Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
8433 results about "Statistical physics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Statistical physics is a branch of physics that uses methods of probability theory and statistics, and particularly the mathematical tools for dealing with large populations and approximations, in solving physical problems. It can describe a wide variety of fields with an inherently stochastic nature. Its applications include many problems in the fields of physics, biology, chemistry, neuroscience, and even some social sciences, such as sociology and linguistics. Its main purpose is to clarify the properties of matter in aggregate, in terms of physical laws governing atomic motion.
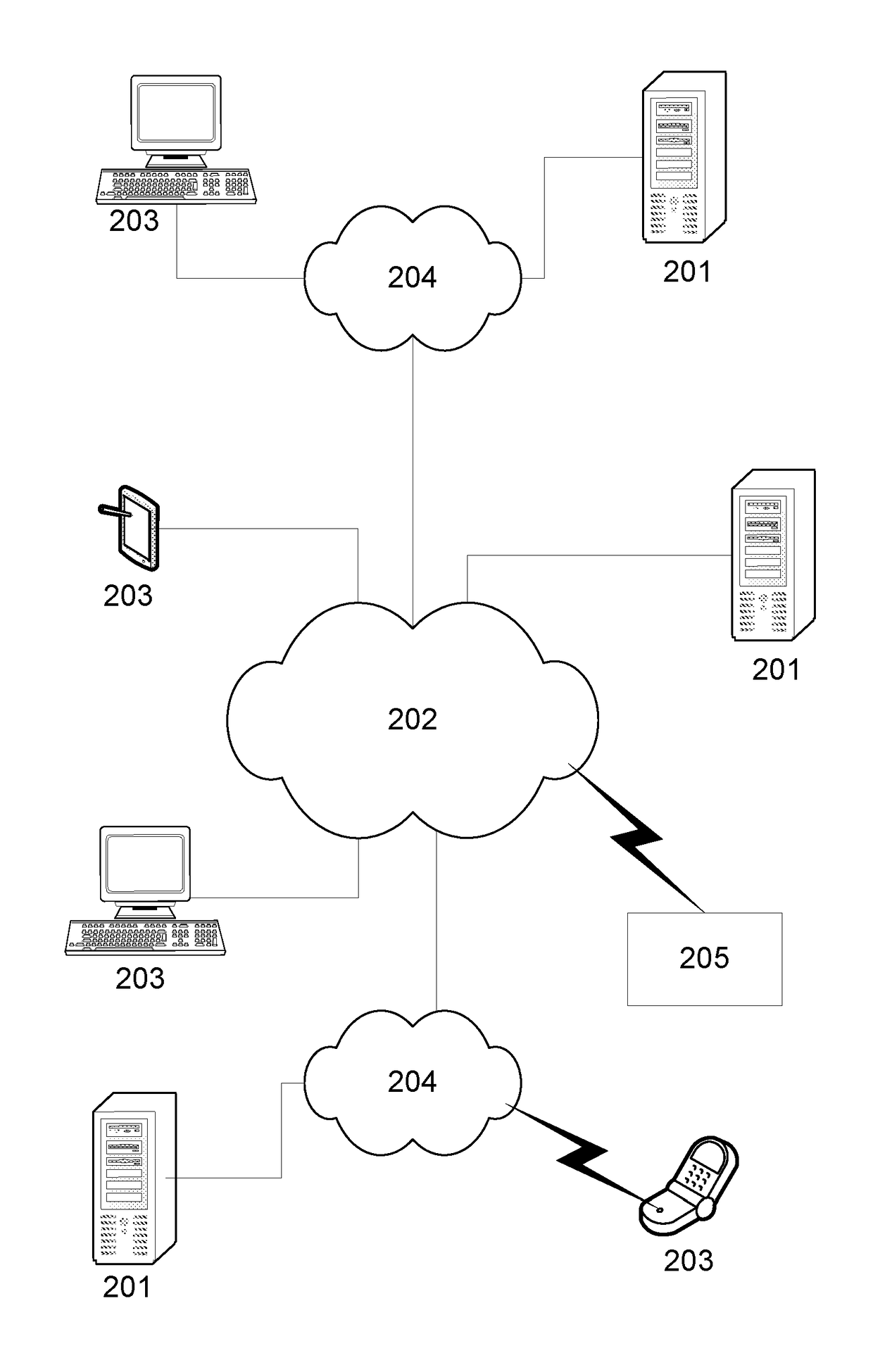
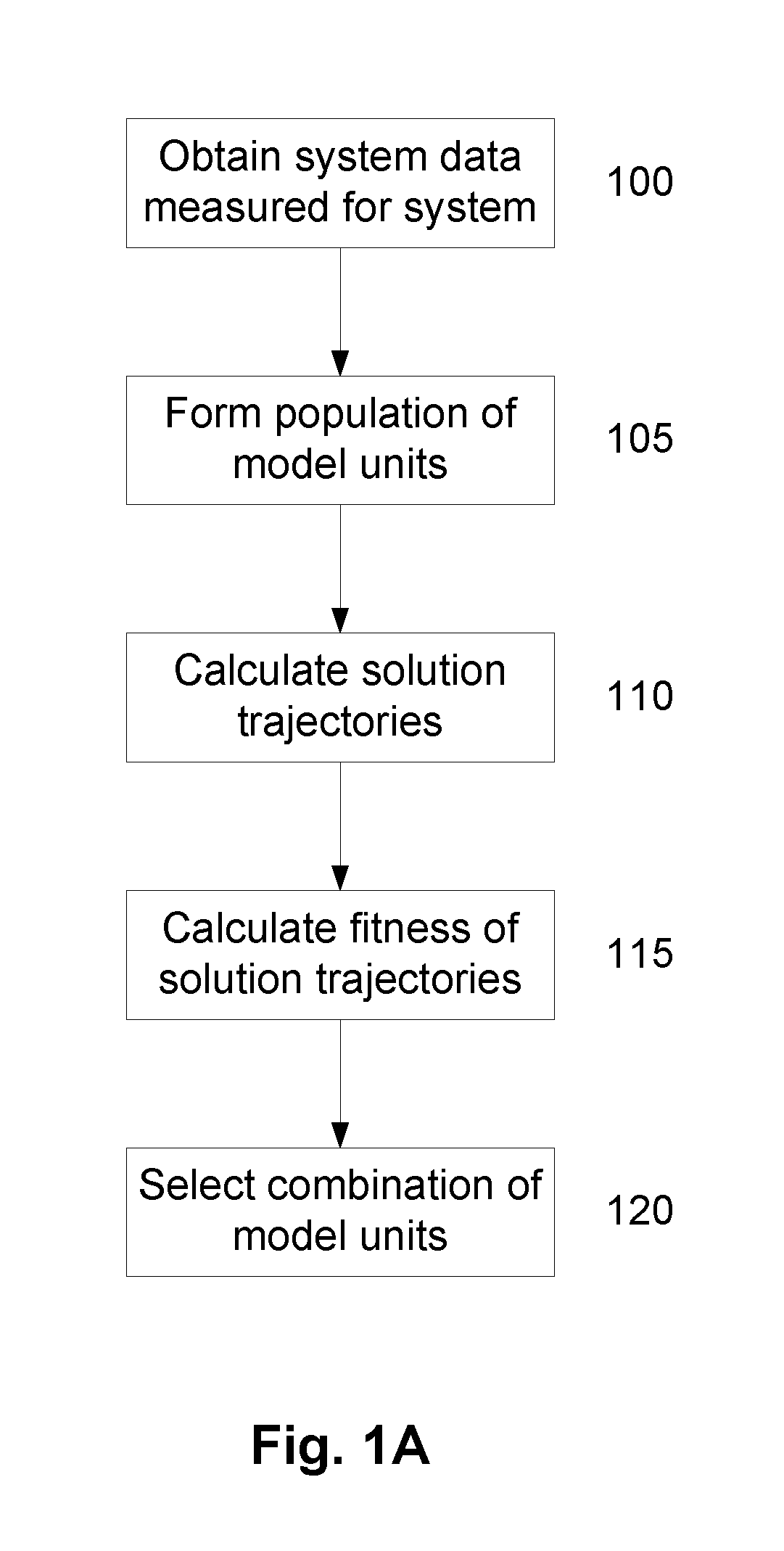
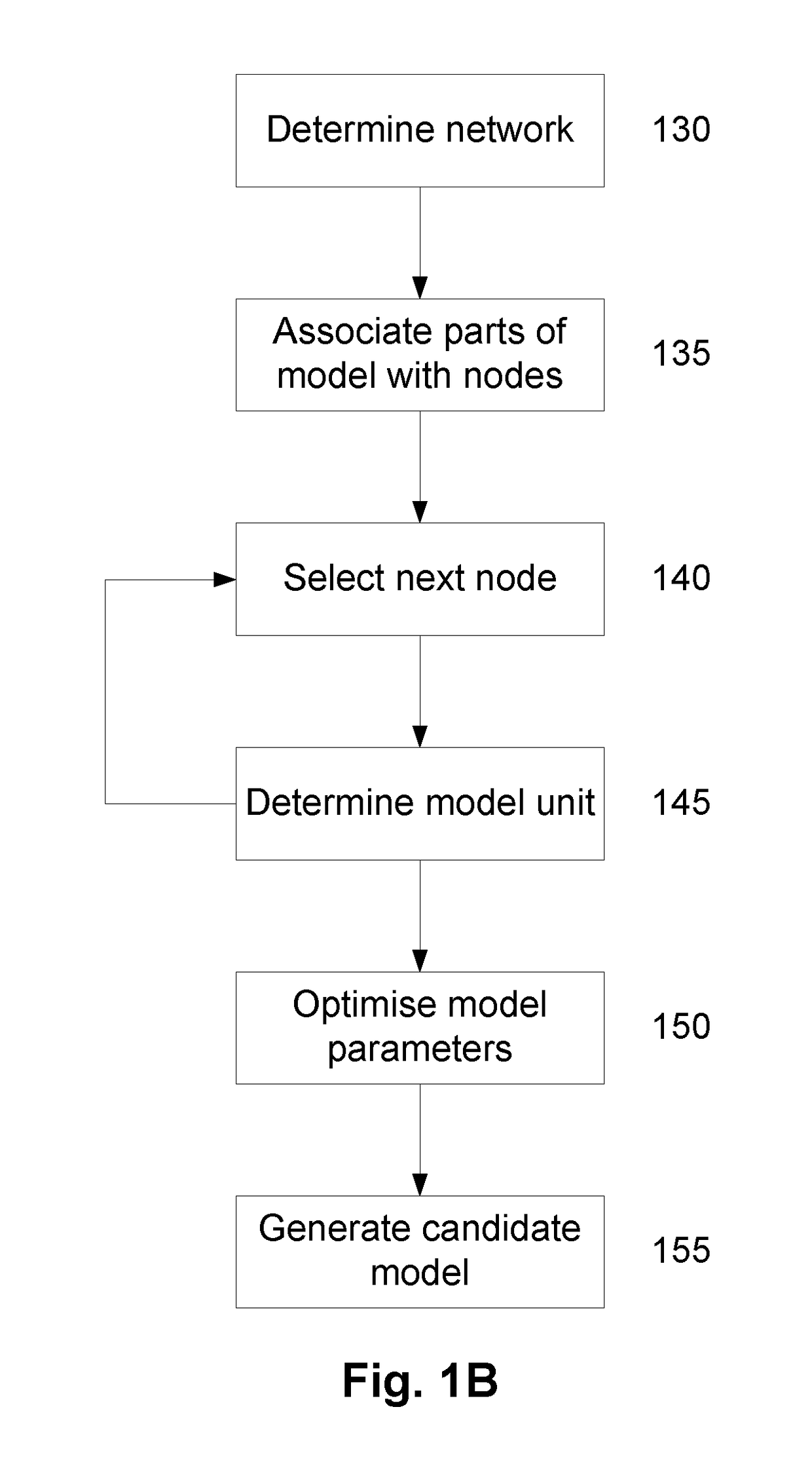
A System and Method for Modelling System Behaviour
ActiveUS20170147722A1Reduce the impactReduce impactMedical simulationDesign optimisation/simulationCollective modelModel system
A method of modelling system behaviour of a physical system, the method including, in one or more electronic processing devices obtaining quantified system data measured for the physical system, the quantified system data being at least partially indicative of the system behaviour for at least a time period, forming at least one population of model units, each model unit including model parameters and at least part of a model, the model parameters being at least partially based on the quantified system data, each model including one or more mathematical equations for modelling system behaviour, for each model unit calculating at least one solution trajectory for at least part of the at least one time period; determining a fitness value based at least in part on the at least one solution trajectory; and, selecting a combination of model units using the fitness values of each model unit, the combination of model units representing a collective model that models the system behaviour.
Owner:EVOLVING MACHINE INTELLIGENCE
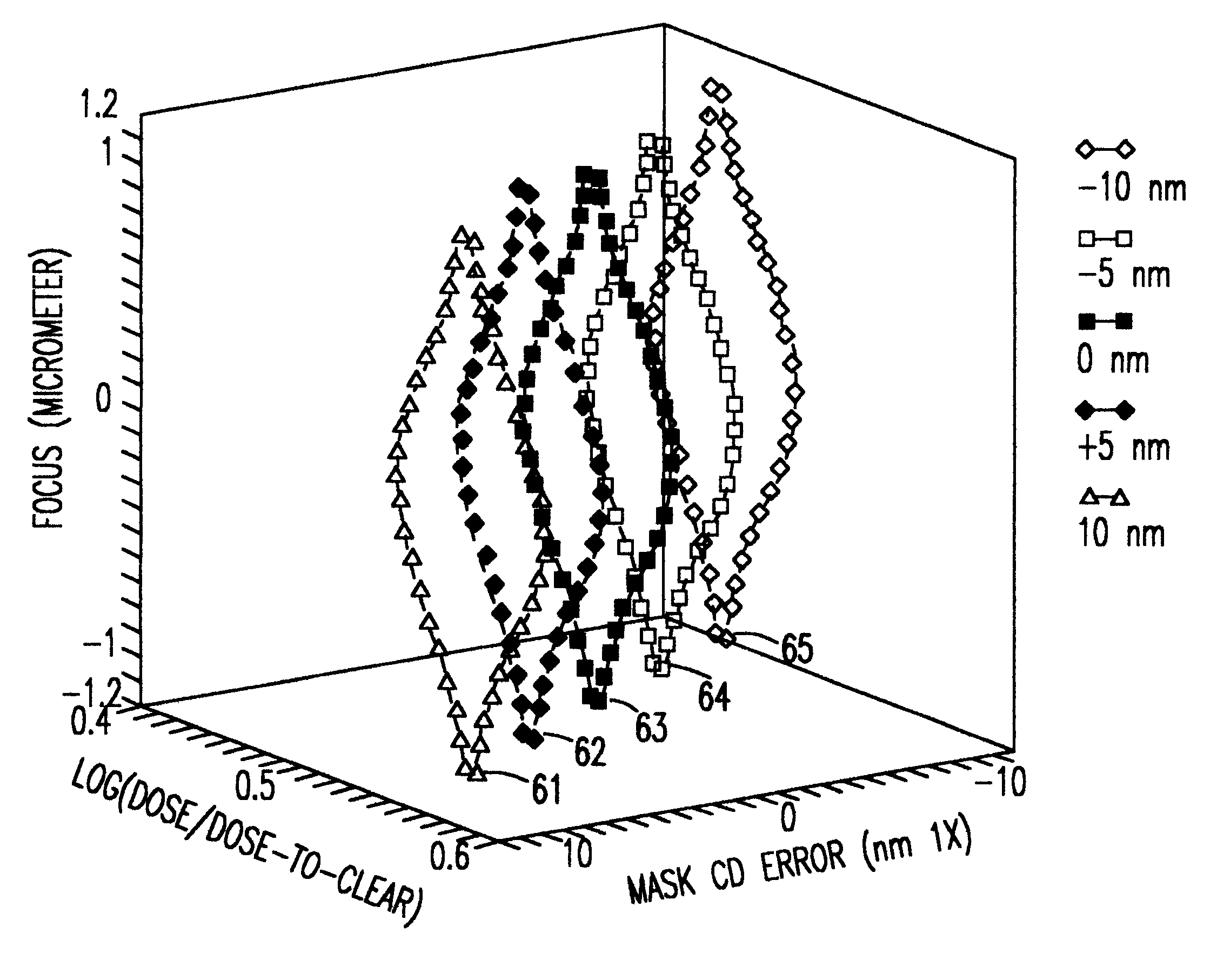
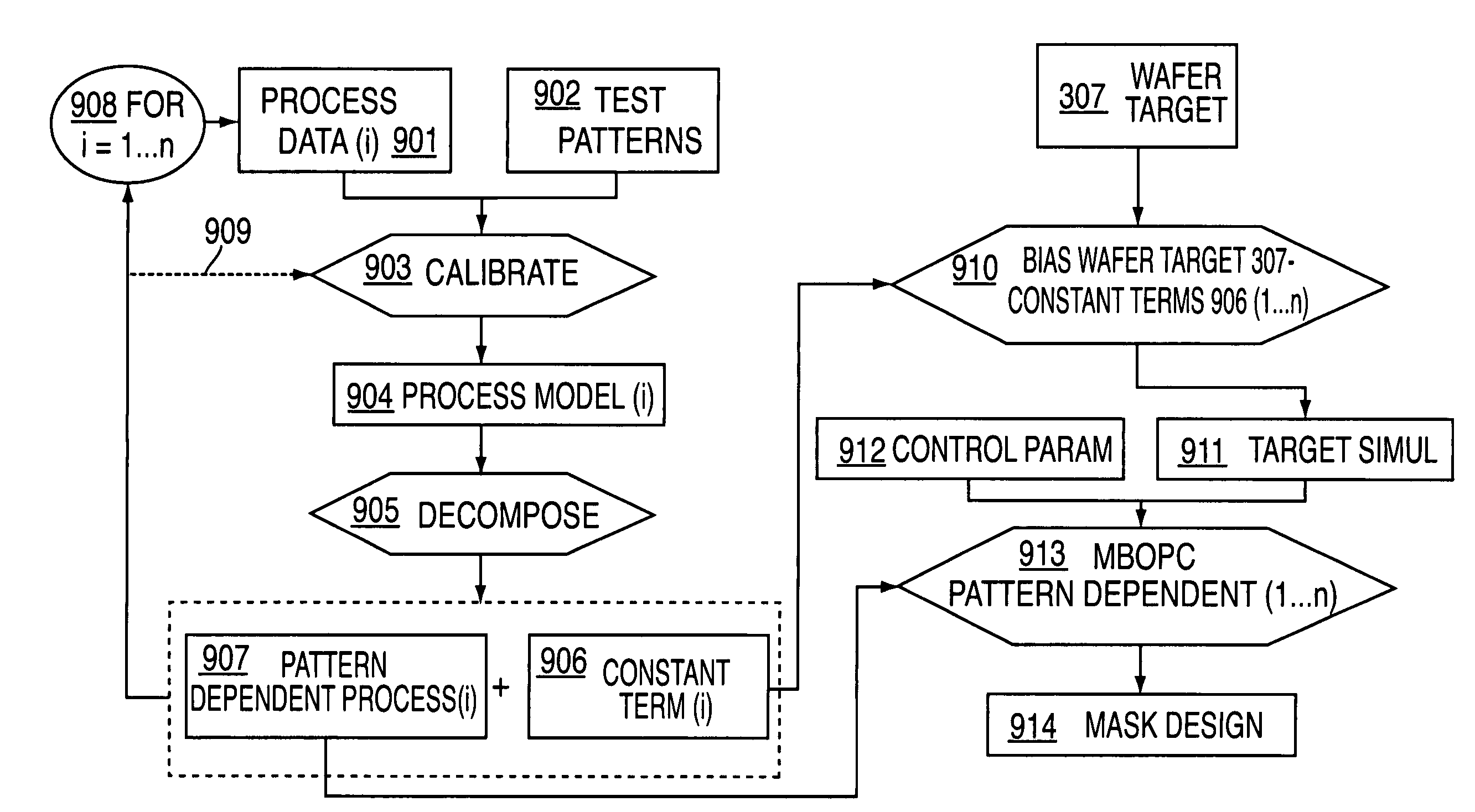
Method to determine optical proximity correction and assist feature rules which account for variations in mask dimensions
InactiveUS6553559B2Photomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentComputational physicsProcess window
Optical proximity correction (OPC) and assist feature rules are generated using a process window (PW) analysis. A reference pitch is chosen and the mask bias is found that optimizes the process window. This can be done using standard process window analysis or through a weighted process window (WPW) analysis which accounts for focus and dose distributions that are expected in a real process. The WPW analysis gives not only the optimum mask bias, but also the center focus and dose conditions for the optimum process centering. A series of other pitches and mask biases are then analyzed by finding the common process window with the reference pitch. For the standard PW analysis, a common process window is found. For the WPW analysis, the WPW is computed at the center focus and dose conditions found for the reference pitch. If mask or lens errors are to be accounted for, then multiple structures can be included in the analysis. Once the common process windows for the mask features of interest have been computed, functional fits to the data can be found. Once the functional forms have been found for each of the OPC parameters, the rules table can be determined by solving for the spacings of interest in the design.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Method for improving optical proximity correction
ActiveUS7350183B2Improve variationDefect minimizationPhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentLine widthComputer science
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
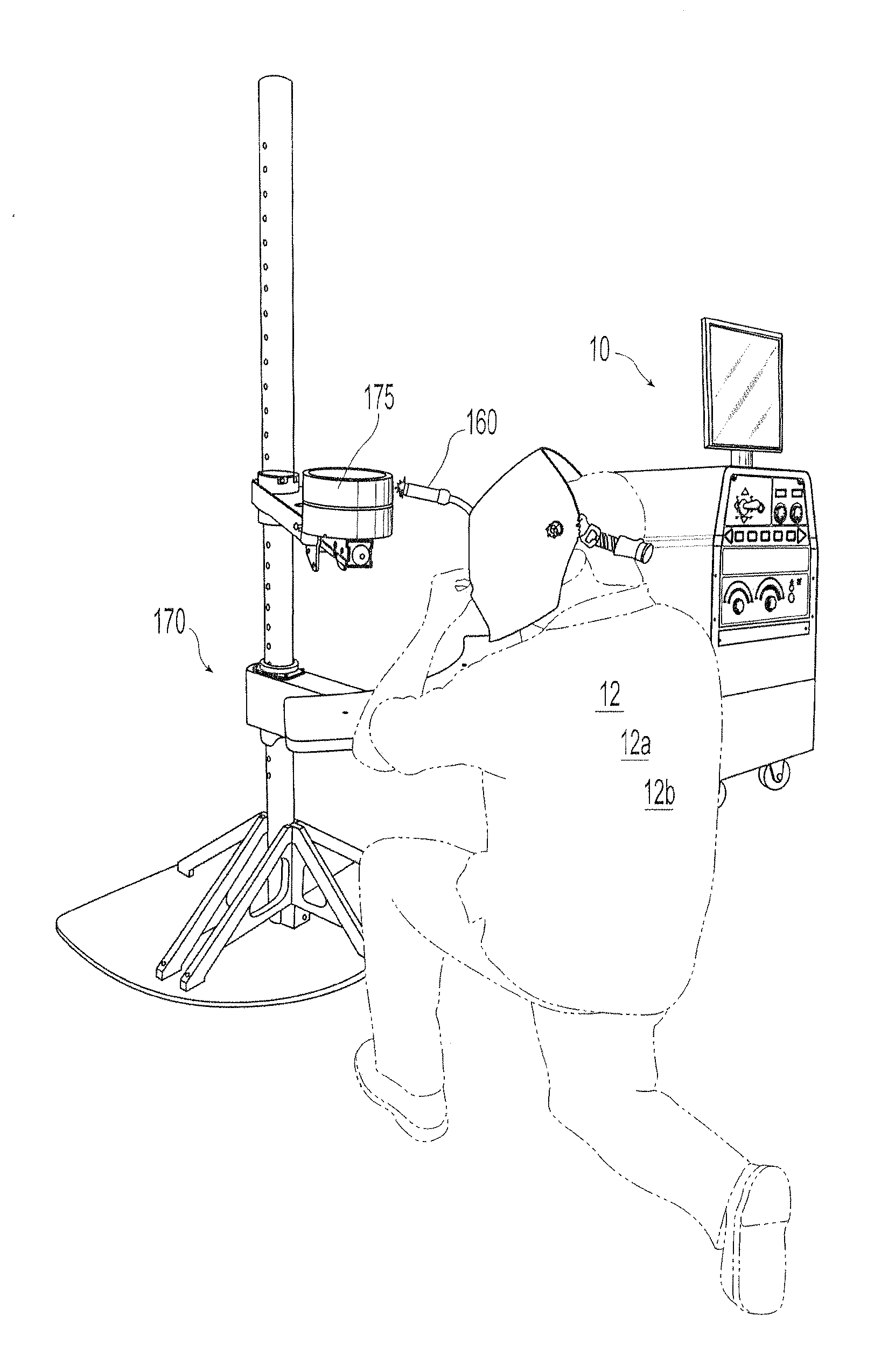
Virtual reality gtaw and pipe welding simulator and setup
ActiveUS20130189657A1Affect characteristicArc welding apparatusEducational modelsSimulationClassical mechanics
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
Spectral data classification of samples
A system and method for classifying tissue by application of discriminant analysis to spectral data. Spectra are recorded as amplitudes at a series of discrete wavelengths. Pluralities of reference spectra are recorded for specimens having known conditions. The reference spectra are subjected to discriminant analysis to determine wavelength regions of interest for the analysis. A plurality of amplitudes are selected for the analysis, and are plotted in an N-dimensional space. For each plurality of reference spectra corresponding to a specific known condition, a characteristic point is determined and plotted, the characteristic point representative of the known condition. A test spectrum is recorded from a test specimen, and the plurality of amplitudes corresponding in wavelength to the wavelength regions of interest are selected. A characteristic point in N-dimensional space is determined for the test spectrum. The distance of the characteristic point of the test spectrum from each of the plurality of characteristic points representative of known conditions is determined. The test specimen is assigned the condition corresponding to the characteristic point of a plurality of reference spectra, based on a distance relationship with at least two distances, provided that at least one distance is less than a pre-determined maximum distance. In some embodiments, the test specimen can comprise human cervical tissue, and the known conditions can include normal health, metaplasia, CIN I and CIN II / III.
Owner:LUMA IMAGING CORP
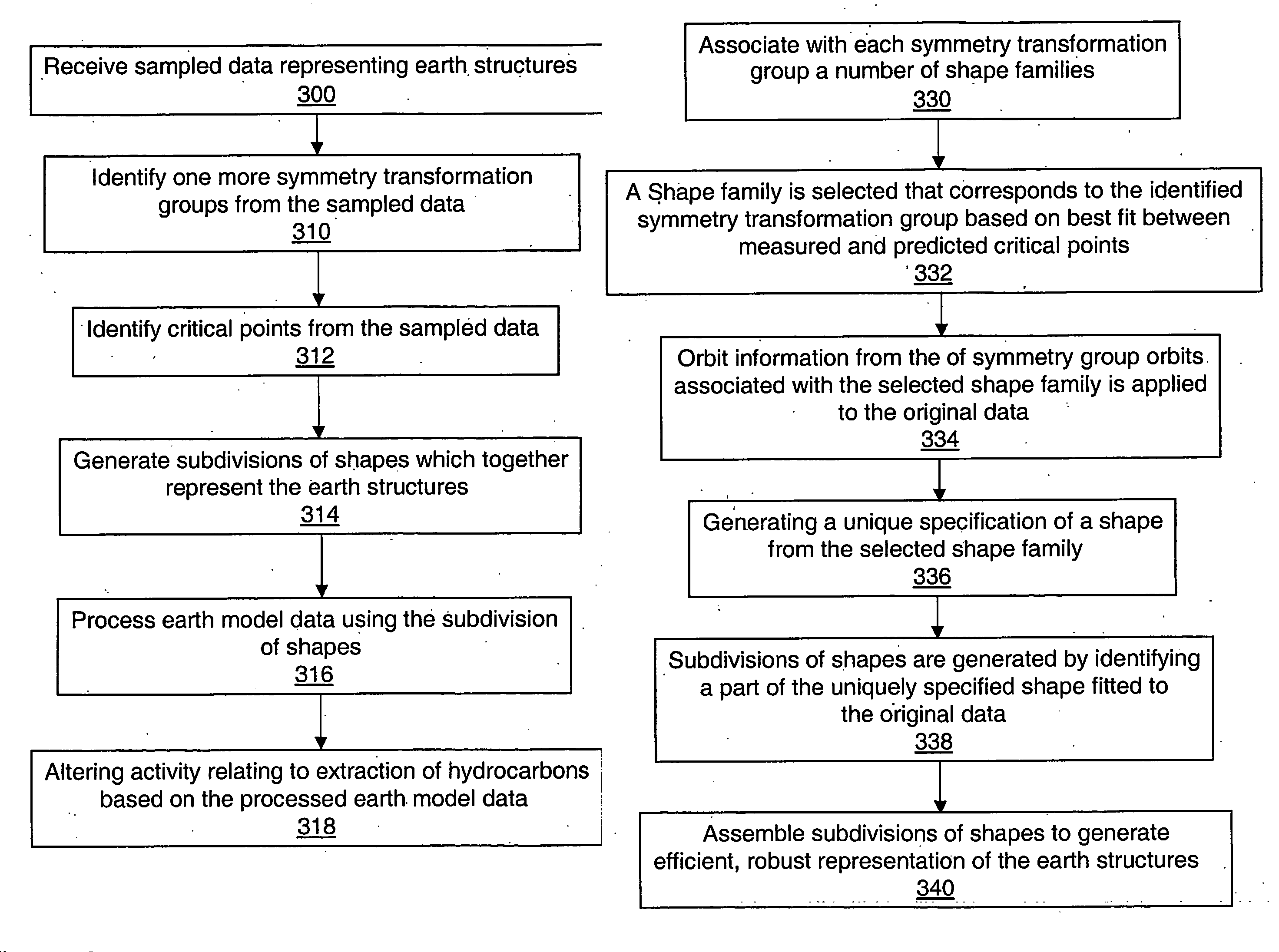
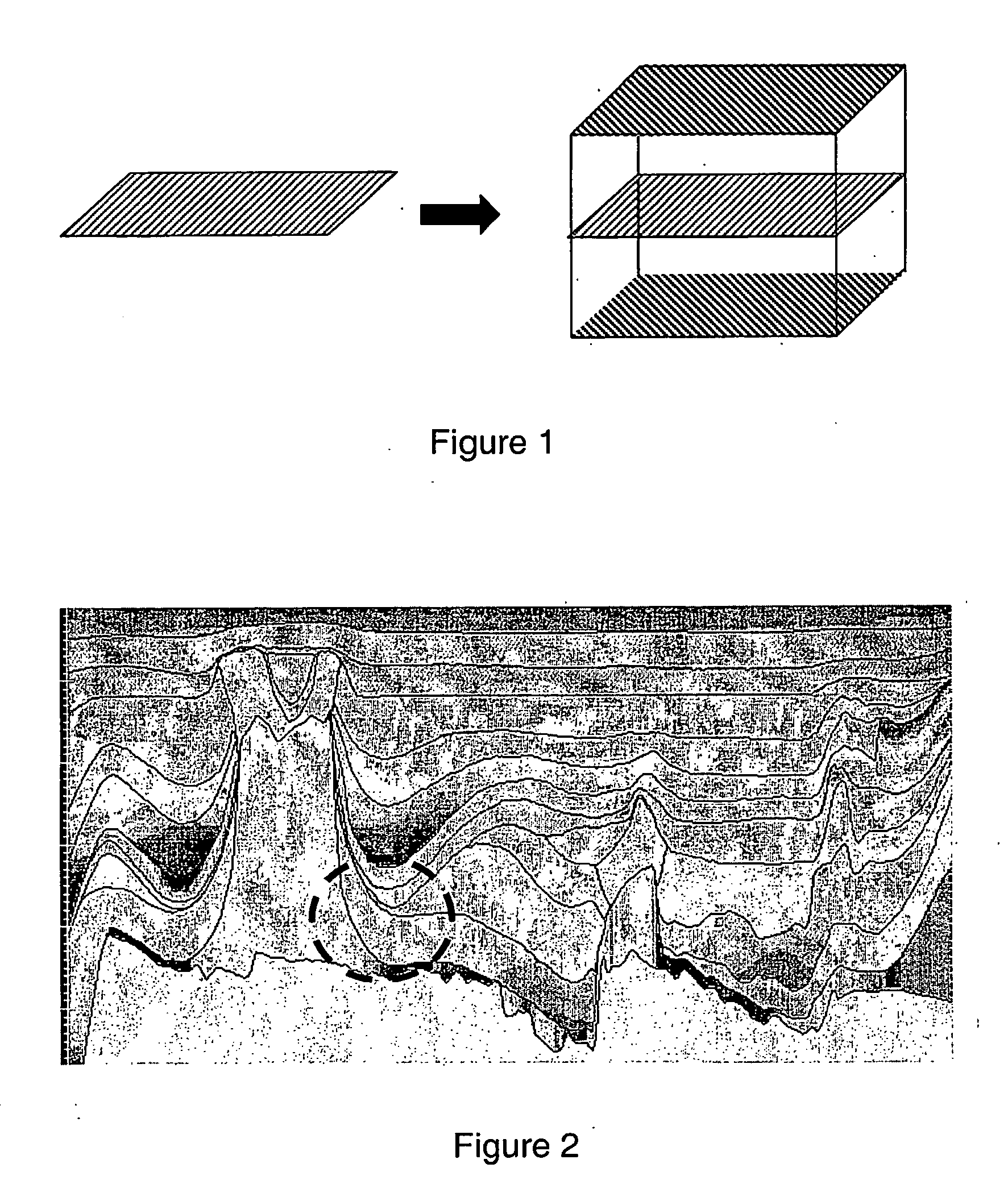
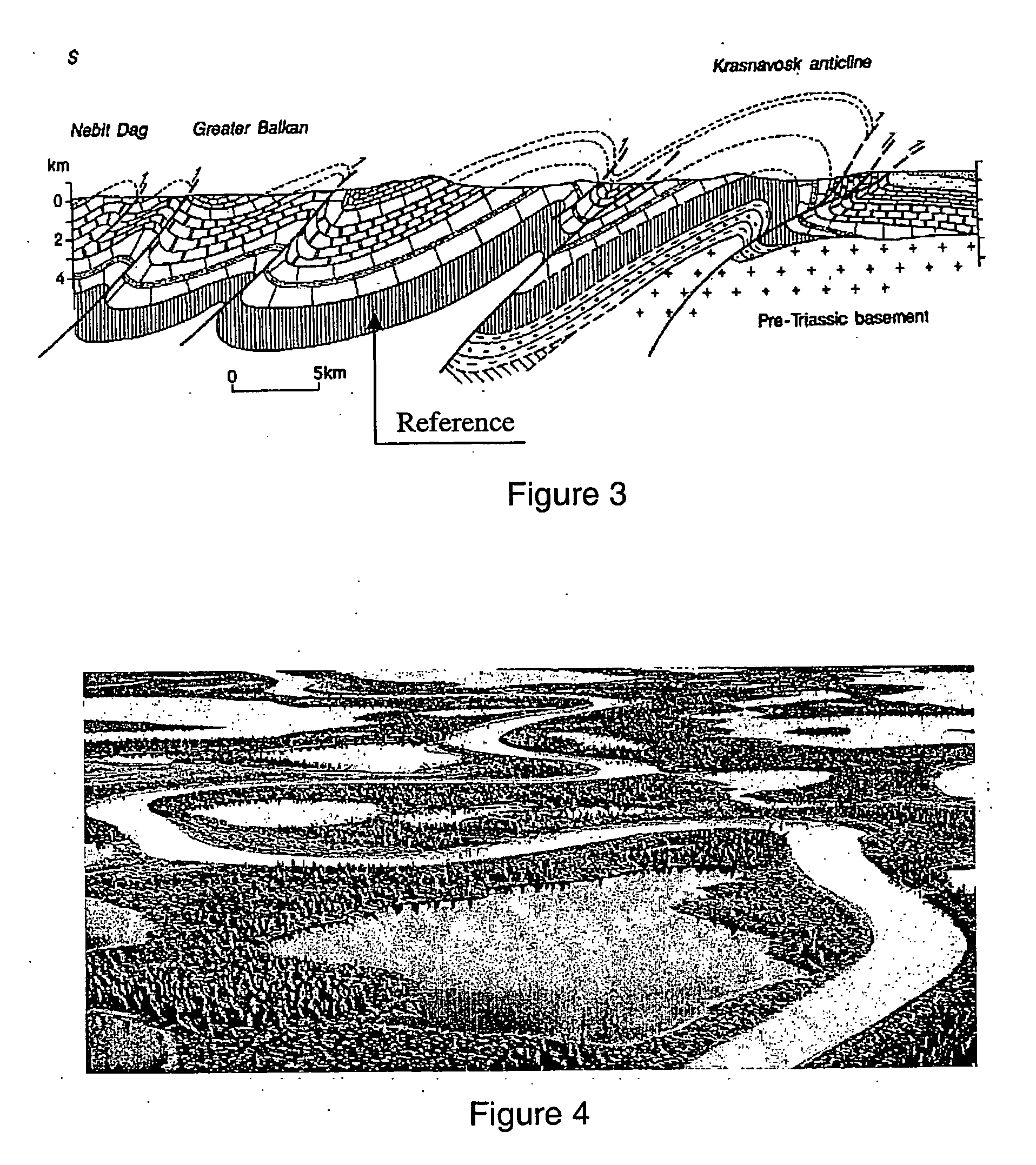
System and method for representing and processing and modeling subterranean surfaces
InactiveUS20060235666A1Enhance memoryImprove efficiencyGeological measurementsAnalogue processes for specific applicationsCrucial pointHydrocotyle bowlesioides
Methods and systems are disclosed for processing data used for hydrocarbon extraction from the earth. Symmetry transformation groups are identified from sampled earth structure data. A set of critical points is identified from the sampled data. Using the symmetry groups and the critical points, a plurality of subdivisions of shapes is generated, which together represent the original earth structures. The symmetry groups correspond to a plurality of shape families, each of which includes a set of predicted critical points. The subdivisions are preferably generated such that a shape family is selected according to a best fit between the critical points from the sampled data and the predicted critical points of the selected shape family.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
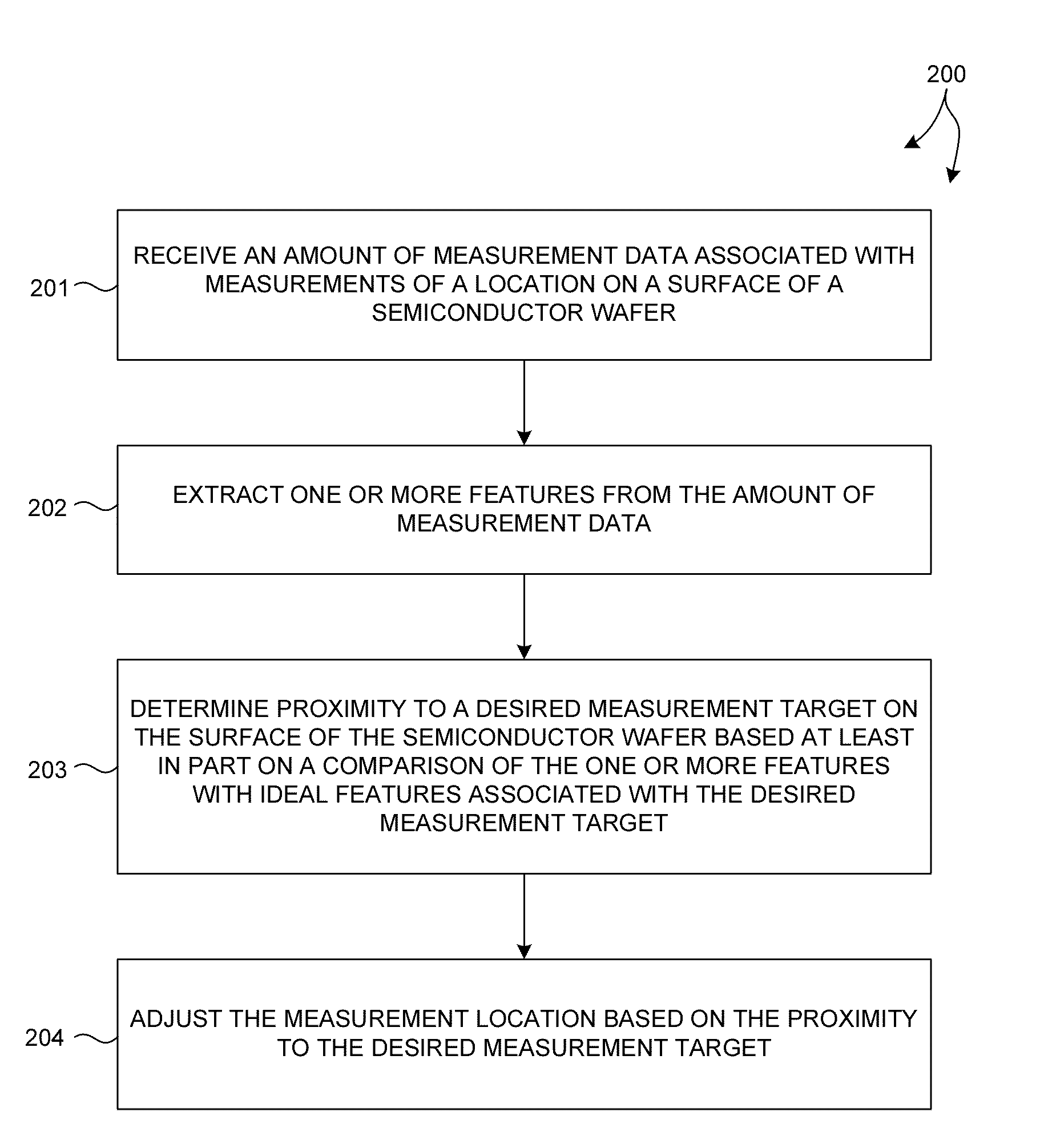
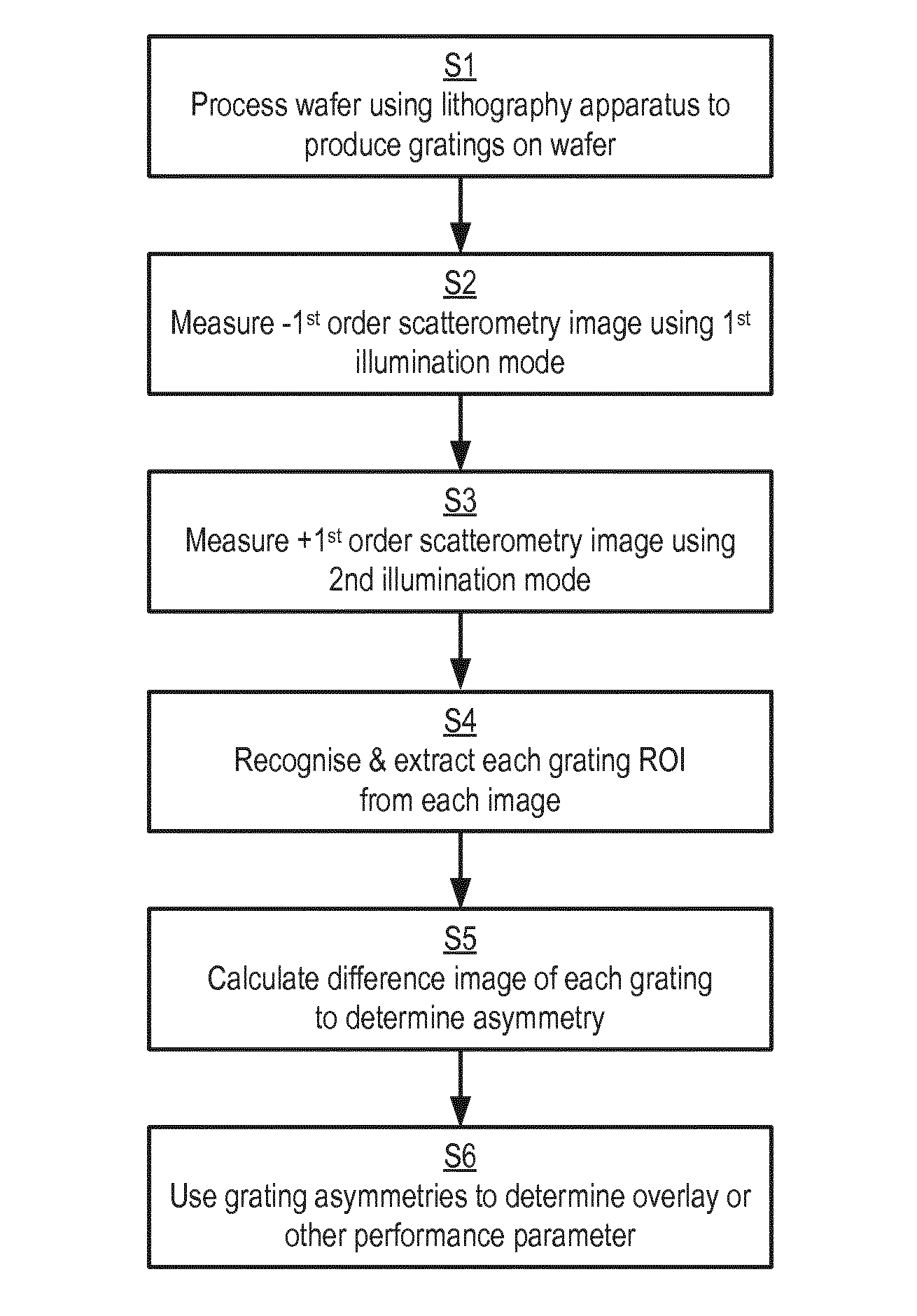
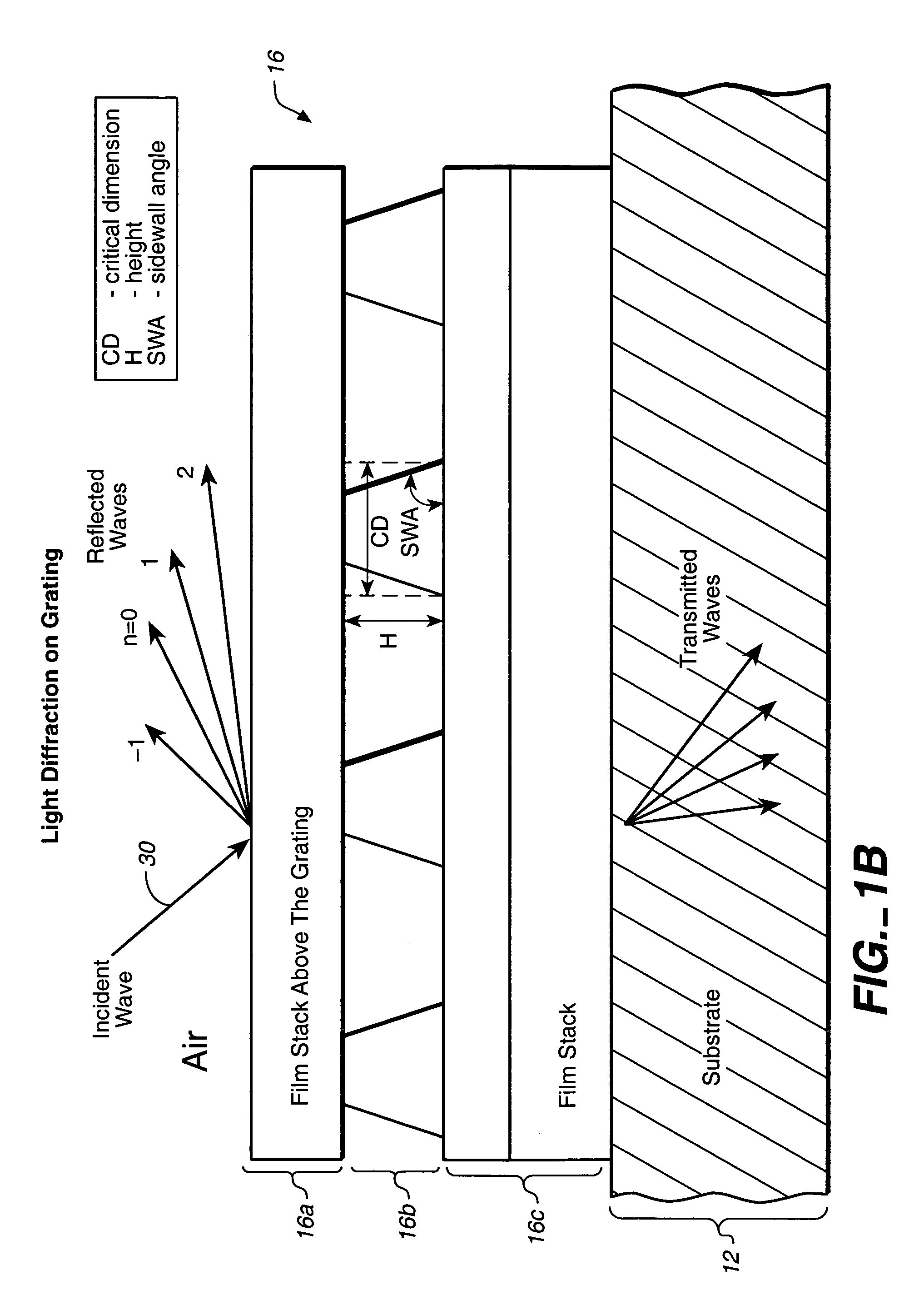
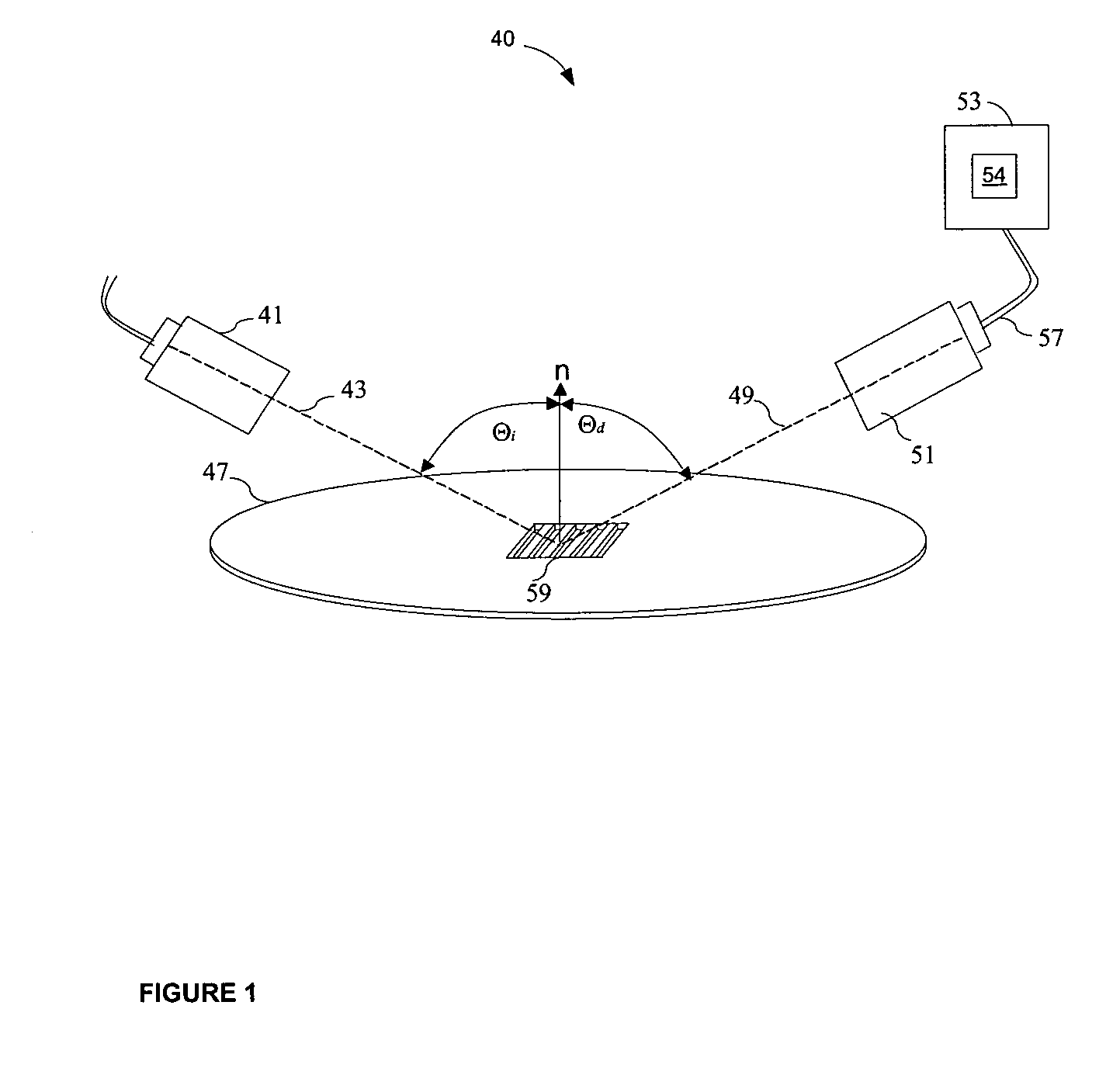
Scatterometry-Based Imaging and Critical Dimension Metrology
ActiveUS20150300965A1Improve the measurement effectMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDiffraction orderMetrology
Methods and systems for performing measurements of semiconductor structures and materials based on scatterometry measurement data are presented. Scatterometry measurement data is used to generate an image of a material property of a measured structure based on the measured intensities of the detected diffraction orders. In some examples, a value of a parameter of interest is determined directly from the map of the material property of the measurement target. In some other examples, the image is compared to structural characteristics estimated by a geometric, model-based parametric inversion of the same measurement data. Discrepancies are used to update the geometric model of the measured structure and improve measurement performance. This enables a metrology system to converge on an accurate parametric measurement model when there are significant deviations between the actual shape of a manufactured structure subject to model-based measurement and the modeled shape of the structure.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
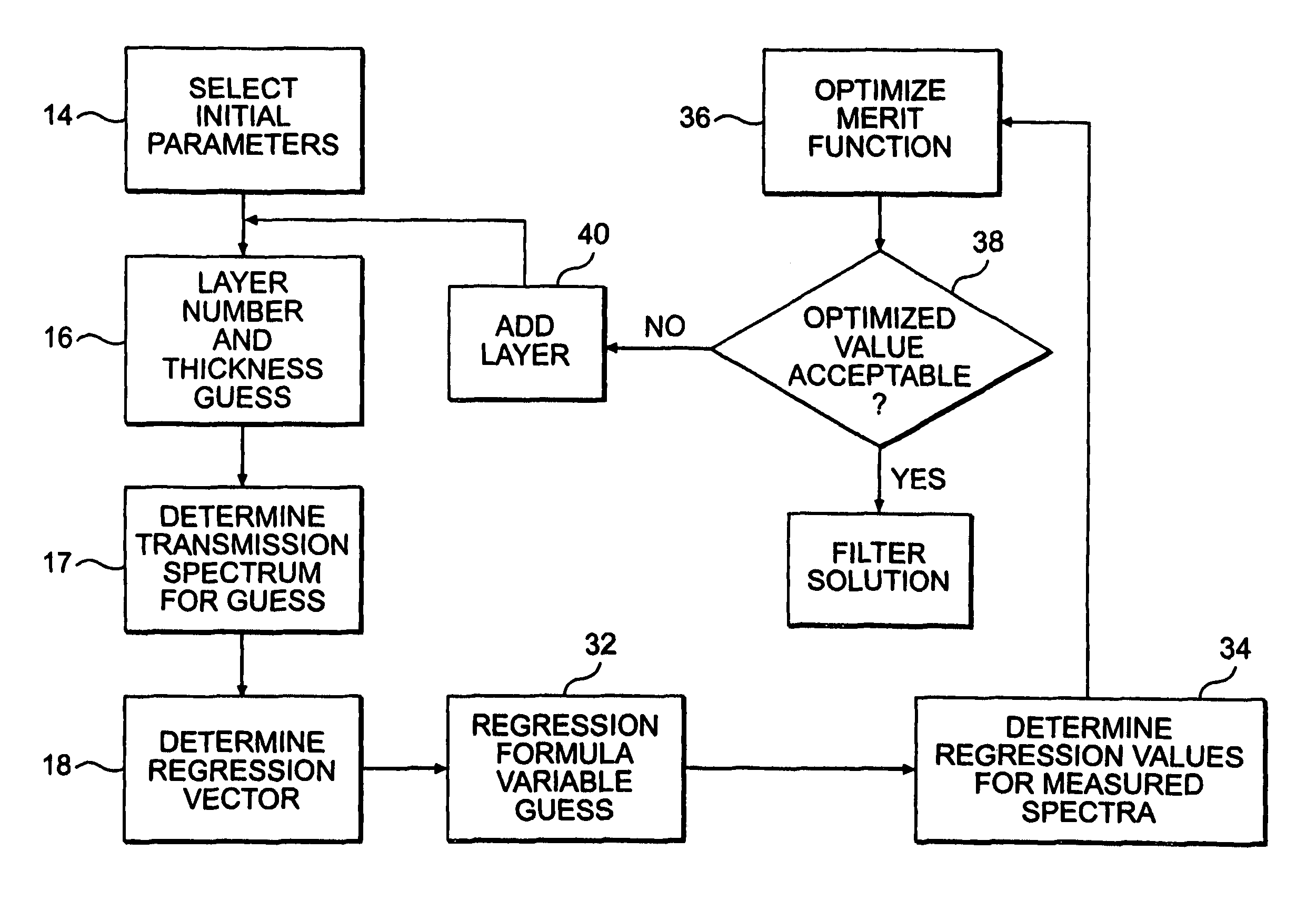
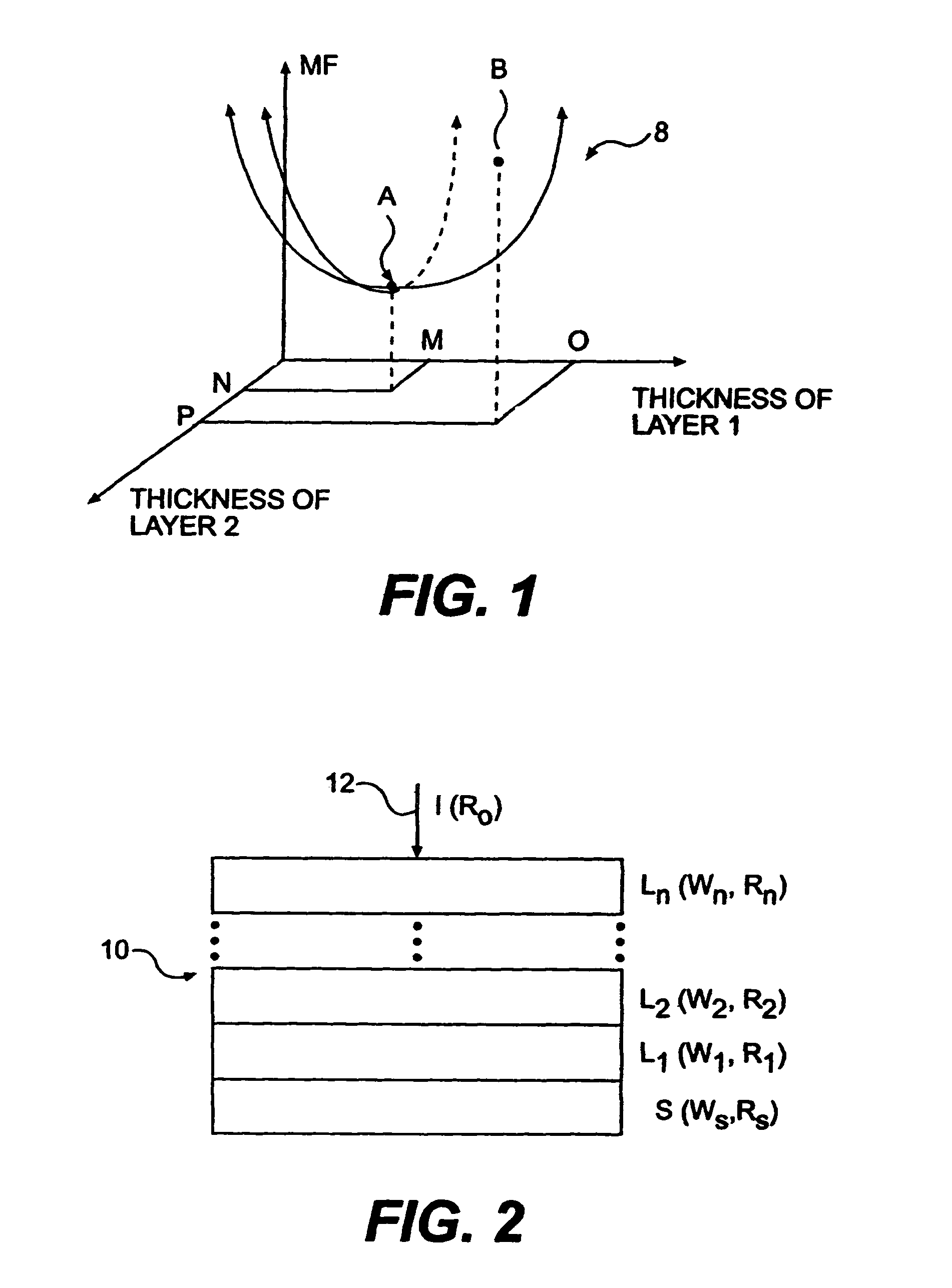
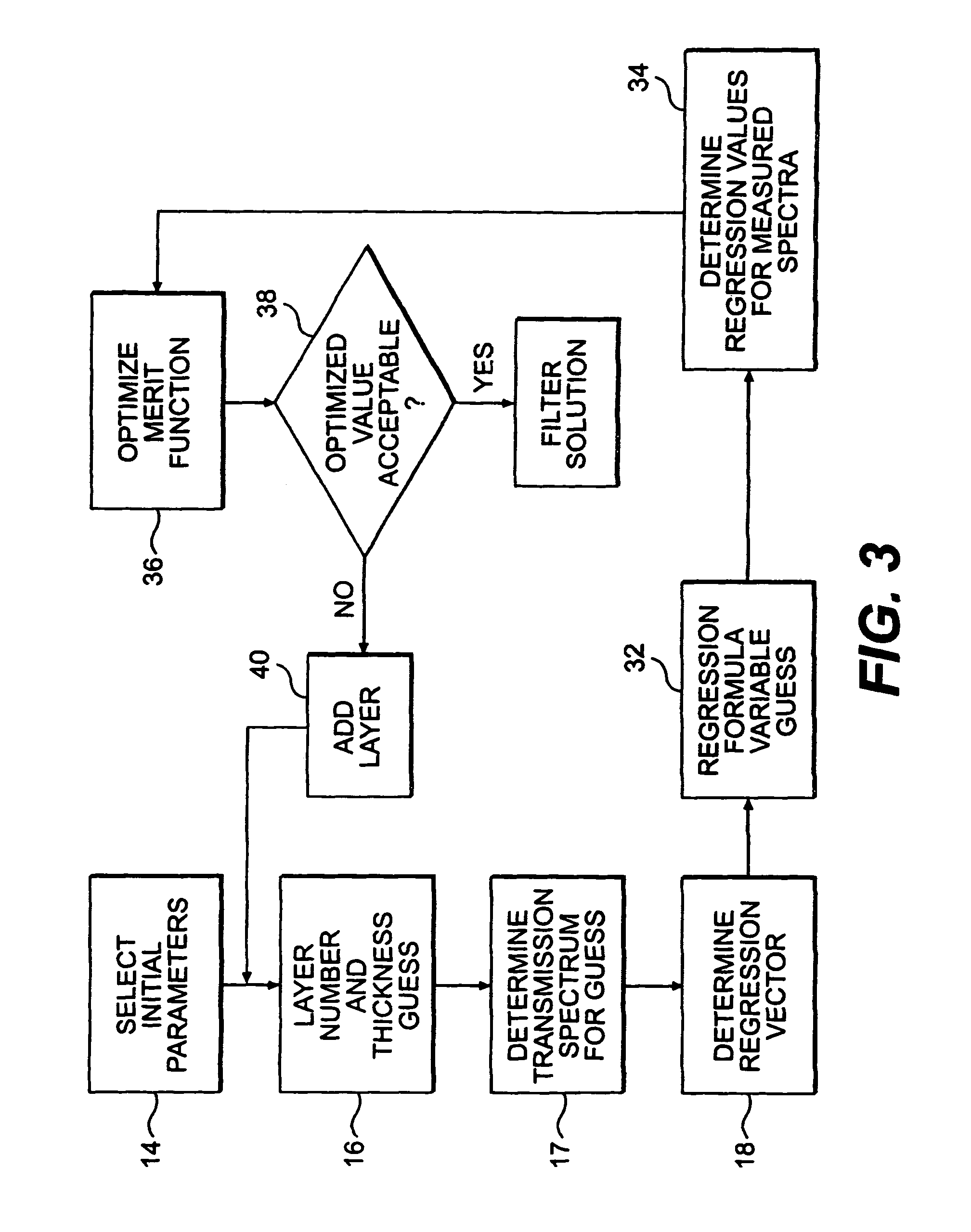
Filter design algorithm for multi-variate optical computing
Within a method of making an optical interference filter, sample spectra and measurements of a predetermined characteristic associated with respective spectra are provided. Upon selection of an initial number of filter layers and a thickness for each layer, a transmission spectrum is determined. Each sample spectrum is applied to a regression formula that relates interaction of light with the transmission spectrum to a regression value. A comparison relationship between the calculated regression values and the sample measurements is defined and optimized, wherein thickness of each layer is an optimization variable.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
On-device metrology
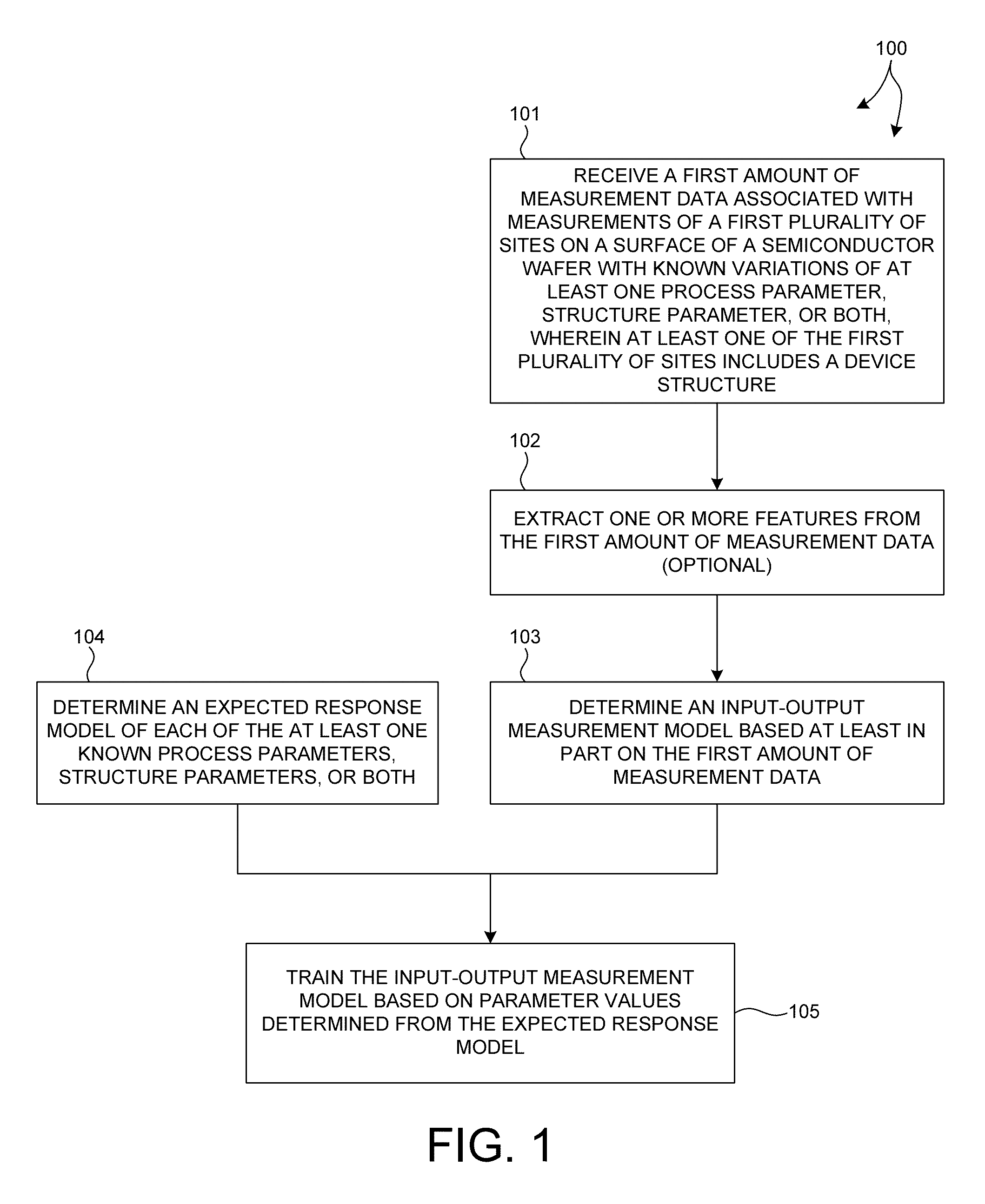
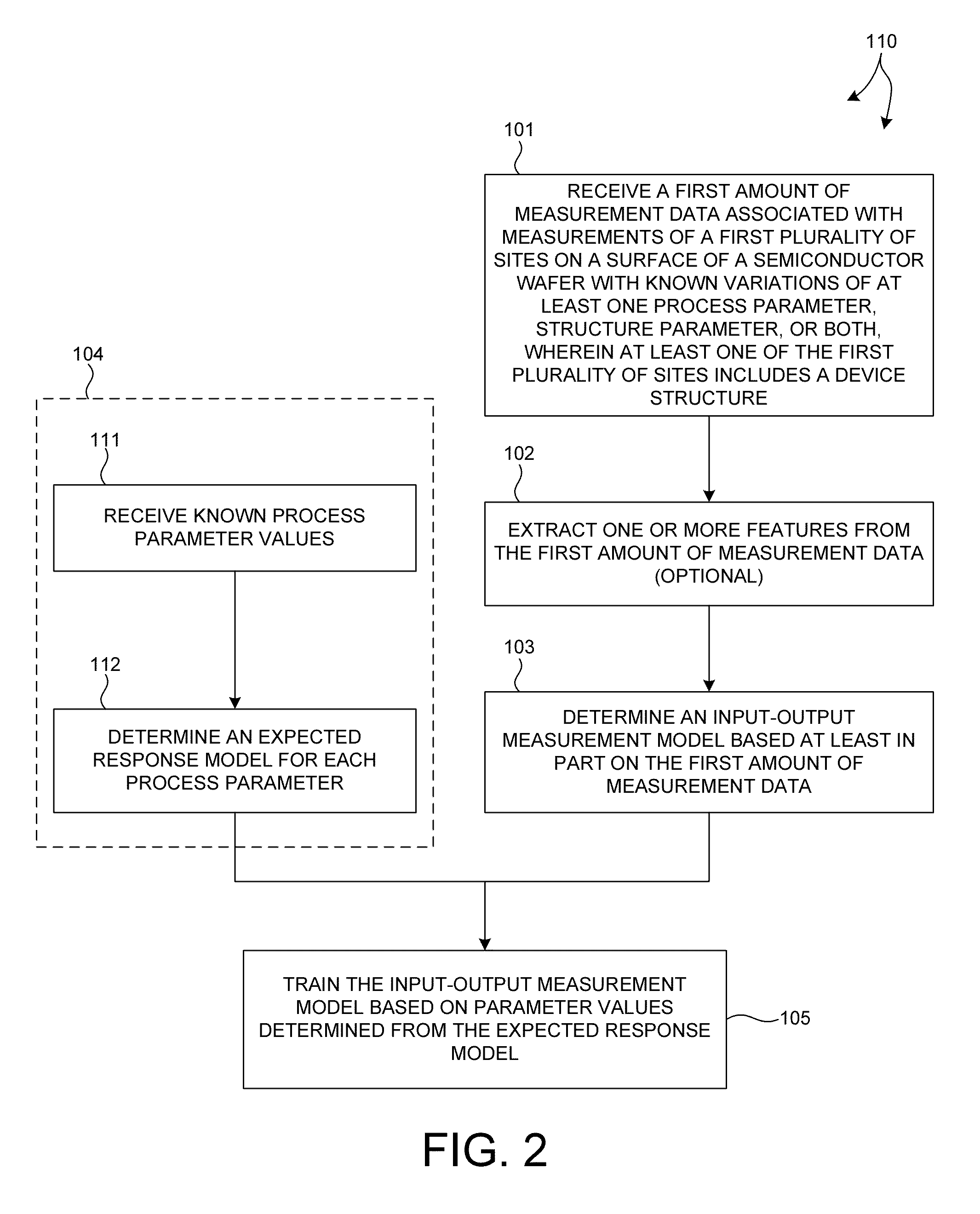
ActiveUS20140316730A1Accurate measurementAvoid poor resultsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesMetrologyComputation process
Methods and systems for performing semiconductor metrology directly on device structures are presented. A measurement model is created based on measured training data collected from at least one device structure. The trained measurement model is used to calculate process parameter values, structure parameter values, or both, directly from measurement data collected from device structures of other wafers. In some examples, measurement data from multiple targets is collected for model building, training, and measurement. In some examples, the use of measurement data associated with multiple targets eliminates, or significantly reduces, the effect of under layers in the measurement result, and enables more accurate measurements. Measurement data collected for model building, training, and measurement may be derived from measurements performed by a combination of multiple, different measurement techniques.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
System and method for efficiently generating cluster groupings in a multi-dimensional concept space
ActiveUS20050010555A1Generate efficientlyData processing applicationsWeb data indexingComputational scienceAlgorithm
A system and method for efficiently generating cluster groupings in a multi-dimensional concept space is described. A plurality of terms is extracted from each document in a collection of stored unstructured documents. A concept space is built over the document collection. Terms substantially correlated between a plurality of documents within the document collection are identified. Each correlated term is expressed as a vector mapped along an angle θ originating from a common axis in the concept space. A difference between the angle θ for each document and an angle σ for each cluster within the concept space is determined. Each such cluster is populated with those documents having such difference between the angle θ for each such document and the angle σ for each such cluster falling within a predetermined variance. A new cluster is created within the concept space those documents having such difference between the angle θ for each such document and the angle σ for each such cluster falling outside the predetermined variance.
Owner:NUIX NORTH AMERICA
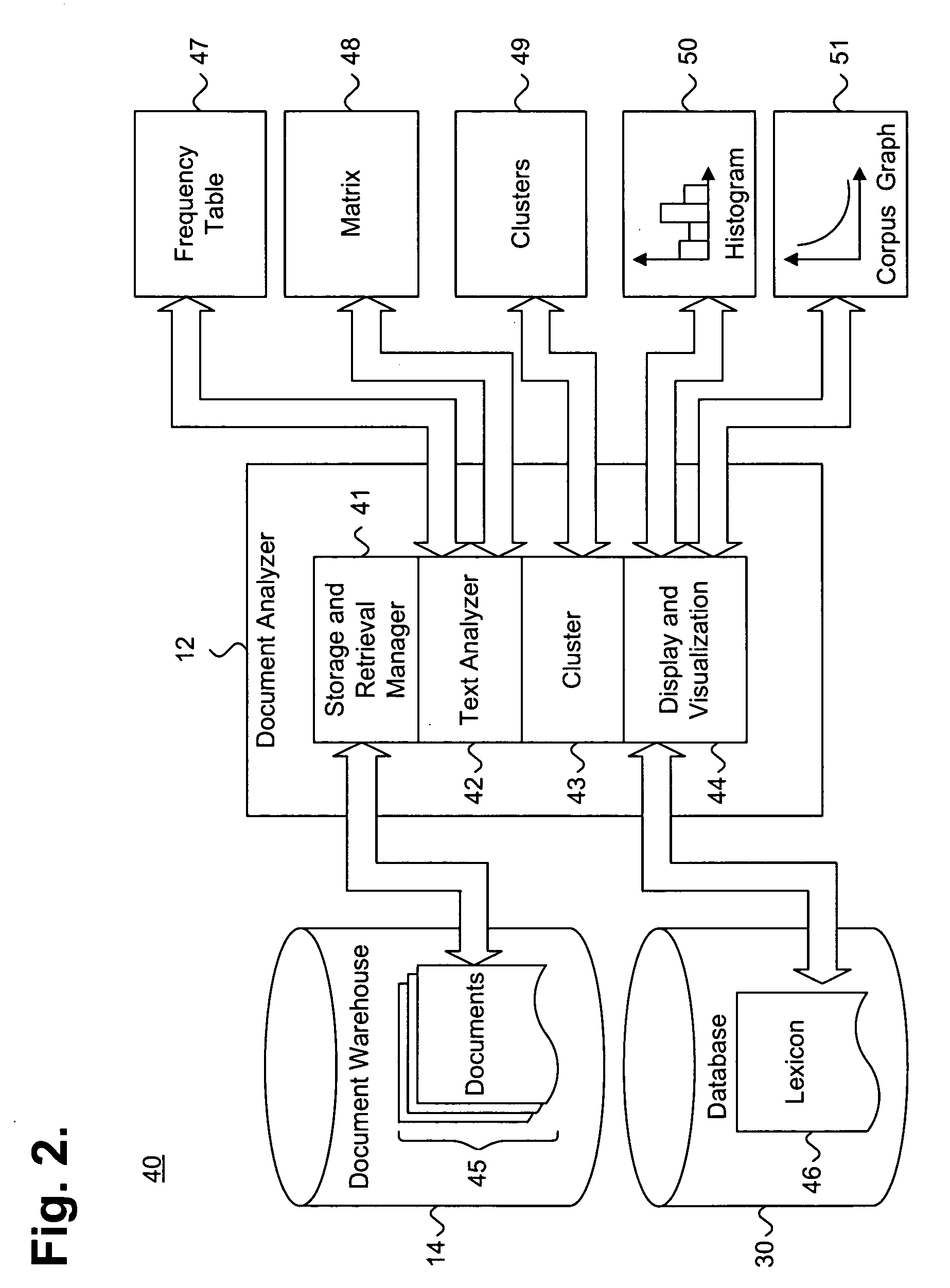
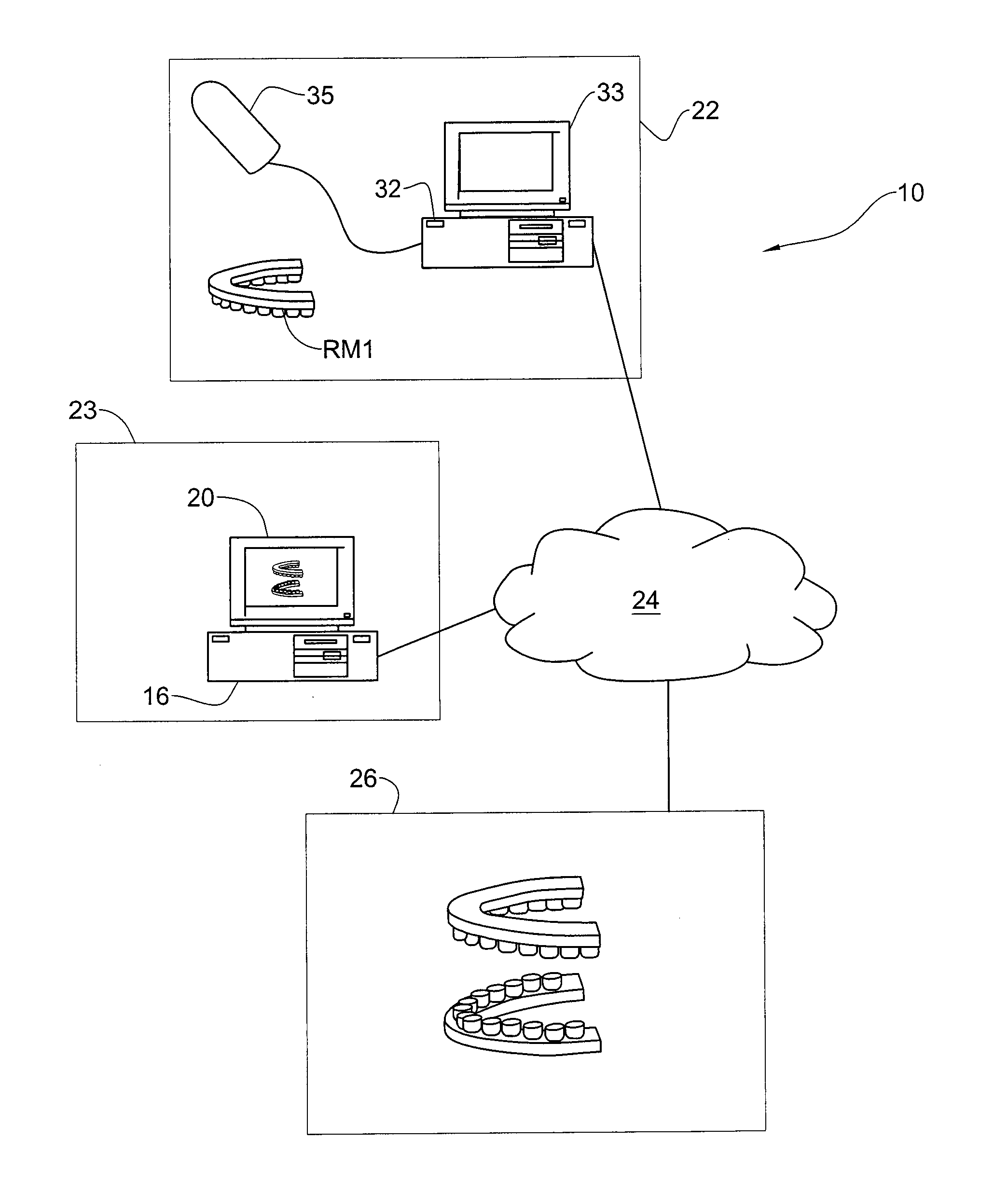
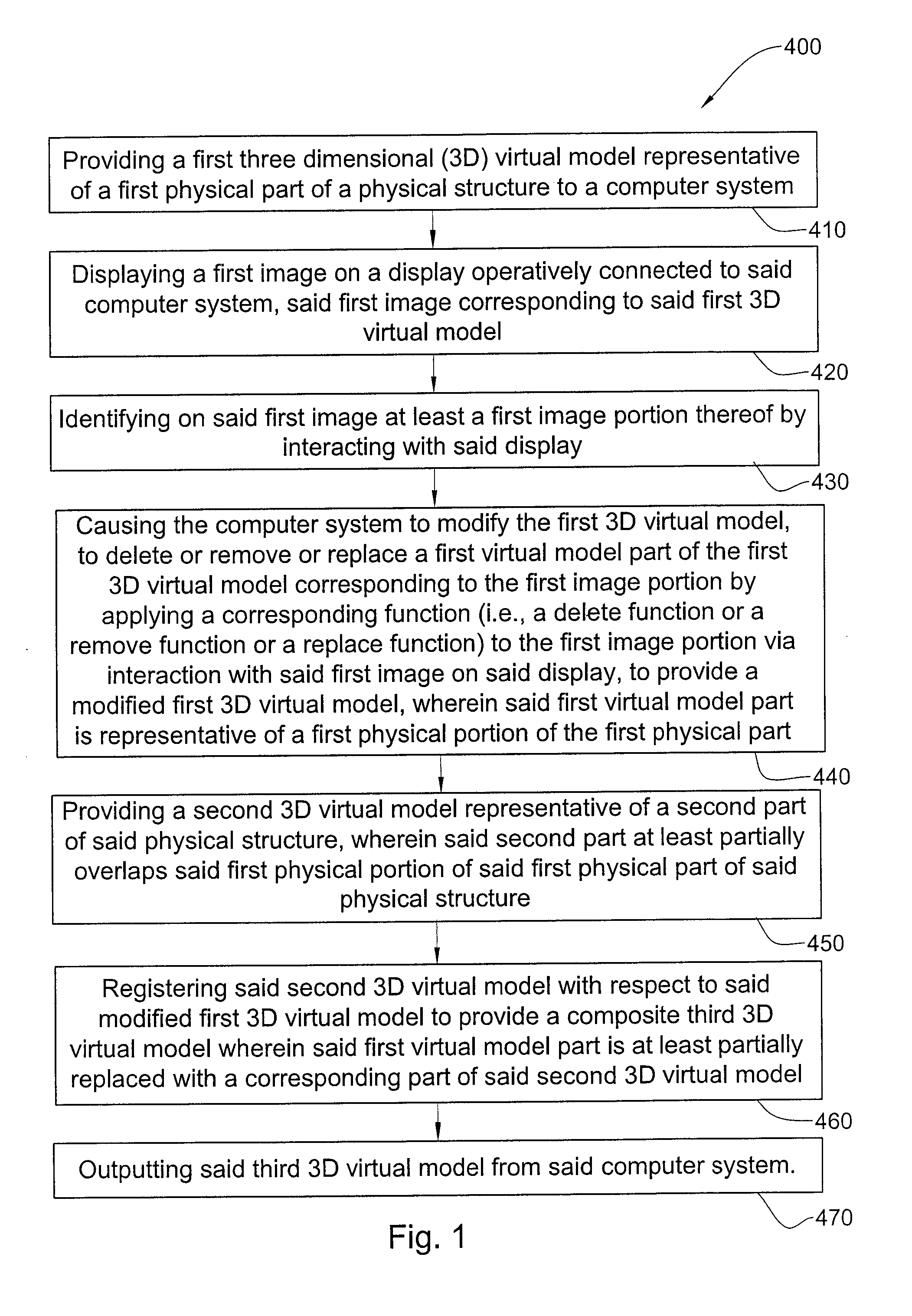
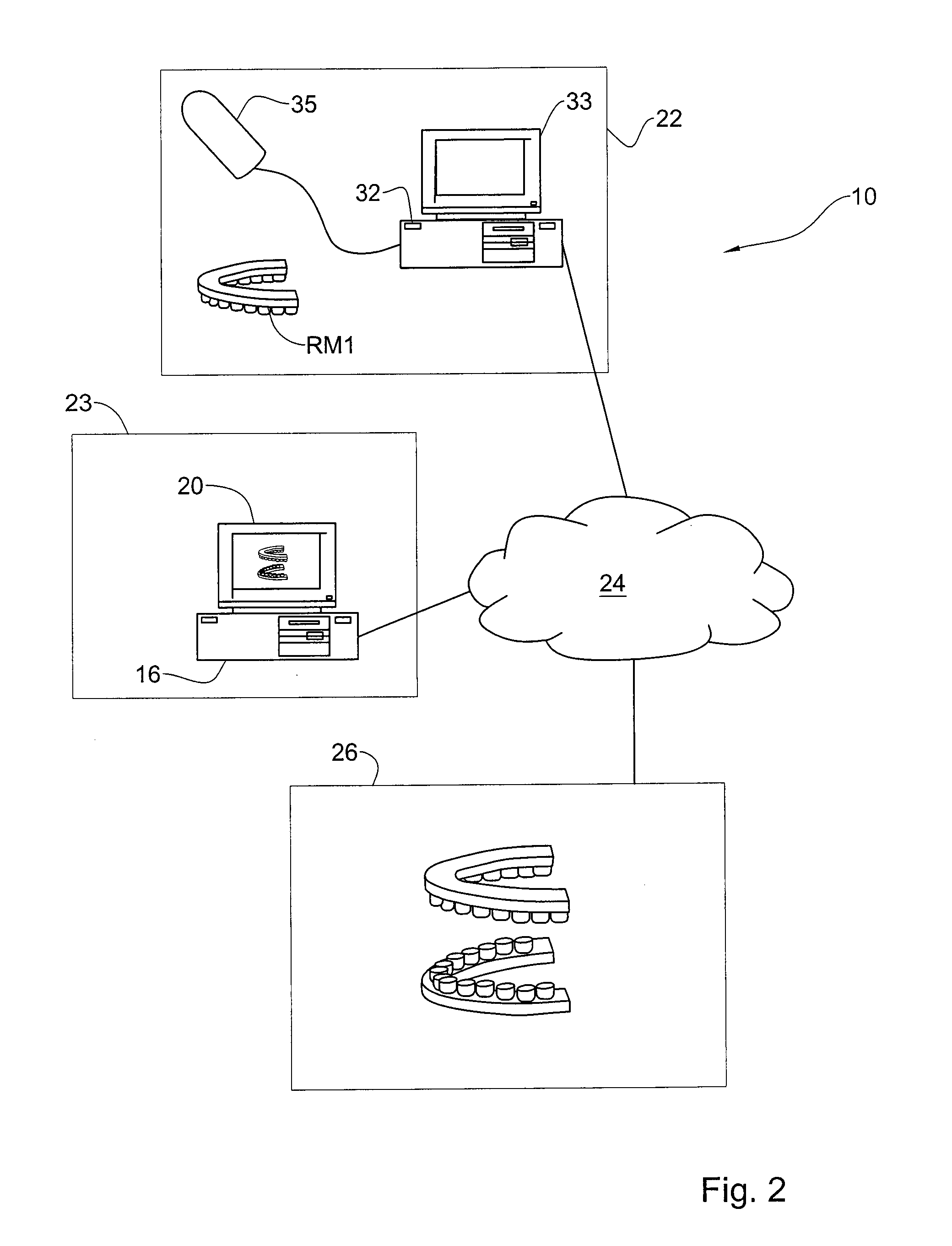
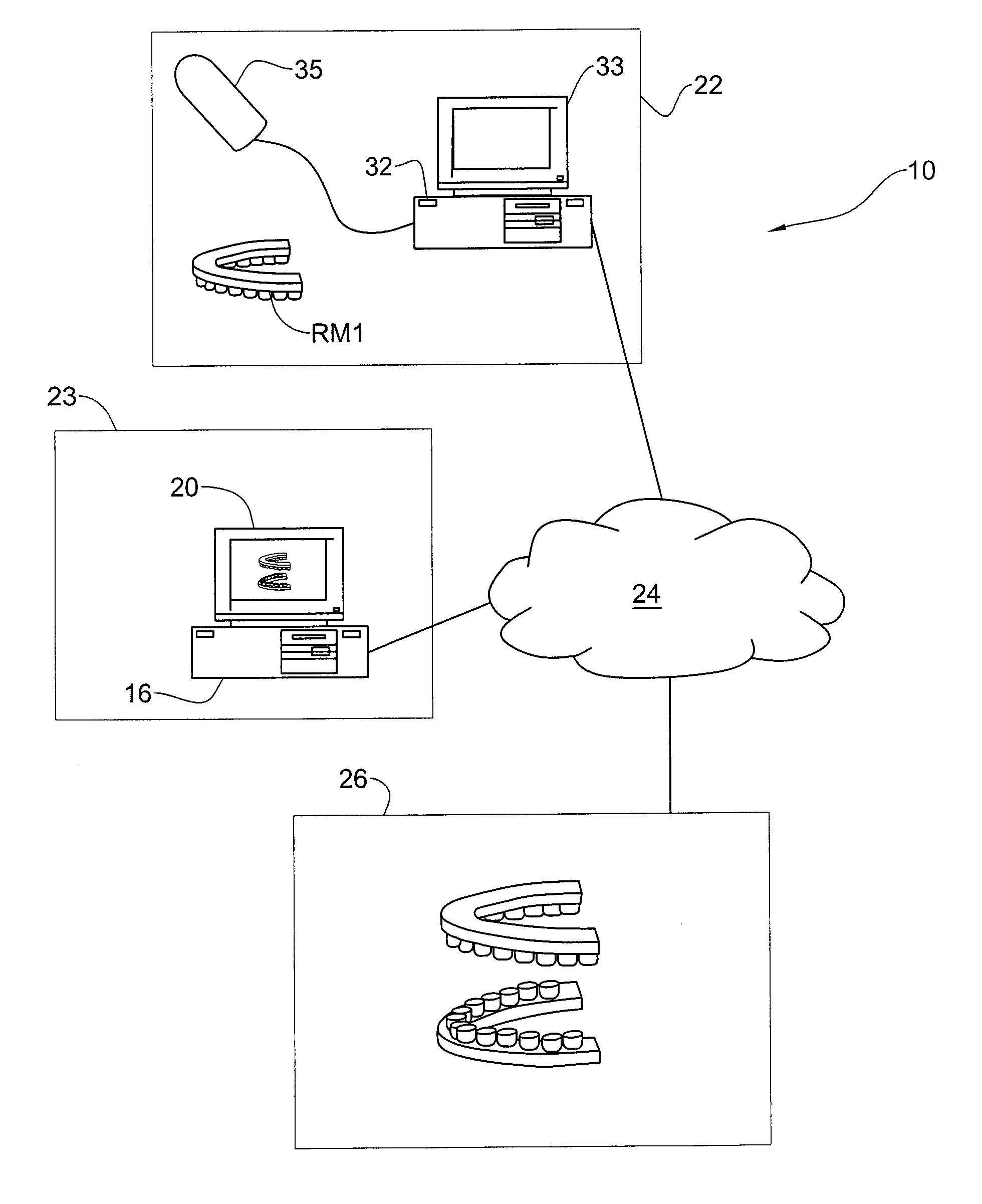
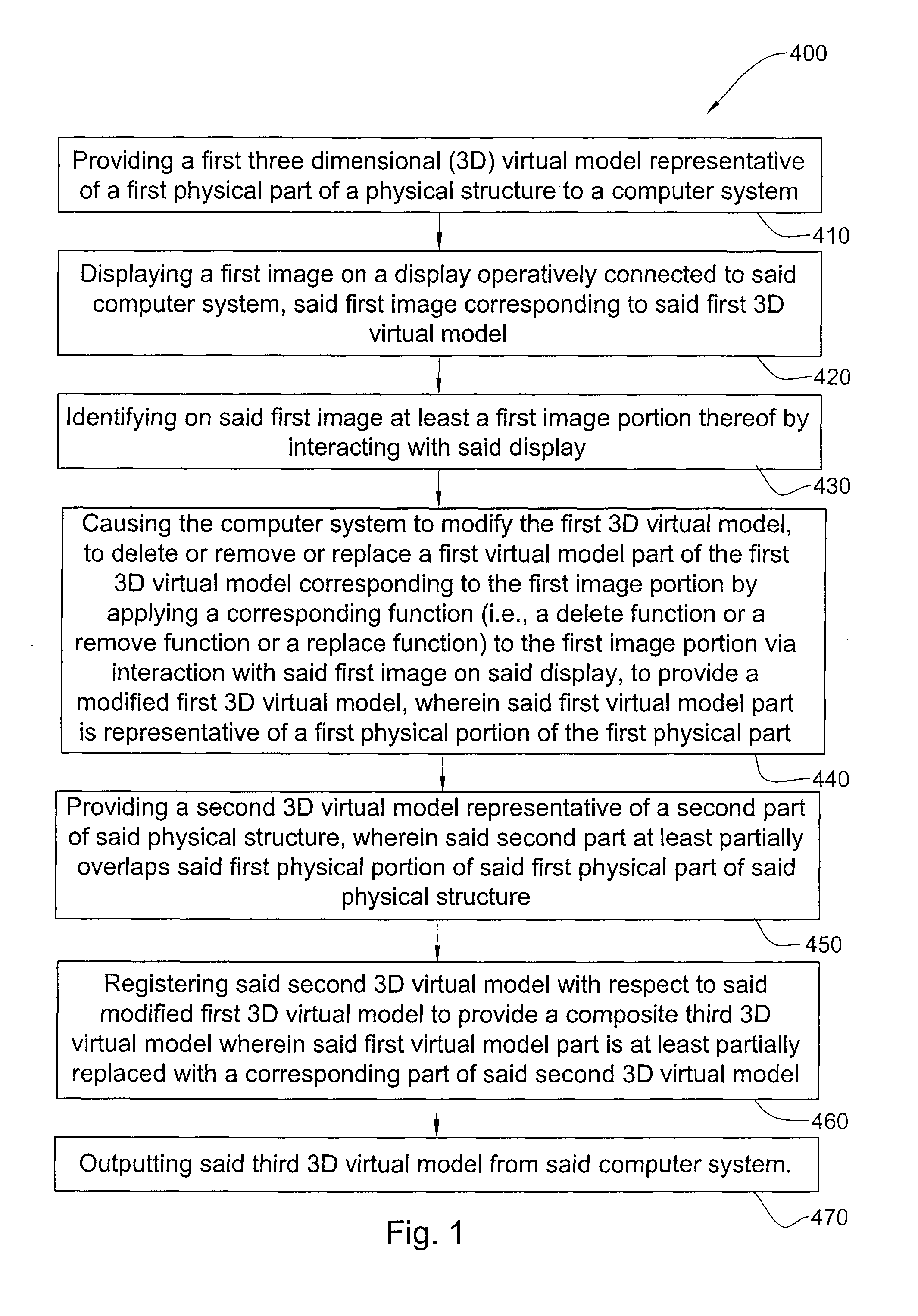
Methods and systems for creating and interacting with three dimensional virtual models
ActiveUS20130110469A1The process is convenient and fastImage enhancementImpression capsComputer graphics (images)Virtual model
Systems and methods are provided for modifying a virtual model of a physical structure with additional 3D data obtained from the physical structure to provide a modified virtual model.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
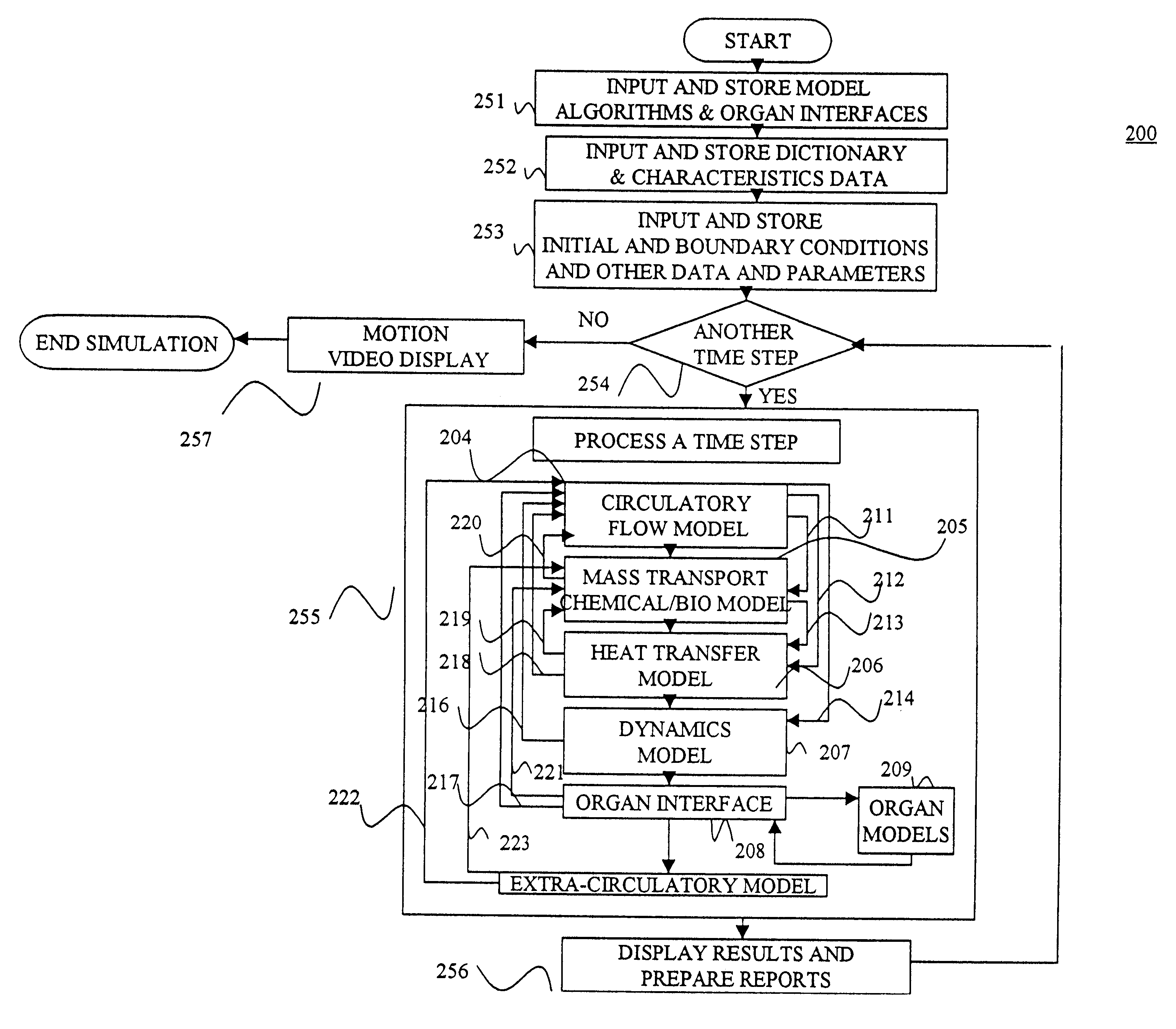
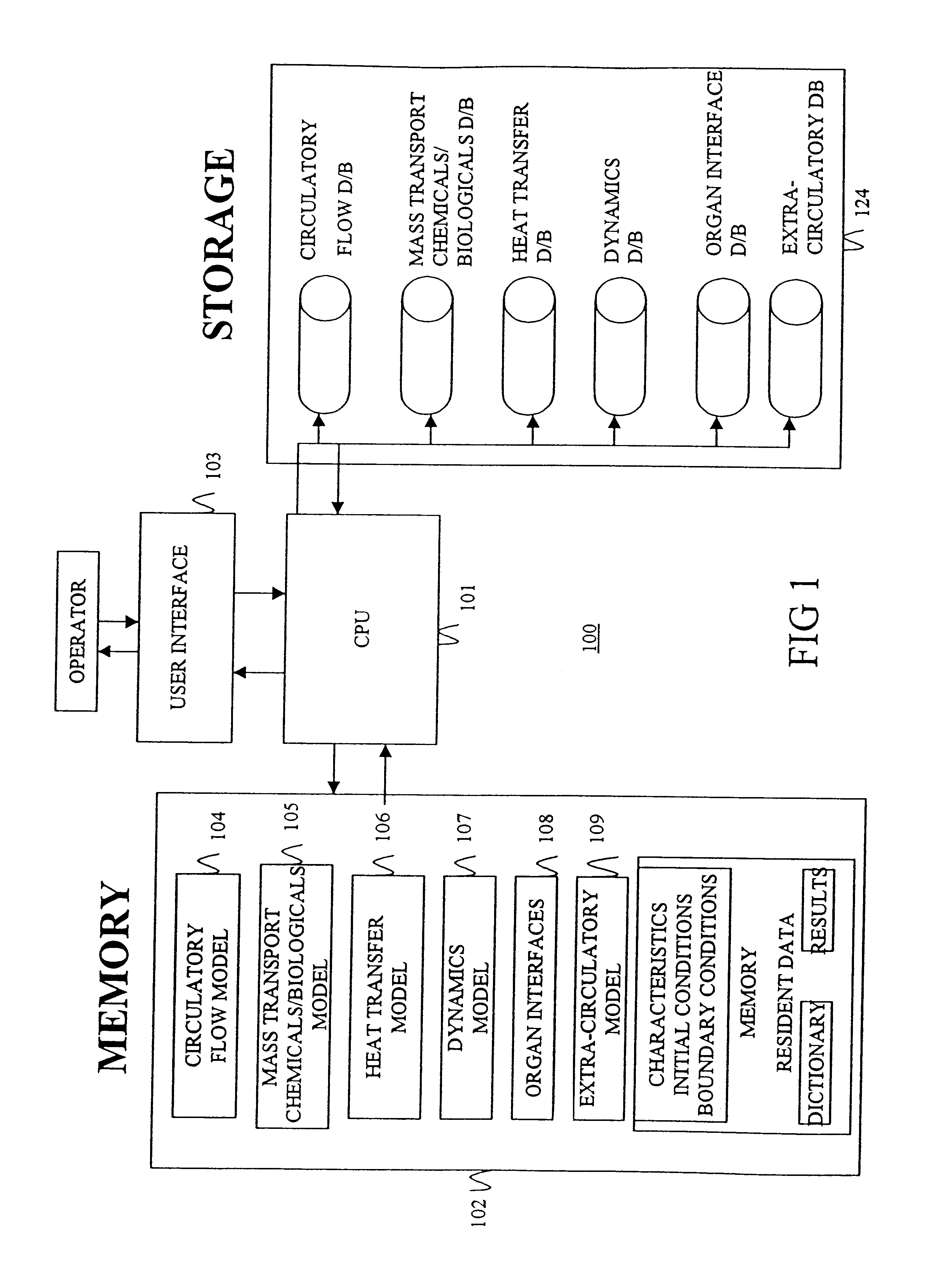
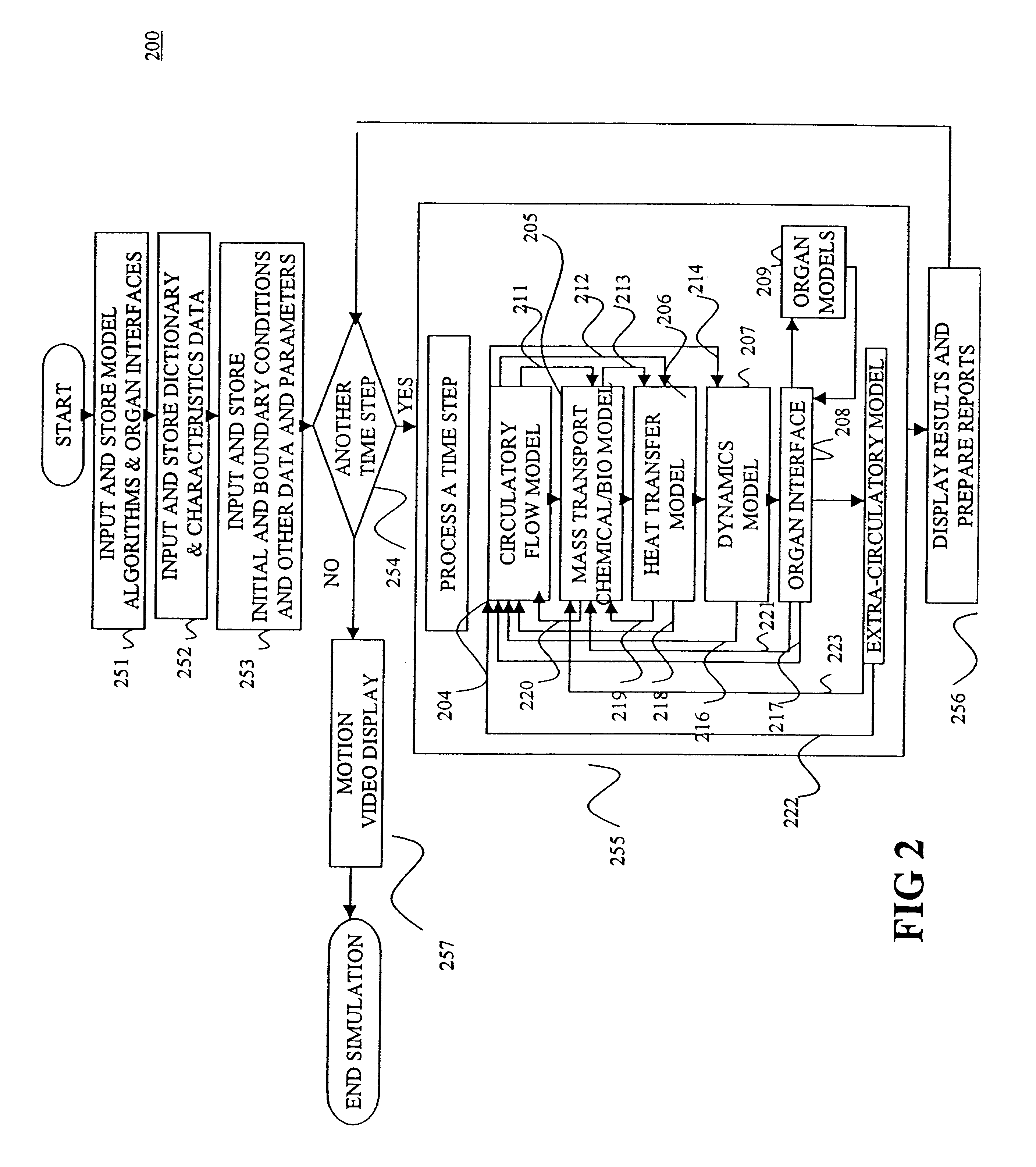
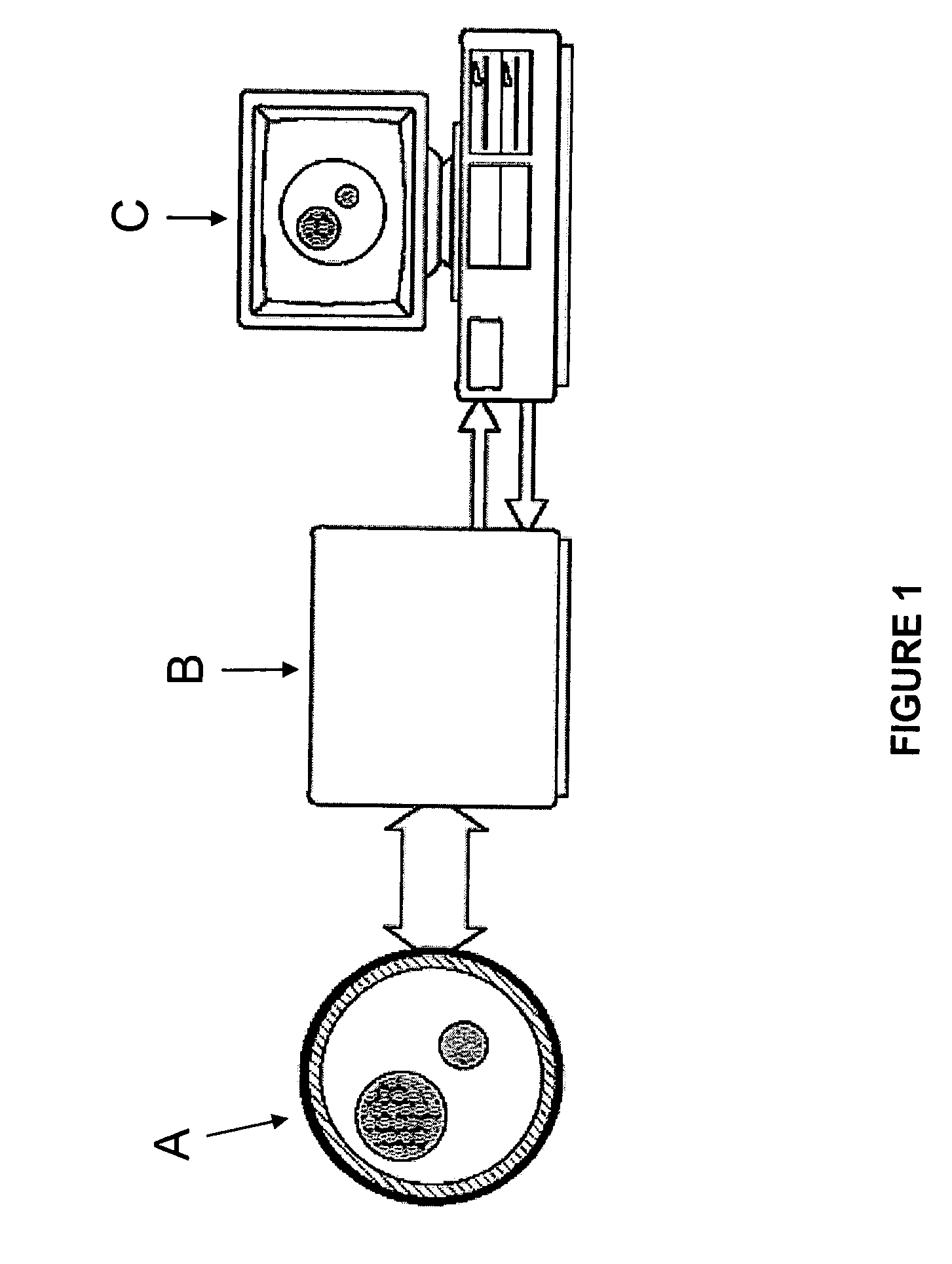
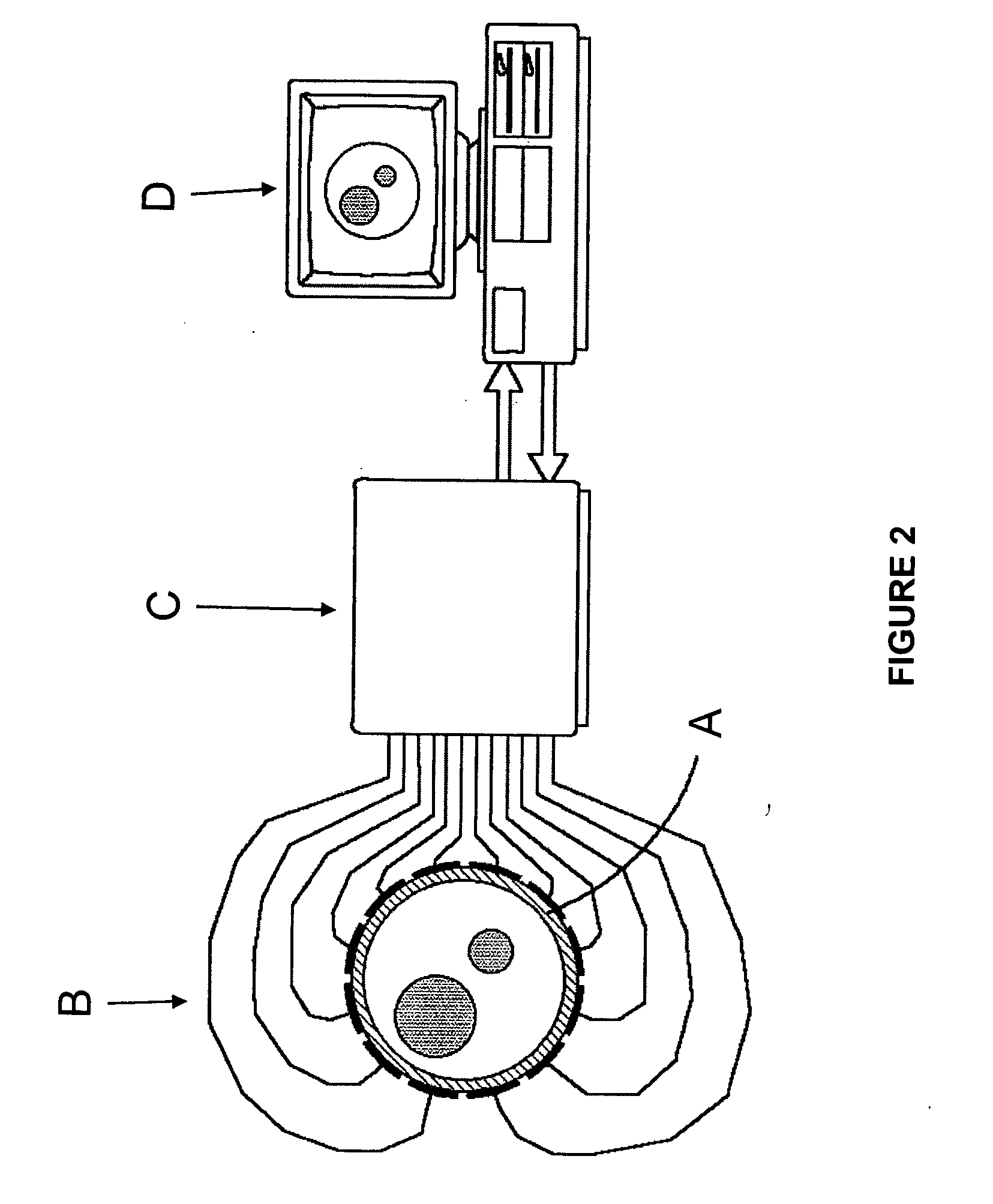
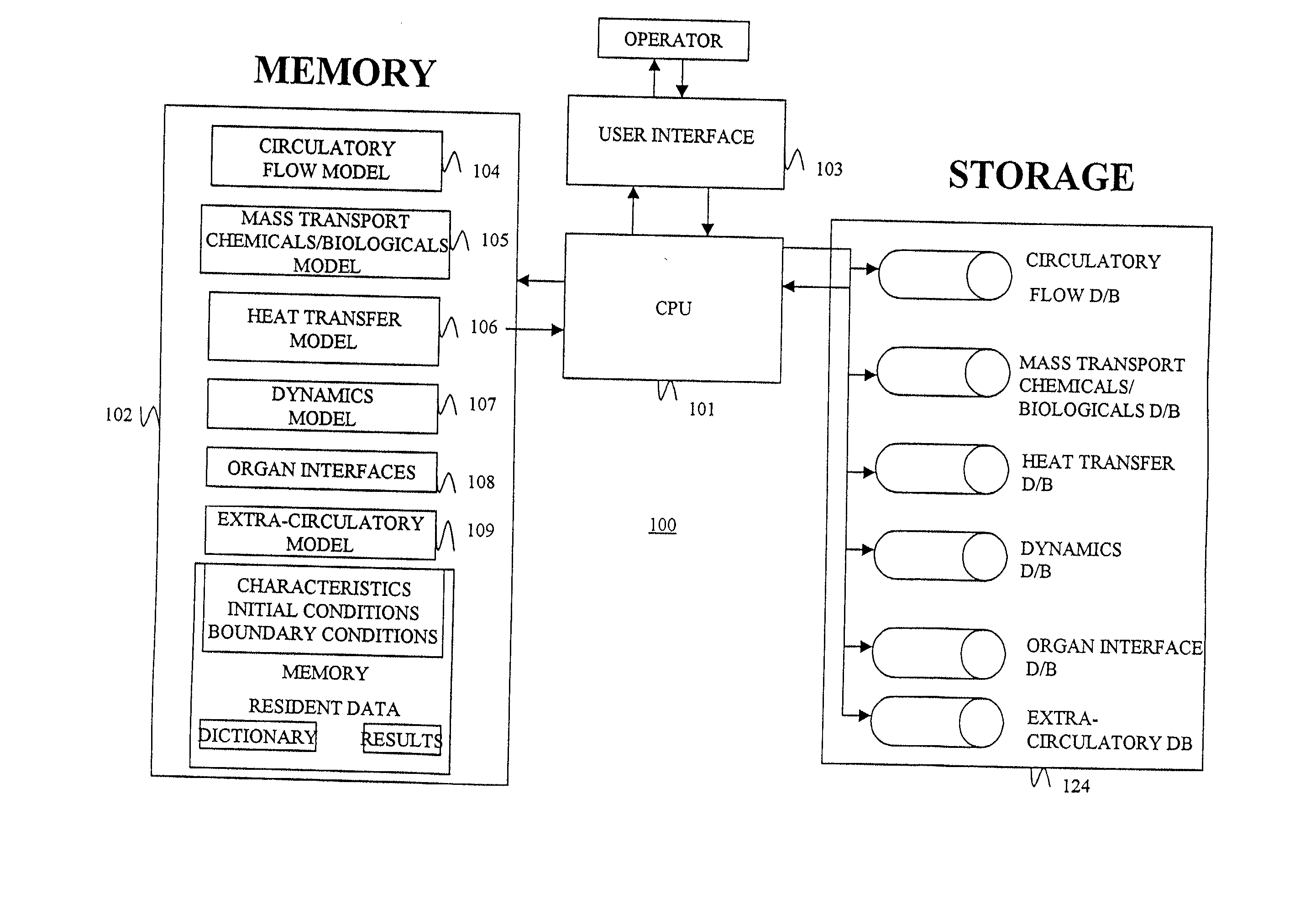
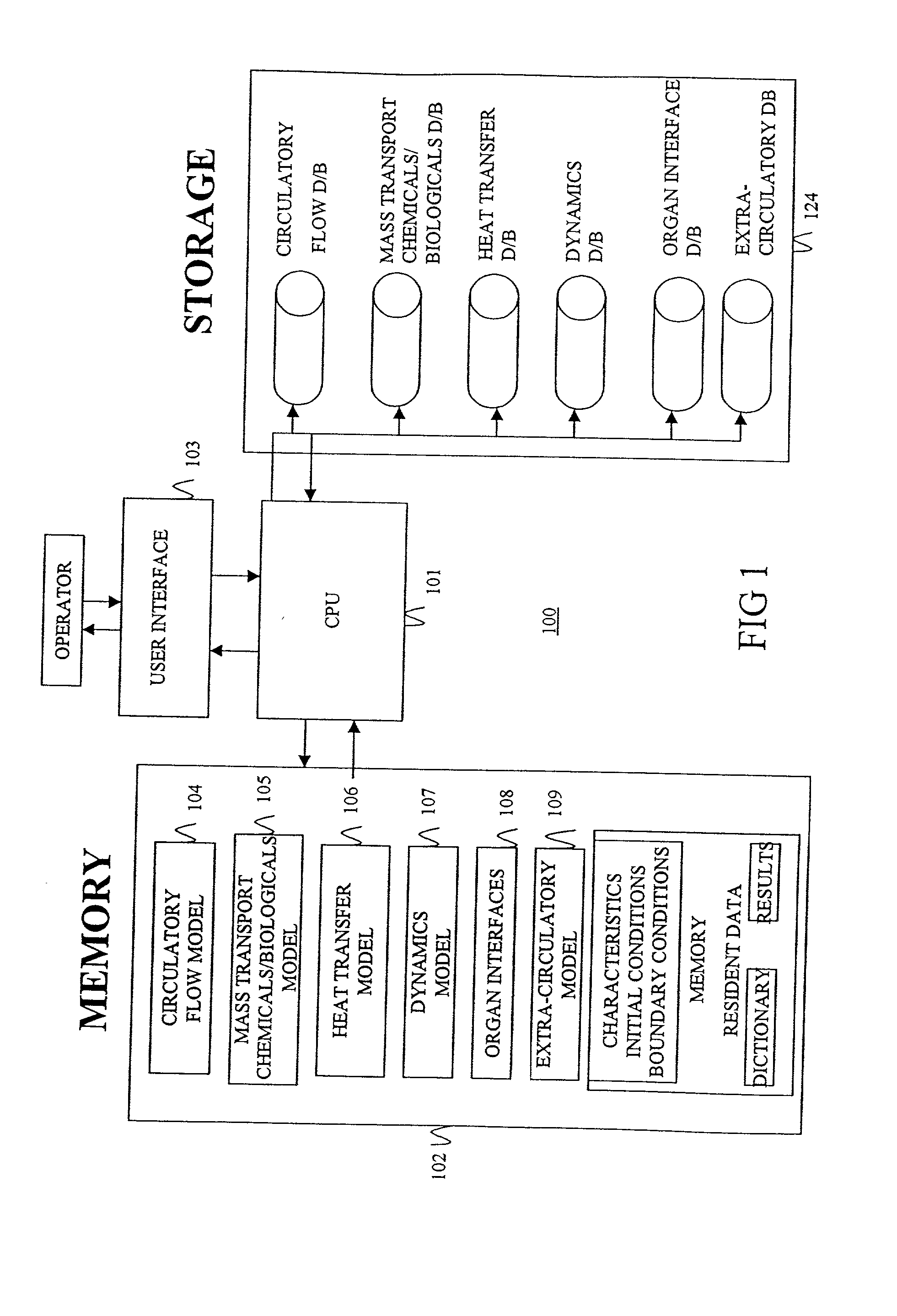
Configurable bio-transport system simulator
InactiveUS6381562B2Easy to customizeSave effortNanoinformaticsAnalogue computers for chemical processesComputational scienceBiological body
A method of simulating a bio-transport system comprising: (a) characterizing one or more elements to represent a bio-transport system of an organism or a portion thereof; (b) constructing one or more mathematical representations that model one or more bio-transport dynamics for each element based on the characterization of the elements to form a configured simulation model; (c) initializing the configured simulation model; (d) executing the configured simulation model to obtain bio-transport dynamics data for one or more elements; and (e) outputting information to a user based on at least a portion of the bio-transport dynamics data.
Owner:KEANE JOHN A
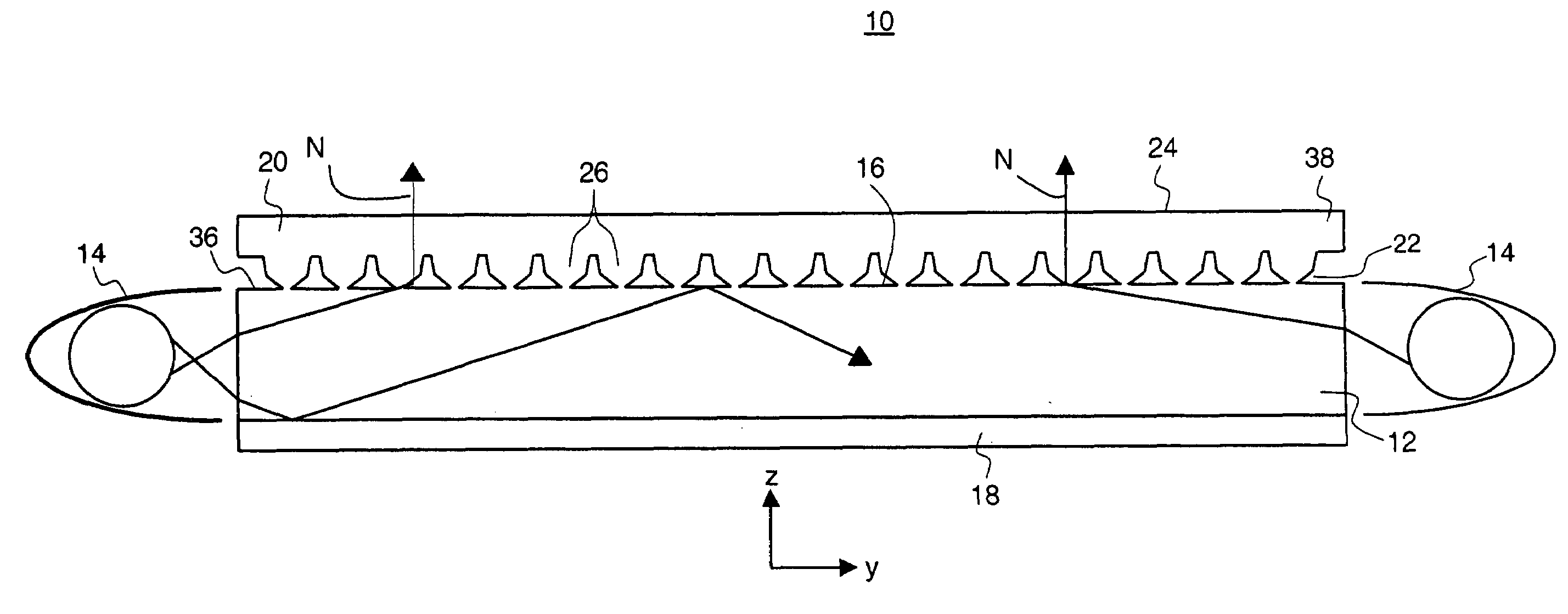
Illumination apparatus and film
InactiveUS20070223252A1Easy to manufactureLow costOptical light guidesReflectorsTotal internal reflectionLight guide
An illumination apparatus comprises:(a) at least one light source;(b) a light guide for accepting light from the at least one light source and for guiding the light using total internal reflection, the light guide having a top surface;(c) a light extracting film having an input surface optically coupled with the top surface and an output surface for providing light,wherein the input surface comprises a plurality of features which are optically coupled to the top surface of the light guide, each feature having:(i) a first side comprising two or more planar segments; and(ii) a second side comprising two or more planar segments, andwherein the first and second sides intersect at an apex.
Owner:SKC HAAS DISPLAY FILMS CO LTD
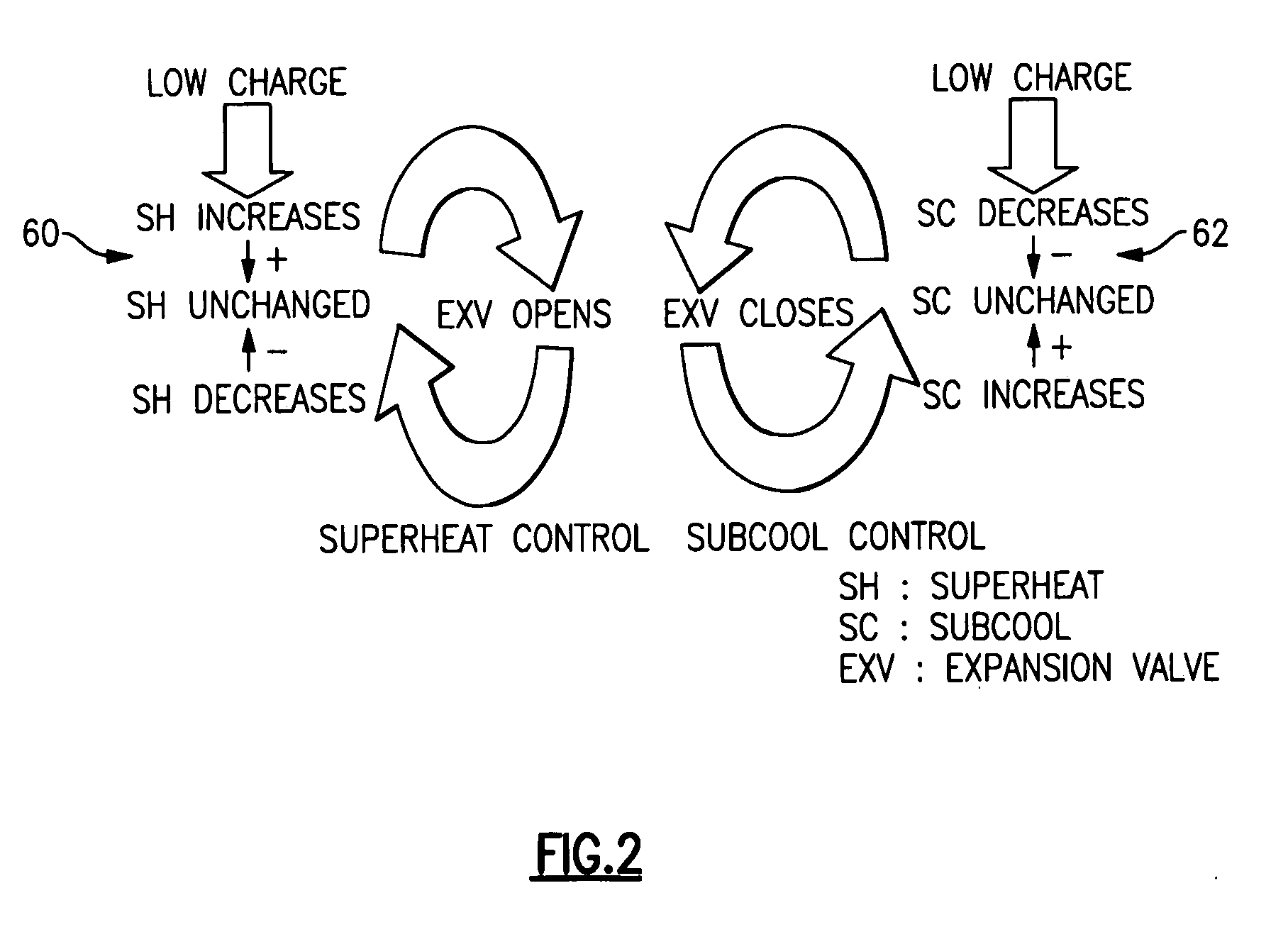
Charge loss detection and prognostics for multi-modular split systems
InactiveUS20060021362A1Compression machines with non-reversible cycleFluid circulation arrangementCharge lossPrognostics
A method for detecting and predicting refrigerant level includes the steps of determining an estimated value for a parameter indicative of refrigerant level and comparing that estimated value to an actual value. The difference between the actual and estimated value provides a refrigerant charge indicator value. The charge indicator value is indicative of the amount of refrigerant contained within the system. A change value is combined with the charge indicator value to provide a prediction for the future value of the charge indicator value. This future value is determined based on a rate of change and charge indicator value over a selected period of time.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
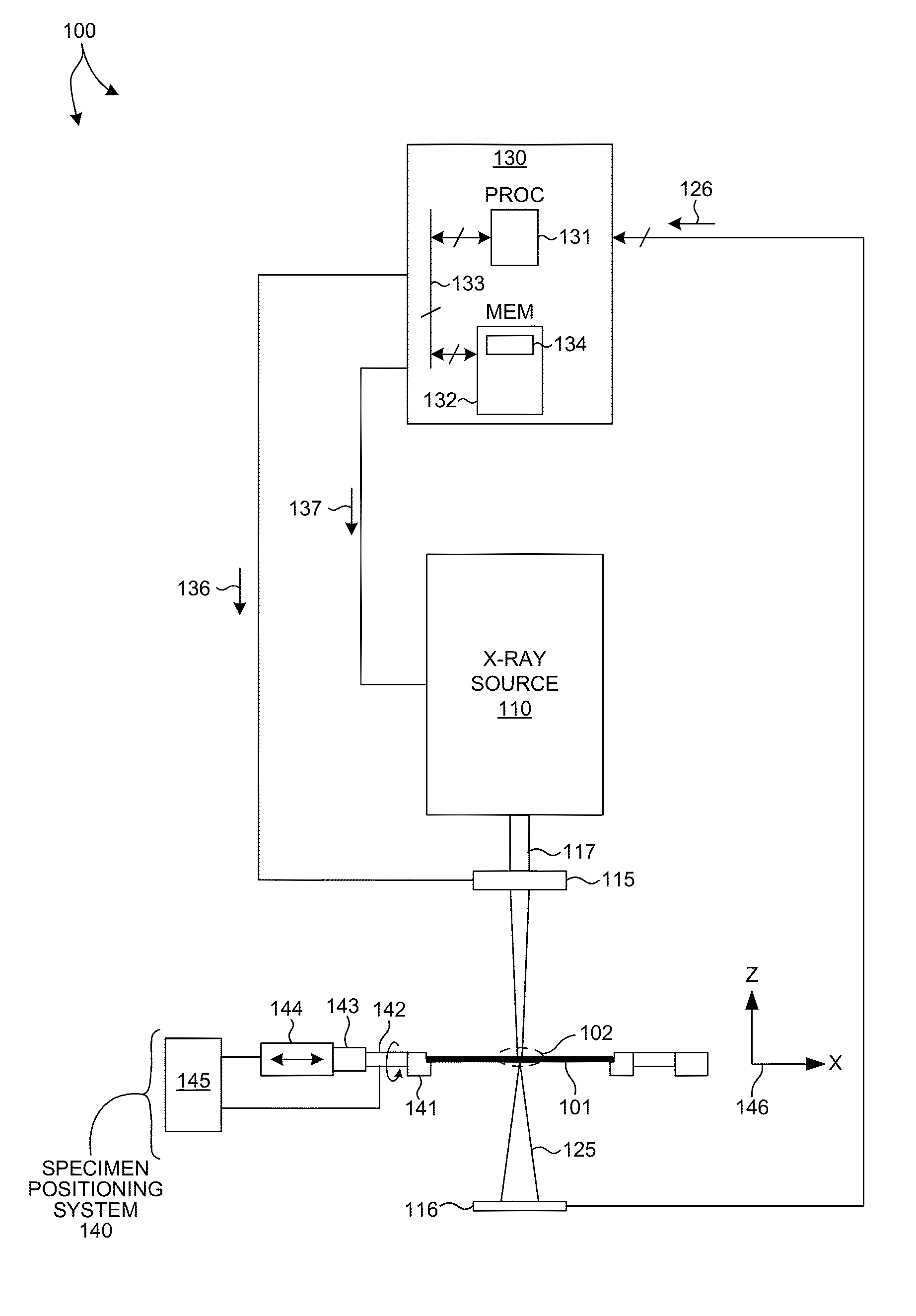
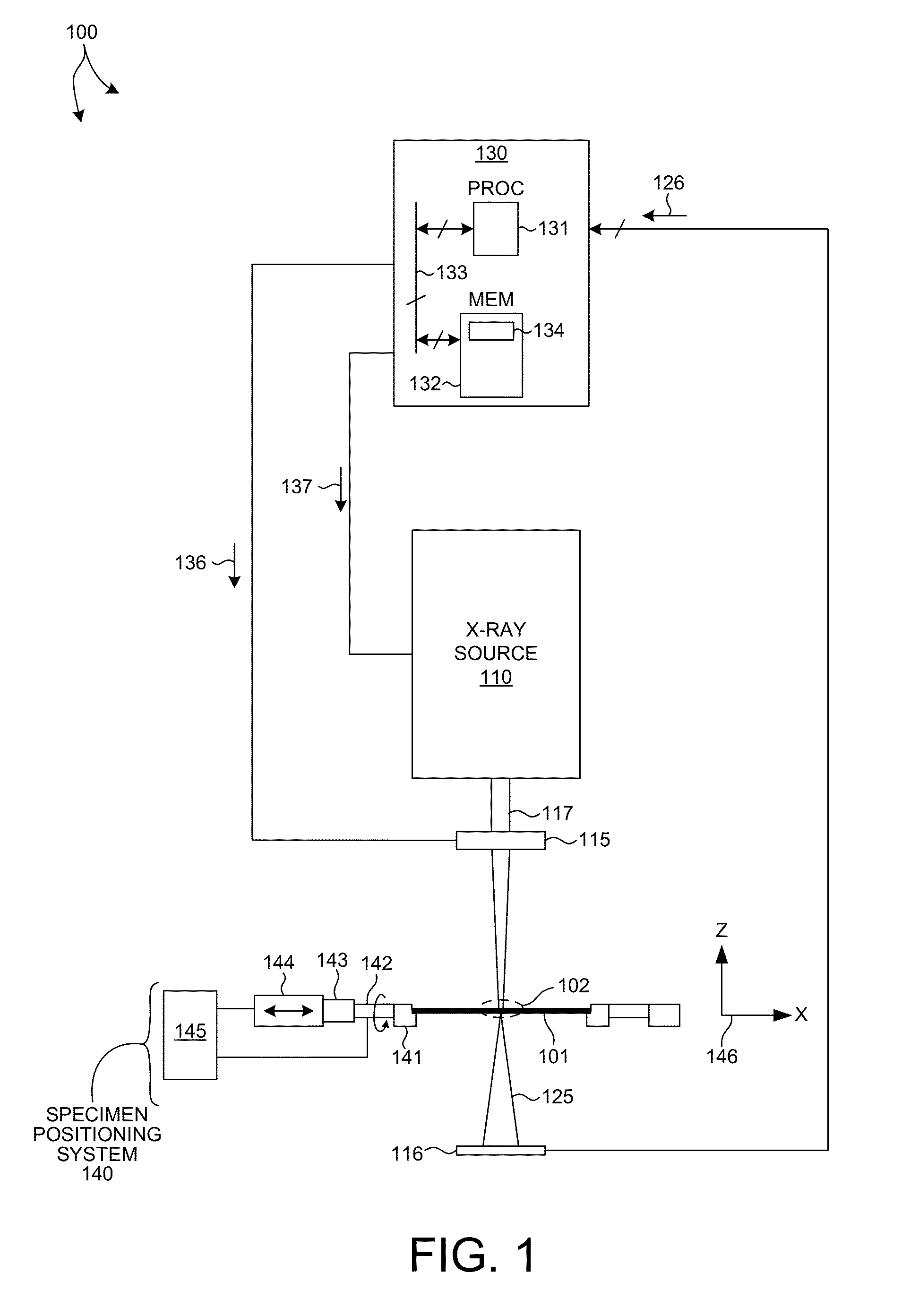
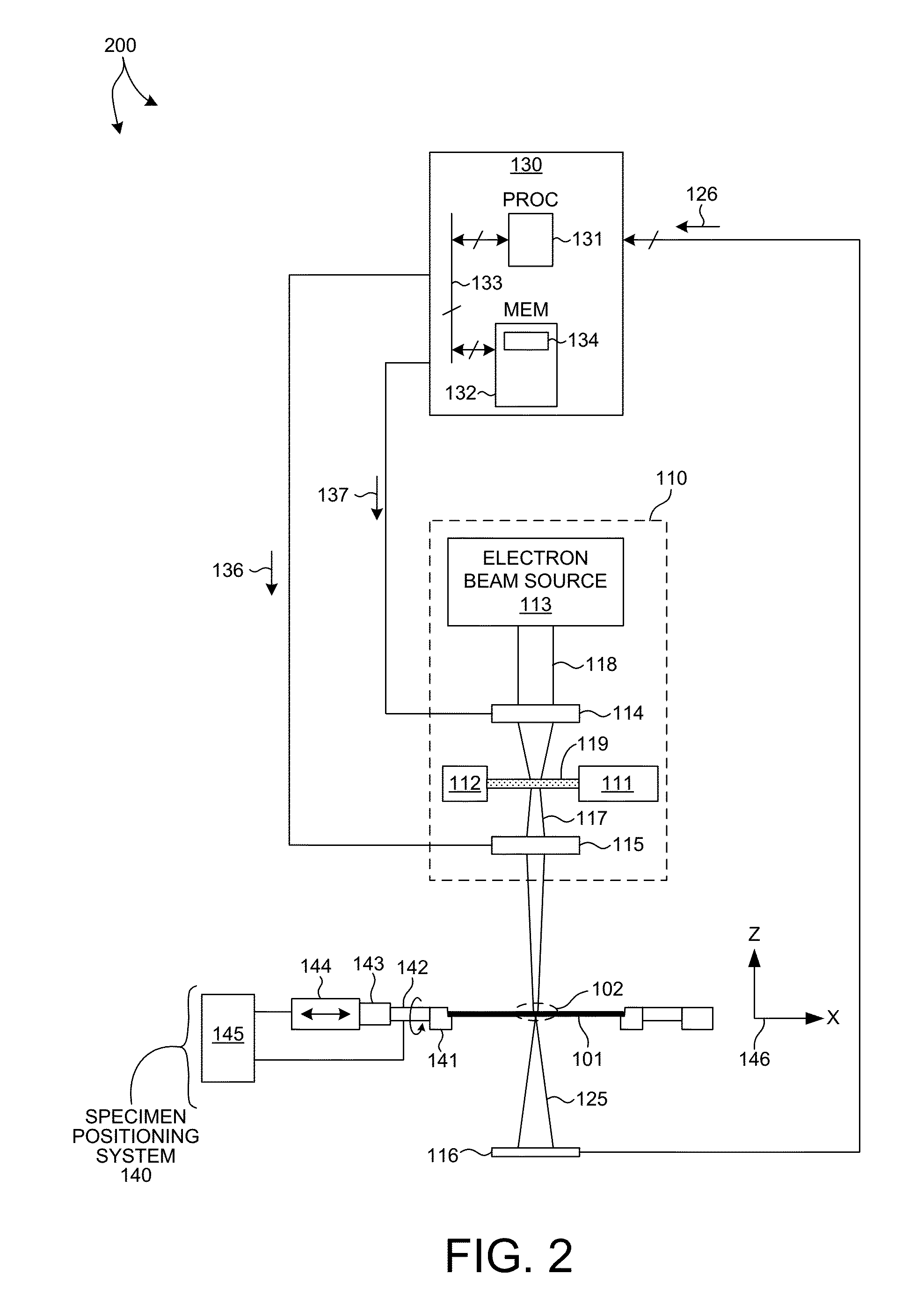
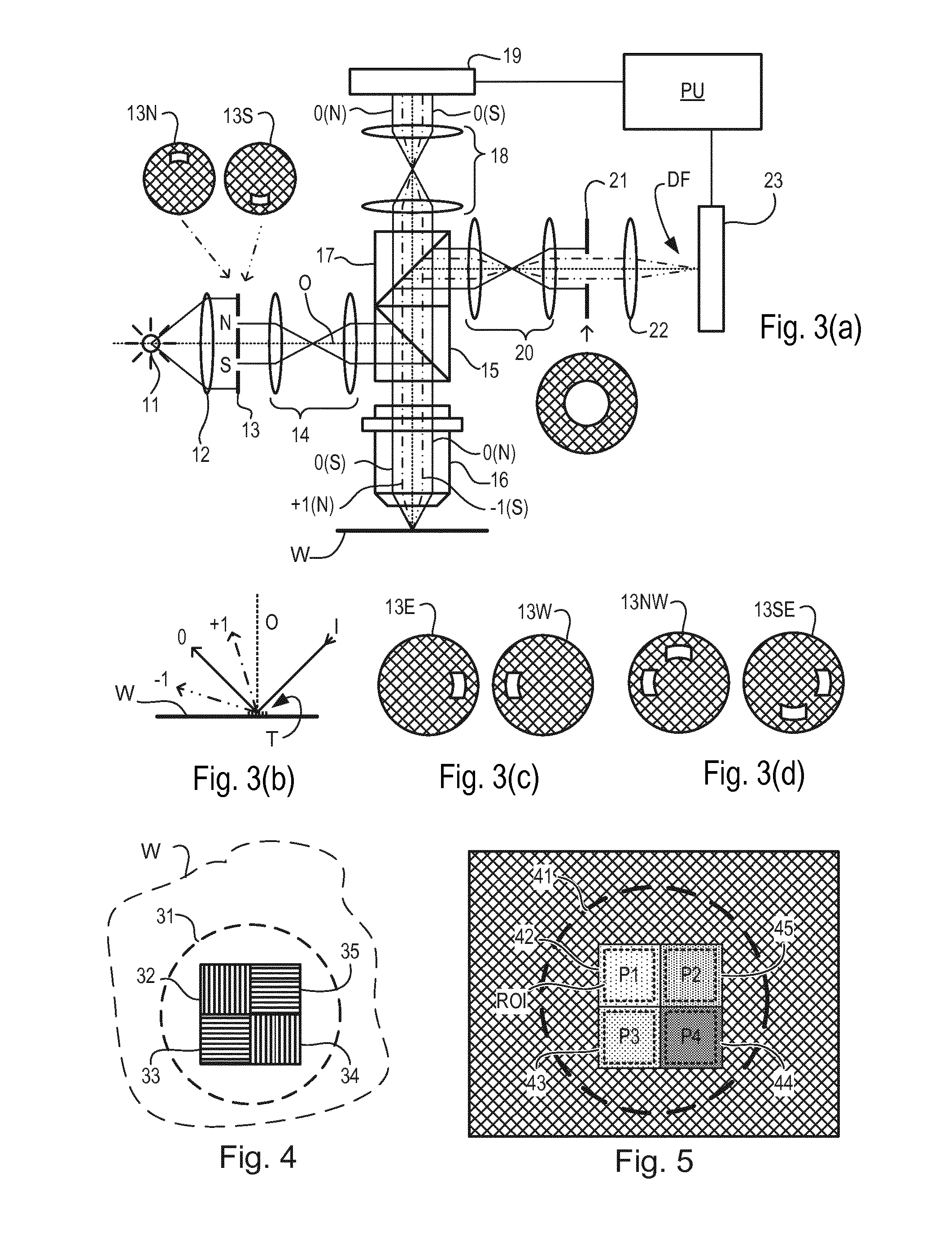
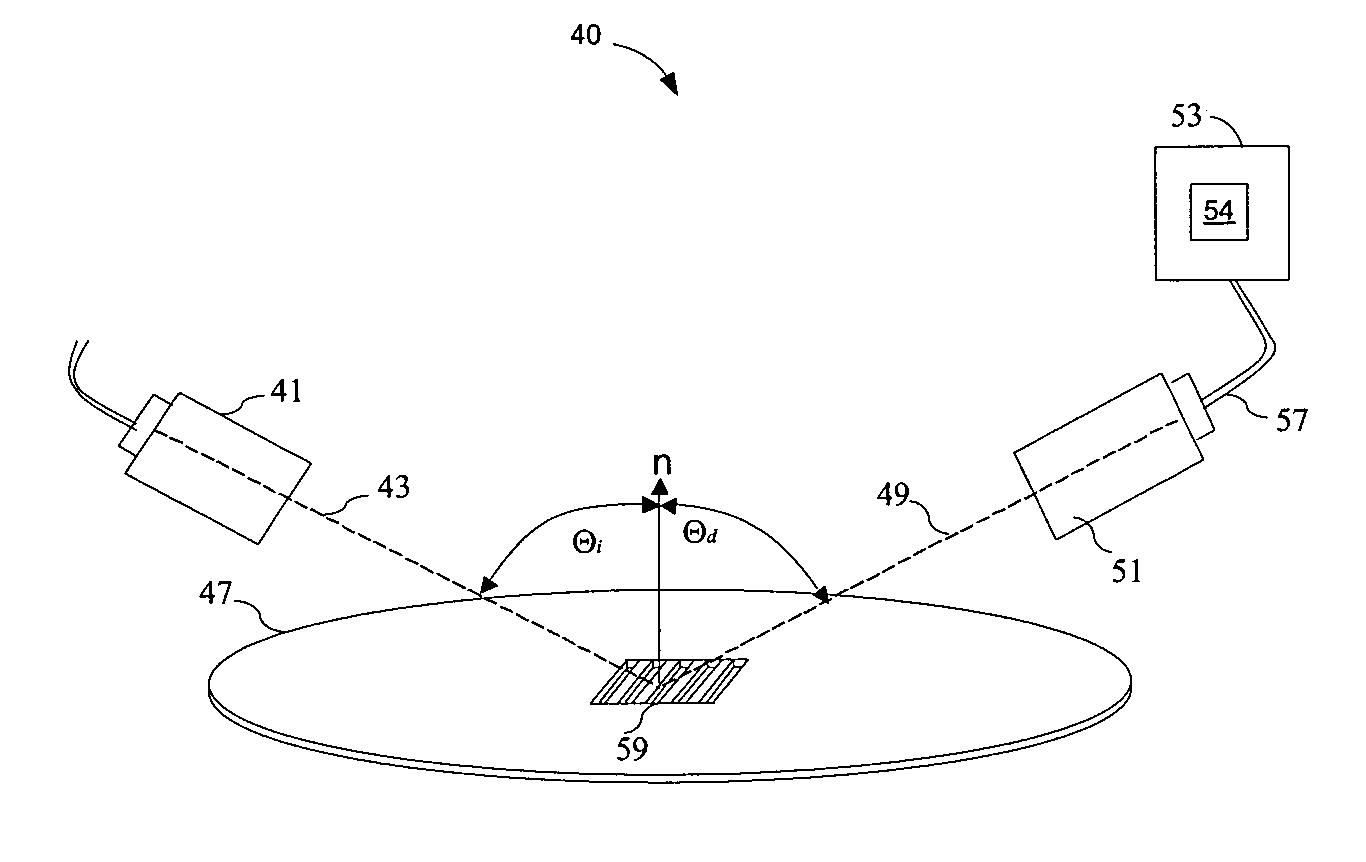
Metrology Method and Apparatus, Lithographic System and Device Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20160161864A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLithography processRegression analysis
Disclosed is a method of measuring a parameter of a litho-graphic process, and associated inspection apparatus. The method comprises measuring at least two target structures on a substrate using a plurality of different illumination conditions, the target structures having deliberate overlay biases; to obtain for each target structure an asymmetry measurement representing an overall asymmetry that includes contributions due to (i) the deliberate overlay biases, (ii) an overlay error during forming of the target structure and (iii) any feature asymmetry. A regression analysis is performed on the asymmetry measurement data by fitting a linear regression model to a planar representation of asymmetry measurements for one target structure against asymmetry measurements for another target structure, the linear regression model not necessarily being fitted through an origin of the planar representation. The overlay error can then be determined from a gradient described by the linear regression model.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
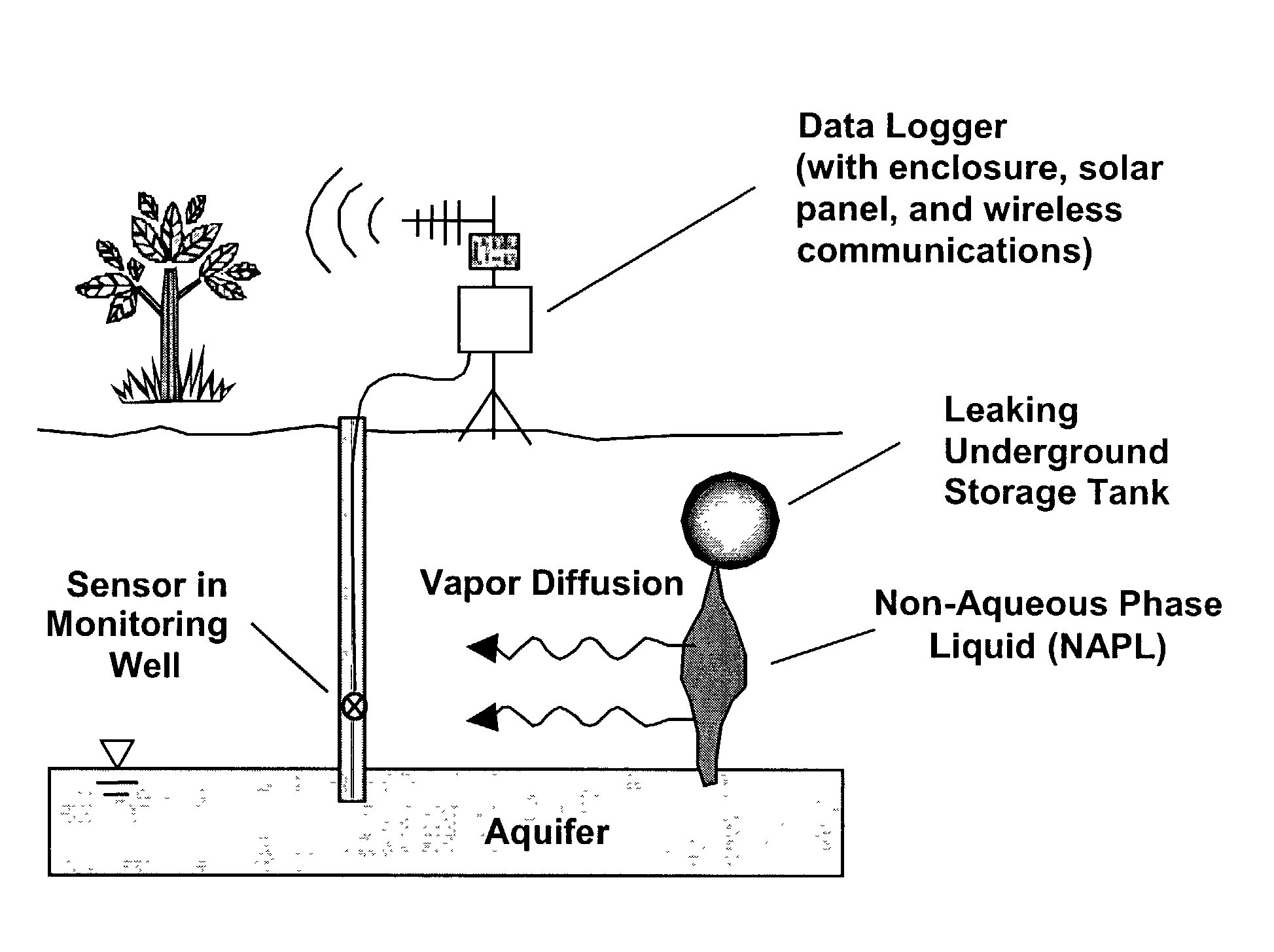
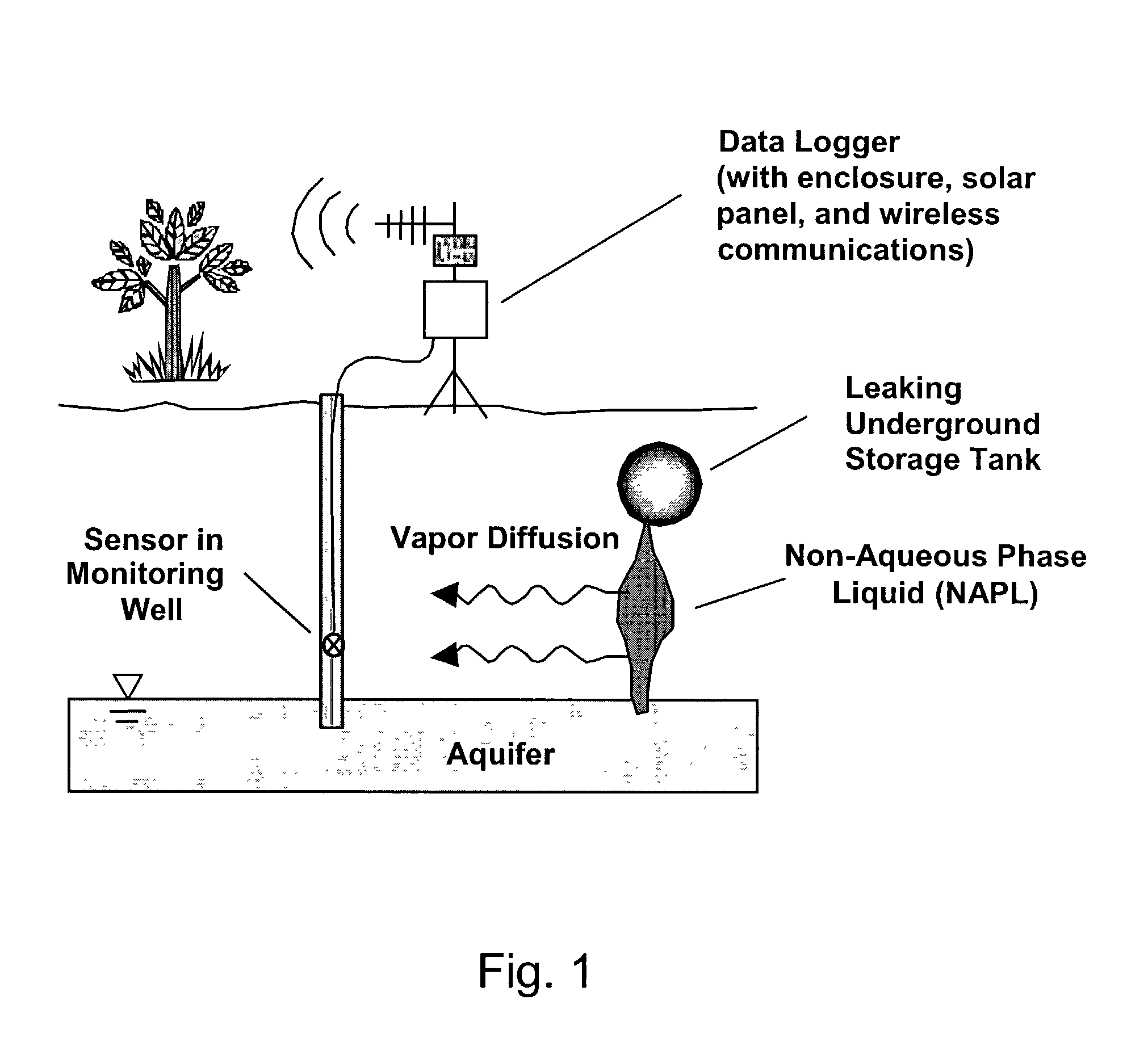
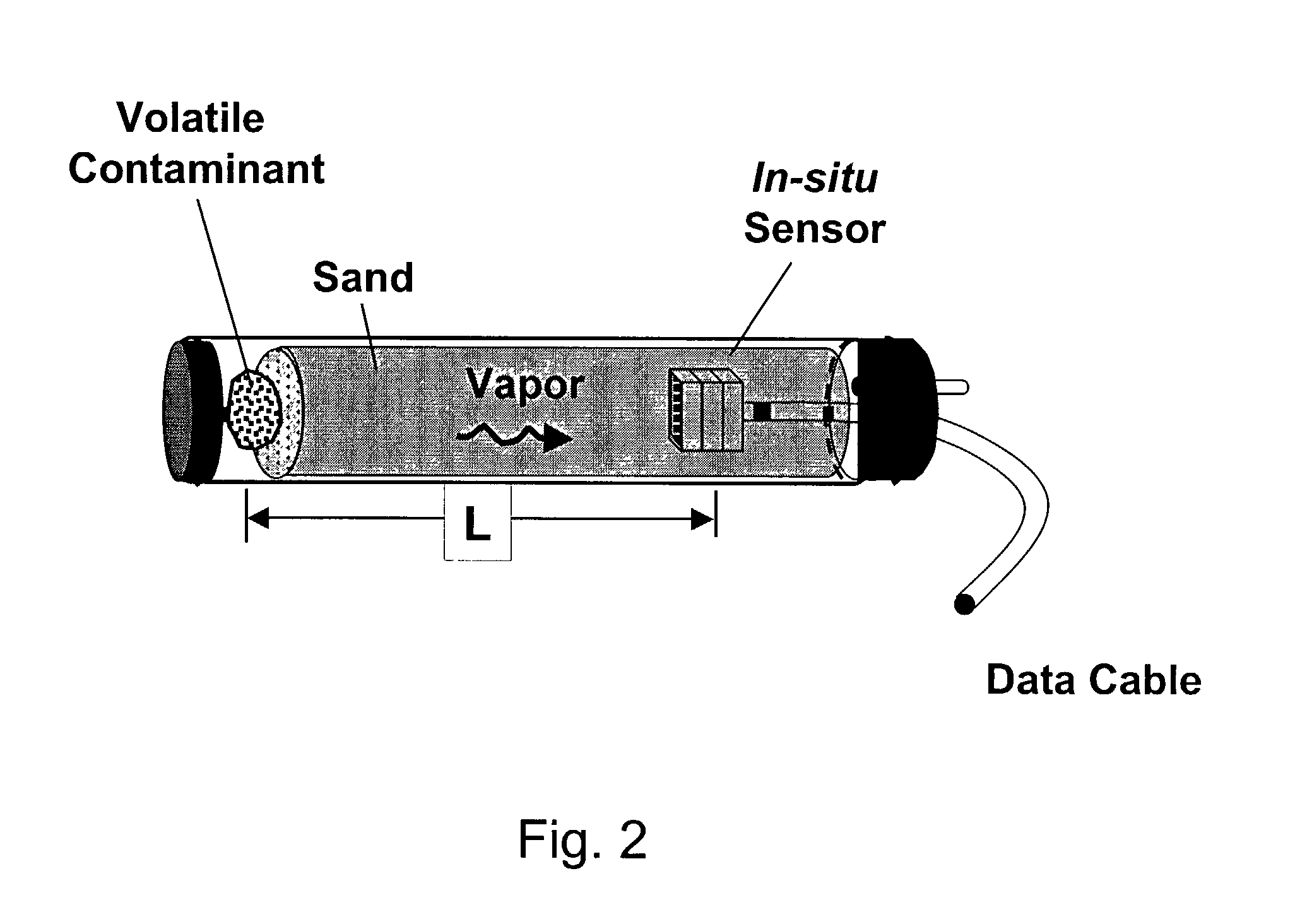
Methods for characterizing subsurface volatile contaminants using in-situ sensors
ActiveUS7003405B1Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConcentration ResponseTriangulation
An inverse analysis method for characterizing diffusion of vapor from an underground source of volatile contaminant using data taken by an in-situ sensor. The method uses one-dimensional solutions to the diffusion equation in Cartesian, cylindrical, or spherical coordinates for isotropic and homogenous media. If the effective vapor diffusion coefficient is known, then the distance from the source to the in-situ sensor can be estimated by comparing the shape of the predicted time-dependent vapor concentration response curve to the measured response curve. Alternatively, if the source distance is known, then the effective vapor diffusion coefficient can be estimated using the same inverse analysis method. A triangulation technique can be used with multiple sensors to locate the source in two or three dimensions. The in-situ sensor can contain one or more chemiresistor elements housed in a waterproof enclosure with a gas permeable membrane.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
Method for imaging multiphase flow using electrical capacitance tomography
InactiveUS20070133746A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGenetics algorithmsEngineering
The invention relates to a novel image-reconstruction technique which is used to view multiphase flows using electrical capacitance tomography (ECT), which is based on non-linear heuristic global optimization methods involving simulated annealing and genetic algorithms. The inventive method consists in obtaining electrical capacitance data which are measured between electrodes positioned on the outer surface of pipeline, well or tank (electrically-insulating) containing fluids. The aforementioned data are dependent on the distribution of the fluids inside the pipeline, well or tank. Moreover, the data are processed in order to reconstruct an image of the spatial distribution of the relative electrical permittivity (also known as the dielectric constant) inside the tube, well or tank, which reflects the distribution of the different phases present in the flow.
Owner:INST MEXICANO DEL GASOLINEEO
Configurable bio-transport system simulator
InactiveUS20020120431A1Easy to customizeSave effortNanoinformaticsAnalogue computers for chemical processesComputational scienceBiological body
A method of simulating a bio-transport system comprising: (a) characterizing one or more elements to represent a bio-transport system of an organism or a portion thereof; (b) constructing one or more mathematical representations that model one or more bio-transport dynamics for each element based on the characterization of the elements to form a configured simulation model; (c) initializing the configured simulation model; (d) executing the configured simulation model to obtain bio-transport dynamics data for one or more elements; and (e) outputting information to a user based on at least a portion of the bio-transport dynamics data.
Owner:KEANE JOHN A
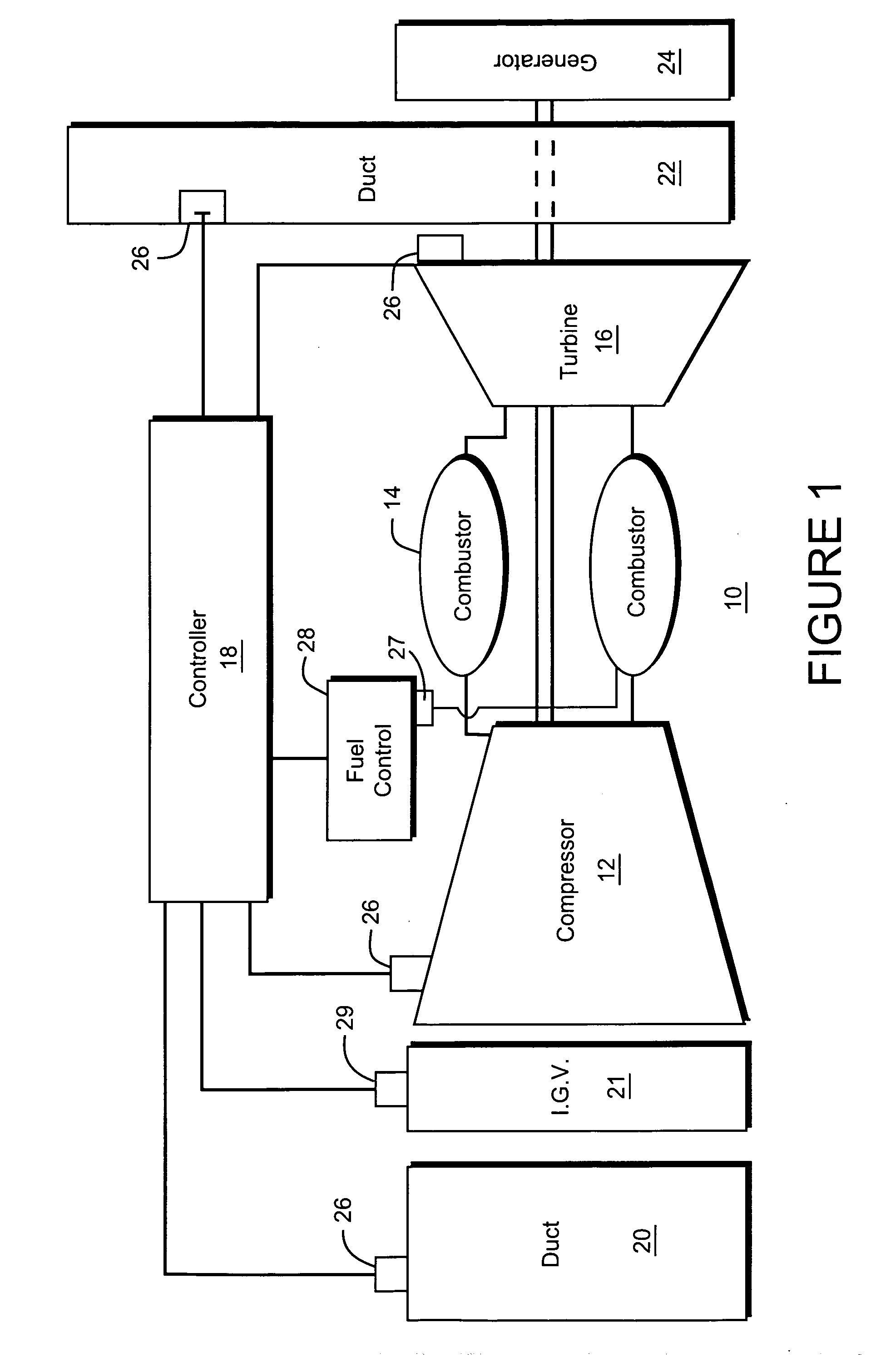
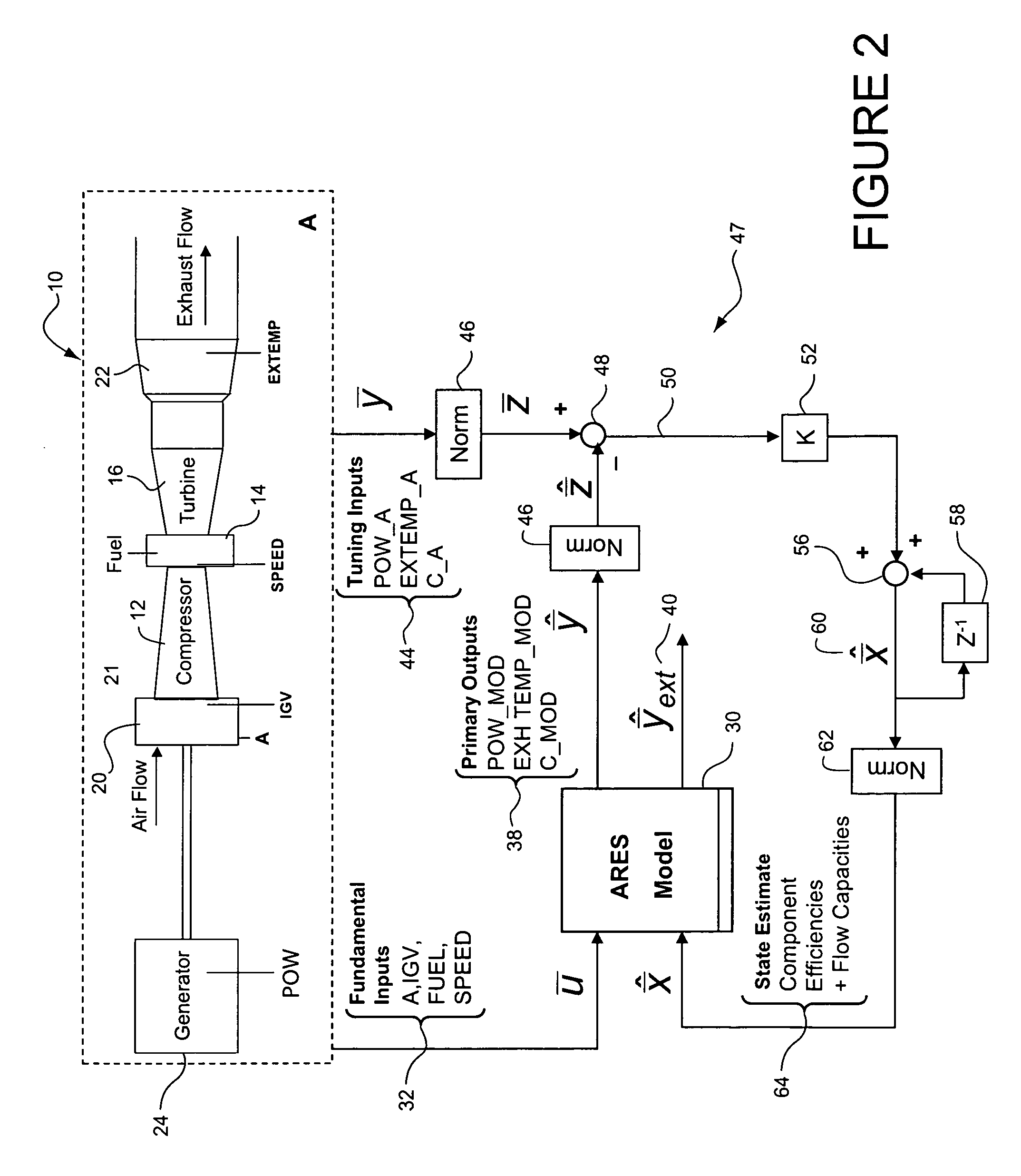
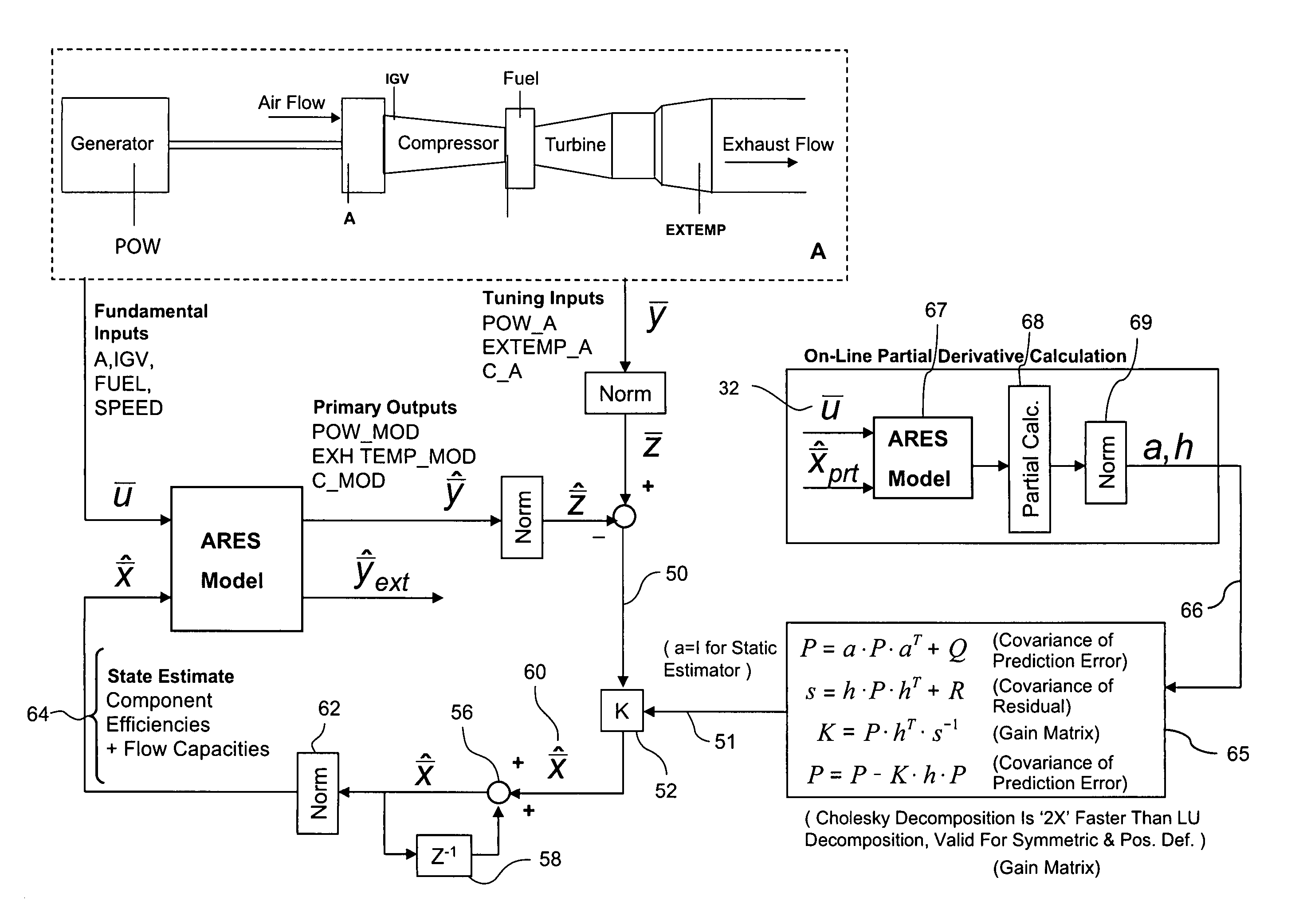
Method and system for gas turbine engine simulation using adaptive Kalman filter
A method for simulating a gas turbine including the steps of: sensing values of a plurality of first operating parameters of an actual gas turbine; applying the sensed values of the first operating parameters to a model of the gas turbine, wherein the model generates a plurality of predicted second operating parameters; determining difference values between the predicted second operating parameters and corresponding sensed second operating parameters of the actual gas turbine; modifying the difference values based on tuning factors generated by a Kalman filter gain matrix during operation of the gas turbine, and using the adjusted difference values to adjust the model of the gas turbine. The method may further comprise generating the tuning factors by applying to the model the sensed values of the plurality of first operating parameters and pertubated values of the adjusted different values to determine optimal tuning factors.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and systems for creating and interacting with three dimensional virtual models
Systems and methods are provided for modifying a virtual model of a physical structure with additional 3D data obtained from the physical structure to provide a modified virtual model.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Focus correction method for inspection of circuit patterns
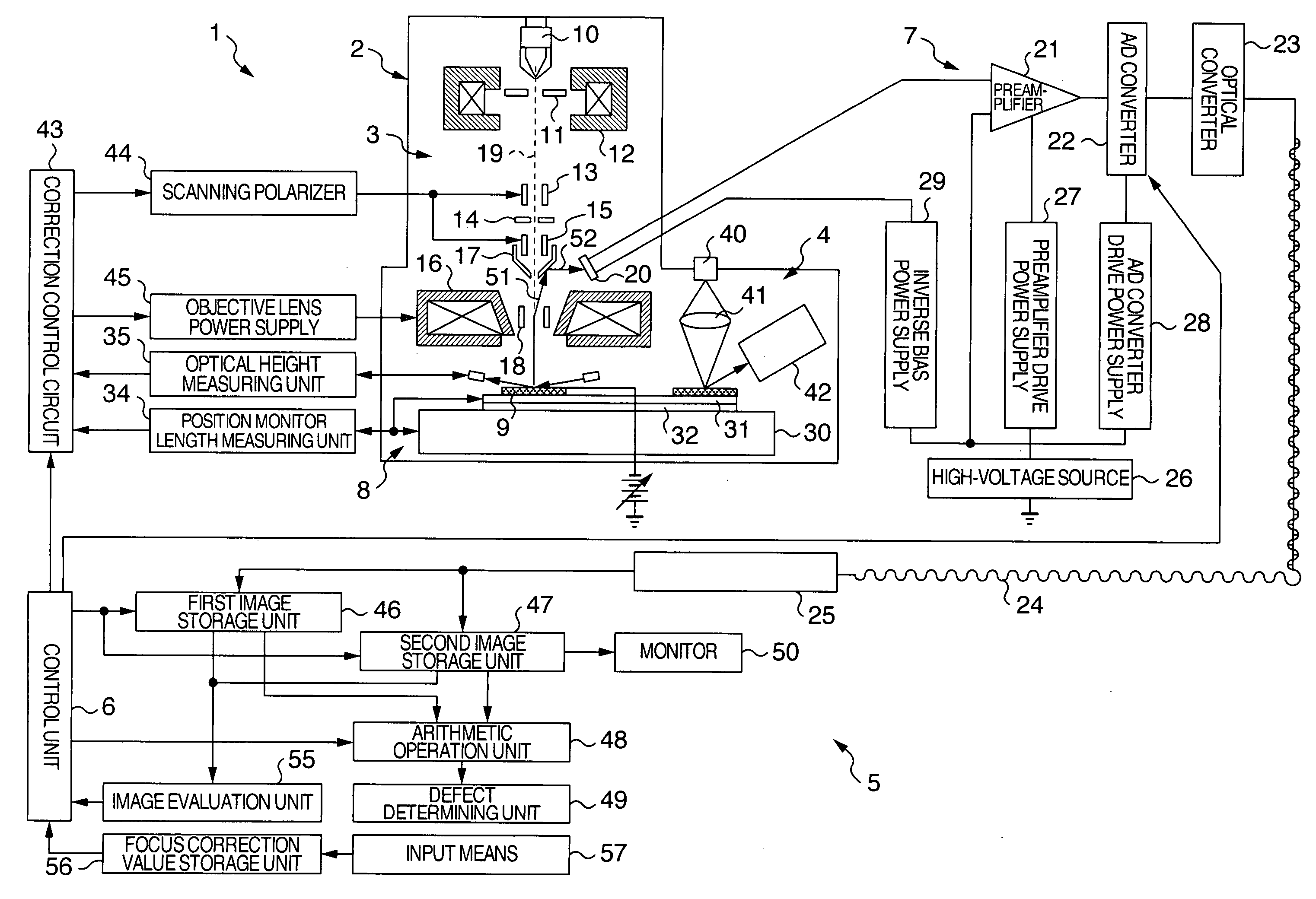
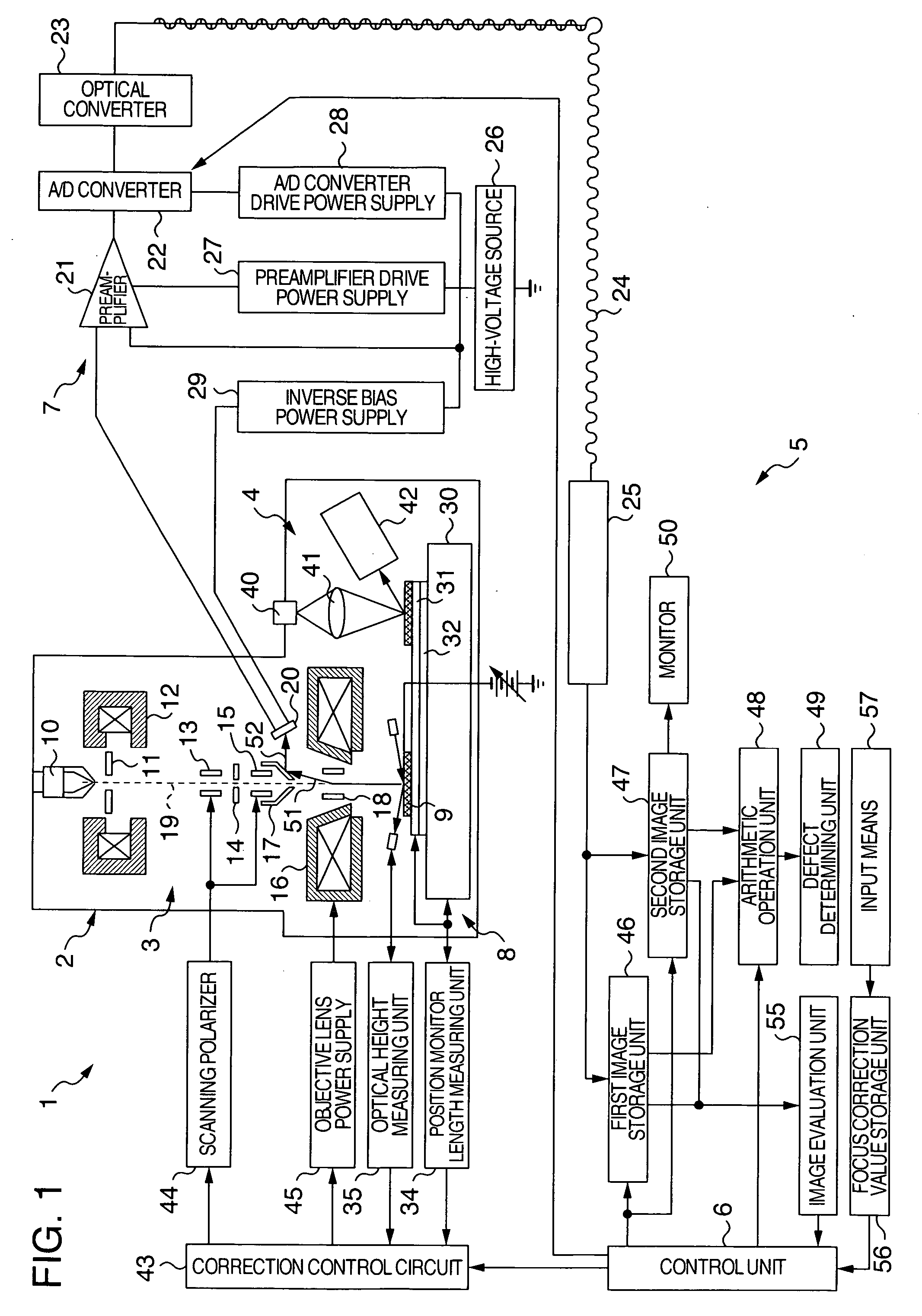
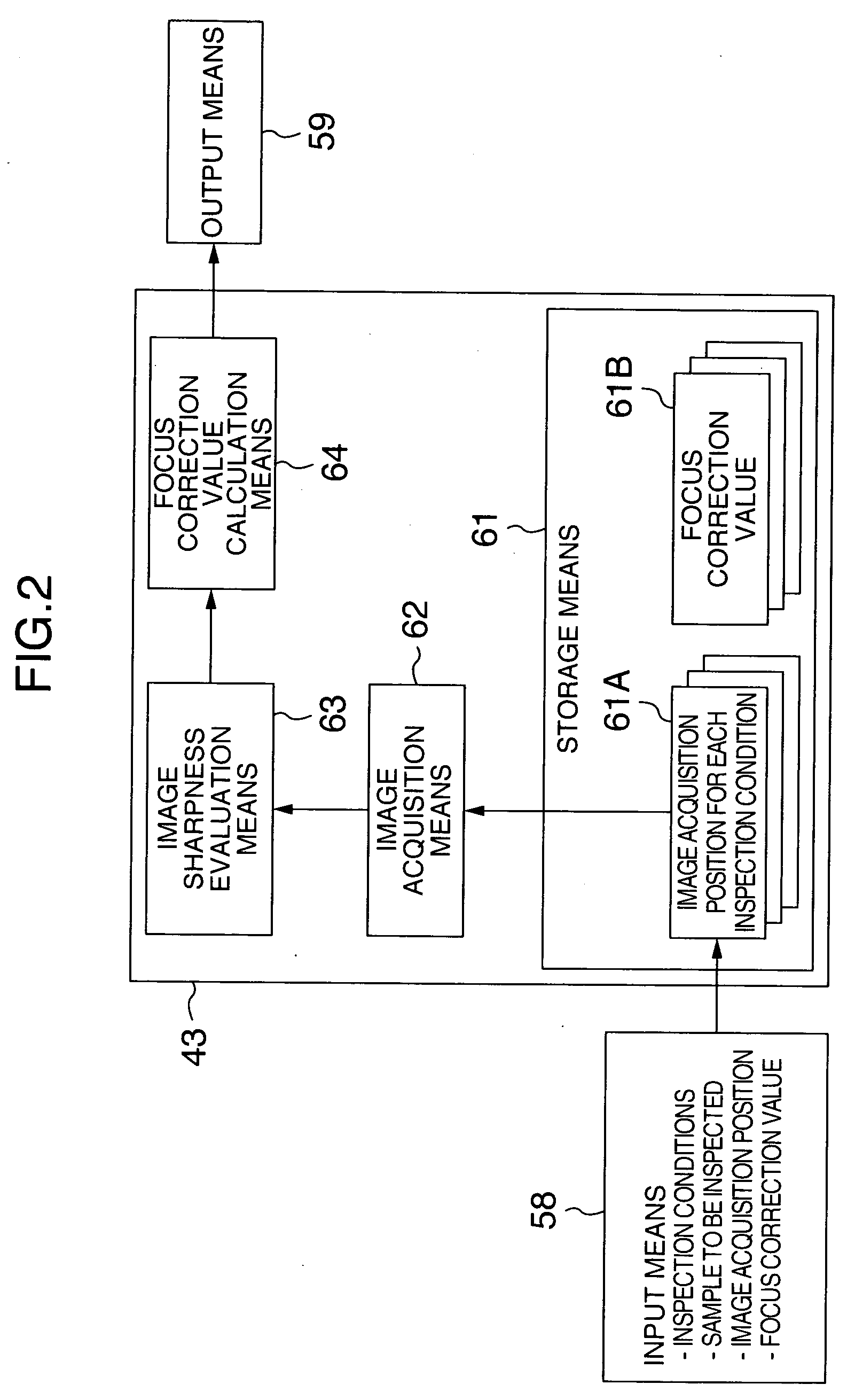
InactiveUS20060284088A1Avoid scrap rateReduce false informationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesComputational physicsEngineering
A charged particle application circuit pattern inspection apparatus and method are disclosed, in which the reduction in the rejection rate attributable to an out-of-focus state due to the change in the charge condition on the sample surface is prevented and the false information is reduced to improve the apparatus reliability. The image acquisition position on a sample is stored in an image acquisition position storage unit, a focus correction value is stored in a focus correction value storage unit in accordance with the image acquisition position and the sample charge condition, the inspection conditions and the sample to be inspected are input from an input unit, the sample charge condition is evaluated in accordance with the image position acquisition position, and the focal point is corrected by a focus correction unit.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Granular channel width for power optimization
ActiveUS20120023473A1Improve performancePower optimizationDetecting faulty computer hardwarePower supply for data processingComputational sciencePower optimization
A storage medium recording a cell library having one or more cells that may be readable by a computer and may be used by the computer to design an integrated circuit. The one or more cells may have a physical dimension parameter and a channel width parameter. The physical dimension parameter may be a footprint of the one or more cells. The channel width parameter may have a minimum driver size and a maximum driver size. The channel width parameter may define a range within which a tool varies the channel width between the maximum driver size and the minimum driver size during a design flow of the integrated circuit based upon one or more power criteria without changing the footprint.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
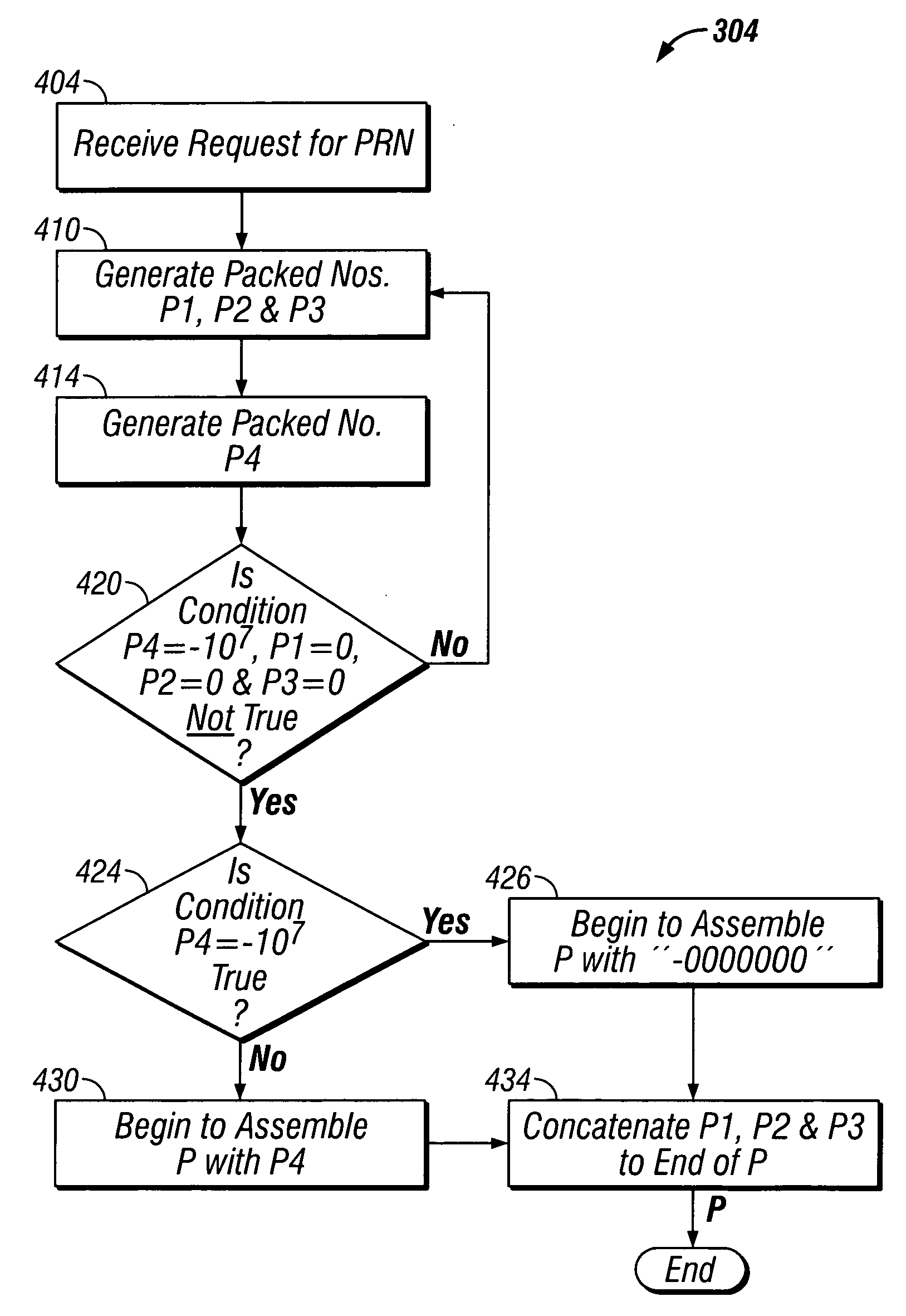
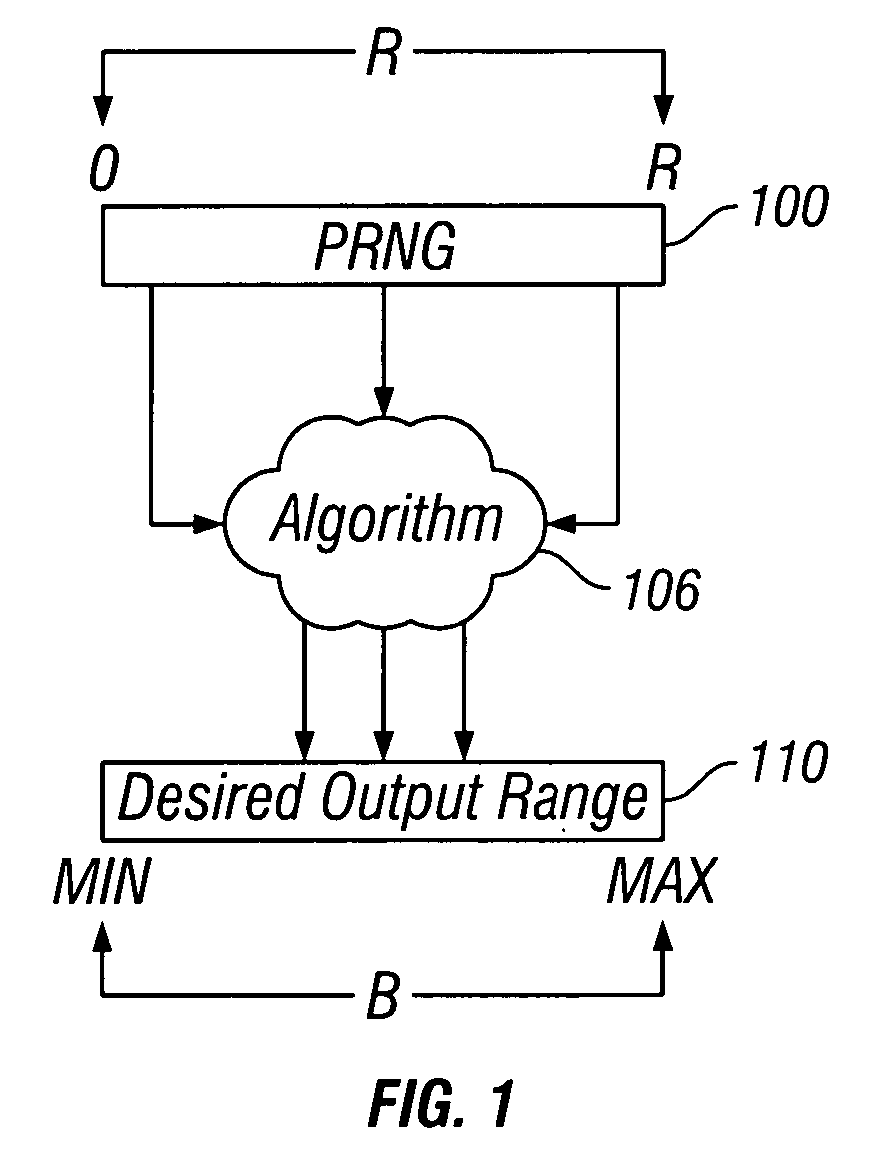
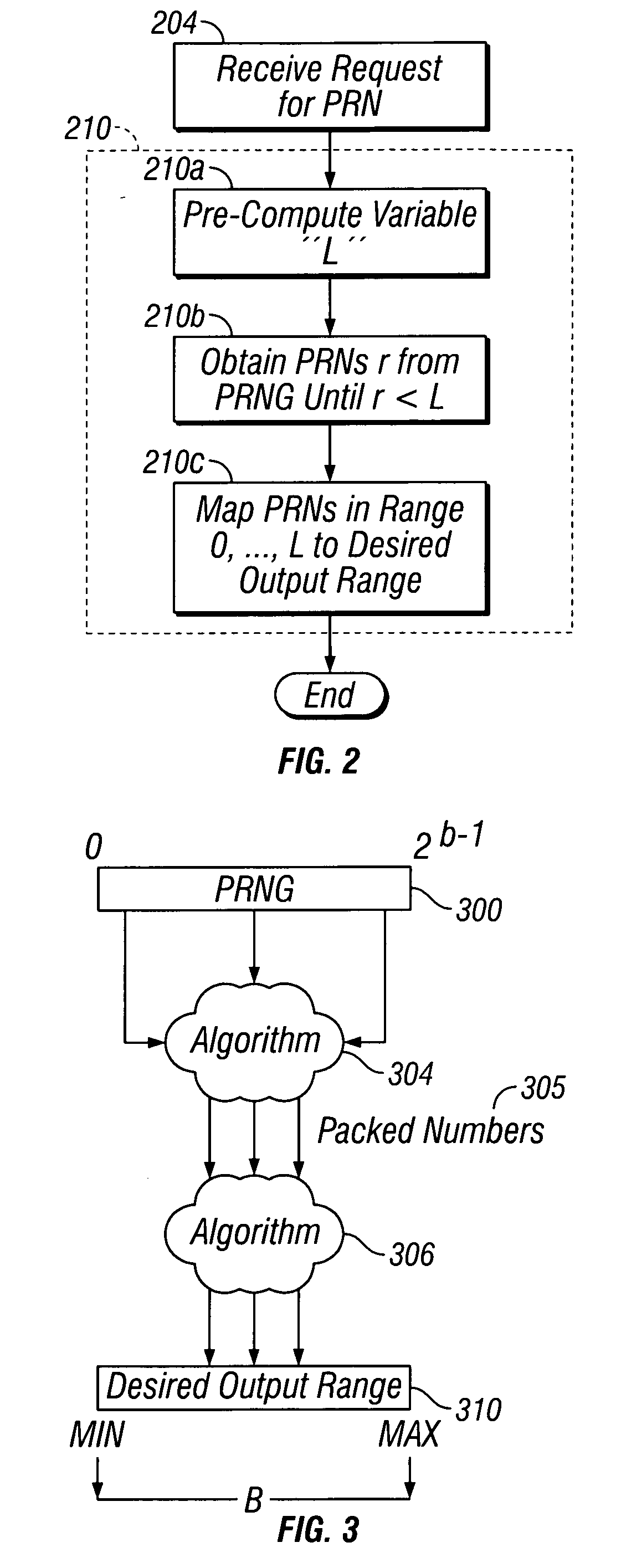
Mapping pseudo-random numbers to predefined number ranges
ActiveUS20050050121A1Low costDiminish pseudo randomnessRandom number generatorsDigital function generatorsSmall targetComputer science
Pseudo-random numbers (PRNs) generated by a PRN generator are mapped to predefined number ranges or target ranges. The target range may be smaller or larger than the range of the PRN generator. Mapping to a smaller target range may include generating PRNs (e.g., integers) from a particular bit-input stream (e.g., 32-bit) having a uniform distribution across the range of numbers; selecting an optimal subset of the generated PRNs to map; and mapping the selected PRNs to a corresponding number in a target range such that the mapped numbers are uniformly distributed across the target range. Mapping to a larger target range may include generating uniformly distributed PRNs; applying a generation function to the PRNs to generate uniformly distributed packed numbers; and applying a mapping function to map selected packed numbers to the target range such that the mapped numbers are uniformly distributed.
Owner:SAP AG
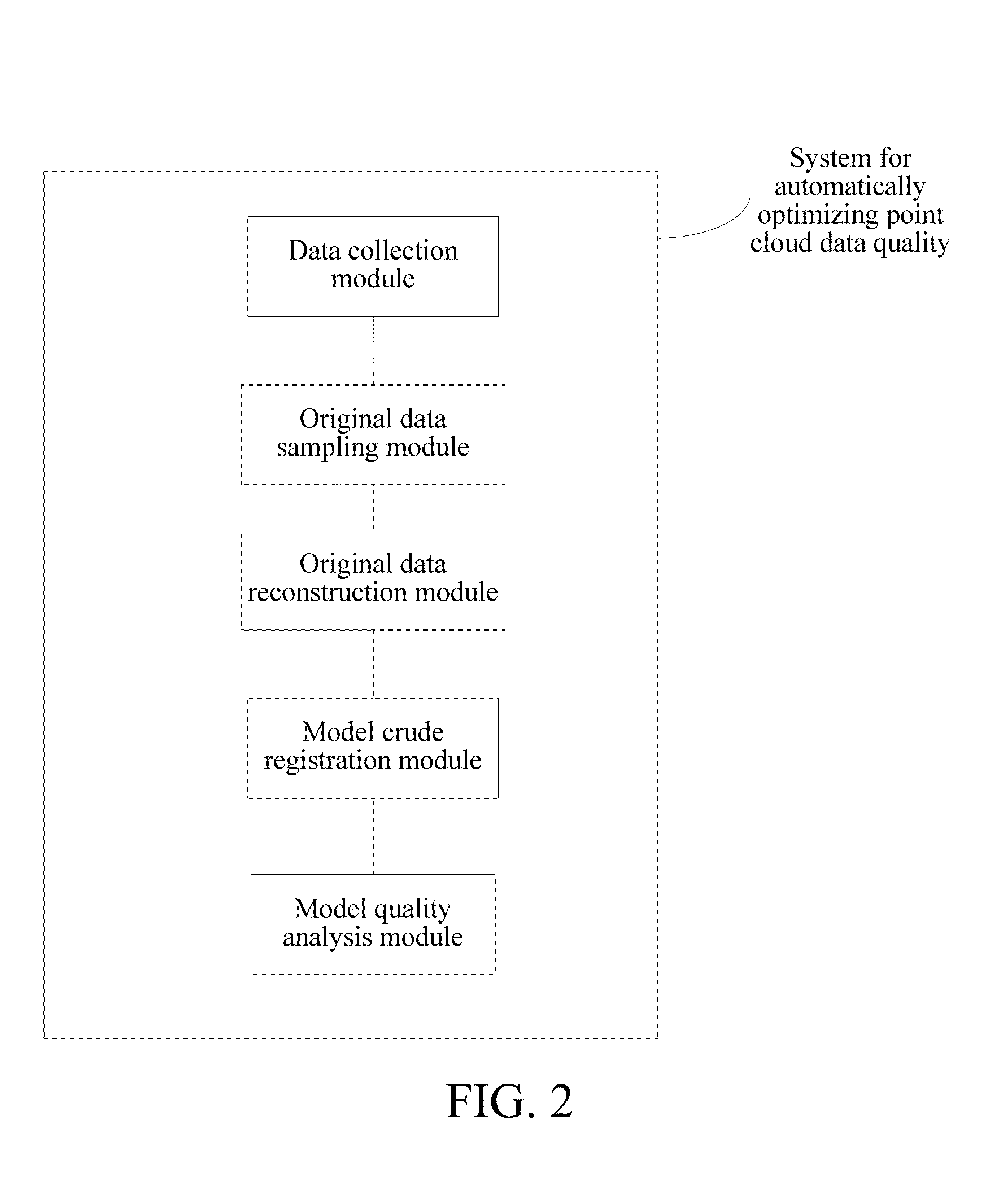
Method and system for automatically optimizing quality of point cloud data
Disclosed is a method for automatically optimizing point cloud data quality, including the following steps of: acquiring initial point cloud data for a target to be reconstructed, to obtain an initial discrete point cloud; performing preliminary data cleaning on the obtained initial discrete point cloud to obtain a Locally Optimal Projection operator (LOP) sampling model; obtaining a Possion reconstruction point cloud model by using a Possion surface reconstruction method on the obtained initial discrete point cloud; performing iterative closest point algorithm registration on the obtained Possion reconstruction point cloud model and the obtained initial discrete point cloud; and for each point on a currently registered model, calculating a weight of a surrounding point within a certain radius distance region of a position corresponding to the point for the point on the obtained LOP sampling model, and comparing the weight with a threshold, to determine whether a region where the point is located requires repeated scanning. Further disclosed is a system for automatically optimizing point cloud data quality.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and system for gas turbine engine simulation using adaptive Kalman filter
A method for simulating a gas turbine including the steps of: sensing values of a plurality of first operating parameters of an actual gas turbine; applying the sensed values of the first operating parameters to a model of the gas turbine, wherein the model generates a plurality of predicted second operating parameters; determining difference values between the predicted second operating parameters and corresponding sensed second operating parameters of the actual gas turbine; modifying the difference values based on tuning factors generated by a Kalman filter gain matrix during operation of the gas turbine, and using the adjusted difference values to adjust the model of the gas turbine. The method may further comprise generating the tuning factors by applying to the model the sensed values of the plurality of first operating parameters and perturbated values of the adjusted different values to determine optimal tuning factors.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
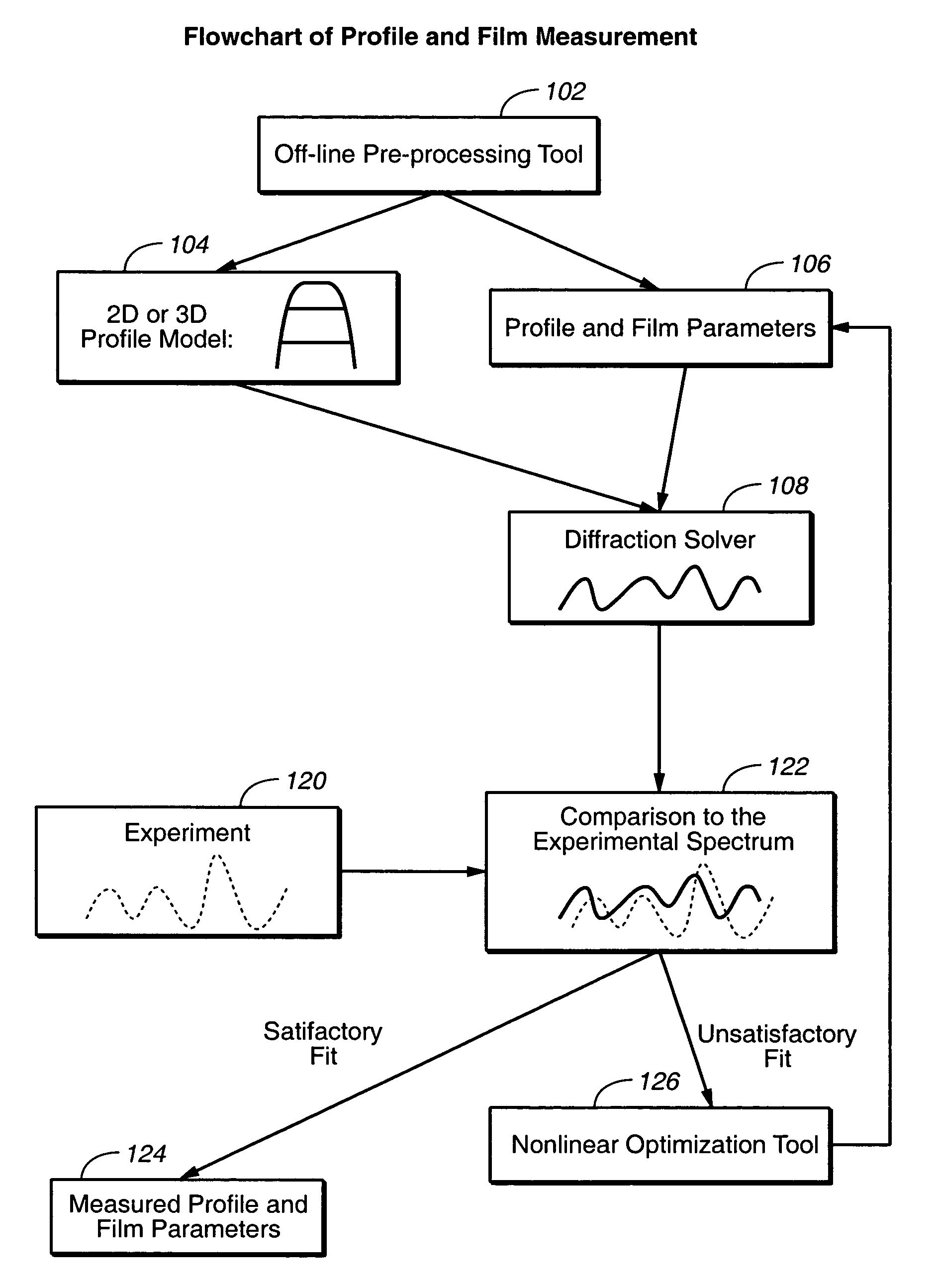
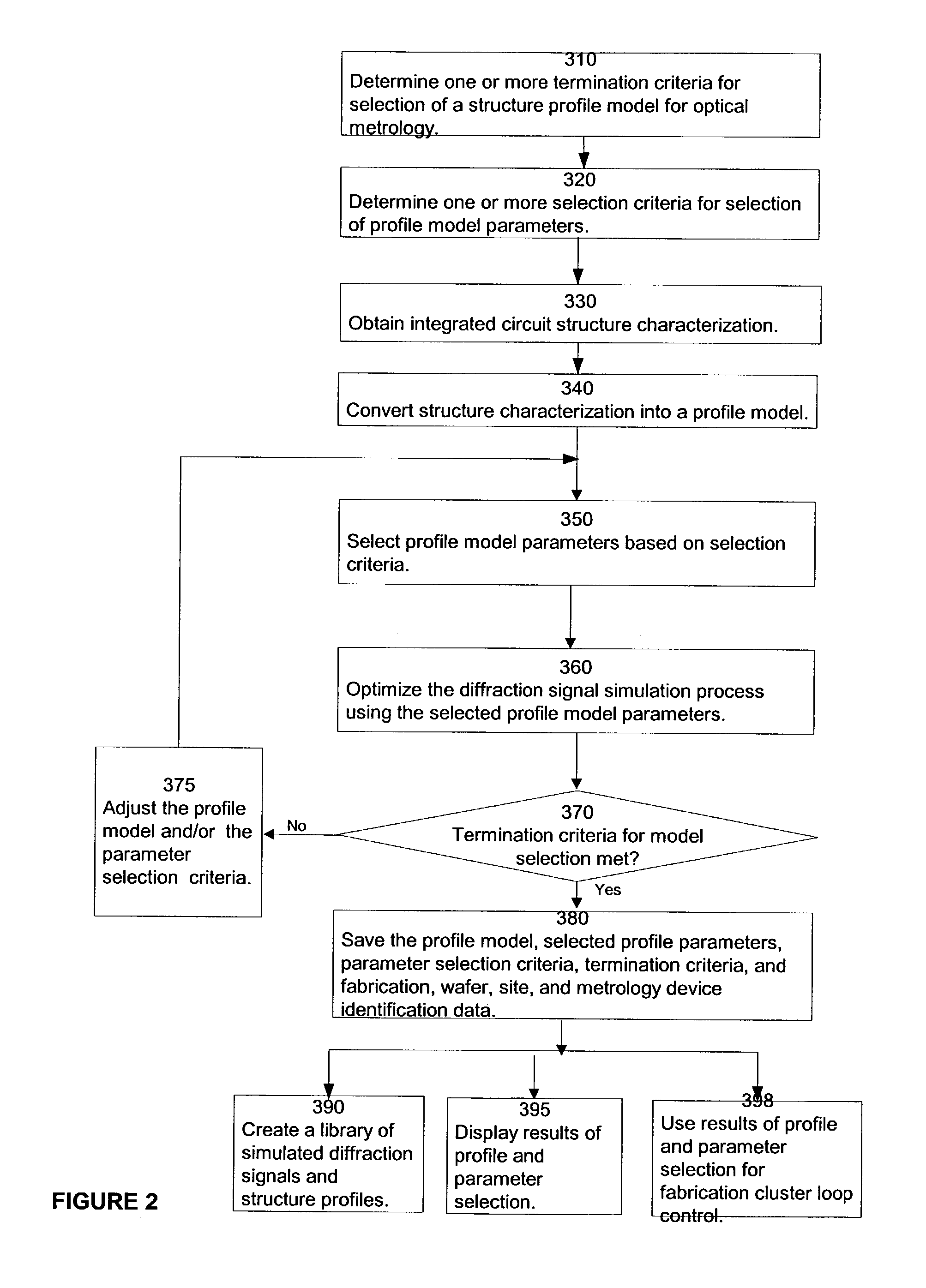
Selecting a profile model for use in optical metrology using a machine learining system
InactiveUS20050192914A1Photomechanical apparatusDigital computer detailsEngineeringOptical metrology
A profile model can be selected for use in examining a structure formed on a semiconductor wafer using optical metrology by obtaining an initial profile model having a set of profile parameters. A machine learning system is trained using the initial profile model. A simulated diffraction signal is generated for an optimized profile model using the trained machine learning system, where the optimized profile model has a set of profile parameters with the same or fewer profile parameters than the initial profile model. A determination is made as to whether the one or more termination criteria are met. If the one or more termination criteria are met, the optimized profile model is modified and another simulated diffraction signal is generated using the same trained machine learning system.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Quasi-monte carlo light transport simulation by efficient ray tracing
Methods, systems, devices and computer program code (software) products operable within a computer graphics system or other computer system enable quasi-Monte Carlo (QMC) light transport simulation by ray tracing: and include constructing a bounding interval hierarchy (BIH), within a computer, using quantized planes to reduce memory requirements while maintaining a selected degree of precision.
Owner:MENTAL IMAGES
Efficient Computation Method for Electromagnetic Modeling
ActiveUS20090006053A1InsulationFluid removalControlled source electro-magneticElectromagnetic shielding
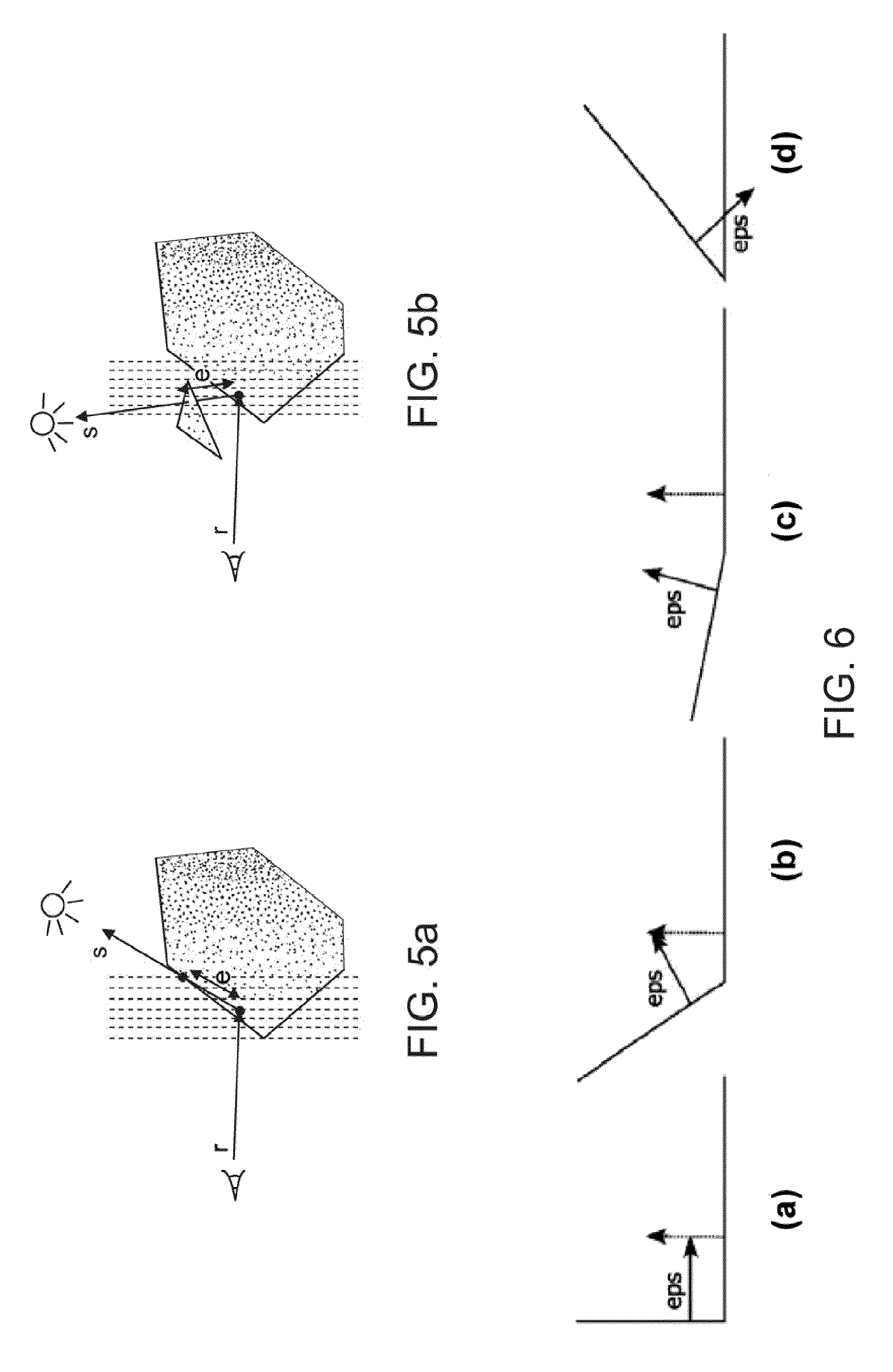
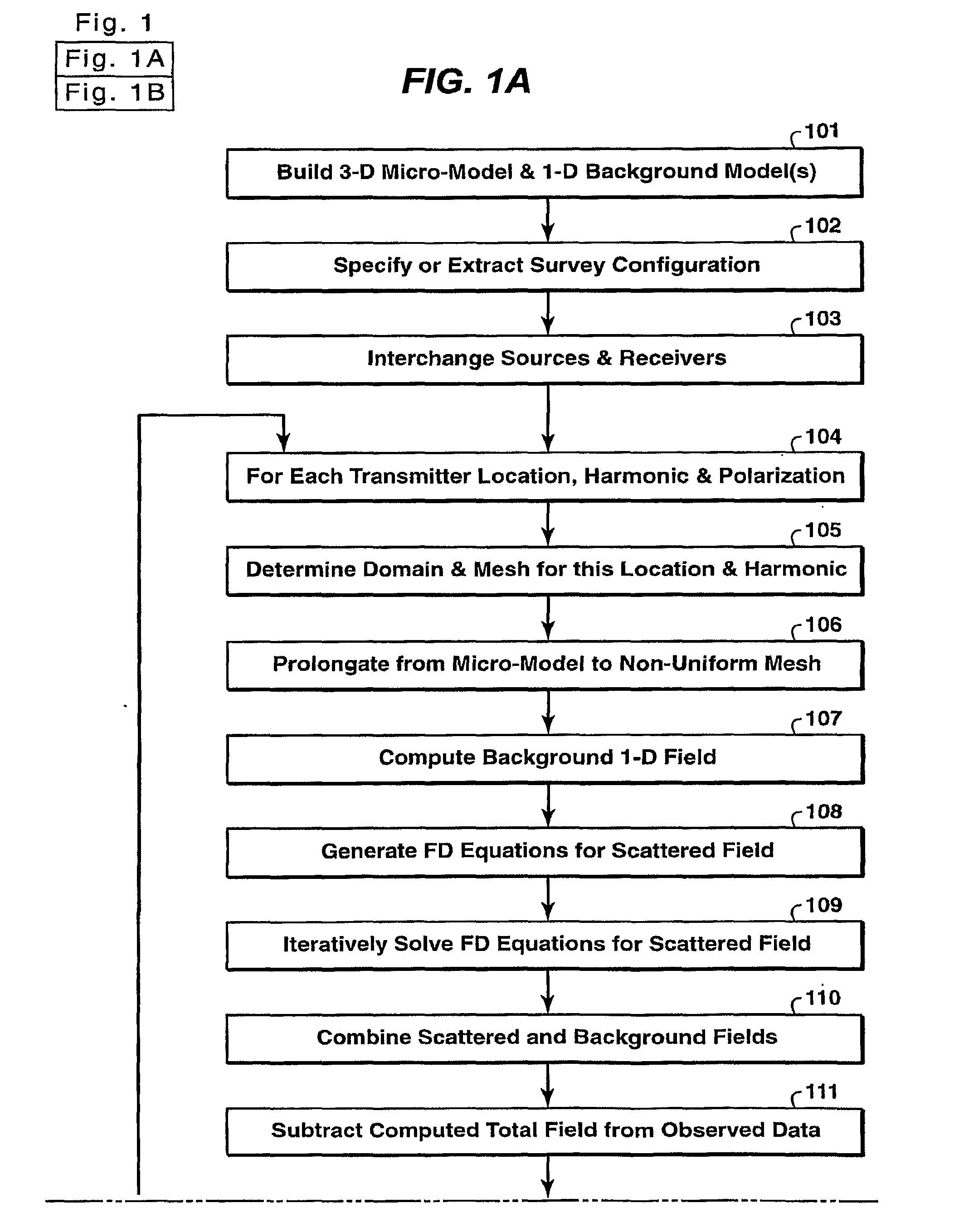
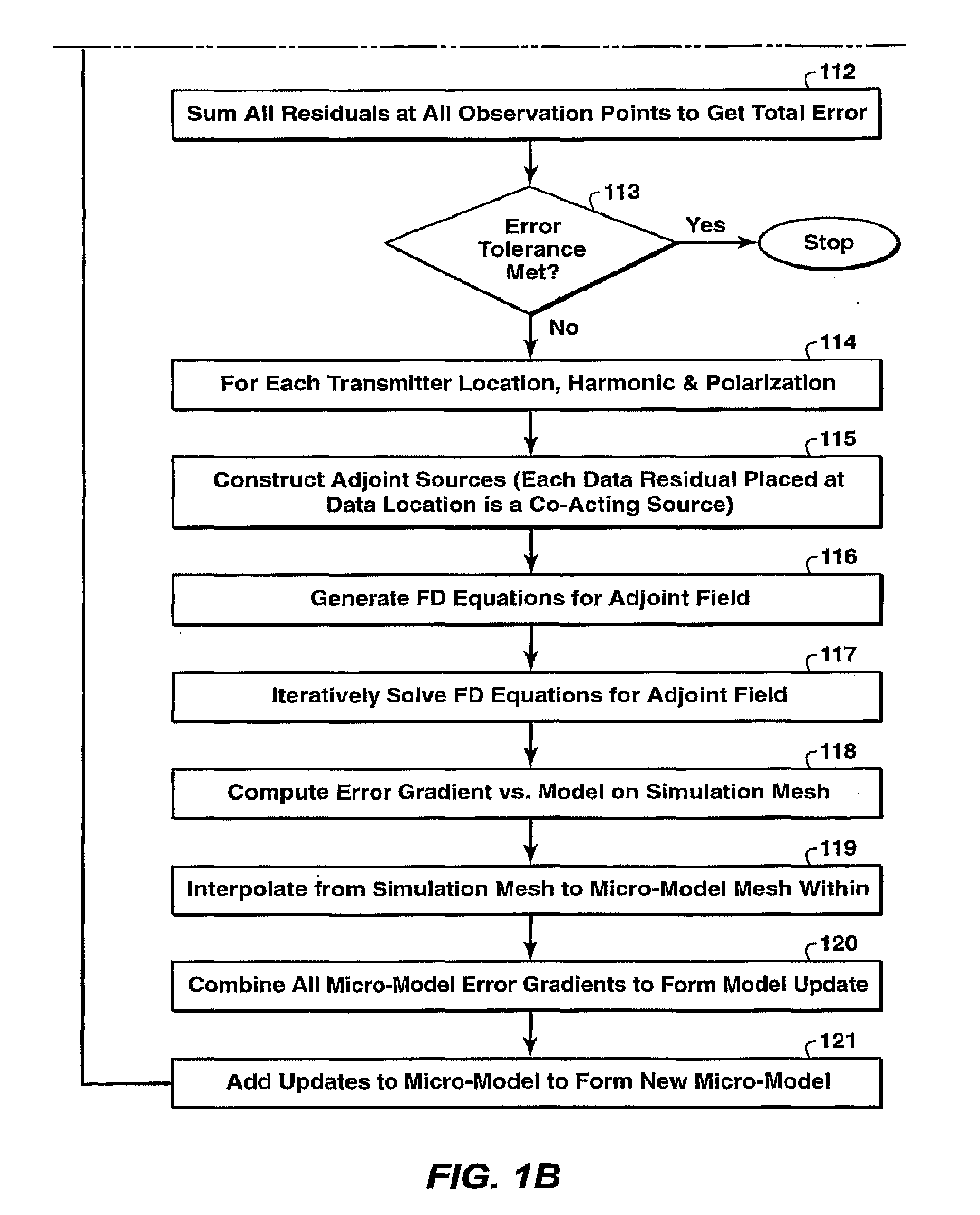
Method for efficient processing of controlled source electromagnetic data, whereby Maxwell's equations are solved [107] by numerical techniques [109] such as finite difference or finite element in three dimensions for each source location and frequency of interest. The Reciprocity Principle is used [103] to reduce the number of computational source positions, and a multi-grid is used [105] for the computational grid to minimize the total number of cells yet properly treat the source singularity, which is essential to satisfying the conditions required for applicability of the Reciprocity Principle. An initial global resistivity model [101] is Fourier interpolated to the computational multi grids [106]. In inversion embodiments of the invention, Fourier prolongation is used to update [120] the global resistivity model based on optimization results from the multi-grids.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
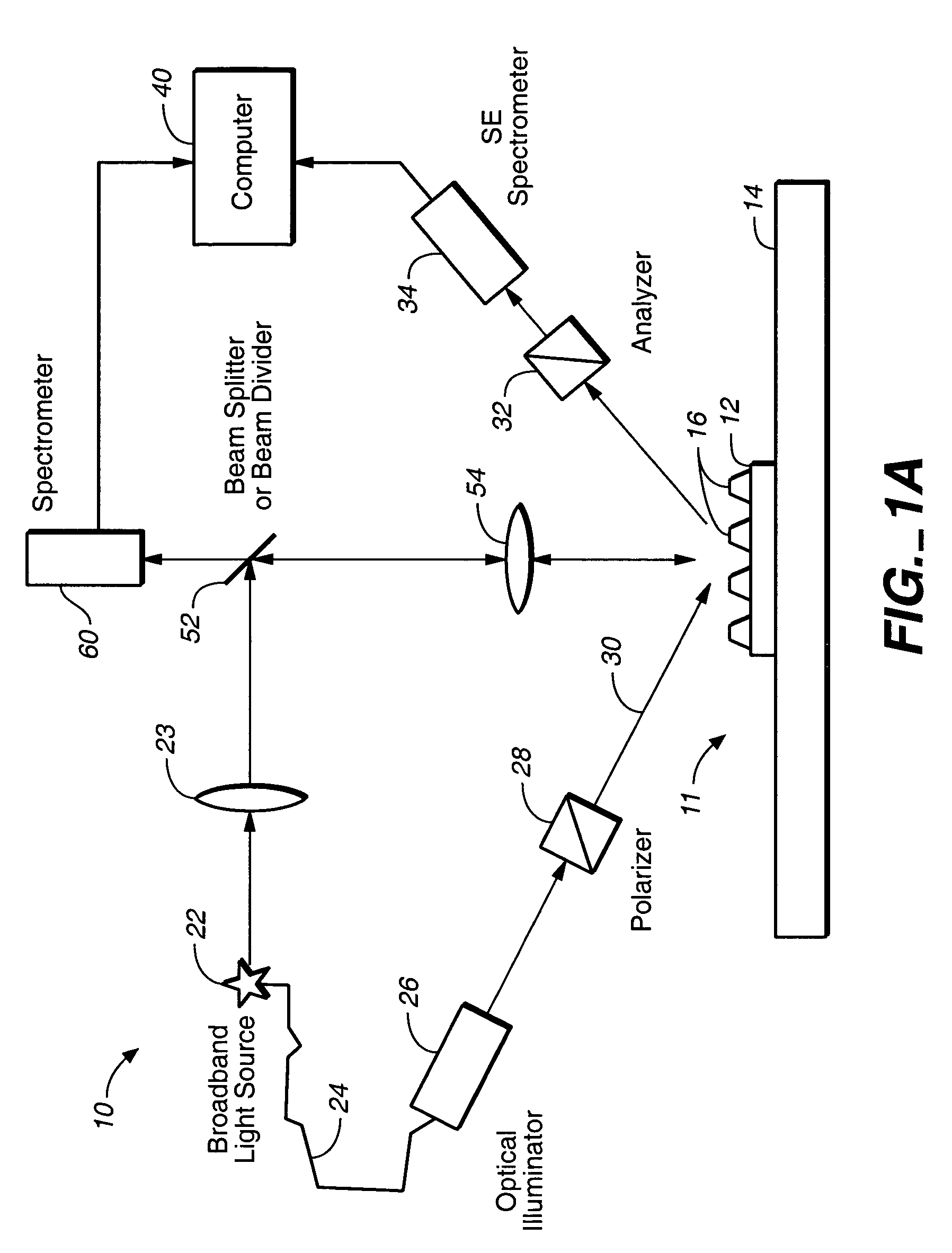
Parametric profiling using optical spectroscopic systems
InactiveUS7280230B2Simplify profile measurementRemove uncertaintyPolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsComputer scienceSemiconductor
A gallery of seed profiles is constructed and the initial parameter values associated with the profiles are selected using manufacturing process knowledge of semiconductor devices. Manufacturing process knowledge may also be used to select the best seed profile and the best set of initial parameter values as the starting point of an optimization process whereby data associated with parameter values of the profile predicted by a model is compared to measured data in order to arrive at values of the parameters. Film layers over or under the periodic structure may also be taken into account. Different radiation parameters such as the reflectivities Rs, Rp and ellipsometric parameters may be used in measuring the diffracting structures and the associated films. Some of the radiation parameters may be more sensitive to a change in the parameter value of the profile or of the films then other radiation parameters. One or more radiation parameters that are more sensitive to such changes may be selected in the above-described optimization process to arrive at a more accurate measurement. The above-described techniques may be supplied to a track / stepper and etcher to control the lithographic and etching processes in order to compensate for any errors in the profile parameters.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Optimized model and parameter selection for optical metrology
A profile model for use in optical metrology of structures in a wafer is selected based on a template having one or more parameters including characteristics of process and modeling attributes associated with a structure in a wafer. The process includes performing a profile modeling process to generate a profile model of a wafer structure based on a template having one or more parameters including characteristics of process and modeling attributes. The profile model includes a set of geometric parameters associated with the dimensions of the structure. The generated profile model may further be tested against termination criteria and the one or more parameters modified. The process of performing a modeling process to generate a profile model and testing the generated profile model may be repeated until the termination criteria are met.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON US HOLDINGS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com