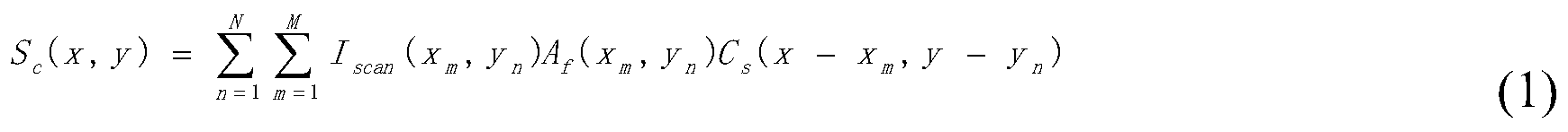Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
223 results about "Dose calculation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
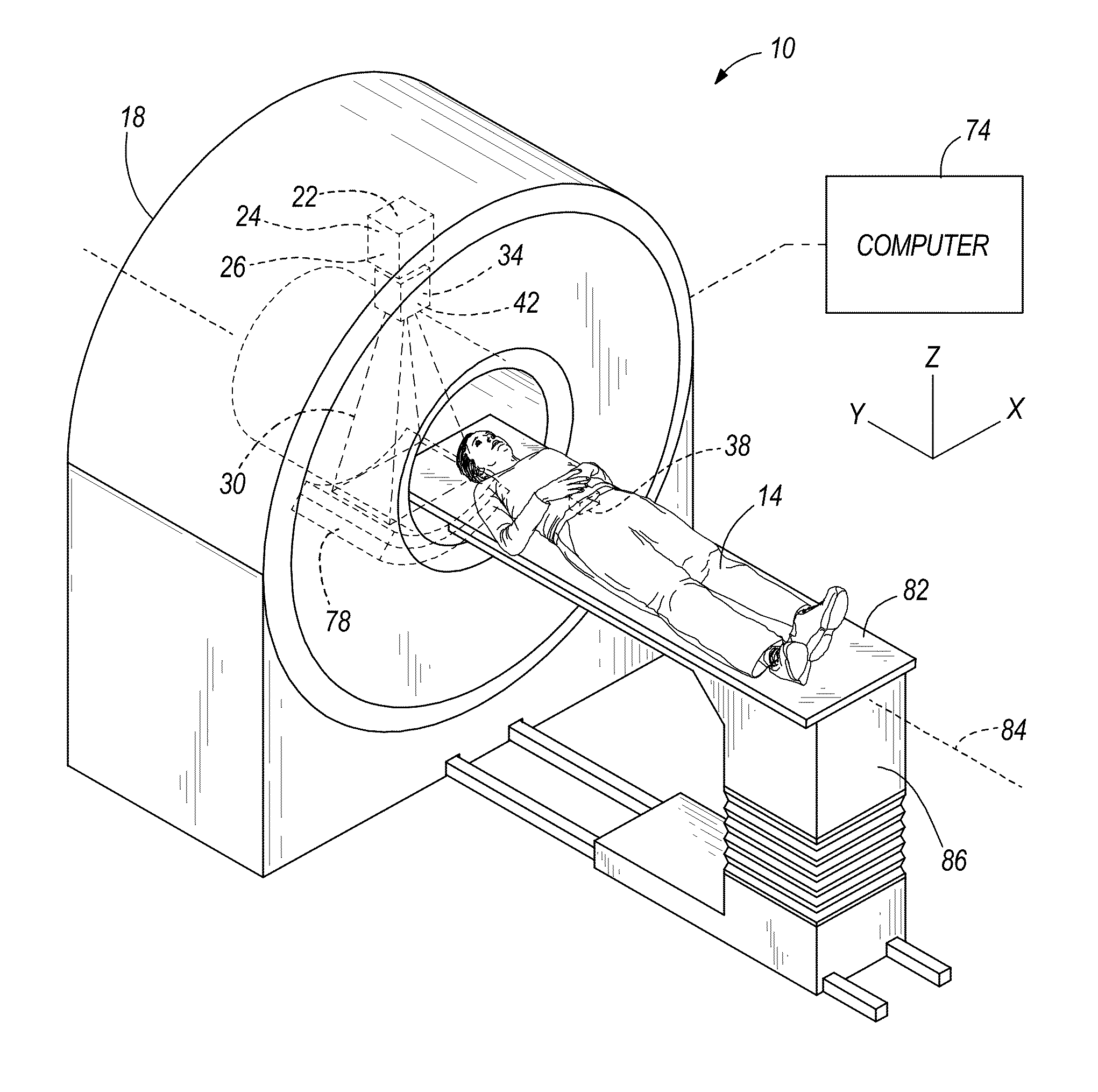
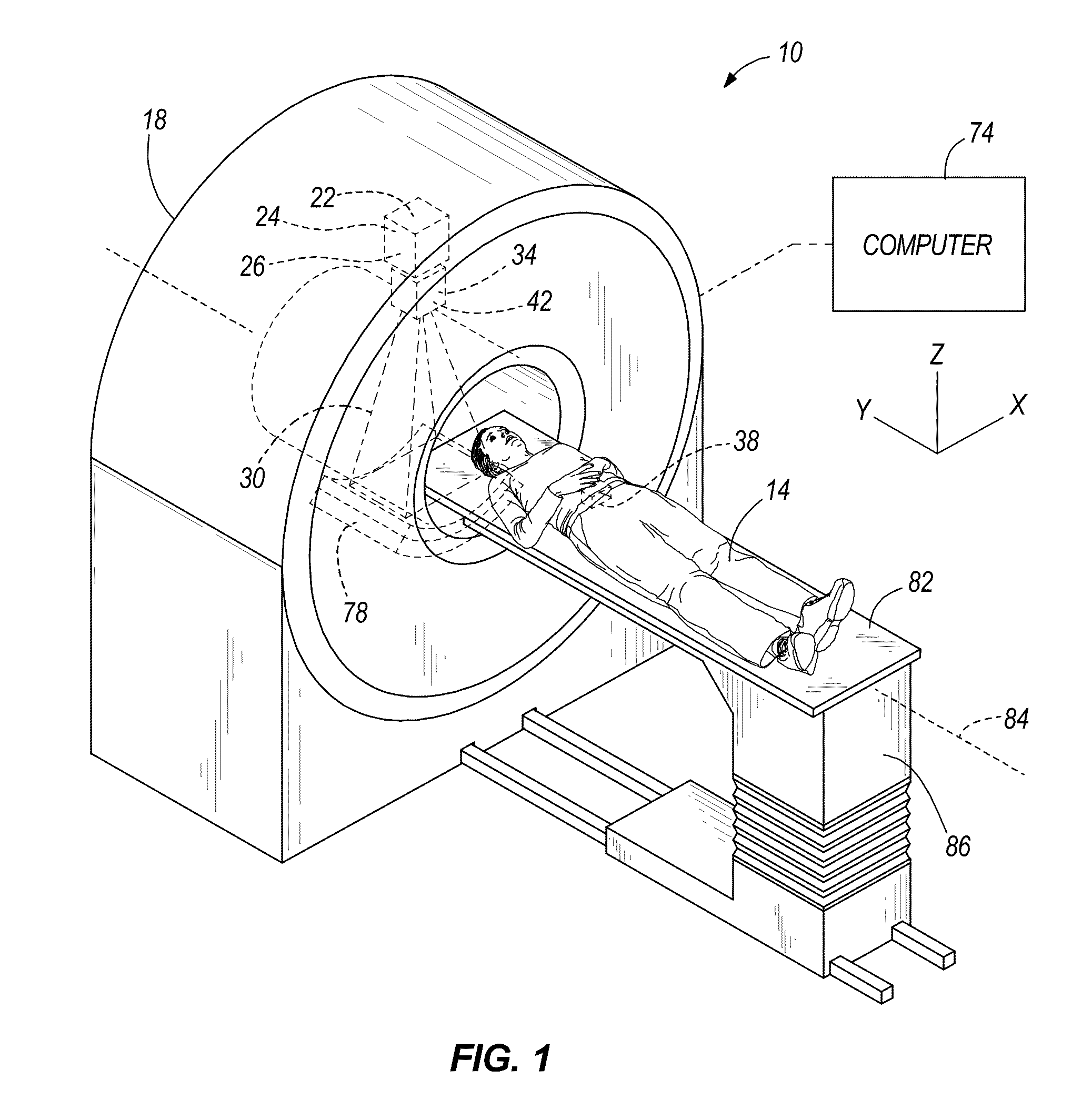
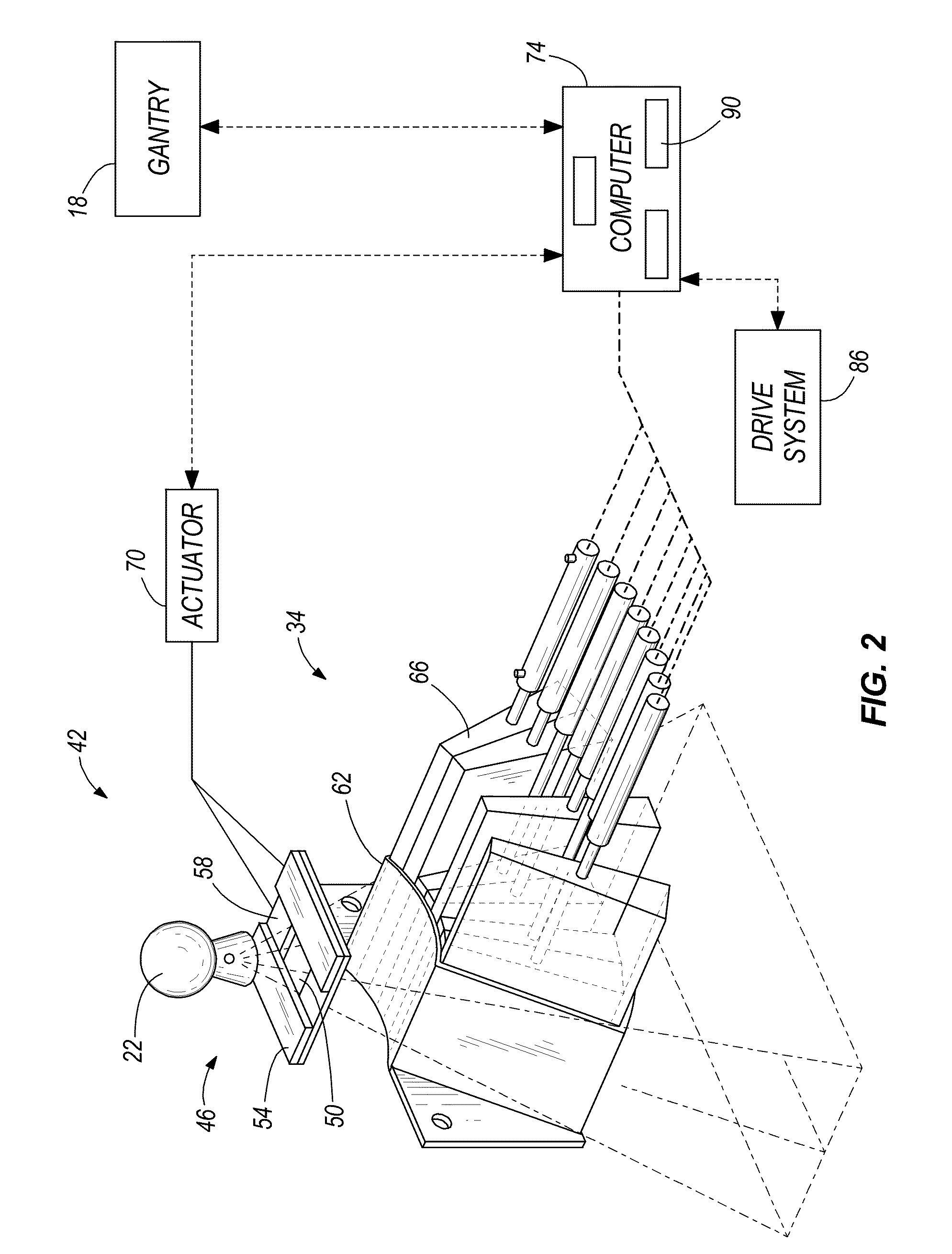
Dose calculation method for multiple fields
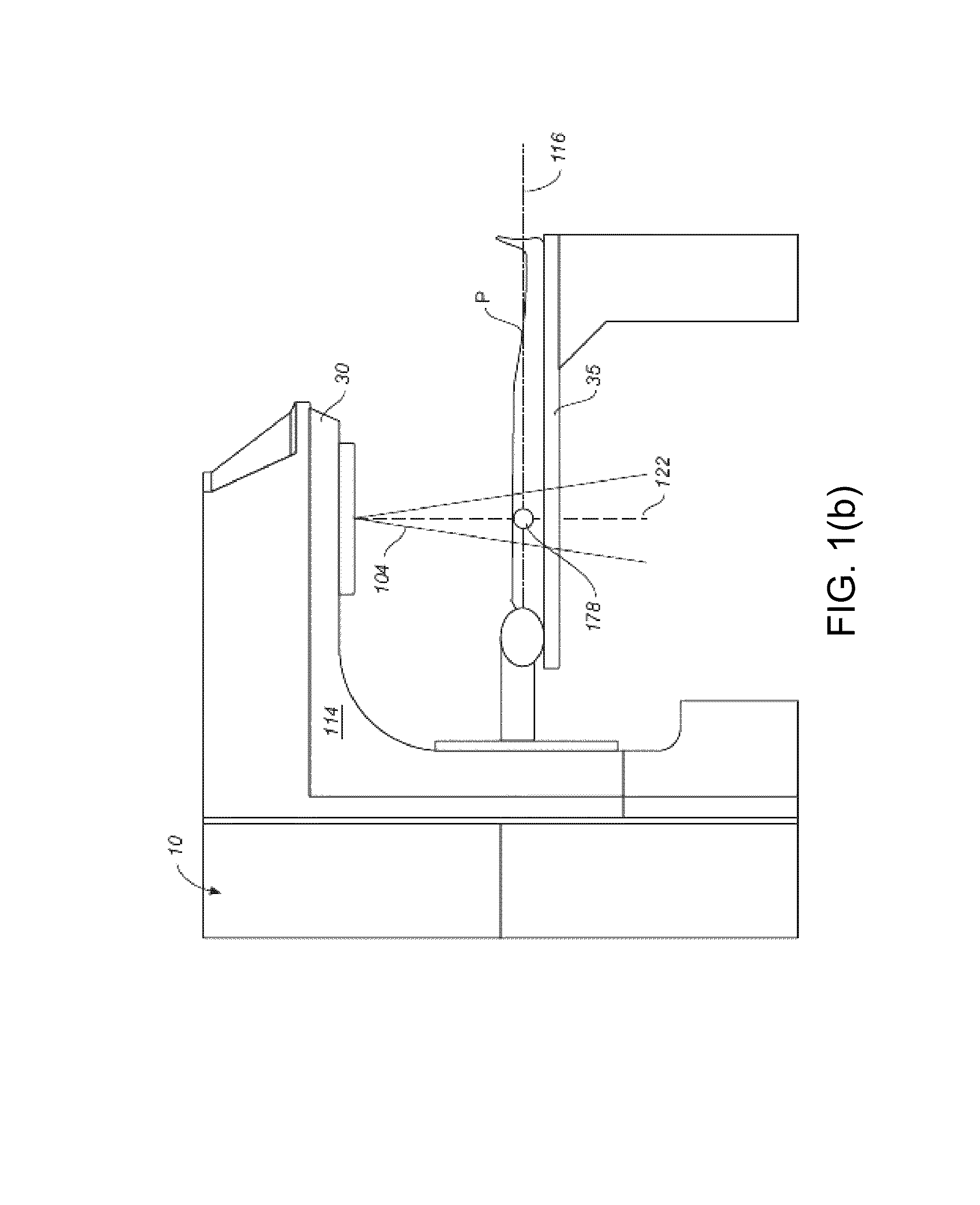
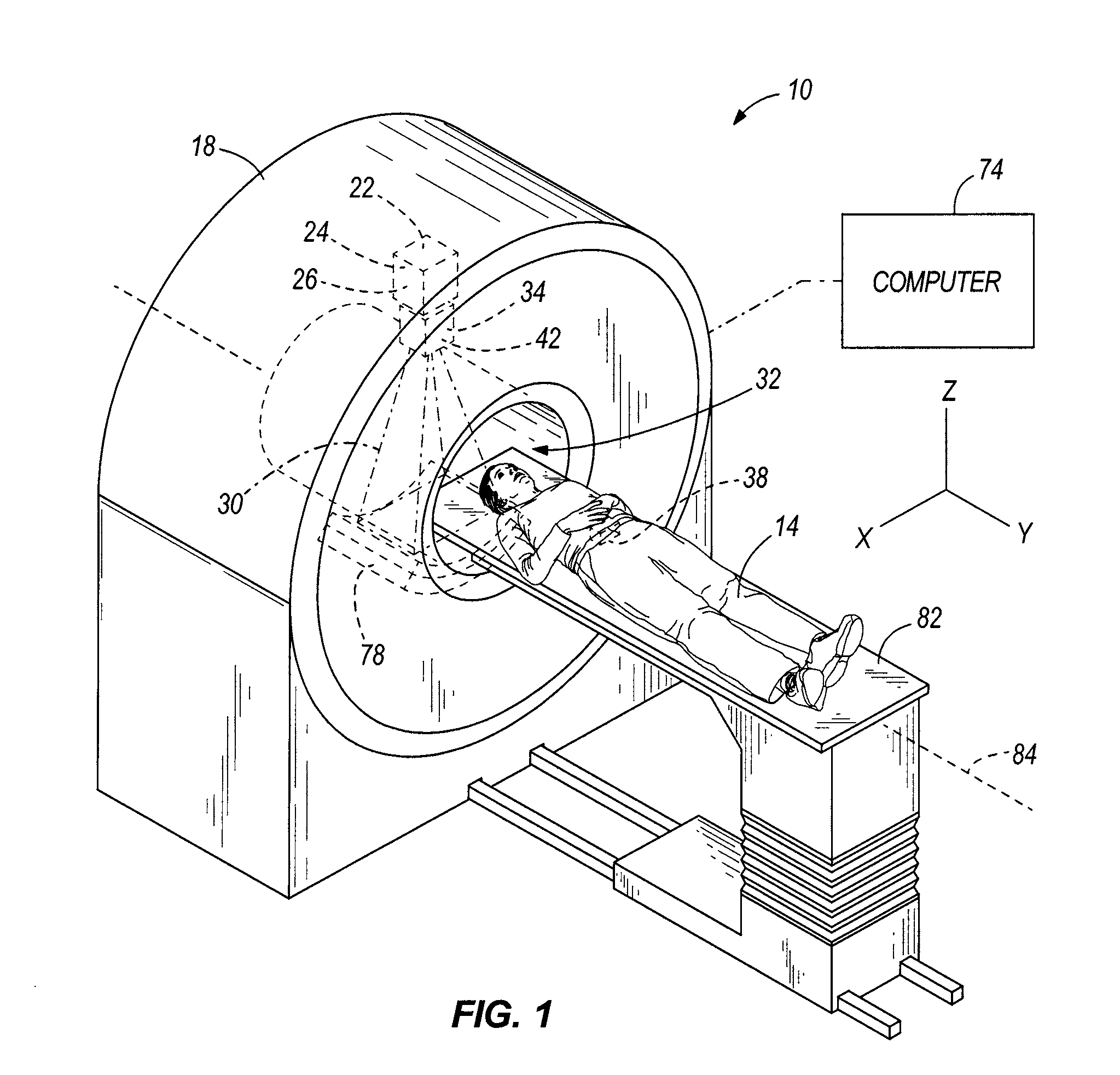
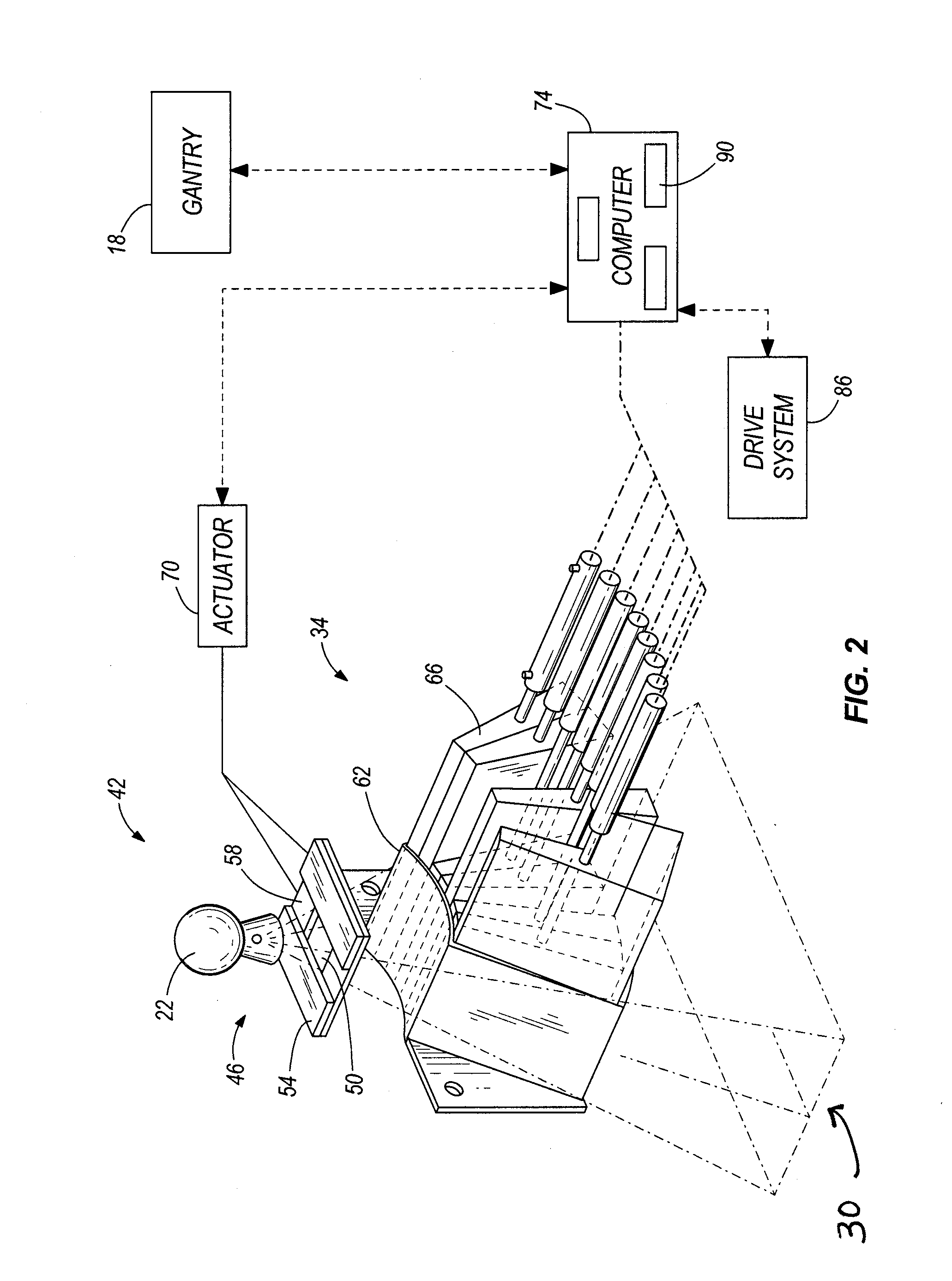
ActiveUS8009804B2X-ray apparatusX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTherapy planningDose calculation
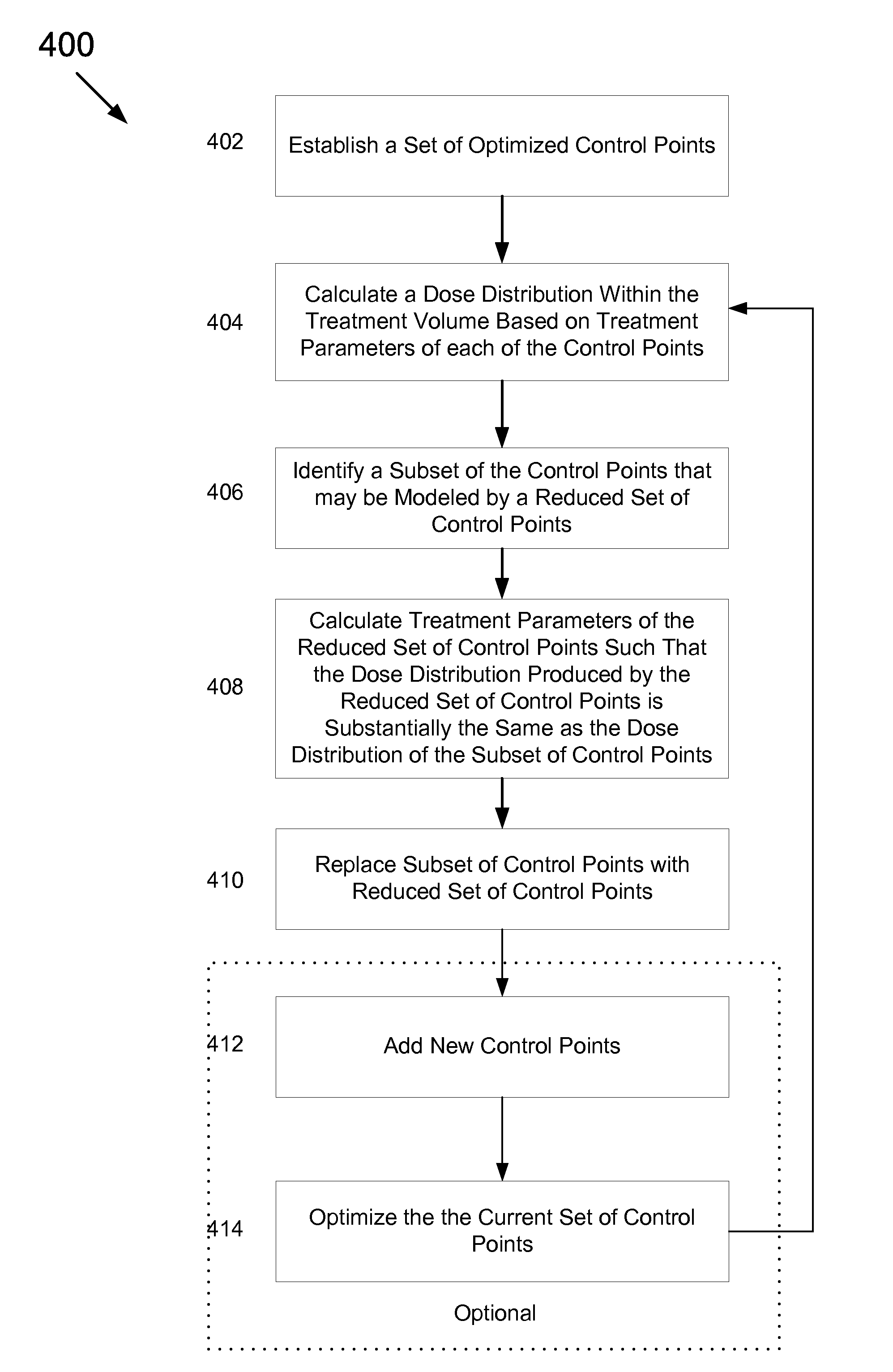
Systems and methods for developing a treatment plan for irradiating a treatment volume within a patient are disclosed. In accordance with the present invention, control points used to calculate a dose of radiation delivered to the treatment volume may be combined to result in a smaller number of control points. The smaller number of control points may allow more efficient calculation of dose distributions resulting in a treatment plan that can be delivered to the patient earlier or may allow additional iterations of treatment plan optimization resulting in a more accurate dose distribution being delivered to the patient.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
Precise radiotherapy planning system
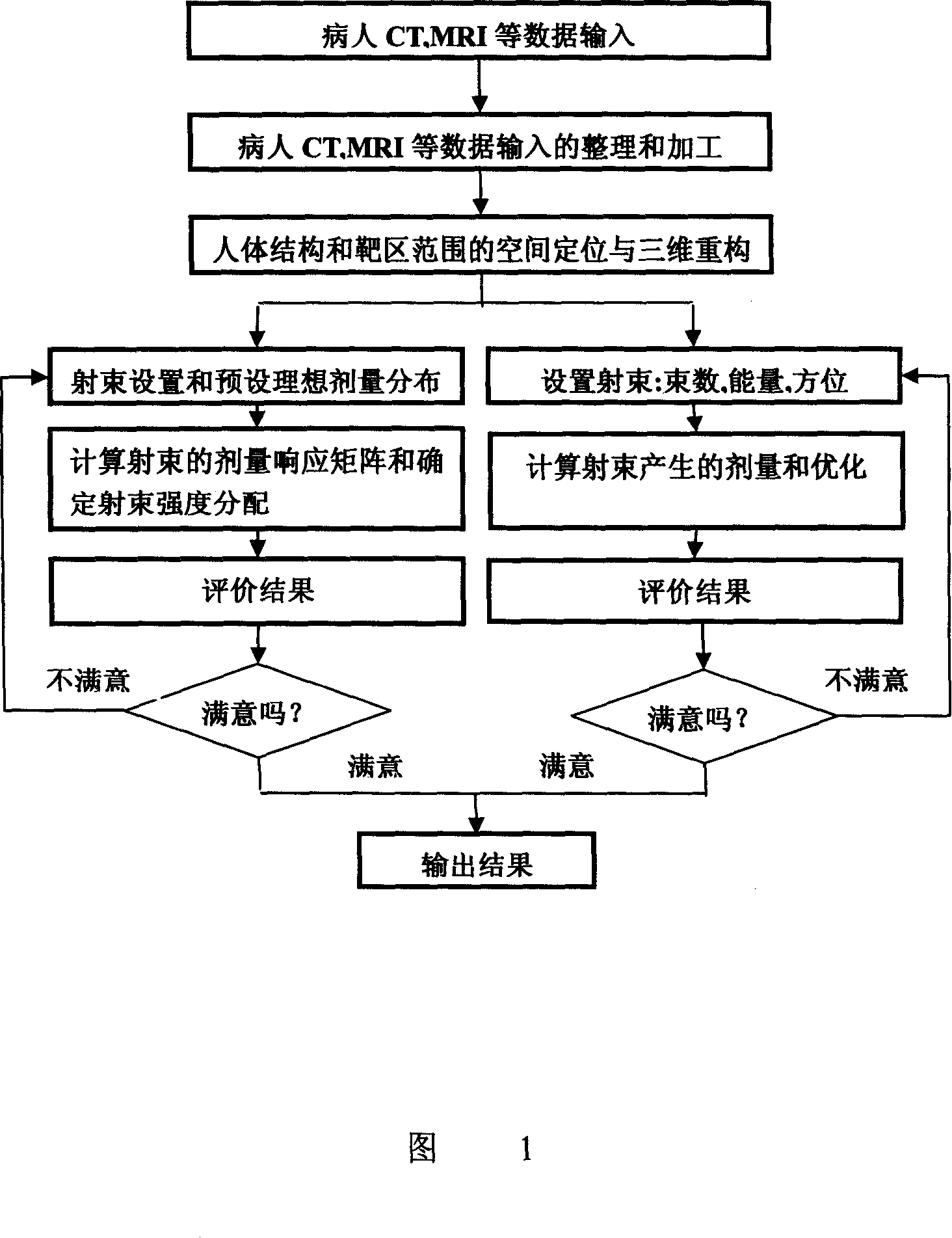
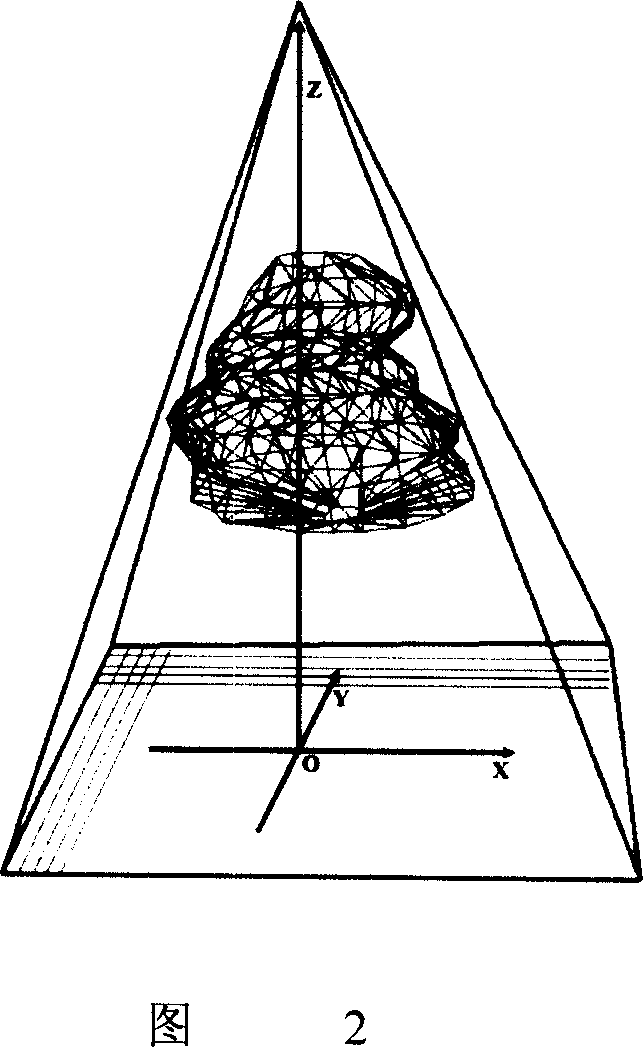
InactiveCN101120871AImprove accuracyImprove the quality of lifeData processing applicationsSurgeryTumor targetLife quality
The present invention discloses an accurate radiation treatment planning system, which mainly comprises a three-dimensional medical image reconstruction module for reconstruction of human organs and the tumor target area, a three-dimensional dose calculation module of high accuracy photon beam, a three-dimensional dose calculation module of high accuracy electron beam, a conventional radiation plan designing module of the photon beam and the electron beam, a conformal radiation designing module of the photon beam and the electron beam, a reverse plan scheme designing module focused on the photon beam treatment. The present invention independently resolves the main and key technology of the radiation treatment planning system. The present invention develops a highly accurate algorithm and a fast precise optimal method of the three-dimensional dose distribution in photon beam and the electron beam, which distributes in non-uniform human medium. The present invention greatly improves accuracy of the embarking dose in tumor target area in patient body. Because the dose calculation speed has been improved dramatically, the advanced conformal radiation treatment planning system and the treatment planning system focused on radiation are feasible for clinical application. The present invention brings important benefits for improving the radiation treatment effect and improving life quality of the patient.
Owner:成都奇林科技有限责任公司
Deterministic computation of radiation doses delivered to tissues and organs of a living organism
InactiveUS20050143965A1Improve computing efficiencyHigh solution accuracyDosimetersComputation using non-denominational number representationInternal radiationIntensity modulation
Various embodiments of the present invention provide methods and systems for deterministic calculation of radiation doses, delivered to specified volumes within human tissues and organs, and specified areas within other organisms, by external and internal radiation sources. Embodiments of the present invention provide for creating and optimizing computational mesh structures for deterministic radiation transport methods. In general these approaches seek to both improve solution accuracy and computational efficiency. Embodiments of the present invention provide methods for planning radiation treatments using deterministic methods. The methods of the present invention may also be applied for dose calculations, dose verification, and dose reconstruction for many different forms of radiotherapy treatments, including: conventional beam therapies, intensity modulated radiation therapy (“IMRT”), proton, electron and other charged particle beam therapies, targeted radionuclide therapies, brachytherapy, stereotactic radiosurgery (“SRS”), Tomotherapy®; and other radiotherapy delivery modes. The methods may also be applied to radiation-dose calculations based on radiation sources that include linear accelerators, various delivery devices, field shaping components, such as jaws, blocks, flattening filters, and multi-leaf collimators, and to many other radiation-related problems, including radiation shielding, detector design and characterization; thermal or infrared radiation, optical tomography, photon migration, and other problems.
Owner:TRANSPIRE
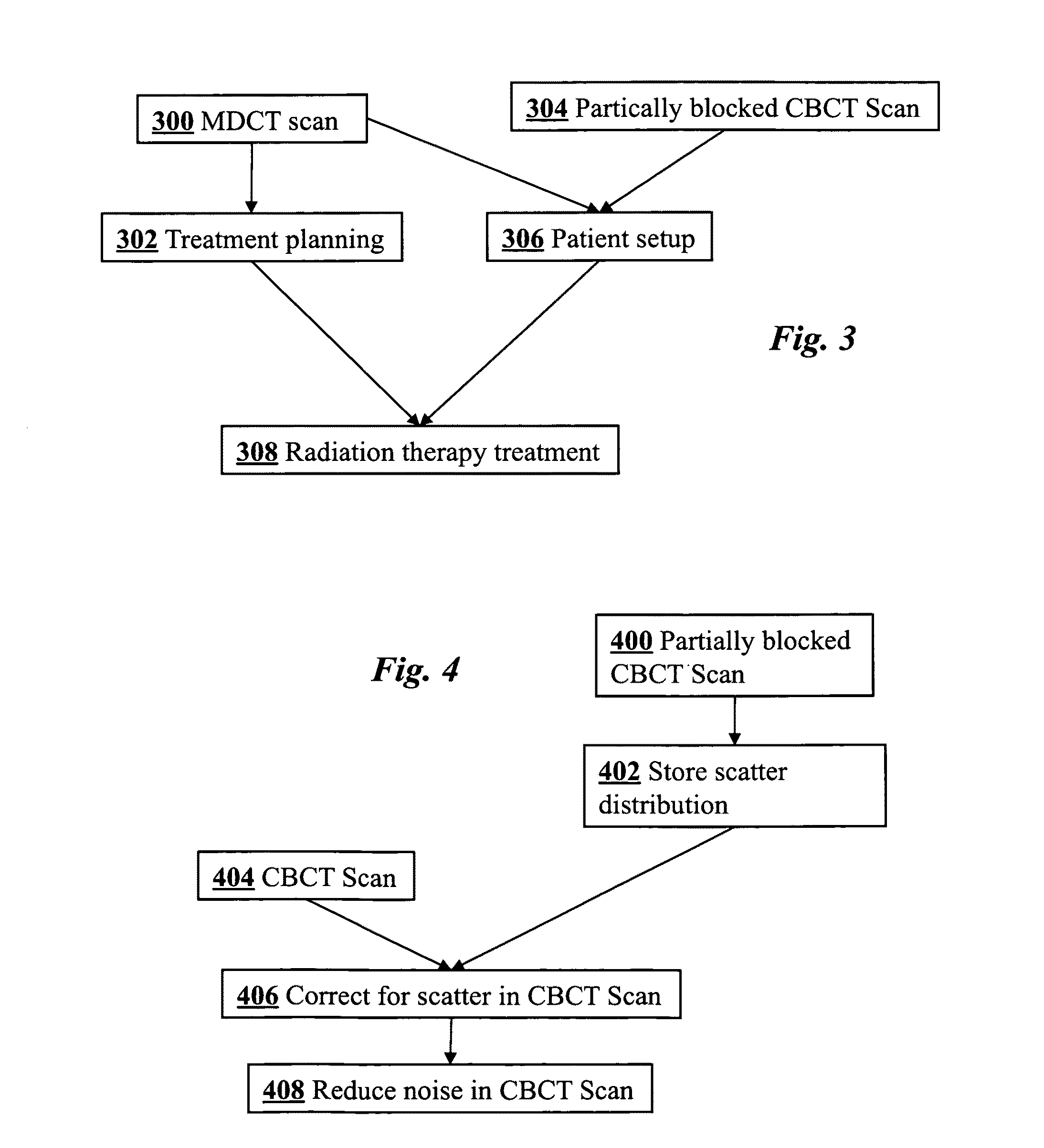
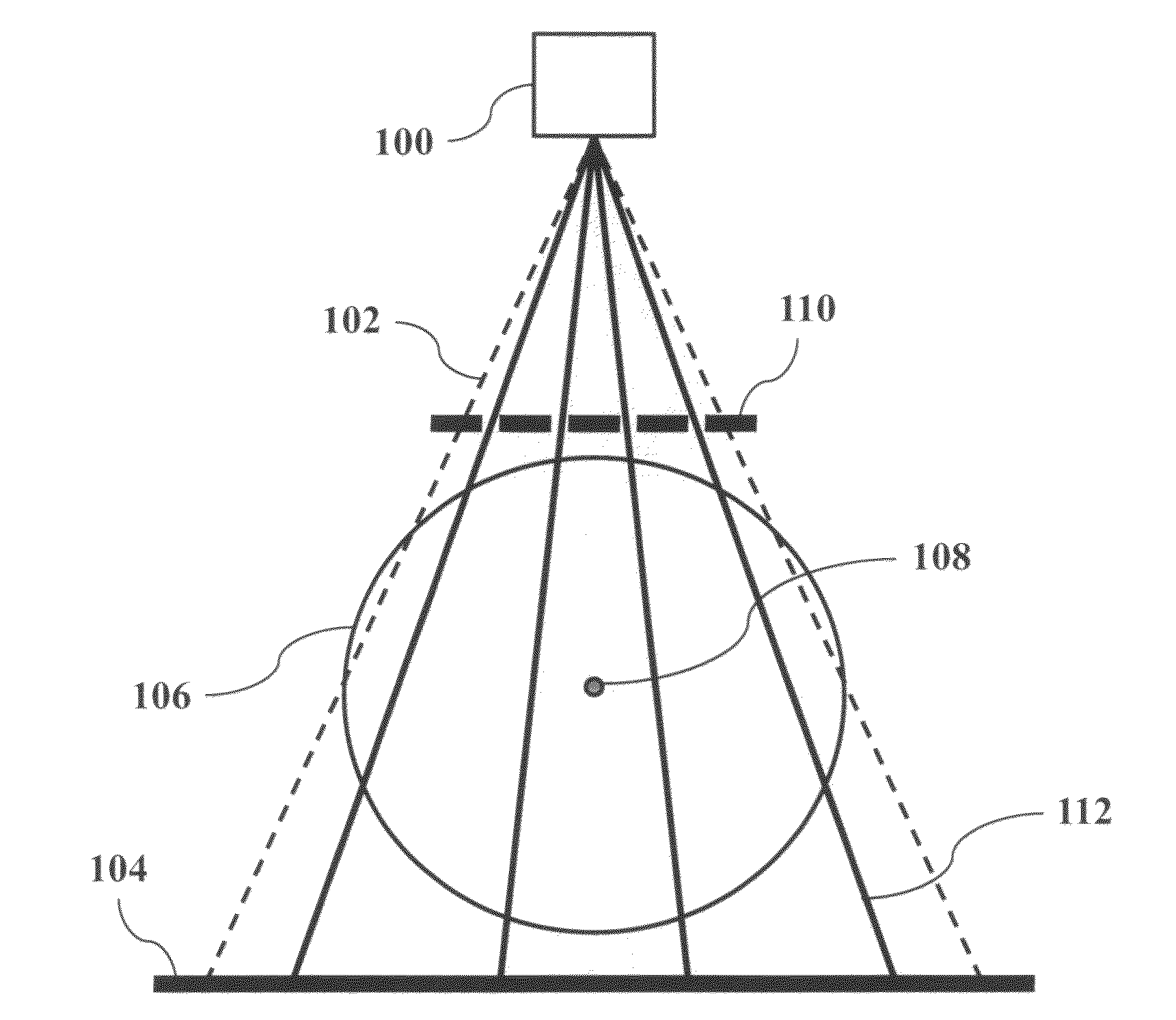
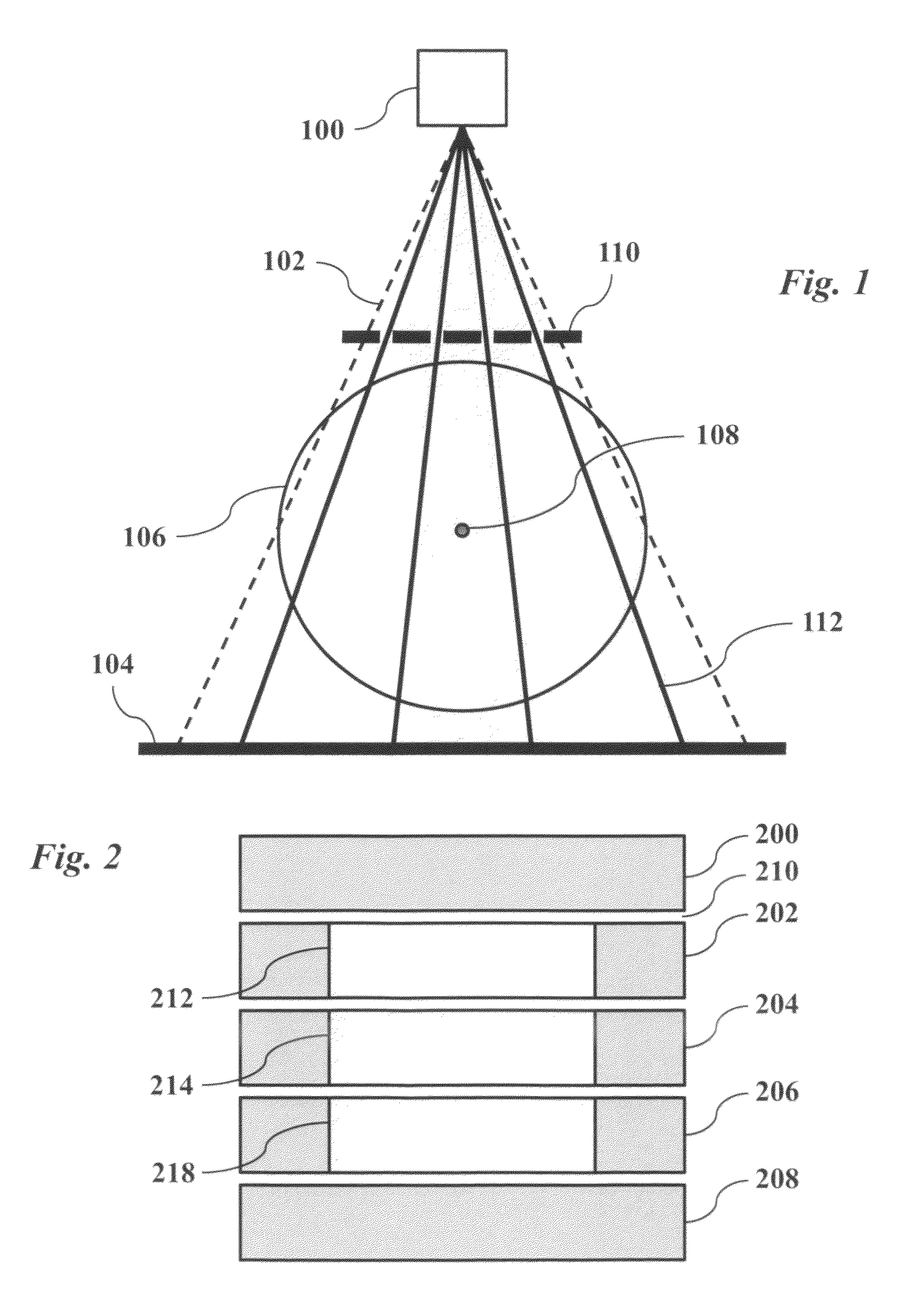
Cone-beam CT imaging scheme
InactiveUS20090225932A1Reduce noiseReduce doseReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationImaging qualityCbct imaging
A general imaging scheme is proposed for applications of CBCT. The approach provides a superior CBCT image quality by effective scatter correction and noise reduction. Specifically, in its implementation of CBCT imaging for radiation therapy, the proposed approach achieves an accurate patient setup using a partially blocked CBCT with a significantly reduced radiation dose. The image quality improvement due to the proposed scatter correction and noise reduction also makes CBCT-based dose calculation a viable solution to adaptive treatment planning.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
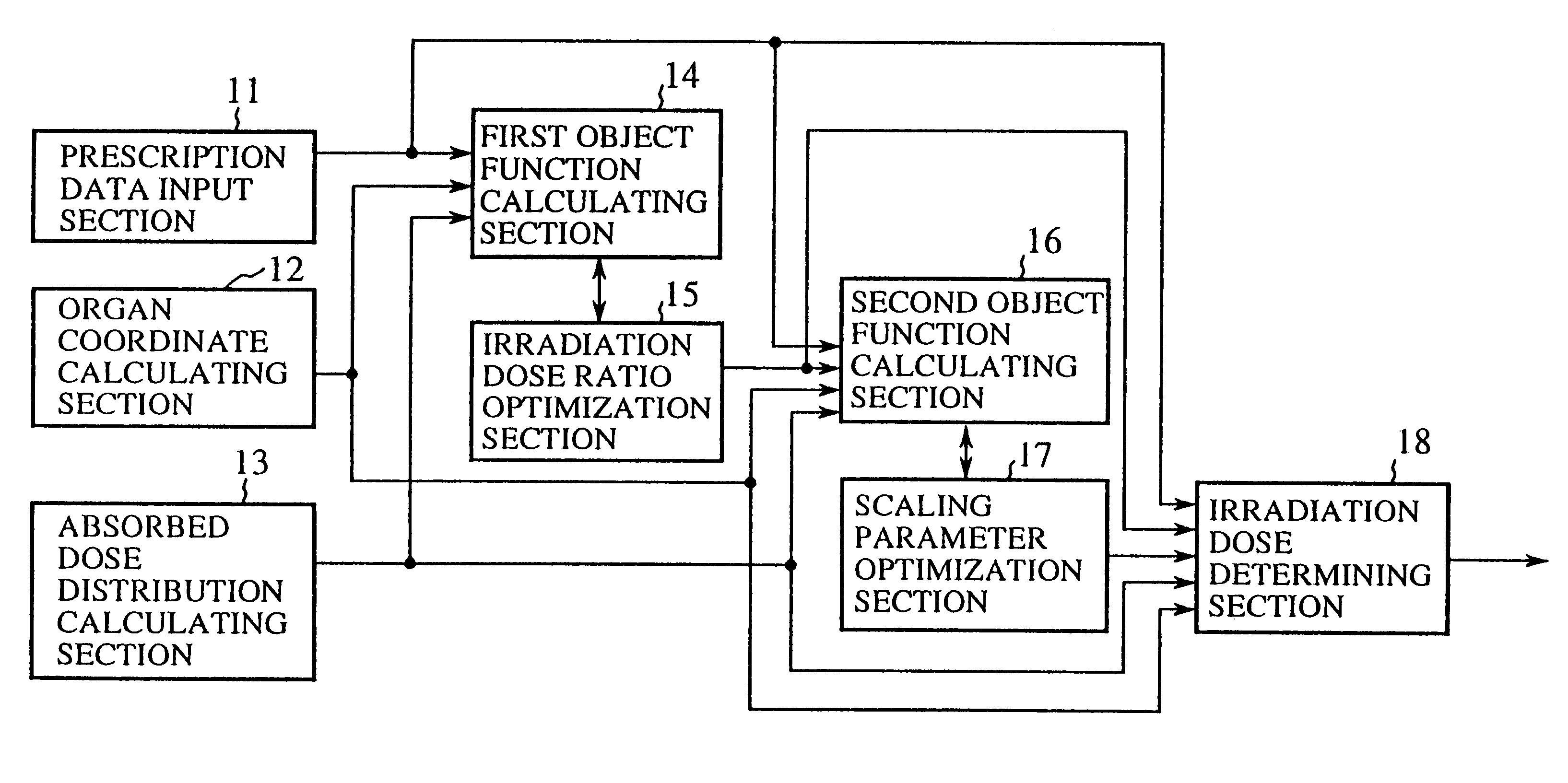
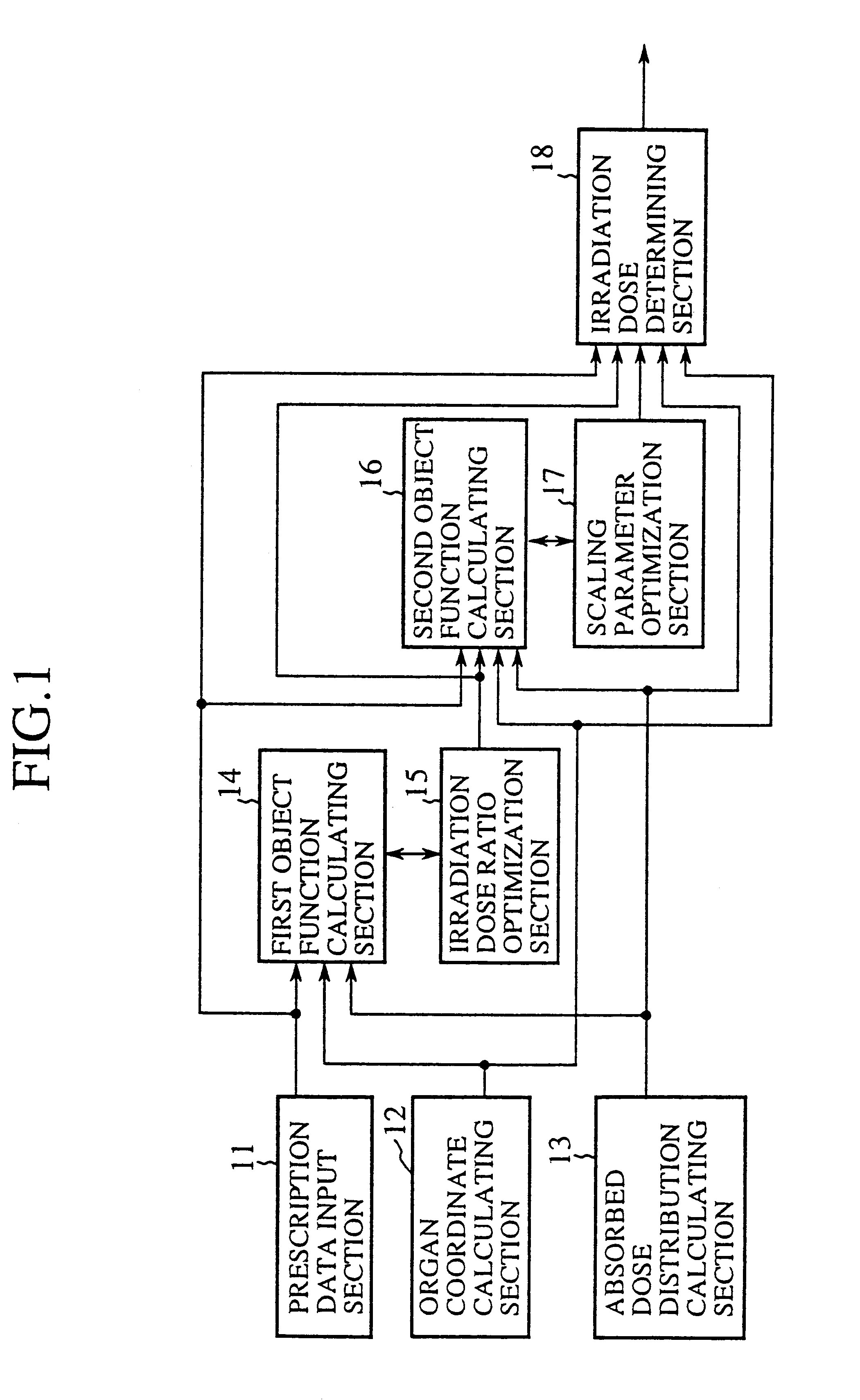
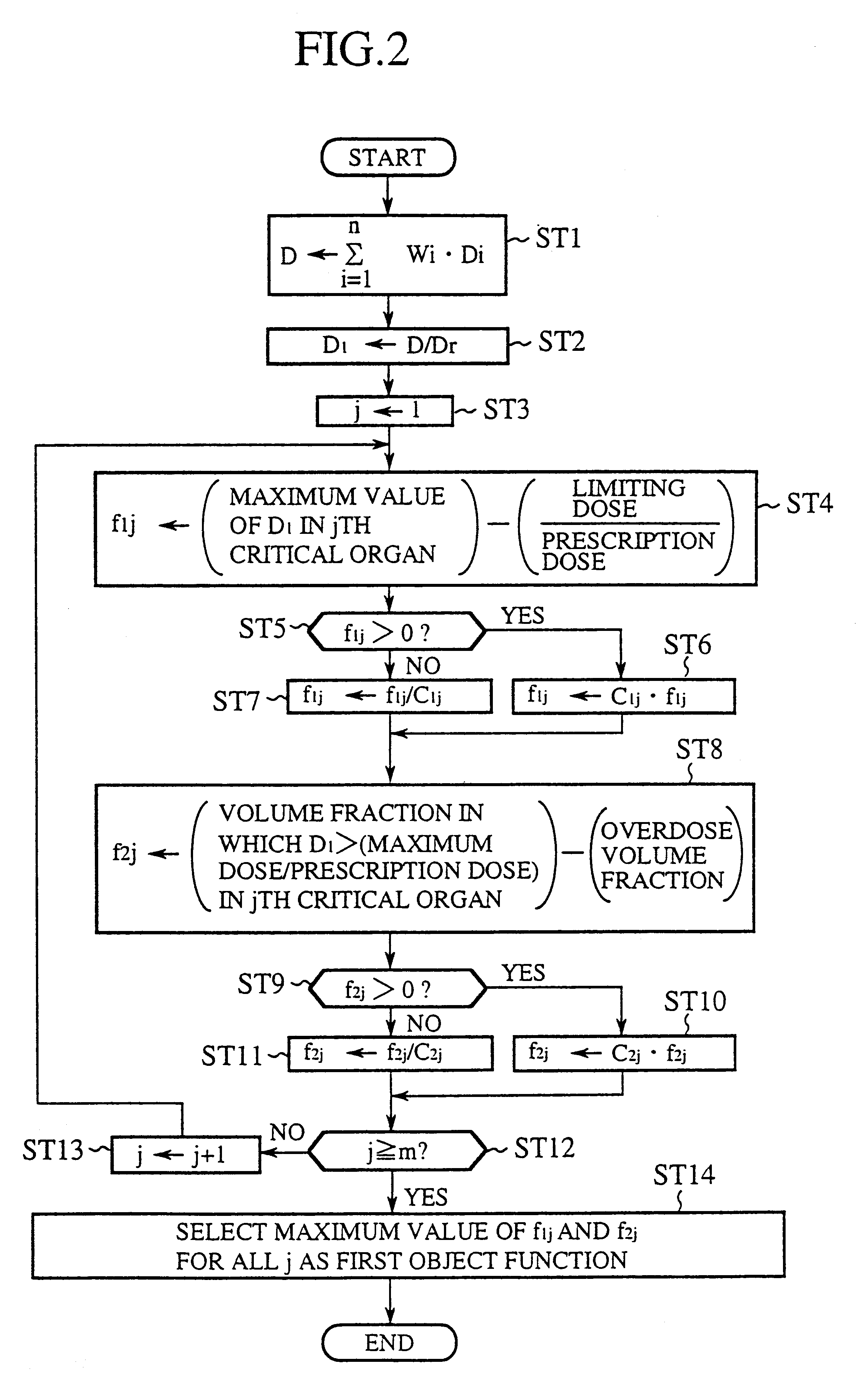
Irradiation dose calculation unit, irradiation dose calculation method and recording medium
An irradiation dose calculating unit can solve a problem of a conventional irradiation dose calculating unit in that since irradiation doses from portals are empirically determined, it is likely that optimum irradiation doses are not established for a target and a critical organ. A prescription data input section is used for a physician to input prescription data designating doses to a target and a critical organ. First and second object function calculating sections each calculate predefined indices, and obtain a first object function representing the level of satisfaction for the critical organ and a second object function representing the level of satisfaction for the target and critical organ. The irradiation doses from the portals are calculated based on these object functions such that the prescription data are satisfied.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Treatment planning system and method for radiotherapy
ActiveUS8085899B2Less precisionLow accuracyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDose calculation algorithmPlanning method
A treatment planning method and system for optimizing a treatment plan used to irradiate a treatment volume including a target volume, such as a tumor, is disclosed. According to the method, two dose calculation algorithms are used to develop the optimized treatment plan. A first dose calculation algorithm is used to obtain substantially complete dose calculations and a second, incremental, dose calculation algorithm is used to make more limited calculations. The incremental calculations may be performed, for example, with less precision, less accuracy or less scope (e.g., focused on a specific subvolume within the treatment volume) in order to reduce the time required to achieve an optimized plan. Each of the dose calculation algorithms may be iterated a plurality of times, and different cutoff criteria can be used to limit the number of iterations in a given pass. A treatment planning system of the invention uses software for implementing the complete and incremental dose calculation algorithms. The method and system are especially useful for IMRT and arc therapy where treatment plan optimization is particularly challenging.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
Single session interactive ultra-short duration super-high biological dose rate radiation therapy and radiosurgery
A medical accelerator system consisting of coplanar and non-coplanar beams, on line magnetic resonance anatomic and functional imaging and cone beam computed tomographic imaging for single session image guided all field simultaneous radiation therapy and radiosurgery is provided. This system enables single session simulation, field-shaping block making, treatment planning, dose calculations and treatment of tumors. The radiation exposure time to the tumor and the normal tissue is reduced to a few seconds to less than a minute. In filed intensity modulated radiation is rendered by combined divergent and pencil beam, multiple smaller fields within a larger field, selectively varying beam's energy, dose rate and beam weight. Since all the treatment fields are treated simultaneously the dose rate at the tumor site is the sum of each of the converging beam's dose rate at depth. This super-high biological dose rate impairs the lethal and sublethal damage repair.
Owner:SAHADEVAN VELAYUDHAN
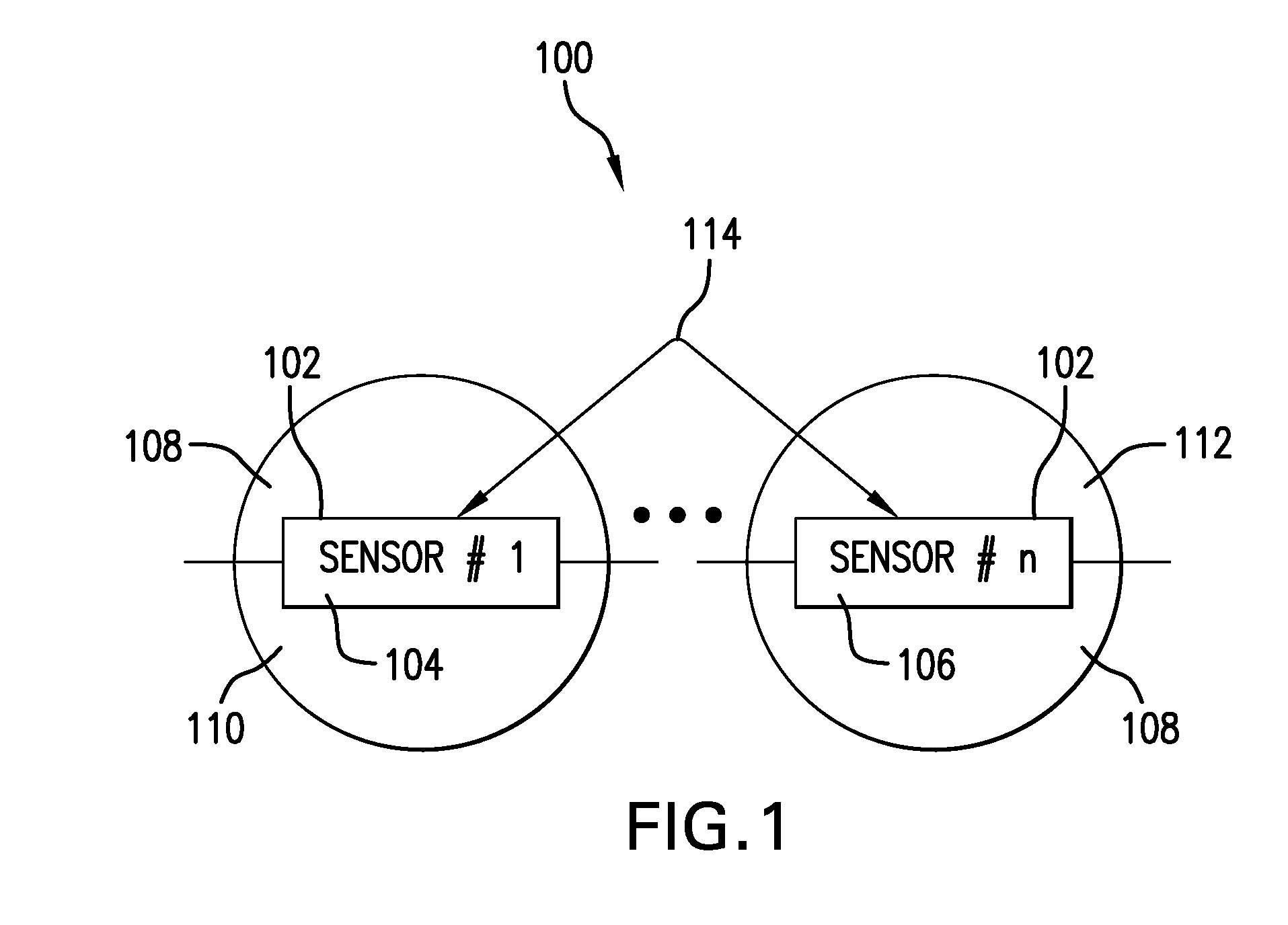
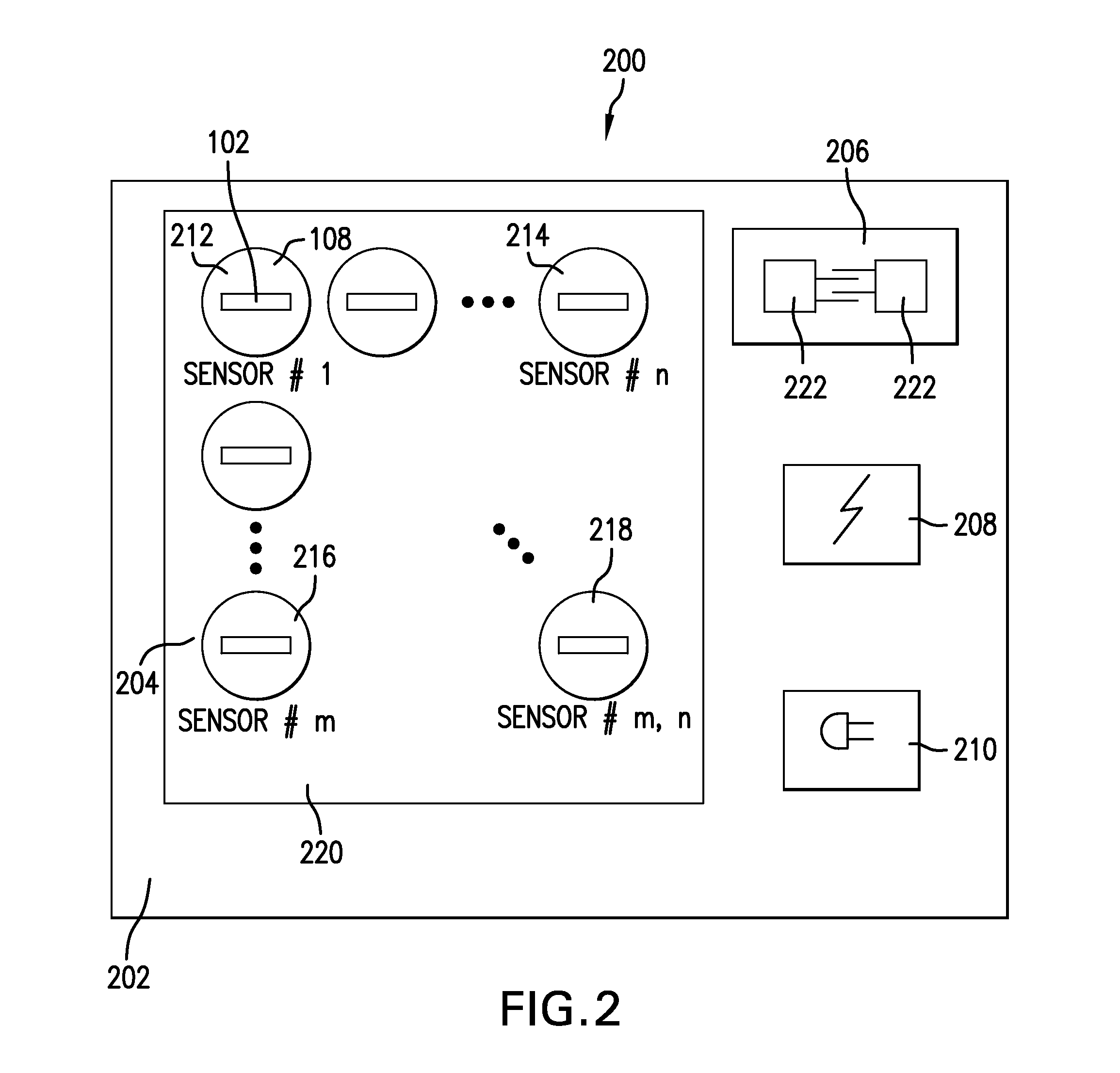
System and method for wireless, motion and position-sensing, integrating radiation sensor for occupational and environmental dosimetry
Described is a radiation dose calculation algorithm based upon the output of a radiation dosimeter including multiple sensor devices (including one or more passive integrating radiation sensors and optionally, a MEMS accelerometers, a wireless transmitters a GPS, a thermistor, or other chemical, biological or EMF sensors). The algorithm is used to convert the sensor output into dose values used to assess the exposure of personnel to ionizing radiation. Sensor output patterns are matched to stored empirically generated sensor outputs thru weighting and optimization calculation processes to determine personnel doses. Algorithm outputs can include personal dose equivalents, radiation types, radiation energy and radiation source identification. Dose calculations can be optimized for specific applications, and matched to different sets of measured data without changing the underlining software calculation programs.
Owner:LANDAUER INC
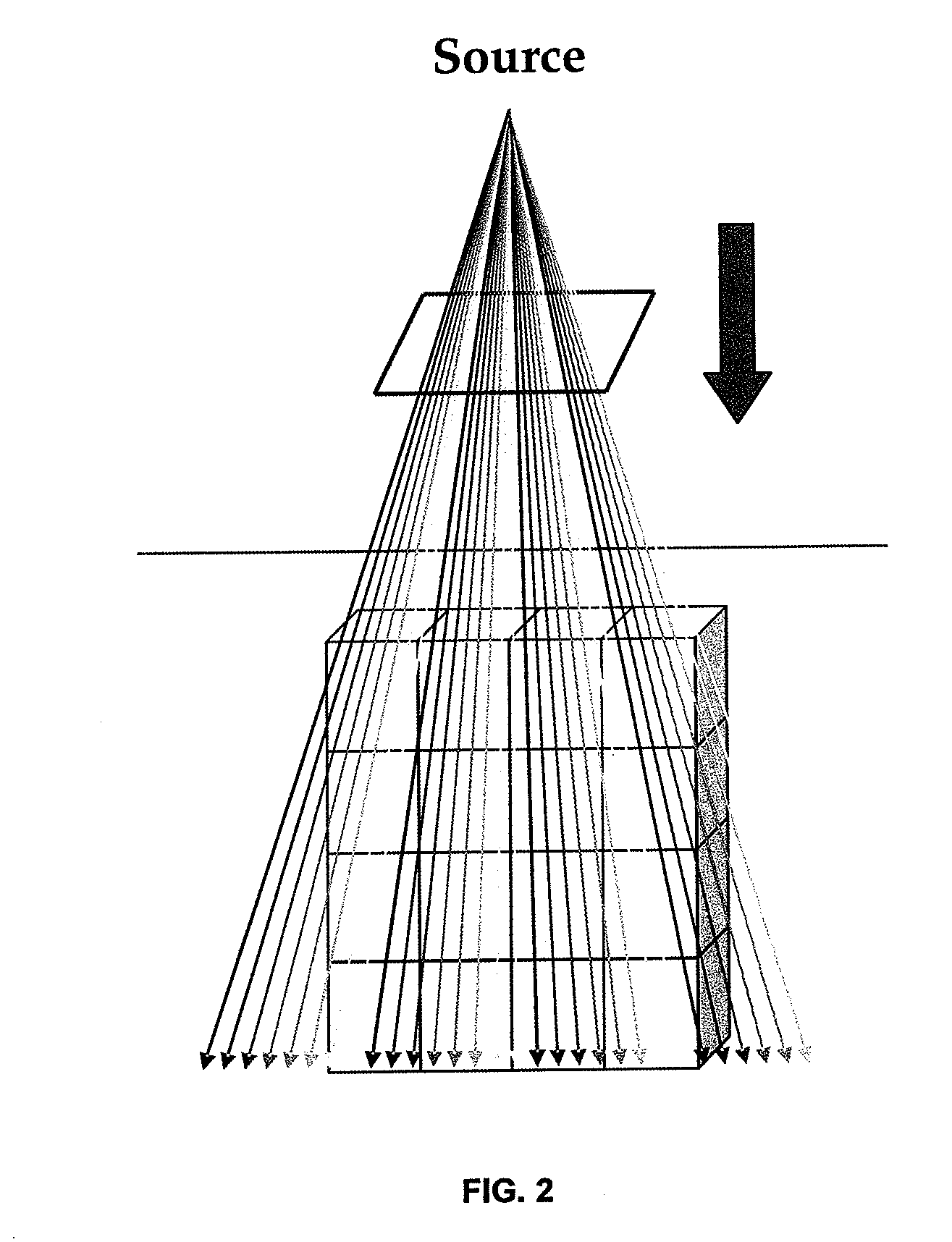
Non-voxel-based broad-beam (NVBB) algorithm for intensity modulated radiation therapy dose calculation and plan optimization
ActiveUS20110122997A1Increase optimization processing timeImprove accuracyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyVoxelDose profile
A method of calculating a dose distribution for a patient for use in a radiation therapy treatment plan. The method includes acquiring an image of a volume within the patient, defining a radiation source, and defining a reference plane oriented between the radiation source and the patient. The method also includes generating a radiation therapy treatment plan, wherein the plan includes a plurality of rays that extend between the radiation source and the patient volume, and calculating a three-dimensional dose volume for the patient volume from the plurality of rays that intersect the reference plane without first having to independently calculate a dose distribution on each of the plurality of rays. The method can also include displaying the three-dimensional dose volume.
Owner:TOMOTHERAPY INC
Real-time dose computation for radiation therapy using graphics processing unit acceleration of the convolution/superposition dose computation method
A system for radiation therapy including a radiation planning system, wherein the radiation planning system comprises a parallel processor adapted to receive input information concerning a body having an intended radiation treatment region and to output information for providing radiation treatment to the intended radiation treatment region of the body, wherein the parallel processor is adapted to perform a plurality of reverse ray tracing calculations based on the input information concerning the body in determining the output information for providing radiation treatment, each of the plurality of reverse ray tracing calculations comprising: calculating a first physical property corresponding to a first sub-region of the intended radiation treatment region of the body that is intersected by a ray traced between a source position and the intended radiation treatment region; and calculating, subsequent to the first-mentioned calculating, a second physical property corresponding to a second sub-region of the intended radiation treatment region that is intersected by the ray at a location closer to the source position than is the first sub-region.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Medication i.v. warning label
An I.V. medication warning label designed to inform attending healthcare workers of possible medication incompatibility combinations. The label includes a flexible, main label with a front surface and a back surface. The back surface has an adhesive applied thereto which allows the main label to be attached to an I.V. bag or I.V. line. Printed on the front surface of the main label is a primary medication indicator which informs the healthcare worker of the medication contained in the I.V. line or administered through the I.V. line. Also printed on the main label is a list of compatible medications, a list of incompatible medications, a dose calculation information section, a date of administration / mixture, and a plurality of removable tags with the primary medication indicator printed thereon. The removable tags may be detached from the main label and attached to other injection ports or lines located upstream or downstream from the I.V. bag.
Owner:LEWIS LEANDER
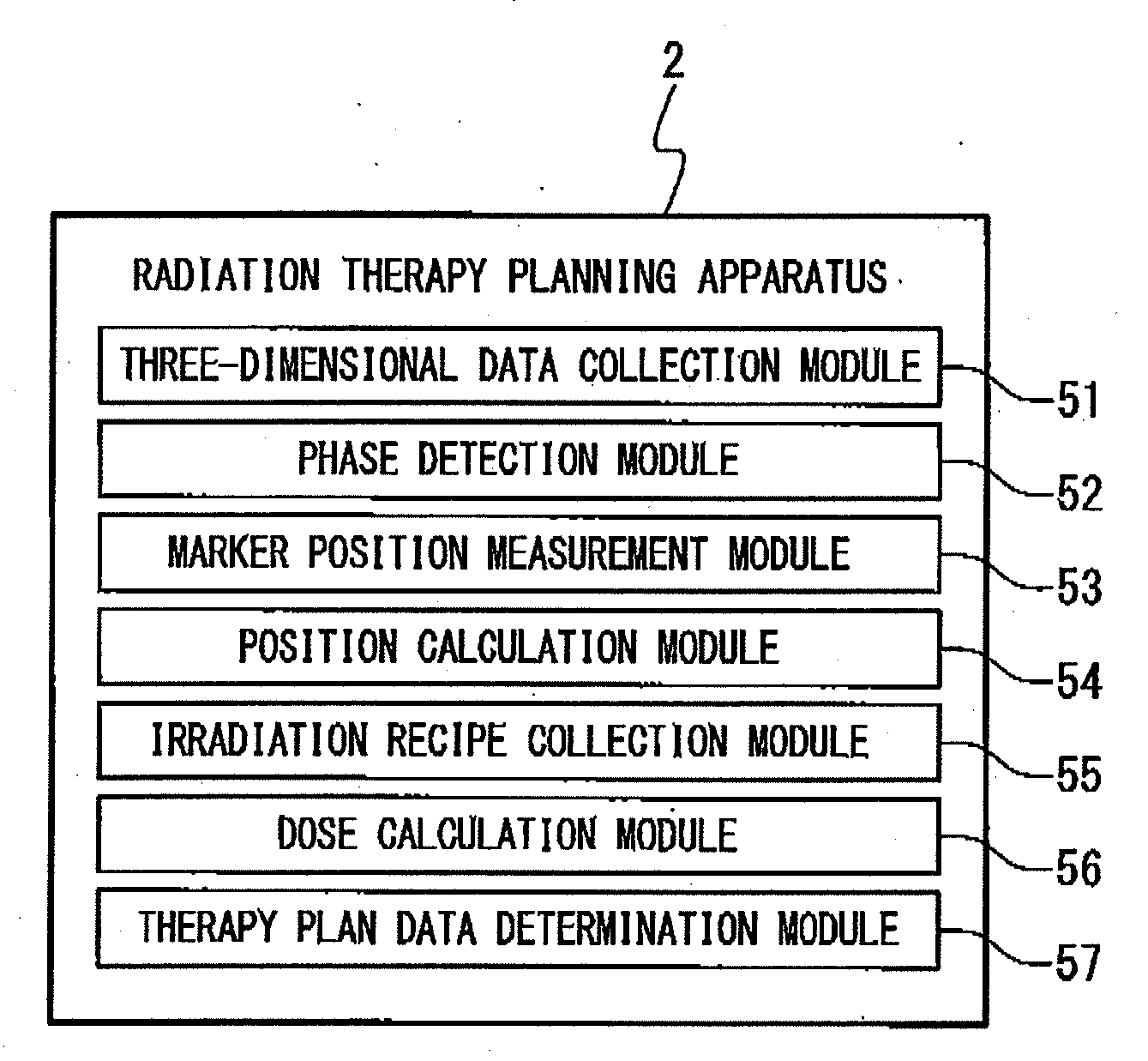
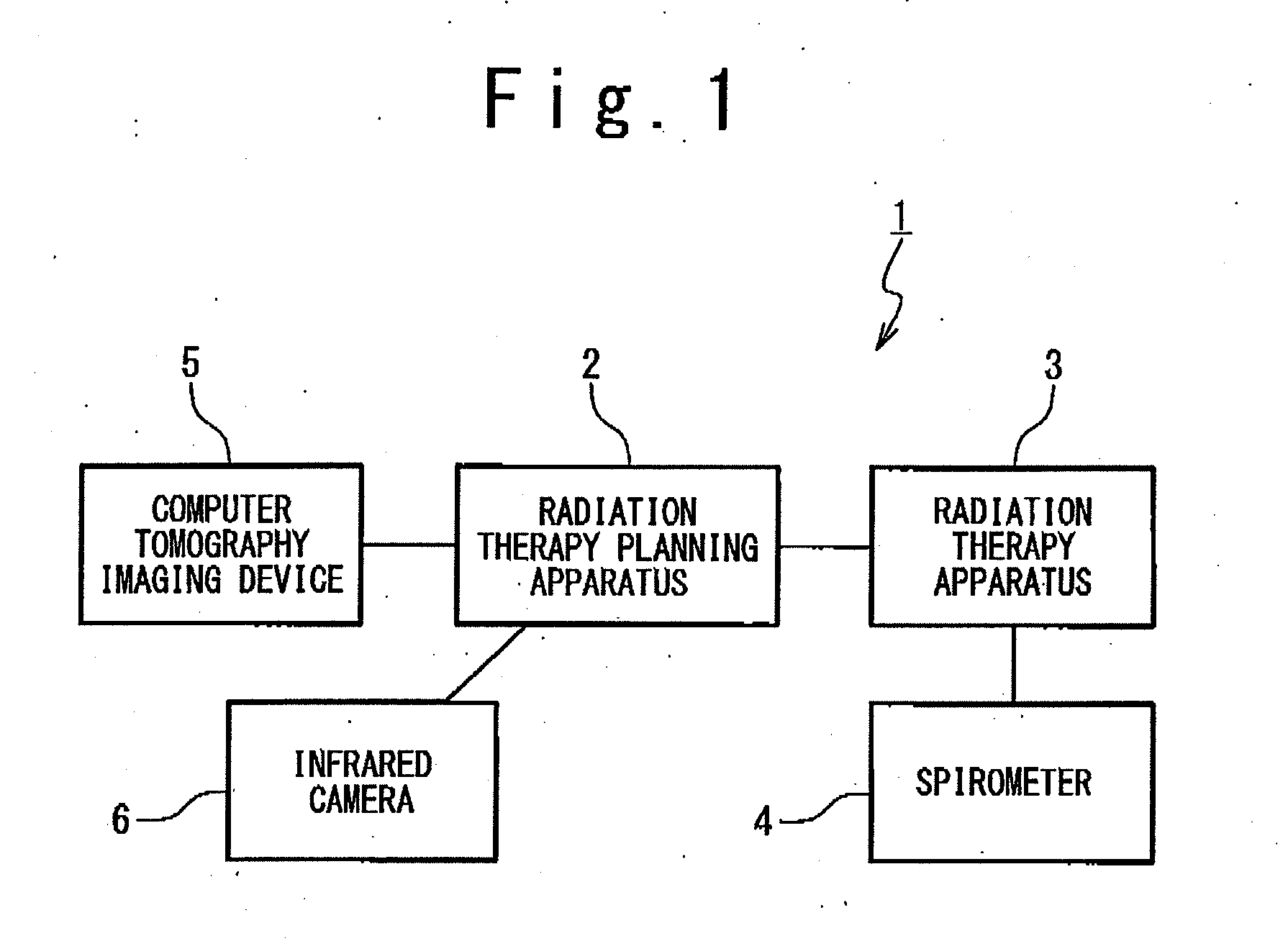
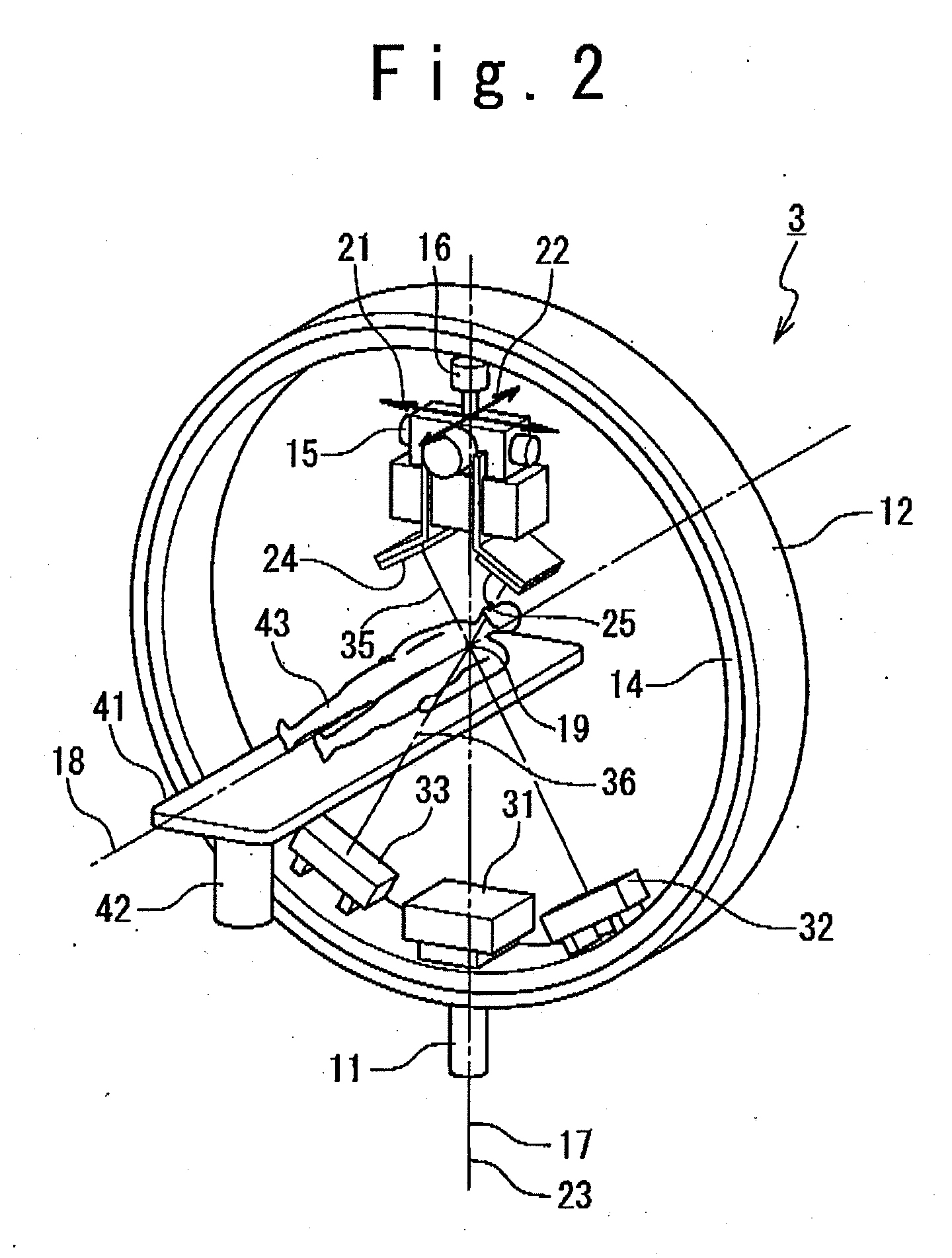
Radiation therapy planning apparatus and radiation therapy planning method
ActiveUS20110044429A1Reduce the burden onReduce doseX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapySubject matterTherapy radiation
A radiation therapy planning apparatus is provided with; a three-dimensional data collection part collecting three-dimensional data representing a plurality of positions where a plurality of portions of a subject are positioned; a marker position measurement part measuring a motion of a marker; and a dose calculation part calculating, when the subject is irradiated with therapeutic radiation changing on the basis of the motion of the subject, the dose of the therapeutic radiation with which each of the plurality of portions is irradiated, based on the motion and the three-dimensional data. The radiation therapy planning apparatus thus constructed can calculate the dose of the therapeutic radiation with which each of the respective portions of the subject is irradiated, more accurately, and reduce the dose of radiation with which the subject is irradiated in calculating the motions of the plurality of portions of the subject.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
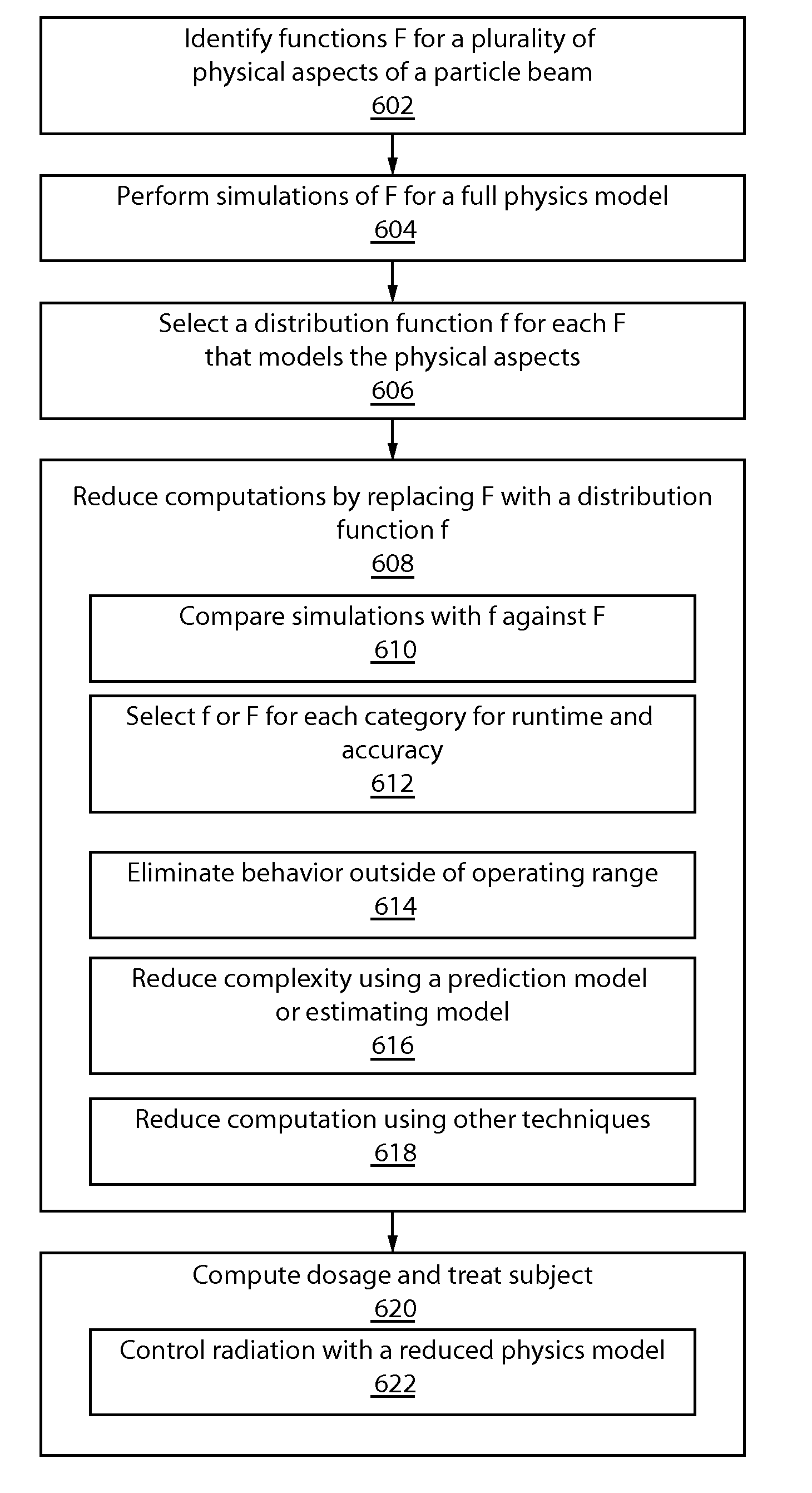
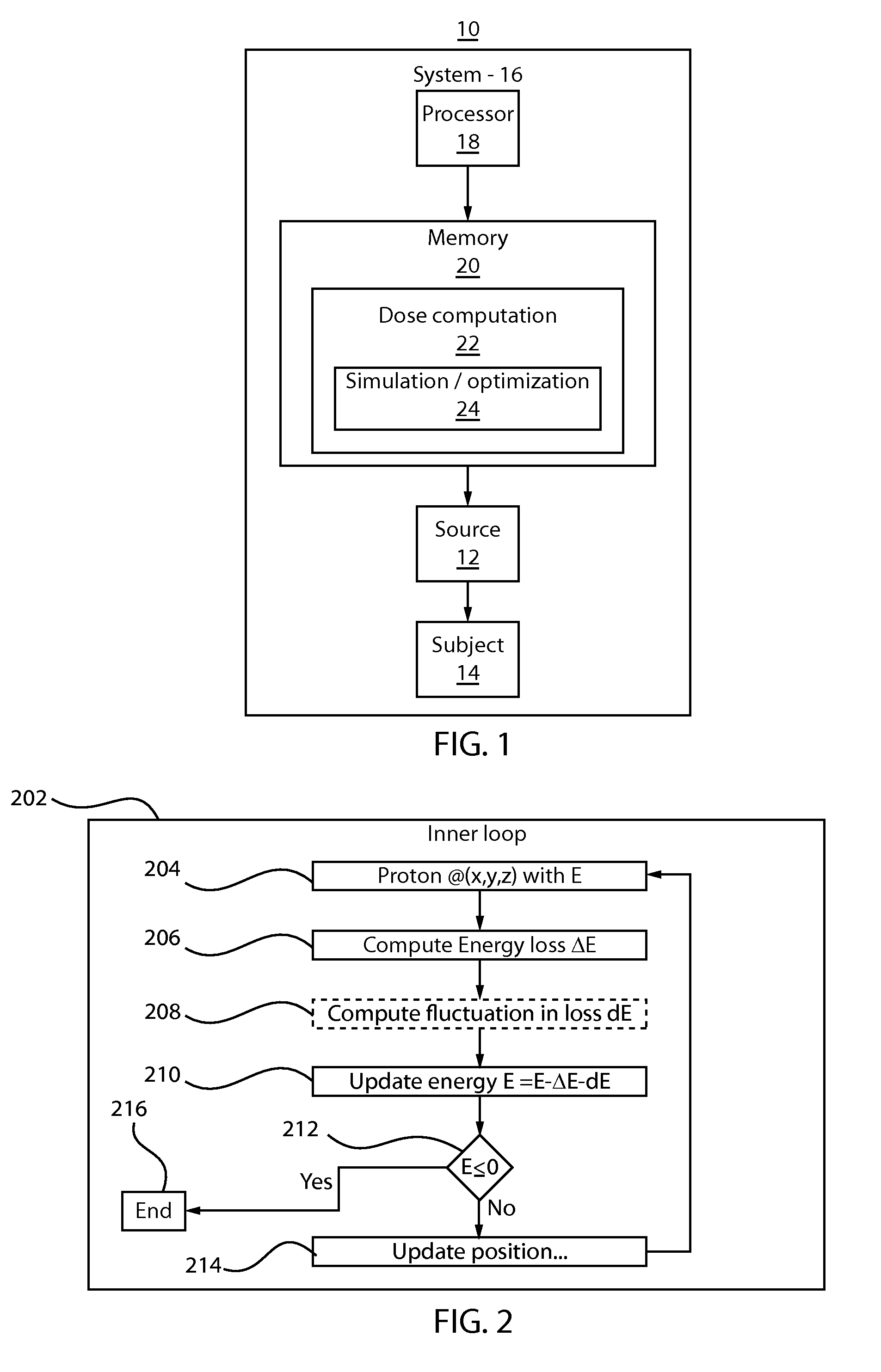
Fast and accurate proton therapy dose calculations
ActiveUS20150352374A1Reduce calculationAccurate modelingMedical simulationComputation using non-denominational number representationSimulation basedComputer science
Simulating particle beam interactions includes identifying a set of n functions F1, F2, . . . , Fn corresponding to a plurality of different physical aspects of a particle beam, performing simulations of each Fi using a full physics model, selecting for each Fi a distribution function fi that models relevant behavior and reducing computation of the full physics model for each Fi by replacing Fi with a distribution function fi. The computation reduction includes comparing a set of simulations wherein each fi replaces its respective Fi to determine if relevant behavior is accurately modeled and selecting one of fi or Fi for each n, for a Monte Carlo simulation based on a runtime and accuracy criteria.
Owner:IBM CORP
Dose Calculation Method for Multiple Fields
ActiveUS20110091014A1X-ray apparatusX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDose calculationRadiation dose
Systems and methods for developing a treatment plan for irradiating a treatment volume within a patient are disclosed. In accordance with the present invention, control points used to calculate a dose of radiation delivered to the treatment volume may be combined to result in a smaller number of control points. The smaller number of control points may allow more efficient calculation of dose distributions resulting in a treatment plan that can be delivered to the patient earlier or may allow additional iterations of treatment plan optimization resulting in a more accurate dose distribution being delivered to the patient.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
Method for comprehensive evaluation of uranium mining and milling atmospheric radiation environment
InactiveCN104424388ASolve the problem that cannot be calculated at the same timeRealize local multi-source prediction functionSpecial data processing applicationsICT adaptationTerrainEarth surface
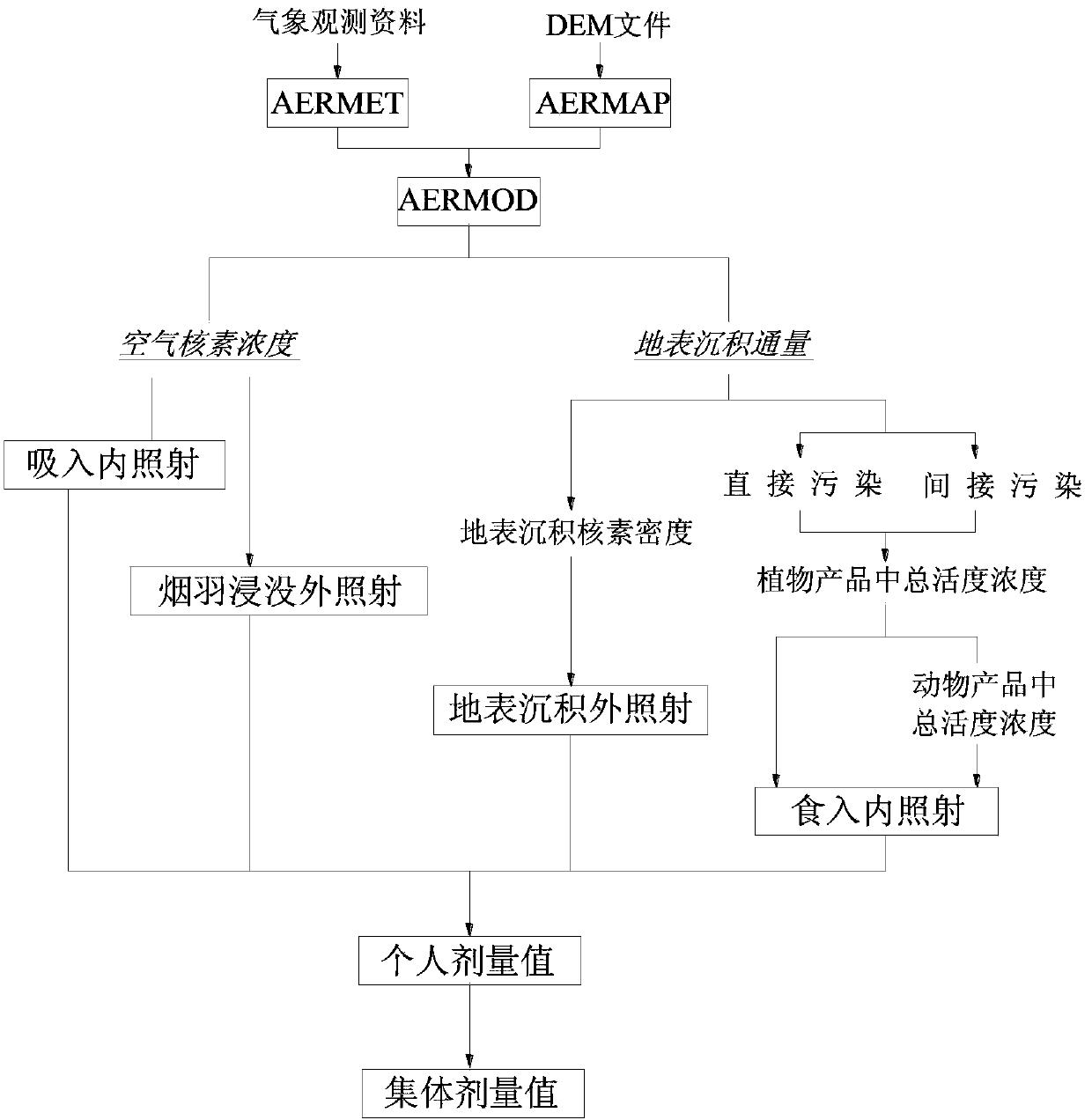
The invention provides a method for comprehensive evaluation of uranium mining and milling atmospheric radiation environment. The method comprises the following steps: pretreating atmosphere; pretreating terrain; calculating atmospheric diffusion; determining breathed internal radiation dose; determining eaten internal radiation dose; determining dose of external radiation deposited on earth surface; determining dose of external radiation immersed in smoke plume; determining public individual dose; determining public group dose and the like. The method disclosed by the invention has the functional characteristics of being scientific, accurate, rapid and comprehensive, and is suitable for prediction and evaluation on influences of the national uranium mining and milling atmospheric radiation environment; by using the method, the calculation results can preferably satisfy the actual relocation diffusion rules of atmospheric pollutants, and the environmental influences and public dose calculation are more scientific and reasonable.
Owner:THE FOURTH INST OF NUCLEAR ENG OF CNNC
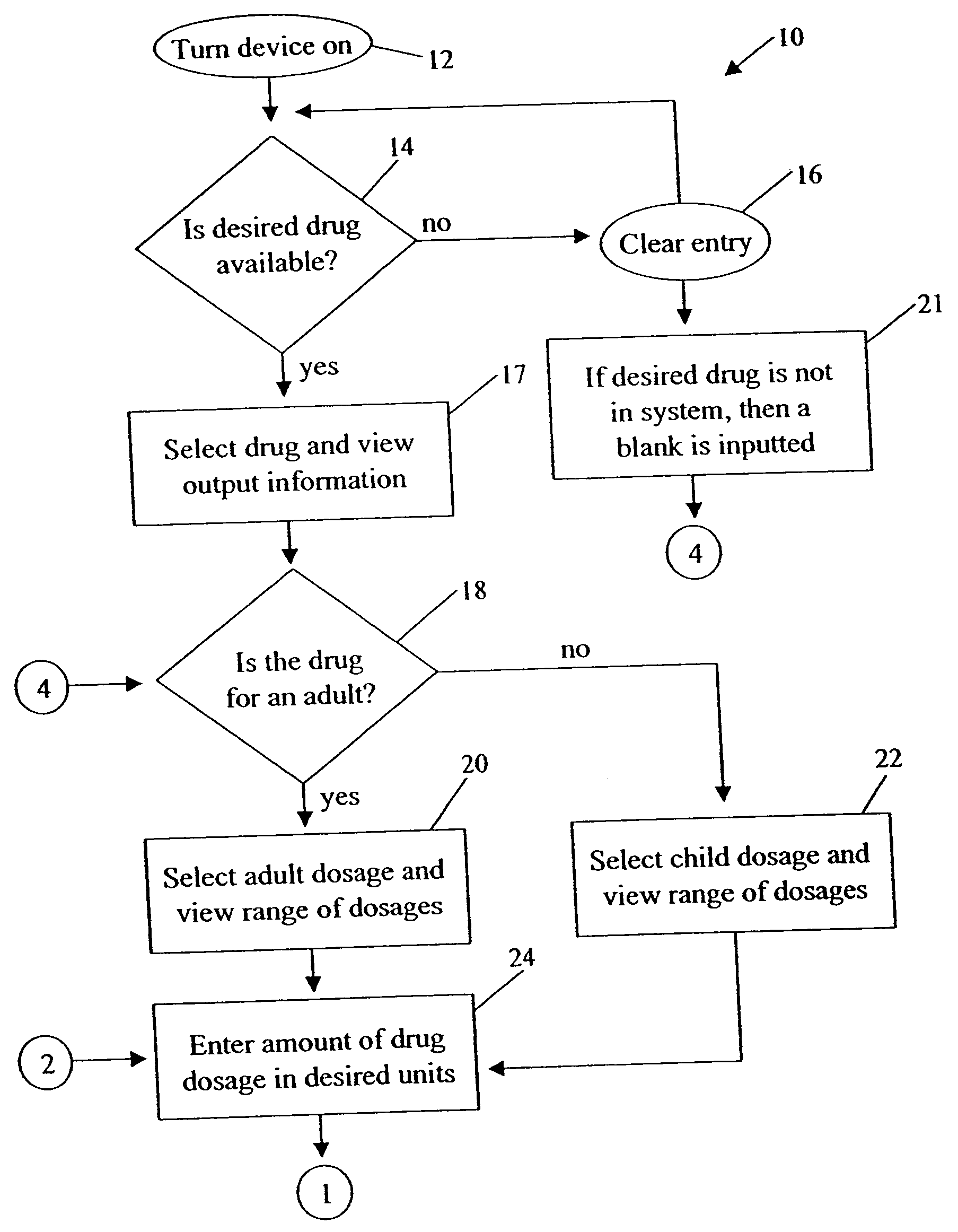
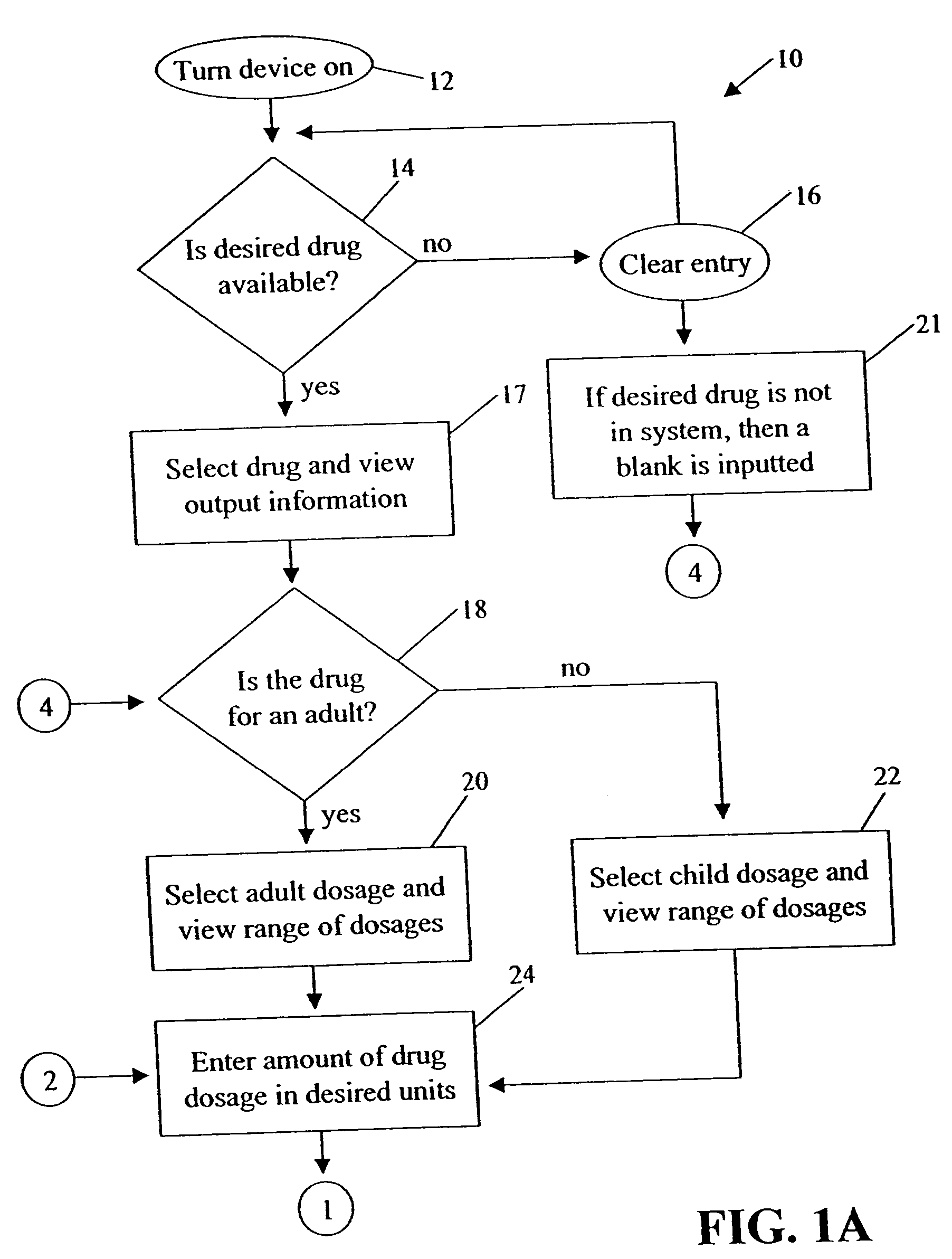
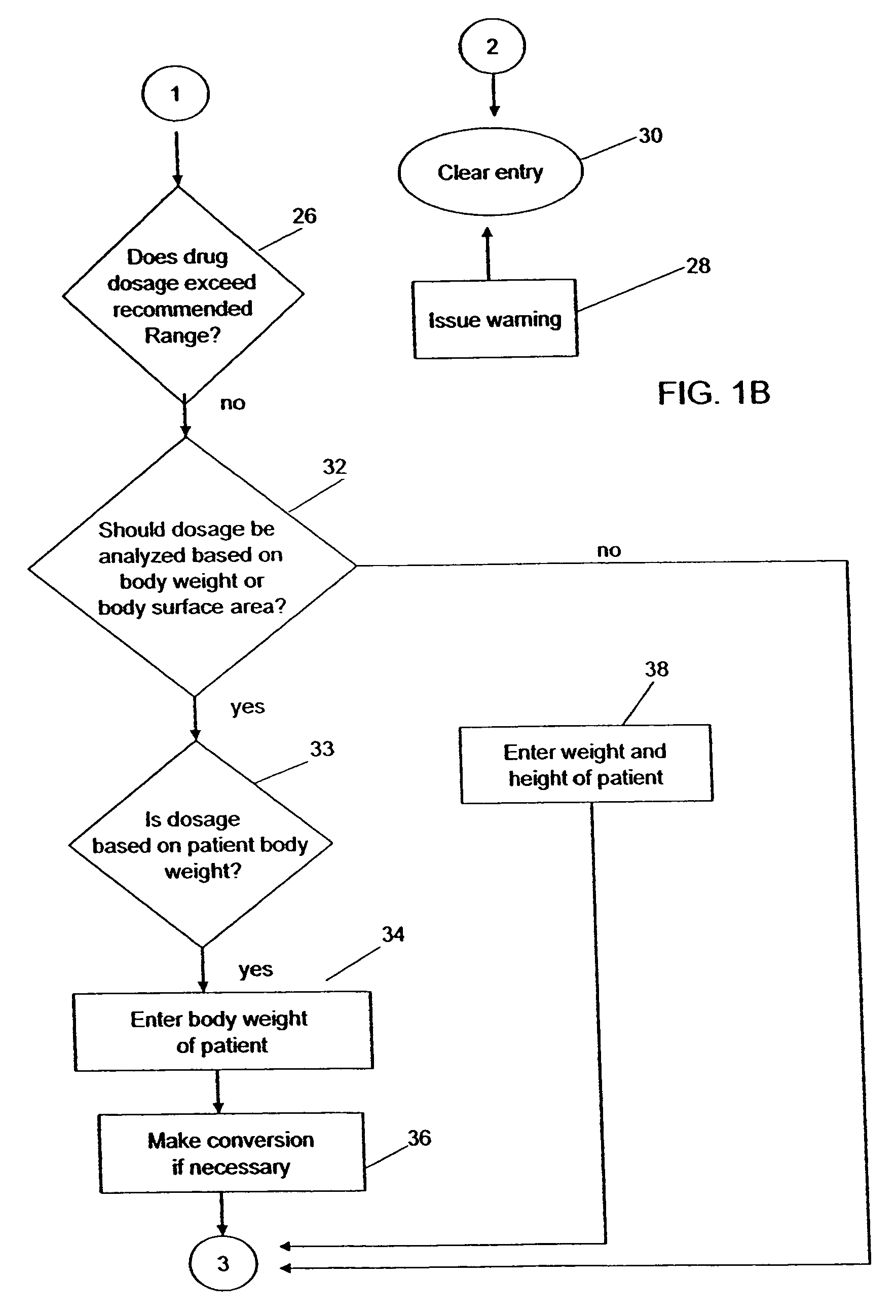
Medication dose calculator
InactiveUS20060129357A1Reduce needData processing applicationsDrug and medicationsMedication doseMedicine
A medication dose calculator and method for comparing an inputted, ordered medication dosage with a known medication dosage range in a database including an input device for inputting a desired drug name, indicating whether the drug is for a child or an adult, an amount of the drugs that are ordered, the body weight or body surface of the patient, and a computing mechanism for determining the dose of the drug to be delivered. The medication dose calculator provides warnings when the inputted amount of drug exceeds the dosage range limits or is incorrect. The medication dose calculator converts an inputted drug unit of measure into a desired unit of measure. In addition, various methods for receiving, recording, storing, transmitting, transferring, and editing information along with various processes utilizing the medication dose calculator are disclosed.
Owner:INFORMMED
System and methods for performing medical physics calculation
ActiveUS20130054670A1Easy and economical and secure accessAlters of calculationMedical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesRadiant energy densityComputer science
A method of calculating radiation fluence and energy deposition distributions on a networked virtual computational cluster is presented. With this method, complex Monte Carlo simulations that require expansive equipment, personnel, and financial resources can be done efficiently and inexpensively by hospitals and clinics requiring radiation therapy dose calculations.
Owner:STC UNM
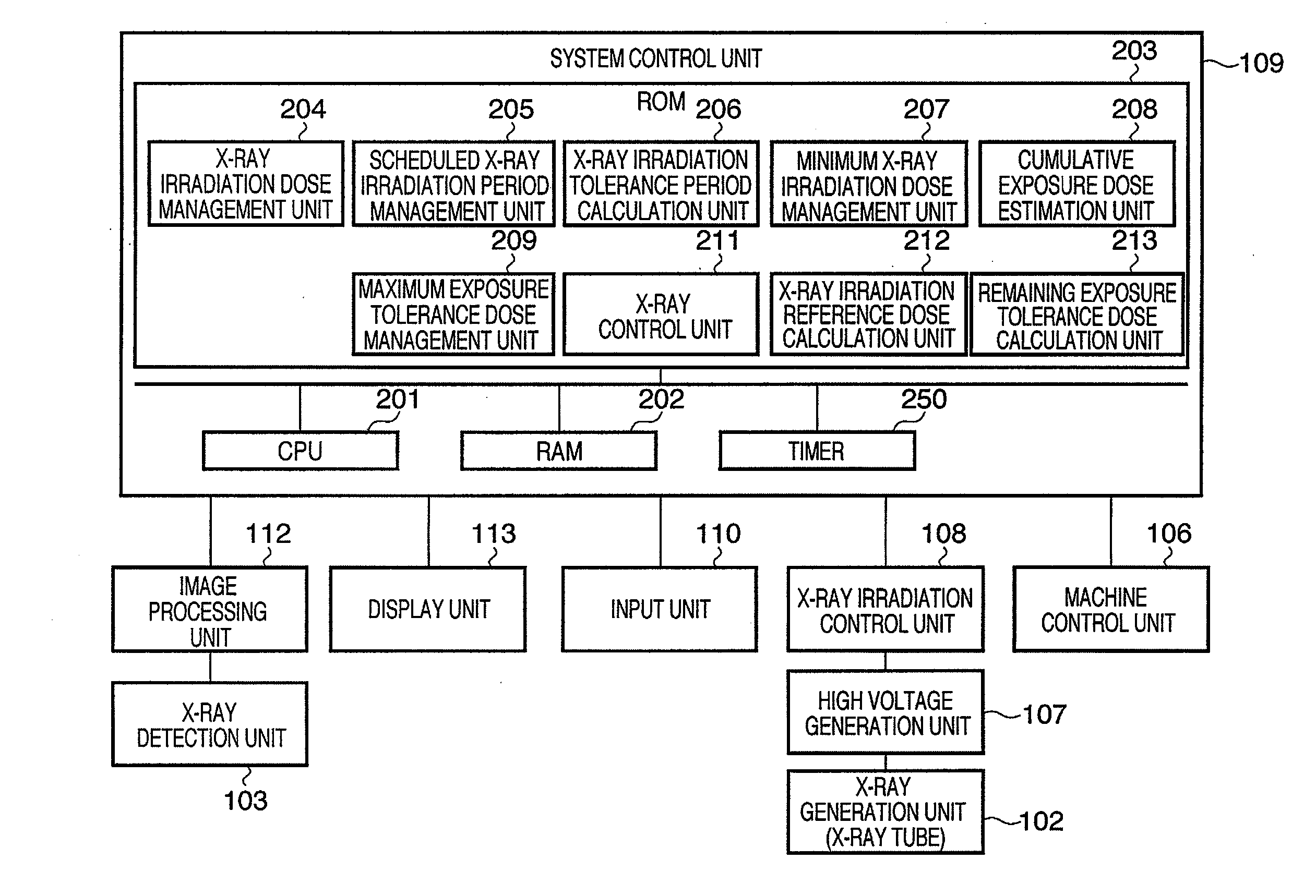
X-ray imaging apparatus and x-ray imaging method
InactiveUS20080317205A1Inhibiting excessive X-ray irradiationExcessive irradiationX-ray apparatusRadiation diagnosticsSoft x rayX-ray
An X-ray imaging apparatus includes an estimation unit (208) that estimates a cumulative exposure dose of X-rays irradiated onto an object, a remaining exposure tolerance dose calculation unit (213) that calculates a remaining exposure tolerance dose using a difference between a tolerated maximum exposure dose and the cumulative exposure dose, an X-ray irradiation tolerance period calculation unit (206) that calculates an X-ray irradiation tolerance period using a difference between a predetermined scheduled X-ray irradiation period and an actual irradiation period of X-rays irradiated onto the object, an X-ray irradiation reference dose calculation unit (212) that calculates an X-ray irradiation reference dose per unit time that will form a basis of X-ray irradiation based on the remaining exposure tolerance dose and the X-ray irradiation tolerance period, and a control unit (211) that controls X-ray irradiation onto the object by setting an X-ray irradiation dose per unit time within the X-ray irradiation tolerance period based on the X-ray irradiation reference dose.
Owner:CANON KK
Non-voxel-based broad-beam (NVBB) algorithm for intensity modulated radiation therapy dose calculation and plan optimization
ActiveUS8401148B2Optimization flexible and efficientImprove accuracyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyVoxelRadical radiotherapy
A method of calculating a dose distribution for a patient for use in a radiation therapy treatment plan. The method includes acquiring an image of a volume within the patient, defining a radiation source, and defining a reference plane oriented between the radiation source and the patient. The method also includes generating a radiation therapy treatment plan, wherein the plan includes a plurality of rays that extend between the radiation source and the patient volume, and calculating a three-dimensional dose volume for the patient volume from the plurality of rays that intersect the reference plane without first having to independently calculate a dose distribution on each of the plurality of rays. The method can also include displaying the three-dimensional dose volume.
Owner:TOMOTHERAPY INC
Treatment planning system and method for radiotherapy
ActiveUS20090154644A1Less precisionLow accuracyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDose calculation algorithmPlanning method
A treatment planning method and system for optimizing a treatment plan used to irradiate a treatment volume including a target volume, such as a tumor, is disclosed. According to the method, two dose calculation algorithms are used to develop the optimized treatment plan. A first dose calculation algorithm is used to obtain substantially complete dose calculations and a second, incremental, dose calculation algorithm is used to make more limited calculations. The incremental calculations may be performed, for example, with less precision, less accuracy or less scope (e.g., focused on a specific subvolume within the treatment volume) in order to reduce the time required to achieve an optimized plan. Each of the dose calculation algorithms may be iterated a plurality of times, and different cutoff criteria can be used to limit the number of iterations in a given pass. A treatment planning system of the invention uses software for implementing the complete and incremental dose calculation algorithms. The method and system are especially useful for IMRT and arc therapy where treatment plan optimization is particularly challenging.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
Radioactive source inversion method based on multi-algorithm
InactiveCN101477205ARebuild pollutionAccurate Radiation Source SpectroscopyX-ray spectral distribution measurementDosimetersPollutionDose calculation
The invention discloses a method for inversing a radiation source, which is to measure a PDD curve by a water tank or other radiation dosimetry measuring equipment. Information of the high accuracy radiation source can be acquired by the method, including photon energy spectrum, or proton energy spectrum, or electron energy spectrum and photon pollution and other radiation information. The method has the advantages that: the information of the photon energy spectrum, the electron energy spectrum, the proton energy spectrum, photon pollution and other radiation source information of the radiation source can be simultaneously reestablished; the defect that the prior energy spectrum calculation method can not accurately acquire multiple radiation source information can be overcome; while the accurate energy spectrum of the radiation source is accurately acquired, the information of the photon pollution and other information can be acquired; correct information of the radiation source can be provided for dose calculation; information of scattered or continuous energy spectrum and the photon pollution can be acquired; and the accurate radiation source can be realized by a plurality of algorithms so as to solve the problem that the prior single algorithm can not ensure that the inverse of the energy spectrum has a solution.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
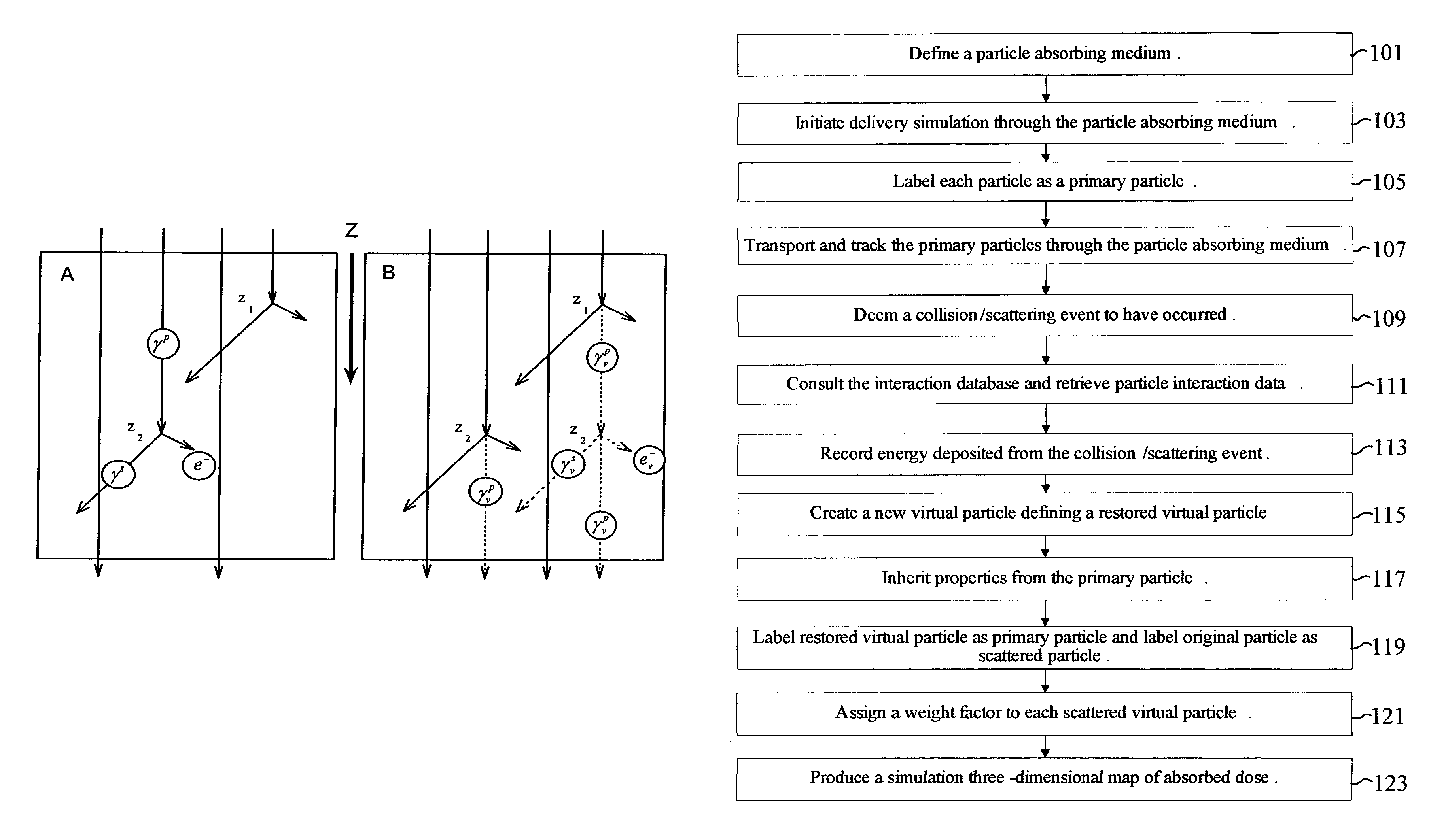
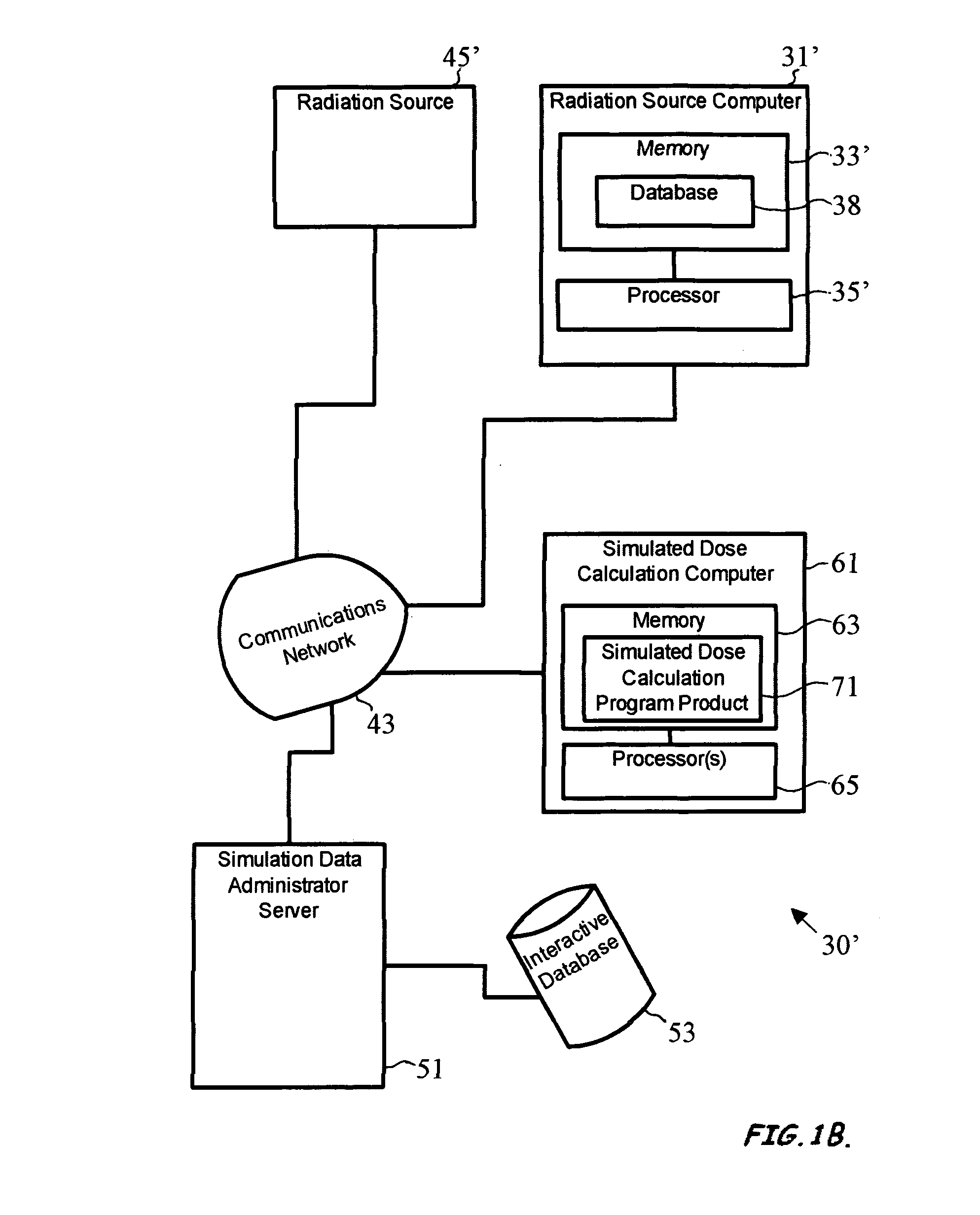
Variance reduction simulation system, program product, and related methods
ActiveUS8125813B2Improve computing efficiencyCost efficientDigital storageProbabilistic CADParticle interactionComputer science
A system to provide enhanced computational efficiency in a simulation of particle transport through a medium, program product, and related methods are provided. The system can include a simulation data administrator server having access to an interaction database including records related to parameters describing interactions of particles in an absorbing medium to provide particle interaction parameters, and a simulated dose calculation computer in communication with the simulation data administrator server through a communications network. The system can also included simulated dose calculation program product stored in memory of the simulated dose calculation computer and including instructions that when executed by a processor causes the processor to perform for each of a plurality of particles deliverable from a particle source the operations of providing parameters for a medium to perform a Monte Carlo simulation to develop a map of simulated absorbed dose in the medium, and artificially adjusting simulation particle fluxes to achieve a substantially constant variance throughout a depth of the medium.
Owner:BEST MEDICAL INT
Cone-beam CT imaging scheme
InactiveUS8144829B2Reduce doseEliminate the effects ofReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationImaging qualityCbct imaging
A general imaging scheme is proposed for applications of CBCT. The approach provides a superior CBCT image quality by effective scatter correction and noise reduction. Specifically, in its implementation of CBCT imaging for radiation therapy, the proposed approach achieves an accurate patient setup using a partially blocked CBCT with a significantly reduced radiation dose. The image quality improvement due to the proposed scatter correction and noise reduction also makes CBCT-based dose calculation a viable solution to adaptive treatment planning.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Multi charged particle beam writing apparatus, and multi charged particle beam writing method
A multi charged particle beam writing apparatus includes a dose calculation unit to calculate a first dose resolving the resist of the target object, for a first beam of the multiple beams, corresponding to a pattern forming region, in which a pattern is arranged, and to calculate a second dose not resolving the resist, for a second beam of the multiple beams, corresponding to a no-pattern forming region, which surrounds the whole perimeter of the pattern and in which no pattern is arranged, and a deflection control unit to control a plural blankers so that a dose of the first beam is to be the first dose calculated and a dose of the second beam is to be the second dose calculated.
Owner:NUFLARE TECH INC
X-ray ct apparatus, scan plan assistance apparatus and method for scan plan assistance
An X-ray CT apparatus that transmits X-rays toward a subject on the basis of a set scan condition and reconstructs images from detected X-rays that passes through the subject, including a scan plan setting unit configured to set the scan condition, a reference dose storage unit configured to store reference dose information, including an relation between an attribute information about a plurality of kinds of subjects and reference doses to be referenced for an exposure dose, and an exposure dose calculation unit configured to calculate the exposure dose corresponding to the set scan condition in accordance with the timing of setting of the scan condition.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Dose distribution simulating method for nuclear installation decommissioning radiation field
ActiveCN107330187ASimple stepsRealize distributed computingDesign optimisation/simulationNeural architecturesNetwork modelRadiation field
The invention provides a dose distribution simulating method for a nuclear installation decommissioning radiation field. The method comprises the steps that firstly, the geometrical information, which needs to be simulated in a nuclear installation decommissioning scene, of the radiation field, the position of a radiation source and the geometrical information of a shielding object are determined; secondly, according to the position of the radiation source and the position of the shielding object, a dose monitoring point distributing network is built and used for extracting sample data; thirdly, according to whether there is the shielding object in the radiation field or not, dose distribution calculation is divided into partitioned dose calculation and non-partitioned dose calculation; fourthly, according to the sample data, a radial basis neural network model is built; fifthly, the dose value of any one point is calculated through an inverse distance weighted method; sixthly, the dose distribution of the radiation field is calculated. By means of the dose distribution simulating method, no radiation source term models are needed, the dose distribution of the radiation field is calculated by depending on a small amount of dose monitoring points, and the steps are simpler. By means of the dose distribution simulating method, the calculation of the dose distribution of the radiation field affecting the shielding effect is achieved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Radiotherapy scheme optimization system capable of automatically determining weight of target function
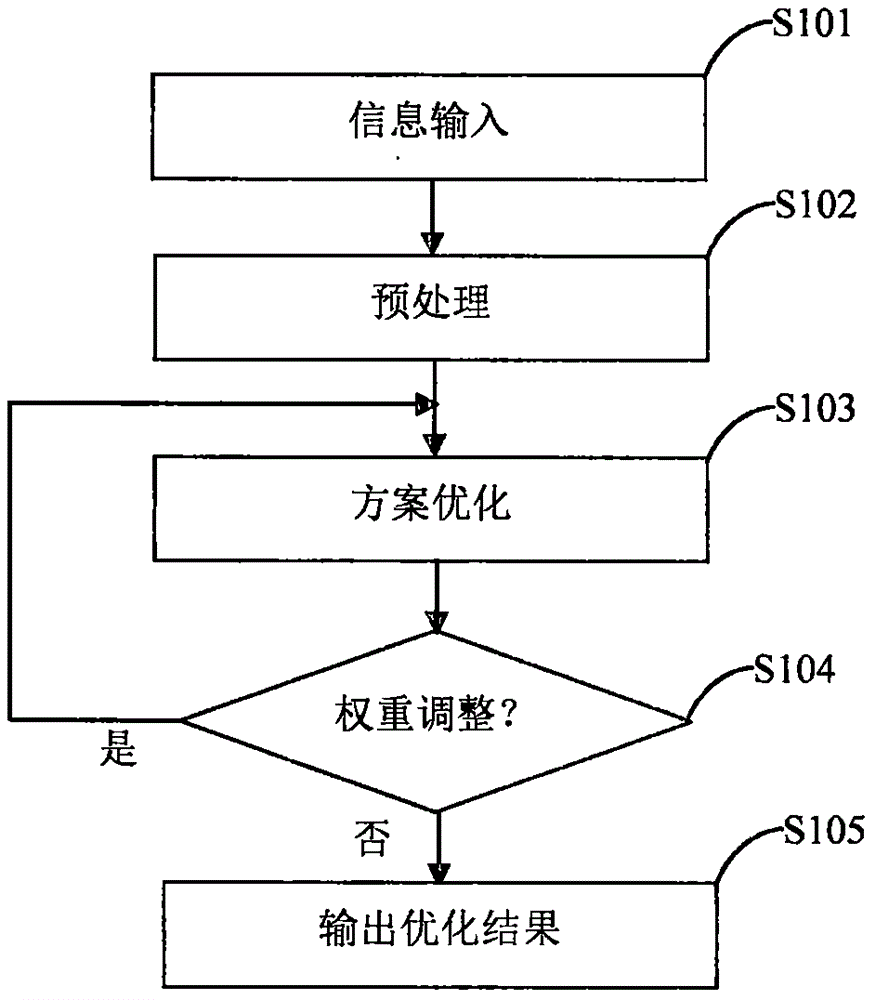
ActiveCN105930636AGuaranteed to proceed normallySatisfaction GuaranteeMedical automated diagnosisSpecial data processing applicationsWeight adjustmentComputer science
The invention discloses a radiotherapy scheme optimization system capable of automatically determining the weight of a target function. The radiotherapy scheme optimization system includes an information input module, a pretreatment module, a scheme optimization module, a weight adjustment module, and a scheme optimization result output module; the information input module acquires patient three-dimensional information, organ drawing information, treatment head information, target function information, and DV restricted parameters of organs used in a target function; the pretreatment module calculates dose deposition matrixes of different radiation directions through a dose calculation engine; the scheme optimization module performs scheme optimization through a scheme optimization engine; the weight adjustment module calculates dose distribution of each organ and the value of each sub target function according to input information of the scheme optimization module, and determines if the all the sub target functions meet an optimization ending condition; and the scheme optimization result output module outputs the scheme optimization information. The automatic scheme optimization is an iterative process without inputting an ideal DVH curve.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Analyte sensor and medicant delivery data evaluation and error reduction apparatus and methods
Apparatus and methods for error modeling and correction in one or both of (i) a partially or fully implanted or non-implanted medicant delivery mechanism (such as a pump), and (ii) implanted physiologic parameter sensor. In one exemplary embodiment, the apparatus and methods employ a training mode of operation, whereby the apparatus conducts “machine learning” to model one or more errors (e.g., unmodeled variable system errors) associated with the medicant dose calculation process, and (ii) generation of a medicant delivery operational model (based at least in part on data collected / received in the training mode), which is applied to correct or compensate for the errors during normal operation of the sensor and pump system. This enhances accuracy of medicant delivery, such as over the lifetime of an implanted pump at a single implantation site, or during multiple relocations of a transcutaneously implanted pump), and enables “personalization” of the pump to each user.
Owner:GLYSENS
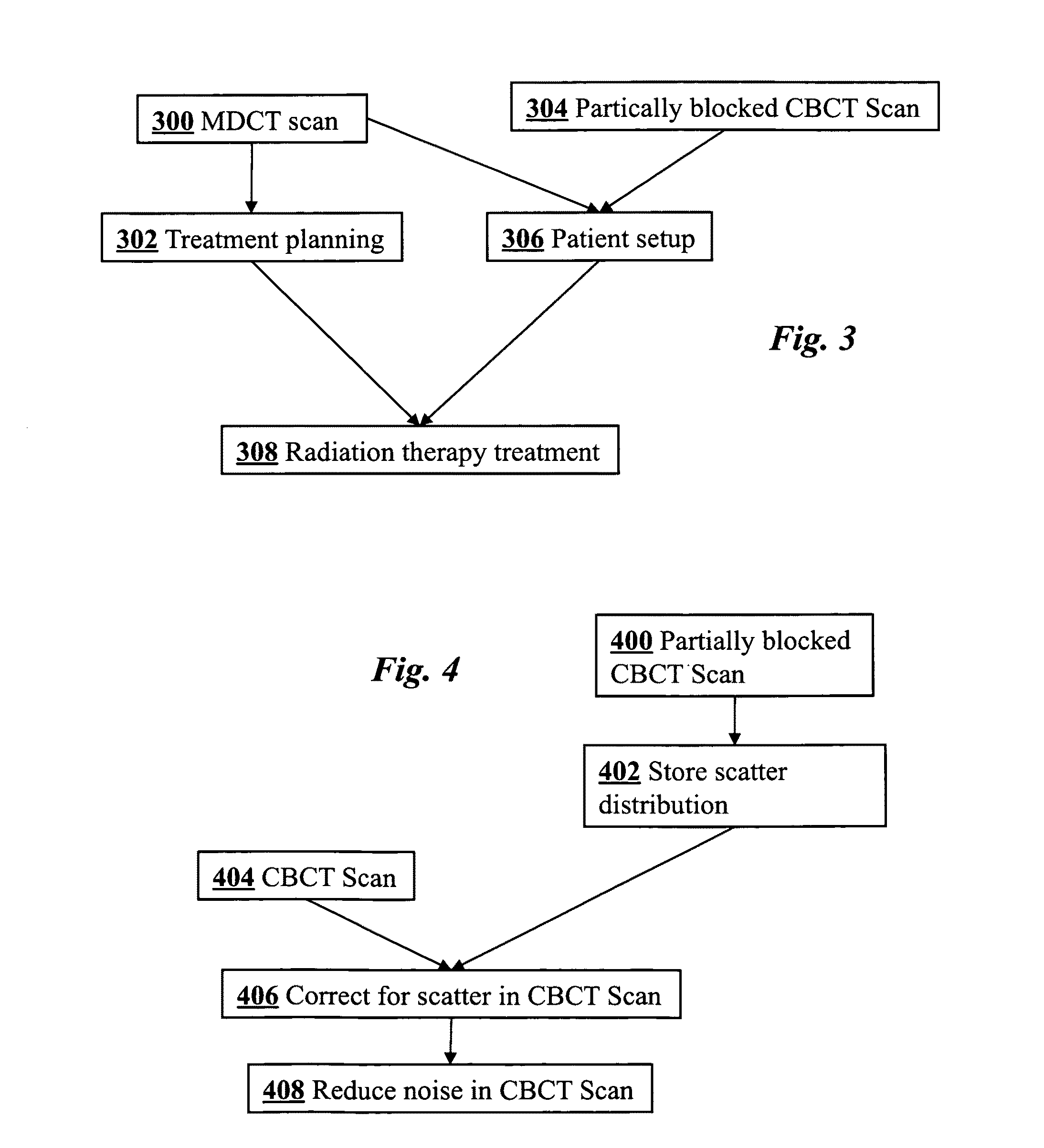
Offline dose verification method based on improved CBCT (cone beam computed tomography) images
InactiveCN104027128AAvoid imaging discrepanciesImprove accuracyImage analysisComputerised tomographsDose verificationCalibration curve
The invention discloses an offline dose verification method based on improved CBCT (cone beam computed tomography) images. The offline dose verification method includes: subjecting the CBCT images of an individual patient to scatter correction on the basis of Monte-Carlo simulation to acquire a first CBCT image; rectifying the first CBCT image with a planned CT (computed tomography) image to acquire target-region deformation field information; verifying outline information of the planned CD image according to the target-region deformation field information, transplanting the verified outline information to the CBCT images to acquire a second CBCT image; establishing HU-ED calibration curves of the CBCT images according to average HU value of a particular tissue area of the individual patient in the second CBCT image and ED value of a particular tissue area of the planned CT image; performing dose calculation and planned validation on the basis of the second CBCT image, the HU-ED calibration curves, the planned CT and standard CT-ED calibration curves. By the technical scheme, treatment time and cost of the patient can be saved, and accurate adaptive radiation therapy and individual radiation therapy are realized.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
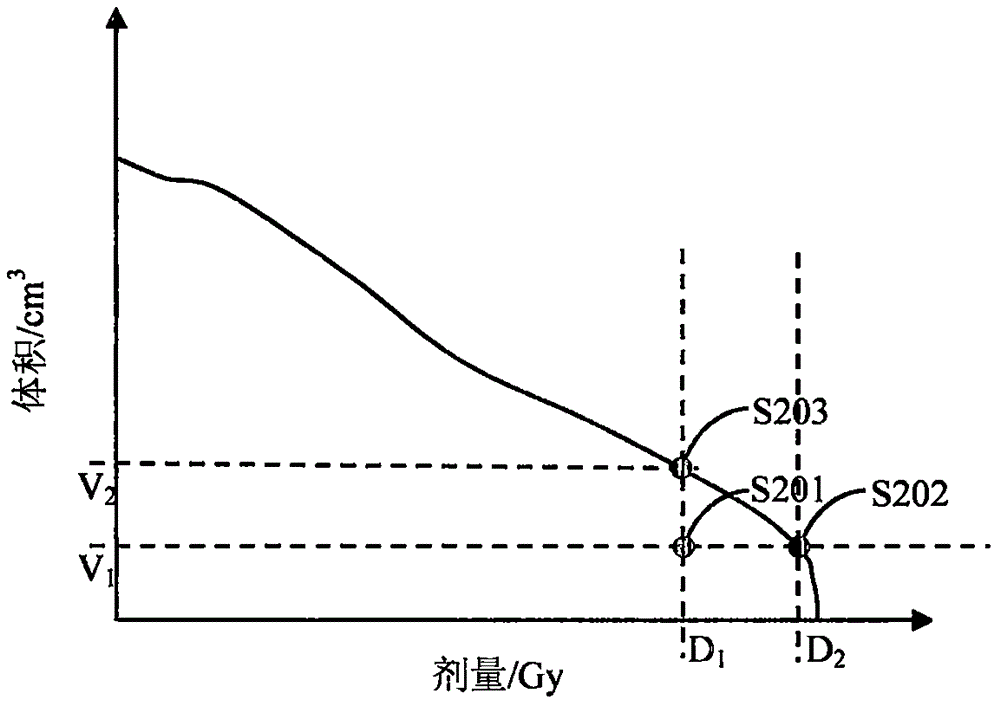
System and method of calculating dose uncertainty
ActiveUS8363784B2Maximum flexibilityExtended treatment timeMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesLocal control/monitoringMedicineDose calculation
A dose calculation tool operable to generate a variance map that represents a dose uncertainty. The variance map illustrates on a point-by-point basis where high uncertainty in the dose may exist and where low uncertainty in the dose may exist. The dose uncertainty is a result of an error in one or more data parameters related to a delivery parameter or a computational parameter.
Owner:TOMOTHERAPY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com