Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
14479 results about "Surface finishing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Surface finishing is a broad range of industrial processes that alter the surface of a manufactured item to achieve a certain property. Finishing processes may be employed to: improve appearance, adhesion or wettability, solderability, corrosion resistance, tarnish resistance, chemical resistance, wear resistance, hardness, modify electrical conductivity, remove burrs and other surface flaws, and control the surface friction. In limited cases some of these techniques can be used to restore original dimensions to salvage or repair an item. An unfinished surface is often called mill finish.
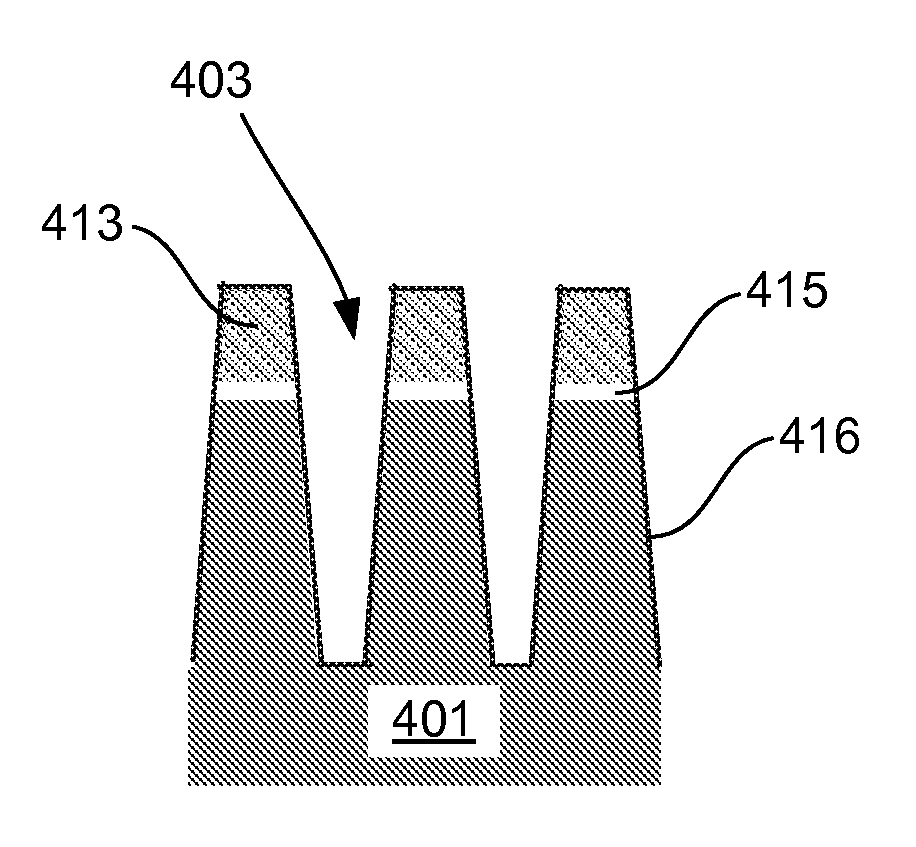
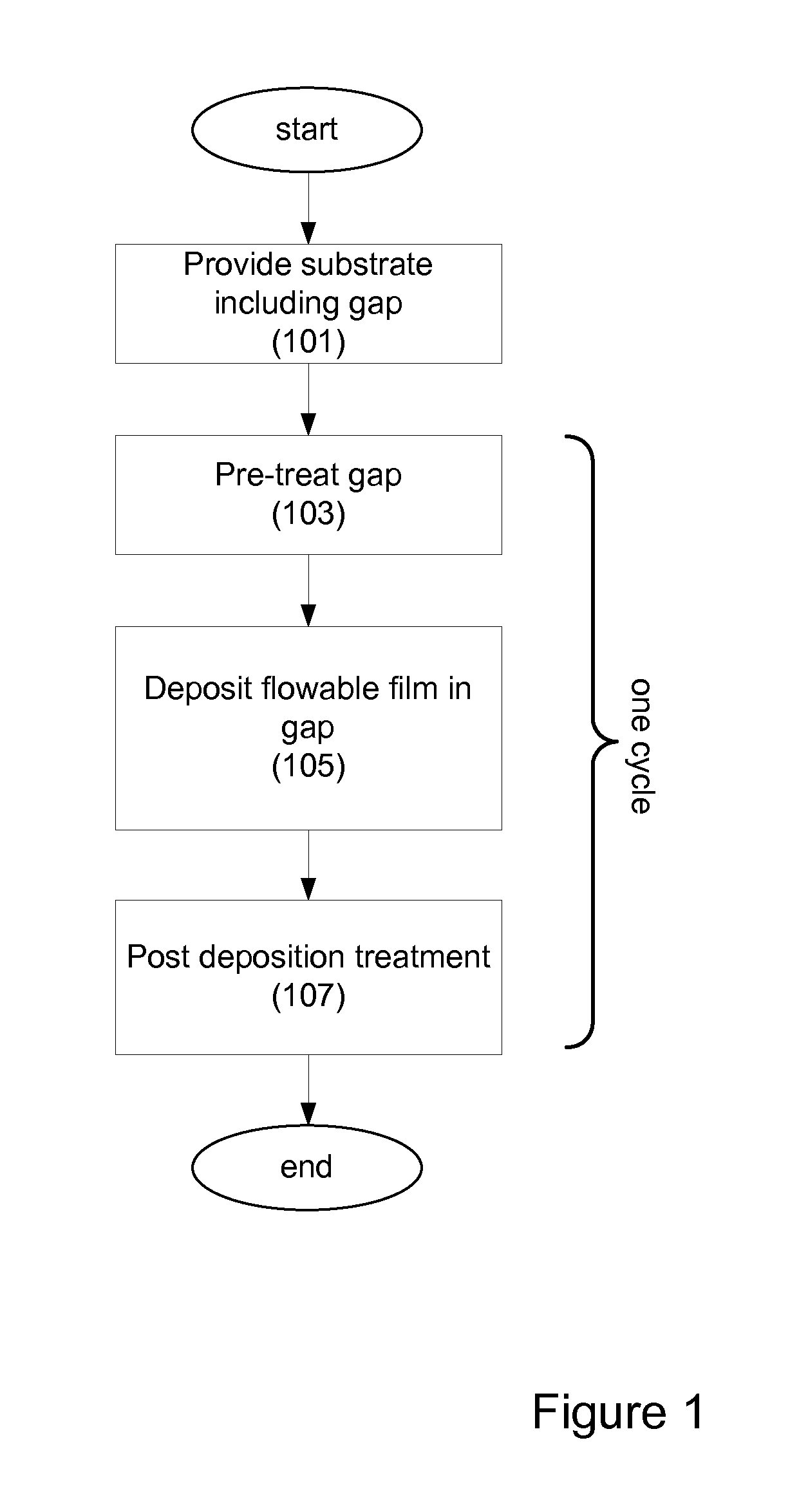
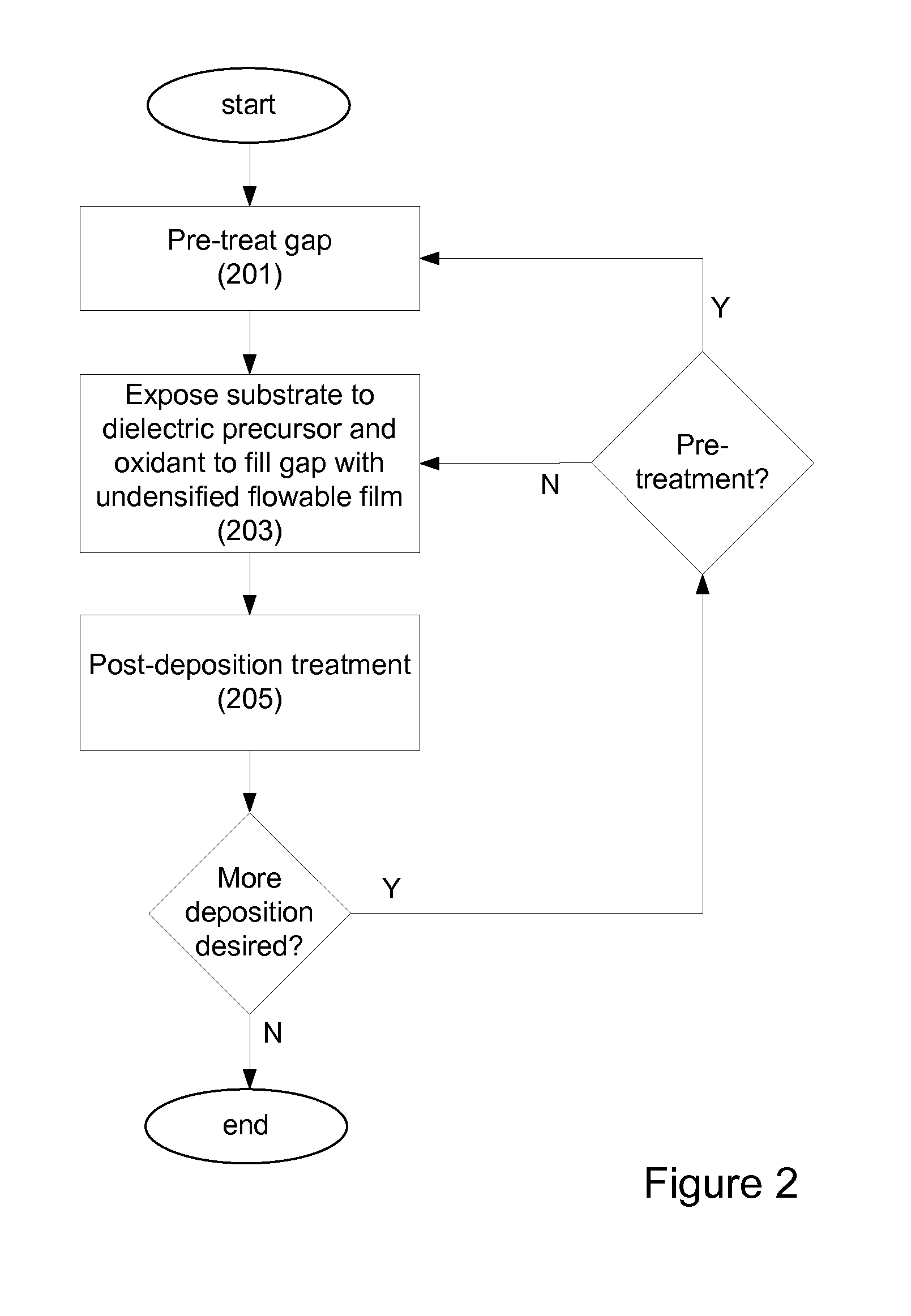
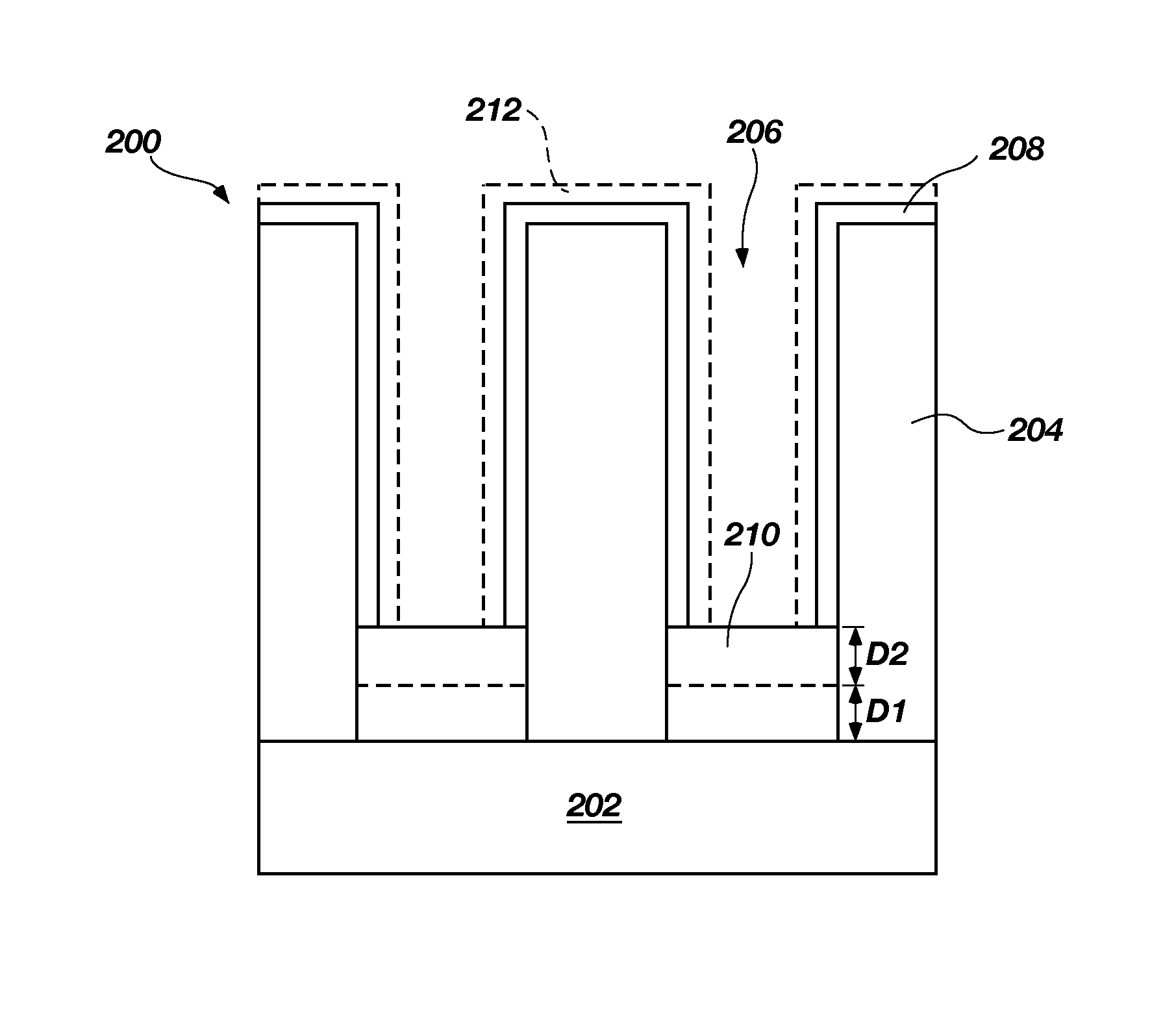
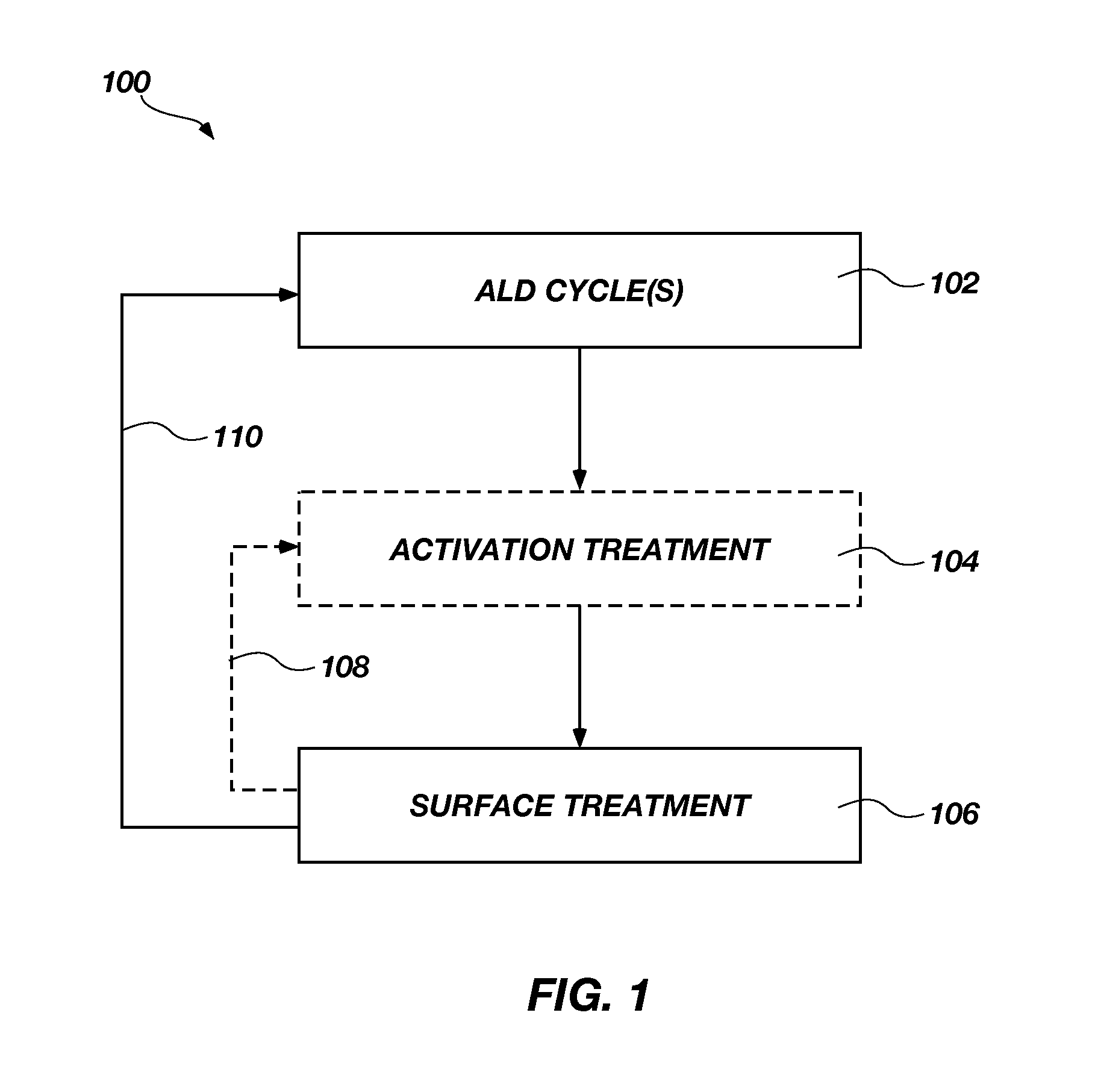
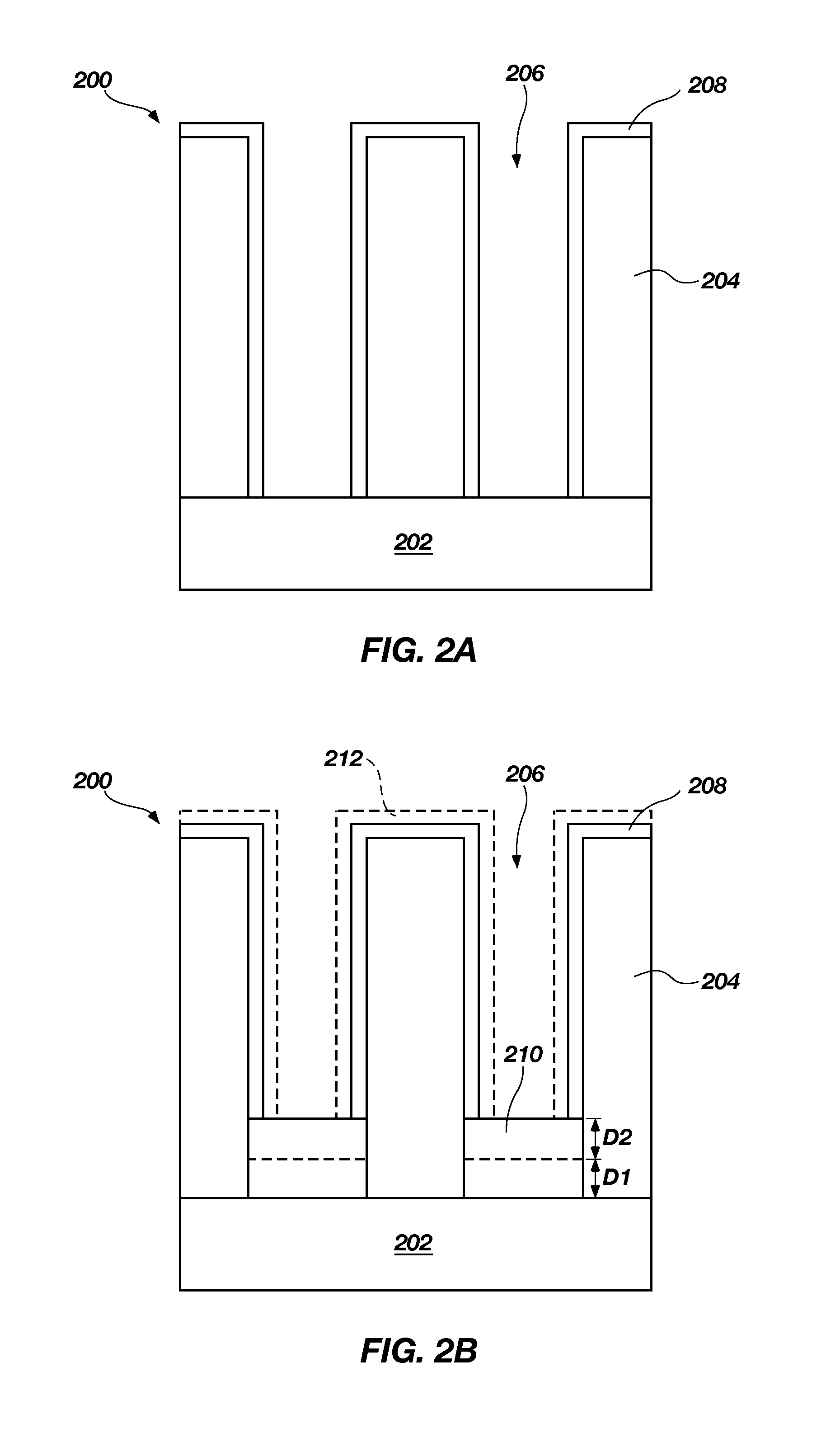
Bottom up fill in high aspect ratio trenches
InactiveUS20120149213A1Improve gap fillingReduce nucleation delayLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenNitrogen
Provided are novel methods of filling gaps with a flowable dielectric material. According to various embodiments, the methods involve performing a surface treatment on the gap to enhance subsequent bottom up fill of the gap. In certain embodiments, the treatment involves exposing the surface to activated species, such as activated species of one or more of nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen. In certain embodiments, the treatment involves exposing the surface to a plasma generated from a mixture of nitrogen and oxygen. The treatment may enable uniform nucleation of the flowable dielectric film, reduce nucleation delay, increase deposition rate and enhance feature-to-feature fill height uniformity.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Methods of selectively forming a material using parylene coating
ActiveUS8945305B2Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor structureSelective deposition
Methods for depositing a material, such as a metal or a transition metal oxide, using an ALD (atomic layer deposition) process and resulting structures are disclosed. Such methods include treating a surface of a semiconductor structure periodically throughout the ALD process to regenerate a blocking material or to coat a blocking material that enables selective deposition of the material on a surface of a substrate. The surface treatment may reactivate a surface of the substrate toward the blocking material, may restore the blocking material after degradation occurs during the ALD process, and / or may coat the blocking material to prevent further degradation during the ALD process. For example, the surface treatment may be applied after performing one or more ALD cycles. Accordingly, the presently disclosed methods enable in situ restoration of blocking materials in ALD process that are generally incompatible with the blocking material and also enables selective deposition in recessed structures.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Phase change material thermal capacitor clothing
InactiveUS6855410B2Good thermal controlFast regenerationExothermal chemical reaction heat productionNatural cellulose pulp/paperSOCKSThermal insulation
An apparatus and method for metabolic cooling and insulation of a user in a cold environment. In its preferred embodiment the apparatus is a highly flexible composite material having a flexible matrix containing a phase change thermal storage material. The apparatus can be made to heat or cool the body or to act as a thermal buffer to protect the wearer from changing environmental conditions. The apparatus may also include an external thermal insulation layer and / or an internal thermal control layer to regulate the rate of heat exchange between the composite and the skin of the wearer. Other embodiments of the apparatus also provide 1) a path for evaporation or direct absorption of perspiration from the skin of the wearer for improved comfort and thermal control, 2) heat conductive pathways within the material for thermal equalization, 3) surface treatments for improved absorption or rejection of heat by the material, and 4) means for quickly regenerating the thermal storage capacity for reuse of the material. Applications of the composite materials are also described which take advantage of the composite's thermal characteristics. The examples described include a diver's wet suit, ski boot liners, thermal socks, gloves and a face mask for cold weather activities, and a metabolic heating or cooling blanket useful for treating hypothermia or fever patients in a medical setting and therapeutic heating or cooling orthopedic joint supports.
Owner:BUCKLEY THERESA M
Passivating solution and surface treatment method for galvanized material
InactiveCN101608306AImprove corrosion resistanceMeet the requirements of the RoHS directiveMetallic material coating processesChromium freeAlcohol
The invention relates to a passivating solution which is aqueous solution containing water-soluble molybdic compound, boric acid, water-soluble organic matter and silica sol, wherein the water-soluble organic matter is a mixture of alcohol and organic carboxylic acid. The invention also provides a surface treatment method for a galvanized material, which comprises the following step: enabling the passivating solution to be in contact with a galvanized material. A galvanized layer can be passivated by the contact between the passivating solution and the galvanized material so as to enable the galvanized material to have excellent corrosion resistance. In addition, the paint composition is chromium free and meets the requirements of a RoHS instruction.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP VANADIUM TITANIUM & RESOURCES +3
Surface coating for chamber components used in plasma systems
ActiveUS20170032942A1Low plasma surface recombination rateHigh trafficElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingBlood plasmaPlasma chamber
Disclosed herein are surface coatings for plasma components that have the benefit of being robust against chemical and plasma physical attack in aggressive (e.g., fluorine-based) plasma environments. The coatings also provide low plasma surface recombination rates for active oxygen, nitrogen, fluorine, and hydrogen species when compared with other known surface treatments. The coatings can be applied to any plasma system component not requiring etching or plasma cleaning including but not limited to materials like quartz, aluminum, or anodized aluminum. Additionally, the efficiency of the system is increased by applying a non-reactive coating to system components thereby increasing the flow of excited plasma species to the plasma chamber of the system.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Precision surface treatments using dense fluids and a plasma
InactiveUS20040003828A1Reduce the temperatureEasy to separateElectric discharge tubesElectrostatic cleaningSolventSolid phases
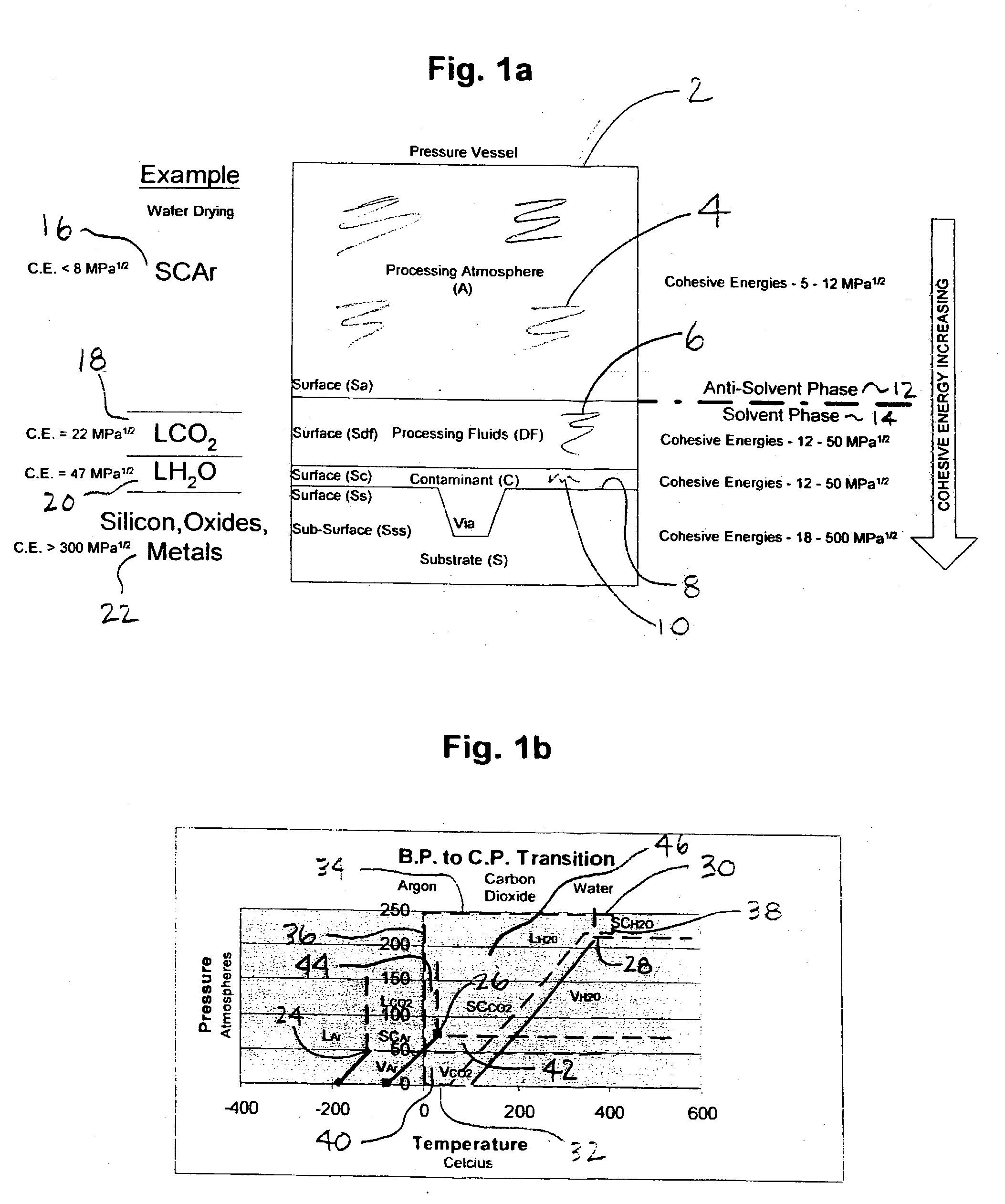
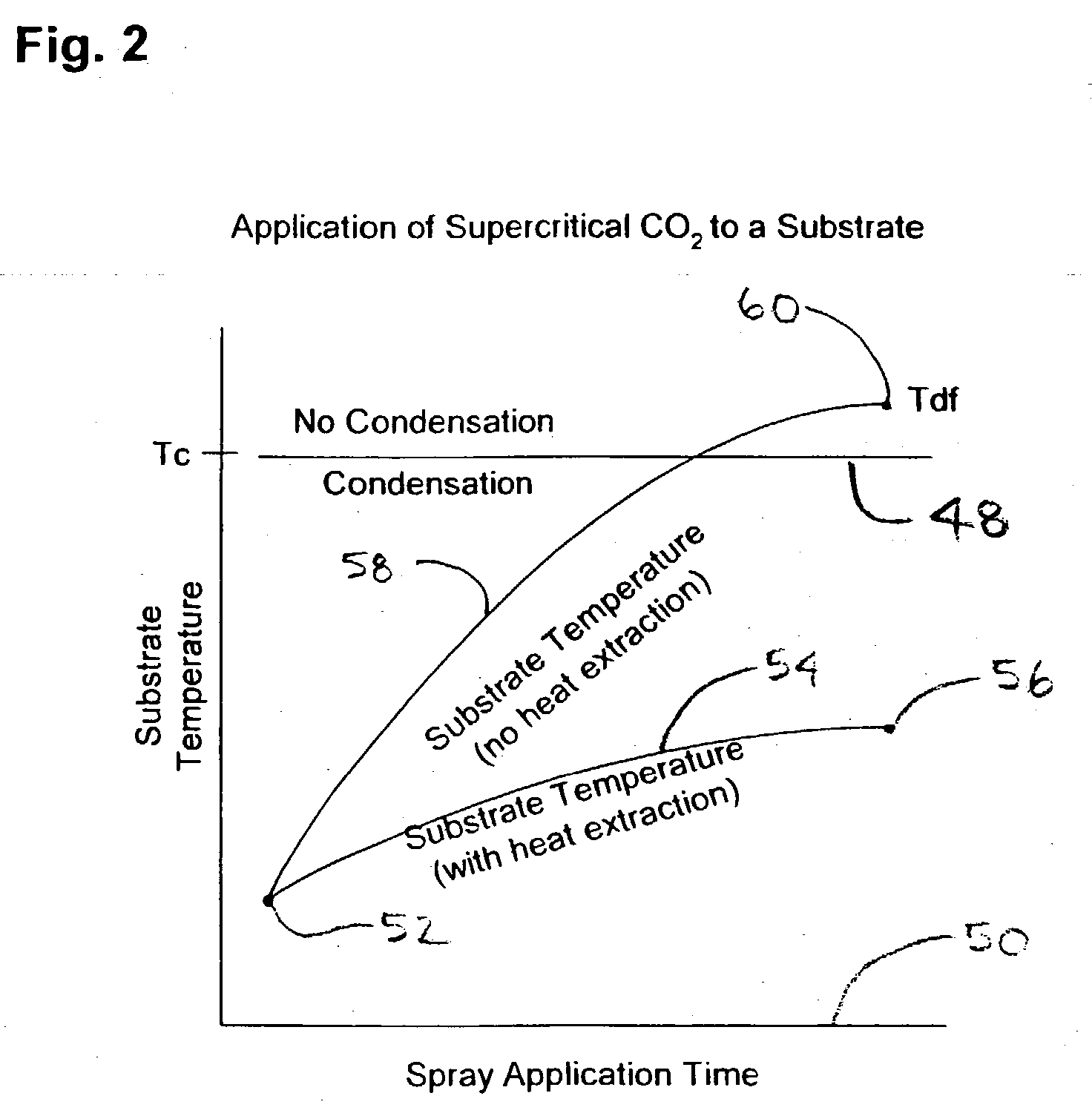
The present invention is a method, process and apparatus for selective cleaning, drying, and modifying substrate surfaces and depositing thin films thereon using a dense phase gas solvent and admixtures within a first created supercritical fluid antisolvent. Dense fluids are used in combination with sub-atmospheric, atmospheric and super-atmospheric plasma adjuncts (cold and thermal plasmas) to enhance substrate surface cleaning, modification, precision drying and deposition processes herein. Moreover, conventional wet cleaning agents such as hydrofluoric acid and ammonium fluoride may be used with the present invention to perform substrate pre-treatments prior to precision drying and cleaning treatments described herein. Finally, dense fluid such as solid phase carbon dioxide and argon may be used as a follow-on treatment or in combination with plasmas to further treat a substrate surface.
Owner:JACKSON DAVID P
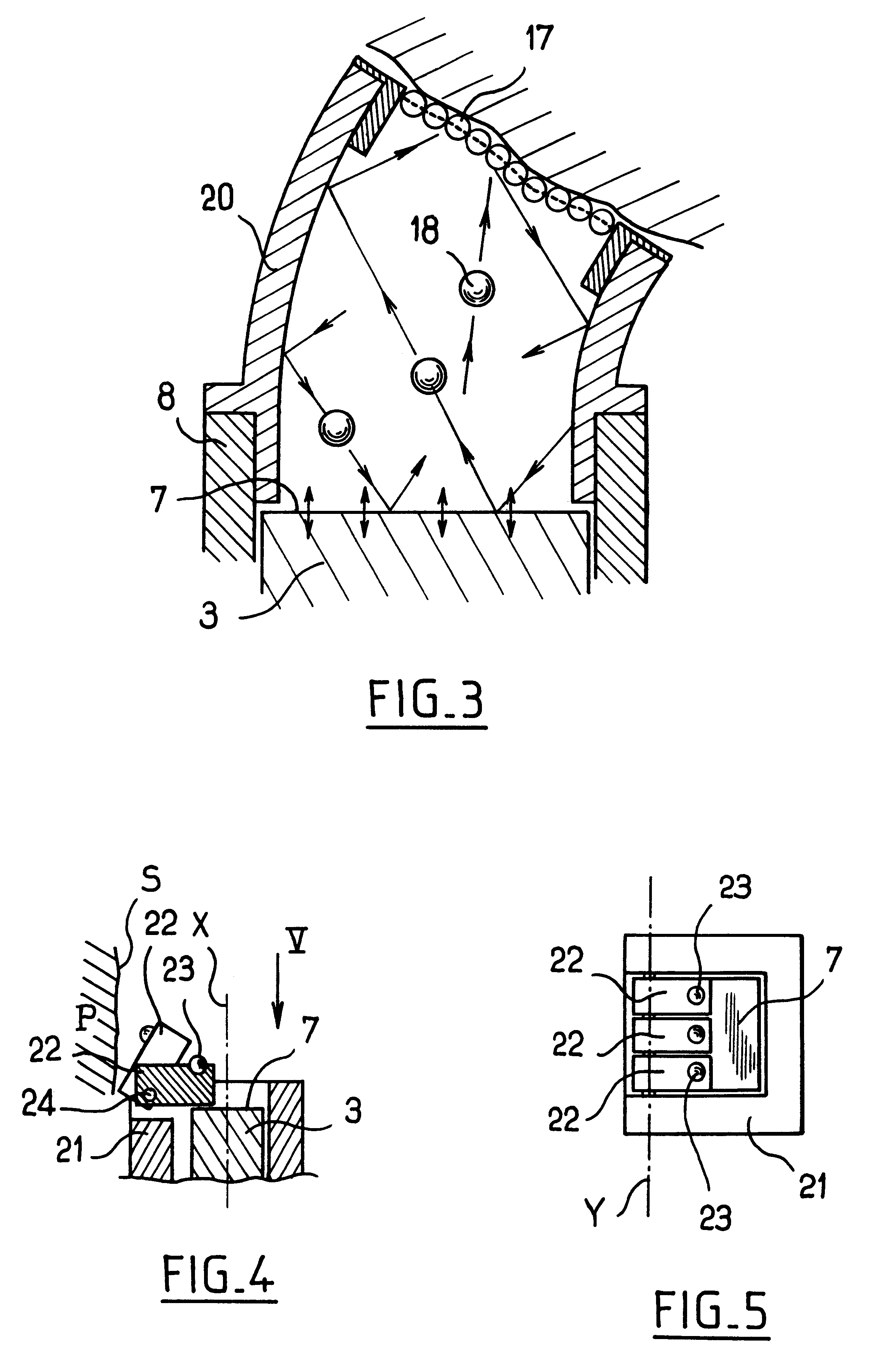
Apparatus for surface treatment by impact
InactiveUS6343495B1Quality improvementSimple treatmentNon-mechanical blast generatorsBurnishing machinesBiomedical engineeringProjectile
The invention relates to apparatus for surface treatment by impact, the apparatus comprising a vibrating surface and at least one projectile suitable for being projected towards the surface to be treated by said vibrating surface. The apparatus includes retaining means for keeping each projectile captive in the apparatus.
Owner:SONATS SOC DES NOUV APPL DES TECHN DE SURFACES
Method and apparatus for depositing tungsten after surface treatment to improve film characteristics
InactiveUS6936538B2Reduce fluorine contentHigh resistivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical speciesNucleation
A method and system to form a refractory metal layer over a substrate includes introduction of a reductant, such as PH3 or B2H6, followed by introduction of a tungsten containing compound, such as WF6, to form a tungsten layer. It is believed that the reductant reduces the fluorine content of the tungsten layer while improving the step coverage and resistivity of the tungsten layer. It is believed that the improved characteristics of the tungsten film are attributable to the chemical affinity between the reductants and the tungsten containing compound. The chemical affinity provides better surface mobility of the adsorbed chemical species and better reduction of WF6 at the nucleation stage of the tungsten layer. The method can further include sequentially introducing a reductant, such as PH3 or B2H6, and a tungsten containing compound to deposit a tungsten layer. The formed tungsten layer can be used as a nucleation layer followed by bulk deposition of a tungsten layer utilizing standard CVD techniques. Alternatively, the formed tungsten layer can be used to fill an aperture.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Surface-treatment method for rapid-manufactured three-dimensional objects
ActiveUS20080169585A1Additive manufacturing apparatusCeramic shaping apparatusComputer visionSolvent
Owner:STRATSYS INC
Formation of discontinuous films during an imprint lithography process
The present invention is directed to a template having a body including a surface with first and second regions. The first region has first wetting characteristics for a given material and the second region has second wetting characteristics for the given material. The first wetting characteristics differ from the second wetting characteristics. Specifically, the first region is formed from a surface treatment layer with a first surface energy to provide the first wetting characteristics. The second region is exposed portions of the body, typically quartz of fused silica, having a second surface energy associated therewith. The second surface energy is greater than the first surface energy to provide the second region with the second wetting characteristics.
Owner:CANON KK +1
Vessels, contact surfaces, and coating and inspection apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20120252709A1Reduce transmission of fluidReduce transmissionInfusion syringesBearing componentsProduct gasSurface barrier
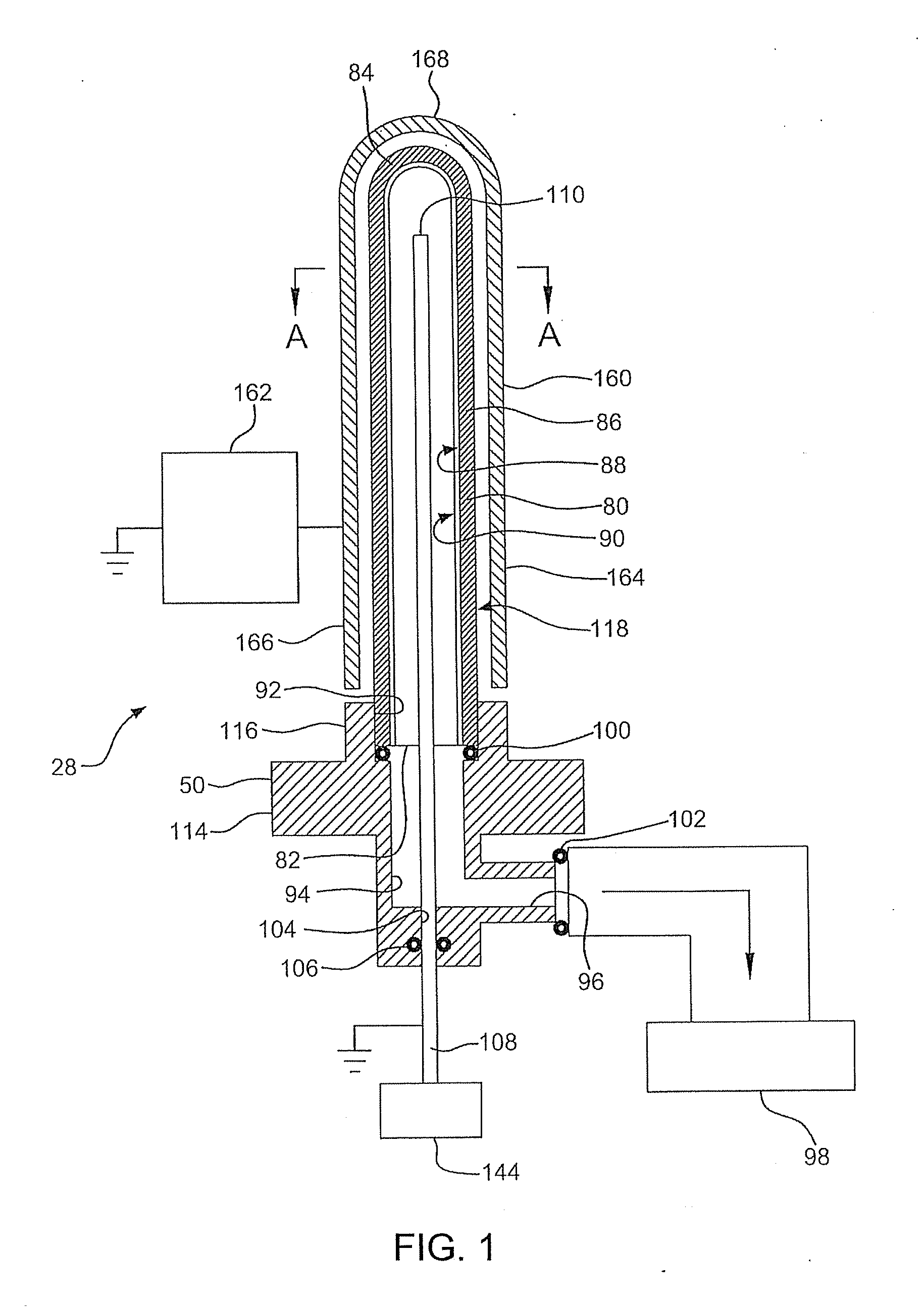
Methods for processing a contact surface, for example to provide a gas barrier or lubricity or to modify the wetting properties on a medical device, are disclosed. First and second PECVD or other contact surface processing stations or devices and a contact surface holder comprising a contact surface port are provided. An opening of the contact surface can be seated on the contact surface port. The interior contact surface of the seated contact surface can be processed via the contact surface port by the first and second processing stations or devices. contact surface barrier, lubricity and hydrophobic coatings and coated contact surfaces, for example syringes and medical sample collection tubes are disclosed. A contact surface processing system and contact surface inspection apparatus and methods are also disclosed.
Owner:SI02 MEDICAL PRODS
Flexible 3D Freeform Techniques
ActiveUS20160151833A1Improve manufacturing speedBuild fine and complexConfectioneryGlass forming apparatusEngineeringInjection molding machine
This invention relates to processes and systems of rapid prototyping and production. Its features includes flexible material deposition along tangential directions of surfaces of a part to be made, thereby eliminating stair-shape surface due to uniform horizontal layer deposition, increasing width of material deposition to increase build up rate, applying the principles of traditional forming / joining processes, such as casting, fusion welding, plastic extrusion and injection molding in the fabrication process so that various industrial materials can be processed, applying comparatively low cost heating sources, such as induction heating and arc-heating. Additional features include varying width and size of material deposition in accordance with geometry to be formed and applying a differential molding means for improved shape formation and surface finishing.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
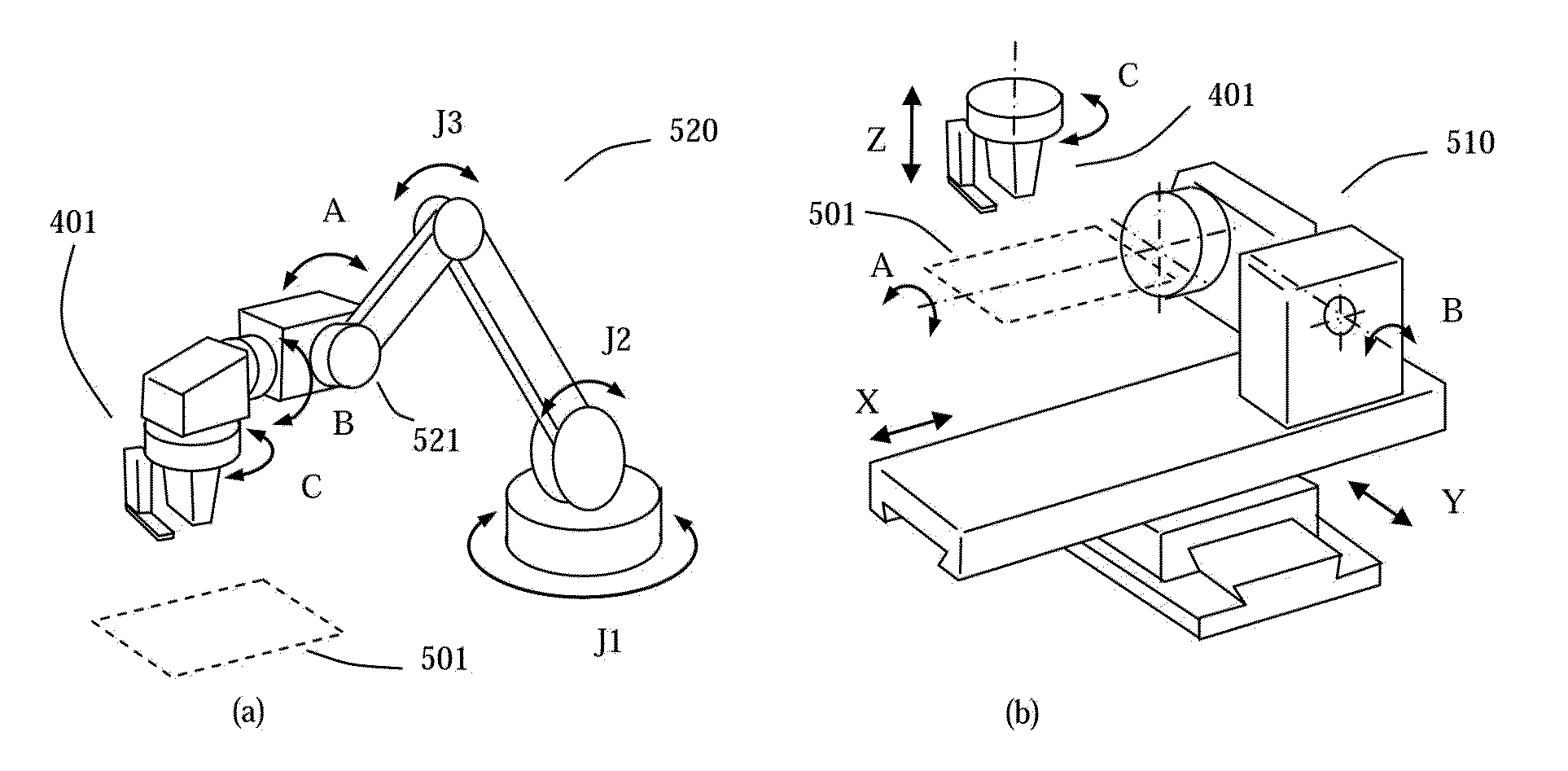
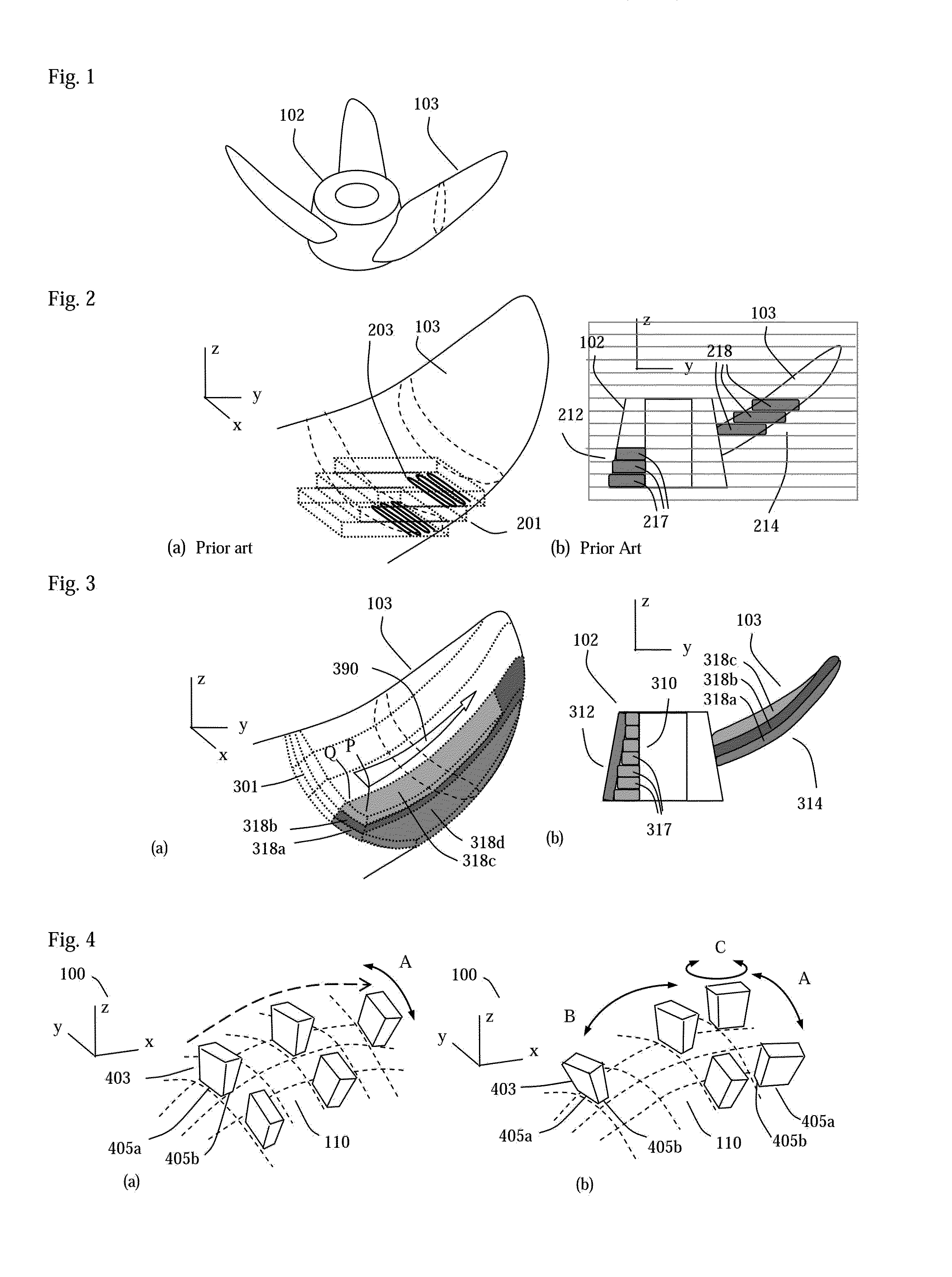
Robotic system for applying surface finishes to large objects
InactiveUS20150375390A1Economically efficientProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpraying apparatusRobotic systemsSurface finishing
A robotic system for performing surface finishing processes on a large object, is provided, the system includes at least one platform having a connected robot, the robot performing a surface finishing process on the large object. Also included is an automatic guided vehicle (AGV) separable of the platform movable independent of the platform for moving under the platform, lifting up the platform and moving the platform multiple locations along or around the large object to extend a useful working envelope of the robot.
Owner:ENCORE AUTOMATION
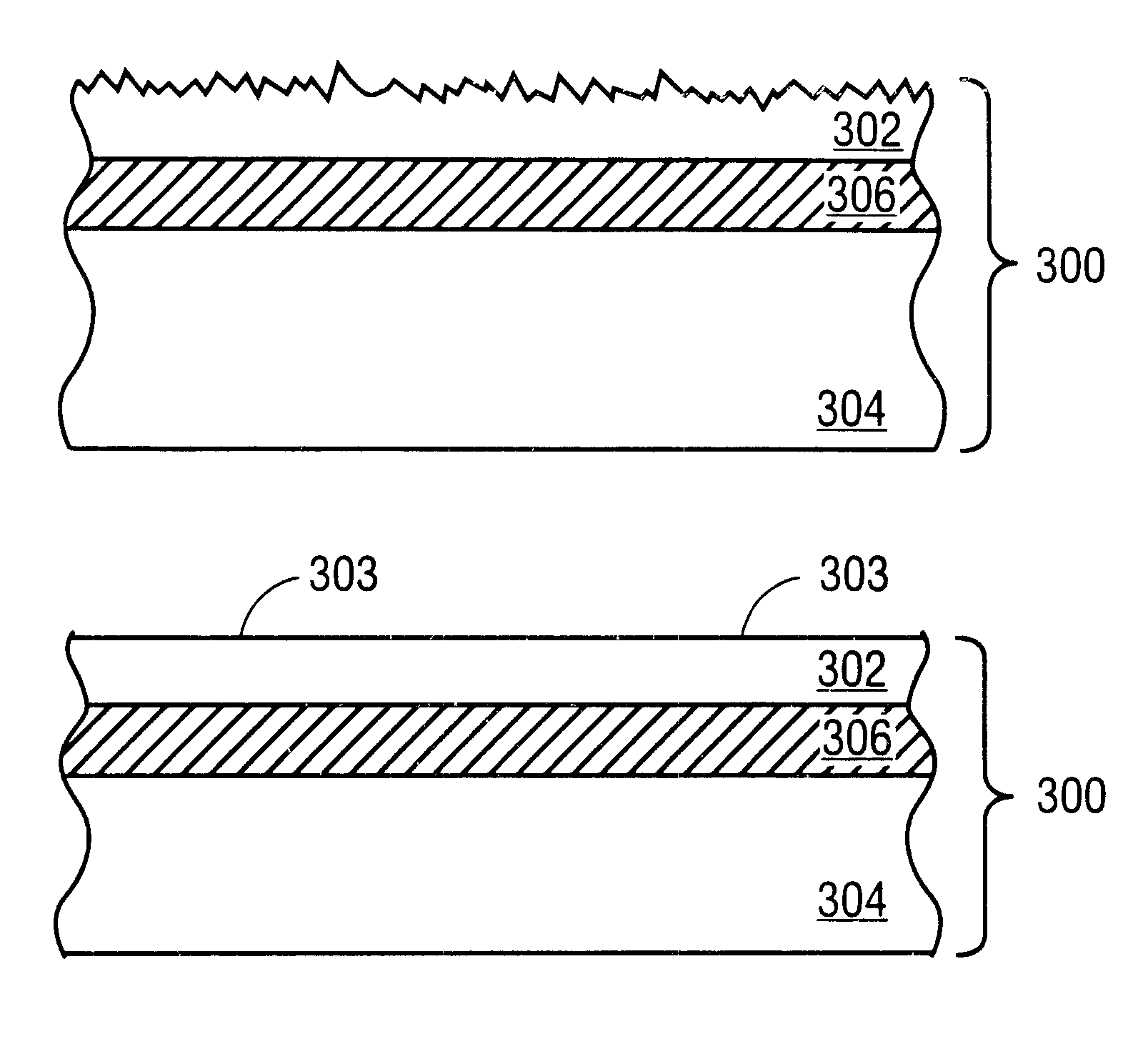
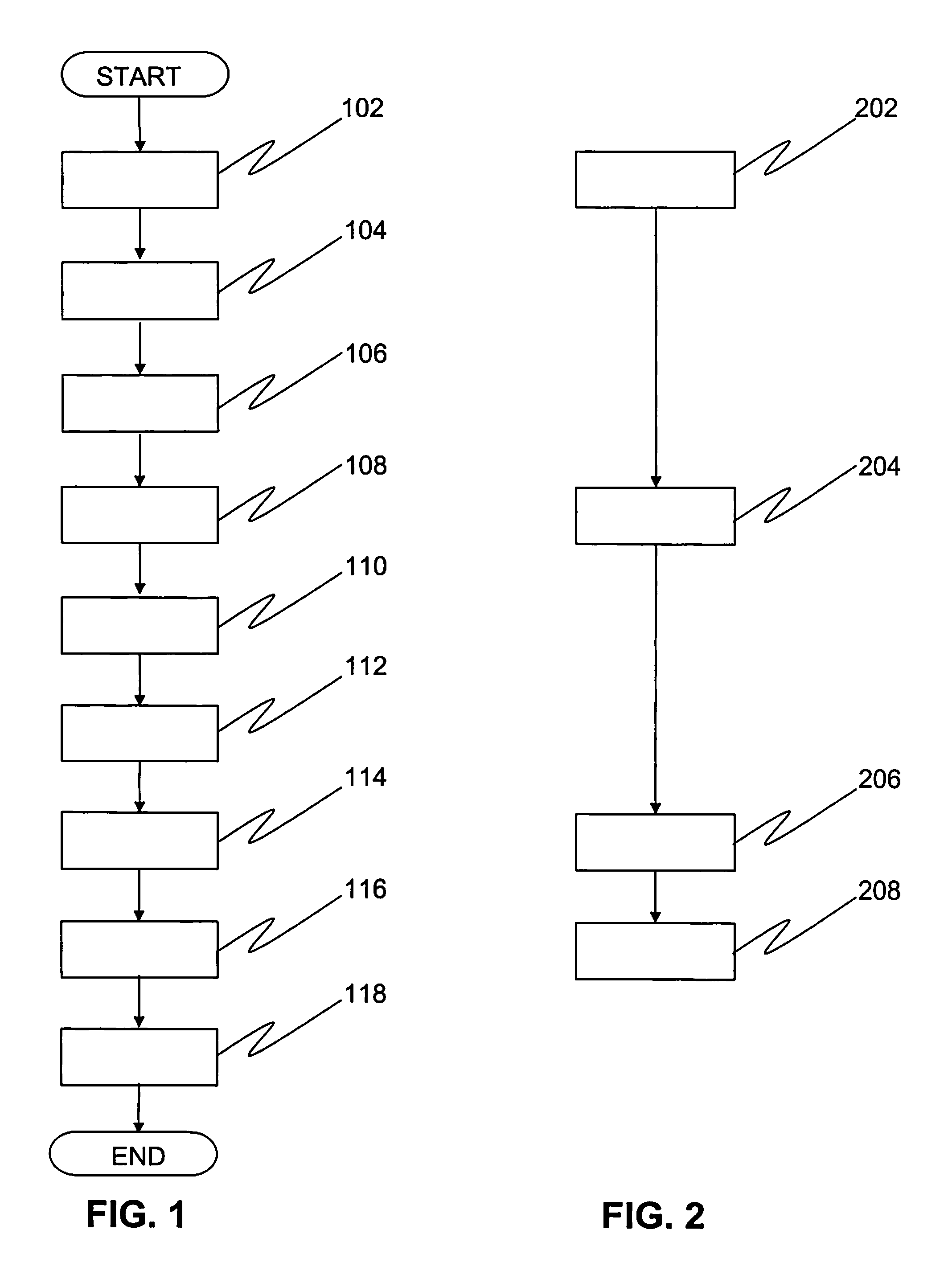
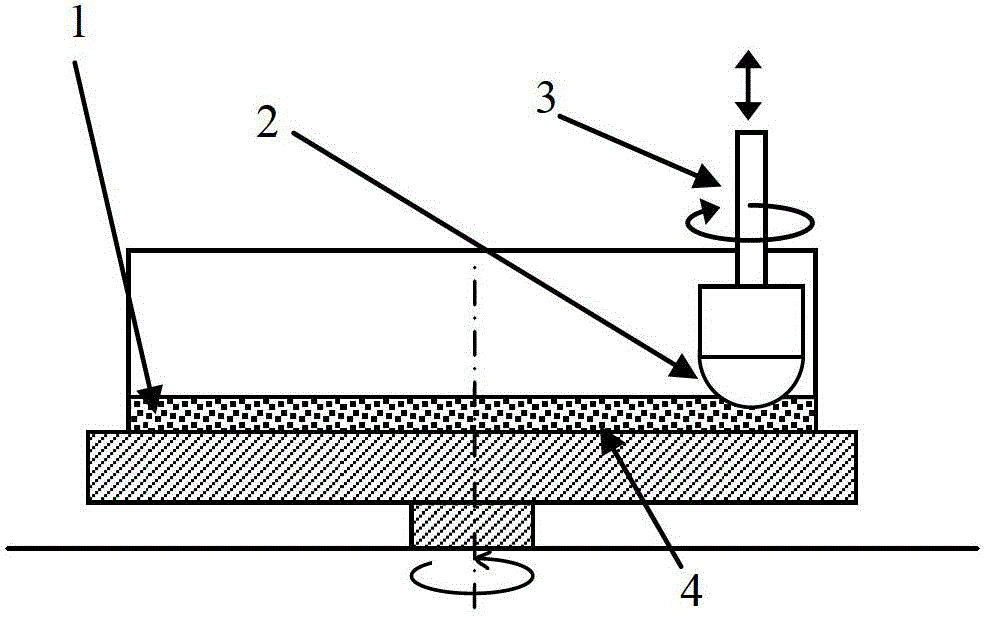
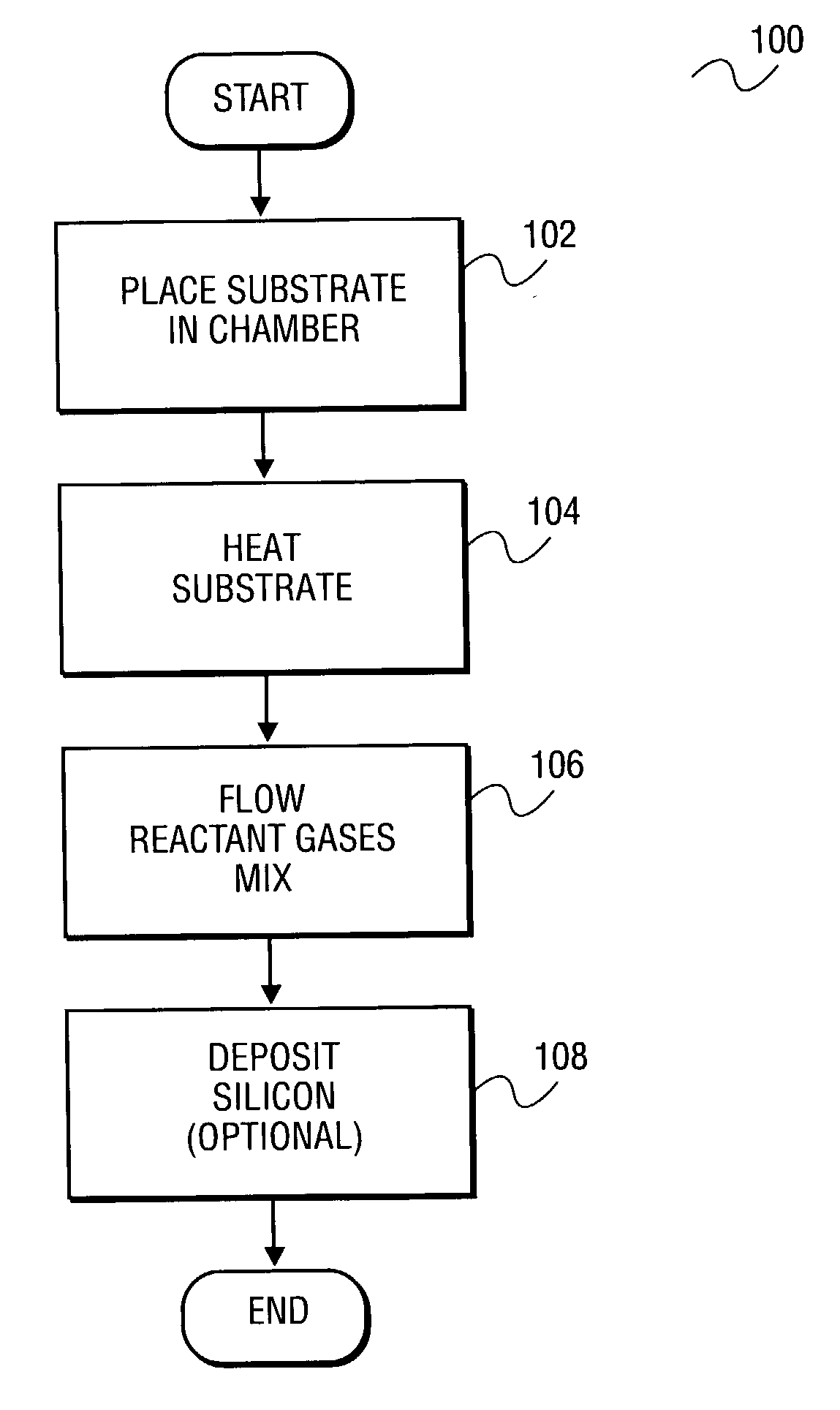
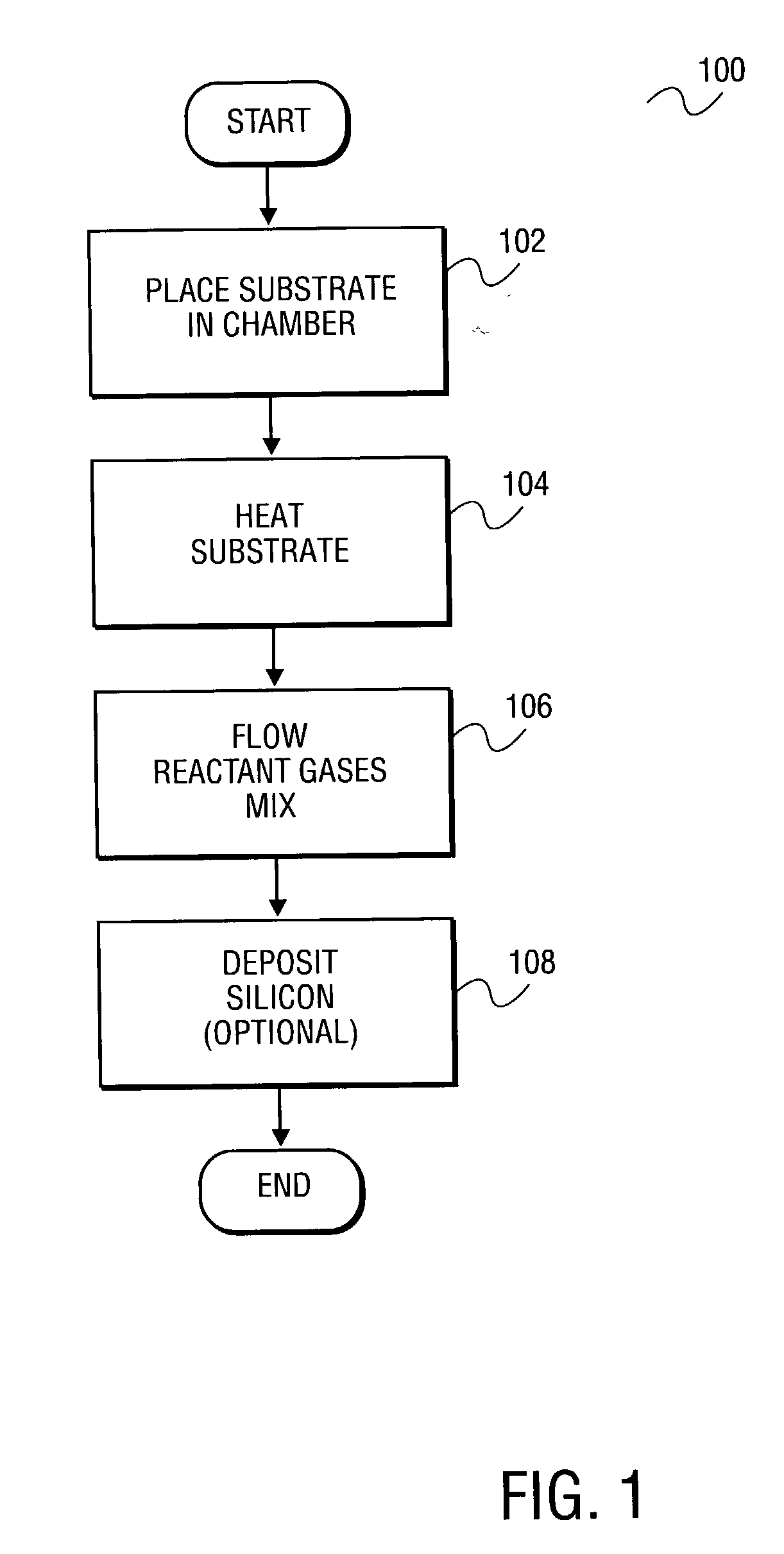
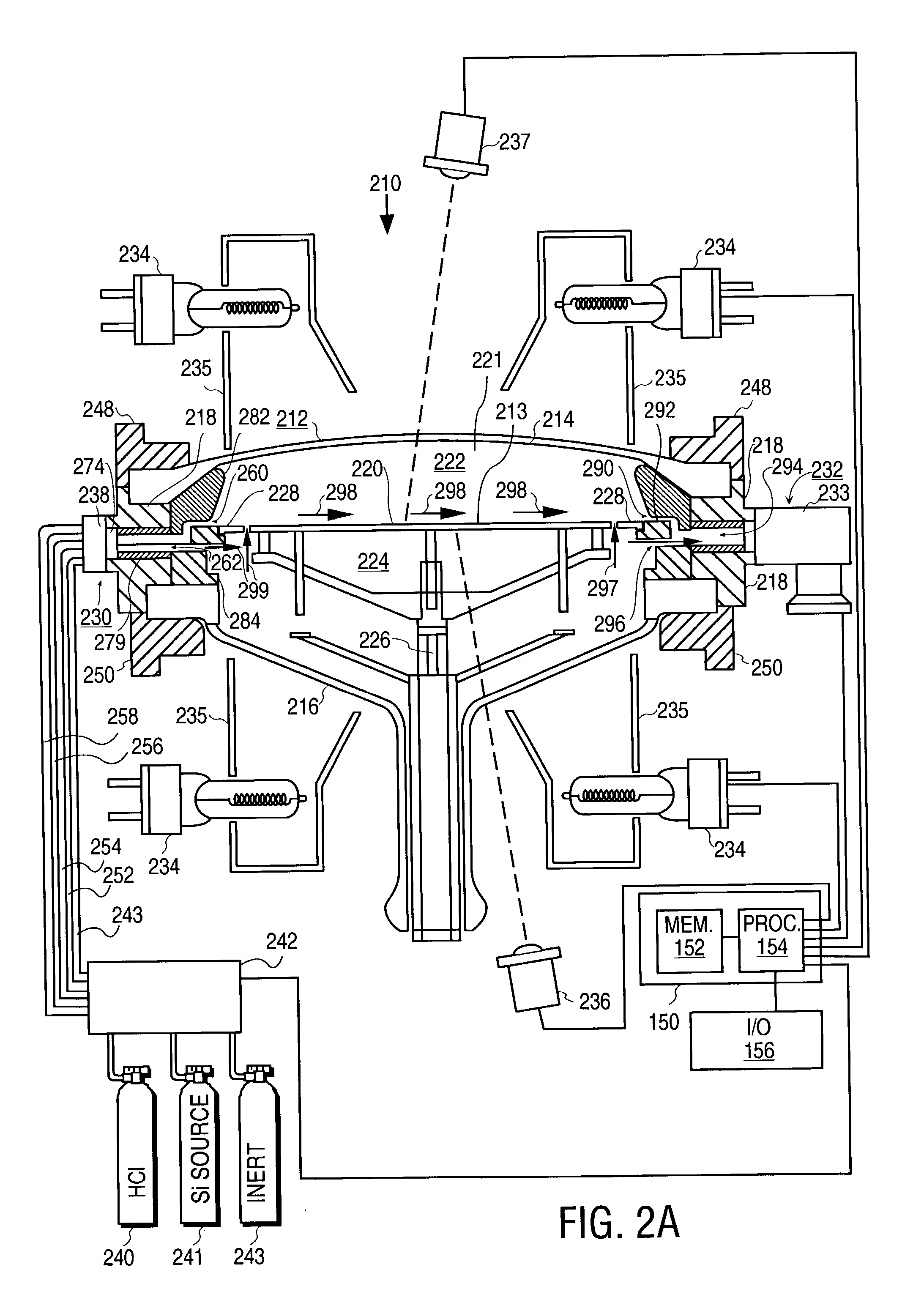
Apparatus and method for surface finishing a silicon film
A method of smoothing a silicon surface formed on a substrate. According to the present invention a substrate having a silicon surface is placed into a chamber and heated to a temperature of between 1000°-1300° C. While the substrate is heated to a temperature between 1000°-1300° C., the silicon surface is exposed to a gas mix comprising H2 and HCl in the chamber to smooth the silicon surface.
Owner:SILICON GENERAL CORPORATION +1
Method for fabricating fine features by jet-printing and surface treatment
A method and system for masking a surface to be etched is described. The method includes the operation of heating a phase-change masking material and using a droplet source to eject droplets of a masking material for deposit on a thin-film or other substrate surface to be etched. The temperature of the thin-film or substrate surface is controlled such that the droplets rapidly freeze after upon contact with the thin-film or substrate surface. The thin-film or substrate is then treated to alter the surface characteristics, typically by depositing a self assembled monolayer on the surface. After deposition, the masking material is removed. A material of interest is then deposited over the substrate such that the material adheres only to regions not originally covered by the mask such that the mask acts as a negative resist. Using such techniques, feature sizes of devices smaller than the smallest droplet printed may be fabricated.
Owner:XEROX CORP
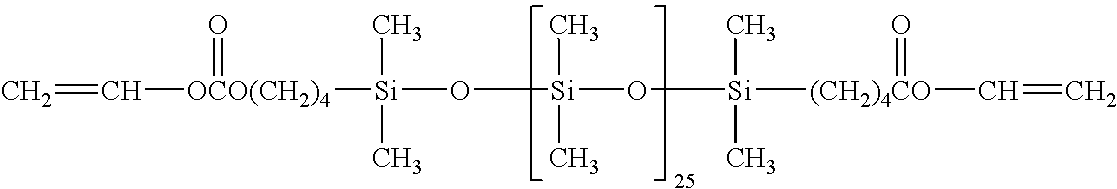
Wettable silicone hydrogel contact lenses and related compositions and methods
ActiveUS8231218B2Comfortable to wearPharmaceutical delivery mechanismOptical articlesInterpenetrating polymer networkChemistry
Silicone hydrogel contact lenses having ophthalmically acceptable surface wettabilities are obtained from pre-extracted polymerized silicone hydrogel contact lens products having relatively large amounts of removable or extractable materials. The silicone hydrogel contact lenses can be obtained from non-polar resin based contact lens molds and without surface treatments or an interpenetrating polymeric network of a polymeric wetting agent. Related lens products, polymerizable compositions, and methods are also described.
Owner:COOPERVISION INT LTD
Plastic profiled bar decorative layer combination material with metal-like natural texture, preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a plastic profiled bar decorative layer combination material with natural texture for co-extrusion molding, formed by mixing 15-80wt% of plastic substrate, 15-80wt% of composite pigment and 0-50wt% of inorganic powder, wherein the composite pigment comprises pigment or dye with natural color texture effect; inorganic pigment and inorganic powder in the composite pigment need to be respectively and actively processed by a surface conditioning agent or a coupling agent; the combination material provides the surface of the plastic profiled bar with a high-polymer material co-extrusion composite layer with stronger adhesion and endows the surface of the plastic profiled bar with the metal-like texture effects, such as the colors of gold, silver, copper or other natural metal materials. The decorative layer has a certain thickness, high hardness, strong scratch resistance and longer product service life and can be used for industries, such as electronic appliance shells, plastic color windows and doors, plastic profiled bars, furniture sheets, and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG SHENGHENGCHANG CHEM IND
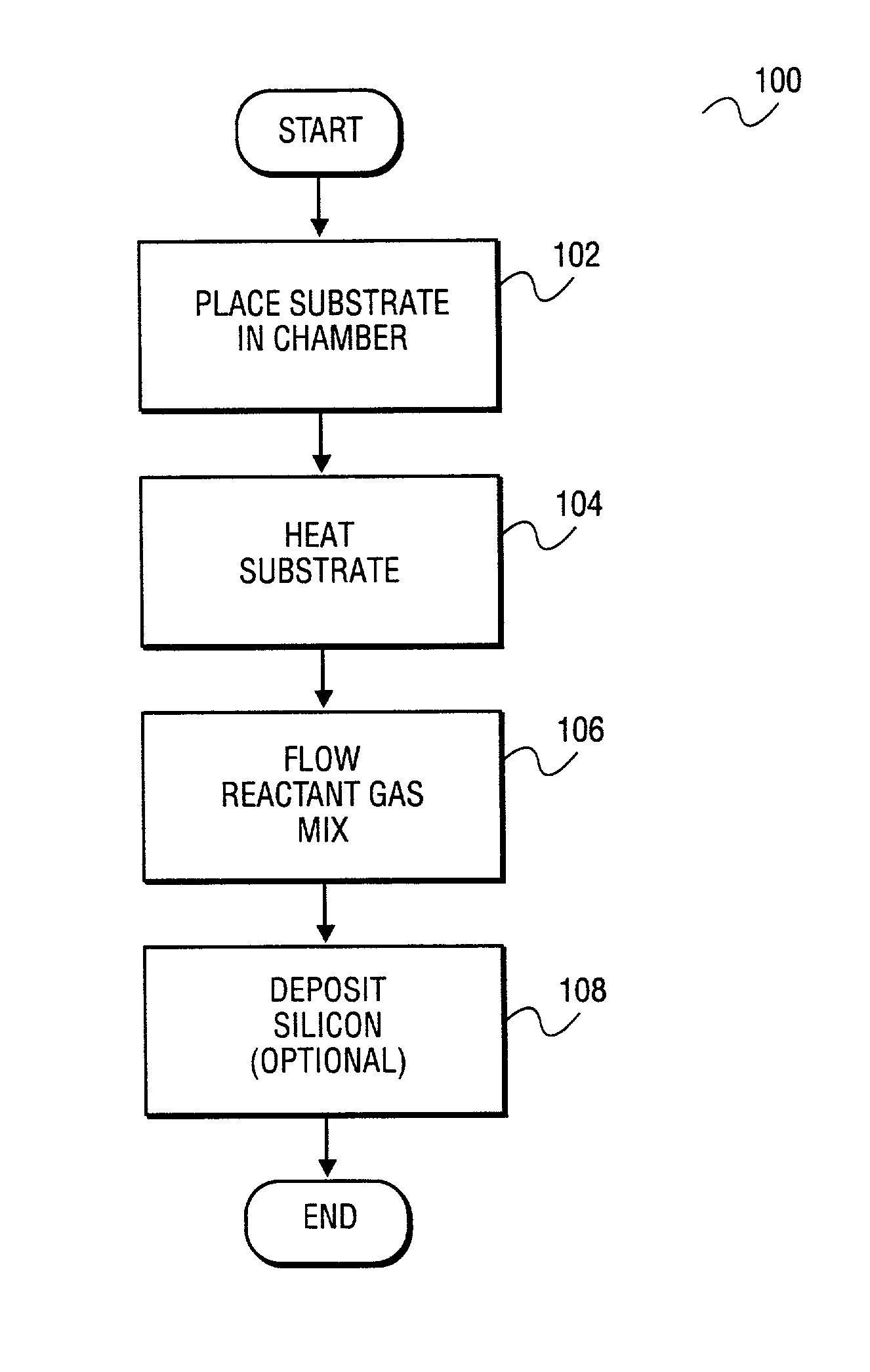
Apparatus and method for surface finishing a silicon film
InactiveUS20020090818A1Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSurface finishSilicon membrane
A method of smoothing a silicon surface formed on a substrate. According to the present invention a substrate having a silicon surface is placed into a chamber and heated to a temperature of between 1000°-1300° C. While the substrate is heated to a temperature between 1000°-1300° C., the silicon surface is exposed to a gas mix comprising H2 and HCl in the chamber to smooth the silicon surface.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC +1
Surface treatment for silicone hydrogel contact lenses comprising hydrophilic polymer chains attached to an intermediate carbon coating
InactiveUS6902812B2Improve hydrophilicityImprove wettabilityOptical articlesPaper/cardboard layered productsCarbon coatingSurface finishing
The present invention provides an optically clear, hydrophilic coating upon the surface of a silicone medical device by sequentially subjecting the surface of the lens to plasma polymerization in a hydrocarbon-containing atmosphere and then covalently attaching a preformed hydrophilic polymer to the surface of the carbon coating. The invention is especially useful for forming a biocompatible coating on a silicone contact lens.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Surface treatment of medical devices
InactiveUS20080142038A1Improve wettabilityElectrostatic cleaningCoatingsHydrophilic monomerCarboxylic acid
A method for improving the wettability of a medical device is provided, the method comprising the steps of (a) providing a medical device formed from a monomer mixture comprising a hydrophilic monomer and a siloxy-containing monomer, (b) subjecting a surface of the medical device to a surface treatment, and (c) contacting the treated surface of the medical device with a wetting agent solution comprising a carboxylic acid-containing polymer or copolymer to form a carboxylic acid-containing polymeric or copolymeric layer on the treated surface of the medical device.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Cleaning implement with interchangeable tool heads
A system for treating a work surface including a handle portion, a first tool head adapted for use with a removable pad and a second tool head, both connectable to the handle portion, and a first fluid reservoir is disclosed. In some arrangements, the second tool head can be used with a removable pad or can include an electric motor. A controller can be provided for releasing and stopping fluid flow from the first fluid reservoir. An optional second fluid reservoir can also be used. The first tool head and the first fluid reservoir can include a first indicium that can be characterized by a feature such as color, shape, picture, text, or sound. The indicium can signify a work surface, a purpose for surface treatment, a mode of operation or instructions. Surface treatments include applying, cleaning, scrubbing, waxing, polishing, disinfecting, killing mites, killing fleas, detoxifying, neutralizing allergens, painting, removing liquids, and fertilizing.
Owner:THE CLOROX CO
Processing technique of cellphone shell with metal luster
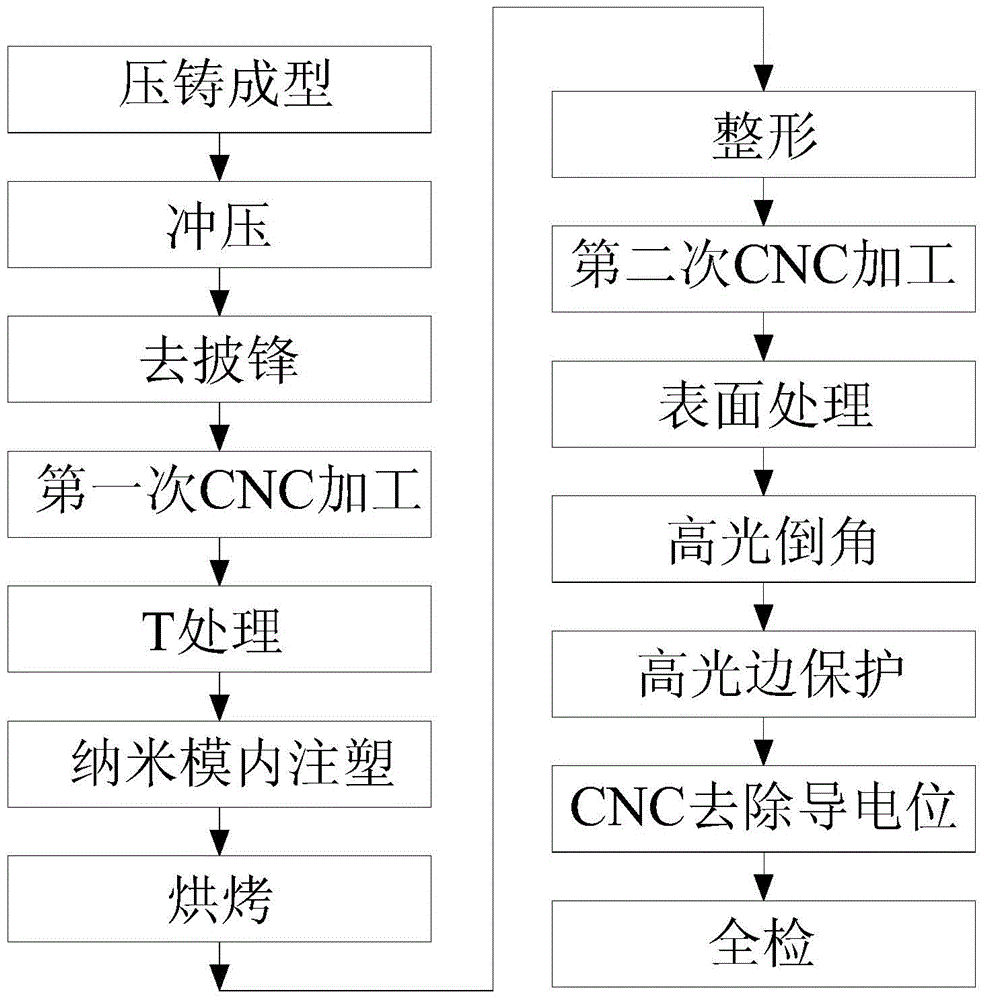
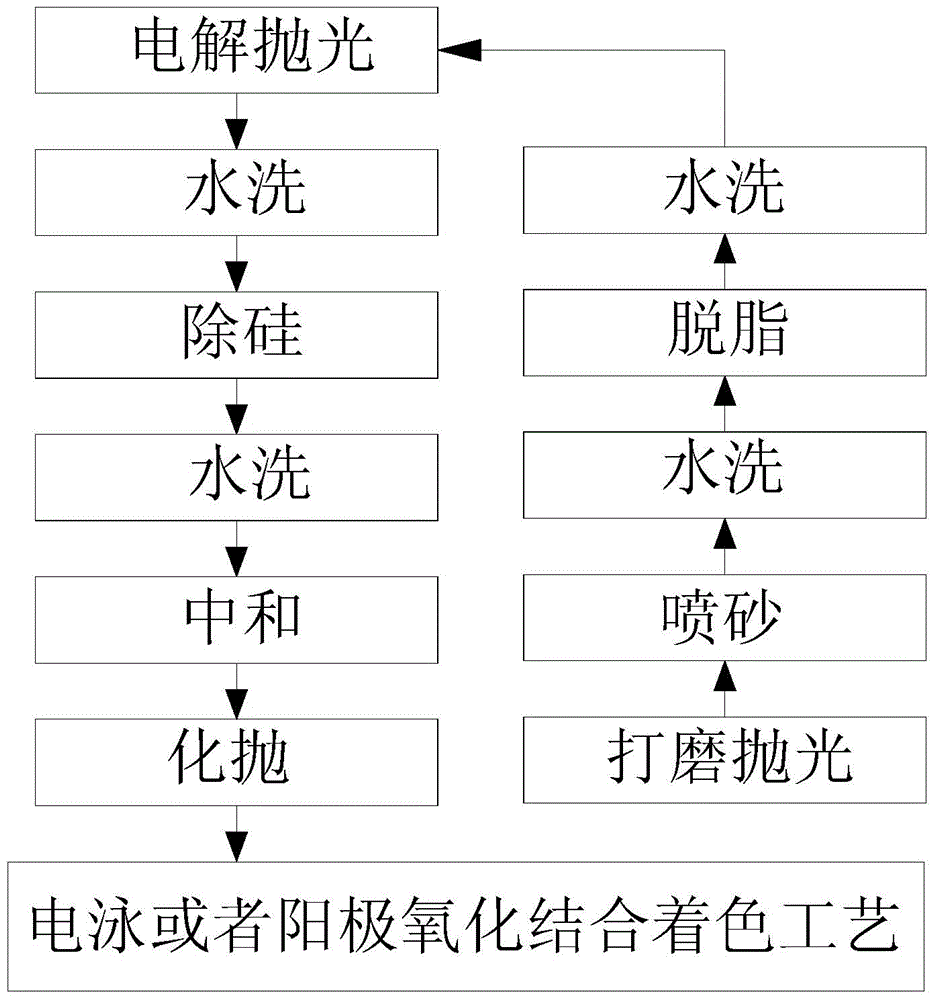
ActiveCN104607884AGuaranteed StrengthReduce processing costsCoatingsNumerical controlAbrasive blasting
The invention provides a processing technique of a cellphone shell with metal luster. The processing technique includes the steps of S1, performing compression molding; S2, performing stamping; S3, performing primary CNC (computer numerical control) machining; S4, performing T treatment; S5, performing injection molding in a nano mold; S6, performing secondary CNC machining; S7, performing surface treatment, to be specific, performing a, polishing, b, shot-blasting, c, degreasing, d, washing, e, electrolytic polishing, f, washing, g, silicon removal aiming to decrease silicon content of the polished surface of the cellphone shell, h, neutralizing, i, chemical polishing, and j, electrophoresis or combination of anodic oxidation and coloring, aiming to impart metal luster to the polished surface of the cellphone shell. The compete cellphone shell is made through the steps S1 to S6, the silicon content of the polished surface of the cellphone shell is processed, the cellphone shell never produces compounds of intervals such as Al-Mg-Si-Fe during following anodic oxidation, defects such as oxide film darkening, bluing or milky-whiting are avoided, and the metal-lustered cellphone shell is manufactured through the complete process.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Expanding fire-proof paint
InactiveCN1380368AGood fire and heat insulationGood adhesionFireproof paintsFoaming agentAcrylic resin
The expansive fire-resisting paint contains the components of acrylic resin, catalyst, carbon-forming agent, foaming agent, fire-resisting agent, reinforcing agent, pigment filling material, adjuvantand smoke inhibiting agent, and is characterized by that it utilizes the modification of acrylic resin, surface treatment of catalyst and addition of smoke inhibiting agent to raise comprehensive property of paint. When the paint film is heated and expanded, it can be formed into fire-resistant carbonized layer with three-D space structure, and can release fire-resisting gas to prevent flame fromspreading. Said paint is suitable for steel structure, and material and electric cable, etc.
Owner:MARINE CHEM RES INST
Methods of cementing pipe in well bores and low density cement compositions therefor
The present invention provides methods of cementing pipe in well bores and low density cement compositions having enhanced compressive, tensile and bond strengths upon setting. The composition of the invention are basically comprised of a hydraulic cement, sufficient water to form a slurry and hollow glass microspheres surface treated with a mixture of organosilane coupling agents present in an amount sufficient to produce a cement composition density in the range of from about 6 to about 12 pounds per gallon.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Polishing pad, method of manufacturing the polishing pad, and cushion layer for polishing pad
InactiveUS20040055223A1Easy to processHigh thickness accuracyOther chemical processesAbrasion apparatusSurface patternEngineering
The polishing pad of this invention is a polishing pad effecting stable planarizing processing, at high polishing rate, materials requiring surface flatness at high level, such as a silicon wafer for semiconductor devices, a magnetic disk, an optical lens etc. This invention provides a polishing pad which can be subjected to surface processing to form a sheet or grooves, is excellent in thickness accuracy, attains a high polishing rate, achieves a uniform polishing rate, and also provides a polishing pad which is free of quality variations resulting from an individual variation, easily enables a change the surface patterns, enables fine surface pattern, is compatible with various materials to be polished, is free of burrs upon forming the pattern. This invention provides a polishing pad which can have abrasive grains mixed at very high density without using slurry, and generates few scratches by preventing aggregation of abrasive grains dispersed therein. The polishing pad of this invention has a polishing layer formed from a curing composition to be cured with energy rays, the polishing layer being formed surface pattern thereon by photolithography. The polishing pad of this invention comprises a polishing layer resin having abrasive grains dispersed therein, the resin containing ionic groups in the range of 20 to 1500 eq / ton.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Ultra-precise curved surface finishing method based on non-Newtonian fluid shear thickening effect
ActiveCN102717325AImprove gripAvoid damagePolishing machinesOther chemical processesSocial benefitsSurface finish
The invention discloses an ultra-precise curved surface finishing method based on non-Newtonian fluid shear thickening effect. The method includes: adding abrasive particles or micropowder into non-Newtonian fluid with shear thickening effect to prepare non-Newtonian fluid polishing solution, wherein the non-Newtonian fluid accounts for 50%-90% of the mass of the polishing solution, the abrasive particles or the micropowder account for 10%-50% of the mass of the polishing solution, and the particle size of the abrasive particles or the micropowder ranges from 0.05 micrometer to 50 micrometers. Relative motion is generated between a workpiece and the polishing solution during polishing, shear thickening is generated at a contact portion of the polishing solution and the workpiece under shearing action, viscosity of the polishing solution in the contact area is increased to enhance holding force to the abrasive particles or the micropowder, and removal of workpiece surface materials is achieved under the micro cutting or chemical mechanical action of the adding abrasive particles or micropowder with polishing effect in the polishing solution on the workpiece, so that polishing of the workpiece surface is achieved. The ultra-precise curved surface finishing method based on the non-Newtonian fluid shear thickening effect can achieve efficient and high-quality polishing to various curved surfaces, in particular to complex curved surfaces and has great economic and social benefits.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
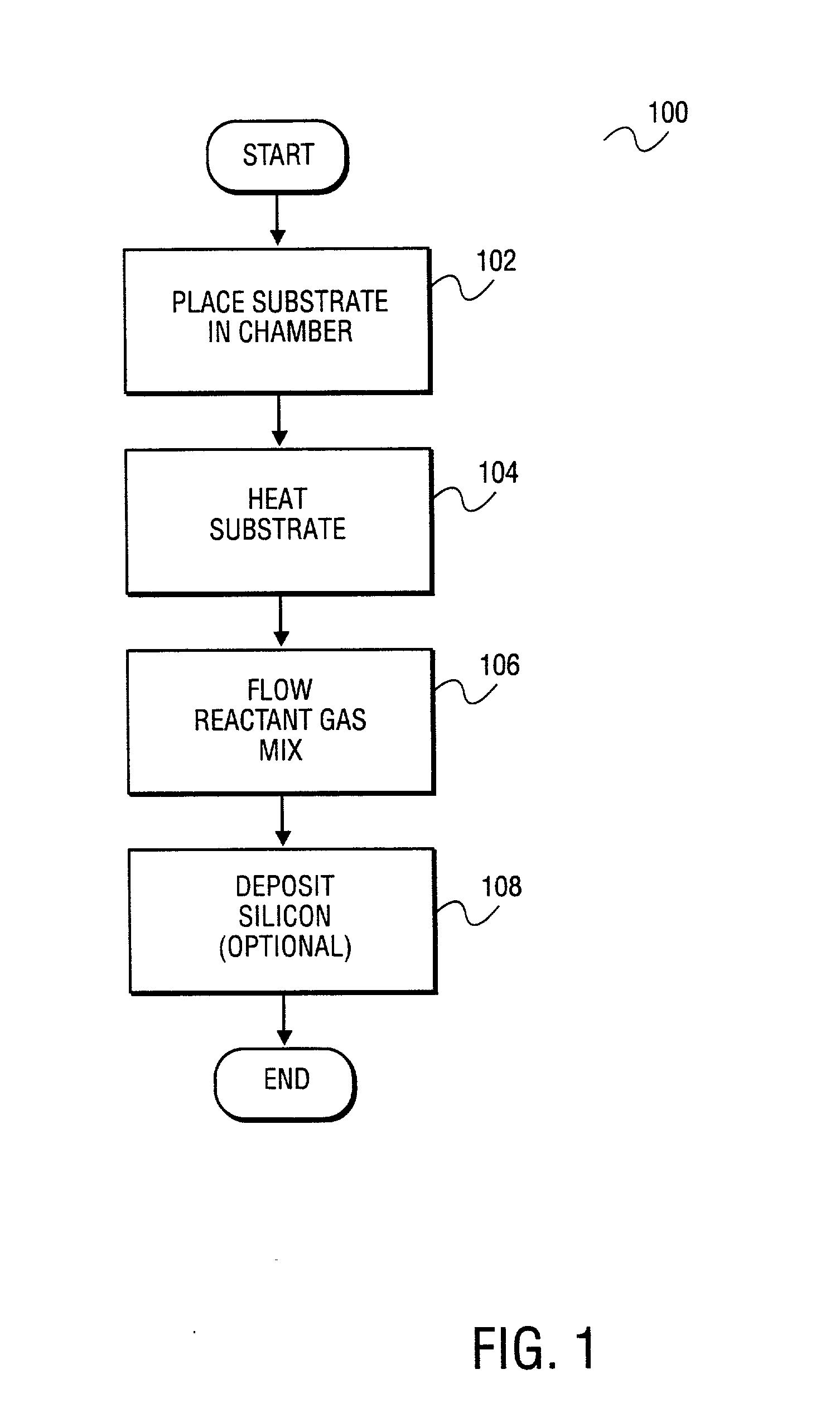
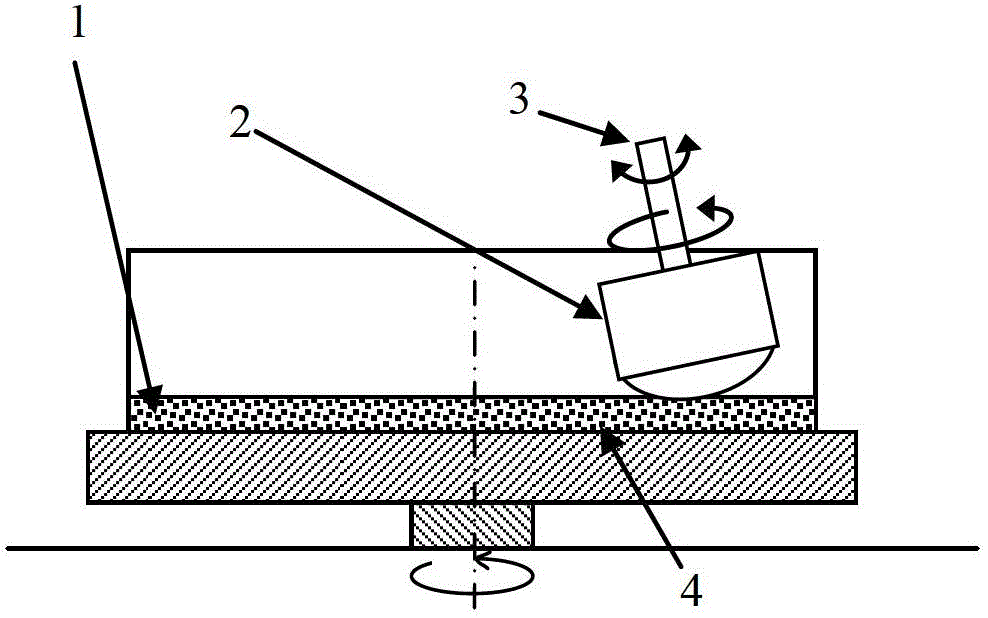
Apparatus and method for surface finishing a silicon film
InactiveUS20040053515A1Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSurface finishSilicon membrane
A method of treating a silicon surface of a substrate that includes heating the substrate in a process chamber to a temperature, exposing a first area adjacent to the silicon surface to a first gas mixture comprising an etchant, a silicon source gas, and a carrier, exposing a second area adjacent to the silicon surface to a second gas mixture, wherein the second gas mixture is different from the first gas mixture.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
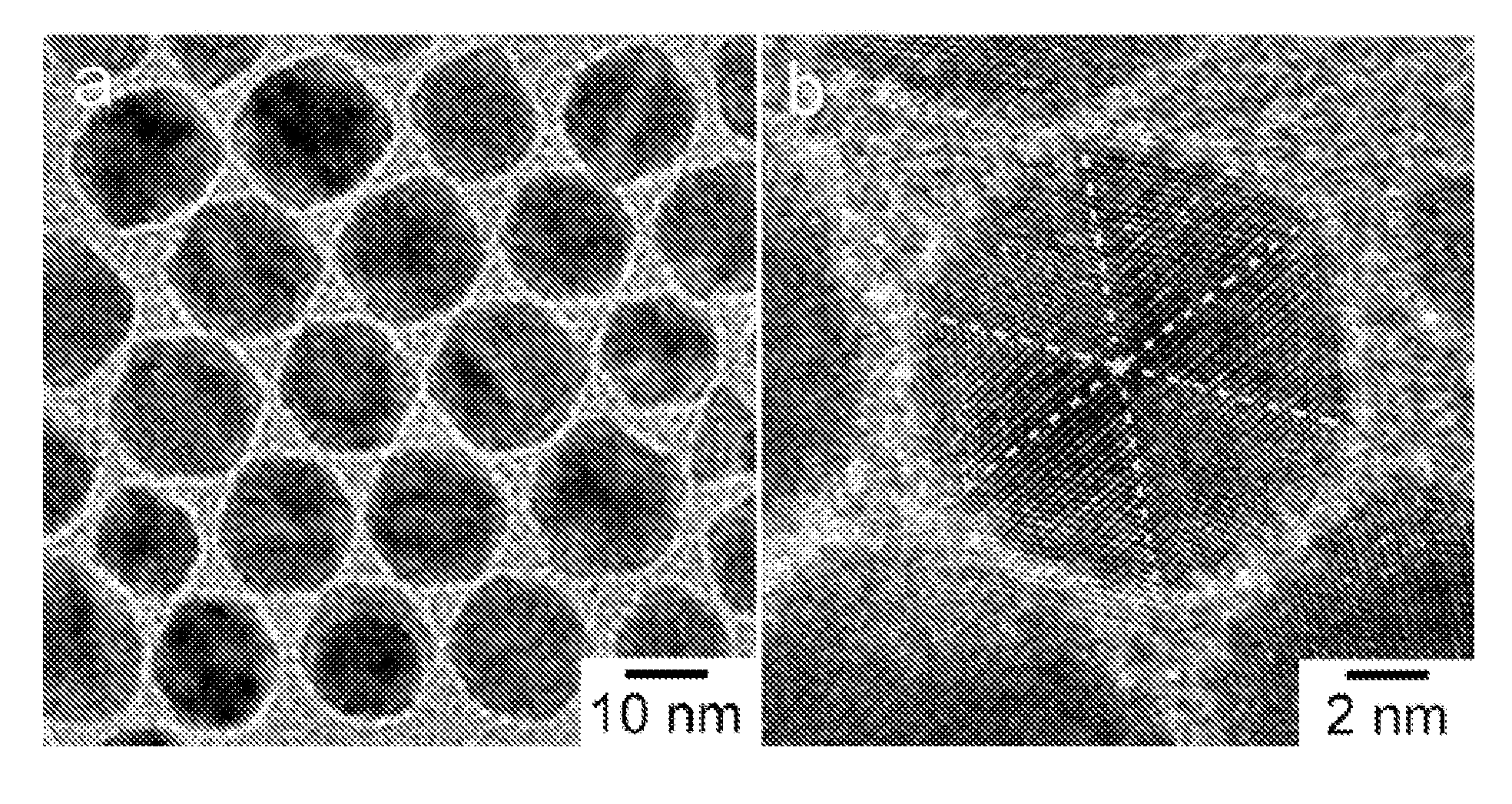
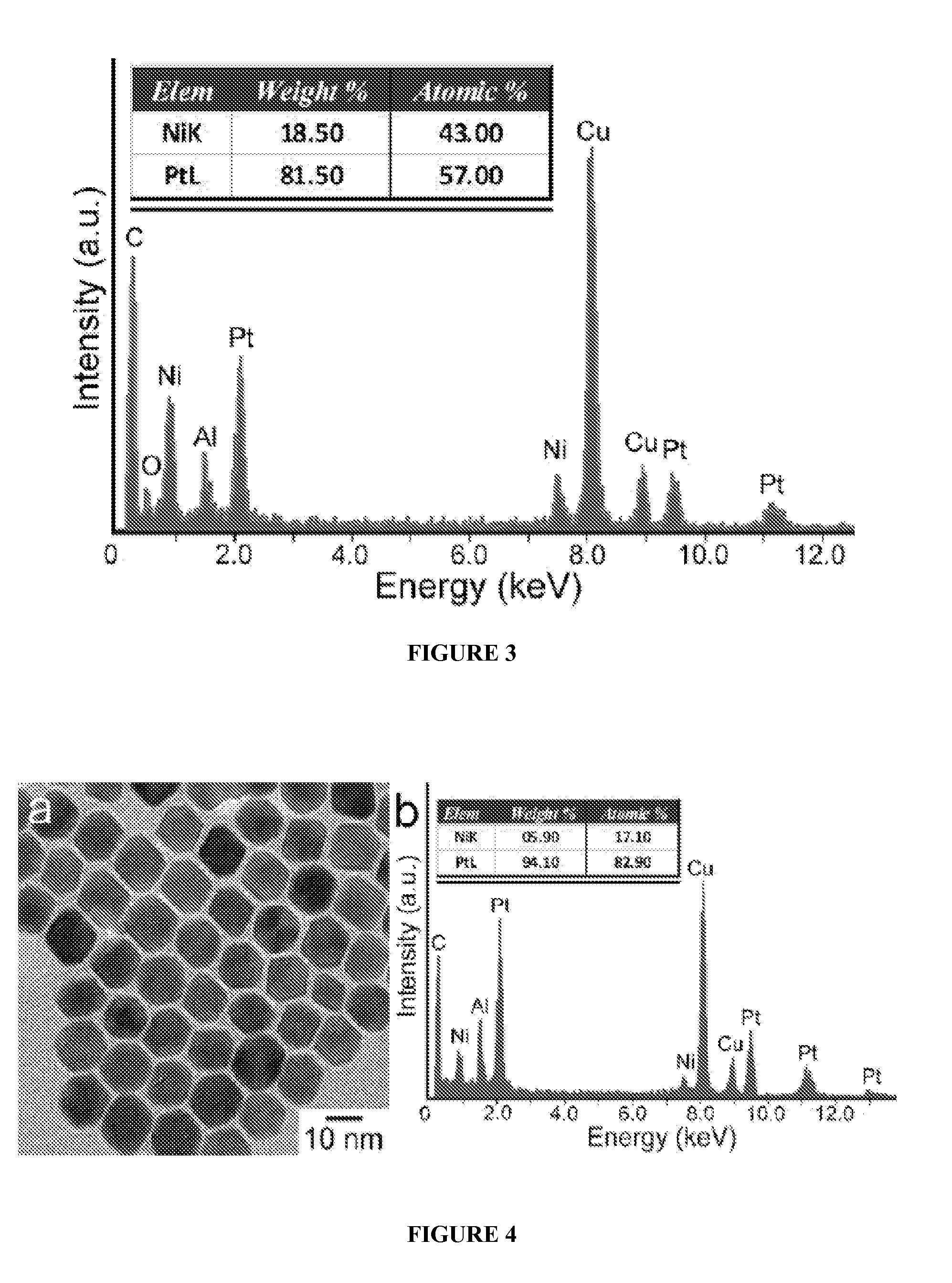
Synthesis of Nanoparticles Using Reducing Gases
Selective gas-reducing methods for making shape-defined metal-based nanoparticles. By avoiding the use of solid or liquid reducing reagents, the gas reducing reagent can be used to make shape well-defined metal- and metal alloy-based nanoparticles without producing contaminates in solution. Therefore, the post-synthesis process including surface treatment become simple or unnecessary. Weak capping reagents can be used for preventing nanoparticles from aggregation, which makes the further removing the capping reagents easier. The selective gas-reducing technique represents a new concept for shape control of nanoparticles, which is based on the concepts of tuning the reducing rate of the different facets. This technique can be used to produce morphology-controlled nanoparticles from nanometer- to submicron- to micron-sized scale. The Pt-based nanoparticles show improved catalytic properties (e.g., activity and durability).
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Method for treating ophthalmic lenses
InactiveUS20090145086A1Reduce material handling stepReduce accompanying costPackage sterilisationOptical articlesAqueous solutionEye lens
A method of treating an ophthalmic lens in a package involves: placing the lens and an aqueous solution in a recess of package, the solution including an organic surface treatment agent that attaches to anterior and posterior surfaces of the lens; and sealing the recess of the package with lidstock and sterilizing the package contents. The bottom of the recess includes raised projections.
Owner:REYNOLDS GER M +4
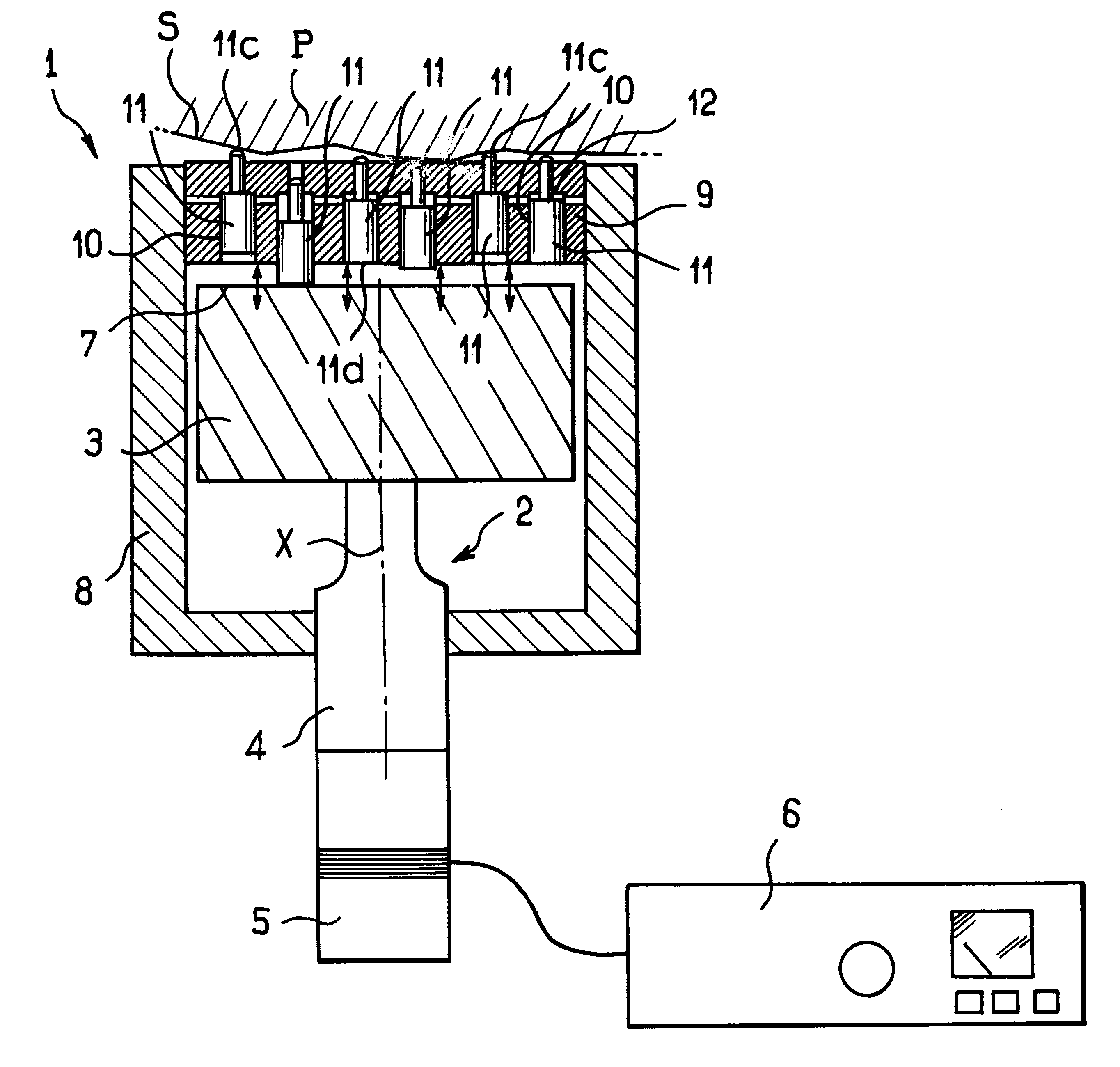
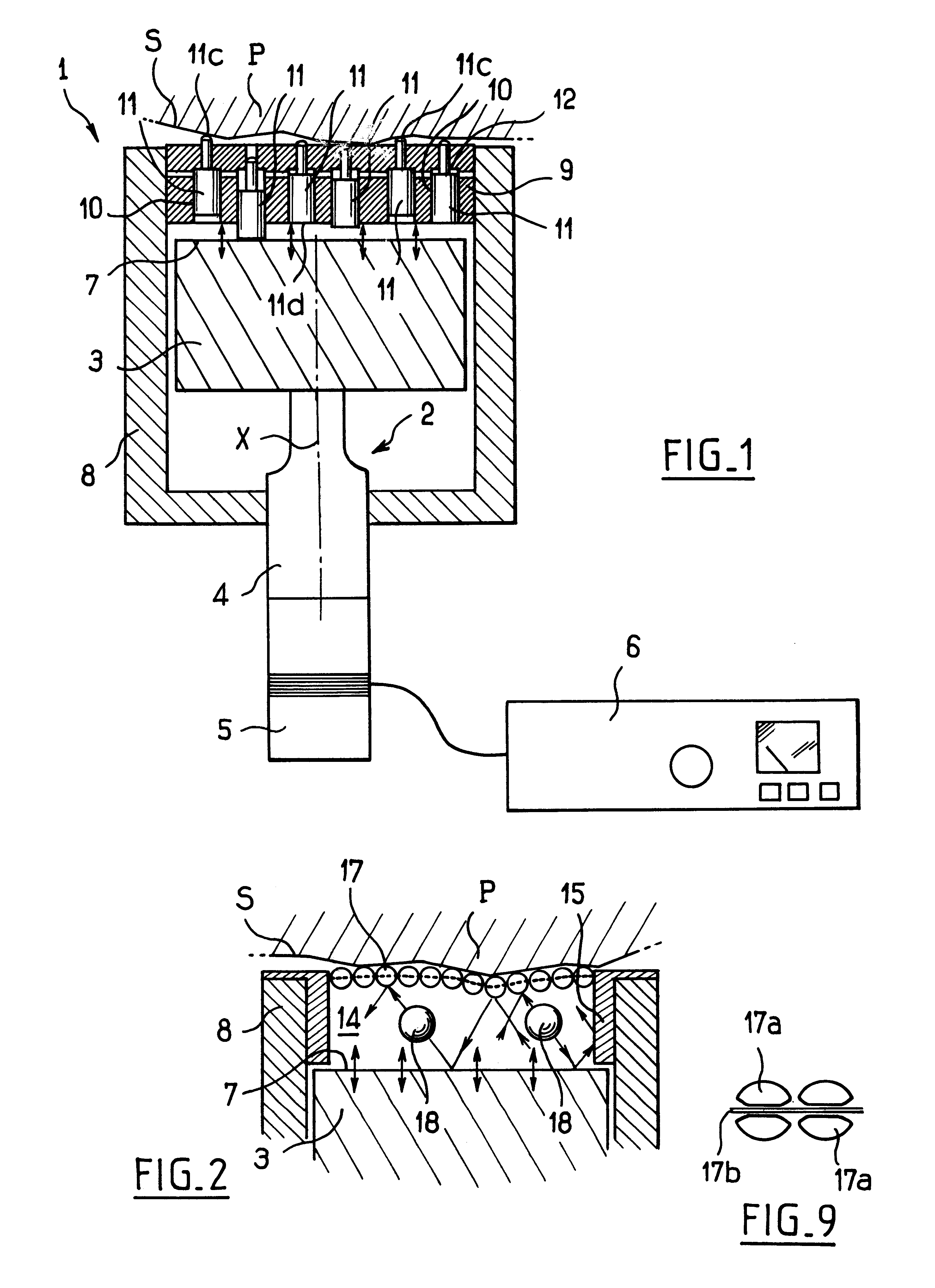
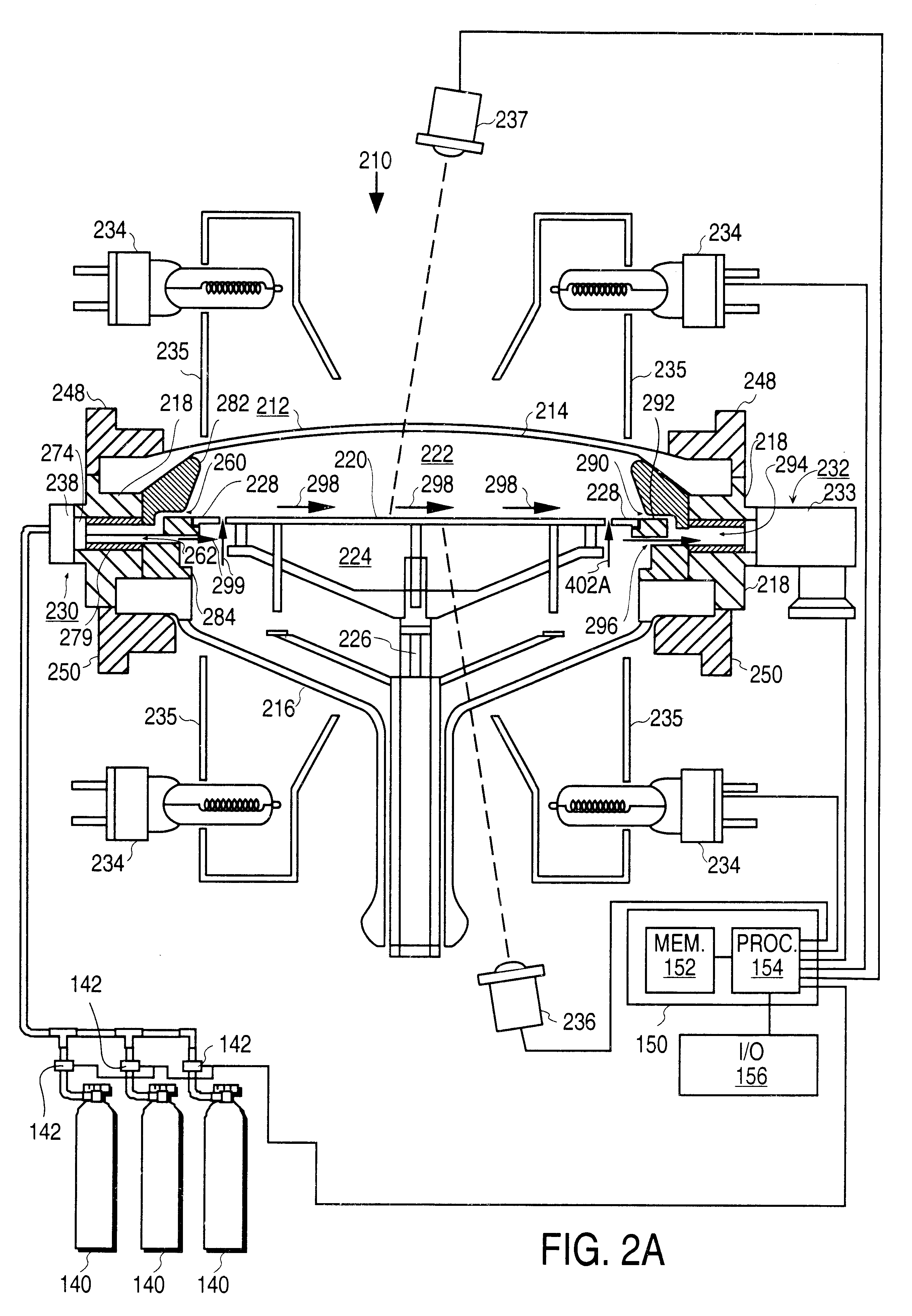
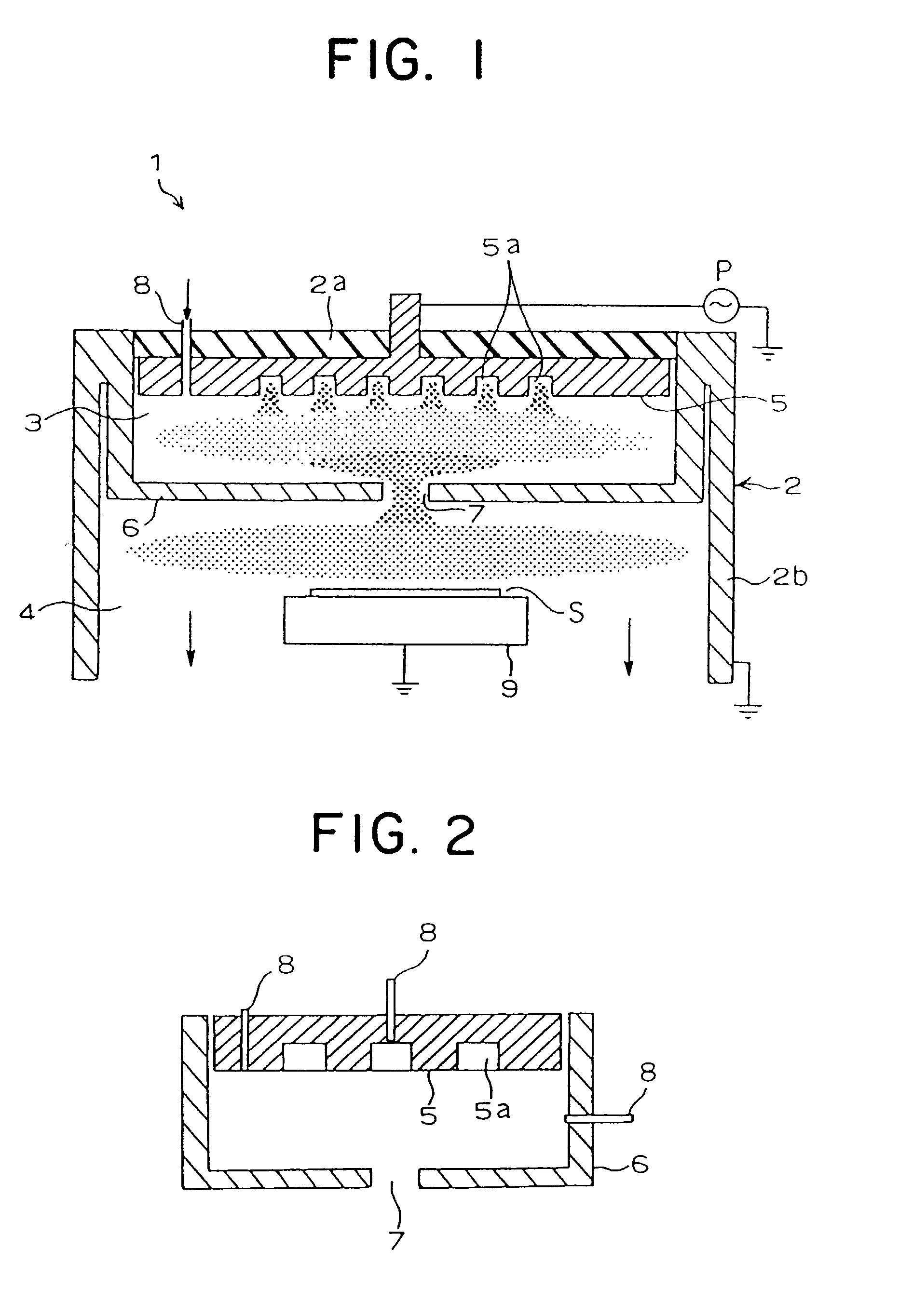
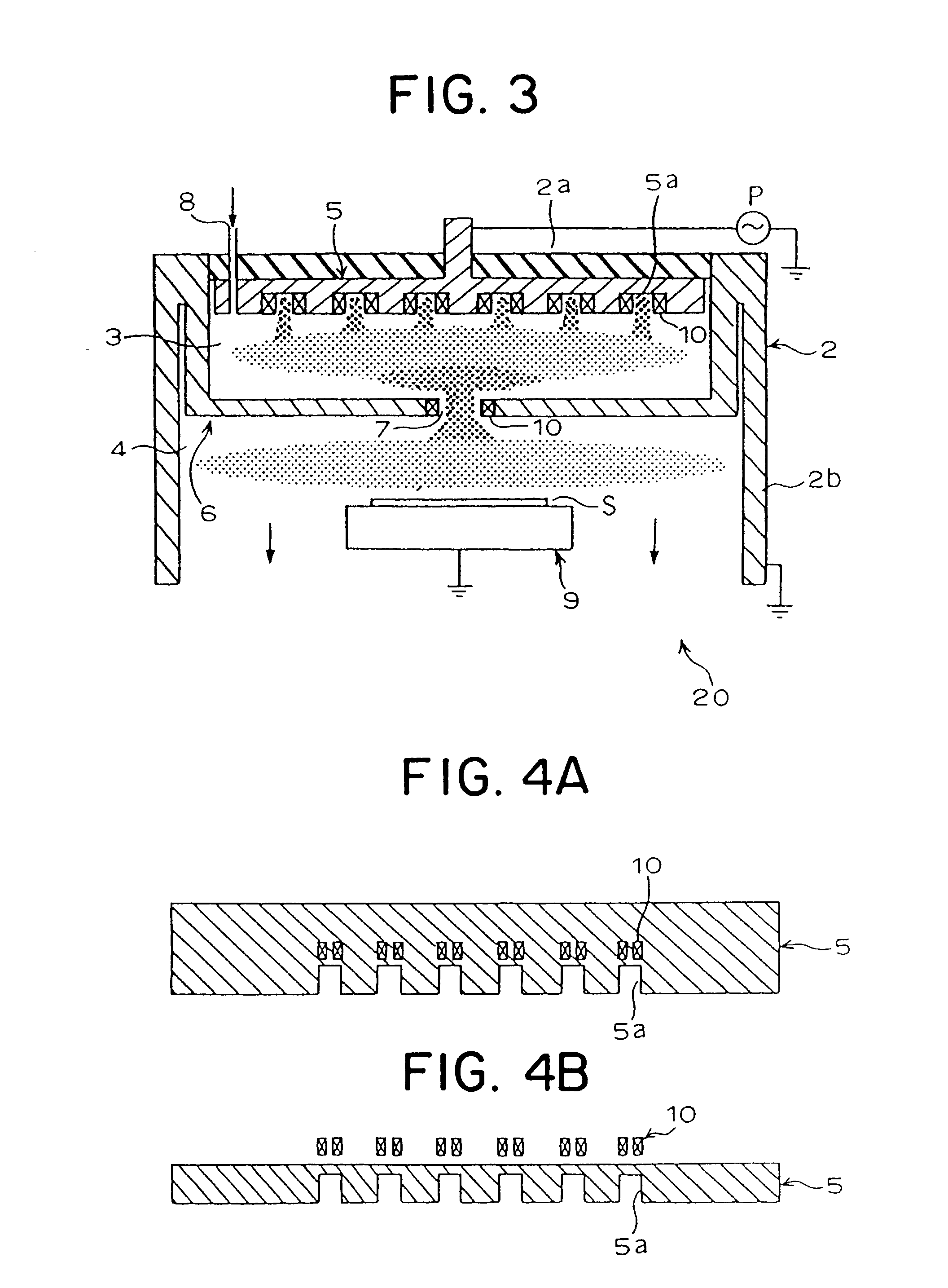
Surface treatment apparatus
InactiveUS20030106643A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsCathode electrode
The present invention provides a surface treatment apparatus which can treat a surface with high speed and high quality. A casing of a surface treatment apparatus is defined into two chambers, a plasma generation chamber provided with a plasma generation electrode and a substrate treatment chamber provided with a substrate support table. A plasma nozzle is formed on an anode electrode constituting a partition wall of the both chambers. A recess is formed on an upper cathode electrode. Further, the plasma nozzle is used as a hollow anode discharge generation area, and the recess as a hollow cathode discharge generation area.
Owner:KOMATSU LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com