Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1097 results about "X ray beam" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
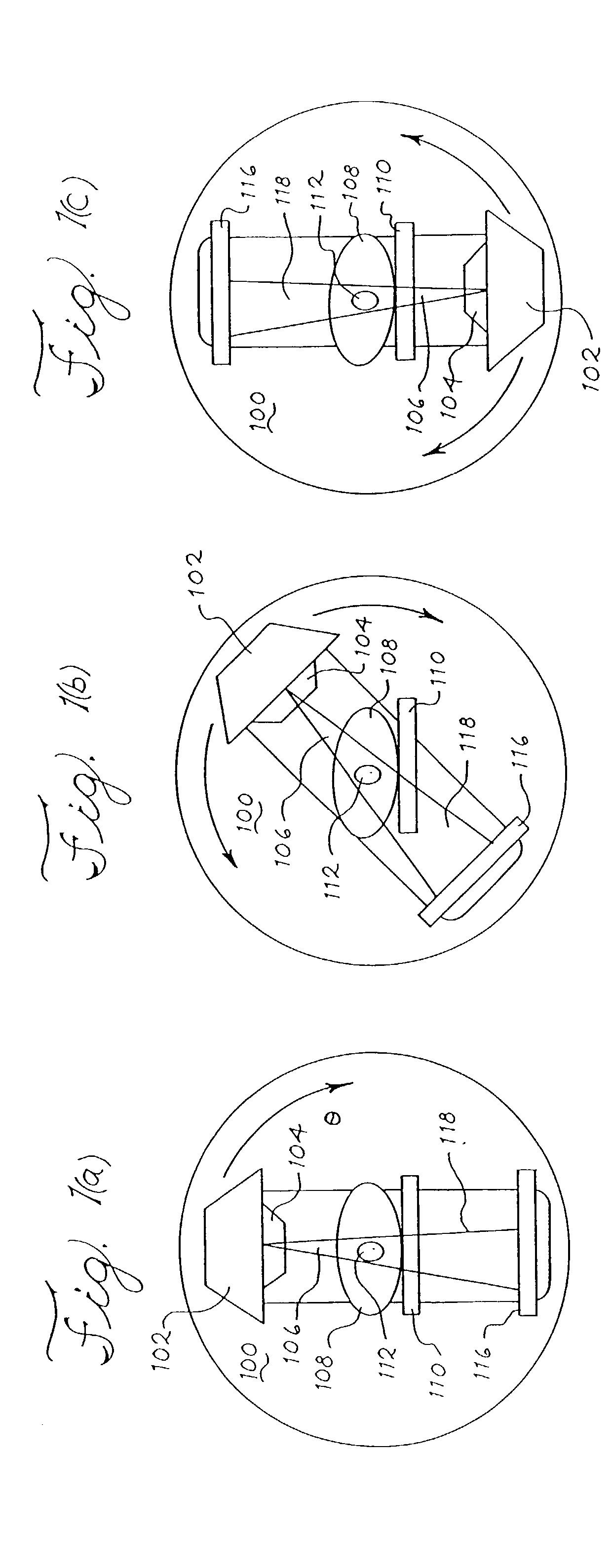
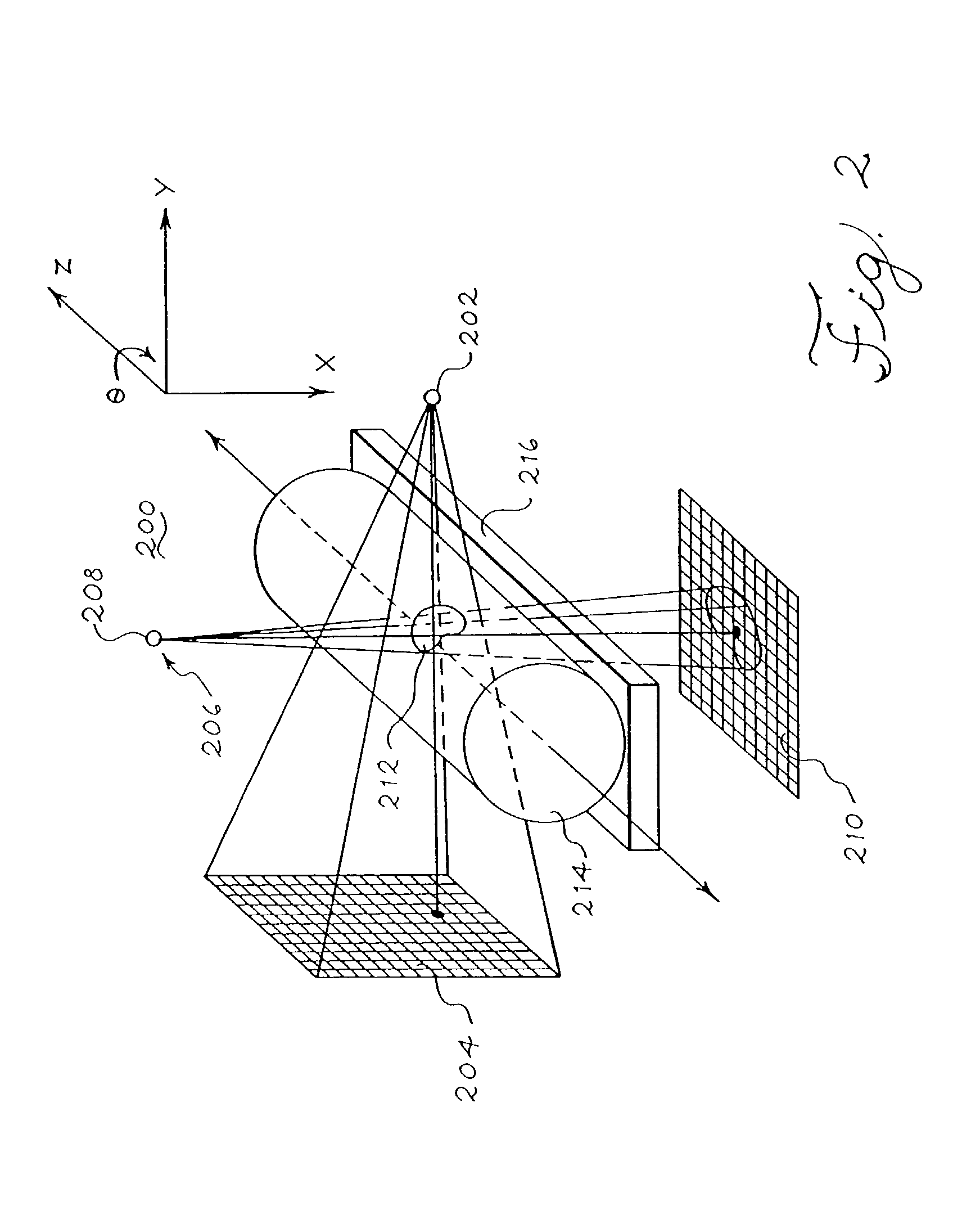
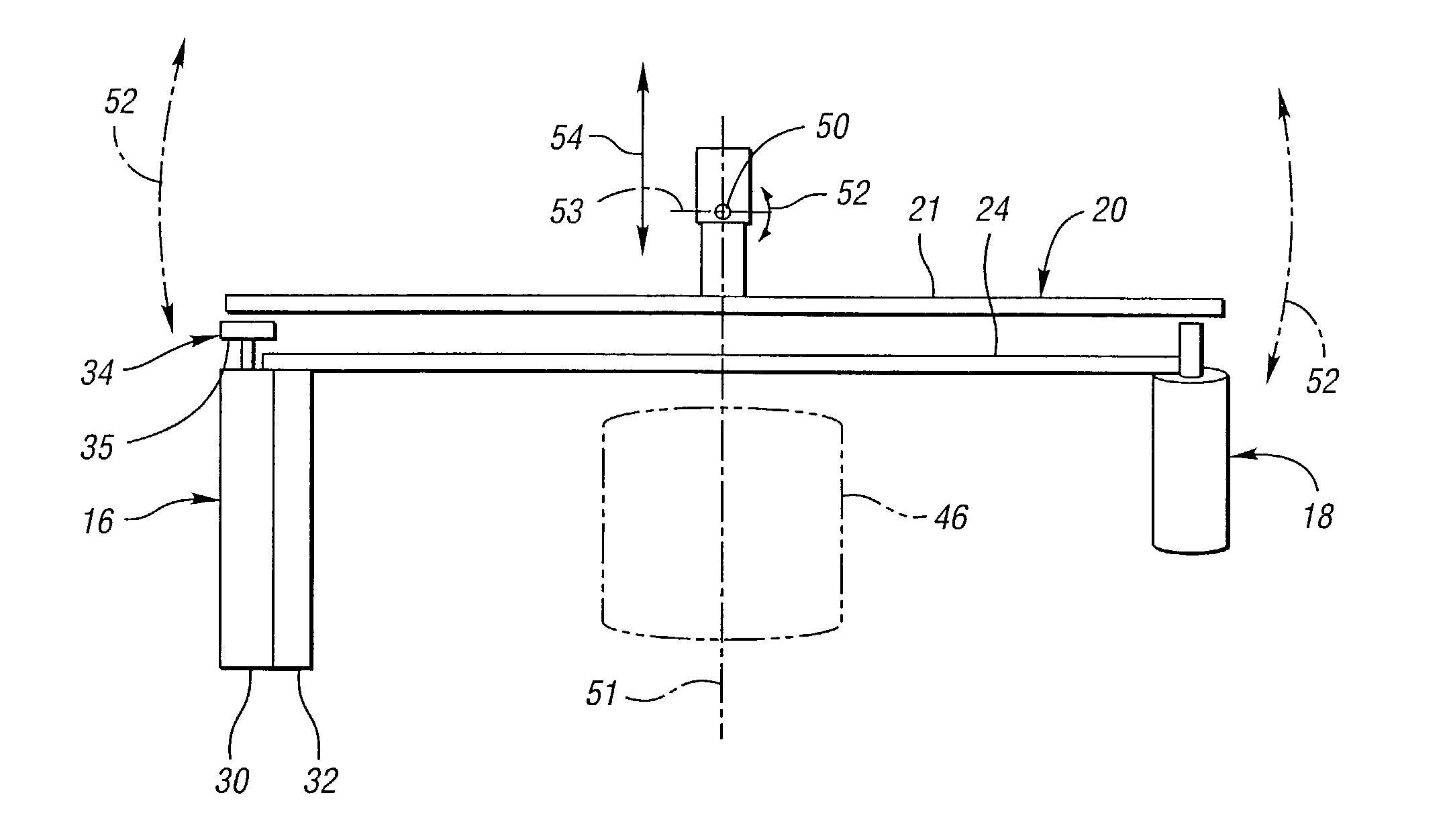
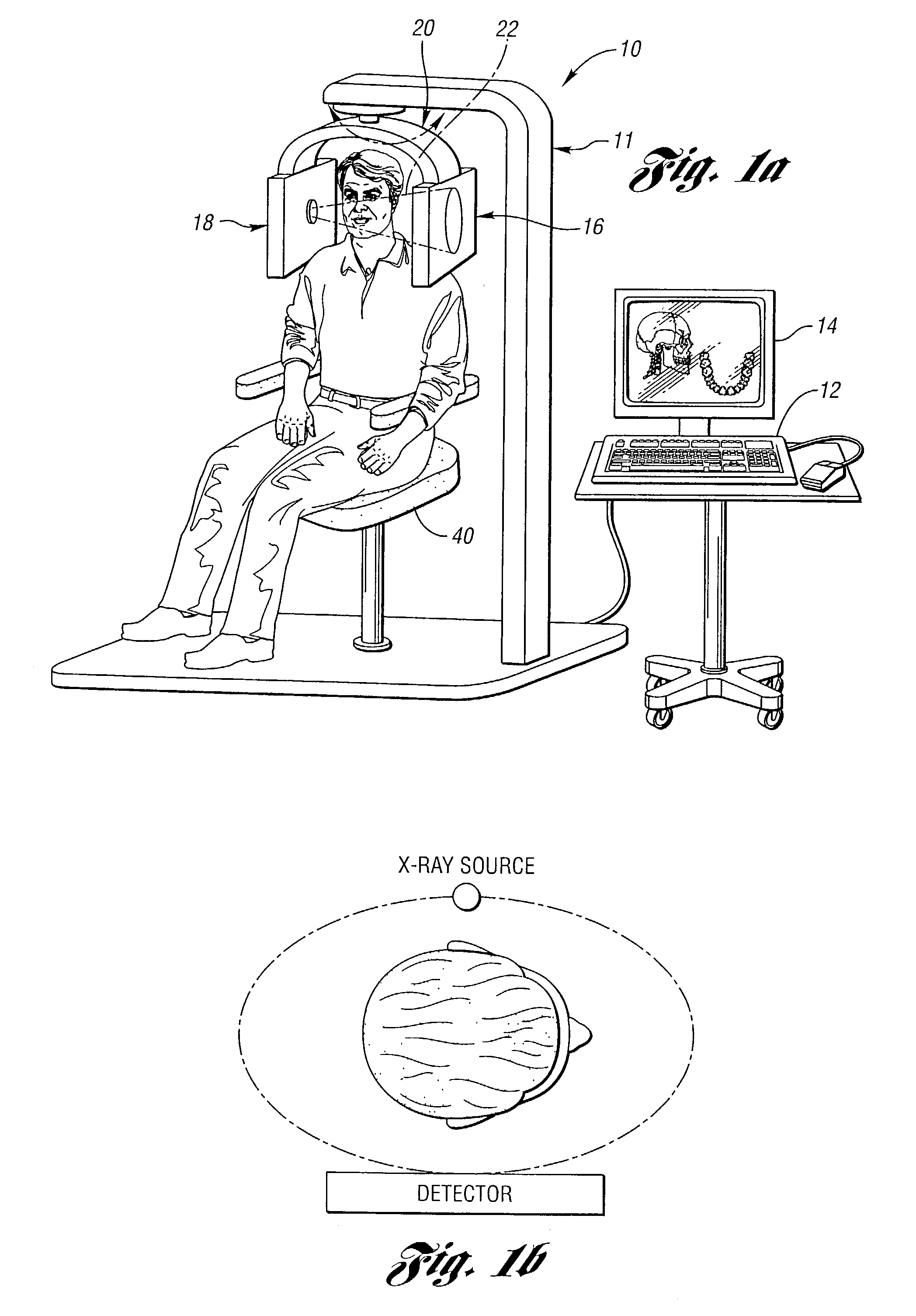
Cone-beam computed tomography systems (CBCT) are a variation of traditional computed tomography (CT) systems. The CBCT systems used by dental professionals rotate around the patient, capturing data using a cone-shaped X-ray beam.
Cone beam computed tomography with a flat panel imager
InactiveUS6842502B2Adequate visualizationReduce errorsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayAmorphous silicon
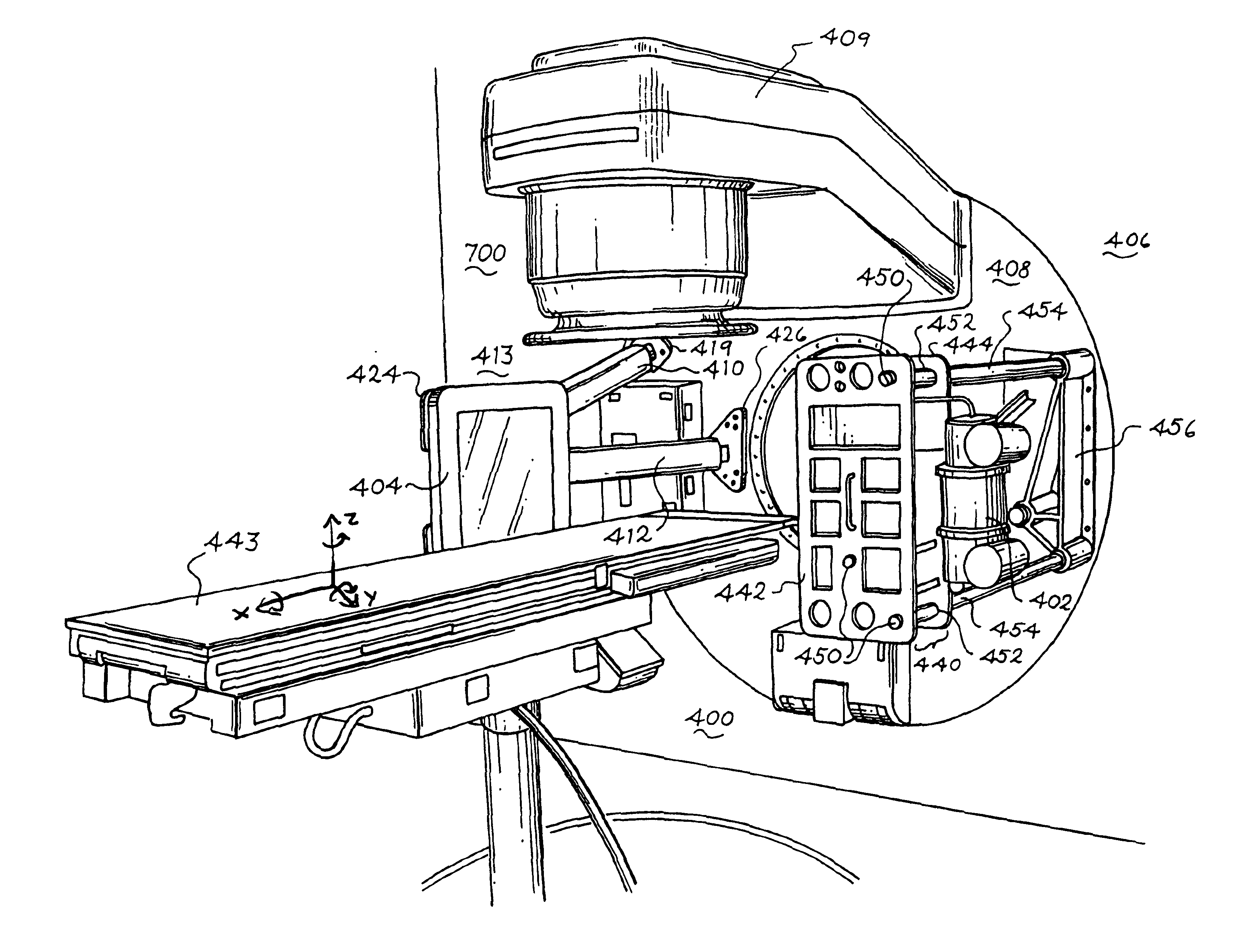
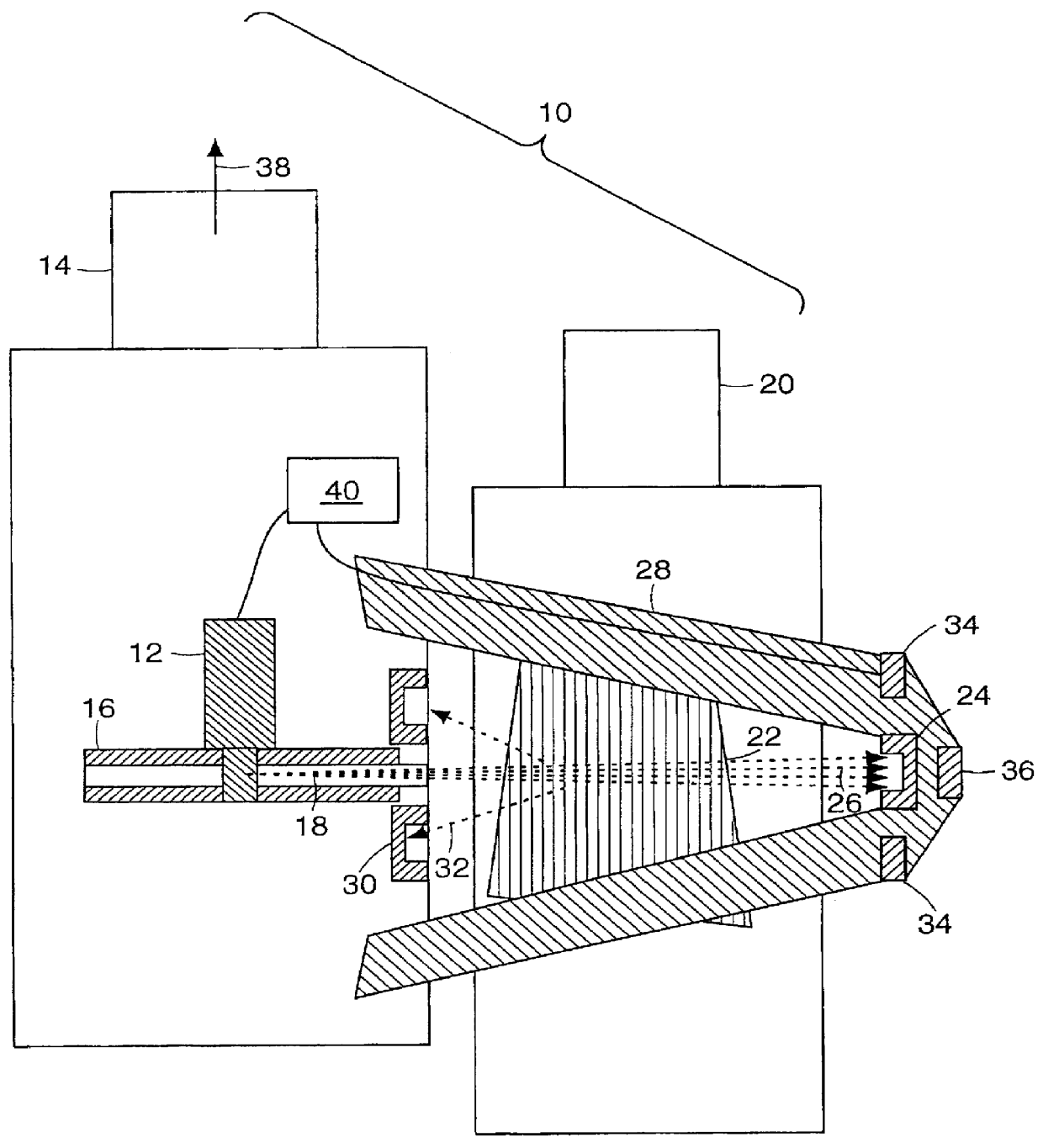
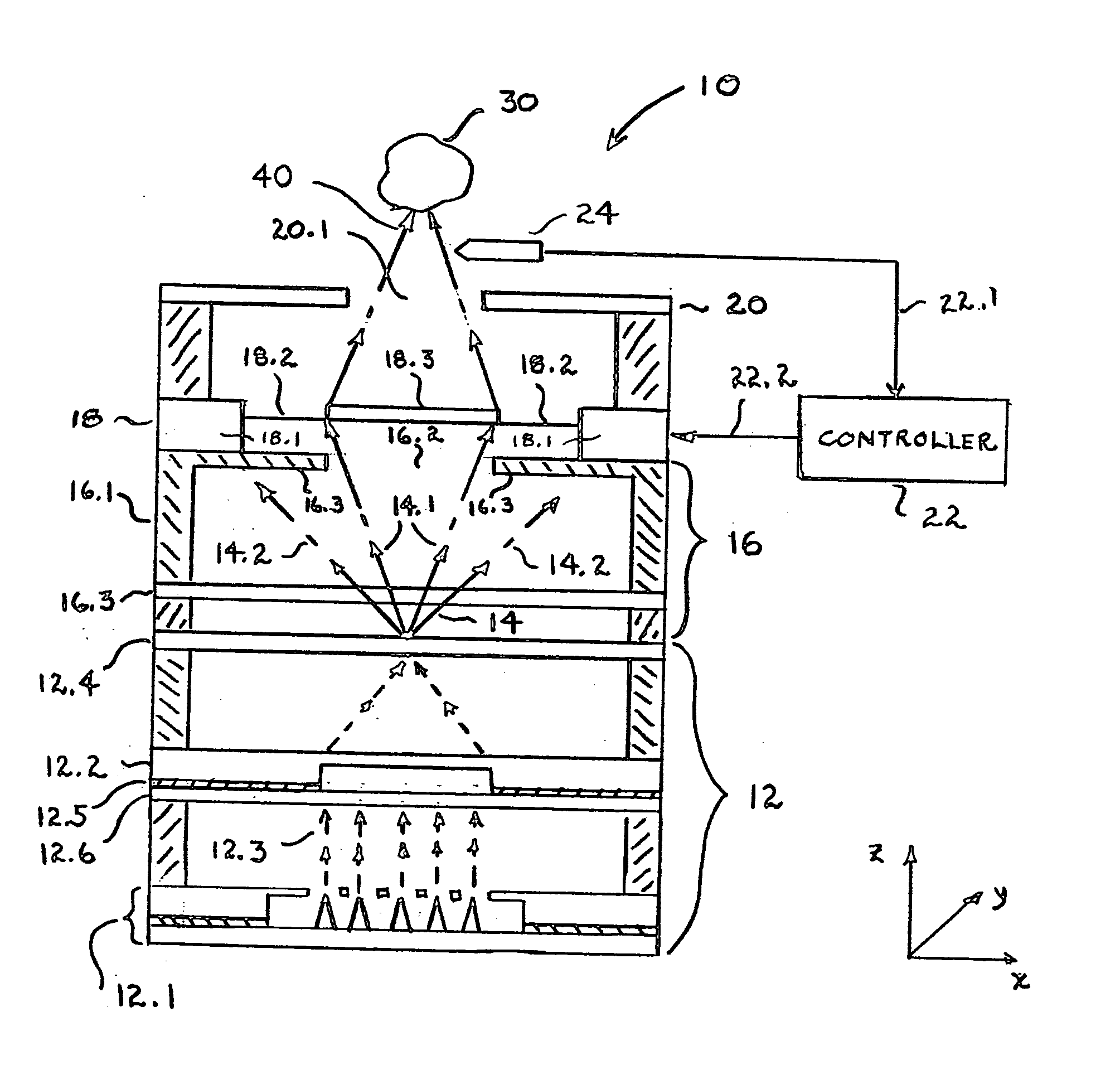
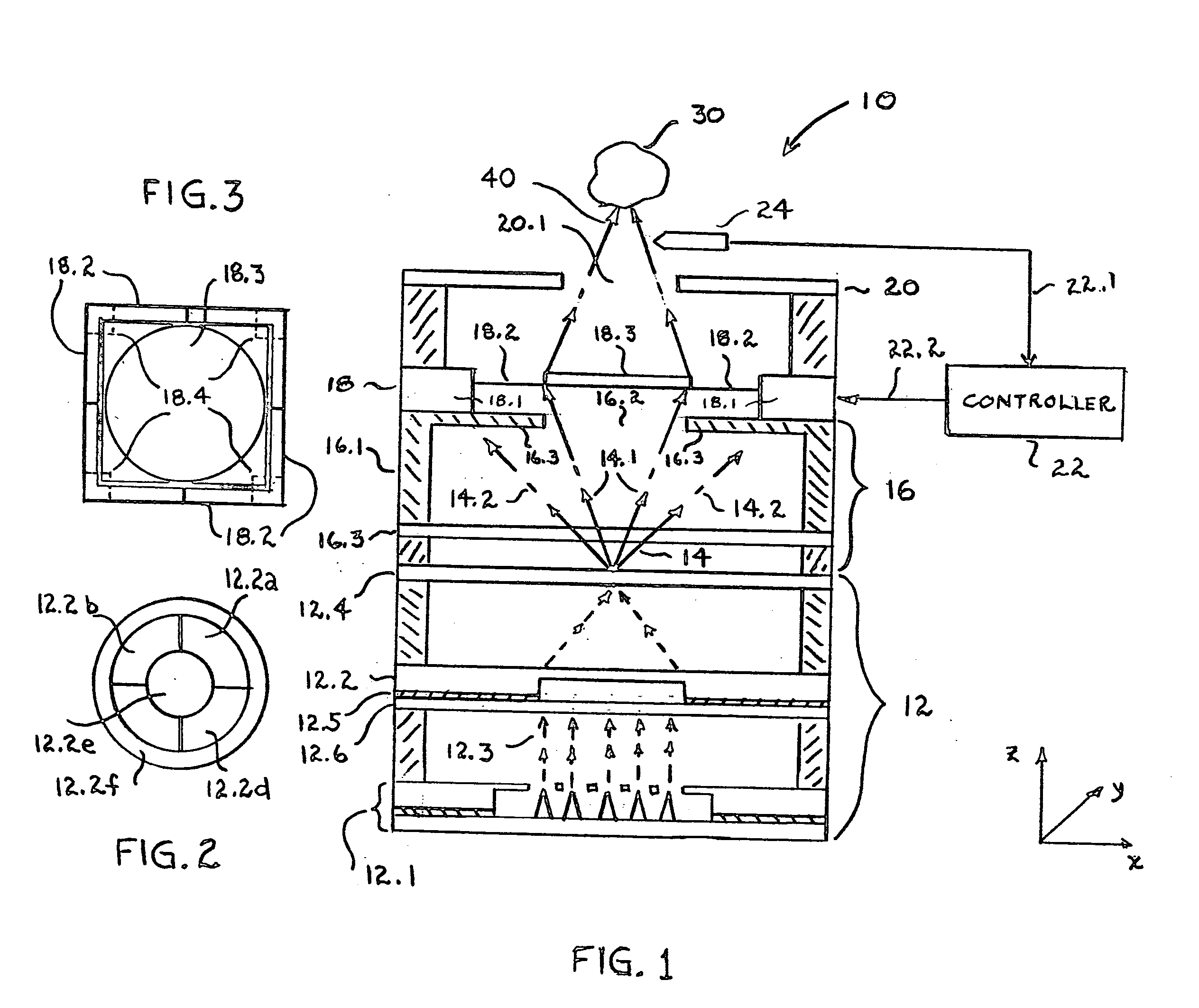
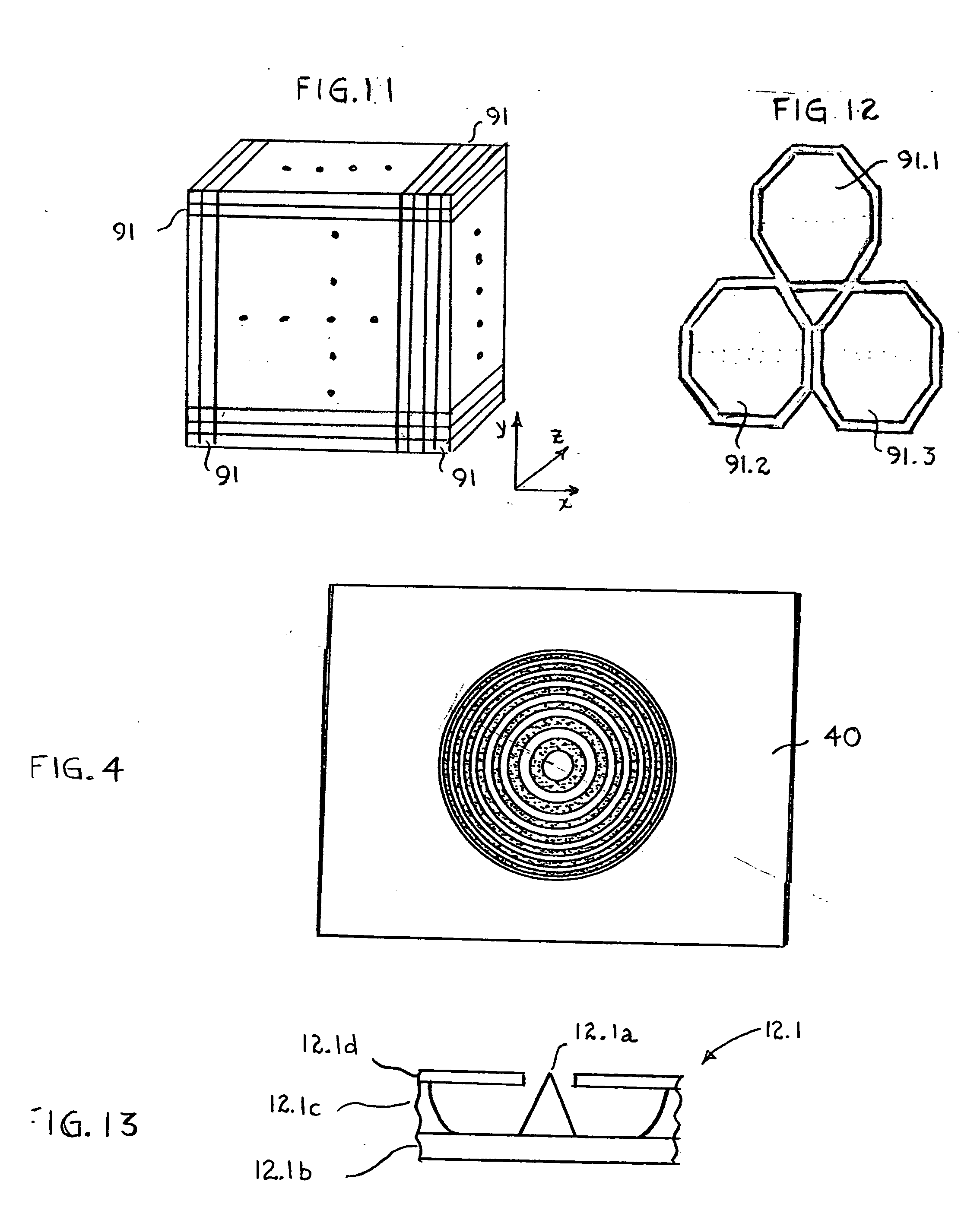
A radiation therapy system that includes a radiation source that moves about a path and directs a beam of radiation towards an object and a cone-beam computer tomography system. The cone-beam computer tomography system includes an x-ray source that emits an x-ray beam in a cone-beam form towards an object to be imaged and an amorphous silicon flat-panel imager receiving x-rays after they pass through the object, the imager providing an image of the object. A computer is connected to the radiation source and the cone beam computerized tomography system, wherein the computer receives the image of the object and based on the image sends a signal to the radiation source that controls the path of the radiation source.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
Cone-beam computerized tomography with a flat-panel imager
InactiveUS20030007601A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingAmorphous siliconX-ray
A radiation therapy system that includes a radiation source that moves about a path and directs a beam of radiation towards an object and a cone-beam computer tomography system. The cone-beam computer tomography system includes an x-ray source that emits an x-ray beam in a cone-beam form towards an object to be imaged and an amorphous silicon flat-panel imager receiving x-rays after they pass through the object, the imager providing an image of the object. A computer is connected to the radiation source and the cone beam computerized tomography system, wherein the computer receives the image of the object and based on the image sends a signal to the radiation source that controls the path of the radiation source.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
High spatial resolution X-ray computed tomography (CT) system
InactiveUS7099428B2Reduce dispersionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingComputed tomographyHigh spatial resolution
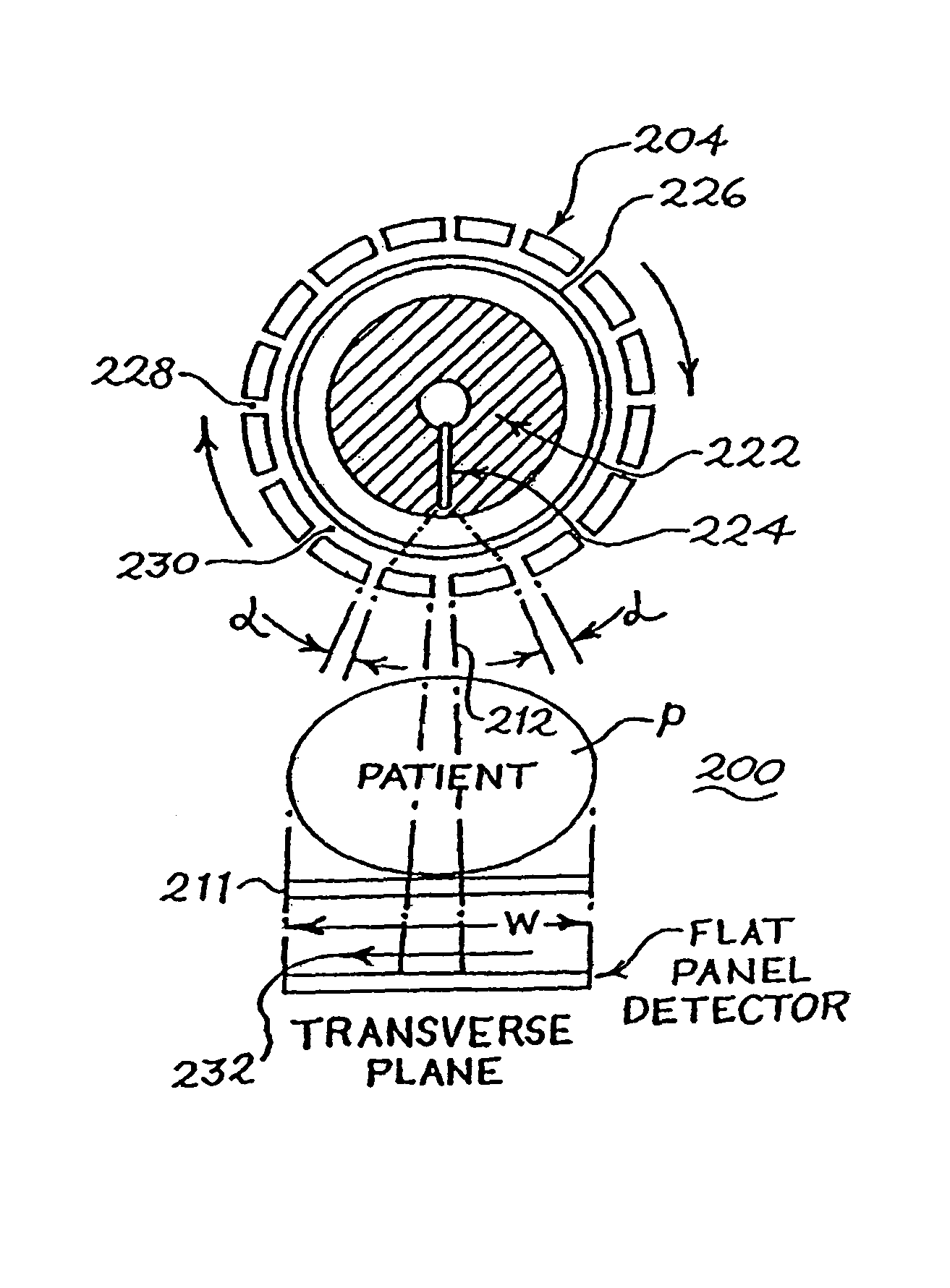
A high spatial resolution X-ray computed tomography (CT) system is provided. The system includes a support structure including a gantry mounted to rotate about a vertical axis of rotation. The system further includes a first assembly including an X-ray source mounted on the gantry to rotate therewith for generating a cone X-ray beam and a second assembly including a planar X-ray detector mounted on the gantry to rotate therewith. The detector is spaced from the source on the gantry for enabling a human or other animal body part to be interposed therebetween so as to be scanned by the X-ray beam to obtain a complete CT scan and generating output data representative thereof. The output data is a two-dimensional electronic representation of an area of the detector on which an X-ray beam impinges. A data processor processes the output data to obtain an image of the body part.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
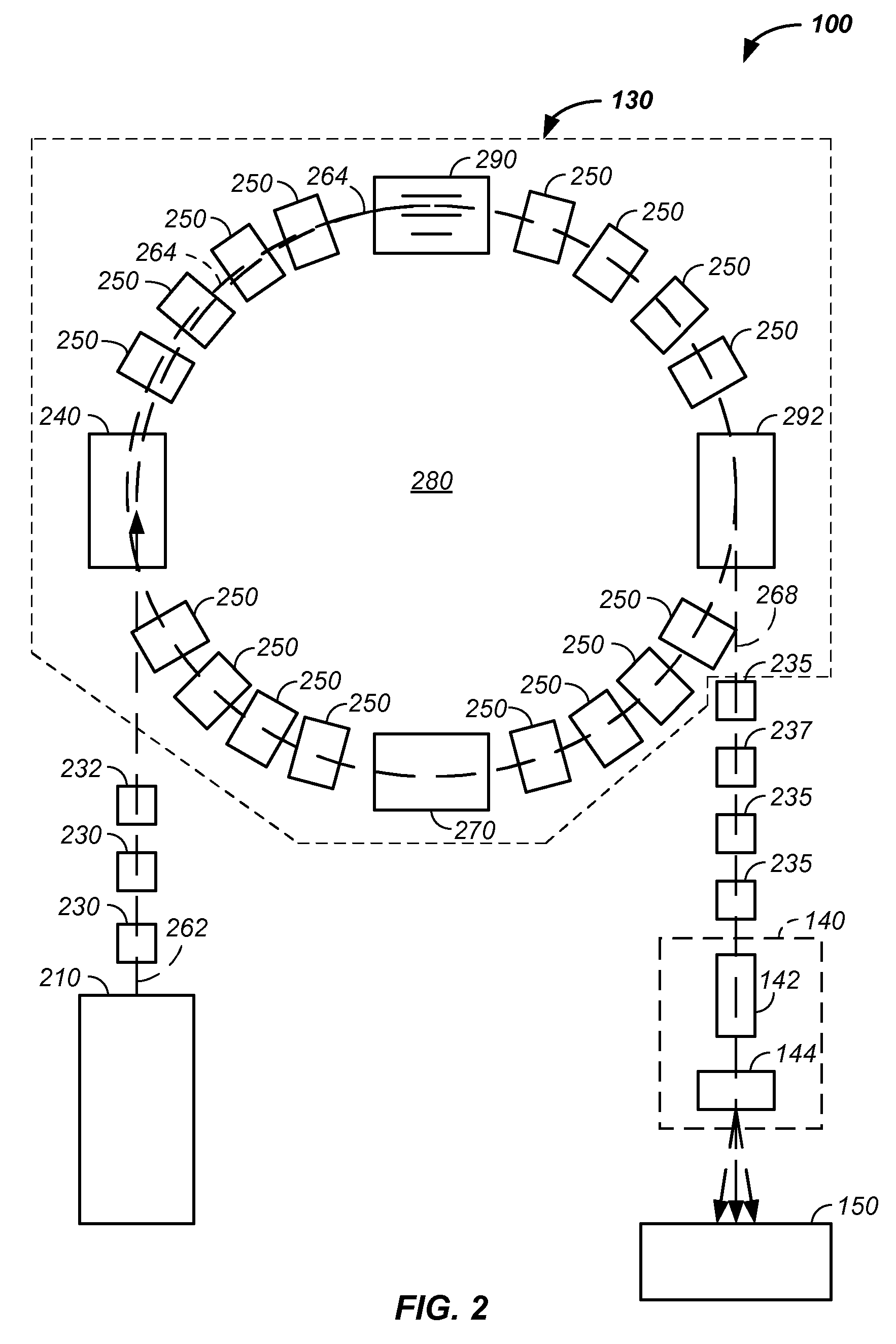
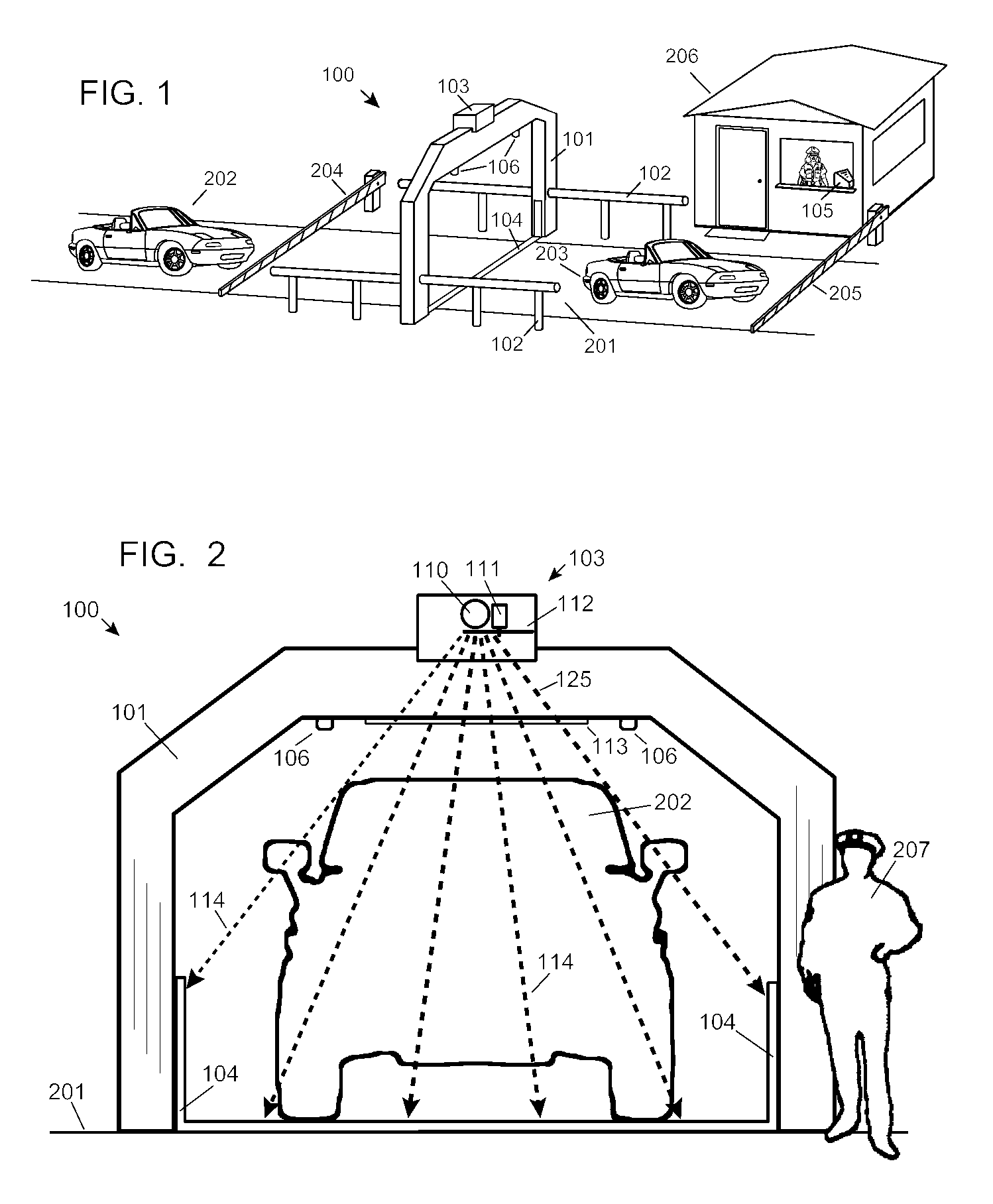
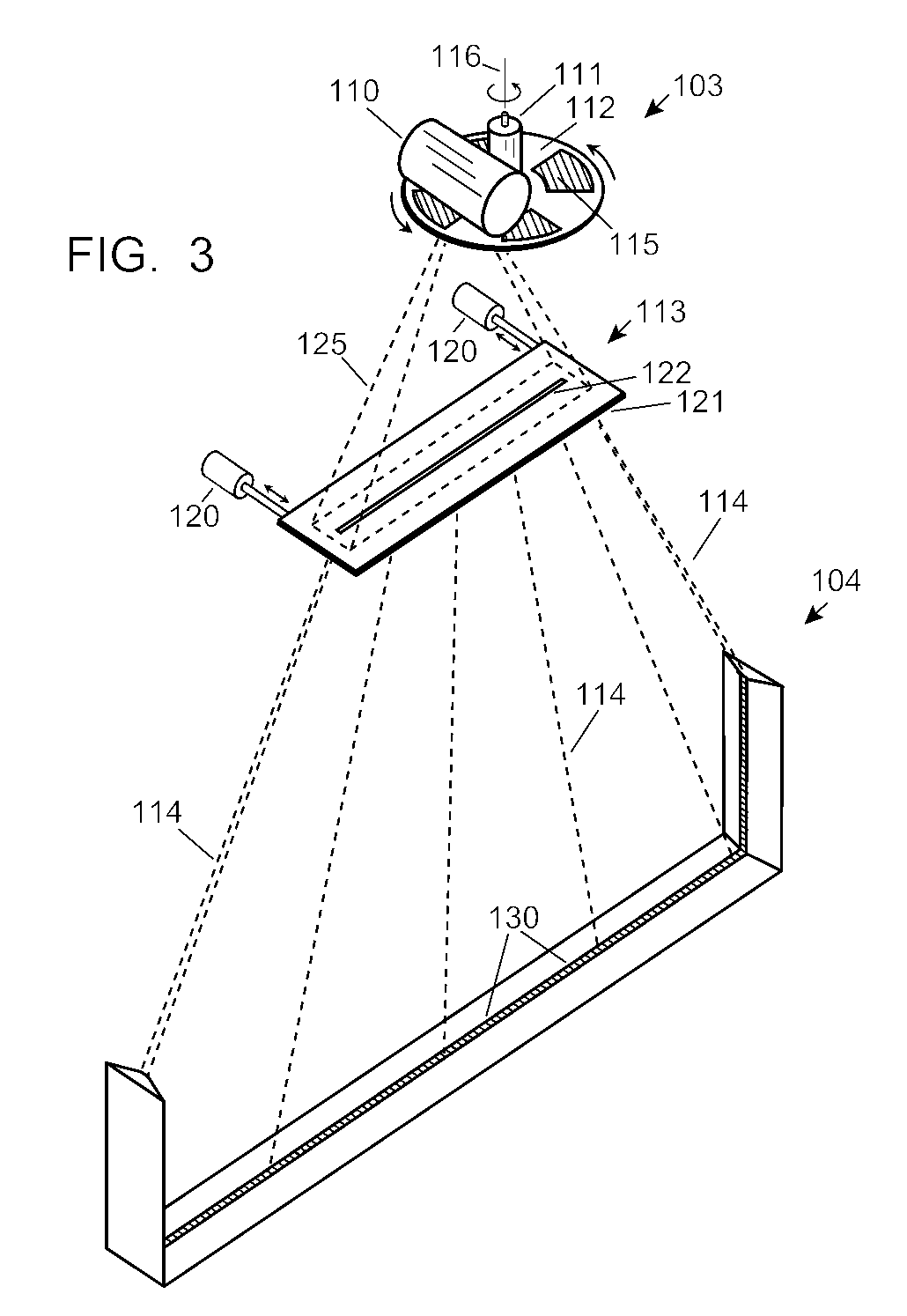
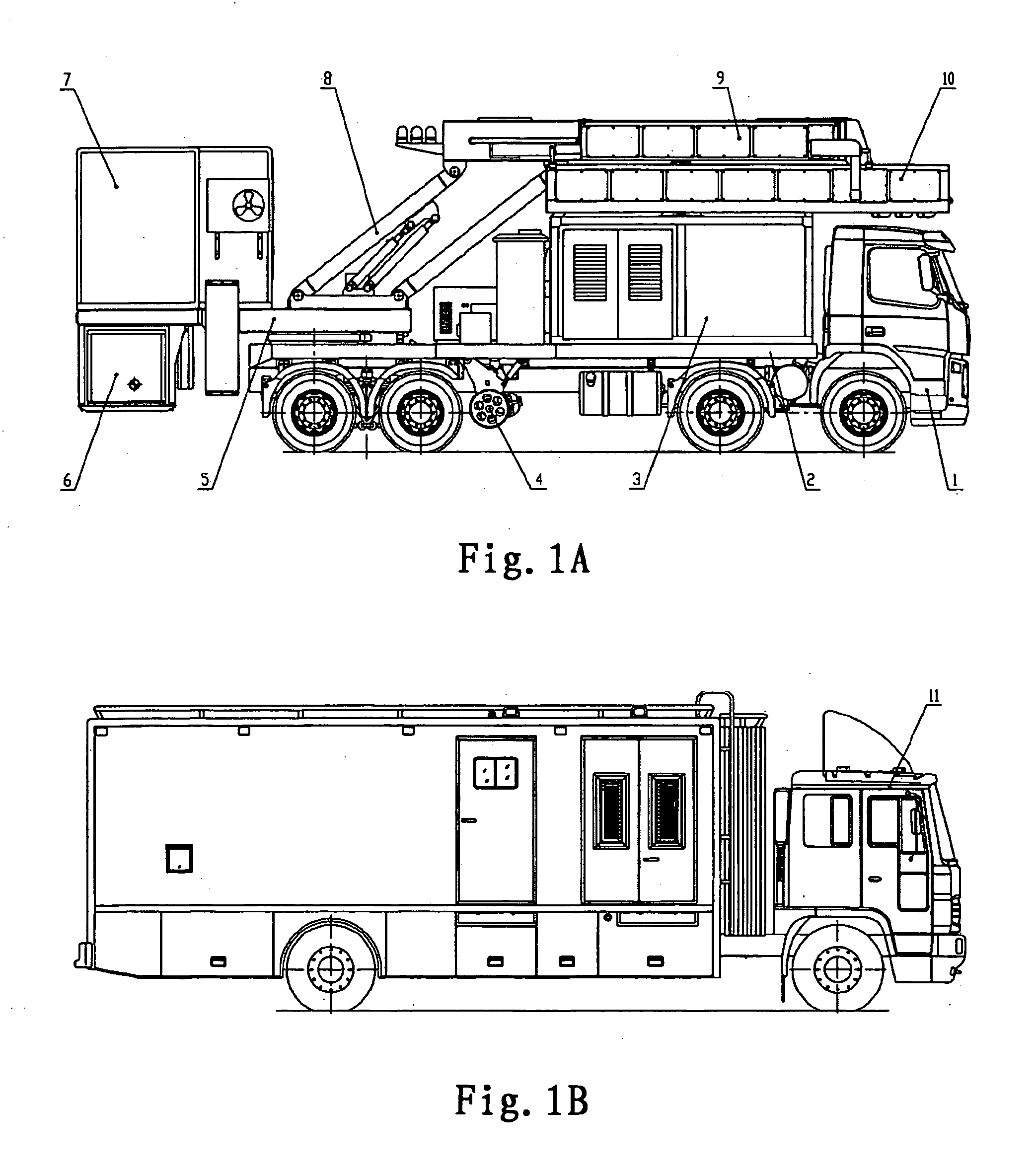
Vehicle-carried mobile container inspection apparatus
ActiveUS6920197B2Wide cross-sectionLower levelItem transportation vehiclesX-ray apparatusIn vehicleComputer module
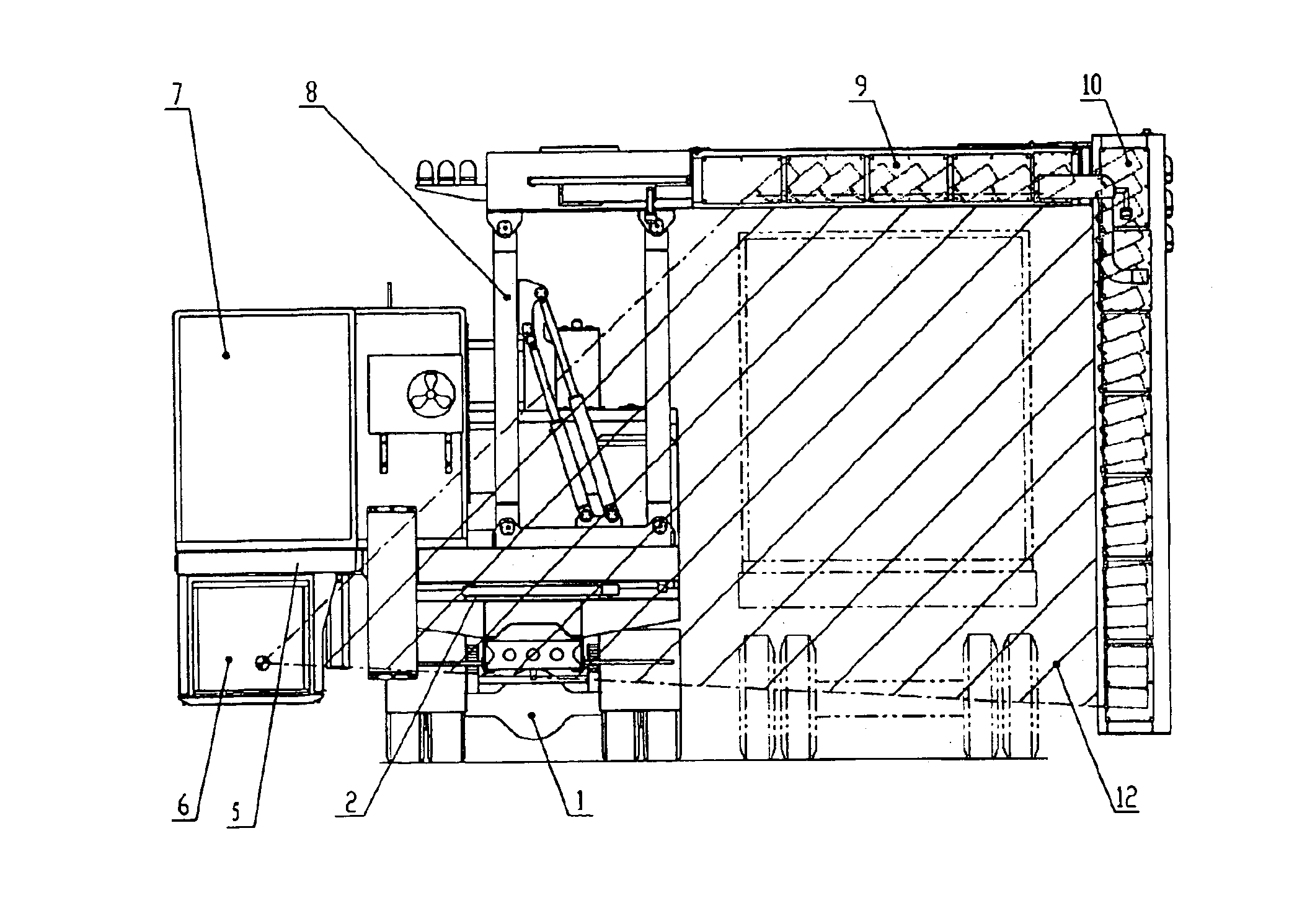
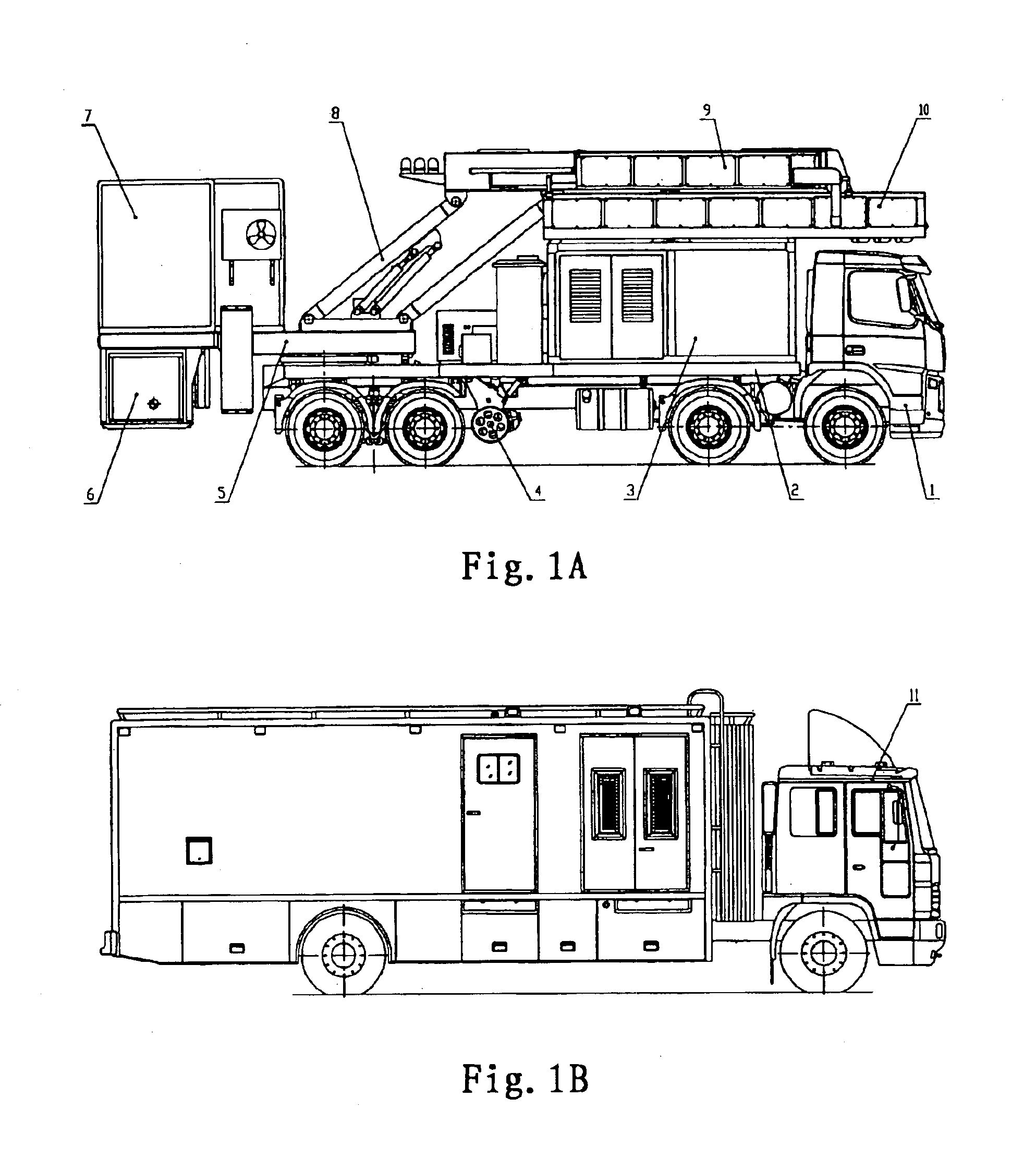
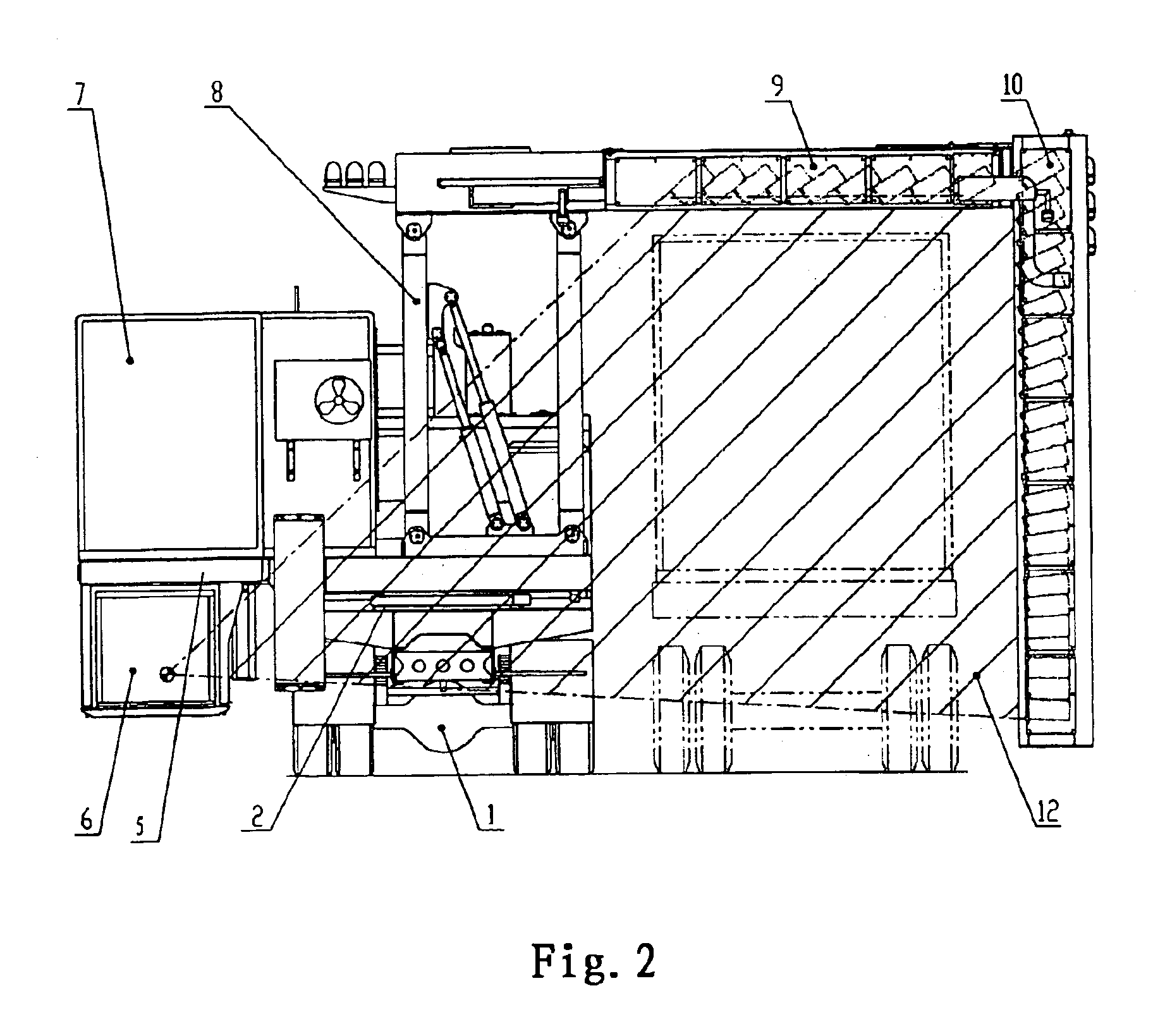
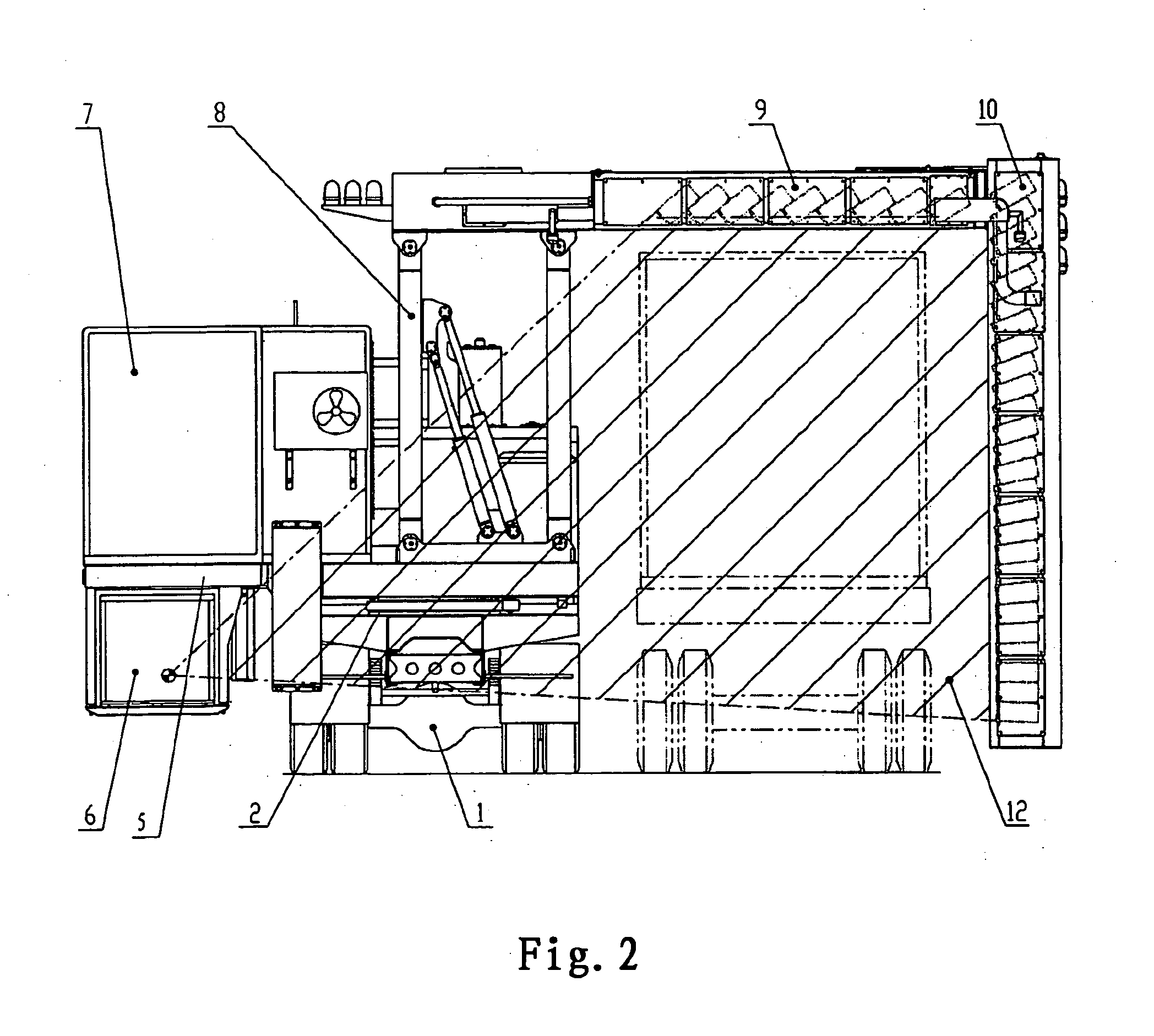
A vehicle-carried mobile container inspection apparatus characterized in that the mobile container inspection apparatus comprises a first box-shaped cabin arranged in the front portion of the chassis and provided with a workroom accommodating a scan control module, an image acquisition module and an operation / inspection module; and a second box-shaped cabin and a third box-shaped cabin both arranged on the rear portion of the rotatable platform, in which the second box-shaped cabin is arranged on the top of the third box-shaped cabin, the control unit of the radiation source is accommodated in the second box-shaped cabin, the third box-shaped cabin is arranged under the rotatable platform, the radiation source is arranged in the third box-shaped cabin, the level of the radiation source from which the X-ray beam emit is arranged below the level of the chassis, the scanning vehicle is provided with a driving means to smoothly move the scanning vehicle the rotatable platform is provided with a rotatably driving means, when inspecting a container, the rotatable platform is driven to turn 90 degrees, and the second arm turns into its vertical gesture, so that a portal-shaped frame is formed by means of the parallelogrammical bracket, the first arm and the second arm. The mobile inspection container apparatus is capable of inspecting as broad area as to reach the vehicle chassis. The apparatus comprises two vehicles, in which usually the both vehicles are used, while only one vehicle is used for fulfilling the inspection work in emergency.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
X-ray ambient level safety system
InactiveUS6067344AX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationSoft x rayImaging quality
A method for modulating the intensity of an x-ray beam in an x-ray inspection system so as to maintain the highest penetration power and optimum image quality subject to keeping the ambient radiation generated by the x-rays below a specified standard.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
Tetrahedron beam computed tomography
ActiveUS7760849B2Reduce exposureReduce the ratioMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisSoft x ray
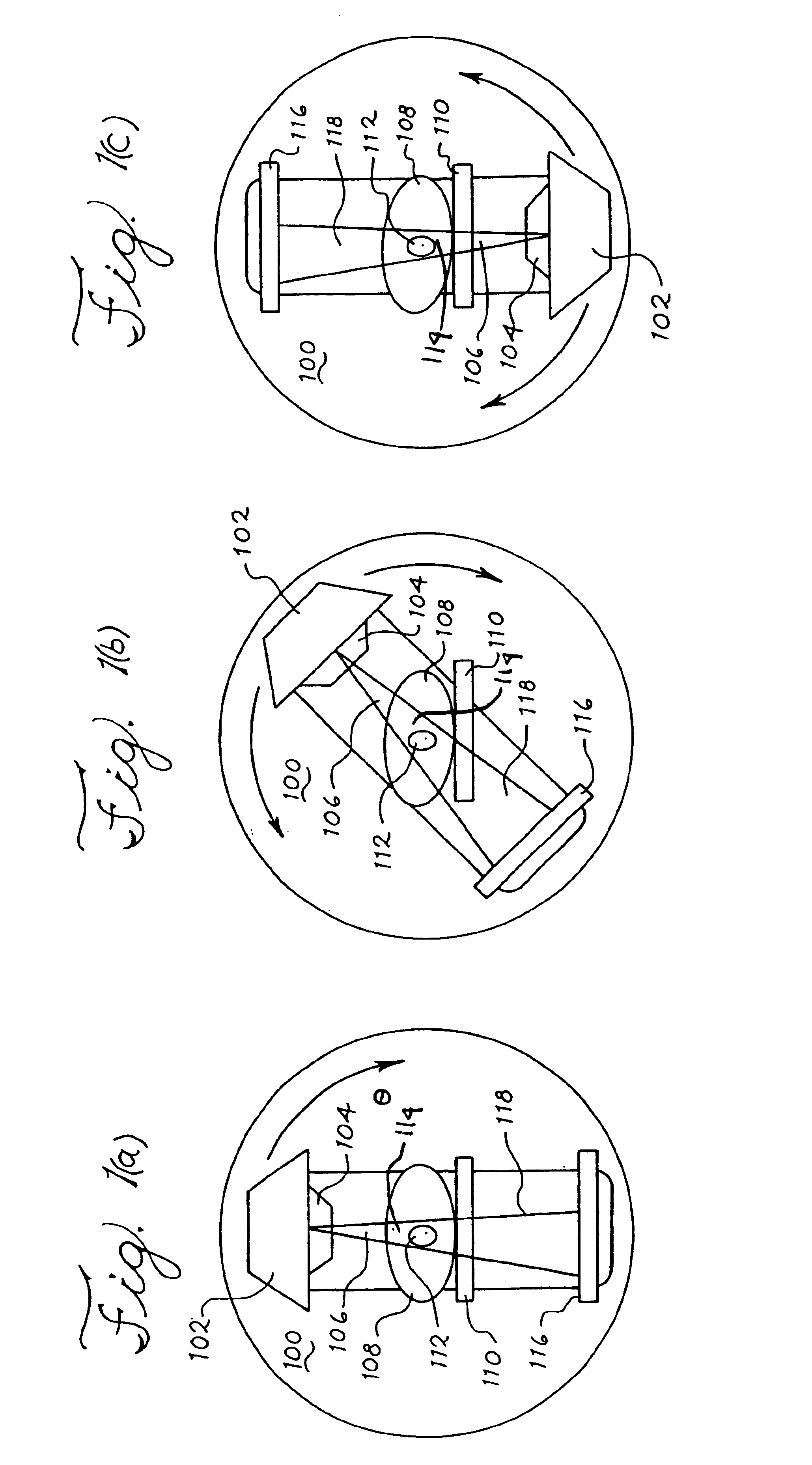
A method of imaging an object that includes directing a plurality of x-ray beams in a fan-shaped form towards an object, detecting x-rays that pass through the object due to the directing a plurality of x-ray beams and generating a plurality of imaging data regarding the object from the detected x-rays. The method further includes forming either a three-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography, digital tomosynthesis or Megavoltage image from the plurality of imaging data and displaying the image.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
Computer tomography imaging device and method
ActiveUS9380984B2Increase speedReduce hardware costsReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayTomography
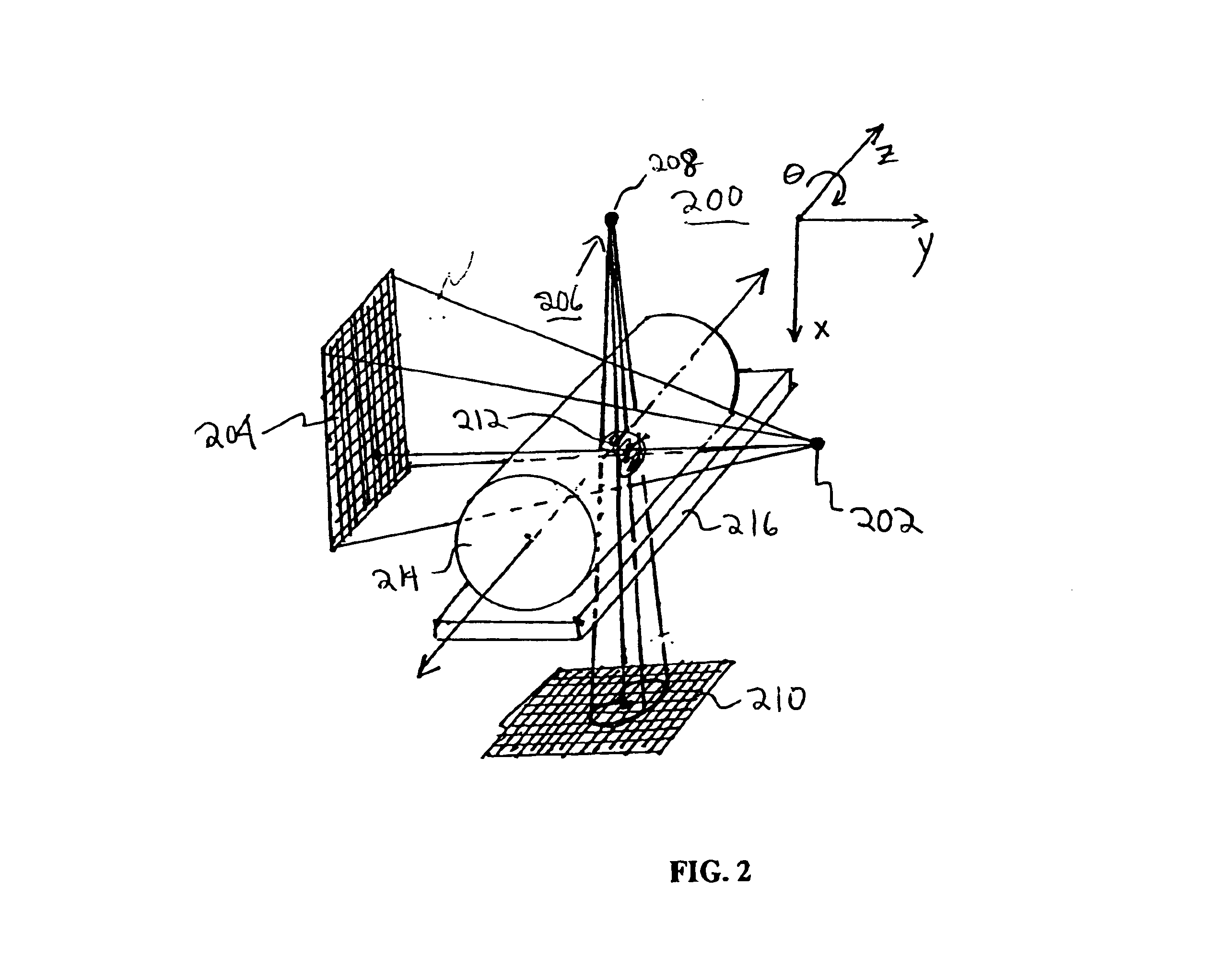
The present invention discloses a method for performing CT imaging on a region of interest of an object under examination, comprising: acquiring the CT projection data of the region of interest; acquiring the CT projection data of region B; selecting a group of PI line segments covering the region of interest, and calculating the reconstruction image value for each PI line segment in the group; and combining the reconstruction image values in all the PI line segments to obtain the image of the region of interest. The present invention further discloses a CT imaging device using this method and a data processor therein. Since the 2D / 3D slice image of the region of interest can be exactly reconstructed and obtained as long as the X-ray beam covers the region of interest and the region B, it is possible to use a small-sized detector to perform CT imaging on the region of interest at any position of a large-sized object, which reduces to a great extent the radiation dose of the X-ray during the CT scanning.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
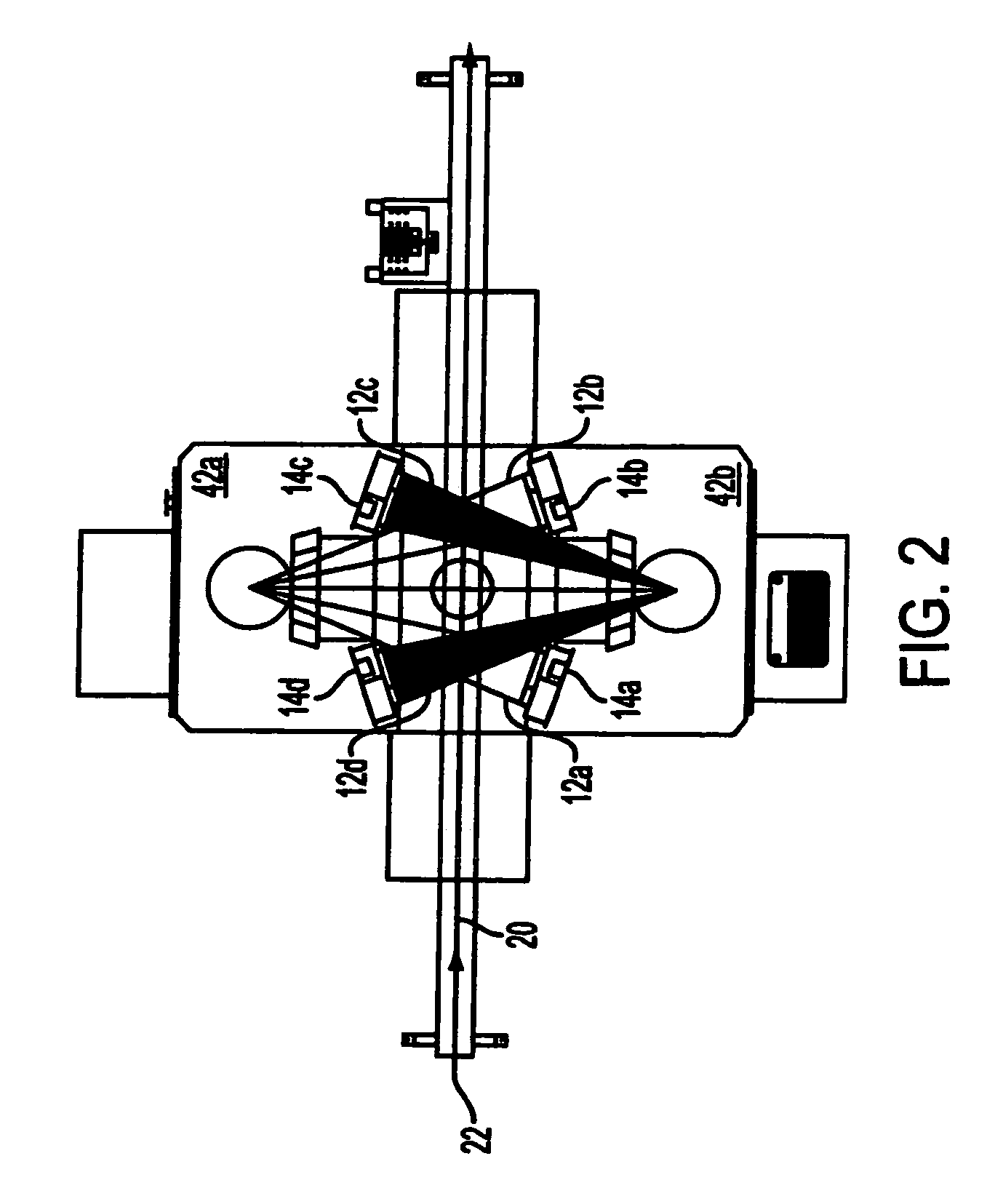
Scanning system for differential phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS9750465B2Reduce contrastReduce X-ray doseComputerised tomographsTomographyX ray imageImaging data
The invention relates to the field of X-ray differential phase contrast imaging. For scanning large objects and for an improved contrast to noise ratio, an X-ray device (10) for imaging an object (18) is provided. The X-ray device (10) comprises an X-ray emitter arrangement (12) and an X-ray detector arrangement (14), wherein the X-ray emitter arrangement (14) is adapted to emit an X-ray beam (16) through the object (18) onto the X-ray detector arrangement (14). The X-ray beam (16) is at least partial spatial coherent and fan-shaped. The X-ray detector arrangement (14) comprises a phase grating (50) and an absorber grating (52). The X-ray detector arrangement (14) comprises an area detector (54) for detecting X-rays, wherein the X-ray device is adapted to generate image data from the detected X-rays and to extract phase information from the X-ray image data, the phase information relating to a phase shift of X-rays caused by the object (18). The object (18) has a region of interest (32) which is larger than a detection area of the X-ray detector (18) and the X-ray device (10) is adapted to generate image data of the region of interest (32) by moving the object (18) and the X-ray detector arrangement (14) relative to each other.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
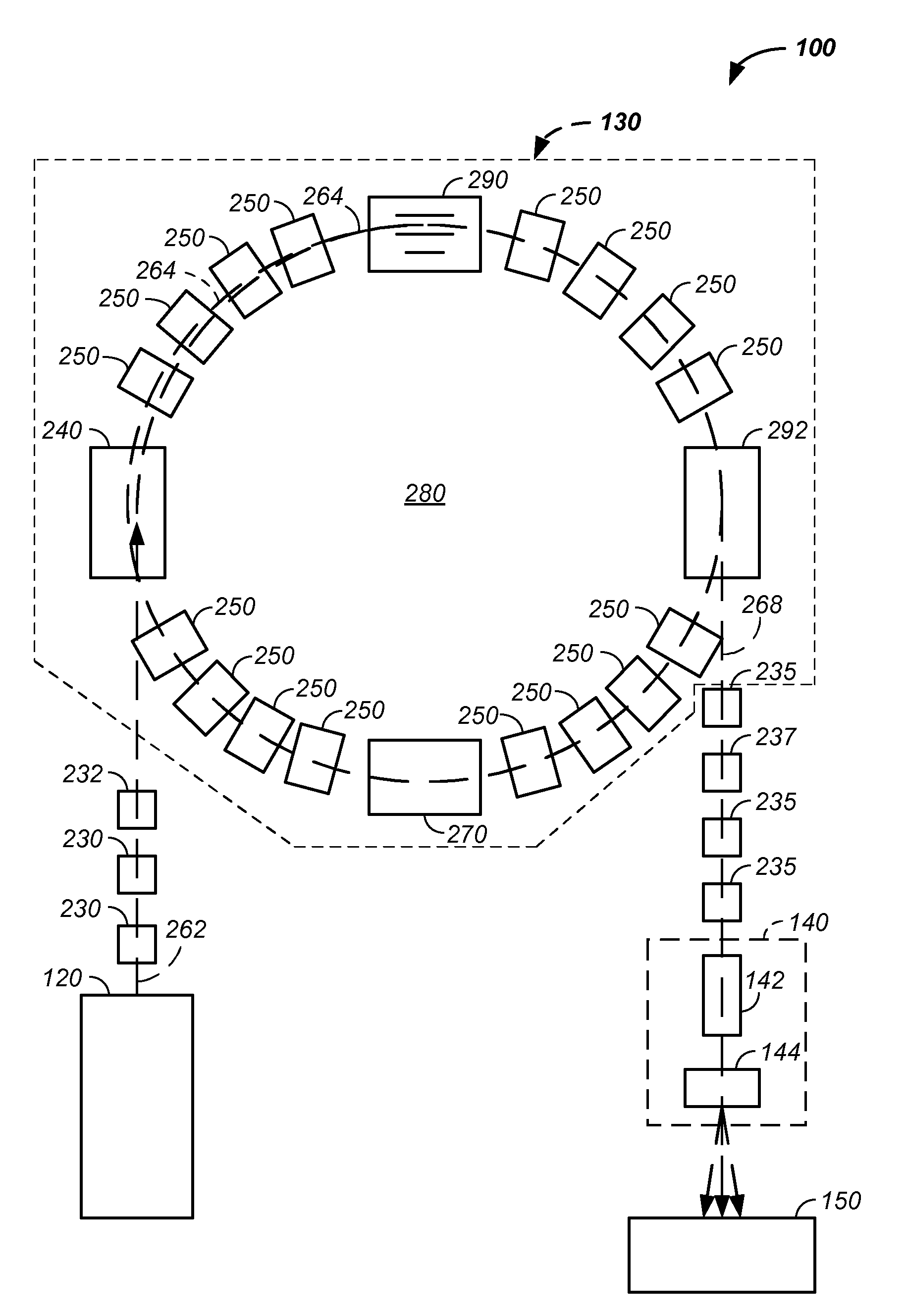
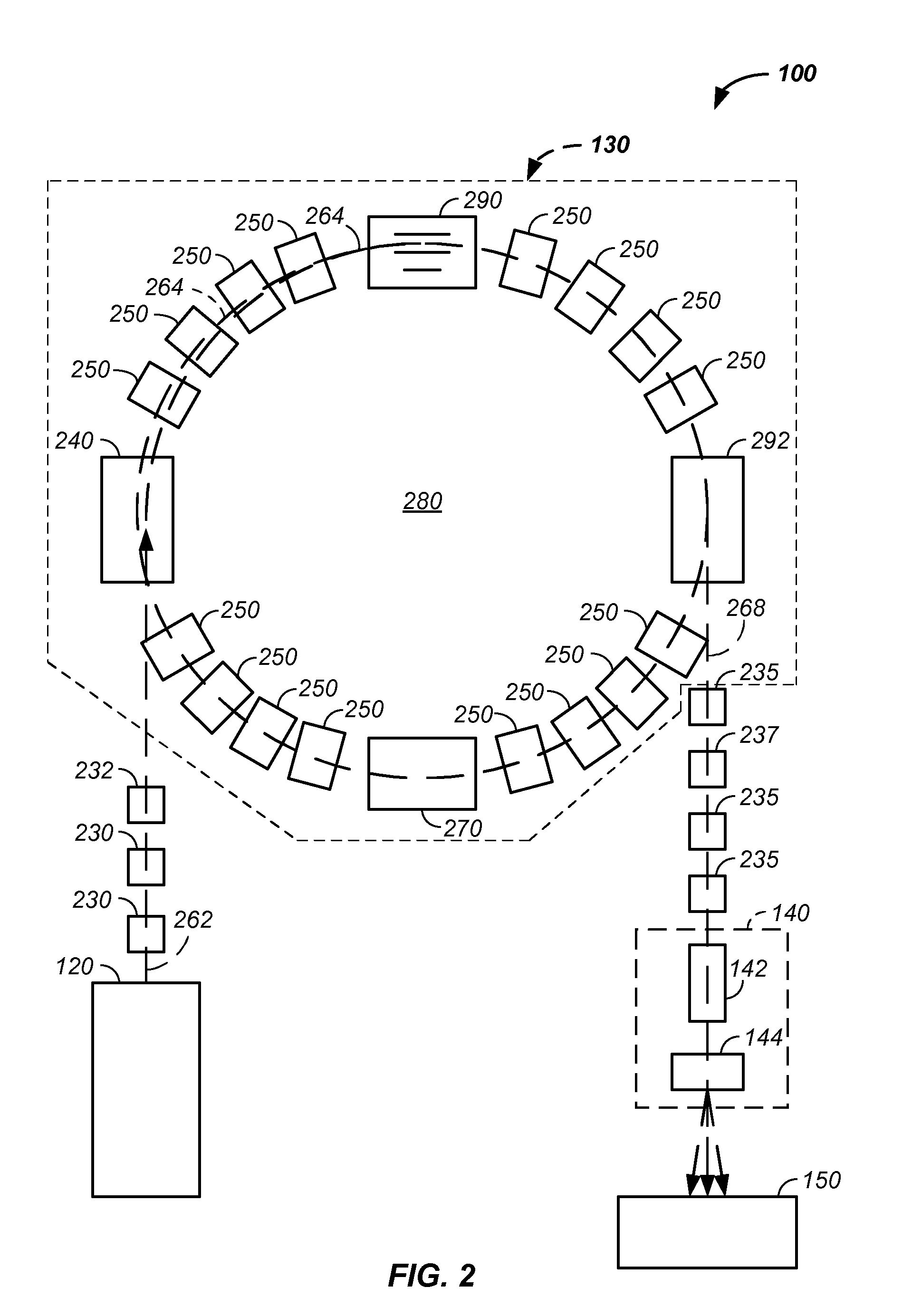
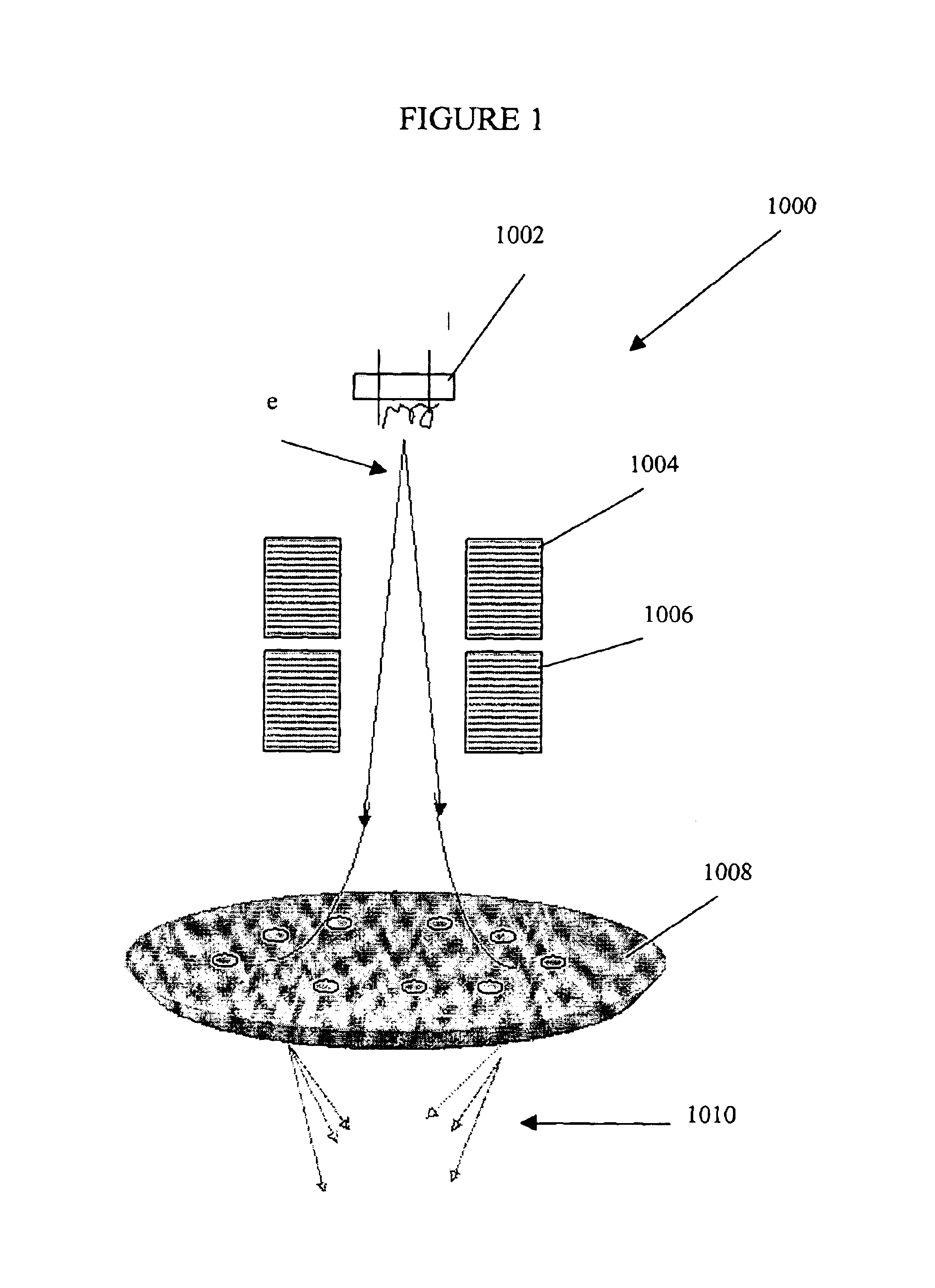
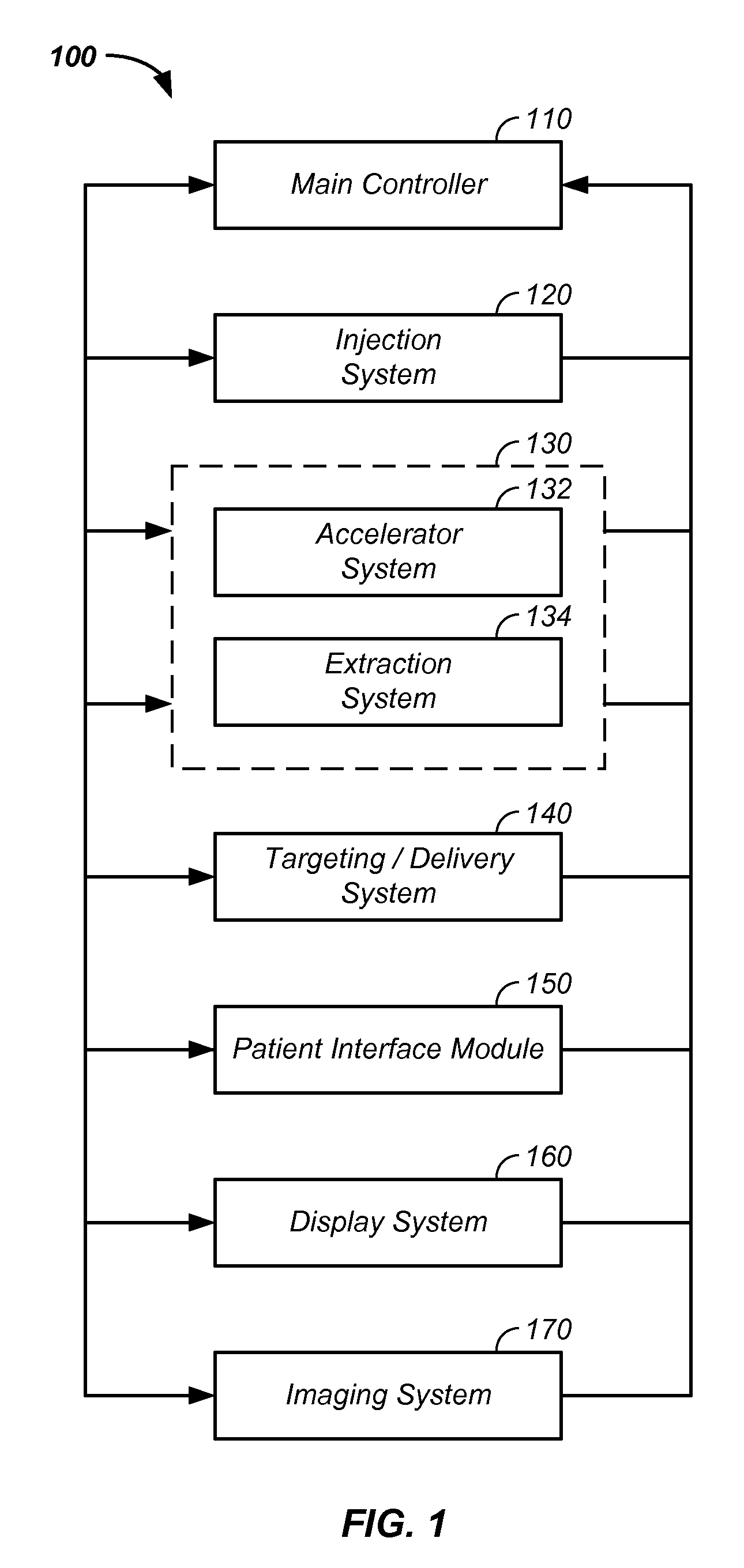
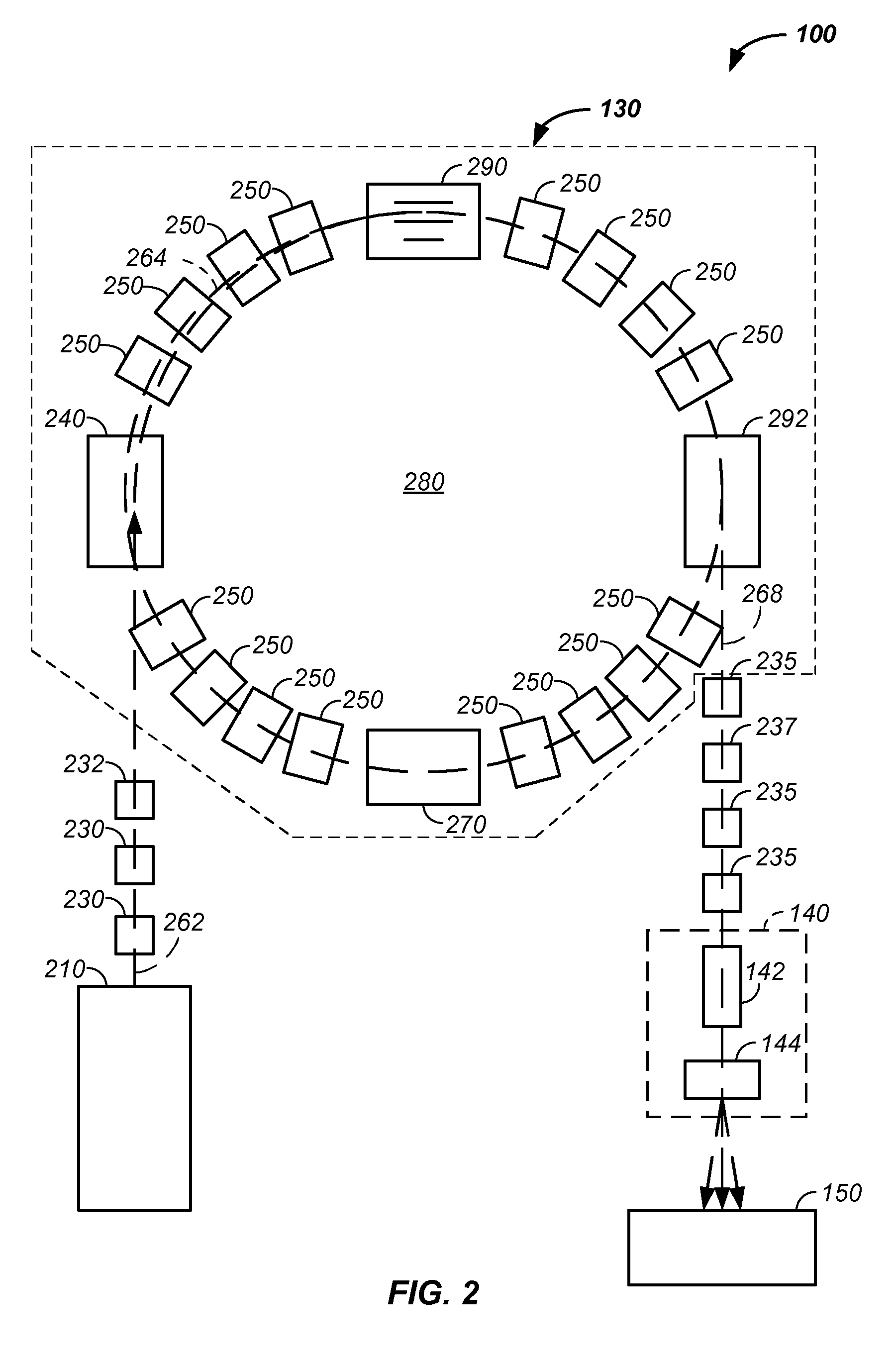
Elongated lifetime x-ray method and apparatus used in conjunction with a charged particle cancer therapy system
ActiveUS20100008469A1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsX-ray tube electrodesX-rayX ray image
The system uses an X-ray imaging system having an elongated lifetime. Further, the system uses an X-ray beam that lies in substantially the same path as a charged particle beam path of a particle beam cancer therapy system. The system creates an electron beam that strikes an X-ray generation source located proximate to the charged particle beam path. By generating the X-rays near the charged particle beam path, an X-ray path running collinear, in parallel with, and / or substantially in contact with the charged particle beam path is created. The system then collects X-ray images of localized body tissue region about a cancerous tumor. Since, the X-ray path is essentially the charged particle beam path, the generated image is usable for precisely target the tumor with a charged particle beam.
Owner:BALAKIN ANDREY VLADIMIROVICH +1
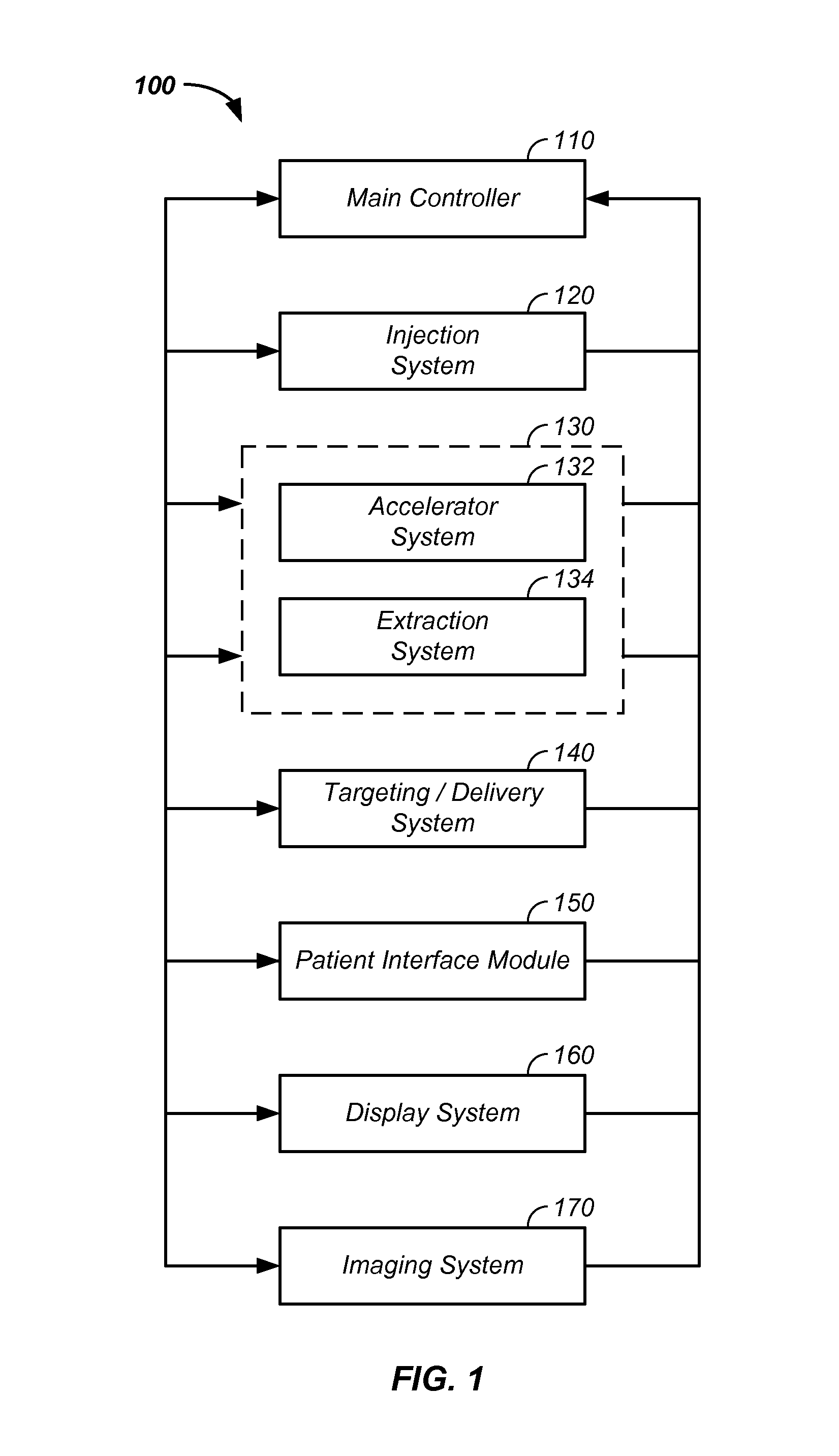
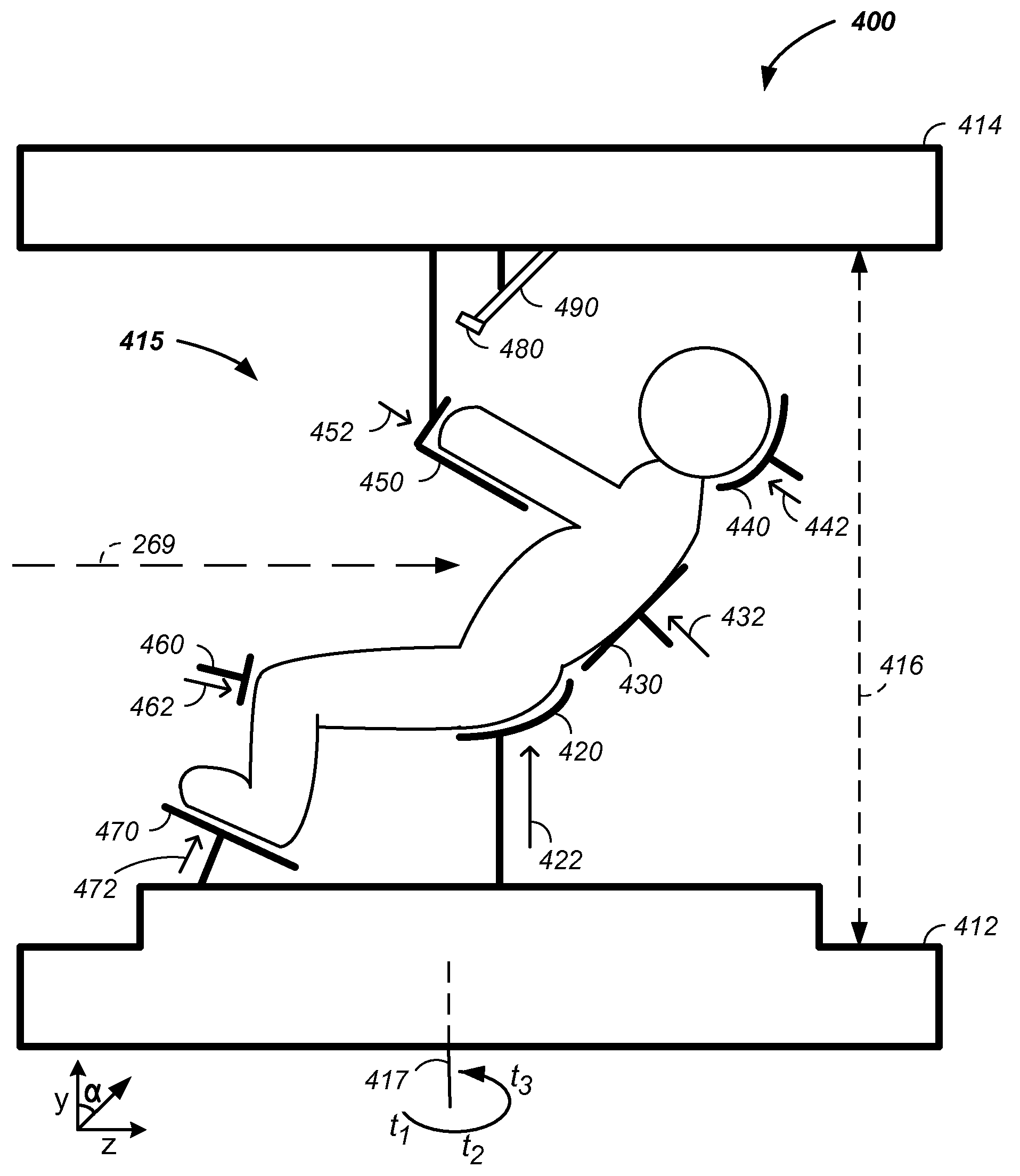
Charged particle cancer therapy and patient positioning method and apparatus
The invention comprises a laying, semi-vertical, or seated patient positioning, alignment, and / or control method and apparatus used in conjunction with multi-axis charged particle or proton beam radiation therapy of cancerous tumors. Patient positioning constraints are used to maintain the patient in a treatment position, including one or more of: a seat support, a back support, a head support, an arm support, a knee support, and a foot support. One or more of the positioning constraints are movable and / or under computer control for rapid positioning and / or immobilization of the patient. The system optionally uses an X-ray beam that lies in substantially the same path as a proton beam path of a particle beam cancer therapy system. The generated image is usable for: fine tuning body alignment relative to the proton beam path, to control the proton beam path to accurately and precisely target the tumor, and / or in system verification and validation.
Owner:BALAKIN ANDREY VLADIMIROVICH +1
Method And System For Dynamic Low Dose X-ray Imaging
InactiveUS20080118023A1Reduce decreaseReduce detectionTomosynthesisHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-rayX ray dose
A method and system for performing fluoroscopic imaging of a subject has high temporal and spatial resolution in a center portion of the captured dynamic images. The system provides for reduced X-ray dose to the patient associated with that part of the X-ray beam associated with a peripheral portion of the captured images although temporal, and in some embodiments spatial, resolution is reduced in the peripheral portion of the image. The system uses a rotating collimator to produce an X-ray beam having narrow wing portions associated with the peripheral portions of the image, and a broader central region associated with the high resolution center portion of the images.
Owner:FOREVISION IMAGING TECH LLC
Small-angle scattering x-ray metrology systems and methods
ActiveUS20150110249A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationTesting semiconductor materialsSoft x rayMetrology
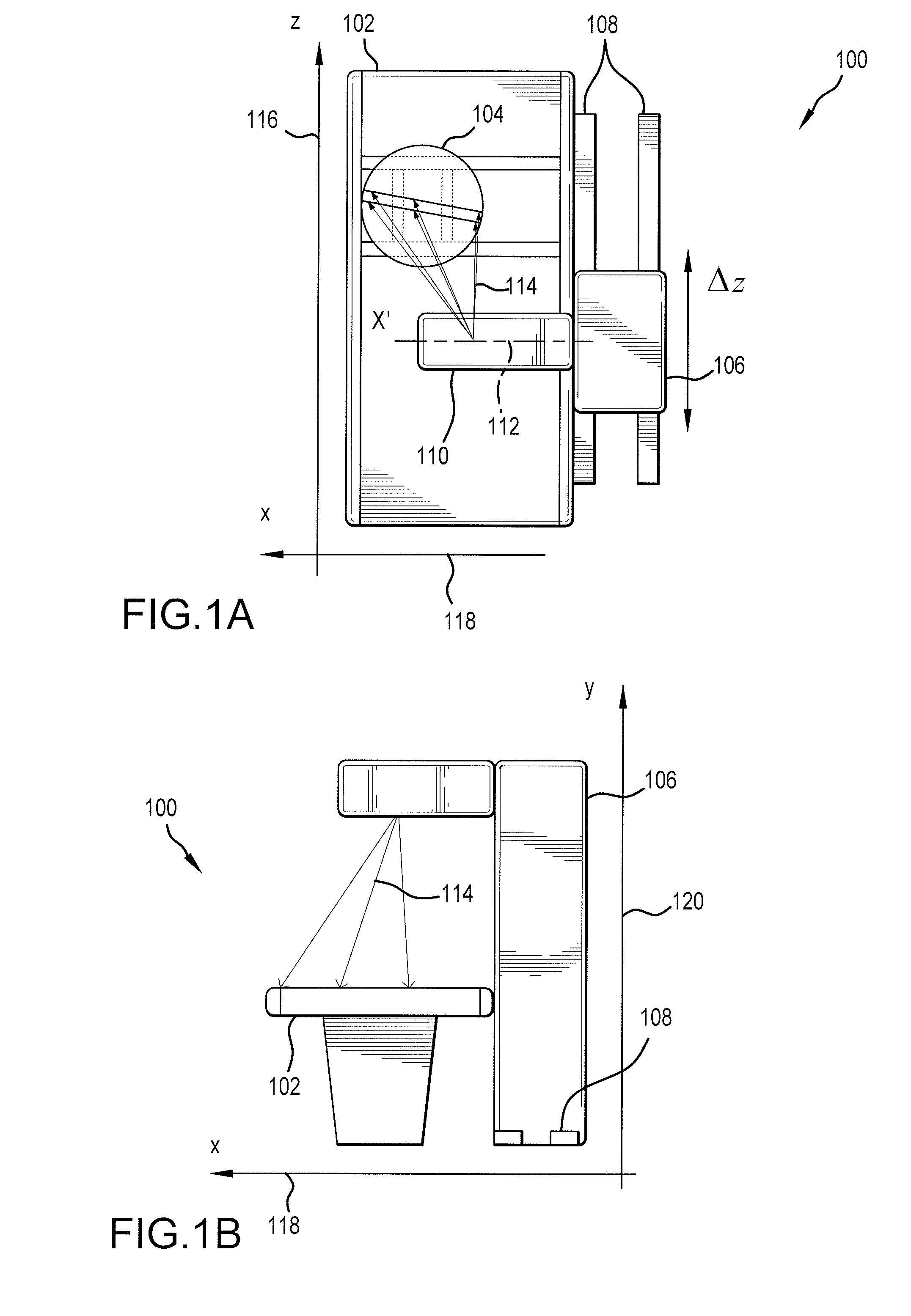
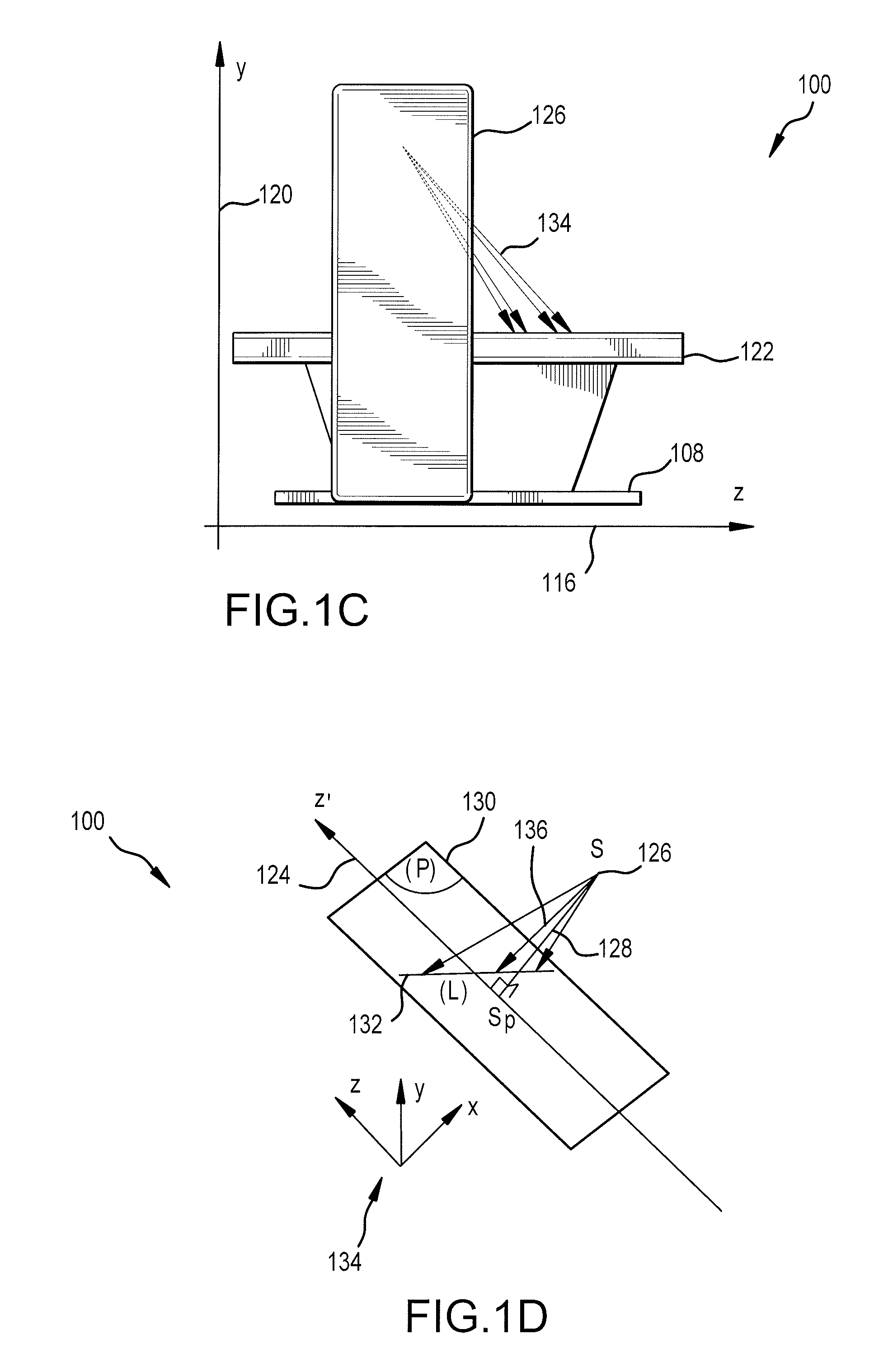
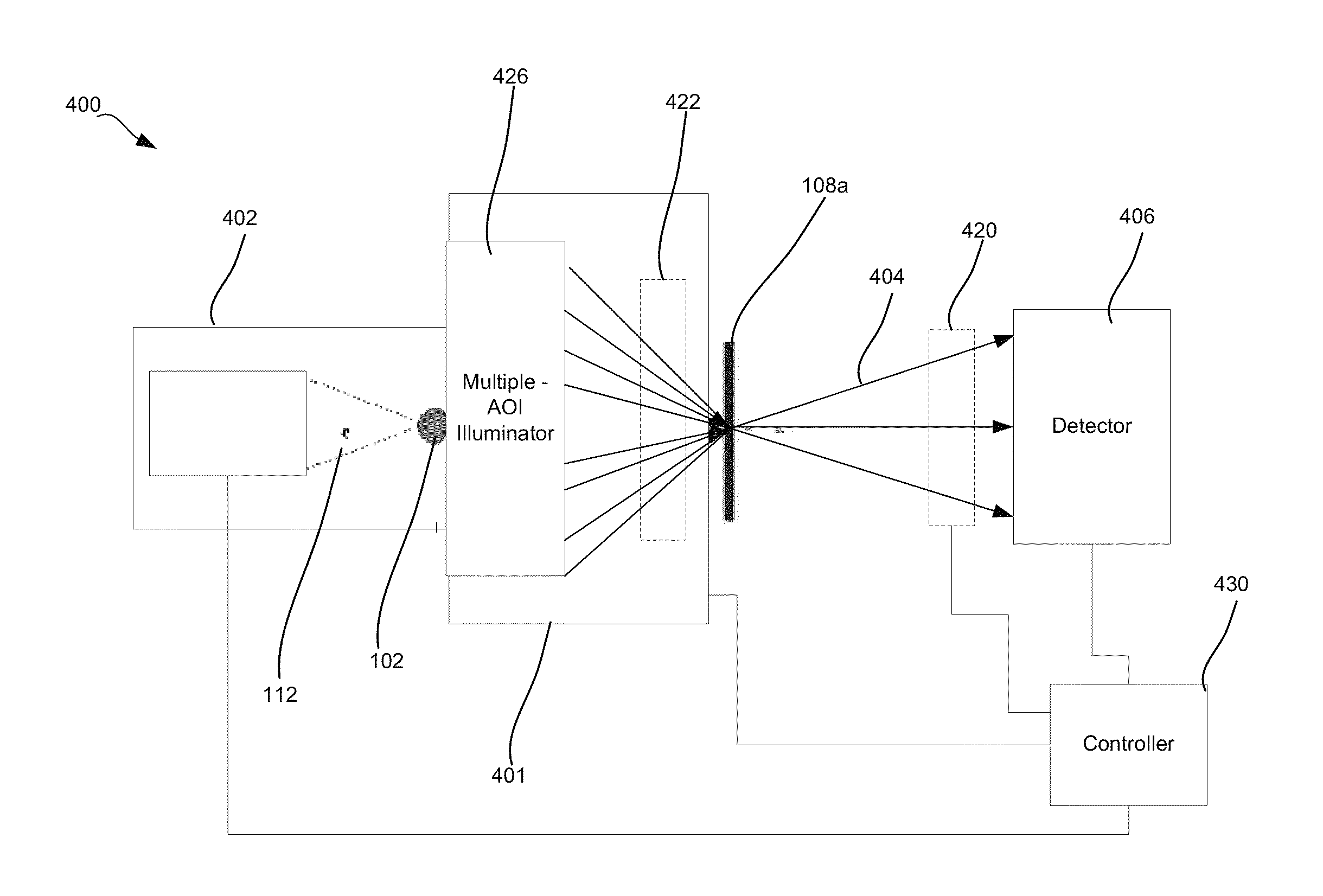
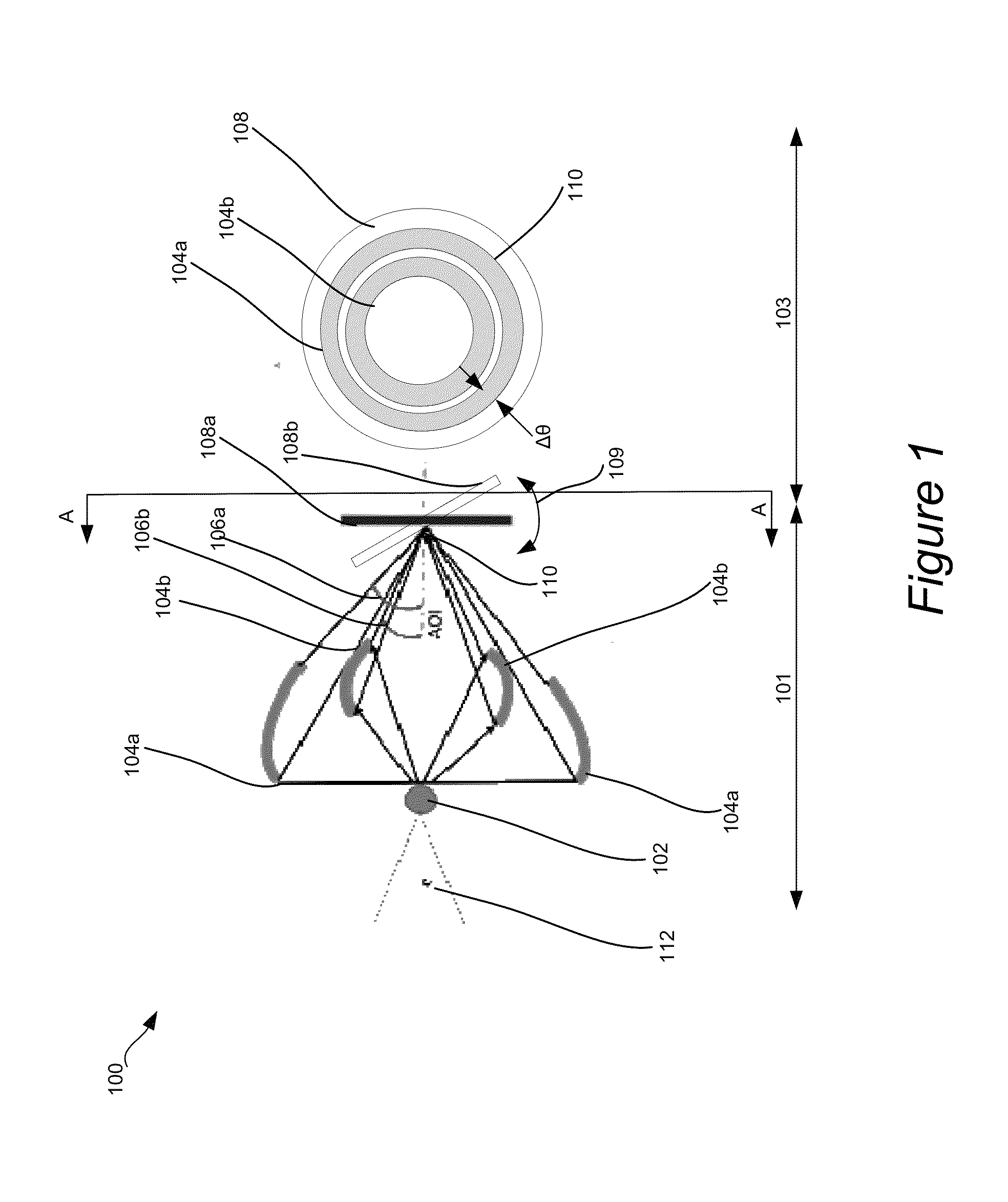
Disclosed are apparatus and methods for performing small angle x-ray scattering metrology. This system includes an x-ray source for generating x-rays and illumination optics for collecting and reflecting or refracting a portion of the generated x-rays towards a particular focus point on a semiconductor sample in the form of a plurality of incident beams at a plurality of different angles of incidence (AOIs). The system further includes a sensor for collecting output x-ray beams that are scattered from the sample in response to the incident beams on the sample at the different AOIs and a controller configured for controlling operation of the x-ray source and illumination optics and receiving the output x-rays beams and generating an image from such output x-rays.
Owner:KLA CORP
Patient positioning method and apparatus used in conjunction with a charged particle cancer therapy system
InactiveUS20090314960A1Chemical conversion by chemical reactionX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapySystem verificationFoot supports
The invention comprises a semi-vertical or seated patient positioning, alignment, and / or control method and apparatus used in conjunction with multi-axis charged particle or proton beam radiation therapy of cancerous tumors. Patient positioning constraints are used to maintain the patient in a treatment position, including one or more of: a seat support, a back support, a head support, an arm support, a knee support, and a foot support. One or more of the positioning constraints are movable and / or under computer control for rapid positioning and / or immobilization of the patient. The system optionally uses an X-ray beam that lies in substantially the same path as a proton beam path of a particle beam cancer therapy system. The generated image is usable for: fine tuning body alignment relative to the proton beam path, to control the proton beam path to accurately and precisely target the tumor, and / or in system verification and validation.
Owner:BALAKIN VLADIMIR
Device for performing and verifying a therapeutic treatment and corresponding computer program and control method
InactiveUS6993112B2Avoid radiationReduce in quantityIrradiation devicesX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyBeam sourceTherapeutic treatment
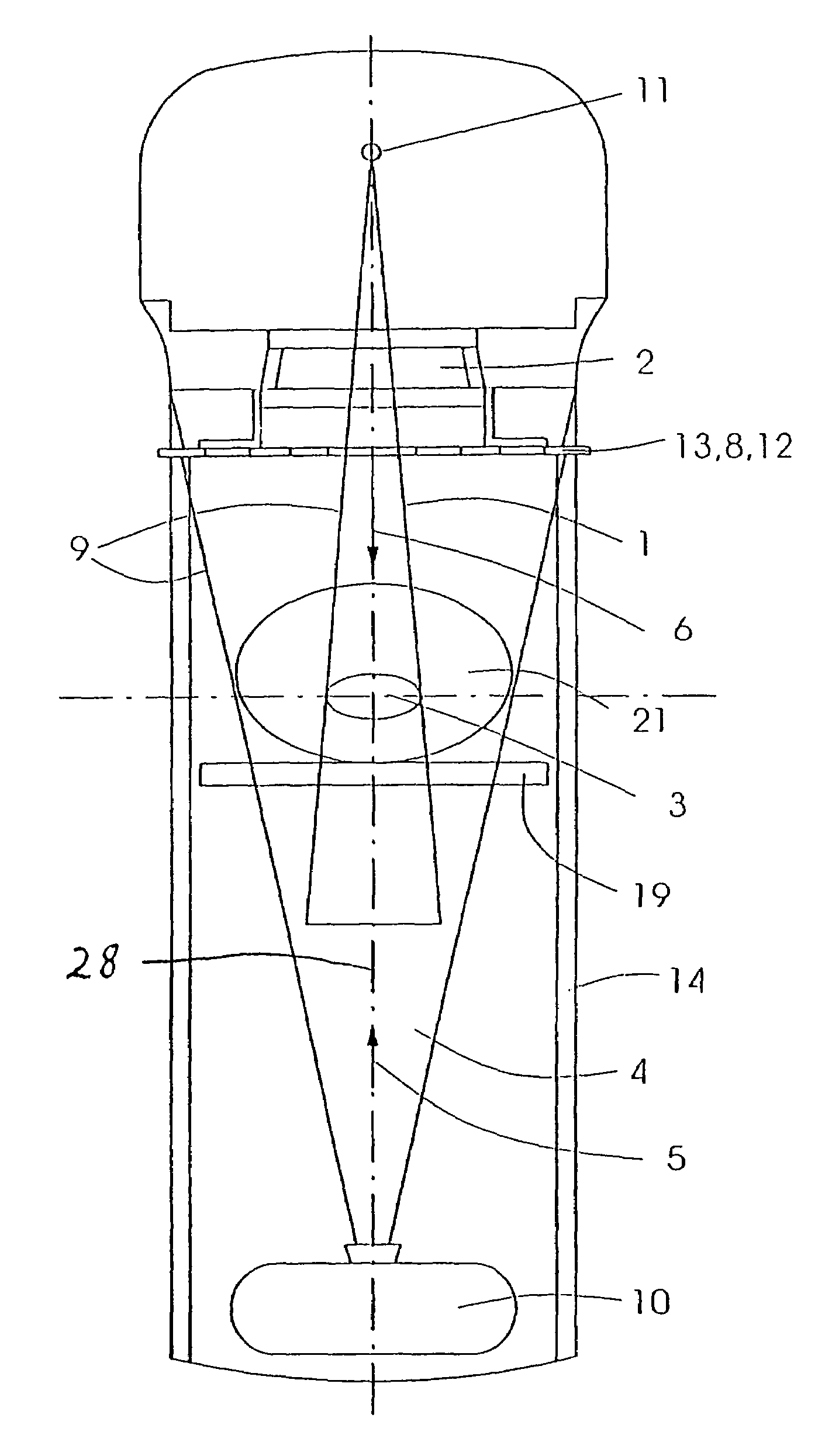
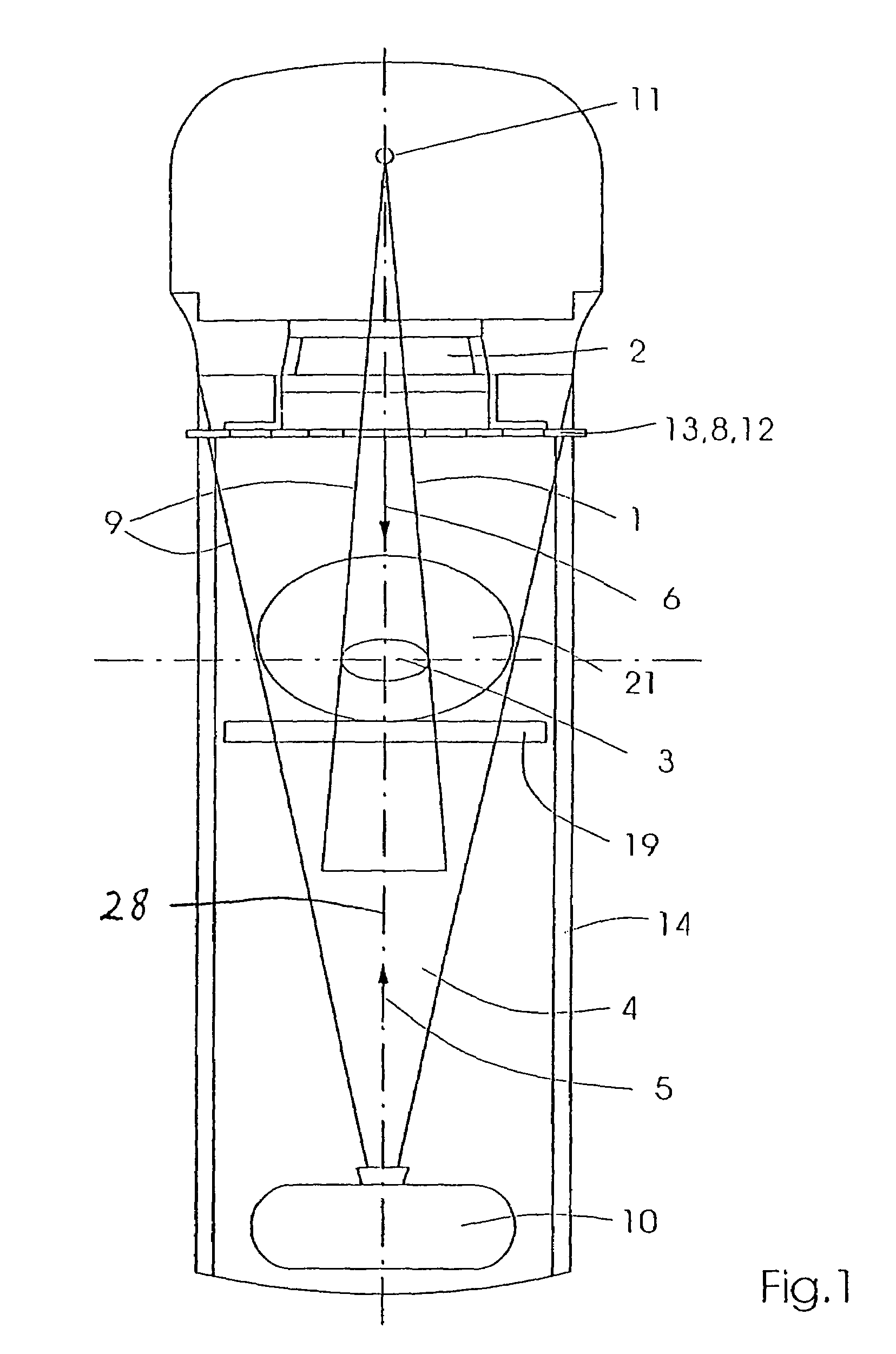
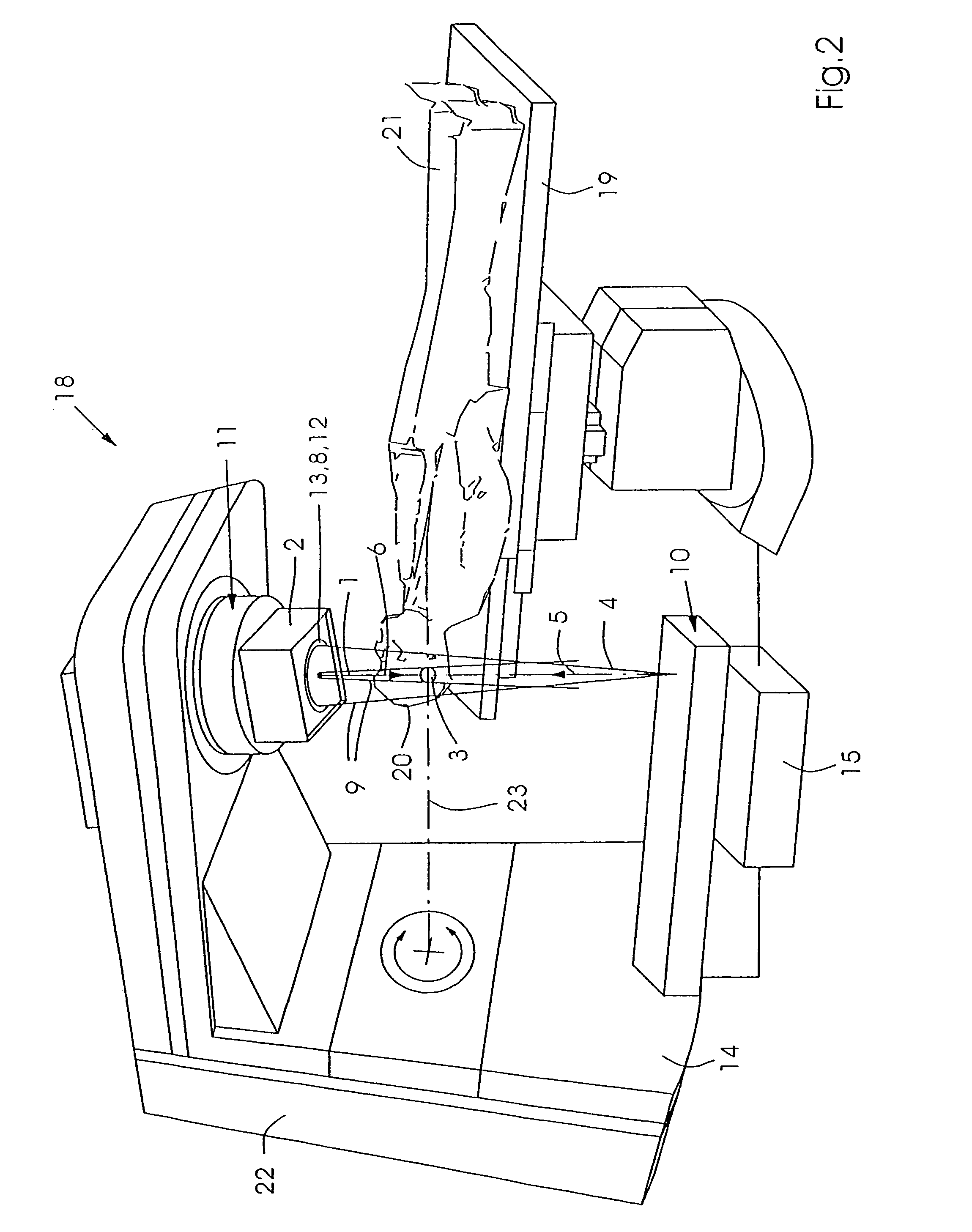
The invention relates to a device for performing and verifying therapeutic radiation. An x-ray beam (4) is arranged across from a target volume (3) of the beam source (11) for the high-energy beam (1) in such a way that the beams (1, 4) run in essentially opposite directions (5, 6). The invention also relates to a computer program and a control method for operating said device. The inventive device makes it possible to exactly verify areas (16, 16′, 16″) that are subjected to different levels of radiation, the entire anatomy of the target volume (3), and the surroundings thereof in addition to the contour of the therapy beam (1). The x-ray beam (4) detects the anatomy and position of the patient (21) within the range of the target volume (3) before the high-energy beam (1) is applied and the shape of the applied high-energy beam (1) is then detected and areas (16, 16′, 16″) that are subjected to different levels of radiation as well as at least one partial segment of the target volume (3) during the emission breaks of the high-energy beam (1). The detected data is used for correcting the treatment plan.
Owner:DEUTES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENT STIFTUNG DES OFFENTLICHEN RECHTS
Devices and methods for producing multiple x-ray beams from multiple locations
InactiveUS6980627B2Efficient in producing multi-beamHighly integrated multiple functionX-ray tube electrodesNanoinformaticsX-rayCold cathode
An x-ray generating device includes at least one field-emission cold cathode having a substrate and incorporating nanostructure-containing material including carbon nanotubes. The device further includes at least one anode target. Associated methods are also described.
Owner:NURAY TECH
Semi-vertical positioning method and apparatus used in conjunction with a charged particle cancer therapy system
The invention comprises a semi-vertical patient positioning, alignment, and / or control method and apparatus used in conjunction with charged particle or proton beam radiation therapy of cancerous tumors. Patient positioning constraints are used to maintain the patient in a treatment position, including one or more of: a seat support, a back support, a head support, an arm support, a knee support, and a foot support. One or more of the positioning constraints are movable and / or under computer control for rapid positioning and / or immobilization of the patient. The system optionally uses an X-ray beam that lies in substantially the same path as a proton beam path of a particle beam cancer therapy system. The generated image is usable for: fine tuning body alignment relative to the proton beam path, to control the proton beam path to accurately and precisely target the tumor, and / or in system verification and validation.
Owner:BALAKIN ANDREY VLADIMIROVICH +1
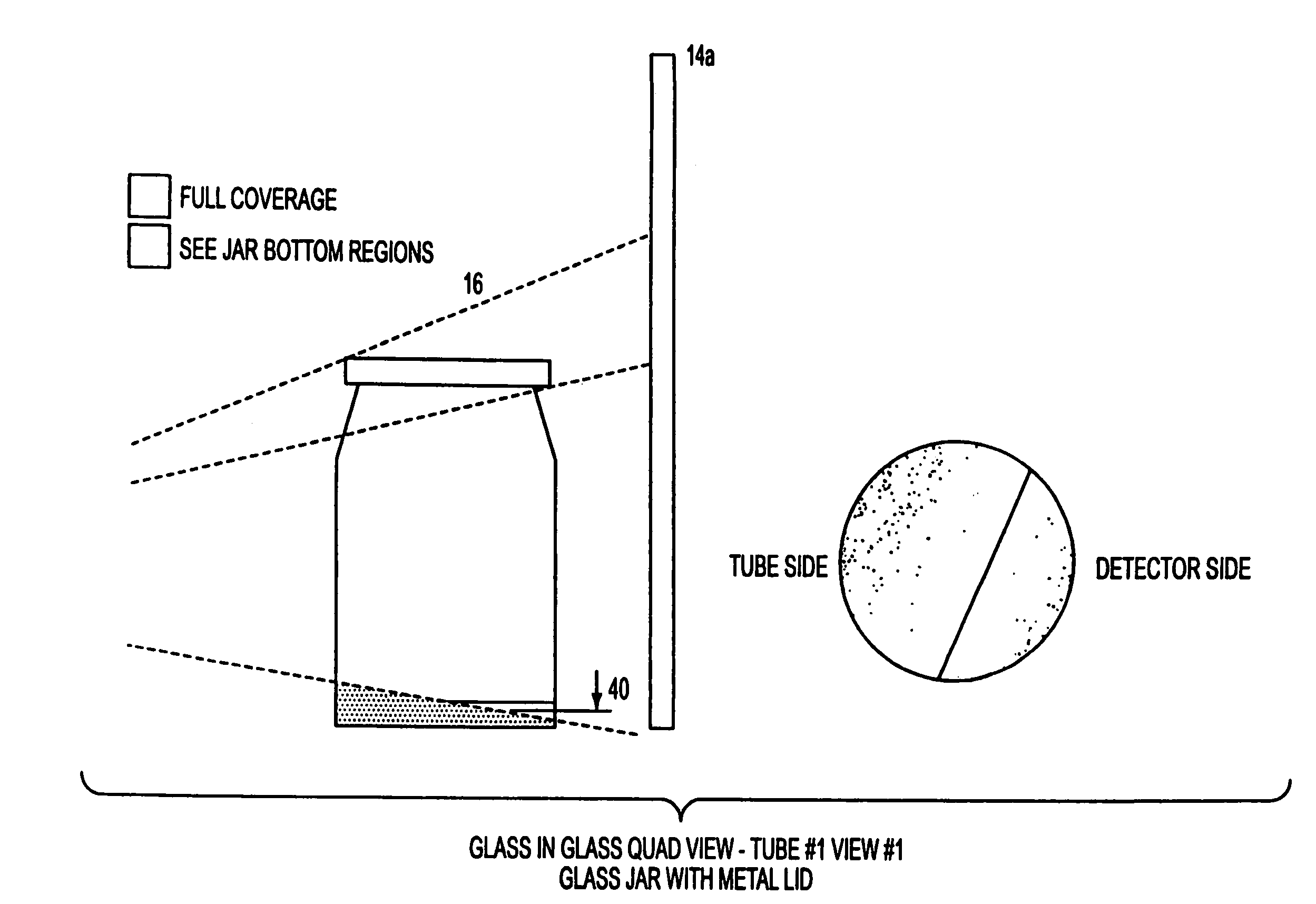
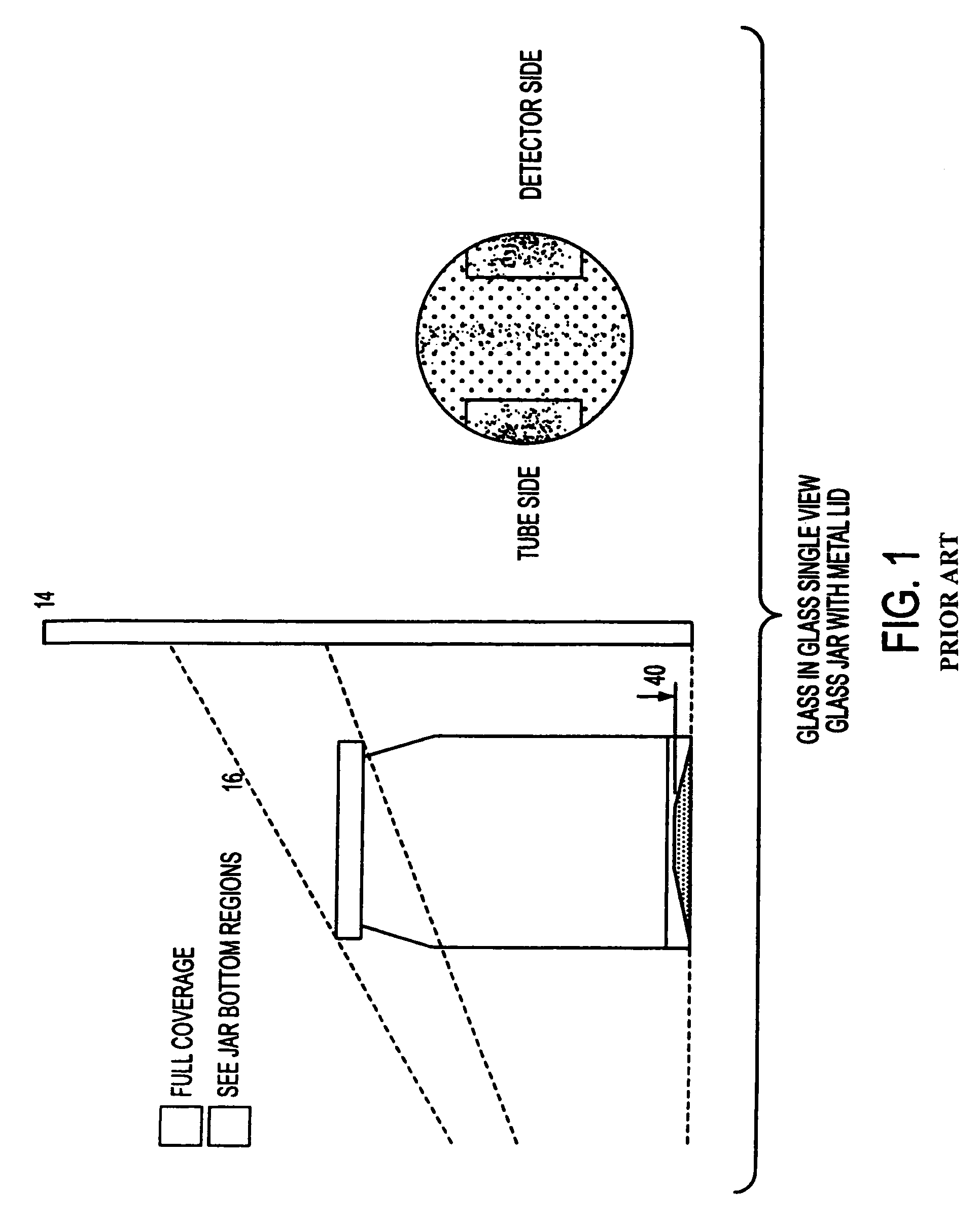
Non-destructive inspection of material in container
InactiveUS7164750B2Using wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationNon destructiveX-ray
An apparatus and method for non-destructive inspection of materials housed in containers involves orienting an X-ray beam emitter and detector to direct and detect an X-ray beam at an angle substantially parallel to a sloped surface of the container to be inspected. A first X-ray apparatus is located opposite a second X-ray apparatus, and both the first and second X-ray apparatus are adapted to provide two X-ray beams. This arrangement provides for imaging of the entire area of a sloped portion of the container without any shadow or hidden spots.
Owner:METTLER TOLEDO INC
Focusable and steerable micro-miniature x-ray apparatus
ActiveUS20050105690A1Inexpensive to fabricateUse disposableX-ray tube windowsHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-rayEngineering
A micro-miniature x-ray apparatus comprises: a first chip subassembly including a source of x-rays including both Bremsstrahlung photons and characteristic x-rays; a second chip subassembly including a filter for transmitting the characteristic x-rays and blocking the Bremsstrahlung photons; a third chip subassembly including a movable element for focusing or collimating the transmitted characteristic x-rays into a beam and means for controlling the position of the focusing element. In one embodiment, the controlling means include a micro-electromechanical system (MEMS). In another embodiment, the position of the movable element determines how the x-ray beam is steered to the focal area. In still another embodiment, the x-ray source includes a field emitter electron source and a target responsive to the electrons for generating x-rays. In this case, the x-ray beam is also steered by selectively energizing the anode segments. In yet another embodiment, the movable element includes a Fresnel zone plate; in still another embodiment it includes an array of poly-capillaries. Advantageously, our x-ray source, including its focusing, collimating and steering components, can be fabricated small enough to be mounted at the end of a catheter. In addition, in some embodiments it can also fabricated sufficiently inexpensively to be disposable after each use.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
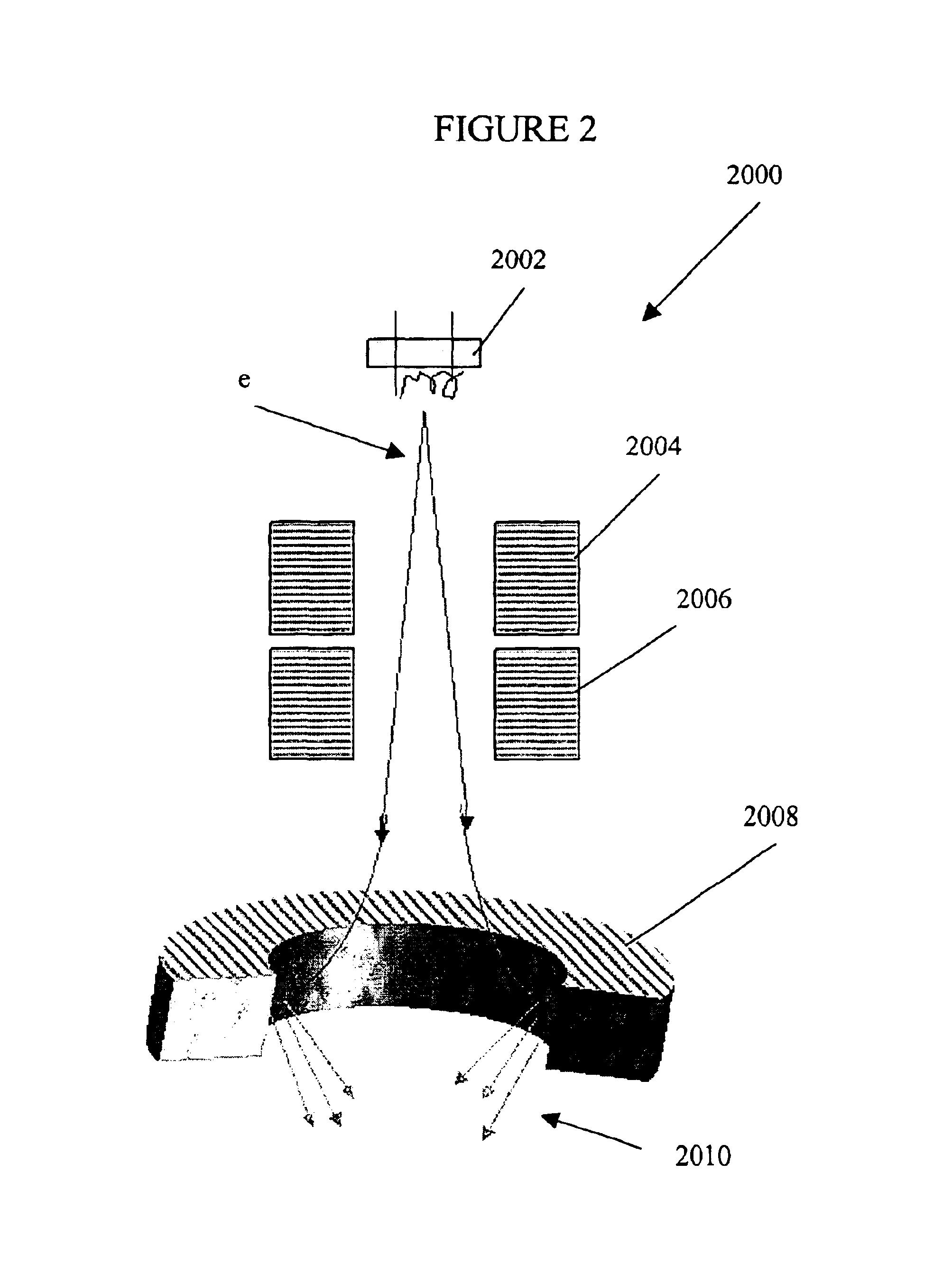
Elongated lifetime X-ray method and apparatus used in conjunction with a charged particle cancer therapy system
ActiveUS7940894B2Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsX-ray tube electrodesSoft x rayParticle beam
The system uses an X-ray imaging system having an elongated lifetime. Further, the system uses an X-ray beam that lies in substantially the same path as a charged particle beam path of a particle beam cancer therapy system. The system creates an electron beam that strikes an X-ray generation source located proximate to the charged particle beam path. By generating the X-rays near the charged particle beam path, an X-ray path running collinear, in parallel with, and / or substantially in contact with the charged particle beam path is created. The system then collects X-ray images of localized body tissue region about a cancerous tumor. Since, the X-ray path is essentially the charged particle beam path, the generated image is usable for precisely target the tumor with a charged particle beam.
Owner:BALAKIN ANDREY VLADIMIROVICH +1
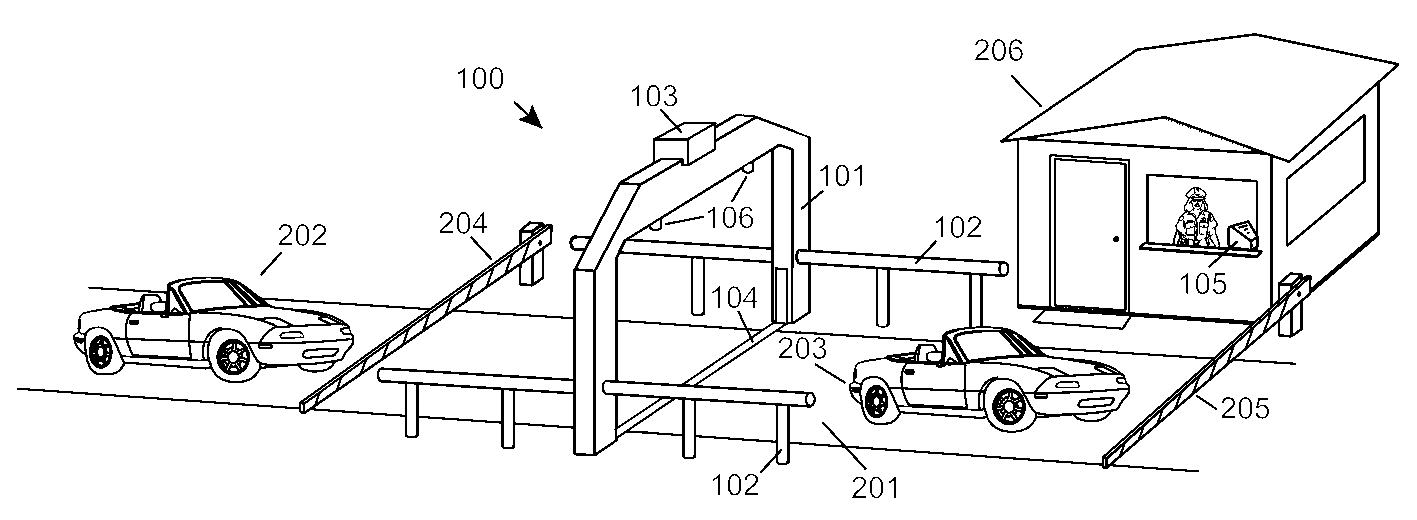
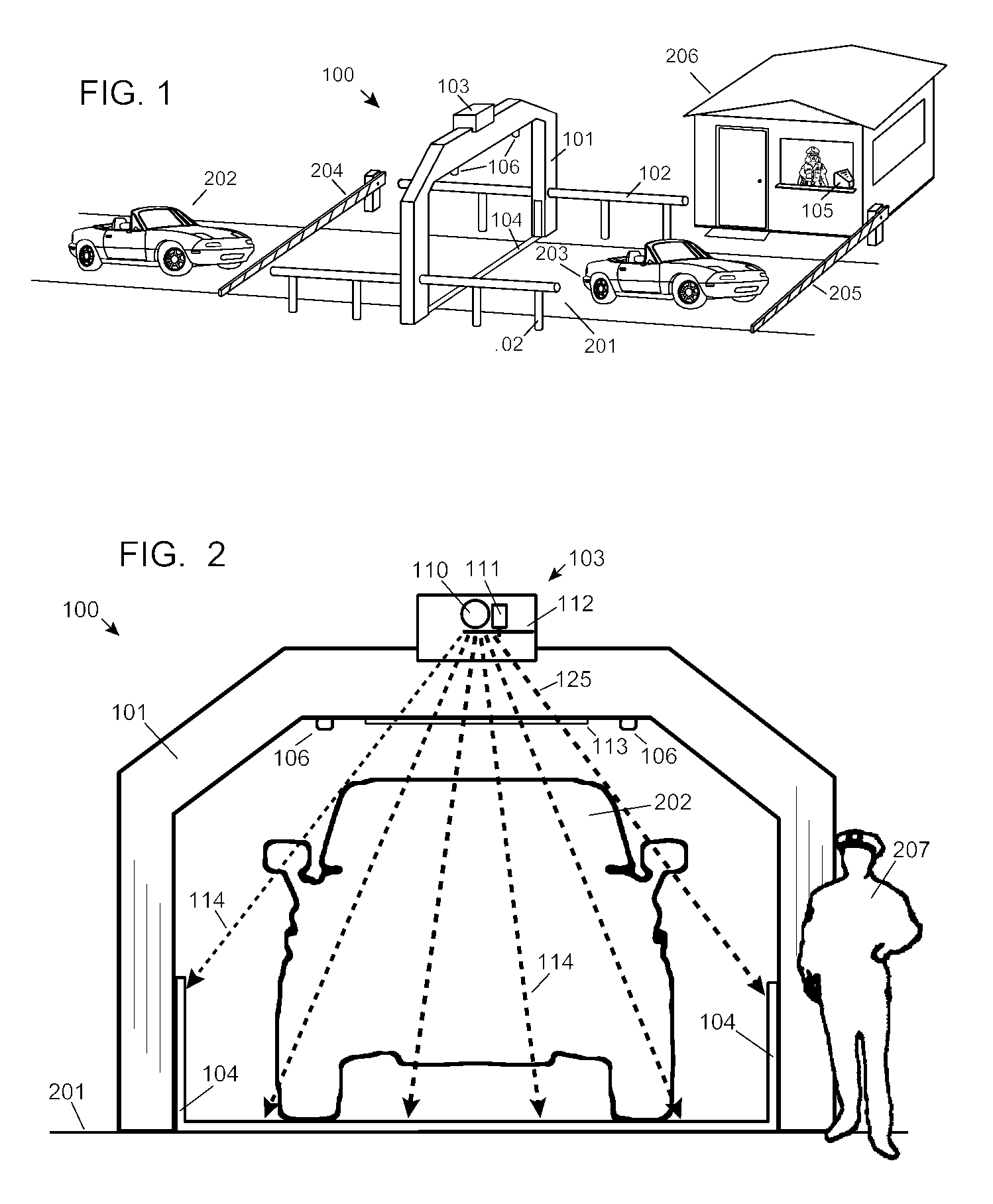
Automobile scanning system
ActiveUS7742568B2Easy to checkUniform exposureX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationAtomic elementHigh energy
A dual-energy x-ray imaging system searches a moving automobile for concealed objects. Dual energy operation is achieved by operating an x-ray source at a constant potential of 100 KV to 150 KV, and alternately switching between two beam filters. The first filter is an atomic element having a high k-edge energy, such as platinum, gold, mercury, thallium, lead, bismuth, and thorium, thereby providing a low-energy spectrum. The second filter provides a high-energy spectrum through beam hardening. The low and high energy beams passing through the automobile are received by an x-ray detector. These detected signals are processed by a digital computer to create a steel suppressed image through logarithmic subtraction. The intensity of the x-ray beam is adjusted as the reciprocal of the measured automobile speed, thereby achieving a consistent radiation level regardless of the automobile motion. Accordingly, this invention provides images of organic objects concealed within moving automobiles without the detritus effects of overlying steel and automobile movement.
Owner:LEIDOS
Coplanar X-ray guided aiming arm for locking of intramedullary nails
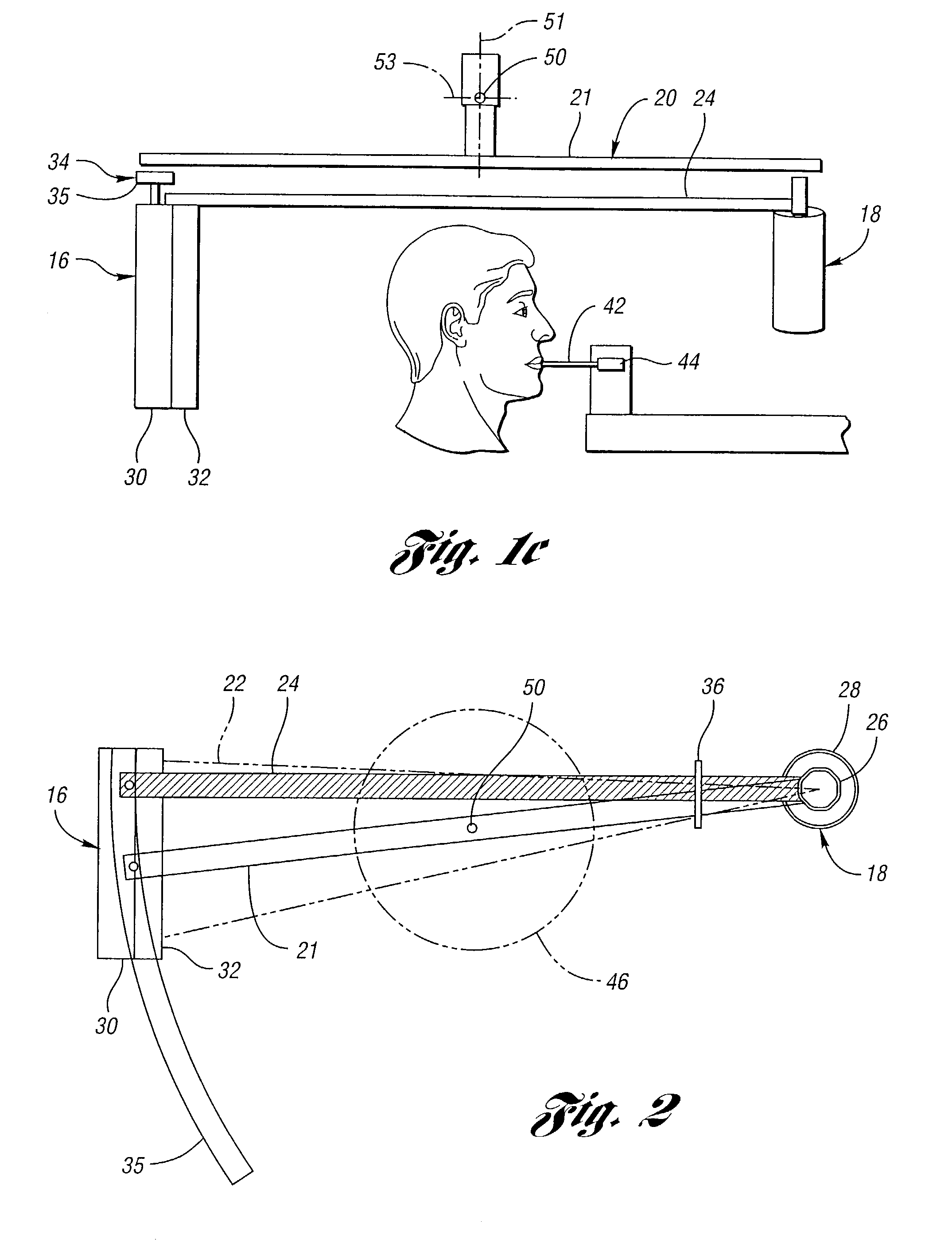
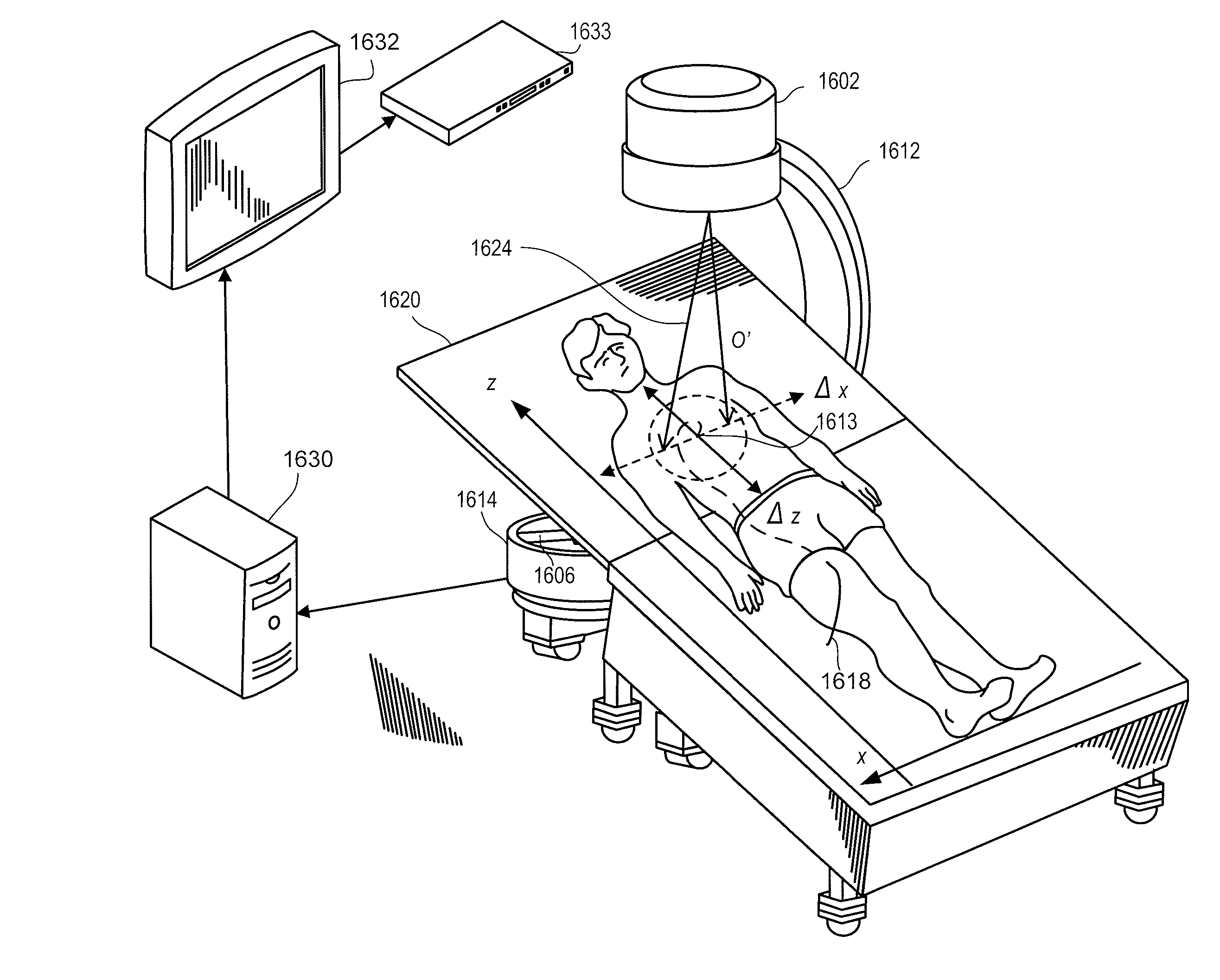
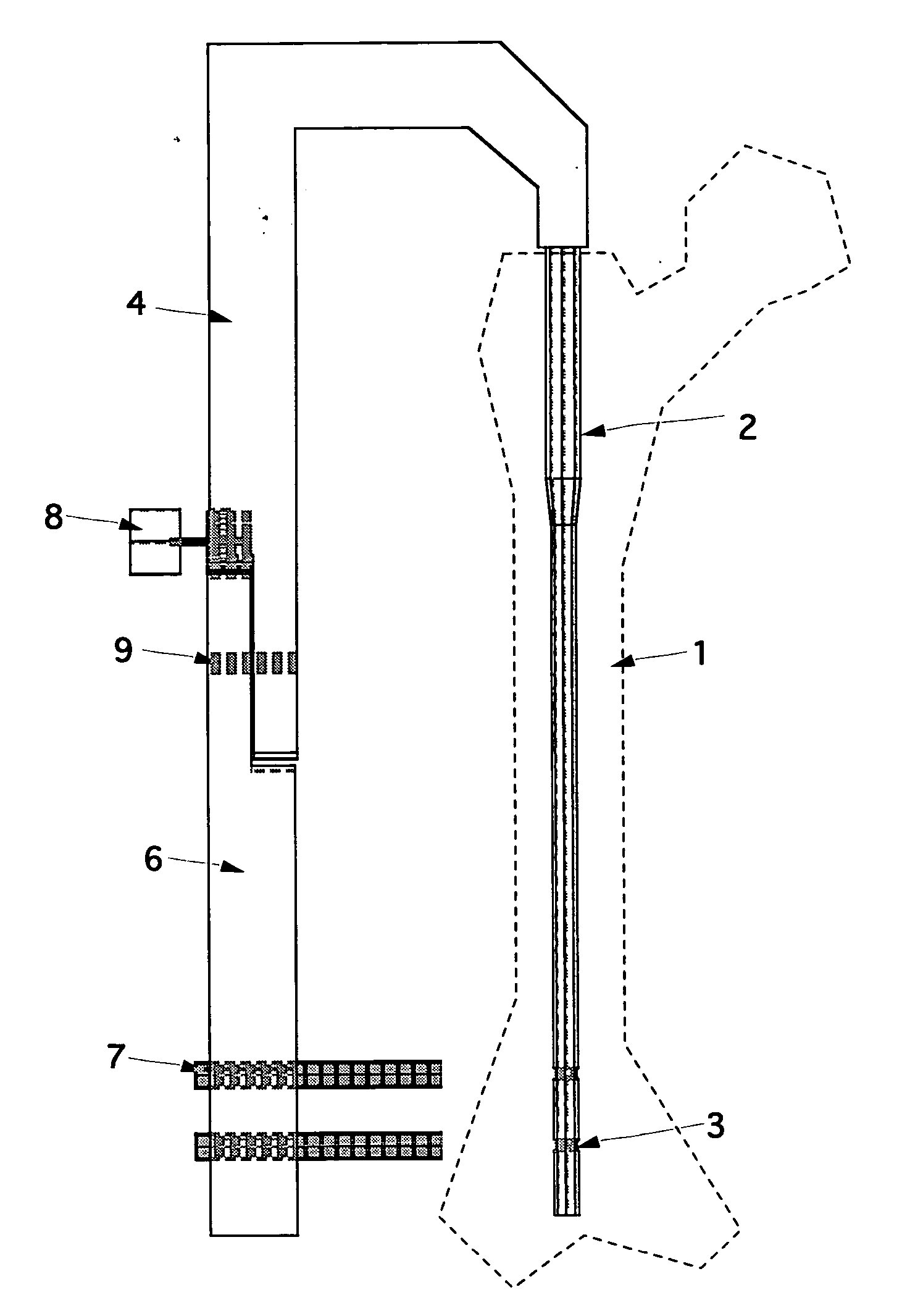
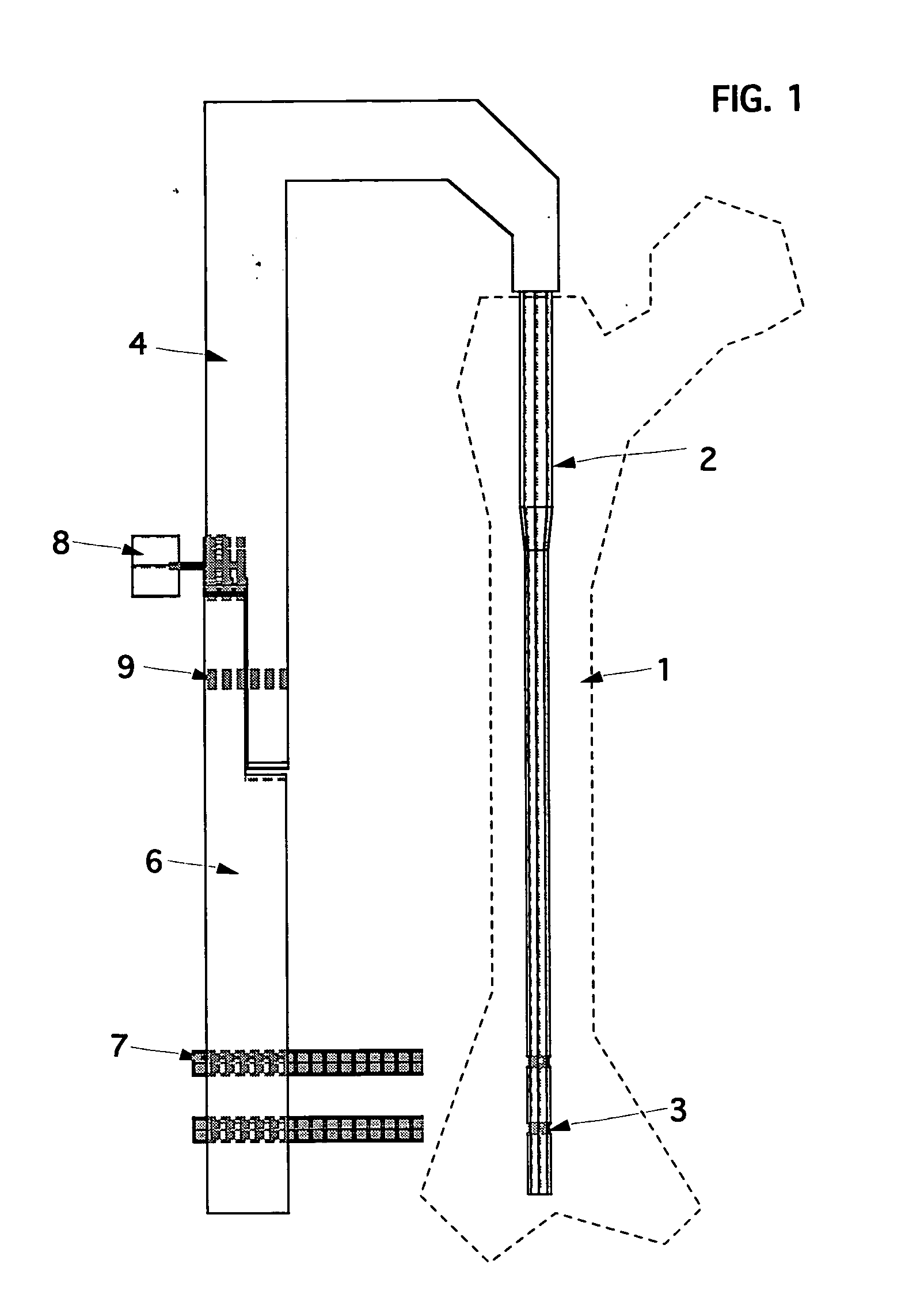
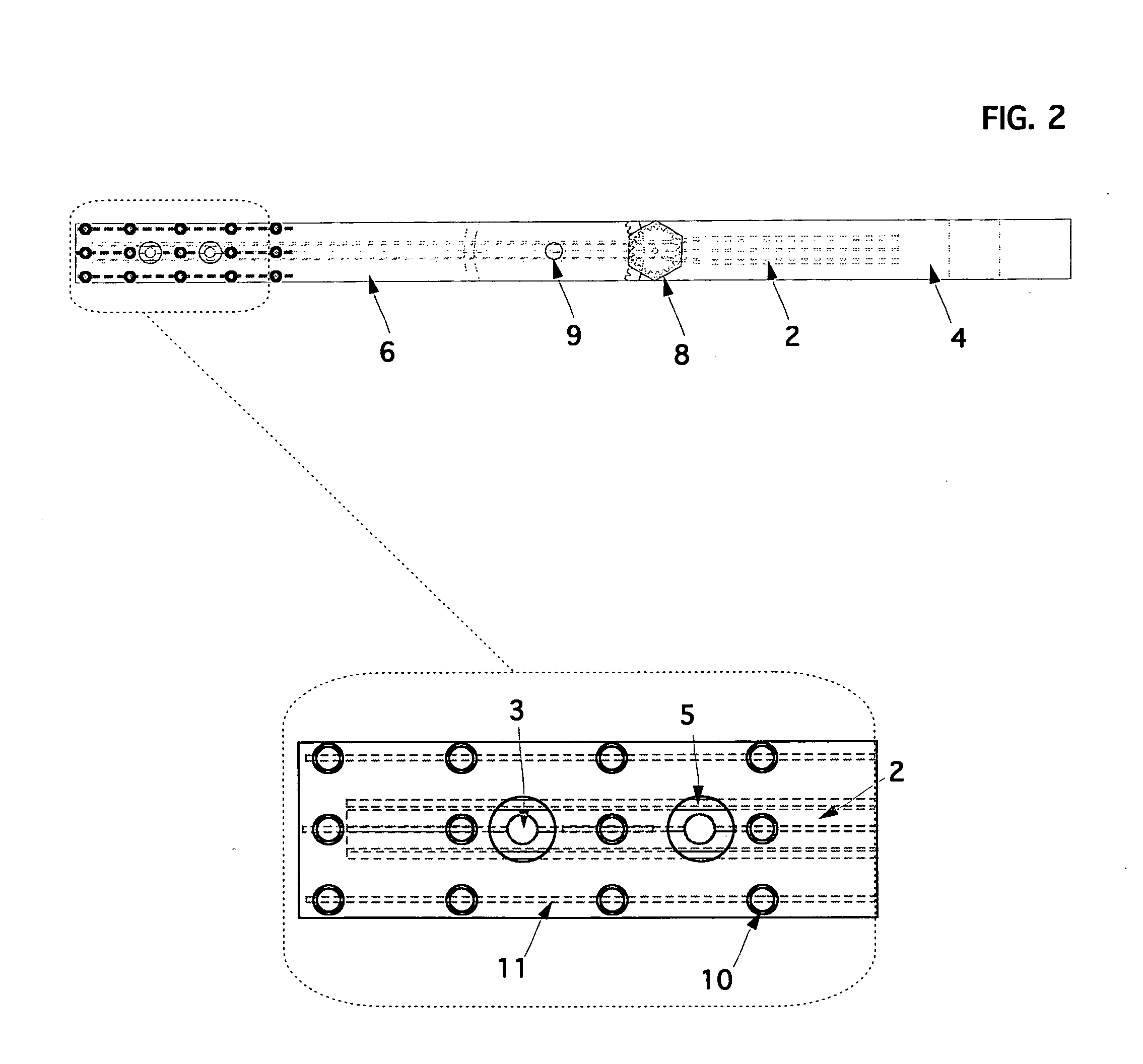
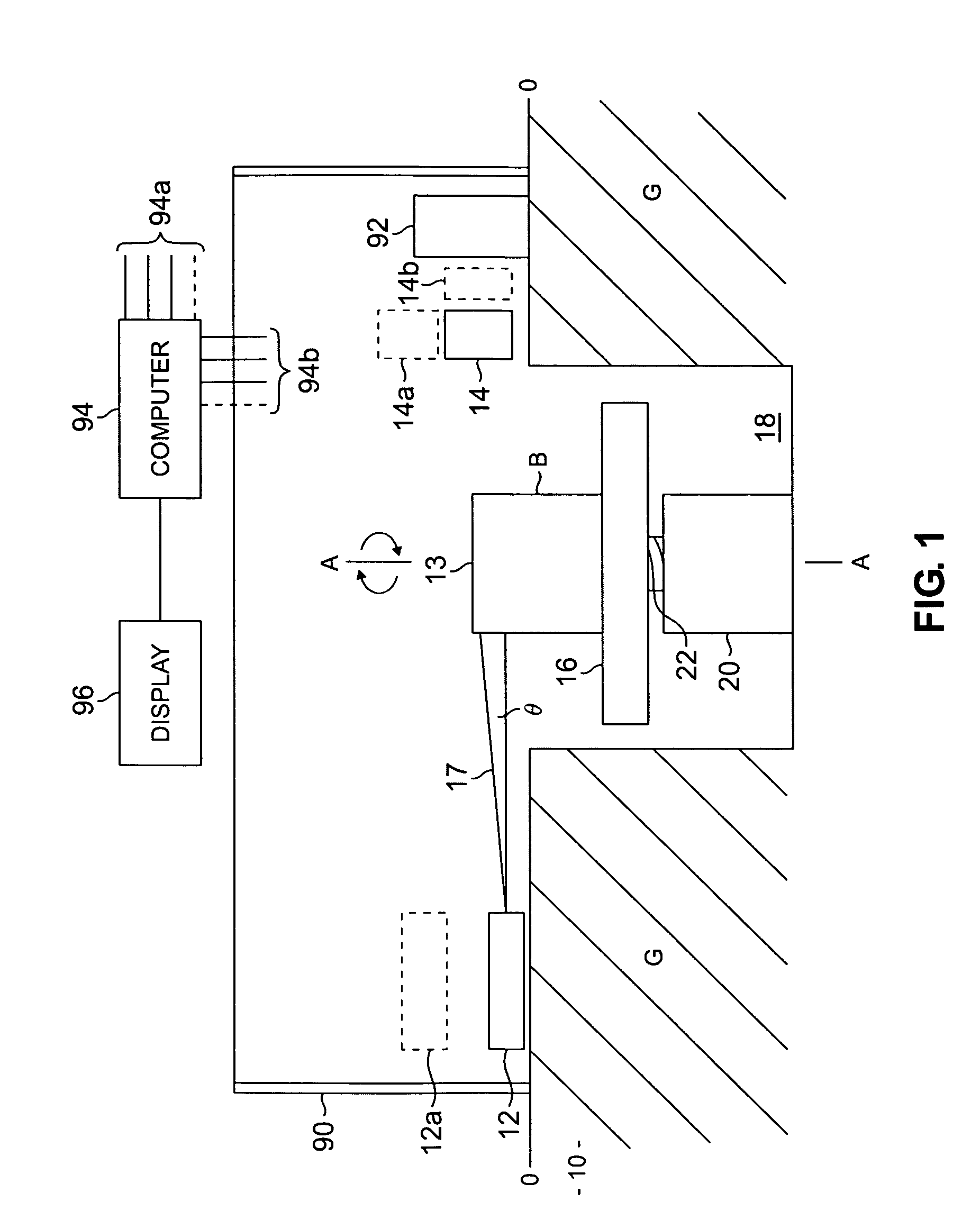
ActiveUS20060064106A1Accurate informationCompensation DistortionDiagnostic markersProsthesisX-raySurgery
A novel coplanar X-ray guided method and device for insertion of distal locking screws in intramedullary bone nails. The device has coplanar holes, which allow insertion of protective sleeves. Bone drill and bone screws can be inserted through the protective sleeves. Radiopaque target markers in the aiming arm enable the easy positioning of an X-ray source such that an X-ray beam is coplanar with the aiming arm transverse holes. After the X-ray source is accurately oriented, a single X-ray snapshot is enough to assess the exact distortion of the implanted intramedullary nail. The X-ray beam does not need to be coaxial with nail holes anymore. The aiming arm has a mobile portion and a fixed portion fastened to the nail, wherein said aiming arm can be adjusted, displacing the mobile portion over the fixed portion, to compensate for the distortion of the intramedullary nail after implanted. Once the aiming arm is precisely positioned, the aiming arm transverse holes and intramedullary nail holes are accurately aligned, protective sleeves are inserted through aiming arm holes, bone drills are drilled through the intramedullary nail holes and surrounding bone material, and bone screws are screwed, locking the intramedullary nail to the bone.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Automobile Scanning System
ActiveUS20090086907A1Easy to checkUniform radiation exposureX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationAtomic elementHigh energy
A dual-energy x-ray imaging system searches a moving automobile for concealed objects. Dual energy operation is achieved by operating an x-ray source at a constant potential of 100 KV to 150 KV, and alternately switching between two beam filters. The first filter is an atomic element having a high k-edge energy, such as platinum, gold, mercury, thallium, lead, bismuth, and thorium, thereby providing a low-energy spectrum. The second filter provides a high-energy spectrum through beam hardening. The low and high energy beams passing through the automobile are received by an x-ray detector. These detected signals are processed by a digital computer to create a steel suppressed image through logarithmic subtraction. The intensity of the x-ray beam is adjusted as the reciprocal of the measured automobile speed, thereby achieving a consistent radiation level regardless of the automobile motion. Accordingly, this invention provides images of organic objects concealed within moving automobiles without the detritus effects of overlying steel and automobile movement.
Owner:LEIDOS
Differential interference phase contrast X-ray imaging system
InactiveUS8073099B2High radiant fluxPhoton energy is highImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesHigh energyPhotoconductive detector
A differential phase-contrast X-ray imaging system is provided. Along the direction of X-ray propagation, the basic components are X-ray tube, filter, object platform, X-ray phase grating, and X-ray detector. The system provides: 1) X-ray beam from parallel-arranged source array with good coherence, high energy, and wider angles of divergence with 30-50 degree. 2) The novel X-ray detector adopted in present invention plays dual roles of conventional analyzer grating and conventional detector. The basic structure of the detector includes a set of parallel-arranged linear array X-ray scintillator screens, optical coupling system, an area array detector or parallel-arranged linear array X-ray photoconductive detector. In this case, relative parameters for scintillator screens or photoconductive detector correspond to phase grating and parallel-arranged line source array, which can provide the coherent X-rays with high energy.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
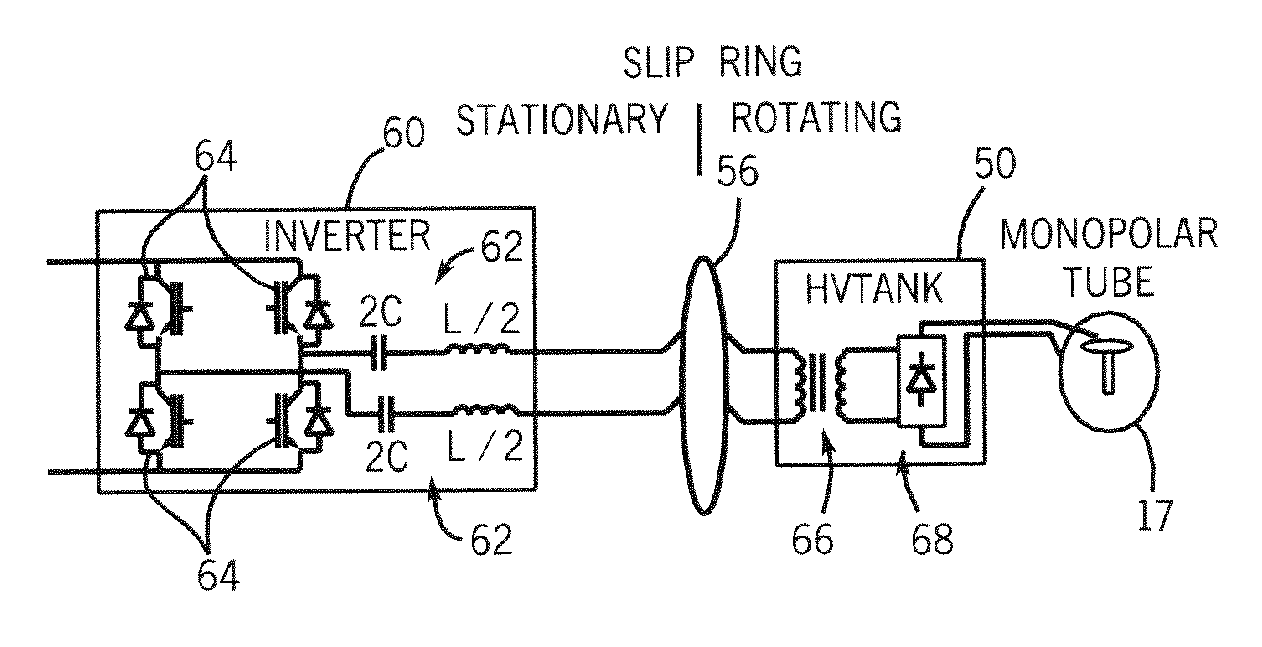
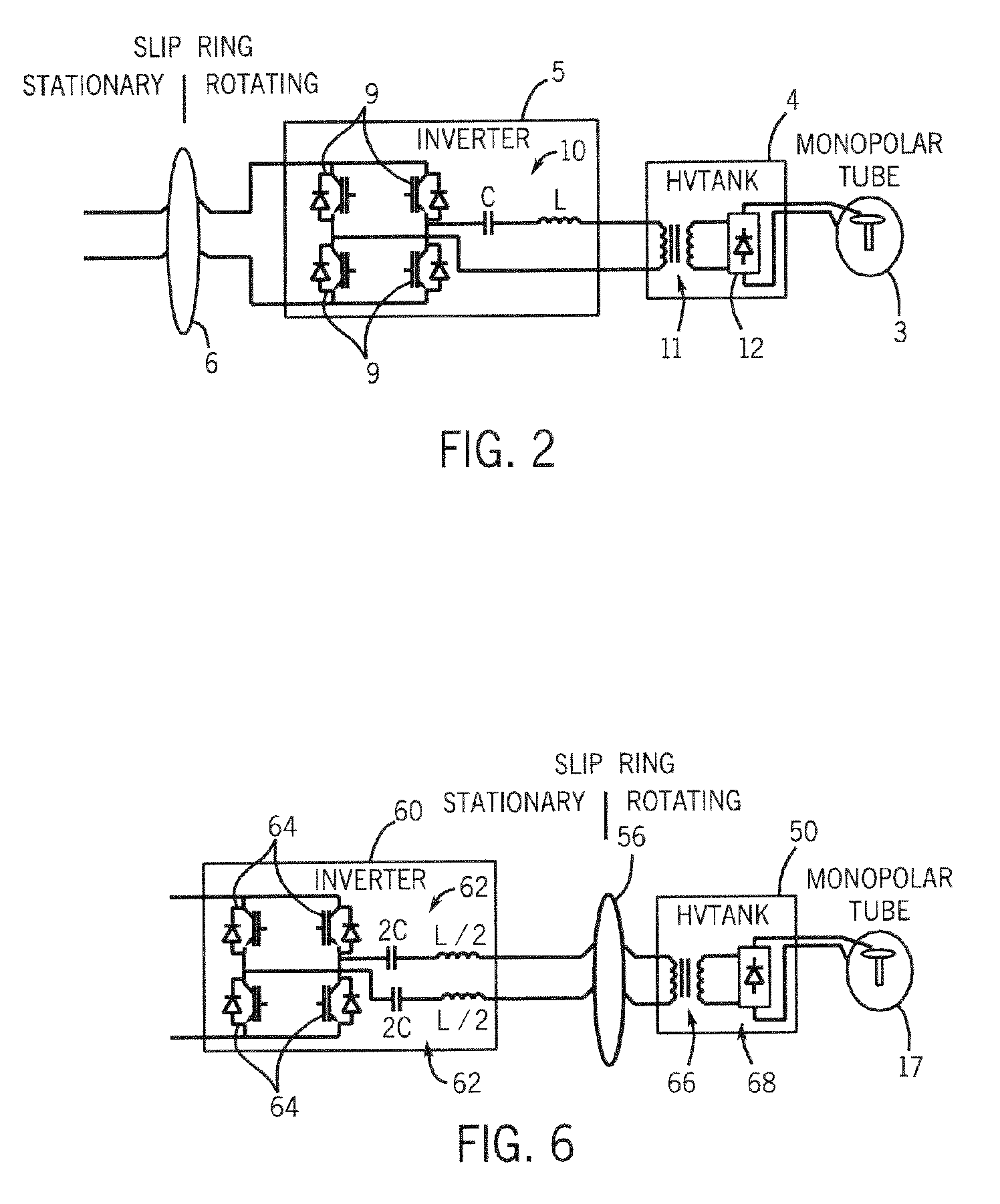
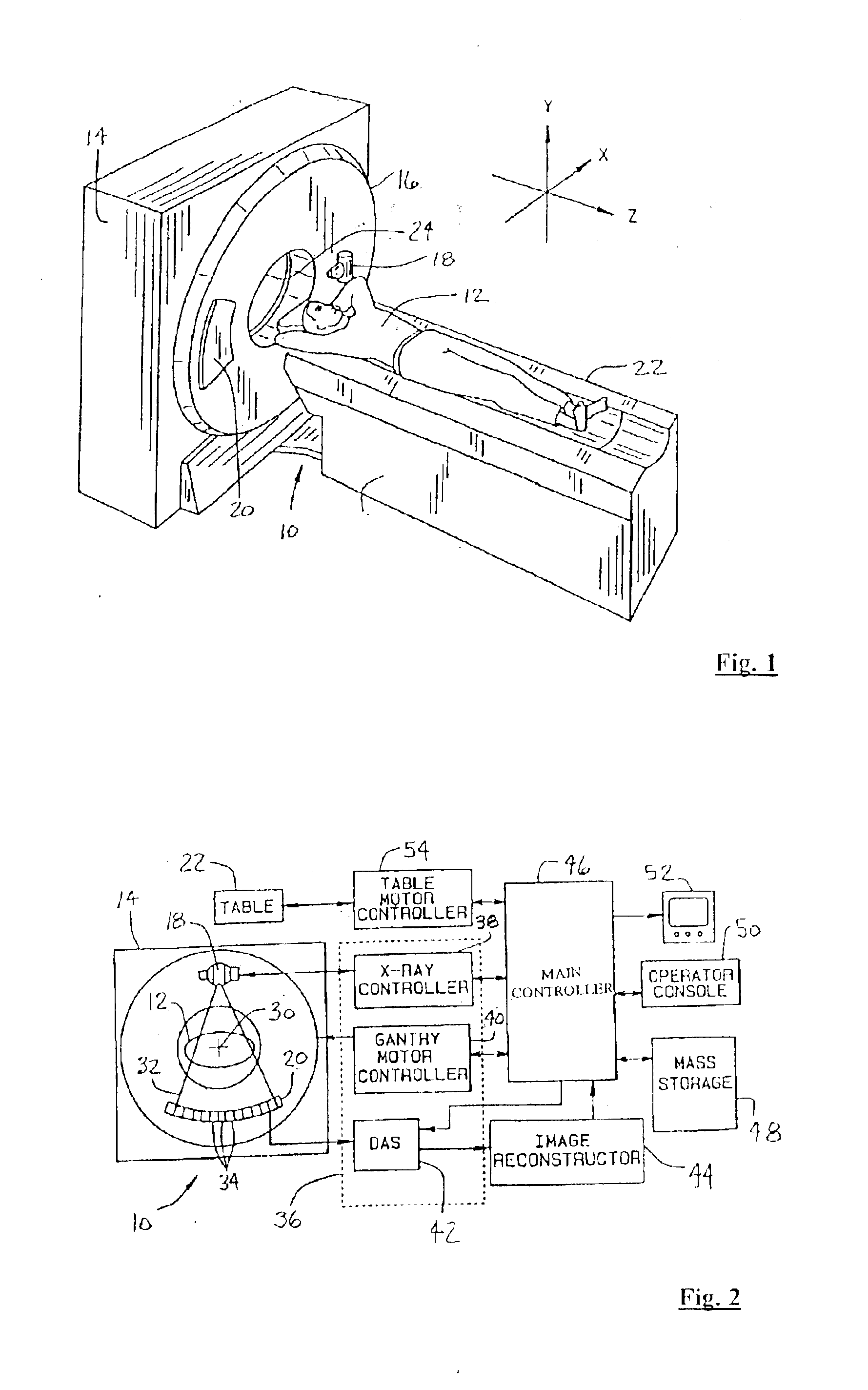
X-ray generator and slip ring for a CT system
InactiveUS6975698B2Radiation diagnosis data transmissionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTransformerFuel tank
The present invention is directed to an apparatus for supplying power to a rotatable x-ray tube for generation of an x-ray beam for acquisition of CT data. The apparatus includes a slip ring to transfer power from a stationary inverter to a rotatable HV tank. The HV tank conditions the transferred power and creates a voltage potential across the x-ray tube for x-ray generation. The inverter has a single or pair of series resonant circuits connected either directly to the slip ring or indirectly through a transformer to limit frequency content and reduce common-mode component of the voltage and current waveforms carried by the slip ring as well as reduce power losses.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
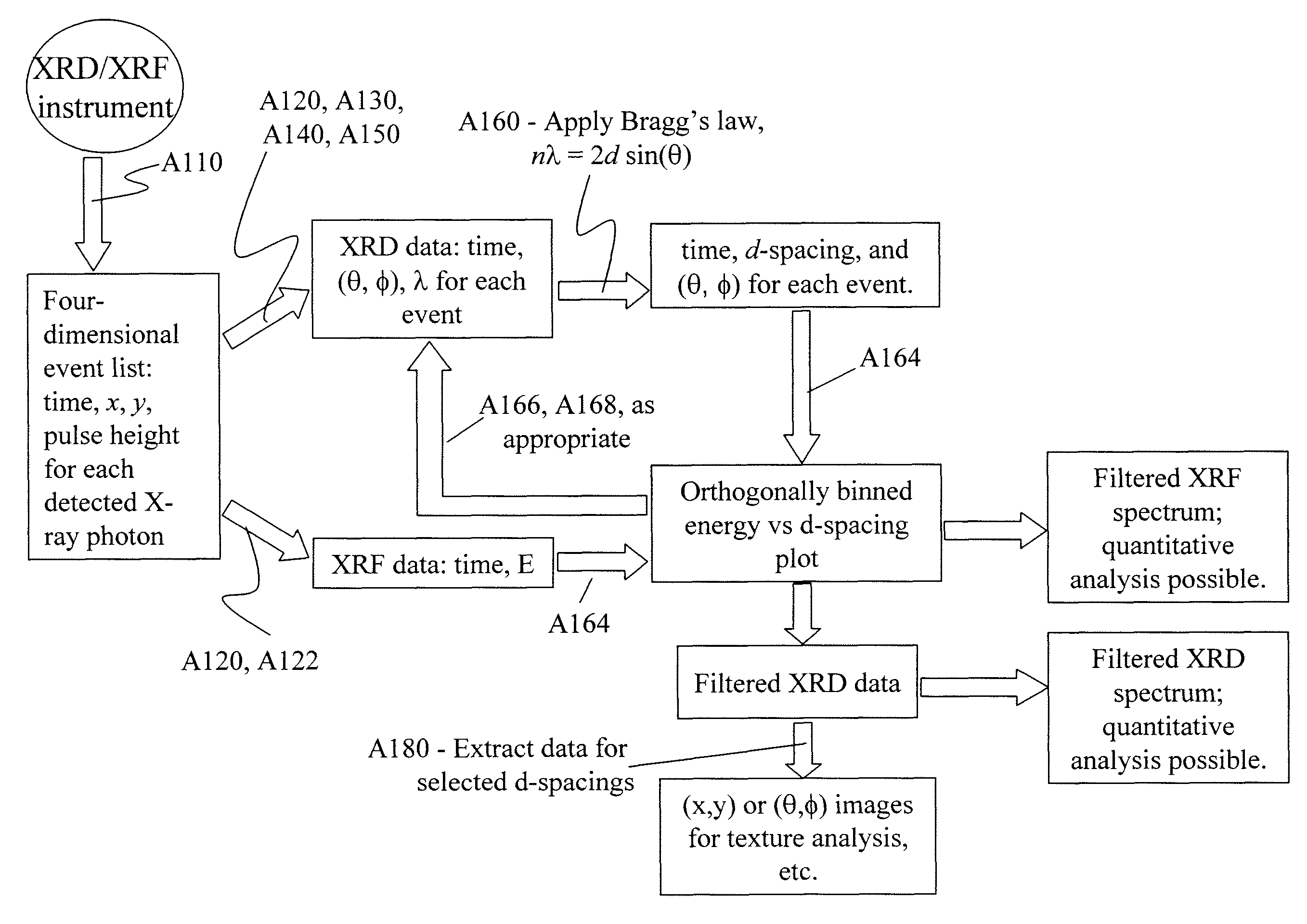
Instrument and method for X-ray diffraction, fluorescence, and crystal texture analysis without sample preparation
InactiveUS7796726B1Reduce power consumptionHigh sensitivityX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionX-rayReflection geometry
An X-ray diffraction and X-ray fluorescence instrument for analyzing samples having no sample preparation includes a X-ray source configured to output a collimated X-ray beam comprising a continuum spectrum of X-rays to a predetermined coordinate and a photon-counting X-ray imaging spectrometer disposed to receive X-rays output from an unprepared sample disposed at the predetermined coordinate upon exposure of the unprepared sample to the collimated X-ray beam. The X-ray source and the photon-counting X-ray imaging spectrometer are arranged in a reflection geometry relative to the predetermined coordinate.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
Scatter correction for x-ray imaging using modulation of primary x-ray spatial spectrum
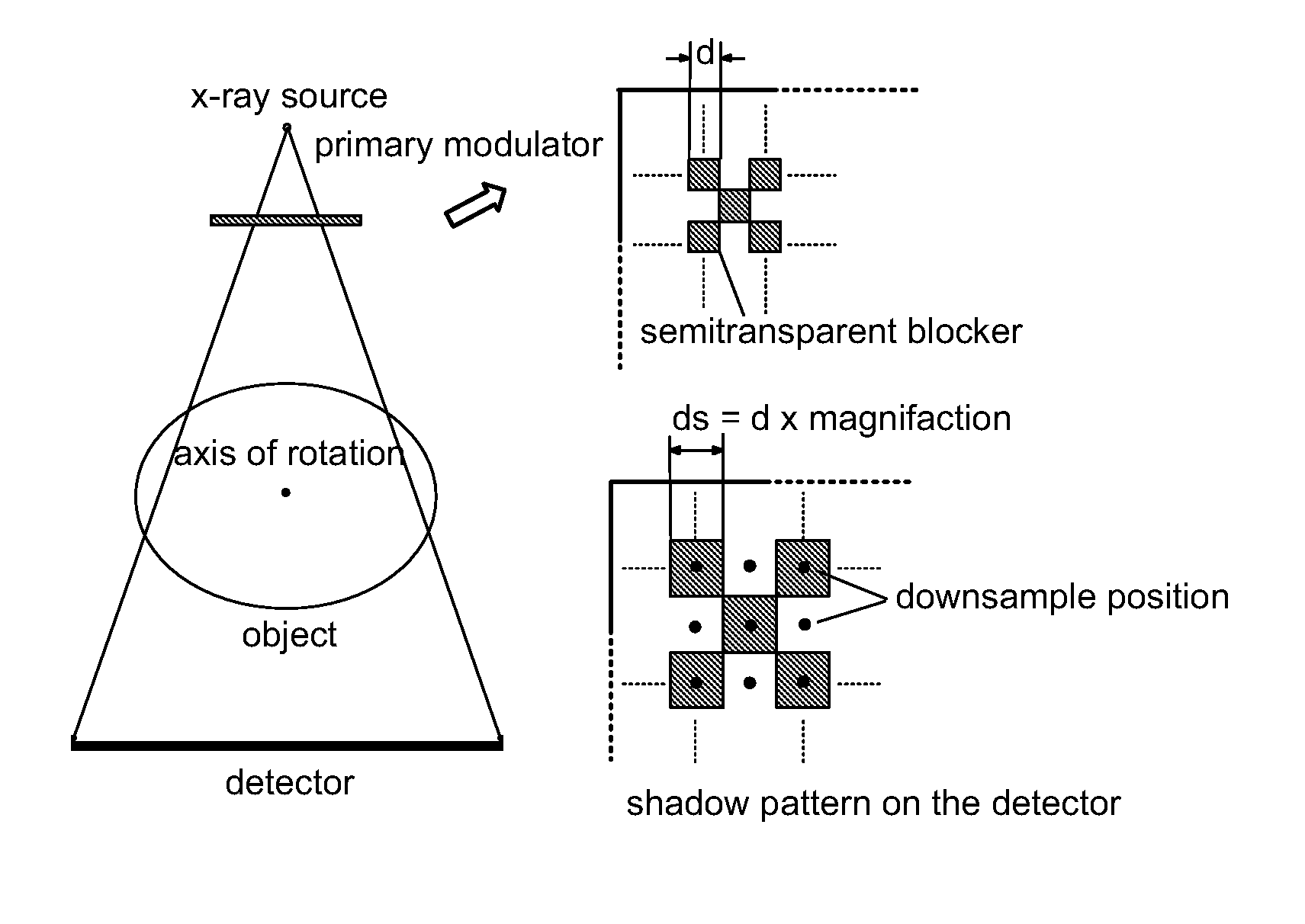
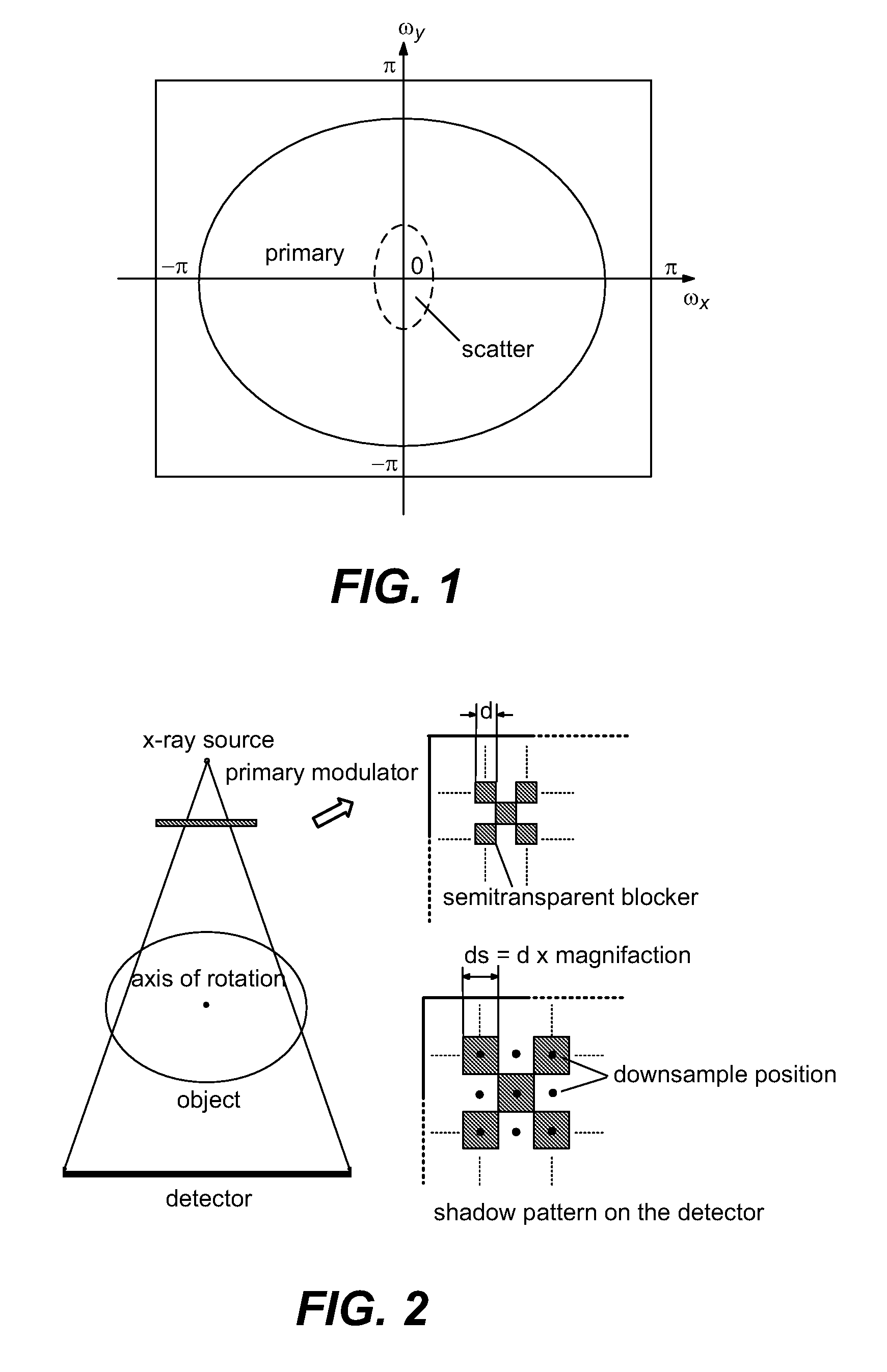
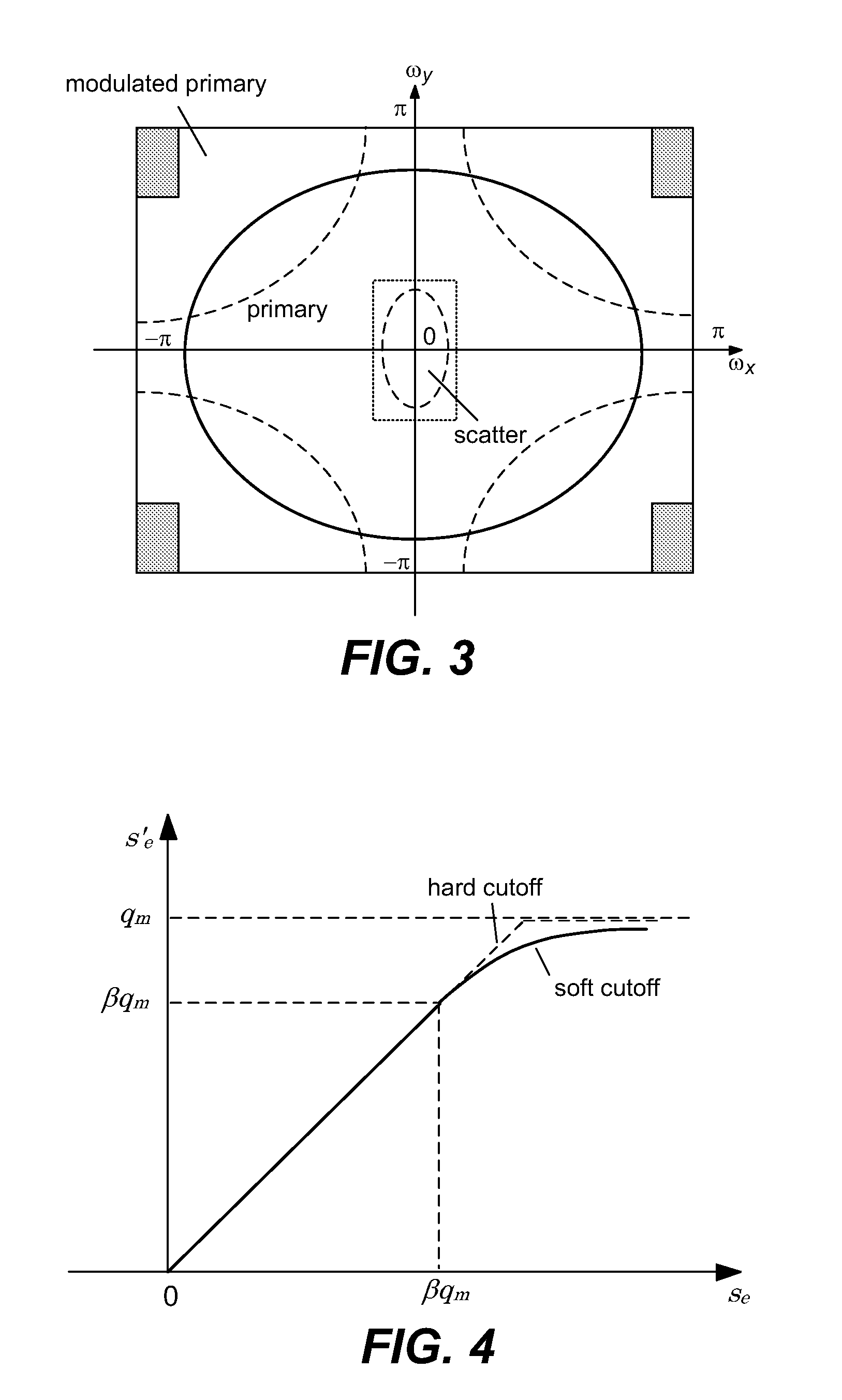
ActiveUS7463712B2Efficient transferMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayX ray image
Scatter radiation in an x-ray imaging system including an x-ray source and an x-ray detector is separated by using amplitude modulation to translate the spatial frequency of a detected x-ray beam to a higher frequency and provide separation from low frequency scatter signal. The low frequency content of the detected x-ray beam is then obtained by demodulating the detected modulated signal.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Vehicle-carried mobile container inspection apparatus
ActiveUS20040125914A1Wide cross-sectionLower levelItem transportation vehiclesX-ray apparatusIn vehicleComputer module
A vehicle-carried mobile container inspection apparatus characterized in that the mobile container inspection apparatus comprises a first box-shaped cabin arranged in the front portion of the chassis and provided with a workroom accommodating a scan control module, an image acquisition module and an operation / inspection module; and a second box-shaped cabin and a third box-shaped cabin both arranged on the rear portion of the rotatable platform, in which the second box-shaped cabin is arranged on the top of the third box-shaped cabin, the control unit of the radiation source is accommodated in the second box-shaped cabin, the third box-shaped cabin is arranged under the rotatable platform, the radiation source is arranged in the third box-shaped cabin, the level of the radiation source from which the X-ray beam emit is arranged below the level of the chassis, the scanning vehicle is provided with a driving means to smoothly move the scanning vehicle; the rotatable platform is provided with a rotatably driving means, when inspecting a container, the rotatable platform is driven to turn 90 degrees, and the second arm turns into its vertical gesture, so that a portal-shaped frame is formed by means of the parallelogrammical bracket, the first arm and the second arm. The mobile inspection container apparatus is capable of inspecting as broad area as to reach the vehicle chassis. The apparatus comprises two vehicles, in which usually the both vehicles are used, while only one vehicle is used for fulfilling the inspection work in emergency.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Radiation scanning units including a movable platform
A scanning unit for inspecting objects comprises in one example a radiation source, a movable platform to support an object, and a detector positioned to receive radiation after interaction of radiation with the object. The platform is movable at least partially within a cavity defined, at least partially, below at least one of the source or the detector. In another scanning unit, a first conveyor conveys an object to a movable platform, and second and third conveyors convey the object from the platform. The second and third conveyors are at different vertical heights. In another scanning unit, images from an energy sensitive detector and a spatial detector are fused. In a method, scanning parameters during CT scanning are changed and images reconstructed before and after the change. In another method, an object is scanned with X-ray beams having first and second energy distributions, generated by the same X-ray source.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
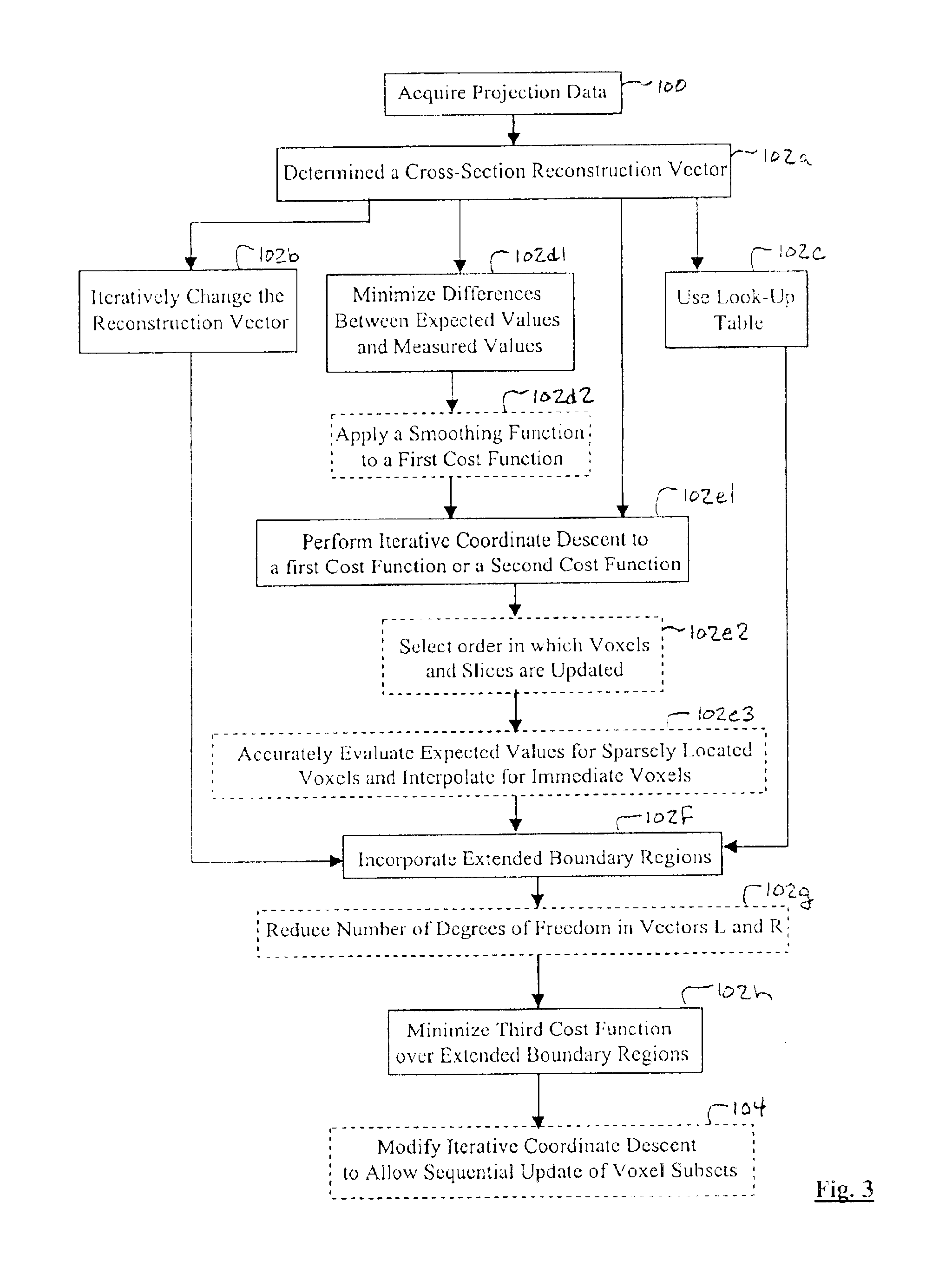
Iterative reconstruction methods for multi-slice computed tomography
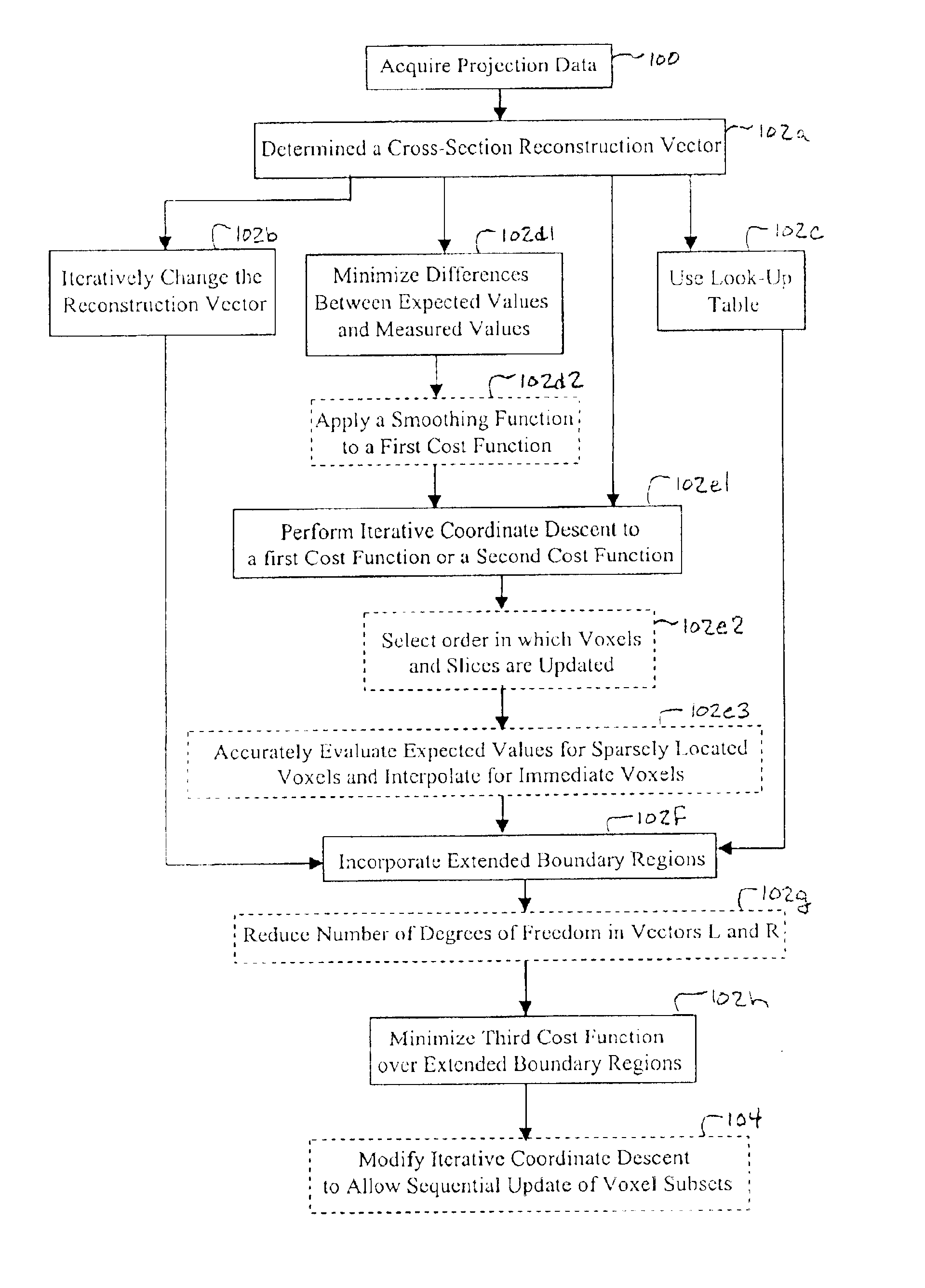
InactiveUS6907102B1Avoid warpingError minimizationReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHelical scanMulti slice
A multi-slice computed tomography imaging system is provided including a source that generates an x-ray beam and a detector array that receives the x-ray beam and generates projection data. A translatable table has an object thereon and is operable to translate in relation to the source and the detector array. The source and the detector array rotate about the translatable table to helically scan the object. An image reconstructor is electrically coupled to the detector array and reconstructs an image in response to the projection data using a computed tomography modeled iterative reconstruction technique. The iterative reconstruction technique includes determining a cross-section reconstruction vector, which approximately matches the projection data via a computed tomography model. Methods for performing the same are also provided including accounting for extended boundary regions.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC +2
Radiation scanning units including a movable platform
InactiveUS20090067575A1Material analysis by transmitting radiationNuclear radiation detectionComputed tomographyX-ray
A scanning unit for inspecting objects comprises in one example a radiation source, a movable platform to support an object, and a detector positioned to receive radiation after interaction of radiation with the object. The platform is movable at least partially within a cavity defined, at least partially, below at least one of the source or the detector. In another scanning unit, a first conveyor conveys an object to a movable platform, and second and third conveyors convey the object from the platform. The second and third conveyors are at different vertical heights. In another scanning unit, images from an energy sensitive detector and a spatial detector are fused. In a method, scanning parameters during CT scanning are changed and images reconstructed before and after the change. In another method, an object is scanned with X-ray beams having first and second energy distributions, generated by the same X-ray source.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com