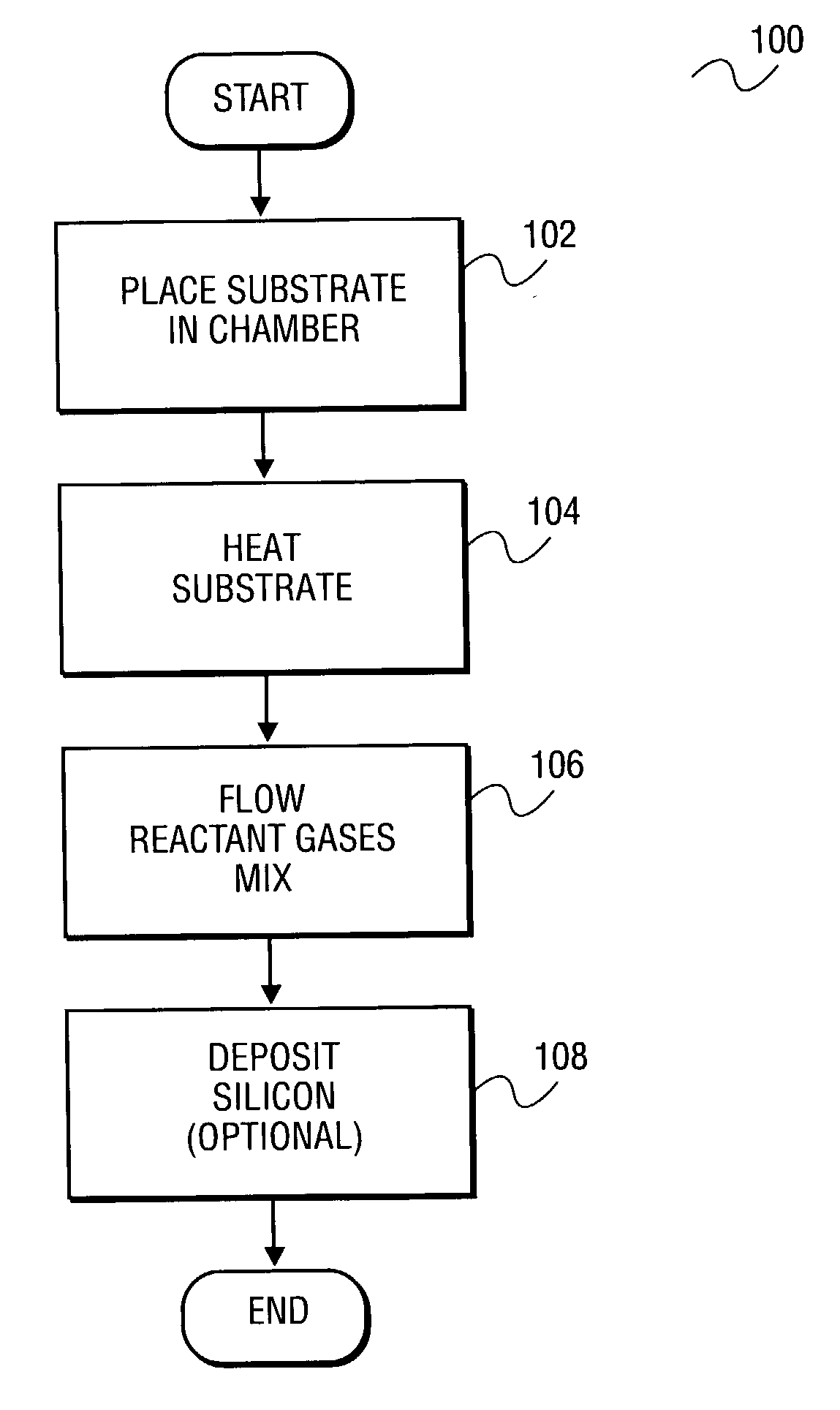
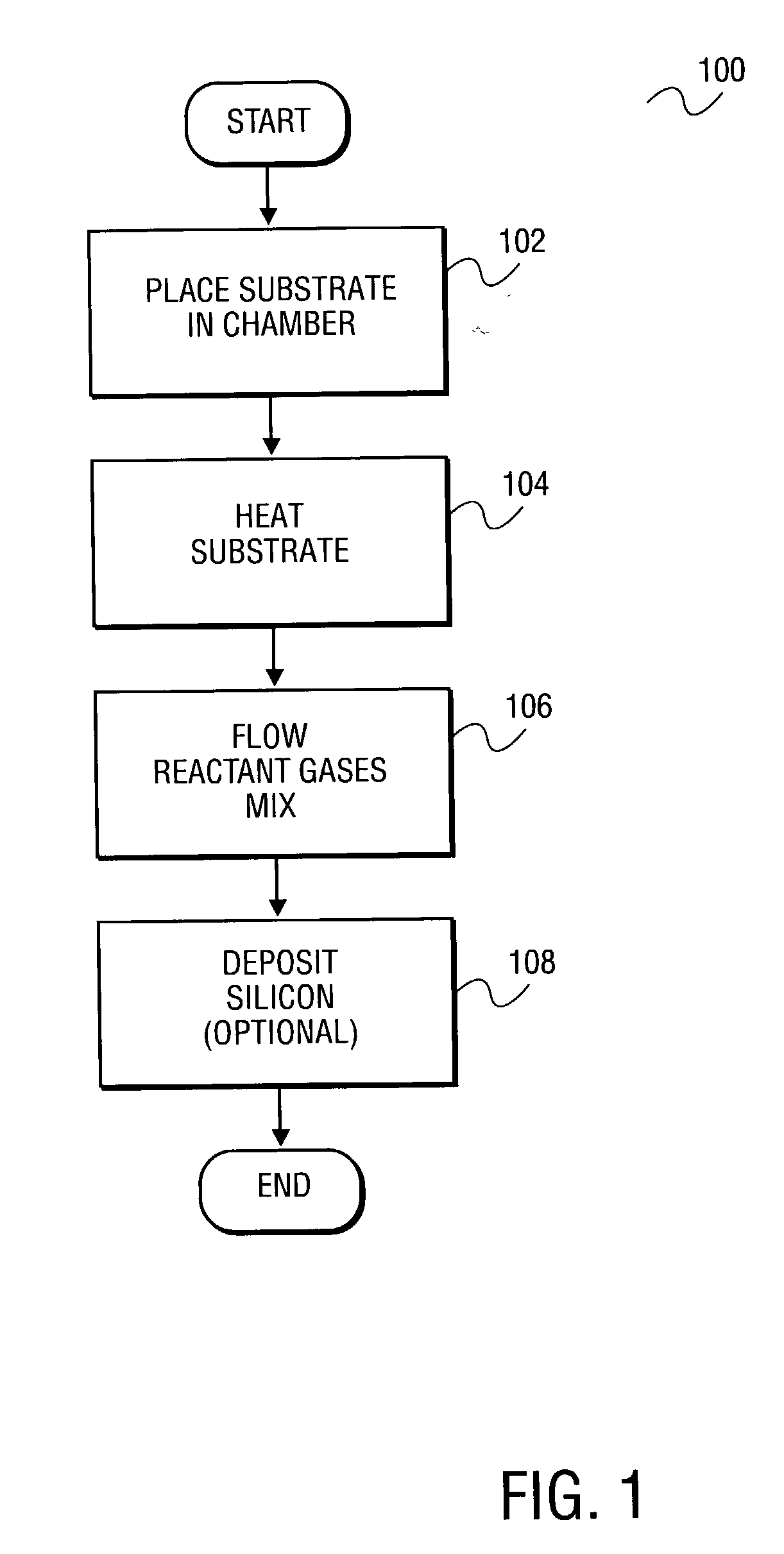
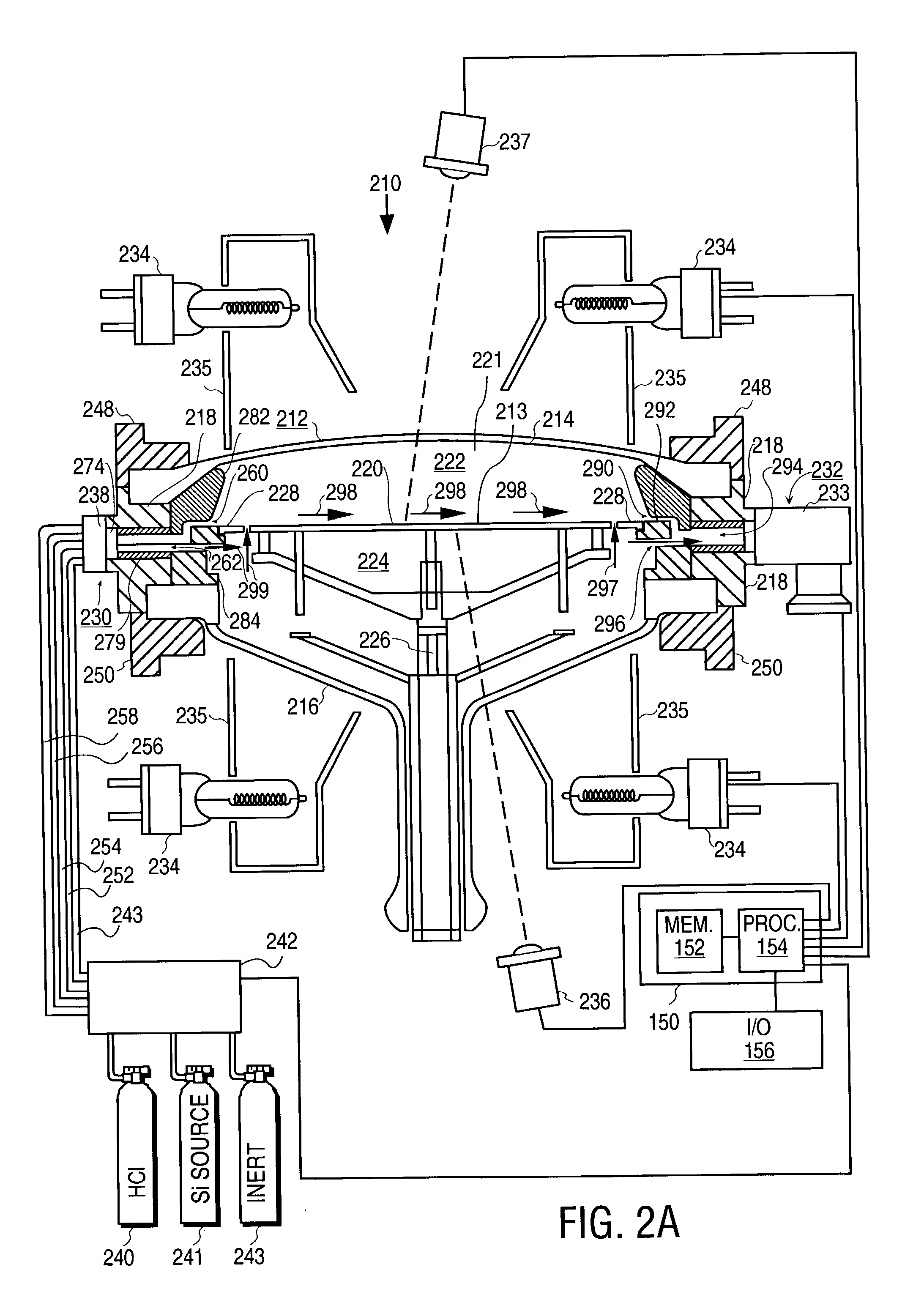
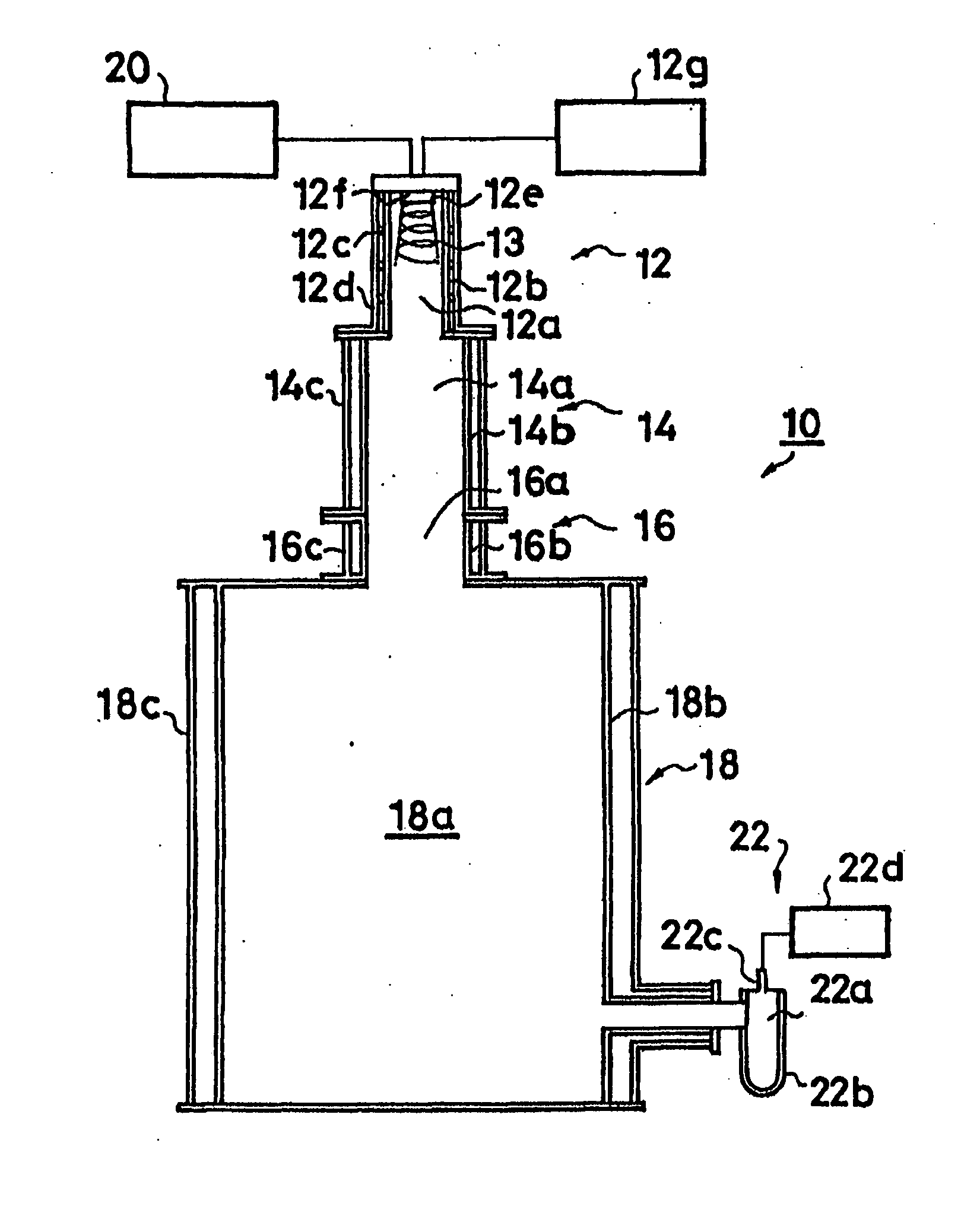
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
635 results about "Silicon membrane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
PermSelect® silicone membrane modules use silicone hollow fibers with exceptional gas transfer properties. Because silicone is dense (non-porous), liquids cannot transfer through the membrane. This enables silicone's use in liquid contacting applications with all compatible liquids regardless of surface tension.
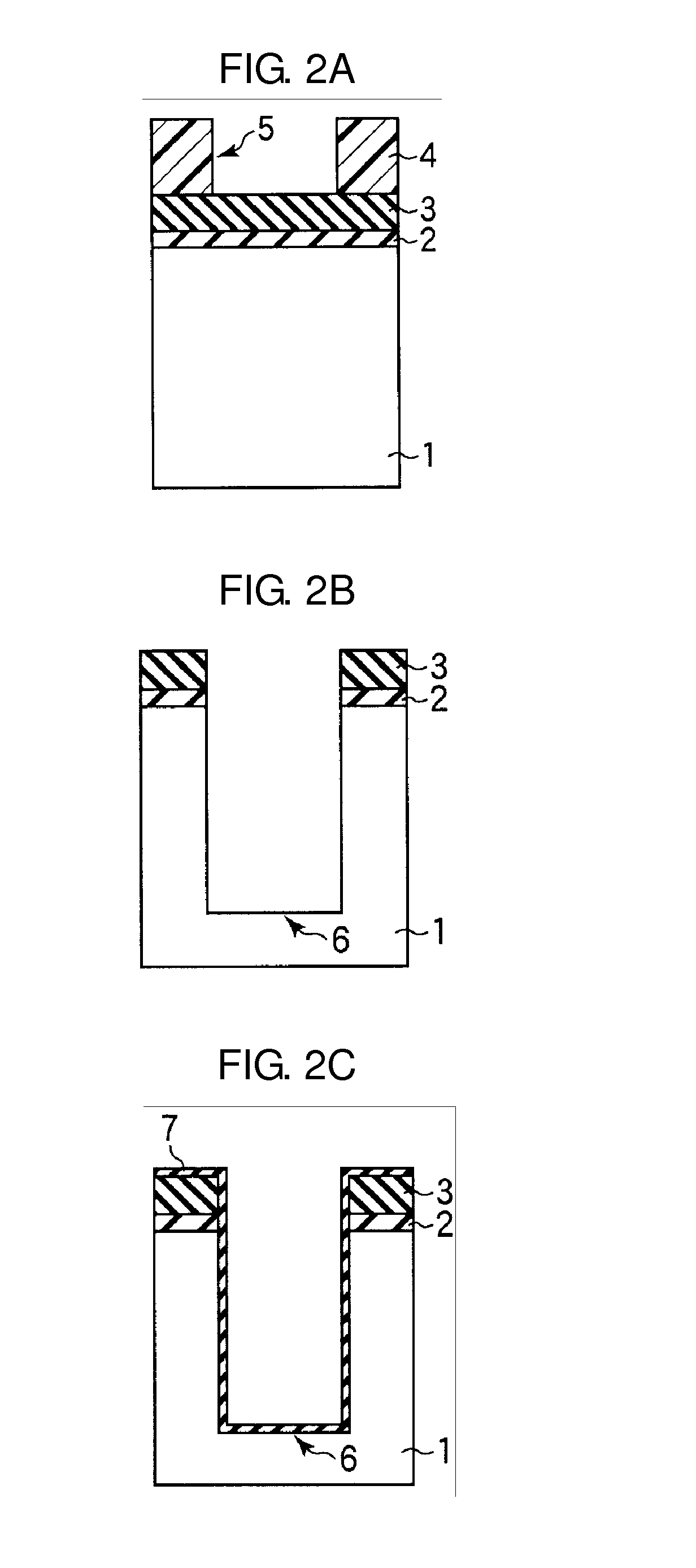
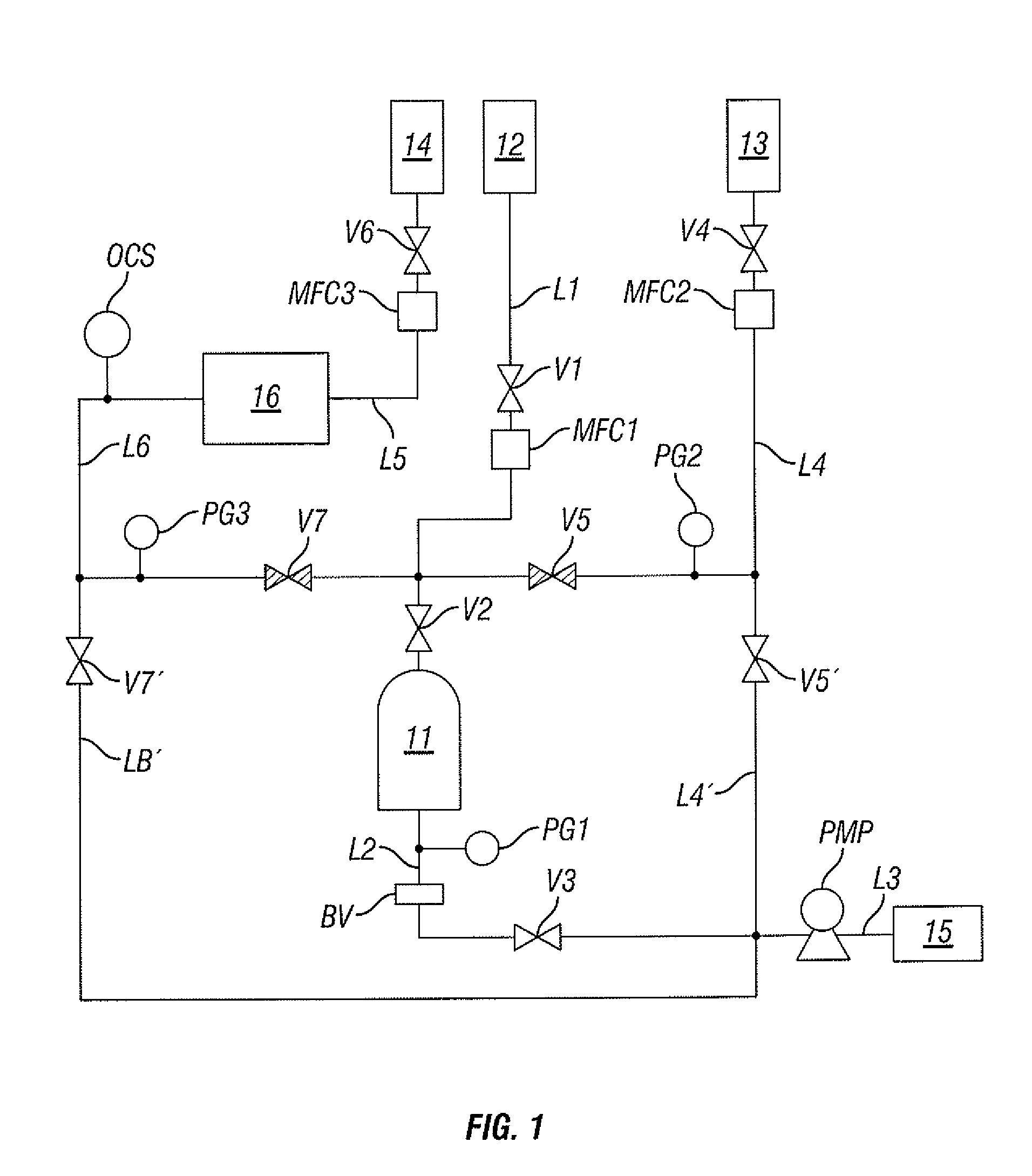
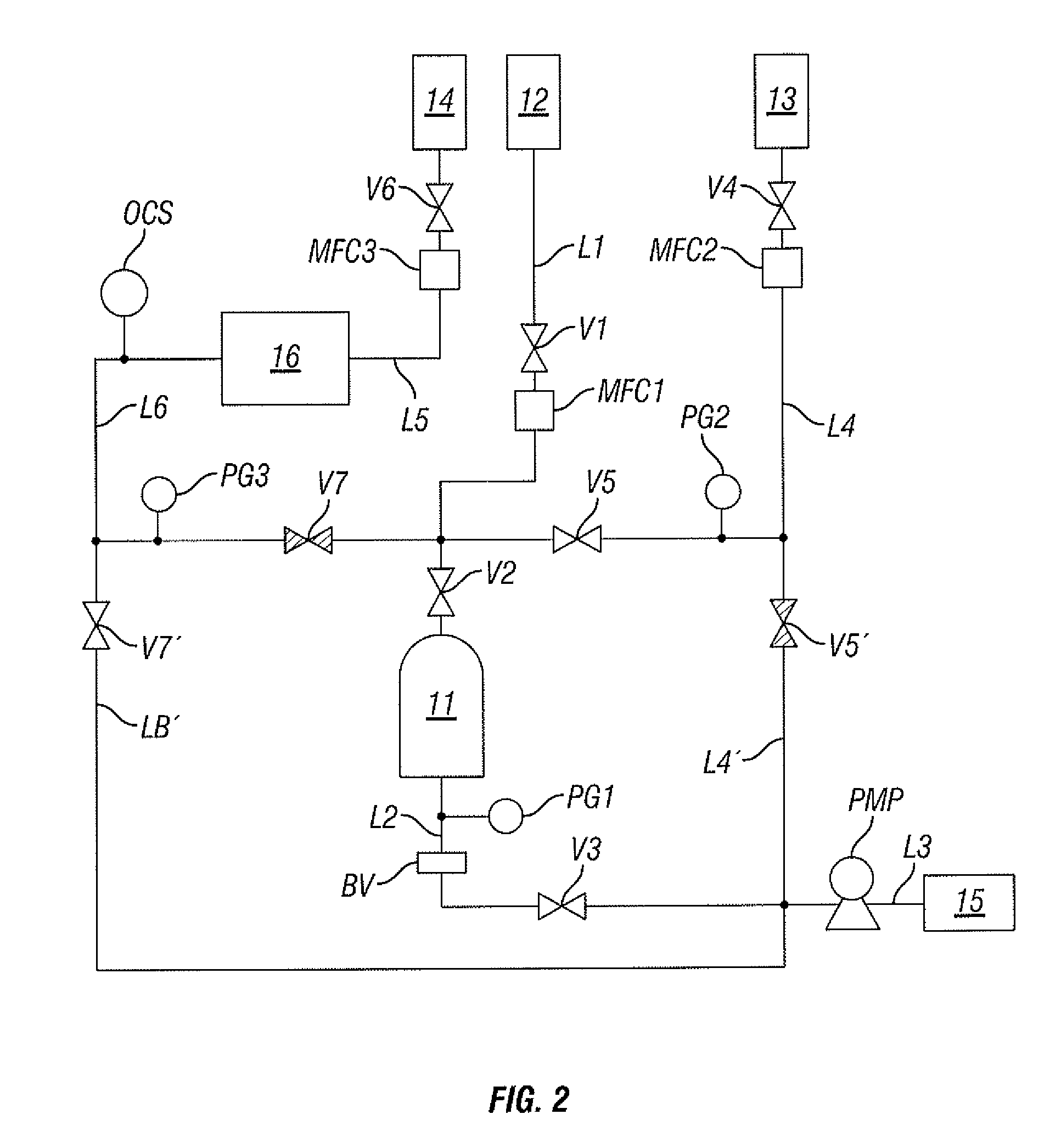
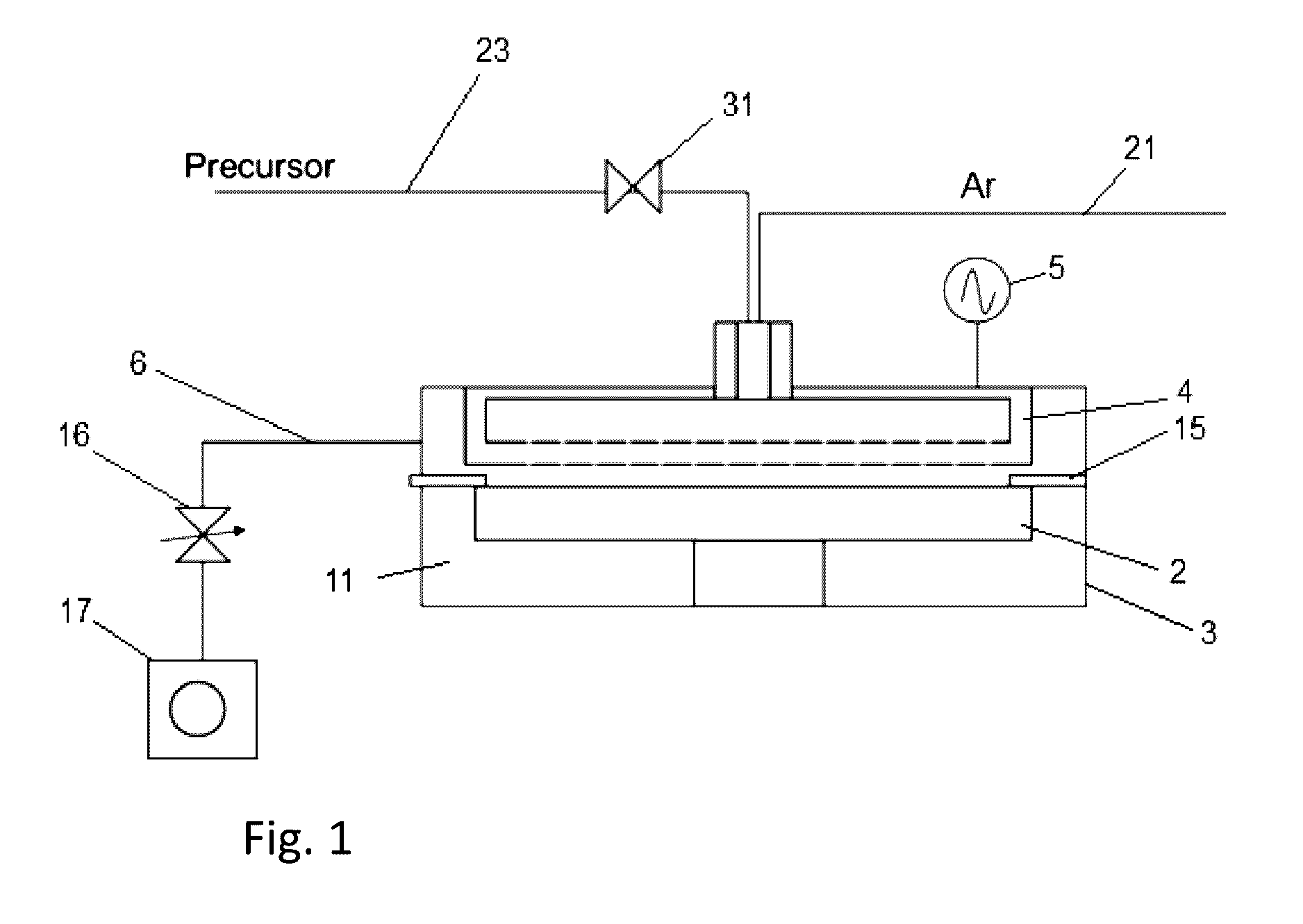
Method and apparatus for cleaning and method and apparatus for etching
InactiveUS20050020071A1Increase flexibilityImprove securitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingProcess engineeringForming gas
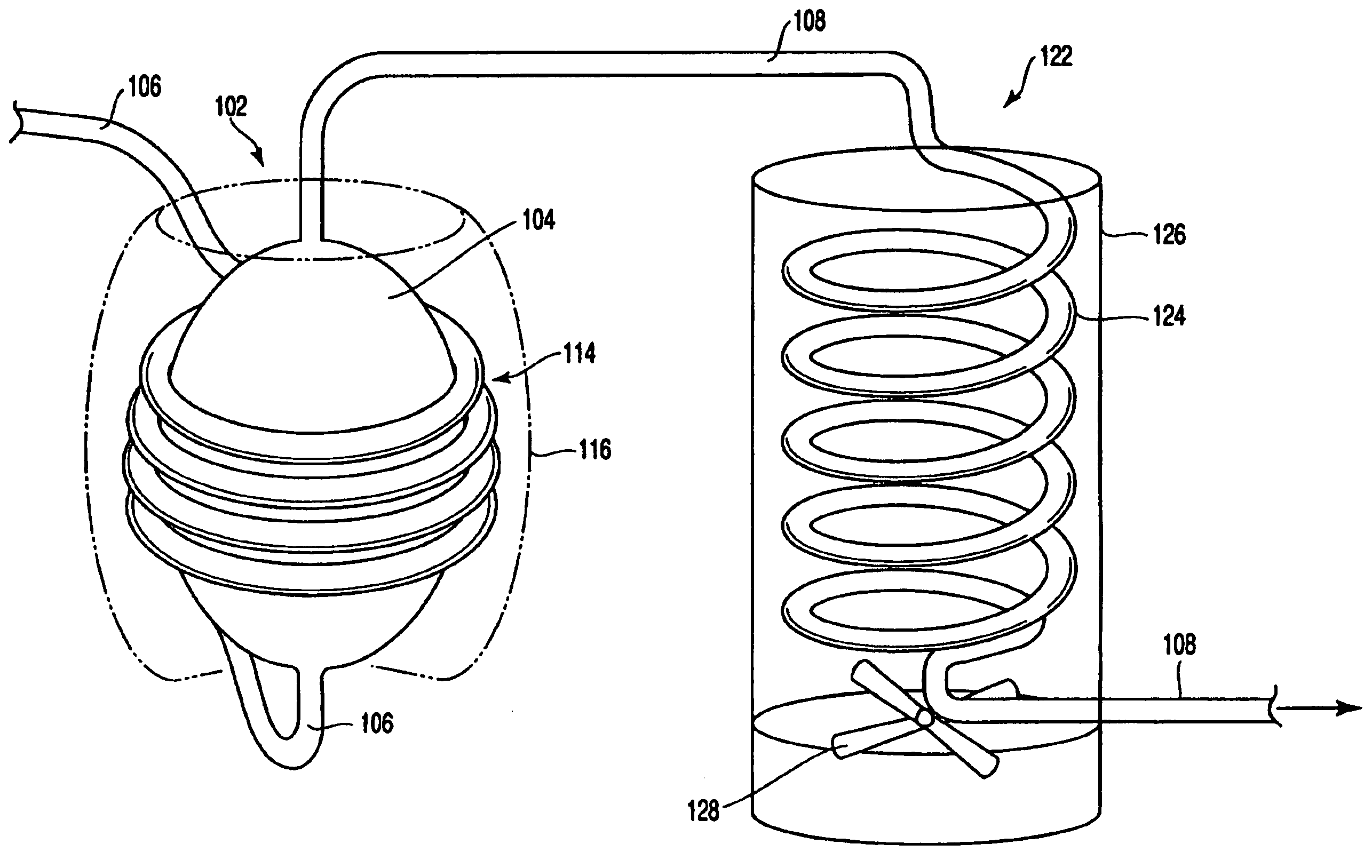
A cleaning apparatus (30) is connected to a treating chamber (12) of a CVD apparatus (10) for forming a silicon film. The cleaning apparatus (30) has a first, a second, and a third gas sources (32, 34, 36) and a chlorine gas, a fluorine gas, and an inert gas are introduced from the gas sources through FMC (38a, 38b, 38c), respectively, with flow rates controlled independently from one another. Those gases are gathered at a pipe (42) and mixed into a mixed gas. The mixed gas is passed through a heated reactor (44) such as a heat exchanger to thereby react the chlorine gas with the fluorine gas and form a formed gas containing fluorinated chlorine gas such as CIF3. The formed gas is supplied to the treating chamber (12) through a cooler (46), an analyzer (48) and a buffer (54).
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
Trench embedding method and film-forming apparatus
ActiveUS20120164842A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSilicon nitrideSilicon membrane
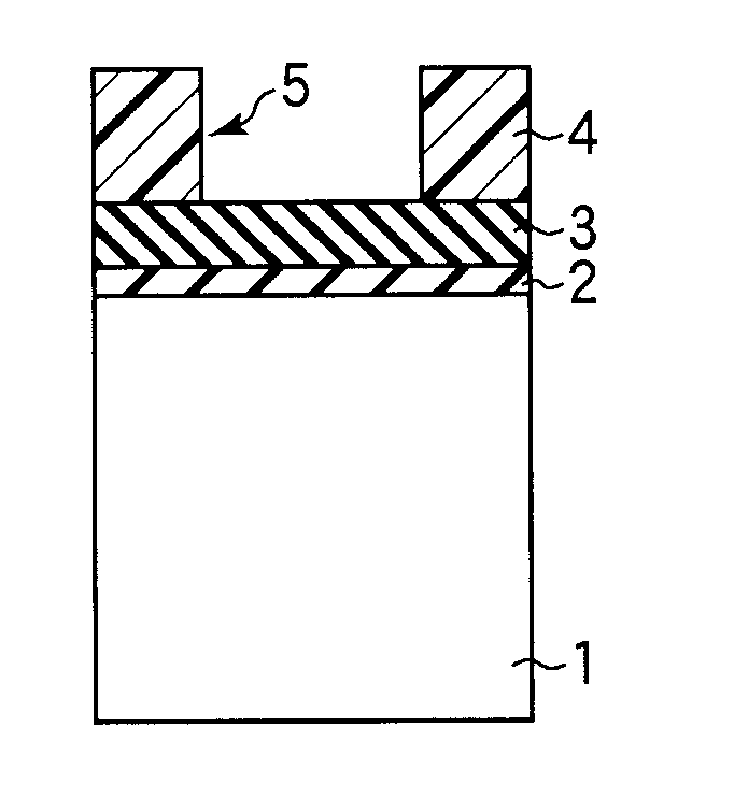
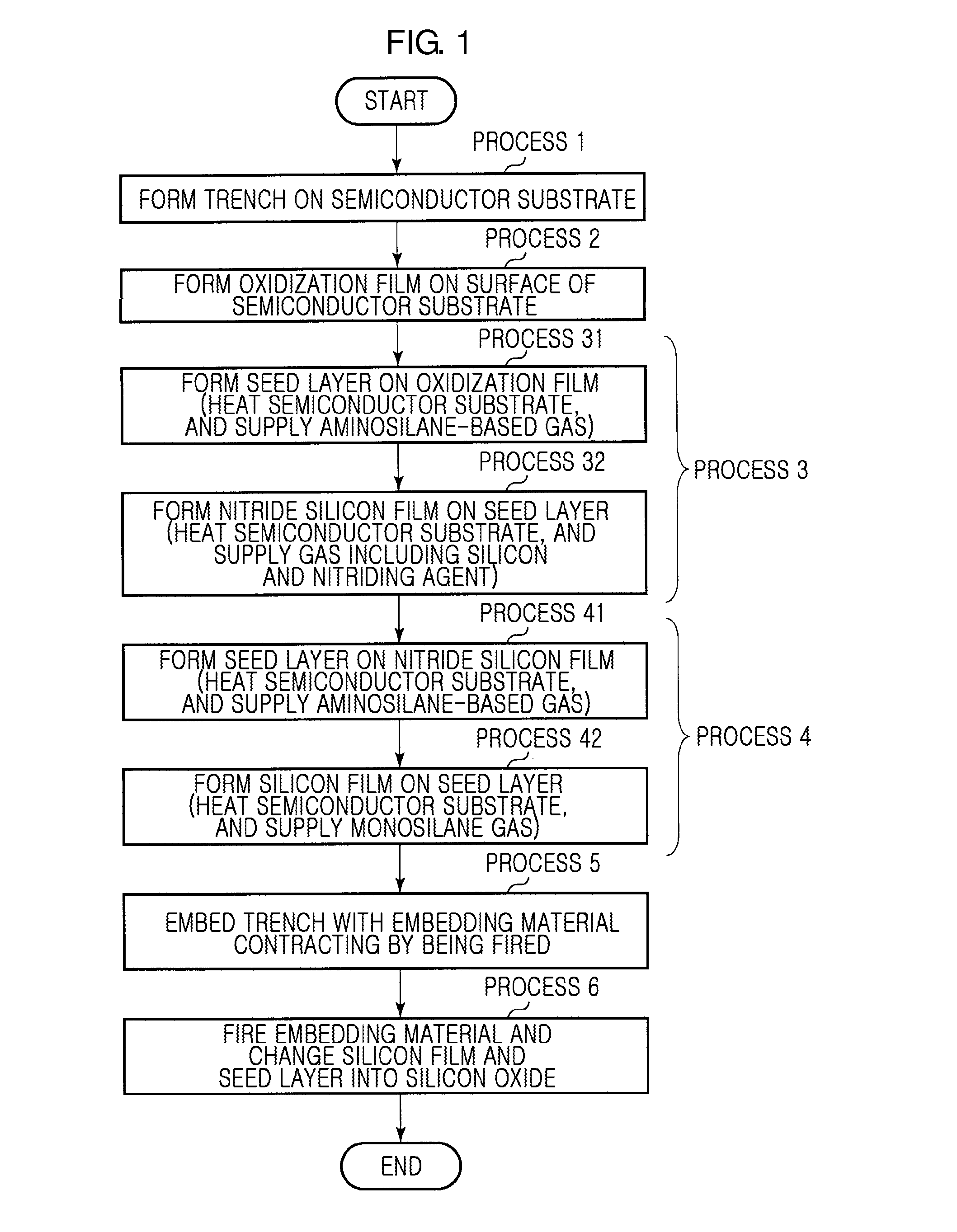
A trench embedding method includes forming an oxidization barrier film on a trench; forming an expandable film on the oxidization barrier film; embedding an embedding material that contracts by being fired on the trench; and firing the embedding material, wherein the forming of the oxidization barrier film includes: forming a first seed layer on the trench by supplying an aminosilane-based gas; and forming a silicon nitride film on the first seed layer, wherein the forming of the expandable film includes: forming a second seed layer on the silicon nitride film by supplying an aminosilane-based gas; and forming a silicon film on the second seed layer.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
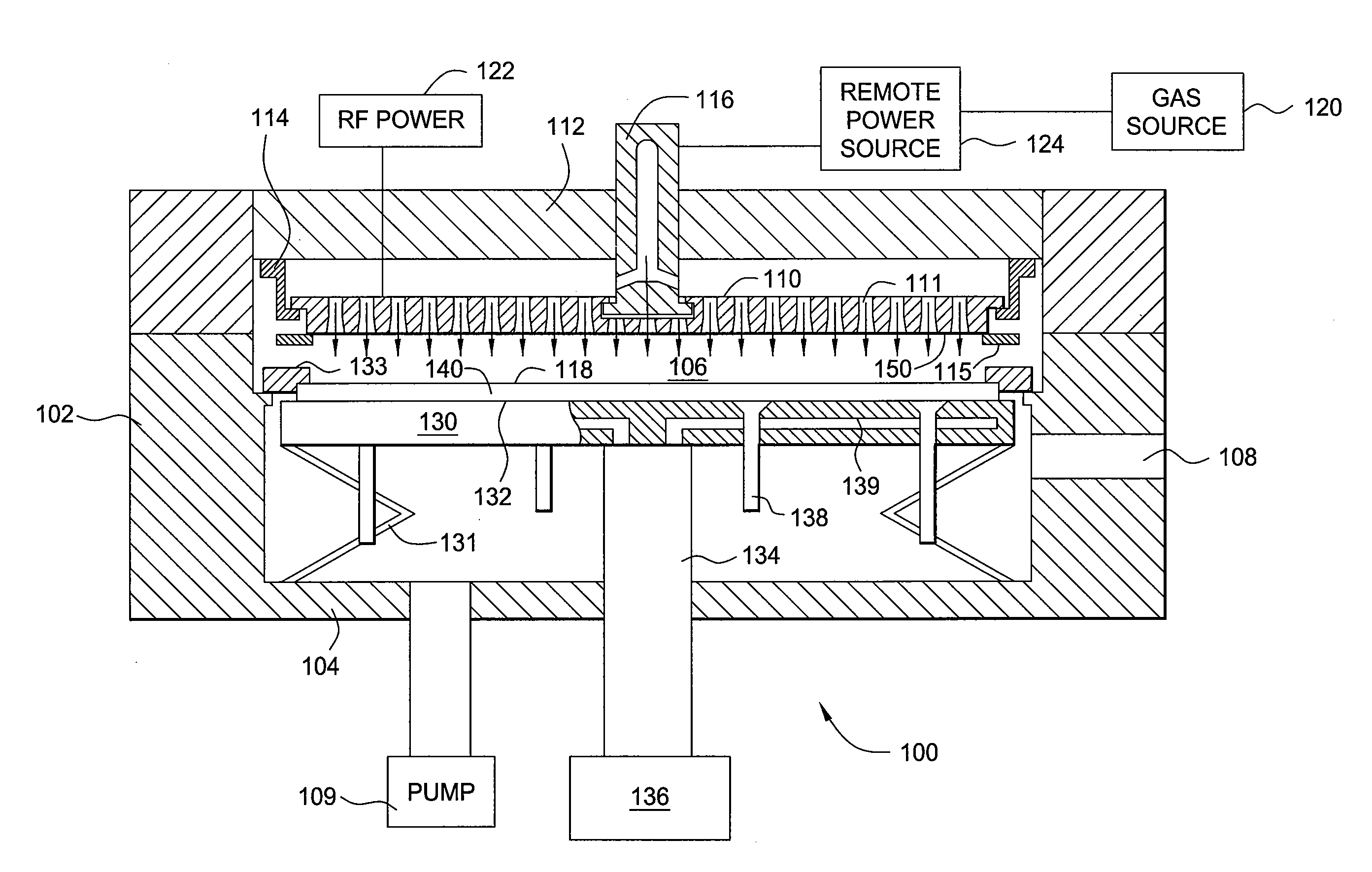
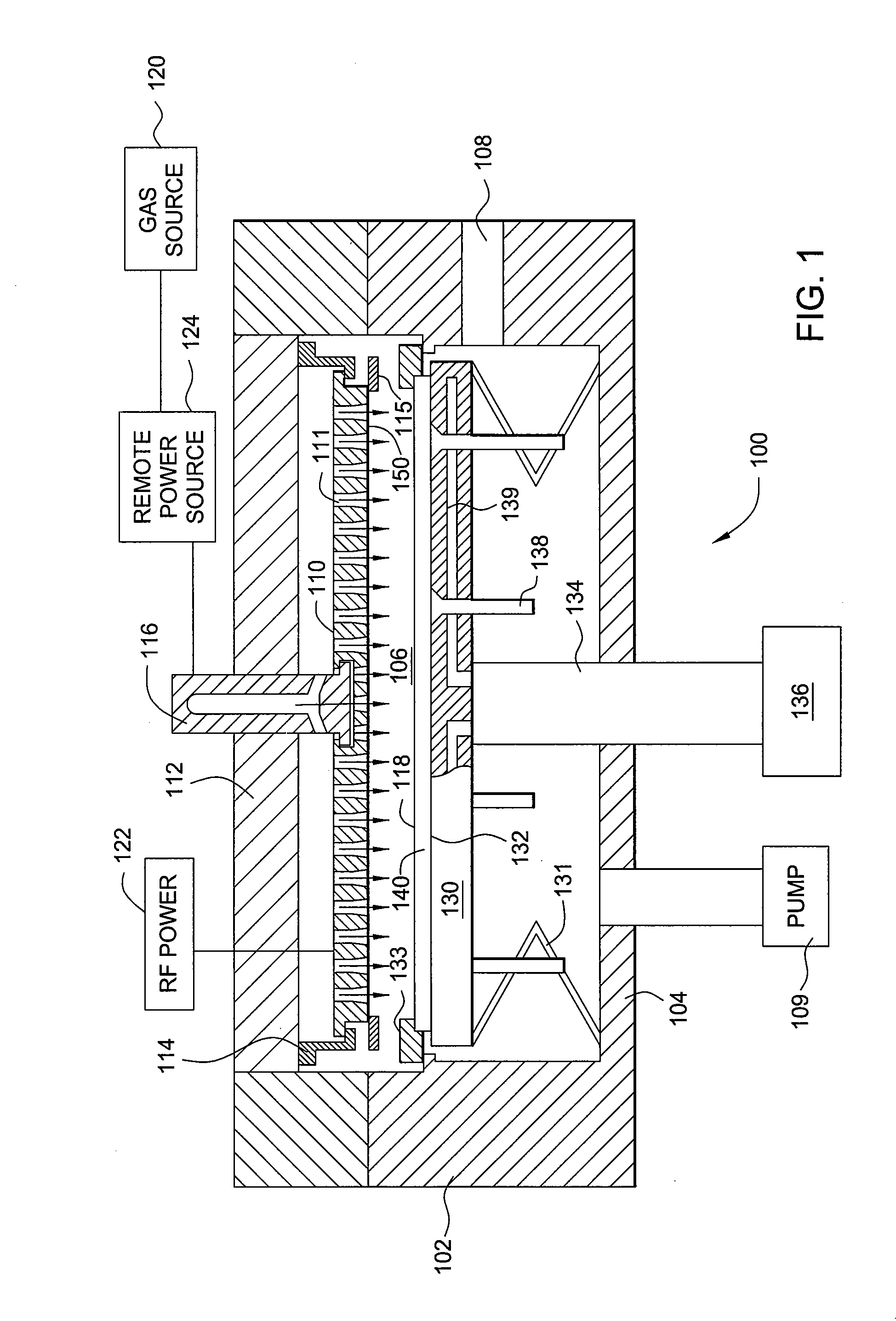
Apparatus for depositing a uniform silicon film and methods for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080305246A1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon membraneProduct gas
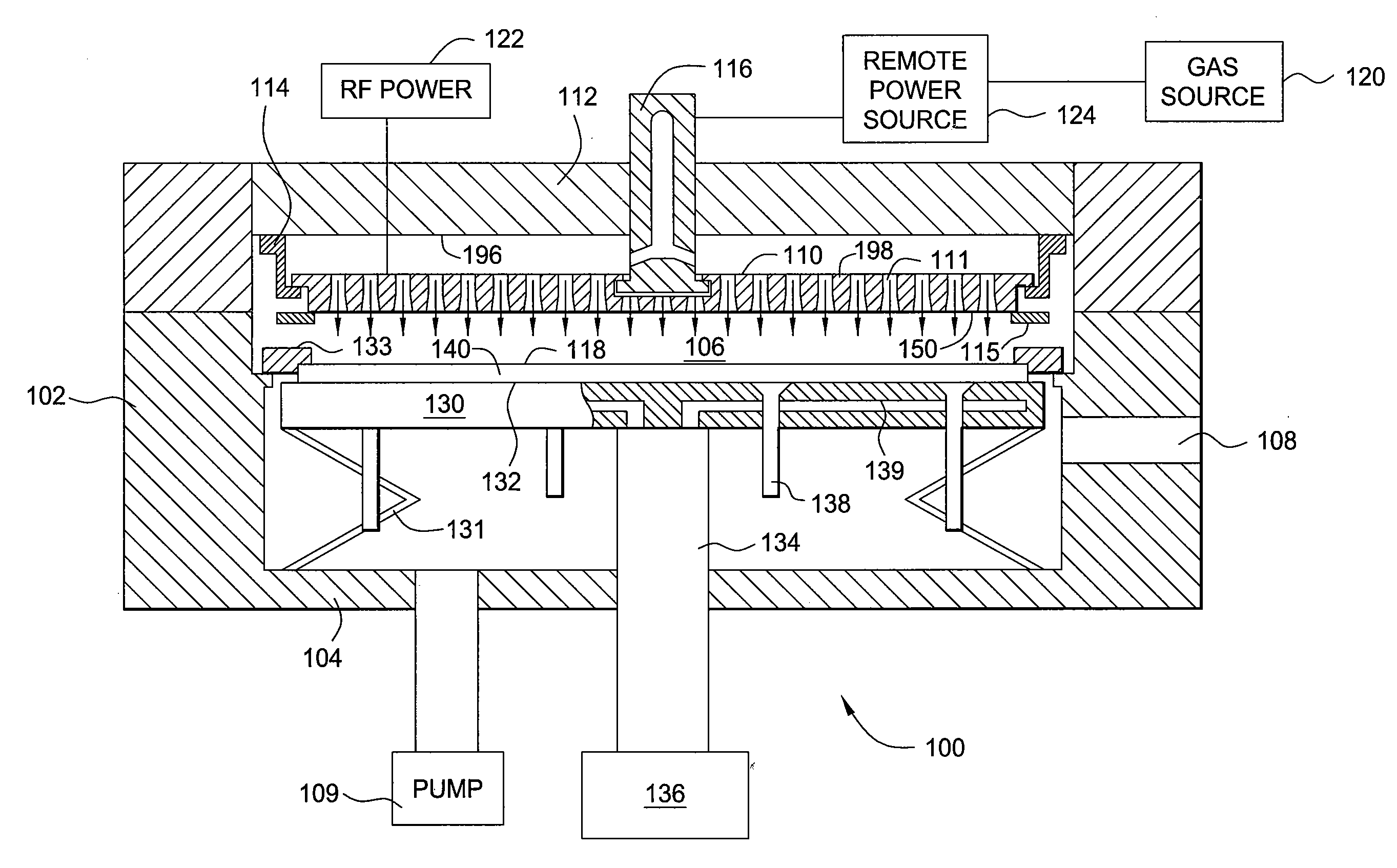
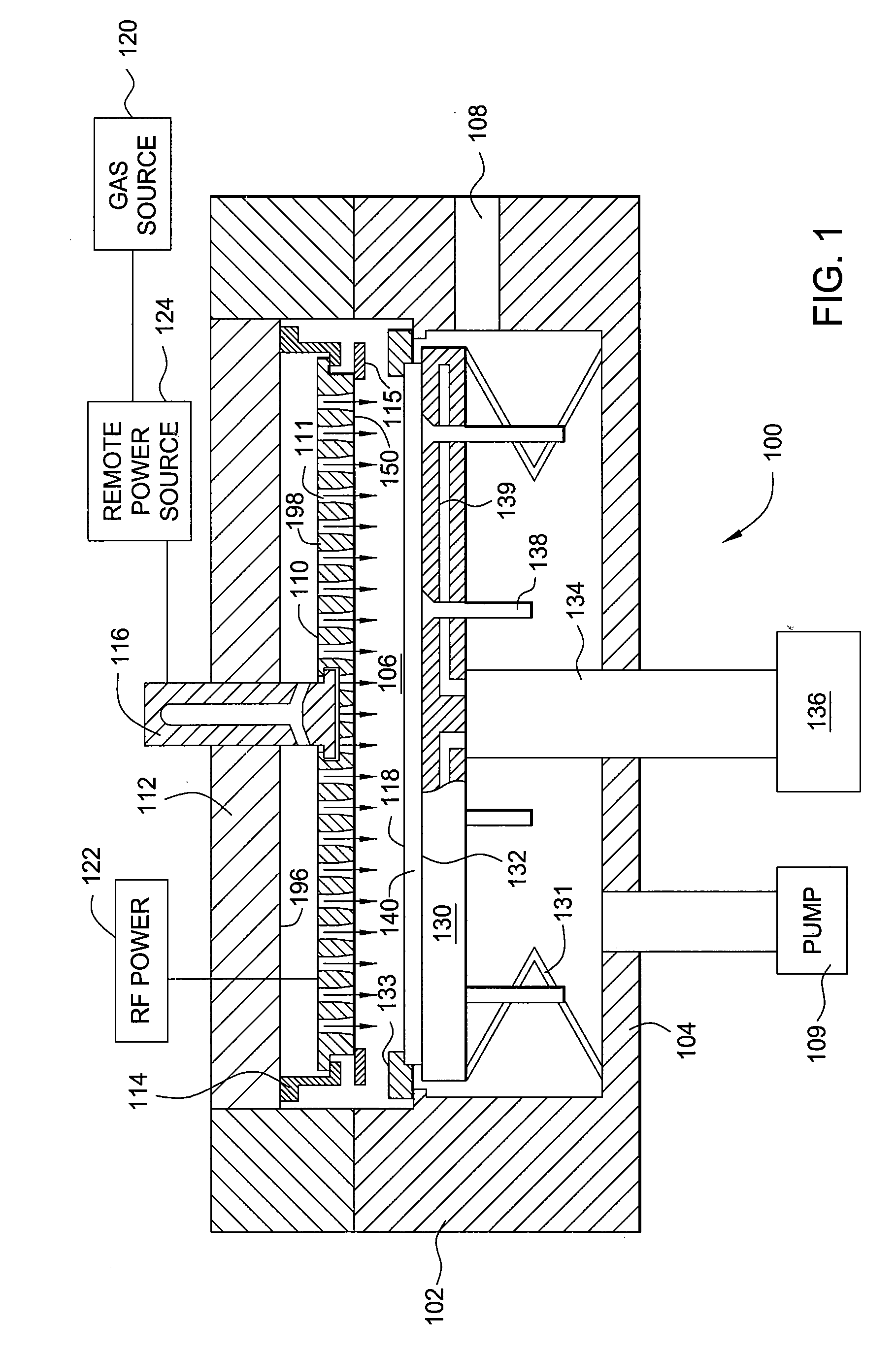
Methods and apparatus having a gradient spacing created between a substrate support assembly and a gas distribution plate for depositing a silicon film for solar cell applications are provided. In one embodiment, an apparatus for depositing films for solar cell applications may include a processing chamber, a substrate support disposed in the processing chamber and configured to support a quadrilateral substrate thereon, and a gas distribution plate disposed in the processing chamber above the substrate support, wherein a bottom surface of the gas distribution plate has a perimeter that includes edges and corners, and wherein the corners of the gas distribution plate are closer to the substrate support than the edges of the gas distribution plate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Organoaminodisilane precursors and methods for depositing films comprising same
Described herein are precursors and methods for forming silicon-containing films. In one aspect, there is provided a precursor of Formula I:wherein R1 is selected from linear or branched C3 to C10 alkyl group, linear or branched C3 to C10 alkenyl group, linear or branched C3 to C10 alkynyl group, C1 to C6 dialkylamino group, electron withdrawing group, and C6 to C10 aryl group; R2 is selected from hydrogen, linear or branched C1 to C10 alkyl group, linear or branched C3 to C6 alkenyl group, linear or branched C3 to C6 alkynyl group, C1 to C6 dialkylamino group, C6 to C10 aryl group, linear or branched C1 to C6 fluorinated alkyl group, electron withdrawing group, and C4 to C10 aryl group; optionally wherein R1 and R2 are linked together to form ring selected from substituted or unsubstituted aromatic ring or substituted or unsubstituted aliphatic ring; and n=1 or 2.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Method for silicon based dielectric chemical vapor deposition
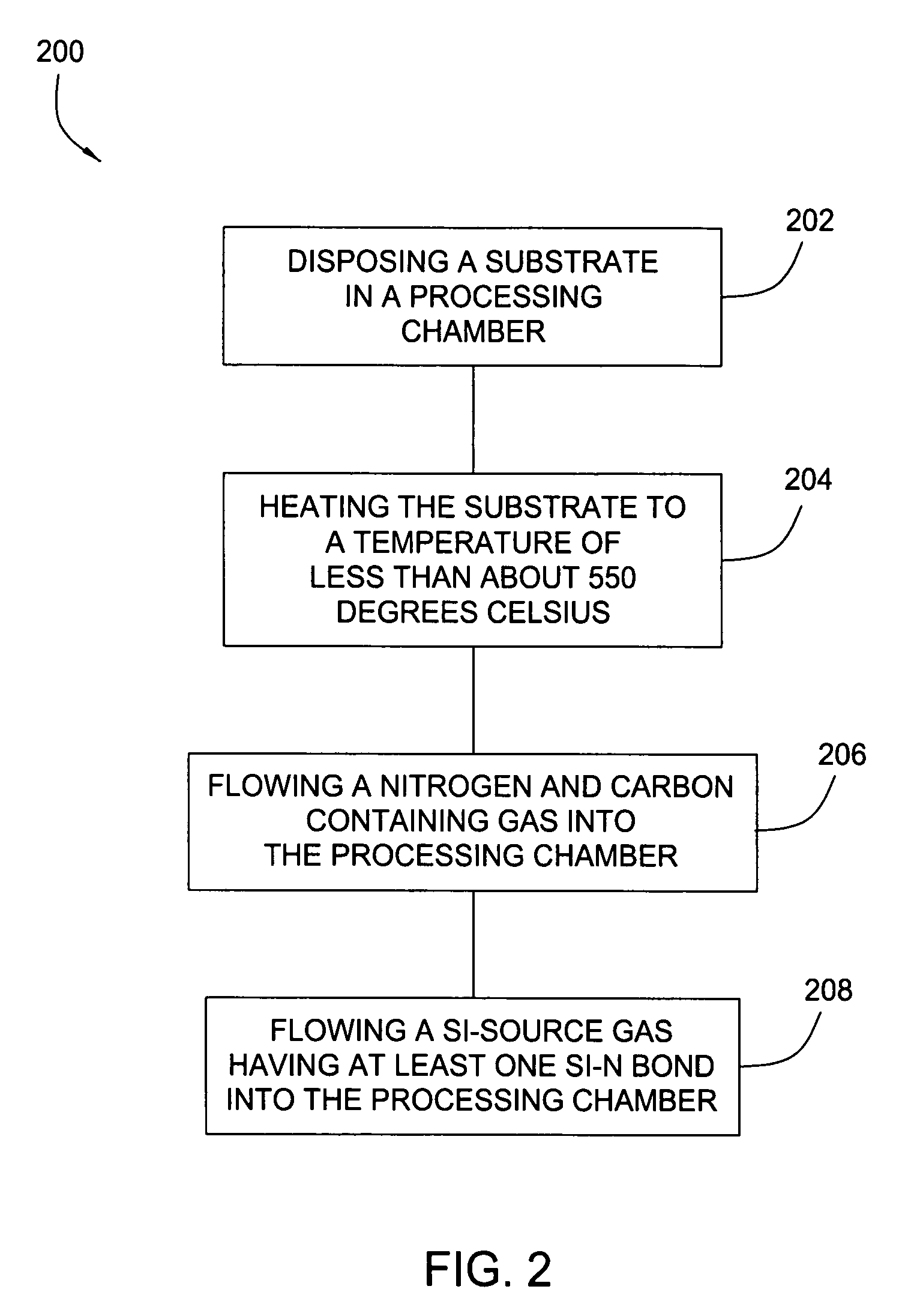
InactiveUS20060286818A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricCelsius Degree
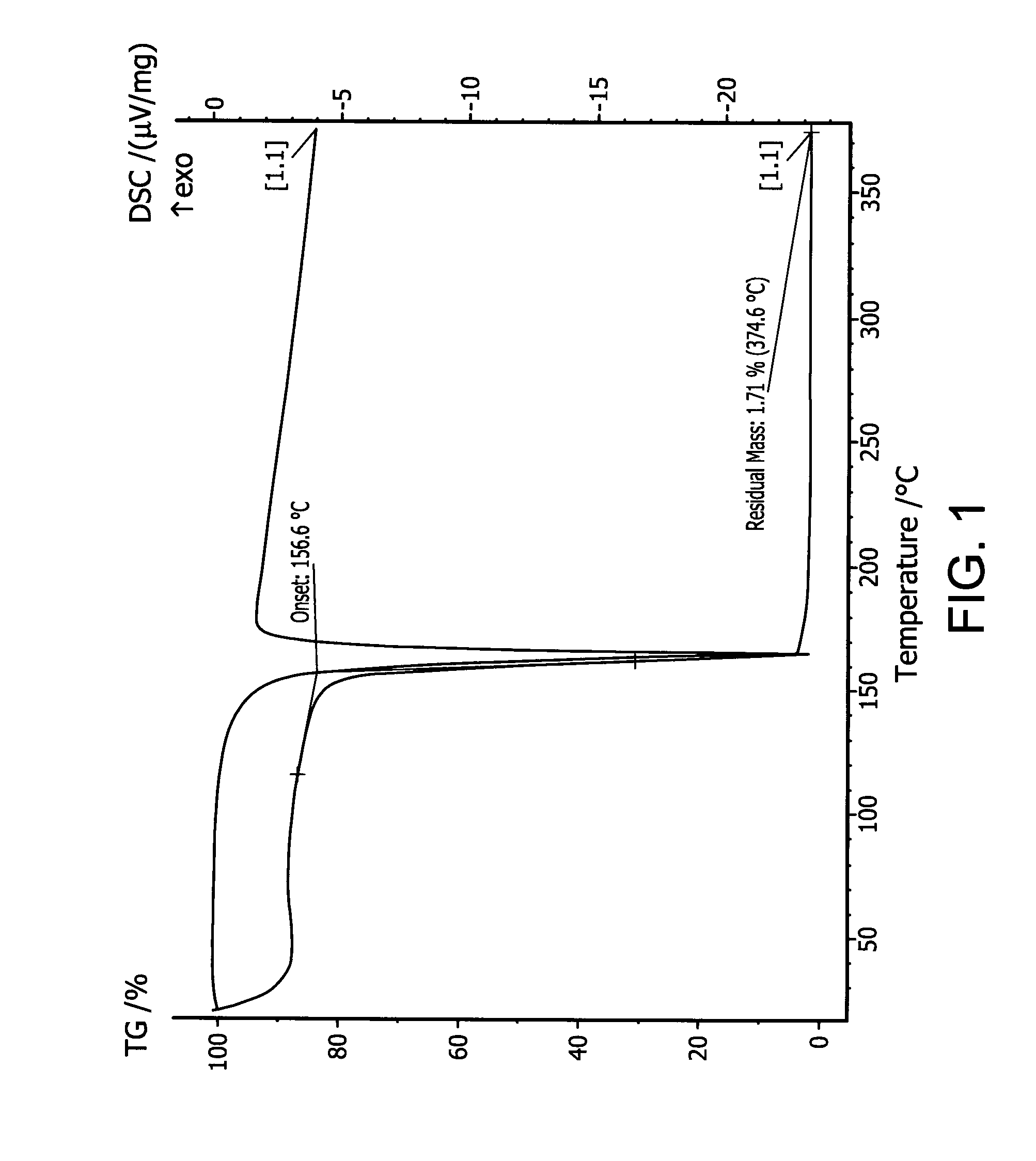
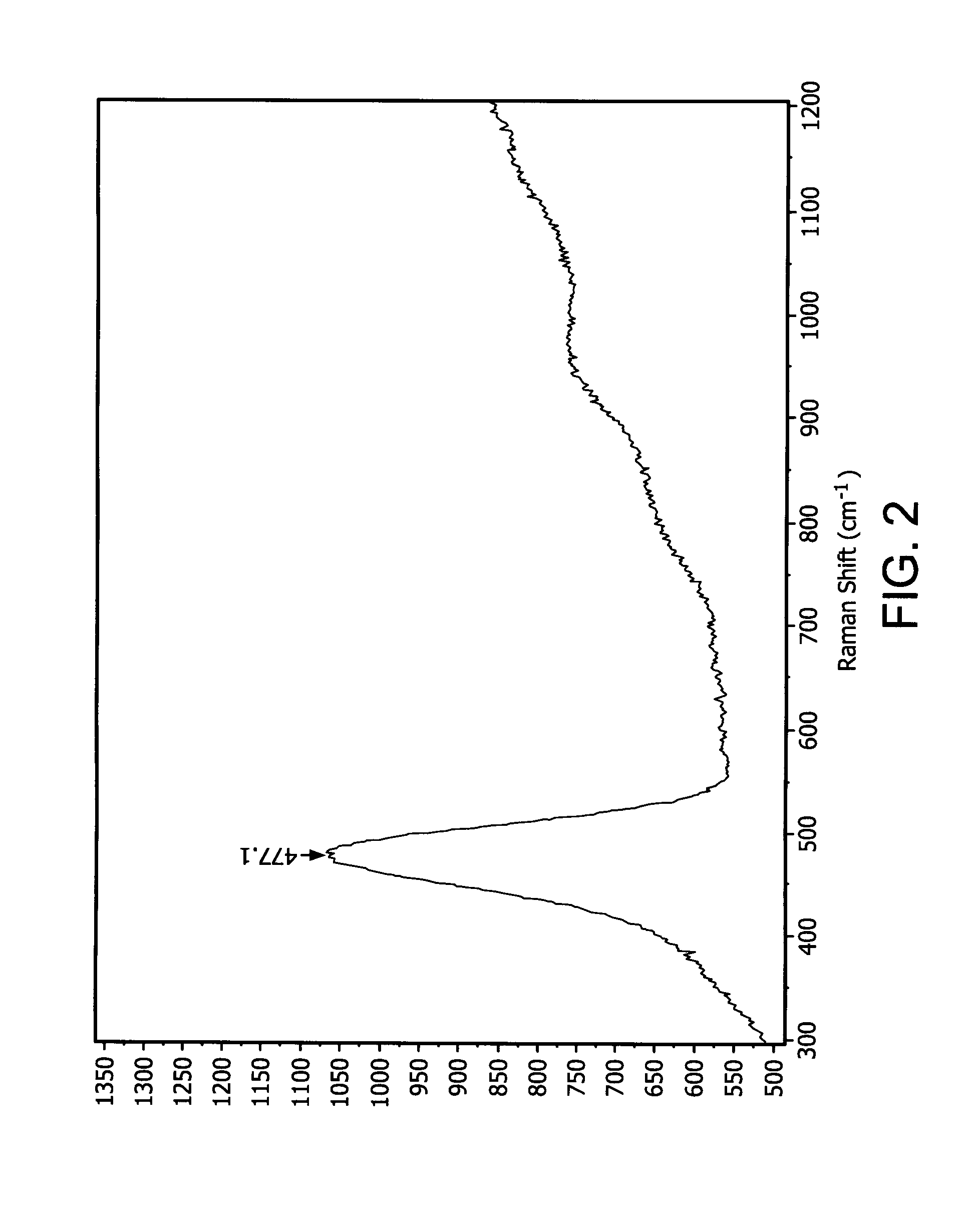
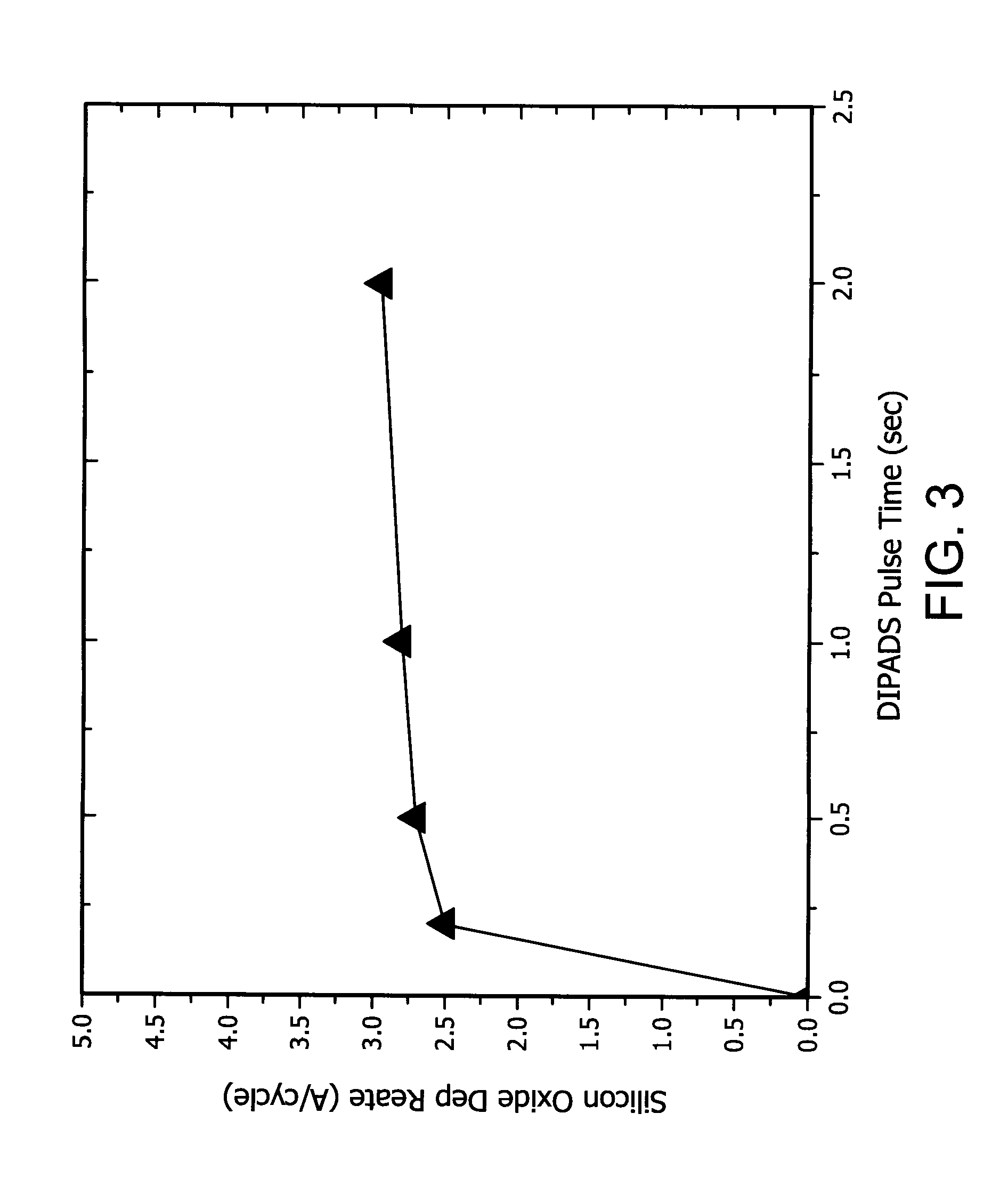
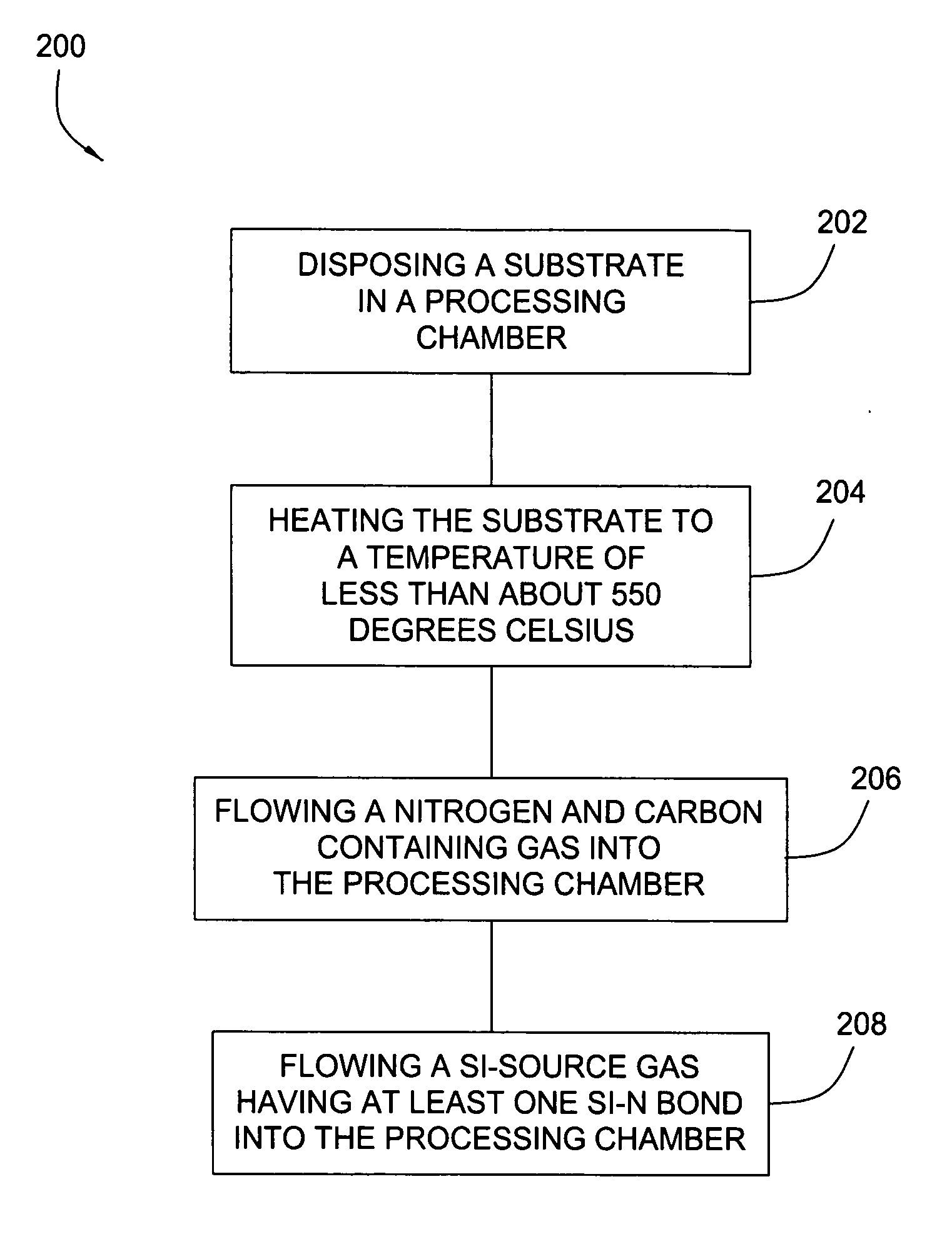
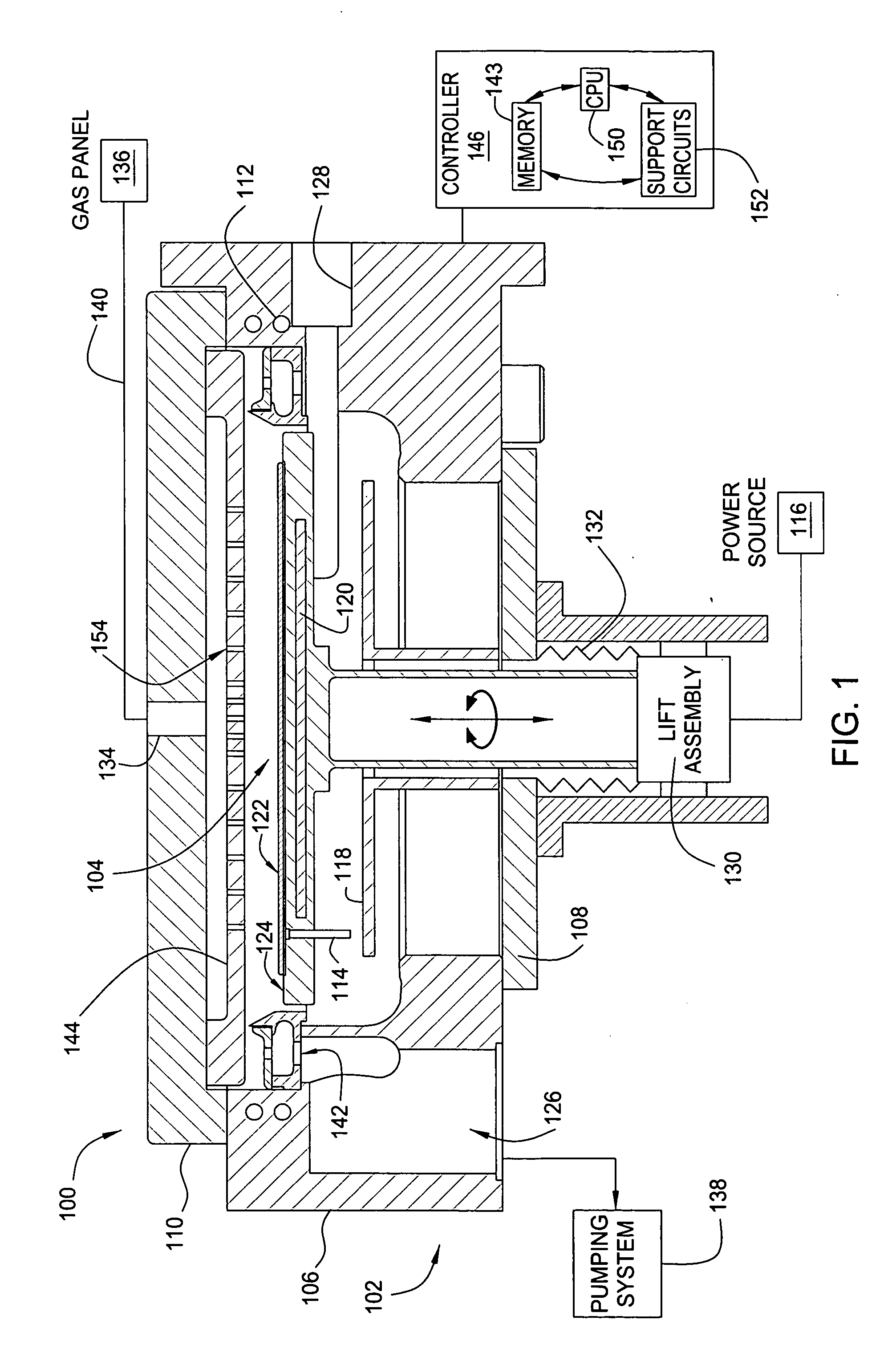
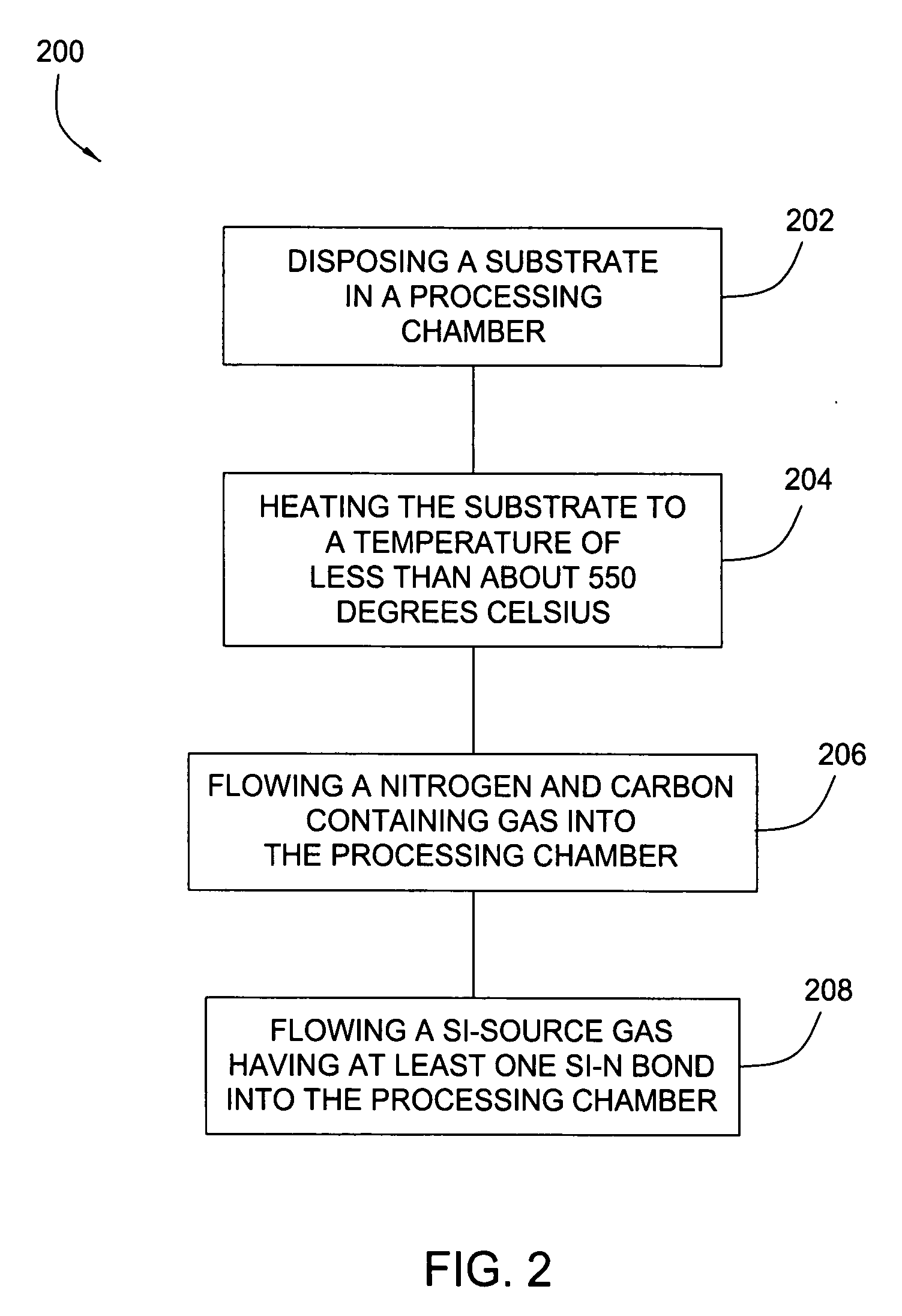
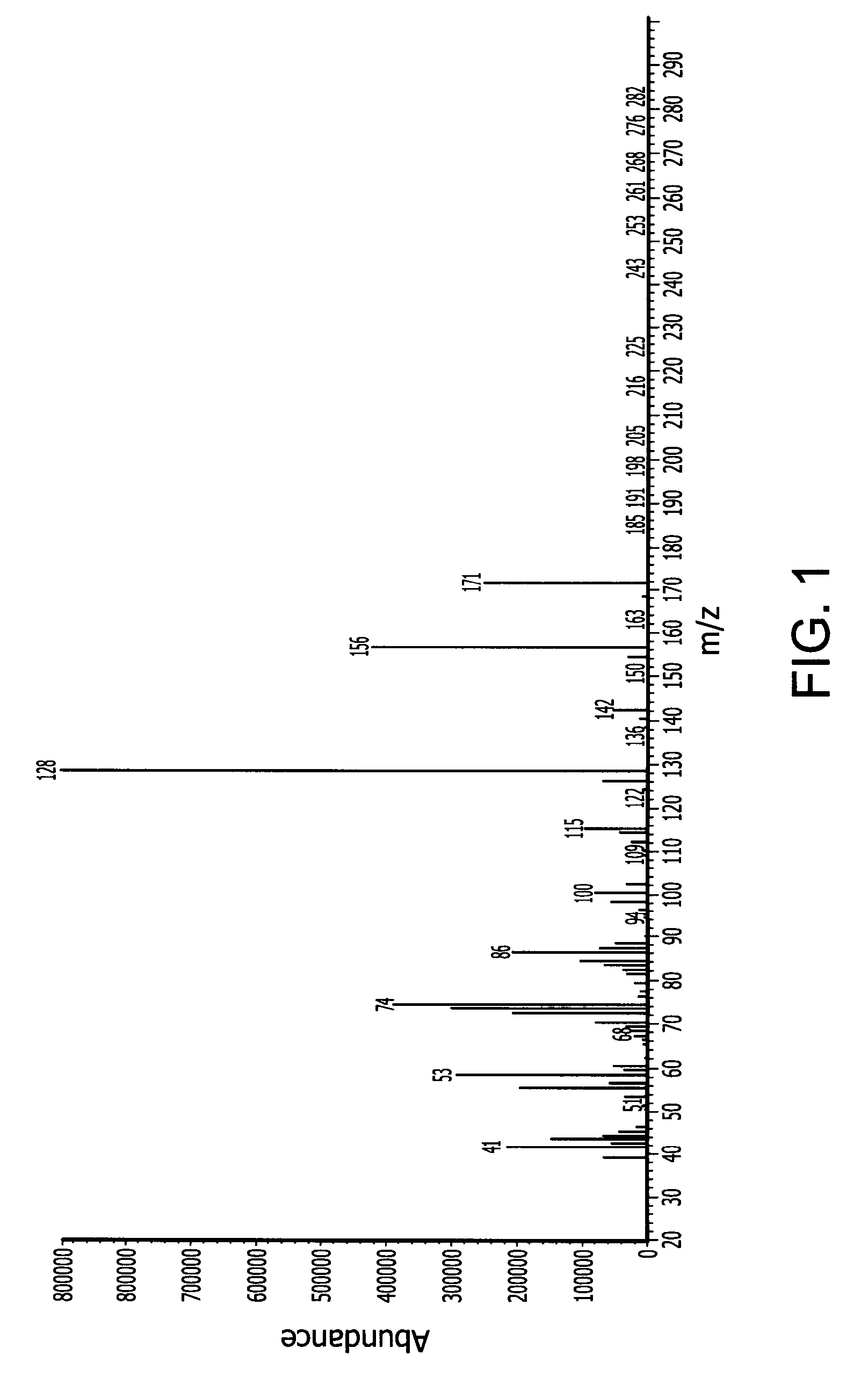
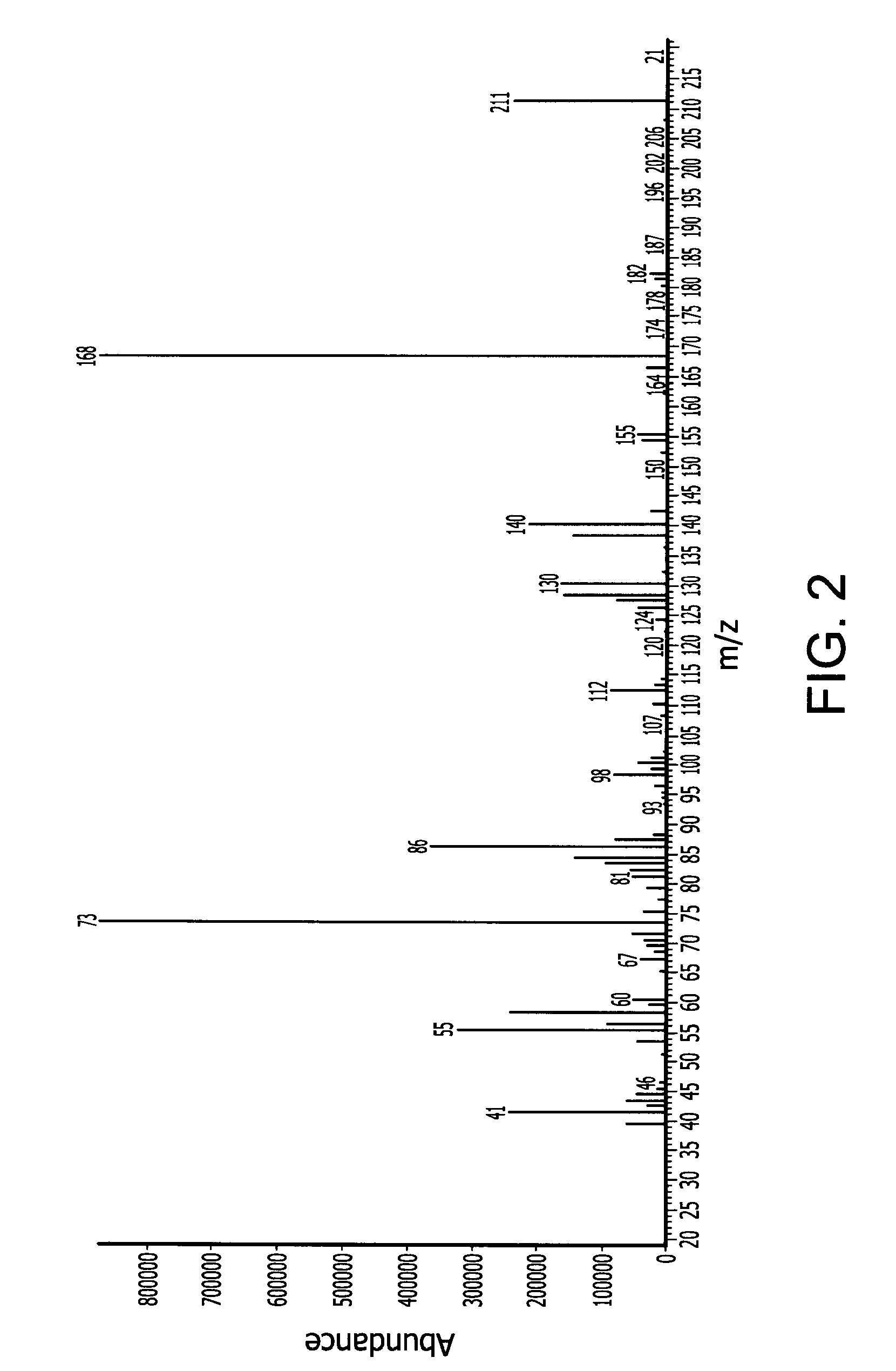
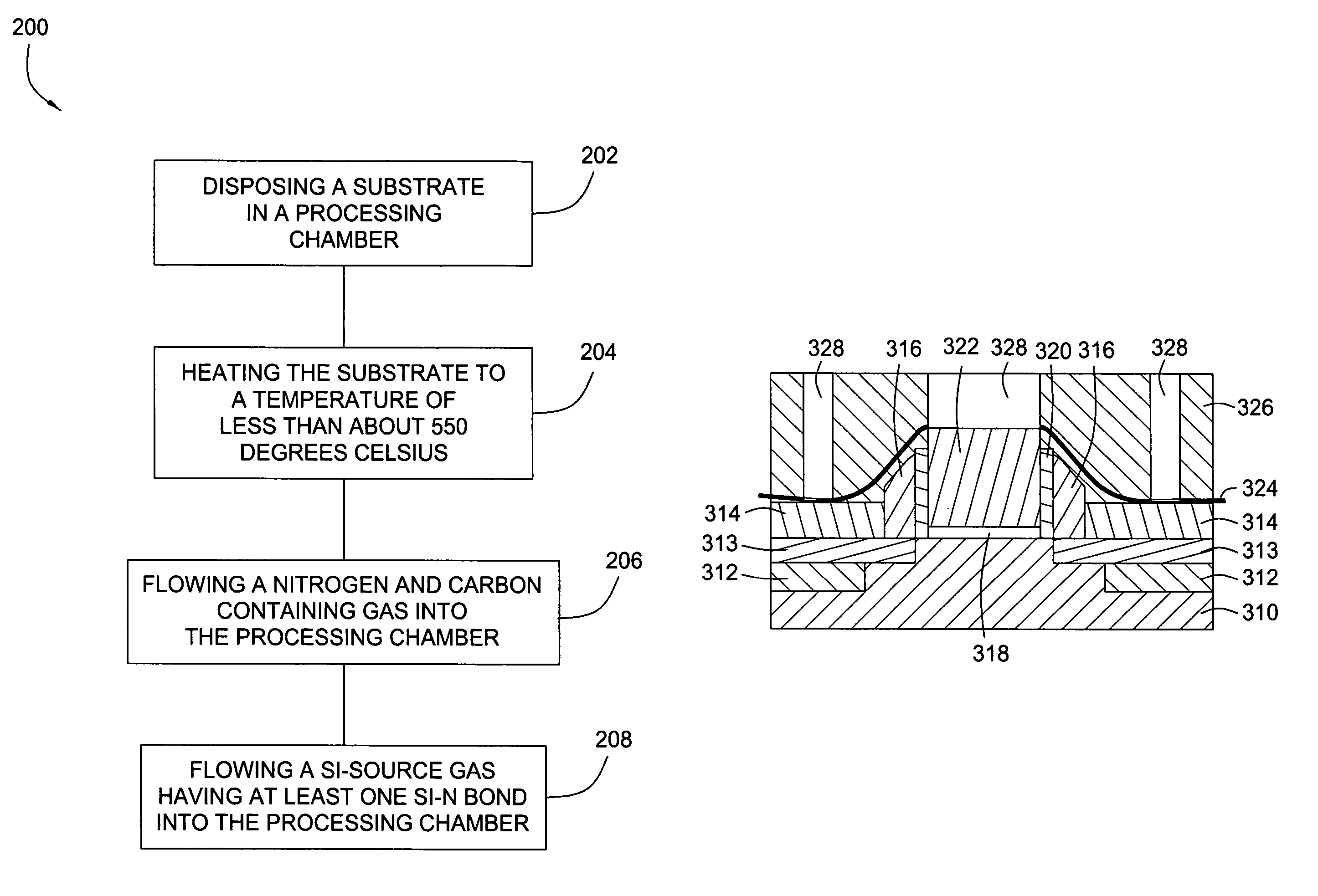
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing silicon-containing films. In one embodiment, a method for depositing silicon-containing material film on a substrate includes flowing a nitrogen and carbon containing chemical into a deposition chamber, flowing a silicon-containing source chemical having silicon-nitrogen bonds into the processing chamber, and heating the substrate disposed in the chamber to a temperature less than about 550 degrees Celsius. In another embodiment, the silicon containing chemical is trisilylamine and the nitrogen and carbon containing chemical is (CH3)3—N.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
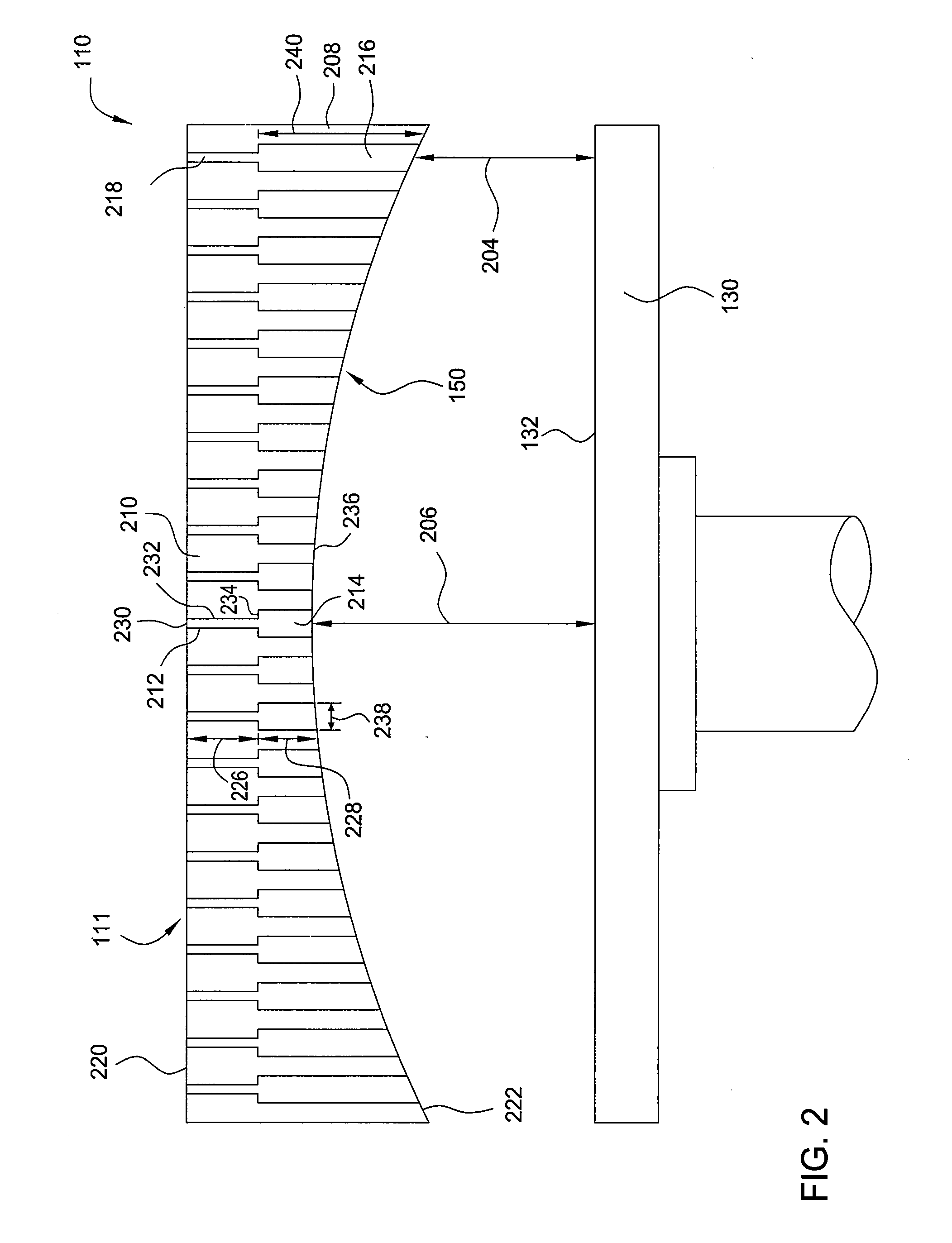
Methods and apparatus for depositing a uniform silicon film with flow gradient designs
Methods and apparatus having a flow gradient created from a gas distribution plate are provided. In one embodiment, the method and apparatus are particularly useful for, but not limited to, depositing a silicon film for solar cell applications. The apparatus for depositing a uniform film for solar cell applications includes a processing chamber, and a quadrilateral gas distribution plate disposed in the processing chamber and having at least four corners separated by four sides. The gas distribution plate further includes a first plurality of chokes formed through the gas distribution plate, the first plurality of chokes located in the corners, and a second plurality of chokes formed through the gas distribution plate, the second plurality of chokes located along the sides of the gas distribution plate between the corner regions, wherein the first plurality of chokes have a greater flow resistance than that of the second plurality of chokes.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
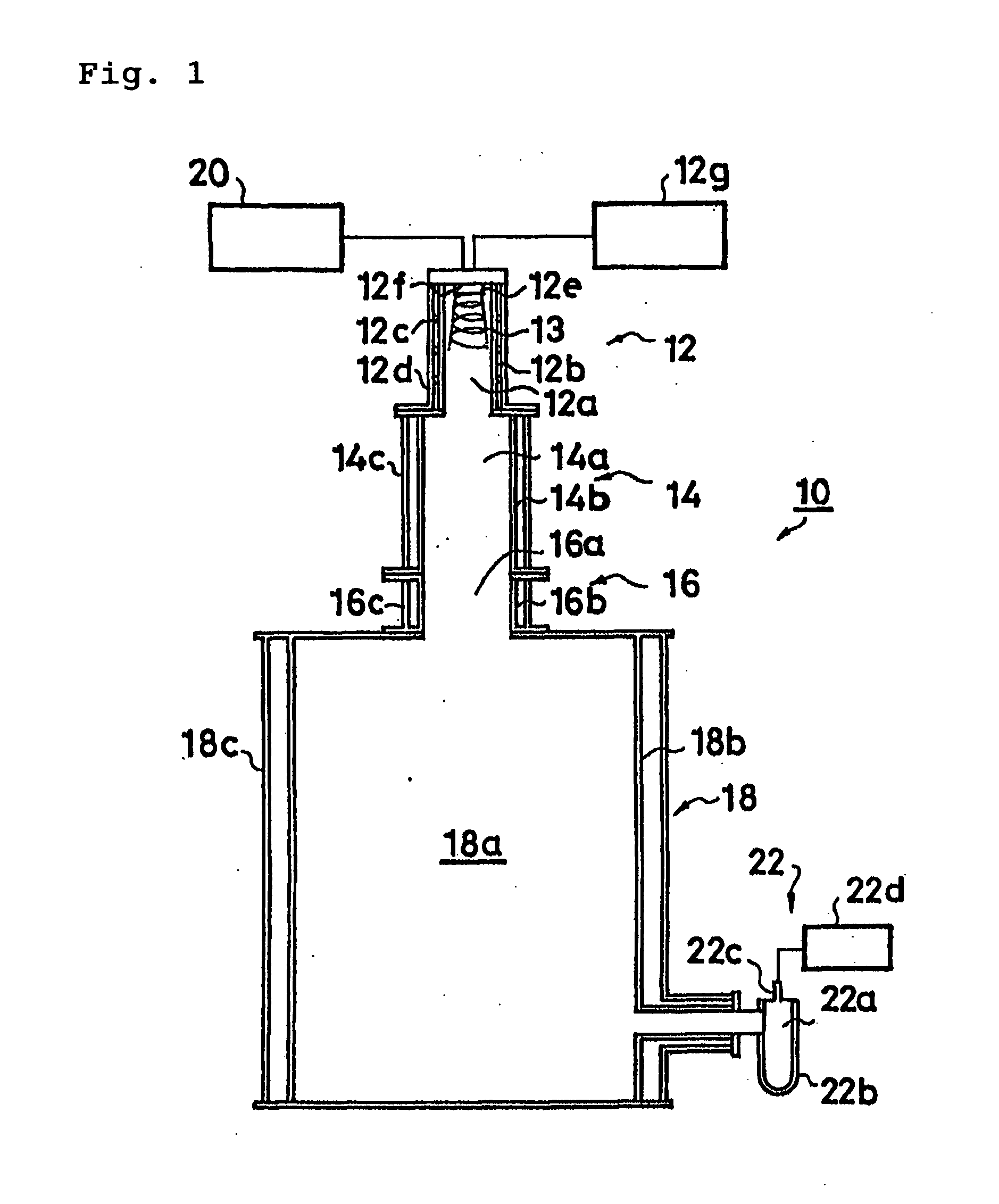
Substrate processing method
ActiveUS20110204025A1Decorative surface effectsPretreated surfacesDecompositionAMMONIUM SILICOFLUORIDE
A silicon-containing film on a substrate is subjected to a plasma process using a process gas containing fluorine and carbon, and is thereafter subjected to plasma process using an ammonia gas, whereby ammonium silicofluoride having toxicity and hygroscopic property is adhered to the substrate. The harmful ammonium silicofluoride is removed by the inventive method. After conducting the plasma process using an ammonia gas, the substrate is heated to a temperature not lower than the decomposition temperature of the ammonium silicofluoride to decompose the ammonium silicofluoride in a process container in which the plasma process was conducted, or in a process container connected with the processing vessel which the plasma process was conducted therein and is isolated from a clean room atmosphere.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
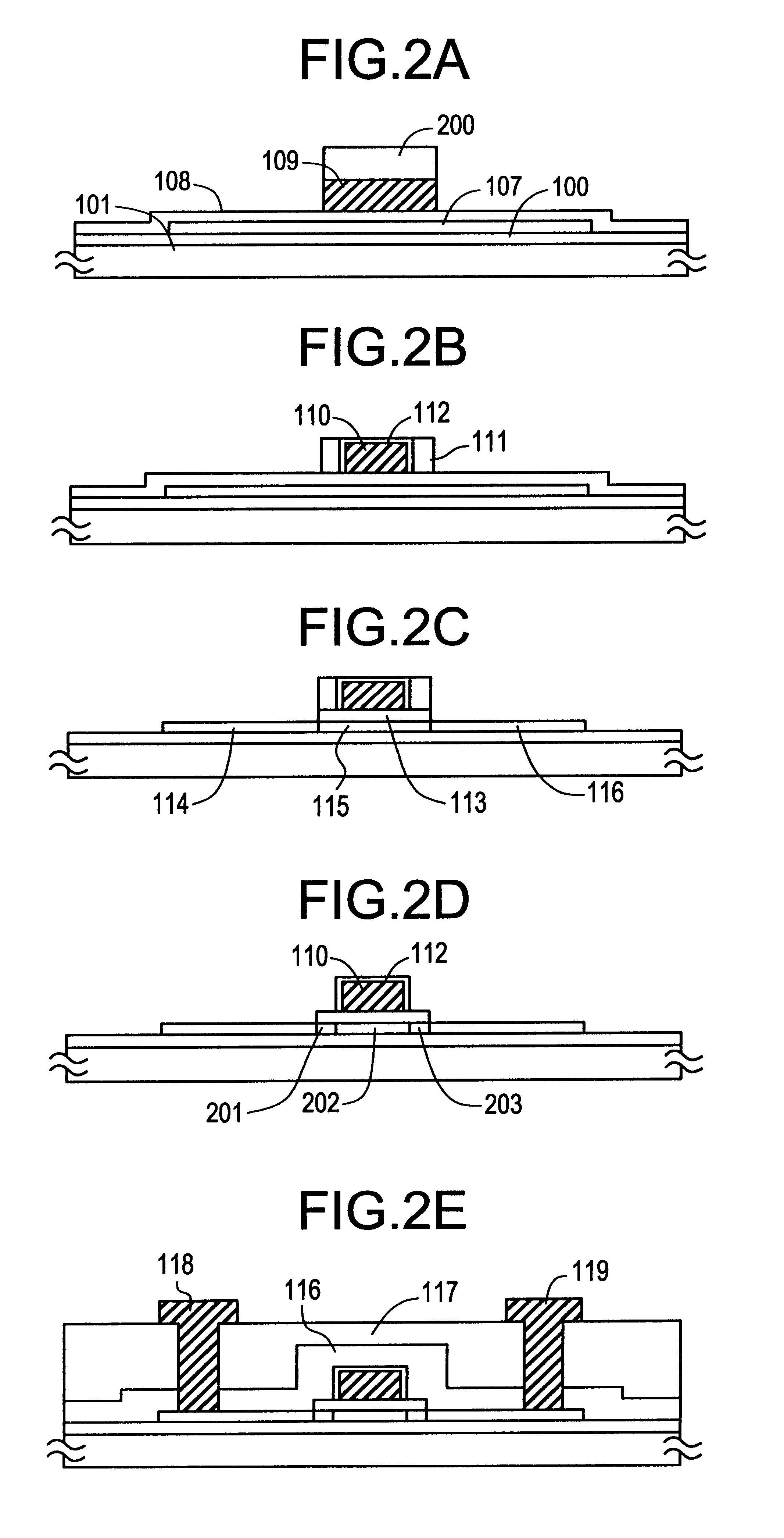
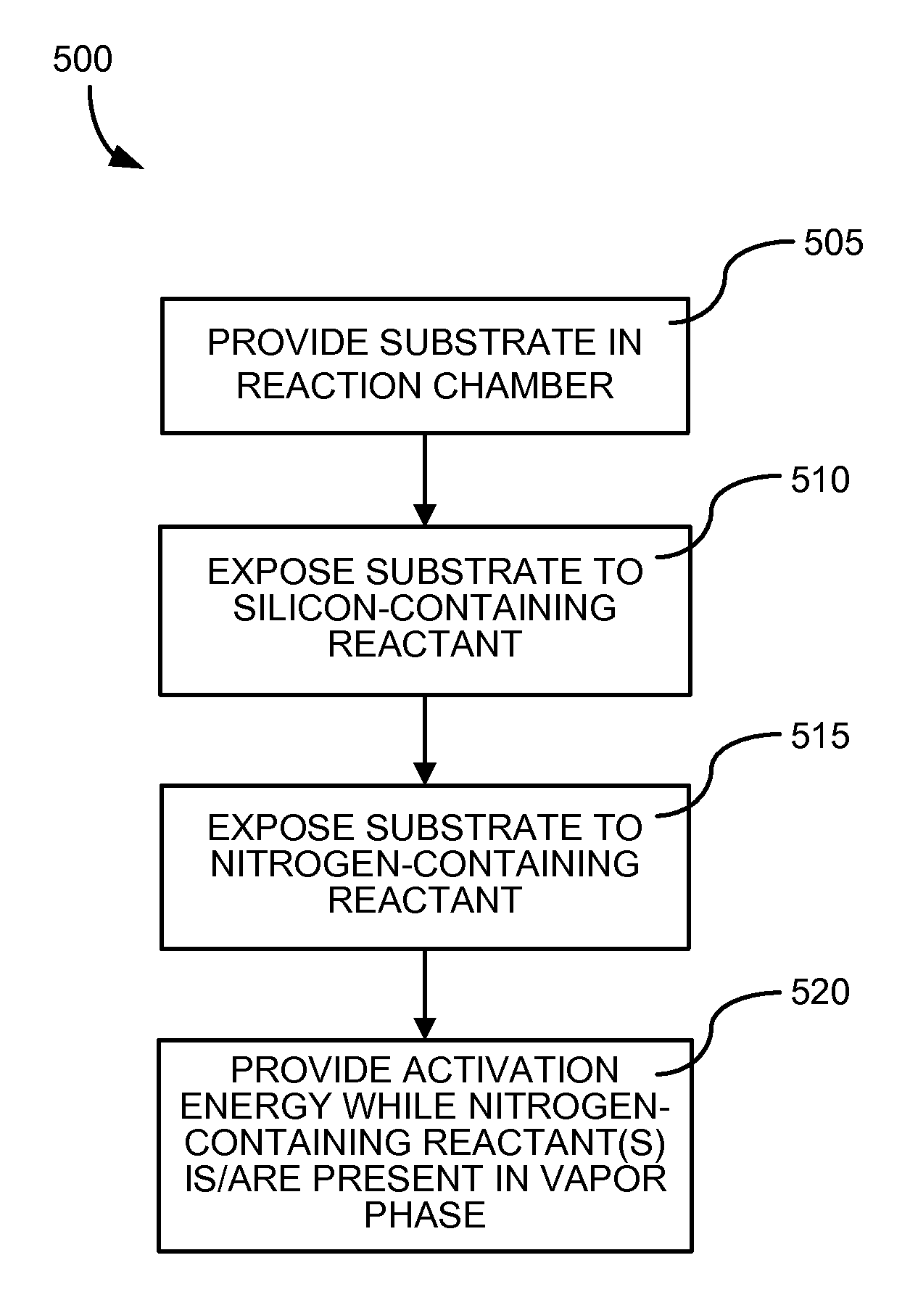
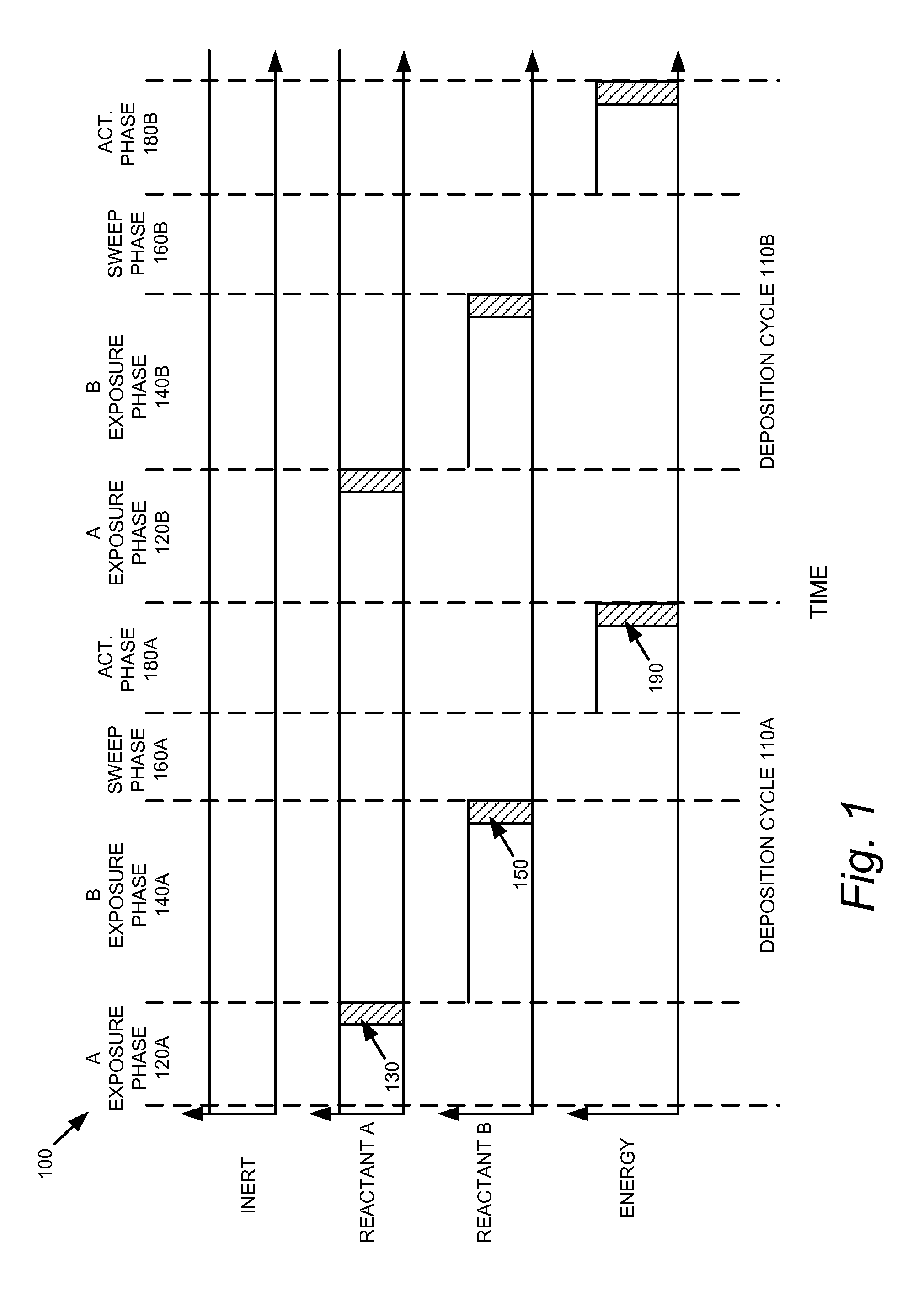
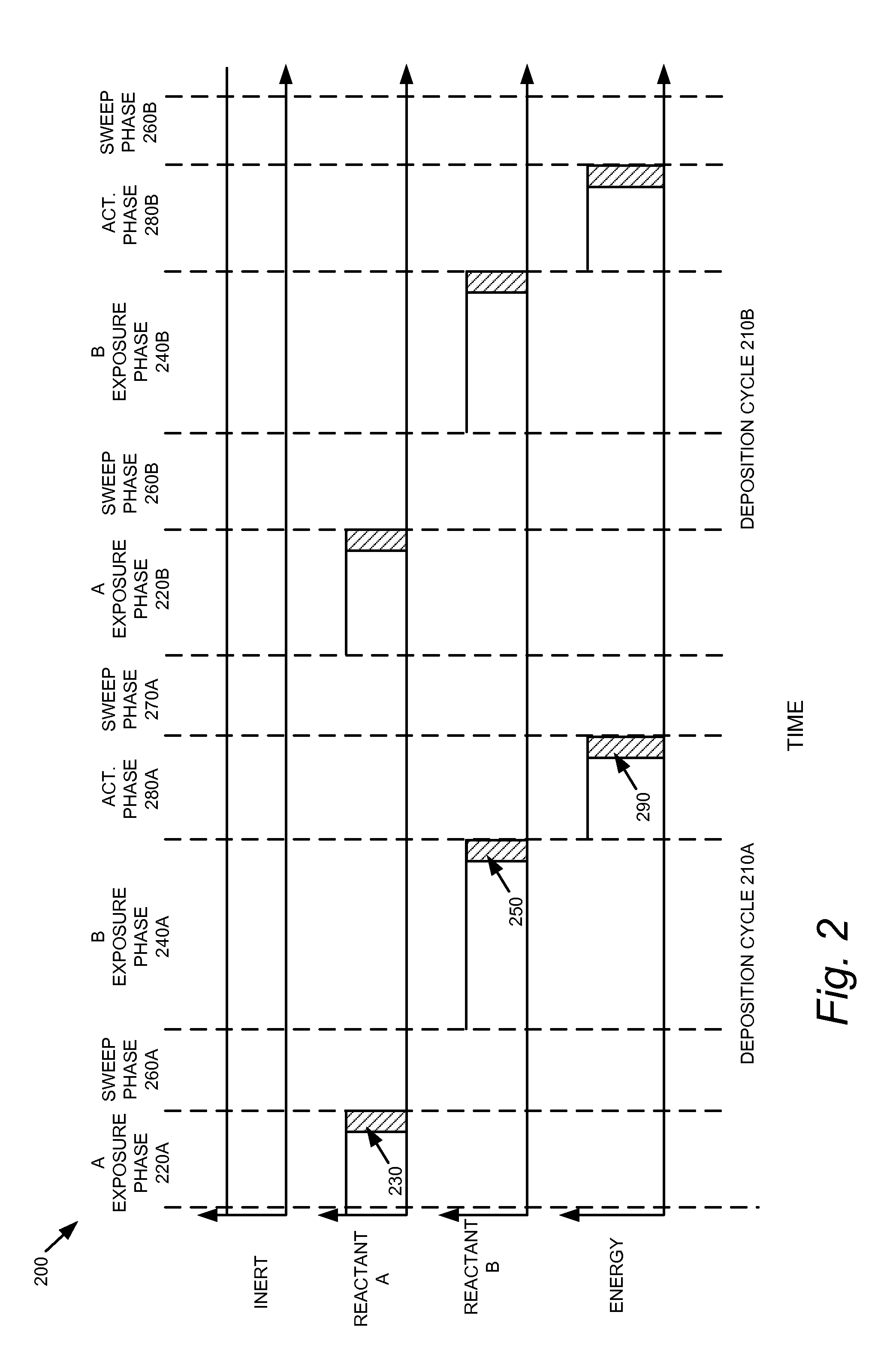
Method of forming silicon-containing films
A method of forming a silicon-containing film comprising providing a substrate in a reaction chamber, injecting into the reaction chamber at least one silicon-containing compound; injecting into the reaction chamber at least one co-reactant in the gaseous form; and reacting the substrate, silicon-containing compound, and co-reactant in the gaseous form at a temperature equal to or less than 550° C. to obtain a silicon-containing film deposited onto the substrate. A method of preparing a silicon nitride film comprising introducing a silicon wafer to a reaction chamber; introducing a silicon-containing compound to the reaction chamber; purging the reaction chamber with an inert gas; and introducing a nitrogen-containing co-reactant in gaseous form to the reaction chamber under conditions suitable for the formation of a monomolecular layer of a silicon nitride film on the silicon wafer.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
Method for forming low-carbon CVD film for filling trenches
ActiveUS20100143609A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolid state diffusion coatingBoiling pointSilicon membrane
A method of forming a low-carbon silicon-containing film by CVD on a substrate having trenches includes: introducing a silicon-containing compound having three or less hydrocarbon units in its molecule and having a boiling temperature of 35° C. to 220° C.; applying RF power to the gas; and depositing a film on a substrate having trenches wherein the substrate is controlled at a temperature such that components of the silicon-containing compound are at least partially liquidified on the substrate, thereby filling the trenches with the film.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
APPARATUSES AND METHODS FOR DEPOSITING SiC/SiCN FILMS VIA CROSS-METATHESIS REACTIONS WITH ORGANOMETALLIC CO-REACTANTS
ActiveUS20140193983A1Liquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon membraneSemiconductor
Disclosed herein are methods of forming SiC / SiCN film layers on surfaces of semiconductor substrates. The methods may include introducing a silicon-containing film-precursor and an organometallic ligand transfer reagent into a processing chamber, adsorbing the silicon-containing film-precursor, the organometallic ligand transfer reagent, or both onto a surface of a semiconductor substrate under conditions whereby either or both form an adsorption-limited layer, and reacting the silicon-containing film-precursor with the organometallic ligand transfer reagent, after either or both have formed the adsorption-limited layer. The reaction results in the forming of the film layer. In some embodiments, a byproduct is also formed which contains substantially all of the metal of the organometallic ligand transfer reagent, and the methods may further include removing the byproduct from the processing chamber. Also disclosed herein are semiconductor processing apparatuses for forming SiC / SiCN film layers.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
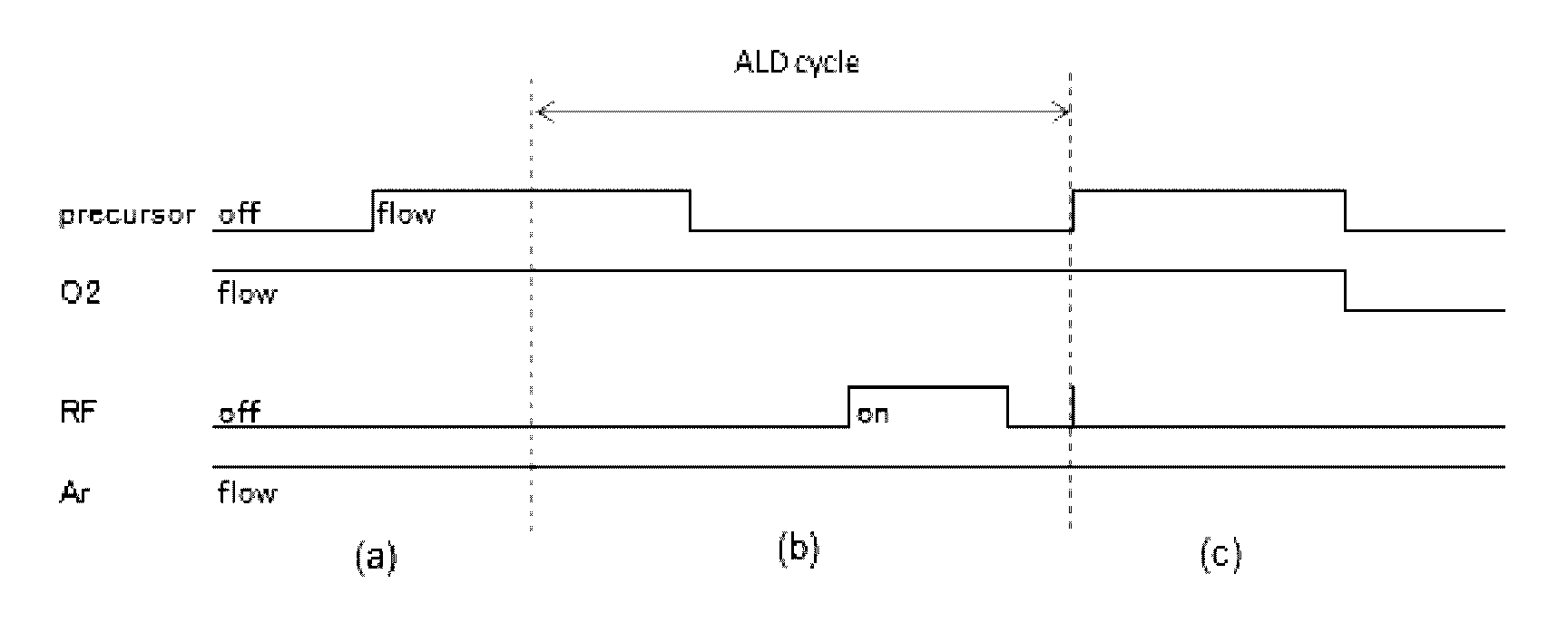
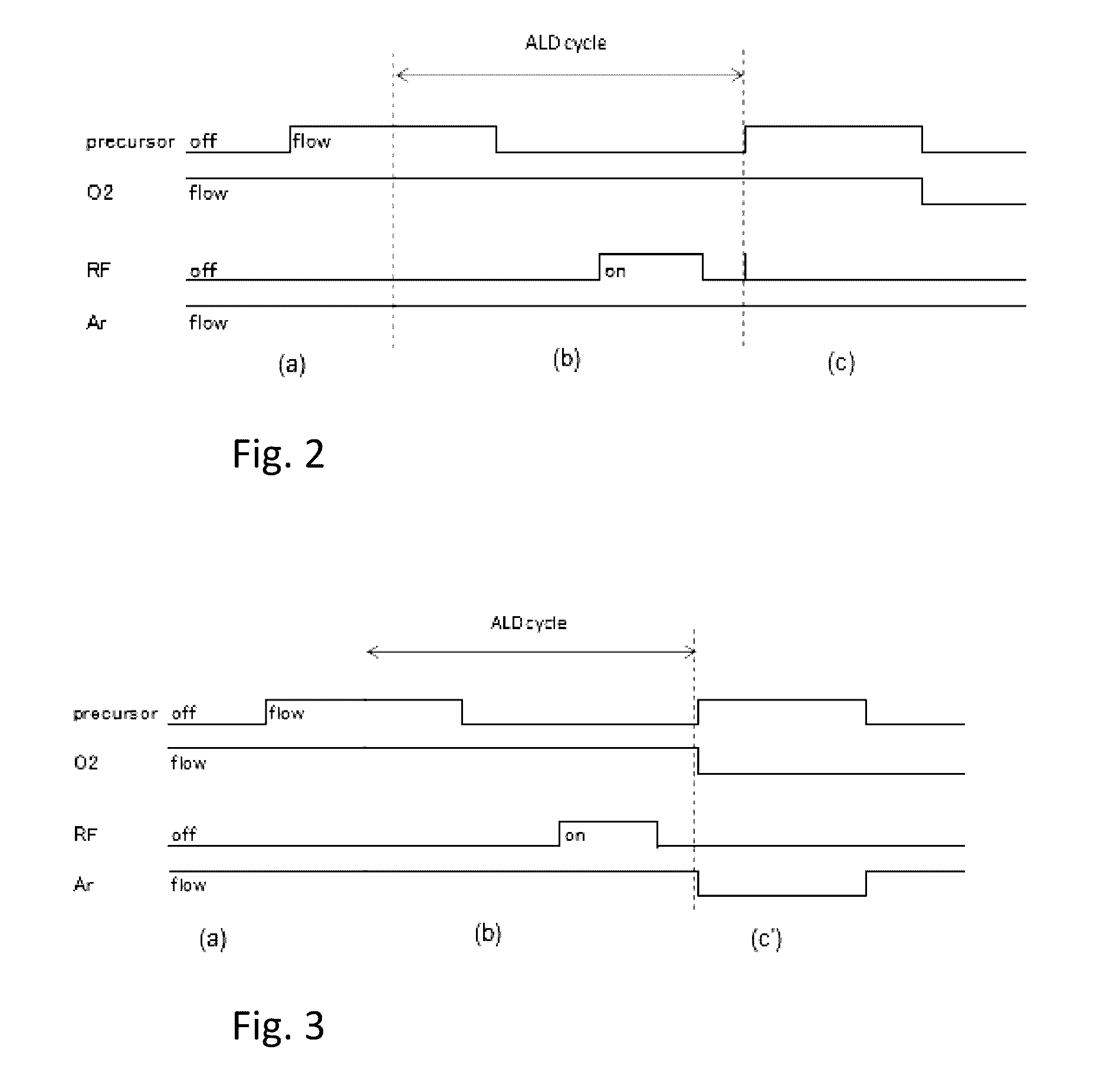
Method for hydrophobization of surface of silicon-containing film by ALD
ActiveUS9478414B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingAtmospheric airChemical adsorption
A method is for hydrophobization of a surface of a silicon-containing film by atomic layer deposition (ALD), wherein the surface is subjected to atmospheric exposure. The method includes: (i) providing a substrate with a silicon-containing film formed thereon; and (ii) forming on a surface of the silicon-containing film a hydrophobic atomic layer as a protective layer subjected to atmospheric exposure, by exposing the surface to a silicon-containing treating gas without exciting the gas. The treating gas is capable of being chemisorbed on the surface to form a hydrophobic atomic layer thereon.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
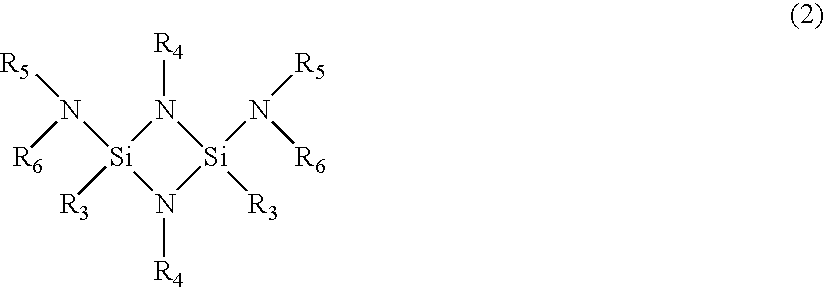
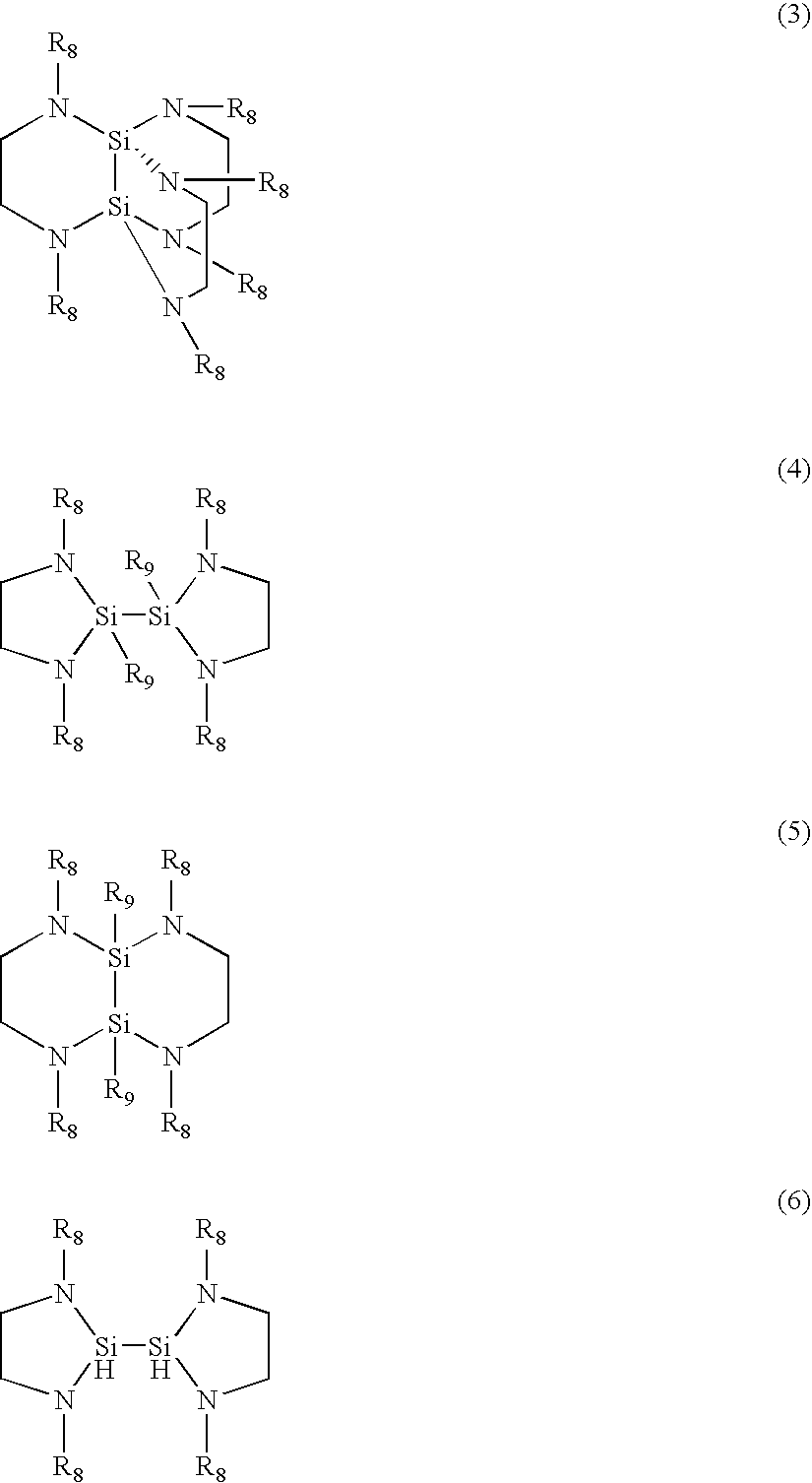
Organoaminosilane precursors and methods for making and using same
Described herein are organoaminosilane precursors which can be used to deposit silicon containing films which contain silicon and methods for making these precursors. Also disclosed herein are deposition methods for making silicon-containing films or silicon containing films using the organoaminosilane precursors described herein. Also disclosed herein are the vessels that comprise the organoaminosilane precursors or a composition thereof that can be used, for example, to deliver the precursor to a reactor in order to deposit a silicon-containing film.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Method for silicon based dielectric chemical vapor deposition
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing silicon-containing films. In one embodiment, a method for depositing silicon-containing material film on a substrate includes flowing a nitrogen and carbon containing chemical into a deposition chamber, flowing a silicon-containing source chemical having silicon-nitrogen bonds into the processing chamber, and heating the substrate disposed in the chamber to a temperature less than about 550 degrees Celsius. In another embodiment, the silicon containing chemical is trisilylamine and the nitrogen and carbon containing chemical is (CH3)3—N.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Organoaminosilane precursors and methods for depositing films comprising same
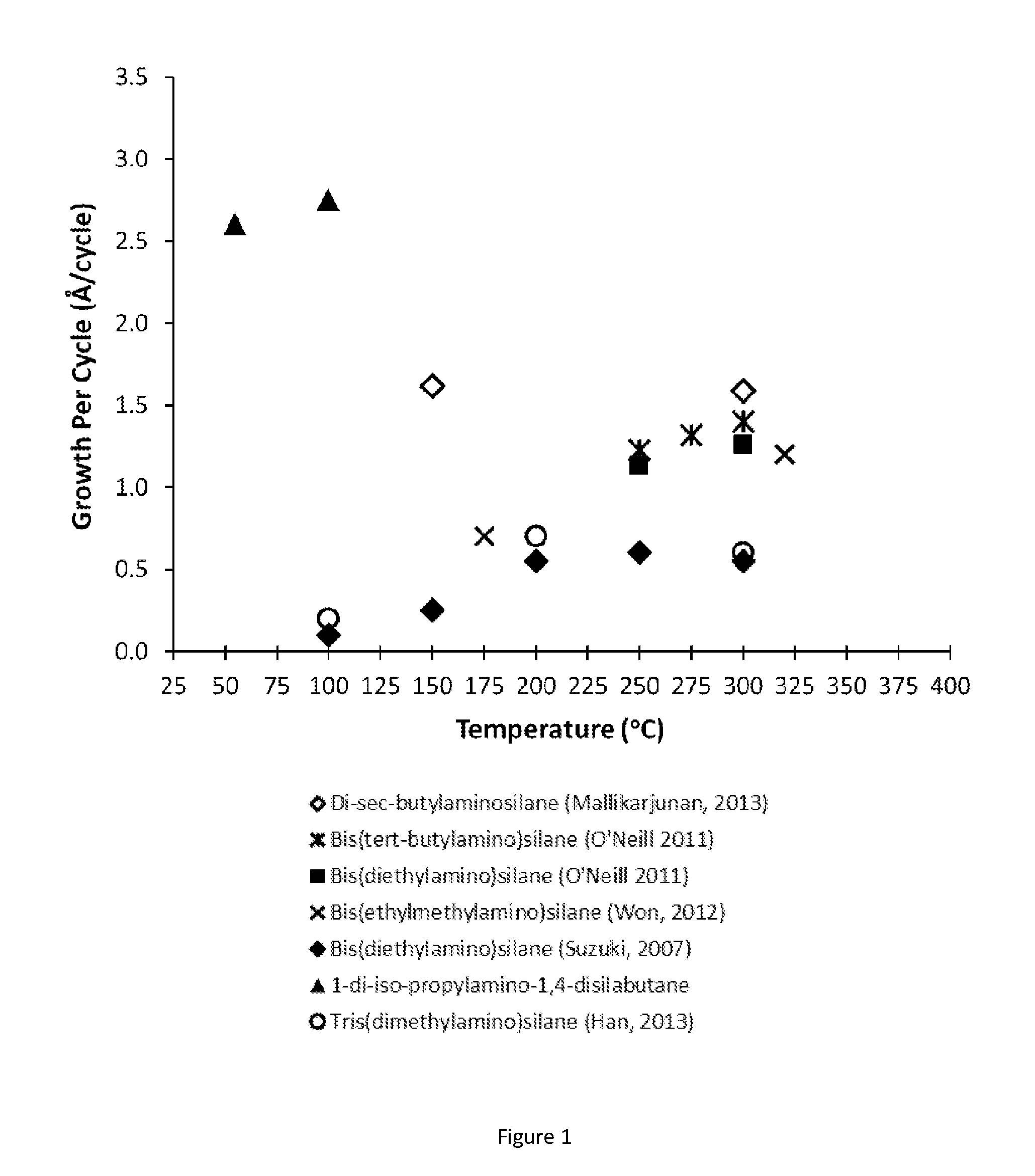
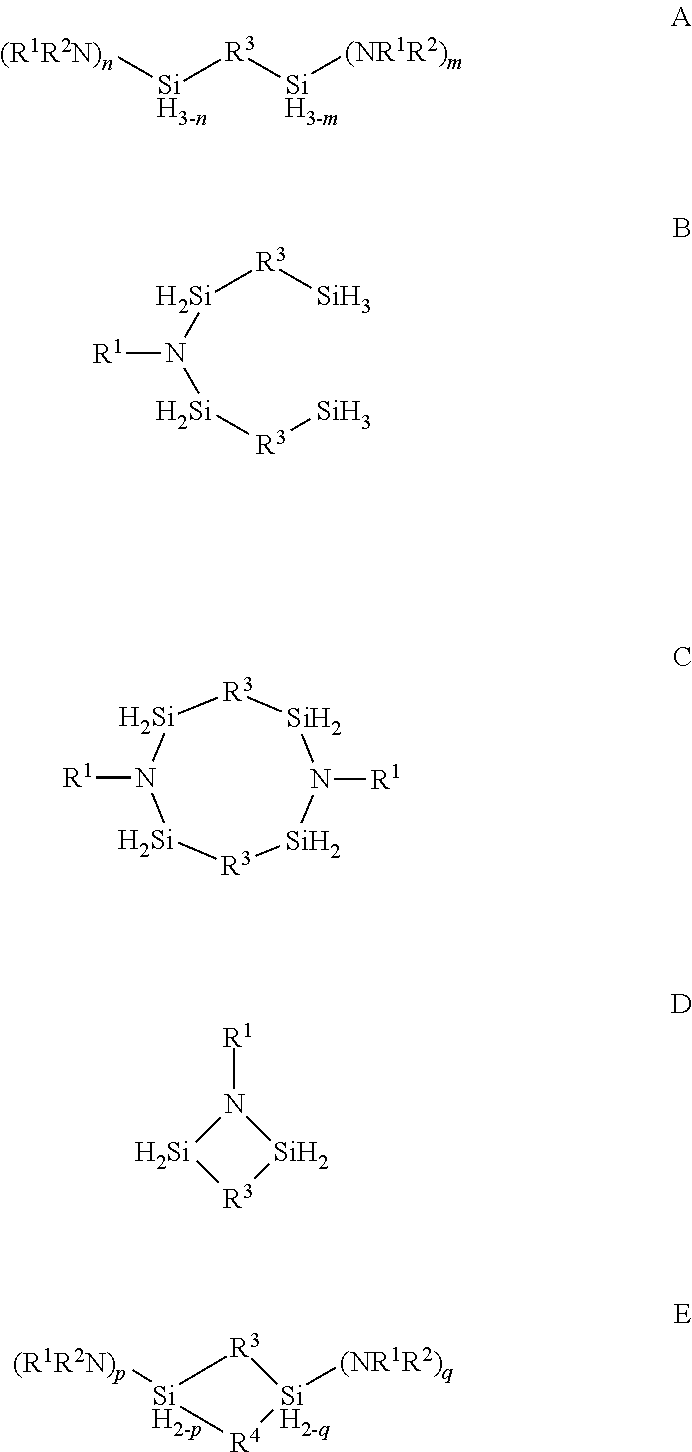
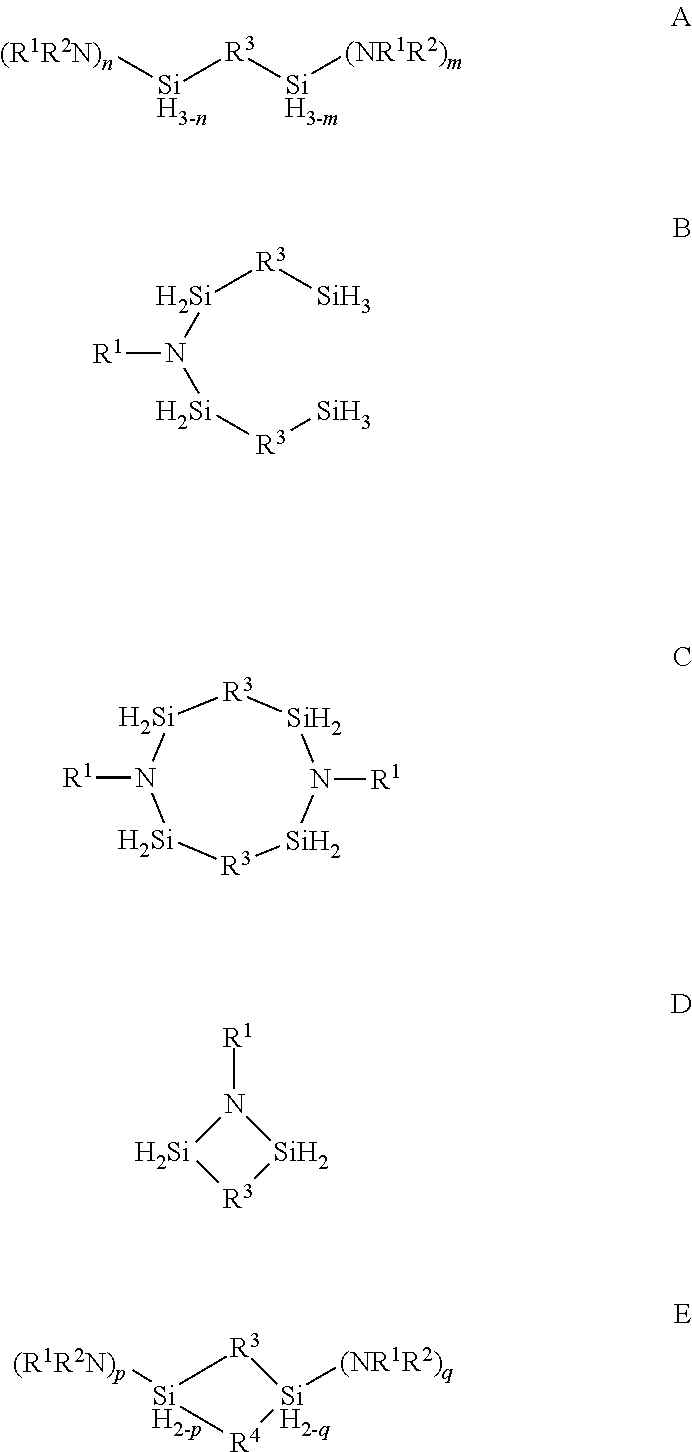
ActiveUS20150087139A1Low temperature efficientlySilicon organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationSilanesPhysical chemistry
Described herein are precursors and methods for forming silicon-containing films. In one aspect, the precursor comprises a compound represented by one of following Formulae A through E below:In one particular embodiment, the organoaminosilane precursors are effective for a low temperature (e.g., 350° C. or less), atomic layer deposition (ALD) or plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD) of a silicon-containing film. In addition, described herein is a composition comprising an organoaminosilane described herein wherein the organoaminosilane is substantially free of at least one selected from the amines, halides (e.g., Cl, F, I, Br), higher molecular weight species, and trace metals.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Precursors and flowable CVD methods for making low-K films to fill surface features
A method for depositing a silicon-containing film, the method comprising: placing a substrate comprising at least one surface feature into a flowable CVD reactor which is at a temperature of from about −20° C. to about 400° C.; introducing into the reactor at least one silicon-containing compound having at least one acetoxy group to at least partially react the at least one silicon-containing compound to form a flowable liquid oligomer wherein the flowable liquid oligomer forms a silicon oxide coating on the substrate and at least partially fills at least a portion of the at least one surface feature. Once cured, the silicon oxide coating has a low k and excellent mechanical properties.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
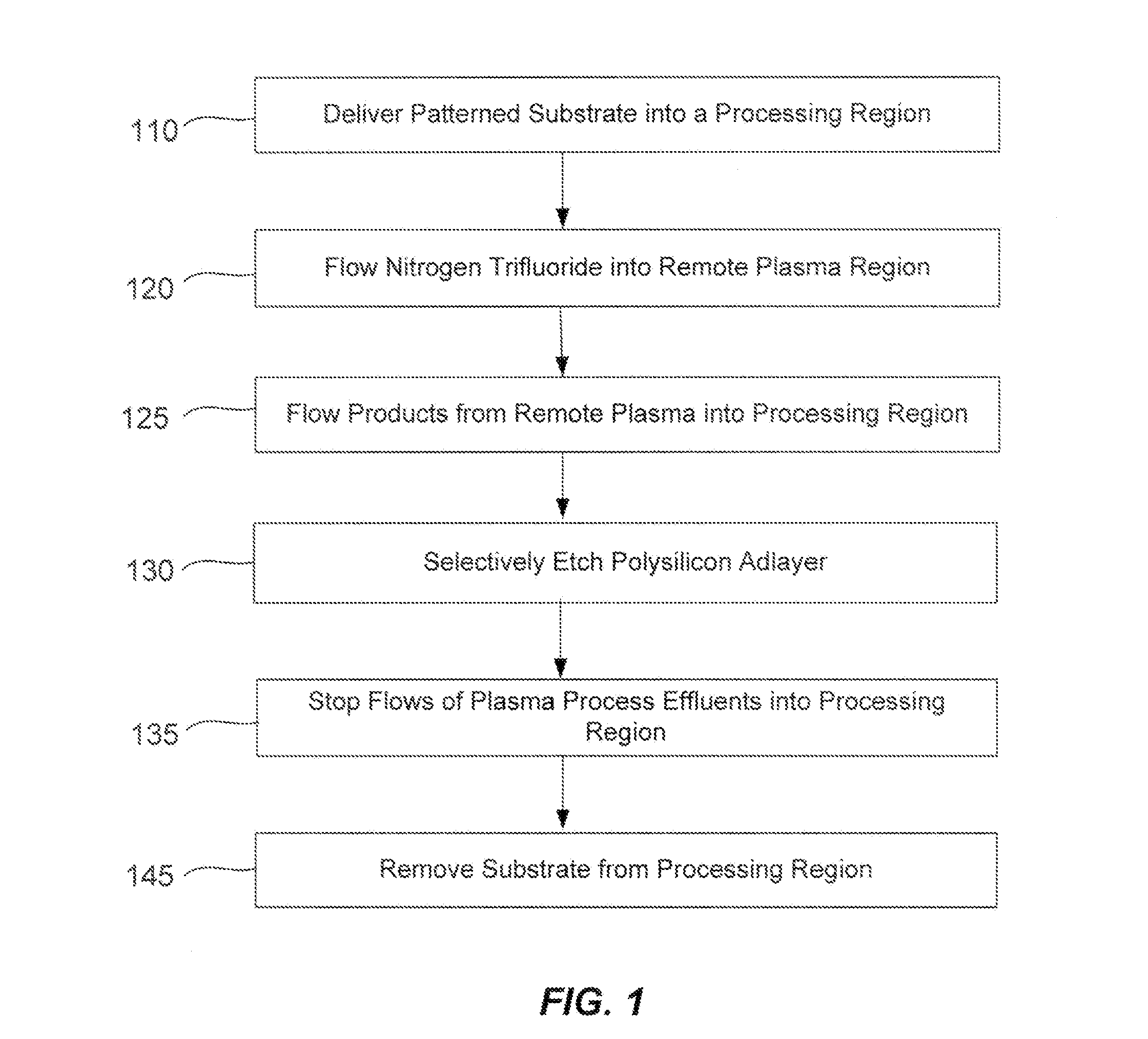
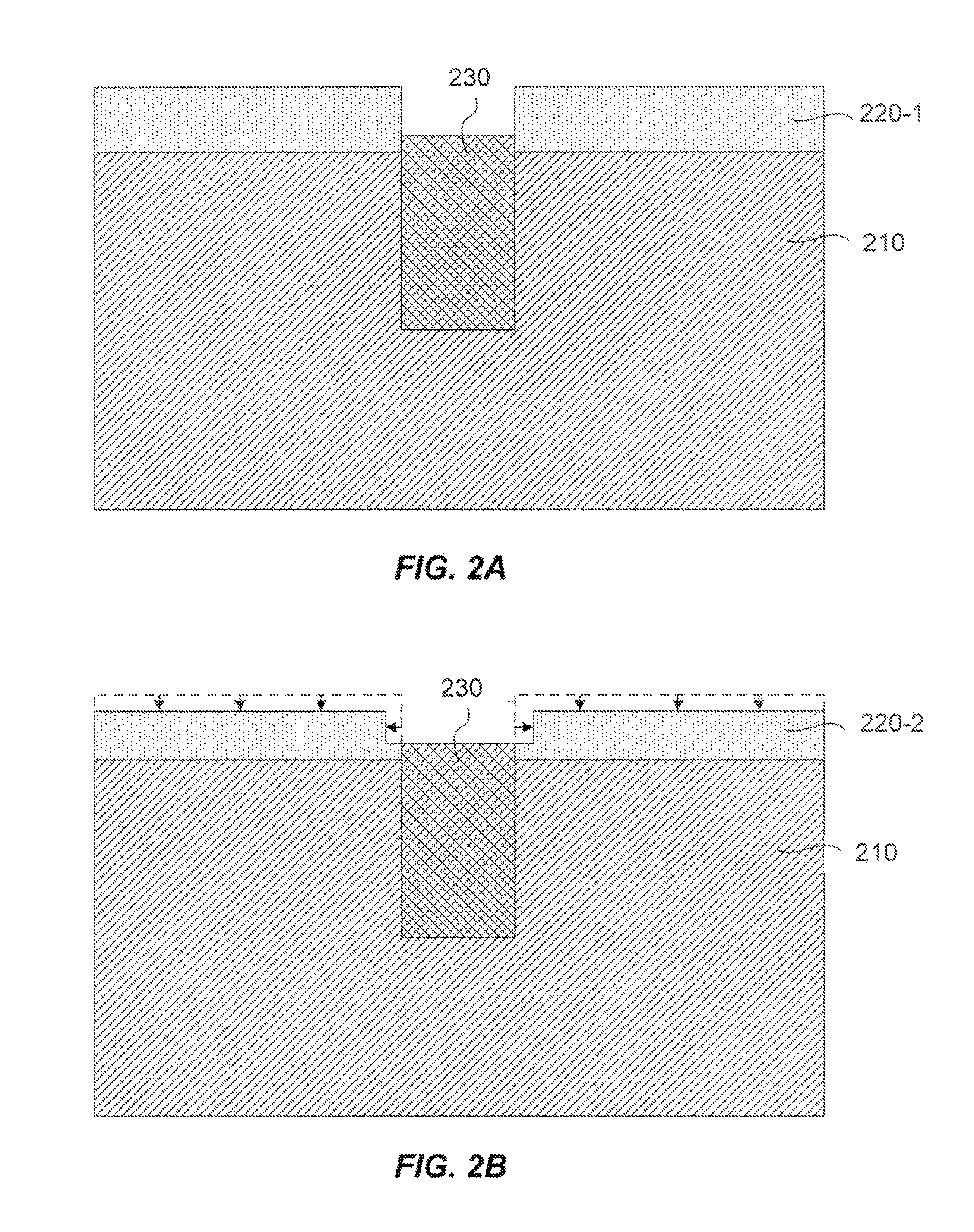
Selective etch for silicon films
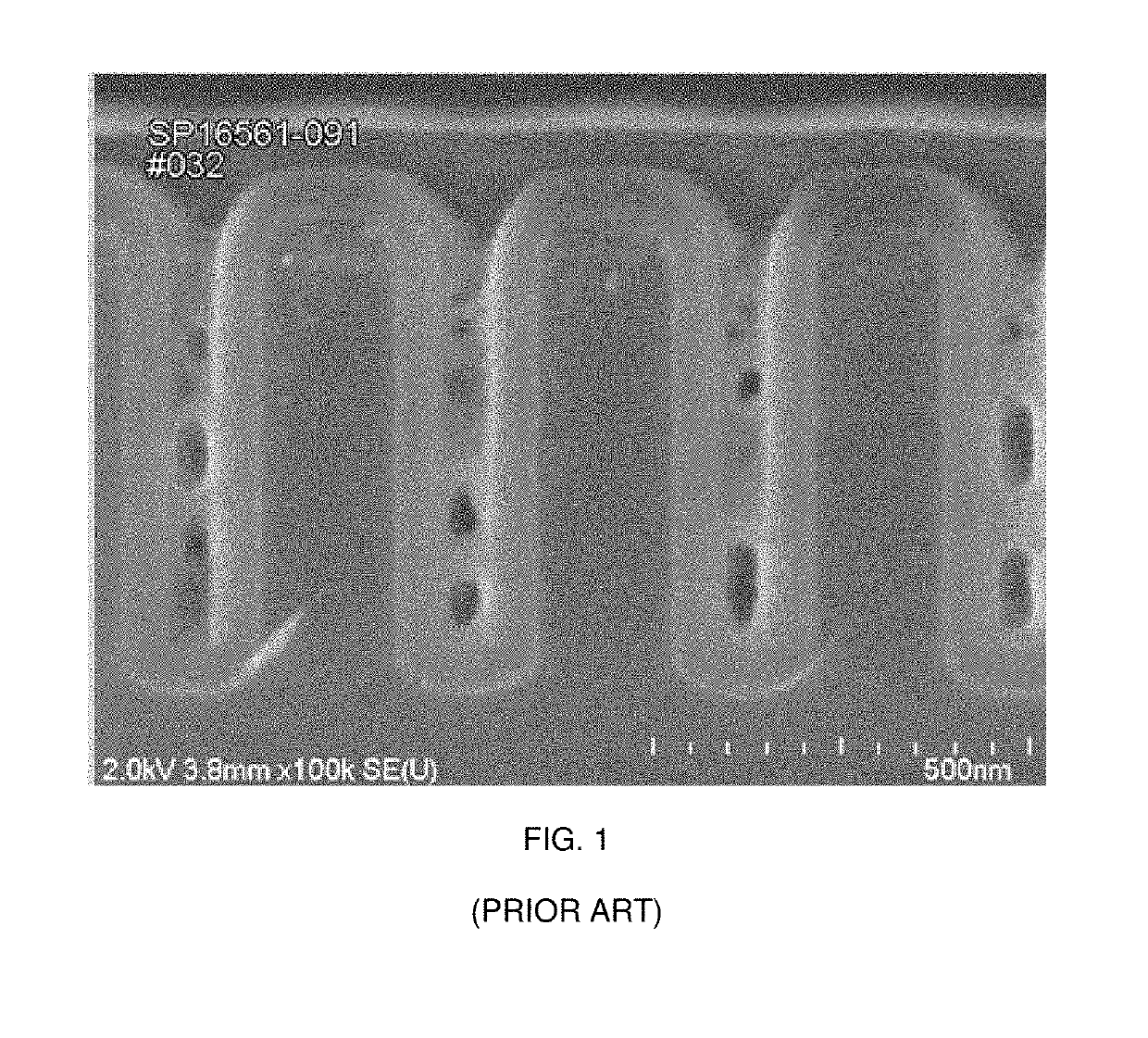
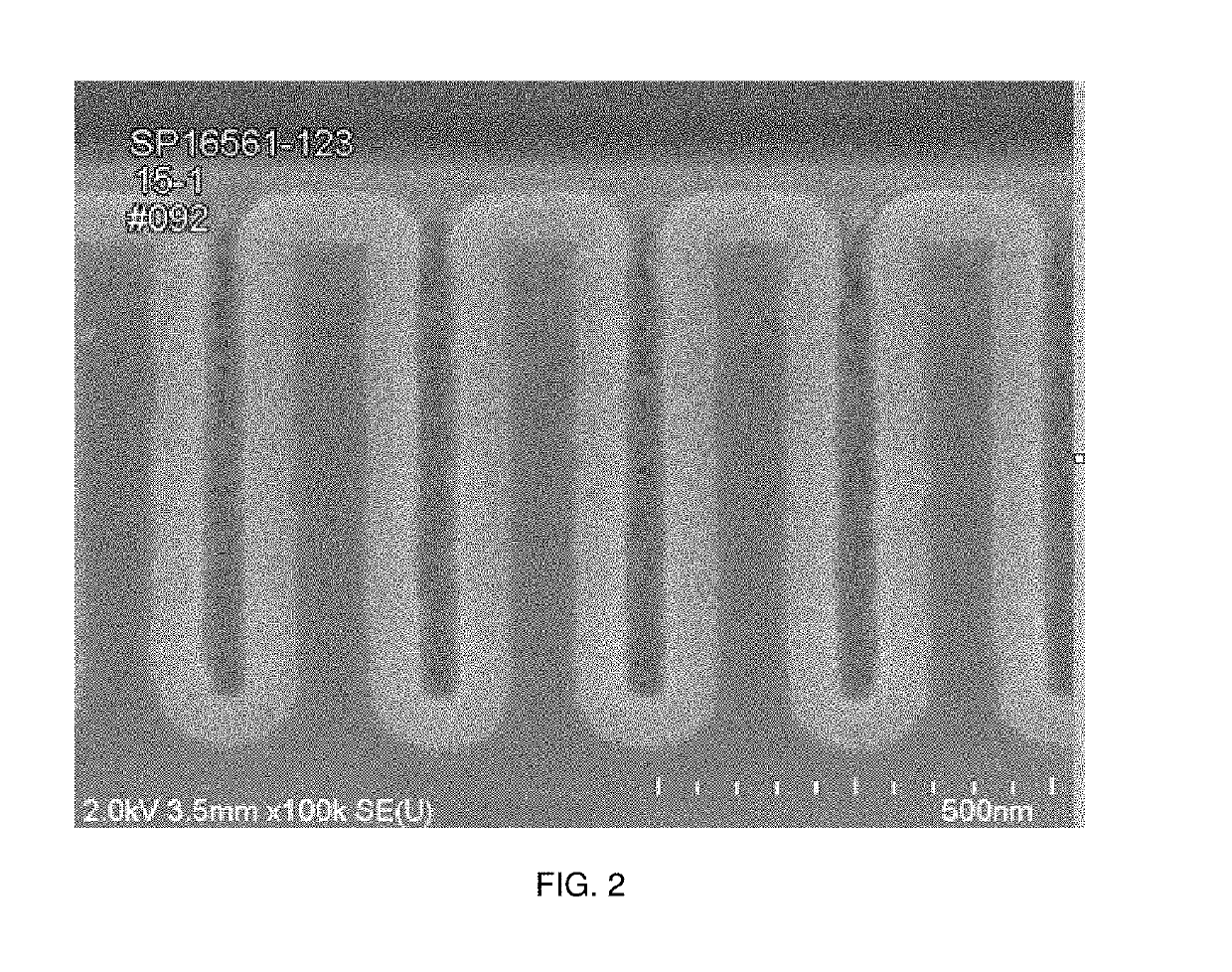
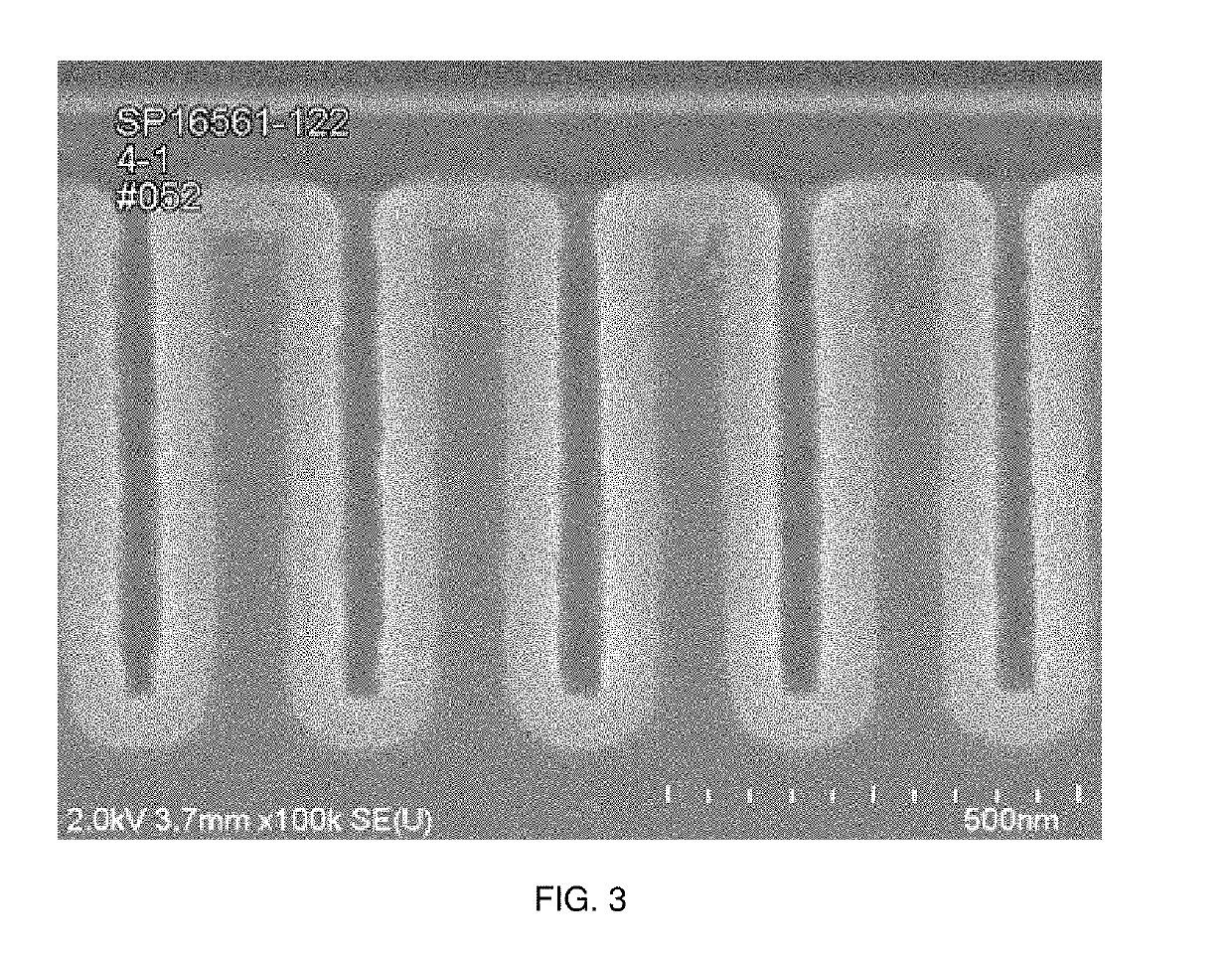
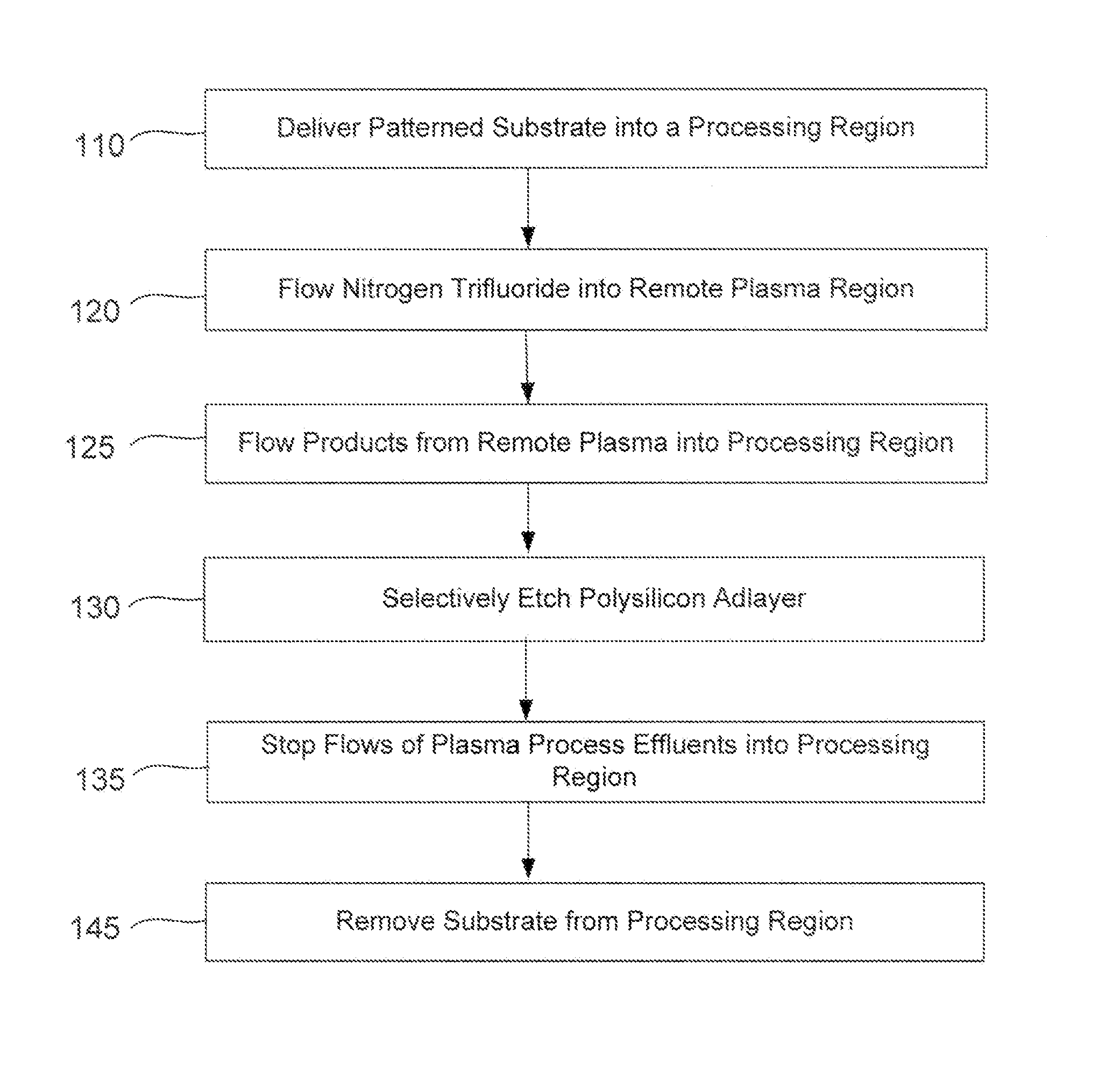
ActiveUS9324576B2Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaSilicon membrane
A method of etching patterned heterogeneous silicon-containing structures is described and includes a remote plasma etch with inverted selectivity compared to existing remote plasma etches. The methods may be used to conformally trim polysilicon while removing little or no silicon oxide. More generally, silicon-containing films containing less oxygen are removed more rapidly than silicon-containing films which contain more oxygen. Other exemplary applications include trimming silicon carbon nitride films while essentially retaining silicon oxycarbide. Applications such as these are enabled by the methods presented herein and enable new process flows. These process flows are expected to become desirable for a variety of finer linewidth structures. Methods contained herein may also be used to etch silicon-containing films faster than nitrogen-and-silicon containing films having a greater concentration of nitrogen.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Composition and method for low temperature deposition of silicon-containing films such as films including silicon nitride, silicon dioxide and/or silicon-oxynitride
ActiveUS20040096582A1Silicon organic compoundsPolycrystalline material growthLow temperature depositionGas phase
Silicon precursors for forming silicon-containing films in the manufacture of semiconductor devices, such as low dielectric constant (k) thin films, high k gate silicates, low temperature silicon epitaxial films, and films containing silicon nitride (Si3N4), siliconoxynitride (SiOxNy) and / or silicon dioxide (SiO2). The precursors of the invention are amenable to use in low temperature (e.g., <500° C.) chemical vapor deposition processes, for fabrication of ULSI devices and device structures.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Method for forming precoat film and method for forming silicon-containing film
PendingUS20210324510A1Quality improvementReduce metal pollutionElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh frequency powerPhysical chemistry
A method for forming a precoat film on a metal surface in a chamber before forming a silicon-containing film having an identical composition system with that of the precoat film on a substrate in the chamber using a PECVD method, wherein the precoat film is formed using a PEALD method in which a first gas and a second gas are supplied into the chamber by shifting timing of supply, the PEALD method comprises an adsorption step comprising supplying the first gas into the chamber so that the source gas component adsorbs on the metal surface, a first purge step comprising discharging an excessive source gas component not adsorbed on the metal surface, and a precoat film forming step comprising supplying the second gas into the chamber and applying high-frequency power to generate plasma in the reactant gas component in the second gas.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Thin Films and Methods of Making Them
InactiveUS20020197831A1Increase productionImprove device yieldTransistorMaterial nanotechnologyAnti-reflective coatingSilicon membrane
<heading lvl="0">Abstract of Disclosure< / heading> Thin, smooth silicon-containing films are prepared by deposition methods that utilize a silicon-containing precursor. In preferred embodiments, the methods result in Si-containing films that are continuous and have a thickness of about 150 Åor less, a surface roughness of about 5 Å rms or less, and a thickness non-uniformity of about 20% or less. Preferred silicon-containing films display a high degree of compositional uniformity when doped or alloyed with other elements. Preferred deposition methods provide improved manufacturing efficiency and can be used to make various useful structures such as wetting layers, HSG silicon, quantum dots, dielectric layers, anti-reflective coatings (ARC s), gate electrodes and diffusion sources.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
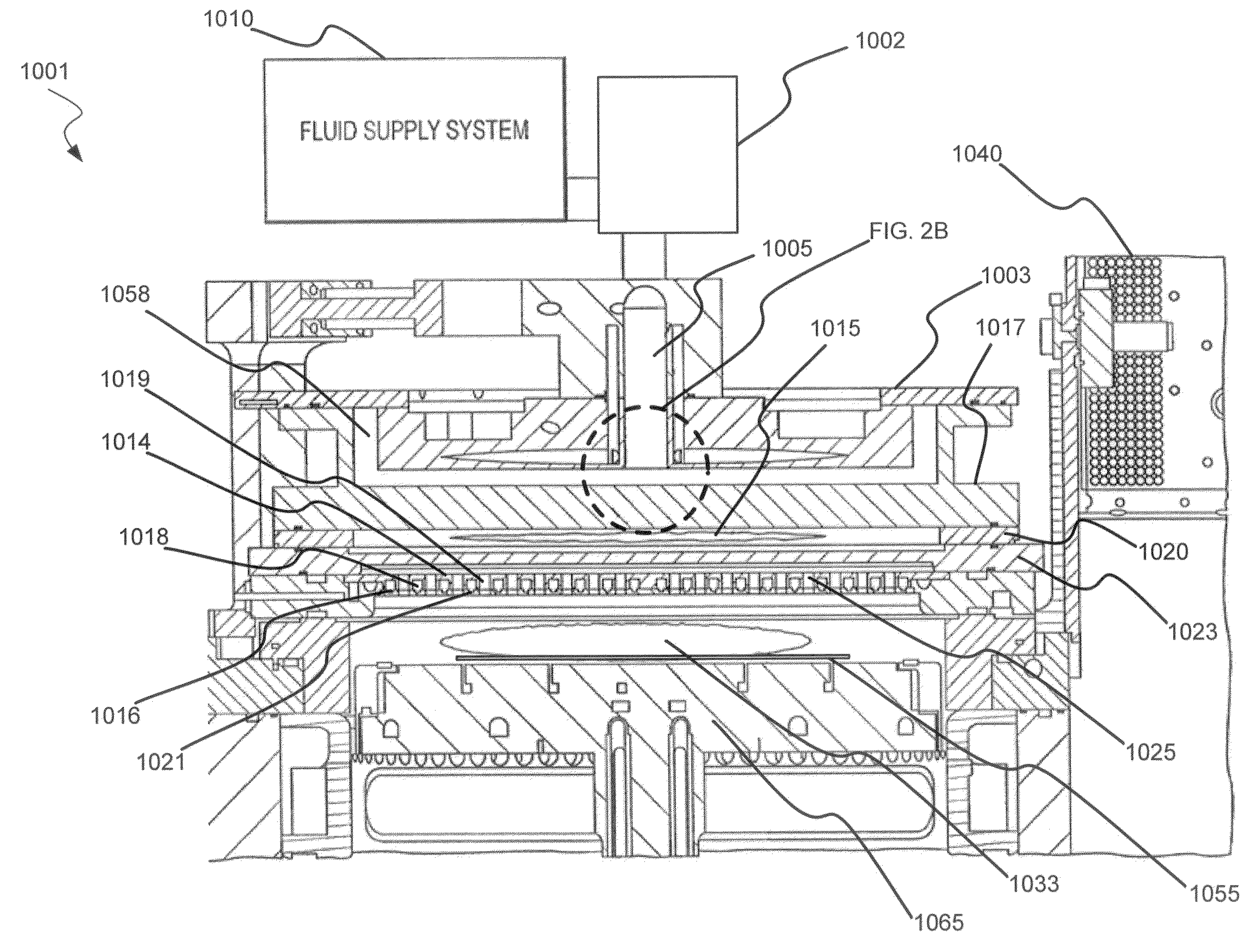
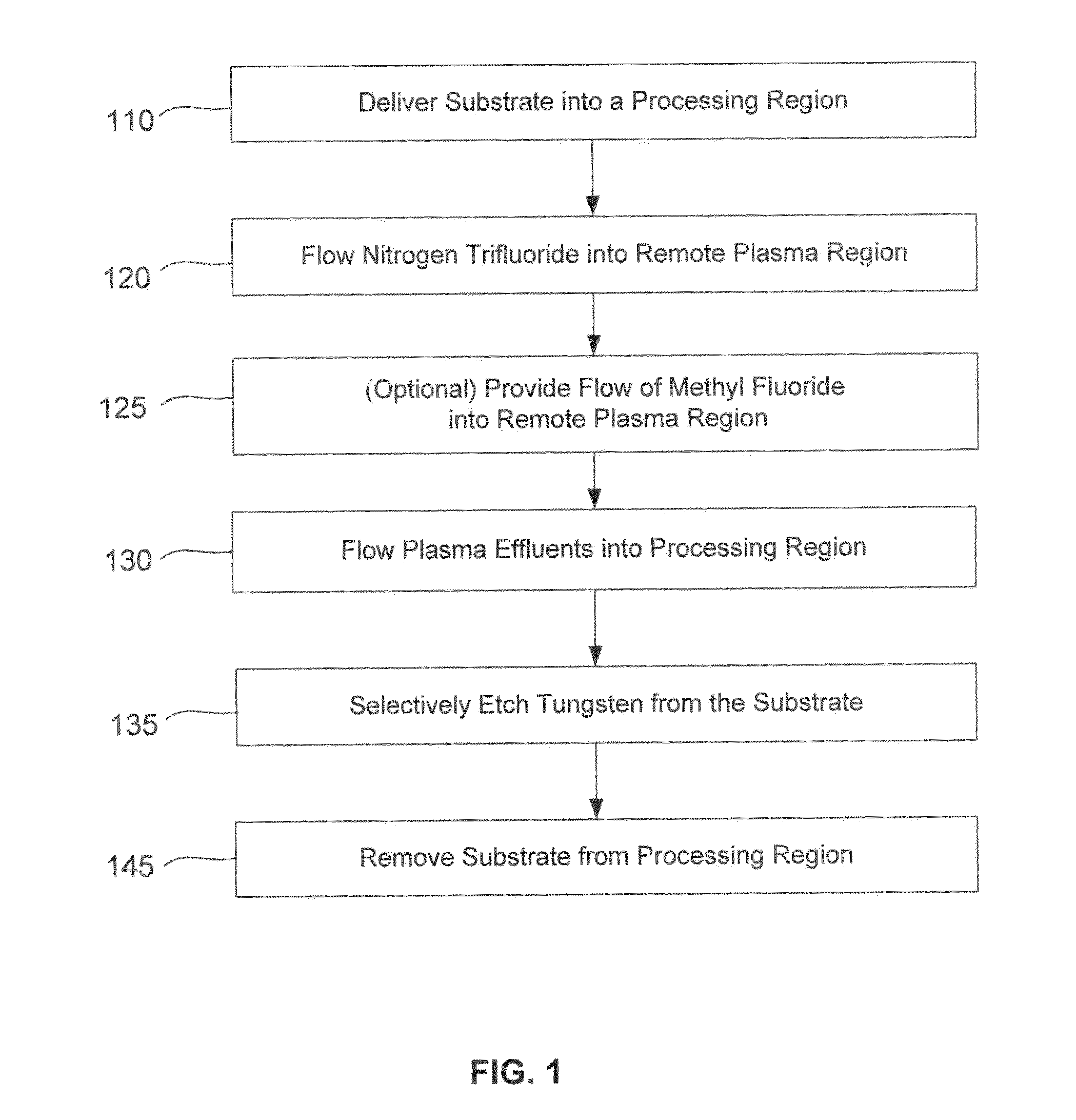
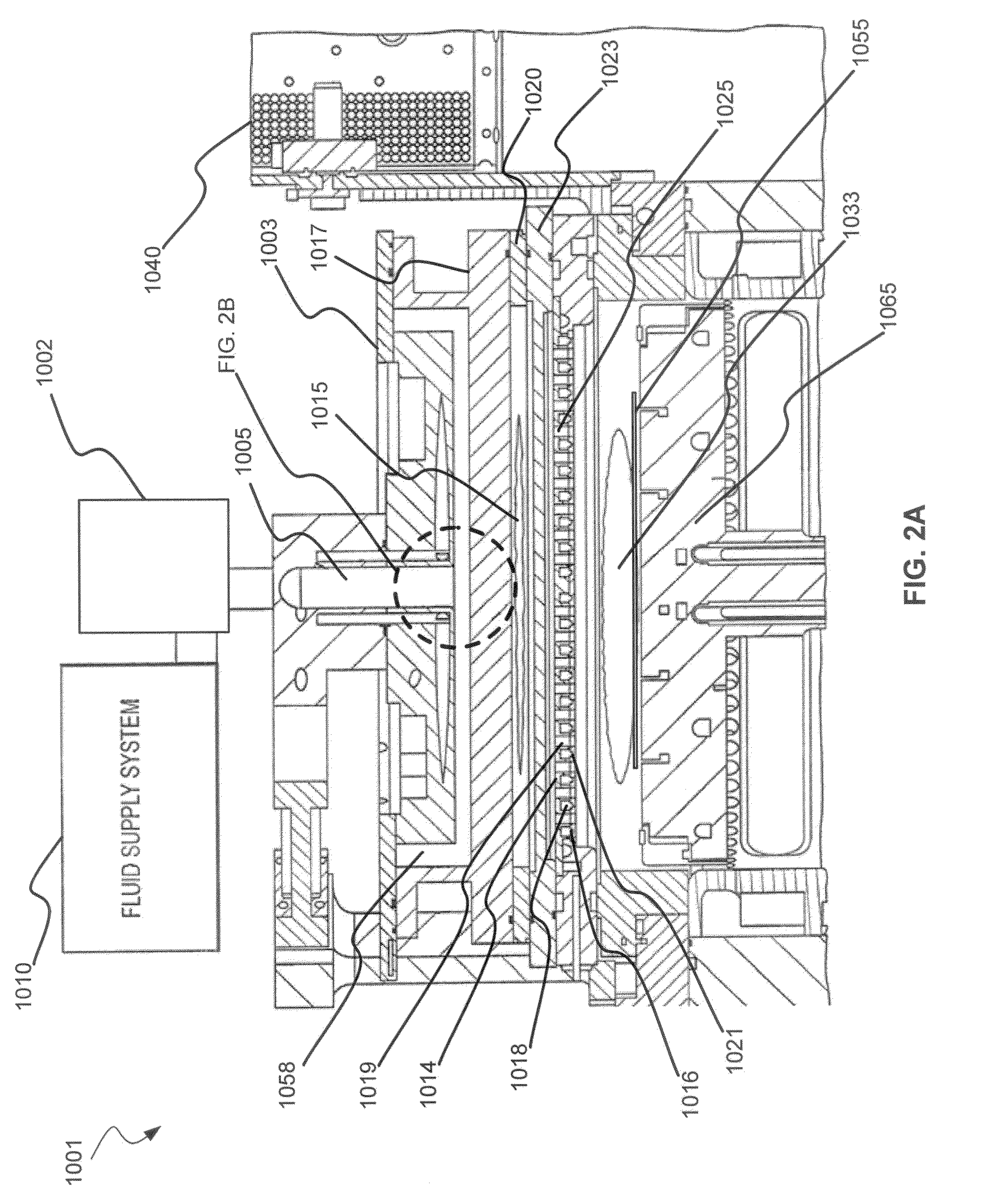
Dry-etch for selective tungsten removal
ActiveUS20140154889A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxideMaterials science
Methods of selectively etching tungsten relative to silicon-containing films (e.g. silicon oxide, silicon carbon nitride and (poly)silicon) as well as tungsten oxide are described. The methods include a remote plasma etch formed from a fluorine-containing precursor and / or hydrogen (H2). Plasma effluents from the remote plasma are flowed into a substrate processing region where the plasma effluents react with the tungsten. The plasma effluents react with exposed surfaces and selectively remove tungsten while very slowly removing other exposed materials. Sequential and simultaneous methods are included to remove thin tungsten oxide which may, for example, result from exposure to the atmosphere.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Precursors for depositing silicon-containing films and processes thereof
InactiveUS20050181633A1Satisfies needSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenReactive gas
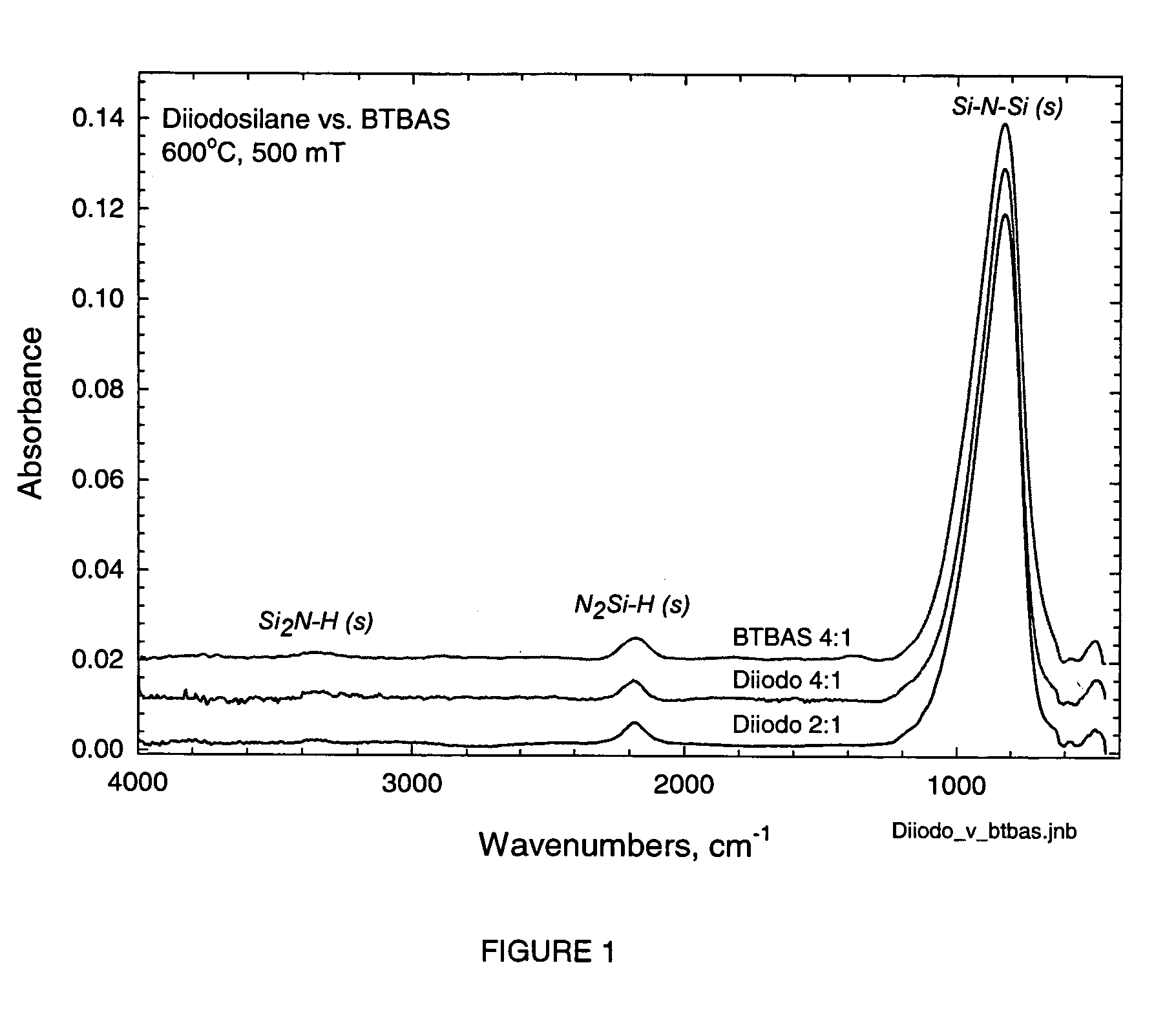
Inorganic precursors, namely iodosilane precursors, for the low temperature, low pressure deposition of silicon-containing films is provided therein. In one aspect, there is provided a process for forming a silicon-containing film process comprising: introducing a substrate and gaseous reagents comprising an iodosilane precursor having three or less iodine atoms bound to the silicon atom and at least one reagent selected from an oxygen-containing reactive gas, a nitrogen-containing reactive gas, a hydrogen-containing reactive gas and mixtures thereof into a reaction chamber; heating the reaction chamber to one or more temperatures ranging from 200° C. to 900° C. to form the silicon containing film on the substrate, provided that if the iodosilane precursor has three iodine atoms bound to the silicon atom then the heating step is conducted at one or more pressures less than 600 Torr.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Apparatus and method for surface finishing a silicon film
InactiveUS20020090818A1Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSurface finishSilicon membrane
A method of smoothing a silicon surface formed on a substrate. According to the present invention a substrate having a silicon surface is placed into a chamber and heated to a temperature of between 1000°-1300° C. While the substrate is heated to a temperature between 1000°-1300° C., the silicon surface is exposed to a gas mix comprising H2 and HCl in the chamber to smooth the silicon surface.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC +1
Apparatus and method for surface finishing a silicon film
InactiveUS20040053515A1Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSurface finishSilicon membrane
A method of treating a silicon surface of a substrate that includes heating the substrate in a process chamber to a temperature, exposing a first area adjacent to the silicon surface to a first gas mixture comprising an etchant, a silicon source gas, and a carrier, exposing a second area adjacent to the silicon surface to a second gas mixture, wherein the second gas mixture is different from the first gas mixture.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Composition for forming silicon film and method for forming silicon film
InactiveUS20050145163A1Polycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsLight treatmentSilicon membrane
There are provided a silicon-film-forming composition containing silicon particles and a dispersion medium and a method for forming a silicon film by forming a coating film of the silicon-film-forming composition on a substrate and subjecting the coating film to instantaneous fusion, a heat treatment or a light treatment. According to the composition and the method, a polysilicon film with a desired thickness which may be used as a silicon film for a solar battery can be formed efficiently and easily.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
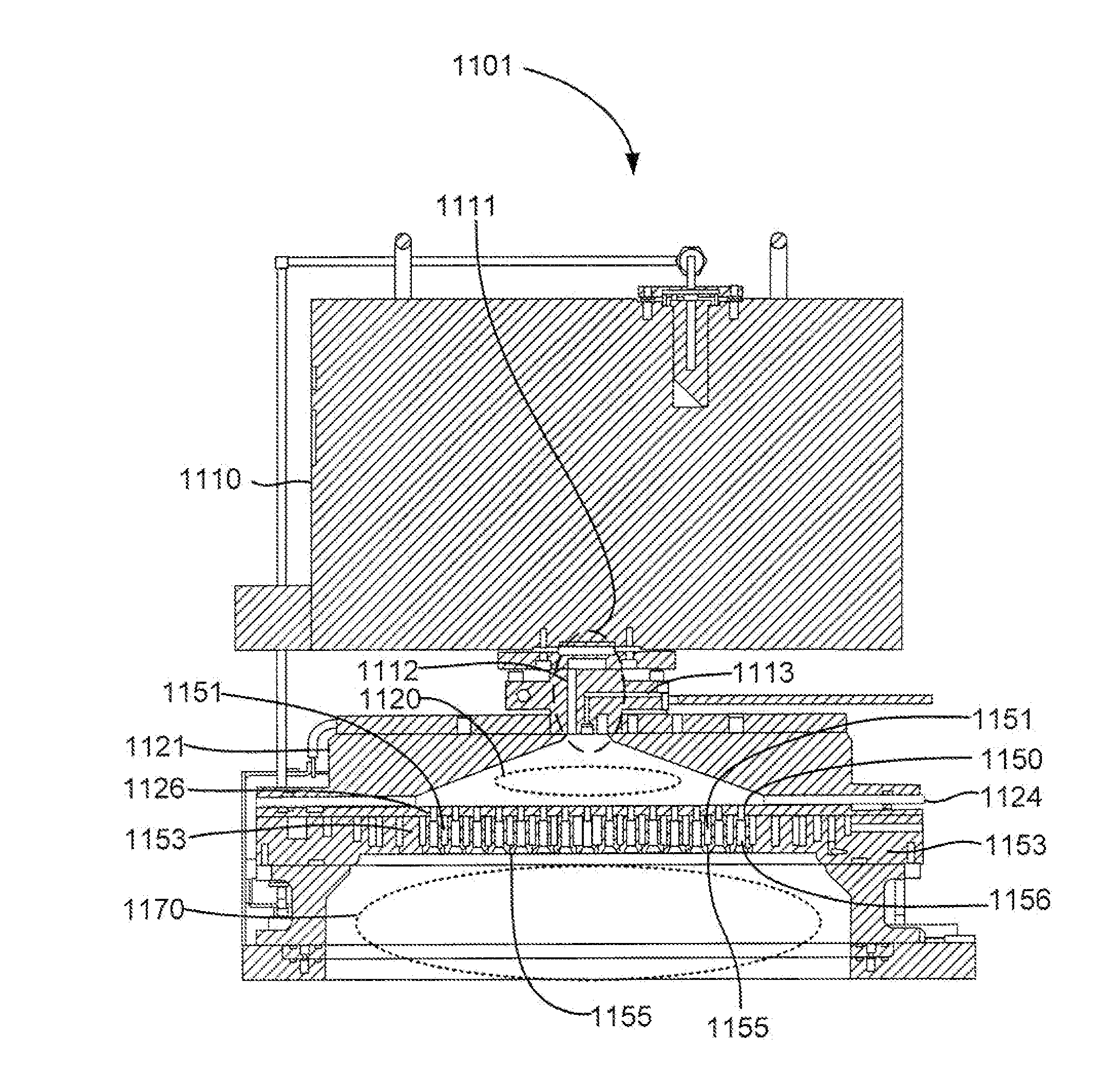
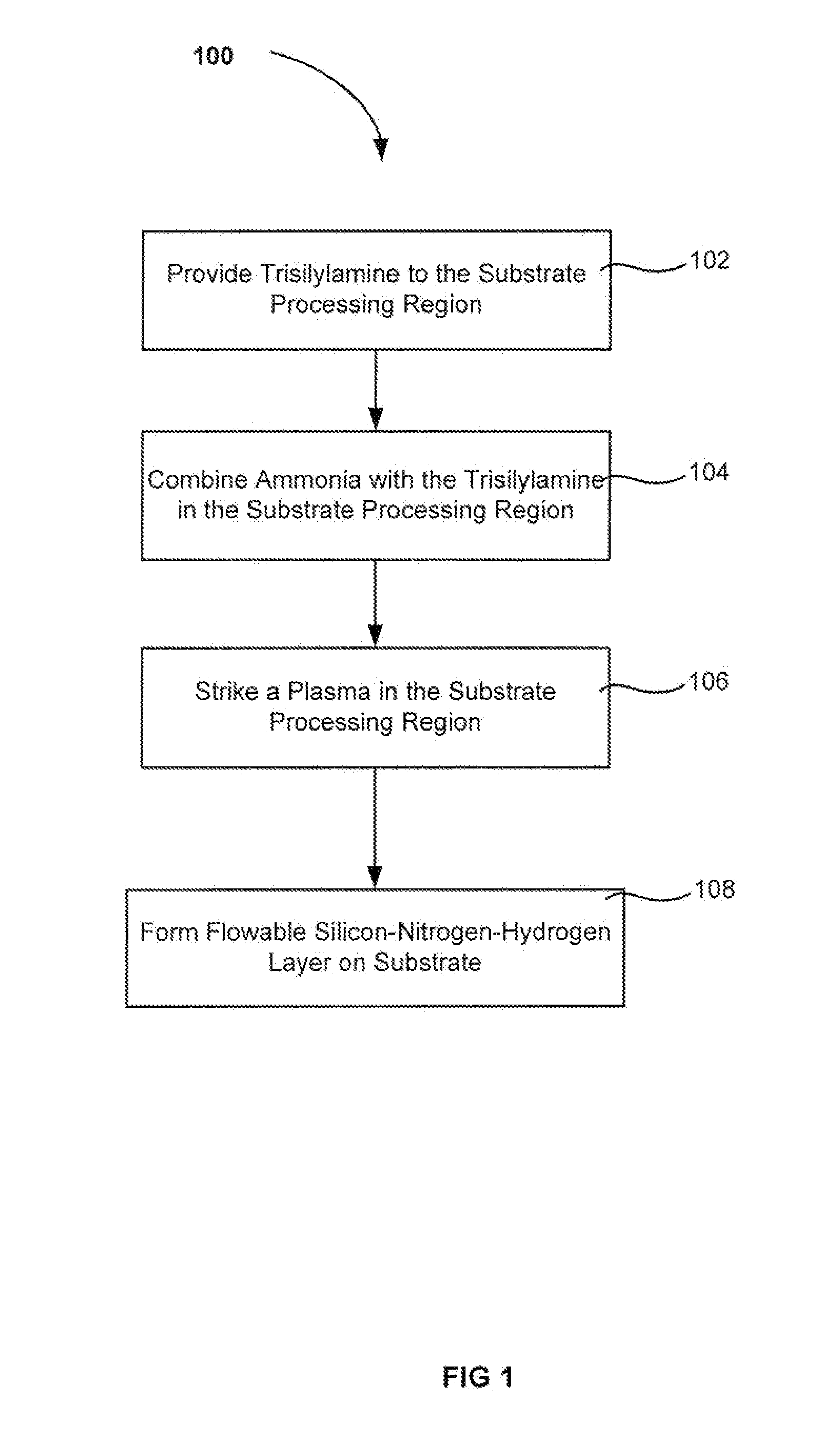
Low cost flowable dielectric films
ActiveUS20140073144A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSilyleneSilanes
A method of forming a dielectric layer is described. The method deposits a silicon-containing film by chemical vapor deposition using a local plasma. The silicon-containing film is flowable during deposition at low substrate temperature. A silicon precursor (e.g. a silylamine, higher order silane or halogenated silane) is delivered to the substrate processing region and excited in a local plasma. A second plasma vapor or gas is combined with the silicon precursor in the substrate processing region and may include ammonia, nitrogen (N2), argon, hydrogen (H2) and / or oxygen (O2). The equipment configurations disclosed herein in combination with these vapor / gas combinations have been found to result in flowable deposition at substrate temperatures below or about 200° C. when a local plasma is excited using relatively low power.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
InactiveUS6893503B1Eliminate the problemTransistorPolycrystalline material growthSilicon membraneCrystalline silicon
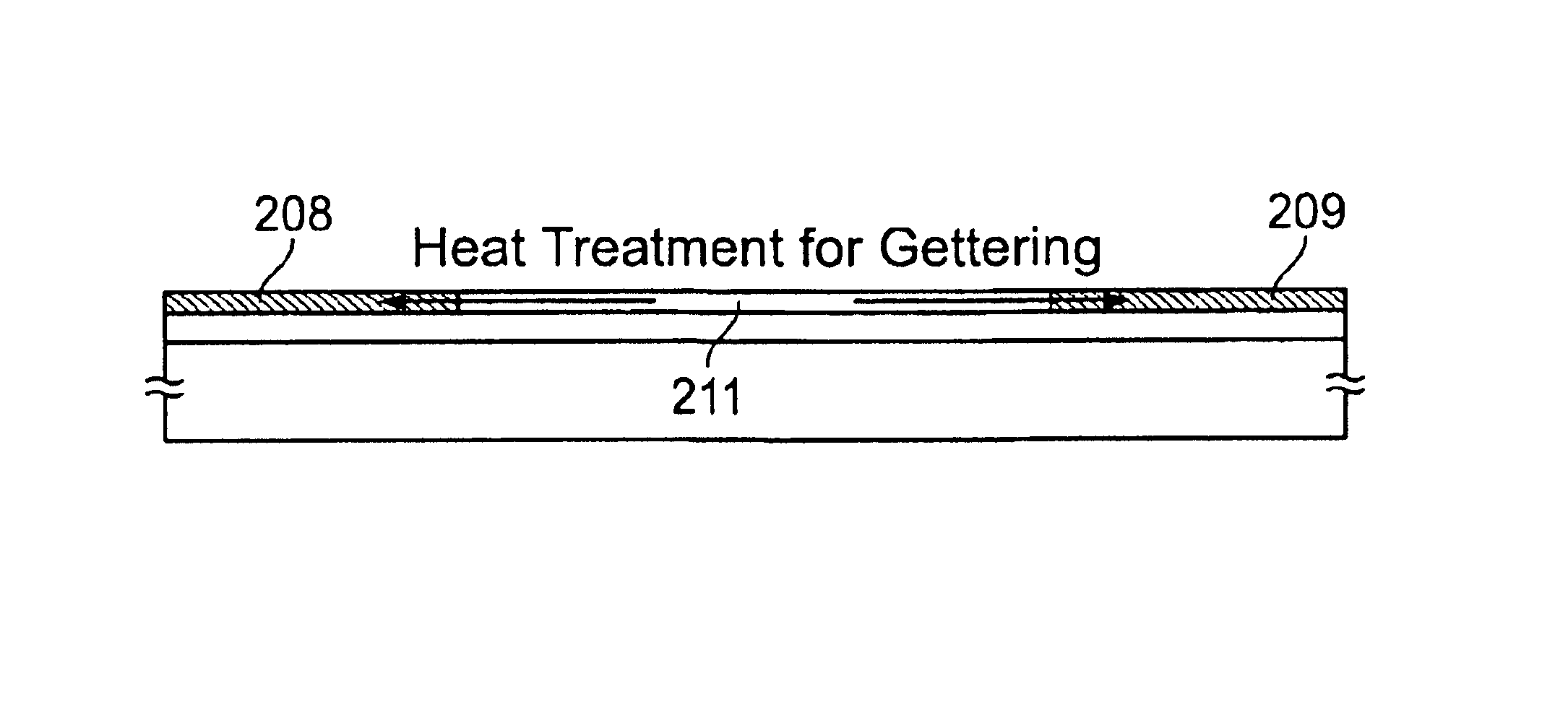
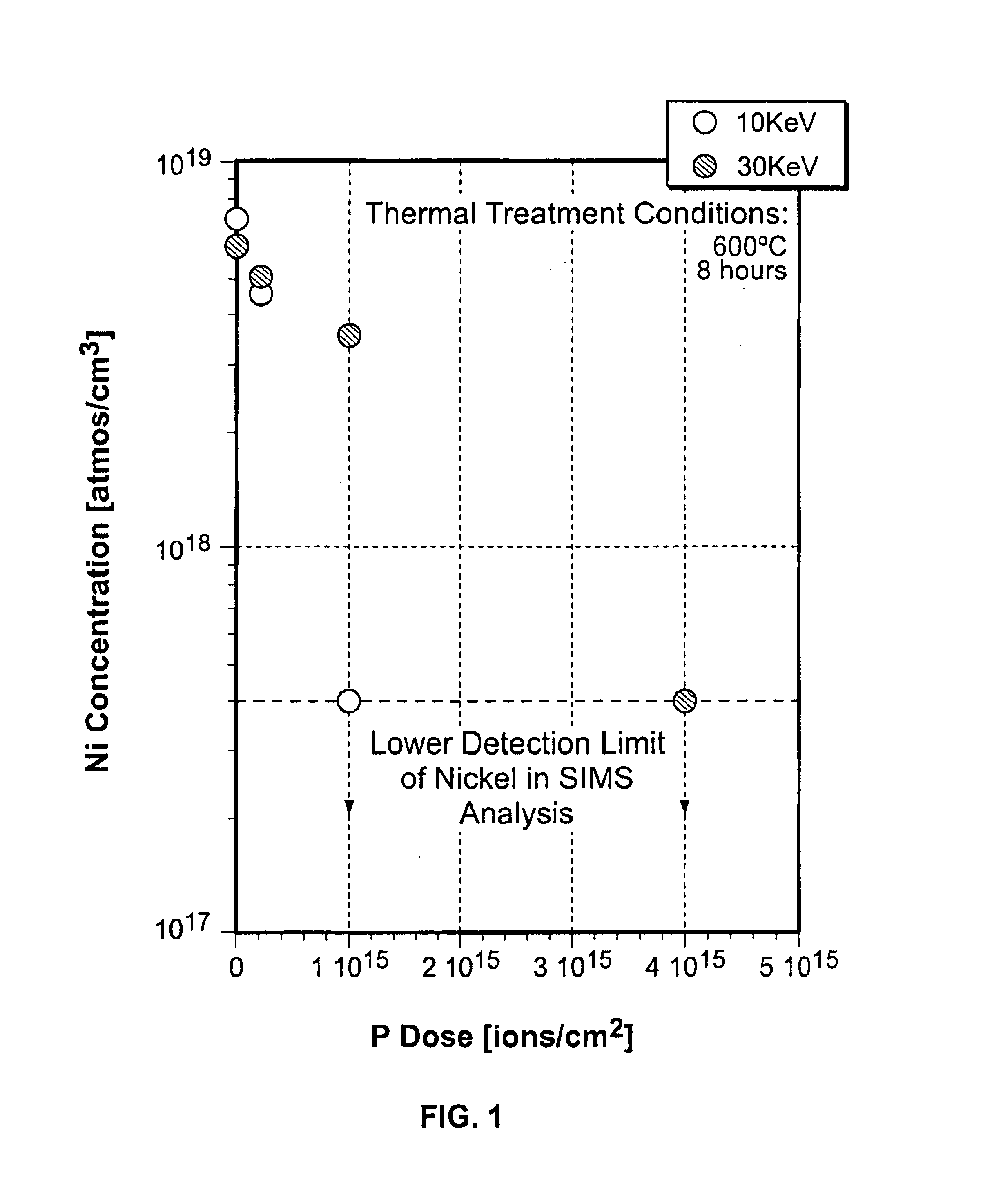
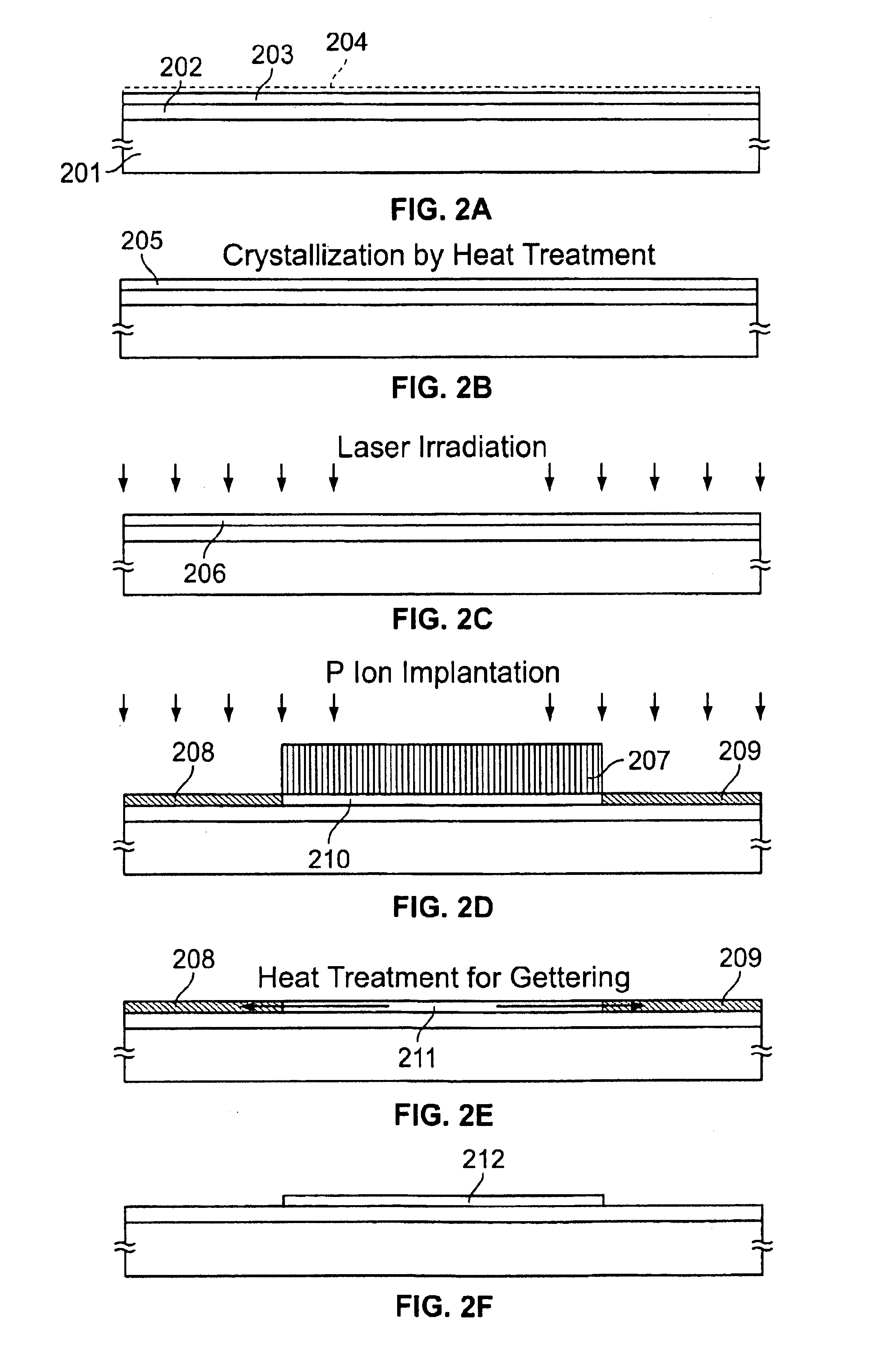
A method of producing a semiconductor device which removes catalyst elements from a silicon-containing semiconductor film while maintaining the advantage of low temperature process is provided. The method comprises the steps of: forming an amorphous semiconductor film containing silicon on a glass substrate to crystallize it by using a catalyst element; selectively introducing into the amorphous semiconductor film an impurity belonging to Group 15 to form gettering regions and regions to be gettered; and causing the catalyst element in the silicon film to move to the gettering regions by heat treatment. Through the gettering process, the crystalline silicon film can be obtained in which the concentration of nickel contained therein is sufficiently reduced.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
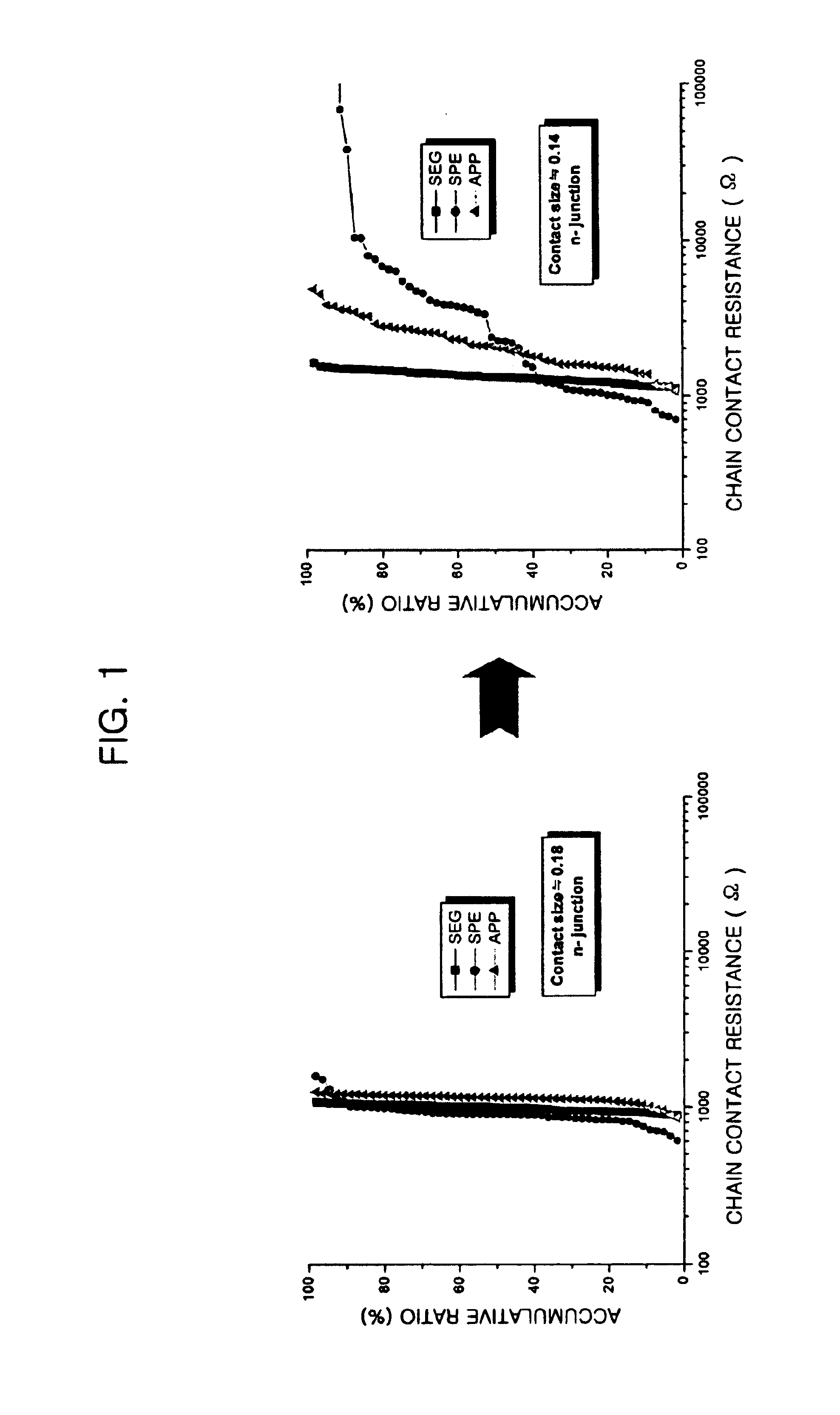
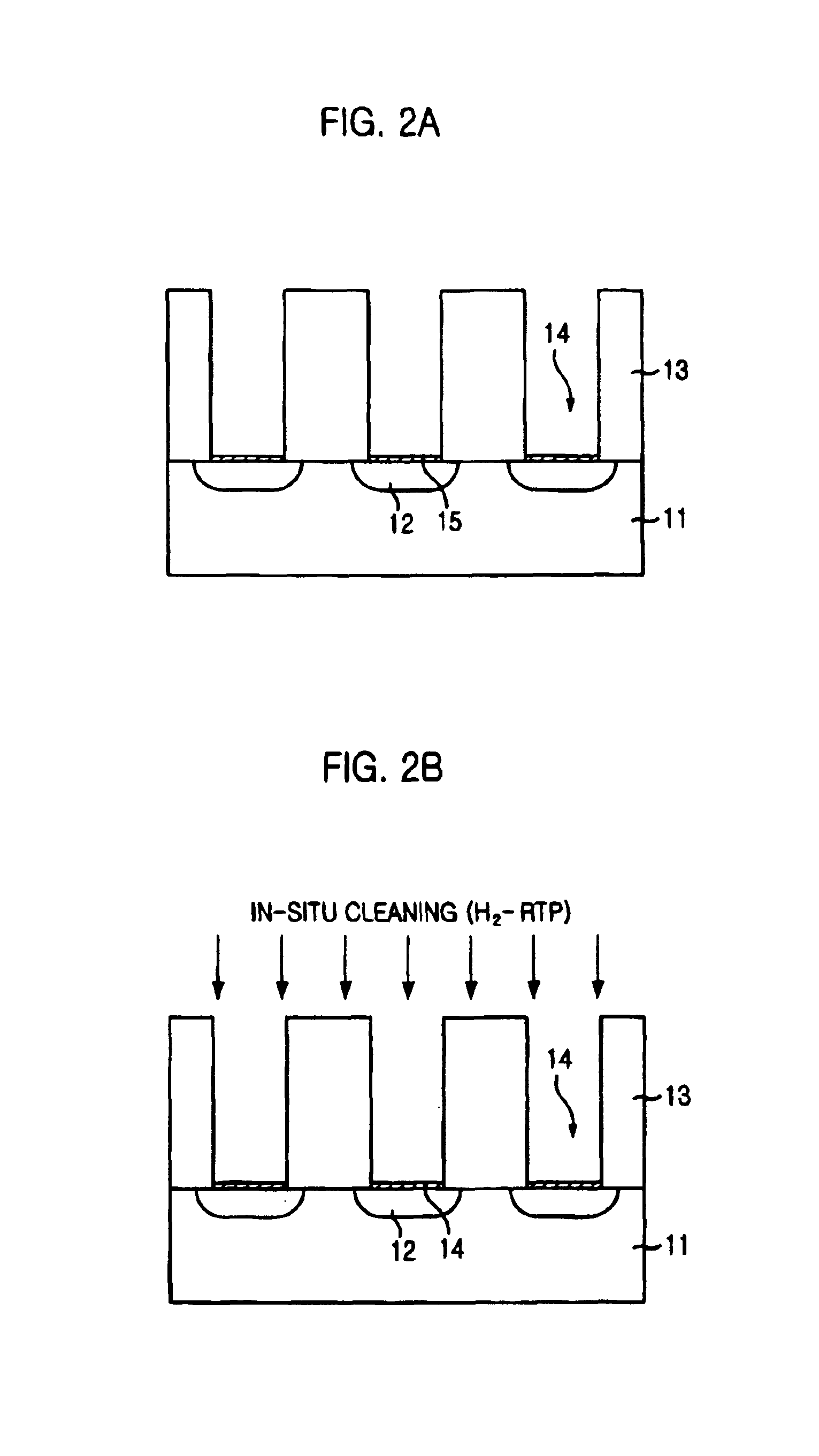
Method for forming contact plug in semiconductor device
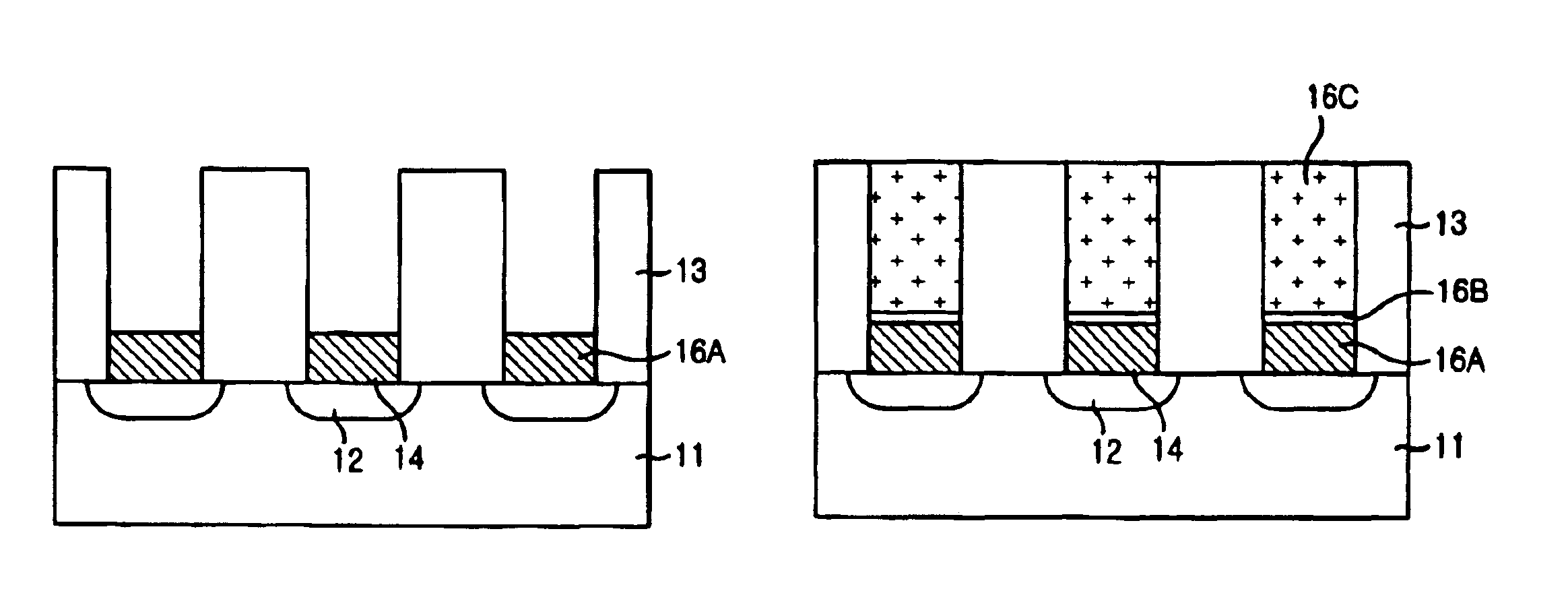
InactiveUS6844259B2Reduce contact resistanceReduce uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSilicon membraneEngineering
The present invention provides a method for forming a contact plug in a semiconductor device capable of preventing an increase of contact resistance even if the contact size becomes smaller and degradation of a step coverage property and of suppressing a decrease of uniformity in the contact resistance. The inventive method includes the steps of: a method for forming a contact plug in a semiconductor device, comprising the steps of: forming a contact hole by etching an insulating layer on a substrate; forming a first silicon film with a first doping concentration on the substrate in the contact hole so that the contact hole is partially filled; flushing a doping gas on a surface of the first silicon film; and forming a second silicon film having a second doping concentration higher than the first doping concentration on the first silicon film until filling the contact hole.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Method of forming a TFT by adding a metal to a silicon film promoting crystallization, forming a mask, forming another silicon layer with group XV elements, and gettering the metal through opening in the mask
InactiveUS6242290B1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon membraneAmorphous silicon
There is disclosed a method of fabricating TFTs using a silicon film crystallized with the aid of nickel. The nickel is removed from the crystallized silicon film. The method starts with maintaining nickel in contact with the surface of an amorphous silicon film. Then, a heat treatment is performed to form a crystalline silicon film. At this time, nickel promotes the crystallization greatly, and nickel diffuses into the film. A mask is formed. A silicon film heavily doped with phosphorus is formed. Thereafter, a heat treatment is performed to move the nickel from the crystalline silicon film into the phosphorus-rich silicon film. This reduces the concentration of nickel in the crystalline silicon film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Methods for uv-assisted conformal film deposition
InactiveUS20130196516A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingBiological activationElectromagnetic radiation
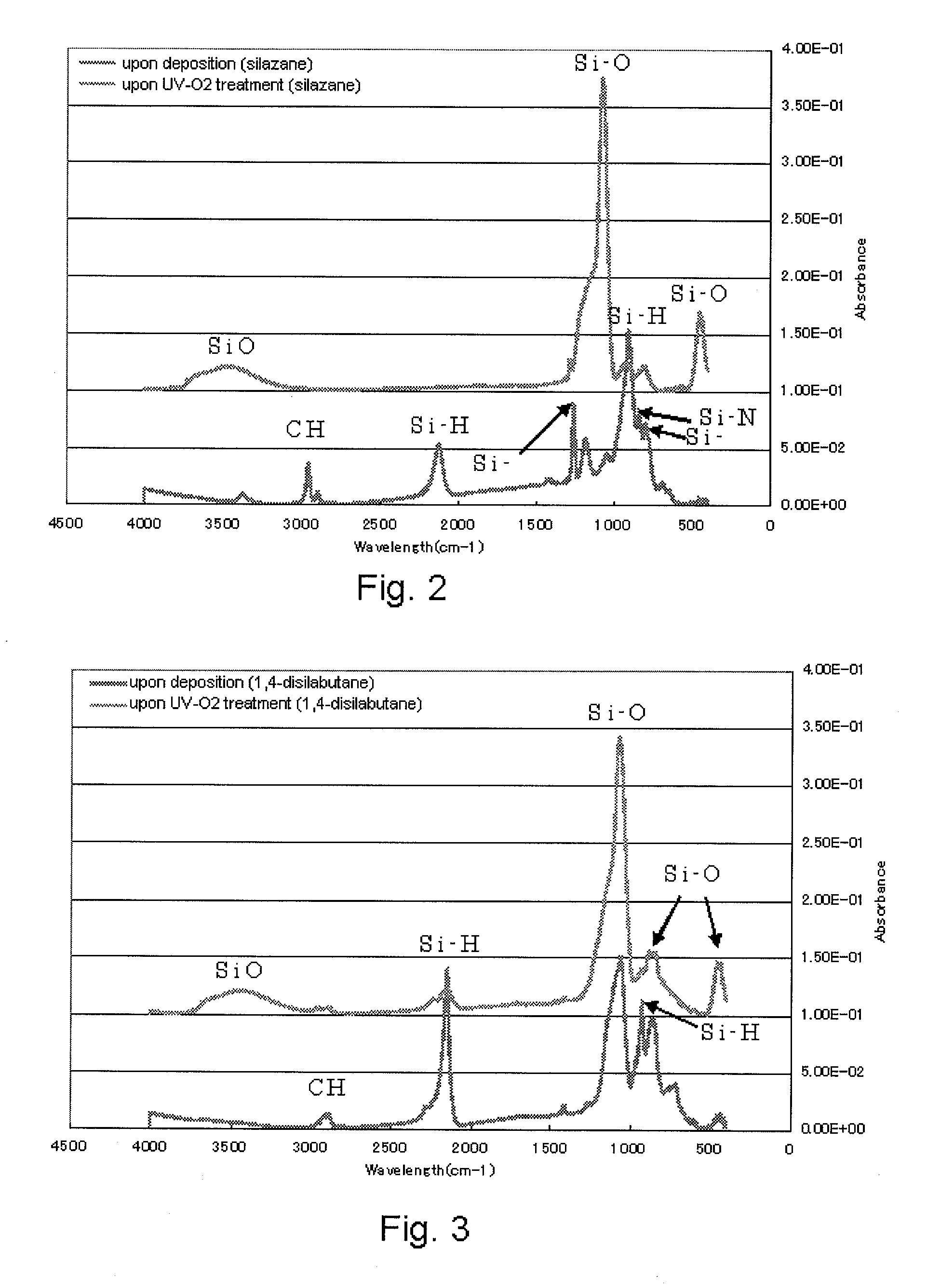
Described are methods of making silicon nitride (SiN) materials and other silicon-containing films, including carbon-containing and / or oxygen-containing films such as SiCN (also referred to as SiNC), SiON and SiONC films, on substrates. According to various embodiments, the methods involve electromagnetic radiation-assisted activation of one or more reactants. In certain embodiments, for example, the methods involve ultraviolet (UV) activation of vapor phase amine coreactants. The methods can be used to deposit silicon-containing films, including SiN and SiCN films, at temperatures below about 400° C.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Silicon-containing film-forming composition, silicon-containing film, silicon-containing film-bearing substrate, and patterning method
ActiveUS20070238300A1Sufficient etching resistanceImprove accuracyPhotosensitive materialsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistAmmonium compounds
A silicon-containing film is formed from a heat curable composition comprising (A) a silicon-containing compound obtained by effecting hydrolytic condensation of a hydrolyzable silicon compound in the presence of an acid catalyst, and substantially removing the acid catalyst from the reaction mixture, (B) a hydroxide or organic acid salt of lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium or cesium, or a sulfonium, iodonium or ammonium compound, (C) an organic acid, and (D) an organic solvent. The silicon-containing film allows an overlying photoresist film to be patterned effectively. The composition is effective in minimizing the occurrence of pattern defects after lithography and is shelf stable.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com