Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
415 results about "Fall time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
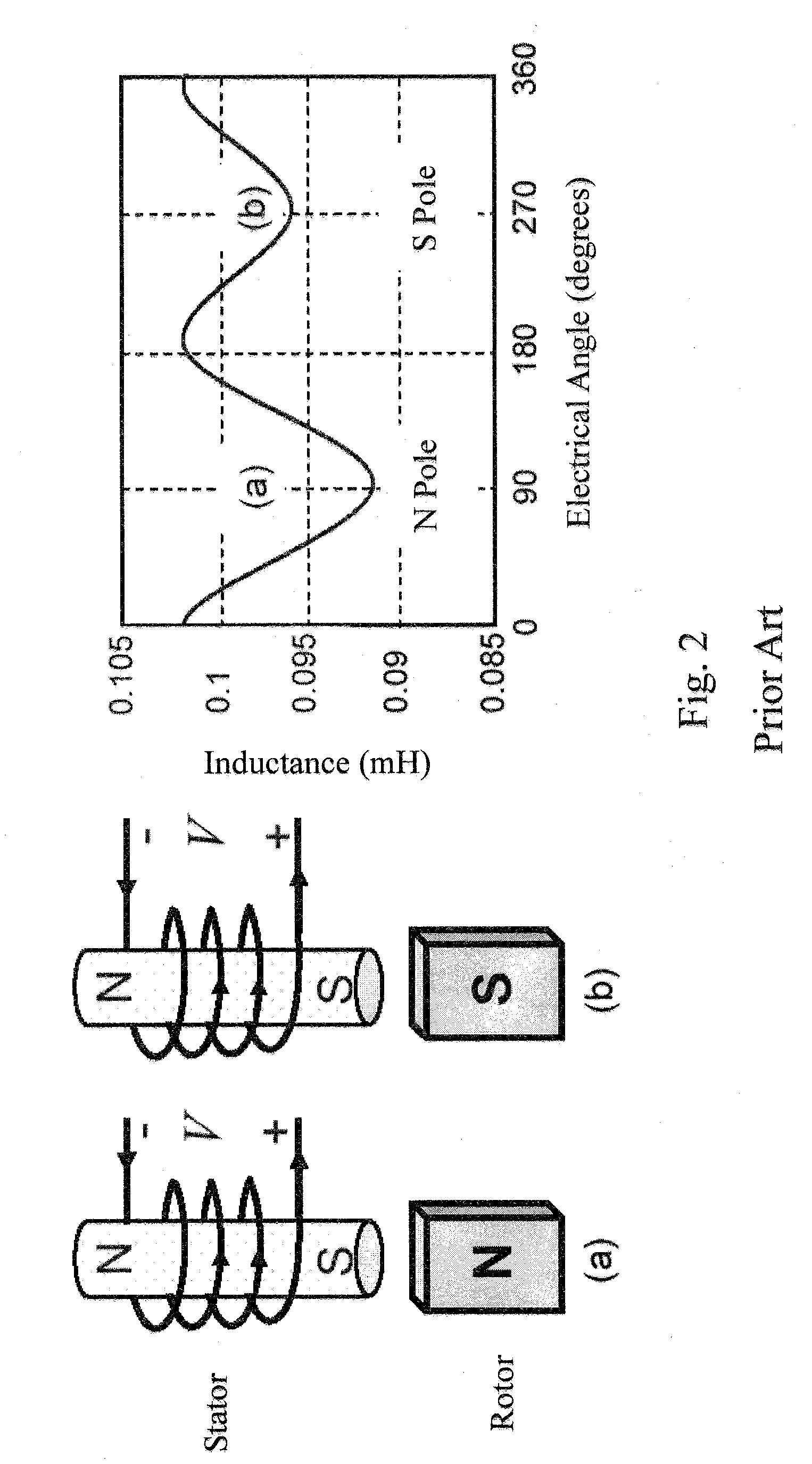
In electronics, fall time (pulse decay time) tf is the time taken for the amplitude of a pulse to decrease (fall) from a specified value (usually 90% of the peak value exclusive of overshoot or undershoot) to another specified value (usually 10% of the maximum value exclusive of overshoot or undershoot). Limits on undershoot and oscillation (also known as ringing and hunting) are sometimes additionally stated when specifying fall time limits.
FMOD transceivers including continuous and burst operated TDMA, FDMA, spread spectrum CDMA, WCDMA and CSMA
InactiveUS6928101B2Improve performanceLow costAsymmetric modulation circuitsPhase-modulated carrier systemsModem deviceFrequency spectrum
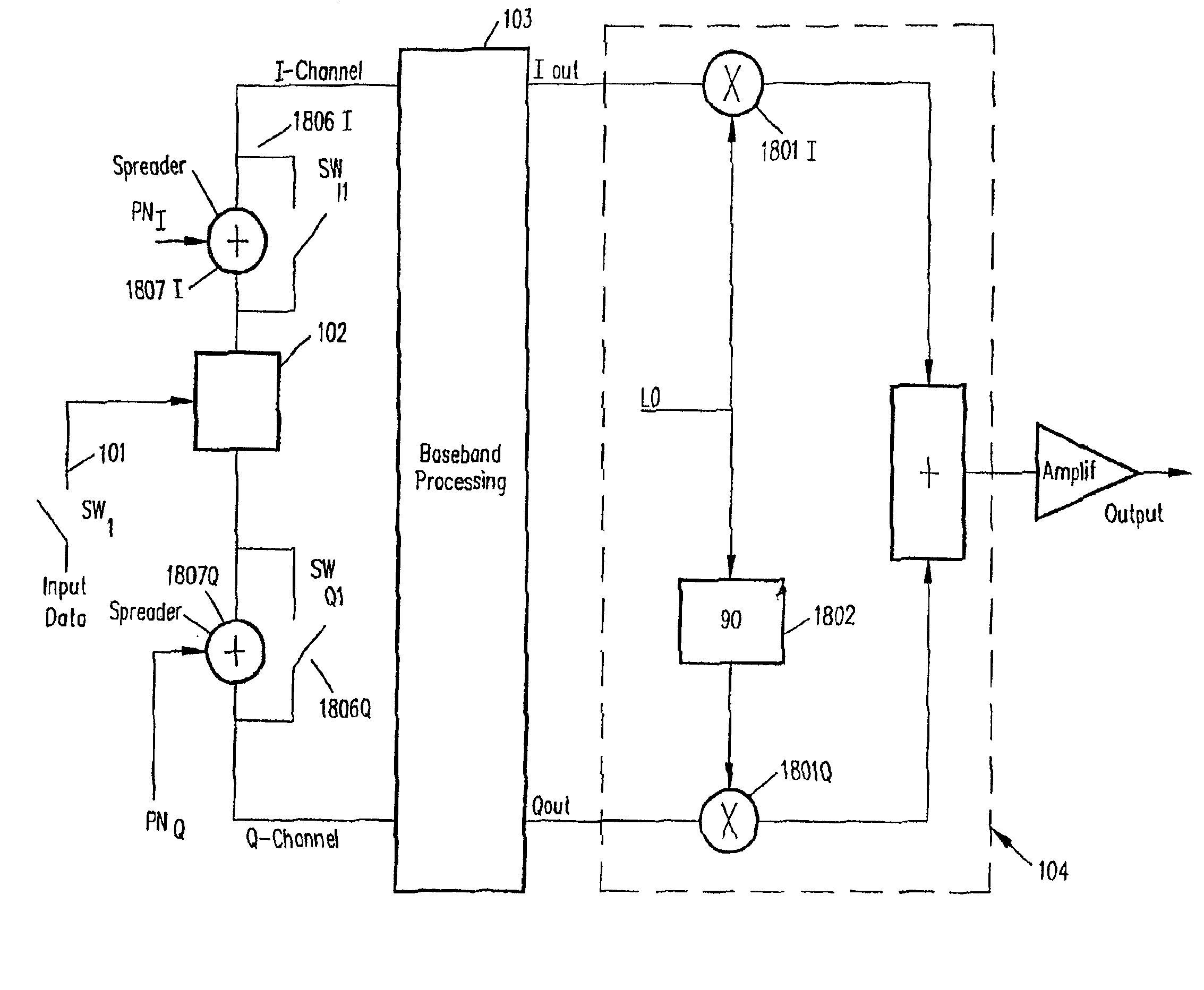
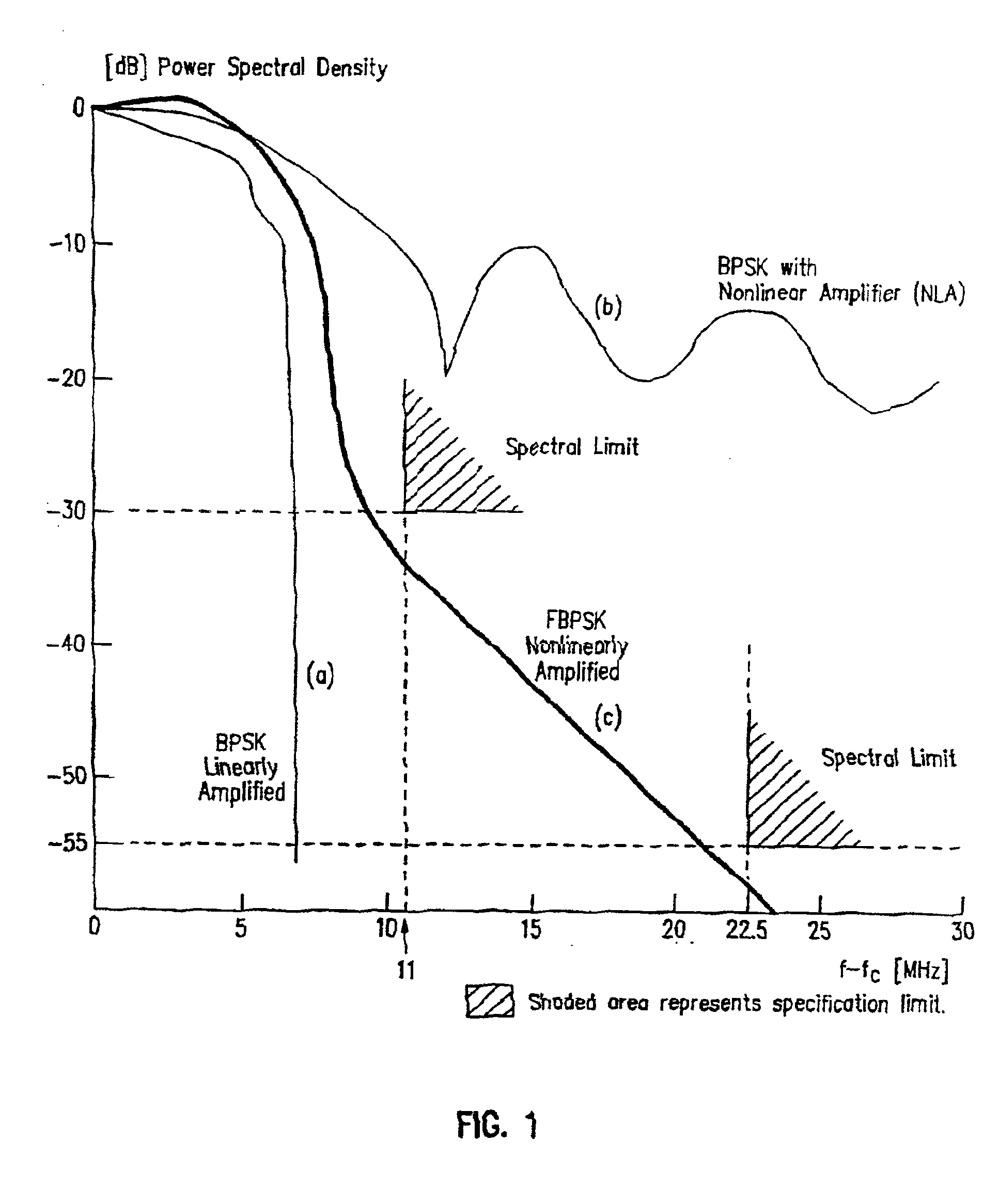
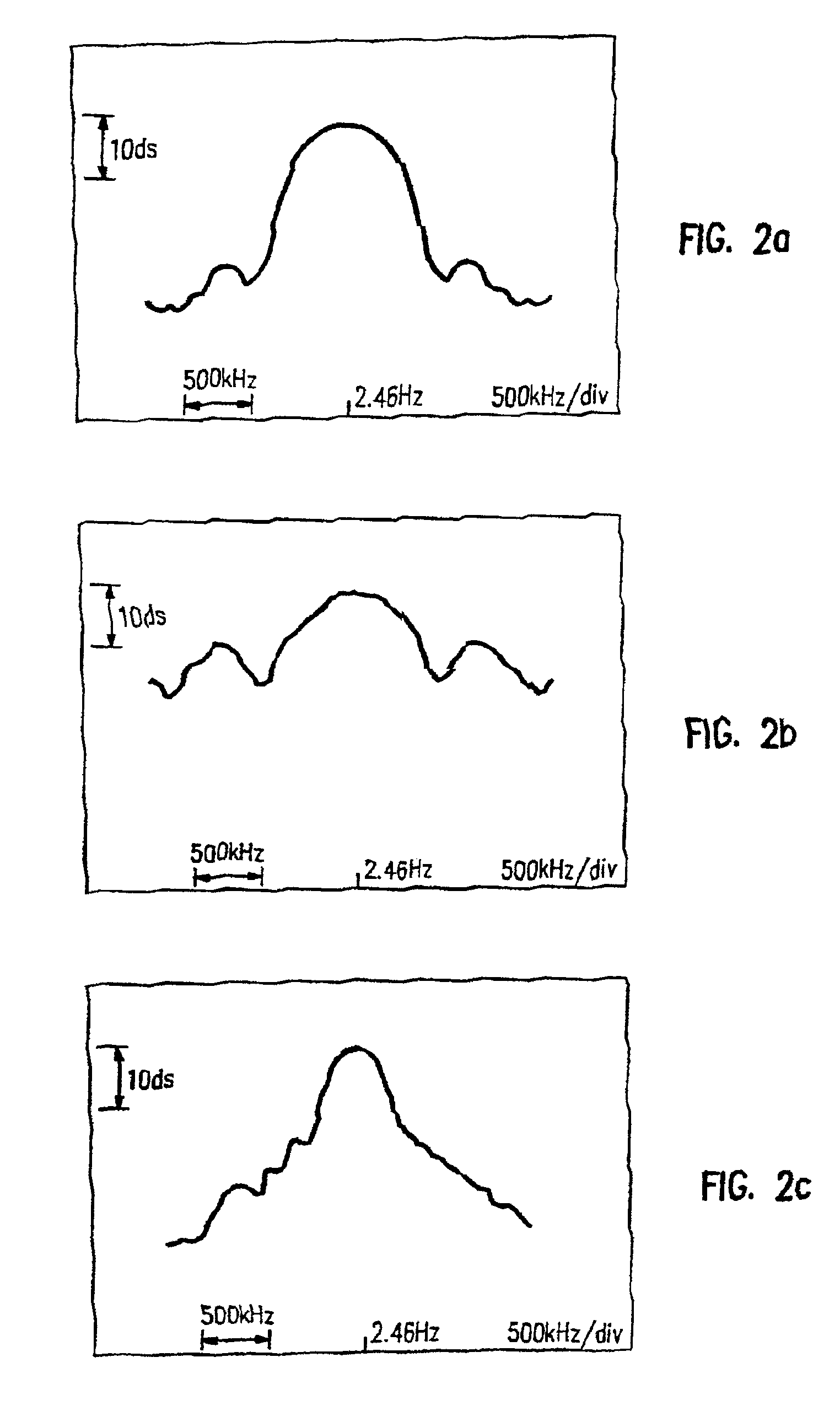
Binary and Quadrature Feher's Modulation (F-Modulation, or FMOD) Transmitter-Receiver systems and circuits exhibit reduced envelope fluctuation and peak radiation, and increased efficiency. A subclass of these systems has a constant envelope. They advantageously provide lower power operation with improved performance including robust BER performance, and compatibility with both linearly and nonlinearly amplified narrow spectrum, and without disadvantages of conventional BPSK, DBPSK QPSK and pi / 4-QPSK. Feher's BPSK (FBPSK) is an improved efficiency transmitter which is compatible with conventional BPSK receivers. FBPSK modems are based on using quadrature structure where Q-channel data is inserted in quadrature with I-channel data for certain applications. The Q-channel data may be “offset” from the I-channel data by an amount selectable between zero and a specified time. Further improvement in the spectrum is attained using correlation between I and Q channels. FBPSK modem is shown to meet the IEEE 802.11 specified spectral direct sequence spread spectrum mask (−30 dB point) for wireless LAN, and leads to an output power gain of 6.5 dB over conventional BPSK modems. The cross-coupled quadrature FMOD structure is also suitable for continuous mode and for burst operated TDMA, FDMA, CDMA, WCDMA and CSMA Frequency Modulation Quadrature AM (QAM), QPSK and offset QPSK, as well as pi / 4-shifted QPSK modems / processors. Reduced modulation index Gaussian FSK (GFSK), multilevel FM and cross-coupled Quadrature Amplitude Modulated (QAM) transmitters and combinations of these modulations and corresponding coherent demodulators are disclosed. Controlled rise and fall time descriptions of burst operated systems are included.
Owner:INTEL CORP
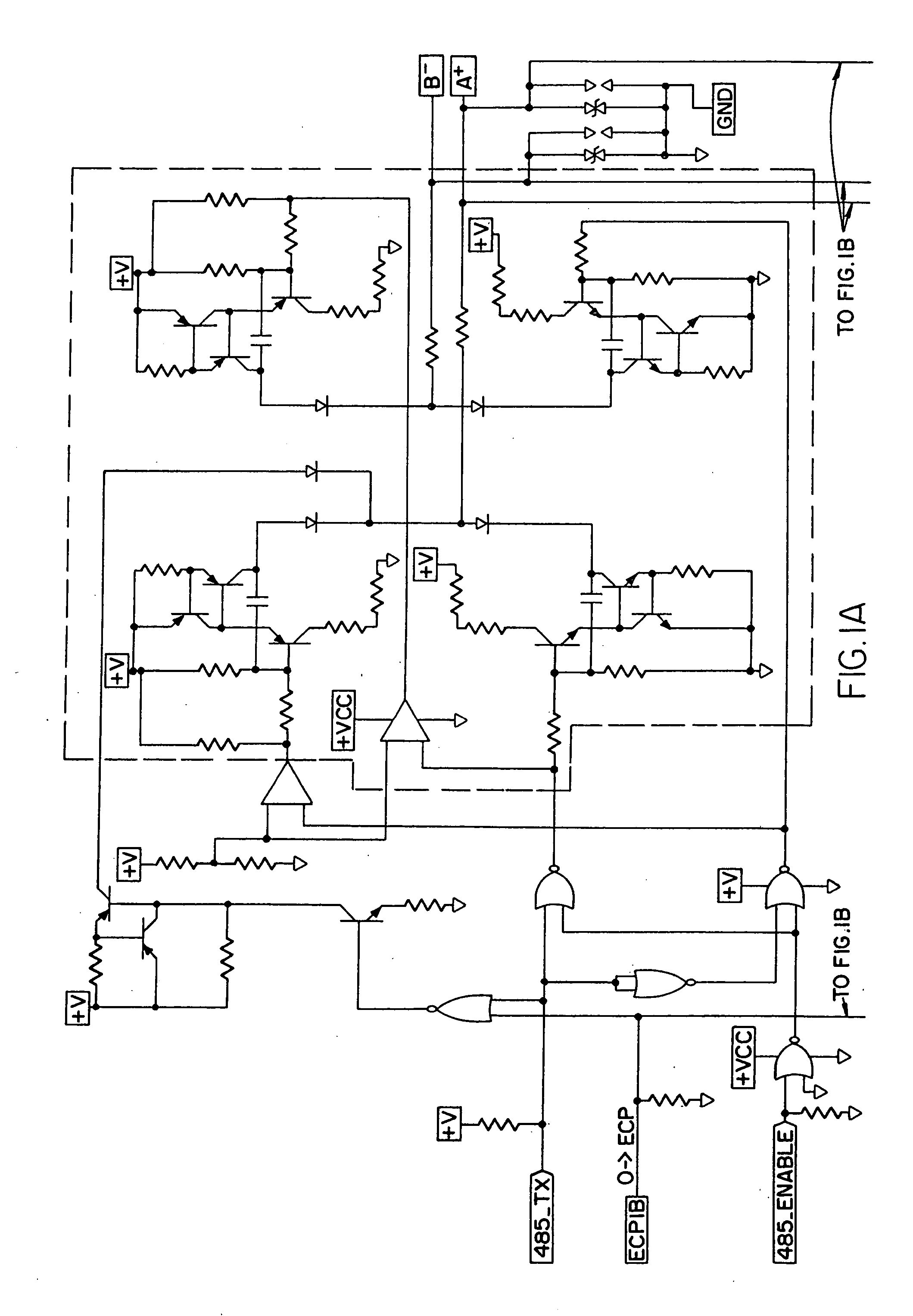
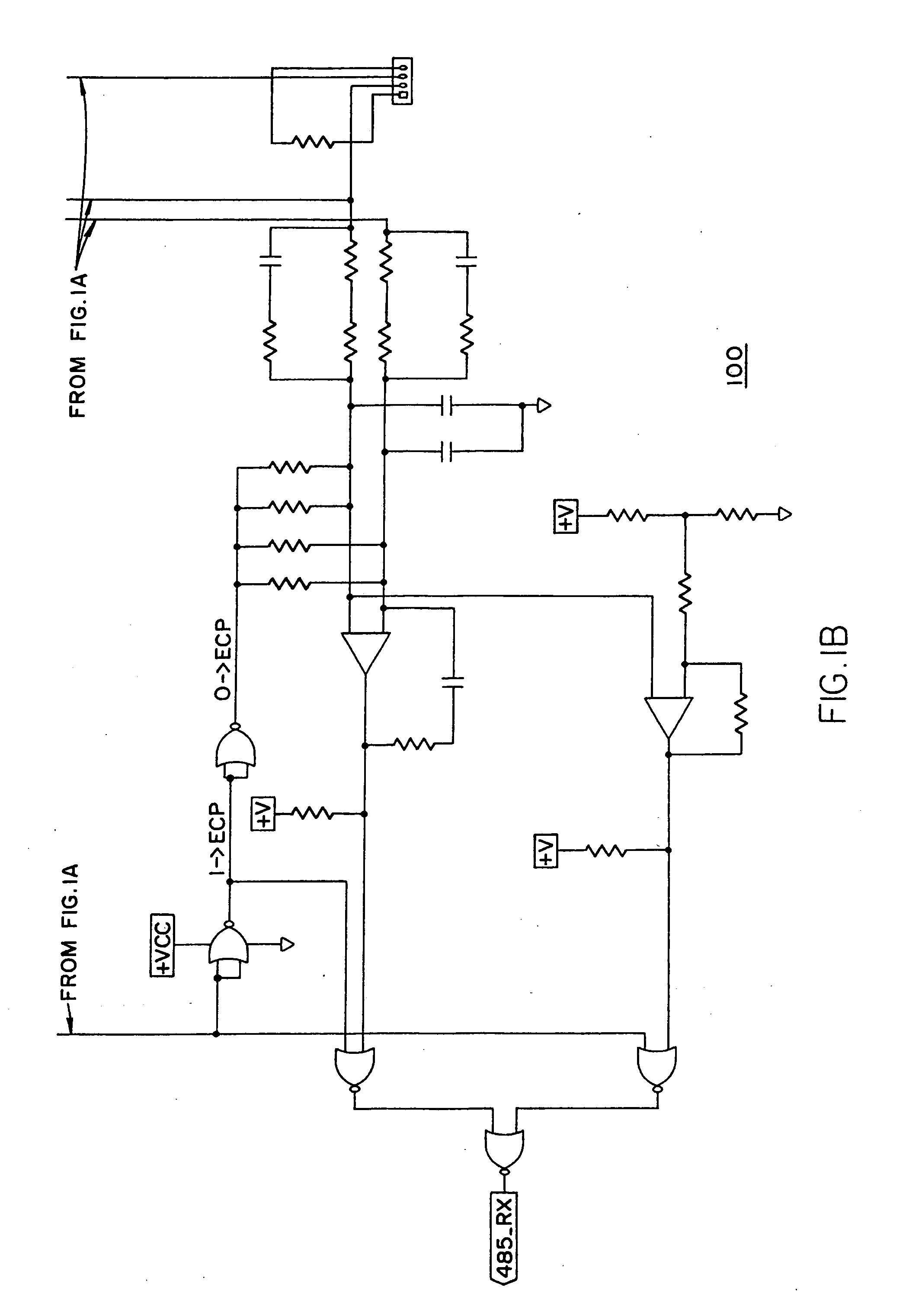
Feedback circuit for line load compensation and reflection reduction
InactiveUS20070164779A1Reduce reflectionReliability increasing modificationsElectronic switchingElectrical resistance and conductanceCapacitance
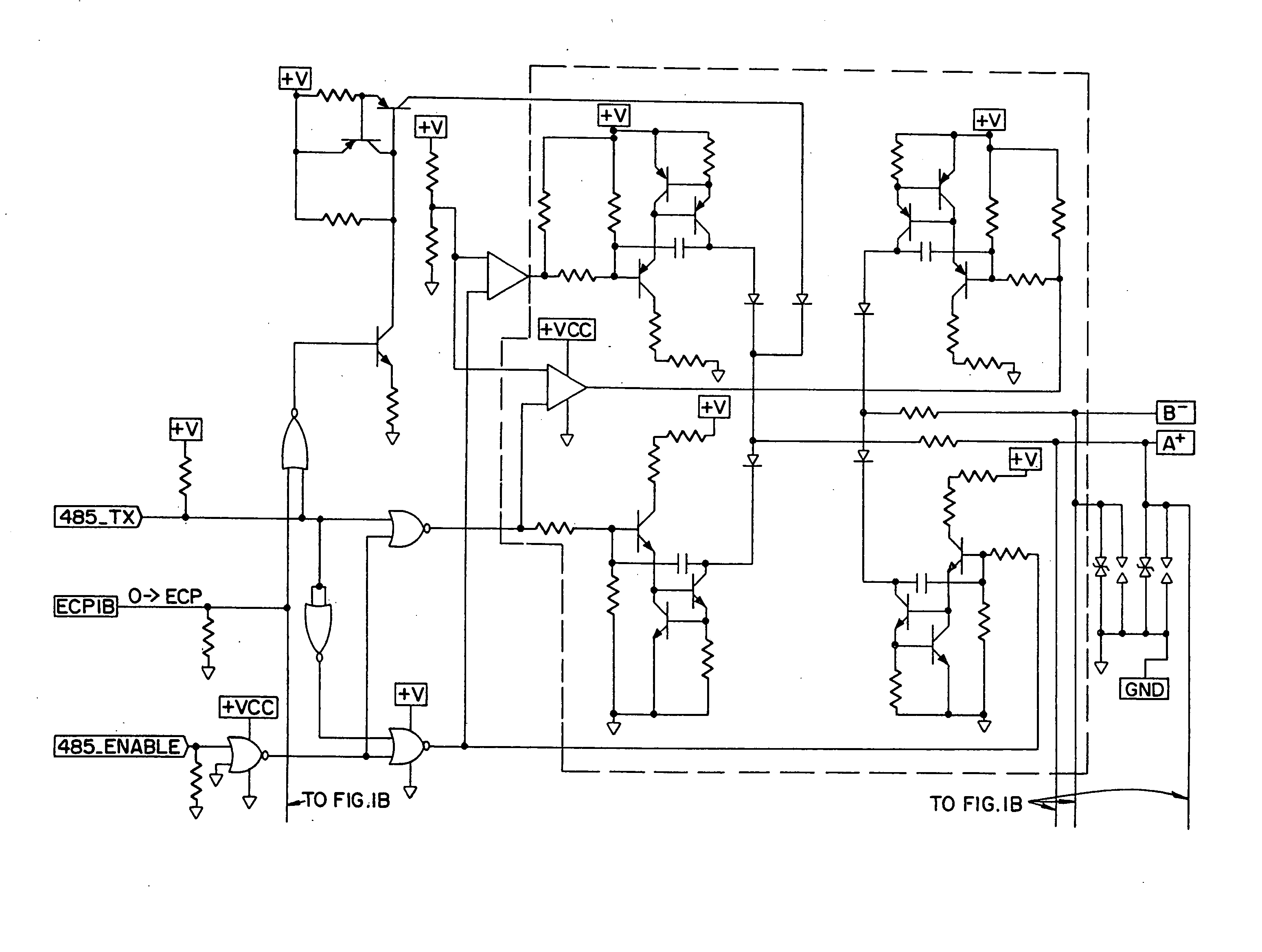
Line load compensation and reflection reduction in a signal transmitting circuit is provided using feedback capacitors. The feedback capacitor serially coupled with a resistance generates an RC rise / fall time that is independent of the line load. Additionally, by selecting a capacitor that yields a rise / fall time of approximately ⅓ of the maximum bit transmission time, signal reflection on the signal line can be reduced. Accordingly, by incorporating the feedback capacitor with a differential drive circuit, such as the IB 485 driver, variations in line load can be compensated for while also reducing signal reflection due to un-terminated or improperly terminated signal lines, thus allowing a free topology implementation.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
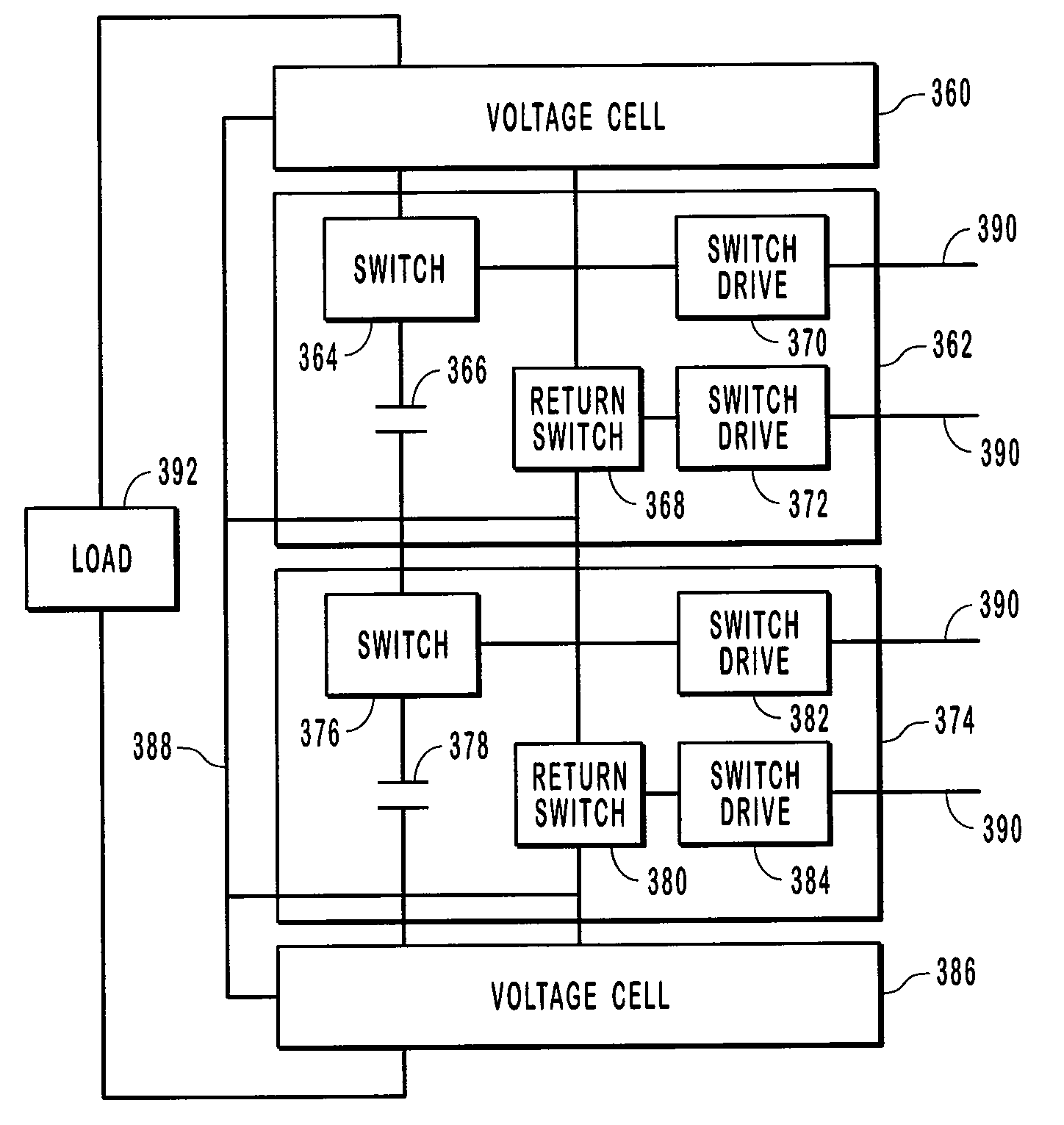
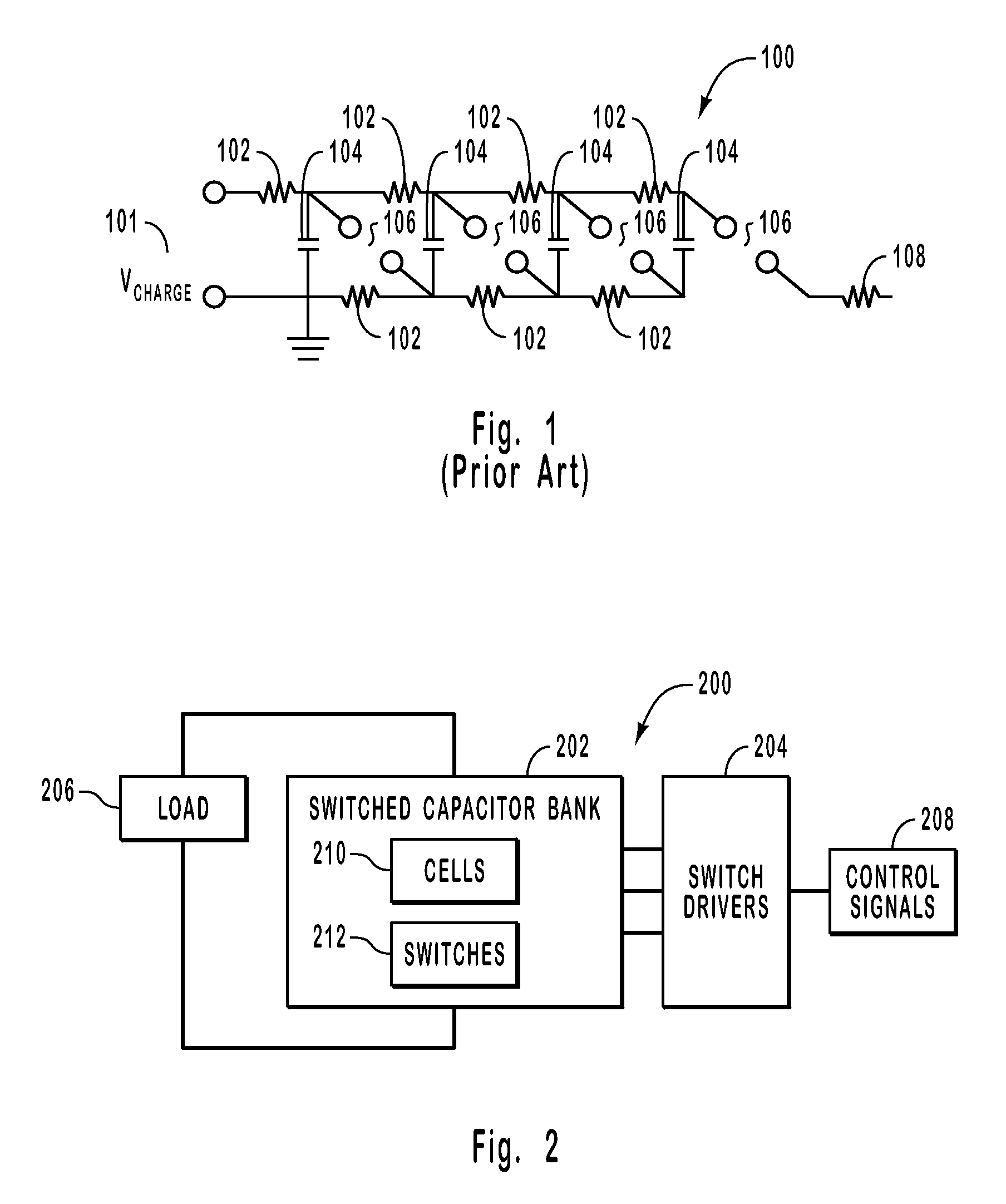
High voltage pulsed power supply using solid state switches
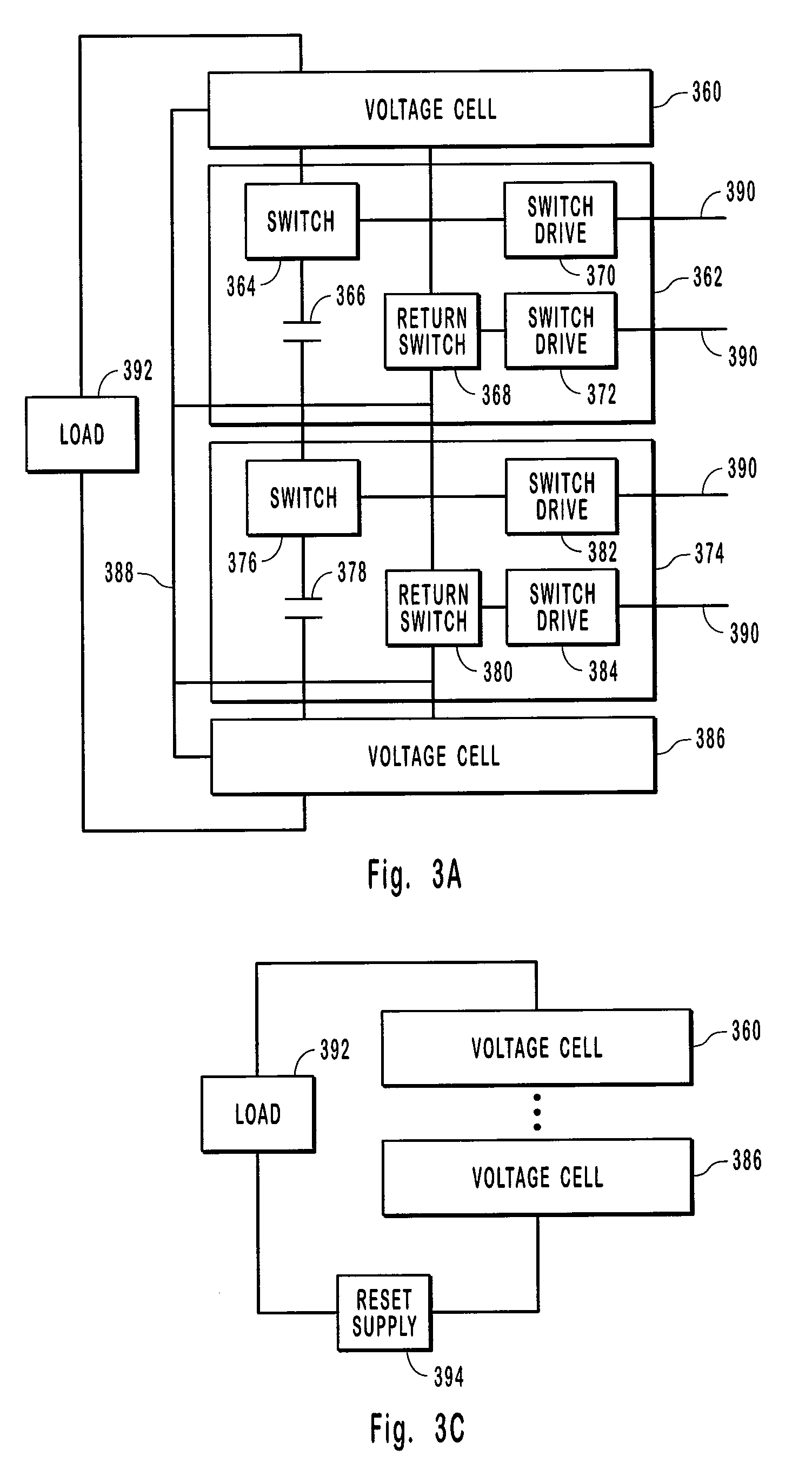
ActiveUS7301250B2Reduce stray capacitanceShortened fall timeApparatus without intermediate ac conversionPulse generation by energy-accumulating elementBalancing networkCapacitance
Systems and methods for generating a high voltage pulse. A series of voltage cells are connected such that charging capacitors can be charged in parallel and discharged in series. Each cell includes a main switch and a return switch. When the main switches are turned on, the capacitors in the cells are in series and discharge. When the main switches are turned off and the return switches are turned on, the capacitors charge in parallel. One or more of the cells can be inactive without preventing a pulse from being generated. The amplitude, duration, rise time, and fall time can be controlled with the voltage cells. Each voltage cell also includes a balance network to match the stray capacitance seen by each voltage cell.
Owner:STANGENES IND INC
Method and apparatus for transmitting a signal using simultaneous FM and AM modulation
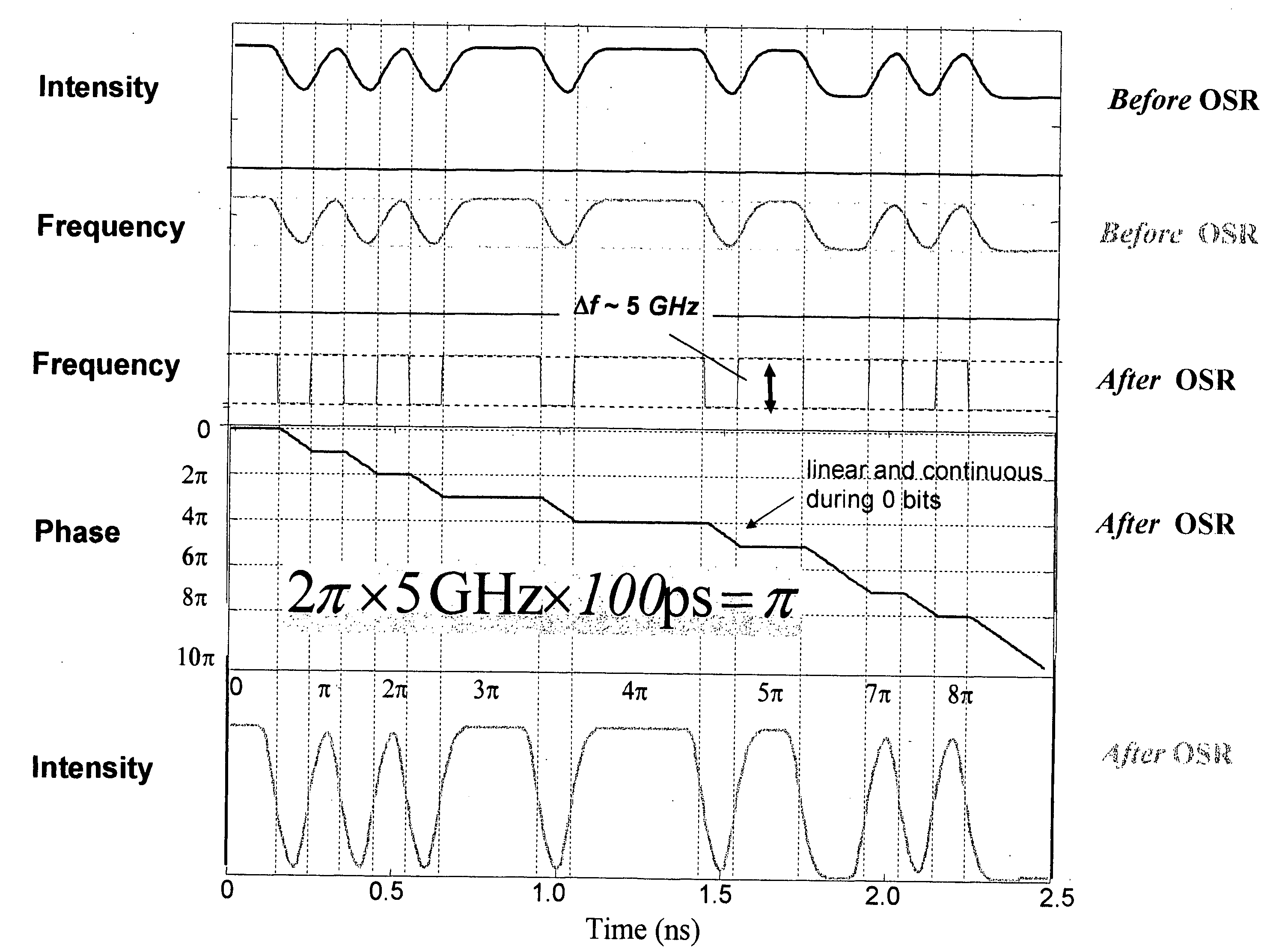
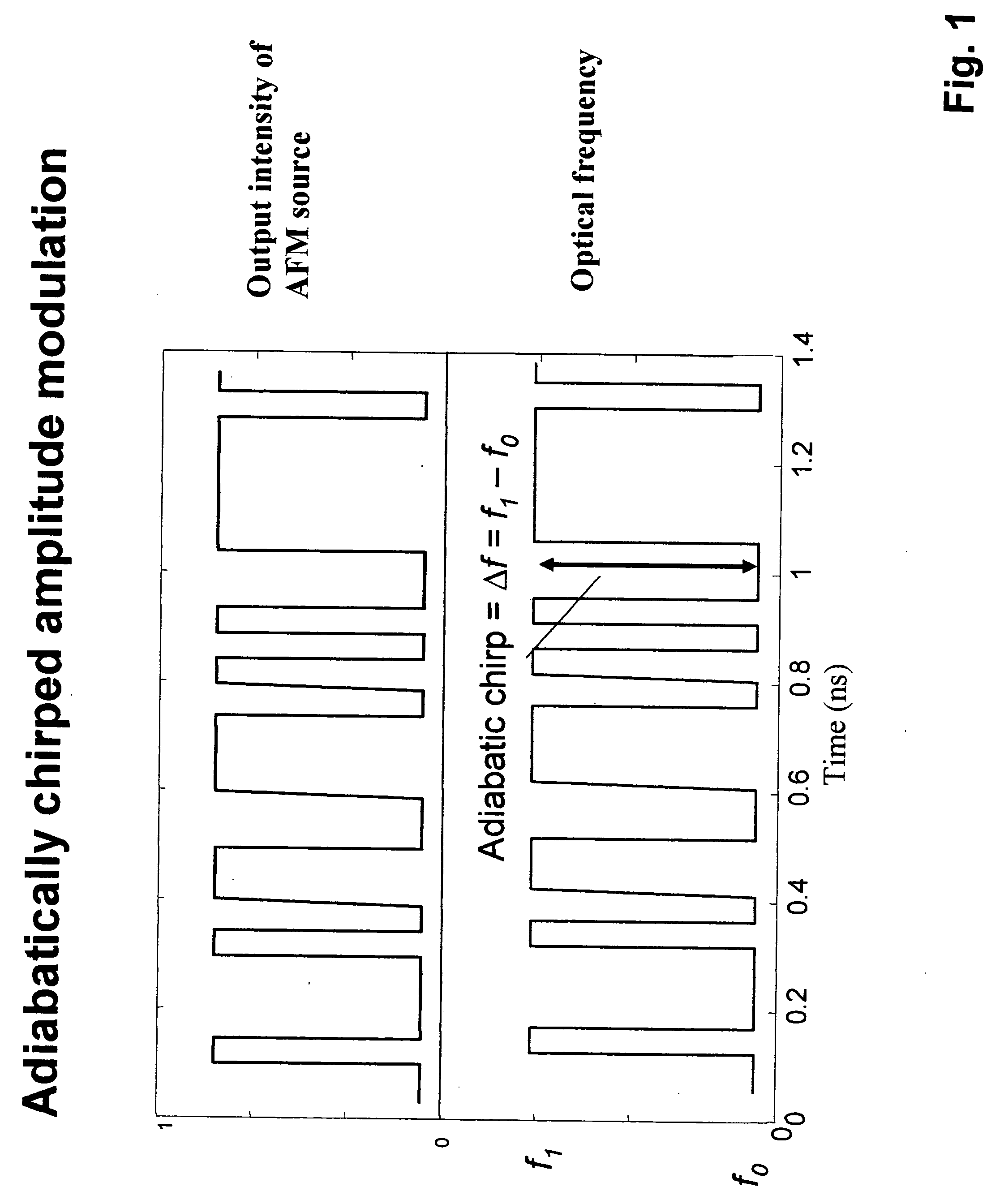
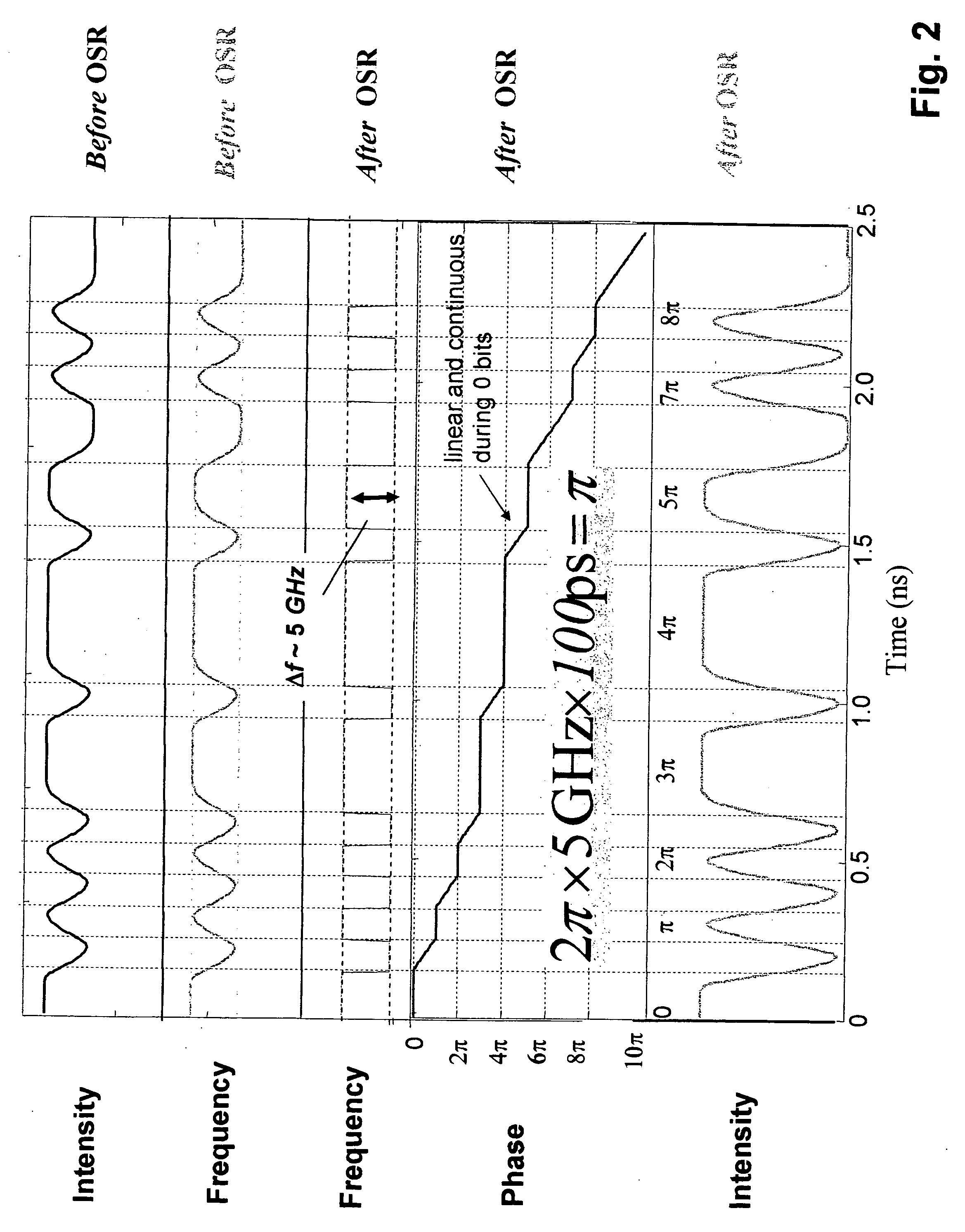
There is provided method for transmitting binary data contained in respective successive time cells, the data being in the form of an optical signal obtained by amplitude modulation and frequency modulation of an optical carrier wave, with a 0 bit data value having a 0 bit mean amplitude having a 0 bit amplitude time duration and a 0 bit frequency having a 0 bit frequency duration, and a 1 bit data value having a 1 bit mean amplitude having a 1 bit amplitude time duration and a 1 bit frequency having a 1 bit frequency duration; the improvement wherein: independently adjusting the 0 bit mean amplitude relative to the 1 bit mean amplitude; independently adjusting the 0 bit frequency relative to the 1 bit frequency; and independently adjusting time duration of the frequency profile of the 1 bit relative to the time duration of the amplitude profile of the 1 bit, whereby to extend the error-free propagation of the optical signal though a dispersive optical fiber beyond the dispersion limit. There is provided a method for transmitting Non-Return-To-Zero (NRZ) binary data contained in respective successive time cells, the data being in the form of an optical signal obtained by amplitude modulation and frequency modulation of an optical carrier wave, with a 0 bit data value having a 0 bit mean amplitude having a 0 bit amplitude time duration and a 0 bit frequency having a 0 bit frequency duration, and a 1 bit data value having a 1 bit mean amplitude having a 1 bit amplitude time duration and a 1 bit frequency having a 1 bit frequency duration; the improvement wherein: the phase across each 1 bit data value is substantially constant, and the phase of the carrier changes across each and every 0 bit by an amount equal to the product of the frequency difference between the 1 bit and the 0 bit and the duration of the 0 bit; whereby to extend the error-free propagation of the optical signal though a dispersive optical fiber beyond the dispersion limit. In accordance with one form of the present invention, there is provided a method for transmitting binary data contained in respective successive time cells, the data being in the form of an optical signal obtained by amplitude modulation and frequency modulation of an optical carrier wave, with a 0 bit data value having a 0 bit mean amplitude having a 0 bit amplitude time duration and a 0 bit frequency having a 0 bit frequency duration, and a 1 bit data value having a 1 bit mean amplitude having a 1 bit amplitude time duration and a 1 bit frequency having a 1 bit frequency duration; the improvement wherein: the amplitude profile of the 1 bit is substantially bell-shaped, and the frequency profile of the 1 bit is substantially square-shaped, with steeper rise and fall time and a wider flat top region; whereby to extend the error-free propagation of the optical signal though a dispersive optical fiber beyond the dispersion limit.
Owner:AZNA +1
Optical disk recording method, optical disk device and optical disk
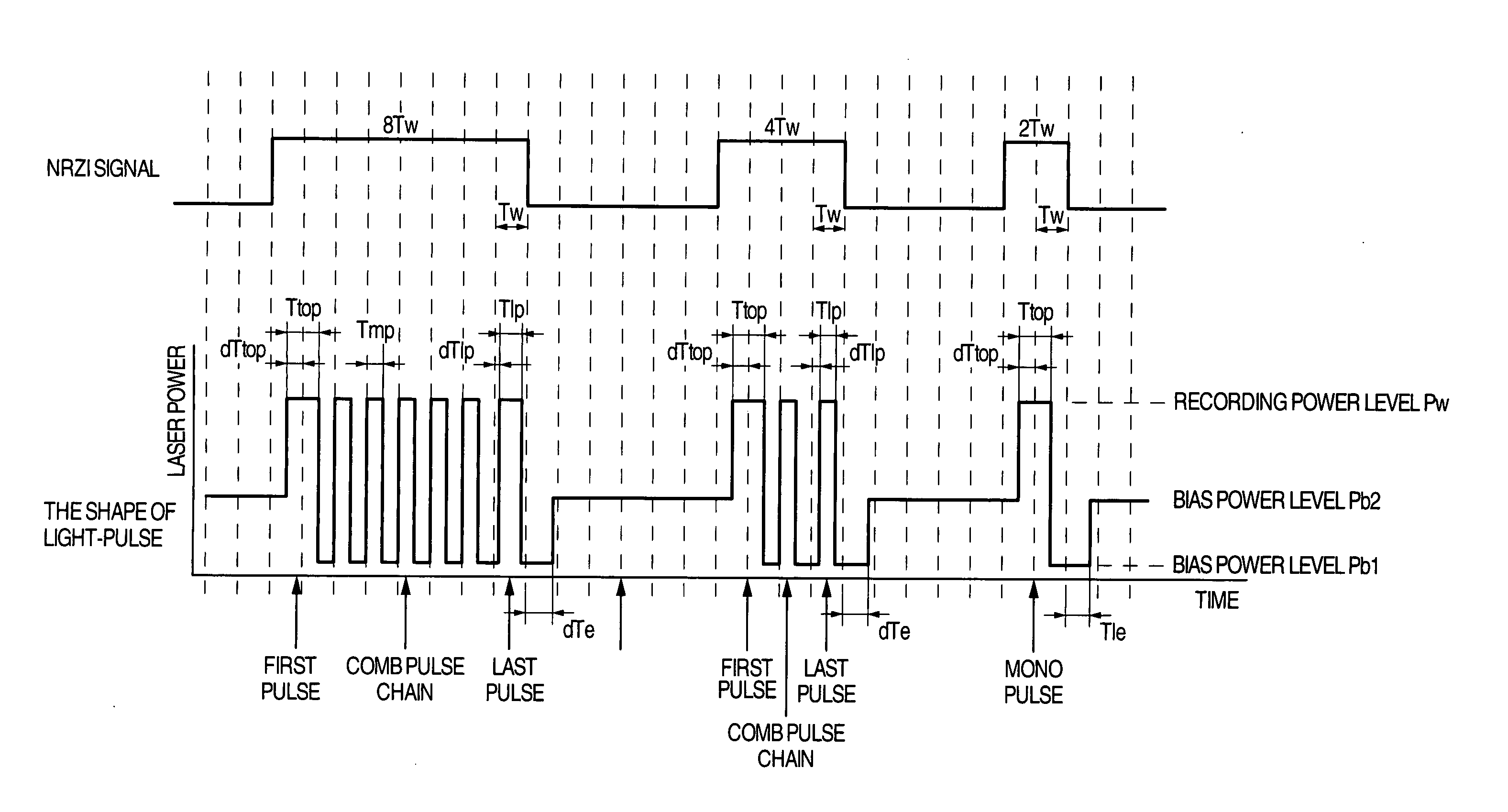
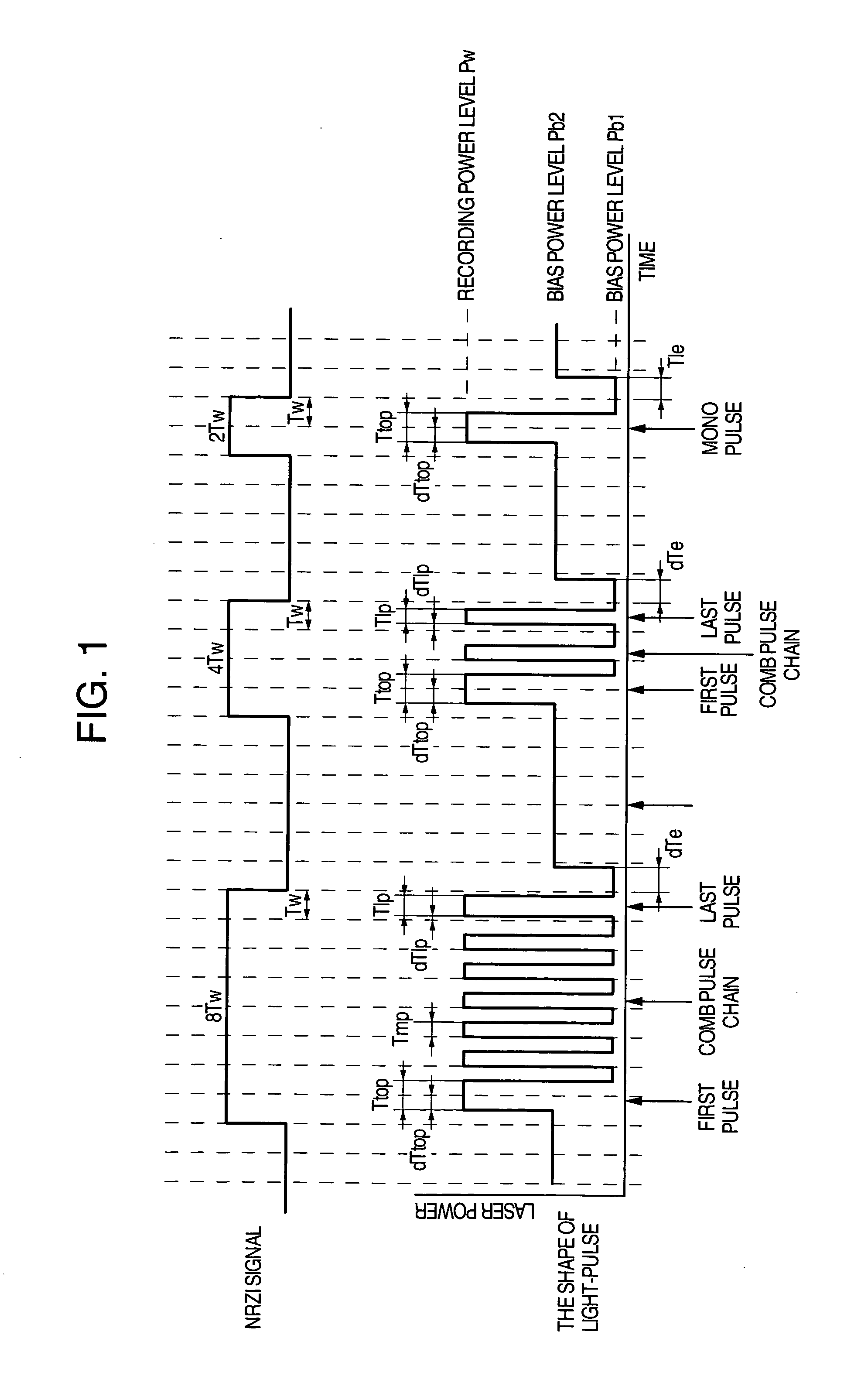
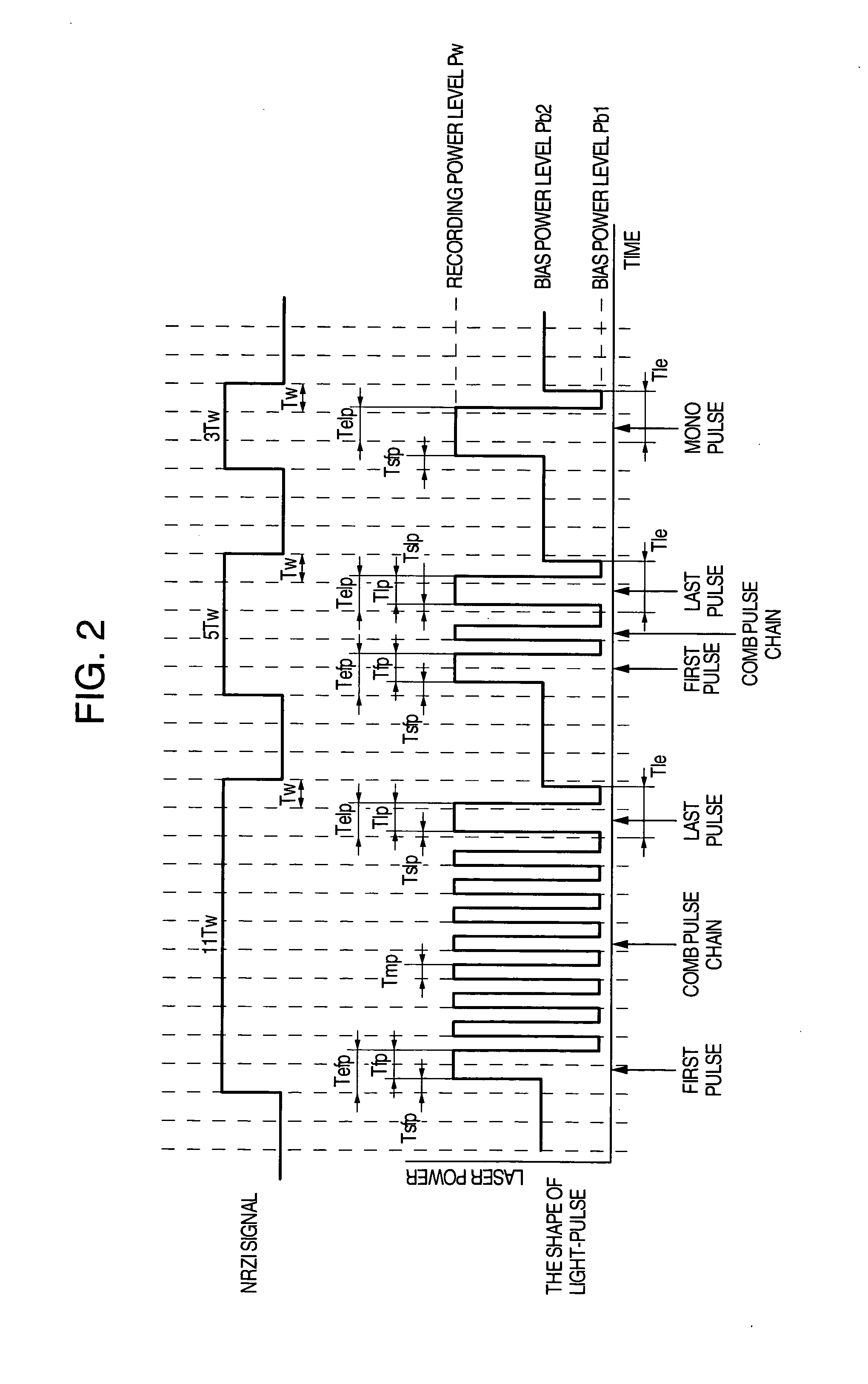
ActiveUS20050058047A1Accurate recordEasy to operateRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsFall timeEngineering
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
Method and apparatus for pulsed electromagnetic therapy
An apparatus and method for applying pulsed electromagnetic therapy to humans and animals. A straight wire element is employed to generate the magnetic field. A power and timer circuit supplies current pulses that approximate square pulses in form, so that the straight wire element generates magnetic pulses having rapid rise and fall times. Peak field strength is approximately 2 gauss at a 1 cm distance from the straight wire element, and the duration of peak field strength is approximately 200 nanoseconds. The pulses are repeated at a frequency of about 70 Hz. The straight wire element and circuit may be housed in a hand-held probe, with an LED illuminating the skin area to provide a visual indication of effective range, or a plurality of the straight wire elements and associated circuits may be embedded in a conformable pad that is placed over the affected area of the body.
Owner:GORDON GLEN A
Low-power, high-modulation-index amplifier for use in battery-powered device
InactiveUS7079901B1Reliably efficiently transmittingEfficient power consumptionNear-field transmissionElectrotherapyElectrical batteryCarrier signal
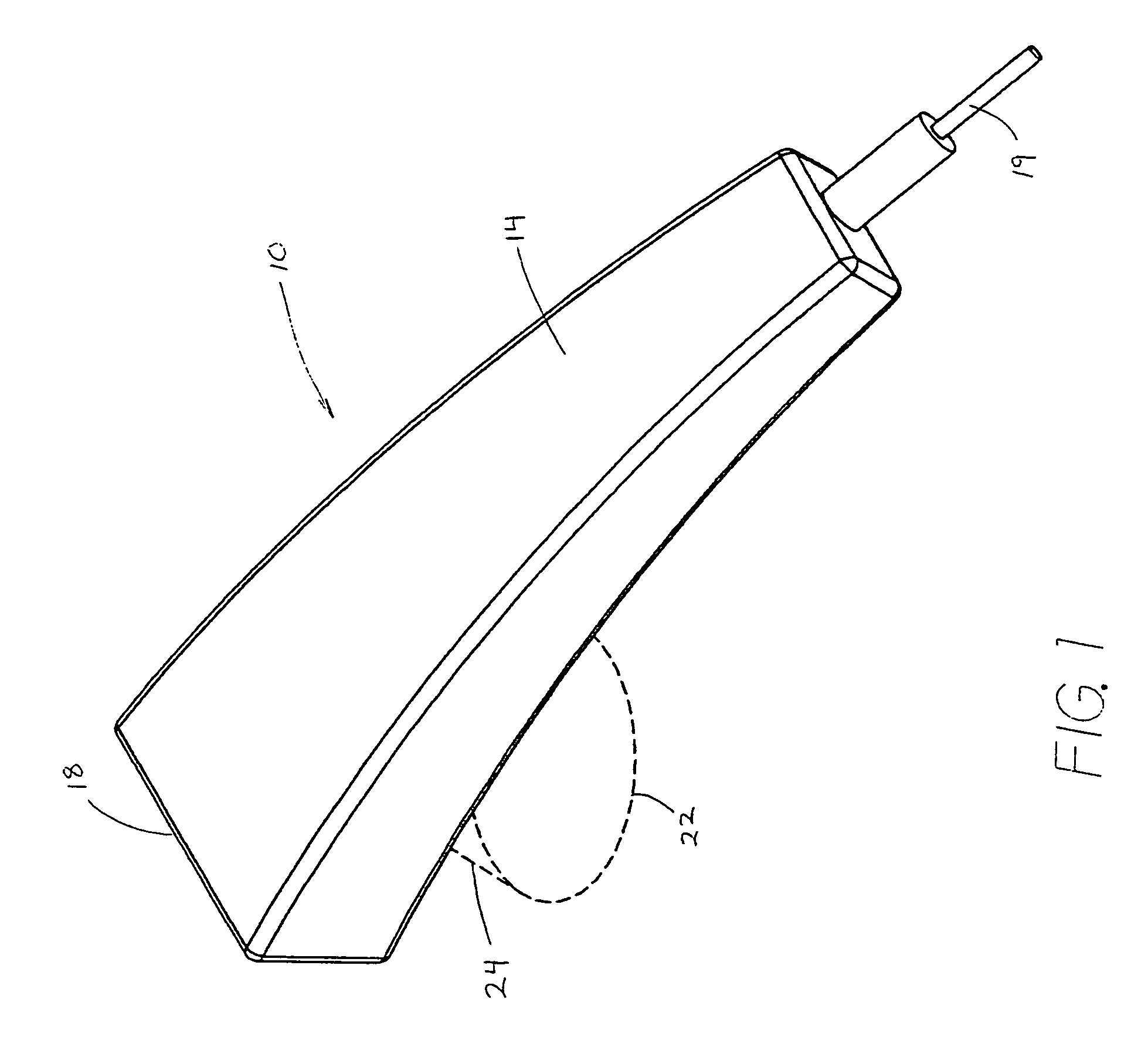
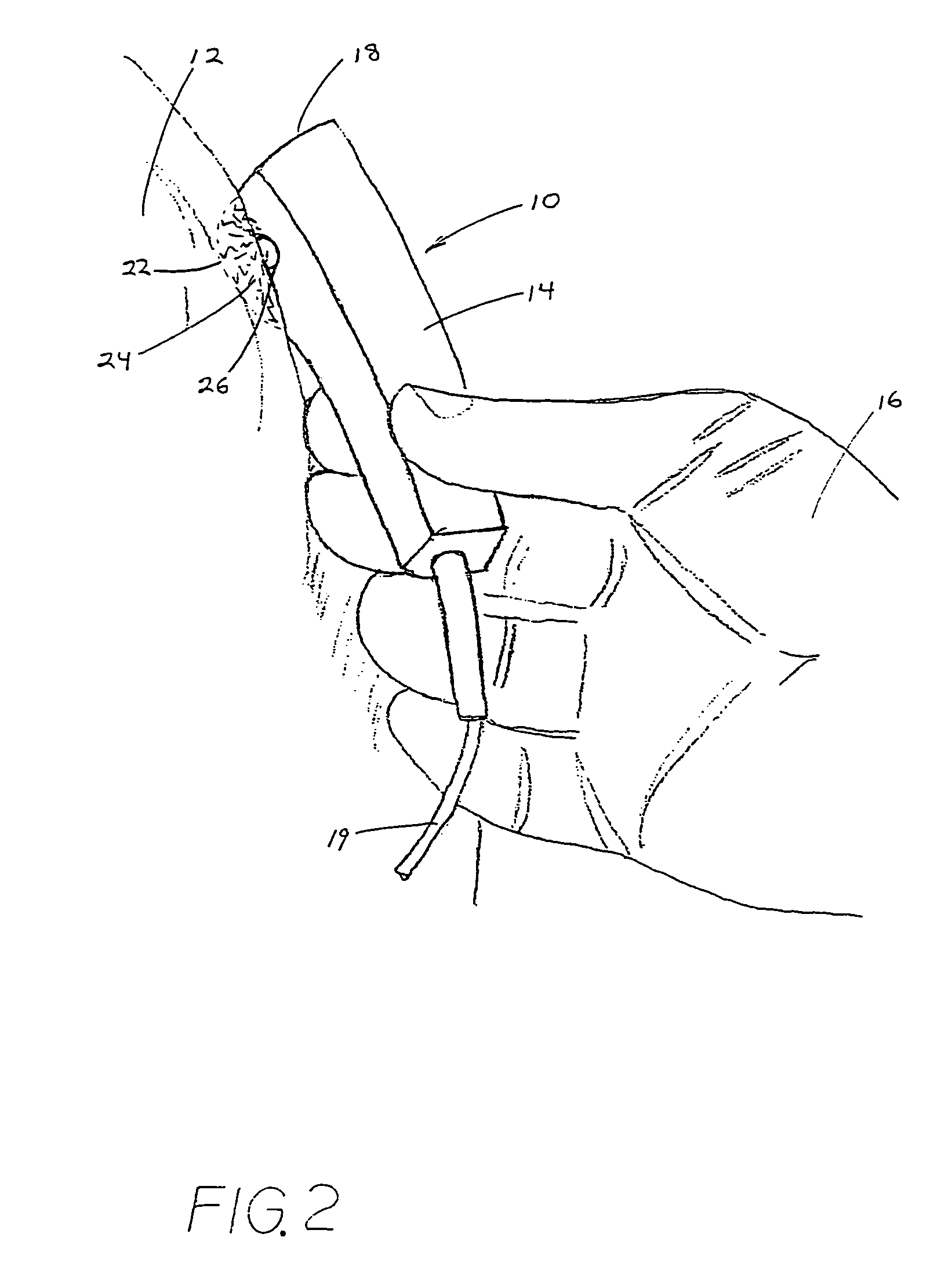
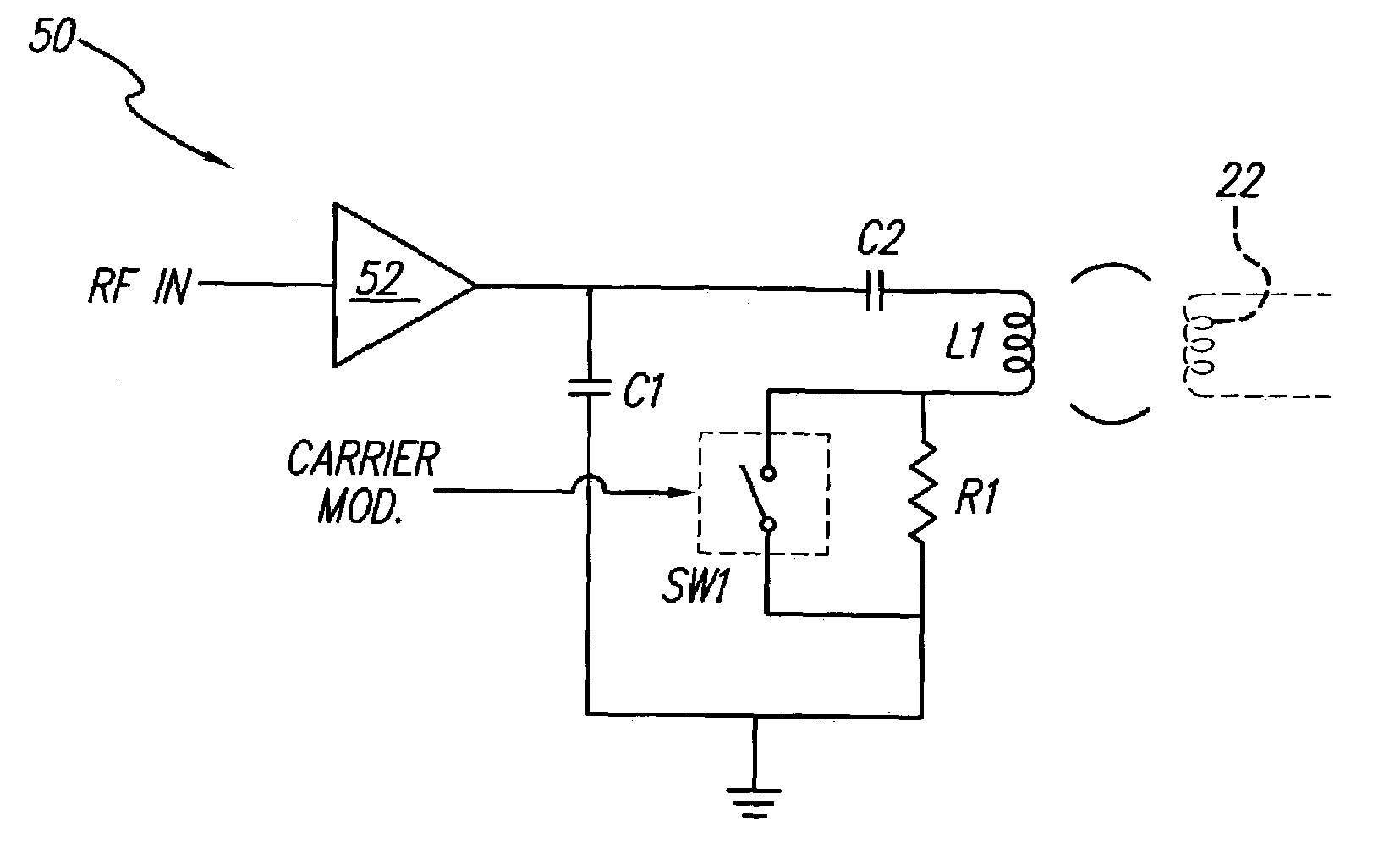
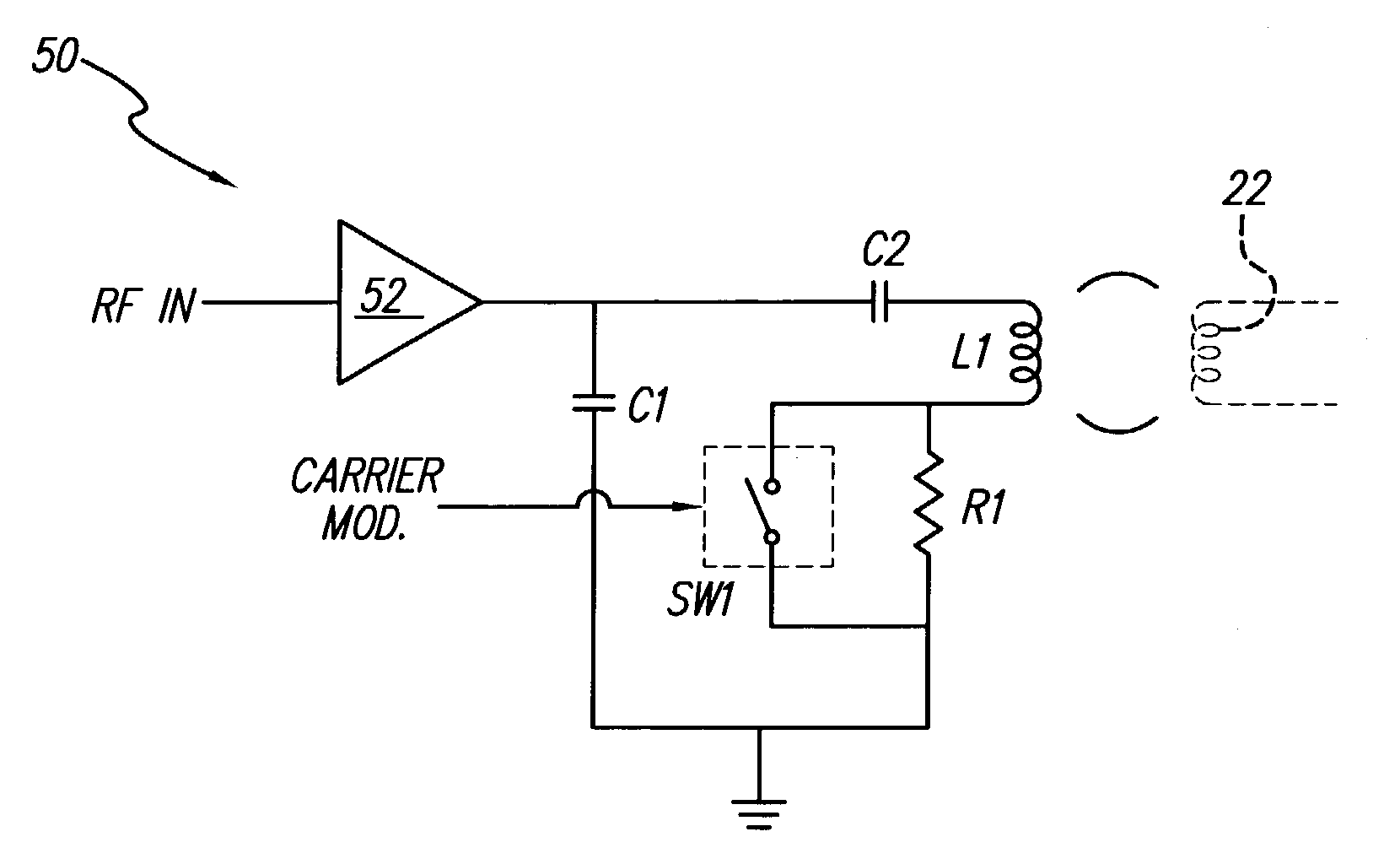
An external transmitter circuit drives an implantable neural stimulator having an implanted coil from a primary coil driven by a power amplifier. For efficient power consumption, the transmitter output circuit (which includes the primary coil driven by the power amplifier inductively coupled with the implanted coil) operates as a tuned resonant circuit. When operating as a tuned resonant circuit, it is difficult to modulate the carrier signal with data having sharp rise and fall times without using a high power modulation amplifier. Sharp rise and fall times are needed in order to ensure reliable data transmission. To overcome this difficulty, the present invention includes an output switch that selectively inserts a resistor in the transmitter output coil circuit in order to de-tune the resonant circuit only during those times when data modulation is needed. Such de-tuning allows sharp rise and fall times in the data modulation without the need for using a high power modulation amplifier. Because data modulation is typically needed for only a small percent of the time that a carrier signal is present, it is thus possible using the present invention to achieve reliable data modulation, transmission and reception without having to use a high power modulation amplifier in the transmitter.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
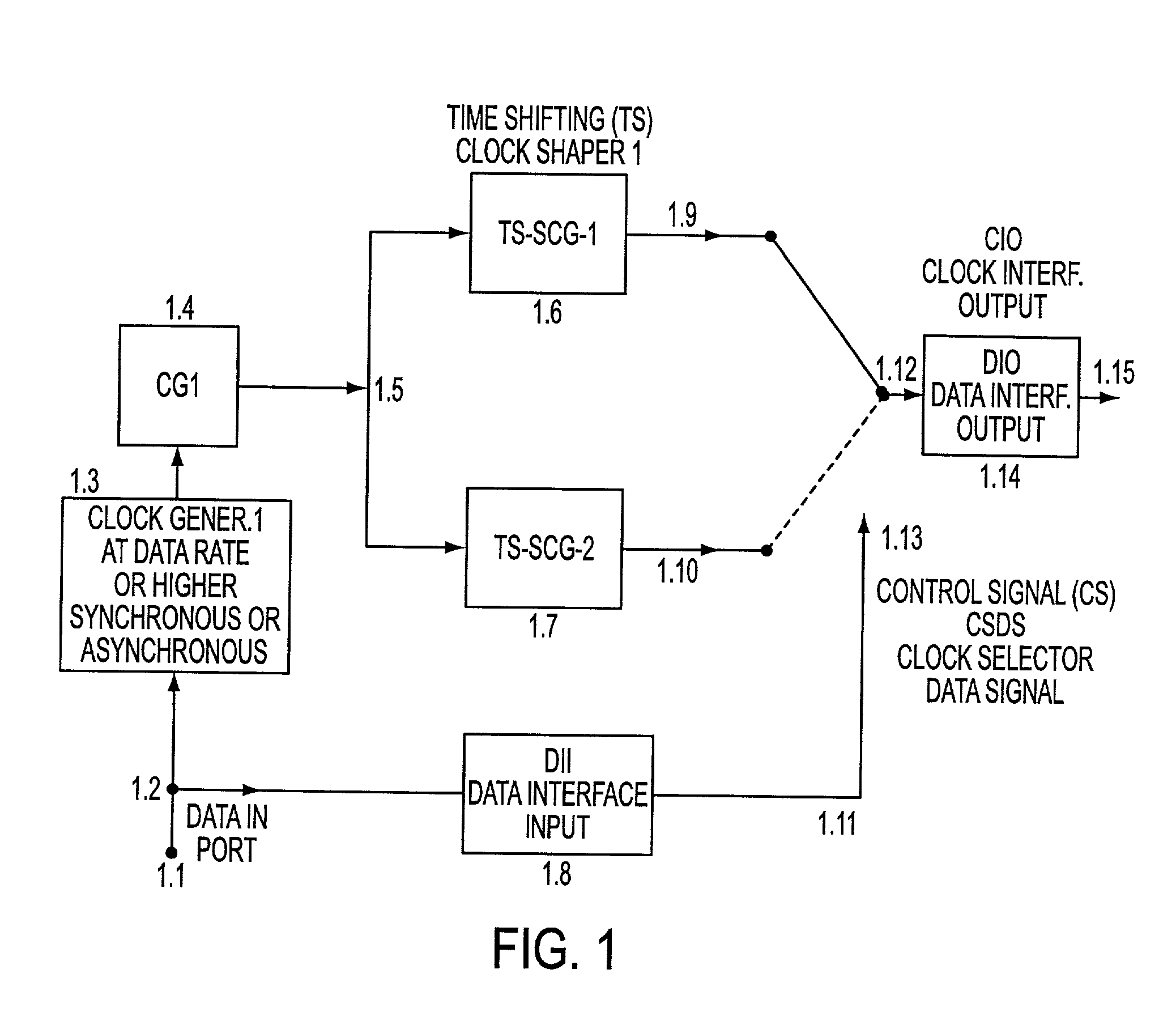
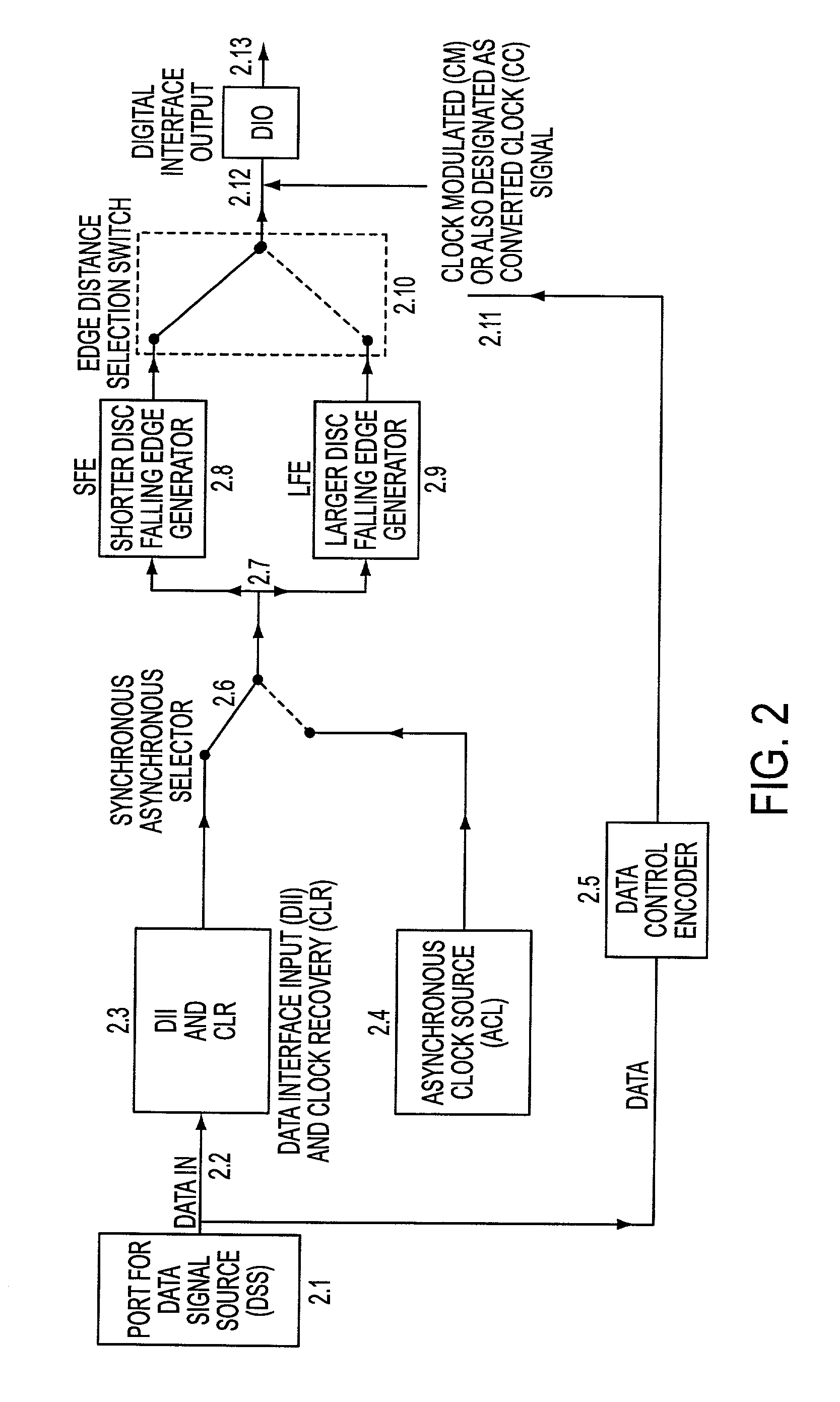
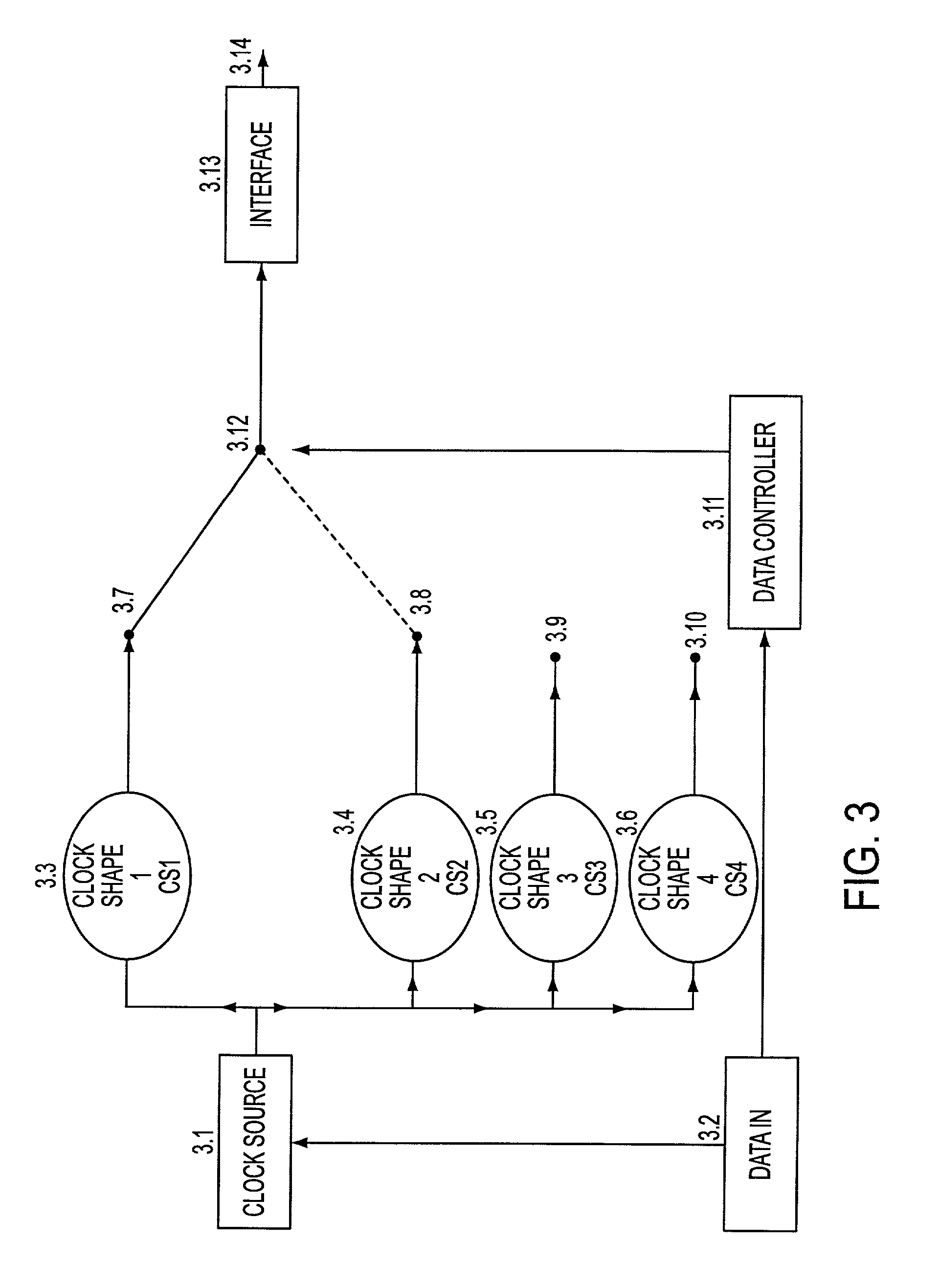
Feher keying (FK) modulation and transceivers including clock shaping processors
InactiveUS20010016013A1Increase powerModulated carrier system with waveletsSynchronisation information channelsFrequency spectrumModem device
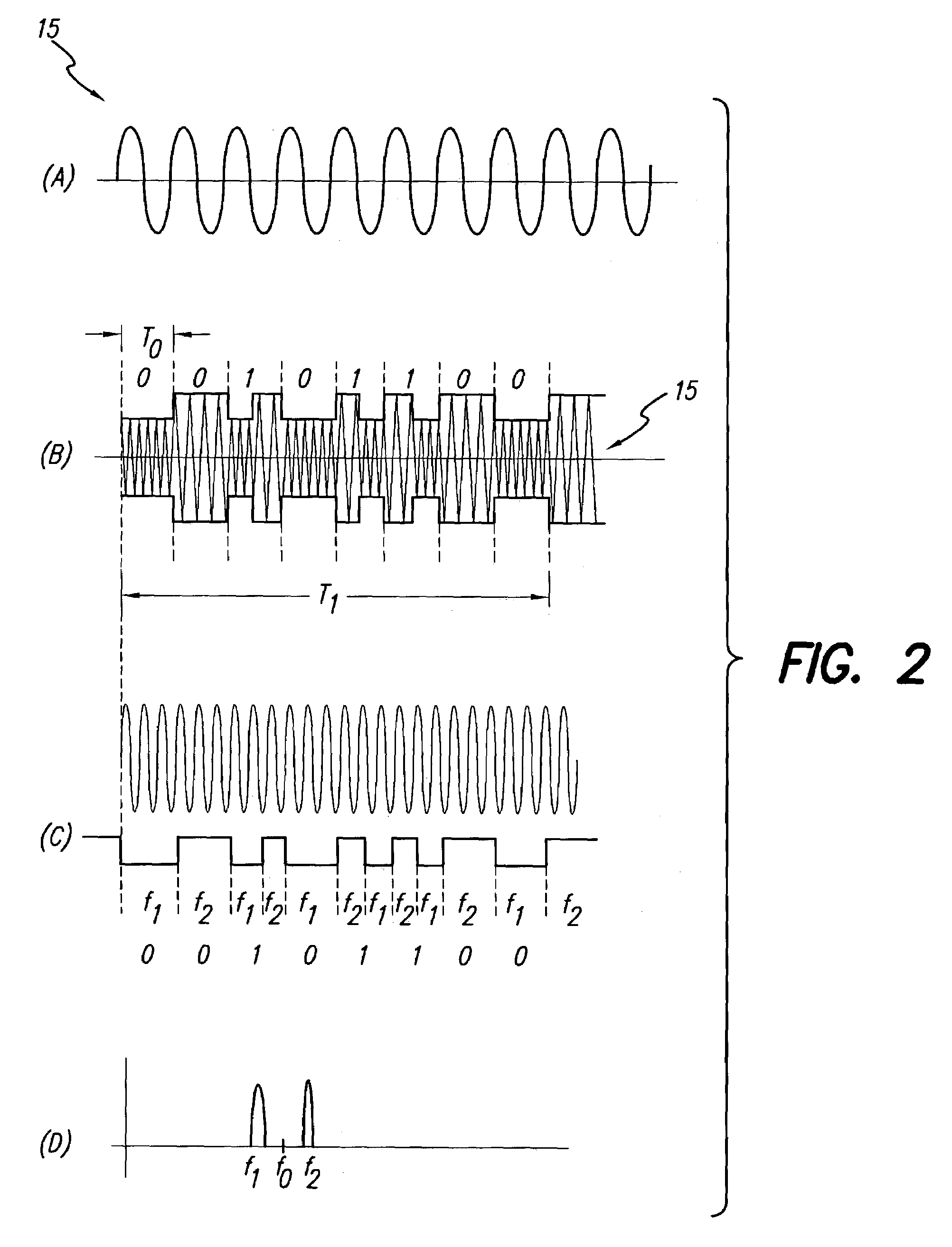
Ultra high spectral efficient Feher Keying (FK) Modulation and Demodulation (Modem), Baseband Processing (BBP), Intermediate Frequency (IF) and Radio Frequency (RF) signal generation and processing methods and implementations, including Clock Modulated (CM) and Shaped Clocked (SC) Transmitters-Receivers (transceivers) are disclosed. Additional embodiments, including Feher Quadrature Shift Keying (FQPSK) and Feher Quadrature Modulation (FQAM), in conjunction with CM and SC are also described. In the FK modulator, specified clock converted and clock shaped signal parameters are generated. These are based on the input data signal patterns and are generated by means of control signals, which are designed in the data input signal interface data signal and / or clock signal encoder units. The selectable clock signal parameters include symmetrical and non-symmetrical clock signals, shaped band-limited continuous clock signal patterns, shaped encoded clock signals, variable rise and fall time clock signals, clock signals having adjustable on and off duration, multilevel and shaped clock signals and asynchronous clock signal information transmission means, where asynchronous clocking is referenced to the incoming data source signals. The FK processors are also used in conjunction with cross-correlated FQPSK quadrature and also non quadrature modem systems as input drive signals to FM VCO based systems to SSB to VSB to DSB-SC to QAM, and FQAM and to coded systems with adaptive equalized receivers, Non Redundant Error Correction (NEC), pseudo-error monitor systems. The FK systems and FT apparatus comprises entire transceiver structures including LIN (linear) and NLA (Non Linear Amplifier) transmitter receiver, AGC, synchronization and demodulation and post demodulation signal processors.
Owner:FEHER KAMILO
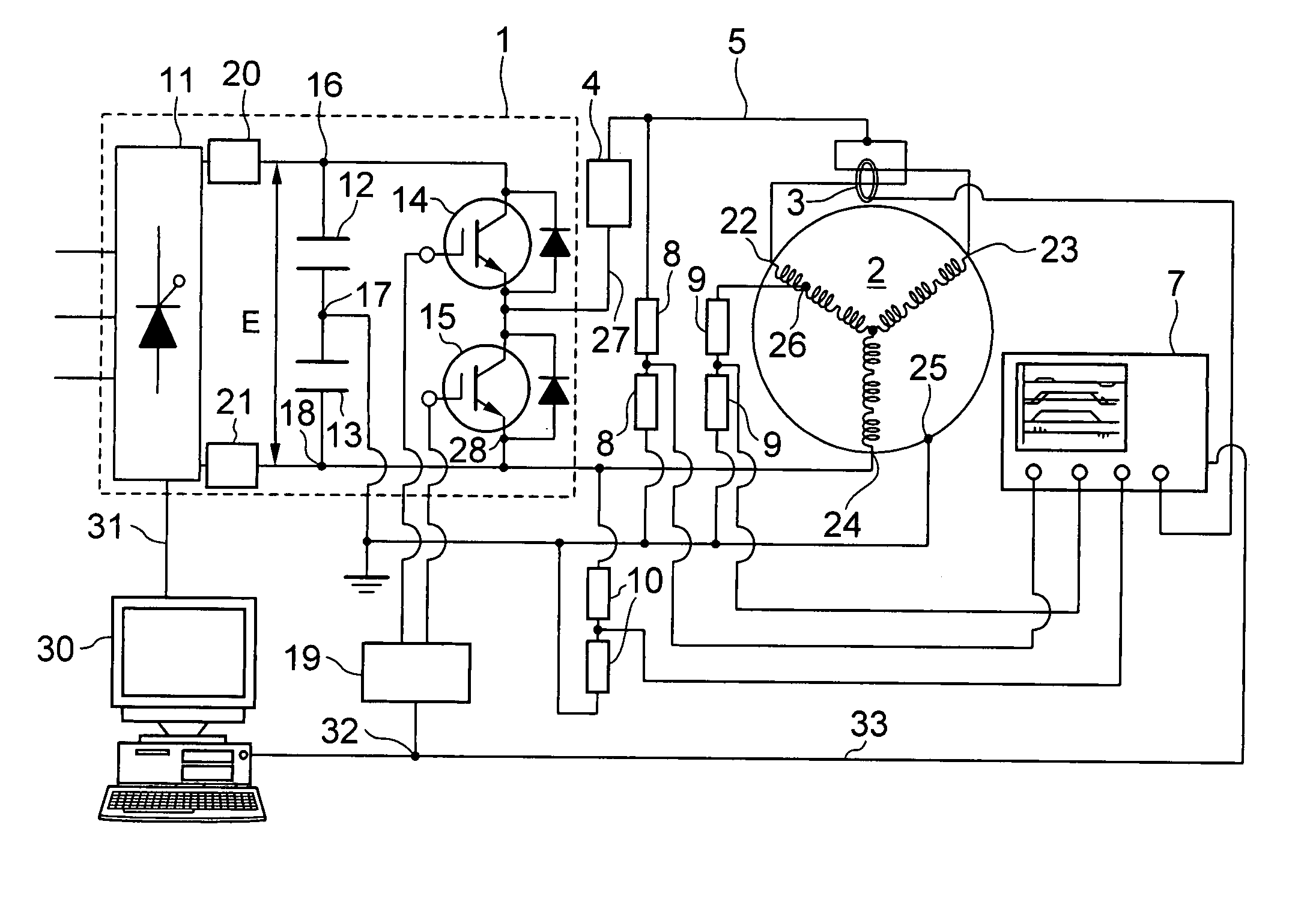
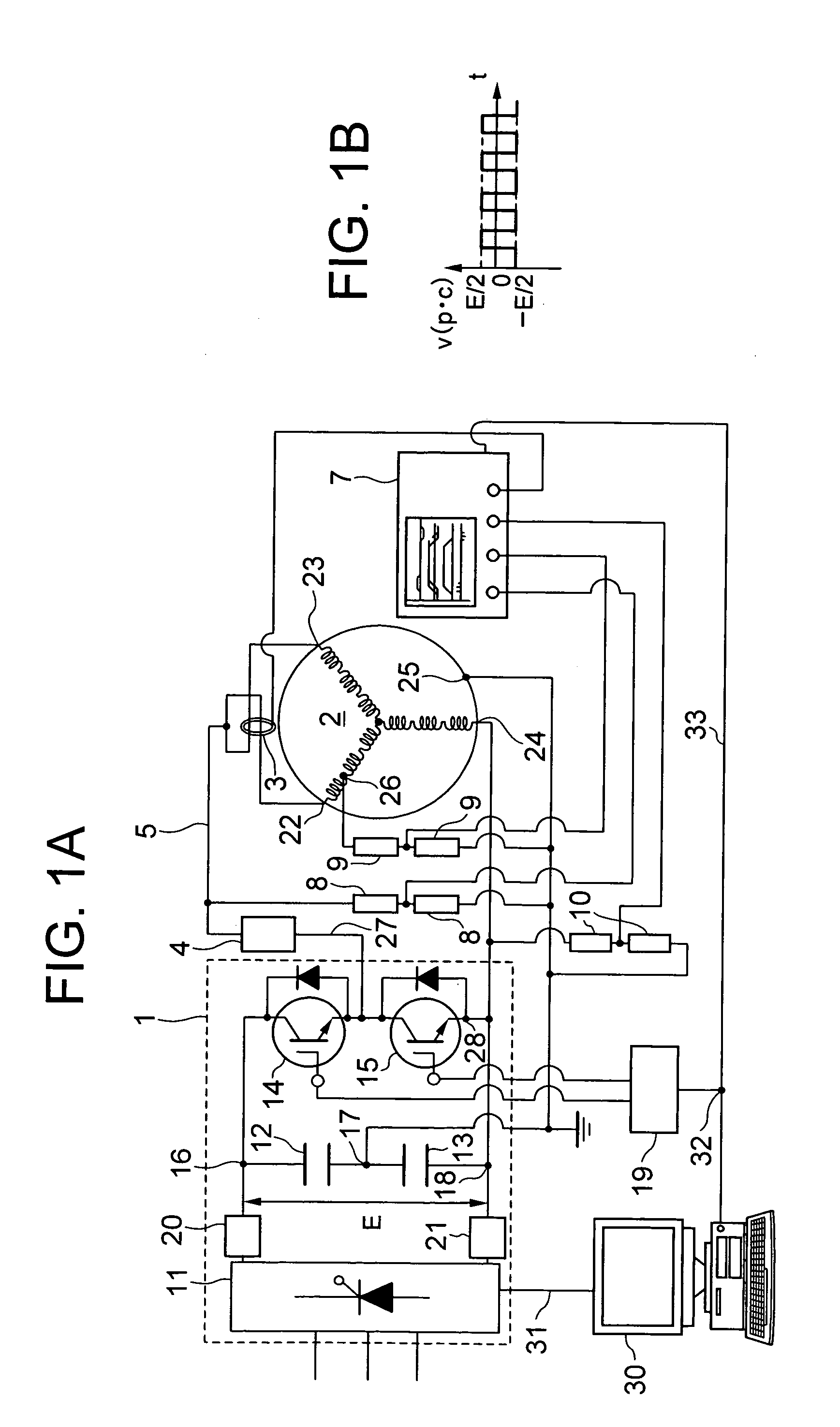
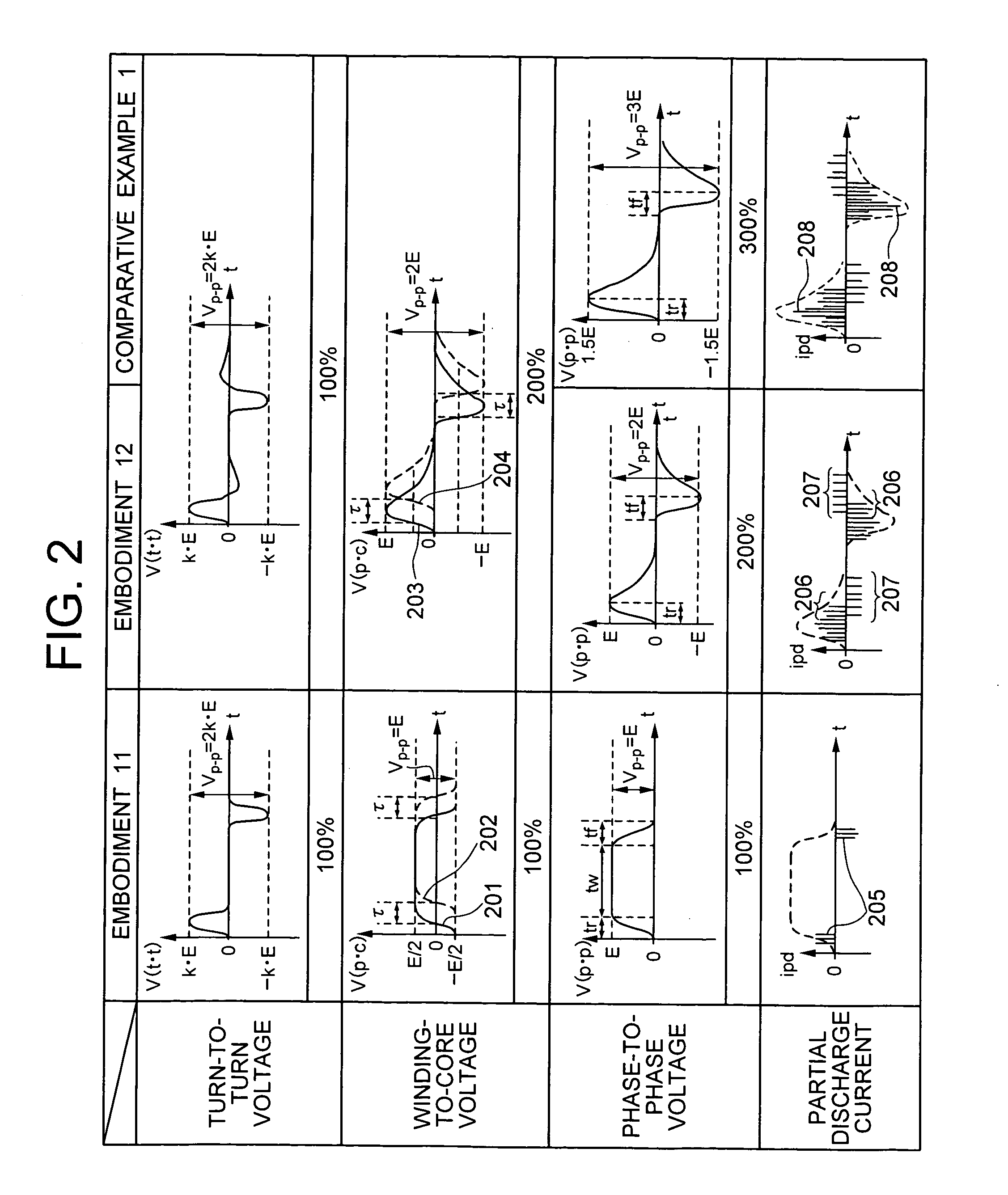
Apparatus for partial discharge detection of turn to turn insulation in motor
ActiveUS20060022679A1Accurate measurementElectric winding testingManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesPower inverterFall time
The apparatus for partial discharge detection of turn-to-turn insulation in motor has a surge generator for generating a surge voltage to the windings of the motor by applying a pulse voltage, and a partial discharge current detector for detecting partial discharge currents between the winding turns of the motor. The surge generator generates in and between the windings of the motor the surge voltage that has the rise time and fall time corresponding to the rise time of the surge voltage observed at the motor terminal when the motor is driven by an inverter, and that is repeated at a frequency of 50 Hz to 20 kHz.
Owner:HITACHI IND EQUIP SYST CO LTD
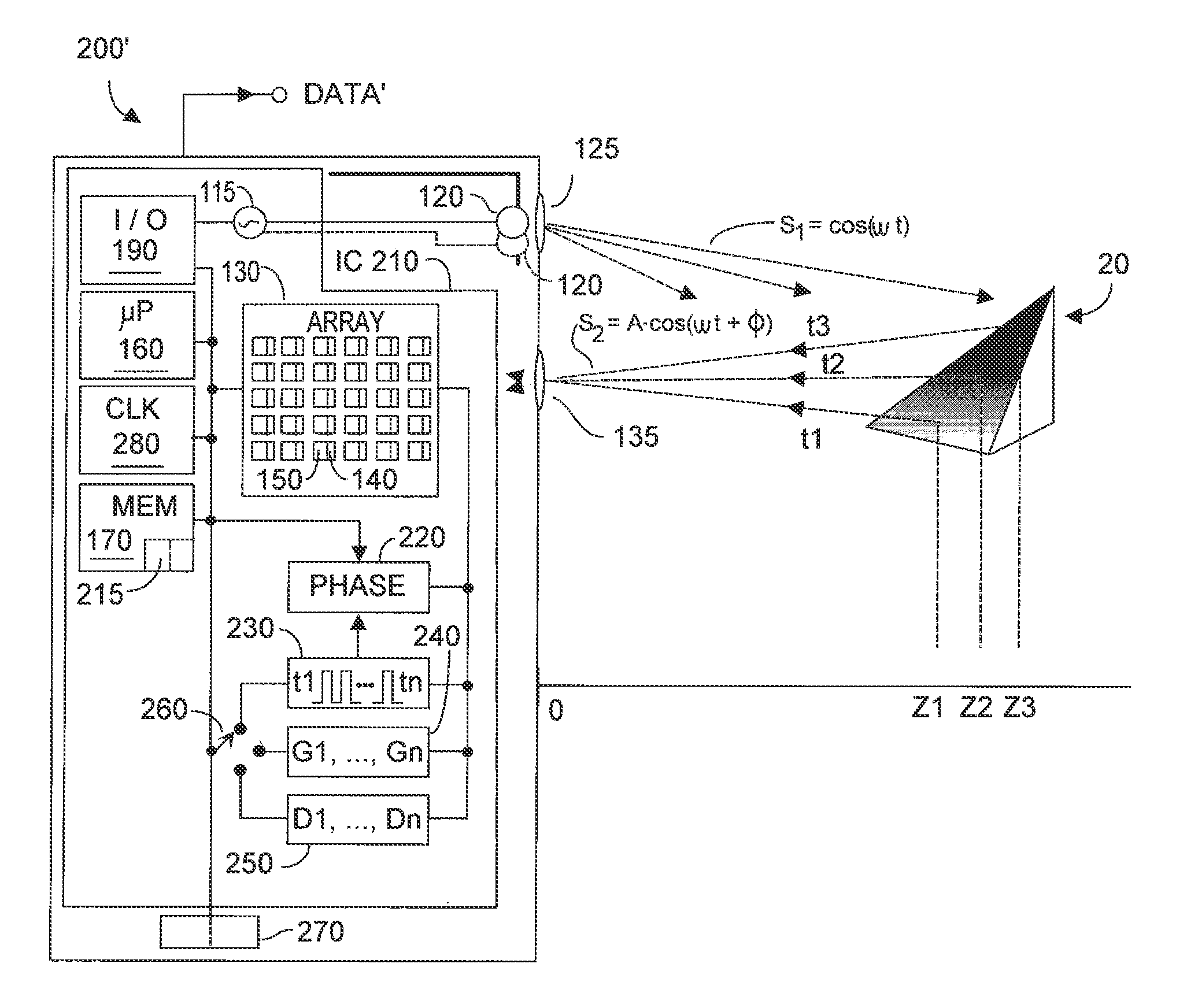
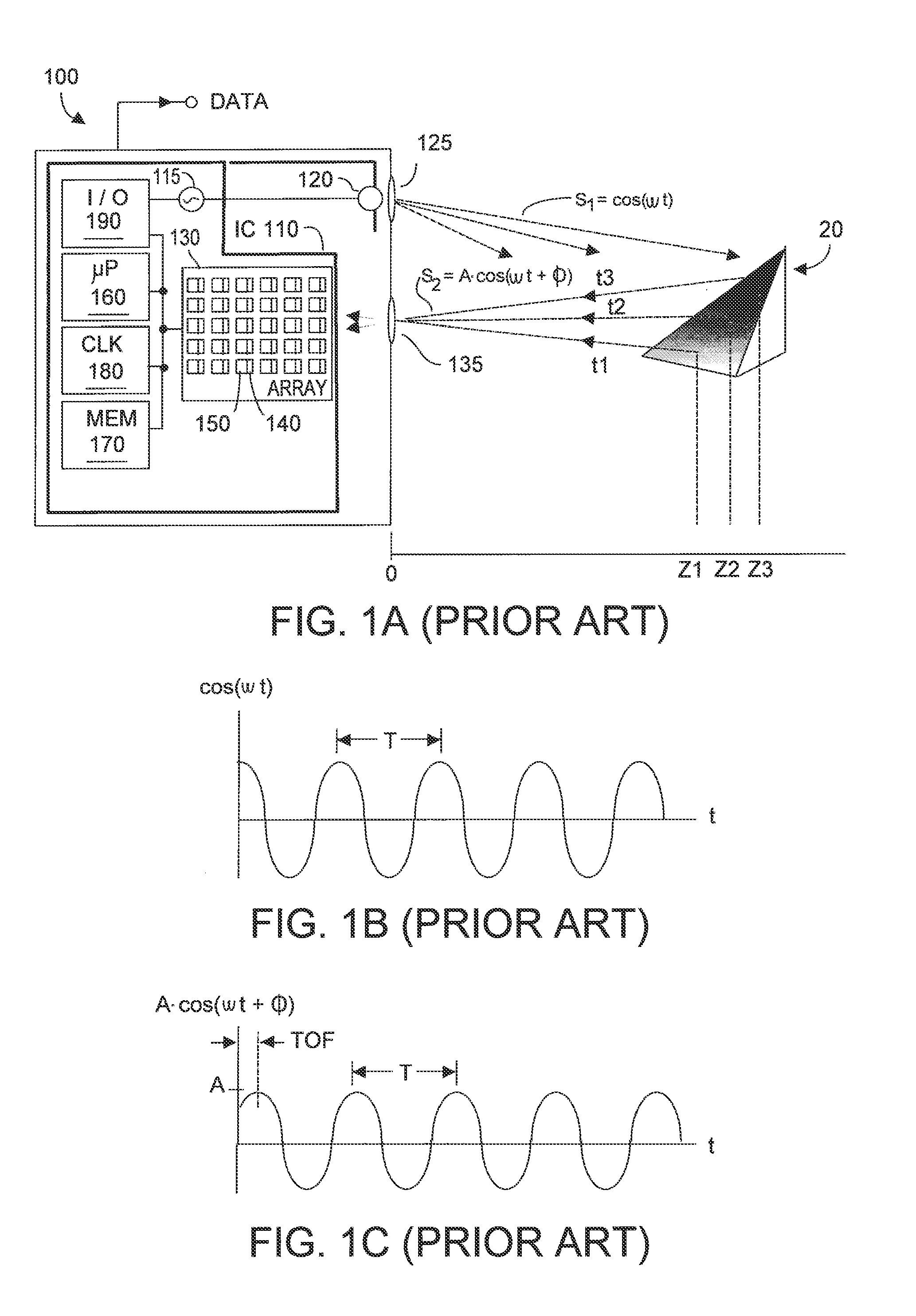
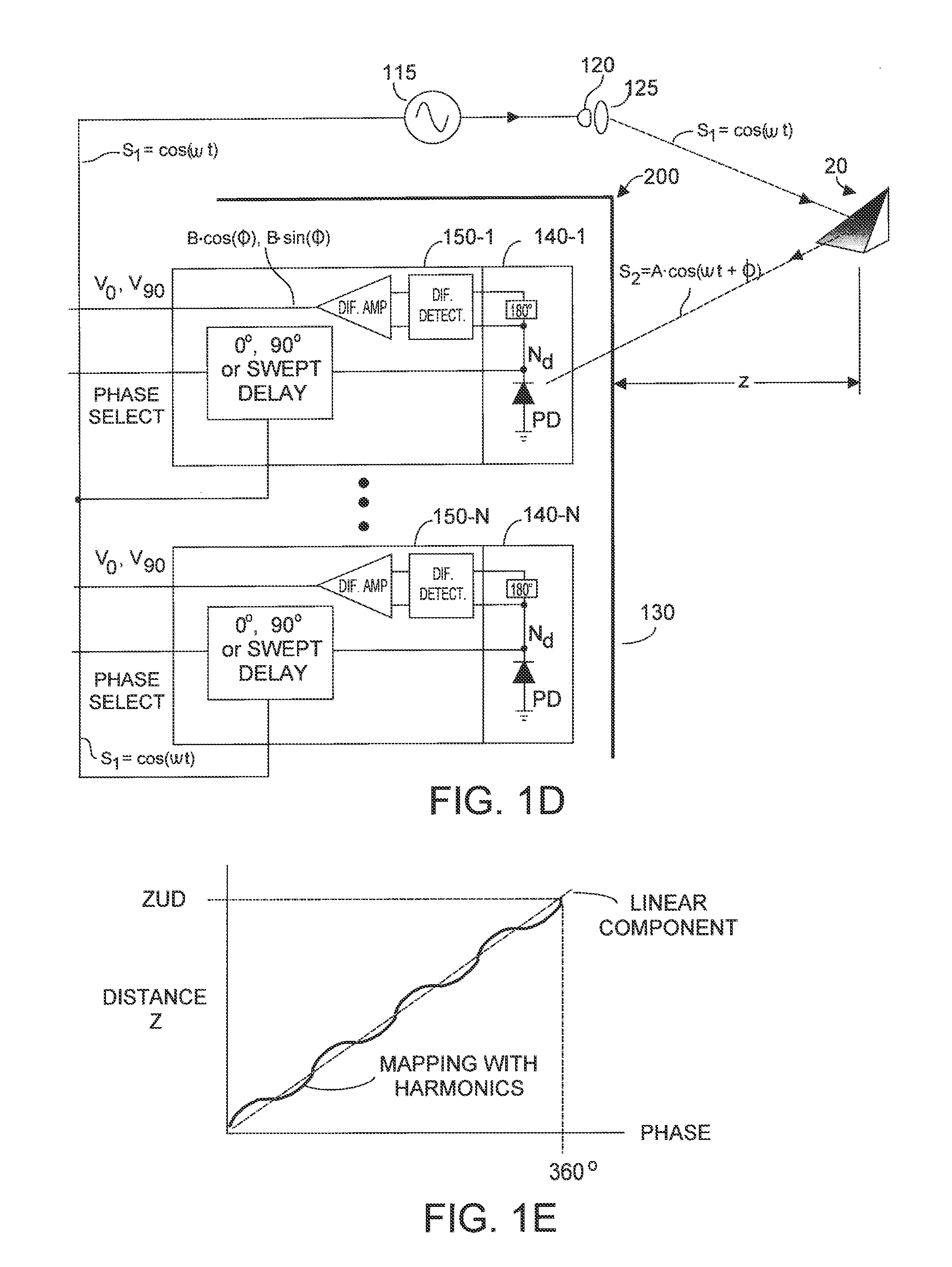
Method and system for multi-phase dynamic calibration of three-dimensional (3D) sensors in a time-of-flight system
ActiveUS20120013887A1Reduces bias errorMaximize modulation contrastOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationAudio power amplifierFall time
A phase-based TOF system preferably generates an optical waveform with fast rise and fall times, to enhance modulation contrast, notwithstanding there will be many high order harmonics. The system is preferably operated with an odd number of phases, to reduce system bias error due to the higher order harmonics, while maintaining good modulation contrast, without unduly increasing system memory requirements. Preferably the system can dynamically calibrate (and compensate for) higher order harmonics in the TOF generated optical energy waveform, over time and temperature. Within the optical energy transmission channel, or within the optical energy detection channel, detection amplifier gain may be modified, and / or detector signal integration time may be varied, and / or digital values may be employed to implement calibration and error reduction The resultant TOF system can operate with improved phase-vs-distance characteristics, with reduced calibration requirements.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
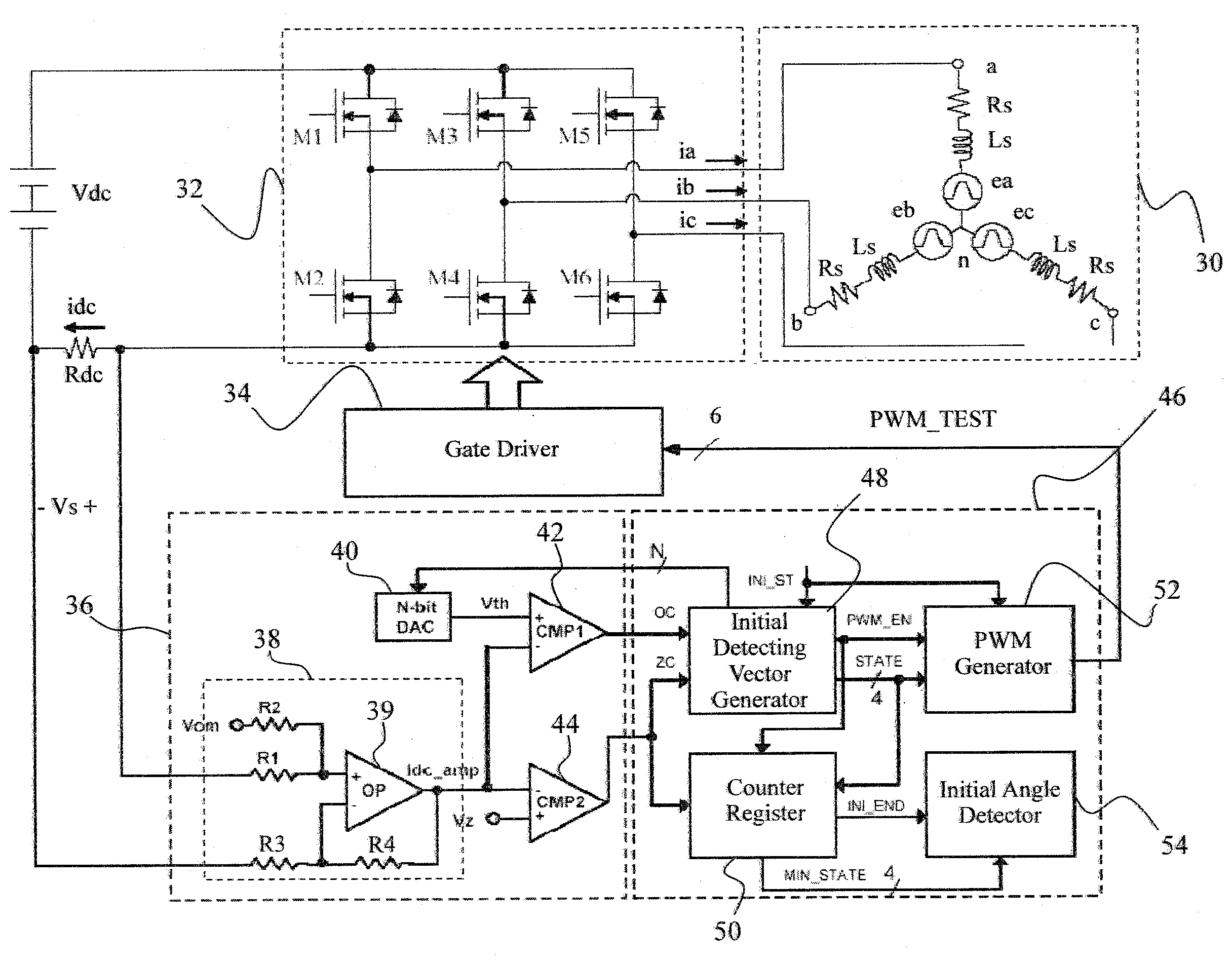
Initial rotor position detection for permanent magnet synchronous motors
ActiveUS20100181952A1High sensitivityAvoid uneven performanceMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersFall timeVoltage vector
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
Low-power, high-modulation-index amplifier for use in battery-powered device
InactiveUS7092762B1Efficient power consumptionSharp rise and fall timeNear-field transmissionElectrotherapyElectrical batteryCarrier signal
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
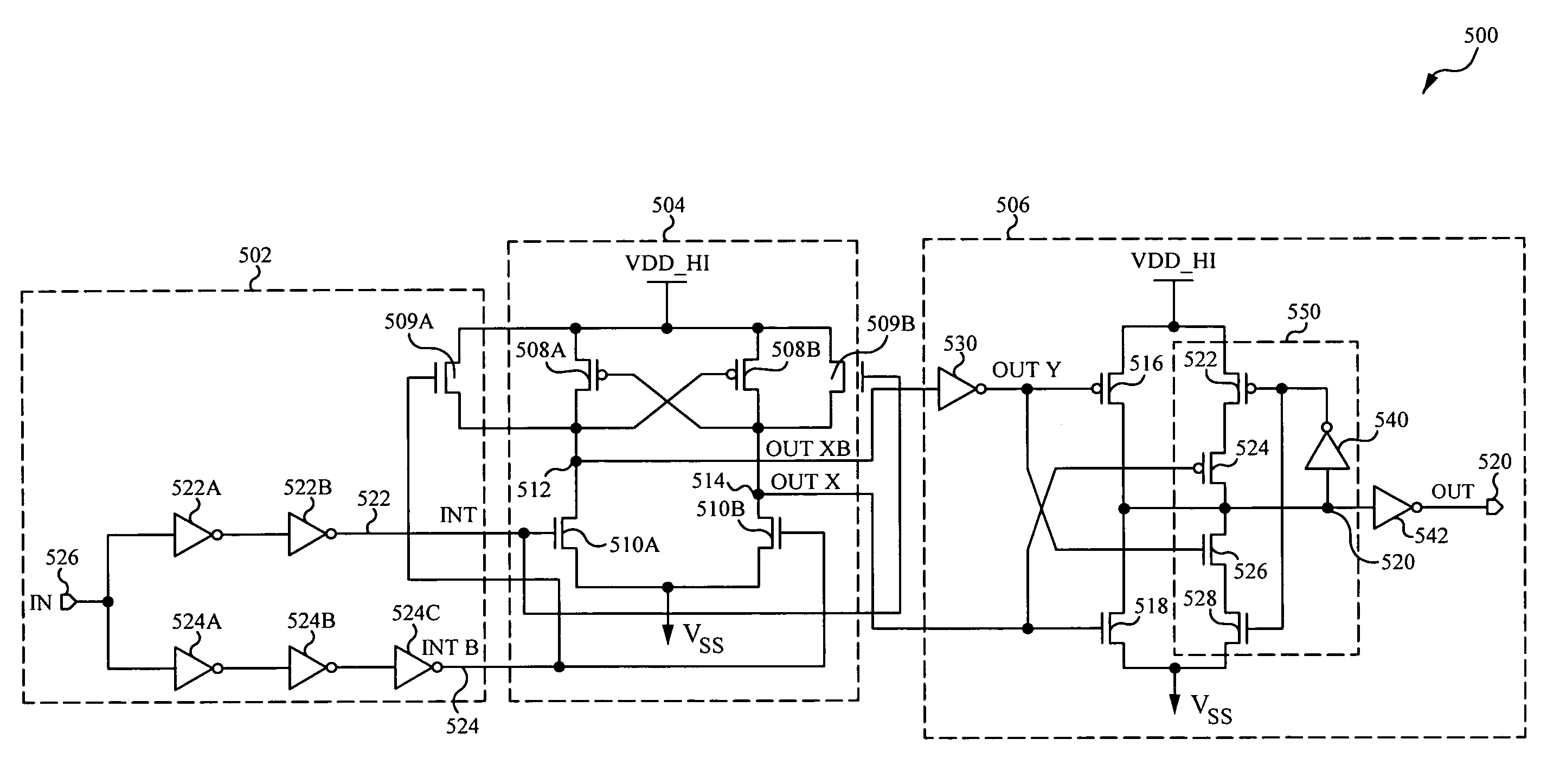
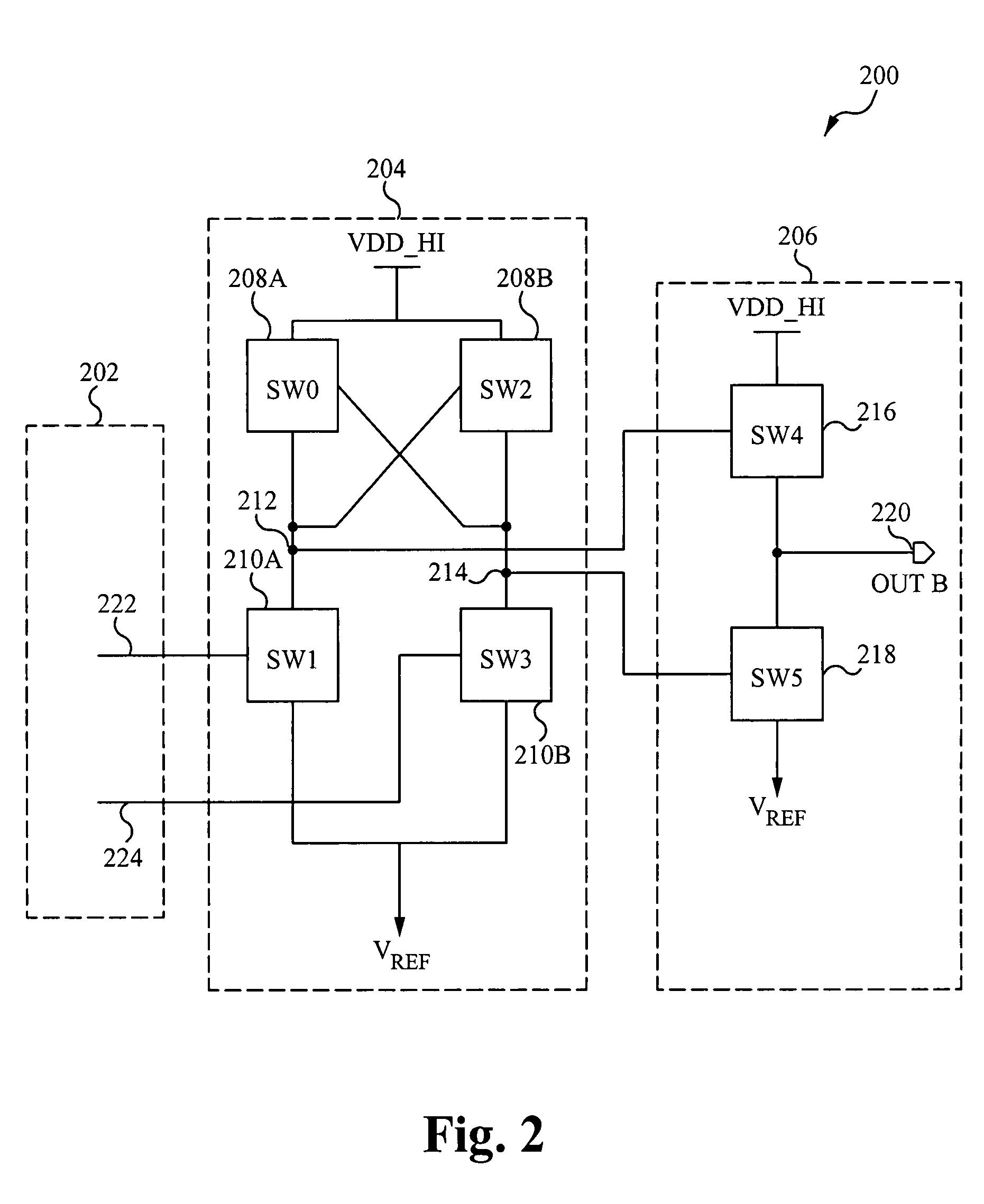
Level shifter with reduced duty cycle variation
InactiveUS20050285658A1Pulse automatic controlAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceLevel shiftingCapacitance
A voltage level shifting circuit (10) transitions an input signal at a first voltage to a second voltage higher than the first voltage. A cross-coupled latch provides the second voltage. Cascode configured transistors (16, 26) are connected in series with input transistors (18, 28) that receive the first voltage in complementary form. Capacitive devices (34, 40) are connected between the first voltage and gates of the cascode configured transistors for allowing independent small signal variations to occur on the gates of the cascode configured transistors for better control of duty cycle and rise and fall time matching of the level shifting circuit. Isolation devices (32, 38) permit independent modification of small signal voltages to occur on the gates of the cascode configured transistors.
Owner:FREESCALE SEMICON INC
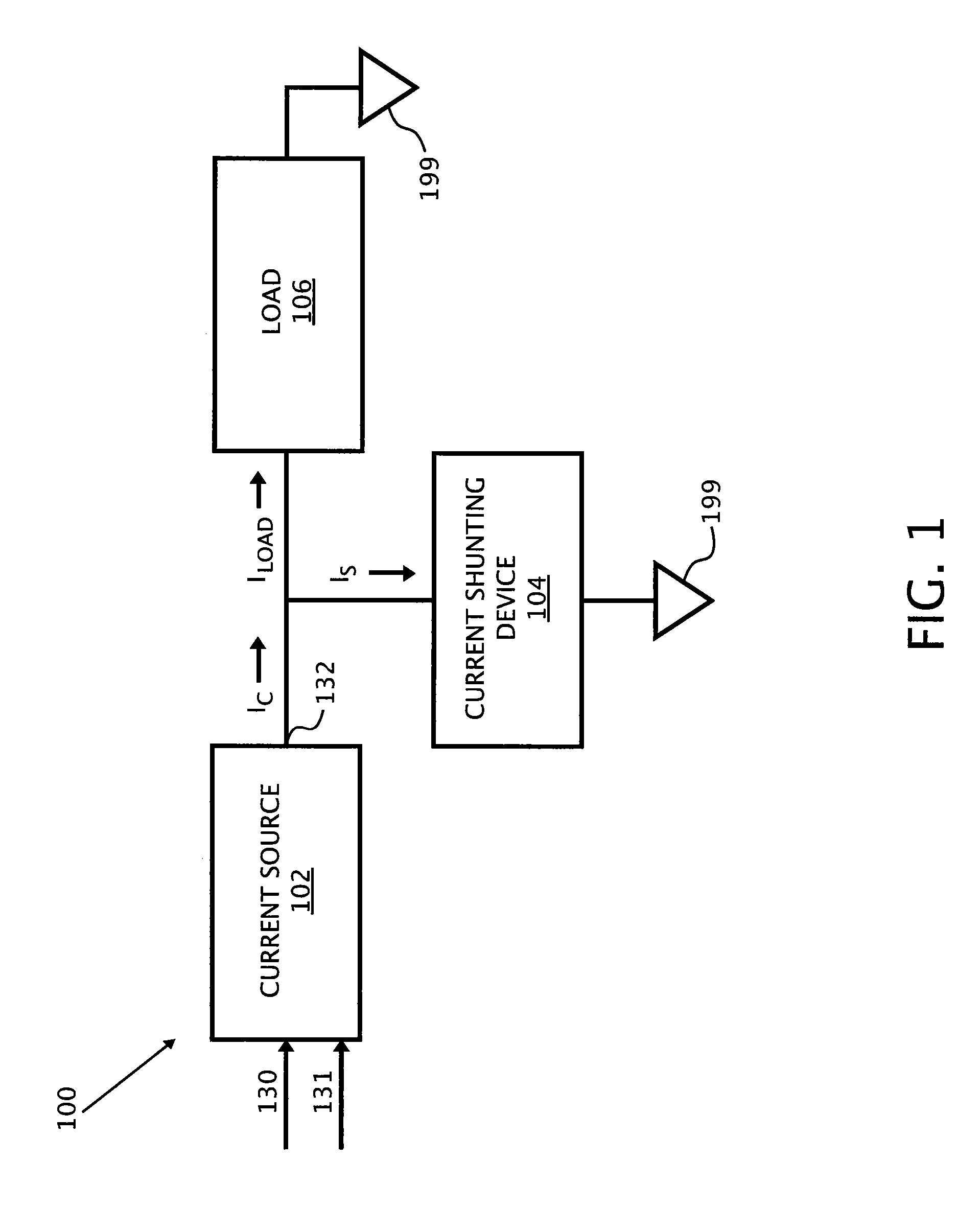
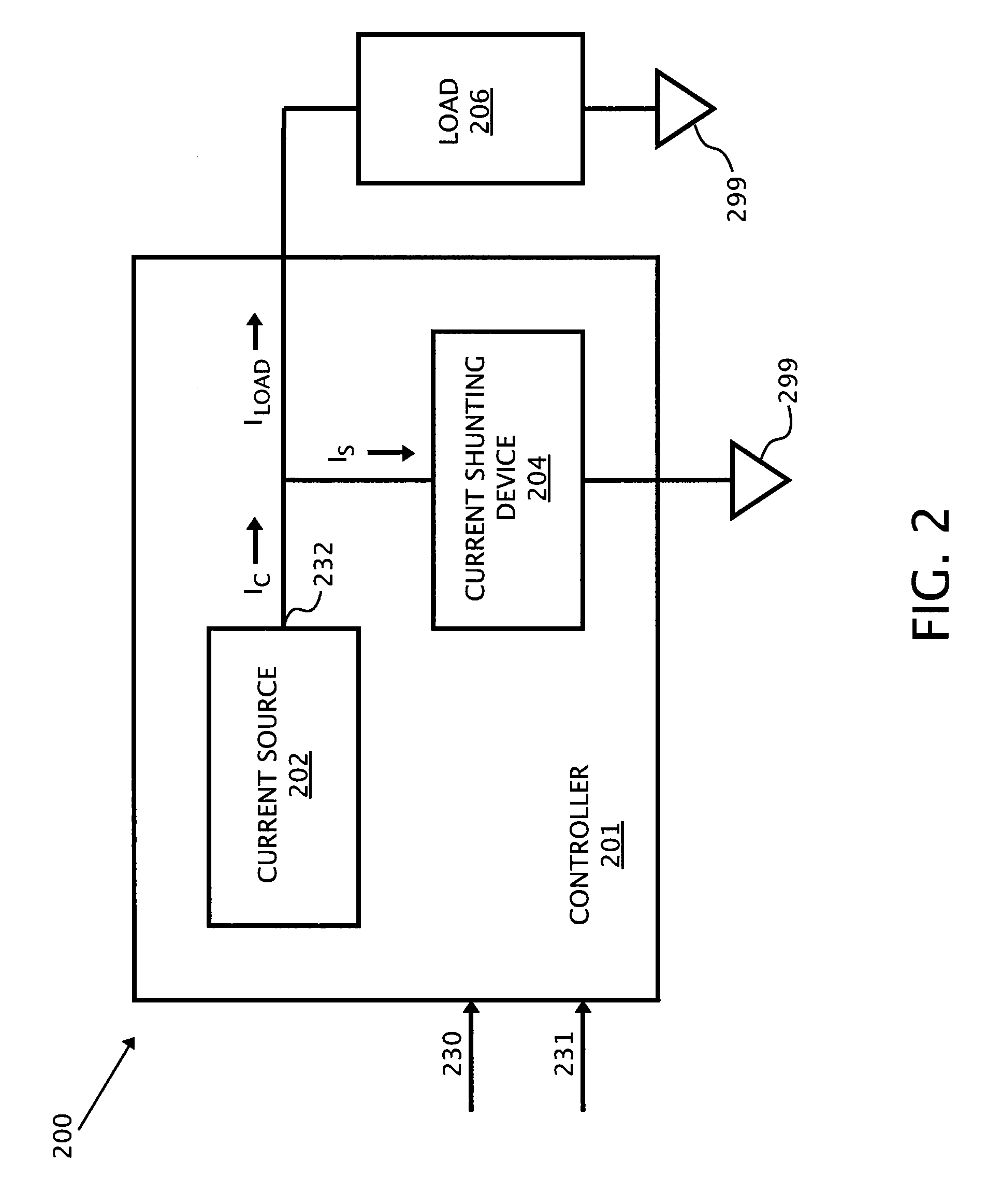
High Current Fast Rise And Fall Time LED Driver
ActiveUS20080012507A1Simple technologyElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesShunt DeviceFall time
The present invention contemplates a variety of improved techniques for the fast switching of current through, among others, LED loads. A current shunting device is utilized to divert current away from a load at high speed when activated, thus enabling the control of the amount current that flows through the load.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
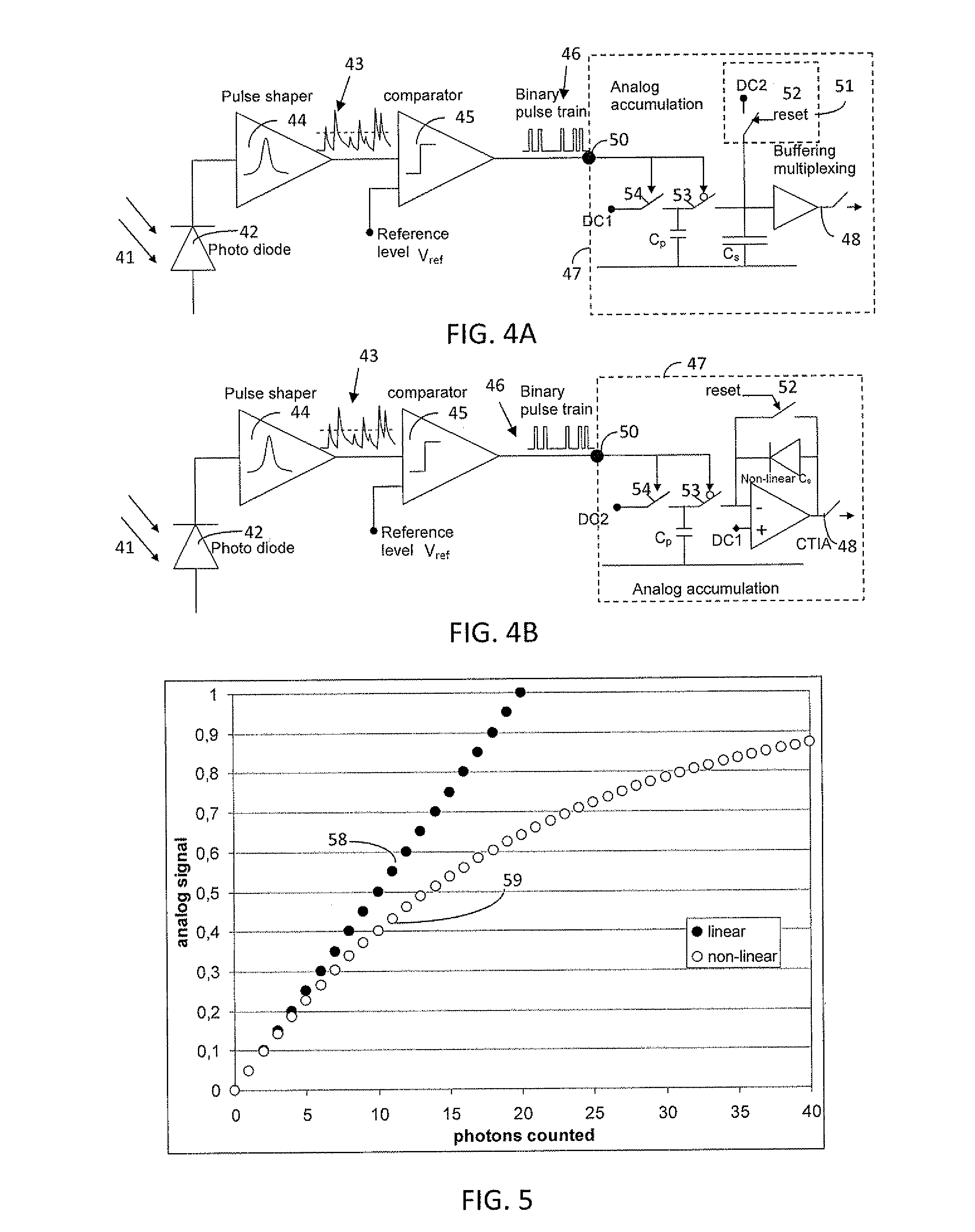
Photon sharpening
ActiveUS20110210235A1Material analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesFall timeHigh energy
The present invention provides an array of pixels for the detection of a flash of electromagnetic radiation or a cloud of impinging high energy particles. Each pixel in the array comprises a radiation receptor for converting the electromagnetic radiation or impinging high energy particles into a radiation signal, and a converter for converting the radiation signal into pulses. The array further comprises a circuit for comparing one or more of the criteria pulse amplitude, pulse arrival time, time to convert a pulse in a digital signal, pulse duration time, pulse rise and fall time or integral of pulse over time for pulses coinciding on pixels in a predetermined neighborhood. The array also comprises a circuit for suppressing those pulses that are compared negatively versus the corresponding pulses in another pixel of the neighborhood for the same one or more criteria. A corresponding method is also provided.
Owner:BART DIERICKX & CAELESTE CVBA
Electronic pulse generator and oscillator
InactiveUS20030151465A1Avoid problemsIncrease lossDelay lines pulse generationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsFall timeFrequency regulation
Improvements in and relating to electronic pulse generation or oscillation circuitry based on a signal path exhibiting endless electromagnetic continuity and affording signal phase inversion in setting pulse duration or half-cycles of oscillation within time of signal traverse of said signal path, and having active switching means associated with said signal path to set rise and fall times of each said pulse or said half-cycle of oscillation, including for frequency adjustment by selective inductance and power saving without stopping pulse generation or oscillation.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
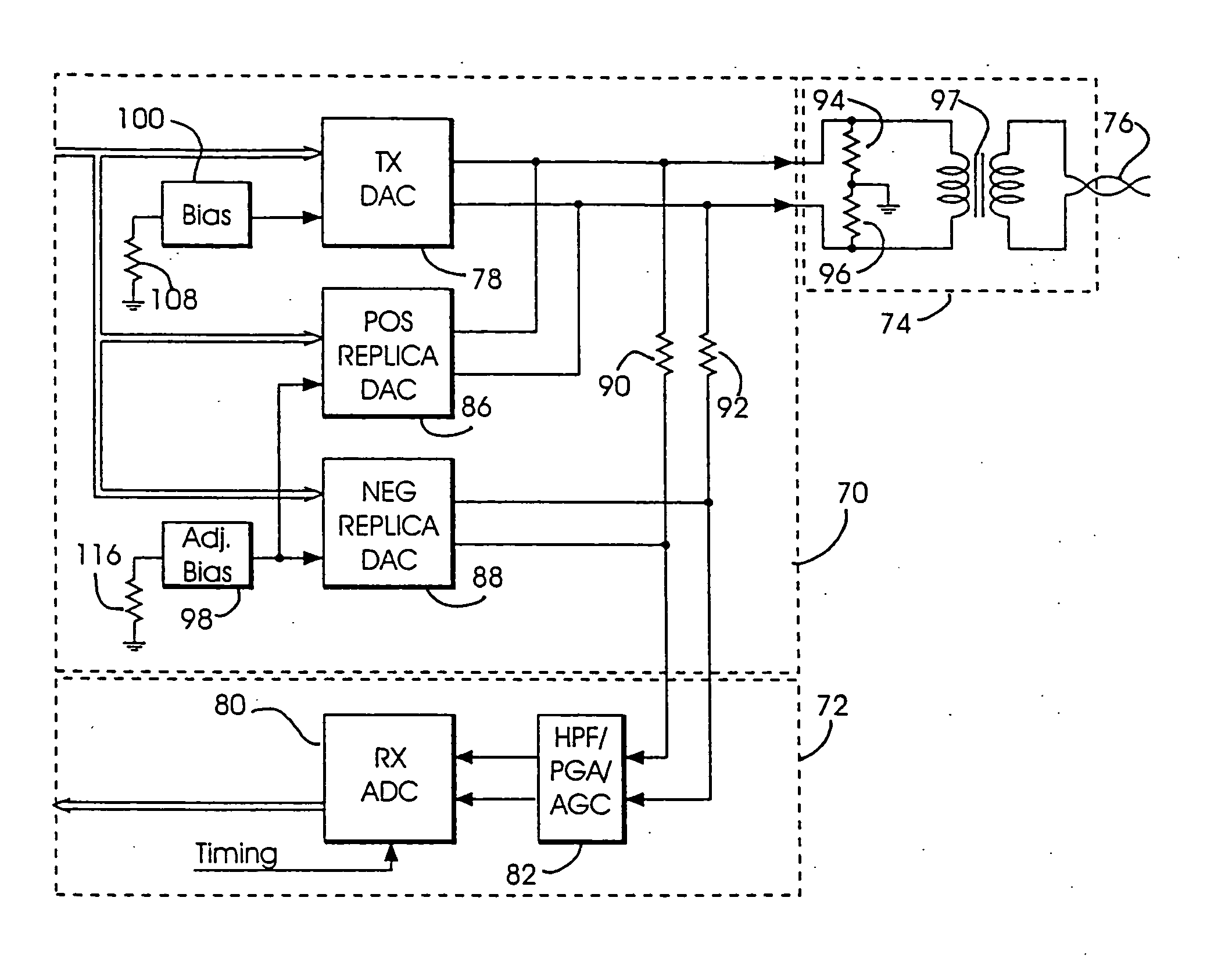
Adaptive electronic transmission signal cancellation apparatus for full duplex communication
An adaptive electronic transmission signal cancellation circuit for separating transmit data from receive data in a bidirectional communication system operating in full duplex mode is disclosed. The output of a main transmitter responsive to a first bias current is connected to the output of a receiver through an internal resistor. A first replica transmitter responsive to a second bias current and matched to the main transmitter current gain and rise / fall time characteristics is connected to the input terminal of the receiver, and produces a cancellation voltage between the output terminal of the main transmitter and the input terminal of the receiver as a function of the second bias current and the internal resistor. A second replica transmitter matched to the current gain and rise / fall time characteristics of the main transmitter and the first replica transmitter and responsive to the second bias current is connected to the output terminal of the main transmitter for canceling excess current, developed by the first replica transmitter, at the output terminal of the main transmitter.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method for collaborative discrimation between authentic and spurious signals in a wireless cognitive network
InactiveUS20100317391A1ConfidenceImprove discriminationRadio transmissionSecurity arrangementPattern recognitionFall time
A WRAN discriminates between authentic incumbent and spurious / malicious signals by collaboratively sensing the frequency environment, classifying and fusing the sensed results, and categorizing each signal as valid or invalid. Embodiments categorize signals according to reports from at least two nodes, thereby increasing detection confidence and resisting denial-of-service attacks. A “voting-rule” can be applied whereby a signal is authentic only if it is detected by a specified percentage of the nodes. Some embodiments categorized signals by comparing sensed analog signal properties, such as amplitude, bandwidth, pulse width, mean, variance, modulation, standard deviation, moments, cumulants, and rise and fall times, with properties of known incumbents and / or known incumbent types. Sensed results can be weighted according to known node locations and / or local topology, sensed signal strengths, and comparisons of sensed analog features with corresponding features of known incumbents and / or known incumbent types in the same class.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
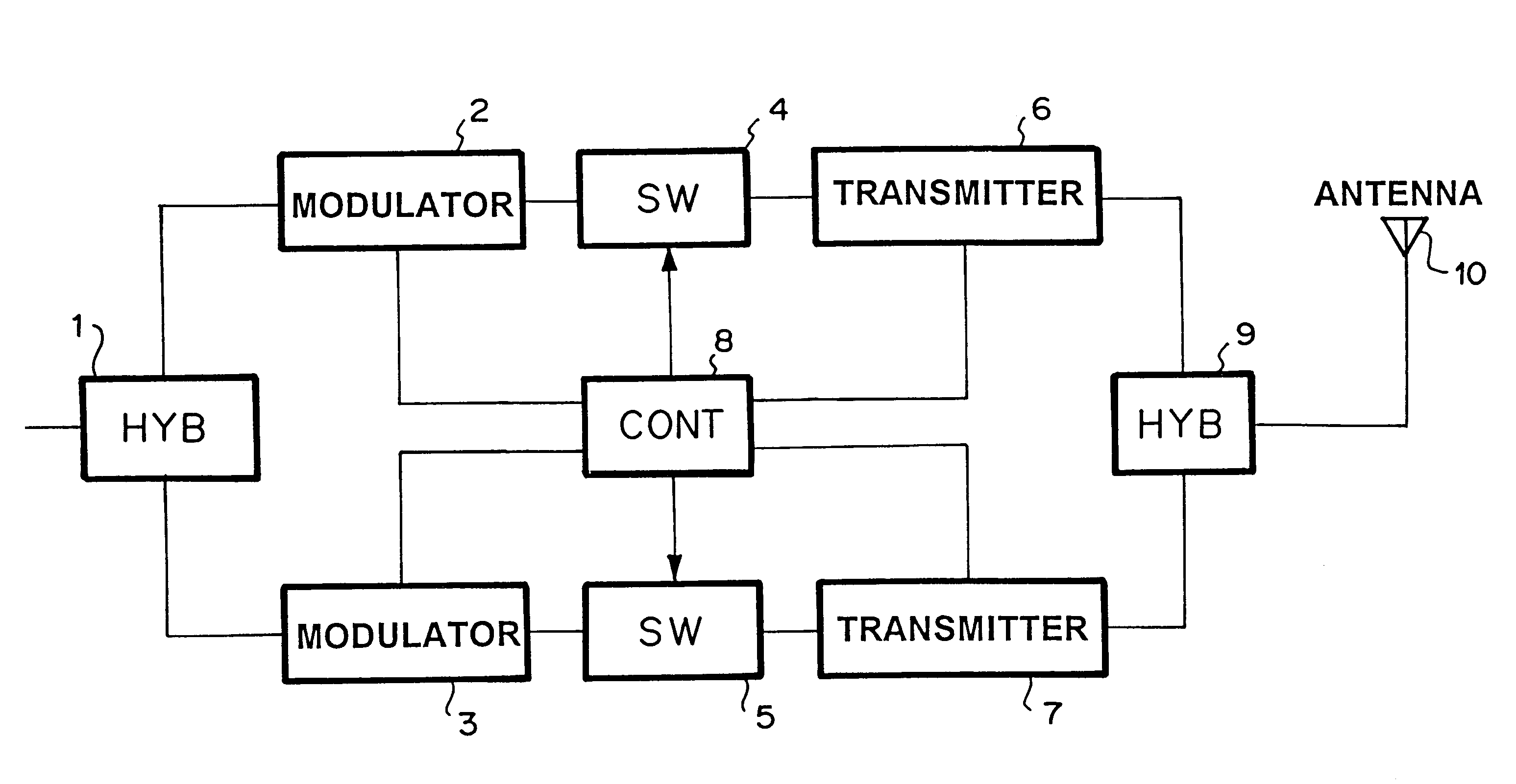
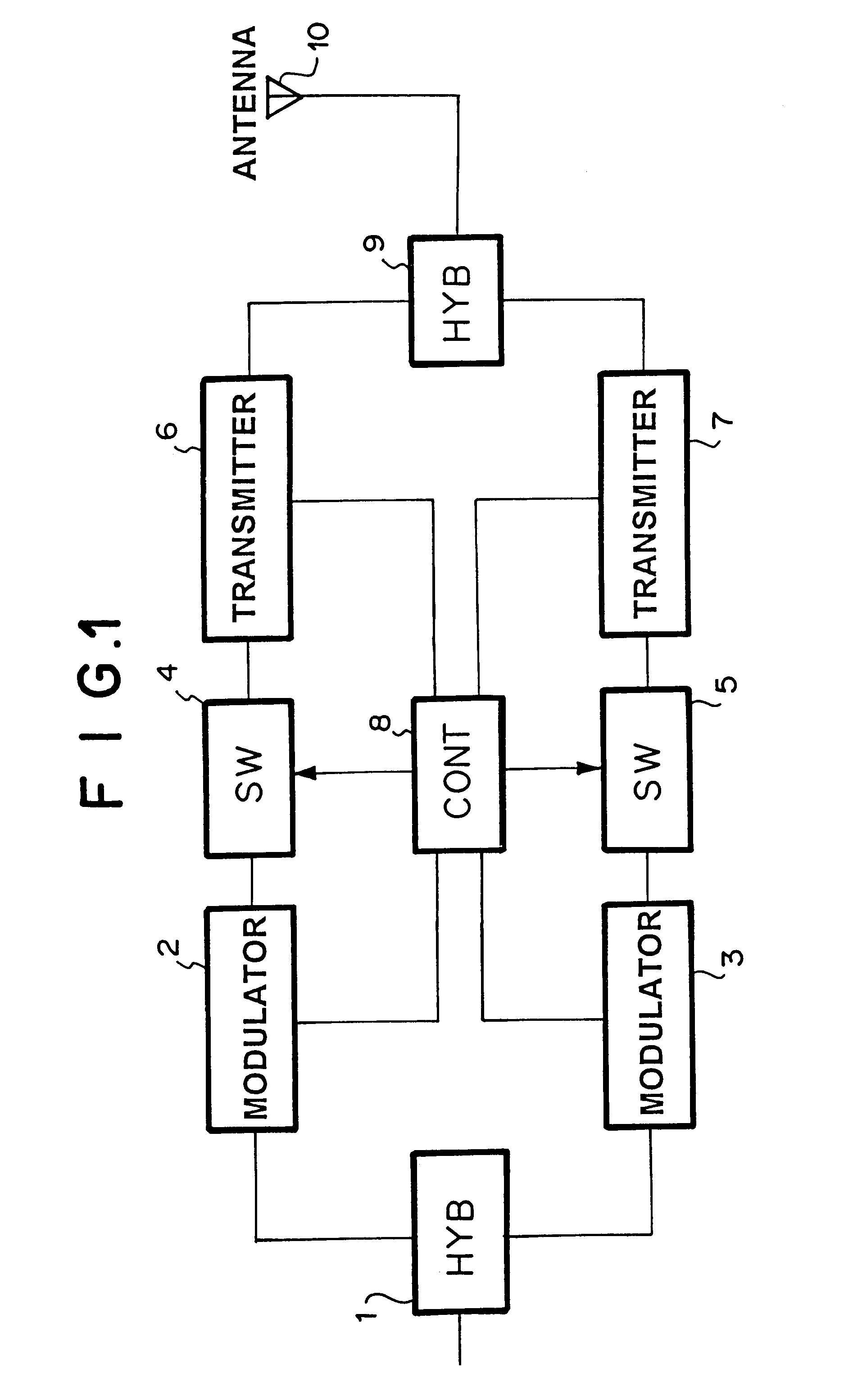
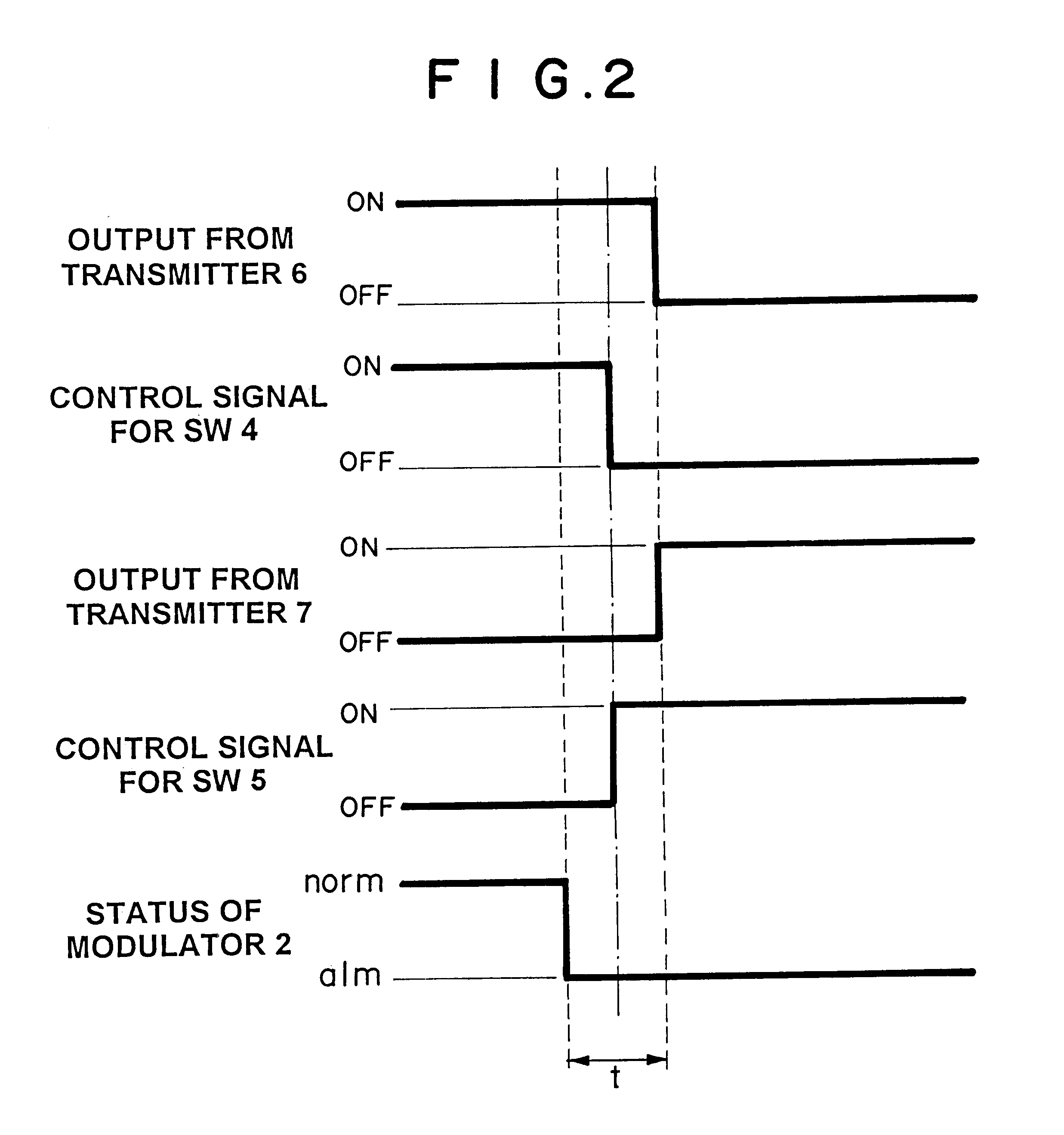
Hot stand-by switching apparatus
InactiveUS6369467B1Batteries circuit arrangementsBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsFall timePower switching
To provide a hot stand-by switching apparatus which is cheaper and more reliable than a conventional RF power switching device. Further, Output level and frequencies during rise and fall times are stabilized. The hot stand-by apparatus of the present invention comprises coupler for outputting either the active signal or the preparative signal, active and preparative transmitters, and switches which are connected with the input terminals of transmitters, respectively.
Owner:NEC CORP
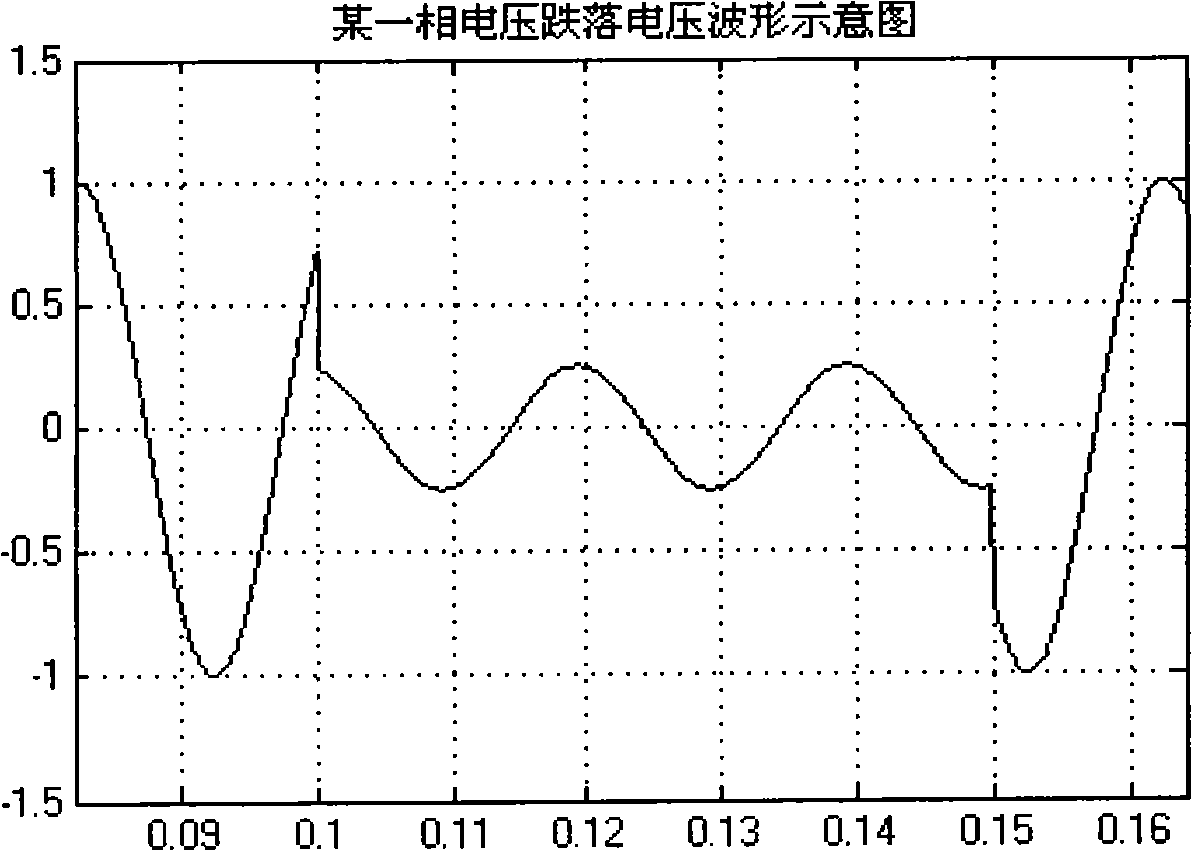
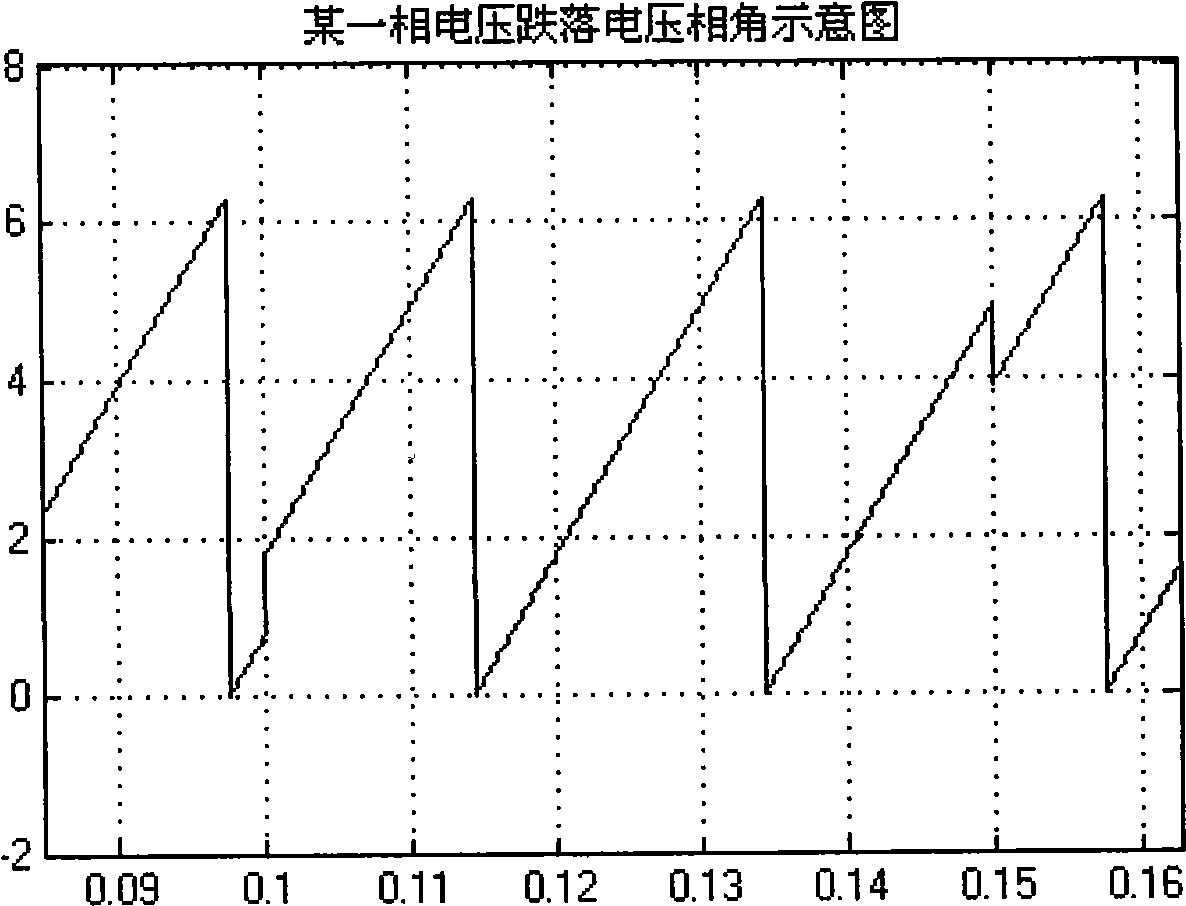
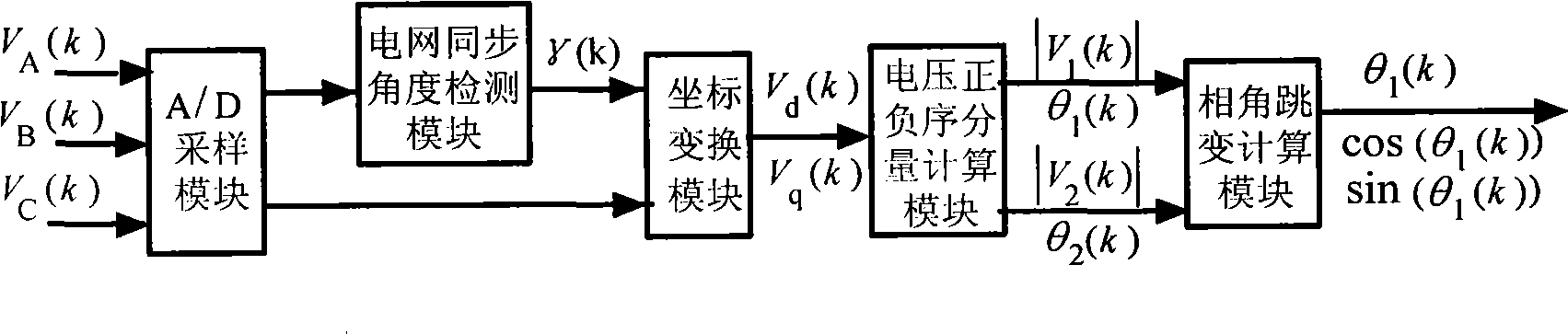
Detection method for electric voltage phase angle jump at network voltage dip
ActiveCN101487861AStrong real-timeGuaranteed real-timeVoltage-current phase angleFall timePower grid
The invention discloses a voltage phase angle jumping detection method at the falling time of network voltages, comprising the following steps of: obtaining, by sampling, three-phase network voltages VA(k), VB(k) and VC(k); detecting a voltage angle [gamma] (k) of synchronous rotation of the network voltages at the sampling time; converting the three-phase network voltages into Vd(k), Vq(k) weights under a d-q synchronous rotation coordinates system; taking the Vd(k), Vq(k) weights under the current d-q coordinates system and Vd(k-1), Vq(k-1) weights at the last sampling time as known quantities, and calculating to obtain an amplitude |V1(k)| of a current positive-sequence weight and a sine and cosine value thereof with a d axis included angle [theta]1(k); directly using an amplitude |V2(k)| of a negative-sequence weight and the sine and cosine value thereof with a d axis included angle [theta]2(k) for the control and calculation subsequent to the falling malfunction of the voltage; or implementing an inverse trigonometric operation on the sine and cosine values of the[theta]1(k) and the[theta]2(k) according to practical requirements so as to obtain voltage positive / negative-sequence phase angle variable quantities [delta][phi]+ and [delta][phi]- that occur on account of the falling of the voltage.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +1
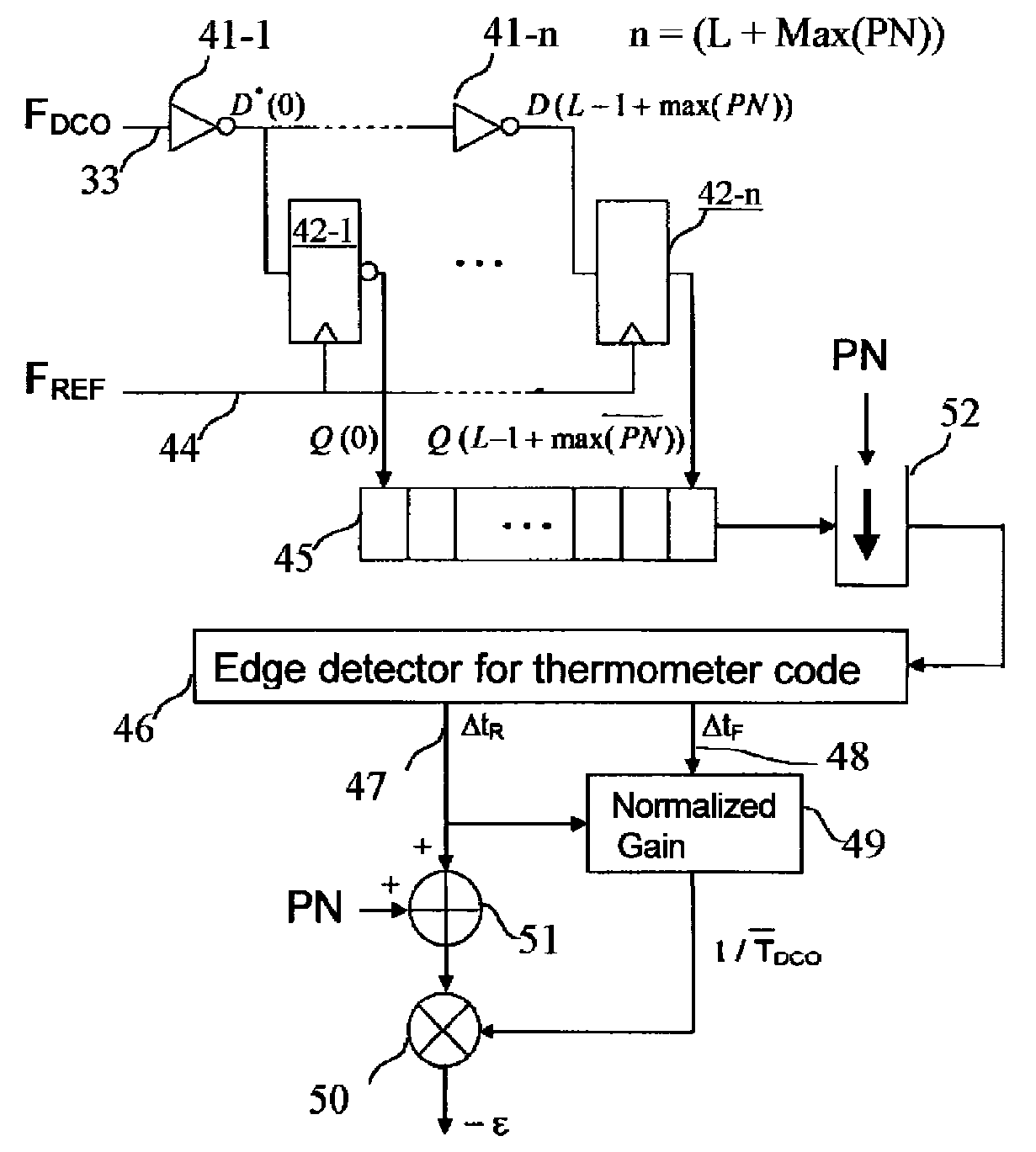
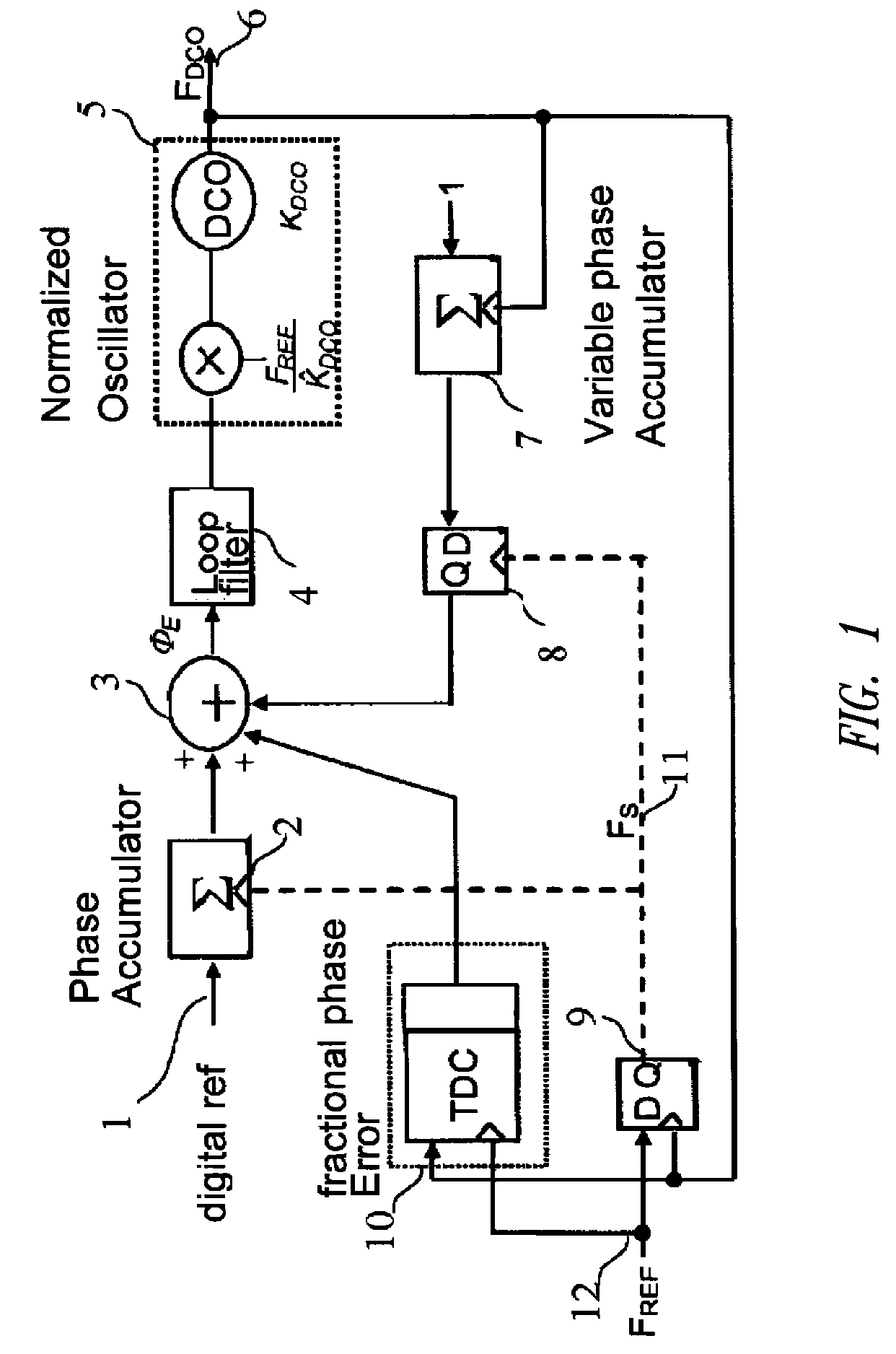
Process for dithering a time to digital converter and circuits for performing said process
ActiveUS20080297208A1Easy to implementLow costElectric signal transmission systemsPulse automatic controlDigital down converterFall time
A process inserts a random noise in a Time to Digital Converter (TDC) designed for calculating the phase error between a first high frequency signal FDCO with respect to a second reference signal, switching at a lower frequency. The process involves: processing of the first signal FDCO by using a chain of delays having a set of n elementary delays which number is chosen so as to extend over a full period of the first signal; storing the outputs of the chain of delays in a set of latches and generation of a thermometer code presenting a stream of “1” separated from a stream of “0” by a border corresponding to the transition of the first signal with respect to the second reference signal; reducing the thermometer code by a random number PN of bits; processing of the result in an edge detecting and thermometer code decoding so as to generate two variables Δtr and Δtf which are representative of the difference between the rise and fall time of the first signal with respect to the second reference signal; computing the normalized gain so as to generate an average value of 1 / TDCO; adding to the value Δtr a binary value corresponding to the number of bits PN; multiplying the preceding result by the average value of 1 / TDCO and computing the phase error between the signals. The delay chain may be arranged with inverters. The process is particularly but not exclusively useful for carrying out a TDC convertor for the purpose of synthesizing of frequencies.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
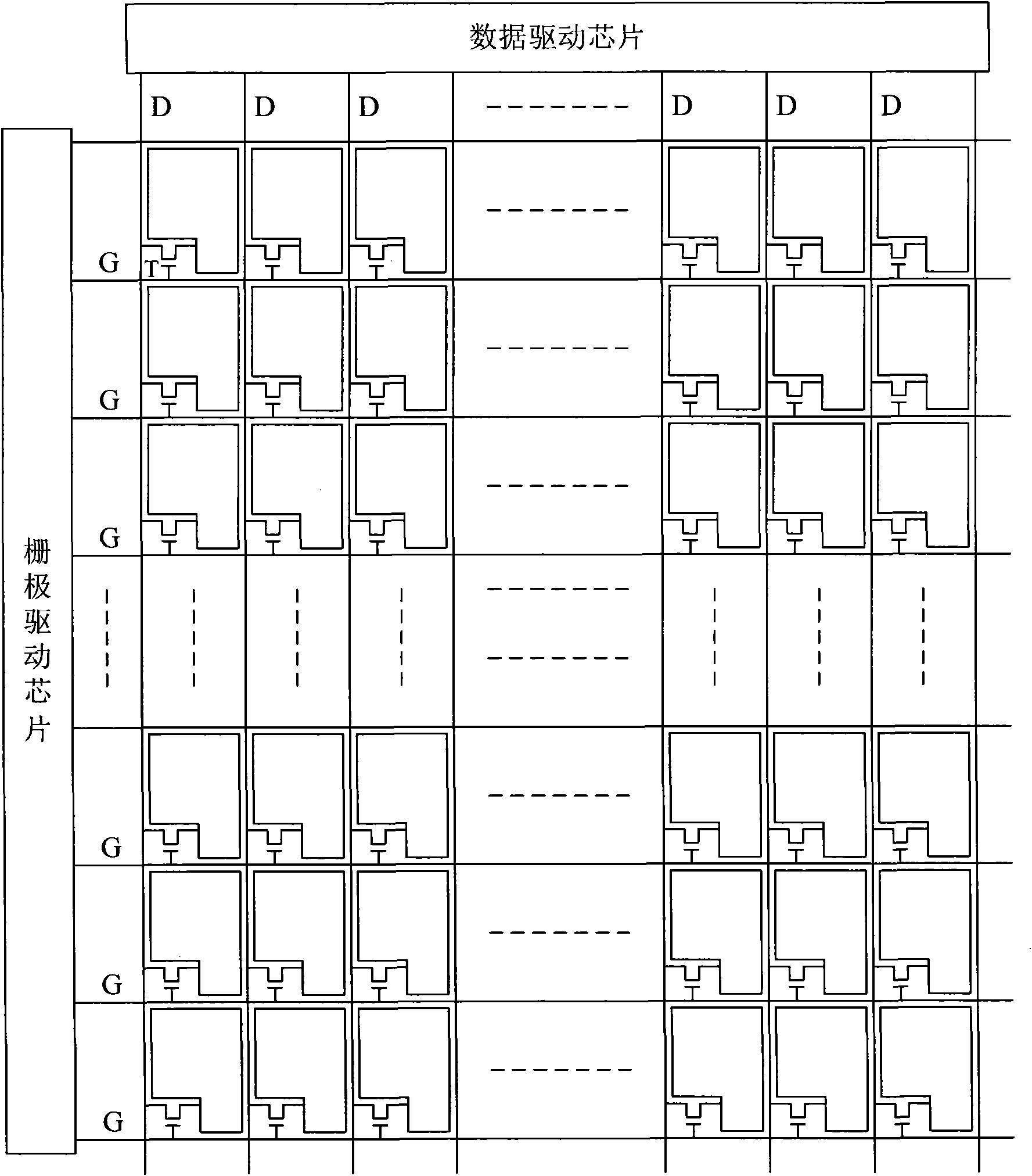
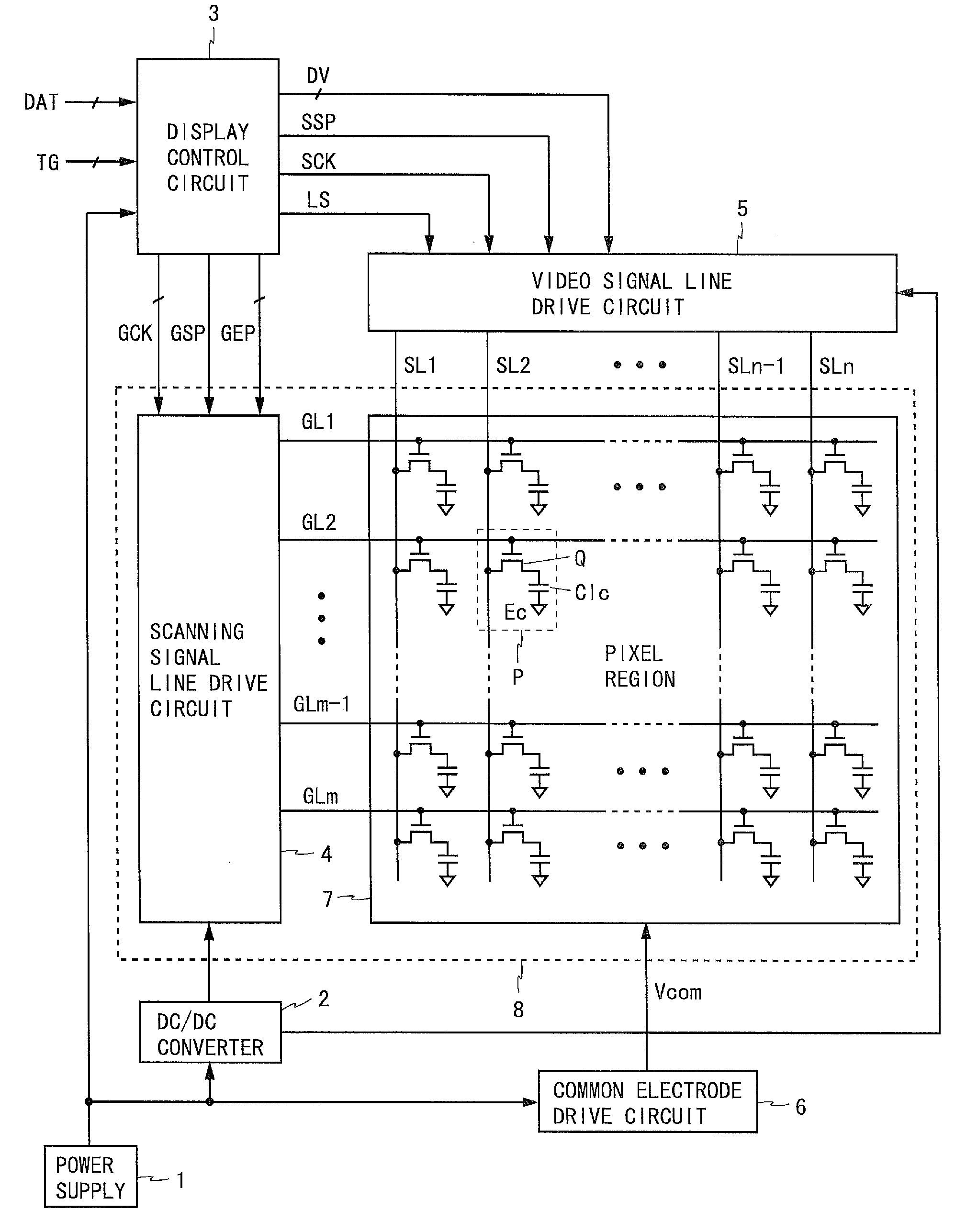
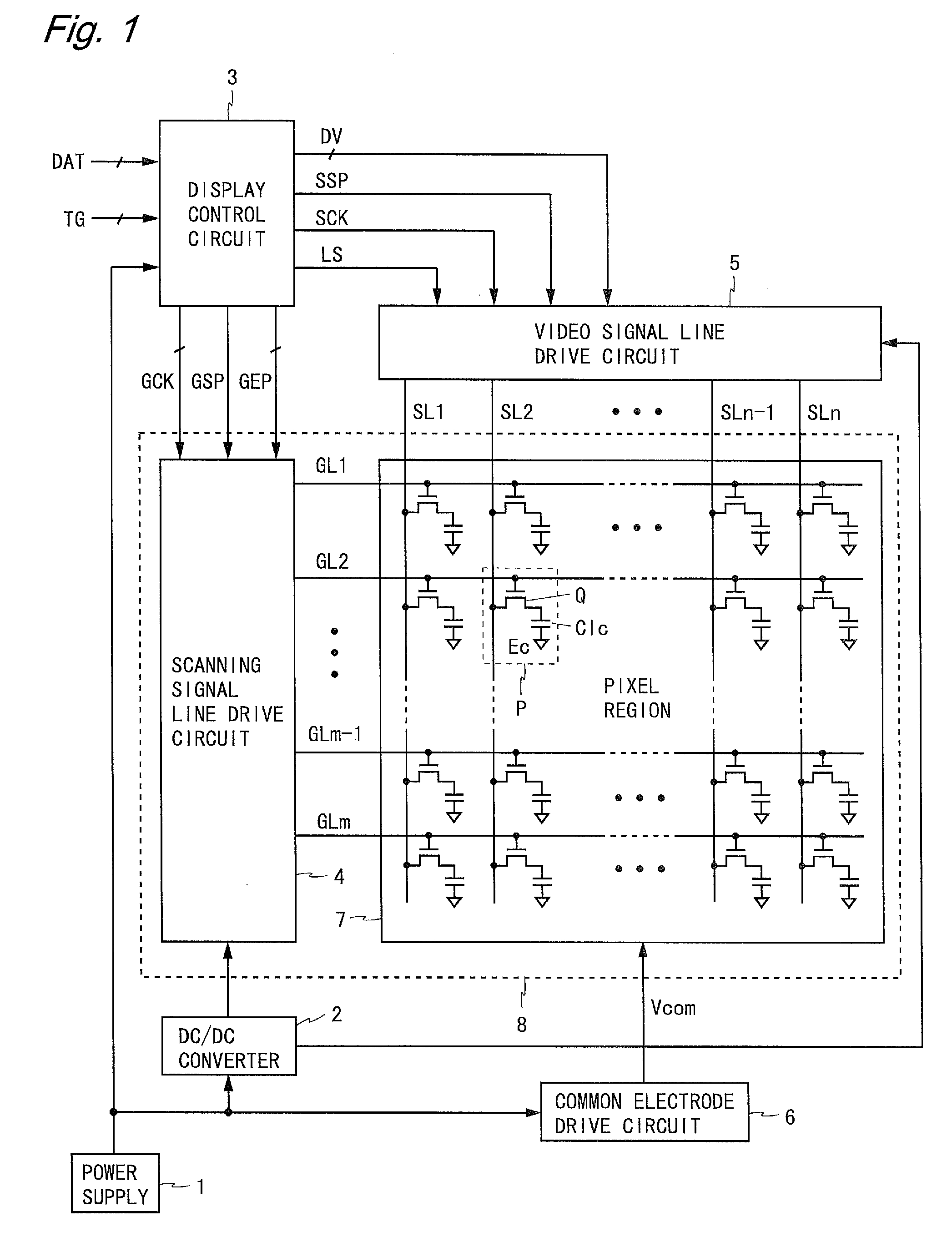
Liquid crystal display driving device
ActiveCN101963724AShorten rise timeMeet the charging timeStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsResistance capacitanceLiquid-crystal display
The invention relates to a liquid crystal display driving device. The liquid crystal display driving device comprises a scan driving unit, a data driving unit, a grid line, a data line and a pixel region which is formed by the grid line and the data line, wherein the grid line comprises a grid scanning line and a redundant grid line; the data line comprises a data signal wire and a redundant data line; and the liquid crystal display driving device also comprises a compensating circuit which is connected with the grid line for compensating a grid scanning signal on the grid scanning line to improve voltage delay phenomenon on the grid scanning line. The liquid crystal display driving device provided by the invention can compensate the grid scanning signal through the compensating circuit which is connected with the grid line, so that the influence of overtime of resistance-capacitance (RC) on the rise time and / or the fall time of the grid scanning signal can be reduced, the charging time requirement of a pixel can be fully met, and the charging rate of the pixel is ensured.
Owner:BEIJING BOE OPTOELECTRONCIS TECH CO LTD
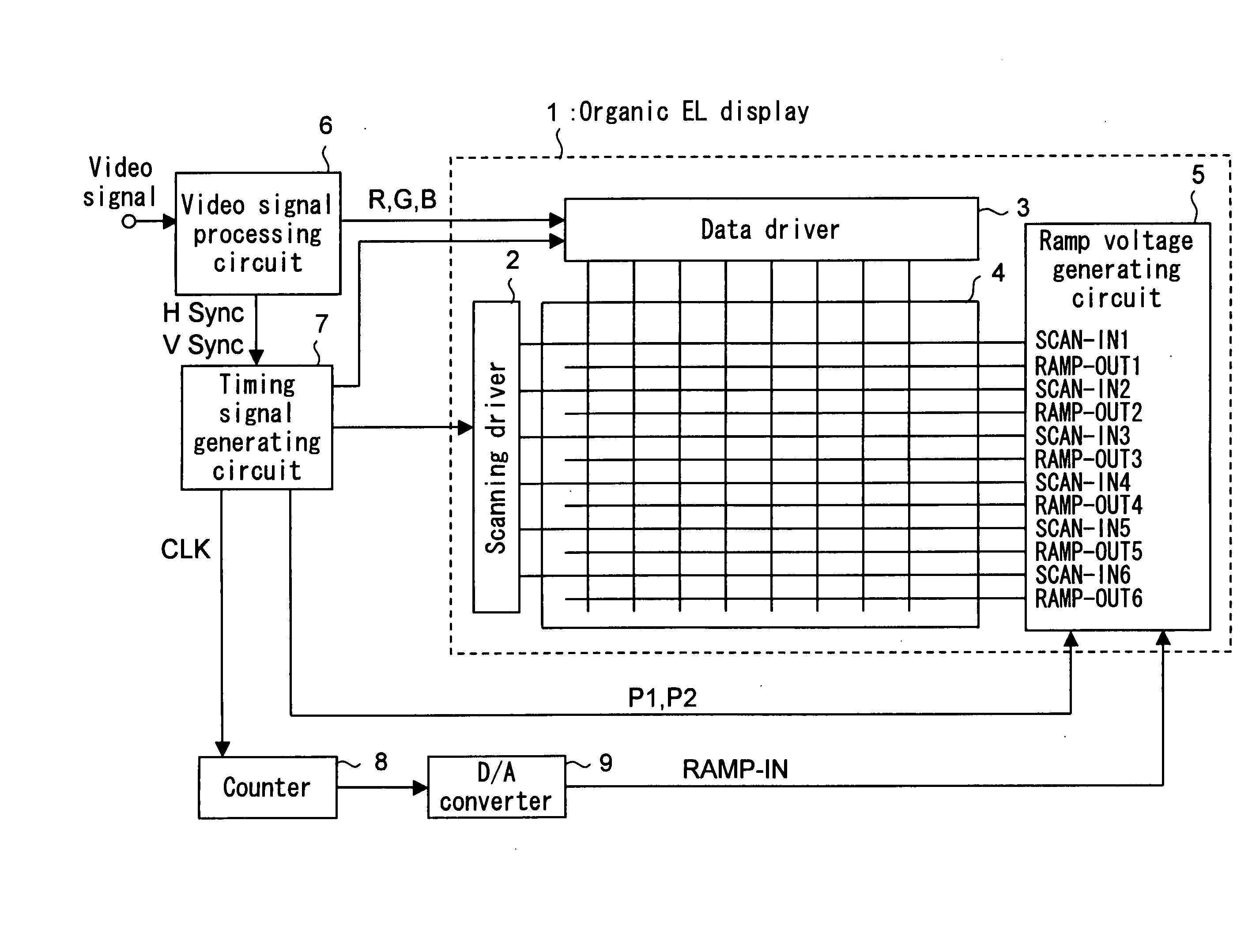
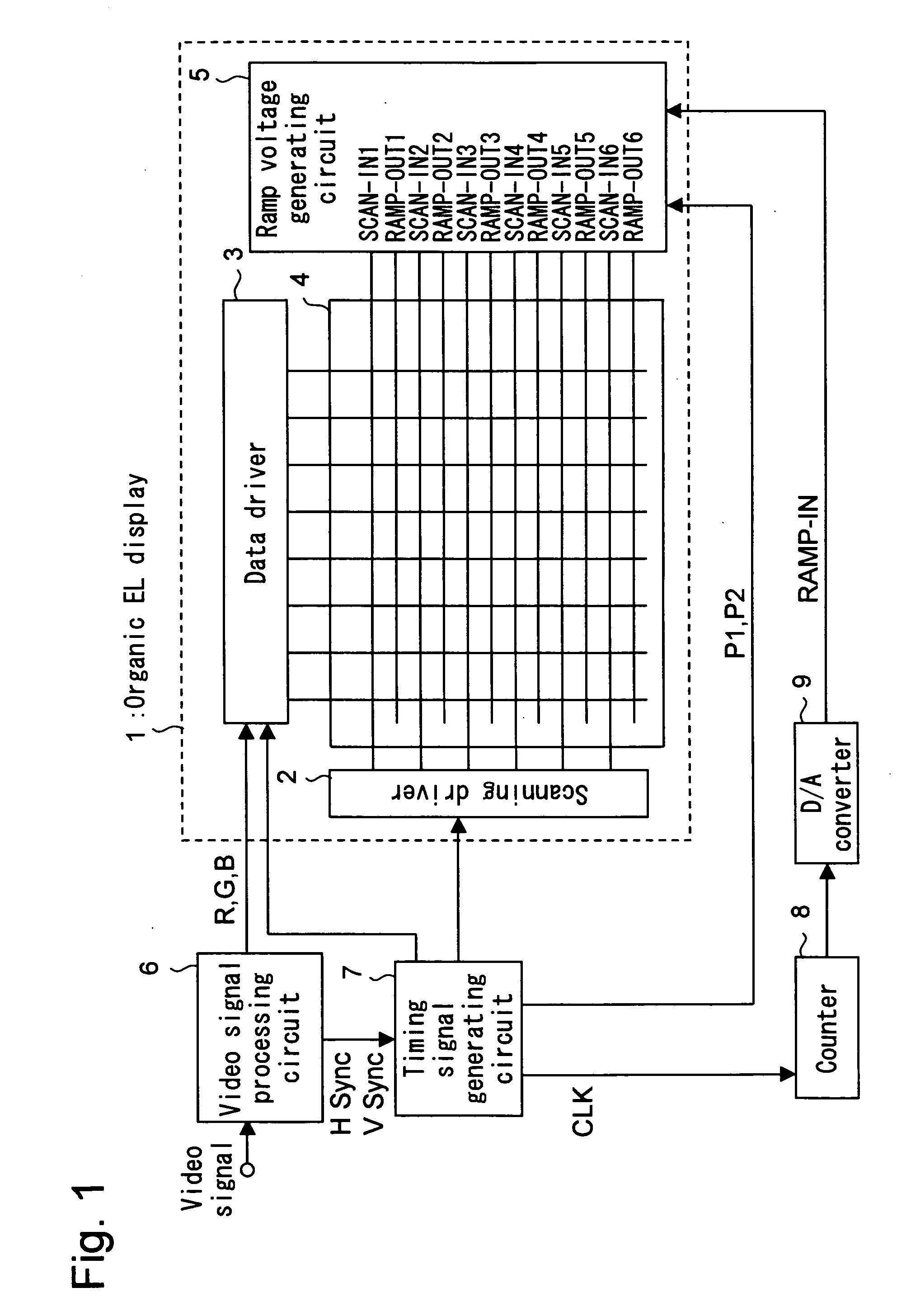
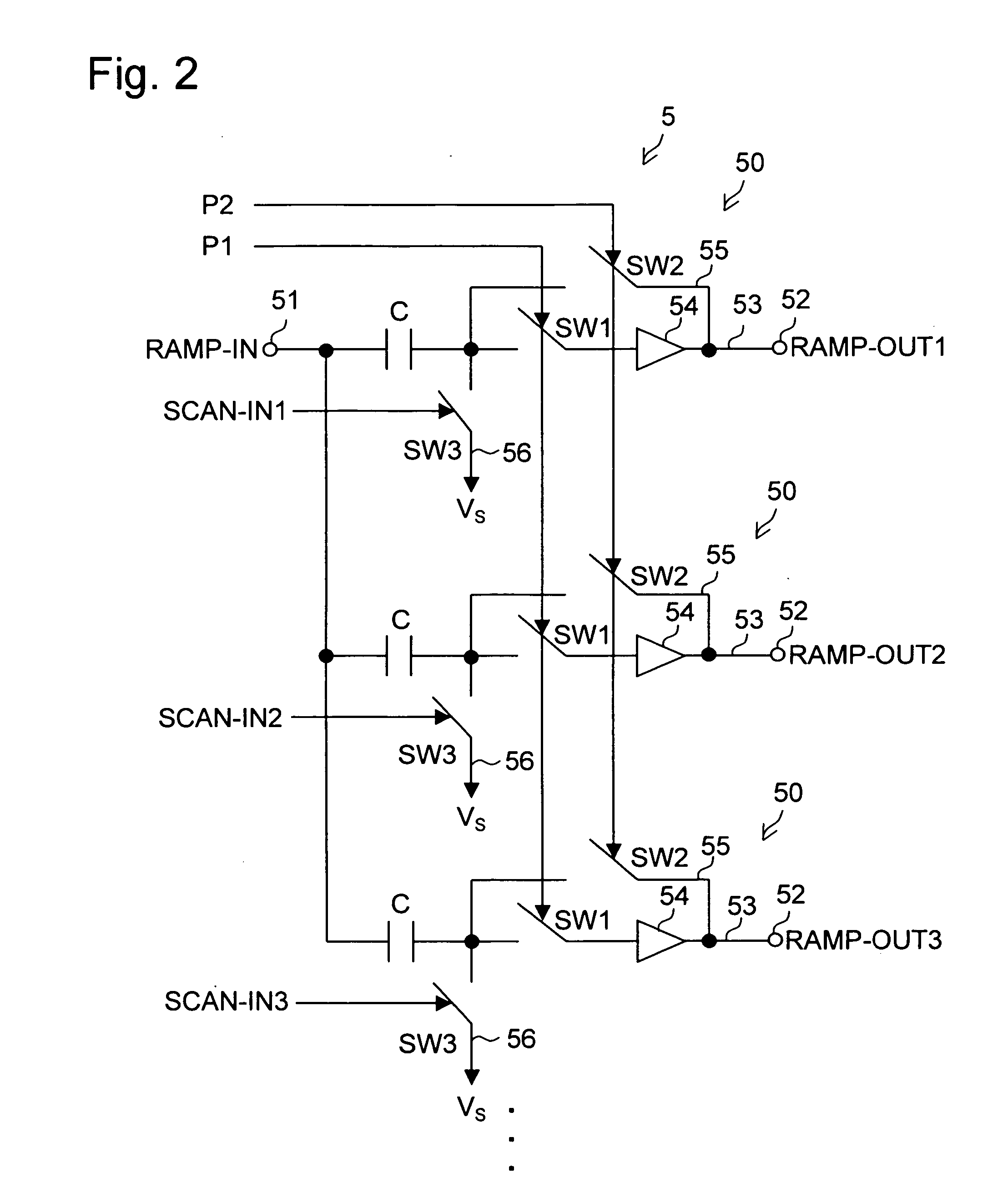
Ramp voltage generating apparatus and active matrix drive-type display apparatus
InactiveUS20050067968A1Reduce the impactSimple circuit configurationPulse generatorElectroluminescent light sourcesFall timeAudio power amplifier
A ramp voltage generating apparatus according to the present invention includes a ramp voltage generating circuit for generating a plurality of ramp voltages out of phase with each other from one ramp voltage, and a control circuit. The ramp voltage generating circuit includes a plurality of voltage generating circuit portions connected in parallel to a voltage input terminal. Each voltage generating circuit portion includes a voltage output terminal, a capacitor, an operational amplifier, a first switch, a second switch and a third switch. The control circuit turns on the third switches while shifting the time point of switching each of the third switches from off to on state, and the control circuit turns off the first switches and, also, turns on the second switches during the period including the fall time point of the ramp voltage input to the voltage input terminal.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
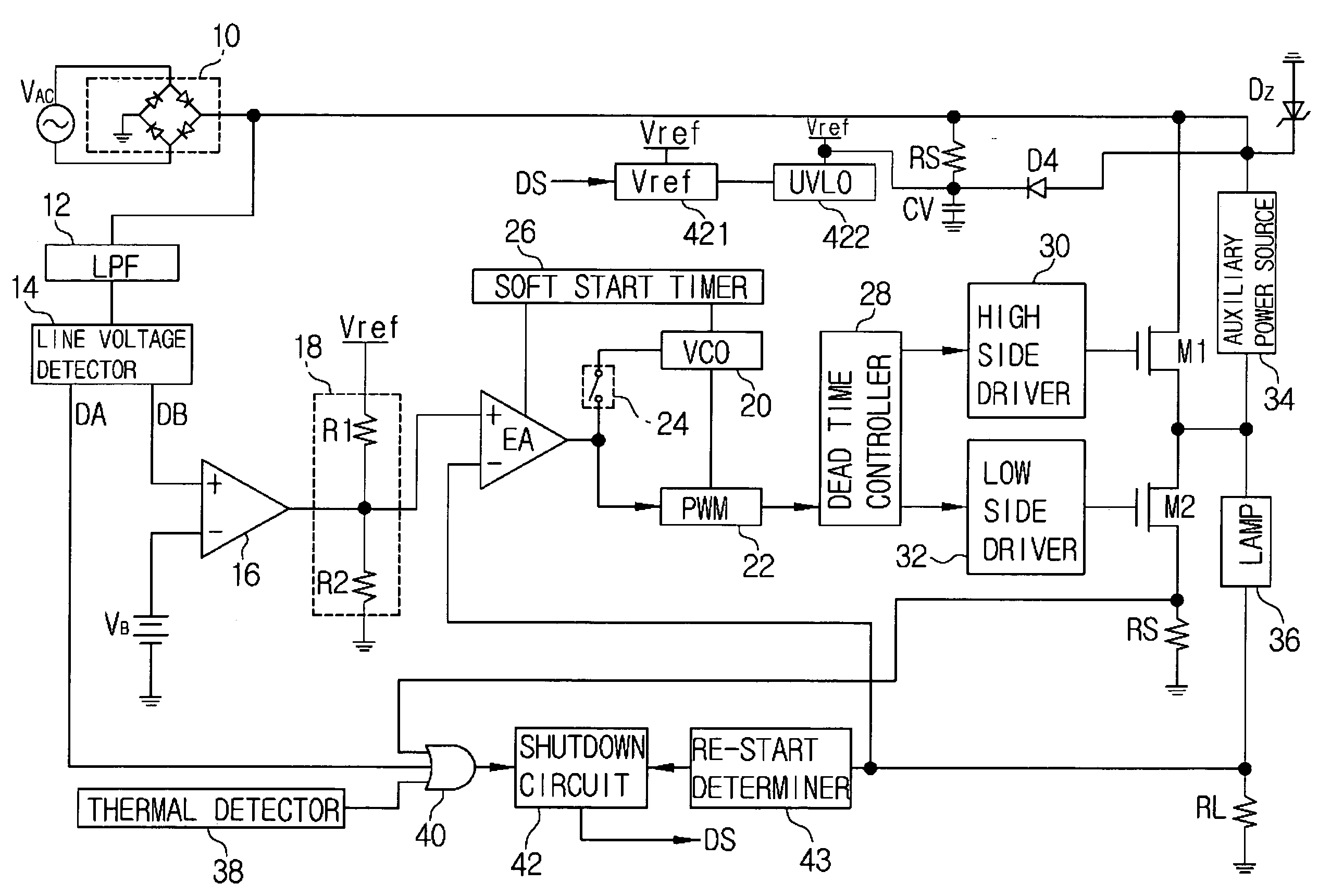
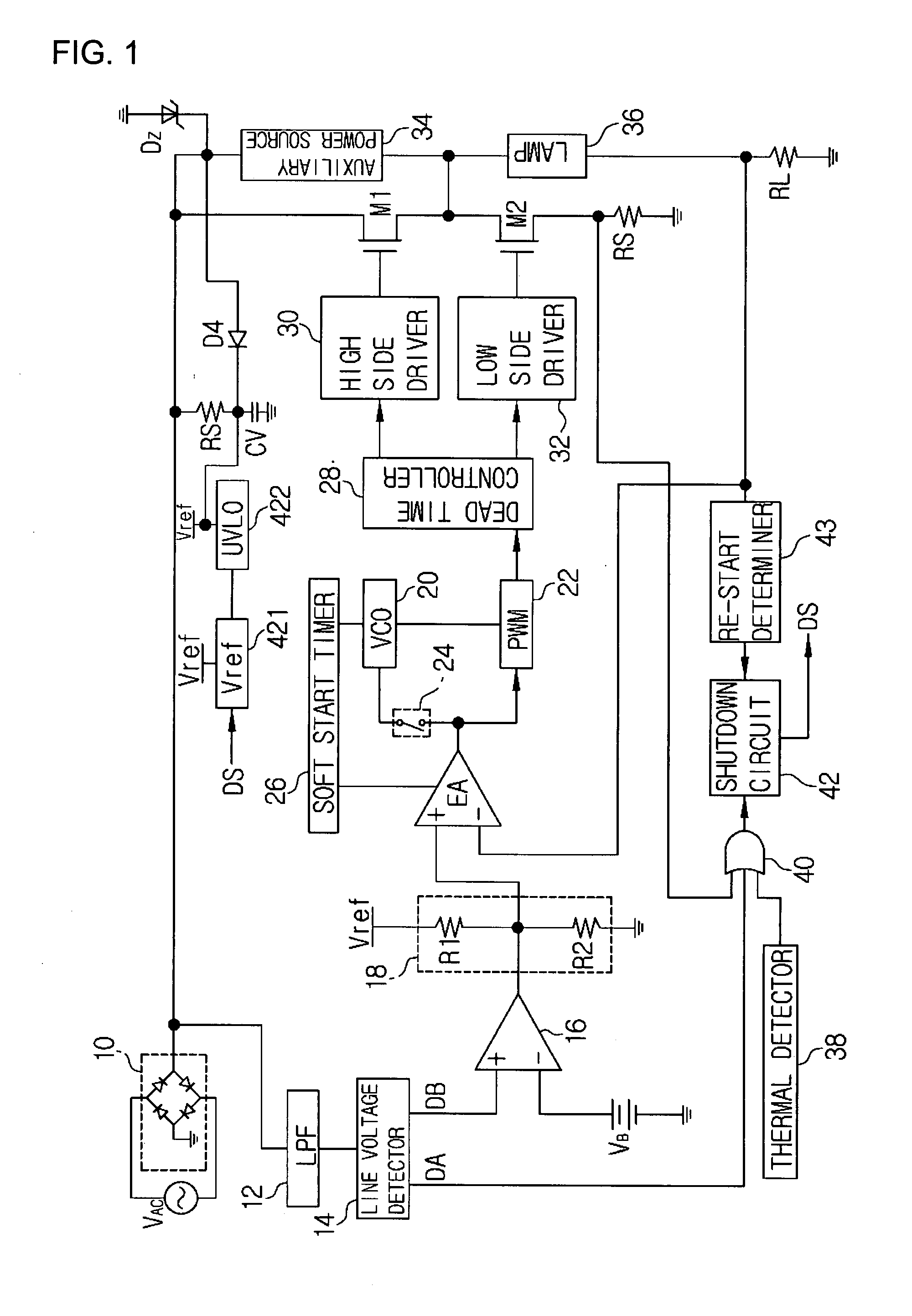
Power supply apparatus using half-bridge circuit
ActiveUS7227763B1Easy to controlImprove power factorConversion with intermediate conversion to dcEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDriver circuitFall time
Disclosed is a power supply apparatus using a half-bridge type driving circuit, which is intended for the purpose of the compensation of a power factor, the achievement of a low crest factor and the maintenance of a constant output. The power supply apparatus using a half-bridge circuit for rectifying an AC power source and providing the rectified power source to a load includes a line voltage detecting means for detecting a voltage of an input power source provided to the load, an error amplifying means for comparing the voltage detected from the line voltage detecting means with a reference voltage and outputting a voltage corresponding to a difference therebetween, a pulse width modulating means for outputting a pulse having a variable width corresponding to an output level of the error amplifying means, a dead time controlling means for outputting a first pulse corresponding to a high side and a second pulse corresponding to a low side by the pulse output from the pulse width modulating means, wherein the first and second pulses have different pulse widths and different rising and falling time points, and a driving means for driving the power source supplied to the load as a constant current state by the first and second pulses.
Owner:AVERD
Nonvolatile memory with multi-frequency charge pump control
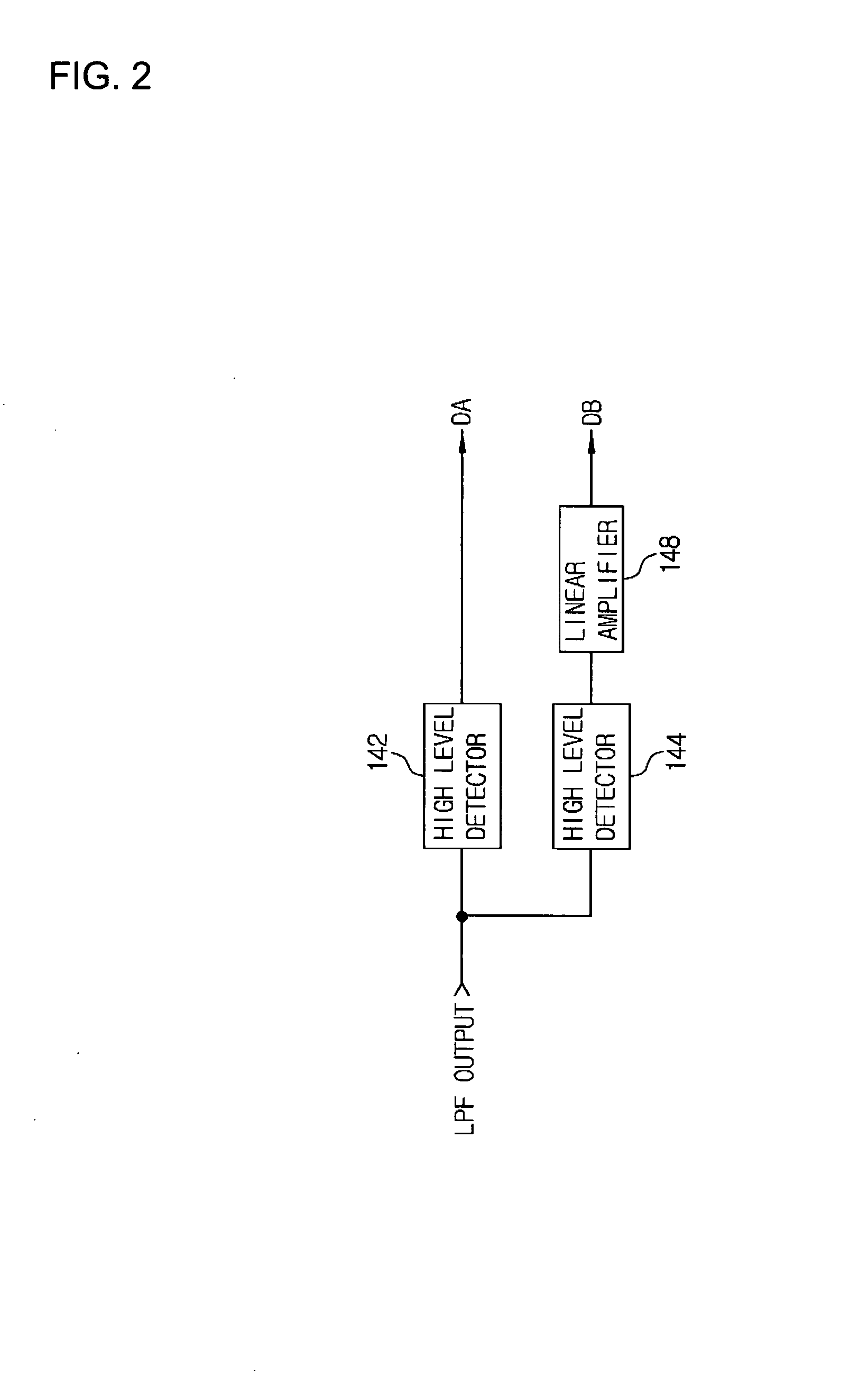
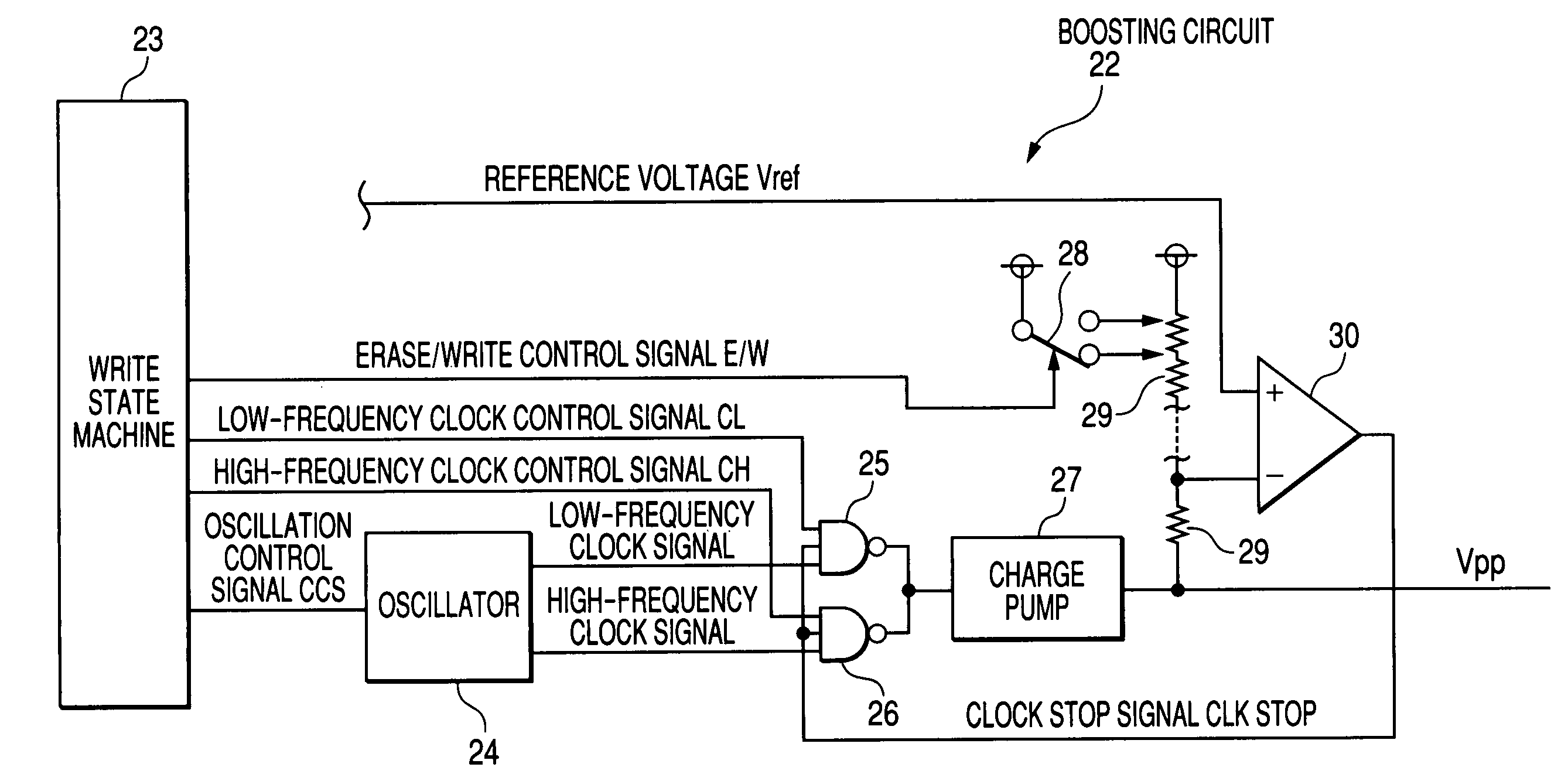
ActiveUS7251162B2Improve communication distanceImprove performanceSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesControl signalPeak value
The present invention is directed to largely reduce peak current at the time of operation of a boosting circuit provided for an EEPROM. In the erase / write operation, first, a low-frequency clock signal as a selection clock signal is input by a low-frequency clock control signal to a charge pump. After lapse of a certain period (about ⅓ of fall time), a high-frequency clock signal having a frequency higher than that of the low-frequency clock signal is output by a high-frequency clock control signal and is input as the selection clock signal to the charge pump to boost a voltage to a predetermined voltage level. In such a manner, while suppressing the peak of consumption current, the fall time of the boosted voltage can be shortened.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Level shifter with balanced rise and fall times
A level shifting circuit can include a shift stage that latches first and second internal nodes to opposite shifted logic potentials in response to different transitions at an input signal node. The input signal node can vary between non-shifted logic potentials. An output stage can enable a first controllable impedance path coupled between an output node and a first shifted power supply node in response to a first type transition at the first internal node, and can enable a second controllable impedance path coupled between the output node and a second shifted power supply node in response to the first type transition at the second internal node.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
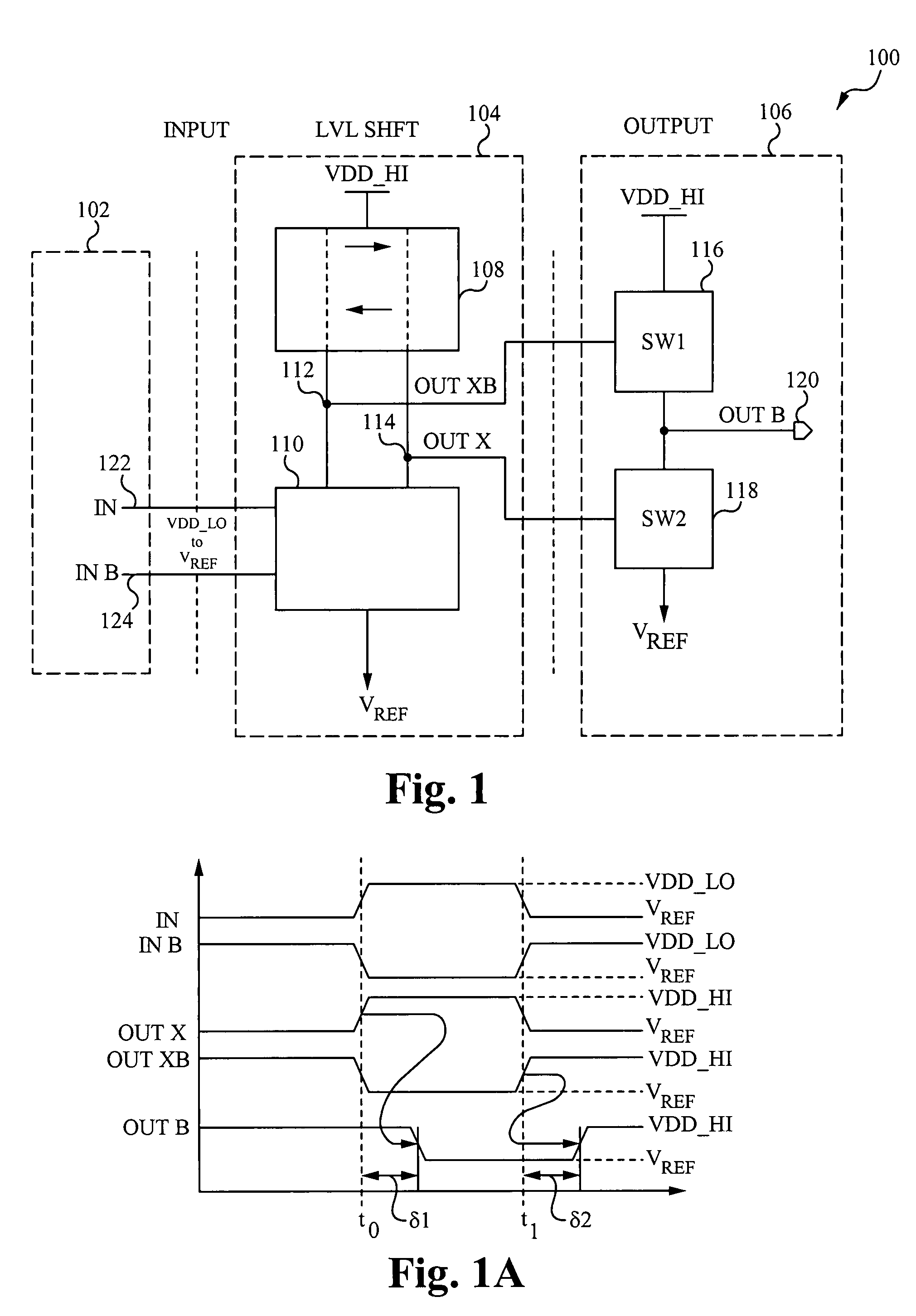
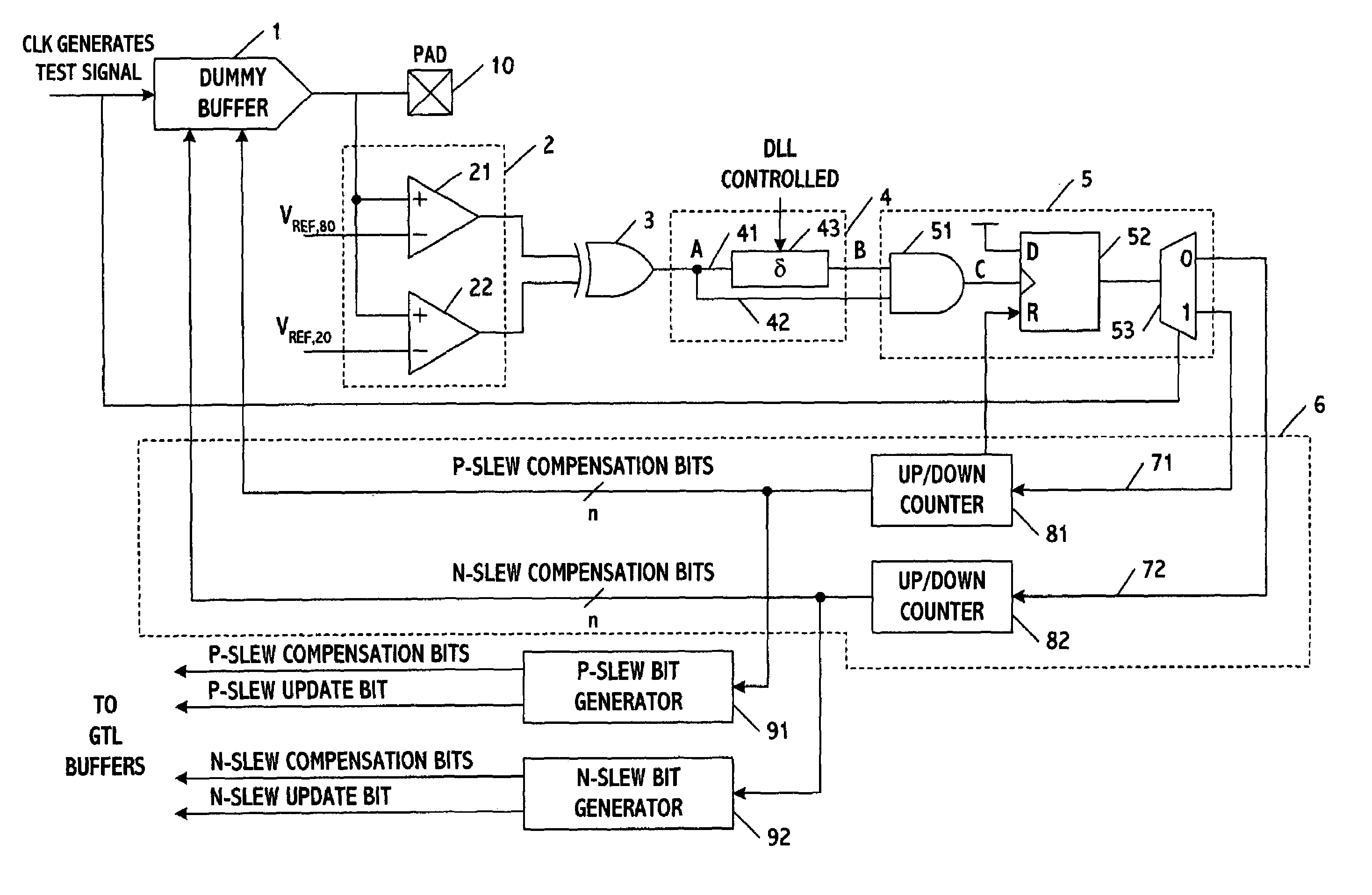
Closed-loop independent DLL-controlled rise/fall time control circuit
A system and method for processing signals determines rise and fall times of a driving signal, compares the rise and fall times to desired values, and independently controls the rise and fall times to equal the desired values. The rise and fall times may be controlled by generating one or more first correction bits based on a difference between the rise time and a corresponding one of the desired values, generating one or more second correction bits based on a difference between the fall time and a corresponding one of the desired values, and then separately applying the bits to independently control the rise and fall times of the driving signal. The driving signal may be an I / O signal or another type of signal.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
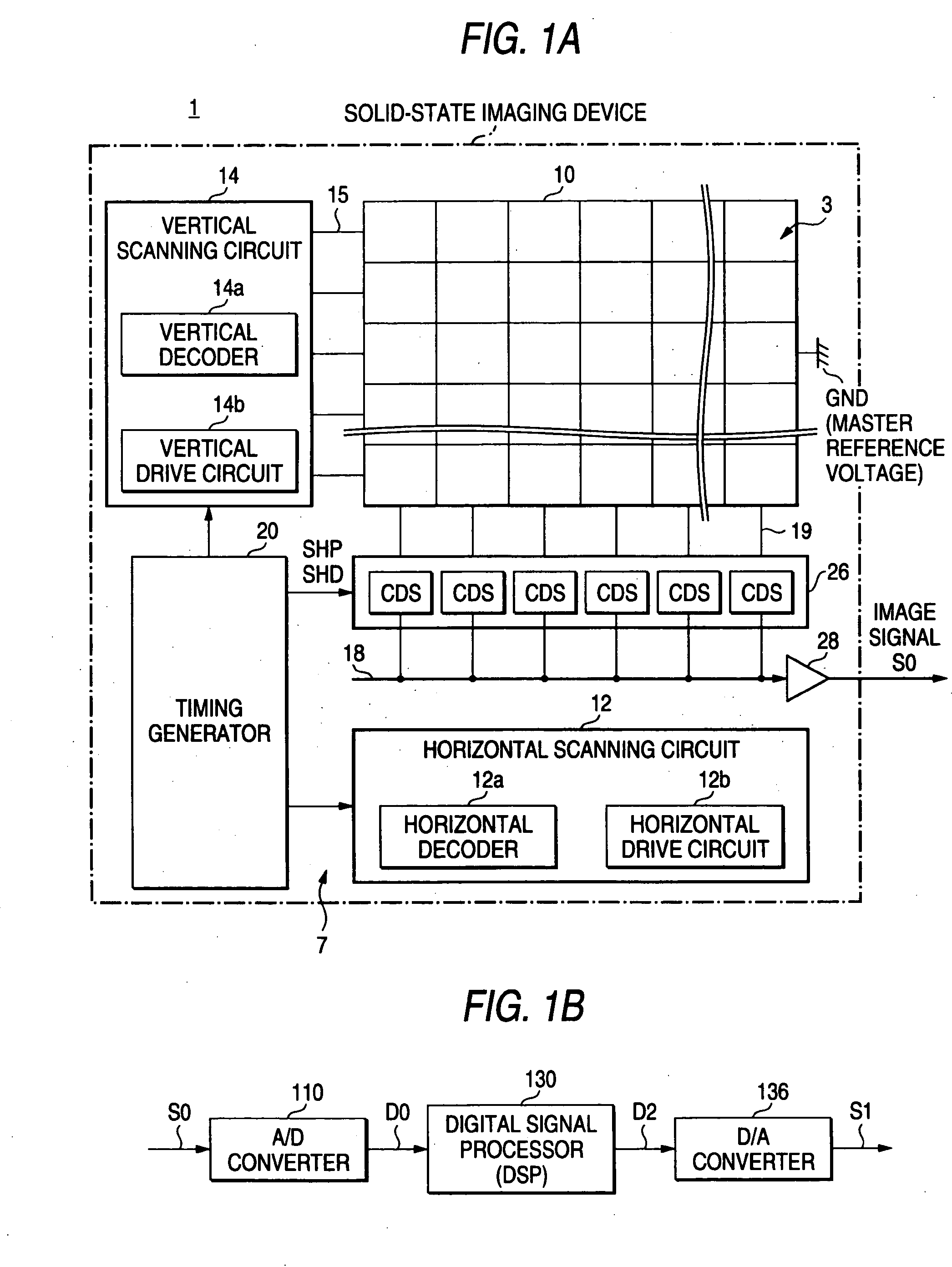
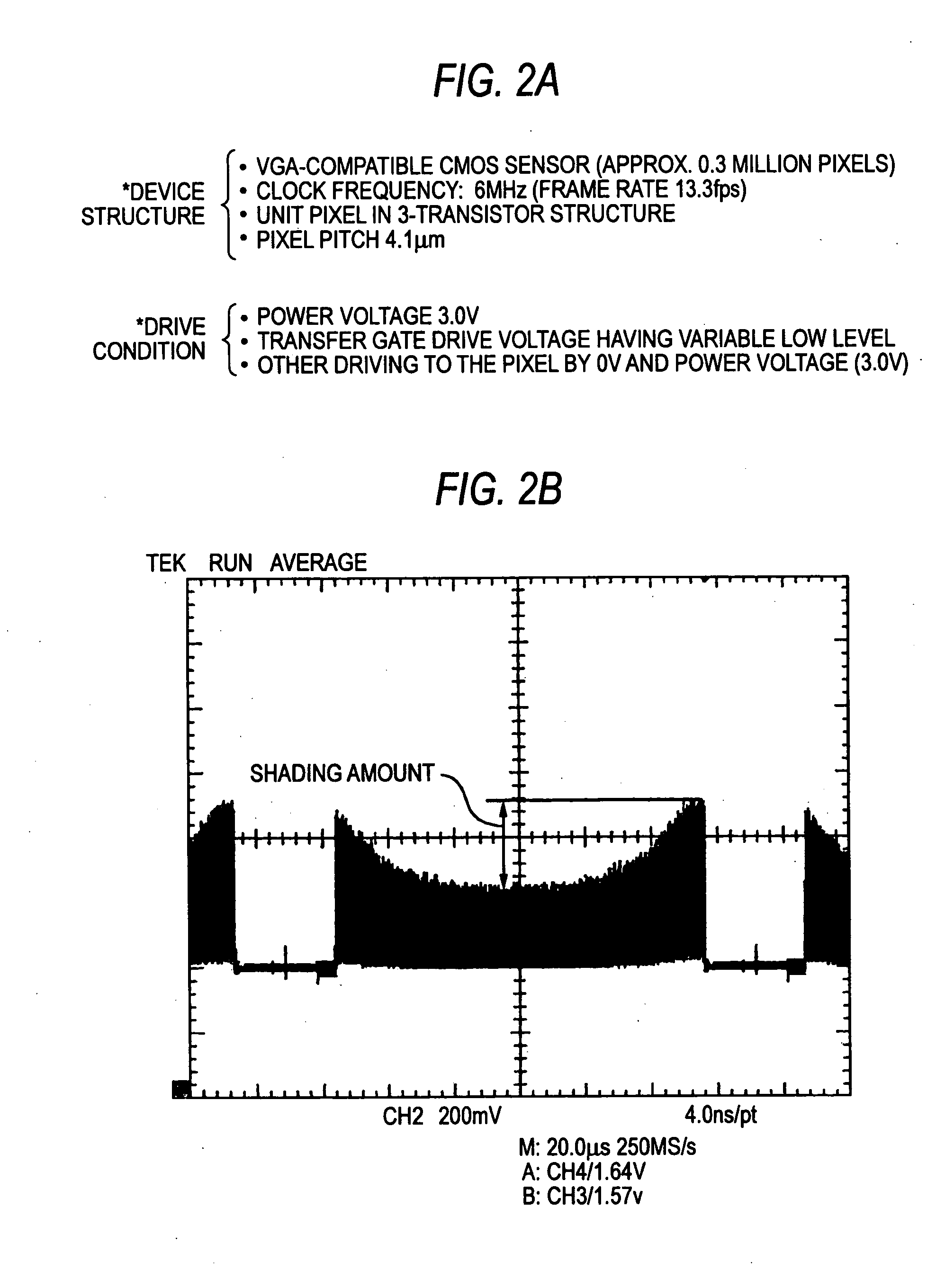
Solid-state imaging device and drive control method for the same
InactiveUS20050001915A1Fall and rise fully shortenedPrevent leakageTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOS sensorElectrical resistance and conductance
A CMOS sensor has unit pixels each structured by a light receiving element and three transistors, to prevent against the phenomenon of saturation shading and the reduction of dynamic range. The transition time (fall time), in switching off the voltage on a drain line shared in all pixels, is given longer than the transition time in turning of any of the reset line and the transfer line. For this reason, the transistor constituting a DRN drive buffer is made proper in its W / L ratio. Meanwhile, a control resistance or current source is inserted on a line to the GND, to make proper the operation current during driving. This reduces saturation shading amount. By making a reset transistor in a depression type, the leak current to a floating diffusion is suppressed to broaden the dynamic range.
Owner:SONY CORP
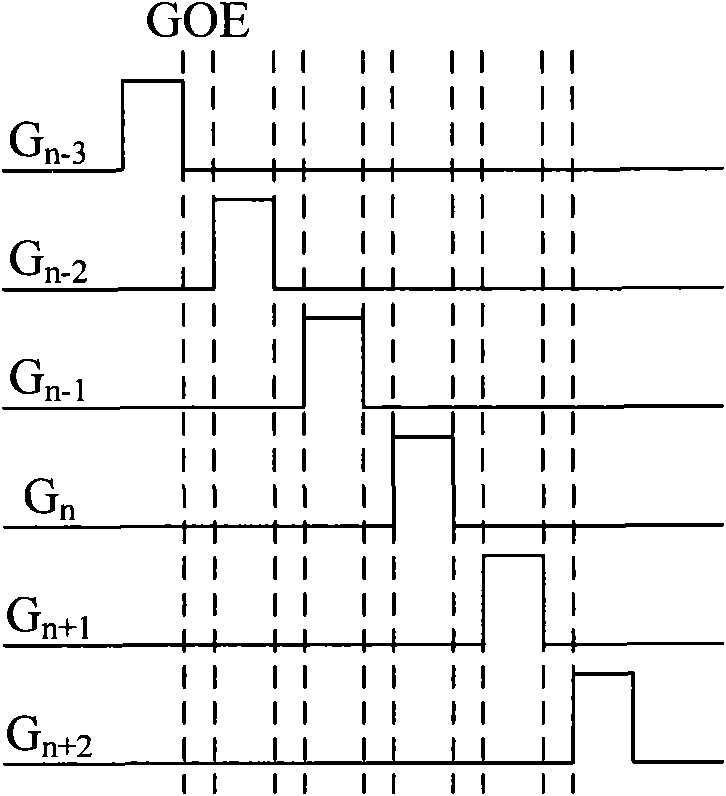
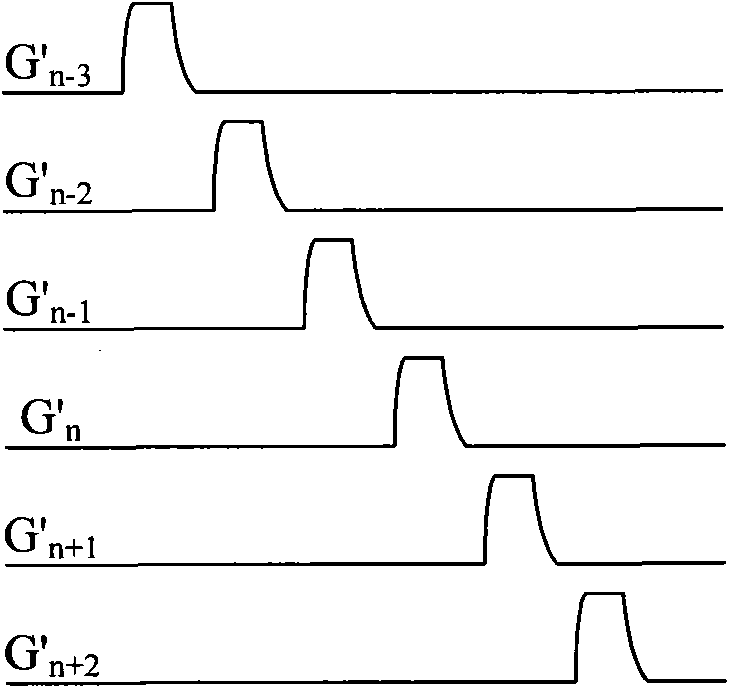
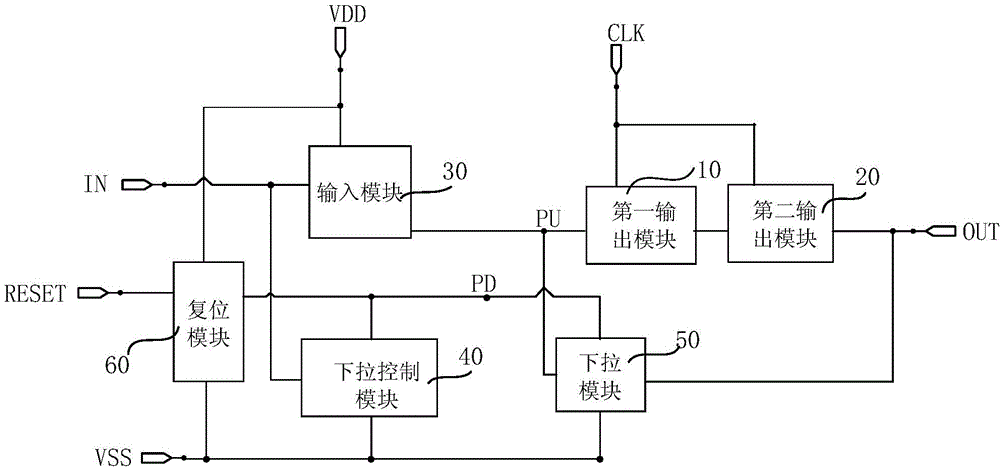
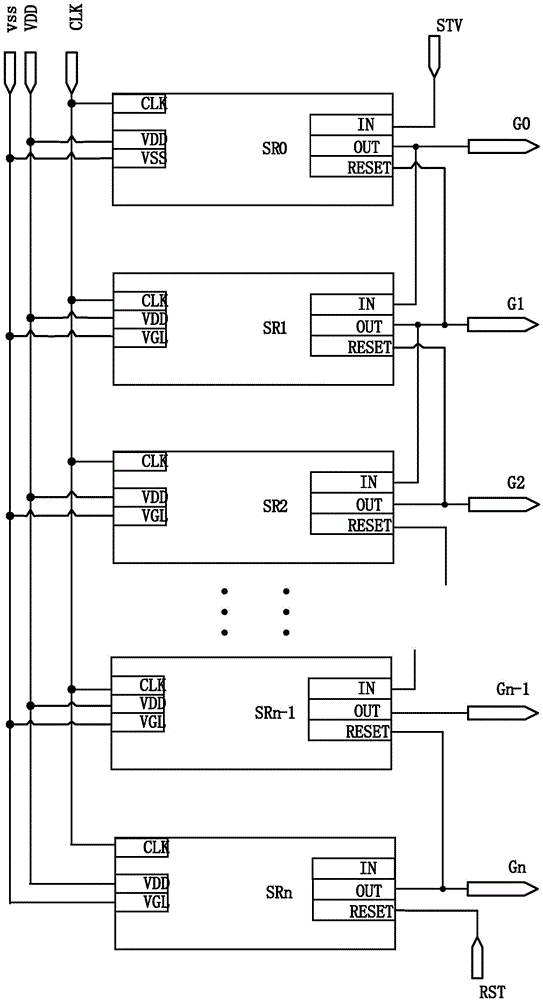
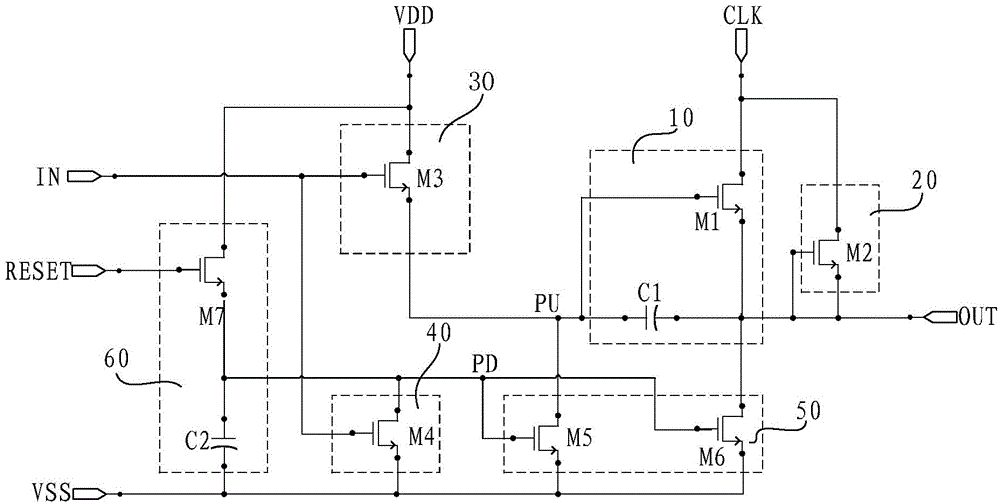
Shift register unit, gate drive circuit and display device
ActiveCN104867472AImprove output performanceImprove output characteristicsStatic indicating devicesDigital storageShift registerFall time
The embodiment of the invention provides a shift register unit, a gate drive circuit and a display device, and can enhance the output capacity of a signal output end and shorten the fall time of output waveform. The shift register unit provided by the invention comprises a first output module, a second output module, an input module, a drop-down control module, a drop-down module and a reset module, wherein under the control of a pull-up control node, the signal of a clock signal end is output to a signal output end; under the signal control of a signal input end, the voltage of a first power supply end is output to the pull-up control node; under the signal control of the signal input end, the signal of a drop-down control node drops down to the voltage of a second power supply end; under the control of the drop-down control node, the signals of the pull-up control node and the signal output end drop down to the voltage of the second power supply end; under the control of a reset signal end, the signal of the first power supply end is output to the drop-down control node. The shift register unit, the gate drive circuit and the display device, provided by the embodiment of the invention, are applied to the production and manufacturing of display panels.
Owner:HEFEI BOE OPTOELECTRONICS TECH +1
Shift register
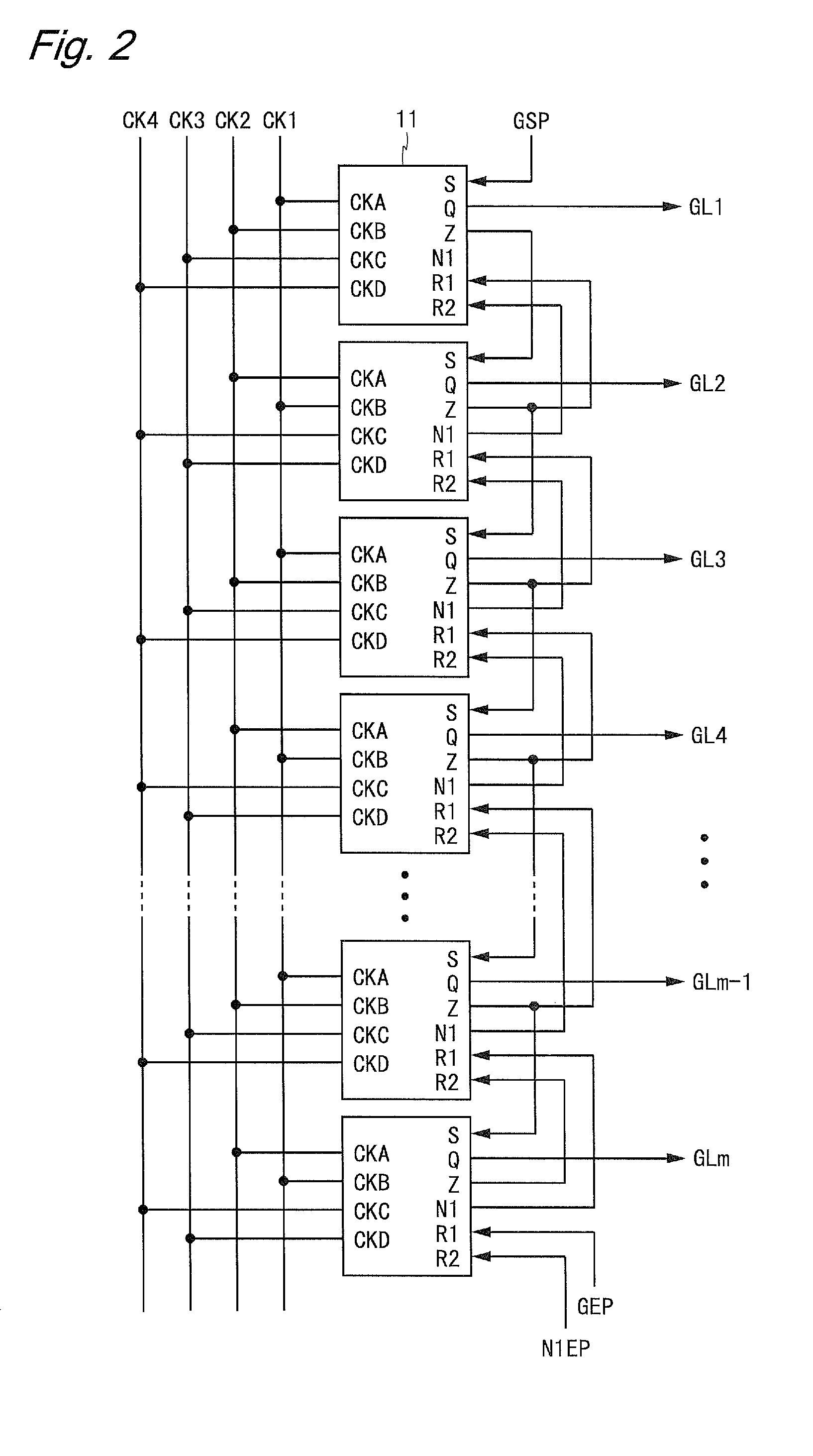
InactiveUS20120242630A1Drive capability can be improvedReduce output timeCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital storageShift registerFall time
Unit circuits 11 each including a TFT T2 (output transistor), a TFT T1 (input transistor), and a TFT T8 (output reset transistor) are cascade-connected, and a gate terminal of the TFT T8 is connected to a gate terminal of the TFT T2 included in a next stage unit circuit 11. By applying a post-boot potential that is higher than an ON potential of the TFT T8 to the gate terminal of the TFT T8, driving capability of the TFT T8 is increased. Accordingly, it is possible to reduce falling time duration of the output signal Q and a layout area of the TFT T8. In this manner, a shift register with a small area capable of resetting an output signal at high speed is provided.
Owner:SHARP KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com