Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1066 results about "Orthotic device" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
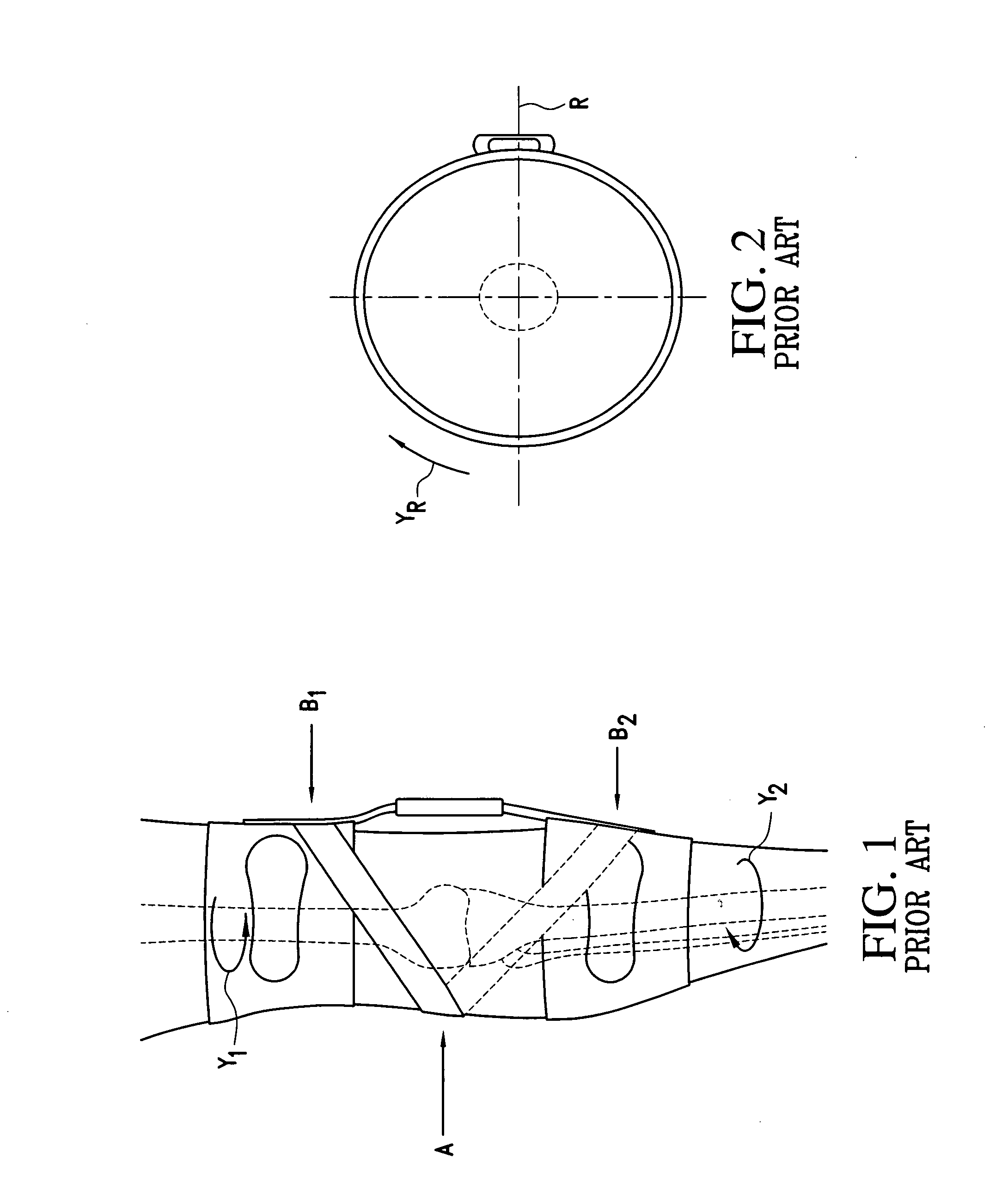
A device applied to a human limb to control or enhance movement or to prevent bone movement or deformity, for example, a splint or an arch support.
Phase change material thermal capacitor clothing
InactiveUS6855410B2Good thermal controlFast regenerationExothermal chemical reaction heat productionNatural cellulose pulp/paperSOCKSThermal insulation
An apparatus and method for metabolic cooling and insulation of a user in a cold environment. In its preferred embodiment the apparatus is a highly flexible composite material having a flexible matrix containing a phase change thermal storage material. The apparatus can be made to heat or cool the body or to act as a thermal buffer to protect the wearer from changing environmental conditions. The apparatus may also include an external thermal insulation layer and / or an internal thermal control layer to regulate the rate of heat exchange between the composite and the skin of the wearer. Other embodiments of the apparatus also provide 1) a path for evaporation or direct absorption of perspiration from the skin of the wearer for improved comfort and thermal control, 2) heat conductive pathways within the material for thermal equalization, 3) surface treatments for improved absorption or rejection of heat by the material, and 4) means for quickly regenerating the thermal storage capacity for reuse of the material. Applications of the composite materials are also described which take advantage of the composite's thermal characteristics. The examples described include a diver's wet suit, ski boot liners, thermal socks, gloves and a face mask for cold weather activities, and a metabolic heating or cooling blanket useful for treating hypothermia or fever patients in a medical setting and therapeutic heating or cooling orthopedic joint supports.
Owner:BUCKLEY THERESA M
Orthoses for joint rehabilitation
InactiveUS6872187B1Physical therapies and activitiesPerson identificationImpaired proprioceptionRange of motion
Orthoses with microprocessor control placed around the joint of a patient are used to perform and to monitor isometric, range-of-motion, proprioception and isotonic exercises of the joint. A variety of improved hardware elements result in an orthosis that is easier to use and interacts more efficiently with the controller to allow the monitoring of a greater range of motions while holding down cost and provide suitable accurate evaluation of the exercises. Efficient ways of programming the exercises, monitoring the exercises and evaluating the exercise provide a comprehensive program for the rehabilitation of an injured or weakened joint.
Owner:IZEX TECH
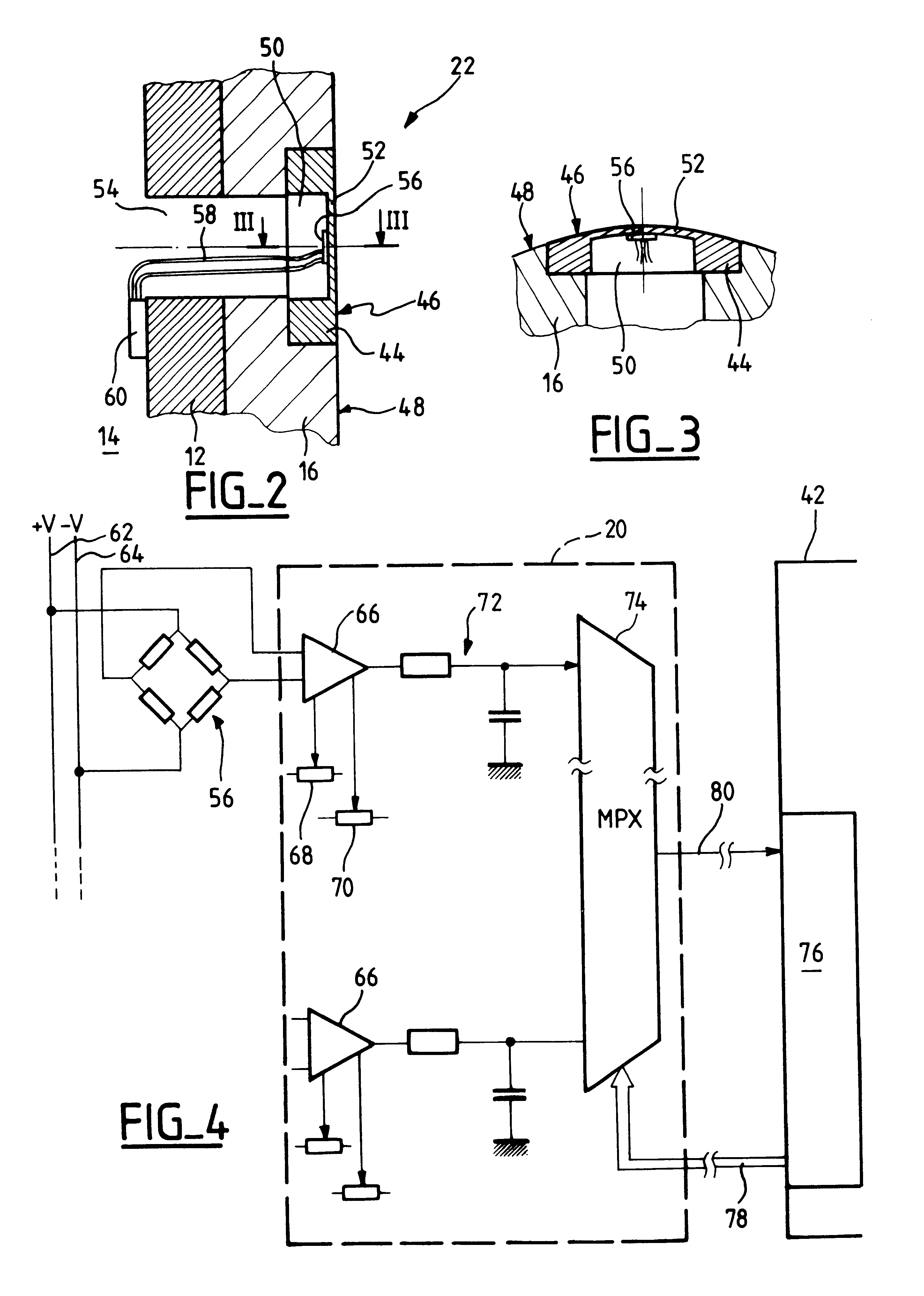
Device for measuring pressure points to be applied by a compressive orthotic device
The device comprises a rigid former reproducing the volume of a portion of the body and suitable for receiving the compressive orthosis. The former (10) incorporates a plurality of sensors (22) distributed over various points of the former and configured in such a manner as to avoid significantly modifying the surface profile of the former, the sensors essentially measuring the pressure applied locally on the former by the orthosis at the location of the sensor and perpendicularly to the surface of the former. Advantageously, at the location of the measurement point, each sensor comprises a thin wall capable of being subjected to microdeformation under the effect of the pressure applied by the orthosis, and means such as a strain gauge bridge, for example. The thin wall can constitute a portion of a support pellet which is fitted to the former in such a manner that its outside surface, which includes the thin wall, is flush with the outside surface of the former.
Owner:INNOTHERA TOPIC INT
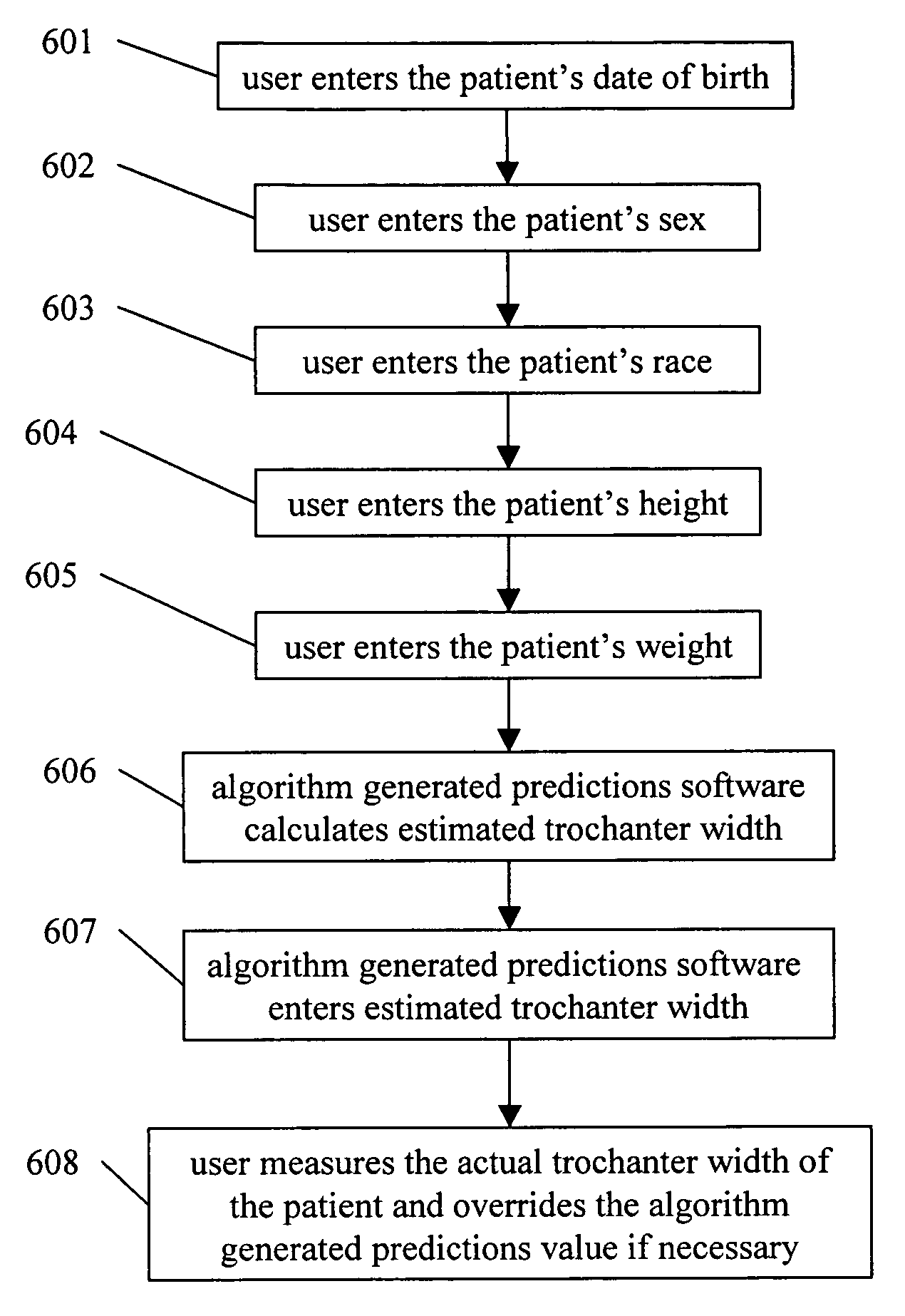
Method a designing, engineering modeling and manufacturing orthotics and prosthetics integrating algorithm generated predictions
InactiveUS20060100832A1More accurateMore scientificComputation using non-denominational number representationProsthesisComputer Aided DesignPhysical model
The present invention represents an advancement on the current processes involved in designing, engineering, modeling and manufacturing of orthotic and prosthetic devices. Orthotic and prosthetic computer aided design software has the option to apply measurements to a template to create a patient specific model. The use of algorithm generated predictions (also referred to as “AGP”) software takes this functionality and makes it more scientific. Algorithm generated predictions is the process of predicting the appropriate size and shape data through the use of complex algorithms. Certain key pieces of data are entered into the software that then calculates the appropriate dimensions and the appropriate computer aided design template. The dimensions are then applied to the computer aided design template. The computer aided design software modifies the templates by reducing and enlarging areas as necessary and a custom computer aided design model is created that can then be transformed into a physical model for the manufacture of the device.
Owner:BOWMAN GERALD DAVID
Devices with internal flexibility sipes, including siped chambers for footwear
ActiveUS20060248749A1Increase flexibilityIncreased flexibility and cushioning and stabilitySolesGolf clubsAnatomical structuresCushioning
The present invention attempts to replicate in footwear, orthotics, and other products the naturally effective anatomical structures like a bare foot that provide superior flexibility, cushioning, and stable support compared to existing products. More specifically, the invention relates to a device for such products including a unitary internal sipe component, said internal sipe providing increased flexibility for said device. Even more specifically, the invention relates to footwear, orthotic or other products with an outer chamber and at least one inner chamber inside the outer chamber; the outer chamber and the inner chamber being separated at least in part by an internal sipe; and the internal sipe providing increased flexibility, cushioning, and stability.
Owner:ELLIS
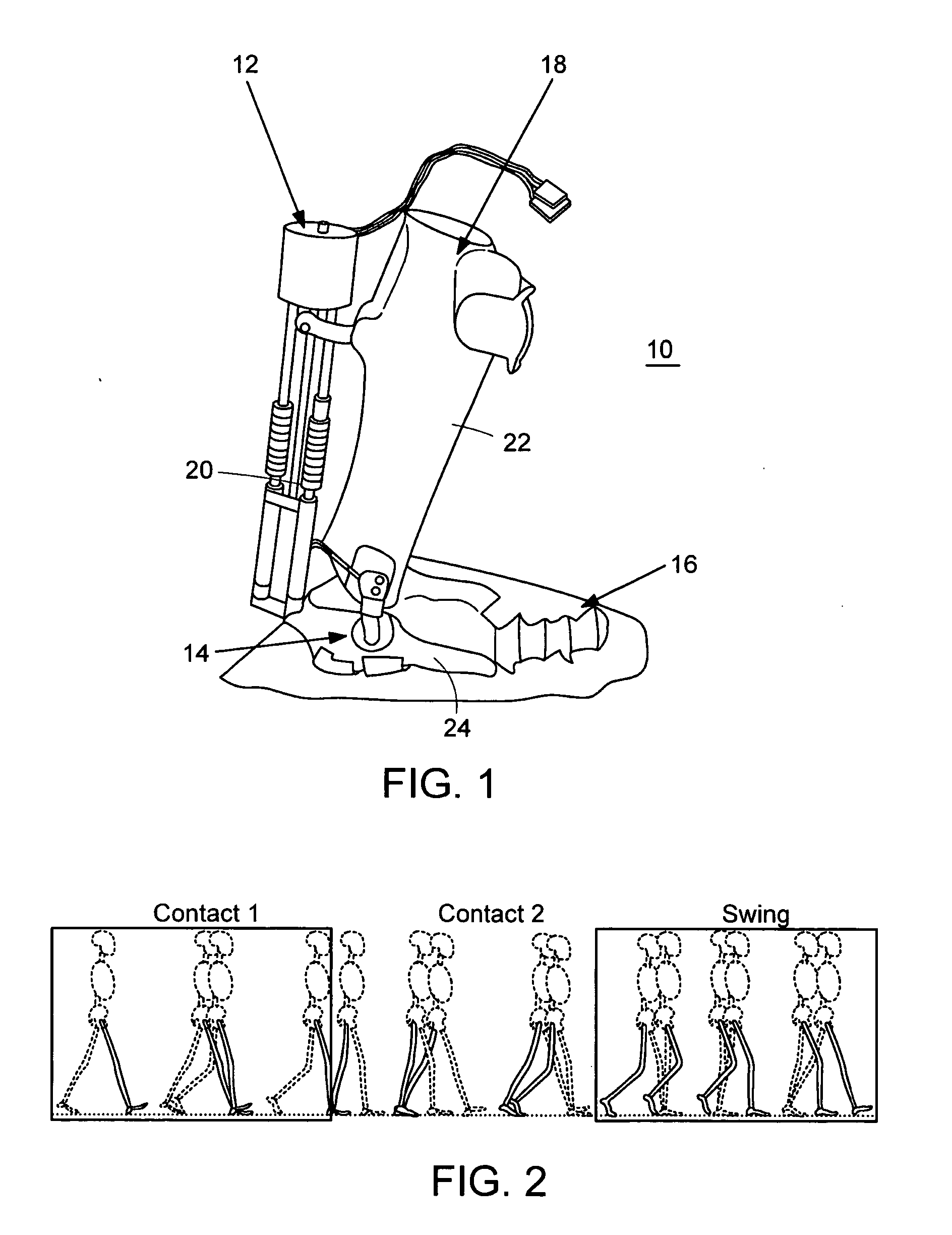
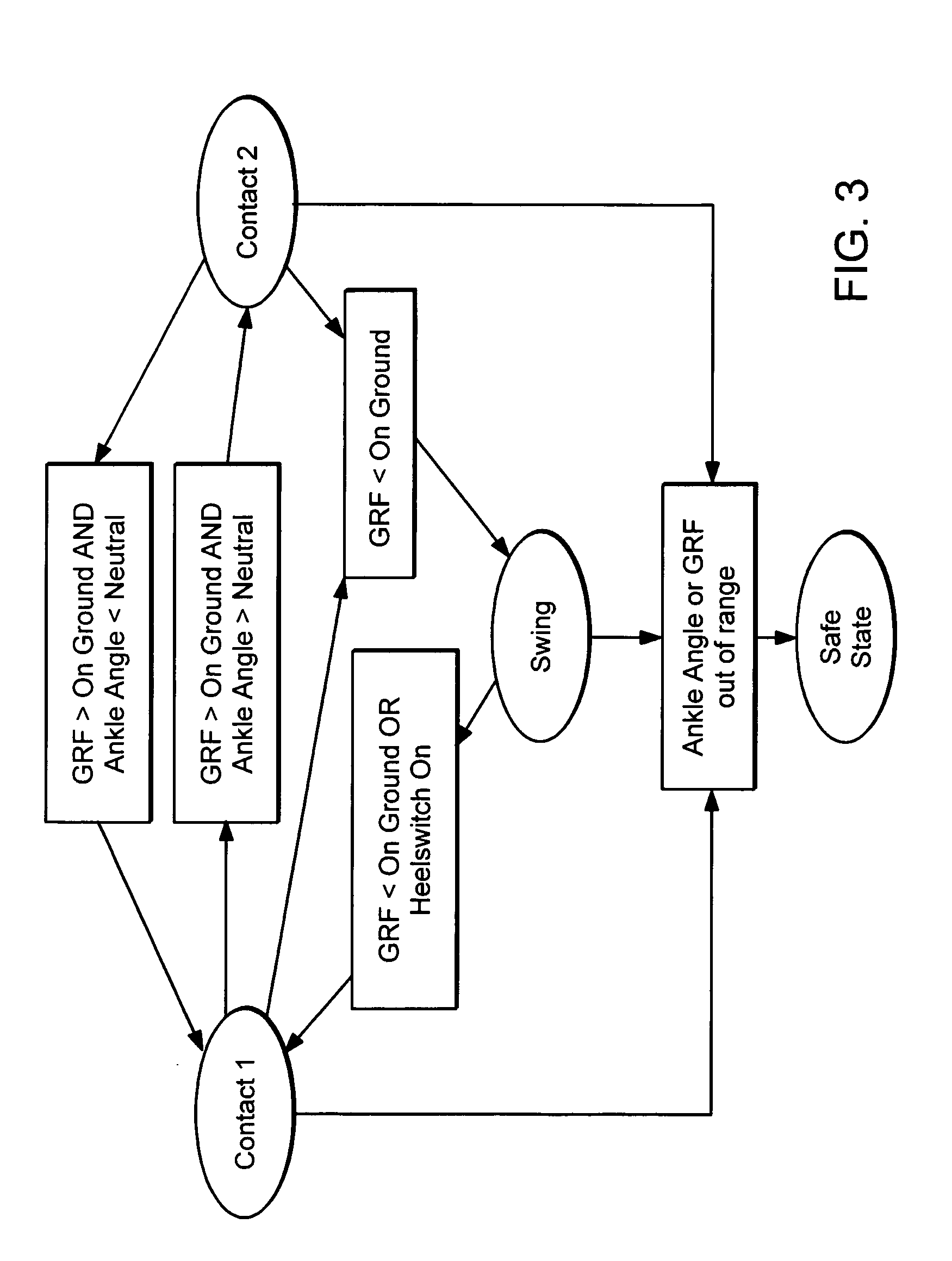
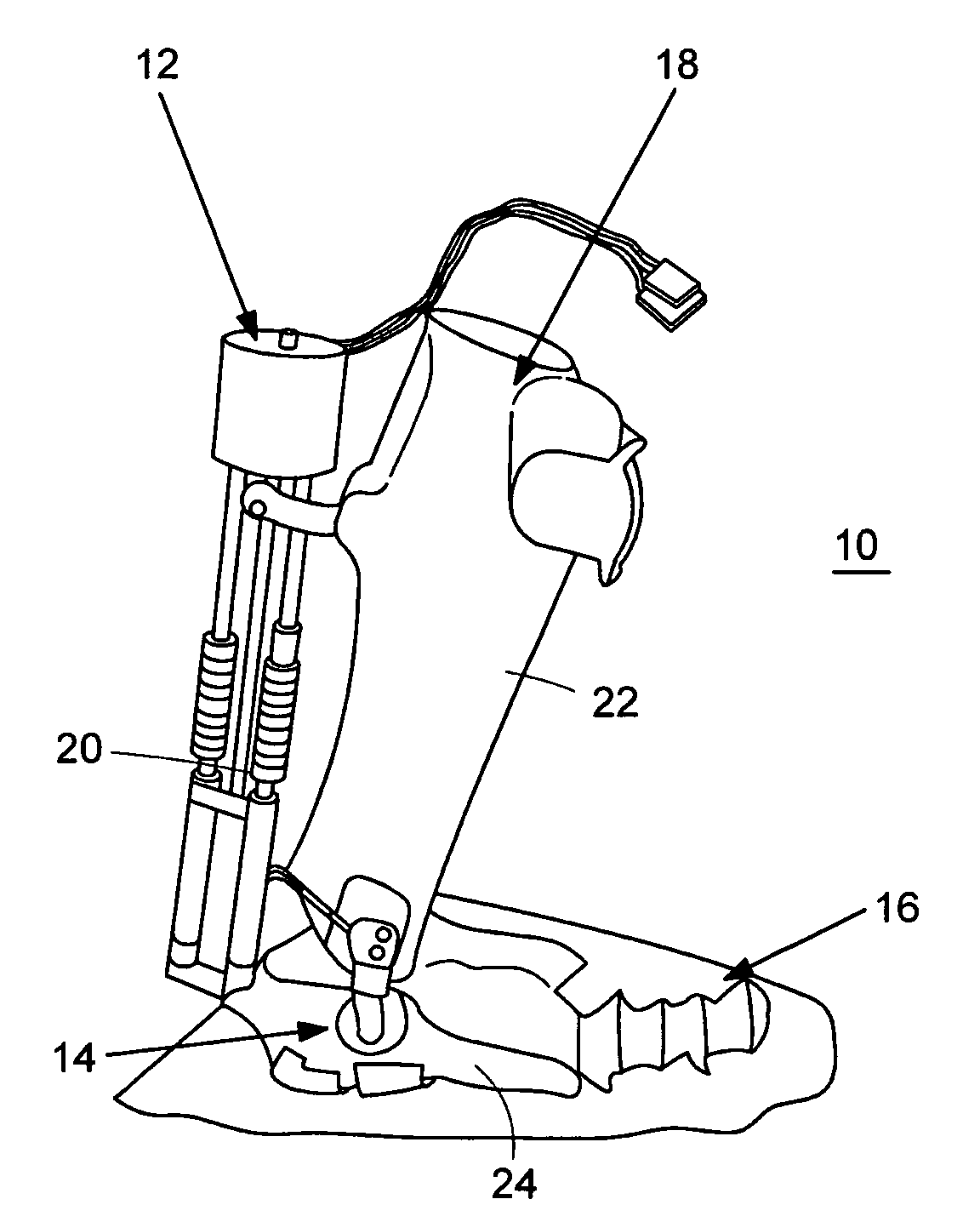
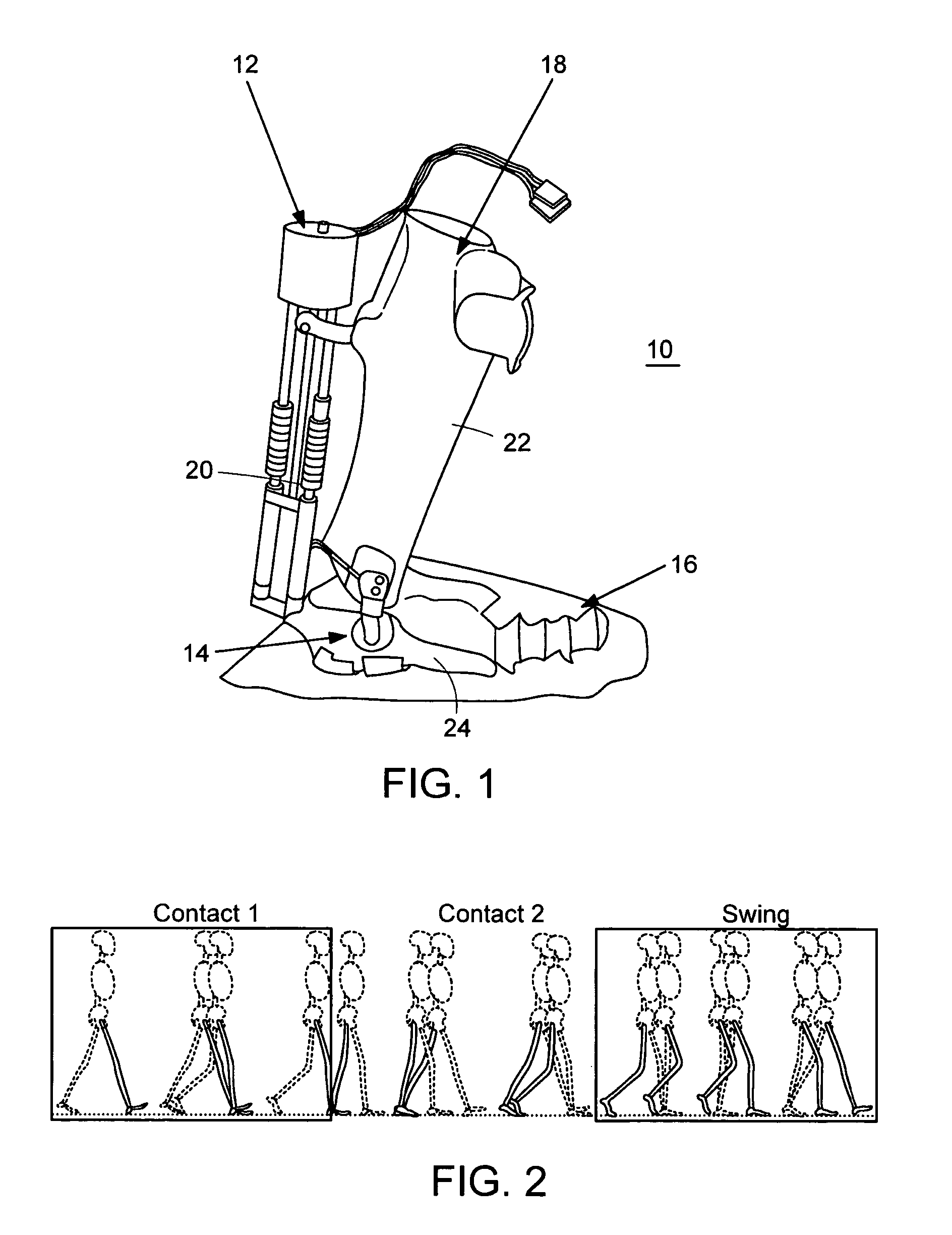
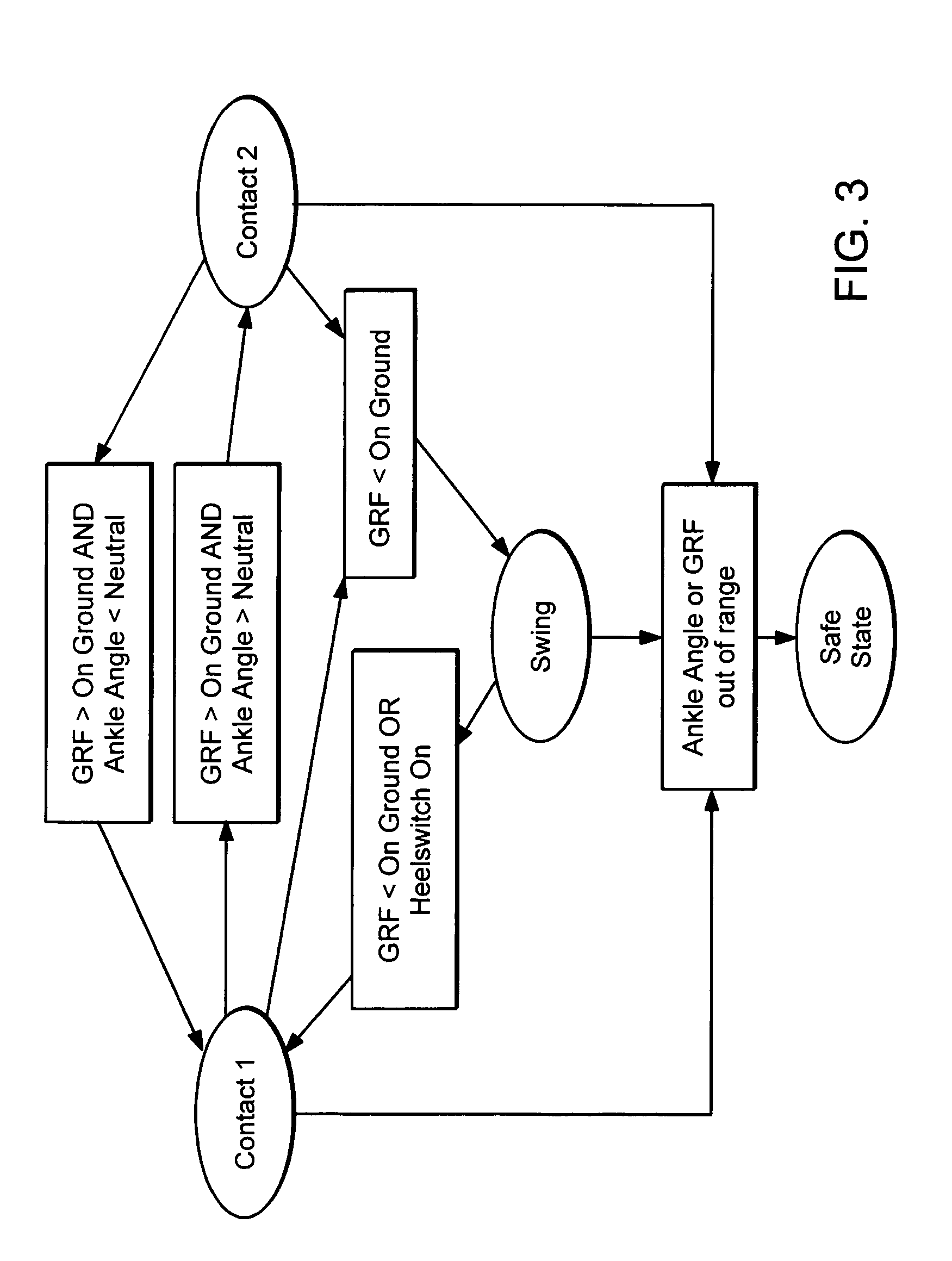
Active Ankle Foot Orthosis
ActiveUS20050070834A1Less kinematic differenceIncrease independenceWalking aidsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesWalking cyclePathology diagnosis
An Active Ankle Foot Orthosis (AAFO) is provided where the impedance of an orthotic joint is modulated throughout the walking cycle to treat ankle foot gait pathology, such as drop foot gait. During controlled plantar flexion, a biomimetic torsional spring control is applied where orthotic joint stiffness is actively adjusted to minimize forefoot collisions with the ground. Throughout late stance, joint impedance is minimized so as not to impede powered plantar flexion movements, and during the swing phase, a torsional spring-damper (PD) control lifts the foot to provide toe clearance. To assess the clinical effects of variable-impedance control, kinetic and kinematic gait data were collected on two drop foot participants wearing the AAFO. It has been found that actively adjusting joint impedance reduces the occurrence of slap foot, allows greater powered plantar flexion, and provides for less kinematic difference during swing when compared to normals.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
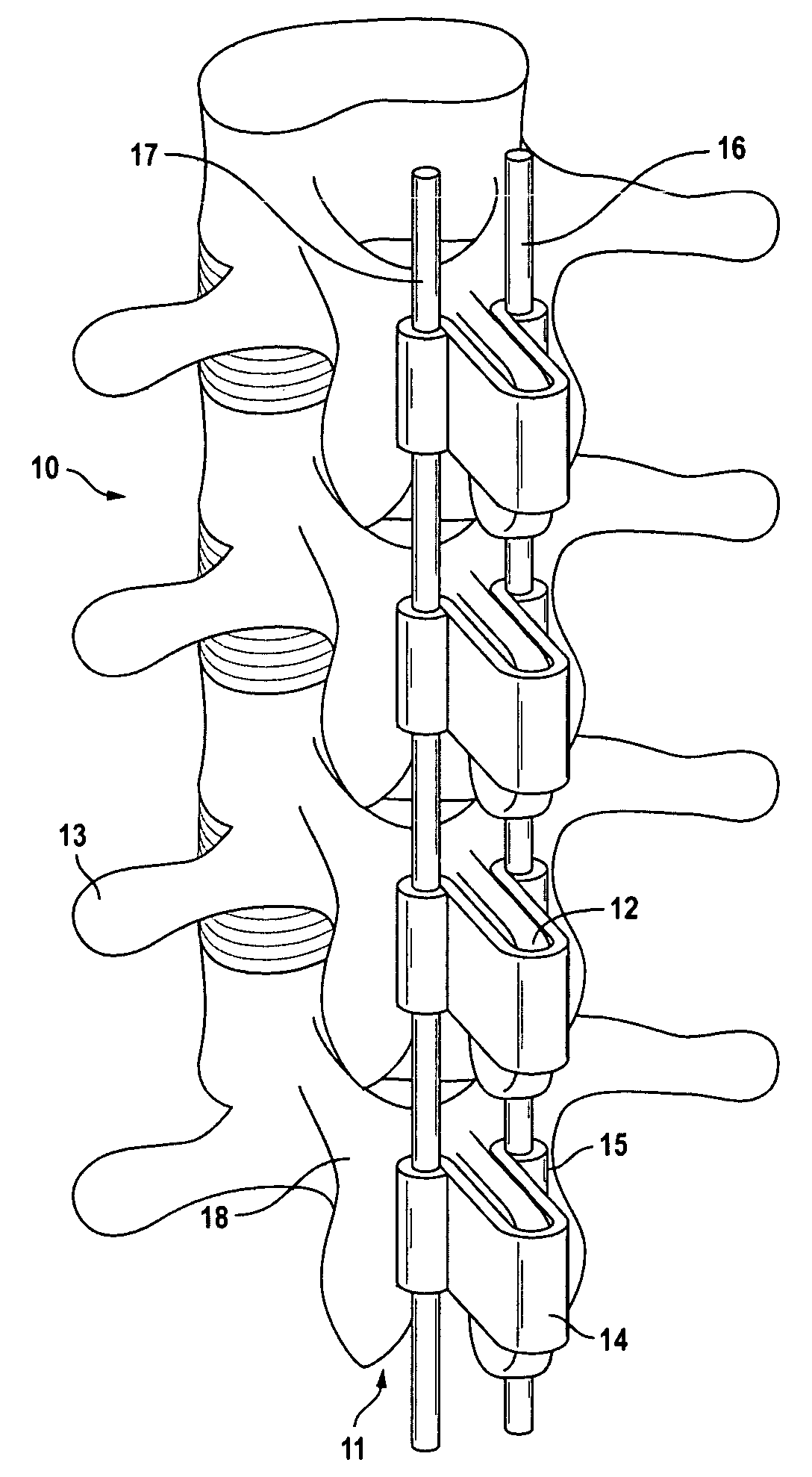
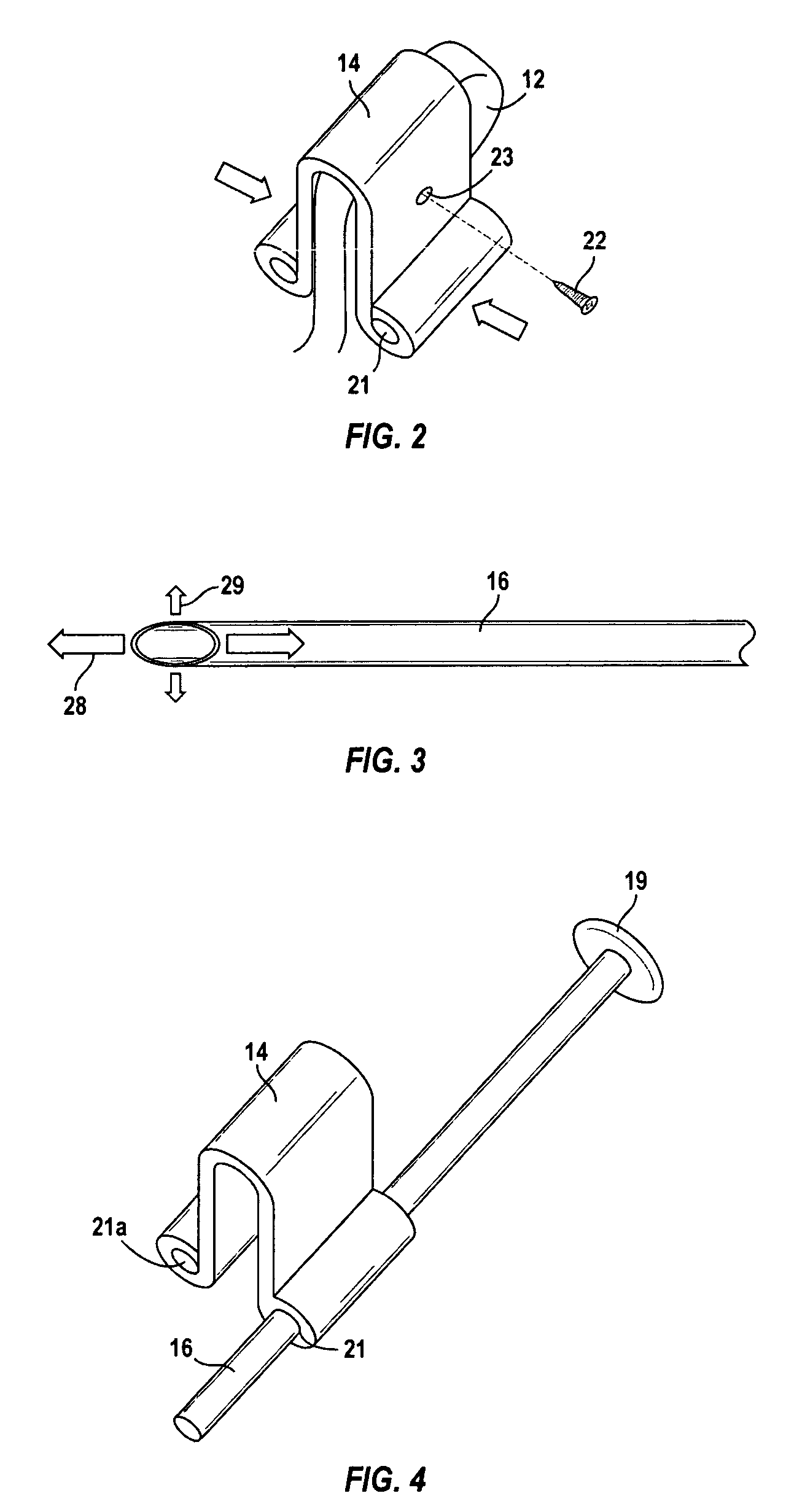
Orthosis to correct spinal deformities
An orthosis for correcting spinal deformities by urging spinal vertebrae toward a vertical axis. The orthosis includes a series of retaining clamps fixed onto the spinous process of said vertebrae, each of said retaining clamps having guides for retaining at least one elastic rod.
Owner:REDUCTION TECH
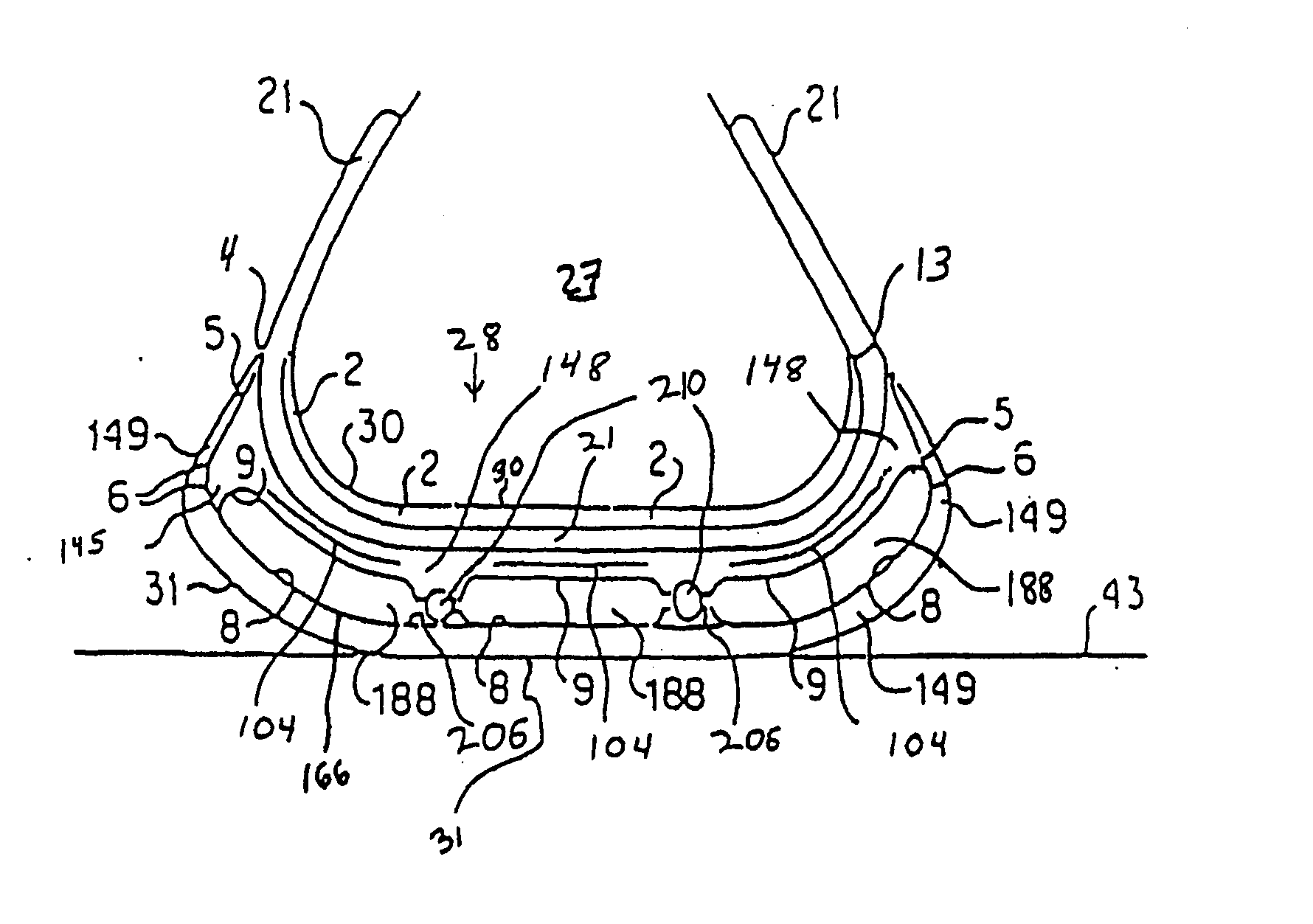
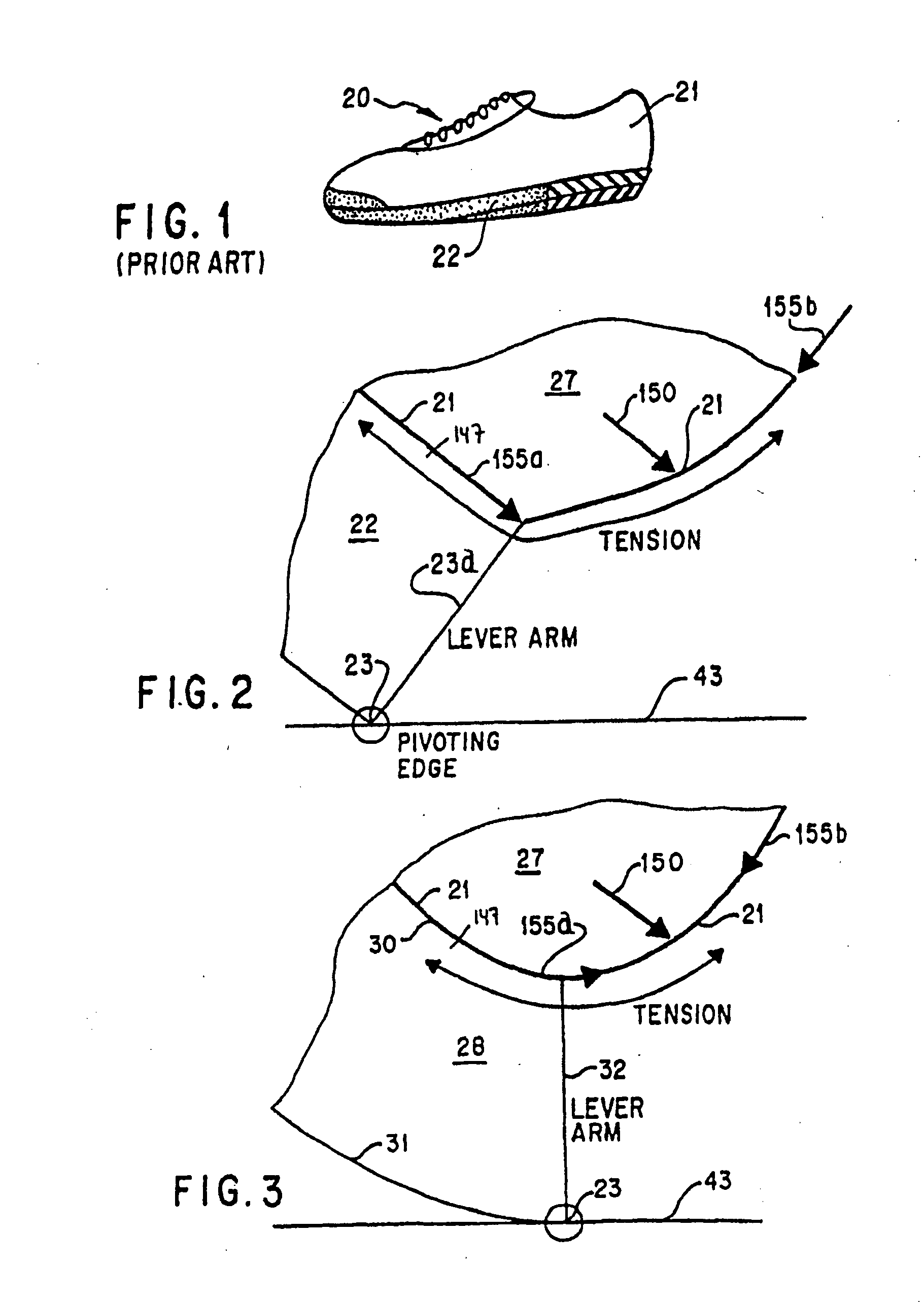
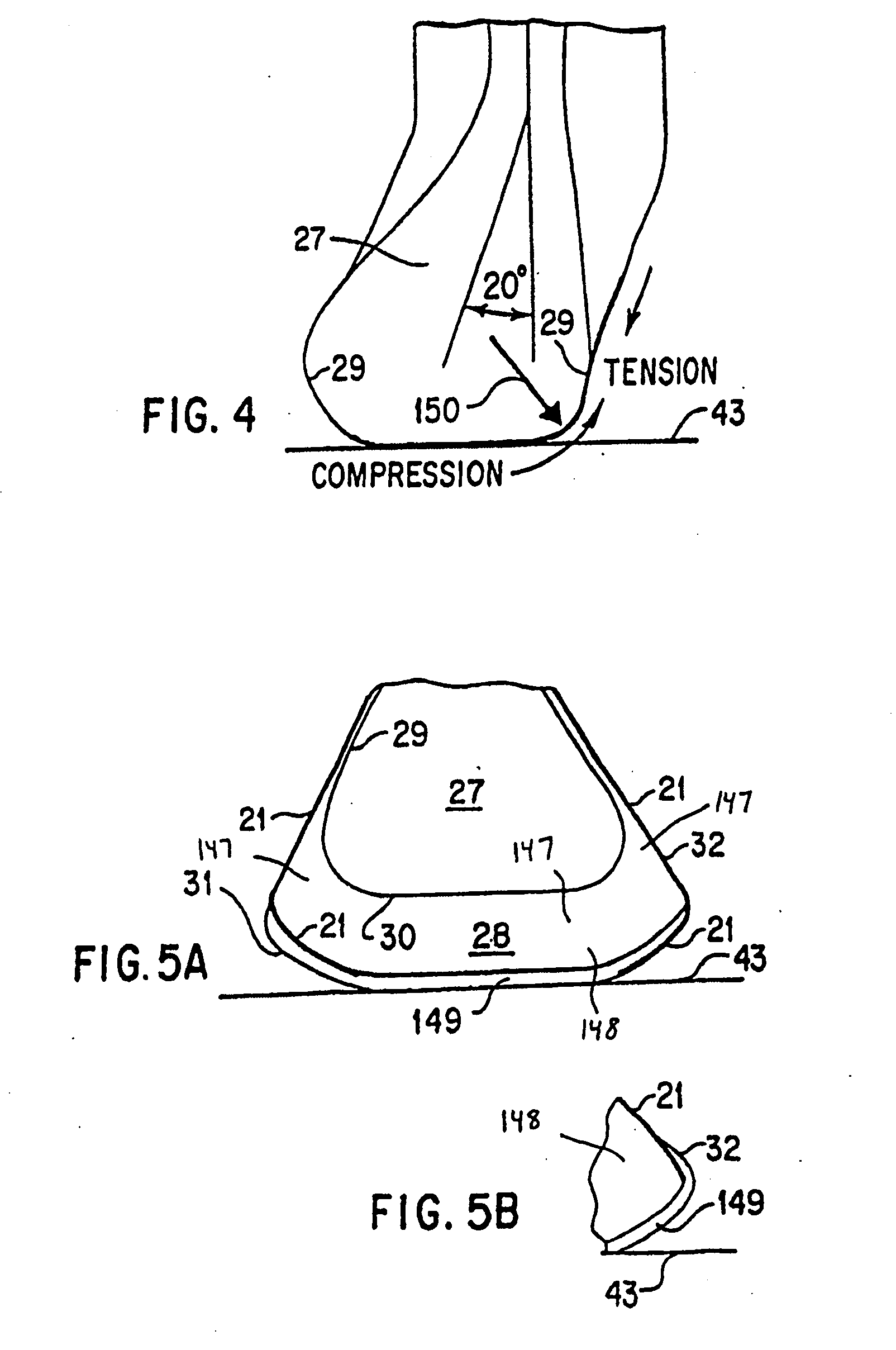
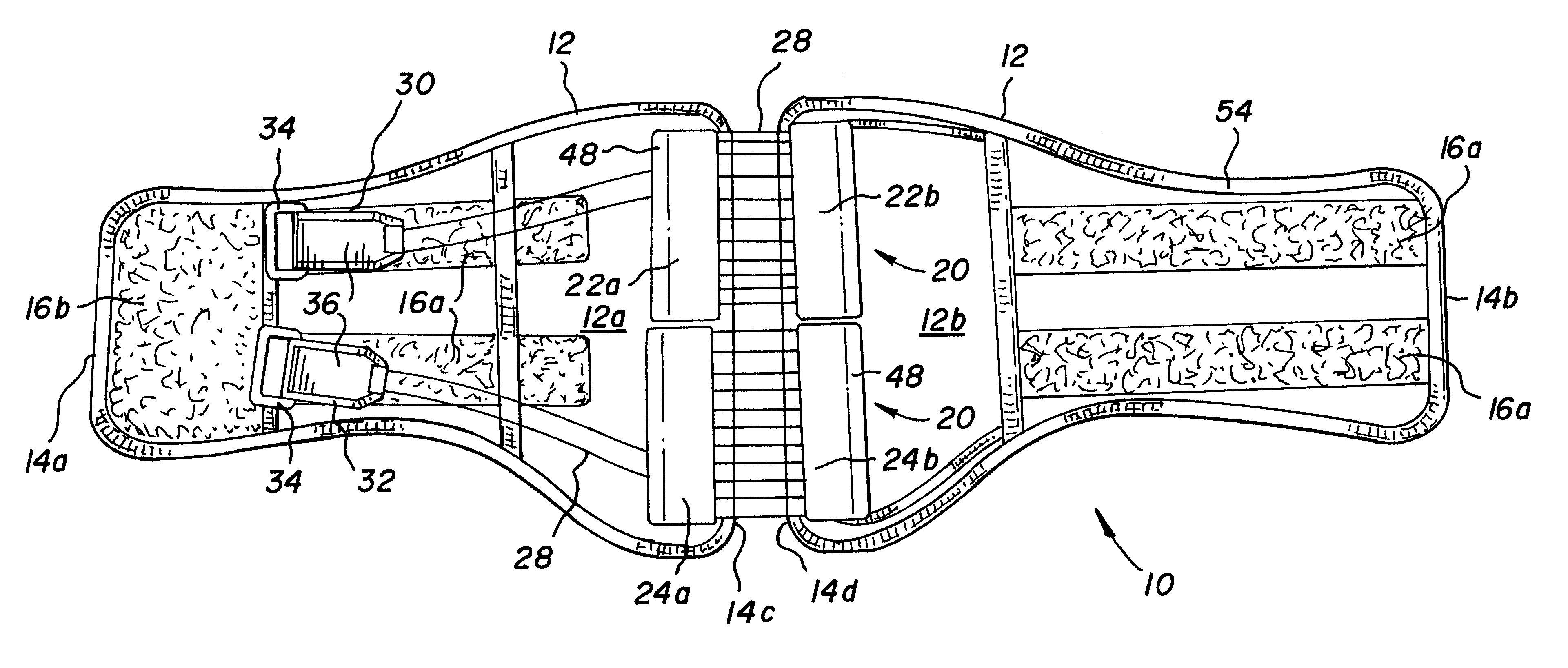
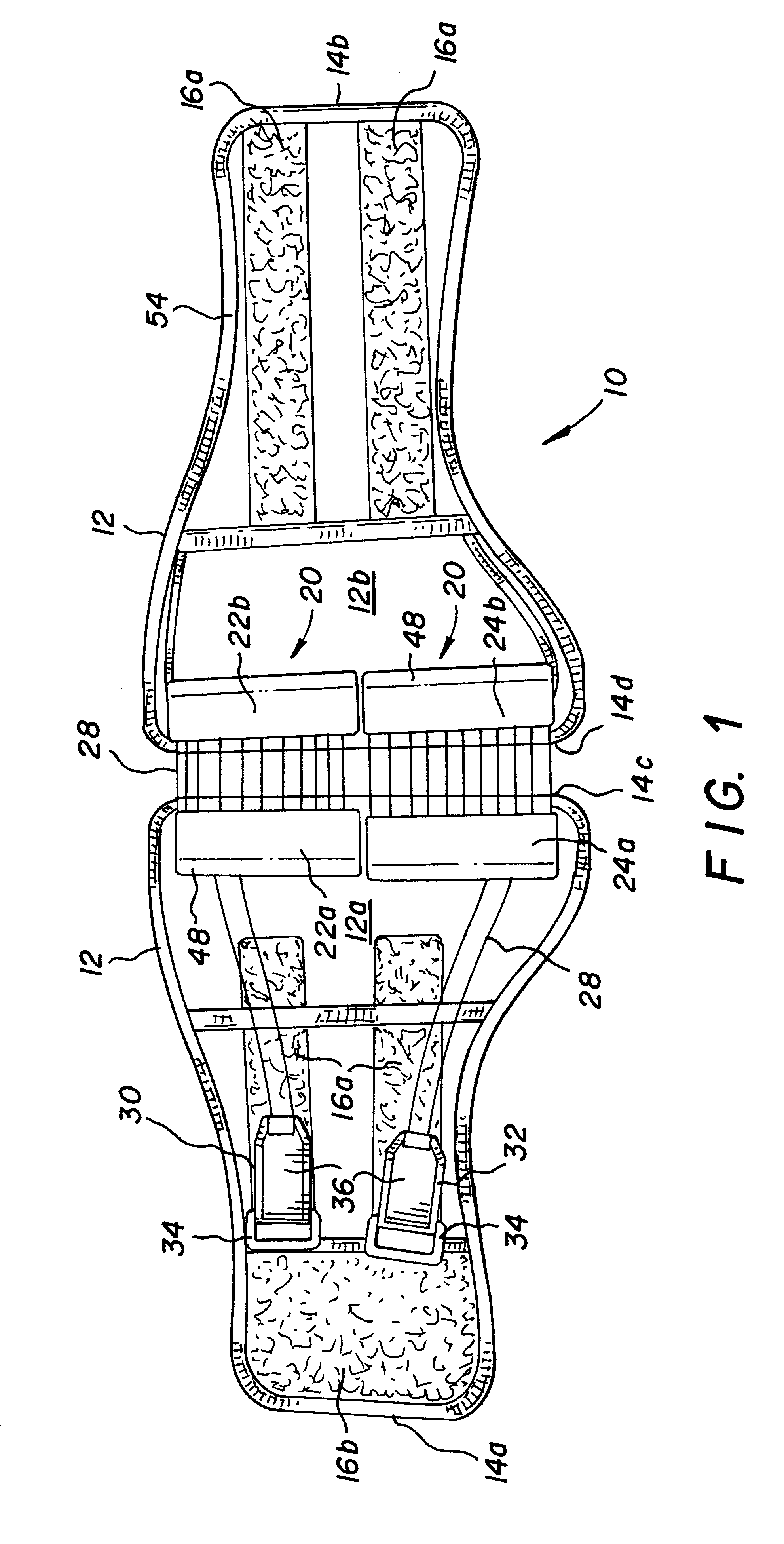
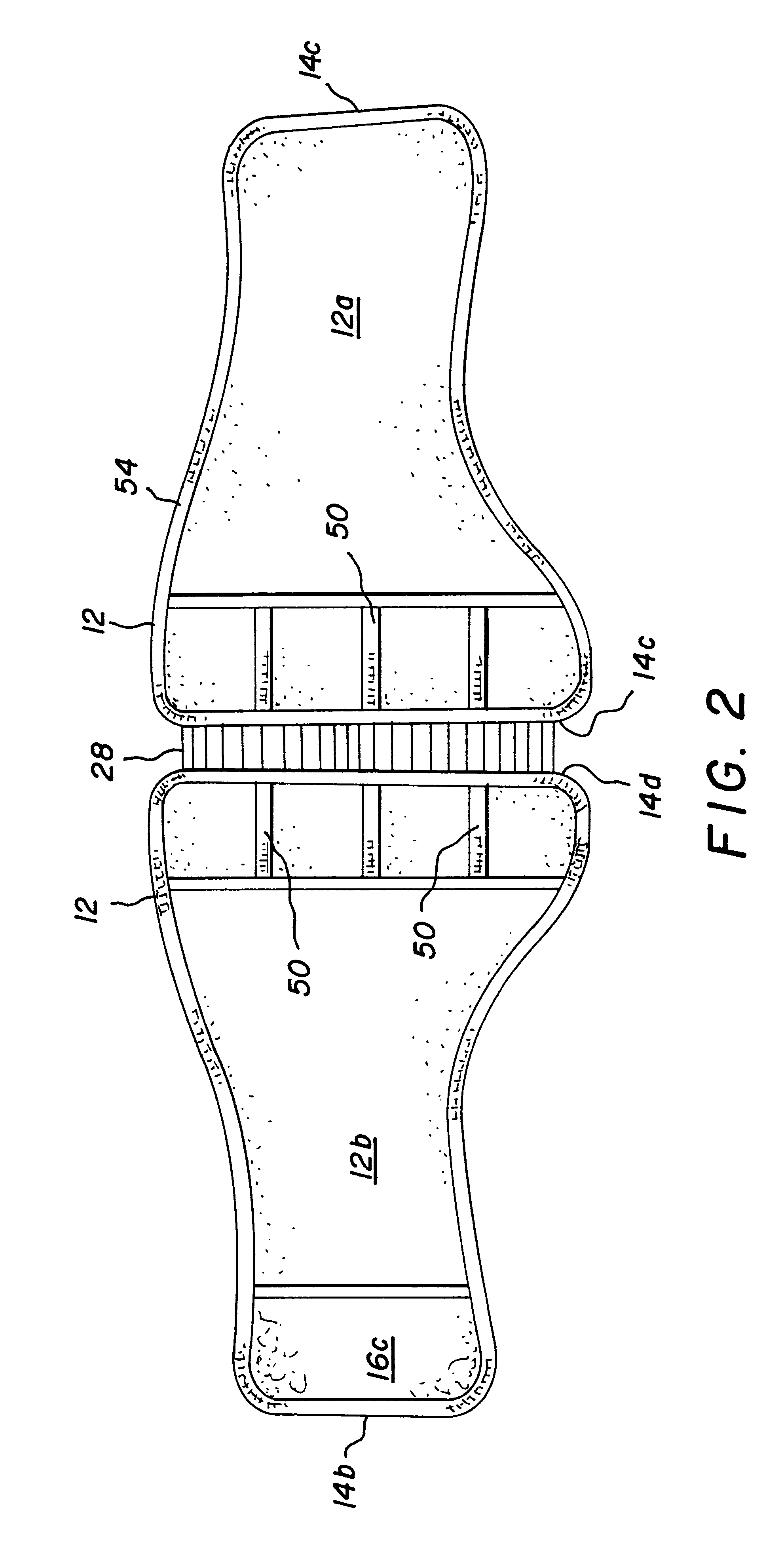
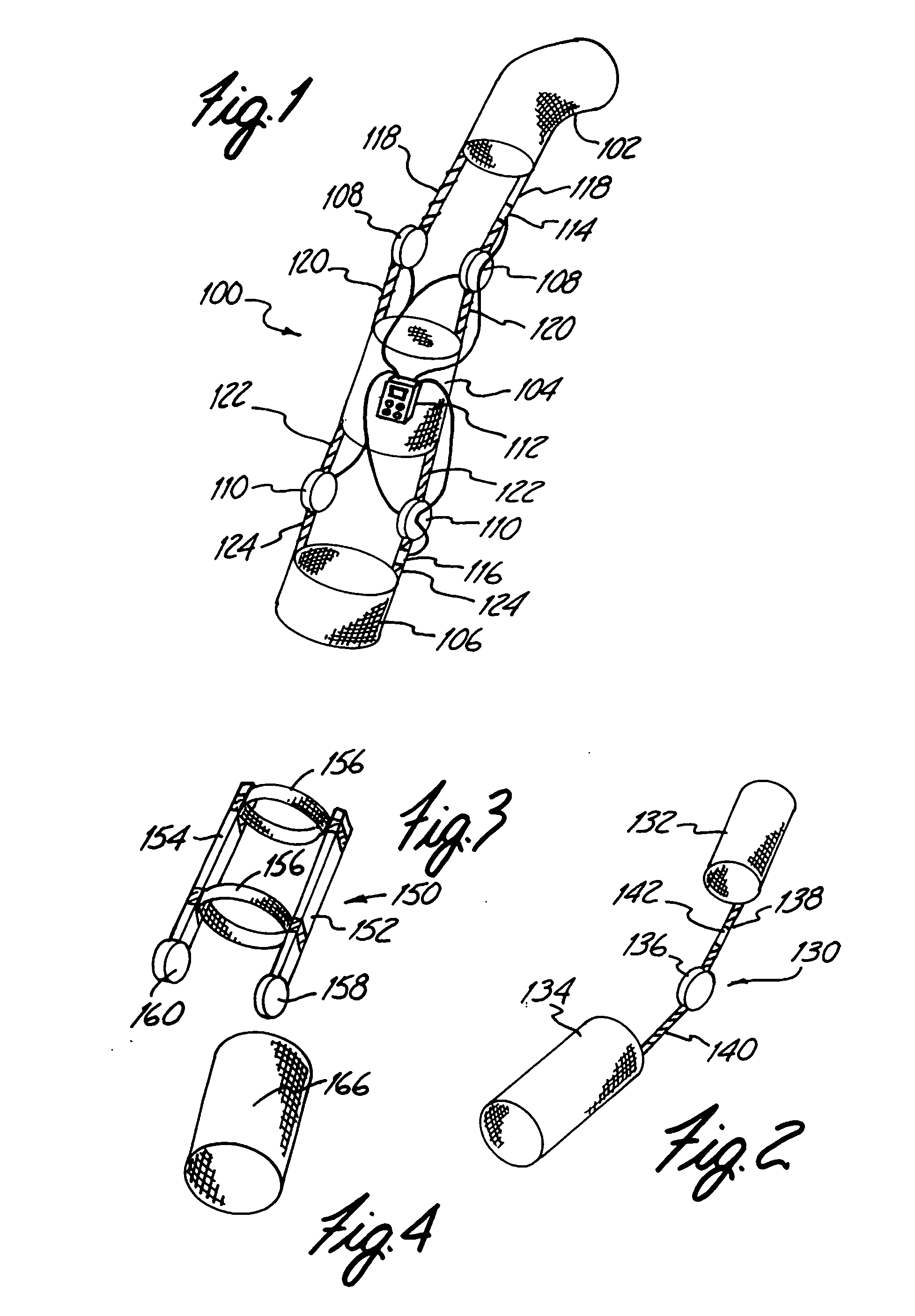
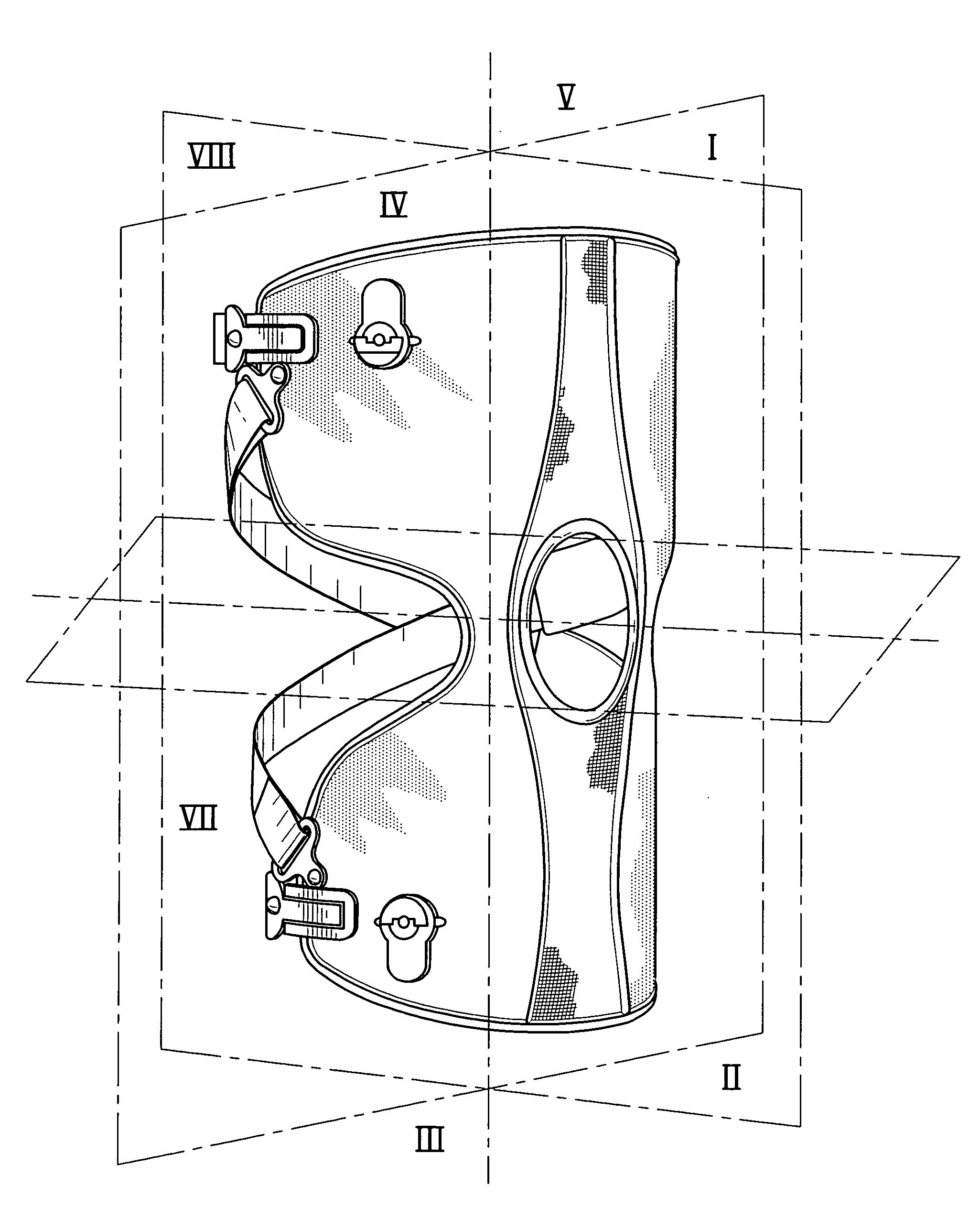
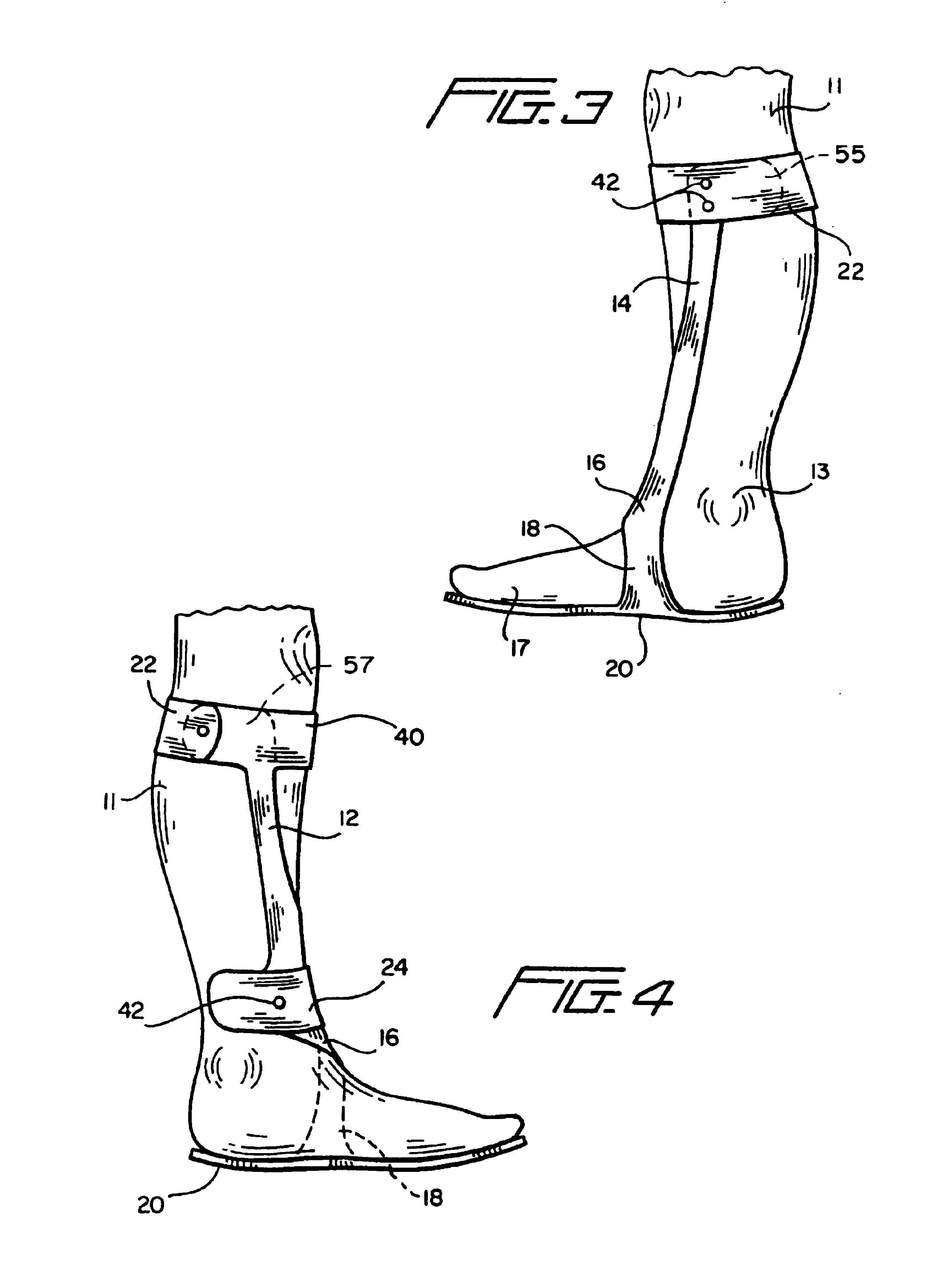
Custom fitted orthotic device
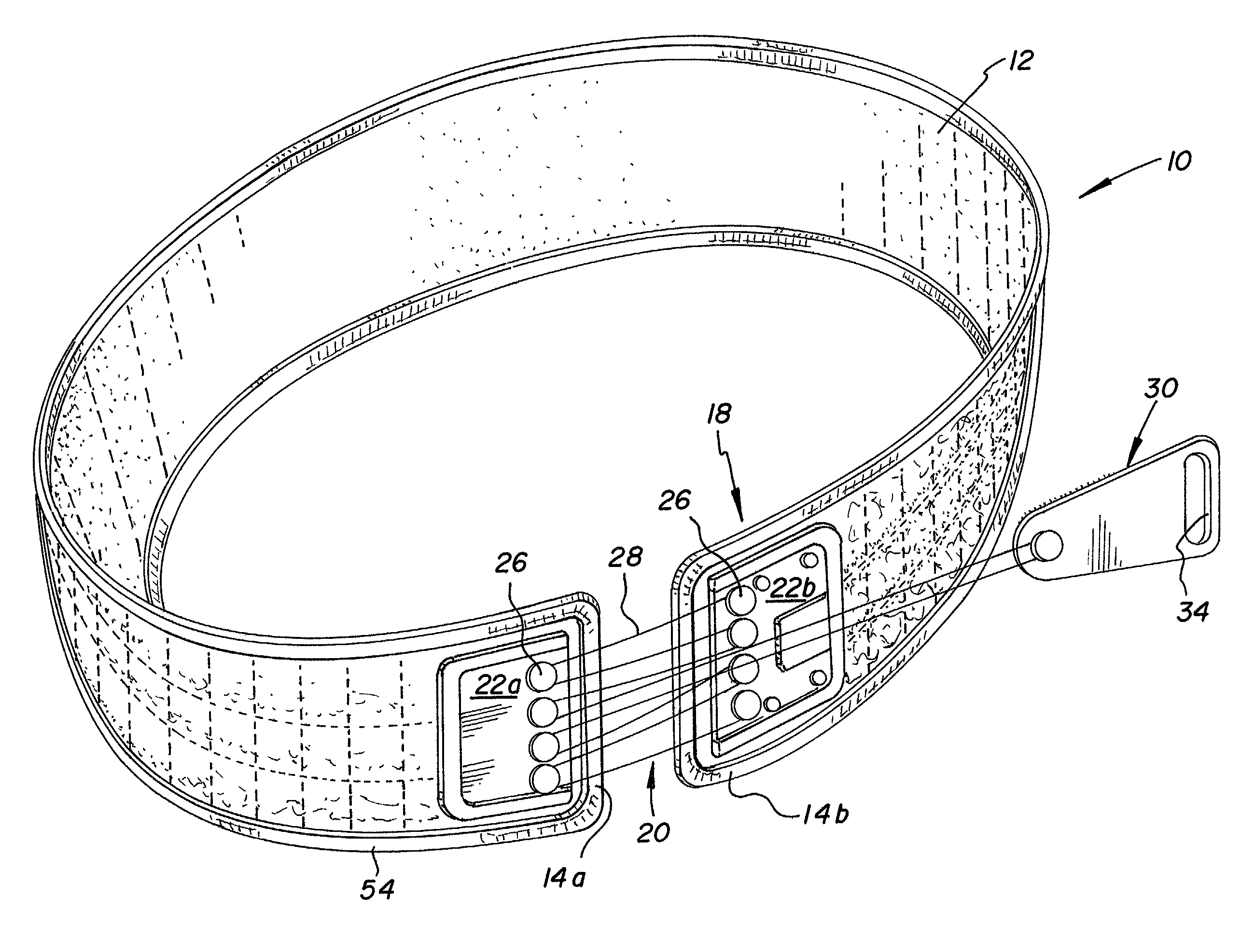
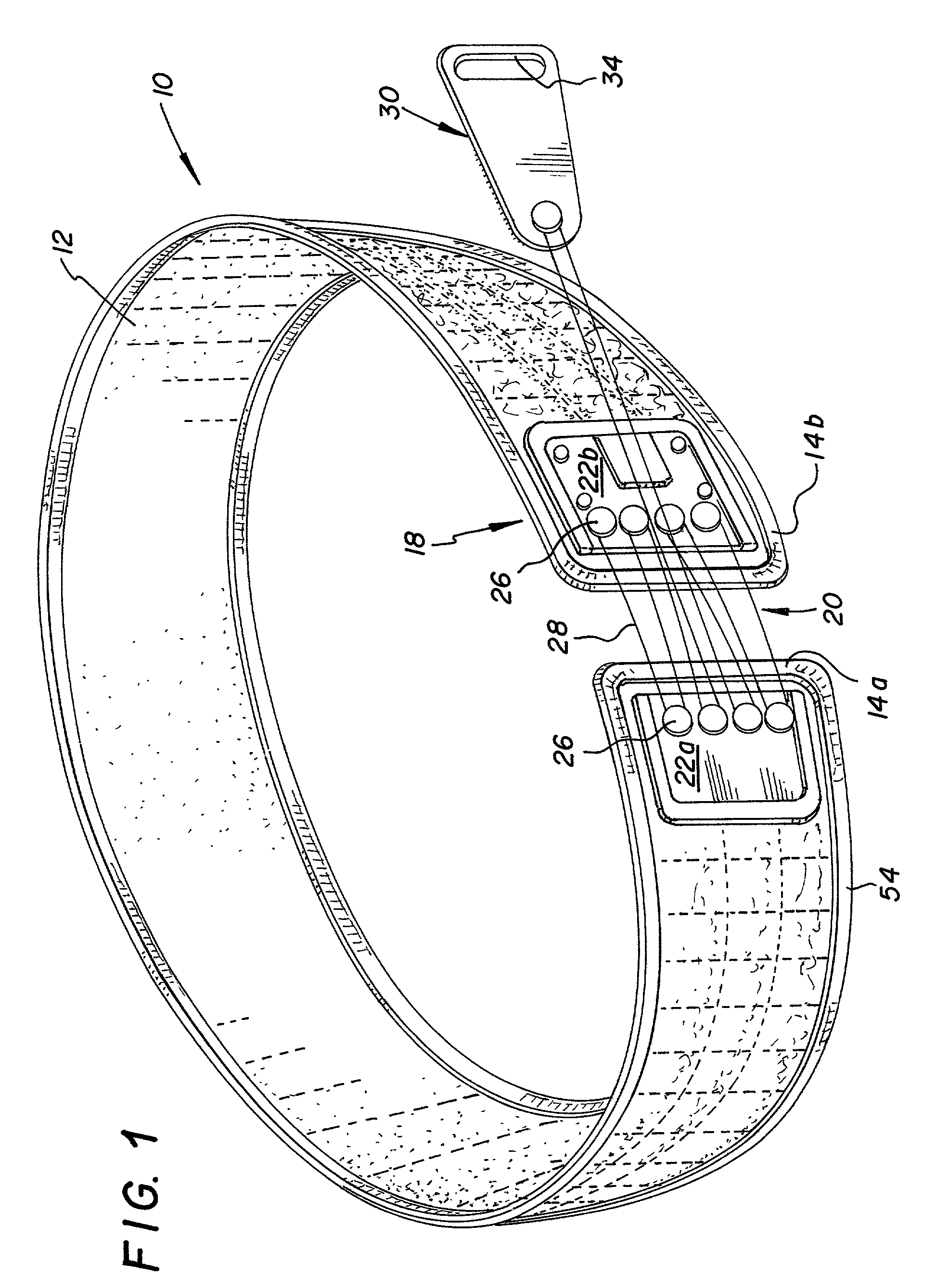
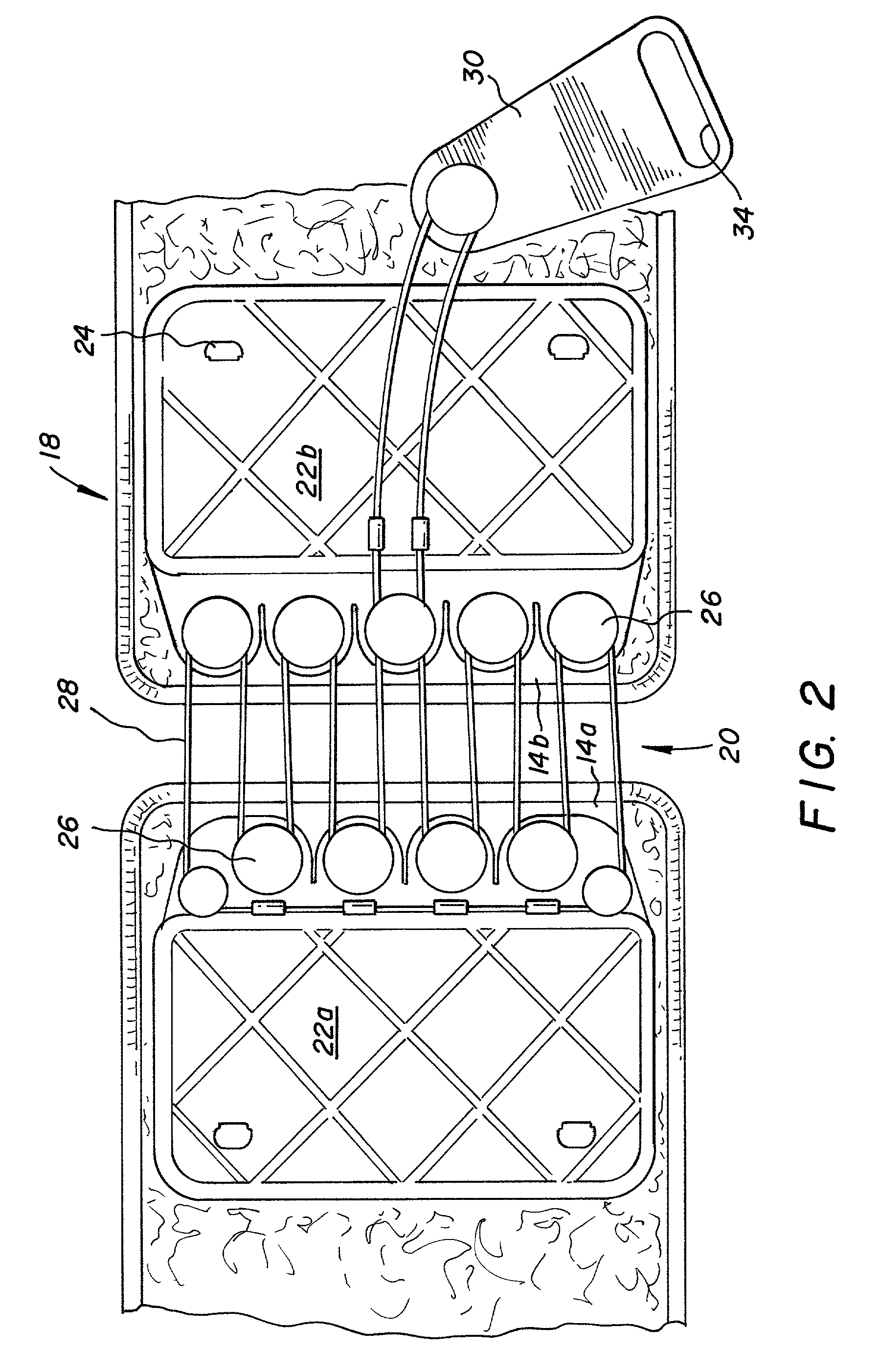
InactiveUS6213968B1Patient compliance is goodEasily and rapidly adjustedOrthopedic corsetsProtective garmentOrthotic deviceMechanical advantage
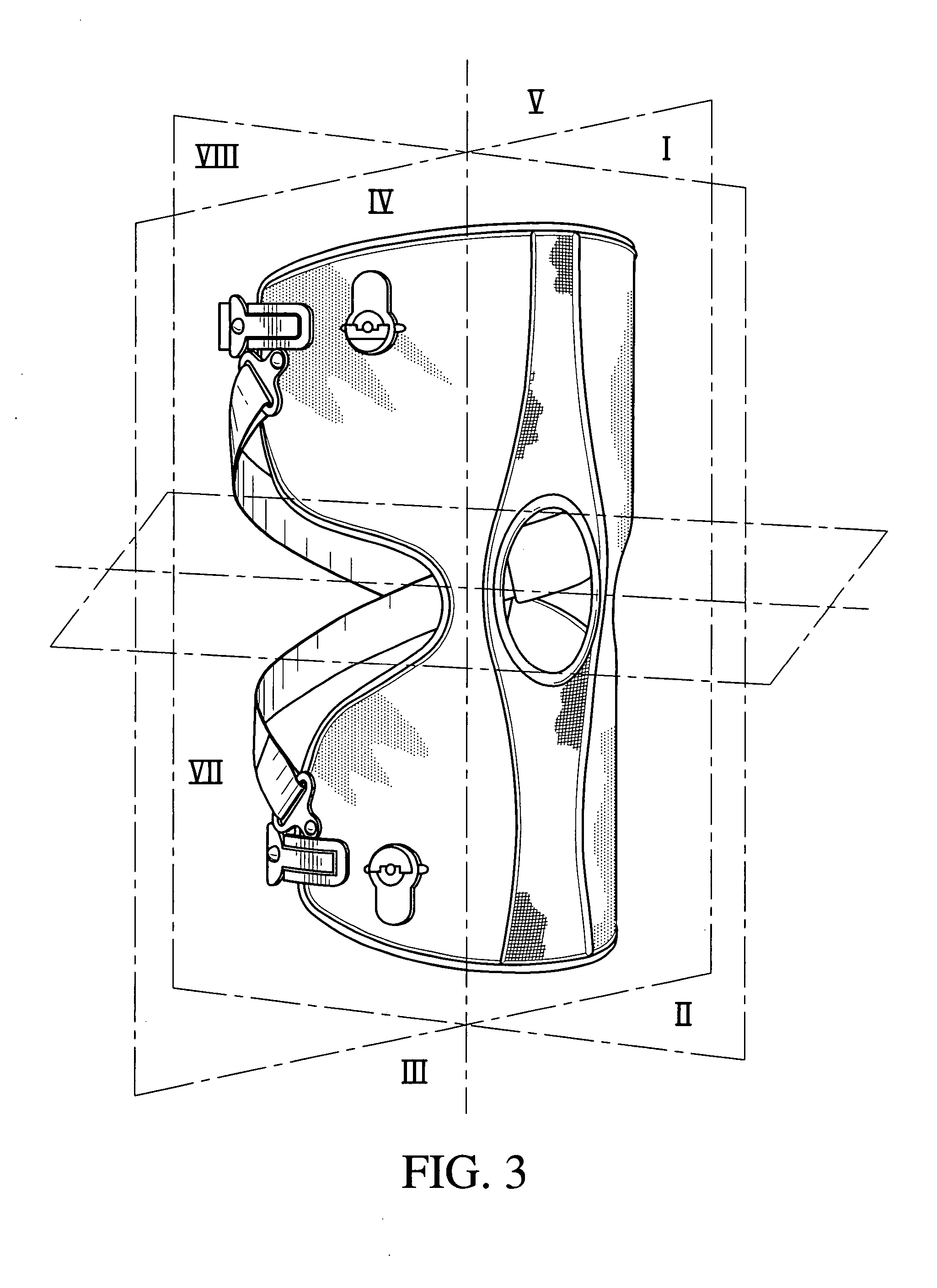
An orthotic device is provided, including an orthosis body adapted to be wrapped around the torso of a wearer of the device, the orthosis body having at least two segments in juxtaposed relationship. Means are provided at free end portions of the at least two segments to releasably secure the free end portions to one another. At least two cables are provided, each cable operatively connected to the at least two segments. At least two sets of pulleys are mounted on the at least two segments with each cable operatively connected to the at least two segments running through a pulley on each of the at least two segments in alteration, shortening of each cable pulling the at least two segments together and tightening the orthotic device with the aid of a mechanical advantage dependent upon the number of pulleys mounted on each of the at least two segments.
Owner:BIO CYBERNETICS INT INC
Spacer element for prosthetic and orthotic devices
ActiveUS20070185425A1Reduce the impactMinimizing rotational forceSynthetic resin layered productsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesProsthesisEngineering
An orthotic or prosthetic spacer element including a ventilated and compressible core having first and second opposed surfaces, and a discrete and continuous web-like silicone-based frictional layer secured to the core first surface. The frictional layer and the core first surface have a plurality of coinciding apertures formed in a pattern. The spacer element may include a foam layer secured to the core second surface such that the foam layer and the core have different rigidities. A layer of hook-receivable material may be directly or indirectly secured to the second core surface.
Owner:KAUPTHING BANK
Systems and methods for manufacturing of multi-property anatomically customized devices
InactiveUS20150165690A1Increase productionOvercomes shortcomingAdditive manufacturing apparatusComputer controlMulti materialEngineering
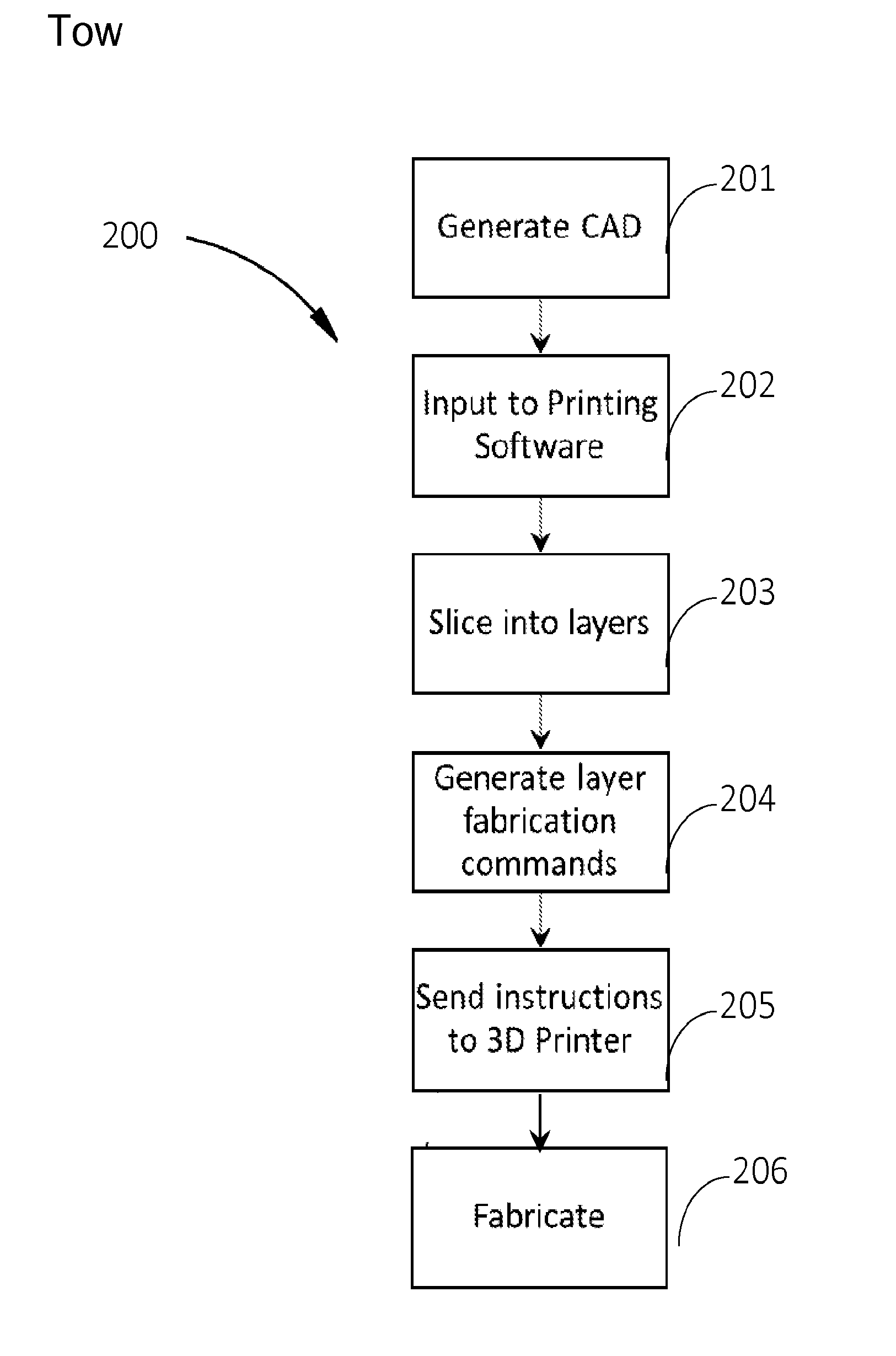
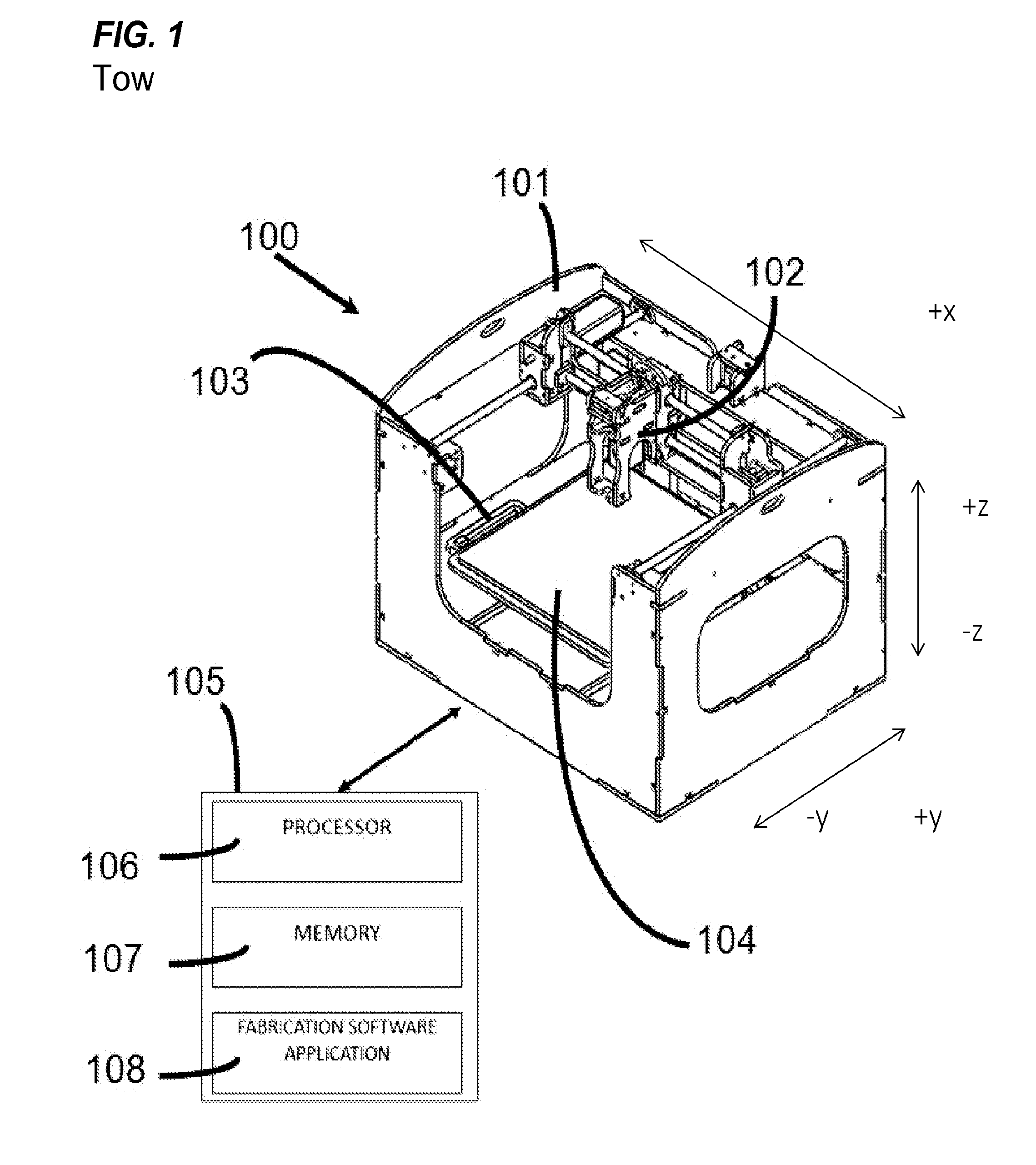
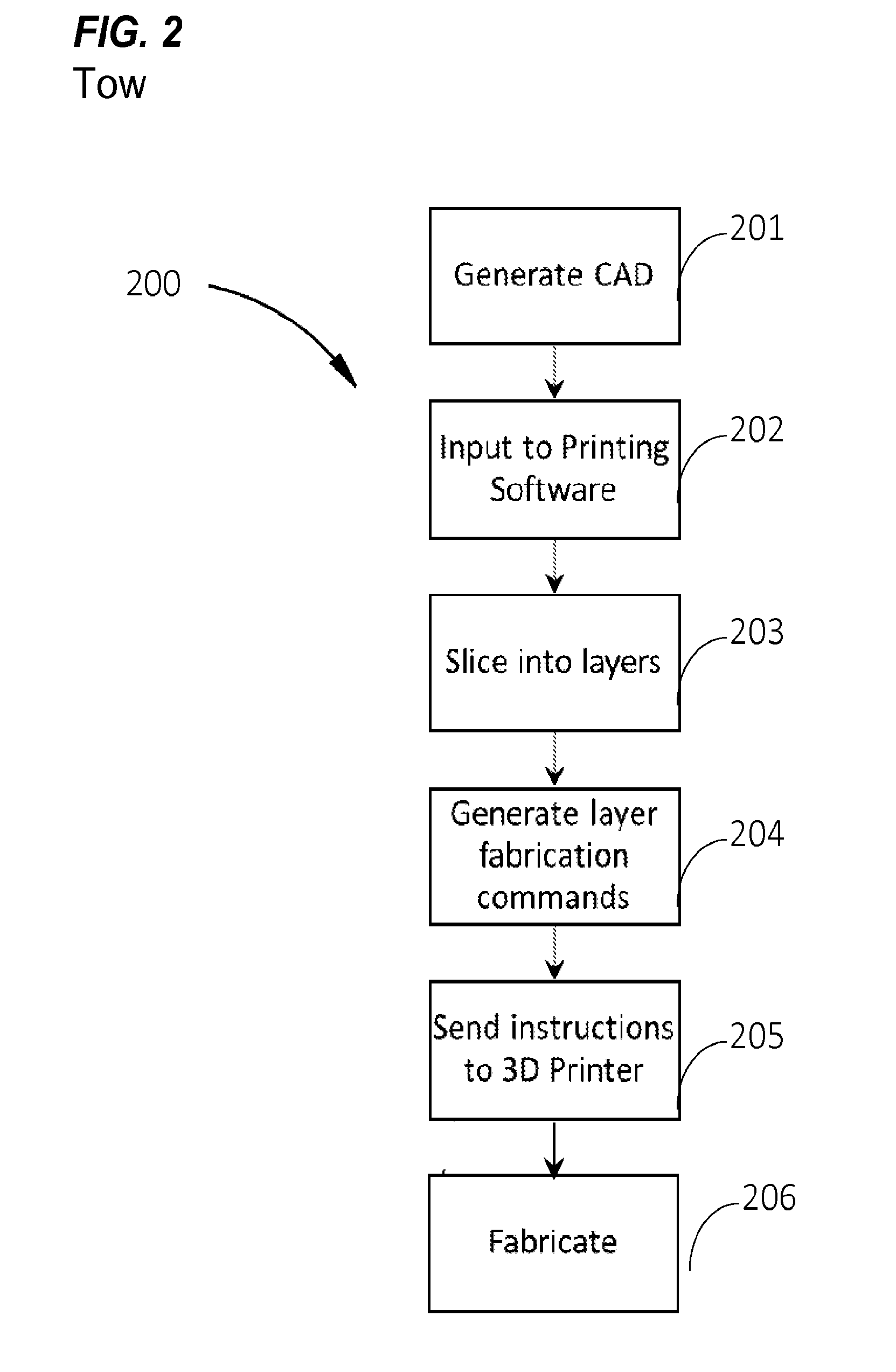
Systems and methods for using a three dimensional fabrication device, like a 3D Printer, for novel automation and additive manufacturing techniques in manufacturing medical devices such as orthotics, customized for a particular person. The systems and methods may use a plurality of work surfaces on the three dimensional fabrication device. The systems and methods may use a plurality of materials or a plurality of fabrication tools and processes to manufacture the customized product.
Owner:TOW ADAM P
Footwear orthosis
The present invention is an apparatus and method of orthopedic footwear for post-surgical or diabetic patients or for sanitary use. The footwear has an ambidextrous bottom sole. In a higher part thereof, there is a groove of at least 10 mm, in which an off-loading plantar insoles or medicine or bandages can be inserted. These have been built-in the bottom sole using an ortho-dynamic concept which allows the patient a controlled deambulation. To that end, the present invention prevents sheer force on the plantar part of the bottom sole and the foot and in particular on the metatarsal and / or tarsal part of the foot.
Owner:SALVATELLI
Devices for management of foot injuries and methods of use and manufacture thereof
The present invention provides orthotic devices for use in managing the treatment and prevention of lower extremity injuries, including foot ulcers. In various aspects, the present invention provides foot-worn orthotics which provide for improved compliance monitoring, and methods of their manufacture and use.
Owner:LASERCURE SCI
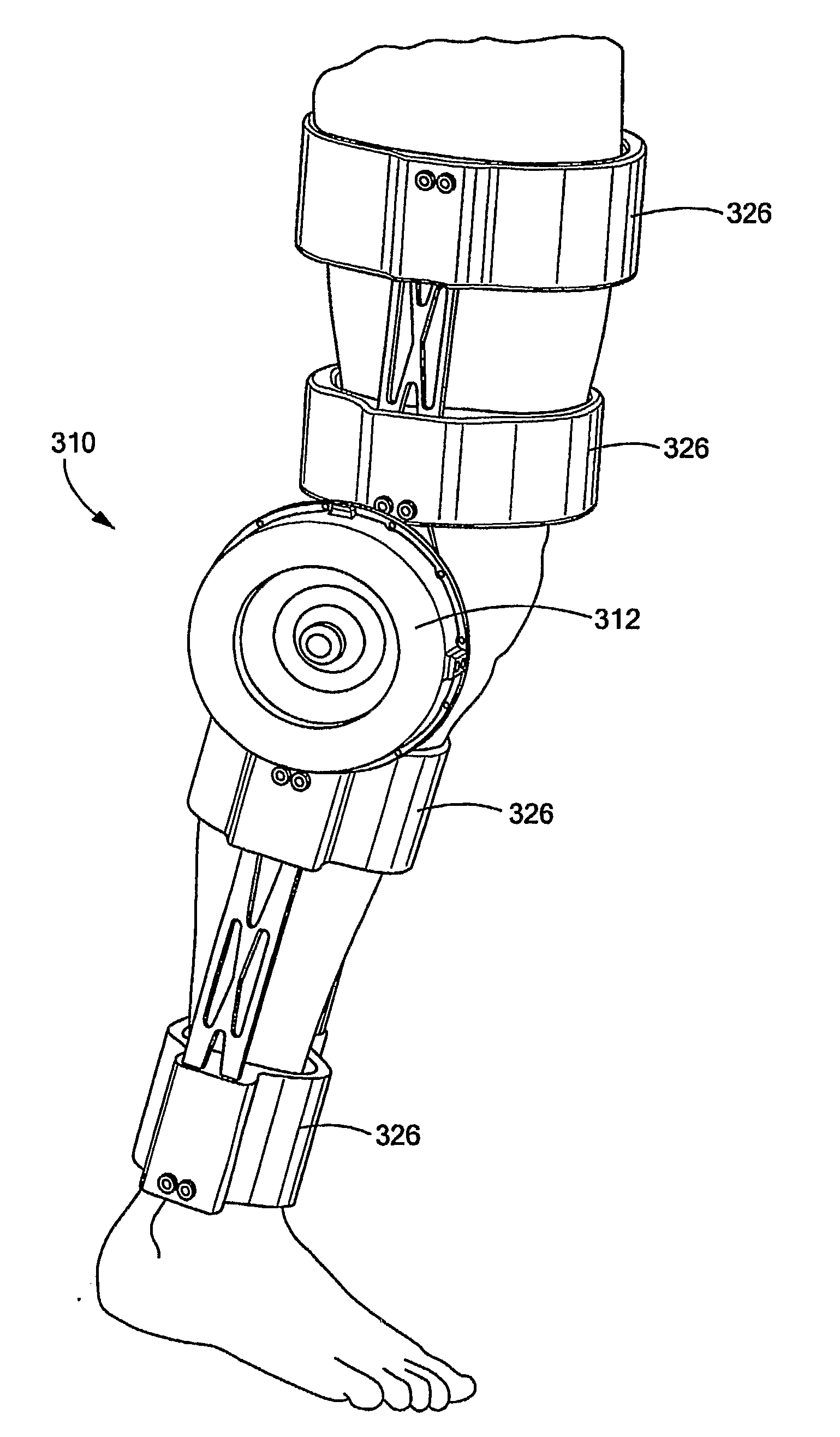
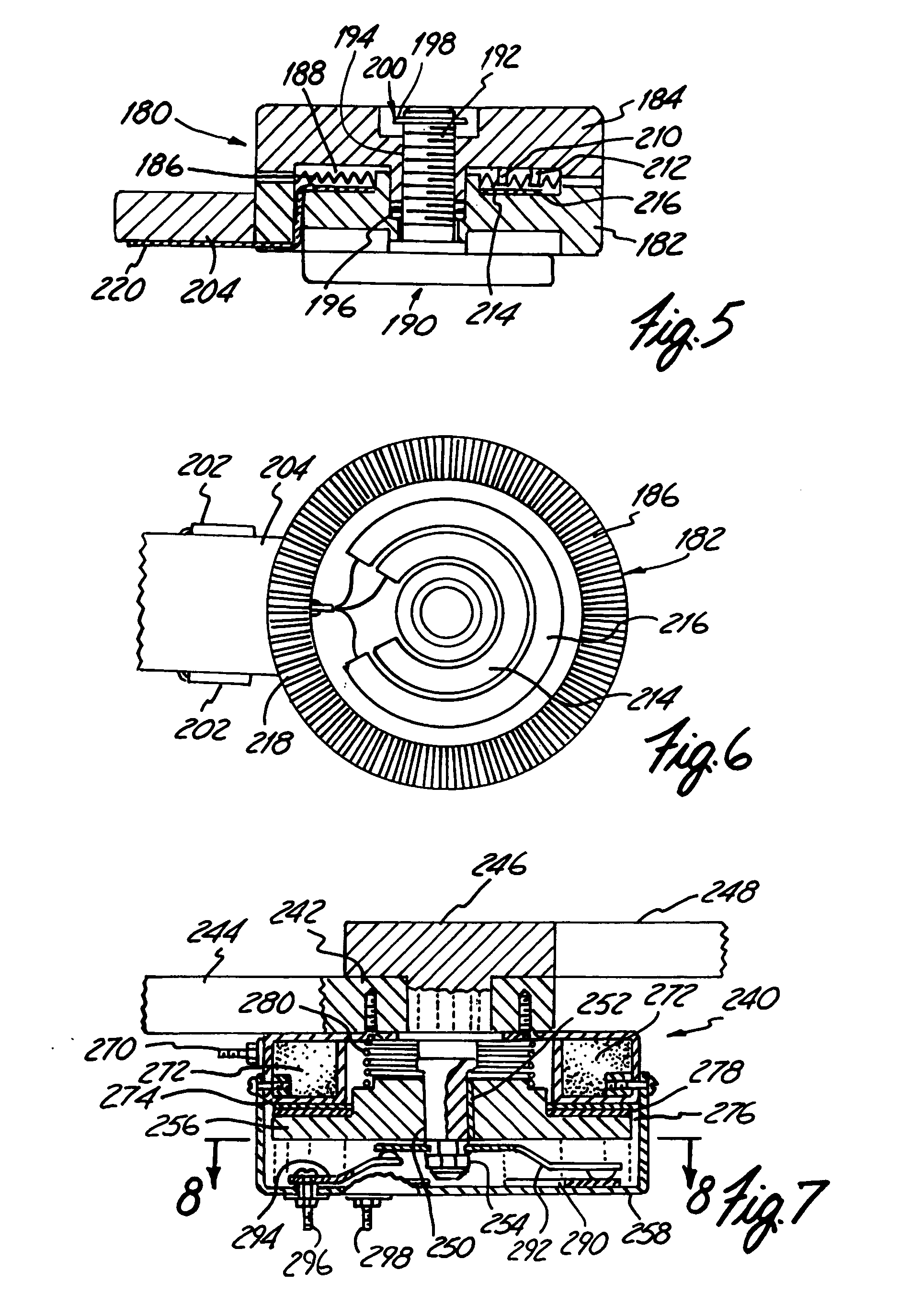
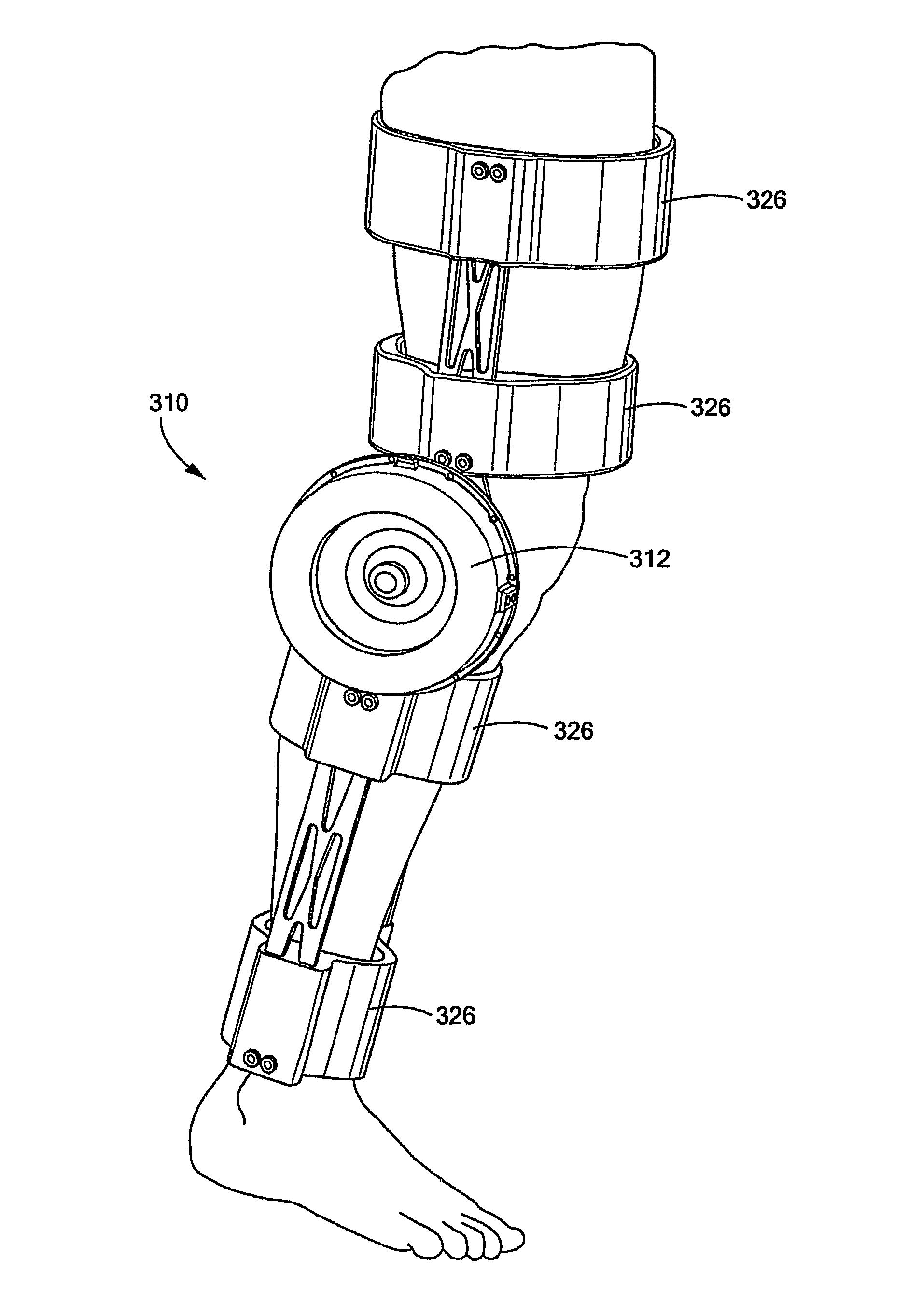
Electro-Rheological Fluid Brake and Actuator Devices and Orthotic Devices Using the Same
InactiveUS20080097269A1Strong and highly tunable torque capabilityLiquid resistance brakesSpringsActuatorOrthotic device
Electro-rheological fluid brake or actuator devices provide controllable resistance with or without inclusion of active torque output in either direction of rotation under manual or computer control. The brake and actuator devices are suitable for use in an orthotic device for a joint, such as the knee or elbow.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
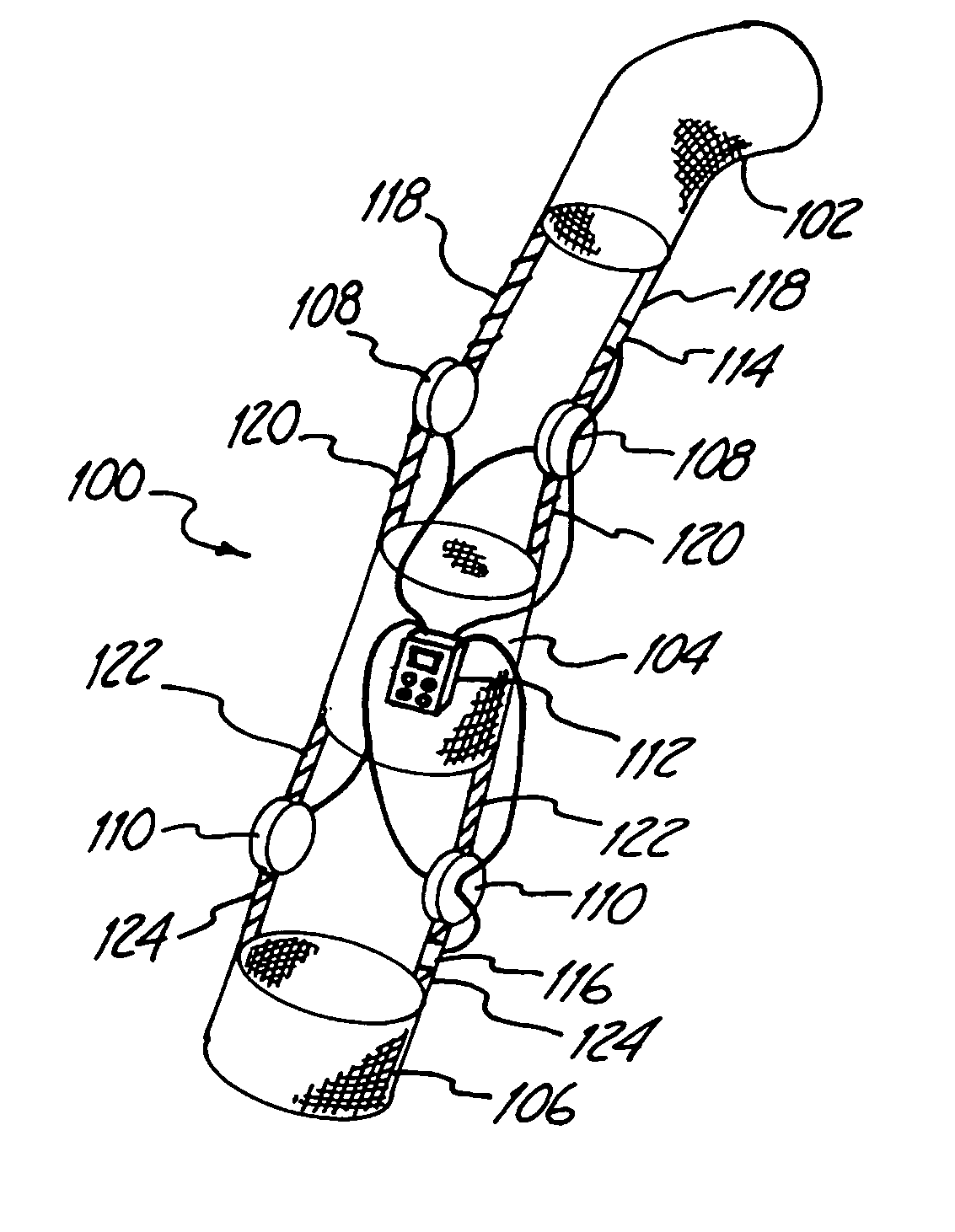
Rehabilitative orthoses
Instrumented orthoses with more sophisticated structures provide for coordinated support and rehabilitation of complex joints and multiple injured joints. Improved instrumented orthoses can include hinges that can rotate in multiple different planes. Particularly preferred embodiments include a shoulder brace with a hand hold and a lower extremities brace. Preferably, a control unit monitors the output of transducers used to instrument the brace. A patient can be prompted by the control unit for the performance of a variety of different monitored exercises.
Owner:IZEX TECH
Systems and methods for processing limb motion
ActiveUS7811333B2Navigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringAccelerometerData set
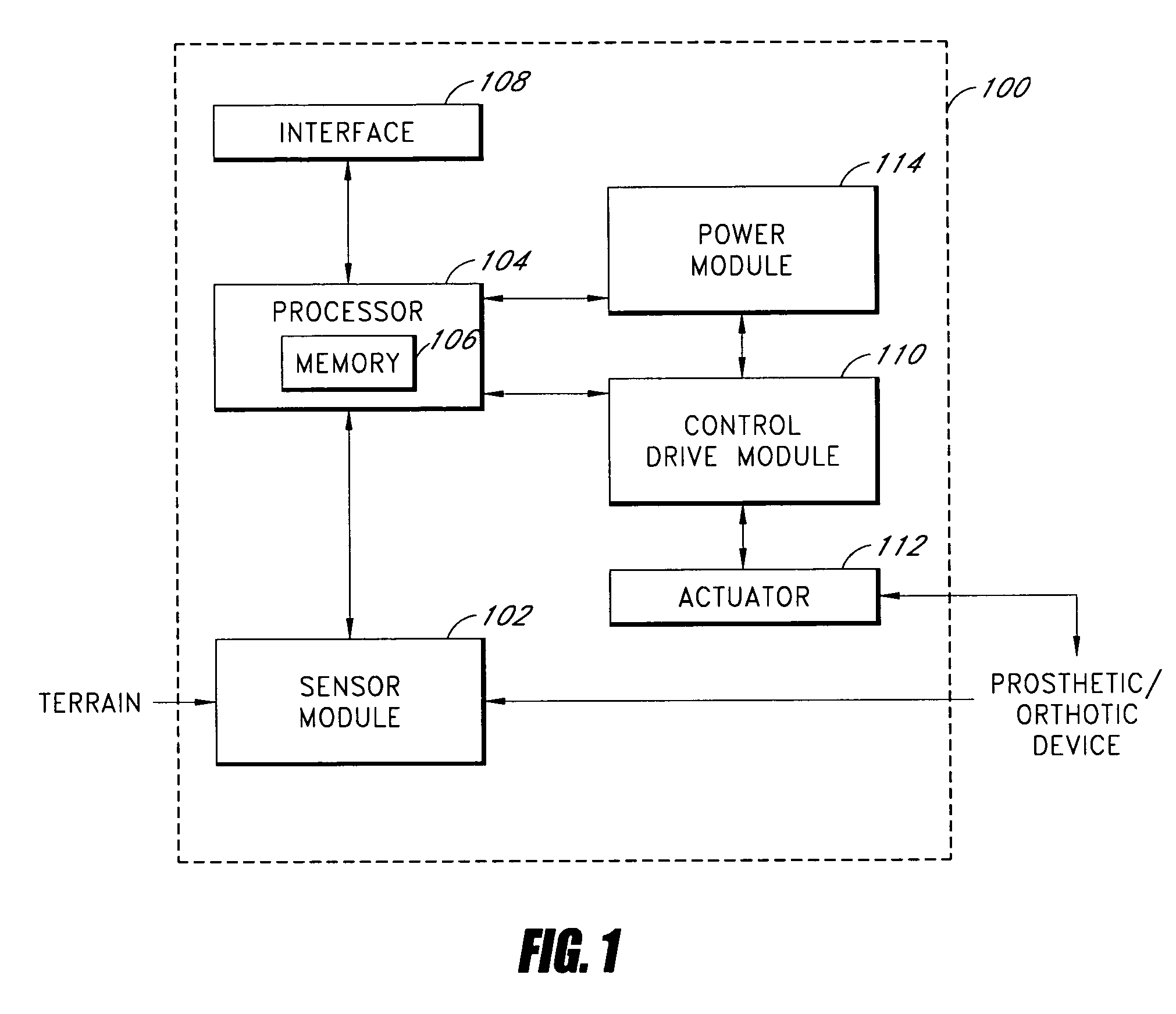
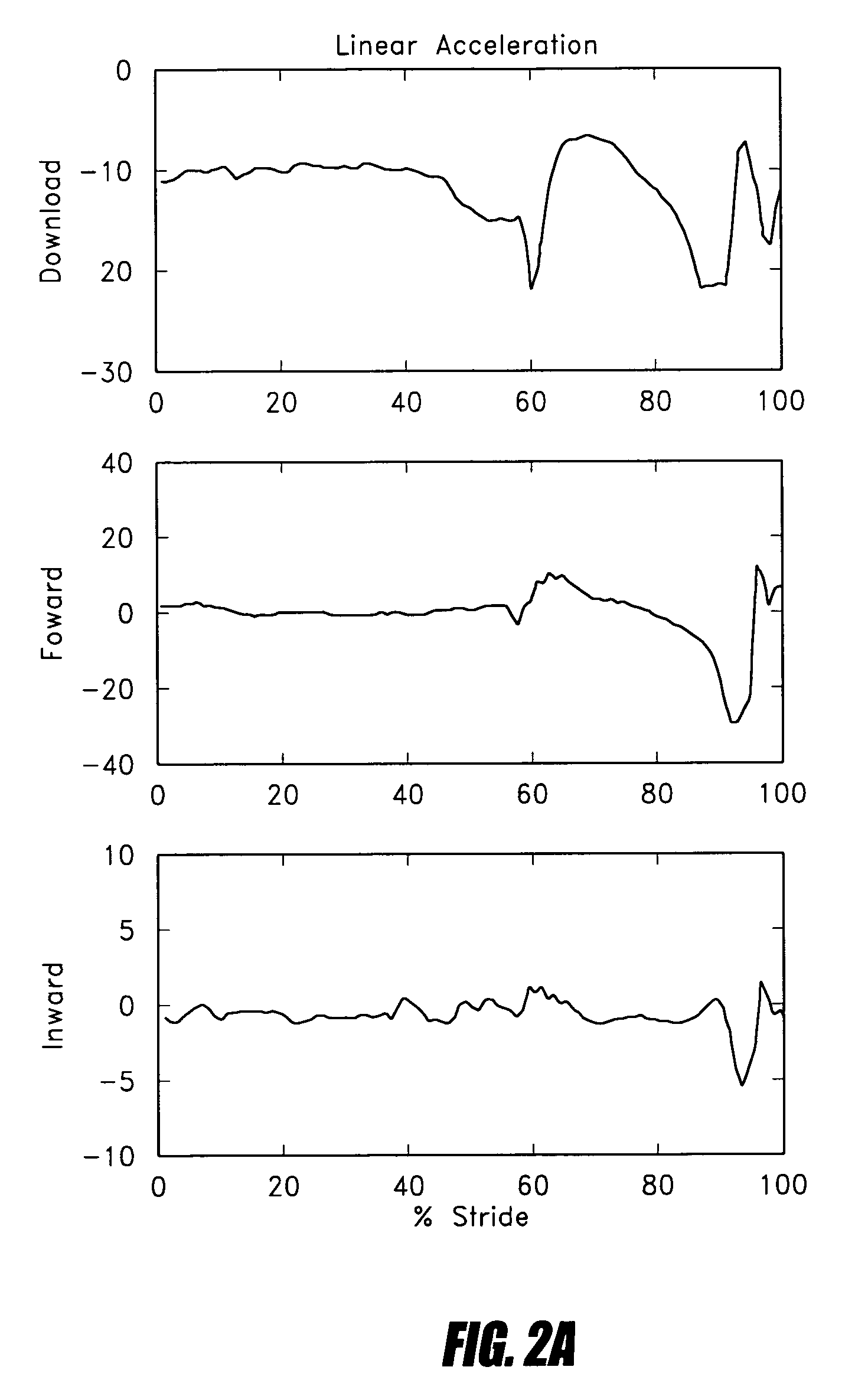
Control systems and methods are disclosed for processing a time series of signals associated with the movement of a device associated with a limb. The time series of motion signals is filtered, such as thorough an autoregressive filter, and compared to stored data sets representing a limb-motion event and / or phase. In certain examples, a plurality of accelerometers generate the time series of motion signals based at least on acceleration measurements in three orthogonal directions and / or planes. The acceleration measurements may relate to the movement of an artificial limb, such as a prosthetic or orthotic device. Upon determining an event and / or phase of limb motion, the control system may trigger an actuator to appropriately adjust one or more prosthetic or orthotic joints.
Owner:OSSUR HF
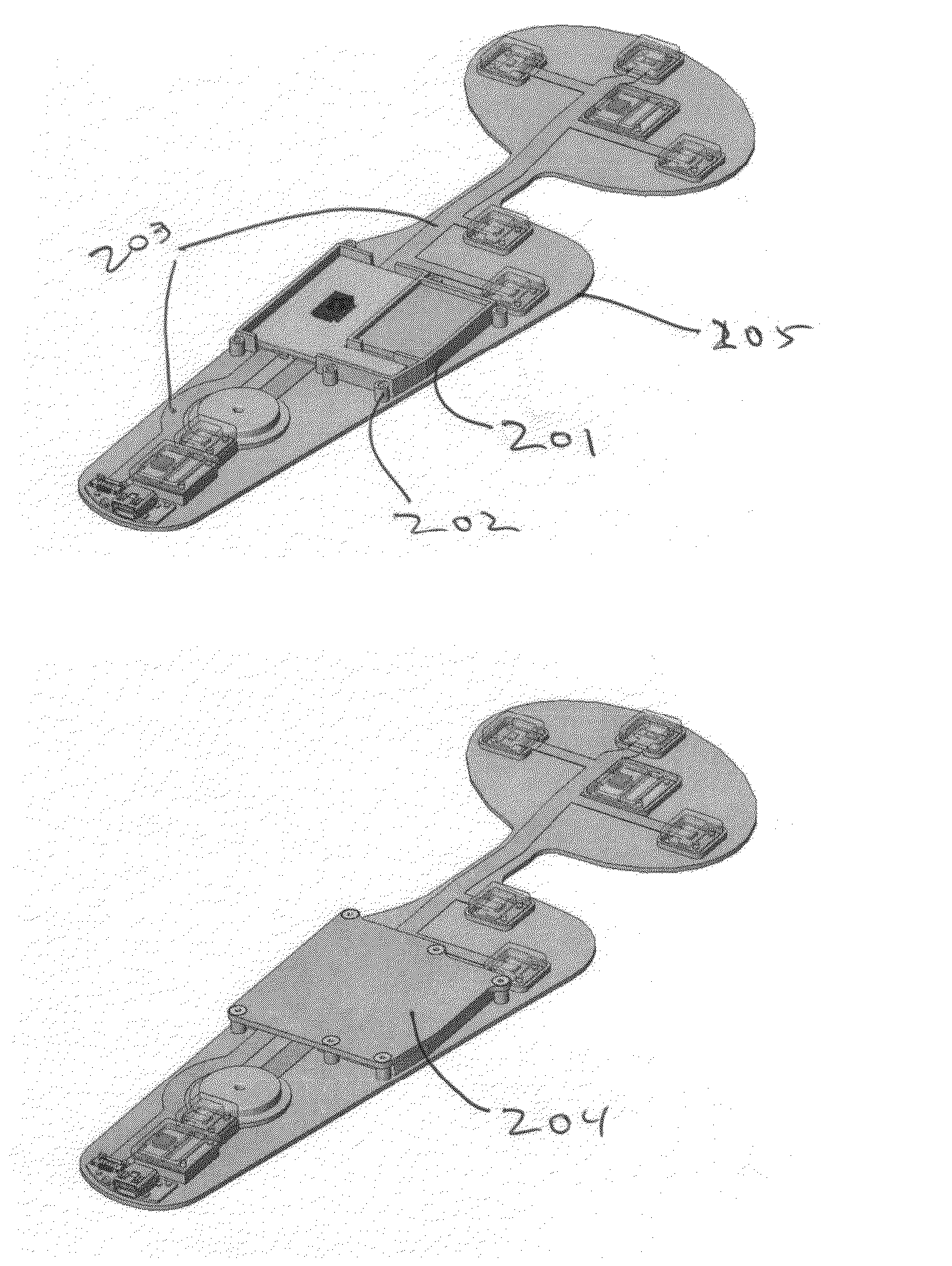
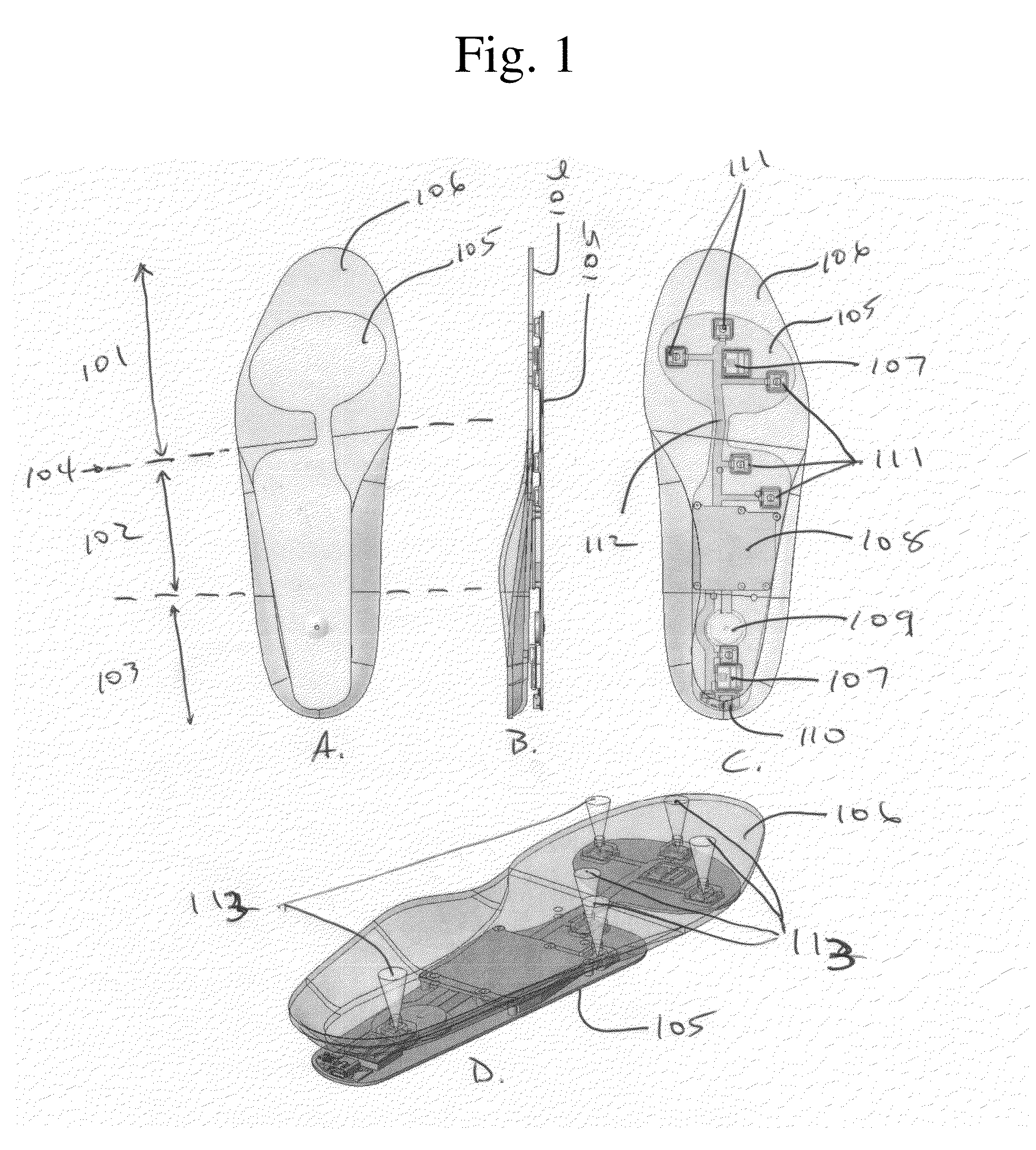
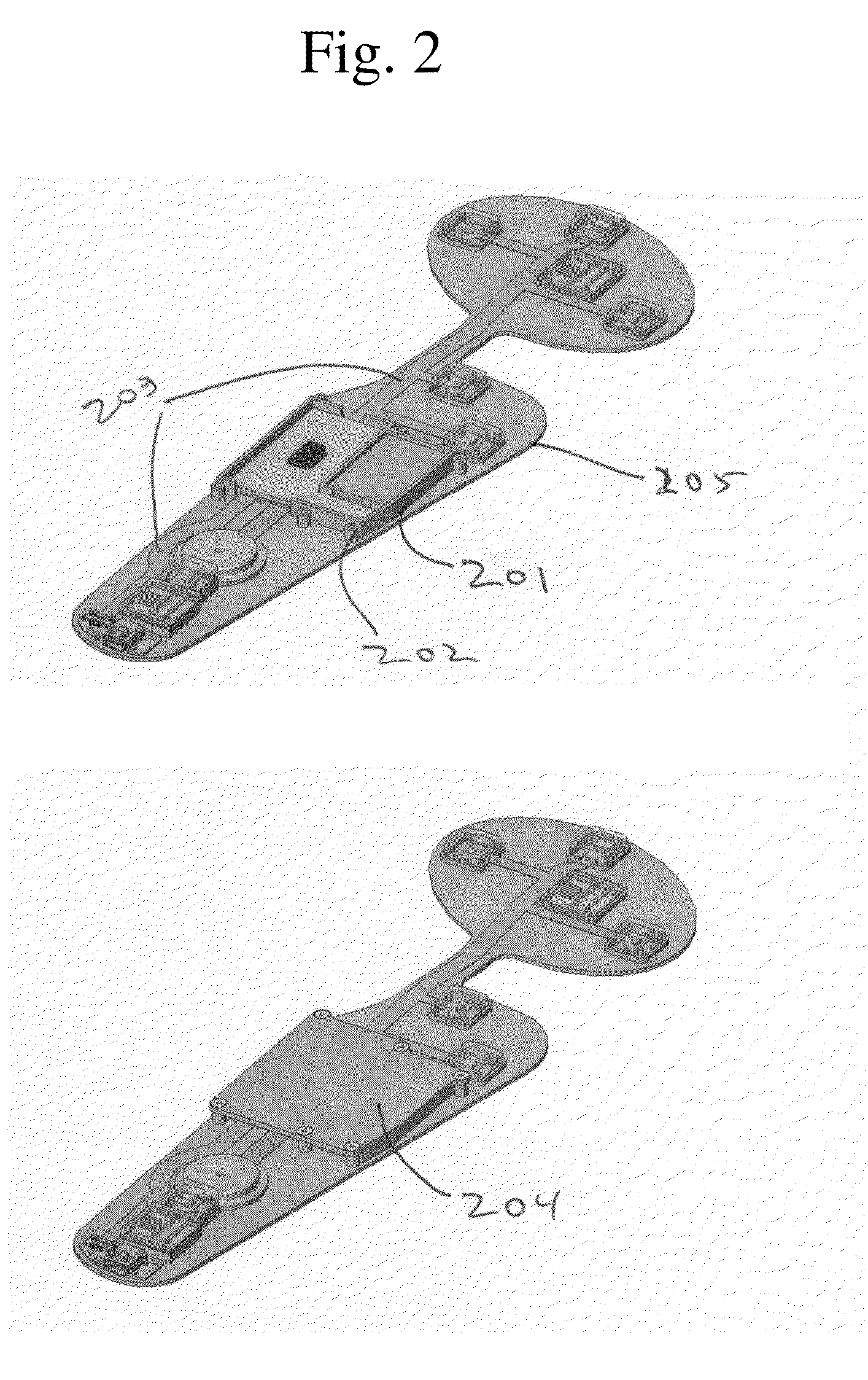
Intelligent orthotic insoles
An intelligent insole for generating time sensitive information about the pressure on the foot. The insole includes a custom-made, semi-custom or generically sized orthotic component. The orthotic is laminated with a top cover and an intermediate pressure sensor having an array of capacitive pressure sensors. Signal processing equipment may be embedded in the insole or placed locally with the insole as on the side of a shoe. The processor also can connect to a wireless transmitter for relaying the information to a remote site.
Owner:ESOLES LLC
Orthotic foot device with removable support components and method of making same
An orthotic foot device for footwear may include a flexible insole chassis adapted to extend substantially between the heel and the toe of the footwear and at least one support component attached at a lower side of the chassis. The chassis may include a cushioned layer composed of conforming resilient material overlying the upper side of the chassis.
Owner:ORTHOSOLE LIMITED A GUERNSEY LIMITED
Spacer element for prosthetic and orthotic devices
ActiveUS7762973B2Reduce impactMinimizing rotational forceSynthetic resin layered productsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesProsthesisEngineering
An orthotic or prosthetic spacer element including a ventilated and compressible core having first and second opposed surfaces, and a discrete and continuous web-like silicone-based frictional layer secured to the core first surface. The frictional layer and the core first surface have a plurality of coinciding apertures formed in a pattern. The spacer element may include a foam layer secured to the core second surface such that the foam layer and the core have different rigidities. A layer of hook-receivable material may be directly or indirectly secured to the second core surface.
Owner:KAUPTHING BANK
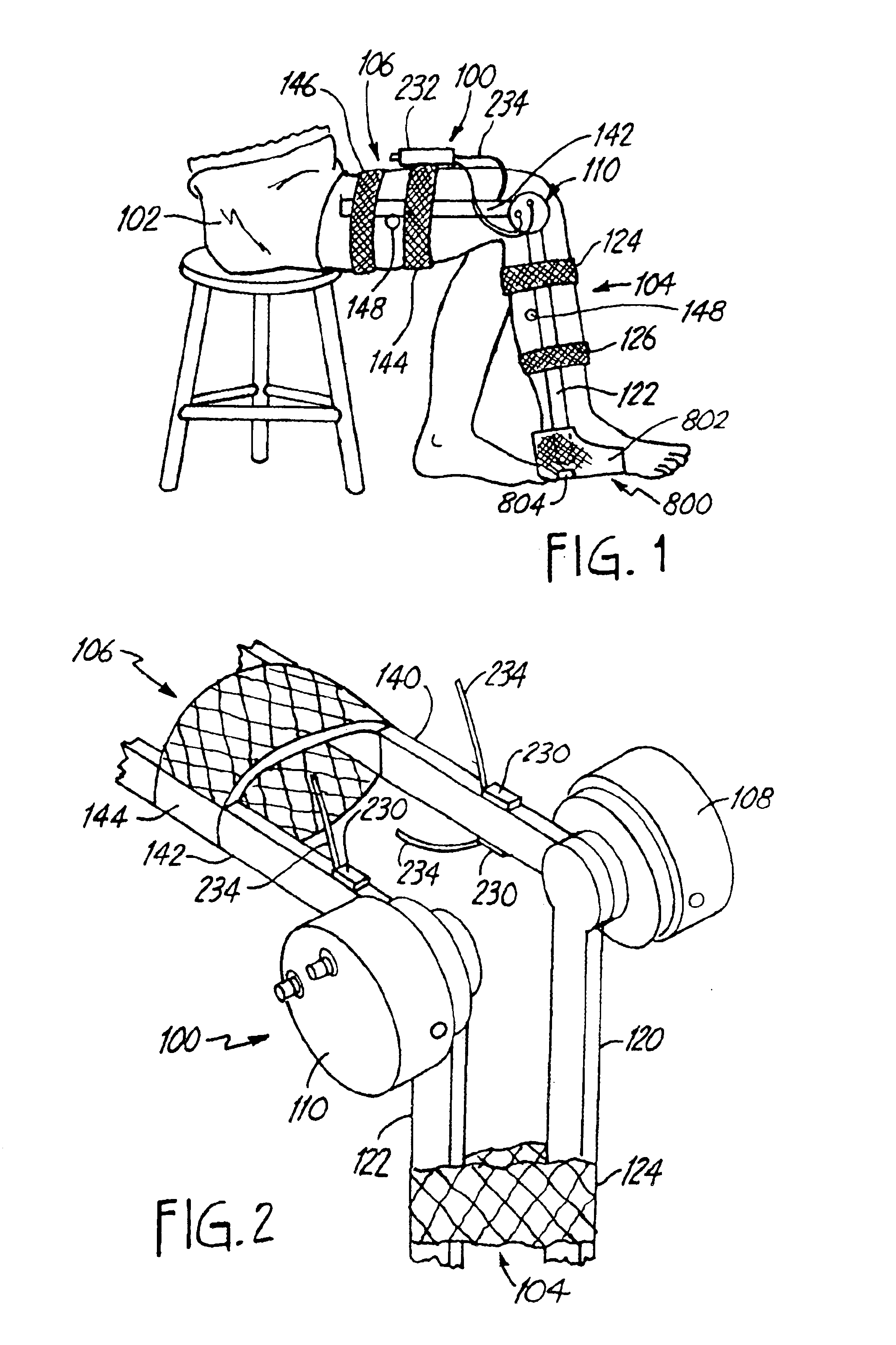
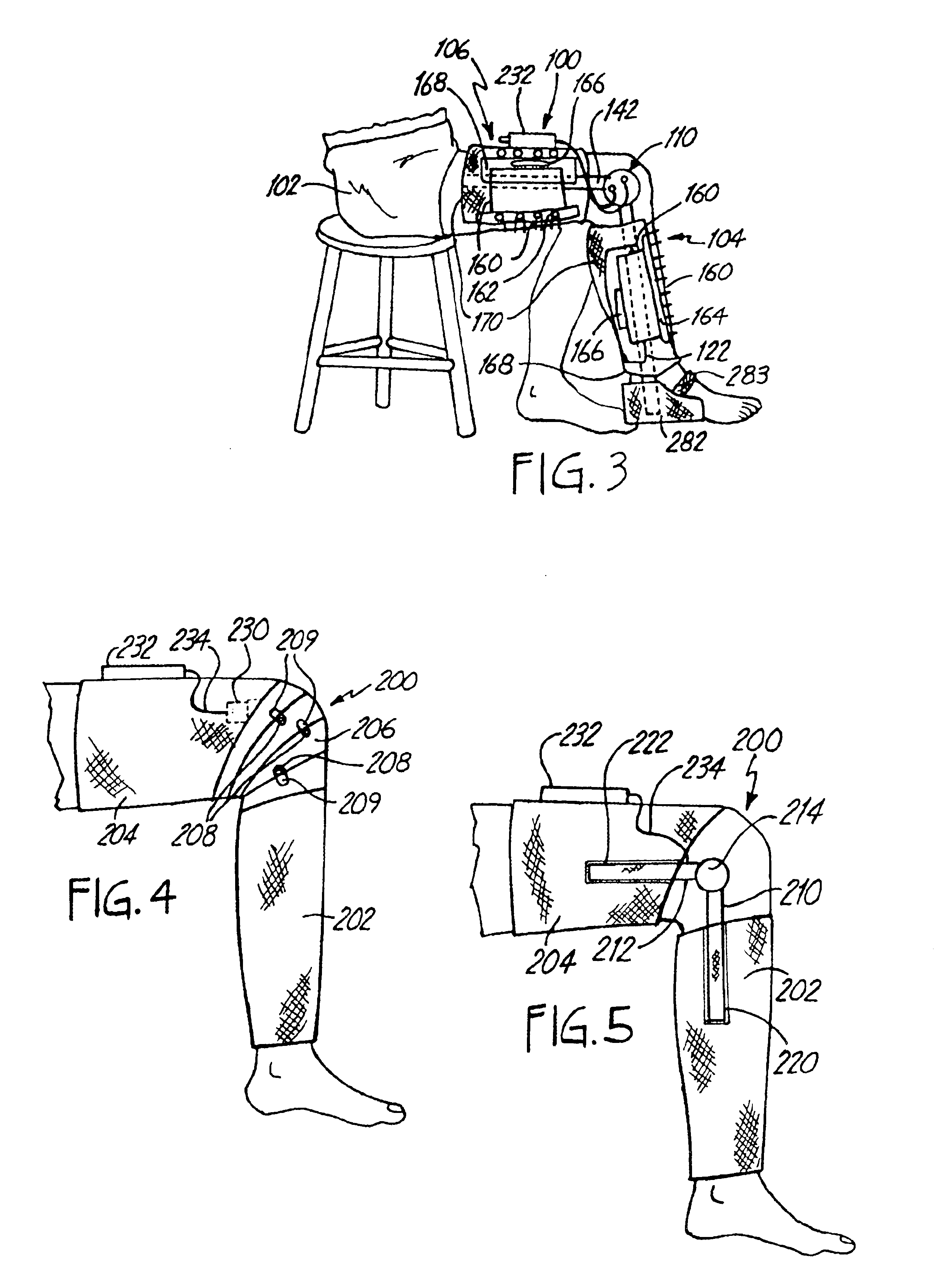
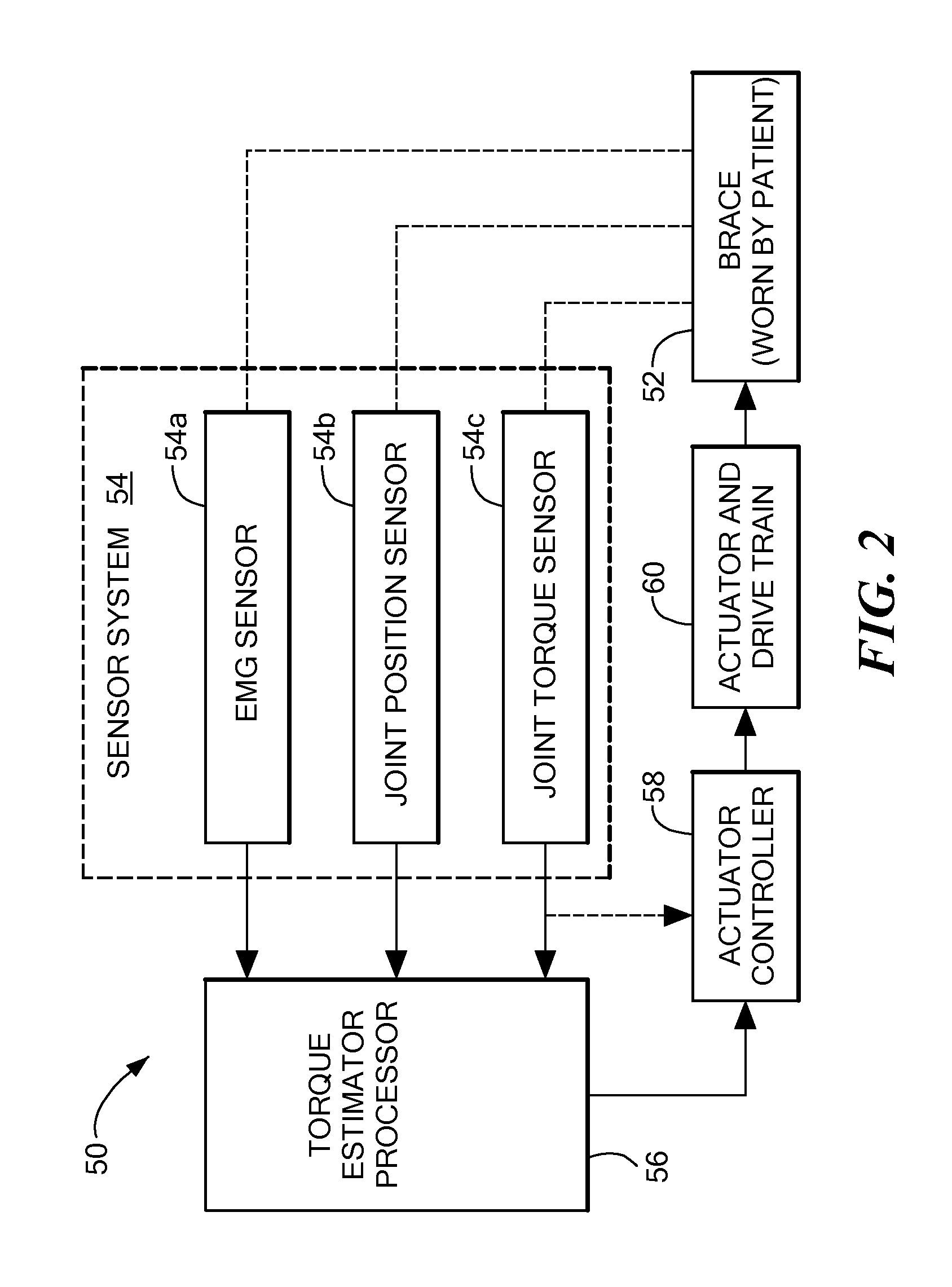
Method of using powered orthotic device
InactiveUS7367958B2Smooth movementHigh strengthElectromyographyChiropractic devicesDiseaseNeuromuscular disease
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Remote psychological evaluation
Instrumented orthoses with more sophisticated structures provide for coordinated support and rehabilitation of complex joints and multiple injured joints. Improved instrumented orthoses can include hinges that can rotate in multiple different planes. Particularly preferred embodiments include a shoulder brace with a hand hold and a lower extremities brace. Preferably, a control unit monitors the output of transducers used to instrument the brace. A patient can be prompted by the control unit for the performance of a variety of different monitored exercises.
Owner:IZEX TECH
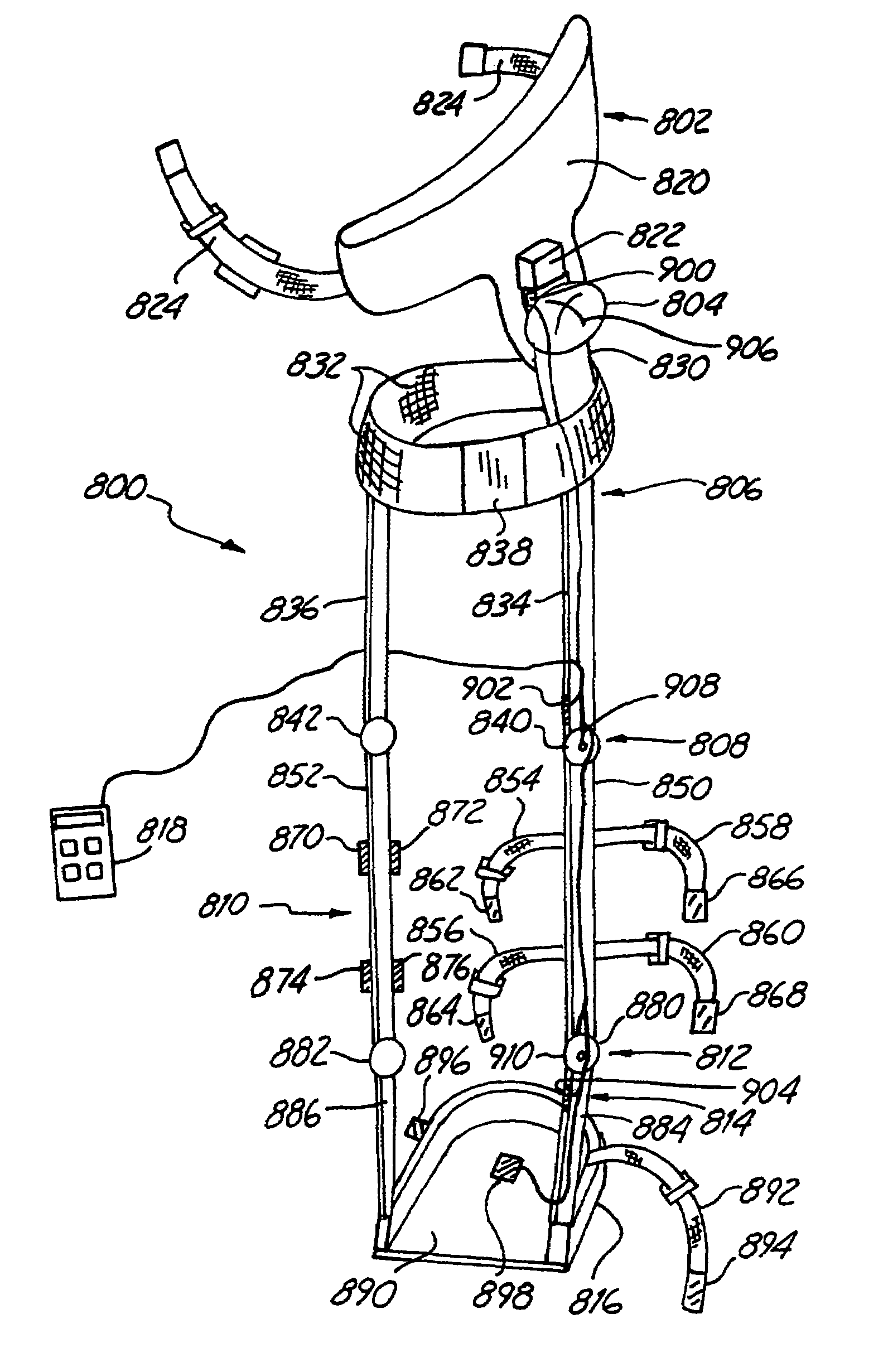
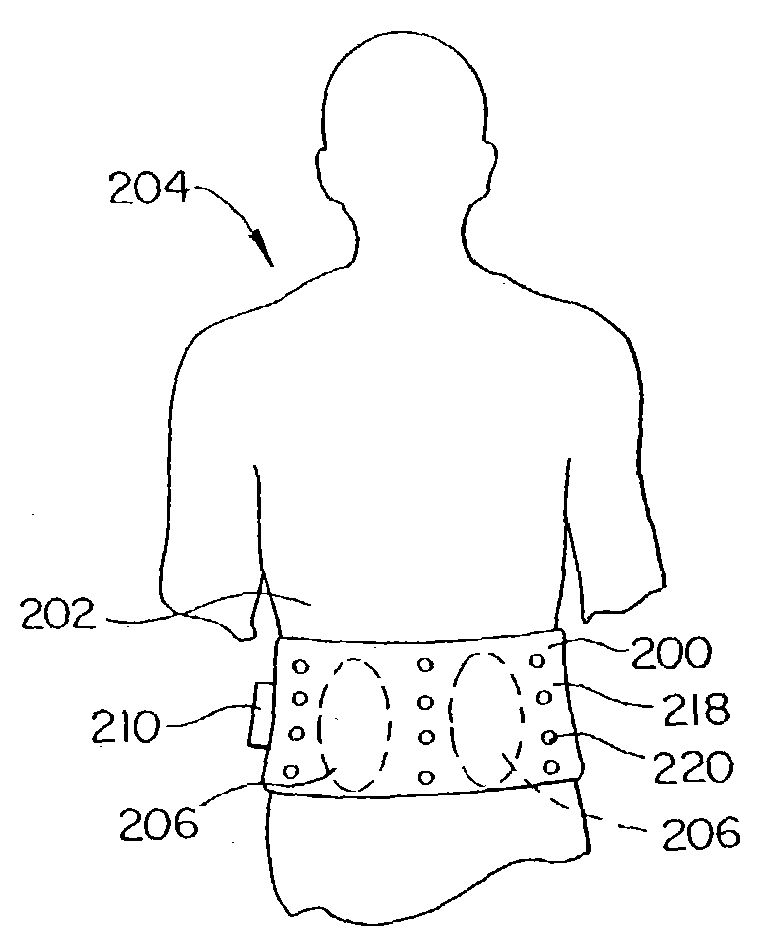
Orthoses
Exercise orthoses are described that include a frame, a fluid bladder held by the frame, a pressure sensor attached to the fluid bladder and a microprocessor receiving the pressure measurements. The microprocessor monitors variations in pressure and determines differences between the measured pressures and predetermined target values. The frame can be designed to support a hinge joint or at least one vertebra. Furthermore, corrective back orthoses are described that include a frame force applicators connected to the frame to apply force to the patient's spine, a sensor that measures forces associated with the force applicators and a control unit that monitors forces measured by the sensor. The corrective back orthosis can include fluid bladders as force applicators. The control unit can include a microprocessor.
Owner:IZEX TECH
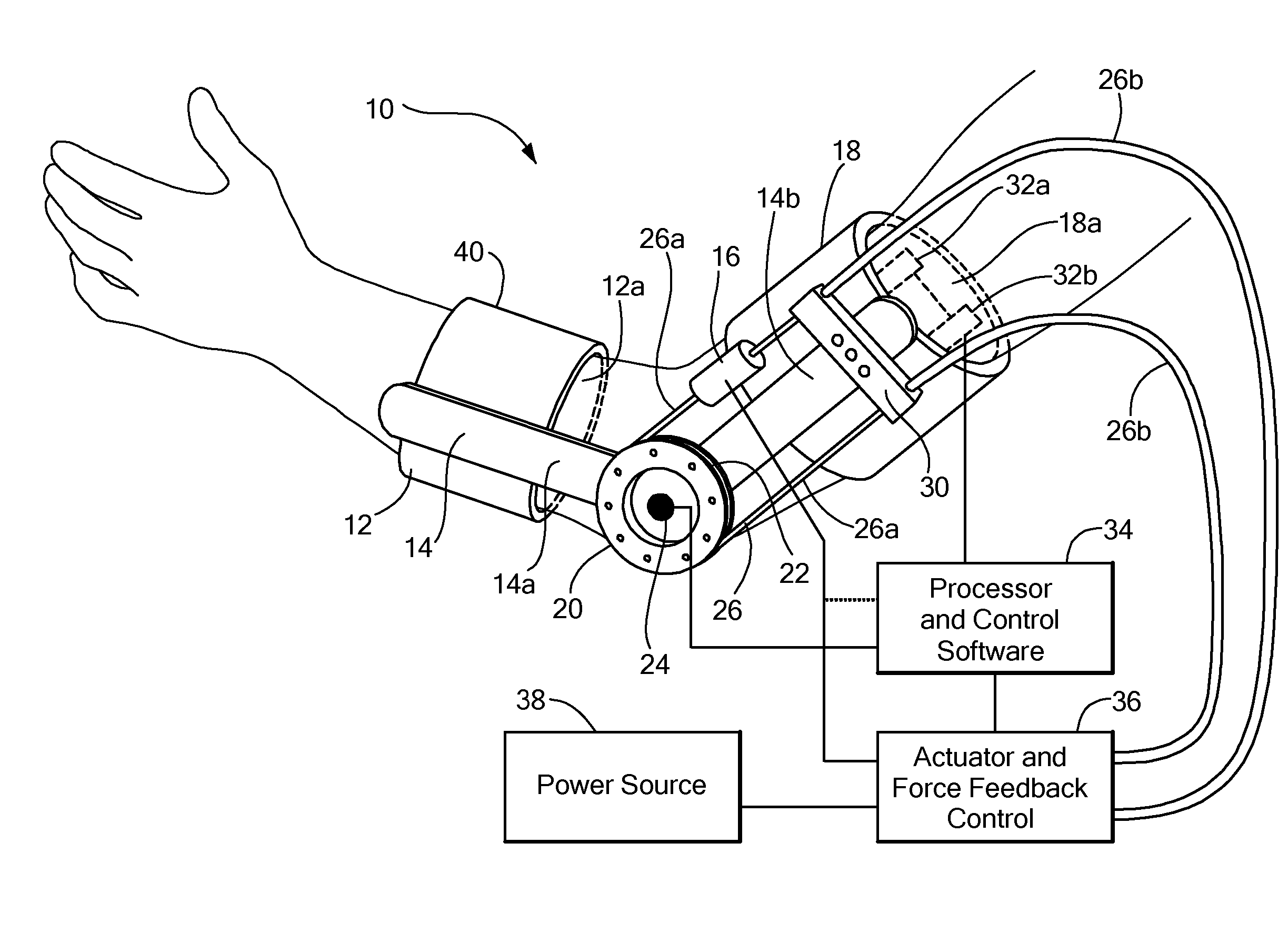
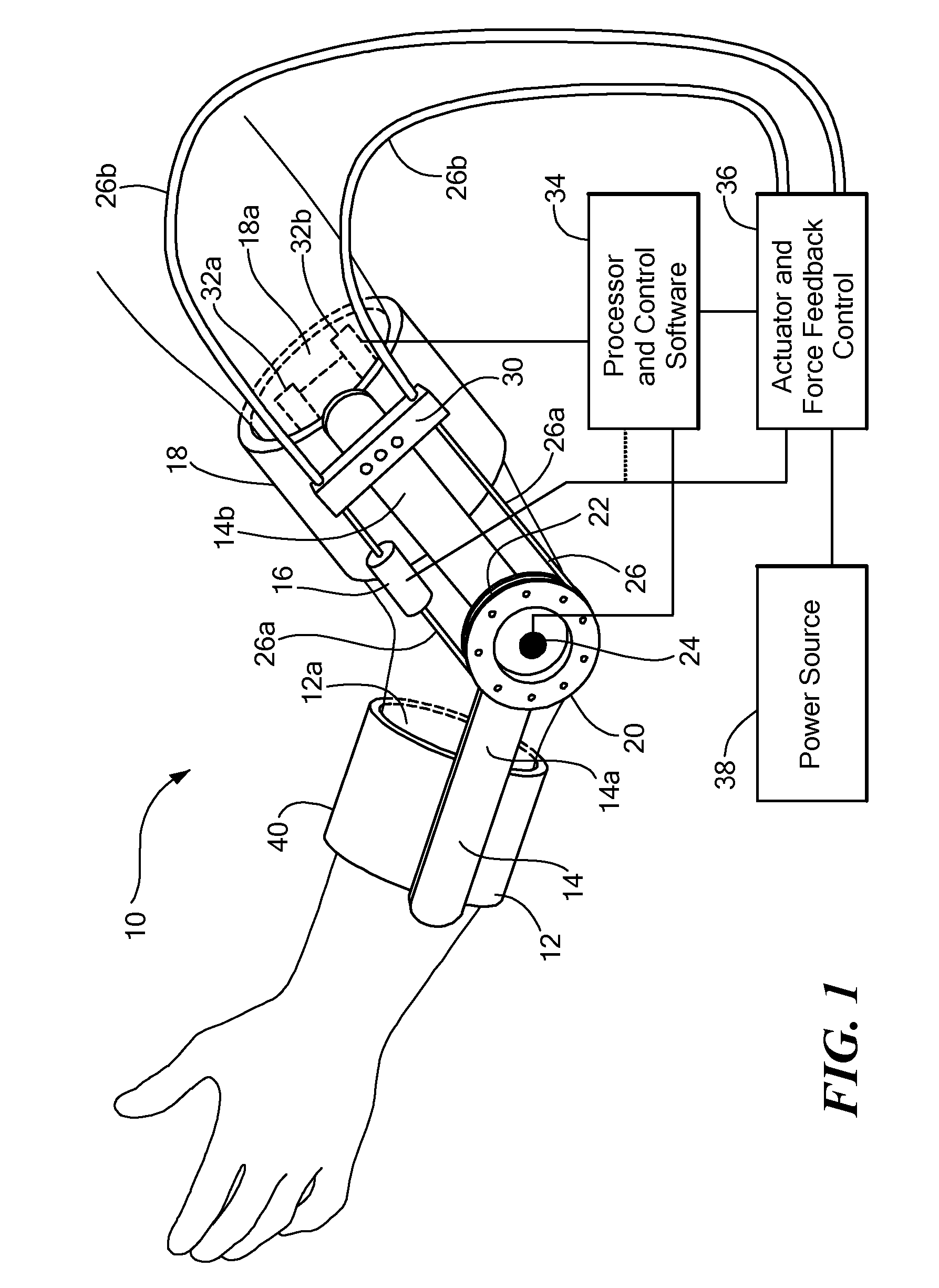
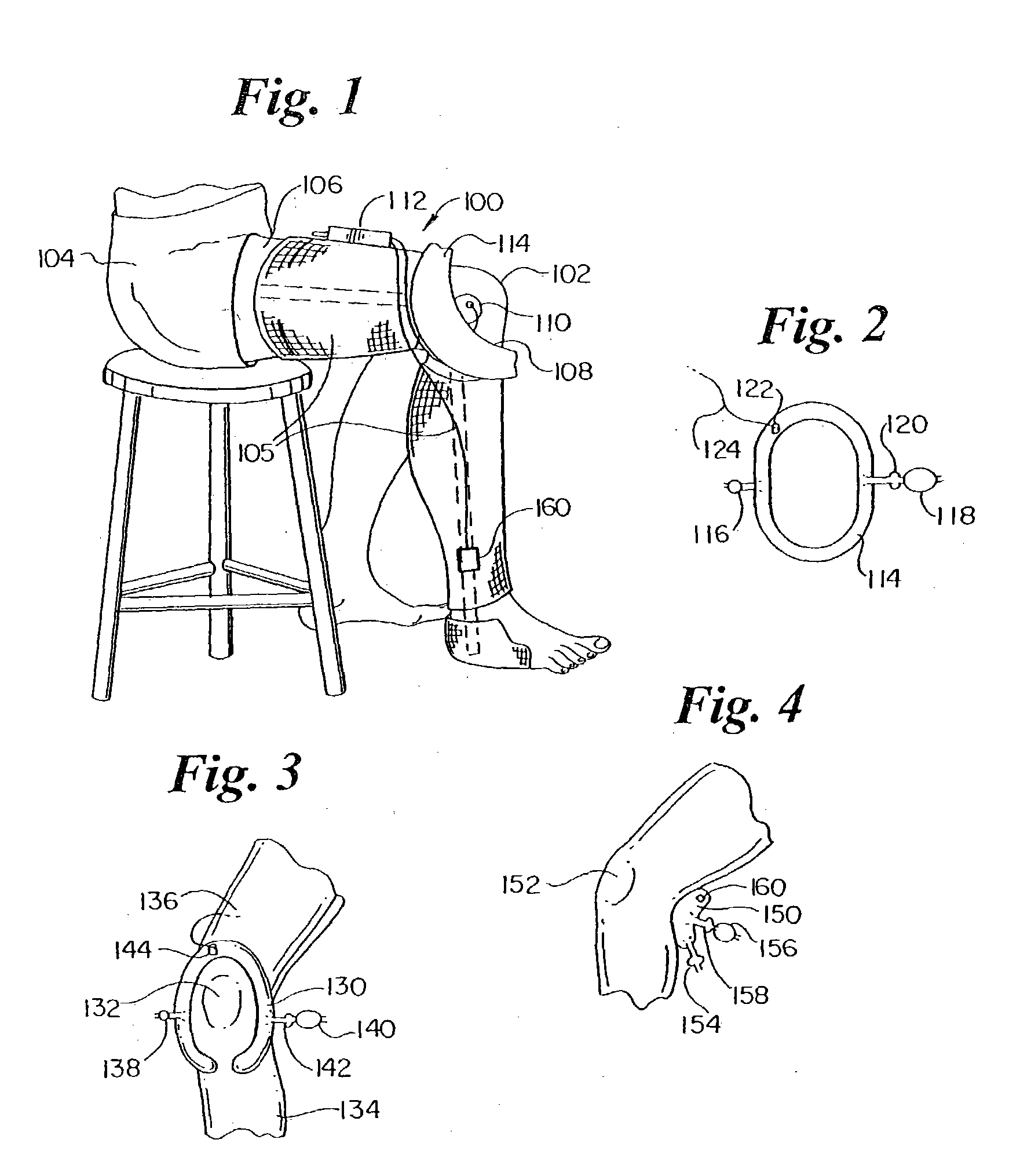
Powered Orthotic Device and Method of Using Same
A powered orthotic system includes a wearable component having a brace with a first section and a second section. The first and second sections are coupled to each other at a pivot. Each section is adapted to be removably attached to a corresponding first and second limb segment such that the pivot is proximate to a joint between each limb segment. The first and the second sections are movable with respect to each other to define flexion and extension directions. The wearable component also includes an electromyographic sensor, an electrically powered actuator assembly in communication with the electromyographic sensor, and a controller in communication with the actuator assembly that provides system parameters to control operation of the actuator assembly. The actuator assembly is coupled to the first and the second sections so as to apply a force that moves the first and the second sections in the flexion and / or extension directions and the force is based on signals from the electromyographic sensor. The actuator assembly is positioned proximate to the pivot. The system also includes a control unit in communication with the wearable component. The control unit includes a processor that modifies the system parameters in the controller and a user interface, in communication with the processor, that permits user selection of the system parameters.
Owner:MYOMO
Active ankle foot orthosis
ActiveUS8075633B2Increase independenceGreat easeWalking aidsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesWalking cyclePostural orientation
An Active Ankle Foot Orthosis (AAFO) is provided where the impedance of an orthotic joint is modulated throughout the walking cycle to treat ankle foot gait pathology, such as drop foot gait. During controlled plantar flexion, a biomimetic torsional spring control is applied where orthotic joint stiffness is actively adjusted to minimize forefoot collisions with the ground. Throughout late stance, joint impedance is minimized so as not to impede powered plantar flexion movements, and during the swing phase, a torsional spring-damper (PD) control lifts the foot to provide toe clearance. To assess the clinical effects of variable-impedance control, kinetic and kinematic gait data were collected on two drop foot participants wearing the AAFO. It has been found that actively adjusting joint impedance reduces the occurrence of slap foot, allows greater powered plantar flexion, and provides for less kinematic difference during swing when compared to normals.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Orthotic device and method for securing the same
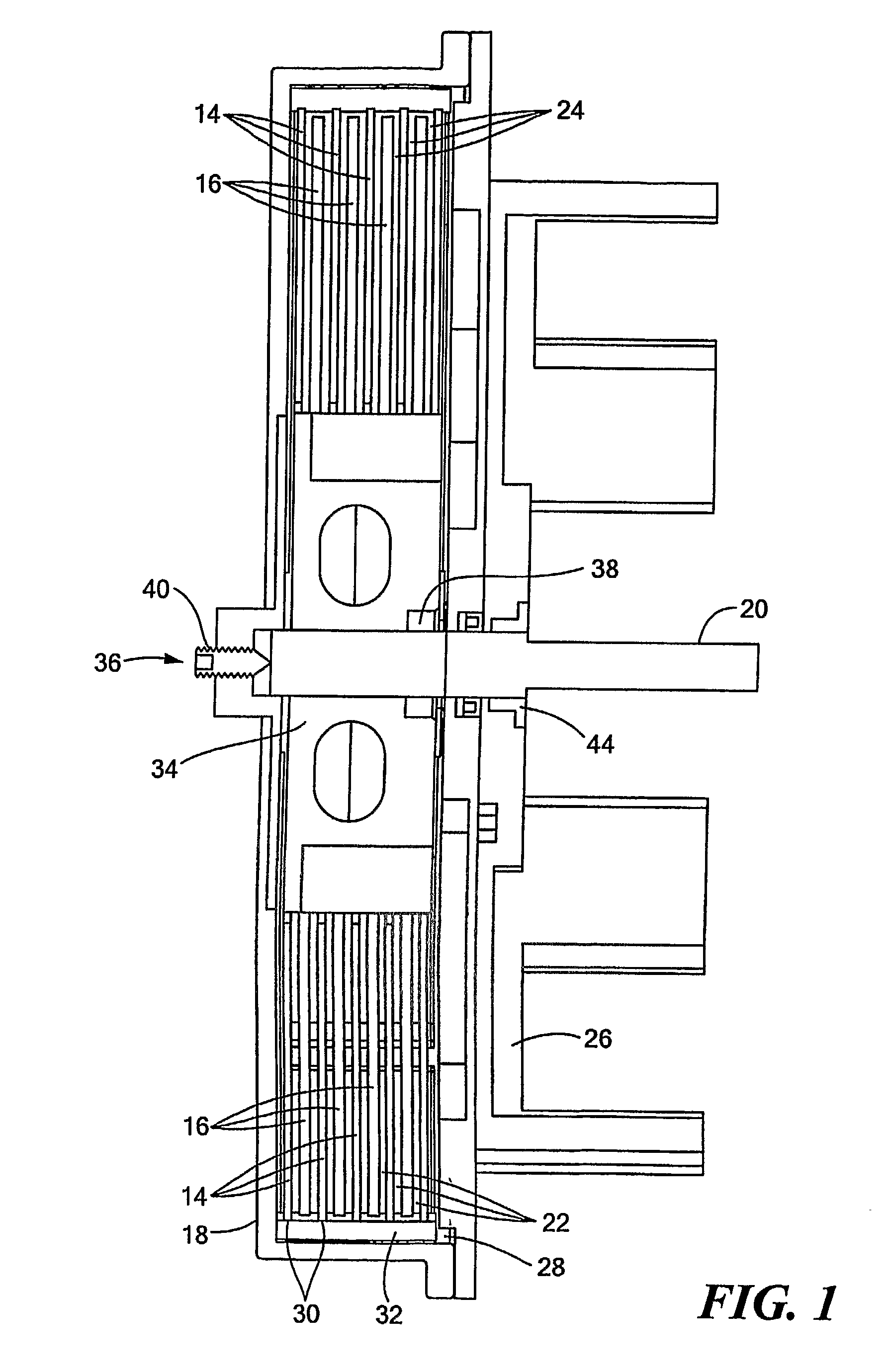
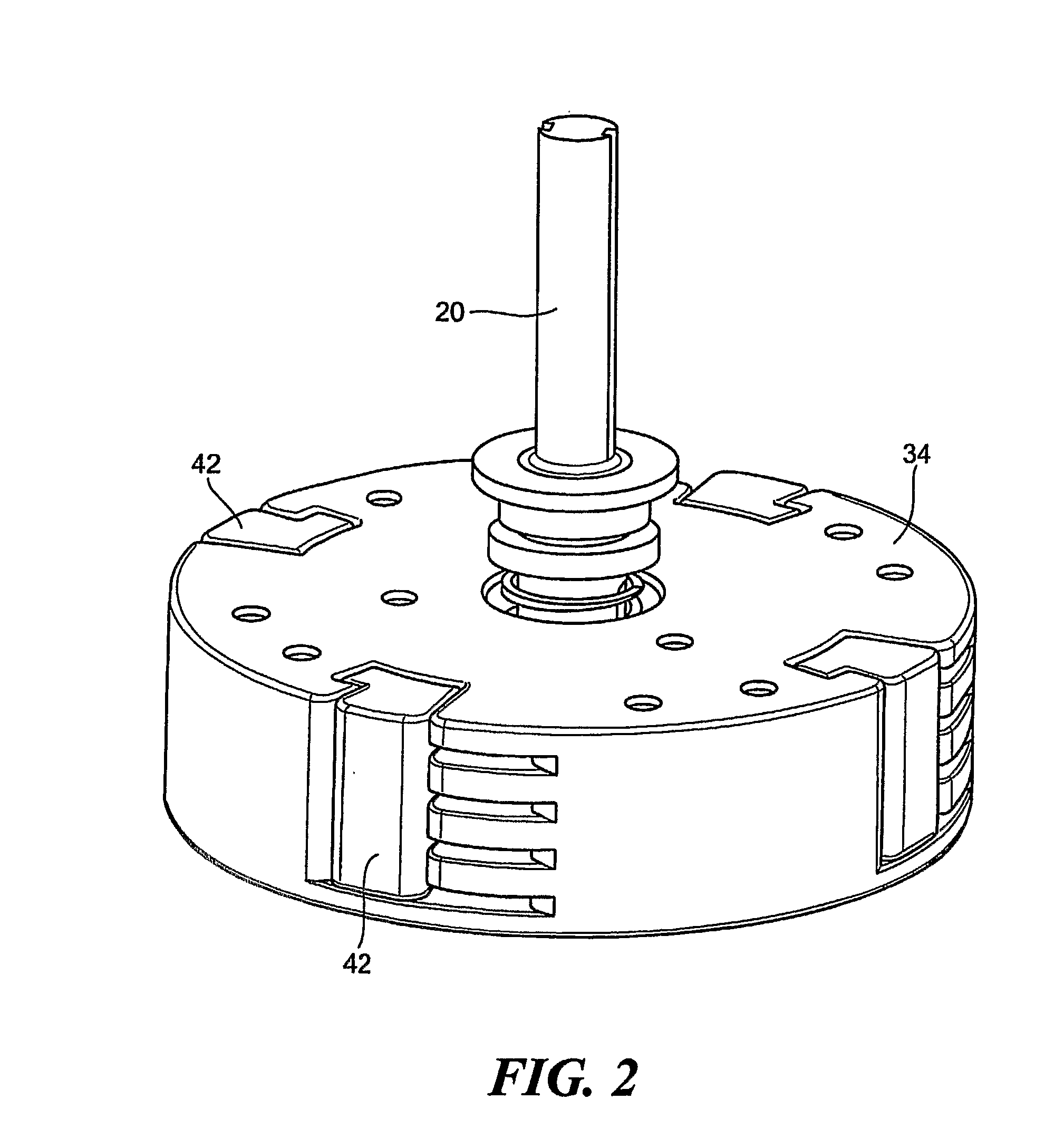
An orthotic device includes a frame having a first shell defining front and rear surfaces, and extending longitudinally into the anterior and posterior sides of the brace. The first shell defining an opening located on the posterior side of the brace. A tightening mechanism is mounted onto the first shell, and has a ratchet strap located along the rear surface of the first shell and a ratchet device mounted on the front surface of the first shell so as to extend partially into the opening and engage the ratchet strap. An elongate tensioning device having a first end portion is connected to the ratchet strap, and the first end portion of the tensioning device extends along the rear surface of the first shell. The tensioning device has a second end portion anchored to a portion of the frame. A channel is mounted to the rear surface of the first shell and entirely encloses at least a portion of the ratchet strap. The tensioning device is a textile-based and substantially inelastic strap.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Ankle-foot orthosis
ActiveUS6945947B2Variable propertySmooth transitionRestraining devicesFeet bandagesMedicineKnee orthosis
An ankle-foot orthosis having a structural frame formed from at least one layer of fabric impregnated with a hardened structural resin. The frame includes at least one anterior support member that extends downwardly from an upper leg engaging portion to define an anterior ankle portion which extends to a medial portion connected to a foot plate.
Owner:KAUPTHING BANK
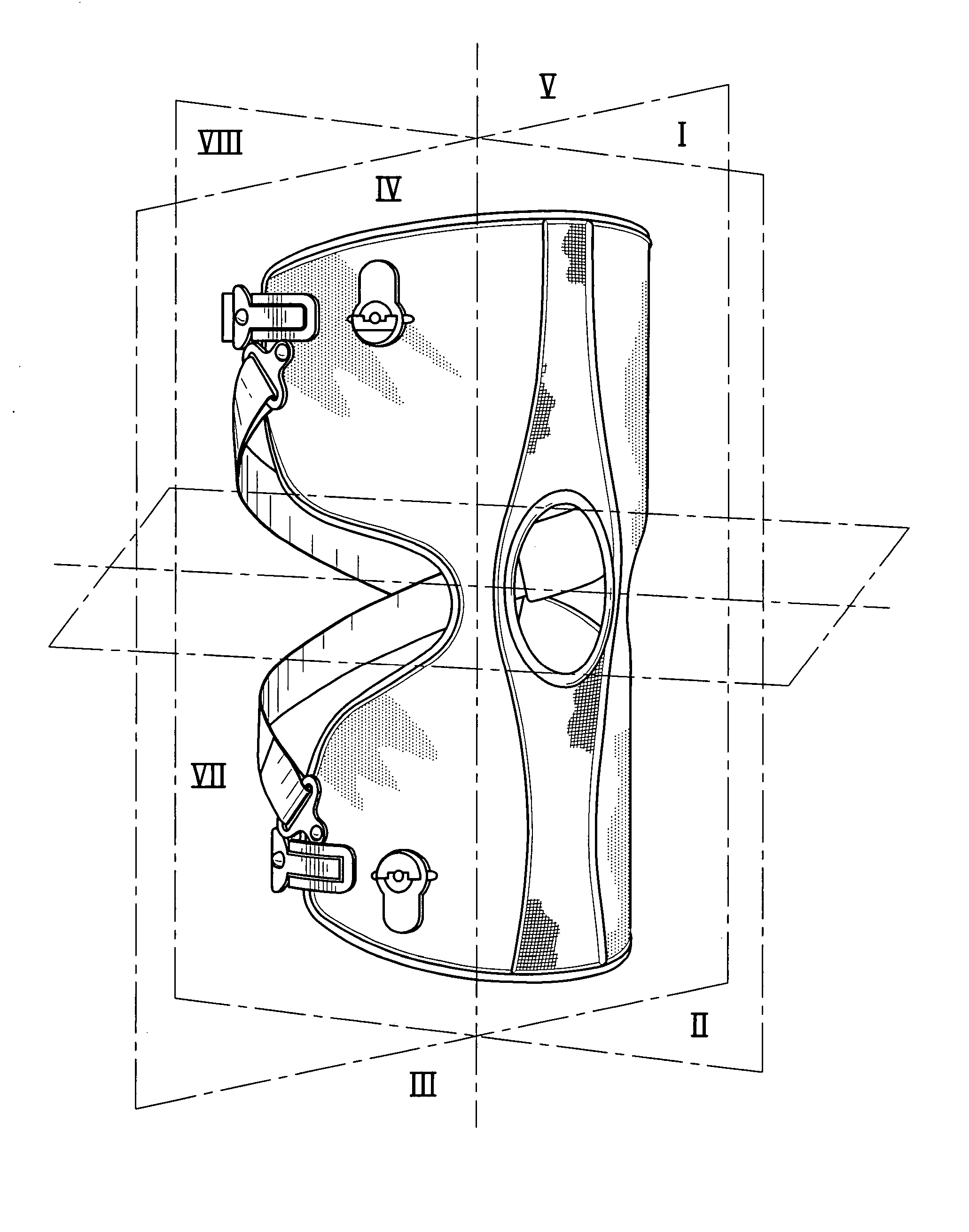
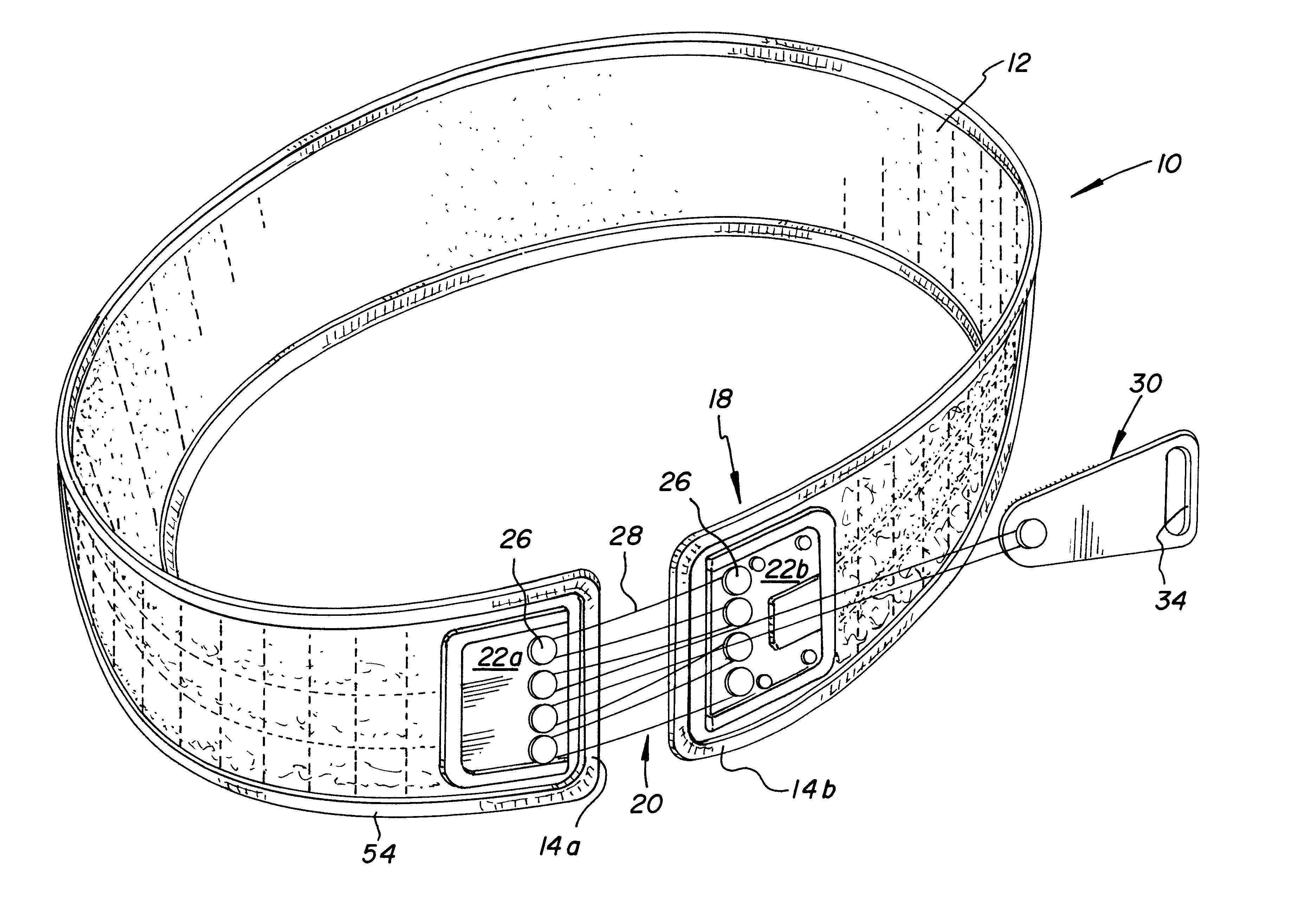
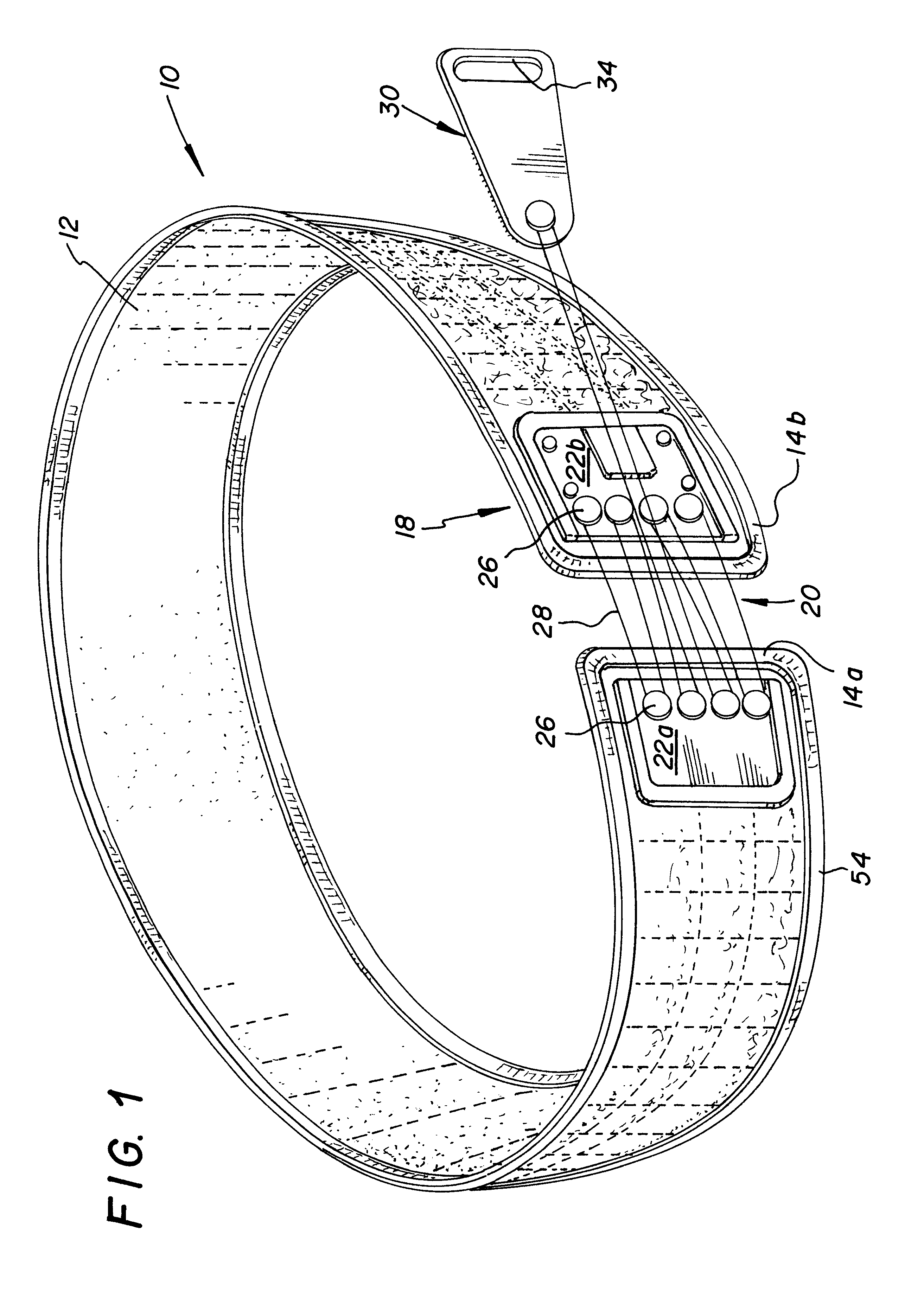
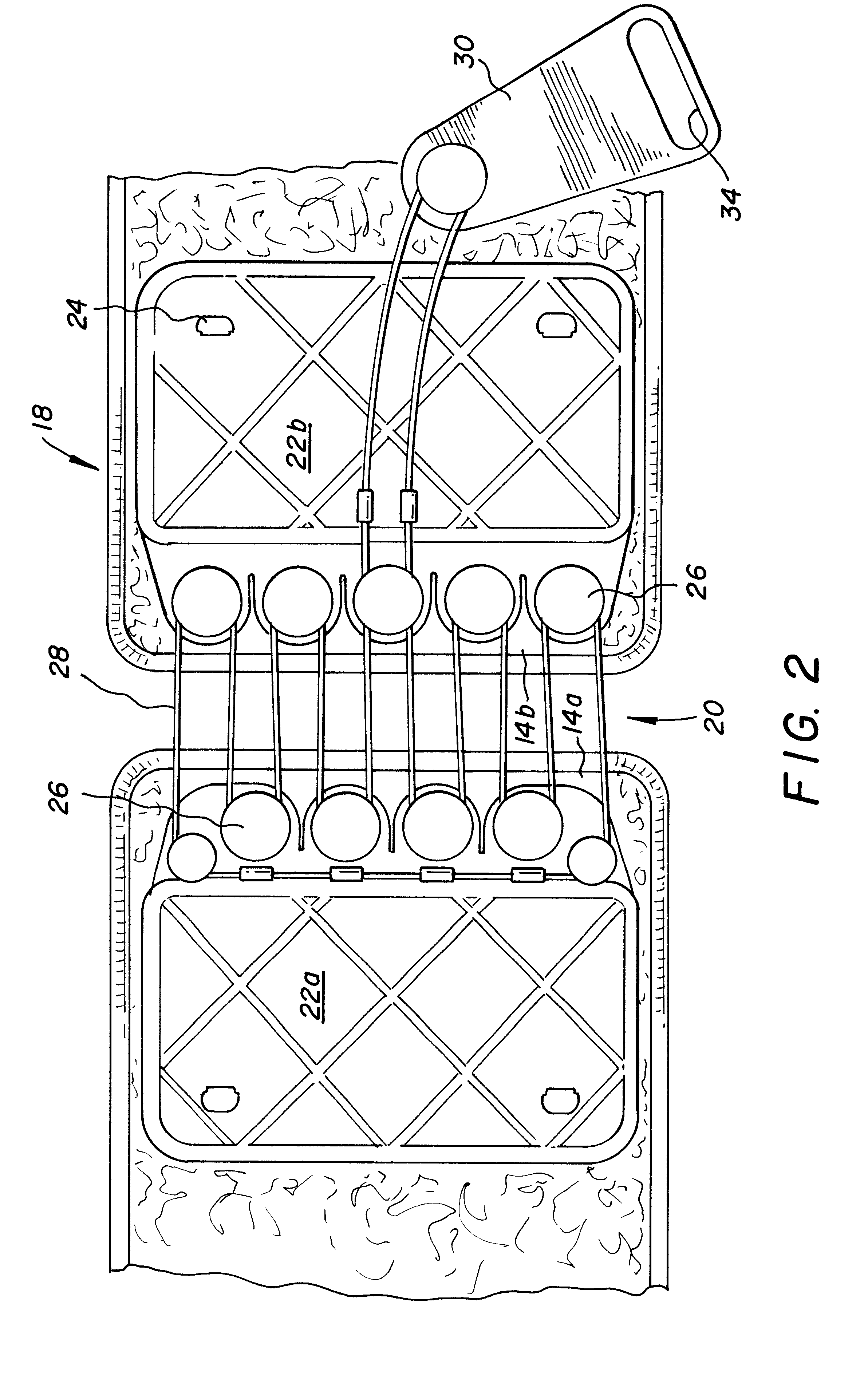
Orthotic trauma device
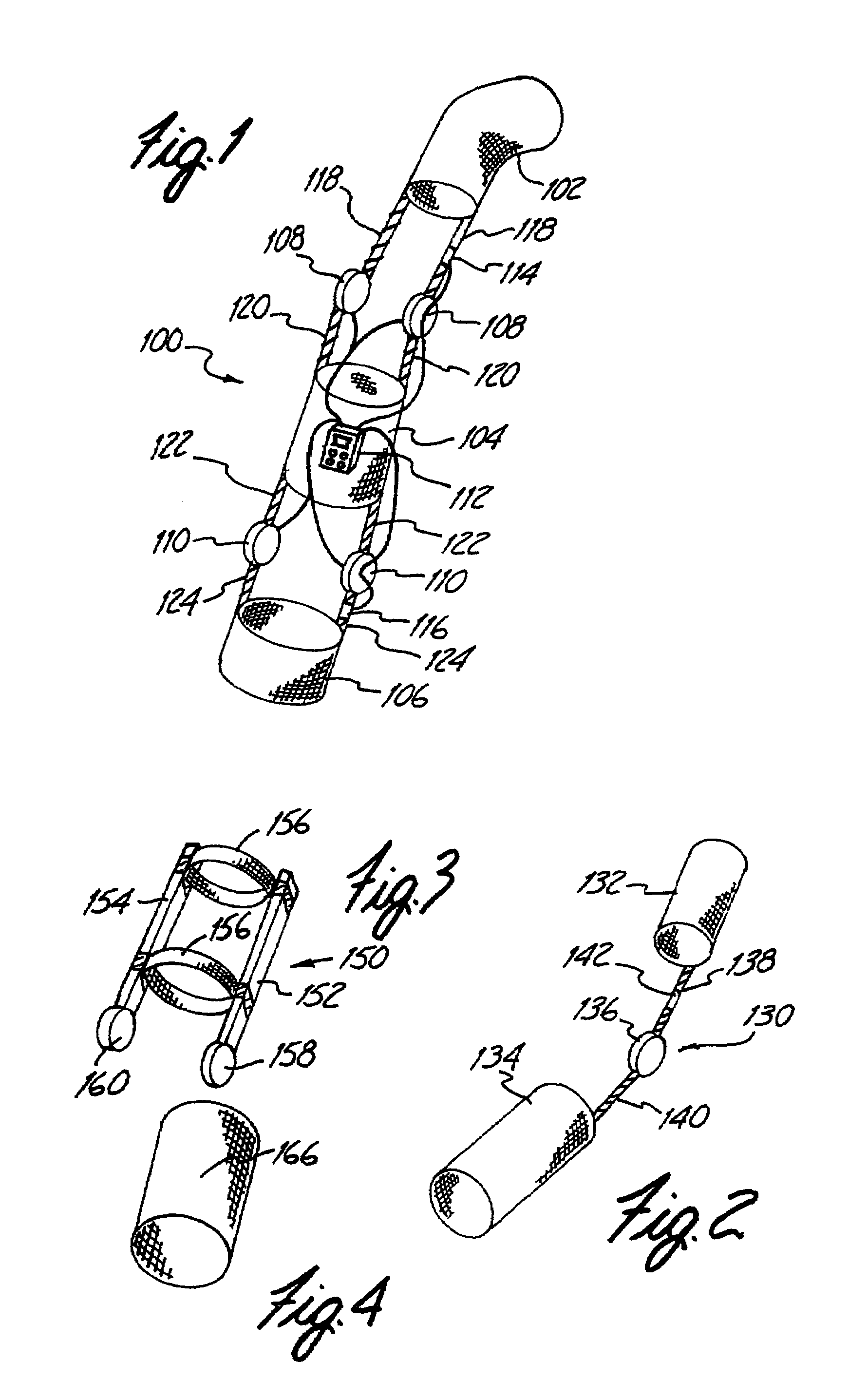
InactiveUS6602214B2Stabilizes broken boneReduce relative motionNon-surgical orthopedic devicesKnee orthosisEngineering
An orthotic trauma device is provided including an elongated orthosis body adapted to be wrapped around a portion of a body, the orthosis body being formed of a pliant material be easily cut with cloth-cutting scissors; a detachable fastening device provided at distal ends of the elongated orthosis body to releasably secure the distal ends to one another; and means for adjusting the tightness of the orthosis body operatively associated with the detachable fastening device. A pulley system for use in an orthotic device includes a pair of pulley banks arranged in a first and second of the pair of pulley banks detachably connected to a first distal end and a second distal end of the orthosis body respectively, a first bank of which is adapted to be detachably disposed on a first distal end of an elongated orthosis body and a second bank of pulleys adapted to be detachably disposed on a second distal end of the elongated orthosis body; and a cable interconnecting the two pulley banks and running through a pulley on each of the pulley banks in alteration, such that shortening of the cable pulls the pulley banks together and tightens the orthotic device with the aid of a mechanical advantage.
Owner:PYNG MEDICAL CORP
Orthotic trauma device
InactiveUS20020148461A1Stabilizes broken boneBlood lossNon-surgical orthopedic devicesKnee orthosisBlock and tackle
An orthotic trauma device is provided including an elongated orthosis body adapted to be wrapped around a portion of a body of a wearer of the device, the orthosis body being formed of a pliant material which is adapted to be easily cut with cloth-cutting scissors; a detachable fastening device provided at distal ends of the elongated orthosis body to releasably secure the distal ends to one another; and means for adjusting the tightness of the orthosis body operatively associated with the detachable fastening device. A pulley system for use in an orthotic device is also provided including a pair of pulley banks arranged in juxtaposed relationship, a first bank of which is adapted to be detachably disposed on a first distal end of an elongated orthosis body and a second bank of pulleys adapted to be detachably disposed on a second distal end of the elongated orthosis body; and a cable interconnecting the two pulley banks and running through a pulley on each of the pulley banks in alteration, such that shortening of the cable pulling the pulley banks together and tightening the orthotic device with the aid of a mechanical advantage dependent upon the number of pulleys mounted on each of the pulley banks.
Owner:PYNG MEDICAL CORP
Electro-rheological fluid brake and actuator devices and orthotic devices using the same
InactiveUS8142370B2Strong and highly tunable torque capabilityLiquid resistance brakesSpringsElectrical resistance and conductanceActuator
Electro-rheological fluid brake or actuator devices provide controllable resistance with or without inclusion of active torque output in either direction of rotation under manual or computer control. The brake and actuator devices are suitable for use in an orthotic device for a joint, such as the knee or elbow.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Dental orthotic and methods of using the same
Apparatuses, systems, and methods for treating oral functions are shown and described. An orthotic dental system for treating oral functions includes an upper dentition orthotic, a lower dentition orthotic, and an articulator system. The articulator system extends between the upper and lower dentition orthotics and can have at least one rigid connector pivotally coupled to the upper dentition orthotic and the lower dentition orthotic. A spacer can be positioned and configured to spatially separate the upper dentition orthotic and the lower dentition orthotic a desired minimum distance. The orthotic dental system can improve various types of oral functions.
Owner:ROBSON FARRAND C
Force sensor system for use in monitoring weight bearing
InactiveUS20060282017A1Quality improvementNormalize gait patternElectrotherapySolesEngineeringBiological activation
A force sensor system for use in monitoring weight bearing on a location. The force sensor system comprises at least one a foot force sensor, a palm force sensor, and a knee force sensor. The foot force sensor comprises a flexible insole containing a plurality of inflatable pockets that are inflated with air or liquid. The palm force sensor and knee force sensor each comprise a wrap to be worn around the palm and knee, respectively. Each wrap comprises a pocket. Each pocket is connected to a tube that, in turn, connects with a pressure sensor and a connector coupling that is remote from the pocket. Each coupling contains a valve. The valve opens to allow inflation and deflation of each inflatable pocket. The pressure sensors measure the air or liquid pressure within each of the inflatable pockets, and convert the corresponding pressure signal into a suitable output signal medium, usually electrical signals. The output signal from the sensors provides accurate real time input data to a weight bearing biofeedback system or to control a stimulator for activation of an electronic orthosis to normalize dynamic gait patterns.
Owner:ANDANTE MEDICAL DEVICES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com