Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
409 results about "Phase grating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
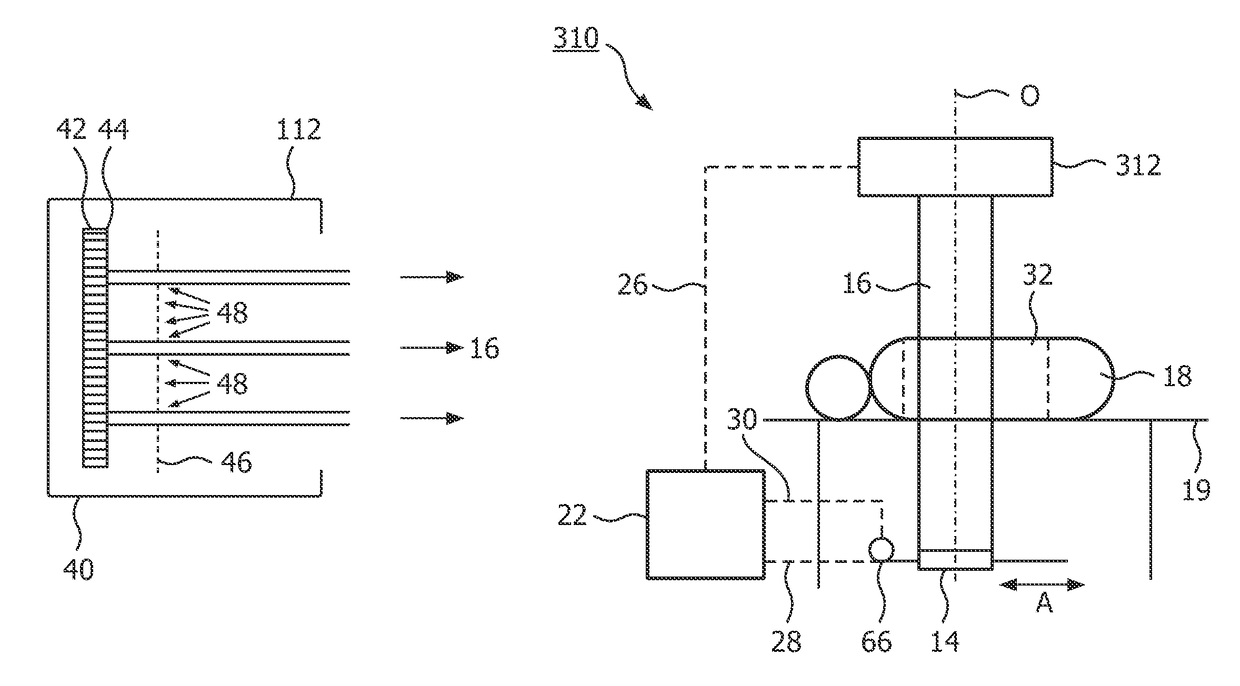
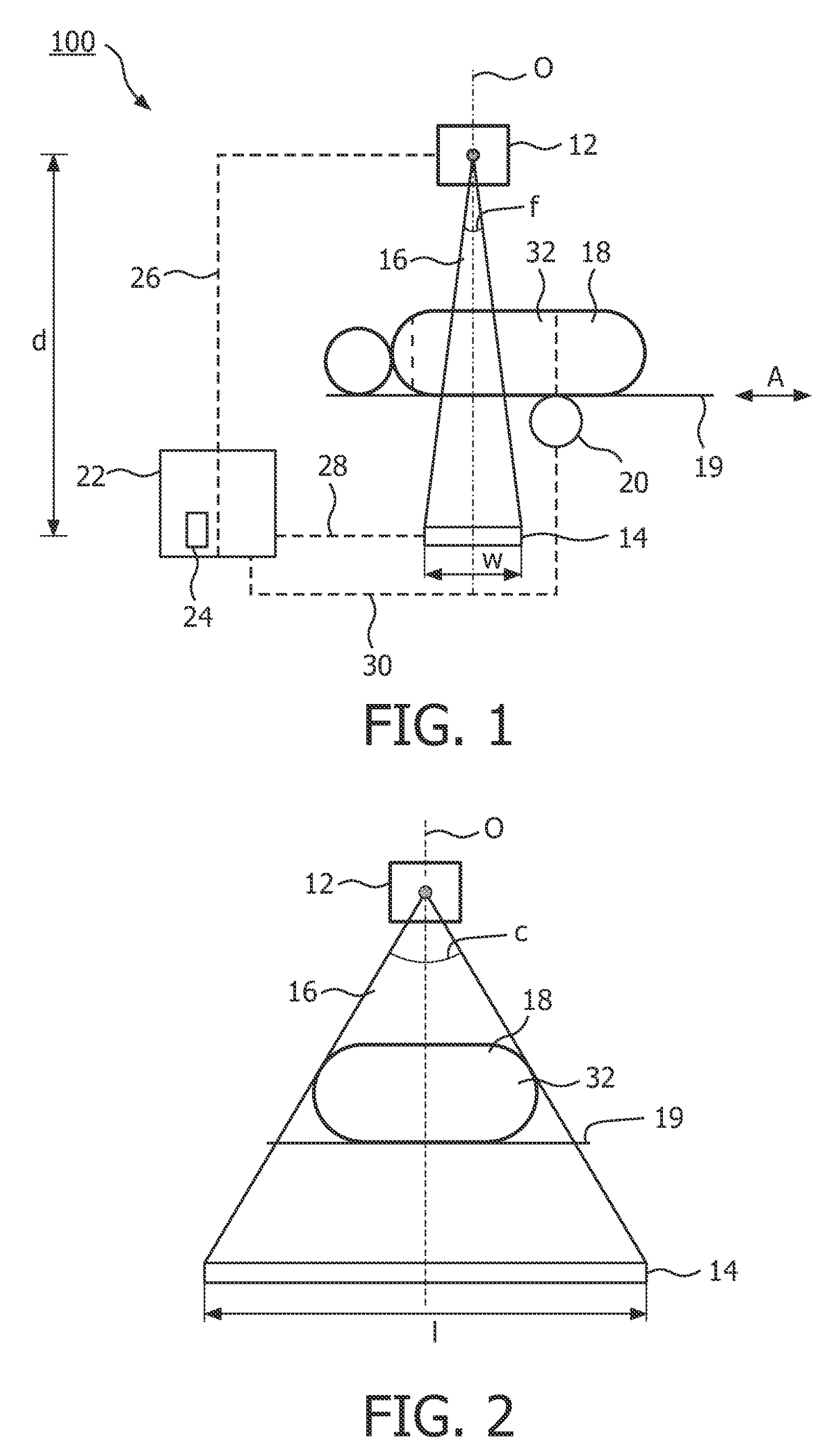
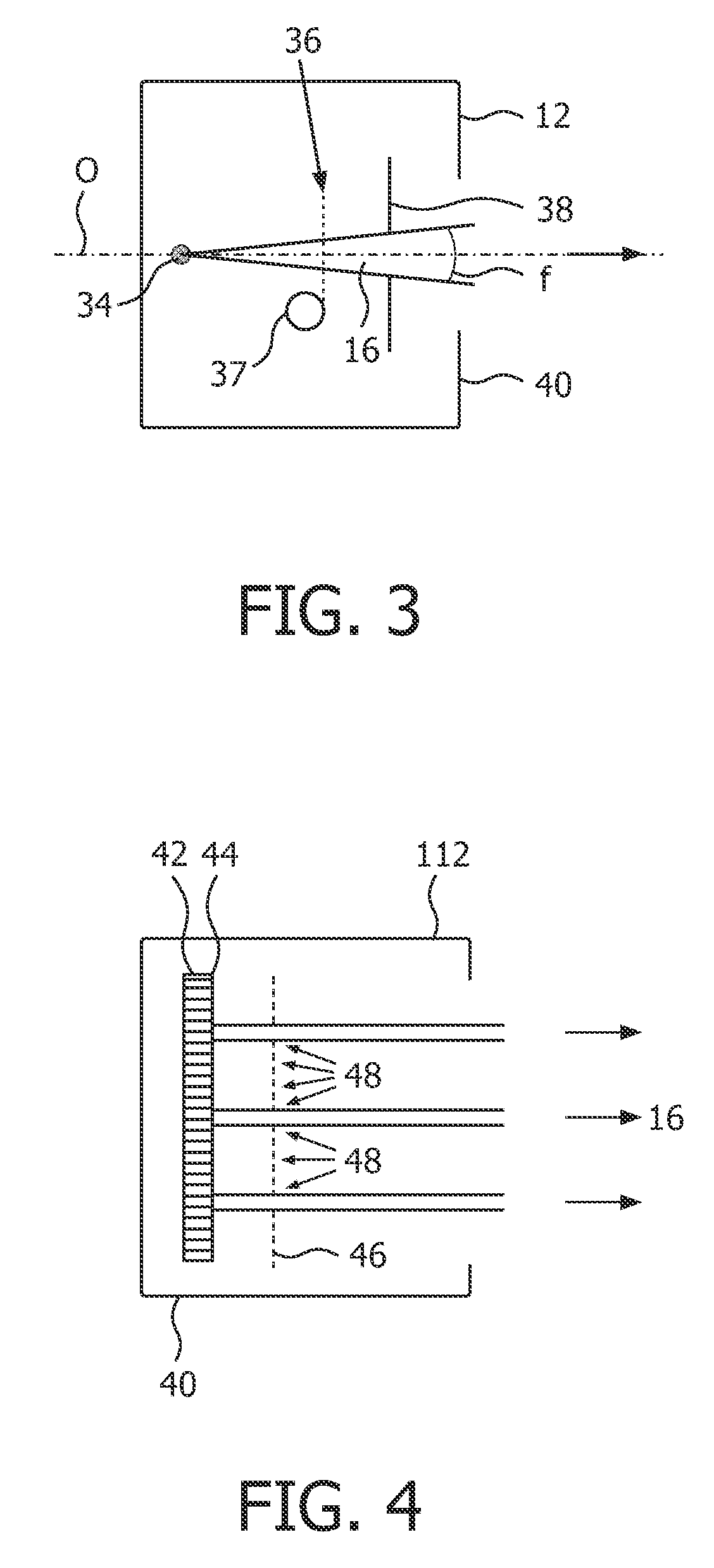
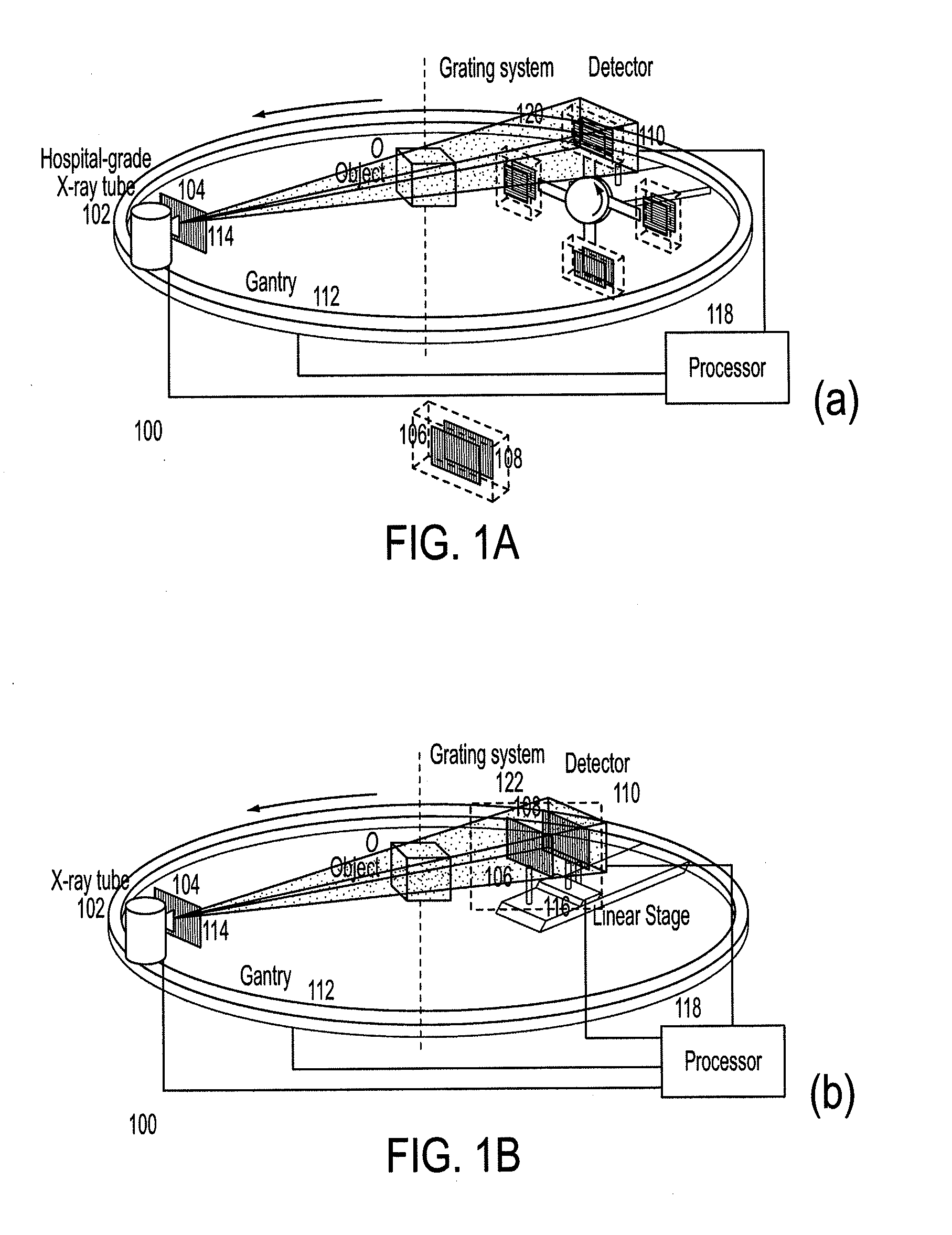
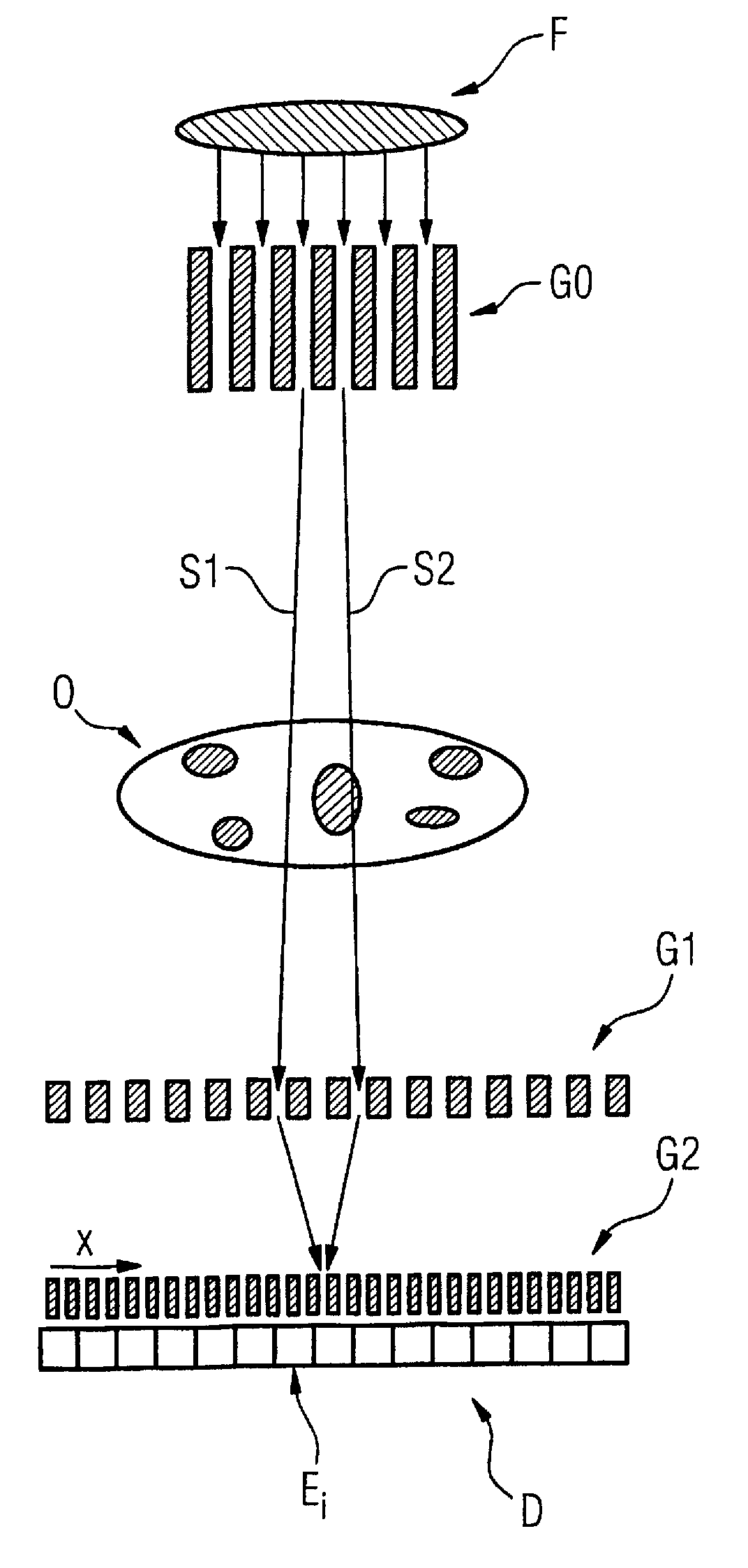
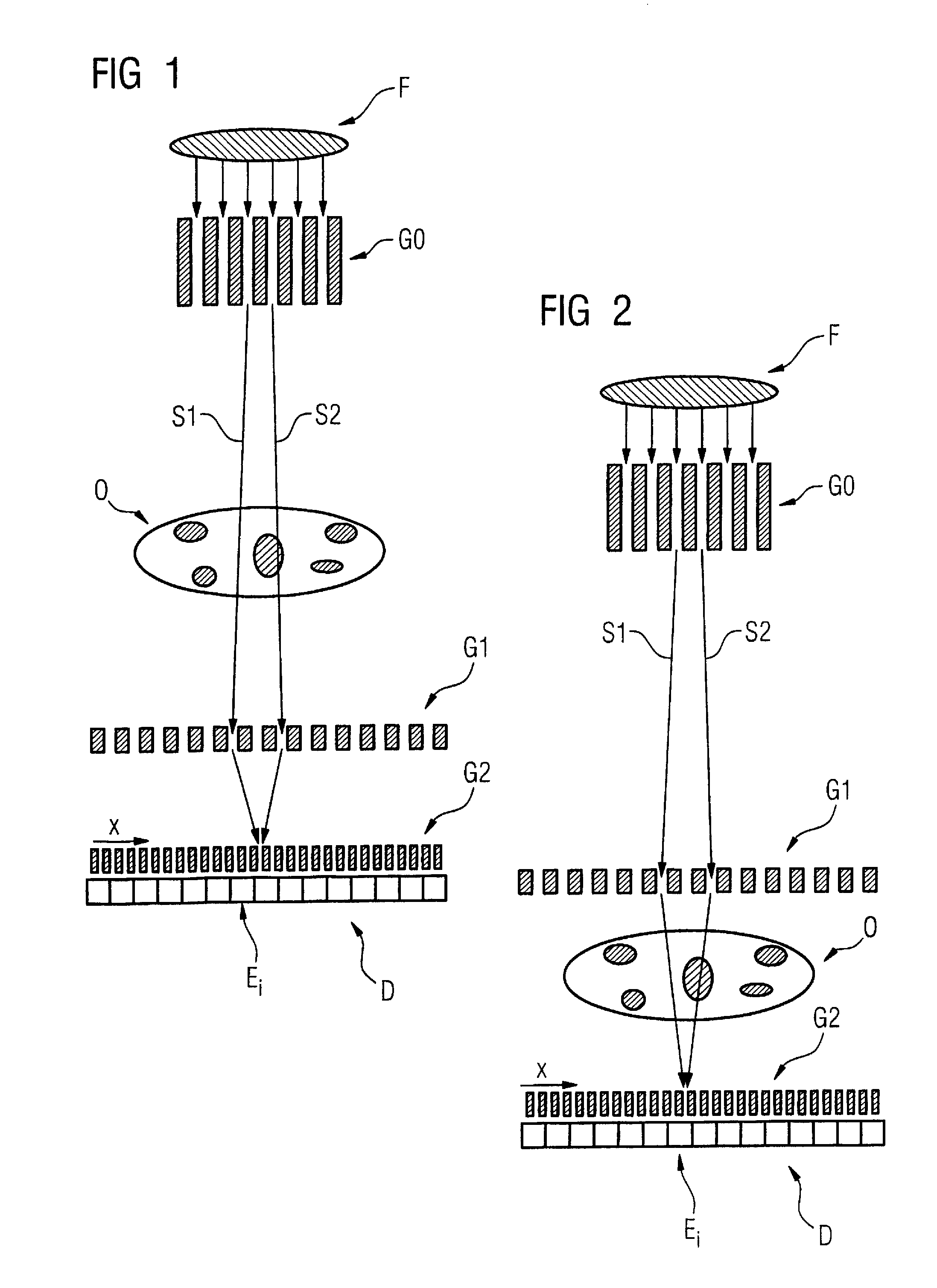
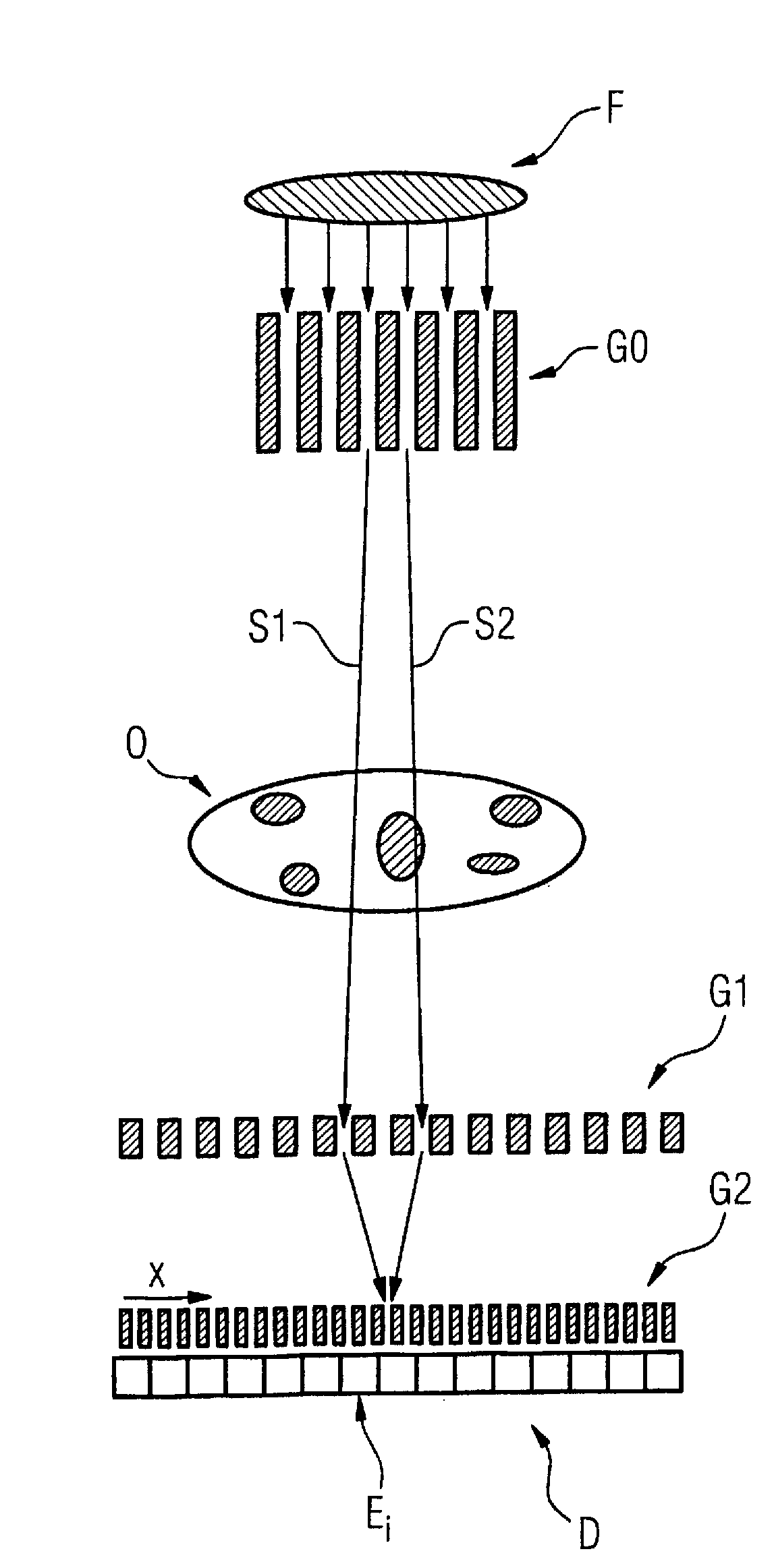
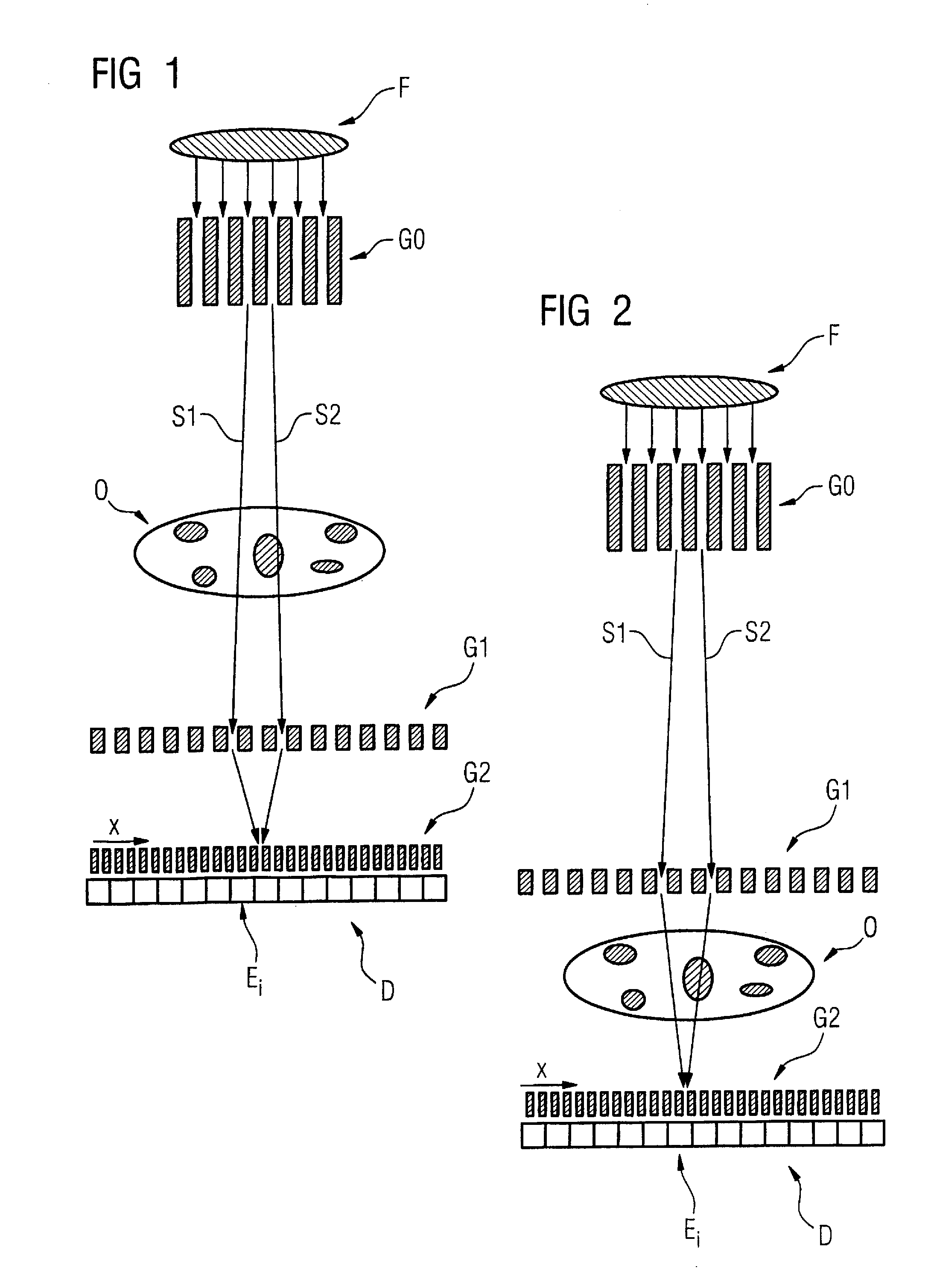
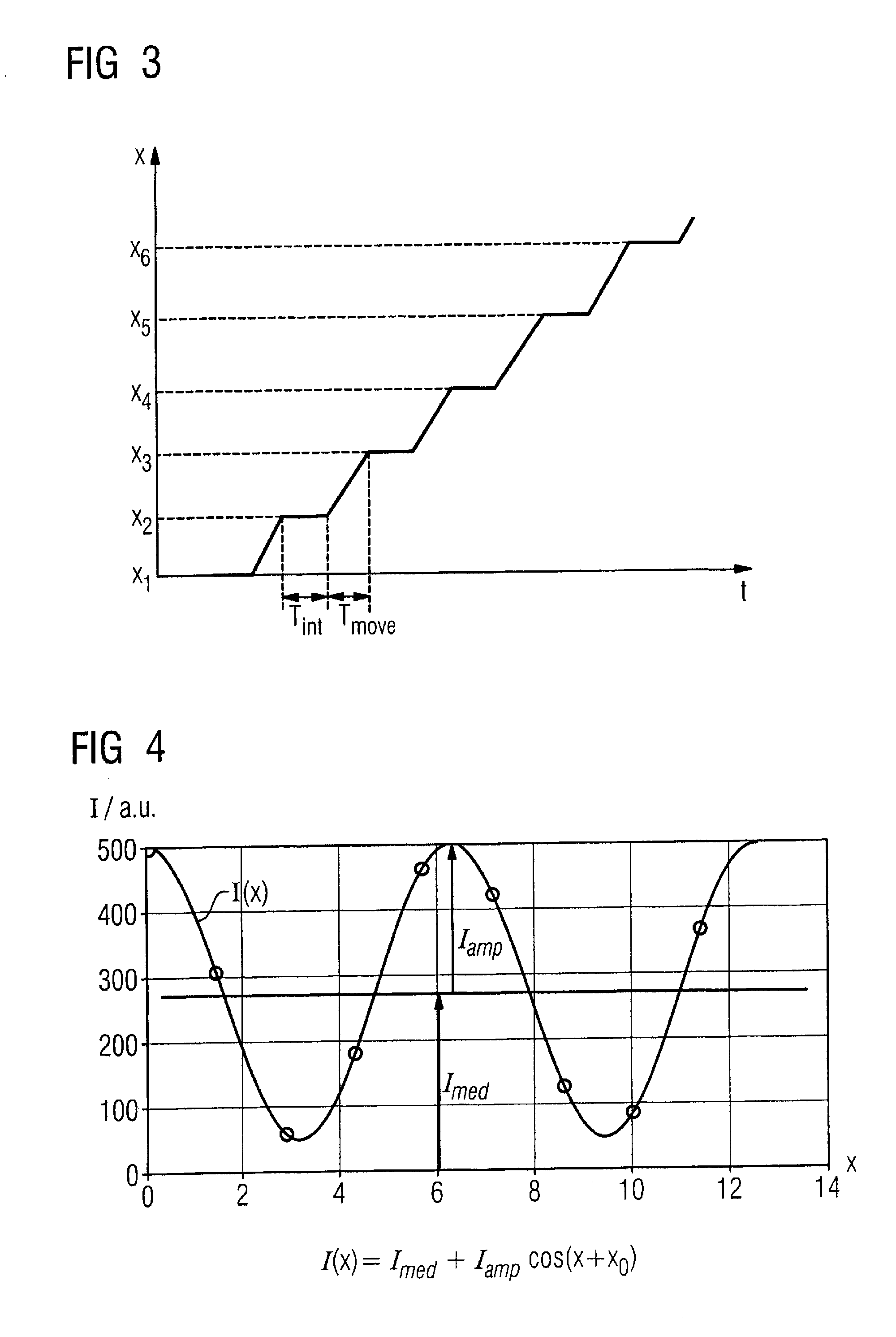
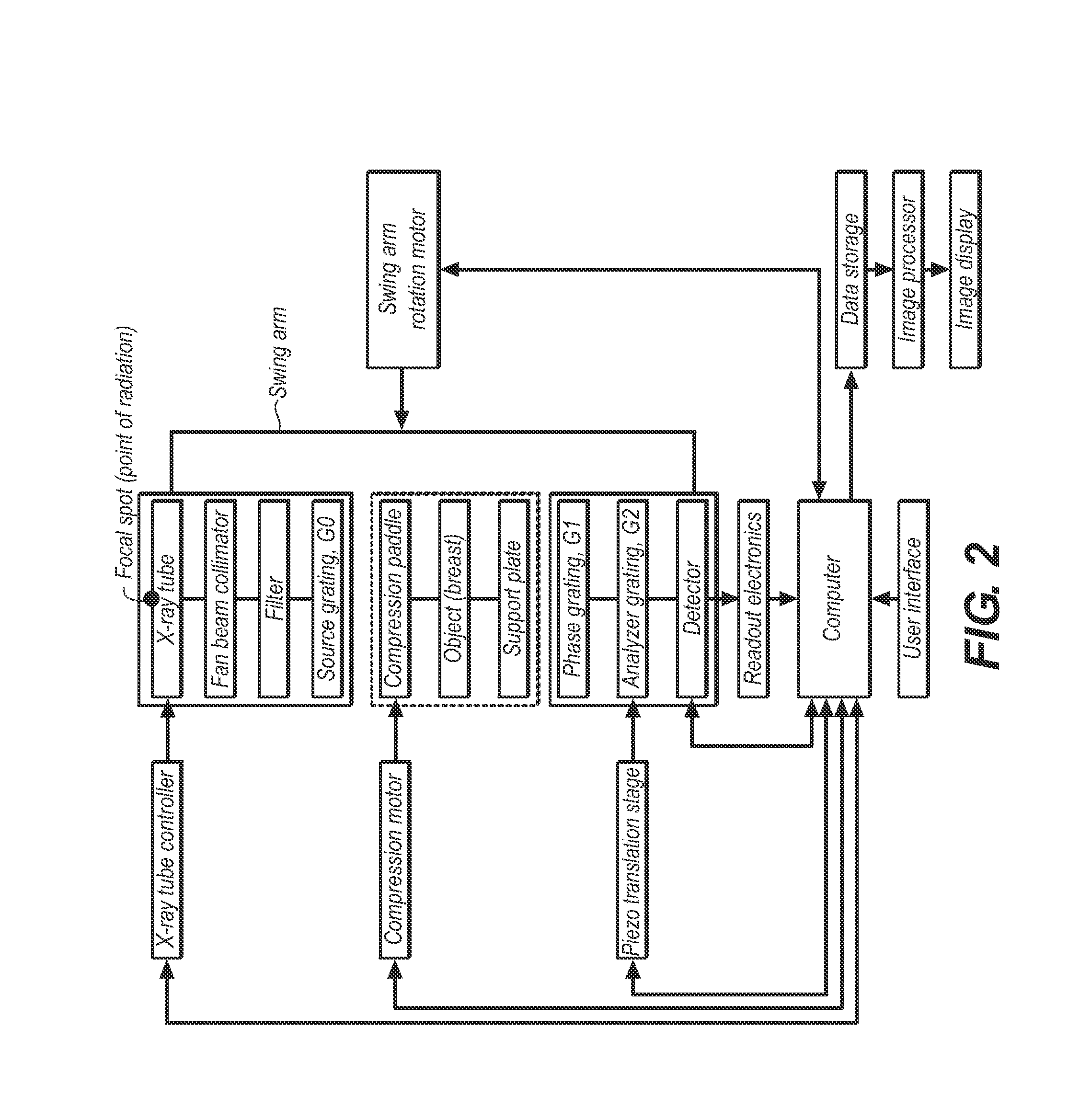
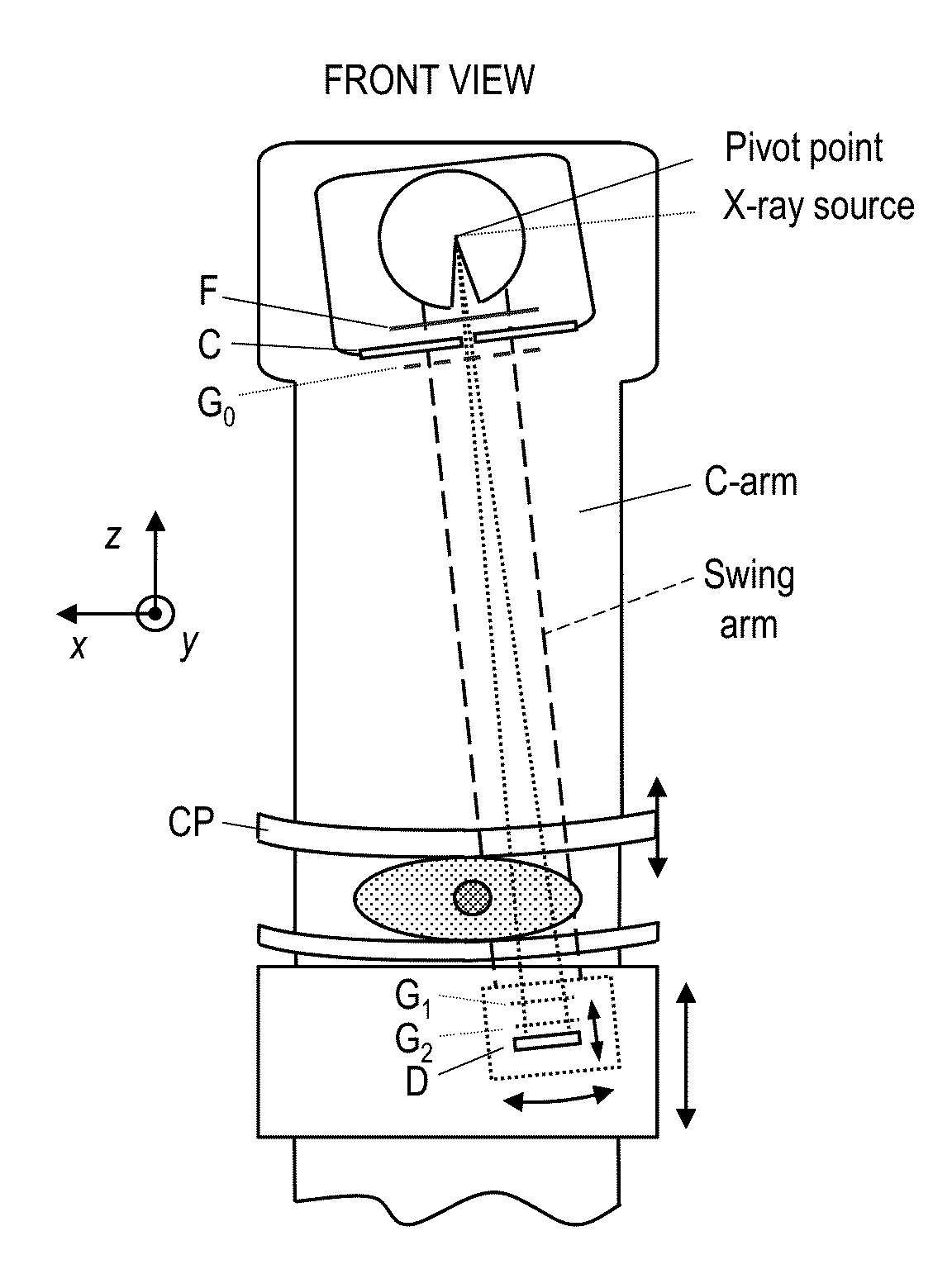
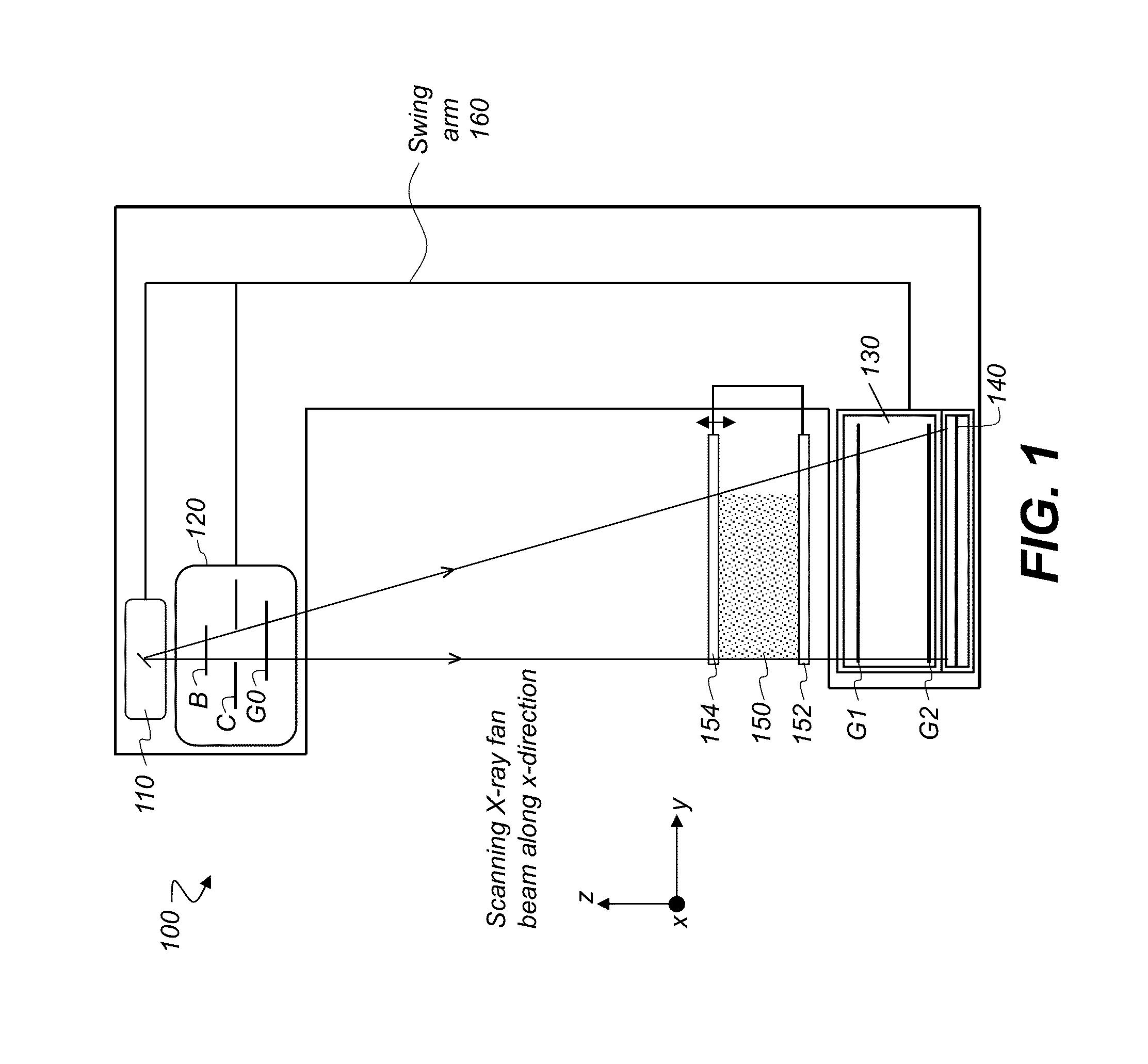
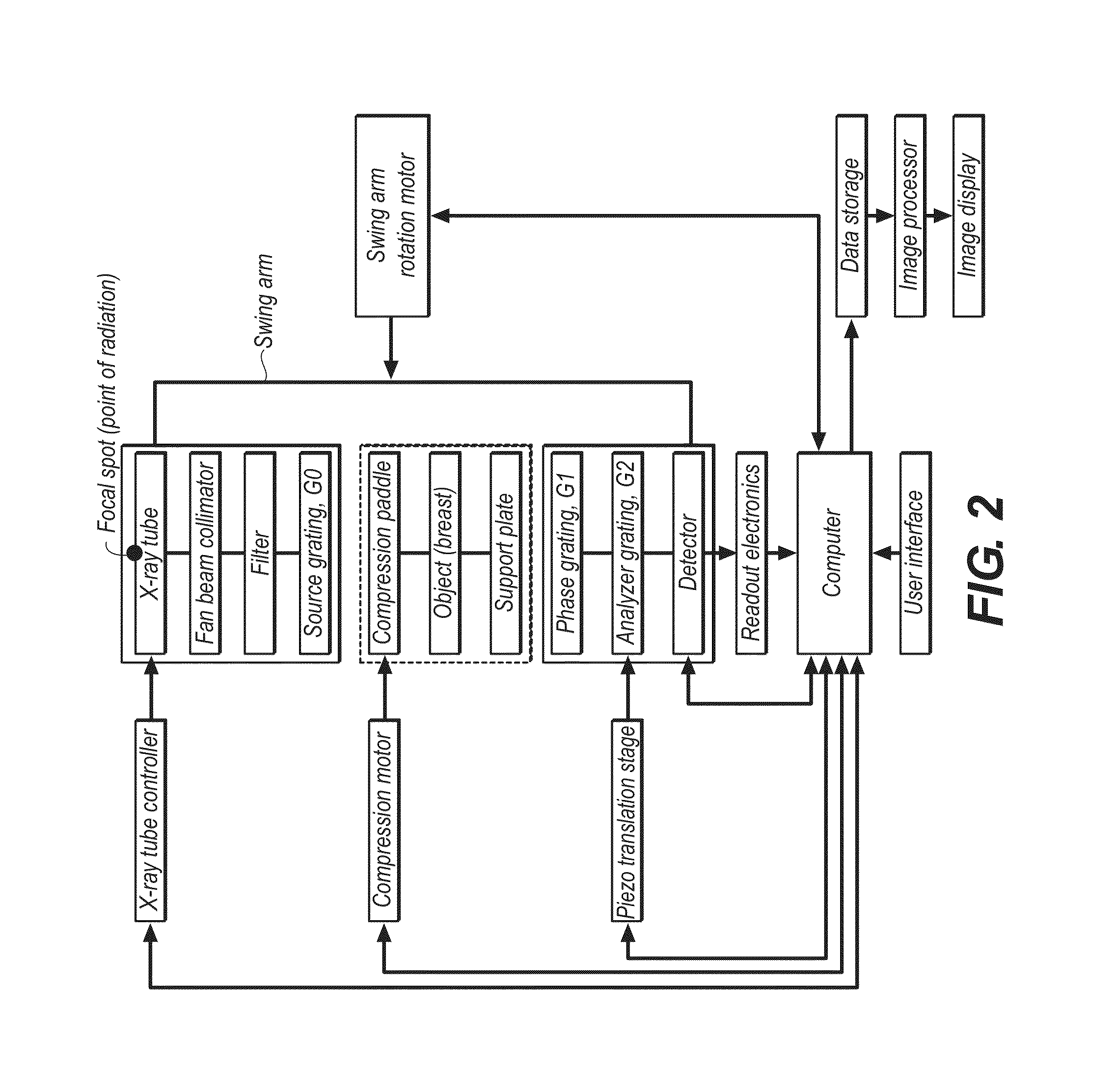
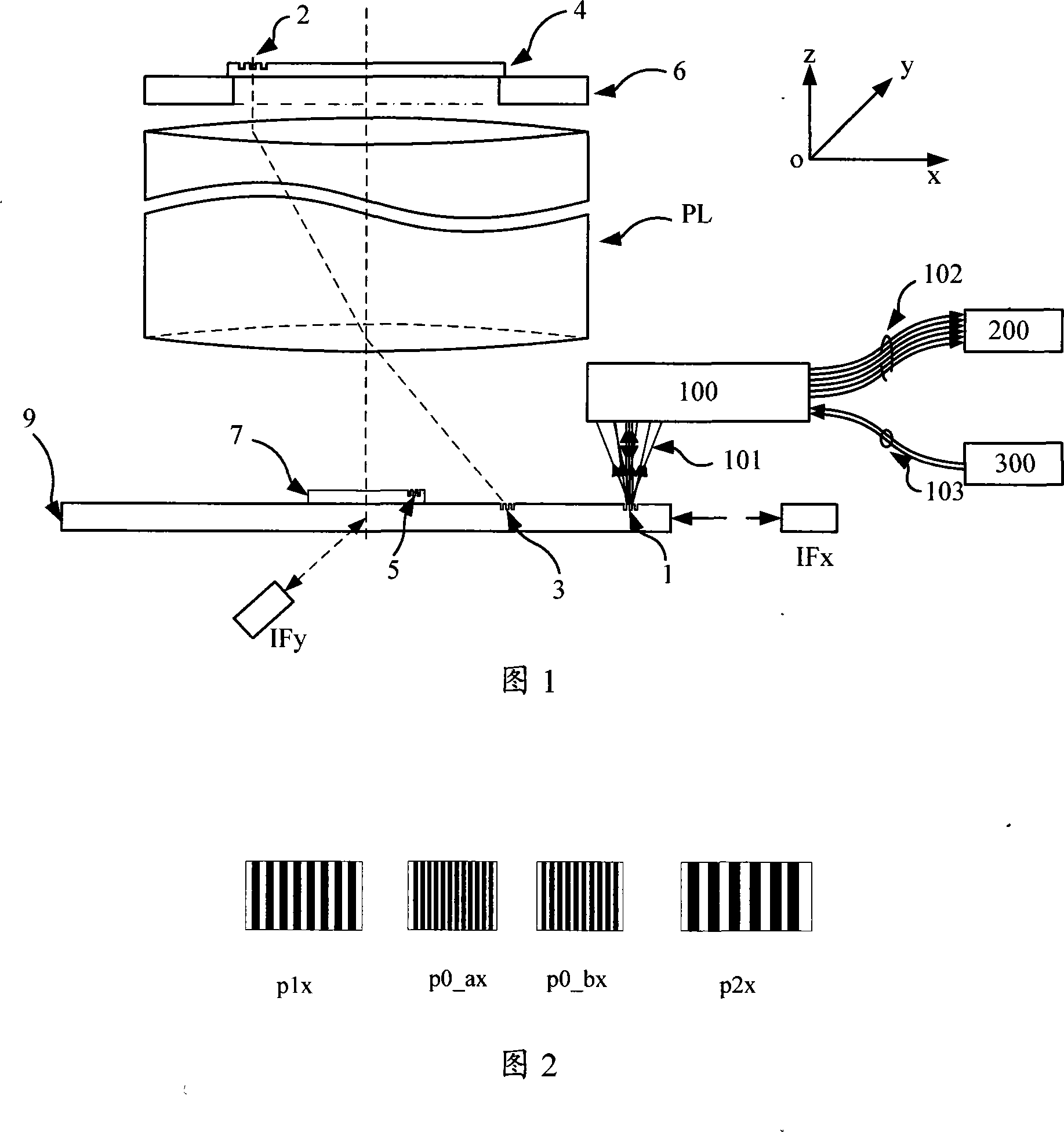
Scanning system for differential phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS9750465B2Reduce contrastReduce X-ray doseComputerised tomographsTomographyX ray imageImaging data
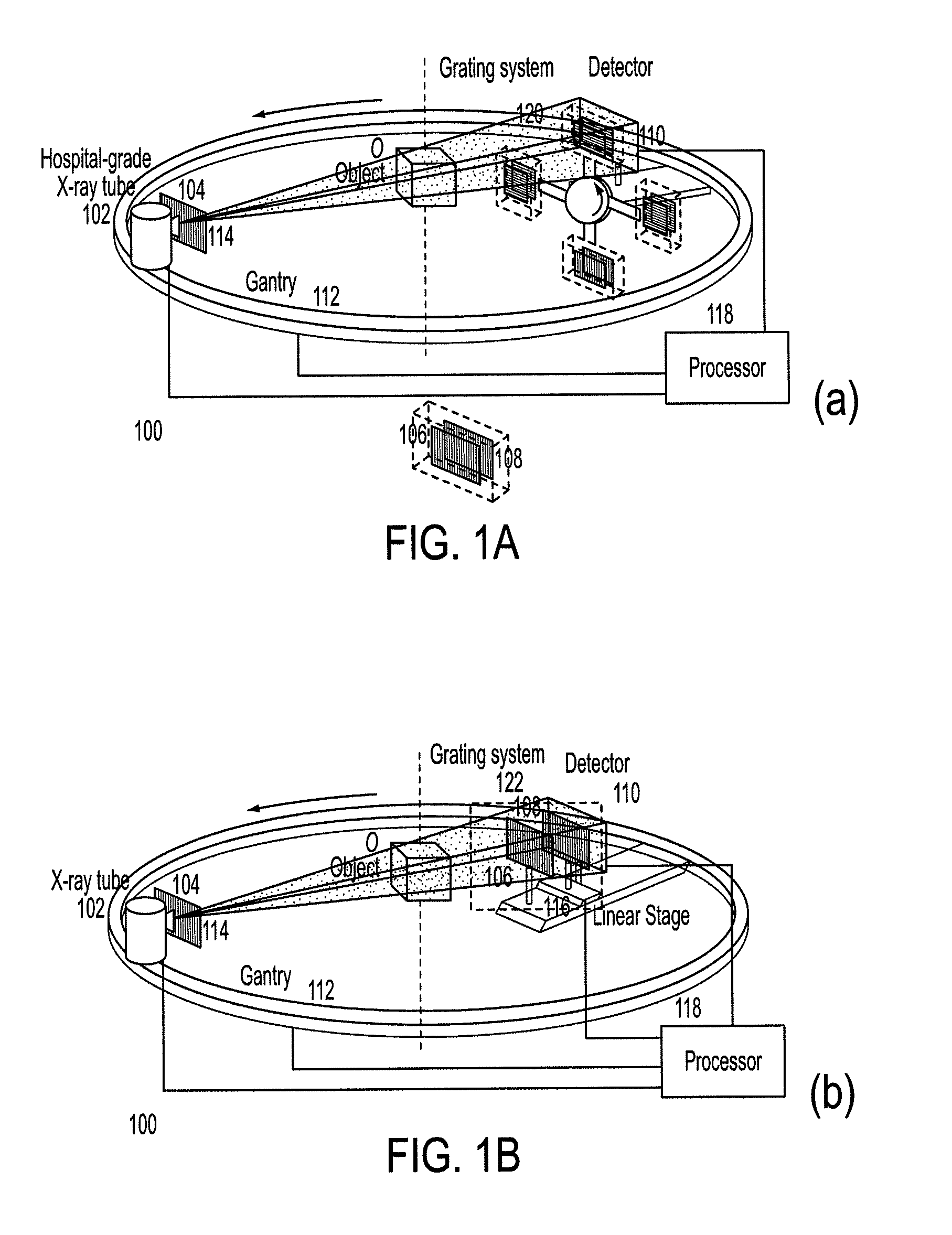
The invention relates to the field of X-ray differential phase contrast imaging. For scanning large objects and for an improved contrast to noise ratio, an X-ray device (10) for imaging an object (18) is provided. The X-ray device (10) comprises an X-ray emitter arrangement (12) and an X-ray detector arrangement (14), wherein the X-ray emitter arrangement (14) is adapted to emit an X-ray beam (16) through the object (18) onto the X-ray detector arrangement (14). The X-ray beam (16) is at least partial spatial coherent and fan-shaped. The X-ray detector arrangement (14) comprises a phase grating (50) and an absorber grating (52). The X-ray detector arrangement (14) comprises an area detector (54) for detecting X-rays, wherein the X-ray device is adapted to generate image data from the detected X-rays and to extract phase information from the X-ray image data, the phase information relating to a phase shift of X-rays caused by the object (18). The object (18) has a region of interest (32) which is larger than a detection area of the X-ray detector (18) and the X-ray device (10) is adapted to generate image data of the region of interest (32) by moving the object (18) and the X-ray detector arrangement (14) relative to each other.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Electronically controlled volume phase grating devices, systems and fabrication methods
InactiveUS20050232530A1Efficient and small device form factorLow costOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsSemiconductor materialsPhase grating
Electrically controlled volume phase gratings and electrically controlled Bragg Gratings can provide variable diffraction gratings that can be operated in a transmissive and / or reflective mode. They can be made from electro-optic materials placed directly on glass or semiconductor materials, utilizing conventional Liquid Crystal on Silicon (LCOS) processes and equipment. Highly efficient and / or small device form factors may be provided.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
Aligning system photolithography equipment
ActiveCN101114135ASimplify design difficultySimplify debugging difficultyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusPhase gratingLithographic artist
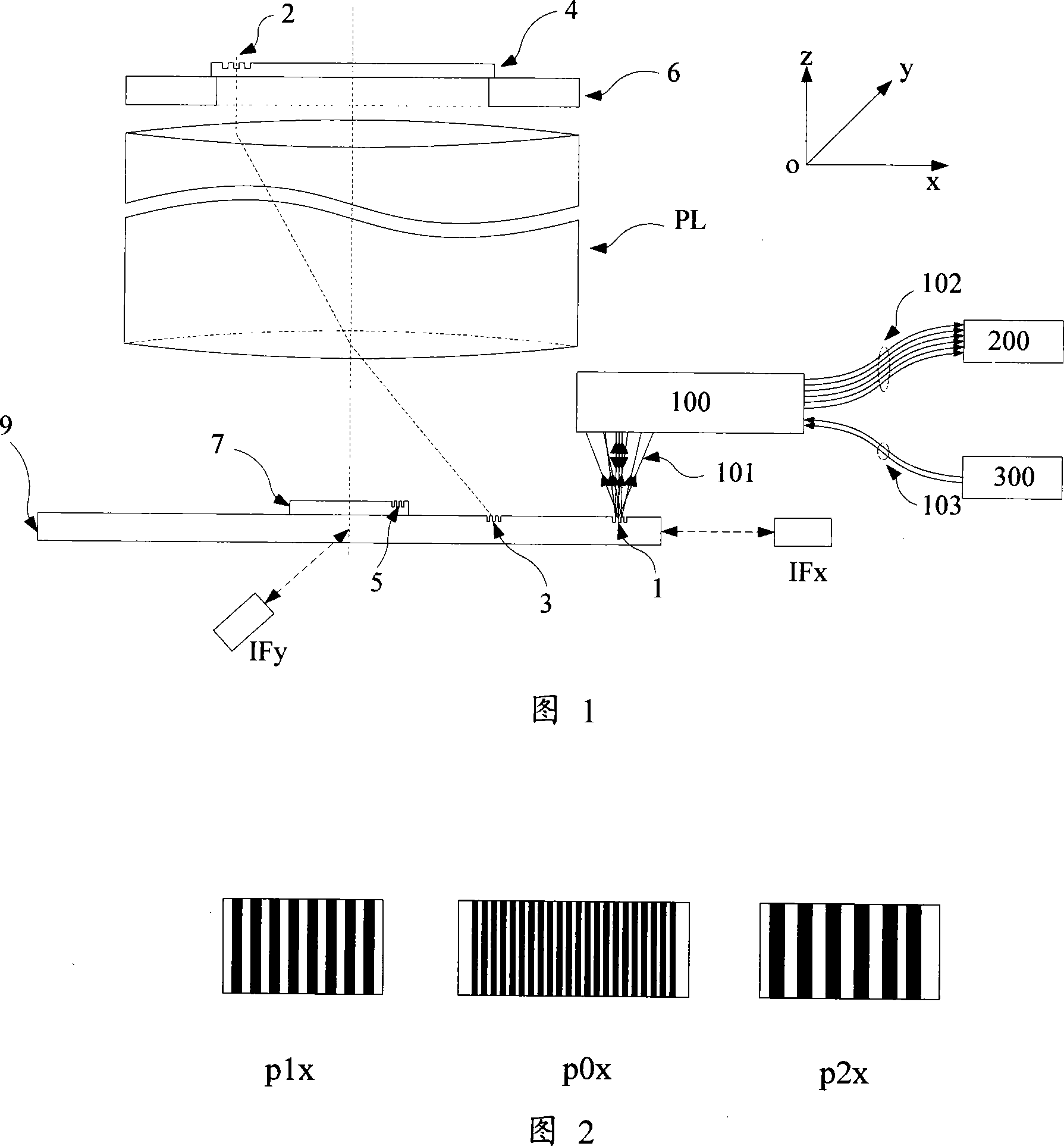
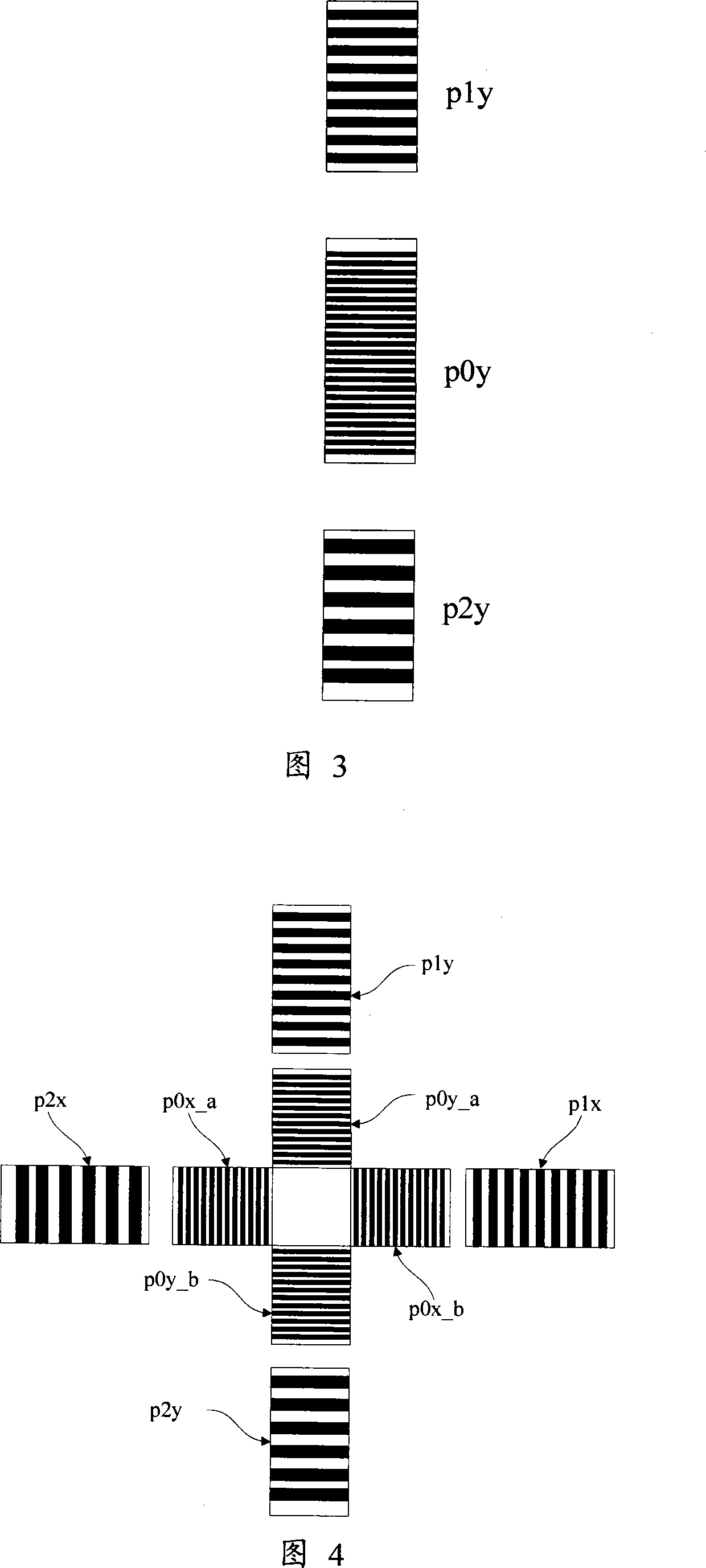
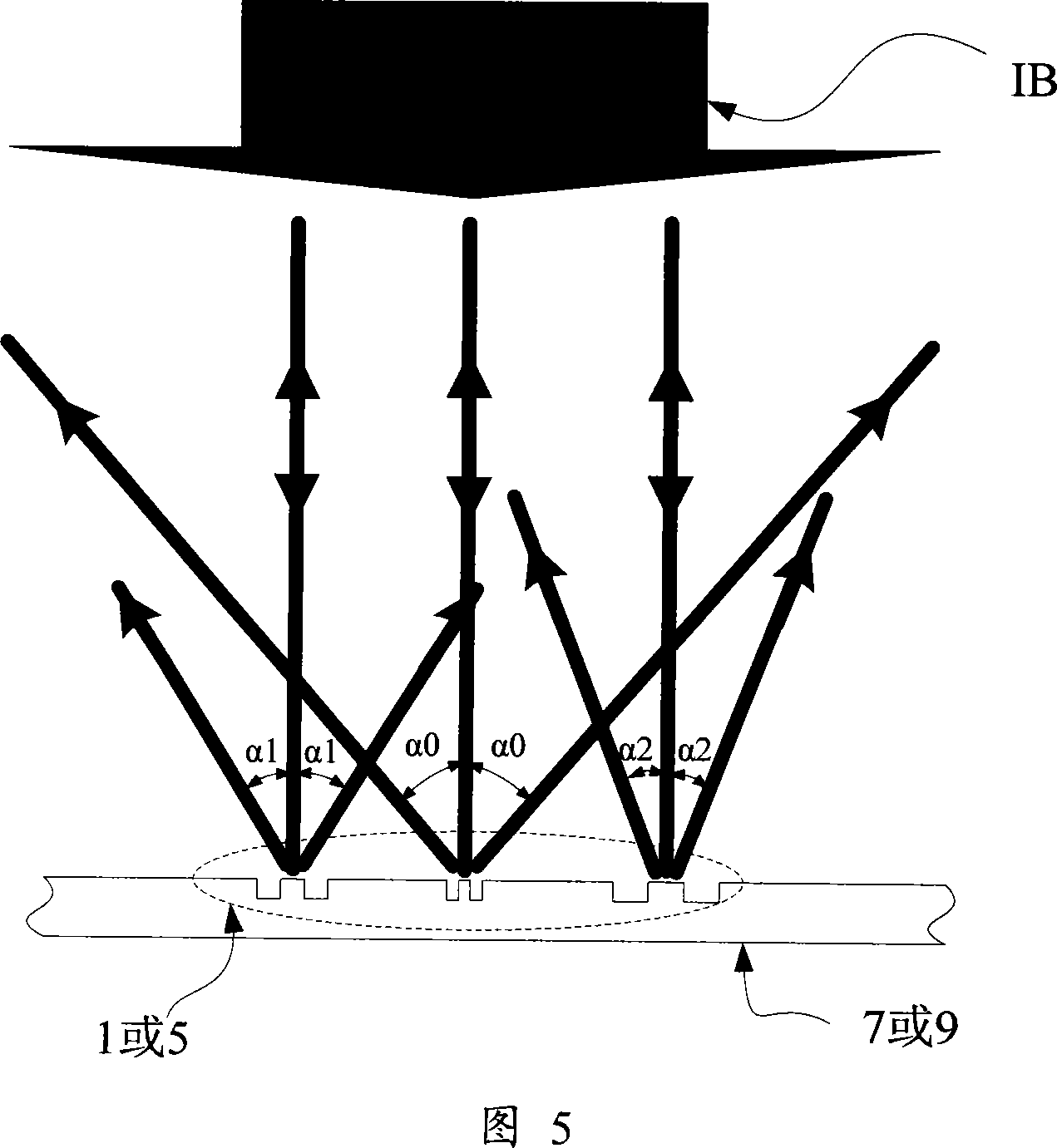
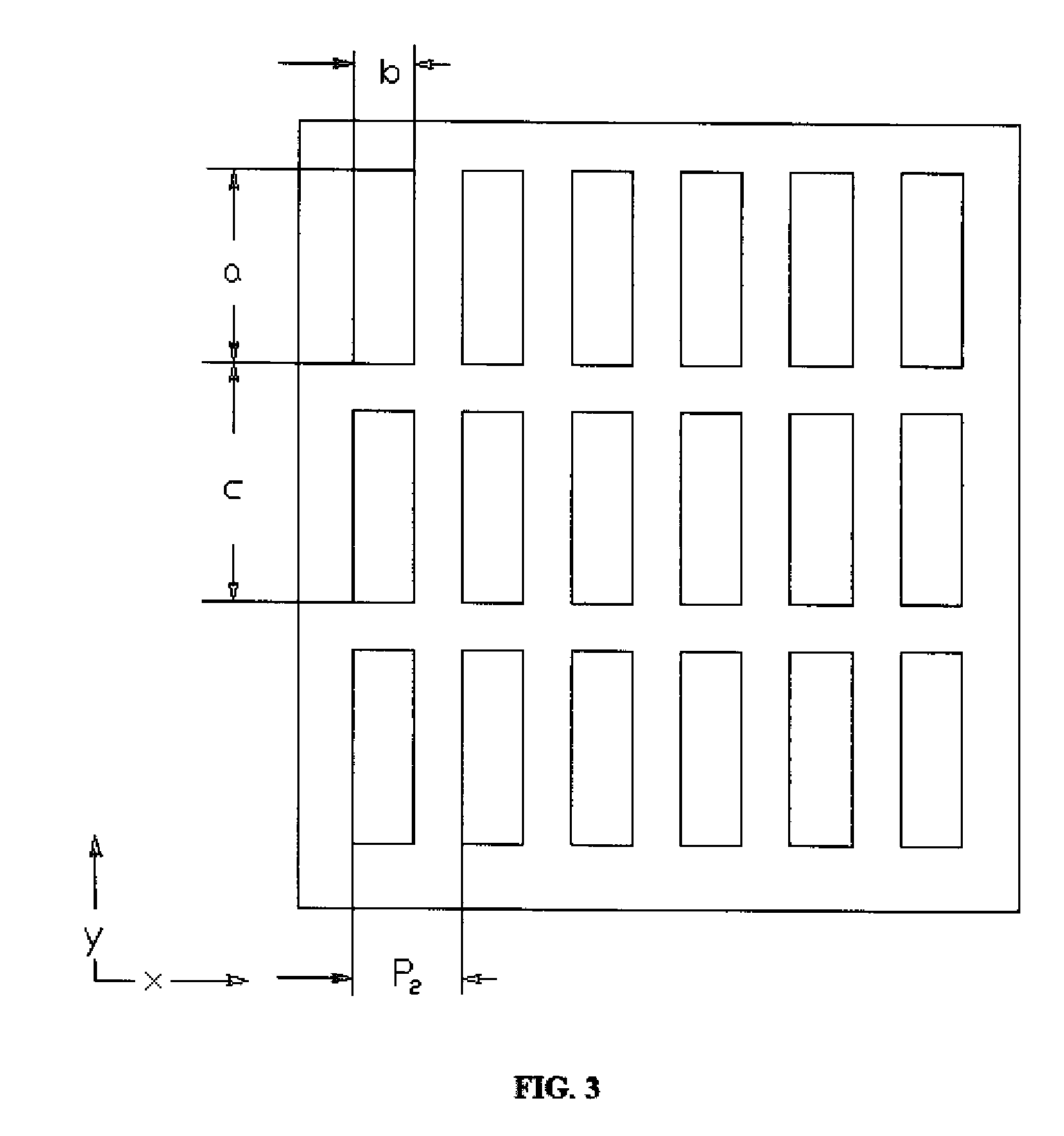
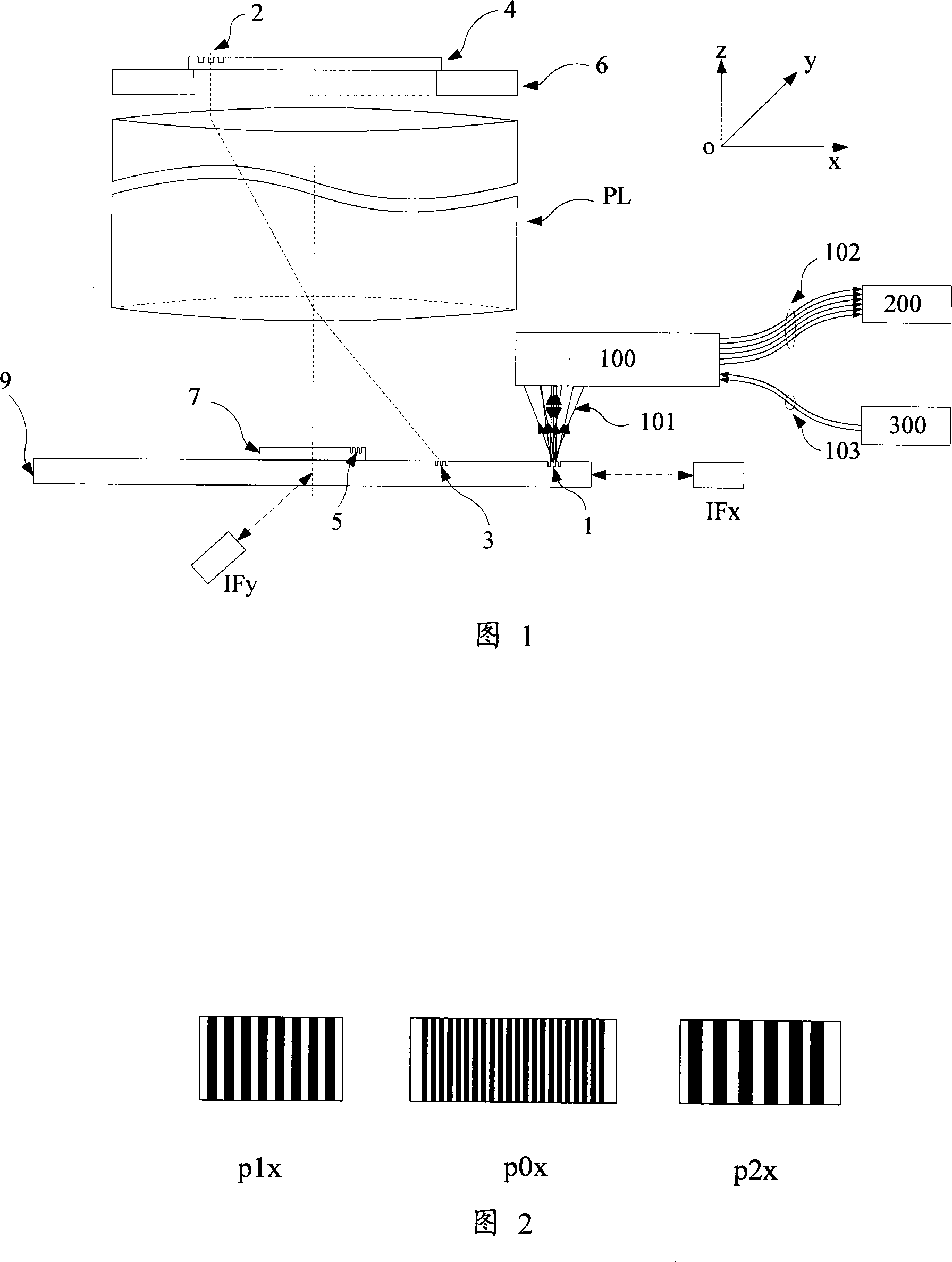
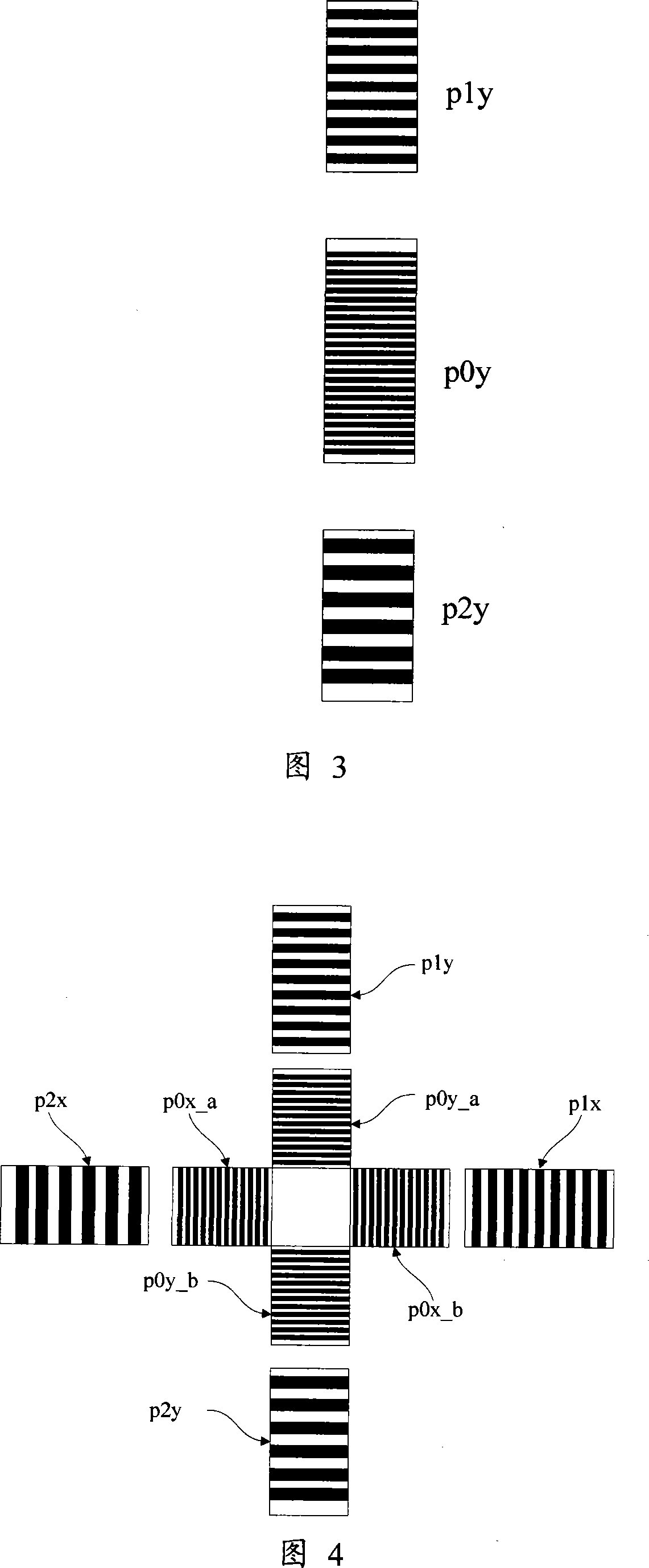
The invention discloses an alignment system applied in a lithography device, which uses three periods phase grating with crude precision combination in a substrate marker or a substrate station reference marker, uses a first order diffraction light of the three periods as an alignment signal, simultaneously realizes a big capture range and gets high alignment precision, gets labeled deformation information and other useful information, and through the optimum design of the match and / or the layout of the three periods, the influence on an alignment position by asymmetrical deformation of the marker is effectively reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Methods and apparatus for differential phase-contrast fan beam ct, cone-beam ct and hybrid cone-beam ct
ActiveUS20100220832A1Improve spatial resolutionIncrease doseImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingHybrid systemPhase grating
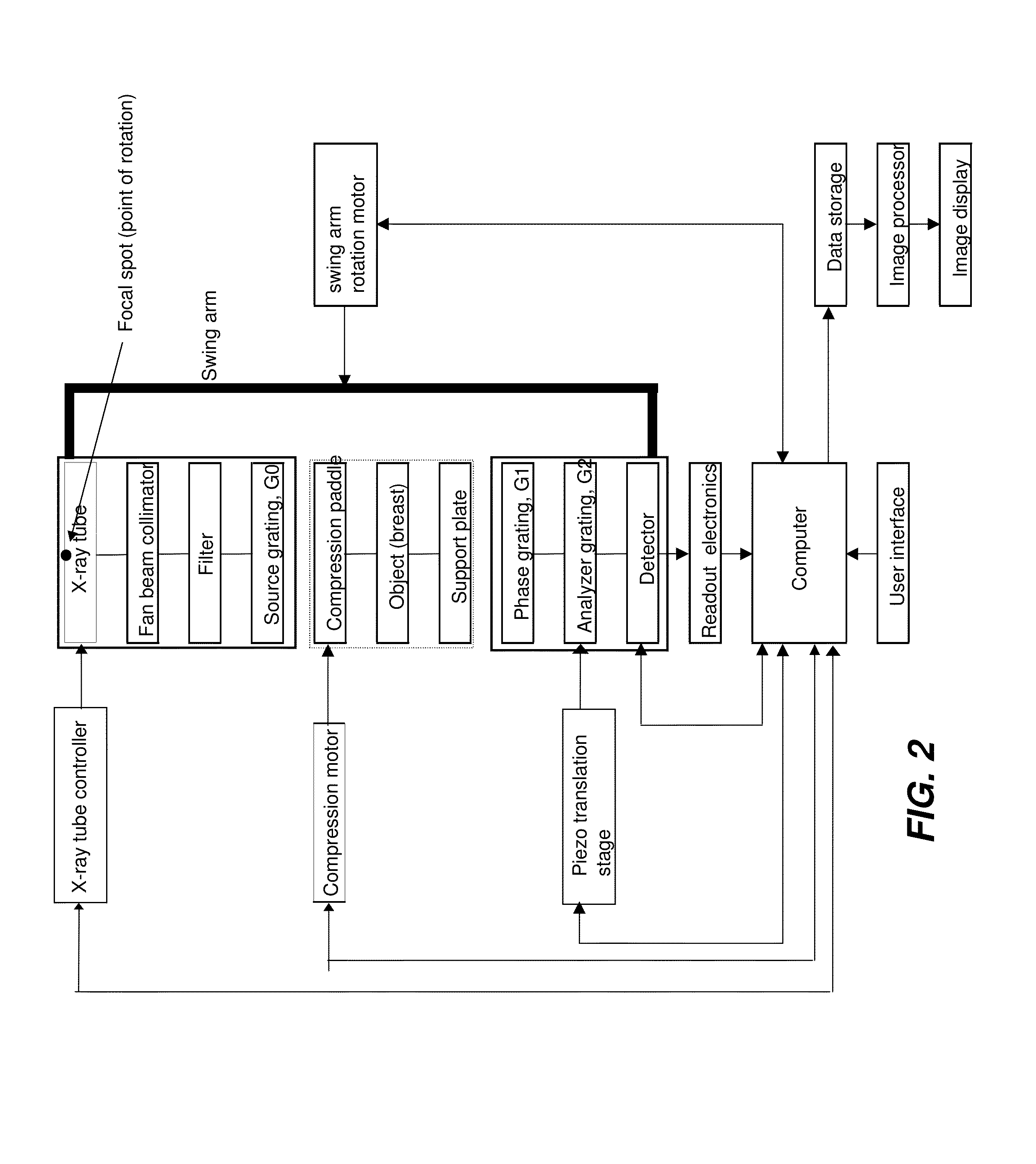
A device for imaging an object, such as for breast imaging, includes a gantry frame having mounted thereon an x-ray source, a source grating, a holder or other place for the object to be imaged, a phase grating, an analyzer grating, and an x-ray detector. The device images objects by differential-phase-contrast cone-beam computed tomography. A hybrid system includes sources and detectors for both conventional and differential-phase-contrast computed tomography.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
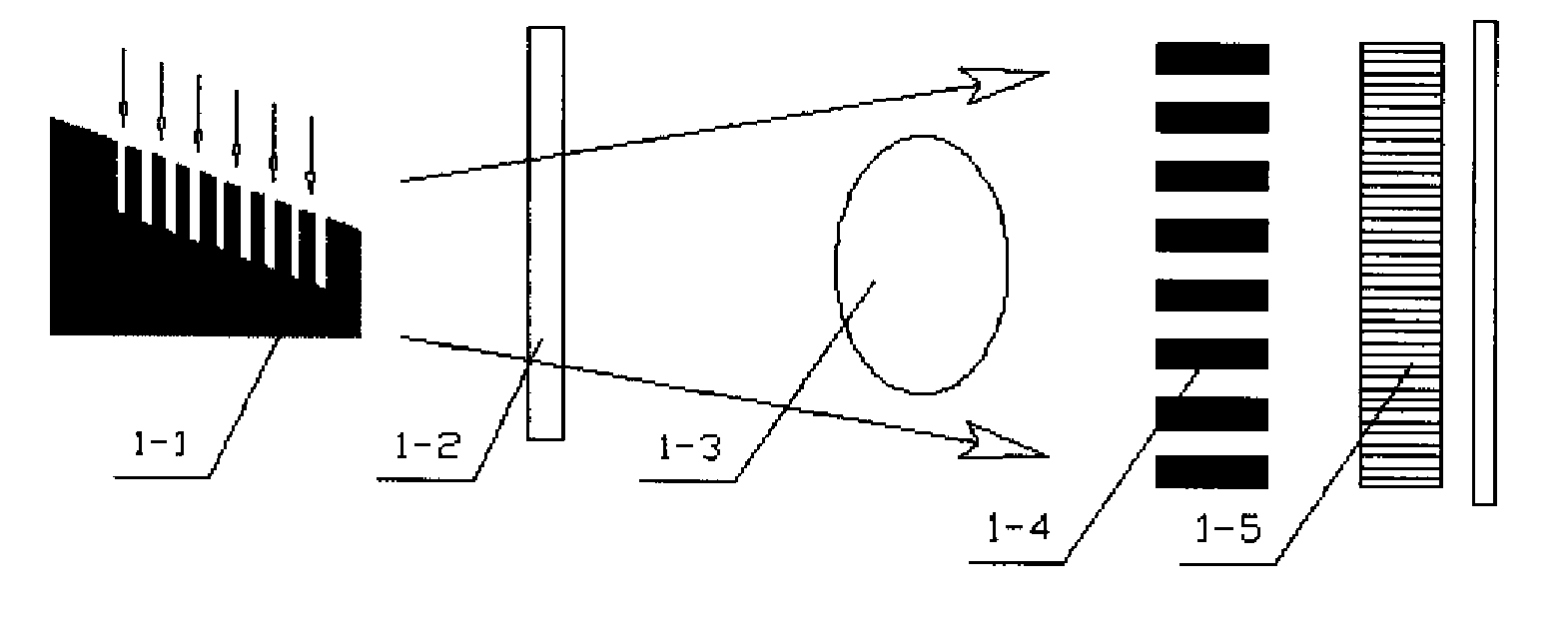
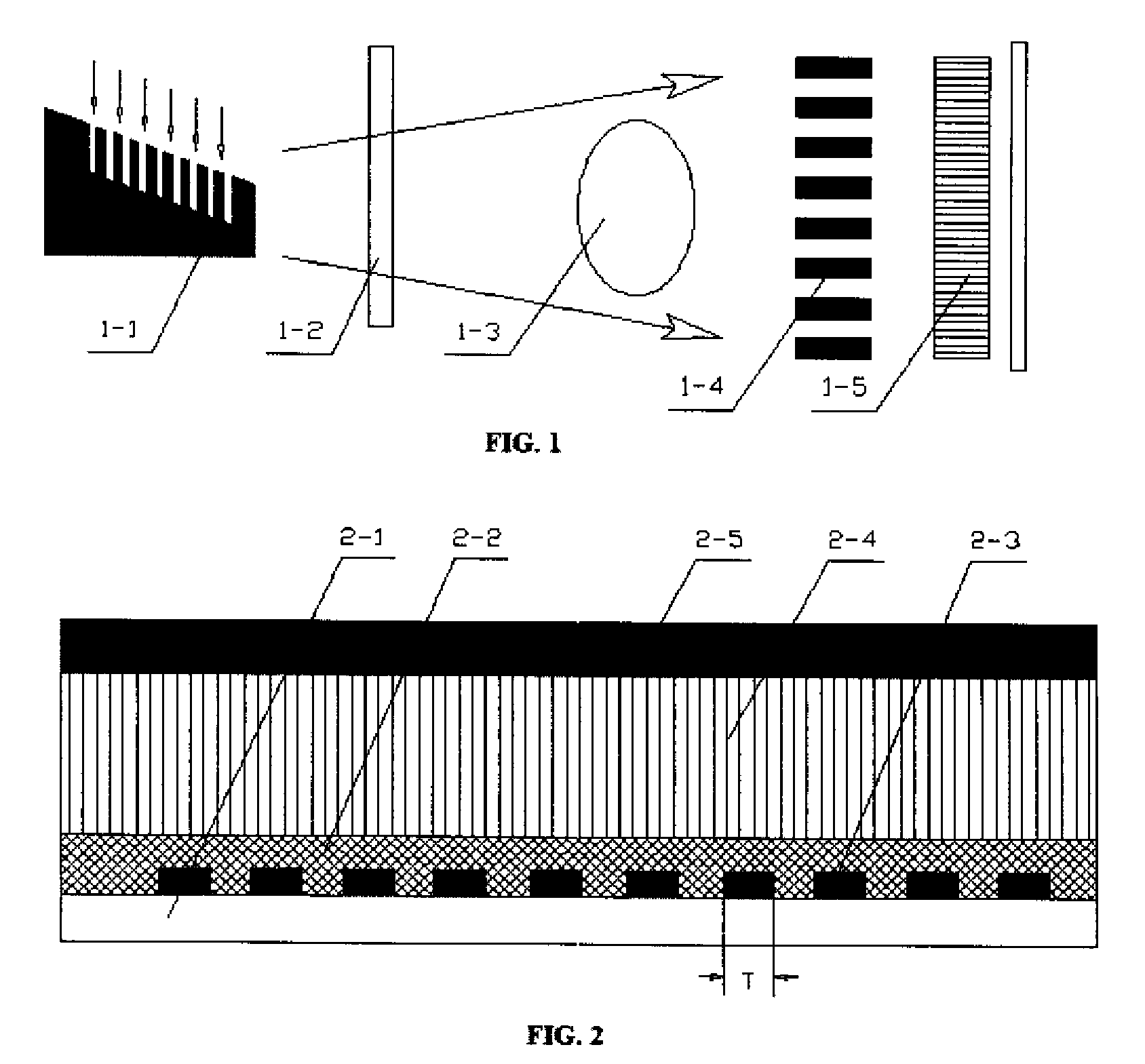
Differential interference phase contrast X-ray imaging system
InactiveUS8073099B2High radiant fluxPhoton energy is highImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesHigh energyPhotoconductive detector
A differential phase-contrast X-ray imaging system is provided. Along the direction of X-ray propagation, the basic components are X-ray tube, filter, object platform, X-ray phase grating, and X-ray detector. The system provides: 1) X-ray beam from parallel-arranged source array with good coherence, high energy, and wider angles of divergence with 30-50 degree. 2) The novel X-ray detector adopted in present invention plays dual roles of conventional analyzer grating and conventional detector. The basic structure of the detector includes a set of parallel-arranged linear array X-ray scintillator screens, optical coupling system, an area array detector or parallel-arranged linear array X-ray photoconductive detector. In this case, relative parameters for scintillator screens or photoconductive detector correspond to phase grating and parallel-arranged line source array, which can provide the coherent X-rays with high energy.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Methods and apparatus for differential phase-contrast fan beam CT, cone-beam CT and hybrid cone-beam CT
ActiveUS7949095B2Increase doseImprove spatial resolutionImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingPhase gratingHybrid system
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Interferometer device and method
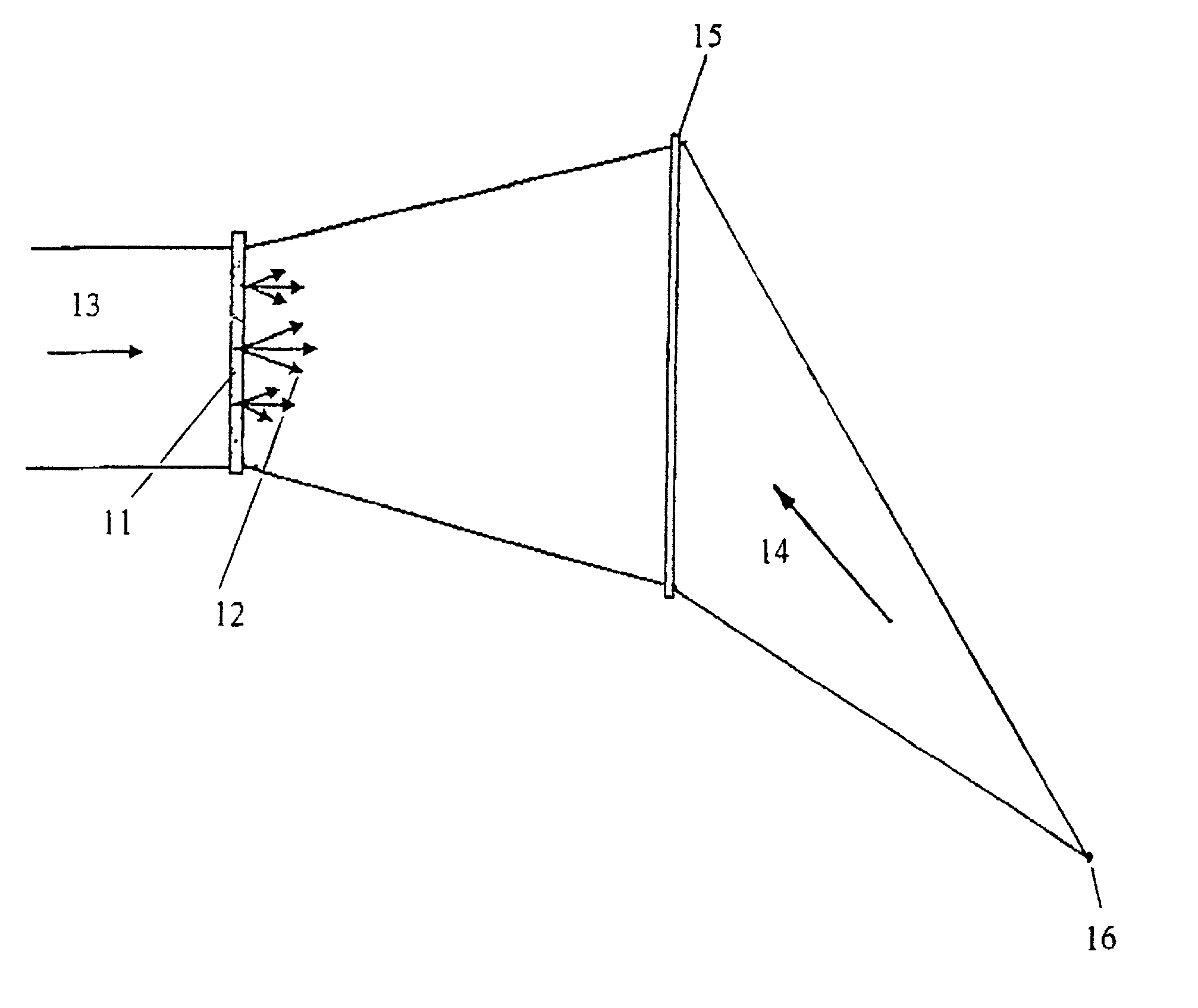
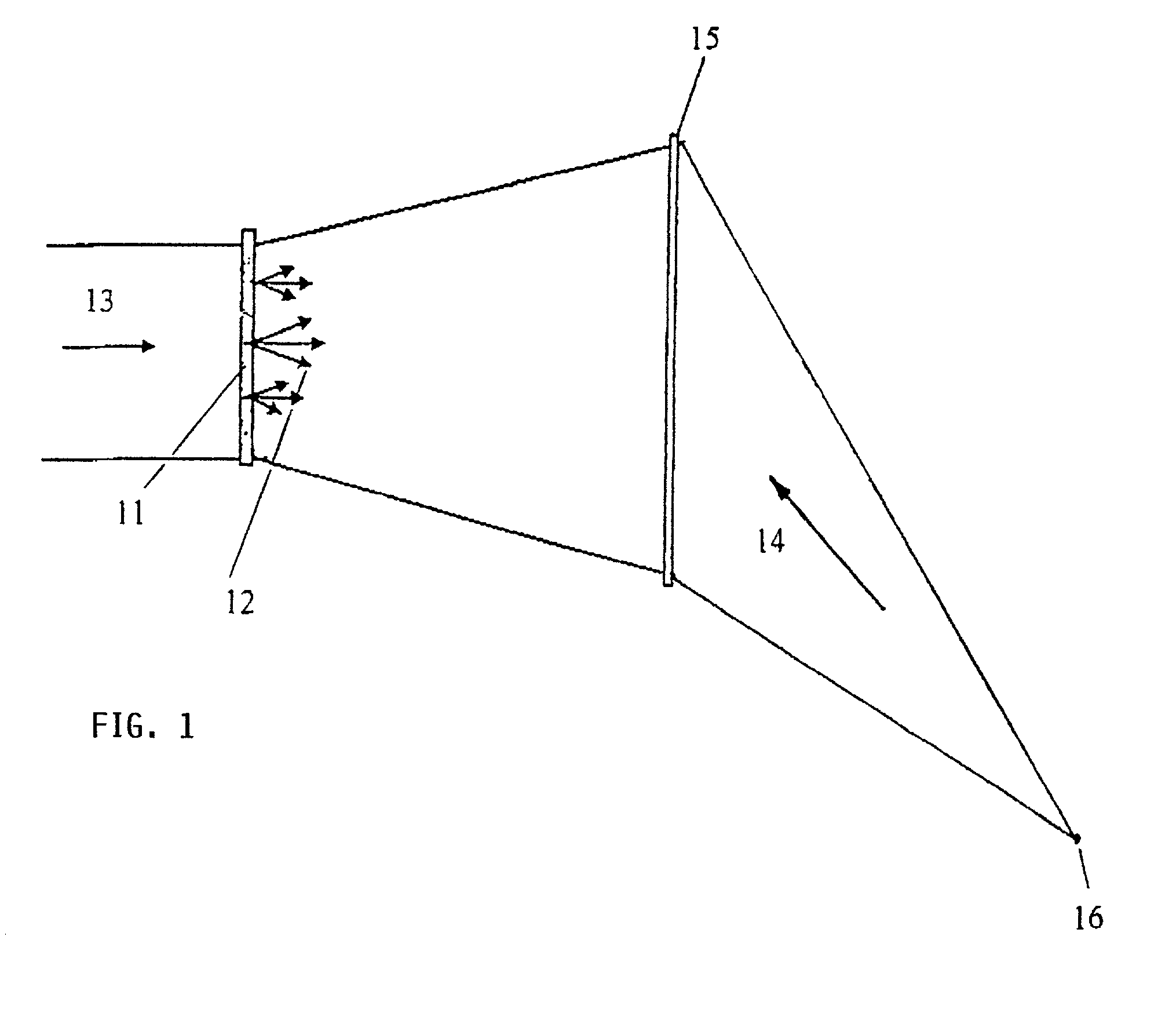
The present invention discloses an interferometer device and method. In embodiments, the device comprises an electromagnetic radiation source emitting radiation having a first mean wavelength λLE; a phase grating having a first aspect ratio; an absorption grating having a second aspect ratio; and a detector. The electromagnetic radiation source, the phase grating, the absorption grating and the detector are radiatively coupled with each other. The absorption grating is positioned between the detector and the phase grating; the electromagnetic radiation source is positioned in front of the source grating; and wherein the phase grating is designed such to cause a phase shift that is smaller than π on the emitted radiation. Additional and alternative embodiments are specified and claimed.
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
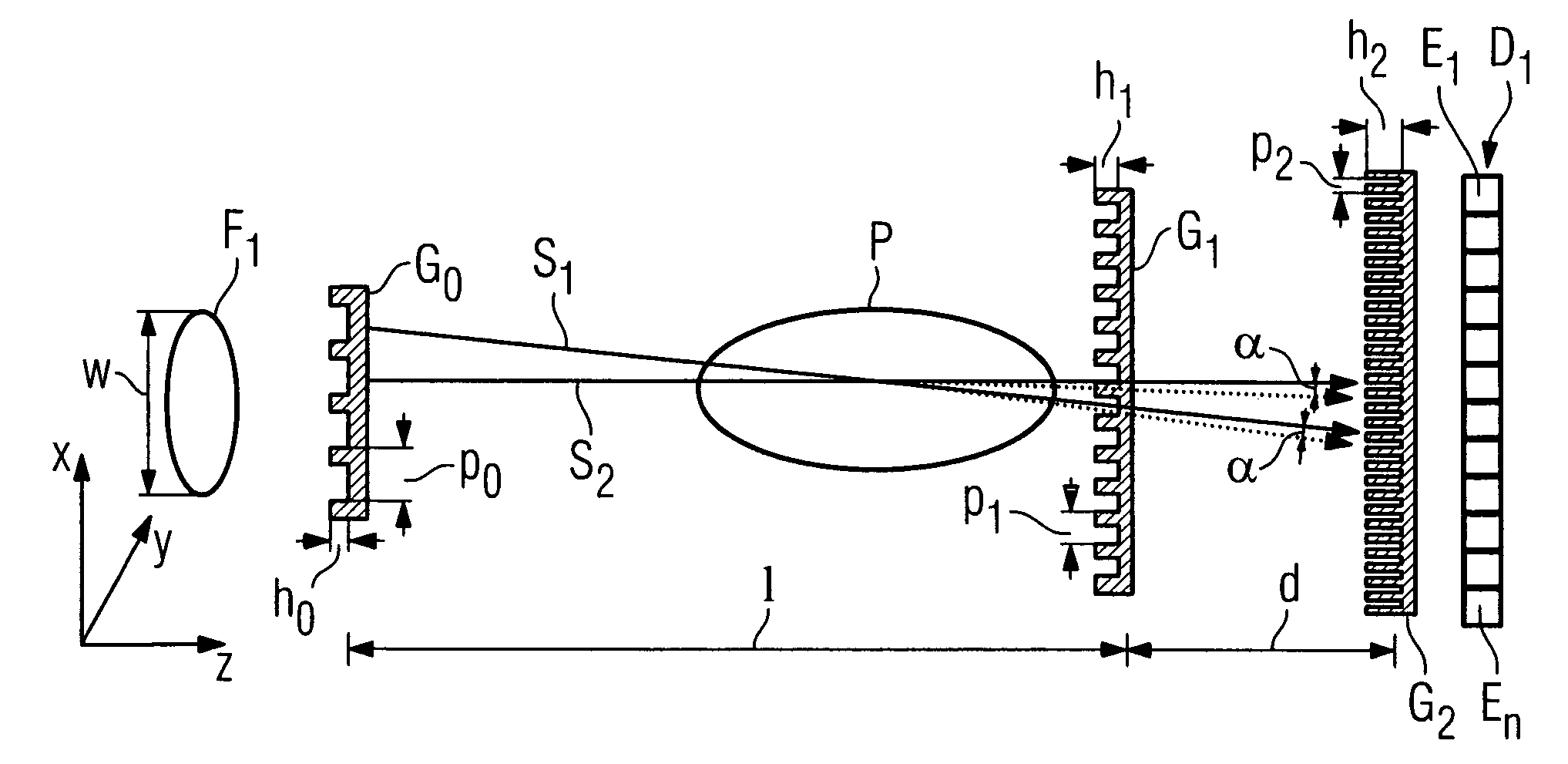
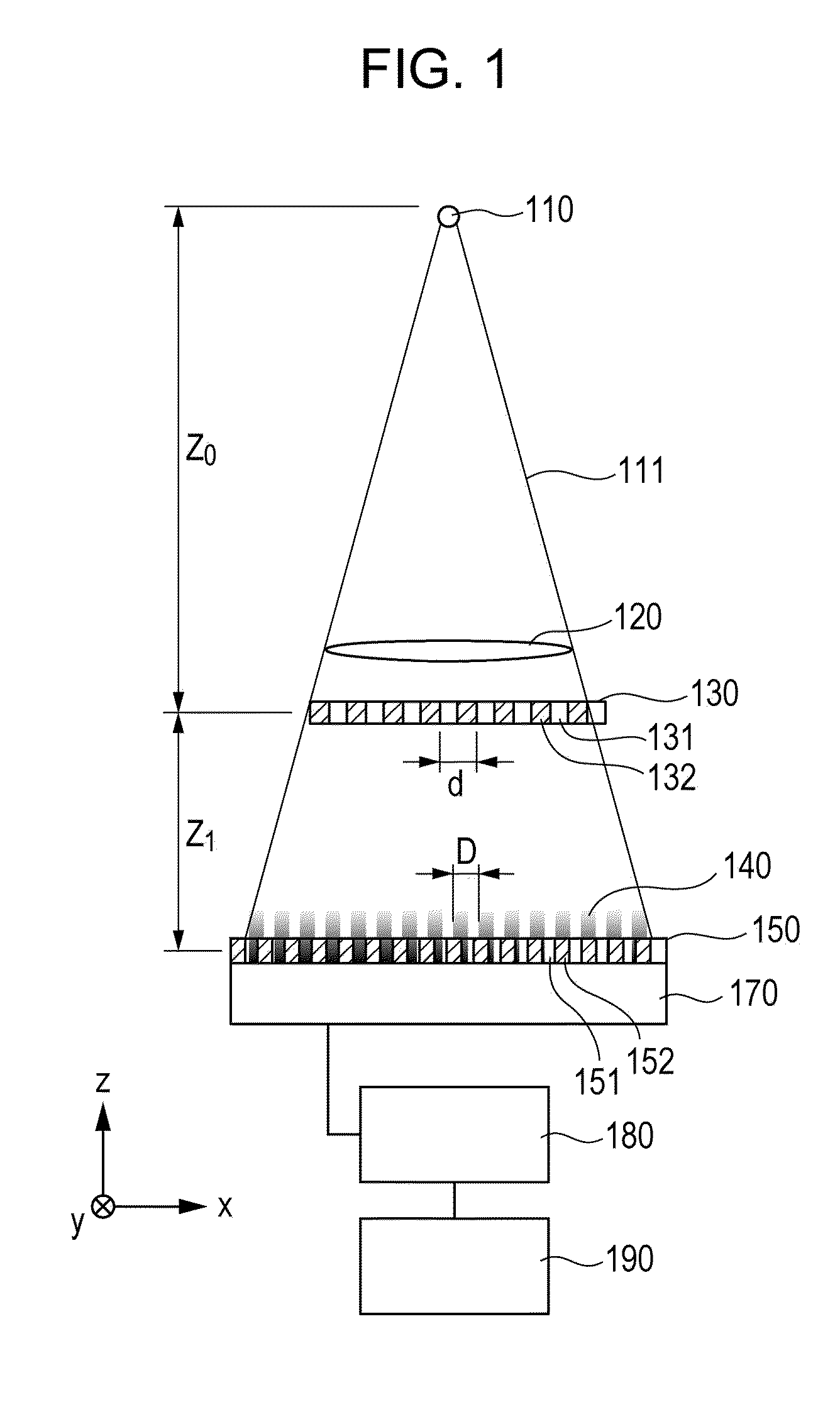
Focus/detector system of an x-ray apparatus for generating phase contrast recordings
InactiveUS7492871B2Improve stabilitySimple structureImaging devicesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhase gratingBeam source
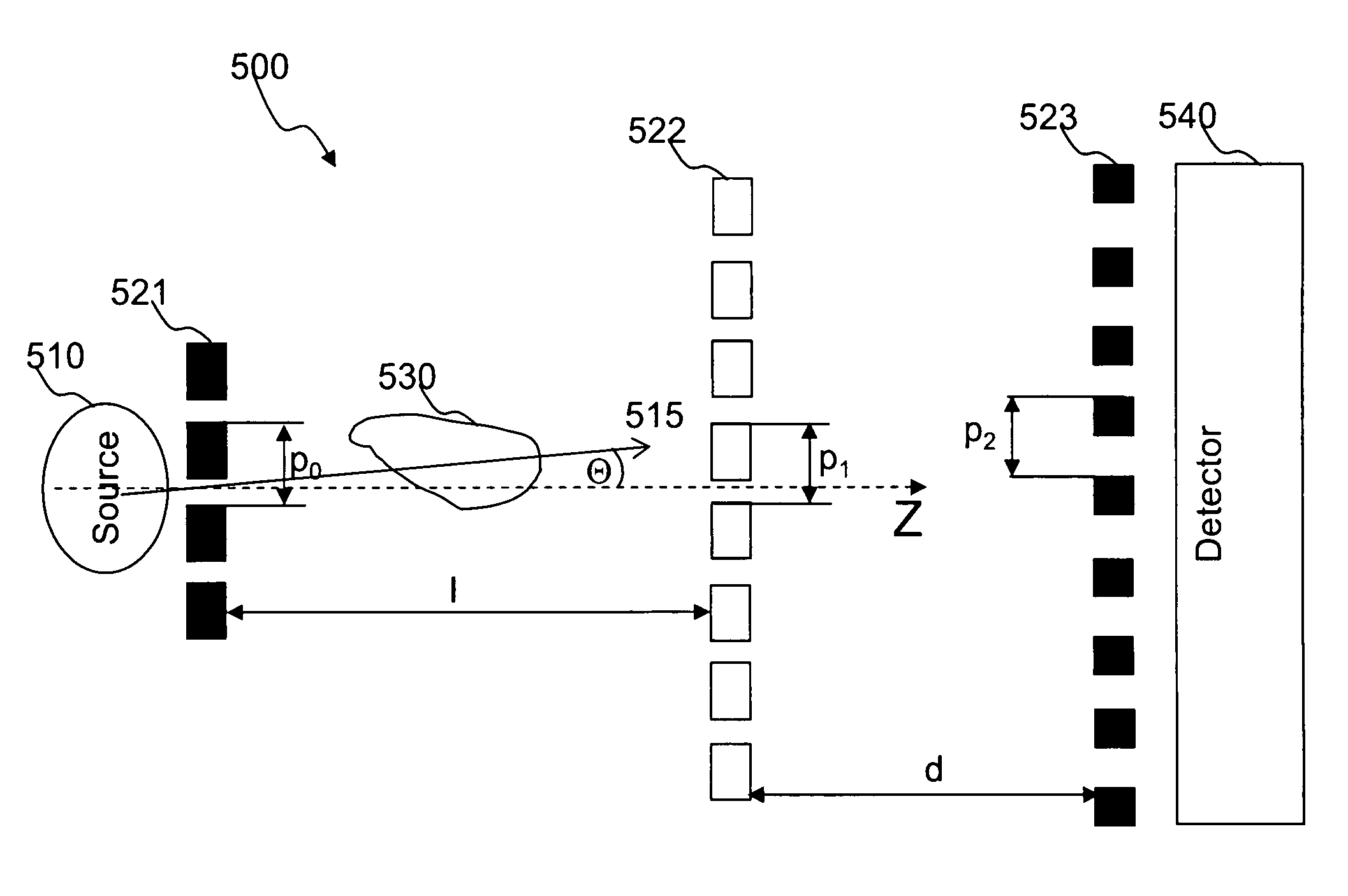
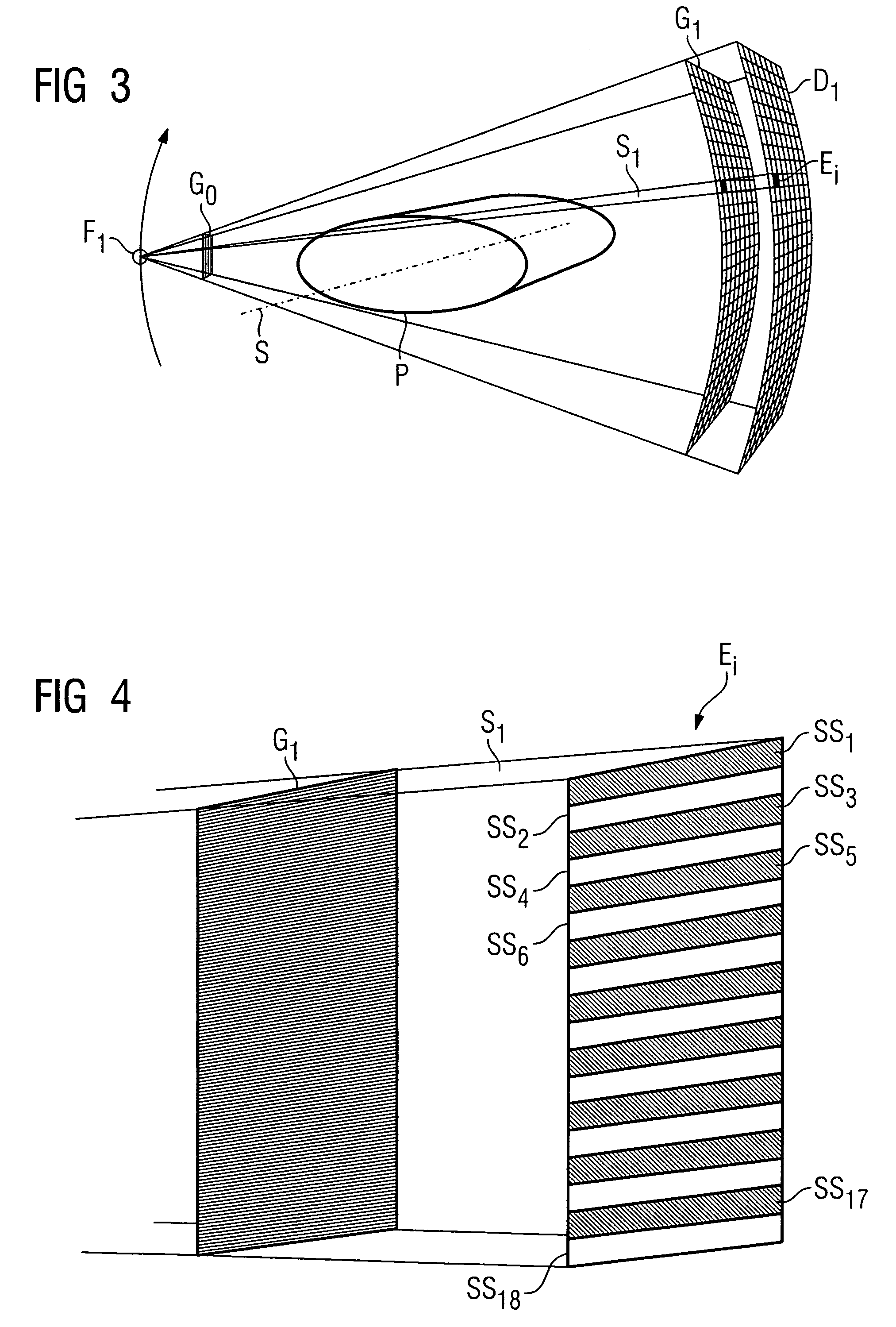
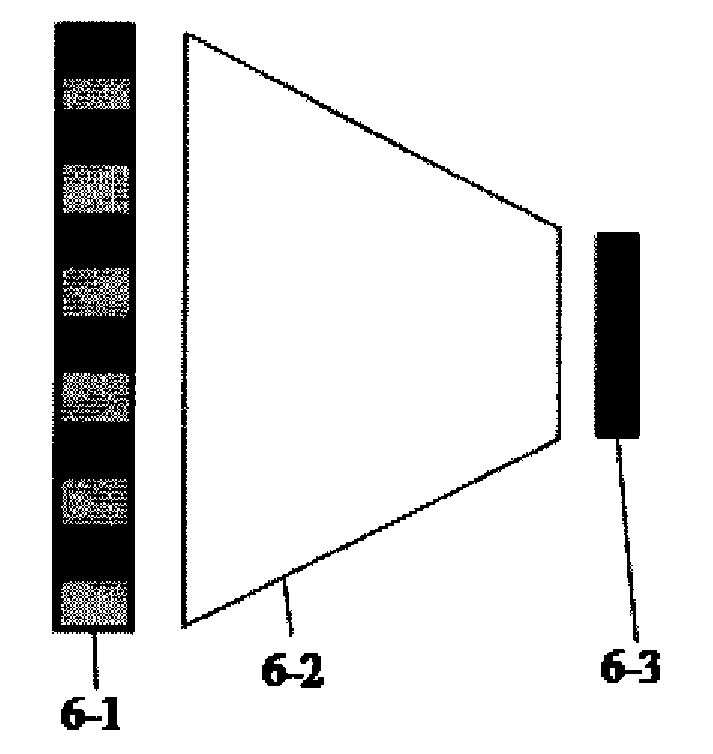
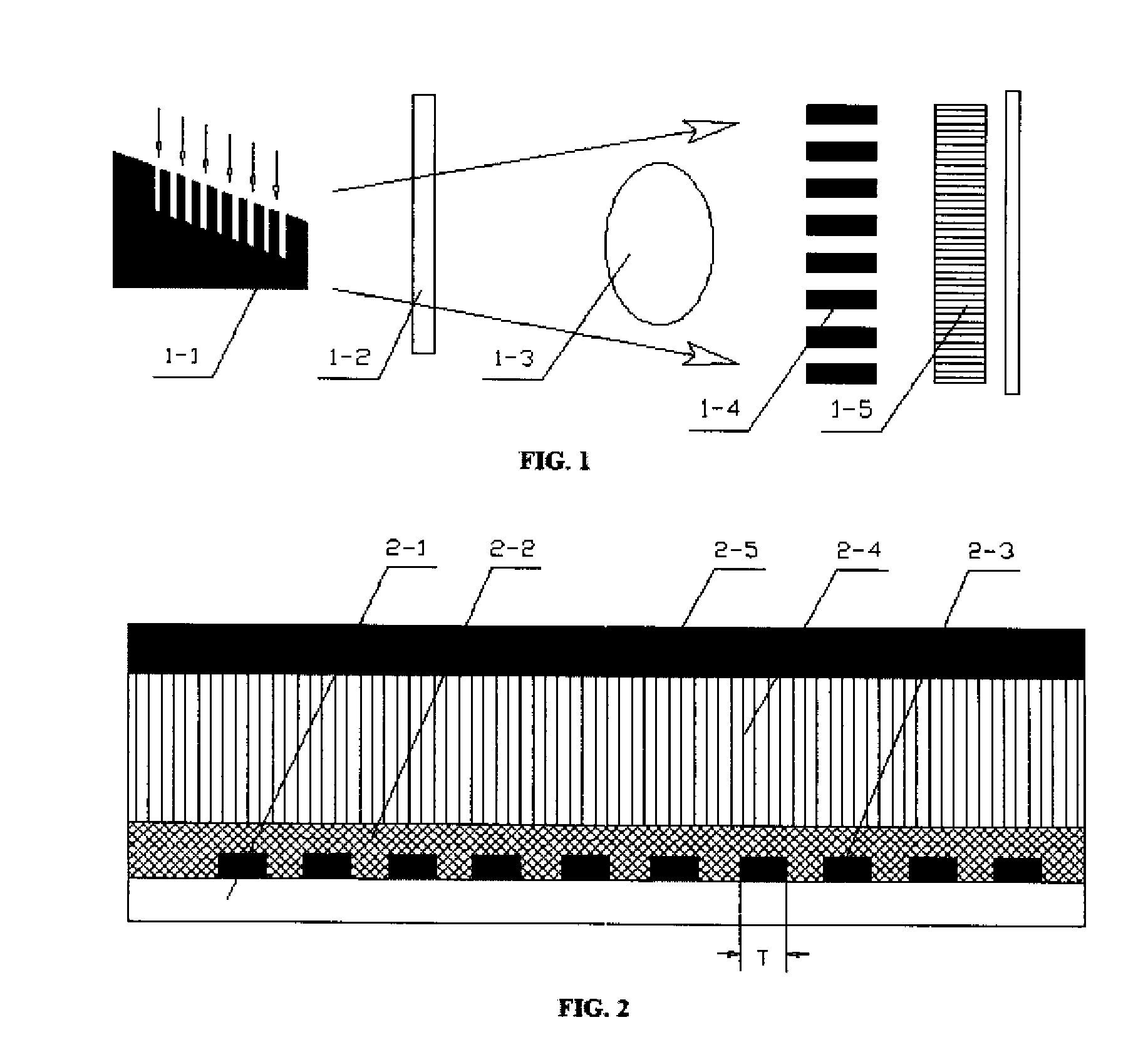
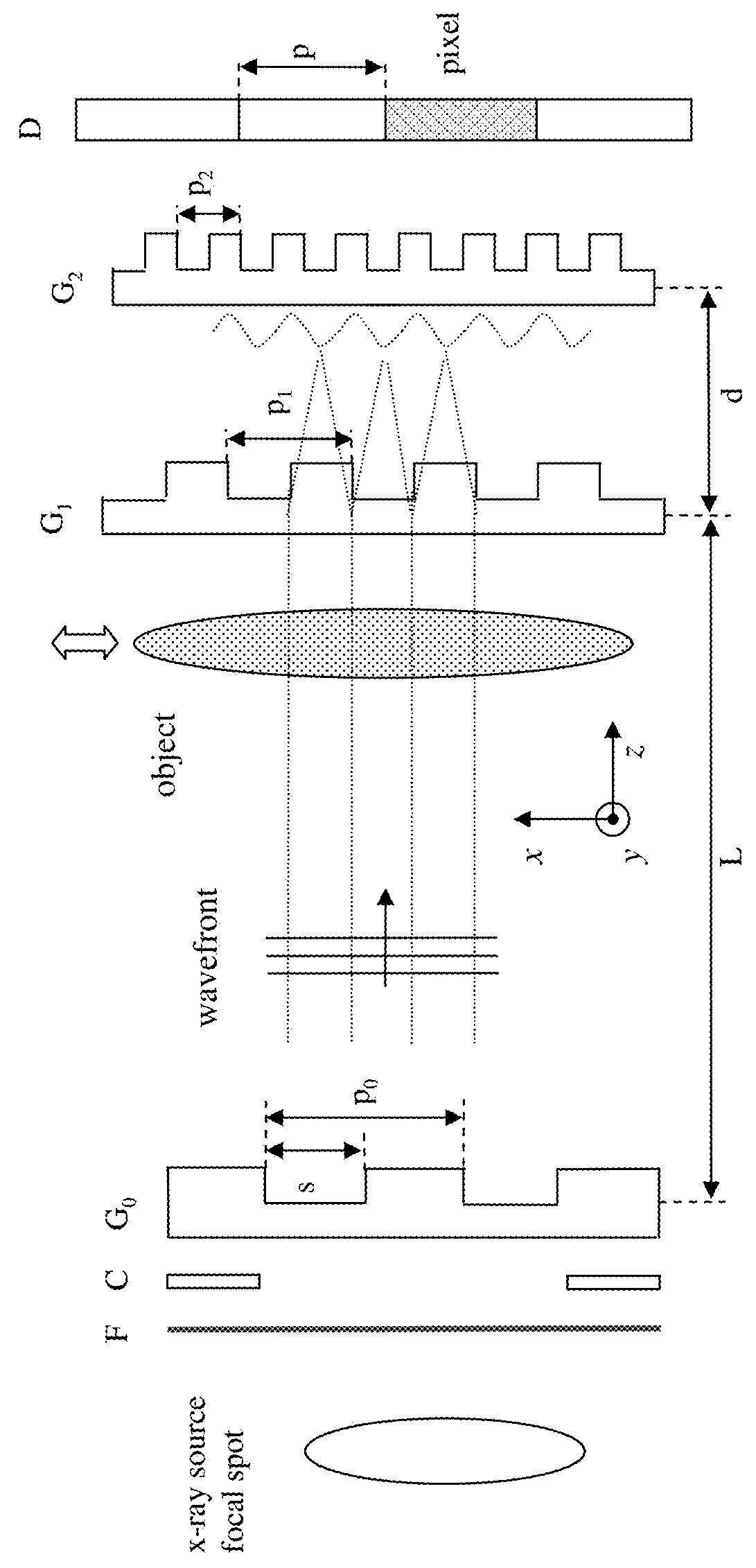
A focus / detector system of an X-ray apparatus and a method for generating projective or tomographic phase contrast recordings, are disclosed. In an embodiment of the system, the system includes a beam source equipped with a focus and a focus-side source grating, arranged in the beam path and generates a field of ray-wise coherent X-rays, a grating / detector arrangement having a phase grating and grating lines arranged parallel to the source grating for generating an interference pattern, and a detector having a multiplicity of detector elements arranged flat for measuring the position-dependent radiation intensity behind the phase grating. Finally, the detector elements are formed by a multiplicity of elongate scintillation strips, which are aligned parallel to the grating lines of the phase grating and have a small period, whose integer multiple corresponds to the average large period of the interference pattern which is formed by the phase grating.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
High accuracy miniature grating encoder readhead using fiber optic receiver channels
InactiveUS6906315B2Robust alignment toleranceHigh resolutionPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
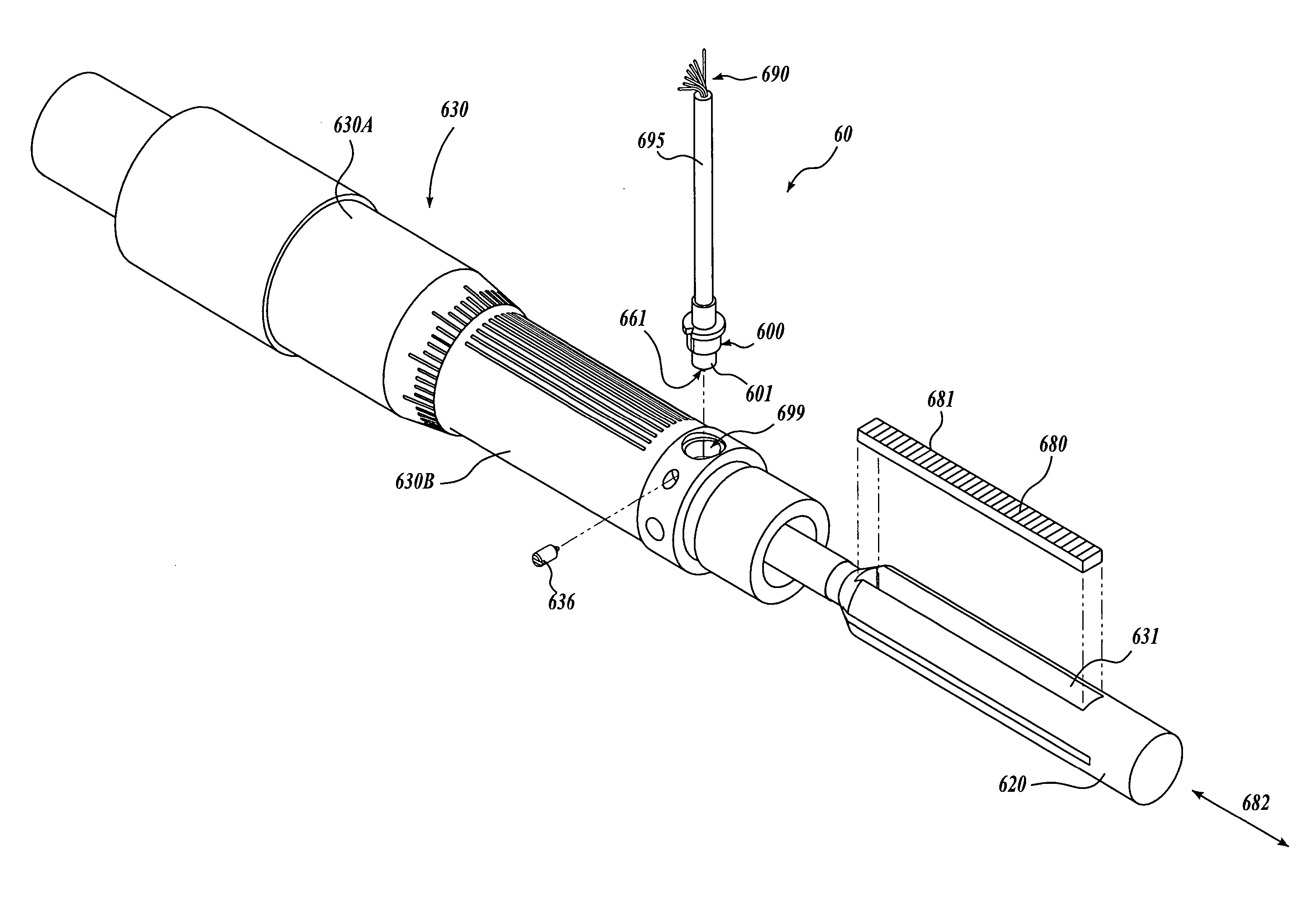
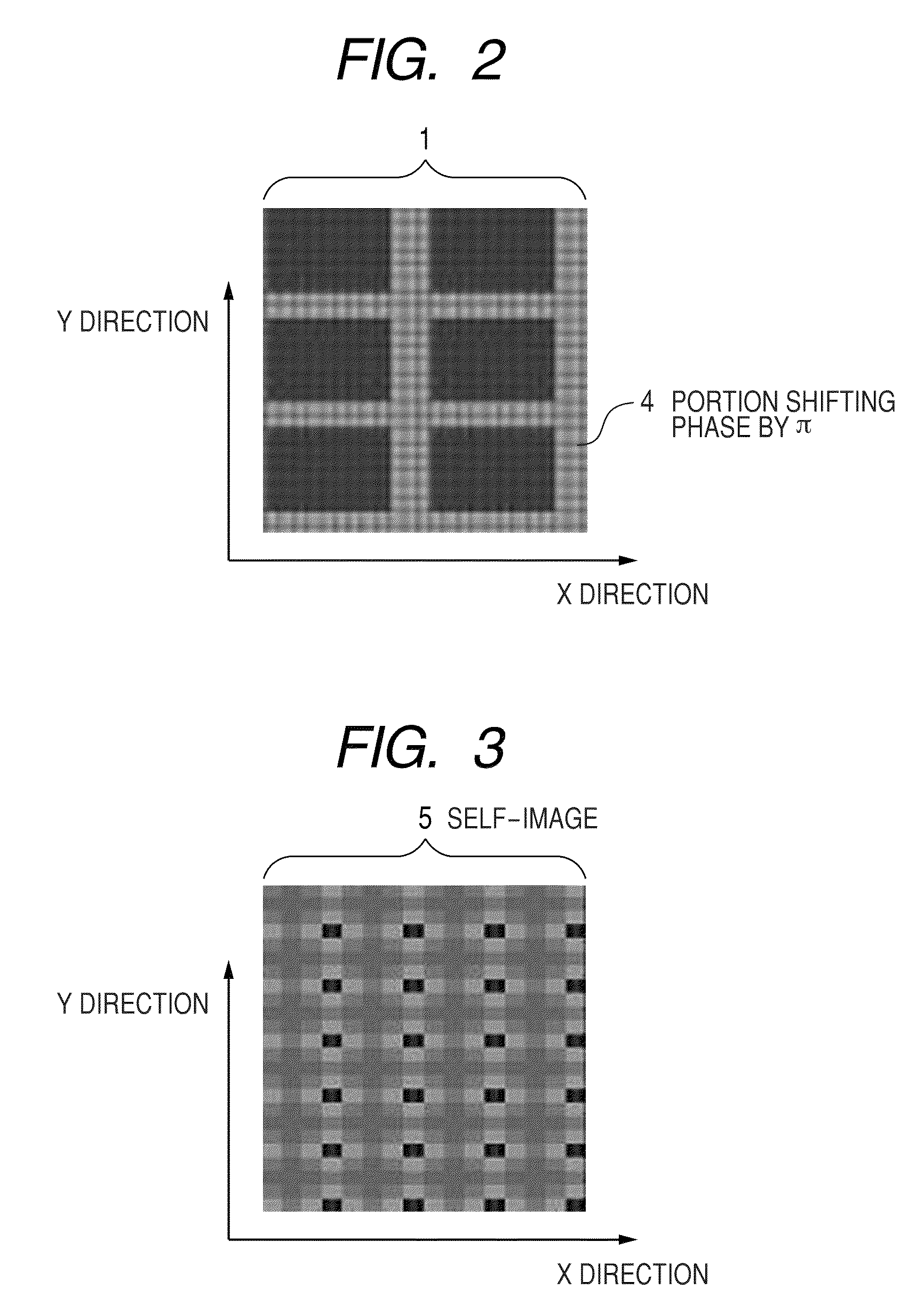
A fiber optic encoder readhead for sensing the displacement of a scale grating is disclosed. The detector channels of the readhead are fiber optic detector channels having respective phase grating masks. The fiber optic encoder readhead is configured to detect the displacement of a self-image of the scale grating. In various exemplary embodiments, the fiber optic readhead is constructed according to various design relationships that insure a robust signal-to-noise ratio. Accordingly, high levels of displacement signal interpolation may be achieved, allowing sub-micrometer displacement measurements. The fiber optic encoder readhead may be assembled in a particularly accurate and economical manner and may be provided in a package with dimensions on the order of 1-2 millimeters.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
X-ray CT system for x-ray phase contrast and/or x-ray dark field imaging
ActiveUS7983381B2Technical requirementPractical operationImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayGrating interferometer
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
X-ray CT system to generate tomographic phase contrast or dark field exposures
InactiveUS8009796B2Easy to measureImprove measurement resultsImaging devicesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationGrating interferometerPhase grating
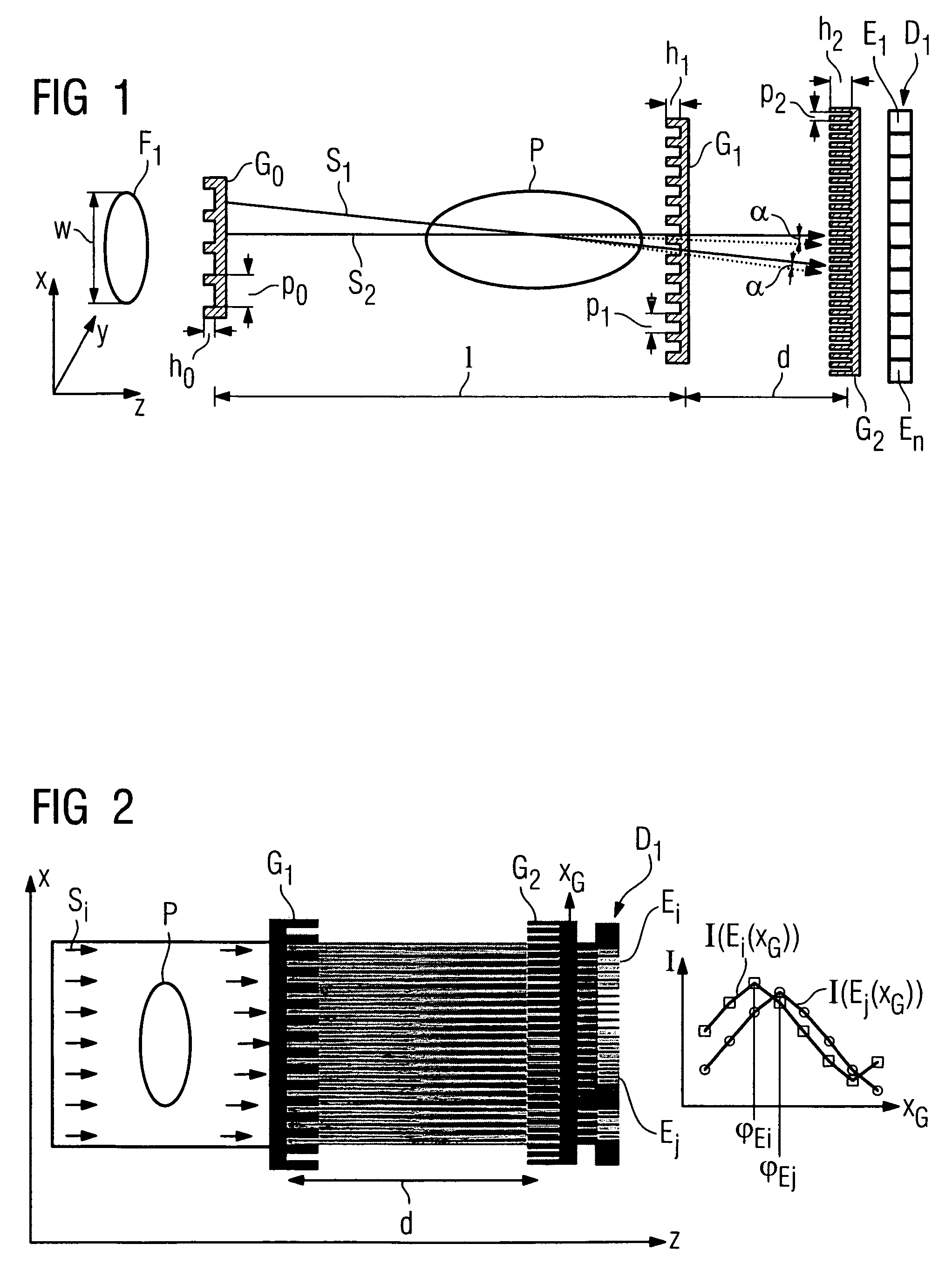
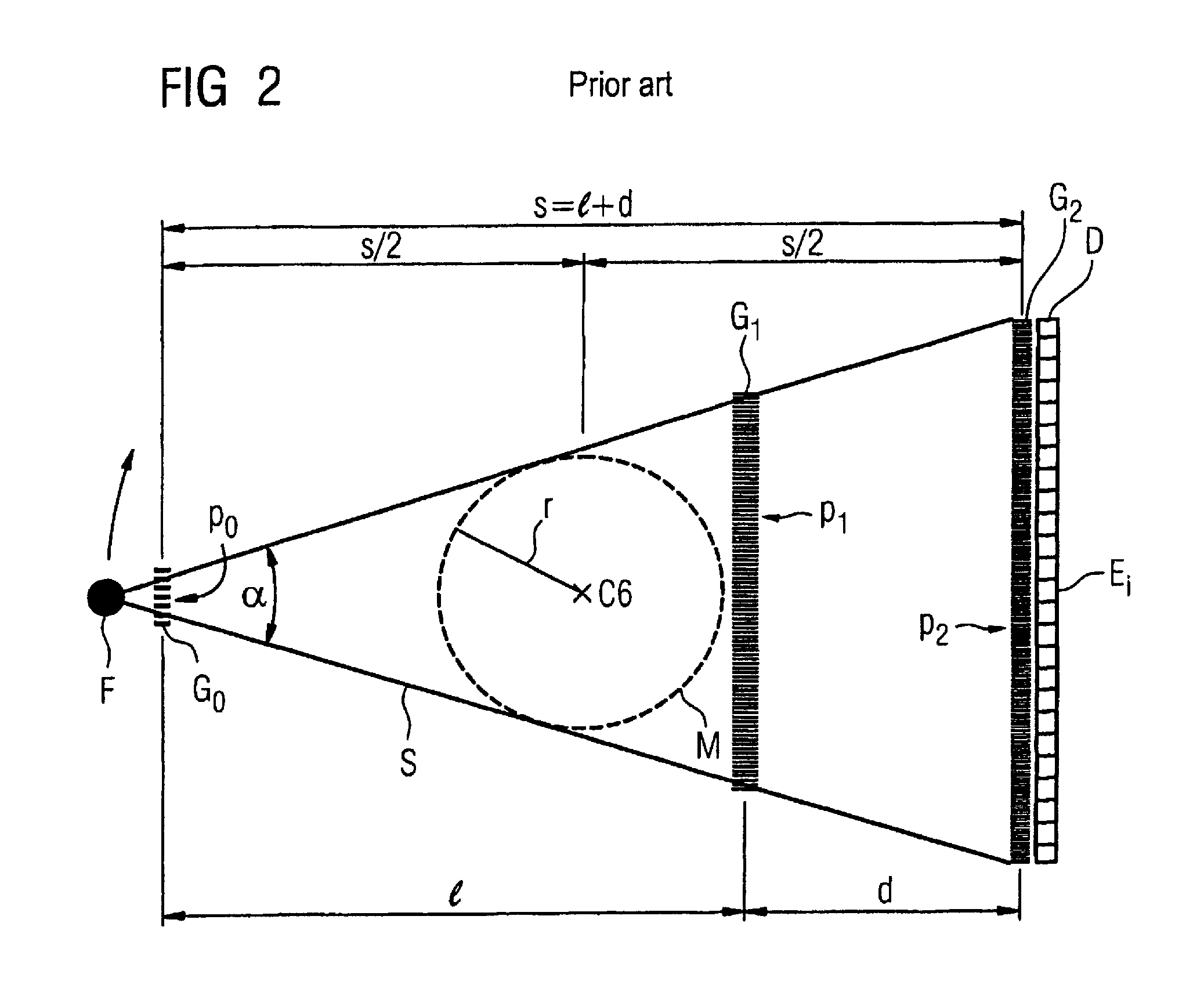
An x-ray CT system that generates tomographic phase contrast or dark field exposures, has at least one grating interferometer with three grating structures arranged in series in the radiation direction, with a modular design of the second and third grating structures. The distance between the first grating structure of the x-ray source and the second grating structure (fashioned as a phase grating) of the respective grating / detector modules is adapted, depending on the fan angle, corresponding to a period of the grating structure of the x-ray source projected onto the grating detector module at a respective fan angle (φi).
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
Differential Interference Phase Contrast X-ray Imaging System
InactiveUS20100091947A1Photon energy is highWide emission angleImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesPhotoconductive detectorHigh energy
A differential phase-contrast X-ray imaging system is provided. Along the direction of X-ray propagation, the basic components are X-ray tube, filter, object platform, X-ray phase grating, and X-ray detector. The system provides: 1) X-ray beam from parallel-arranged source array with good coherence, high energy, and wider angles of divergence with 30-50 degree. 2) The novel X-ray detector adopted in present invention plays dual roles of conventional analyzer grating and conventional detector. The basic structure of the detector includes a set of parallel-arranged linear array X-ray scintillator screens, optical coupling system, an area array detector or parallel-arranged linear array X-ray photoconductive detector. In this case, relative parameters for scintillator screens or photoconductive detector correspond to phase grating and parallel-arranged line source array, which can provide the coherent X-rays with high energy.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Interferometric miniature grating encoder readhead using fiber optic receiver channels
ActiveUS7126696B2Easy to measureEasy to installPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansPhase gratingEngineering
An interferometric fiber optic encoder readhead for sensing the displacement of a scale grating is disclosed. The detector channels of the readhead are fiber optic detector channels having respective phase grating masks. The fiber optic encoder readhead is configured to detect the displacement of interference fringes arising from the scale grating. In various exemplary embodiments, the fiber optic readhead is constructed and operably positioned according to various design relationships that insure a compact mounting and a relatively ideal sinusoidal signal as a function of displacement. Accordingly, high levels of displacement signal interpolation may be achieved, allowing sub-micrometer displacement measurements. The fiber optic encoder readhead may be assembled in a particularly accurate and economical manner and may be provided in a package with dimensions on the order of 1–2 millimeters.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Precision measuring gauges with optical fiber output channels
ActiveUS20050224705A1Improve accuracySmall scaleRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansPhase gratingImage resolution
All-optical output precision measuring gauges that sense the displacement of an internal scale grating are disclosed. Each type of gauge includes a compact, miniature, or ultra-miniature optical readhead that includes a light source for transmitting light to the scale grating, and optical-fiber detector channels for receiving light from the scale grating and outputting optical measuring signals from the gauge. In various embodiments, the optical-fiber detector channels have respective phase grating masks for receiving a periodic light pattern that moves in correspondence to the scale grating, and the channels are arranged in balanced pairs. In various embodiments, the optical readhead is an interferometric-type optical readhead that provides a measuring resolution as fine as 10-50 nanometers or less. In various embodiments, the gauge is provided in an unprecedented miniature size. In various embodiments, the gauge is motorized to provide a precision actuator.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
External grating structures for interfacing wavelength-division-multiplexed optical sources with thin optical waveguides
A coupling arrangement for allowing multiple wavelengths to be coupled into and out of a relatively thin silicon optical waveguide layer utilizes a diffractive optical element, in the form of a volume phase grating, in combination with a prism coupling structure. The diffractive optical element is formed to comprise a predetermined modulation index sufficient to diffract the various wavelengths through angles associated with improving the coupling efficiency of each wavelength into the silicon waveguide. The diffractive optical element may be formed as a separate element, or formed as an integral part of the coupling facet of the prism coupler.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Alignment method and micro-device manufacturing method used for shadow cast scan photo-etching machine
ActiveCN101114134ASimplify design difficultySimplify debugging difficultySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Phase grating
The invention discloses an alignment method of phase grating detection by using three basic grating periods applied in a scanning projection lithography tool and a micro-device manufacturing way by using the method. The alignment method of the invention applied in the scanning projection lithography tool uses three periods phase grating in a substrate marker or a substrate station reference marker, uses a first order diffraction light of the three periods as an alignment signal, simultaneously realizes a big capture range and gets high alignment precision and strong signal intensity, improves system signal to noise ratio, simplifies optical design and debugging difficulty, simplifies hardware realization, reduces signal processing cost and improves alignment efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
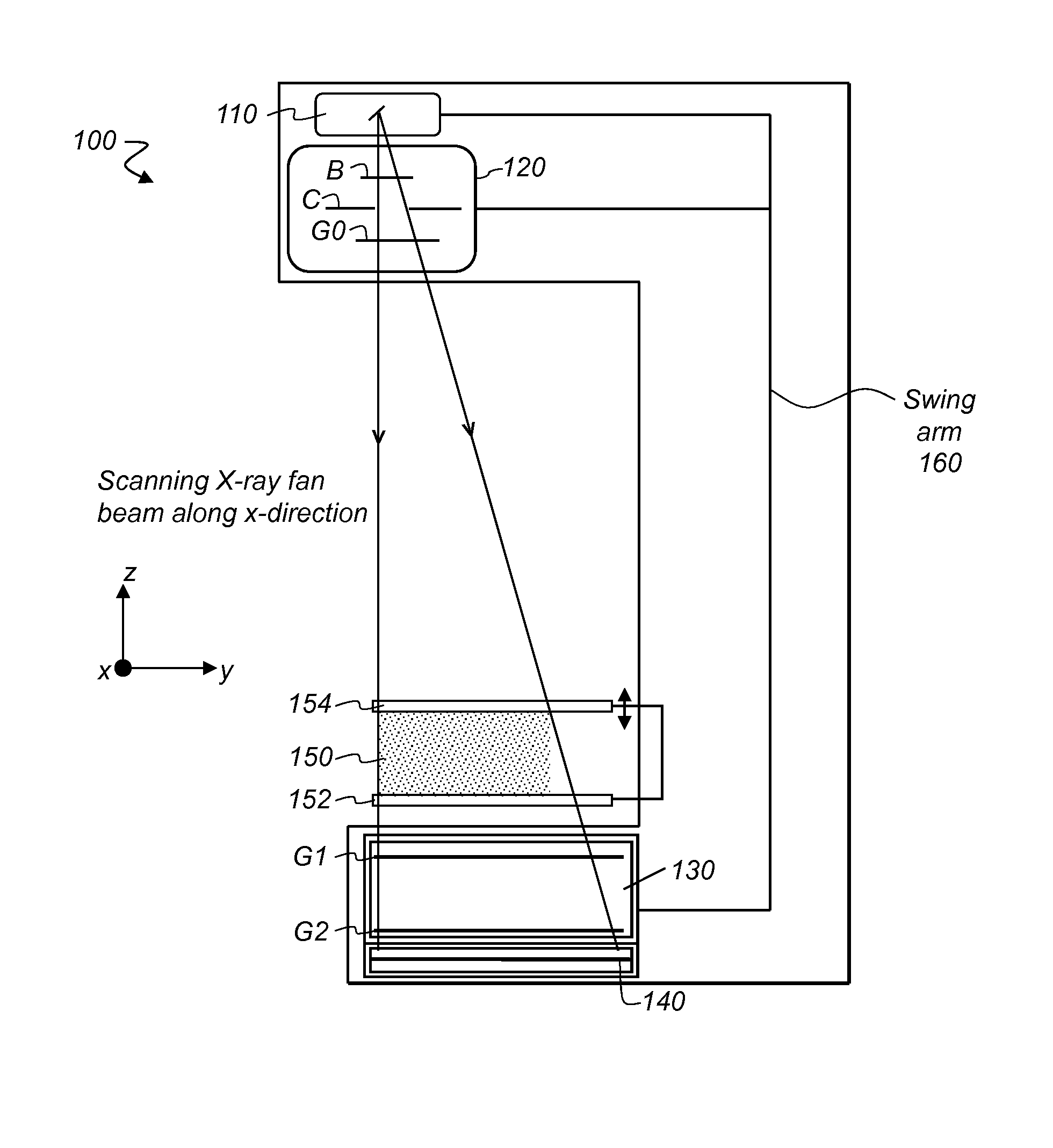
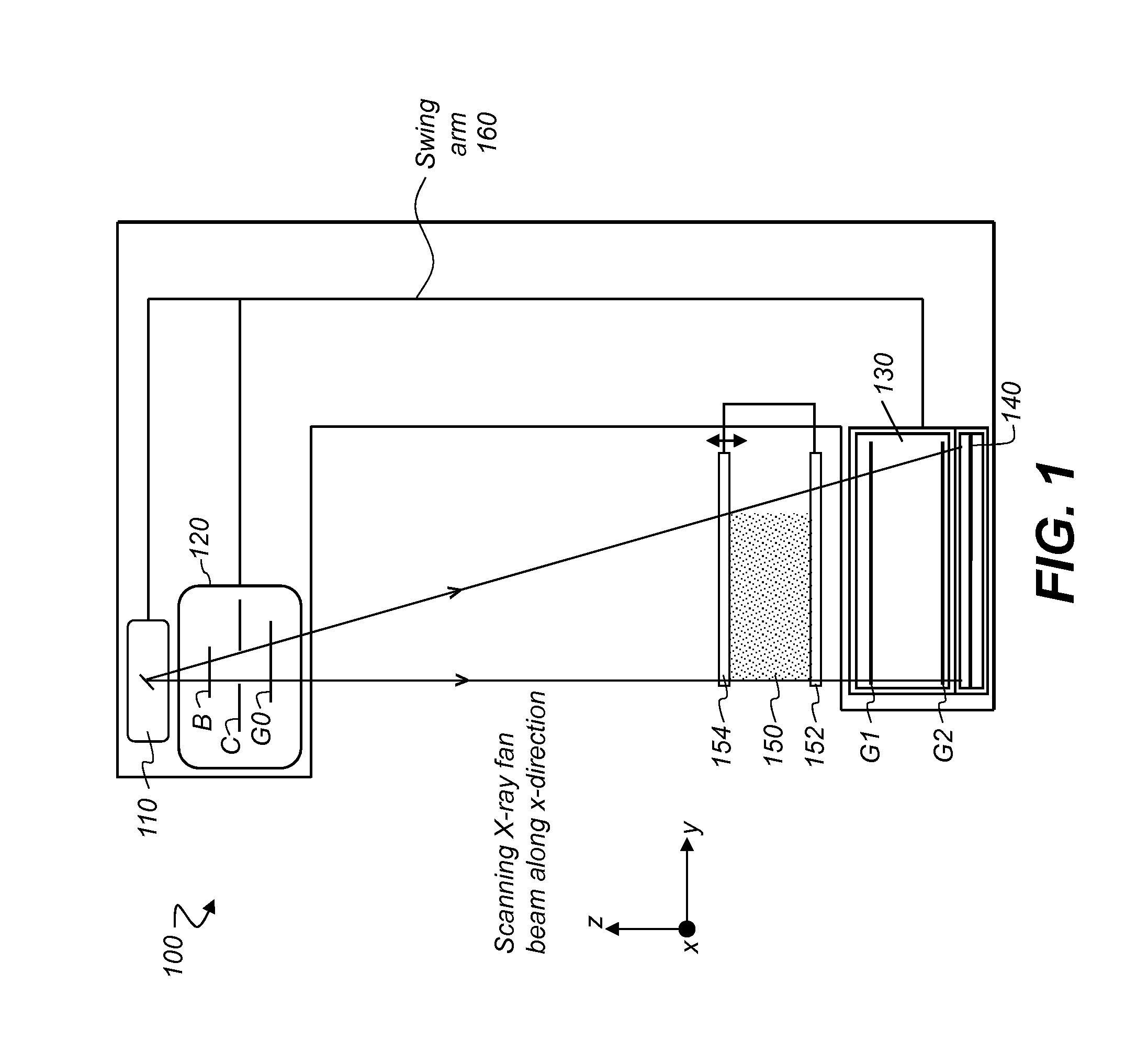
Rotational X ray device for phase contrast imaging
InactiveUS8565371B2Reduce lossesImaging devicesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayPhase grating
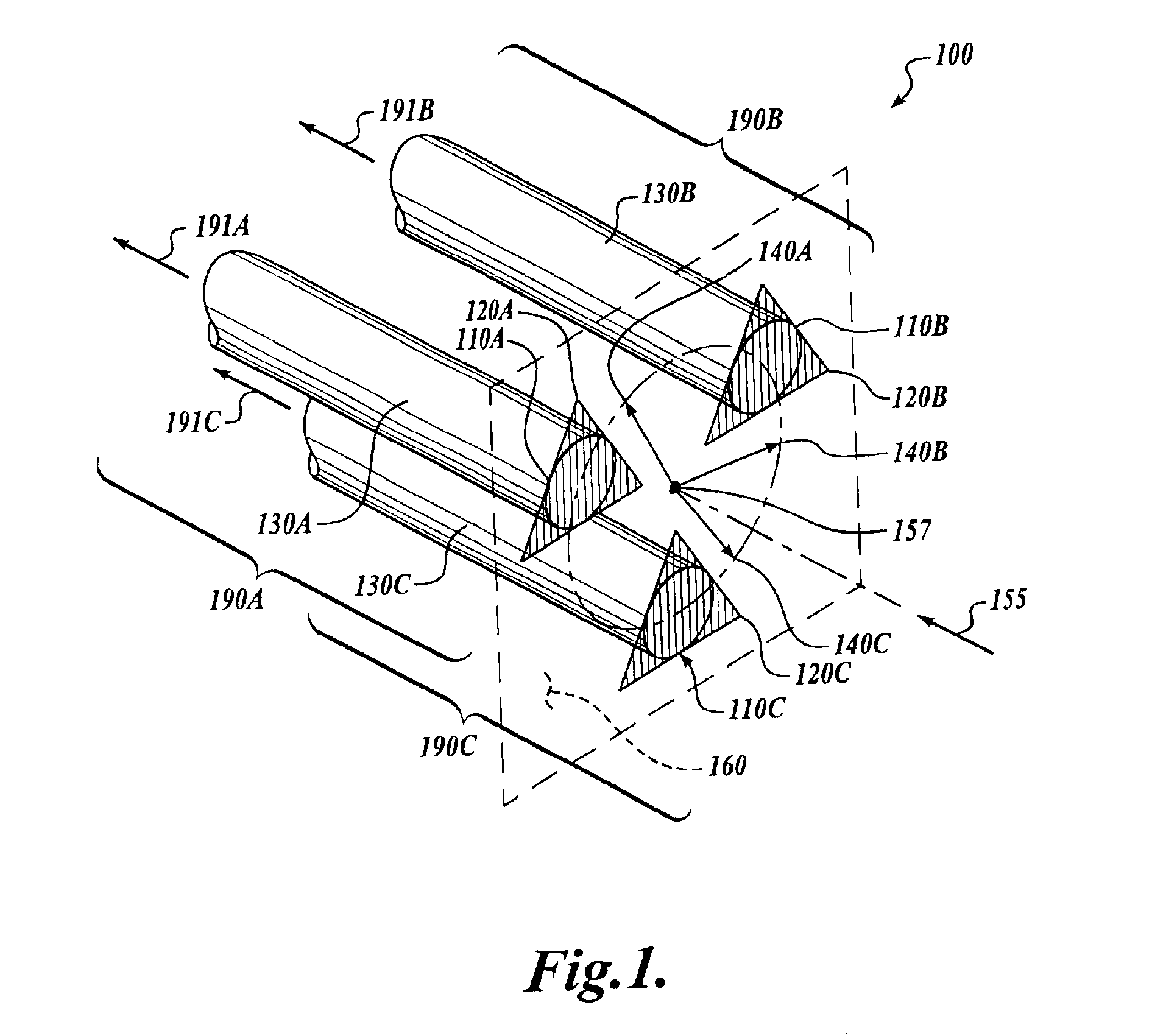
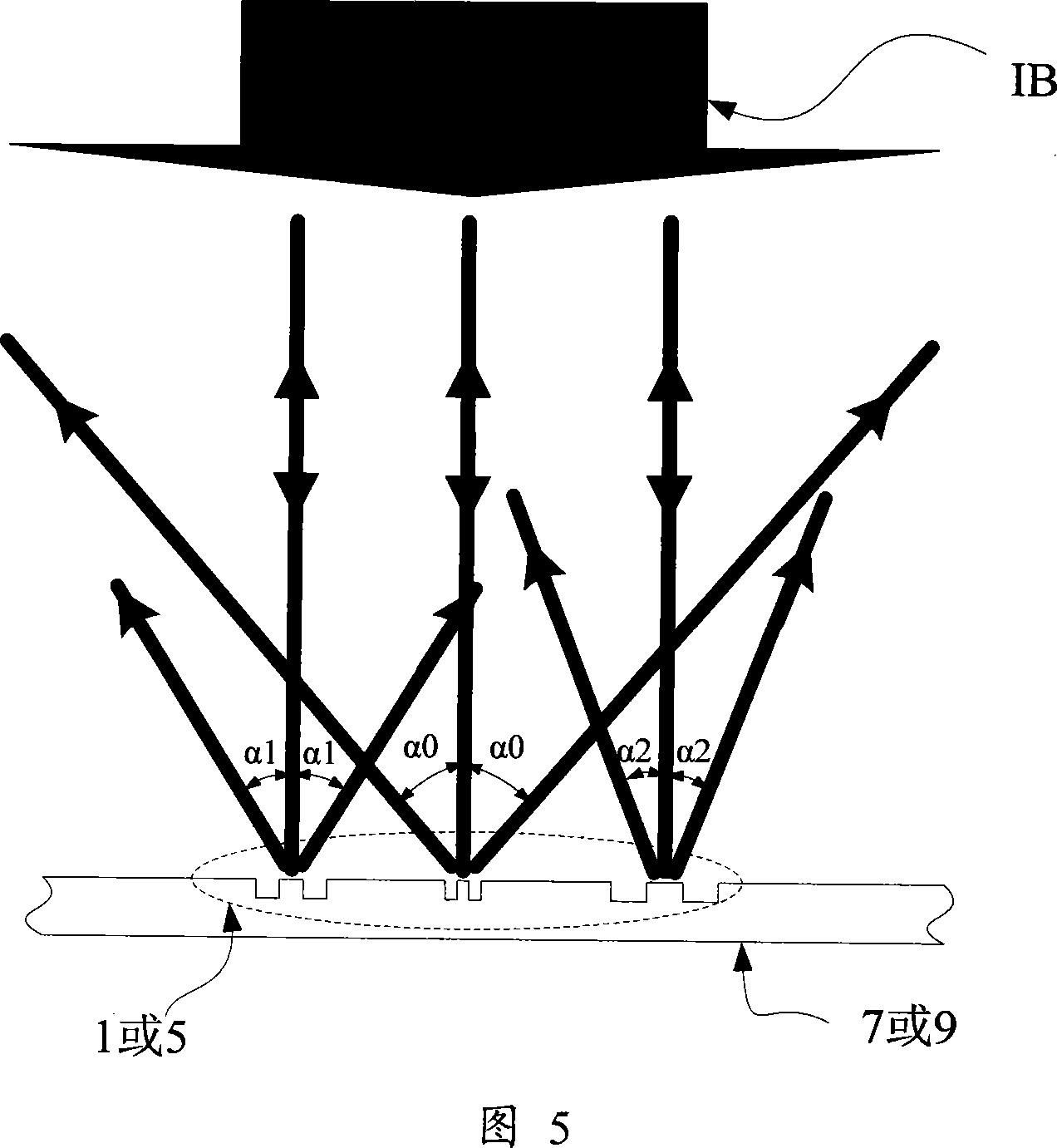
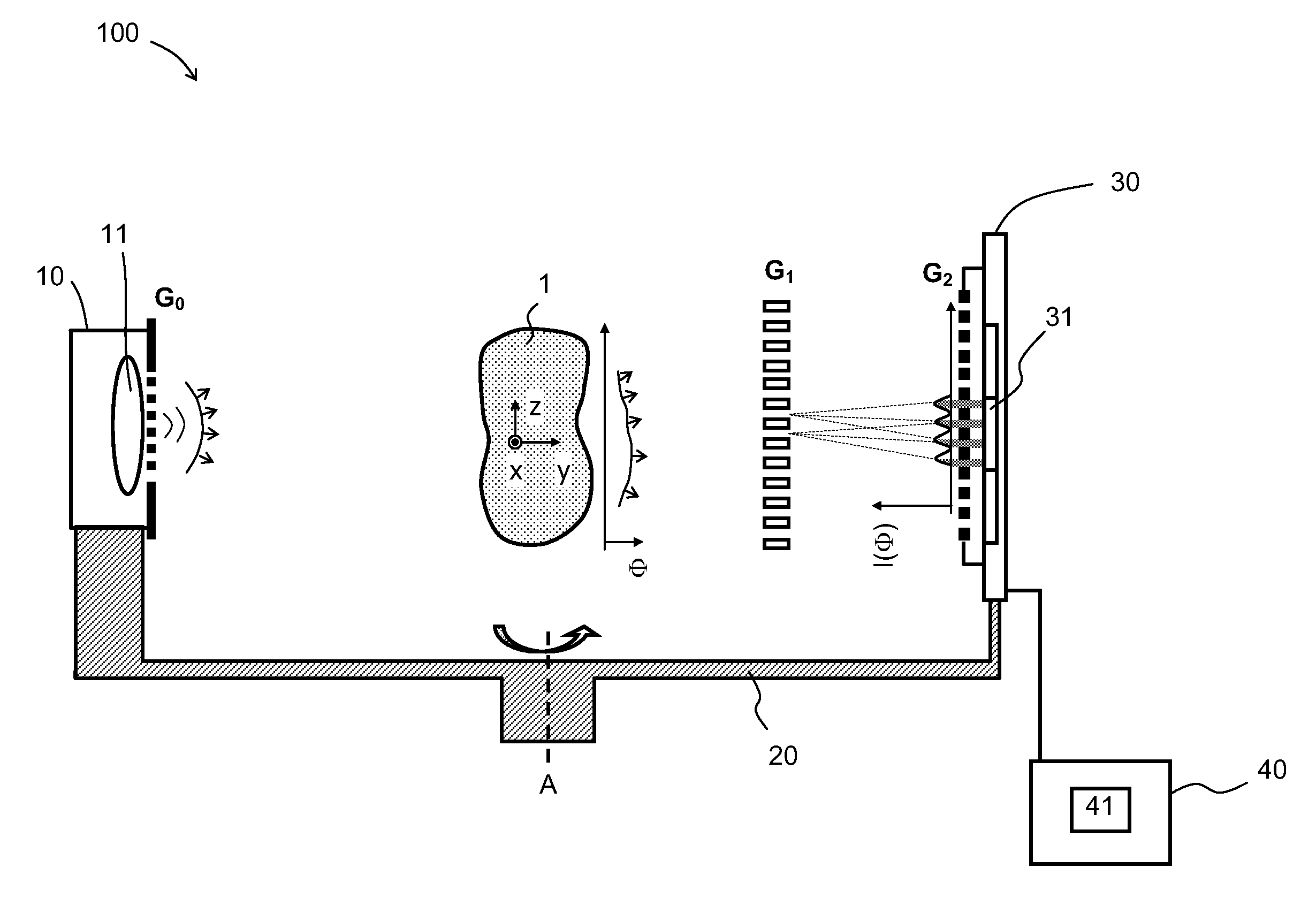
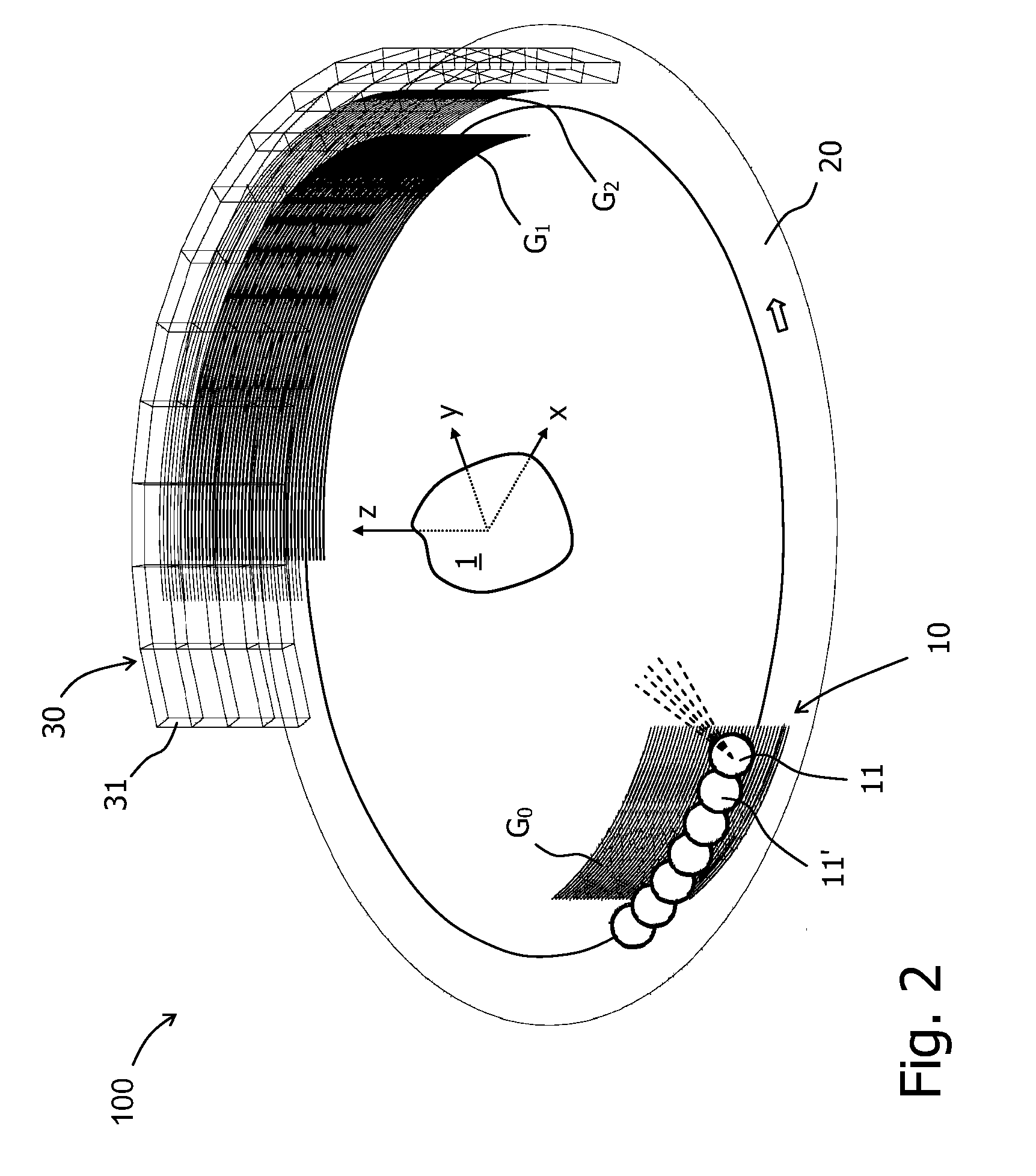
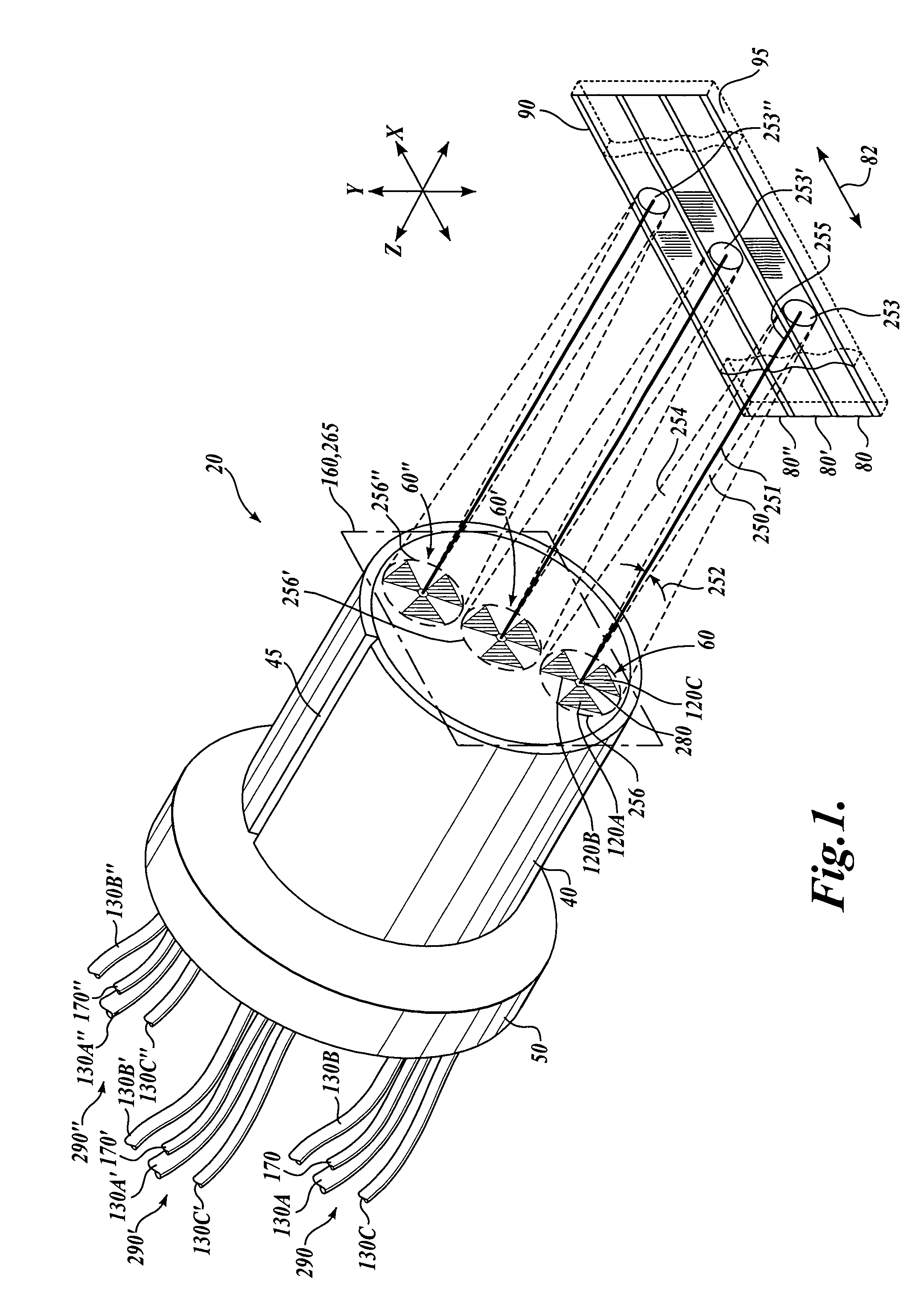
The invention relates to a rotational X-ray device (100), for example a CT scanner, for generating phase contrast images of an object (1). In a particular embodiment of the device (100), a plurality of X-ray sources (11), an X-ray detector (30), and an analyzer grating (G2) are attached to a rotatable gantry (20), while a ring-shaped phase grating (G1) is stationary. The X-ray sources are disposed such that X-rays first pass an object under study before traversing the phase grating (G1) and subsequently the analyzer grating (G2). This is achieved by either shifting the X-ray sources axially with respect to the ring-shaped phase grating (G1) or by disposing the X-ray sources in the interior of the ring. Moreover, the phase grating (G1) and the analyzer (G2) shall have spatially varying relative phase (and / or periodicity), for example realized by line grids that are tilted with respect to each other. During the rotation of the gantry (20), the synchronized activation of X-ray sources (11) allows to generate projection images of an object (1) from the same viewing angle with different relative positions (and therefore phases) between the phase grating (G1) and the analyzer (G2).
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
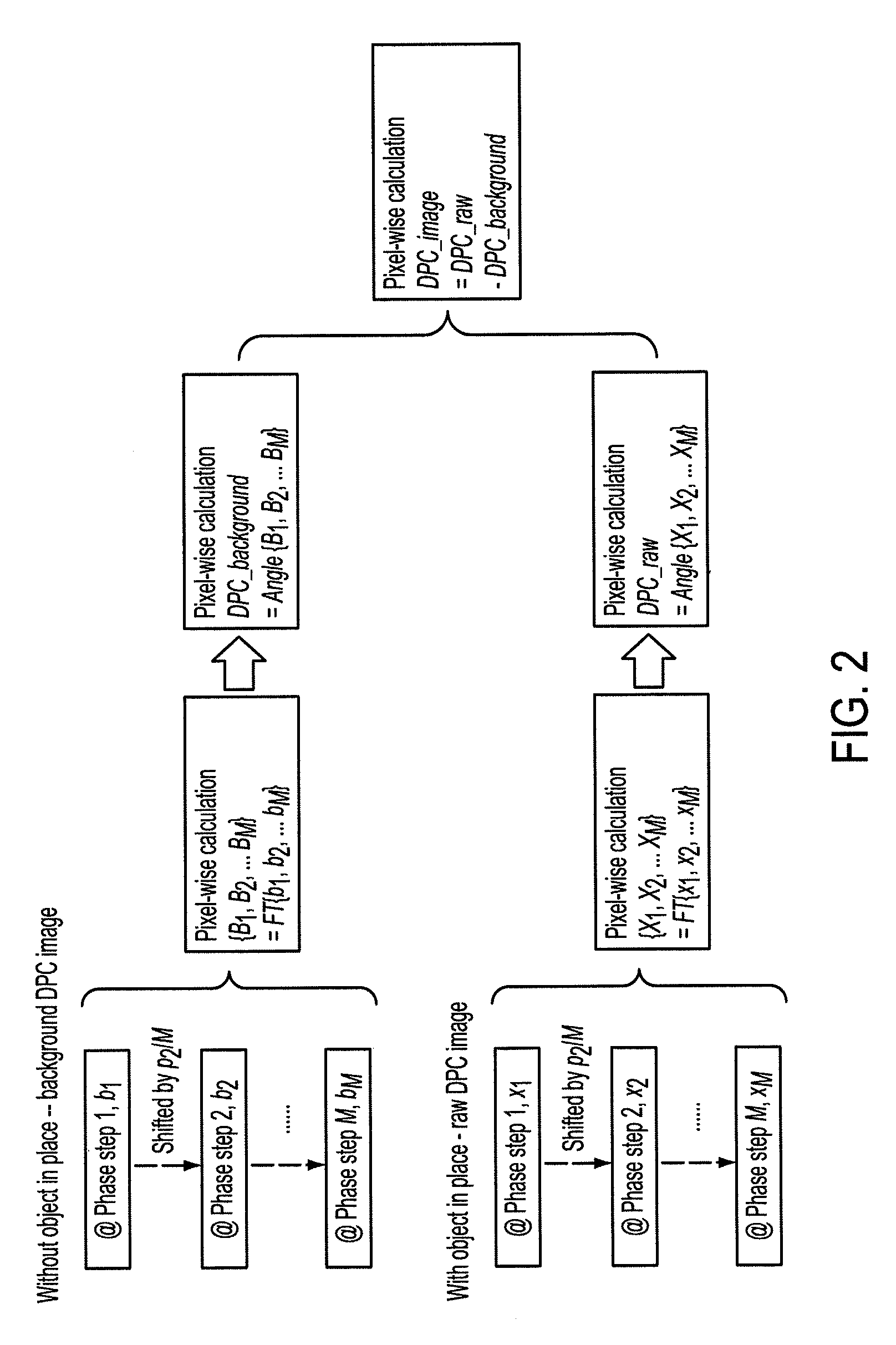
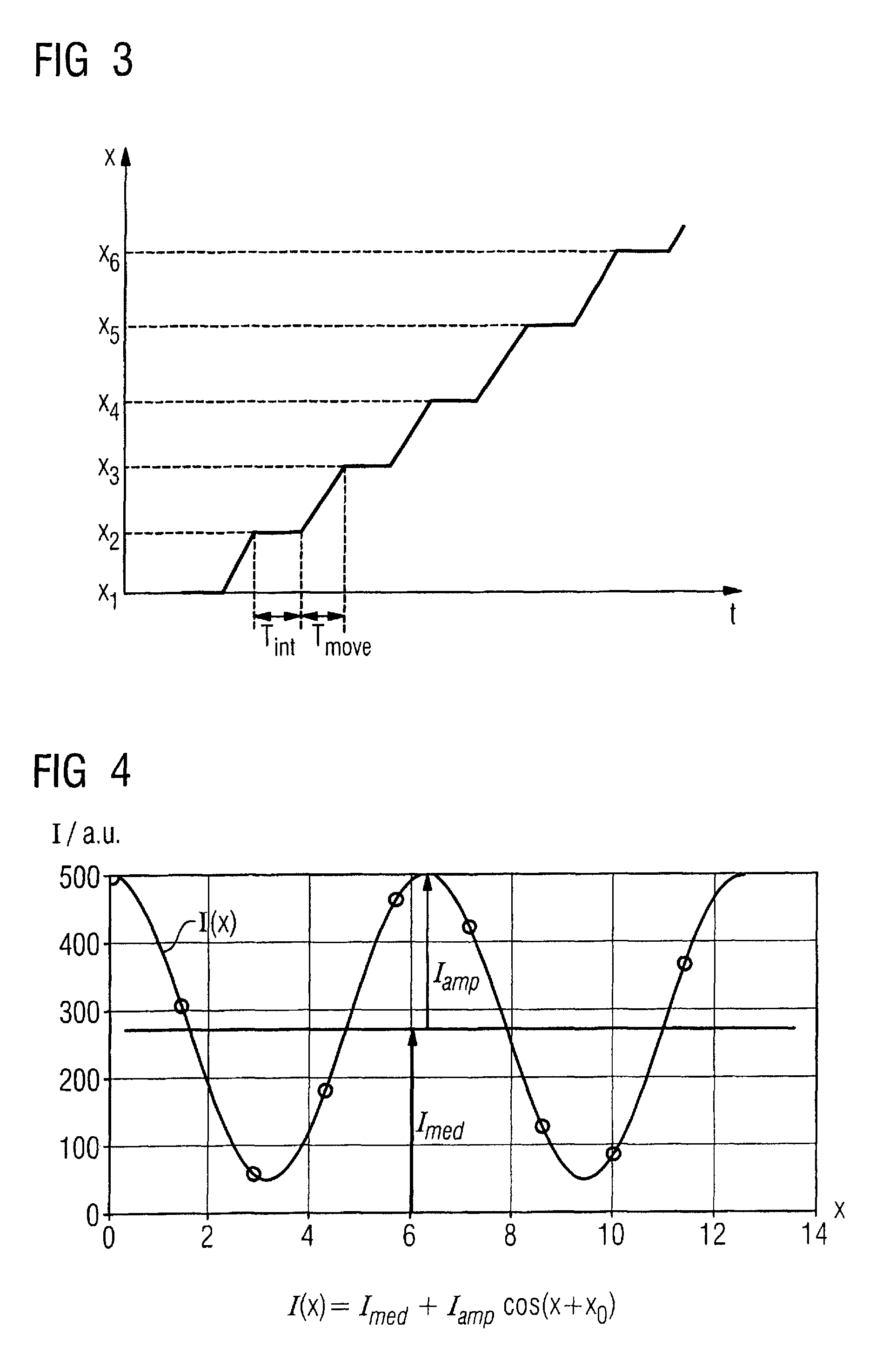
Method to determine phase and/or amplitude between interfering, adjacent x-ray beams in a detector pixel in a talbot interferometer
ActiveUS8005185B2Imaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingPhase gratingX-Ray Phase-Contrast Imaging
In a method to determine phase and / or amplitude between interfering, adjacent x-ray beams in a detector pixel in a Talbot interferometer for projective and tomographical x-ray phase contrast imaging and / or x-ray dark field imaging, after an irradiation of the examination subject with at least two coherent or quasi-coherent x-rays, an interference of the at least two coherent or quasi-coherent x-rays with the aid of an irradiated phase grating is generated, and the variation of multiple intensity measurements in temporal succession after an analysis grating is determined in relation to known displacements of one of the gratings or of an x-ray source fashioned like a grating, positioned upstream in the beam path, relative to one of the gratings. The integrating intensity measurements ensue during a relative movement—thus not during the standstill—of one of the upstream gratings or of the x-ray source fashioned like a grating or of the examination subject, with known speed behavior over a final time interval of a final distance.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method to determine phase and/or amplitude between interfering, adjacent x-ray beams in a detector pixel in a talbot interferometer
ActiveUS20100074395A1Simplify mannerImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayPhase grating
In a method to determine phase and / or amplitude between interfering, adjacent x-ray beams in a detector pixel in a Talbot interferometer for projective and tomographical x-ray phase contrast imaging and / or x-ray dark field imaging, after an irradiation of the examination subject with at least two coherent or quasi-coherent x-rays, an interference of the at least two coherent or quasi-coherent x-rays with the aid of an irradiated phase grating is generated, and the variation of multiple intensity measurements in temporal succession after an analysis grating is determined in relation to known displacements of one of the gratings or of an x-ray source fashioned like a grating, positioned upstream in the beam path, relative to one of the gratings. The integrating intensity measurements ensue during a relative movement—thus not during the standstill—of one of the upstream gratings or of the x-ray source fashioned like a grating or of the examination subject, with known speed behavior over a final time interval of a final distance.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
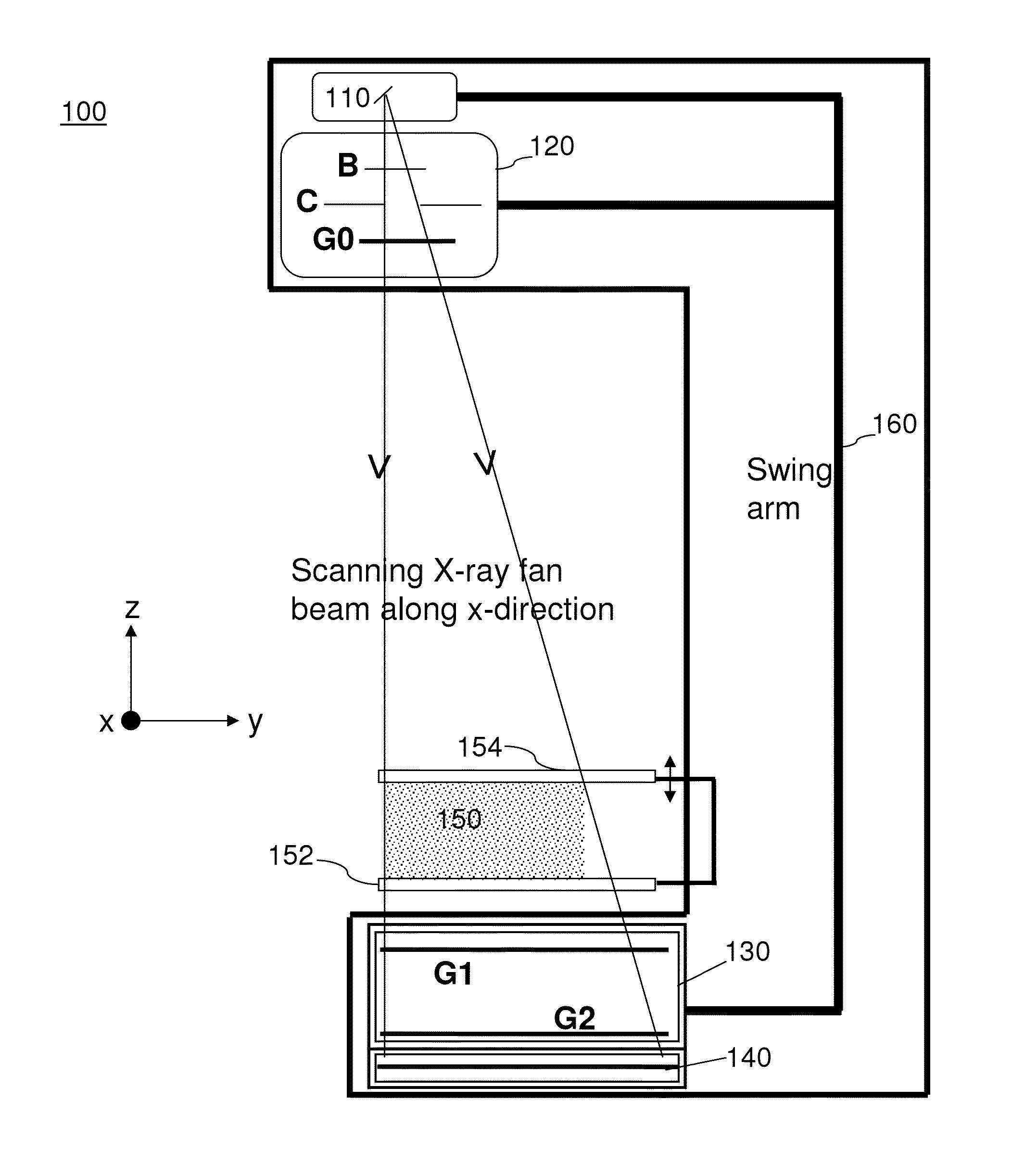
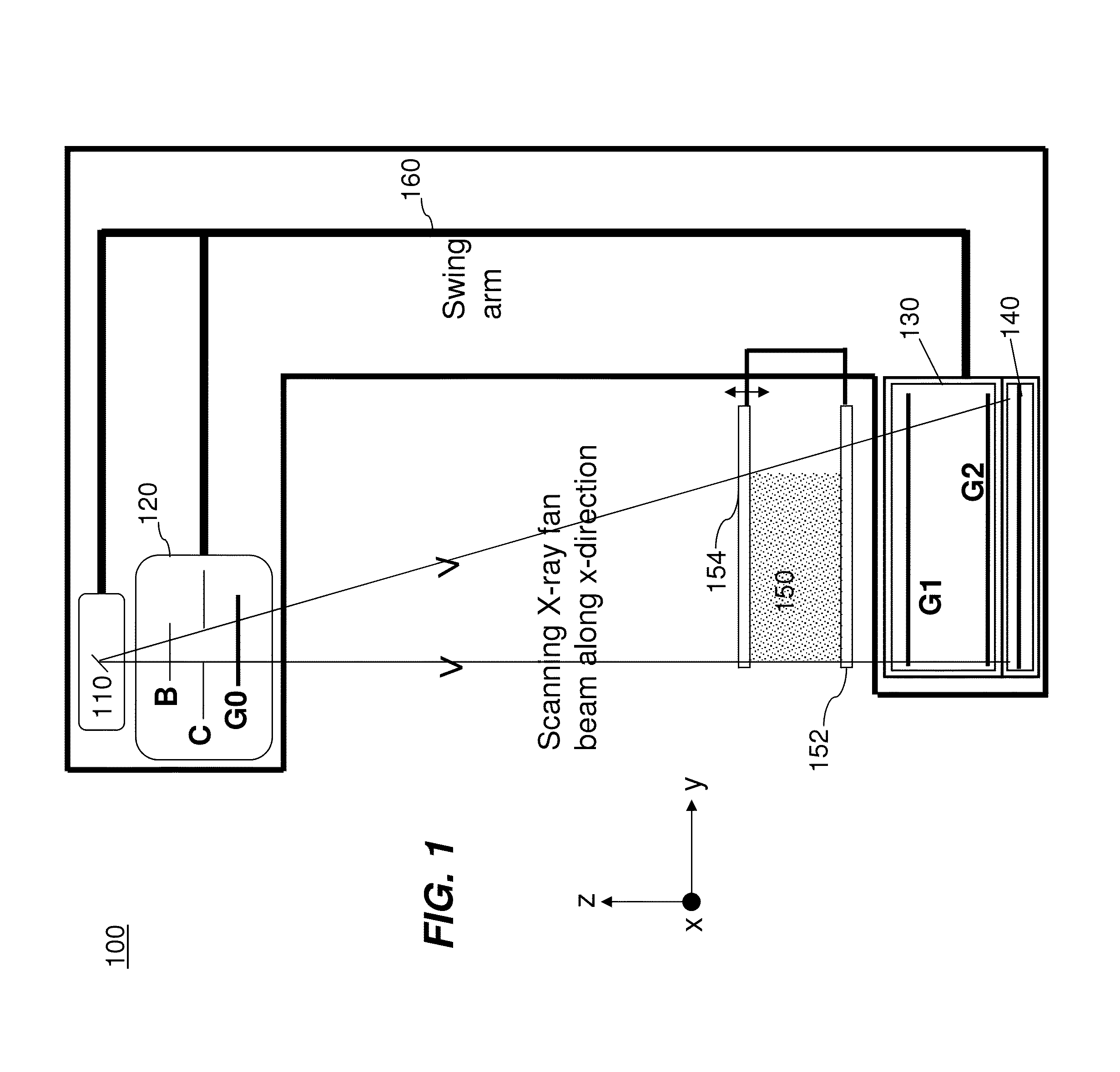
Spectral grating-based differential phase contrast system for medical radiographic imaging
ActiveUS20140185746A1Imaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionBeam energyBeam shaping
Embodiments of methods and apparatus are disclosed for obtaining a phase-contrast digital radiographic imaging system and methods for same that can include an x-ray source for radiographic imaging; a beam shaping assembly including a collimator and a source grating, an x-ray grating interferometer including a phase grating, and an analyzer grating; and an x-ray detector, where a single arrangement of the beam shaping assembly, the x-ray grating interferometer and a position of the detector is configured to provide spectral information (e.g. at least two images obtained at different relative beam energies).
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Spectral grating-based differential phase contrast system for medical radiographic imaging
Embodiments of methods and apparatus are disclosed for obtaining a phase-contrast digital radiographic imaging system and methods for same that can include an x-ray source for radiographic imaging; a beam shaping assembly including a collimator and a source grating, an x-ray grating interferometer including a phase grating, and an analyzer grating; and an x-ray detector, where a single arrangement of the beam shaping assembly, the x-ray grating interferometer and a position of the detector is configured to provide spectral information (e.g. at least two images obtained at different relative beam energies).
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Marker for photo-etching machine aligning and aligning using the same
ActiveCN101158814APrecise alignmentPrecision Alignment MarksPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusPhase gratingLithographic artist
The present invention discloses an alignment mark and an alignment signal treatment method used for projection scanning lithography machine based on four-cycle phase grating. The method makes use of a marked coarse grating branch signal for the determination of capture range and position of the coarse alignment, and makes use a marked fine grating branch signal for the determination of the fine alignment position, thereby ensuring the obtainment of high-precision alignment position by only adopting diffraction optical signal of plus or minus 1 grade, improving the alignment efficiency and simplifying the alignment optical system.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Interferometer device and method
InactiveUS20090128830A1Imaging devicesX-ray spectral distribution measurementPhase gratingPhase shifted
The present invention discloses an interferometer device and method. In embodiments, the device comprises an electromagnetic radiation source emitting radiation having a first mean wavelength λLE; a phase grating having a first aspect ratio; an absorption grating having a second aspect ratio; and a detector. The electromagnetic radiation source, the phase grating, the absorption grating and the detector are radiatively coupled with each other. The absorption grating is positioned between the detector and the phase grating; the electromagnetic radiation source is positioned in front of the source grating; and wherein the phase grating is designed such to cause a phase shift that is smaller than π on the emitted radiation. Additional and alternative embodiments are specified and claimed.
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
X-ray imaging apparatus, X-ray imaging method, and X-ray imaging program
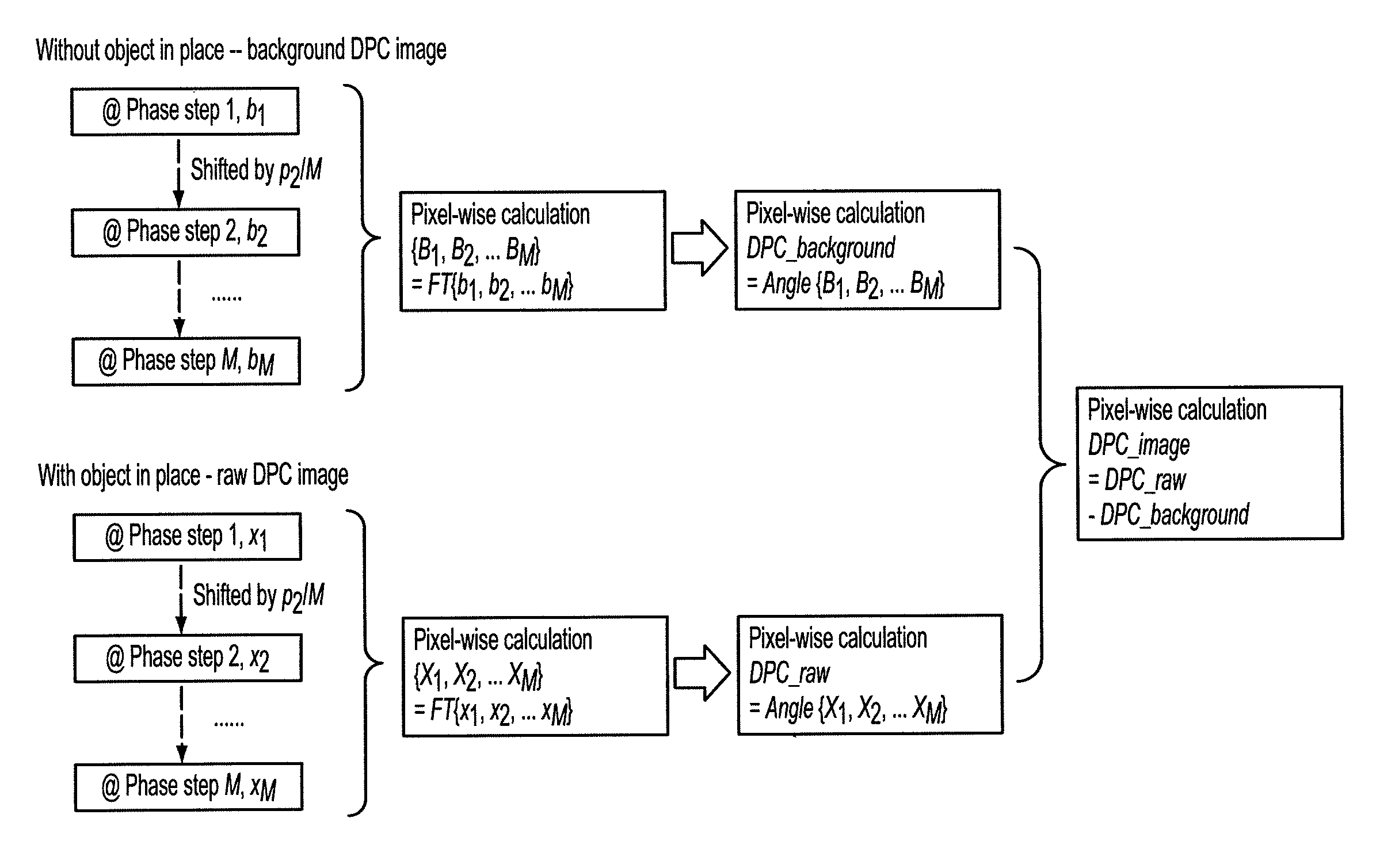
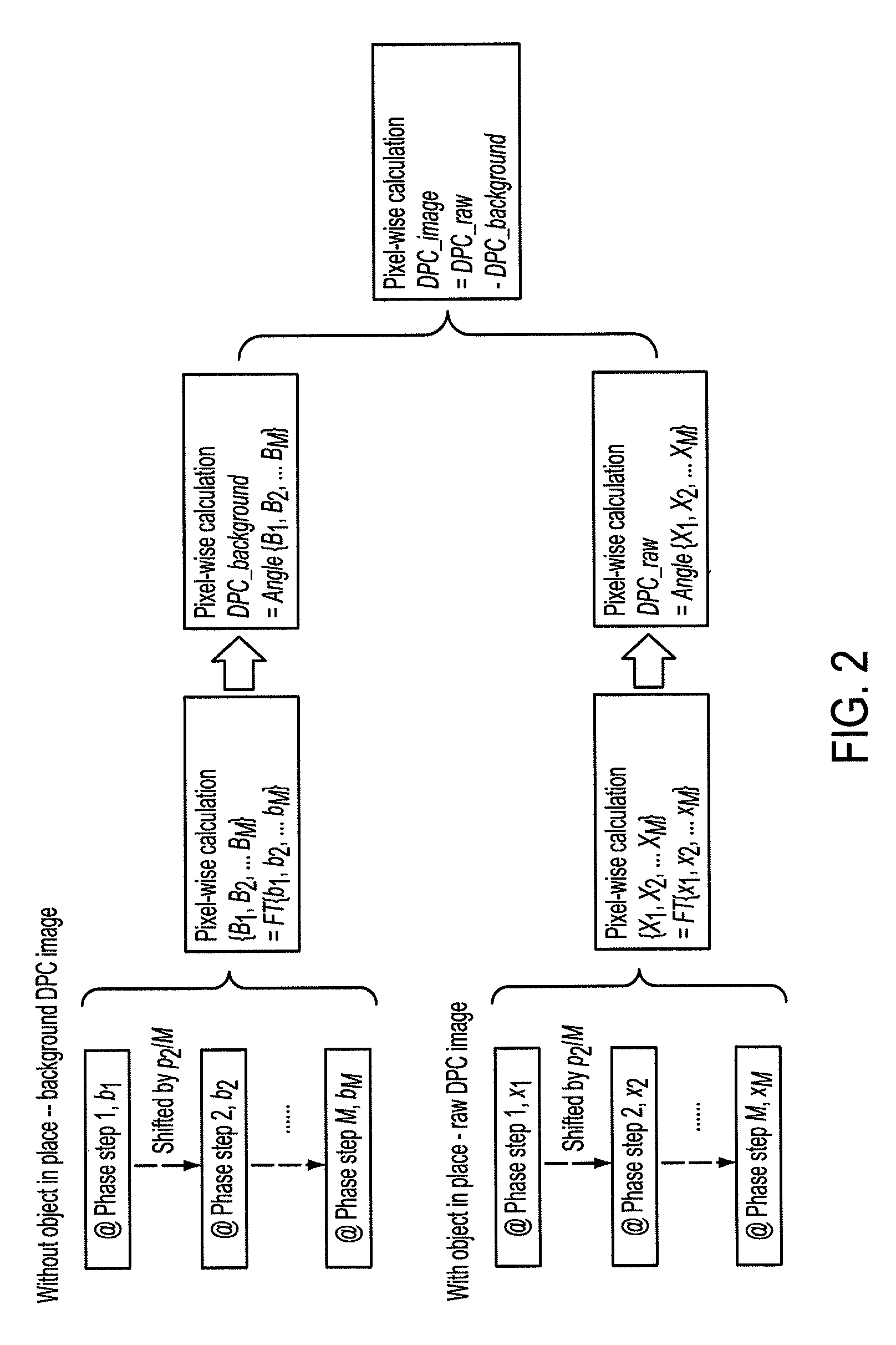
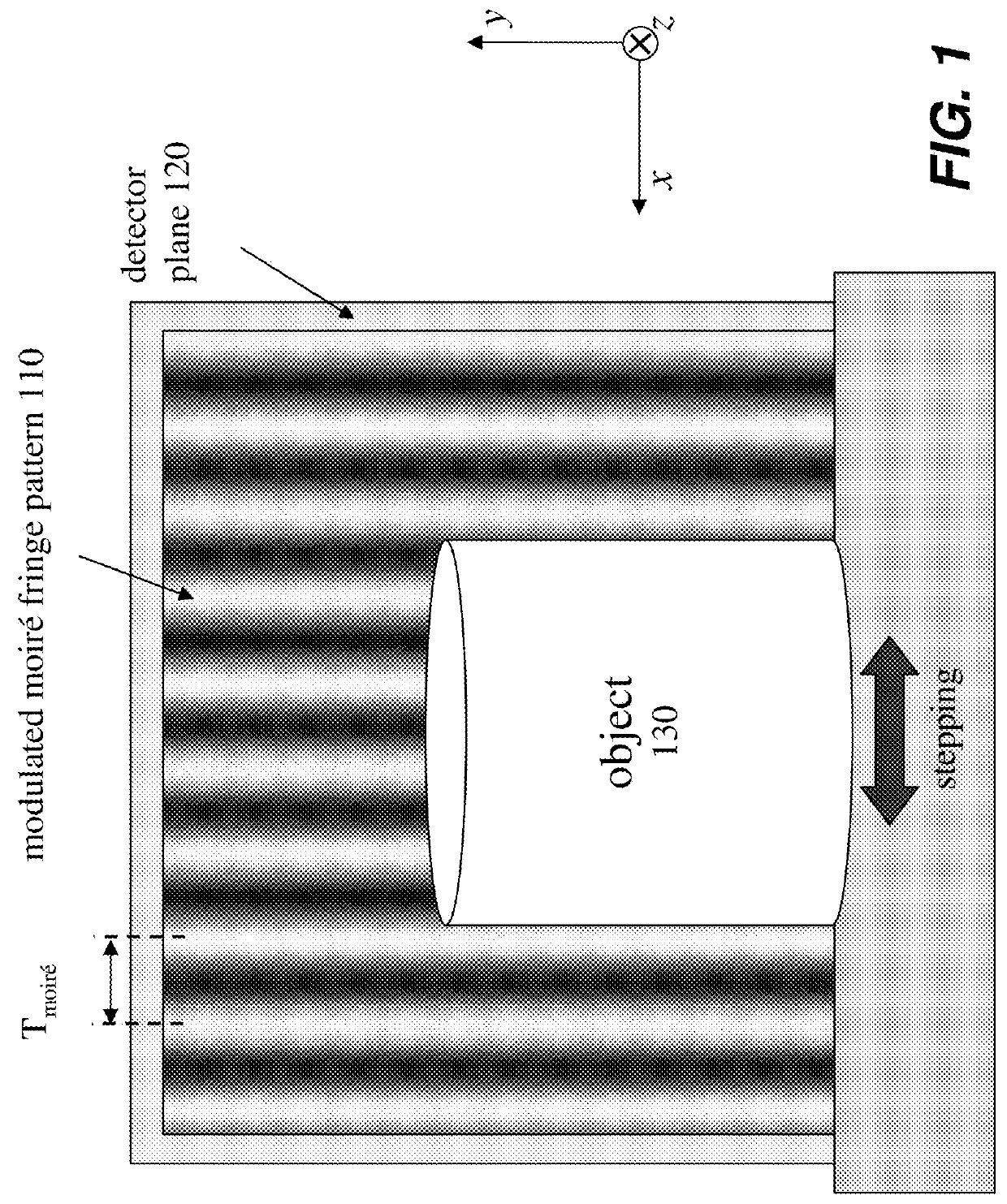
An X-ray imaging apparatus includes a phase grating, an absorption grating, a detector, and an arithmetic unit. The arithmetic unit executes a Fourier transform step of performing Fourier transform for an intensity distribution of a Moiré acquired by the detector, and acquiring a spatial frequency spectrum. Also, the arithmetic unit executes a phase retrieval step of separating a spectrum corresponding to a carrier frequency from a spatial frequency spectrum acquired in the Fourier transform step, performing inverse Fourier transform for the separated spectrum, and acquiring a differential phase image.
Owner:CANON KK
Hybrid slot-scanning grating-based differential phase contrast imaging system for medical radiographic imaging
InactiveUS20130259194A1Imaging devicesPatient positioning for diagnosticsDigital mammographyBeam shaping
Embodiments of methods and apparatus are disclosed for obtaining a phase-contrast digital mammography system and methods for same that can include an x-ray source for radiographic imaging; a beam shaping assembly including a filter or a tunable monochromator, a collimator, a source grating, an x-ray grating interferometer including a phase grating, and an analyzer grating; and an x-ray detector; where the source grating, the phase grating, and the analyzer grating are aligned in such a way that the grating bars of these gratings are parallel to each other.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Large FOV phase contrast imaging based on detuned configuration including acquisition and reconstruction techniques
ActiveUS9357975B2Reduce disadvantagesAchieve effectImaging devicesRadiation diagnostic device controlLarge fovDigital imaging
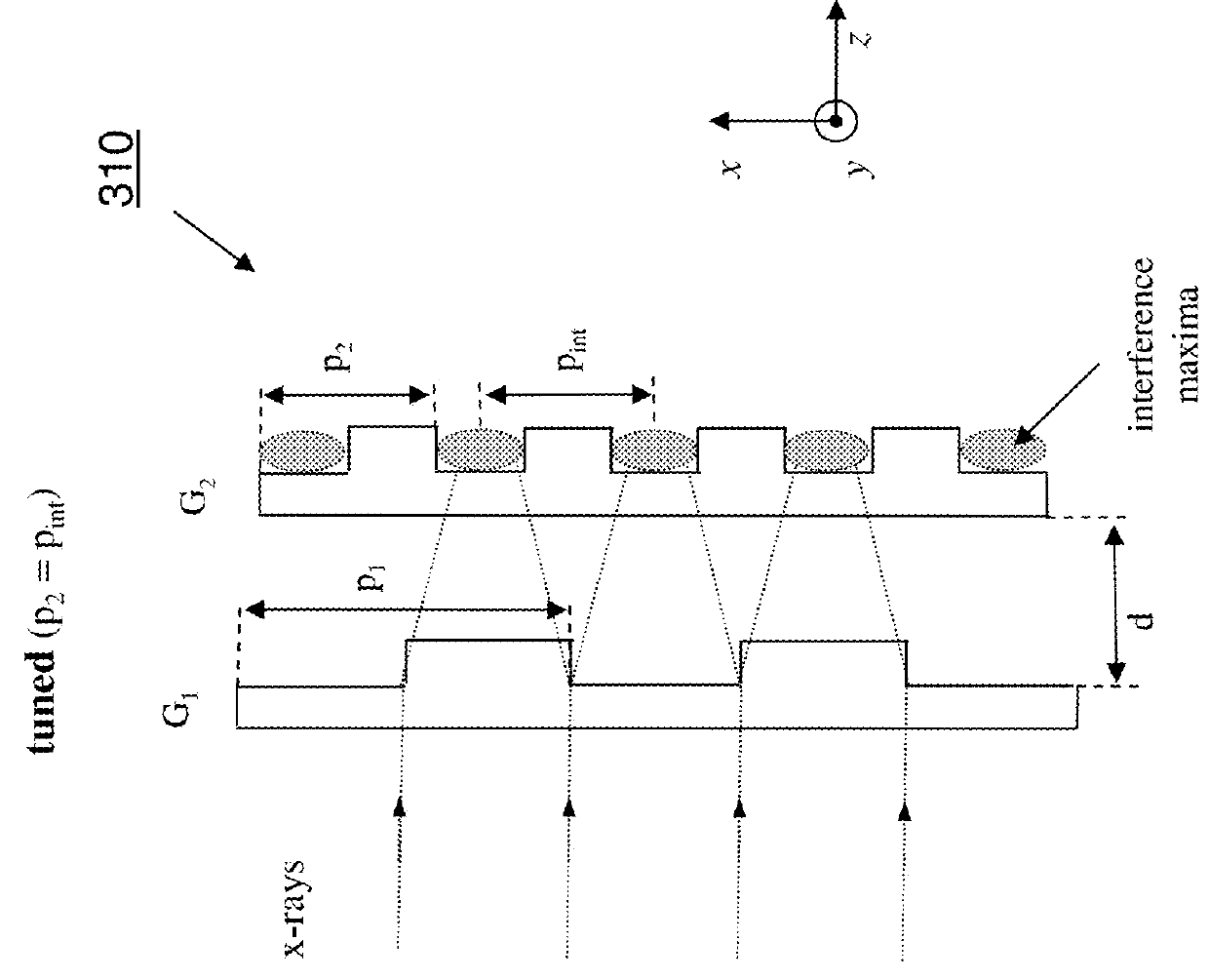
Embodiments of methods and apparatus are disclosed for obtaining a phase-contrast digital imaging system and methods for same that can include an x-ray source for radiographic imaging; a beam shaping assembly, an x-ray grating interferometer including a phase grating and an analyzer grating; and an x-ray detector; where the source grating, the phase grating, and the analyzer grating are detuned and a plurality of uncorrelated reference images are obtained for use in imaging processing with the detuned system.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Phase grating used to take X-ray phase contrast image, imaging system using the phase grating, and X-ray computer tomography system
InactiveUS8351570B2Imaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionSoft x rayPhase grating
To provide a phase grating capable of acquiring, in photographing of an X-ray phase contrast image by use of X-ray with two wavelengths, an X-ray phase contrast image by a phase grating in the same size as when a single wavelength is used, provided is a phase grating used when an X-ray is directed to take an X-ray phase contrast image, the phase grating including a periodic structure for generating a phase difference between an X-ray transmitted through the structure and an X-ray not transmitted through the structure. The periodic structure has different periods in a plurality of directions in a same surface.
Owner:CANON KK
Absolute position miniature grating encoder readhead using fiber optic receiver channels
ActiveUS7053362B2Highly accurate and economical and high configurationOvercome disadvantagesMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansFiberPhase grating
An absolute position fiber optic encoder readhead having multiple readhead portions for sensing the displacement of respective scale grating tracks of a scale is disclosed. The detector channels of the readhead portions are fiber optic detector channels having respective phase grating masks. The fiber optic encoder readhead portions are configured to detect the displacement of a self-image of a respective scale grating track of the scale. In various exemplary embodiments, the fiber optic readhead portions are constructed according to various design relationships that provide a relatively high signal-to-noise ratio. Accordingly, high levels of displacement signal interpolation may be achieved, allowing submicrometer displacement measurements. The fiber optic encoder readhead portions may be assembled in a particularly accurate and economical manner and may be provided in a package with dimensions on the order of 1–2 millimeters, resulting in a very small overall absolute readhead dimension that is dependent on the number of readhead portions that are incorporated. Optical fiber receiver channels carrying binary optical signals derived from a scale code track may be provided in the readhead, to provide an extended absolute measurement range.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Holographic display screen and method for producing the screen
InactiveUS20020154349A1Large viewing angleFulfil requirementsVehicle componentsOptical elementsHolographic screenPhase grating
A transparent holographic display screen for laser projection of at least one or more monochromatic wavelengths, is constructed to selectively diffuse an incident narrow-band laser beam at a predetermined solid angle and simultaneously to pass wide-band ambient light unobstructed through the display screen. The transparent holographic display screen has at least one holographic volume phase grating which is optically coupled to or integrated with a transparent carrier plate. The holographic display screen with its volume grating is produced by illuminating a real screen as an object into a primary hologram and recording a real holographic image of said real screen into a secondary hologram.
Owner:EADS DEUT GMBH
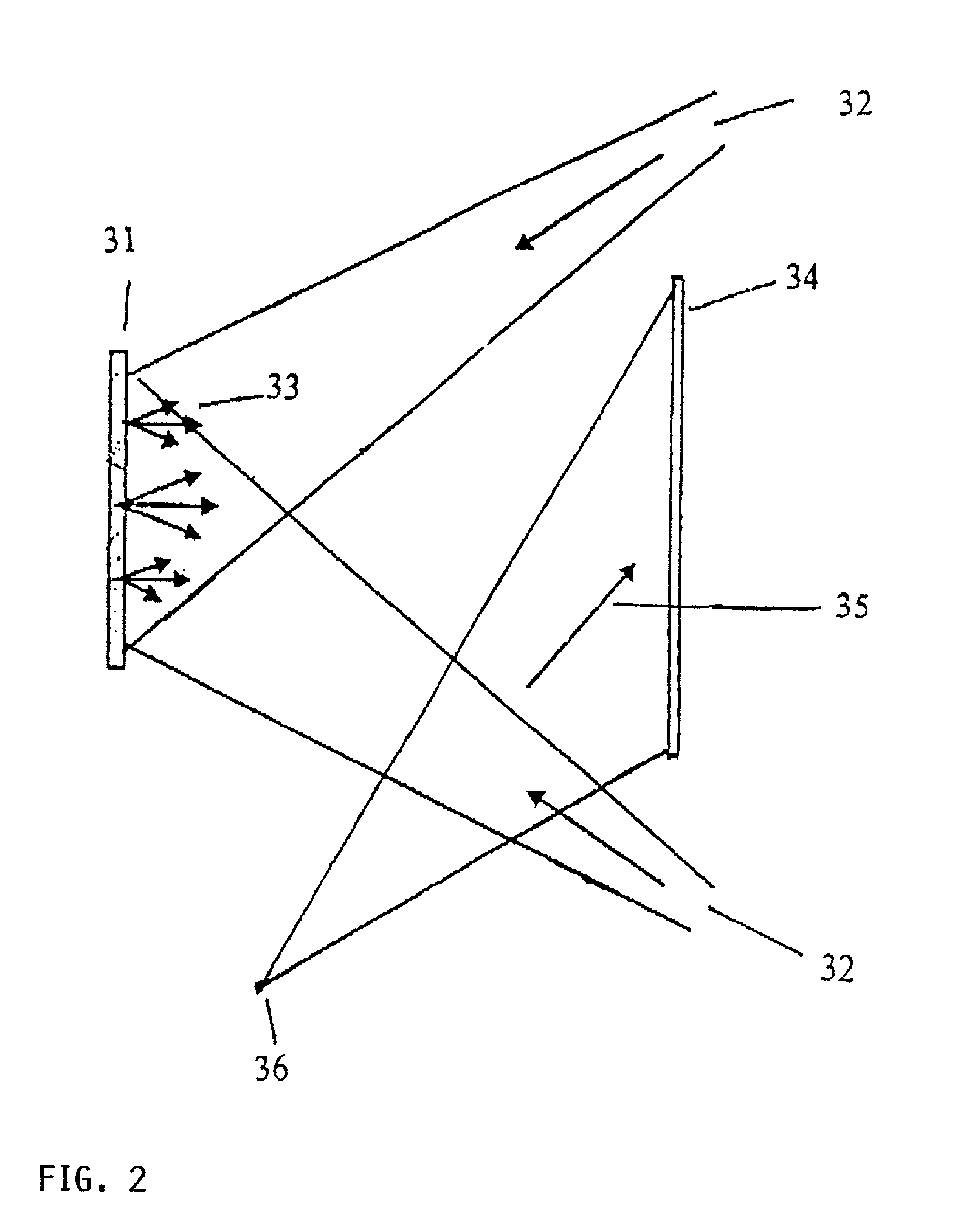
Structure for wavelength selection switch
The invention relates to a structure for a wavelength selection switch composed of a collimator array 1, a beam-expanding prism group 2, a polarization independent transmission phase grating 3, a focusing lens 4 and an MEMS (Micro-electromechanical System) micro-mirror array 5. The volumes of the devices can be reduced by adding a reflector 6 or a steering prism 7 in an optical path. One of the collimator array 1 is used as an input port while the others are used as output ports; DWDM (Dense WaveLength Division Multiplexing) light beams are input and converted to elliptical light beams via the beam-expanding prism group 2, then the light beams with different wavelengths are diffracted to be different deflection angles via the polarization independent transmission phase grating 3, focused by the focusing lens and emitted to different micro-mirrors on the MEMS micro-mirror array 5; each micro-mirror independently controls the reflection direction of every wavelength; the light beams are output to the target output port in the collimator array 1 through the focusing lens 4, the polarization independent transmission phase grating 3 and the beam-expanding prism group 2.
Owner:孙方红 +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com