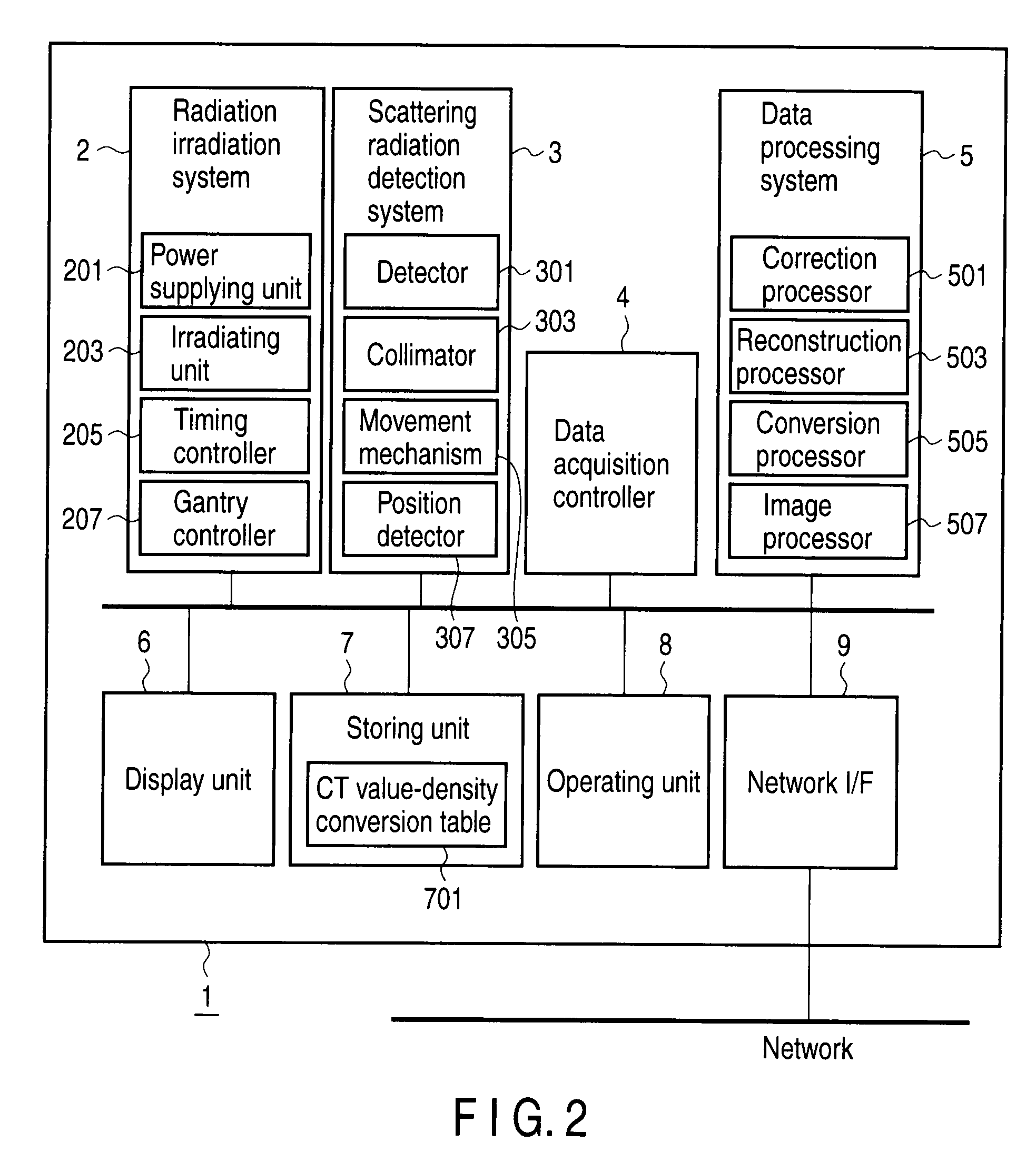
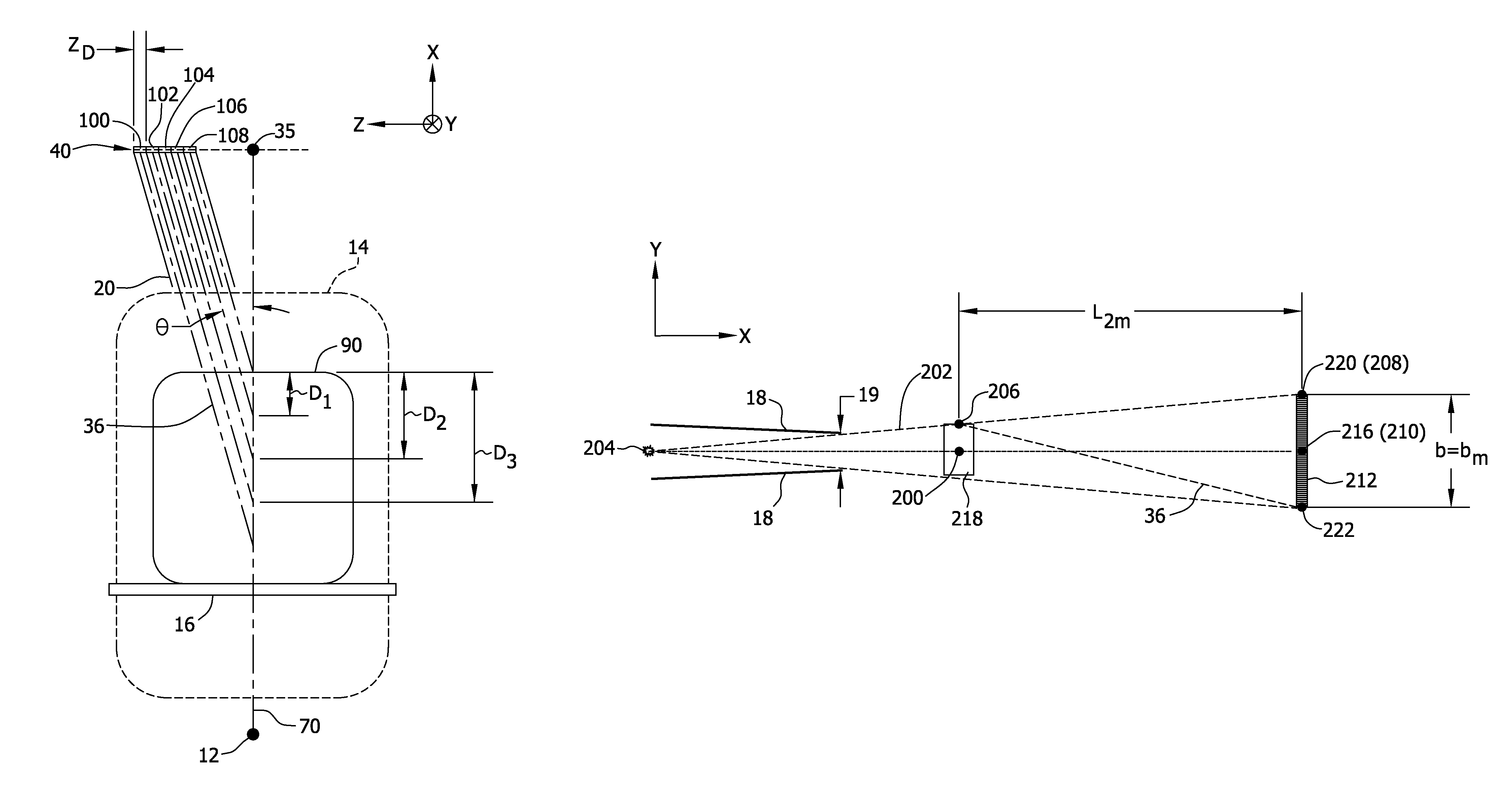
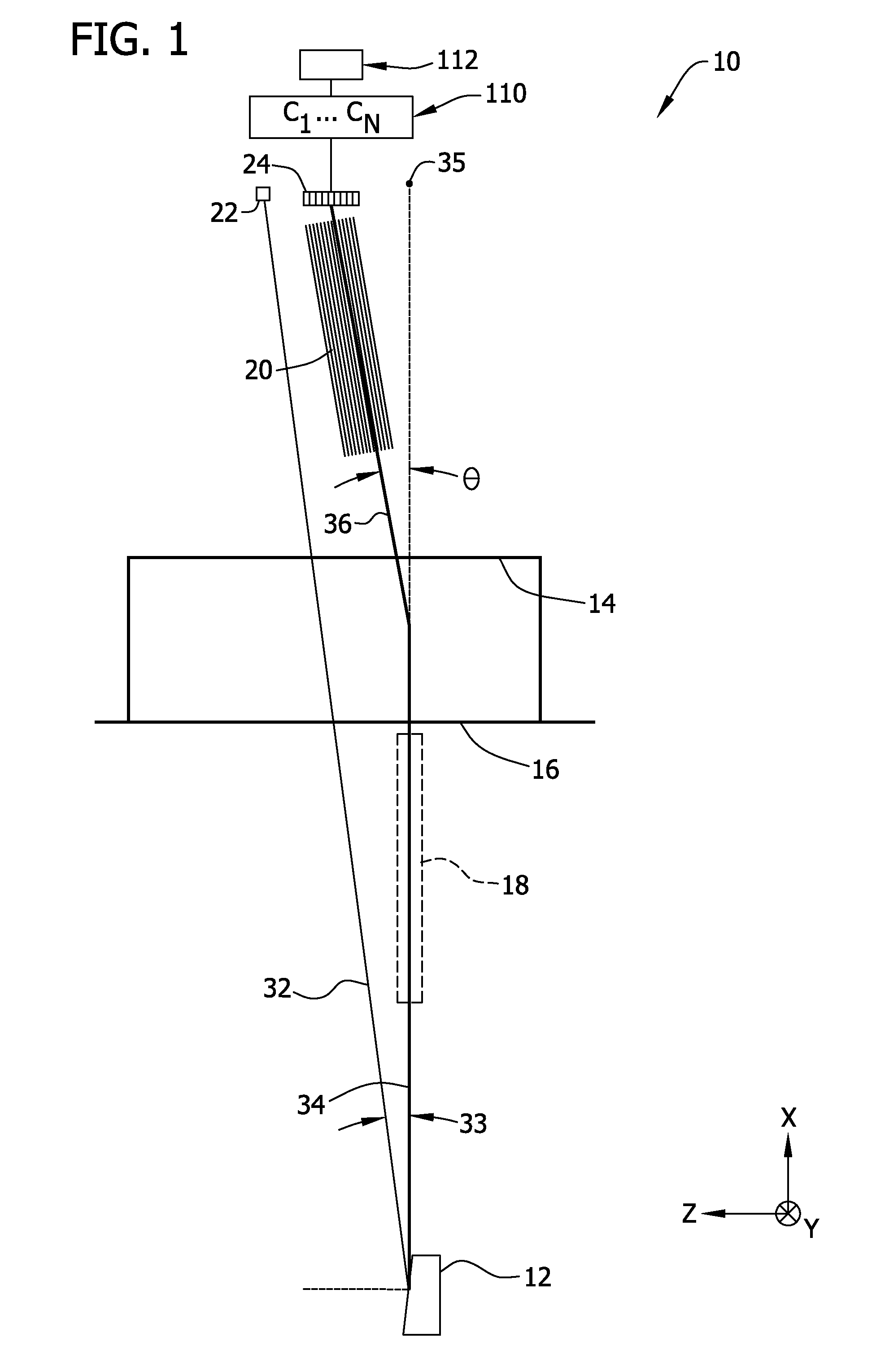
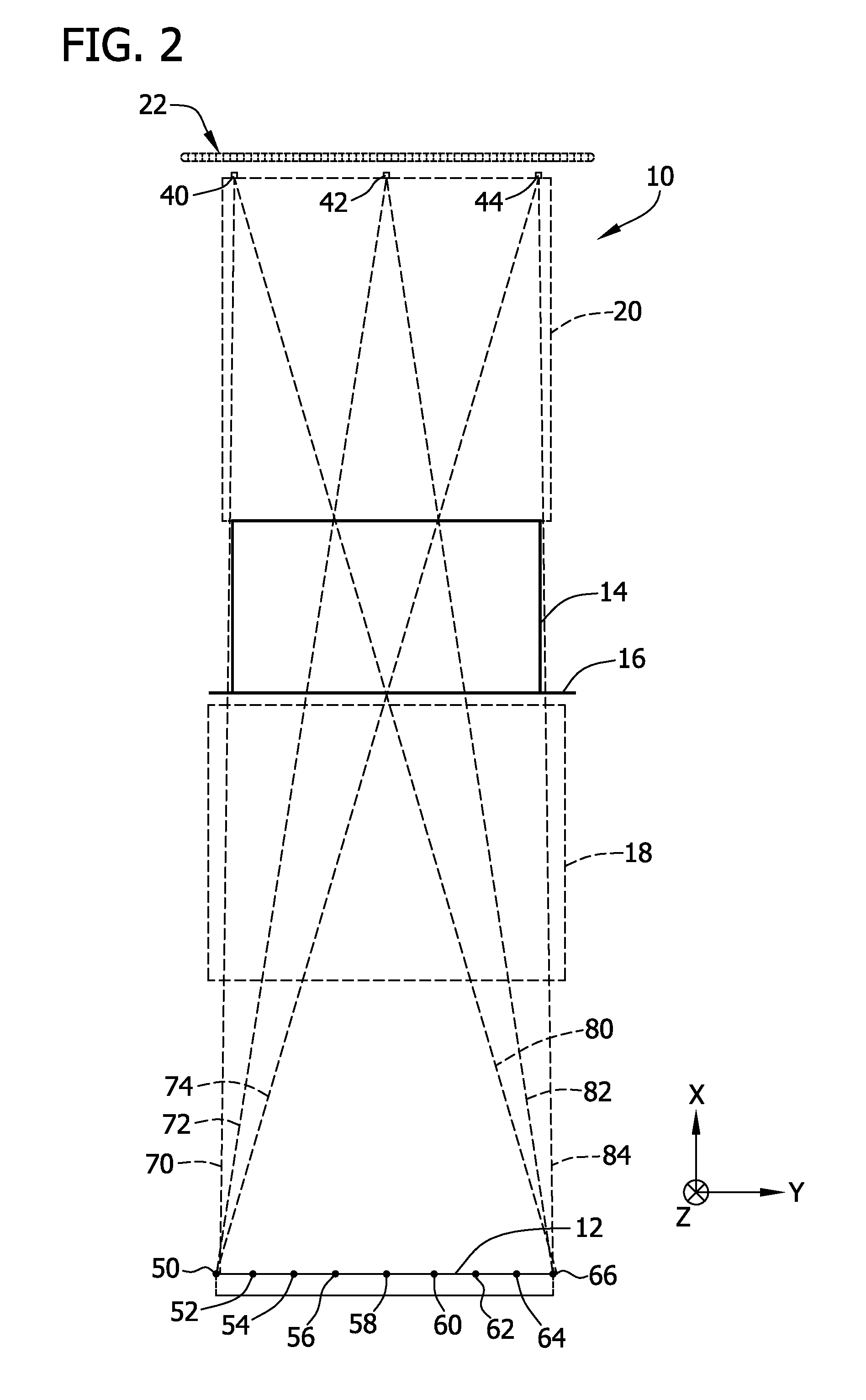
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
343 results about "Scatter radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
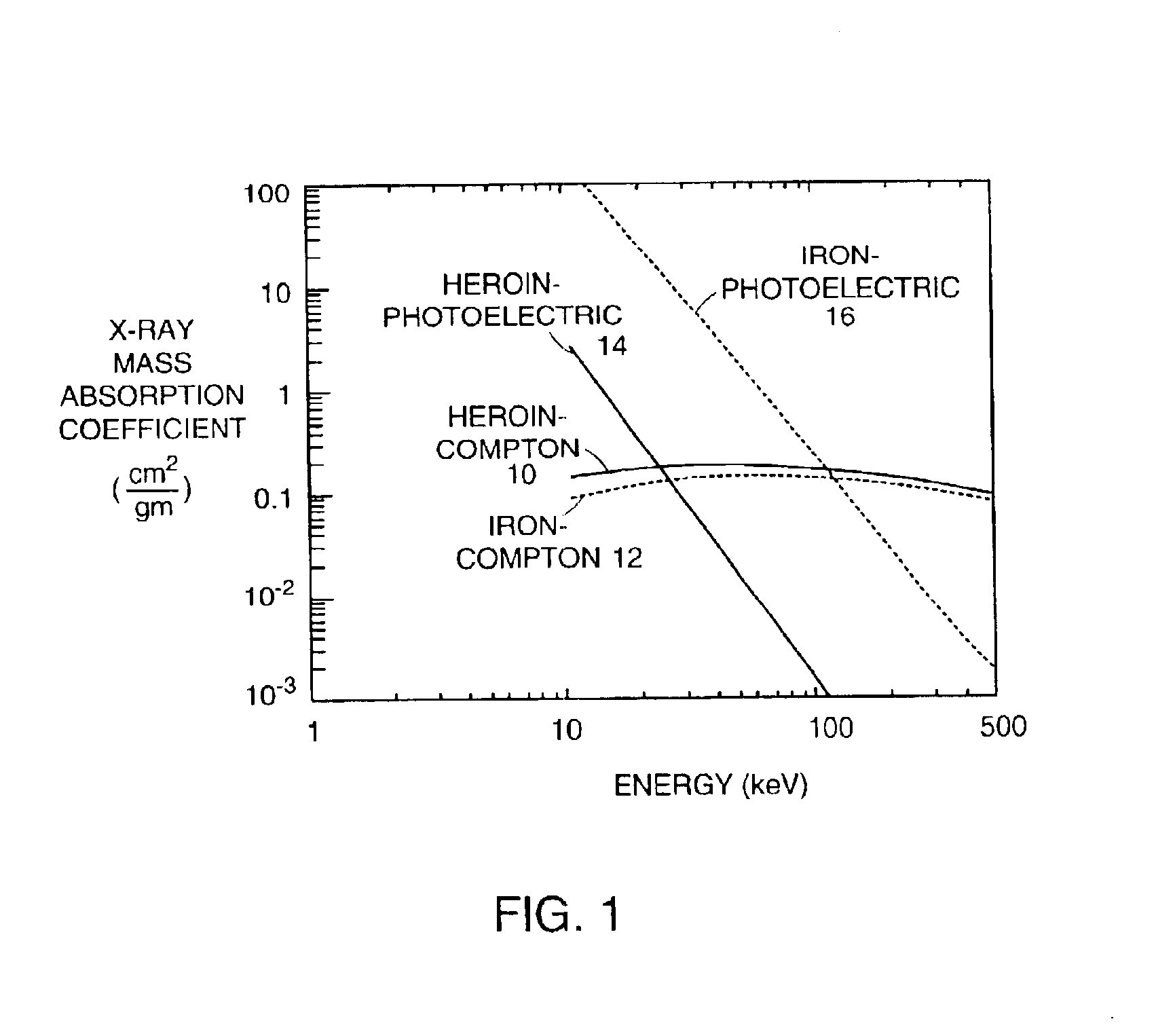
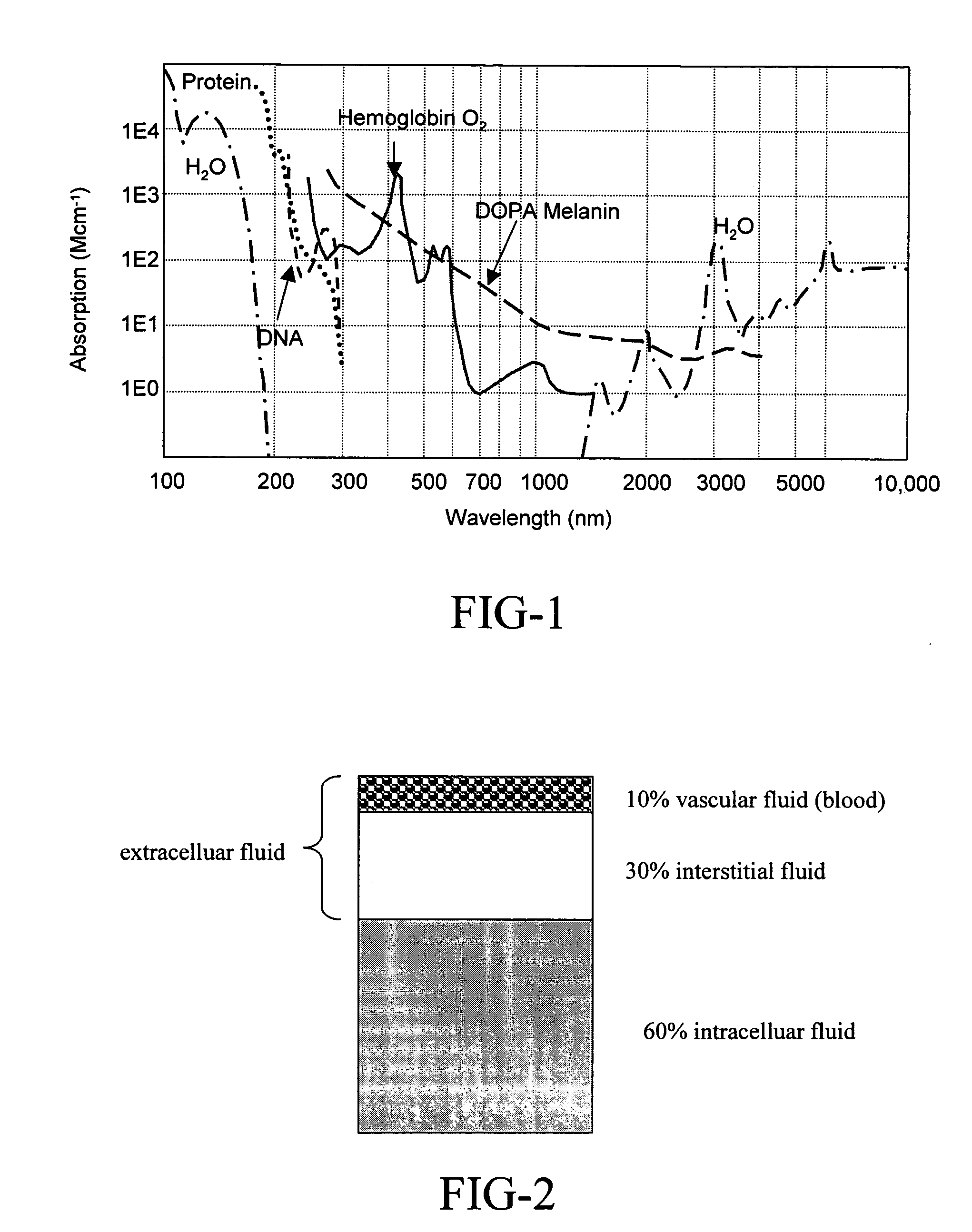
Scatter Radiation is a type of secondary radiation that occurs when the useful beam intercepts any object, causing some x-rays to be scattered. During an x-ray or fluoroscopic exam the patient is the most significant source of scatter radiation.
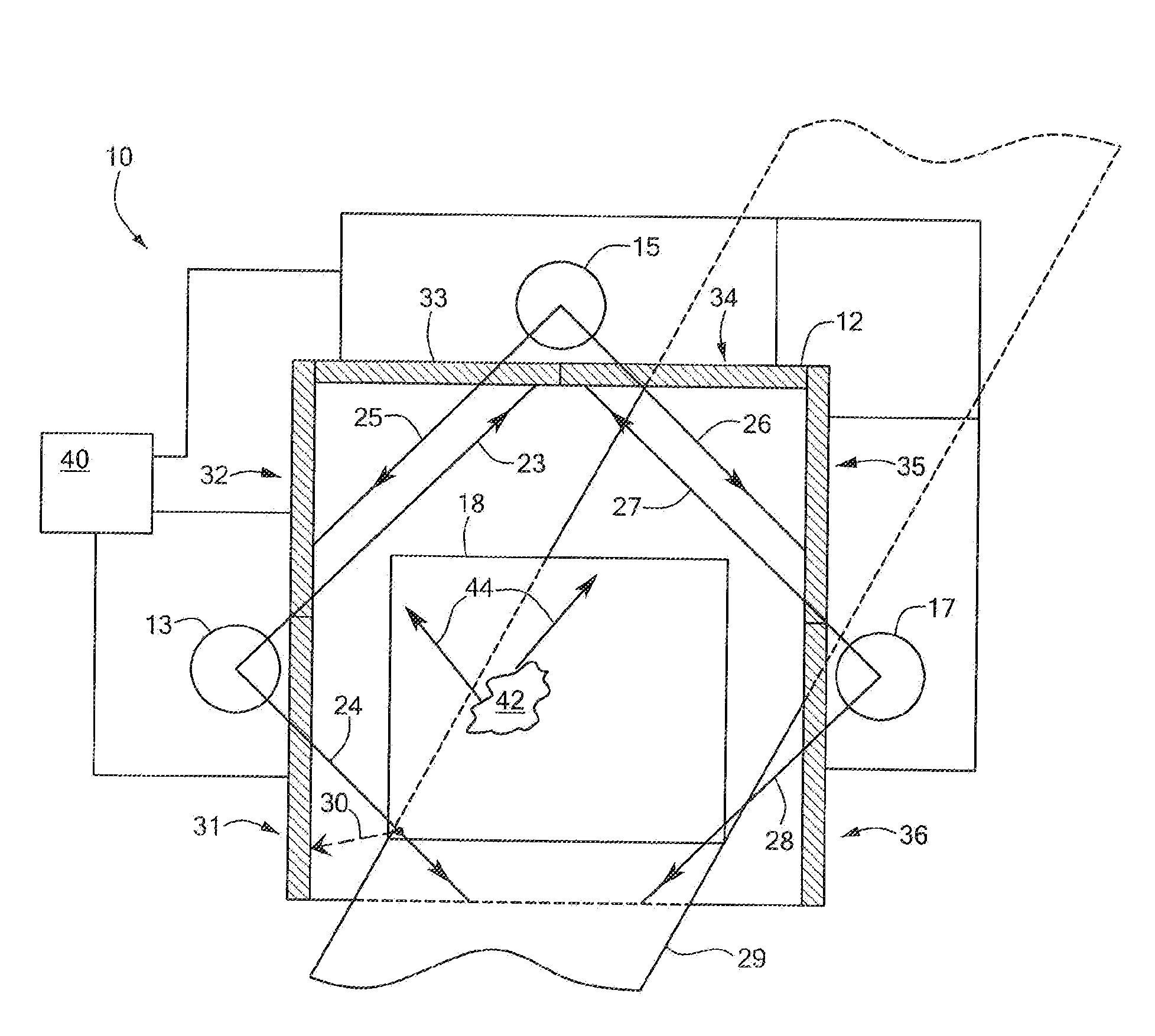
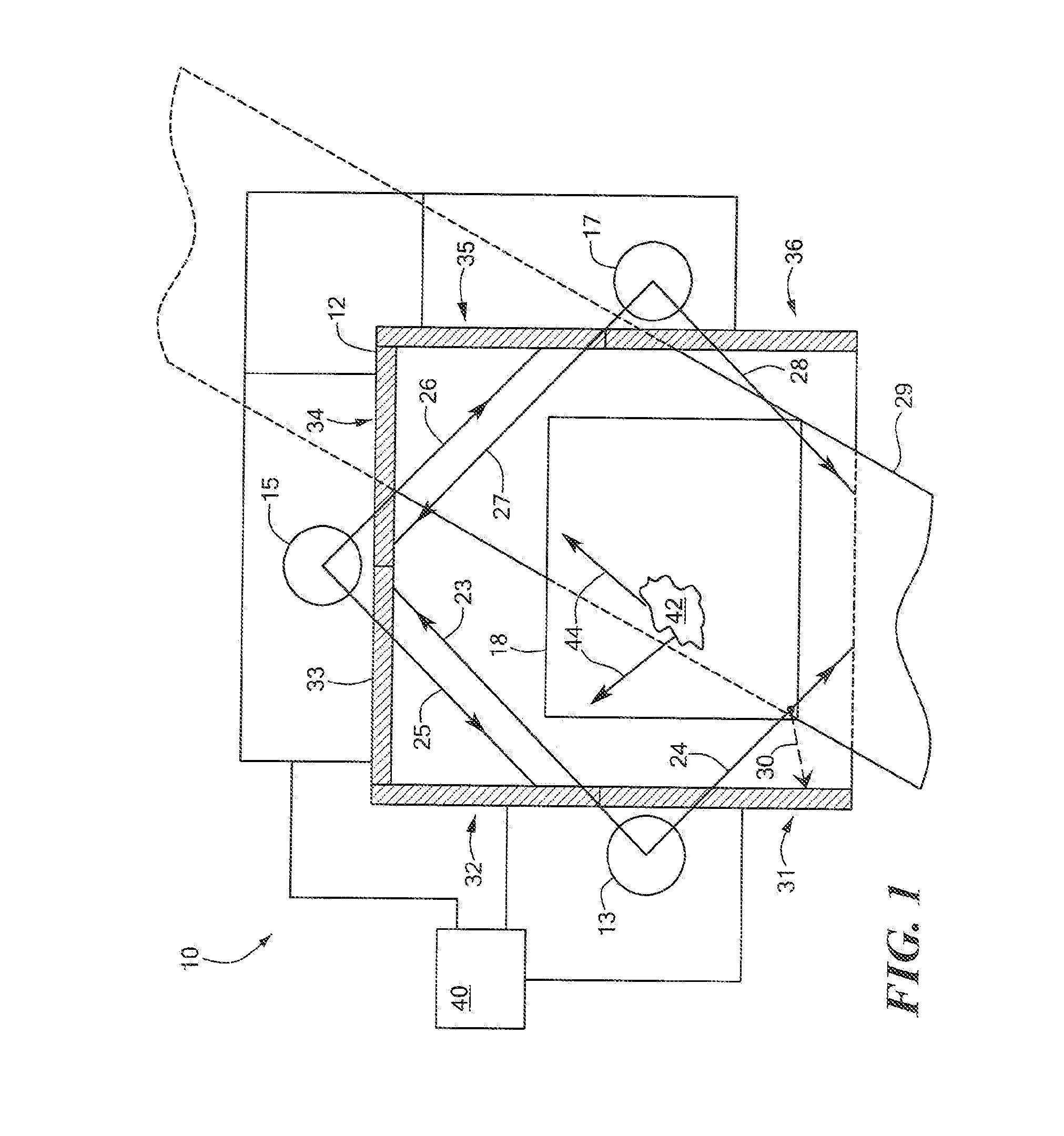
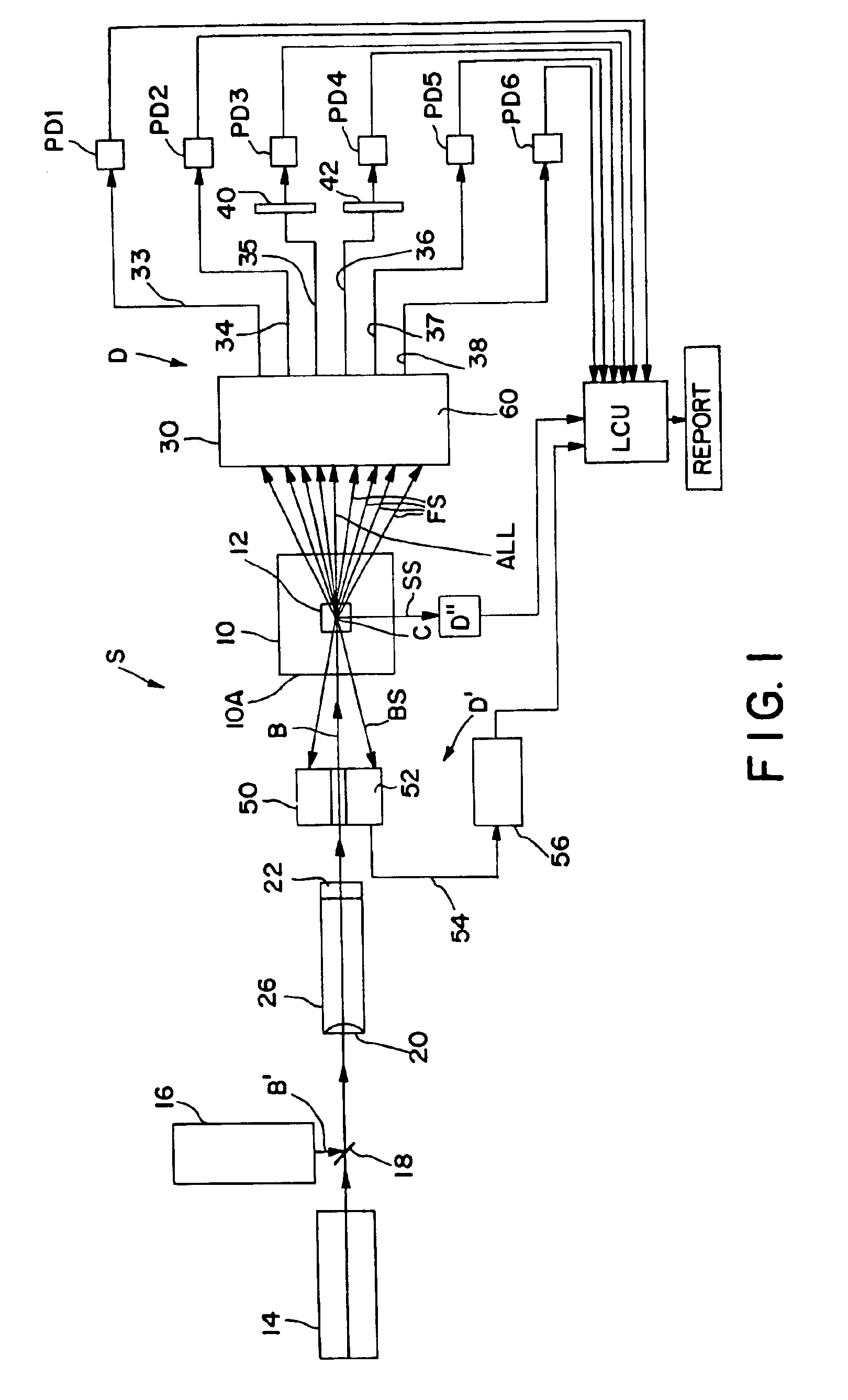
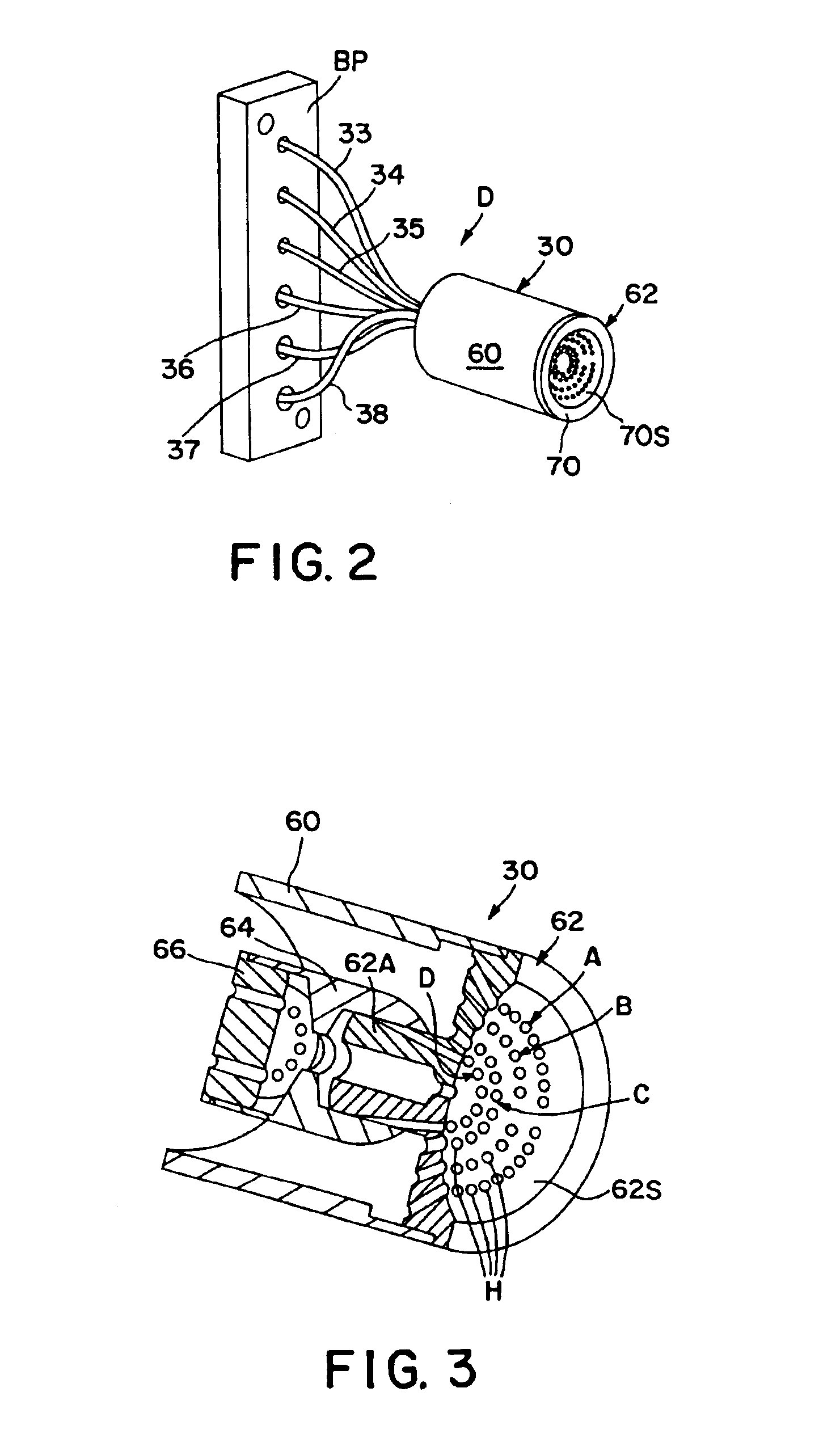
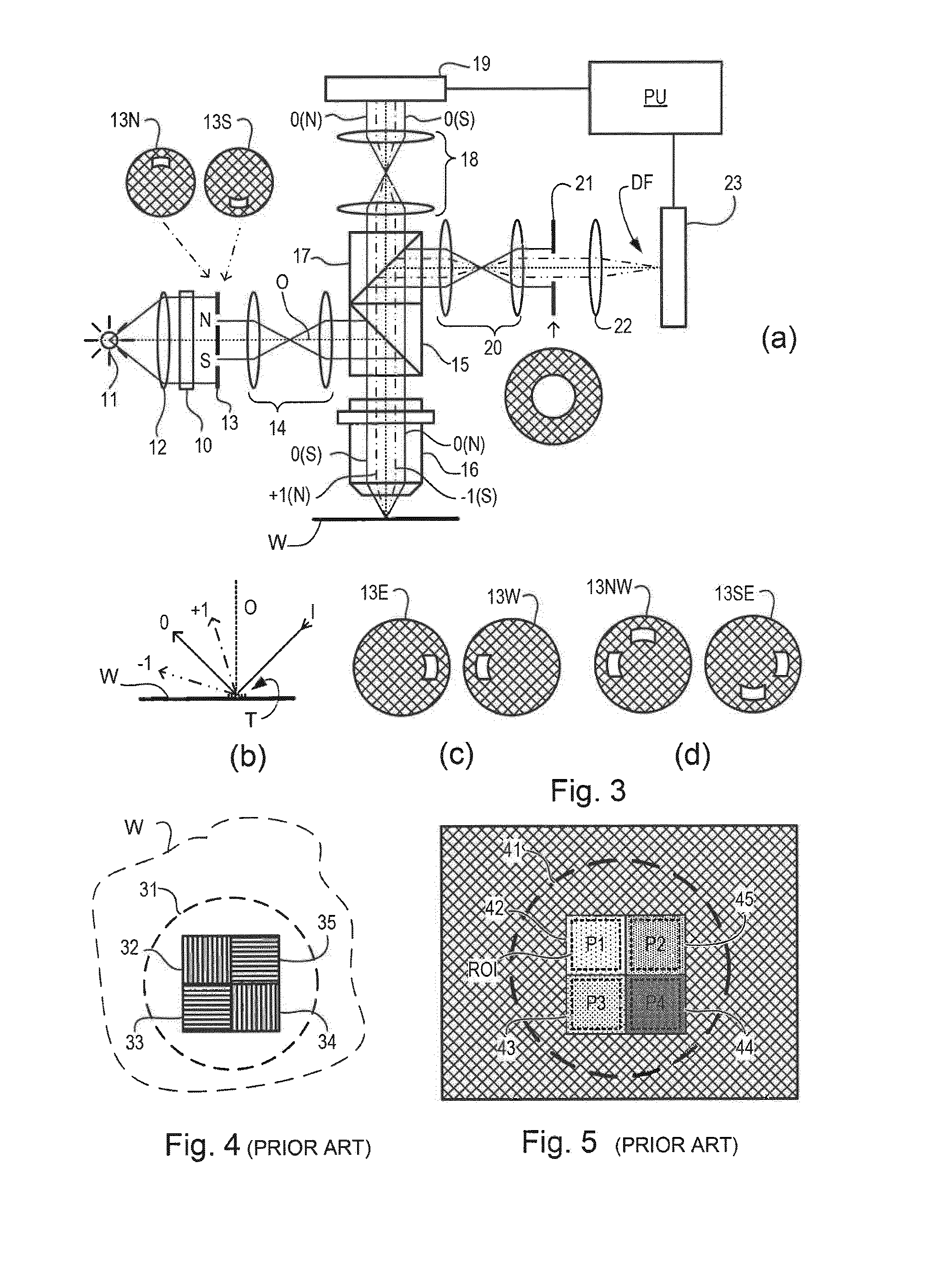
Backscatter inspection portal
ActiveUS7400701B1X/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationImaging qualityLight beam
Owner:AMERICAN SCI & ENG INC
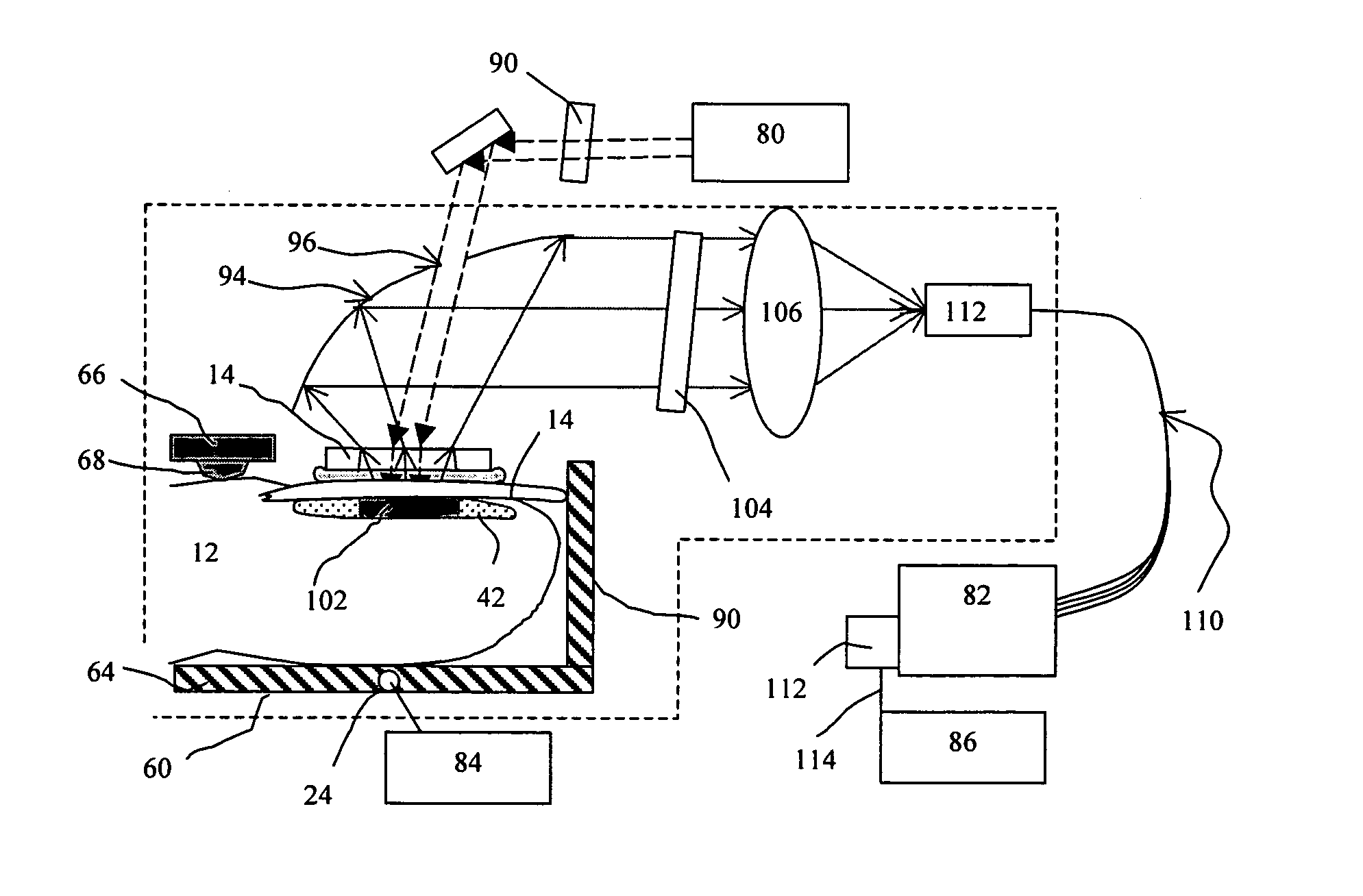
Apparatus and method for non-invasive and minimally-invasive sensing of parameters relating to blood
InactiveUS20060253007A1Reduce disadvantagesImprove accuracyDiagnostics using lightOrgan movement/changes detectionNon invasiveThree vessels
Medical diagnostic system, apparatus and methods are disclosed. Optical transmitters generate radiation-containing photons having a specific interaction with at least one target chromophore in a target structure, preferably a blood vessel such as the interior jugular vein. The optical transmitters transmit the radiation into at least a first area including a substantial portion of the target structure and into a second area not including a substantial portion of the target structure. Optical receivers detect a portion radiation scattered from at least the first area and the second area. A processor estimates oxygenation, pH or cardiac output based on the scattered radiation detected from the first area, and the scattered radiation from the second area.
Owner:SKYLINE BIOMEDICAL
X-ray inspection based on scatter detection
ActiveUS7551715B2Minimize bounceAvoid damageX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationX-rayLight beam
Systems and methods for inspecting an object with a scanned beam of penetrating radiation are disclosed. Scattered radiation from the beam is detected, in either the backward or forward direction. Characteristic values of the backscattered radiation are compared to expected reference values to characterize the object. Additionally, penetrating radiation transmitted through the inspected object may be combined with scatter information. In certain embodiments, the inspected field of view is less than 0.1 steradians, and the detector is separate from the source of penetrating radiation and is disposed, with respect to the object, such as to subtend greater than 0.5 steradians in the field of view of the object.
Owner:AMERICAN SCI & ENG INC
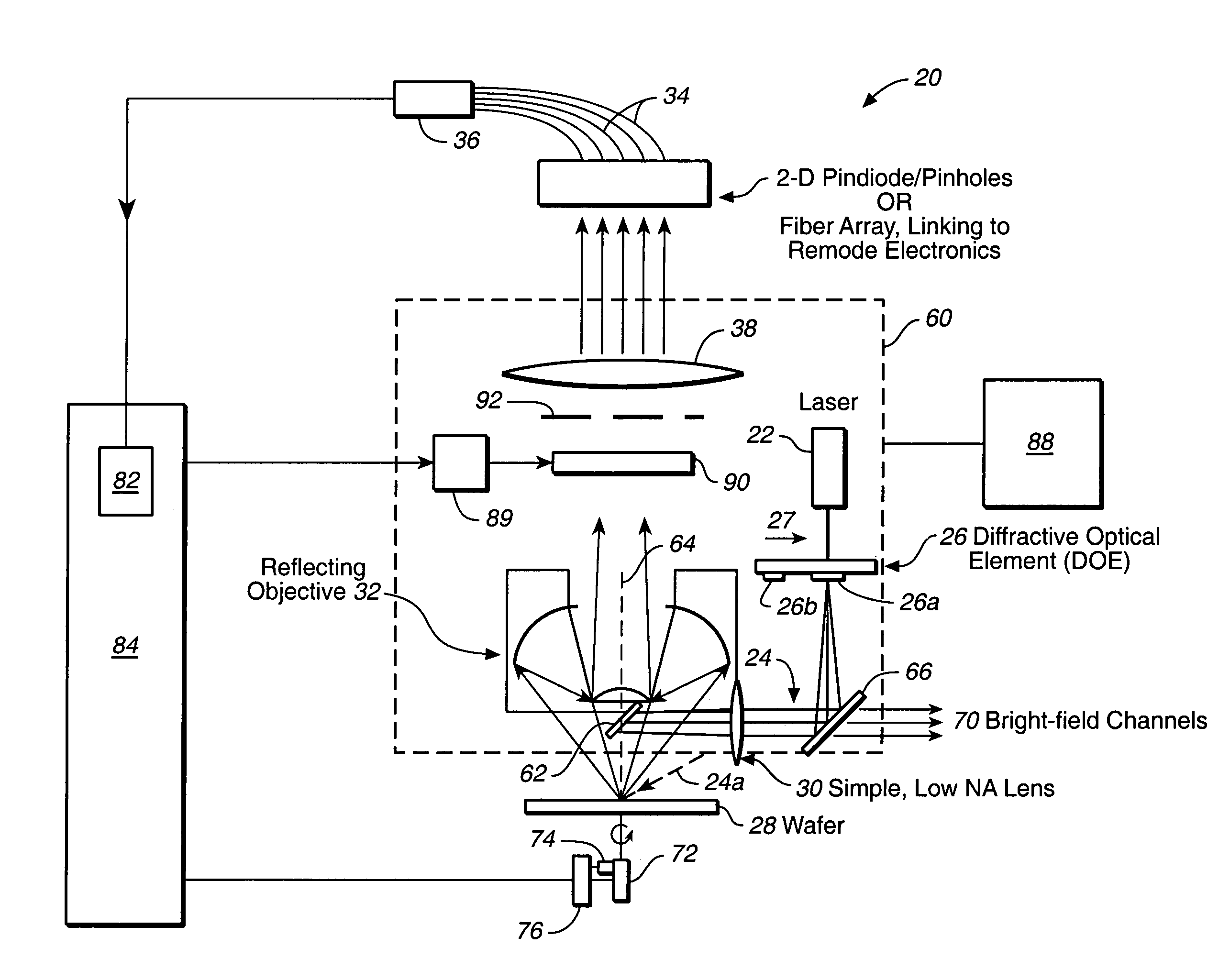
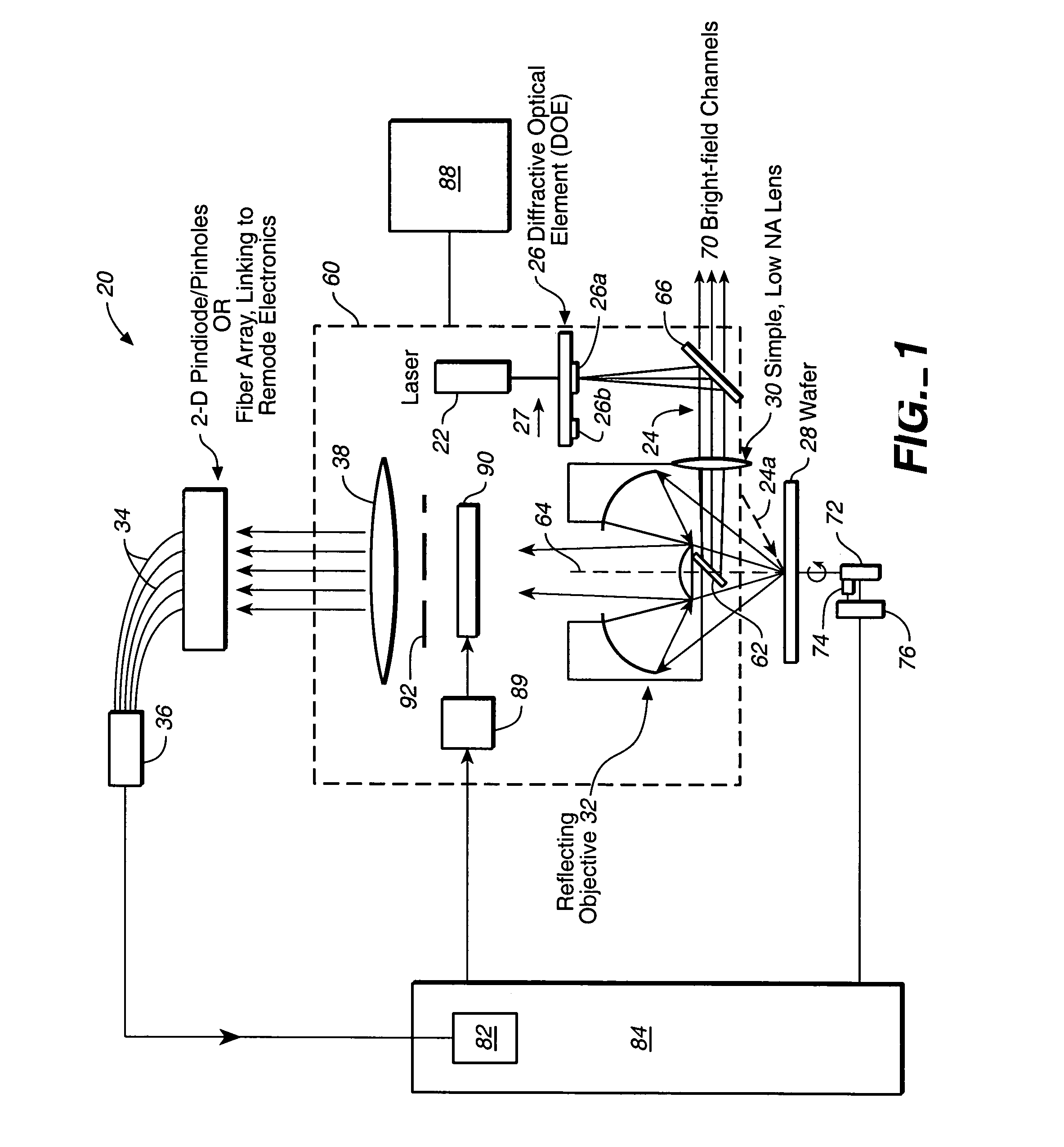
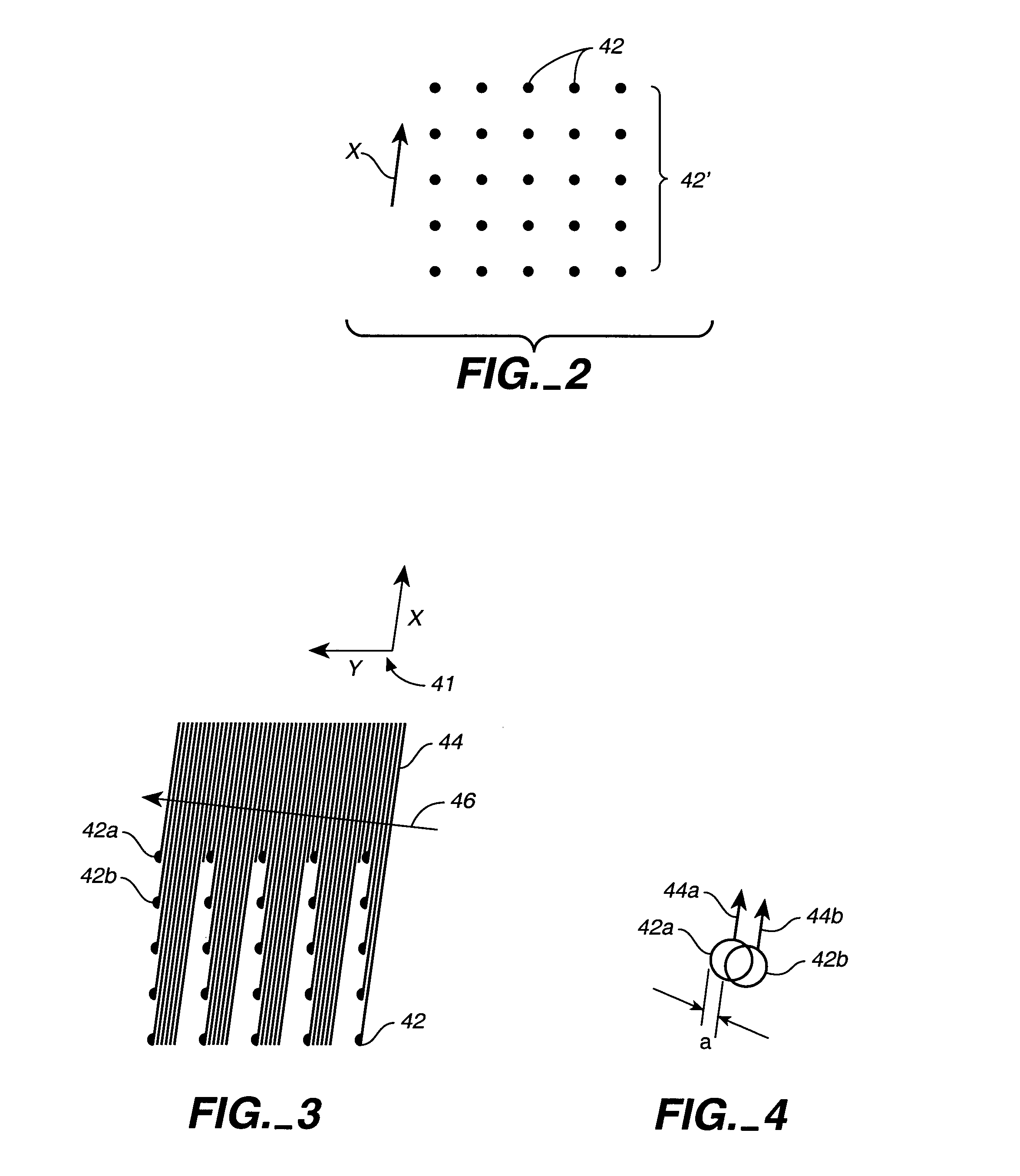
Simultaneous multi-spot inspection and imaging
InactiveUS7130039B2High detection sensitivityImprove performanceAnalysis by electrical excitationOptically investigating flaws/contaminationDetector arrayAnnular aperture
A compact and versatile multi-spot inspection imaging system employs an objective for focusing an array of radiation beams to a surface and a second reflective or refractive objective having a large numerical aperture for collecting scattered radiation from the array of illuminated spots. The scattered radiation from each illuminated spot is focused to a corresponding optical fiber channel so that information about a scattering may be conveyed to a corresponding detector in a remote detector array for processing. For patterned surface inspection, a cross-shaped filter is rotated along with the surface to reduce the effects of diffraction by Manhattan geometry. A spatial filter in the shape of an annular aperture may also be employed to reduce scattering from patterns such as arrays on the surface. In another embodiment, different portions of the same objective may be used for focusing the illumination beams onto the surface and for collecting the scattered radiation from the illuminated spots simultaneously. In another embodiment, a one-dimensional array of illumination beams are directed at an oblique angle to the surface to illuminate a line of illuminated spots at an angle to the plane of incidence. Radiation scattered from the spots are collected along directions perpendicular to the line of spots or in a double dark field configuration.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
X-Ray Inspection Based on Scatter Detection
ActiveUS20070098142A1Minimize bounceAvoid damageX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationX-rayLight beam
Systems and methods for inspecting an object with a scanned beam of penetrating radiation are disclosed. Scattered radiation from the beam is detected, in either the backward or forward direction. Characteristic values of the backscattered radiation are compared to expected reference values to characterize the object. Additionally, penetrating radiation transmitted through the inspected object may be combined with scatter information. In certain embodiments, the inspected field of view is less than 0.1 steradians, and the detector is separate from the source of penetrating radiation and is disposed, with respect to the object, such as to subtend greater than 0.5 steradians in the field of view of the object.
Owner:AMERICAN SCI & ENG INC
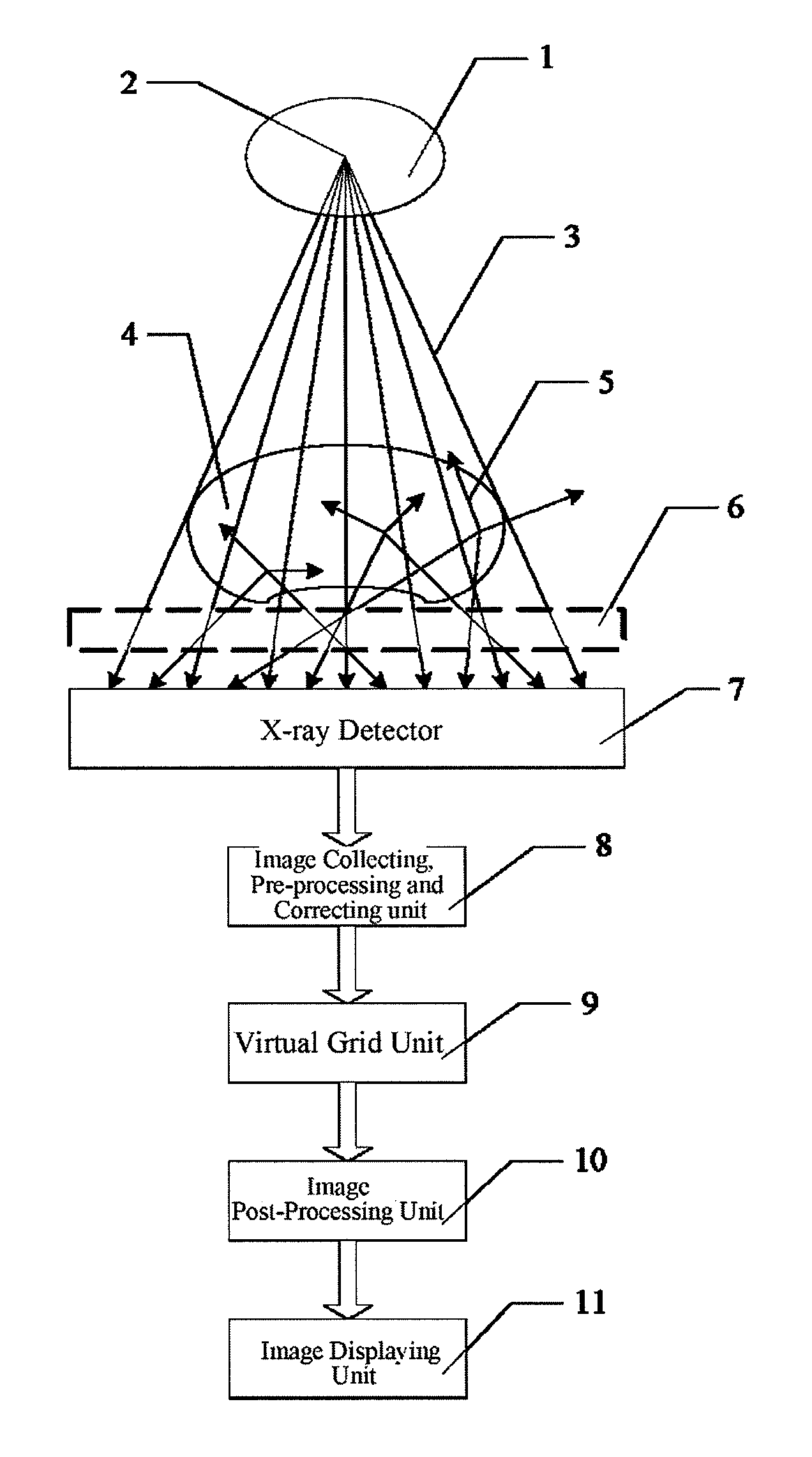
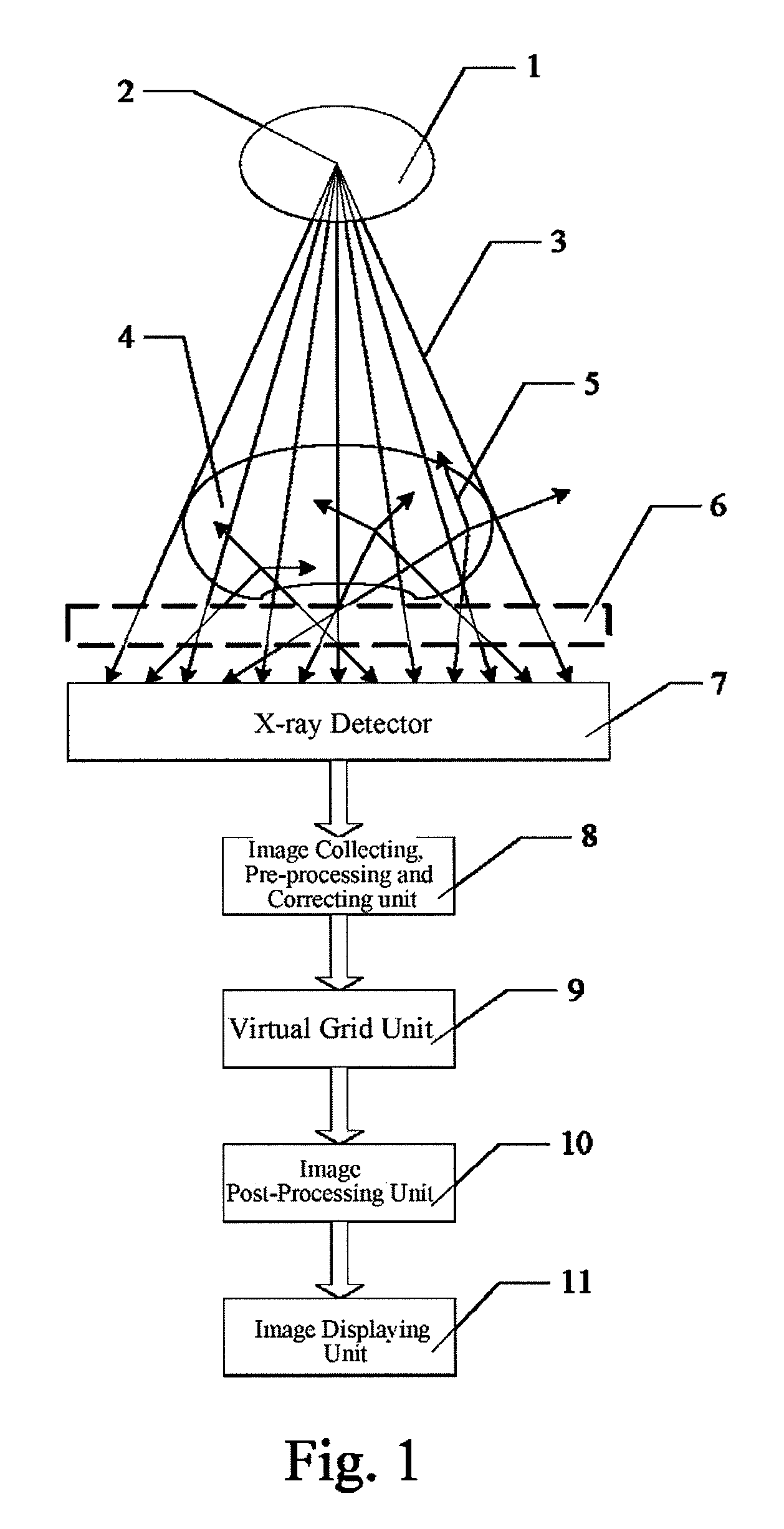
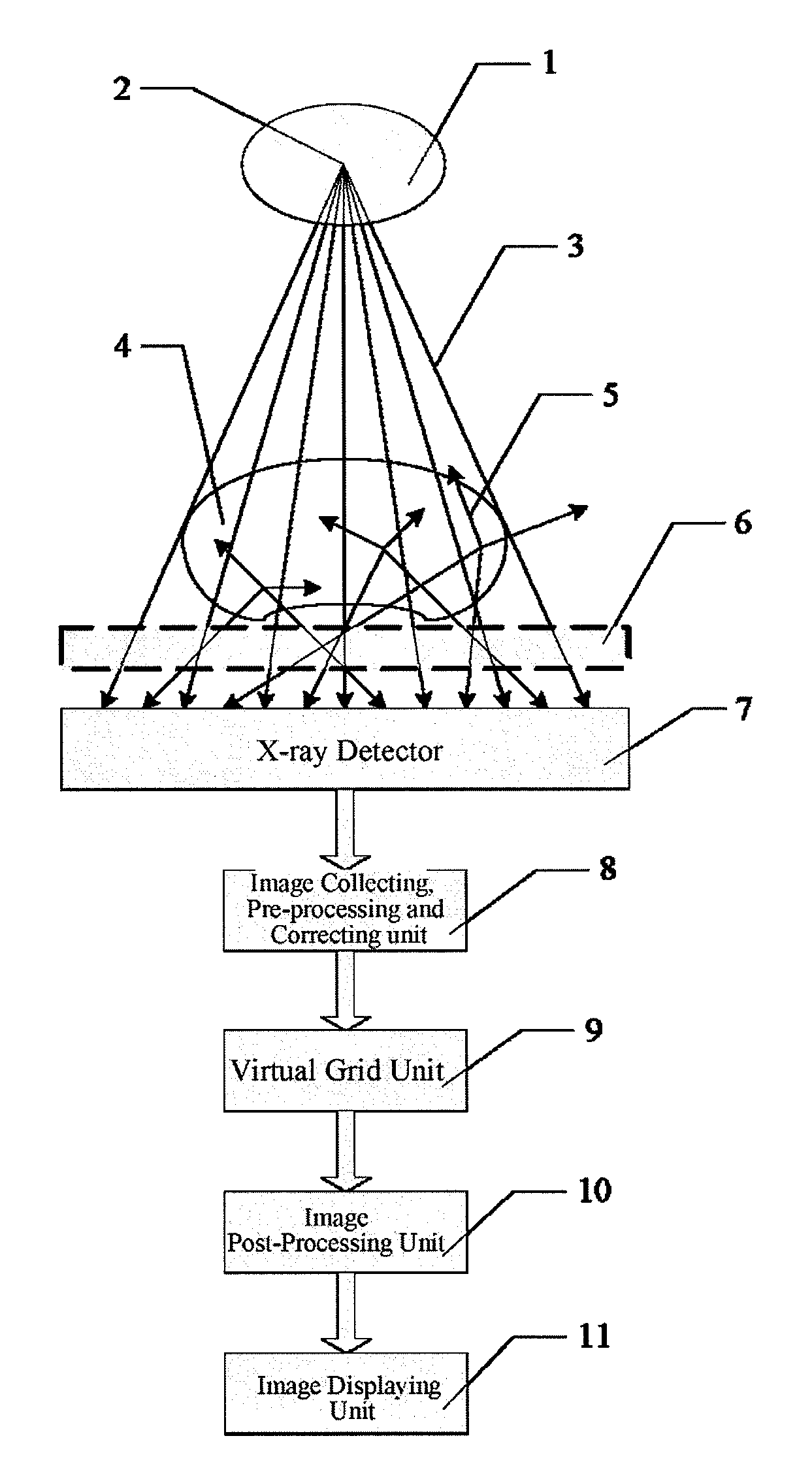
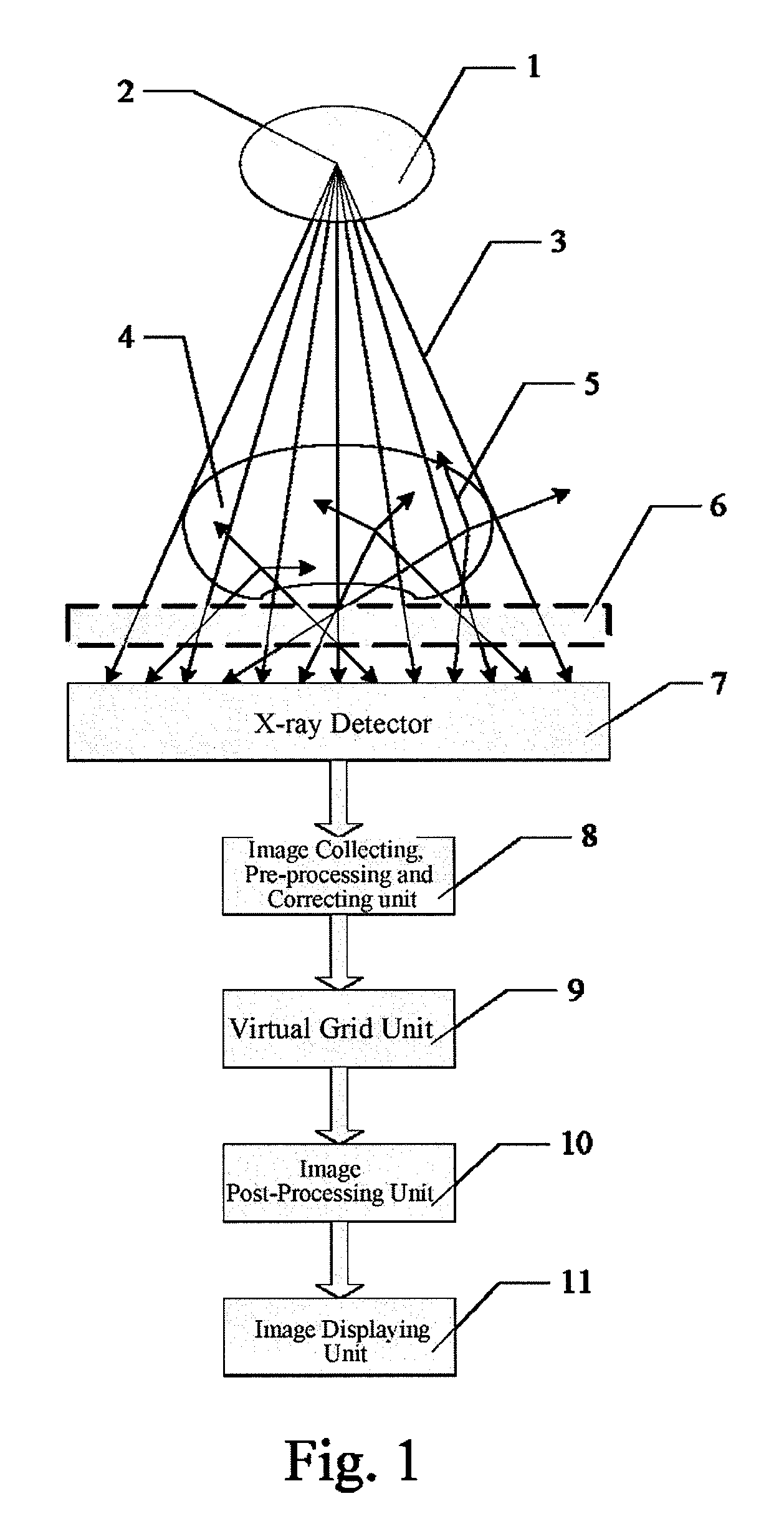
Virtual grid imaging method and system for eliminating scattered radiation effect
InactiveUS8064676B2Eliminate the effects ofComponent can be removedImage enhancementImage analysisMulti bandHigh energy
Owner:BEIJING SINOPHARM HUNDRIC MEDLINE INFO TECH
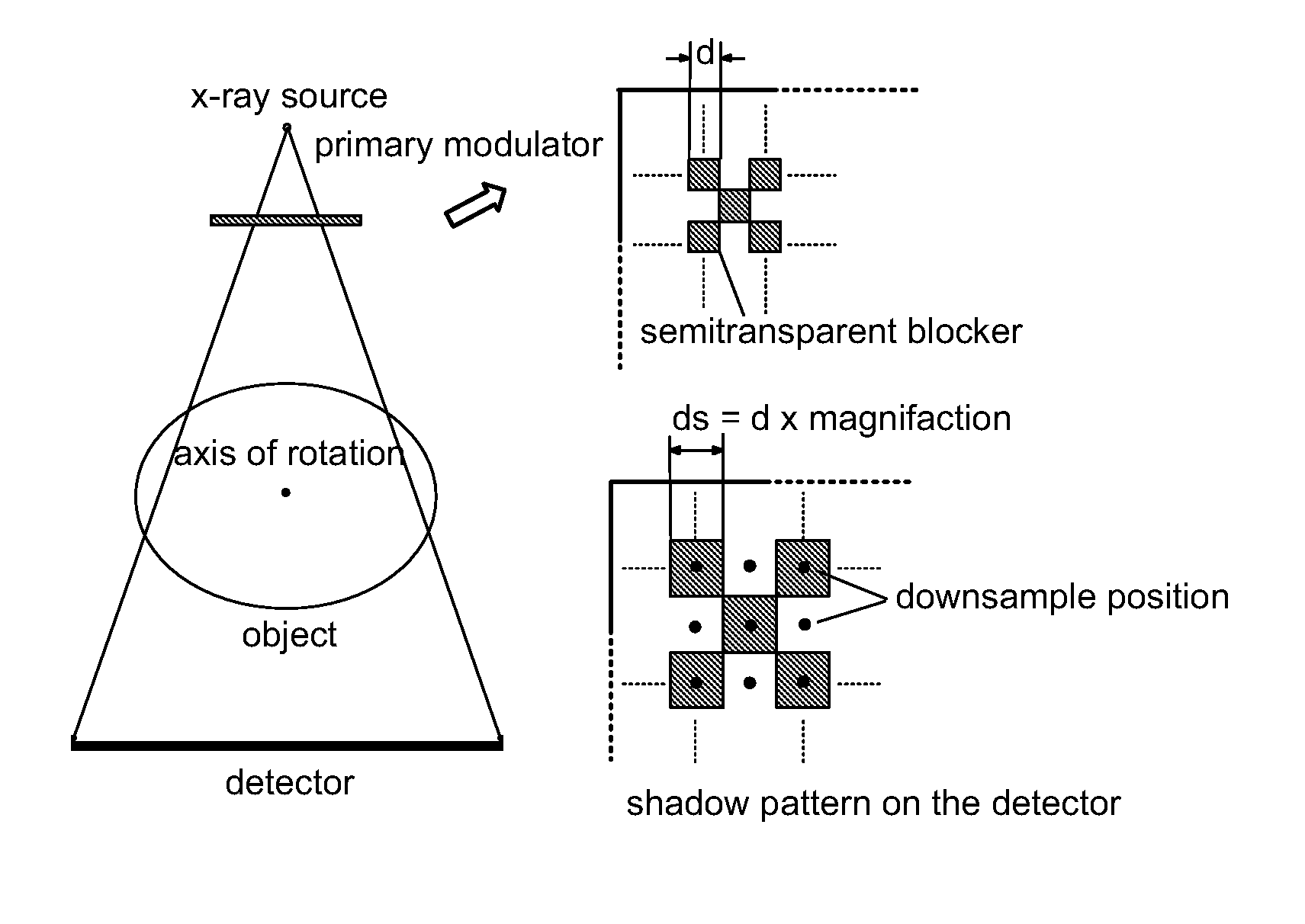
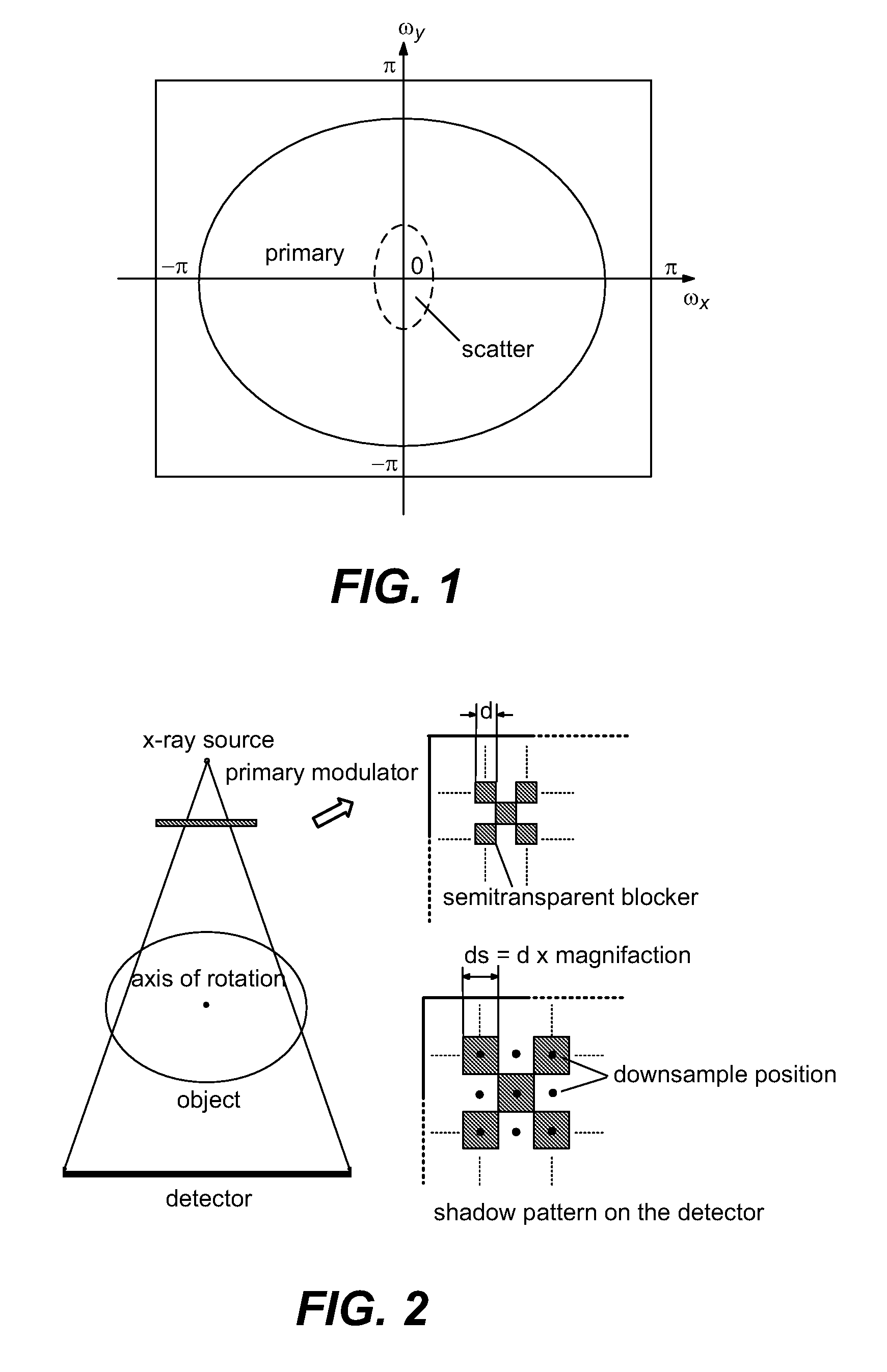
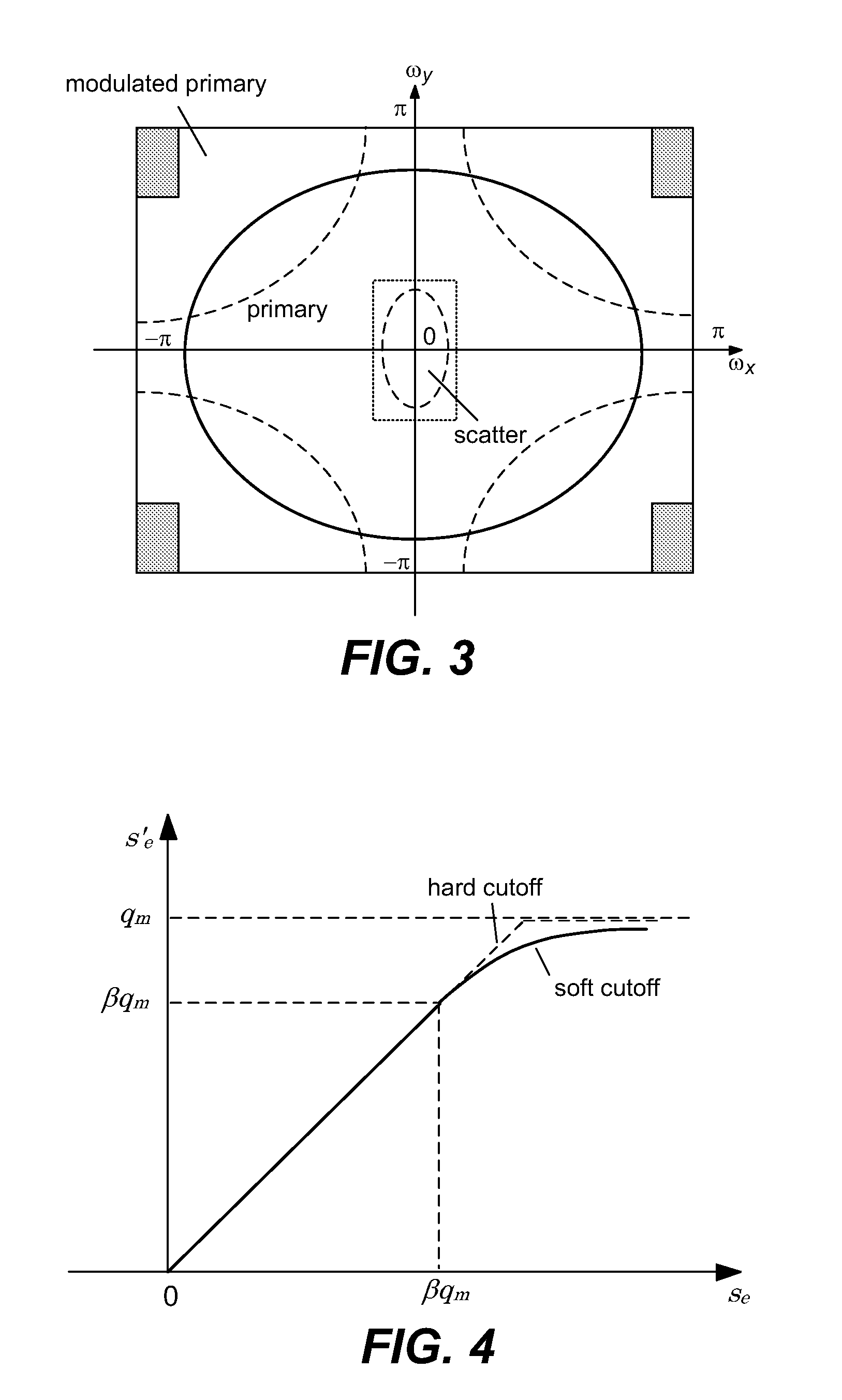
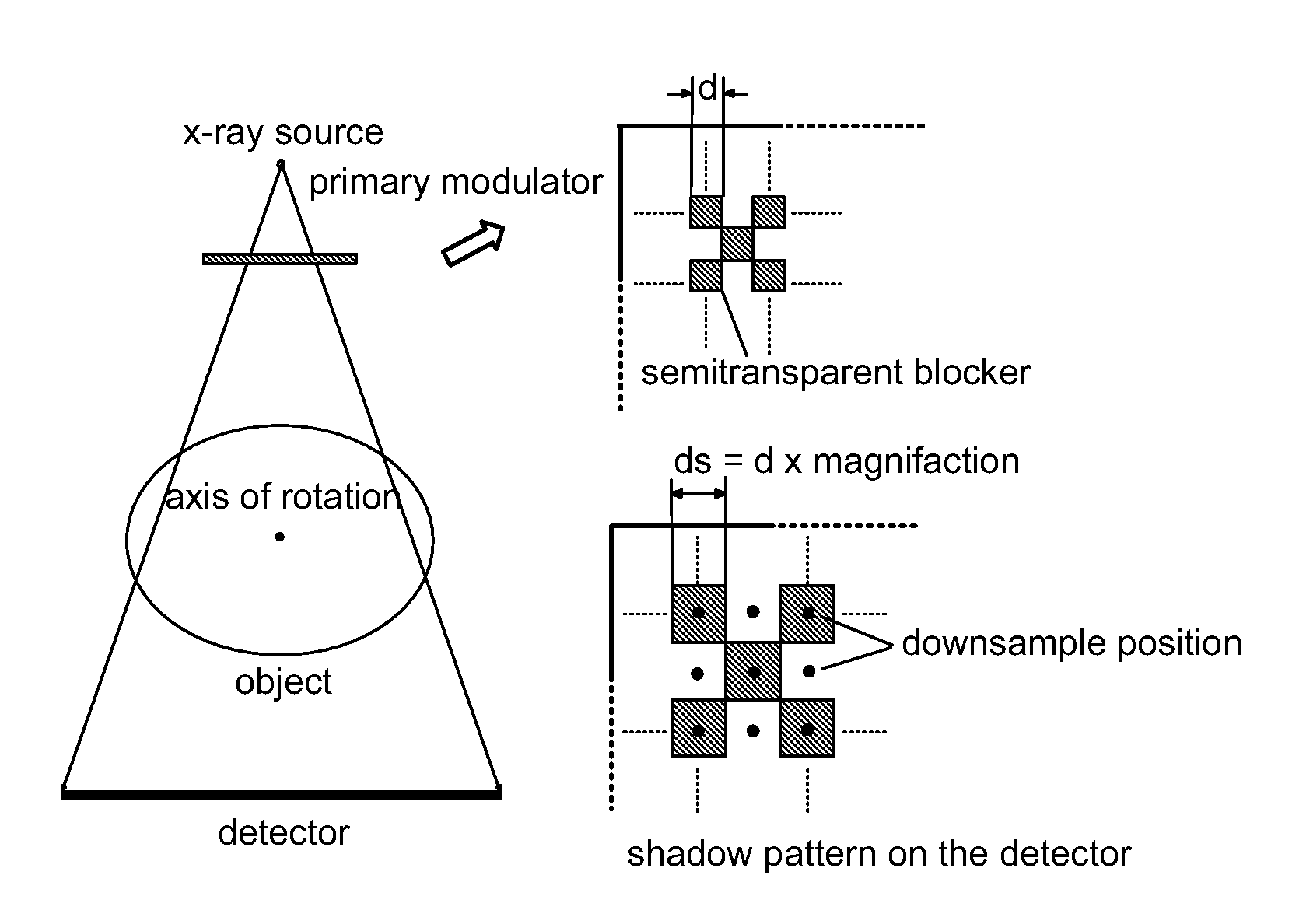
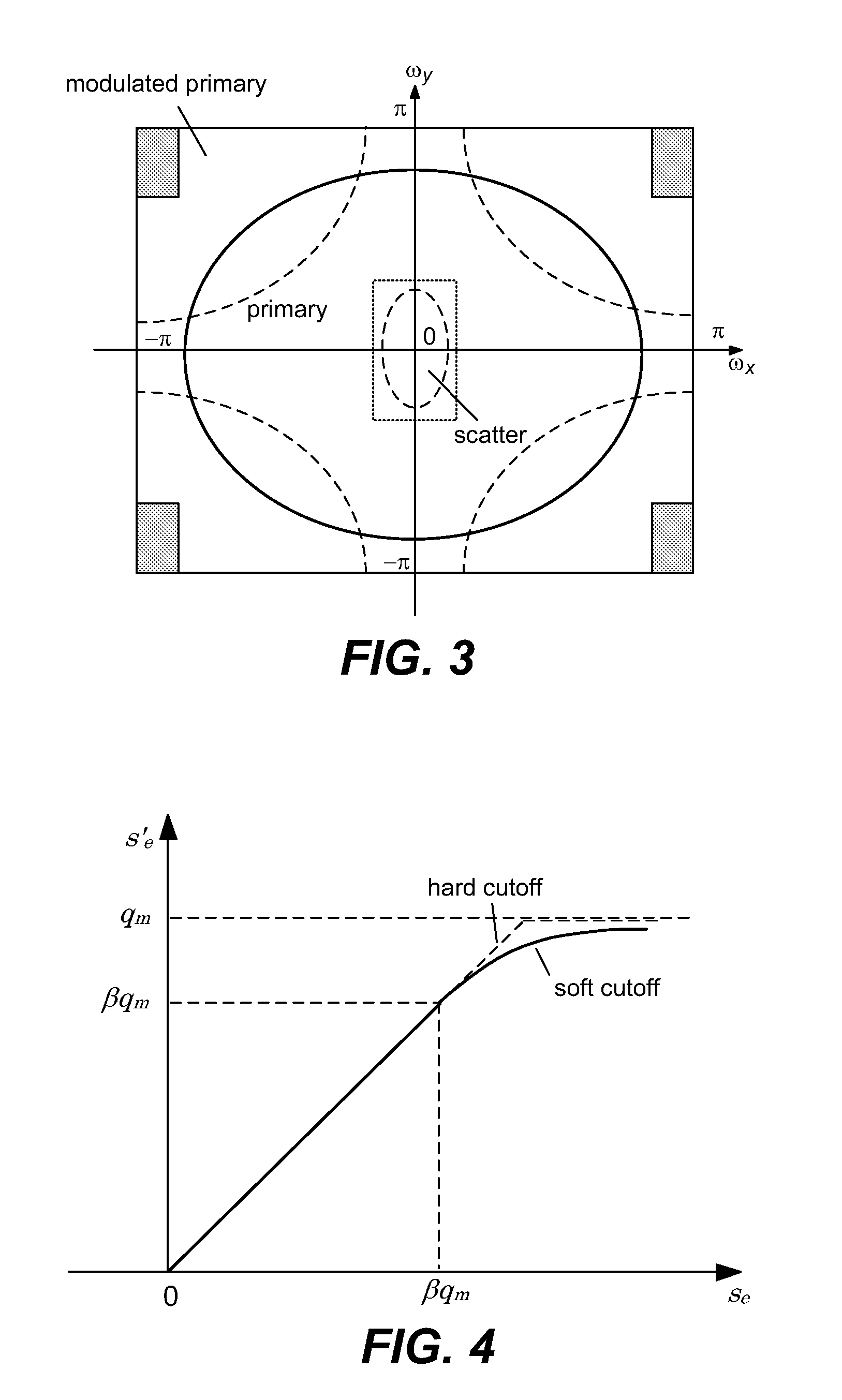
Scatter correction for x-ray imaging using modulation of primary x-ray spatial spectrum
ActiveUS7463712B2Efficient transferMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayX ray image
Scatter radiation in an x-ray imaging system including an x-ray source and an x-ray detector is separated by using amplitude modulation to translate the spatial frequency of a detected x-ray beam to a higher frequency and provide separation from low frequency scatter signal. The low frequency content of the detected x-ray beam is then obtained by demodulating the detected modulated signal.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Virtual, grid imaging method and system for eliminating scattered radiation effect
InactiveUS20100046822A1Eliminate the effects ofComponent can be removedImage enhancementImage analysisMulti bandHigh energy
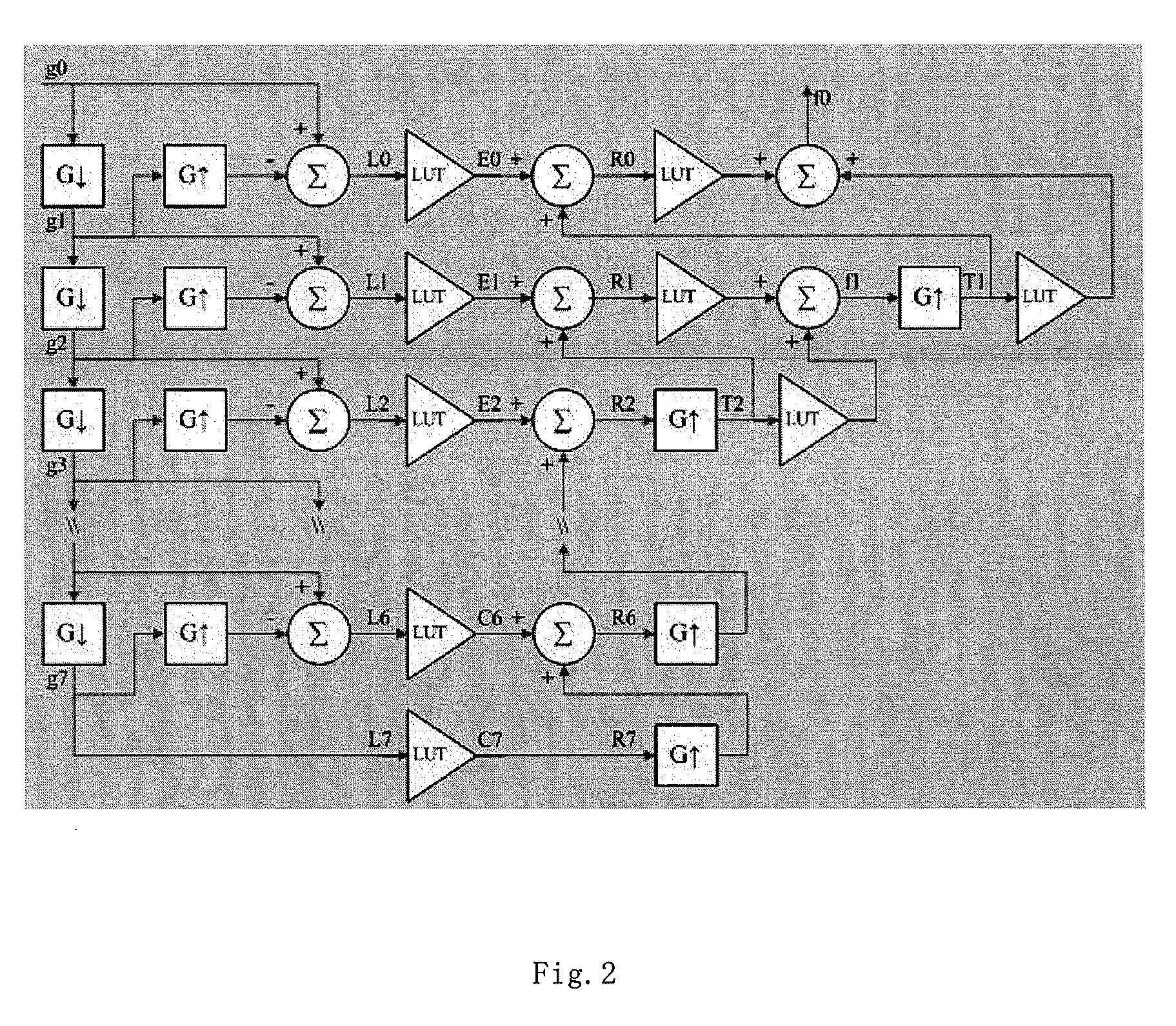
A virtual grid imaging method capable of eliminating scattered radiation effect and an imaging system thereof are provided. The method is mainly applicable for imaging with high energy rays, in which scattered rays reaching a surface of a detector are not filtered, and data of the scattered rays and straight rays are all sampled, and then, separation and inhibition of scattered ray component are performed for the sampled data, thereby eliminating the scattered ray component in the resulted image. The method particularly includes the following steps: (1) decomposing a digital image into multi-band images from high to low according to frequencies; (2) performing de-scattering process for low-frequency band images; (3) performing contrast enhancement process for high-frequency band images; and (4) merging the images of various frequency bands processed in the step (2) and the step (3), and forming an output image. Experiment shows that, in digital X-ray imaging, the present invention can obviously eliminate the scattered radiation effect, and meanwhile significantly reduce the dosage of the rays, in which only one third of the required dosage of a common grid is used to obtain the same image brightness.
Owner:BEIJING SINOPHARM HUNDRIC MEDLINE INFO TECH
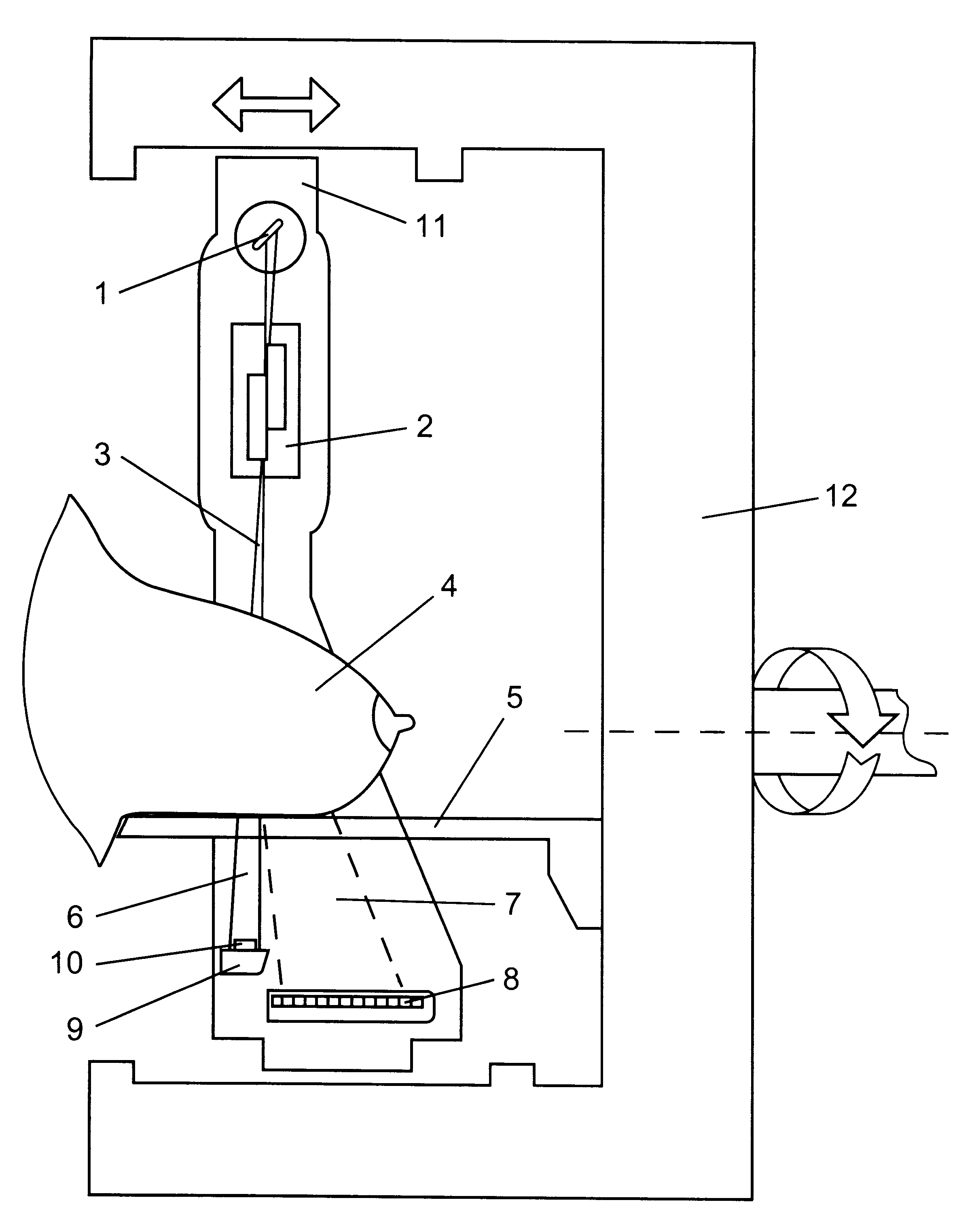
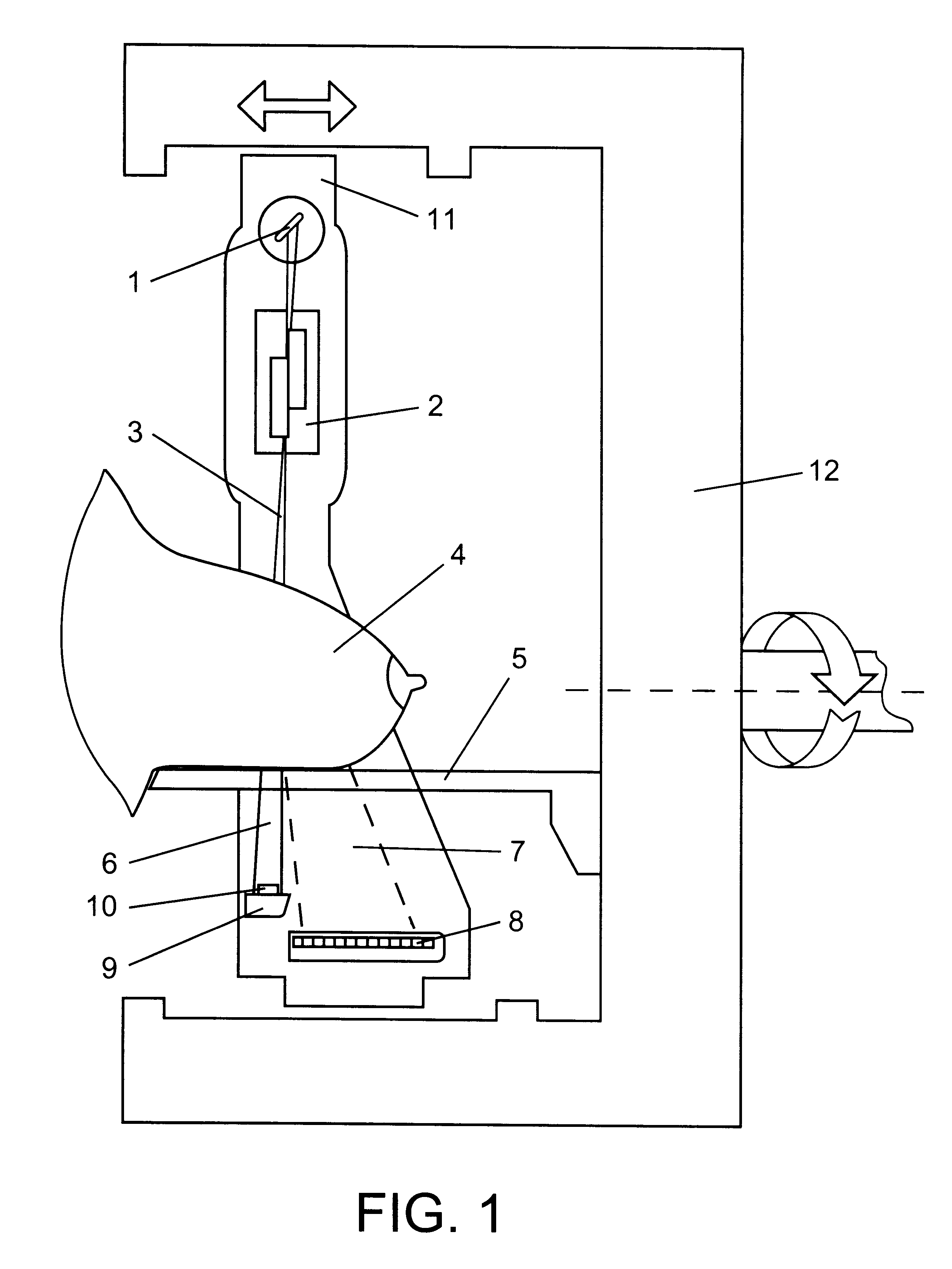
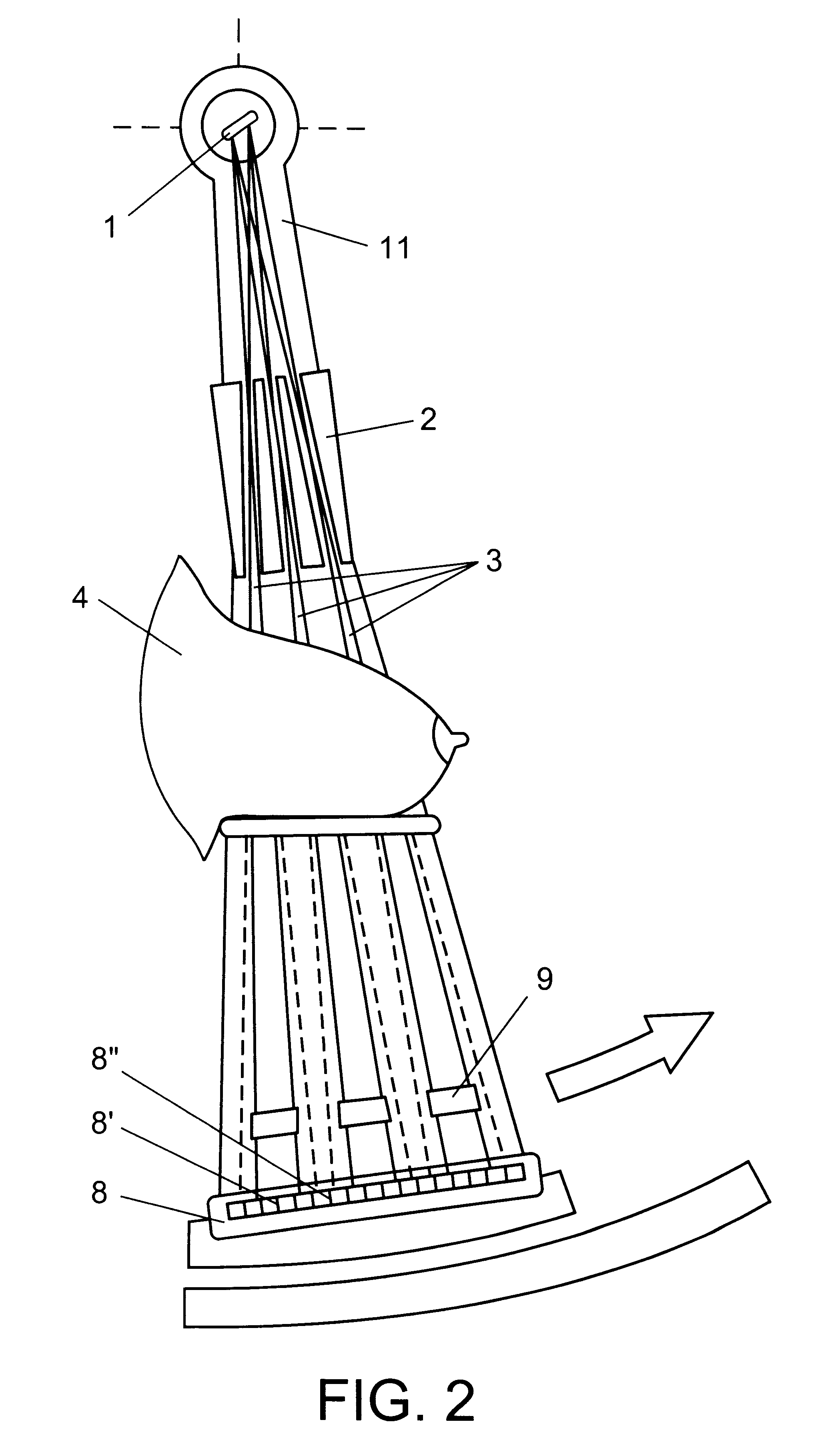
Radiological image detection apparatus, radiographic apparatus and radiographic system
InactiveUS20120163554A1Reduce scattered radiationReduce radiationMusculoskeletal system evaluationRadiation/particle handlingImage detectionGrating pattern
A radiological image detection apparatus includes a first grating unit, a grating pattern unit, a radiological image detector, and an anti-scatter grating. The grating pattern unit has a period that substantially coincides with a pattern period of a radiological image formed by radiation having passed through the first grating unit. The radiological image detector detects the radiological image masked by the grating pattern unit. The anti-scatter grating is arranged on a path of the radiation incident onto the radiological image detector and removes scattered radiation. A smoothing process is performed for at least one of a surface and a backside of the anti-scatter grating intersecting with a traveling direction of the radiation.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
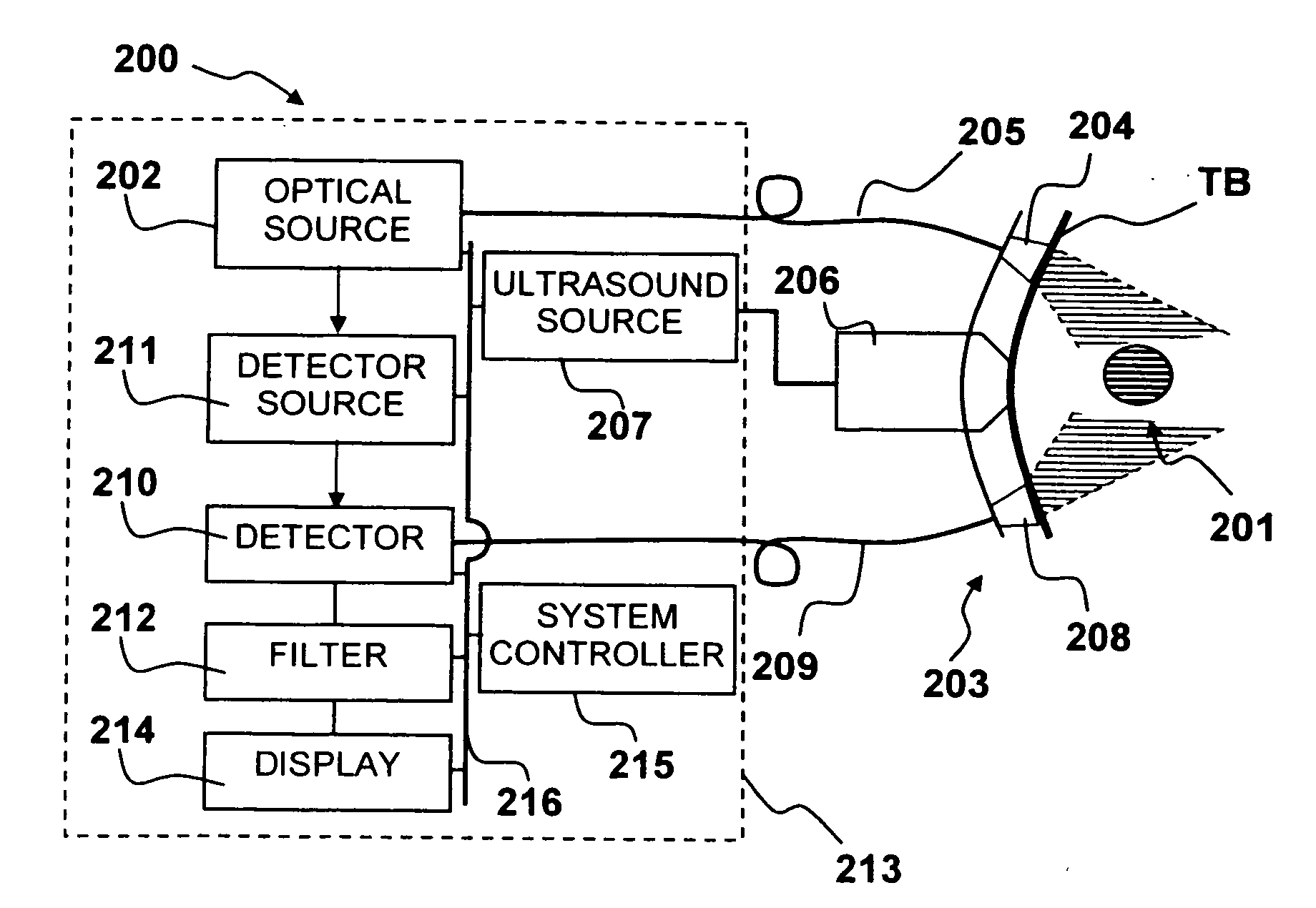
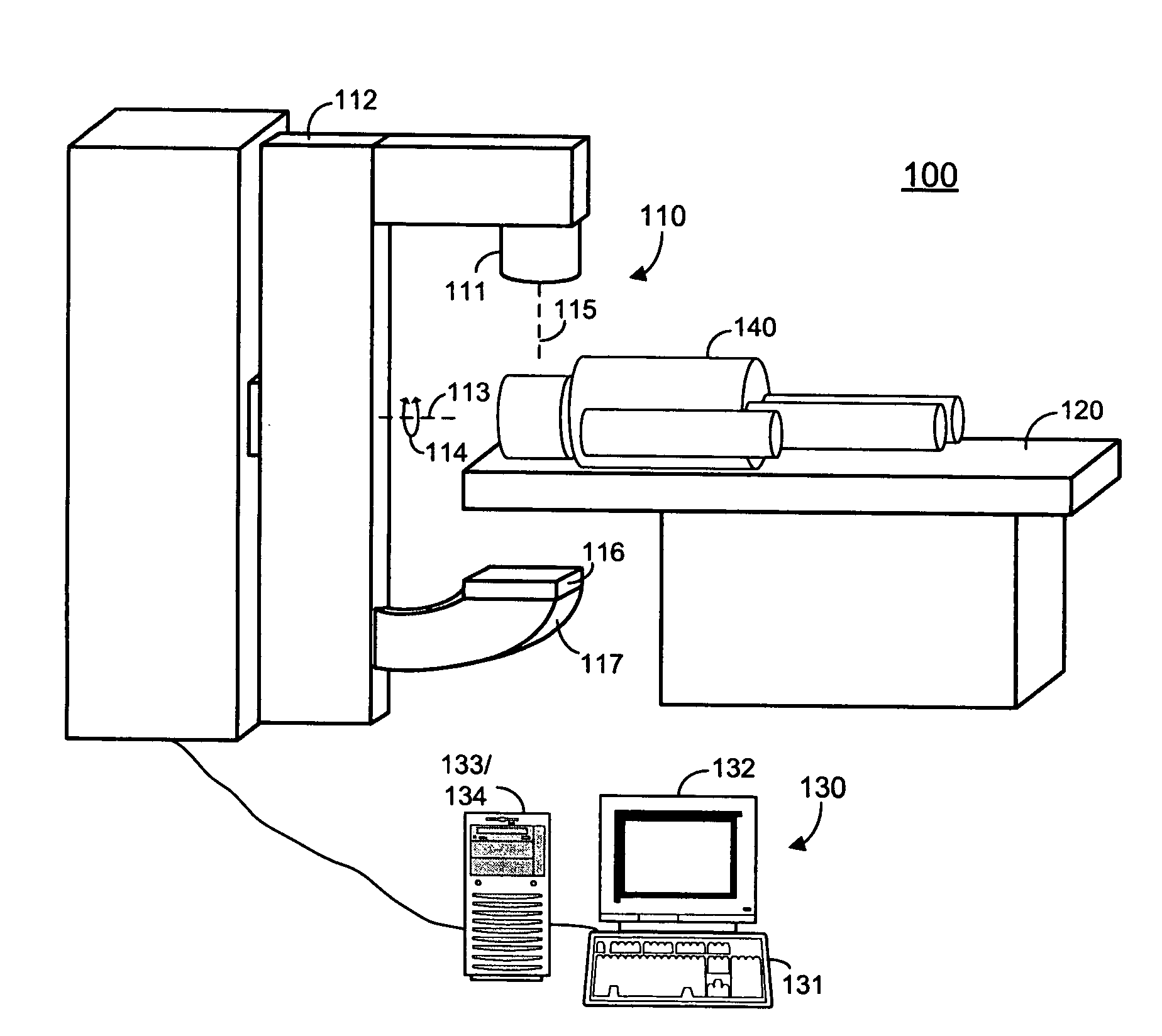
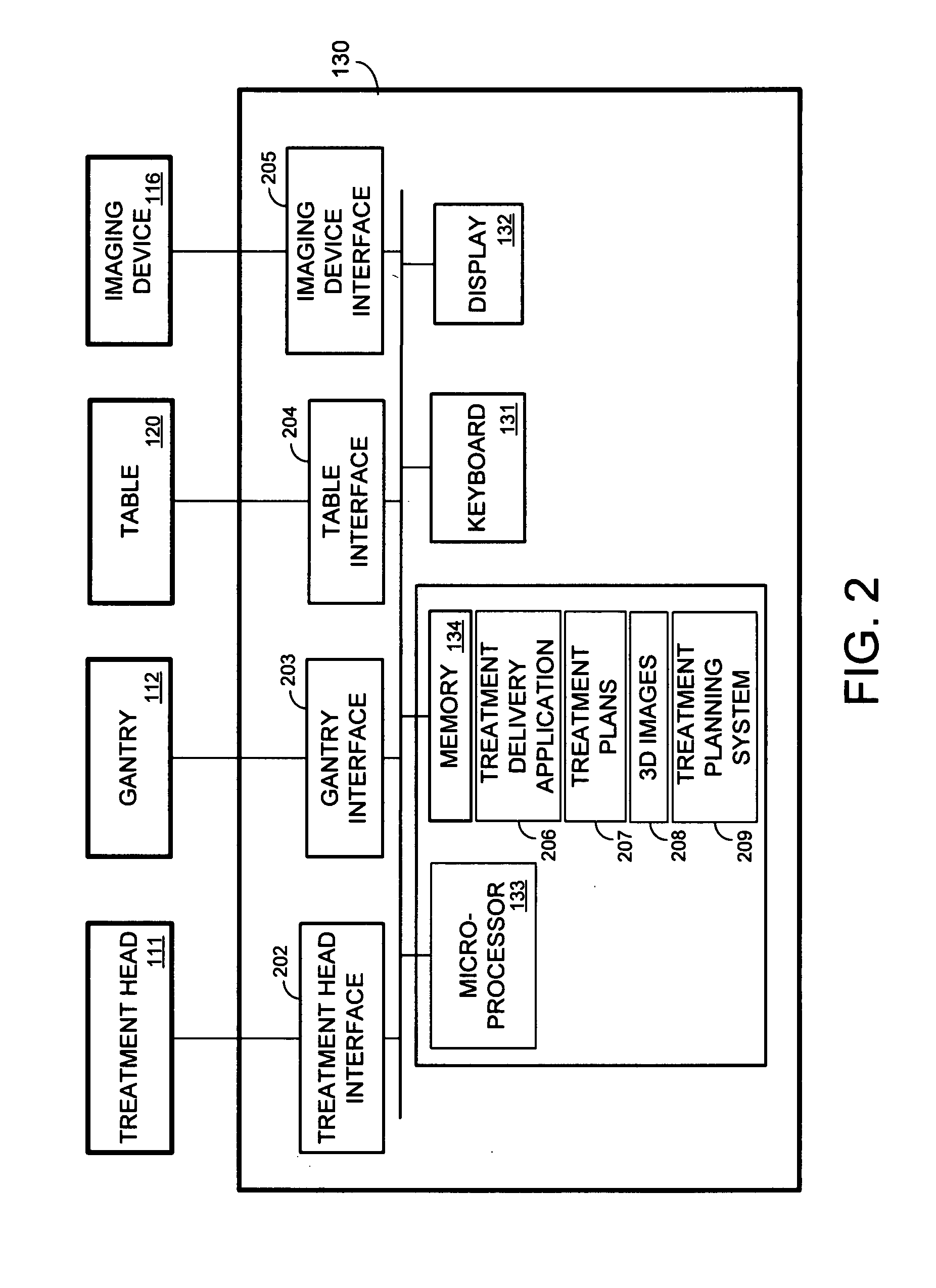
Dose-guided radiation therapy using cone beam CT
ActiveUS20090003512A1Easy to adaptMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingRadiation therapyScattering radiation
A system includes acquisition of a three-dimensional cone beam image, and determination of a dose to be delivered based on the three-dimensional image and on parameters of a treatment beam to deliver the dose. Some systems may include modification of a three-dimensional cone beam image to correct for scatter radiation, and determination of a dose based on the modified three-dimensional cone beam image.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +2
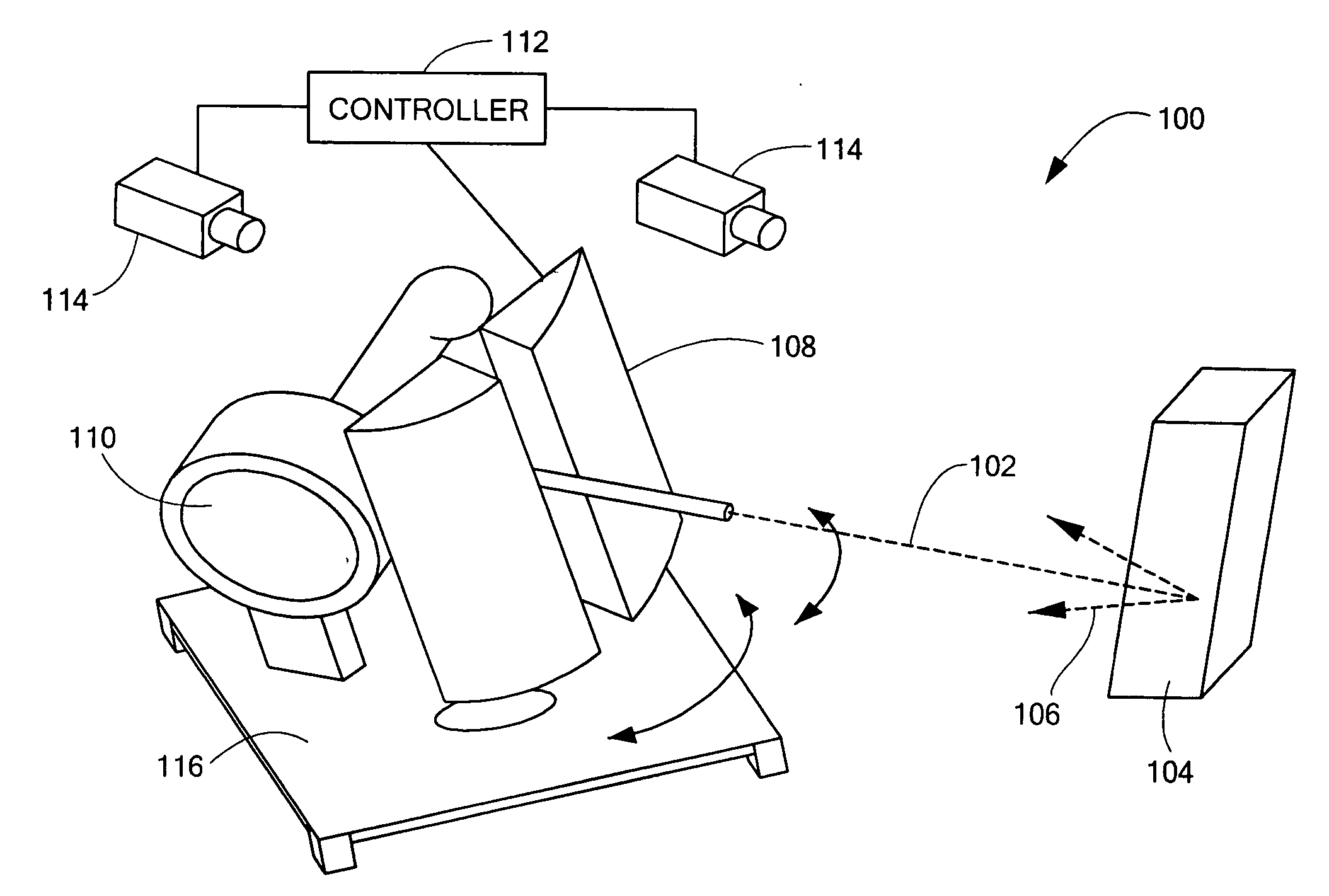
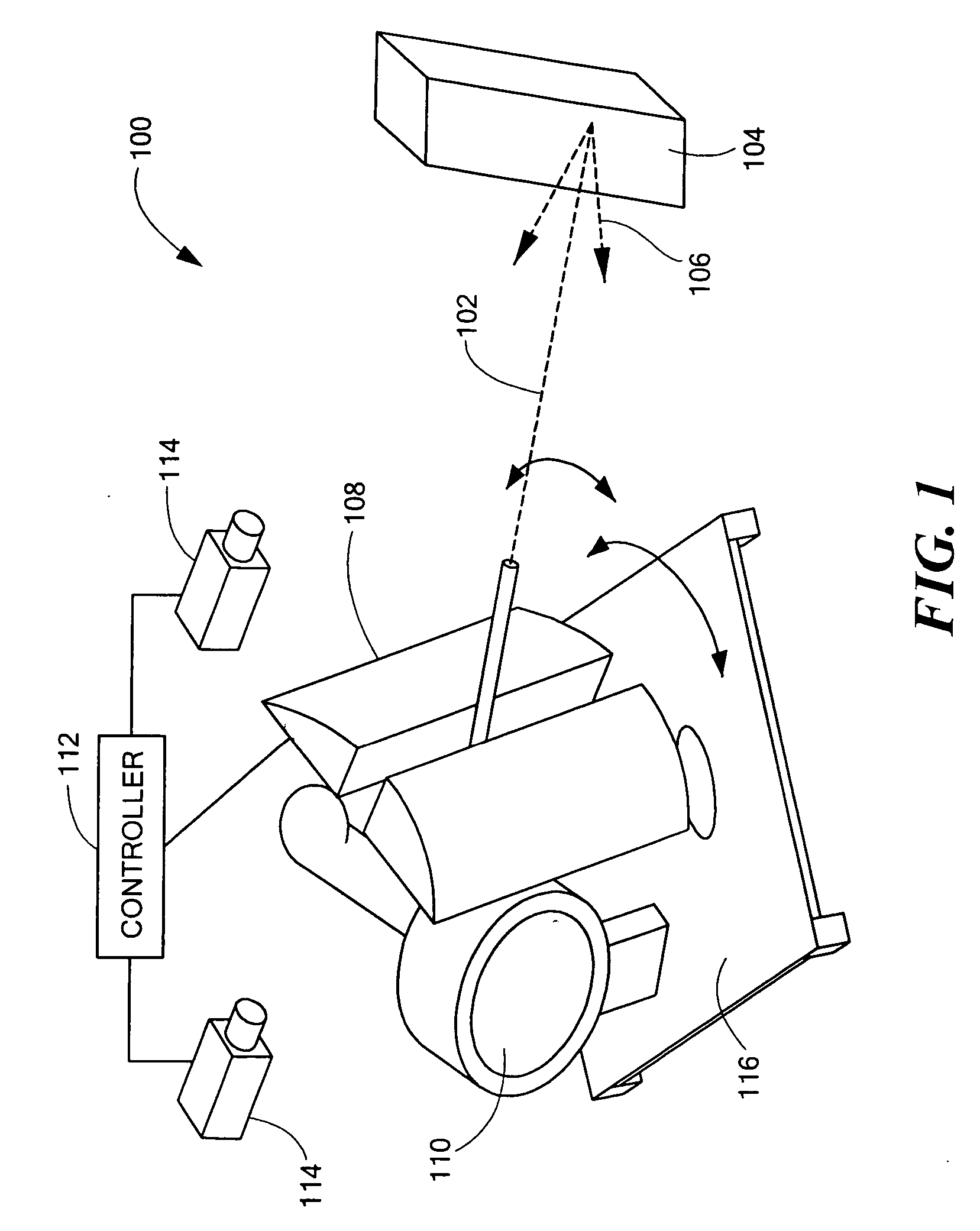
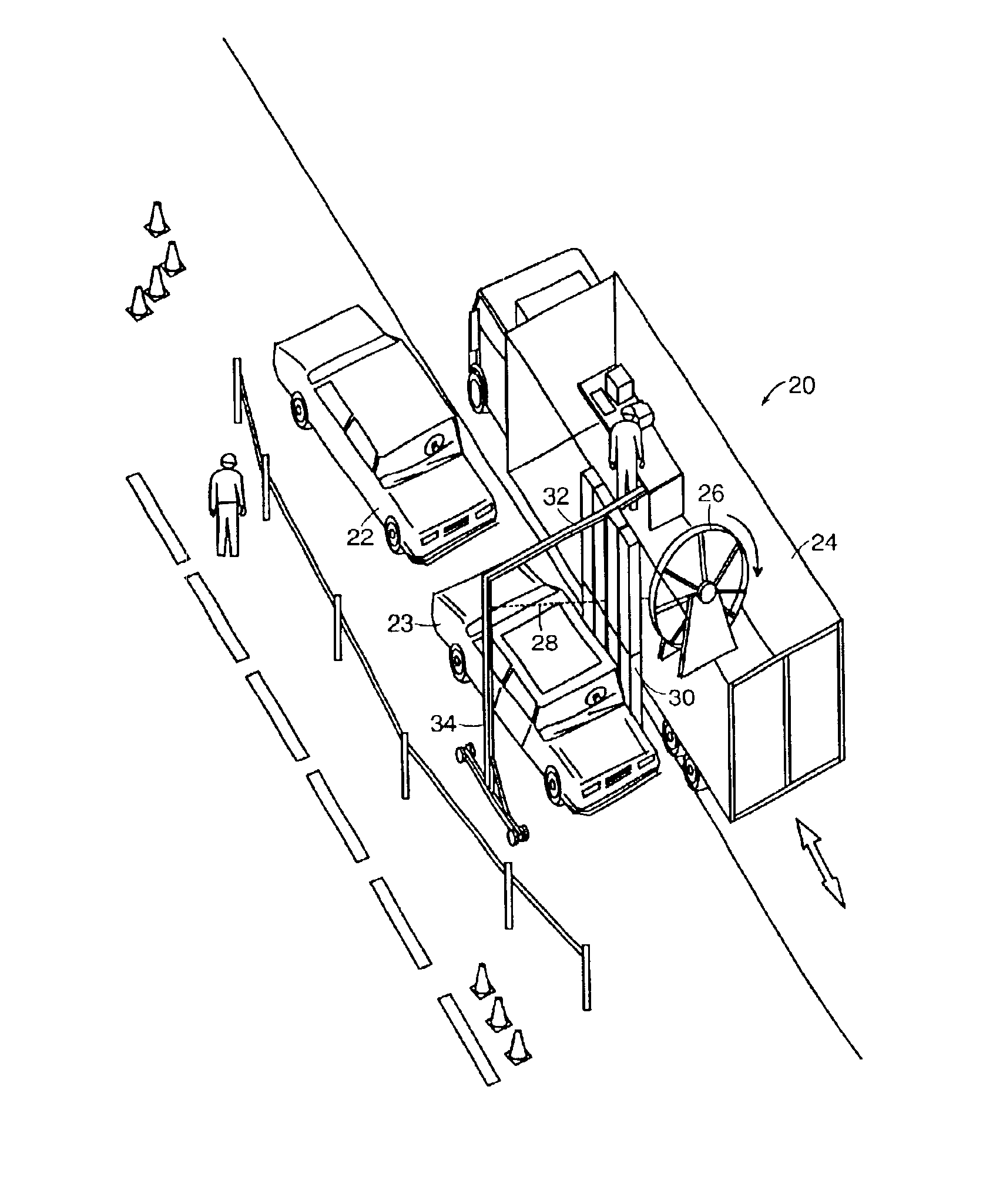
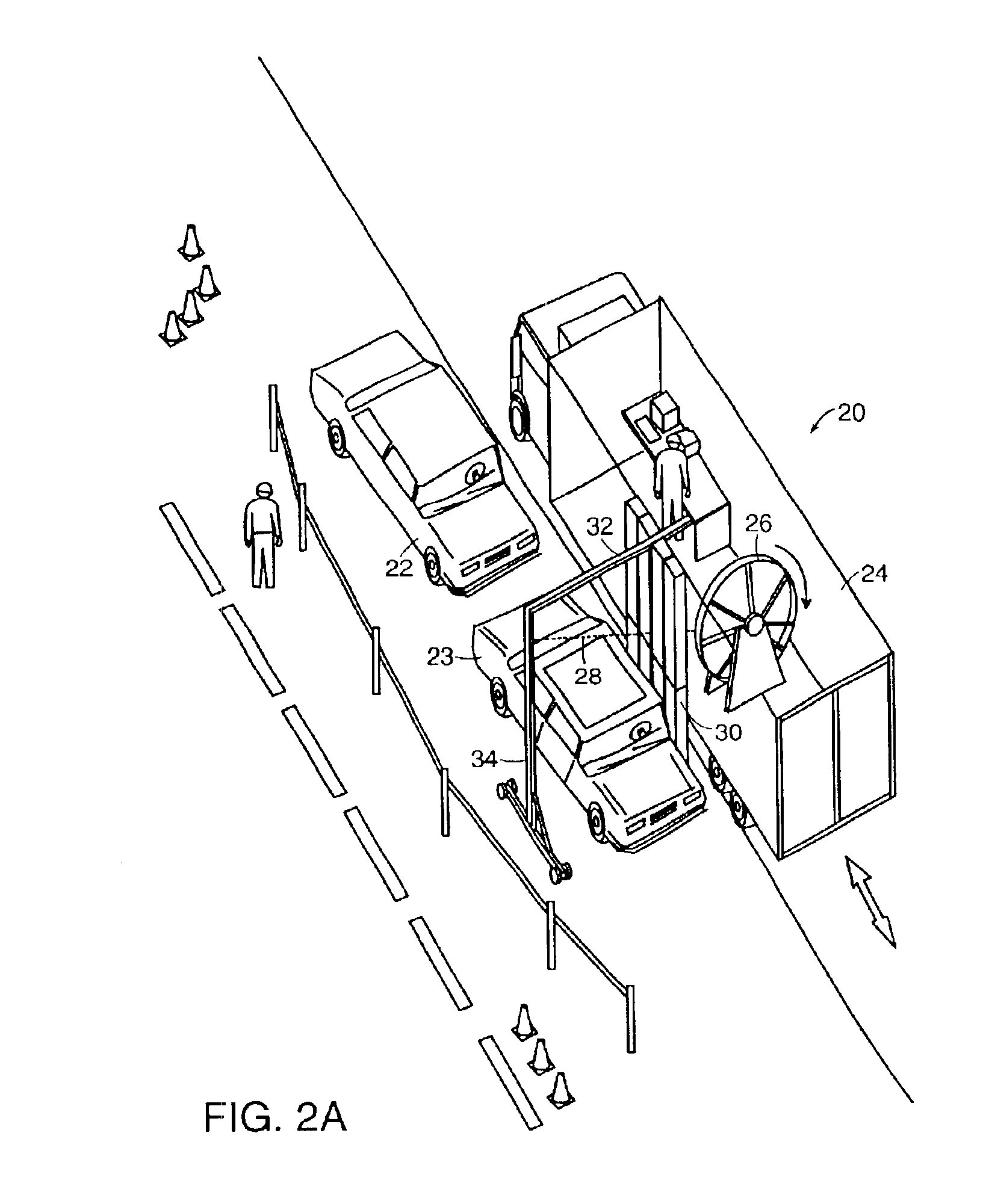
Mobile x-ray inspection system for large objects
InactiveUSRE39396E1Material analysis by transmitting radiationMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionX-rayLight beam
A device for inspecting a cargo container such as a motor vehicle or freight pallet, with penetrating radiation. A source of penetrating radiation is mounted on a moveable bed, thereby allowing a beam of penetrating radiation to sweep the large container. At least one detector is also mounted on the bed, either on the side of the source or on a boom, so that, as the beam is scanned across the container, the container and any contents of the container are characterized by transmitted or scattered radiation, or both.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
Reduced-angle mammography device and variants
InactiveUS6483891B1Easy to useHigh sensitivityPatient positioning for diagnosticsTomographyLight beamRelative motion
The invention relates to the mammography devices based on registration of a reduced-angle coherently scattered radiation when an object is rayed by a penetrating radiation. Registration of the radiation coherently scattered by an object allows to produce an image of an object in the form of distribution of its structural characteristics. The device comprises a system for forming a directed on a tested object, narrow small-divergence beams, or a beam, having the same characteristics, and a system for extracting the radiation that is coherently scattered in small angles by an object. The invention proposes versions of a device that also provide for registration of the radiation passed through an object to make allowance for its thickness so that to obviate the necessity to compress the breast. The device allows to carry out relative movements of an object and system of irradiation-registration, as well as irradiate an object at different angles and by a number of radiation sources simultaneously. The possibility to register the coherently scattered radiation in ultra-small angles within the range of several angular seconds to 0.5 degree, and also the possibility to form the primary radiation beam having a sharp boundary are provided as well.
Owner:QUANTA VISION
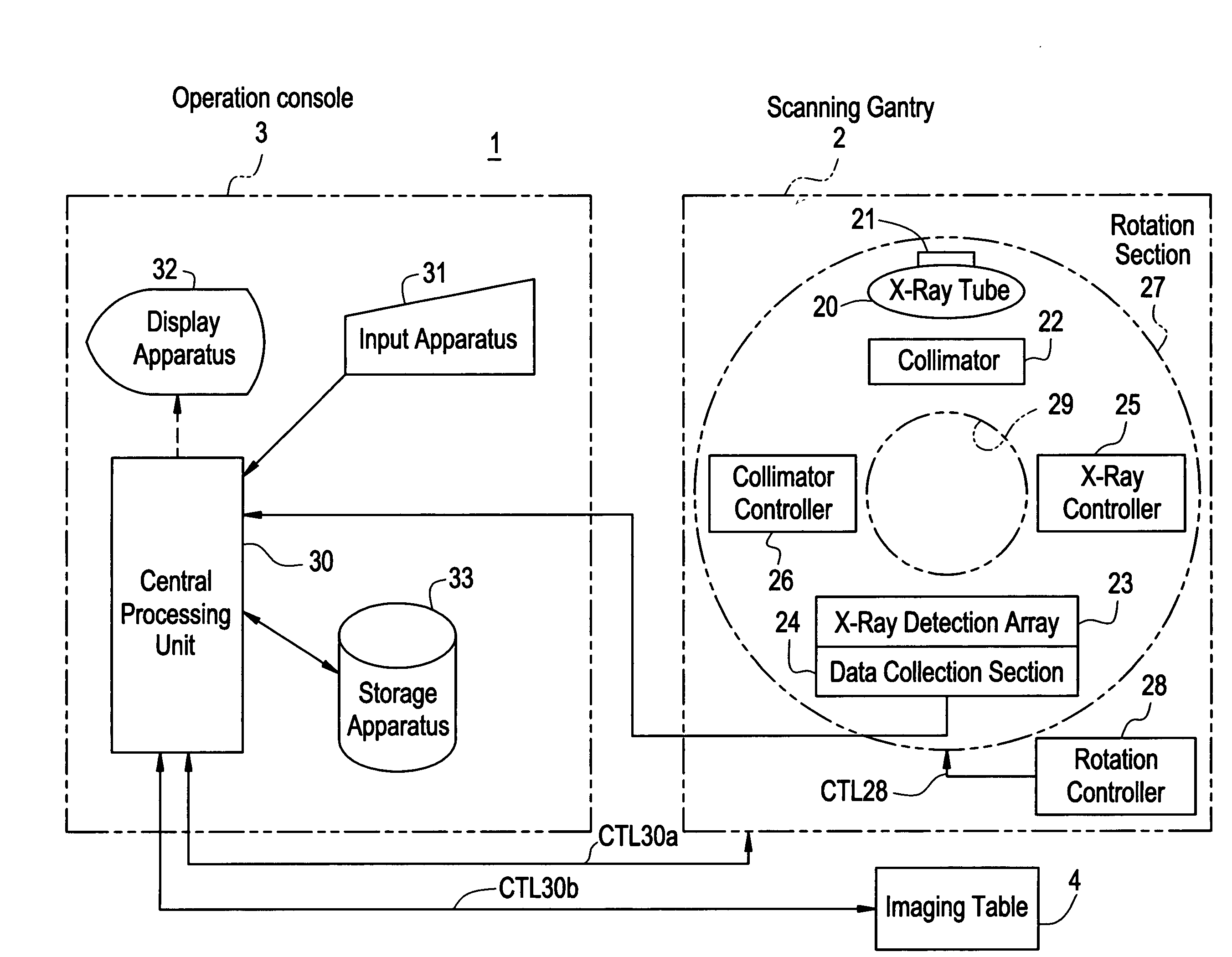
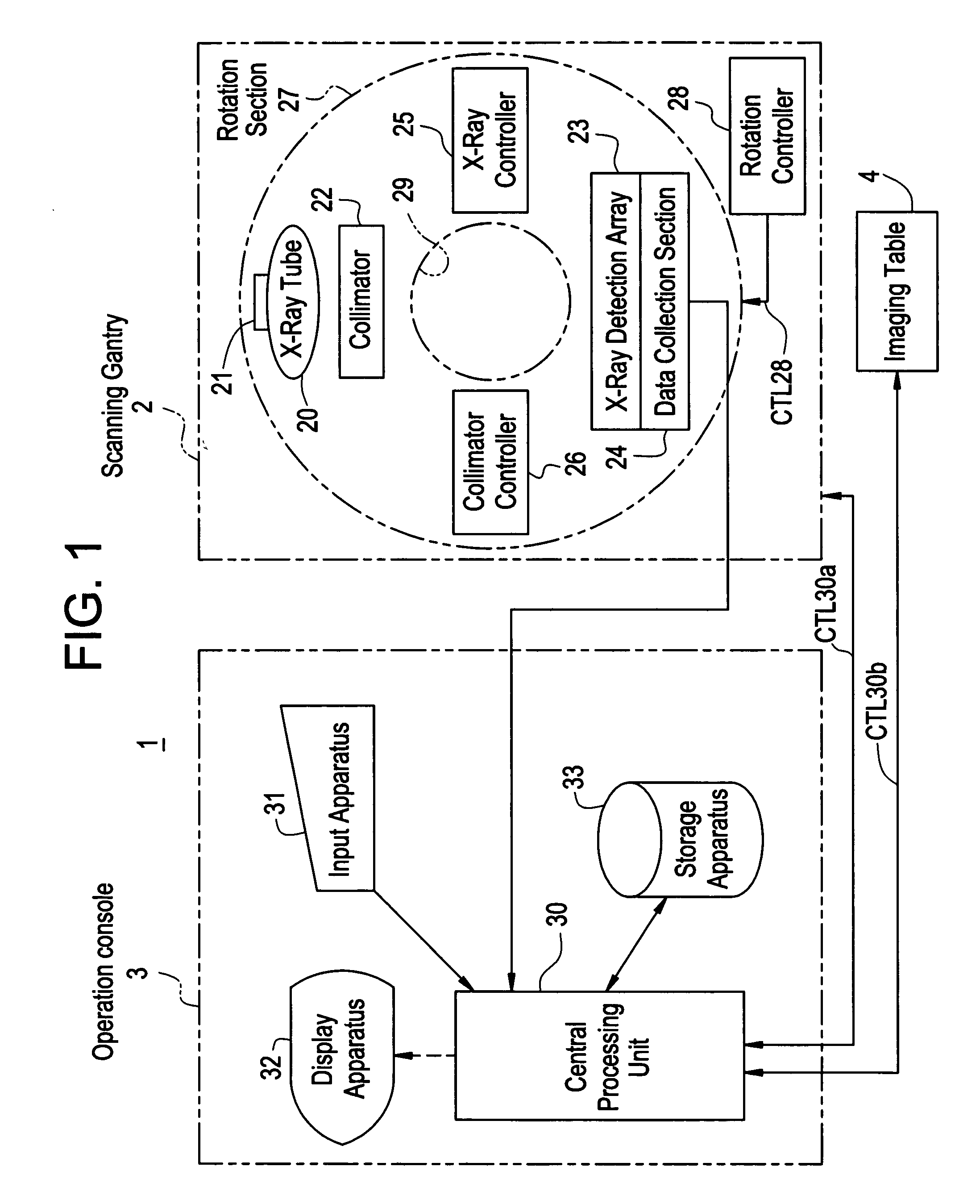
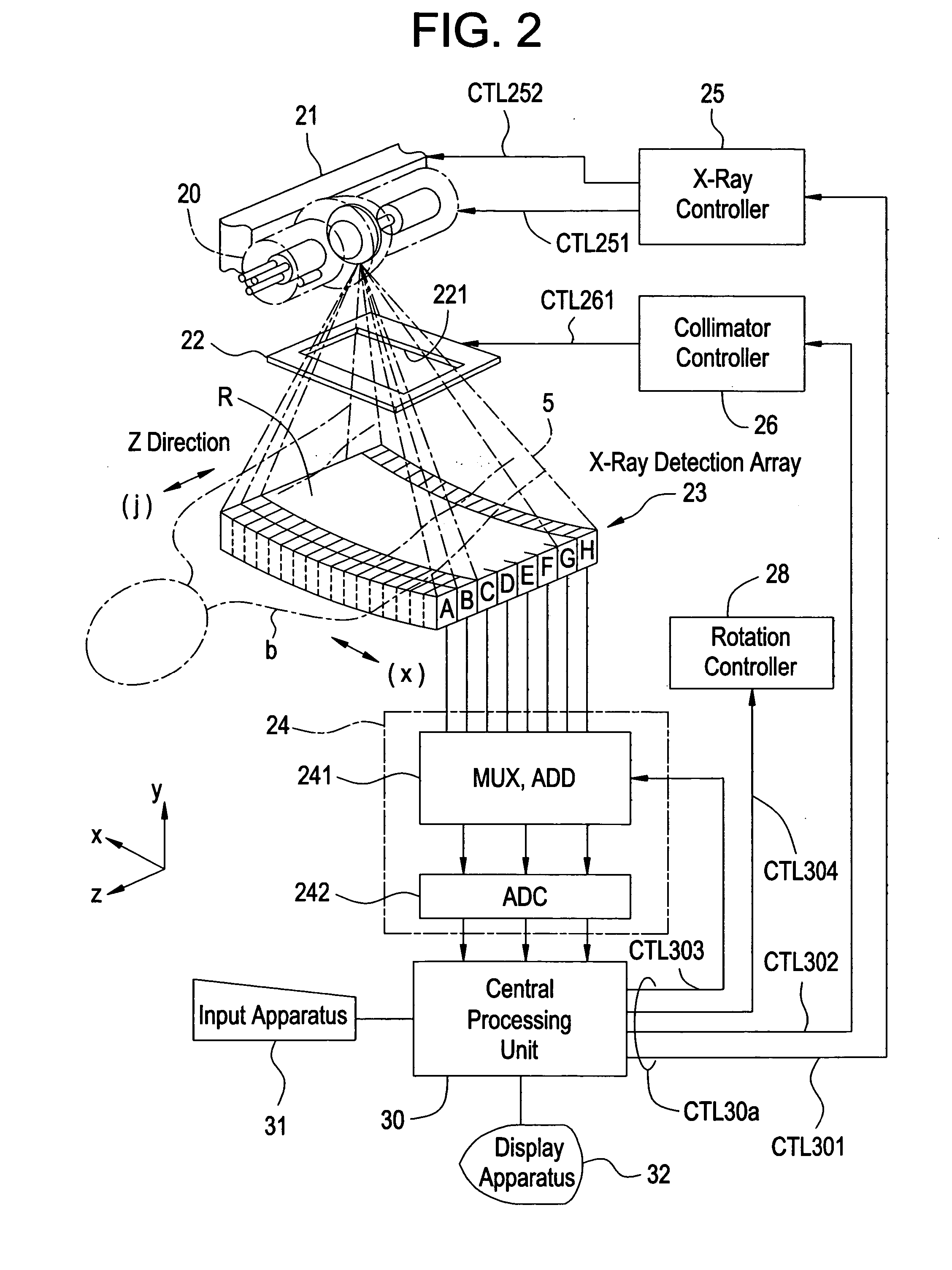
Radiation tomography apparatus
InactiveUS20050053188A1Improving tomographic image qualityEasy to useHandling using diaphragms/collimetersComputerised tomographsX-rayTomography
An apparatus for improving the tomographic image quality by preventing the tomographic image contrast from degrading and preventing artifact from occurring even if many scattered radiations occur. An X-ray detection array obtains first detection data using the X-ray detection elements corresponding to an area not shielded by a collimator. Further, the X-ray detection array obtains second detection data using the X-ray detection elements corresponding to an area shielded by the collimator. A central processing unit corrects the first detection data based on the detection data including the first and second detection data. Finally, the central processing unit generates a tomographic image for an imaging area of the imaging object.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
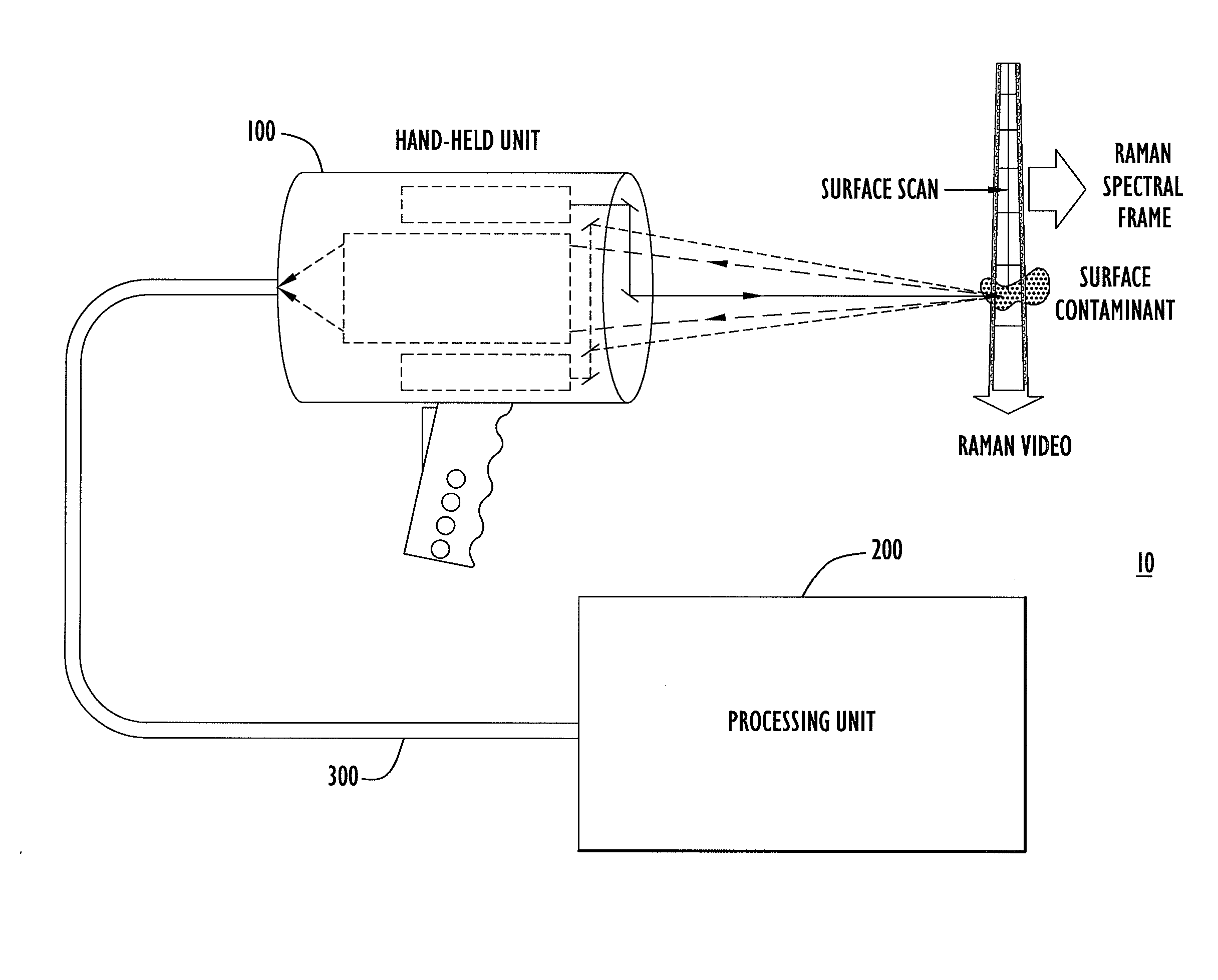
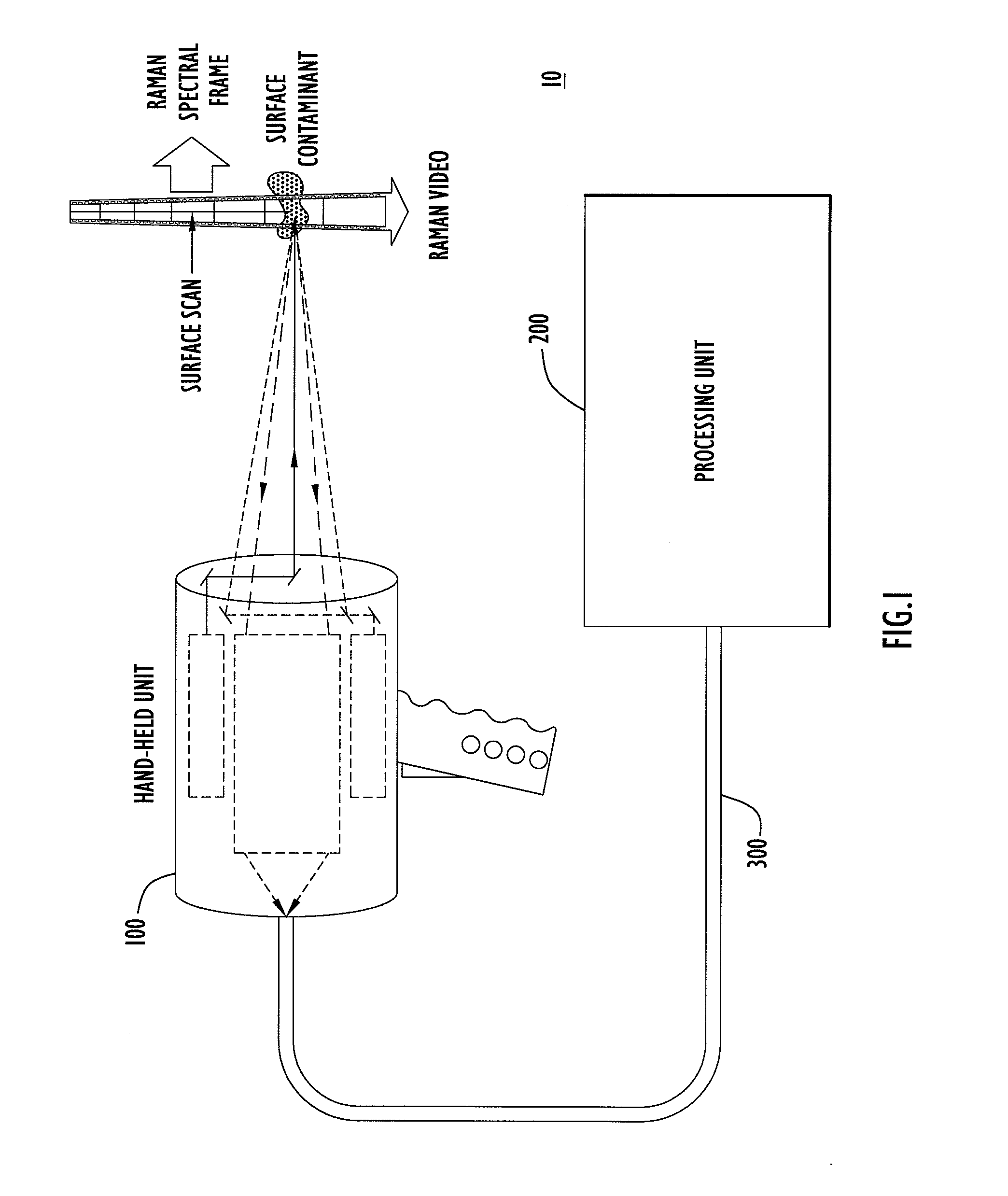
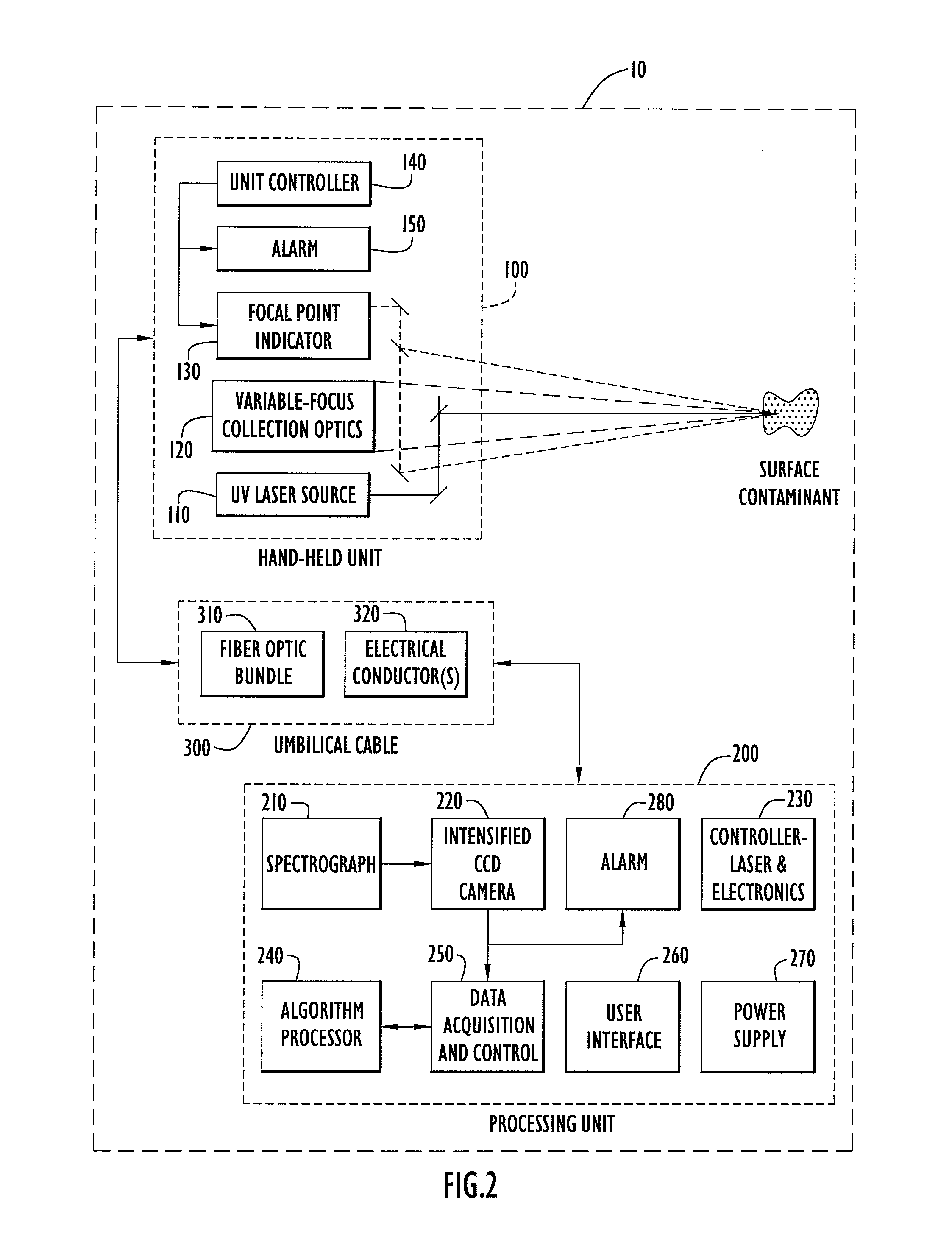
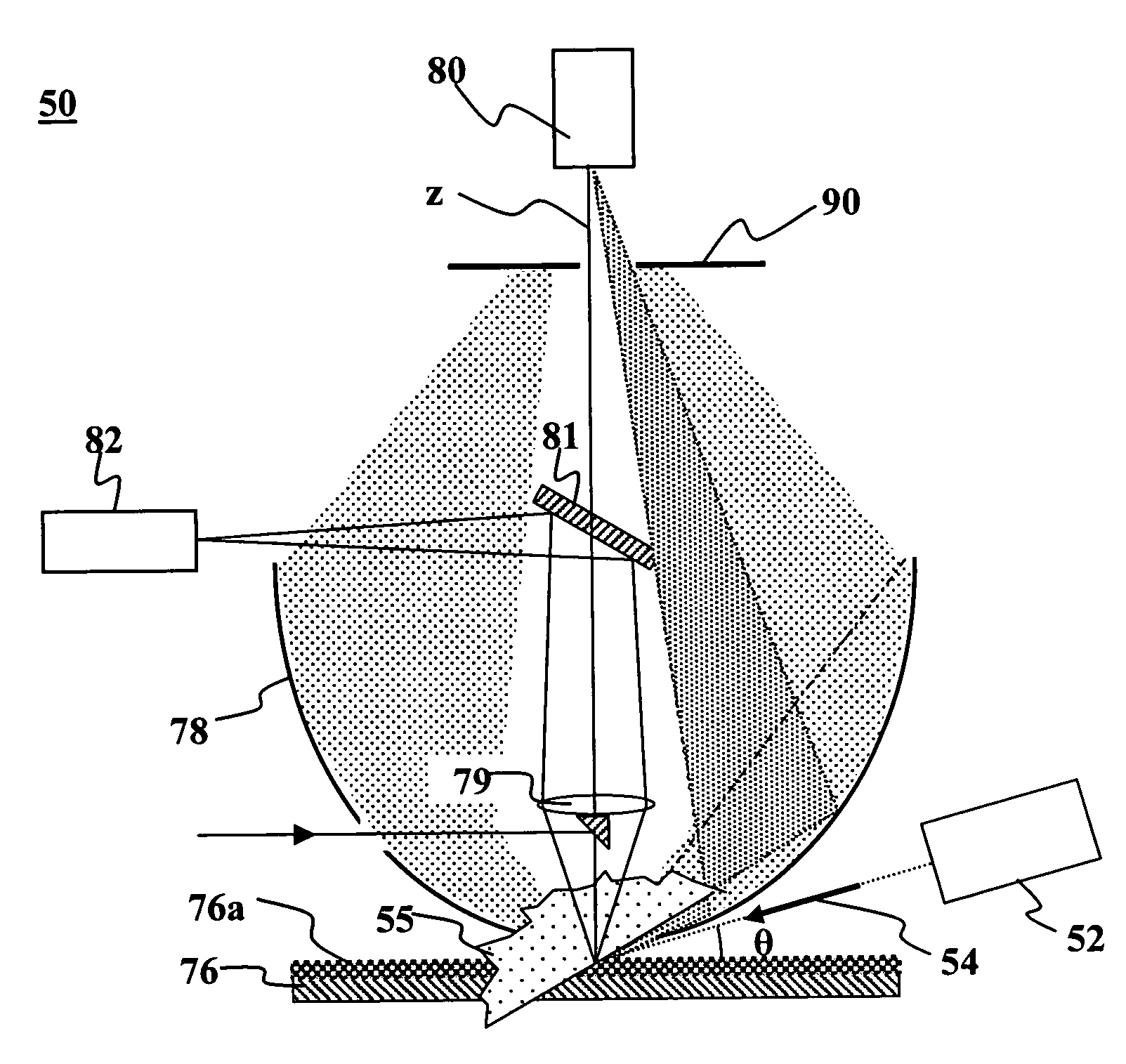
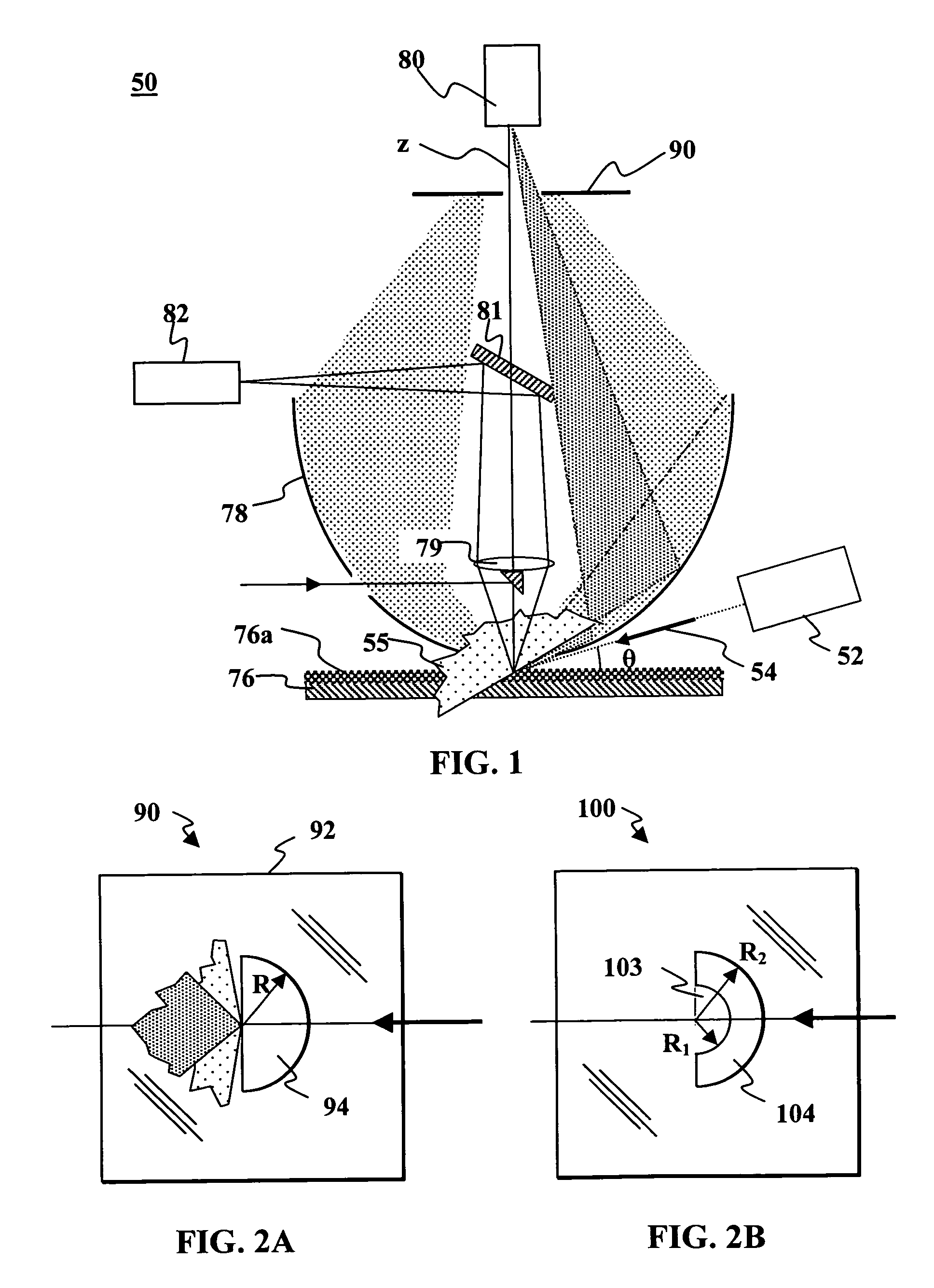
Method, Apparatus and System for Rapid and Sensitive Standoff Detection of Surface Contaminants
ActiveUS20070222981A1Fast and sensitive standoffImprove spatial resolutionRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringExcitation beamHazardous substance
Systems and methods for fast and sensitive standoff surface-hazard detection with high data throughput, high spatial resolution and high degree of pointing flexibility. The system comprises a first hand-held unit that directs an excitation beam onto a surface that is located a distance away from the first unit and an optical subsystem that captures scattered radiation from the surface as a result of the beam of light. The first unit is connected via a link that includes a bundle of optical fibers, to a second unit, called the processing unit. The processing unit comprises a fiber-coupled spectrograph to convert scattered radiation to spectral data, and a processor that analyzes the collected spectral data to detect and / or identify a hazardous substance. The second unit may be contained within a body-wearable housing or apparatus so that the first unit and second unit together form a man-portable detection assembly. In one embodiment, the system can continuously and without interruptions scan a surface from a 1-meter standoff while generating Raman spectral-frames at rates of 25 Hz.
Owner:PERATON INC
Scatter correction for x-ray imaging using modulation of primary x-ray spatial spectrum
ActiveUS20070268997A1Efficient transferMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayX ray image
Scatter radiation in an x-ray imaging system including an x-ray source and an x-ray detector is separated by using amplitude modulation to translate the spatial frequency of a detected x-ray beam to a higher frequency and provide separation from low frequency scatter signal. The low frequency content of the detected x-ray beam is then obtained by demodulating the detected modulated signal.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
System for detecting anomalies and/or features of a surface
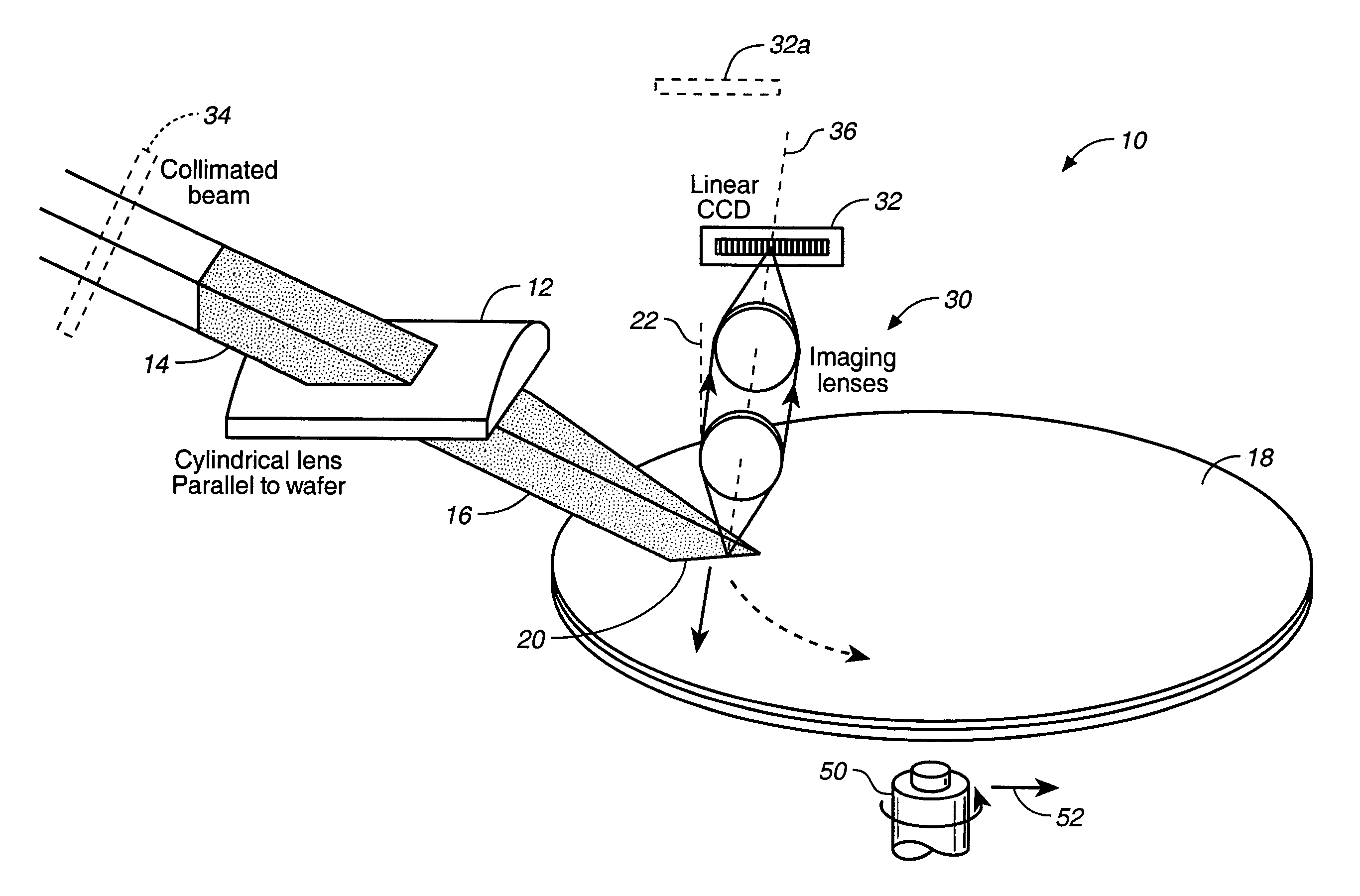
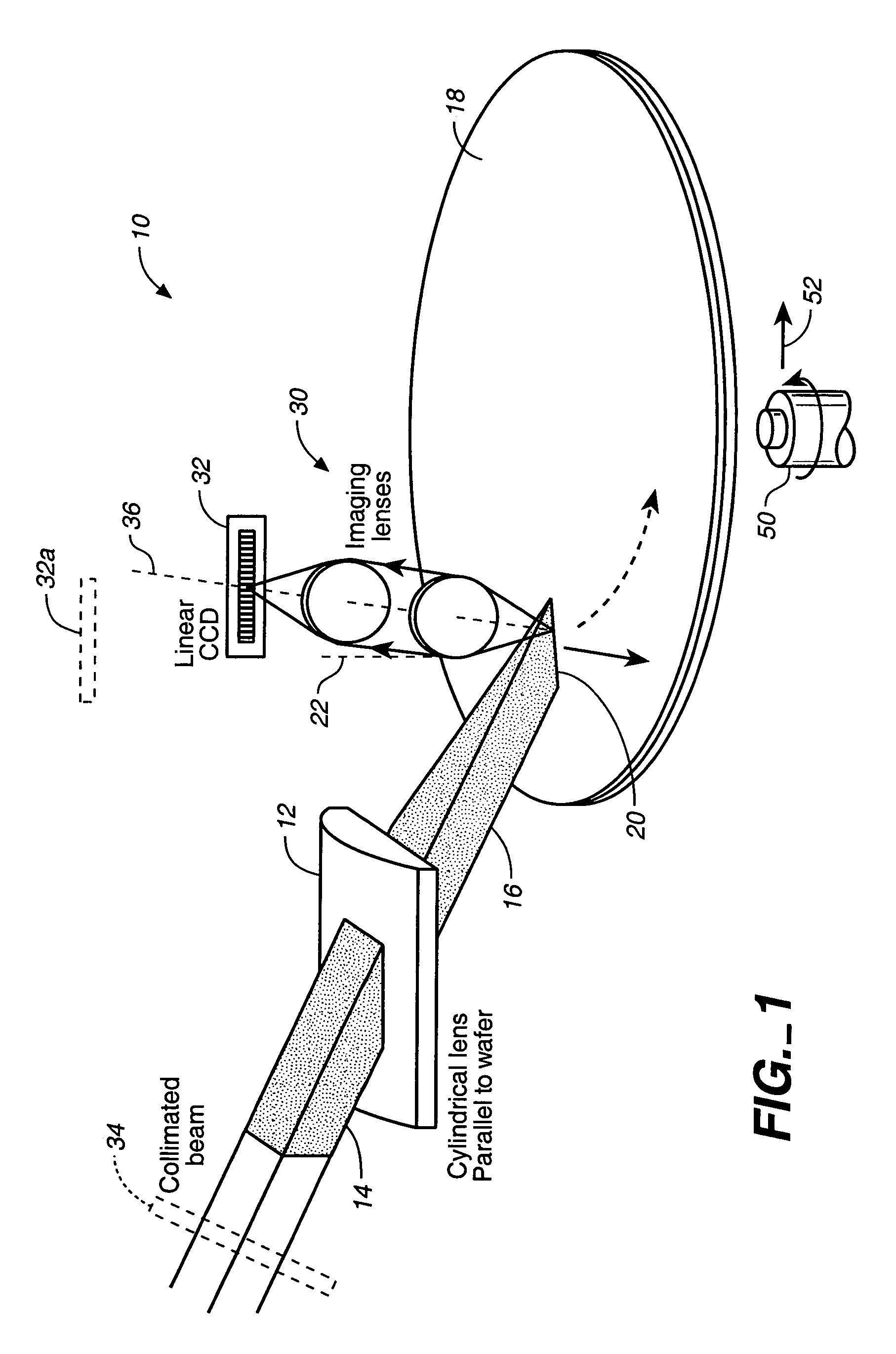
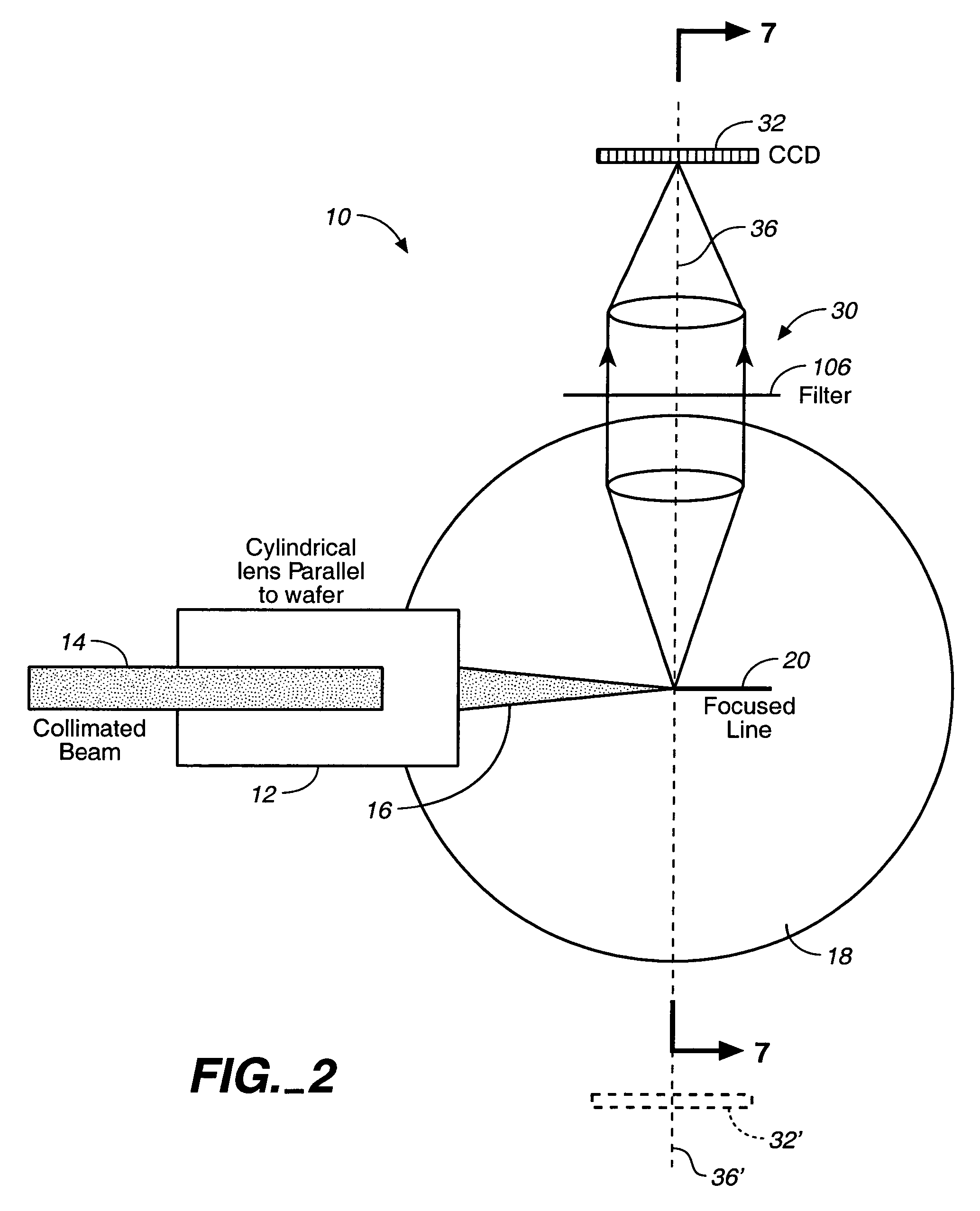
InactiveUS7088443B2Improved sensitivity and performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementScattering properties measurementsRelative motionCharge couple device
A cylindrical mirror or lens is used to focus an input collimated beam of light onto a line on the surface to be inspected, where the line is substantially in the plane of incidence of the focused beam. An image of the beam is projected onto an array of charge-coupled devices parallel to the line for detecting anomalies and / or features of the surface, where the array is outside the plane of incidence of the focused beam. For inspecting surface with a pattern thereon, the light from the surface is first passed through a spatial filter before it is imaged onto the charge-coupled devices. The spatial filter includes stripes of scattering regions that shift in synchronism with relative motion between the beam and the surface to block Fourier components from the pattern. The spatial filter may be replaced by reflective strips that selectively reflects scattered radiation to the detector, where the reflective strips also shifts in synchronism with the relative motion.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Apparatus for differentiating blood cells using back-scatter
InactiveUS6869569B2Material thermal conductivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPhotodetectorRed blood cell
Blood cells of interest are readily distinguishable from other blood cells and look-a-like particles found in a blood sample by their back-scatter signature. A preferred method for differentiating platelets in a blood sample is to irradiate the cells and particles, one at a time, with a beam of radiation, and to detect back-scattered (reflected) radiation using a plurality of optical fibers to transmit the back-scattered radiation to a high-gain photodetector, e.g. a photomultiplier tube. Preferably, the back-scatter signal so obtained is combined with a second signal representing, for example, either the level of forward-scatter within a prescribed, relatively narrow angular range, or the level of side-scattered radiation, or the level of attenuation of the cell-irradiating beam caused by the presence of the irradiated cell or particle in the beam, or the electrical impedance of the irradiated cell or particle, to differentiate the cells of interest. The method and apparatus of the invention are particularly useful in differentiating platelets and basophils in a blood sample.
Owner:COULTER INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
X-ray CT system
InactiveUS7190758B2Excessive radiationHigh precision calibrationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayDirect radiation
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
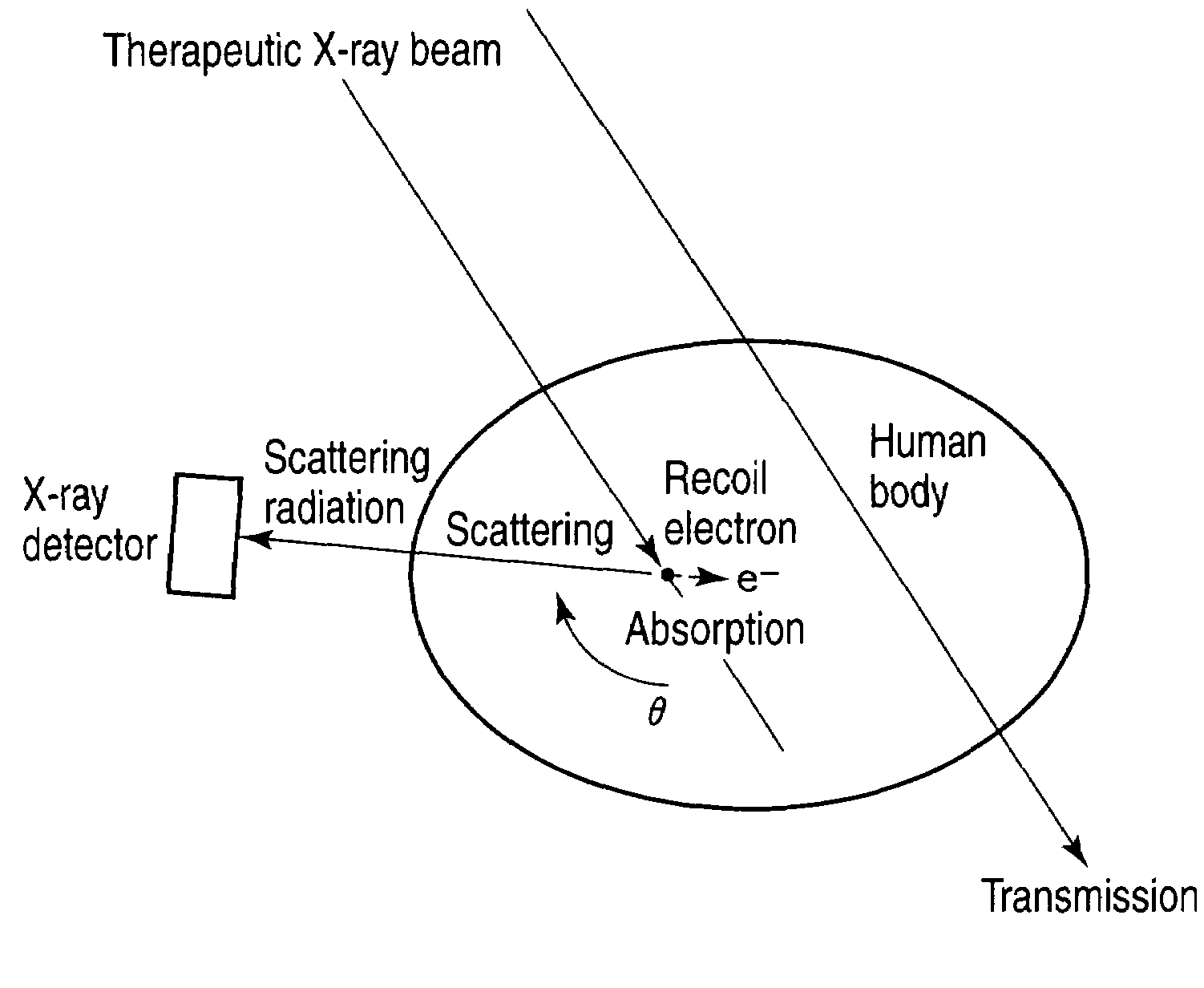
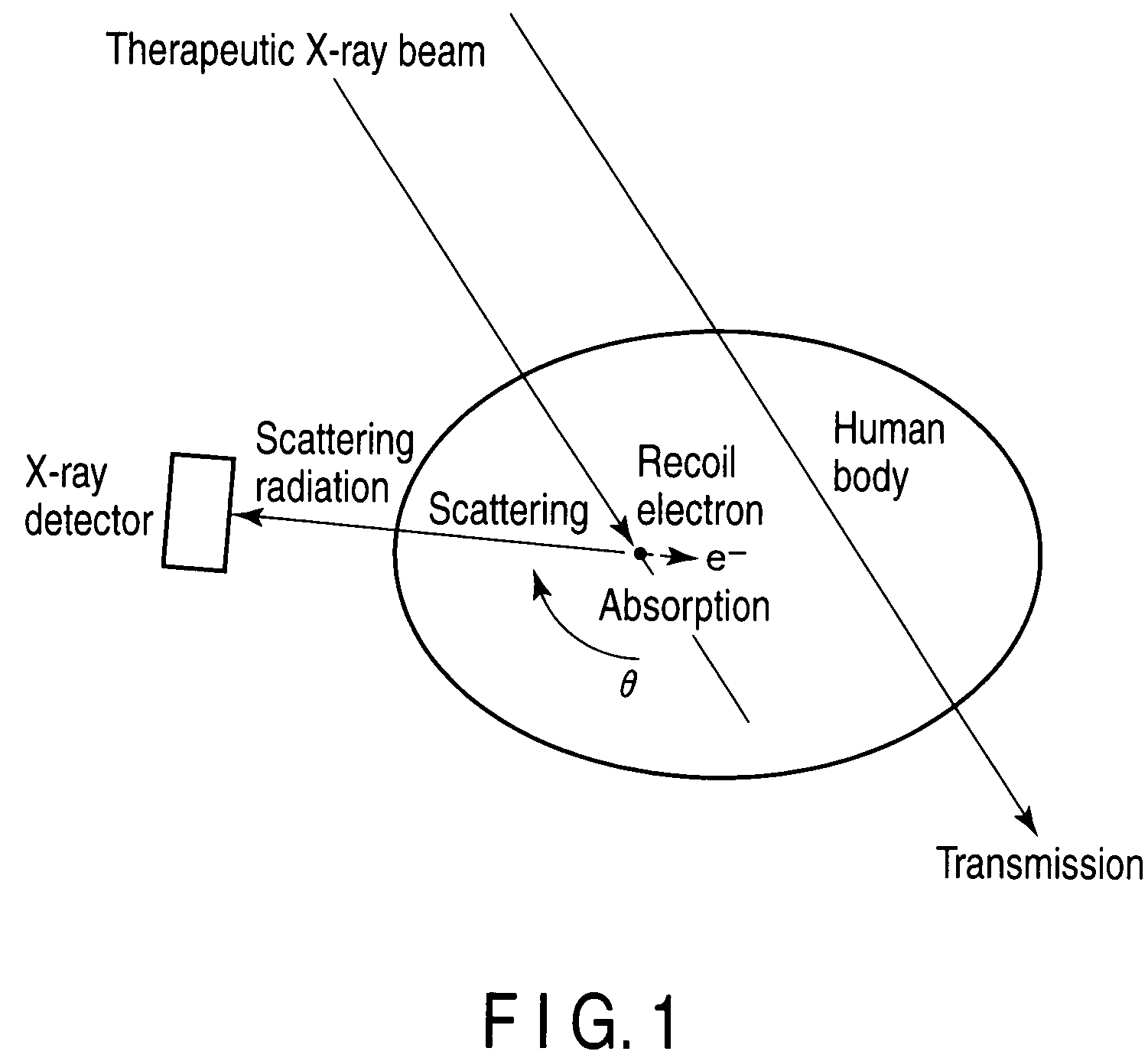
Radiotherapeutic system and radiotherapeutic dose distribution measuring method
ActiveUS20090161818A1Avoid problemsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-rayCompton scattering
A detector having a collimator in a position at a specific angle with respect to a therapeutic X-ray beam is mounted to selectively detect only scattering radiation in the direction. To three-dimensionally obtain a distribution of places where scattering occurs in a patient body, a detector is rotated during irradiation and scattering radiation is measured from all of directions. After that, a reconstructing process is performed, and a distribution of occurrence of scattering radiation in the subject is three-dimensionally imaged. Since angles and amounts of X-rays scattered by Compton scattering are known theoretically, if scattering radiation at a certain angle can be detected, the number of scattering radiation at other angles can be also estimated. On the basis of the theory, images of distribution of scattering radiation sources are converted to images of distribution of absorption of radiation.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
System and method for X-ray diffraction imaging
An X-ray diffraction imaging system is provided. The X-ray diffraction imaging system includes an X-ray source configured to emit an X-ray pencil beam and a scatter detector configured to receive scattered radiation having a scatter angle from the X-ray pencil beam. The scatter detector is located substantially in a plane and includes a plurality of detector strips. A first detector strip has a first width equal to a linear extent of the X-ray pencil beam measured at the plane in a direction parallel to the first width.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
Anti-stokes raman in vivo probe of analyte concentrations through the human nail
A system and method are provided for detecting and quantifying an analyte in vivo. Anti-Stokes Raman scattered radiation emitted from a sample under incident radiation excitation is collected and analyzed. The intensity response is corrected for temperature effects using a Boltzmann correction factor based on the temperature of the sample. The sampled tissue is advantageously the sterile matrix beneath the nail of either a toe or a finger. The incident excitation radiation is projected onto the sterile matrix through the nail, which operates as a window. The present invention may be applied in both the blue / UV and the red / IR regions of the spectrum.
Owner:SKYMOON RES & DEV
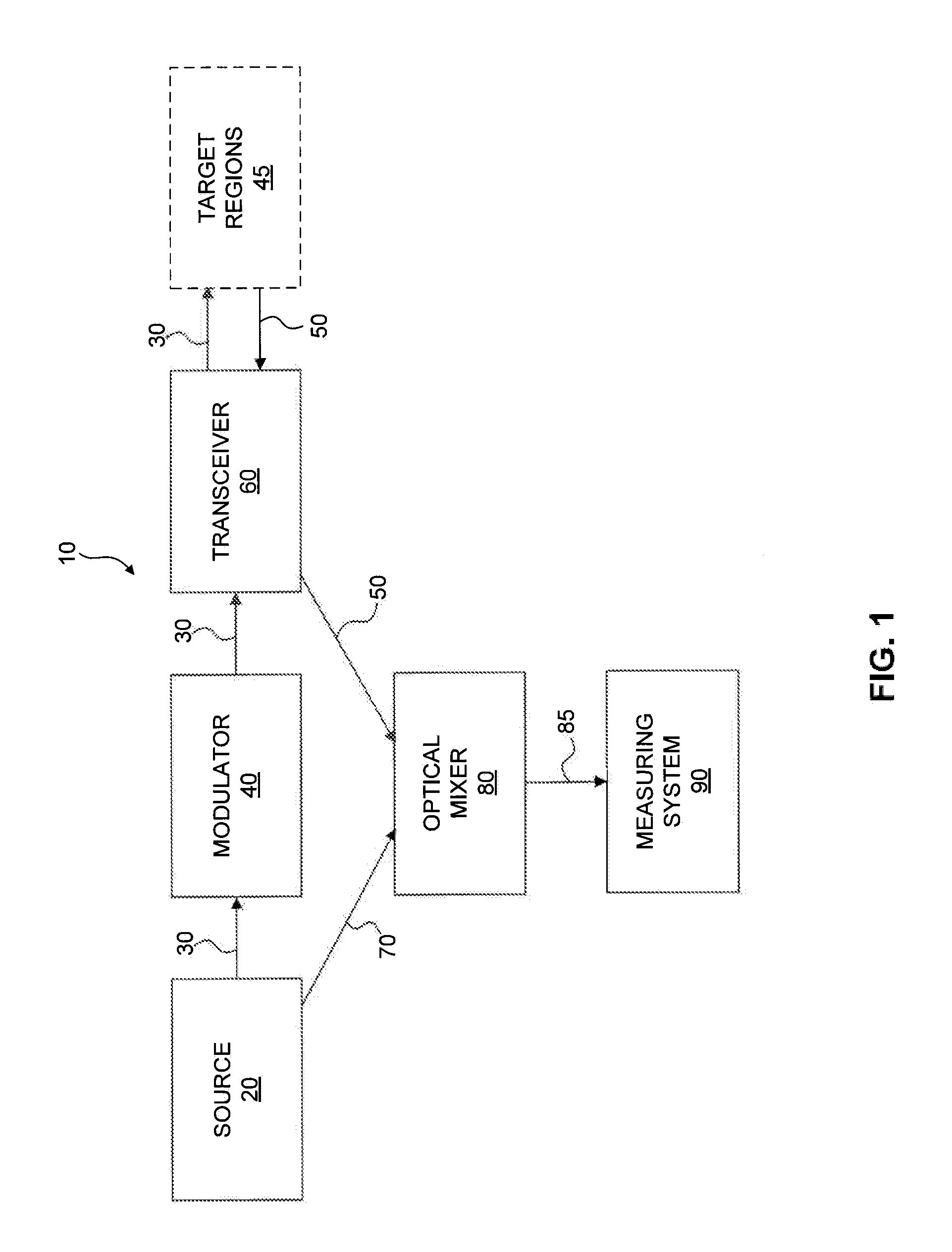
Optical Air Data System Suite of Sensors
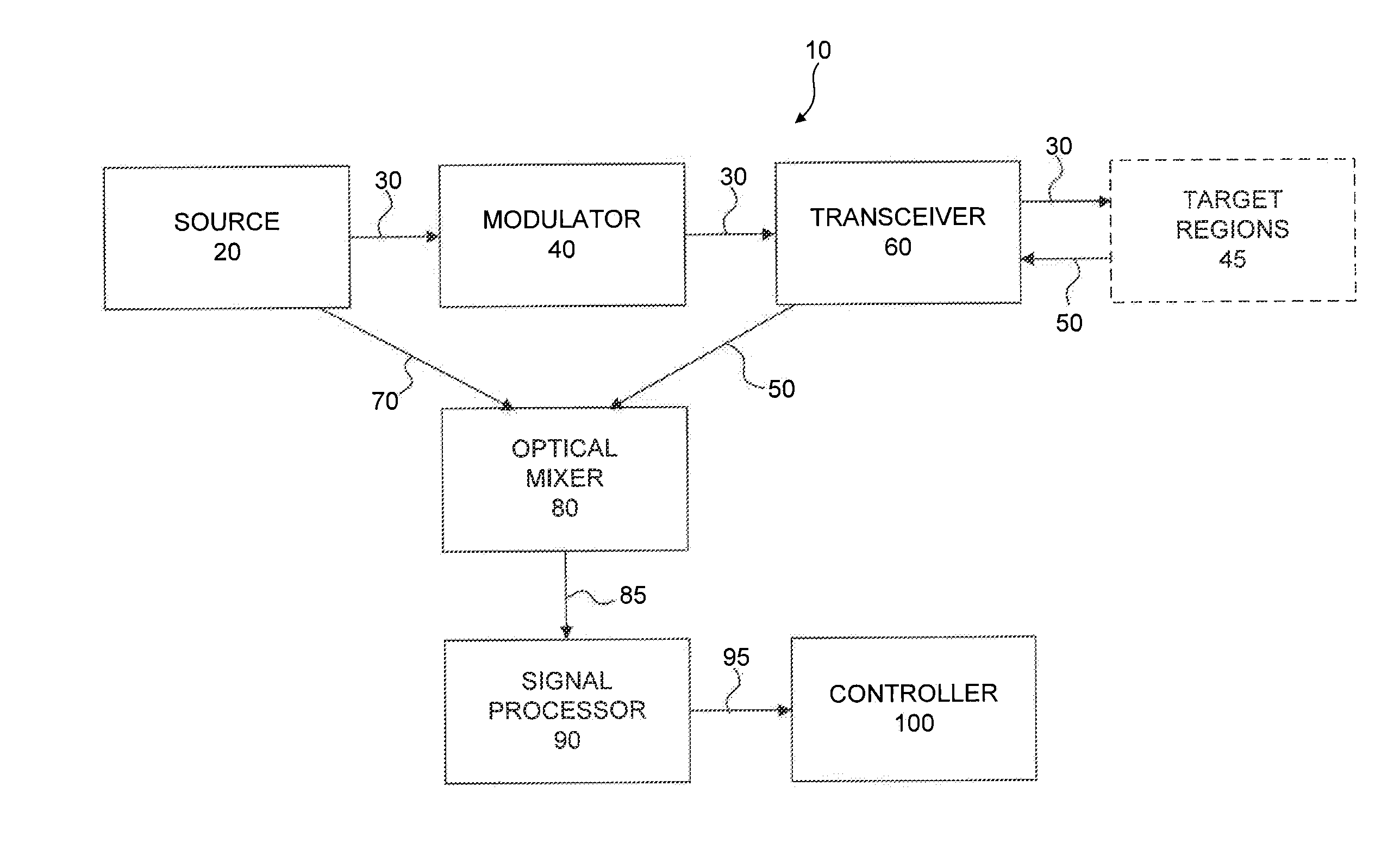
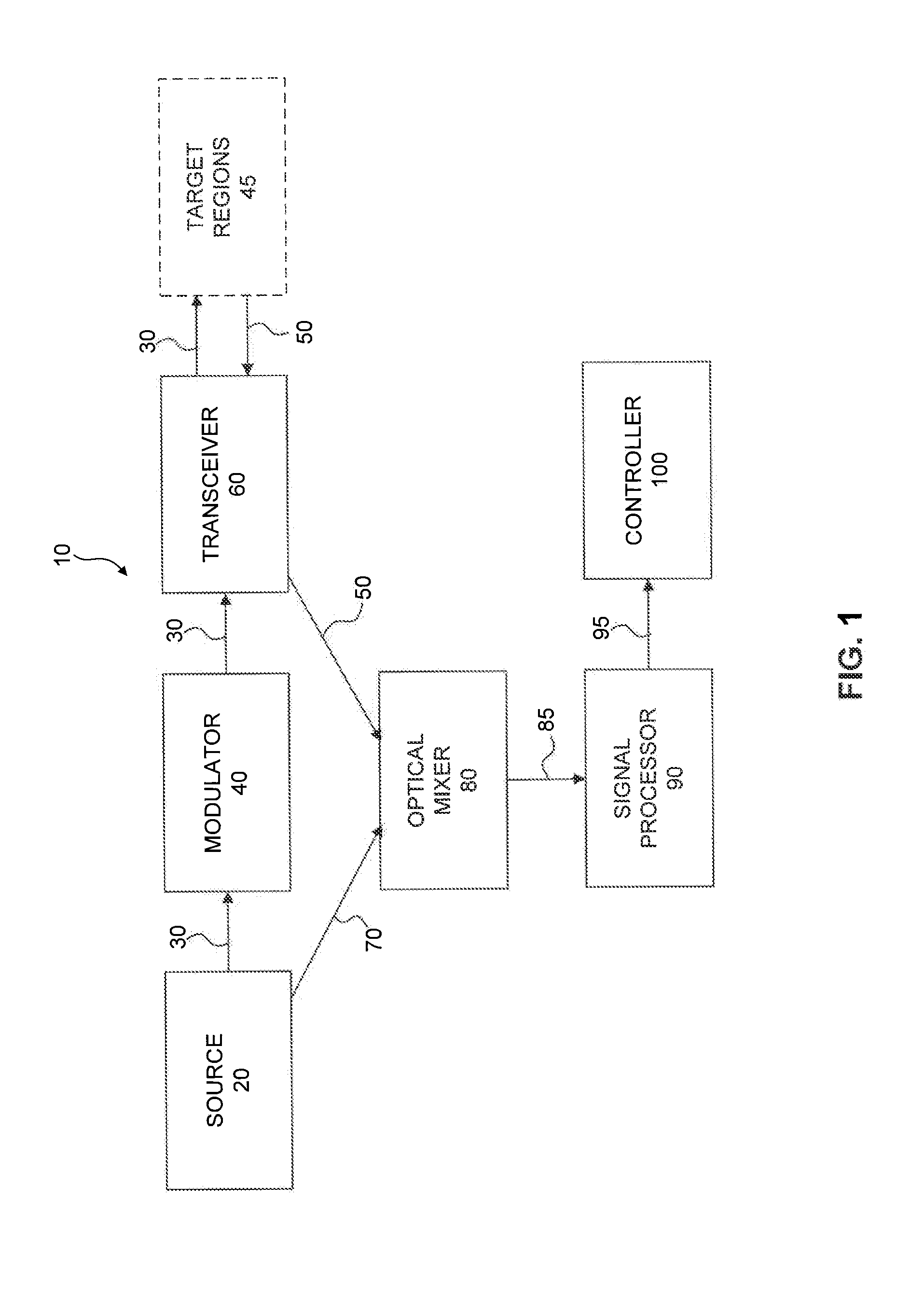
ActiveUS20130162974A1Minimize turbulenceTurbulence experienced by the airborne vehicle is minimizedScattering properties measurementsIndication/recording movementTransceiverFrequency mixer
Systems and methods for laser based measurement of air parameters for use, e.g., on aircraft are disclosed. An example system includes a coherent source of radiation, a modulator, a transceiver, an optical mixer, and a measuring system. The coherent source produces a coherent radiation beam, and the modulator is configured to modulate the coherent radiation beam. The transceiver is configured to transmit the modulated radiation beam to, and receive a scattered radiation signal from a target region. The optical mixer is configured to determine a difference between the scattered radiation signal and the reference radiation beam. The measuring system is configured to determine at least one of velocity, air density, pressure, temperature, barometric altitude, angle of attack, angle of side slip, icing and turbulence based on the difference between the scattered radiation signal and the reference radiation beam.
Owner:RD2 LLC
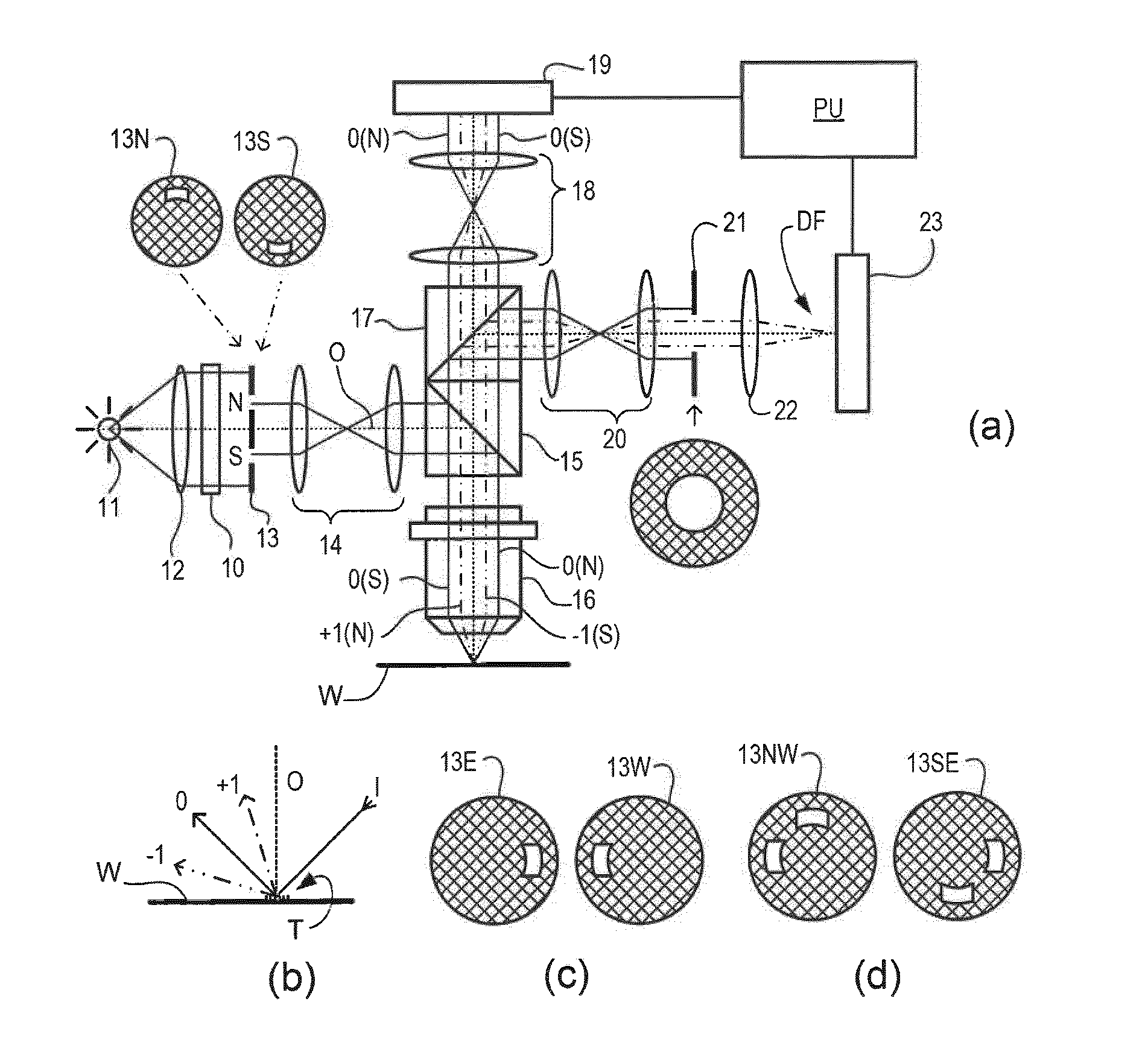
Method of Determining Dose and Focus, Inspection Apparatus, Patterning Device, Substrate and Device Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20150293458A1Improve accuracyPhotometry using reference valueScattering properties measurementsLithography processScatterometer
A method of determining exposure dose of a lithographic apparatus used in a lithographic process on a substrate. Using the lithographic process to produce a first structure on the substrate, the first structure having a dose-sensitive feature which has a form that depends on exposure dose of the lithographic apparatus on the substrate. Using the lithographic process to produce a second structure on the substrate, the second structure having a dose-sensitive feature which has a form that depends on the exposure dose of the lithographic apparatus but which has a different sensitivity to the exposure dose than the first structure. Detecting scattered radiation while illuminating the first and second structures with radiation to obtain first and second scatterometer signals. Using the first and second scatterometer signals to determine an exposure dose value used to produce at least one of the first and second structures.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Apparatus and method for detecting items in objects
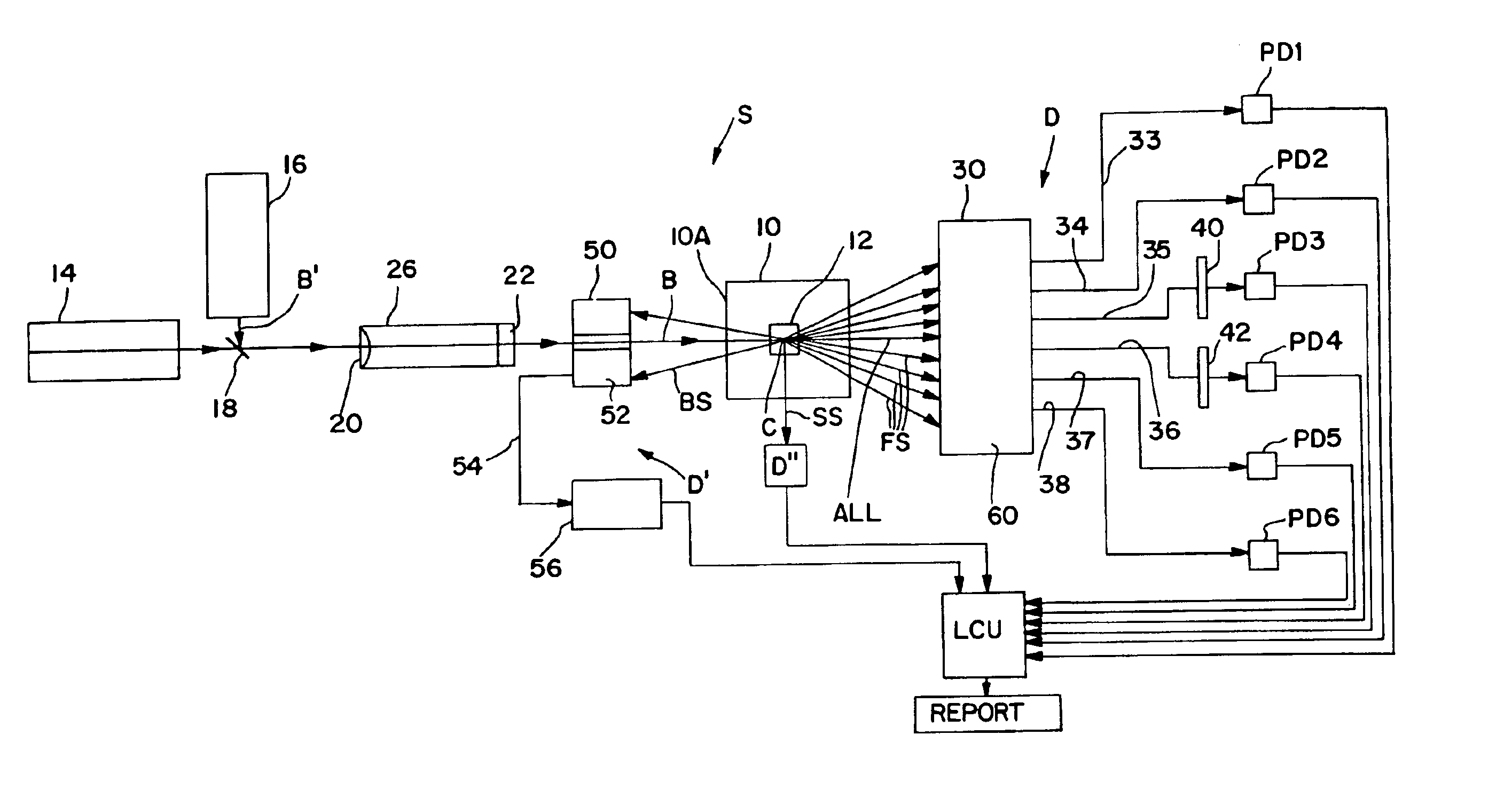
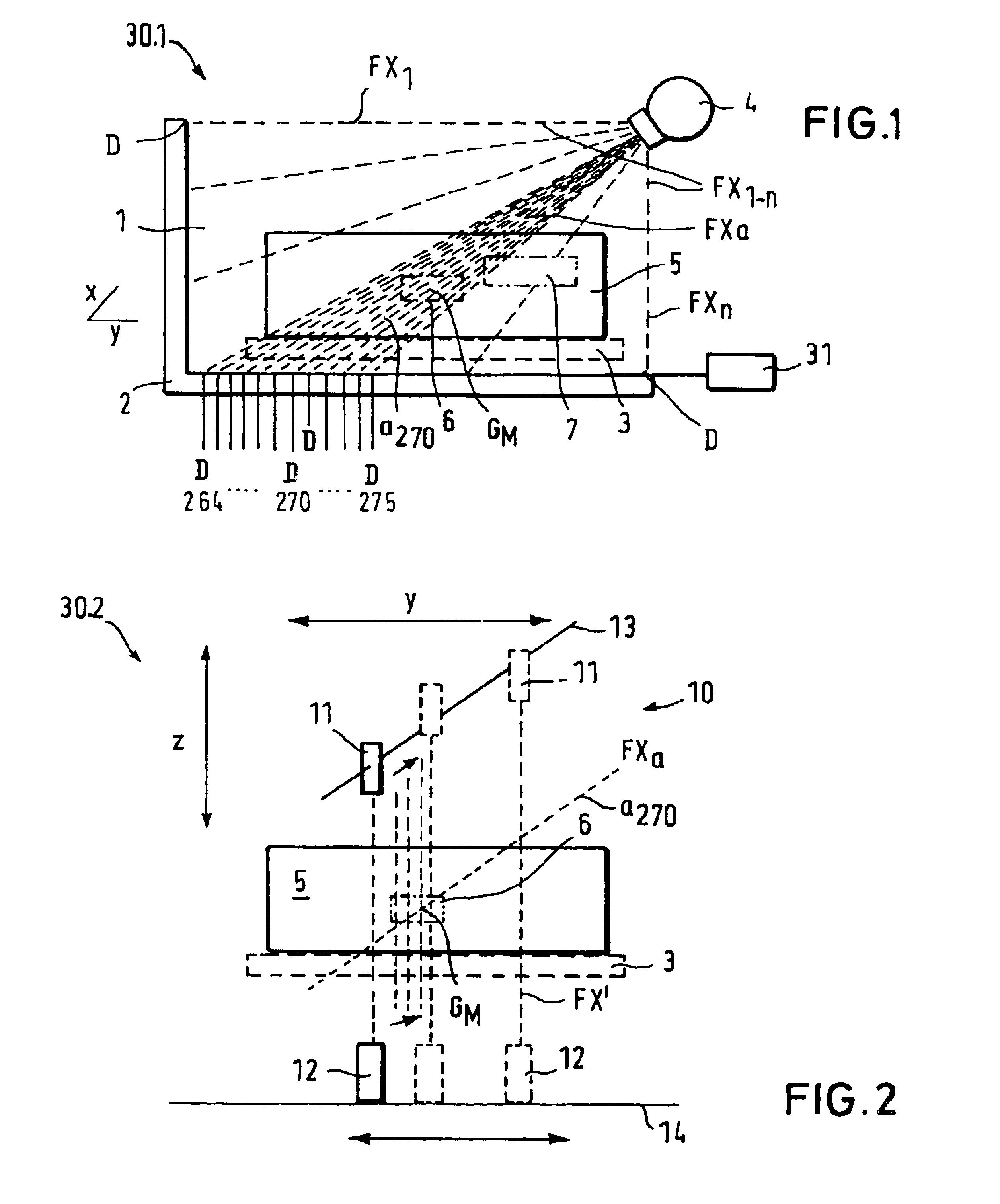
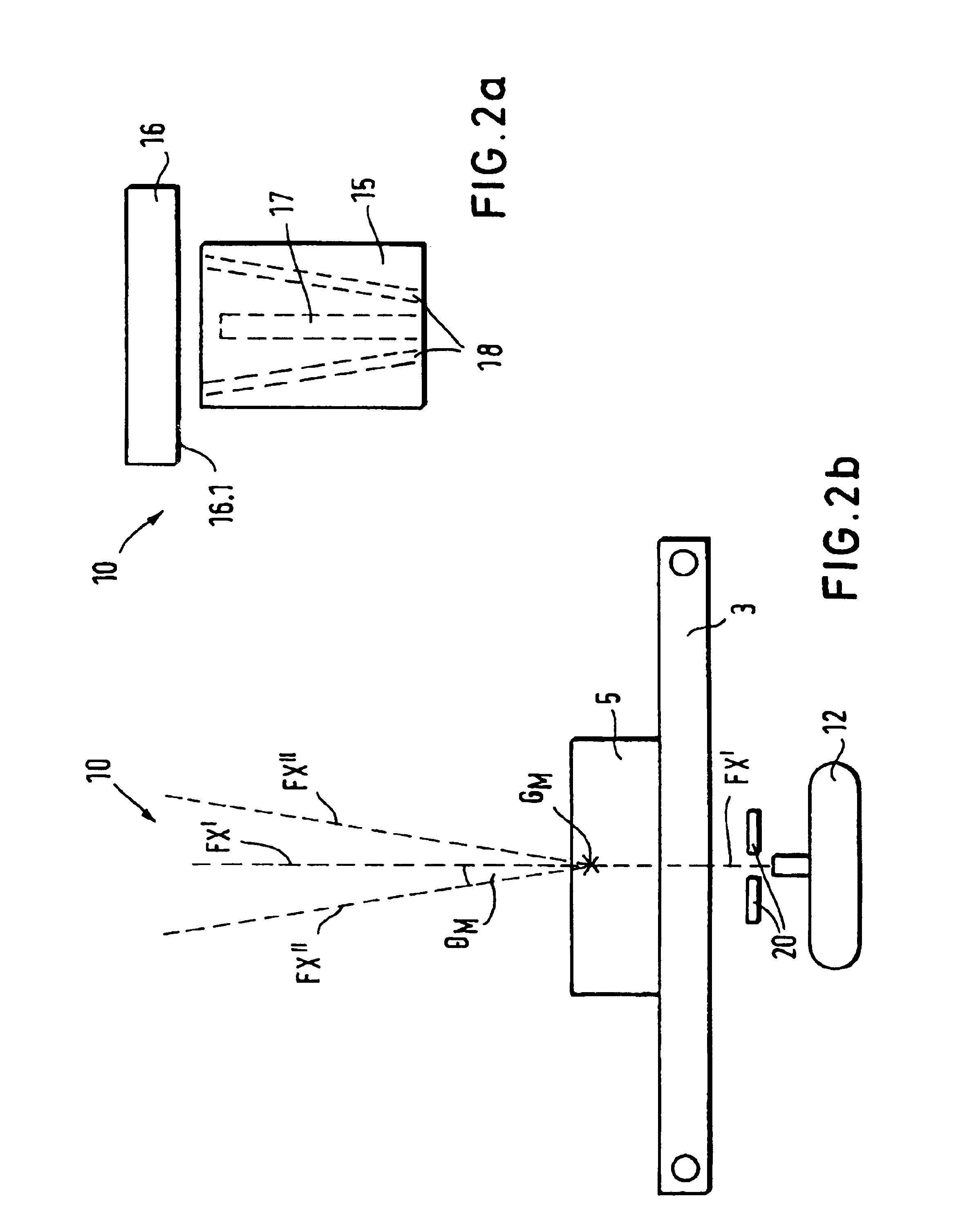
InactiveUS6839406B2Quick checkQuickly and simply and automatically testingUsing wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationX-rayTest phase
A method and an apparatus for detecting items in objects, such as in luggage, wherein a detector apparatus, functioning as a second detector is divided into a lower testing stage and a higher testing stage. In the lower testing stage, the coordinates of the object location are determined, and subsequently, a diffraction apparatus is moved to this location in the higher testing stage. In particular, X-ray diffraction can be employed to determine the explosive material of the item in the object. The diffraction apparatus comprises a collimator / detector arrangement, which is disposed to be adjusted height-wise and laterally in the higher testing stage, with a laterally-adjustable X-ray source, which is synchronized with the collimator / detector arrangement. The collimator / detector arrangement preferably has only one collimator and one detector. The collimator preferably has a conically-expanding ring slot, which a predetermined angle ΘM of a scatter radiation.
Owner:SMITHS HEIMANN
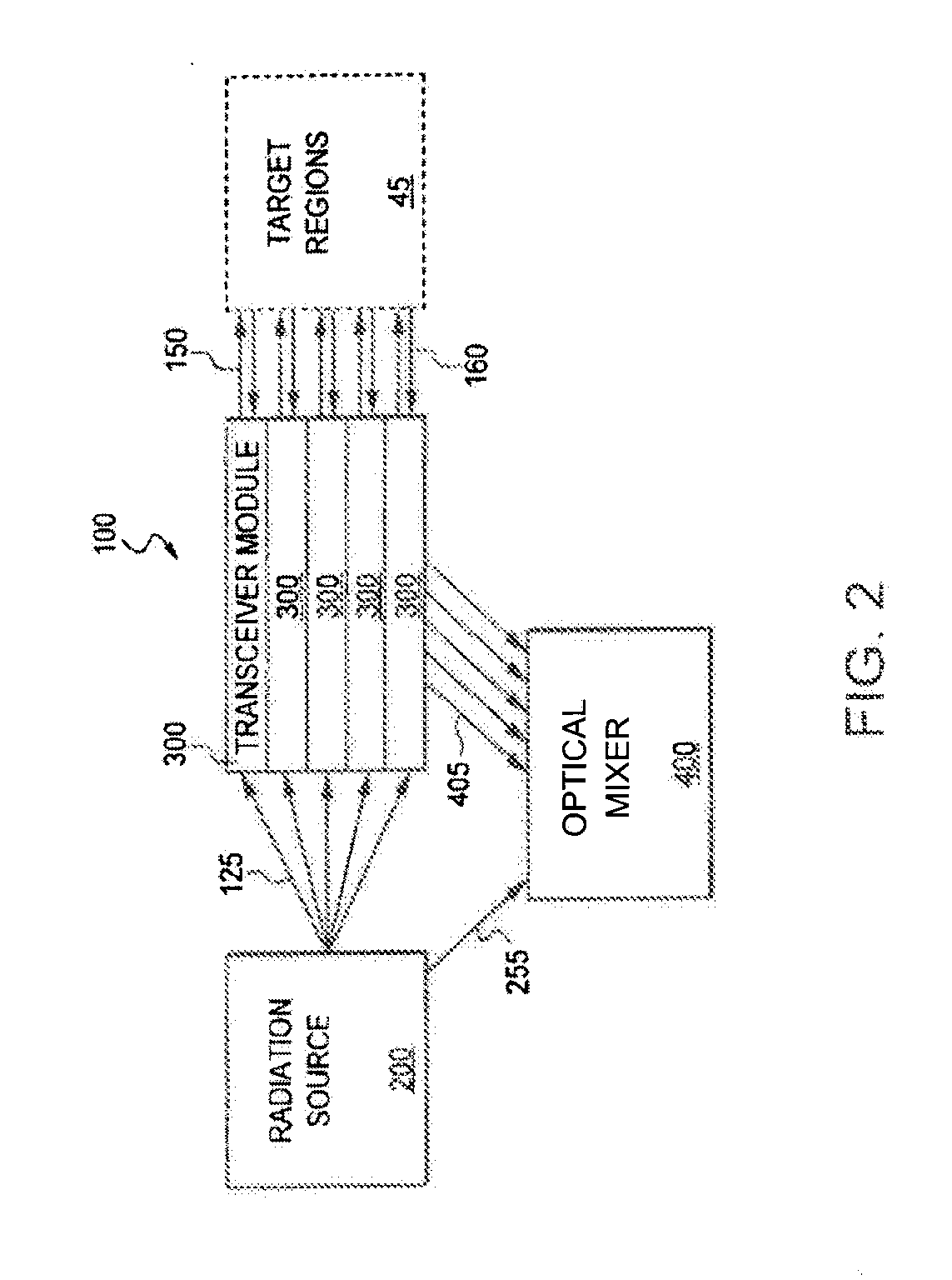
Laser Doppler Velocimeter With Intelligent Optical Device
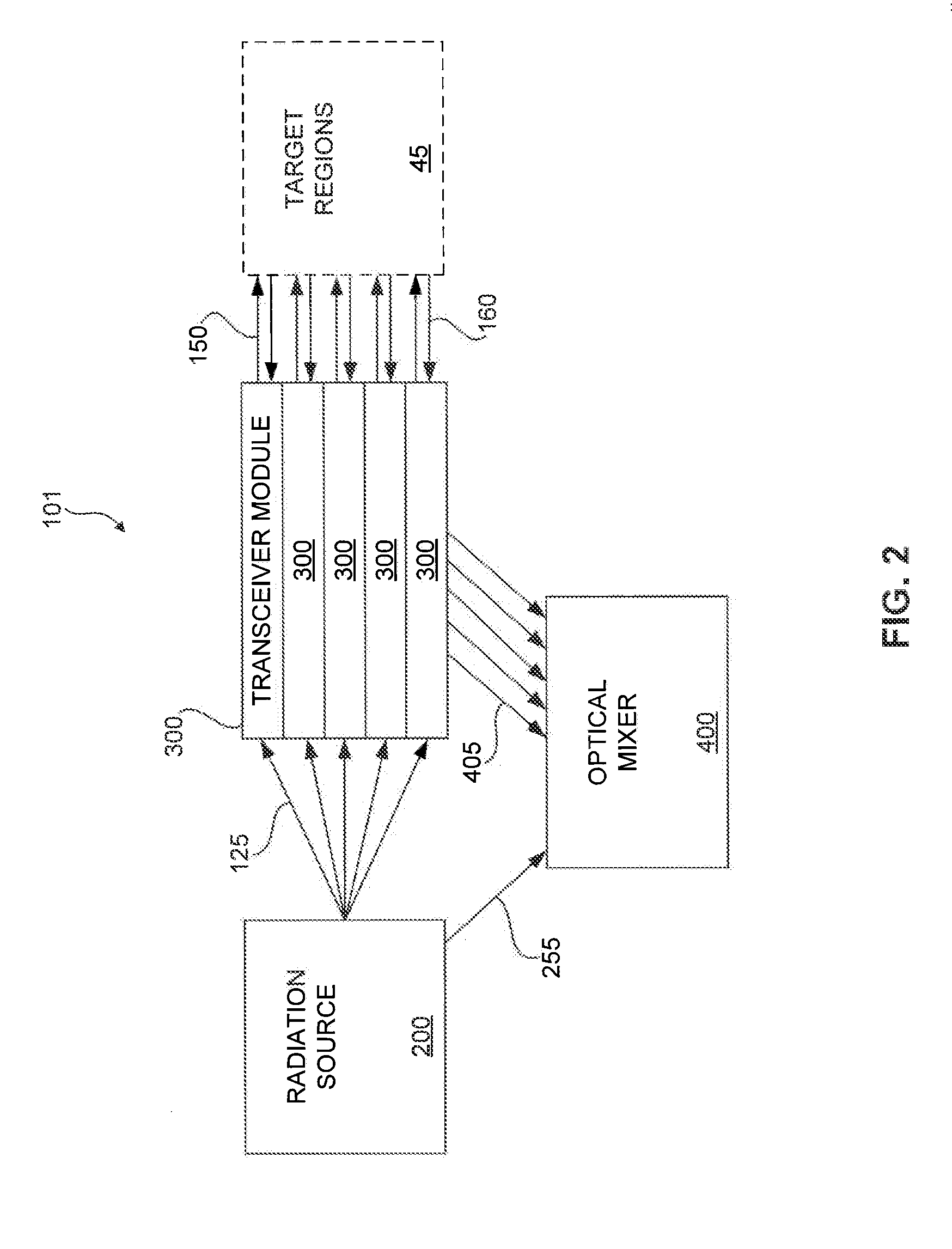
InactiveUS20150185246A1Provide controlDevices using optical meansFluid speed measurementTransceiverLaser Doppler vibrometer
Systems and methods for laser based measurement of air parameters are disclosed. An example system includes a coherent source of radiation, a transceiver, an optical mixer, and an intelligent optical device. The coherent source produces a coherent radiation beam that is then transmitted to a target region by the transceiver. The transceiver is further configured to receive a scattered radiation signal from the target region. The optical mixer is configured to receive the scattered radiation signal from the transceiver, receive a reference radiation beam from the coherent source, and to determine a difference between the scattered radiation signal and the reference radiation beam. In certain embodiments, the intelligent optical device is configured to steer, modulate, or condition, at least one of the coherent radiation beam, the scattered radiation signal, and the reference radiation beam.
Owner:OPTICAL AIR DATA SYST
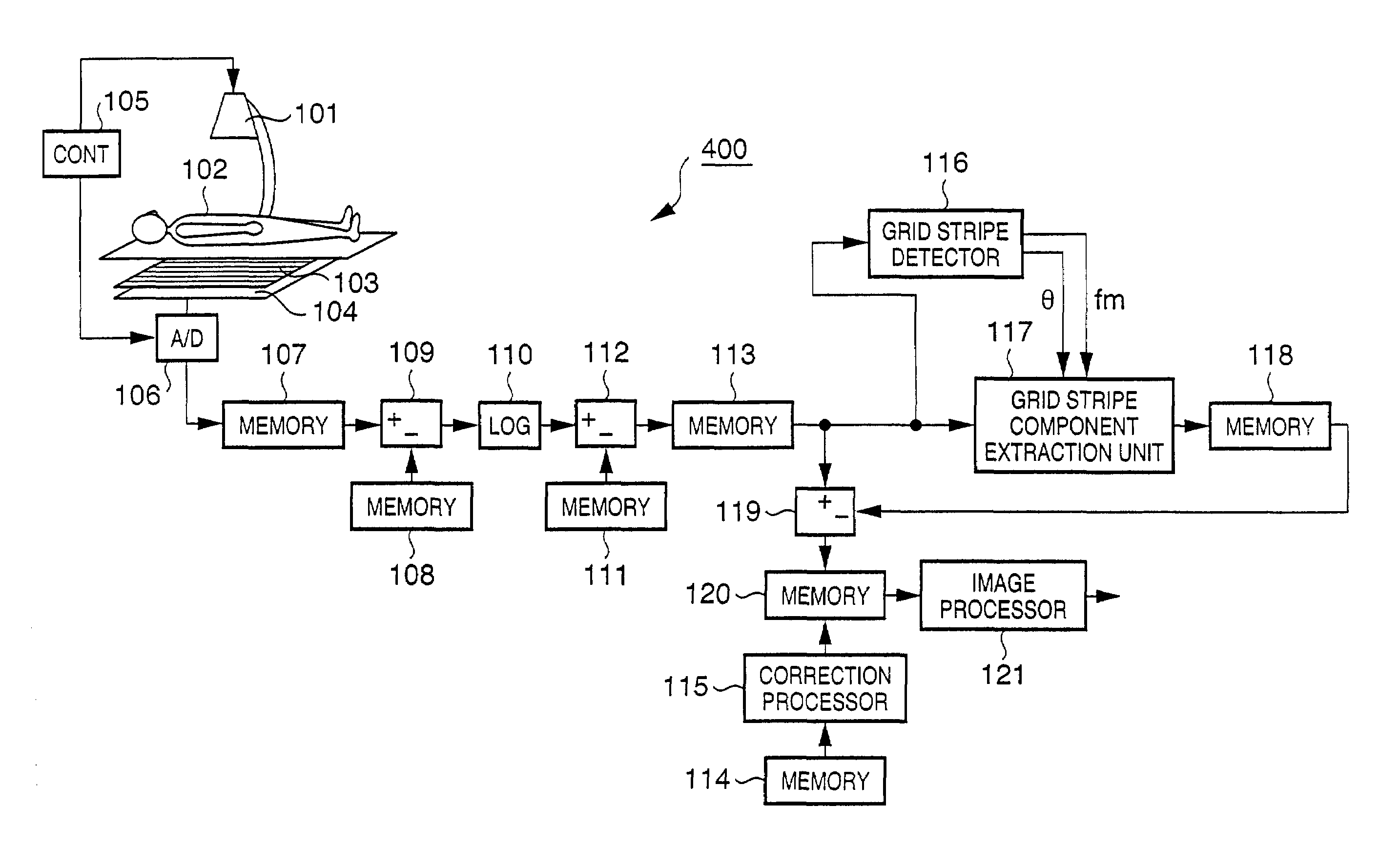
Radiation image processing apparatus, image processing system, radiation image processing method, storage medium, and program
The disclosure is made for an apparatus for processing a radiation image of an object obtained by radiography using a grid which is used to remove scattered radiation from the object.The apparatus includes generation means for generating image components due to the grid on the basis of data of the radiation image, to remove the image components due to the grid from the radiation image.
Owner:CANON KK
Methods, systems, and computer-program products for estimating scattered radiation in radiographic projections
ActiveUS8326011B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTomographic reconstructionScattering kernel
Several related inventions for estimating scattered radiation in radiographic projections are disclosed. Several of the inventions use scatter kernels of various forms, including symmetric and asymmetric forms. The inventions may be used alone or in various combinations with one another. The resulting estimates of scattered radiation may be used to correct the projections, which can improve the results of tomographic reconstructions. Still other inventions of the present application generate estimates of scattered radiation from shaded or partially shaded regions of a radiographic projection, which may be used to correct the projections or used to adjust the estimates of scattered radiation generated according to inventions of the present application that employ kernels.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
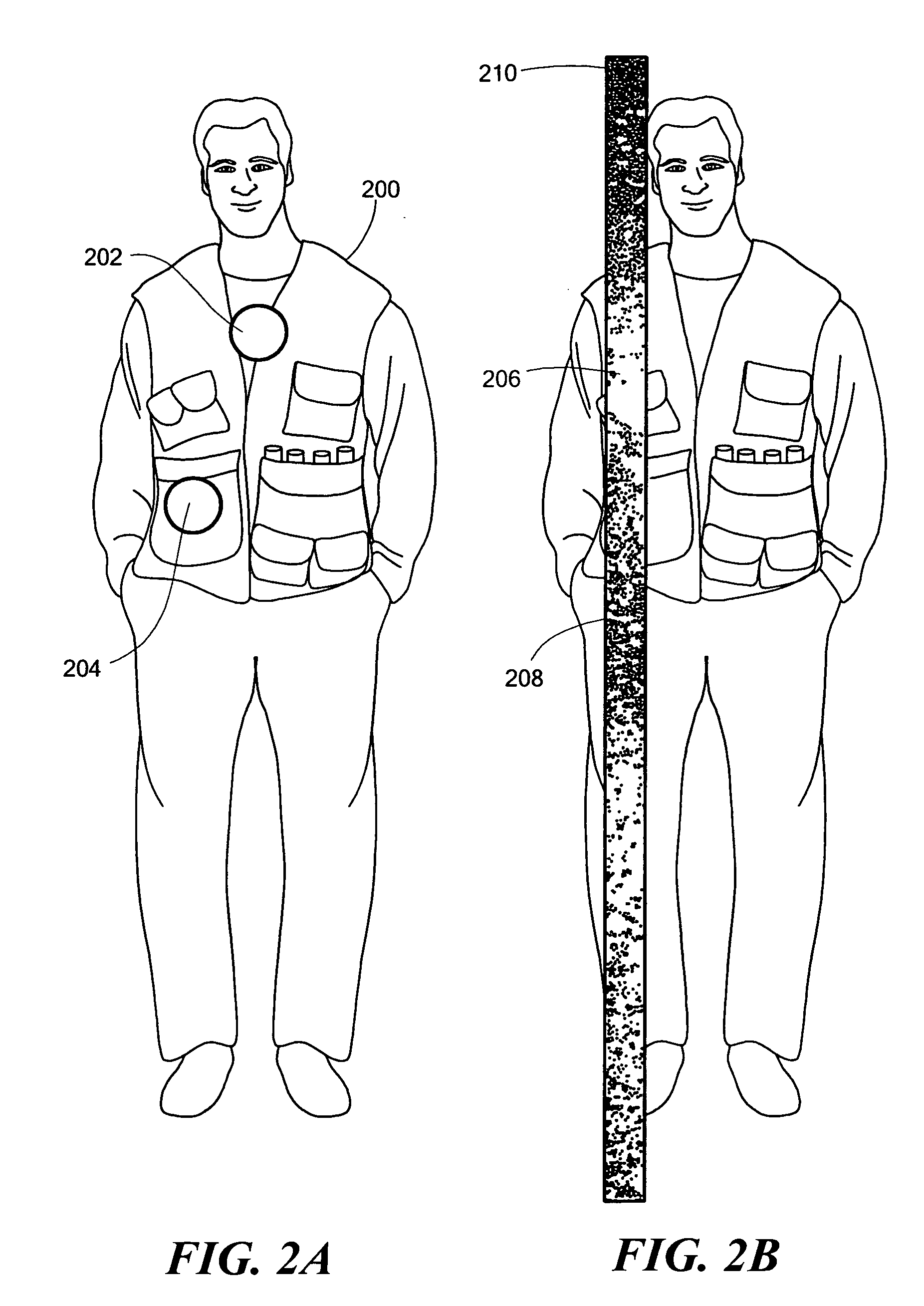
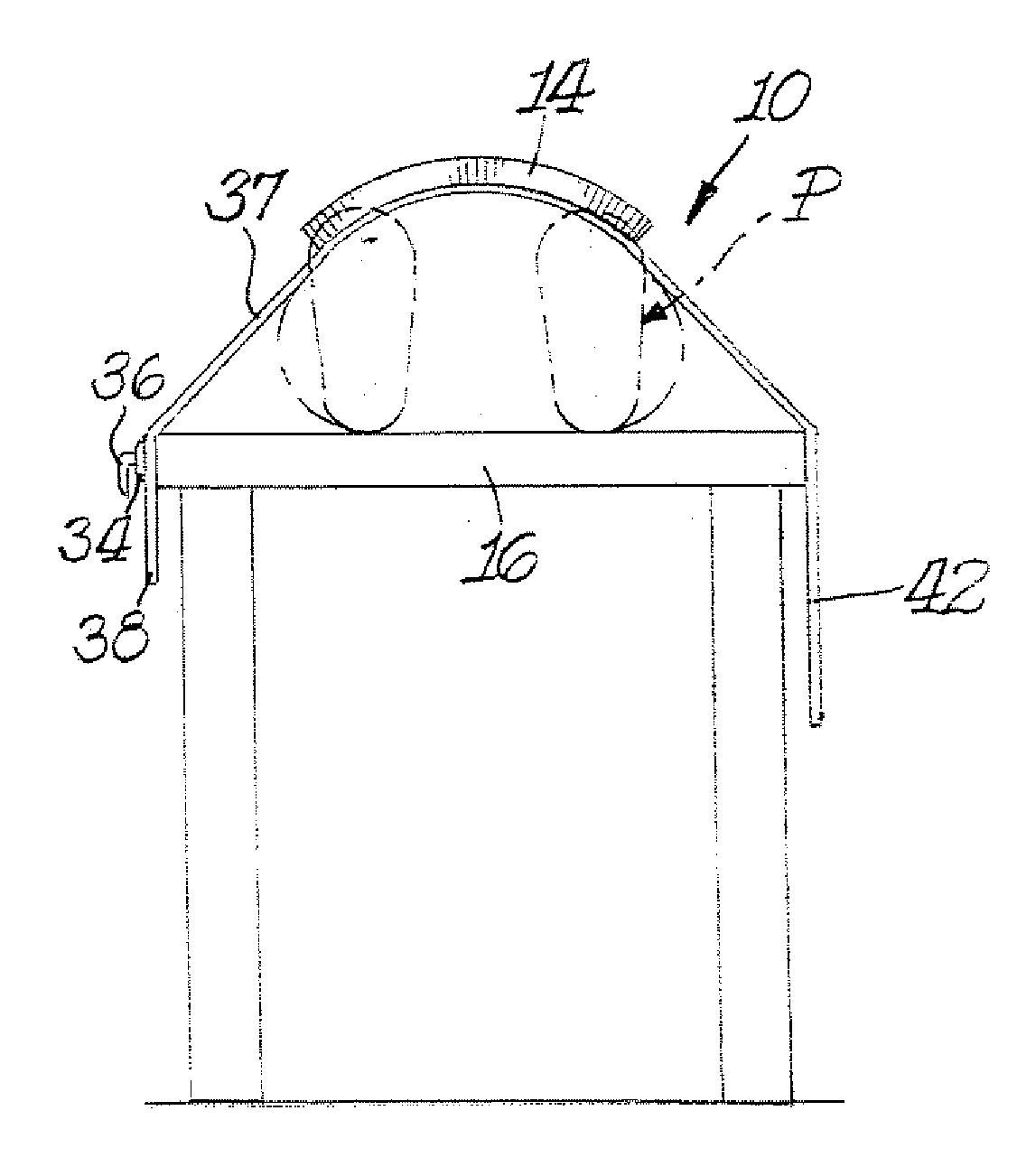
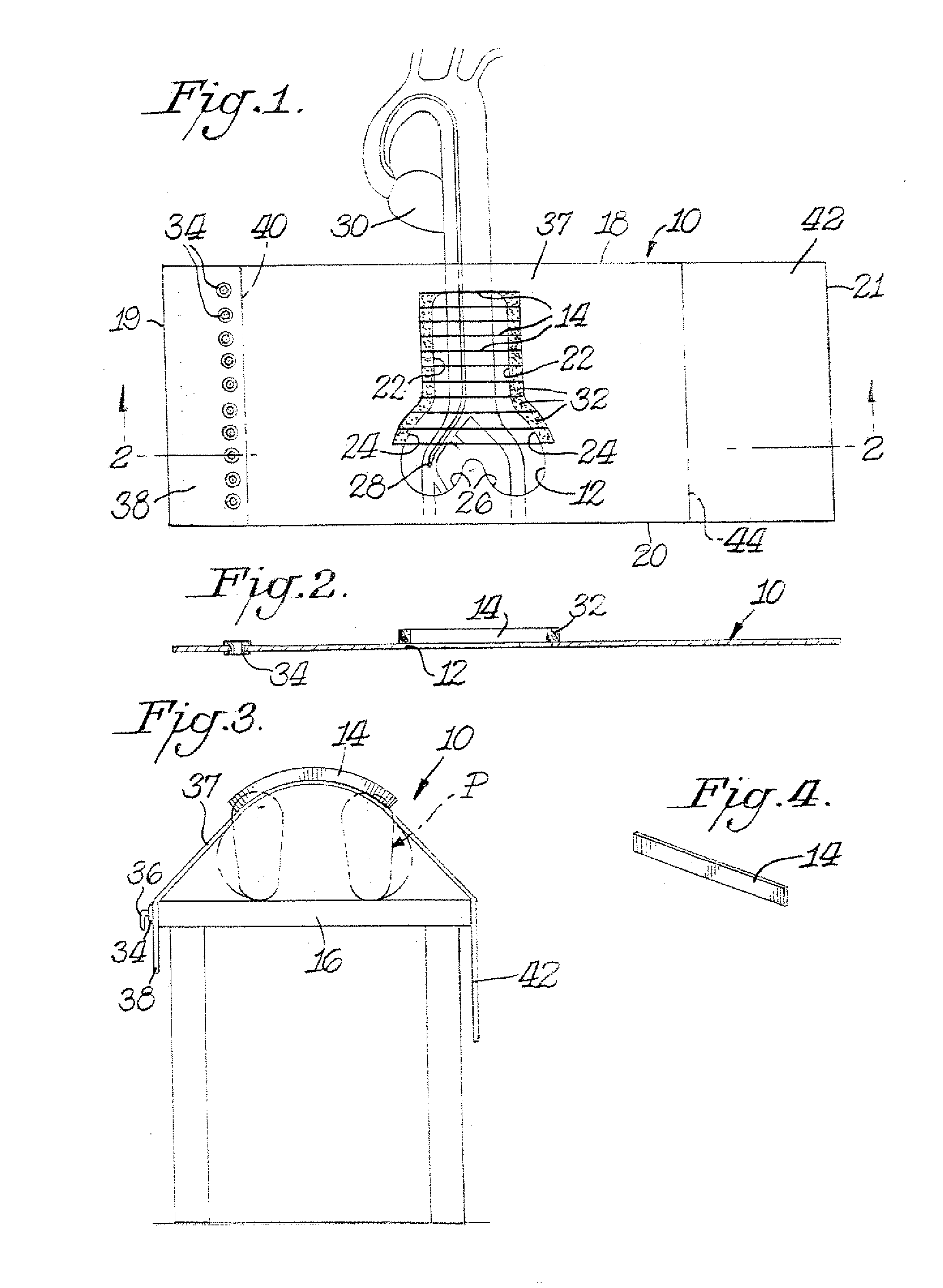
Radiation shield
InactiveUS20070029513A1Direct visualizationReduce radiation exposureRadiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsObservation pointRadiation shield
A radiation shield includes a radio-opaque drape which has an open area extending completely through the drape to provide a viewing site. Radiation control structure in the form of a vent system is located in the open area. The vent system includes a plurality of radio-opaque slats extending at least partially across at least a portion of the open area. The slats preferably extend outwardly away from the surface of the drape to facilitate the capturing of scattered radiation.
Owner:TREUTH MARK G
Spatial filter for sample inspection system
ActiveUS7184138B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansElevation angleForward scatter
Spatial filtering is disclosed that improves the signal to noise ration of a sample inspection system of the type having a detector and collection optics that receive radiation scattered from a point on a sample surface and direct the scattered radiation toward the detector. The spatial filtering may screen the detector from substantially all of the forward-scattered radiation from back-scattered radiation that is scattered in a at an elevation angle less than about 45° with respect to a normal to the surface. Forward scattered noise is screened from the detector while backscattered signal reaches the detector. Programmable spatial filters may be used to selectively block scattered noise due to surface roughness while transmitting scattered signal due to surface defects.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Scatter attenuation tomography using a monochromatic radiation source
InactiveUS8842808B2Material analysis by transmitting radiationMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionVoxelTomographic image
A system and methods for characterizing an inspected object on the basis of attenuation between identified regions of scattering and a plurality of detectors. An incident beam of substantially monochromatic penetrating radiation is generated by a source, which may be a radioactive source. The incident beam is characterized by a propagation axis and a source energy. Radiation scattered by the object is detected by means of a plurality of detector elements disposed about the beam of penetrating radiation, each detector element generating a detector signal characterizing a detected energy of scattered radiation. The detector signal provides for determining a displacement for each scattering point of the object relative to a fiducial position on the propagation axis of the incident beam, based upon the detected energy of the scattered radiation. By calculating the attenuation of penetrating radiation between pairs of scattering voxels, a tomographic image is obtained characterizing the three-dimensional distribution of attenuation in the object of one or more energies of penetrating radiation, and thus of material characteristics.
Owner:AMERICAN SCI & ENG INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com