Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
350results about How to "Reduce radiation exposure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
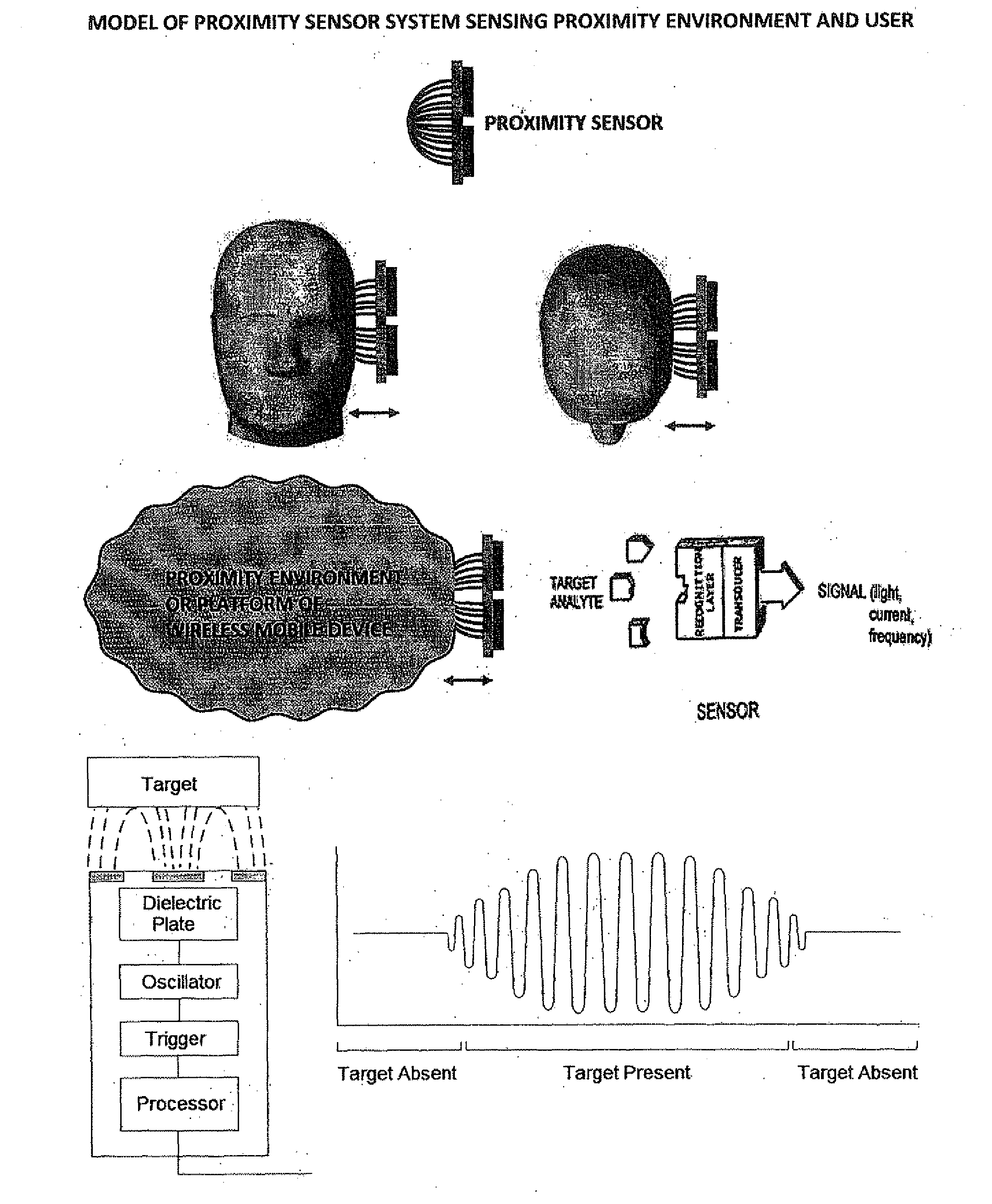
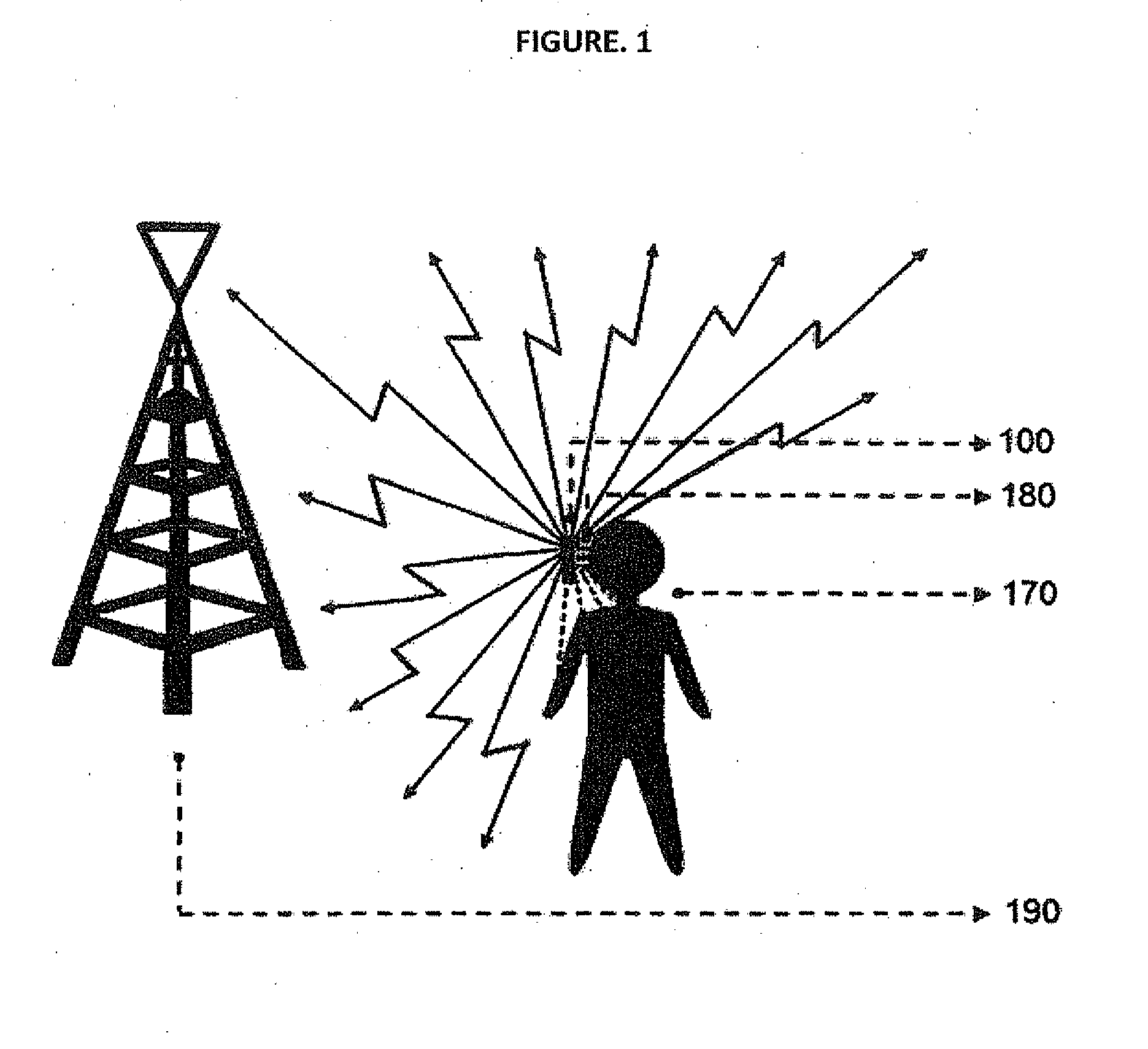
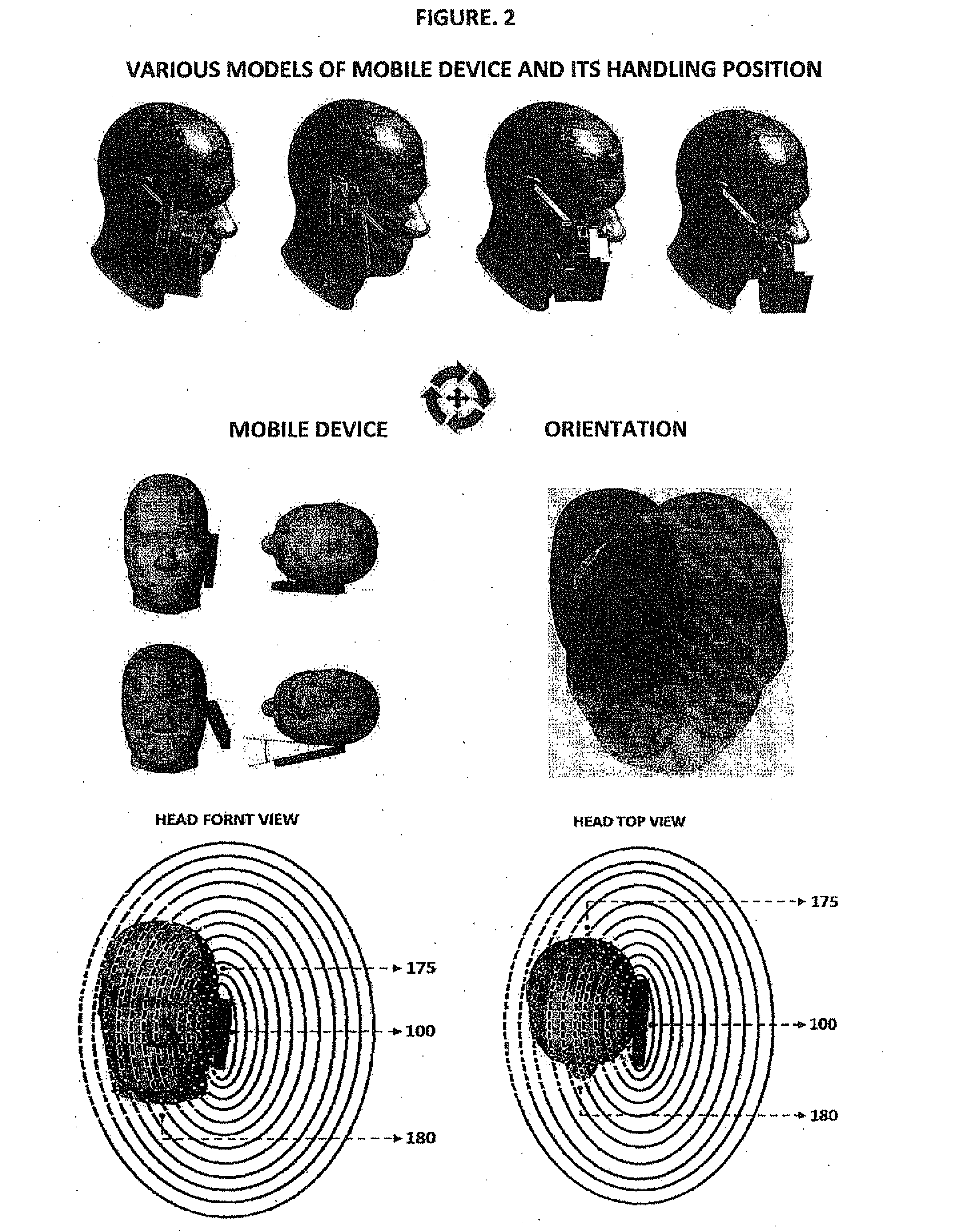
Smart Active Antenna Radiation Pattern Optimising System For Mobile Devices Achieved By Sensing Device Proximity Environment With Property, Position, Orientation, Signal Quality And Operating Modes
ActiveUS20140128032A1Save battery powerImprove signal qualityPower managementUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionDistortionActive antenna
The smart dynamic radiation pattern optimising system is a design and technique to actively shape & optimise the radiation pattern of mobile device controlled by smart RF / Antenna system with signal processing algorithm that works by sensing the change in device proximity environment with nature or property, range, orientation, position, location, signal quality parameters and ambient intelligence to protect the user by controlling radiation exposure, enhance RF signal quality and to save battery power. Mobile devices are handled in different proximity environment which influence the antenna performance due to electromagnetic interaction based on environments properties that leads to detuning, radiation pattern distortion, impedance mismatch etc which in turn degrades the signal quality. Also change in device orientation according to usage leads to power loss due to polarization mismatch. So when the signal quality degrades the system will sense & compute in an adaptive closed loop manner to actively optimise the radiation pattern according to scenarios. The design consist of (a) a sensor system 220 to determine the change in proximity environment [close vicinity] with sensing its property, sensing multi-direction, dimension, layer, position & range of proximity environment with respect to device, sensing device (antenna) orientation, visual sensing, infrared or thermal vision, user recognition, user head & hand hold effect, location, usage scenarios & operating modes and accordingly generate the trigger signal 230; (b) a processing unit 150 for computing the interrupt control signal 140 according to the nature of trigger signal & existing signal quality parameters; (c) Smart active radiation pattern optimiser 120 that works based on control signal; (d) Antenna system 110 capable of achieving dynamic radiation pattern coupled with radiation pattern optimiser that actively shapes and controls the radiation pattern accordingly to protect the user and also restores radiation according to scenarios to optimise communication. Other aspects of the present invention are the same sensor system 220 is utilised to develop an application that guides the user locate & position the mobile device in living space to achieve optimised performance, protect the mobile device from theft and ambient intelligence to alert & interact with the user.
Owner:MUTHUKUMAR PRASAD
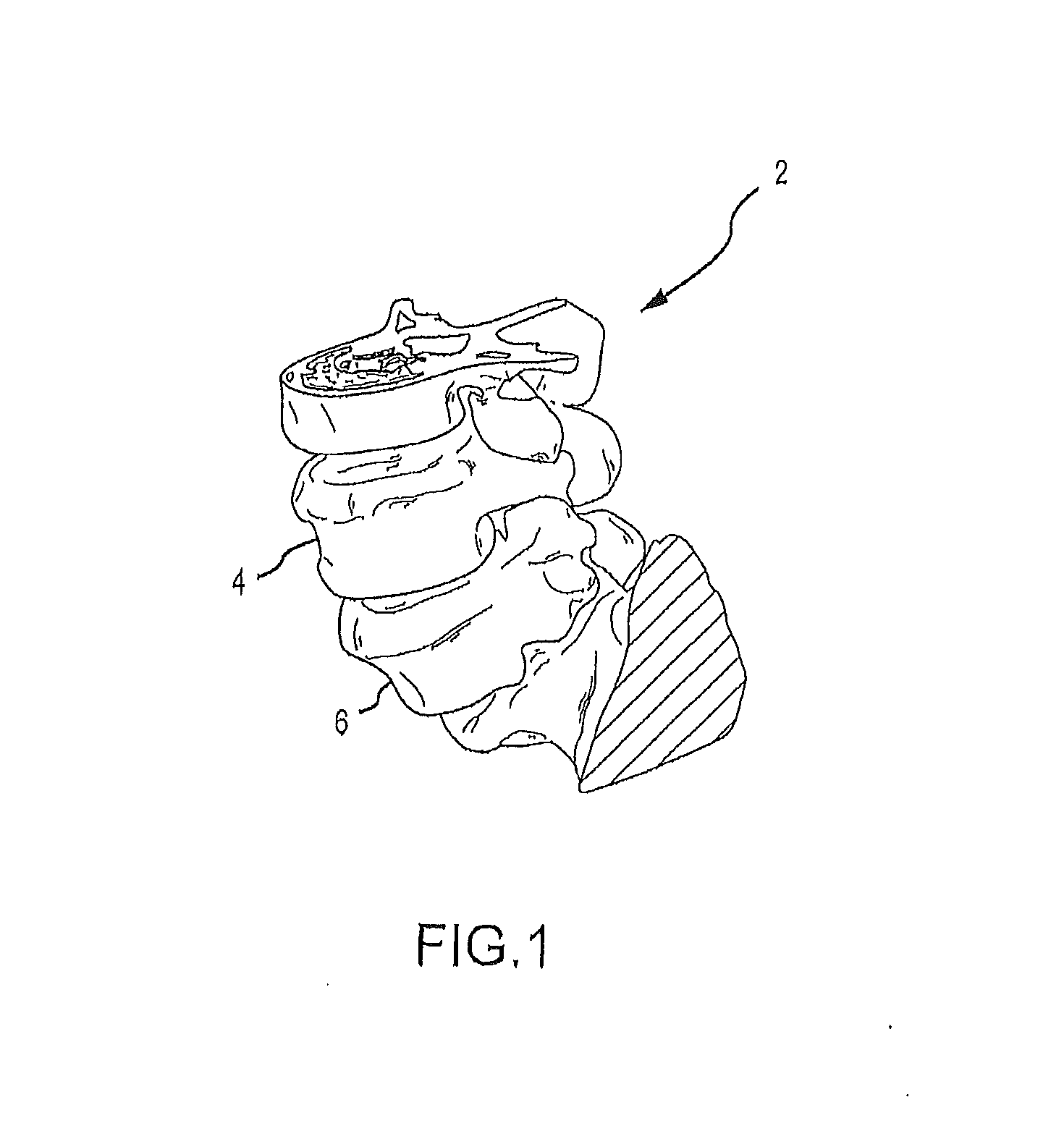
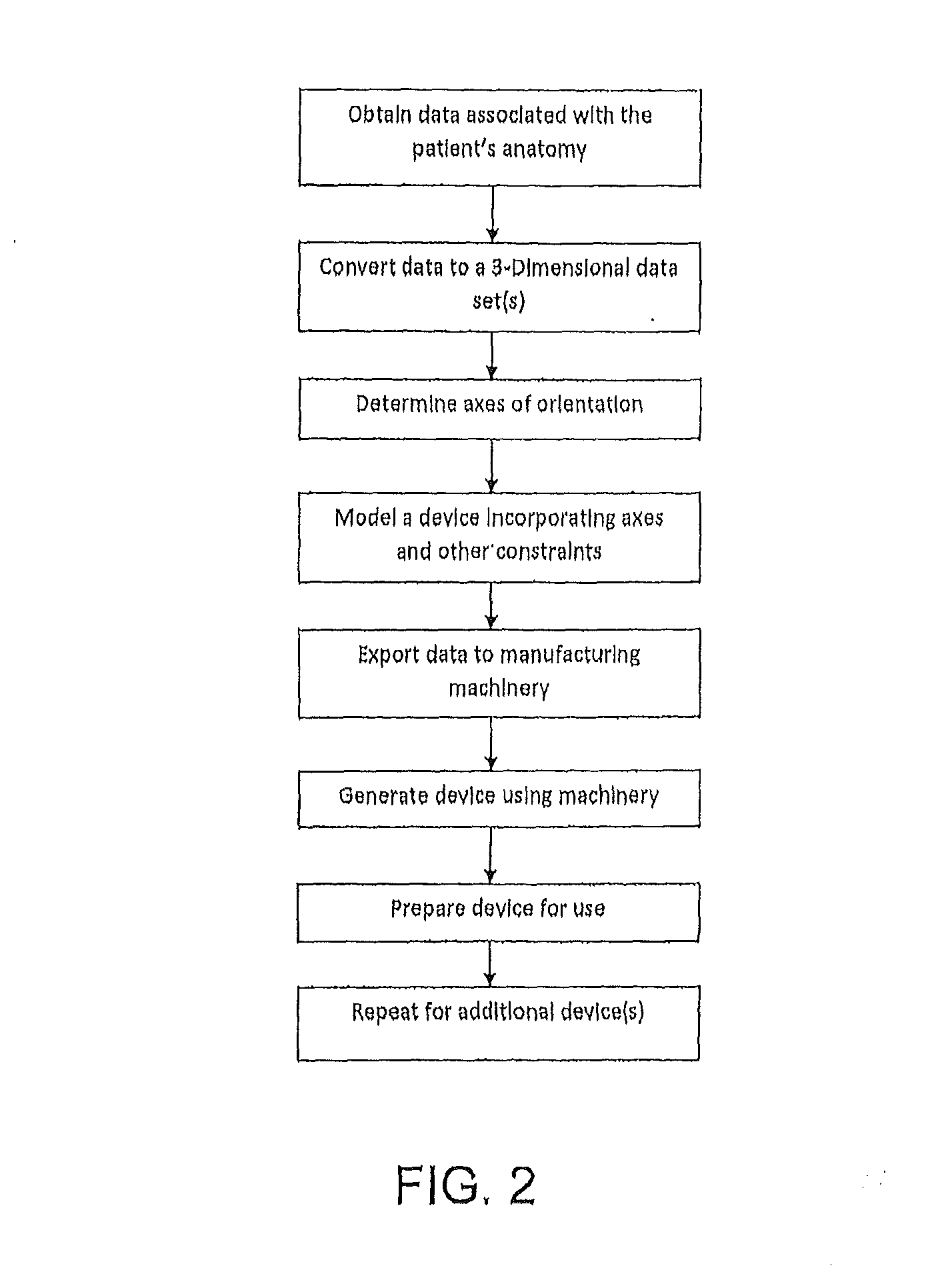
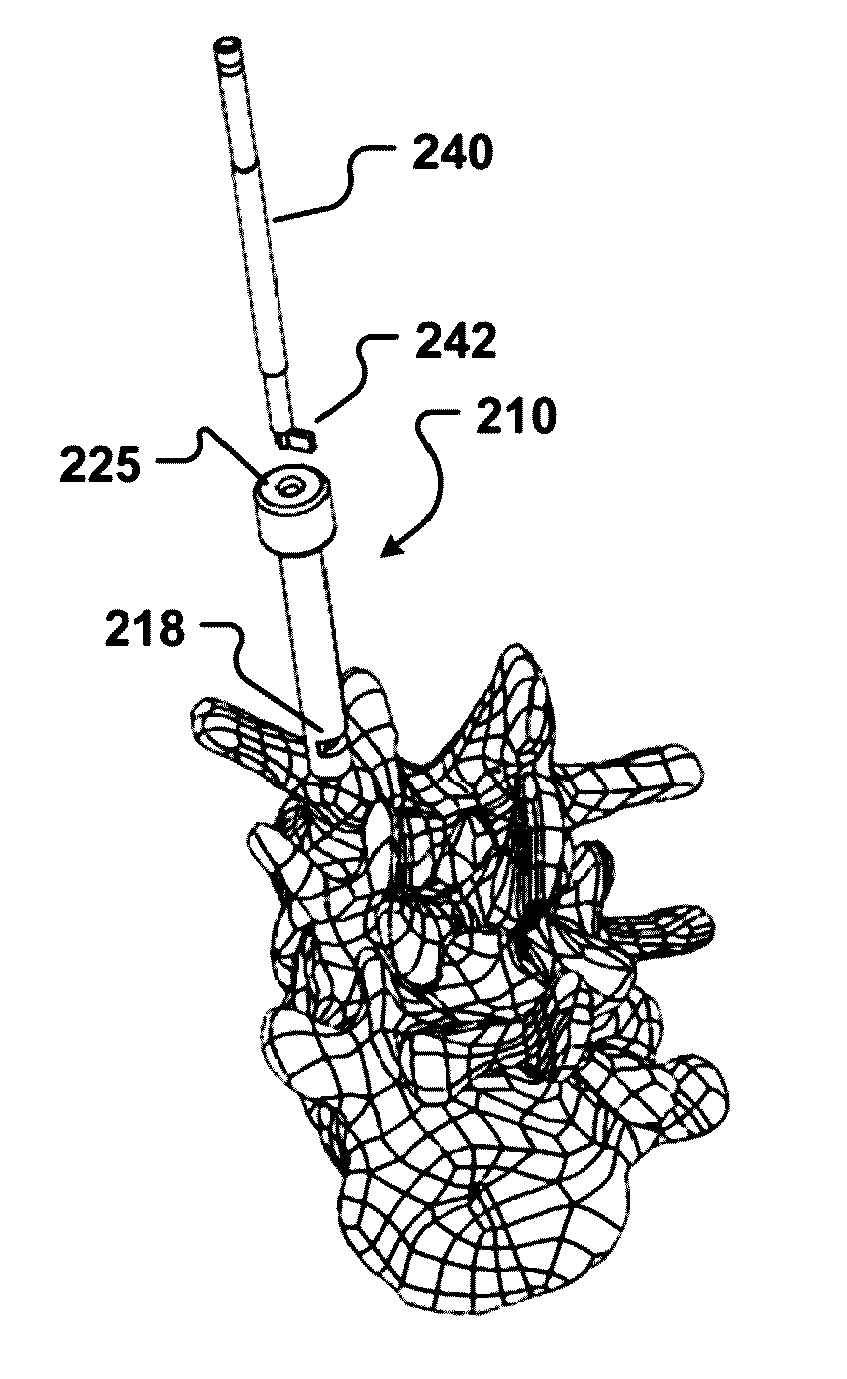
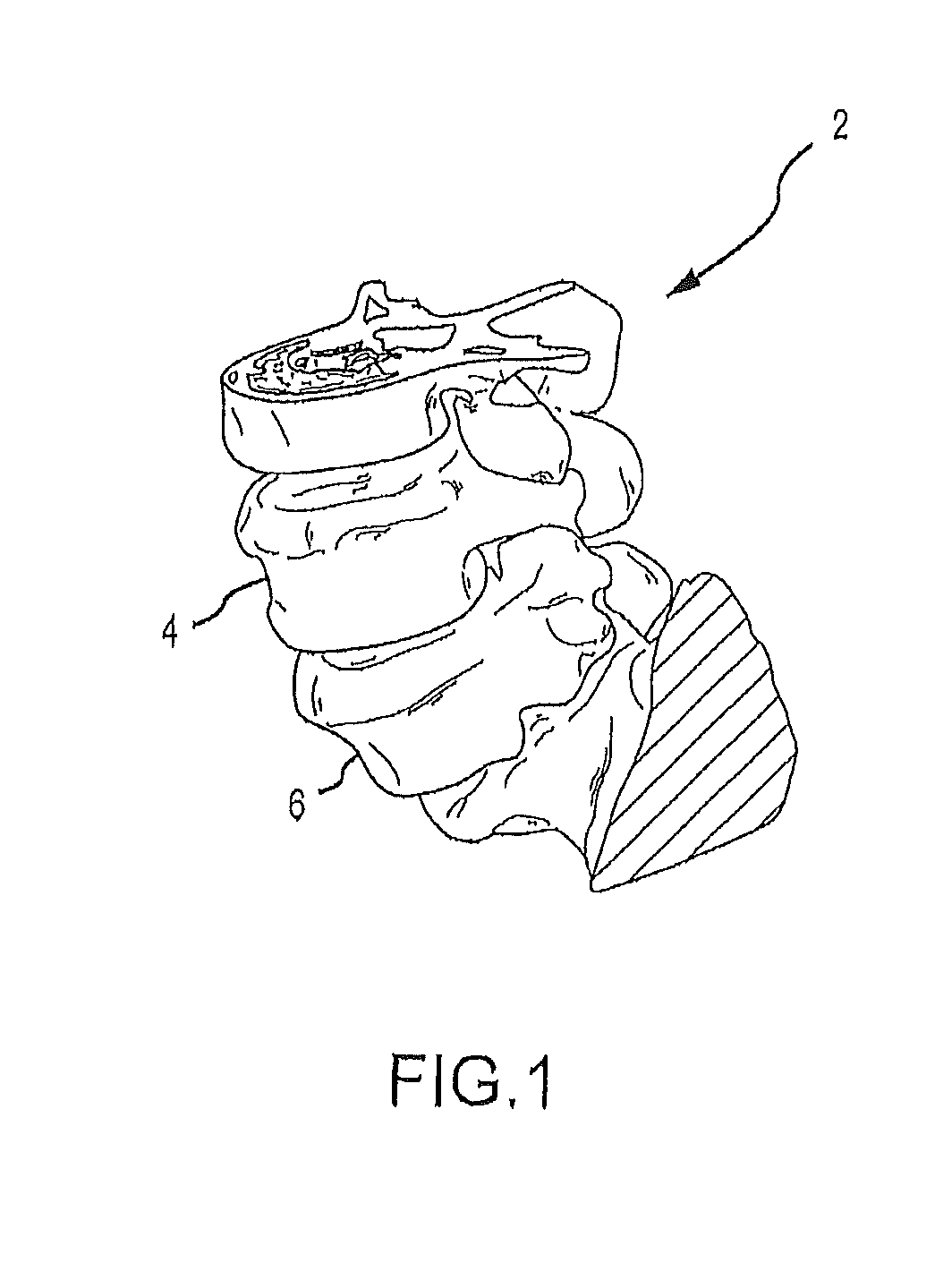
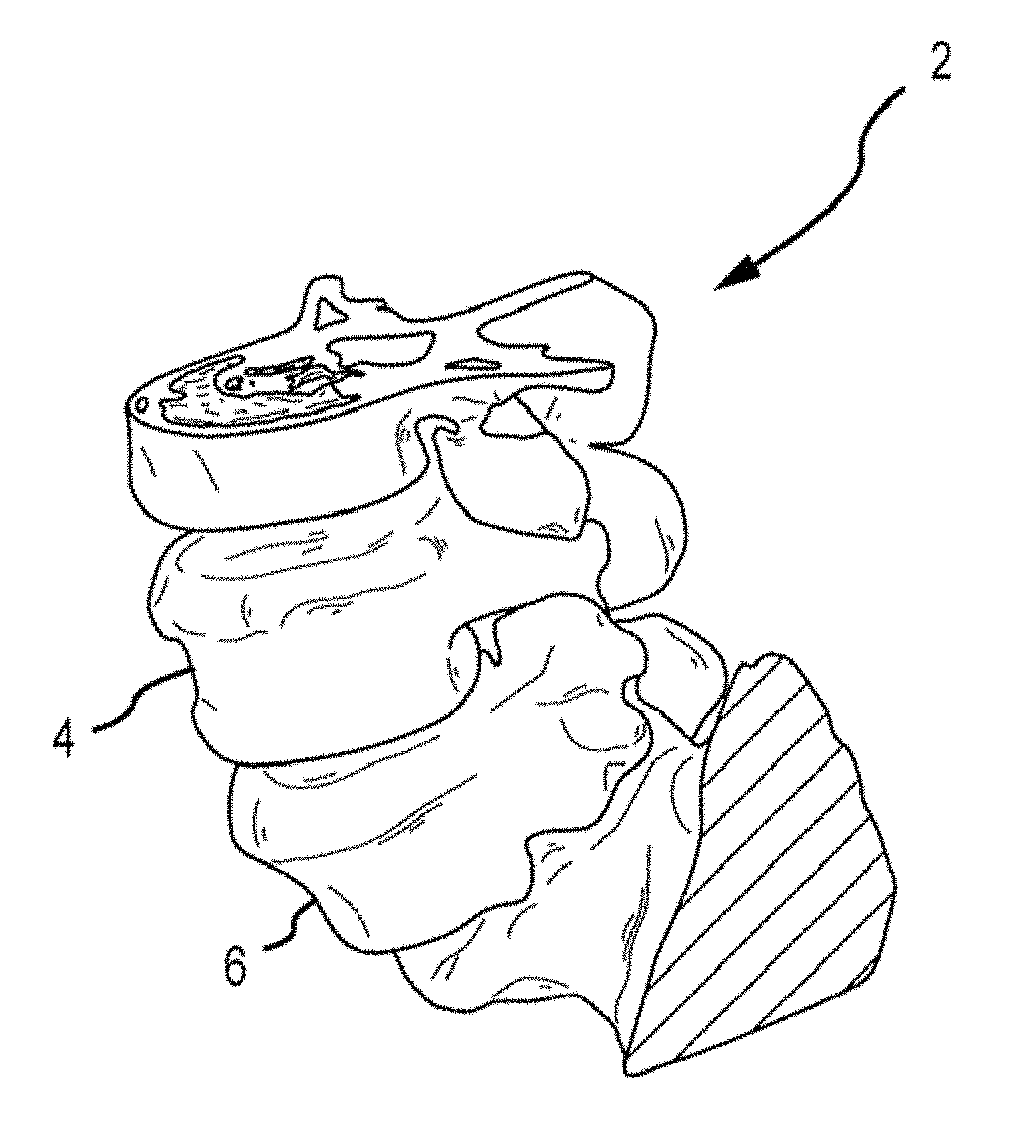
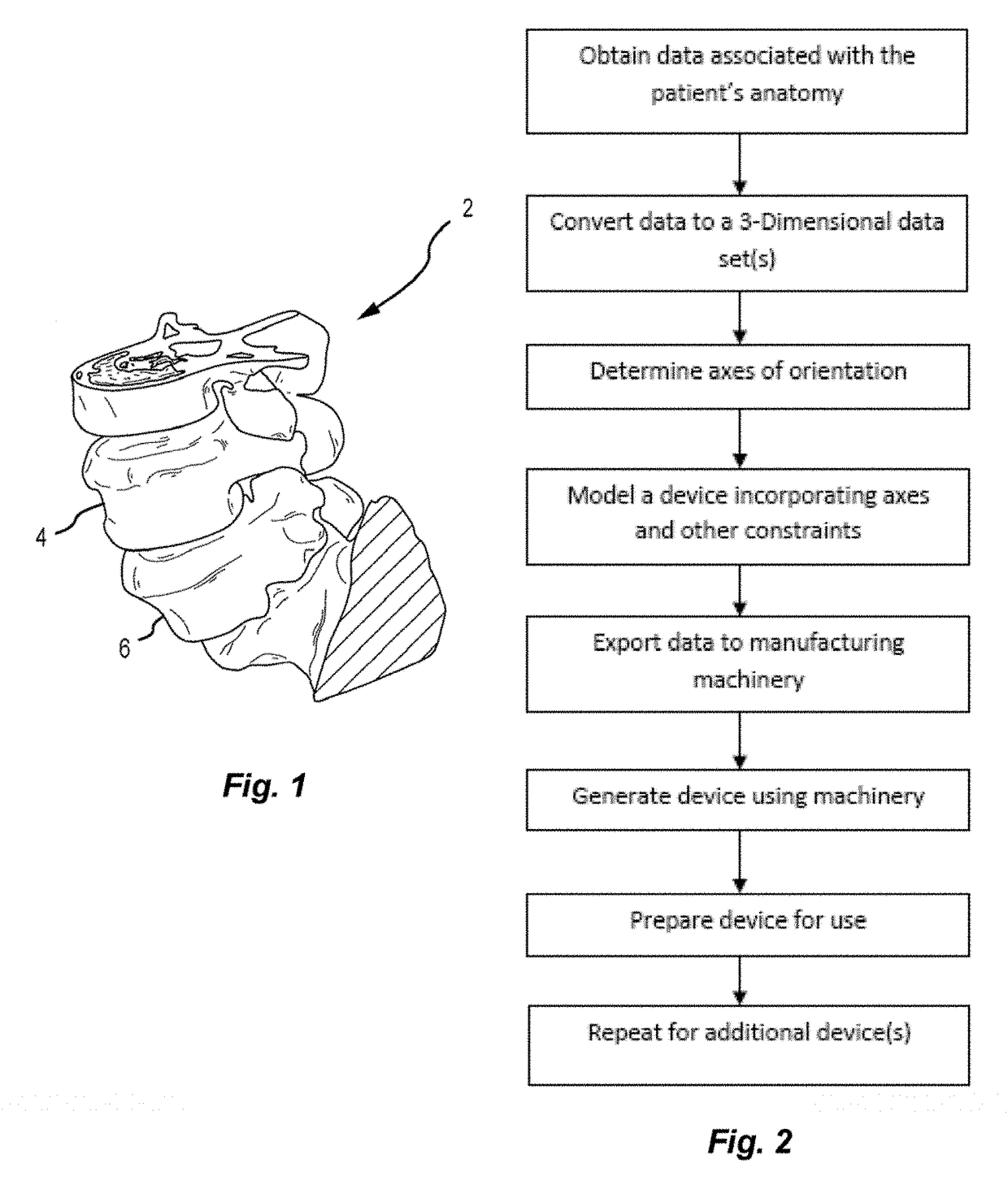
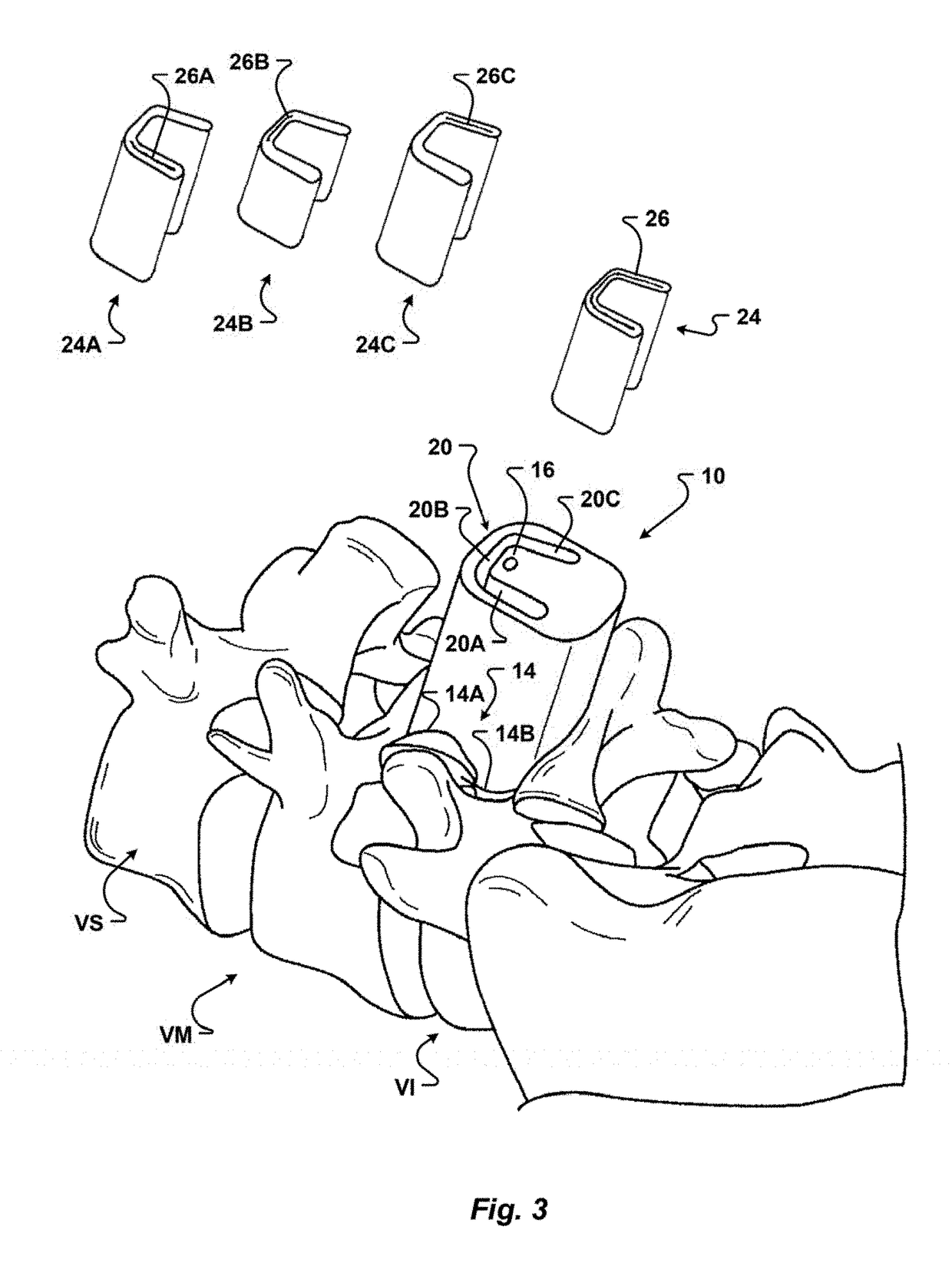
Patient matching surgical guide and method for using the same
ActiveUS20130218163A1Control over orientationReduce the numberInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsAnatomical featureBiomedical engineering
A system and method for developing customized apparatus for use in one or more surgical procedures is disclosed. The system and method incorporates a patient's unique anatomical features or morphology, which may be derived from capturing MRI data or CT data, to fabricate at least one custom apparatus. According to a preferred embodiment, the customized apparatus comprises a plurality of complementary surfaces based on a plurality of data points from the MRI or CT data. Thus, each apparatus may be matched in duplicate and oriented around the patient's own anatomy, and may further provide any desired axial alignments or insertional trajectories. In an alternate embodiment, the apparatus may further be aligned and / or matched with at least one other apparatus used during the surgical procedure.
Owner:MIGHTY OAK MEDICAL INC
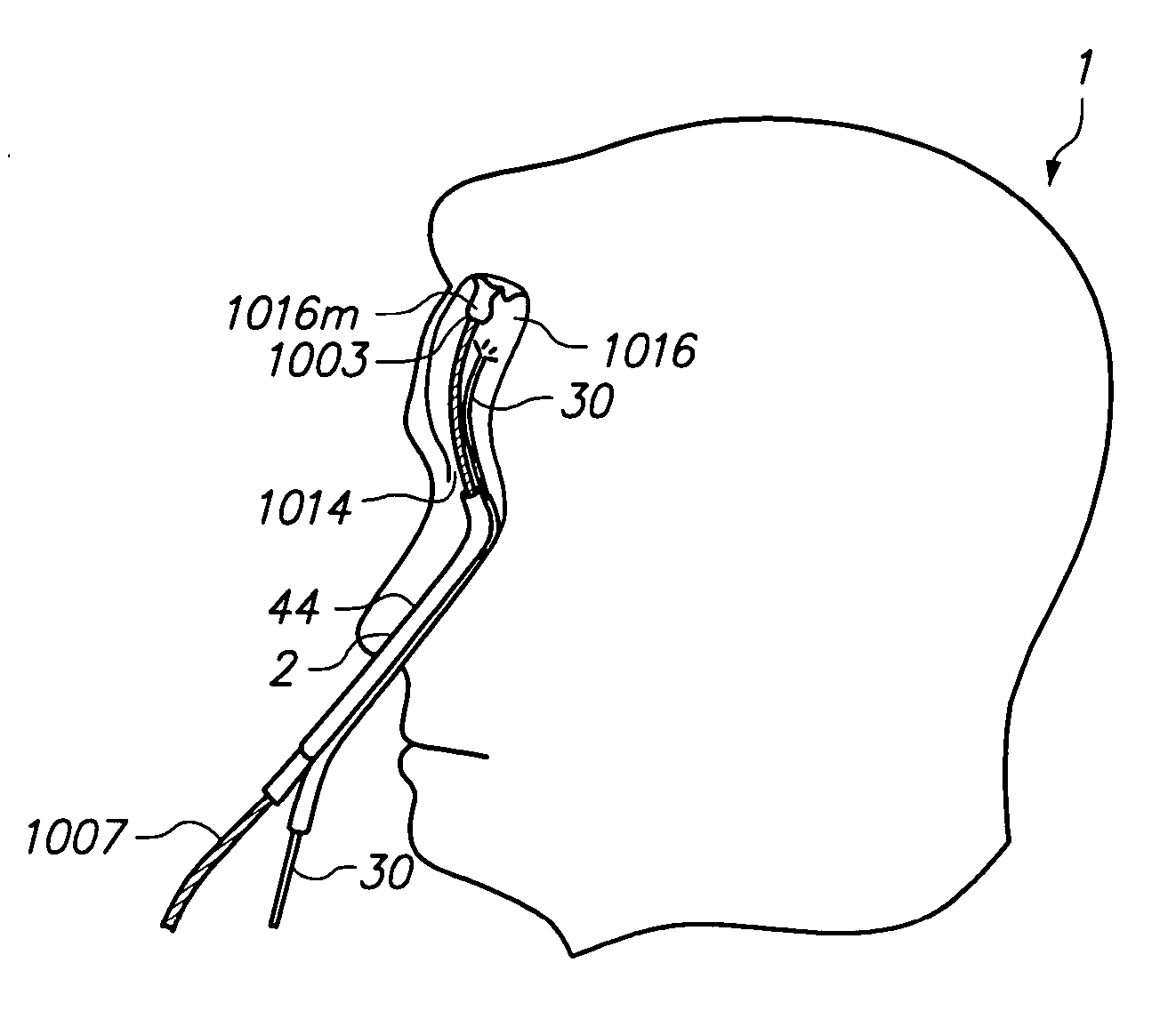
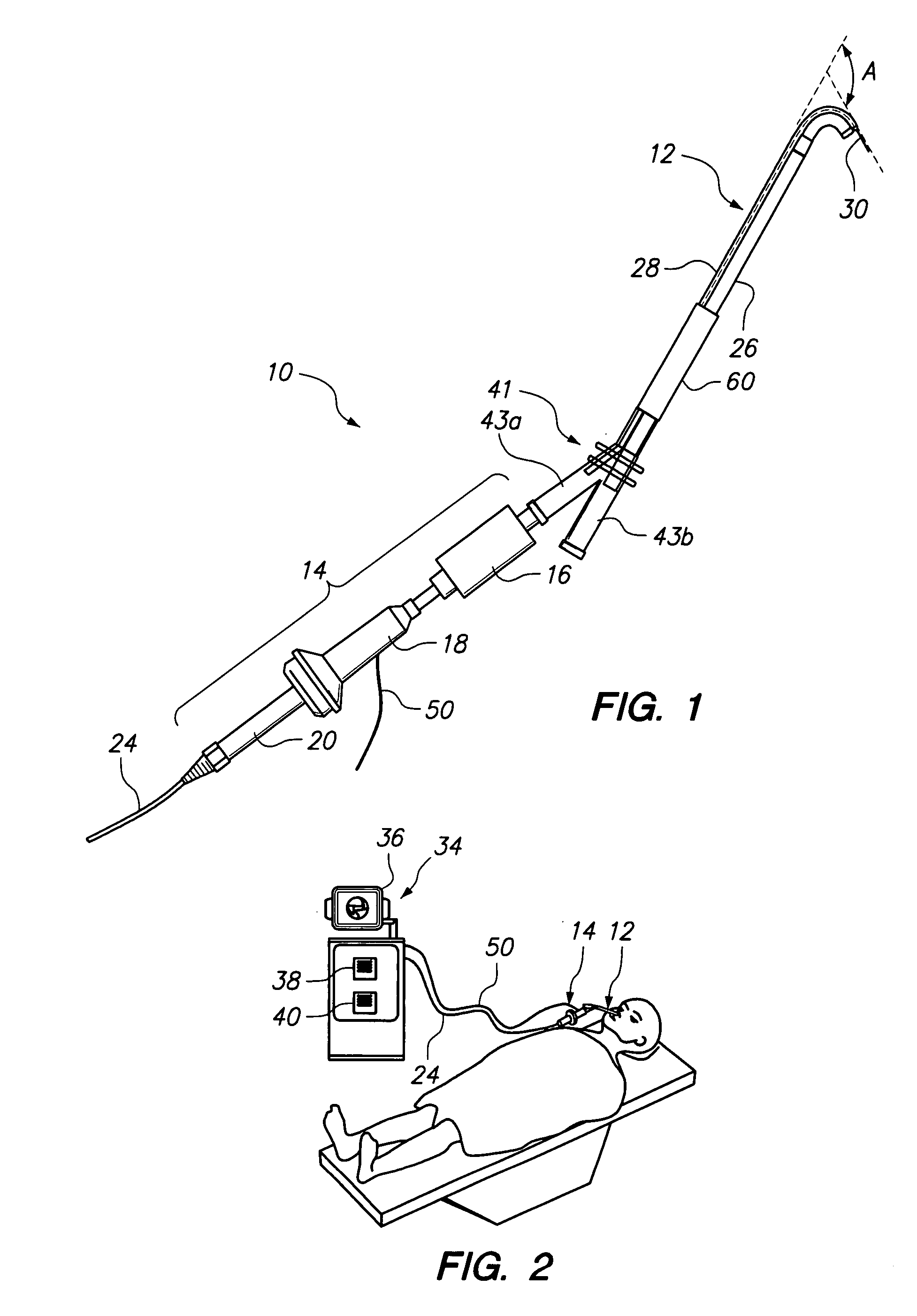
Endoscopic methods and devices for transnasal procedures
Medical devices, systems and methods that are useable to facilitate transnasal insertion and positioning of guidewires and various other devices and instruments at desired locations within the ear, nose, throat, paranasal sinuses or cranium. Direct viewing of such placements via an endoscope.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
Optical-acoustic imaging device
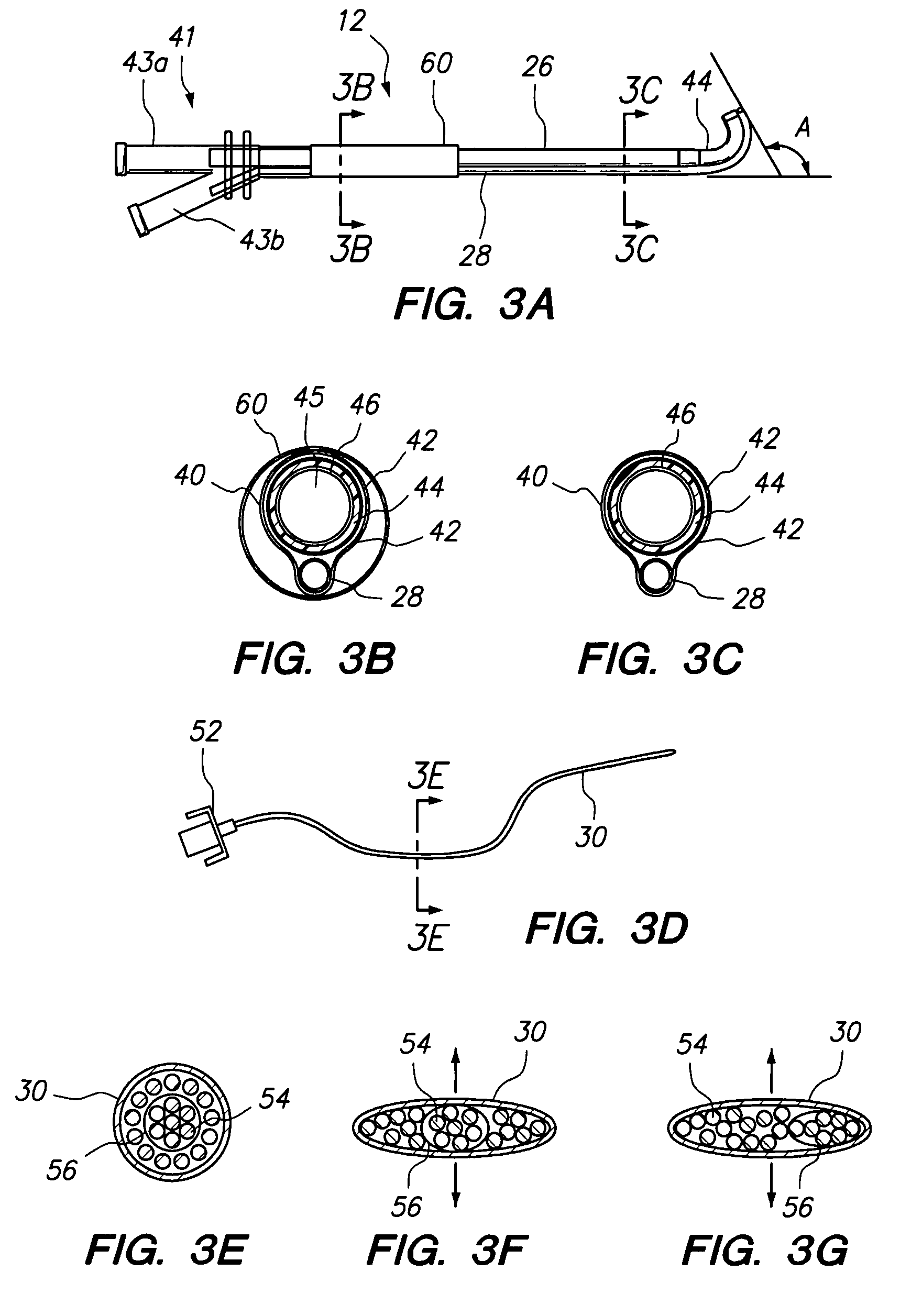
InactiveUS20080119739A1Reduce radiation exposureShorten operation timeMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementGratingRadiation exposure
The present invention is a guide wire imaging device for vascular or non-vascular imaging utilizing optic acoustical methods, which device has a profile of less than 1 mm in diameter. The ultrasound imaging device of the invention comprises a single mode optical fiber with at least one Bragg grating, and a piezoelectric or piezo-ceramic jacket, which device may achieve omnidirectional (360°) imaging. The imaging guide wire of the invention can function as a guide wire for vascular interventions, can enable real time imaging during balloon inflation, and stent deployment, thus will provide clinical information that is not available when catheter-based imaging systems are used. The device of the invention may enable shortened total procedure times, including the fluoroscopy time, will also reduce radiation exposure to the patient and to the operator.
Owner:PHYZHON HEALTH INC
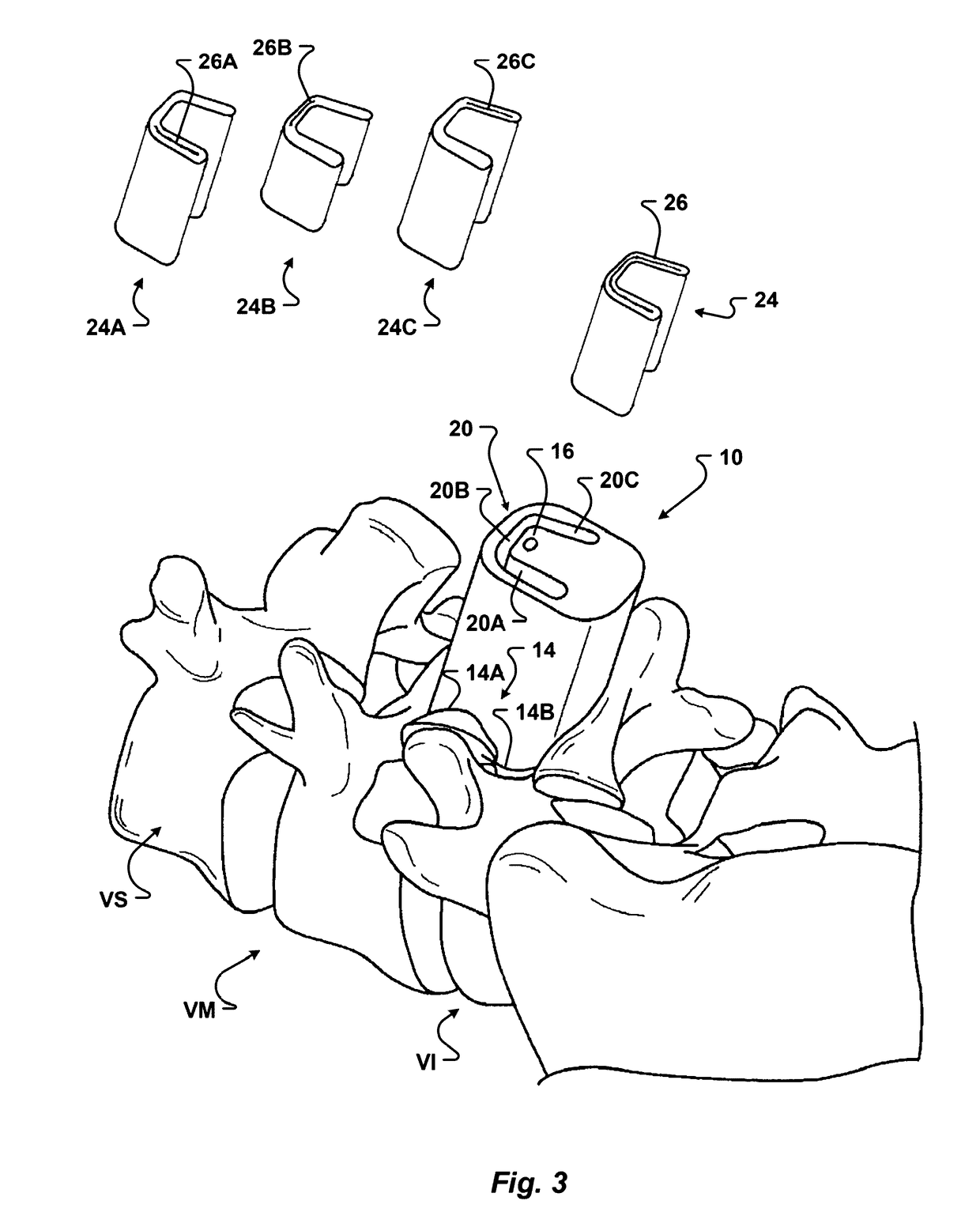
Patient-matched apparatus and methods for performing surgical procedures
ActiveUS20170135706A1Eliminate relative motionPain can be reduced avoidedInternal osteosythesisSurgical furniturePatient specificAnatomical structures
A system and method for developing customized apparatus, such as guides, for use in one or more surgical procedures is disclosed. The system and method incorporates a patient's unique anatomical features or morphology, which may be derived from capturing MRI data or CT data, to fabricate at least one custom apparatus or guide. According to a preferred embodiment, the customized apparatus comprises at least one patient-specific surface and or contour, which may be derived from MRI or CT data. Apparatus may be matched in duplicate and oriented around the patient's own anatomy, and may further provide any desired axial alignments or insertional trajectories. In an alternate embodiment, the apparatus may further be aligned and / or matched with at least one other apparatus during the surgical procedure.
Owner:MIGHTY OAK MEDICAL INC
Image-overlay medical evaluation devices and techniques
InactiveUS20130172731A1Easy to makePromote lowerImpression capsAdditive manufacturing apparatusDisplay deviceComputer access
A system and methods are provided for evaluating the position of surgical implants or openings formed in anatomical tissue during medical procedures, in which an initial 3-dimensional image of the anatomical tissue is combinable with one or more subsequent 3-dimensional images of the same or correlating tissue, and without the use of ionizing radiation on a patient for at least the subsequent images. The system includes a software program, a computer with display, a radiographic image scanning device, and a non-radiographic image scanning device. The computer accesses a medical patient information database and a medical implant database for images used by the software program. A pre-operative image is combined with subsequent images to facilitate evaluation of the proposed placement of a surgical implant or opening relative to tissues of the patient anatomy. Methods of evaluating the accuracy of surgical guides and of fabricating surgical guides are also disclosed.
Owner:GOLE PHILIP D
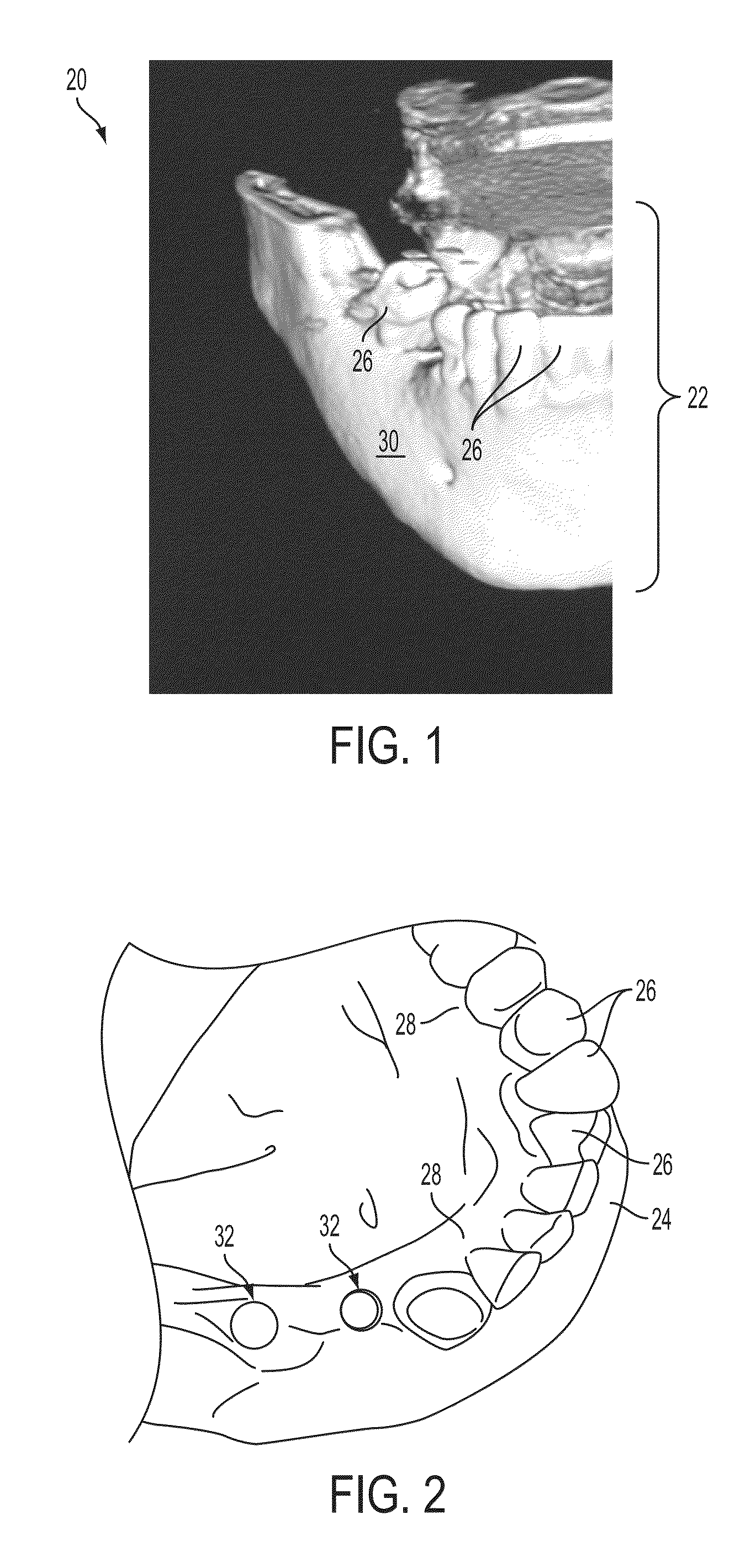
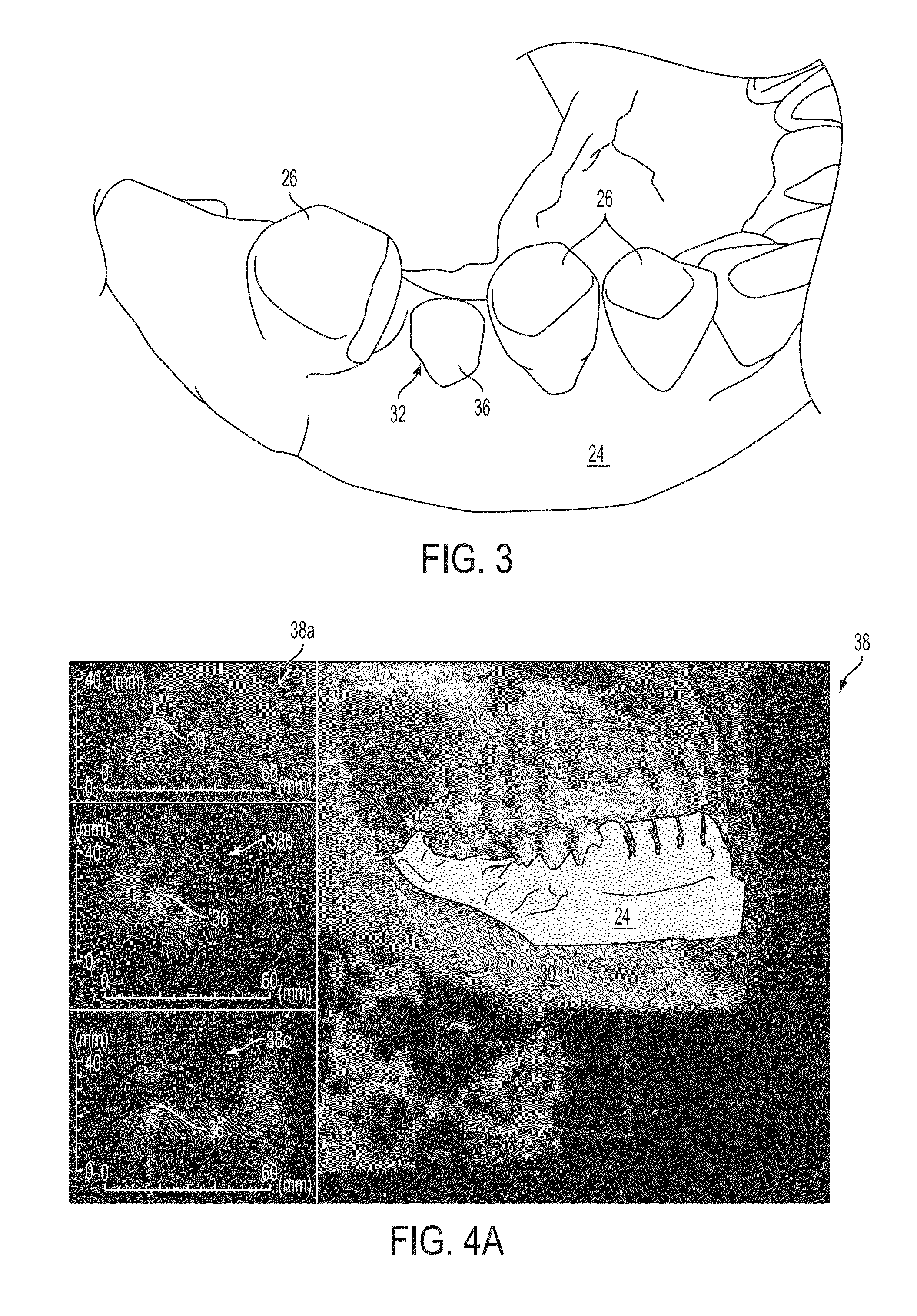
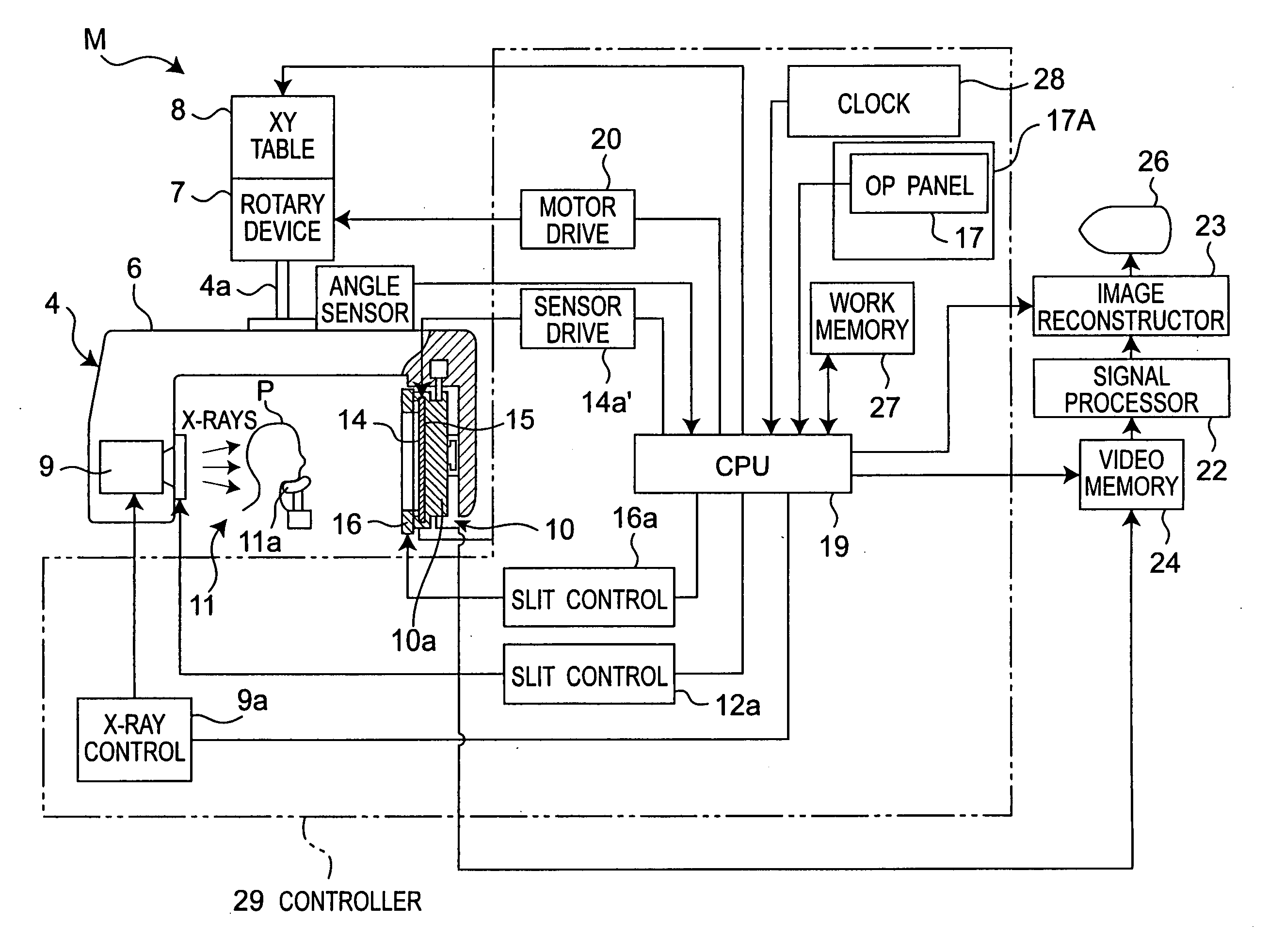
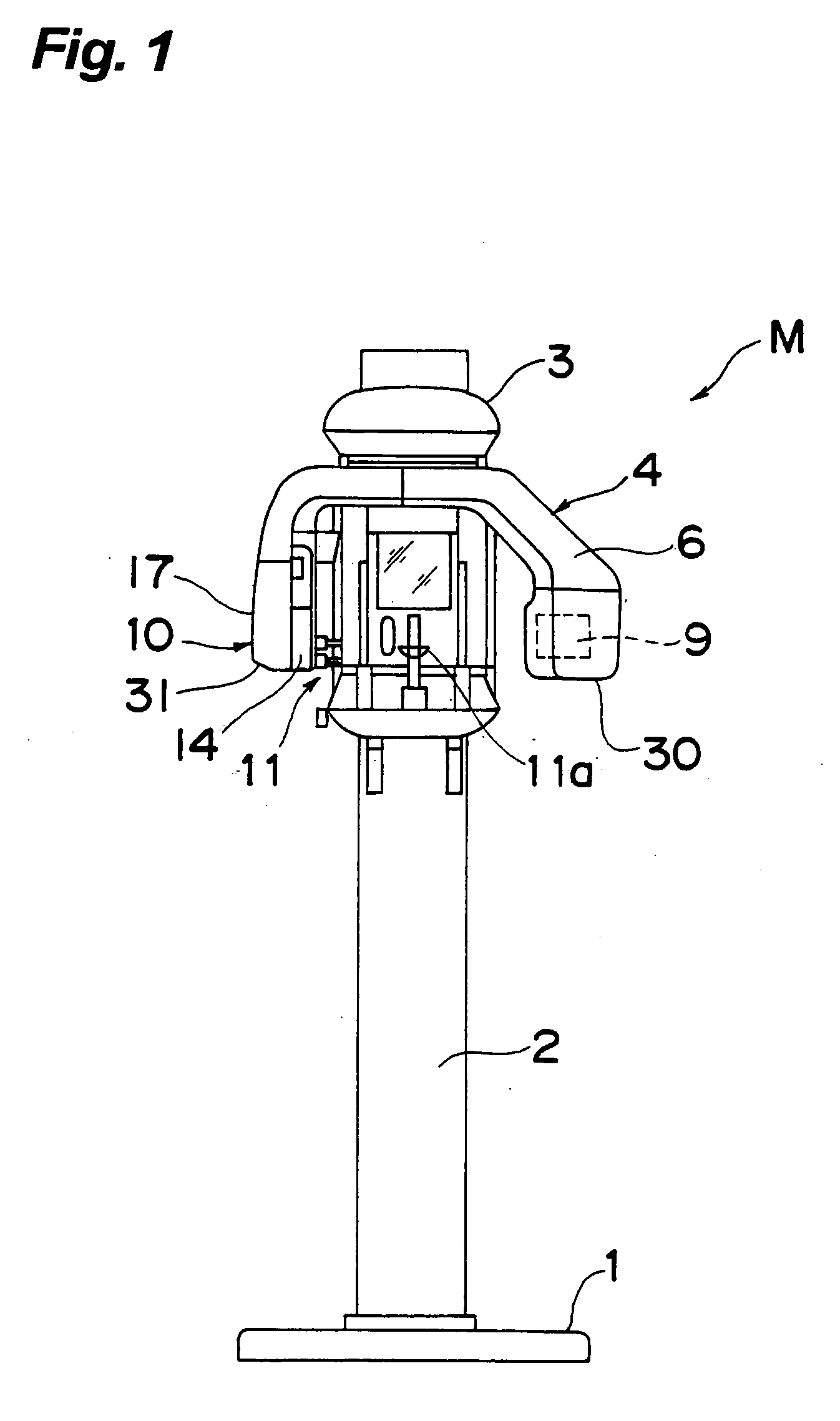
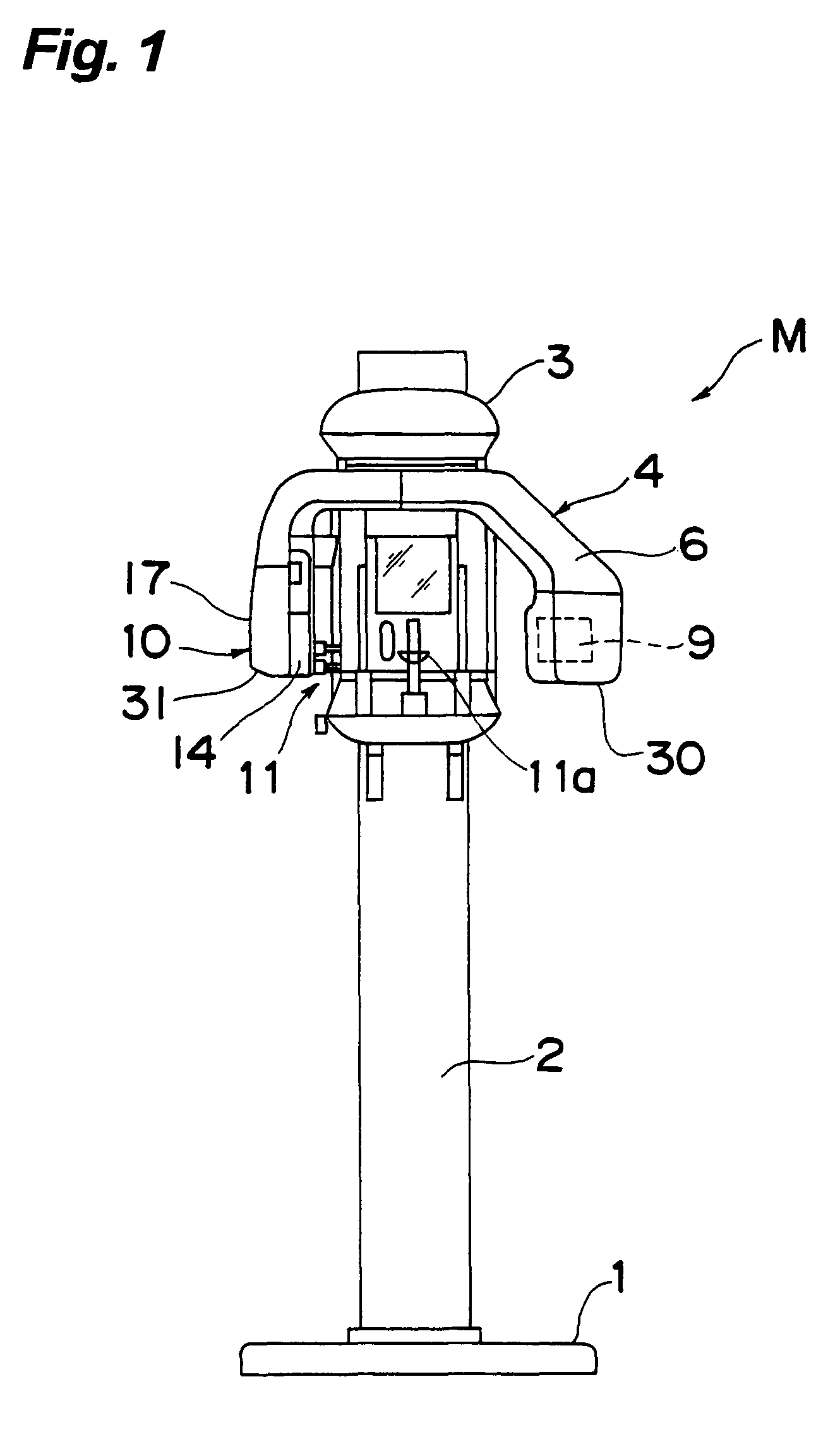
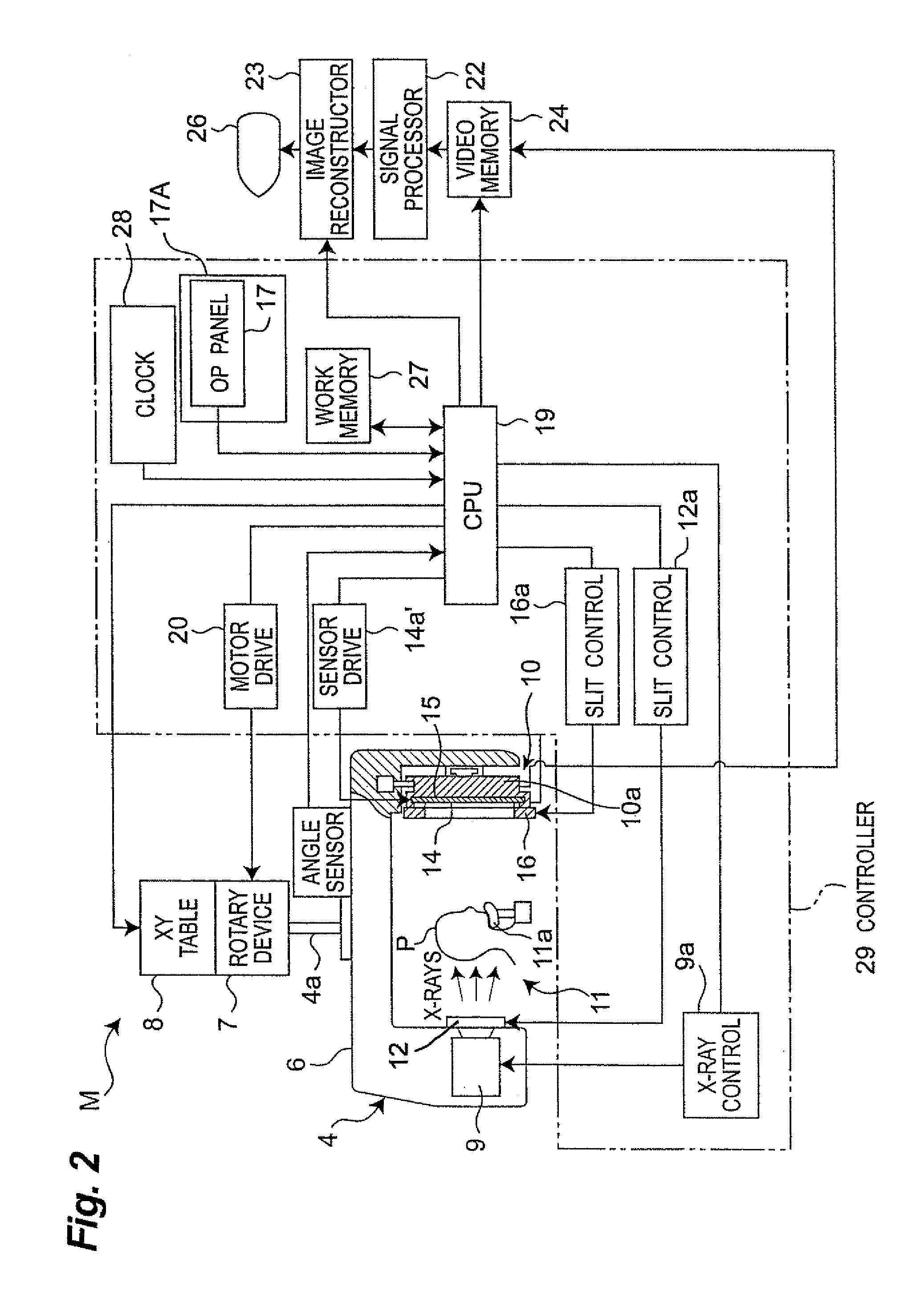
Medical Digital X-Ray Imaging Apparatus and Medical Digital X-Ray Sensor
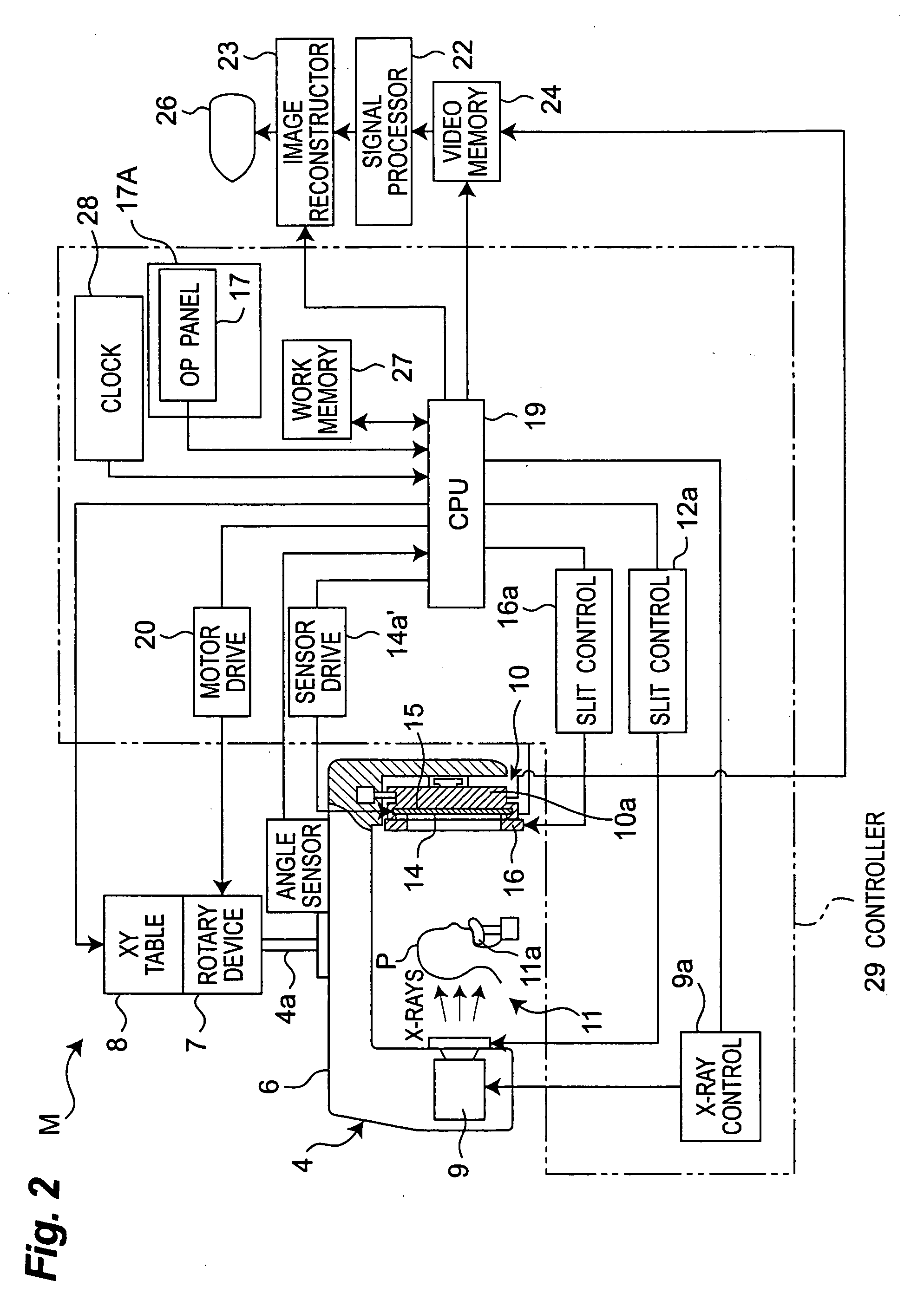
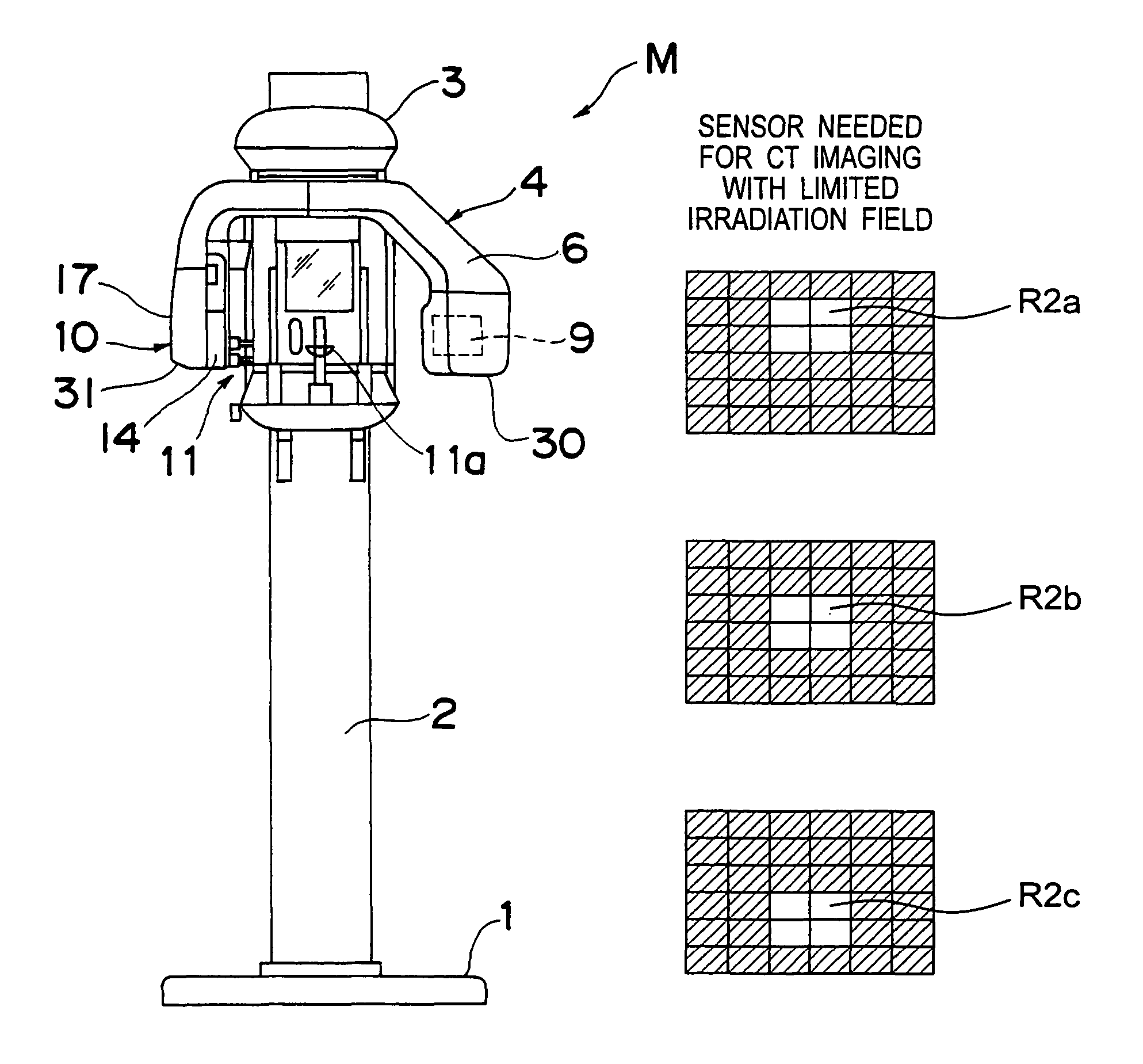
ActiveUS20090168966A1Increase data capacityMany timesTomographyDiaphragms for radiation diagnosticsX-rayComputing tomography
In a medical digital X-ray imaging apparatus having a plurality of imaging modes including computed tomography mode, a supporter supports an X-ray source and a digital X-ray sensor having a two-dimensional detection plane for detecting X-rays, while interposing an object between them. An image reconstructor acquires data from the digital X-ray sensor and reconstructs an image based on the acquired data. An operator selects one of a first imaging mode and a second imaging mode. The second imaging mode has an irradiation field different from the first imaging mode and has an area to be read in the digital X-ray sensor smaller than that in the first imaging mode.
Owner:MORITA MFG CO LTD
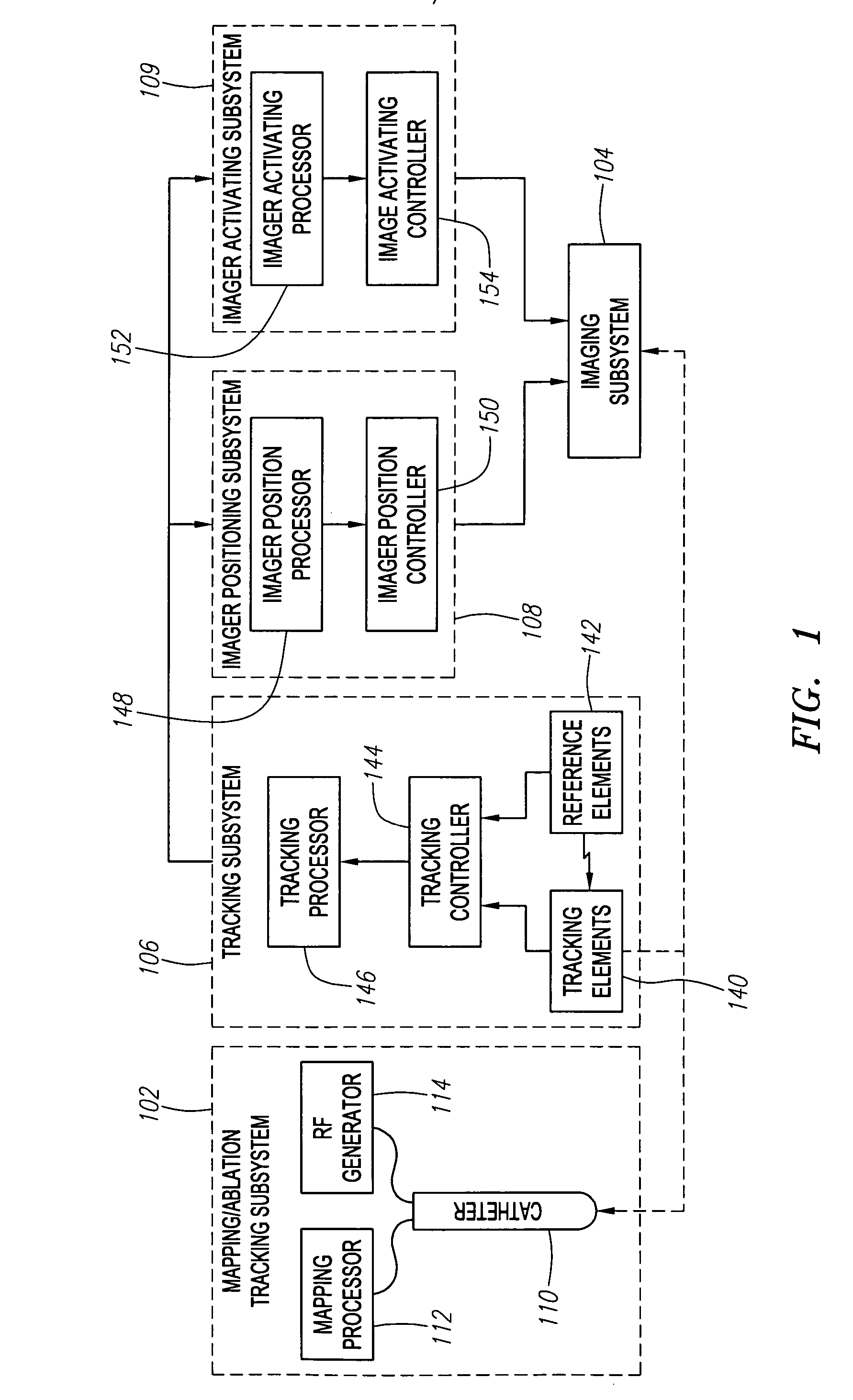
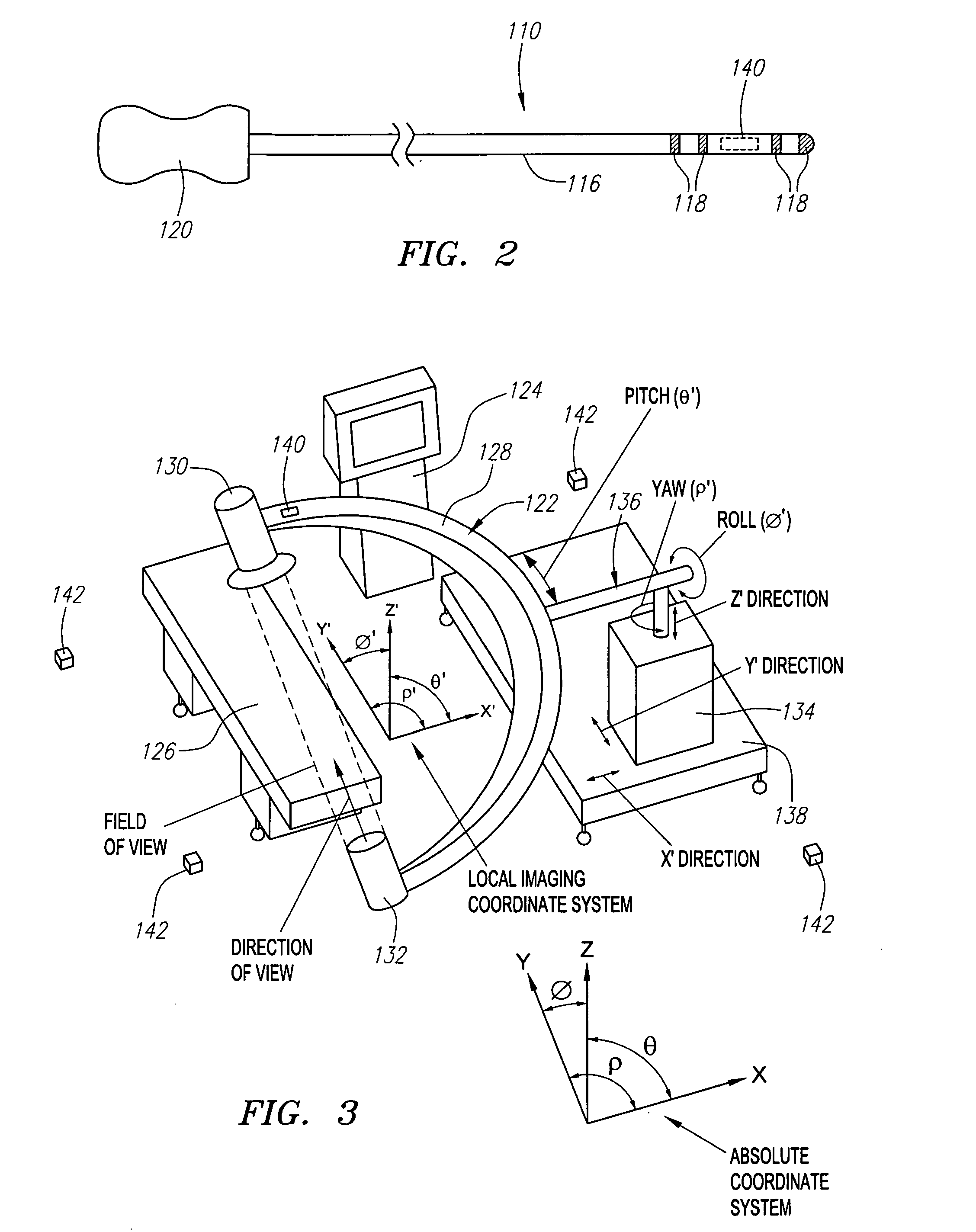
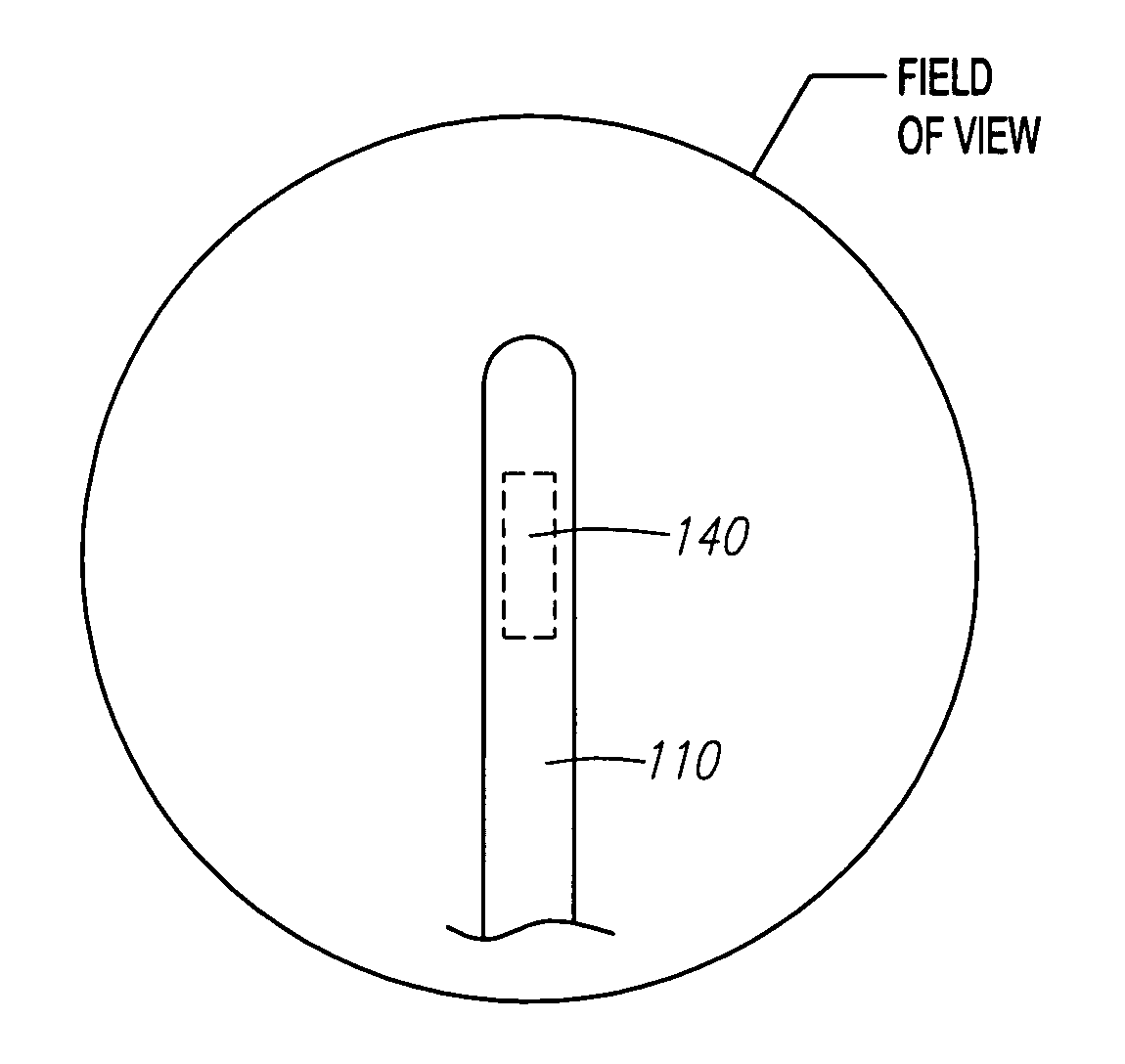
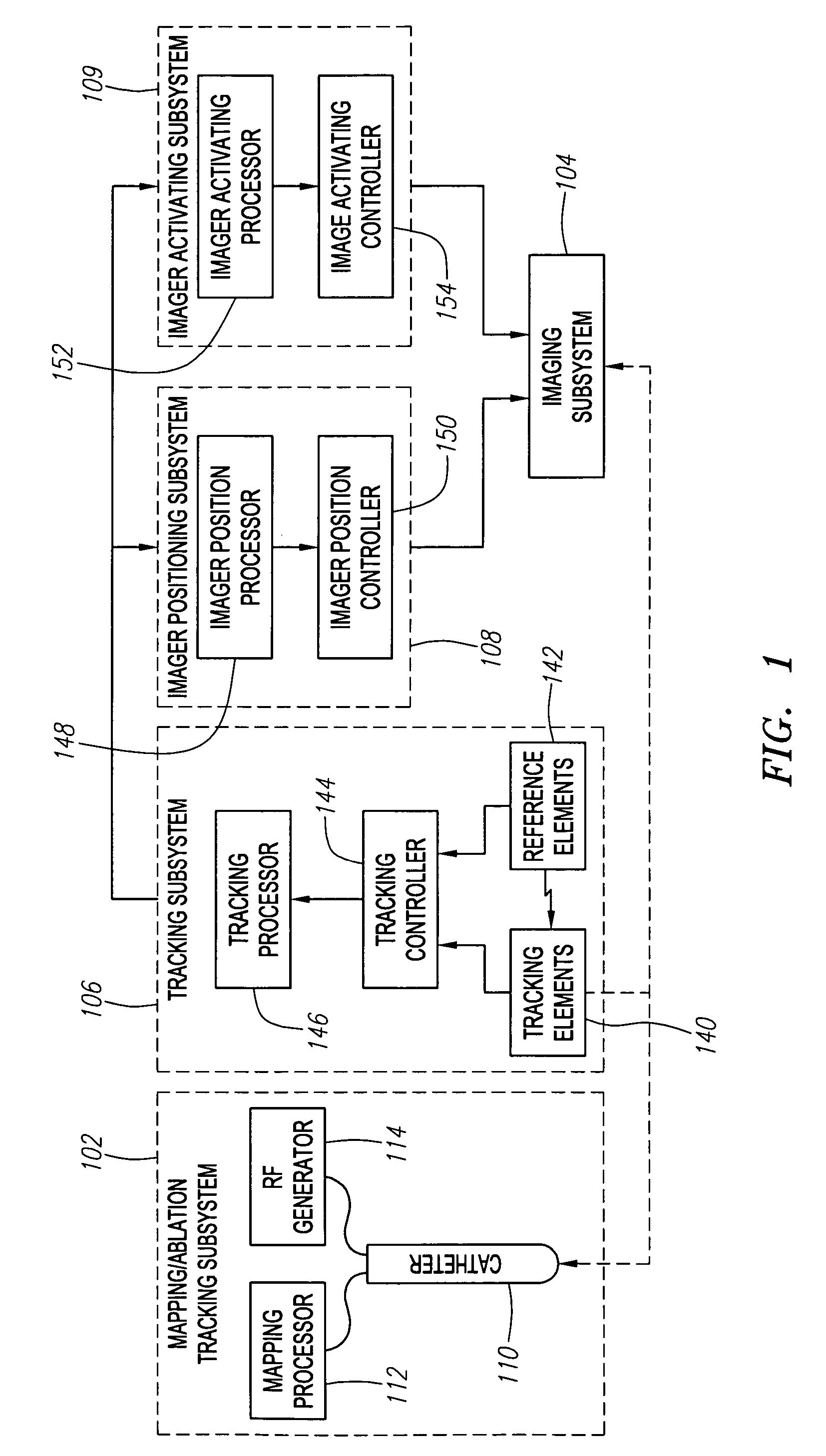
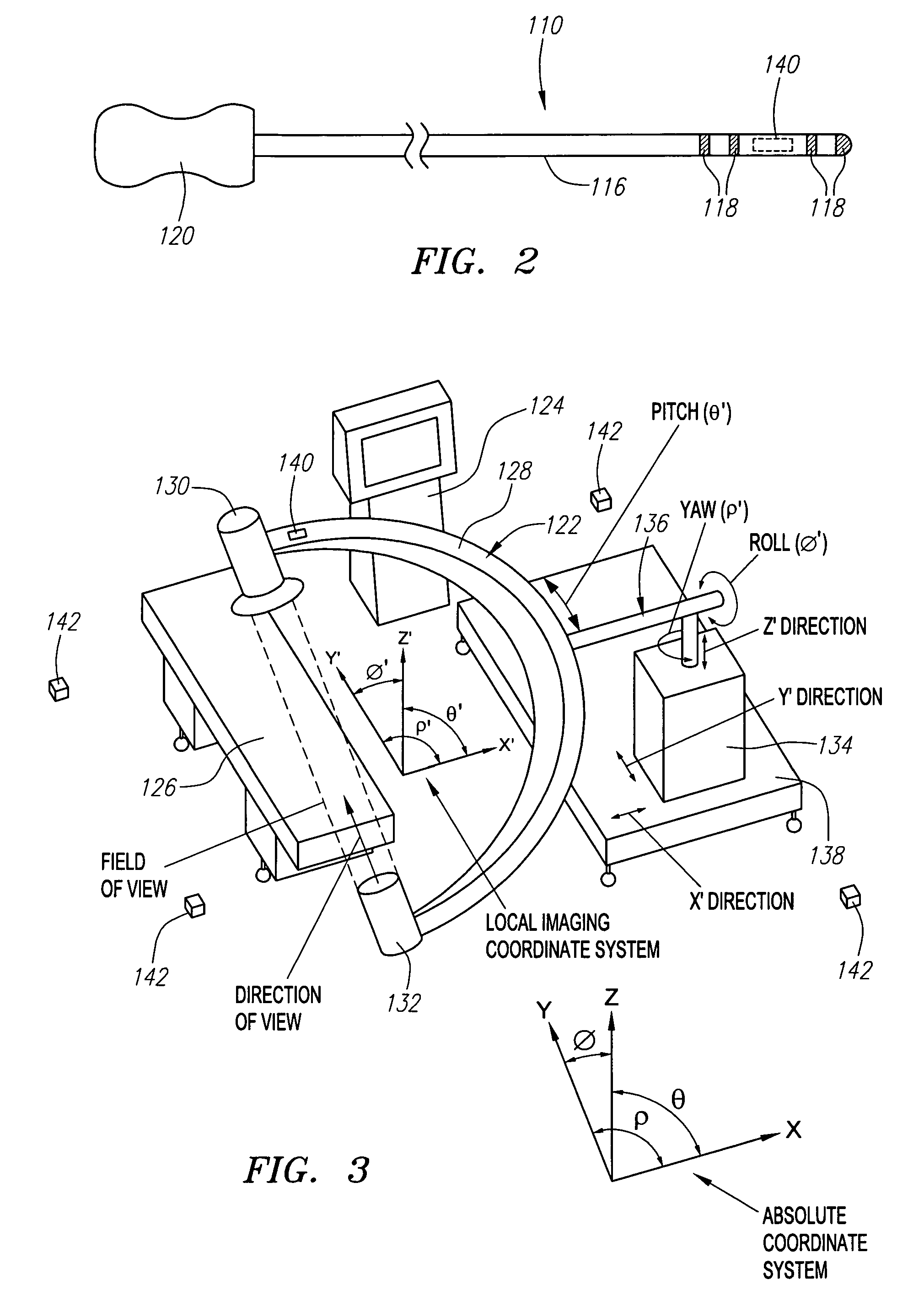
Automated manipulation of imaging device field of view based on tracked medical device position
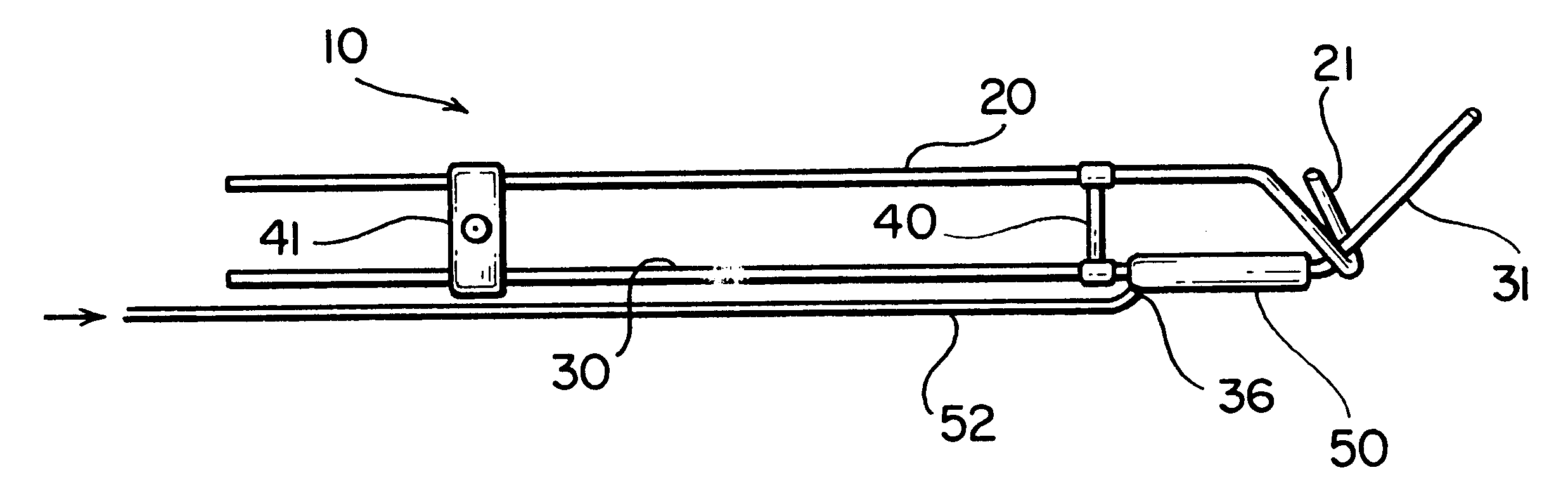
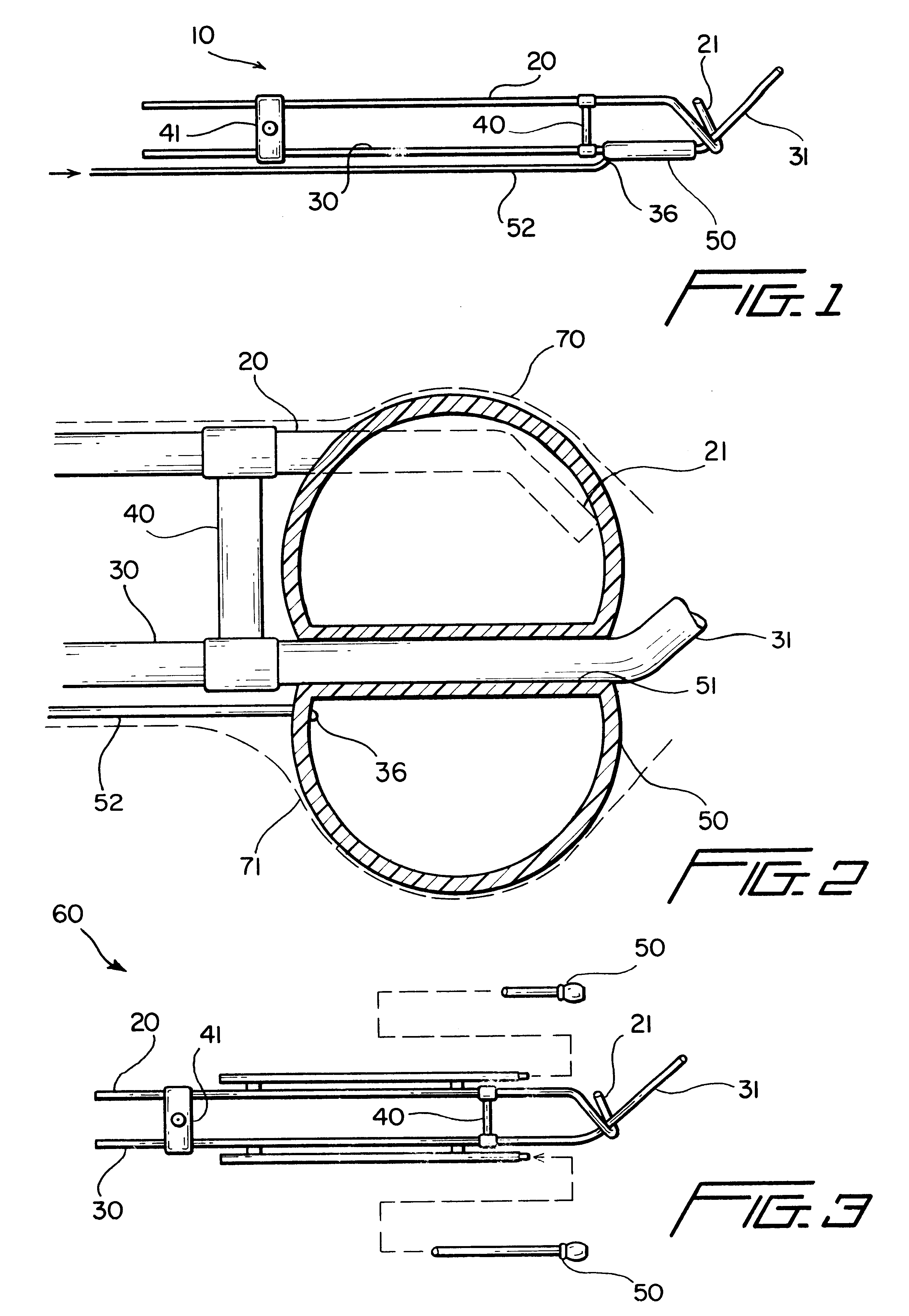
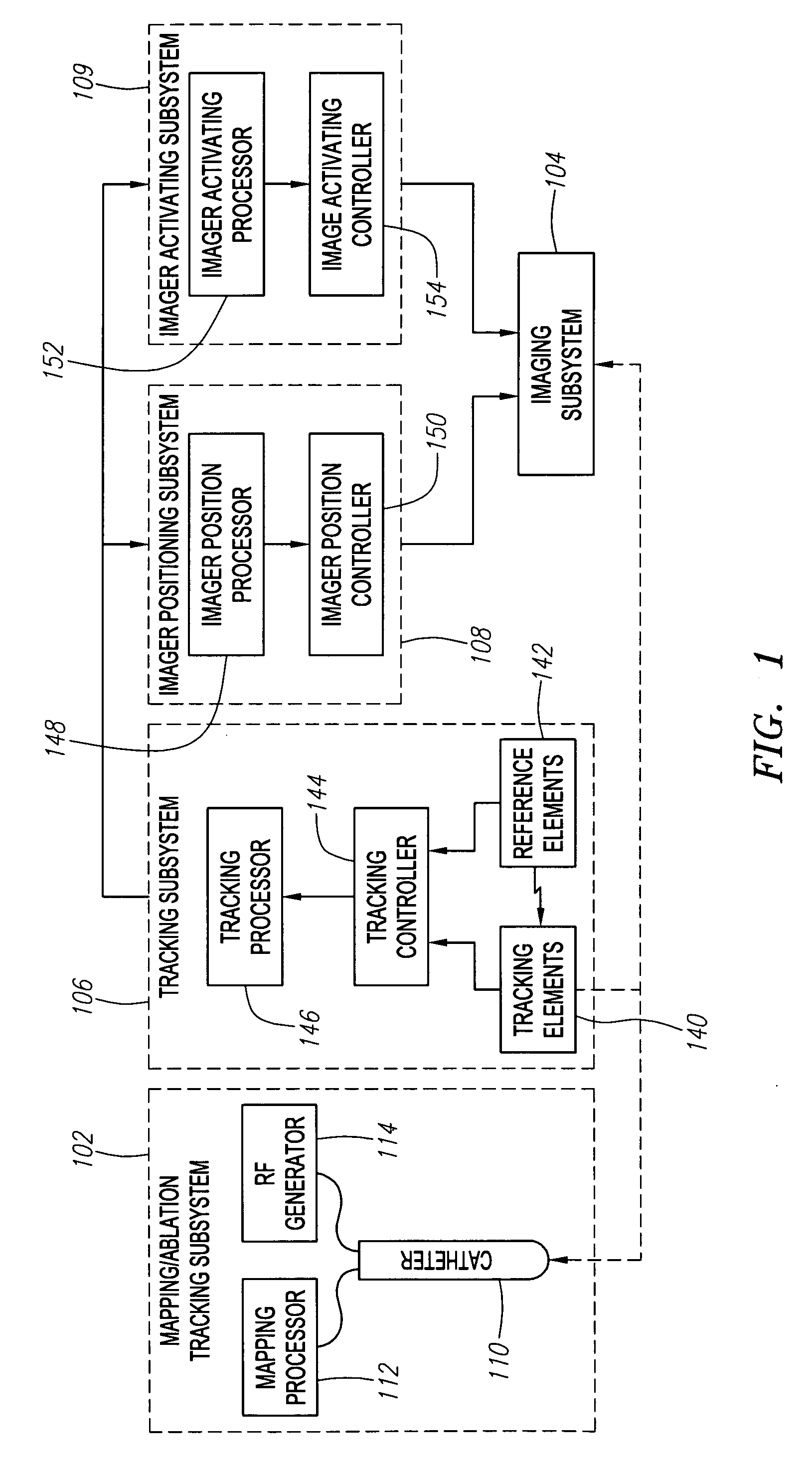
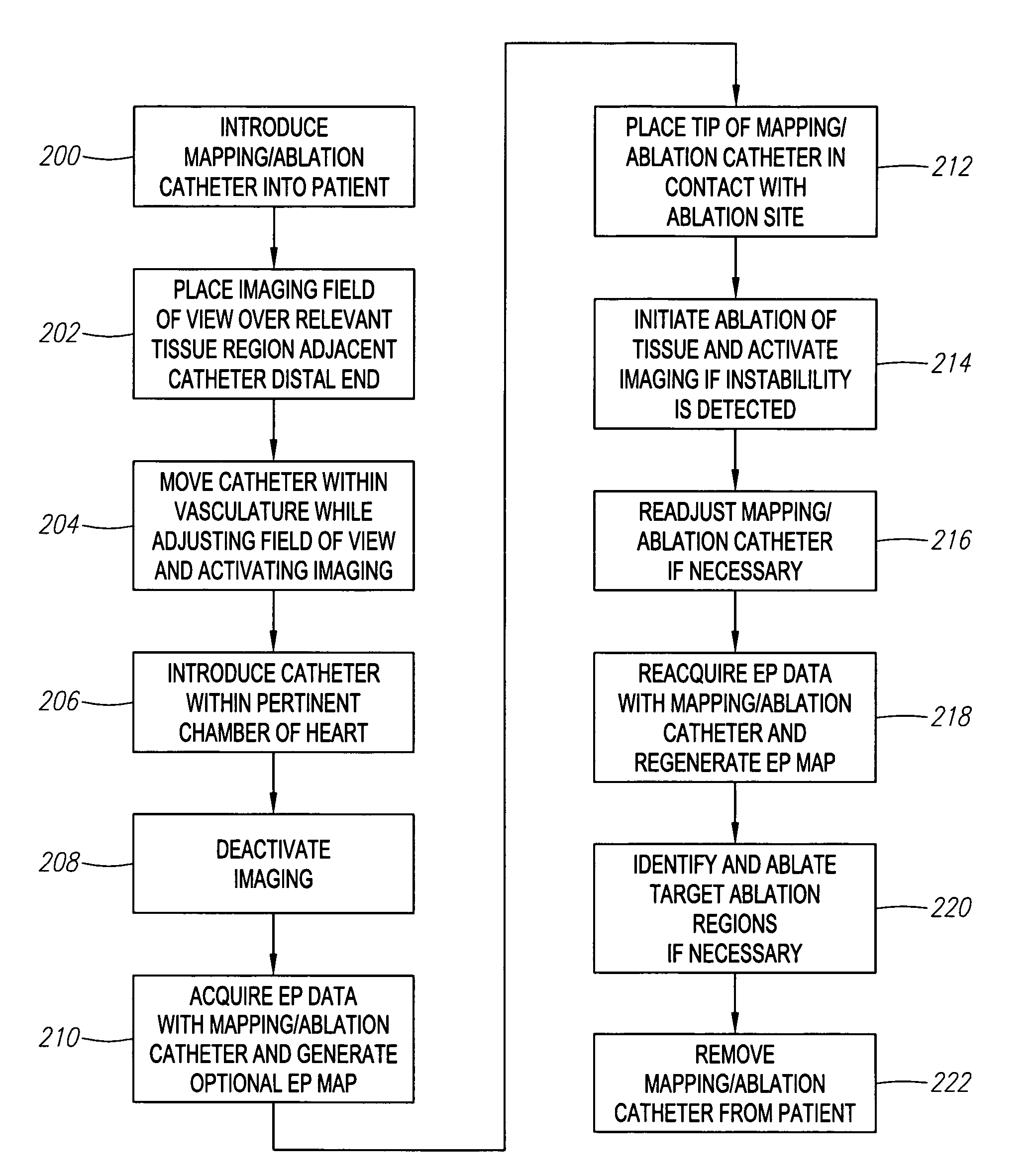
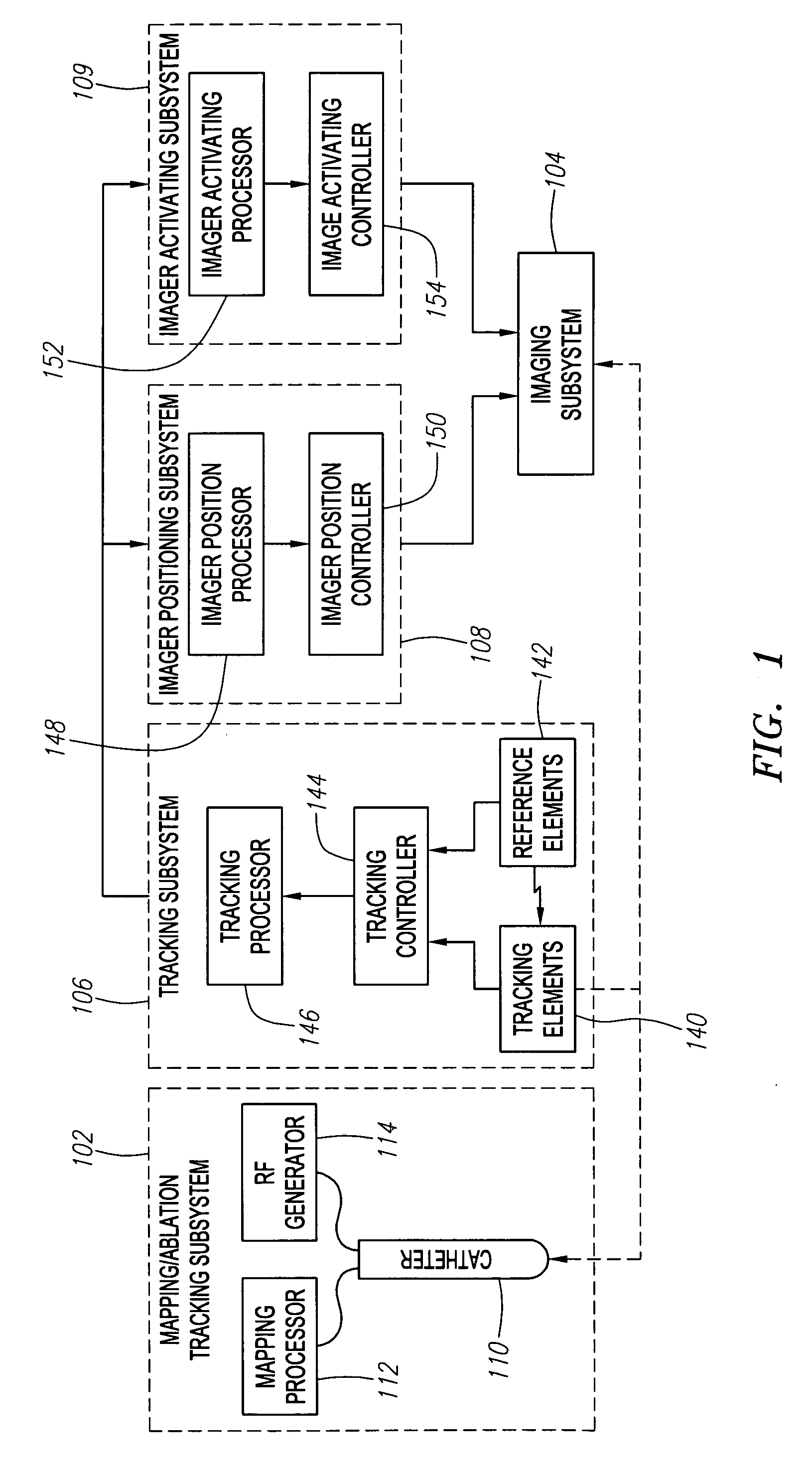
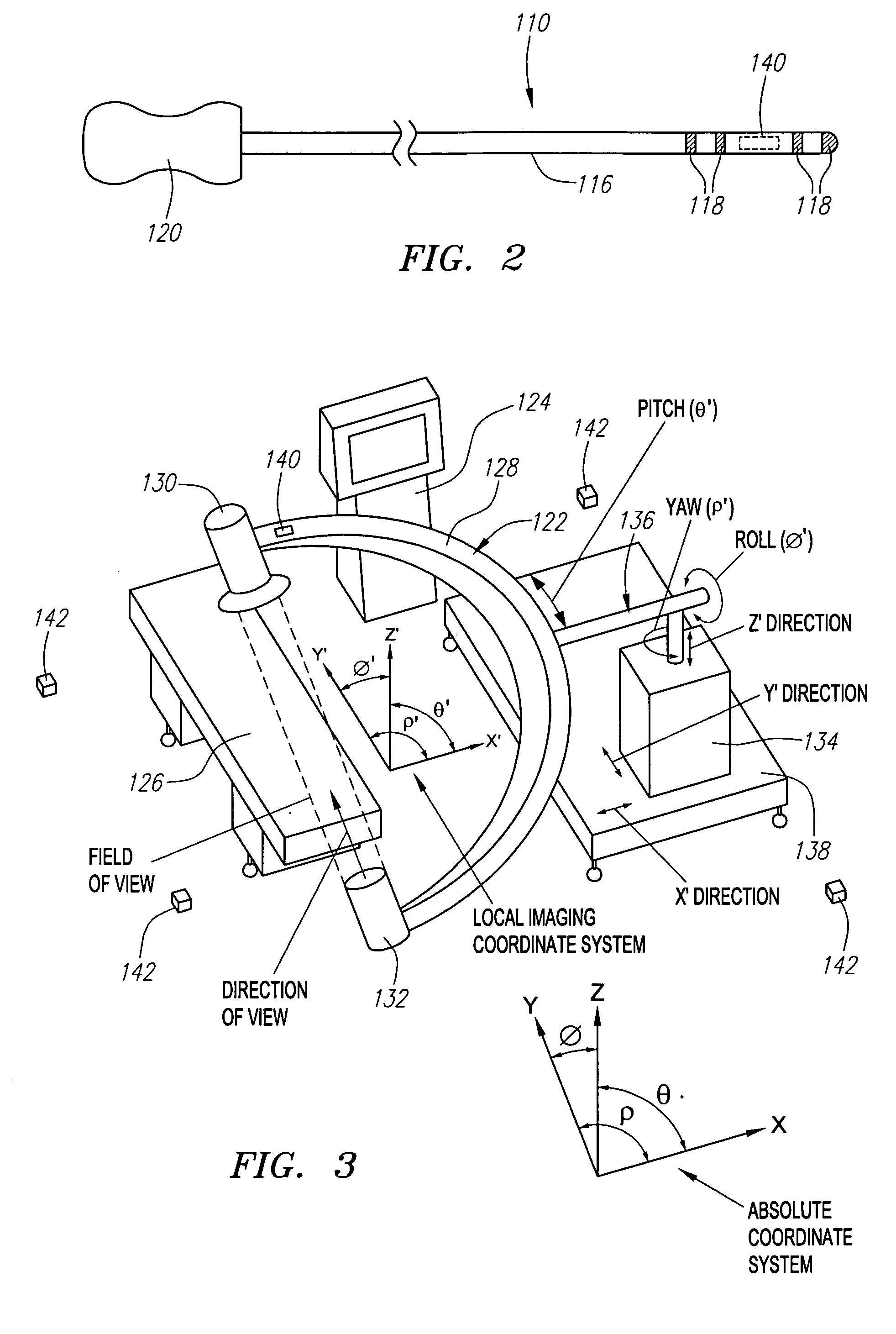
ActiveUS20060247520A1Accurate measurementLow costSurgical navigation systemsCatheterThree vesselsField of view
Methods and systems for navigating medical devices are provided. A patient is imaged while a medical device is moved within the patient. A position (e.g., a location and / or orientation) of the moving medical device is detected within a coordinate system (e.g., a three-dimensional coordinate system), a position of the imaging field of view relative to the patient is adjusted based on the detected medical device position, such that the relevant tissue region of the patient is within the field of view. For example, the field of view can be centered over the medical device or centered just distal to the medical device portion. The direction of view may be oriented at an angle perpendicular to the axis of the medical device, e.g., for more accurately measuring the length of objects within the field of view, or oriented at an angle parallel to the axis of the medical device portion, e.g., for more accurately measuring the diameter of the channel (e.g., blood vessel) in which the medical device is disposed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Radiotomography apparatus
ActiveUS20070189436A1Improve spatial resolutionImprove temporal resolutionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTemporal resolutionData segment
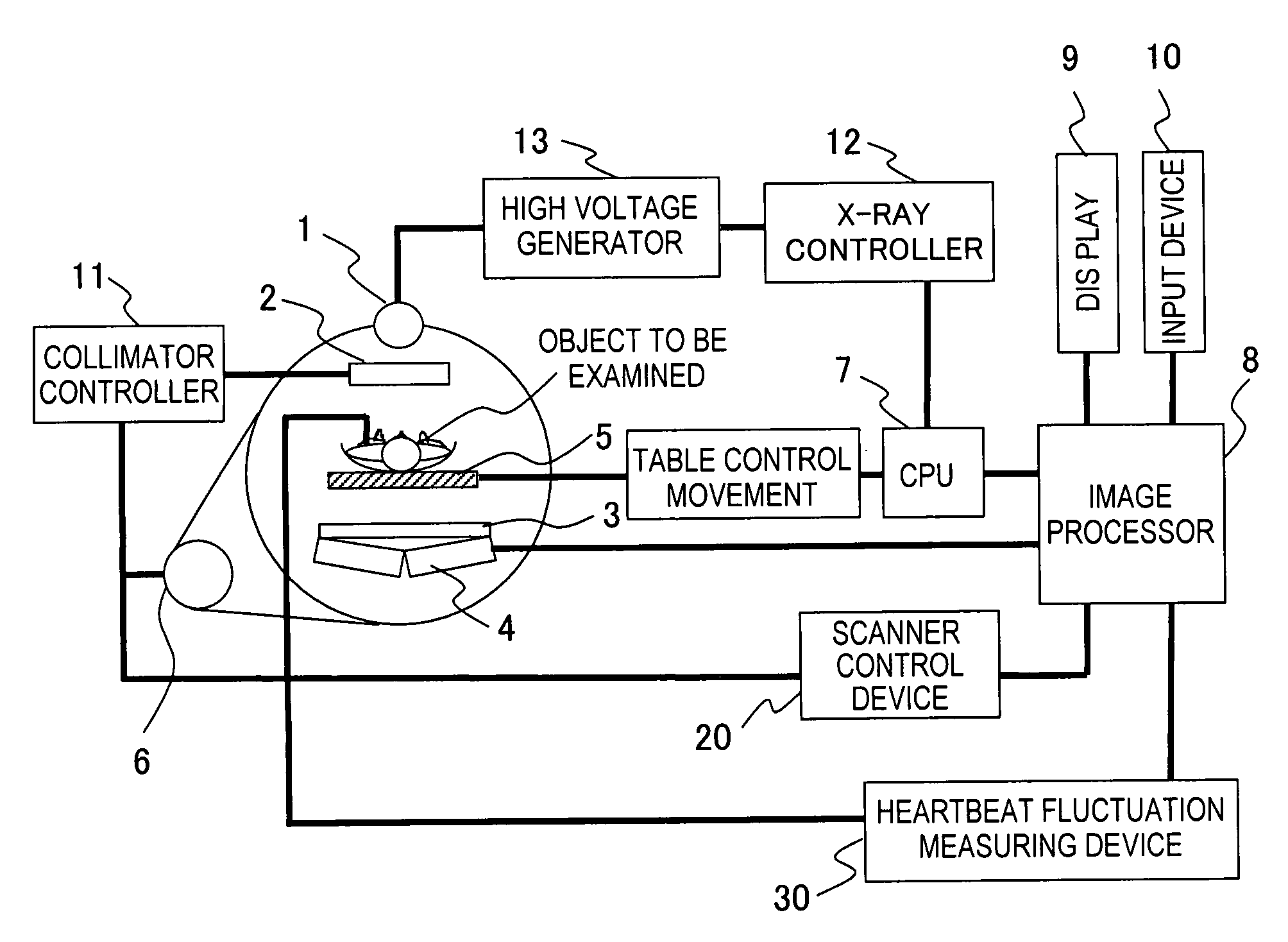
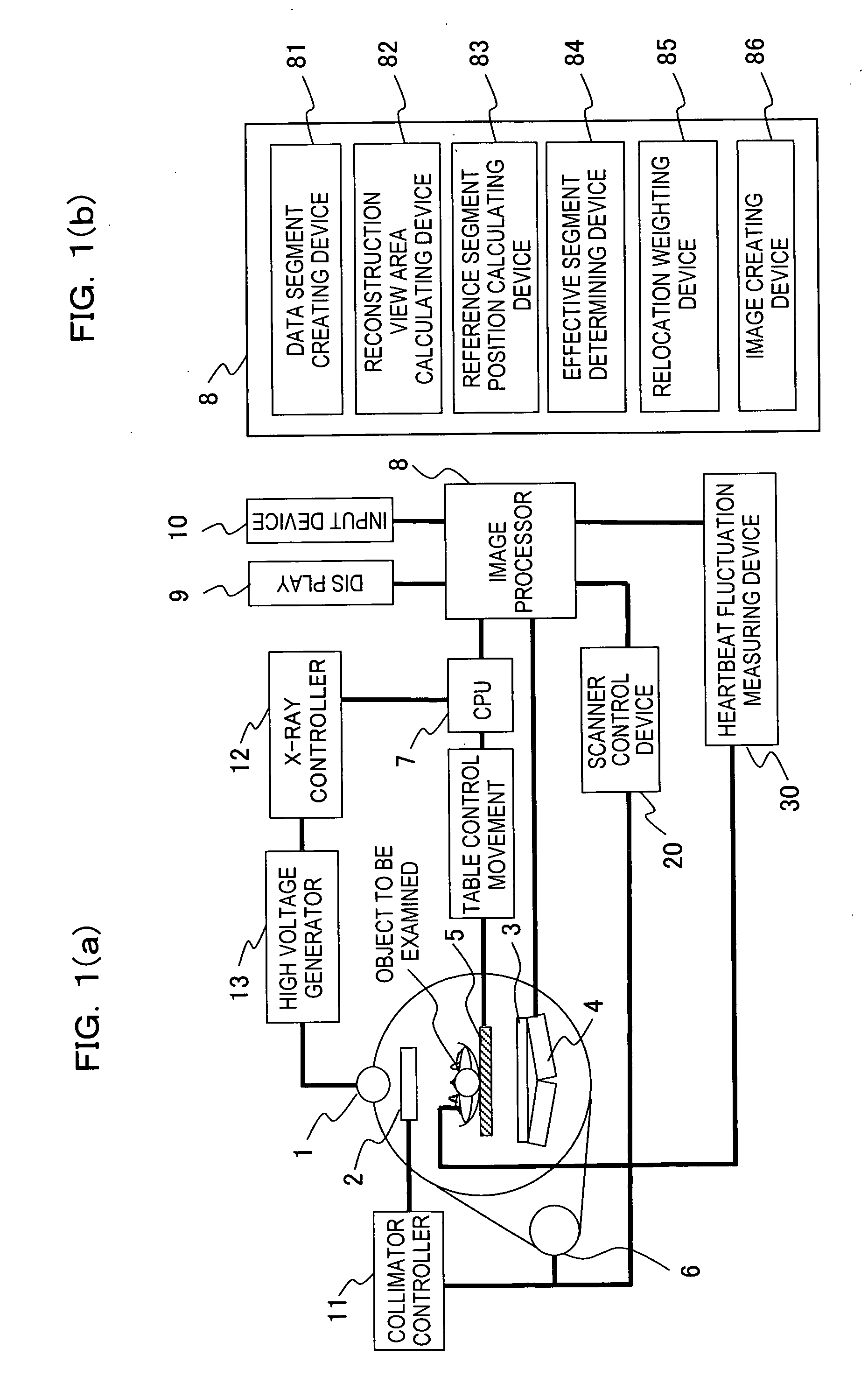
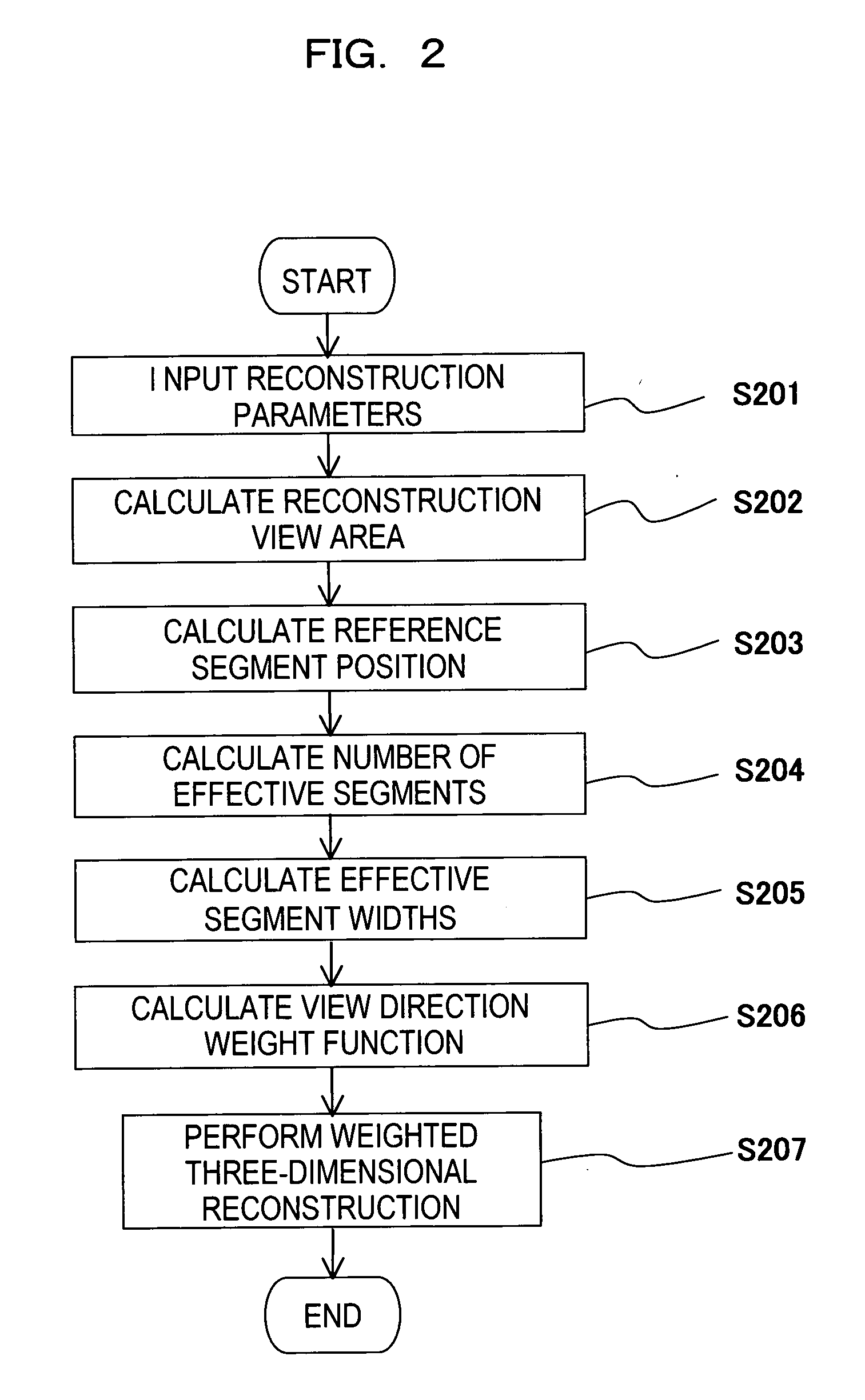
A radiotomography apparatus according to the present invention includes a radiation detection device that irradiates radiation from a radiation source in multiple directions around an object to be examined and detects radiation transmitted through the object from the multiple directions; a table on which the object lies and which can move the object in a body axis direction of the object; reconstruction parameter setting device that sets reconstruction parameters that include an amount of movement of the table in the body axis direction, and that are used to reconstruct an image of the object; a reconstruction view area calculating device that calculates a reconstruction view area for at least one data segment that is necessary for a reconstruction calculation that is determined for each spatial position that is reconstructed based on the set reconstruction parameters; a reference segment position setting device that sets a reference segment position in the calculated reconstruction view area according to a phase signal that is obtained by dynamic analysis of the object; an effective segment calculating device that calculates a data segment including the set reference segment position as an effective segment using a predetermined weight function; and an image creating device that creates an image by reconstructing the calculated effective segments. It is thus possible to provide a radiotomography apparatus that can both enhance temporal resolution and reduce ineffective radiation exposure.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
Patient matching surgical guide and method for using the same
ActiveUS8870889B2Reduce the numberReduce needInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsAnatomical featureBiomedical engineering
A system and method for developing customized apparatus for use in one or more surgical procedures is disclosed. The system and method incorporates a patient's unique anatomical features or morphology, which may be derived from capturing MRI data or CT data, to fabricate at least one custom apparatus. According to a preferred embodiment, the customized apparatus comprises a plurality of complementary surfaces based on a plurality of data points from the MRI or CT data. Thus, each apparatus may be matched in duplicate and oriented around the patient's own anatomy, and may further provide any desired axial alignments or insertional trajectories. In an alternate embodiment, the apparatus may further be aligned and / or matched with at least one other apparatus used during the surgical procedure.
Owner:MIGHTY OAK MEDICAL INC
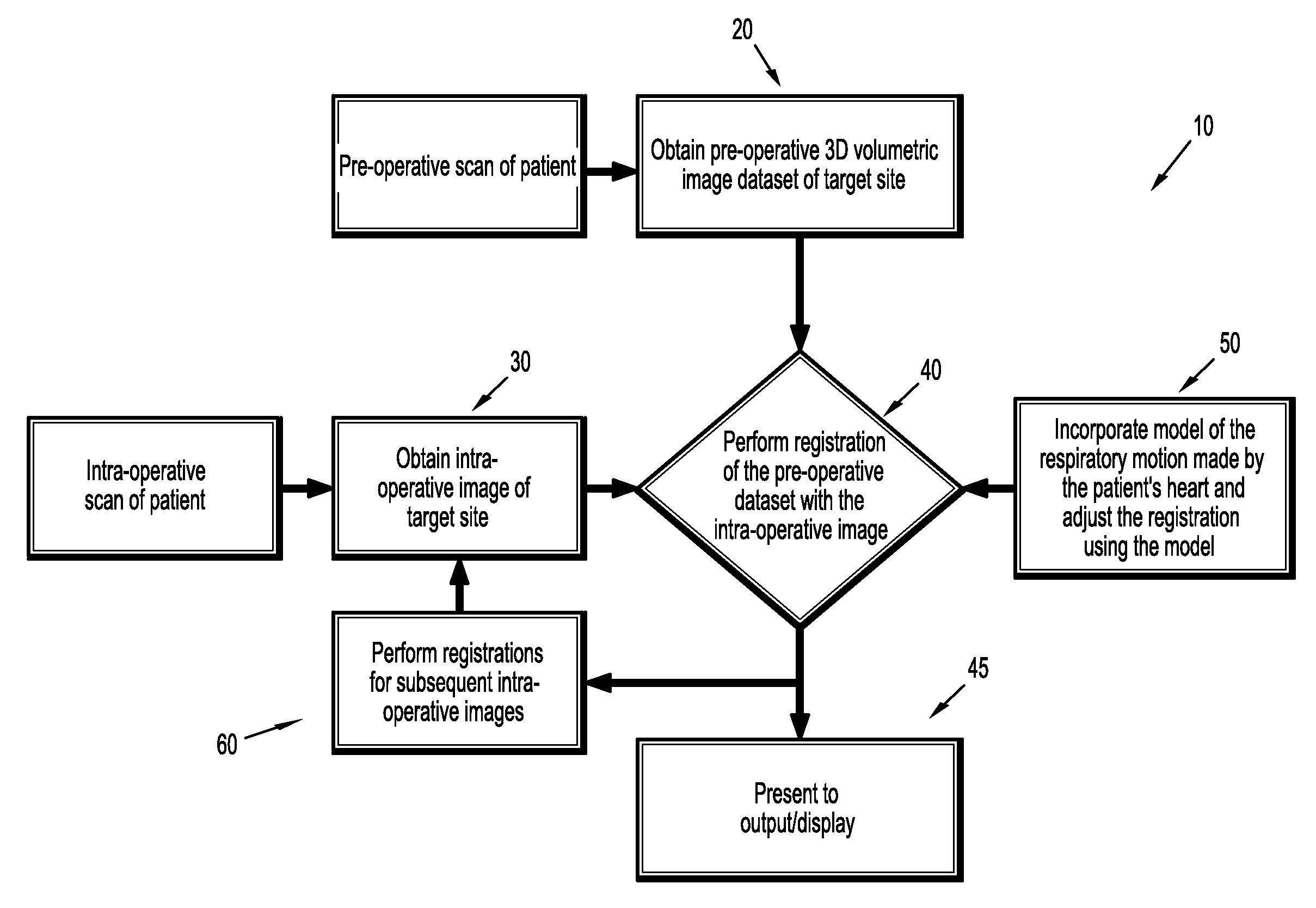
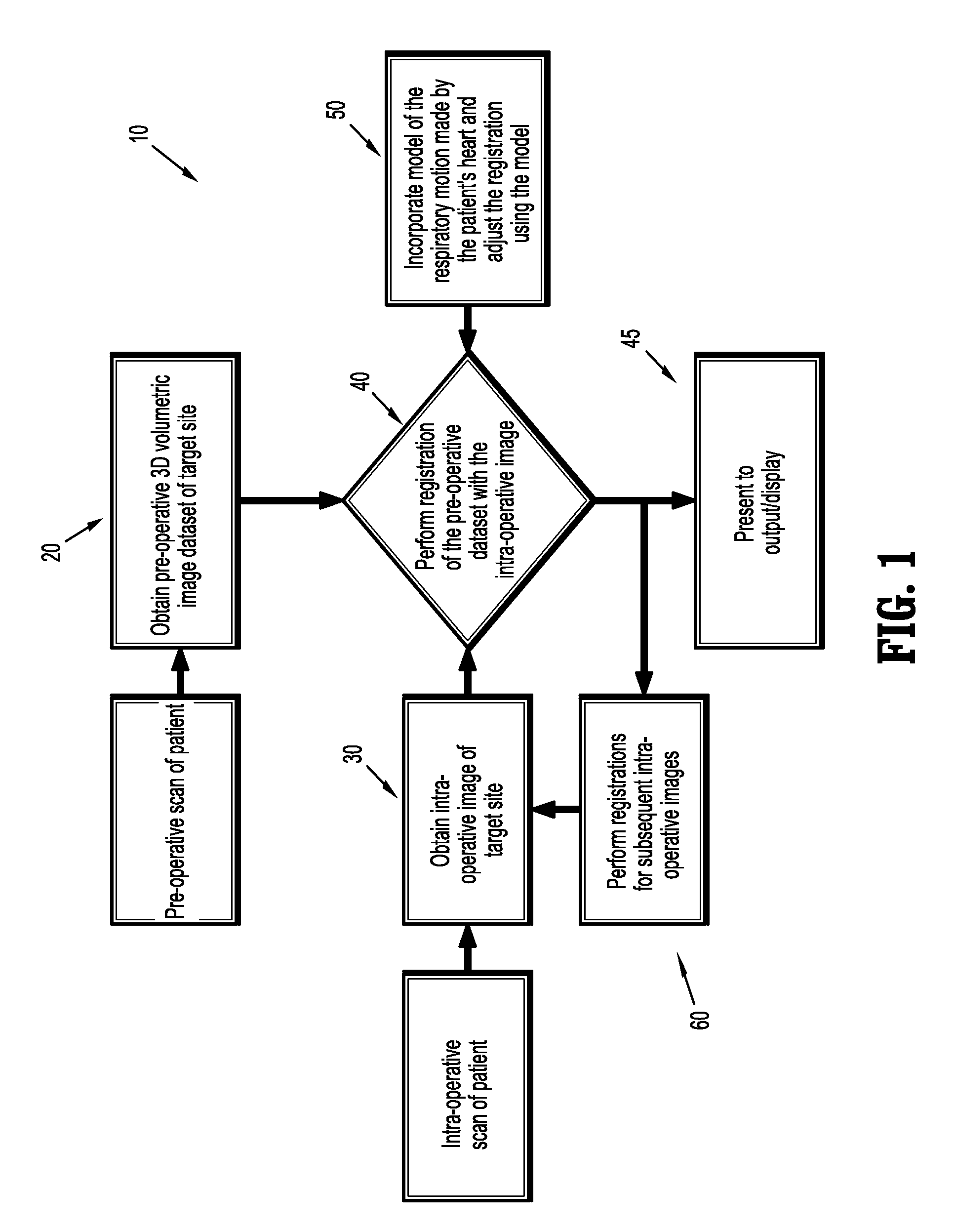
Method of compensation of respiratory motion in cardiac imaging
ActiveUS20100310140A1Improve accuracyImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisCardiac imagingRespiratory motion
A method (10) for respiratory motion compensation by applying principle component analysis (PCA) on cardiac imaging samples obtained using 2D / 3D registration of a pre-operative 3D segmentation of the coronary arteries.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
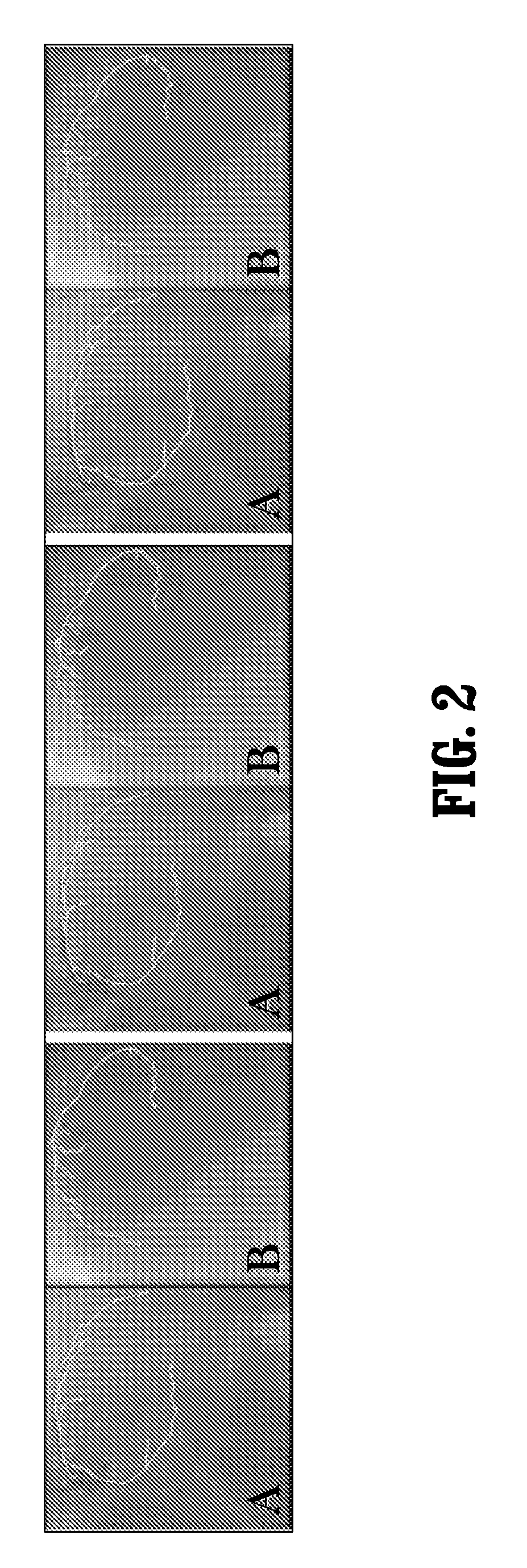
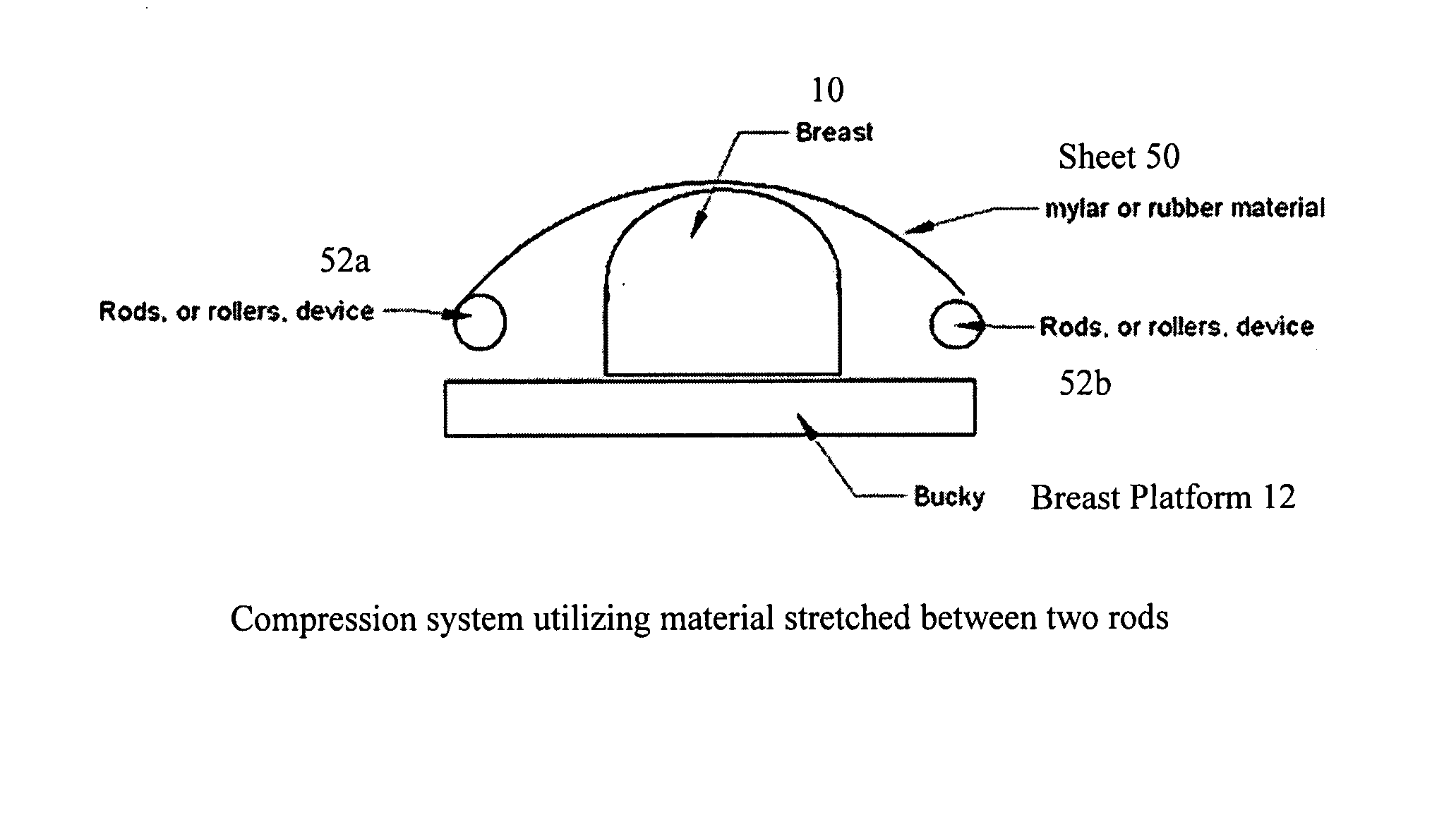
Breast compression for digital mammography, tomosynthesis and other modalities
ActiveUS20070280412A1Spread out the breast tissuesReduce radiation exposureTomosynthesisPatient positioning for diagnosticsTomosynthesisDigital mammography
A breast x-ray imaging method and system that is particularly suited for tomosynthesis imaging but also is useful for conventional mammography. A fluid containing pillow or bag is placed between the breast and a paddle that compresses the breast against a breast platform covering an imaging device, to enhance patient comfort and provide other benefits. Alternatives include a flexible sheet compressing the breast, and a compressible foam, preferably contoured to accommodate a patient's breast.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Medical Procedure Localizing Aid
InactiveUS20120302863A1Reduce radiation exposureAccurately locate the target siteSurgeryDiagnostic markersMedical imagingAssistive device
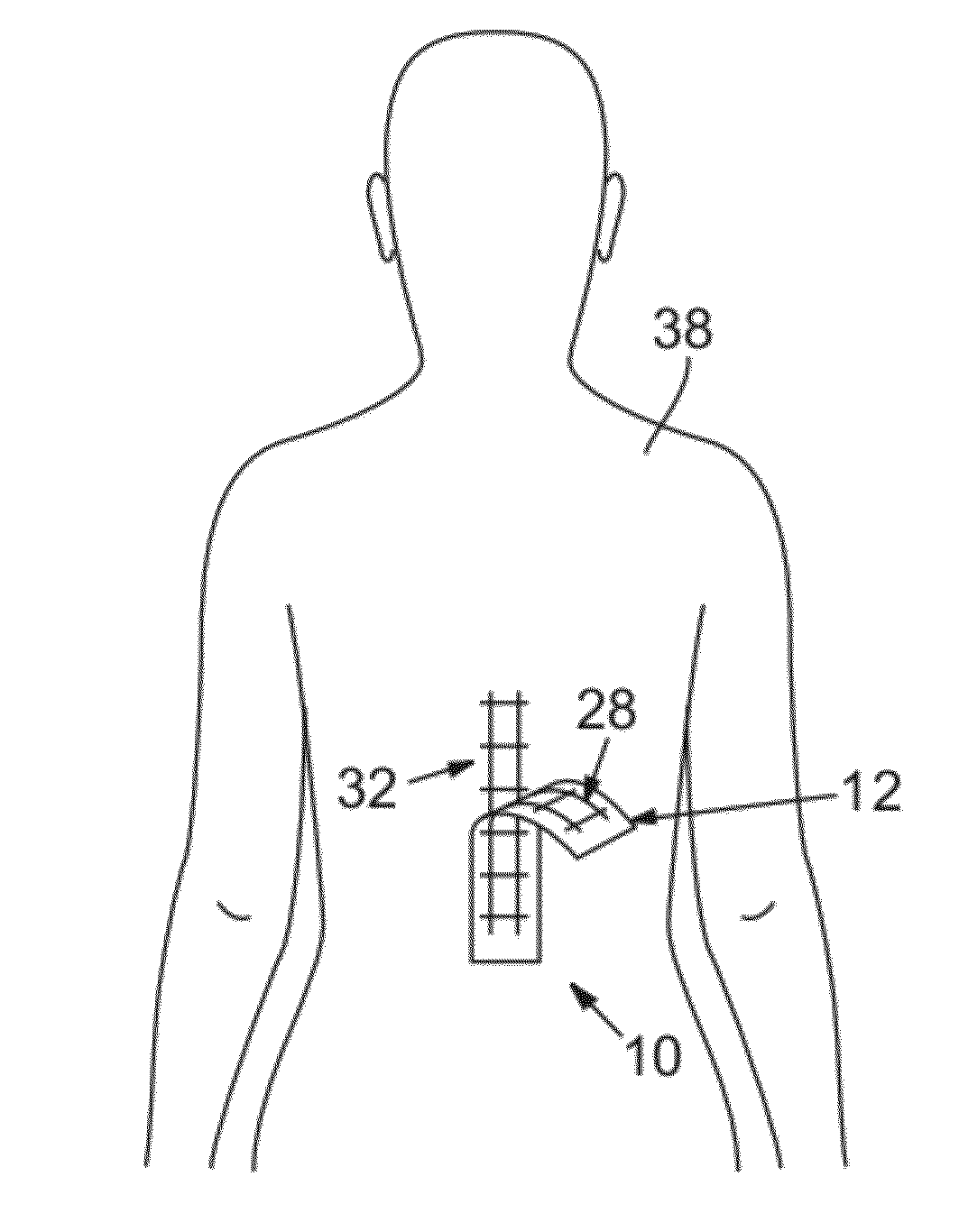
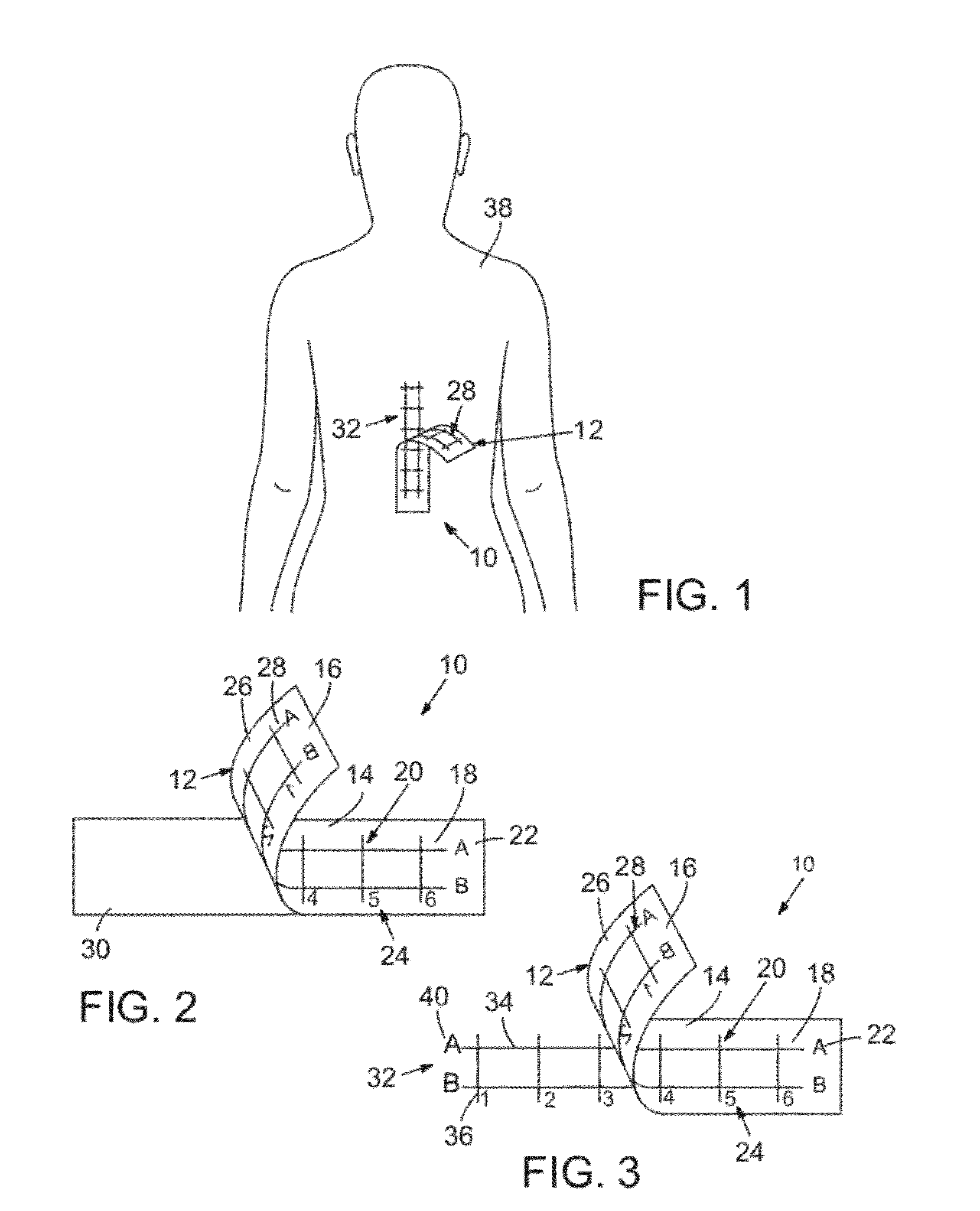
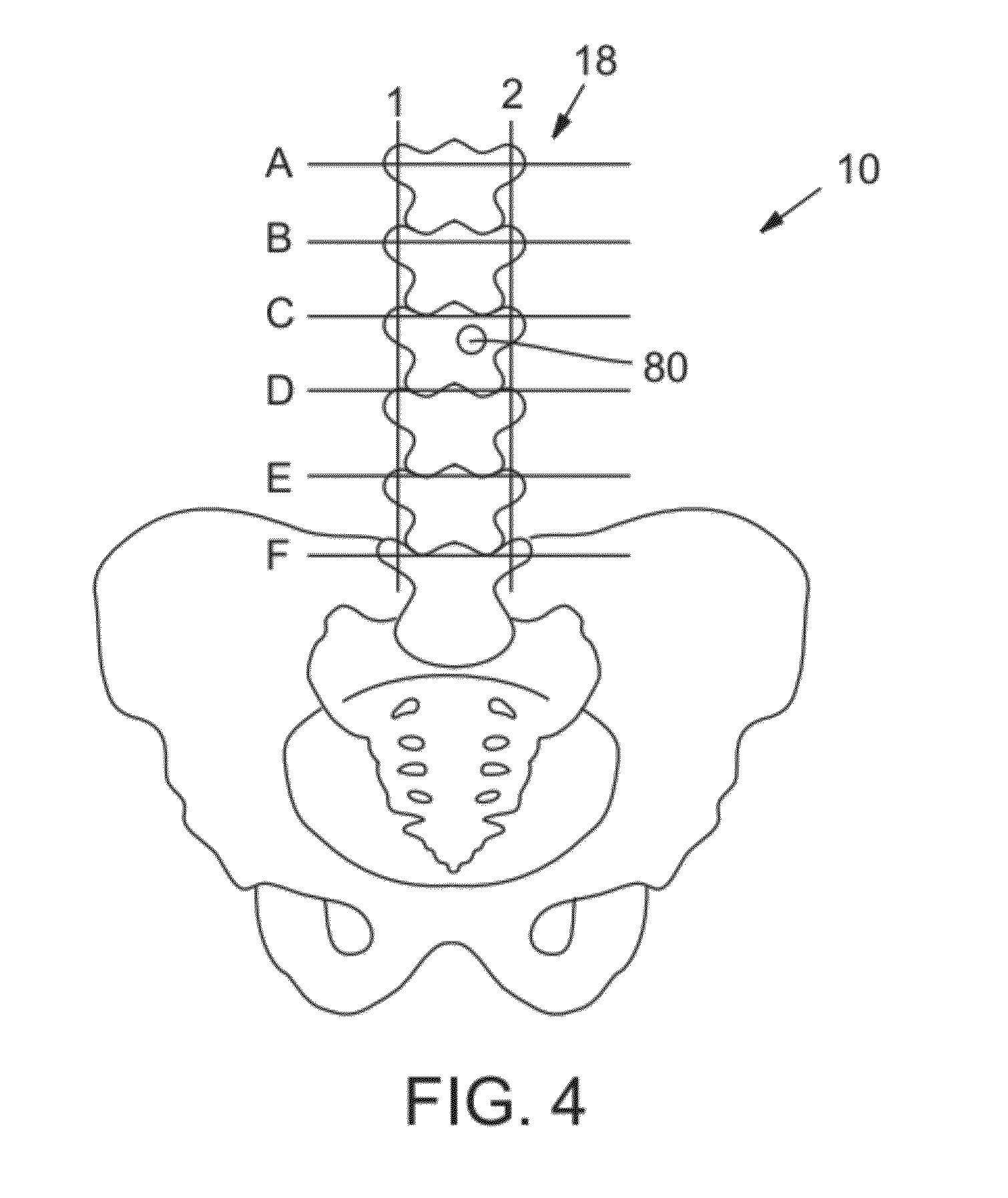
A medical procedure localization aid produces reference marks on both the patient and the medical imaging scan. The aid is defined by a substrate sheet having indicia on one side that is opaque to medical imaging radiation and indicia on a second side that is transferable to a patient. The indicia on the first side is displayed on the scan image and the indicia on the second side is imprinted on the patient. By visualizing the location of a target on the scan image relative to the indicia on the scan image and comparing that with indicia on the patient, a medical professional may reliably locate where a medical procedure should be performed.
Owner:TARGET TAPE
Methods and apparatus for loading radioactive seeds into brachytherapy needles
InactiveUS6846283B2Rapid seed loadingFast loadingMedical devicesInfusion needlesCombined useEngineering
Methods and apparatus are provided for loading therapeutic materials into brachytherapy needles. The apparatus comprises an apparatus with chambers, and radioactive seed and spacer cartridges received therein. The apparatus may be used in conjunction with a standard brachytherapy needle coupled to the distal end of the apparatus. The plunger dislodges seeds and spacers from the cartridge chambers to load the needle with a predetermined packing arrangement.
Owner:NEOSEED TECH
Method and apparatus for treating packaging and an installation for filling and closing packaging, including an apparatus for treating packaging
ActiveUS20110016829A1Increase doseReduce radiation intensityClosing machinesCapsTrademarkConstruction engineering
A method and apparatus for treating packaging and an installation for filling and closing packaging, including an apparatus for treating packaging. The abstract of the disclosure is submitted herewith as required by 37 C.F.R. §1.72(b). As stated in 37 C.F.R. §1.72(b): A brief abstract of the technical disclosure in the specification must commence on a separate sheet, preferably following the claims, under the heading “Abstract of the Disclosure.” The purpose of the abstract is to enable the Patent and Trademark Office and the public generally to determine quickly from a cursory inspection the nature and gist of the technical disclosure. The abstract shall not be used for interpreting the scope of the claims. Therefore, any statements made relating to the abstract are not intended to limit the claims in any manner and should not be interpreted as limiting the claims in any manner.
Owner:KHS GMBH
Cervical applicator for high dose radiation brachytherapy
InactiveUS6699171B2Reduce deliveryMinimizing patient discomfortMedical devicesX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyVaginal wallBrachytherapy
A modified Fletcher-Suit tandem tube applicator includes a balloon which can be inflated to both positionally secure the applicator within the vaginal canal and to distend the confronting vaginal wall thereby increasing the distance of such tissue from the radioactive source contained in the tandem tube of applicator and correspondingly reducing radiation damage to nearby tissues and organs such as the rectum and bladder.
Owner:PAXTON EQUITIES
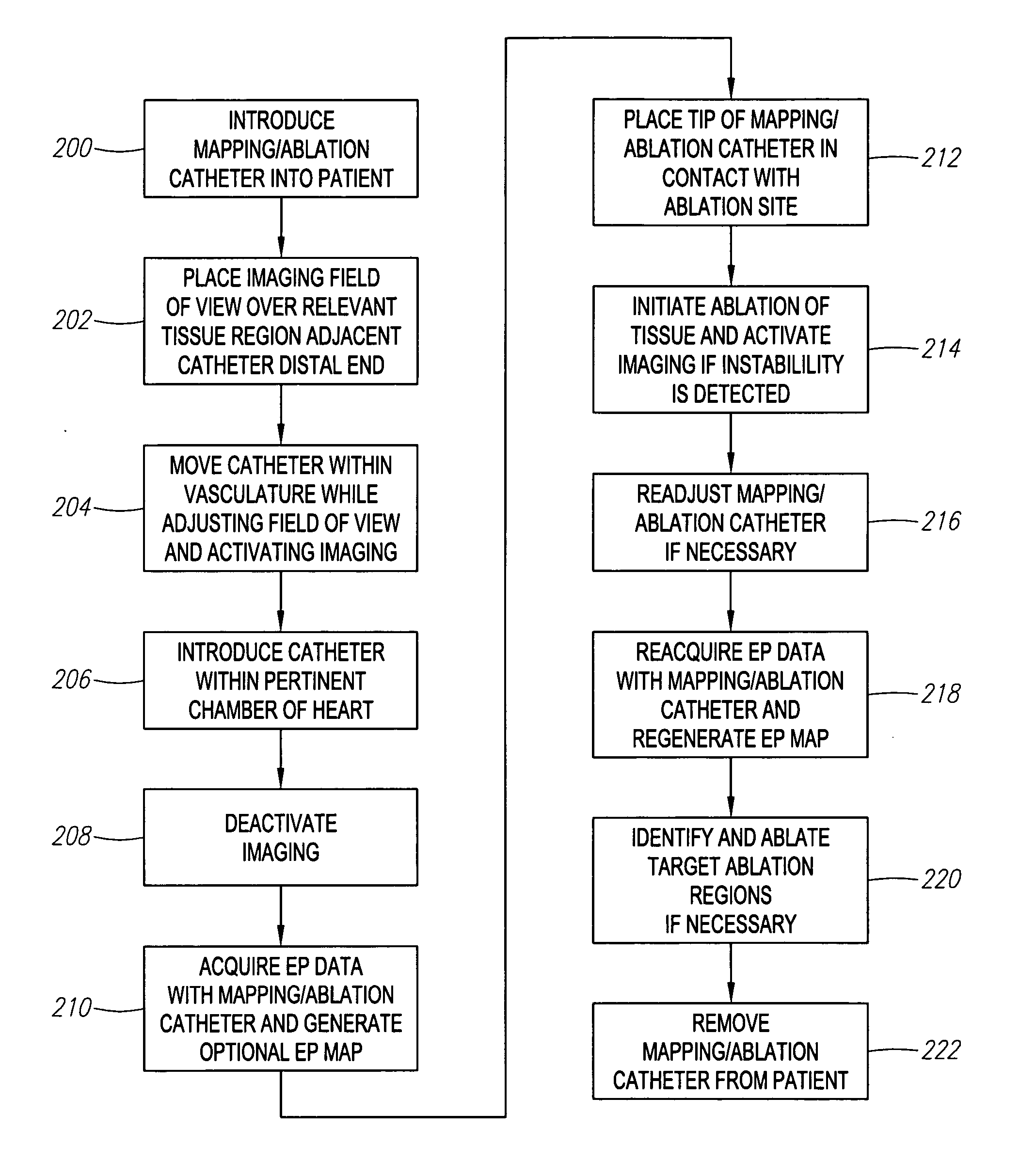
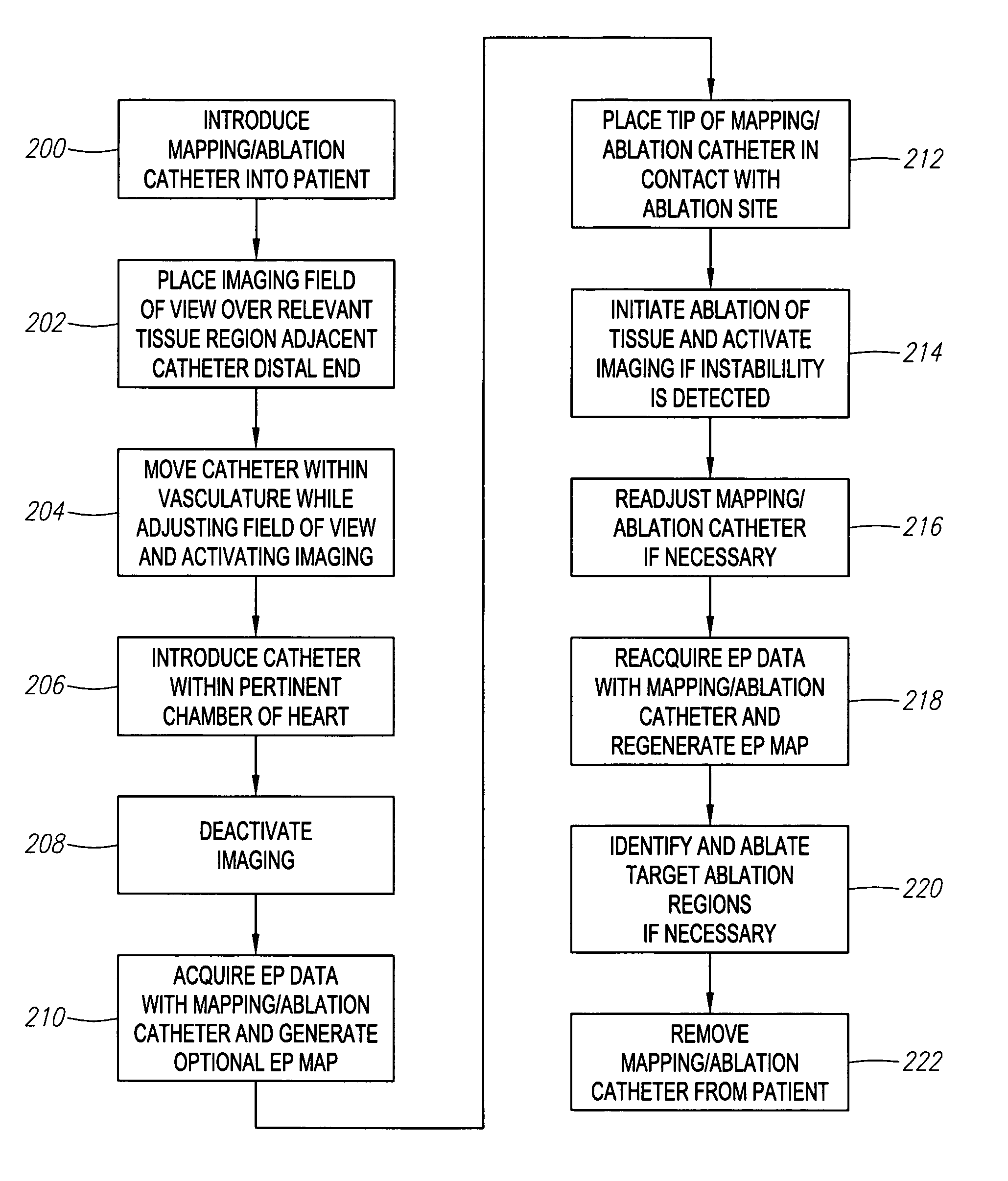
Automated activation/deactivation of imaging device based on tracked medical device position
ActiveUS8571635B2Accurate measurementLow costElectrotherapySurgical navigation systemsMedical equipmentExAblate
Methods and systems for controlling an imaging procedure are provided. A medical device is introduced within a patient, and a position (e.g., location and / or orientation) of the medical device is detected within the patient relative to a reference position (e.g., a previously detected position of the medical device or a position within a desired path). Imaging of the patient is automatically activated based on the detected relative position, such that the patient is imaged only during relevant times. In one method, instability / stability of the medical device is detected, in which case, the imaging is automatically activated when the medical device is unstable, and deactivated when the medical device is stable. For example, if tissue is to be ablated with the medical device, medical personnel can be made aware of inadvertent movement of the medical device via the image, and can correct any displacement of the medical device from the ablation site.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Bone drill
A radiolucent bone drill and / or impact drill is provided, which includes a first portion connected to a second portion. The first portion defines a first axis and the second portion defines a second axis. The second axis is disposed at an angle relative to the first axis. A third portion is connected to the second portion. The third portion has a shaft extending therefrom. The shaft includes a distal end configured to engage bone. The bone drill may include a radiation protection guard mounted to the first portion. Specific drill bits, access sheaths / conduits / tube, curettes, and screwdriver bits designed to be used with the devices are provided. The bone drill may be used to place an access sheath / conduit / tube / needle into a bone in a single step. Methods of use are also disclosed.
Owner:OSTEO INNOVATIONS
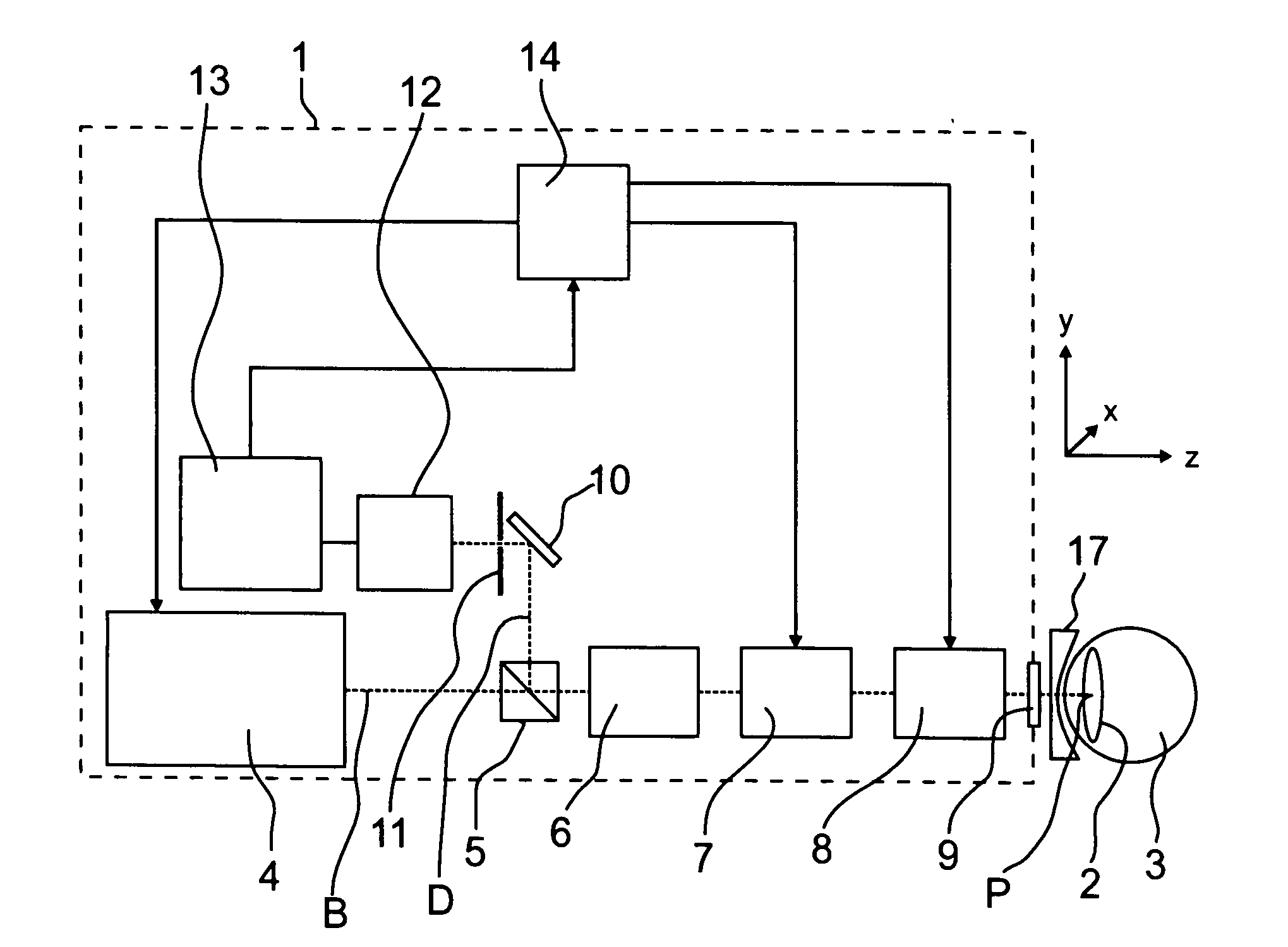
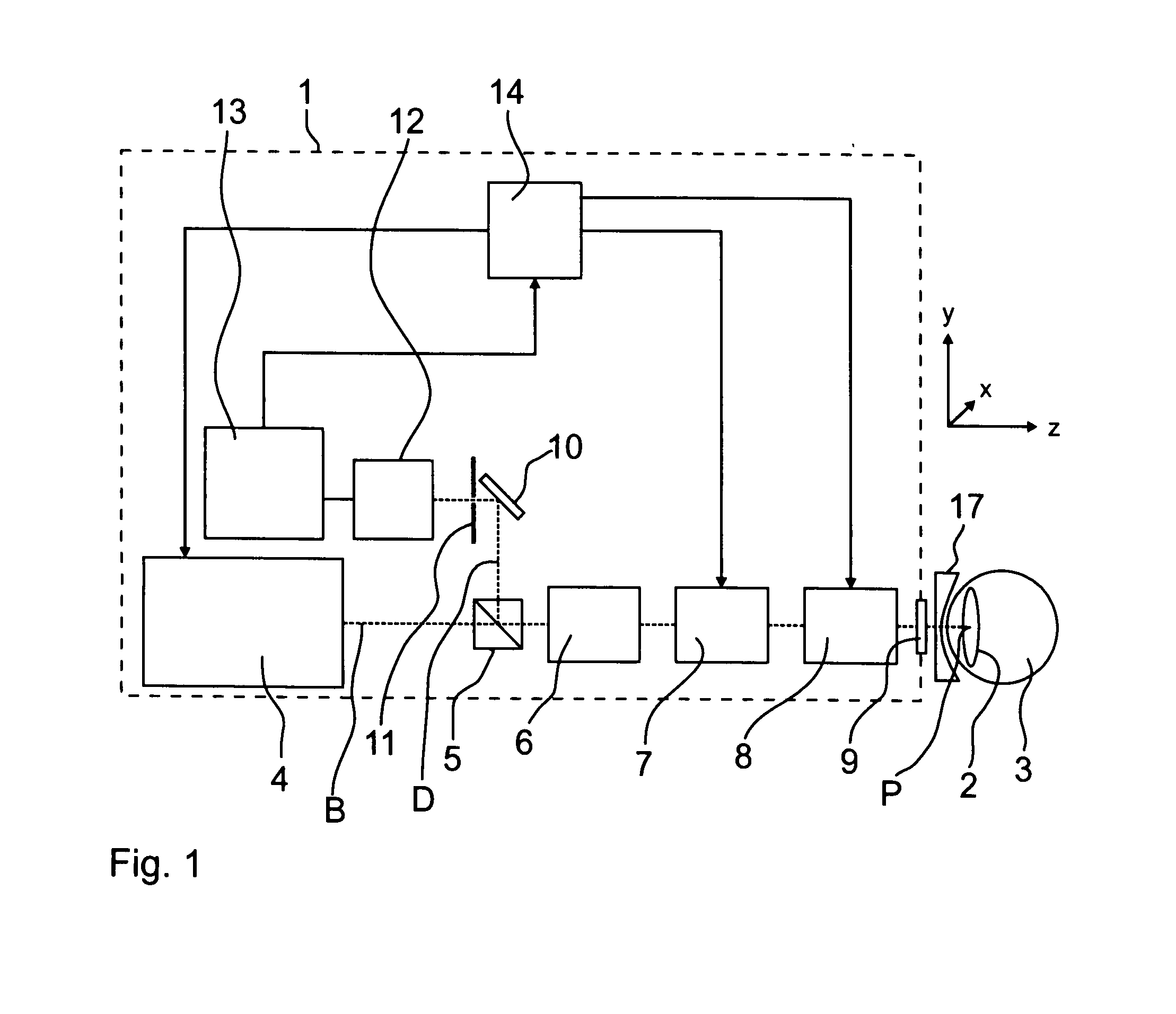
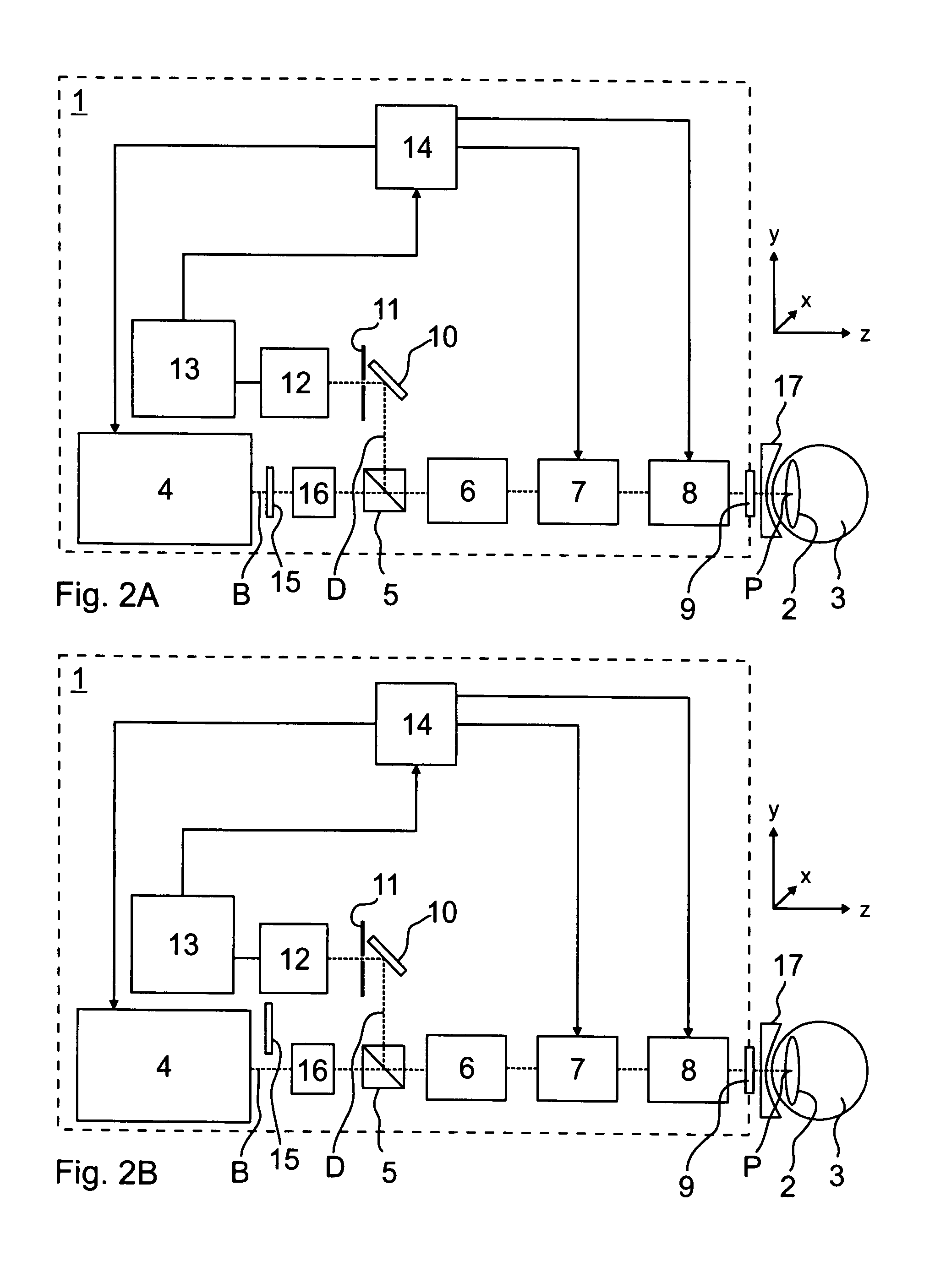
Ophthalmological laser system and operating method
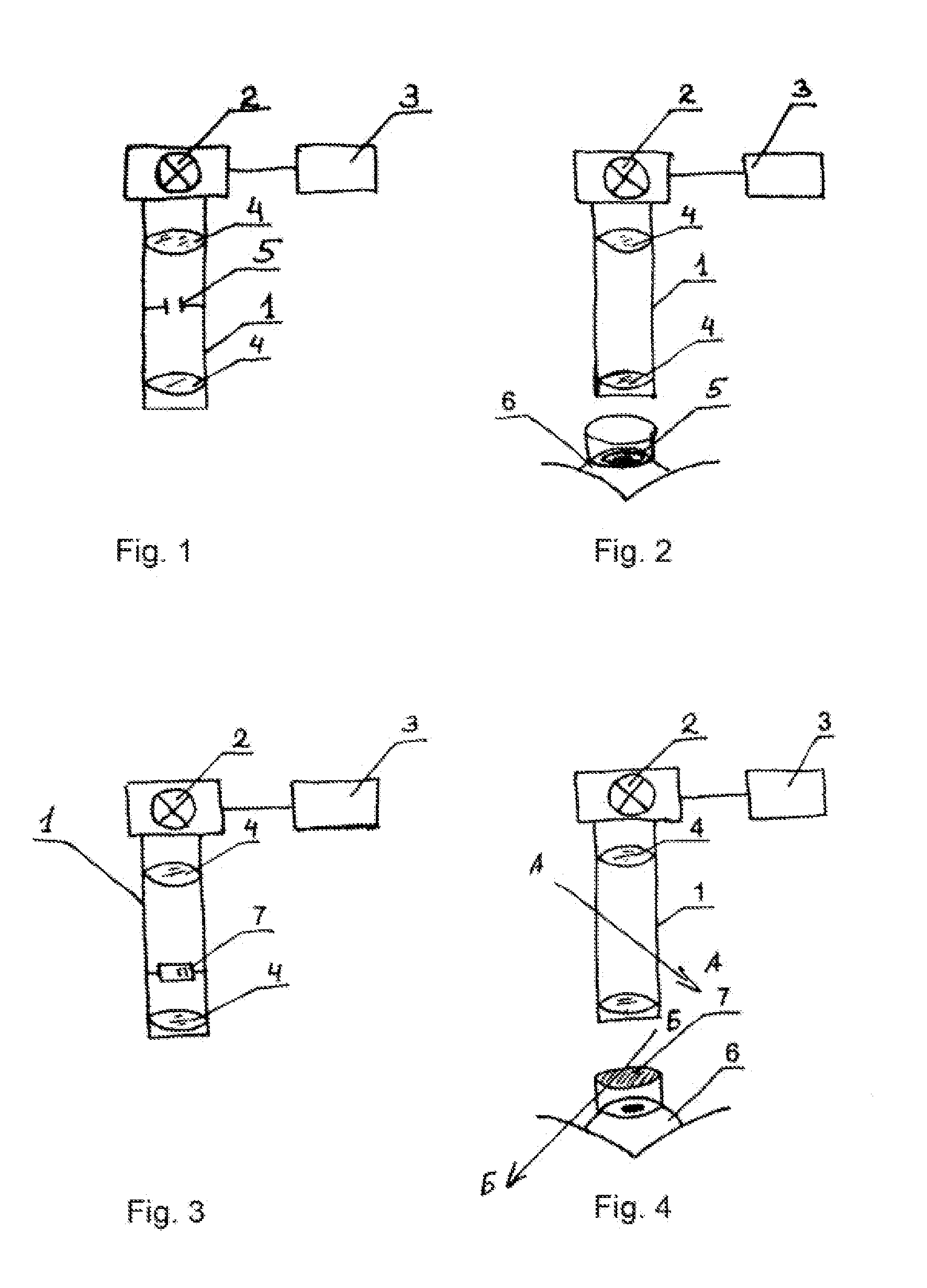
ActiveUS20110264081A1Improve accuracyUnnecessary immobilizationLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsEye lensPartial reflection
A polarization beam splitter selectively decouples detection light onto a detector such that it has a polarization direction that differs from the emitted illumination light. This enables the detection of the light scattered back in the eye lens at a high level of accuracy, since stray light from reflections at optical components of the light path is suppressed. In the generating of photo disruptions or other incisions, the ray exposure of the retina may be reduced in that the incisions being furthest away from the laser are induced first such that laminar gas inclusions with an existence duration time of at least 5 seconds result. In this manner the laser radiation propagated in the direction of the retina in further incisions are scattered and partially reflected such that the influence impinging upon the retina is reduced.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Method for treating keratoconus by UV radiation and a device for carrying out said method (variants)
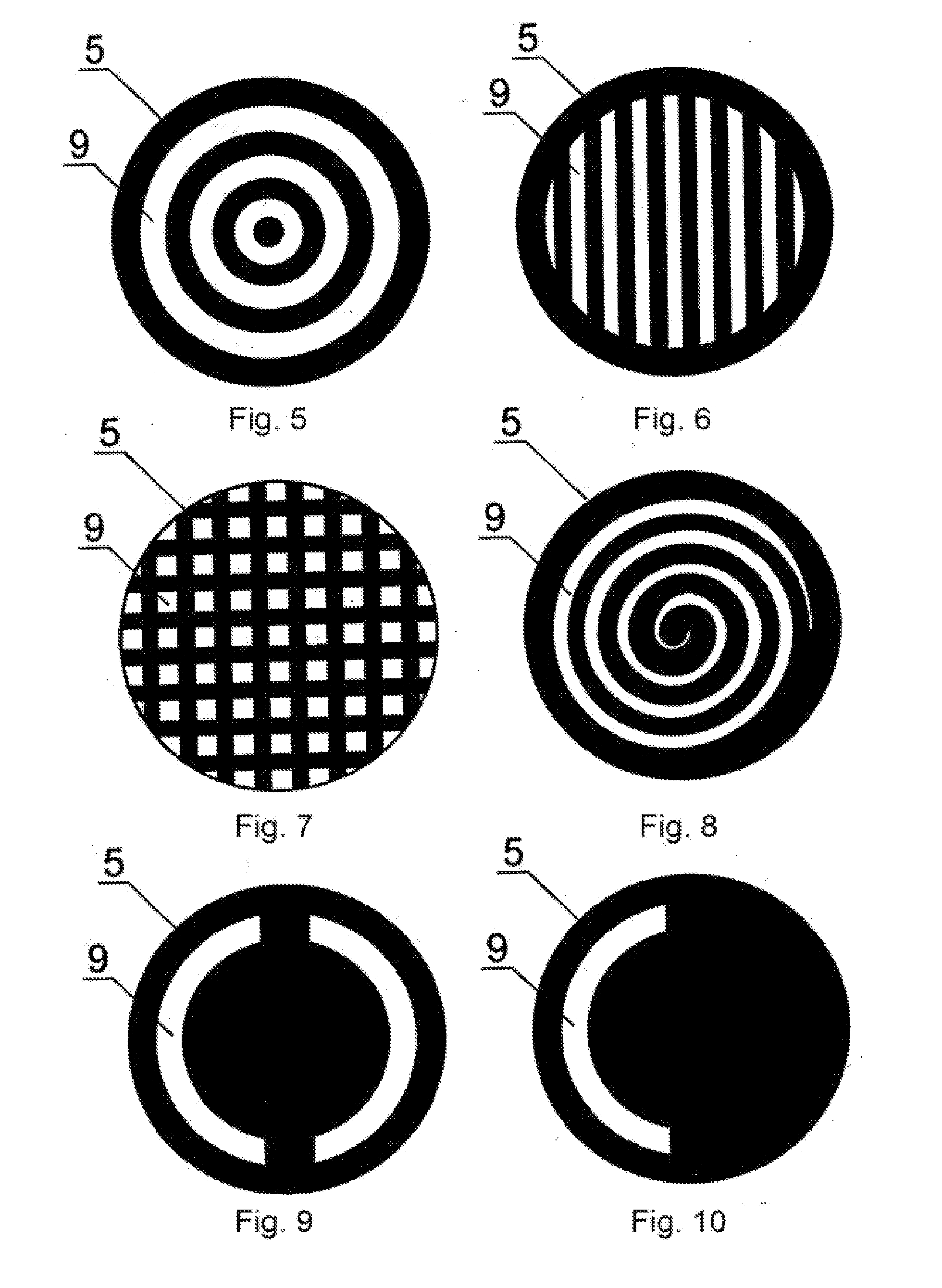
InactiveUS20110190742A1Reduce adverse effectsEfficacy of treatmentLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsOptical axisUltraviolet
The invention relates to ophthalmology and is used for treating keratoconus. The inventive method comprises forming one or more radiation areas of different shape, comprising concentric circles, arcs, parallel lines, cells, grids, spirals or other geometrical figures. In the other variant, the method comprises polarizing UV radiation and adjusting the depth of the UV radiation action by directing the UV radiation polarization plane at an angle of 1-180° to the plane of light polarization by the cornea, thereby using the effect of light polarization by the cornea. The device for treating keratoconus comprises, positioned on the optical axis common with an UV radiation source optical focusing elements and a diaphragm. The diaphragm is situated on the optical axis common with the UV radiation source and is made in the form of a mask with alternating transparent and shaded elements in the form of concentric circles, arcs, parallel lines, cells, grids, spirals or other geometrical figures. In the other variant, the device comprises, situated on the optical axis common with the UV radiation source, the optical focusing elements, the diaphragm and a polarisor.
Owner:ANISIMOV SERGEY IGOREVICH
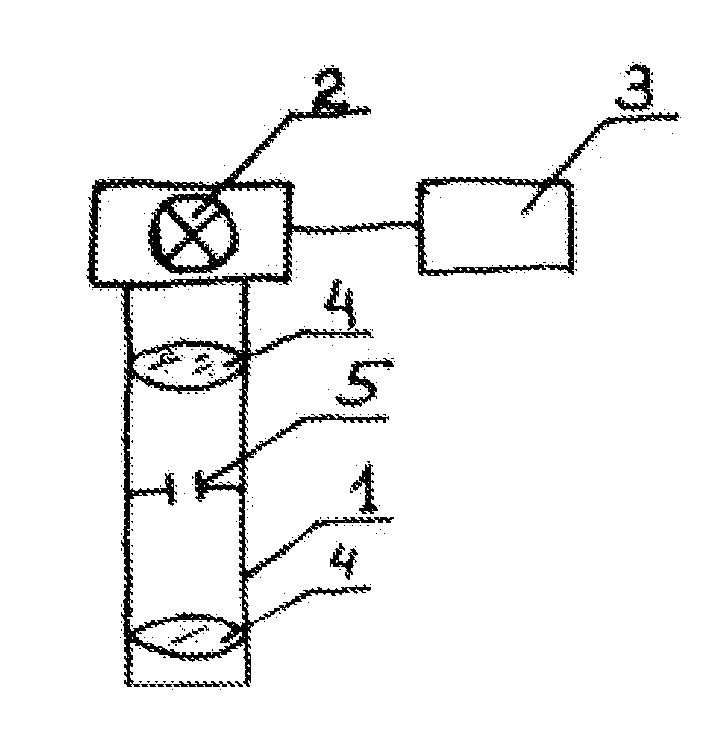
Ophthalmologic laser system
ActiveUS20120016352A1Interference minimizationReduce radiation exposureLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsLens crystallineUltra short pulse
An ophthalmological laser system for photodisruptive irradiation of ocular tissue, including a crystalline lens or a cornea. The system includes an ultra-short pulse laser, the radiation of which is focusable as illumination light via an illumination beam path including a scanner unit and focusing optics. A control unit is programmed to execute determining irradiation control data for photodisruptions at irradiation points in an interior of the ocular tissue distributed three-dimensionally and non-equidistantly to create at least one predetermined target incision. The laser system then irradiates the ocular tissue according to the determined irradiation control data.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Guide forceps device for use with vertebral treatment device, system and methods of use
InactiveUS20070282372A1Minimizing health riskFacilitates guidanceJoint implantsDiagnostic markersForcepsEngineering
A forceps is provided, which is adapted for treating a vertebral body. The forceps has a handle including an actuator pivotably connected therewith. A shaft extends from the handle with the proximal end being operatively engageable with the actuator. An elongated member extends through the shaft and has a proximal end and a distal end. The proximal end being fixed to the handle and the distal end includes opposing arms configured to grasp. The forceps may be configured for use with a bone drill. Portions of the forceps may be radiolucent. A vertebral treatment system and methods of use are also provided.
Owner:OSTEO INNOVATIONS
Automated activation/deactivation of imaging device based on tracked medical device position
ActiveUS20060247521A1Reduce radiation exposureEnhance the imageElectrotherapySurgical navigation systemsInstabilityBiological activation
Methods and systems for controlling an imaging procedure are provided. A medical device is introduced within a patient, and a position (e.g., location and / or orientation) of the medical device is detected within the patient relative to a reference position (e.g., a previously detected position of the medical device or a position within a desired path). Imaging of the patient is automatically activated based on the detected relative position, such that the patient is imaged only during relevant times. In one method, instability / stability of the medical device is detected, in which case, the imaging is automatically activated when the medical device is unstable, and deactivated when the medical device is stable. For example, if tissue is to be ablated with the medical device, medical personnel can be made aware of inadvertent movement of the medical device via the image, and can correct any displacement of the medical device from the ablation site.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Medical digital X-ray imaging apparatus and medical digital X-ray sensor
ActiveUS8005187B2Increase capacityReduce data capacityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayComputing tomography
In a medical digital X-ray imaging apparatus having a plurality of imaging modes including computed tomography mode, a supporter supports an X-ray source and a digital X-ray sensor having a two-dimensional detection plane for detecting X-rays, while interposing an object between them. An image reconstructor acquires data from the digital X-ray sensor and reconstructs an image based on the acquired data. An operator selects one of a first imaging mode and a second imaging mode. The second imaging mode has an irradiation field different from the first imaging mode and has an area to be read in the digital X-ray sensor smaller than that in the first imaging mode.
Owner:MORITA MFG CO LTD
Medical Procedure Localizing Aid
InactiveUS20150223906A1Reduce dependenceReduce radiation exposurePatient positioningSurgeryMedical imagingAnchor point
A medical procedure localization aid produces reference marks on both the patient and the medical imaging scan. The aid is defined by an imaging substrate having indicia on one side that is opaque to medical imaging and a second substrate having indicia that appears on the patient's surface for the procedure. Anchor points align the second substrate to the same position as the first substrate on the patient. By visualizing the location of a target on the scan image relative to the indicia on the scan image and comparing that with indicia on the patient, a medical processional may reliably locate where a medical procedure should be performed.
Owner:TARGET TAPE
Breast compression for digital mammography, tomosynthesis and other modalities
ActiveUS7489761B2Spread out the breast tissuesReduce radiation exposureTomosynthesisPatient positioning for diagnosticsTomosynthesisDigital mammography
A breast x-ray imaging method and system that is particularly suited for tomosynthesis imaging but also is useful for conventional mammography. A fluid containing pillow or bag is placed between the breast and a paddle that compresses the breast against a breast platform covering an imaging device, to enhance patient comfort and provide other benefits. Alternatives include a flexible sheet compressing the breast, and a compressible foam, preferably contoured to accommodate a patient's breast.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Automated manipulation of imaging device field of view based on tracked medical device position
ActiveUS7706860B2Accurate measurementLow costSurgical navigation systemsCatheterVisual field lossImage manipulation
Methods and systems for navigating medical devices are provided. A patient is imaged while a medical device is moved within the patient. A position (e.g., a location and / or orientation) of the moving medical device is detected within a coordinate system (e.g., a three-dimensional coordinate system), a position of the imaging field of view relative to the patient is adjusted based on the detected medical device position, such that the relevant tissue region of the patient is within the field of view. For example, the field of view can be centered over the medical device or centered just distal to the medical device portion. The direction of view may be oriented at an angle perpendicular to the axis of the medical device, e.g., for more accurately measuring the length of objects within the field of view, or oriented at an angle parallel to the axis of the medical device portion, e.g., for more accurately measuring the diameter of the channel (e.g., blood vessel) in which the medical device is disposed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Radiation shield
InactiveUS20070029513A1Direct visualizationReduce radiation exposureRadiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsObservation pointRadiation shield
A radiation shield includes a radio-opaque drape which has an open area extending completely through the drape to provide a viewing site. Radiation control structure in the form of a vent system is located in the open area. The vent system includes a plurality of radio-opaque slats extending at least partially across at least a portion of the open area. The slats preferably extend outwardly away from the surface of the drape to facilitate the capturing of scattered radiation.
Owner:TREUTH MARK G
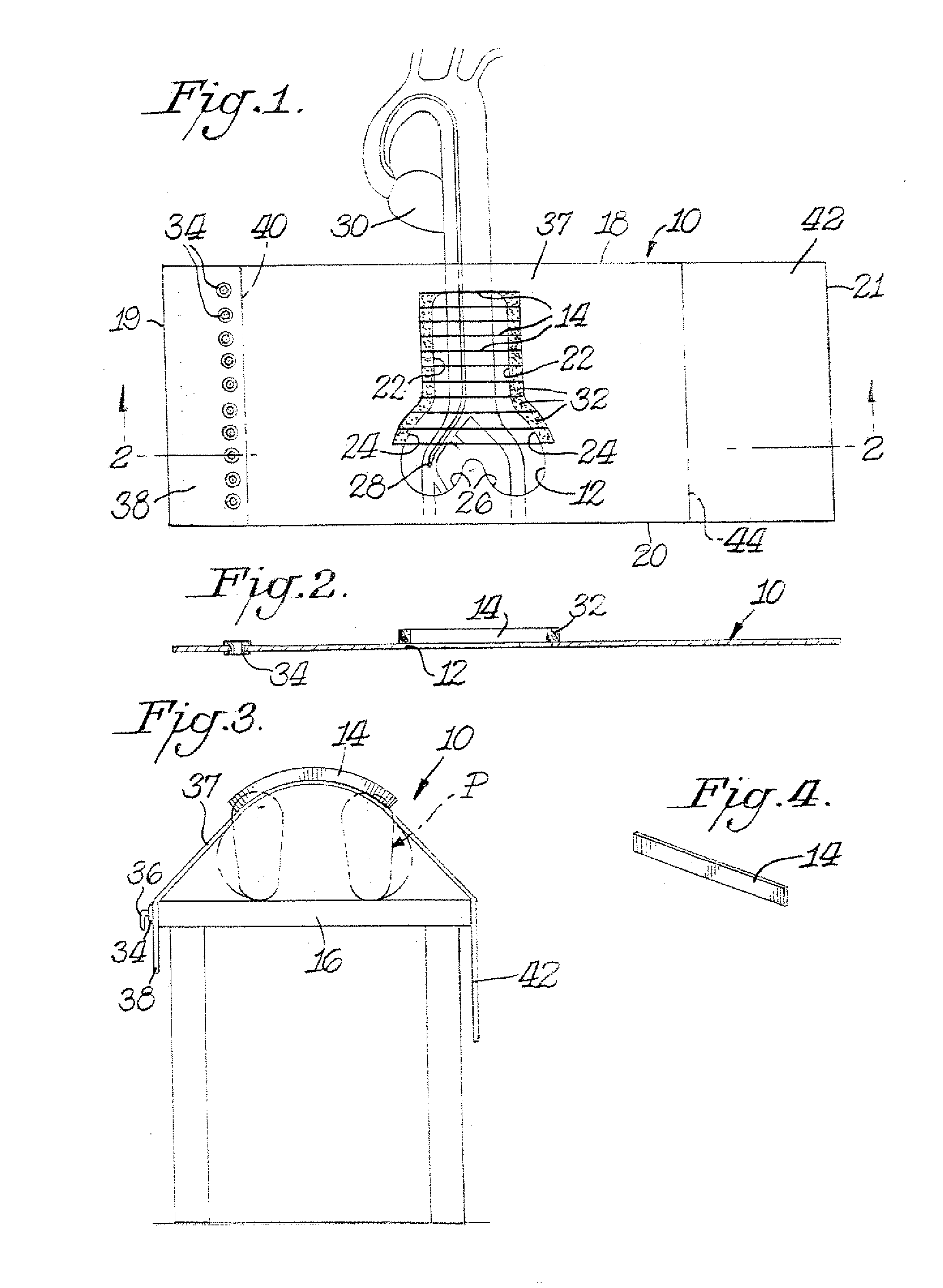
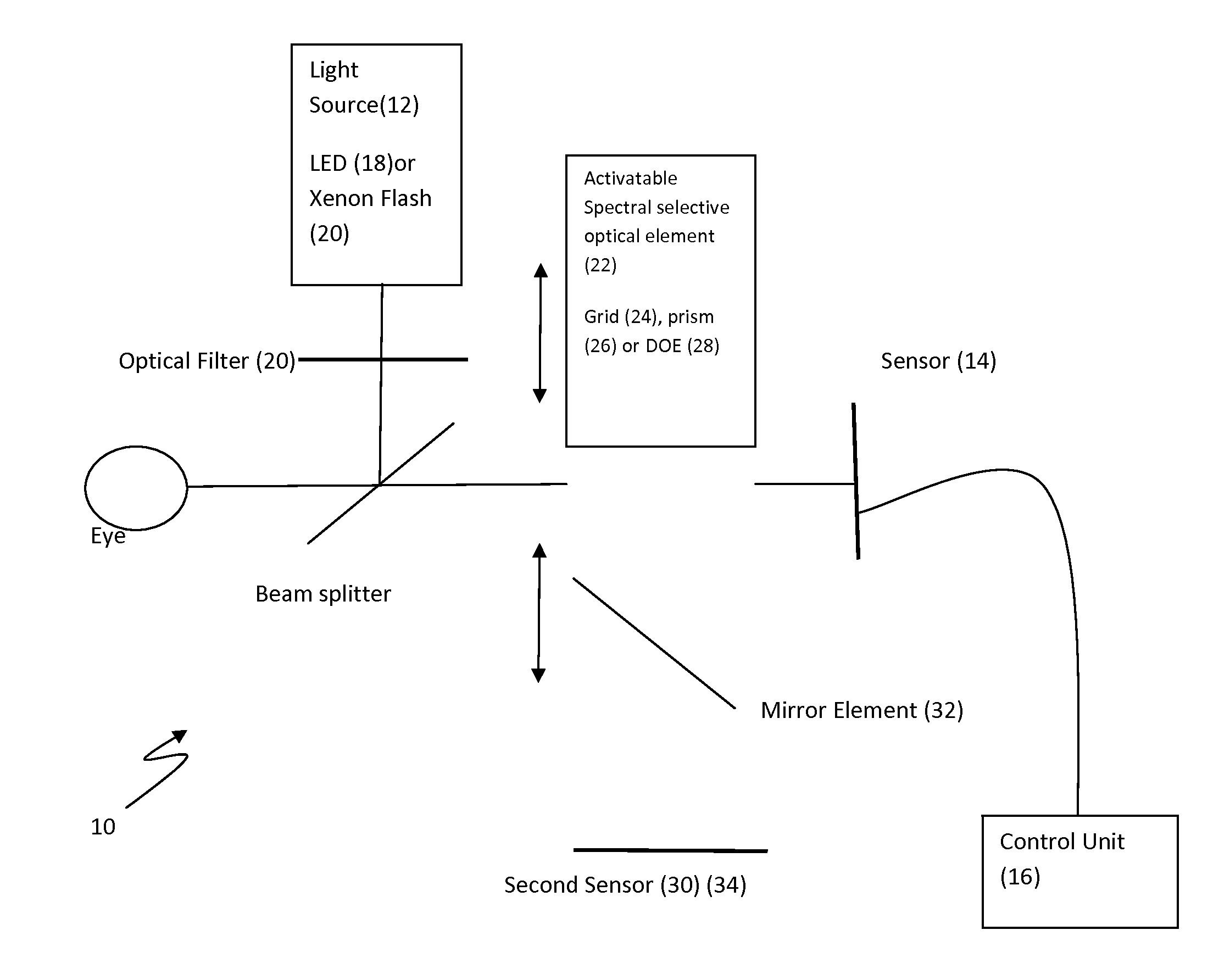
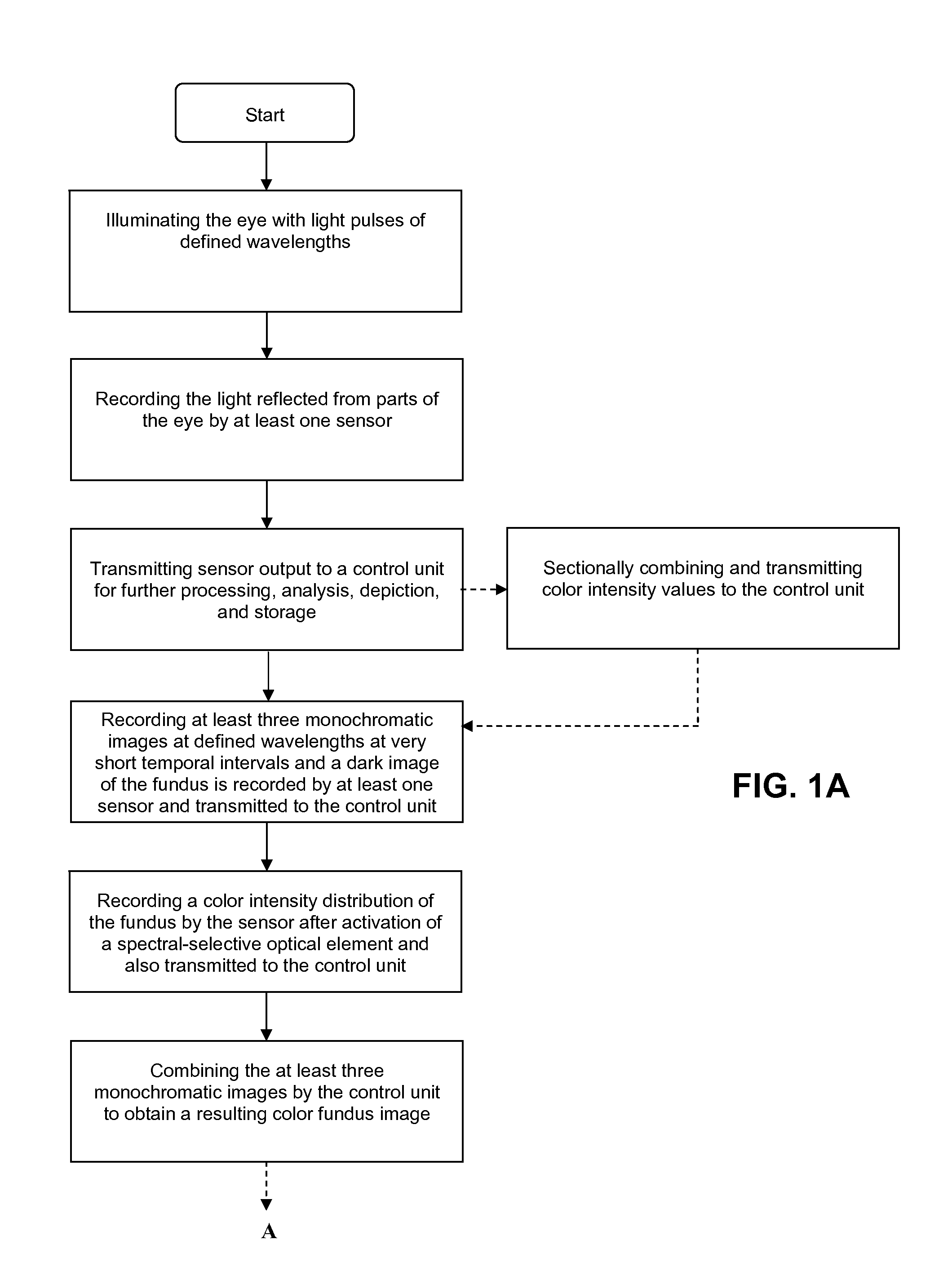
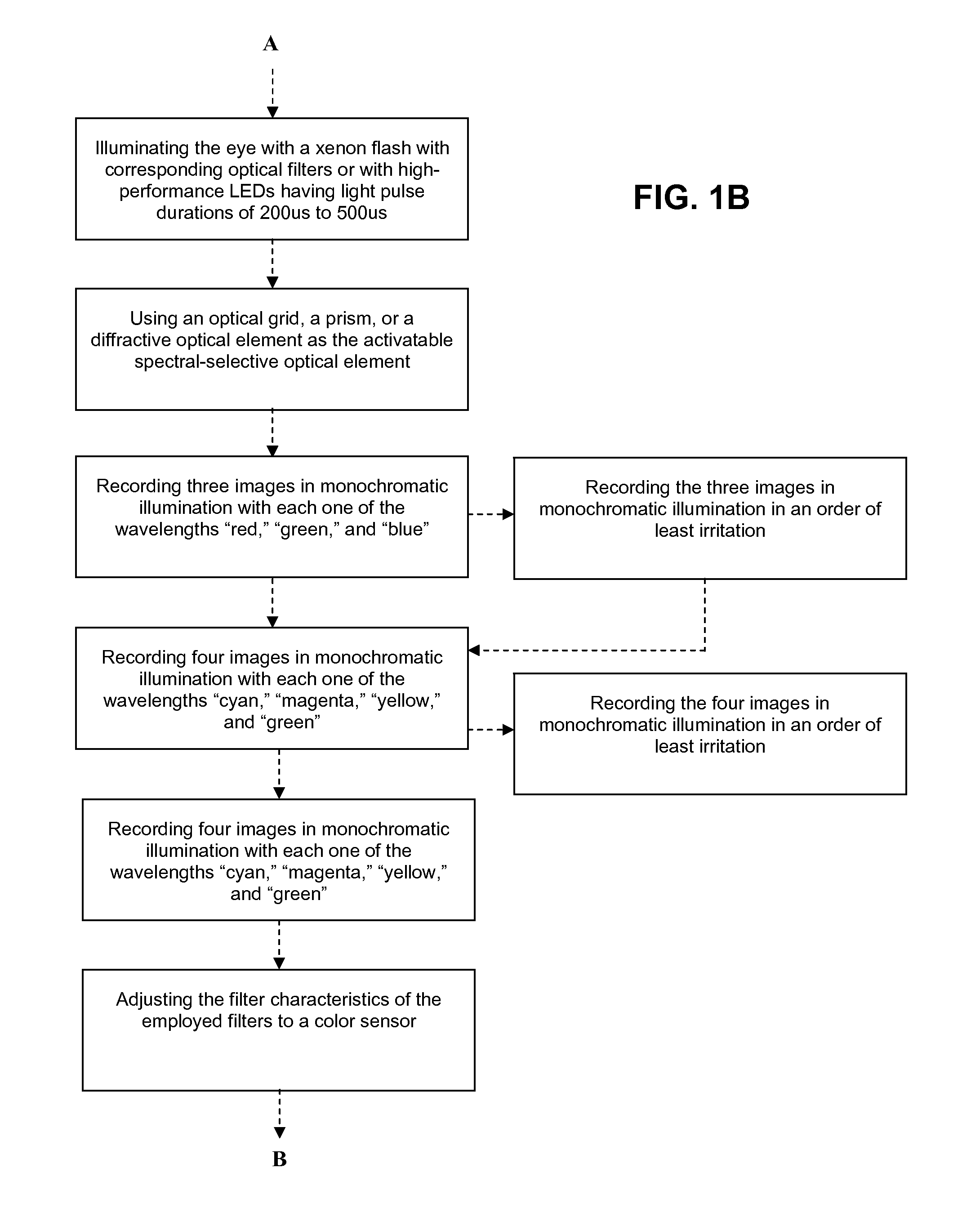
Method and device for producing high-quality fundus images
To produce a color fundus image, the eye is illuminated with light pulses of defined wavelengths. Light reflected is recorded by a sensor and transmitted to a control unit. At least three monochromatic images at very short temporal intervals and a dark image of the fundus are recorded. After activation of a spectral-selective optical element, a color intensity distribution of the fundus is recorded by the sensor at white illumination. The monochromatic images are combined by the control unit to obtain a resulting color fundus image, wherein the color intensity distribution is used for the correction of color composition and the dark image is used for taking into account the noise of the sensor. The solution permits monitoring, documenting and / or diagnosing of the fundus and can also be executed with ophthalmological systems based on the principle of optical coherence and / or confocal imaging.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Patient-matched apparatus and methods for performing surgical procedures
ActiveUS9987024B2Eliminate relative motionPain can be reduced avoidedSurgical furnitureInternal osteosythesisSurgical departmentAnatomical feature
A system and method for developing customized apparatus, such as guides, for use in one or more surgical procedures is disclosed. The system and method incorporates a patient's unique anatomical features or morphology, which may be derived from capturing MRI data or CT data, to fabricate at least one custom apparatus or guide. According to a preferred embodiment, the customized apparatus comprises at least one patient-specific surface and or contour, which may be derived from MRI or CT data. Apparatus may be matched in duplicate and oriented around the patient's own anatomy, and may further provide any desired axial alignments or insertional trajectories. In an alternate embodiment, the apparatus may further be aligned and / or matched with at least one other apparatus during the surgical procedure.
Owner:MIGHTY OAK MEDICAL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com