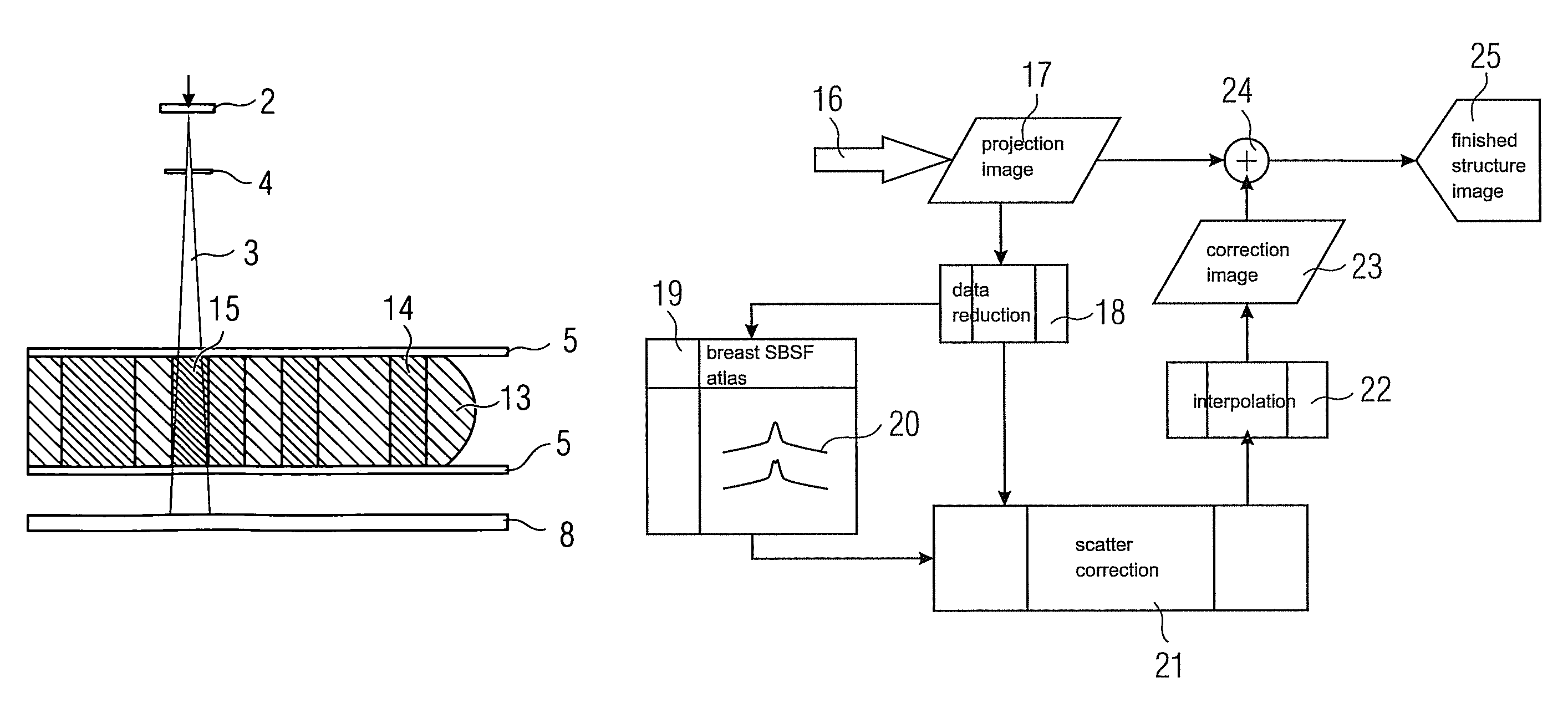
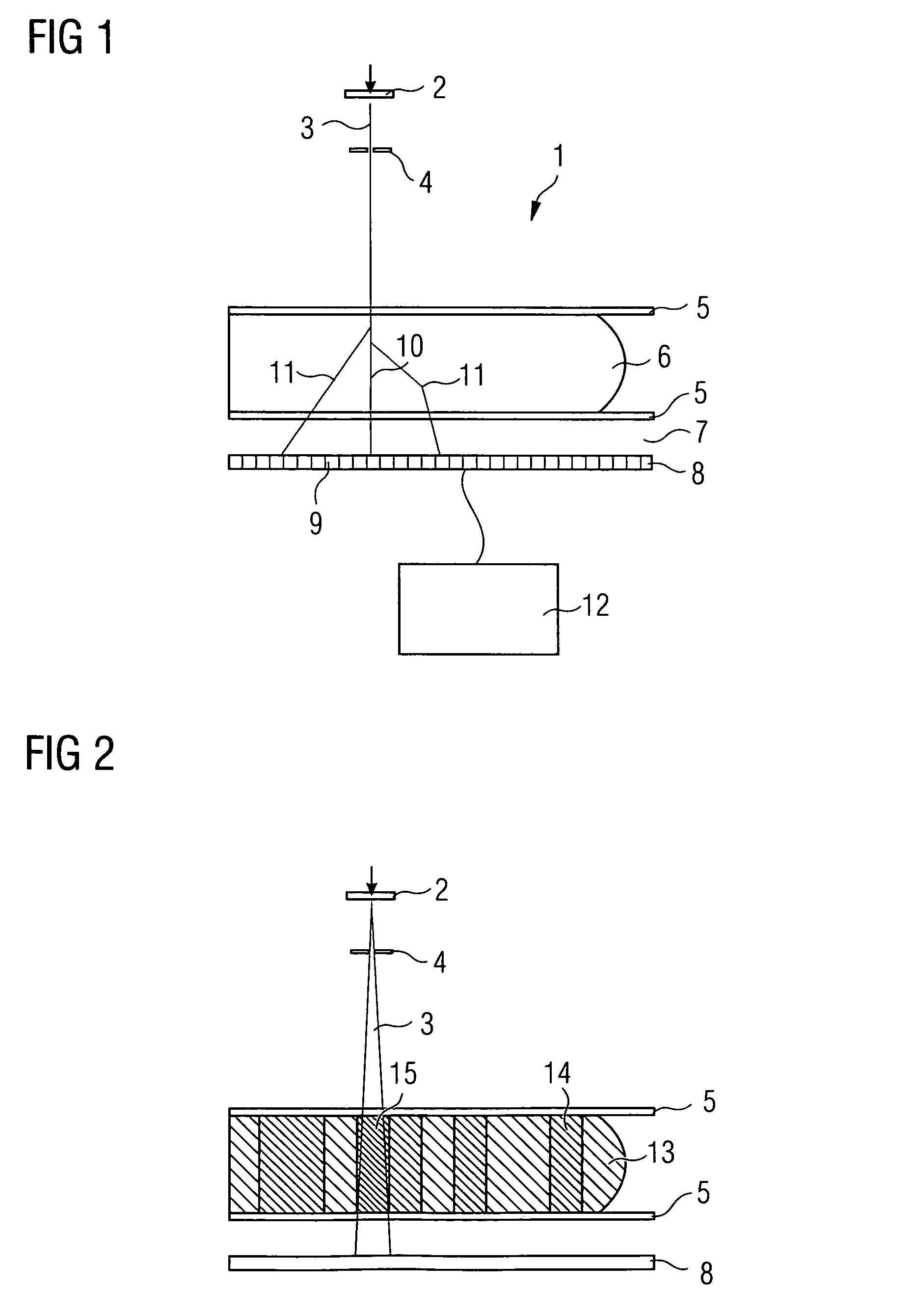
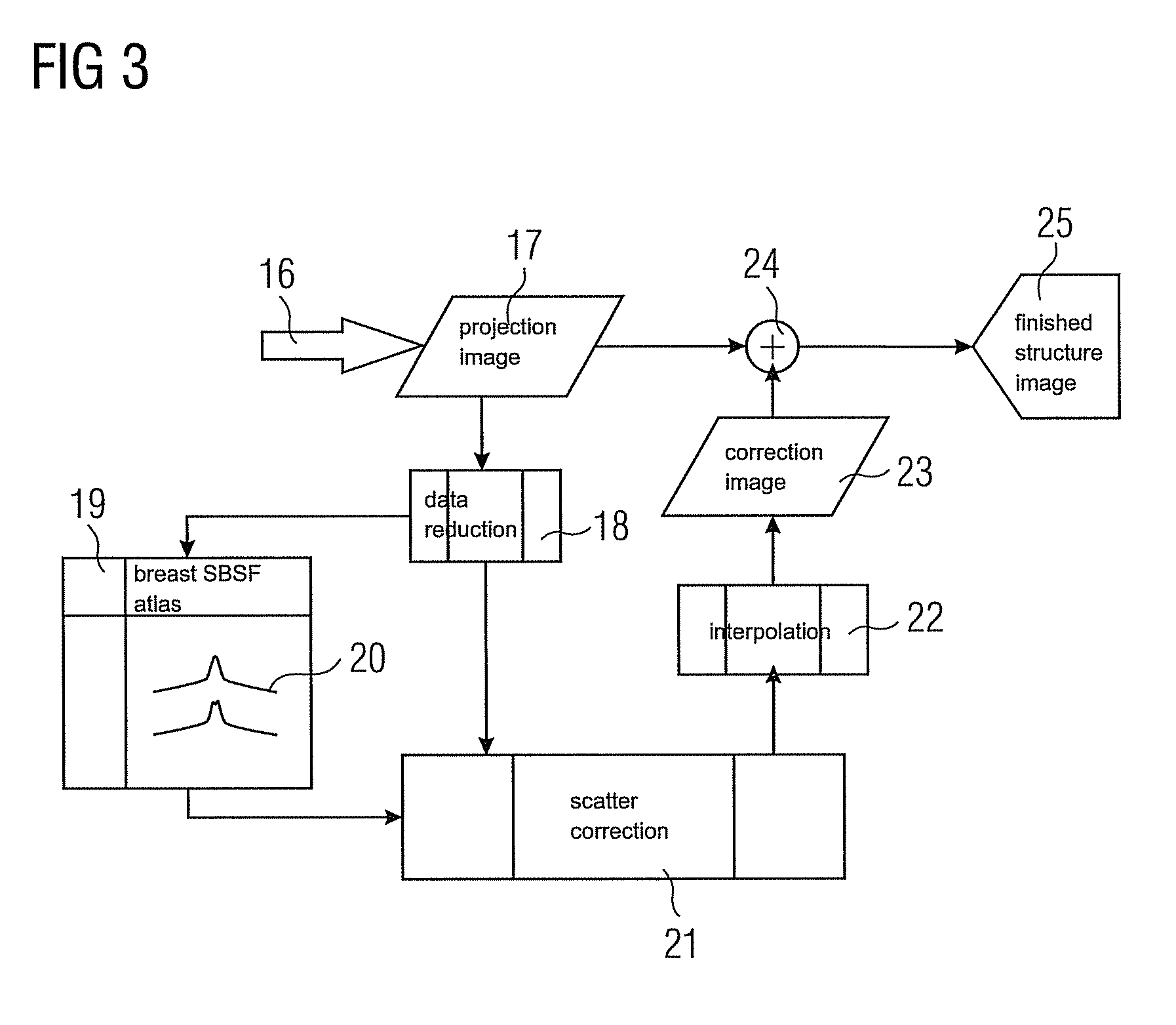
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
199 results about "Scatter correction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
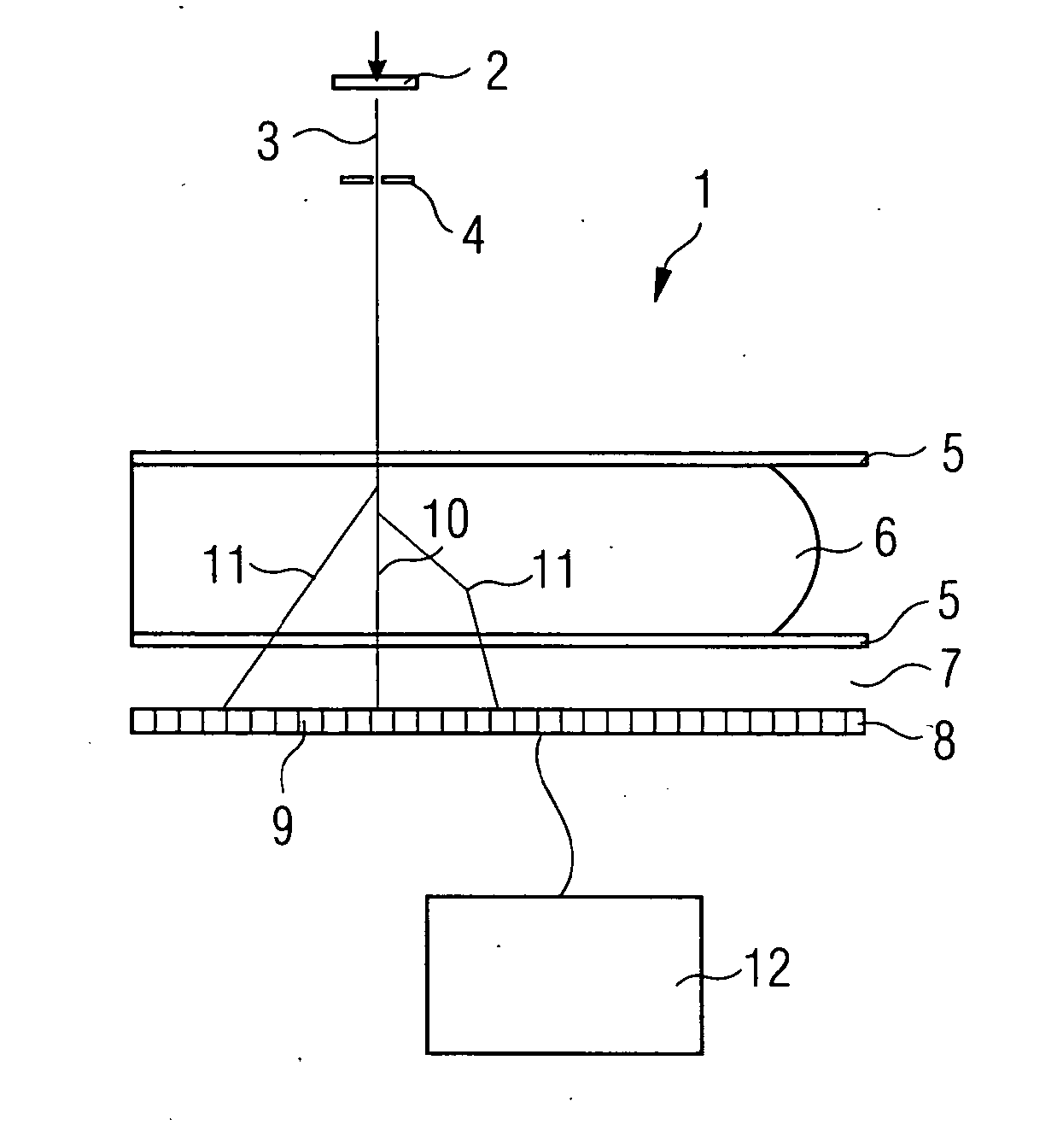
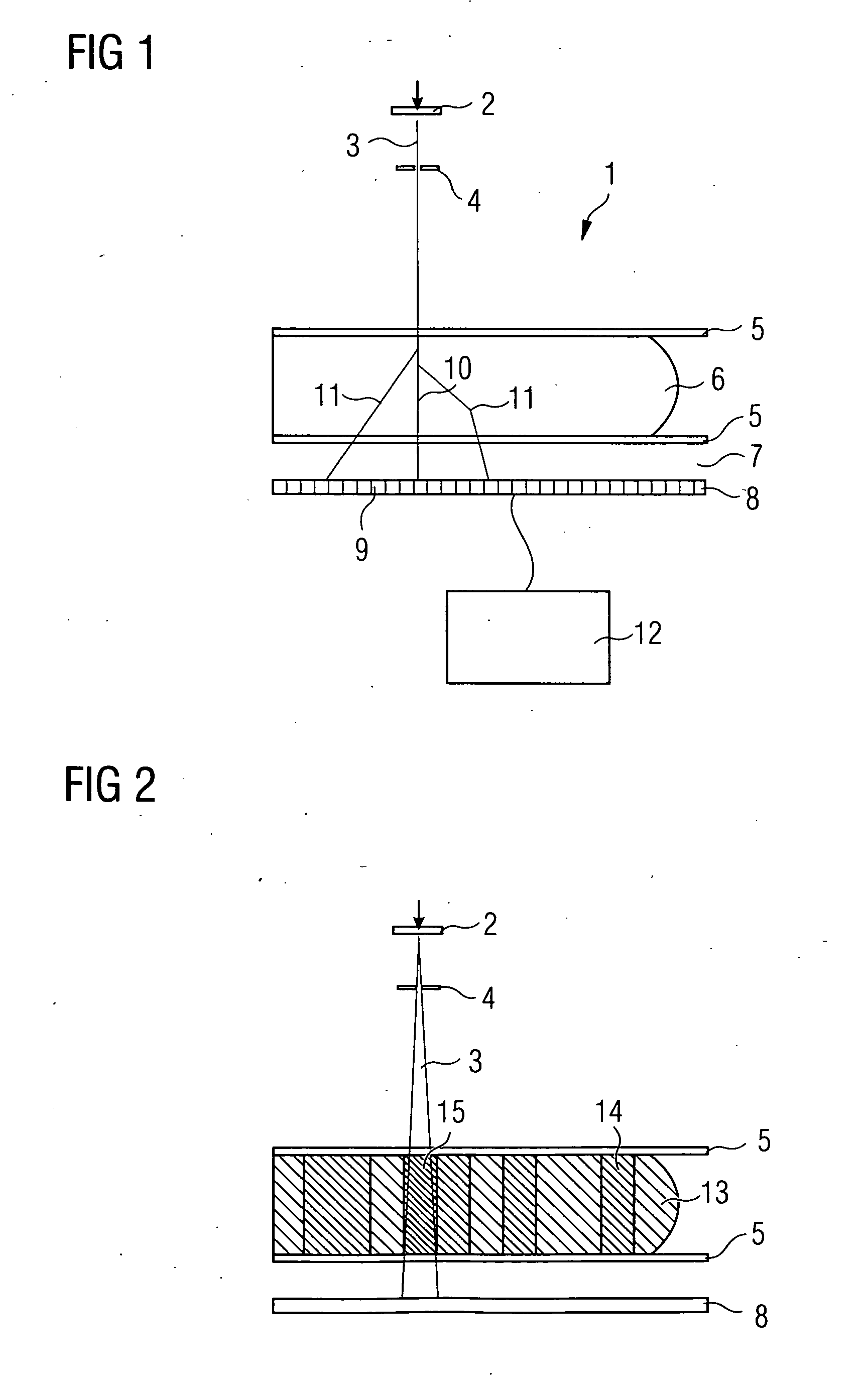
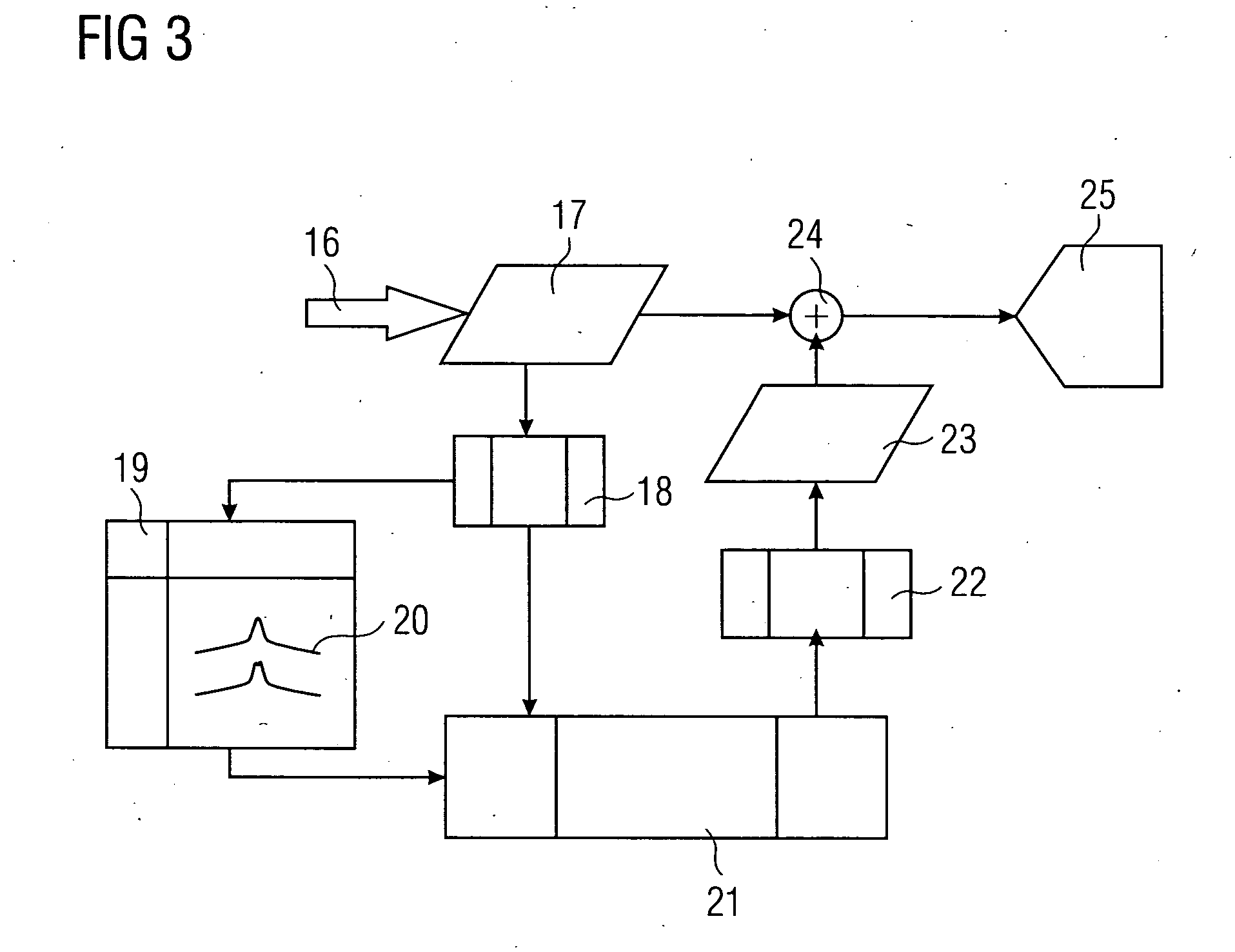
Cone-beam CT imaging scheme
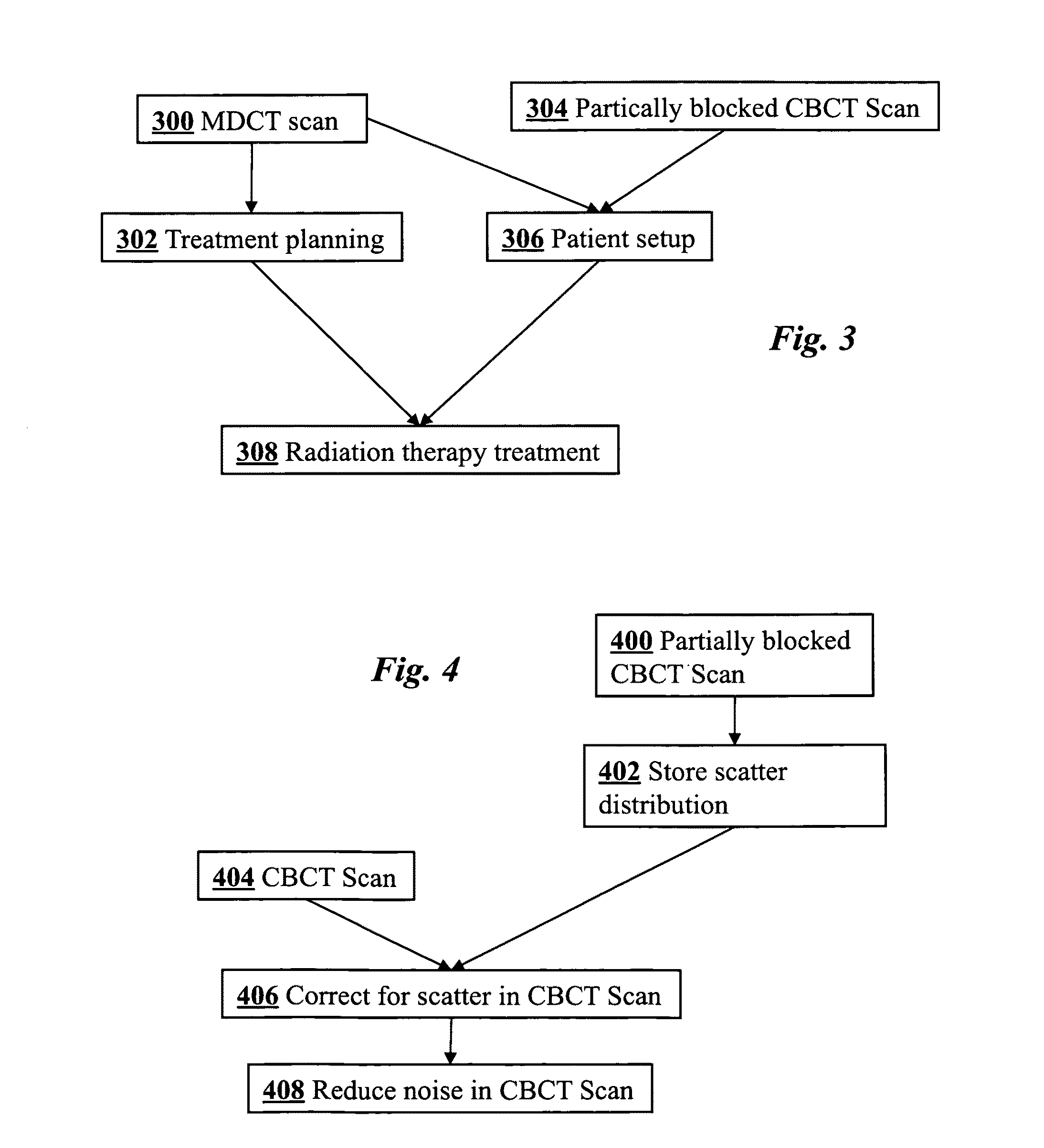
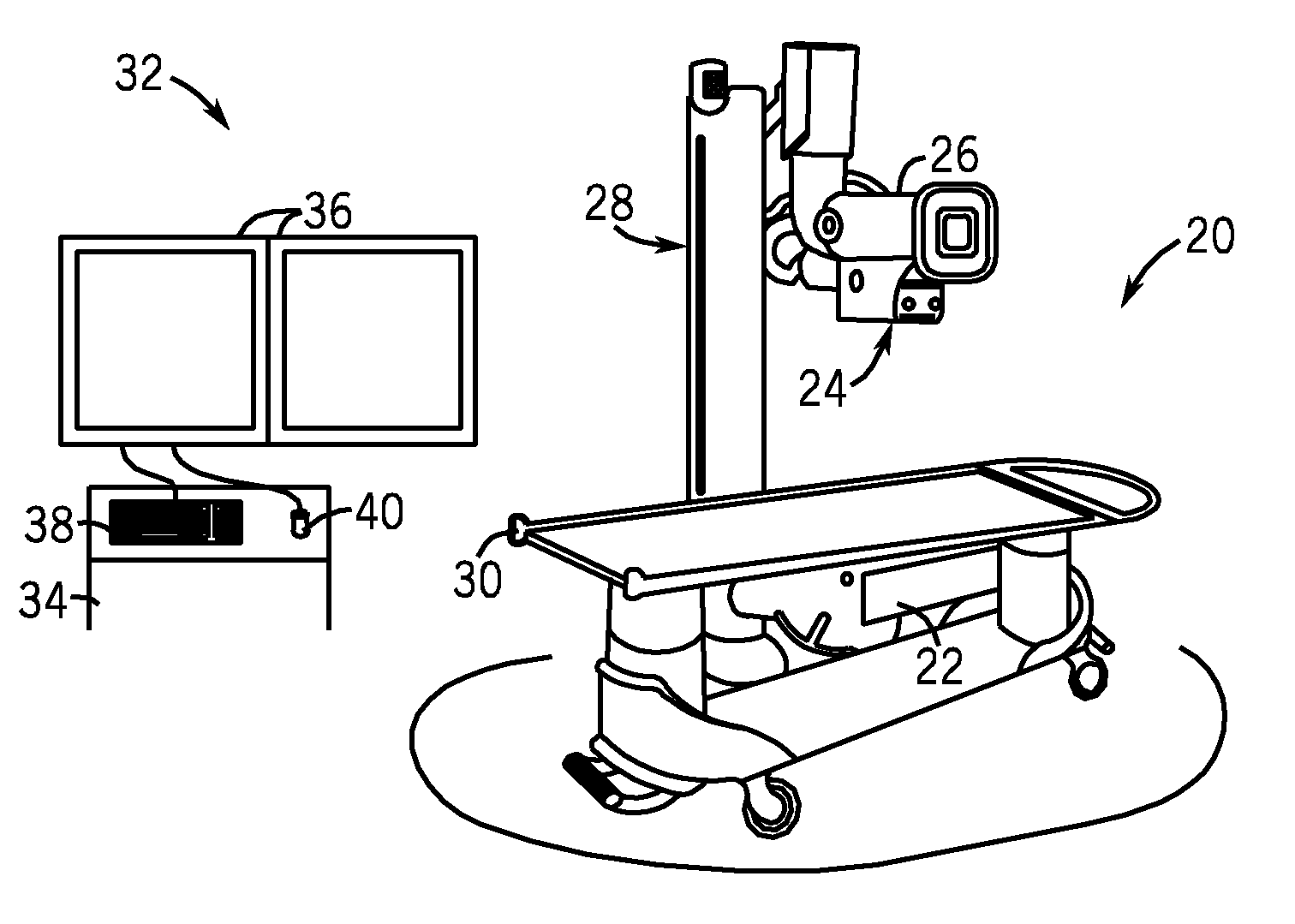
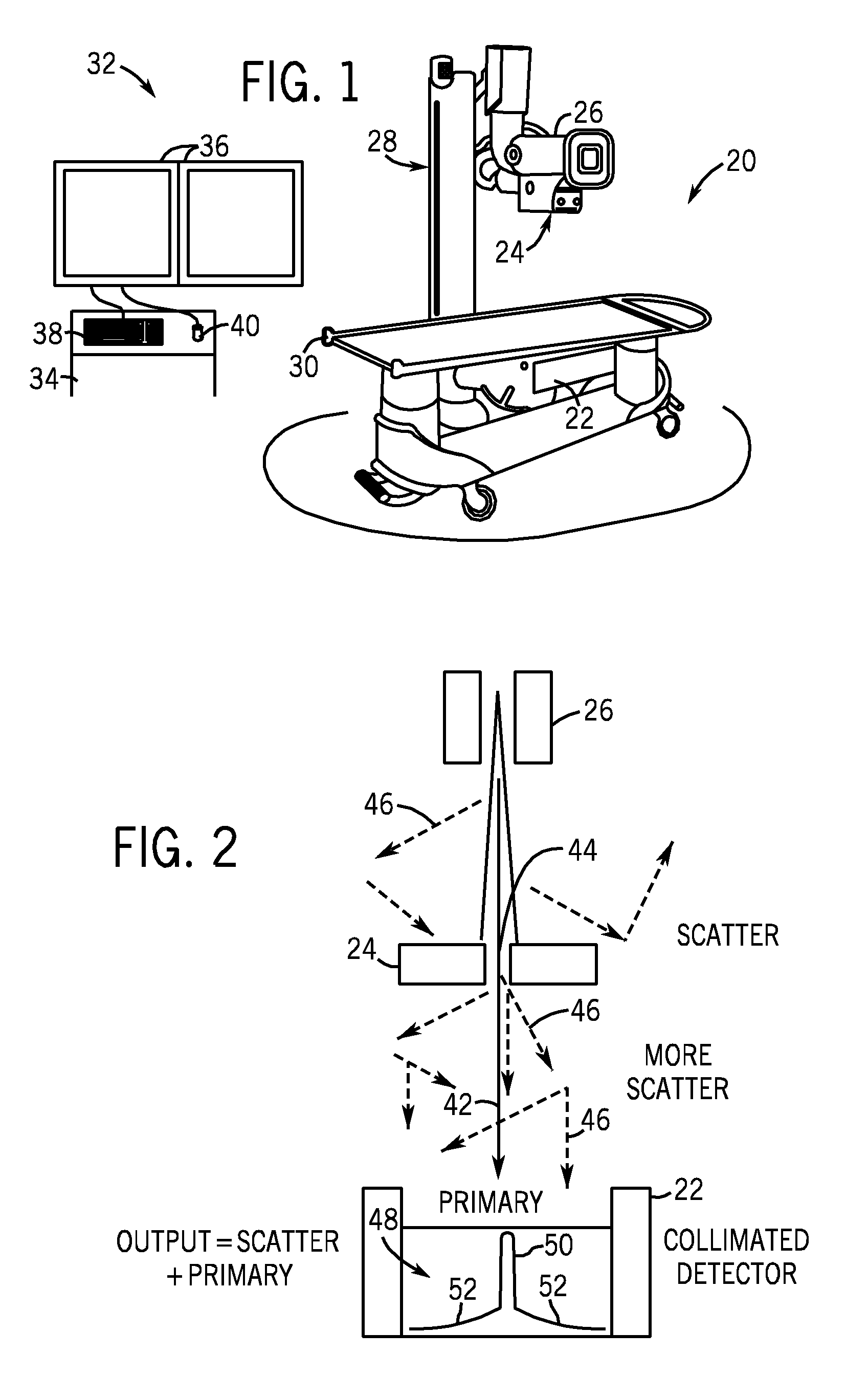
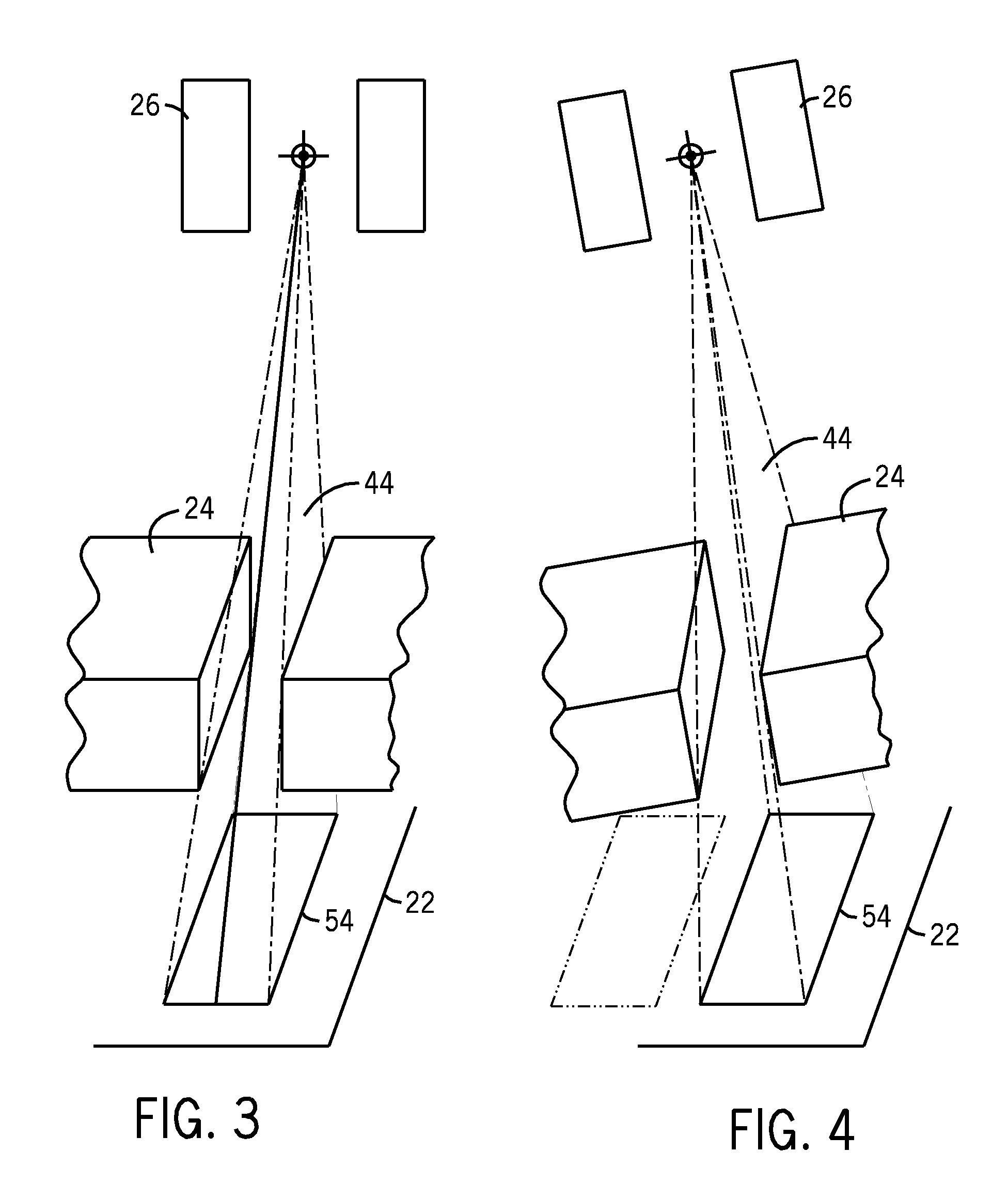
InactiveUS20090225932A1Reduce noiseReduce doseReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationImaging qualityCbct imaging
A general imaging scheme is proposed for applications of CBCT. The approach provides a superior CBCT image quality by effective scatter correction and noise reduction. Specifically, in its implementation of CBCT imaging for radiation therapy, the proposed approach achieves an accurate patient setup using a partially blocked CBCT with a significantly reduced radiation dose. The image quality improvement due to the proposed scatter correction and noise reduction also makes CBCT-based dose calculation a viable solution to adaptive treatment planning.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
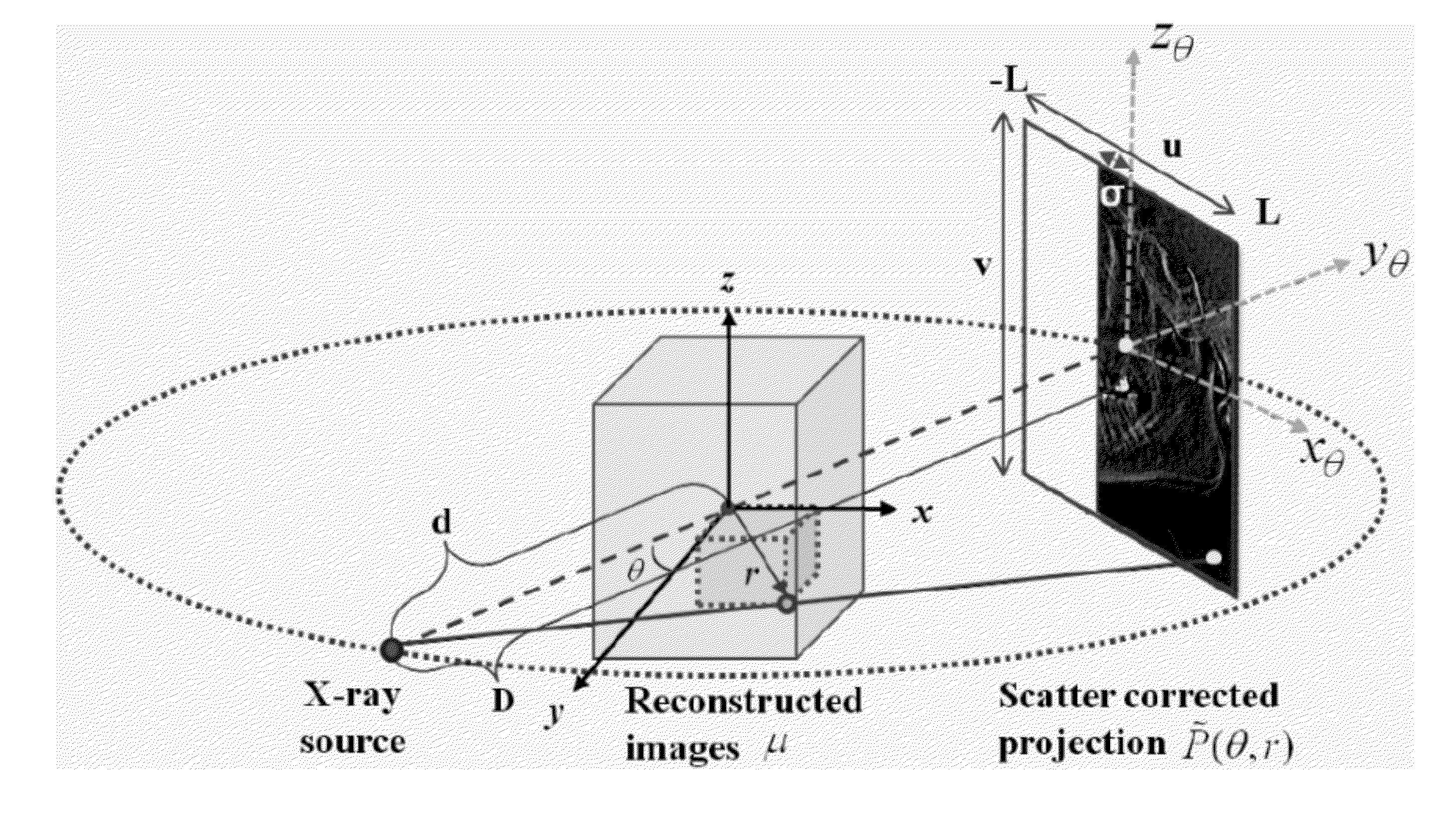
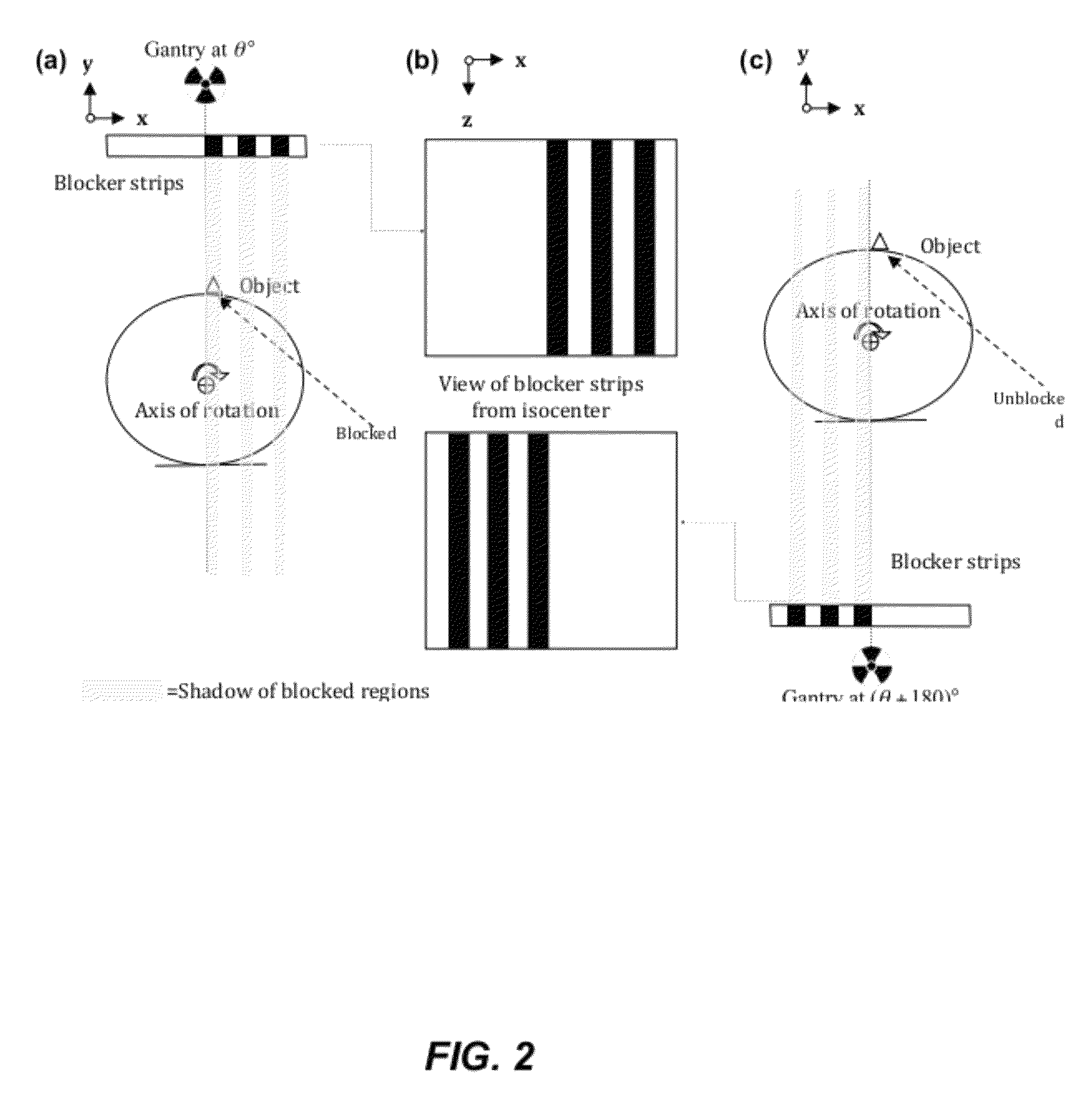
Systems and Methods for Simultaneous Acquisition of Scatter and Image Projection Data in Computed Tomography
InactiveUS20120207370A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationComputed tomographyRegularization algorithm
A method of acquiring scatter data and image projection data in computed tomography is provided that includes attenuating a radiation source using a pattern of blockers arranged to provide blocked and unblocked regions of the radiation source, and acquiring image data and scatter data of a target using an imaging device. A scatter map in the projection image can be estimated by interpolation and / or extrapolation of the projection image using an appropriately programmed computer, subtracting the estimated scatter map from the projection image to obtain scatter-corrected projections, reconstructing a CBCT volume using a total variation regularization algorithm, and applying an iterative regularization process to suppress the noise level on the reconstructed CBCT volume. Reconstructing a CBCT volume can include using a total variation regularization algorithm and applying an iterative regularization process to suppress the noise level on the reconstructed CBCT volume, where scatter-induced artifacts are corrected in the projection image.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
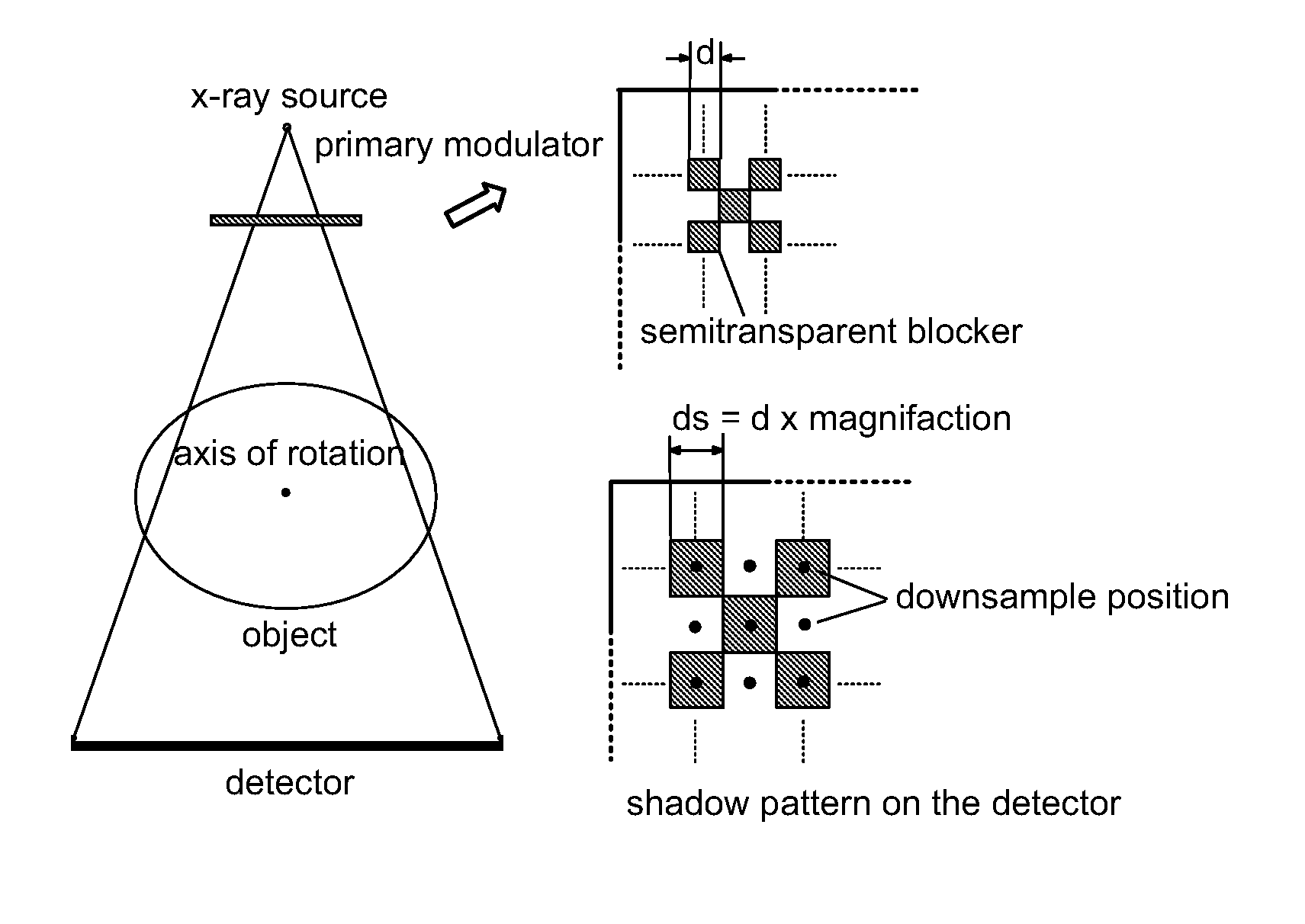
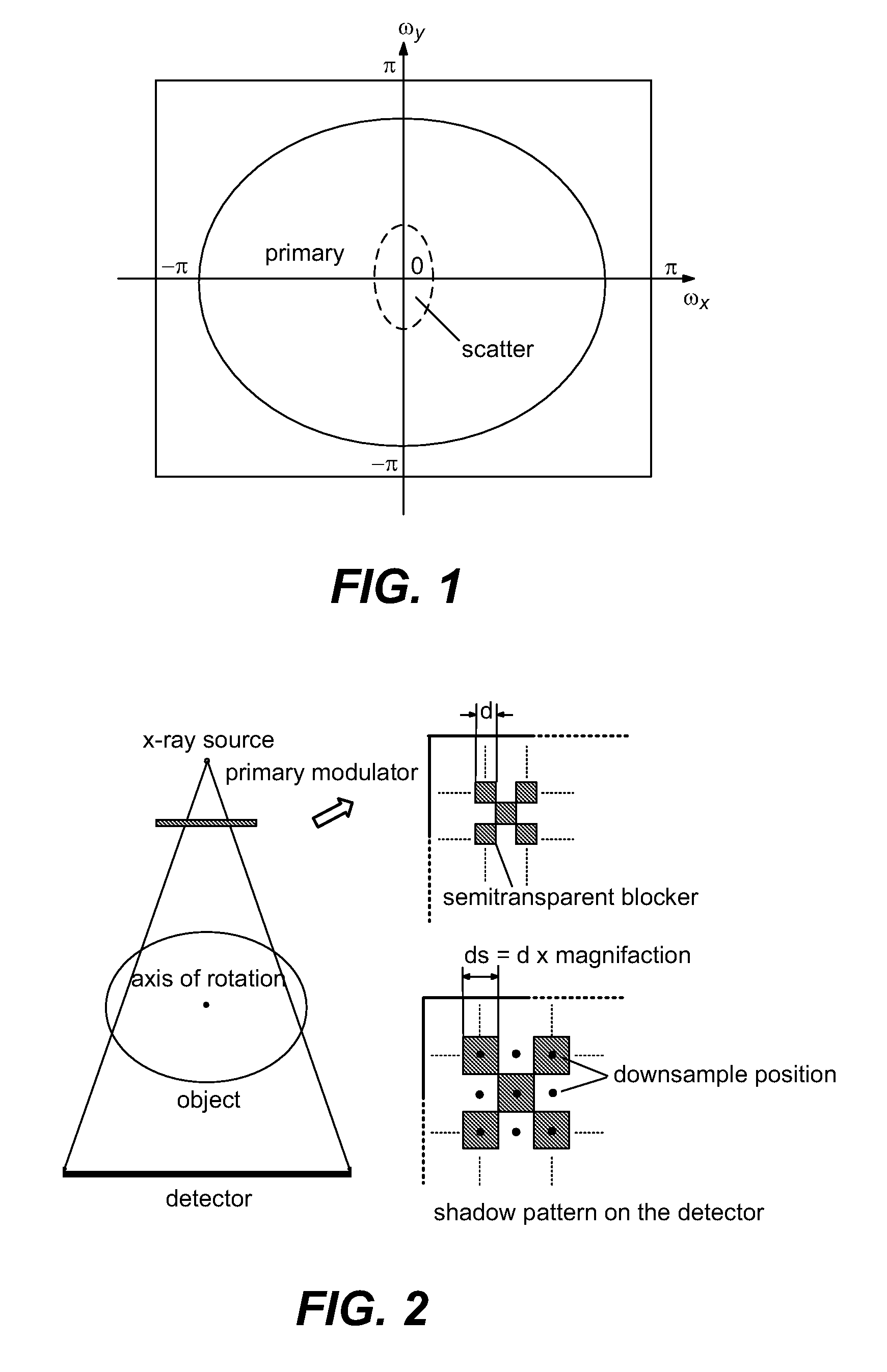
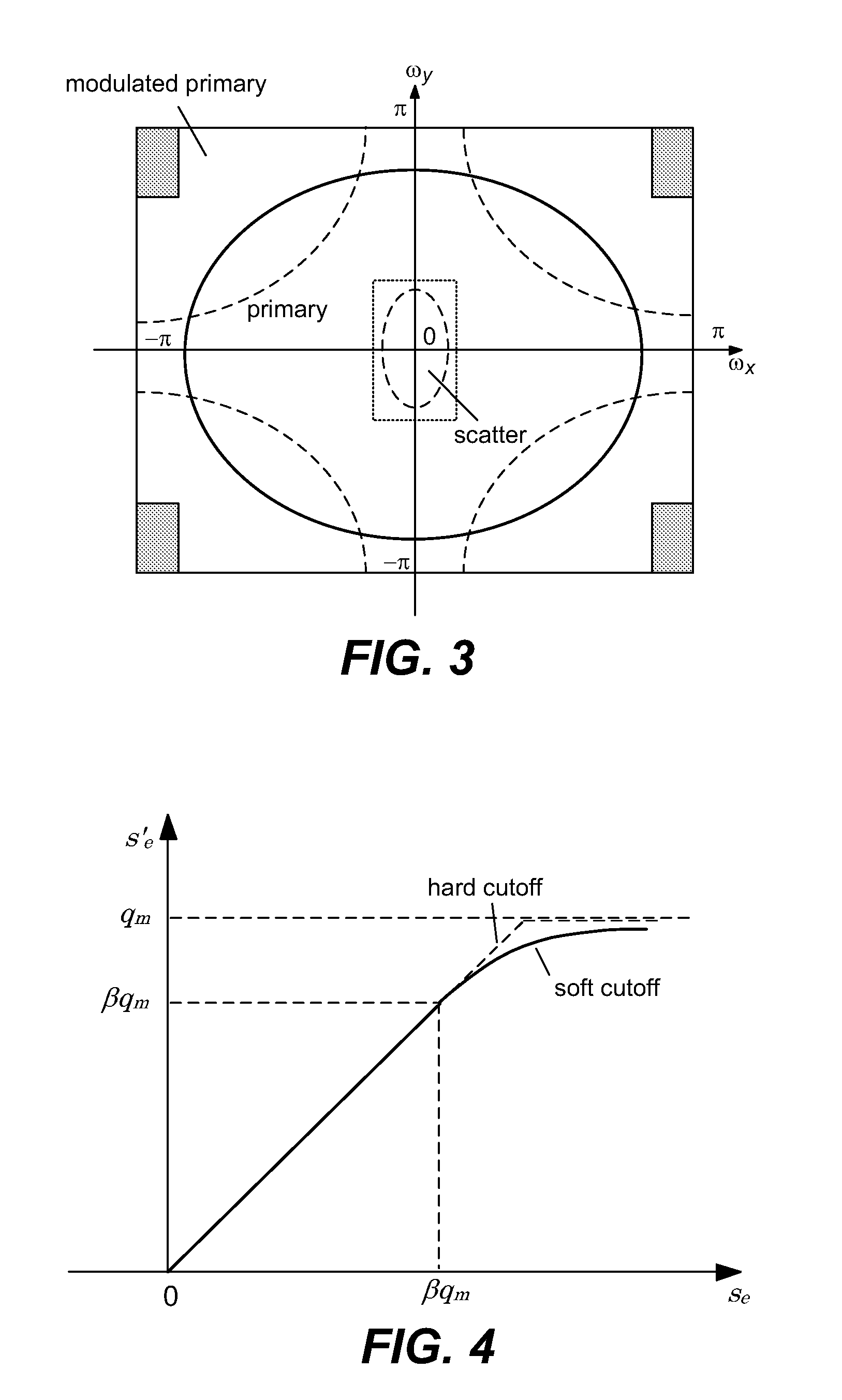
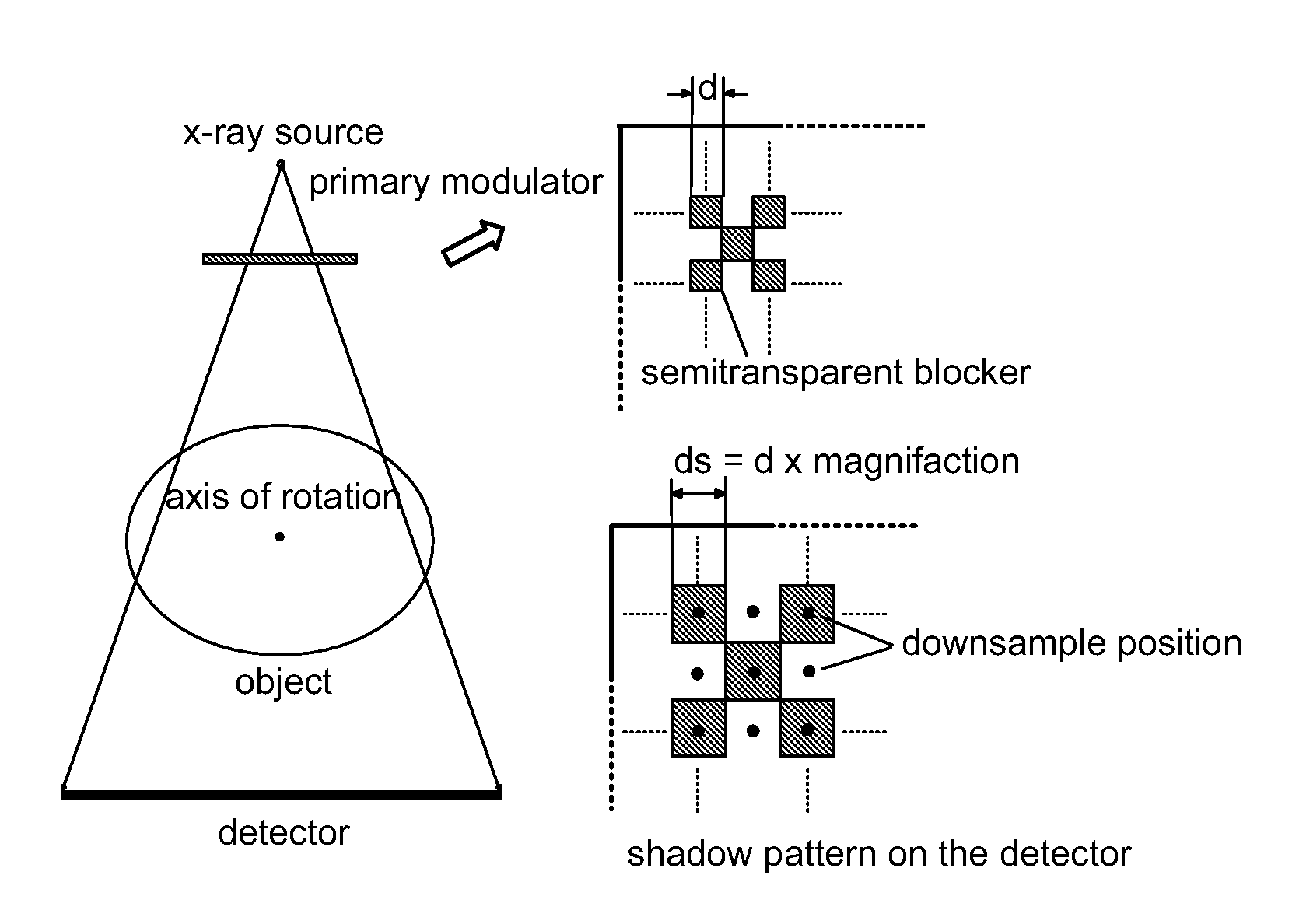
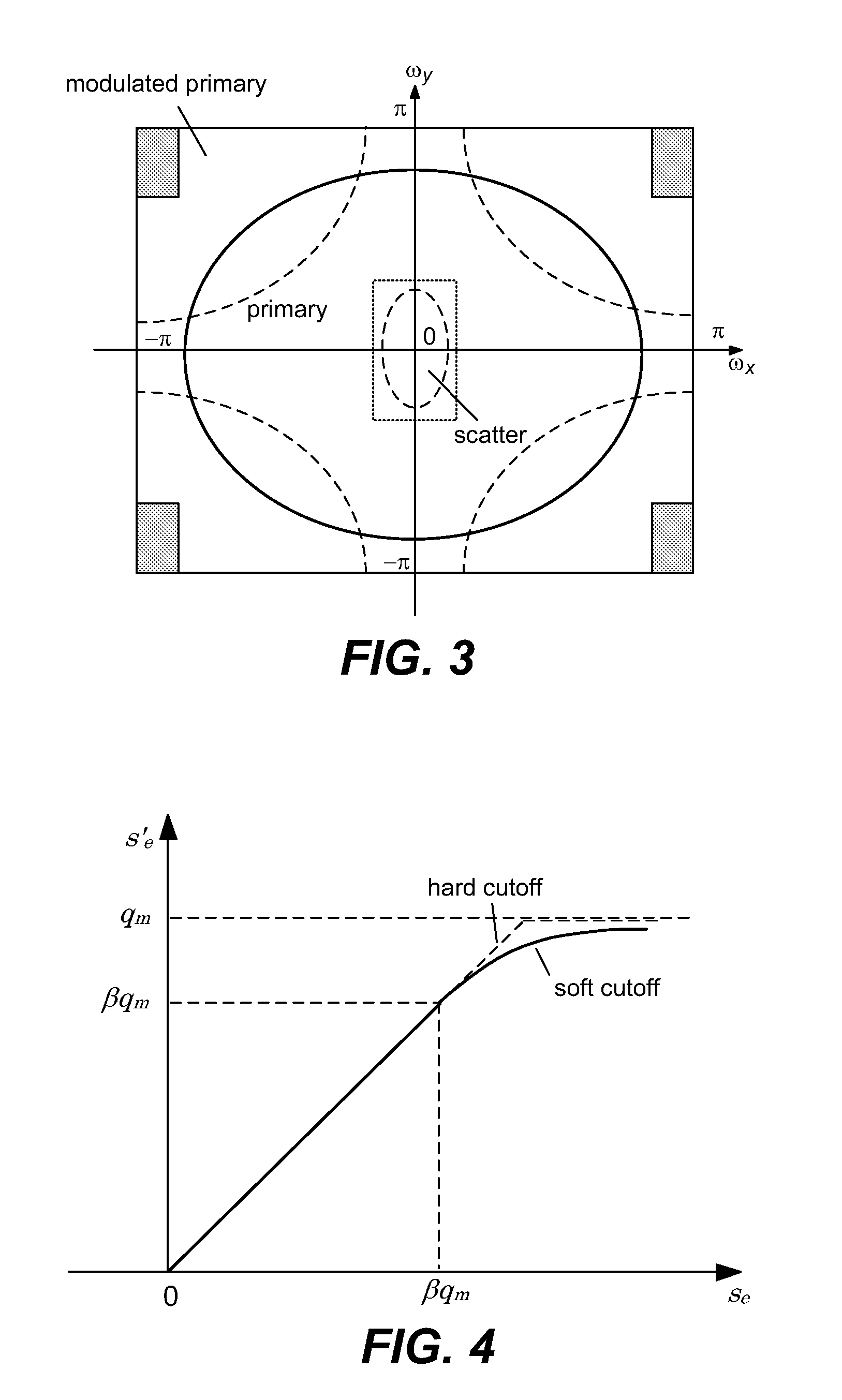
Scatter correction for x-ray imaging using modulation of primary x-ray spatial spectrum
ActiveUS7463712B2Efficient transferMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayX ray image
Scatter radiation in an x-ray imaging system including an x-ray source and an x-ray detector is separated by using amplitude modulation to translate the spatial frequency of a detected x-ray beam to a higher frequency and provide separation from low frequency scatter signal. The low frequency content of the detected x-ray beam is then obtained by demodulating the detected modulated signal.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
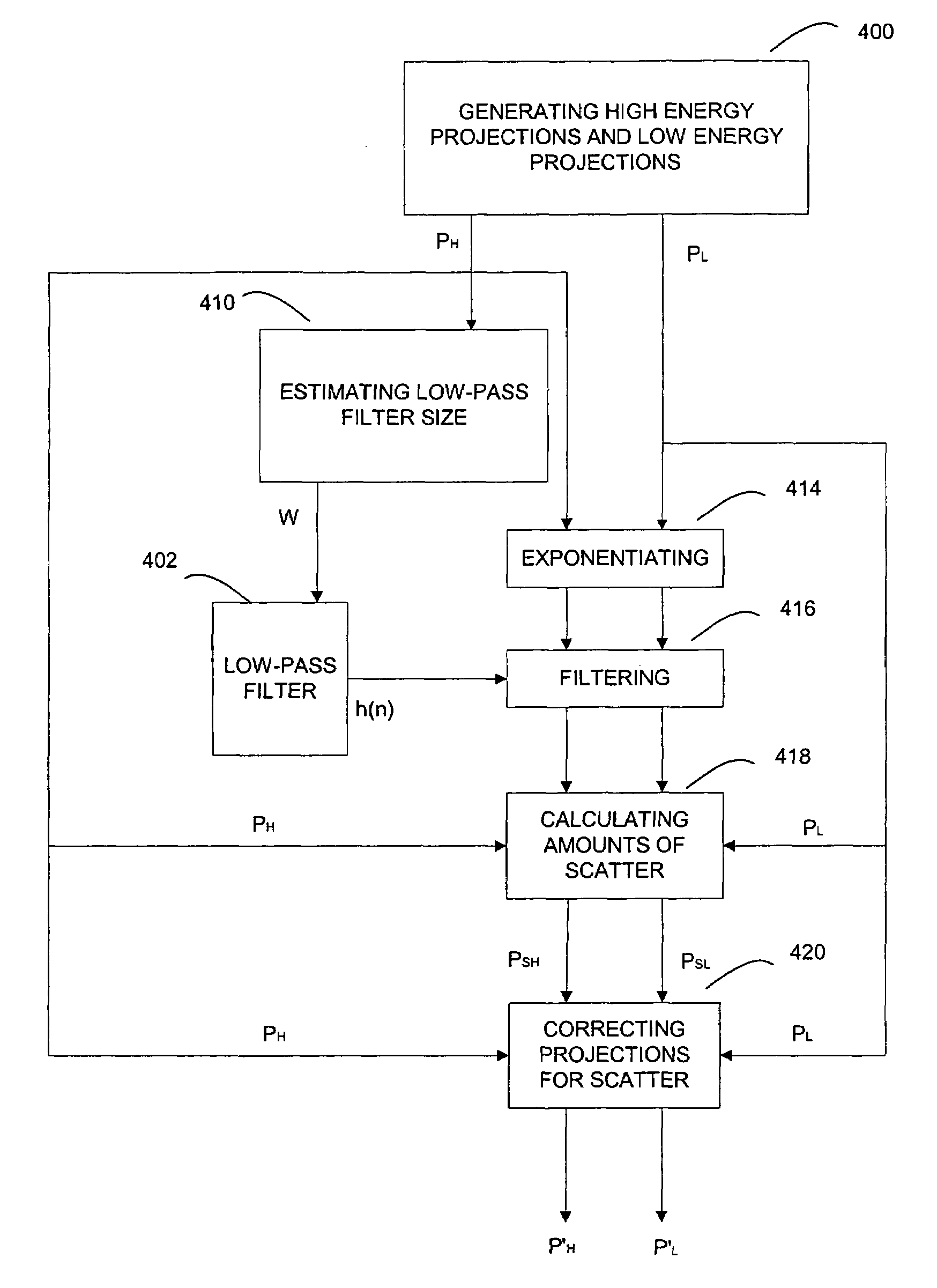
Method of and system for adaptive scatter correction in multi-energy computed tomography
InactiveUS7136450B2Reconstruction from projectionRadiation/particle handlingHigh energyX ray spectra
Owner:ANLOGIC CORP (US)
Grain moisture content detecting method based on hyperspectral image technology
InactiveCN102033043AFast wayMethod stableBiological neural network modelsColor/spectral properties measurementsMoving averagePattern recognition
The invention discloses a grain moisture content detecting method based on a hyperspectral image technology, which comprises the following steps: respectively acquiring an all black calibrated image B, an all white calibrated image W and a hyperspectral original data image I of grains the moisture content of which is given; carrying out reflection spectral correction on the hyperspectral original data image I of grains by the all black calibrated image B and the all white calibrated image W to obtain a corrected image R of grains; extracting the grain image from the corrected image R; carrying out spectral correction by a moving average method and multiplicative scatter correction; calculating the correlation coefficients of spectral reflection values and the moisture content; selecting a correlation coefficient as the maximum spectral reflection value to be input into an artificial neural network; and establishing a grain moisture prediction model. In the invention, the grain moisture content is detected by the artificial neural network according to the spectral signature of the grains caused by the moisture content, a quick stable method is provided, and the detecting efficiency is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
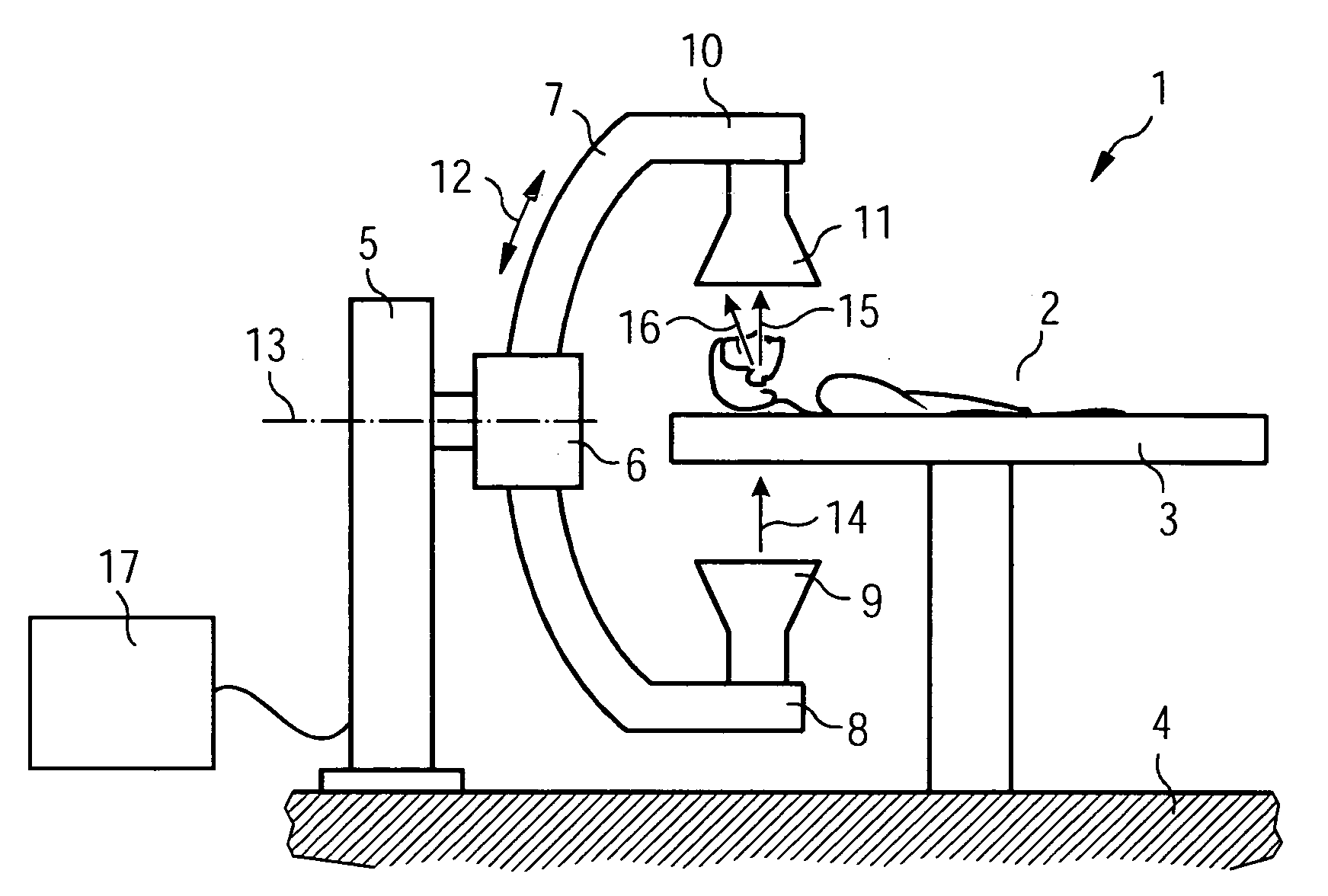
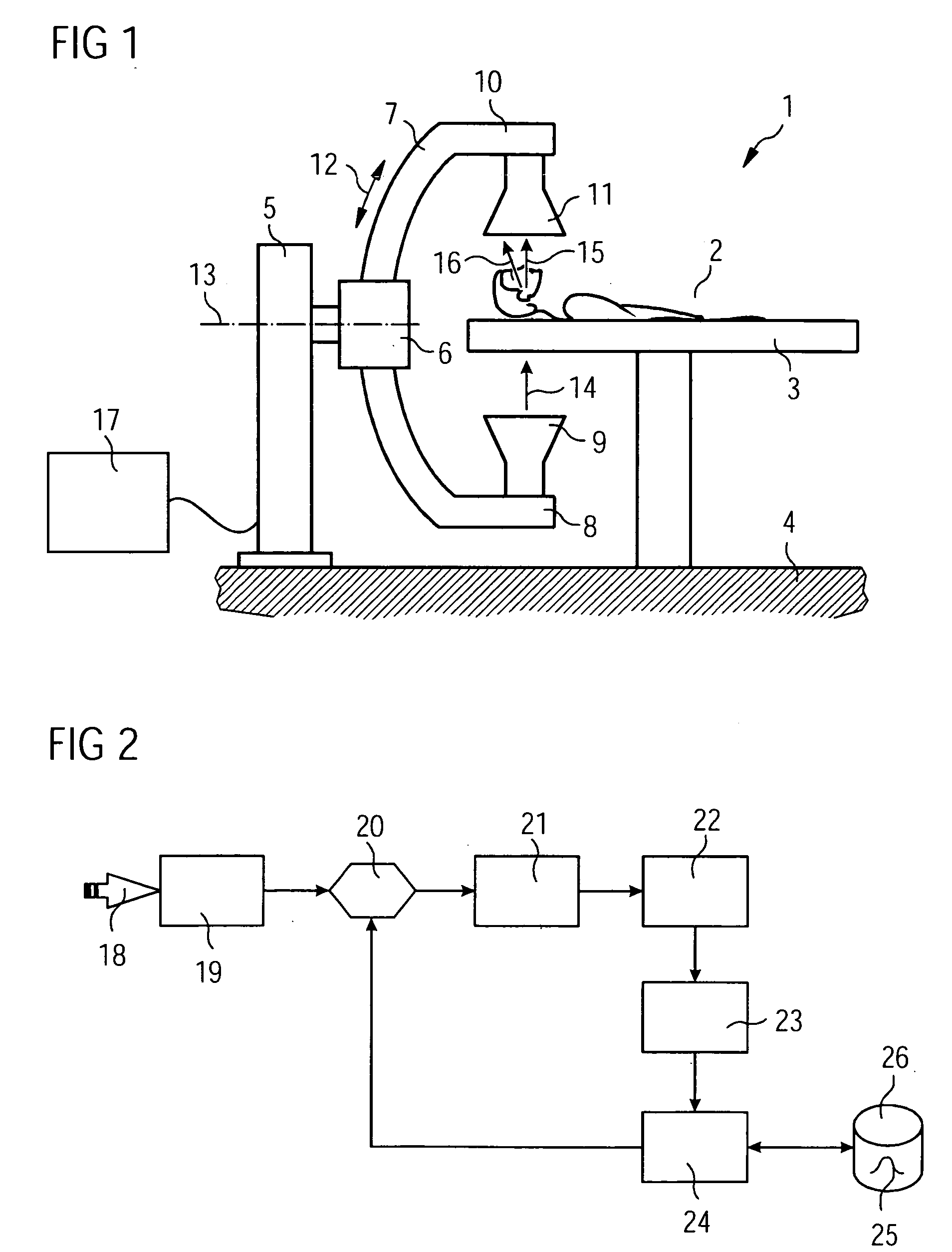
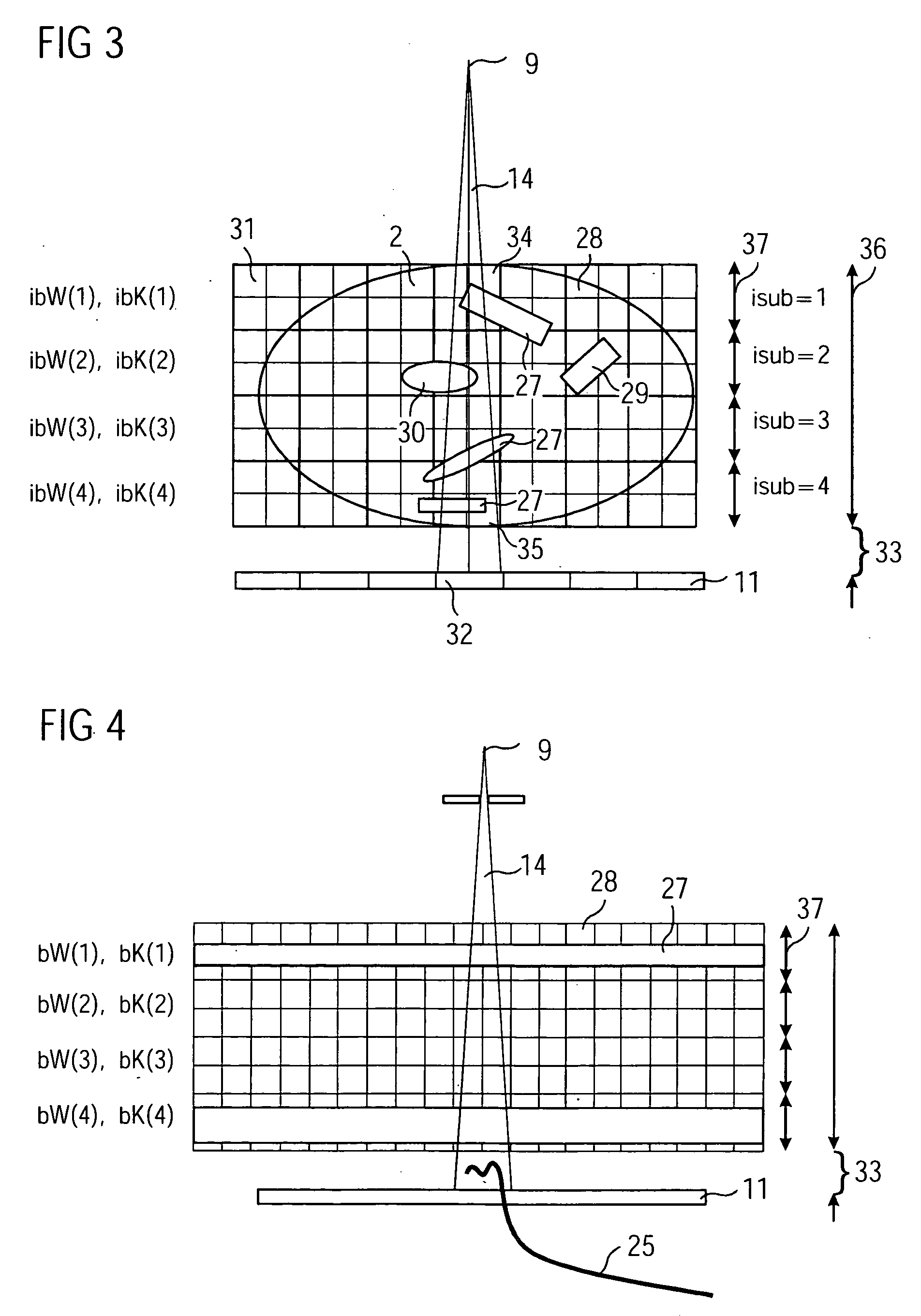
Device and method for x-ray scatter correction in computer tomography
InactiveUS20060008046A1Simple parameter settingSimple calculationReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayTomography
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
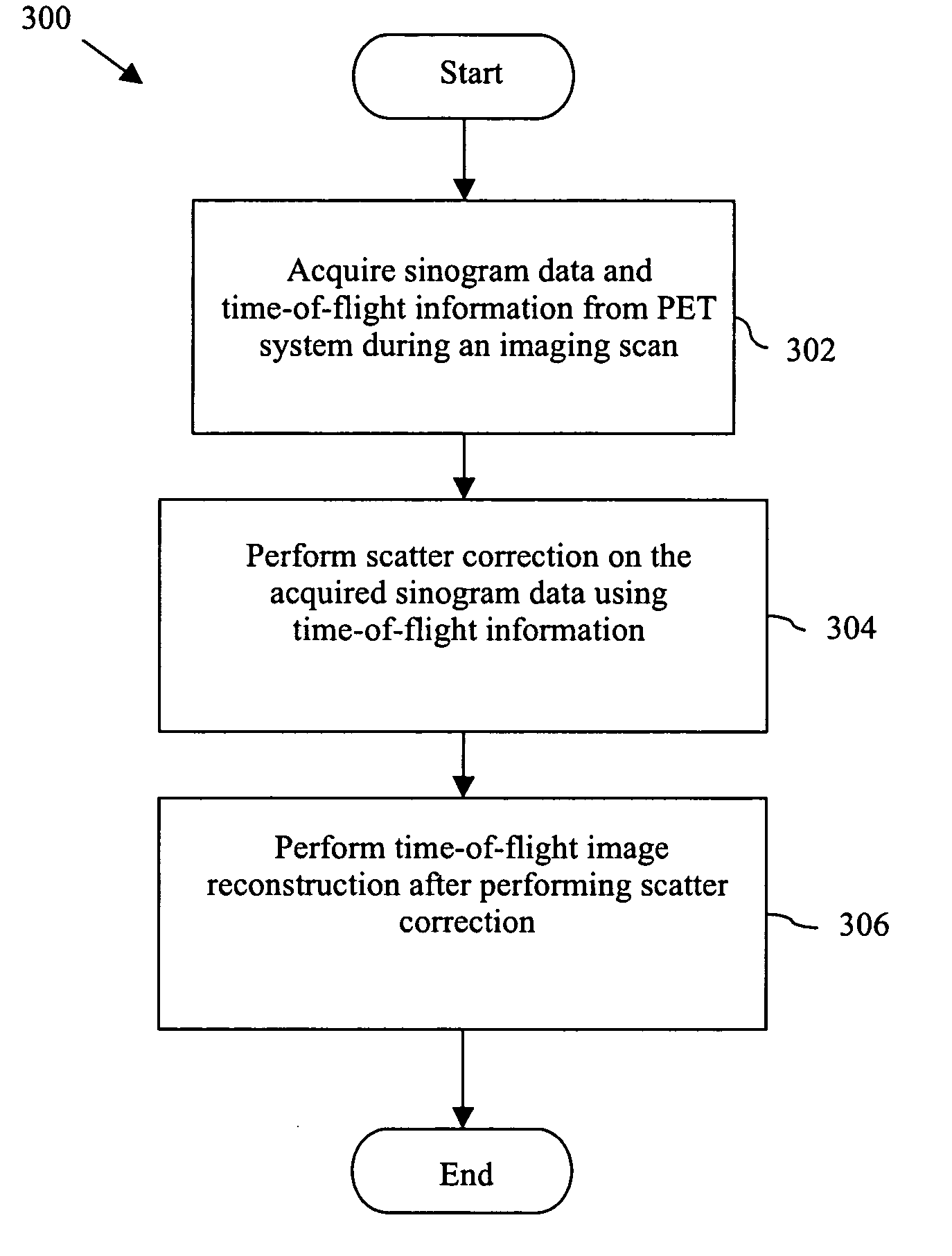
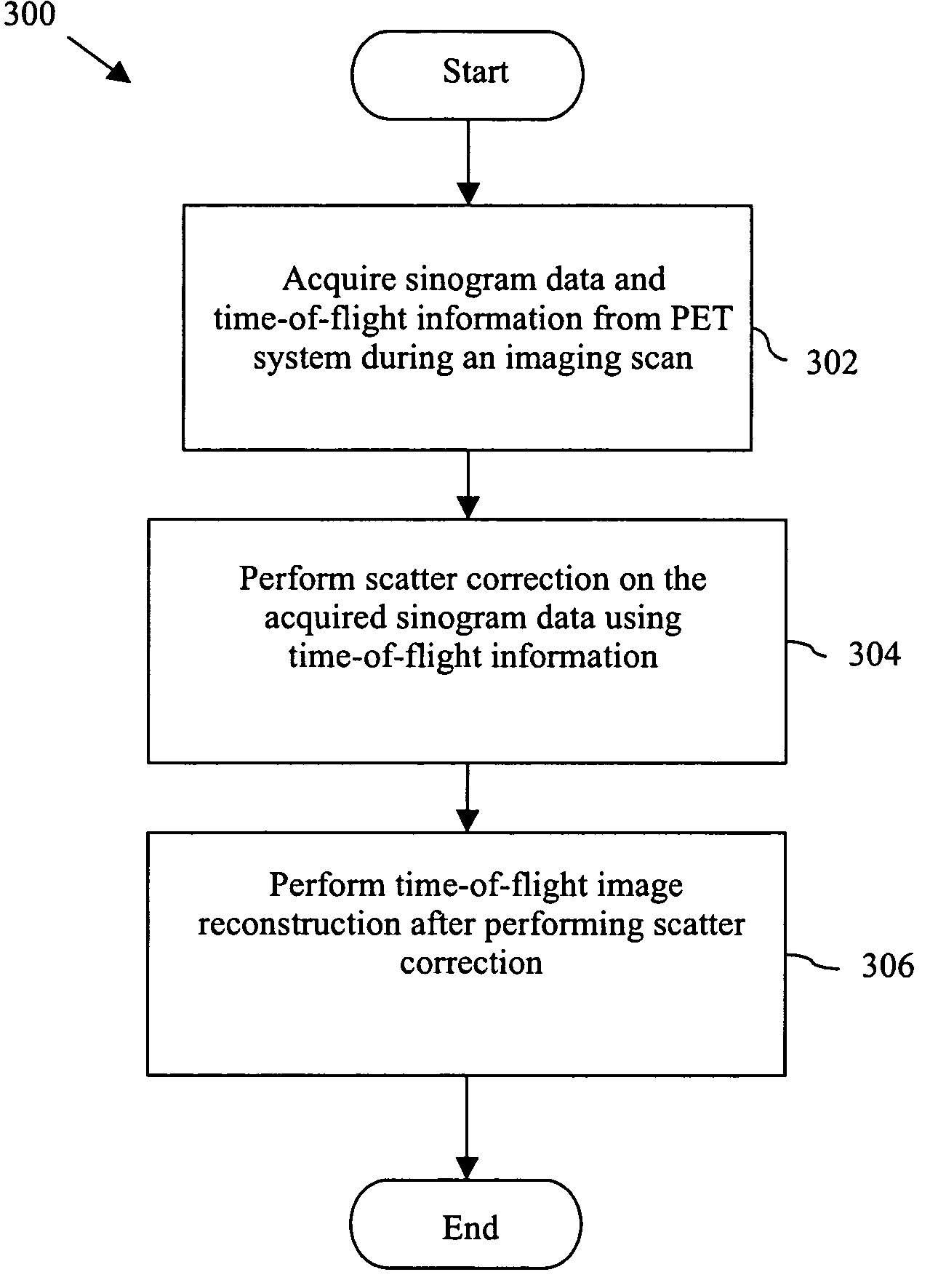
Method and system for scattered coincidence estimation in a time-of-flight positron emission tomography system
ActiveUS20060163485A1Material analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentTomographyCompanion animal
A method and system for controlling a positron emission tomography (PET) system is disclosed. The method includes acquiring image data and time-of-flight information from a PET system during an imaging scan. Further, the method includes performing scatter correction on the image data using the time-of-flight information.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Scatter correction for x-ray imaging using modulation of primary x-ray spatial spectrum
ActiveUS20070268997A1Efficient transferMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayX ray image
Scatter radiation in an x-ray imaging system including an x-ray source and an x-ray detector is separated by using amplitude modulation to translate the spatial frequency of a detected x-ray beam to a higher frequency and provide separation from low frequency scatter signal. The low frequency content of the detected x-ray beam is then obtained by demodulating the detected modulated signal.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
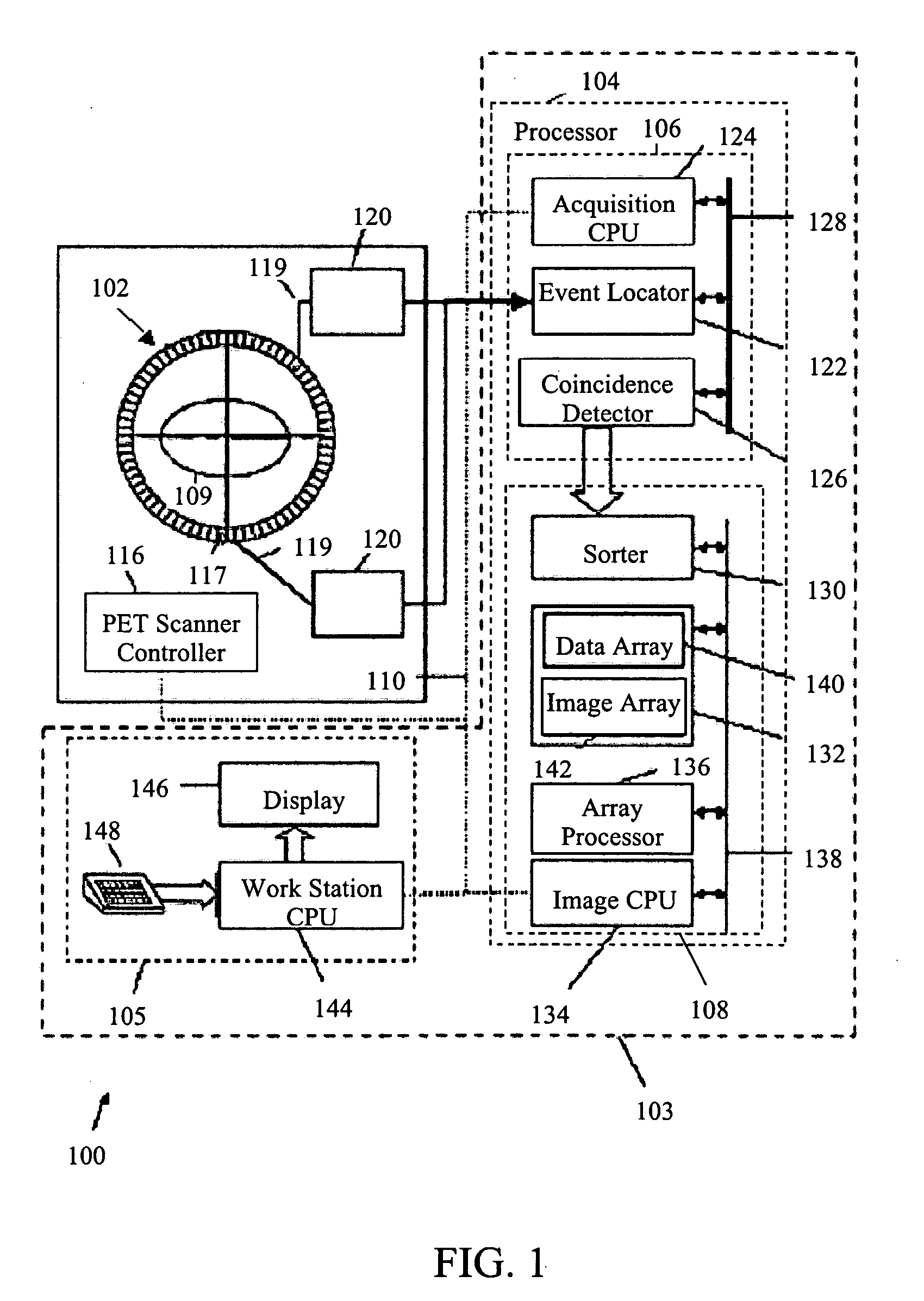
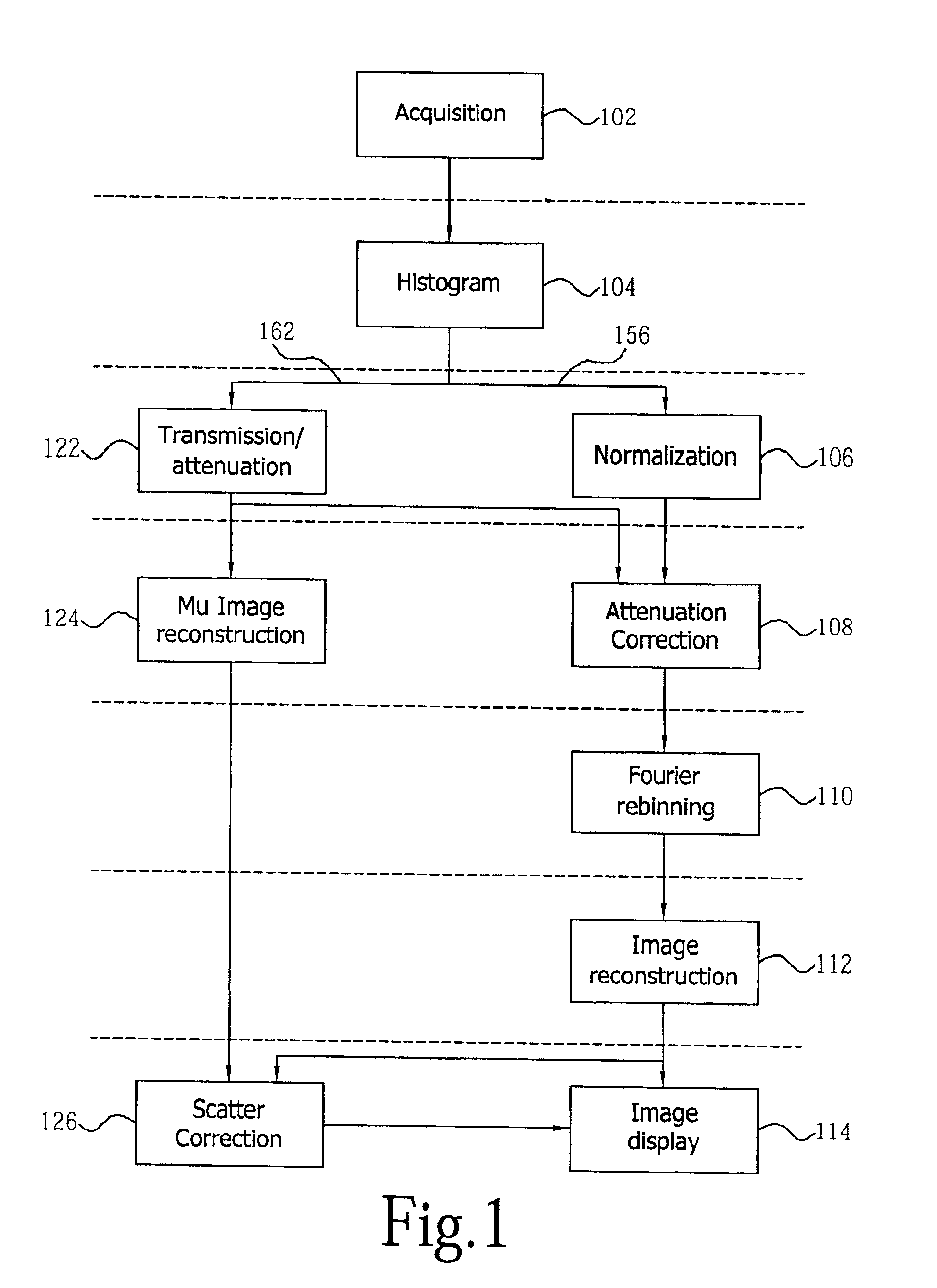
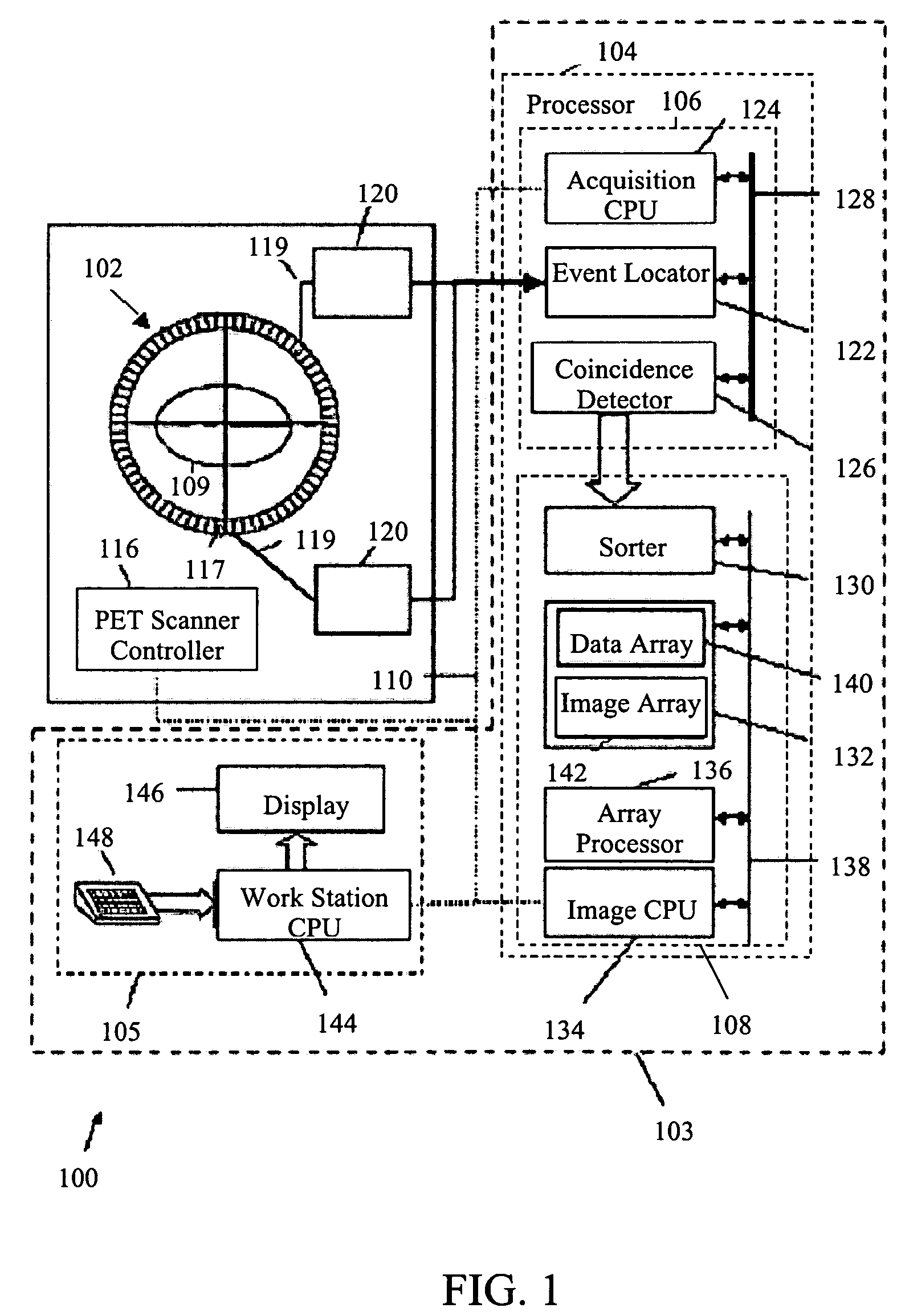
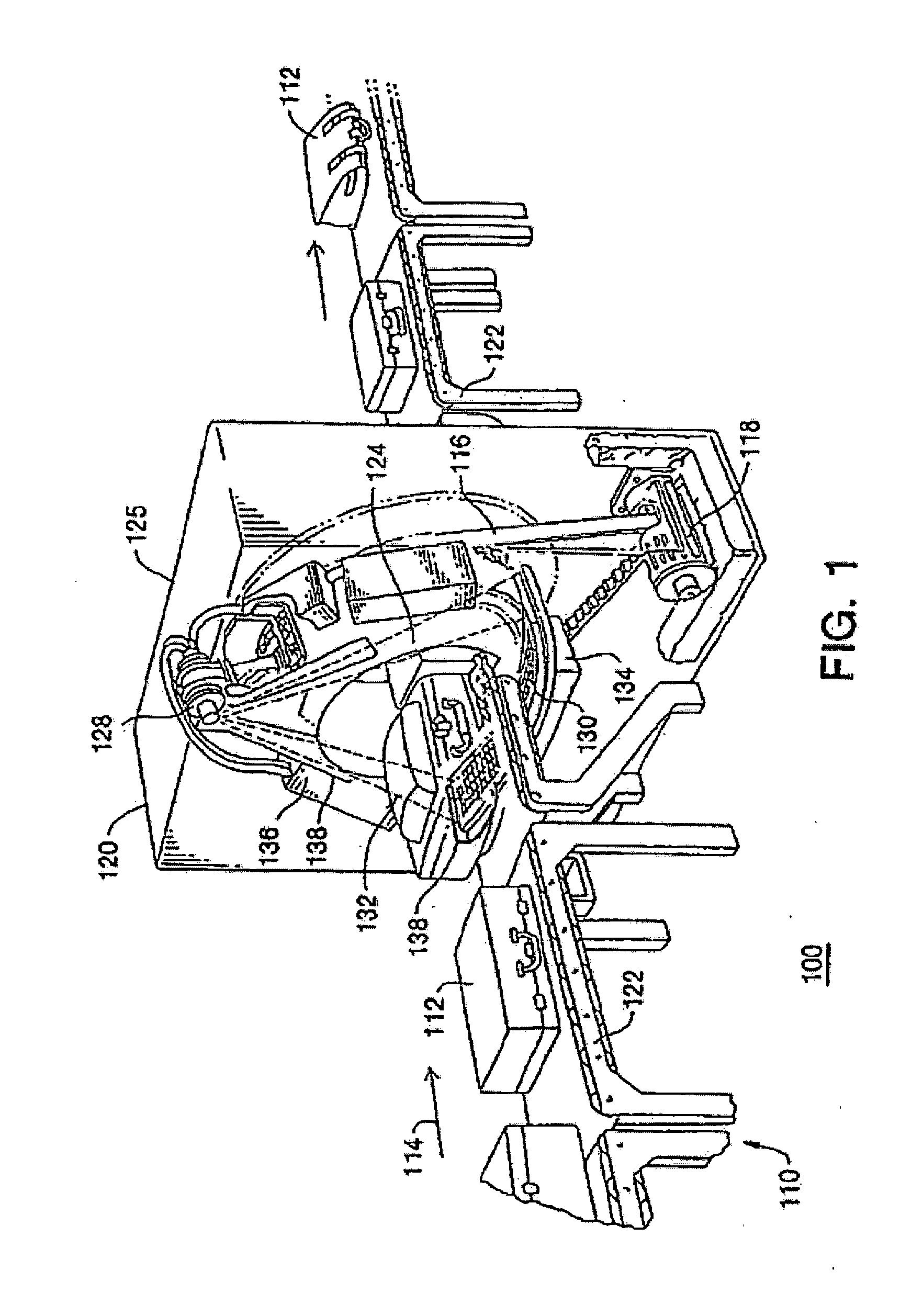
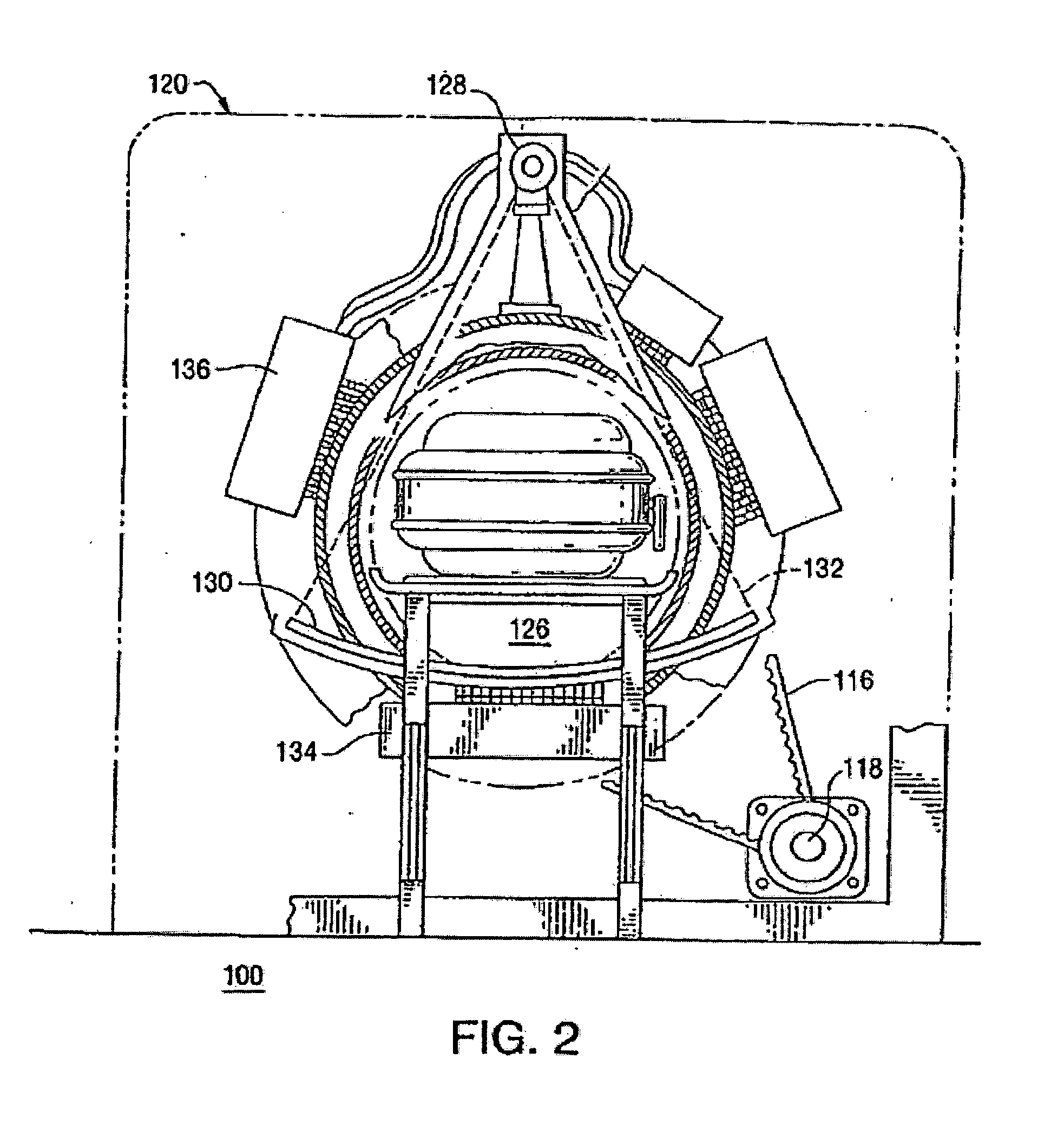
Continuous tomography bed motion data processing apparatus and method
InactiveUS6915004B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationData synchronizationUltrasound attenuation
Apparatus and methods for three dimensional image reconstruction from data acquired in a positron emission tomograph (PET). This invention uses a parallel / pipelined architecture for processing the acquired data as it is acquired from the scanner. The asynchronously acquired data is synchronously stepped through the stages performing histogramming, normalization, transmission / attenuation, Mu image reconstruction, attenuation correction, rebinning, image reconstruction, scatter correction, and image display.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Method and system for scattered coincidence estimation in a time-of-flight positron emission tomography system
ActiveUS7129496B2Material analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentCompanion animalComputer science
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
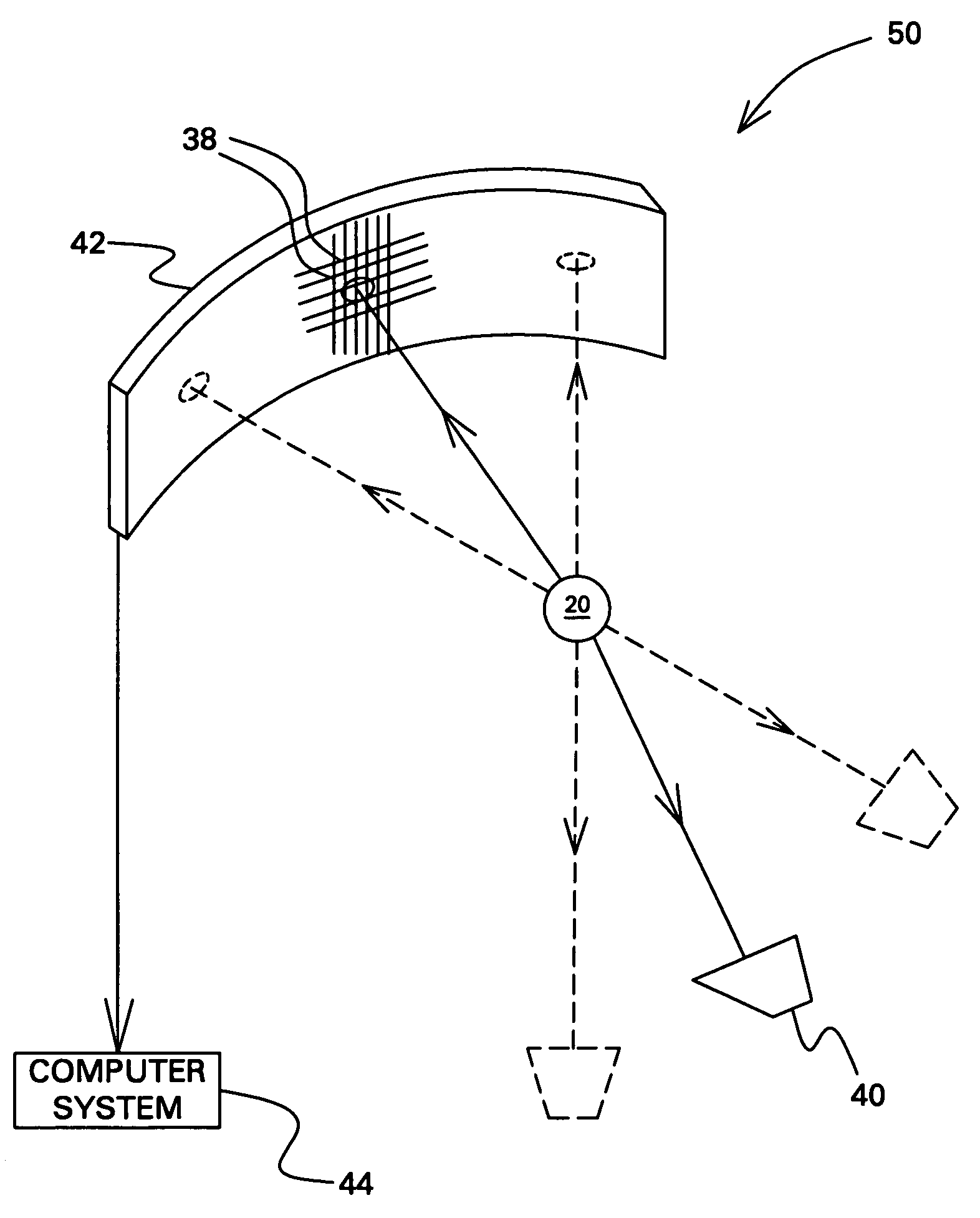
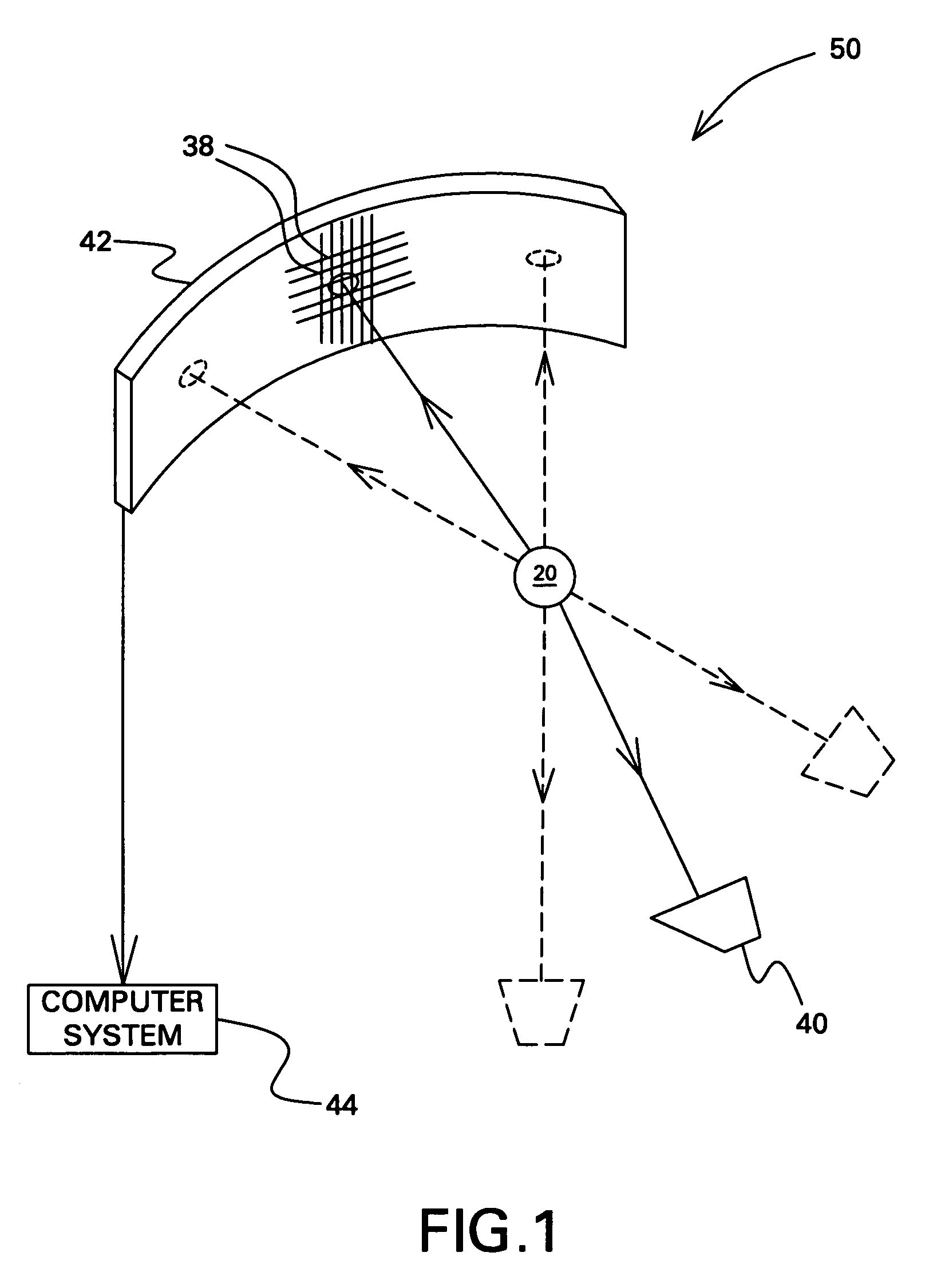
Apparatus and Method for Scatter Correction in Projection Radiography
ActiveUS20080013673A1Reduce computational complexityImprove modeling accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisData memoryArtificial intelligence
An apparatus for projection radiography is set up for correcting stray radiation. The apparatus comprises an evaluation unit which evaluates the distribution of stray radiation, which is arranged in a tabular manner in a data memory, for correcting stray radiation, said distribution being initially determined with the aid of Monte-Carlo-Simulation which takes into account multiple interactions of the photons with the object which is to be analyzed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
Ct scanner with scatter radiation correction and method of using same
ActiveUS20090304142A1Television system detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationCt scannersX-ray
A CT scanner with scatter correction device and a method for scatter correction are provided. The method of correcting CT images from artifacts caused by scattered radiation comprises affixing to the non-rotating frame of the CT gantry a plurality of shields for shielding some of the CT detector elements from direct X ray radiation, while allowing scattered radiation to arrive at said shielded elements; measuring scatter signals from said shielded elements, indicative of scattered radiation intensity; and correcting for scatter by subtracting scatter intensity values estimated from said measured scatter signals from signals measured by unshielded detector elements.
Owner:ARINETA
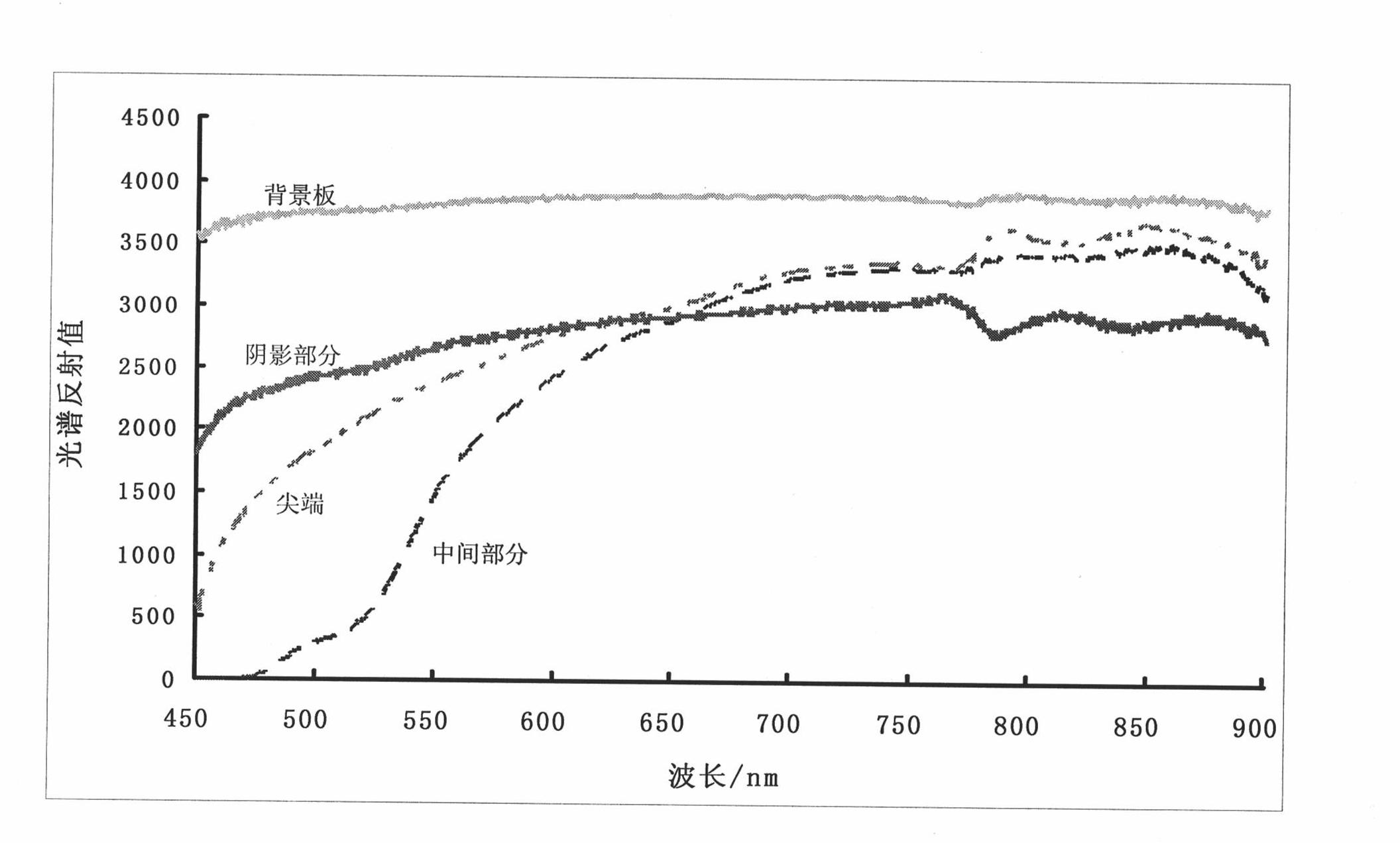
Method for identifying red sandalwood by near-infrared ray
InactiveCN1936552AFast and non-destructive identificationSimple methodMaterial analysis by optical meansRosewoodScatter correction
This invention relates to a method for identifying near infrared spectrum of rosewood including the following steps: applying rosewood and non-rosewood samples to collect several times of near infrared spectrums at different positions on the surface of the sample by a near infrared spectrum device and collect spectrums of 3-19 positions at a same sample to set up distinguishing models of true and false rosewood and its kind through spectrum pre-process such as smoothing, base line correction, a first stage derivative, a second stage derivative, multiple dispersion correction or pre-process of dimensionality reduction of data by a multivariable data analysis method of soft independent modeling sorting or deflection of the least square differential analysis so as to realize quick and harmless identification to true and false of rosewood and their kinds in several minutes.
Owner:INST OF WOOD INDUDTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Apparatus and method for scatter correction in projection radiography
An apparatus for projection radiography is set up for correcting stray radiation. The apparatus comprises an evaluation unit which evaluates the distribution of stray radiation, which is arranged in a tabular manner in a data memory, for correcting stray radiation, said distribution being initially determined with the aid of Monte-Carlo-Simulation which takes into account multiple interactions of the photons with the object which is to be analyzed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method of and system for adaptive scatter correction in multi-energy computed tomography
InactiveUS20050276373A1Quality improvementReconstruction from projectionRadiation/particle handlingHigh energyX ray spectra
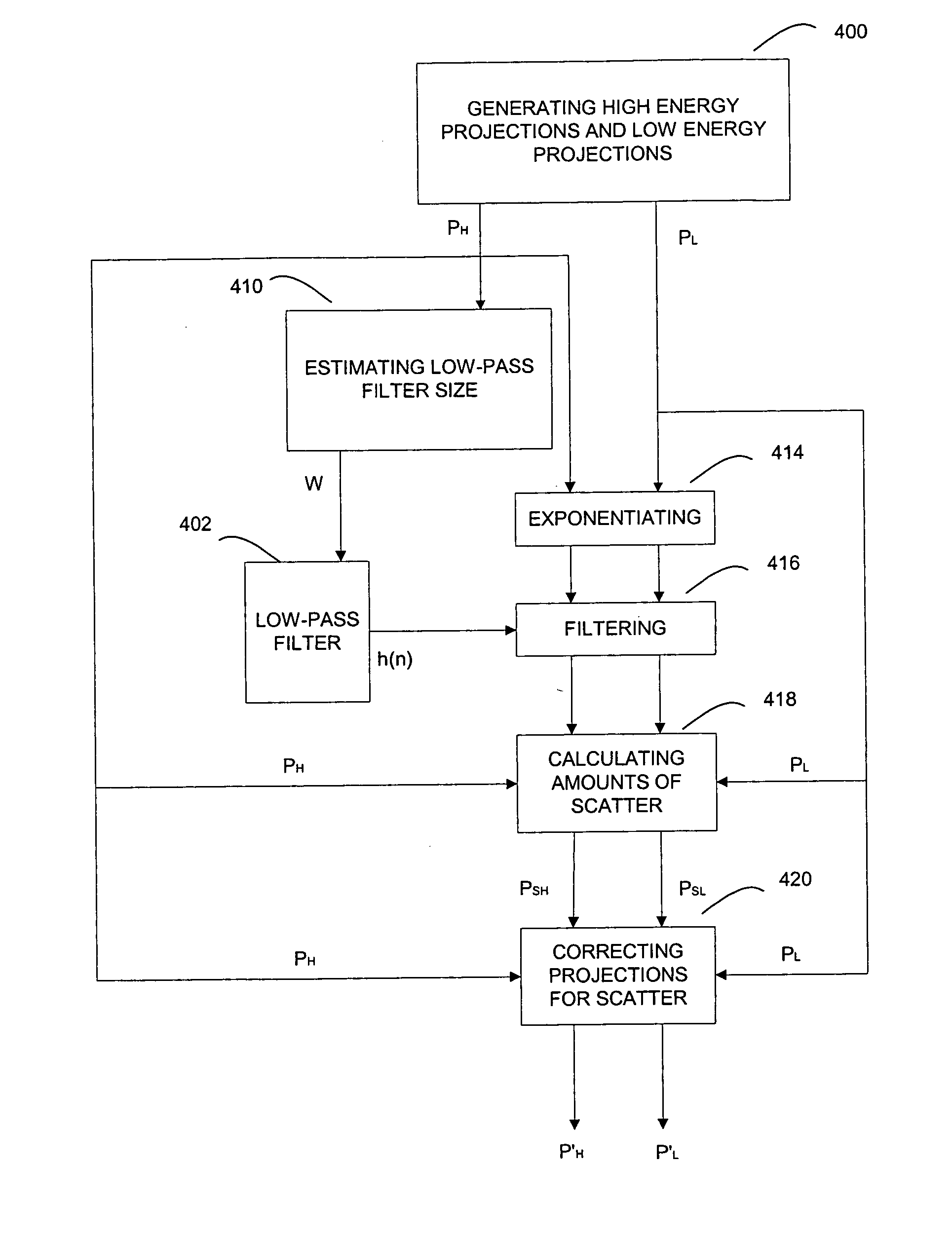
Method of and system for adaptive scatter correction in the absence of scatter detectors in multi-energy computed tomography are provided, wherein input projection data acquired using at least two x-ray spectra for scanned objects may include a set of low energy projections and a set of high energy projections; wherein a low-pass filter of variable size is provided; the method comprises estimating the size of the low-pass filter; computing amounts of scatter; and correcting both sets of projections for scatter. The estimation of low-pass filter size comprises thresholding high energy projections into binary projections; filtering the binary projections; finding the maximum of the filtered binary projections; calculating the low-pass filter size from the found maximum. The computation of amounts of scatter comprises exponentiating input projections; low-pass filtering the exponentiated projections with the estimated filter size; computing the amounts of scatter from the filtered projections.
Owner:ANLOGIC CORP (US)
Method and system for acquiring PET image
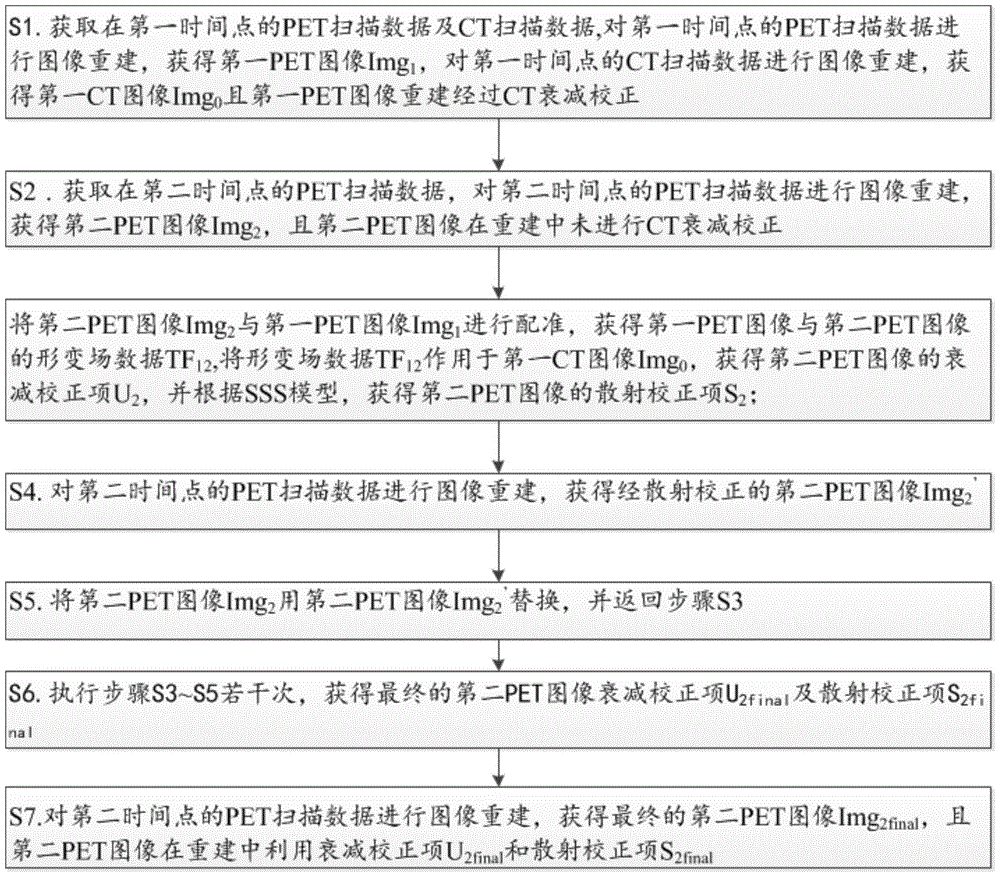
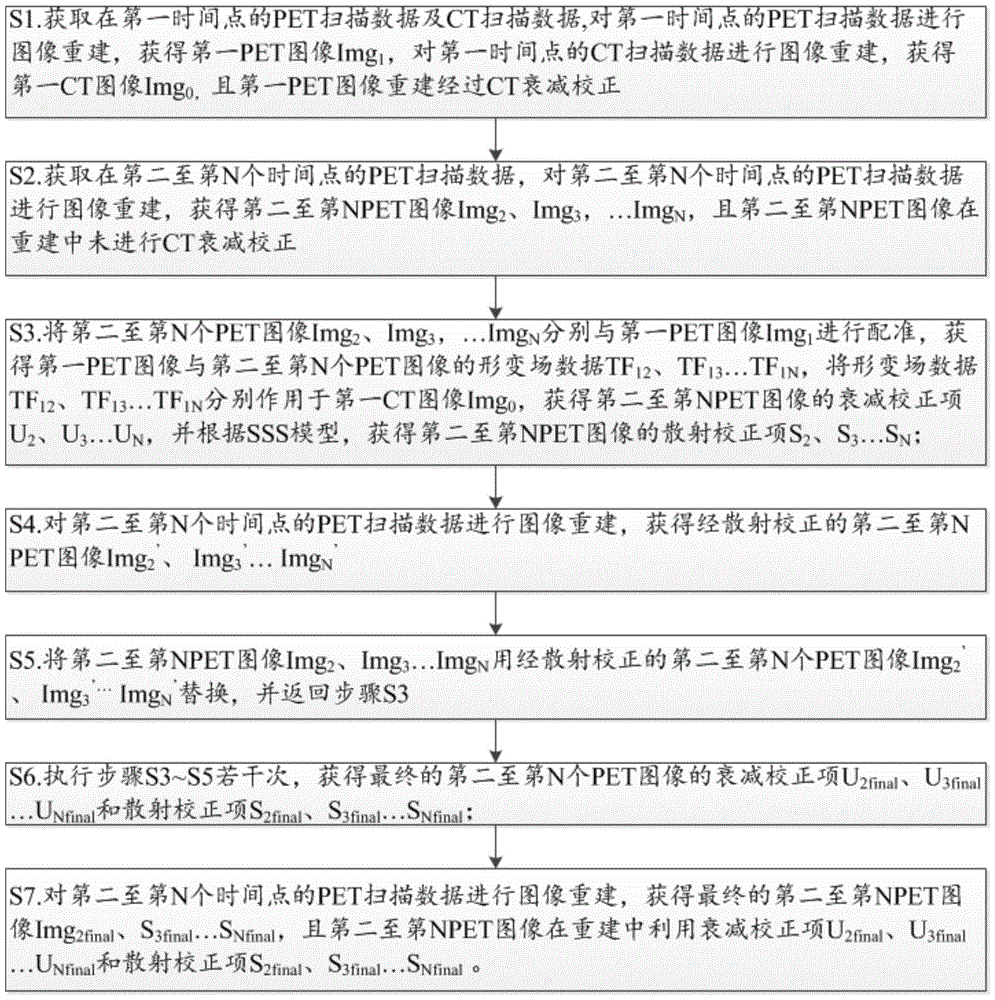
ActiveCN106491151ANo need to restrict movement for long periods of timeAvoid Multiple CT RadiationsComputerised tomographsTomographyUltrasound attenuationField data
The invention discloses a method and system for acquiring a PET image. The method comprises the steps that PET scanning data and CT scanning data at a first time point are acquired, and a first PET image Img1 and a first CT image Img0 are acquired; PET scanning data at a second time point and a second PET image Img2 are acquired, wherein CT attenuation correction is not carried out to the second PET image during reconstruction; registration is conducted the second PET image Img2 and the first PET image Img1, deformation field data TF12 between the two images is acquired and acts on the first CT image Img0, an attenuation correction item U2 of the second PET image is acquired, and a scattering correction item S2 of the second PET image is acquired according to an SSS model; an attenuation correction item U2final and a scattering correction item S2final of the final second PET image are acquired; and the final second PET image is acquired.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Image guided acquisition of quantitative dual energy data
A technique for establishing texture metrics and bone mineral density (BMD) within an anatomical region of interest. A digital imaging system is used to acquire a standard digital X-ray image with a wide field of view. The standard digital X-ray image is used to guide the imaging system to obtain an image of a region of interest. The standard digital X-ray image is used to calculate various texture metrics, such as a length of a fracture. A dual-energy digital X-ray image of the region of interest is acquired. The dual-energy digital X-ray image is corrected for scatter. The BMD of the region of interest may be established from the scatter-corrected dual-energy digital X-ray image. The BMD, the texture metrics, and / or the scatter-corrected dual-energy X-ray image may be displayed on the standard digital X-ray image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Systems and methods for simultaneous acquisition of scatter and image projection data in computed tomography
InactiveUS8989469B2SurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsComputed tomographyRegularization algorithm
A method of acquiring scatter data and image projection data in computed tomography is provided that includes attenuating a radiation source using a pattern of blockers arranged to provide blocked and unblocked regions of the radiation source, and acquiring image data and scatter data of a target using an imaging device. A scatter map in the projection image can be estimated by interpolation and / or extrapolation of the projection image using an appropriately programmed computer, subtracting the estimated scatter map from the projection image to obtain scatter-corrected projections, reconstructing a CBCT volume using a total variation regularization algorithm, and applying an iterative regularization process to suppress the noise level on the reconstructed CBCT volume. Reconstructing a CBCT volume can include using a total variation regularization algorithm and applying an iterative regularization process to suppress the noise level on the reconstructed CBCT volume, where scatter-induced artifacts are corrected in the projection image.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
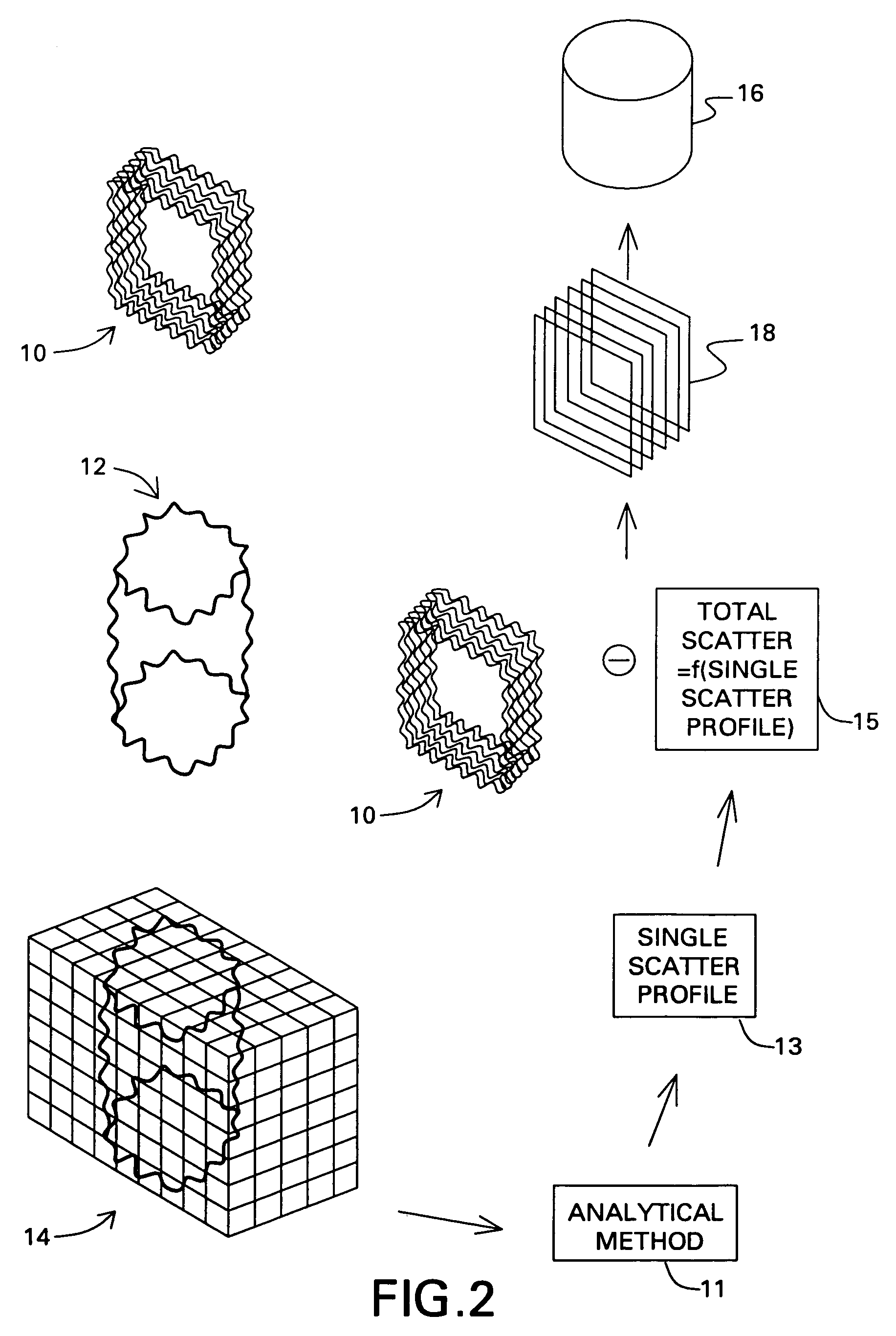
Scatter and beam hardening correction in computed tomography applications
InactiveUS7065234B2Reconstruction from projectionRadiation/particle handlingSpectral response3d image
A method of correcting scatter includes obtaining a voxellized representation of a 3D image of an object from a plurality of projection data. A single scatter profile for the object is calculated using the voxellized representation of the 3D image of the object. A total scatter profile for the object is determined using the single scatter profile and an adjustment factor and the projection data is corrected using the total scatter profile to obtain a scatter corrected projection data. A beam hardening correction method includes simulating a number of attenuation data for an x-ray spectrum, at least one object material, and a detector spectral response. A function is fitted to the attenuation data to obtain an attenuation curve. A number of projection data for an object are corrected using the attenuation curve to obtain a number of beam hardening corrected projection data. A corrected image of the object is reconstructed from the beam hardening corrected image data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
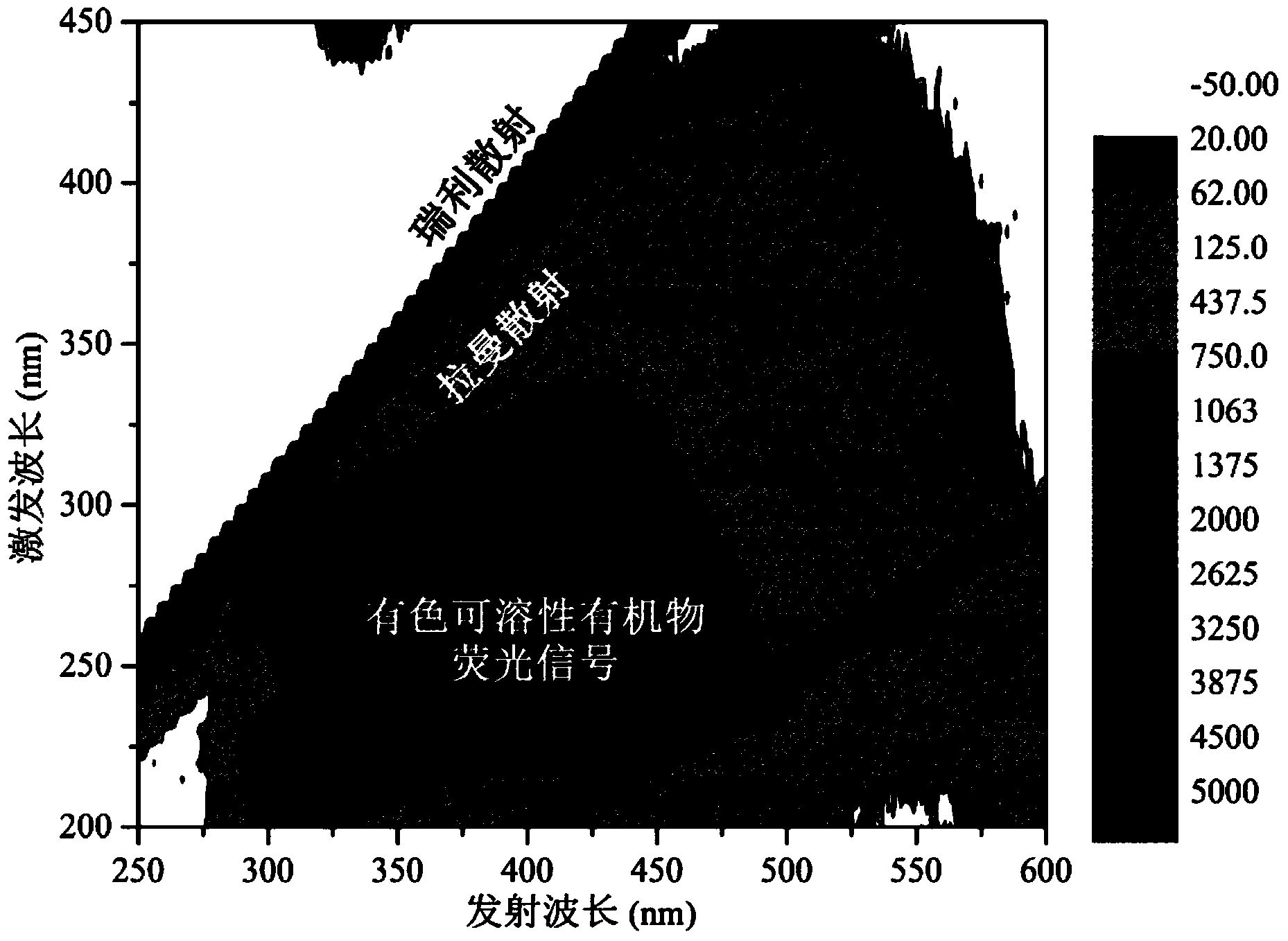
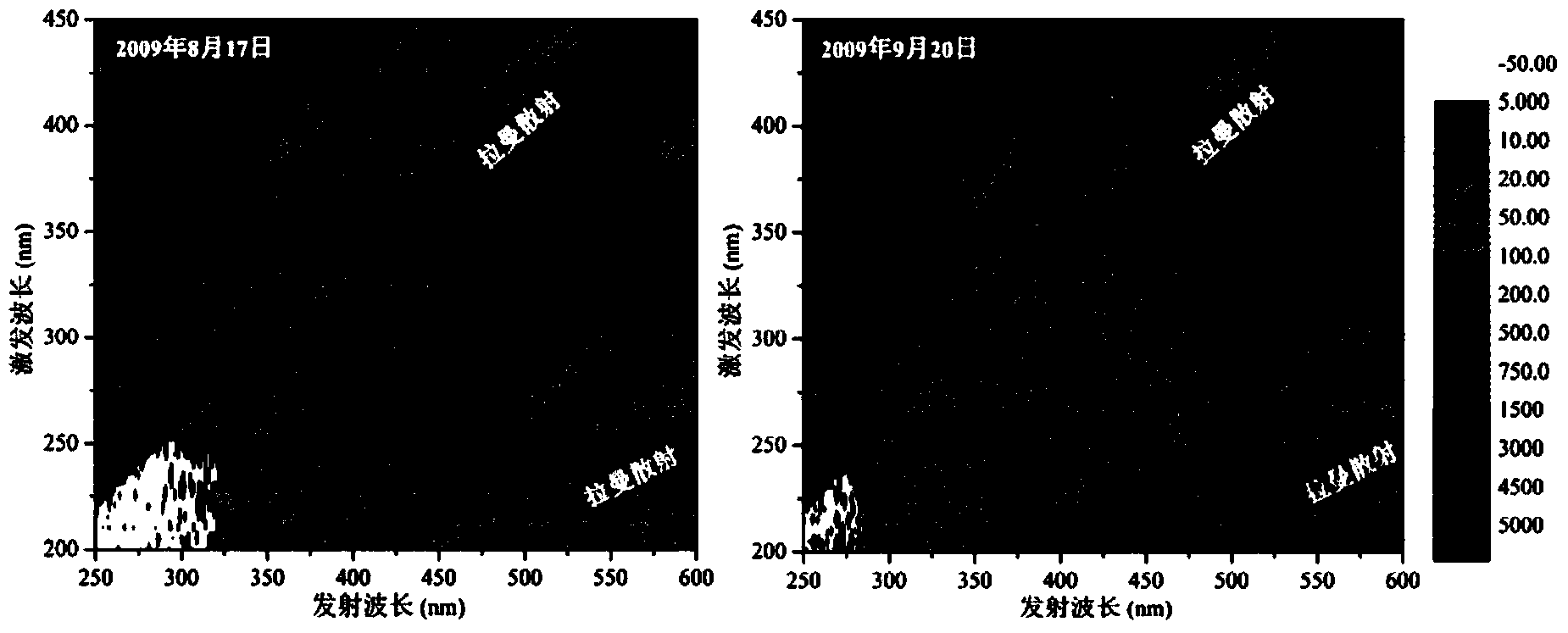
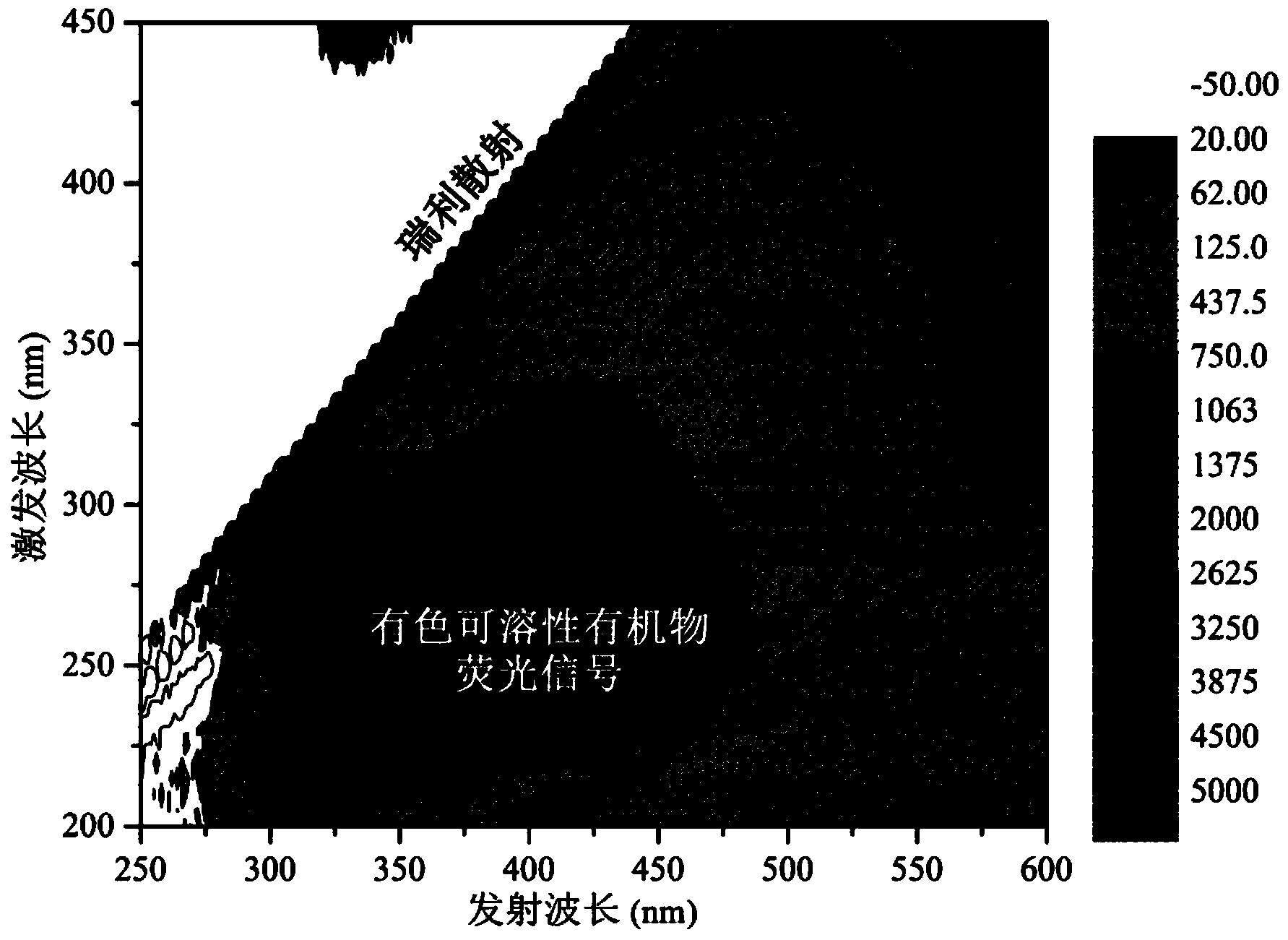
Method for correcting and calibrating three-dimensional fluorescence data of colored soluble organic matters
InactiveCN103630522ADoes not damage the structureHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceRayleigh scatteringHigh concentration
The invention provides a method for correcting and calibrating three-dimensional fluorescence data of colored soluble organic matters. The method comprises the steps of setting measurement conditions such as three-dimensional fluorescence excitation, a wavelength generation range and a scanning speed; measuring a three-dimensional fluorescence spectrum of a sample; measuring a three-dimensional fluorescence spectrum of ultrapure water; performing Raman scattering correction by subtracting excitation-emission three-dimensional fluorescence spectrum of the ultrapure water from the excitation-emission three-dimensional fluorescence spectrum of the sample; assigning 0 to a triangular region of each three-dimensional fluorescence spectrum to perform Rayleigh scattering correction; performing calibration on the fluorescence intensity through the excitation wavelength of 350nm and the emission wavelength of 371-428nm of the ultrapure water; measuring an absorption spectrum of the sample to obtain the absorbency of the sample; performing inner filering effect correction on the three-dimensional fluorescence data according to the absorbency of the sample. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the influence of the inner filtering effect of the high-concentration sample on the fluorescence intensity can be eliminated without dilution of the sample.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Model generation method, image processing method and medical imaging equipment
ActiveCN107516330ALow costImprove securityTelevision system detailsImage enhancementMedical equipmentX-ray
An embodiment of the invention provides a model generation method, an image processing method and medical imaging equipment. The model generation method includes: under specified imaging parameters, acquiring first image data with scattering component and second image data without scattering component, selecting input data from the first image data or related data thereof, and selecting label data from the second image data or related data thereof; according to the input data and the label data, performing machine learning by adopting a neutral network to generate a scattering-correction model. Machine learning is performed by the aid of the neutral network to generate the scattering-correction model, the scattering-correction model is used for performing scattering correction on DR (digital radiography) images, increasing of radiation dose of X-rays is not needed, better safety is achieved, adding of a grid in DR equipment is not needed, cost of the DR equipment can be reduced, and problems that the DR equipment with the grid is poor in safety and high in cost in the prior art are solved to some extent.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Scattering correction method for projected image and device
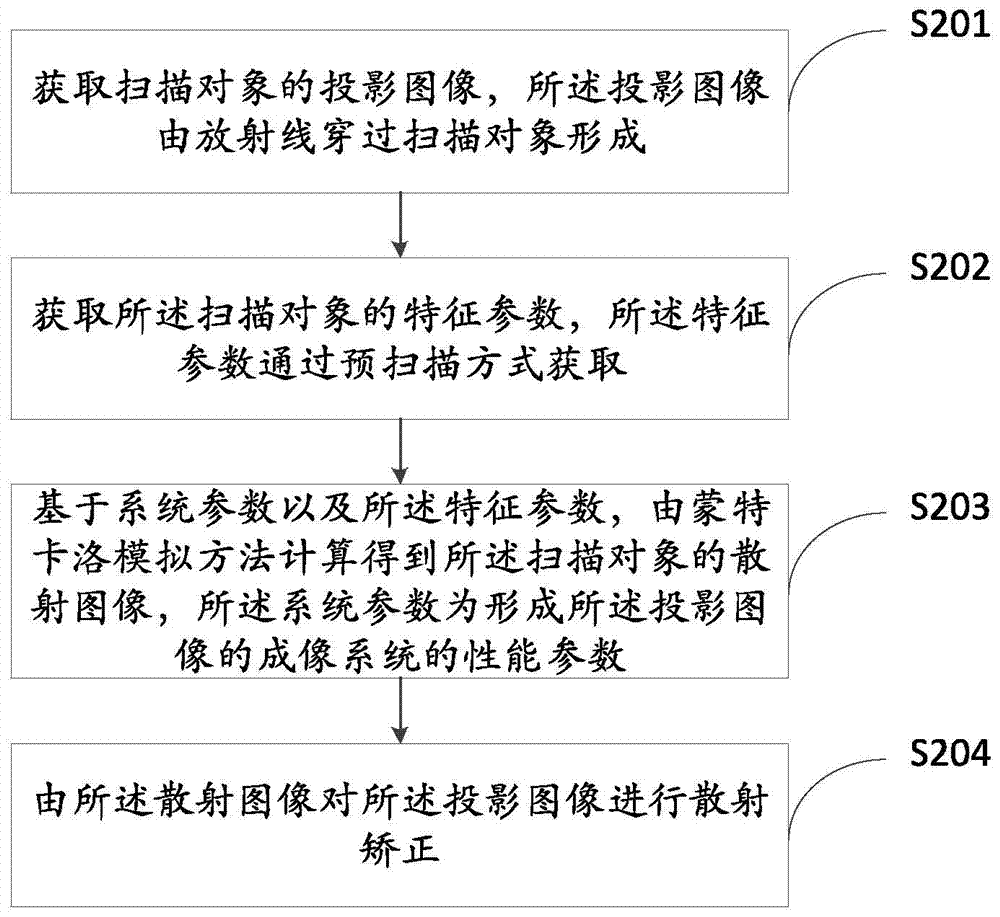
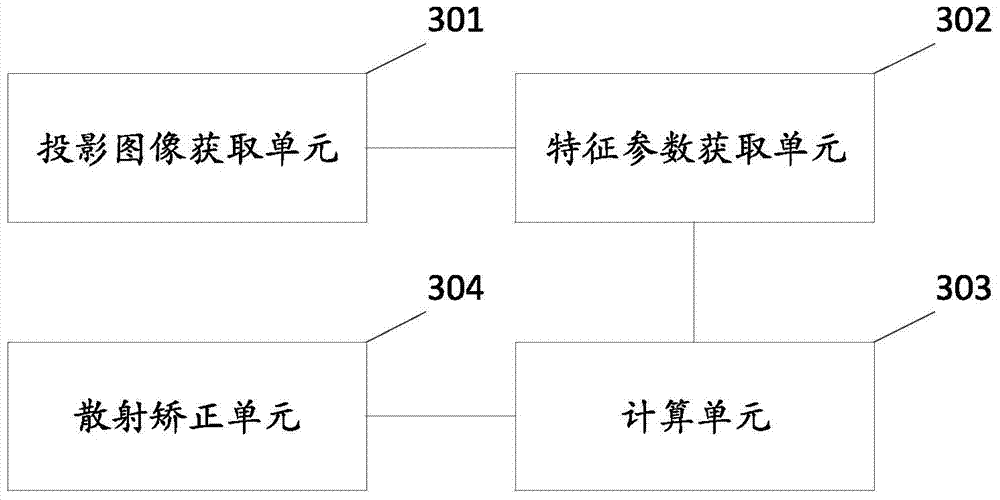
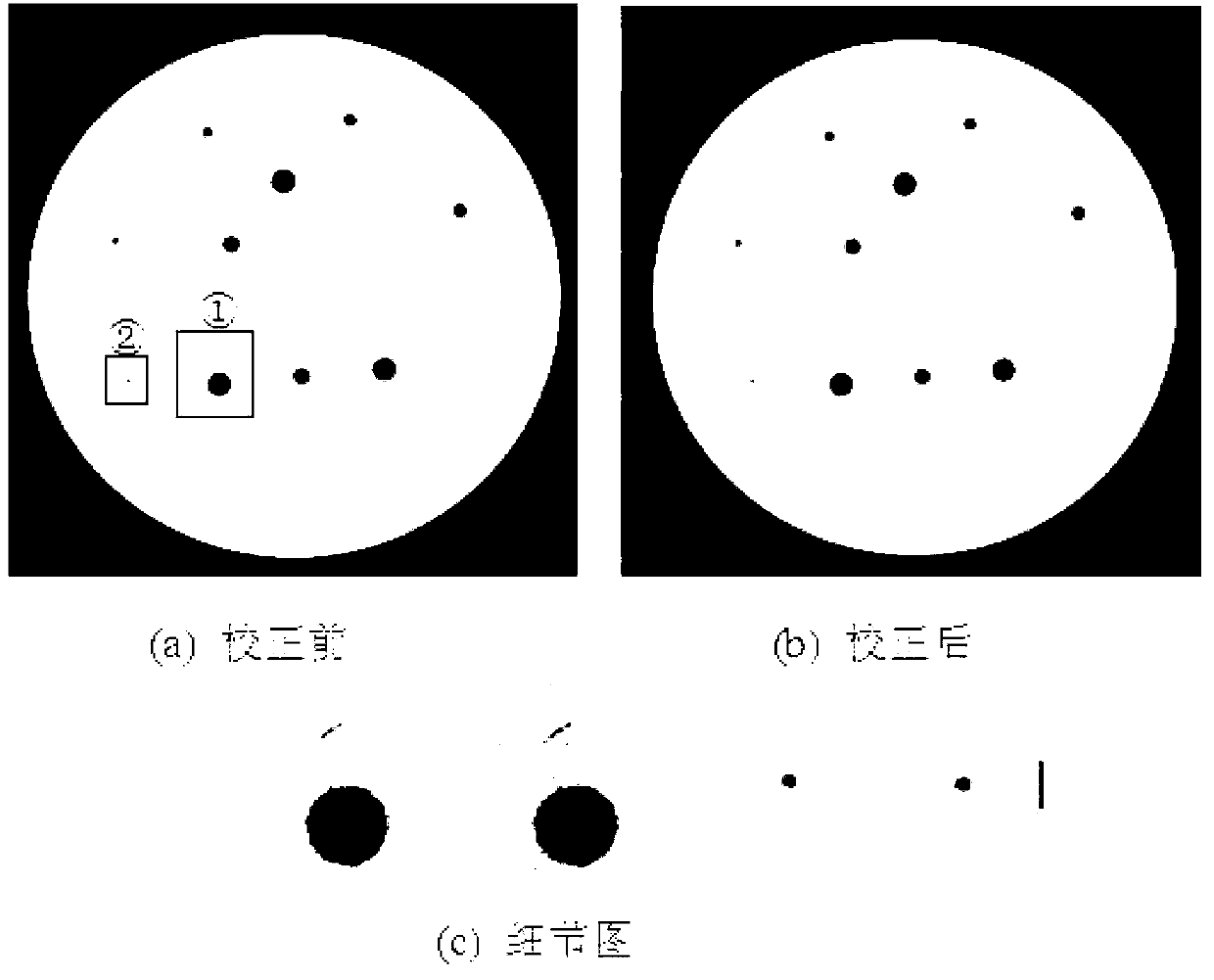
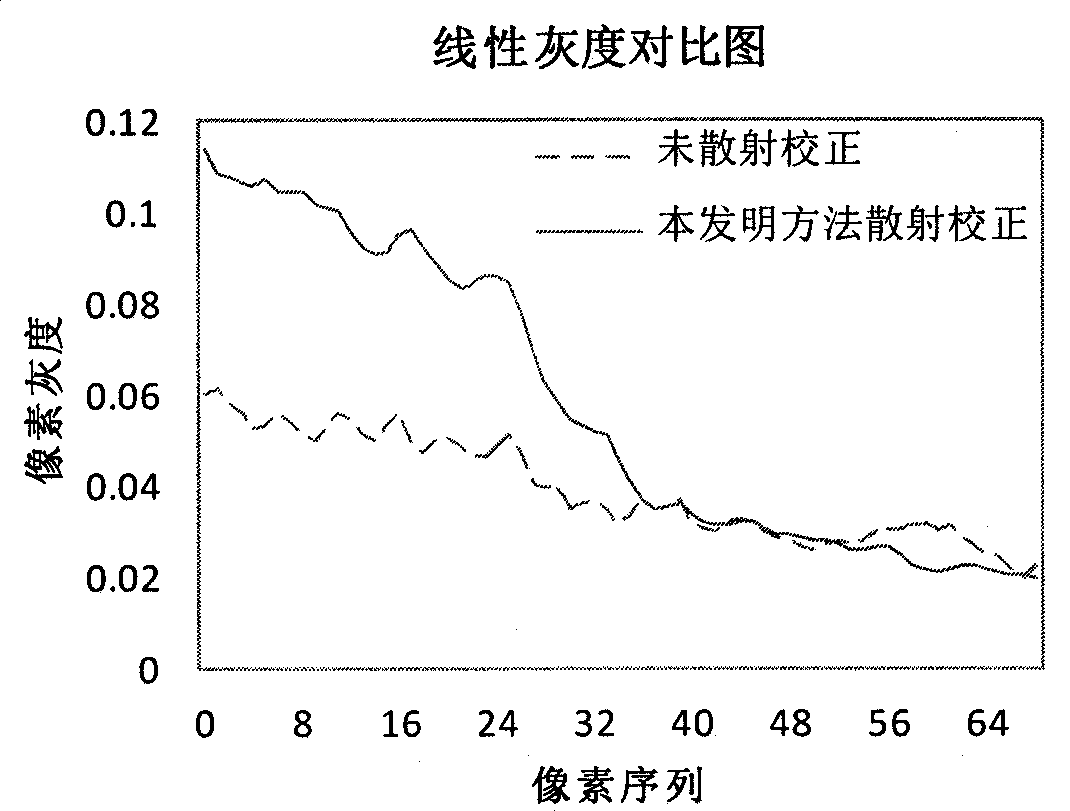
ActiveCN104840211AImprove image qualityLess discomfort2D-image generationPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryRadiation DosagesImaging quality
The invention provides a scattering correction method for a projected image and a device, wherein the scattering correction method comprises: obtaining the projected image of a scanned object; obtaining the characteristic parameter of the scanned object; obtaining the scattering image of the scanned object through calculation according to the Monte Carlo simulation method on the basis of a system parameter and the characteristic parameter; carrying out scattering correction to the projected image through the scattering image. According to the technical scheme of the invention, on the premise of not increasing radiation dosage absorbed by a patient, the discomfort and pain suffered by the patient in the checking process are reduced, in consideration of the impact of physical factors such as secondary and higher scattering, energy response and the like on scattering, the calculation for the scattering is closer to the physical situation, and the image quality of the projected image is enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Convolution-based X-ray CT system beam hardening correction method
InactiveCN103134823ANo lossSignificant beam hardening correctionMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationBeam hardeningAluminum foil
The invention discloses a convolution-based X-ray CT system beam hardening correction method, belonging to the applying field of industrial CT systems. The method comprises the following steps of: I. conducting scattering correction by clinging an aluminum foil filter plate to a rear collimator; II. setting the scanning parameter of a CT system; III. collecting the background value of the system with a ray source not opening; IV. opening the ray source, and scanning the air in the current laboratory to obtain the ray strength of the current air; V. scanning a group of standard parts, and collecting the projection data under different thicknesses; VI. fitting a curve to obtain a hardening model and a convolution correction model; VII. conducting hardening correction by utilizing the function of the convolution correction model to obtain the corrected ray strength data; and VIII. conducting image reconstruction by using the corrected ray strength data. With the correction method, the beam hardening correction effect is obvious, the edge of a detected object can be well maintained, the detail part of the detected object can be saved, and the high-precision detection need can be met.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Scattered radiation correction method of computerized tomography system and computerized tomography system
The present invention relates to a method for scattered radiation correction of a CT system, including at least two focus / detector systems operated angularly offset from one another, is disclosed. In the method, at at least one phantom, similar to the examined object at least in a subregion, for at least one of the focus / detector systems, the scattered radiation intensity occurring is determined in the detector of a focus / detector system during the operation of the at least one focus of at least one other focus / detector system. Further, the spatial distribution thereof is stored for a number of angles of rotation of the focus / detector systems. During scanning of the object, the scattered radiation intensities, determined with the aid of a similar phantom that originate from the at least one other focus / detector system, are subtracted from the measured intensities of the first focus / detector system while taking account of the spatial orientation of the focus / detector systems and the beam respectively considered. Finally, absorption values are calculated with the aid of the intensity values thus corrected, and CT pictures or CT volume data are thereby reconstructed.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
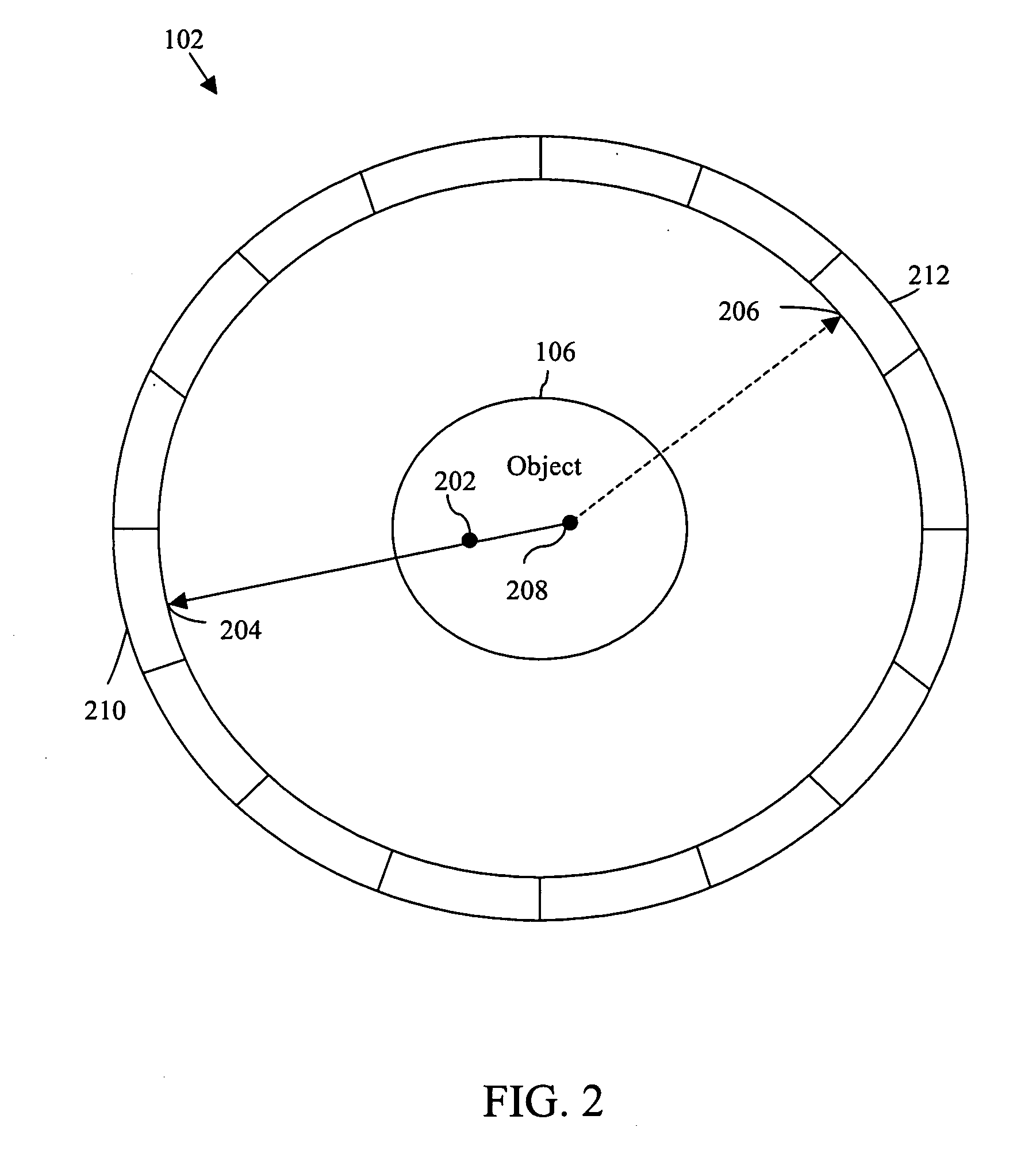
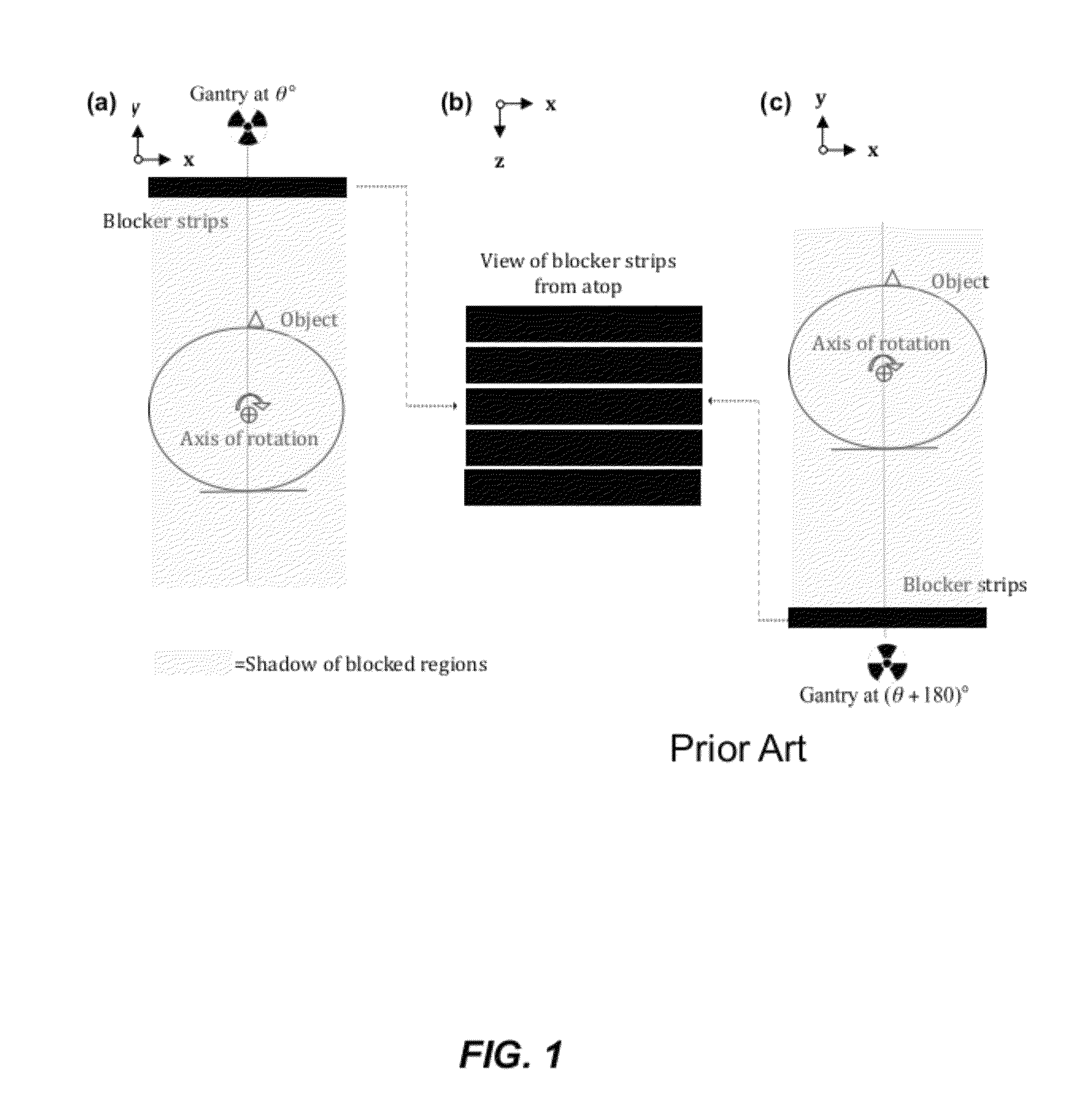
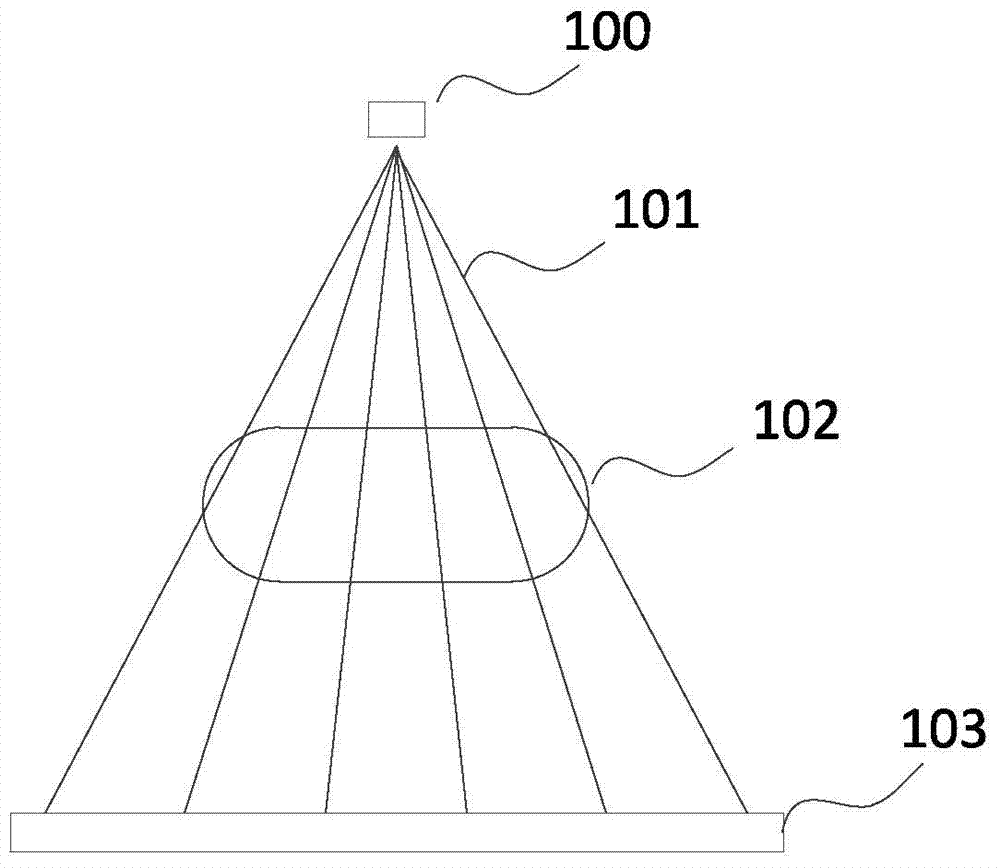
Scatter correction device for radiative tomographic scanner
InactiveUS20050072929A1Improve accuracySharp contrastRadiation/particle handlingMaterial analysis by optical meansCt scannersLight beam
A scatter correction device for radiative tomographic scanners is disclosed. The device comprises at least one steady support component and multiple beam stoppers made of high Z materials such as lead and wolfram. Each beam stopper has two ends fixed on the steady support component respectively. Theses beam stoppers can thus be sustained at fixed locations by the steady support component. During scanning an object, the device is placed between the object and detectors. But when the scatter correction device is applied to a CT scanner, the device is placed between object and radiation source. It attenuates part of the primary radiation with very small affects on the scattered radiation.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Method of and Software for Calculating a Scatter Estimate for Tomographic Scanning and System for Tomographic Scanning
InactiveUS20080224050A1Reduce computing timeShorten the timeMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyUltrasound attenuationTomography
The method calculates a scatter estimate for annihilation photons in a subject having a distribution of attenuation. The method can be used for scatter correction of detection data from a positron emission tomographic scanner. The method uses the following steps: —select a first scatter point S1 and a second scatter point S2, —determine a first scatter probability for scattering of a photon at scatter point S1 and a second scatter probability for scattering of a photon at scatter point S2, —determine an integral of the attenuation over a line connecting S1 and S2, —multiply the integral and the scatter probabilities and use the product in the calculation of the scatter estimate.
Owner:HAMMERSMITH IMANET
Cone beam CT scatter correction method and system
InactiveCN103578082ADo not change the main structureNo change in stabilityImage enhancementComputerised tomographsUltrasound attenuationAttenuation coefficient
The invention relates to a cone beam CT scatter correction method and system. The method comprises the following steps that an attenuation coefficient matrix of an X-ray passing through an attenuation screen on a detector is calculated; under the condition that the attenuation screen is included, projected images of a radiated object are acquired; scatter correction is conducted on each projected image; the projected image of a template body without the attenuation screen is estimated through the attenuation coefficient matrix; the image is reconstructed through a FDK algorithm. The cone beam CT scatter correction method can effectively lower the scatter influence on cone beam CT image reconstruction, and the image quality is improved. Circular scanning is only conducted on cone beam CT for one time, and irradiation dose is not additionally increased. The cone beam CT scatter correction method is simple to implement, and the main structure and the stability of the cone beam CT are not changed. The cone beam CT scatter correction system can effectively lower the scatter influence on cone beam CT image reconstruction, improve the image quality, and overcome the technical difficulty of poor cone beam CT imaging quality.
Owner:JIANGSU CHAOWEI TECH DEV
Scatter and beam hardening correctoin in computed tomography applications
InactiveUS20050185753A1Reconstruction from projectionRadiation/particle handlingSpectral response3d image
A method of correcting scatter includes obtaining a voxellized representation of a 3D image of an object from a plurality of projection data. A single scatter profile for the object is calculated using the voxellized representation of the 3D image of the object. A total scatter profile for the object is determined using the single scatter profile and an adjustment factor and the projection data is corrected using the total scatter profile to obtain a scatter corrected projection data. A beam hardening correction method includes simulating a number of attenuation data for an x-ray spectrum, at least one object material, and a detector spectral response. A function is fitted to the attenuation data to obtain an attenuation curve. A number of projection data for an object are corrected using the attenuation curve to obtain a number of beam hardening corrected projection data. A corrected image of the object is reconstructed from the beam hardening corrected image data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
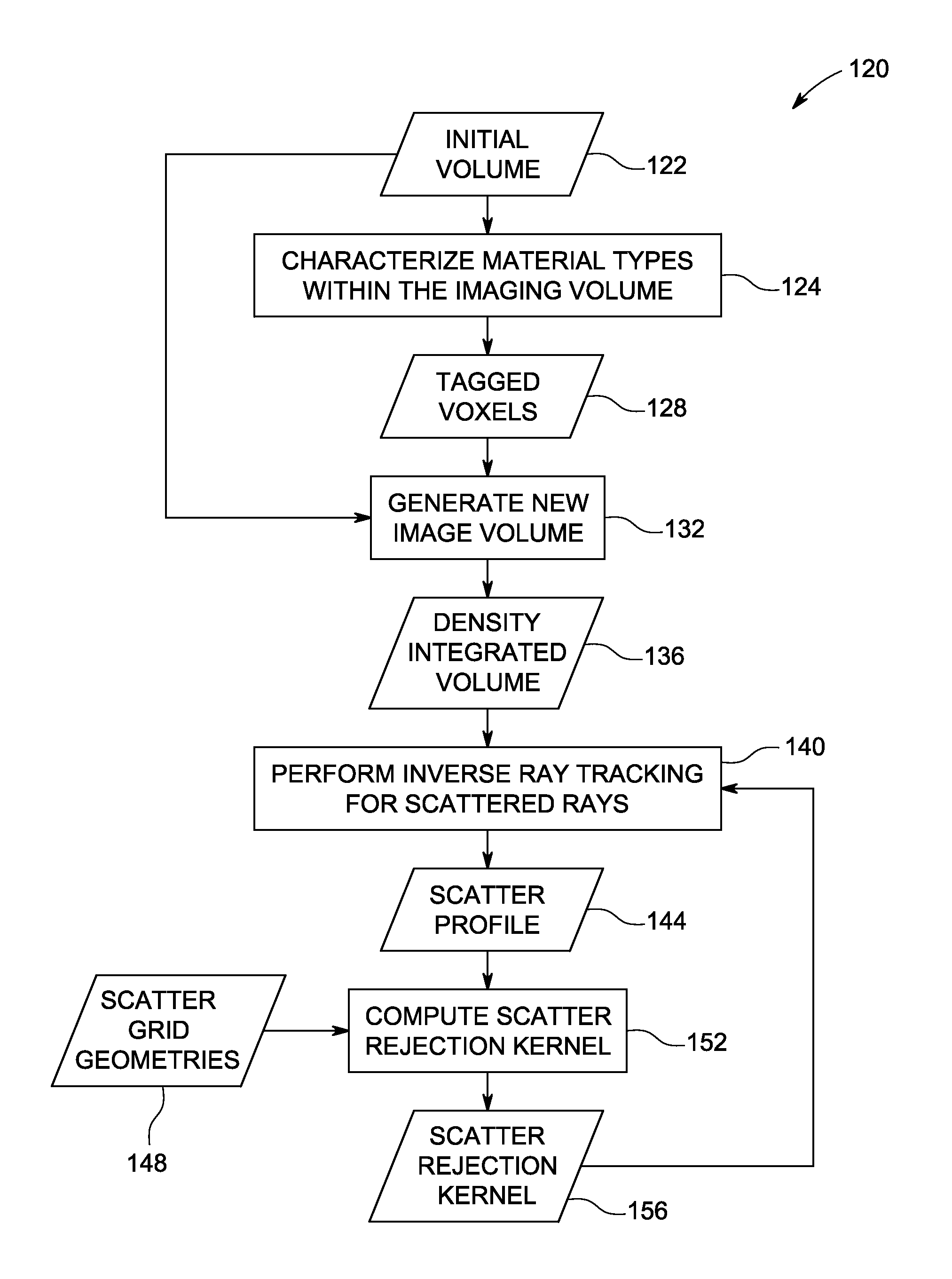
Method and system for scatter correction in x-ray imaging
Approaches for deriving scatter information using inverse tracking of scattered X-rays is disclosed. In certain embodiments scattered rays are tracked from respective locations on a detector to a source of the X-ray radiation, as opposed to tracking schemes that proceed from the source to the detector. In one such approach, the inverse tracking is implemented using a density integrated volume that reduces the integration steps performed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Cone beam CT scatter correction method and device based on complementary gratings
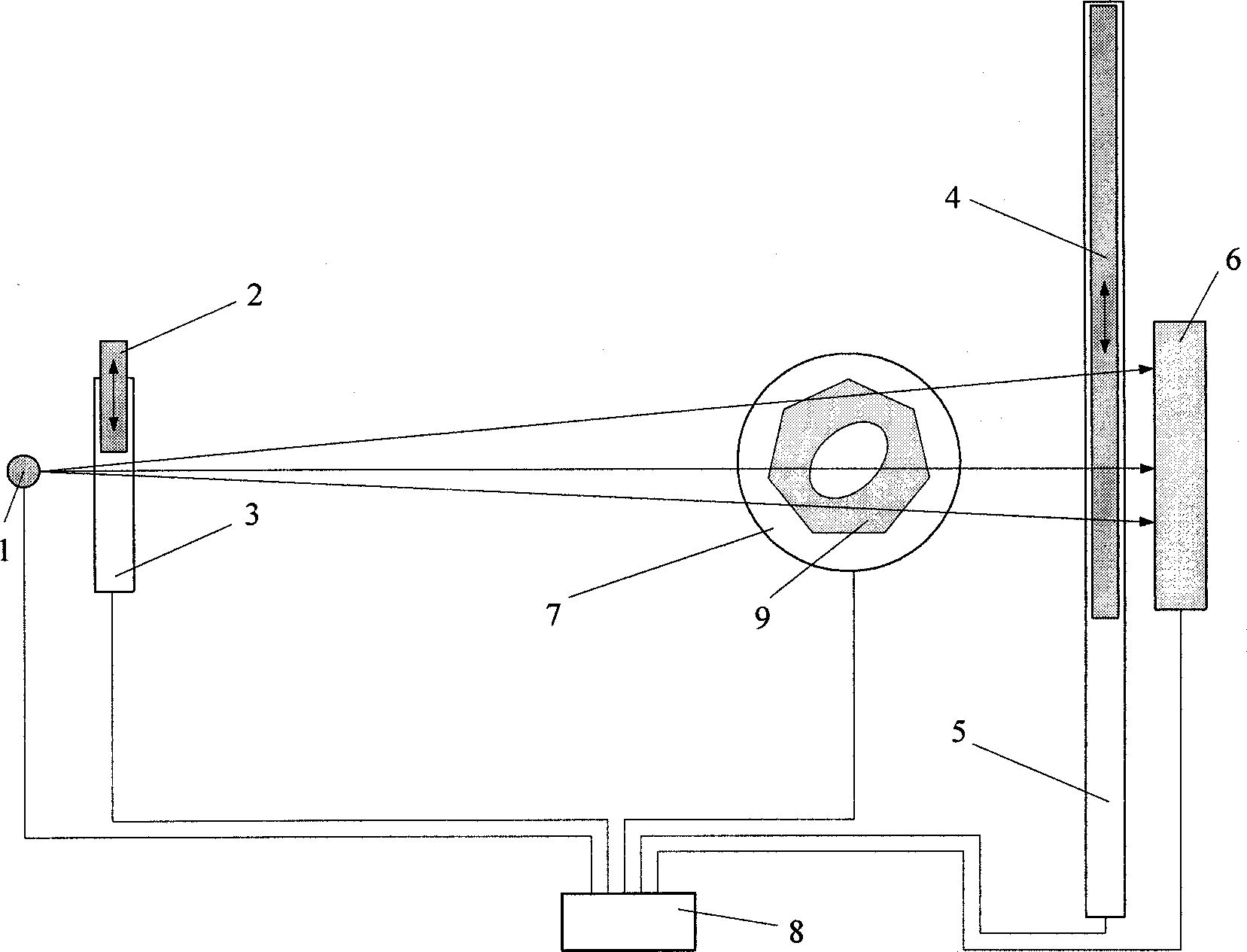
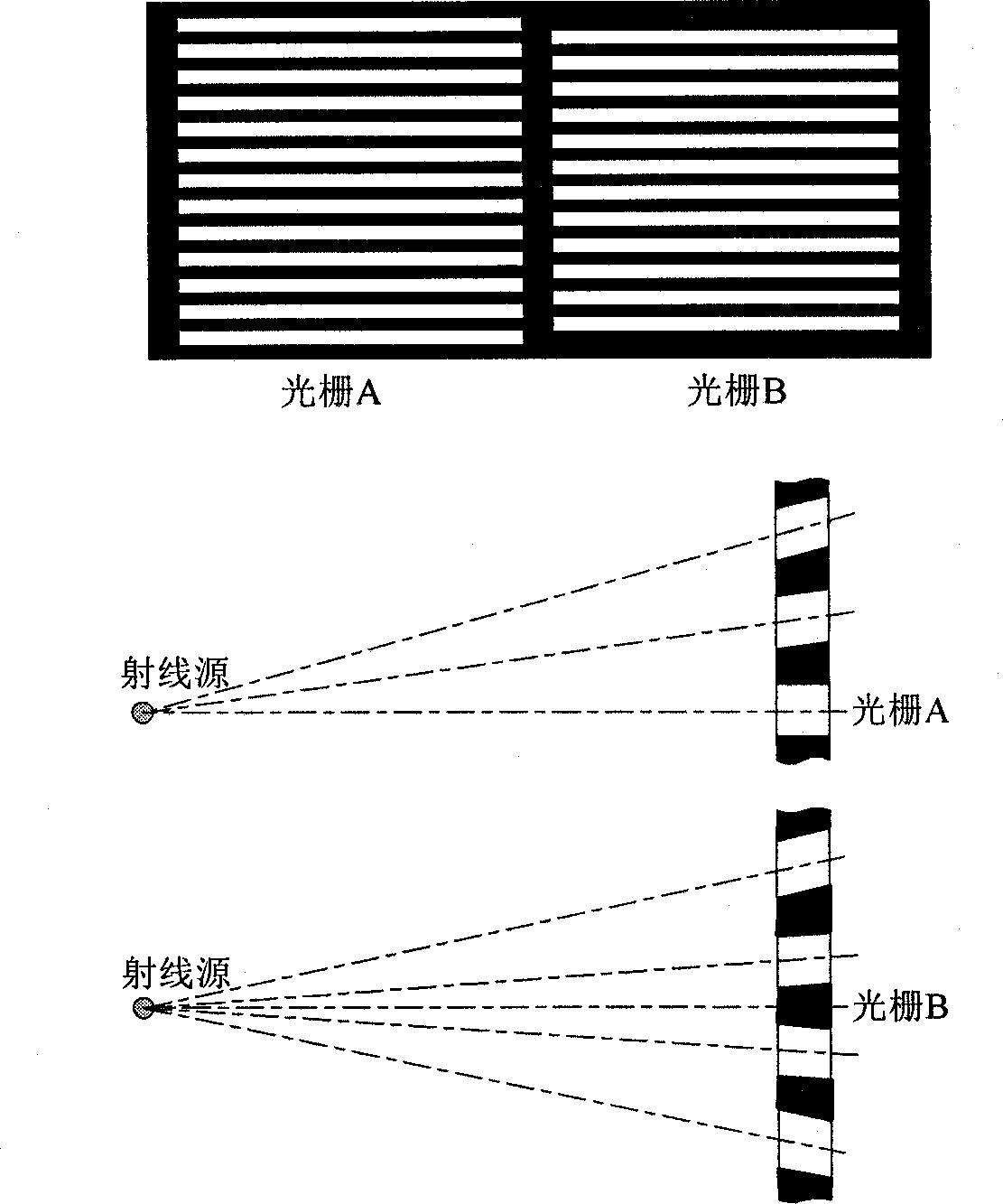
ActiveCN104161536AQuality improvementImprove accuracyComputerised tomographsTomographyGratingRaster scan
The invention discloses a cone beam CT scatter correction method and device based on complementary gratings. The scatter correction of projected images is achieved through simple and reliable complementary grating scanning and a small amount of calculation, and scatter correction slice images can be rebuilt out through the projected images obtained after scatter correction is finished. The cone beam CT scatter correction method and device based on the complementary gratings are suitable for tested objects of any complexities, the method is good in accuracy, reliability, stability and convenience, adverse effects on cone beam CT images from scattering are reduced to the maximum extent, and therefore the quality of the cone beam CT slice images is improved obviously.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com