Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44 results about "Digital mammography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Digital mammography is a specialized form of mammography that uses digital receptors and computers instead of x-ray film to help examine breast tissue for breast cancer. The electrical signals can be read on computer screens, permitting more manipulation of images to theoretically allow radiologists to more clearly view the results. Digital mammography may be "spot view", for breast biopsy, or "full field" for screening. Digital mammmography is also utilized in stereotactic biopsy. Breast biopsy may also be performed using a different modality, such as ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging. While radiologists had hoped for more marked improvement, the effectiveness of digital mammography was found comparable to traditional x-ray methods in 2004, though there may be reduced radiation with the technique and it may lead to fewer retests. Specifically, it performs no better than film for post-menopausal women, who represent more than three-quarters of women with breast cancer. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force concluded that there was insufficient evidence to recommend for or against digital mammography.
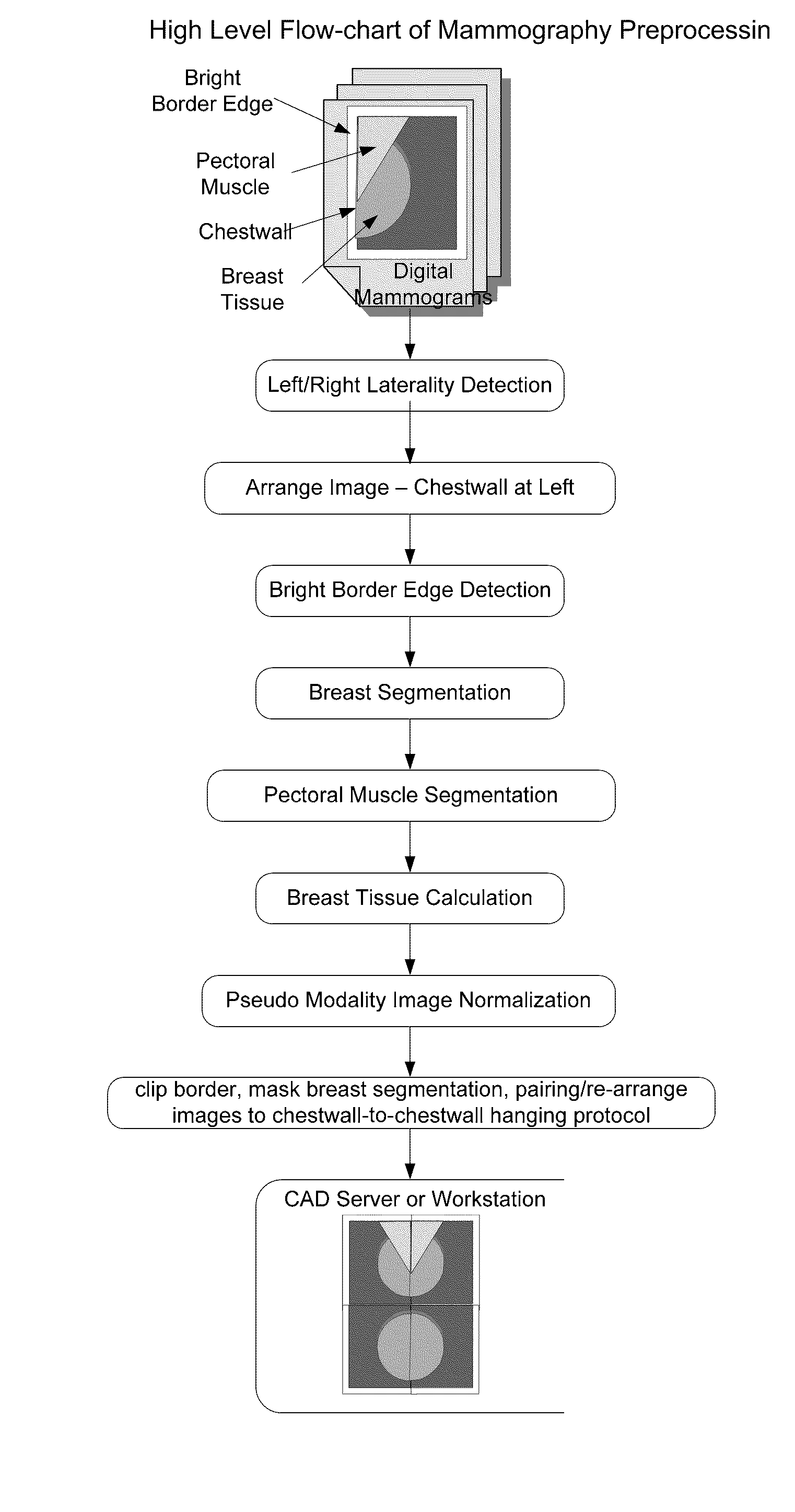
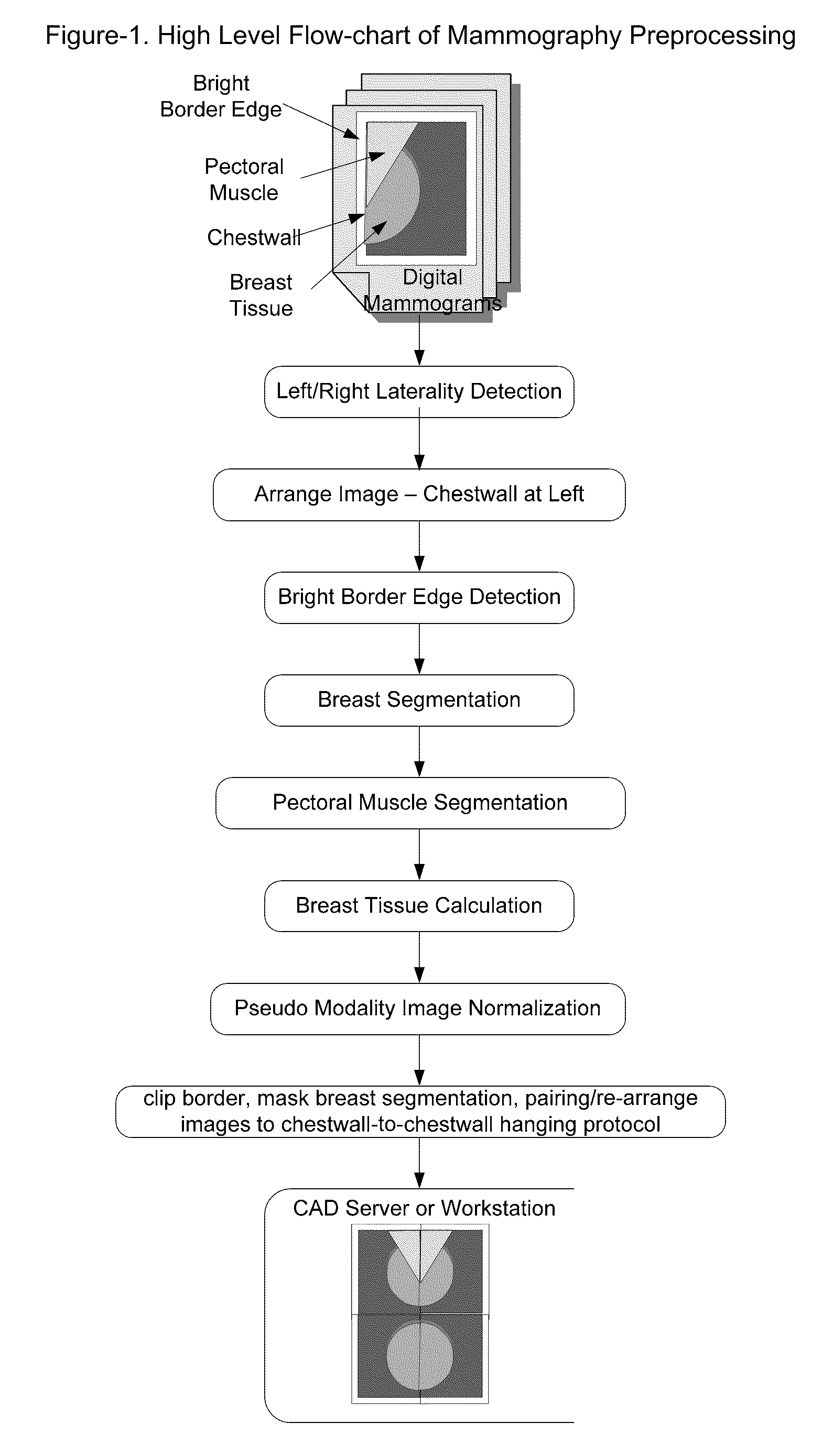
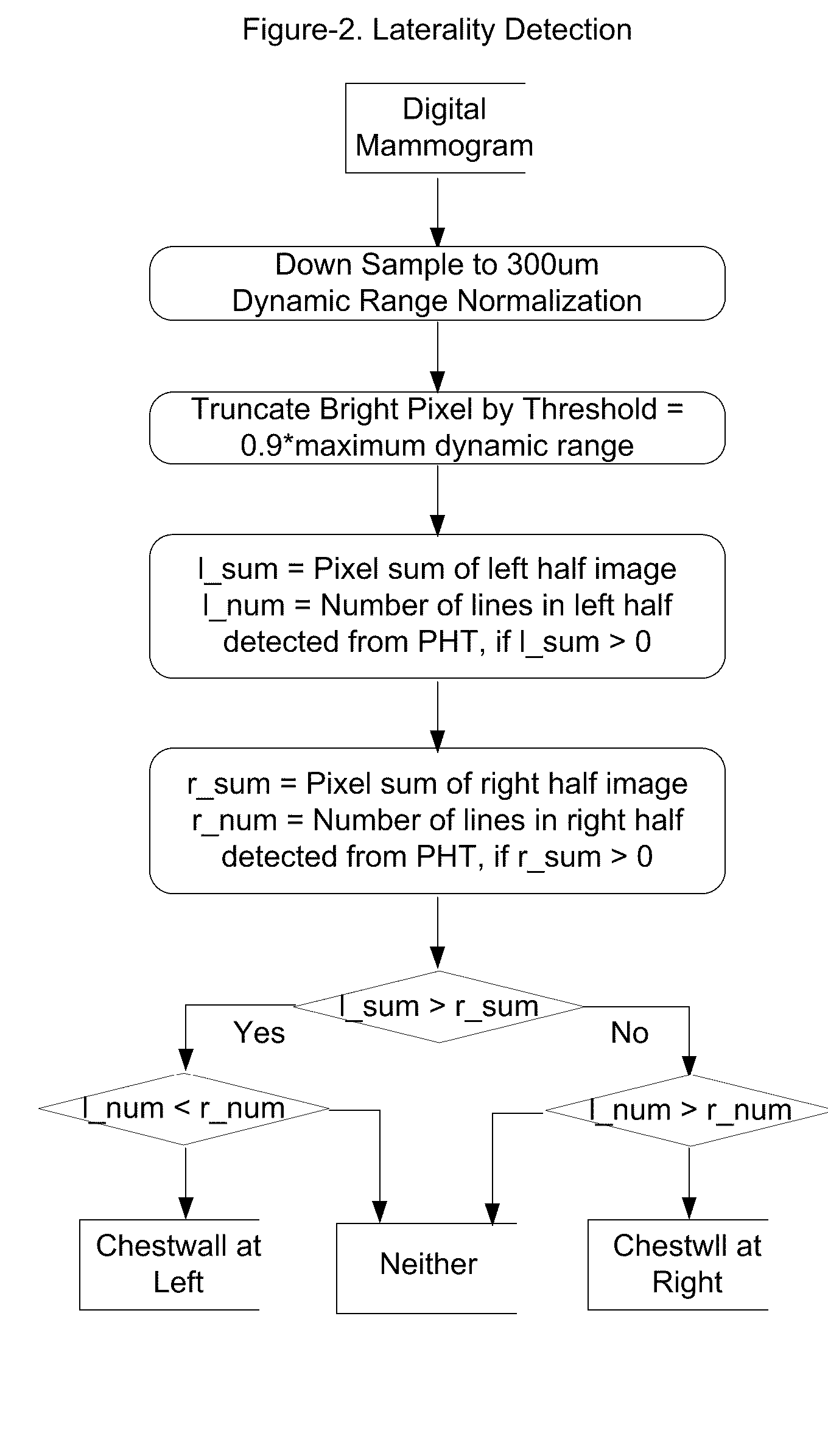
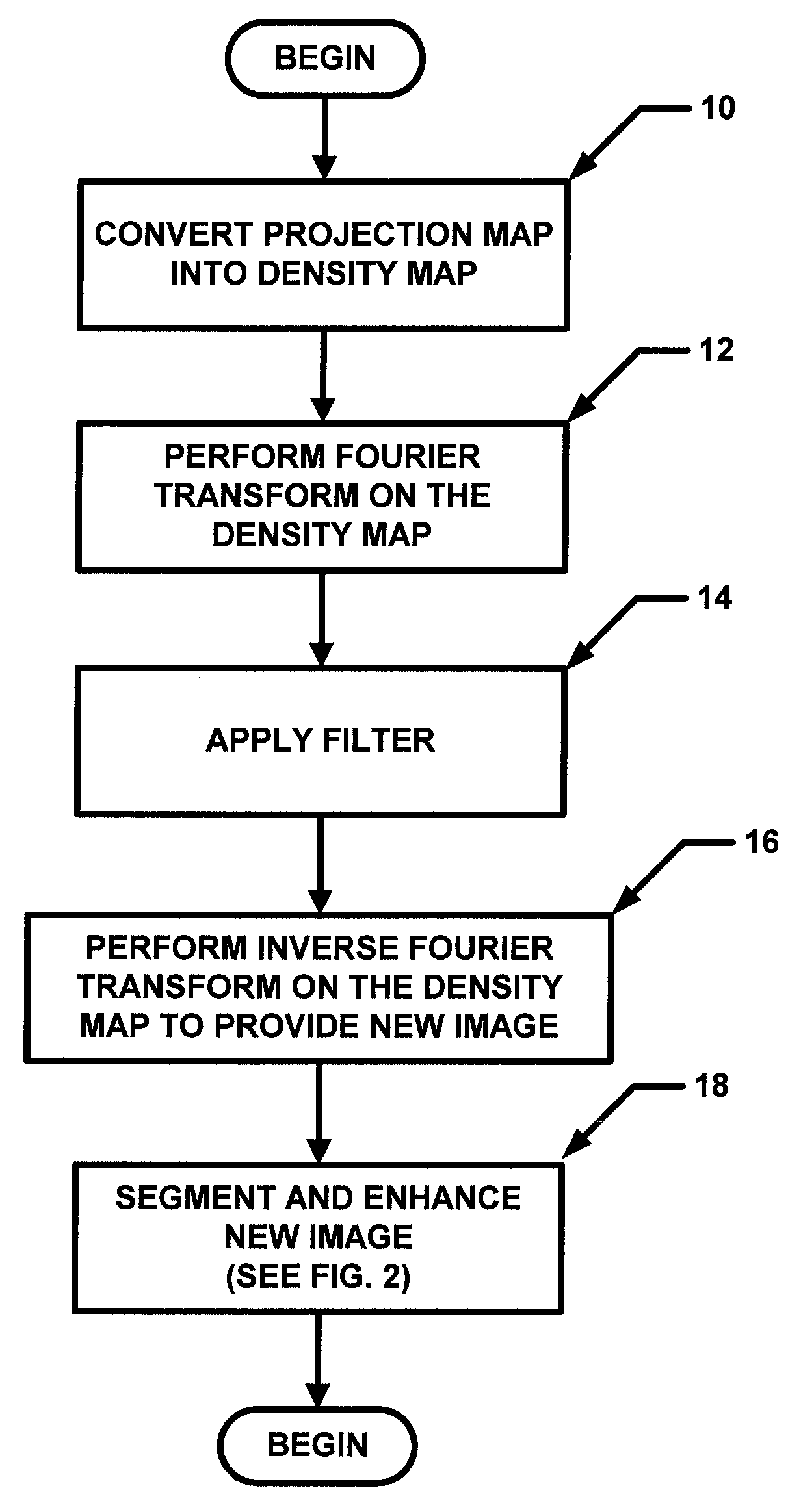
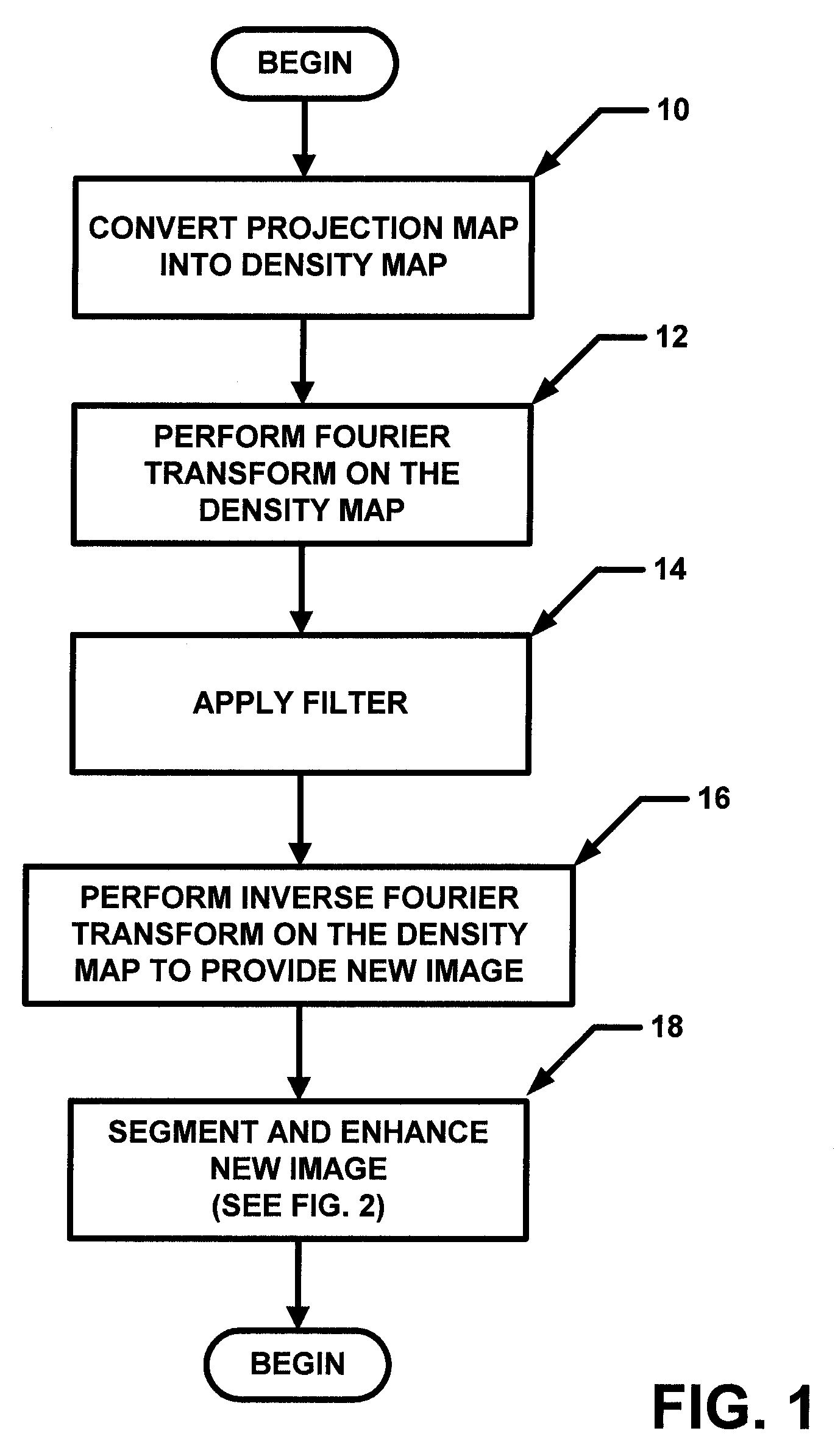
Fast preprocessing algorithms for digital mammography CAD and workstation
ActiveUS20090220138A1Faster and accurate segmentation algorithmAutomatic detectionImage enhancementImage analysisDigital mammographyImage contrast
A method and apparatus are disclosed for an image preprocessing device that automatically detects chestwall laterality; removes border artifacts; and segments breast tissue and pectoral muscle from digital mammograms. The algorithms in the preprocessing device utilize the computer cache, a vertical Sobel filter and a probabilistic Hough transform to detect curved edges. The preprocessing result, along with a pseudo-modality normalized image, can be used as input to a CAD (computer-aided detection) server or to a mammography image review workstation. In the case of workstation input, the preprocessing results improve the protocol for chestwall-to-chestwall image hanging, and support optimal image contrast display of each segmented region.
Owner:THREE PALM SOFTWARE
Computer aided detection (CAD) for 3D digital mammography
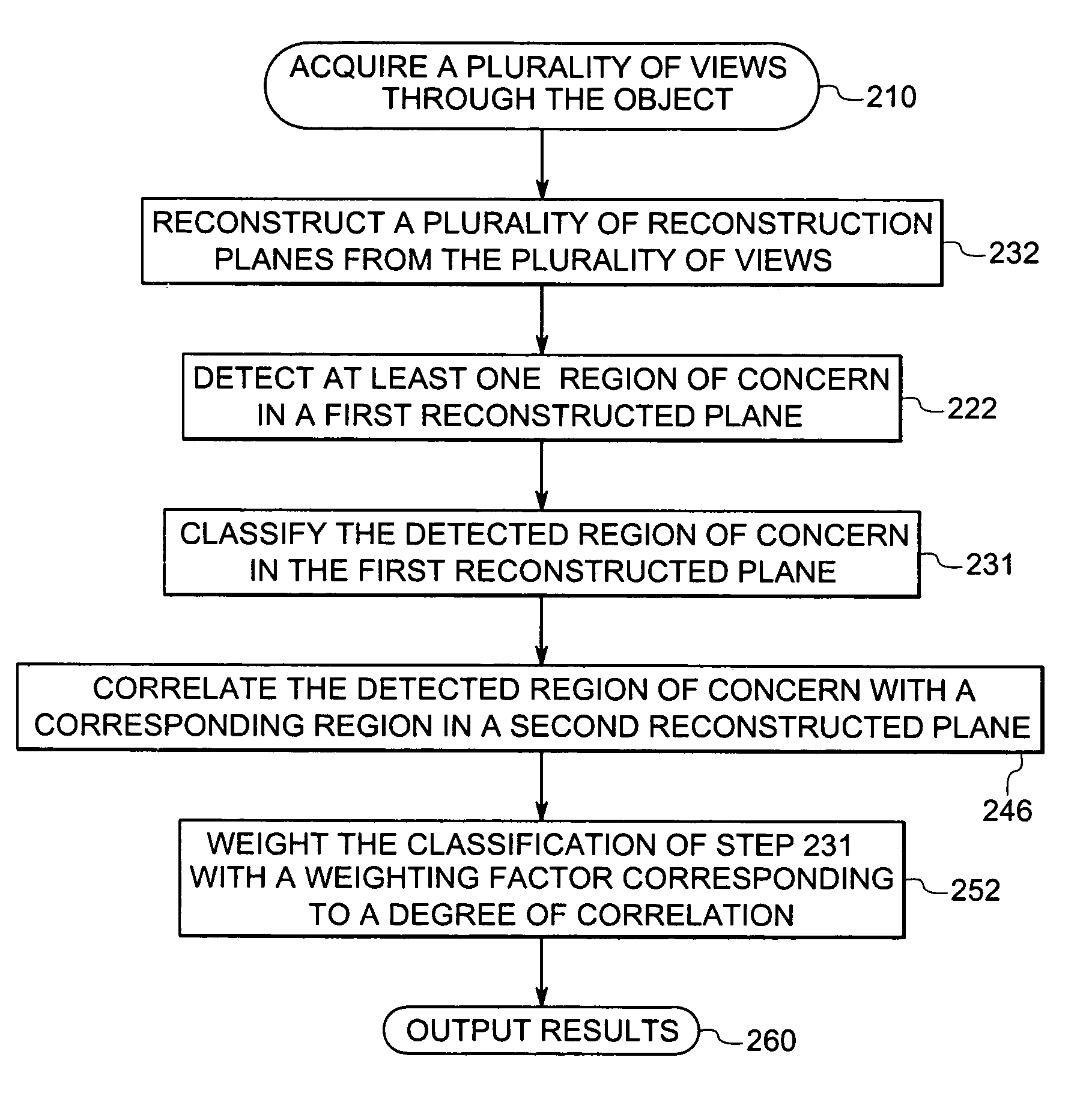
ActiveUS7218766B2Solve lack of contrastReduce contrastUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementDigital mammographyComputer vision
There is provided a method of analyzing a plurality of views of an object, the object including an edge portion partially extending from a surface of the object into an internal volume of the object, comprising the step of analyzing each acquired view. The step of analyzing each acquired view includes analysis of the edge portion. Preferably, the object comprises breast tissue.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
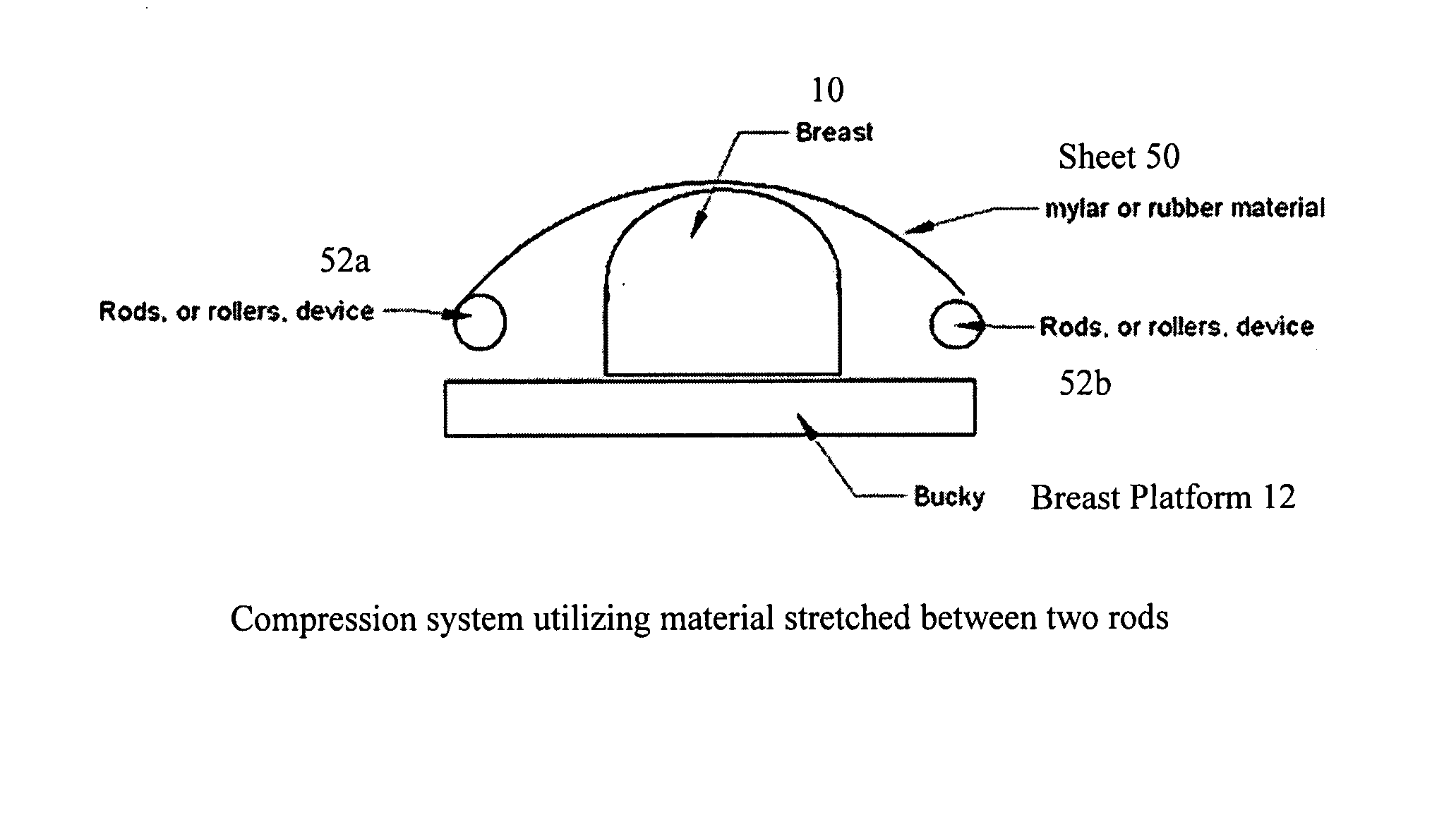
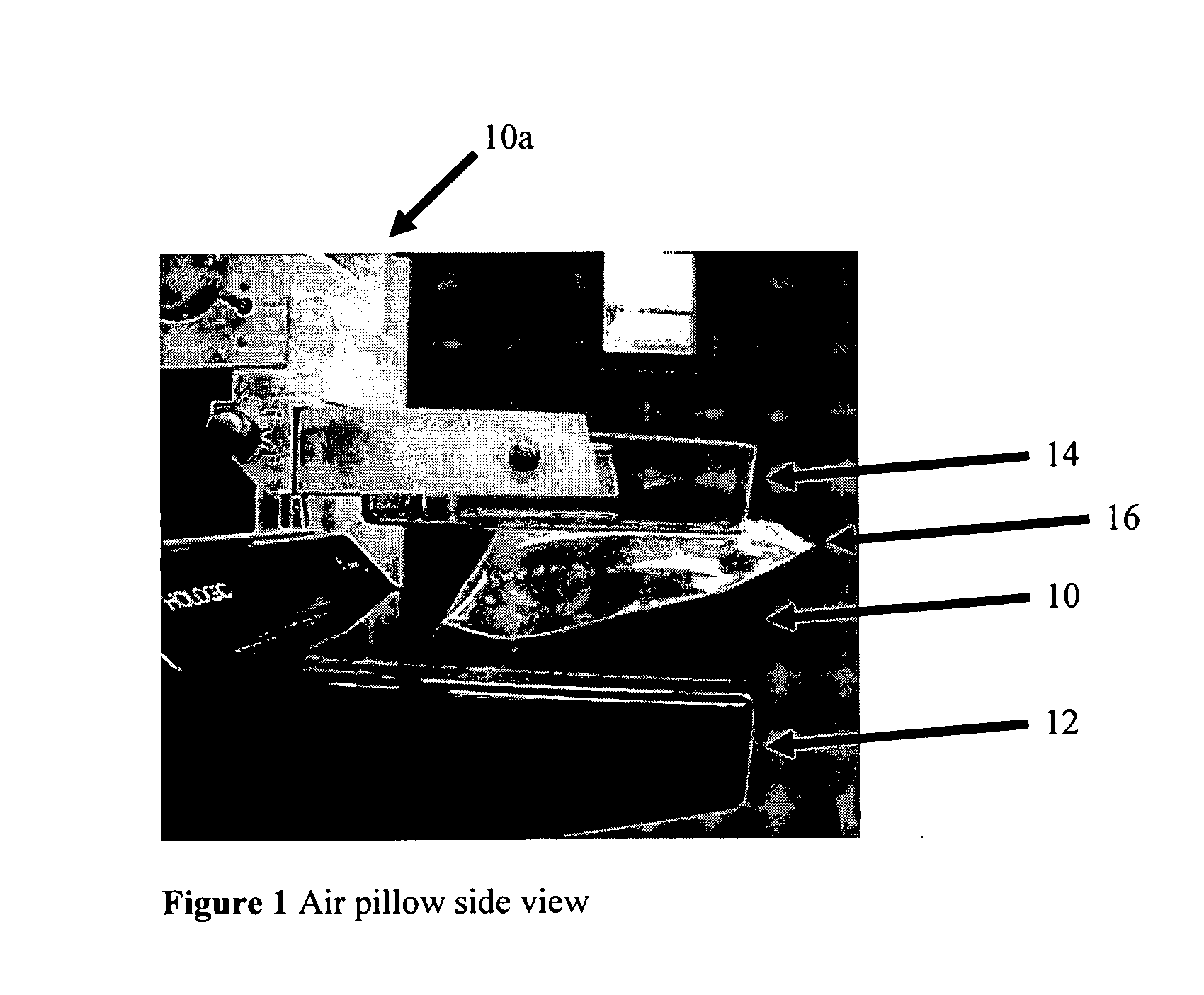
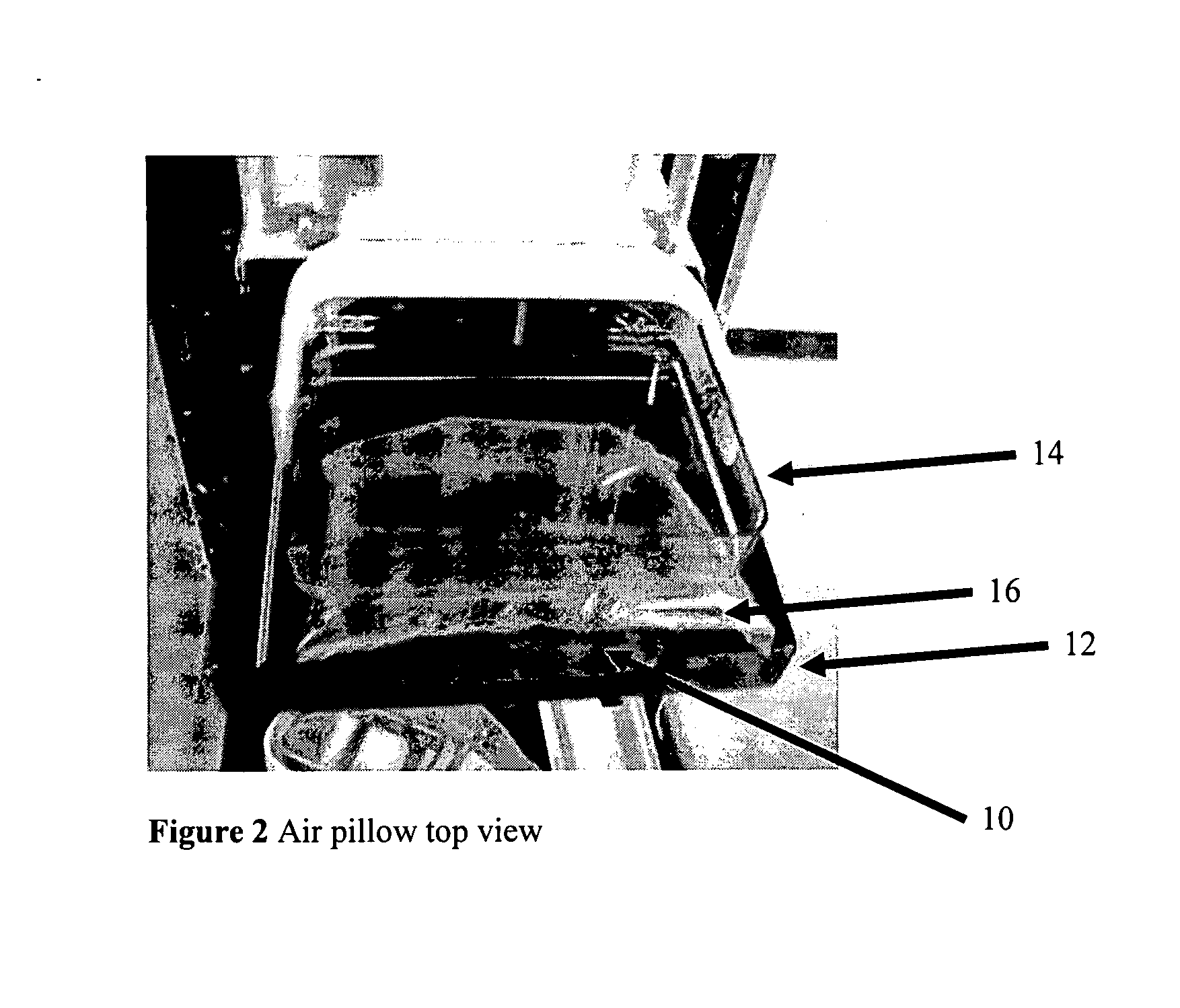
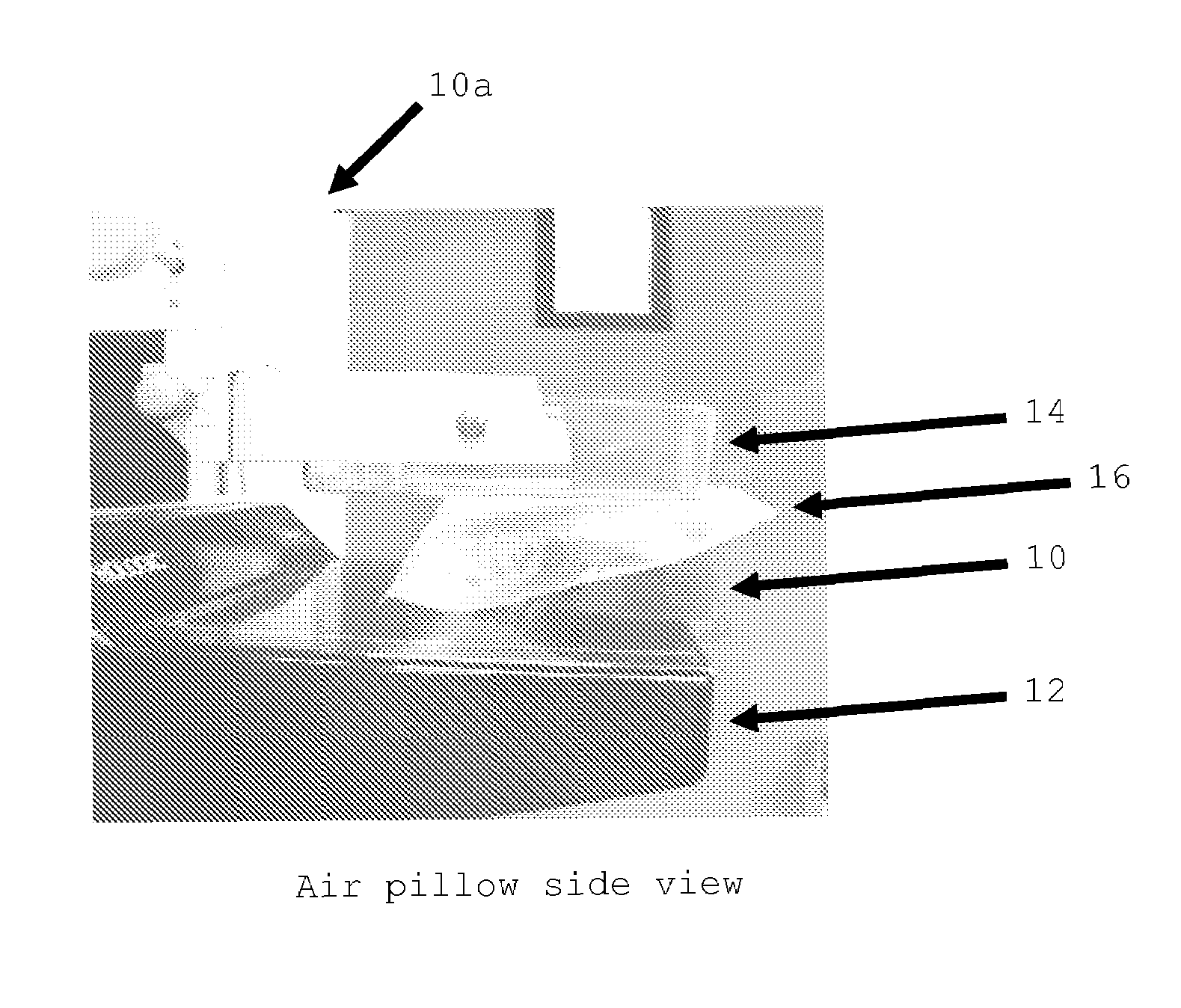
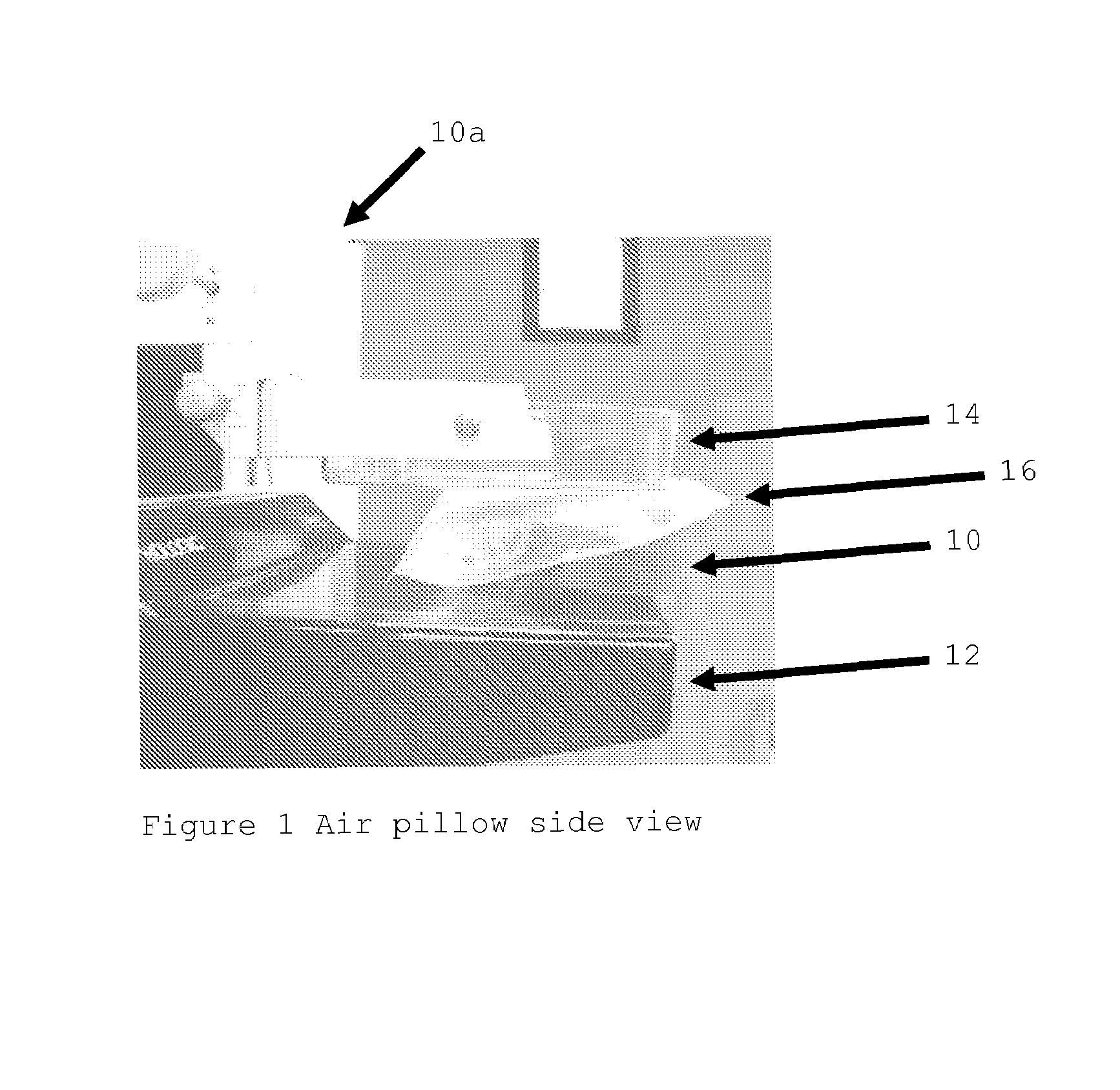
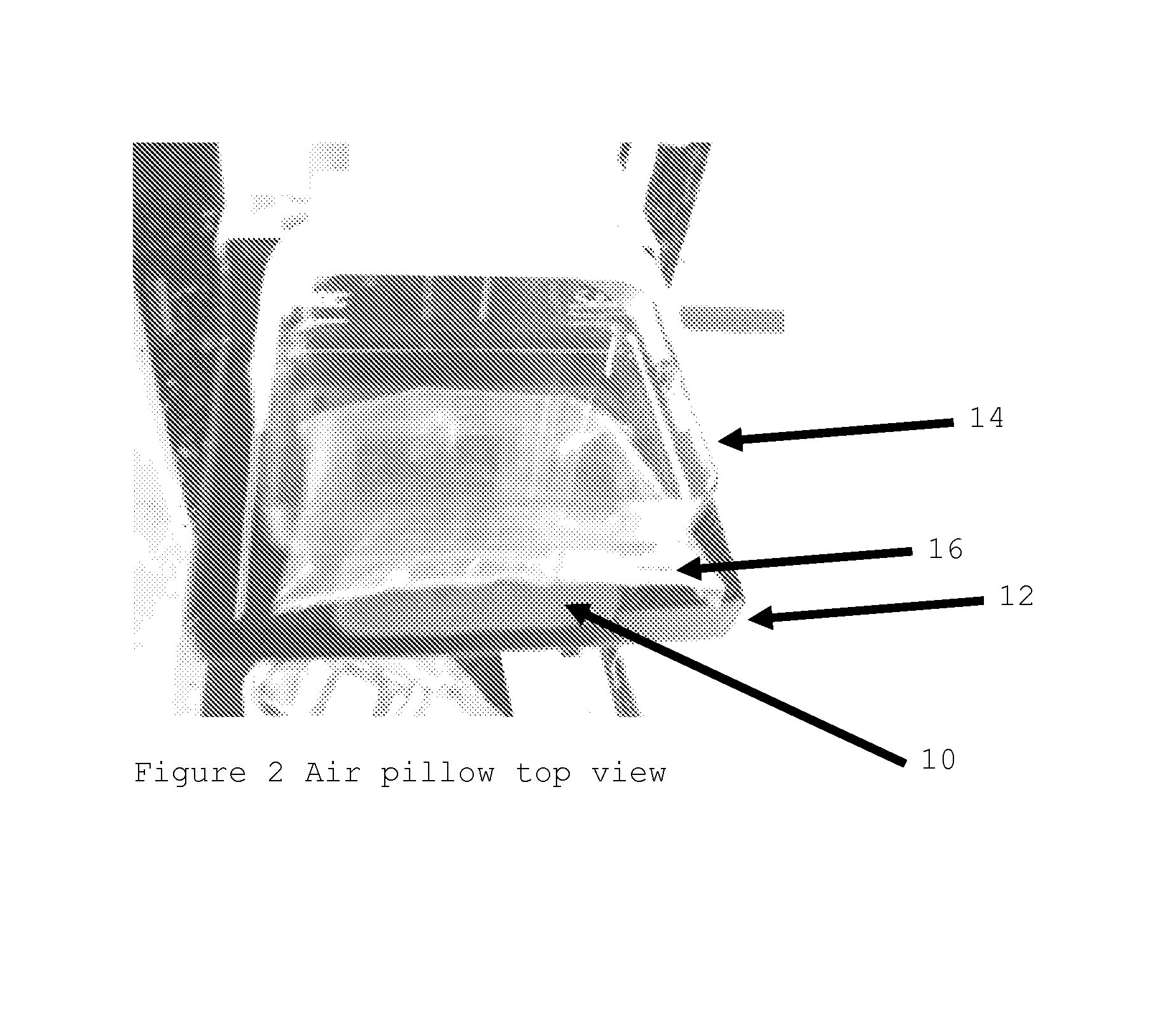
Breast compression for digital mammography, tomosynthesis and other modalities
ActiveUS20070280412A1Spread out the breast tissuesReduce radiation exposureTomosynthesisPatient positioning for diagnosticsTomosynthesisDigital mammography
A breast x-ray imaging method and system that is particularly suited for tomosynthesis imaging but also is useful for conventional mammography. A fluid containing pillow or bag is placed between the breast and a paddle that compresses the breast against a breast platform covering an imaging device, to enhance patient comfort and provide other benefits. Alternatives include a flexible sheet compressing the breast, and a compressible foam, preferably contoured to accommodate a patient's breast.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
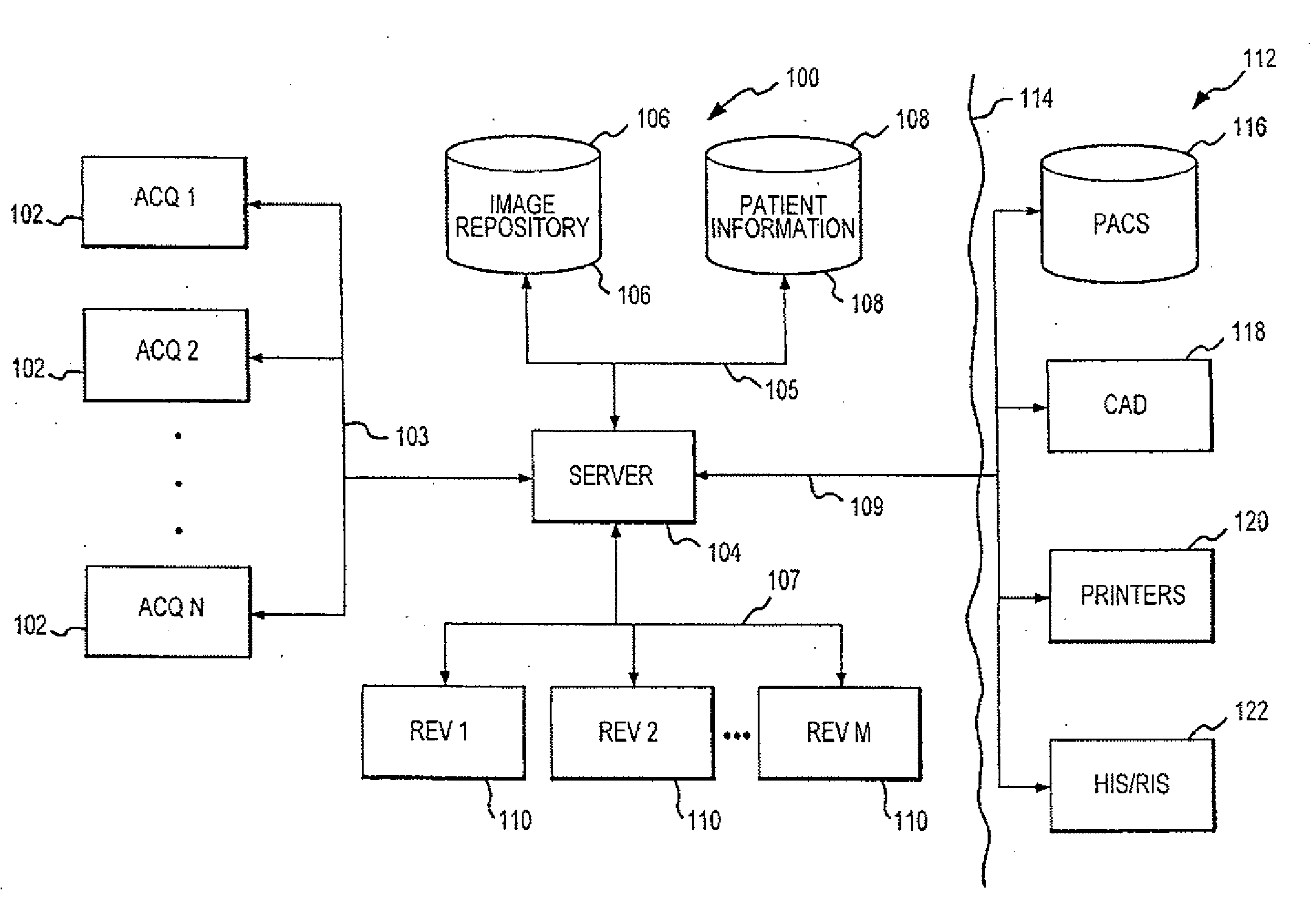
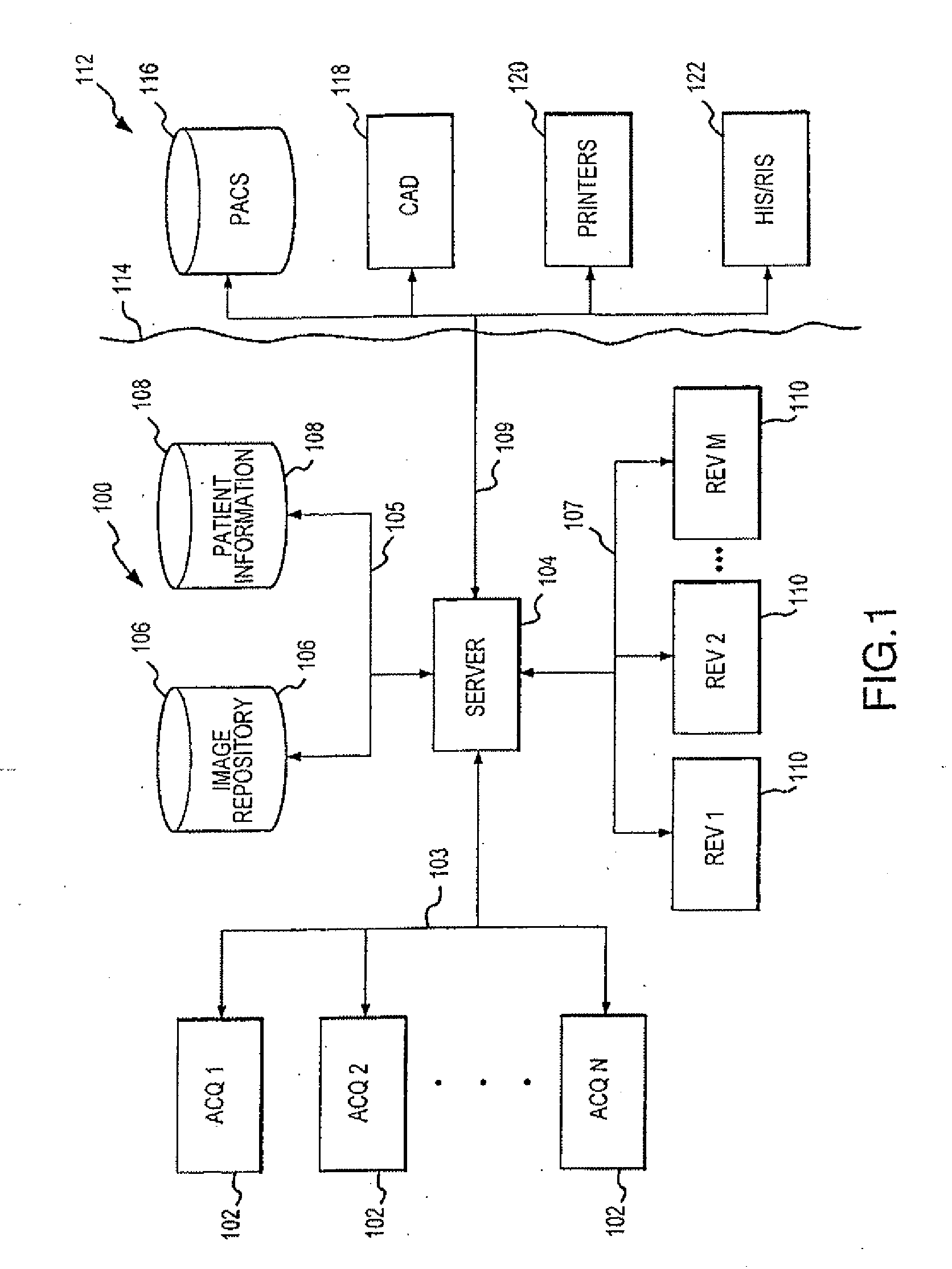
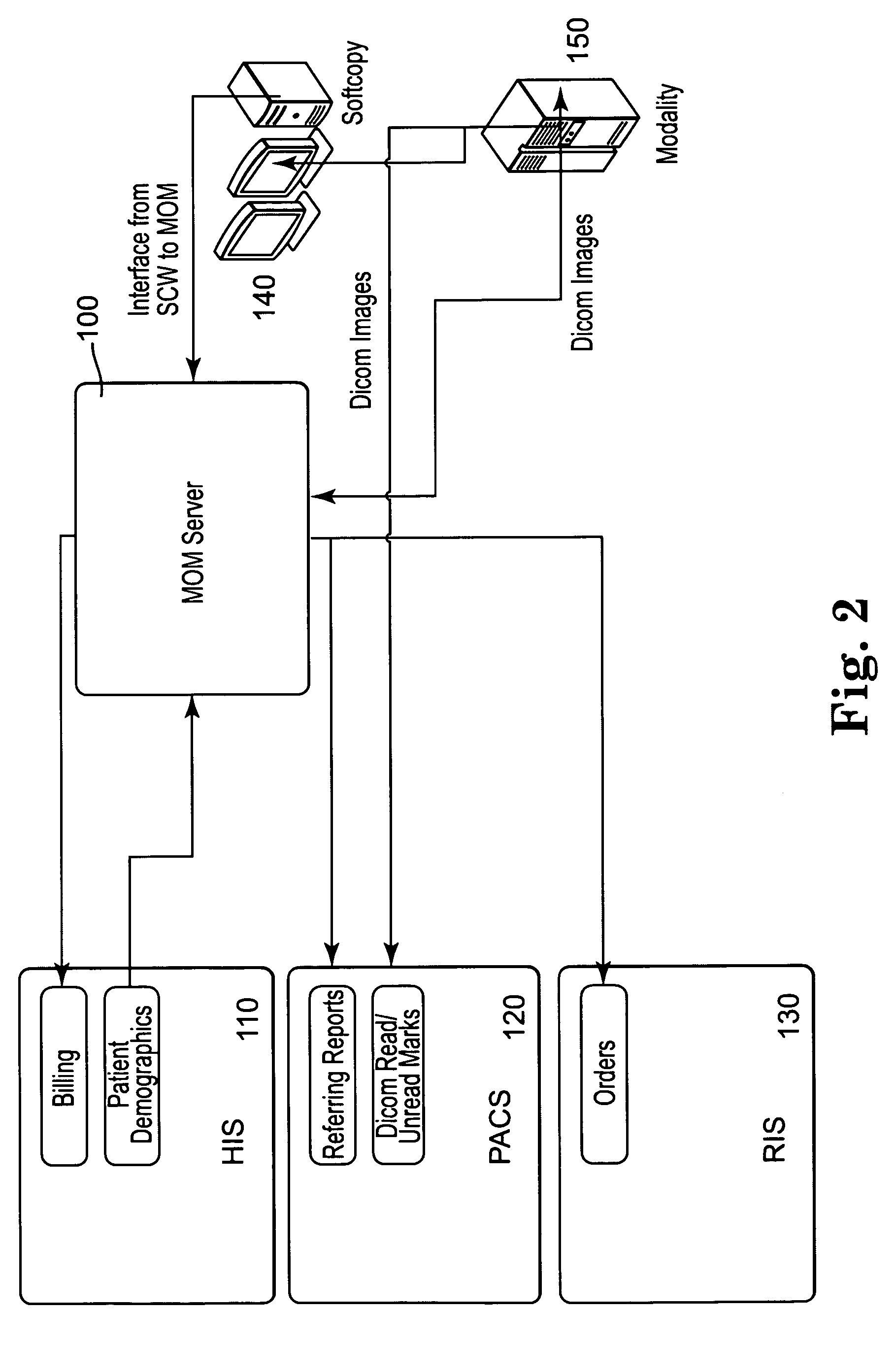
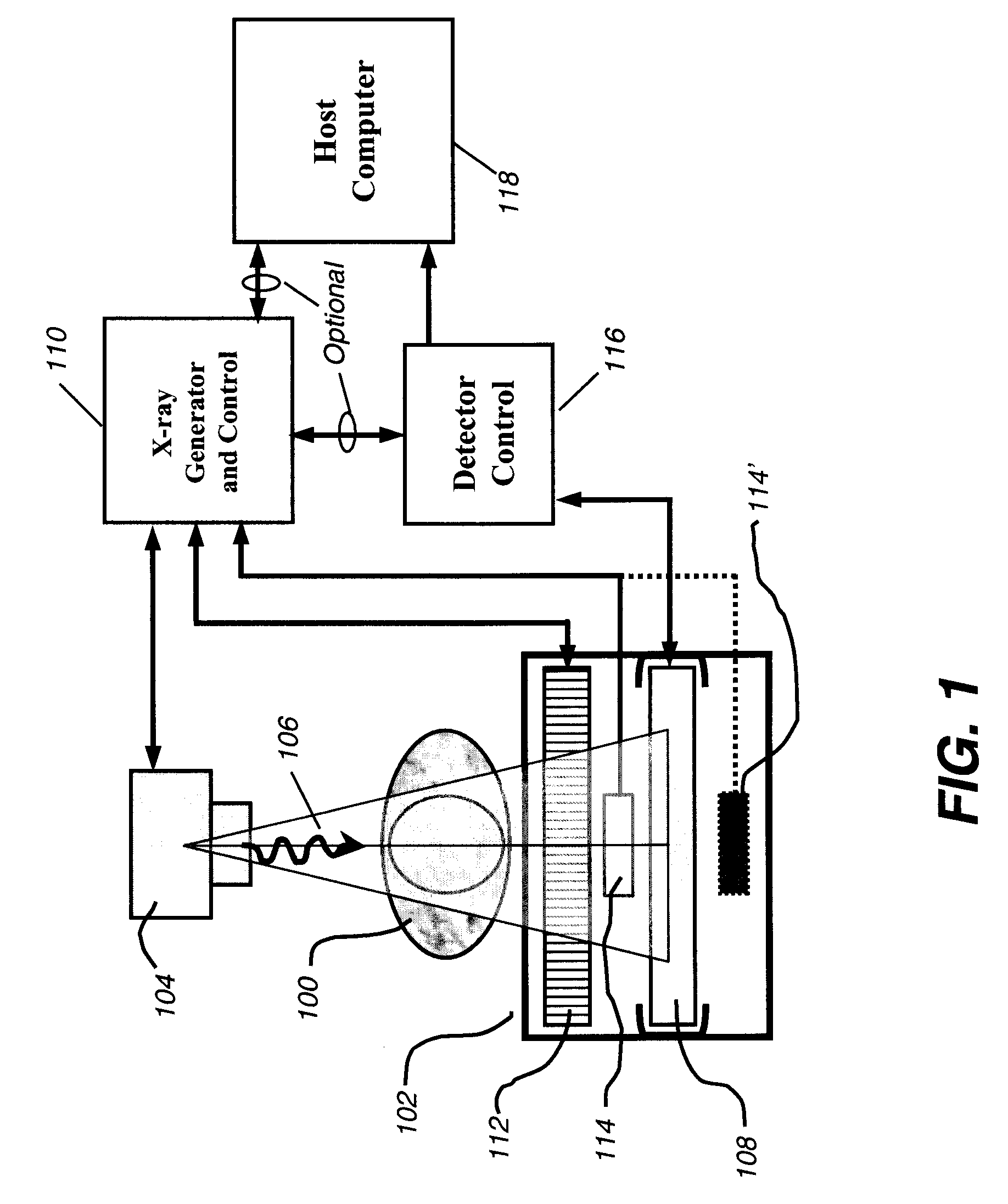
Distributed Architecture for Mammographic Image Acquisition and Processing
InactiveUS20080279439A1Easy to useOrgan movement/changes detectionPatient positioning for diagnosticsImage InspectionDICOM
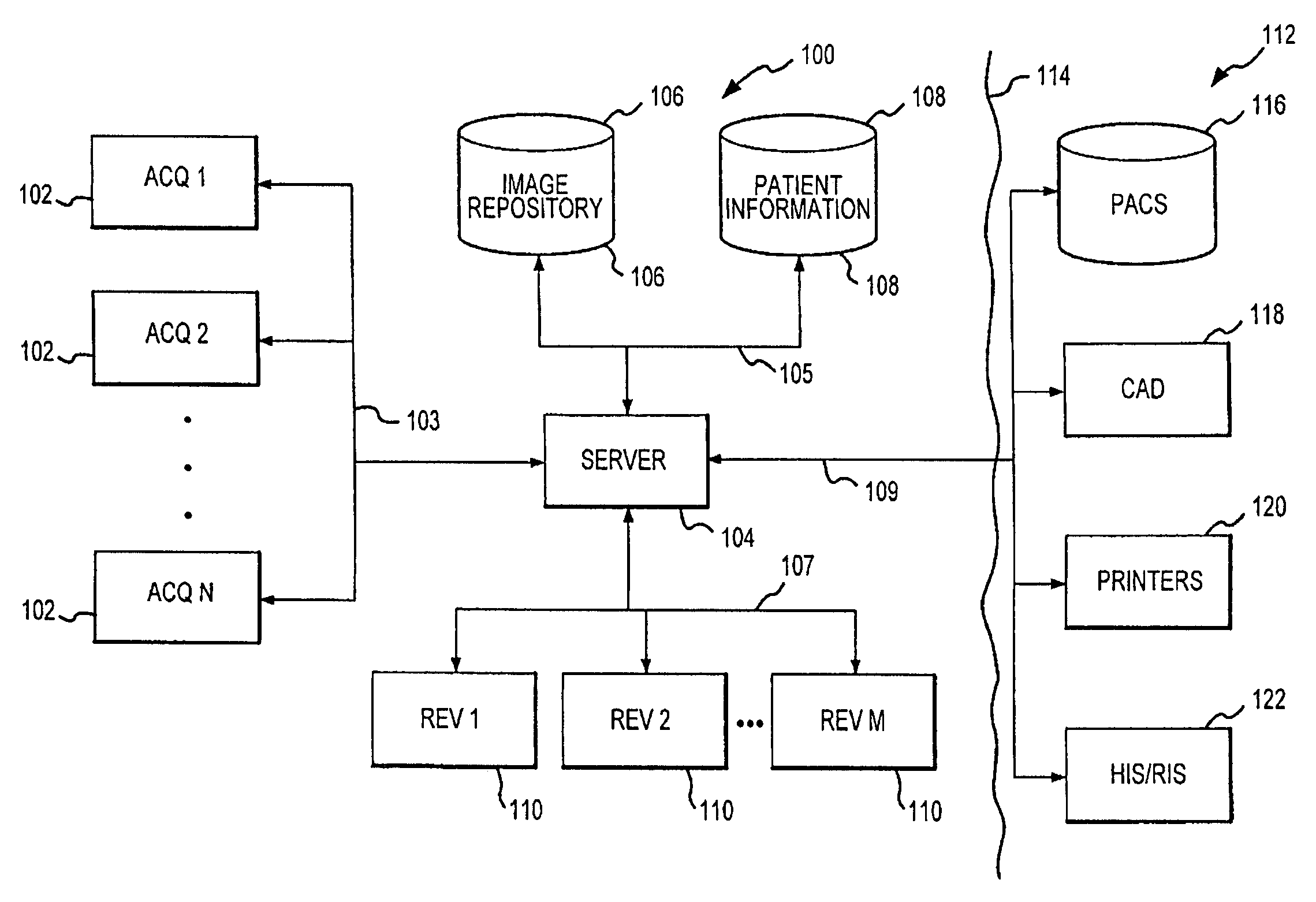
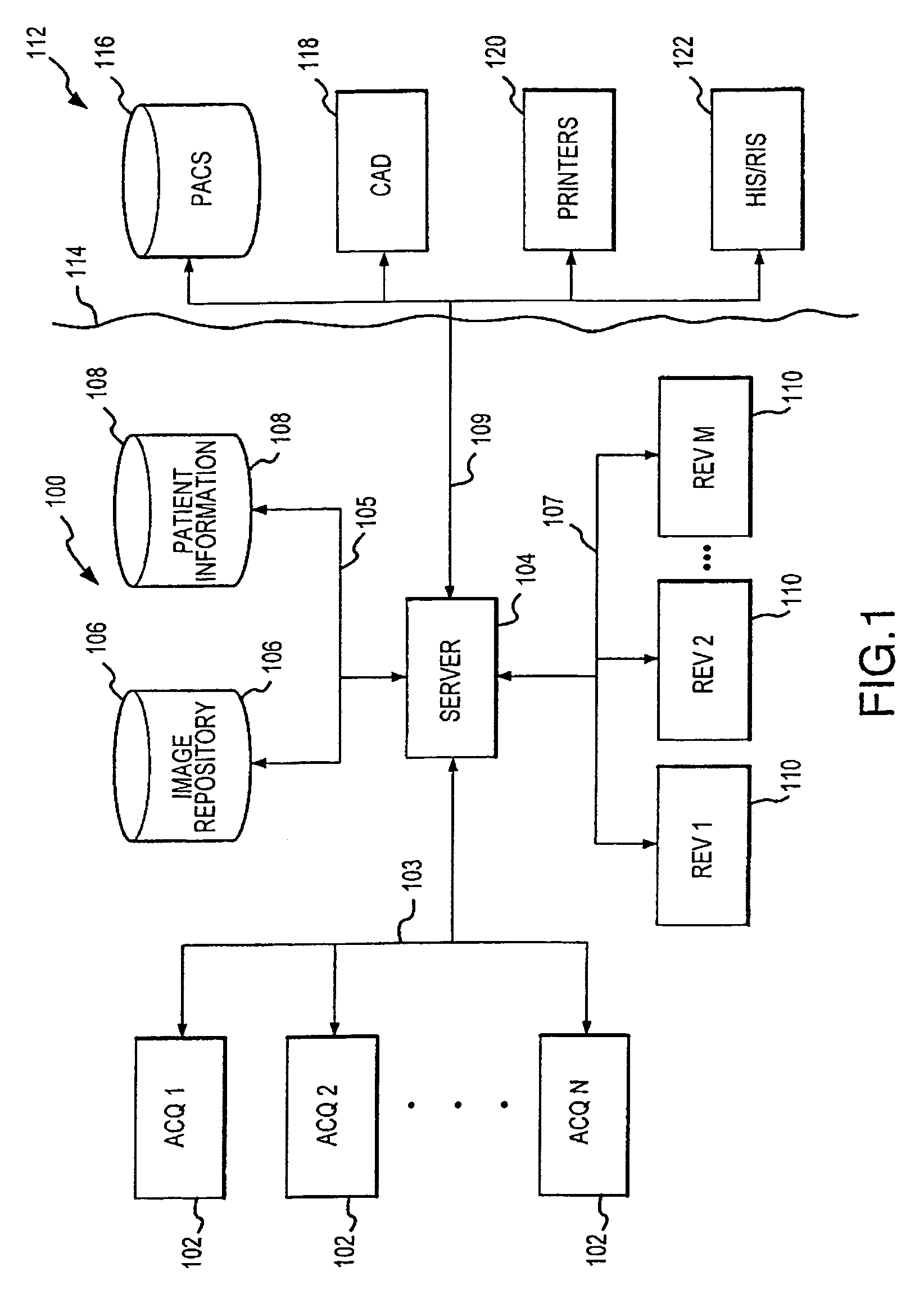
A distributed architecture allows for decoupling of mammographic image acquisition and review, thereby enabling more efficient use of resources and enhanced processing. In one embodiment, the system (100) includes a number of image acquisition stations (102) and a number of image review stations (110) all associated with a central server (104). The server (104) is operative to access an image repository (106), a patient information data base (108) and a number of DICOM tools (112). The invention allows for more efficient and / or more convenient use of the image acquisition equipment and image processing stations. Moreover, the distributed architecture including the central image repository provides certain processing and analysis advantages. The invention also provides certain processing and workflow enhancements that allow for a more full realization of potential digital mammography advantages.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
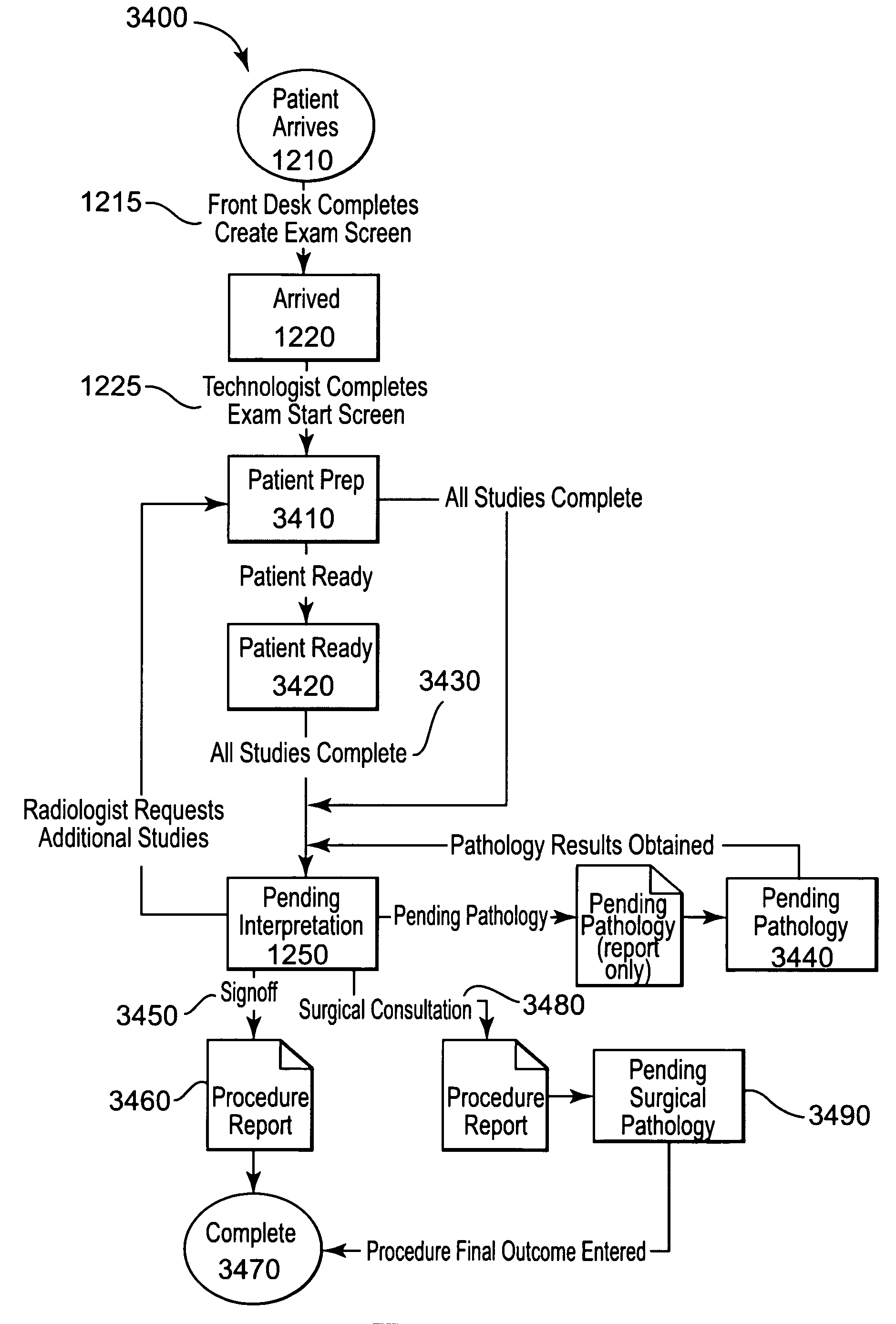
Mammography operational management system and method
InactiveUS20060212317A1Character and pattern recognitionMedical report generationDigital mammographyScreening Examination
In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, a method in a computer system is provided for managing mammography examination information. The method includes receiving electronically personal information of a patient, such as name, demographic information, and insurance information. Next, digital mammography images of the patient are produced by a modality for a screening examination and / or diagnostic examination, and mammography procedure results data is generated that reflect the results of a procedure examination, such as a biopsy. Then, the personal information, digital images, and procedure data of the user are stored in a database and are logically linked to each other. When a system user, such as a radiologist, is prepared to interpret examination results, the digital images and procedure data of the user are electronically displayed to the user responsive to a user request. At least a first portion of the digital images is electronically retrieved from the database, and at least a second portion of the digital images is retrieved from a Picture Archive and Communications System (PACS). Data from the user representing a medical interpretation of the digital images and procedure data are received, and a medical report based on the medical interpretation is automatically generated responsive to receipt of the interpretation.
Owner:NU DESIGN MEDICAL TECH
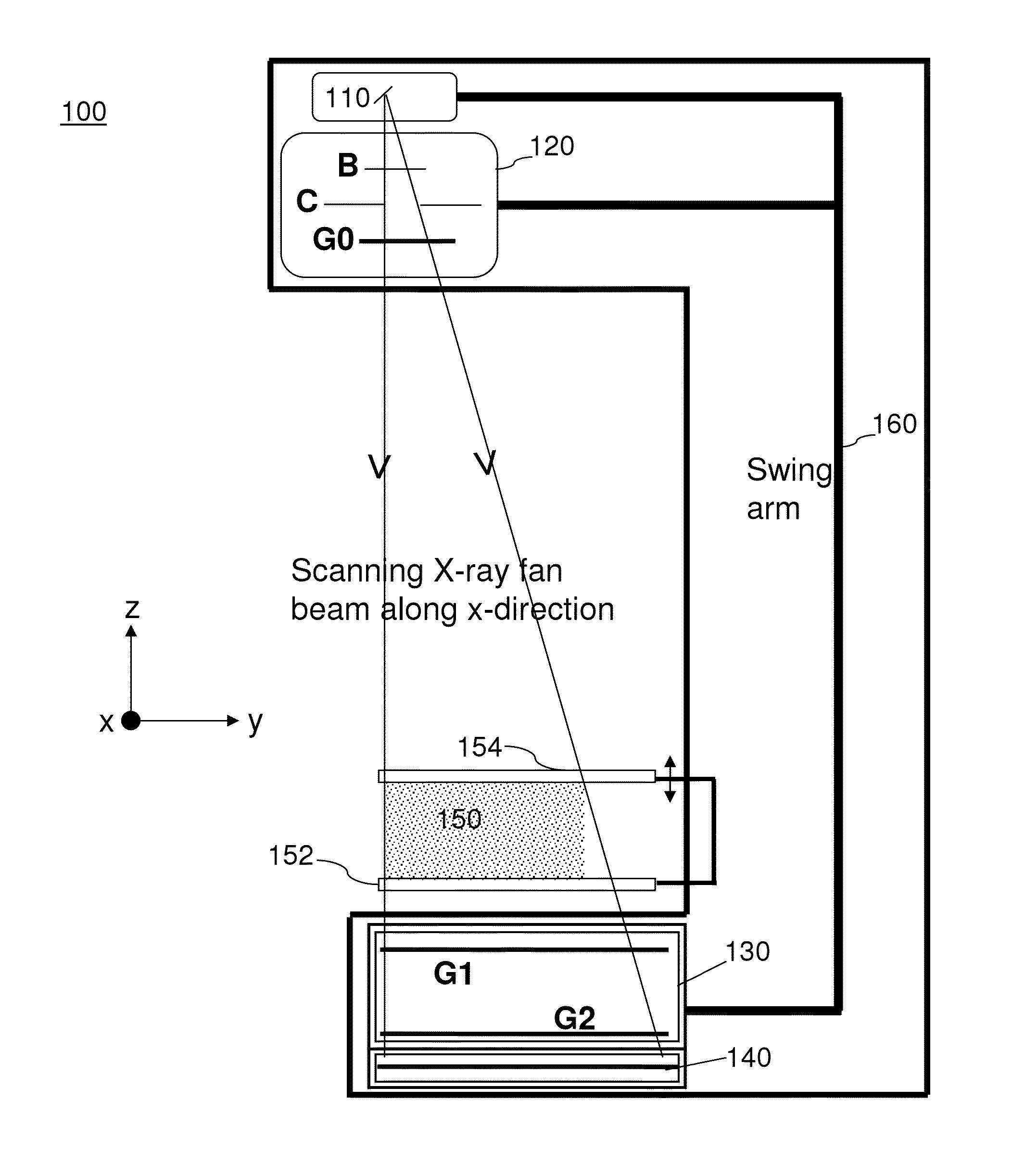
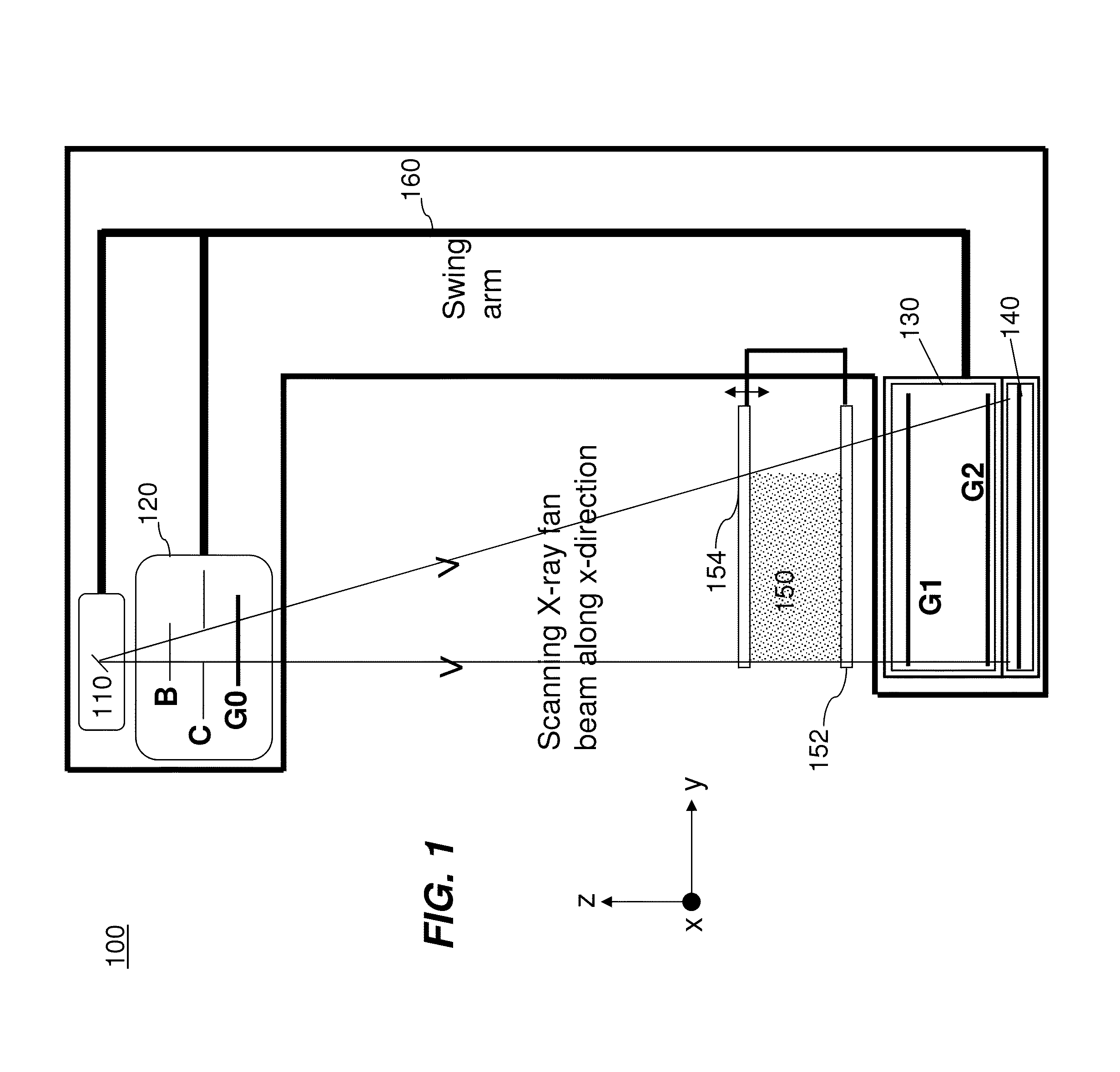
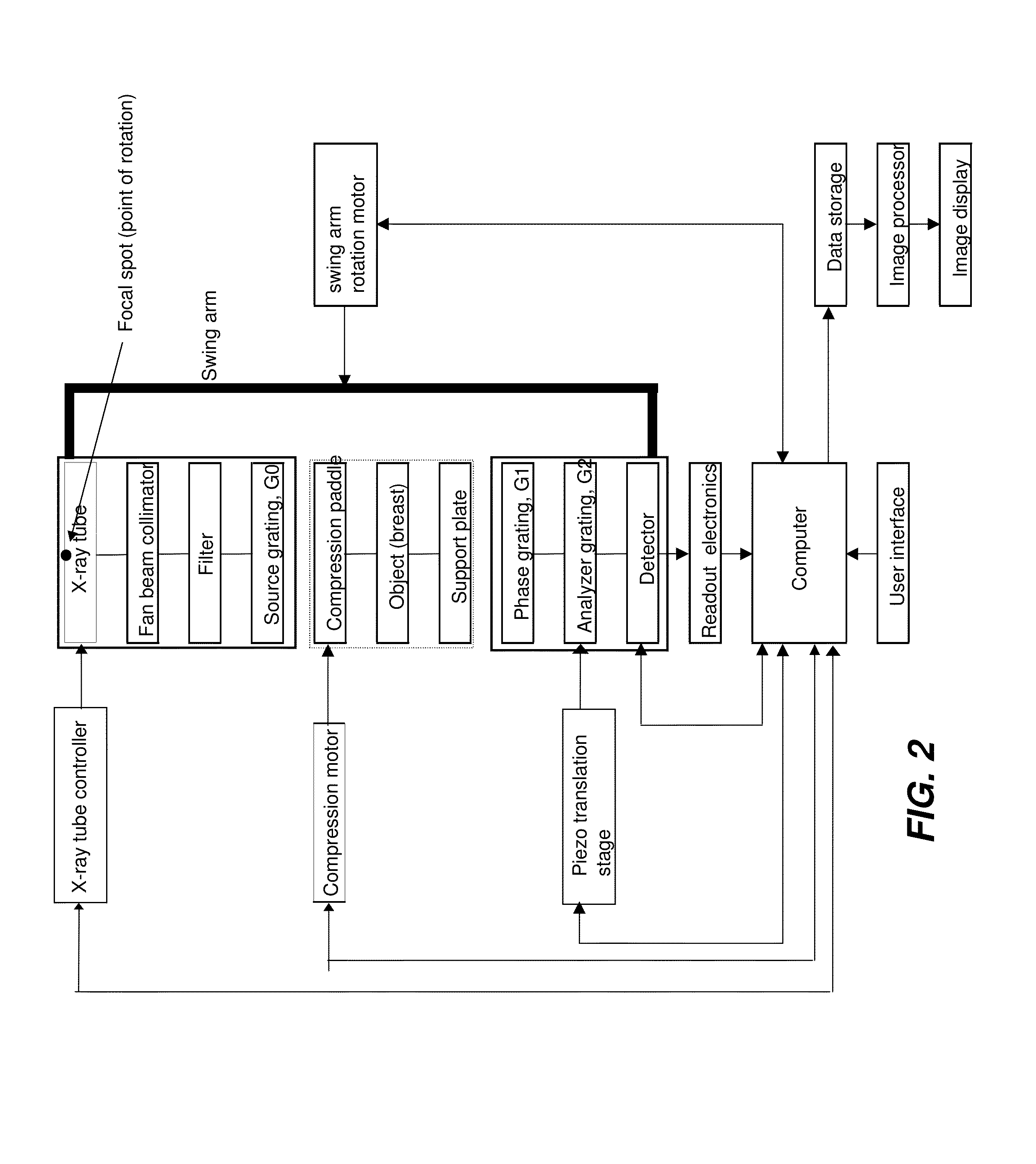
Hybrid slot-scanning grating-based differential phase contrast imaging system for medical radiographic imaging
InactiveUS20130259194A1Imaging devicesPatient positioning for diagnosticsDigital mammographyBeam shaping
Embodiments of methods and apparatus are disclosed for obtaining a phase-contrast digital mammography system and methods for same that can include an x-ray source for radiographic imaging; a beam shaping assembly including a filter or a tunable monochromator, a collimator, a source grating, an x-ray grating interferometer including a phase grating, and an analyzer grating; and an x-ray detector; where the source grating, the phase grating, and the analyzer grating are aligned in such a way that the grating bars of these gratings are parallel to each other.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
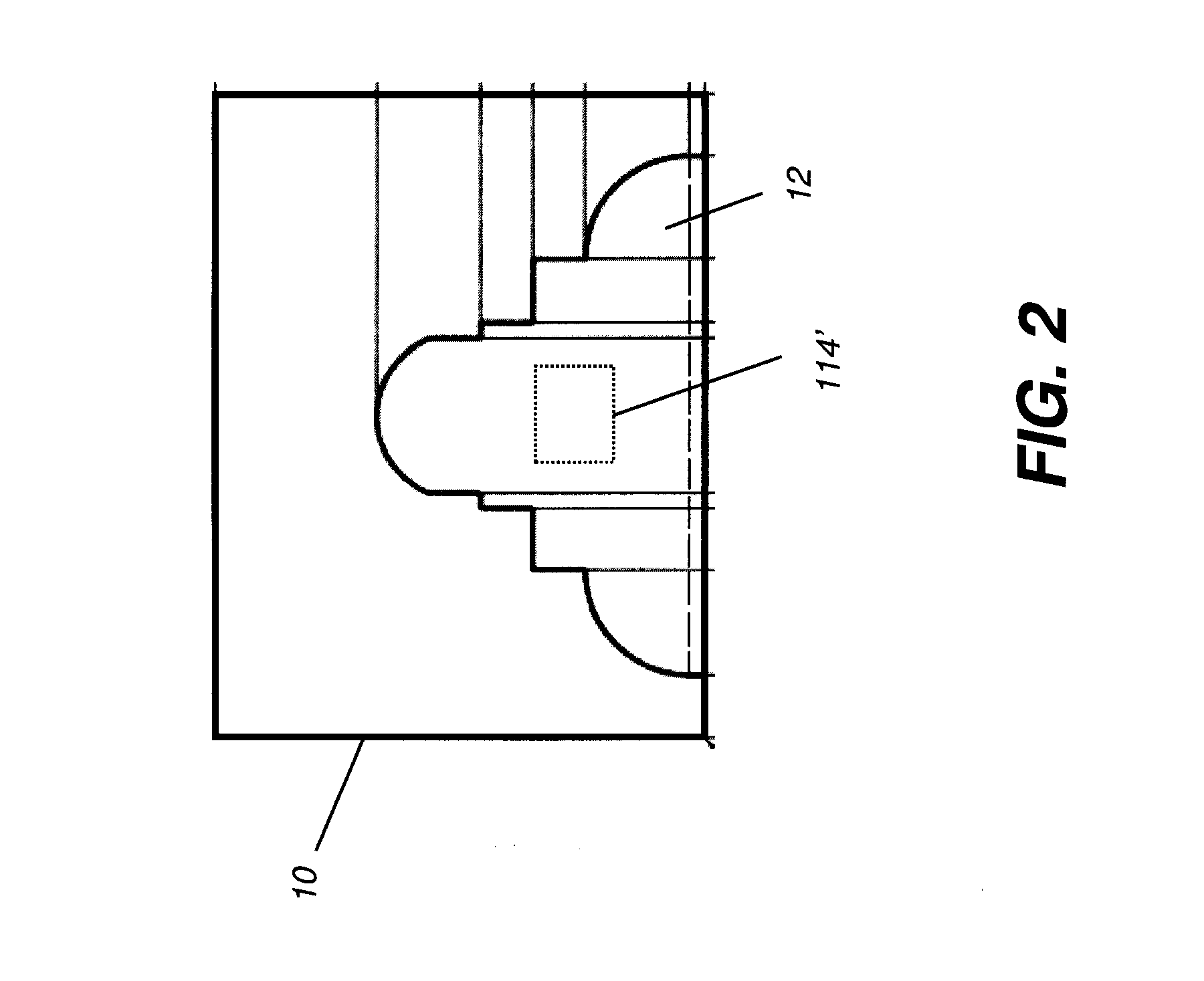
Retrofit digital mammography detector
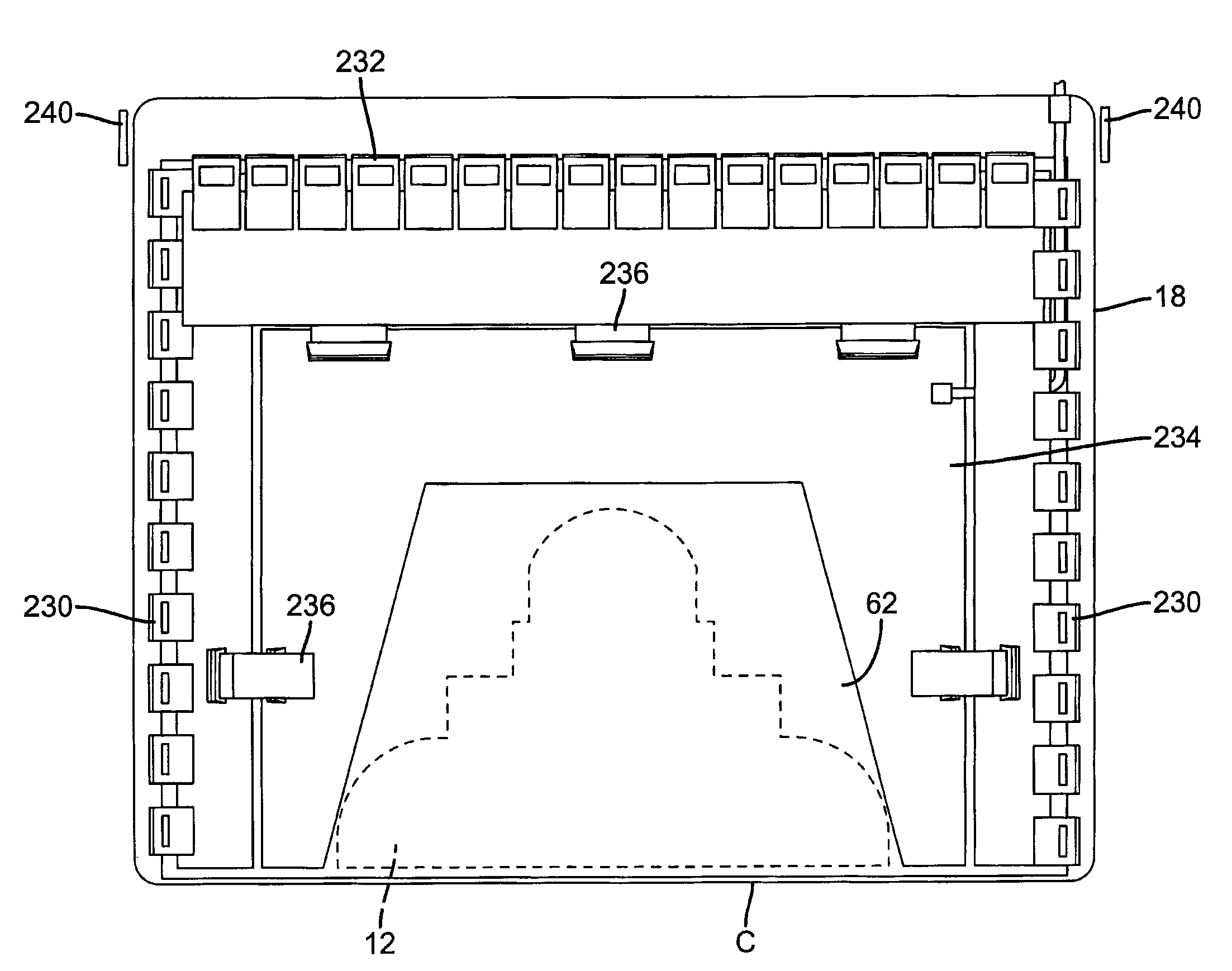
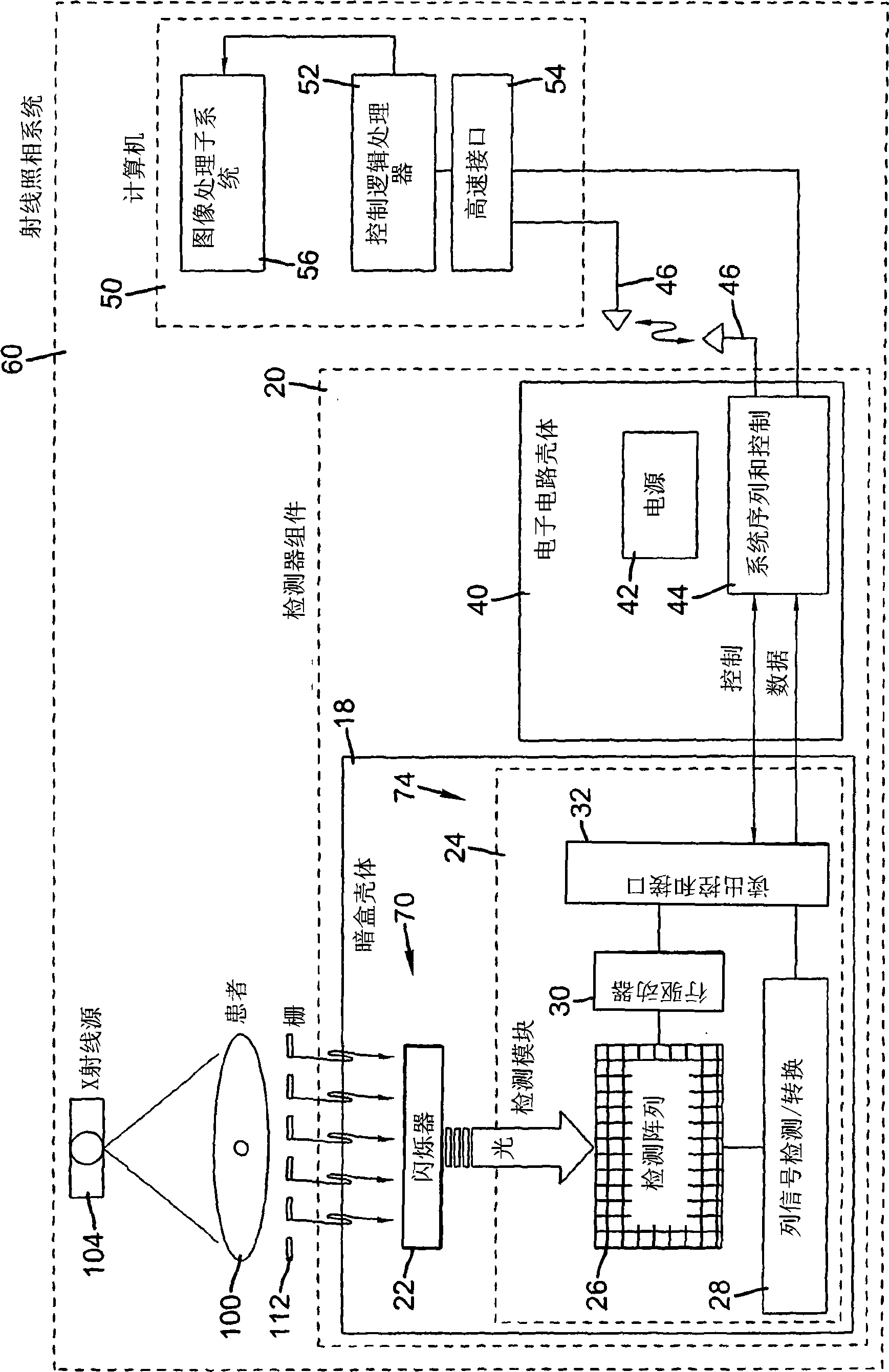
ActiveUS7429737B2Solid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansX-ray shieldDigital mammography
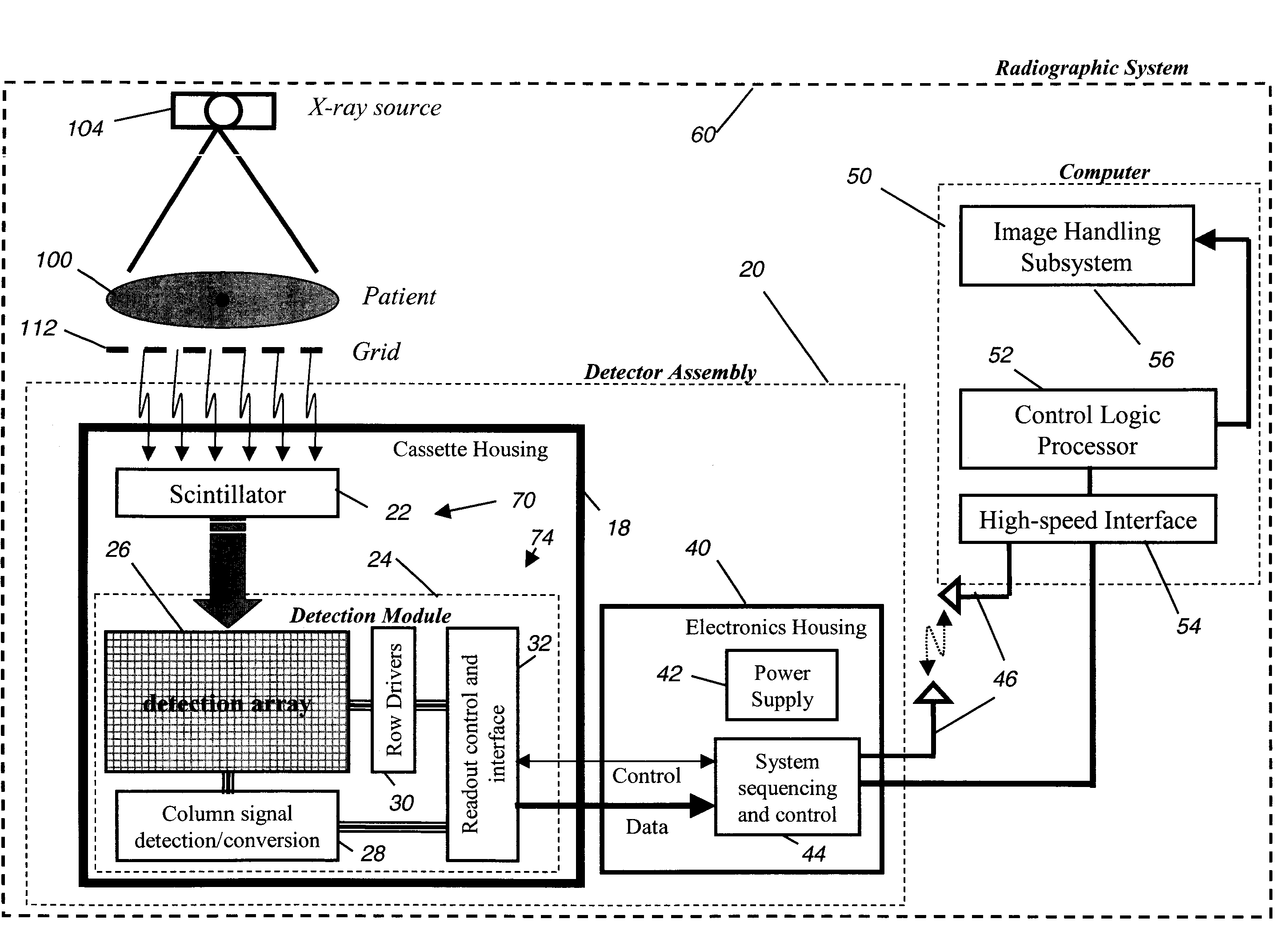
A digital radiography (20) detector has a first housing (18) having substantially the form factor of a film cassette and having a chest wall edge (C). The first housing (18) has an X-ray converter (70) with a detection array (26), each detector generating a signal according to an amount of radiation received. Readout electronics (74) are coupled with switching elements in the detection array for obtaining the signals therefrom. The readout electronics (74) include elements formed from crystalline silicon and are distributed toward outer edges of the first housing (18) and away from the chest wall edge (C). X-ray shielding selectively protects the readout electronics (74) and is located beneath a portion of the detection array. A second housing (40), electrically connected to the first housing (18) has a power source for the detector, readout and control electronics for obtaining signals provided from the detection array (26).
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
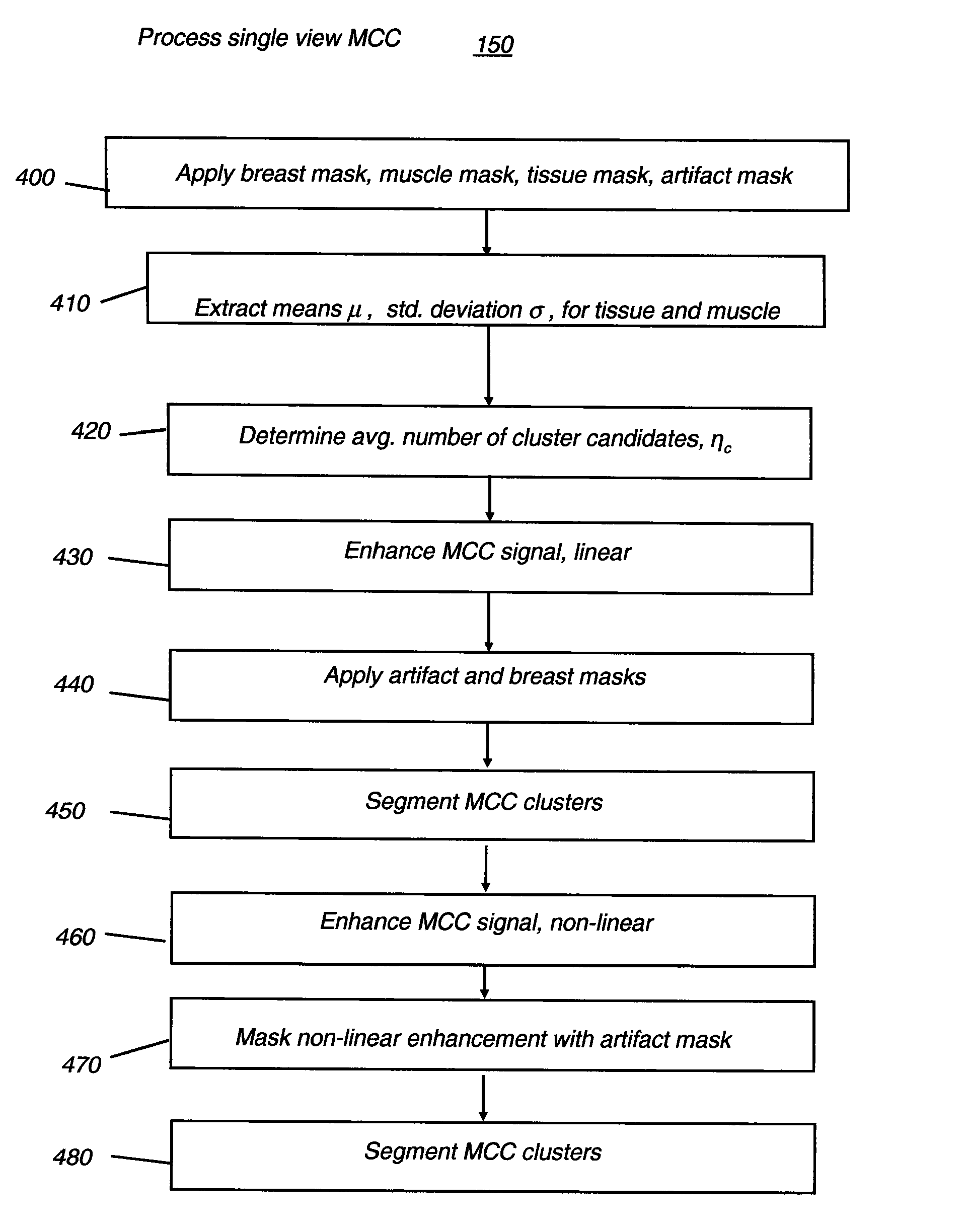
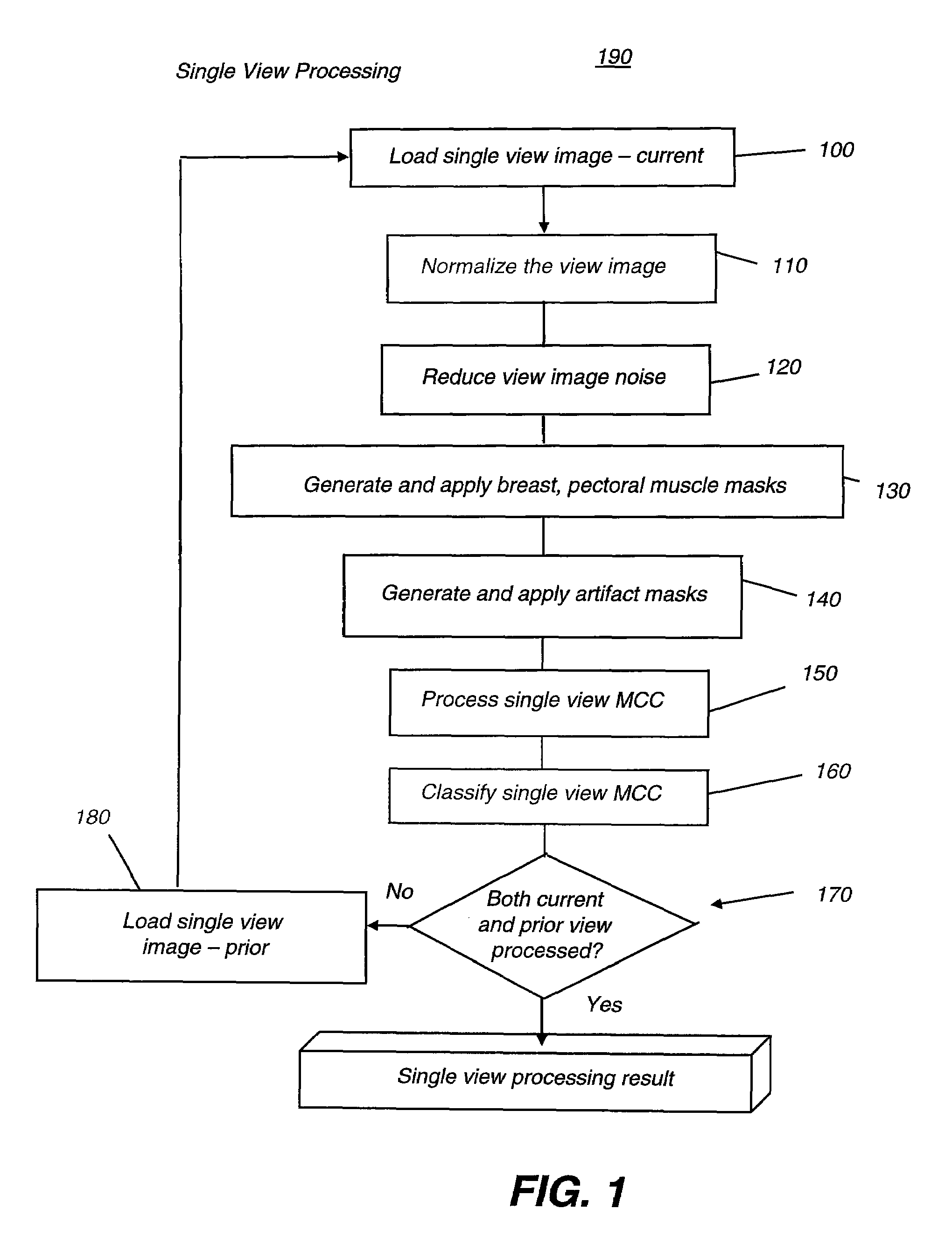
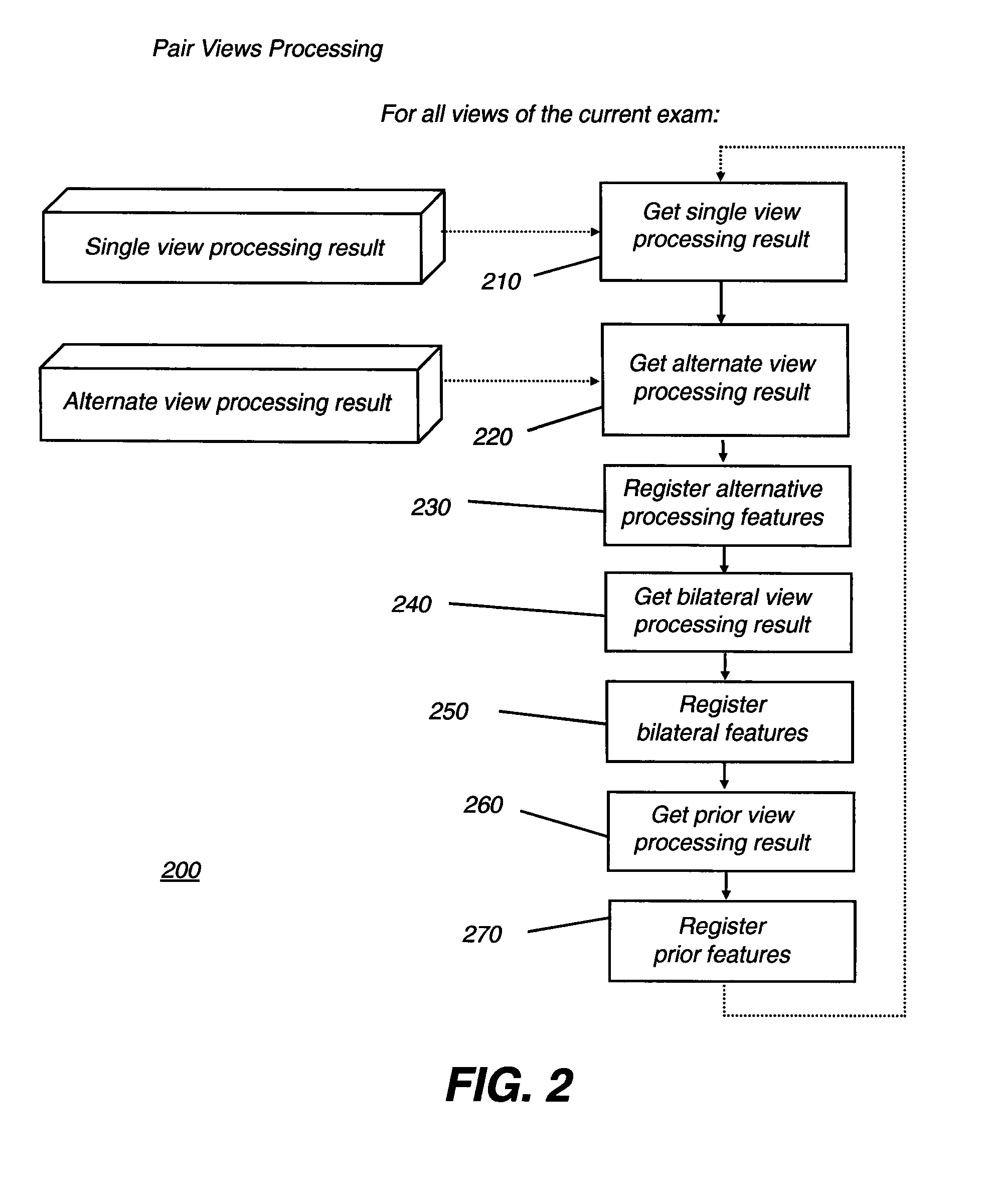
Computer aided detection of microcalcification clusters
InactiveUS20060147101A1Reduce edge effectsReduce image noiseImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
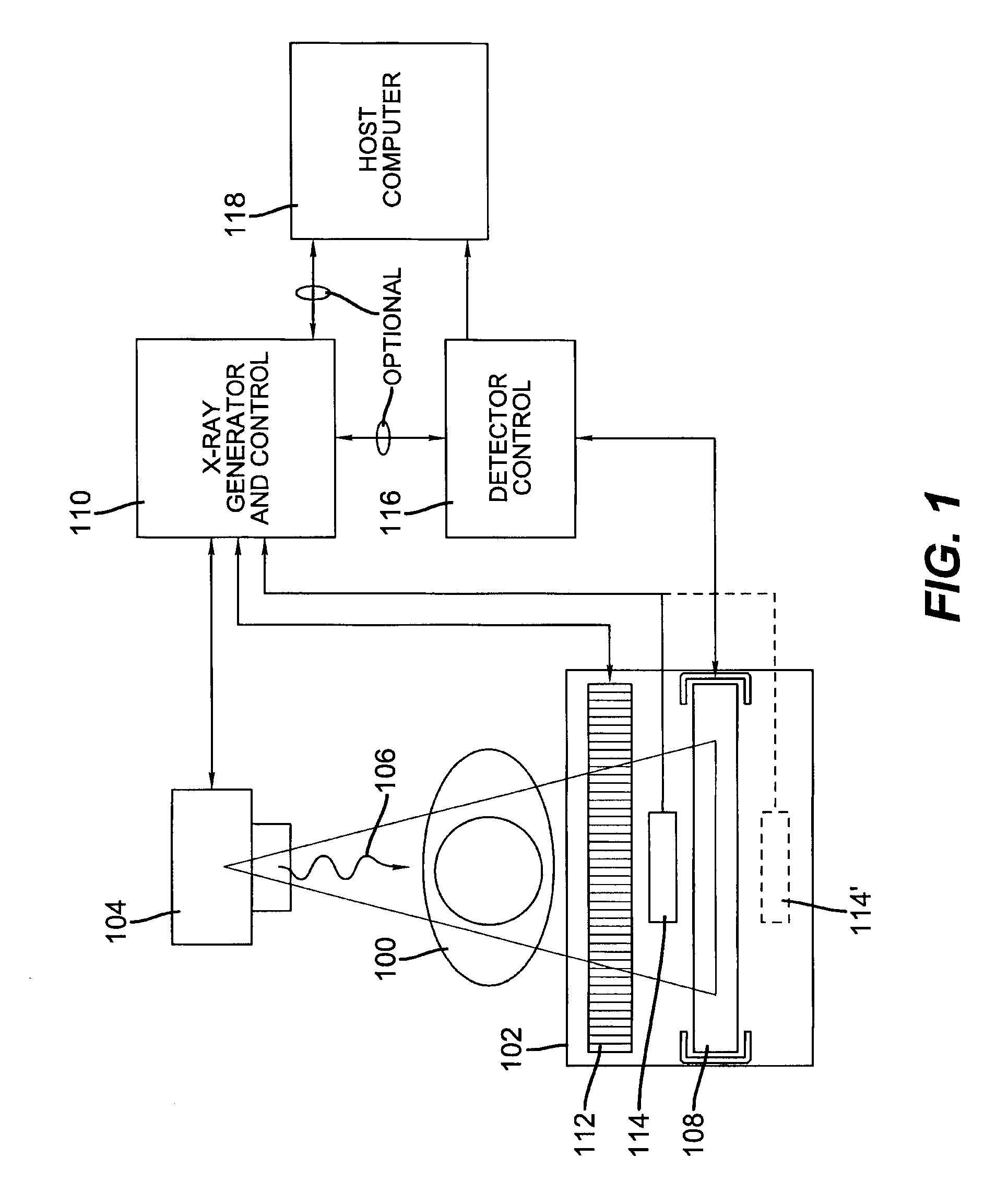
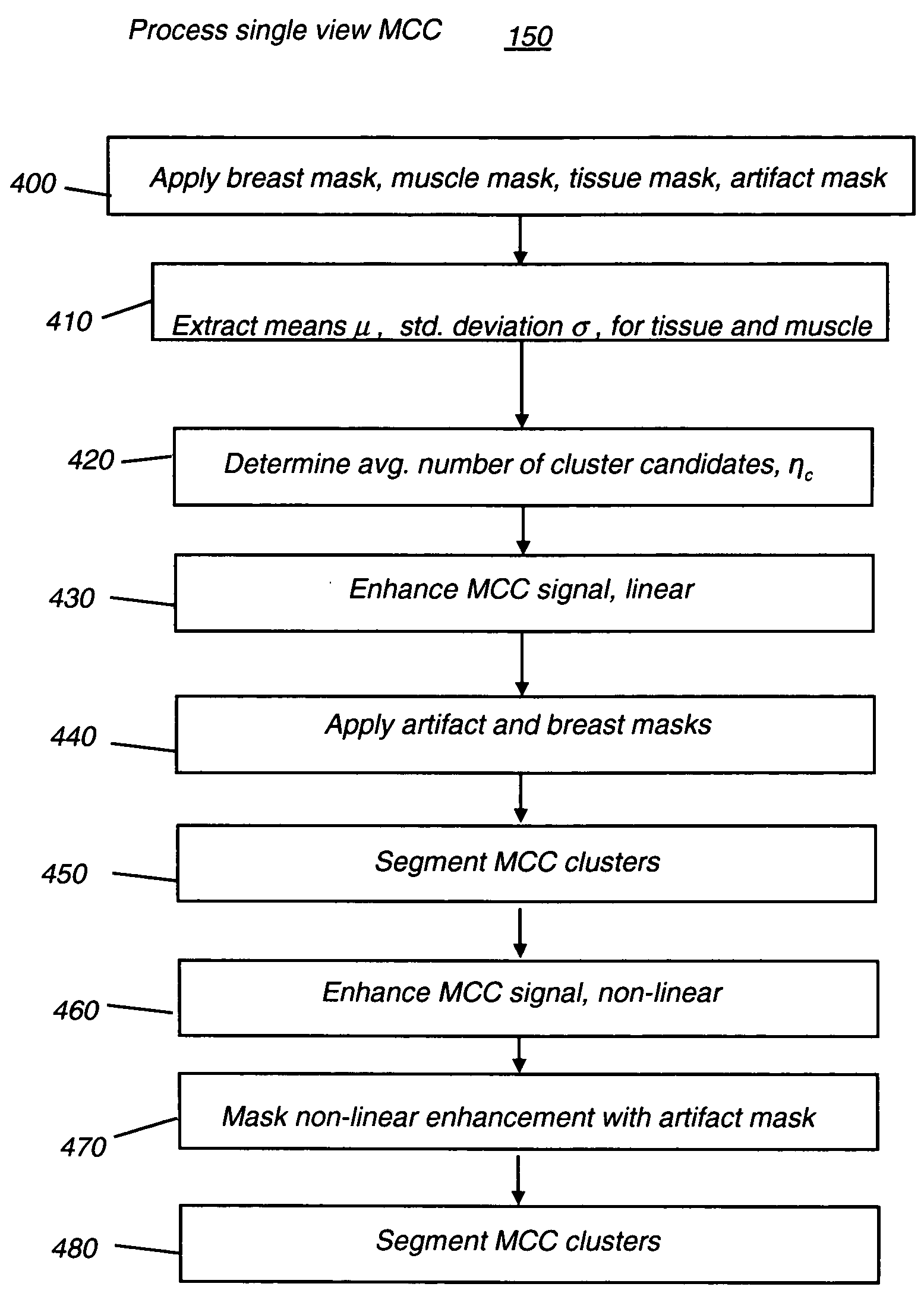
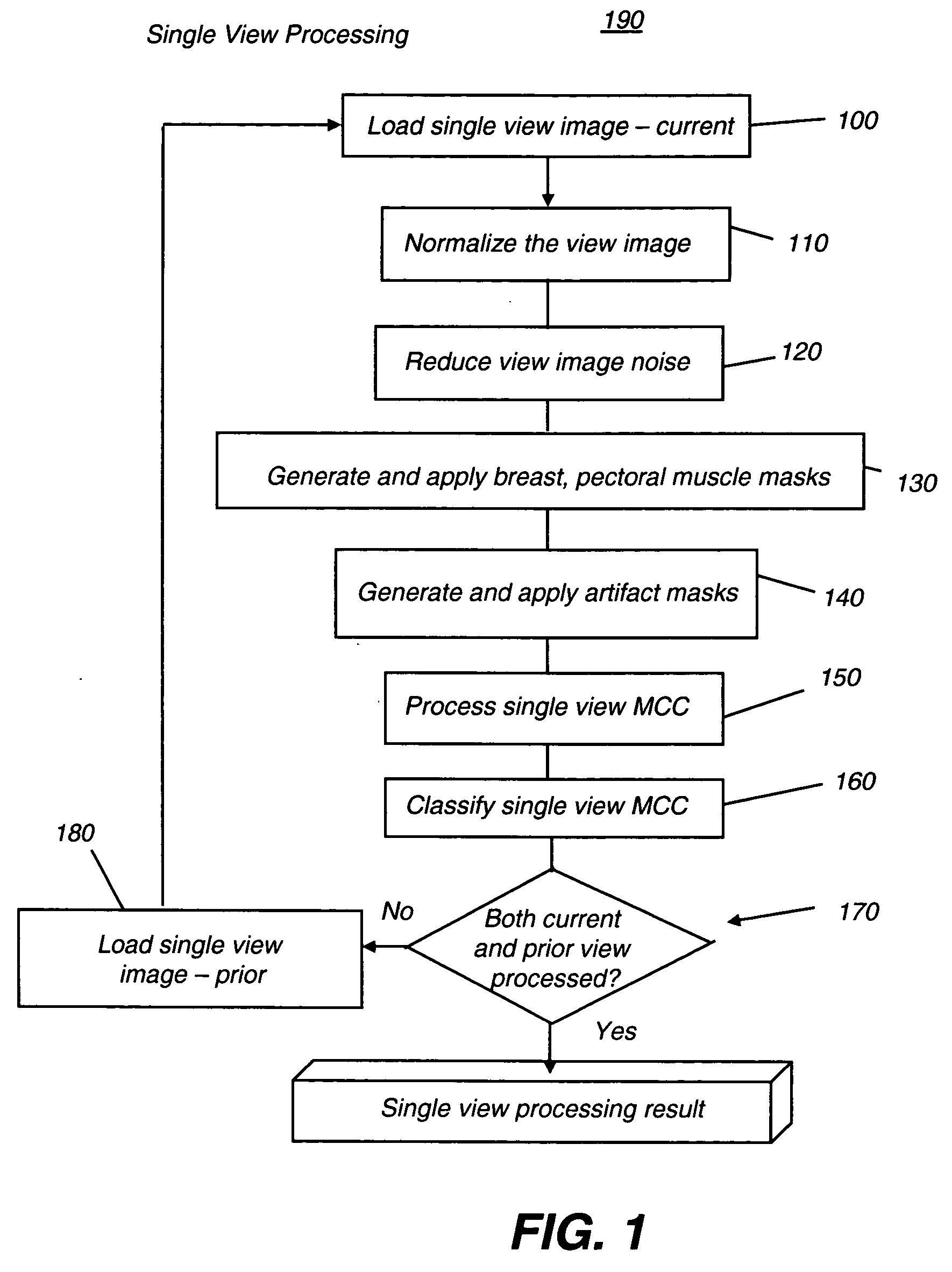
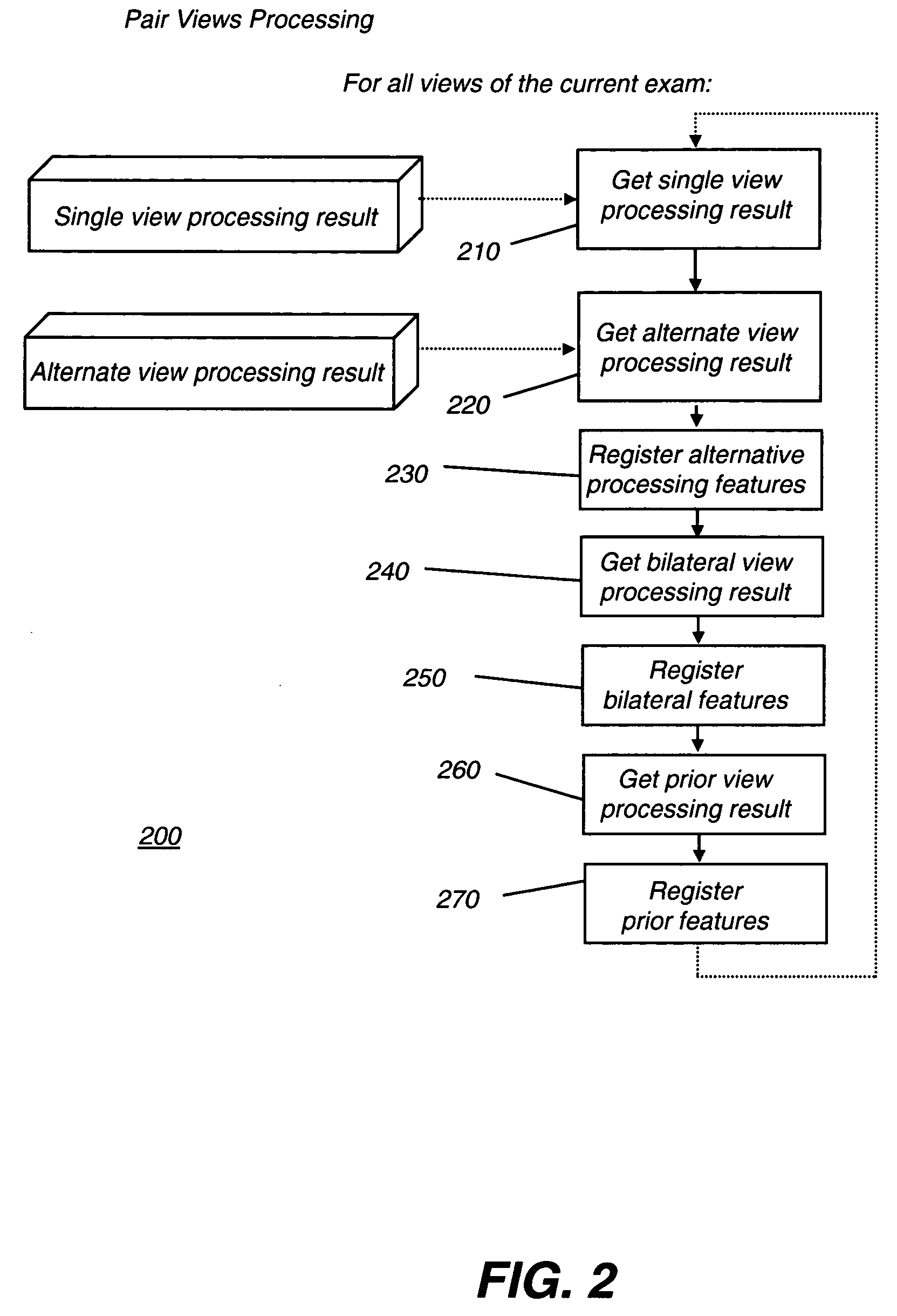
A method for computer-aided detection of microcalcification clusters obtains digital mammography data for a single view image and normalizes and filters the image data to reduce noise. A first mask is generated and applied to the image data for defining the breast structure, forming a first cropped image. A second mask is generated and applied to the image data for defining muscle structure, forming a second cropped image. An artifact mask corresponding to vascular calcifications and known imaging artifacts is generated and applied to the first and second cropped images, defining first and second artifact-masked cropped images. In a repeated sequence, portions of each artifact-masked cropped image are processed using an enhancement algorithm and reducing edge effects to obtain a set of microcalcification cluster candidates and suspected microcalcification clusters. Image processing algorithms remove false positives from the listing of microcalcification clusters and classify candidate microcalcification clusters to identify true positives.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
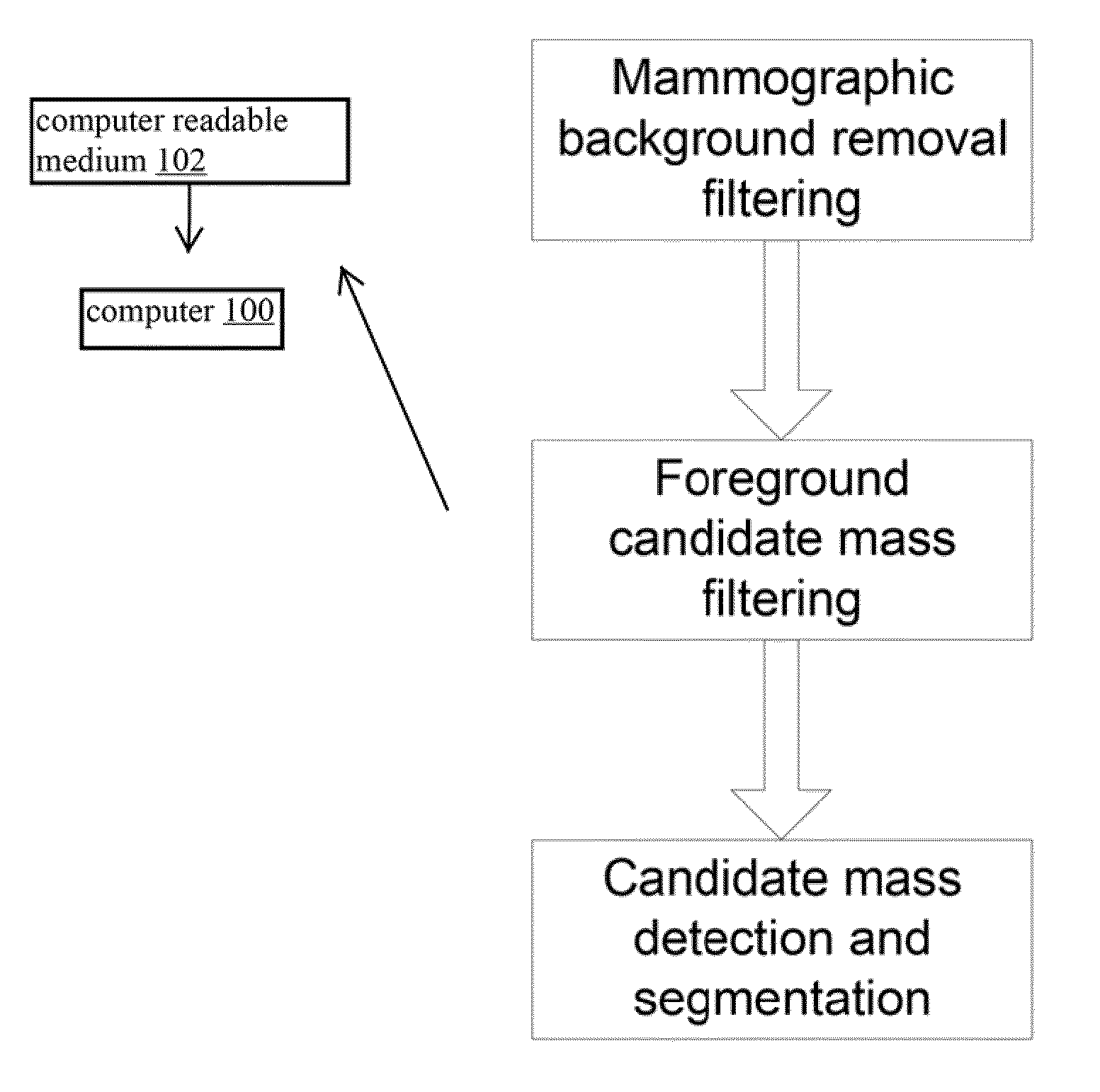
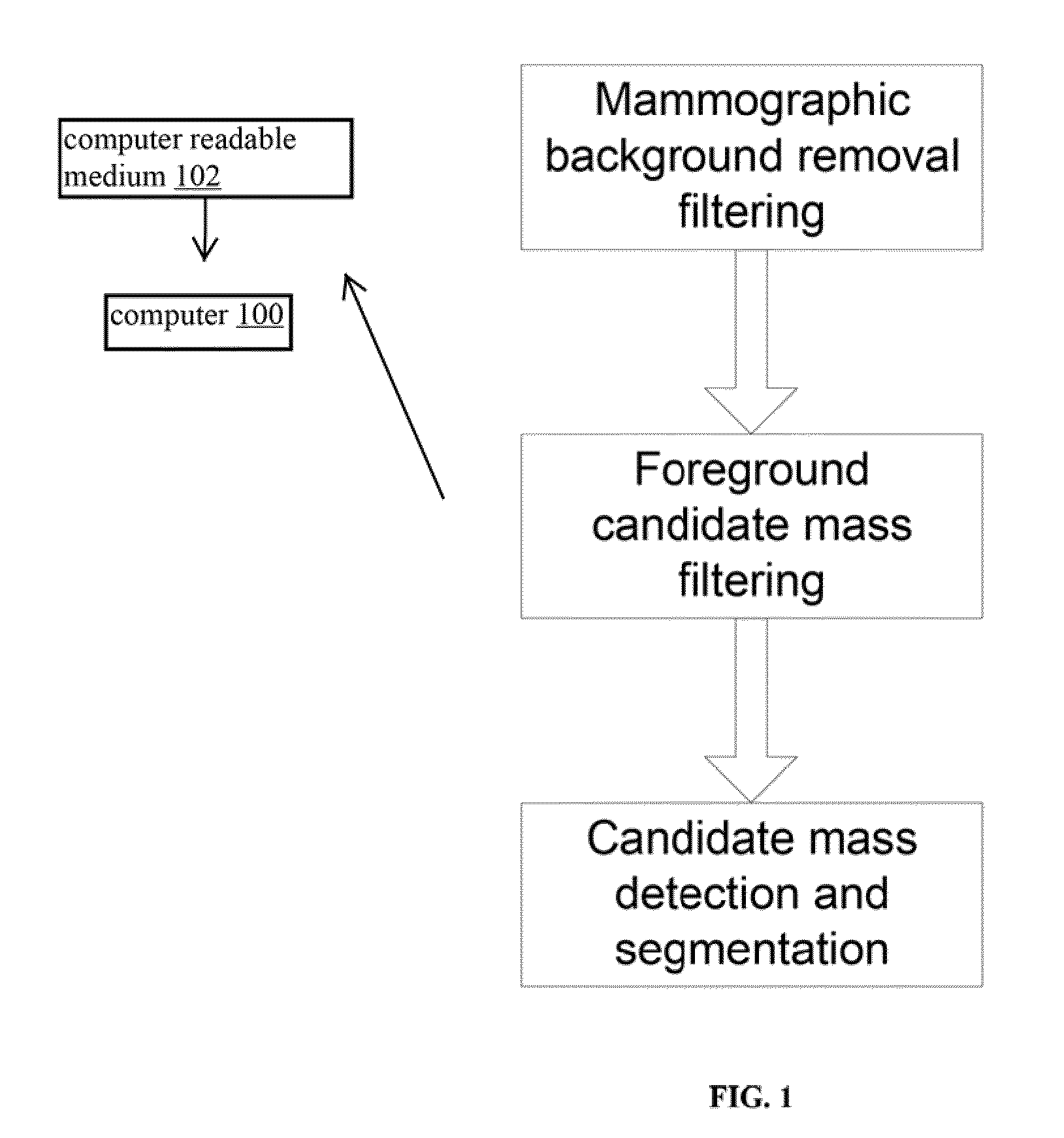
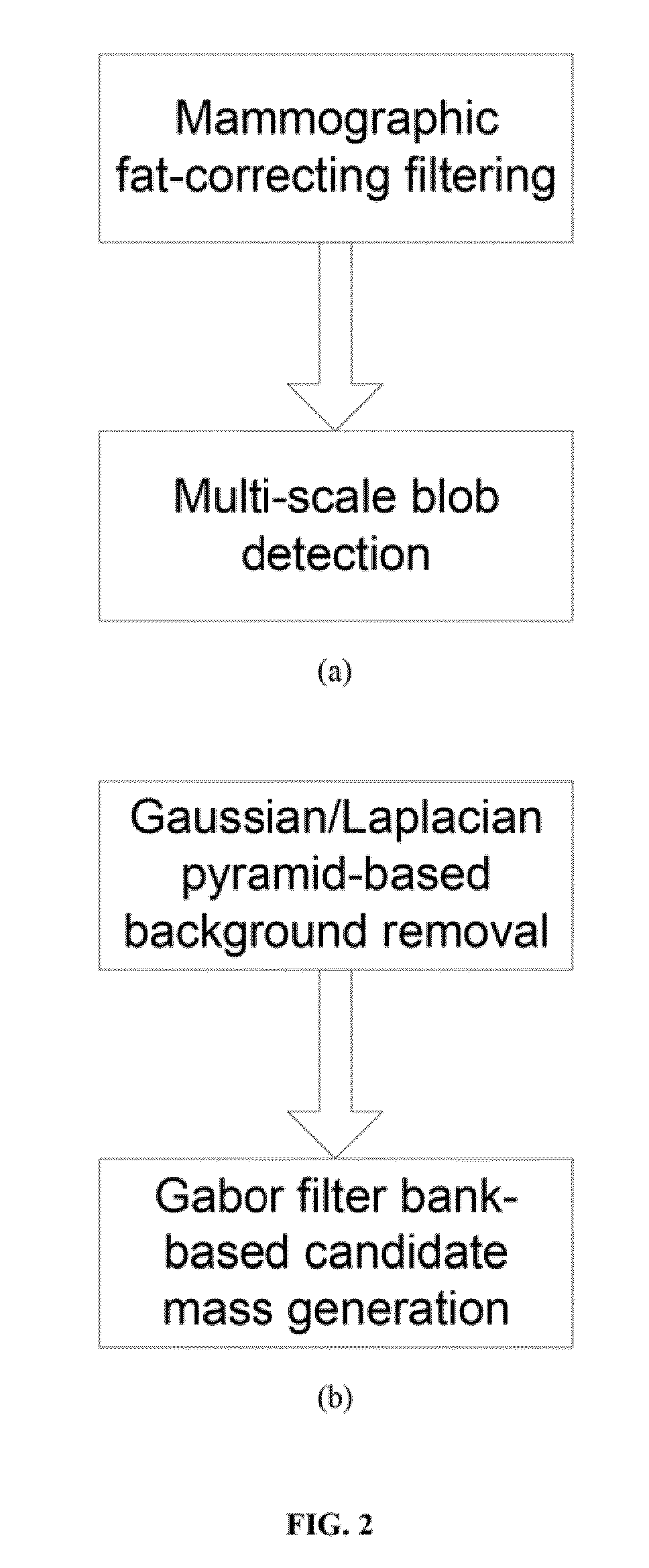
Method for Mass Candidate Detection and Segmentation in Digital Mammograms
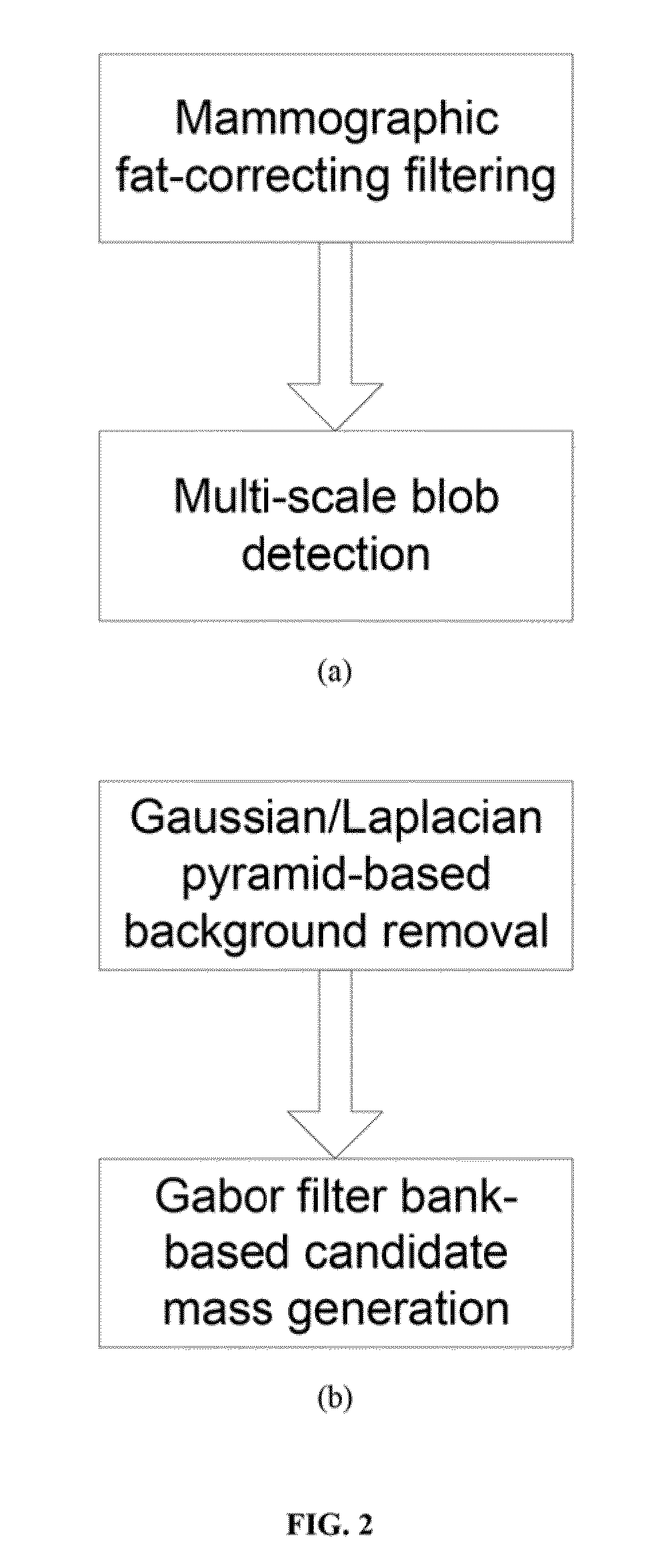
A basic component of Computer-Aided Detection systems for digital mammography comprises generating candidate mass locations suitable for further analysis. A component is described that relies on filtering either the background image or the complementary foreground mammographic detail by a purely signal processing method on the one hand or a processing method based on a physical model on the other hand. The different steps of the signal processing approach consist of band-pass filtering the image by one or more band pass filters, multidimensional clustering, iso-contouring of the distance to centroid of the one or more filtered values, and finally candidate generation and segmentation by contour processing. The physics-based approach also filters the image to retrieve a fat-corrected image to model the background of the breast, and the resulting image is subjected to a blob detection filter to model the intensity bumps on the foreground component of the breast that are associated with mass candidates.
Owner:AGFA NV
Retrofit digital mammography detector
A digital radiography (20) detector has a first housing (18) having substantially the form factor of a film cassette and having a chest wall edge (C). The first housing (18) has an X-ray converter (70) with a detection array (26), each detector generating a signal according to an amount of radiation received. Readout electronics (74) are coupled with switching elements in the detection array for obtaining the signals therefrom. The readout electronics (74) include elements formed from crystalline silicon and are distributed toward outer edges of the first housing (18) and away from the chest wall edge (C). X-ray shielding selectively protects the readout electronics (74) and is located beneath a portion of the detection array. A second housing (40), electrically connected to the first housing (18) has a power source for the detector, readout and control electronics for obtaining signals provided from the detection array (26).
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Breast compression for digital mammography, tomosynthesis and other modalities
ActiveUS7489761B2Spread out the breast tissuesReduce radiation exposureTomosynthesisPatient positioning for diagnosticsTomosynthesisDigital mammography
A breast x-ray imaging method and system that is particularly suited for tomosynthesis imaging but also is useful for conventional mammography. A fluid containing pillow or bag is placed between the breast and a paddle that compresses the breast against a breast platform covering an imaging device, to enhance patient comfort and provide other benefits. Alternatives include a flexible sheet compressing the breast, and a compressible foam, preferably contoured to accommodate a patient's breast.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Computer-aided detection of microcalcification clusters
InactiveUS7593561B2Reduce edge effectsReduce image noiseImage enhancementImage analysisEdge effectsImaging processing
A method for computer-aided detection of microcalcification clusters using a digital computer obtains digital mammography data for a single view image and normalizes and filters the image data to reduce noise. A first mask is generated and applied to the image data for defining the breast structure, forming a first cropped image. A second mask is generated and applied to the image data for defining muscle structure, forming a second cropped image. An artifact mask corresponding to vascular calcifications and known imaging artifacts is generated and applied to the first and second cropped images, defining first and second artifact-masked cropped images. In a repeated sequence, portions of each artifact-masked cropped image are processed using an enhancement algorithm and reducing edge effects to obtain a set of microcalcification cluster candidates and suspected microcalcification clusters. Image processing algorithms remove false positives from the listing of microcalcification clusters and classify candidate microcalcification clusters to identify true positives.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Distributed architecture for mammographic image acquisition and processing
InactiveUS7406150B2Easy to useHigh patient throughputOrgan movement/changes detectionPatient positioning for diagnosticsImage InspectionDICOM
A distributed architecture allows for decoupling of mammographic image acquisition and review, thereby enabling more efficient use of resources and enhanced processing. In one embodiment, the system (100) includes a number of image acquisition stations (102) and a number of image review stations (110) all associated with a central server (104). The server (104) is operative to access an image repository (106), a patient information data base (108) and a number of DICOM tools (112). The invention allows for more efficient and / or more convenient use of the image acquisition equipment and image processing stations. Moreover, the distributed architecture including the central image repository provides certain processing and analysis advantages. The invention also provides certain processing and workflow enhancements that allow for a more full realization of potential digital mammography advantages.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Automatic Positioning Quality Assessment for Digital Mammography
InactiveUS20070248210A1Improve overall mammography processReduce in quantityImage enhancementImage analysisDigital mammographyQuality assessment
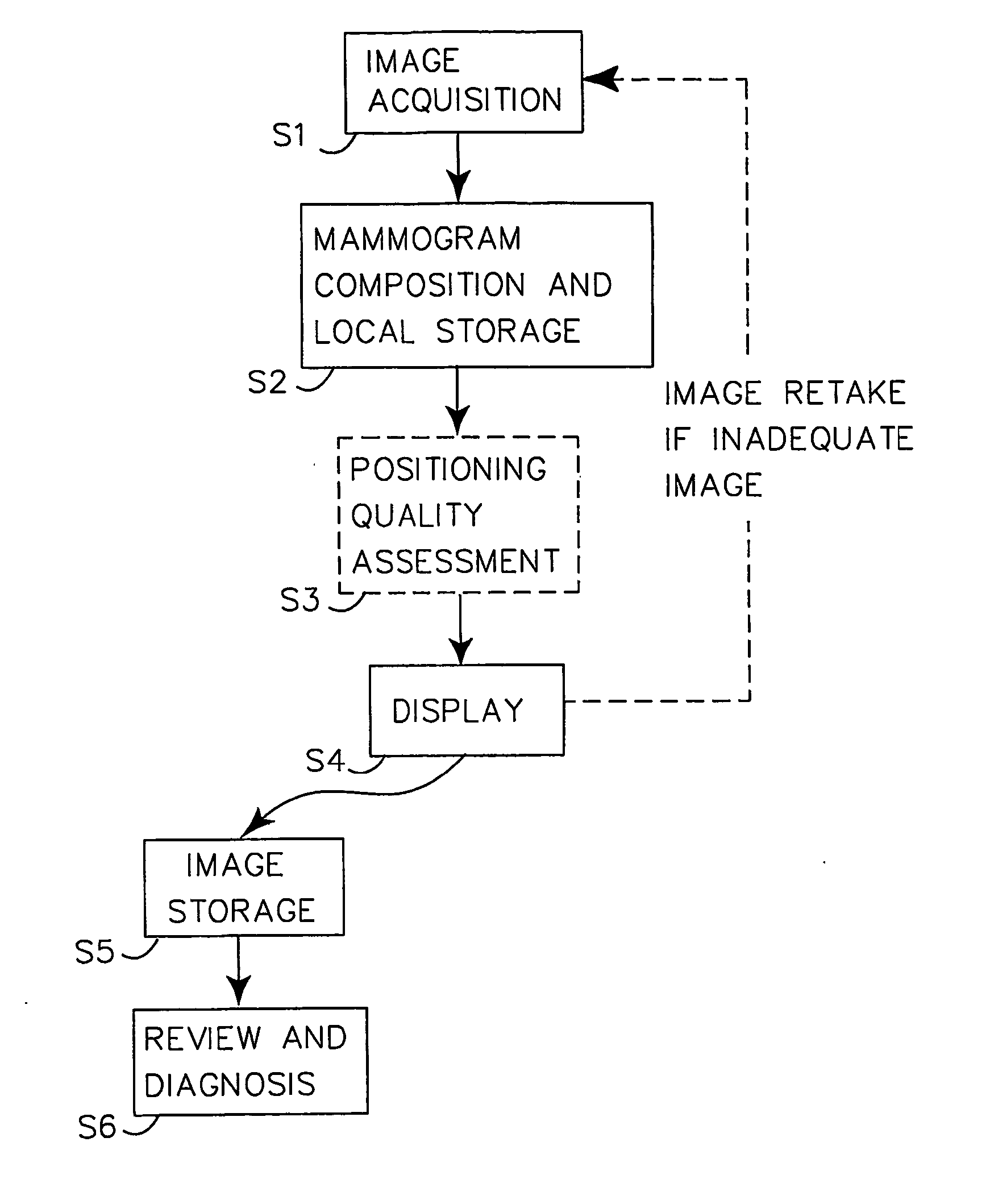
The invention presents a way to automatically assess the quality of acquired (S1, S2) digital mammographic images with respect to the image positioning of a patient's breast. The automated digital quality assessment (S3) is executed in real time and preferably notifies (S4) the technologist instantly if the image positioning quality of a mammographic image is inadequate. This makes it possible to retake the image while the patient is still present at the examination facility. The quality assessment notification includes information to the technologist, preferably both visually and statistically of land-mark positioning measurements. Alternatively, the digital quality assessment is accompanied by a computerized decision of whether the mammogram needs to be retaken, requiring a minimum of involvement, if at all, from the technologist. The invention hence provides a set of quality-assured mammographic images that can be stored (S5) and later accessed by a radiologist for review and diagnosis (S6).
Owner:SECTRA IMTEC
Multi-threshold peripheral equalization method and apparatus for digital mammography and breast tomosynthesis
ActiveUS20070047793A1Improve efficiencyHigh strengthImage enhancementImage analysisTomosynthesisDigital mammography
A peripheral equalization (PE) method and apparatus for compensating for thickness reduction in outer edges of the breast in a mammogram (i.e. a two-dimensional image) while keeping the central area substantially unchanged. The PE method and apparatus can also be applied to three dimensional (tomosynthesis) images of a breast. The peripheral equalization is achieved by segmenting the image of the breast into at least two regions and using a multi-threshold technique to process the data in at least one of the two regions.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
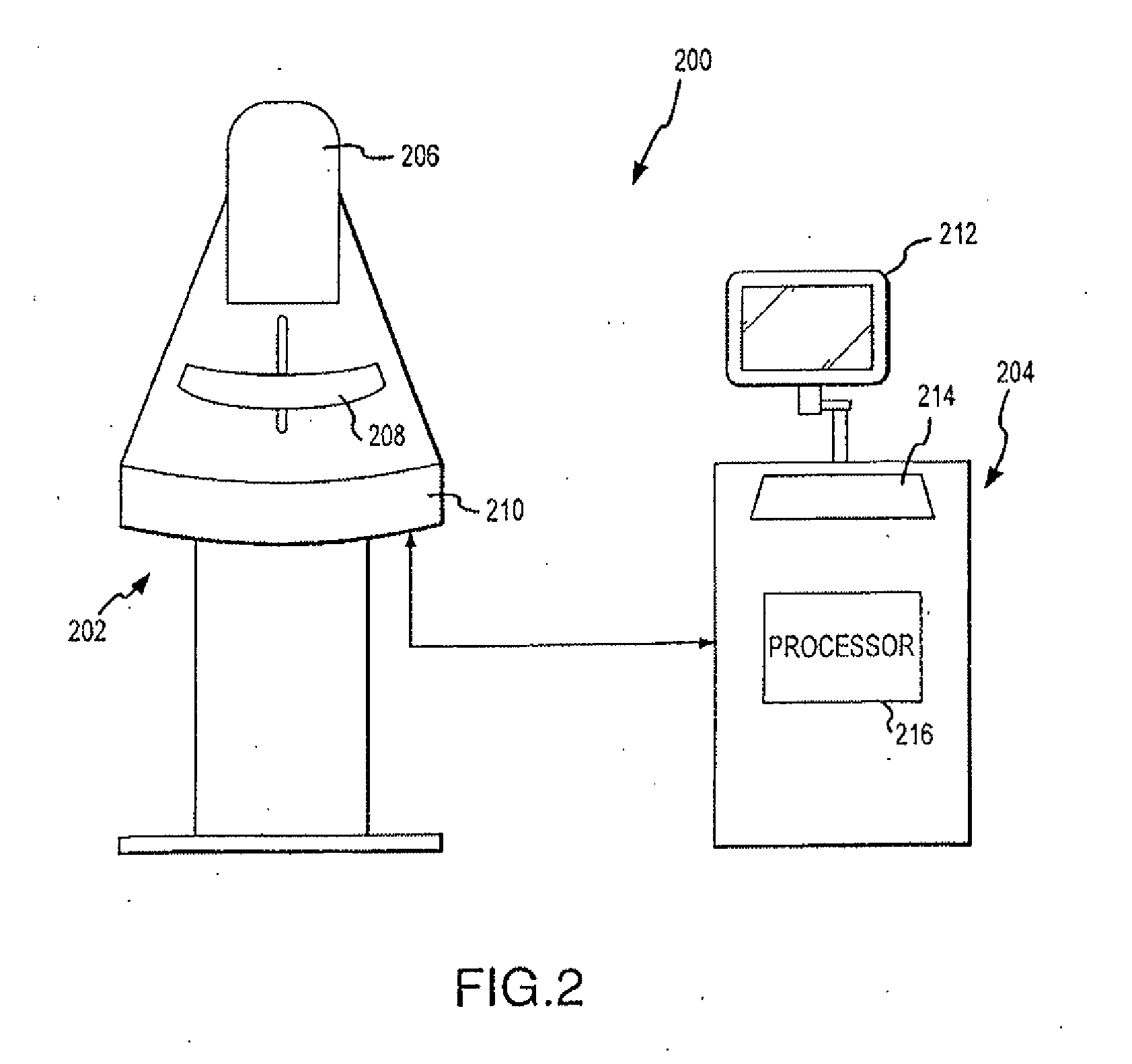
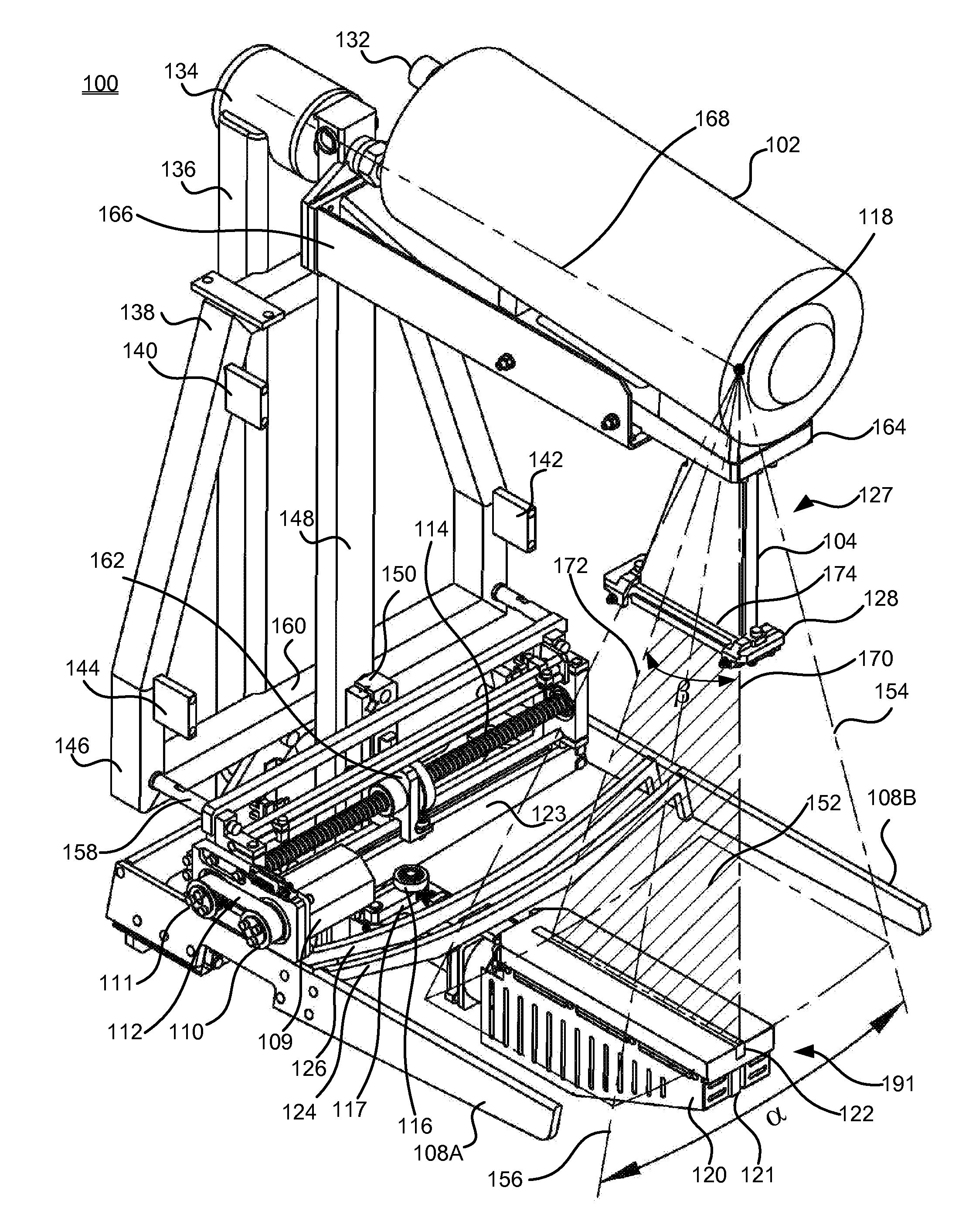
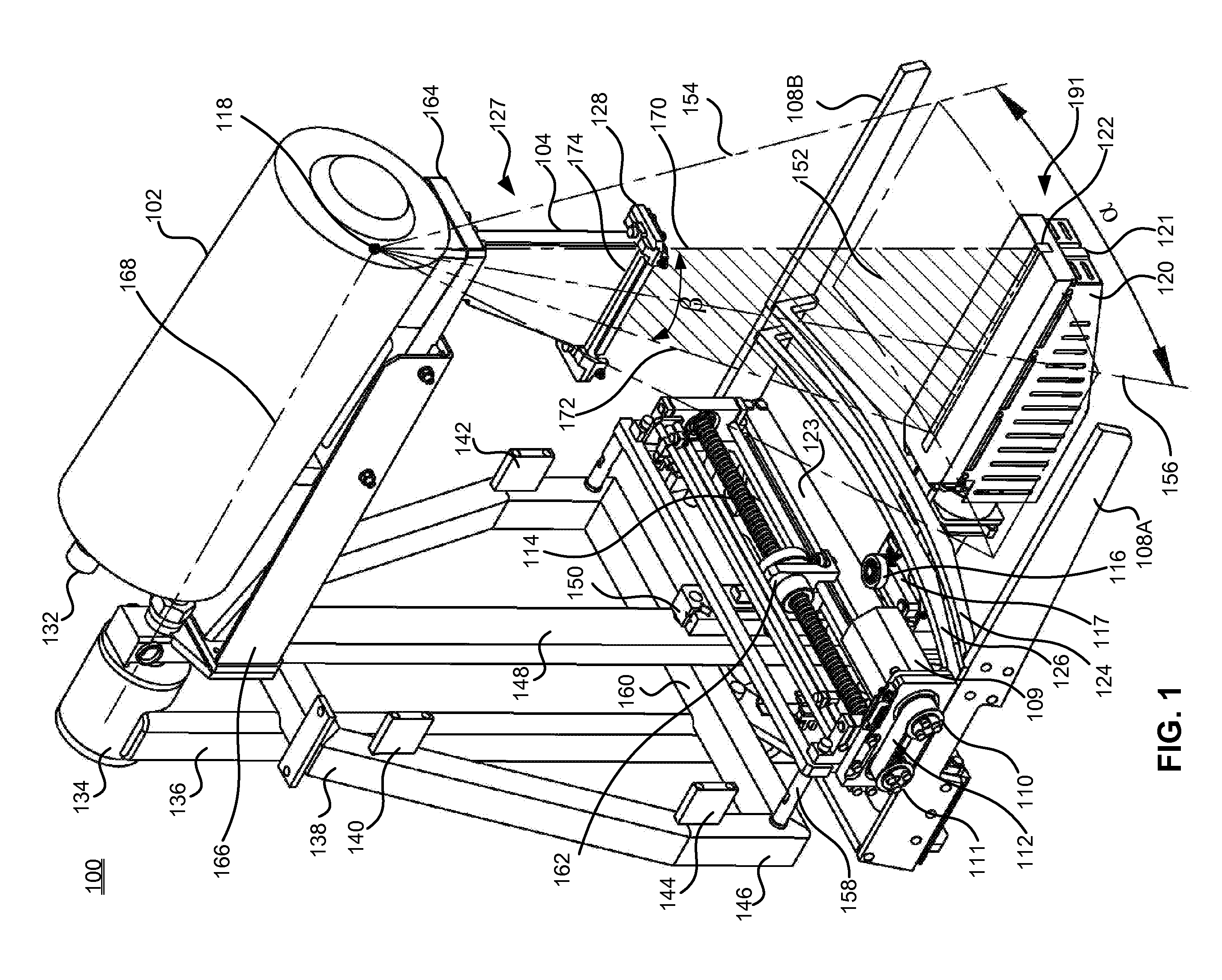
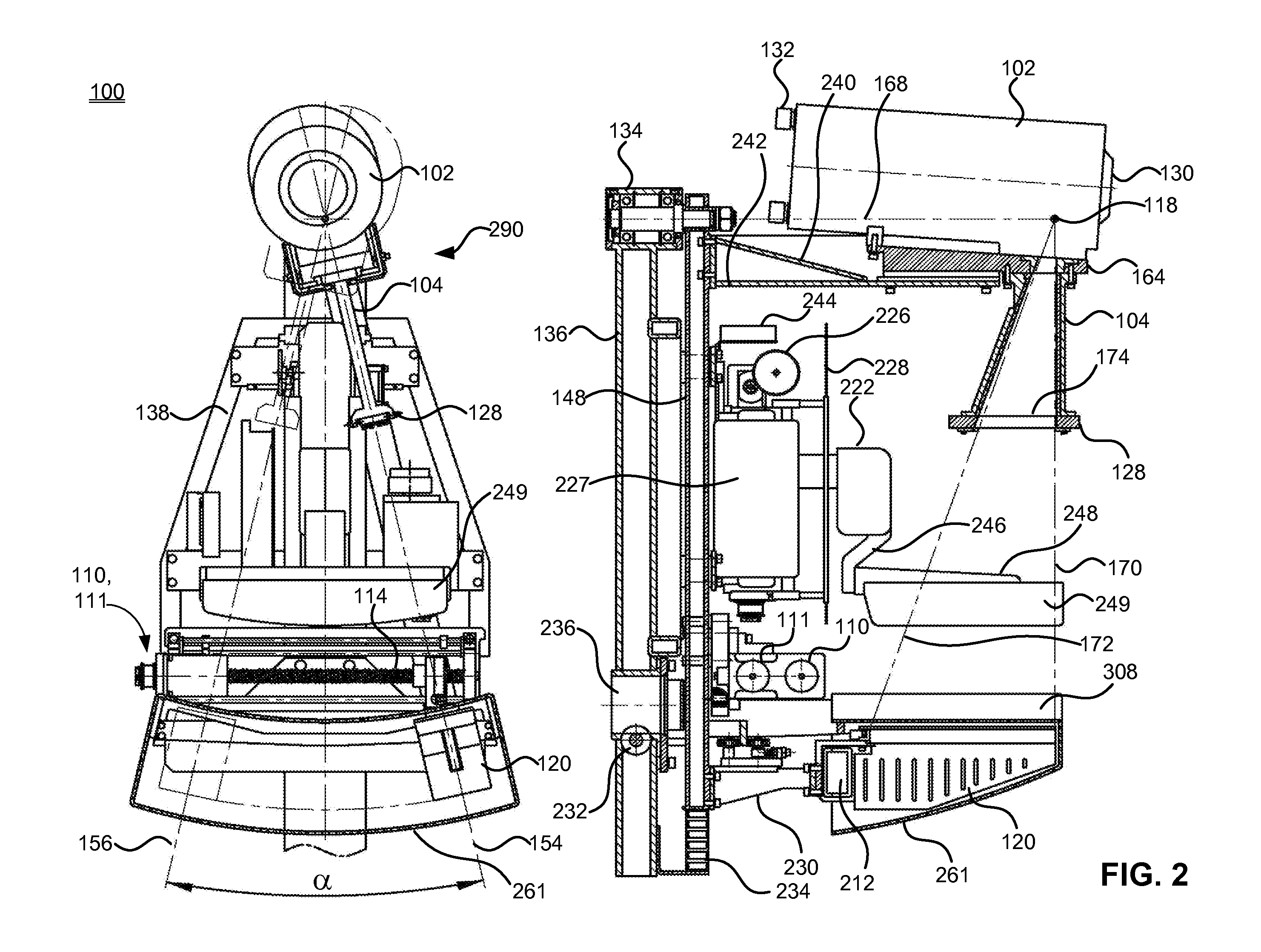
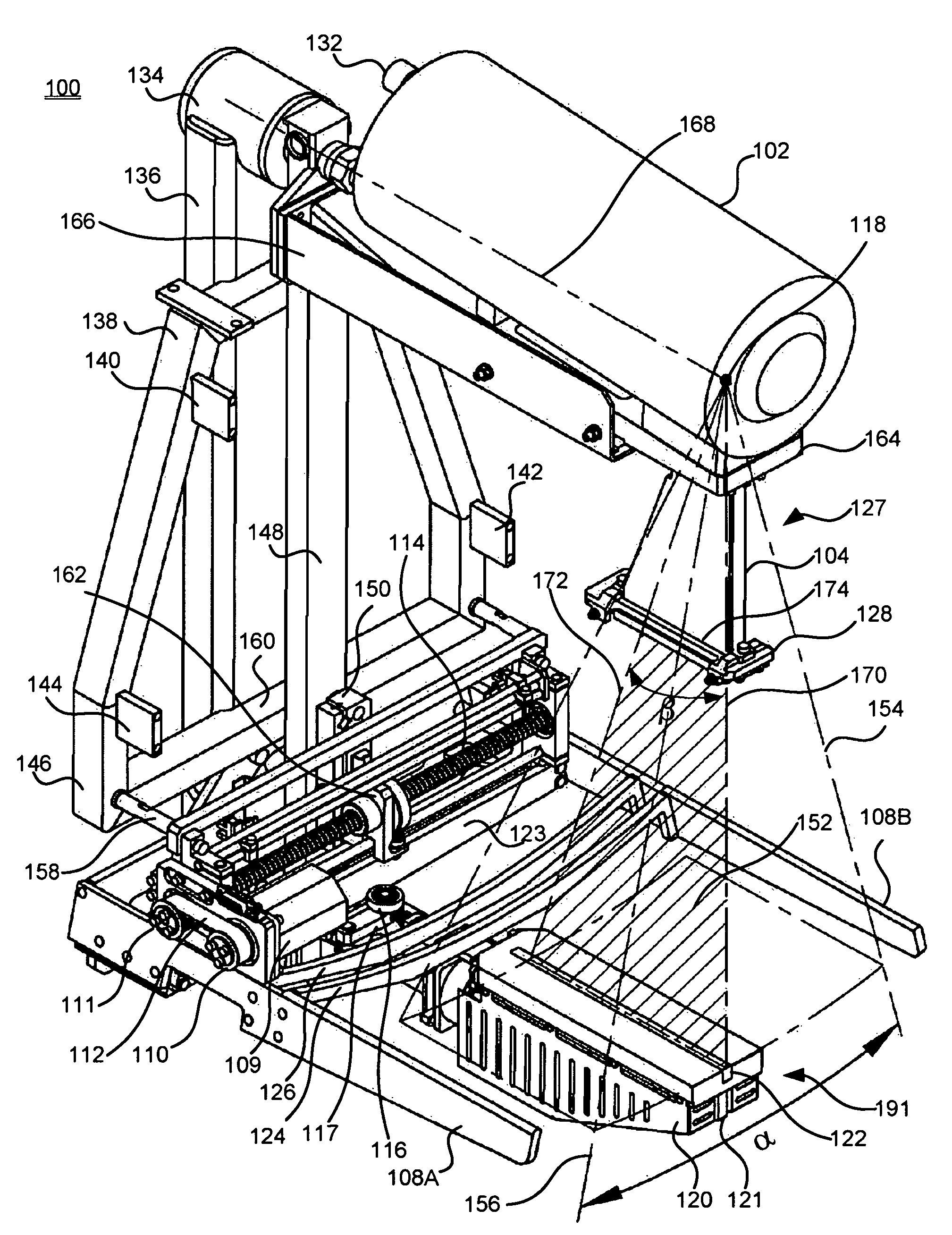
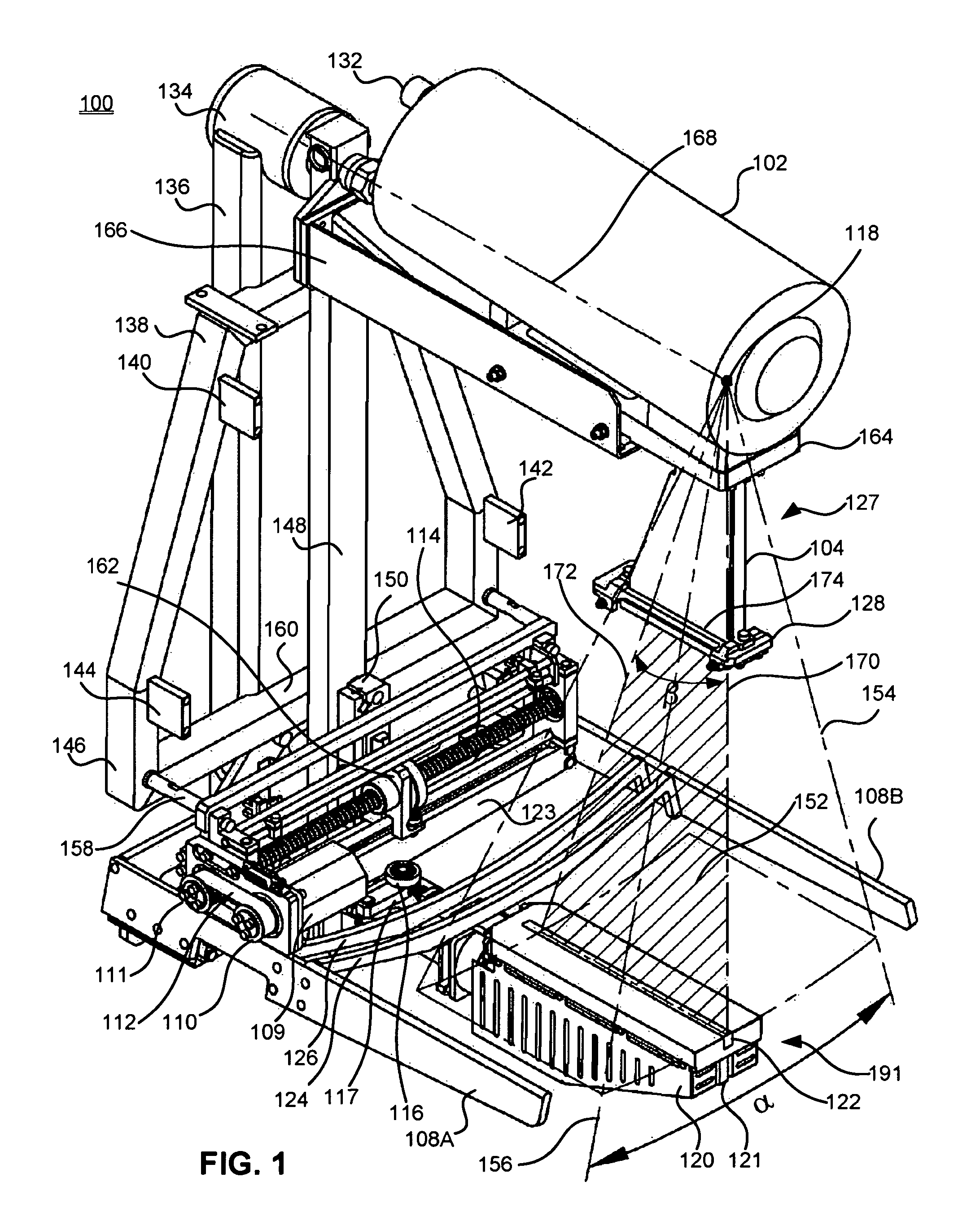
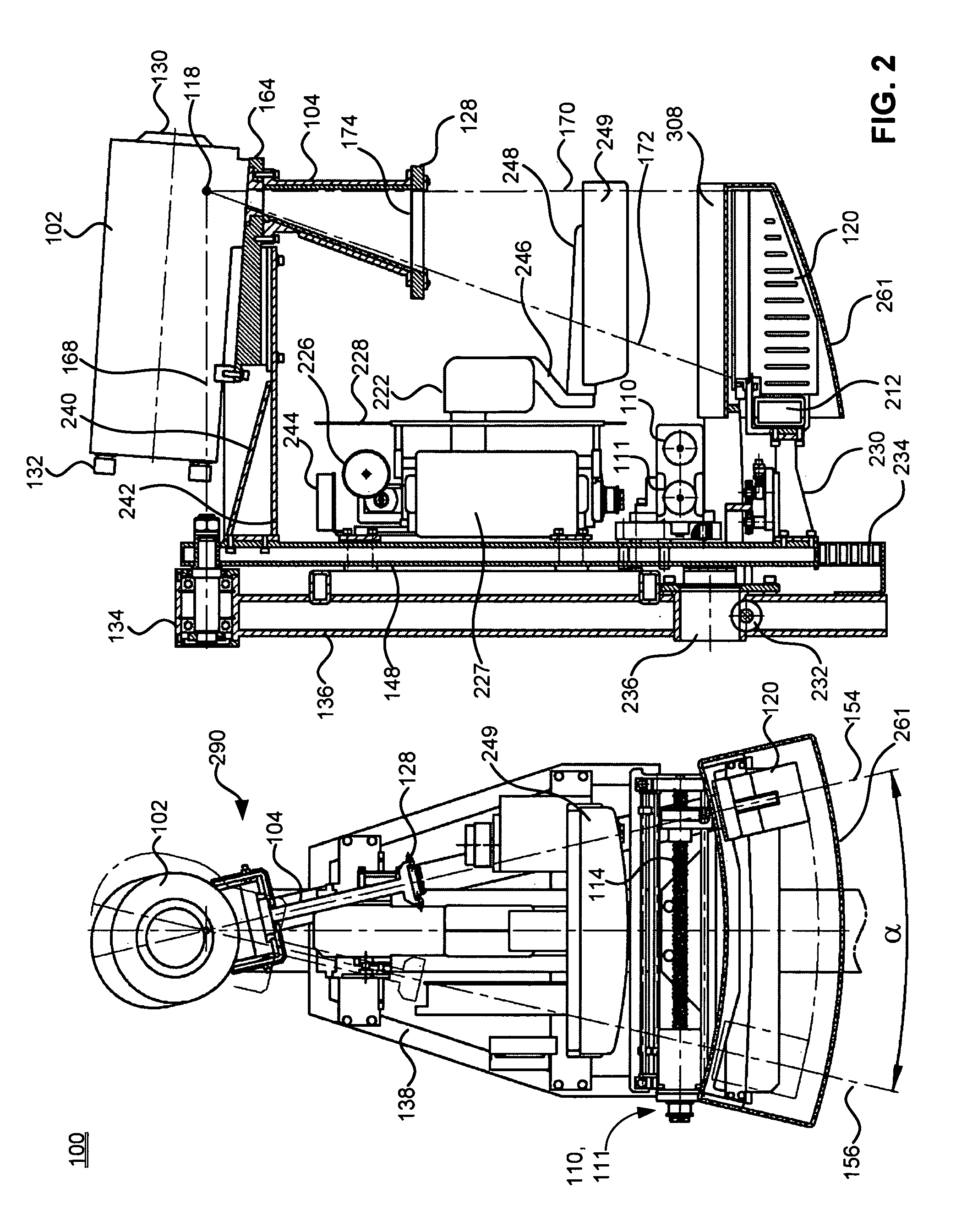
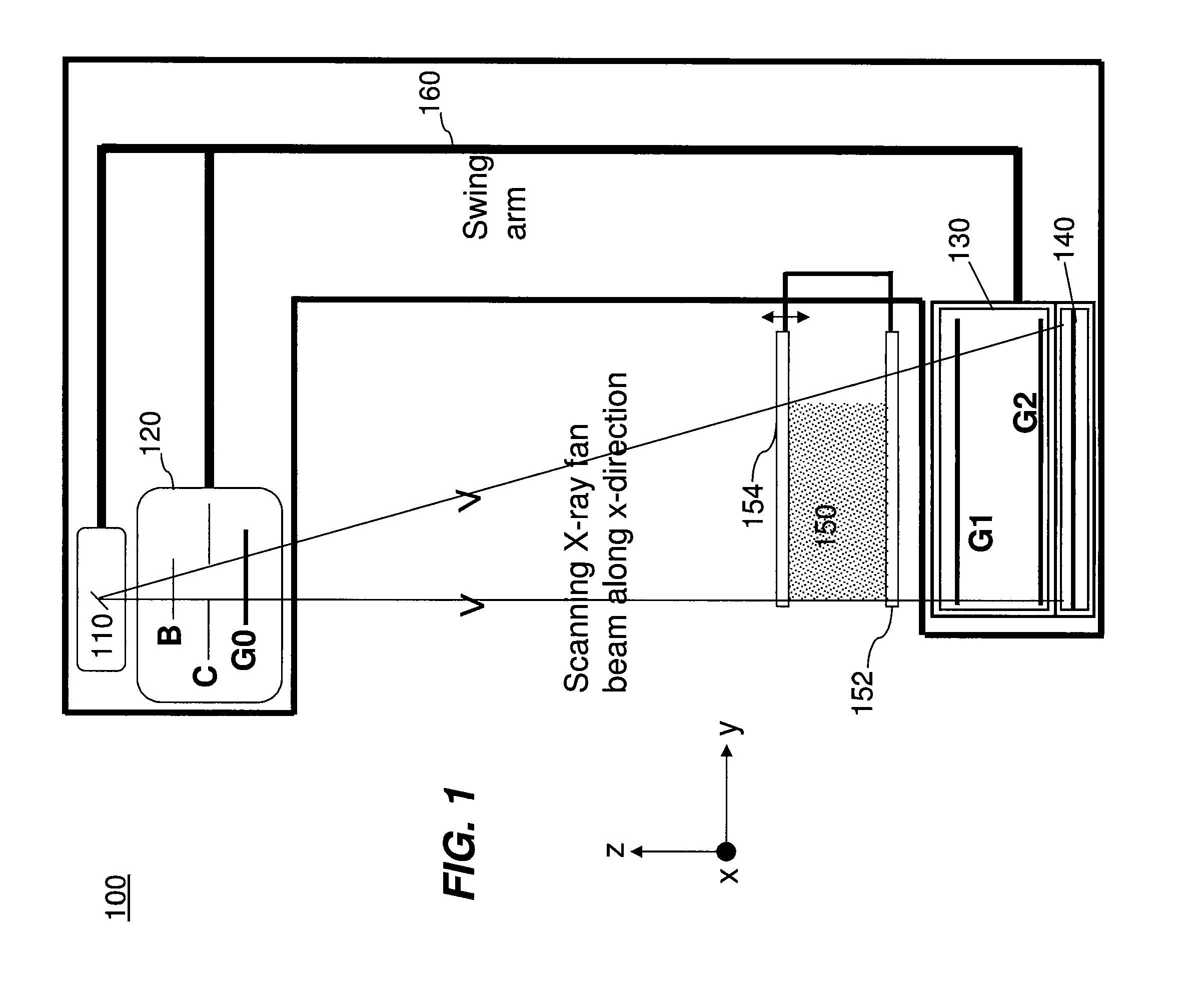
Digital mammography scanning system
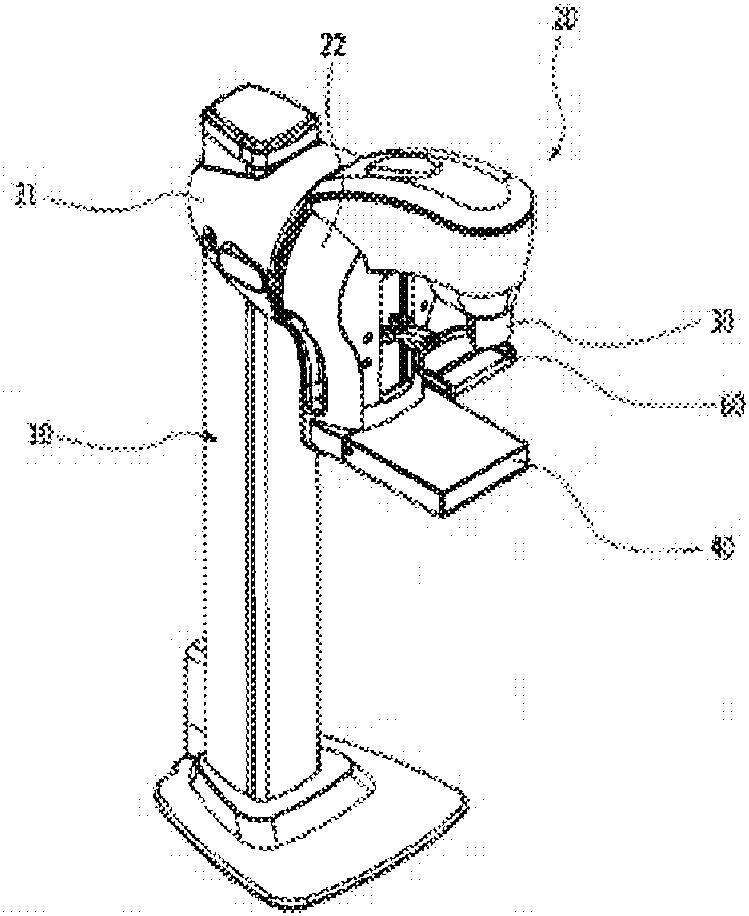
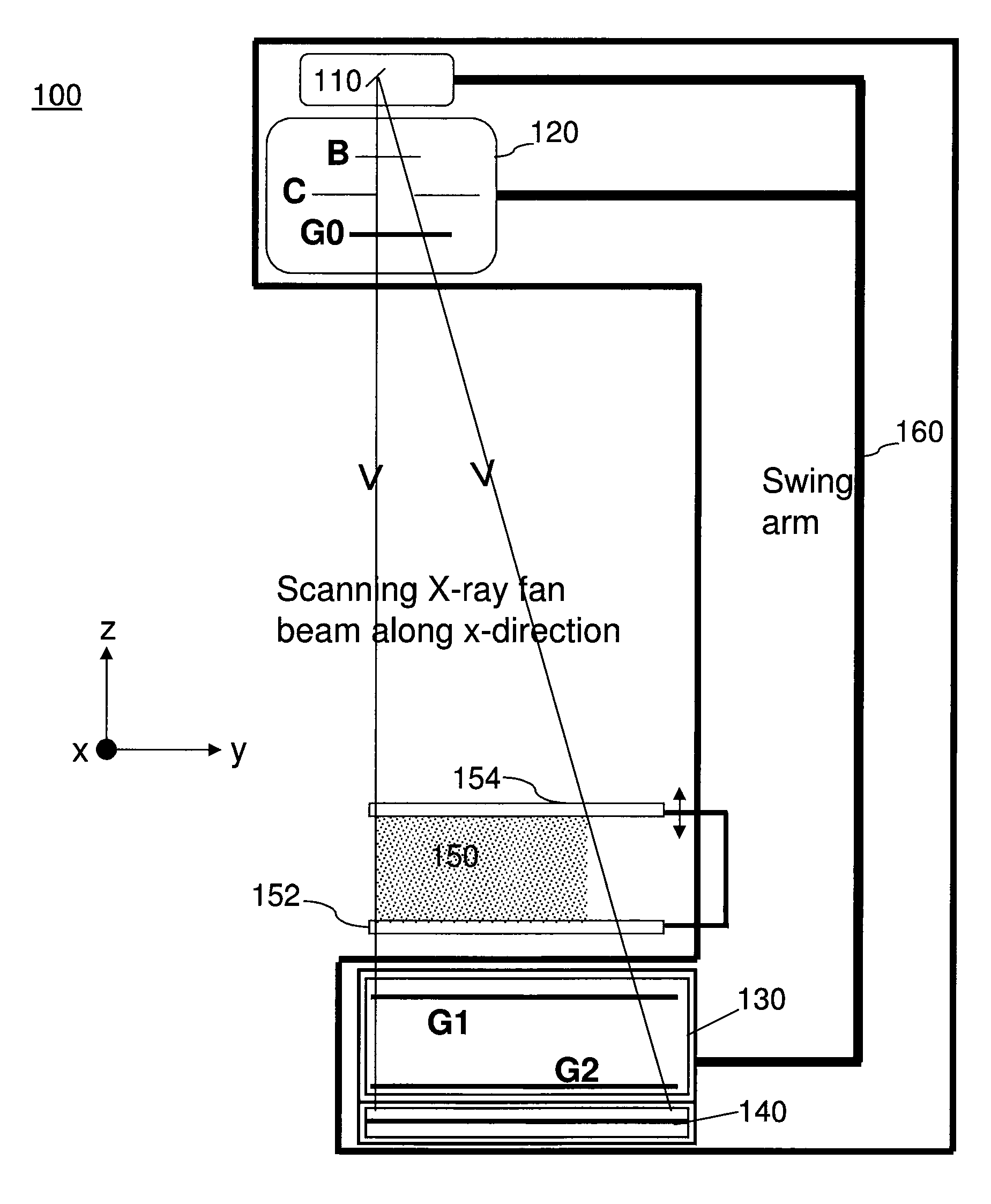
ActiveUS20110206181A1Reduce impactImprove fidelityPatient positioning for diagnosticsTomographyDigital mammographyHorizontal axis
An apparatus for use in imaging an area of interest within a patient's body, including a stationary frame; a rotating assembly mounted on the stationary frame, the rotating assembly including an axle assembly having a substantially horizontal axis of rotation, an X-ray source having a focal spot that coincides with the horizontal axis of rotation; a collimator from which a fan-shaped X-ray beam exits towards a detector assembly, and a rotating frame mechanically coupled to the detector assembly and pivoting about the horizontal axis of rotation. The detector assembly includes a linear X-ray detector for detecting radiation of the fan-shaped X-ray beam after the beam passes through the area of interest, and is mechanically coupled to a motor that enables arcuate movement of the detector assembly in a transverse direction. The motor is mechanically coupled to the rotating assembly to enable rotational movement of the rotating assembly.
Owner:ADANI
Digital mammography scanning system
ActiveUS7940890B1Reduce impactImprove fidelityPatient positioning for diagnosticsTomographyDigital mammographyHorizontal axis
An apparatus for use in imaging an area of interest within a patient's body, including a stationary frame; a rotating assembly mounted on the stationary frame, the rotating assembly including an axle assembly having a substantially horizontal axis of rotation, an X-ray source having a focal spot that coincides with the horizontal axis of rotation; a collimator from which a fan-shaped X-ray beam exits towards a detector assembly, and a rotating frame mechanically coupled to the detector assembly and pivoting about the horizontal axis of rotation. The detector assembly includes a linear X-ray detector for detecting radiation of the fan-shaped X-ray beam after the beam passes through the area of interest, and is mechanically coupled to a motor that enables arcuate movement of the detector assembly in a transverse direction. The motor is mechanically coupled to the rotating assembly to enable rotational movement of the rotating assembly.
Owner:ADANI
Method for mass candidate detection and segmentation in digital mammograms
A basic component of Computer-Aided Detection systems for digital mammography comprises generating candidate mass locations suitable for further analysis. A component is described that relies on filtering either the background image or the complementary foreground mammographic detail by a purely signal processing method on the one hand or a processing method based on a physical model on the other hand. The different steps of the signal processing approach consist of band-pass filtering the image by one or more band pass filters, multidimensional clustering, iso-contouring of the distance to centroid of the one or more filtered values, and finally candidate generation and segmentation by contour processing. The physics-based approach also filters the image to retrieve a fat-corrected image to model the background of the breast, and the resulting image is subjected to a blob detection filter to model the intensity bumps on the foreground component of the breast that are associated with mass candidates.
Owner:AGFA NV
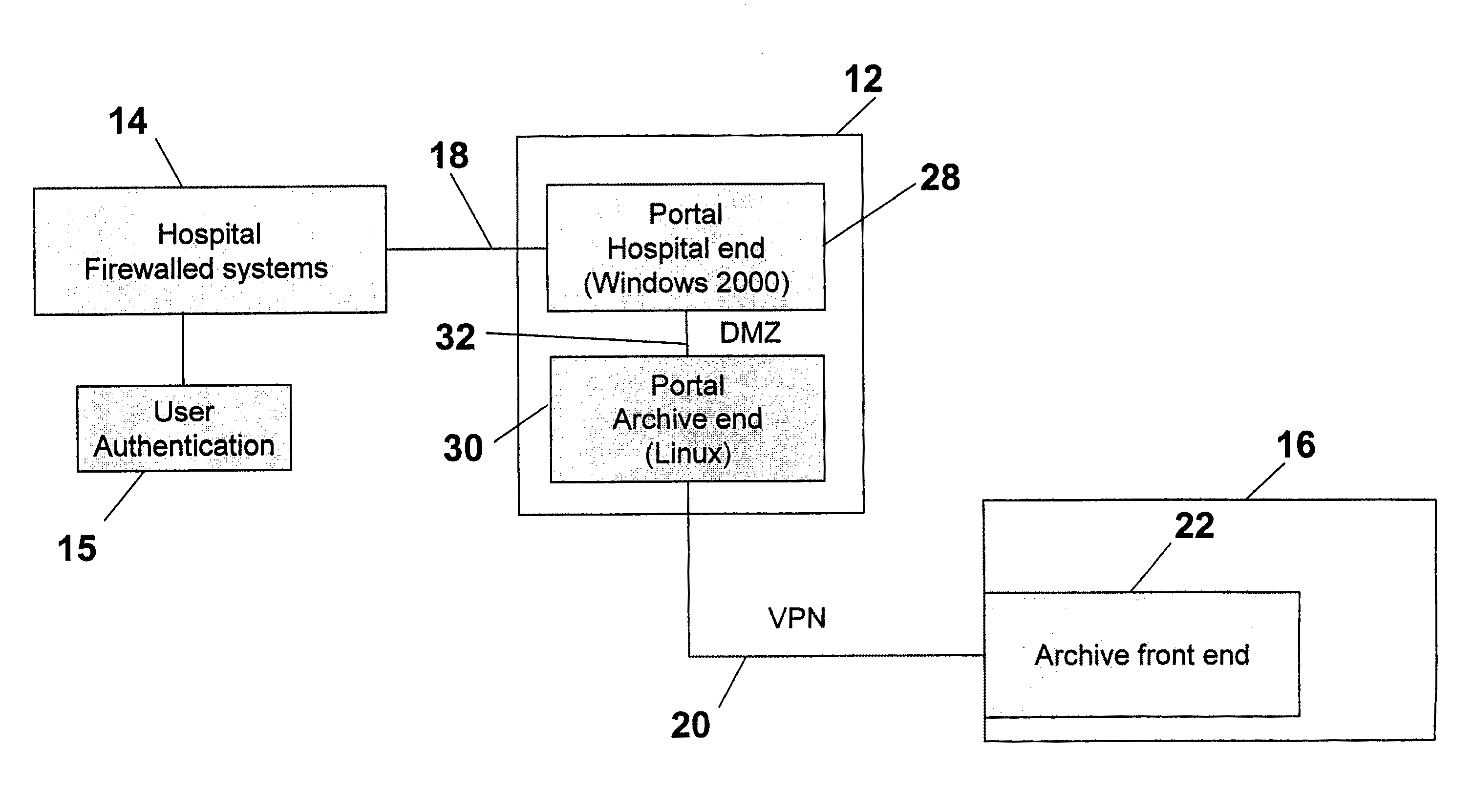
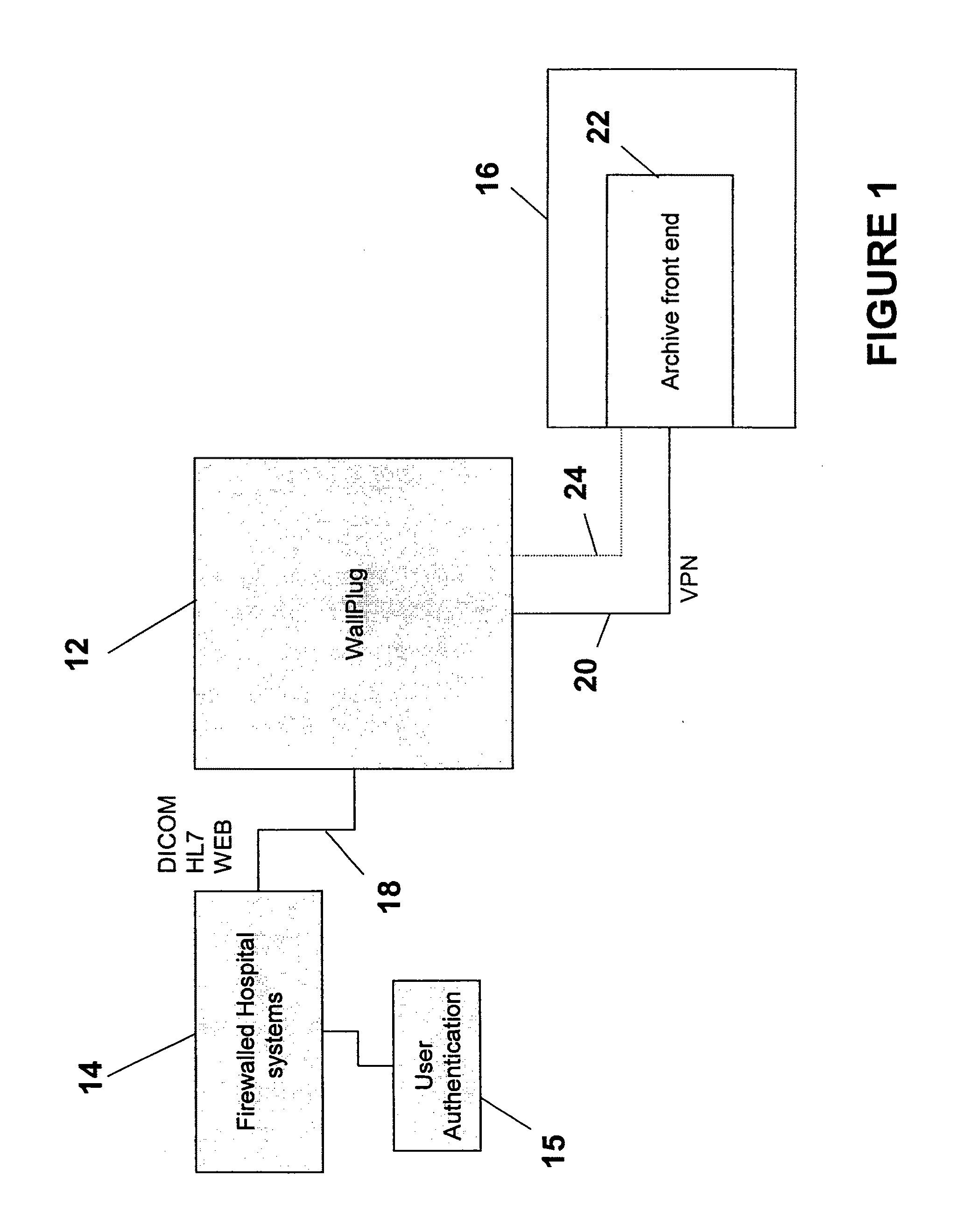
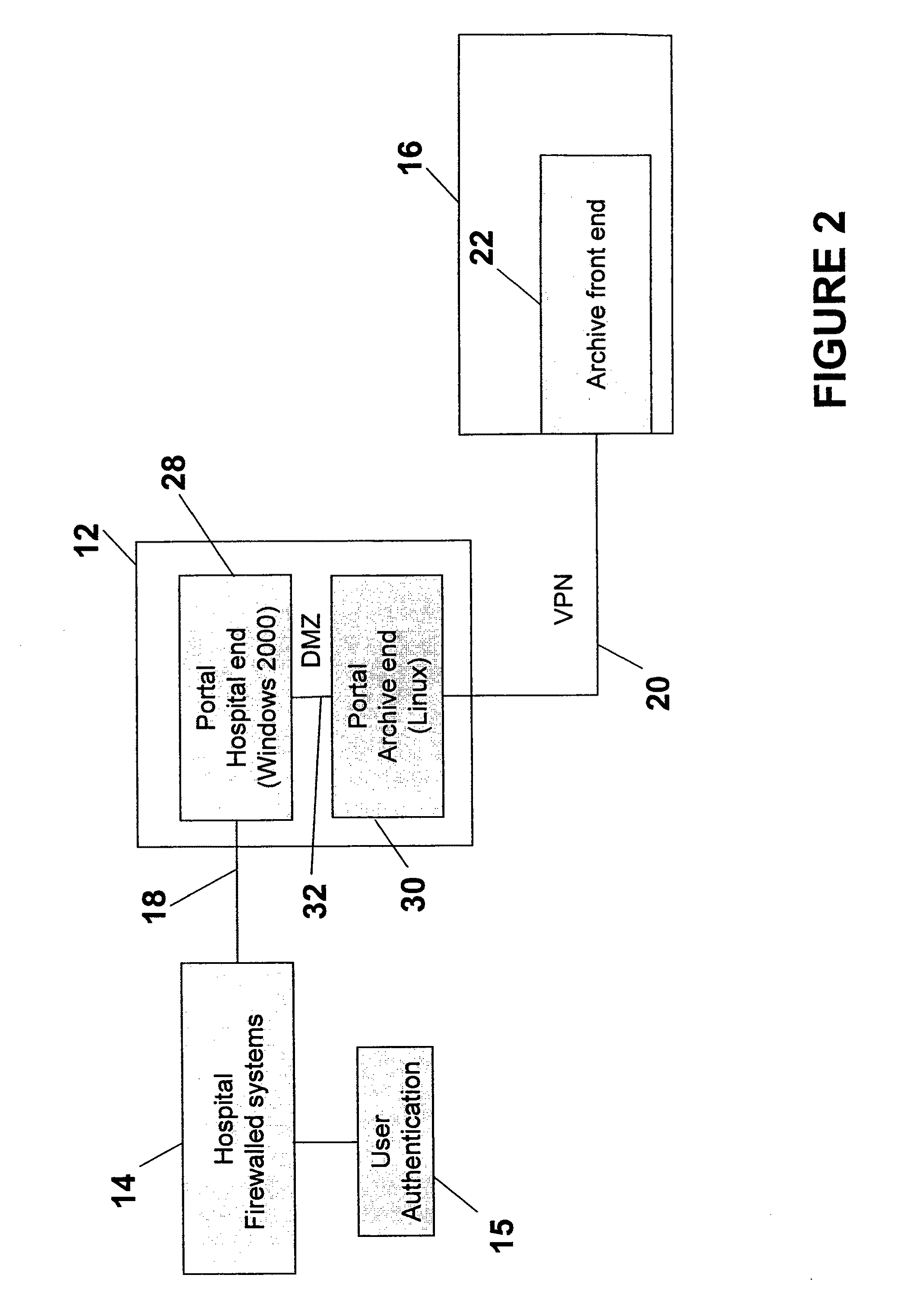
Cross-enterprise wallplug for connecting internal hospital/clinic imaging systems to external storage and retrieval systems
InactiveUS20090313368A1Communication securityComputer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsSecure communicationDICOM
A WallPlug (interface) connects DICOM devices located at a hospital to external storage and retrieval systems. The external storage and retrieval systems can be part of the National Digital Mammography Archive. The WallPlug allows secure communications within the hospital setting, and allows only selected data to be transferred between the hospital devices and the archive. The WallPlug enables cross-enterprise distribution of medical content with proper authentication and logging of transfers. The WallPlug includes two portals connected together by a private secure network. The use of two separate devices greatly enhances the security, redundancy, and manageability of the combined device.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Large area array single exposure digital mammography
InactiveUS6416218B1Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsDigital imagingDigital mammography
A unique digital imaging device includes the digital imager, a mammography machine including the digital imager, a method for processing the digital image obtained by the digital imager, a local area network (LAN) comprising a number of mammography machines and one or more work stations, and a wide area network (WAN) for transmitting digital images to remote locations. The digital imager according to the present invention comprises a large area, single exposure digital imaging device is provided that allows a number of electronic imagers to be butted together to form an array of electronic imagers large enough to image an entire breast in a single exposure. A preferred embodiment of the digital imager comprises an optical system, such as fiber optic bundles, optically coupled with the surface of the electronic imager. The optical systems may have a surface larger than the electronic sensors, and may be butted together to provide a gap-free imaging surface.
Owner:TREX MEDICAL CORP
Positioning method and positioning system for breast lesion puncture point
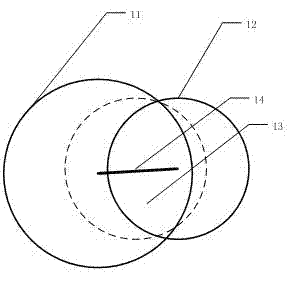
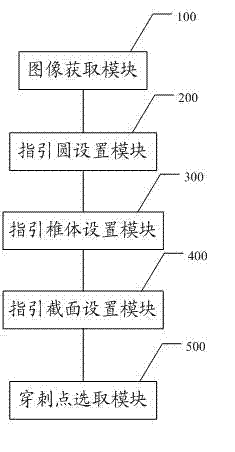
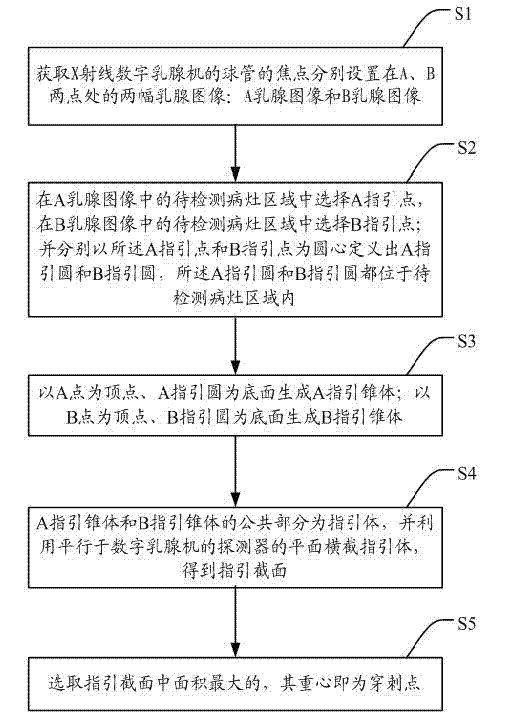
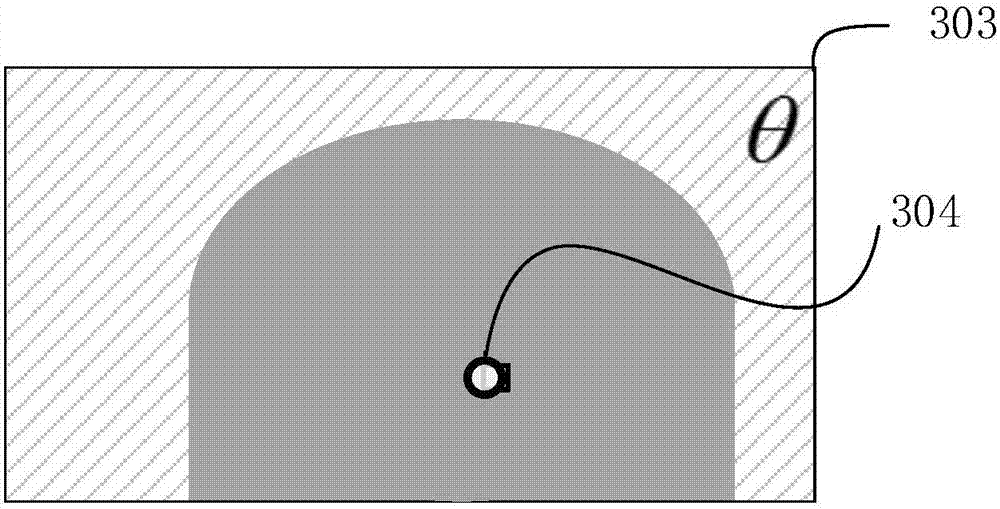
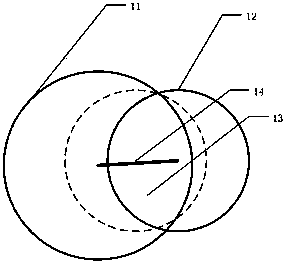
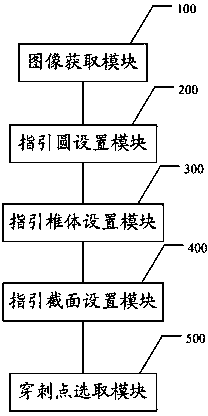
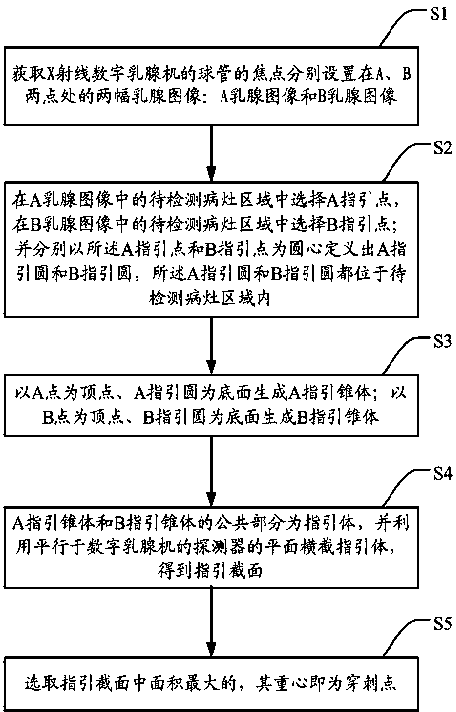
ActiveCN102860834ASophisticated calculationTheoretical perfectionRadiation diagnosticsPuncture BiopsyDigital mammography
The invention discloses a positioning method and a positioning system for a breast lesion puncture point. The positioning method comprises the following steps of: acquiring breast images shot at two different angles by a bulb tube of an X-ray digital mammography machine, and establishing a lesion projection light cone to generate a puncture guide body model. The maximum cross section is obtained by using a plane cross section guide body of a detector which is parallel with the X-ray digital mammography machine, and a point which is far away from the edge is picked on the maximum cross section to serve as the puncture point. The puncture point determined by the positioning method is located in a breast lesion, and is remote from the edge of the lesion, and more enough lesion tissues can be obtained when puncture biopsy is performed. Compared with other puncture point coordinate computing methods, the positioning method for the breast lesion puncture point has the advantages that puncture point computation is exquisite; the theory is perfect; the result accuracy is higher; the operation is simple; and the computing speed is high.
Owner:SHENZHEN ANKE HIGH TECH CO LTD
Retrofit digital mammography detector
A digital radiography ( 20 ) detector has a first housing ( 18 ) having substantially the form factor of a film cassette and having a chest wall edge (C). The first housing ( 18 ) has an X-ray converter ( 70 ) with a detection array ( 26 ), each detector generating a signal according to an amount of radiation received. Readout electronics ( 74 ) are coupled with switching elements in the detection array for obtaining the signals therefrom. The readout electronics ( 74 ) include elements formed from crystalline silicon and are distributed toward outer edges of the first housing ( 18 ) and awayfrom the chest wall edge (C). X-ray shielding selectively protects the readout electronics ( 74 ) and is located beneath a portion of the detection array. A second housing ( 40 ), electrically connected to the first housing ( 18 ) has a power source for the detector, readout and control electronics for obtaining signals provided from the detection array ( 26 ).
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
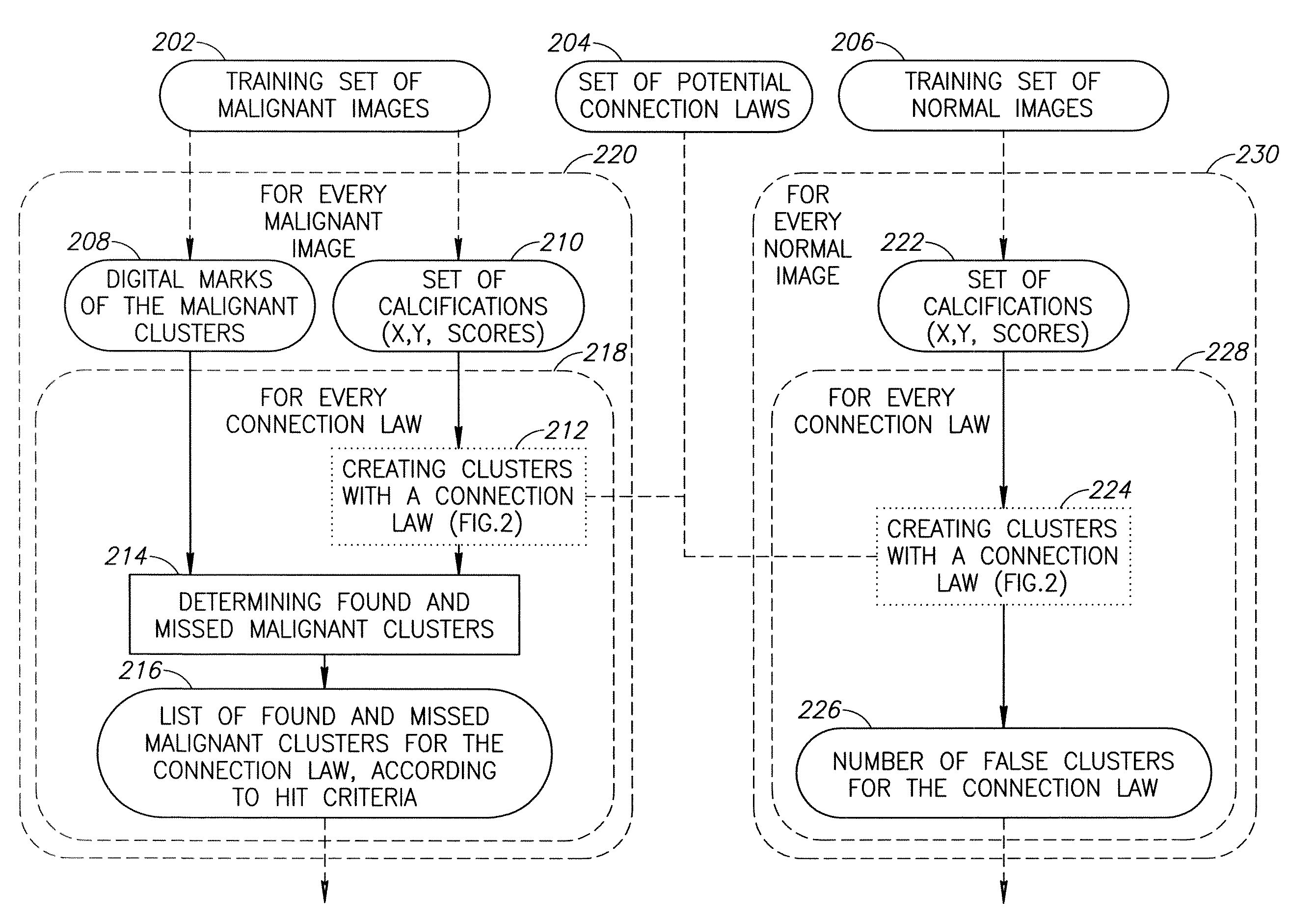
Clusterization of Detected Micro-Calcifications in Digital Mammography Images
InactiveUS20080144945A1Effective and time-saving methodHigh sensitivityImage enhancementImage analysisDigital mammographyCalcification
An iterative method for clusterization of objects in a digital image is taught. Recursivity occurs in both a forward and backward direction and connection is tested using a moving reference object. An optimized set of connection laws is used. A method for optimizing the connection laws to be used is also provided.
Owner:SIEMENS COMP AIDED DIAGNOSIS
Method and system for reconstructing digital breast tomosynthesis image
ActiveCN107545551ASuppress interlayer artifactsQuality improvementImage enhancementImage analysisVoxelHigh density
The invention relates to a method and system for reconstructing a digital breast tomosynthesis image. The method comprises a step of obtaining projection images of a scanned object at different angles, a step of calculating position coordinates of corresponding projections of a voxel to be reconstructed in the projection images, a step of identifying the types of the projections according to preset projection mask values in the position coordinates, wherein the types comprises a high-density material projection or a normal tissue projection, a step of judging that the voxel to be reconstructedis a normal tissue voxel if the ratio of a high-density material projection number in the projections to a total projection angle number is smaller than a set threshold, a step of removing high-density material projections in the projections corresponding to the voxel to be reconstructed of the normal tissue in the reconstruction process, and a step of carrying out back-projection reconstructionof remaining projections of the voxel to be reconstructed and obtaining a reconstruction image with a corrected artifact. Through the above method for reconstructing a digital breast tomosynthesis image, an inter-layer artifact in the reconstruction image is suppressed, and the quality of the reconstructed image is improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HUARUI TECH
Multi-threshold peripheral equalization method and apparatus for digital mammography and breast tomosynthesis
ActiveUS7764820B2Improve efficiencyHigh strengthImage enhancementImage analysisTomosynthesisDigital mammography
A peripheral equalization (PE) method and apparatus for compensating for thickness reduction in outer edges of the breast in a mammogram (i.e. a two-dimensional image) while keeping the central area substantially unchanged. The PE method and apparatus can also be applied to three dimensional (tomosynthesis) images of a breast. The peripheral equalization is achieved by segmenting the image of the breast into at least two regions and using a multi-threshold technique to process the data in at least one of the two regions.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Digital mammography device
ActiveCN105188548APatient positioning for diagnosticsComputerised tomographsDigital mammographyElectric signal
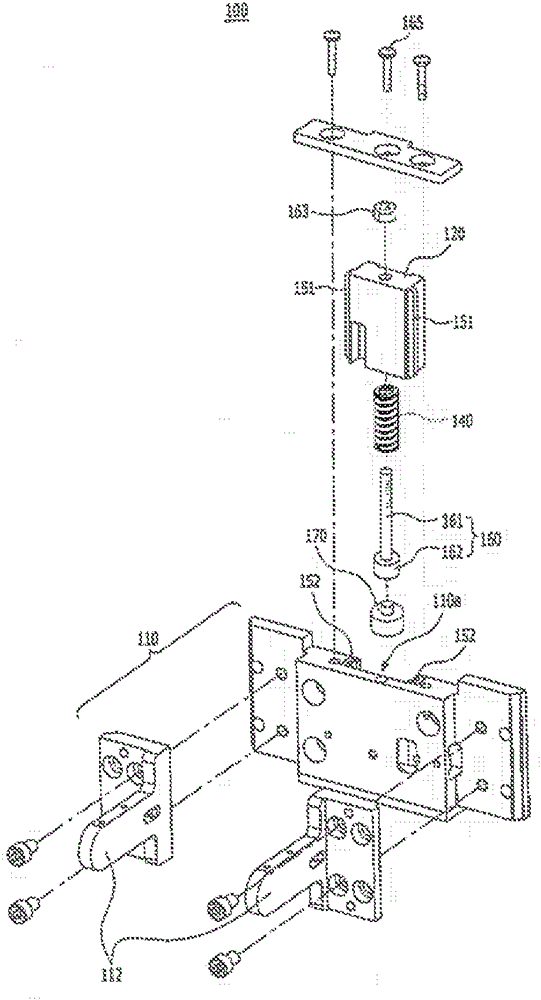
Disclosed is a digital mammography device. The digital mammography device according to the present invention comprises: a pressure pad provided so as to be able to move between an X-ray generator for irradiating X-rays and a detector for receiving X-rays that have passed through an object to be imaged, in such a way as to apply pressure to the object to be imaged; a pressure-pad drive unit provided with a motor and with a power transmission unit for moving the pressure pad by means of the power of the motor; and a pressurising force transmission unit having a coupling block to which the pressure pad is secured and having a mobile block which is secured to the power transmission unit and is linked so as to be able to move relative to the coupling block, and which said pressuring force transmission unit provides an electrical signal in accordance with relative motional displacement between the coupling block and the mobile block.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Hybrid slot-scanning grating-based differential phase contrast imaging system for medical radiographic imaging
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
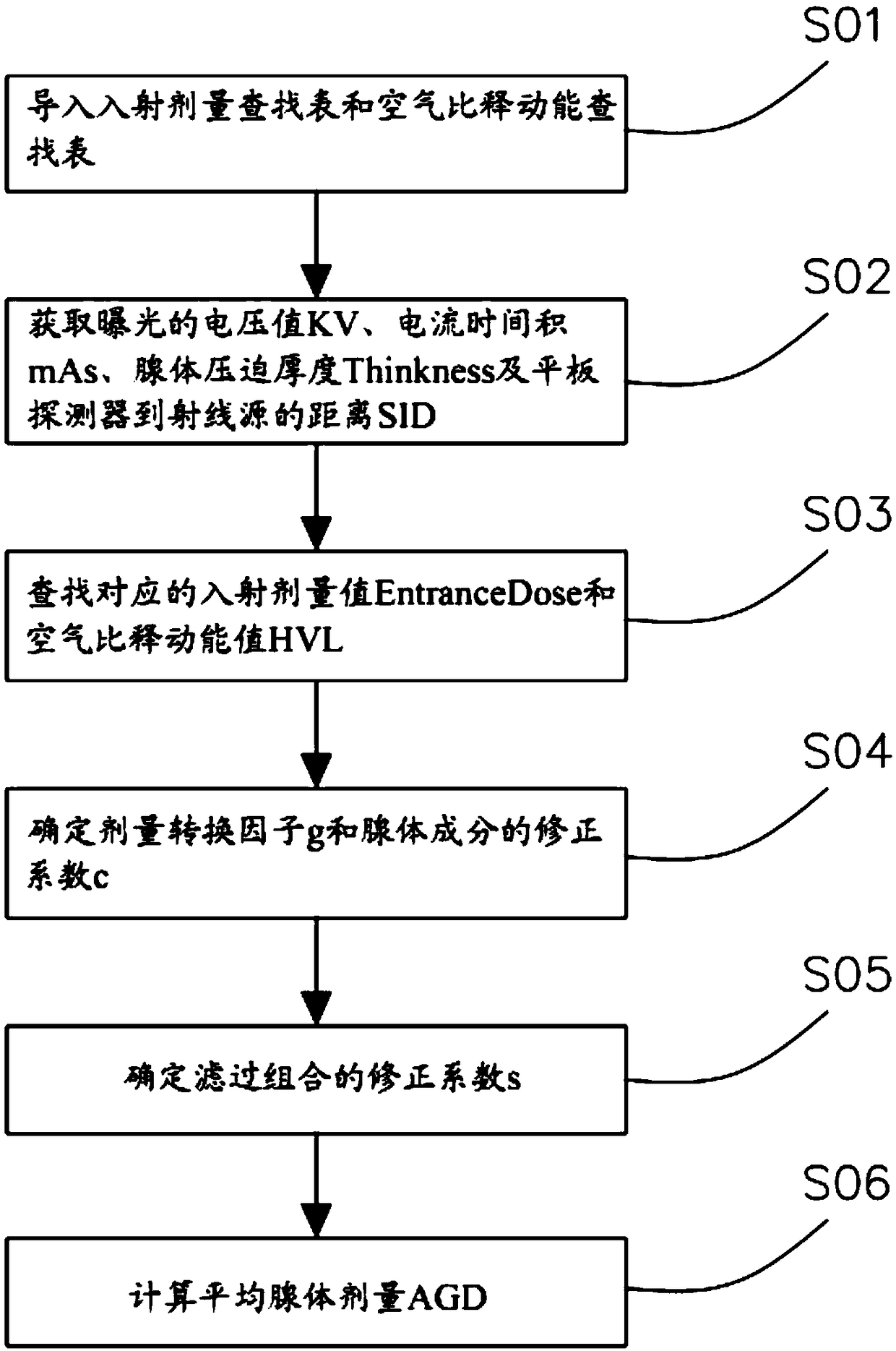
Method, system, device, and medium for calculating average gland dose of mammography system
InactiveCN109239755AQuick calculationDosimetersRadiation diagnosticsFlat panel detectorDose conversion
The invention discloses a method, a system, a device, and a medium for calculating the average gland dose of a mammography system. The method comprises the steps of: introducing an incident dose lookup table and an air kerma lookup table; obtaining an exposure voltage value KV, a current time product mAs, a gland compression thickness Thinkness, and a distance SID from a flat panel detector to a radiation source; searching a corresponding incident dose value EntranceDose and a corresponding air kerma value HVL from the incident dose lookup table and the air kerma lookup table; determining a dose conversion factor g and a correction factor c of the gland component; determining a correction factor s of the filtered combination; calculating the average gland dose AGD. According to the method,the system, the device, and the medium for calculating the average gland dose of a mammography system, the incident dose value and the air kerma value can be obtained quickly through the lookup tables, and the average gland dose value can be calculated according to the dose conversion factor, the correction factor of the gland component, and the correction factor of the filtered combination, so that the method, the system, the device, and the medium have the characteristics of rapid calculation, can ensure that the total average dosage does not exceed the guidance level, and is suitable for aconventional digital mammography system.
Owner:深圳蓝影医学科技股份有限公司
Positioning method and positioning system for breast lesion puncture point
ActiveCN102860834BSophisticated calculationTheoretical perfectionRadiation diagnosticsPuncture BiopsyDigital mammography
The invention discloses a positioning method and a positioning system for a breast lesion puncture point. The positioning method comprises the following steps of: acquiring breast images shot at two different angles by a bulb tube of an X-ray digital mammography machine, and establishing a lesion projection light cone to generate a puncture guide body model. The maximum cross section is obtained by using a plane cross section guide body of a detector which is parallel with the X-ray digital mammography machine, and a point which is far away from the edge is picked on the maximum cross section to serve as the puncture point. The puncture point determined by the positioning method is located in a breast lesion, and is remote from the edge of the lesion, and more enough lesion tissues can be obtained when puncture biopsy is performed. Compared with other puncture point coordinate computing methods, the positioning method for the breast lesion puncture point has the advantages that puncture point computation is exquisite; the theory is perfect; the result accuracy is higher; the operation is simple; and the computing speed is high.
Owner:SHENZHEN ANKE HIGH TECH CO LTD
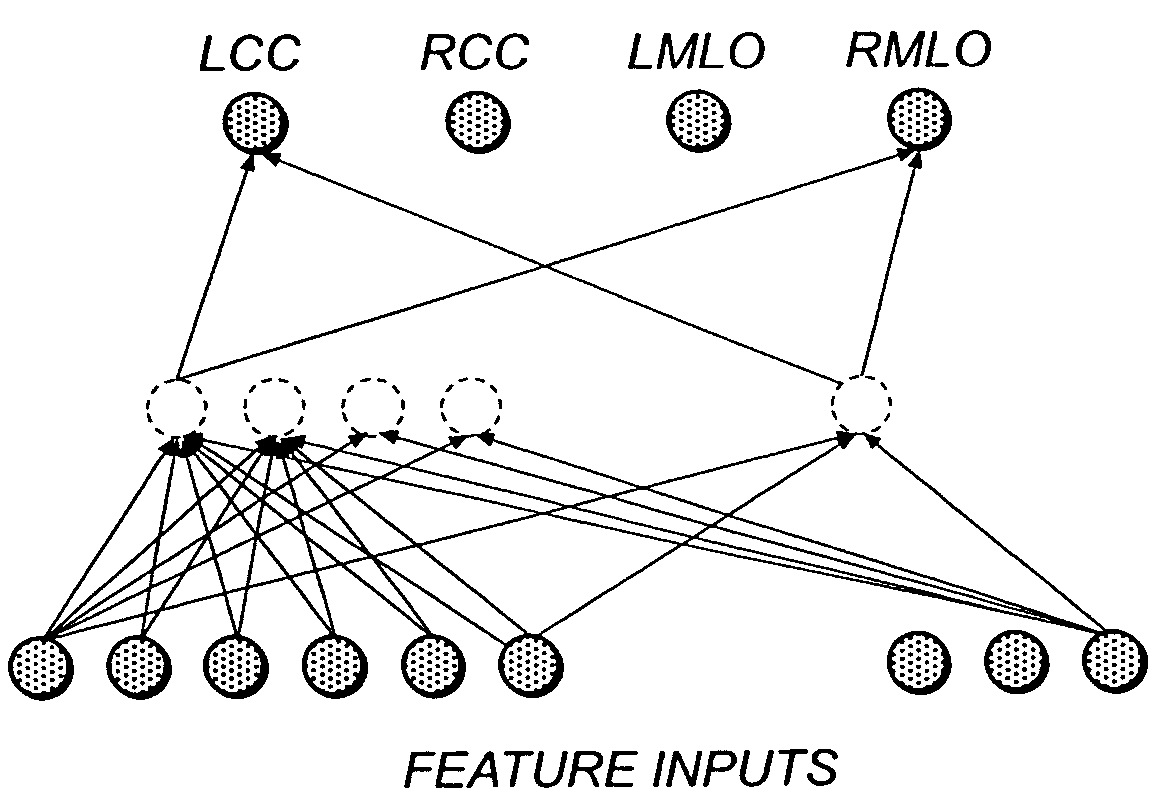
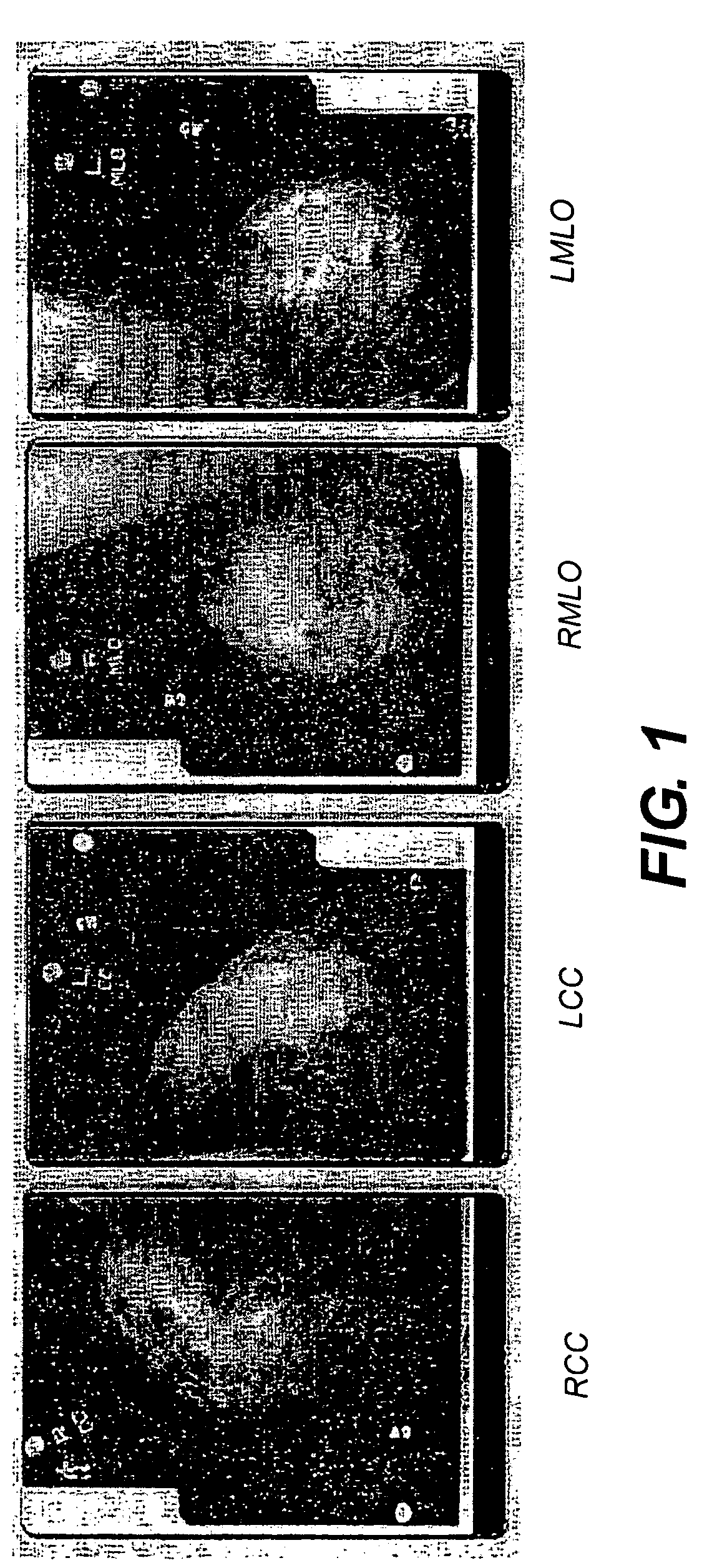
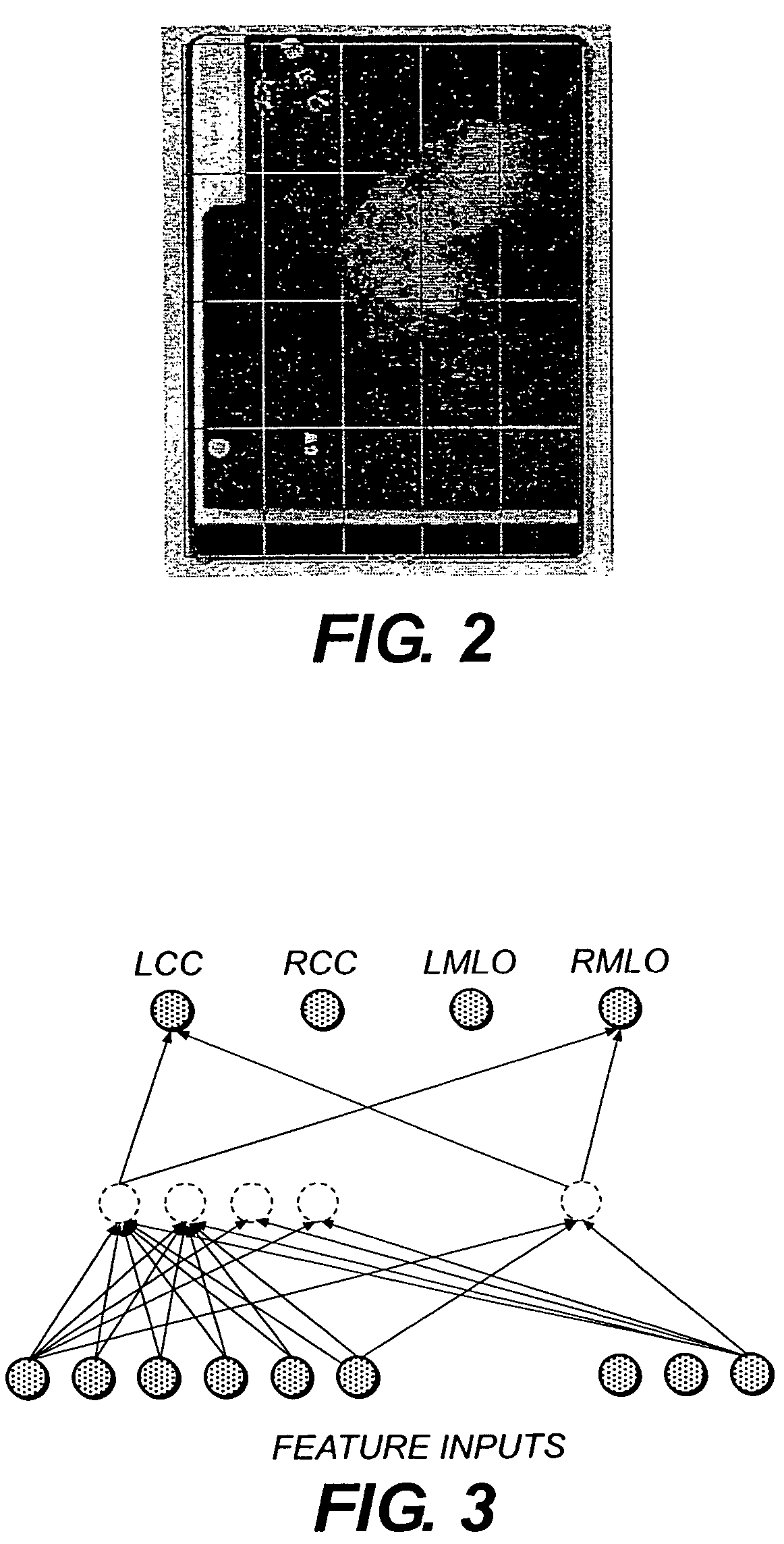
System and method for assigning mammographic view and laterality to individual images in groups of digitized mammograms
A method for identifying a type of a mammographic view for a digital mammography image. The method comprises the steps of: identifying two or more candidate view types; identifying at least one feature capable of distinguishing between the two or more candidate view types; determining the feature for the digital mammography image; and corresponding the determined feature of the digital mammography image with one of the two or more candidate view types to identify the type of a mammographic view of the digital mammography image in accordance with the correspondence.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com