Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
614results about How to "Reduce relative motion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
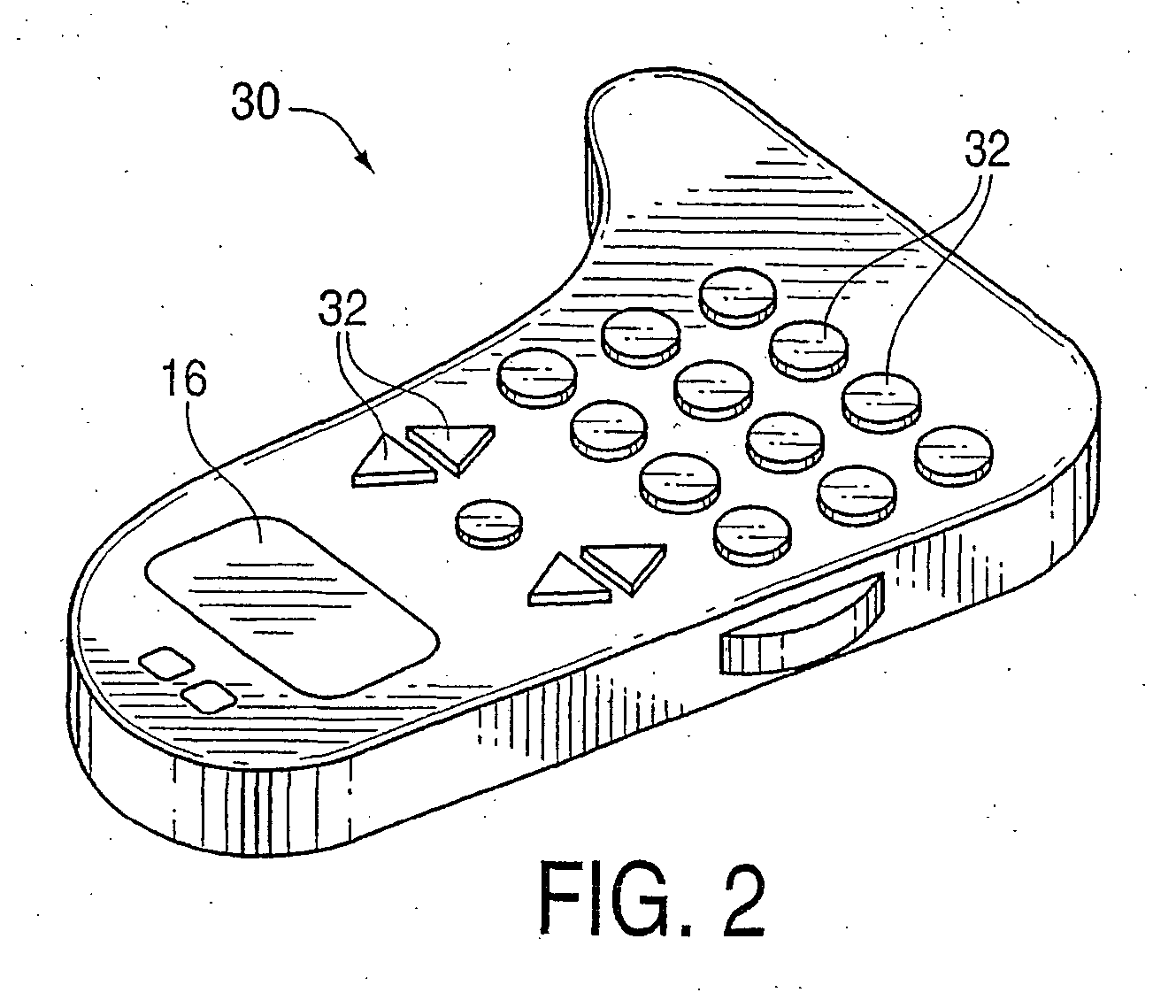
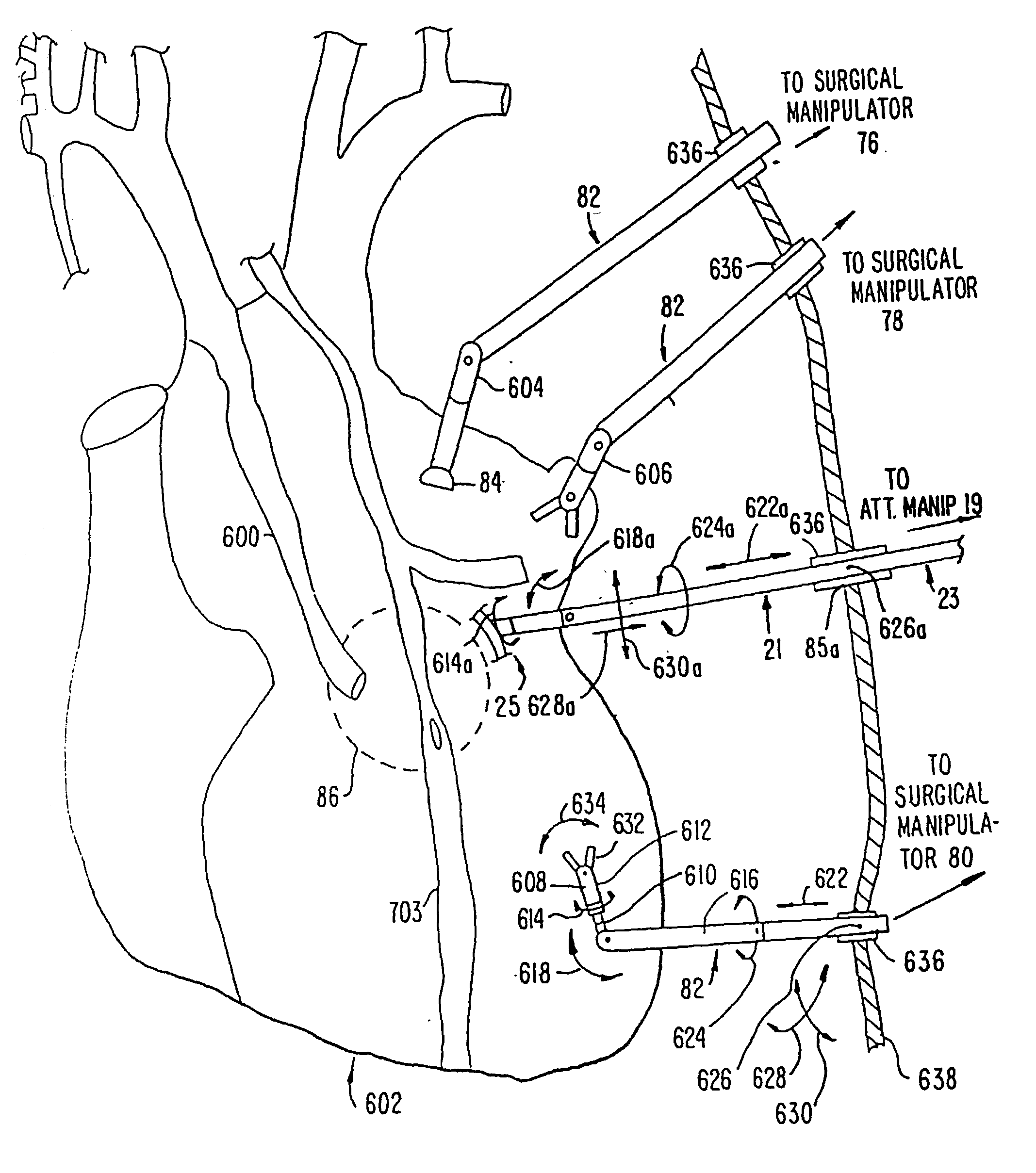
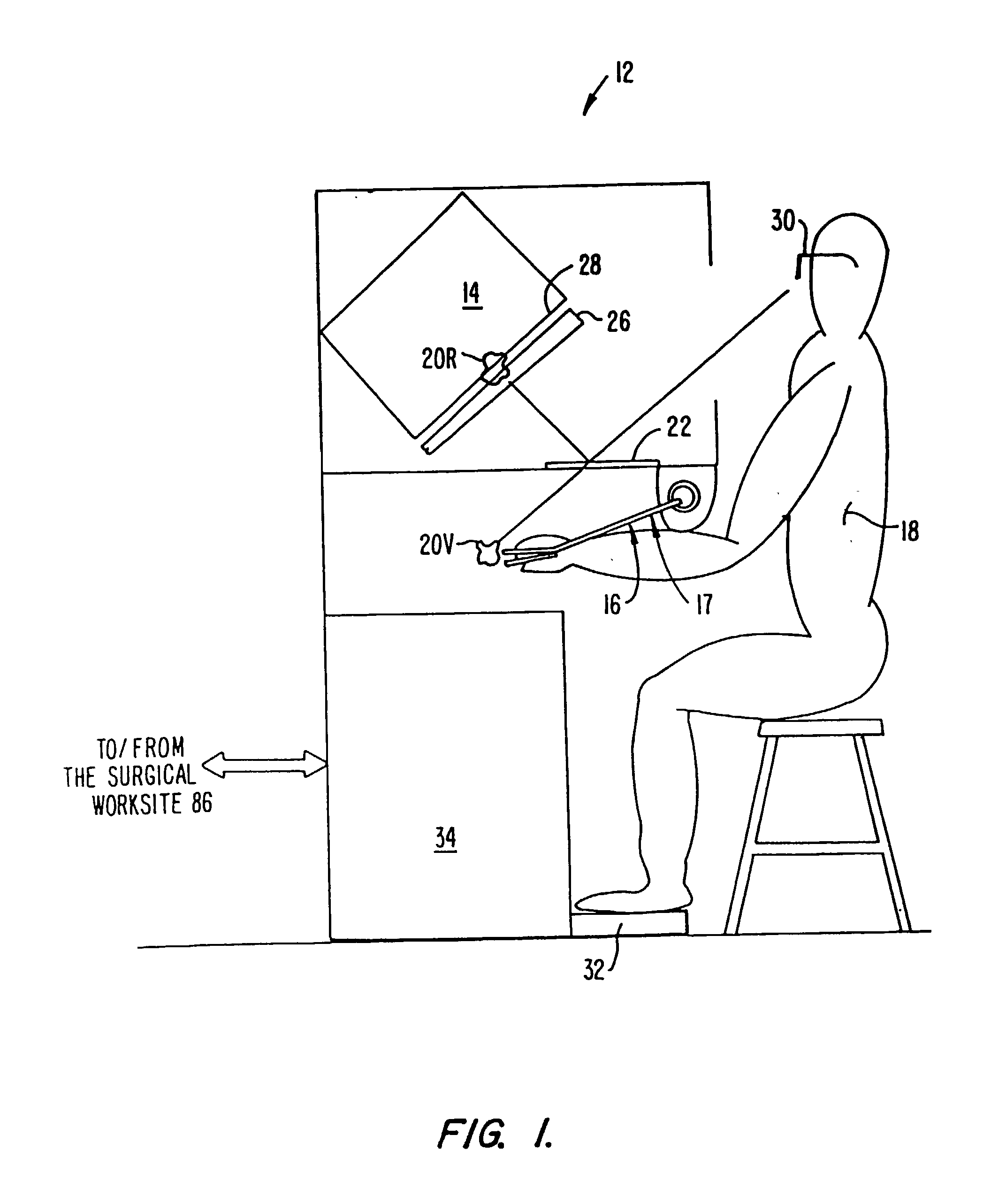
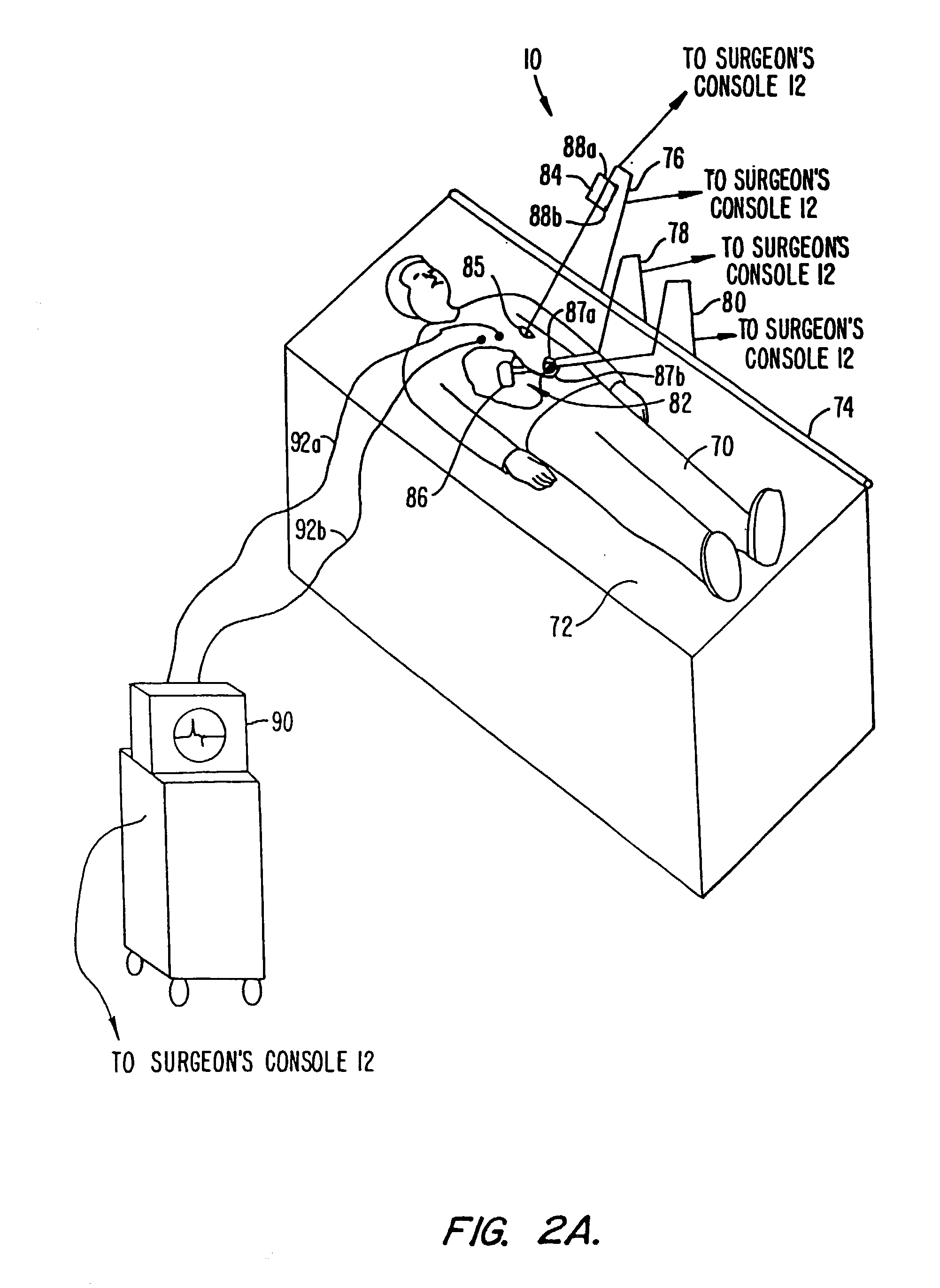
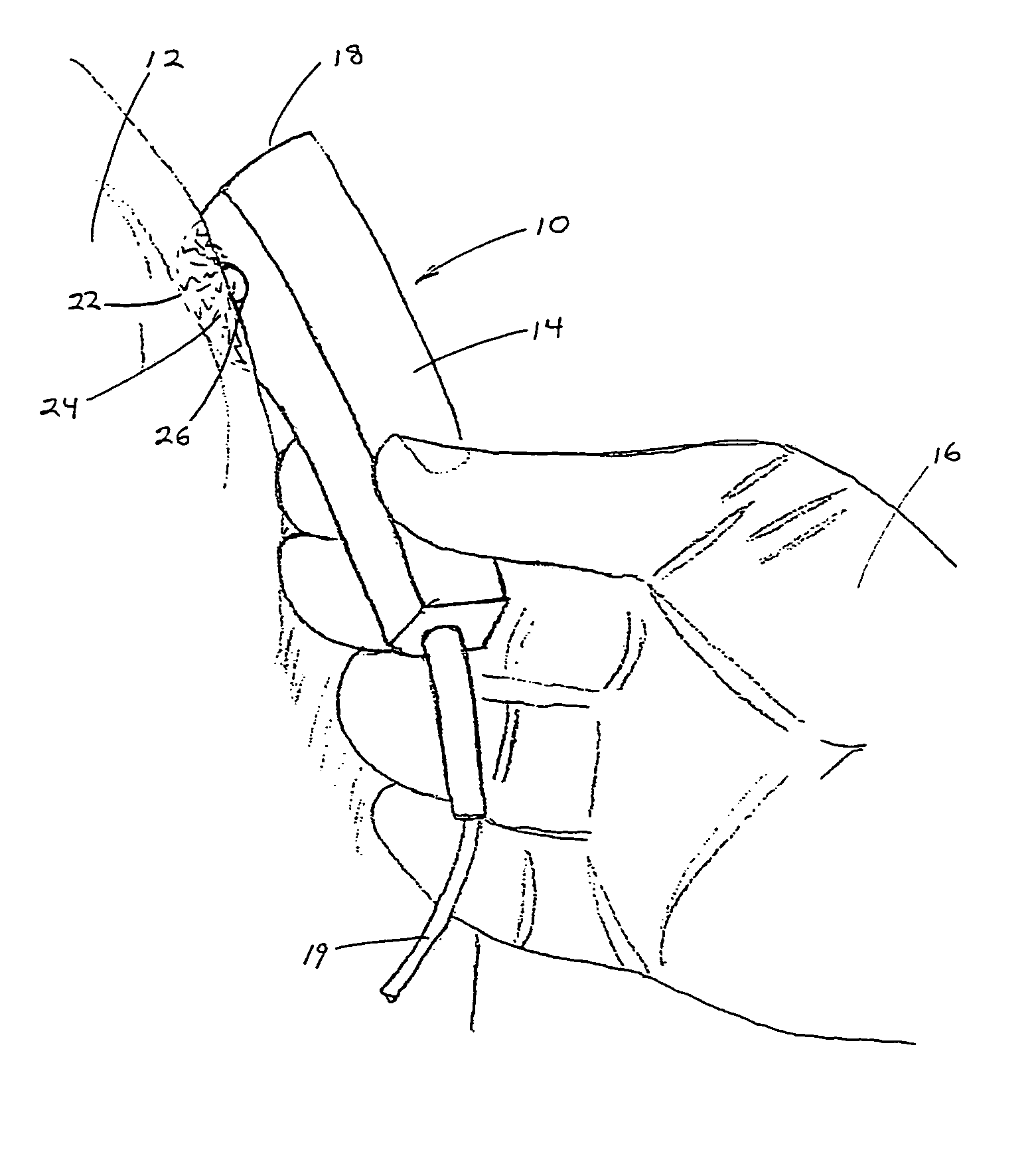
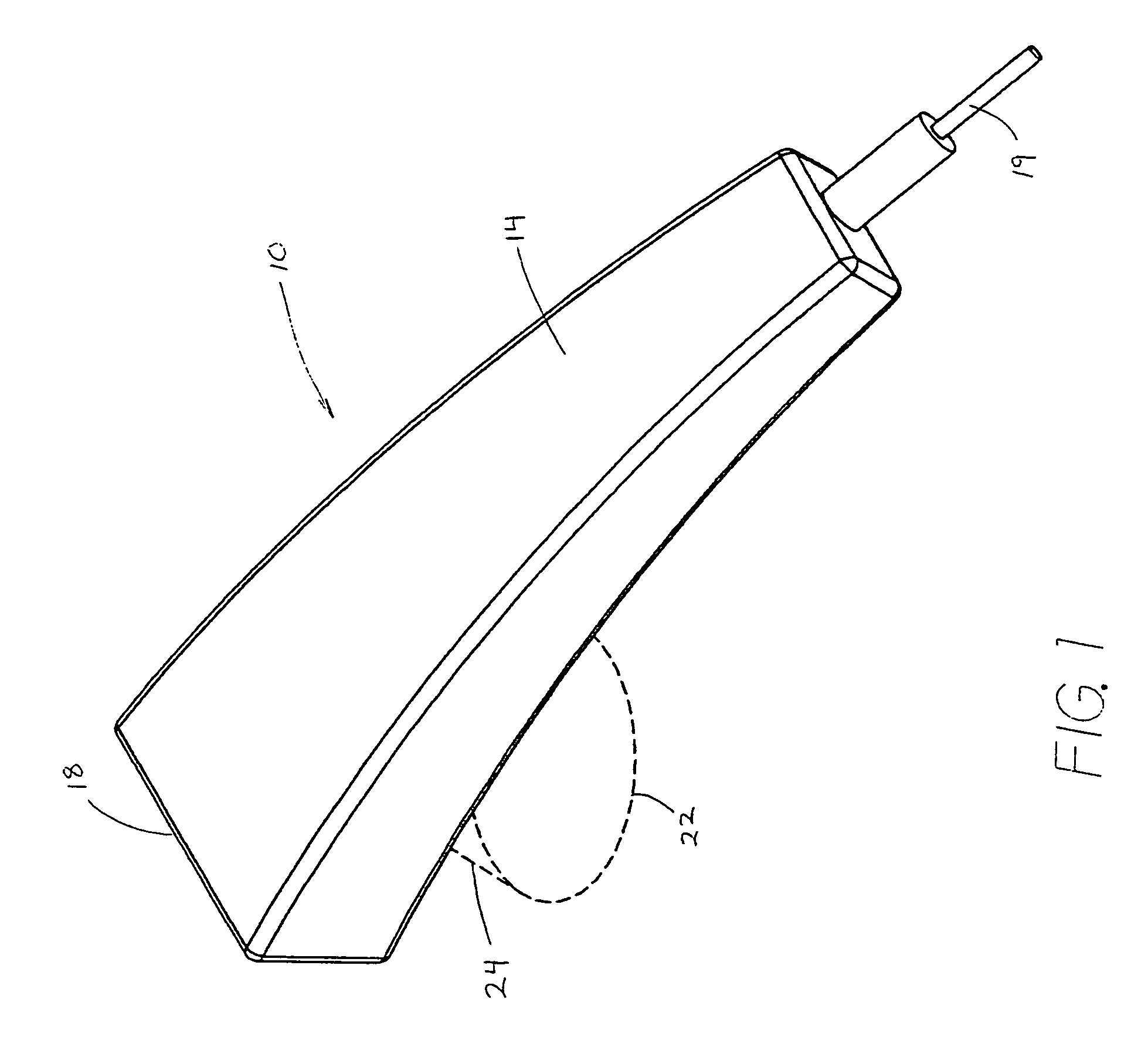
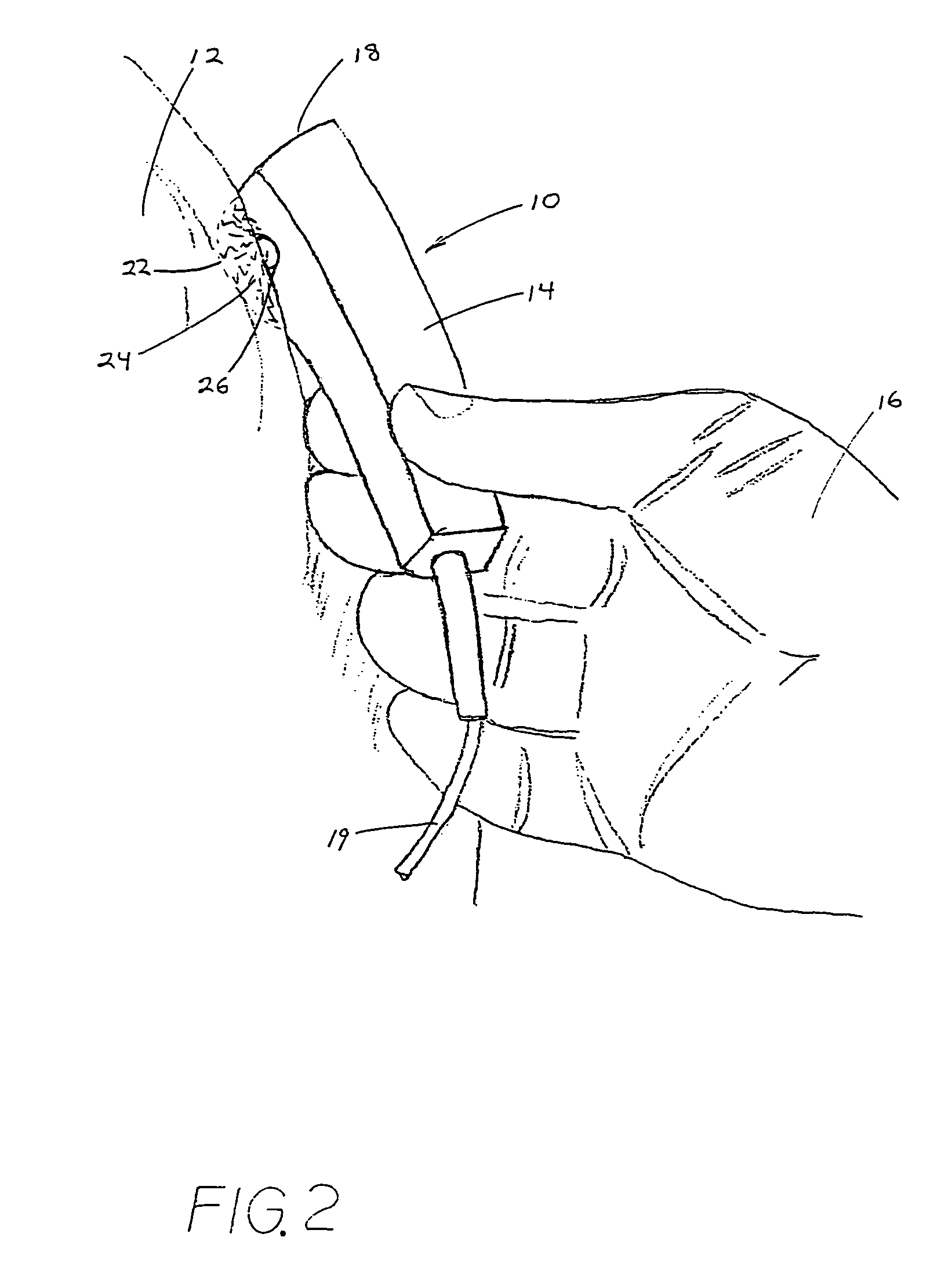
Performing cardiac surgery without cardioplegia
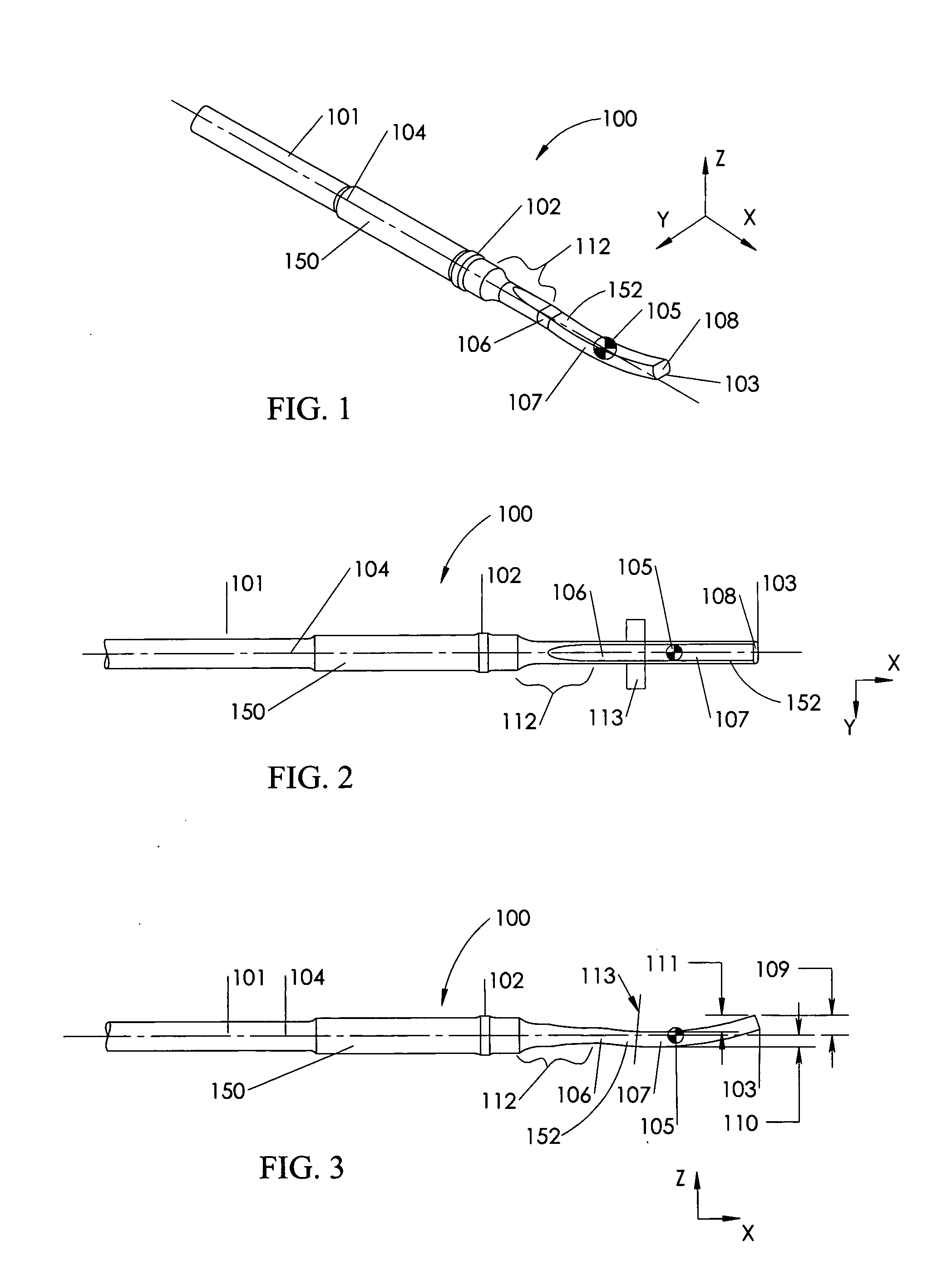
InactiveUS6468265B1Improve abilitiesEasy to controlSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsForcepsMotion tracking system
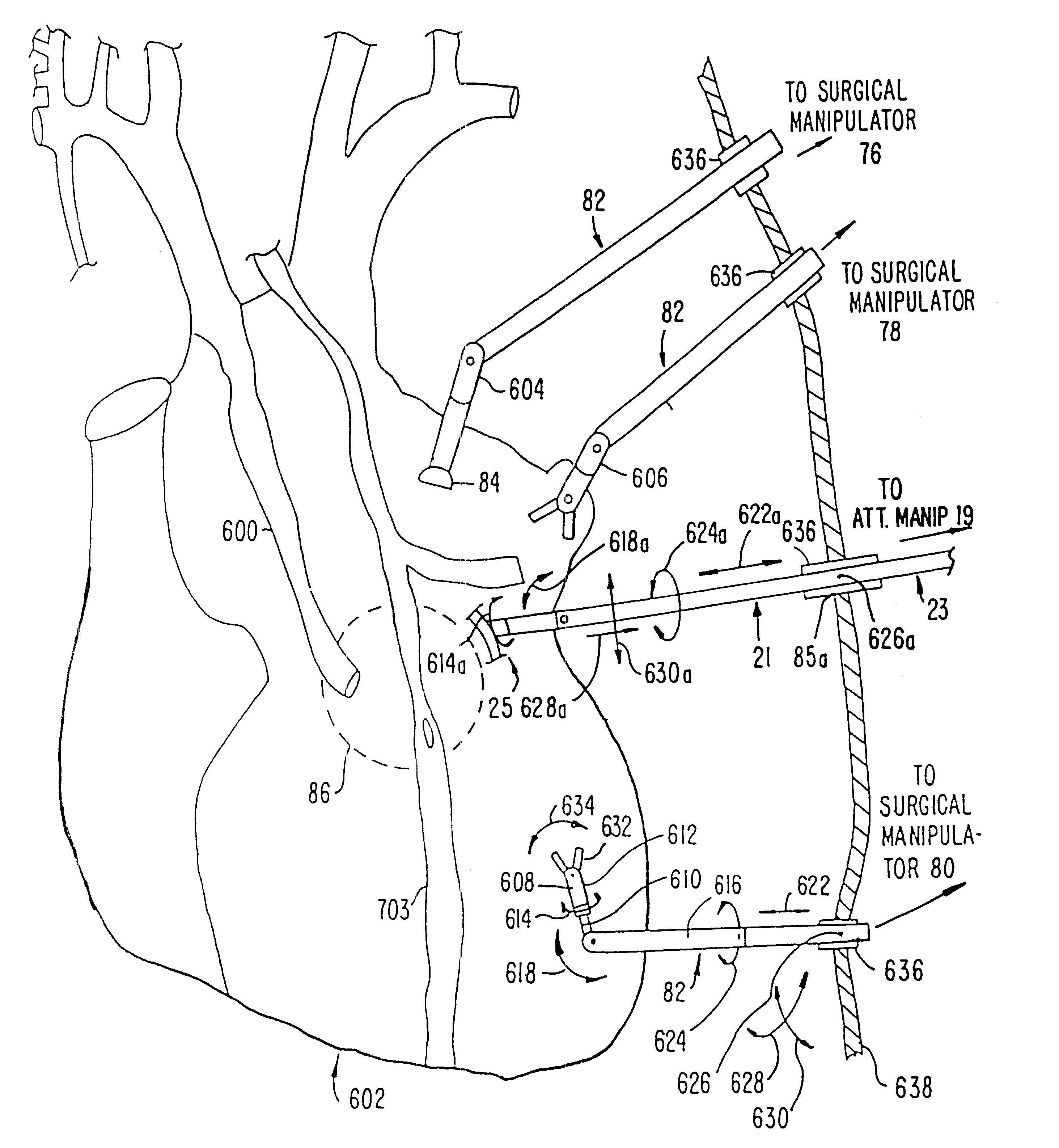
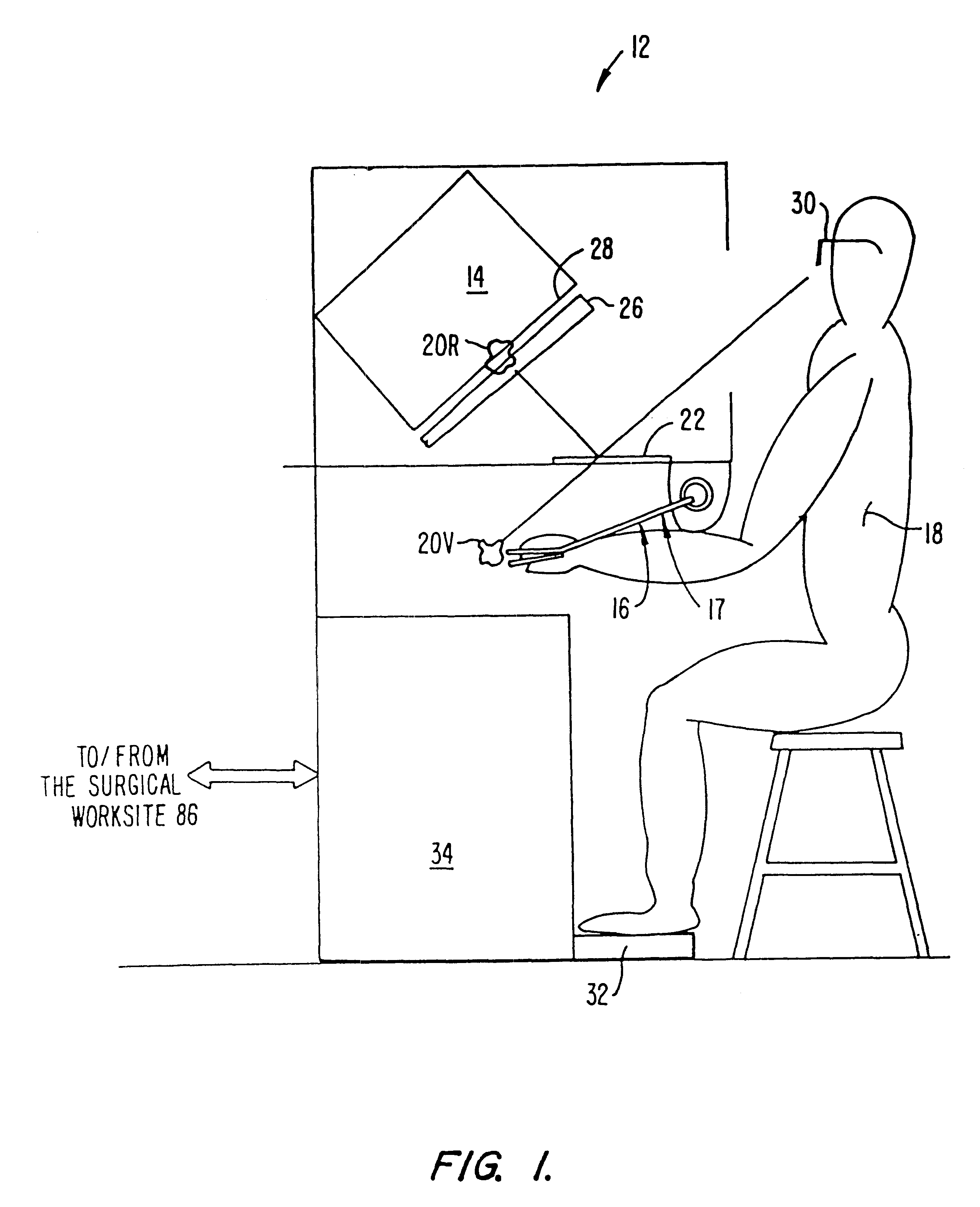
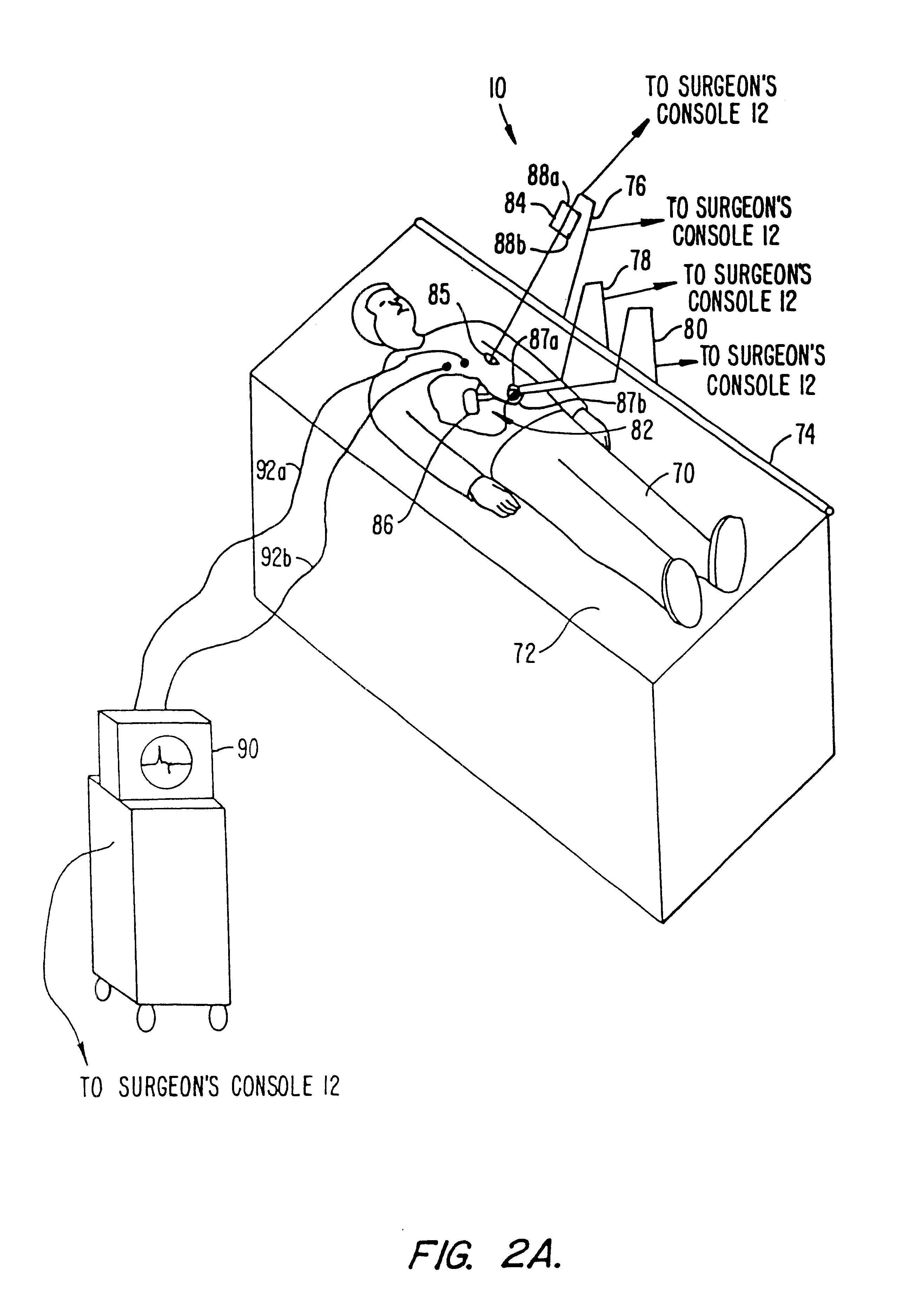
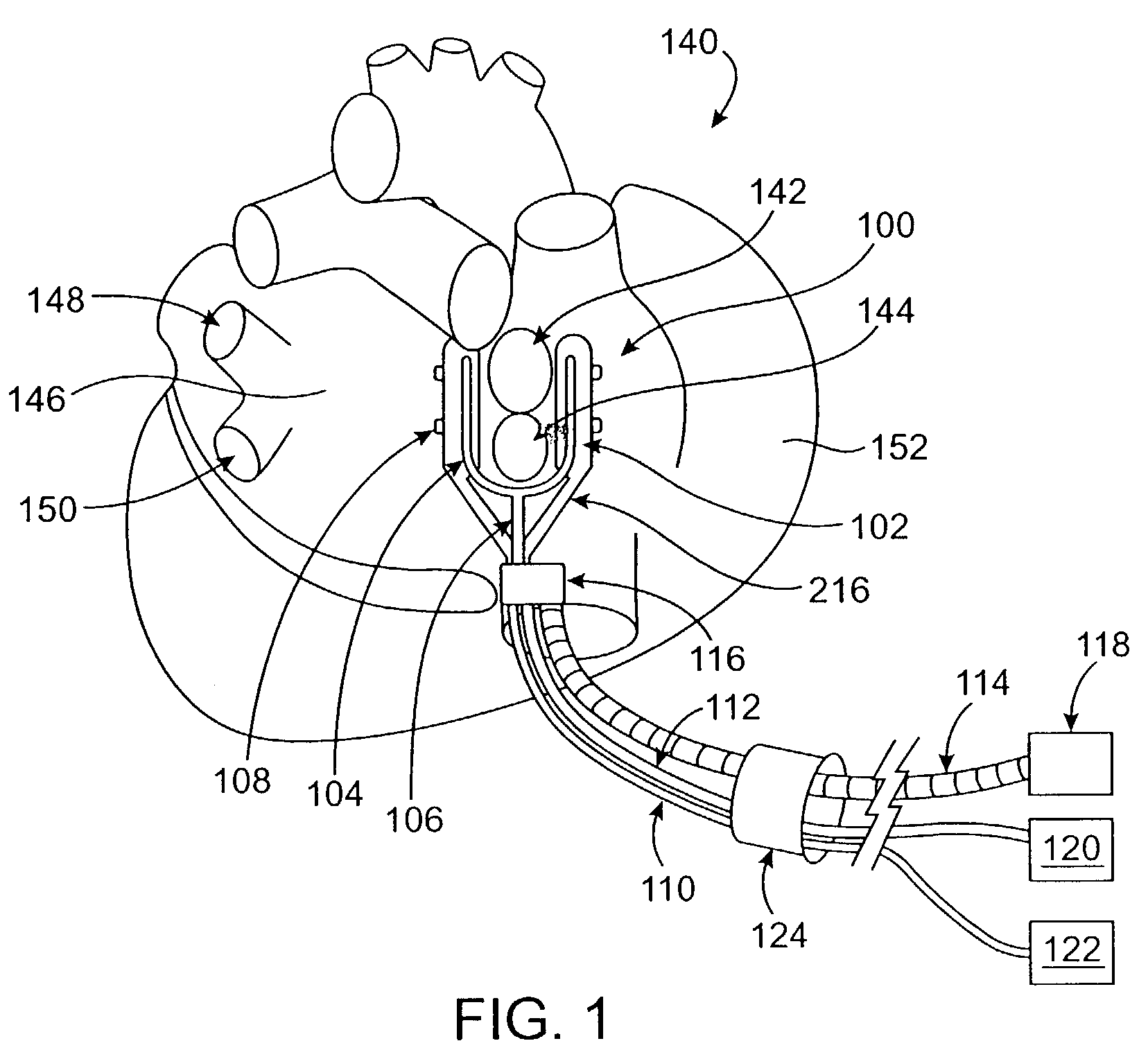
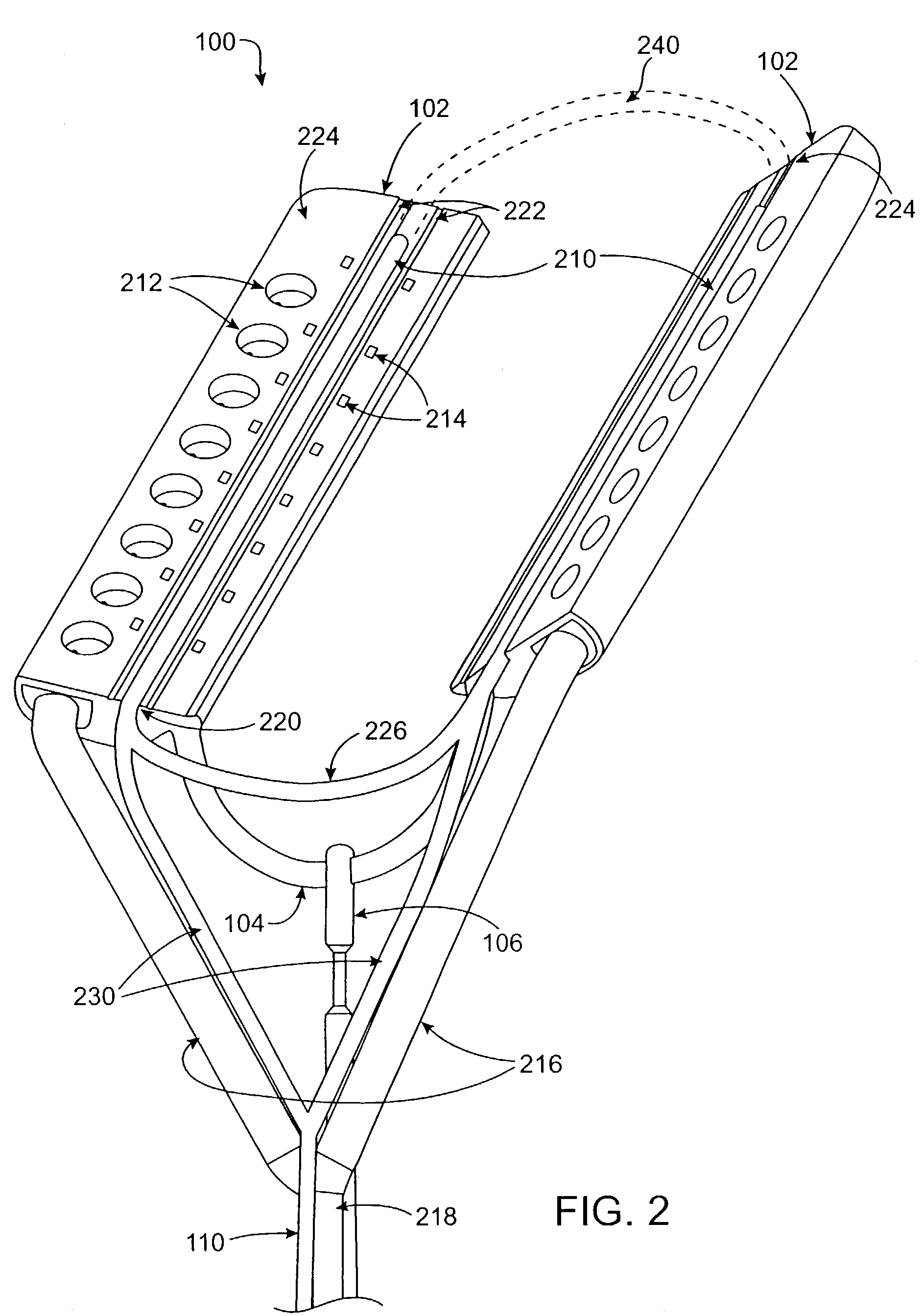
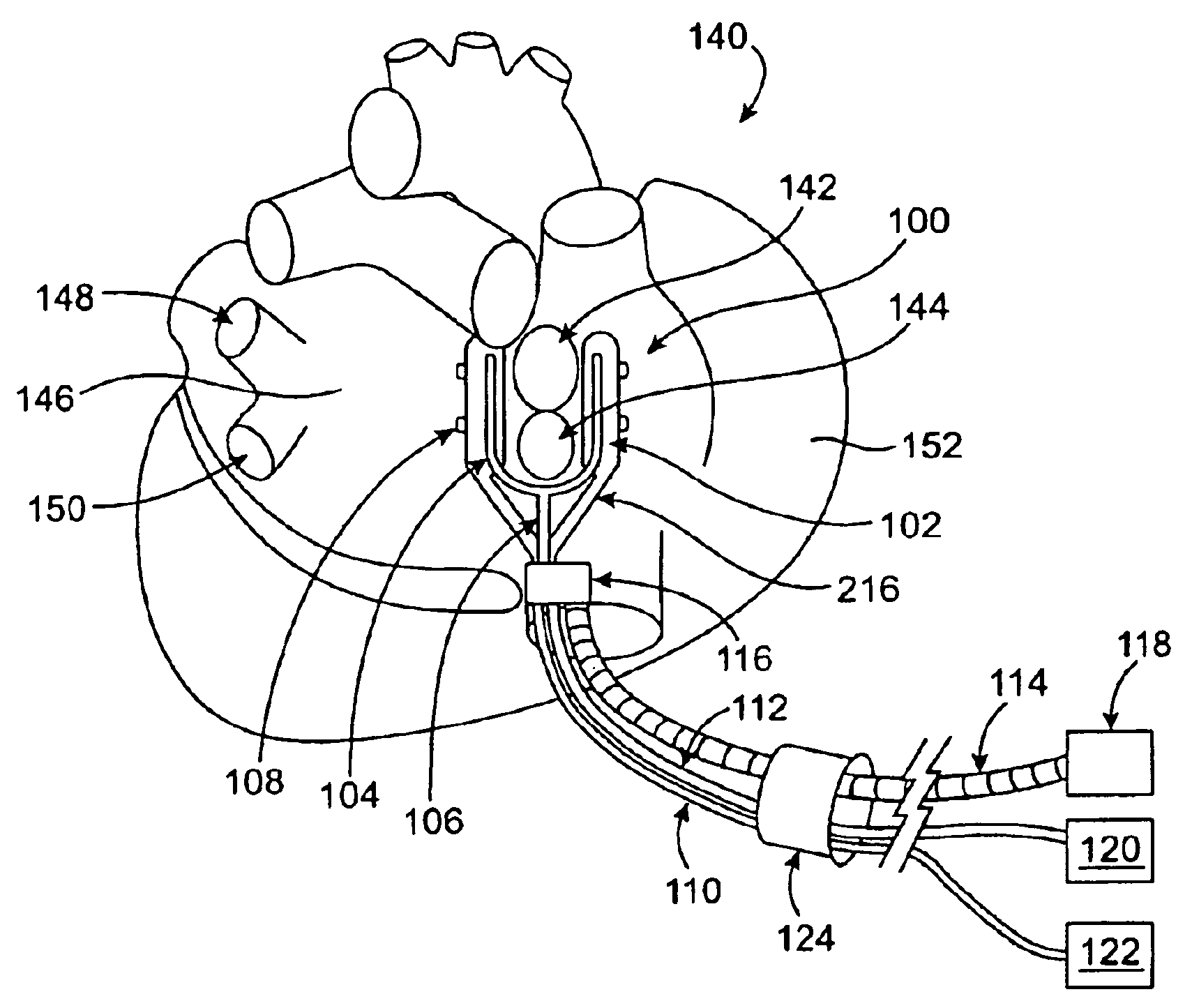
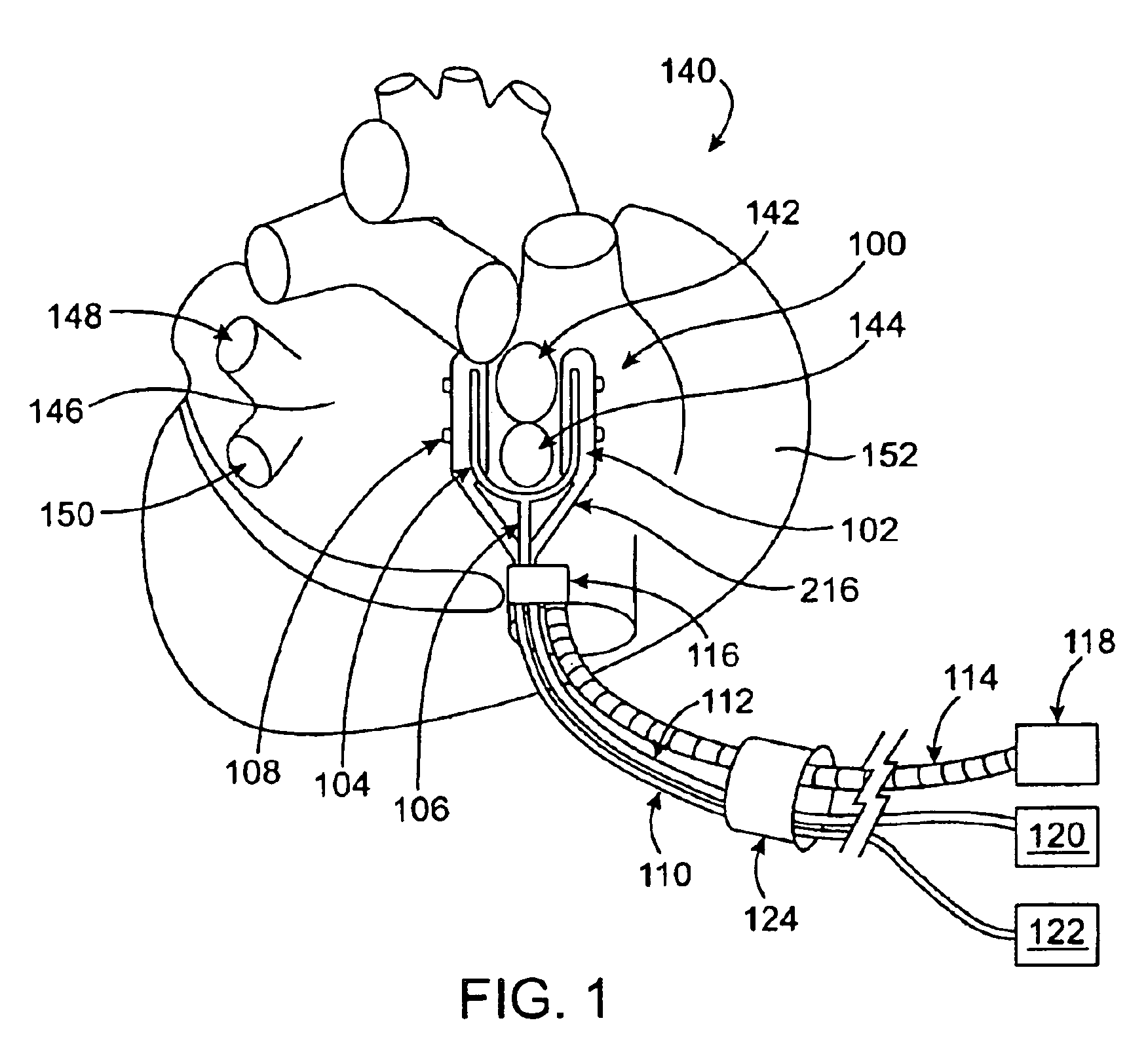
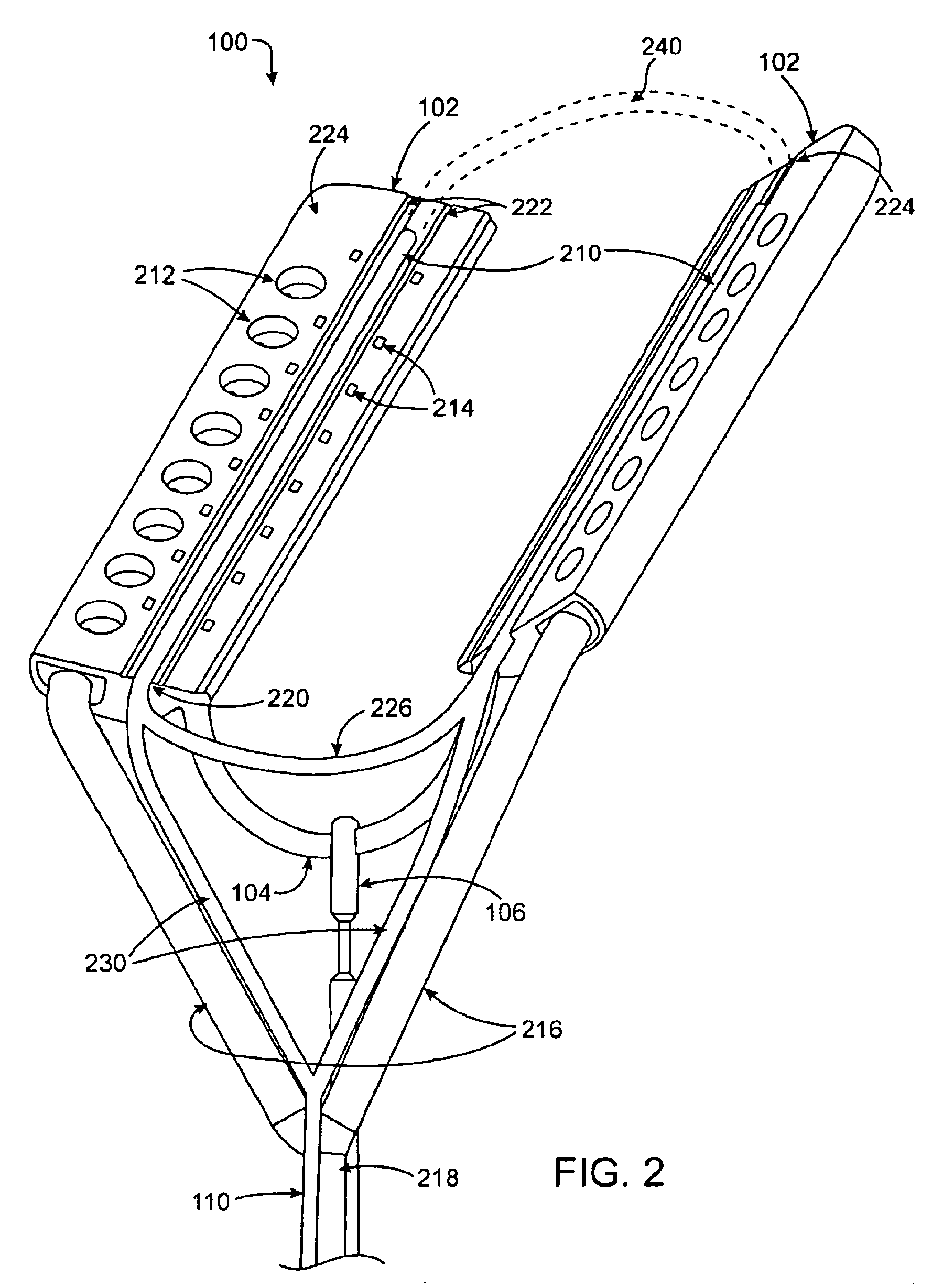
A surgical system or assembly for performing cardiac surgery includes a surgical instrument; a servo-mechanical system engaged to the surgical instrument for operating the surgical instrument; and an attachment assembly for removing at least one degree of movement from a moving surgical cardiac worksite to produce a resultant surgical cardiac worksite. The surgical system or assembly also includes a motion tracking system for gathering movement information on a resultant surgical cardiac worksite. A control computer is engaged to the attachment assembly and to the motion tracking system and to the servo-mechanical system for controlling movement of the attachment assembly and for feeding gathered information to the servo-mechanical system for moving the surgical instrument in unison with the resultant surgical cardiac worksite such that a relative position of the moving surgical instrument with respect to the resultant surgical cardiac worksite is generally constant. A video monitor is coupled to the control computer; and an input system is coupled to the servo-mechanical system and to the control computer for providing a movement of the surgical instrument. The video monitor displays movement of the surgical instrument while the resultant surgical cardiac worksite appears substantially stationary, and while a relative position of the surgical instrument moving in unison with the resultant surgical cardiac worksite, as a result from the movement information gathered by the motion tracking system, remains generally constant. A method of performing cardiac surgery without cardioplegia comprising removing at least one degree of movement freedom from a moving surgical cardiac worksite to produce at least a partially stationary surgical cardiac worksite while allowing a residual heart section, generally separate from the at least partially stationary surgical cardiac worksite, to move as a residual moving heart part. Cardiac surgery is performed on the at least partially stationary cardiac worksite with a surgical instrument such as needle drivers, forceps, blades and scissors.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Cardiac treatment devices and methods
Devices and methods provide for ablation of cardiac tissue for treating cardiac arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation. Although the devices and methods are often be used to ablate epicardial tissue in the vicinity of at least one pulmonary vein, various embodiments may be used to ablate other cardiac tissues in other locations on a heart. Devices generally include at least one tissue contacting member for contacting epicardial tissue and securing the ablation device to the epicardial tissue, and at least one ablation member for ablating the tissue. Various embodiments include features, such as suction apertures, which enable the device to attach to the epicardial surface with sufficient strength to allow the tissue to be stabilized via the device. For example, some embodiments may be used to stabilize a beating heart to enable a beating heart ablation procedure. Many of the devices may be introduced into a patient via minimally invasive introducer devices and the like. Although devices and methods of the invention may be used to ablate epicardial tissue to treat atrial fibrillation, they may also be used in veterinary or research contexts, to treat various heart conditions other than atrial fibrillation and / or to ablate cardiac tissue other than the epicardium.
Owner:ESTECH ENDOSCOPIC TECH +1
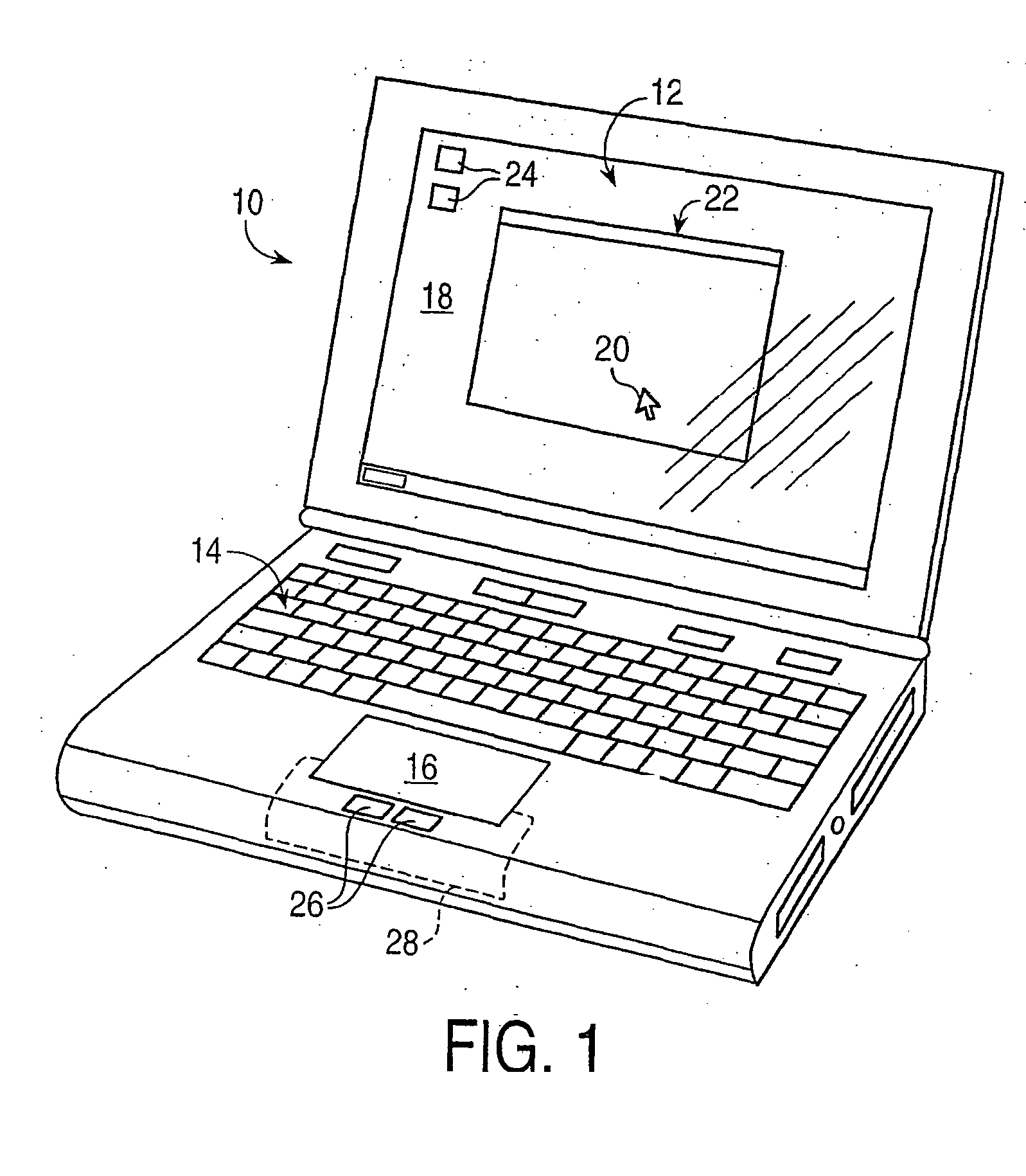
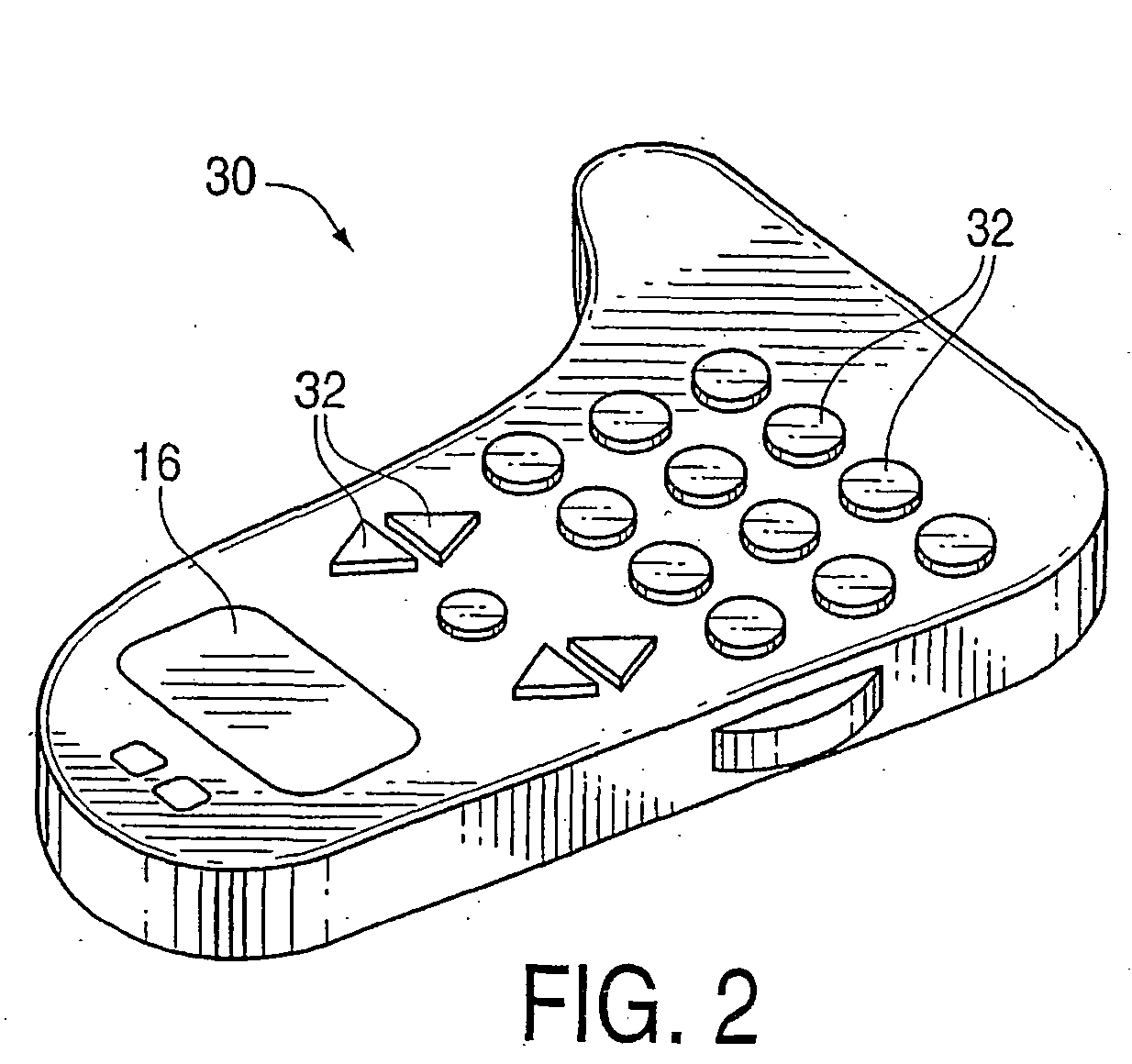
Haptic input devices
InactiveUS20050017947A1Enhanced interactionEnhance manipulationInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsPiezoelectric actuators
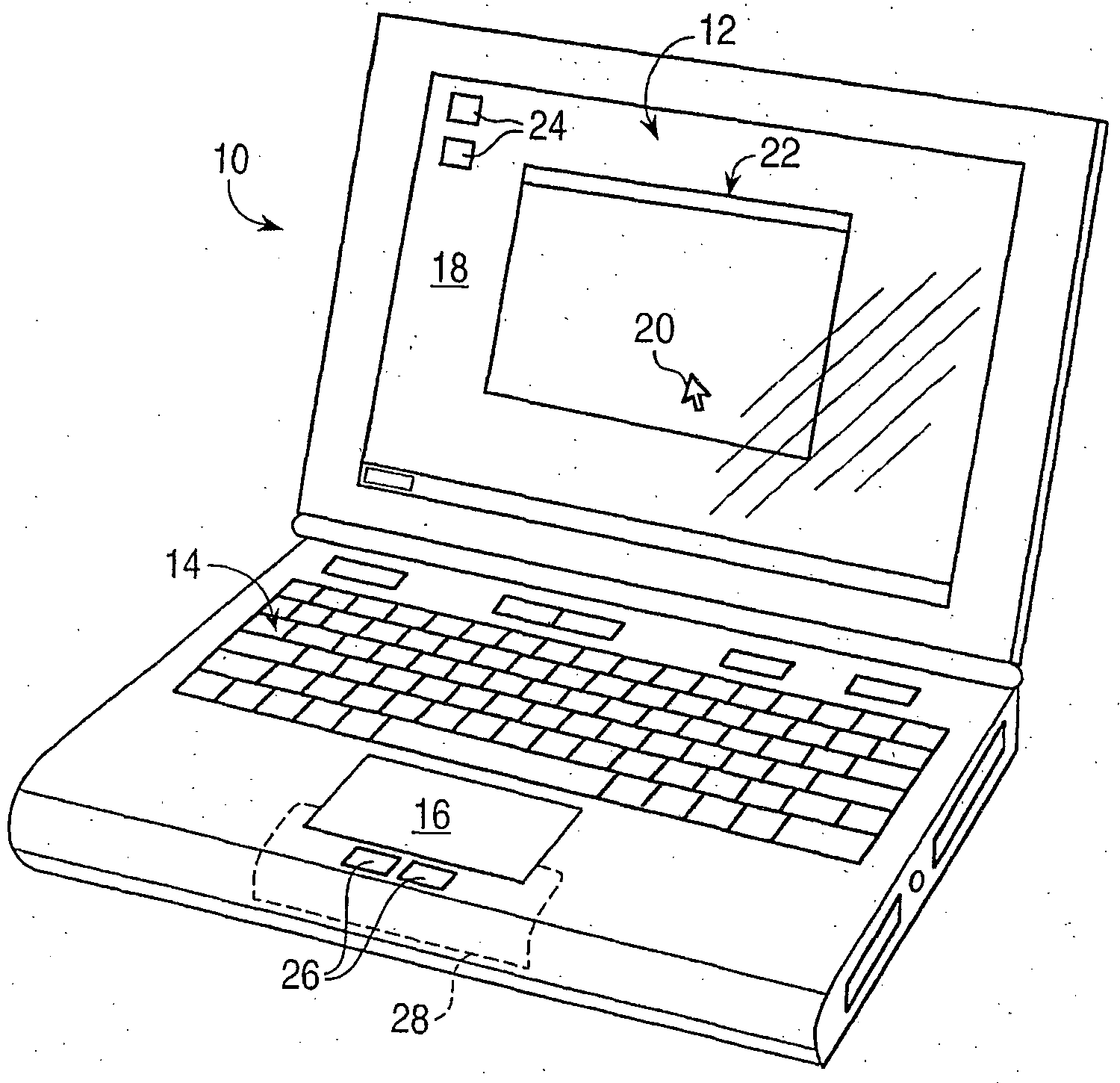
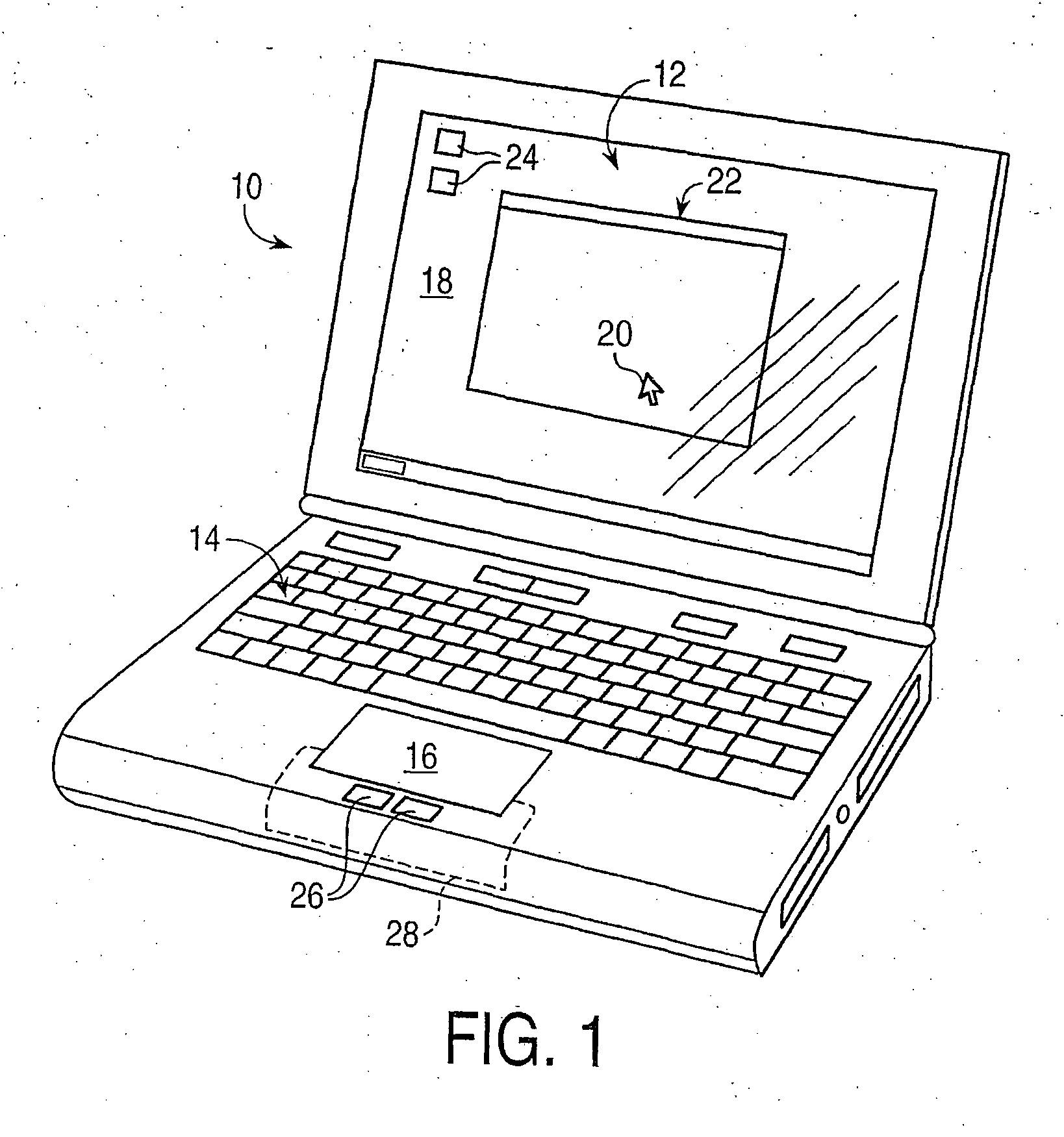
A haptic feedback touch control used to provide input to a computer. A touch input device includes a planar touch surface that provides position information to a computer based on a location of user contact. The computer can position a cursor in a displayed graphical environment based at least in part on the position information, or perform a different function. At least one actuator is also coupled to the touch input device and outputs a force to provide a haptic sensation to the user. The actuator can move the touchpad laterally, or a separate surface member can be actuated. A flat E-core actuator, piezoelectric actuator, or other types of actuators can be used to provide forces. The touch input device can include multiple different regions to control different computer functions.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Performing cardiac surgery without cardioplegia
InactiveUS20030055410A1Improve abilitiesEasy to controlSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsForcepsMotion tracking system
A surgical system or assembly for performing cardiac surgery includes a surgical instrument; a servo-mechanical system engaged to the surgical instrument for operating the surgical instrument; and an attachment assembly for removing at least one degree of movement from a moving surgical cardiac worksite to produce a resultant surgical cardiac worksite. The surgical system or assembly also includes a motion tracking system for gathering movement information on a resultant surgical cardiac worksite. A control computer is engaged to the attachment assembly and to the motion tracking system and to the servo-mechanical system for controlling movement of the attachment assembly and for feeding gathered information to the servo-mechanical system for moving the surgical instrument in unison with the resultant surgical cardiac worksite such that a relative position of the moving surgical instrument with respect to the resultant surgical cardiac worksite is generally constant. A video monitor is coupled to the control computer; and an input system is coupled to the servo-mechanical system and to the control computer for providing a movement of the surgical instrument. The video monitor displays movement of the surgical instrument while the resultant surgical cardiac worksite appears substantially stationary, and while a relative position of the surgical instrument moving in unison with the resultant surgical cardiac worksite, as a result from the movement information gathered by the motion tracking system, remains generally constant. A method of performing cardiac surgery without cardioplegia comprising removing at least one degree of movement freedom from a moving surgical cardiac worksite to produce at least a partially stationary surgical cardiac worksite while allowing a residual heart section, generally separate from the at least partially stationary surgical cardiac worksite, to move as a residual moving heart part. Cardiac surgery is performed on the at least partially stationary cardiac worksite with a surgical instrument such as needle drivers, forceps, blades and scissors.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
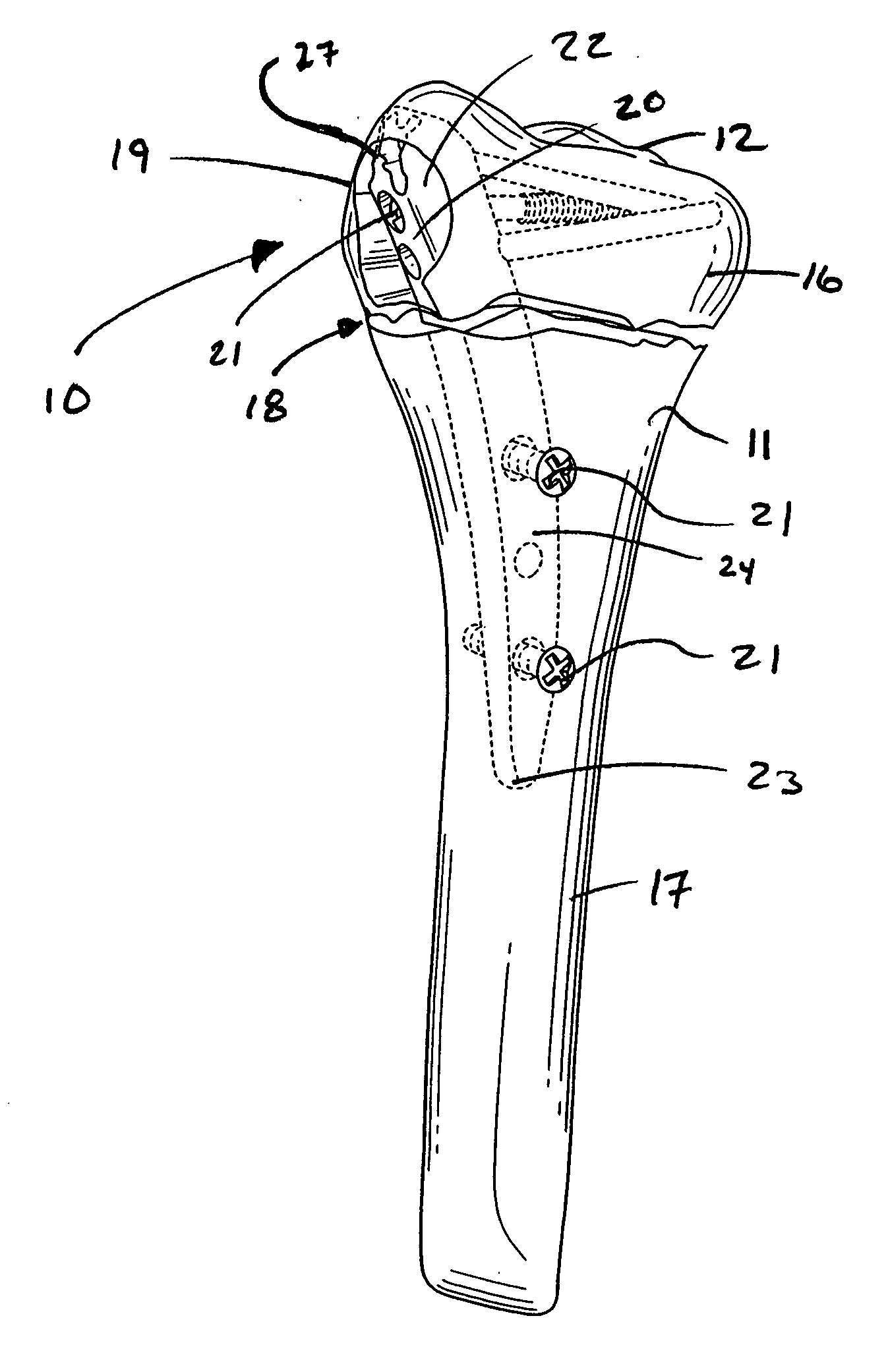
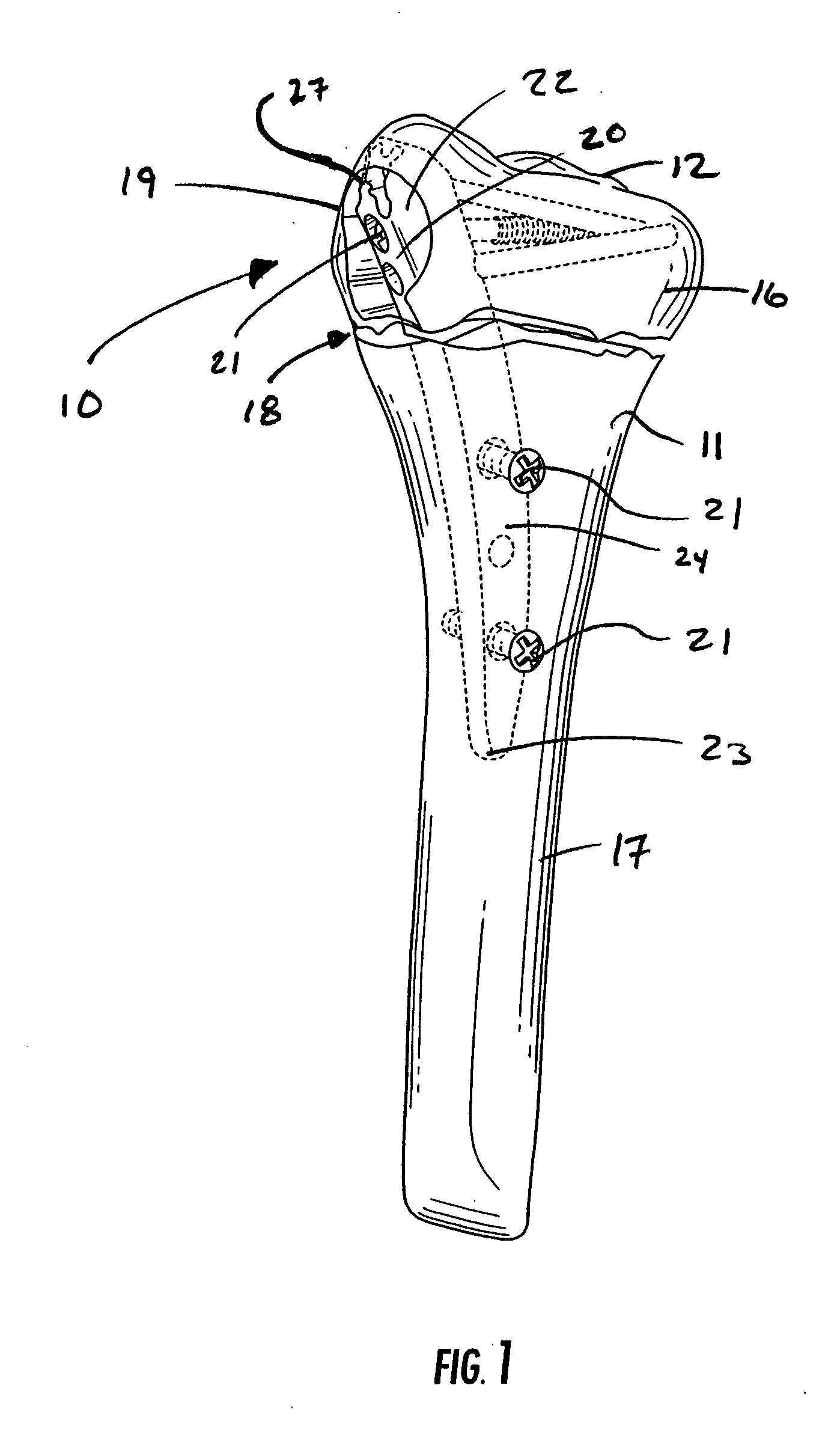
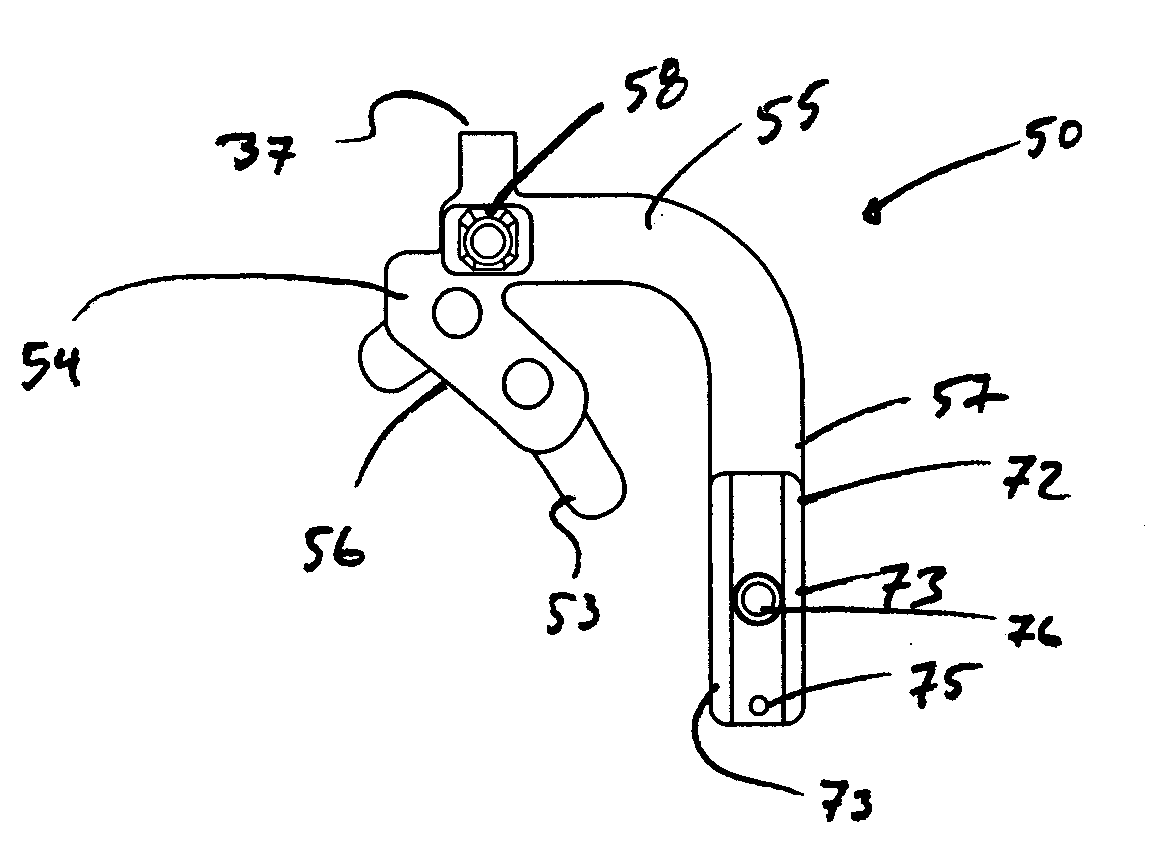
Intramedullary fixation assembly and devices and methods for installing the same
InactiveUS20060015101A1Precise positioningEasy to installInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsBone fragmentBiomedical engineering
An intramedullary fixation assembly usable with different long bone types and a guide assembly for guiding deployment of the intramedullary fixation assembly. The intramedullary fixation assembly includes a fixation member that has ends and a curved body extending between the ends. The curved body of the fixation member has a radius of curvature configured to extend through the medullary canal regardless of the long bone anatomy. Fasteners fix the fixation member to the bone fragments and are guided by a guide assembly. The guide assembly includes a guide body defining openings configured to guide the fasteners through openings defined in the fixation member and into the bone fragments. A fixation end of the guide body includes a pair of opposing, converging surfaces that are configured to engage in a positive fit with an exposed end of the fixation member accessible through the side aperture in the first fragment.
Owner:WRIGHT MEDICAL TECH
Balanced ultrasonic curved blade
InactiveUS20090270891A1Reduce axial torsionReduce lateral movementSurgeryEngineeringUltrasound energy
Methods and devices that provide reduced transverse motion in a curved ultrasonic blade and / or ultrasonic surgical instrument with functional asymmetries. An ultrasonic blade in accordance with embodiments of the present invention includes a curved functional portion of an ultrasonic blade, wherein the center of mass of the curved functional portion lies on the mid-line of a waveguide delivering ultrasonic energy to the blade. Balancing in accordance with embodiments of the present invention, using placement of the center of mass of the curved portion of the blade appropriately, provides blade balance in a proximal portion of the blade, without reduction of mass and inherent stress increase proximal to the end-effector.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
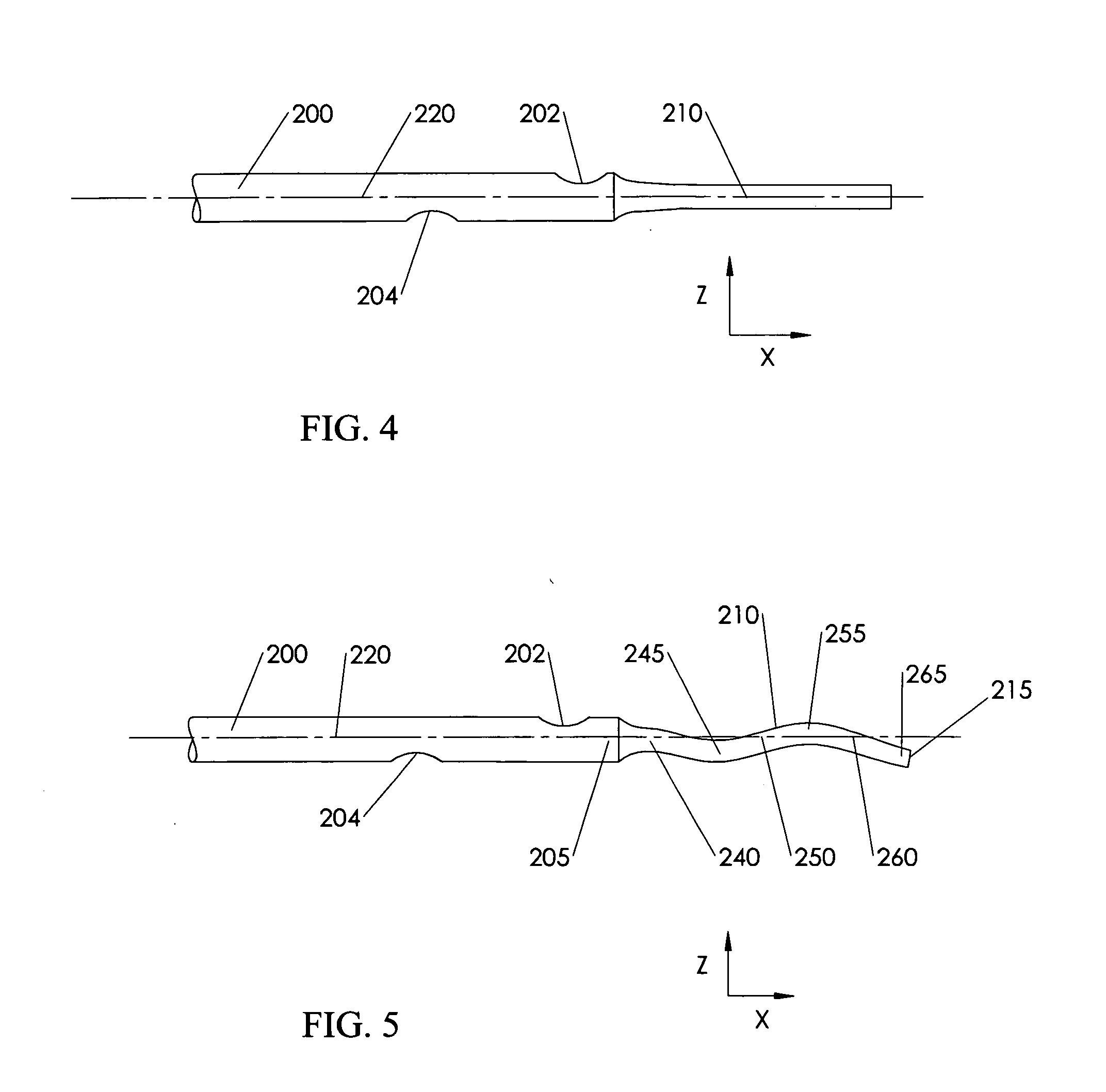
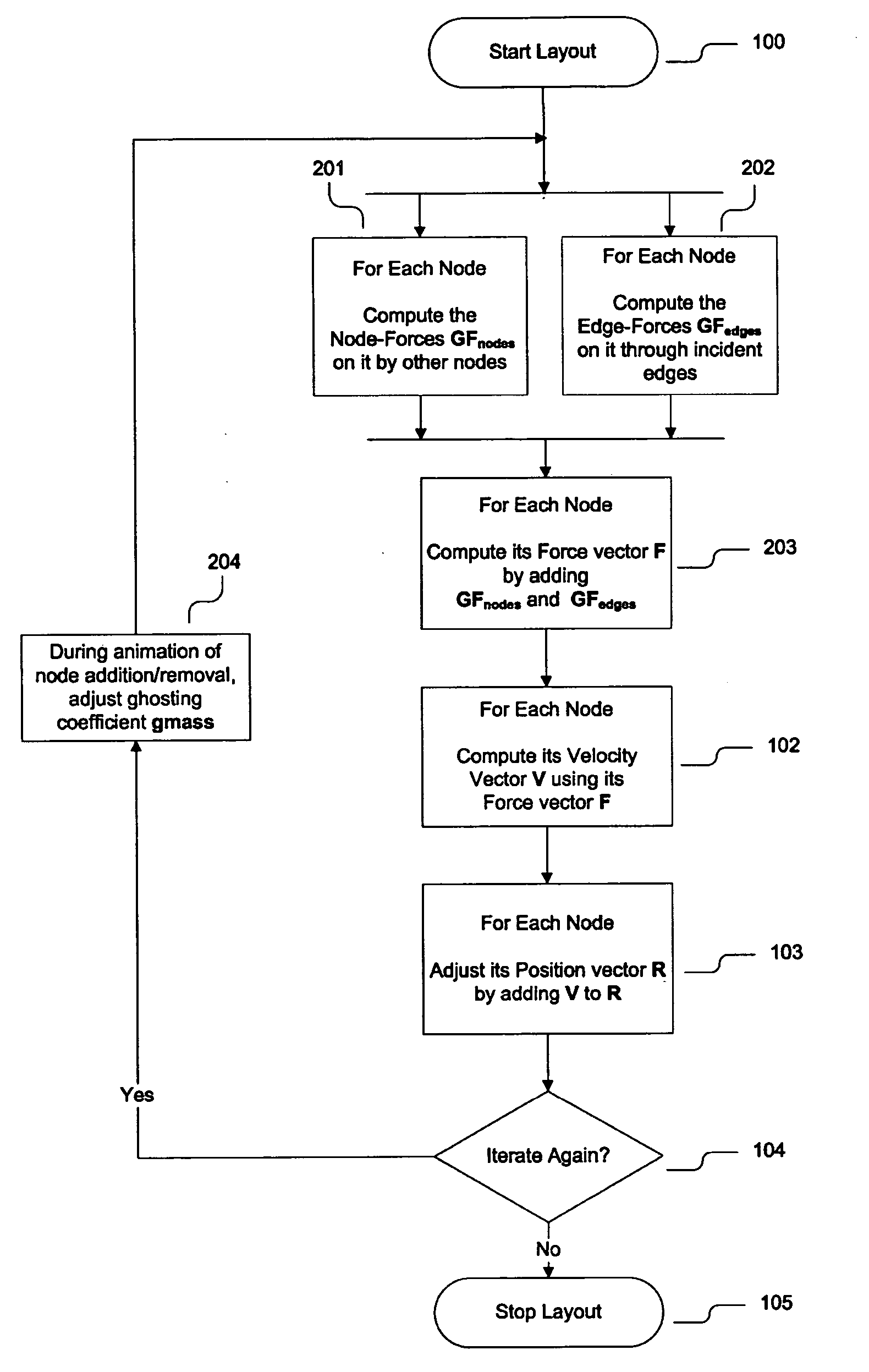
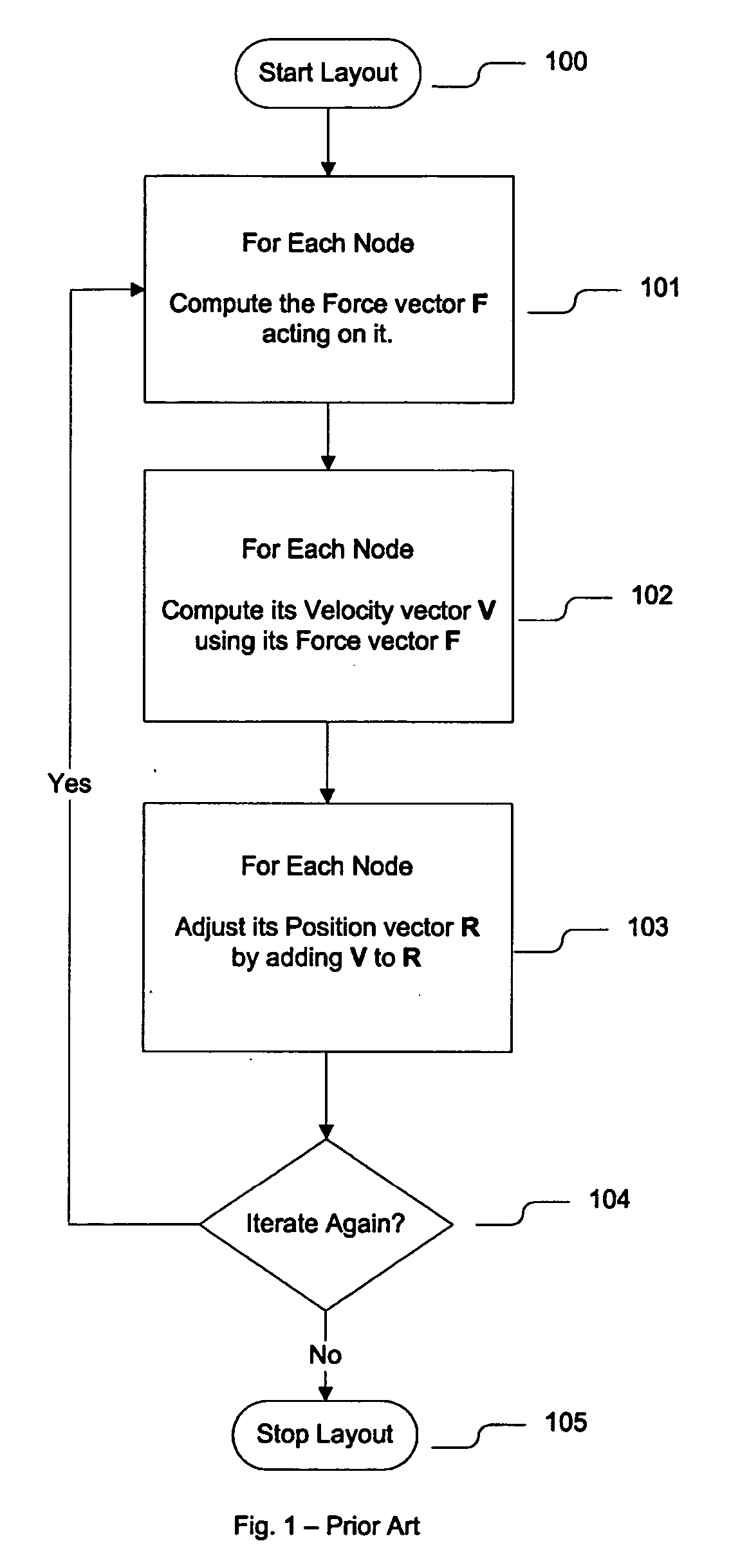
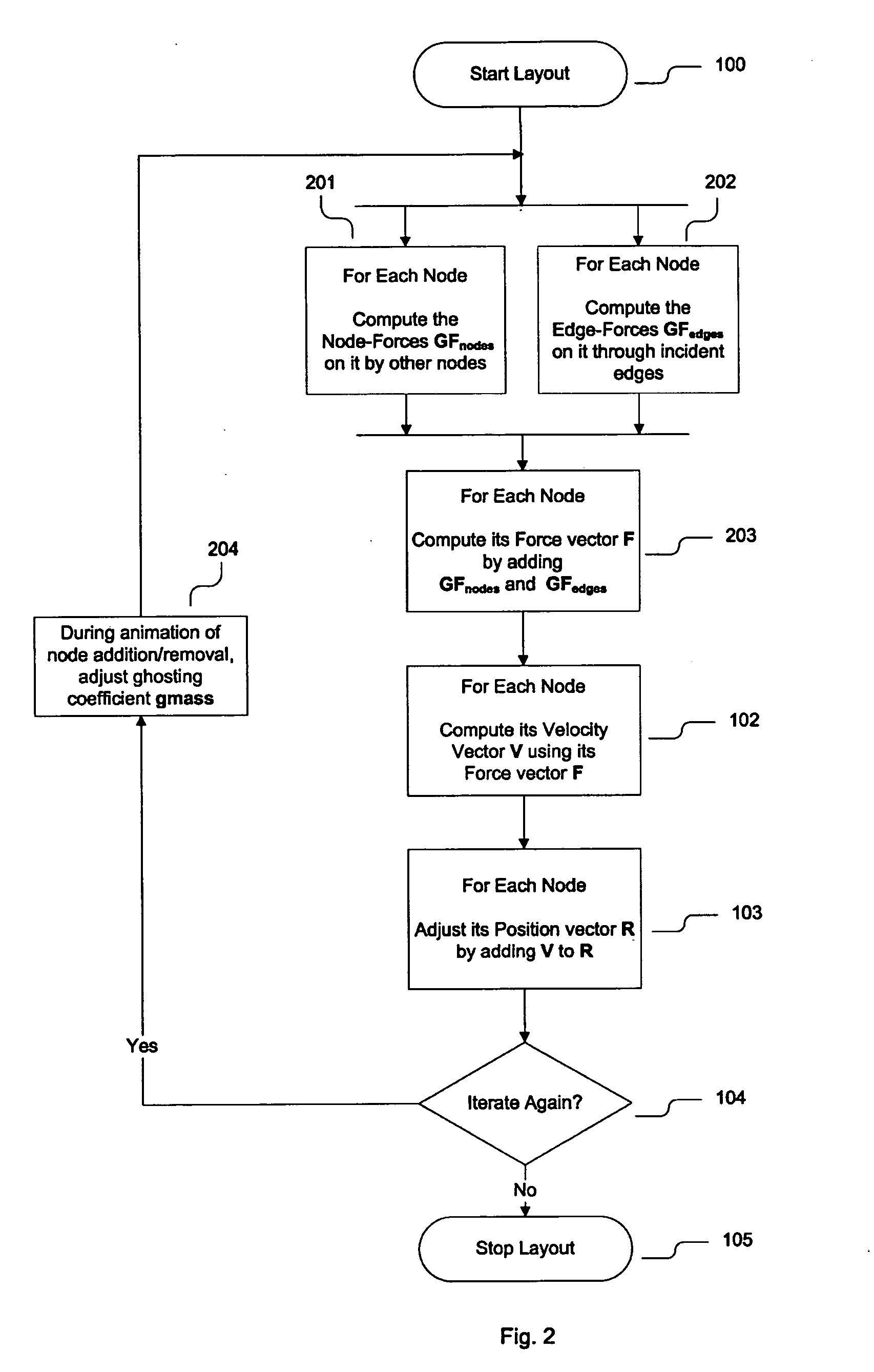
Method of animating transitions and stabilizing node motion during dynamic graph navigation
InactiveUS20050180330A1Avoid relative motionQuickly arrangedDrawing from basic elementsError preventionMarine navigationLayout algorithm
In a system and method for arranging a graph according to a Force-Directed Layout algorithm, a node-set transition in the graph may be animated by iteratively reducing or increasing an impact value of one node on another node, and a velocity of a node may be reduced in proportion the to the degree of its non-directional movement.
Owner:TOUCHGRAPH
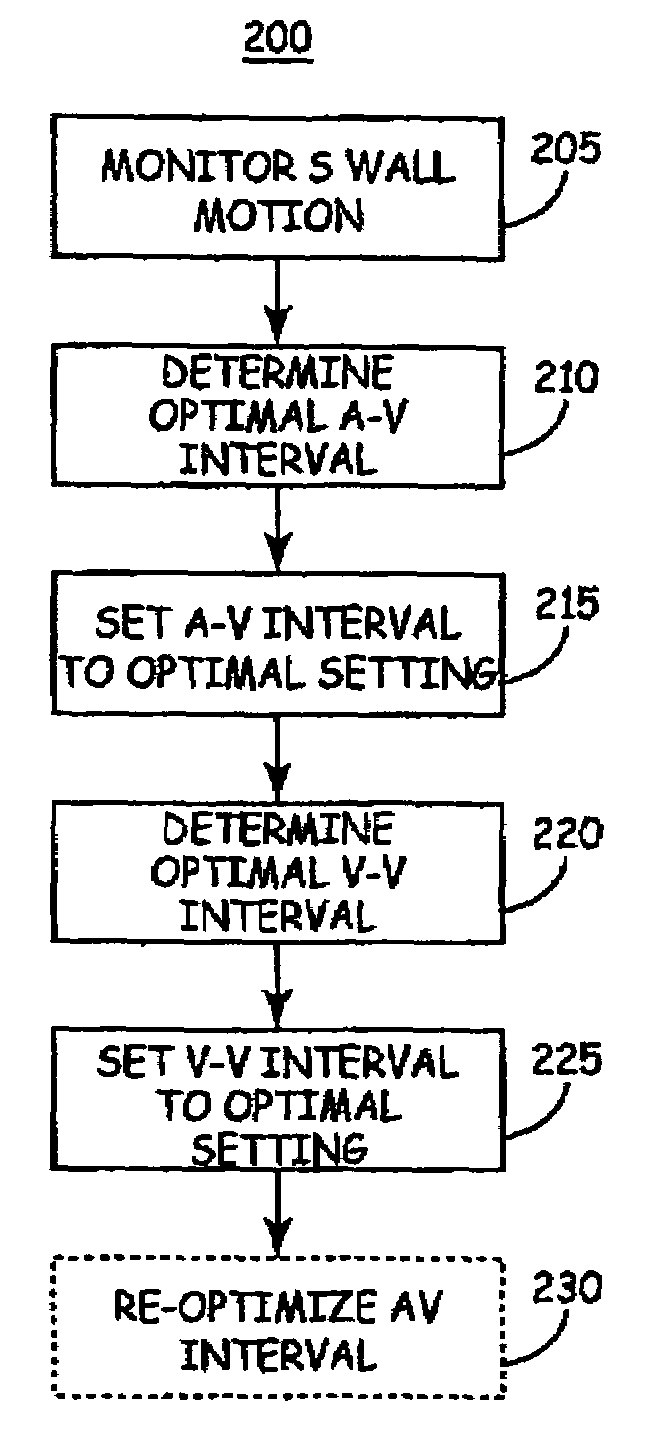
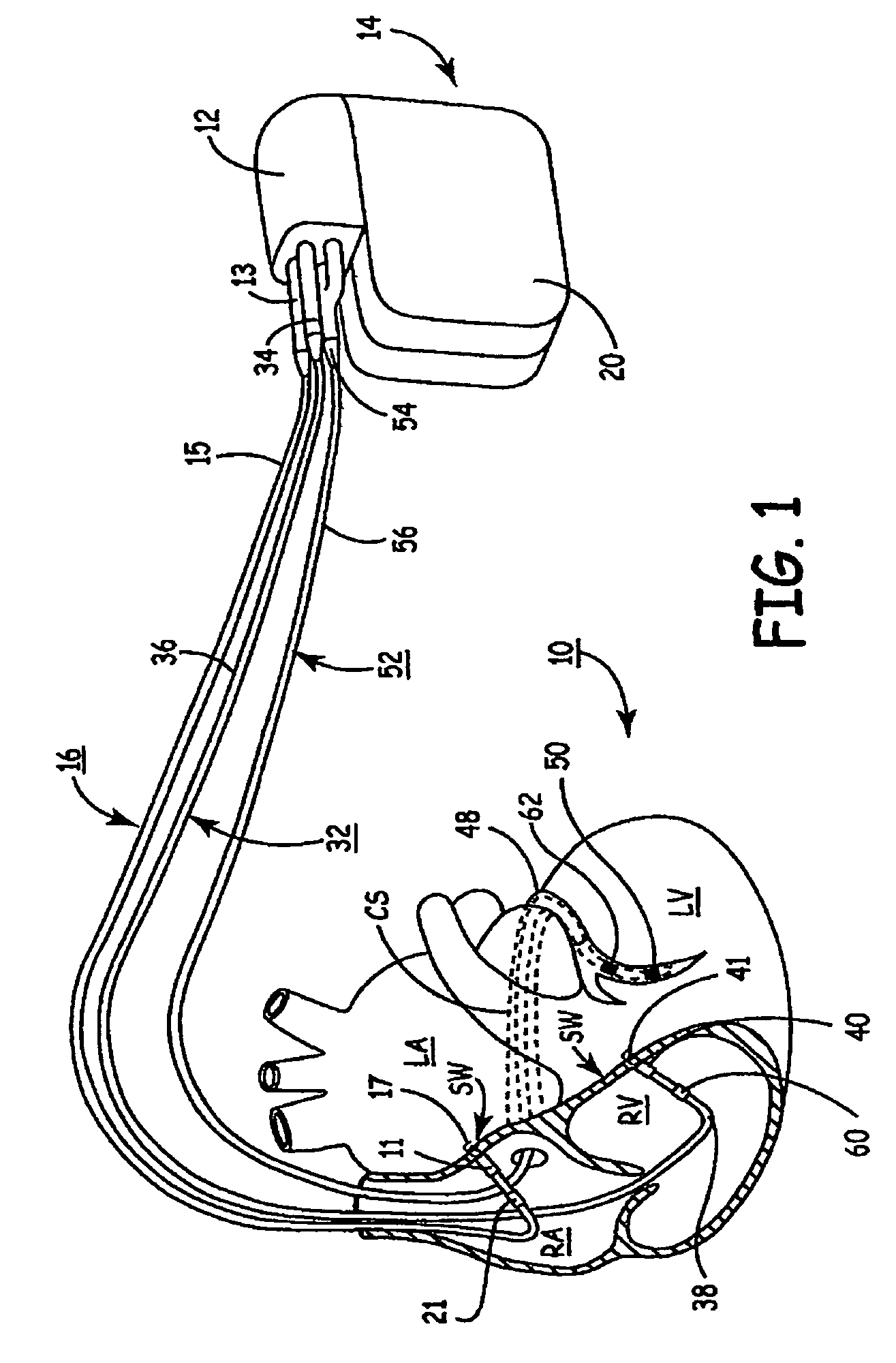
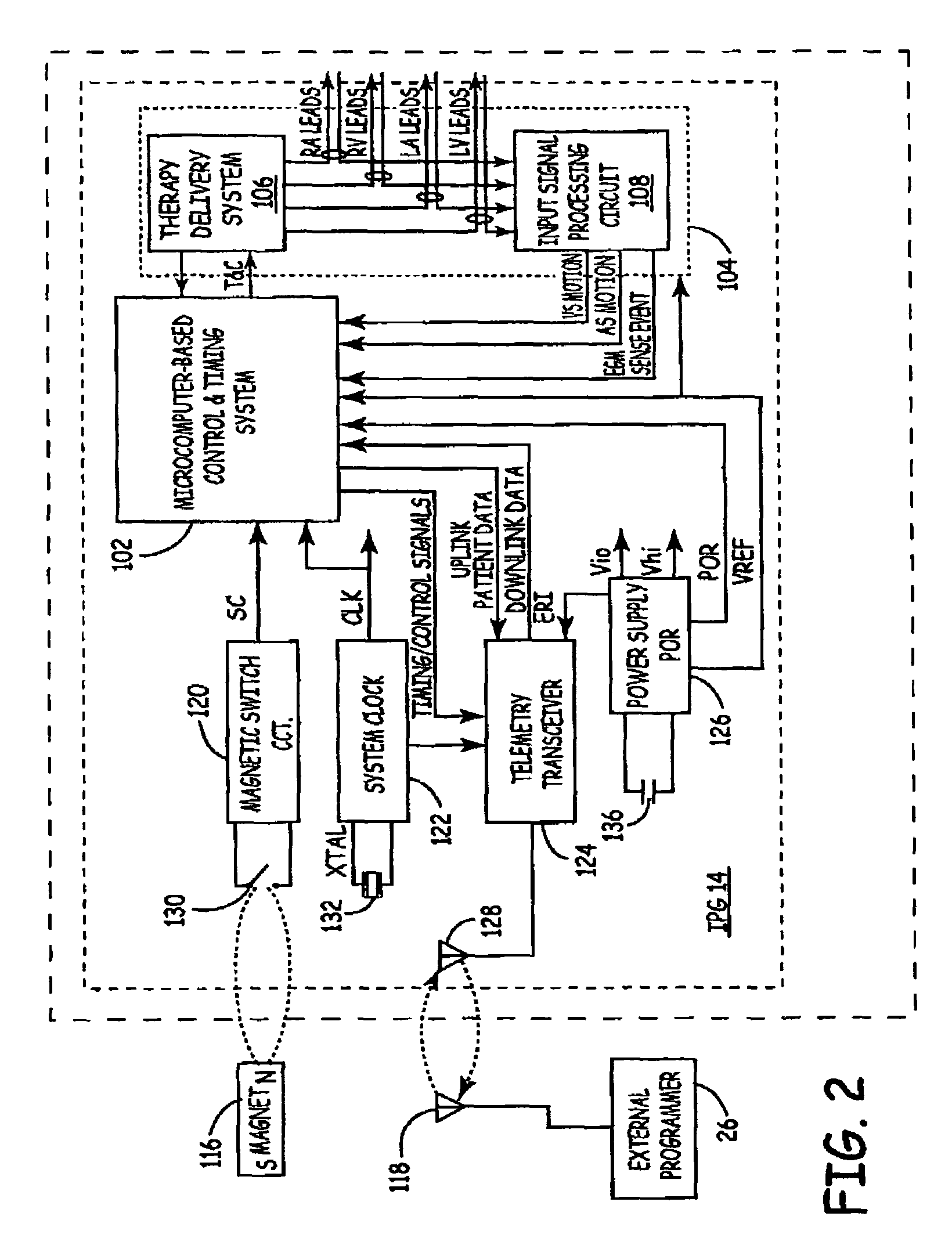
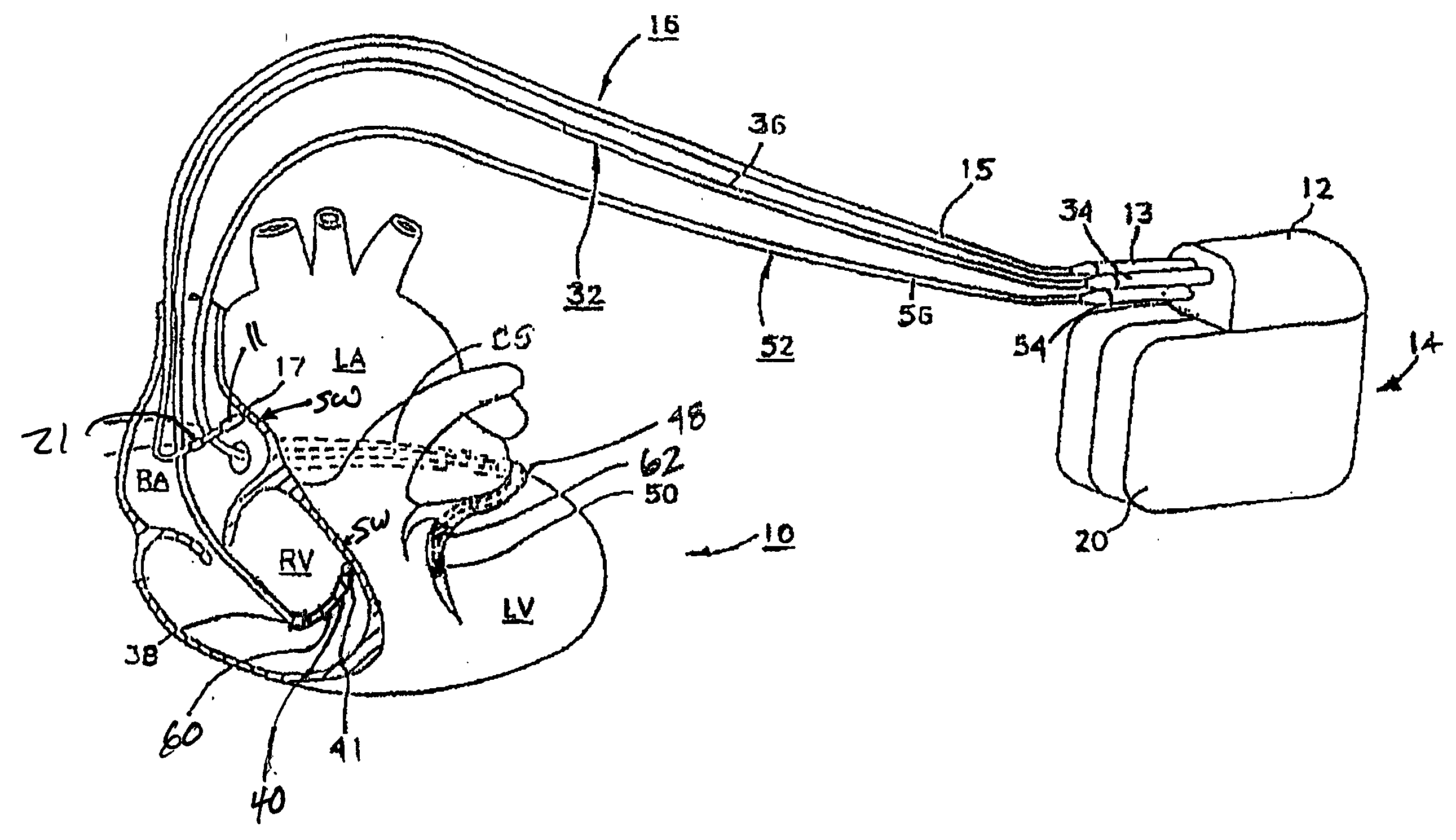
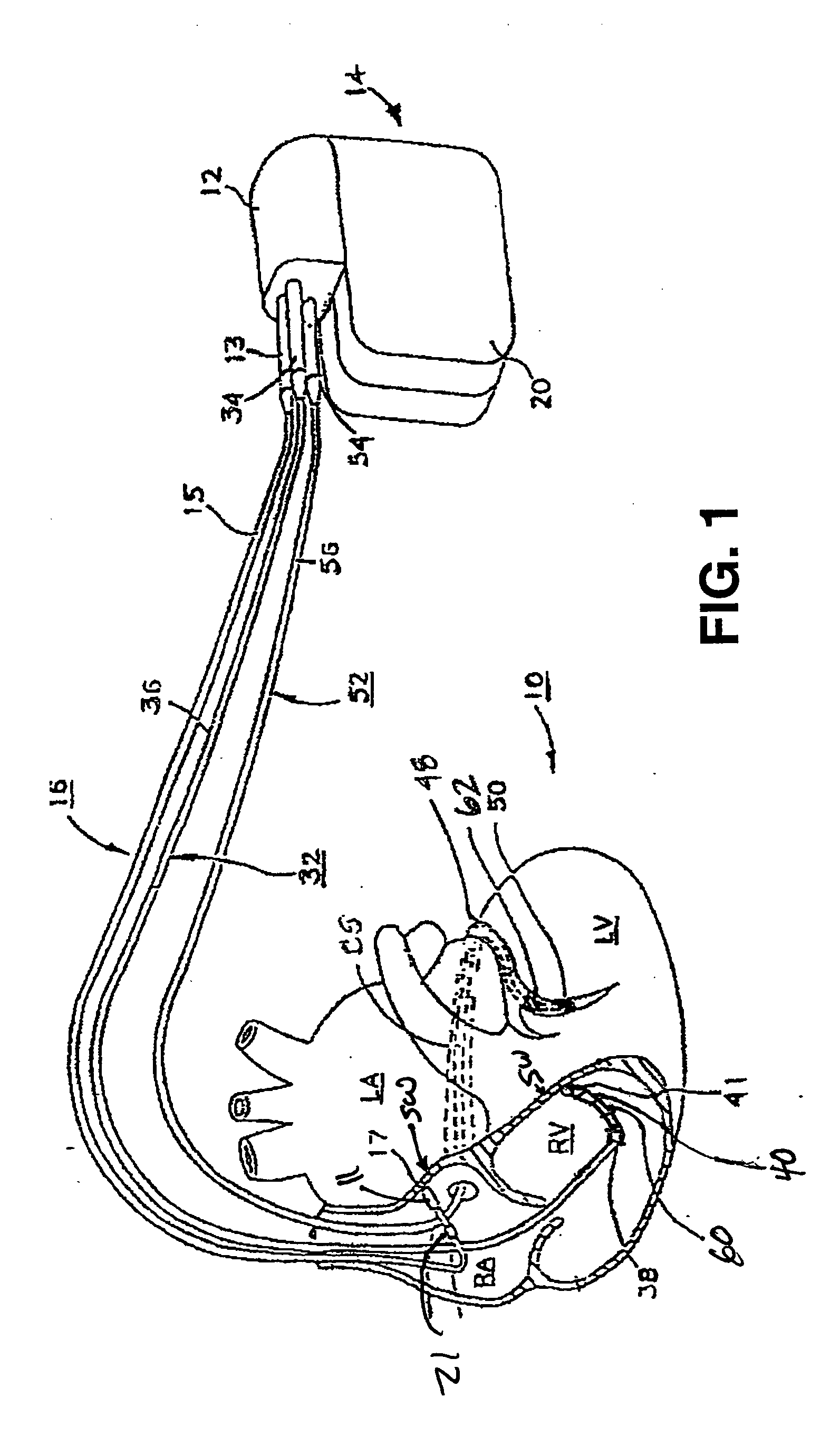
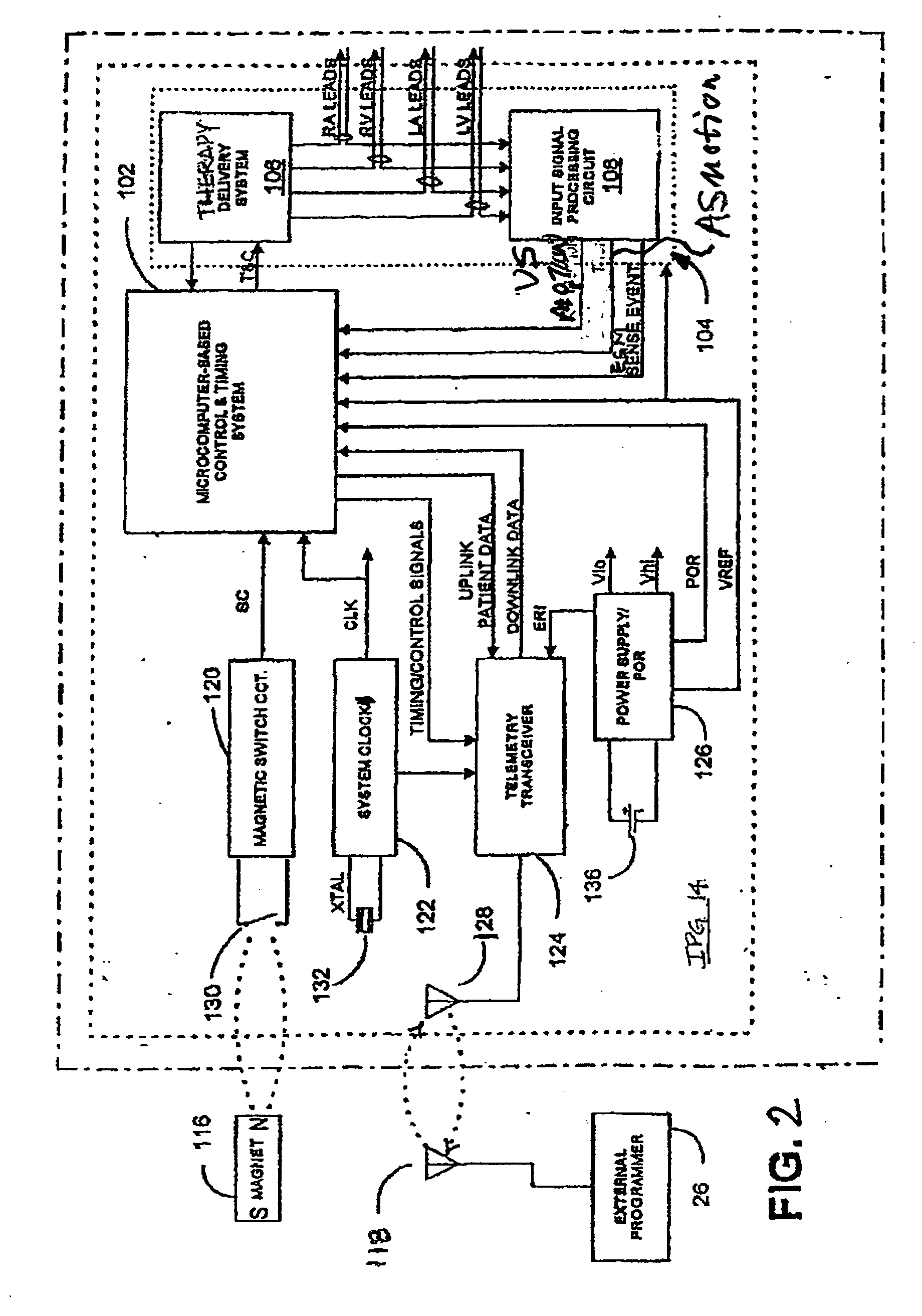
Method of optimizing cardiac resynchronization therapy using sensor signals of septal wall motion
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
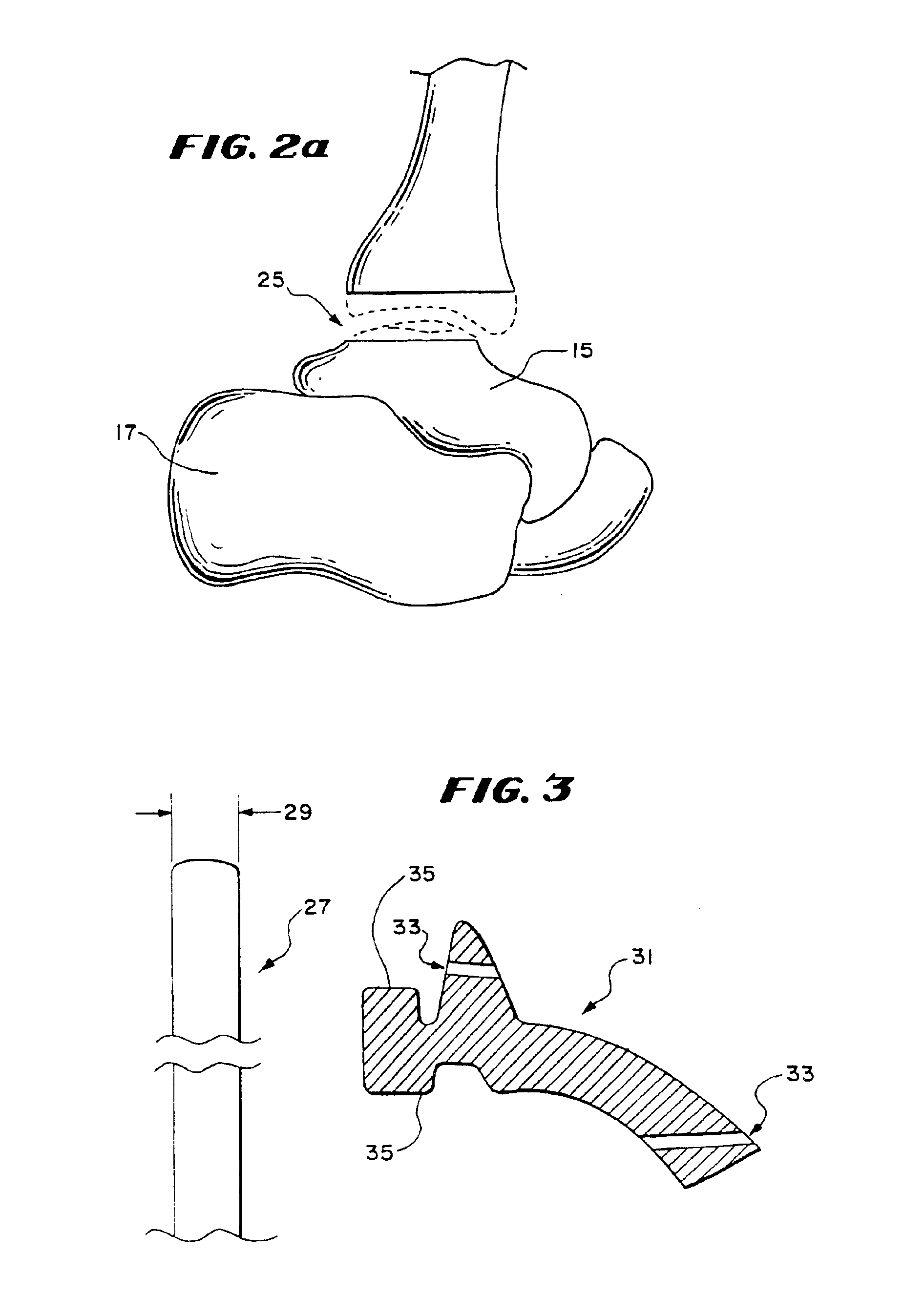
Spinal implants and methods
InactiveUS20090149959A1Reduce relative motionSmooth motionDiagnosticsBone implantPosterior regionIntervertebral disk
Owner:MAGELLAN SPINE TECH
In-Line Legged Robot Vehicle and Method for Operating
ActiveUS20110231050A1Improve mobilityReduce body motionProgramme-controlled manipulatorInstruments for road network navigationControl systemLegged robot
A legged vehicle includes a body, wherein the body includes a major axis corresponding to a primary direction of travel; a plurality of leg mechanisms attached to the body, wherein each leg is attached at its proximal end at one or more discrete attachment points, wherein the attachment points are arranged in-line, one behind the other, with respect to the body, each of the legs including actuators attached between the legs and the body and between adjacent leg members, said legs being actuated for movement of a distal end in three dimensions; a control system in communication with the leg mechanisms to coordinate movements of the leg mechanisms according to approximately single track foot placement, and movement of the legged vehicle in three dimensions over the ground; and a power source connected to and driving the control system components and the plurality of actuators and joints which drive the legs.
Owner:GOULDING JOHN R
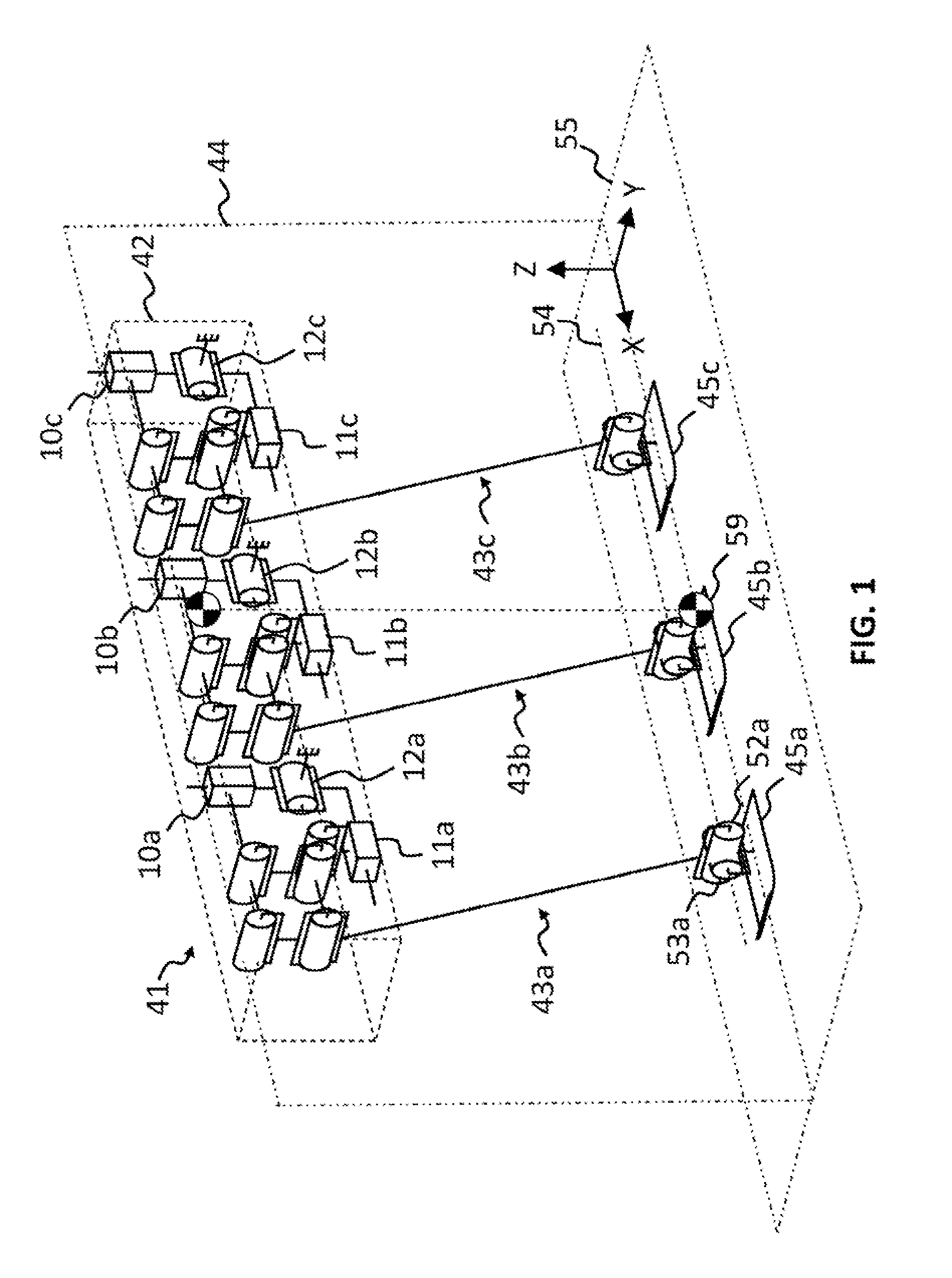
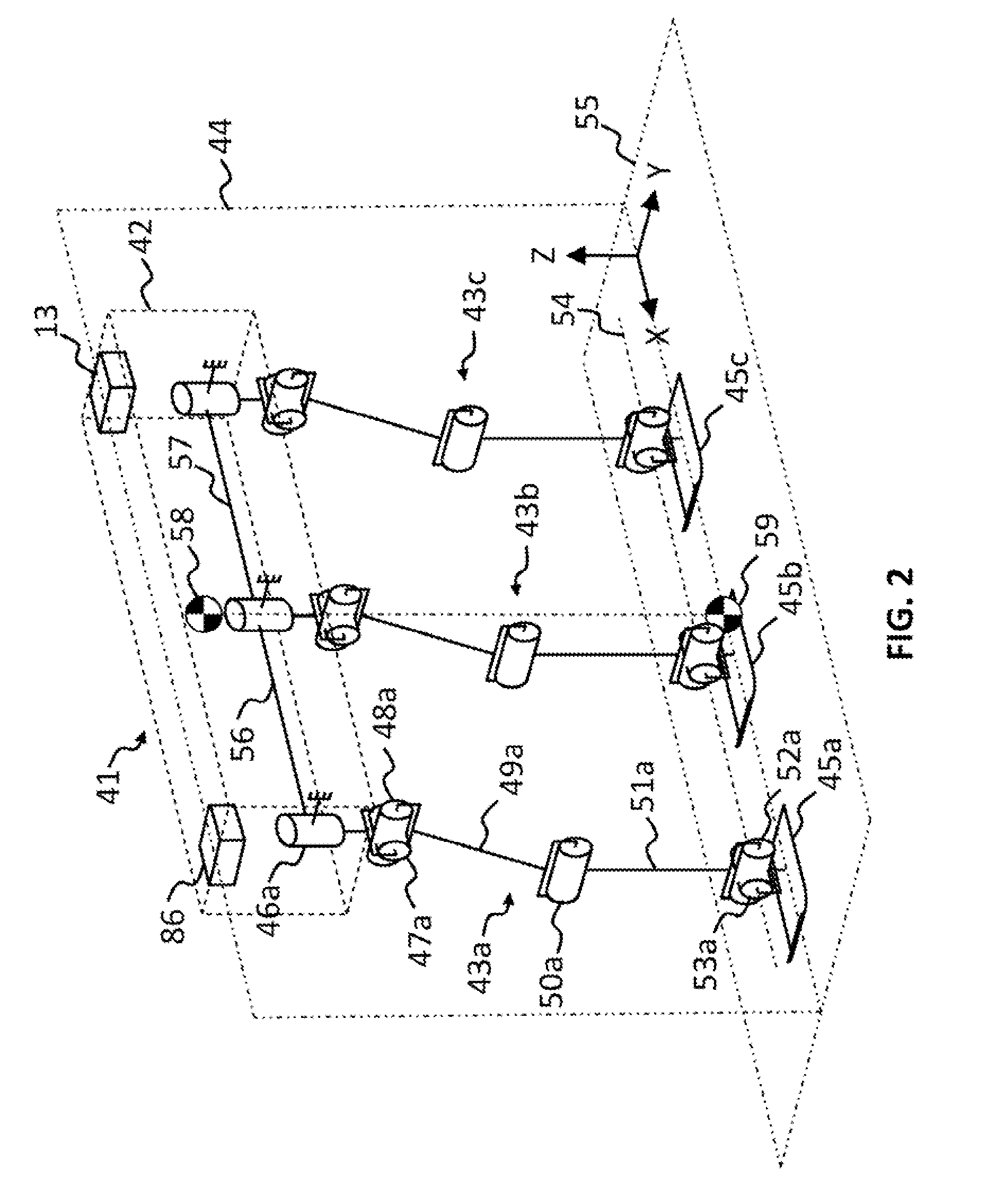
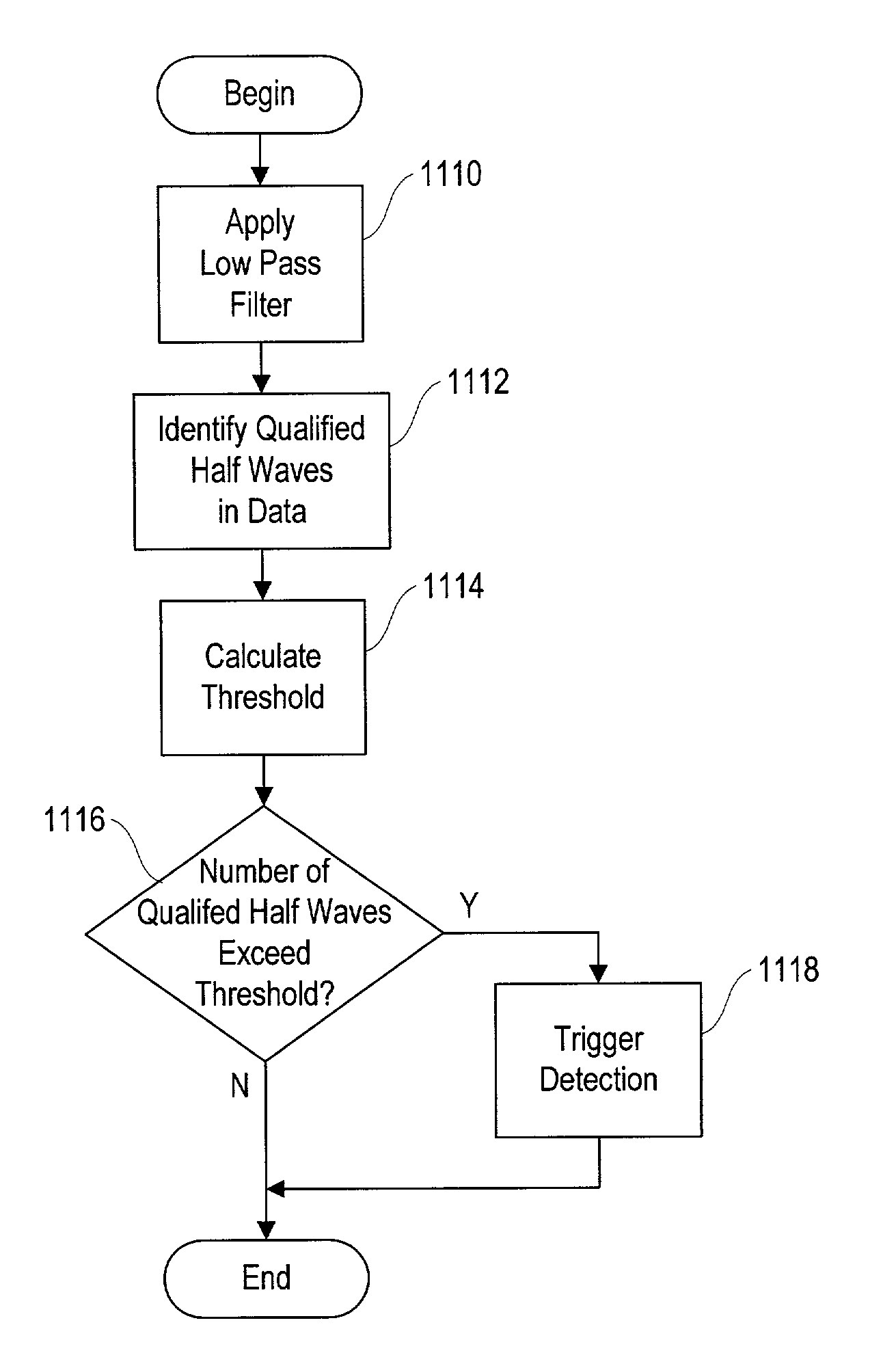
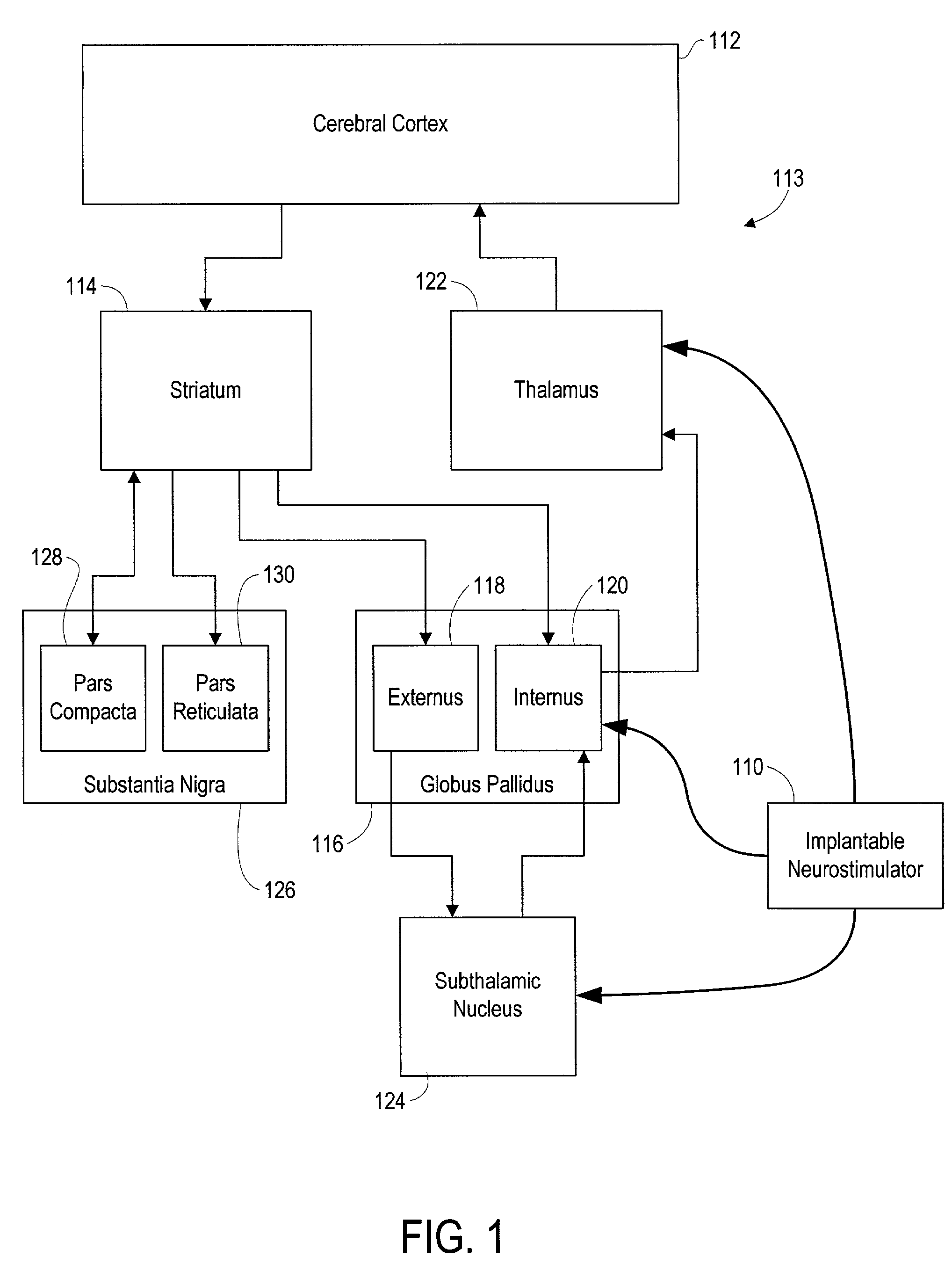
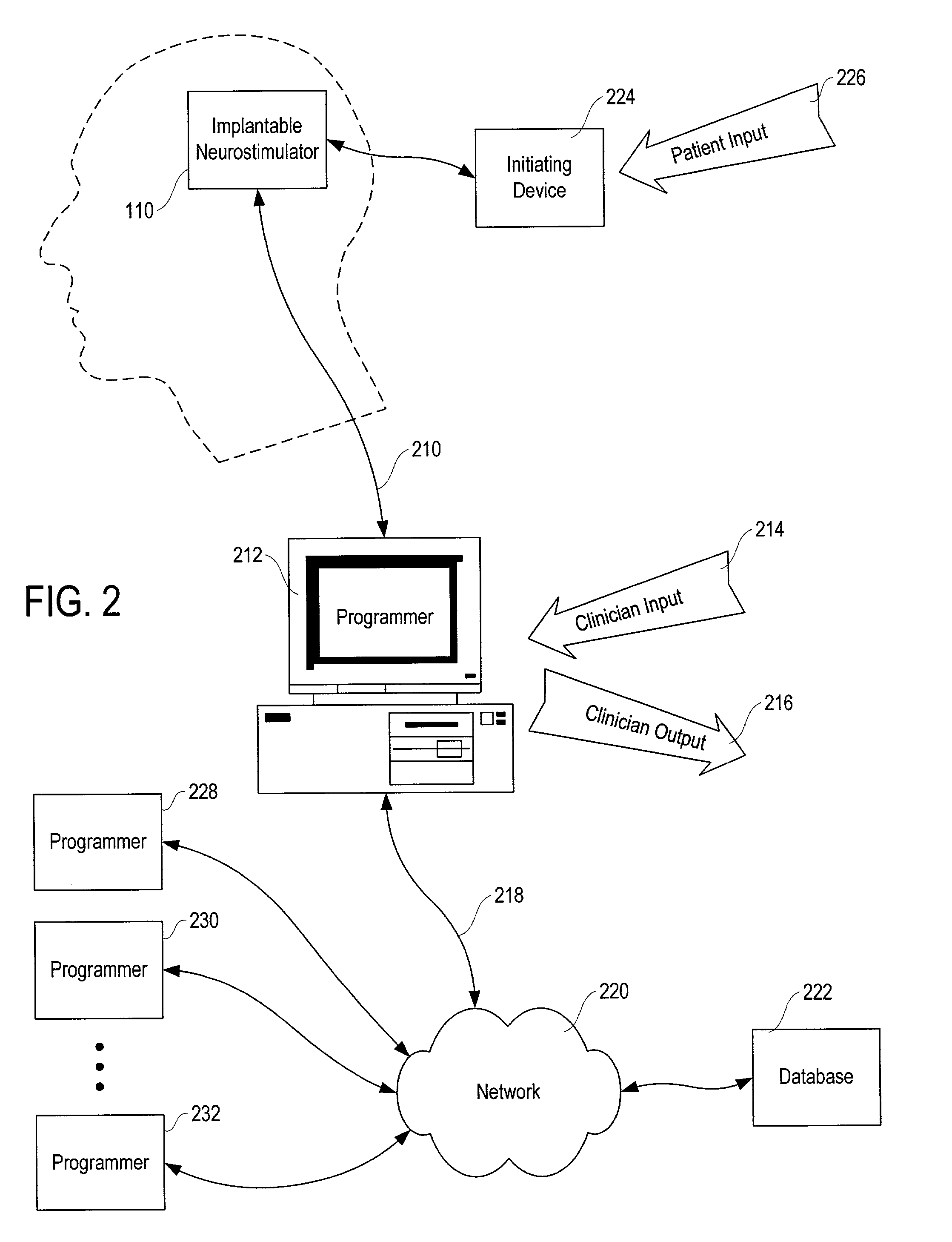
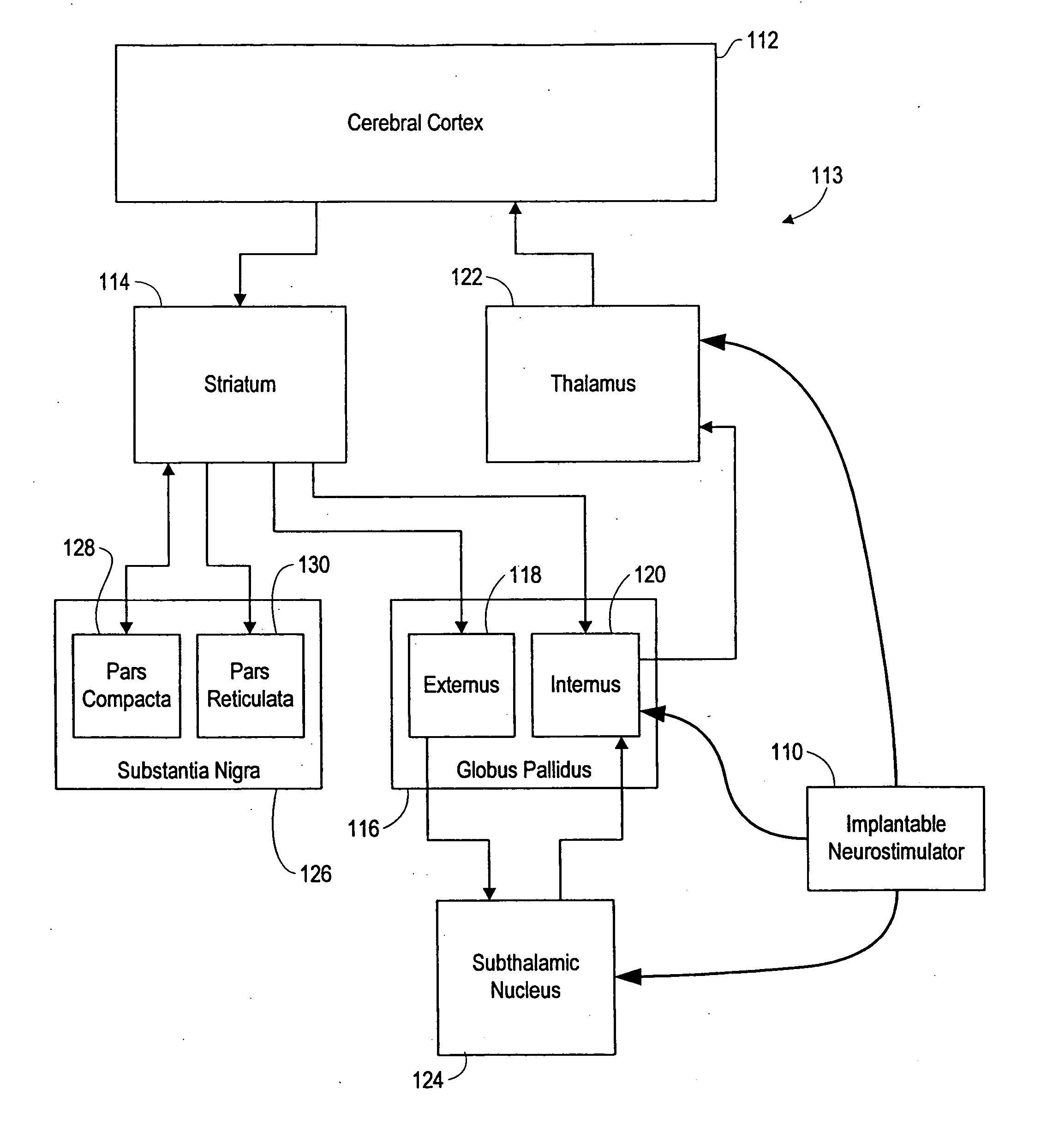
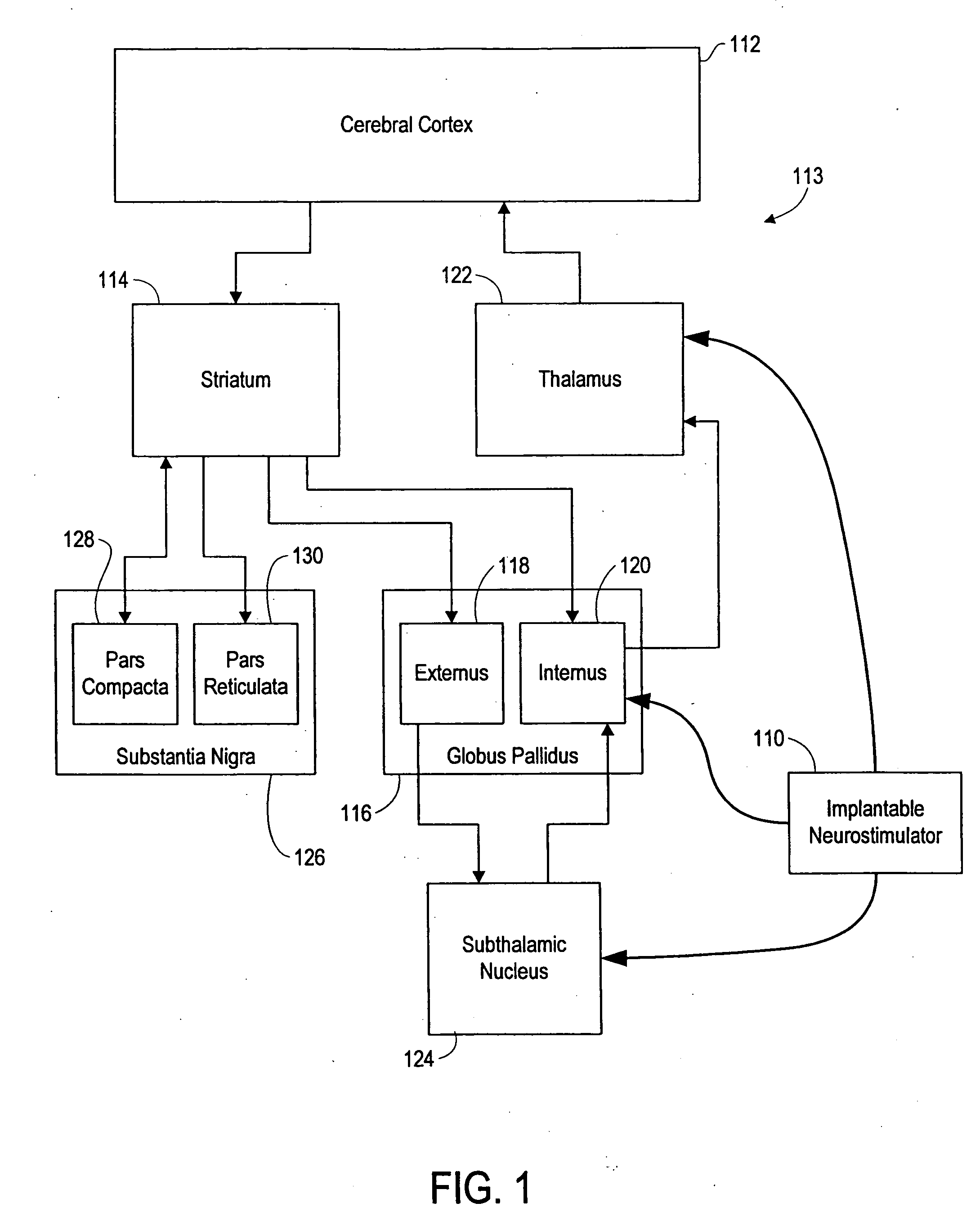
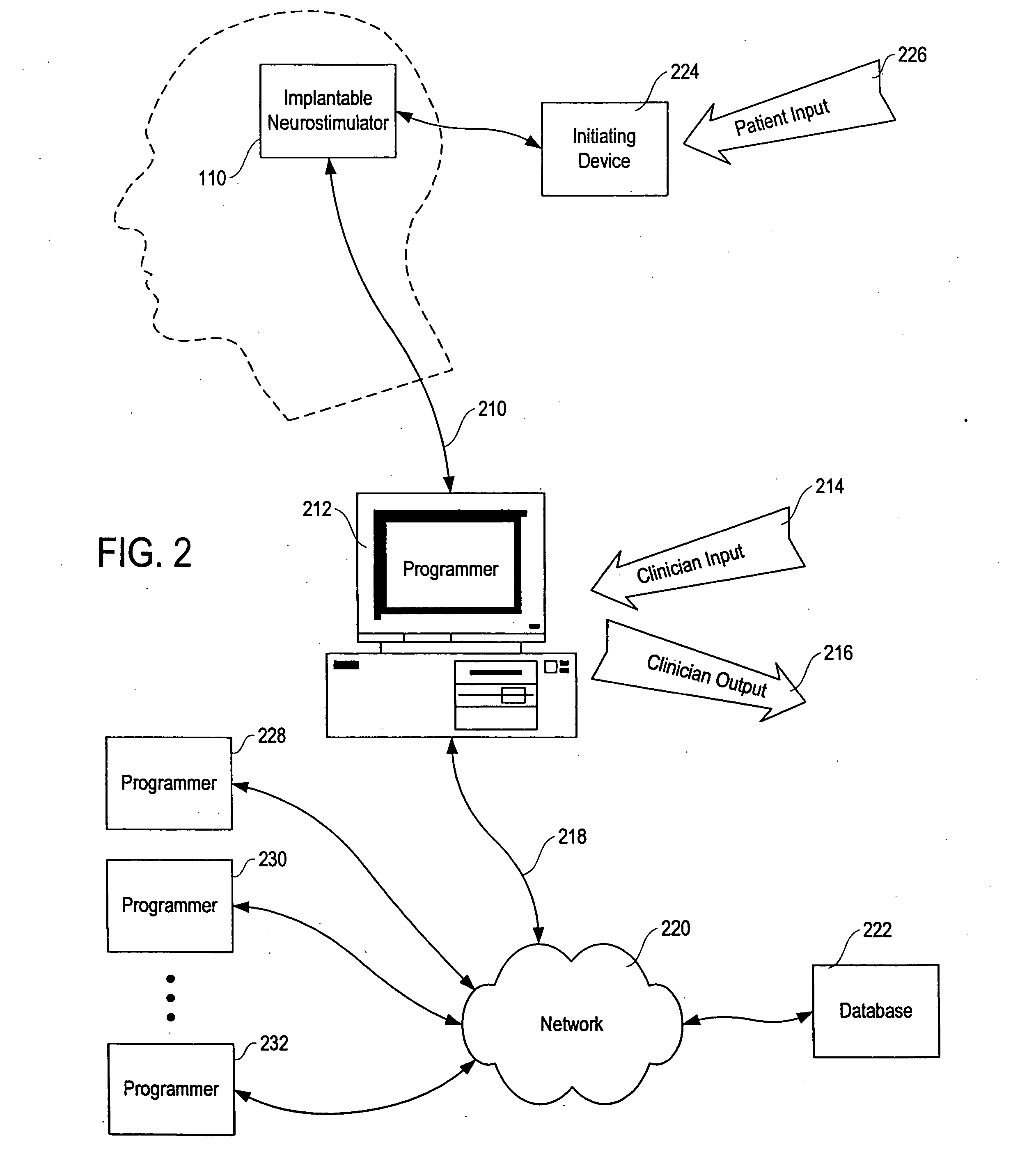
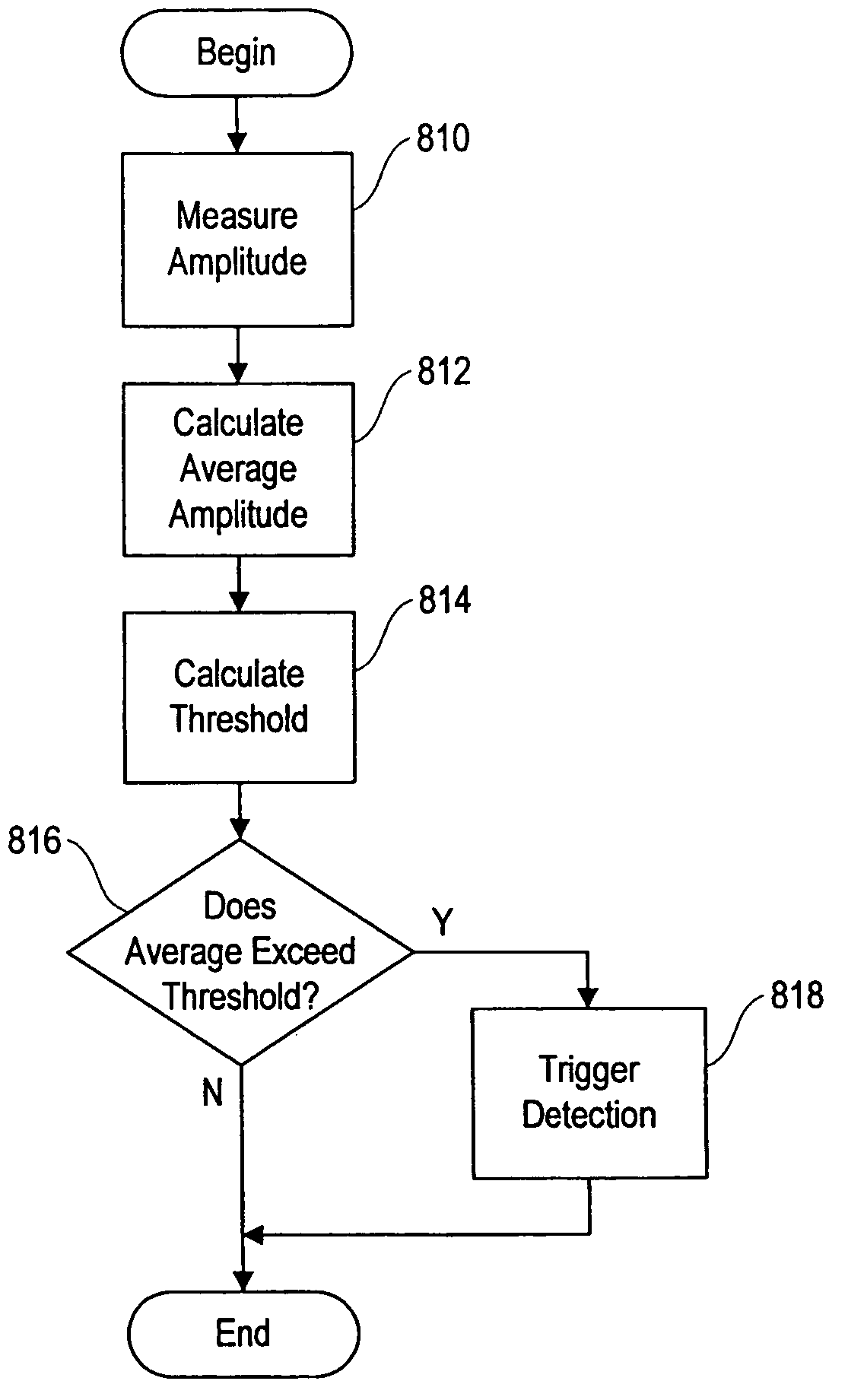
Responsive electrical stimulation for movement disorders
InactiveUS7110820B2Reduce relative motionSetting deviceElectrotherapyArtificial respirationPhysical therapyElectrical stimulations
An implantable neurostimulator system for treating movement disorders includes a sensor, a detection subsystem capable of identifying episodes of a movement disorder by analyzing a signal received from the sensor, and a therapy subsystem capable of applying therapeutic electrical stimulation to treat the movement disorder. The system treats movement disorders by detecting physiological conditions characteristic of an episode of symptoms of the movement disorder and selectively initiating therapy when such conditions are detected.
Owner:NEUROPACE
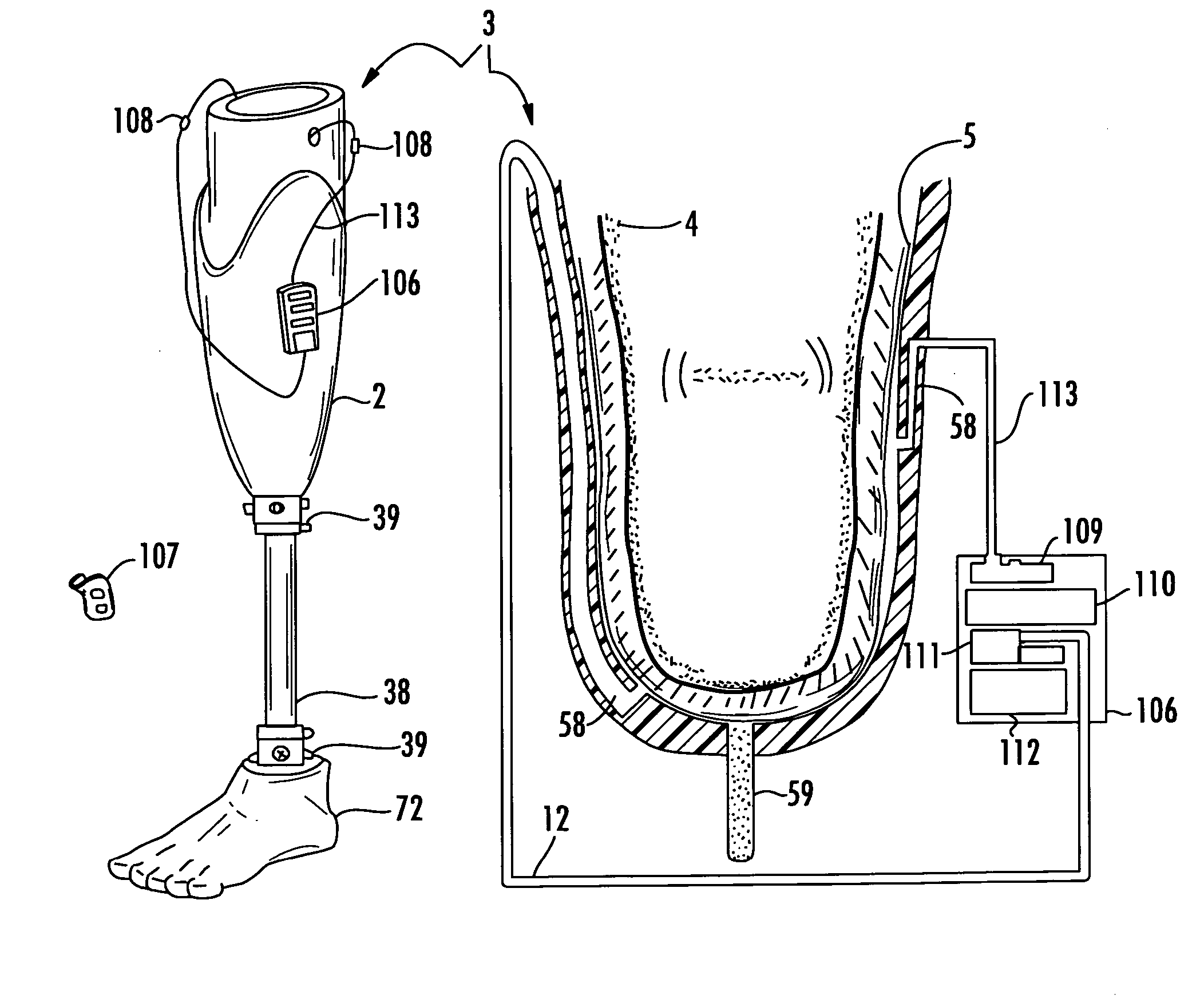
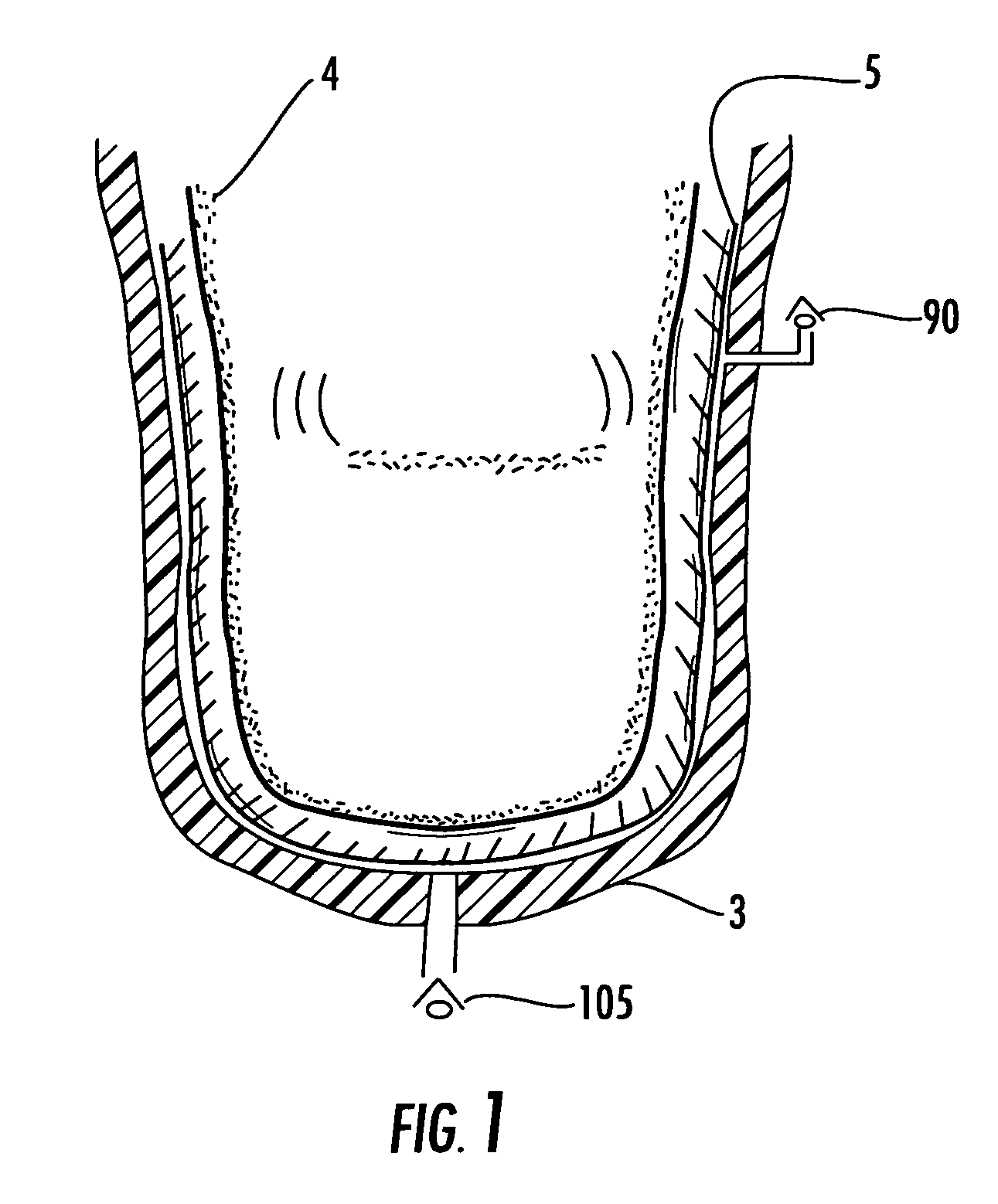
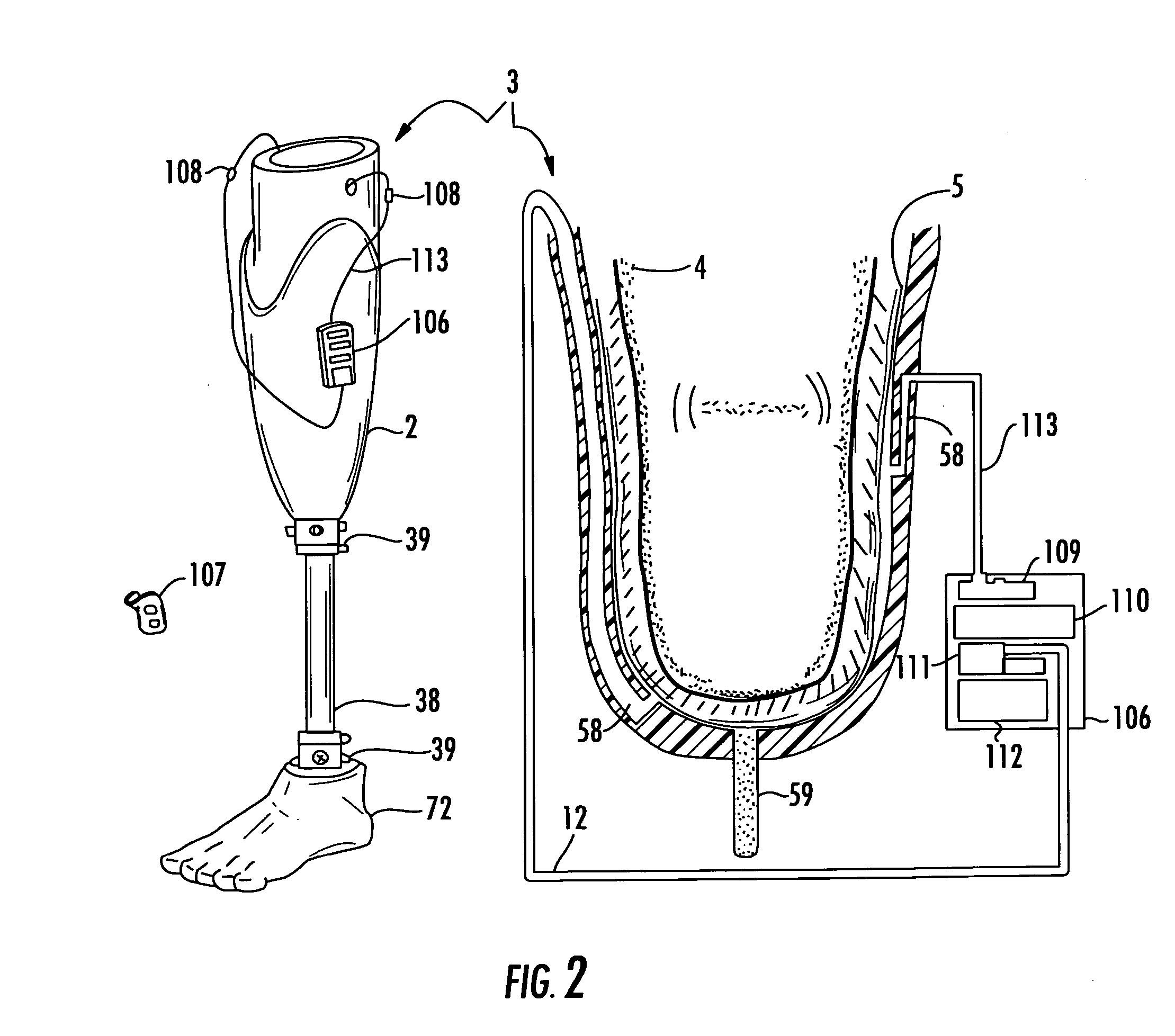
Vacuum assisted heat/perspiration removal system and limb volume management for prosthetic device
InactiveUS20070055383A1Reduce relative motionEasy to hangTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingVacuum assistedPerspiration
The vacuum assisted liner system is for use with a prosthetic device to be attached to a residual limb. The liner system includes a hypobaric prosthetic liner, and a porous wicking material layer to surround at least a portion of the residual limb and define a regulated vacuum environment between the hypobaric prosthetic liner and the residual limb. The hypobaric prosthetic liner has at least one passageway therethrough defining at least one vacuum port, such as an inlet port and outlet port, in fluid communication with the regulated vacuum environment. Internal liner passageways may connect the inlet and outlet ports to the regulated vacuum environment. A vacuum regulation device may include an electric vacuum pump or a motion activated pump connected to the outlet port.
Owner:KING CHARLES
Responsive electrical stimulation for movement disorders
InactiveUS20070038265A1Reduce relative motionSetting deviceElectrotherapyArtificial respirationPhysical therapyElectrical stimulations
An implantable neurostimulator system for treating movement disorders includes a sensor, a detection subsystem capable of identifying episodes of a movement disorder by analyzing a signal received from the sensor, and a therapy subsystem capable of applying therapeutic electrical stimulation to treat the movement disorder. The system treats movement disorders by detecting physiological conditions characteristic of an episode of symptoms of the movement disorder and selectively initiating therapy when such conditions are detected.
Owner:NEUROPACE
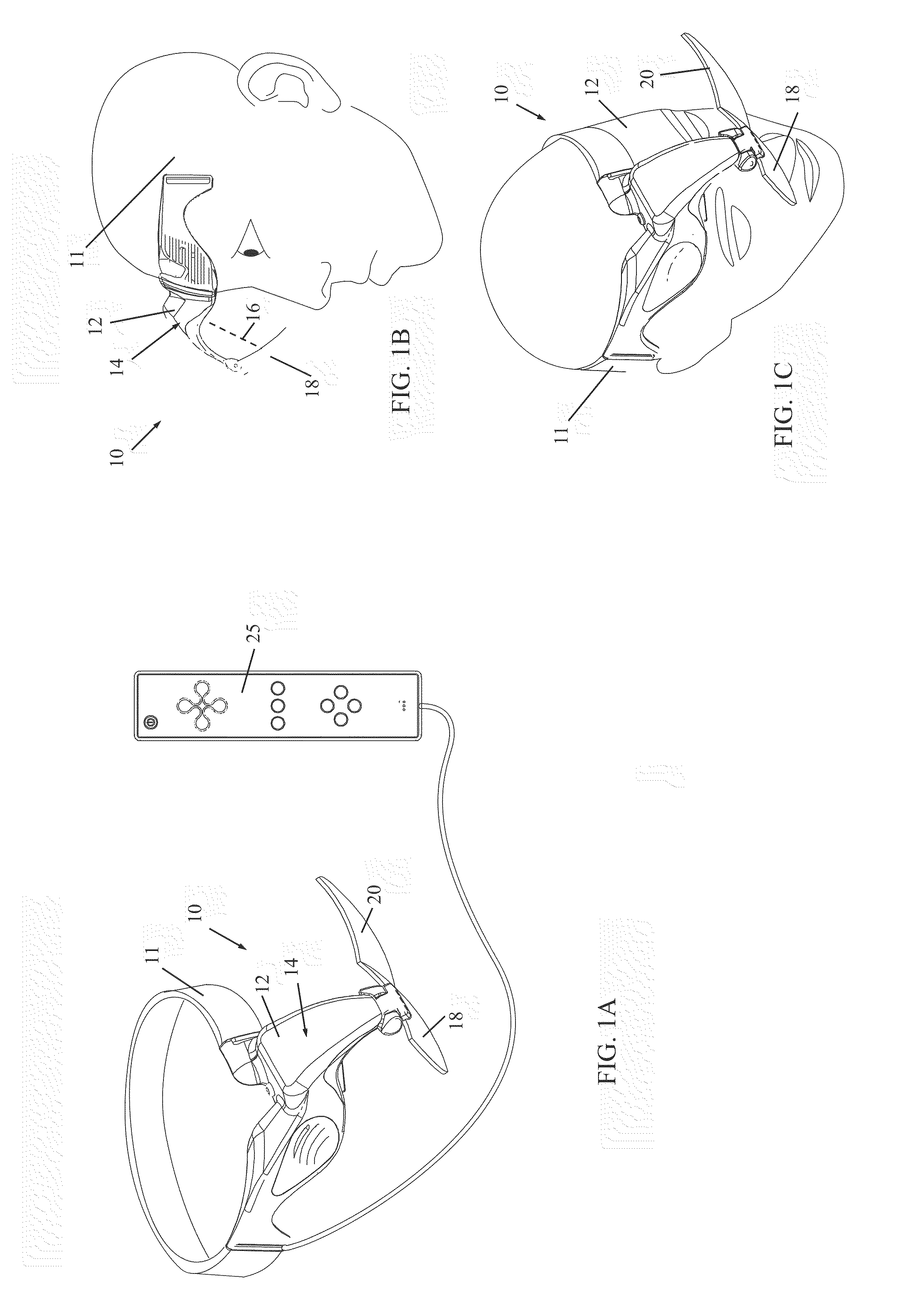
Head mounted 3D display
InactiveUS20100309097A1Reduce fatigueReduce motion sicknessCathode-ray tube indicatorsVideo gamesLight beamDisplay device
A head mounted display (HMD) including a display screen attached to a housing and aligned to be in a line of sight of a first eye of a user, an optics module disposed in the housing, for generating an image and projecting a beam of the image on the display screen, and a non-display screen attached to the housing and aligned to be in a line of sight of a second eye of the user, wherein the image displayed on the display screen is displayed at a virtual display distance different than a distance at which an image of the non-display screen is perceived.
Owner:SIROCCO VISION
Method of optimizing cardiac resynchronization therapy using sensor signals of septal wall motion
The present invention relates to monitoring septal wall motion of the atrial and / or ventricular chambers of a heart for optimizing cardiac pacing intervals based on signals derived from said wall motion. At least one lead of medical device is equipped with a motion sensor adapted to couple to septal tissue. The device receives and may post-process (e.g., suitably filter, rectify and / or integrate) motion signals to determine acceleration, velocity or displacement. During pacing interval optimization the wall motion is measured for many pacing intervals and the pacing interval setting(s) that produce minimal wall motion are implemented for therapy delivery. In addition, the present invention provides methods for periodically determining whether to cease or resume delivery of a bi-ventricular pacing therapy to a patient that may have experienced beneficial reverse remodeling of the heart.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
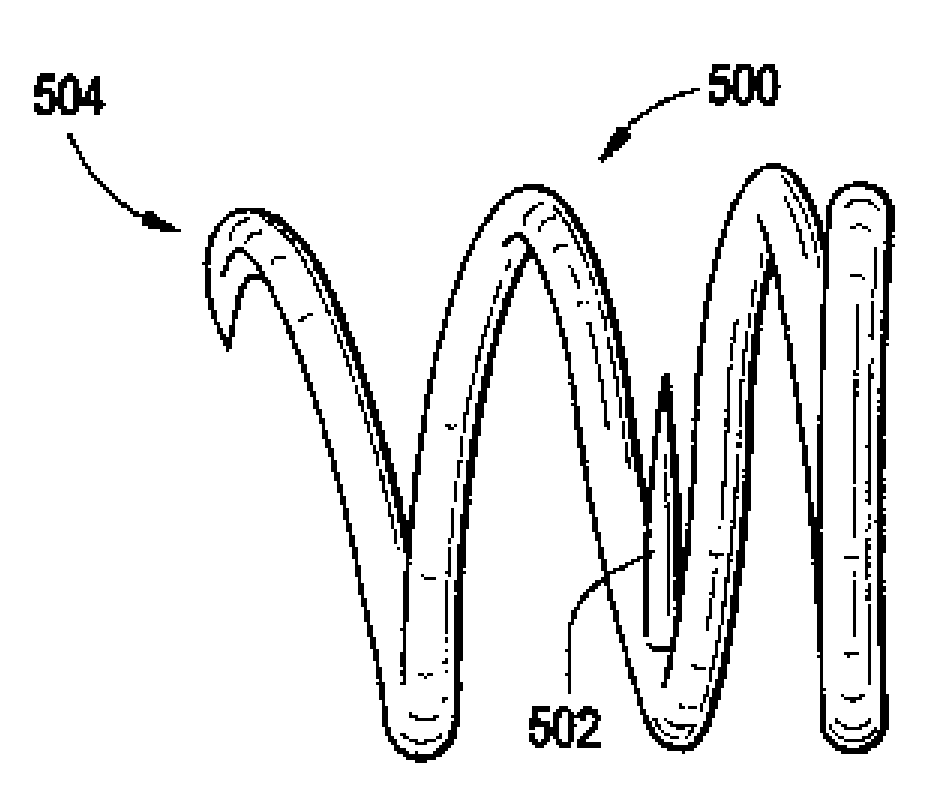
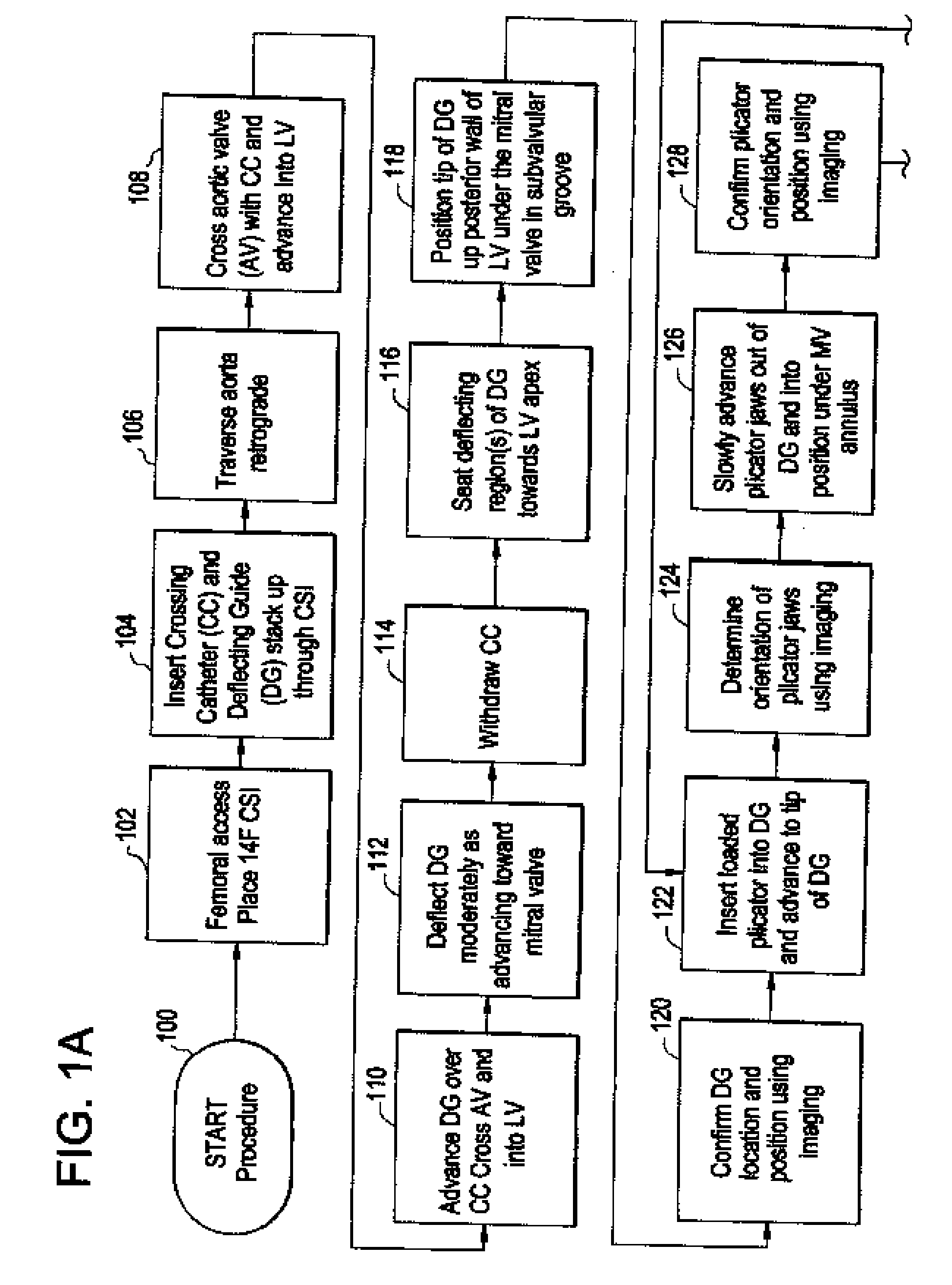
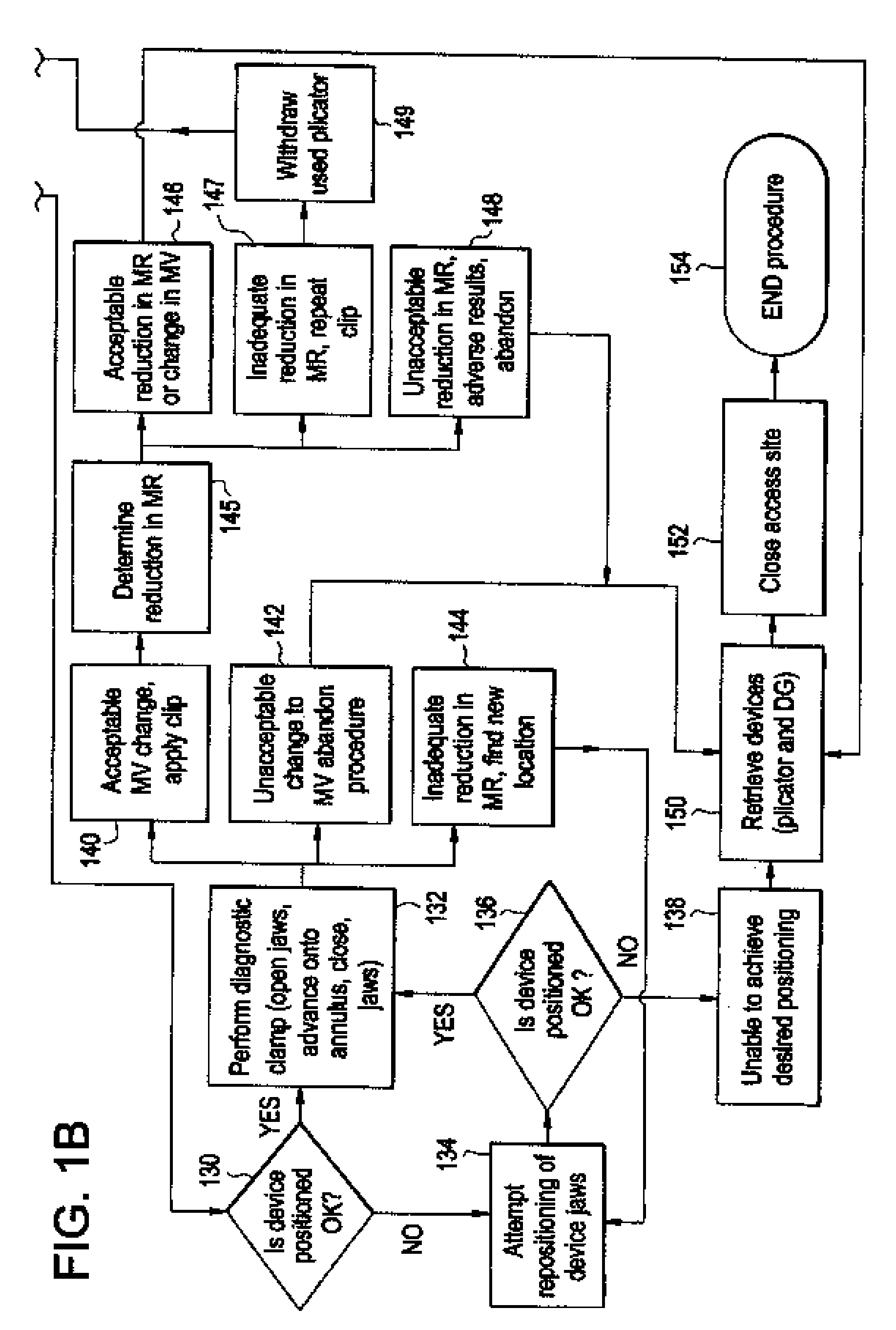
System using a helical retainer in the direct plication annuloplasty treatment of mitral valve regurgitation
InactiveUS20090105816A1Reduce the possibilityReducing interference leaflet motionHeart valvesTubular organ implantsCardiac valve annulusPlication annuloplasty
A system for using a helical retainer in the treatment of mitral valve regurgitation by reshaping the mitral valve annulus using one or more plications of annular tissue each fixed by a retaining clip is described. The system includes four devices to achieve such percutaneous direct plication annuloplasty. The first is a preferably prolapsable crossing catheter. Second, a deflecting guide catheter is used to provide a means for guiding the plication device into proper position at the subvalvular region of the mitral valve annulus. Third, the plication device is then used to make plications in at or near the subvalvular region of the mitral valve annulus. Fourth, a helical retainer clip deployed by the plication device in order to retain the plicated tissue in the plicated form. Alternatively, the fourth device is a retainer delivery catheter that enables delivery of a helical retainer over the outside of the plication device.
Owner:CORDIS CORP
Conduction block verification probe and method of use
ActiveUS20060015165A1Lower impedanceImprove conductivityEpicardial electrodesSurgical needlesVeinCardiac arrhythmia
Devices and methods provide for ablation of cardiac tissue for treating cardiac arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation. Although the devices and methods are often be used to ablate epicardial tissue in the vicinity of at least one pulmonary vein, various embodiments may be used to ablate other cardiac tissues in other locations on a heart. Devices generally include at least one tissue contacting member for contacting epicardial tissue and securing the ablation device to the epicardial tissue, and at least one ablation member for ablating the tissue. Various embodiments include features, such as suction apertures, which enable the device to attach to the epicardial surface with sufficient strength to allow the tissue to be stabilized via the device. For example, some embodiments may be used to stabilize a beating heart to enable a beating heart ablation procedure. Many of the devices may be introduced into a patient via minimally invasive introducer devices and the like. Although devices and methods of the invention may be used to ablate epicardial tissue to treat atrial fibrillation, they may also be used in veterinary or research contexts, to treat various heart conditions other than atrial fibrillation and / or to ablate cardiac tissue other than the epicardium.
Owner:ATRICURE
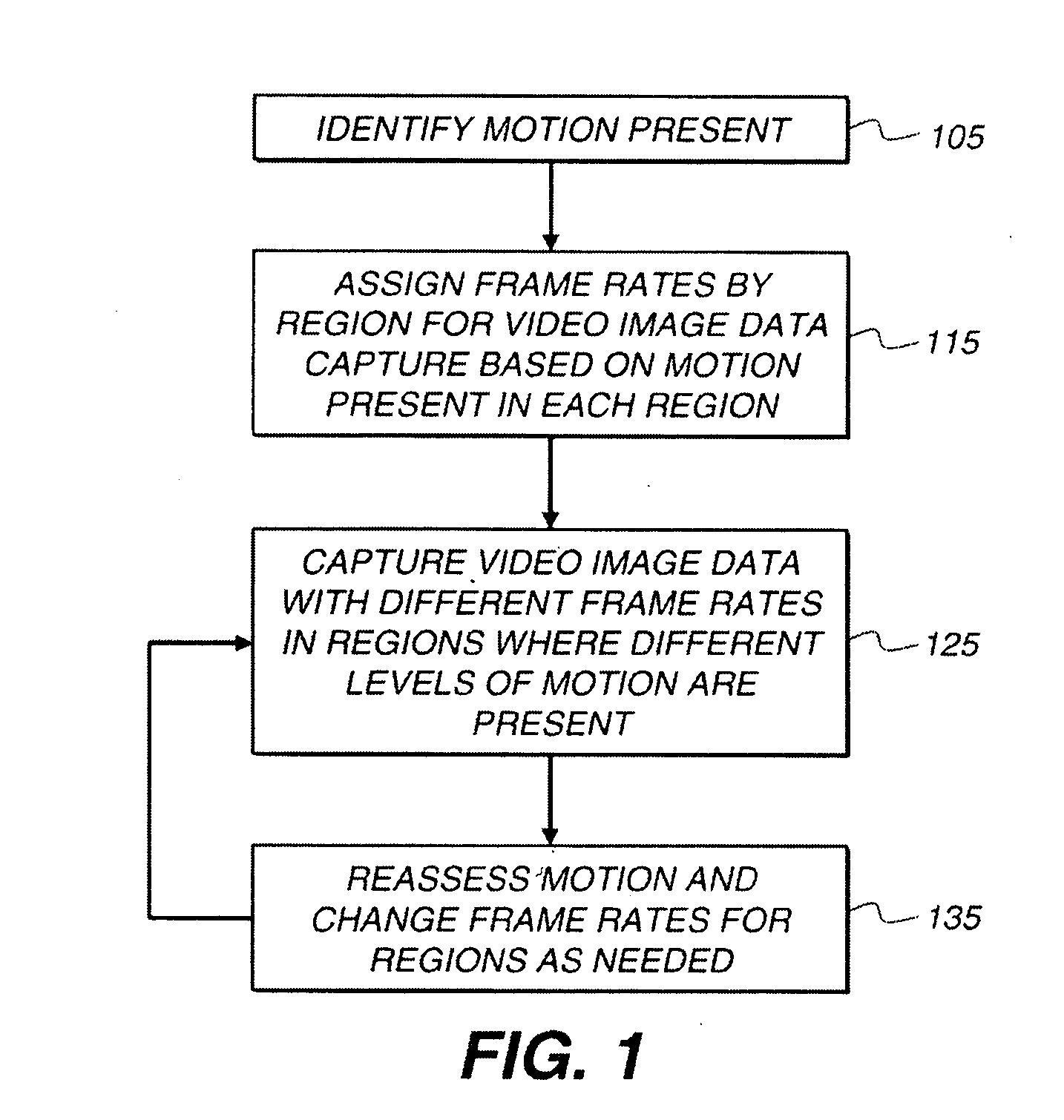
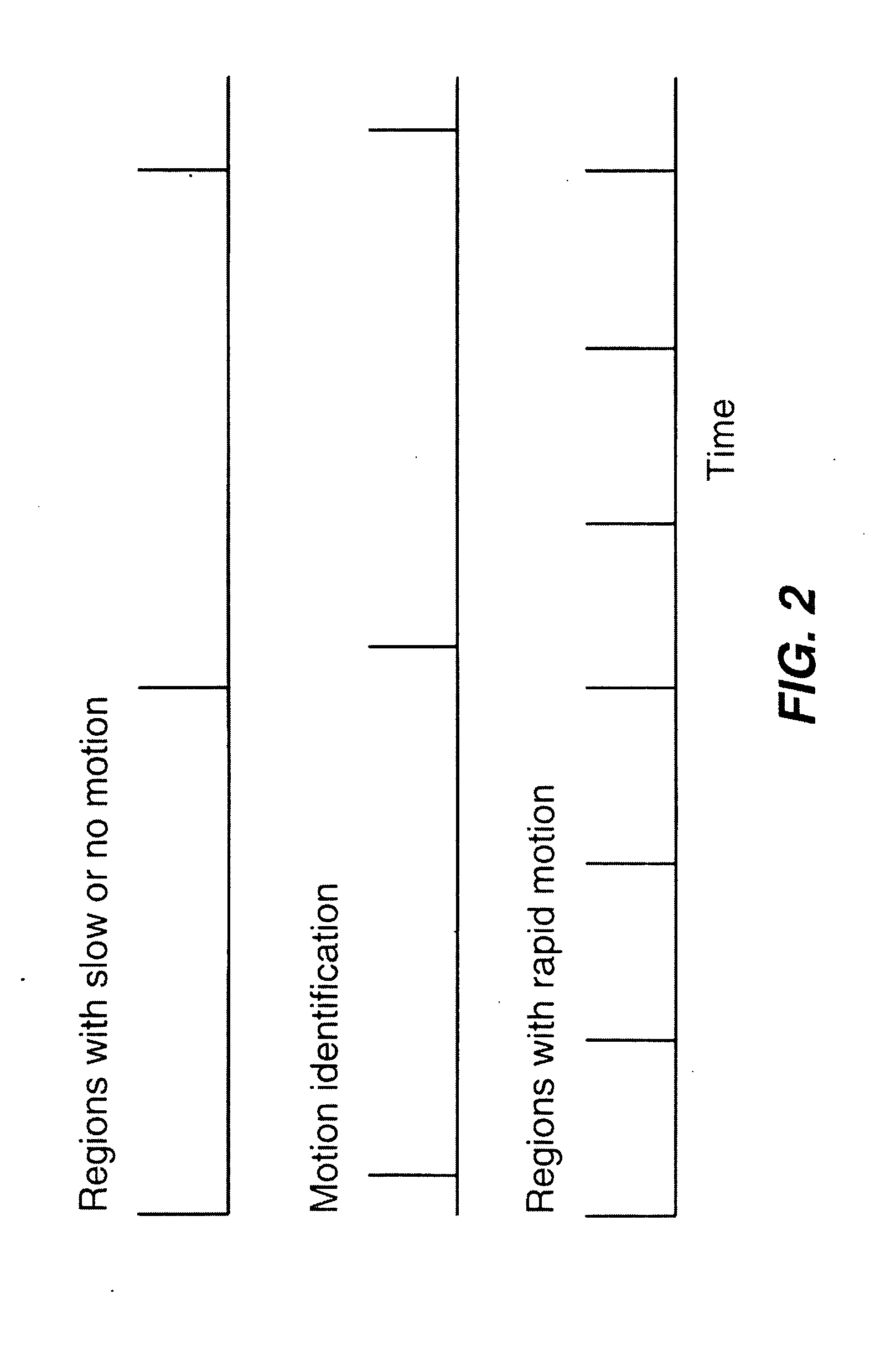
Capture of video with motion
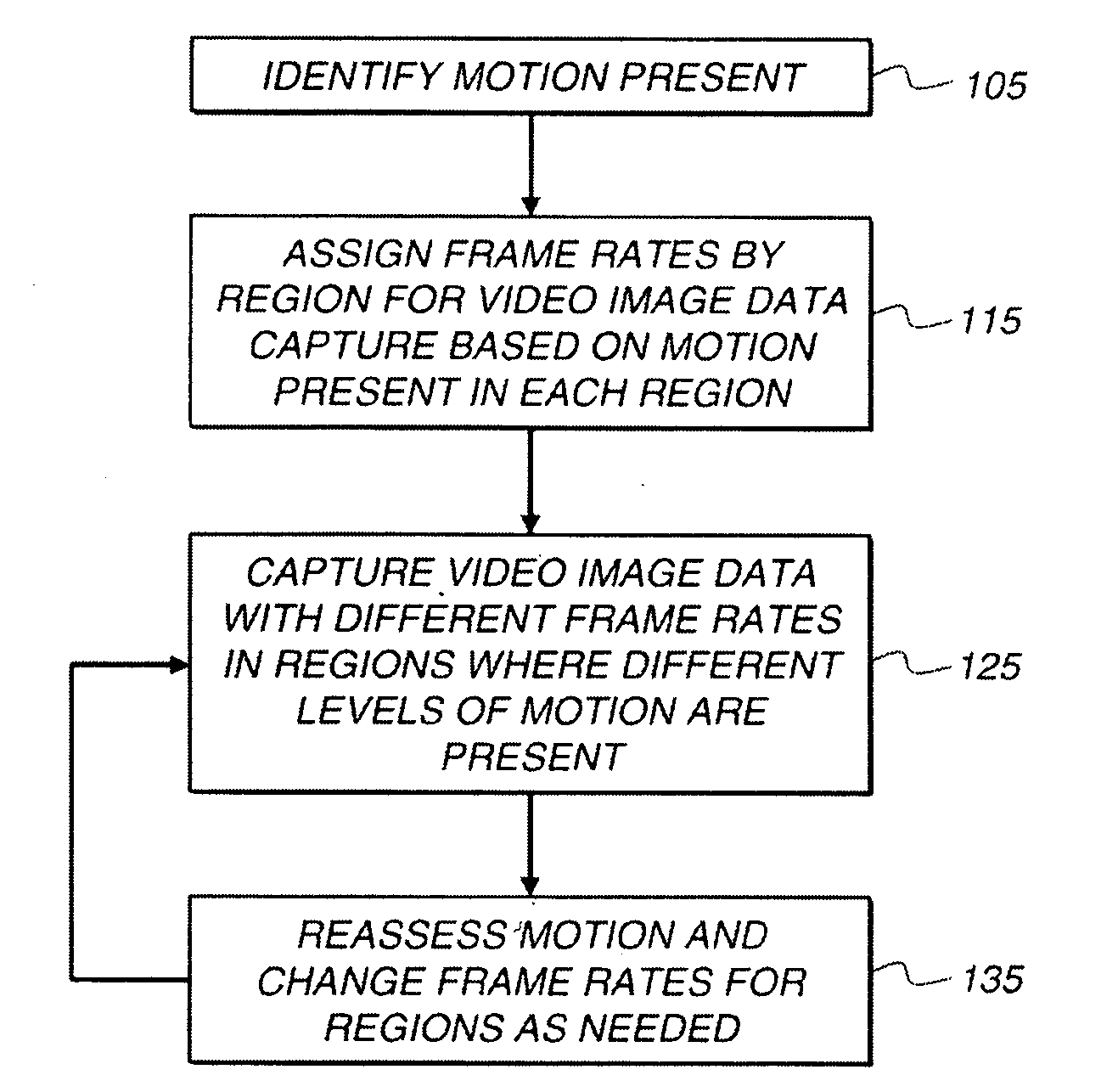
ActiveUS20100231738A1Reduce relative motionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsRelative motionMotion capture
A method of capturing a video of a scene depending on the speed of motion in the scene, includes capturing a video of the scene; determining the relative speed of motion within a first region of the video of the scene with respect to the speed of motion within a second region of the video of the scene; and causing a capture rate of the first region of the video of the scene to be greater than a capture rate of the second region of the video of the scene, or causing an exposure time of the first region to be less than exposure time of the second region.
Owner:APPLE INC
Spinal implants and methods
InactiveUS20090138015A1Reduce relative motionSmooth motionBone implantDiagnosticsPosterior regionIntervertebral disk
Spinal implants are disclosed that can be used for annular repair, facet unloading, disc height preservation, disc decompression, or for sealing a portal through which an intervertebral implant was placed. In some embodiments, an implant is placed within the intervertebral disc space, primarily within the region of the annulus fibrosus. In some embodiments, the implant is expandable. In some embodiments, the implant has a sealing tail structure comprising a tail flange and a linkage. In some embodiments, the sealing tail structure limits the extrusion or expulsion of disc material, either annulus fibrosus or nucleus, into the posterior region of the spine where it could impinge on nerves. In some embodiments, the tail structure is retained in place within the annulus fibrosus by means of an anchor. In some embodiments, the anchor is constructed from multiple components.
Owner:CONNER E SCOTT DR
Pointing device for use in air with improved cursor control and battery life
ActiveUS7696980B1Reduce resolutionImprove cursor controlCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingElectrical batteryImage resolution
One aspect of the present invention is an apparatus and method for improved cursor control in a device which can operate both on a work surface and in air. Cursor resolution is reduced as the user engages with the device for clicking, leading to more precise movement closer to the target, as well as reduced parasitic and other unintentional motion of the cursor during clicking. Moreover, one aspect of the present invention is an apparatus and method for improved battery life in an in-air pointing device. In another aspect, the present invention is a method a system for improved user interface interaction, for UI controls such as sliders, pop-up boxes, menus, lists and button groups.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
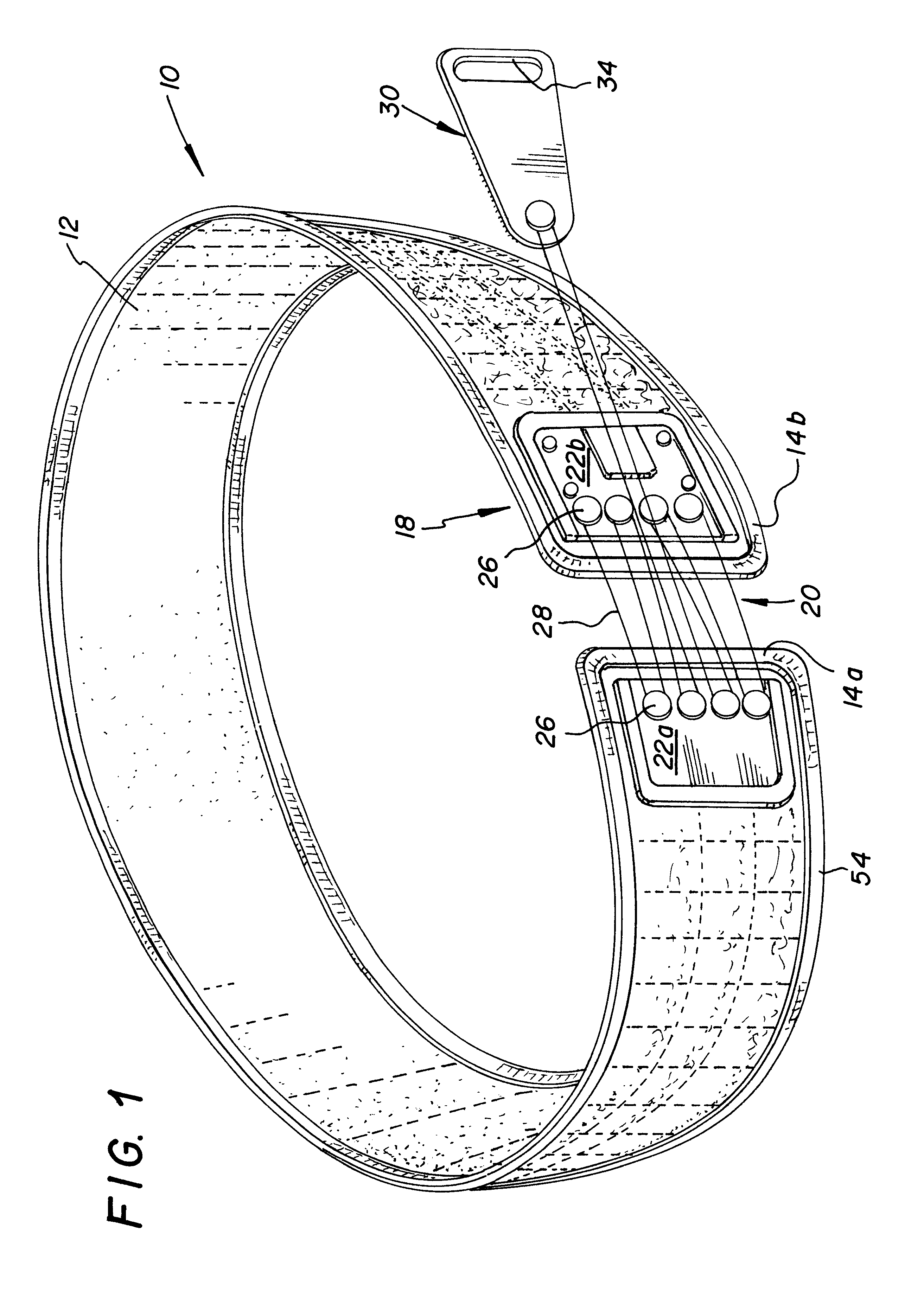
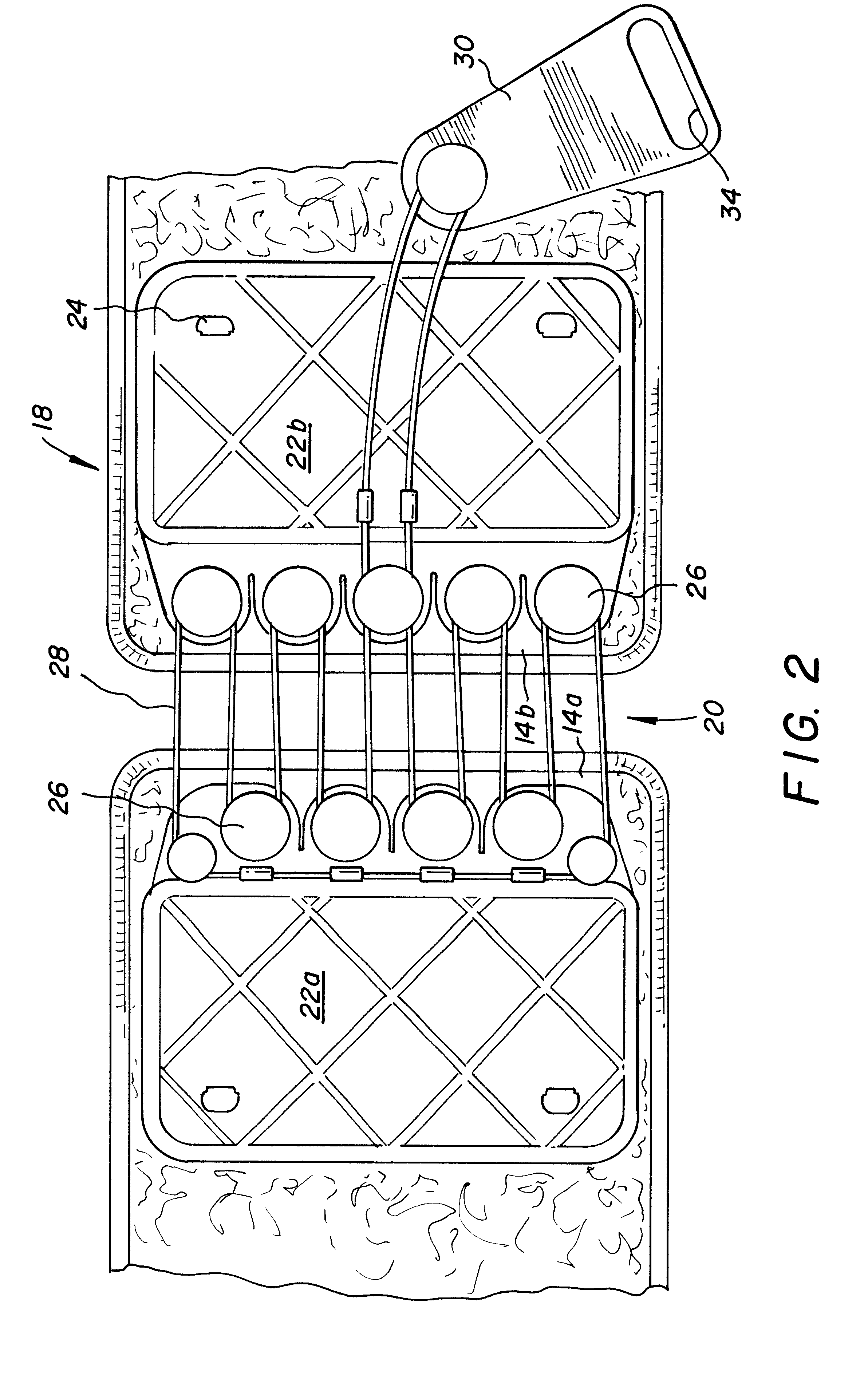
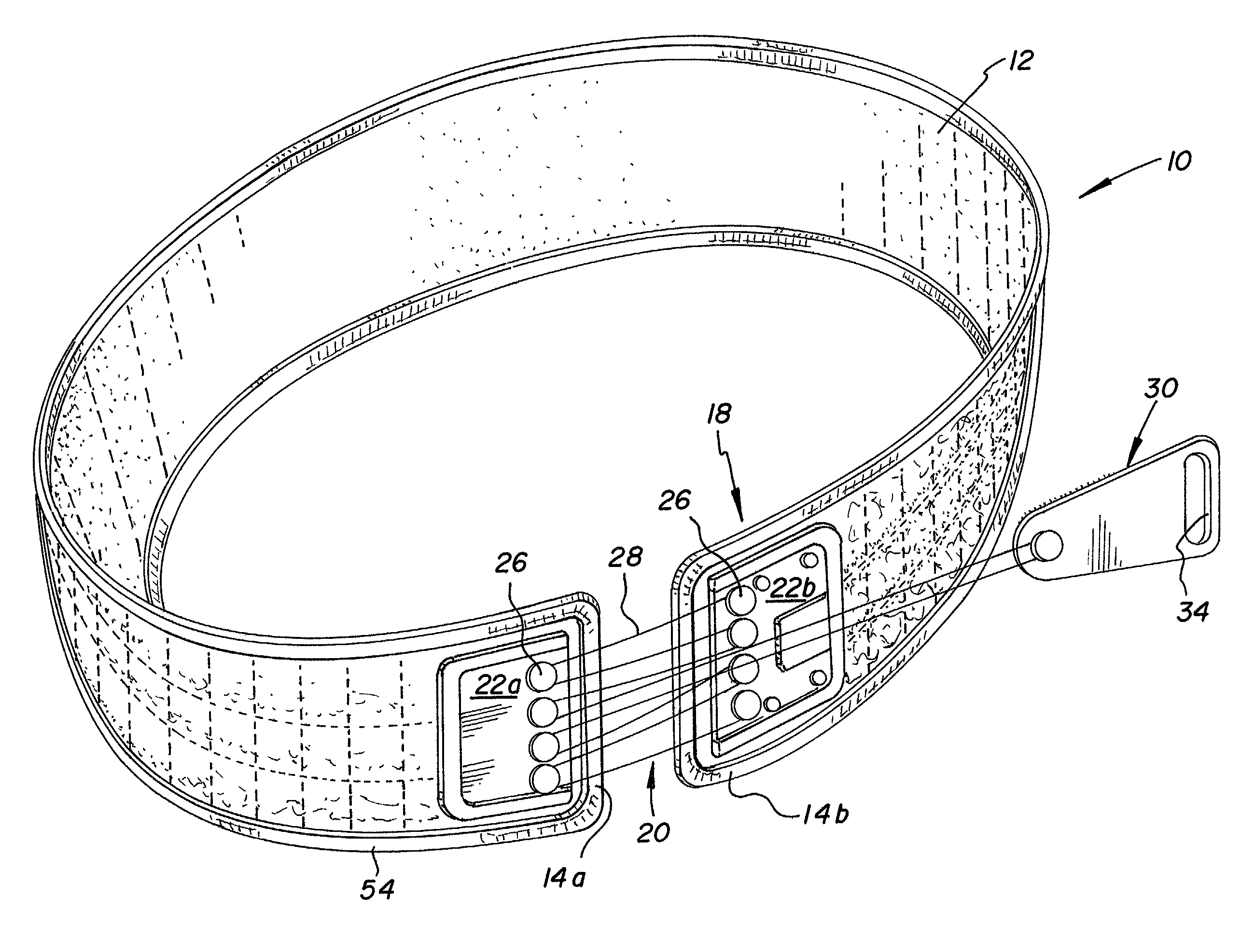
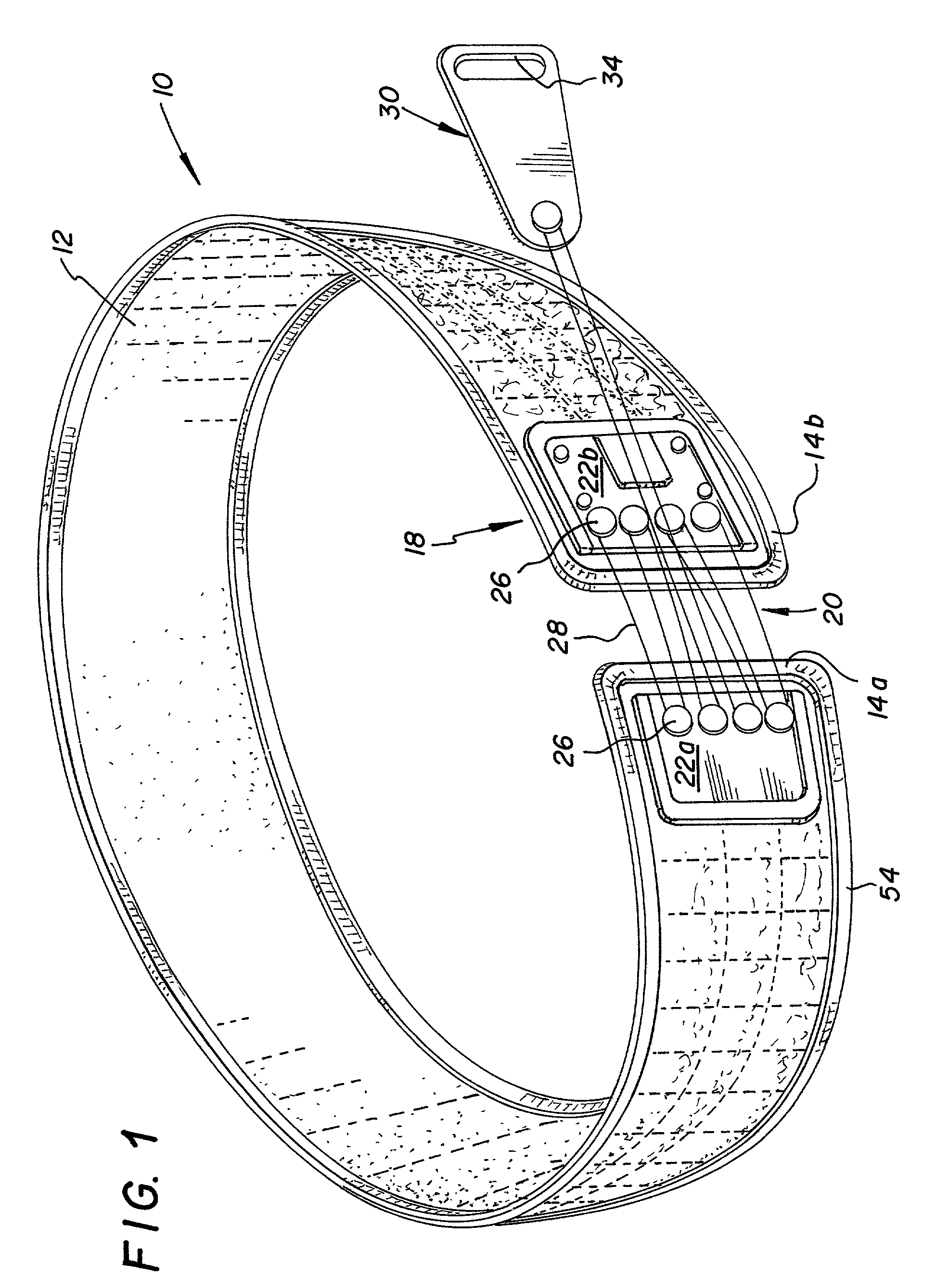
Orthotic trauma device
InactiveUS6602214B2Stabilizes broken boneReduce relative motionNon-surgical orthopedic devicesKnee orthosisEngineering
An orthotic trauma device is provided including an elongated orthosis body adapted to be wrapped around a portion of a body, the orthosis body being formed of a pliant material be easily cut with cloth-cutting scissors; a detachable fastening device provided at distal ends of the elongated orthosis body to releasably secure the distal ends to one another; and means for adjusting the tightness of the orthosis body operatively associated with the detachable fastening device. A pulley system for use in an orthotic device includes a pair of pulley banks arranged in a first and second of the pair of pulley banks detachably connected to a first distal end and a second distal end of the orthosis body respectively, a first bank of which is adapted to be detachably disposed on a first distal end of an elongated orthosis body and a second bank of pulleys adapted to be detachably disposed on a second distal end of the elongated orthosis body; and a cable interconnecting the two pulley banks and running through a pulley on each of the pulley banks in alteration, such that shortening of the cable pulls the pulley banks together and tightens the orthotic device with the aid of a mechanical advantage.
Owner:PYNG MEDICAL CORP
Orthotic trauma device
InactiveUS20020148461A1Stabilizes broken boneBlood lossNon-surgical orthopedic devicesKnee orthosisBlock and tackle
An orthotic trauma device is provided including an elongated orthosis body adapted to be wrapped around a portion of a body of a wearer of the device, the orthosis body being formed of a pliant material which is adapted to be easily cut with cloth-cutting scissors; a detachable fastening device provided at distal ends of the elongated orthosis body to releasably secure the distal ends to one another; and means for adjusting the tightness of the orthosis body operatively associated with the detachable fastening device. A pulley system for use in an orthotic device is also provided including a pair of pulley banks arranged in juxtaposed relationship, a first bank of which is adapted to be detachably disposed on a first distal end of an elongated orthosis body and a second bank of pulleys adapted to be detachably disposed on a second distal end of the elongated orthosis body; and a cable interconnecting the two pulley banks and running through a pulley on each of the pulley banks in alteration, such that shortening of the cable pulling the pulley banks together and tightening the orthotic device with the aid of a mechanical advantage dependent upon the number of pulleys mounted on each of the pulley banks.
Owner:PYNG MEDICAL CORP
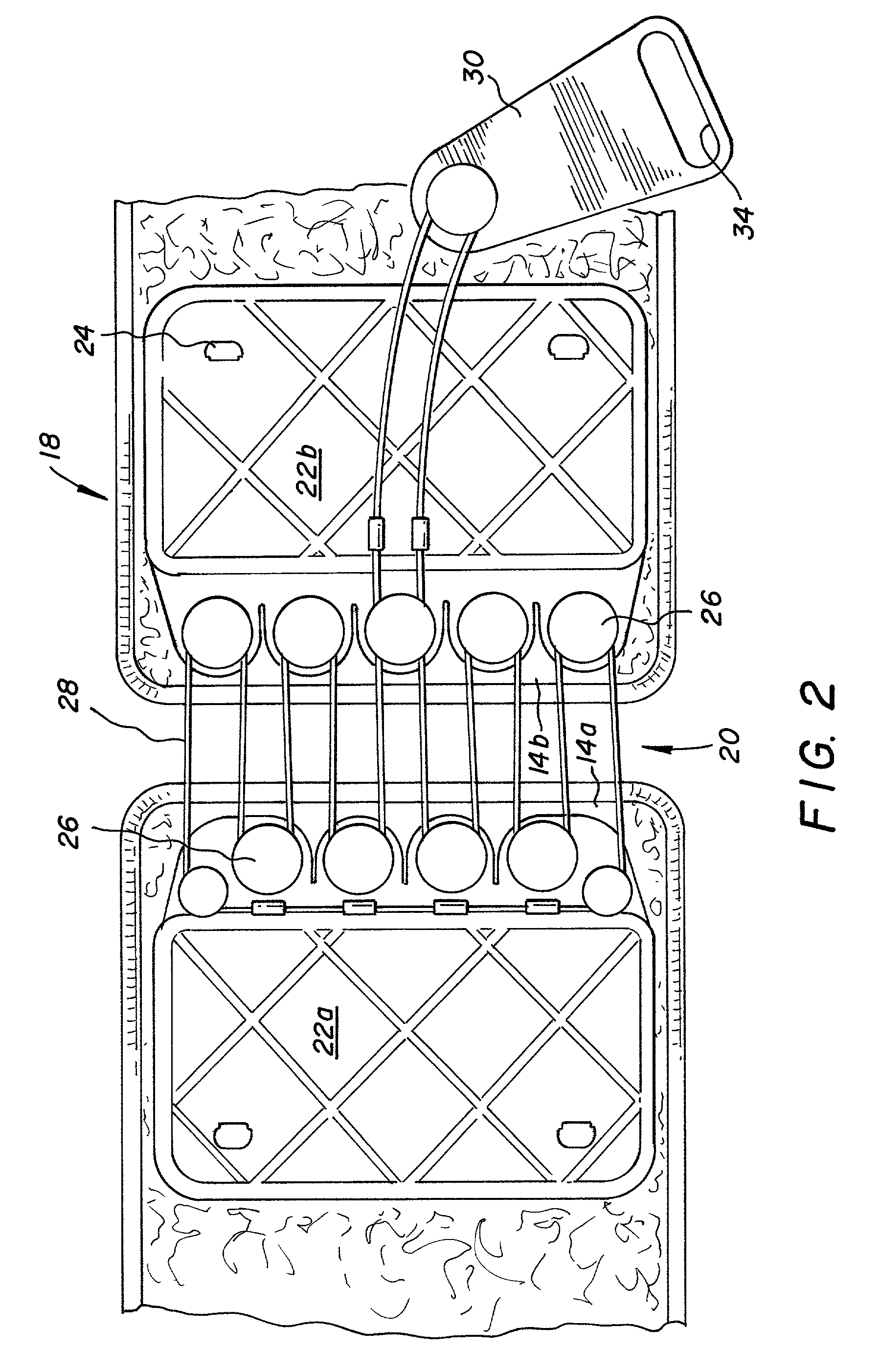
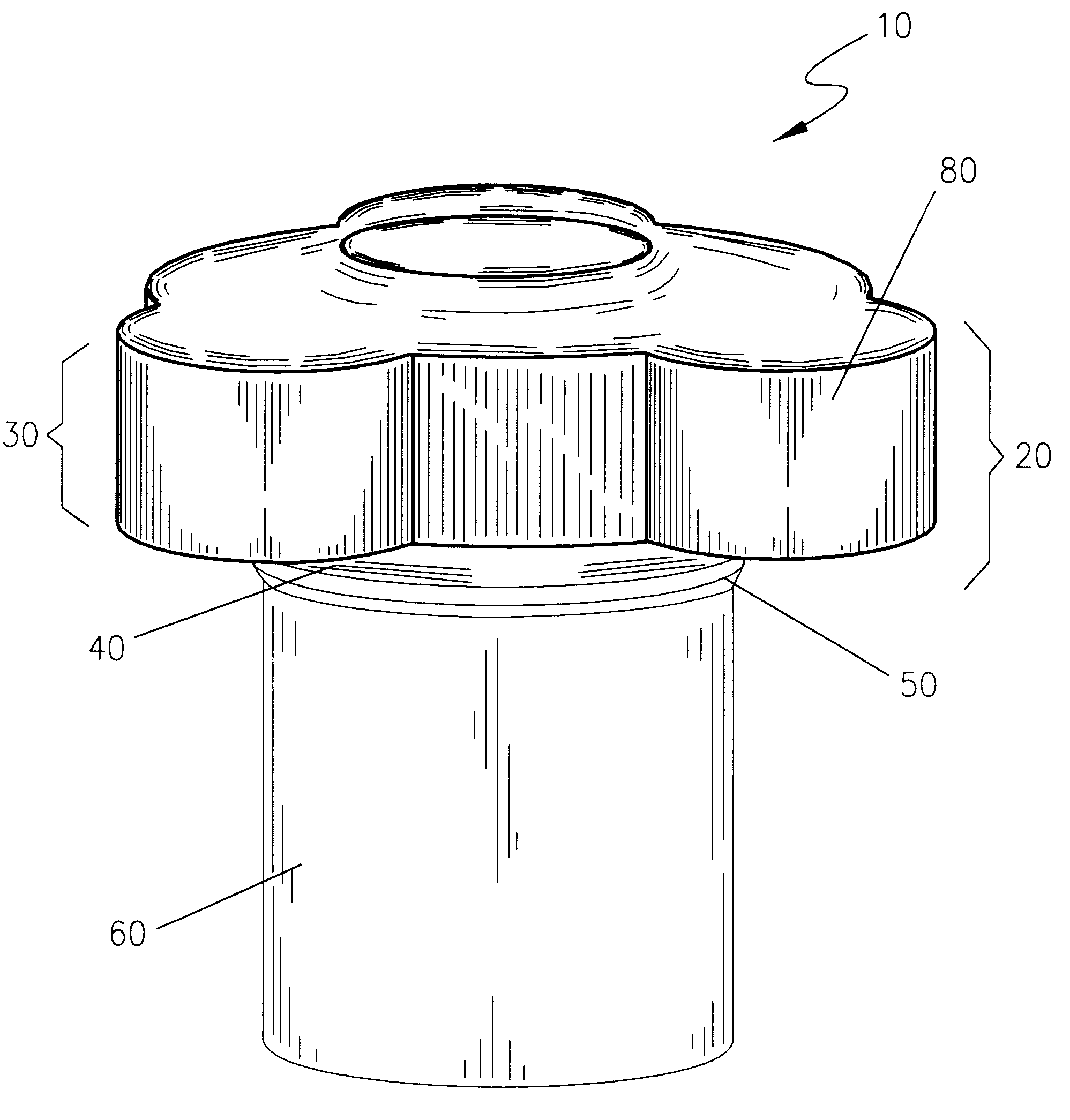
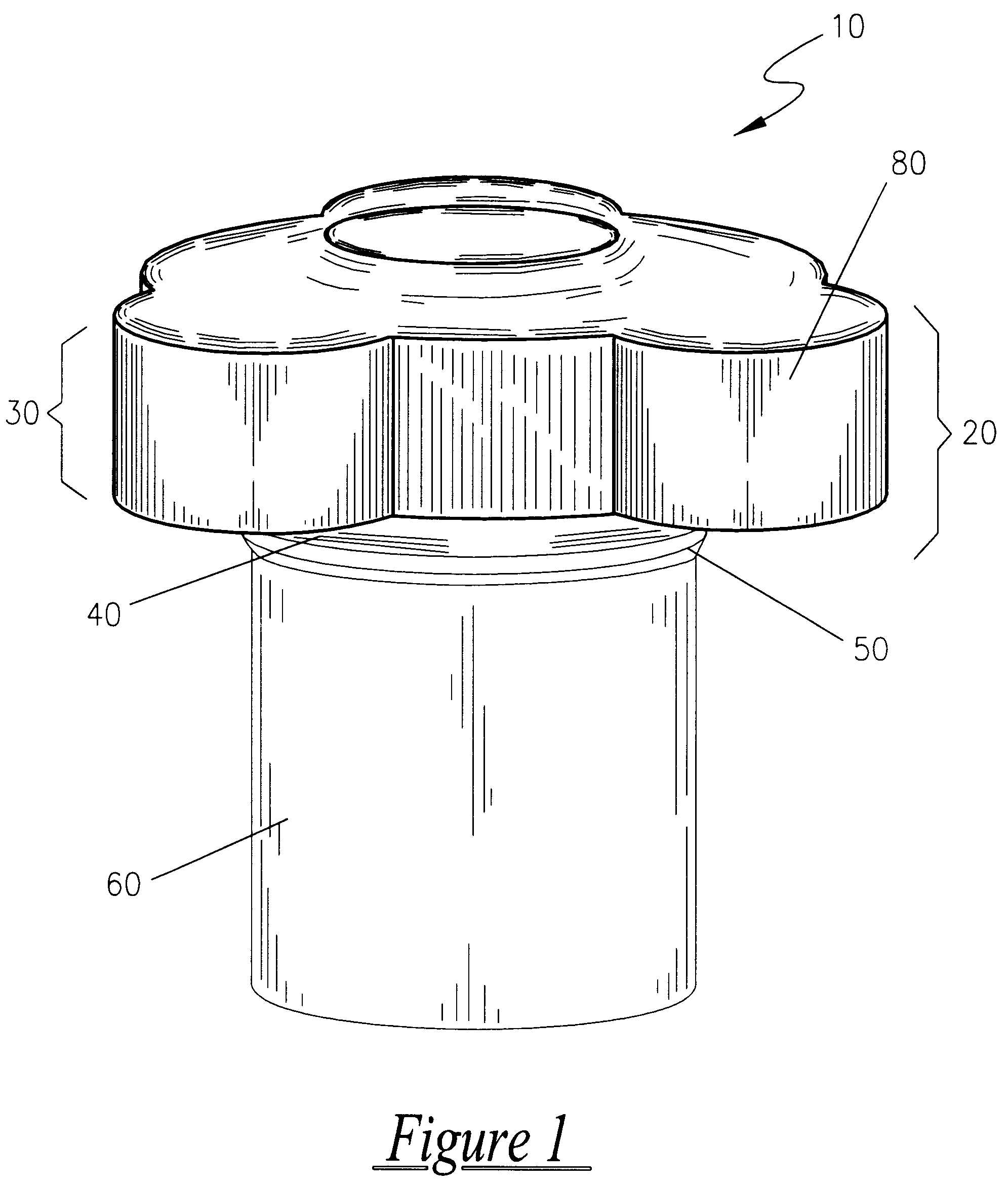
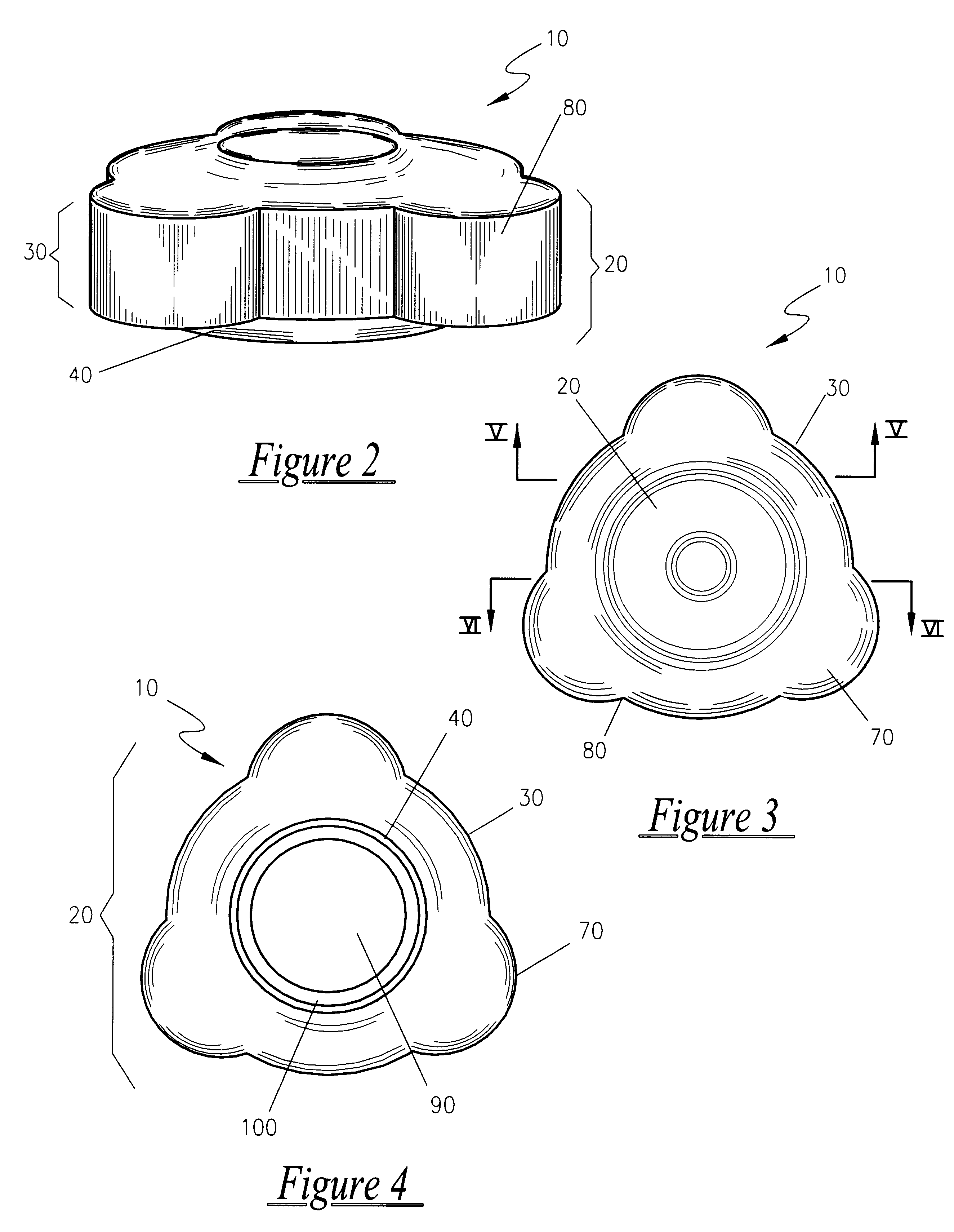
Easy opening, screw cap for threaded opening type containers
An improved, easy opening, screw-cap for threaded opening type containers is disclosed, consisting of a plastic or metal cap of generally cylindrical shape. Located along the upper section of the cap's outer circumferential surface are three, equally spaced, grasping protrusions, that extend radially outward from the radial center of the cap, so as to form a cap of a generally rounded, triangular configuration as seen from above. These grasping protrusions provide torsional, mechanical interference for the hand and it applies rotational force to screw on or off the cap. A series of vertically extending, gripping ribs, are equally spaced along the outer circumferential surface of the upper section of the cap, and are designed to make it easier to screw the cap on and off the neck of a conventional container, such as a bottle. Conventional internal screw threads are used on the internal cavity of the cap to attach the cap to the neck of a conventional container, such as a bottle.
Owner:ELIAS RICHARD I
Responsive electrical stimulation for movement disorders
InactiveUS7813802B2Reduce relative motionSetting deviceElectrotherapyArtificial respirationPhysical therapyElectrical stimulations
An implantable neurostimulator system for treating movement disorders includes a sensor, a detection subsystem capable of identifying episodes of a movement disorder by analyzing a signal received from the sensor, and a therapy subsystem capable of applying therapeutic electrical stimulation to treat the movement disorder. The system treats movement disorders by detecting physiological conditions characteristic of an episode of symptoms of the movement disorder and selectively initiating therapy when such conditions are detected.
Owner:NEUROPACE
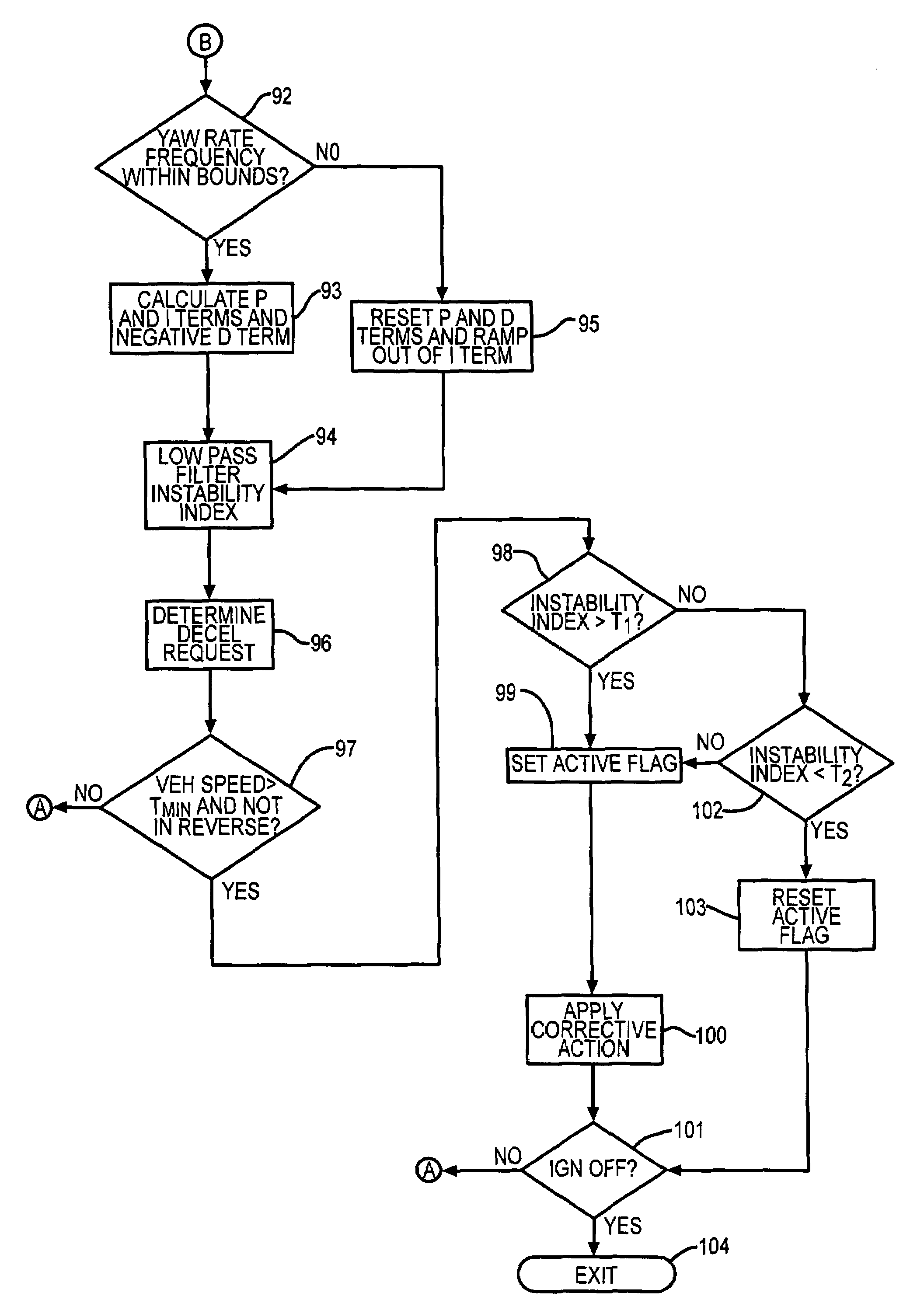
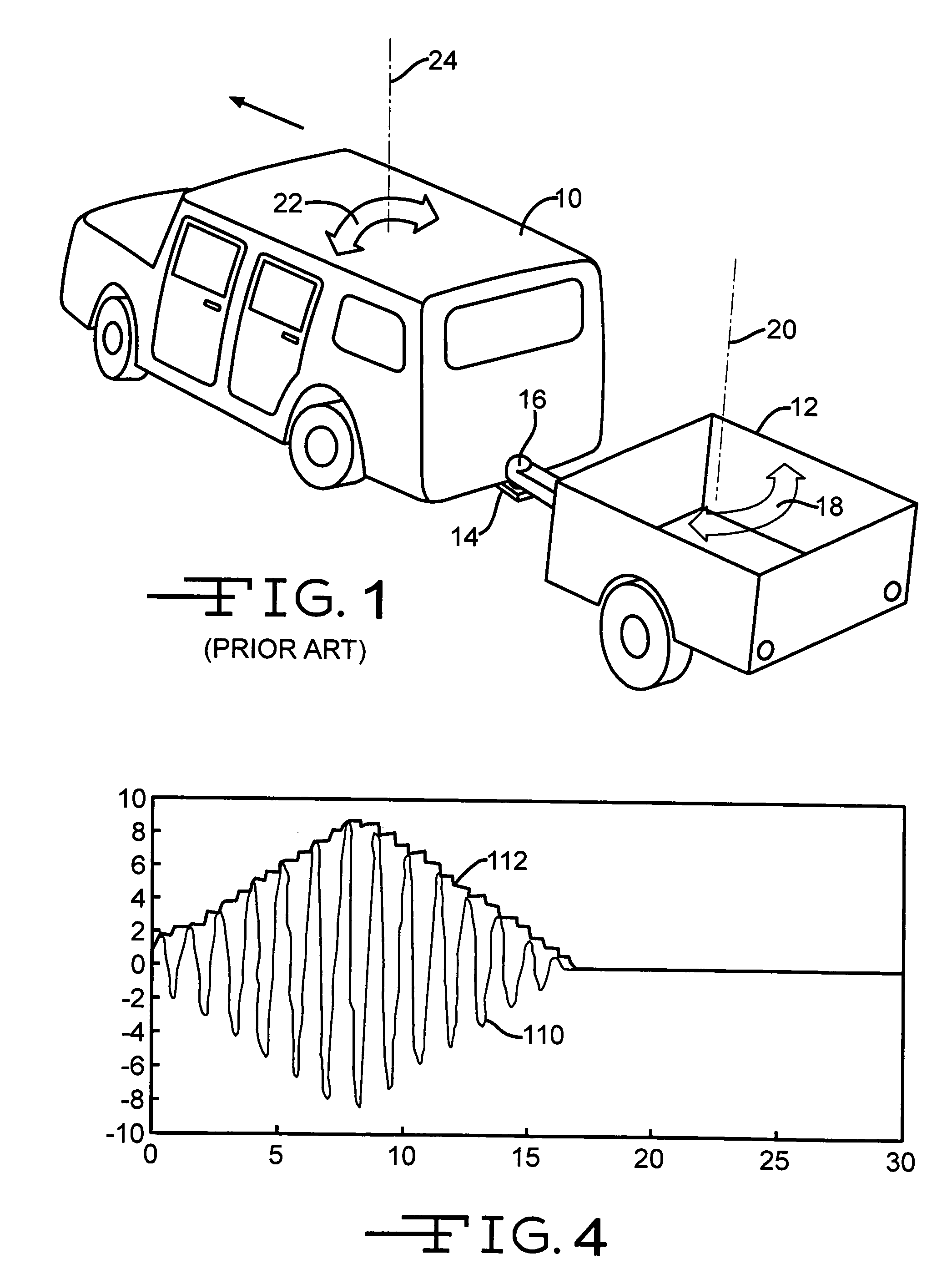
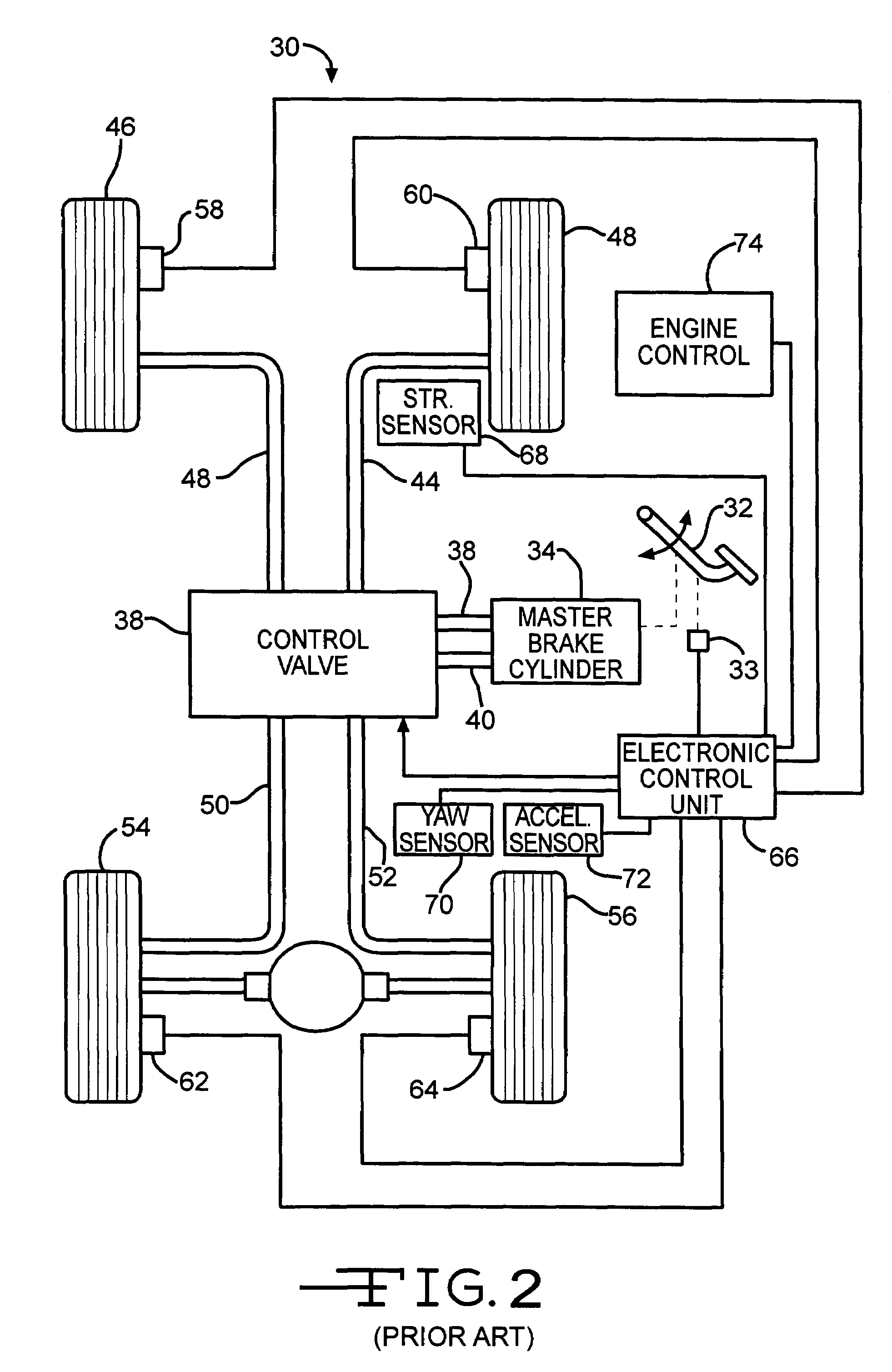
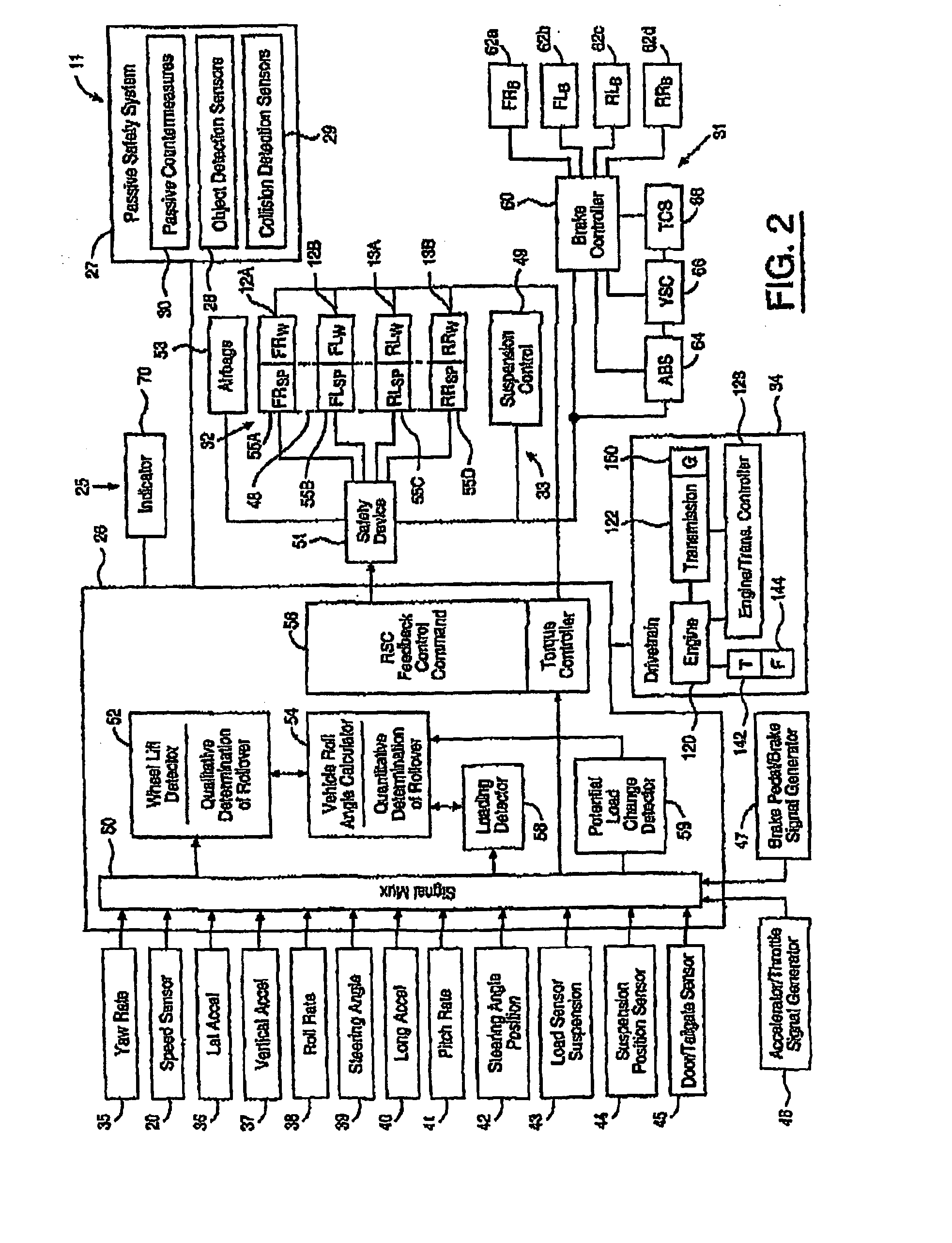
Method and apparatus for detecting and correcting trailer induced yaw movements in a towing vehicle
InactiveUS7272481B2Reduce yaw rateReduce relative motionAnalogue computers for trafficComputations using stochastic pulse trainsControl theoryMechanical engineering
An apparatus and method for determining the presence of excessive yaw rate in a vehicle by calculating an instability index that is a function of the vehicle yaw rate and generating an excessive yaw rate signal when the instability index exceeds a yaw rate threshold.
Owner:KELSEY HAYES CO
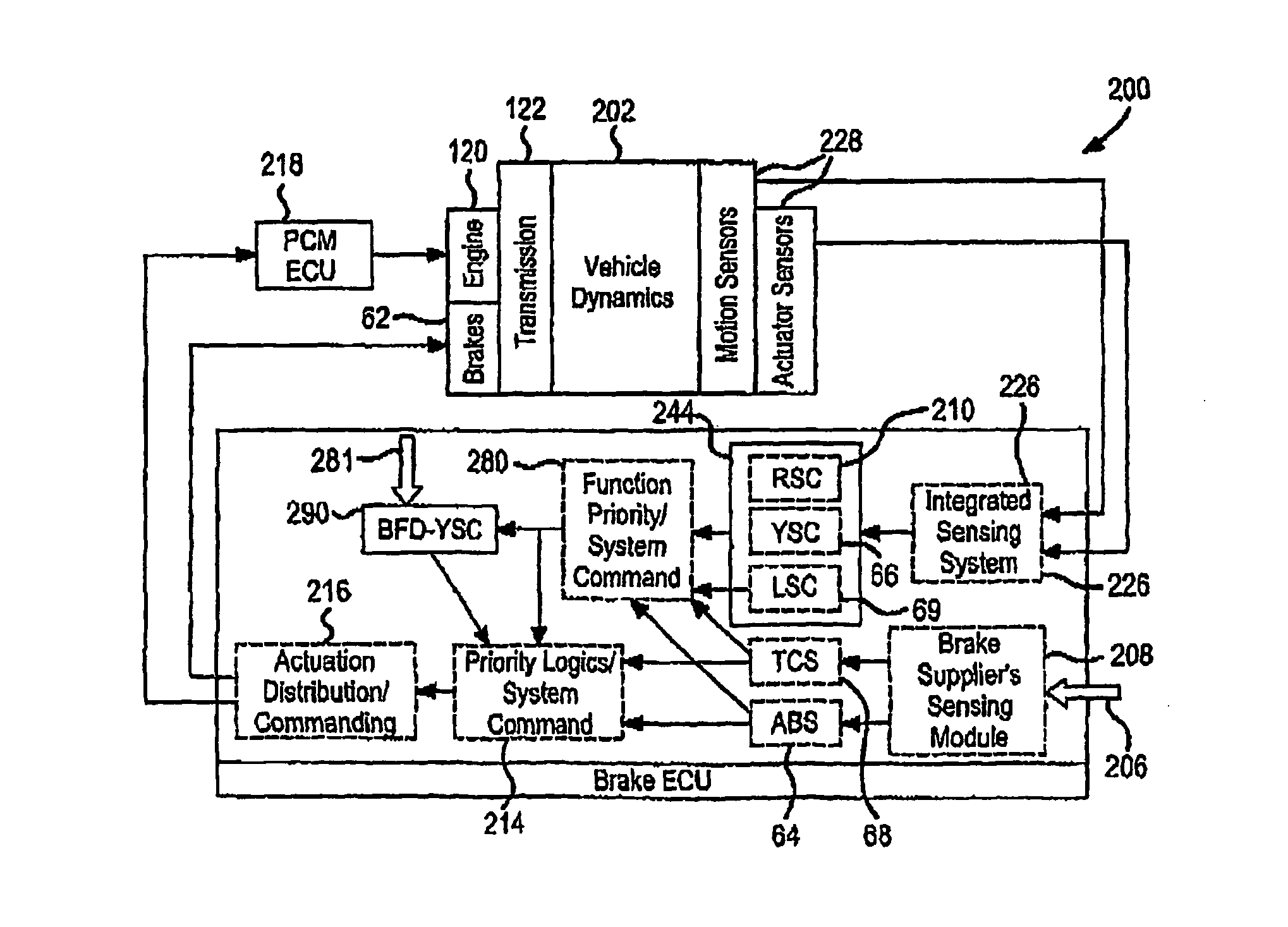
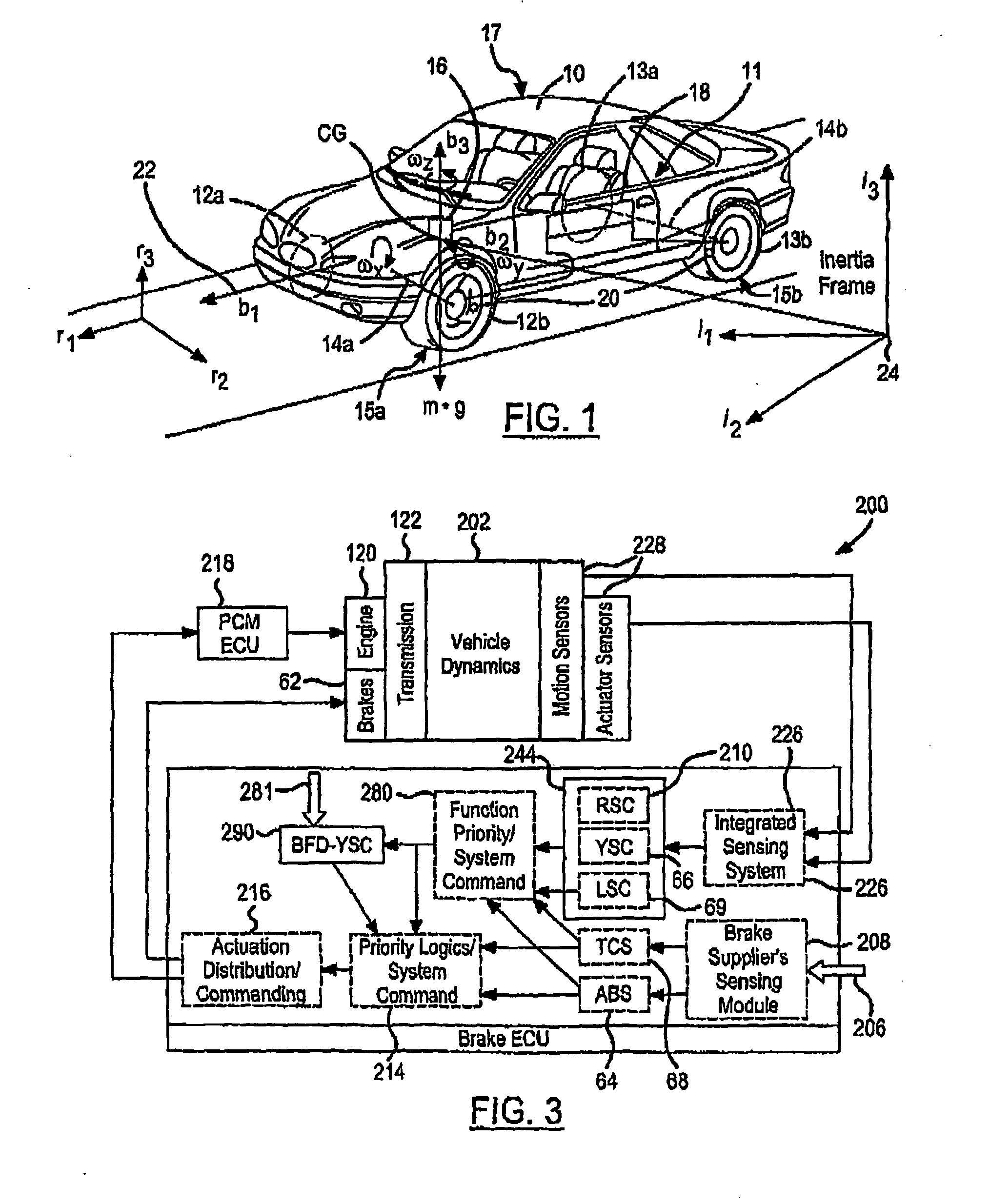
Enhanced Yaw Stability Control to Mitigate a Vehicle's Abnormal Yaw Motion Due to a Disturbance Force Applied to Vehicle Body
ActiveUS20110166744A1Reduce yaw motionEasy to operateVehicle testingAnalogue computers for trafficControl systemNormal functioning
An enchanced stability control system (200) for a vehicle includes a vehicle status sensor that generates a sensor signal. A driver input sensor that generates an input signal. A controller (214) may disable normal yaw stability control operation and enable body-force- disturbance (BDF) yaw stability control (YSC) operation, which includes at least partially reducing response functions of the normal yaw stability control associated with the input signal, in response to the sensor signal and performing BFD-YSC functions to achieve desired control performance upon the detection of BFD reception. The controller (214) may also or alternatively compare the sensor signal to a threshold and detect an improperly functioning / inoperative vehicle status sensor. The controller (214) disregards information associated with the improperly functioning / inoperative vehicle status sensor, and continues to perform enhanced yaw stability control operations.
Owner:VOLVO CAR CORP
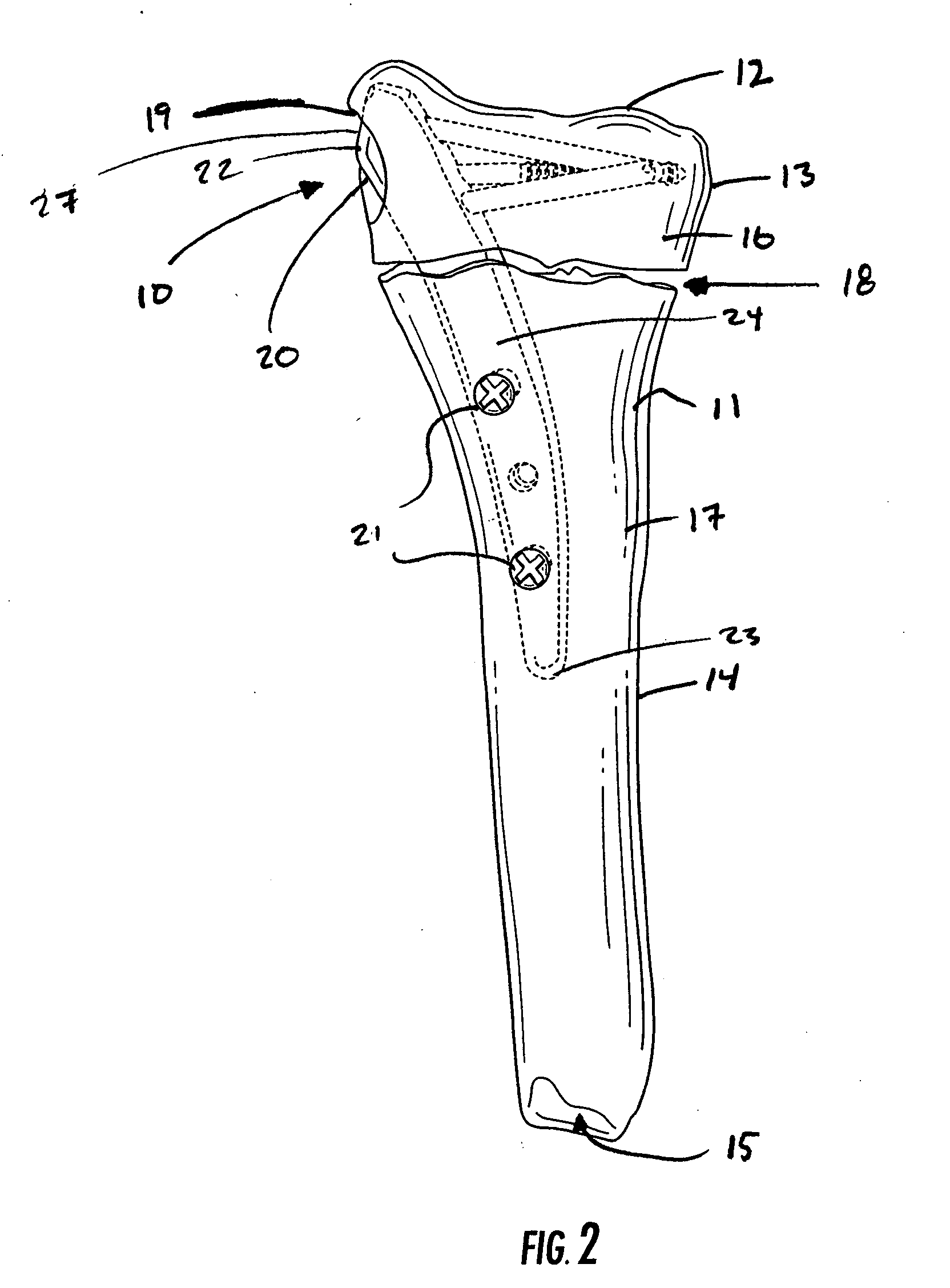
Guide assembly for intramedullary fixation and method of using the same
ActiveUS20060015123A1Precise positioningEasy to installInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsBone fragmentBiomedical engineering
An intramedullary fixation assembly usable with different long bone types and a guide assembly for guiding deployment of the intramedullary fixation assembly. The intramedullary fixation assembly includes a fixation member that has ends and a curved body extending between the ends. The curved body of the fixation member has a radius of curvature configured to extend through the medullary canal regardless of the long bone anatomy. Fasteners fix the fixation member to the bone fragments and are guided by a guide assembly. The guide assembly includes a guide body defining openings configured to guide the fasteners through openings defined in the fixation member and into the bone fragments. A fixation end of the guide body includes a pair of opposing, converging surfaces that are configured to engage in a positive fit with an exposed end of the fixation member accessible through the side aperture in the first fragment.
Owner:WRIGHT MEDICAL TECH
Haptic interface for laptop computers and other portable devices
InactiveUS20050052430A1Enhanced interactionEnhance manipulationInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsPiezoelectric actuators
A haptic feedback touch control used to provide input to a computer. A touch input device includes a planar touch surface that provides position information to a computer based on a location of user contact. The computer can position a cursor in a displayed graphical environment based at least in part on the position information, or perform a different function. At least one actuator is also coupled to the touch input device and outputs a force to provide a haptic sensation to the user. The actuator can move the touchpad laterally, or a separate surface member can be actuated. A flat E-core actuator, piezoelectric actuator, or other types of actuators can be used to provide forces. The touch input device can include multiple different regions to control different computer functions.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
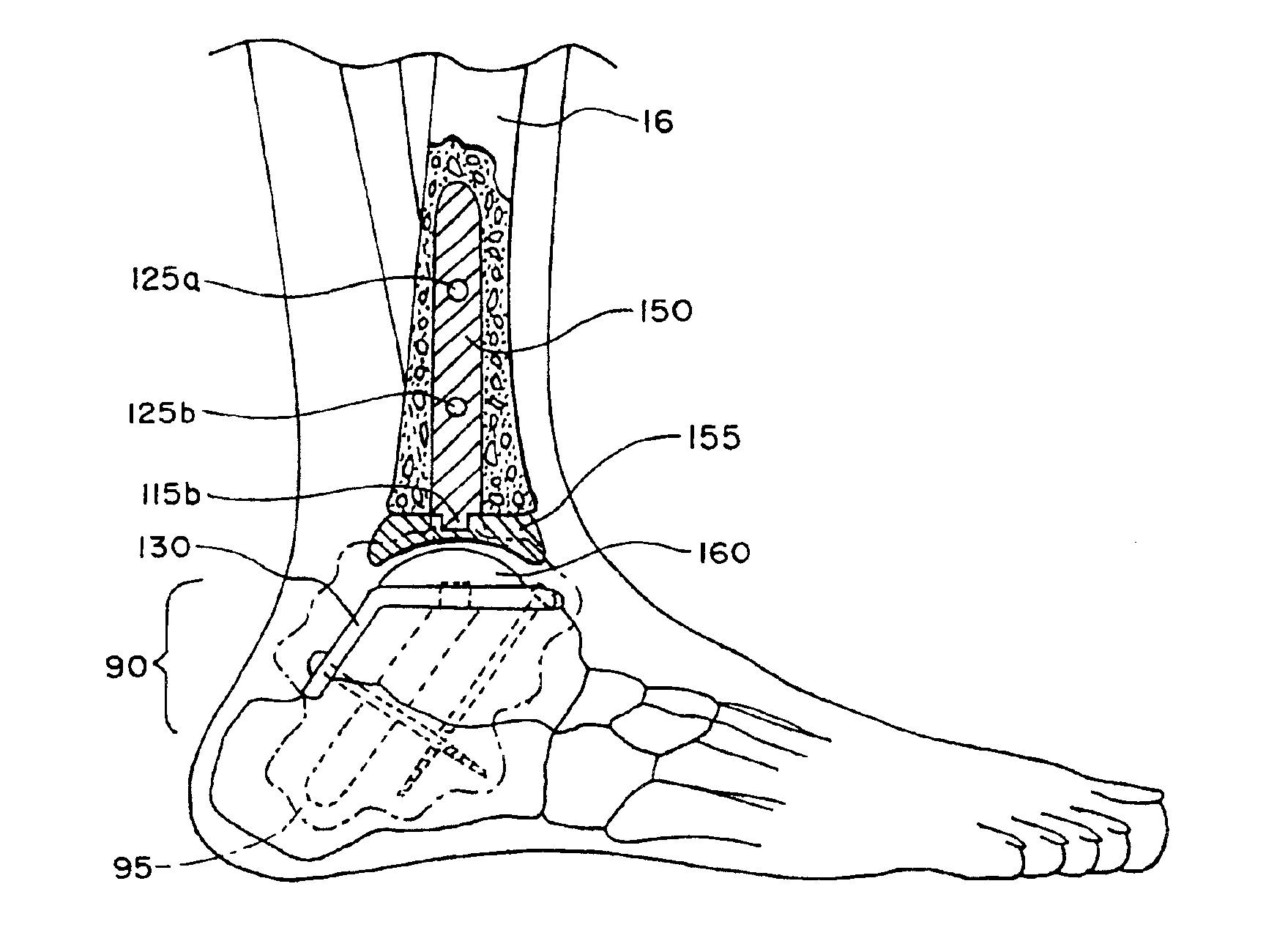
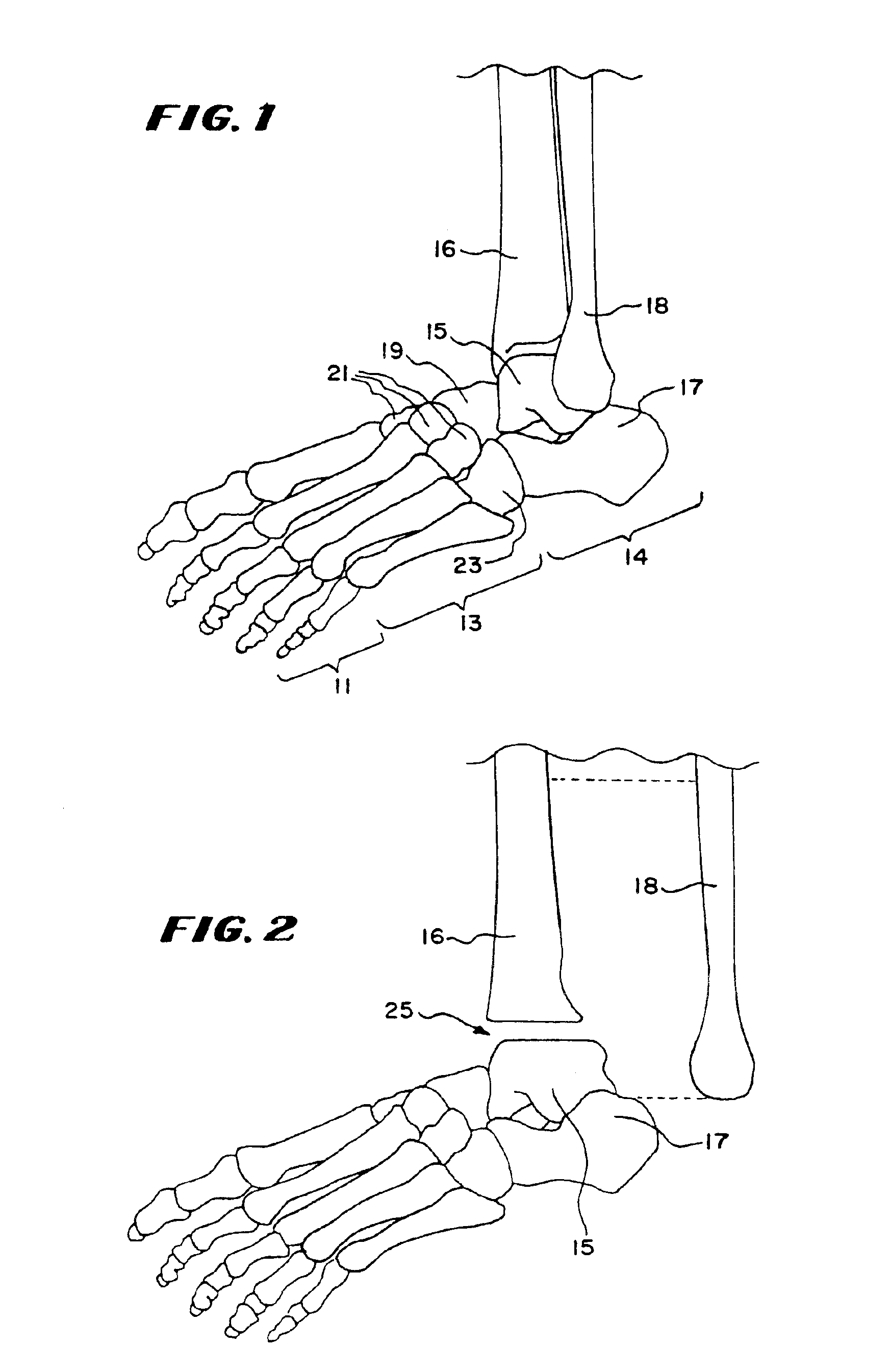
Intramedullary guidance systems and methods for installing ankle replacement prostheses
InactiveUS6875236B2ResultGuaranteed long-term resultsInternal osteosythesisAnkle jointsGuidance systemAnkle joint prosthesis
Intramedullary guidance systems and methods introduce some and / or all surgical tools and ankle prostheses components through the tibia, using minimal invasive exposure in the tibia tubercle, or retrograde through the talus, using minimal invasive exposure in planar surface of the calcaneus. The systems and methods align the talus and tibia for the installation of one or more ankle prostheses components, and also maintain that alignment during the installation using intramedullary guidance, e.g., by use of a guide pin to form an intramedullar passage along which surgical tools and prosthetic components are guided.
Owner:INBONE TECH
Method and apparatus for pulsed electromagnetic therapy
An apparatus and method for applying pulsed electromagnetic therapy to humans and animals. A straight wire element is employed to generate the magnetic field. A power and timer circuit supplies current pulses that approximate square pulses in form, so that the straight wire element generates magnetic pulses having rapid rise and fall times. Peak field strength is approximately 2 gauss at a 1 cm distance from the straight wire element, and the duration of peak field strength is approximately 200 nanoseconds. The pulses are repeated at a frequency of about 70 Hz. The straight wire element and circuit may be housed in a hand-held probe, with an LED illuminating the skin area to provide a visual indication of effective range, or a plurality of the straight wire elements and associated circuits may be embedded in a conformable pad that is placed over the affected area of the body.
Owner:GORDON GLEN A
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com