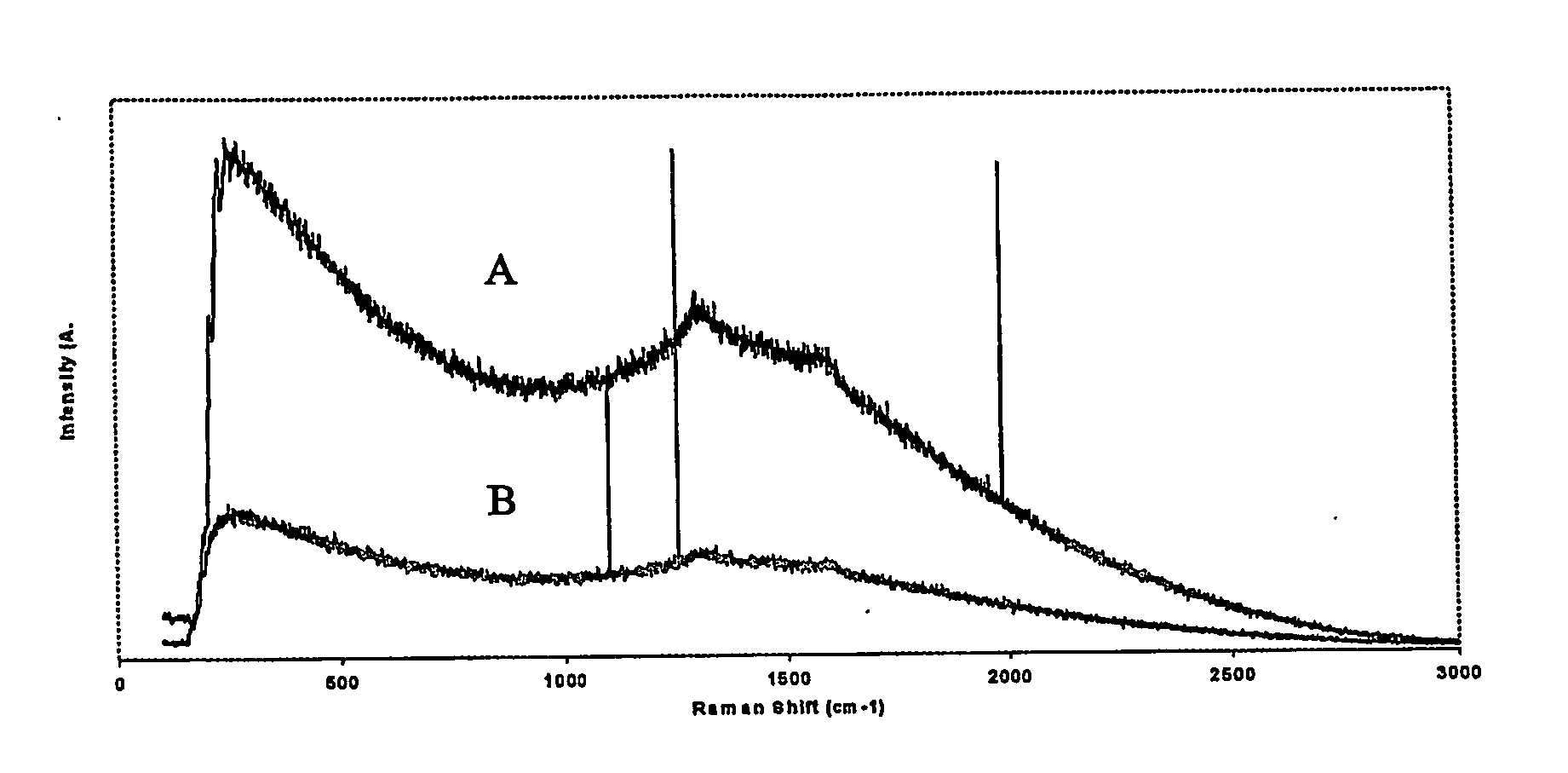
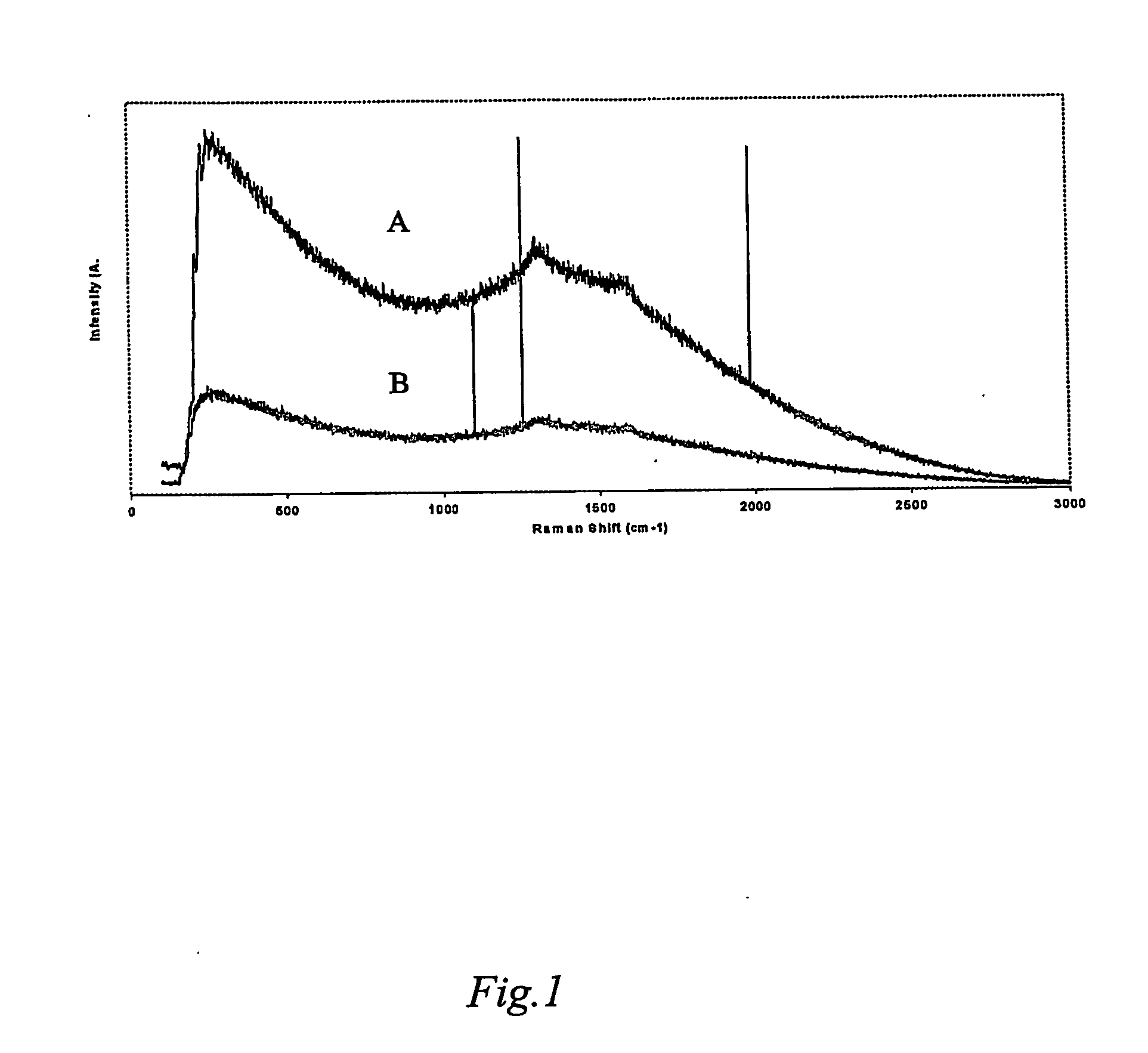
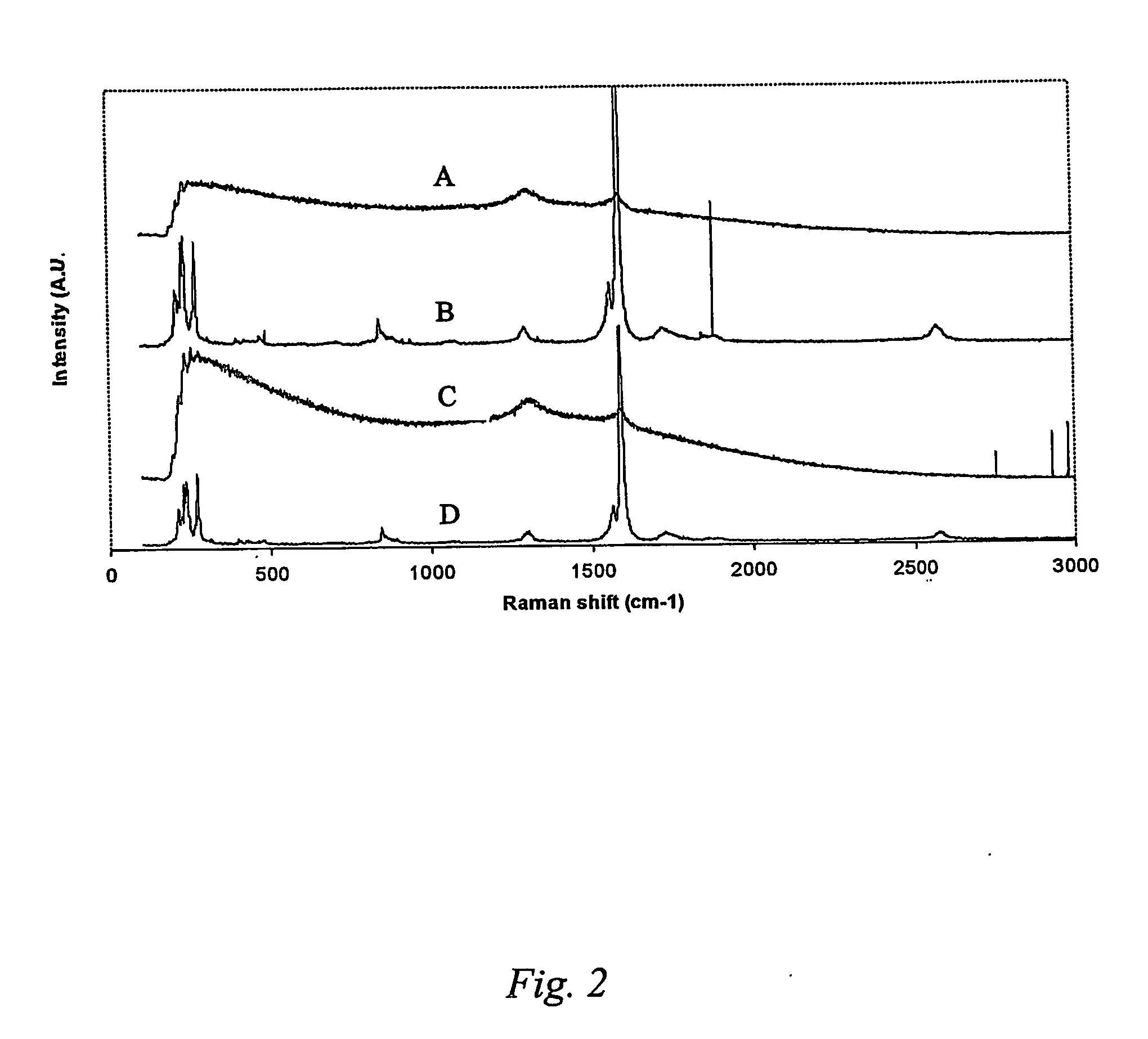
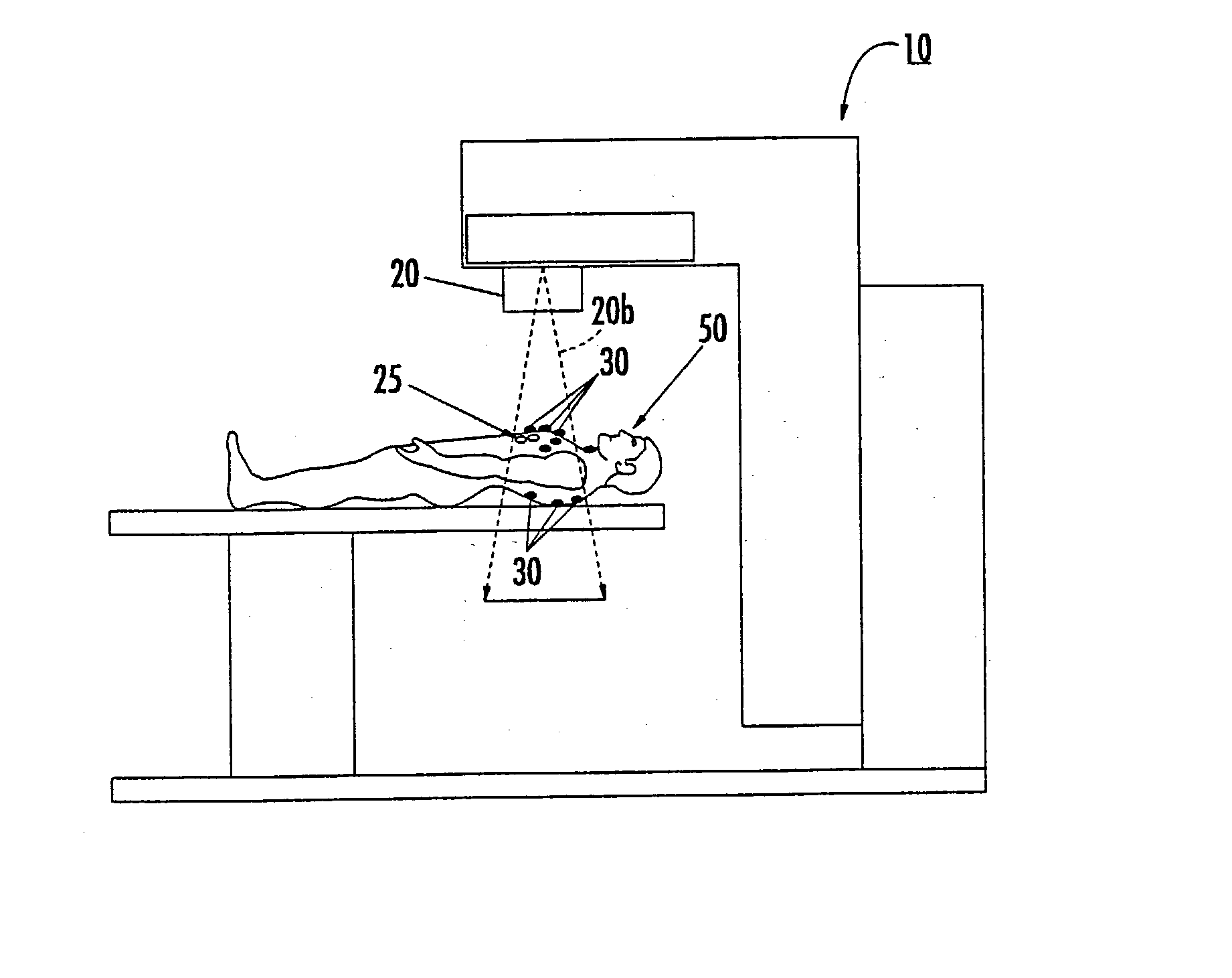
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1160results about "Dosimeters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
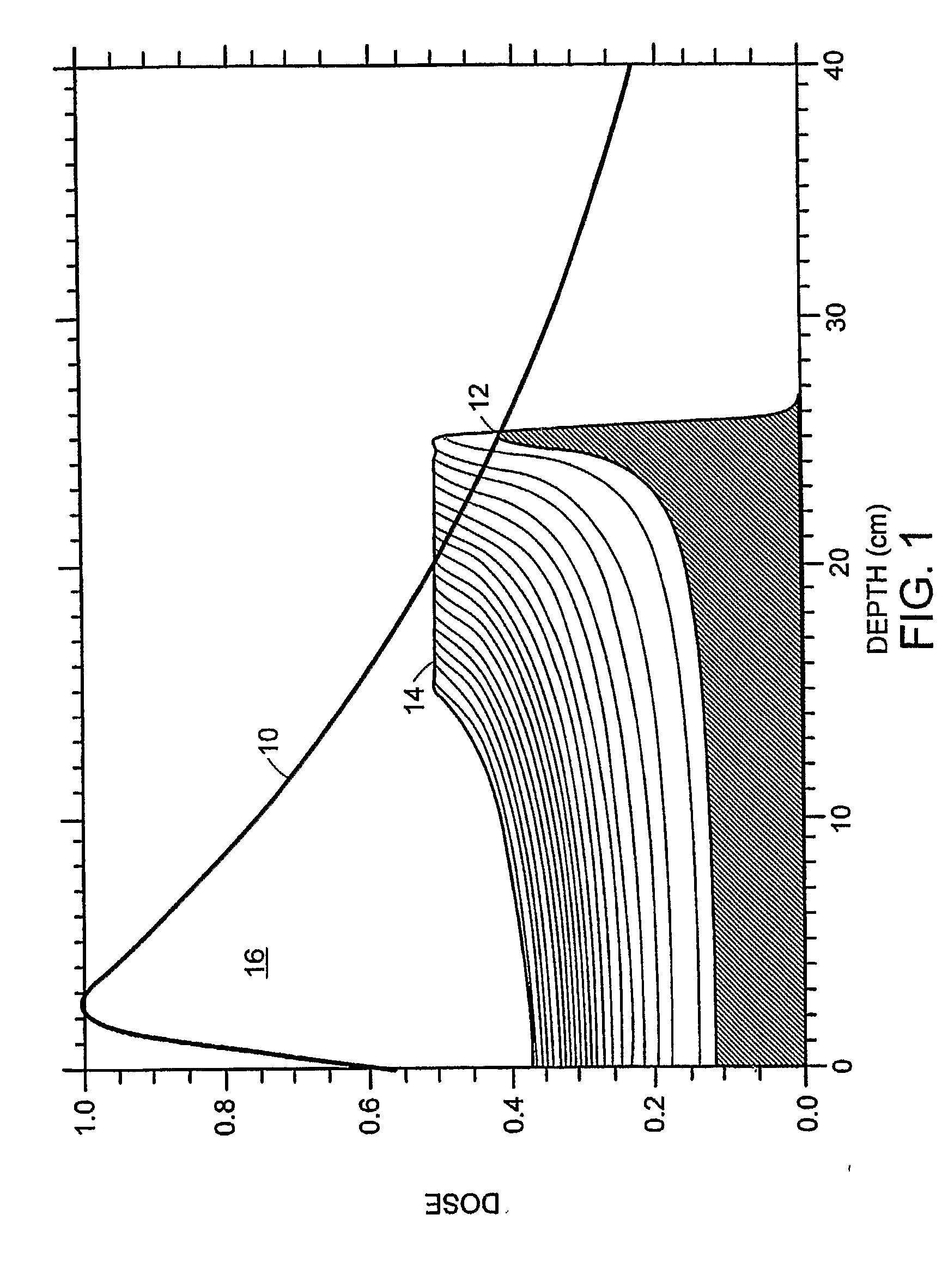
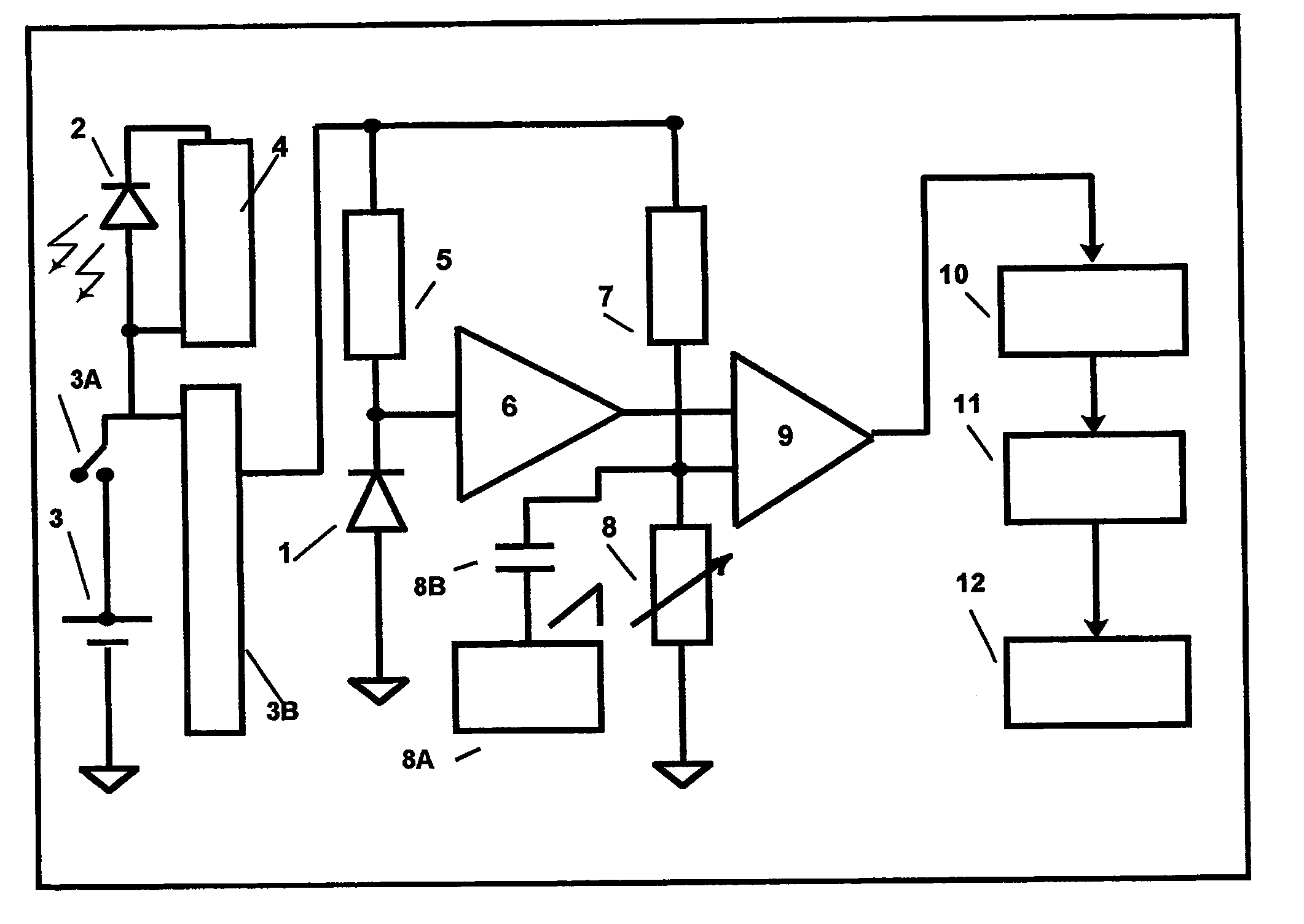
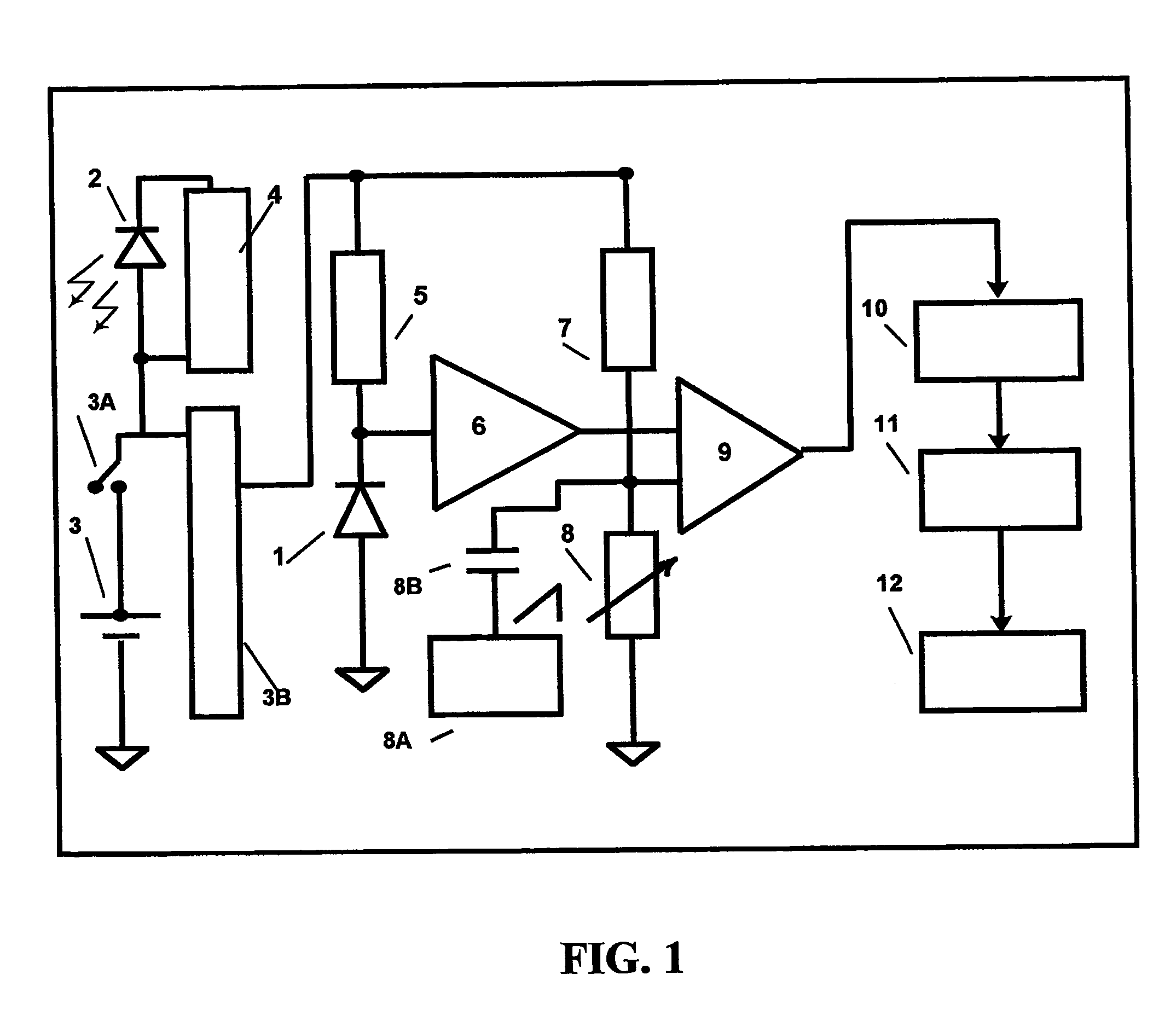
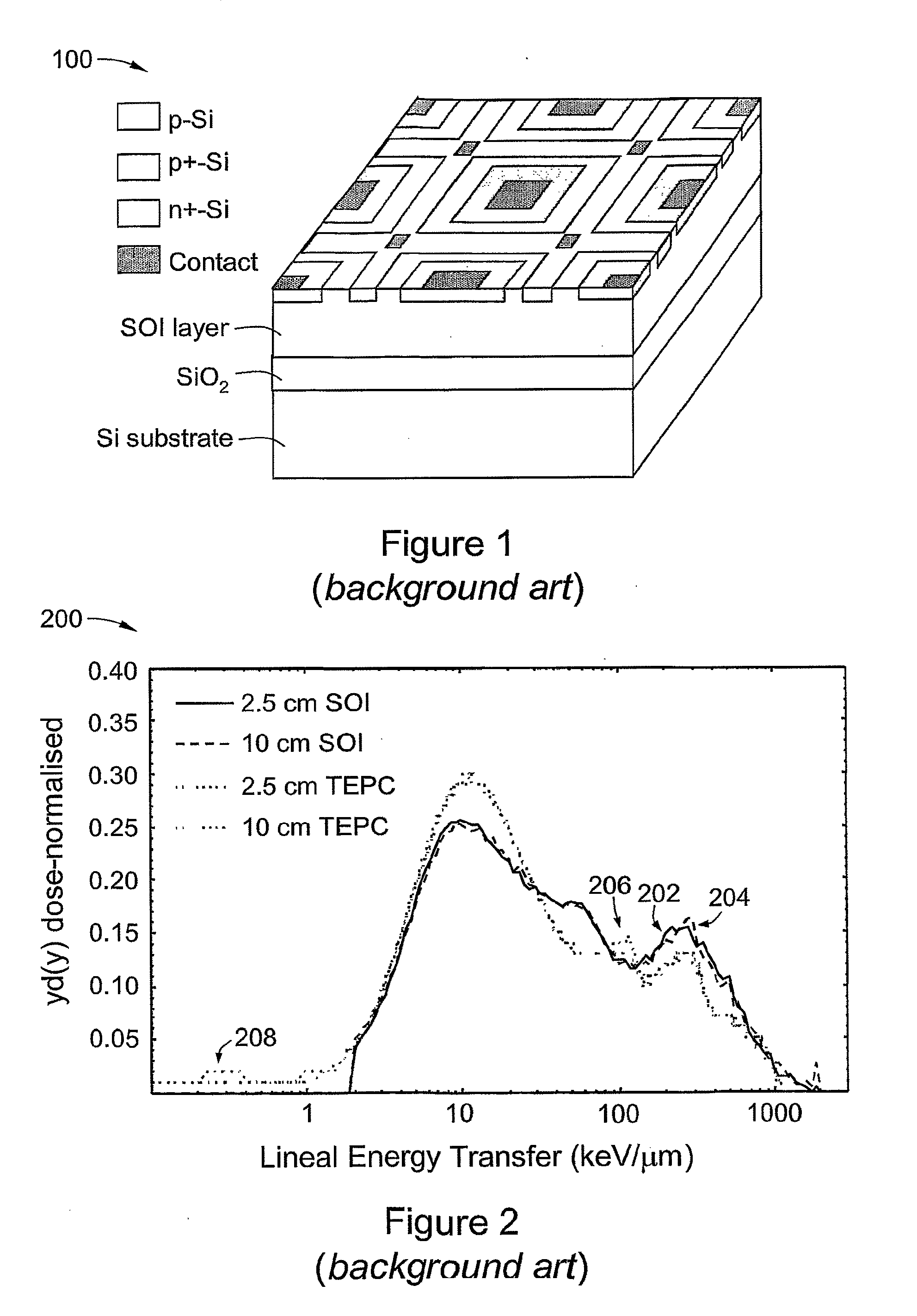
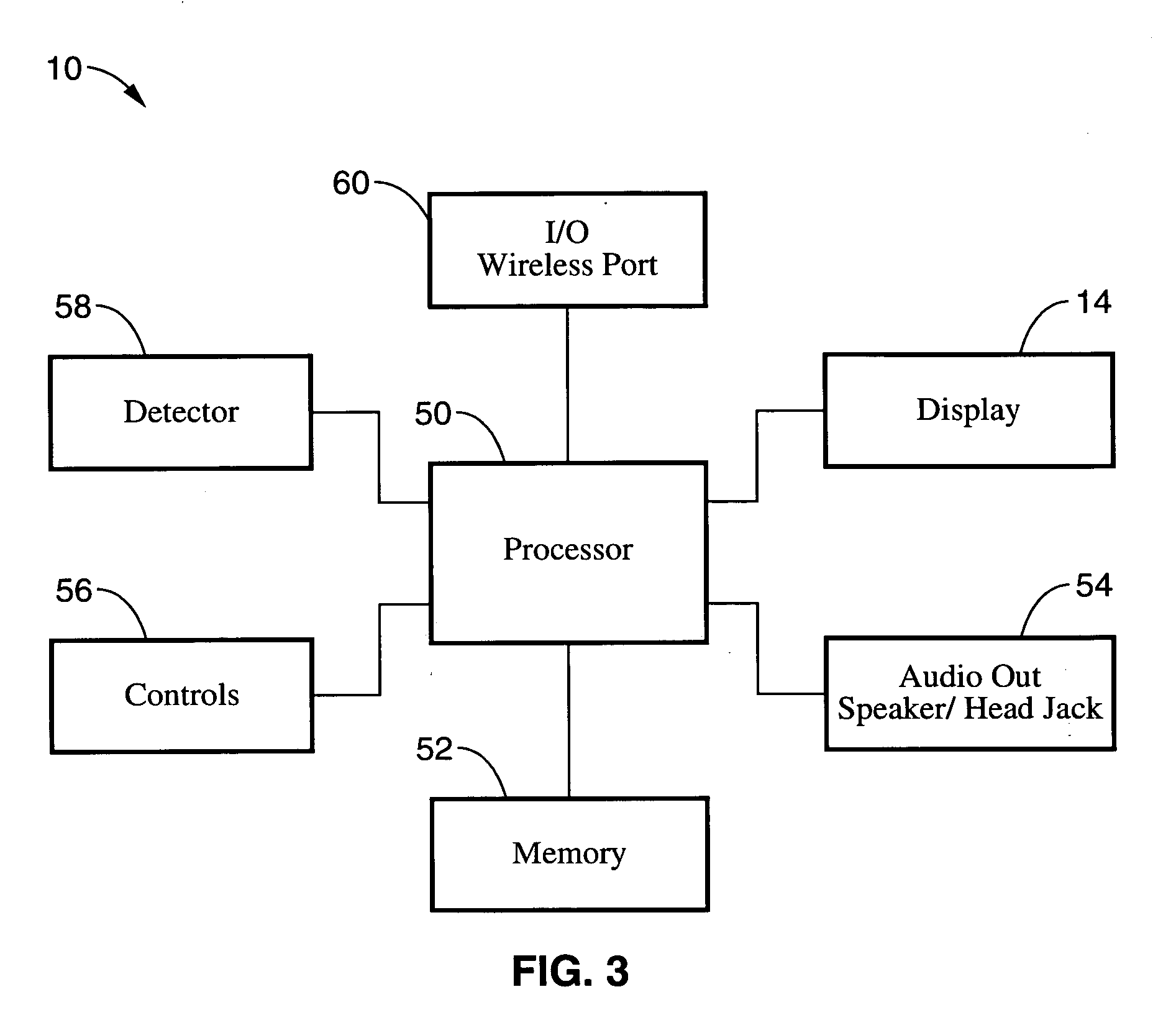
Safety indicator and method
InactiveUS7378954B2Eliminate saturationReduce the noise floorDosimetersPhotometryExposure durationRadiation exposure
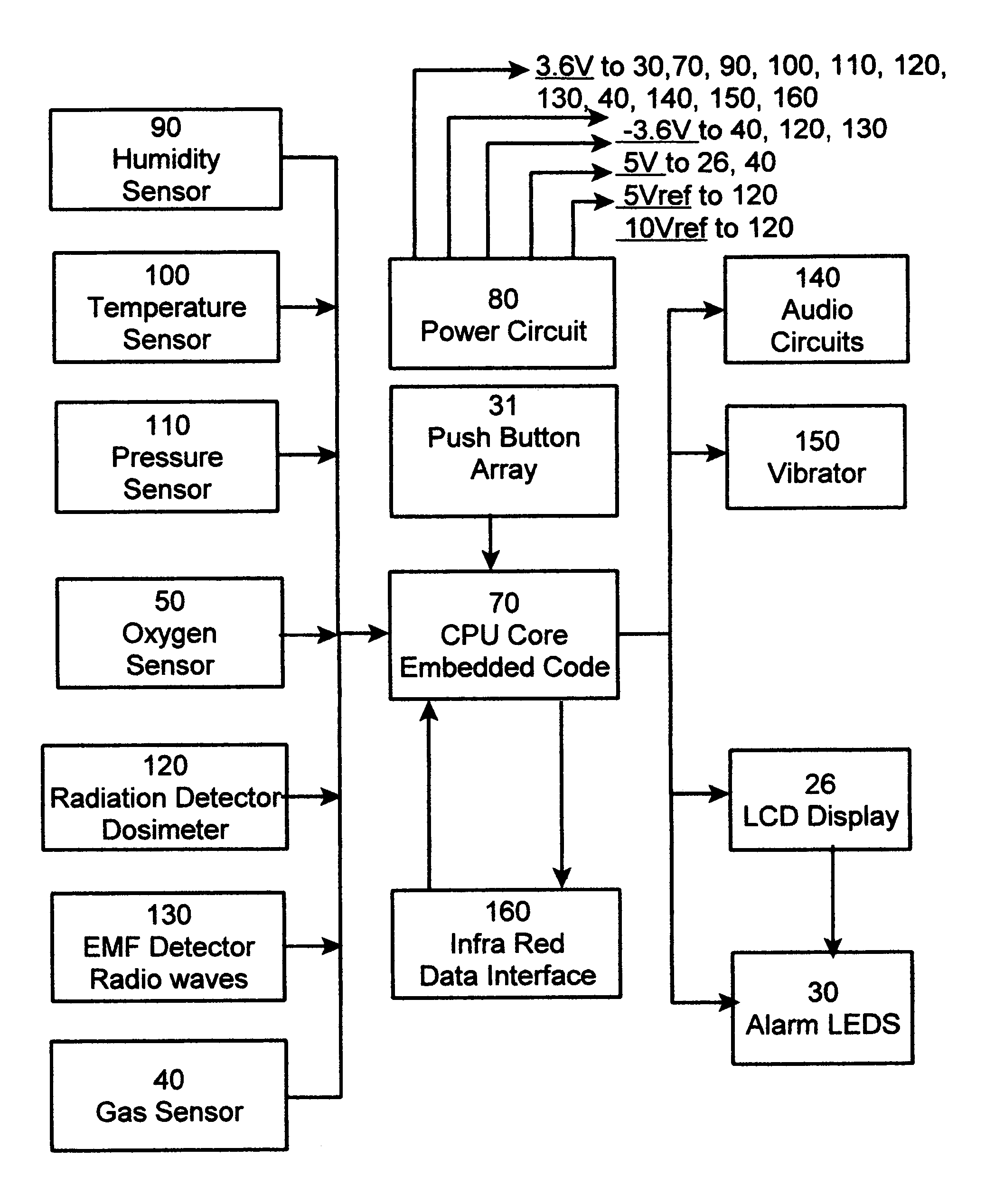
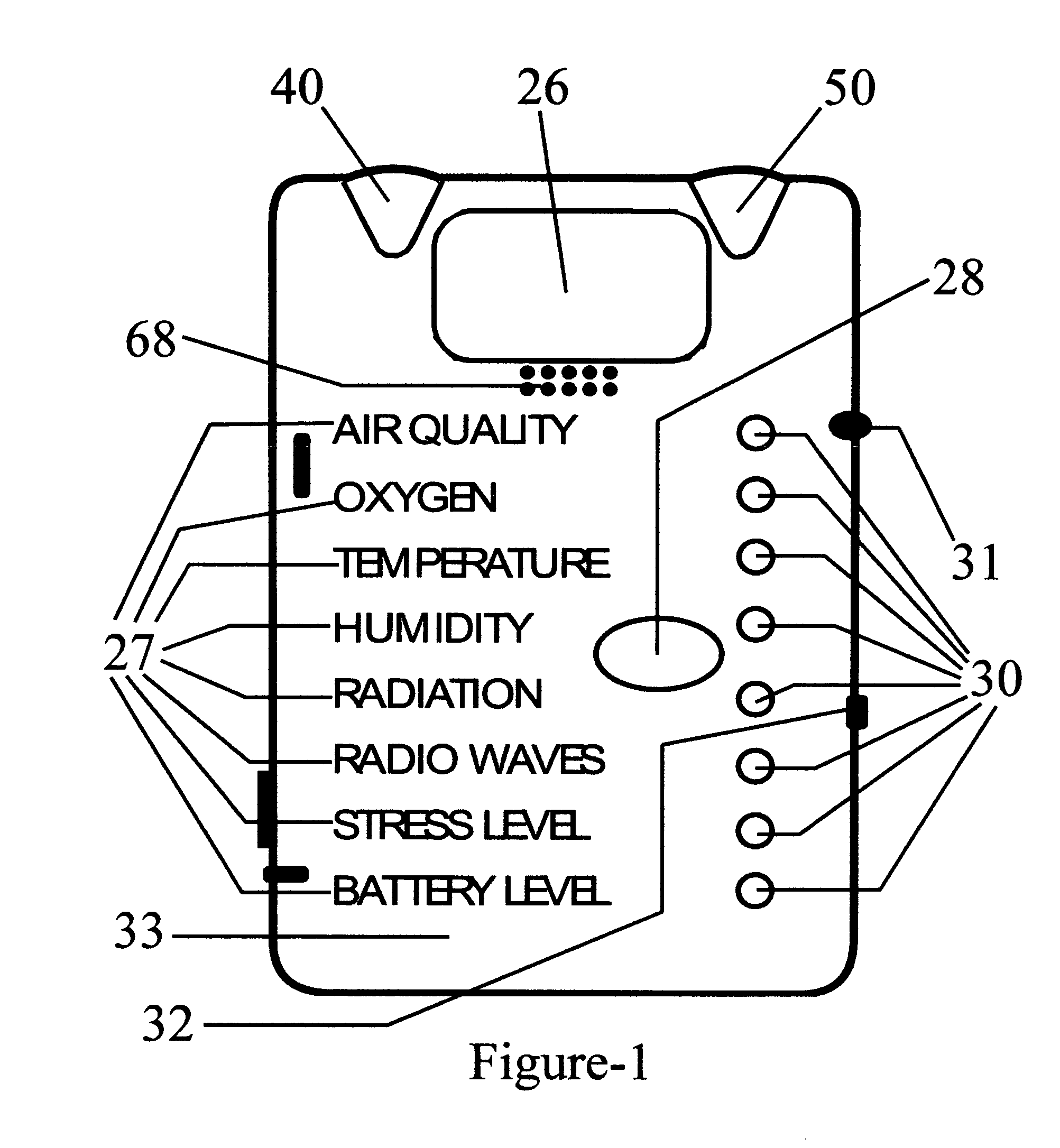
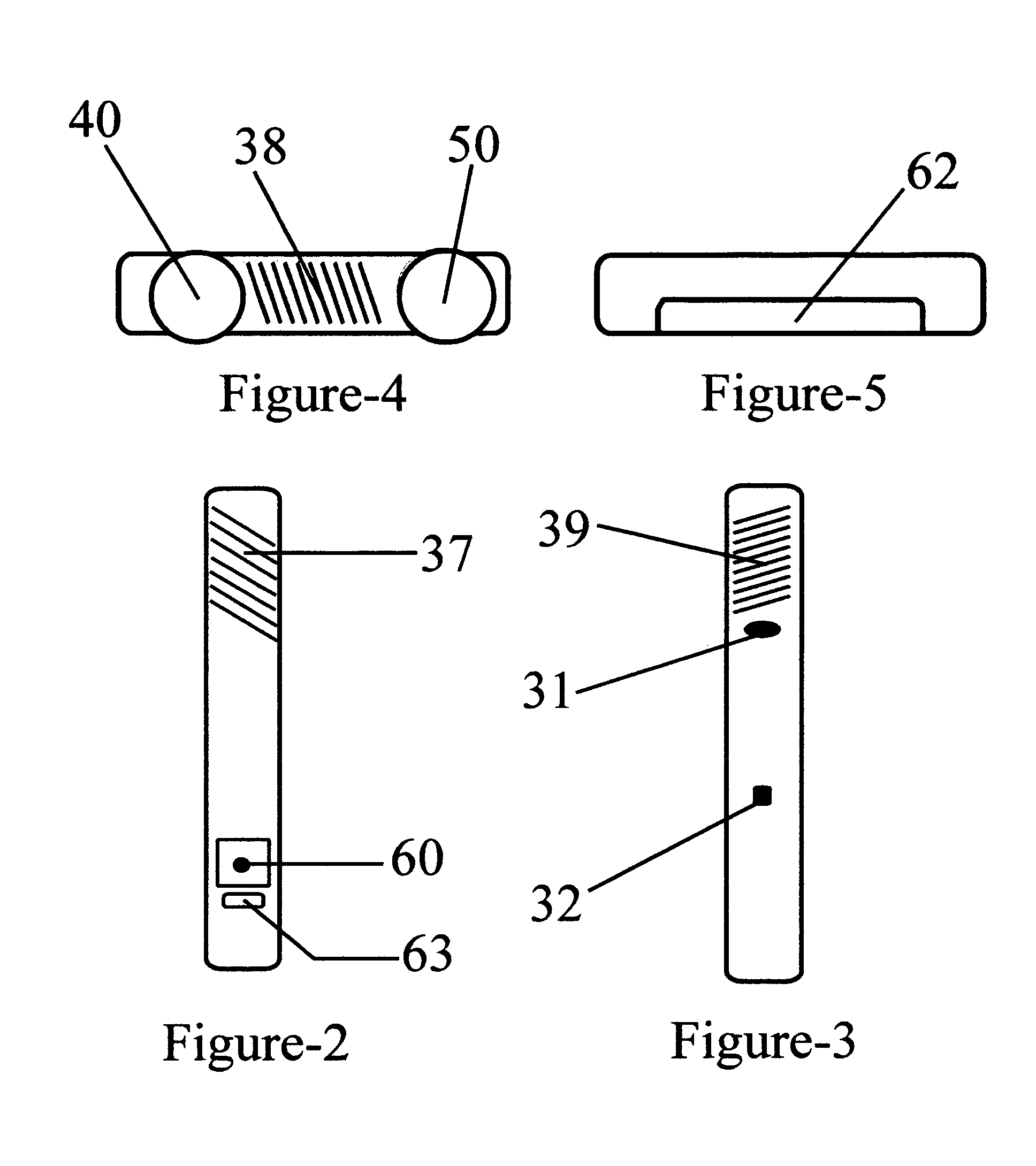
A safety indicator monitors environment conditions detrimental to humans e.g., hazardous gases, air pollutants, low oxygen, radiation levels of EMF or RF and microwave, temperature, humidity and air pressure retaining a three month history to upload to a PC via infra red data interface or phone link. Contaminants are analyzed and compared to stored profiles to determine its classification and notify user of an adversity by stored voice messages from, via alarm tones and associated flashing LED, via vibrator for silent operation or via LCD. Environmental radiation sources are monitored and auto-scaled. Instantaneous radiation exposure level and exposure duration data are stored for later readout as a detector and dosimeter. Scans for EMF allow detection with auto scaling of radiation levels and exposure durations are stored for subsequent readout. Electronic bugs can be found with a high sensitivity EMF range setting. Ambient temperature measurements or humidity and barometric pressure can be made over time to predict weather changes. A PCS RF link provides wireless remote communications in a first responder military use by upload of alarm conditions, field measurements and with download of command instructions. The link supports reception of telemetry data for real time remote monitoring of personnel via the wrist band for blood pressure, temperature, pulse rate and blood oxygen levels are transmitted. Commercial uses include remote environmental data collection and employee assignment tasking. GPS locates personnel and reporting coordinates associated with alarm occurrences and associated environmental measurements.
Owner:NTCG
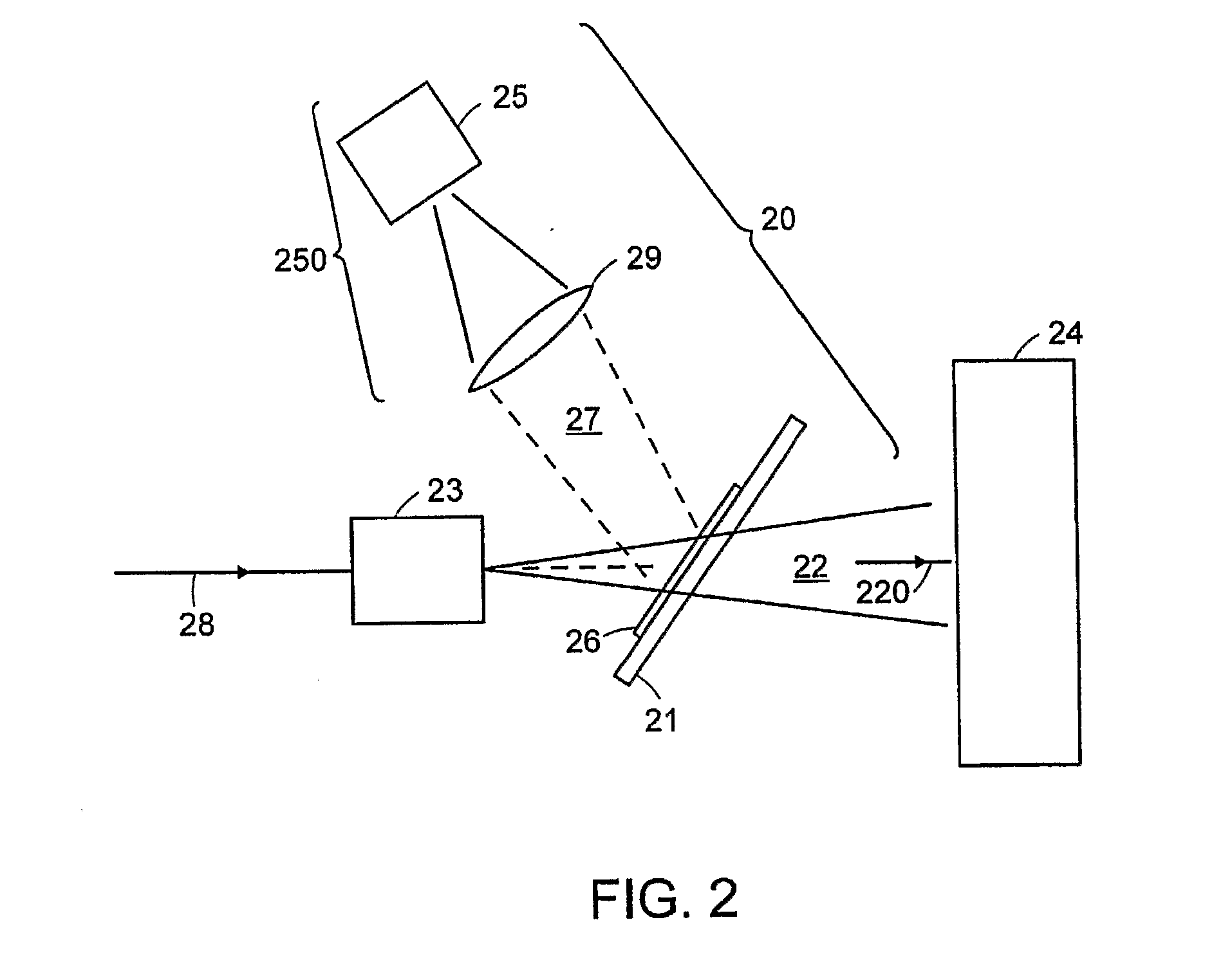
High resolution proton beam monitor
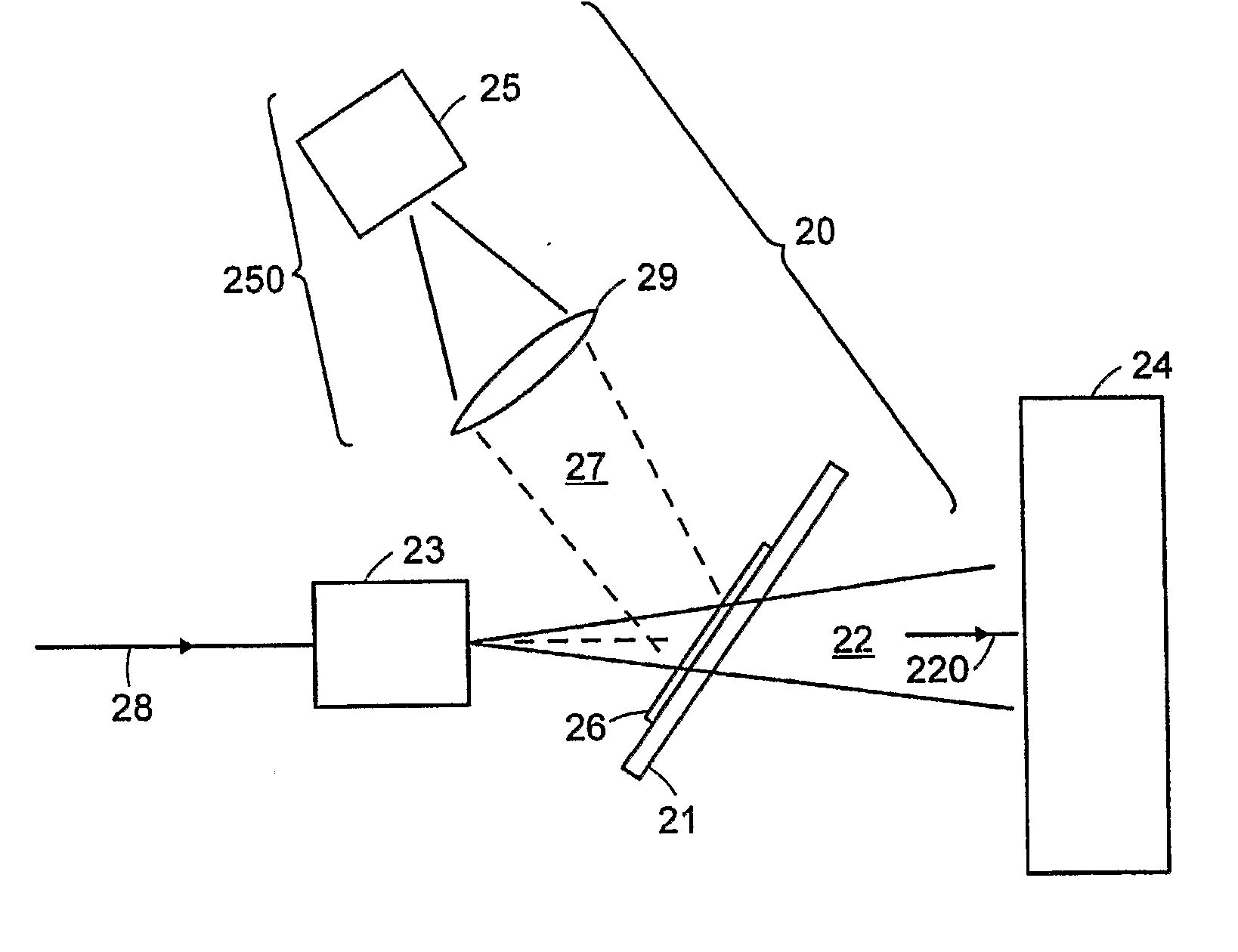
InactiveUS20070181815A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingLight beamProton
A method and apparatus for monitoring a scanning beam of penetrating radiation, such as a scanning proton beam used to irradiate tissue. The position of the beam is tracked in real time by interposing a scintillator film between a source and an object of irradiation. An imaging detector, in optical communication with the scintillator, provides an output that is indicative of the position of the radiation and its variation with time. The accumulated dose over a scan may also be monitored.
Owner:LEXITEK
Method of scanning, analyzing and identifying electro magnetic field sources
InactiveUS20100125438A1Easy to identifyAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDosimetersProbable CaseElectromagnetic field
A method for determining the energy level of an electromagnetic field (EMF) received from an EMF source (EMFS) and for identifying the EMFS is provided, the method comprising: receiving an EMF signal, separating the EMF signal into EMF sub-signals; determining, when possible, the energy level of EMF sub-signals; identify, when possible, the EMFS corresponding to the EMF sub-signals; and recording EMF related data. An apparatus, a system and a user graphical interface is also provided herein. Further, a network of EMFDD adapted to share EMF data therebetween is also provided herein.
Owner:MAUTECH
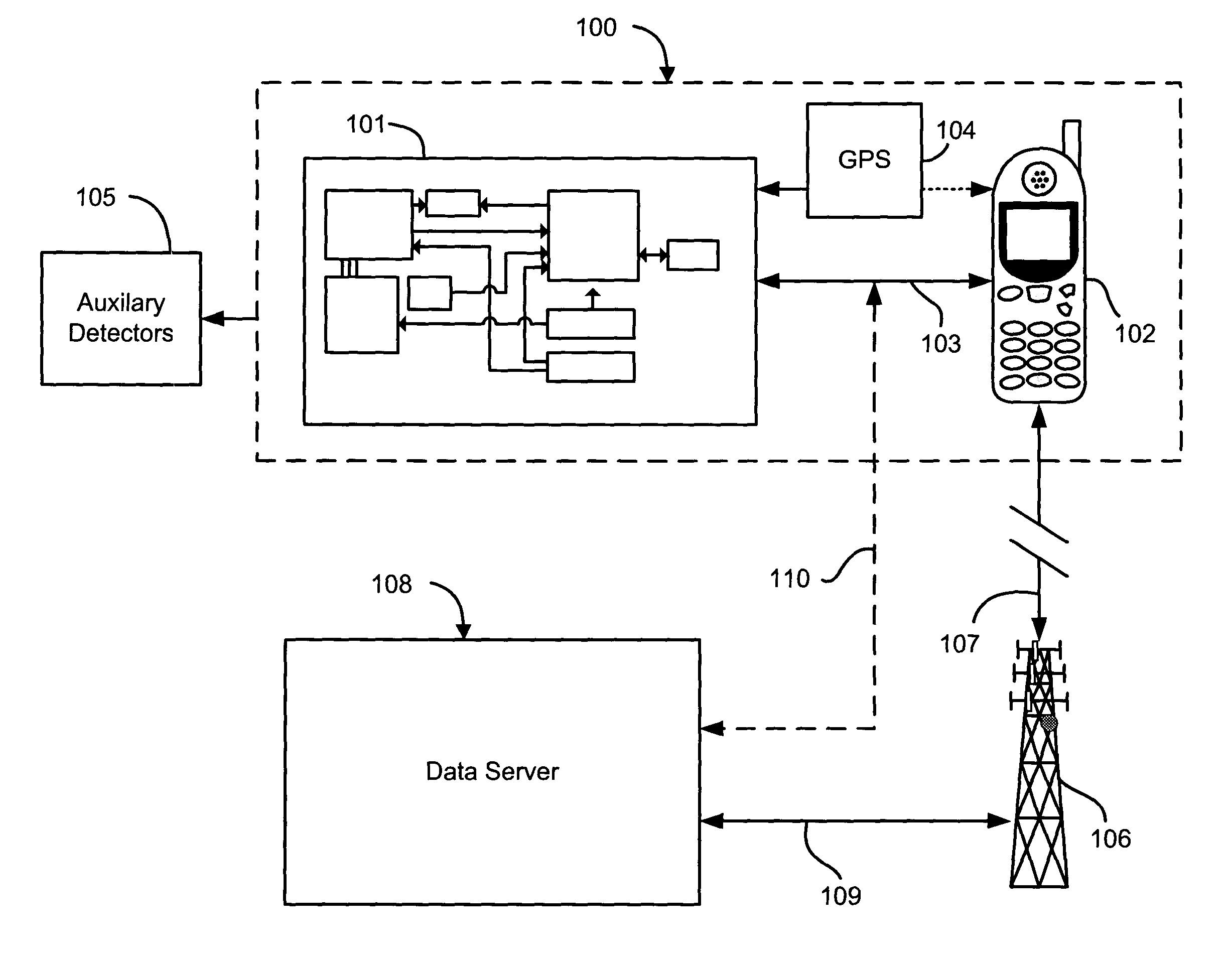
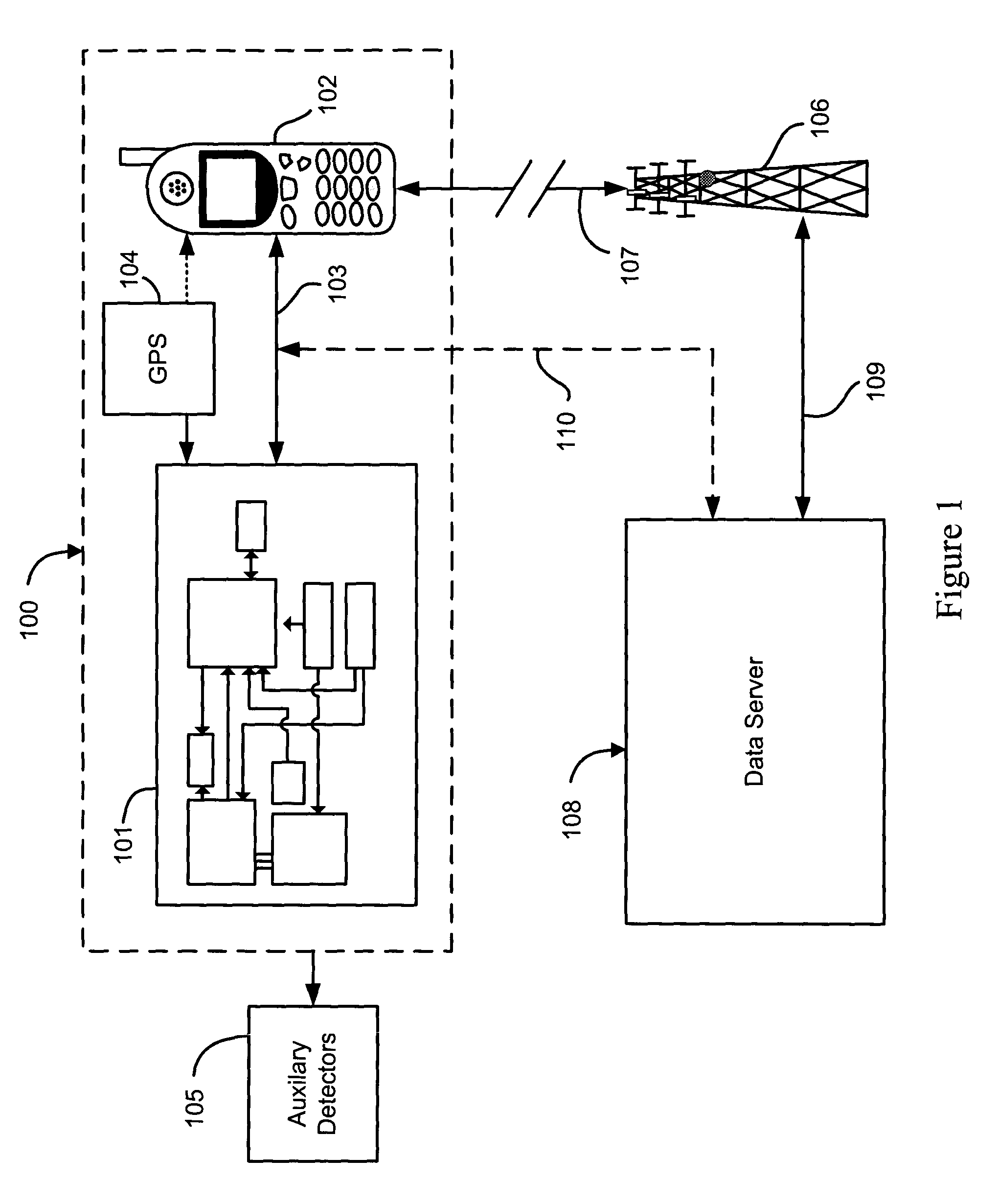
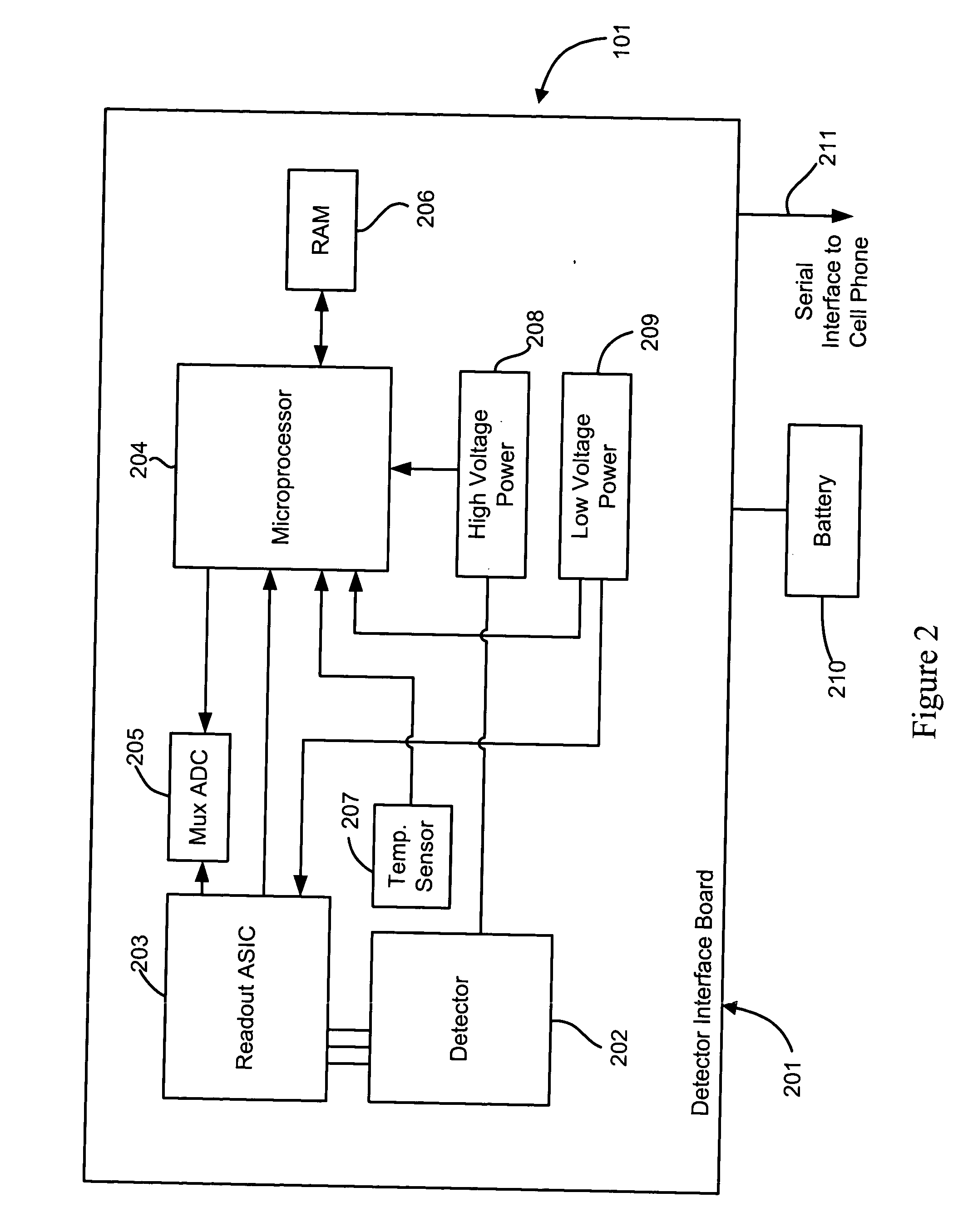
Cellular telephone-based radiation sensor and wide-area detection network
A network of radiation detection instruments, each having a small solid state radiation sensor module integrated into a cellular phone for providing radiation detection data and analysis directly to a user. The sensor module includes a solid-state crystal bonded to an ASIC readout providing a low cost, low power, light weight compact instrument to detect and measure radiation energies in the local ambient radiation field. In particular, the photon energy, time of event, and location of the detection instrument at the time of detection is recorded for real time transmission to a central data collection / analysis system. The collected data from the entire network of radiation detection instruments are combined by intelligent correlation / analysis algorithms which map the background radiation and detect, identify and track radiation anomalies in the region.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
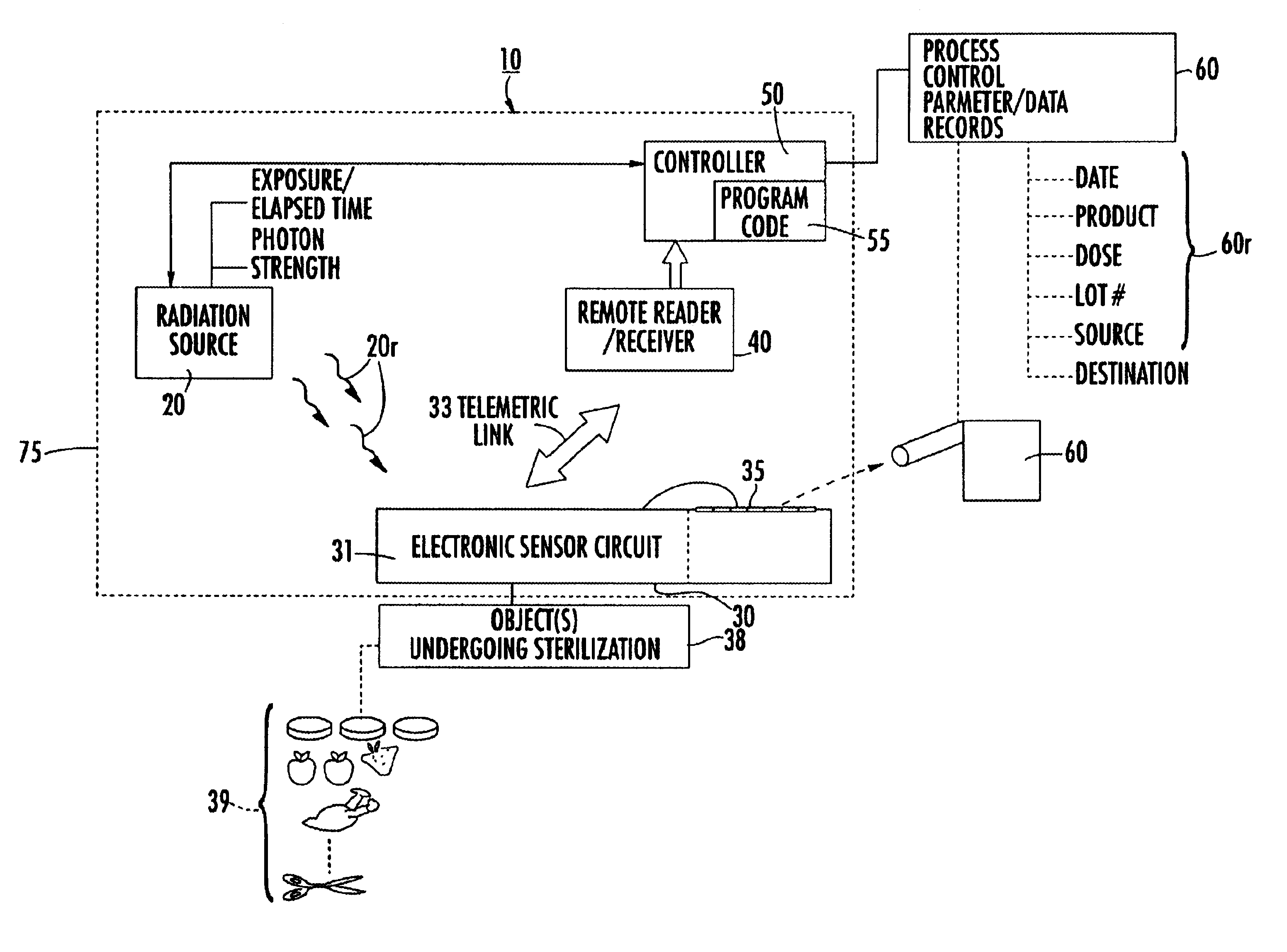
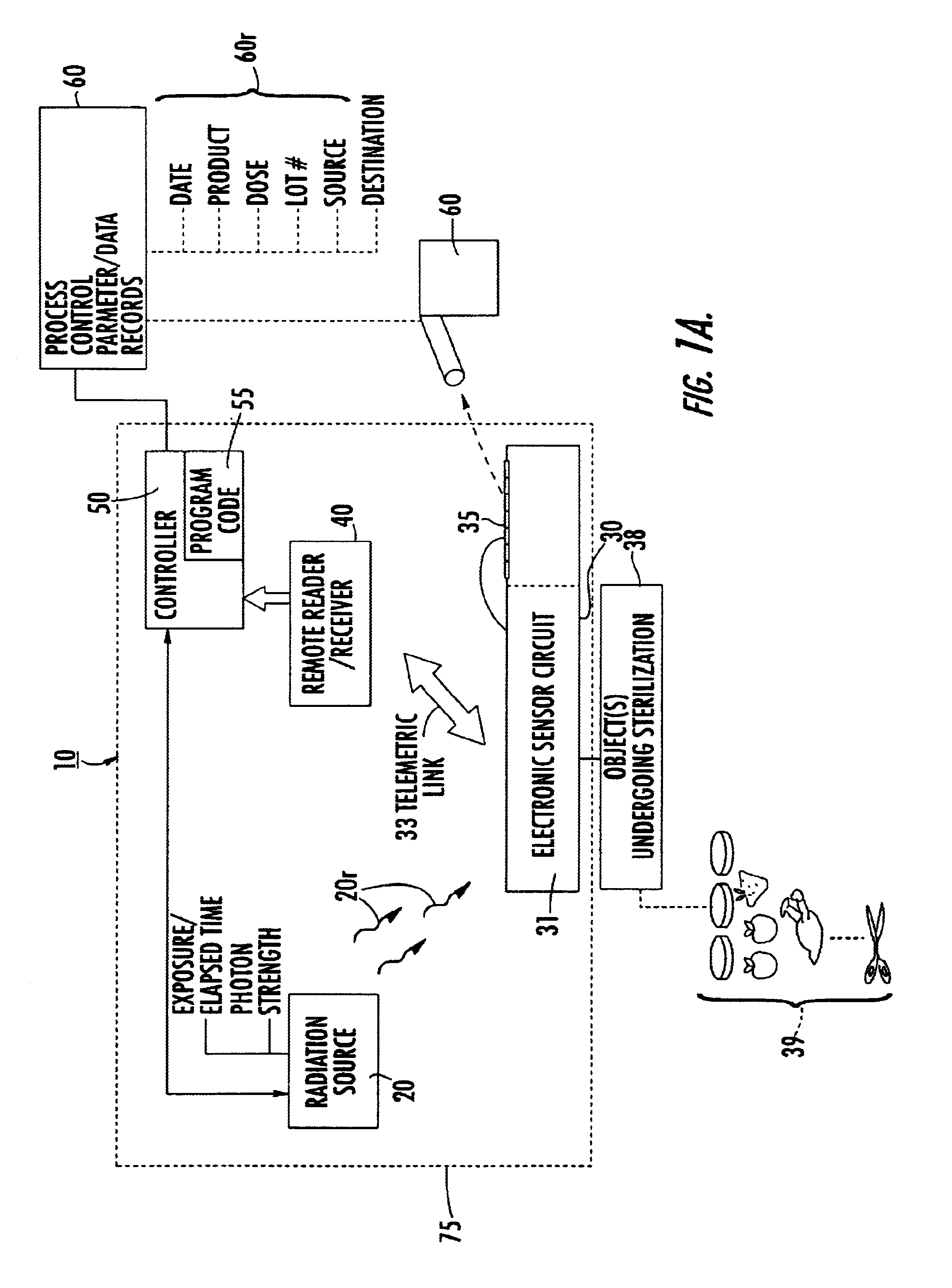
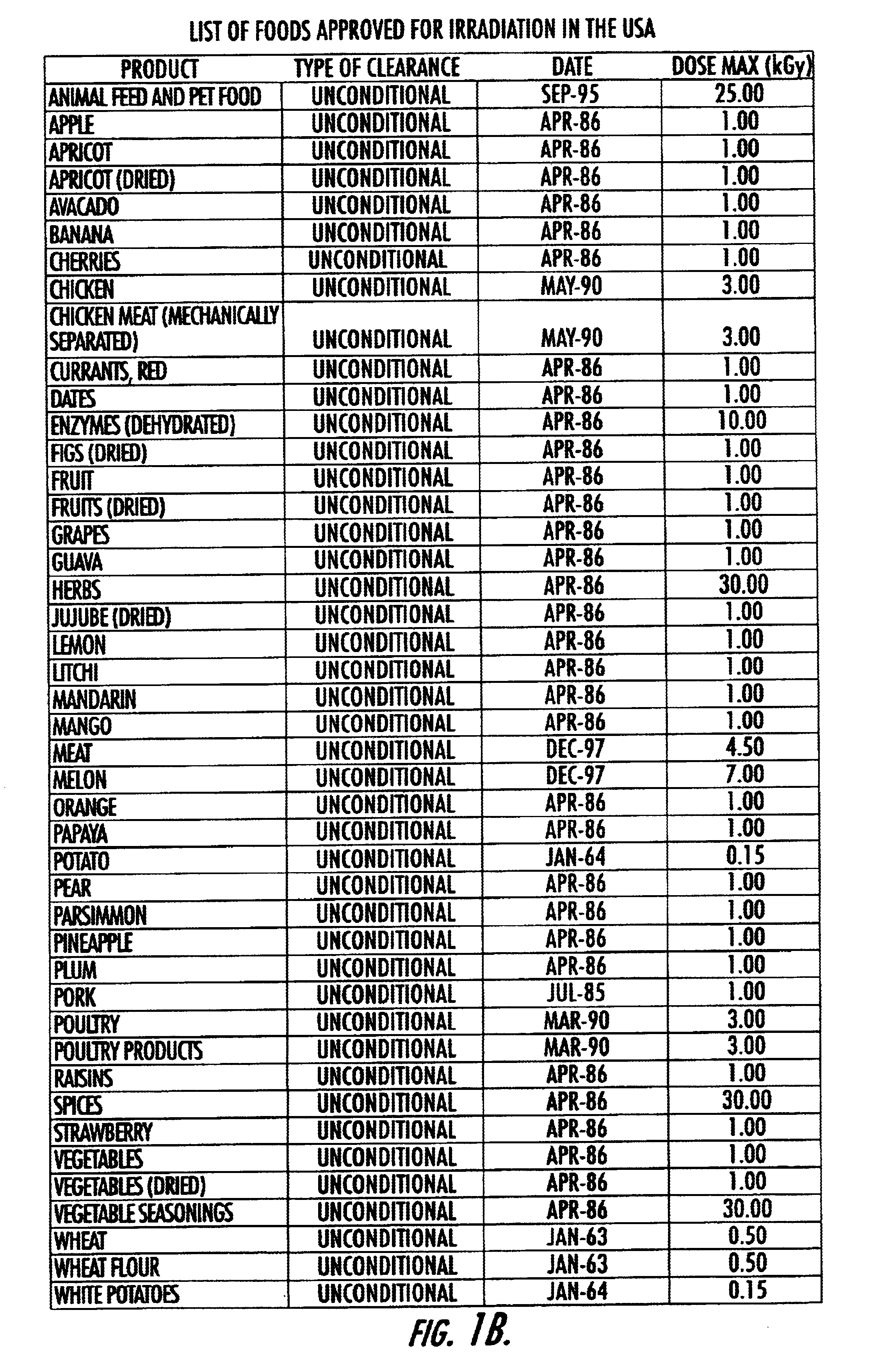
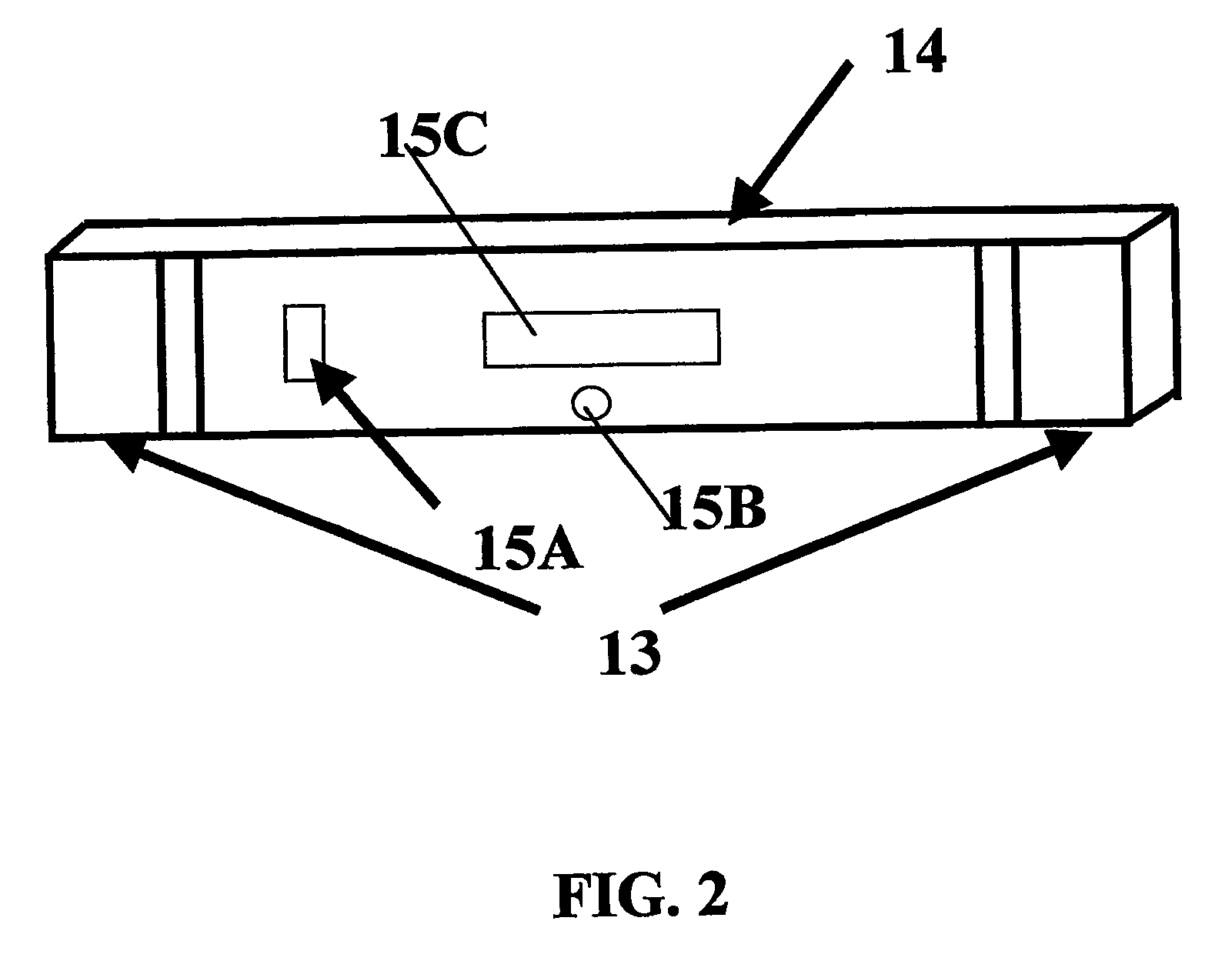
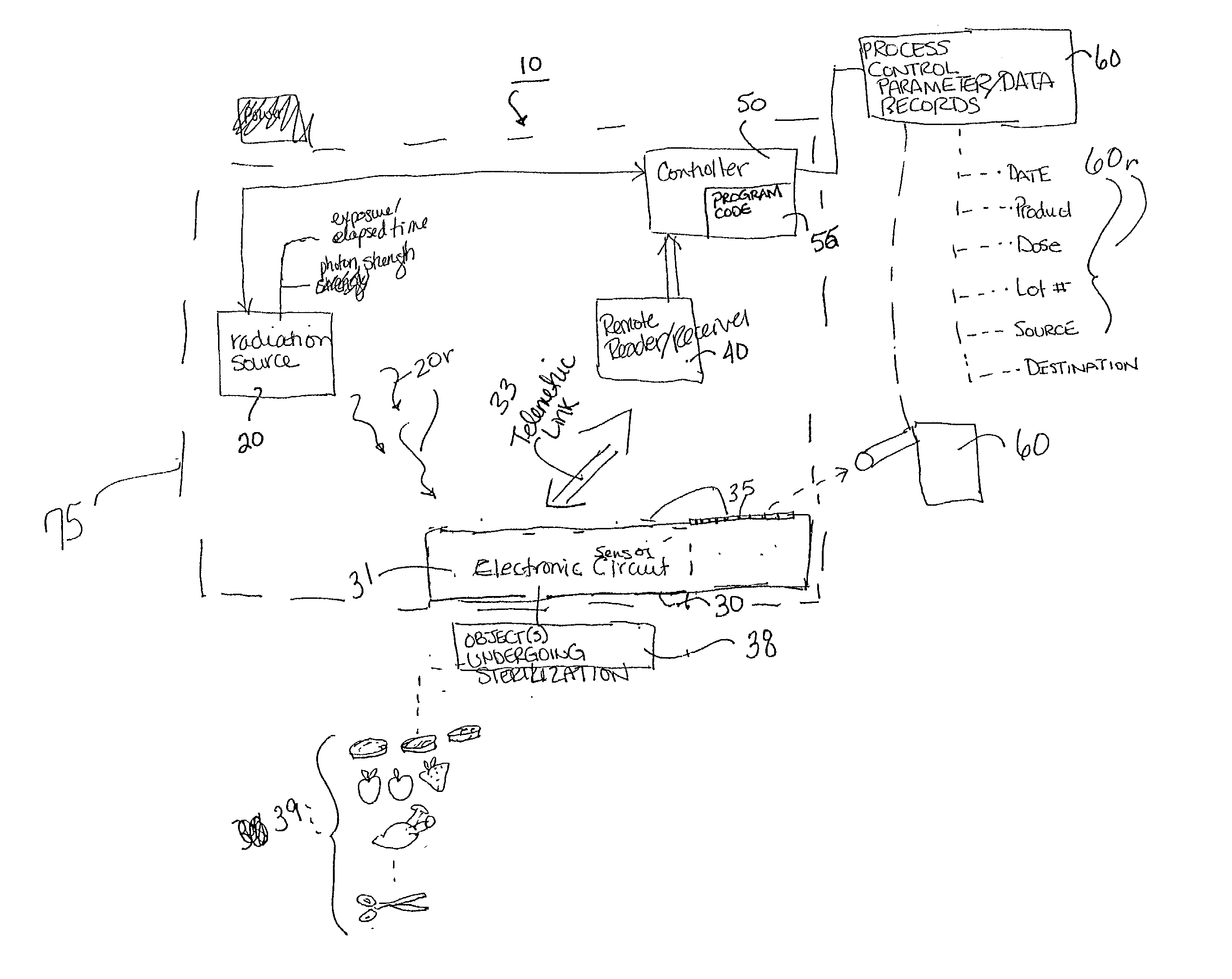
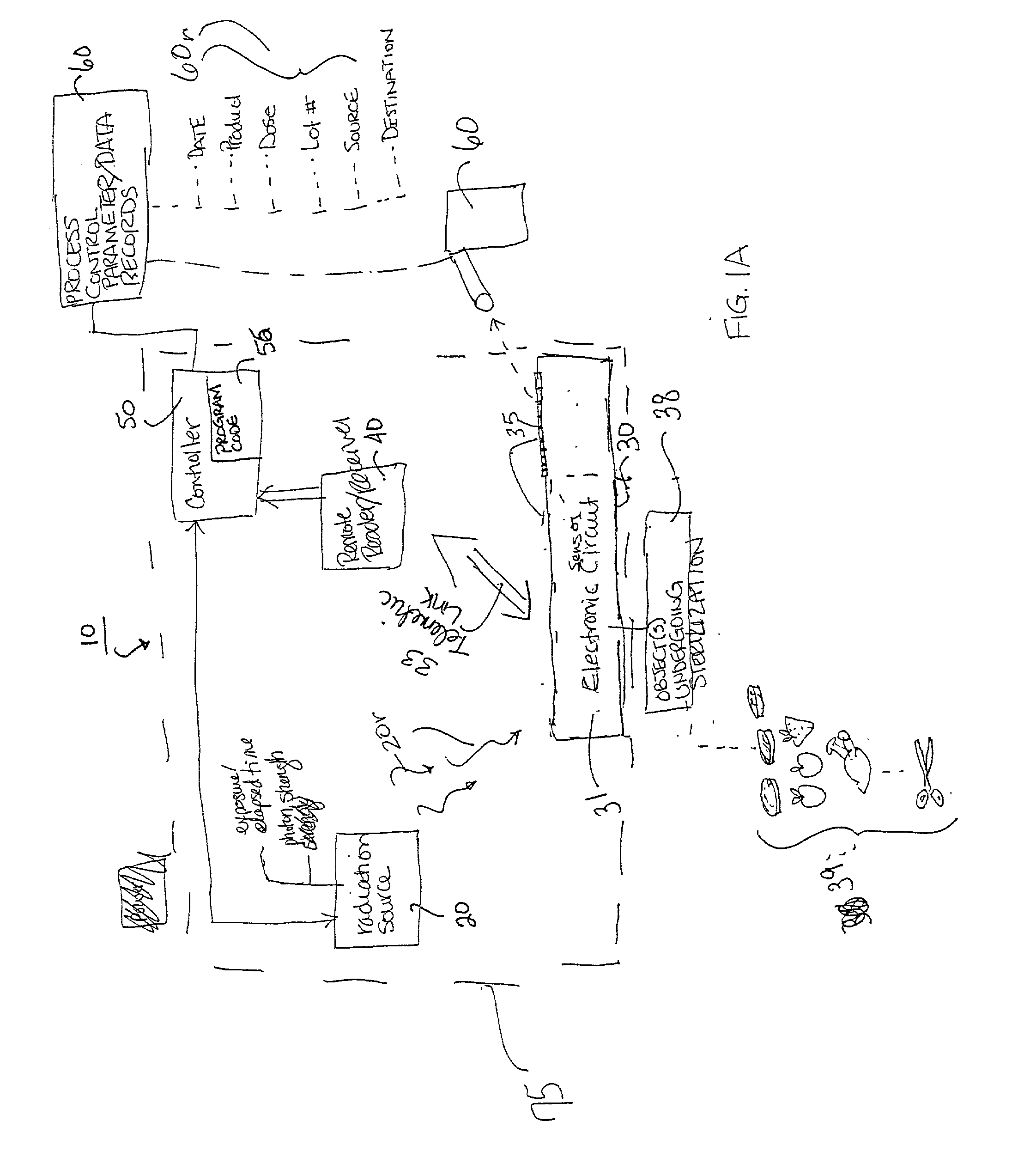
Evaluation of irradiated foods and other items with telemetric dosimeters and associated methods
InactiveUS6717154B2Simple methodEasy to processThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsDosimeterIrradiation
Methods for quantifying the irradiation dose received by an item or items, such as food items and medical items, undergoing irradiation-based sterilization, includes the steps of monitoring a selected electronic parameter associated with an economic single use sensor positioned adjacent the item or items and telemetrically relaying data associated with the monitored electronic parameter to a computer. The computer includes a computer program which is configured to determine the radiation dose received by the item or items by correlating the value of the monitored electronic parameter to a corresponding amount of radiation associated with the value. Related sensors and systems are also described.
Owner:VTQ IP HLDG
Deterministic computation of radiation doses delivered to tissues and organs of a living organism
InactiveUS20050143965A1Improve computing efficiencyHigh solution accuracyDosimetersComputation using non-denominational number representationInternal radiationIntensity modulation
Various embodiments of the present invention provide methods and systems for deterministic calculation of radiation doses, delivered to specified volumes within human tissues and organs, and specified areas within other organisms, by external and internal radiation sources. Embodiments of the present invention provide for creating and optimizing computational mesh structures for deterministic radiation transport methods. In general these approaches seek to both improve solution accuracy and computational efficiency. Embodiments of the present invention provide methods for planning radiation treatments using deterministic methods. The methods of the present invention may also be applied for dose calculations, dose verification, and dose reconstruction for many different forms of radiotherapy treatments, including: conventional beam therapies, intensity modulated radiation therapy (“IMRT”), proton, electron and other charged particle beam therapies, targeted radionuclide therapies, brachytherapy, stereotactic radiosurgery (“SRS”), Tomotherapy®; and other radiotherapy delivery modes. The methods may also be applied to radiation-dose calculations based on radiation sources that include linear accelerators, various delivery devices, field shaping components, such as jaws, blocks, flattening filters, and multi-leaf collimators, and to many other radiation-related problems, including radiation shielding, detector design and characterization; thermal or infrared radiation, optical tomography, photon migration, and other problems.
Owner:TRANSPIRE
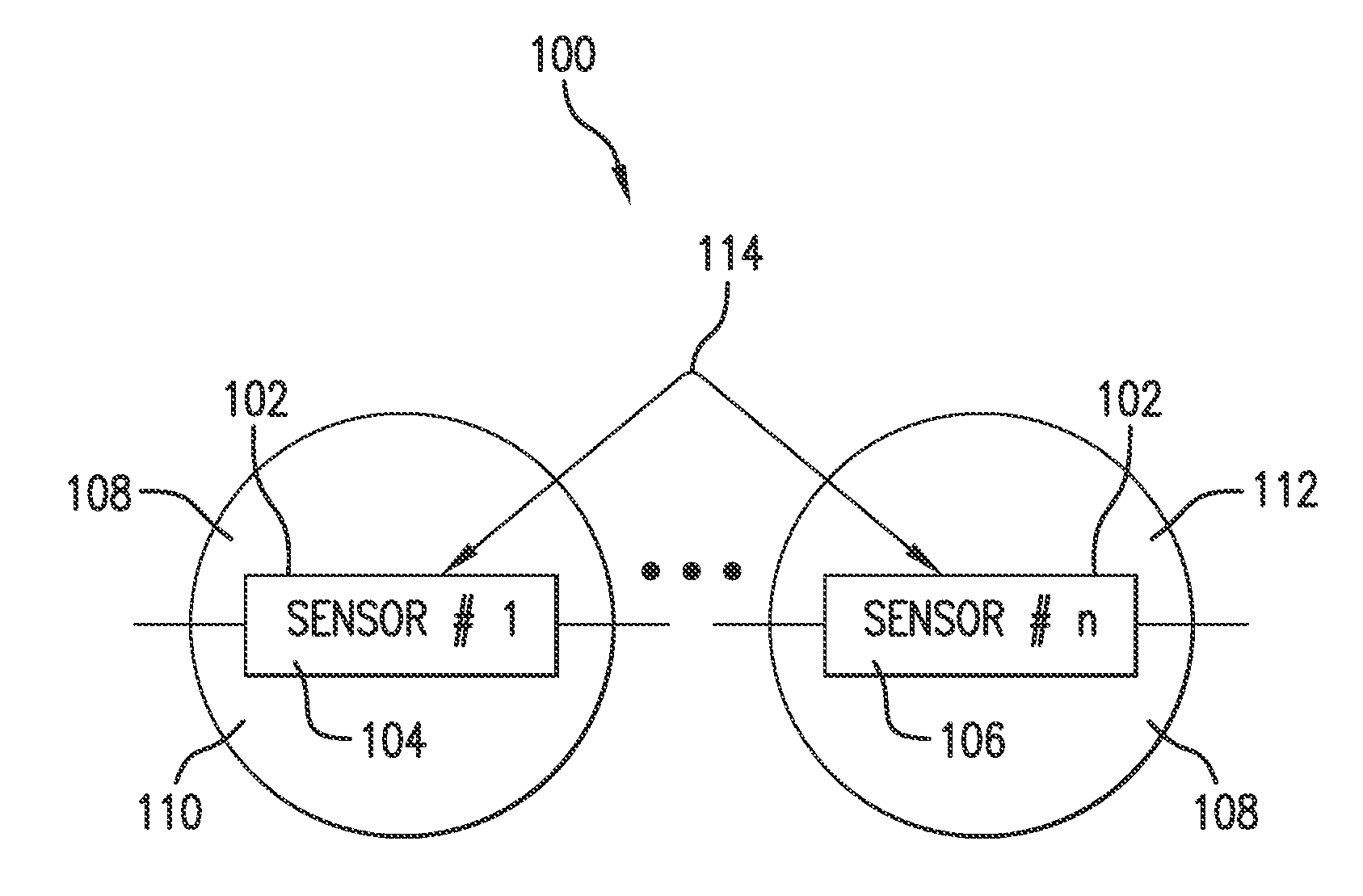
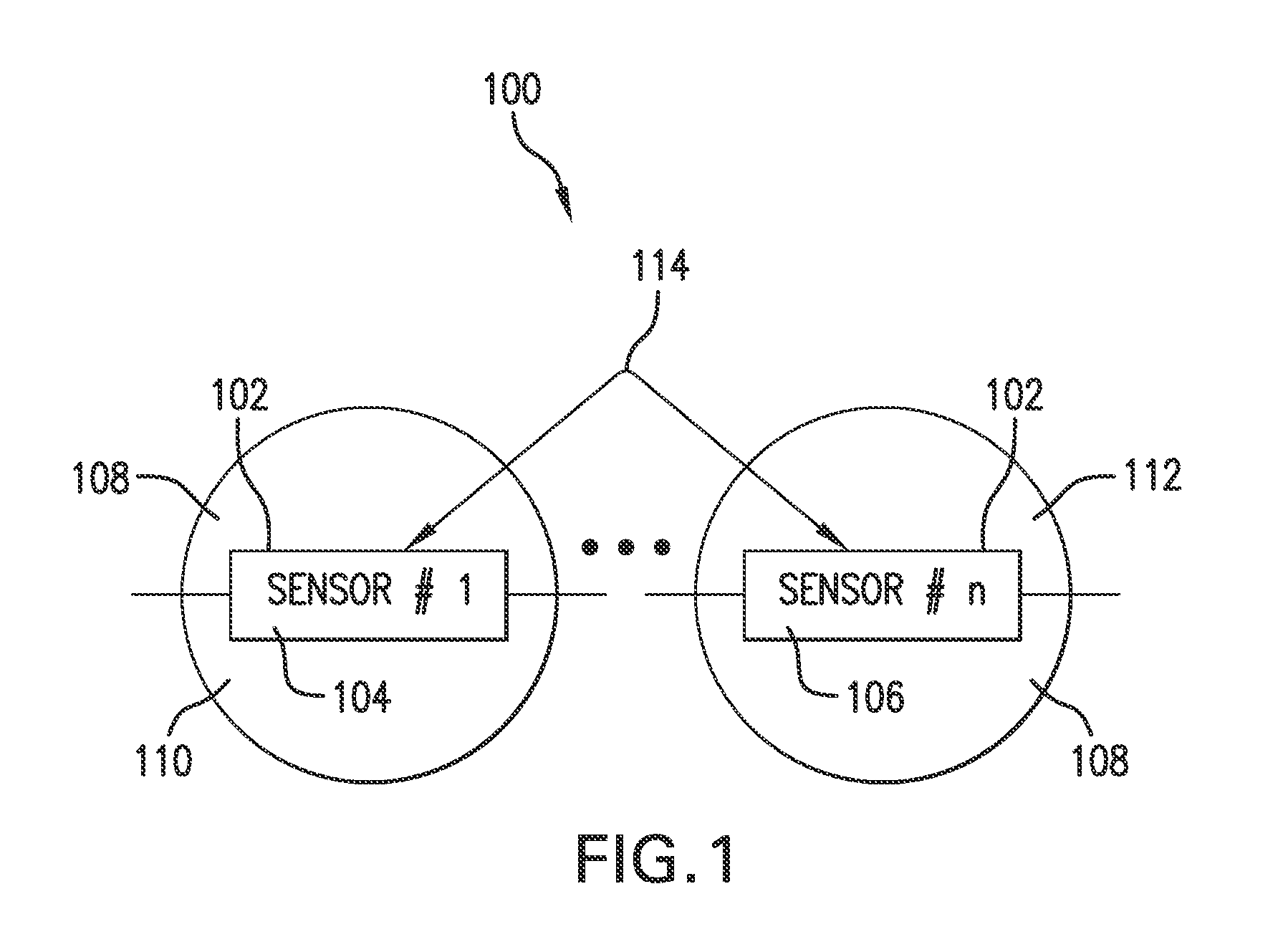
Wireless, motion and position-sensing, integrating radiation sensor for occupational and environmental dosimetry
ActiveUS20130320212A1Excellent angular responseSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDosimetry radiationAccelerometer
Described is a radiation dosimeter including multiple sensor devices (including one or more passive integrating electronic radiation sensor, a MEMS accelerometers, a wireless transmitters and, optionally, a GPS, a thermistor, or other chemical, biological or EMF sensors) and a computer program for the simultaneous detection and wireless transmission of ionizing radiation, motion and global position for use in occupational and environmental dosimetry. The described dosimeter utilizes new processes and algorithms to create a self-contained, passive, integrating dosimeter. Furthermore, disclosed embodiments provide the use of MEMS and nanotechnology manufacturing techniques to encapsulate individual ionizing radiation sensor elements within a radiation attenuating material that provides a “filtration bubble” around the sensor element, the use of multiple attenuating materials (filters) around multiple sensor elements, and the use of a software algorithm to discriminate between different types of ionizing radiation and different radiation energy.
Owner:LANDAUER INC
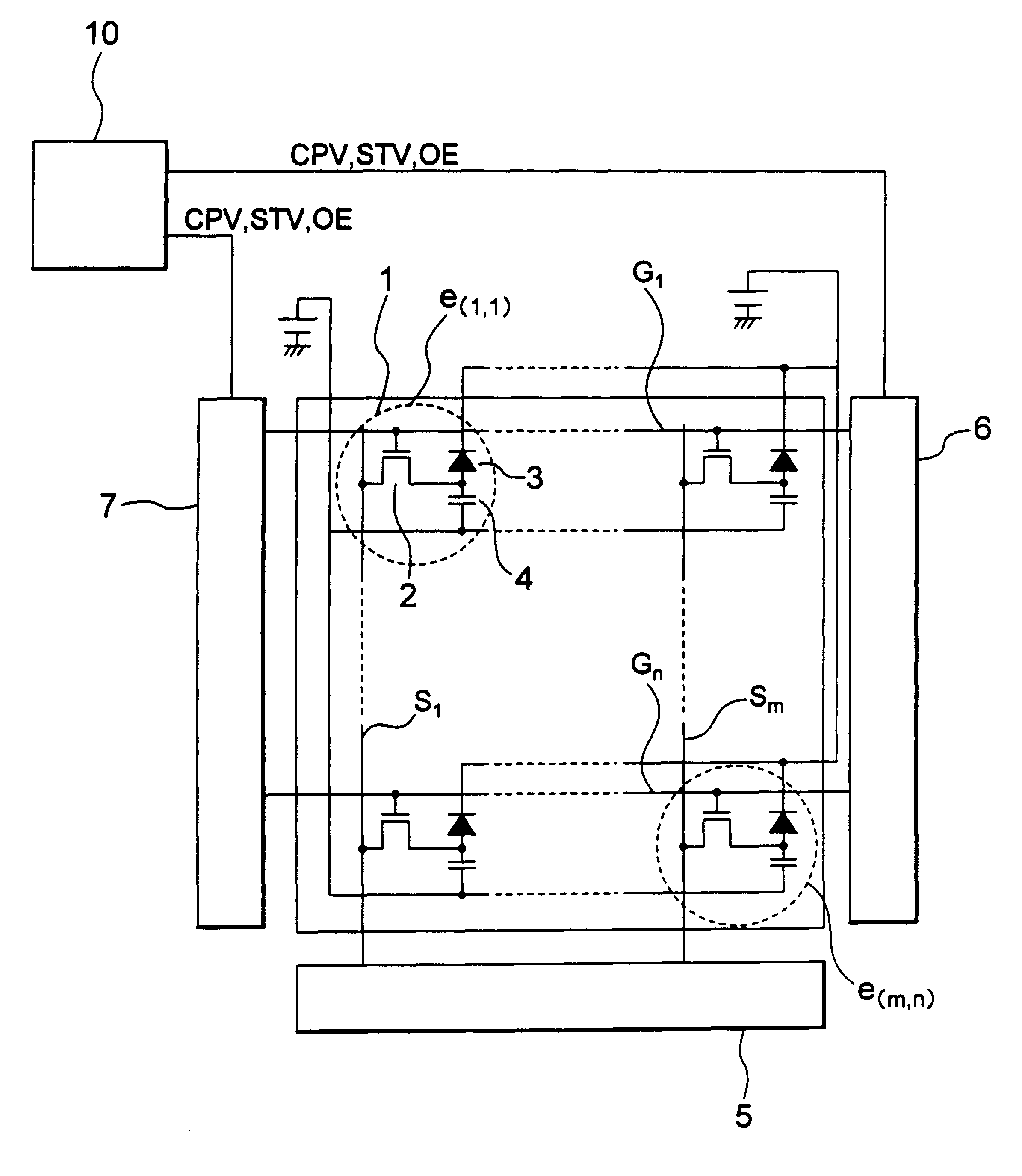
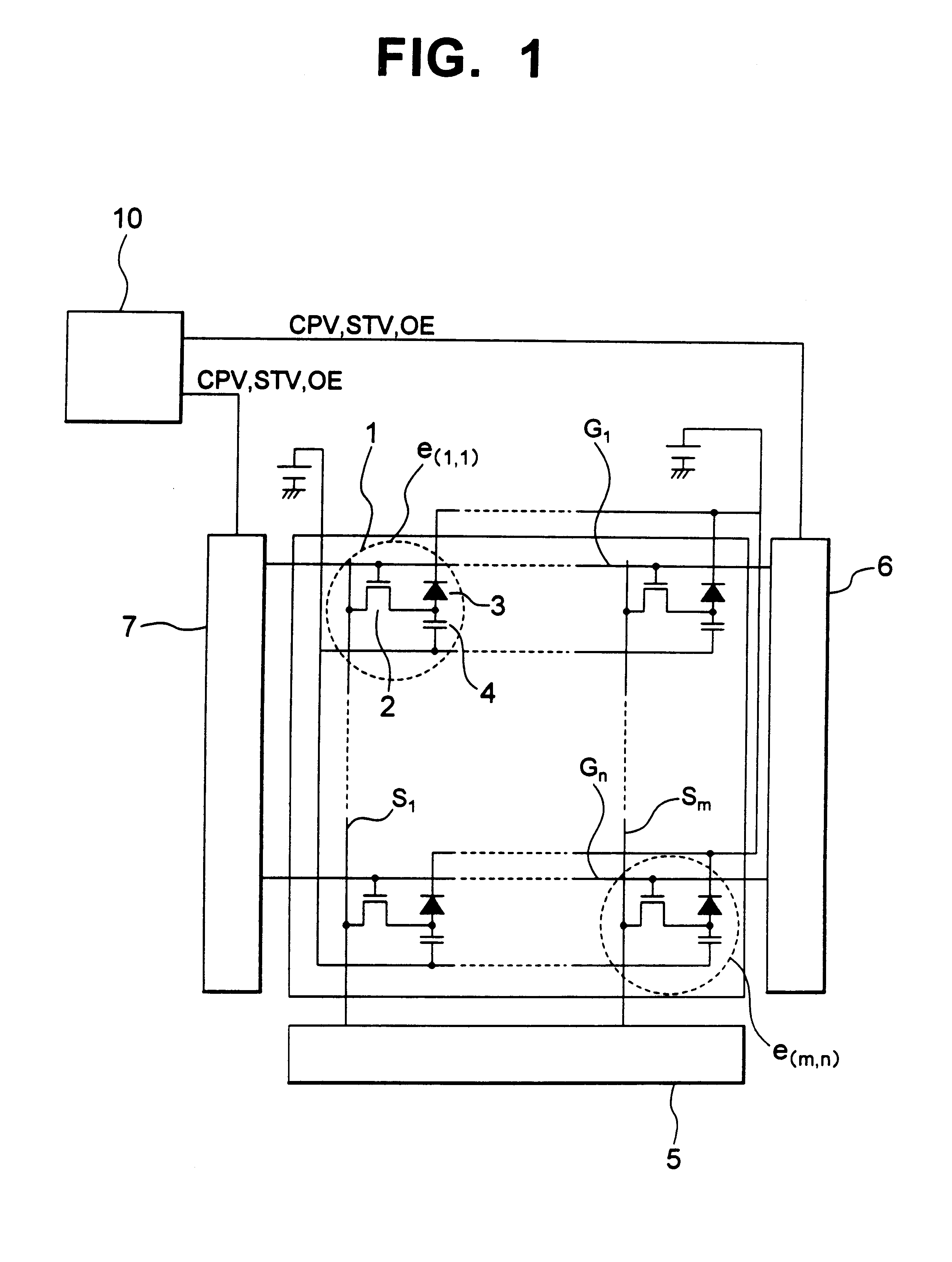
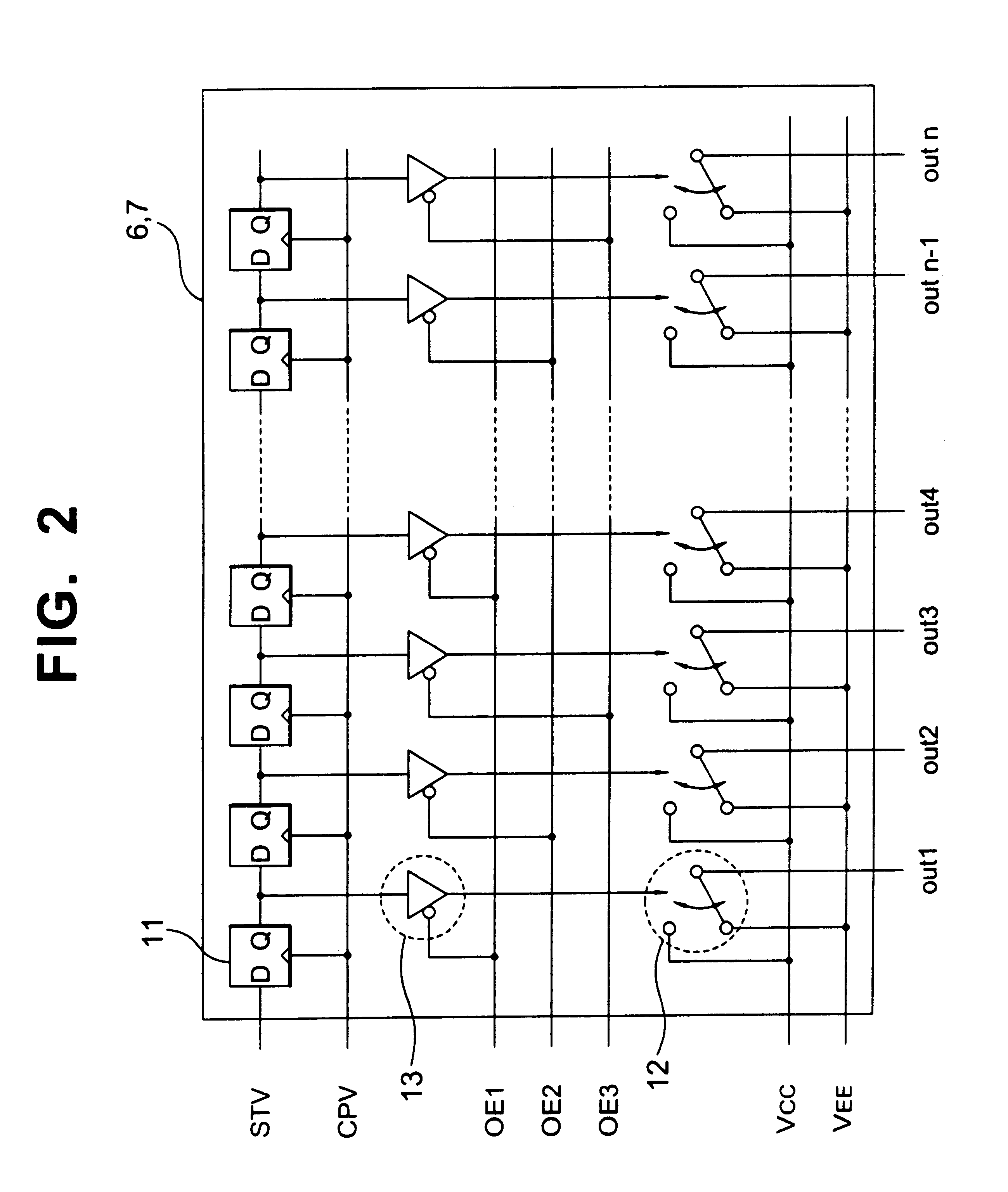
Image detecting device and an X-ray imaging system
An image detecting device has a large dynamic range that deals with a plurality of image detecting modes. The image detecting device is composed of pixels e (i, j) arranged in a matrix array. Each pixel has a photoelectric element. In each pixel, a capacitor 102 and a protecting diode 103 are disposed. The capacitor 102 stores electric charge corresponding to the intensity of penetrated light to the relevant pixel. The protecting diode limits the capacitance. A bias voltage is supplied to the protecting diode 103 through a bias line Bias. The bias voltage is adjusted by a bias voltage controlling system 133 corresponding to the frame rate. Thus, the influence of a leak current in the off-state of the protecting diode 103 can be alleviated against electric charge stored in the capacitor 102. Consequently, an image with a high S / N ratio can be obtained regardless of the frame rate.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
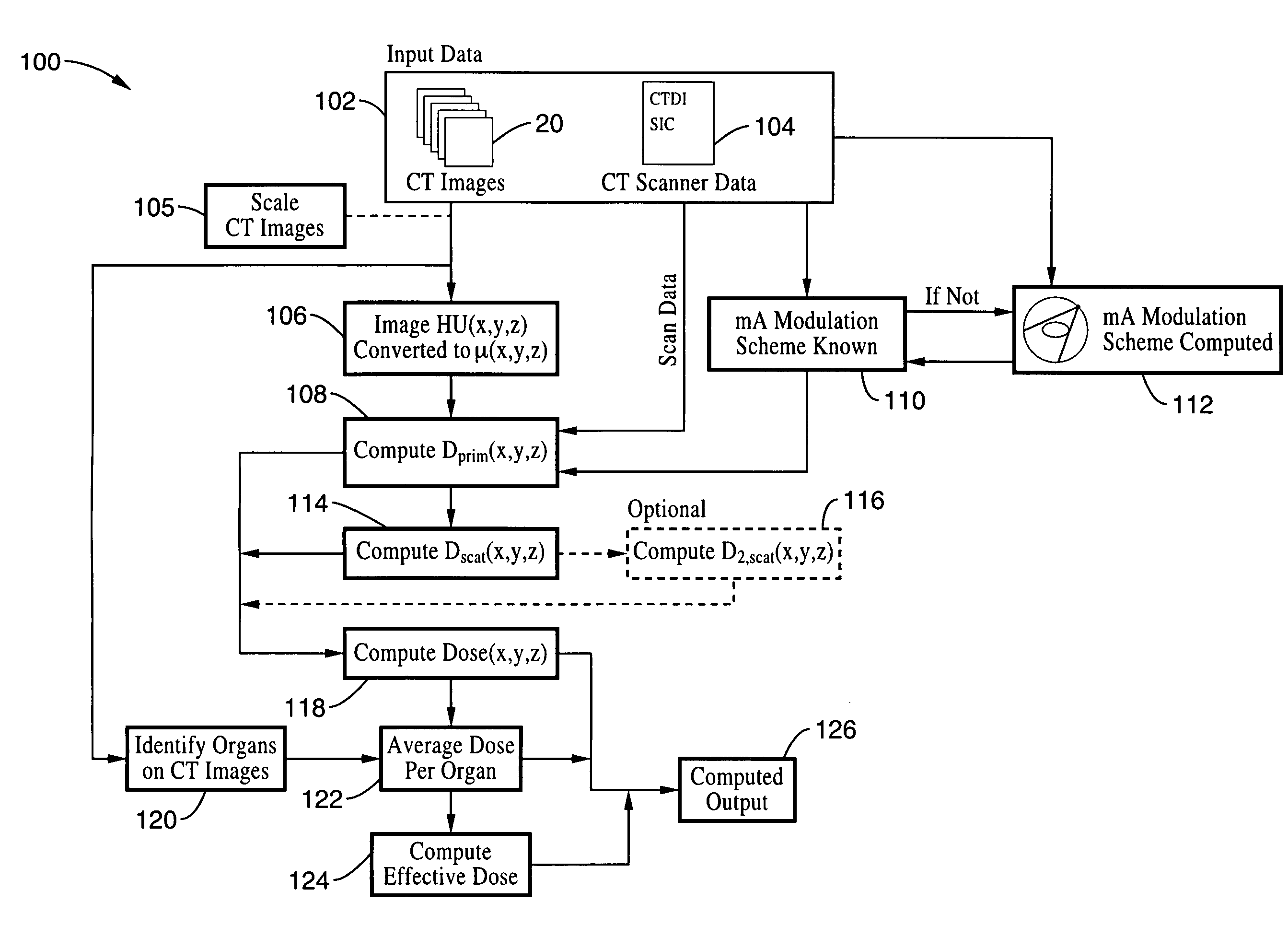
Method for computing patient radiation dose in computed tomography
ActiveUS20080292055A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingComputed tomographyX-ray
A system and method are disclosed for computing a radiation dose delivered to a patient during a computed tomography (CT) scan of the patient. The CT image dataset generated during the scan of the patient, and one or more parameters relating to a x-ray source are used to calculate the radiation dose delivered to the patient as a function of the CT image data set and the one or more parameters of the x-ray source. The radiation dose is generally found by calculating a primary x-ray dose distribution and scattered x-ray dose distribution from the CT image dataset and taking the sum of the primary x-ray dose distribution and scattered x-ray dose distribution.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Functionalized carbon nanotube-polymer composites and interactions with radiation
The present invention involves the interaction of radiation with functionalized carbon nanotubes that have been incorporated into various host materials, particularly polymeric ones. The present invention is directed to chemistries, methods, and apparatuses which exploit this type of radiation interaction, and to the materials which result from such interactions. The present invention is also directed toward the time dependent behavior of functionalized carbon nanotubes in such composite systems.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY +1
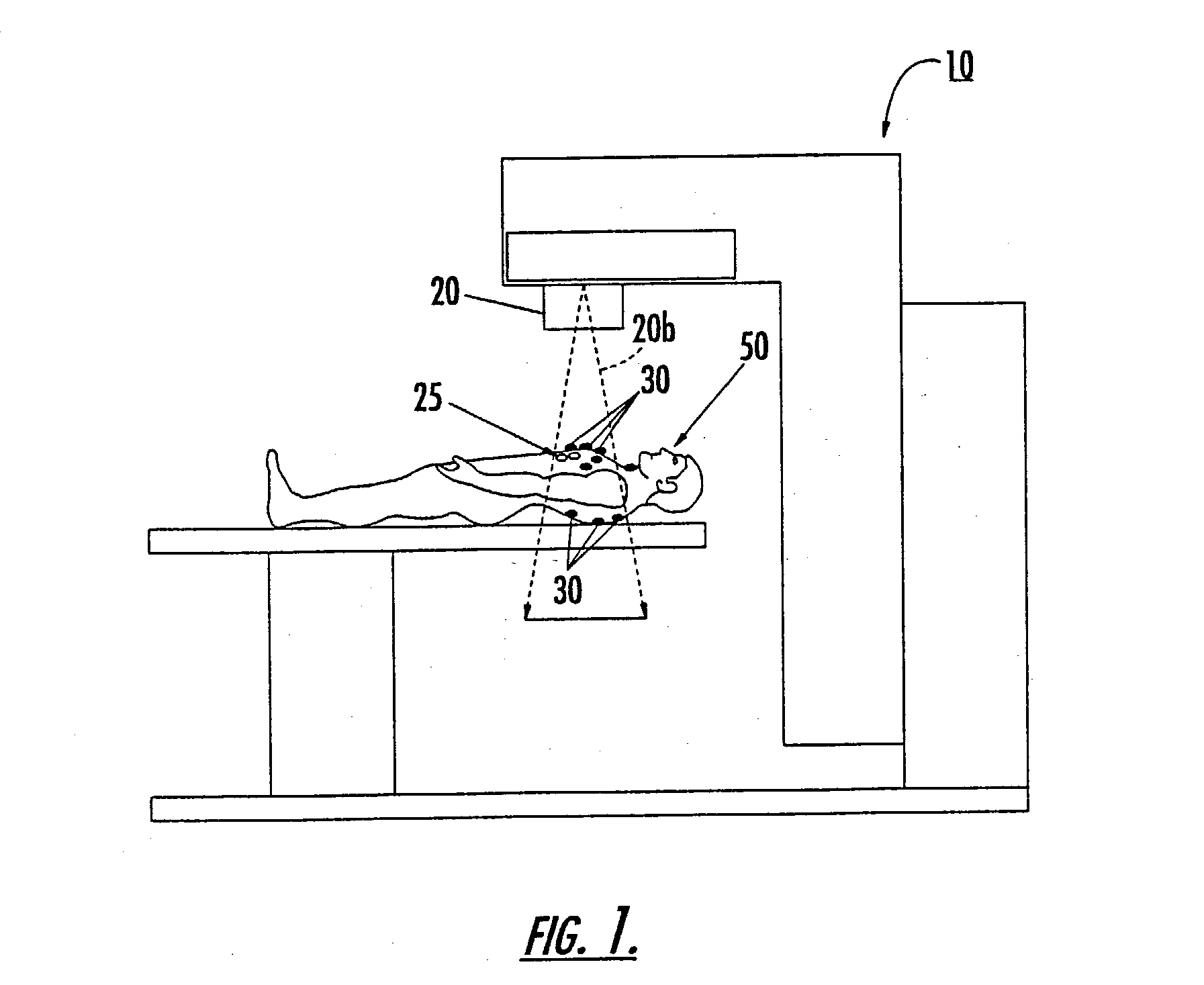
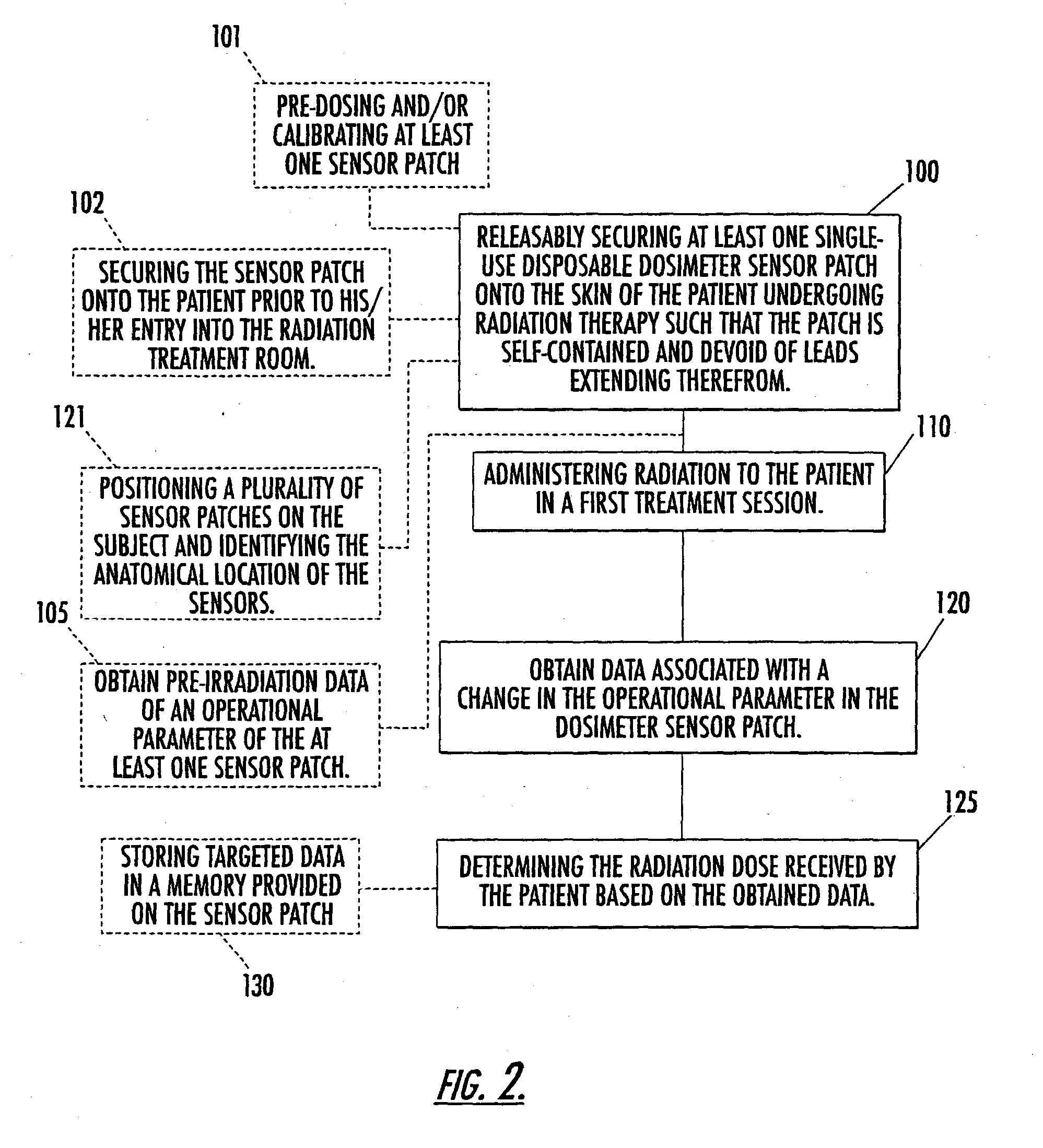
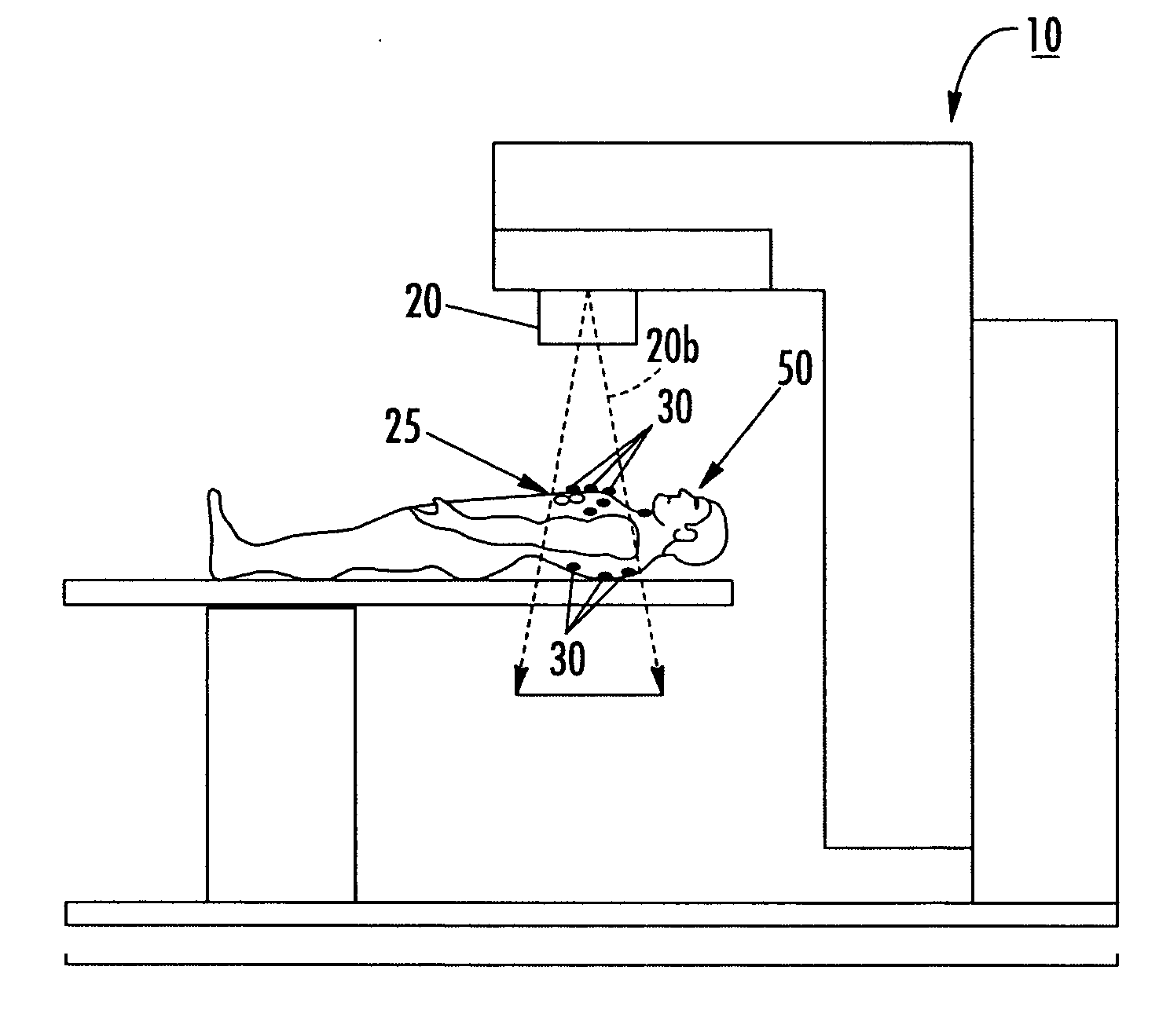
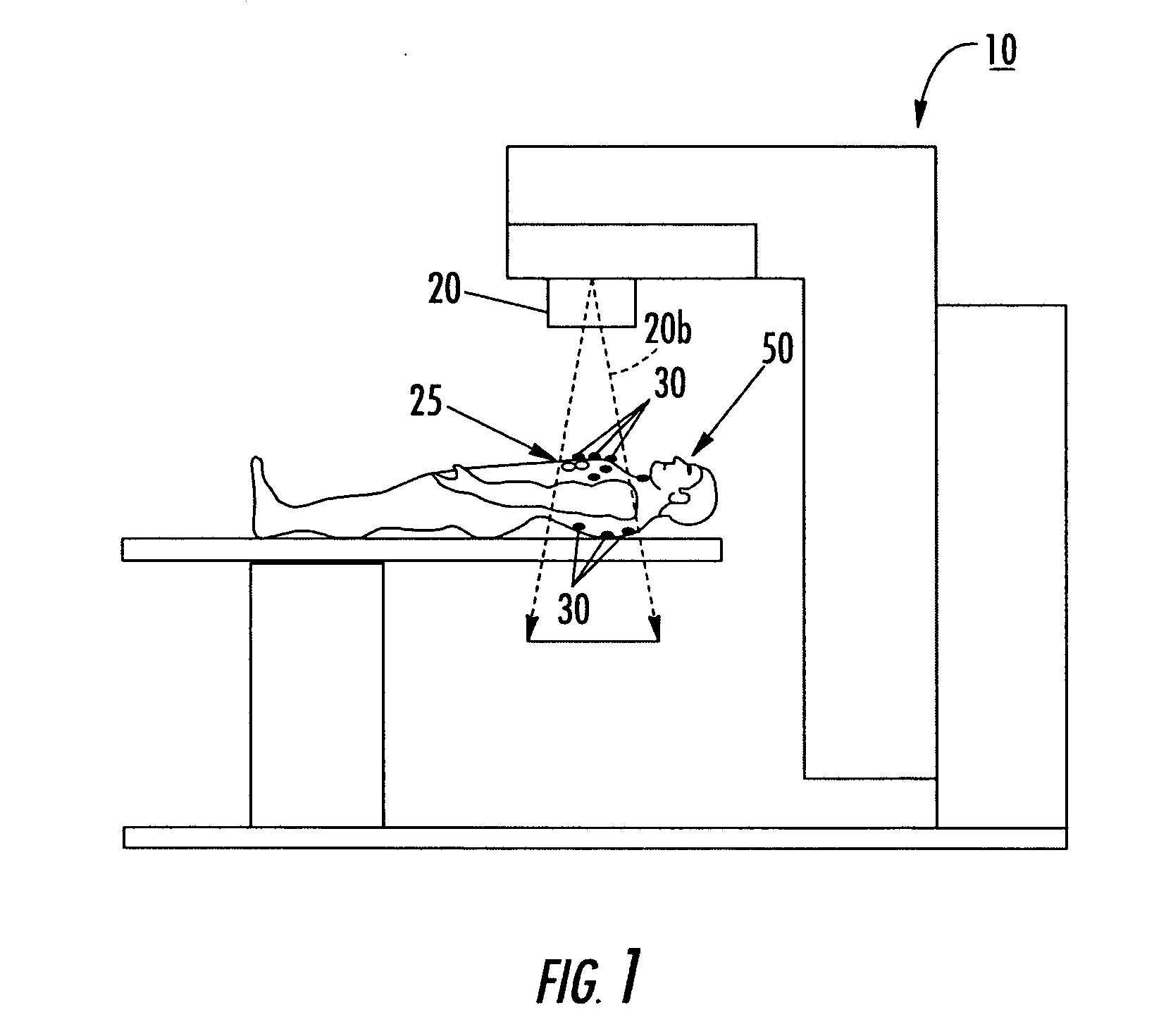
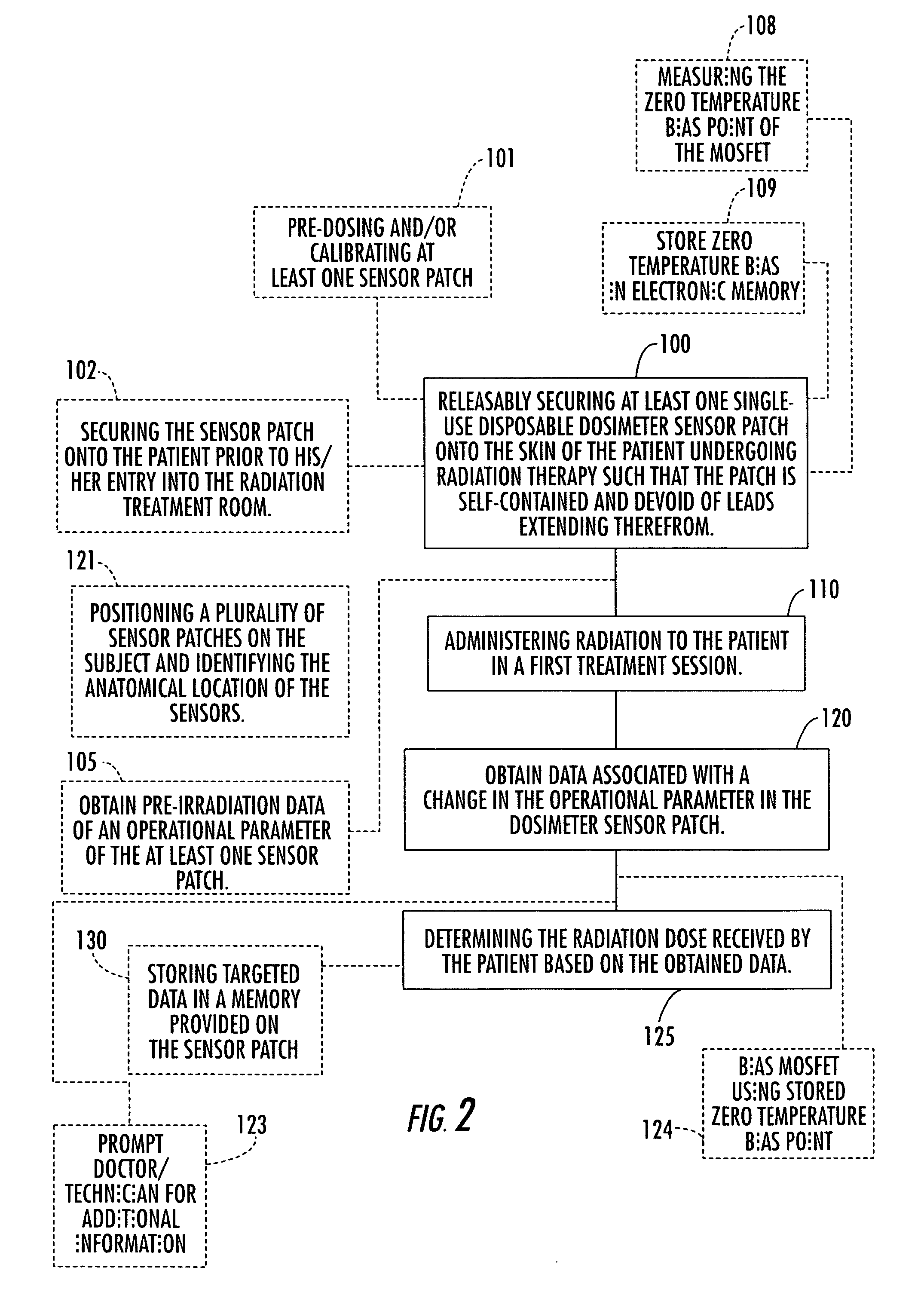
Disposable single-use external dosimeters for use in radiation therapies
ActiveUS20030125616A1Cost-effectiveReduce labor set-up timeDosimetersDiagnostic recording/measuringDosimeterRadiation sensor
Methods, systems, devices, and computer program products include positioning disposable single-use radiation sensor patches that have adhesive means onto the skin of a patient to evaluate the radiation dose delivered during a treatment session. The sensor patches are configured to be minimally obtrusive and operate without the use of externally extending power chords or lead wires.
Owner:VTQ IP HLDG
Device to prevent the risk of overexposure to harmful solar radiation
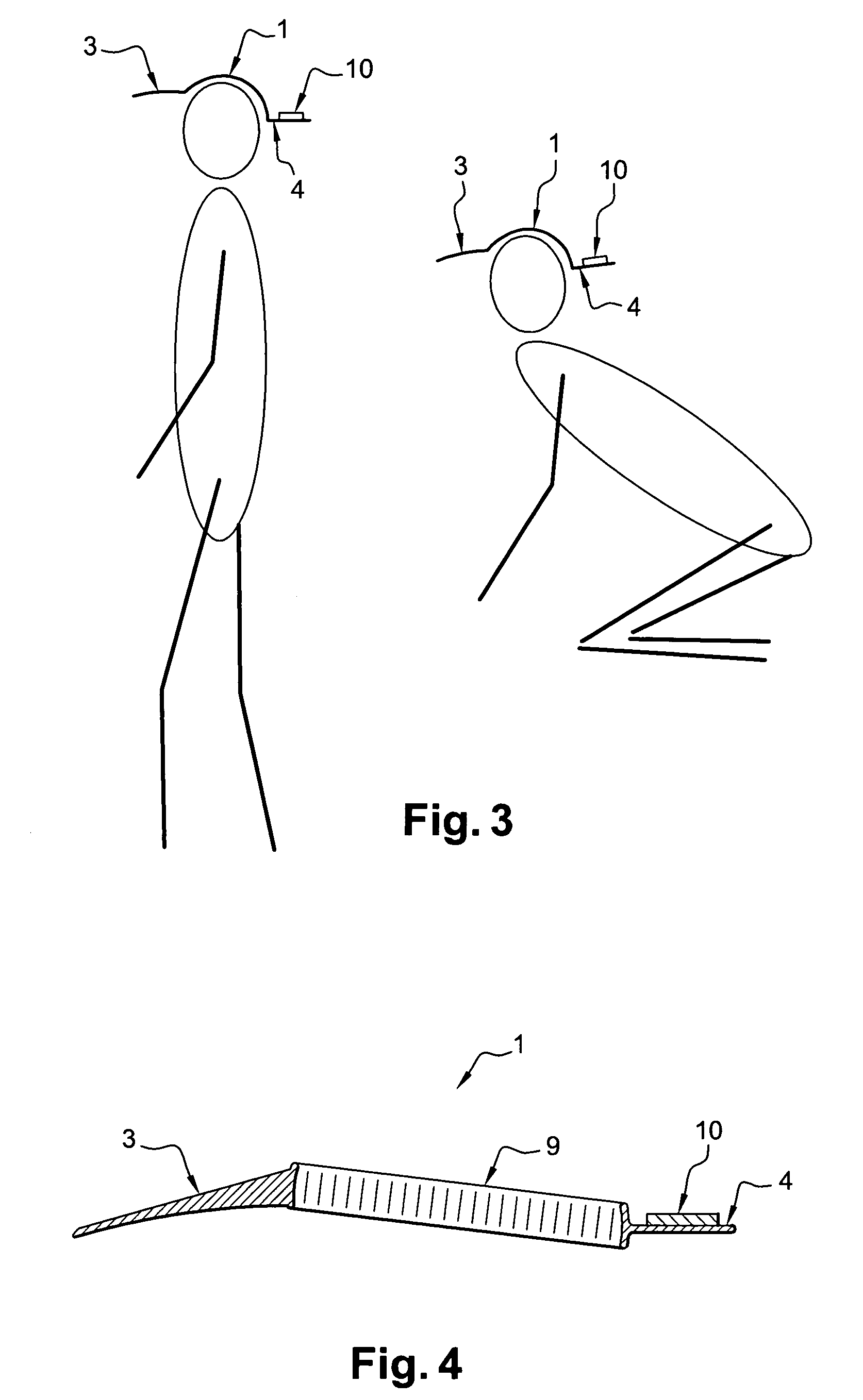
InactiveUS7265358B2Reduce riskReliable informationRadiation pyrometryDosimetersVertical planeEngineering
A device intended to reduce the risks of overexposure to harmful solar radiation. The device includes a detection arrangement, including at least one sensor sensitive to solar radiation, in particular UV. In addition, an arrangement is linked to the detection arrangement to generate a signal representing the quantity of radiation received by the detection means. An attachment arrangement is provided to attach the device to the head of a subject, such that the sensor(s) is (are) oriented in a substantially perpendicular manner to the vertical plane of the subject when the latter is active in the sun. The device is preferably configured in the form of a cap, with the detection arrangement arranged on a first visor intended to be positioned over the back of the individual's neck. The cap also preferably includes a second visor located opposite the first.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Real time radiation monitoring system and portable telepositional radiation dosimeter
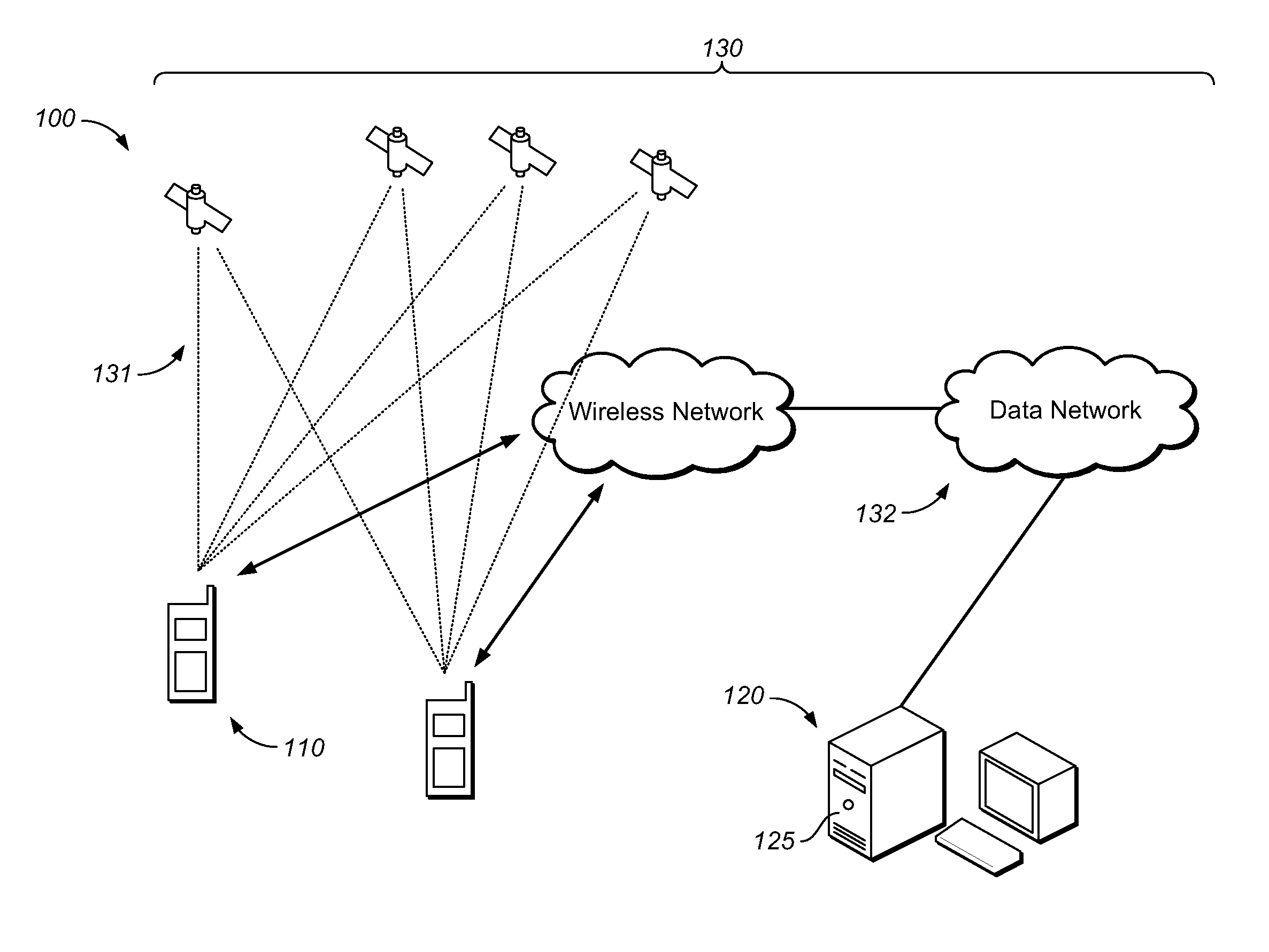
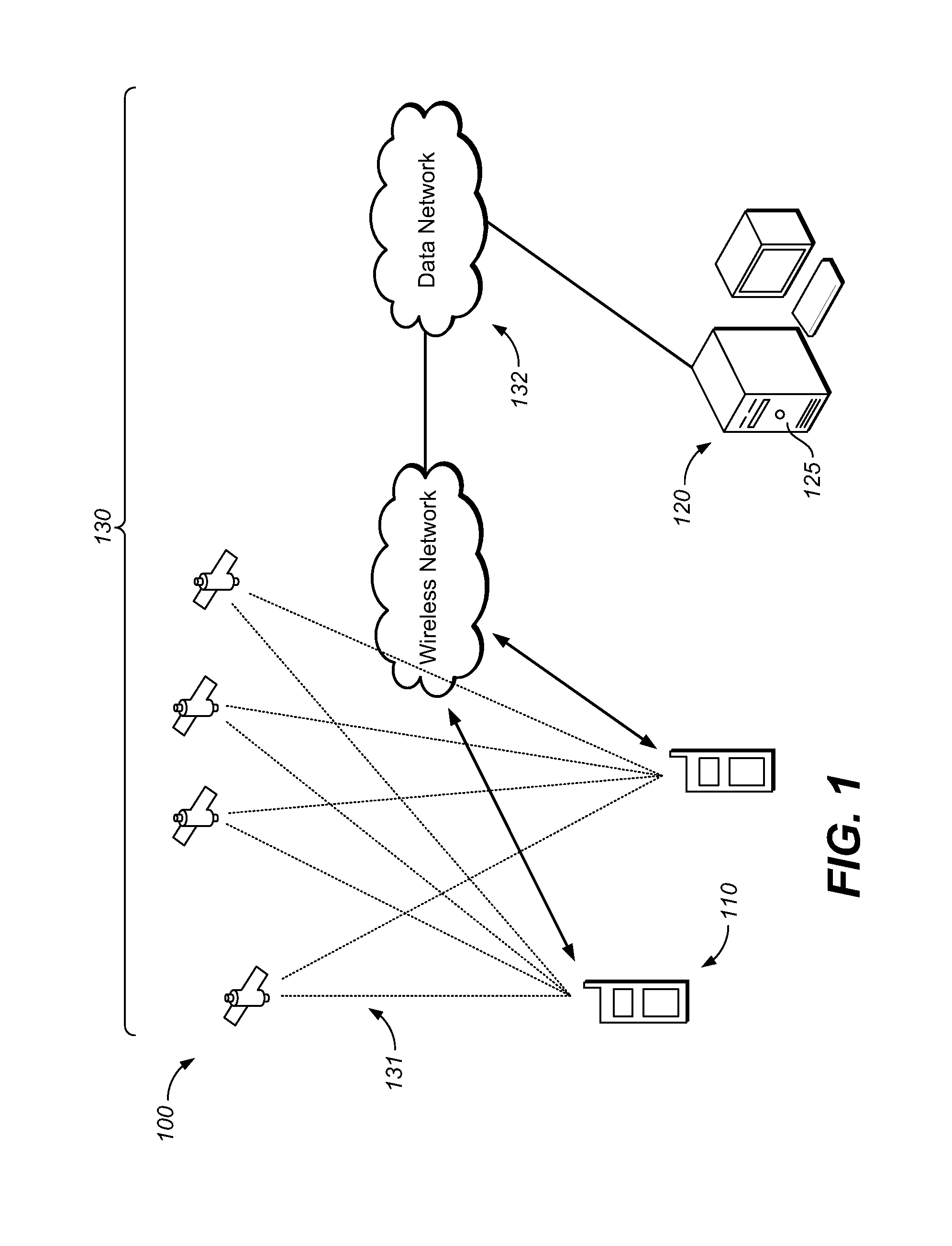
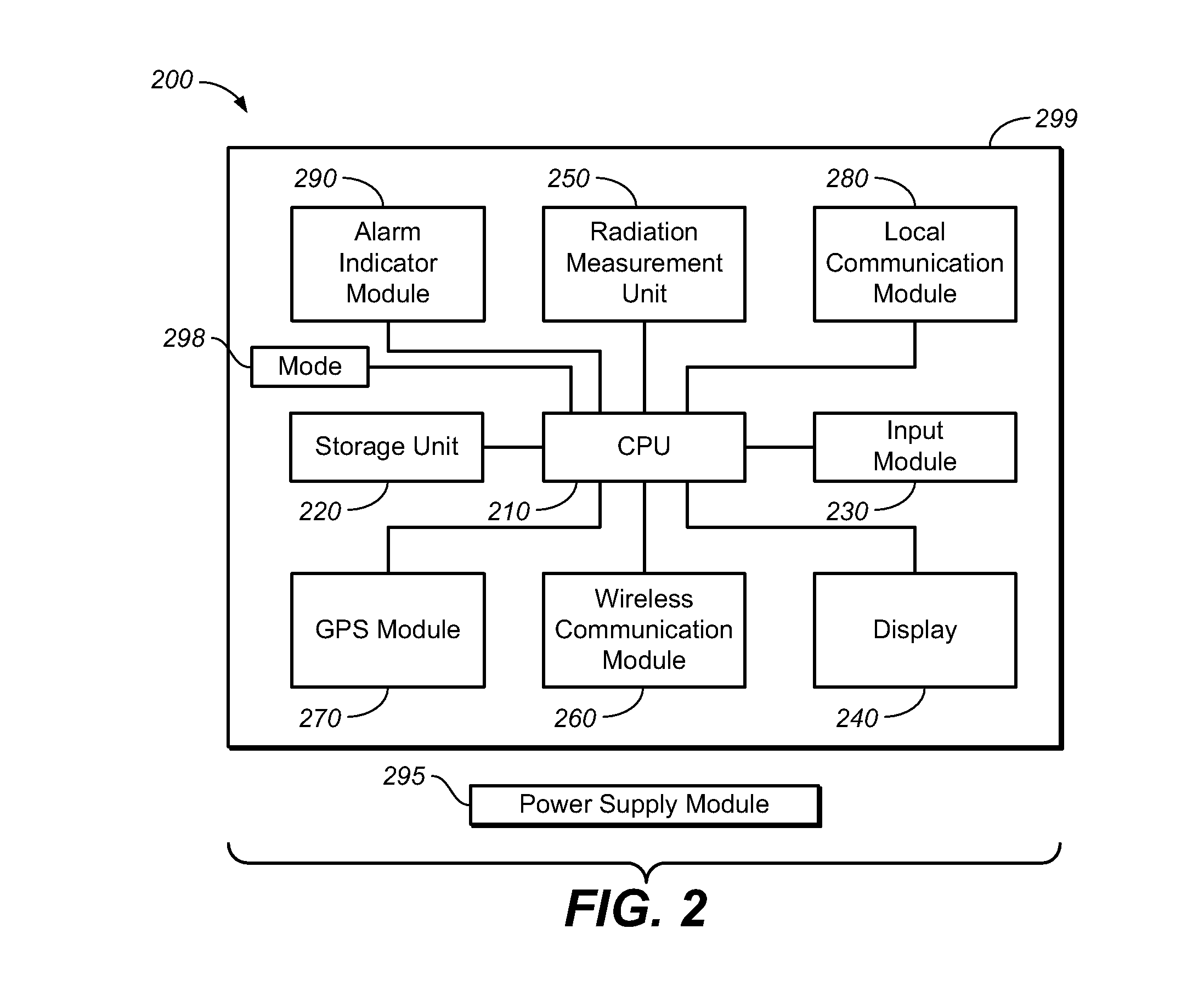
The present invention provides a system, device, computer program product and article for a telepositional dosimeter (TPD) and a radiation measurement system (RMS) having one or more TPDs capable of communicating environmental radiation measurements to a network, database or other data management technology. The present invention combines radiation measurement technology, wireless network and mobile communication technology, software, and related technologies to enable applications in various environments including the areas of environmental protection, homeland security, anti-terrorism, nuclear safety, radiation material handling and safety, and emergency response.
Owner:ZHANG CHONG +1
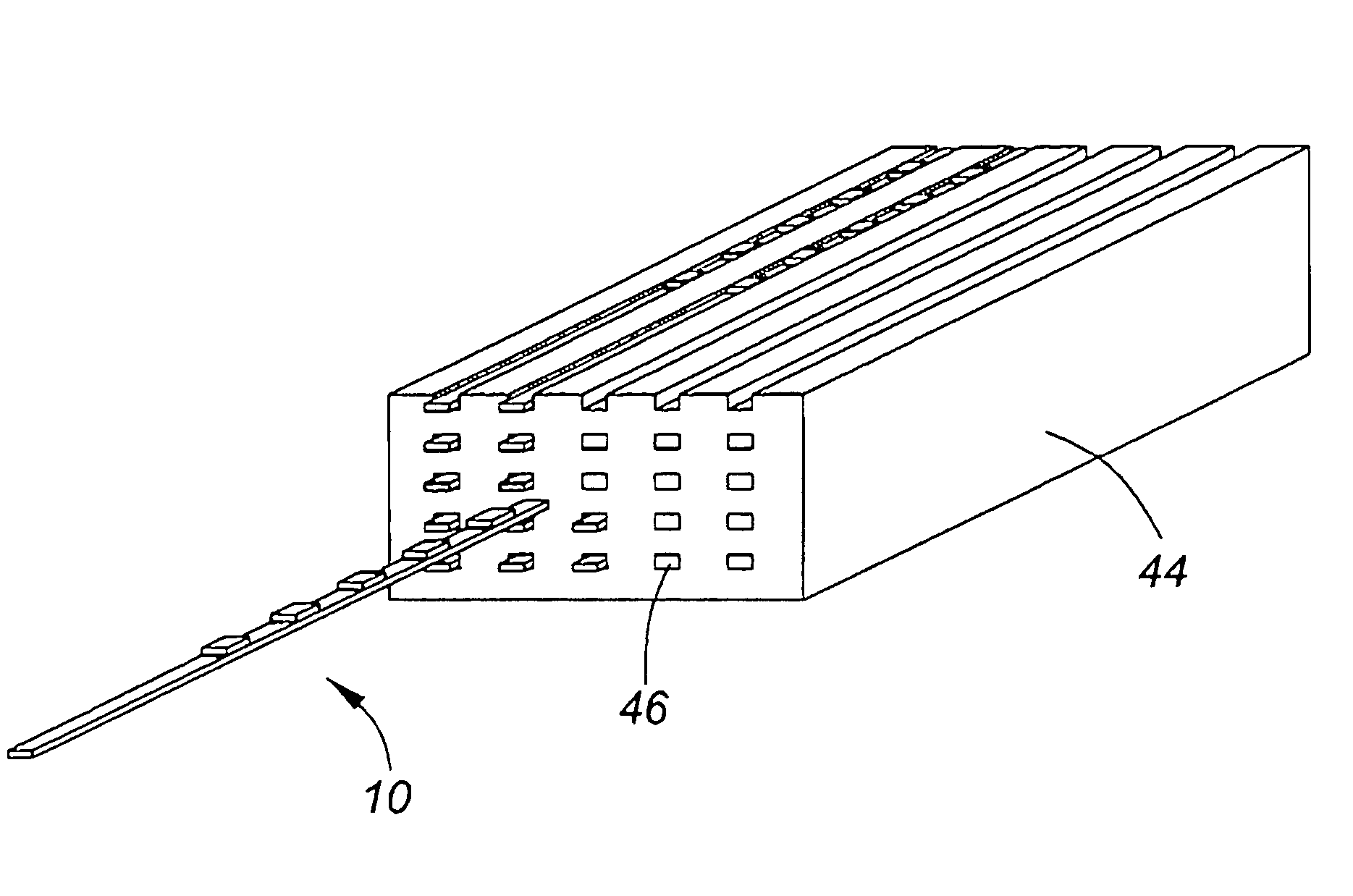
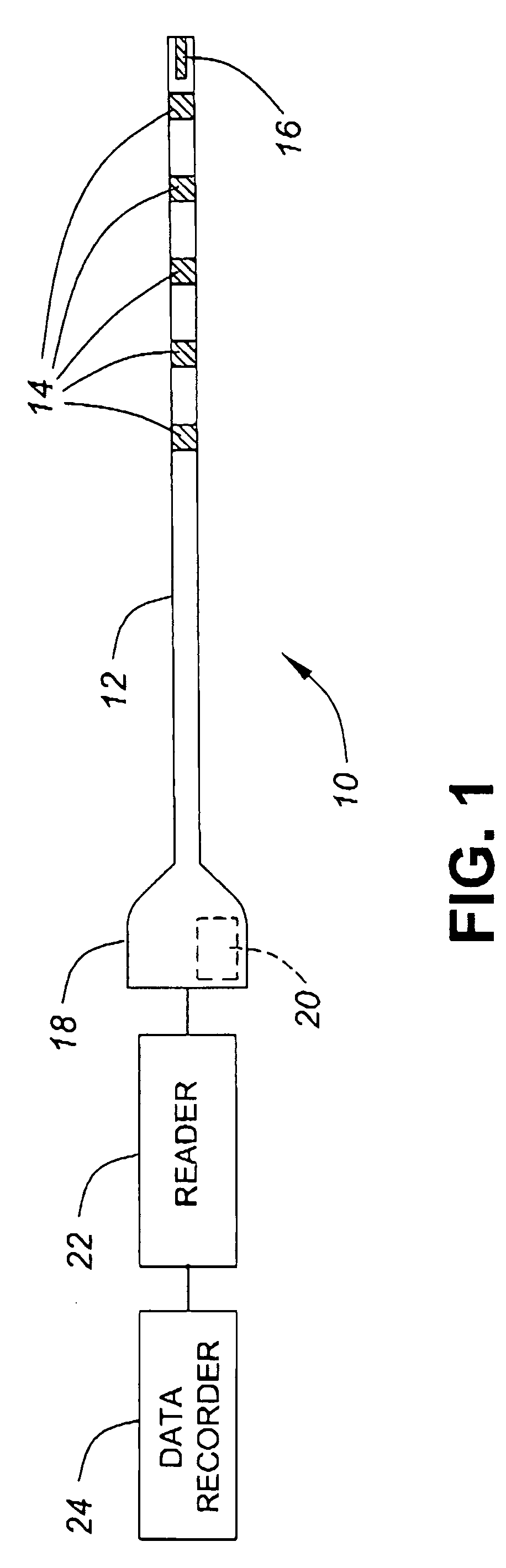
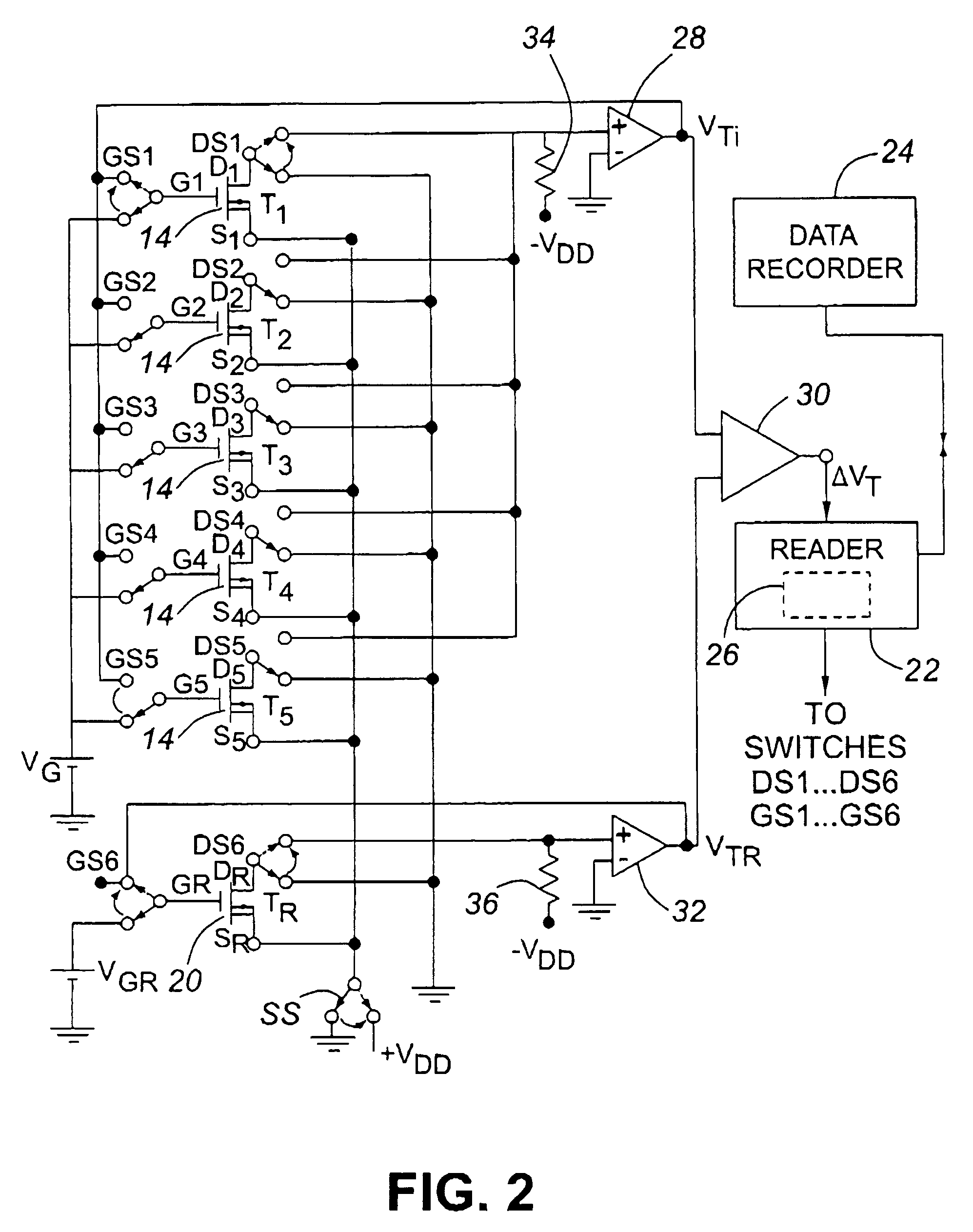
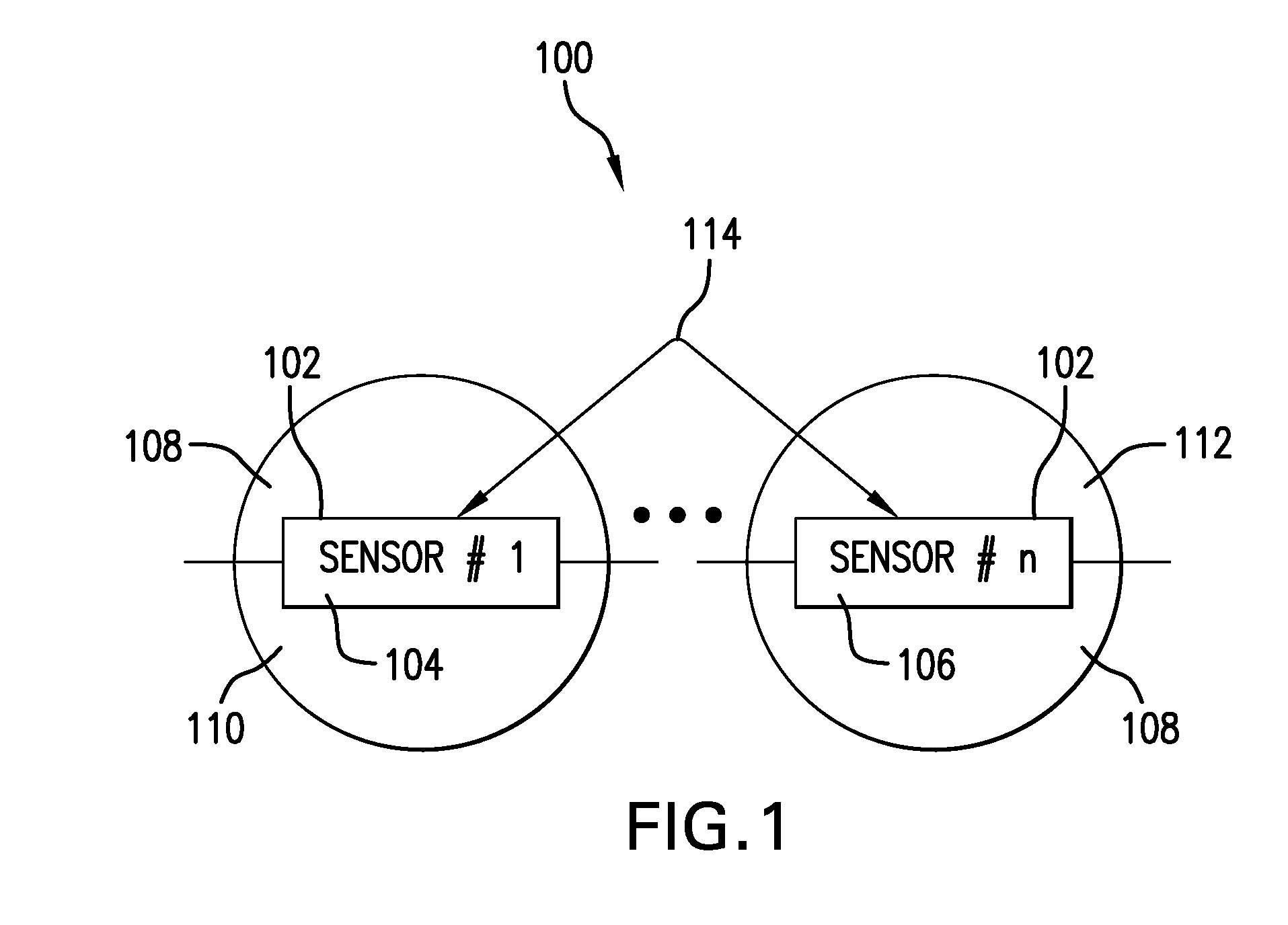
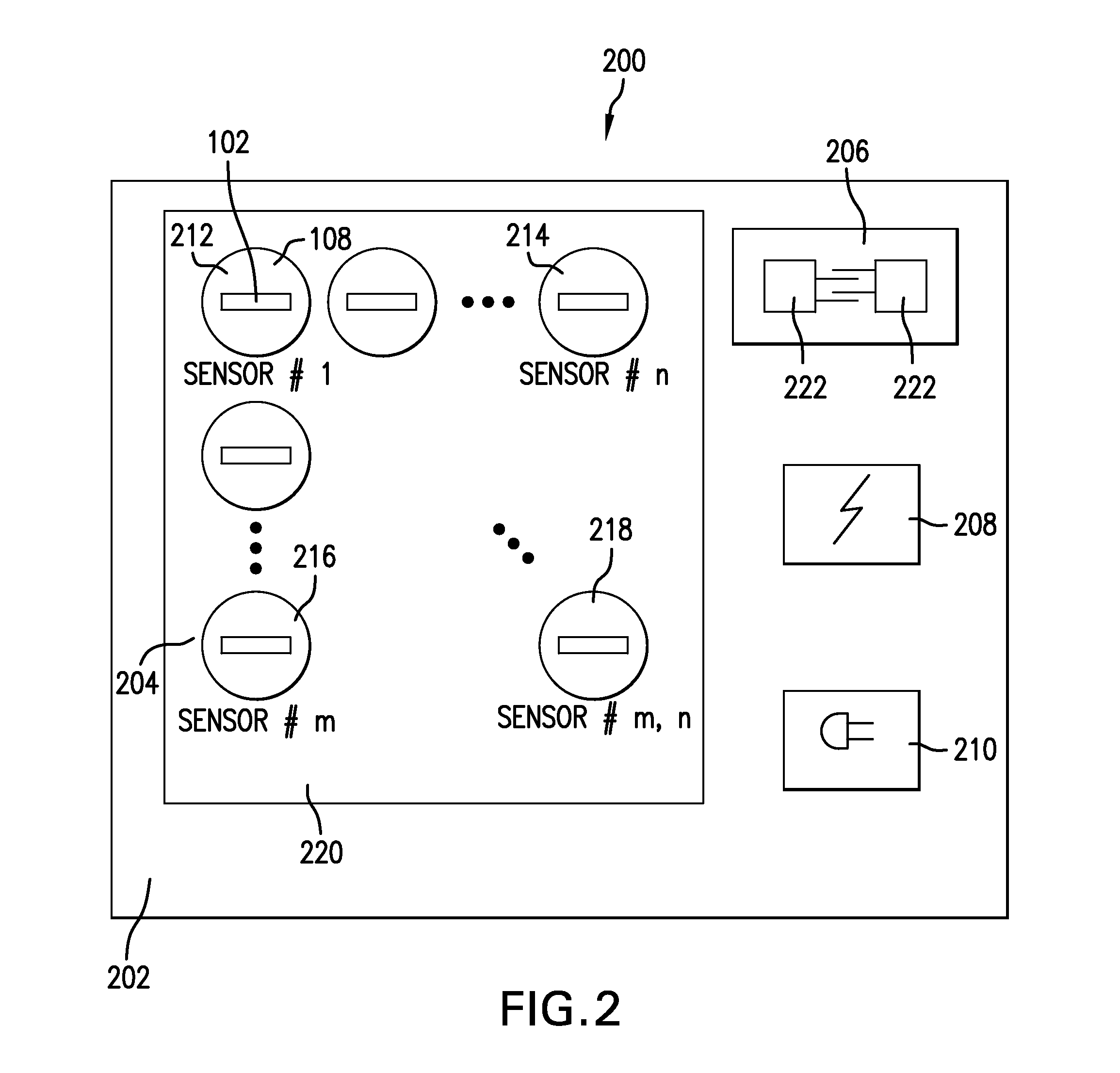
Dosimeter having an array of sensors for measuring ionizing radiation, and dosimetry system and method using such a dosimeter
InactiveUS20060027756A1Limit reduction of width and thicknessEfficient measurementDosimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansSensor arrayElectrical conductor
In a dosimeter for measuring levels of ionizing radiation, for example during radiotherapy, a plurality of radiation sensors, such as insulated gate field effect transistors (IGFETs), are spaced apart at predetermined intervals on a support, for example a flexible printed circuit strip, and connected to a connector which can be coupled to a reader for reading the sensors. The sensors may each be connected to a reference device, which may also be an insulated gate field effect transistor, and the absorbed radiation dose may be determined by measuring, before and after the irradiation, the difference between the threshold voltages of the individual sensors and the threshold voltage reference device. Corresponding terminals of the sensors may be connected to the connector by a single conductor, thereby reducing the number of conductors required.
Owner:BEST THERATRONICS +1
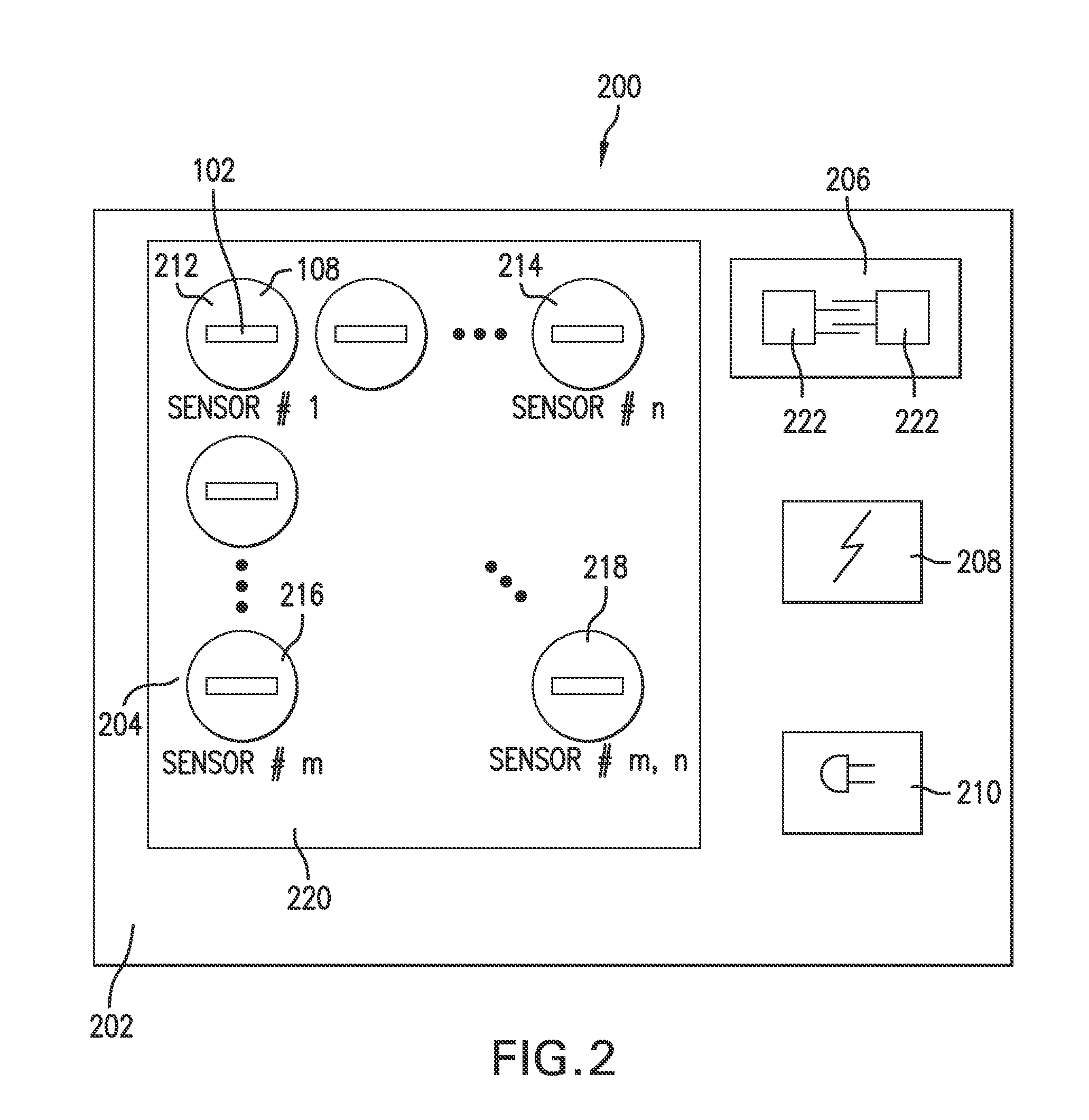
System and method for wireless, motion and position-sensing, integrating radiation sensor for occupational and environmental dosimetry
Described is a radiation dose calculation algorithm based upon the output of a radiation dosimeter including multiple sensor devices (including one or more passive integrating radiation sensors and optionally, a MEMS accelerometers, a wireless transmitters a GPS, a thermistor, or other chemical, biological or EMF sensors). The algorithm is used to convert the sensor output into dose values used to assess the exposure of personnel to ionizing radiation. Sensor output patterns are matched to stored empirically generated sensor outputs thru weighting and optimization calculation processes to determine personnel doses. Algorithm outputs can include personal dose equivalents, radiation types, radiation energy and radiation source identification. Dose calculations can be optimized for specific applications, and matched to different sets of measured data without changing the underlining software calculation programs.
Owner:LANDAUER INC
Low cost digital pocket dosemeter
The invention relates to a pocket type digital radiation dosemeter comprising of a detector, which converts the ionisation in the detector caused by the incidence of ionising radiation of certain energy range into electrical impulses, a low power pulse amplifier, that amplifies the electrical pulses from the detector to detectable amplitudes, a discriminator circuit, that is used to reject pulses of origin other than those caused by the ionising radiation, a programmable divider circuit for calibrating the dosemeter, an electronic counting circuit and a six digit LCD display. The sensitivity of the dosemeter is 1 count per μSv (micro Sievert) and the accuracy is within ±15% from 60 keV to 1.25 Mev of X or Gamma radiation. A metallic energy compensation filter and a discriminator threshold modulation circuit are used to provide uniform response within ±15% from 60 KeV to 1.25 MeV. The Digital display indicates at any instant the total X or Gamma radiation dose, in μSv, received by the dosemeter since the time at which the dosemeter was switched on. The dosemeter is designed for very low power consumption and is powered by two coin type Li batteries (Type CR2320). It is capable of over 500 hours of continuous operation before having to replace the batteries. A blinking LED indicates low battery condition when 8 hours of battery life is still left. The entire circuitry and the battery holder are mounted on a single printed circuit board. Surface mount components are used to make the unit compact. The dosemeter is compact (110 mm L×30 mm W×14 mm H excluding Clip) and light in weight (60 gm).
Owner:DEPT OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Radioactive source on-line monitoring system based on Internet of Things technology
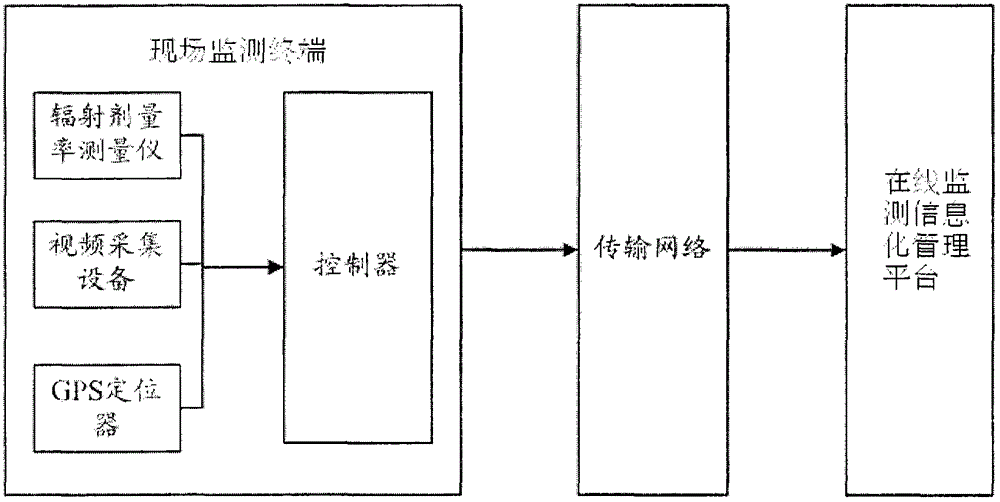
ActiveCN104808237AComprehensive monitoringImprove monitoring efficiencyDosimetersInformatizationMeasuring instrument
The invention provides a radioactive source on-line monitoring system based on an Internet of Things technology. The radioactive source on-line monitoring system comprises RF (radio frequency) cards, field monitoring terminals, a transmission network and an on-line monitoring informatization management platform, wherein the RF card is fixedly arranged in each monitoring site with a preset distance from a radiation source, unique identity information of a radiation source, approved geographical position information and the standard radiation dose rate are stored in the RF cards, each field monitoring terminal is arranged in the corresponding monitoring site, and comprises an RF card reader-writer, a radiation dose rate measuring instrument, video collecting equipment, a GPS (global positioning system) positioning device, a controller, an in-site warning device, a communication interface and a power supplying power supply, and the processor is respectively connected with the RF card reader-writer, the radiation dose rate measuring instrument, the video collecting equipment, the GPS positioning device, the field warning device, the communication interface and the power supplying power supply. The radioactive source on-line monitoring system has the advantages that the radiation source can be comprehensively monitored, then, through a communication network, the monitoring information can be remotely obtained in time, and the monitoring efficiency is effectively improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SOS TECH
Evaluation of irradiated foods and other items with telemetric dosimeters and associated methods
InactiveUS20020040968A1Cost-effectiveSimple methodThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsDosimeterIrradiation
Methods for quantifying the irradiation dose received by an item or items, such as food items and medical items, undergoing irradiation-based sterilization, includes the steps of monitoring a selected electronic parameter associated with an economic single use sensor positioned adjacent the item or items and telemetrically relaying data associated with the monitored electronic parameter to a computer. The computer includes a computer program which is configured to determine the radiation dose received by the item or items by correlating the value of the monitored electronic parameter to a corresponding amount of radiation associated with the value. Related sensors and systems are also described.
Owner:VTQ IP HLDG
High resolution proton beam monitor
InactiveUS7515681B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingProtonLight beam
A method and apparatus for monitoring a scanning beam of penetrating radiation, such as a scanning proton beam used to irradiate tissue. The position of the beam is tracked in real time by interposing a scintillator film between a source and an object of irradiation. An imaging detector, in optical communication with the scintillator, provides an output that is indicative of the position of the radiation and its variation with time. The accumulated dose over a scan may also be monitored.
Owner:LEXITEK
Disposable single-use internal dosimeters for detecting radiation in medical procedures/therapies
Methods, systems, devices, and computer program products include positioning single-use radiation internal dosimeters with MOSFETs into a patient to evaluate the radiation dose delivered during a medical procedure or treatment session. The MOSFETs can be unpowered during irradiation.
Owner:VTQ IP HLDG
Functionalized carbon nanotube-polymer composites and interactions with radiation
The present invention involves the interaction of radiation with functionalized carbon nanotubes that have been incorporated into various host materials, particularly polymeric ones. The present invention is directed to chemistries, methods, and apparatuses which exploit this type of radiation interaction, and to the materials which result from such interactions. The present invention is also directed toward the time dependent behavior of functionalized carbon nanotubes in such composite systems.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY +1
Method and apparatus for validation of sterilization process
InactiveUS20050135965A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDosimeterEngineering
An apparatus, system and method for verifying the achievement of a desired sterility assurance level (SAL) for components manipulated within a low-energy electron beam sterilization chamber. The components are preferably pre-sterilized and connected together in an assembly fashion which creates and maintains the sterility of the connection by subjecting the components to low-energy (less than 300 KeV) electron beam radiation. The verification is completed by measuring the sterilization dose delivered to a sensor, also known as a dosimeter, positioned within the sterilization process to simulate the components.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC
Dosimetry device for charged particle radiation
ActiveUS8044364B2Low costElectric discharge tubesDosimetersAudio power amplifierSignal processing circuits
A dosimetry device for charged particle radiation that can be exclusive of cables and connectors between substrates is provided. A plurality of first electrodes are formed on one surface of a printed circuit board, a second electrode substrate having a second electrode opposing each of the plurality of first electrodes through an ionized space is provided, and a signal processing circuit is provided on the other surface opposing the surface of the printed circuit board. The signal processing circuit includes at least one amplifying circuit, a plurality of integrating capacitors corresponding to the amplifying circuit for integrating charge at each corresponding one of the first electrodes, and at least one selector switch that switchably connects each of the integrating capacitors to the amplifying circuit. The printed circuit board may be a multi-layer printed circuit board.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method and apparatus for tissue equivalent solid state microdosimetry
ActiveUS8421022B2Little noiseReduce errorsX-ray/infra-red processesDosimetersSemiconductor detectorP–n junction
A microdosimeter, comprising an array of three-dimensional p-n junction semiconductor detectors, each providing a sensitive volume-target and a tissue equivalent medium for generating secondary charged particles. The array is manufactured from a semiconductor on insulator wafer and the detectors are located to detect secondary charged particles generated in the tissue equivalent medium.
Owner:UNIV OF WOLLONGONG
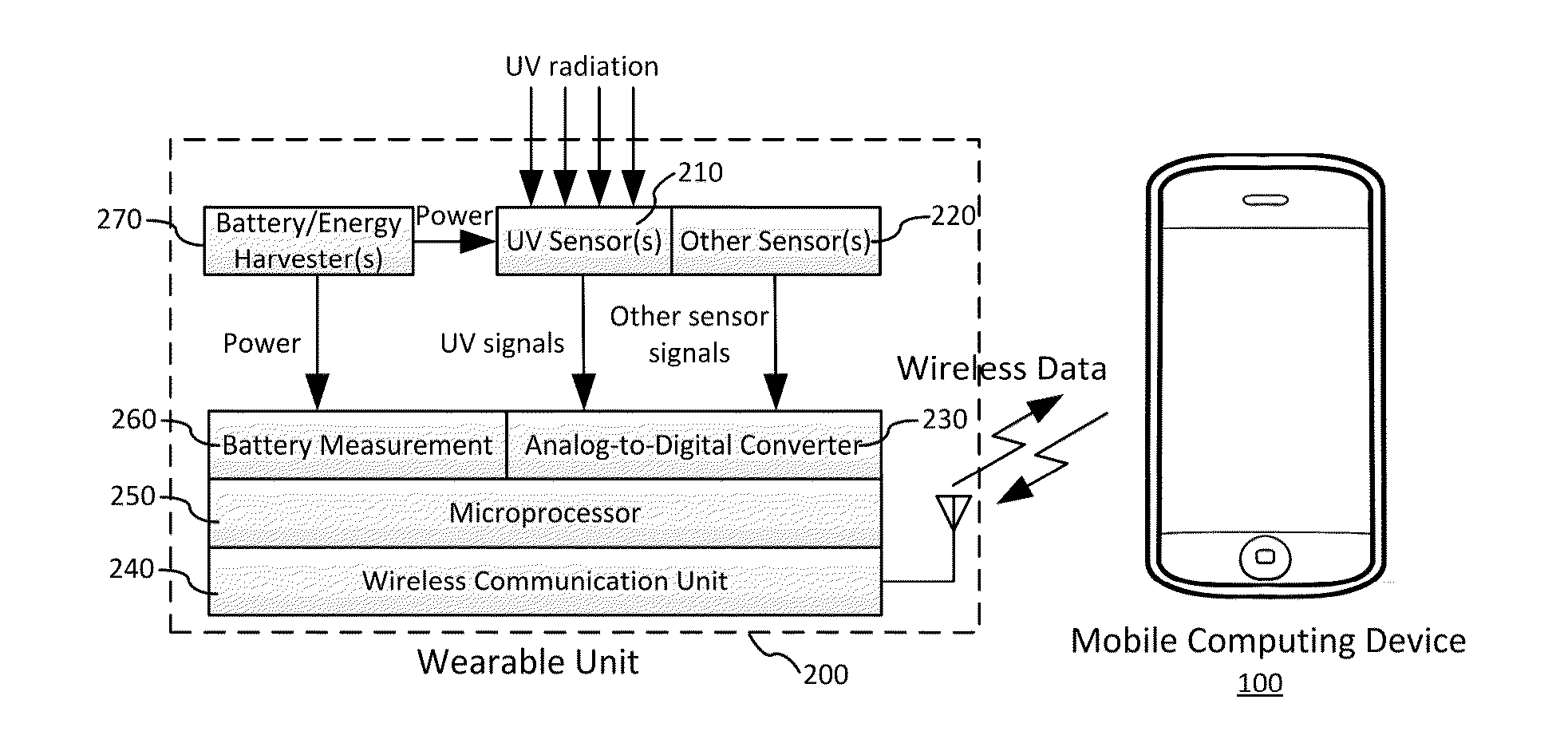
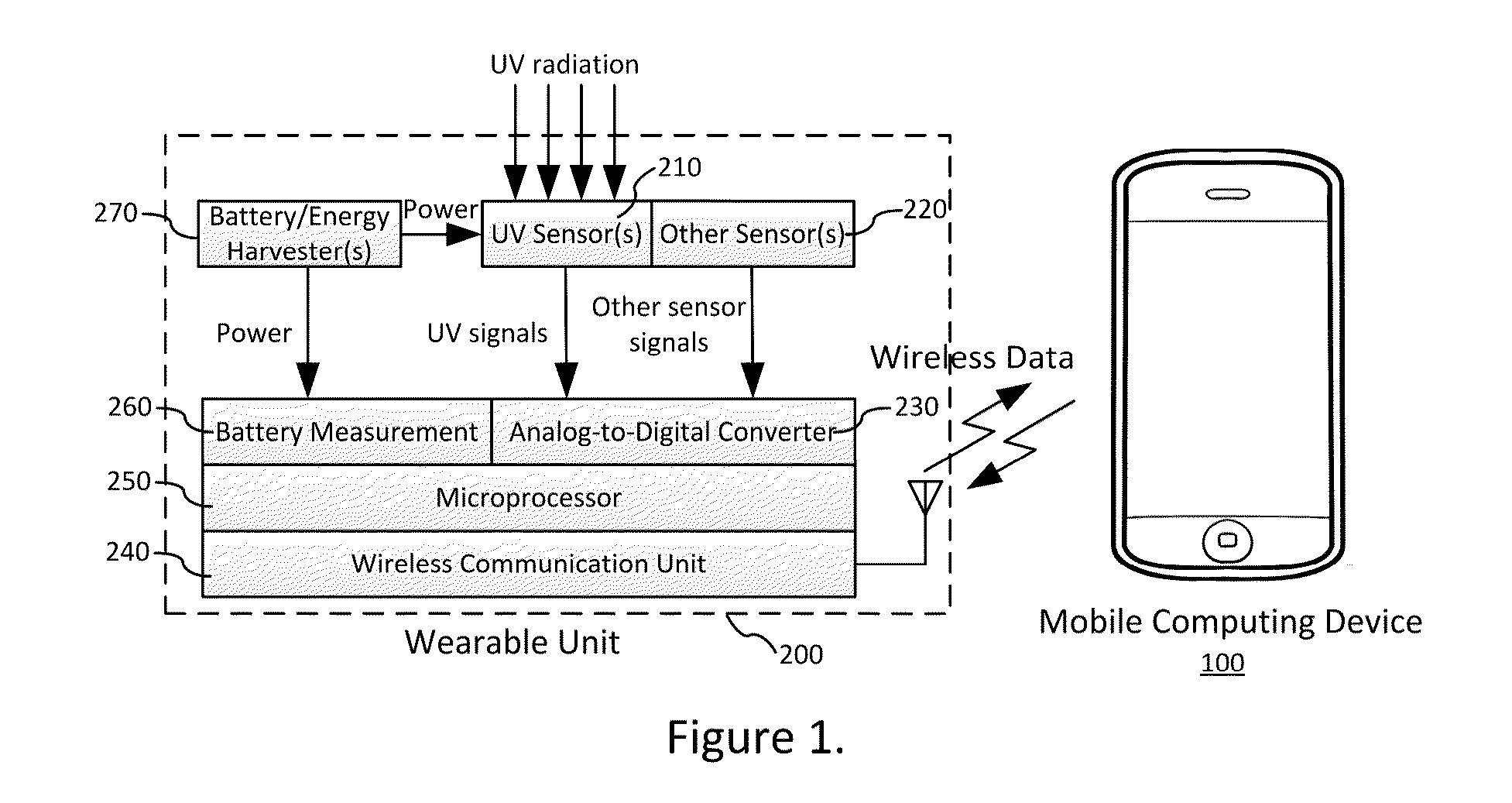
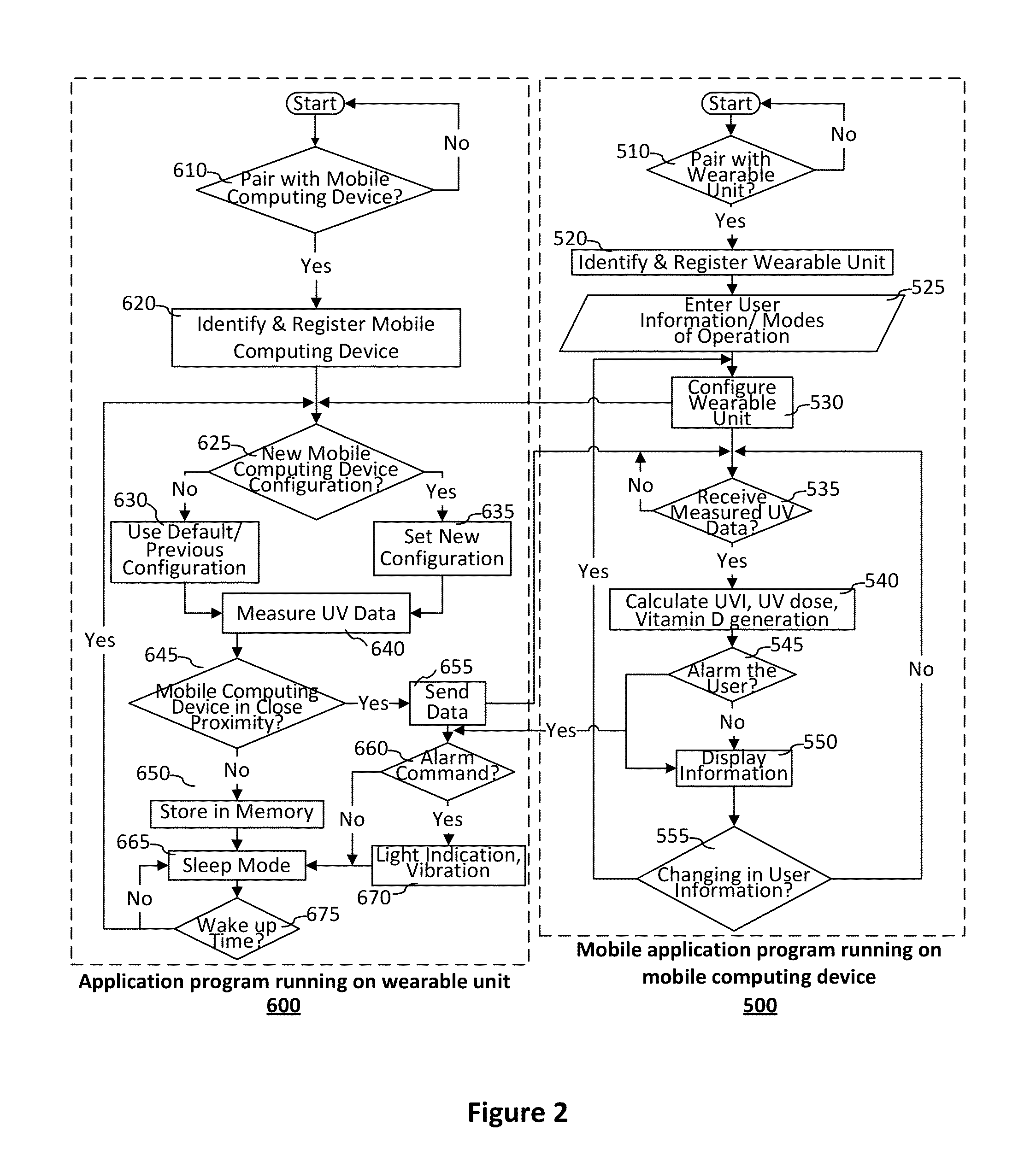
UV dosimetry system with sensor data correction
ActiveUS20150177063A1Accurate estimateAvoid skin damageDosimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansUltravioletTime integral
A UV exposure dosimetry system includes at least one UV sensor that accurately measures the UV irradiance intensity. The system can generate extrapolated UV intensity data based on measured UV intensity data to correct unreliable UV measurement due to inconsistent irradiation of UV light. The UV dosimetry system integrates the extrapolated UV intensity data over time to calculate the real-time UV dosage and the vitamin D production by taking into account factors comprising UV sensor location, body surface area, clothing coverage, and sunscreen usage. Based on the measurement, the system can predict the time remaining to skin burn and the time remaining to reach daily goal of vitamin D production. The UV dosimetry system supports multi-user control through an advanced and user friendly input and output interface.
Owner:ULTRA
Miniaturized, low power fgmosfet radiation sensor and wireless dosimeter system
ActiveUS20100096556A1Reduce capacitanceHigh sensitivityDosimetersSolid-state devicesCapacitanceMOSFET
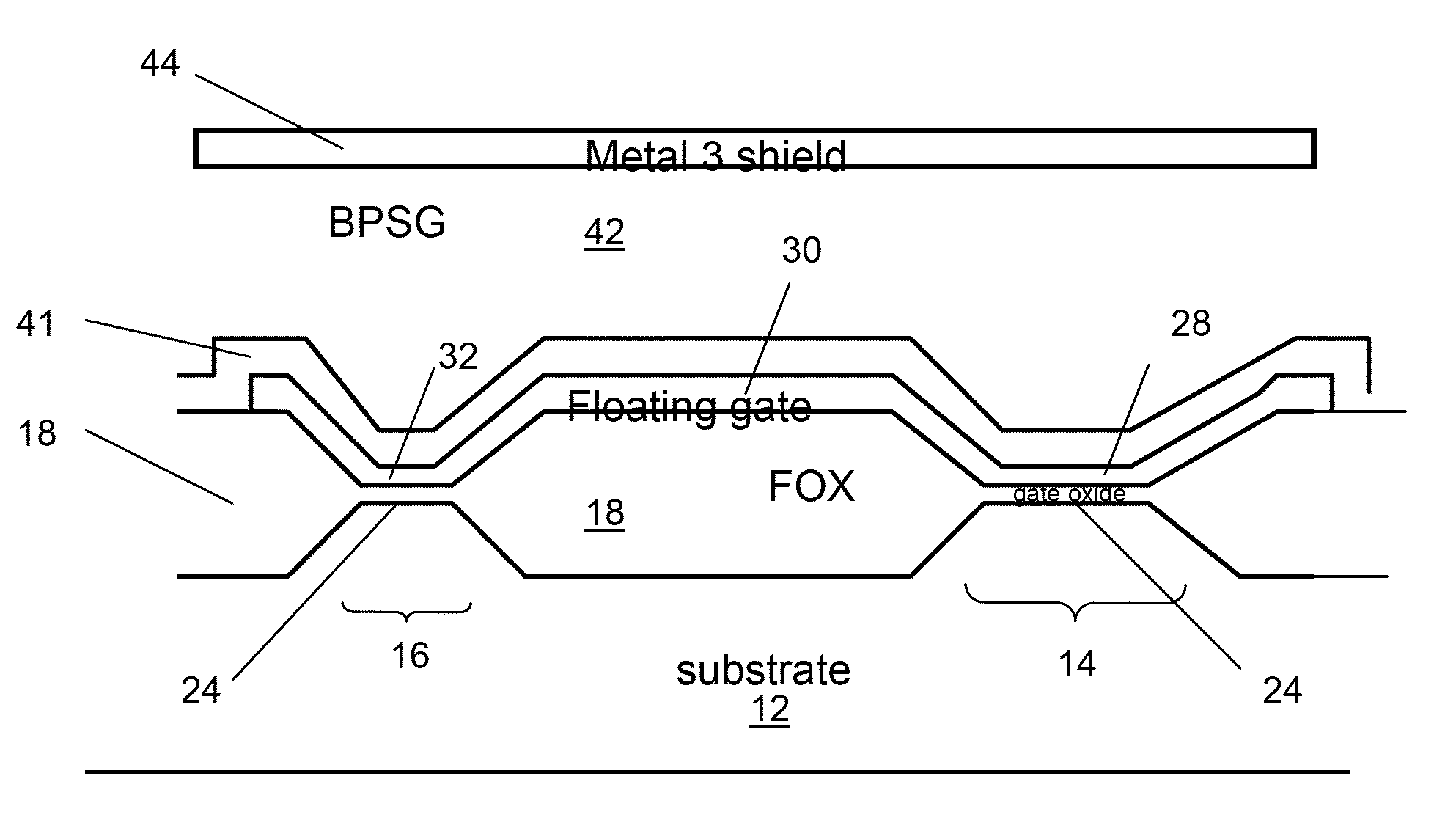
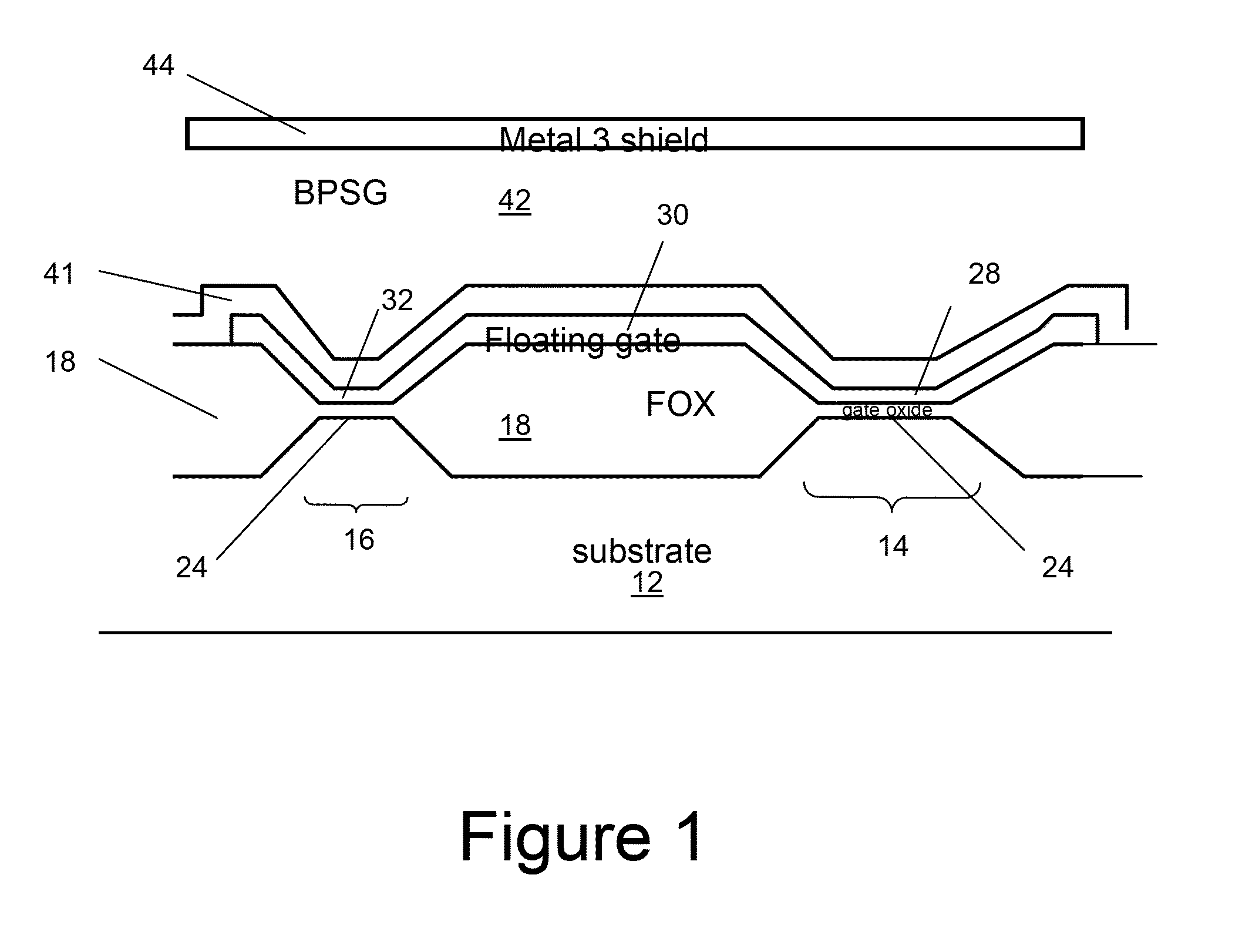
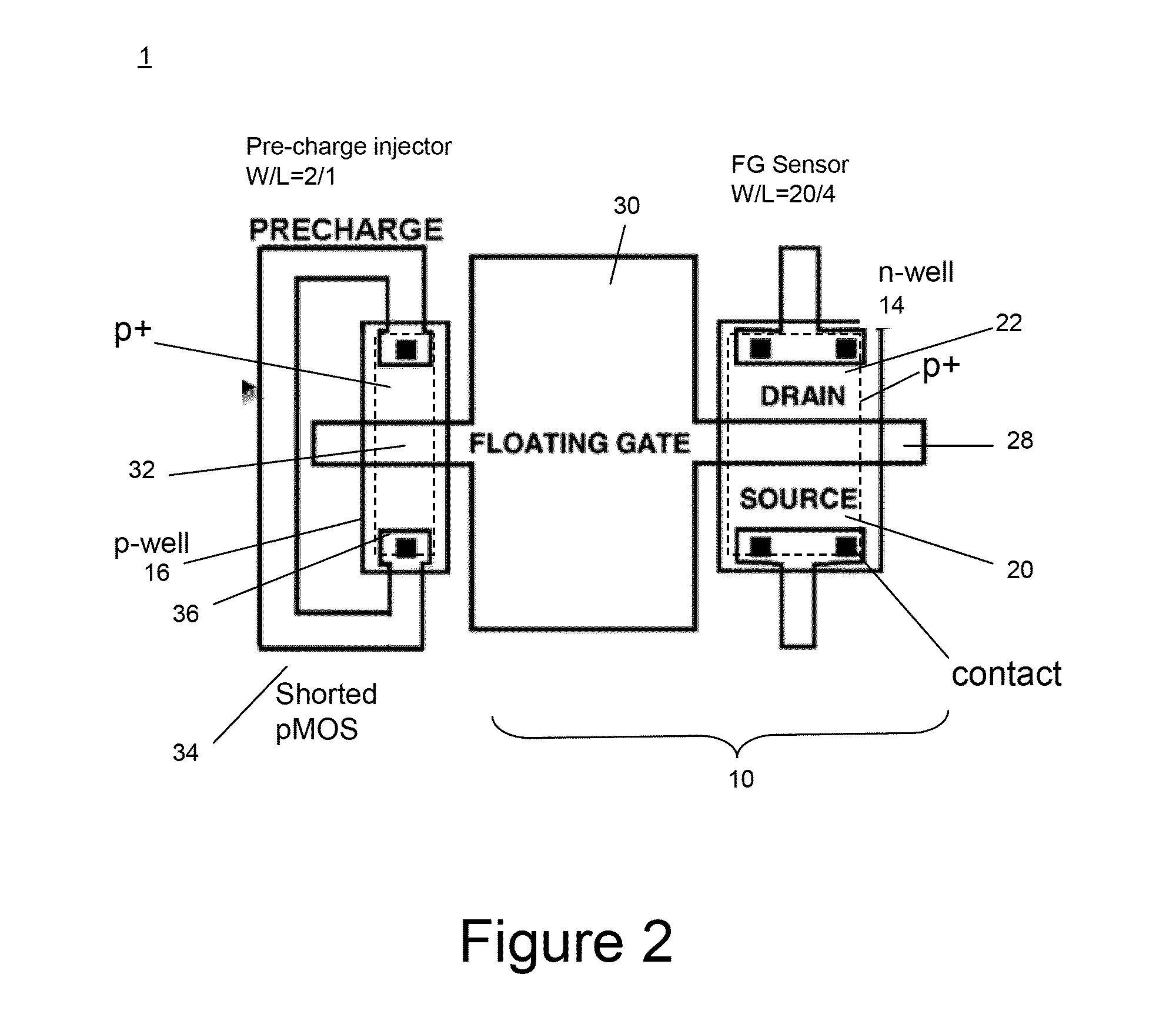
A miniaturized floating gate (FG) MOSFET radiation sensor system is disclosed, The sensor preferably comprises a matched pair of sensor and reference FGMOSFETs wherein the sensor FGMOSFET has a larger area floating gate with an extension over a field oxide layer, for accumulation of charge and increased sensitivity. Elimination of a conventional control gate and injector gate reduces capacitance, and increases sensitivity, and allows for fabrication using standard low cost CMOS technology. A sensor system may be provided with integrated signal processing electronics, for monitoring a change in differential channel current ID, indicative of radiation dose, and an integrated negative bias generator for automatic pre-charging from a low voltage power source. Optionally, the system may be coupled to a wireless transmitter. A compact wireless sensor System on Package solution is presented, suitable for dosimetry for radiotherapy or other biomedical applications.
Owner:KING ABDULLAH UNIV OF SCI & TECH
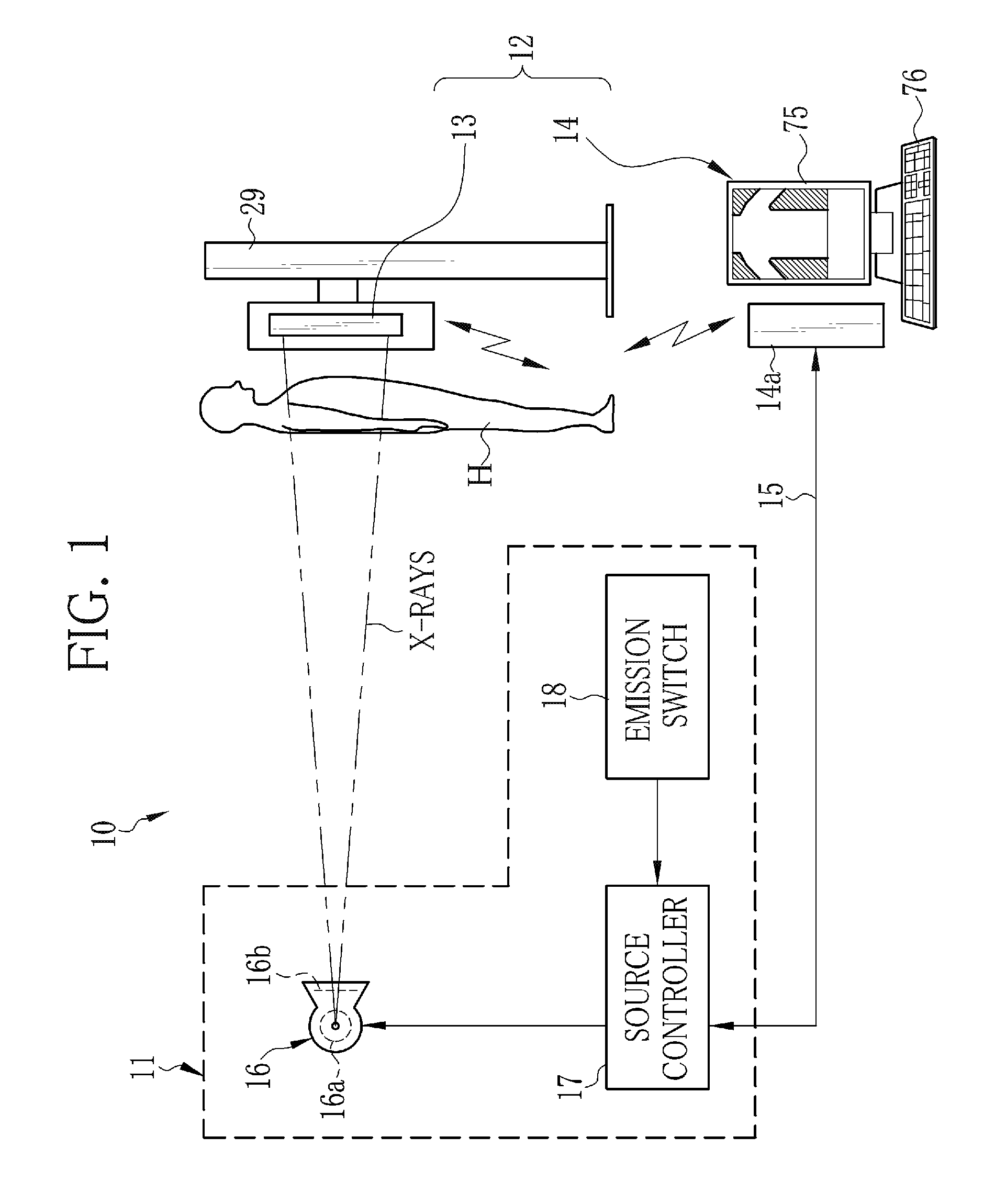
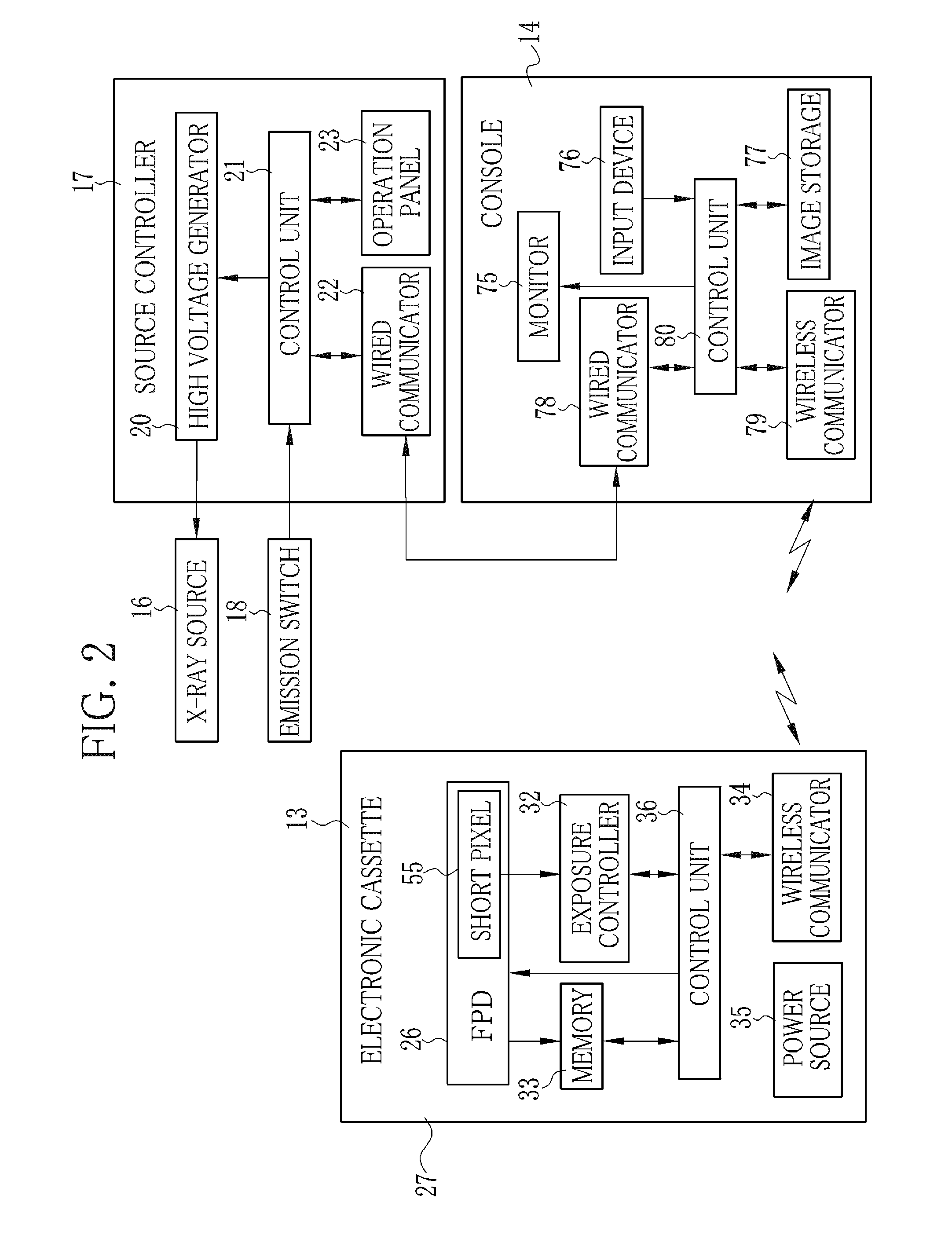
Radiation imaging apparatus and control method thereof, and radiation imaging system
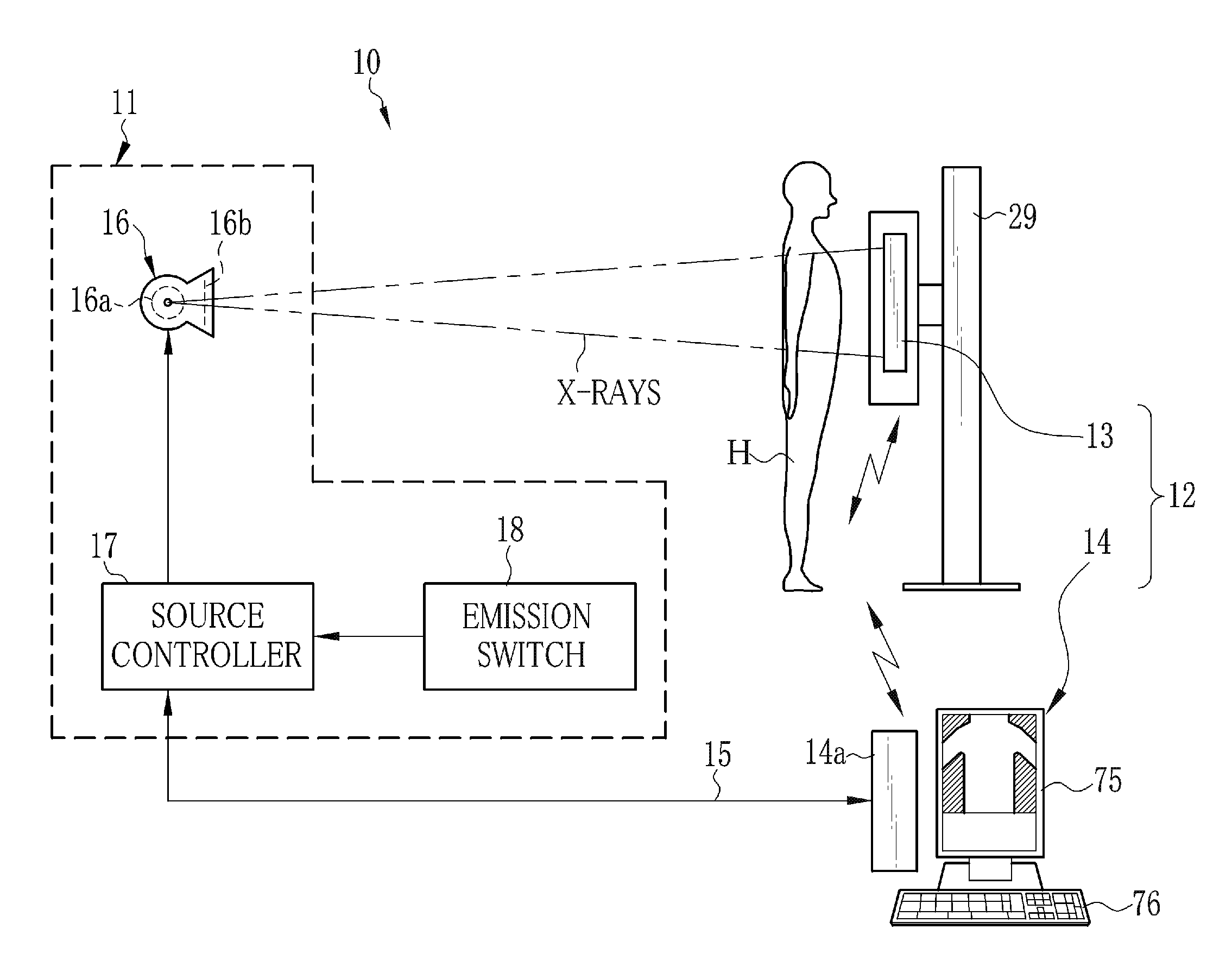
ActiveUS20130202086A1Improve image qualitySimple structureRadiation diagnostic image/data processingDosimetersRadiation imagingExposure control
An FPD detects an X-ray image of an object. The FPD includes a plurality of pixels arranged in its image capturing field. Each pixel receives X-rays emitted from an X-ray source, and outputs a pixel value in accordance with an X-ray dose applied thereto. A pixel determiner determines a minimum-value pixel out of the pixels based on the pixel values of the pixels. The minimum-value pixel is a pixel whose pixel value is the lowest. The pixel determiner sets the minimum-value pixel as an exposure control pixel. A comparator compares a first integrated value, which is an integrated value of the pixel values of the minimum-value pixel, with a predetermined first threshold value. The comparator performs X-ray emission control such that, when the first integrated value has reached the first threshold value, the X-ray source stops emitting the X-rays.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Dynamic emergency radiation monitor
A dynamic radiation monitor having a detector coupled to a computer to determine at any given location, the amount of time a person has before a pre-selected maximum permissible radiation exposure is received. The device dynamically calculates and outputs the user's permissible stay time for a given area based on a personalized maximum permissible dose, and adjusts in real time the output based on elapsed time and changing exposure rate. The device also provides the user audio and visual feedback such as varying background colors for different stay time ranges.
Owner:BUSHBERG JERROLD T
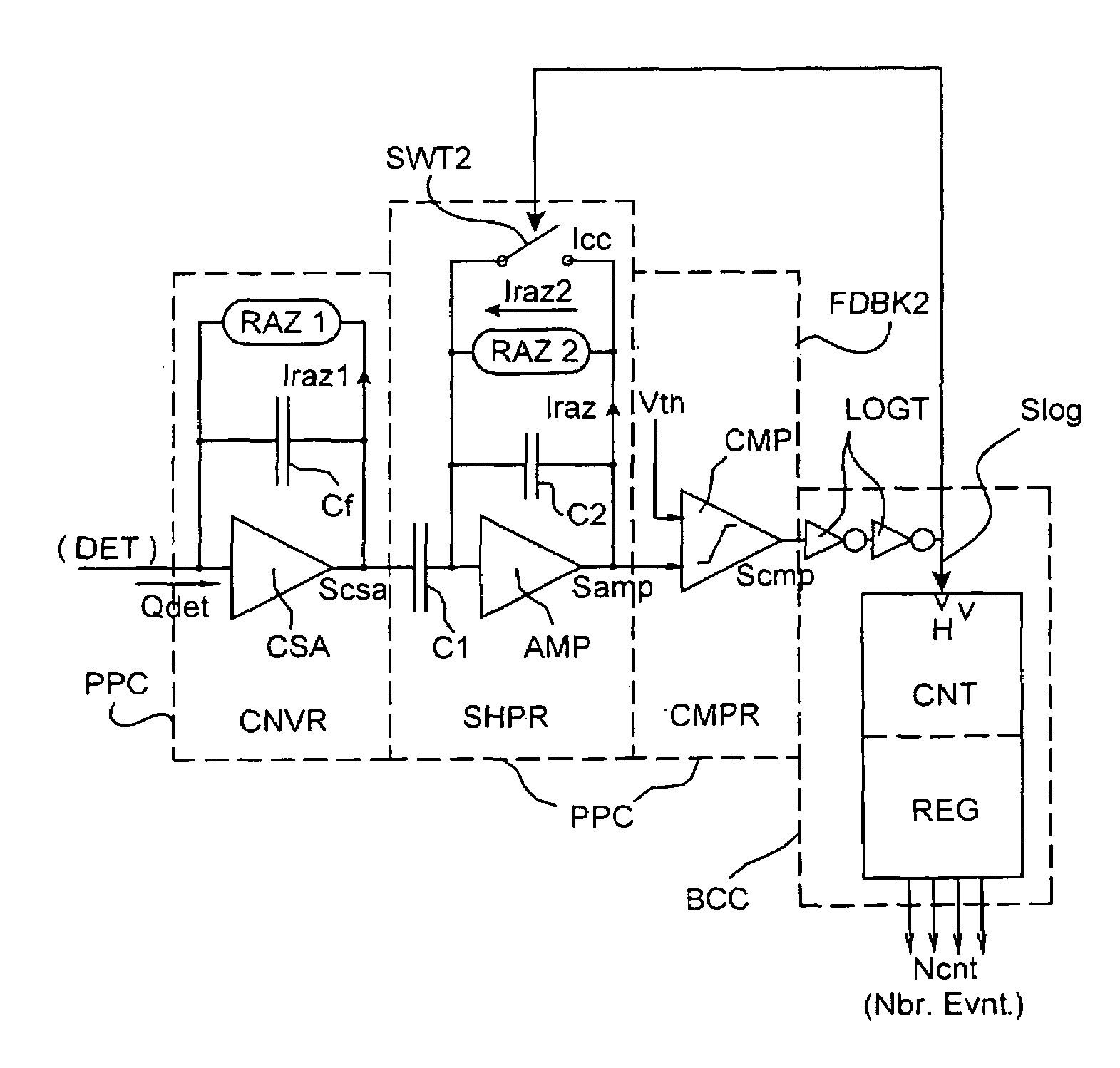
Radiation detecting system with double resetting pulse count
InactiveUS7615753B2Increase amplitudeImprove signal-to-noise ratioMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDosimetersPhotonPulse counting
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Single-use external dosimeters for use in radiation therapies and related methods, systems and computer program products
ActiveUS20040236207A1Cost-effectiveReduce labor set-up timeDosimetersDiagnostic recording/measuringDosimeterRadiation sensor
Methods, systems, devices, and computer program products include positioning disposable single-use radiation sensor patches that have adhesive means onto the skin of a patient to evaluate the radiation dose delivered during a treatment session. The sensor patches are configured to be minimally obtrusive and operate without the use of externally extending power chords or lead wires.
Owner:VTQ IP HLDG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com