Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
519 results about "Dose distribution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
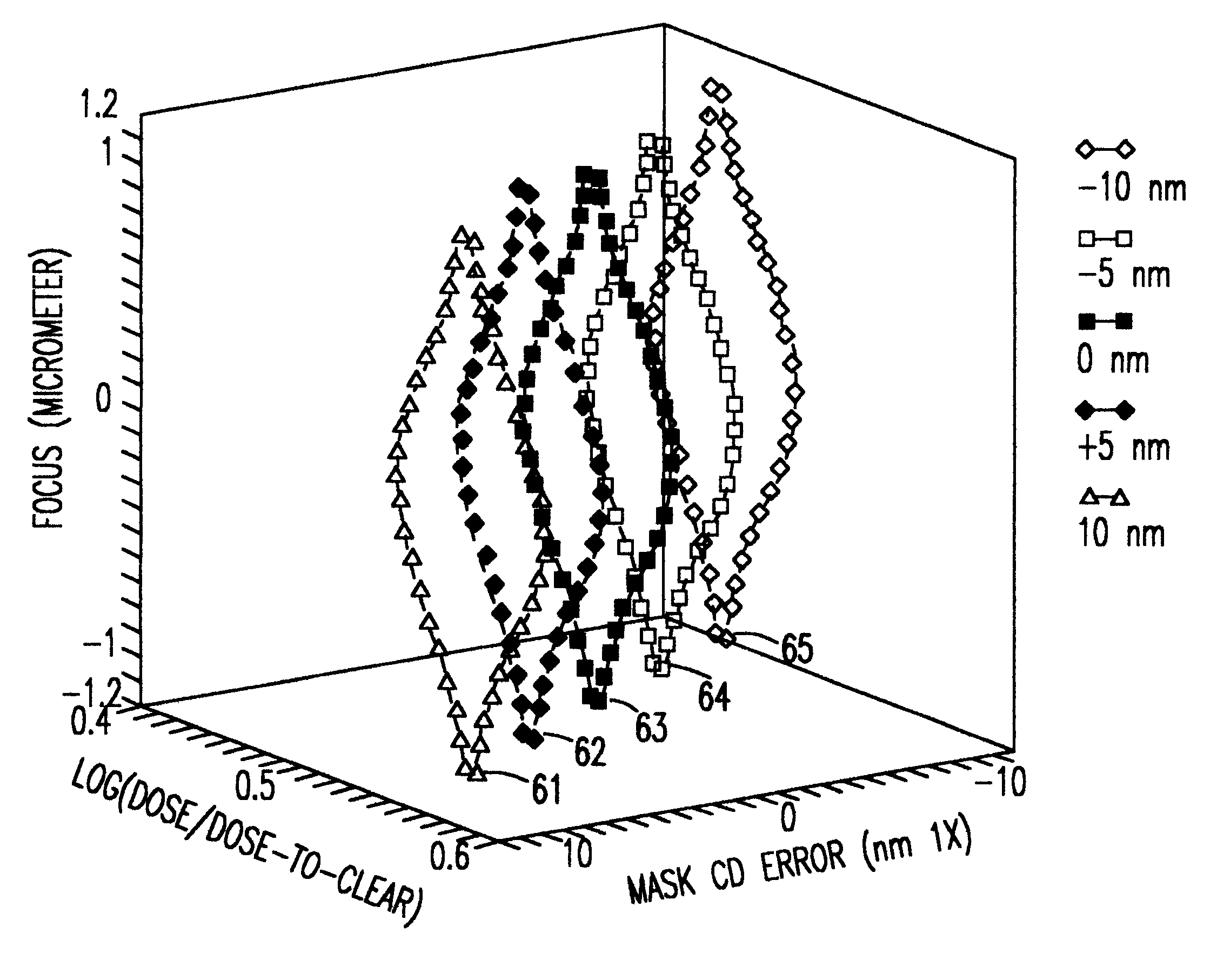
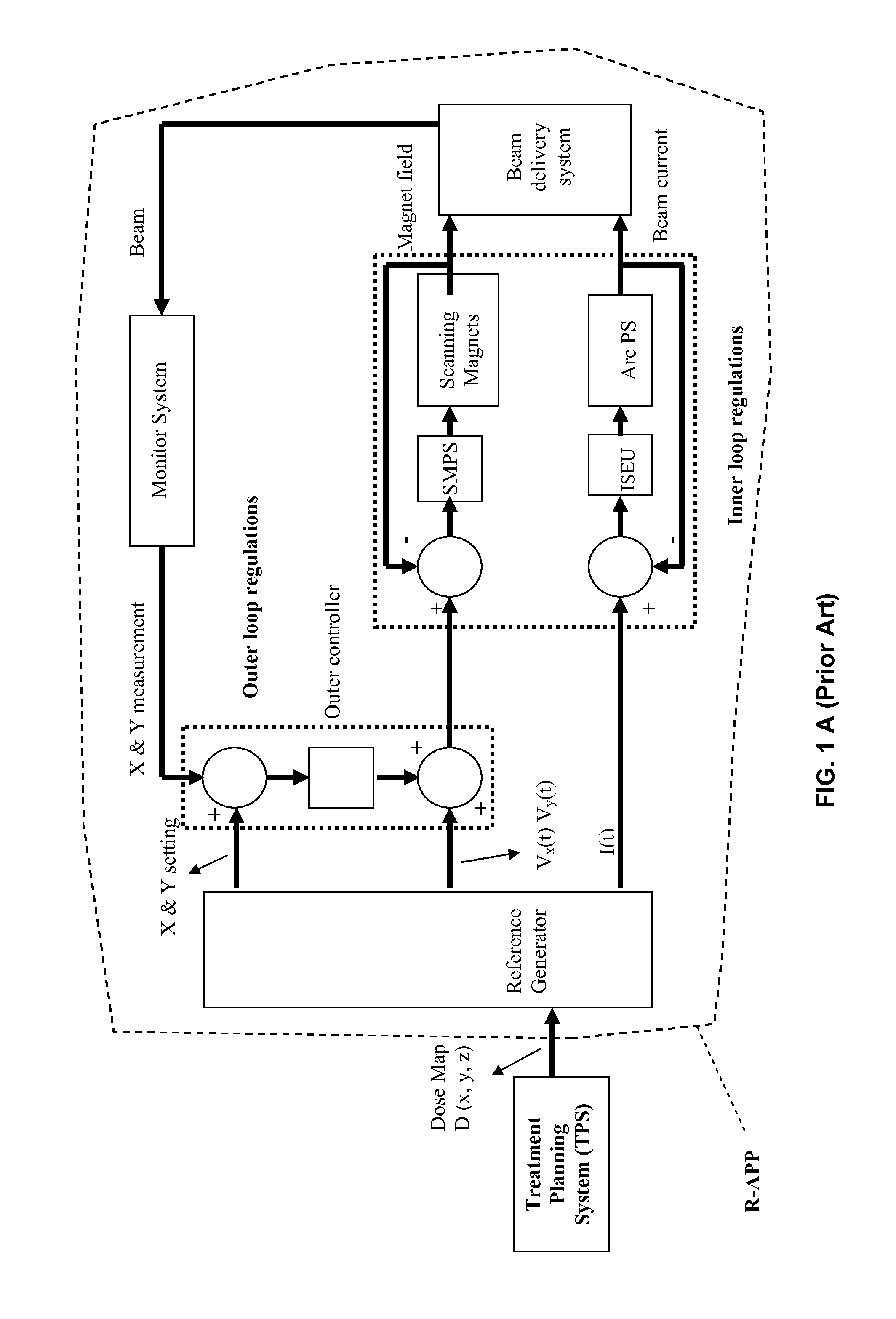
Method to determine optical proximity correction and assist feature rules which account for variations in mask dimensions
InactiveUS6553559B2Photomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentComputational physicsProcess window
Optical proximity correction (OPC) and assist feature rules are generated using a process window (PW) analysis. A reference pitch is chosen and the mask bias is found that optimizes the process window. This can be done using standard process window analysis or through a weighted process window (WPW) analysis which accounts for focus and dose distributions that are expected in a real process. The WPW analysis gives not only the optimum mask bias, but also the center focus and dose conditions for the optimum process centering. A series of other pitches and mask biases are then analyzed by finding the common process window with the reference pitch. For the standard PW analysis, a common process window is found. For the WPW analysis, the WPW is computed at the center focus and dose conditions found for the reference pitch. If mask or lens errors are to be accounted for, then multiple structures can be included in the analysis. Once the common process windows for the mask features of interest have been computed, functional fits to the data can be found. Once the functional forms have been found for each of the OPC parameters, the rules table can be determined by solving for the spacings of interest in the design.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
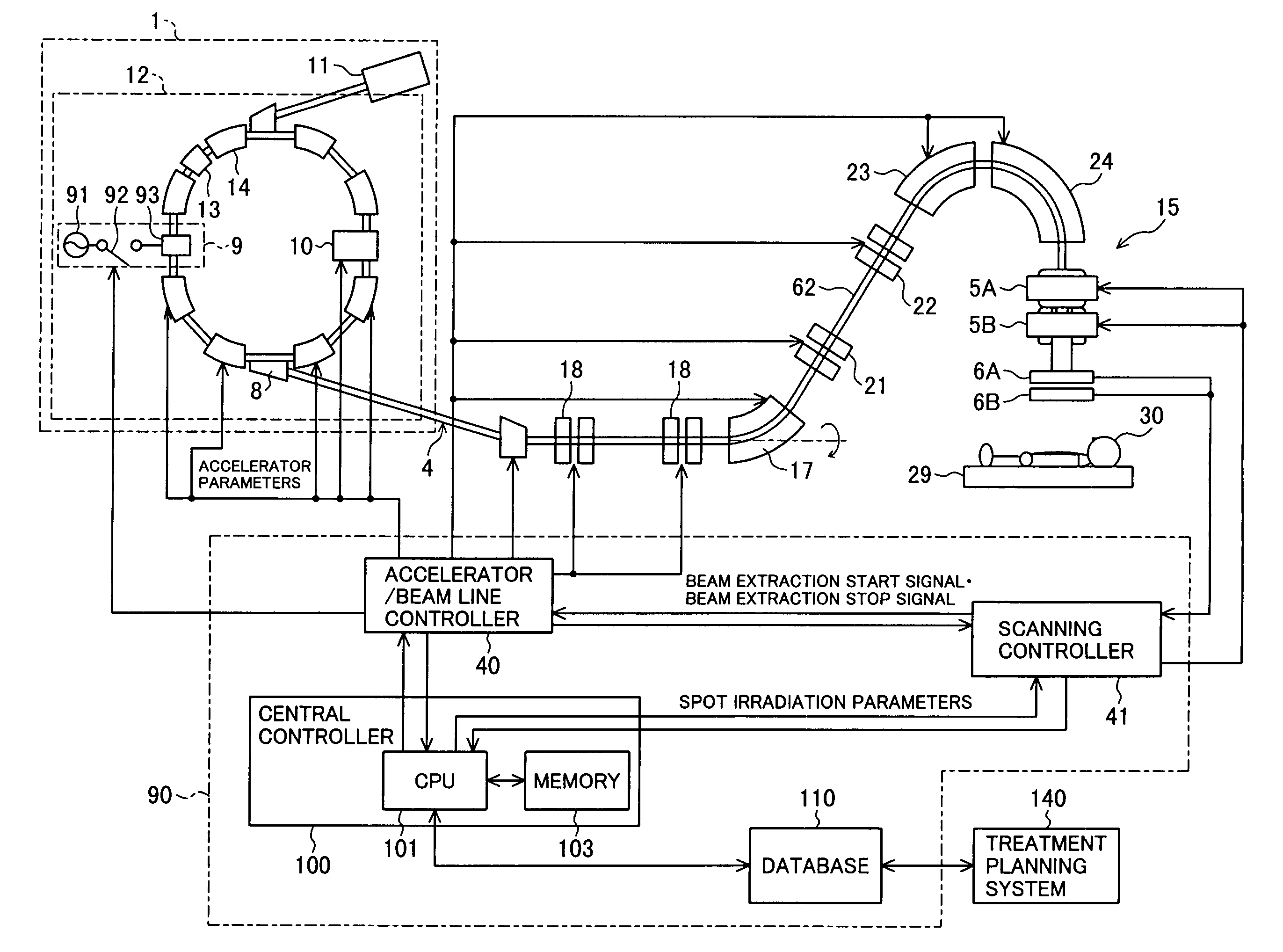
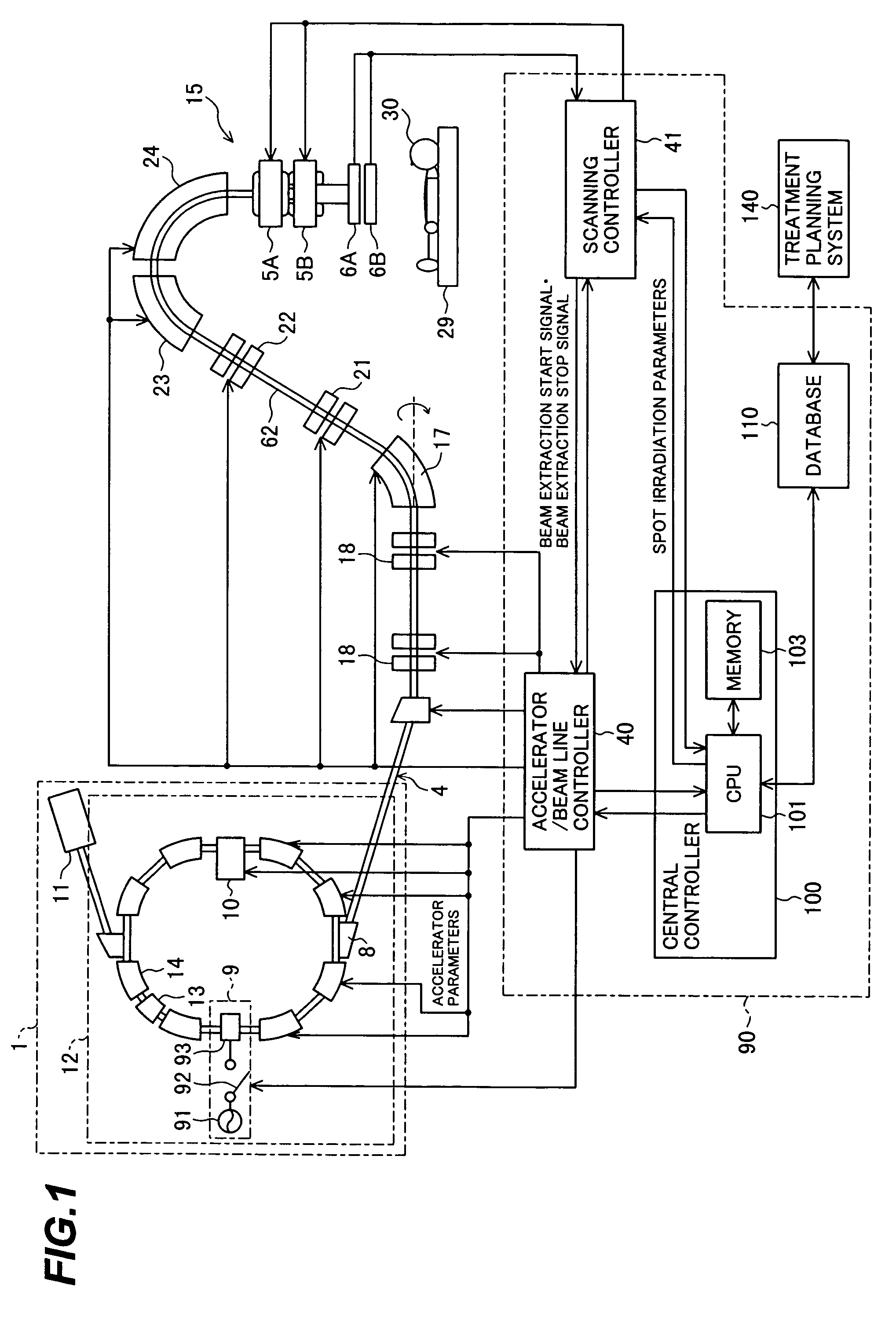
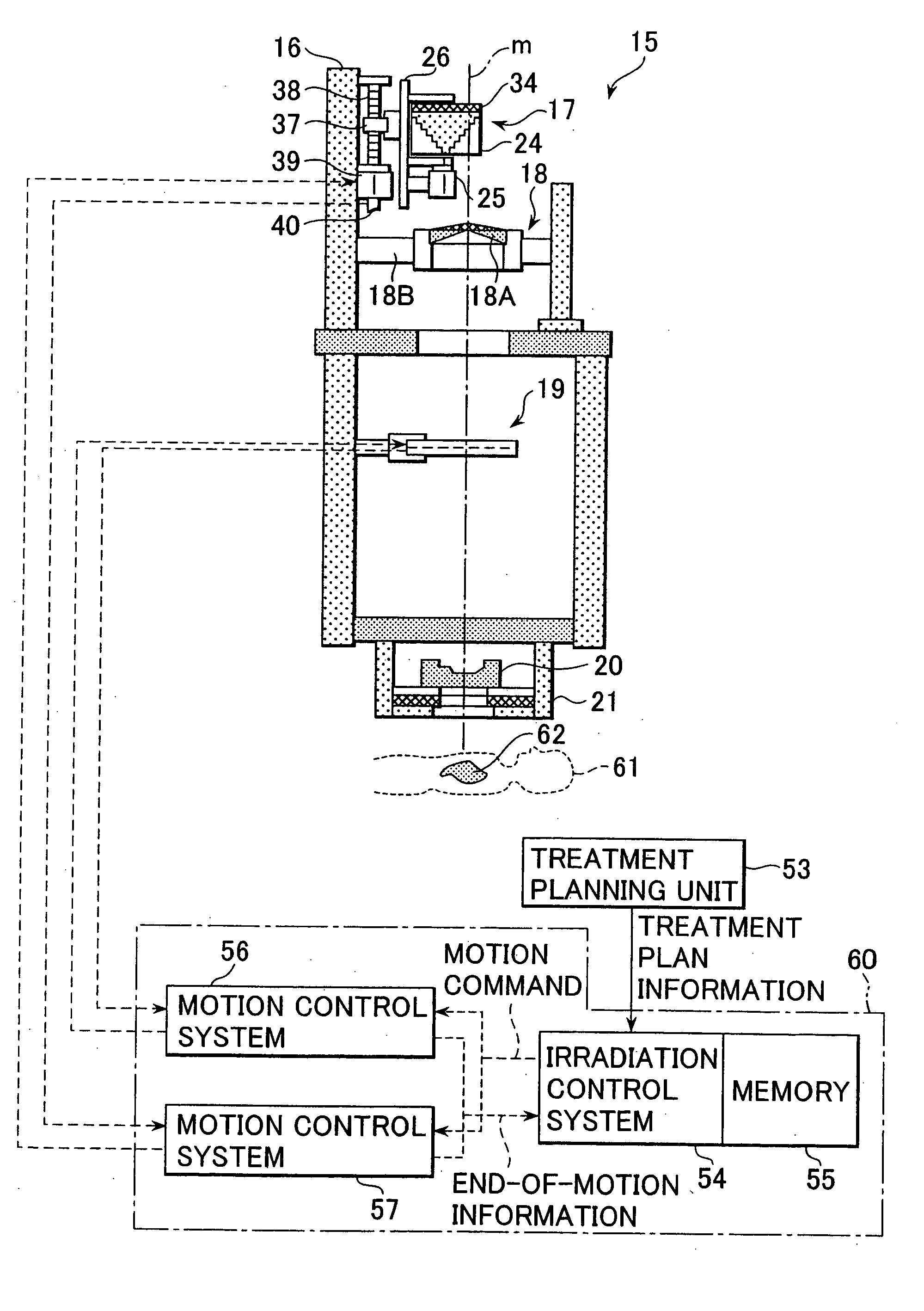
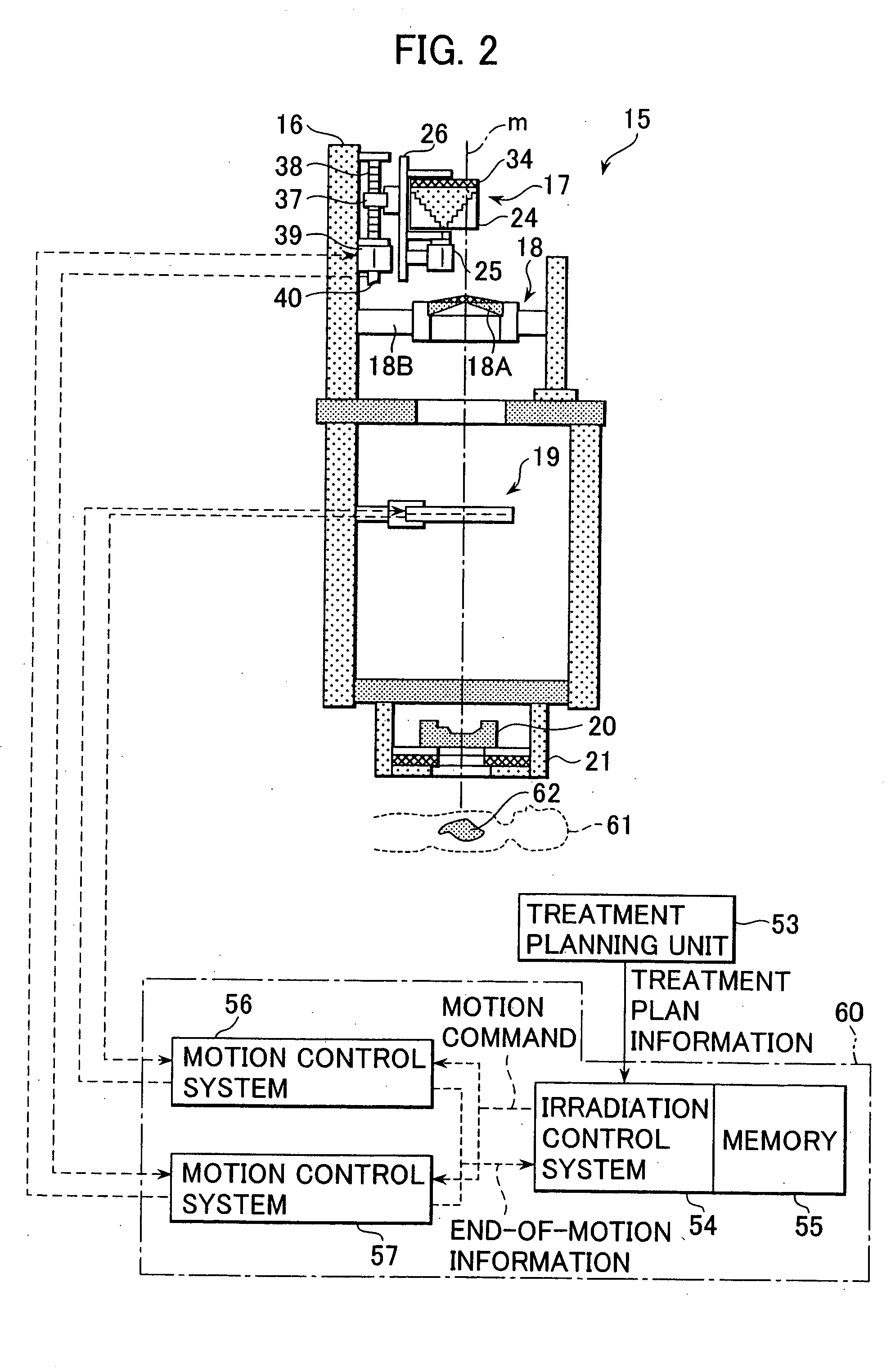
Particle beam irradiation system and method of adjusting irradiation field forming apparatus
ActiveUS7049613B2Increase in sizePenumbra can be reducedElectrotherapyRadiation/particle handlingParticle beamLight beam
A particle therapy system, as one example of a particle beam irradiation system, comprises a charged particle beam generator and an irradiation field forming apparatus. An ion beam from the charged particle beam generator is irradiated to a diseased part in the body of a patient through the irradiation field forming apparatus. A scattering compensator and a range modulation wheel (RMW) are disposed on the upstream side in a direction of beam advance and are movable along a beam axis. The movement of the scattering compensator and the RMW adjusts a size of the ion beam entering a scatterer device, whereby a change in scattering intensity of the ion beam in the scatterer device is adjusted. As a result, a penumbra in dose distribution is reduced and a more uniform dose distribution in a direction perpendicular to the direction of beam advance is obtained in the diseased part.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Particle beam irradiation system
ActiveUS7301162B2Minimize exposureUniform dose distributionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingParticle beamLight beam
A particle beam irradiation system capable of ensuring a more uniform dose distribution at an irradiation object even when a certain time is required from output of a beam extraction stop signal to the time when extraction of a charged particle beam from an accelerator is actually stopped. The particle beam irradiation system comprises a synchrotron, an irradiation device including scanning magnets and outputting an ion beam extracted from the synchrotron, and a control unit. The control unit stops the output of the ion beam from the irradiation device in accordance with the beam extraction stop signal, controls the scanning magnets to change an exposure position in a state in which the output of the ion beam is stopped, and after the change of the exposure position, starts the output of the ion beam from the irradiation device again. The control unit further outputs a next beam extraction stop signal when an increment of dose integrated from the time of a preceding beam extraction stop signal as a start point reaches a setting dose stored in advance.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Dose calculation method for multiple fields
ActiveUS8009804B2X-ray apparatusX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTherapy planningDose calculation
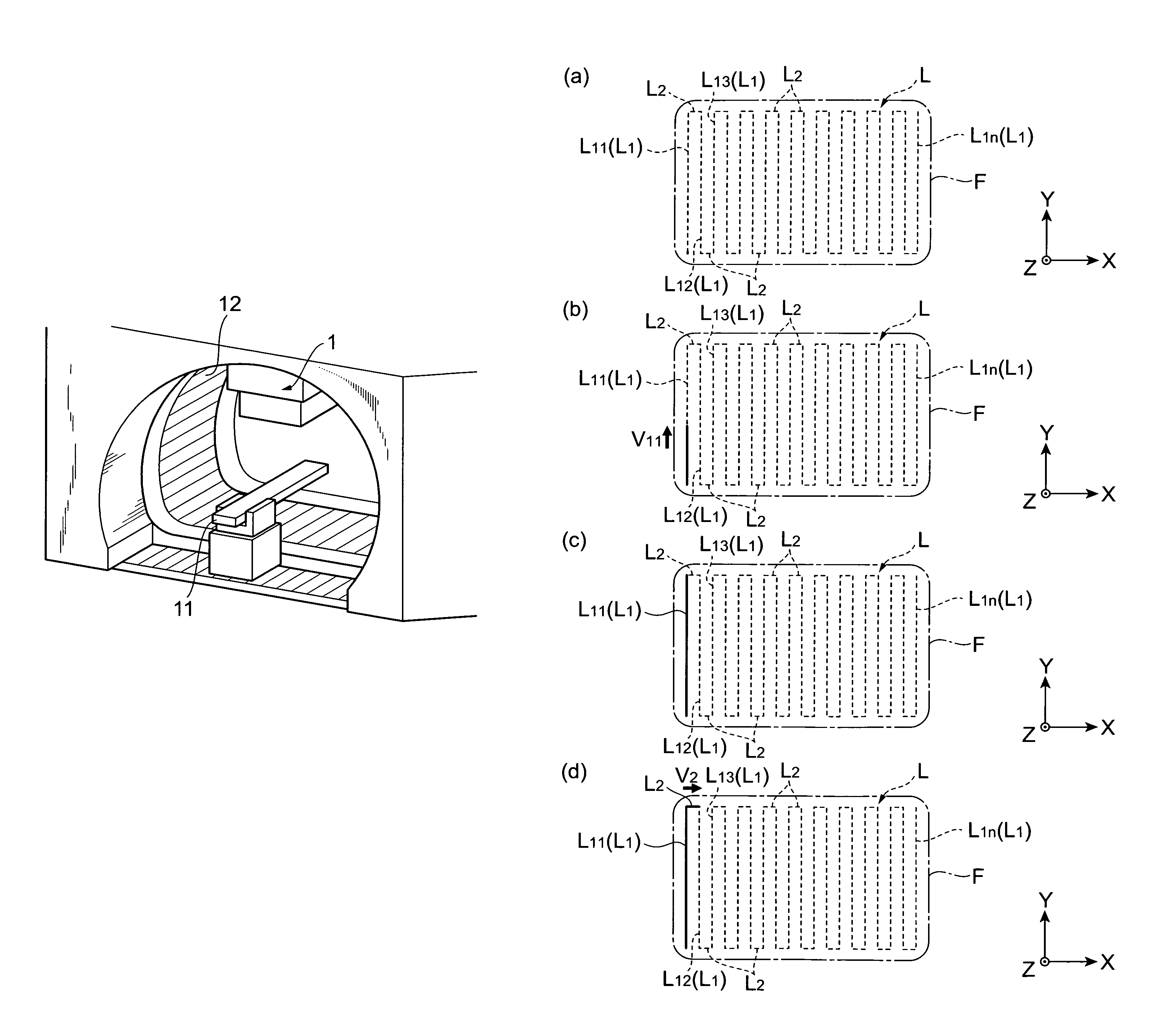
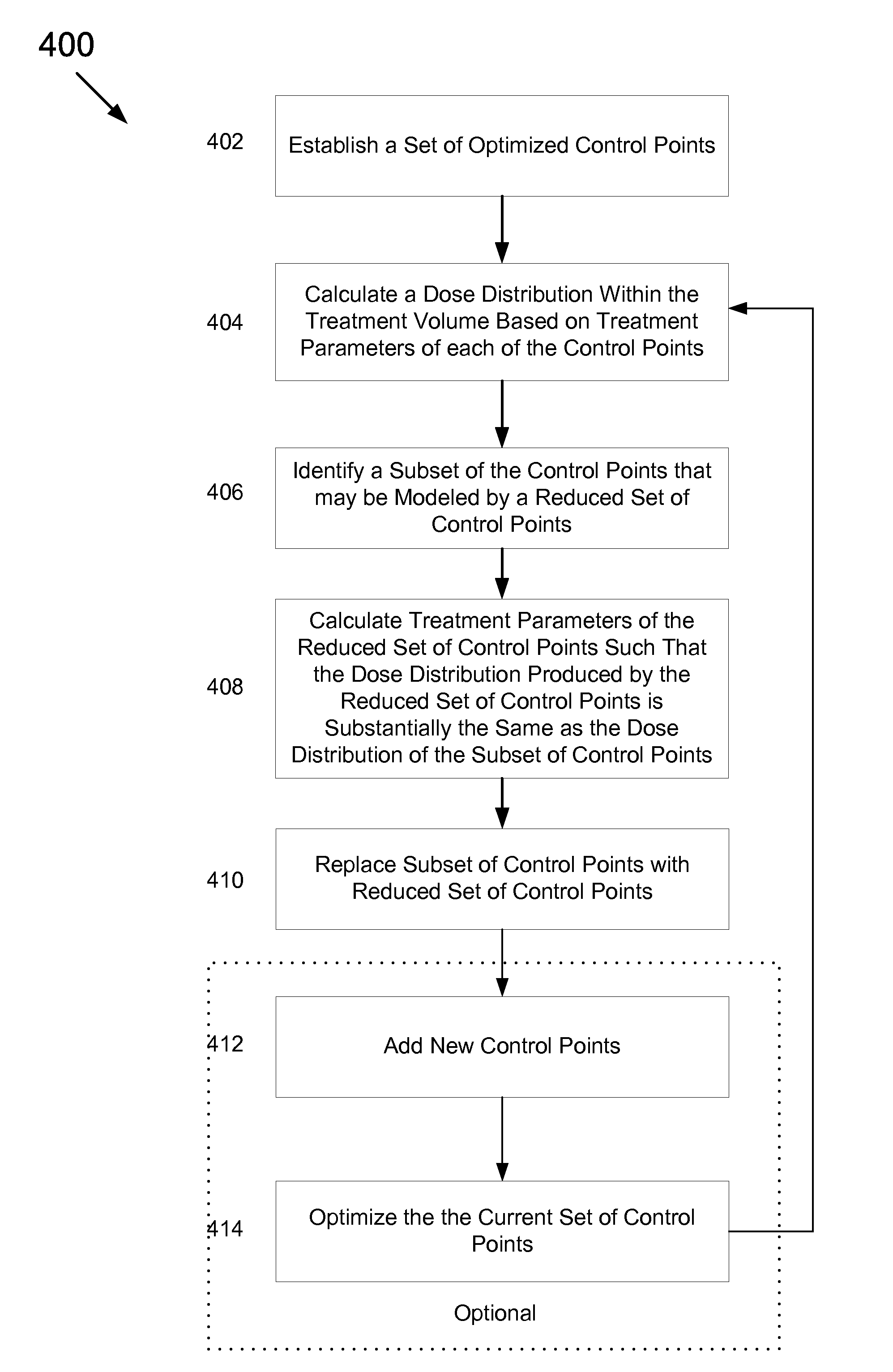
Systems and methods for developing a treatment plan for irradiating a treatment volume within a patient are disclosed. In accordance with the present invention, control points used to calculate a dose of radiation delivered to the treatment volume may be combined to result in a smaller number of control points. The smaller number of control points may allow more efficient calculation of dose distributions resulting in a treatment plan that can be delivered to the patient earlier or may allow additional iterations of treatment plan optimization resulting in a more accurate dose distribution being delivered to the patient.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
Precise radiotherapy planning system
InactiveCN101120871AImprove accuracyImprove the quality of lifeData processing applicationsSurgeryTumor targetLife quality
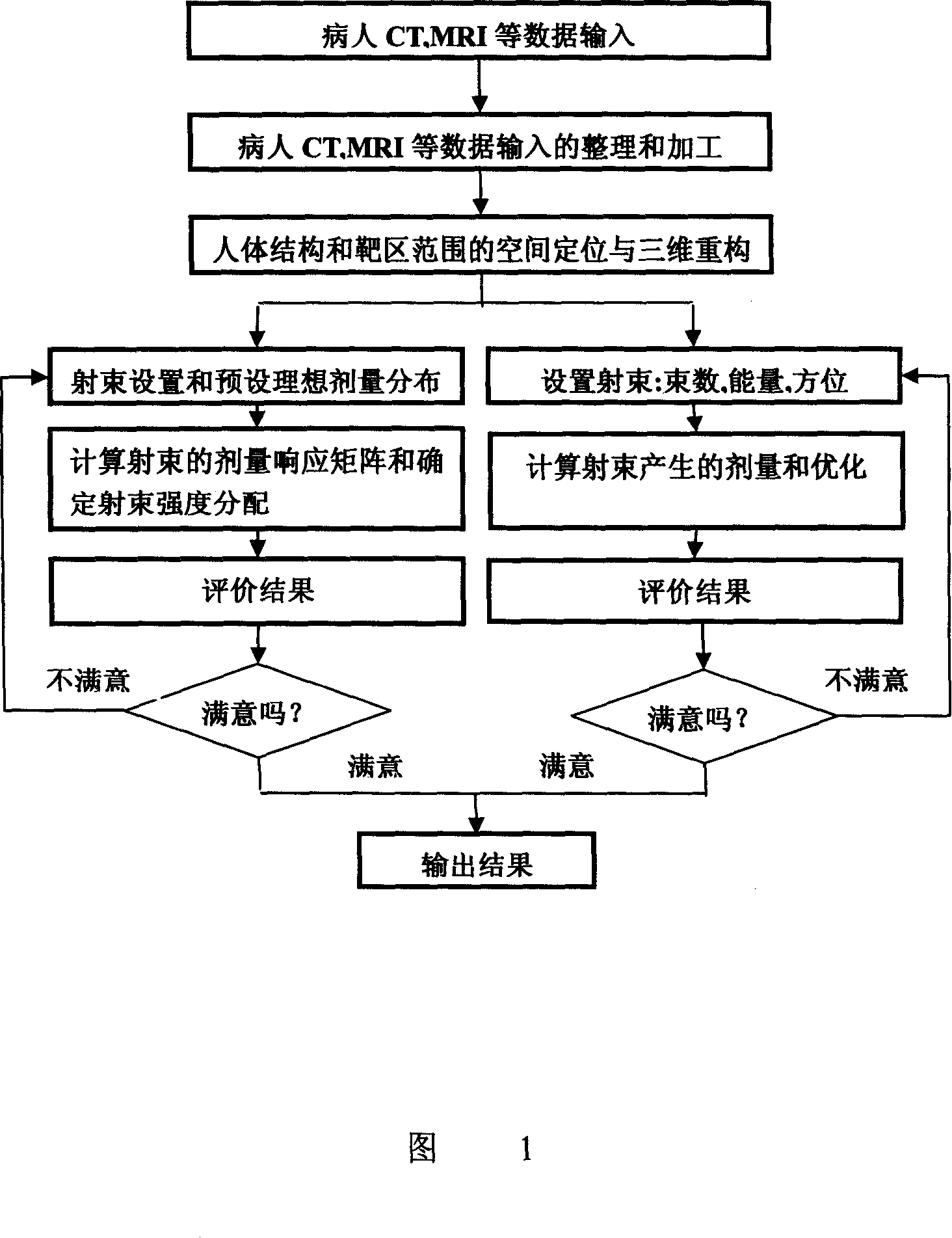
The present invention discloses an accurate radiation treatment planning system, which mainly comprises a three-dimensional medical image reconstruction module for reconstruction of human organs and the tumor target area, a three-dimensional dose calculation module of high accuracy photon beam, a three-dimensional dose calculation module of high accuracy electron beam, a conventional radiation plan designing module of the photon beam and the electron beam, a conformal radiation designing module of the photon beam and the electron beam, a reverse plan scheme designing module focused on the photon beam treatment. The present invention independently resolves the main and key technology of the radiation treatment planning system. The present invention develops a highly accurate algorithm and a fast precise optimal method of the three-dimensional dose distribution in photon beam and the electron beam, which distributes in non-uniform human medium. The present invention greatly improves accuracy of the embarking dose in tumor target area in patient body. Because the dose calculation speed has been improved dramatically, the advanced conformal radiation treatment planning system and the treatment planning system focused on radiation are feasible for clinical application. The present invention brings important benefits for improving the radiation treatment effect and improving life quality of the patient.
Owner:成都奇林科技有限责任公司
Mixed irradiation evaluation support system
InactiveUS7186991B2Radiation/particle handlingChemical conversion by chemical reactionSupporting systemMedicine
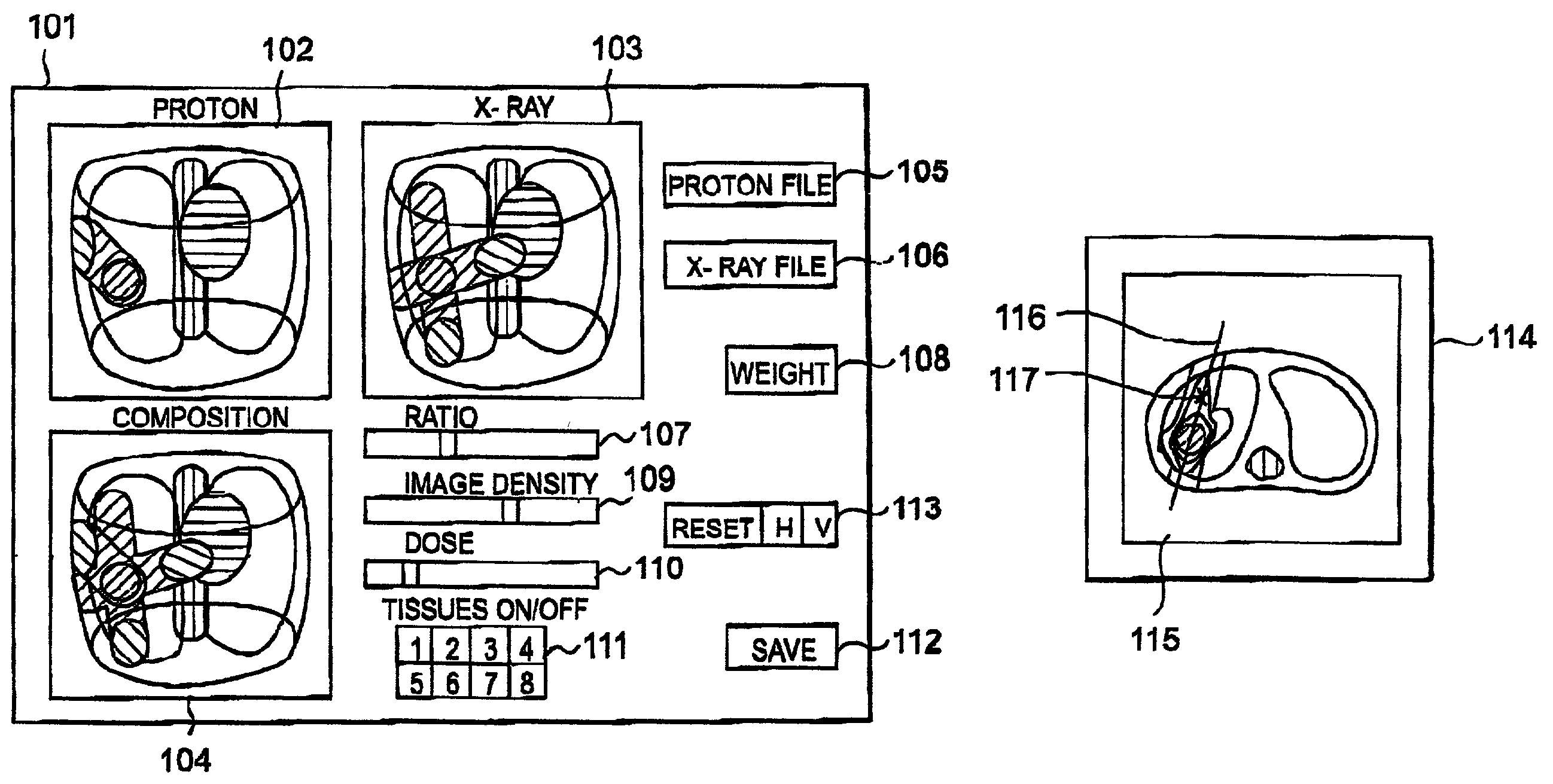
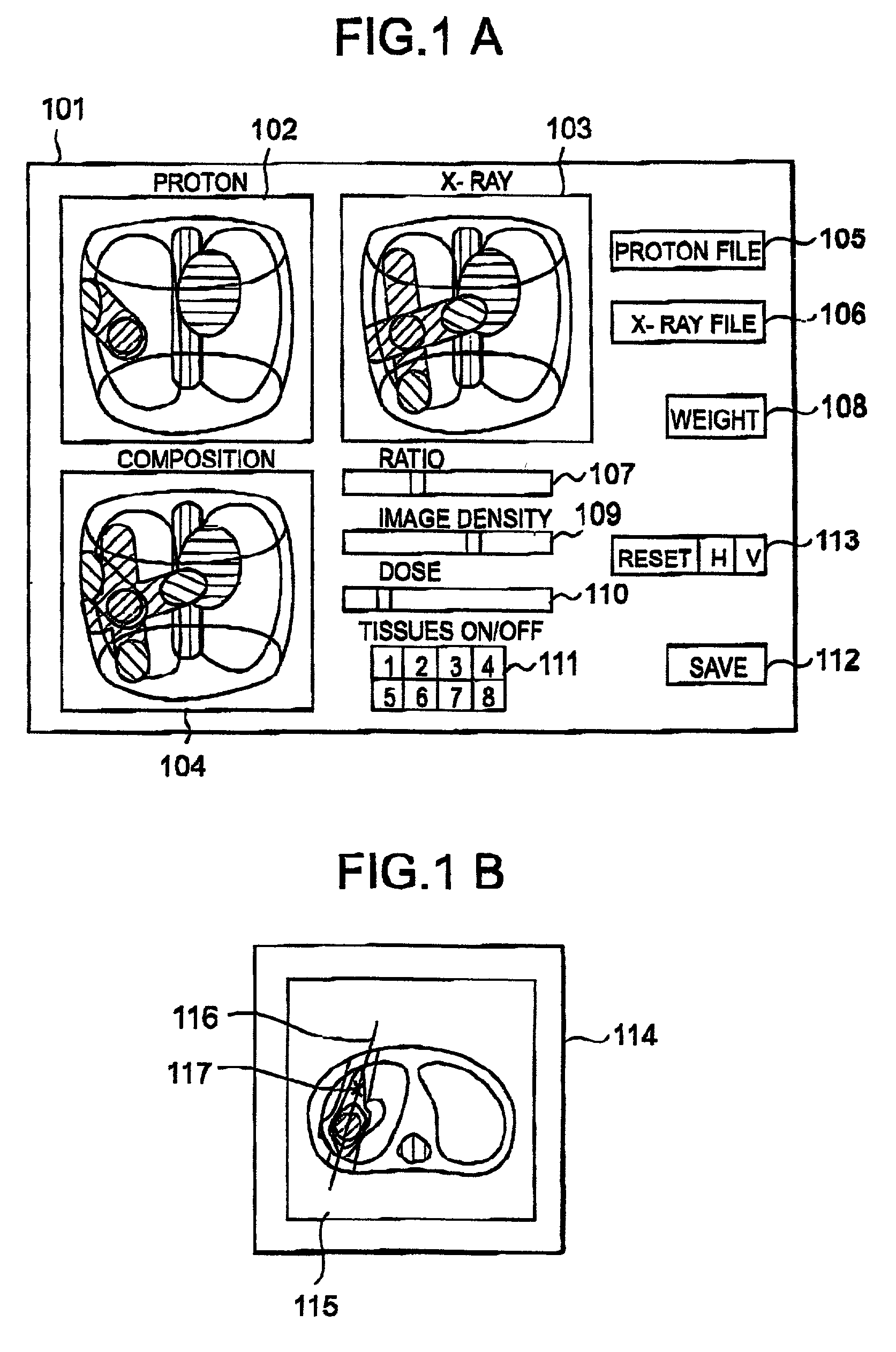
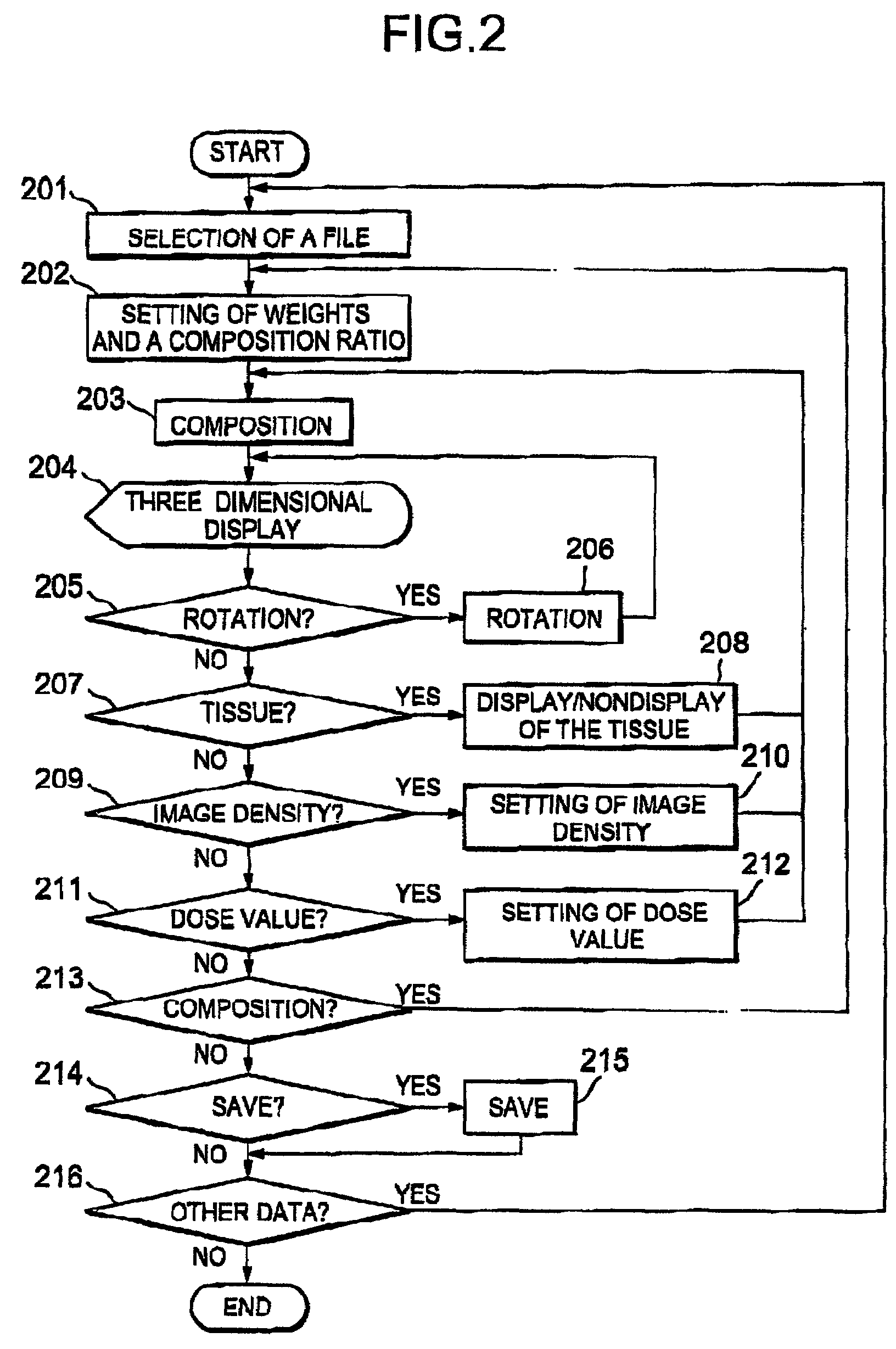
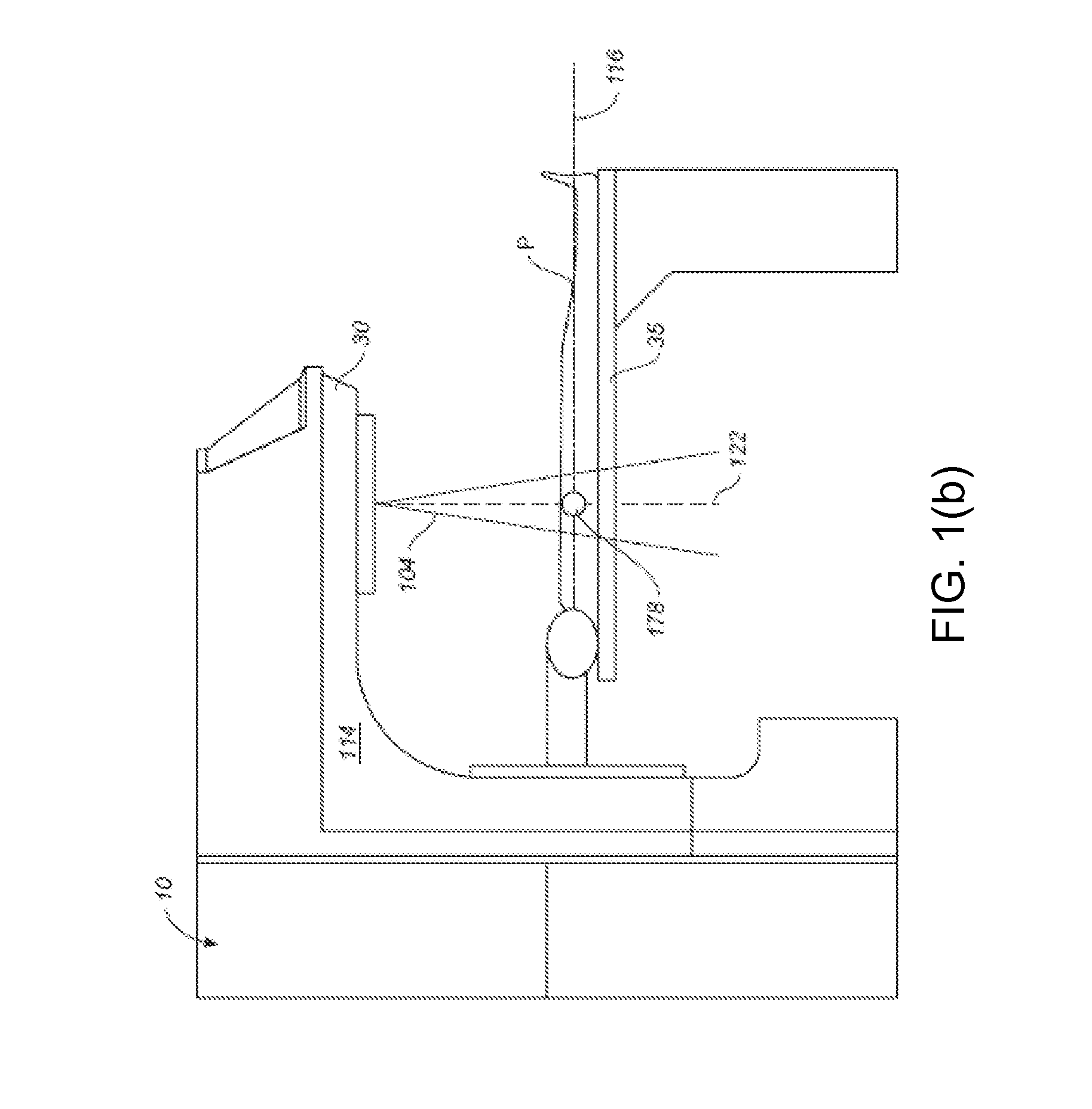
A mixed irradiation evaluation support system for supporting judgment and determination of allocation of contribution in mixed irradiation using proton beams and X-rays. According to a composition ratio designated by a composition ratio scroll bar 107, a dose distribution by a proton beam and a dose distribution by an X-ray are composed, and the result of the composition is displayed three-dimensionally in a three-dimensional display part 104. Further, when a cross section is designated in the three-dimensional display part 104, an isodose map 115 in the designated cross section is displayed in a cross section window 114.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
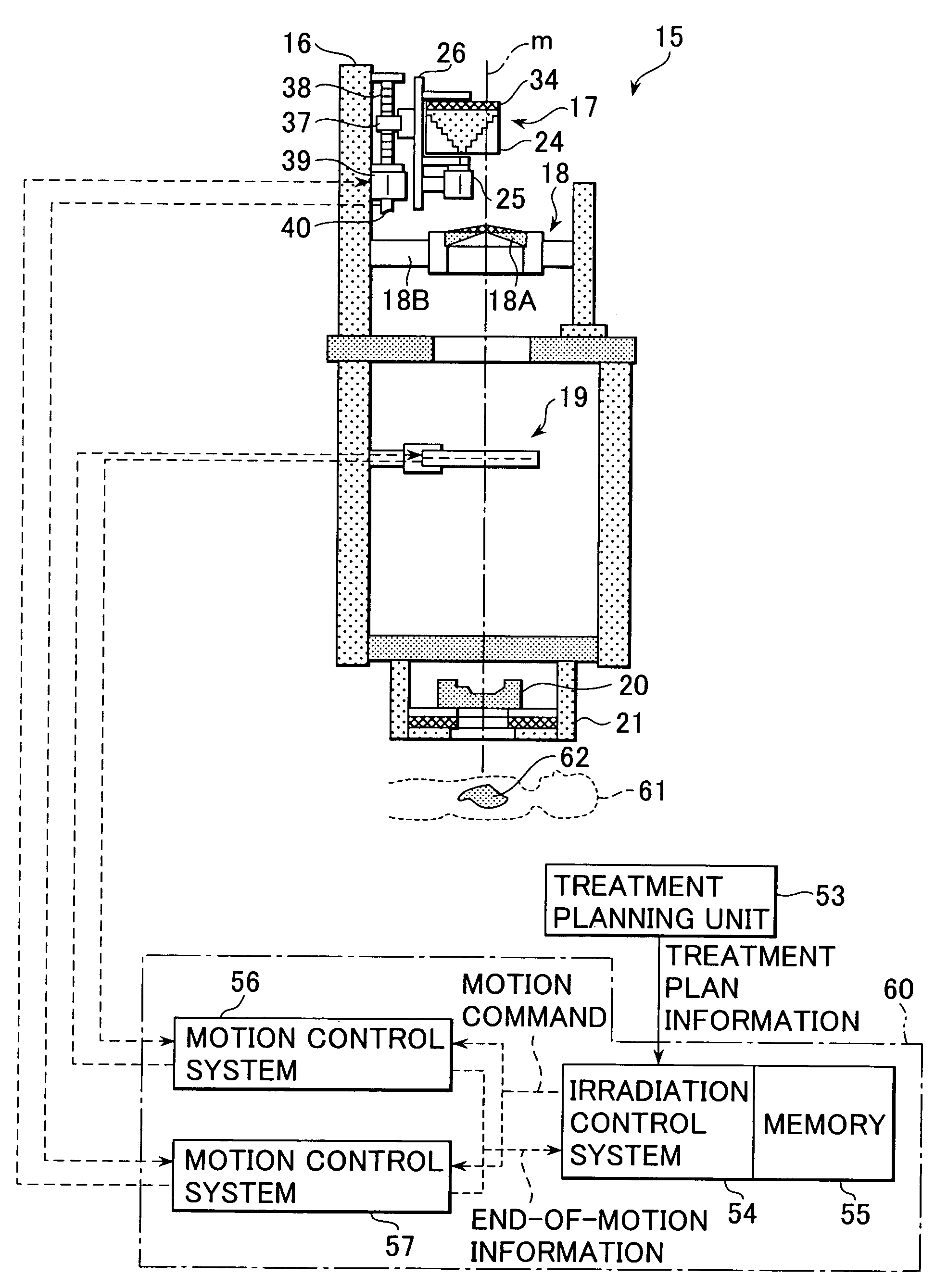
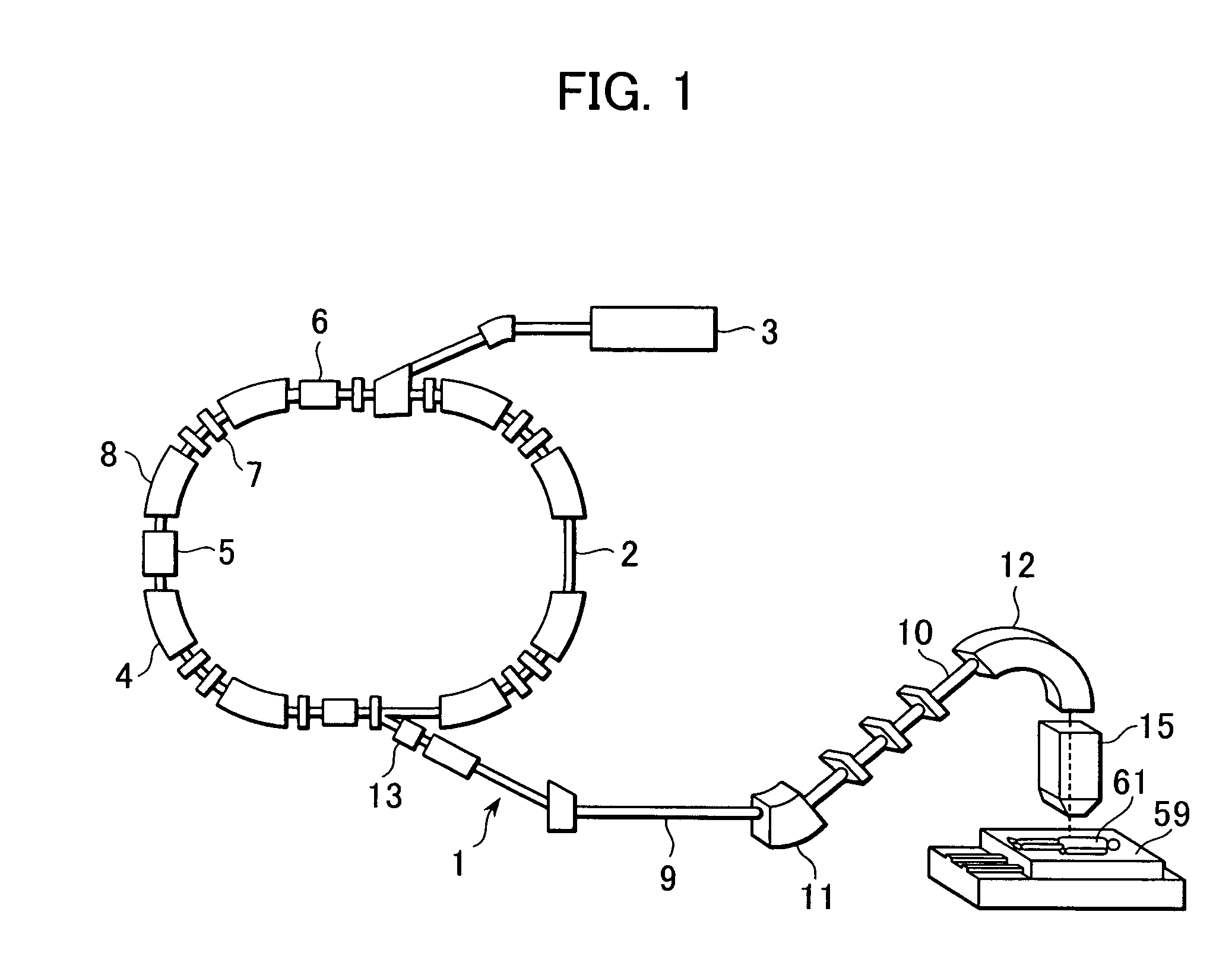
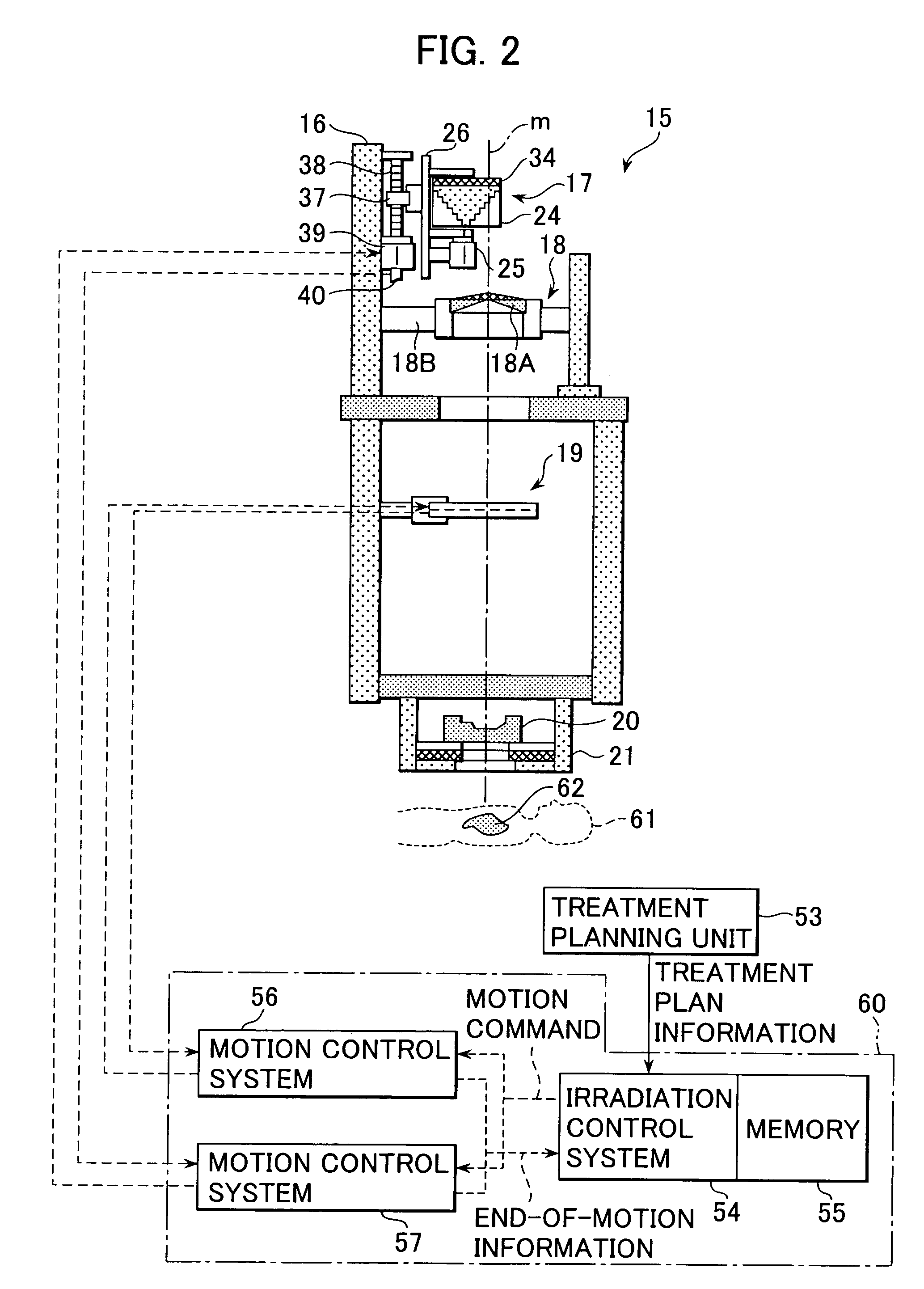
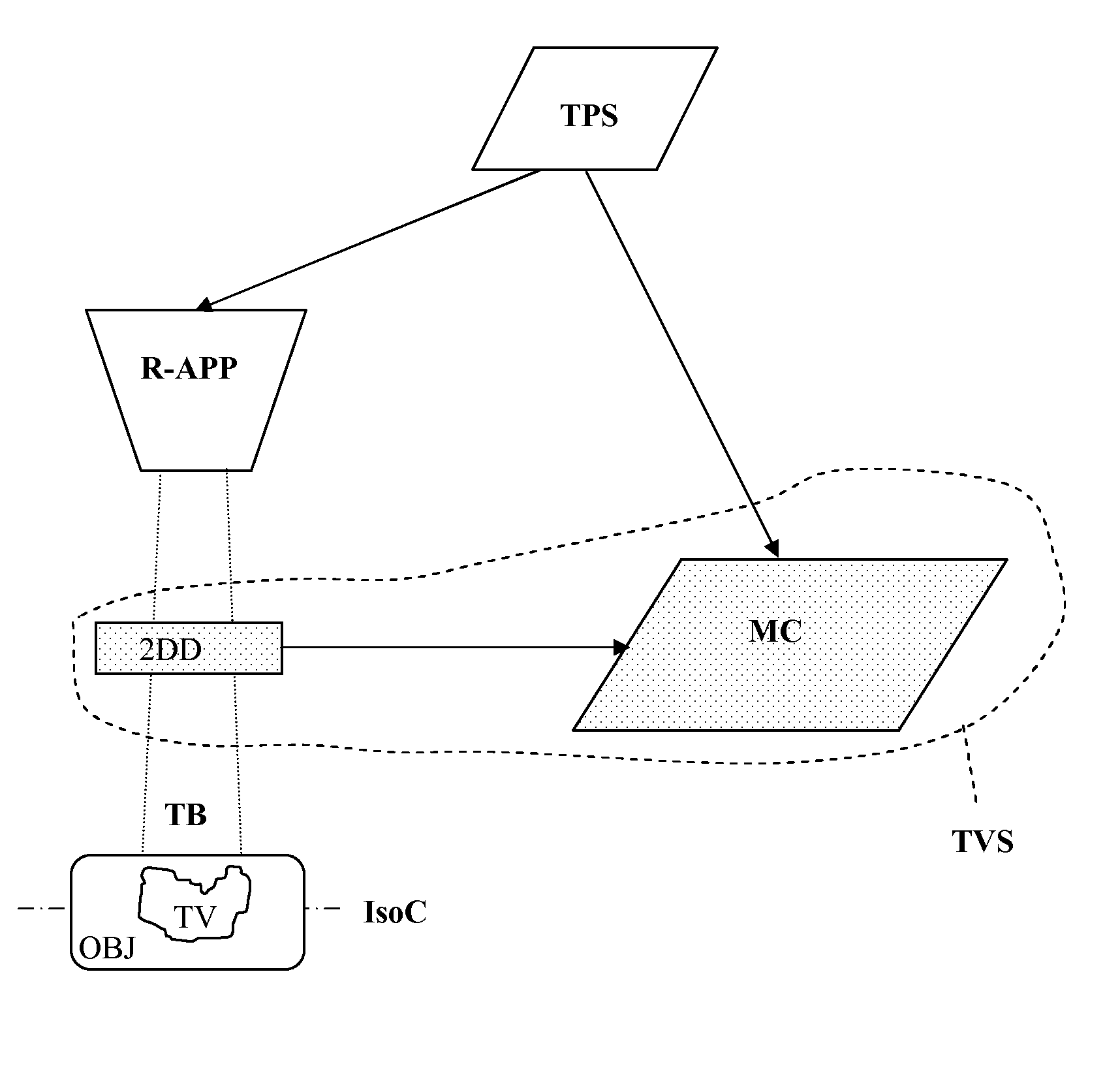
Device And Method For Particle Therapy Monitoring And Verification
ActiveUS20110248188A1Reduce in quantityChemical conversion by chemical reactionX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyConformal radiation therapyParticle physics
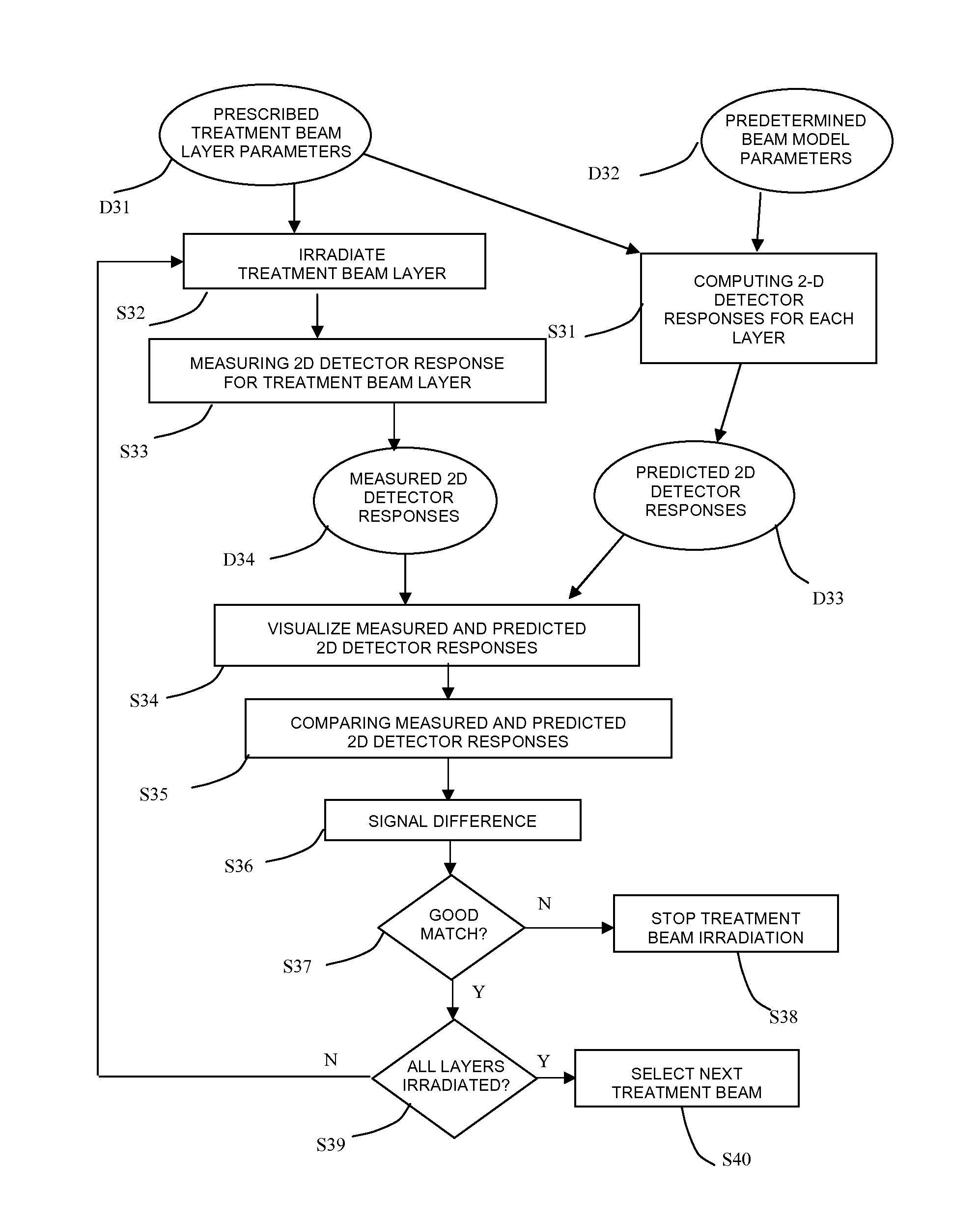
The present invention relates to a device and method for monitoring and verification of the quality of a radiation treatment beam in conformal radiation therapy, and in particular for IMPT (Intensity Modulated Particle Therapy) applications. The device comprises a 2D electronic detector measuring 2D responses to the delivered treatment beam. These 2D responses are compared with predicted 2D responses and differences in responses are signalled. Based on the measured 2D responses the effectively delivered 3D dose distribution in the target can be reconstructed.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Method for calculation radiation doses from acquired image data
InactiveUS20080091388A1Fast rebuildMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesComputation using non-denominational number representationDeterministic methodComputer science
Various embodiments of the present invention provide processes for applying deterministic radiation transport solution methods for calculating doses and predicting scatter in radiotherapy and imaging applications. One method embodiment of the present invention is a process for using deterministic methods to calculate dose distributions resulting from radiotherapy treatments, diagnostic imaging, or industrial sterilization, and for calculating image scatter for the purposes of image reconstruction. In one embodiment of the present invention, a method provides a means for transport of external radiation sources through field-shaping devices. In another embodiment of the present invention, a method includes a process for calculating the dose response at selected points and volumes prior to radiotherapy treatment planning.
Owner:FAILLA GREGORY A +3
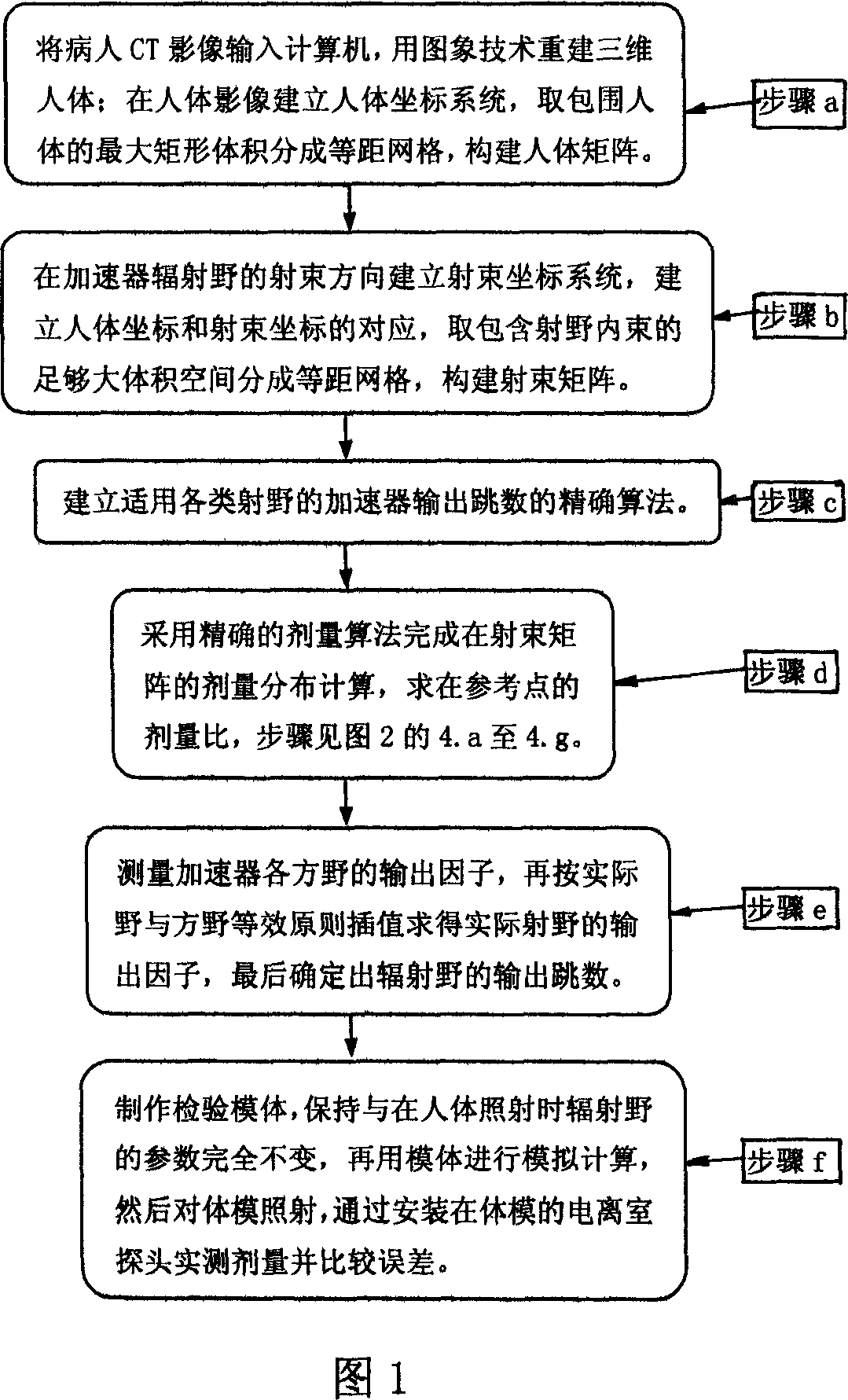
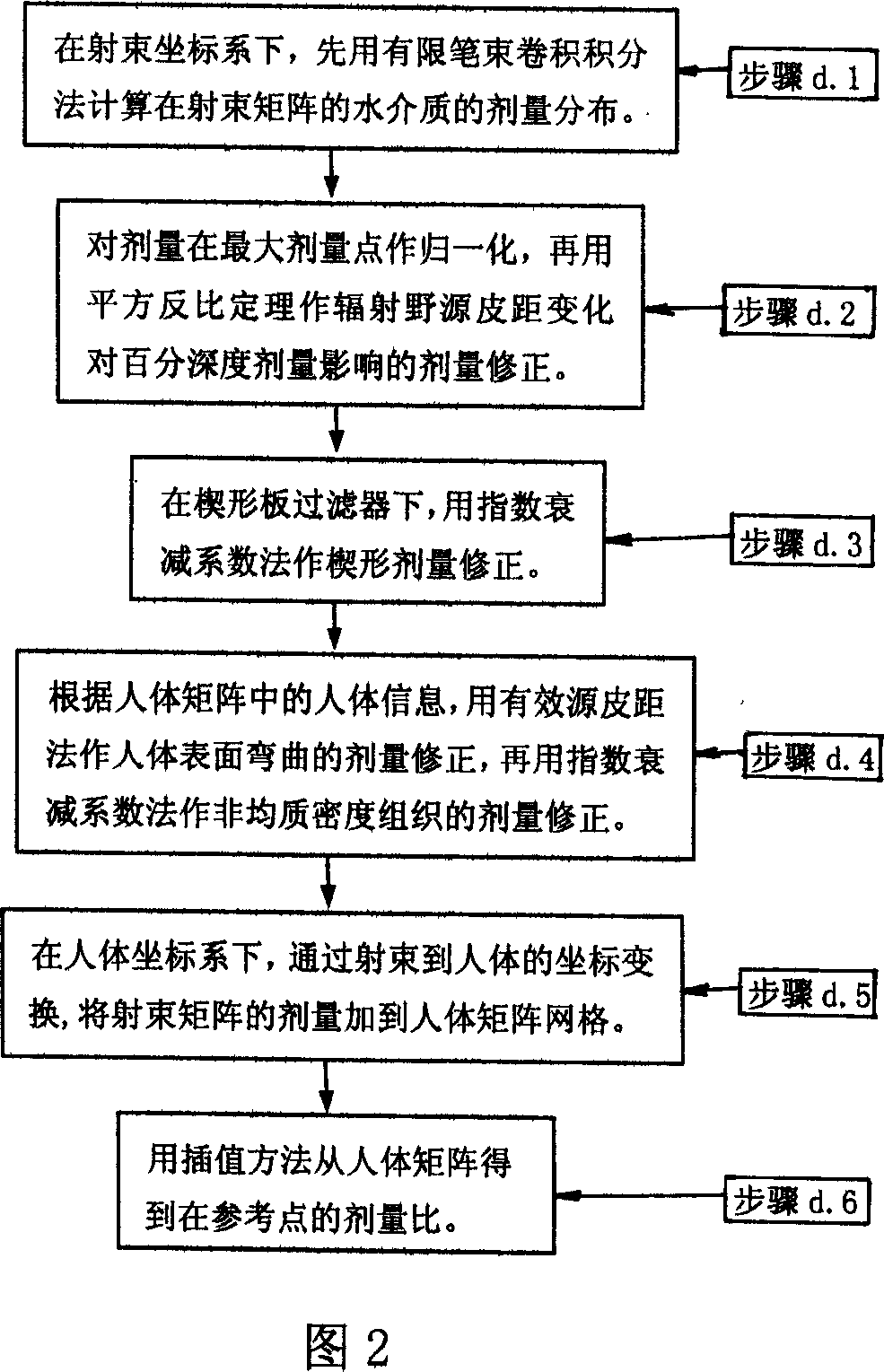
Method for determining radiating field output dose accurately in conformalradiotherapy
The invention relates to a method for accurately fixing the radiation output amount in radiotheraphy, which comprises that setting coordinate on patient, to obtain the information of ill part; setting the radiation coordinate at the injection direction of accelerator, building the projection between the human coordinate and the injection coordination; calculating out the agent distribution generated in the injection grid matrix of injection coordinate; building the formula of output MU; building the body model, processing radiation analogue calculation on the body model, radiating with machine, detecting the radiation amount via the detector in the body model, checking the error between the analogue calculated agent and the detected agent, to reach the demand. The invention builds accurate algorism (A) to be used in variable radiation systems with high accuracy.
Owner:成都奇林科技有限责任公司
Inhaler device
ActiveUS20070240708A1Show reliableEasy to manufactureRespiratorsLiquid surface applicatorsHand heldEngineering
The invention relates to a hand-held device for the dosed distribution of sprayable substances, especially medicaments to be inhaled, said device comprising a cartridge that can be displaced into the distribution-opening position by means of pressure in a housing, and a feeding mechanism moved by the opening course of the cartridge and used to register and display the distribution actuation carried out. Said feeding mechanism is arranged in the centre of a housing below the front wall of the cartridge, on the opening side, overlapping the cartridge valve tube. The aim of the invention is to provide one such hand-held device in a spatially favourable manner, with more reliability in terms of handling, and a simplified structure. To this end, a stepped feeding mechanism arranged in a plate-shaped housing is provided with control elements which rotate about the axis located in the longitudinal direction of the cartridge.
Owner:VON SCHUCKMANN ALFRED
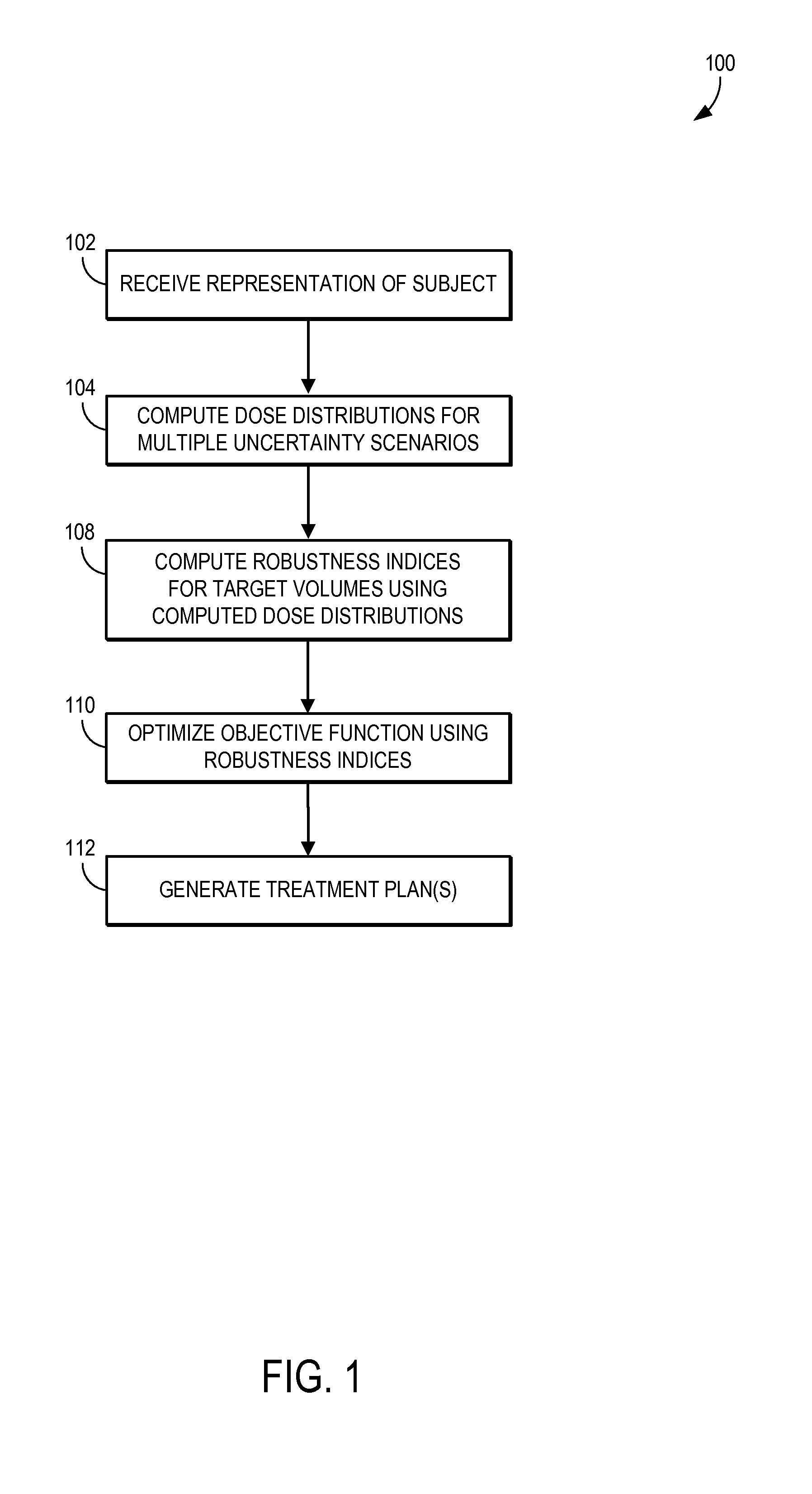
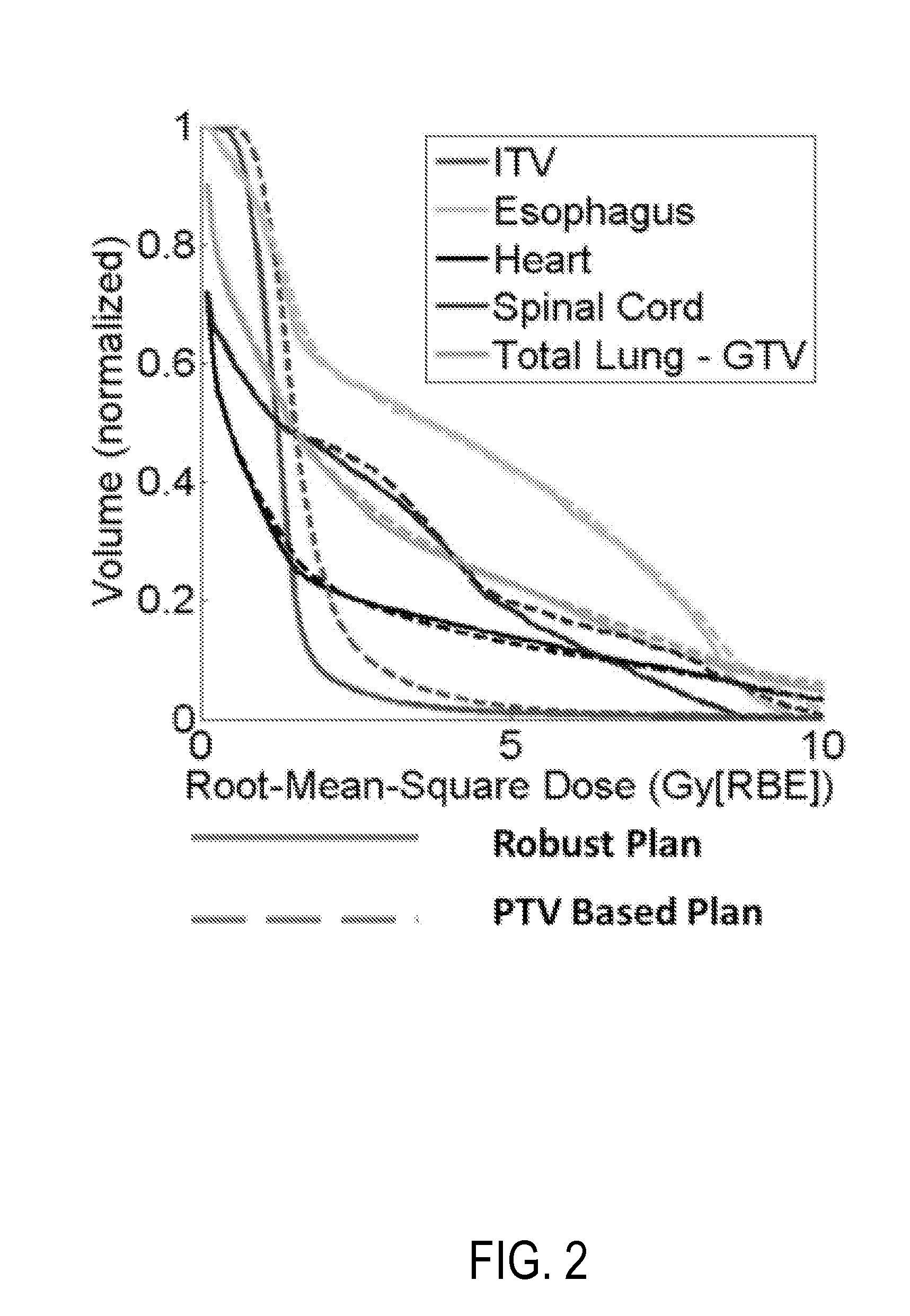
System and method for robust intensity-modulated proton therapy planning
ActiveUS20160059039A1Reduce the impact of uncertaintyEasy to controlHealth-index calculationComputerised tomographsProgram planningProton
The present invention provides a system and method for generating intensity modulated proton therapy plans. The method includes receiving a representation of a subject that includes information related to target and non-target volumes of interest, and computing, using the representation and a proton beam configuration that describes a number of beamlets and their respective arrangement, a dose distribution for each one of a plurality of uncertainty scenarios. The method also includes computing a robustness index for respective locations in the target volumes of interest using the dose distributions, and optimizing an objective function to determine a set of intensity weights for each beamlet in the proton beam configuration, wherein the objective function is based at least in part on deviations of the robustness indices from a prescribed robustness index. The method further includes generating a treatment plan using the determined intensity weights.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
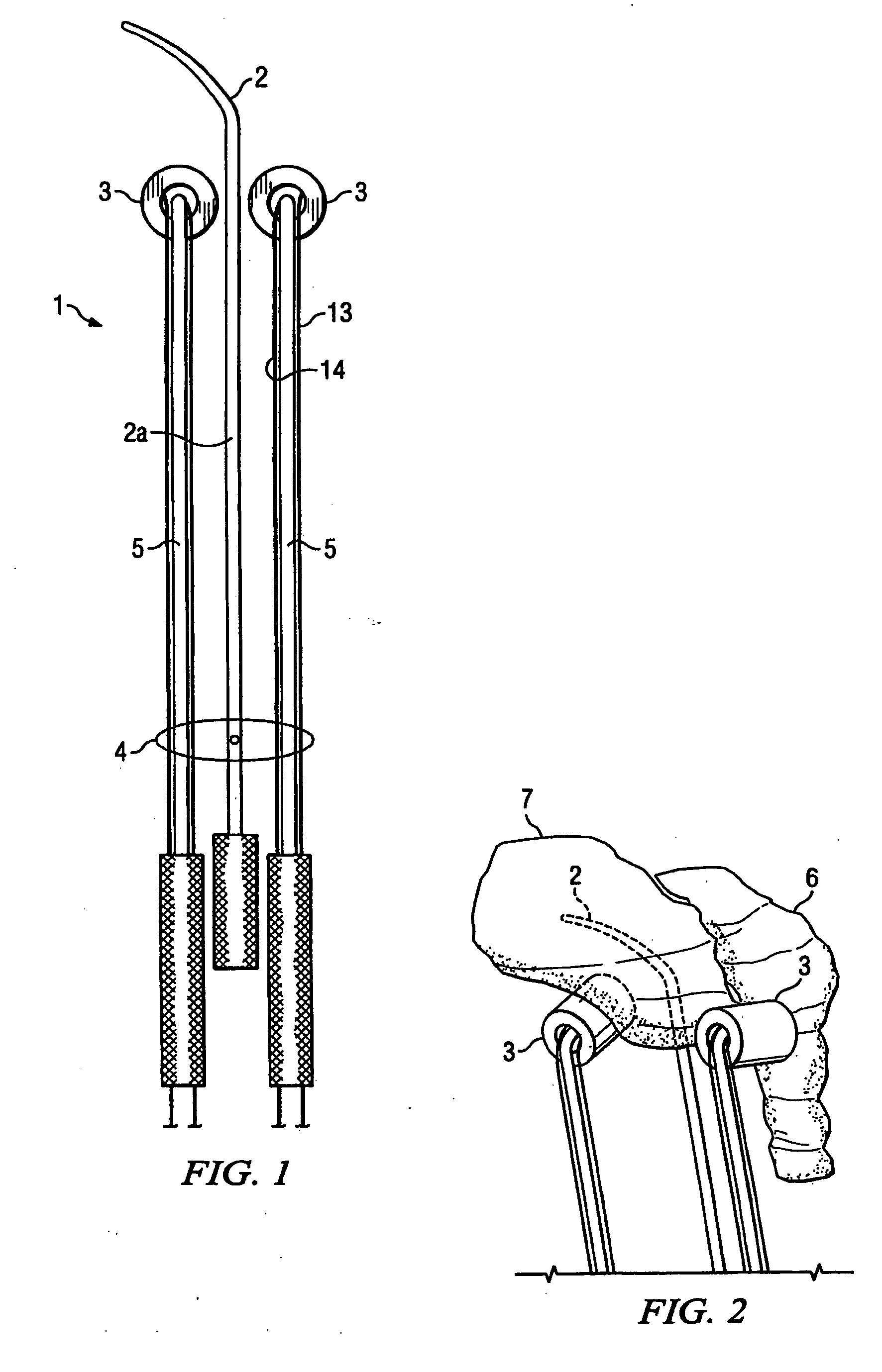
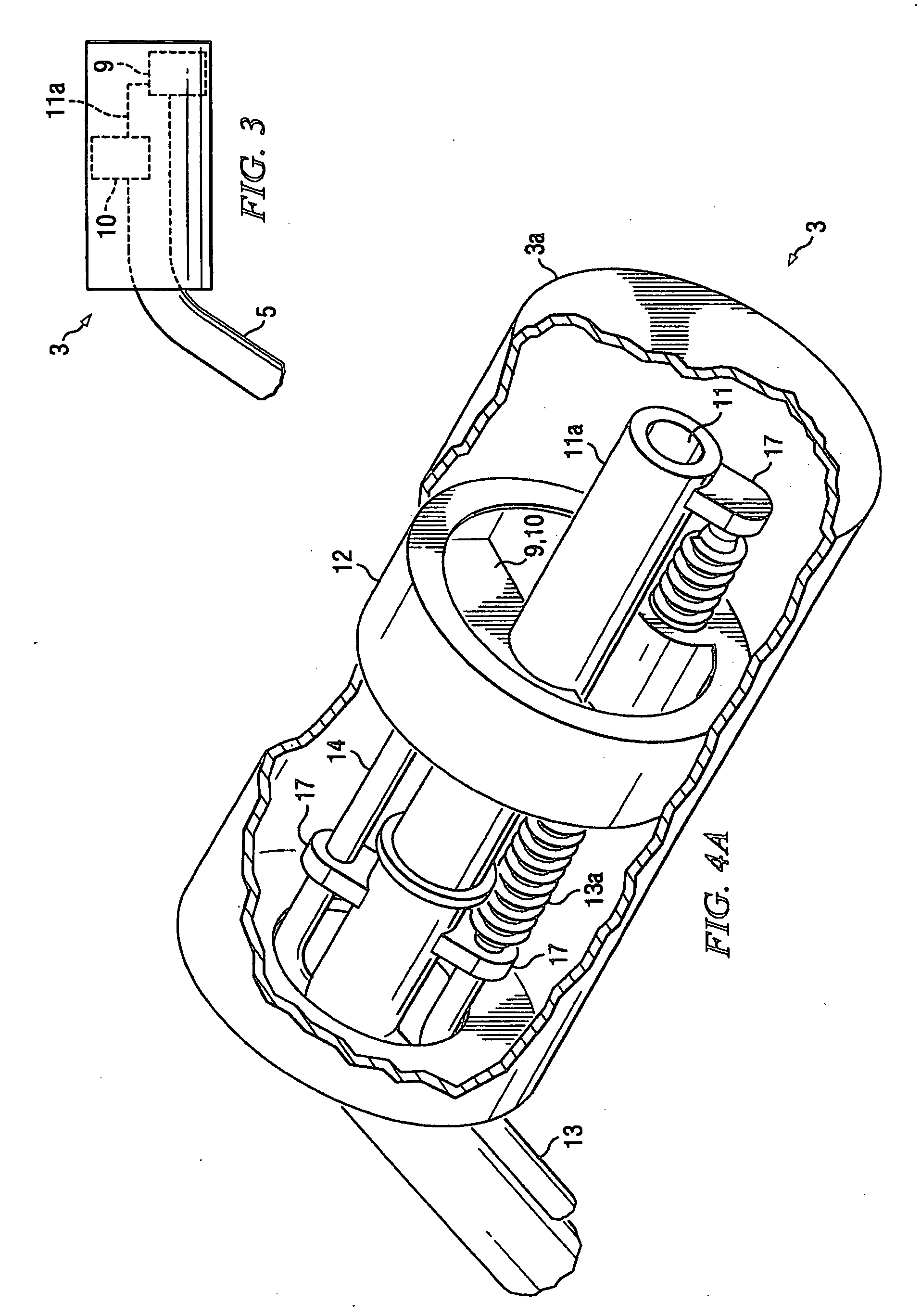
Adaptive intracavitary brachytherapy applicator
ActiveUS20060235260A1Improve on current brachytherapy clinical outcomeReduce complication rateRadiation therapyBrachytherapy deviceNormal tissue
The invention is a novel adaptive CT-compatible brachytherapy applicator with remotely-controlled radial and longitudinal motion radioactive source lumen shields that can be manipulated by the radiation oncologist to optimize the dose distribution to the target and normal tissue structures for brachytherapy procedures.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Device and method for particle therapy monitoring and verification
ActiveUS8716663B2PhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansConformal radiation therapyParticle physics
The present invention relates to a device and method for monitoring and verification of the quality of a radiation treatment beam in conformal radiation therapy, and in particular for IMPT (Intensity Modulated Particle Therapy) applications. The device comprises a 2D electronic detector measuring 2D responses to the delivered treatment beam. These 2D responses are compared with predicted 2D responses and differences in responses are signalled. Based on the measured 2D responses the effectively delivered 3D dose distribution in the target can be reconstructed.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Method and a system for optimizing a radiation treatment plan
A computer-based method for generating an improved radiation therapy treatment plan for a treatment volume having a target and an organ-at-risk. The method includes a step of accessing an existing radiation therapy treatment plan from a memory of a computer, a dose distribution of the existing radiation therapy treatment plan serving as a reference dose distribution; and performing machine parameter optimization on the existing radiation therapy treatment plan with the computer by pursuing an optimization goal to minimize doses to the organ-at-risk, thereby generating the improved radiation therapy treatment plan.
Owner:RAYSEARCH LAB
Radiotherapeutic system and radiotherapeutic dose distribution measuring method
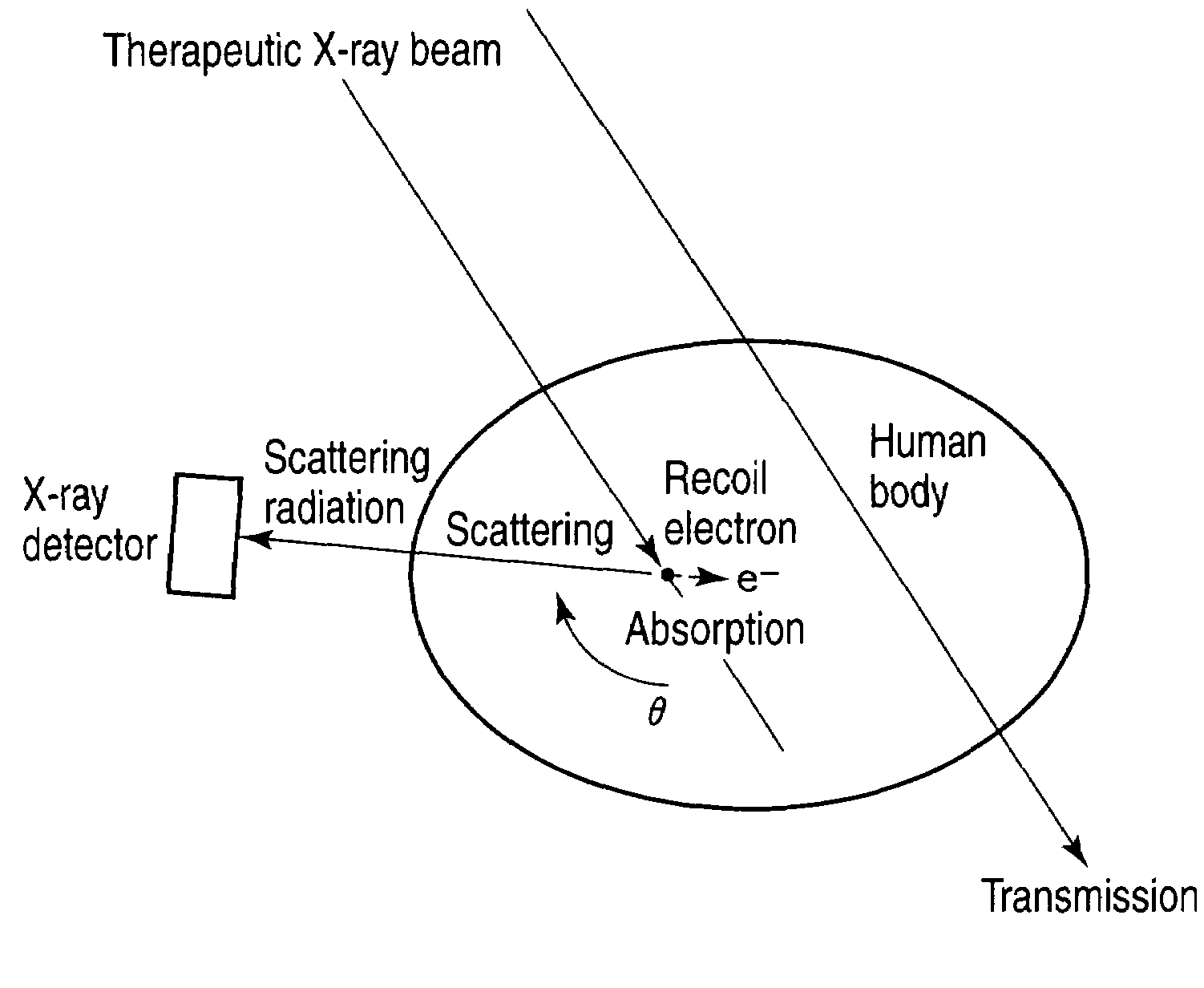
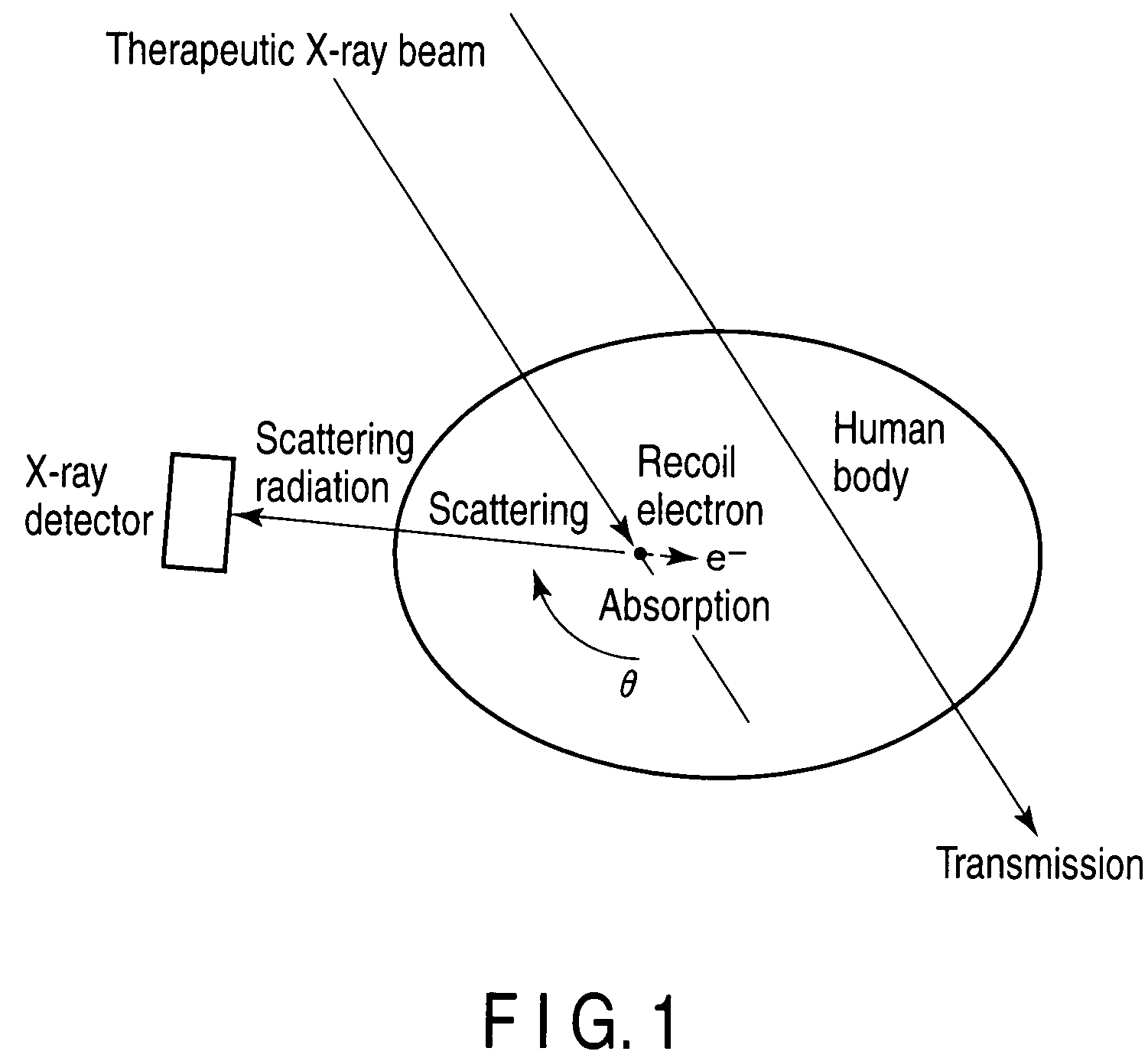
ActiveUS20090161818A1Avoid problemsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-rayCompton scattering
A detector having a collimator in a position at a specific angle with respect to a therapeutic X-ray beam is mounted to selectively detect only scattering radiation in the direction. To three-dimensionally obtain a distribution of places where scattering occurs in a patient body, a detector is rotated during irradiation and scattering radiation is measured from all of directions. After that, a reconstructing process is performed, and a distribution of occurrence of scattering radiation in the subject is three-dimensionally imaged. Since angles and amounts of X-rays scattered by Compton scattering are known theoretically, if scattering radiation at a certain angle can be detected, the number of scattering radiation at other angles can be also estimated. On the basis of the theory, images of distribution of scattering radiation sources are converted to images of distribution of absorption of radiation.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
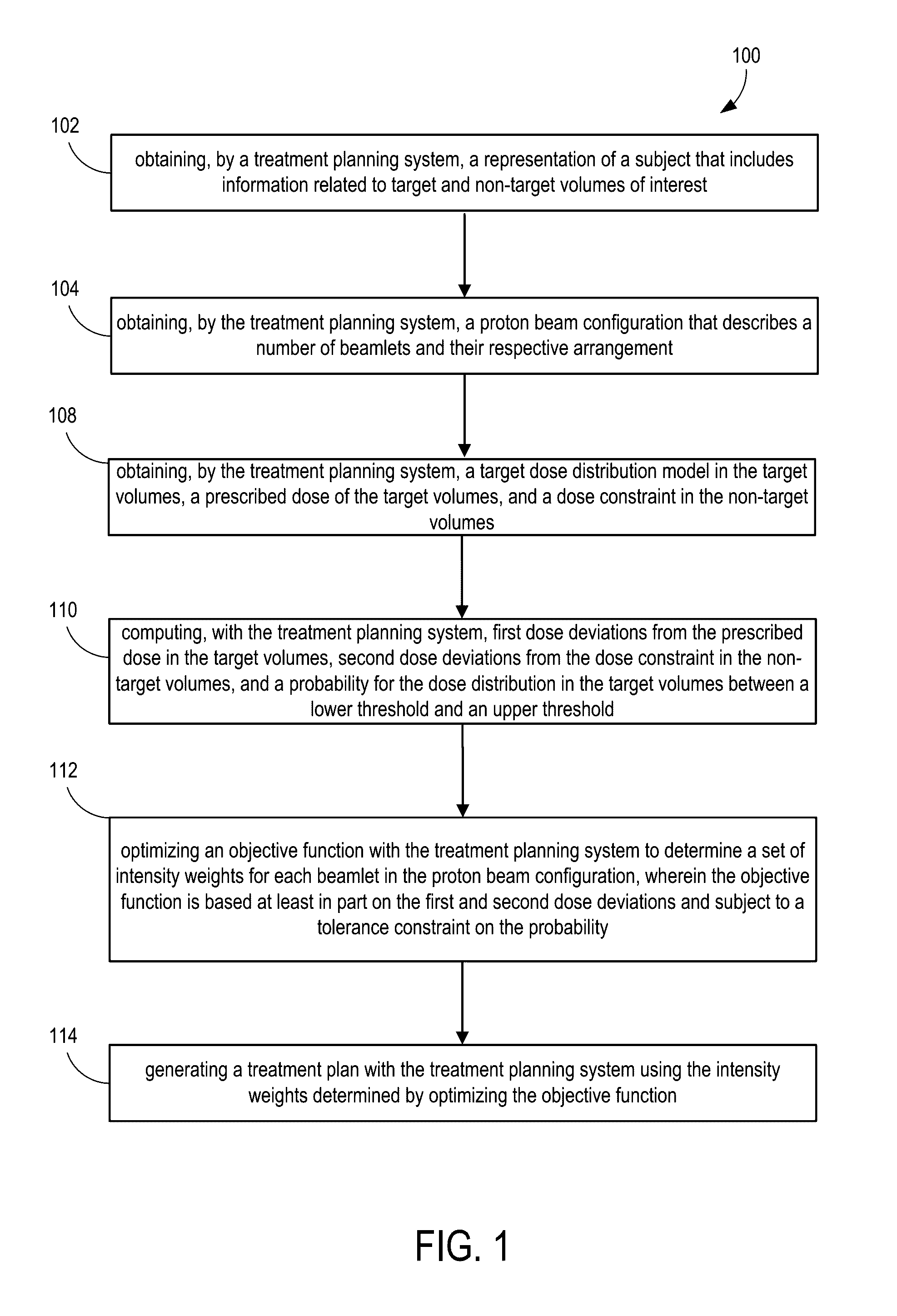
System and method for novel chance-constrained optimization in intensity-modulated proton therapy planning to account for range and patient setup uncertainties
A system and methods are provided for generating intensity modulated proton therapy plans robust to various kinds of delivery uncertainties with the capability for treatment planners to control the balance between plan quality and robustness. The system obtains a representation of a subject and a proton beam configuration that describes a number of beamlets and their respective arrangement. The system computes an objective function, in the treatment planning system, first part of which is about dose deviations from the prescribed dose in the target volumes, second part of which is about dose deviations from the dose constraint in the non-target volumes, and computing dose volume constraints for targets using a probability to control the dose distribution in the target volumes to be between a lower threshold and an upper threshold. Based on this information, the system obtains a robust chance-constrained treatment planning model with a user-adjustable tolerance level.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES +1
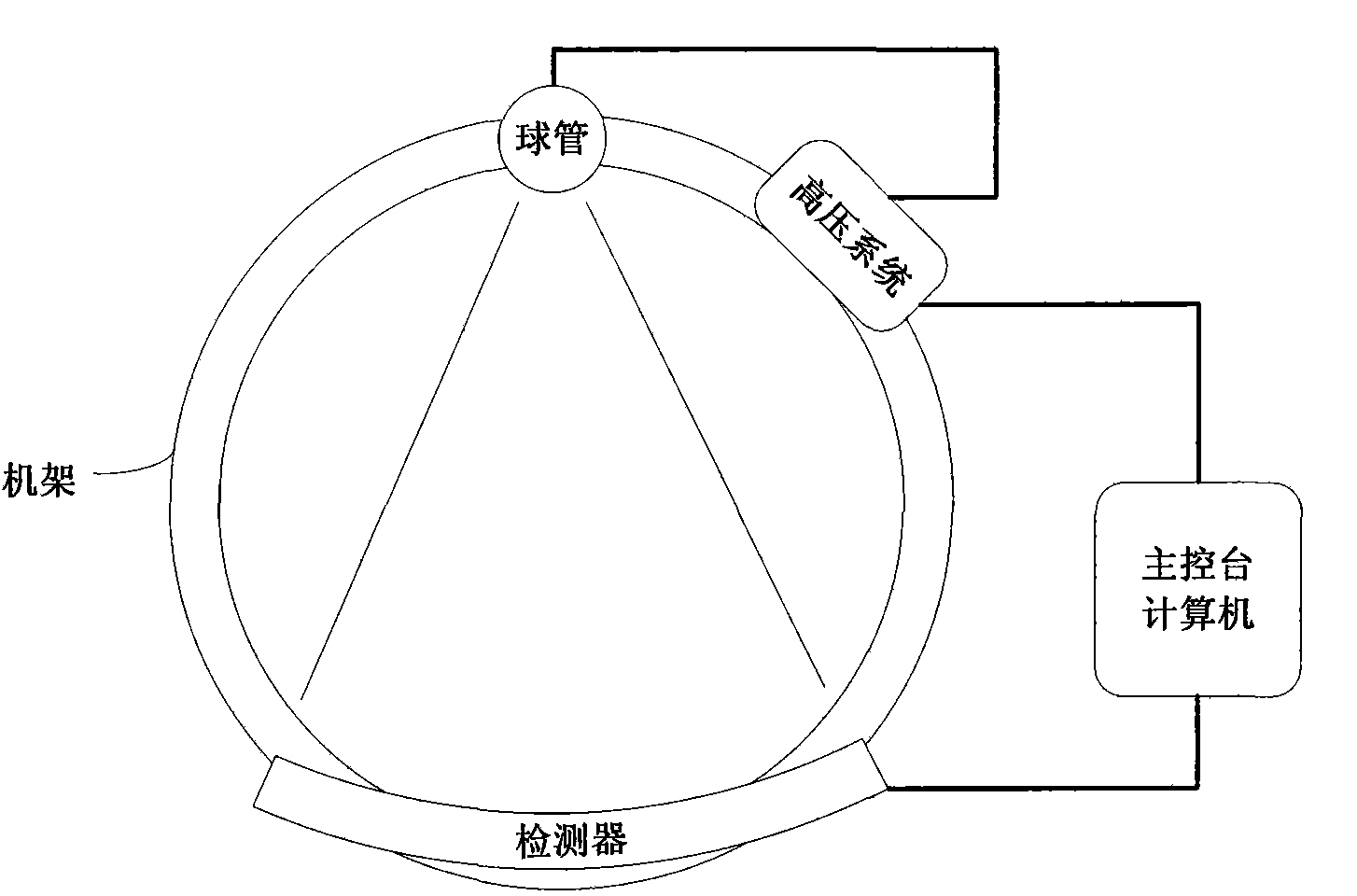
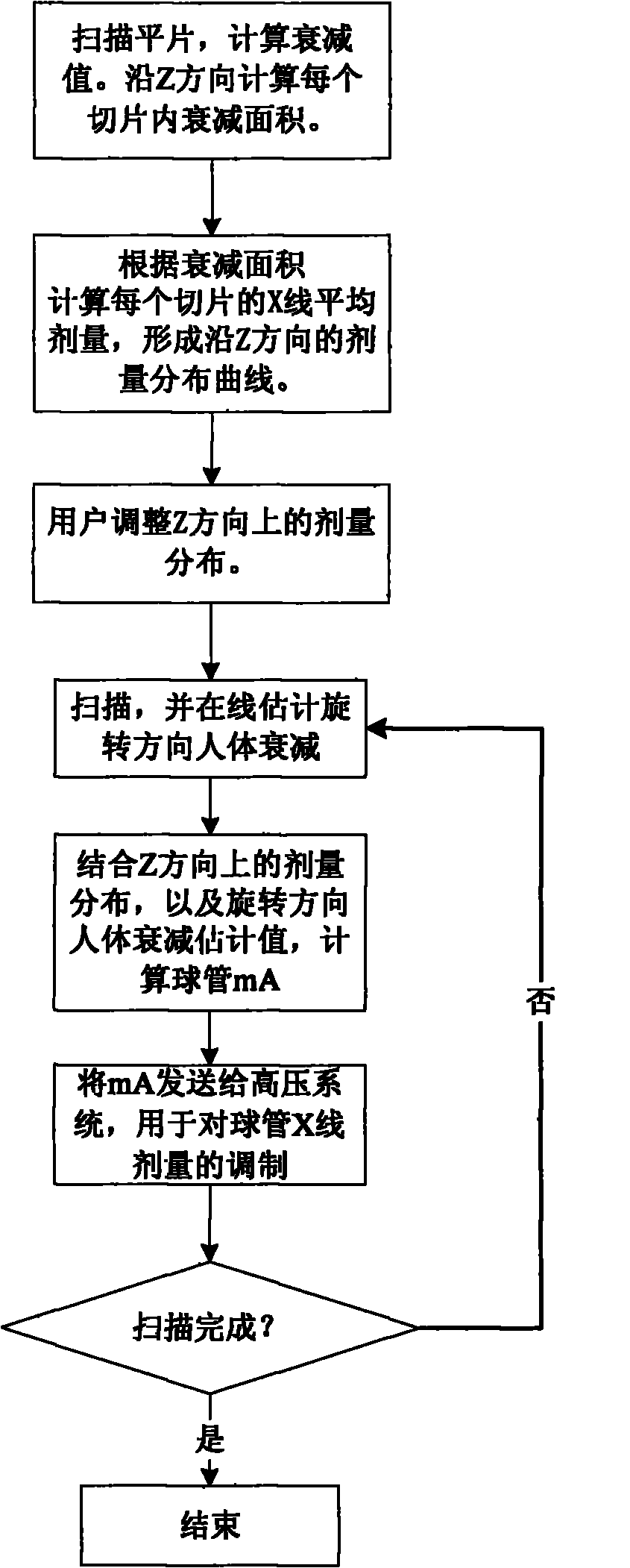
On-line dose modulation method of X-ray CT (Computed Tomography) machine
ActiveCN102100562AReduce overexposureReduce the problem of underexposureComputerised tomographsTomographyUltrasound attenuationComputed tomography
The invention relates to an on-line dose modulation method of an X-ray CT (Computed Tomography) machine, which comprises the following steps: scanning plain film data, extracting Z-direction attenuation information of a human body, and calculating the attenuation area of the human body in each cut film along the Z direction; according to the attenuation area, calculating the average X-ray dose in each cut film to form a dose distribution curve along the Z direction, and supplying to a user as an initial recommended value, so that the user can adjust the dose distribution in the Z direction as required; scanning a patient, and simultaneously carrying out on-line estimation on the attenuation value of the rotation direction of the patient to obtain an attenuation estimated value; combining the dose distribution in the Z direction with the attenuation estimated value of the human body in the rotation direction to calculate a bulb tube mA value; transmitting the mA value to a high-pressure system, and carrying out high-frequency dose adjustment; and finishing the on-line dose modulation process if the scanning is completed. The invention reduces the overexposure and underexposure possibly caused by assuming sine laws. Besides, the invention does not assume that what passes through the central passage is the maximum attenuation, so that the dose modulation is better matched with the shape of the actual object.
Owner:NEUSOFT MEDICAL SYST CO LTD
Particle beam irradiation system and method of adjusting irradiation field forming apparatus
InactiveUS20050167616A1Increase in sizePenumbra can be reducedElectrotherapyRadiation/particle handlingParticle beamLight beam
Owner:HITACHI LTD
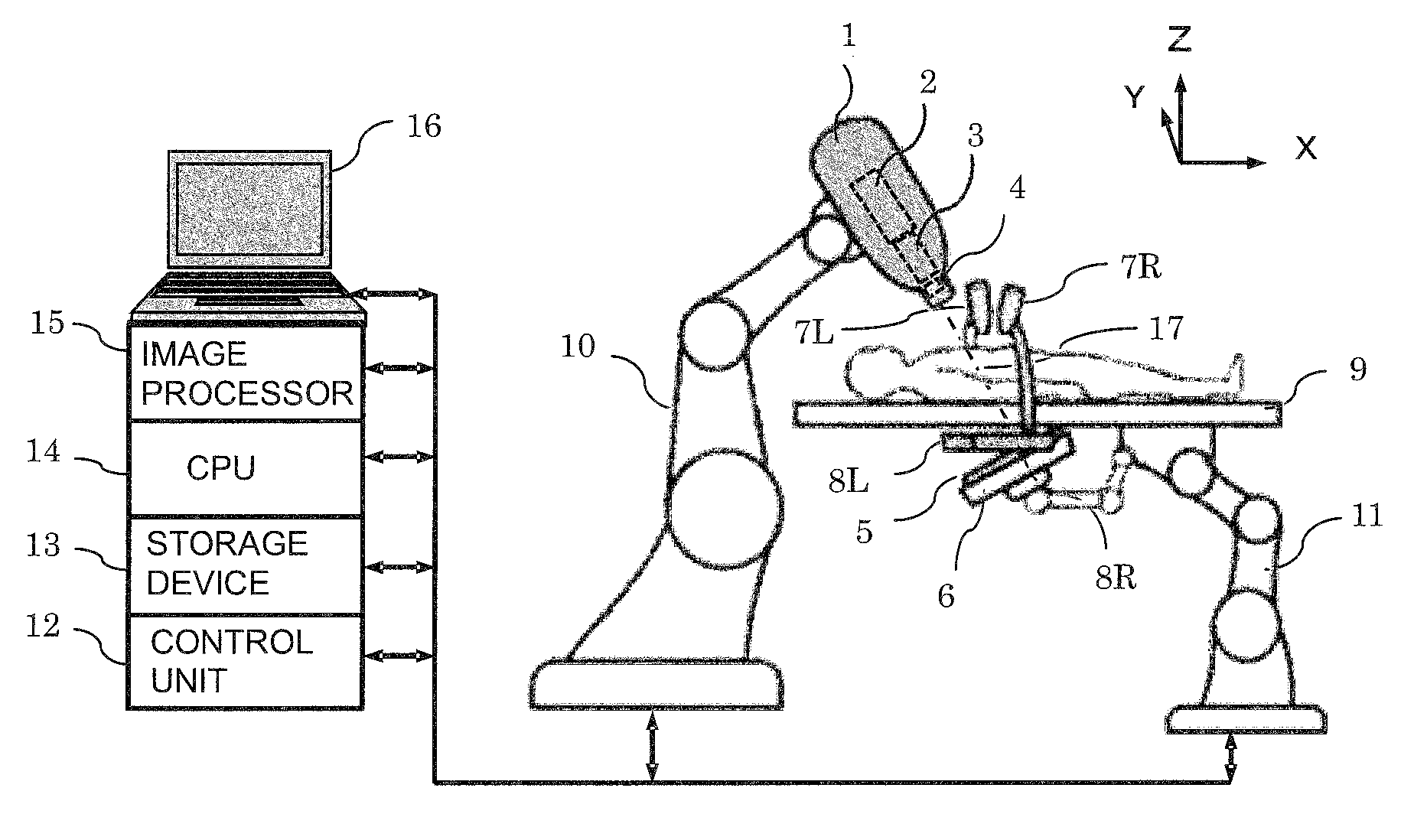
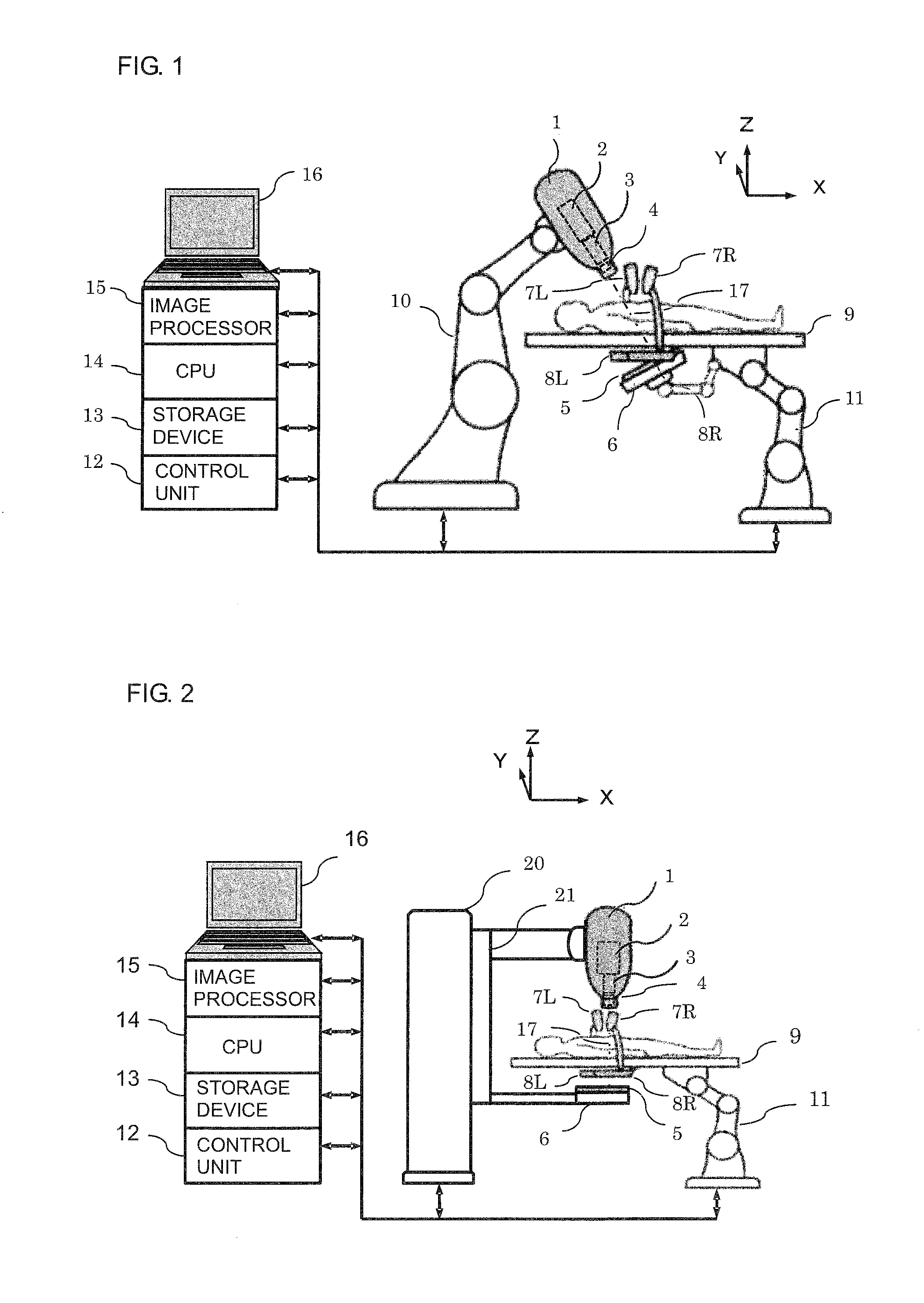
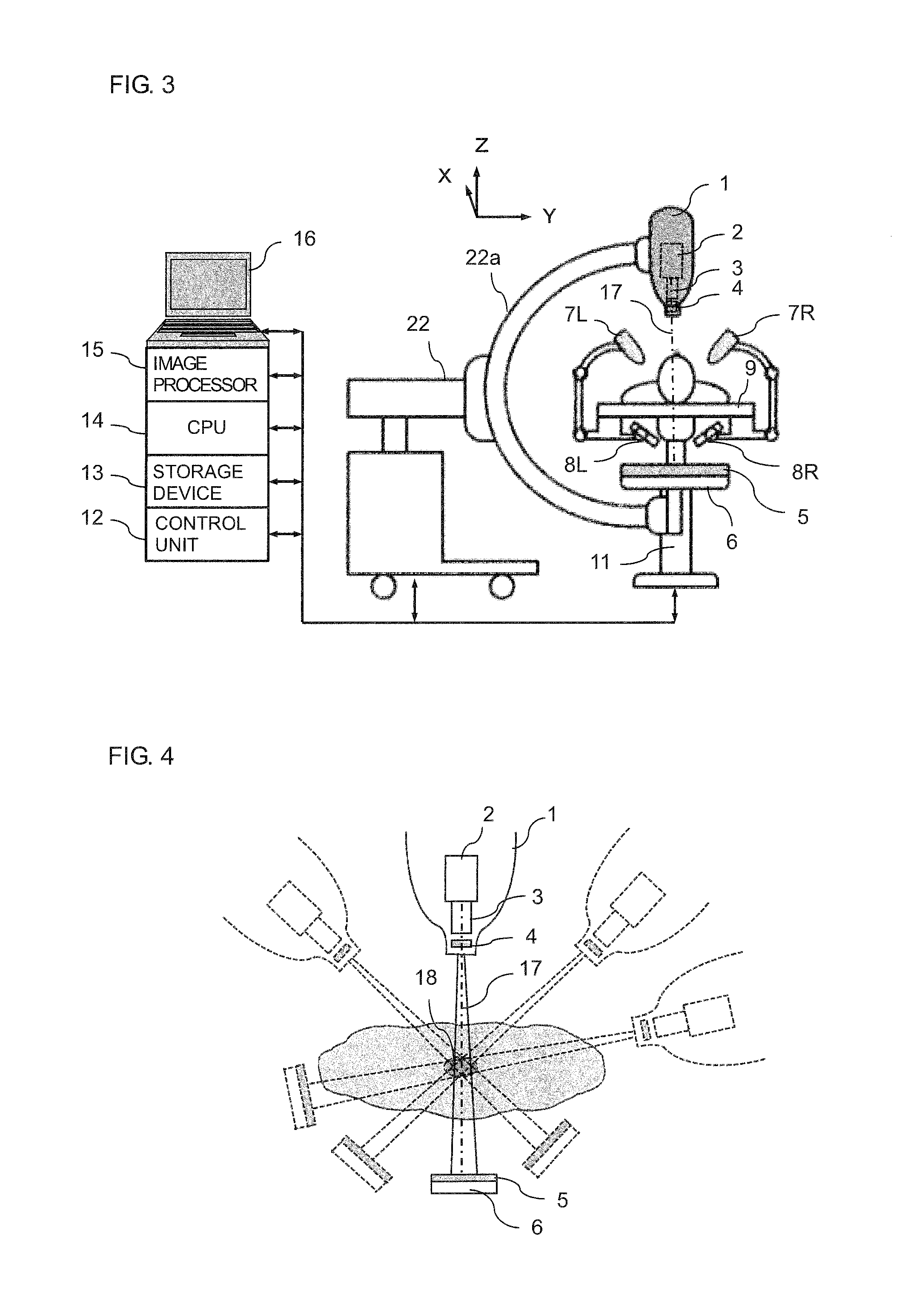
Real-time three-dimensional radiation therapy apparatus and method
InactiveUS9149656B2High precisionIncrease speedMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTreatment targetsX-ray
A radiation therapy apparatus including a robot supporting a robot head; a therapeutic radiation source attached to the robot head; a collimator for adjusting a radiation field shape of therapeutic radiation radiated from the therapeutic radiation source; a first therapeutic radiation detector attached to the robot head; a couch configured to support a patient lying supine thereon; a second therapeutic radiation detector for detecting the therapeutic radiation, disposed opposite the first therapeutic radiation detector with the couch disposed therebetween; at least two X-ray sources and detectors for position detection of a marker and / or a treatment target; an image processor for reconstructing an image of the treatment target; and a CPU that computes the intensity, irradiation direction, dose, and dose distribution of the therapeutic radiation, and dose absorbed by the treatment target, radiation field shape, and position of the treatment target in real time for feedback to a next irradiation.
Owner:ACCUTHERA
Method for pre treatment verification in radiation therapy
ActiveUS20060203967A1Accurate distributionReduce directional and energy dependencyX-ray apparatusRadiation diagnosticsTreatment verificationPre treatment
The present invention relates to a method to measure dose distribution in a patient-shaped phantom with high accuracy. The invention consists of a method of measuring dose distribution in a phantom for radiation therapy treatment verification, a detector configuration in such a phantom, detector improvement and measurement methodology to enable application of correction factors in an accurate way.
Owner:NILSSON GORGEN
Brachytherapy apparatus and methods
InactiveUS6846282B1Accurate storageX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyAdemetionineRadioactive seed
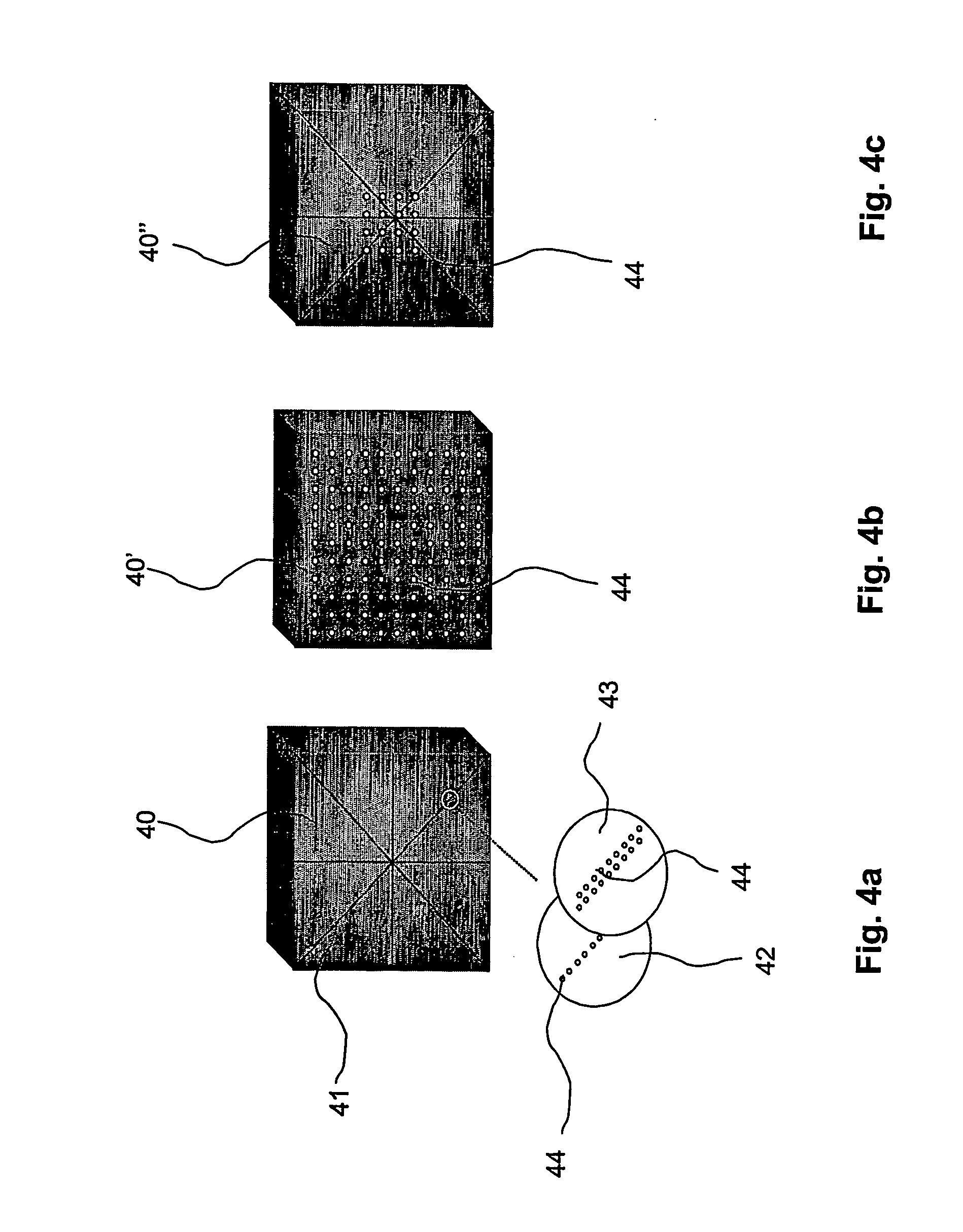
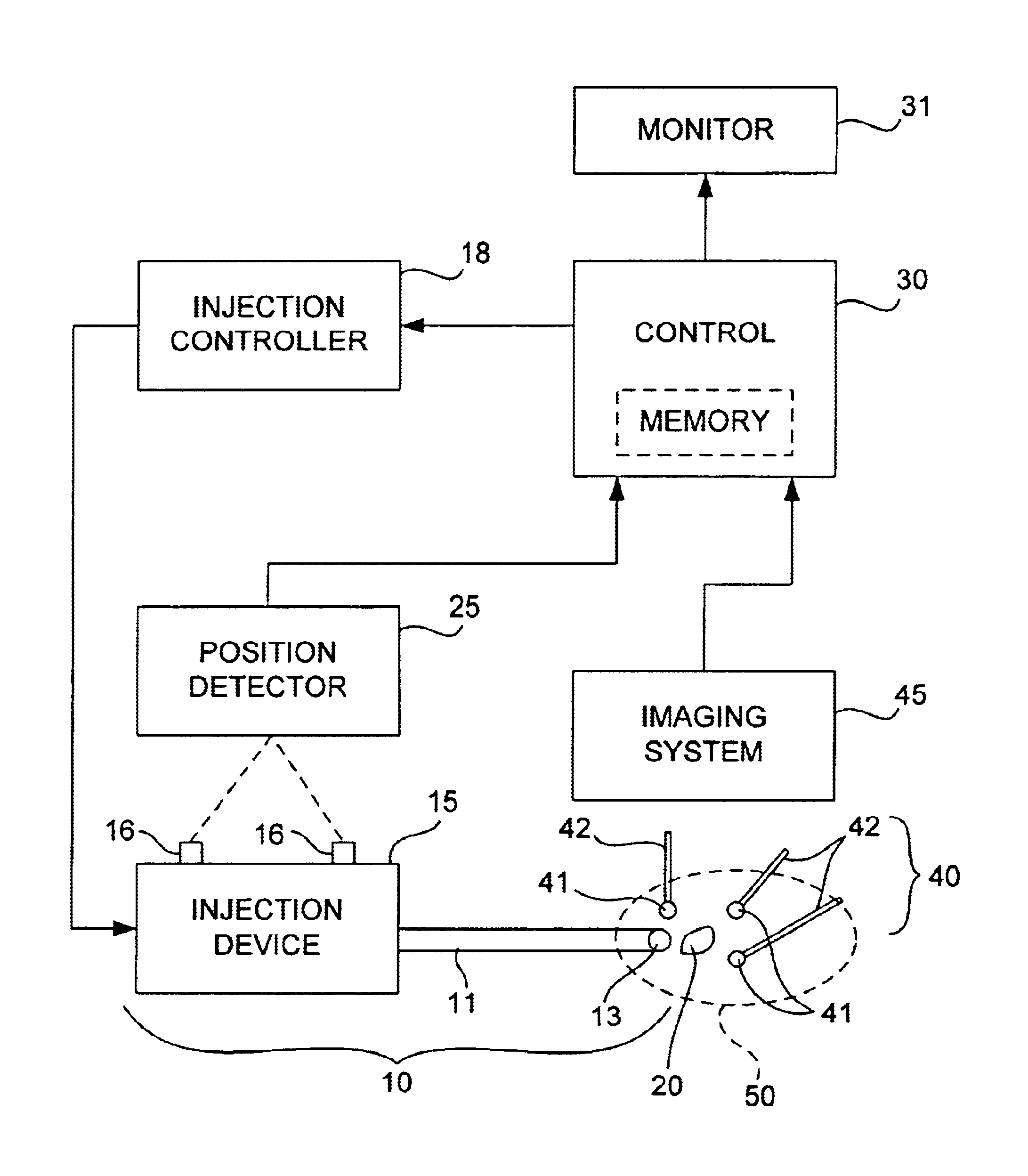
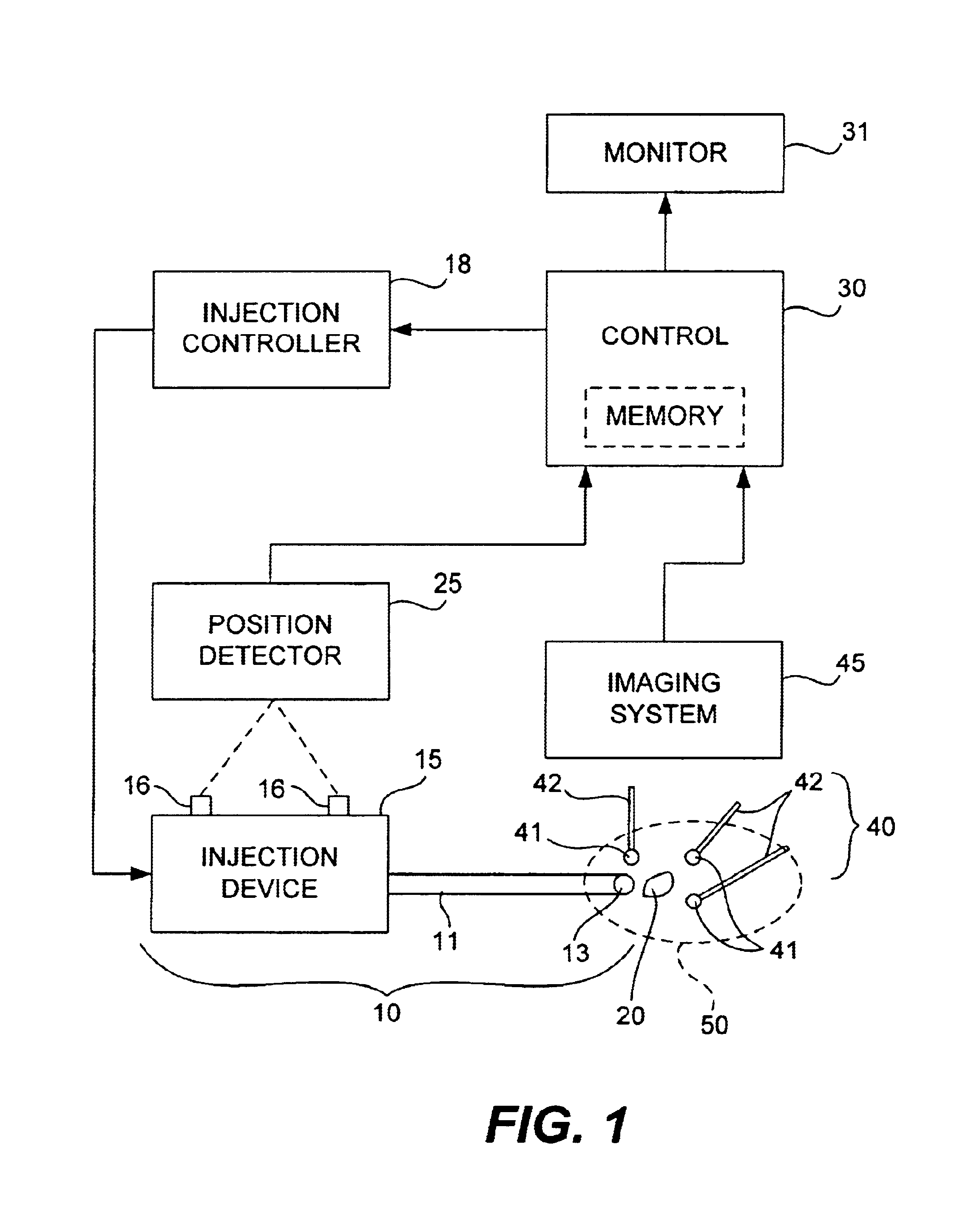
Brachytherapy is carried out with a needle to inject a radioactive seed into a patient's body. A space-fixed detector detects radiation from radiation emitters to determine the position of a deposited seed from the needle with reference to a space-fixed coordinate system. Markers may be affixed to the patient's body such that a body-fixed coordinate system can be determined in real time by an imaging device. Alternatively, earlier obtained patient's anatomical data may be referenced. After positions of earlier injected seeds are thus ascertained in real time in the body-fixed coordinate system, the stored anatomical data may be updated and a radiation dose distribution can be calculated from the determined seed positions. The calculated radiation dose distribution can be displayed and compared with a planned distribution.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Laser-Accelerated Proton Therapy Units And Superconducting Electromagnet Systems For Same
InactiveUS20090050819A1Material analysis by optical meansMagnetic discharge controlSuperconducting CoilsLight beam
Compact particle selection and collimation devices are disclosed for delivering beams of protons with desired energy spectra. These devices are useful with laser-accelerated proton therapy systems, in which the initial protons have broad energy and angular distributions. Superconducting magnet systems produce a desired magnetic field configuration to spread the protons with different energies and emitting angles for particle selection. The simulation of proton transport in the presence of the magnetic field shows that the selected protons are successfully refocused on the beam axis after passing through the magnetic field with the optimal magnet system. Dose distributions are also provided using Monte Carlo simulations of the laser-accelerated proton beams for radiation therapy applications.
Owner:INST FOR CANCER RES
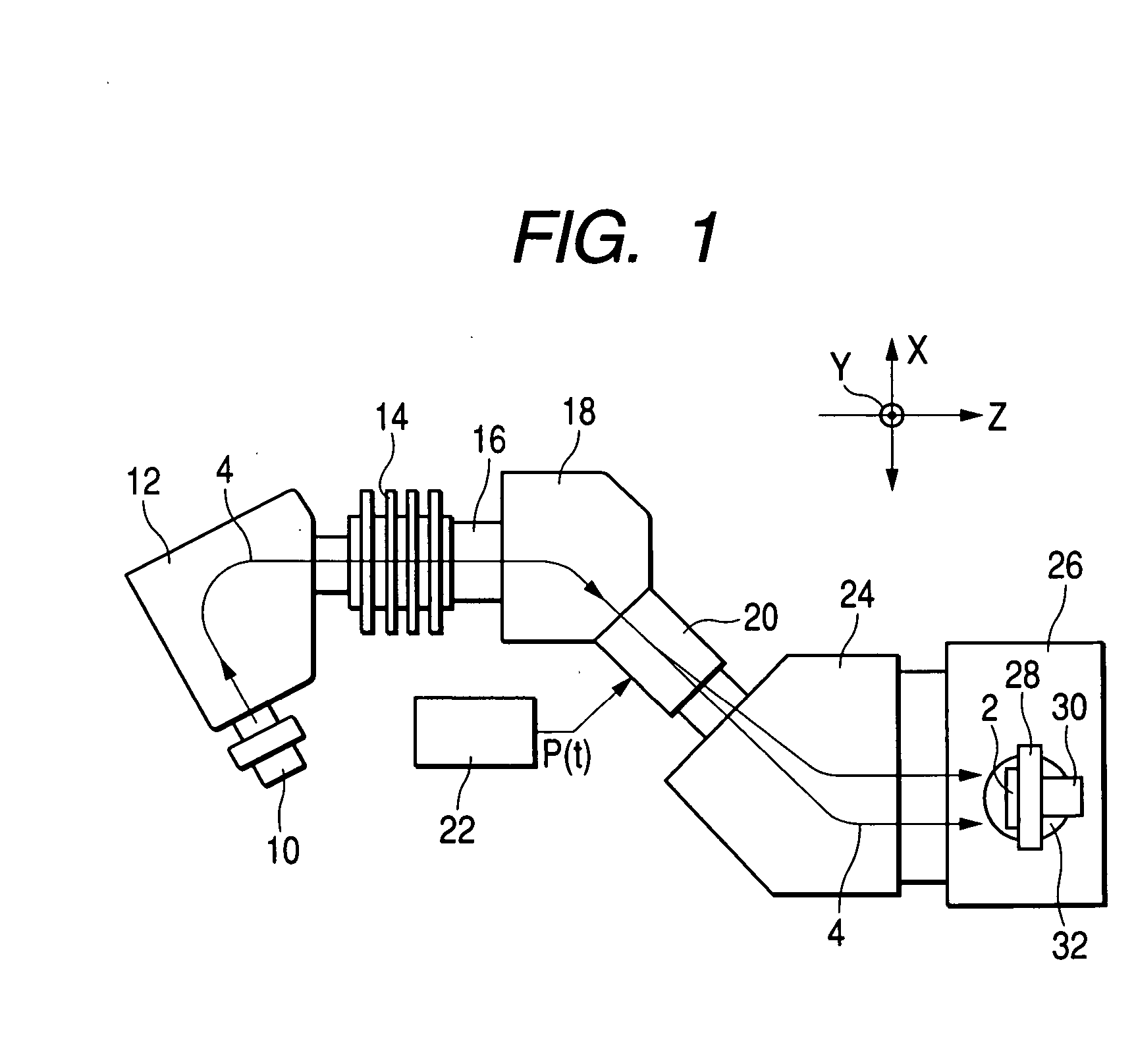
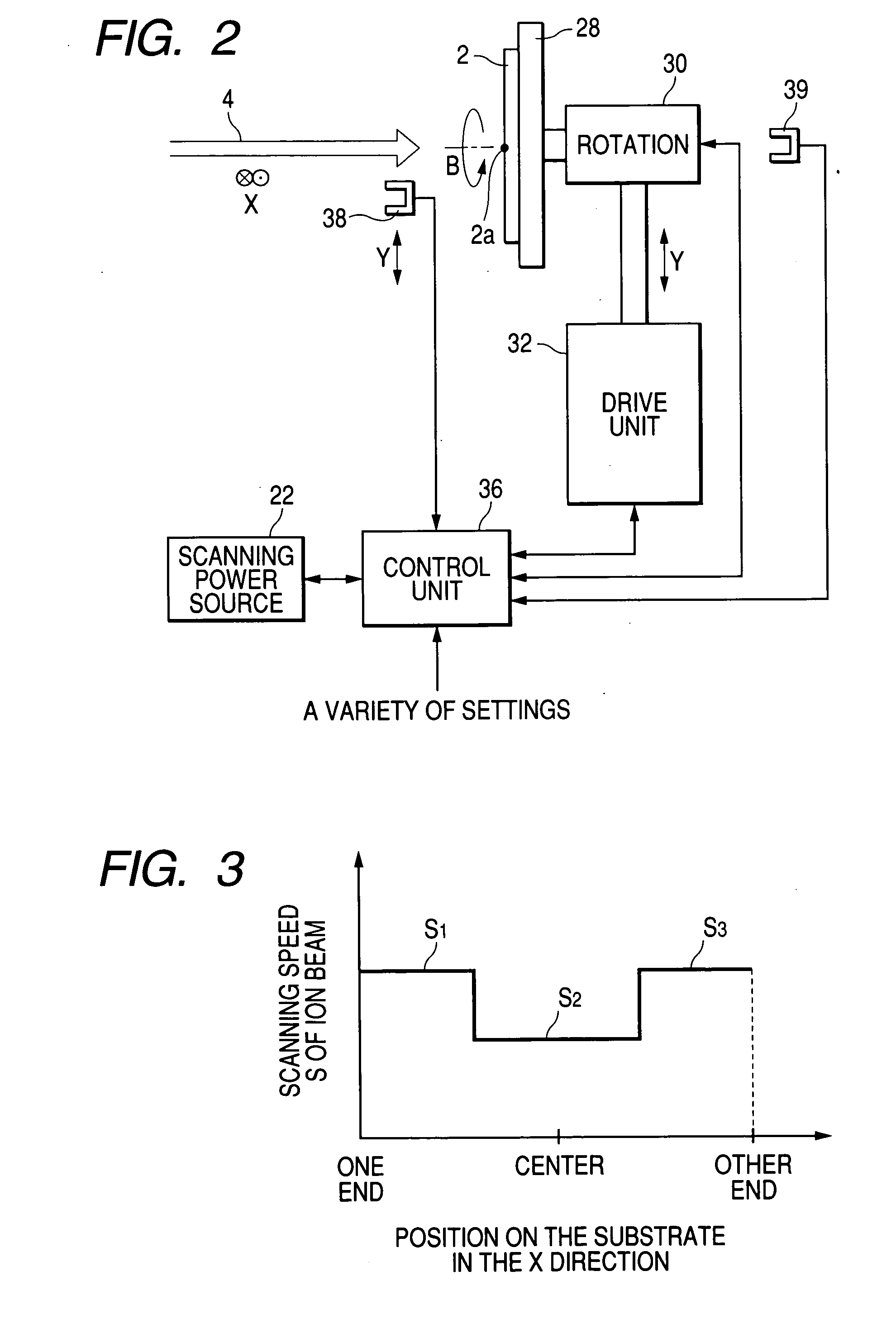
Ion implantation method and apparatus
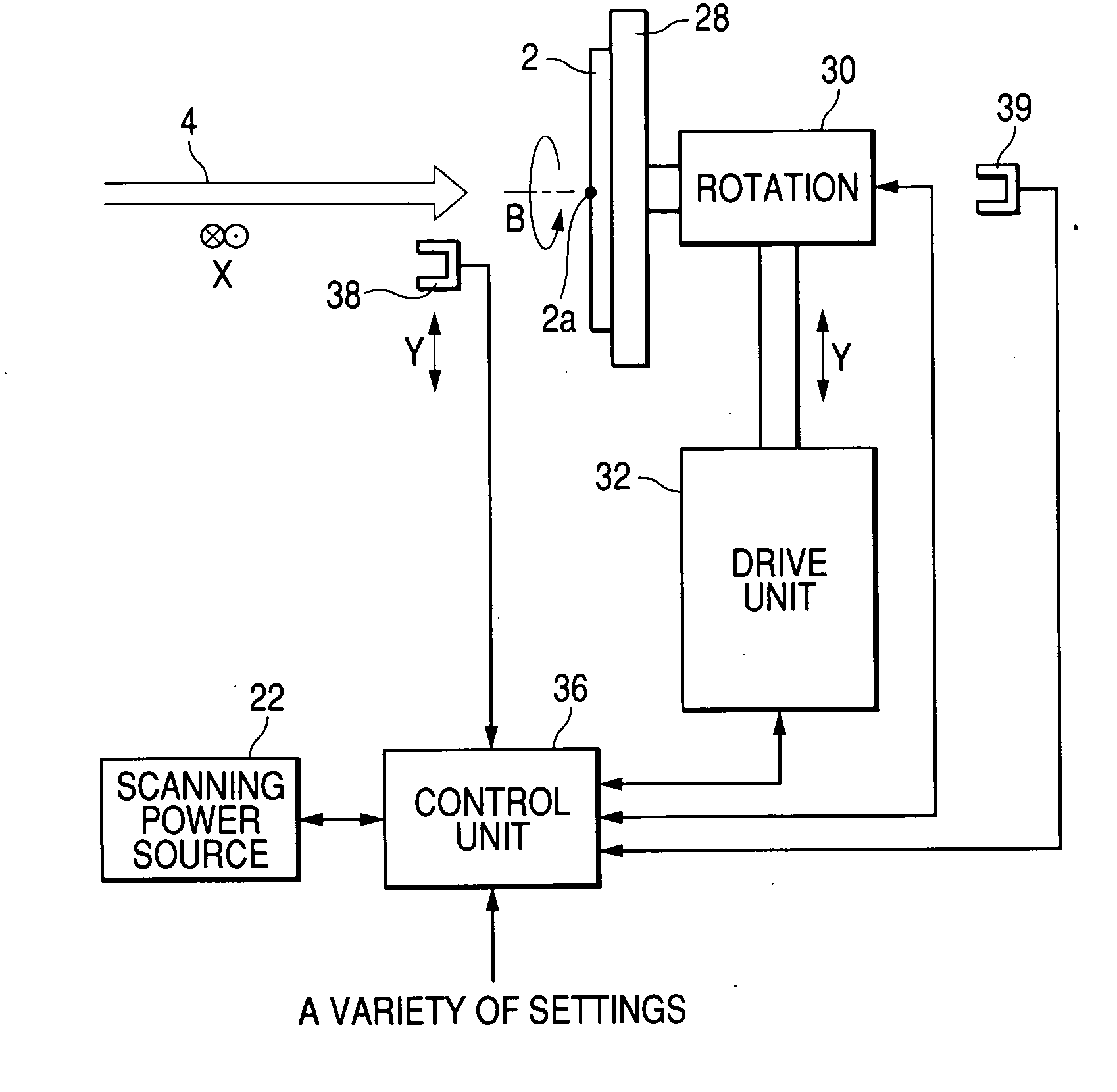
An ion implantation method includes scanning reciprocatingly an ion beam in an X direction by an electric field or magnetic field and mechanically driving reciprocatingly a substrate in a Y direction orthogonal to the X direction to implant ions over the entire surface of the substrate. A dose distribution that is non-uniform within the plane of the substrate is formed within the plane of the substrate by changing at least one of a scanning speed of the ion beam and a driving speed of the substrate within an area where the ion beam is incident on the substrate.
Owner:NISSIN ION EQUIP CO LTD
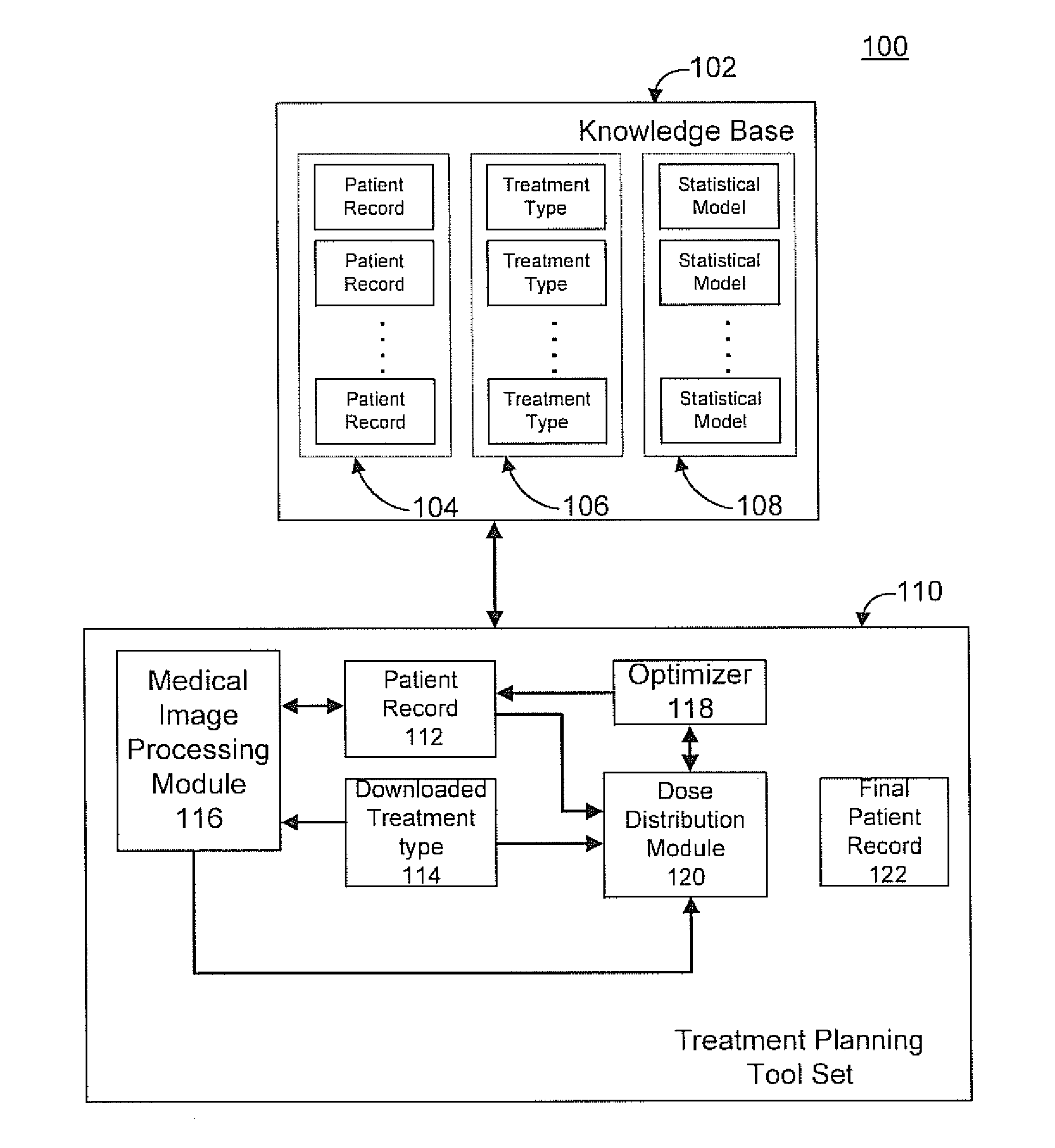
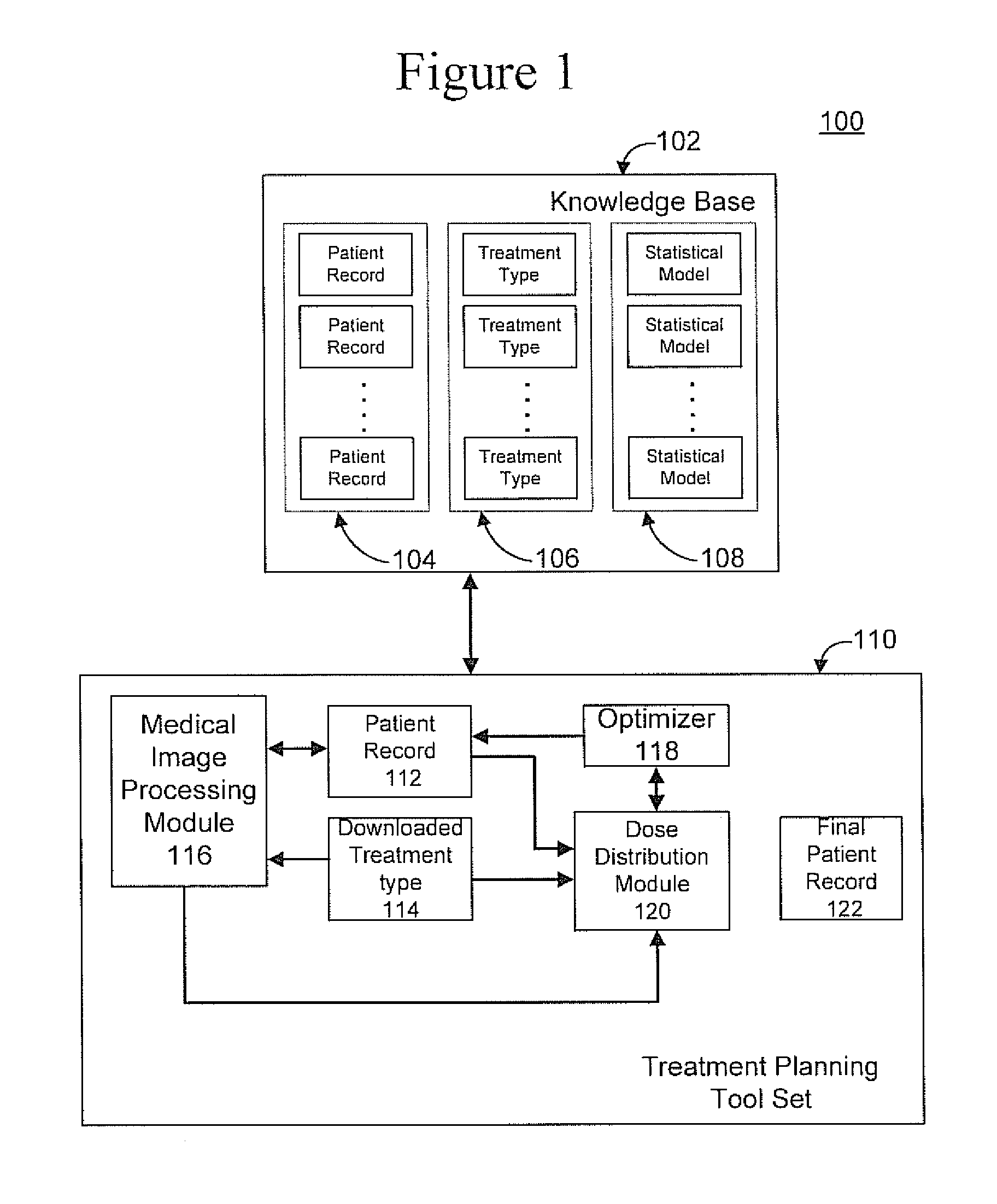
Radiation therapy treatment plan improvement through use of knowledge base
A radiation therapy dose distribution method starts with selecting a treatment type. Then an organ at risk (OAR) distance to target map is determined. The OAR distance to target map comprises distances to a target organ for portions of an OAR. The OAR distances are determined from at least one segmented patient organ image. A cohort average dose distance to target histogram is selected. A dose value to the portions of the OAR are assigned to form a first 3D dose distribution map. The dose values are from the selected cohort average dose distance to target histogram. A second 3D dose distribution map is determined based on a field arrangement determined by the treatment type and the first 3D dose distribution map. A dose distance to target histogram is calculated using the second 3D dose distribution map and the distance to target map.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Charged particle beam irradiating apparatus
ActiveUS8153989B2Avoid unevennessStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsParticle physicsIrradiation
The present invention provides a charged particle beam irradiating apparatus capable of simply preventing unevenness or reduction in a peripheral portion of the dose distribution of a charged particle beam.A charged particle beam irradiating apparatus includes scanning electromagnets that scan a charged particle beam and a control device that controls the operations of the scanning electromagnets. In the charged particle beam irradiating apparatus, the control unit changes a scanning speed when the charged particle beam is irradiated along an irradiation line such that a peripheral portion of the dose distribution of the charged particle beam is corrected.
Owner:SUMITOMO HEAVY IND LTD
Dose Calculation Method for Multiple Fields
ActiveUS20110091014A1X-ray apparatusX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDose calculationRadiation dose
Systems and methods for developing a treatment plan for irradiating a treatment volume within a patient are disclosed. In accordance with the present invention, control points used to calculate a dose of radiation delivered to the treatment volume may be combined to result in a smaller number of control points. The smaller number of control points may allow more efficient calculation of dose distributions resulting in a treatment plan that can be delivered to the patient earlier or may allow additional iterations of treatment plan optimization resulting in a more accurate dose distribution being delivered to the patient.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
Method for inversing patient target region dosage in radiation therapy
InactiveCN101209367AHigh precisionTroubleshooting Accurate ExecutionImage data processing detailsRadiation diagnosticsFlat panel detectorImage resolution
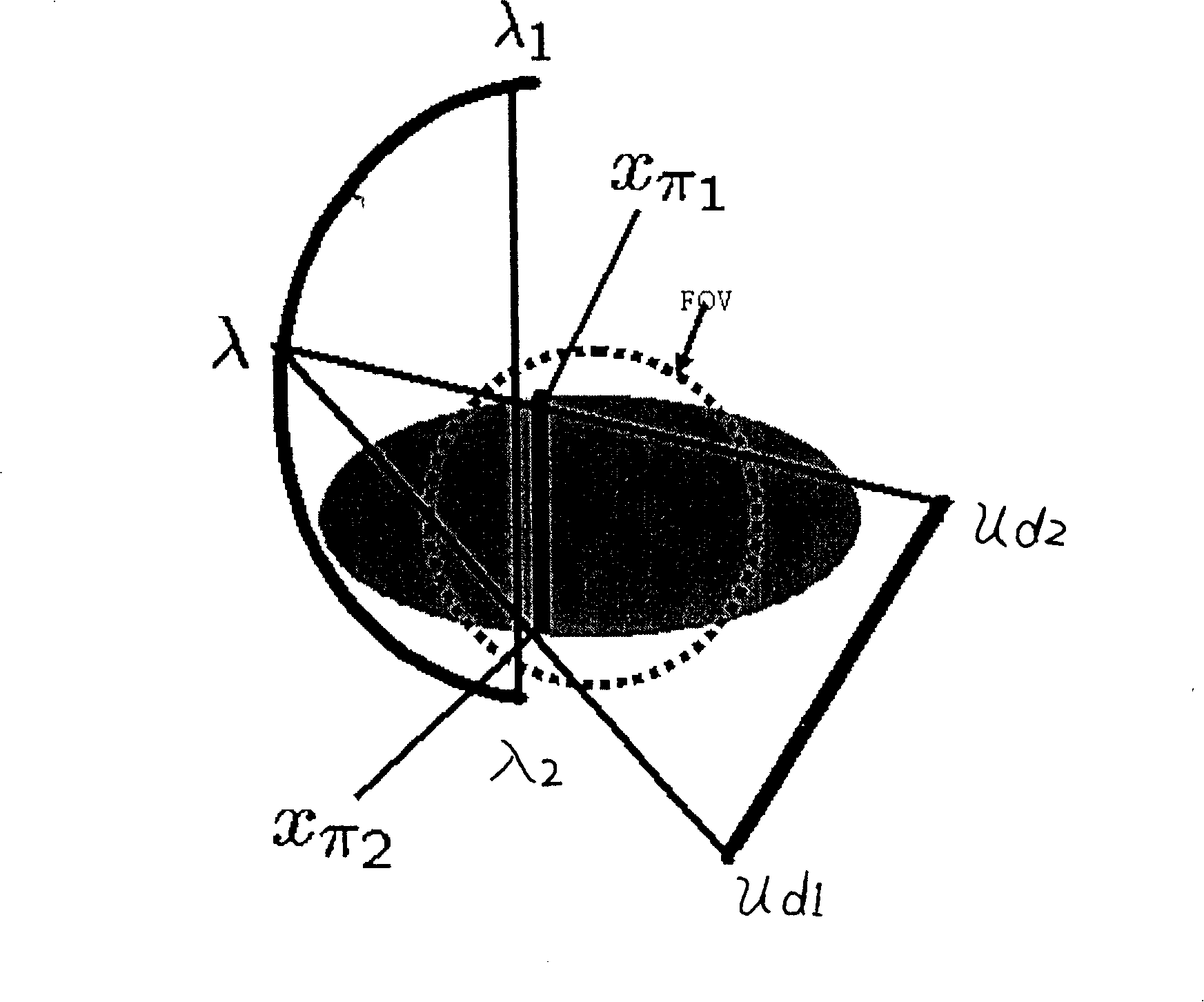
The invention discloses a method of dose reversal of the target of a patient in radiotherapy, the method makes use of a light source and a flat panel detector to carry out the rotary scanning around the target of the patient, so as to obtain the data of the target image of the patient and the dose data which penetrates the target of the patient; the invention applies a virtual PI line reconstruction algorithm to carry out the reconstruction and processing, and the treatment is carried out by adjusting the position of the patient and the input dose distribution data according to the processing results. As the invention adopts a true three-dimensional image reconstruction algorithm which is based on the flat panel detector, the spatial resolution of the true three-dimensional image is isotropic, the invention does not need interpolation, and can directly realize the processing of the image on the three-dimensional space, thus greatly improving the imaging precision and solving the problem that the imaging is not precise due to the interpolation error during the integration process into a quasi three-dimensional image of the existing radiotherapy, which can further affect the accurate implementation of the treatment plan of focus.
Owner:SHEN ZHEN HYPER TECH SHENZHEN +1
Treatment planning system, device for calculating a scanning path and particle therapy system
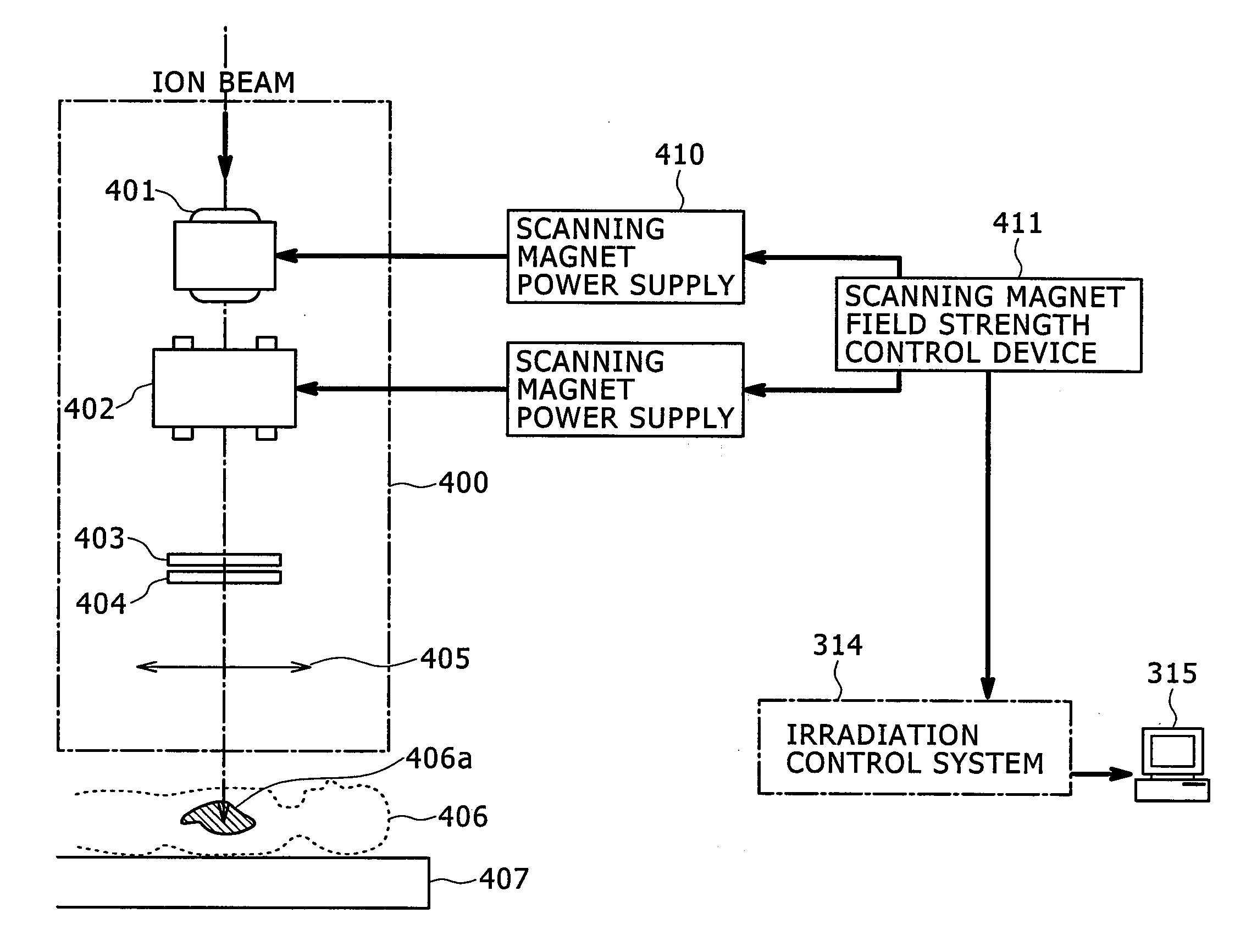
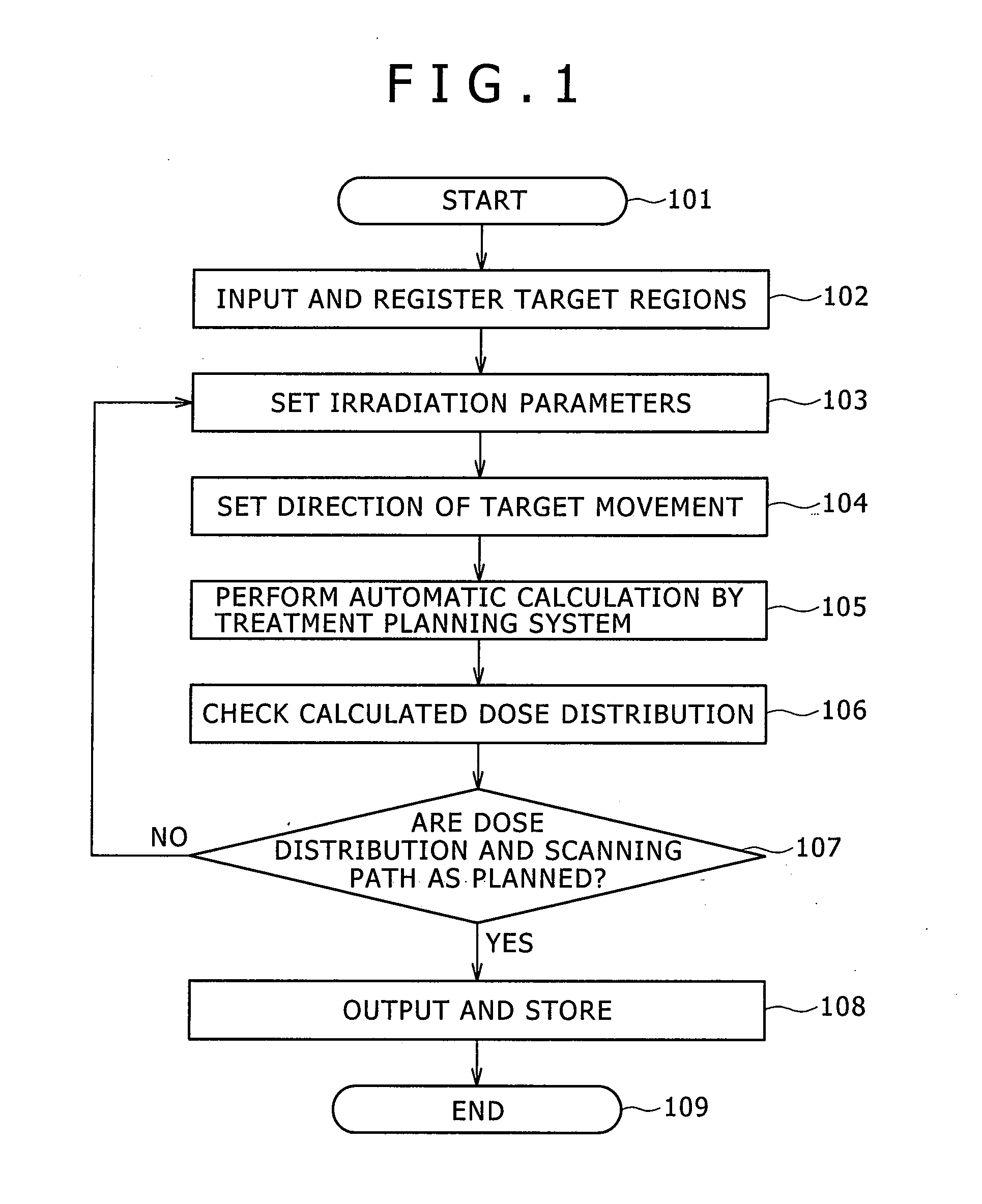
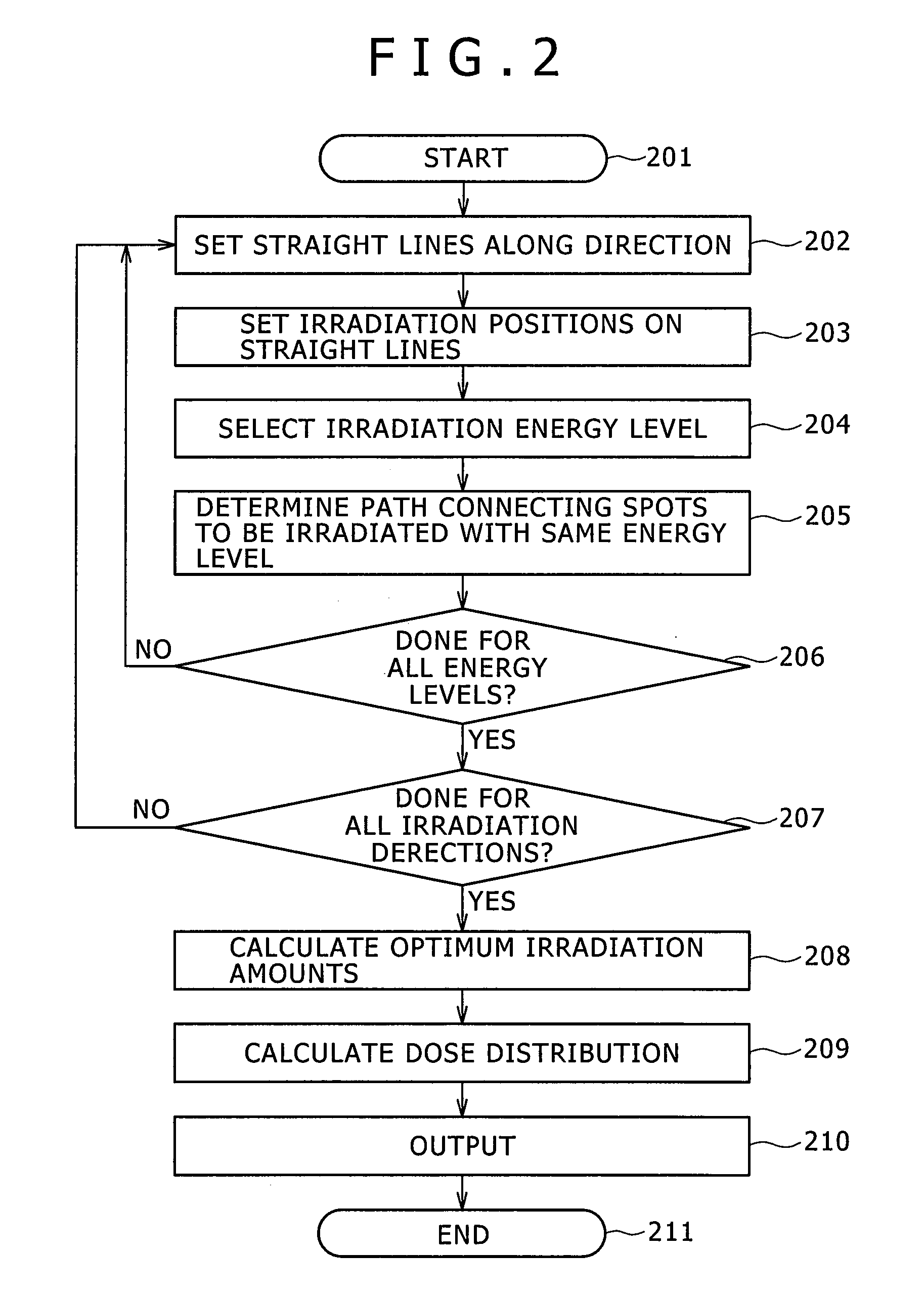
ActiveUS20120001085A1Improve uniformityThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsTomographyNuclear medicine
In a particle therapy treatment planning system for creating treatment plan data, the movement of a target (patient's affected area) is extracted from plural tomography images of the target, and the direction of scanning is determined by projecting the extracted movement on a scanning plane scanned by scanning magnets. Irradiation positions are arranged on straight lines parallel with the scanning direction making it possible to calculate a scanning path for causing scanning to be made mainly along the direction of movement of the target. The treatment planning system can thereby realize dose distribution with improved uniformity.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
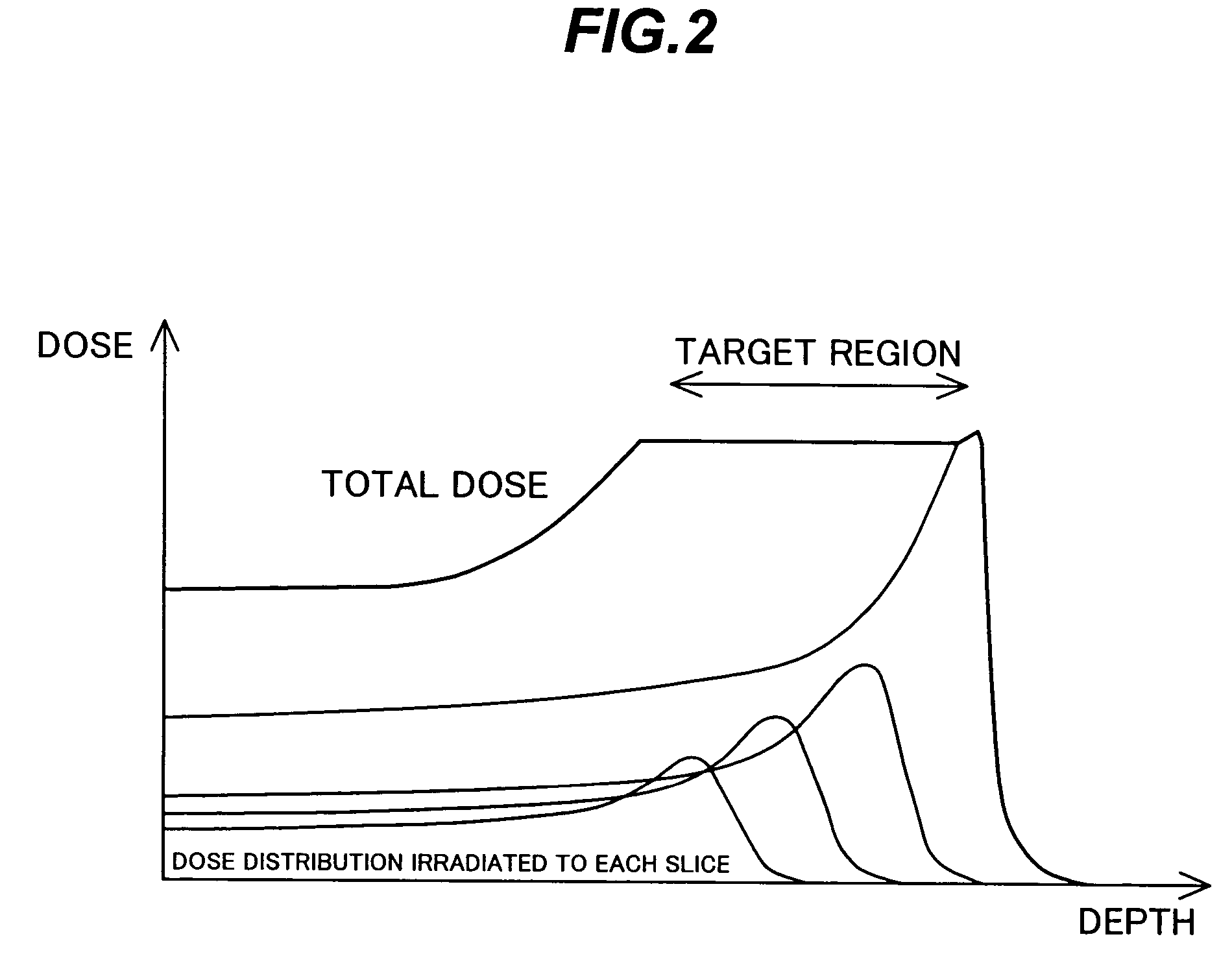
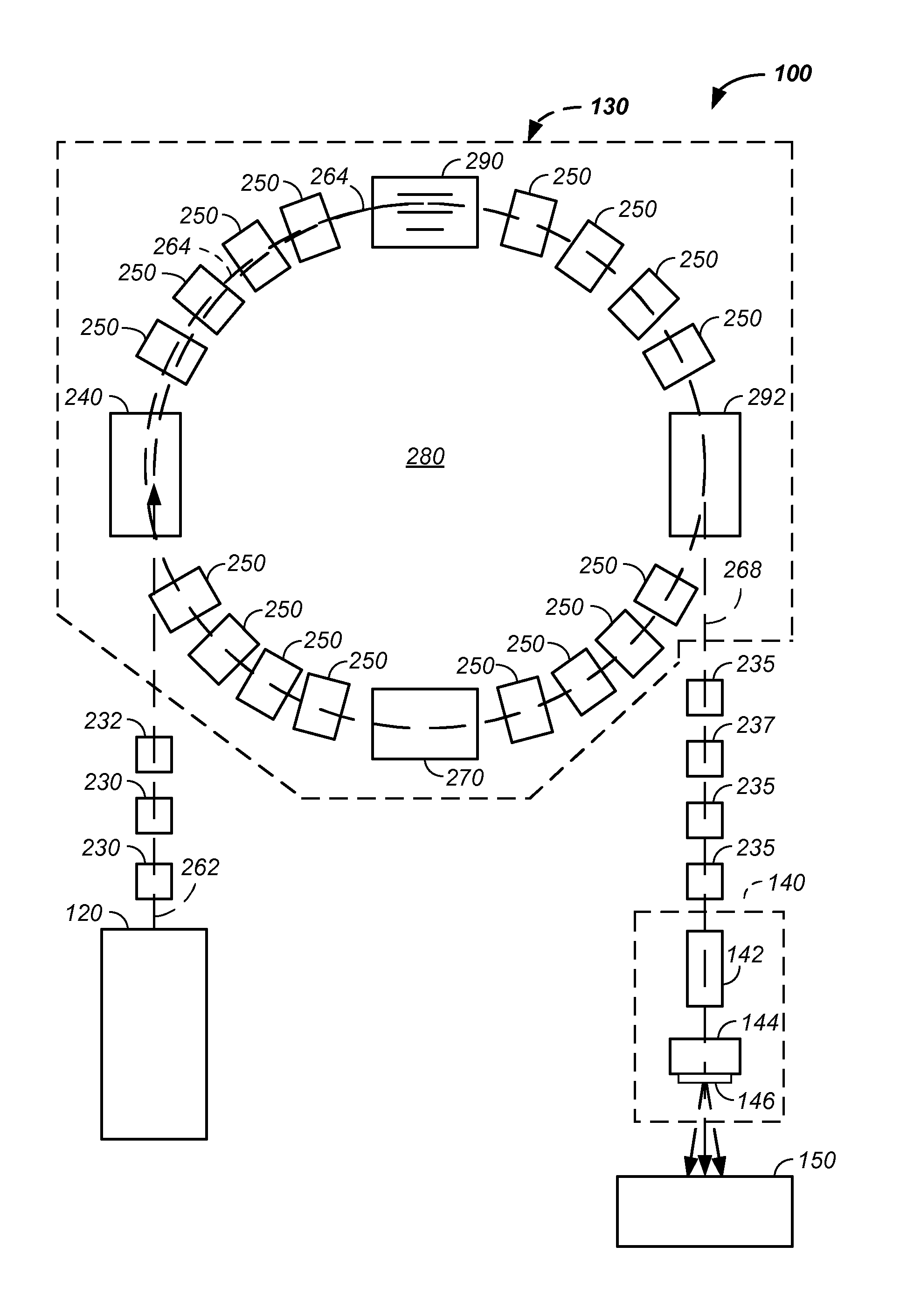
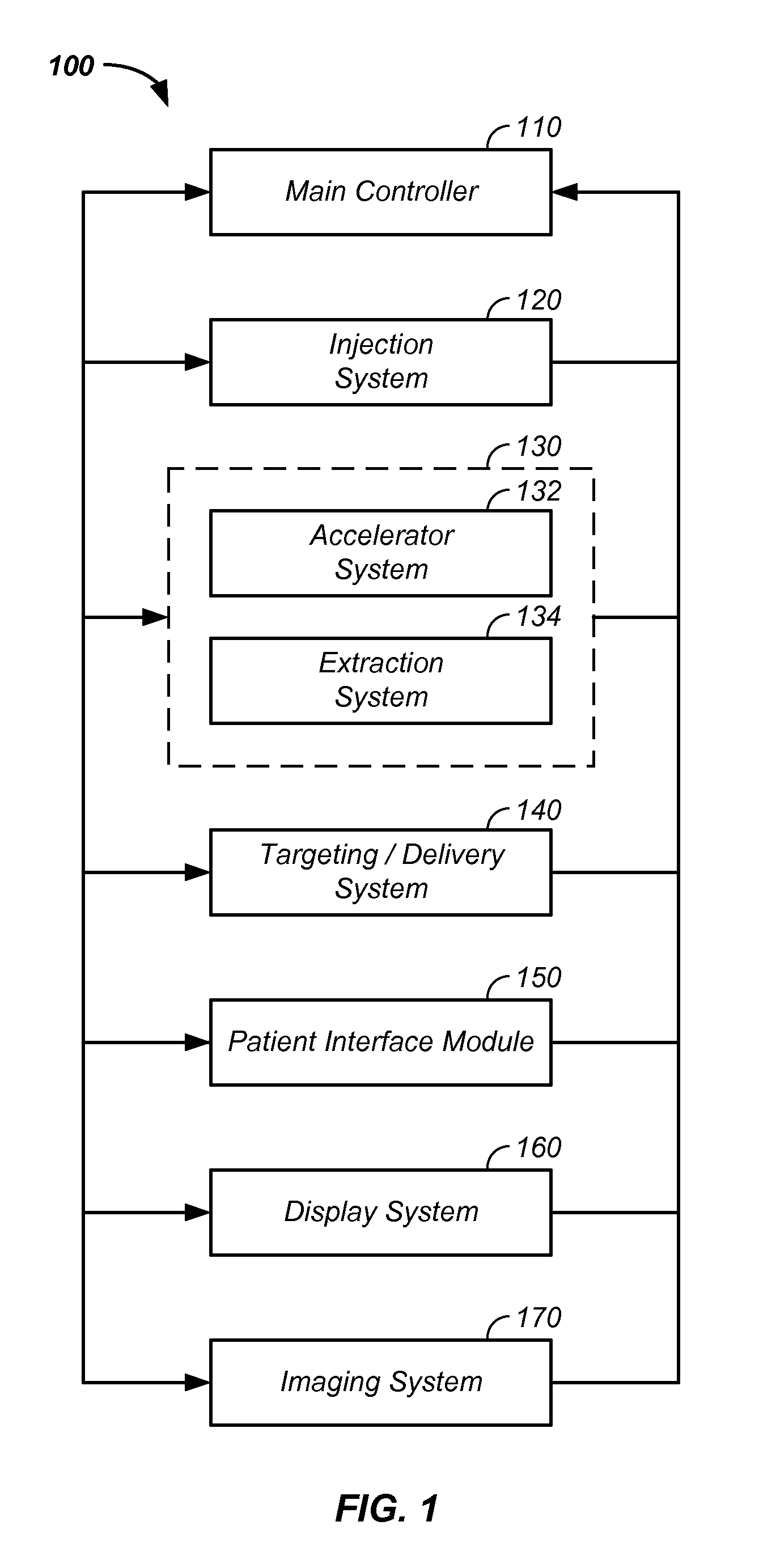
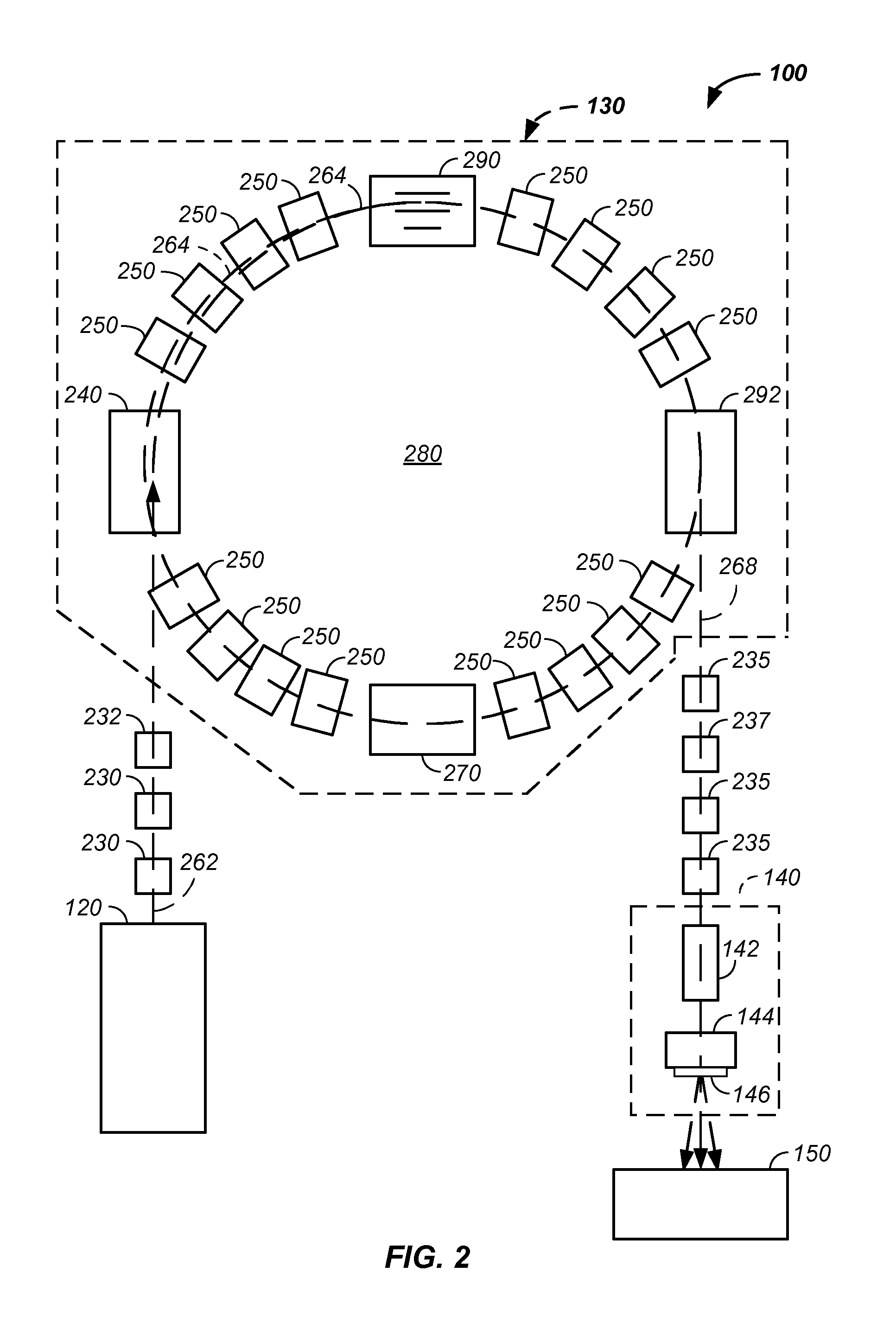
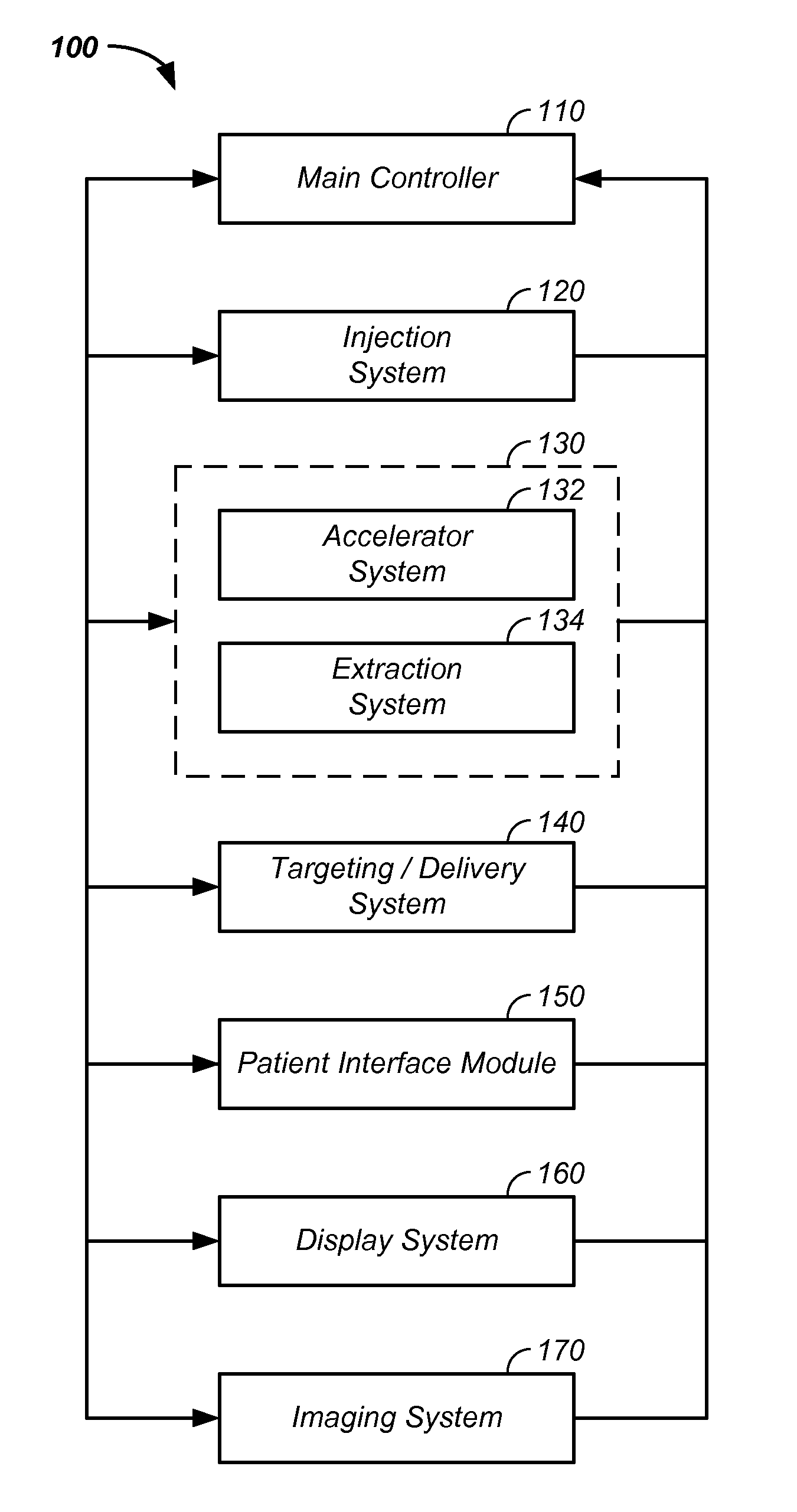
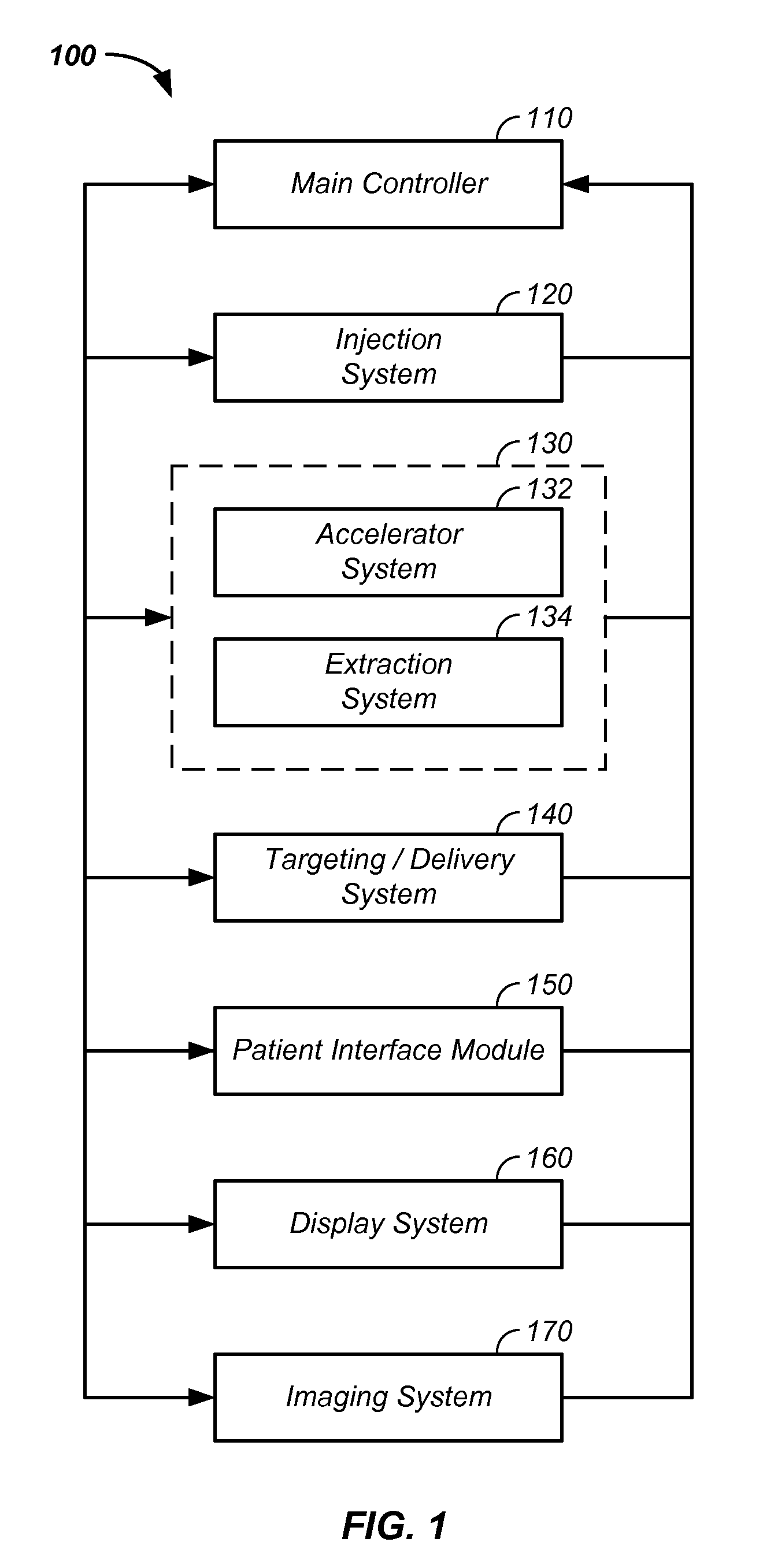
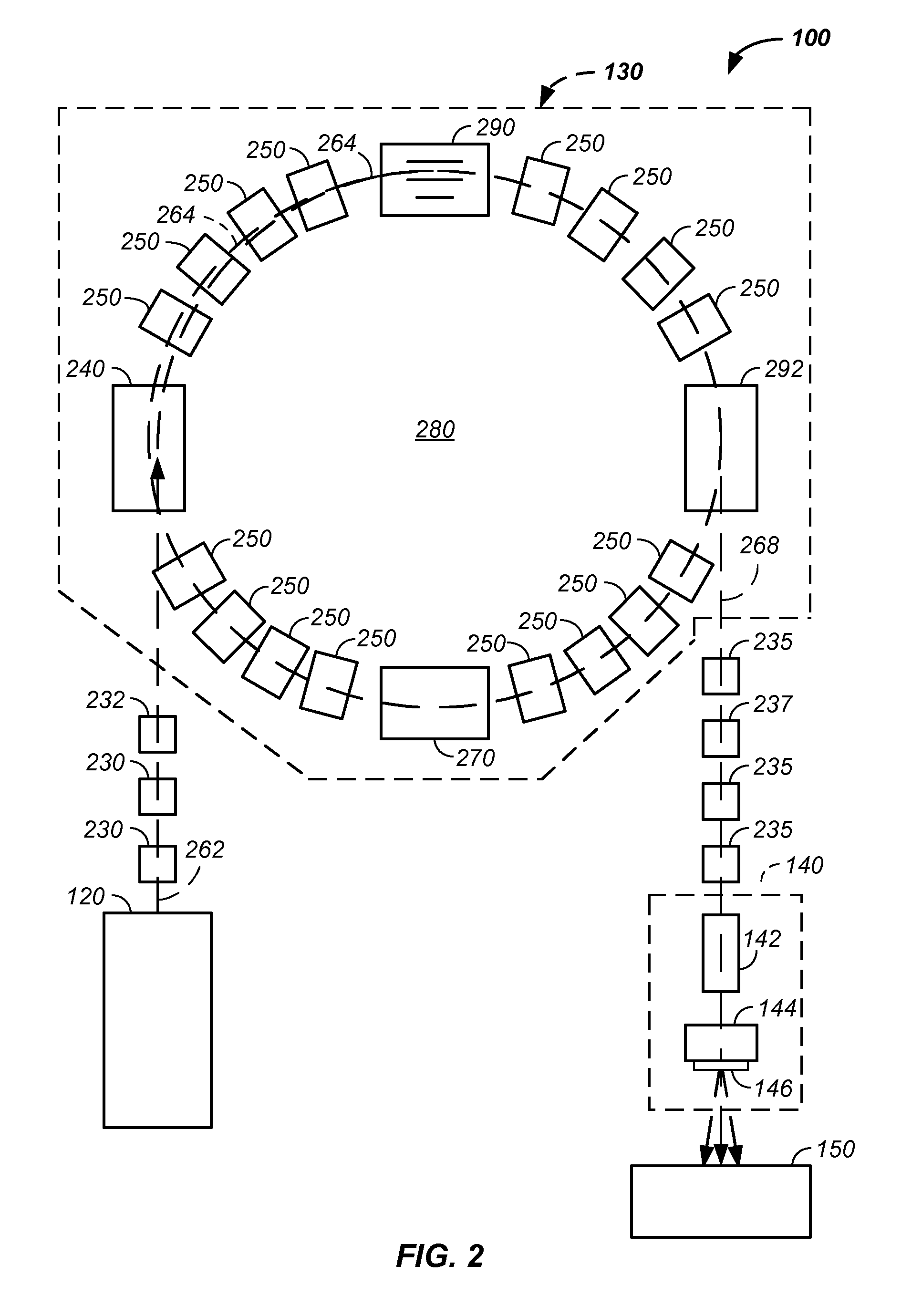
Charged particle cancer therapy dose distribution method and apparatus
ActiveUS20100127184A1Efficient dosage deliveryStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsBragg peakAbnormal tissue growth
The invention relates generally to treatment of solid cancers. More particularly, a method and apparatus for efficient radiation dose delivery to a tumor is described. Preferably, radiation is delivered through an entry point into the tumor and Bragg peak energy is targeted to a distal or far side of the tumor from an ingress point. Delivering Bragg peak energy to the distal side of the tumor from the ingress point is repeated from multiple rotational directions. Beam intensity is proportional to radiation dose delivery efficiency. The multi-field irradiation process with energy levels targeting the far side of the tumor from each irradiation direction provides even and efficient charged particle radiation dose delivery to the tumor. Preferably, the charged particle therapy is timed to patient respiration via control of charged particle beam injection, acceleration, extraction, and / or targeting methods and apparatus.
Owner:BALAKIN ANDREY VLADIMIROVICH +1
Charged particle cancer therapy dose distribution method and apparatus
ActiveUS8642978B2Stability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsBragg peakMulti field
The invention relates generally to treatment of solid cancers. More particularly, a method and apparatus for efficient radiation dose delivery to a tumor is described. Preferably, radiation is delivered through an entry point into the tumor and Bragg peak energy is targeted to a distal or far side of the tumor from an ingress point. Delivering Bragg peak energy to the distal side of the tumor from the ingress point is repeated from multiple rotational directions. Beam intensity is proportional to radiation dose delivery efficiency. The multi-field irradiation process with energy levels targeting the far side of the tumor from each irradiation direction provides even and efficient charged particle radiation dose delivery to the tumor. Preferably, the charged particle therapy is timed to patient respiration via control of charged particle beam injection, acceleration, extraction, and / or targeting methods and apparatus.
Owner:BALAKIN ANDREY VLADIMIROVICH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com