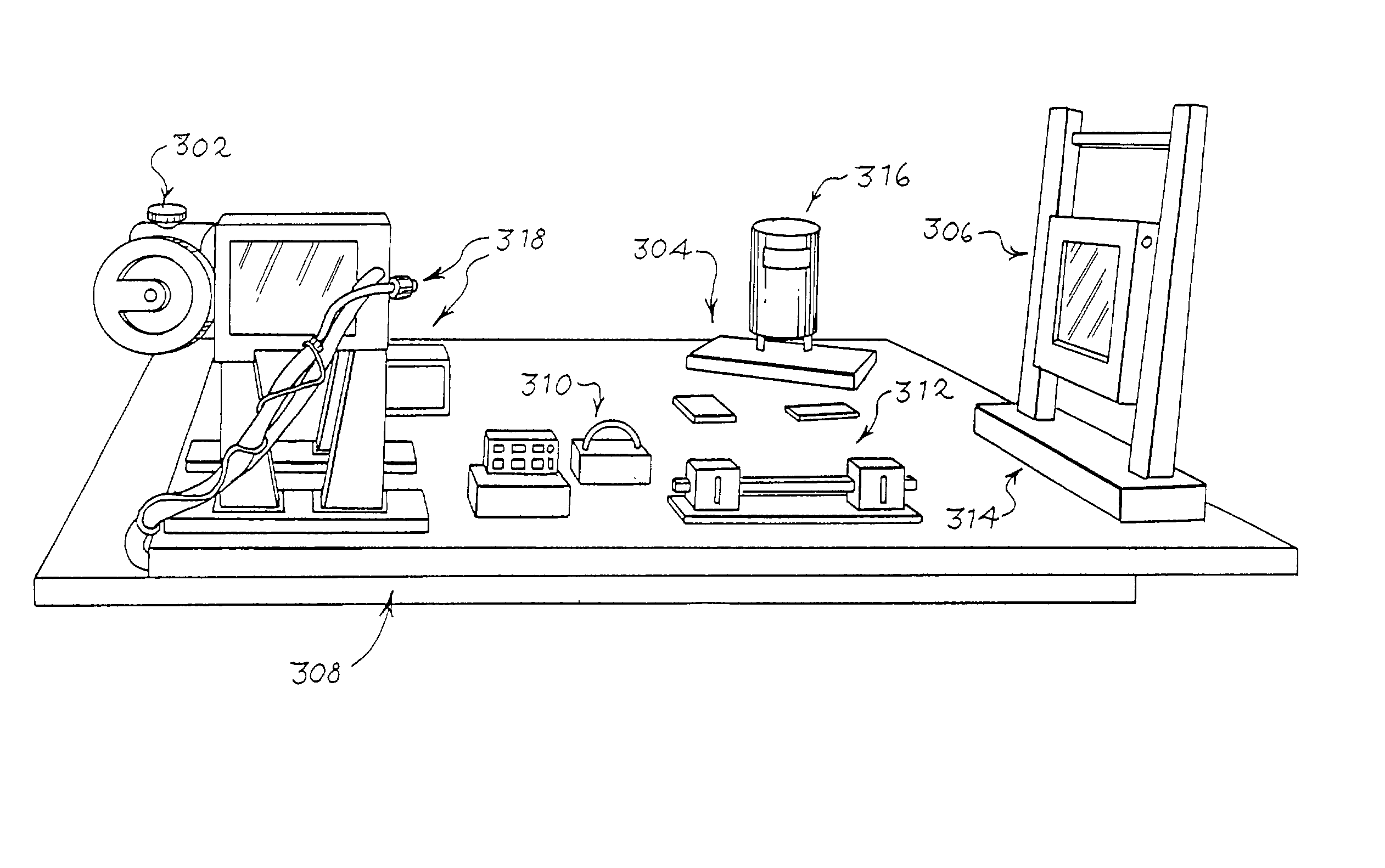
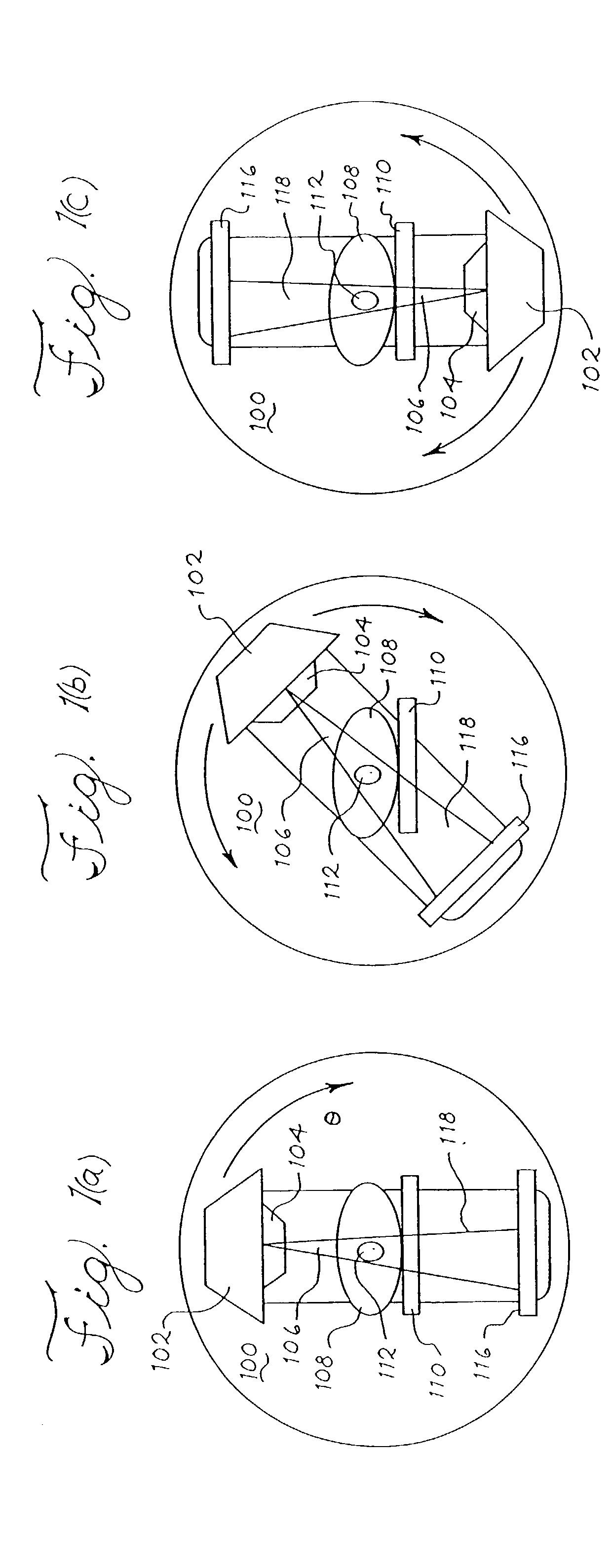
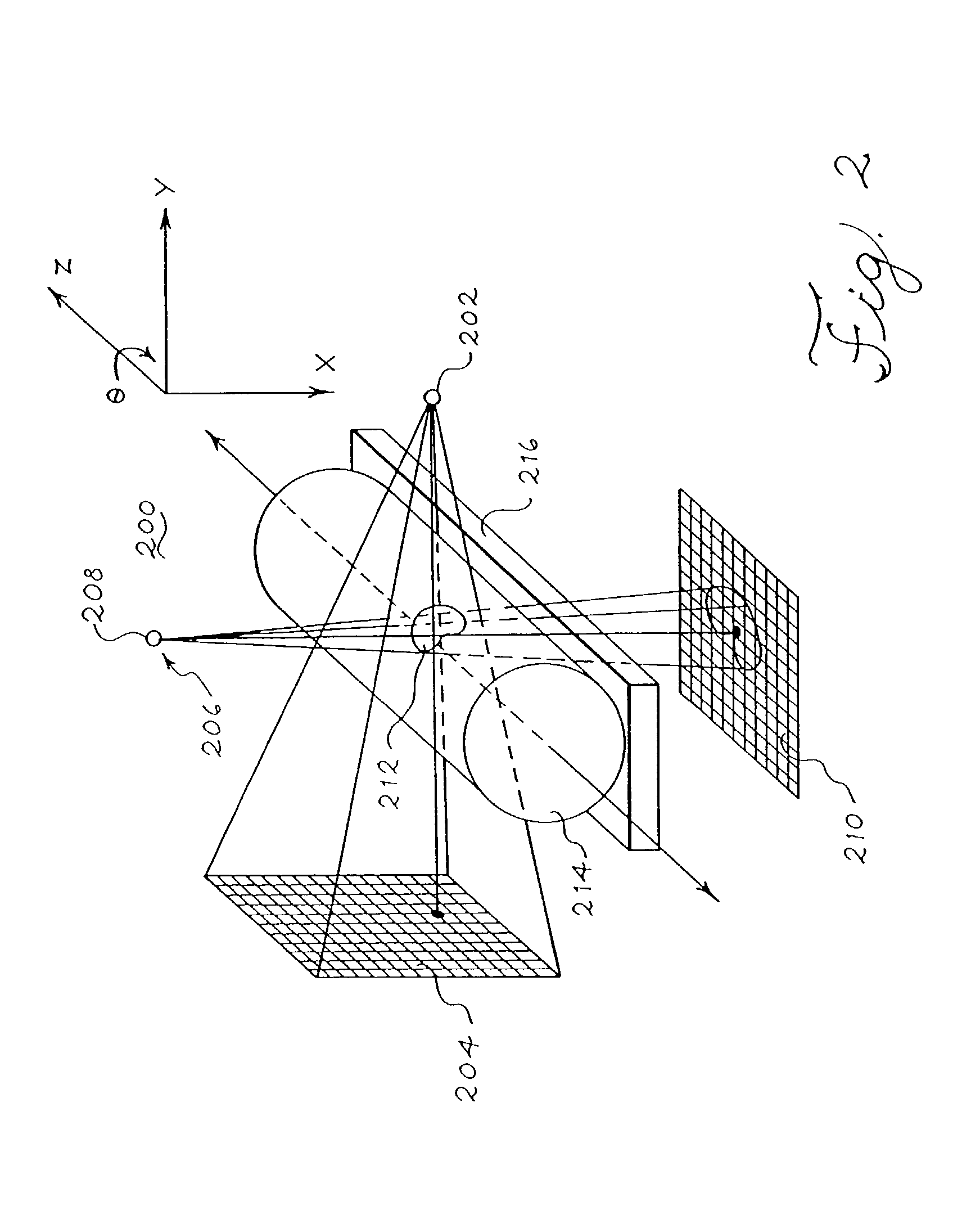
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
165 results about "Conical beam" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
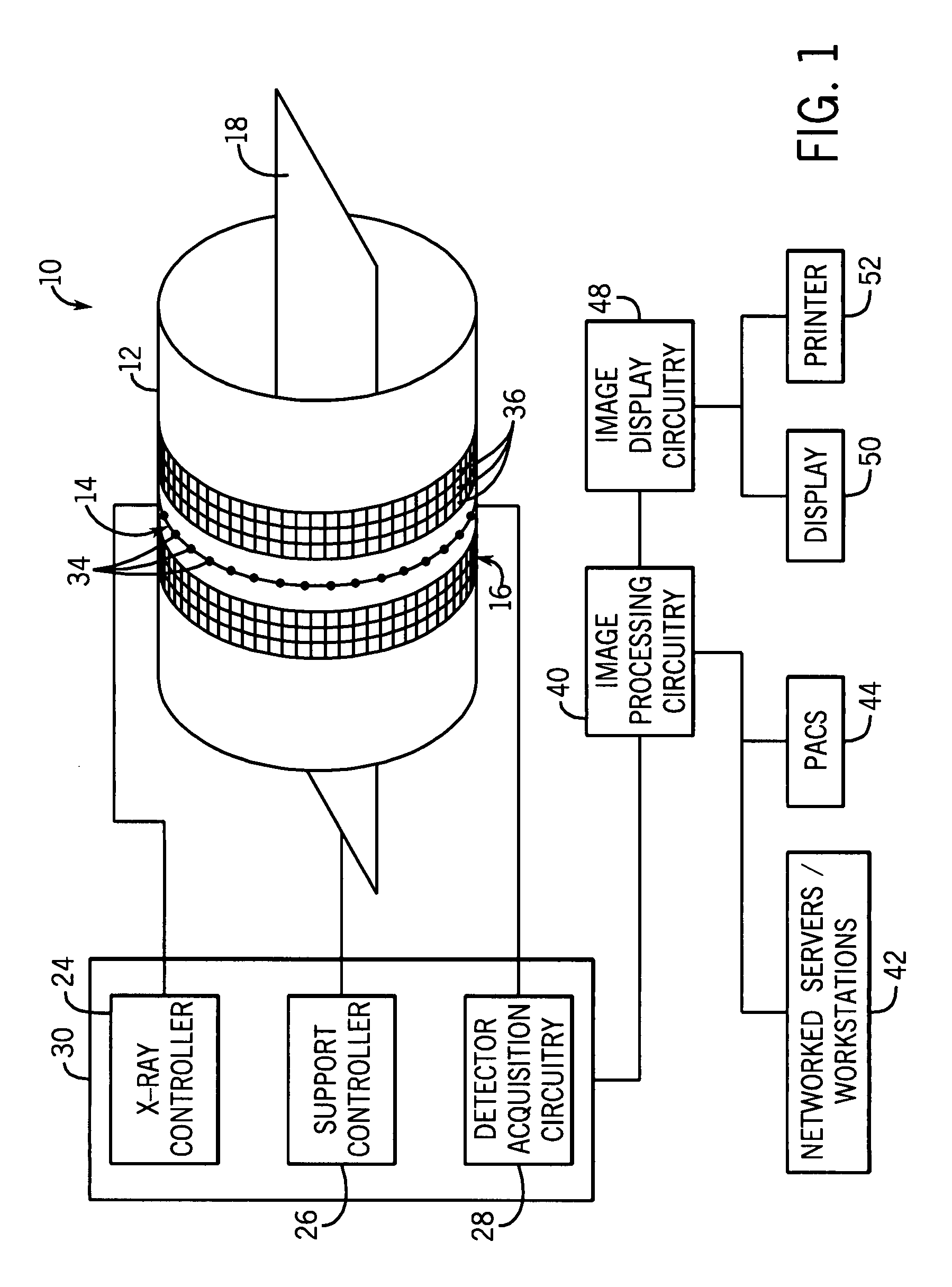
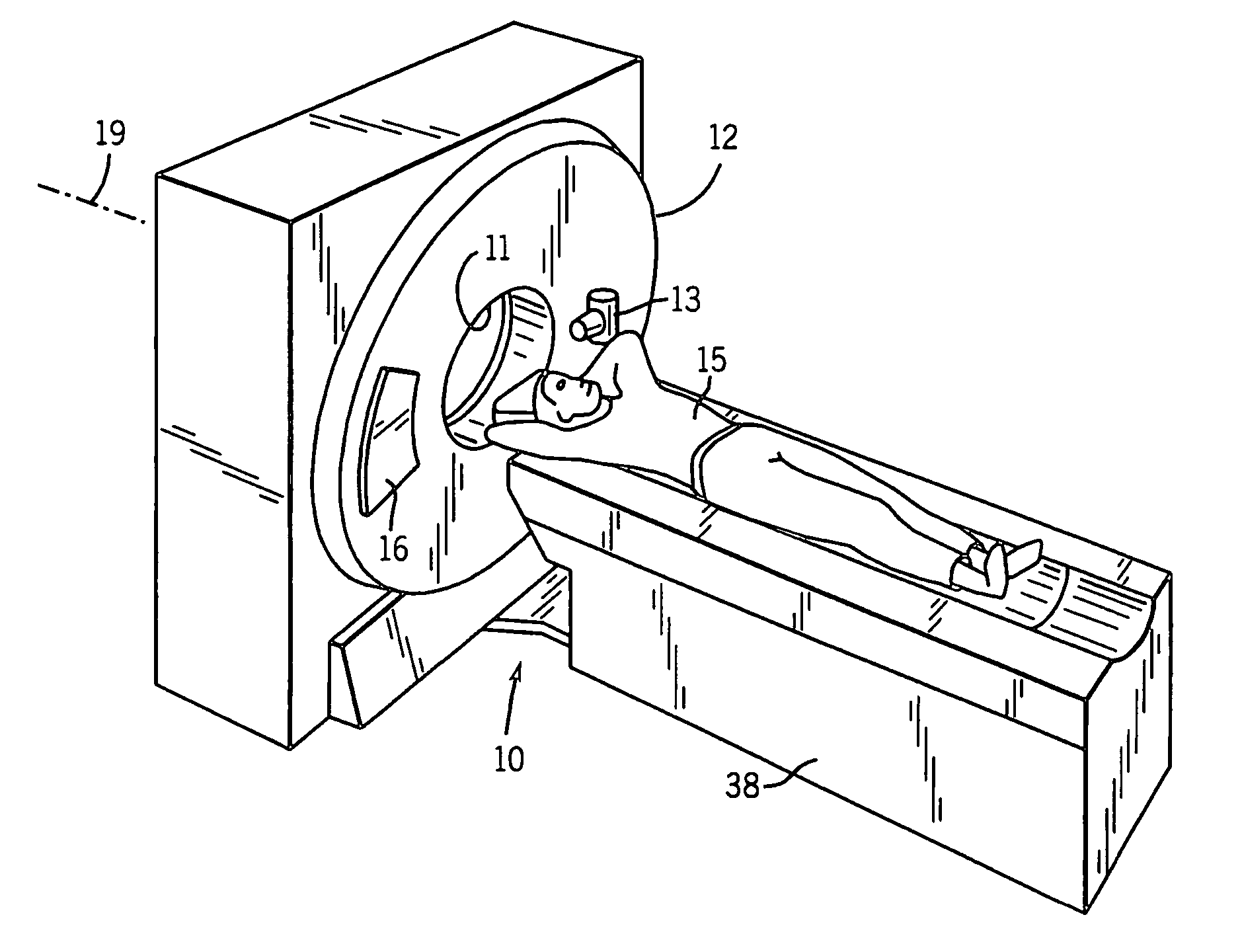
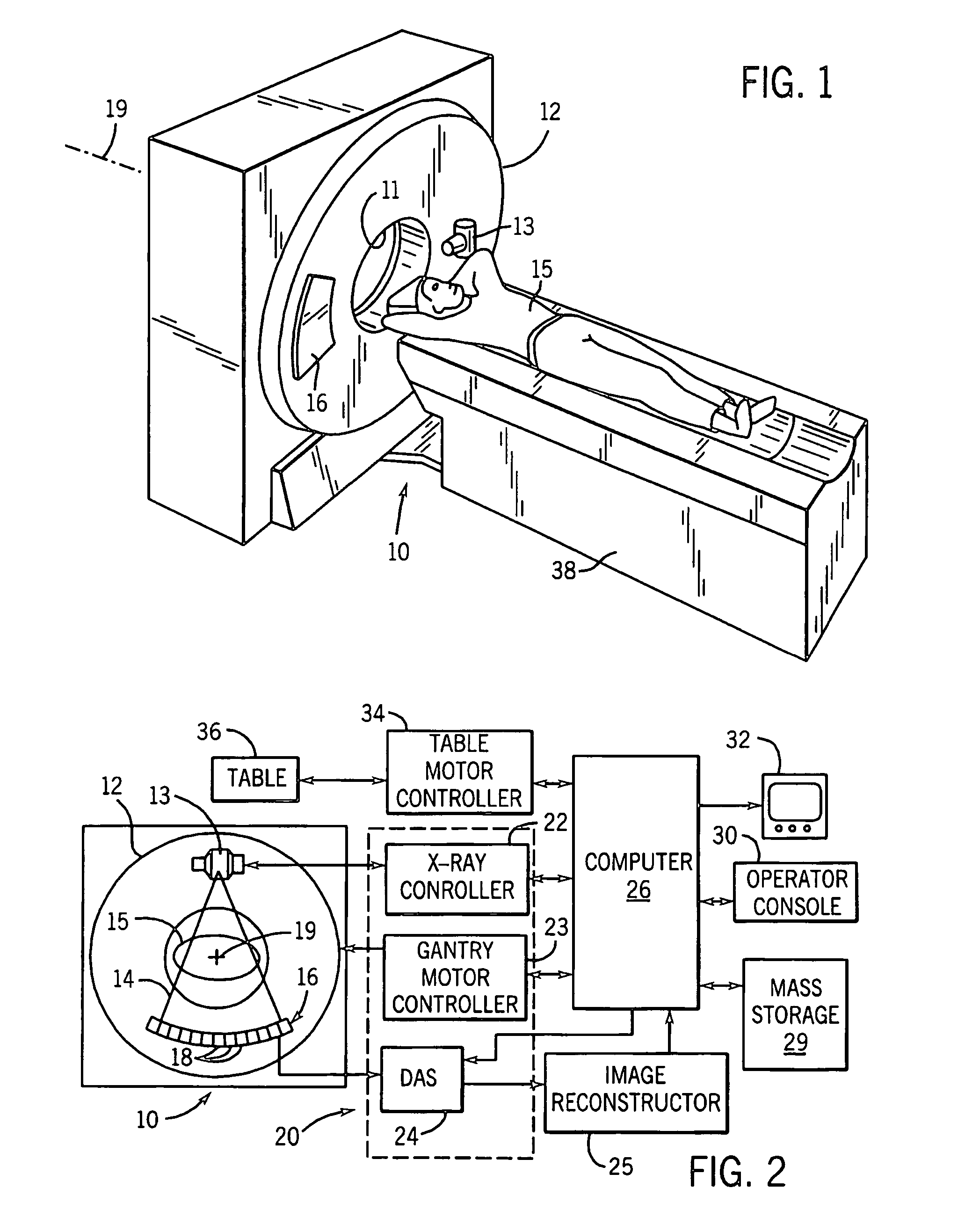
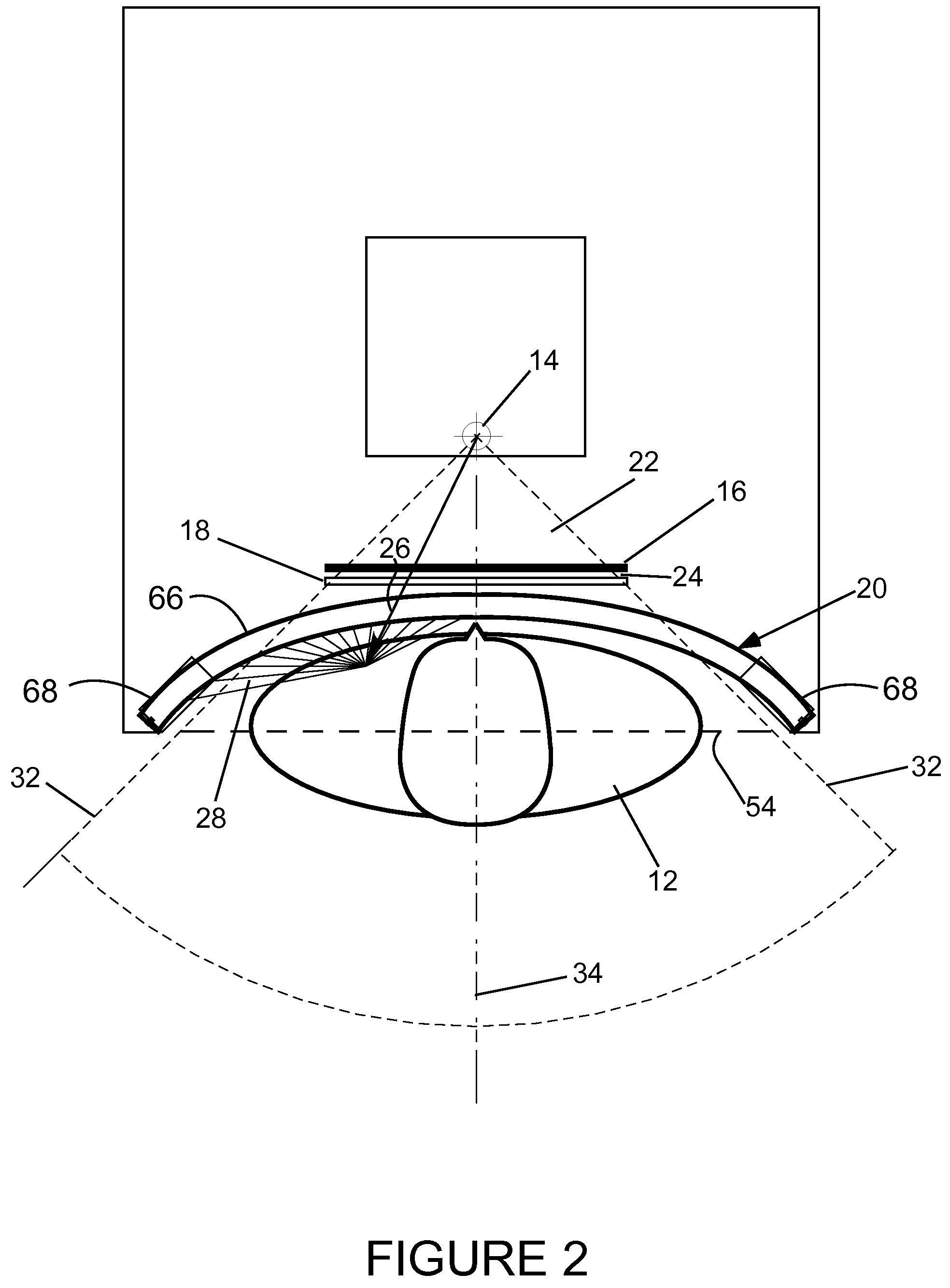
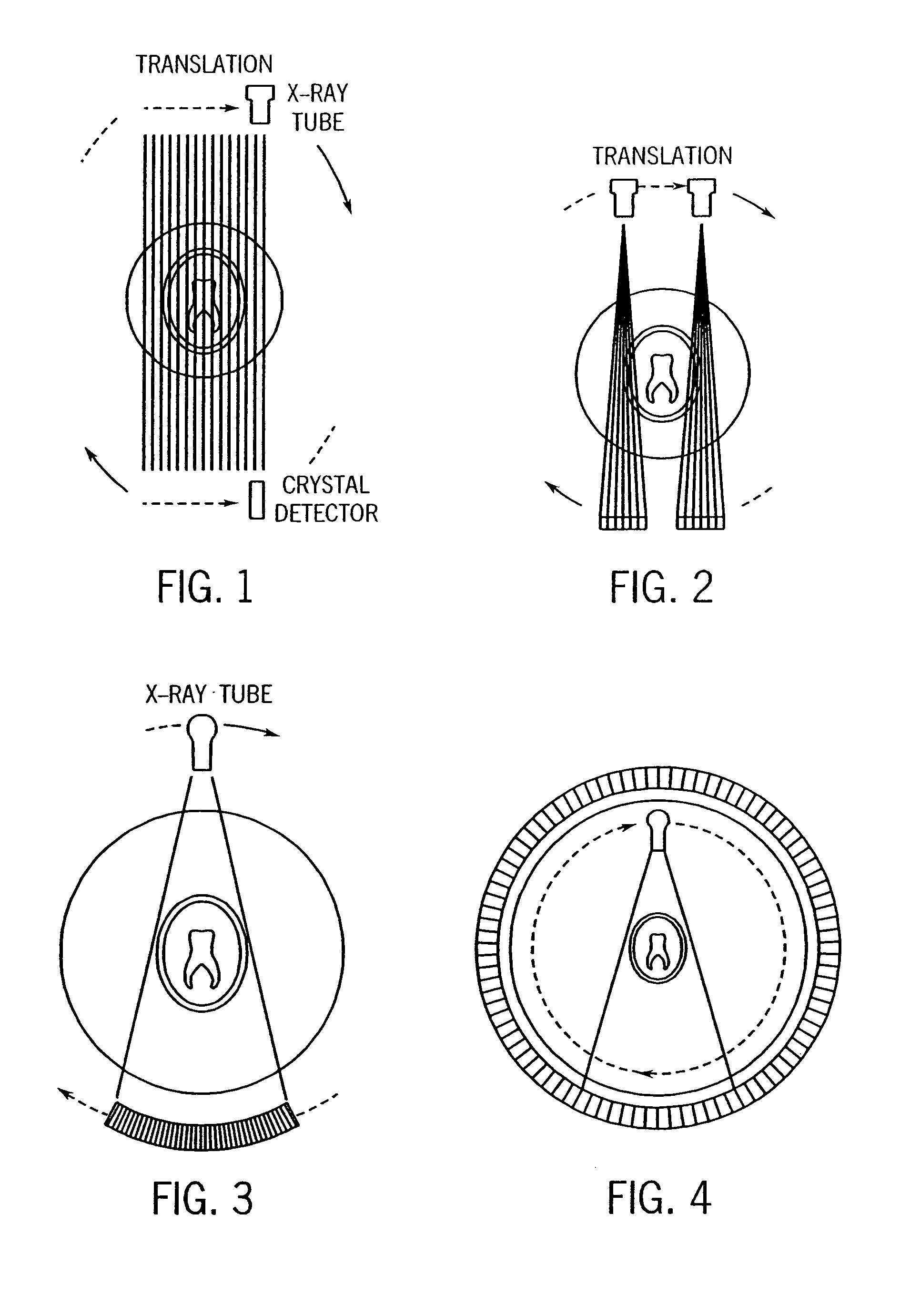
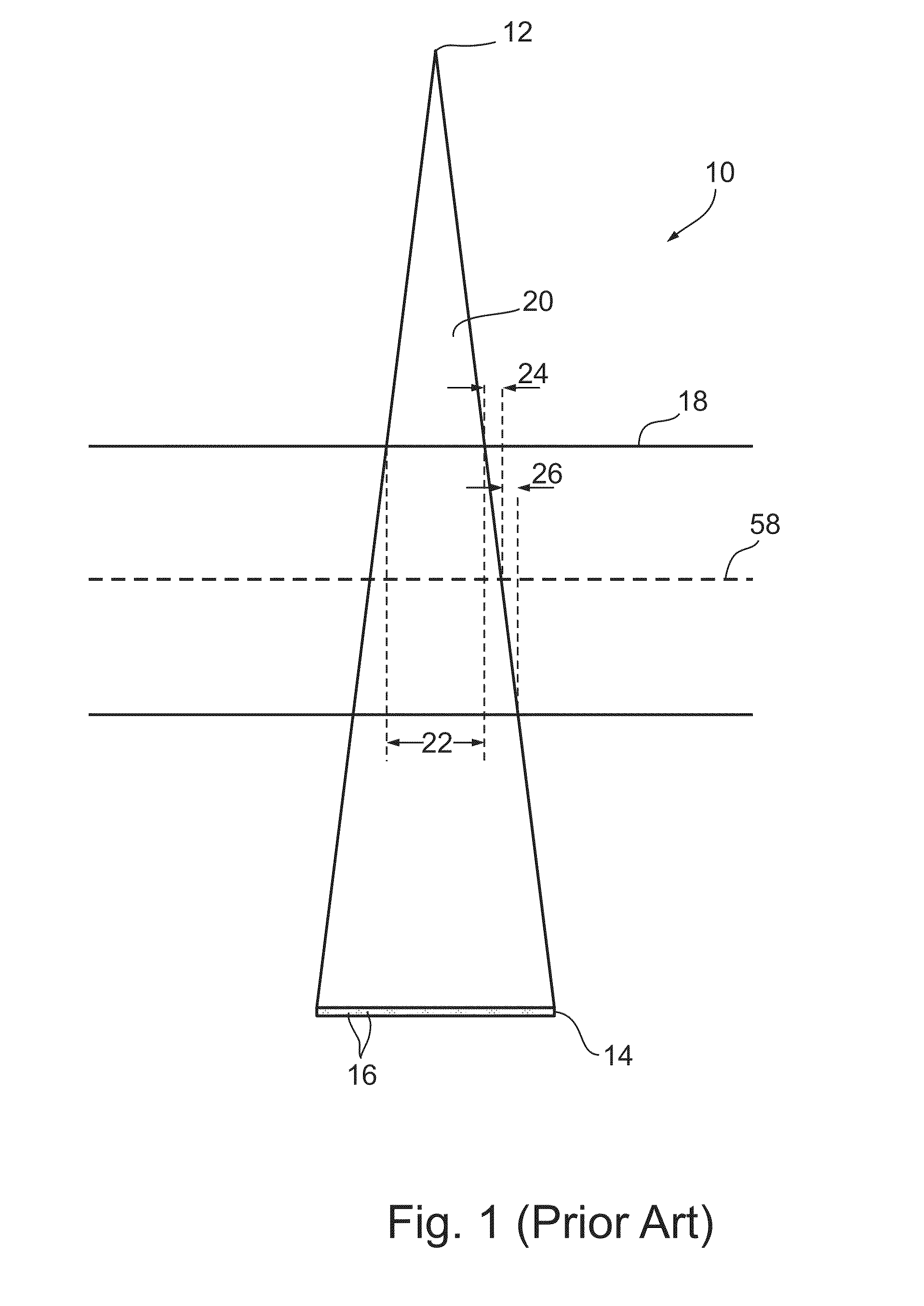
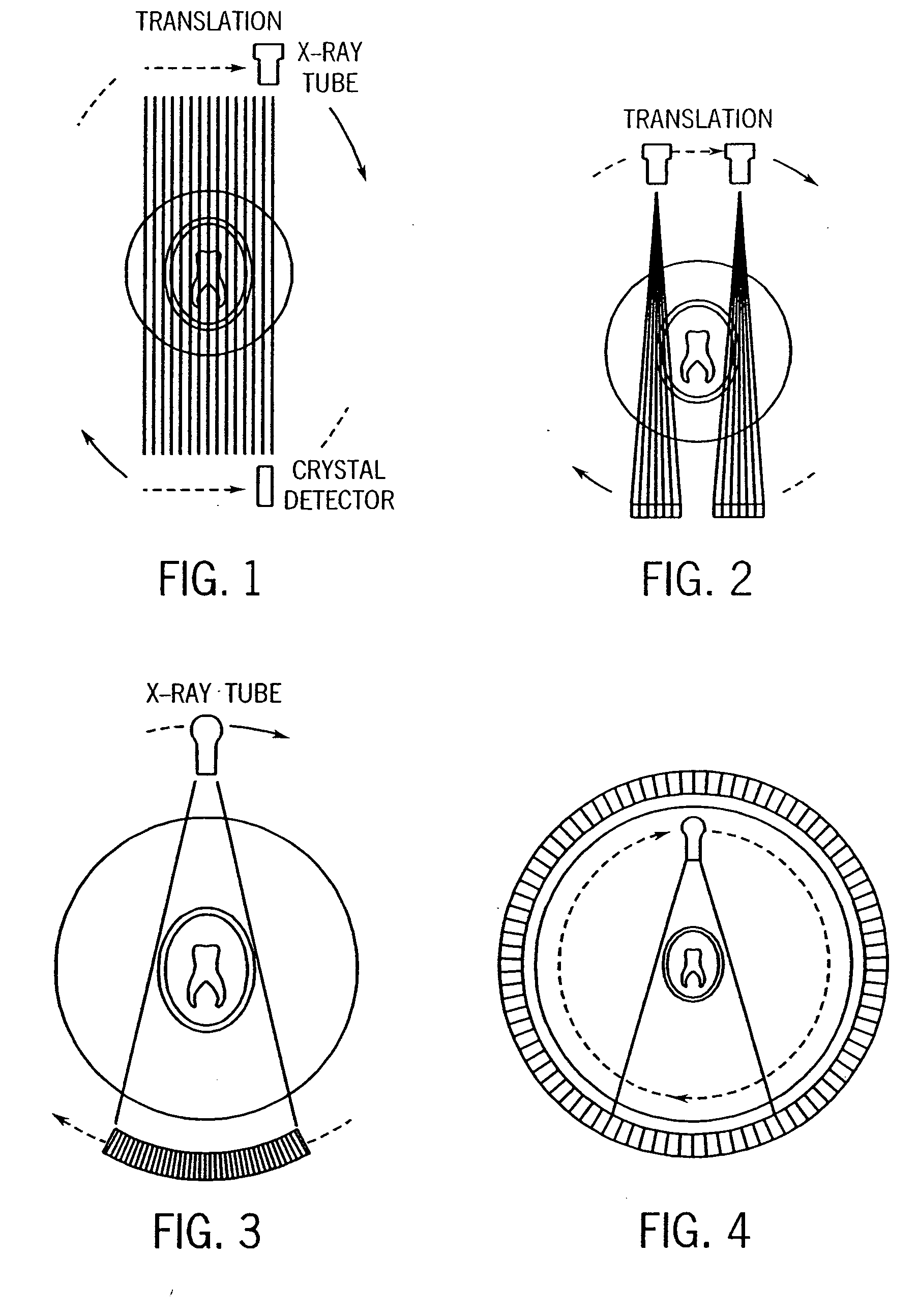
Conical Beam. Description: Also known as "pinpoint illumination", a small circular aperture of light is focused on a specific point on the cornea, or aimed through the pupil to reveal anterior chamber details. Uses for Conical Beam:
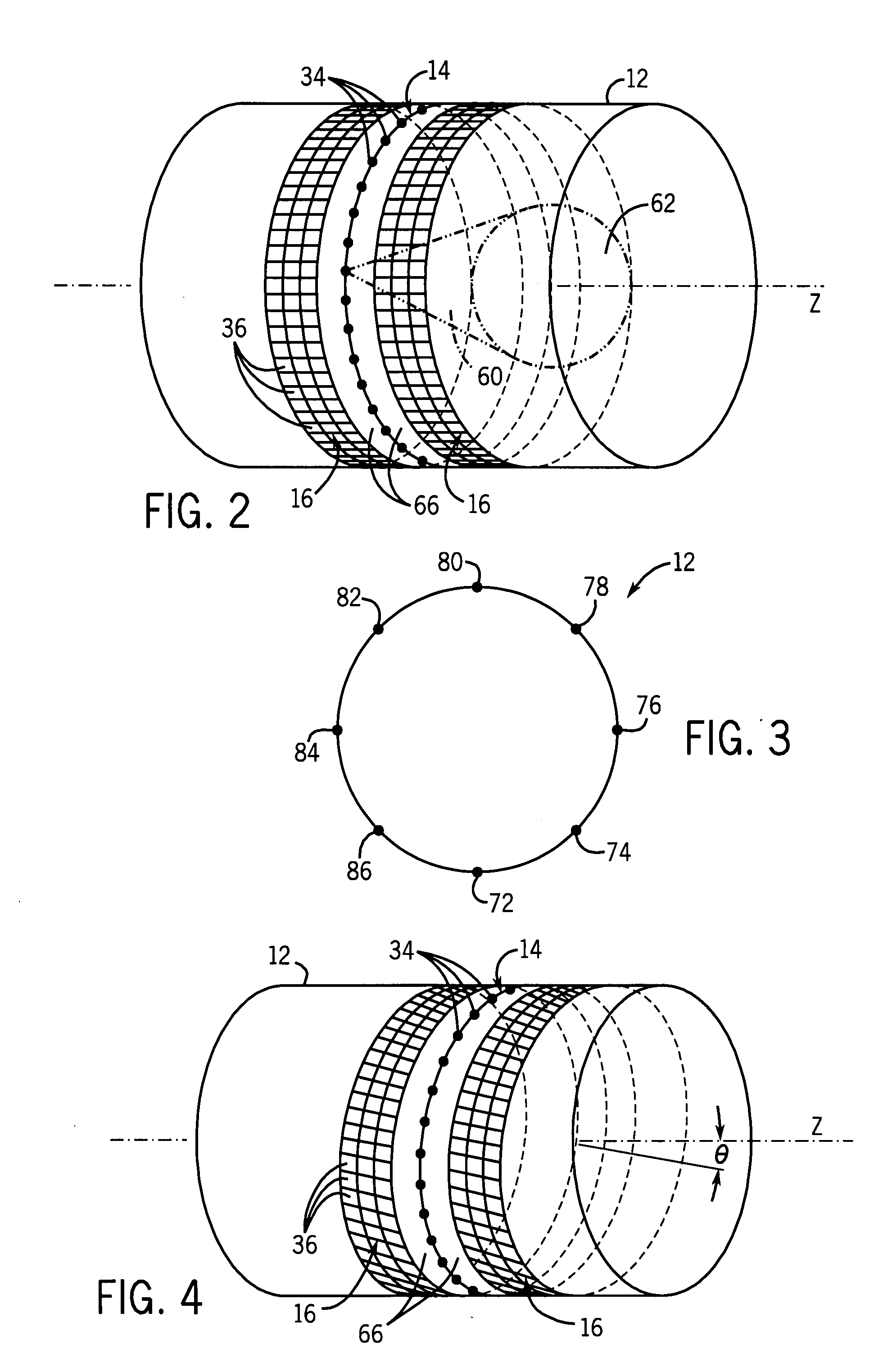
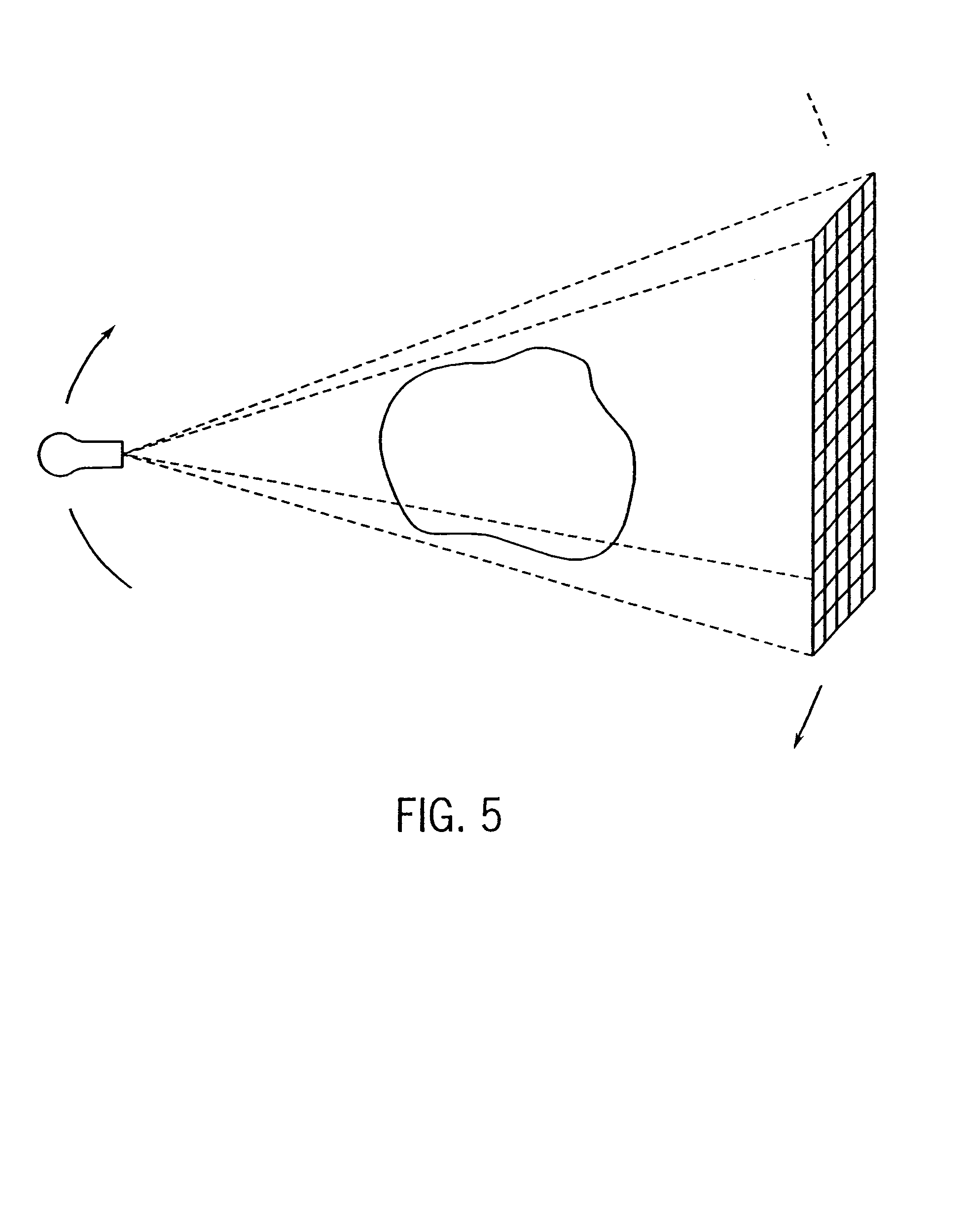
Cone-beam computerized tomography with a flat-panel imager
InactiveUS20030007601A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingAmorphous siliconX-ray
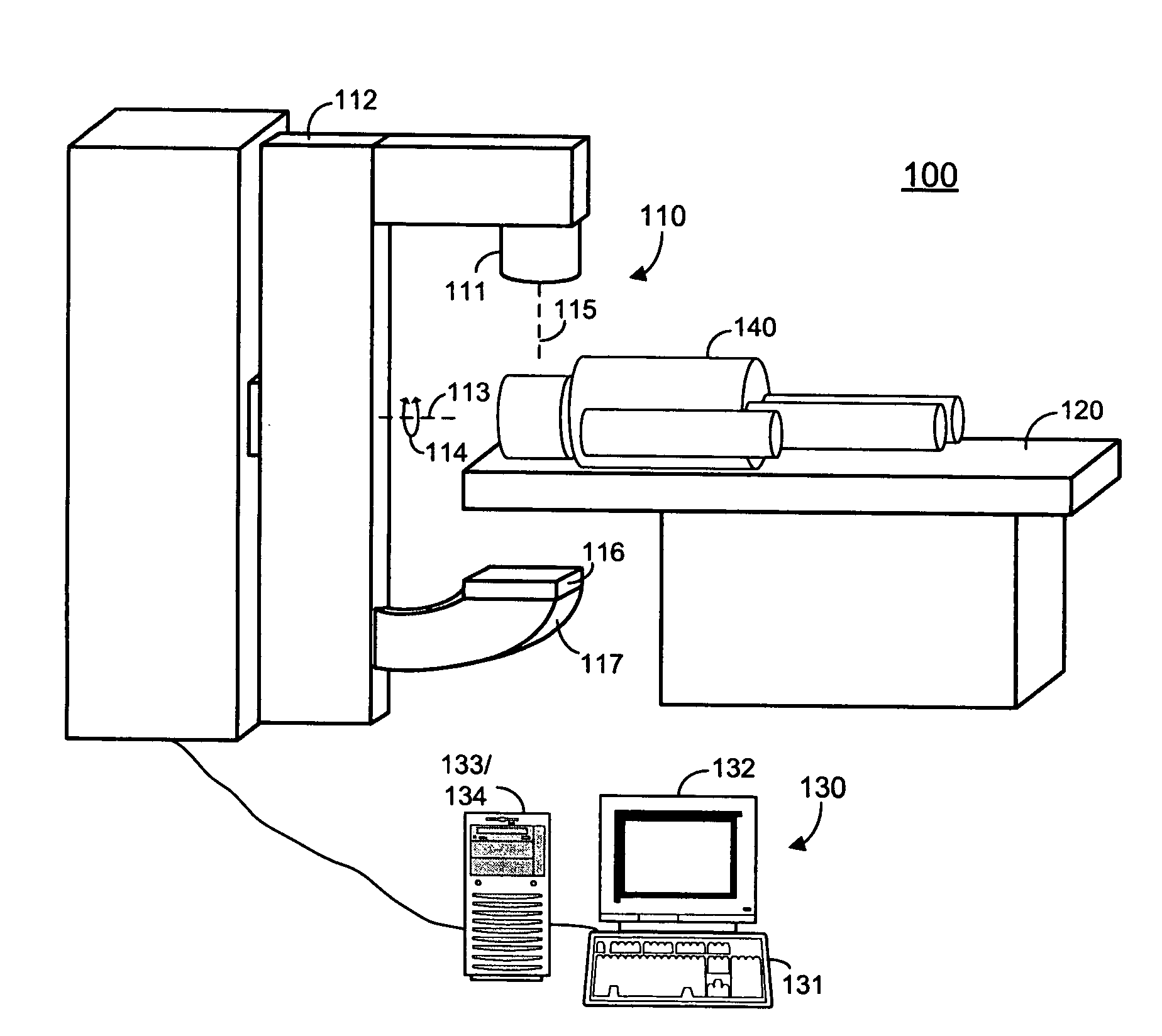
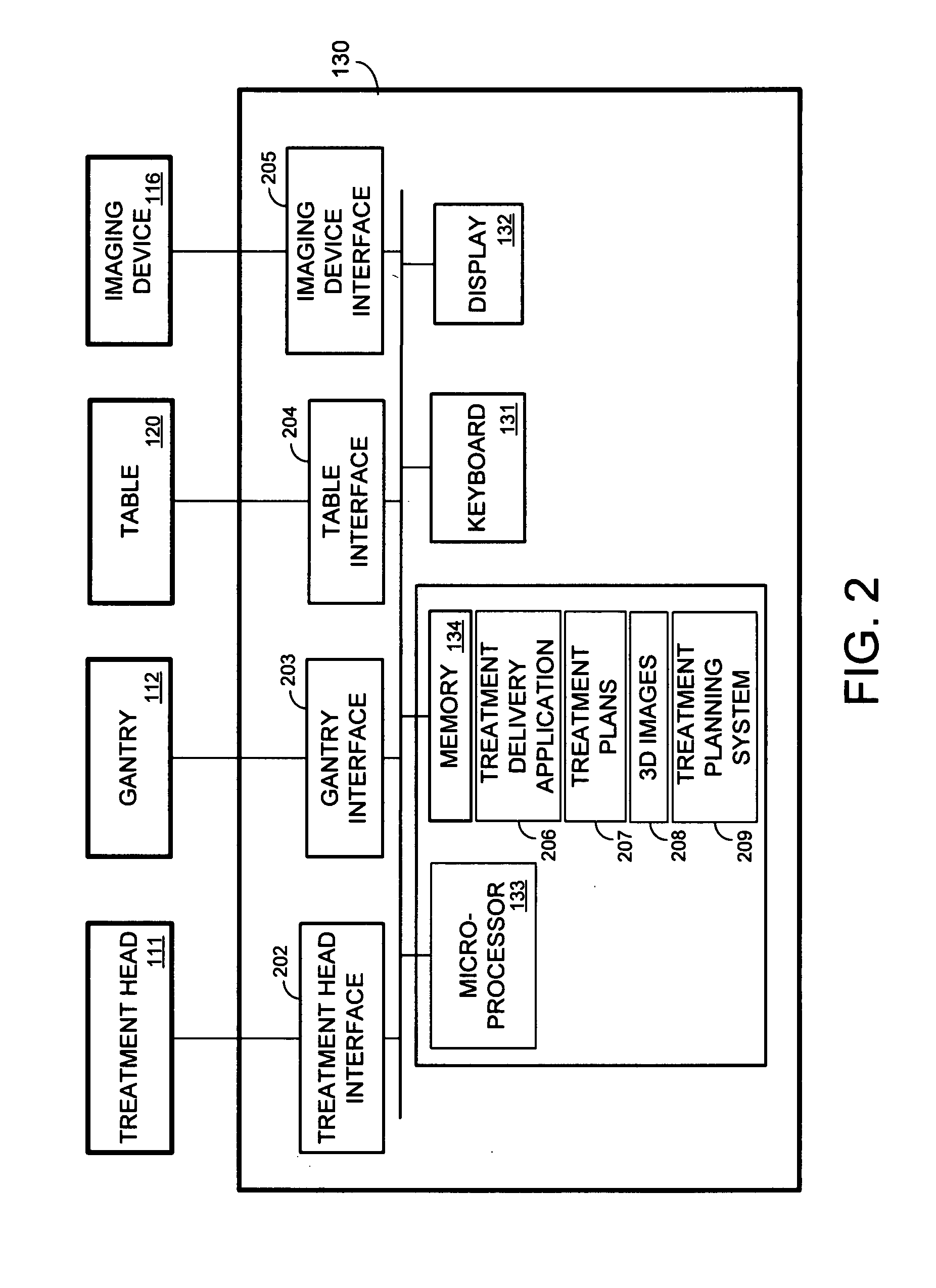
A radiation therapy system that includes a radiation source that moves about a path and directs a beam of radiation towards an object and a cone-beam computer tomography system. The cone-beam computer tomography system includes an x-ray source that emits an x-ray beam in a cone-beam form towards an object to be imaged and an amorphous silicon flat-panel imager receiving x-rays after they pass through the object, the imager providing an image of the object. A computer is connected to the radiation source and the cone beam computerized tomography system, wherein the computer receives the image of the object and based on the image sends a signal to the radiation source that controls the path of the radiation source.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
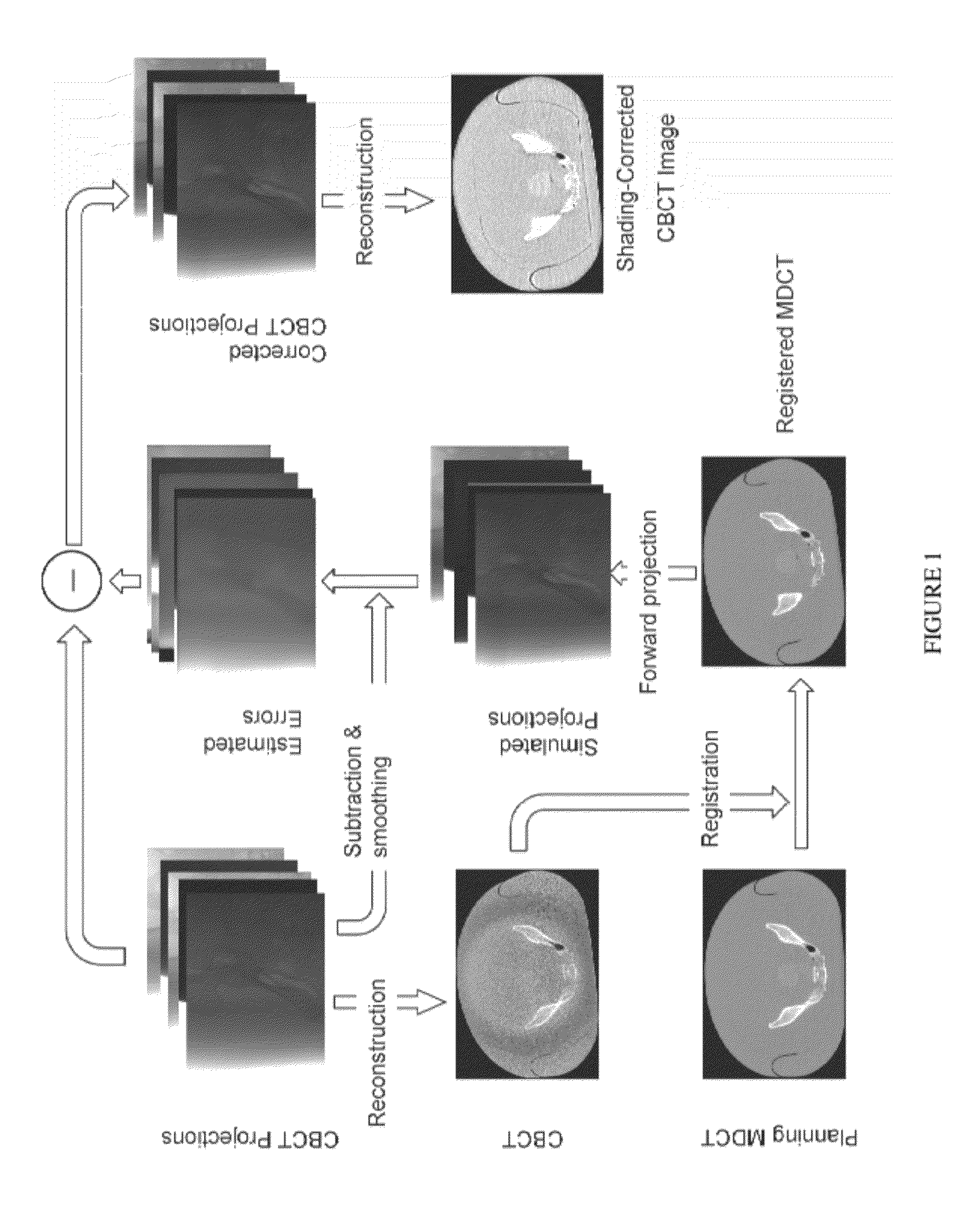
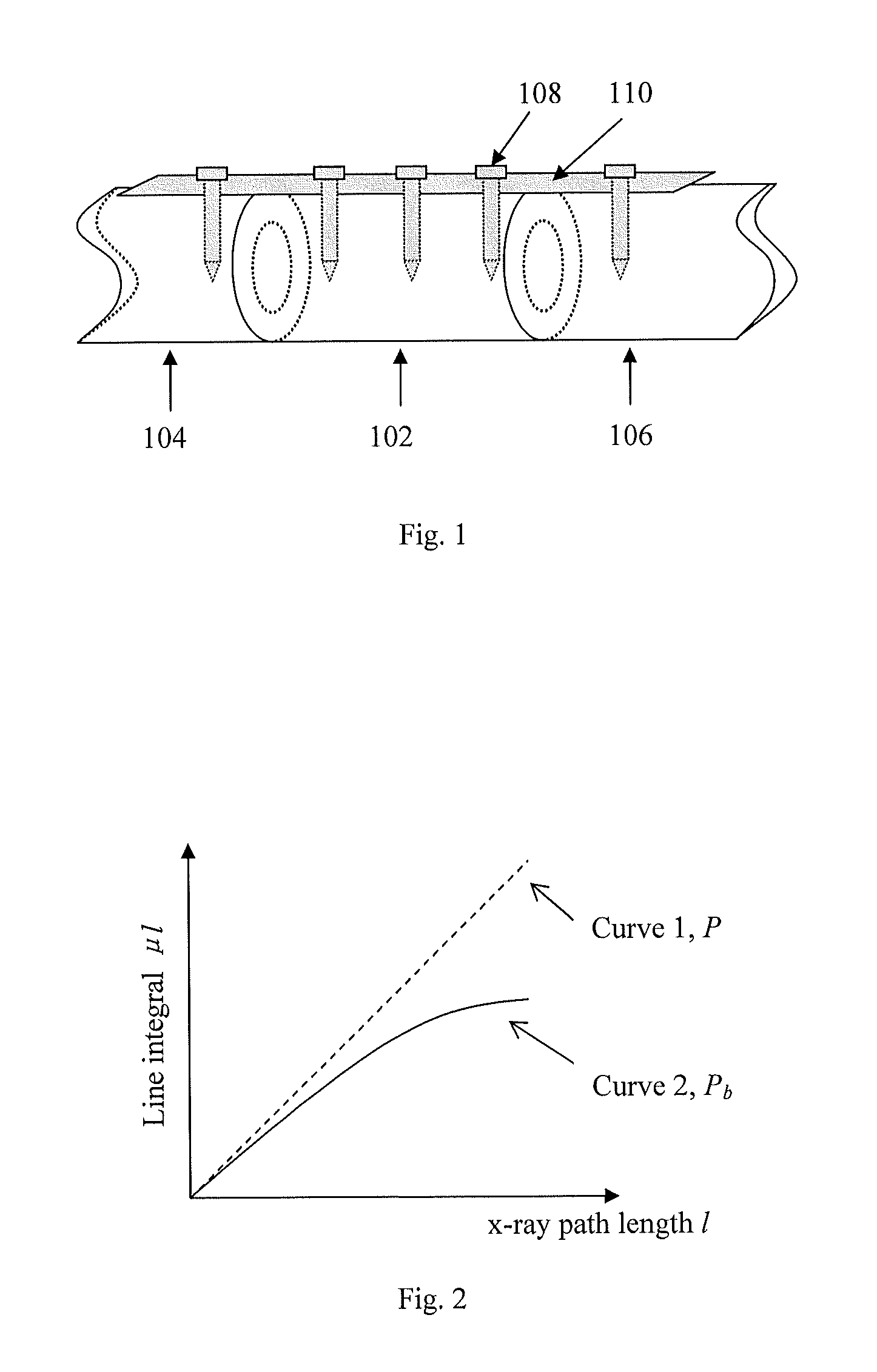
Scatter correction methods
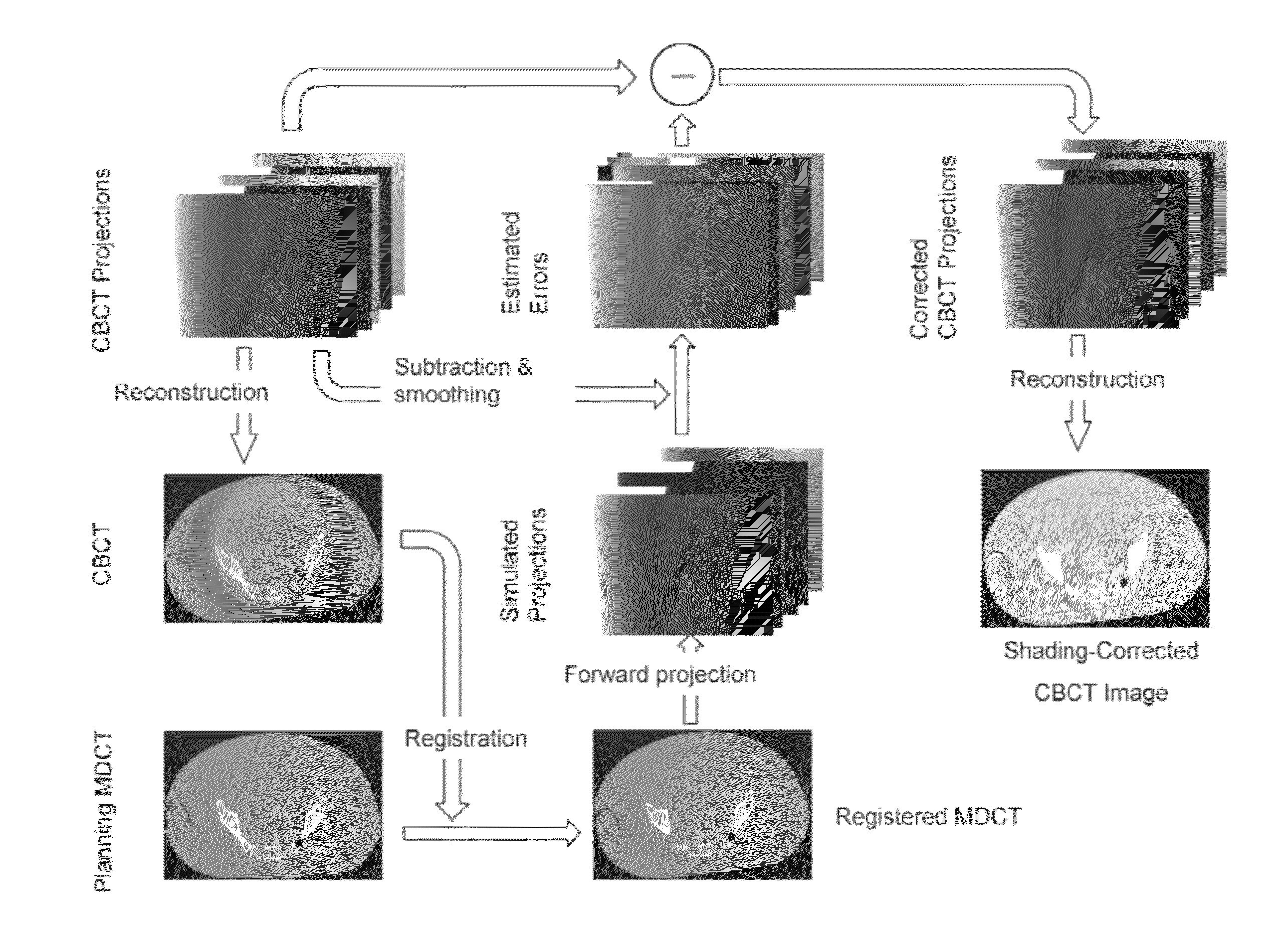
ActiveUS20120263360A1Reduce pollutionAccurate methodImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionProjection imageImproved method
Described herein are improved methods for correcting cone beam computed tomography signals to reduce scatter contamination contained therein. Generally, the improved methods involve generating a plurality of two-dimensional projection images of a subject from a three-dimensional multi-detector computed tomography image of the subject. This is followed by subtracting the plurality of two-dimensional projection images from a plurality of two-dimensional cone beam projection images of the subject to produce a plurality of two-dimensional estimated error projections that comprise an estimated error in the plurality of two-dimensional cone beam projection images. The plurality of two-dimensional estimated error projection images are subtracted from the plurality of two-dimensional cone beam projection images to generate a plurality of two-dimensional corrected cone beam projection images. A three-dimensional corrected cone beam computed tomography image of the subject is then constructed from the plurality of two-dimensional corrected cone beam projection images.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Single session interactive ultra-short duration super-high biological dose rate radiation therapy and radiosurgery
A medical accelerator system consisting of coplanar and non-coplanar beams, on line magnetic resonance anatomic and functional imaging and cone beam computed tomographic imaging for single session image guided all field simultaneous radiation therapy and radiosurgery is provided. This system enables single session simulation, field-shaping block making, treatment planning, dose calculations and treatment of tumors. The radiation exposure time to the tumor and the normal tissue is reduced to a few seconds to less than a minute. In filed intensity modulated radiation is rendered by combined divergent and pencil beam, multiple smaller fields within a larger field, selectively varying beam's energy, dose rate and beam weight. Since all the treatment fields are treated simultaneously the dose rate at the tumor site is the sum of each of the converging beam's dose rate at depth. This super-high biological dose rate impairs the lethal and sublethal damage repair.
Owner:SAHADEVAN VELAYUDHAN
Reconstruction of CT projection data
InactiveUS20080056432A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationData setComputing tomography
Systems and methods are provided for reconstructing projection data that is mathematically complete or sufficient acquired using a computed tomography (CT) system. In one embodiment, a set of projection data representative of a sampled portion of a cylindrical surface is provided. The set of projection data is reconstructed using a suitable cone-beam reconstruction algorithm. In another embodiment, two or more sets of spatially interleaved helical projection data are processed using helical interpolation. The helically interpolated set of projection data is reconstructed using a two-dimensional axial reconstruction algorithm or a three-dimensional reconstruction algorithm.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
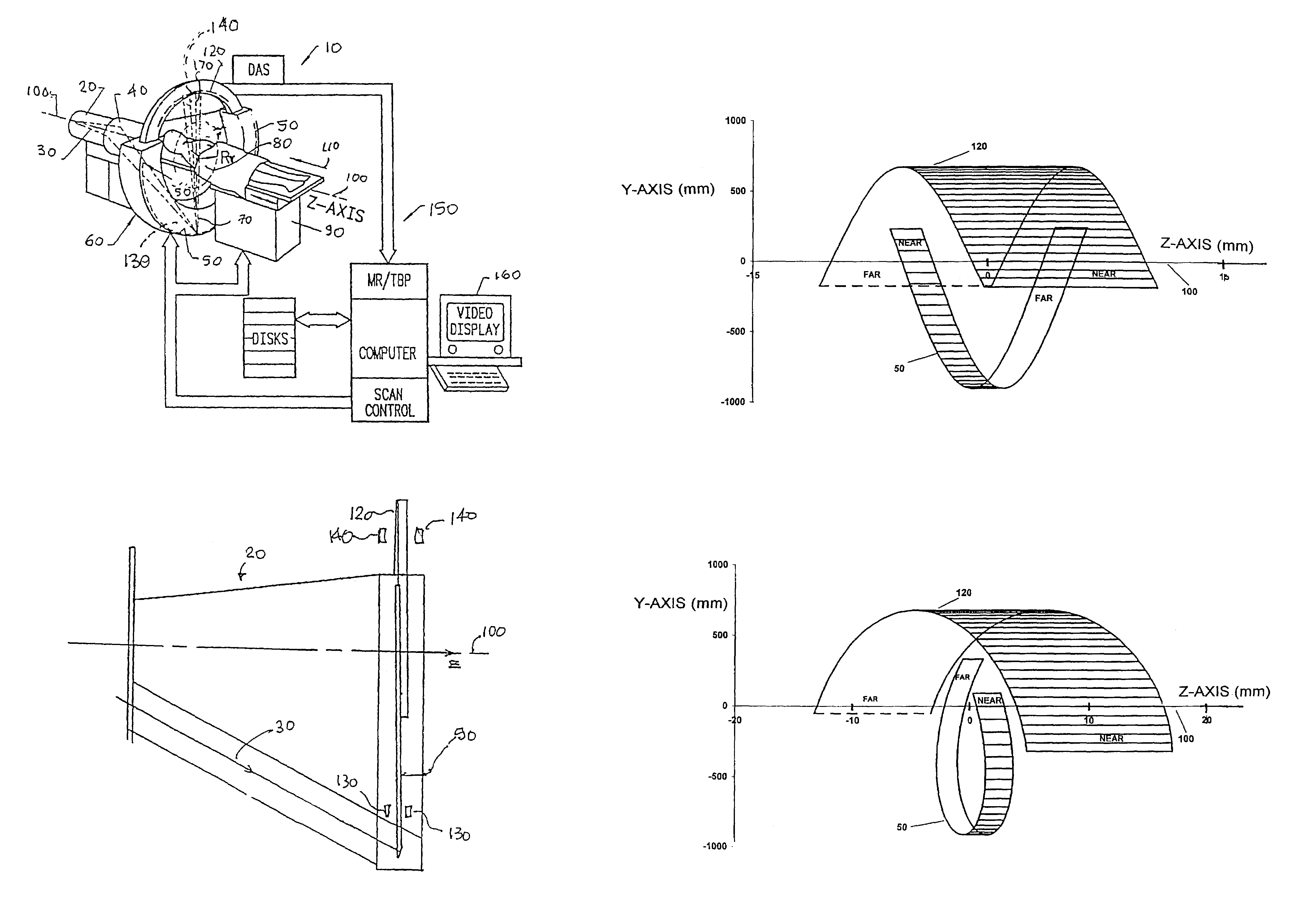
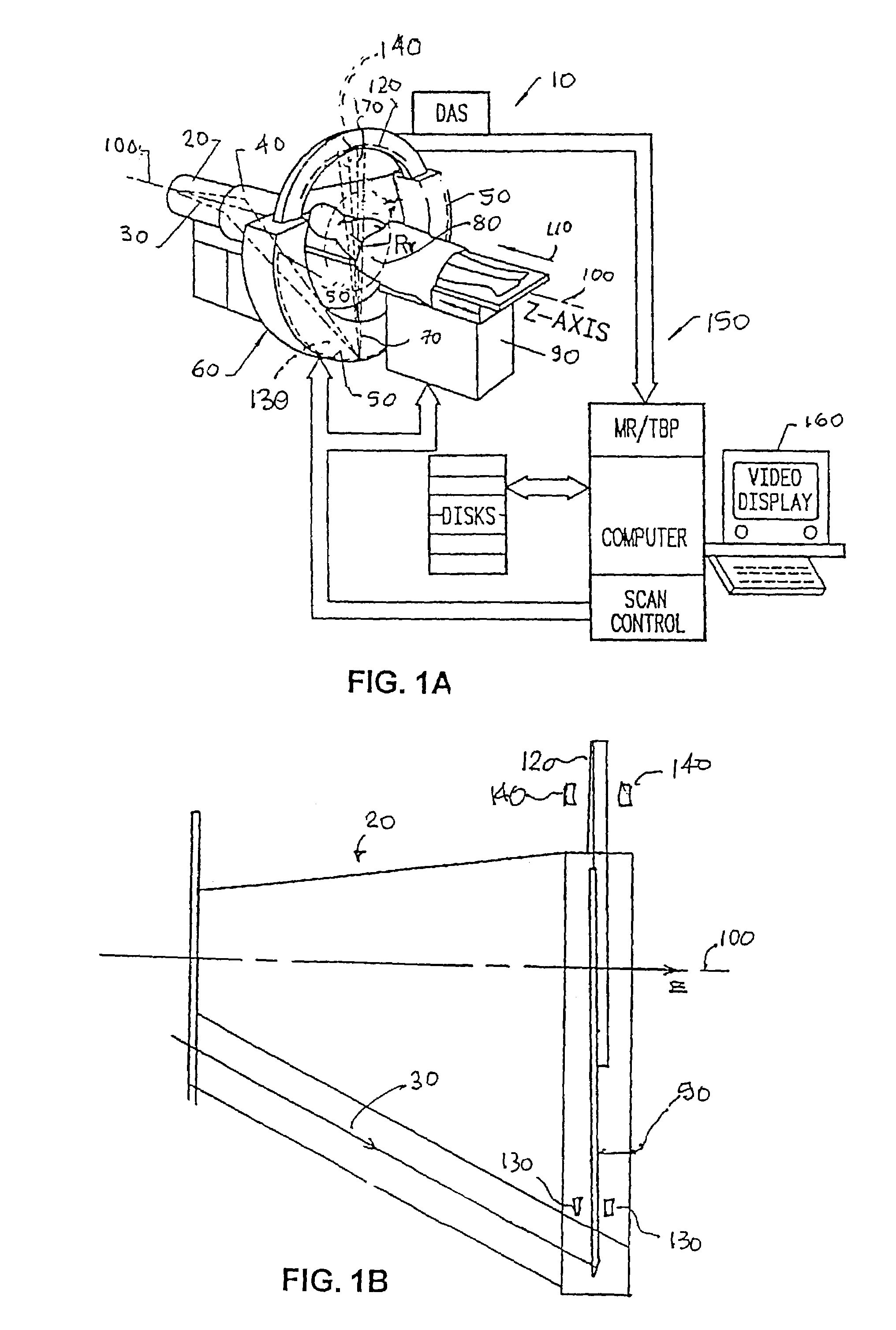
Computed tomography with z-axis scanning
InactiveUS20050100126A1Reduce relative motionShort time intervalMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTwo dimensional detectorX-ray
A CT imaging system includes a two-dimensional detector array and an x-ray source that both revolve around the subject during a scan. The x-ray source produces a cone beam of x-rays and the focal point of this cone beam is electrically moved to different locations along the z-axis to increase the z-axis extent of the ROI that can be imaged without patient table movement. Different focal point scan patterns are described for a variety of different clinical applications.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC +1
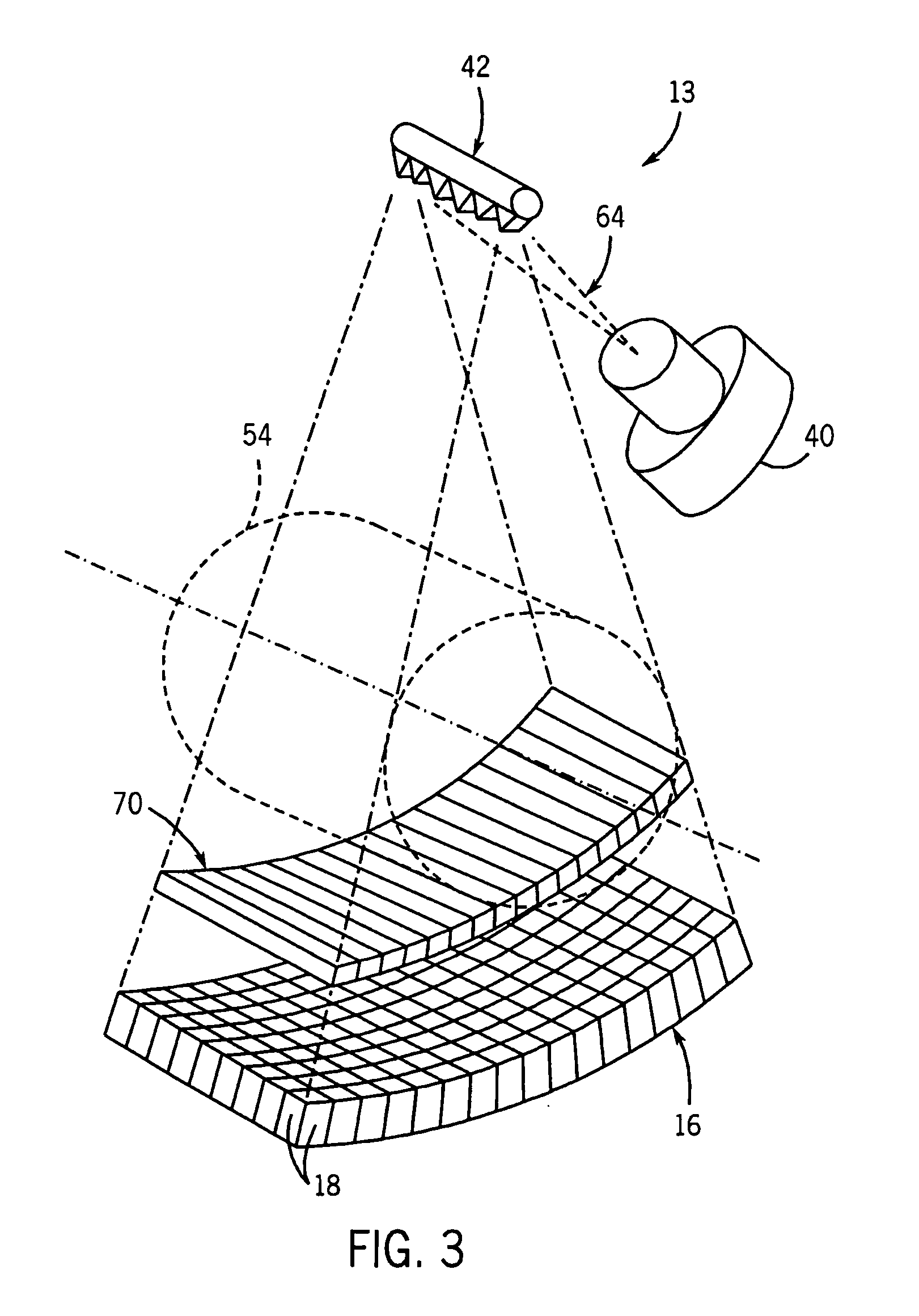
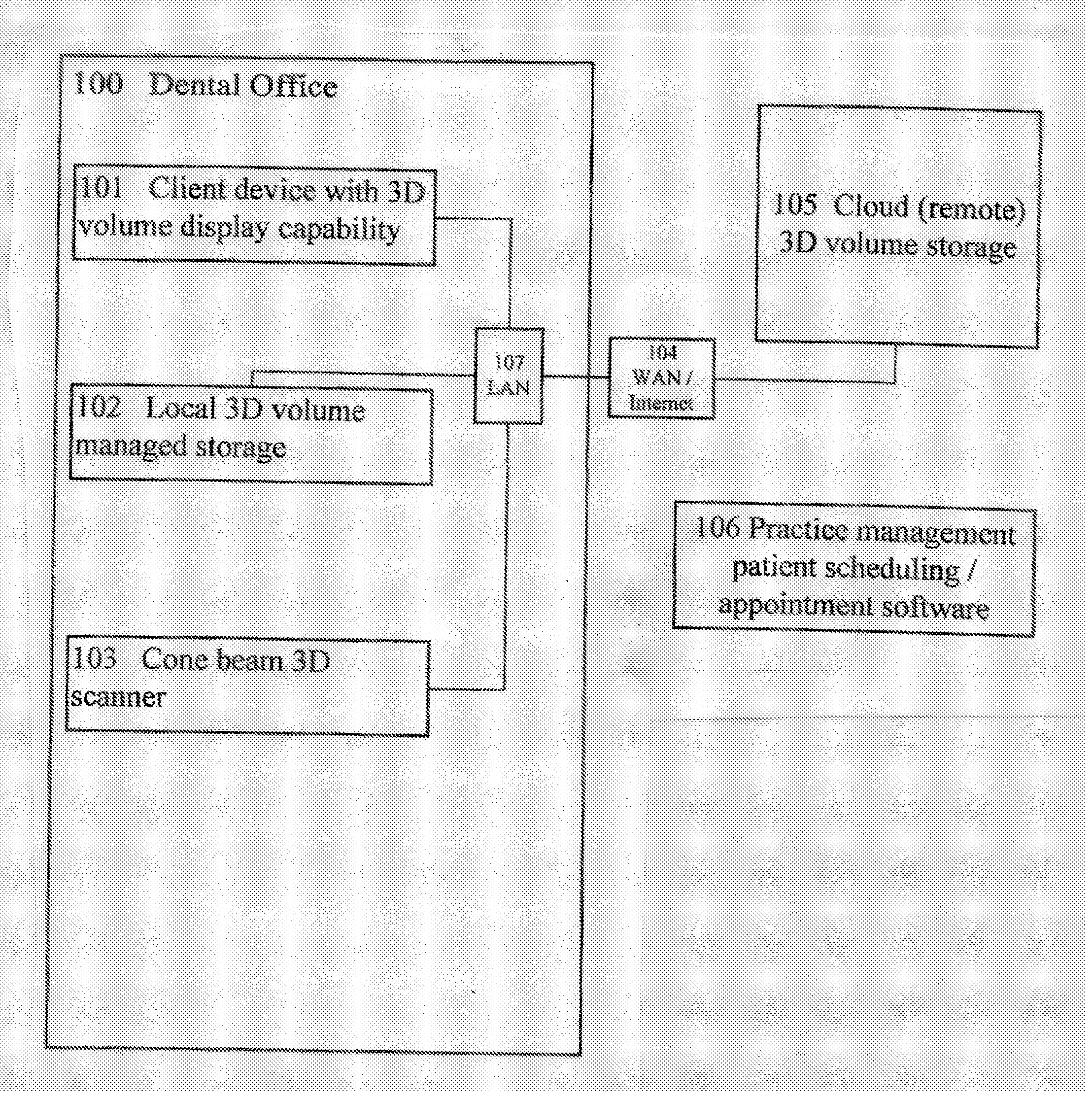
3D cone beam dental imaging system
A 3D dental imaging system which is used for producing and transferring 3D volumes of a patient from a remote cloud storage device and which includes a 3D volume imaging software for displaying cone beam images. The software retrieves volumes from storage located in the dental office. The 3D volumes are acquired via a cone beam scanner. There is storage located in the dentist office for storage of 3D volumes that were acquired via a cone beam scanner. There is also storage located remotely of the dentist office for storage of 3D volumes that were acquired via a cone beam scanner located in the dentist office. The 3D volumes are transferred between the local storage and the remote storage. The patient appointment information is retrieved for patient's future appointments from a patient scheduling software. The 3D volumes automatically are downloaded from remote storage to local storage based upon patient's future appointment information.
Owner:GOLAY DOUGLAS A
Dose-guided radiation therapy using cone beam CT
ActiveUS20090003512A1Easy to adaptMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingRadiation therapyScattering radiation
A system includes acquisition of a three-dimensional cone beam image, and determination of a dose to be delivered based on the three-dimensional image and on parameters of a treatment beam to deliver the dose. Some systems may include modification of a three-dimensional cone beam image to correct for scatter radiation, and determination of a dose based on the modified three-dimensional cone beam image.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +2
Personnel x-ray inspection system
ActiveUS7561666B2Less powerDistanceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentSoft x rayLight beam
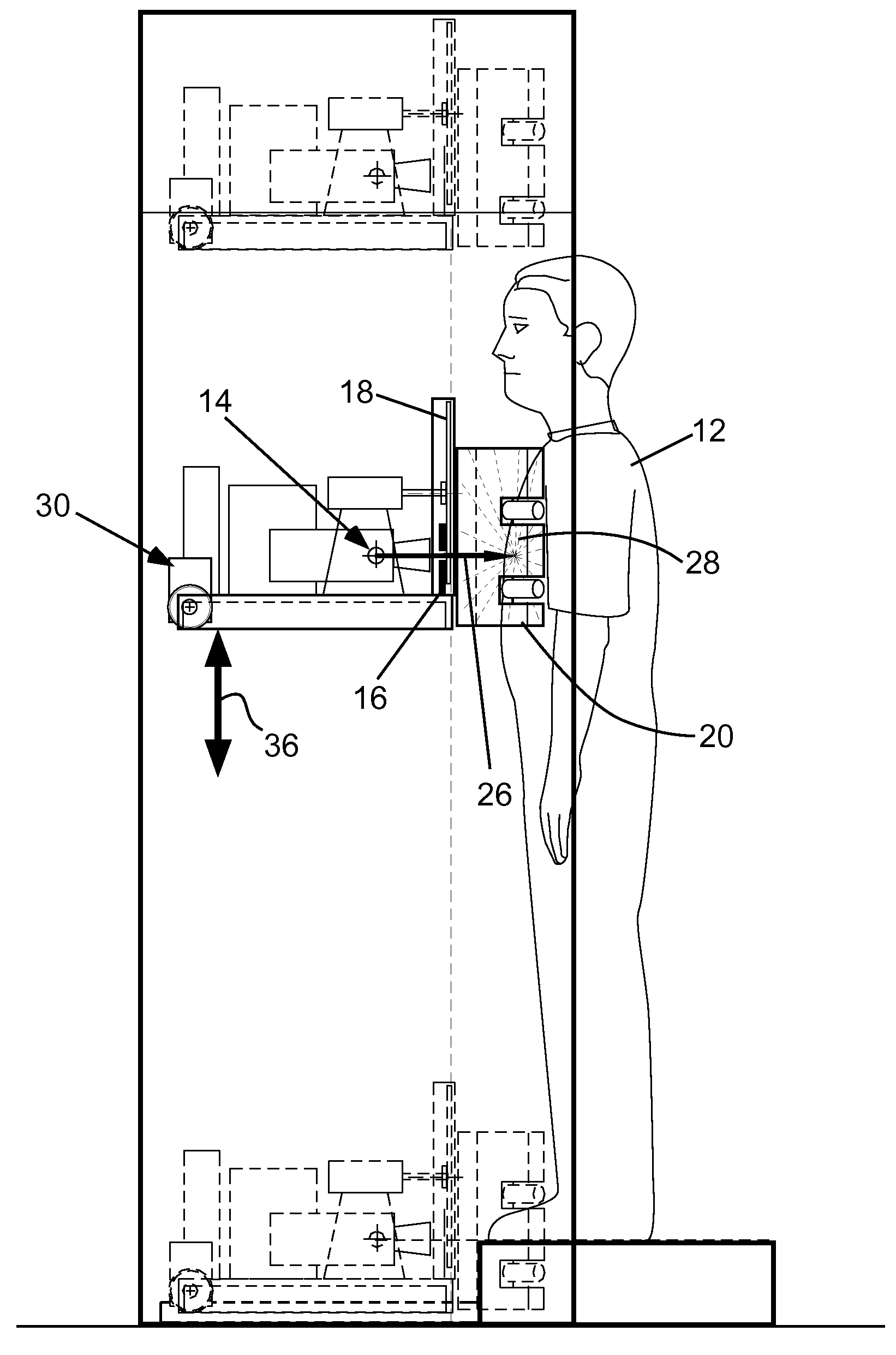
A dual-energy x-ray source located a distance of one half of the maximum width of the subject from the subject emits a cone beam to a horizontal slit in an x-ray-blocking sheet, producing a fan beam that is chopped into a pencil beam by a rotating disk with radial slots. The pencil beam sweeps a subject, producing backscatter read by a plastic scintillator detector situated very close to and curved around the sides of the subject. The entire assembly translates vertically to produce a complete image of the subject. Pencil beam area is increased farther from the center by increasing the width of the slit toward both ends and increasing the width of the slots toward the outer end. High and low peak x-ray energies of 50 KeV or more and 30 KeV or less, respectively, enable differentiation between innocent and contraband materials that both contain low Z materials.
Owner:REVEAL IMAGING TECH
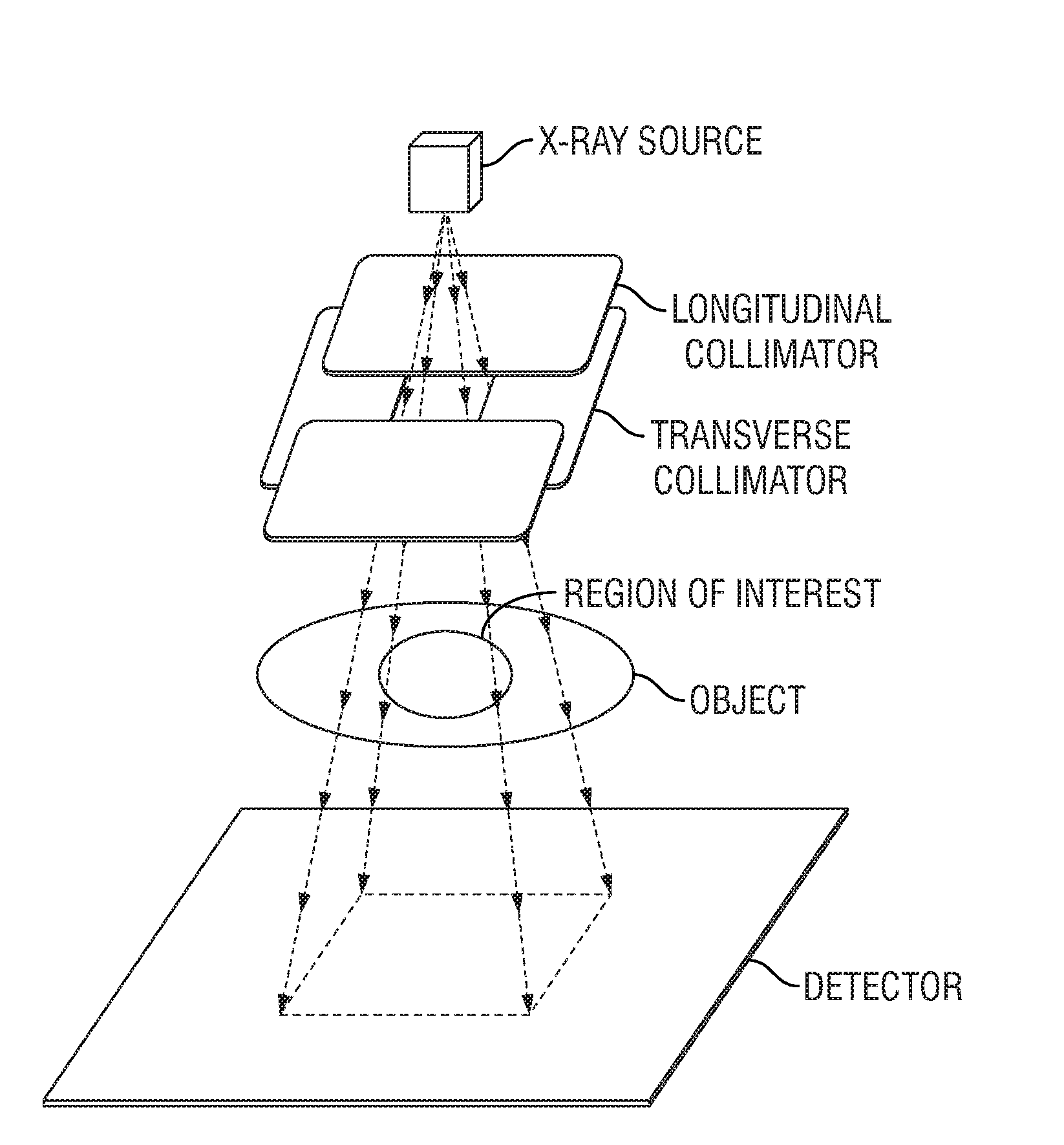
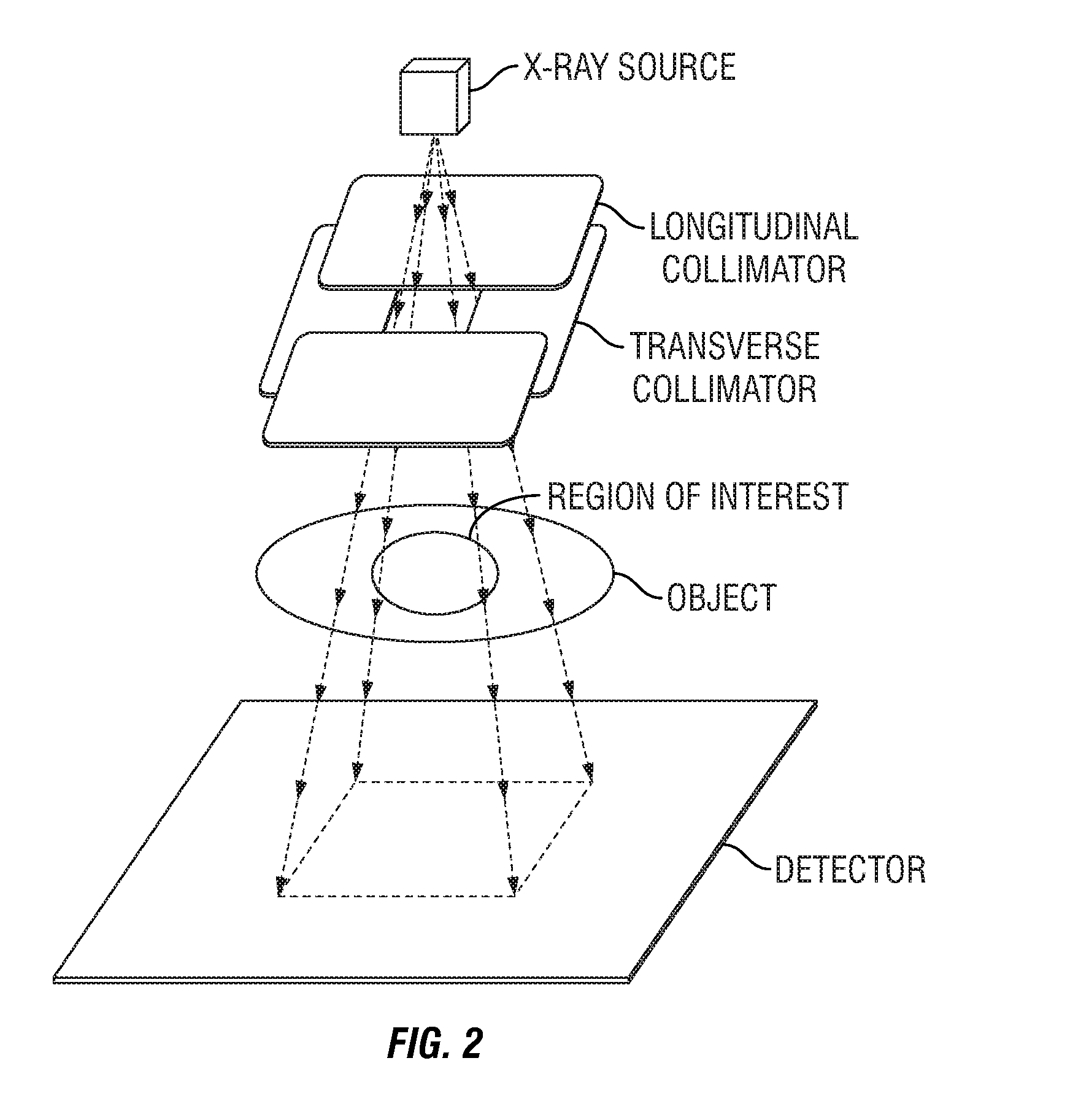
Intensity-modulated, cone-beam computed tomographic imaging system, methods, and apparatus
InactiveUS20100119033A1Reduce radiation exposureNarrowed windowMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersImaging processing3d image
Owner:THE METHODIST HOSPITAL RES INST
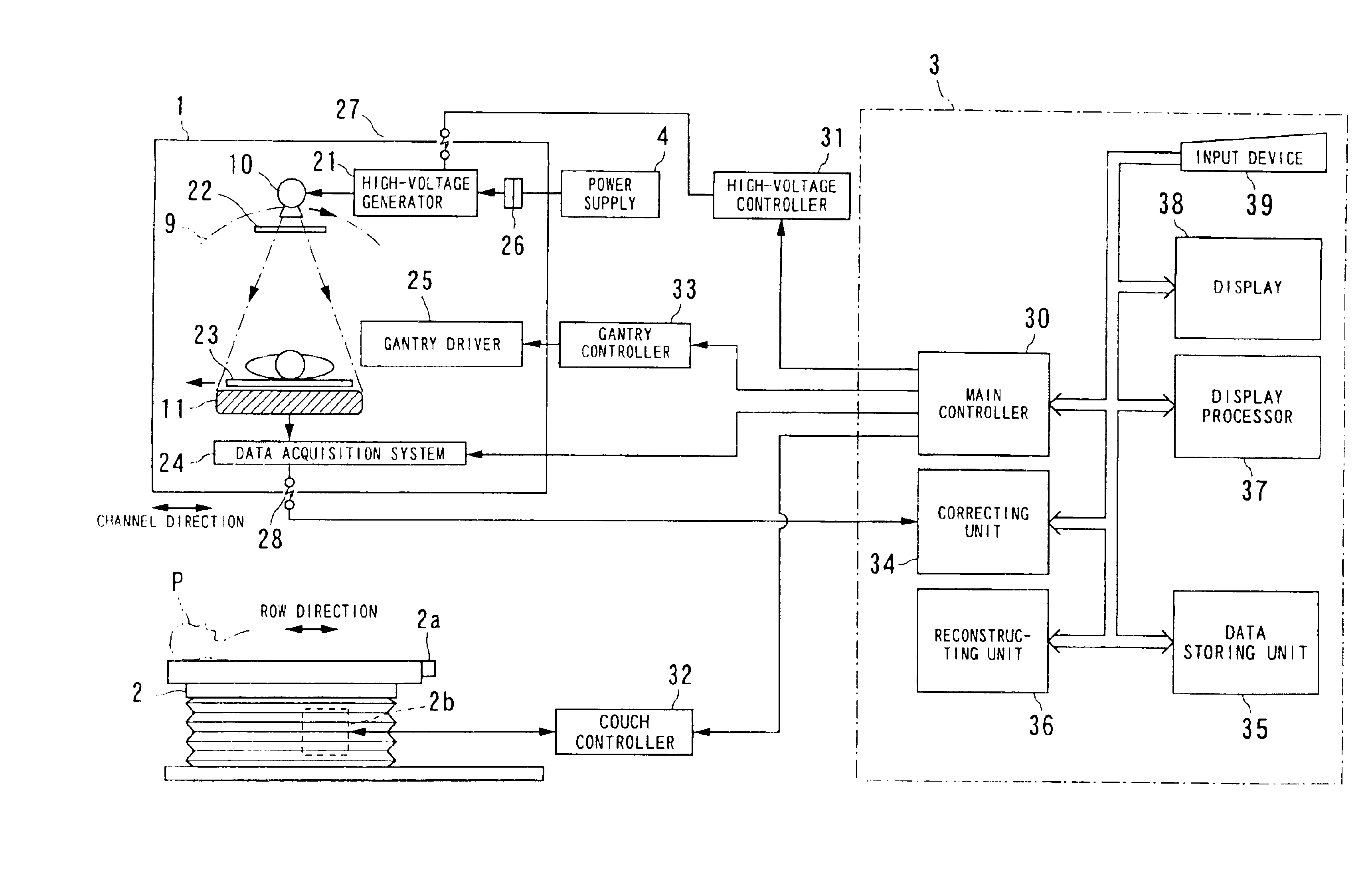
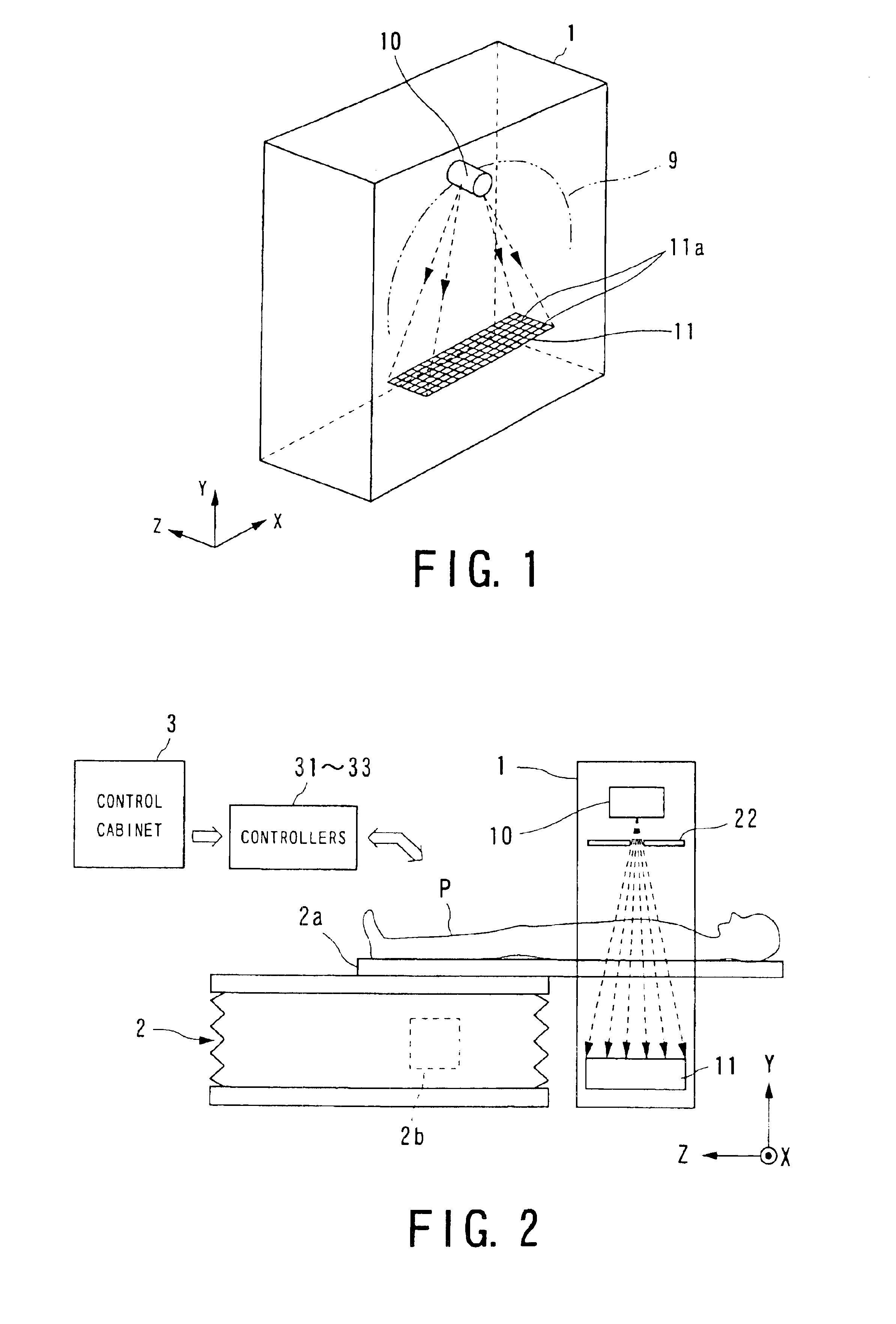
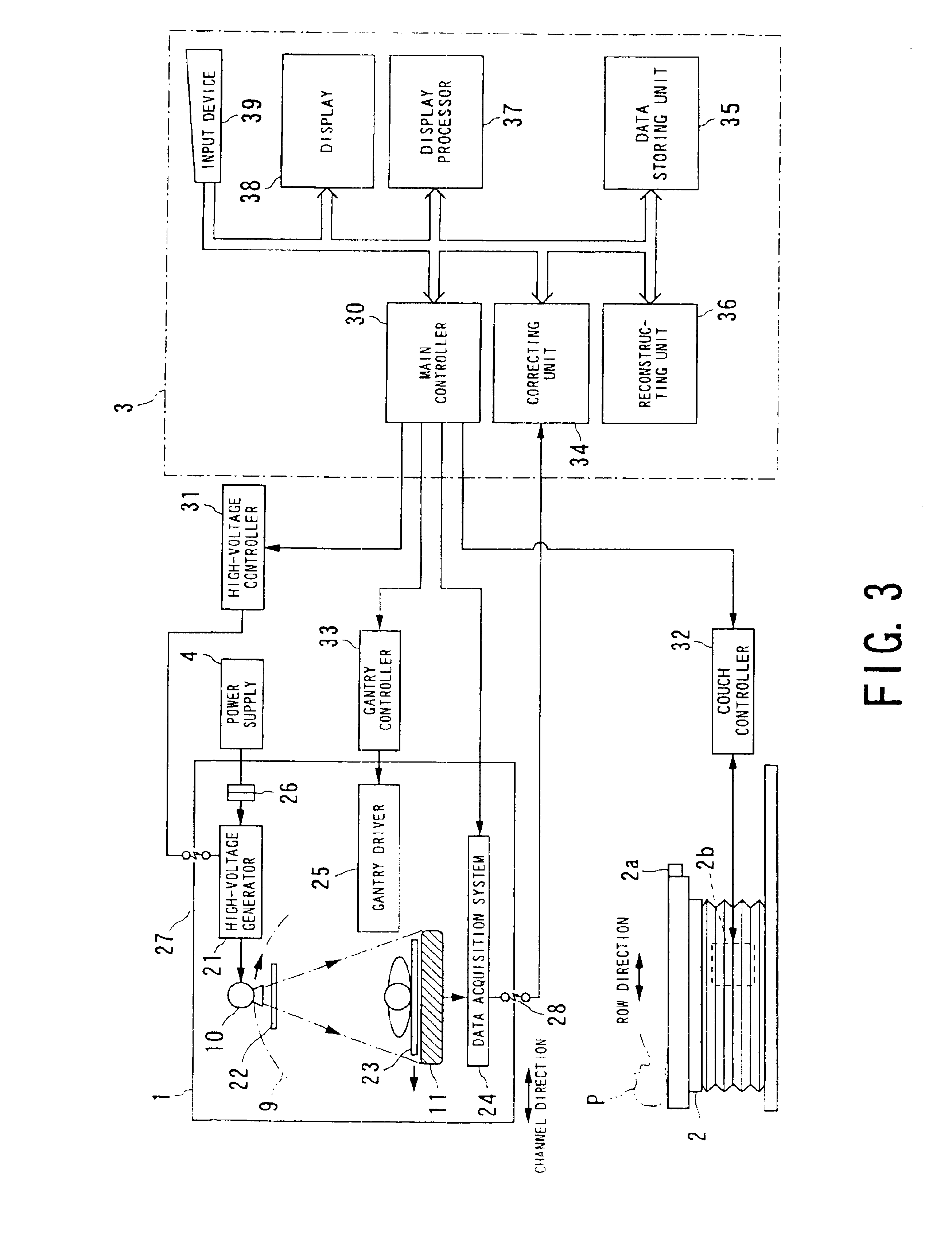
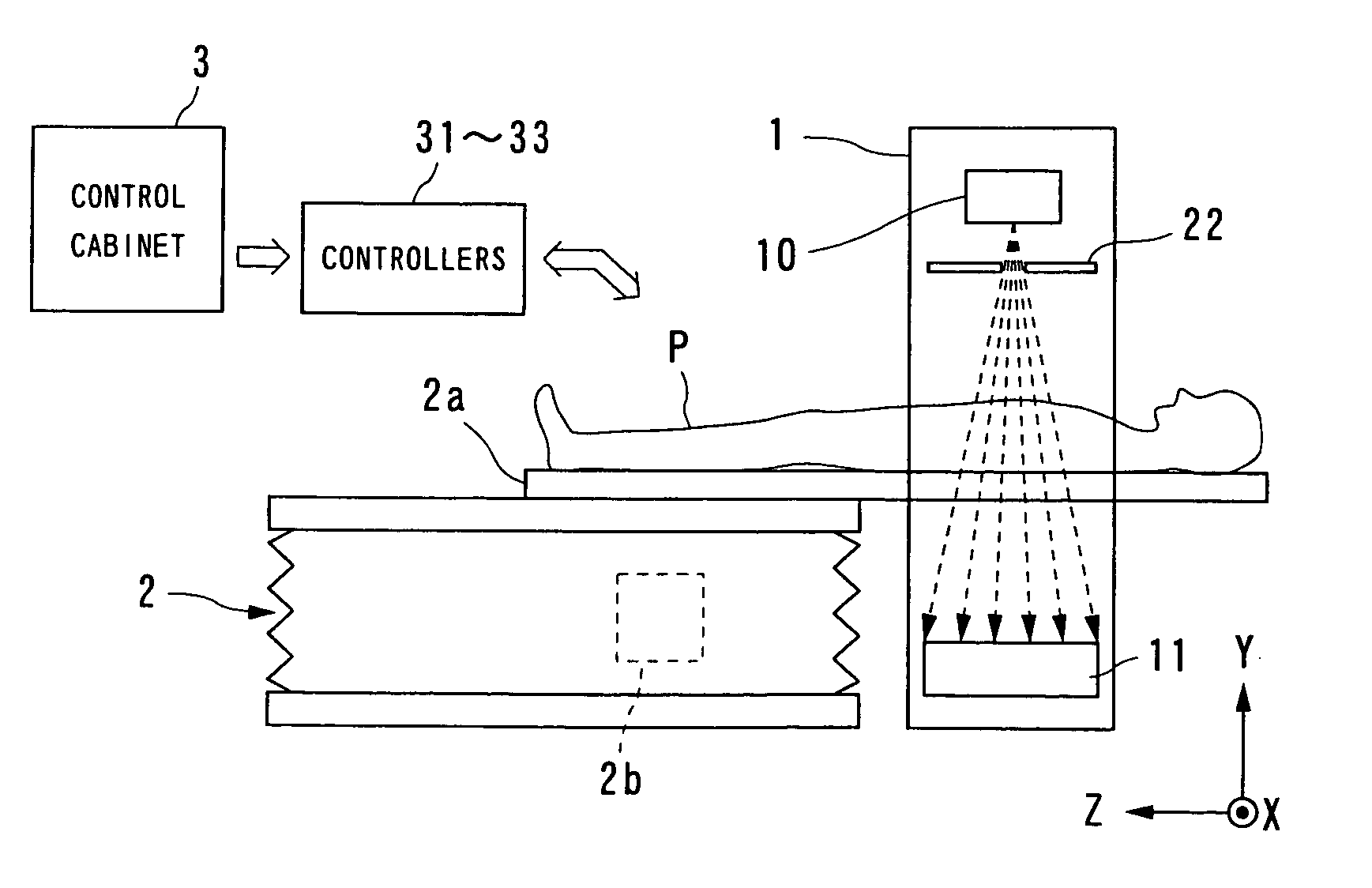
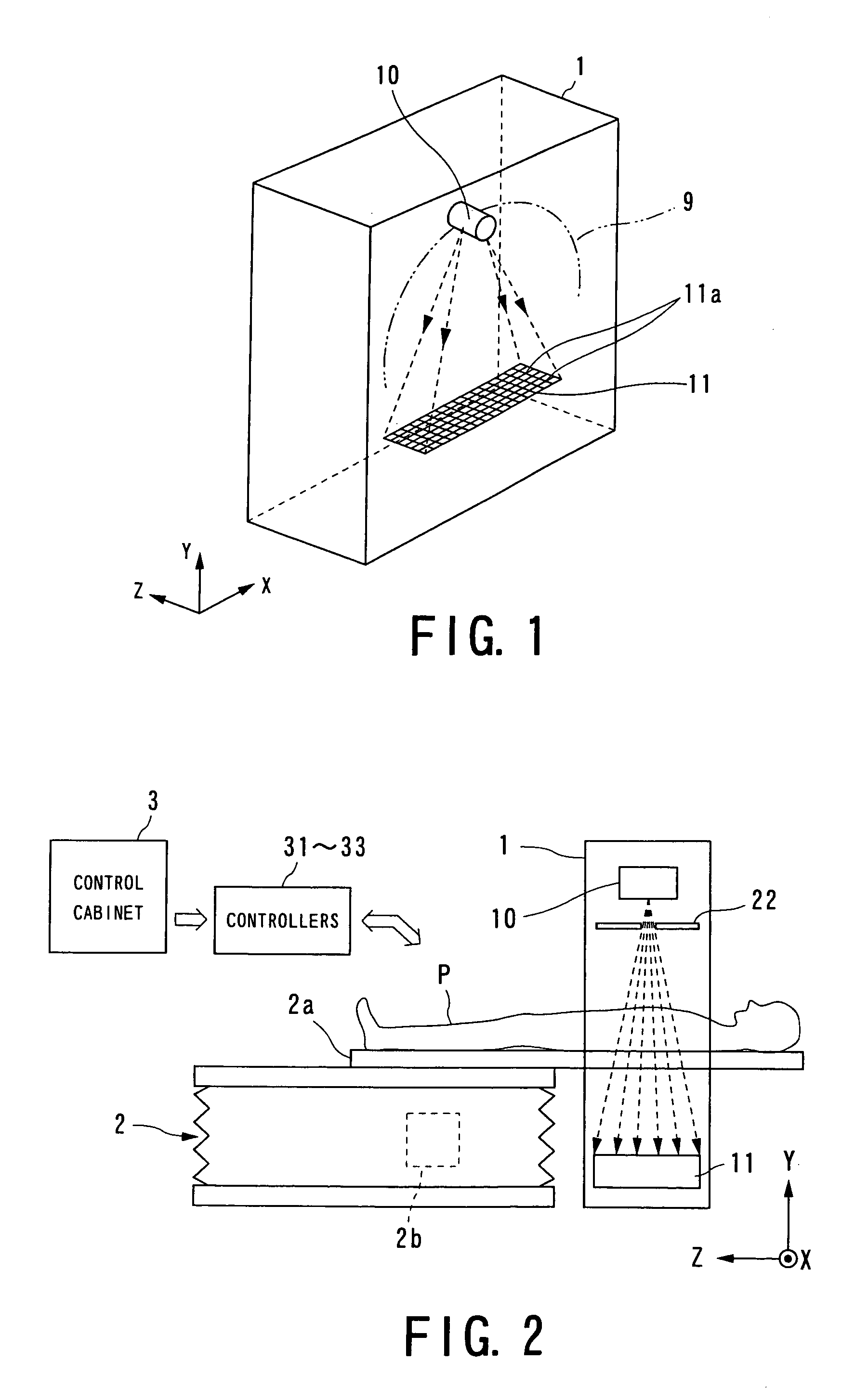
Cone beam type of X-ray CT system for three-dimensional reconstruction
InactiveUS6907100B2Reduce resultHigh resolutionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTemporal resolutionAcquisition time
An X-ray CT system is equipped with a gantry, couch and control cabinet and configured to scan a cone-beam X-ray toward an object along a given orbit to acquire cone-beam data in which a three-dimensional distribution of an X-ray absorption coefficient within the object is reflected. The control cabinet decides a degree of reliability for the cone-beam data according to an acquisition time of the cone-beam data, and then decides a weight for three-dimensional Radon data from the cone-beam data on the basis of the degree of reliability. Using this weight, the control cabinet reconstructs the three-dimensional Radon data based on a three-dimensional reconstruction algorithm. Thus, when the three-dimensional reconstruction algorithm for cone-beam CT is applied to medical CT, artifacts attributable to object's motion can be suppressed and temporal resolution can be improved.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Volumetric computed tomography (VCT)
InactiveUS20060002506A1Fast and reliableMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handling2d arrayX-ray
The present invention provides a volumetric computed tomography (VCT) system capable of producing data for reconstructing an entire three-dimensional (3D) image of a subject during a single rotation without suffering from cone beam artifacts. The VCT system comprises an array of source positions distributed along a line parallel to an axis of rotation, a plurality of collimators, and an array of x-ray detectors. In a preferred embodiment, a reversed imaging geometry is used. A 2D array of source positions provides x-rays emanating from each focal spot toward an array of detectors. The x-rays are restricted by a collimator array and measured by a detector array separately per each source position. The axial extent of the source array and the detector array are comparable to or larger than the axial extent of the portion of the object being imaged.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Cone beam type of x-ray CT system for three-dimensional reconstruction
InactiveUS20040086074A1High resolutionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTemporal resolutionAcquisition time
An X-ray CT system is equipped with a gantry, couch and control cabinet and configured to scan a cone-beam X-ray toward an object along a given orbit to acquire cone-beam data in which a three-dimensional distribution of an X-ray absorption coefficient within the object is reflected. The control cabinet decides a degree of reliability for the cone-beam data according to an acquisition time of the cone-beam data, and then decides a weight for three-dimensional Radon data from the cone-beam data on the basis of the degree of reliability. Using this weight, the control cabinet reconstructs the three-dimensional Radon data based on a three-dimensional reconstruction algorithm. Thus, when the three-dimensional reconstruction algorithm for cone-beam CT is applied to medical CT, artifacts attributable to object's motion can be suppressed and temporal resolution can be improved.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
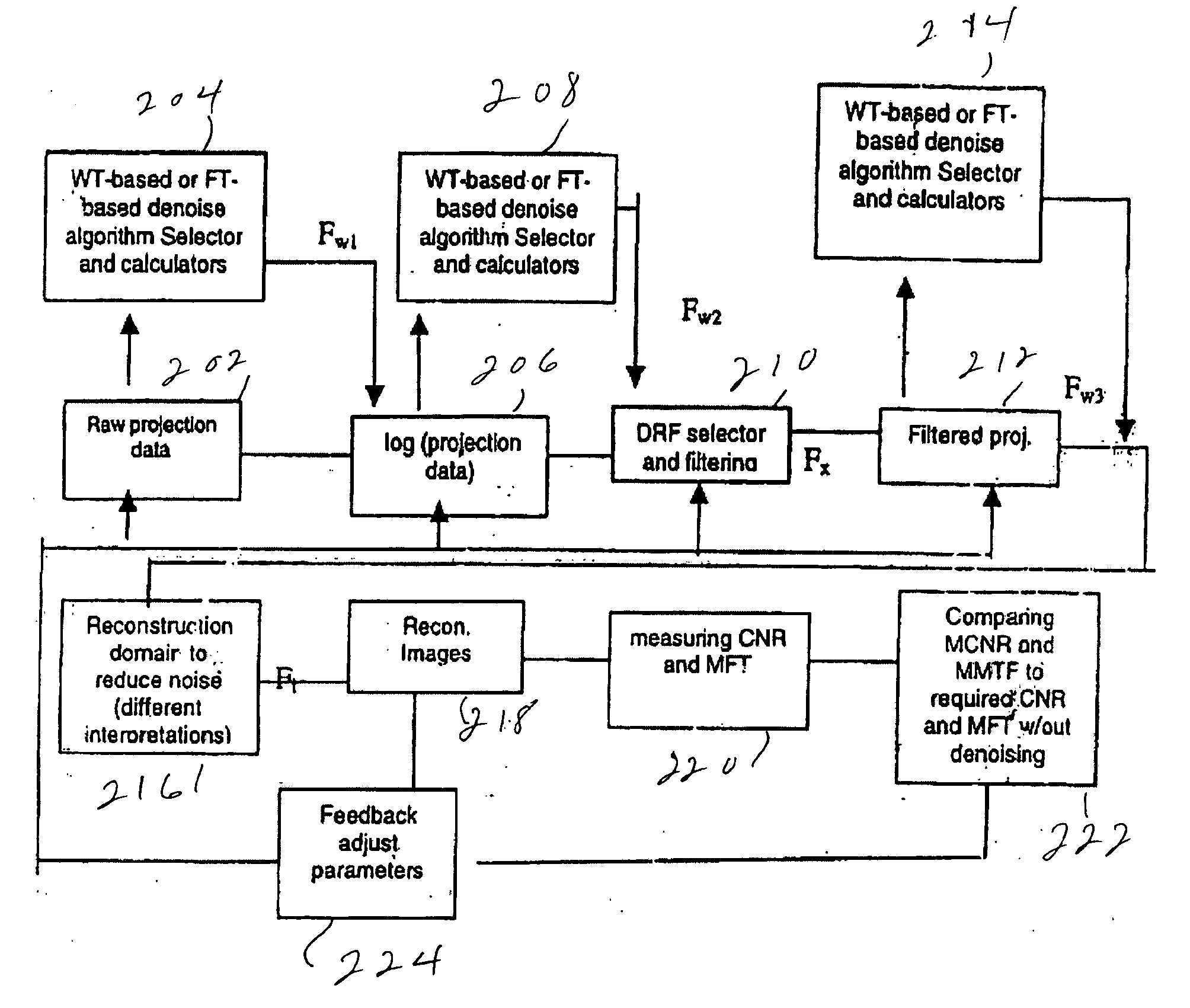
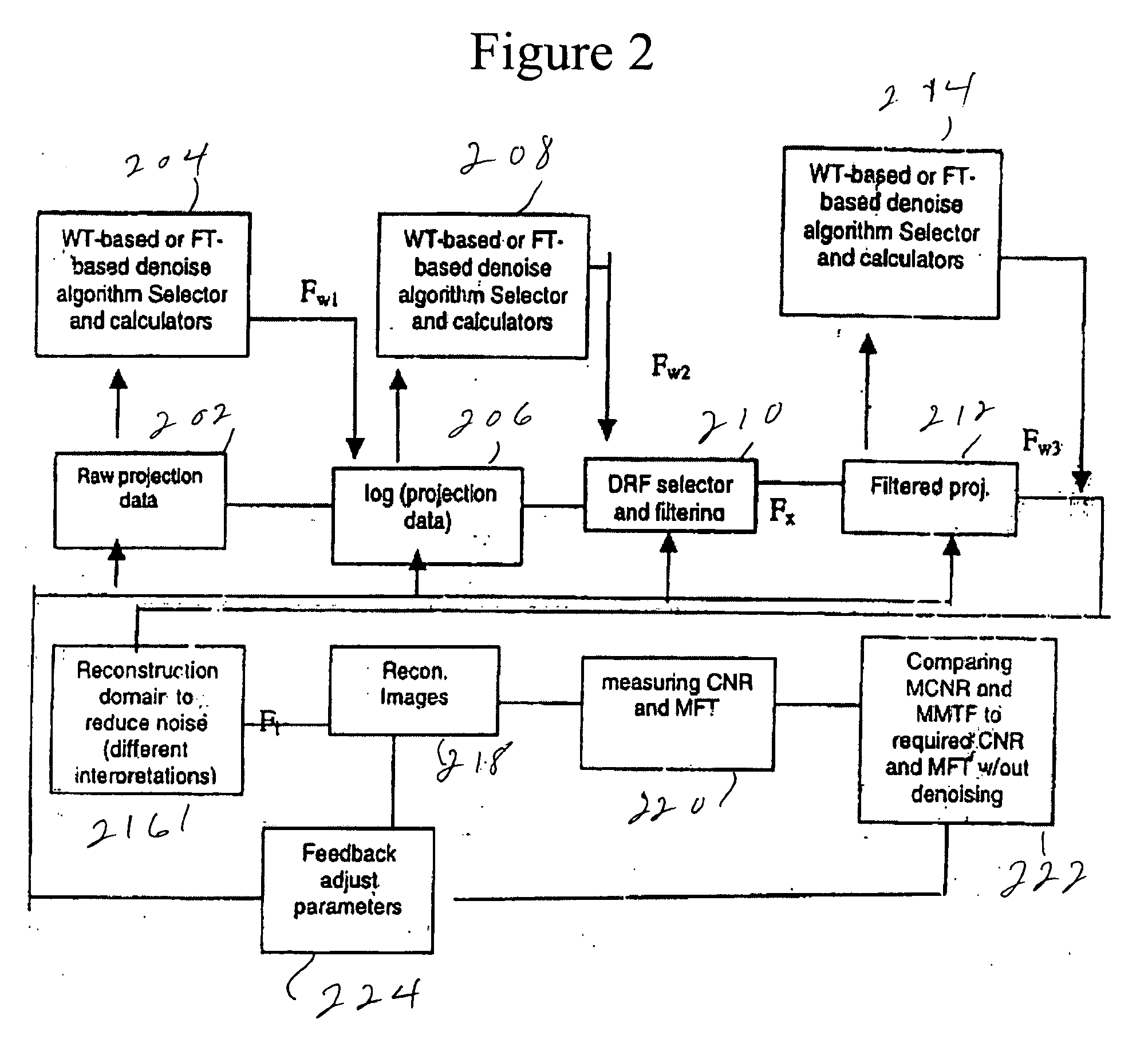
Method and apparatus of global de-noising for cone beam and fan beam CT imaging
ActiveUS20070053477A1Reduce X-ray doseEfficient and effectiveImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionProjection imageTomography
Raw cone beam tomography projection image data are taken from an object and are denoised by a wavelet domain denoising technique and at least one other denoising technique such as a digital reconstruction filter. The denoised projection image data are then reconstructed into the final tomography image using a cone beam reconstruction algorithm, such as Feldkamp's algorithm.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
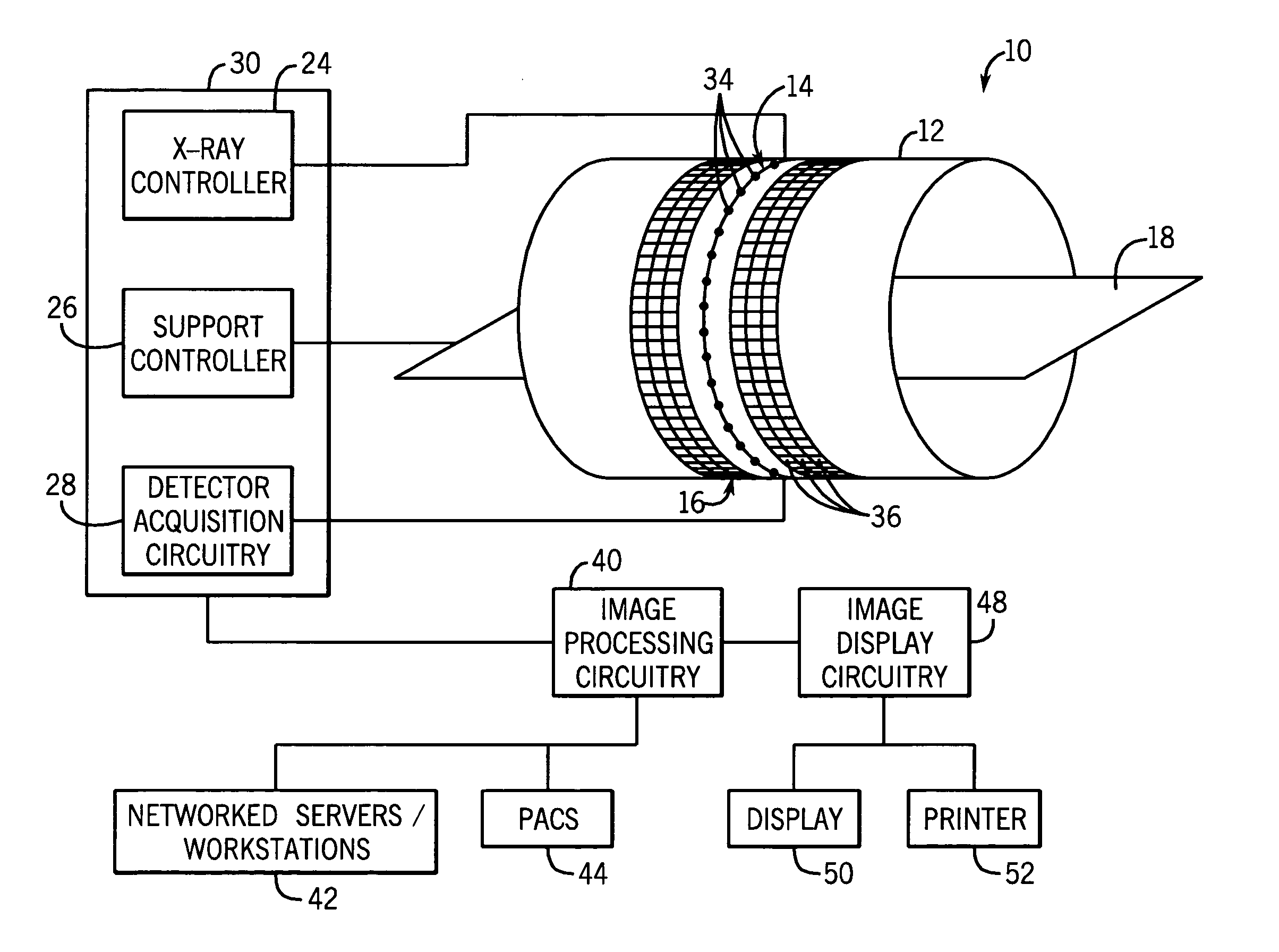
CT scanning system with interlapping beams
InactiveUS7460636B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingLight beamX-ray
A CT scanning system including a gantry operable to rotate about a rotation axis, and a plurality of X-ray imagers mounted on the gantry, each X-ray imager including a radiation source and a detector, wherein the radiation source is operative to emit a radiation beam (e.g., a cone beam) and the detector is positioned to receive the radiation beam so as to acquire partial projections set of an object through which the beams pass, wherein a union of the partial projections sets forms a projection set sufficient for CT reconstruction of the object.
Owner:EIN GAL MOSHE
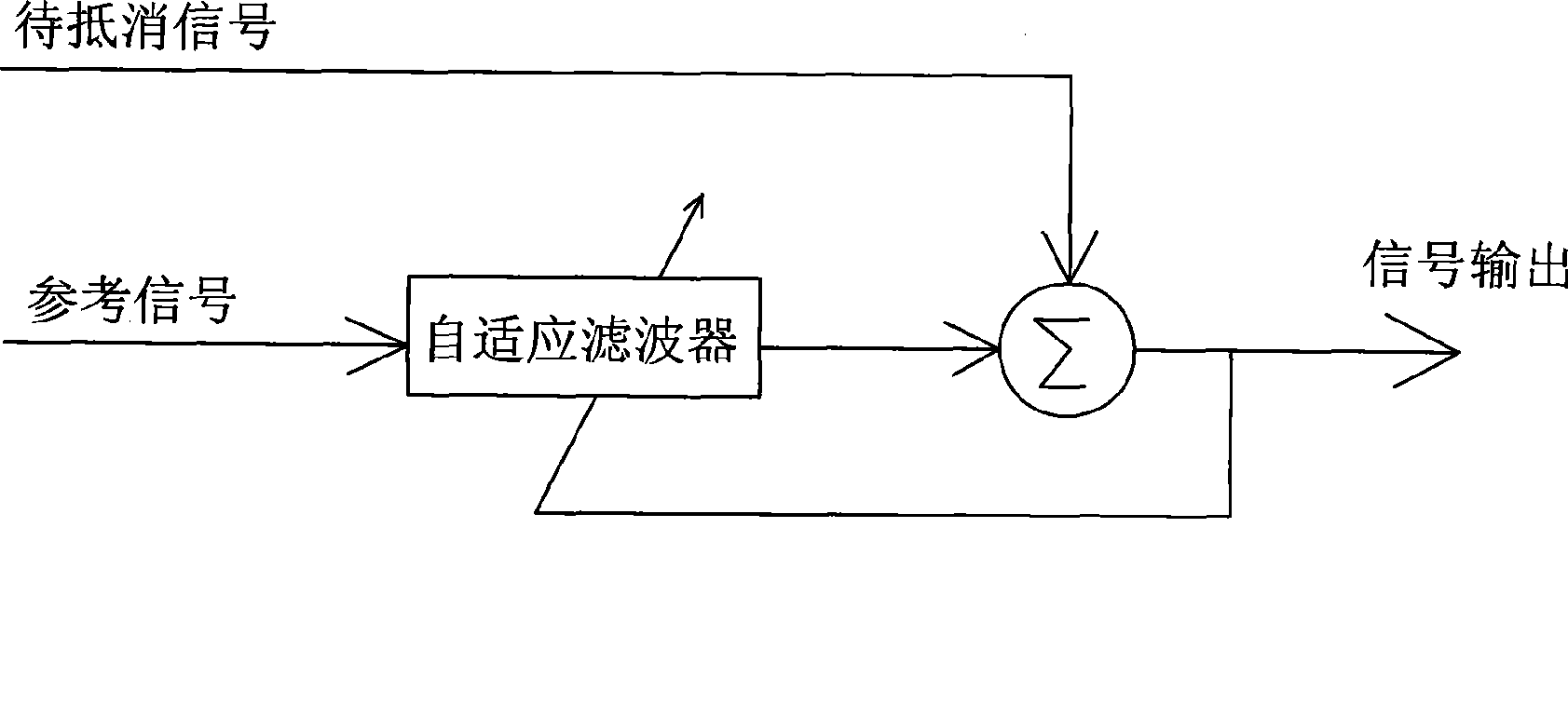
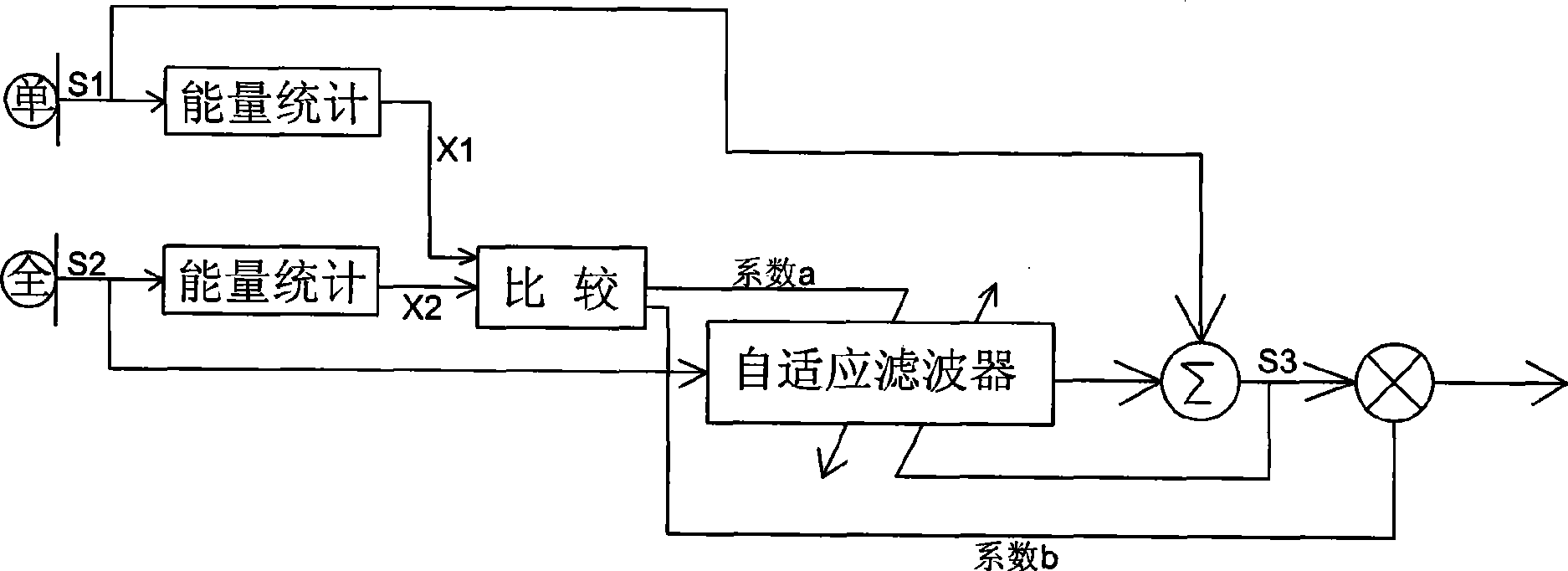
Minitype microphone array device and beam forming method thereof
InactiveCN101466055ACancel noiseAchieving Cone Beam DirectivityTransducer circuitsEngineeringMicrophone array
The invention provides a microphone array device and a beam forming method thereof. The microphone array device can effectively eliminate noise and realize the directive property of a conical beam. Compared with prior art, the invention restrains the noise by controlling the updating of the coefficient of a self-adapting filter with the coefficient a, and the efficiency is pretty high.
Owner:瑞声声学科技(常州)有限公司
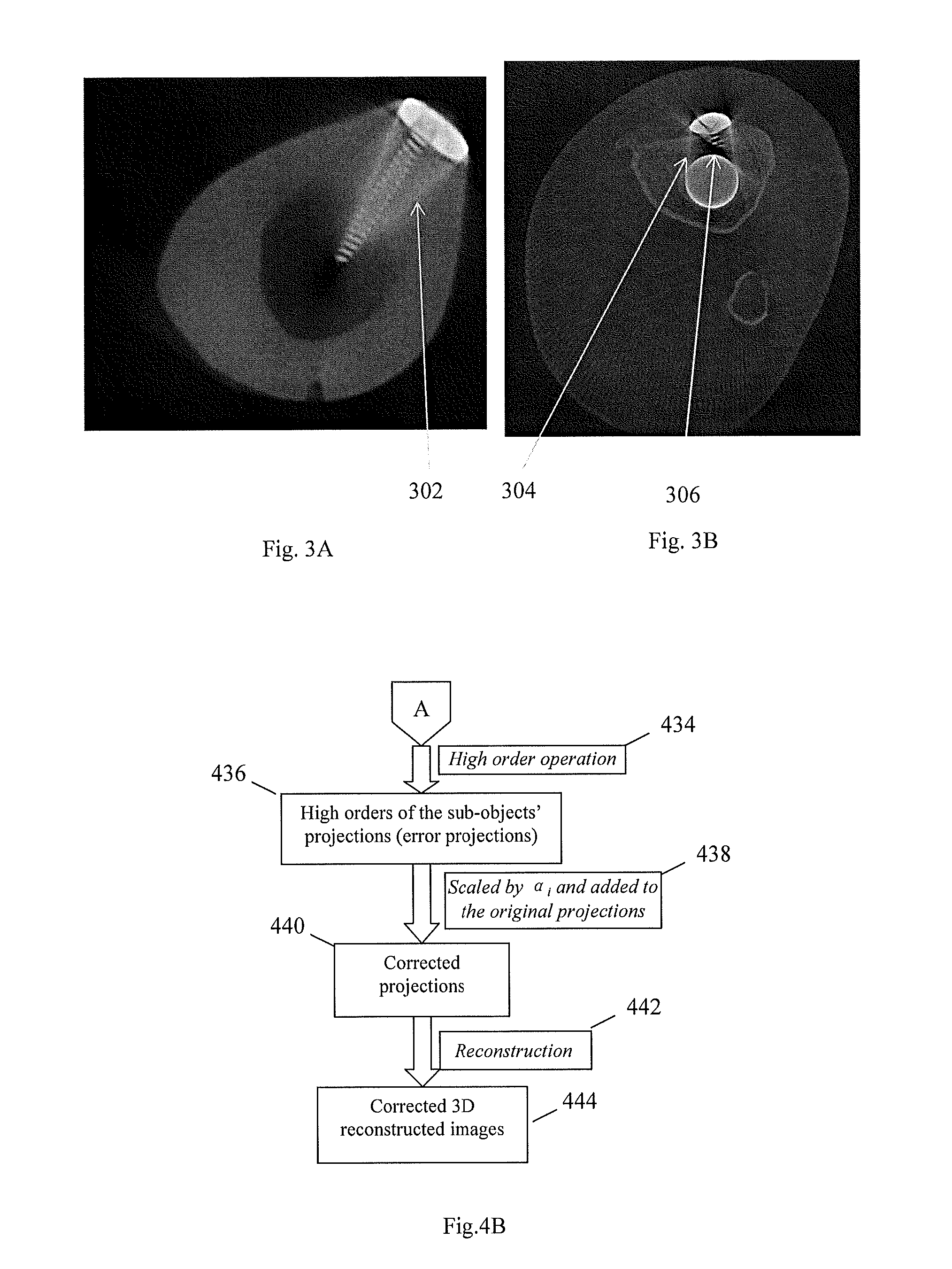
Method and apparatus for 3D metal and high-density artifact correction for cone-beam and fan-beam CT imaging
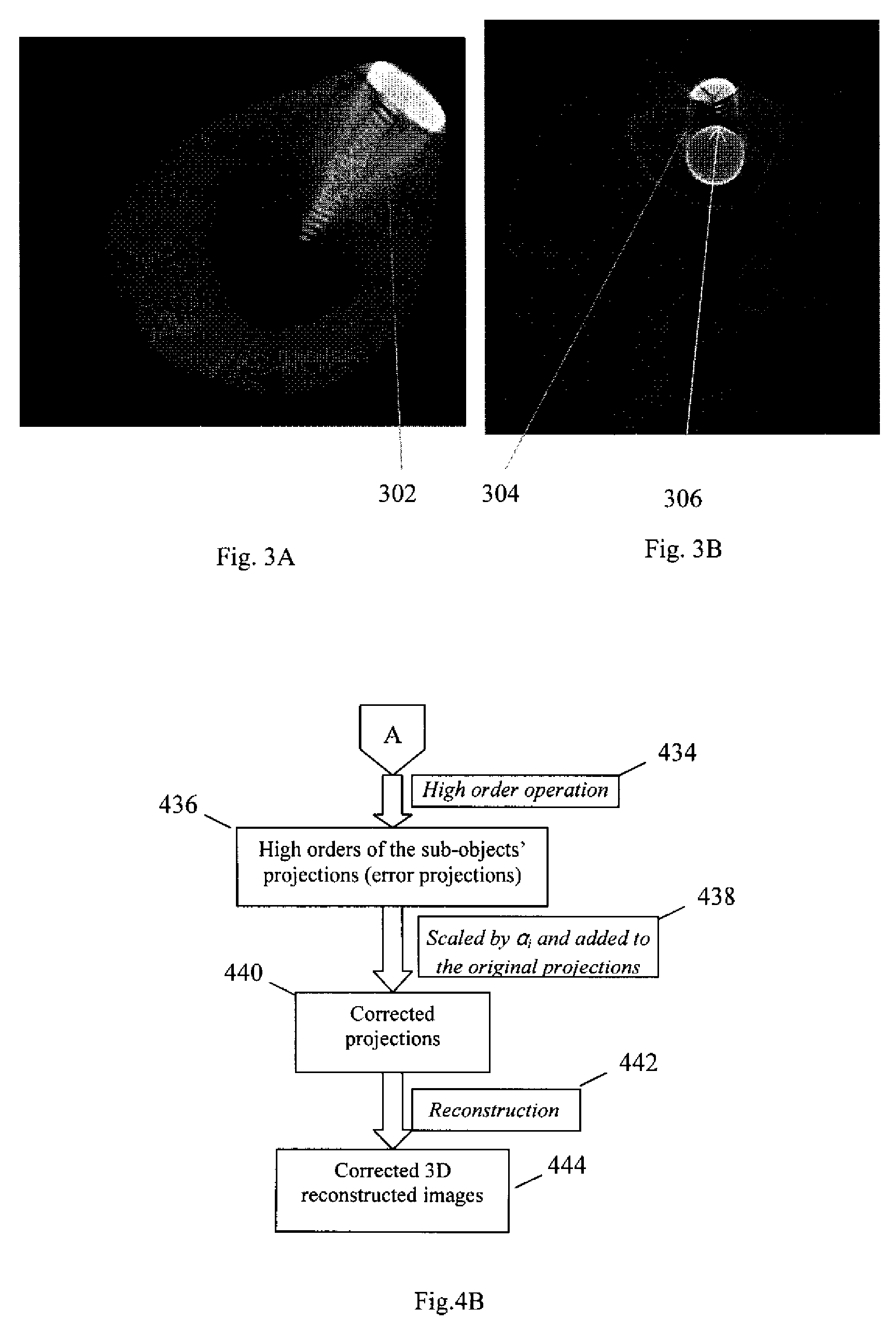
ActiveUS8023767B1Correction of artifactAccurate reconstruction imageImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionMetal ArtifactHigh density
A 3D metal artifacts correction technique corrects the streaking artifacts generated by titanium implants or other similar objects. A cone-beam computed tomography system is utilized to provide 3D images. A priori information (such as the shape information and the CT value) of high density sub-objects is acquired and used for later artifacts correction. An optimization process with iterations is applied to minimize the error and result in accurate reconstruction images of the object.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
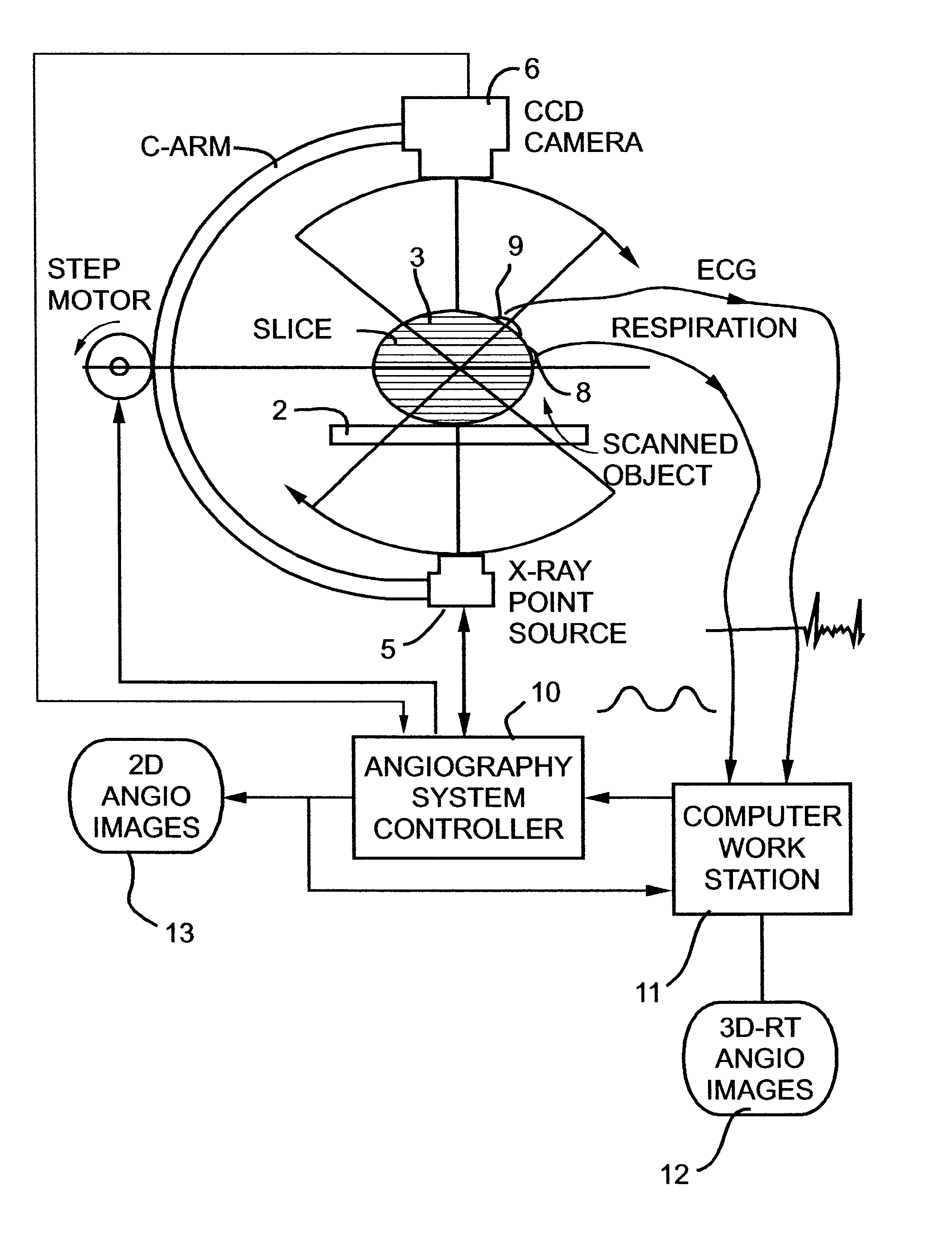
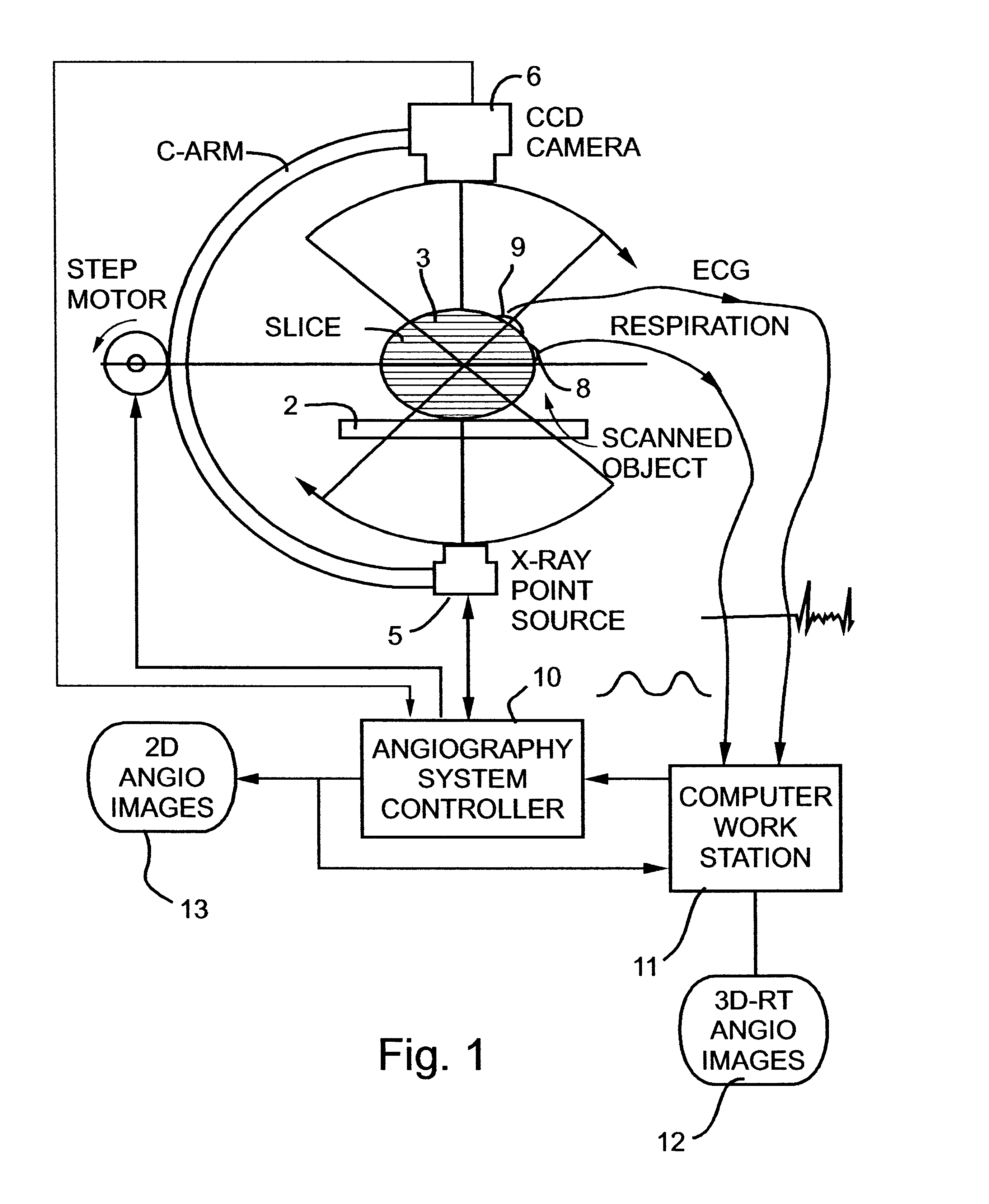
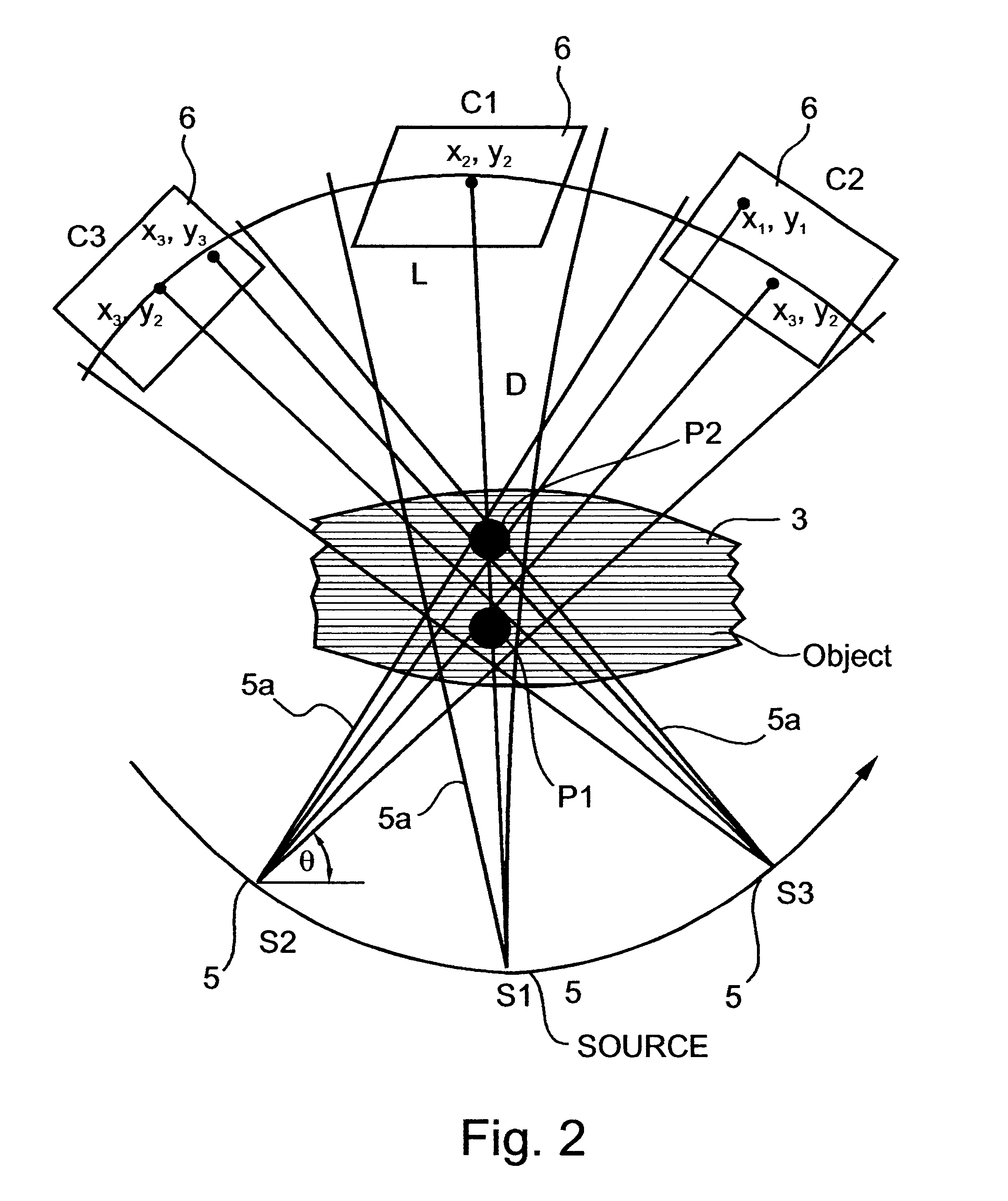
Imaging methods and apparatus particularly useful for two and three-dimensional angiography
InactiveUS6574500B2Enhance CNRRaise the ratioVolume/mass flow measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionElectricityAngio ct
Owner:MEDIMAG C V I
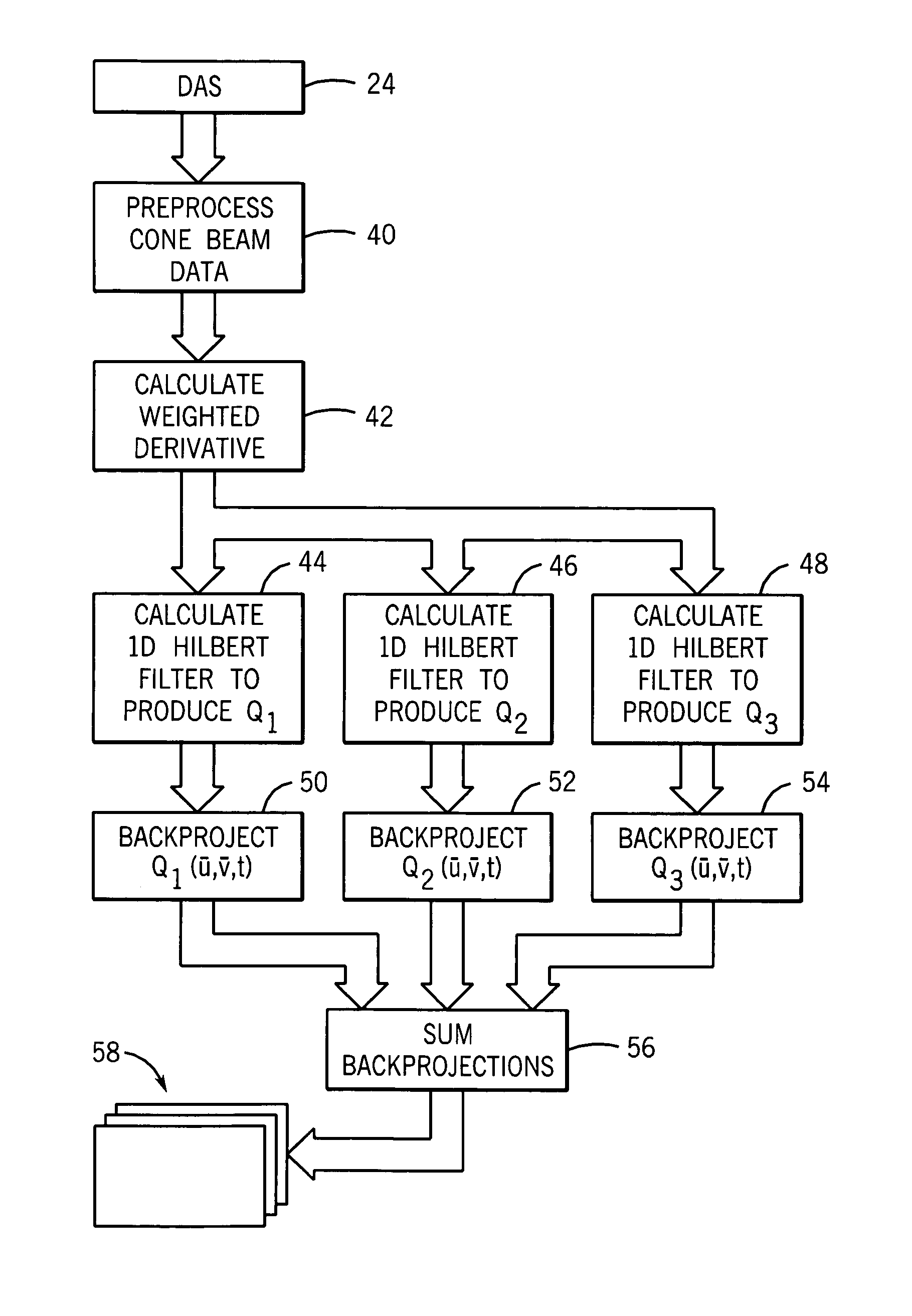
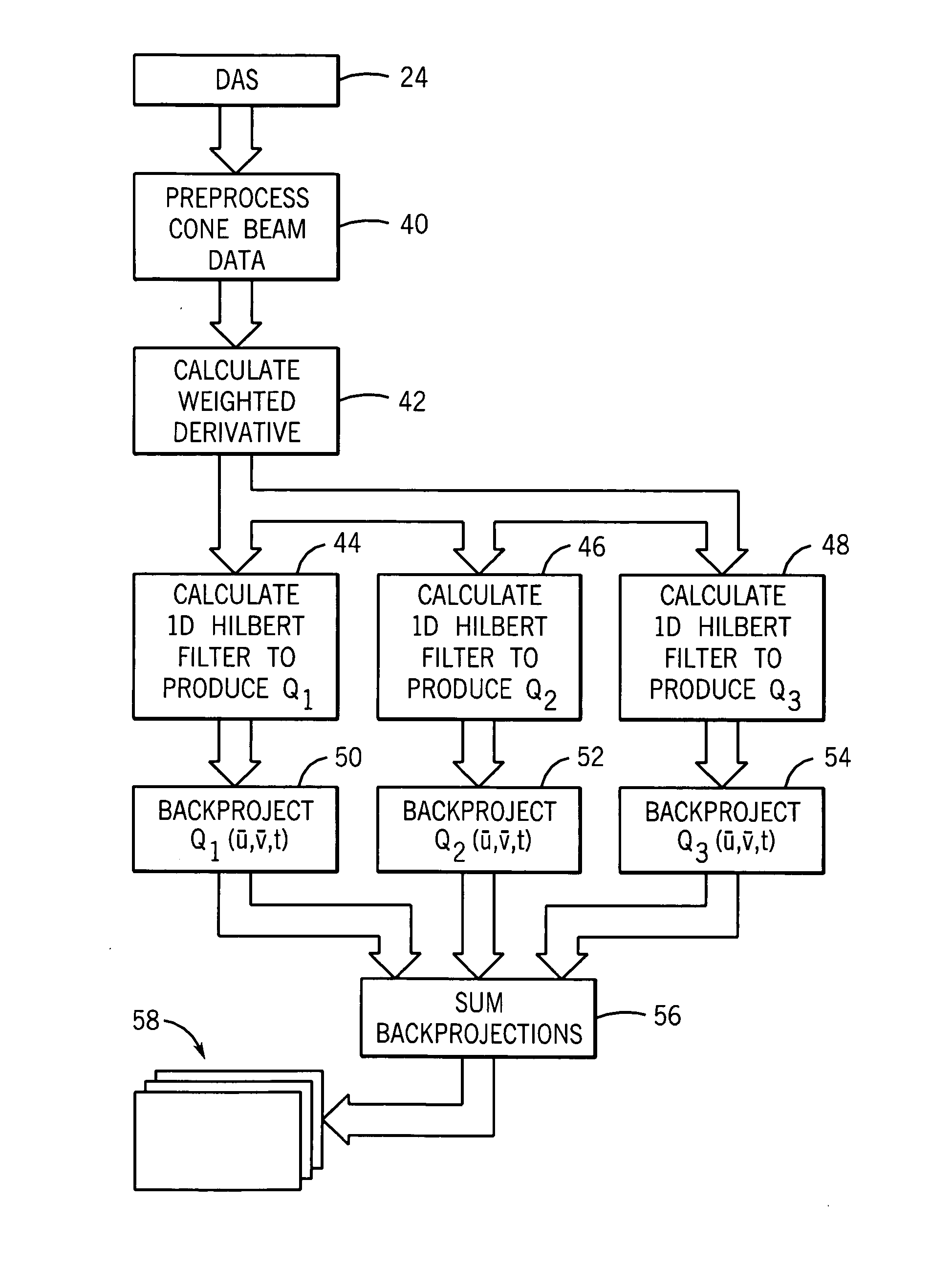
Cone-beam filtered backprojection image reconstruction method for short trajectories
ActiveUS7203272B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationReconstruction methodX-ray
An image reconstruction method for cone beam x-ray attenuation data acquired over a super-short-scan, short-scan or full-scan includes backproejcting over three adjacent segments of the arc traversed by the x-ray source. Each backprojection consists of a weighted combination of 1D Hilbert filtering of the modified cone-beam data along both horizontal and non-horizontal directions.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Cone-beam CT
ActiveUS7869561B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingElement spaceX-ray
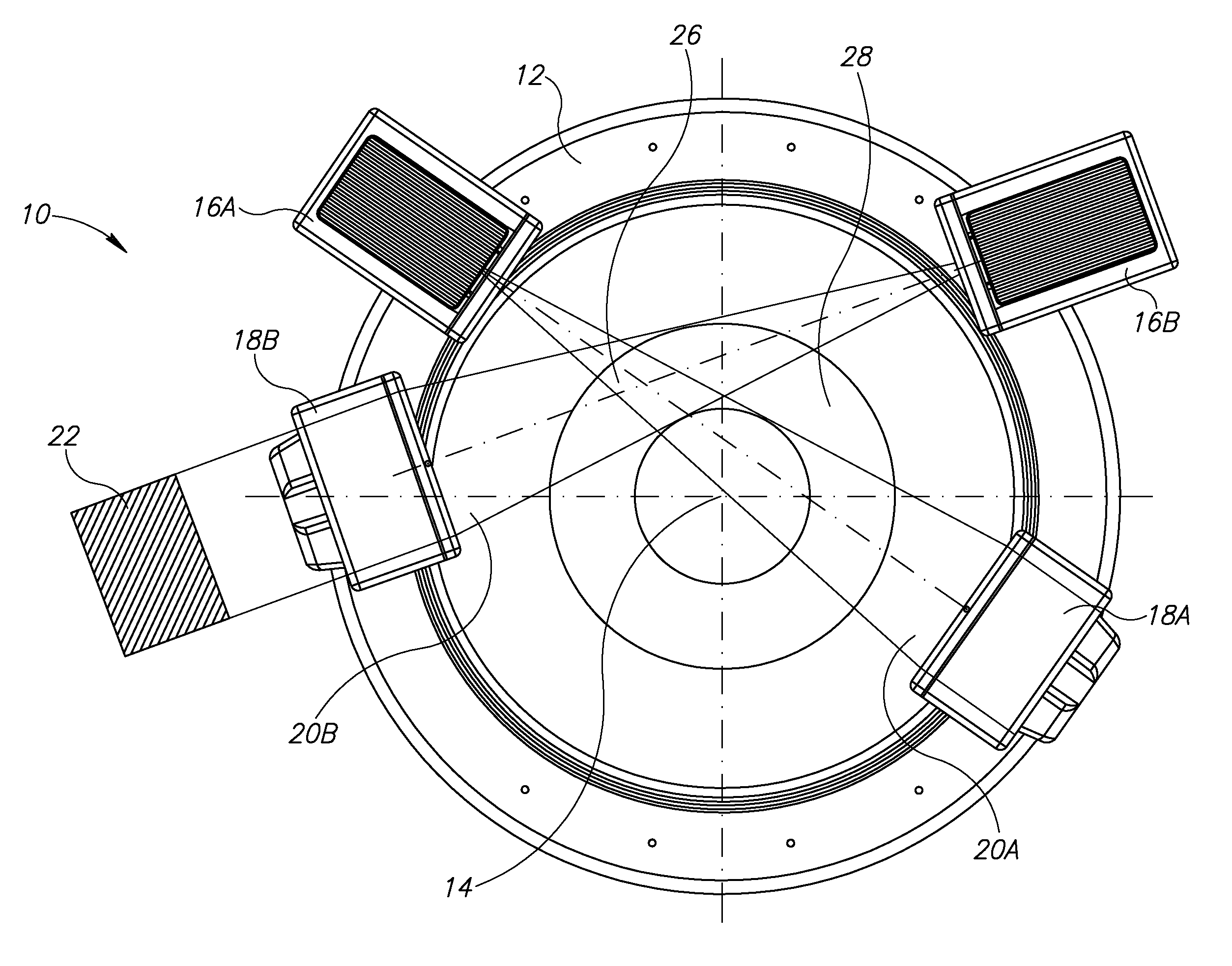
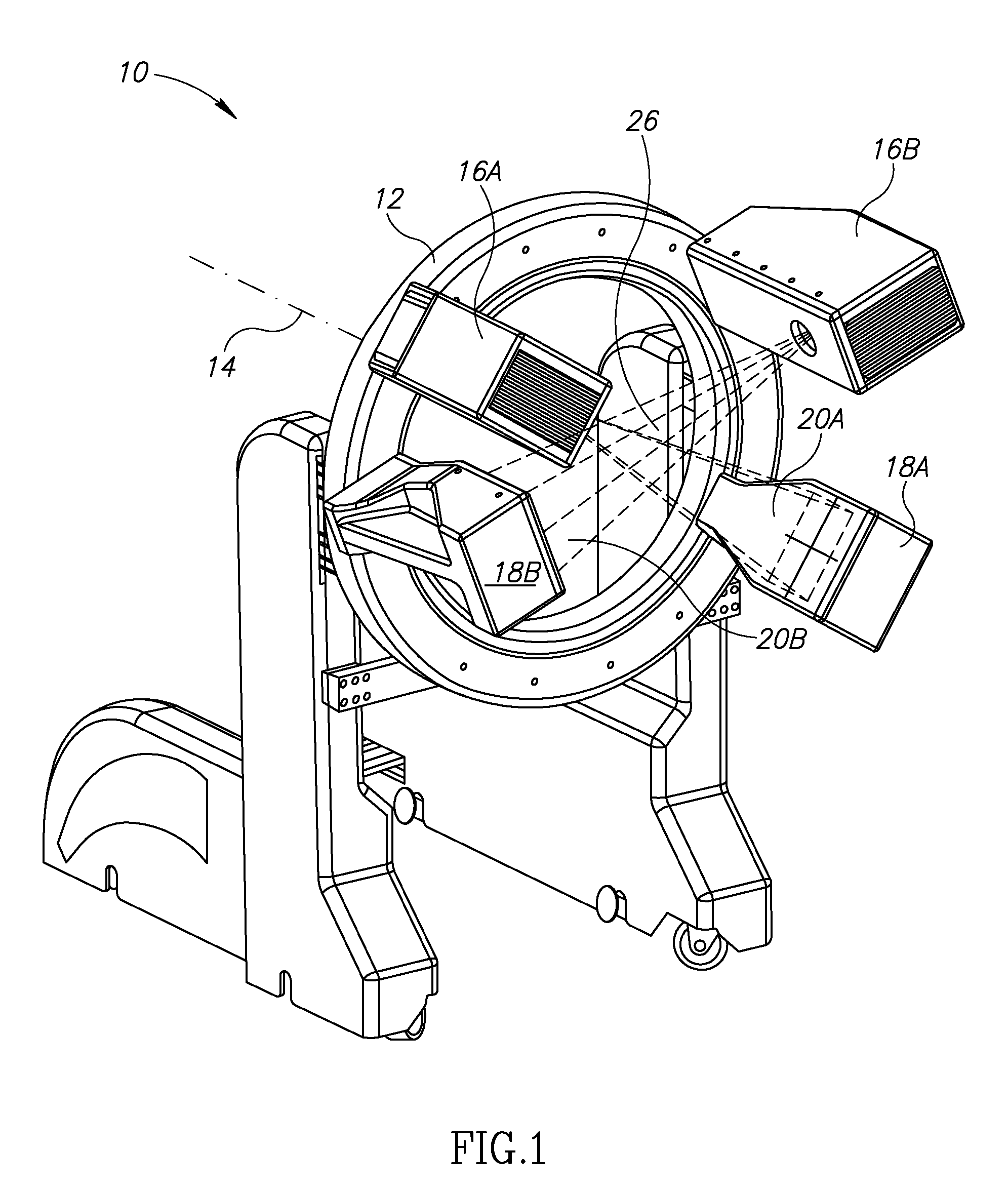
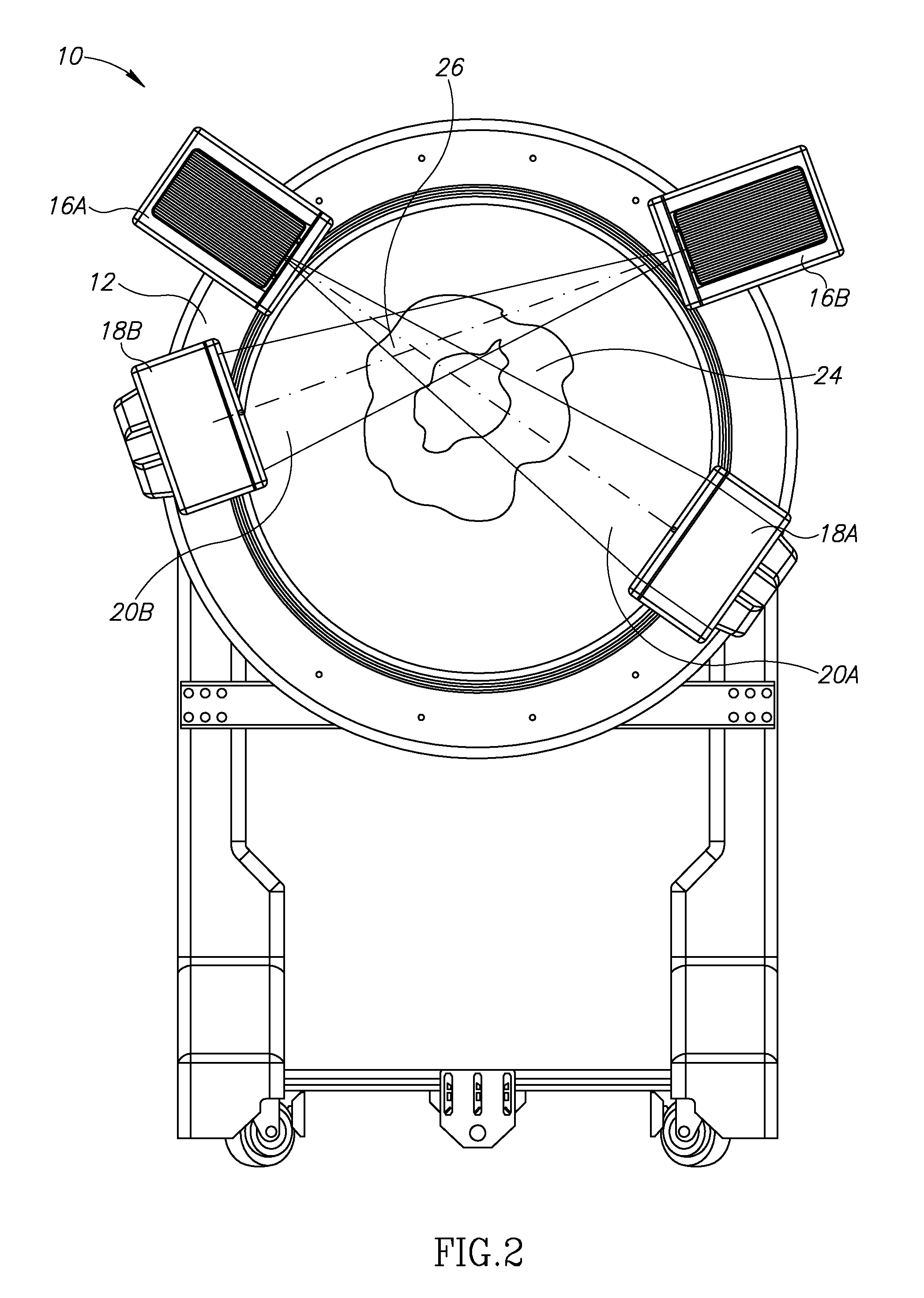
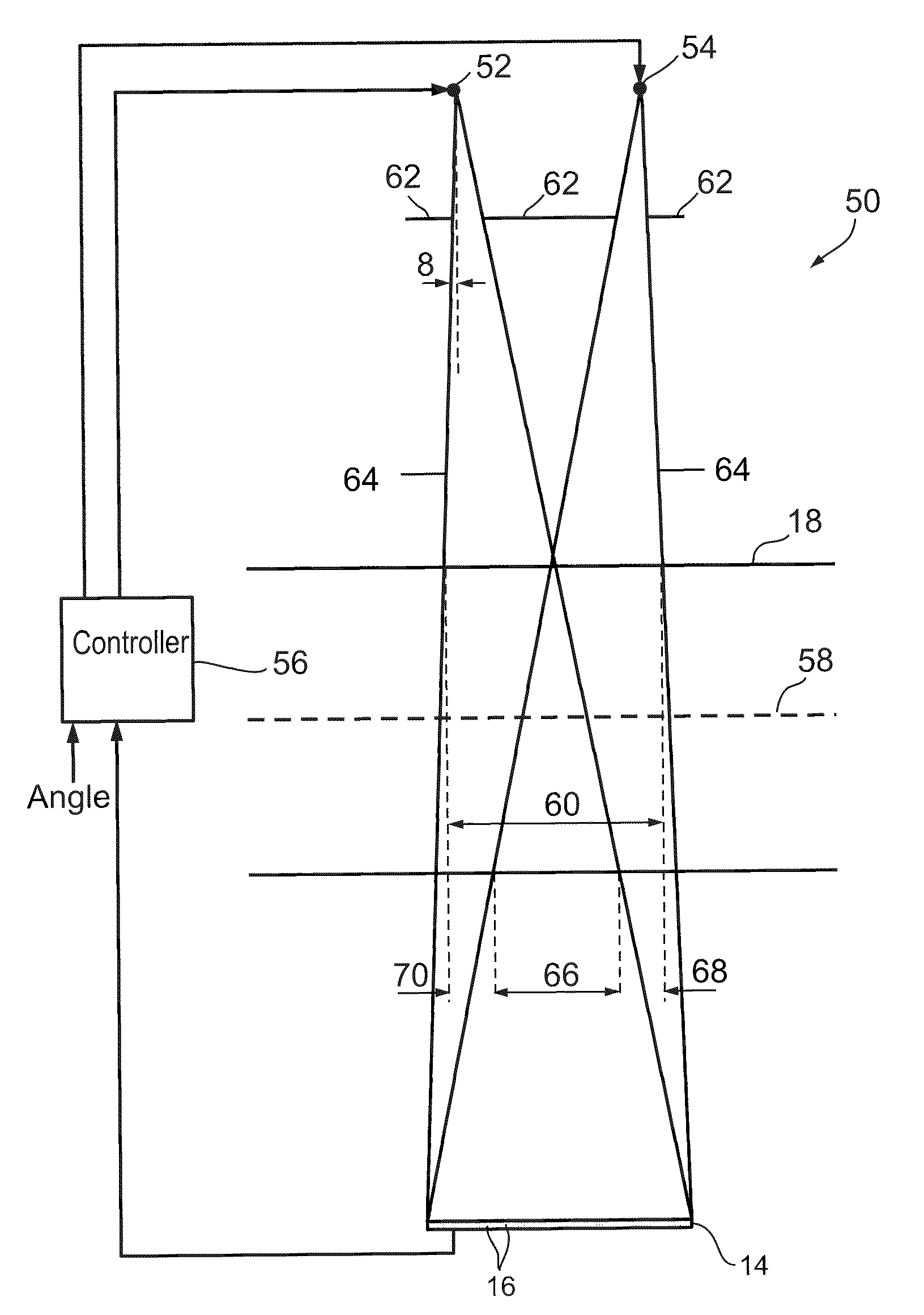
Apparatus for CT cone beam scanning, comprising:a table for holding a subject;a gantry;a first detector array, having a given number of rows of detector elements spaced along an rotation axis of the gantry, mounted on the gantry;a first plurality of x-ray sources mounted on the gantry for rotation about the patient table on a rotation axis, the number of rows being at least twice the number of sources; anda controller that acquires data responsive to radiation from the sources from the detector array attenuated by at least part of the common volume of the subject irradiated by the plurality of radiation sources.
Owner:ARINETA
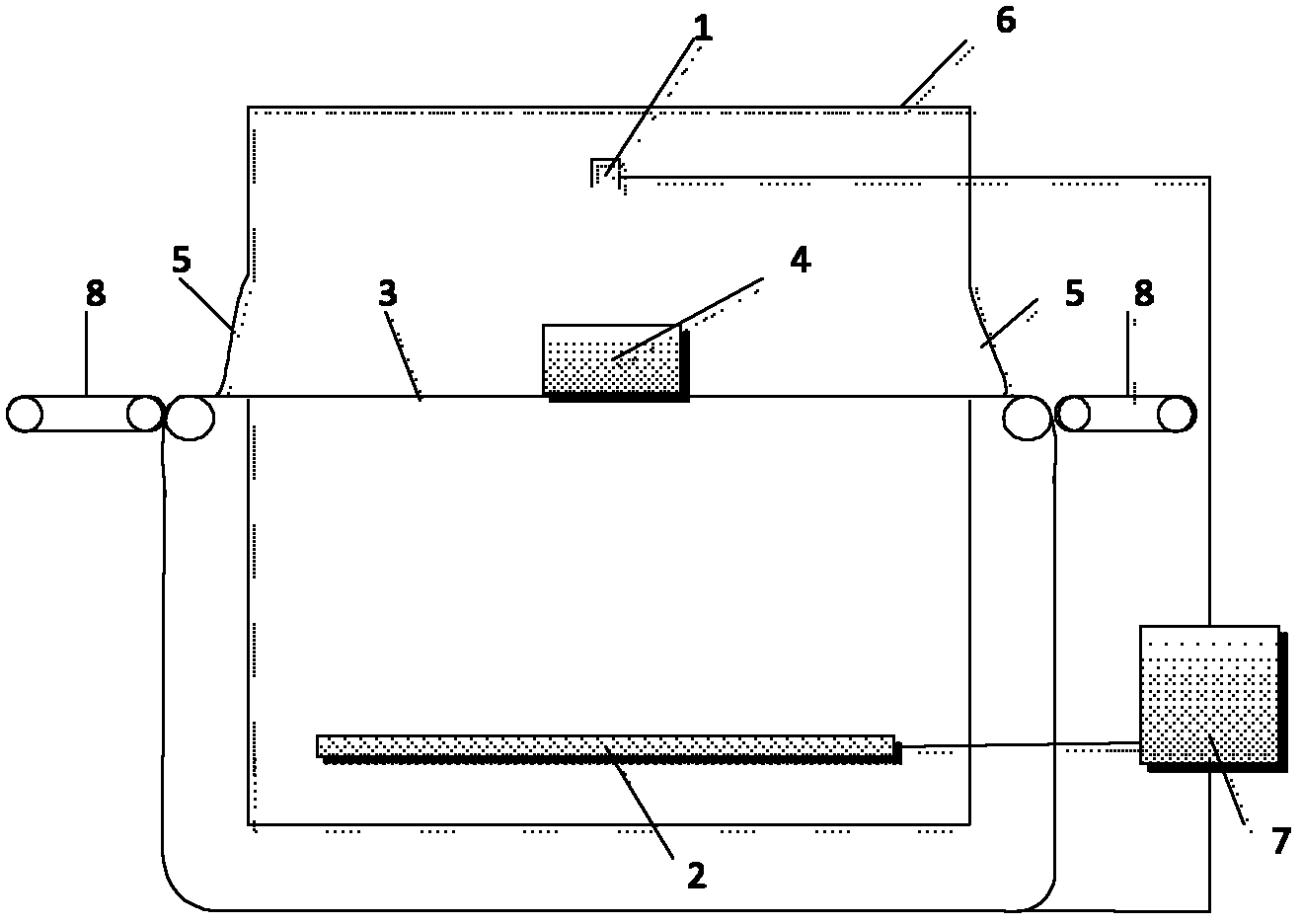
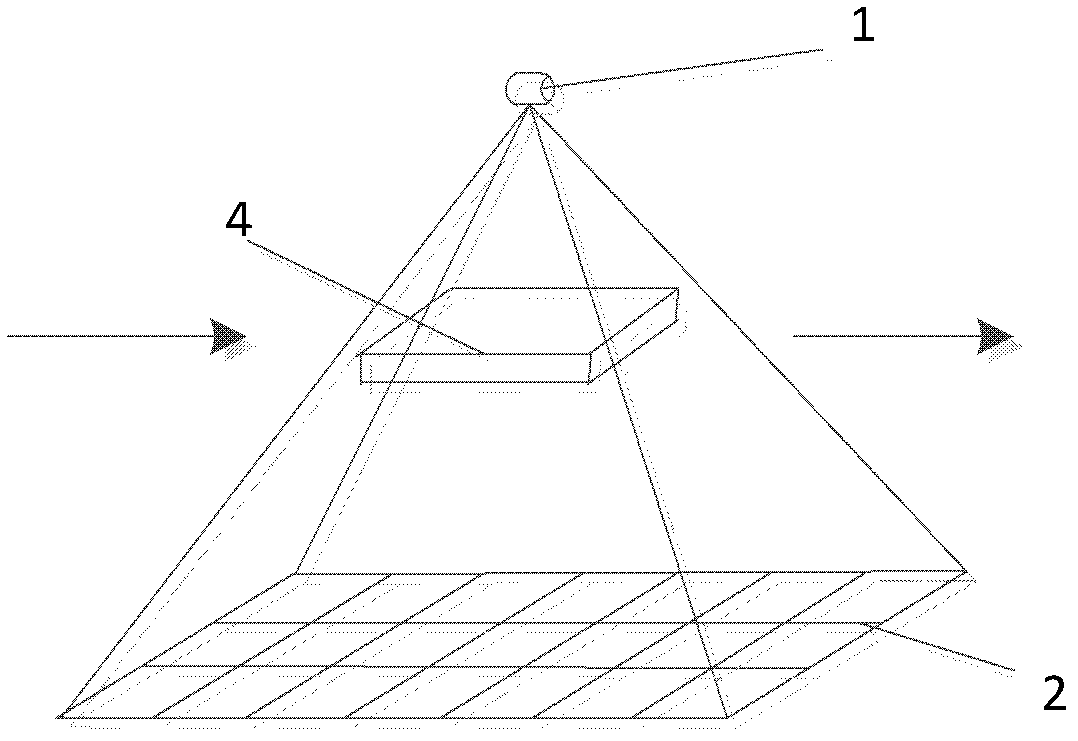
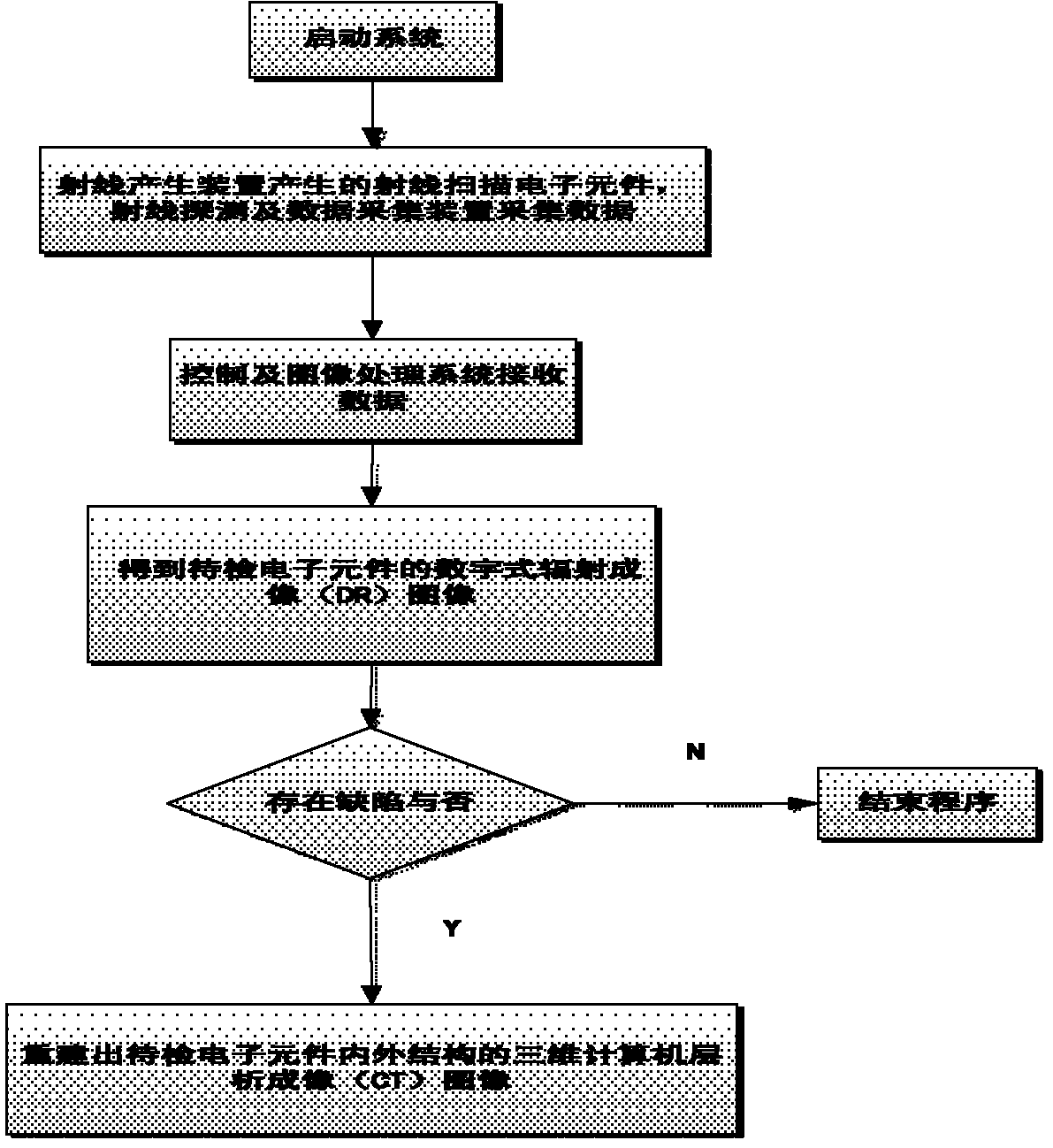
Method for online detecting electronic element by translational type micro focus CT (Computerized Tomography) detection device
ActiveCN102590248AImprove scanning efficiencyReduce volumeMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationThree dimensional ctProduction line
The invention discloses a method for online detecting an electronic element by a translational type micro focus CT (Computerized Tomography) detection device, and the method is realized as follows: when the detection is started, the electronic element is scanned by a conical ray beam generated by a ray generation device; and ray projection data is acquired by a ray detection and data acquisition device, and then is transmitted to a control and image processing system for imaging including digital radiation (DR) imaging and computerized tomography (CT) imaging. When the CT imaging is performed, the CT image can be reconstructed according to incomplete projection data acquired through ray scanning by the translational type conical beam and adopting translational type conical beam CT iterative reconstruction algorithm based on subdomain equalization and total variation minimization, so as to obtain a high quality three-dimensioanl CT image. The method is used for online detecting the electronic element on the production line with high precision, can perform amplification DR image and three-dimensional CT image for internal and external structures of the electronic element; the device has simple structure and high scanning efficiency; and further, material deficiency and assembly deficiency of the electronic element can be detected efficiently.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
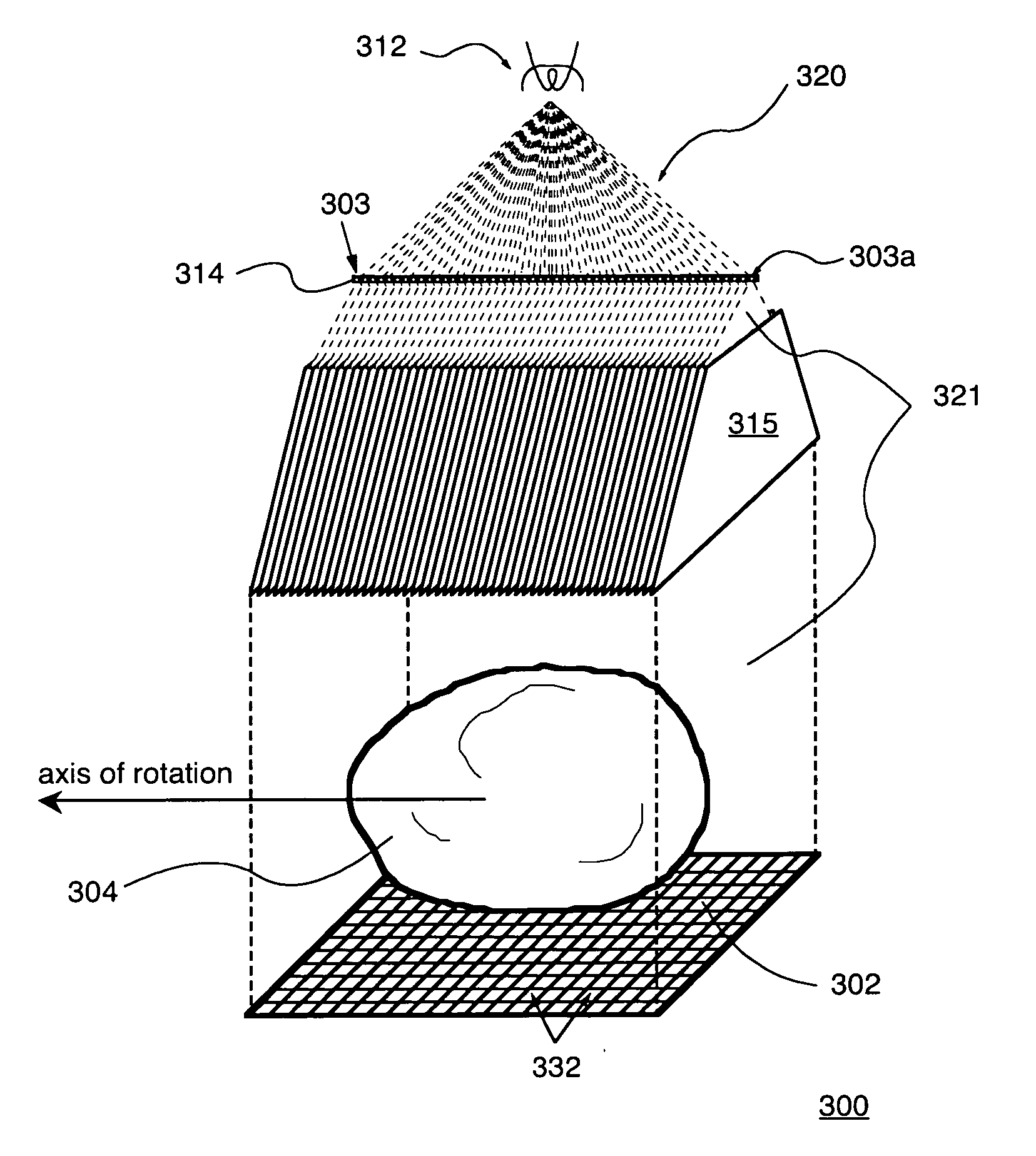
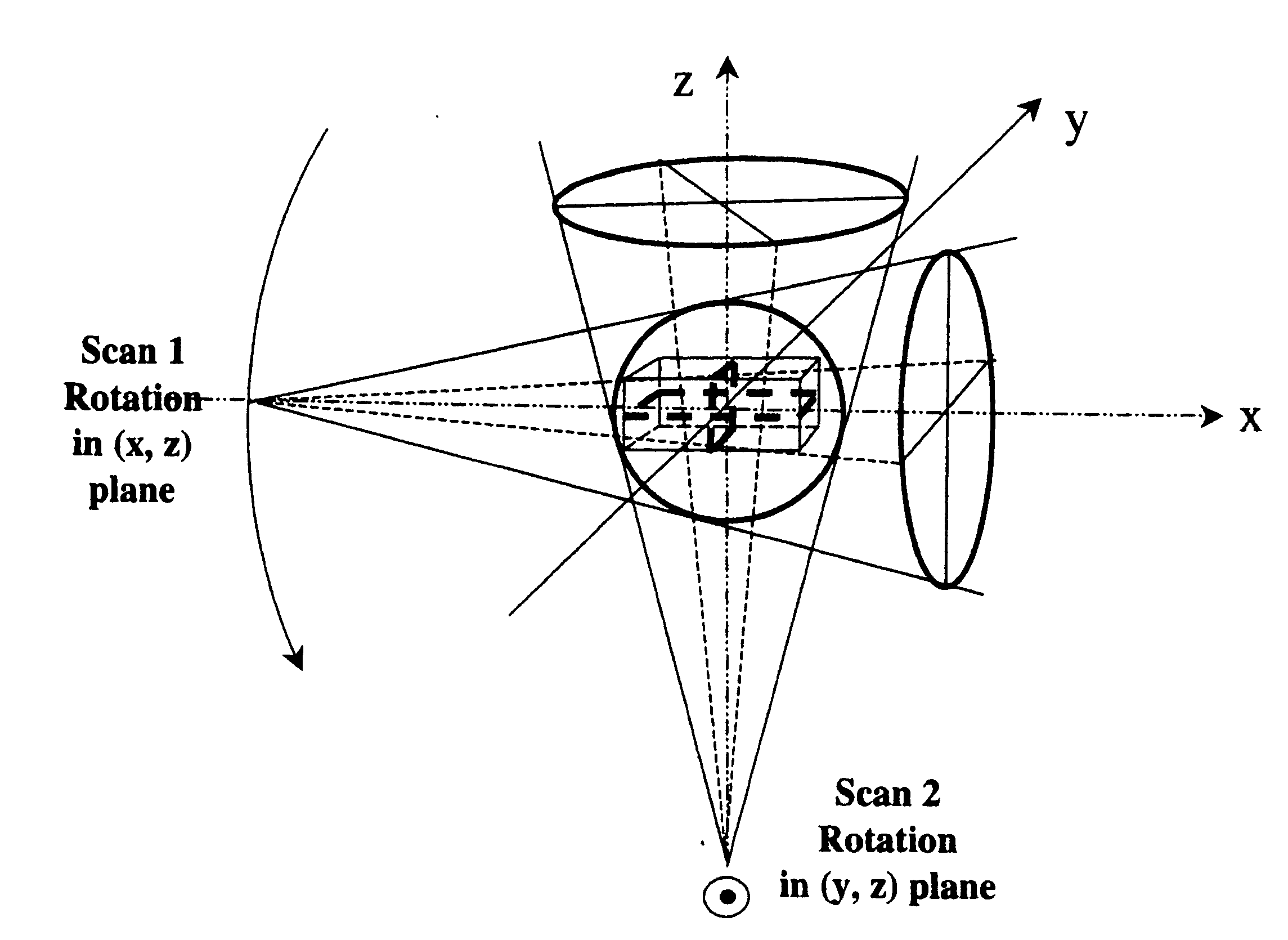
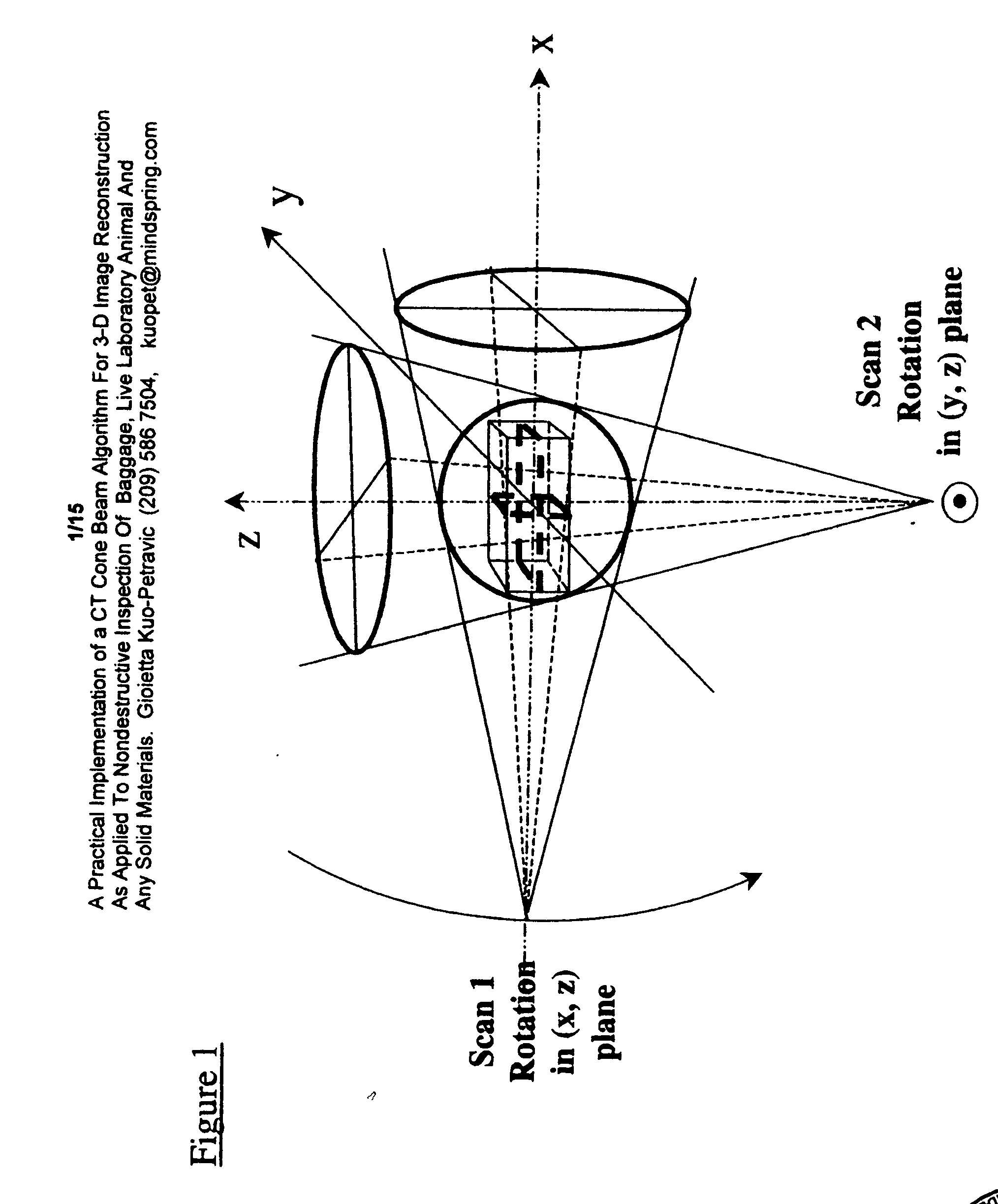
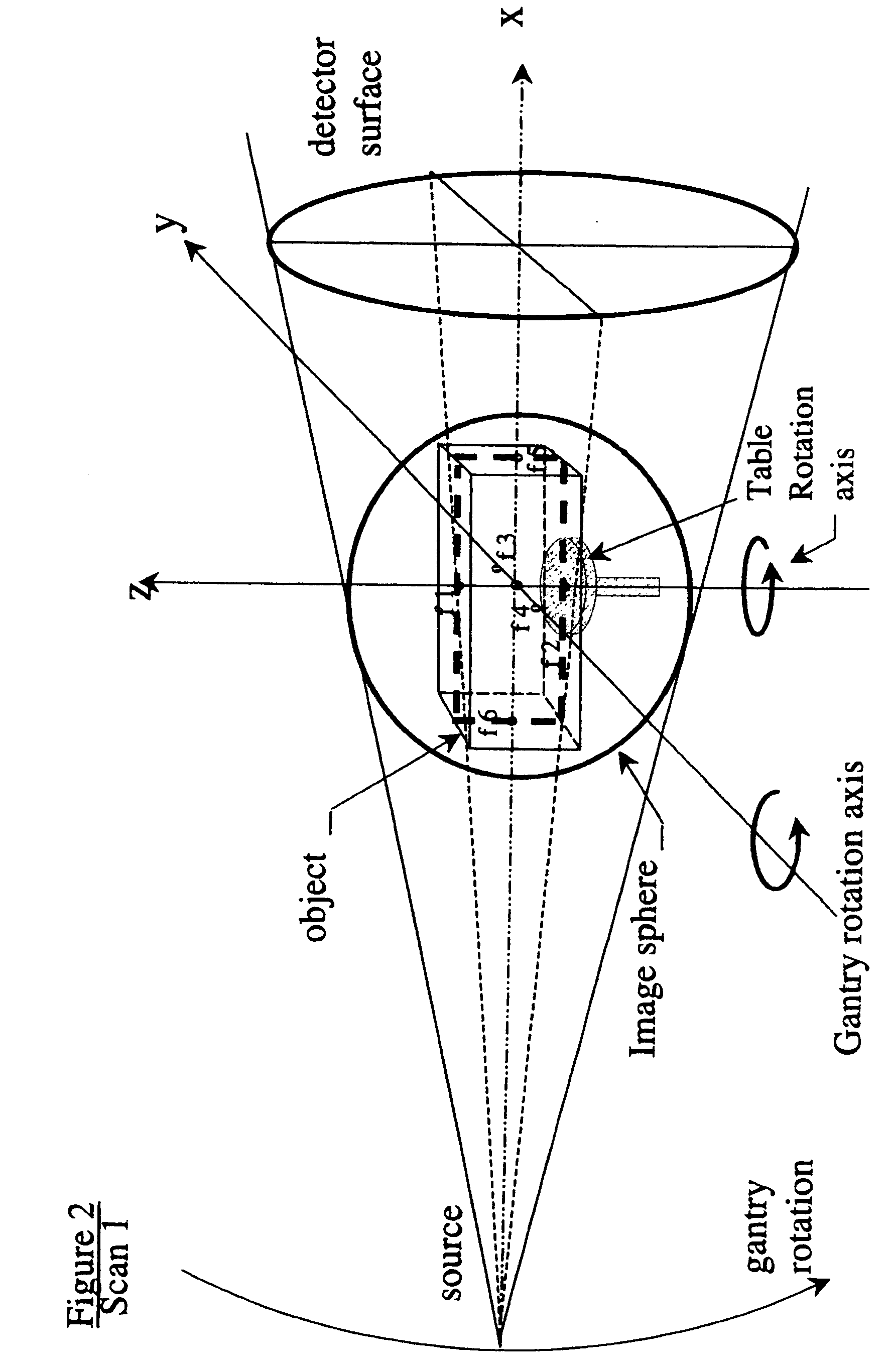
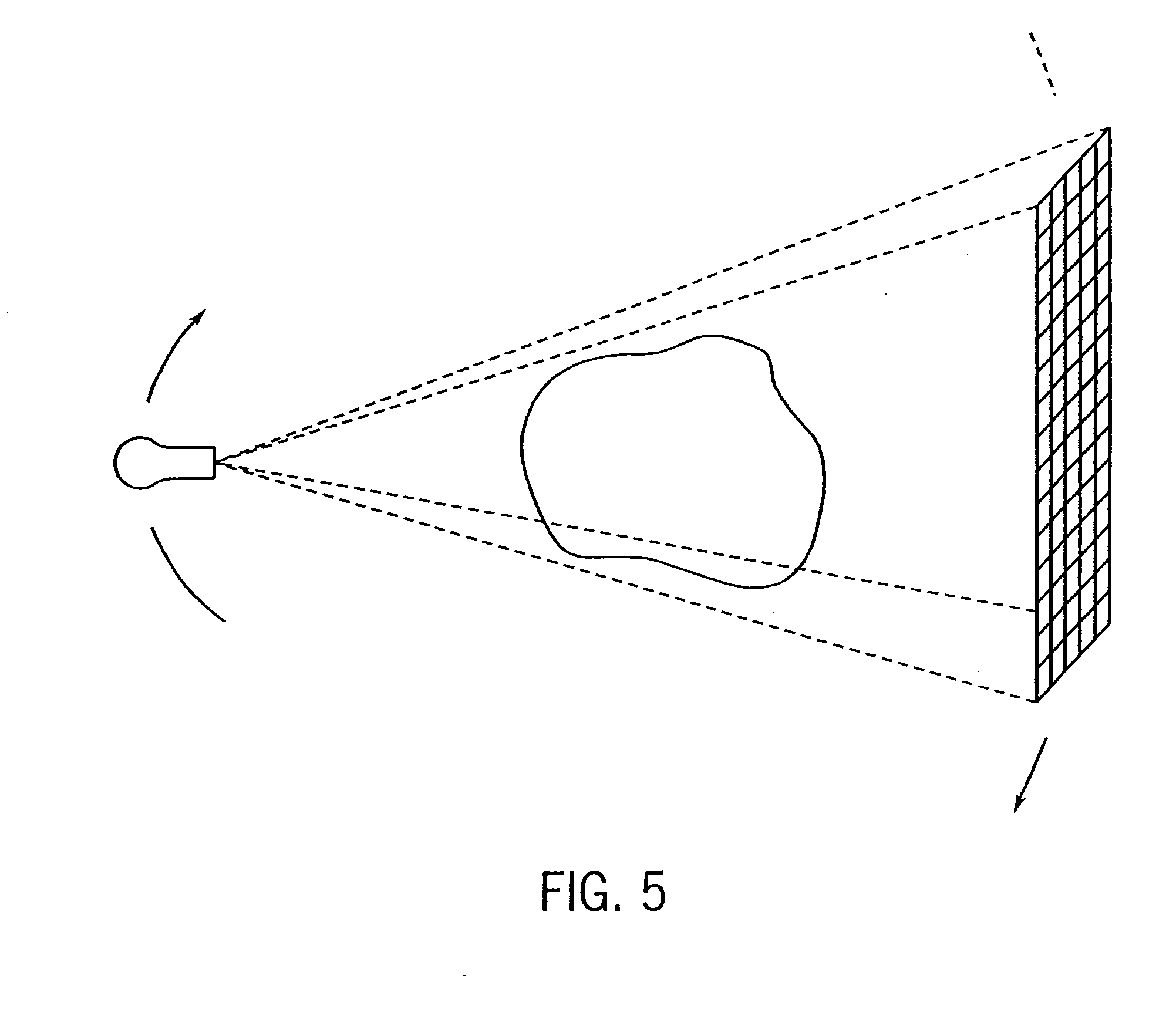
Practical implementation of a CT cone beam algorithm for 3-D image reconstruction as applied to nondestructive inspection of baggage, live laboratory animal and any solid materials
InactiveUS20050041771A1Enhance the imageReconstruction from projectionRadiation/particle handlingData setBeam source
This invention uses the CT (Computer Tomography) principle to obtain nondestructive image of different x-ray attenuation inside an object. In order to have fast data acquisition and high resolution, a cone beam source and a 2-D detector surface are necessary. However, for good cone beam image reconstruction datasets from 2 orthogonal planes about the object are required (U.S. Pat. No. 5,375,156,) December 1994 of Kuo-Petravic and Hupke), thus making its implementation difficult as well as raising the cost of the scanner. Here, we suggest a practical way of implementing the 2 orthogonal planes theory by replacing the 2 gantry rotations by 2 rotations of only one fixed gantry and one movement of the object position, making it simple and low cost. This method is applied to the nonintrusive inspection of baggage or imaging of mice for pharmaceutical purposes where the object has to remain in a horizontal plane throughout the procedure. This algorithm can also be applied to nondestructive testing of any solid materials, for example: imperfections in semi-conductors, fracture in turbo-engine blades, composition of uranium drums etc.
Owner:KUO PETRAVIC GIOIETTA +2
Method and device for realizing laser focusing
InactiveCN101770076APlay a focal roleFocusLaser beam welding apparatusOptical elementsLight spotLight beam
The invention discloses a method for realizing laser focusing, which utilizes reflection of a reflector and focusing of a focus lens to exchange an inner position and an outer position of a light spot of a laser beam in rings along the radial direction and to focalize. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: the laser beam is reflected to a turbinate annular beam; the turbinate annular beam is converted into an annular beam; the annular beam is focused, so as to form an annular conical beam, and a hollow conical dark area is formed in the middle of the annular conical beam, thus obtaining a focusing spot of hollow annular light. The method solves the defects of laser focusing in the prior art and obtains a focusing spot with strong light encompassing weak light, almost uniform energy distribution and small gradient, thus improving the processing effect.
Owner:SUZHOU LEAD LASER TECH
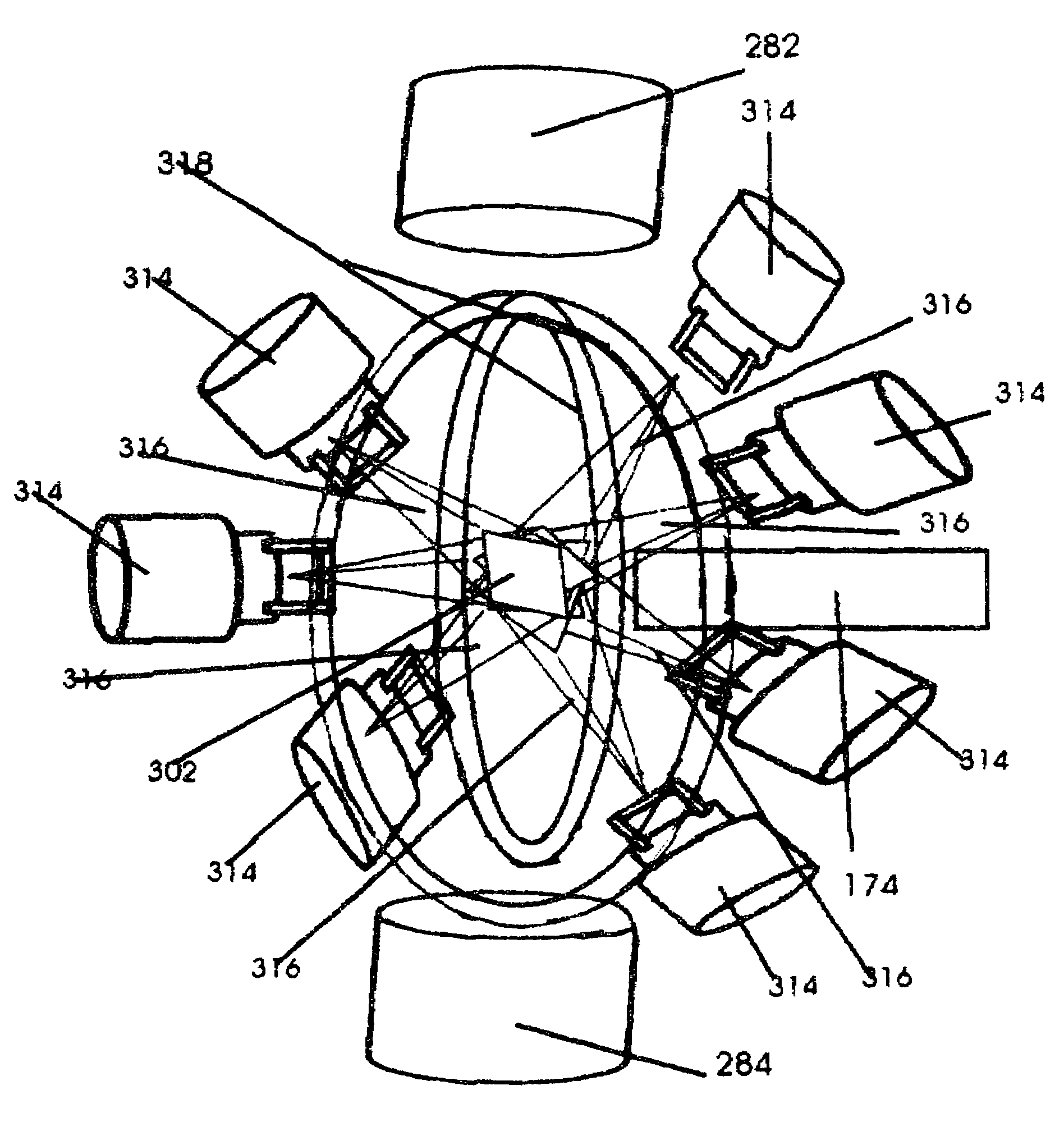
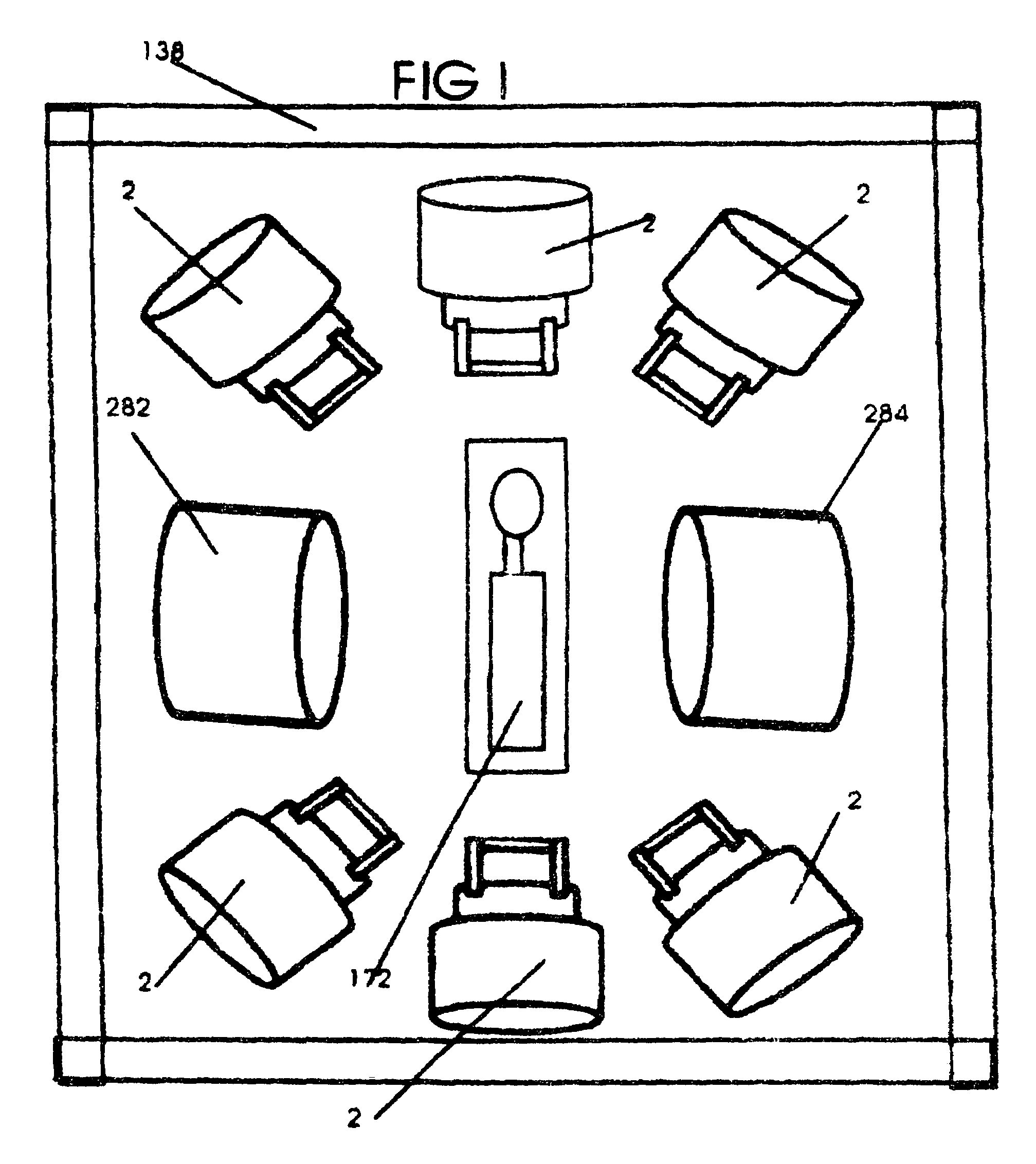
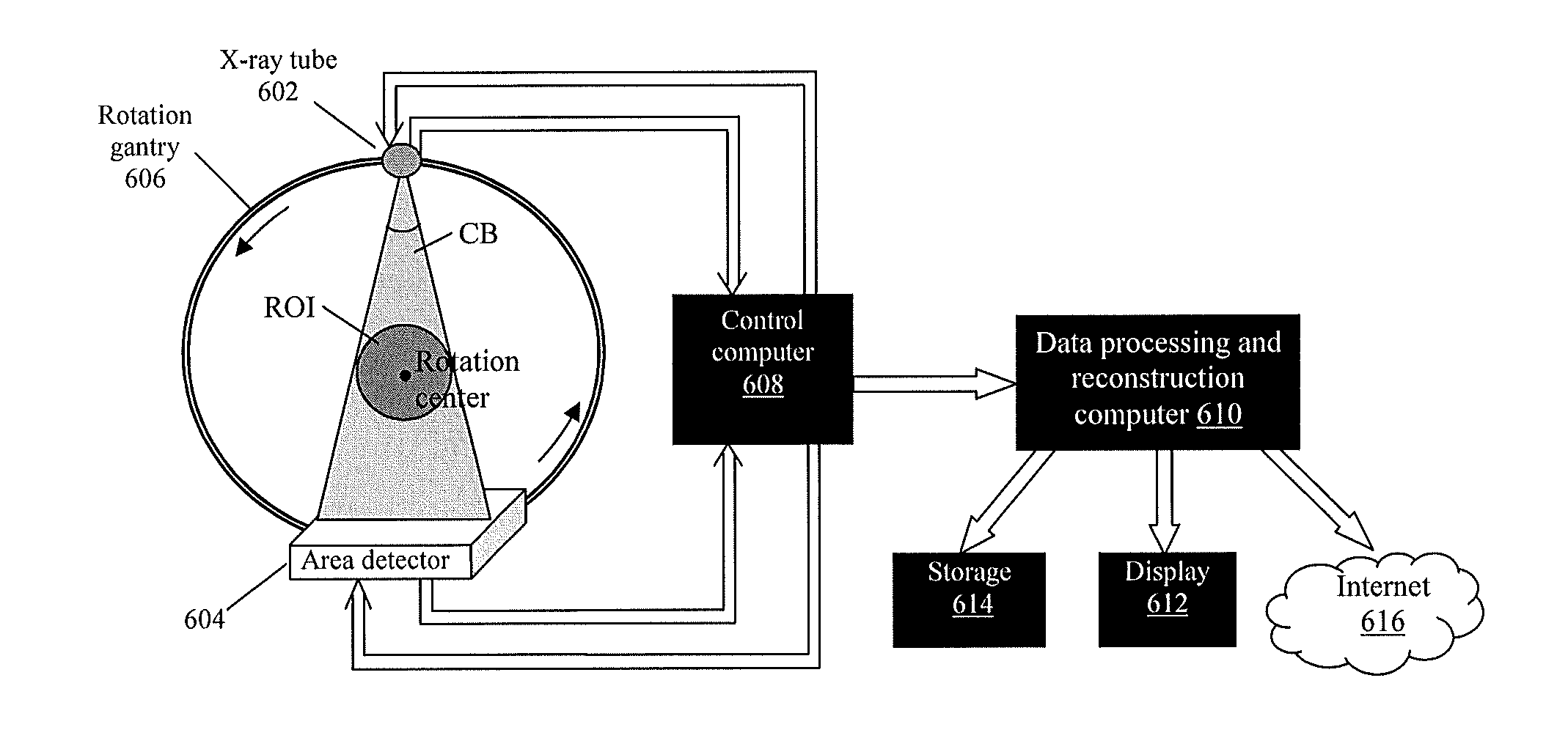
System and method for cone beam computed tomography
ActiveUS20130077737A1Easy accessRadiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsX-rayHorizontal axis
A cone beam computed tomography system with a horizontally disposed, cylindrical gantry and a method for its use are provided. The cylindrical gantry includes a rotatable cylindrical frame fixed to a support frame. A cone beam X-ray source and X-ray detector are mounted to the circumference of the cylindrical frame at diametrically opposed positions. The cylindrical frame is actuated to revolve the X-ray source-detector arrangement around a horizontal axis, thereby scanning a recumbent subject positioned in the aperture of the cylindrical frame.
Owner:QUEENSLAND RAIL LIMITED
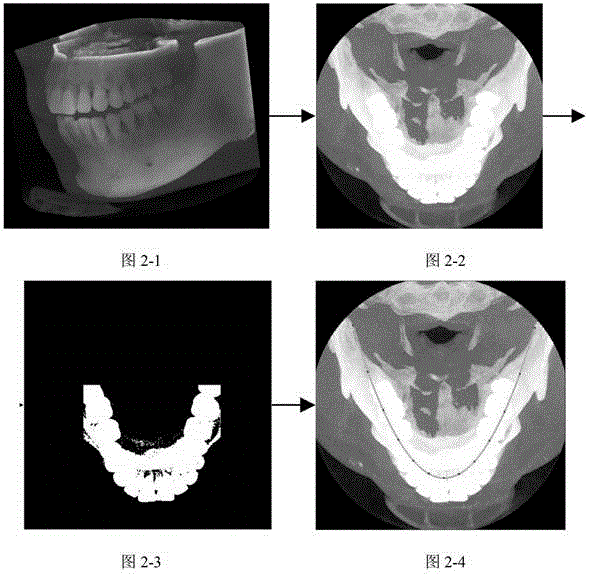
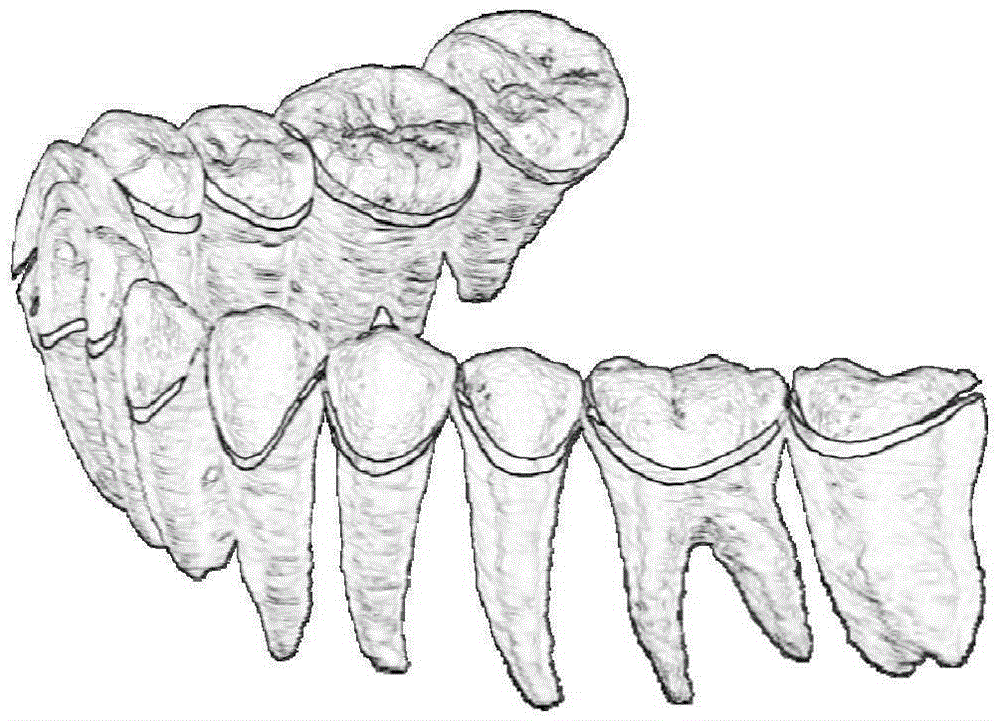
Method for extracting panoramic image from three-dimensional conical beam CT data of dentistry department
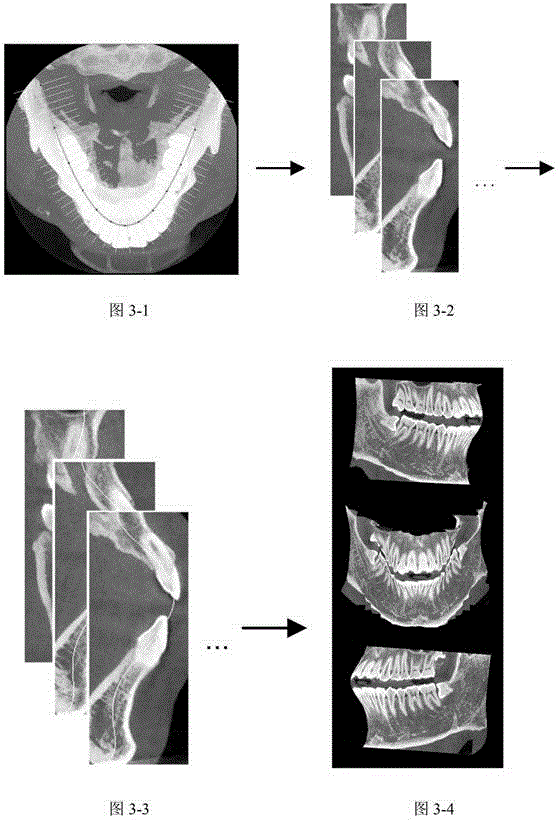
ActiveCN105608747AIdentify anatomyStructural solutionDetails involving 3D image dataGeometric image transformationAnatomical structuresThree dimensional ct
The invention relates to a method for extracting panoramic image from three-dimensional conical beam CT data of a dentistry department, and the method comprises the following steps: (1), generating a dental arch curve according to the three-dimensional conical beam CT data of the dentistry department; (2), extracting a three-dimensional oral cavity panoramic curved surface according to the generated dental arch curve; (3), expanding the three-dimensional oral cavity panoramic curved surface and obtaining an oral cavity panoramic image. The method can extract a tooth curved surface faultage image through the three-dimensional CT data, solves problems of structure overlapping and image fuzzy, and improves the diagnosis precision. The method can obtain a single-frame oral cavity panoramic image, and the single-frame oral cavity panoramic image can display all teeth. The method can clearly recognize the anatomical structure of teeth, such as enamel, dentin and dental pulp, effectively avoids image fuzzy caused by perspective, and has no structure overlapping.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for 3d metal and high-density artifact correction for cone-beam and fan-beam ct imaging
ActiveUS20120008845A1Accurate reconstruction imageHigh artifactImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionMetal ArtifactHigh density
A 3D metal artifacts correction technique corrects the streaking artifacts generated by titanium implants or other similar objects. A cone-beam computed tomography system is utilized to provide 3D images. A priori information (such as the shape information and the CT value) of high density sub-objects is acquired and used for later artifacts correction. An optimization process with iterations is applied to minimize the error and result in accurate reconstruction images of the object.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
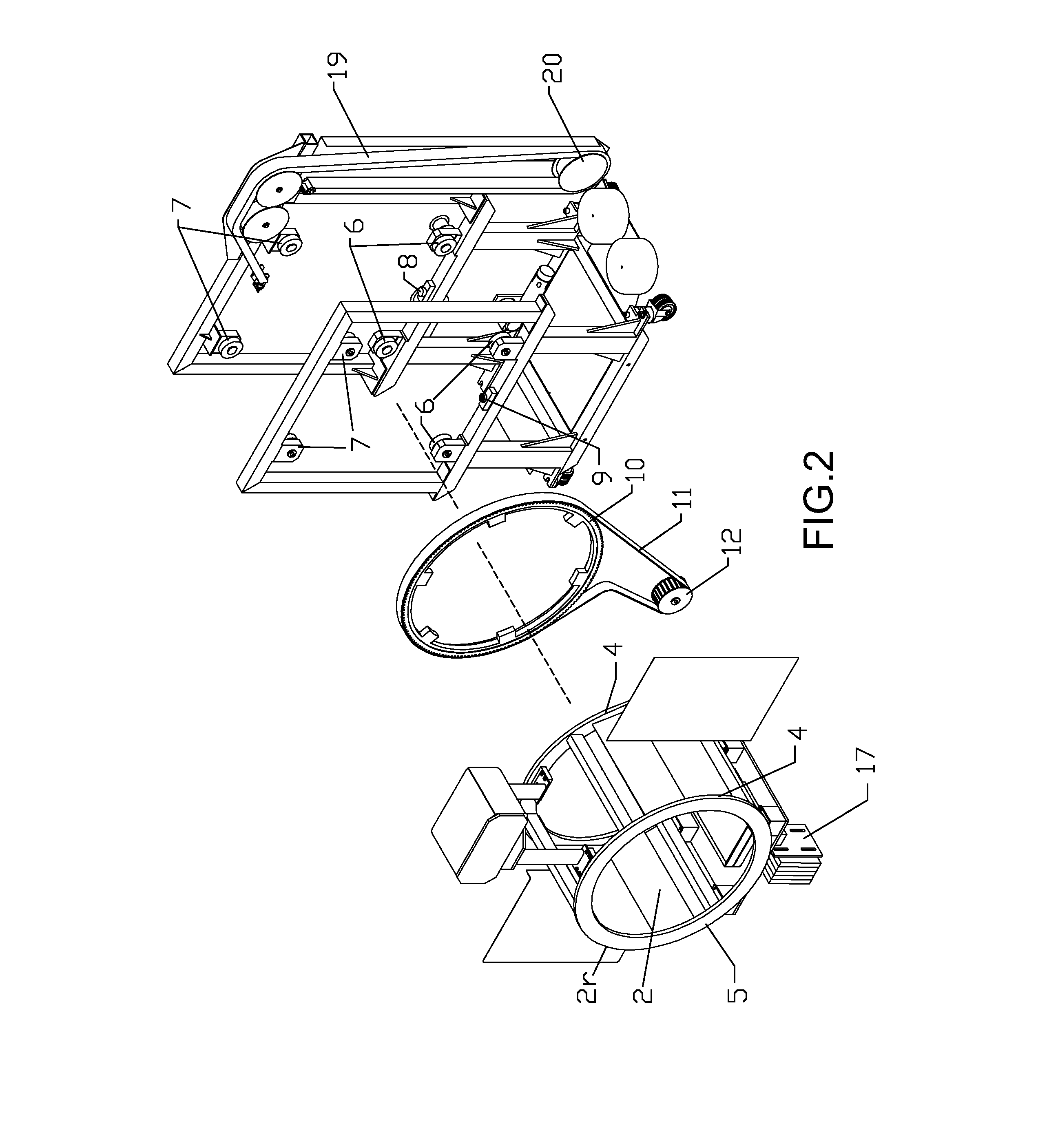
Electron beam computed tomographic scanner system with helical or tilted target, collimator and detector components to eliminate cone beam error and to scan continuously moving objects
InactiveUS7020232B2Reduce system costReduce computational overheadReconstruction from projectionHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHelical scanMulti slice
A scanning electron beam computed tomographic system eliminates axial offset between target and detector by disposing the target, collimator, and detector such that active portions of the target and detector are always diametrically opposite each other. This result is achieved by providing a helical target, collimator, and detector, or by providing planar target, collimator, and detector components that are inclined relative to the vertical axis such that active portions of the target and detector are always diametrically opposite each other. Either configuration eliminates cone beam error and the necessity to correct for same. Further, the system can provide multi-slice scanning of an object that is in constant motion at a critical velocity, without having to interpolate data. Conventional helical scanning may still be undertaken. Detector elements can be disposed axially to improve signal / noise ratio and to produce a cone beam cancellation effect.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Crown root three-dimensional model merging method
ActiveCN106806030AAchieve natural transition fusionDental prostheticsDenturesInductively coupled plasma
The invention relates to a crown root three-dimensional model merging method, which comprises the following steps of preparing a denture mold or a dental jaw gypsum mold; performing optical scanning to obtain a three-dimensional digital denture mold; rebuilding a three-dimensional digital denture mold with complete tooth root information through maxillofacial region conical beam CT (Computed Tomography) scanning data extraction; on the basis of an ICP (inductively coupled plasma) algorithm, performing positioning registering on optical scanning and CBCT (cone beam computerized tomography) re-building three-dimensional denture mold according to the dental crown common region; building an occlusion plane modeling coordinate system; creating the crown gingival boundary line by a method of crown gingival boundary line extraction and quantitative bias and projection; on the basis of the crown gingival and crown root boundary line, respectively performing division cutting on the optical scanning and CBCT re-building denture mold; completing the integral fusion of three-dimensional dental crown and tooth root data based on a curvature continuous algorithm. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the natural transition fusion of the optical scanning dental crown data and CBCT rebuilding tooth root data is realized, so that the crown root three-dimensional fusion model more similar to the real teeth can be obtained.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SCHOOL OF STOMATOLOGY
Cone-beam filtered backprojection image reconstruction method for short trajectories
ActiveUS20060115040A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayReconstruction method
An image reconstruction method for cone beam x-ray attenuation data acquired over a super-short-scan, short-scan or full-scan includes backproejcting over three adjacent segments of the arc traversed by the x-ray source. Each backprojection consists of a weighted combination of ID Hilbert filtering of the modified cone-beam data along both horizontal and non-horizontal directions.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Focus detector arrangement for generating phase-contrast X-ray images and method for this
ActiveCN101011250AHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHandling using diaphragms/collimetersSoft x rayPhase grating
A focus-detector arrangement and an X-ray apparatus for generating projective or tomographic phase contrast recordings of a subject are disclosed. In at least one embodiment, the focus-detector arrangement includes a radiation source with a focus, arranged on a first side of the subject, for generating a fan-shaped or conical beam of rays; at least one X-ray optical grating arranged in the beam path, with at least one phase grating arranged on the opposite second side of the subject in the beam path generating an interference pattern of the X-radiation preferably, in a particular energy range; and an analysis-detector system which detects at least the interference pattern generated by the phase grating in respect of its phase shift with position resolution. According to at least one embodiment of the invention, at least one X-ray optical grating including bars which are free from overhangs form shadows in the beam path of the fan-shaped or conical beam of rays.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
Underwater acoustic beacon location system
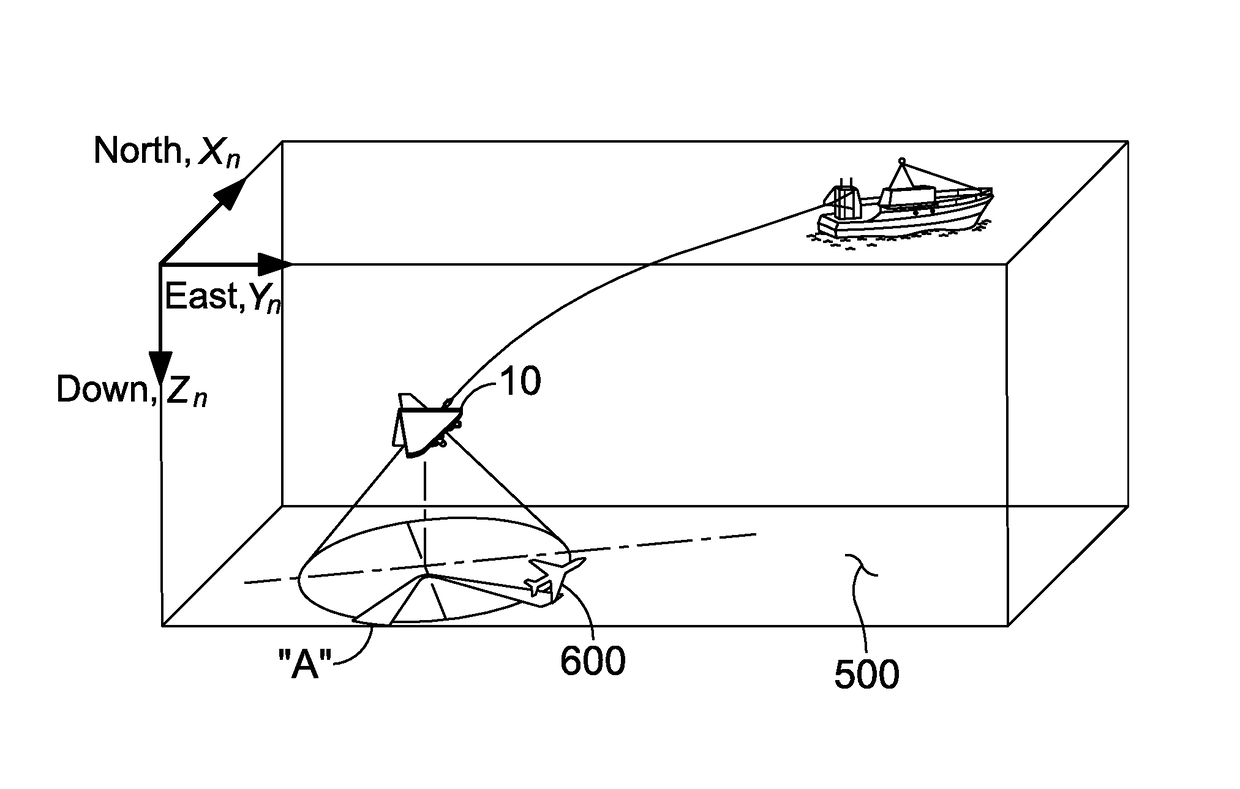
ActiveUS9829565B1Accurate estimatePosition fixationAcoustic wave reradiationOcean bottomSensor array
A method using a tow body and sensor array for locating an underwater location beacon is provided. The steps of the method are moving the body and array in a direction of motion; orientating the array orthogonal to the direction of motion; beamforming acoustic conical beams from the array onto a seafloor; detecting a time series of acoustic data channels from the beacon; converting the data channels into spatial beams of acoustic frequency; determining if a signal of the underwater location beacon is present from each spatial beam; calculating likelihood functions for locations of the beacon to represent an area of the seafloor from which the signal of the underwater location beacon is to have originated; accumulating likelihood functions for the location of the underwater location beacon over the course of a search pattern; and producing a grid for a beacon location based on the likelihood functions.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com