Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1251results about "Pulse generator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
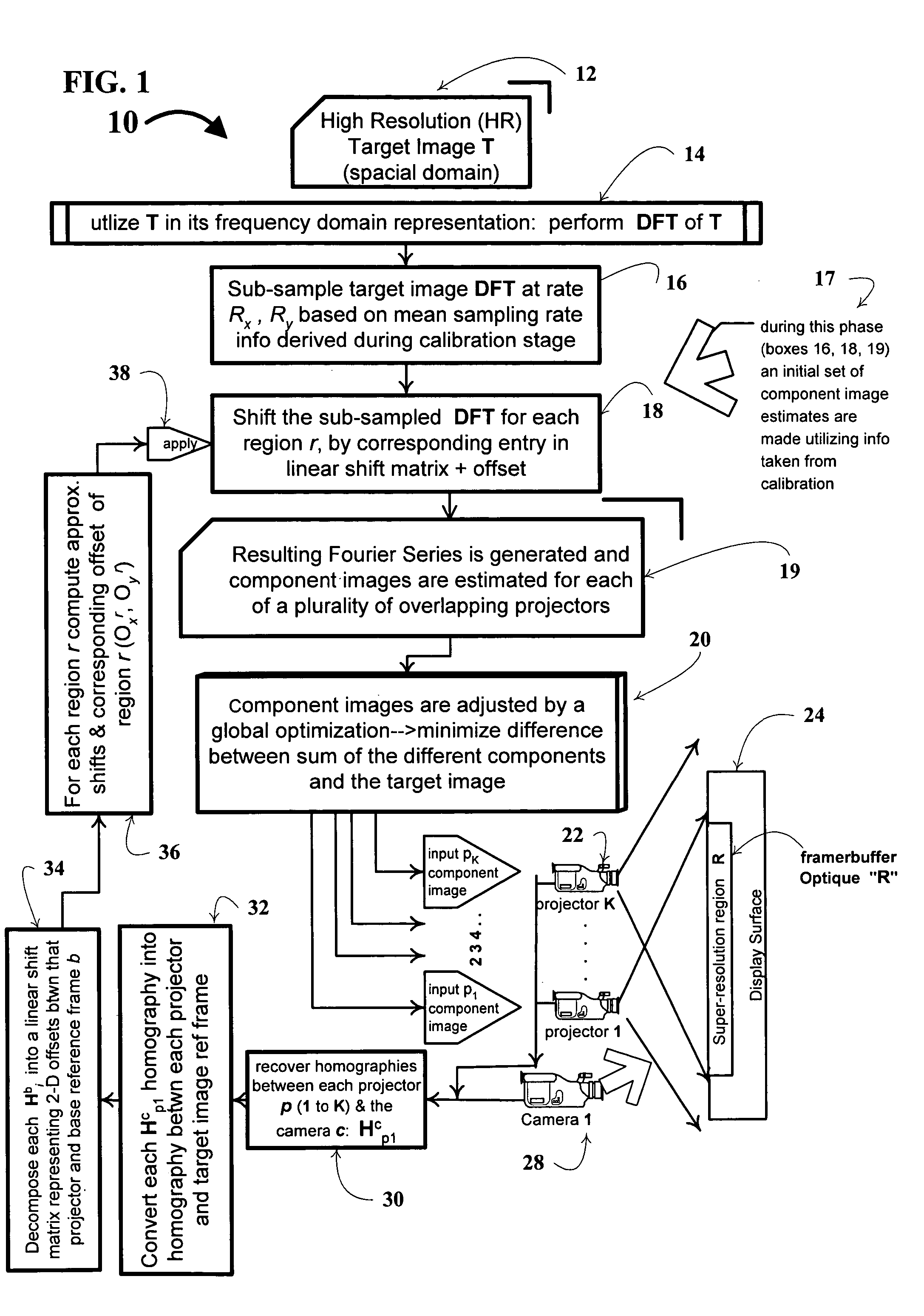
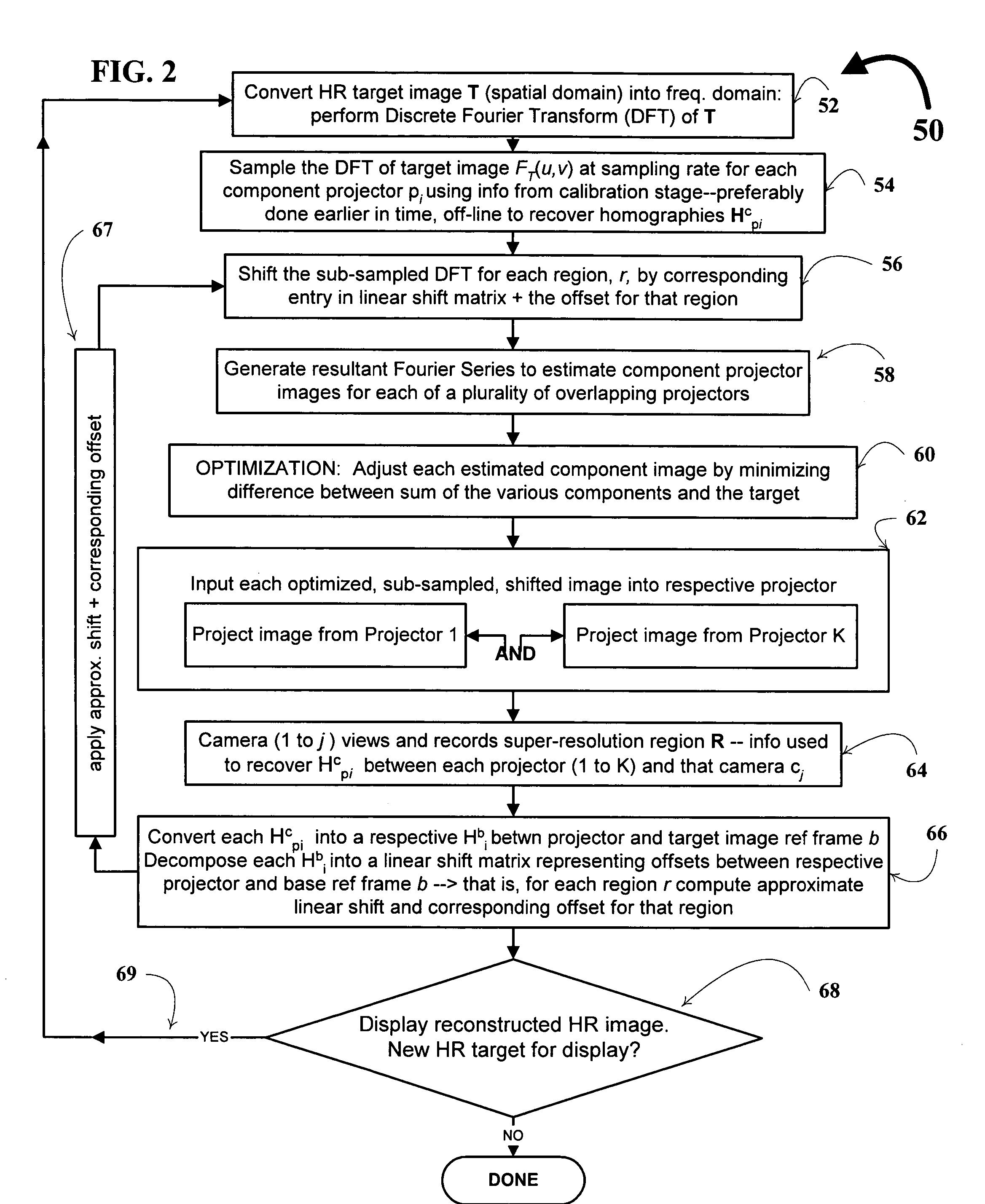
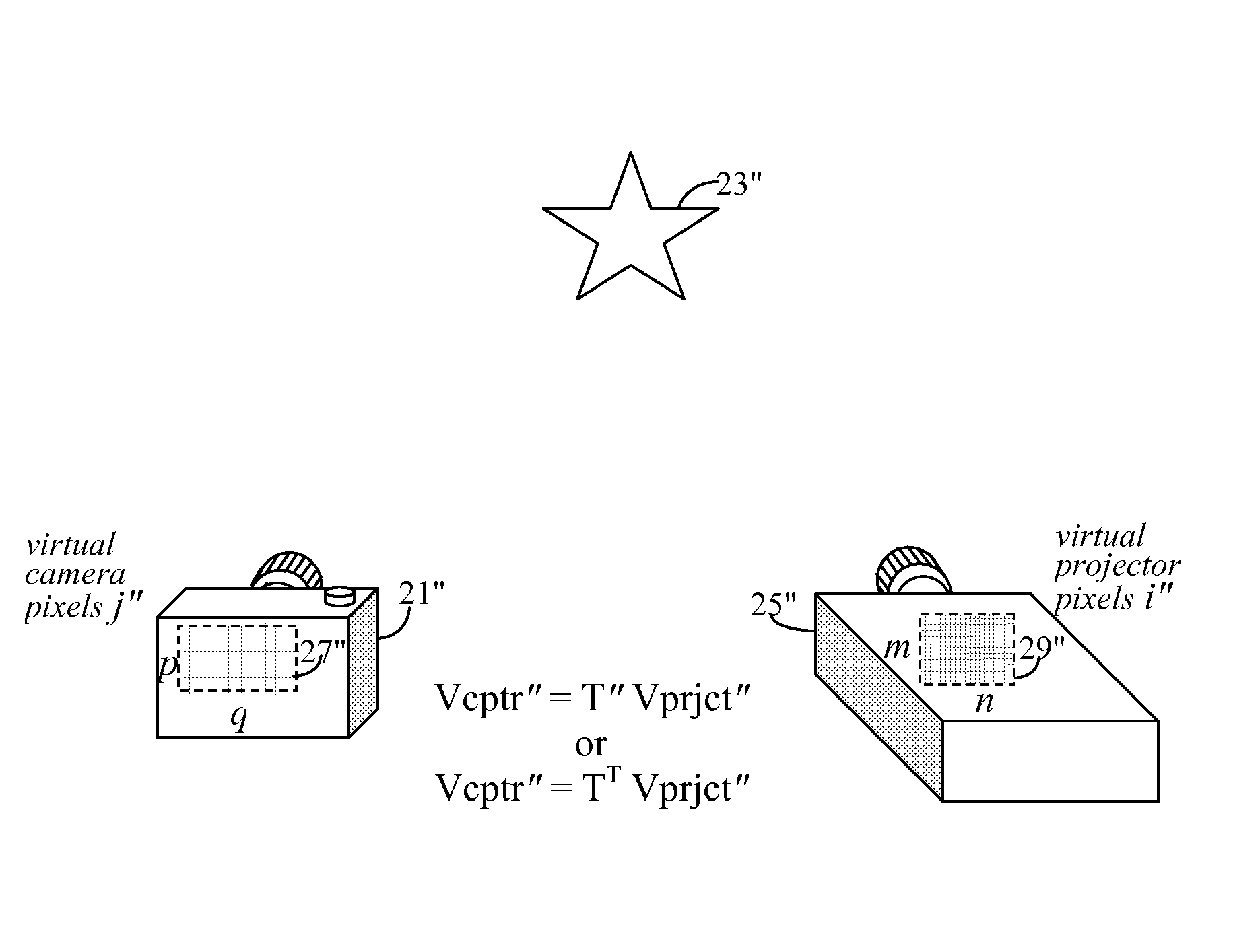
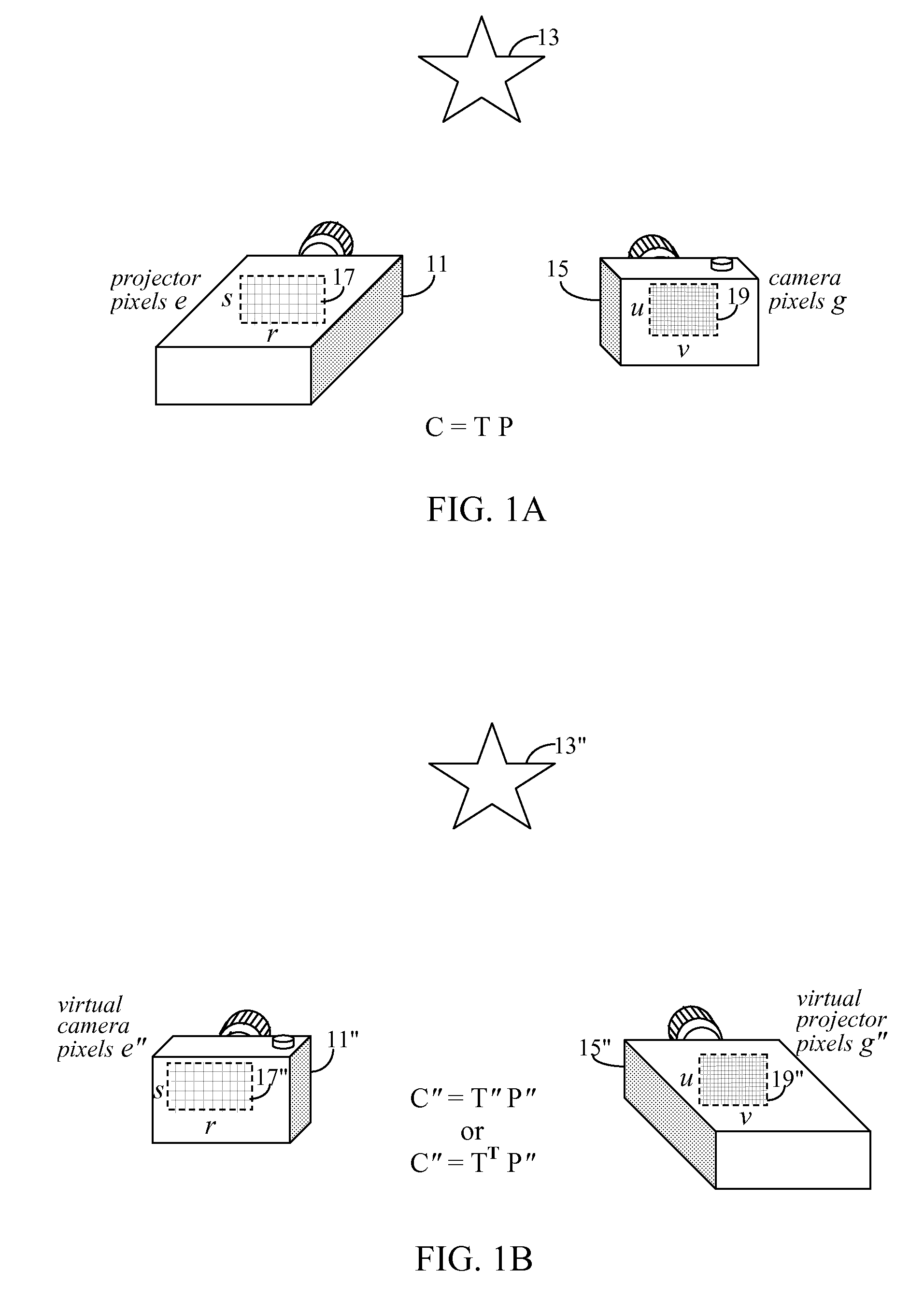
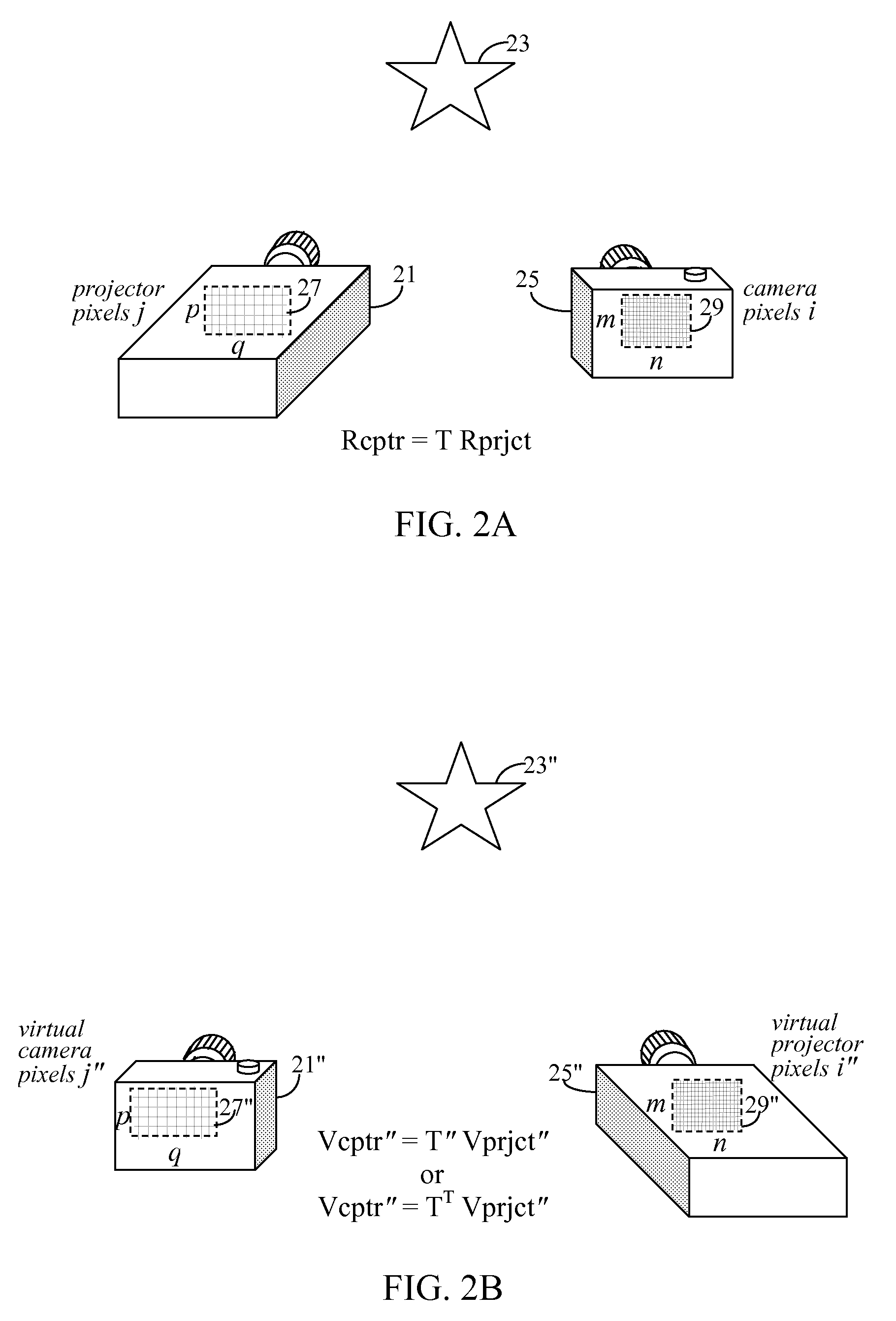
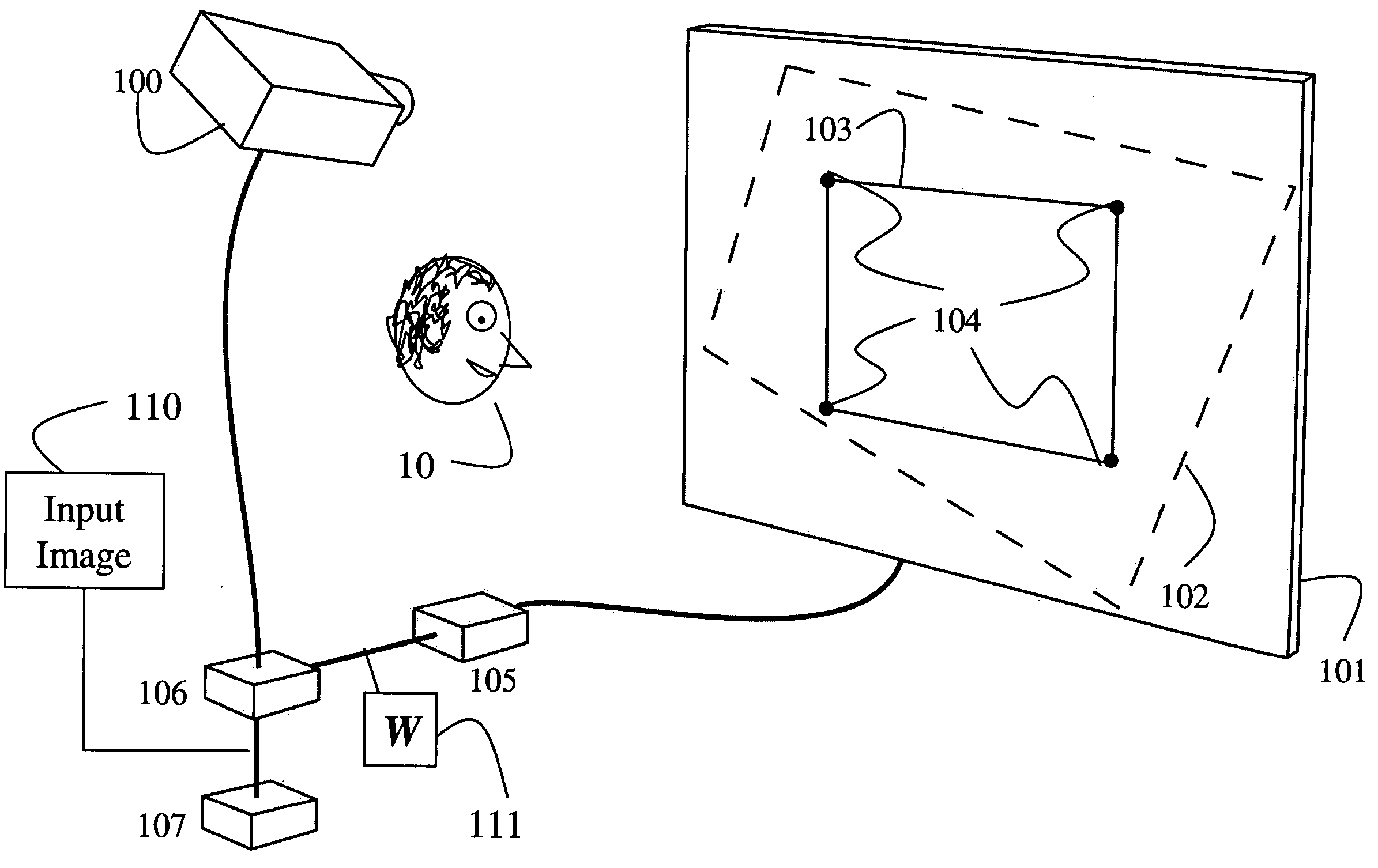
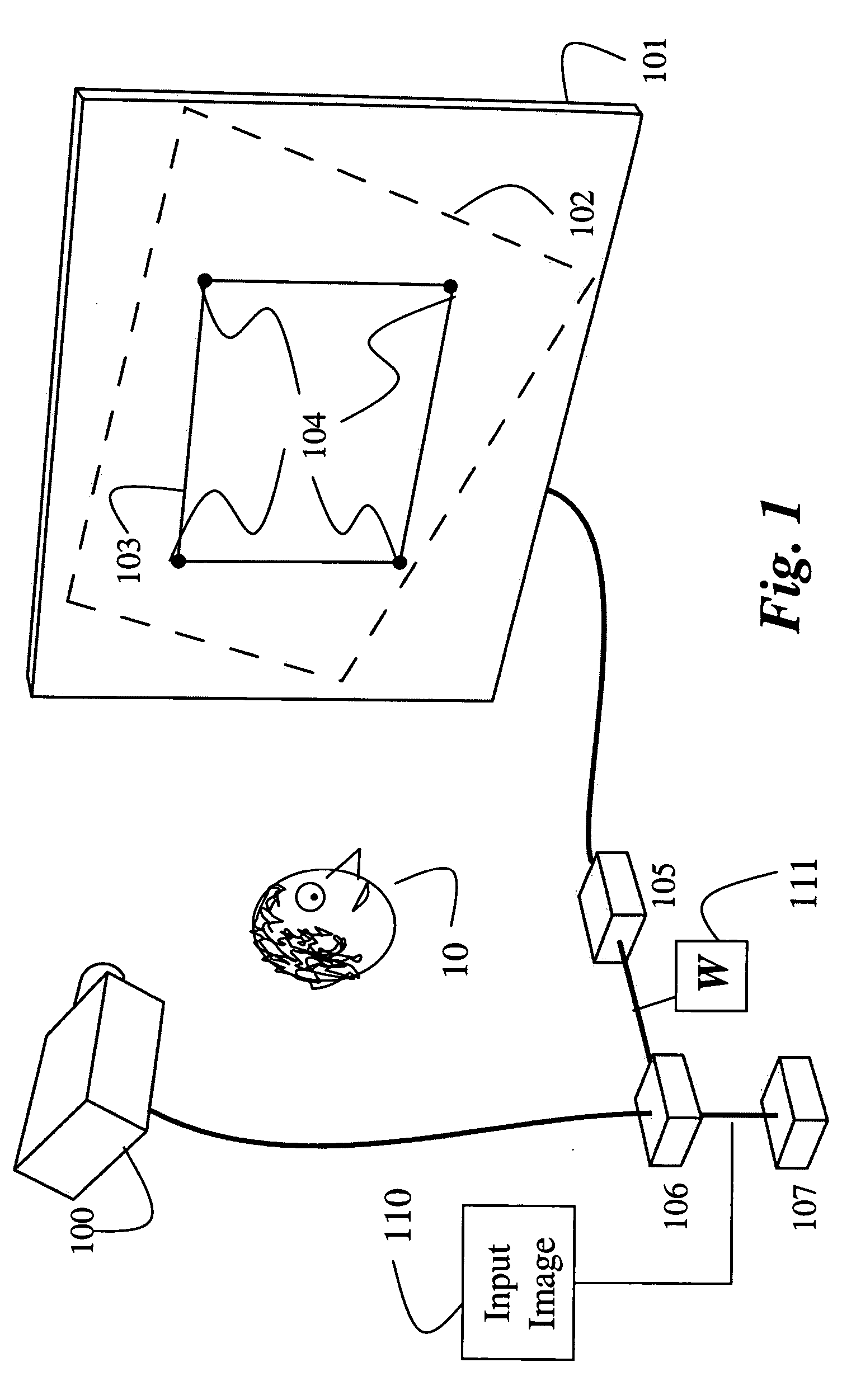
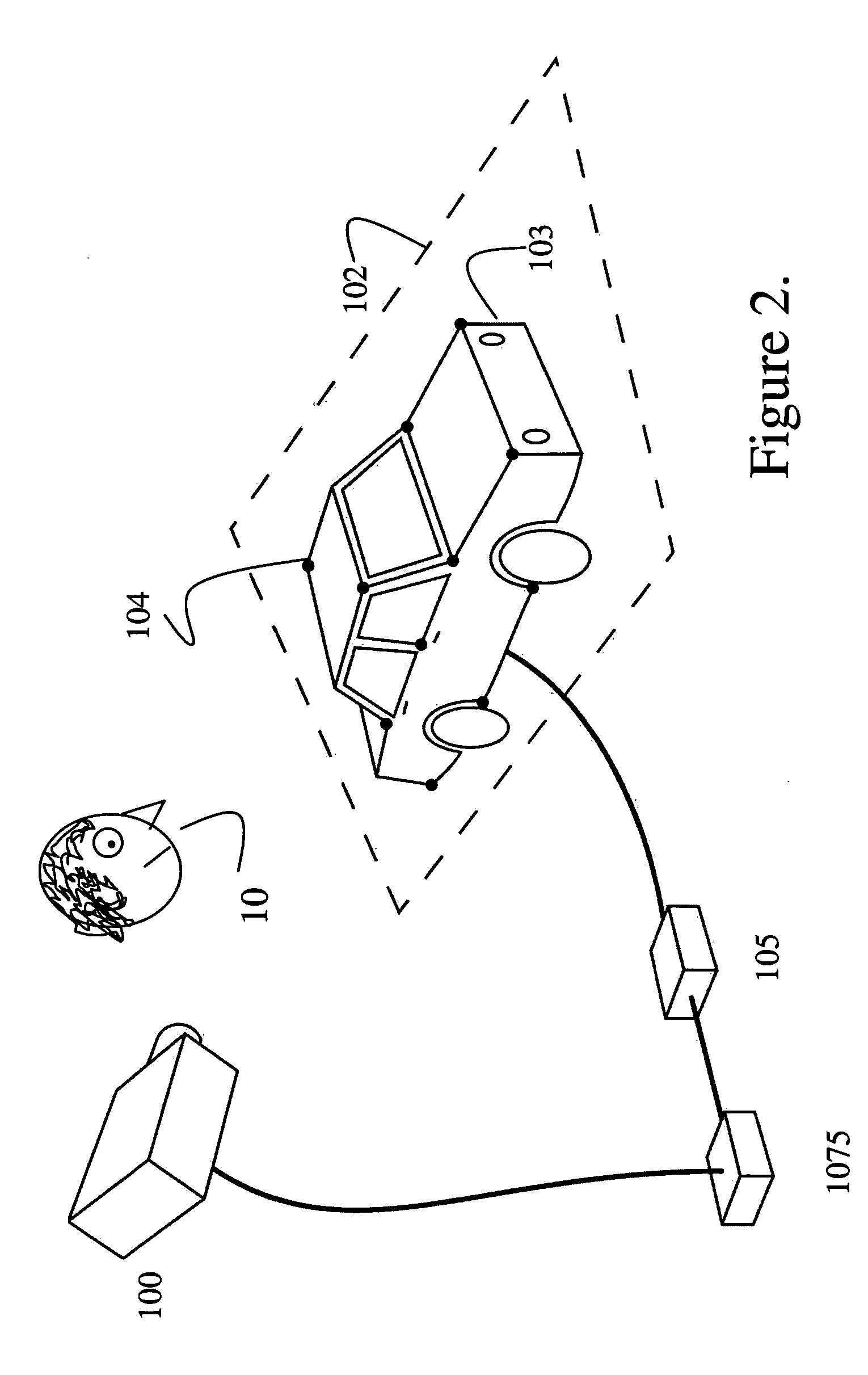
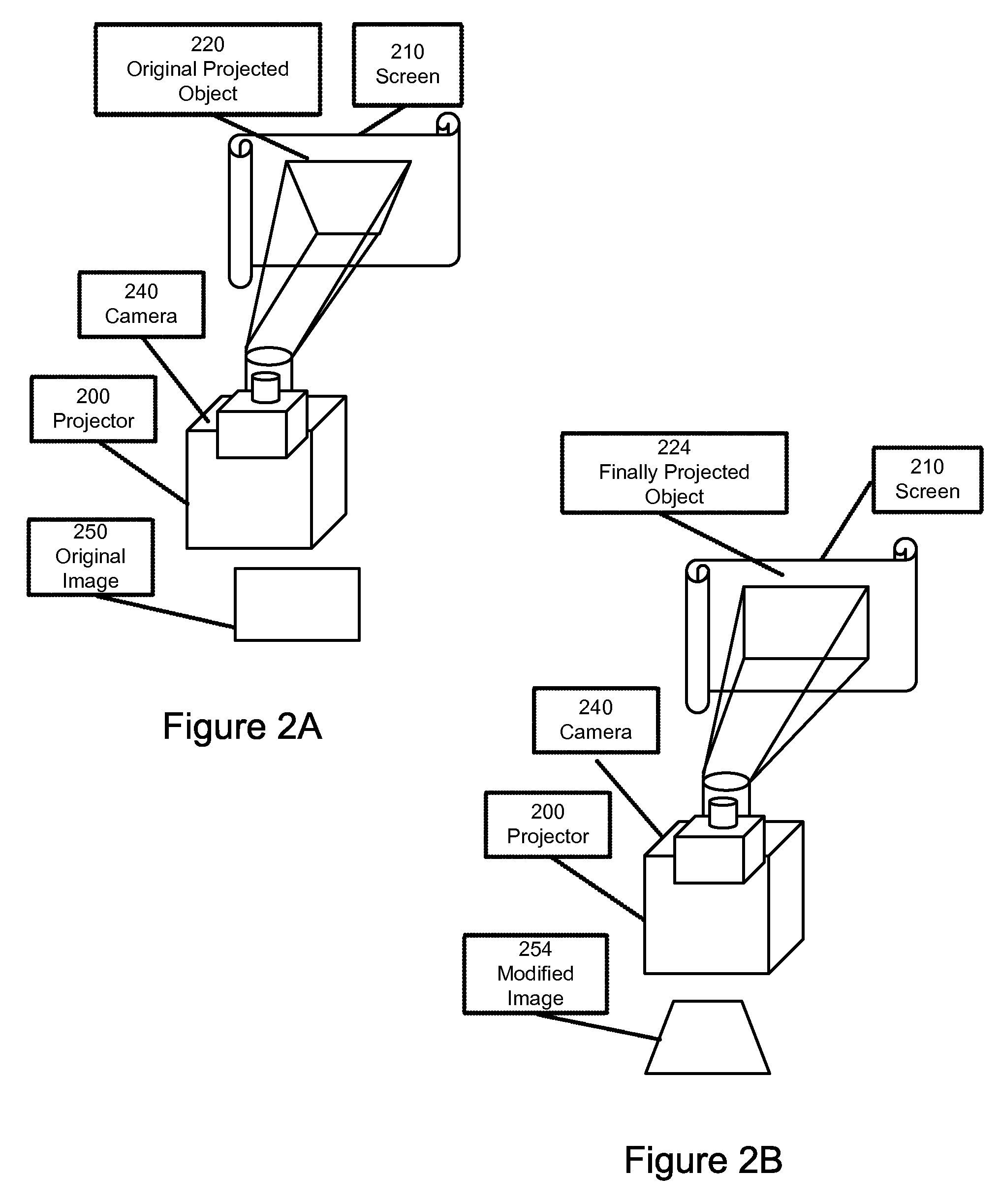
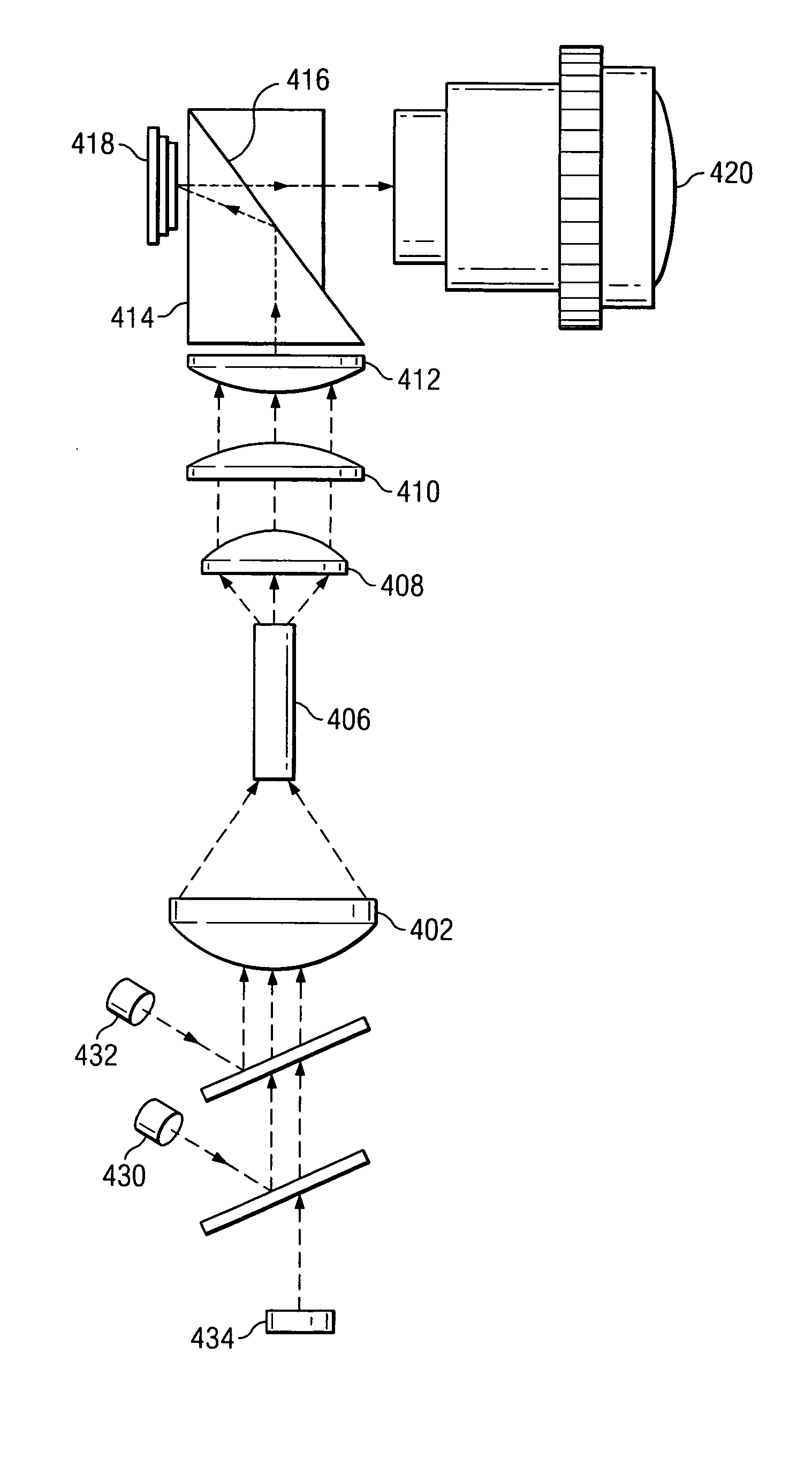
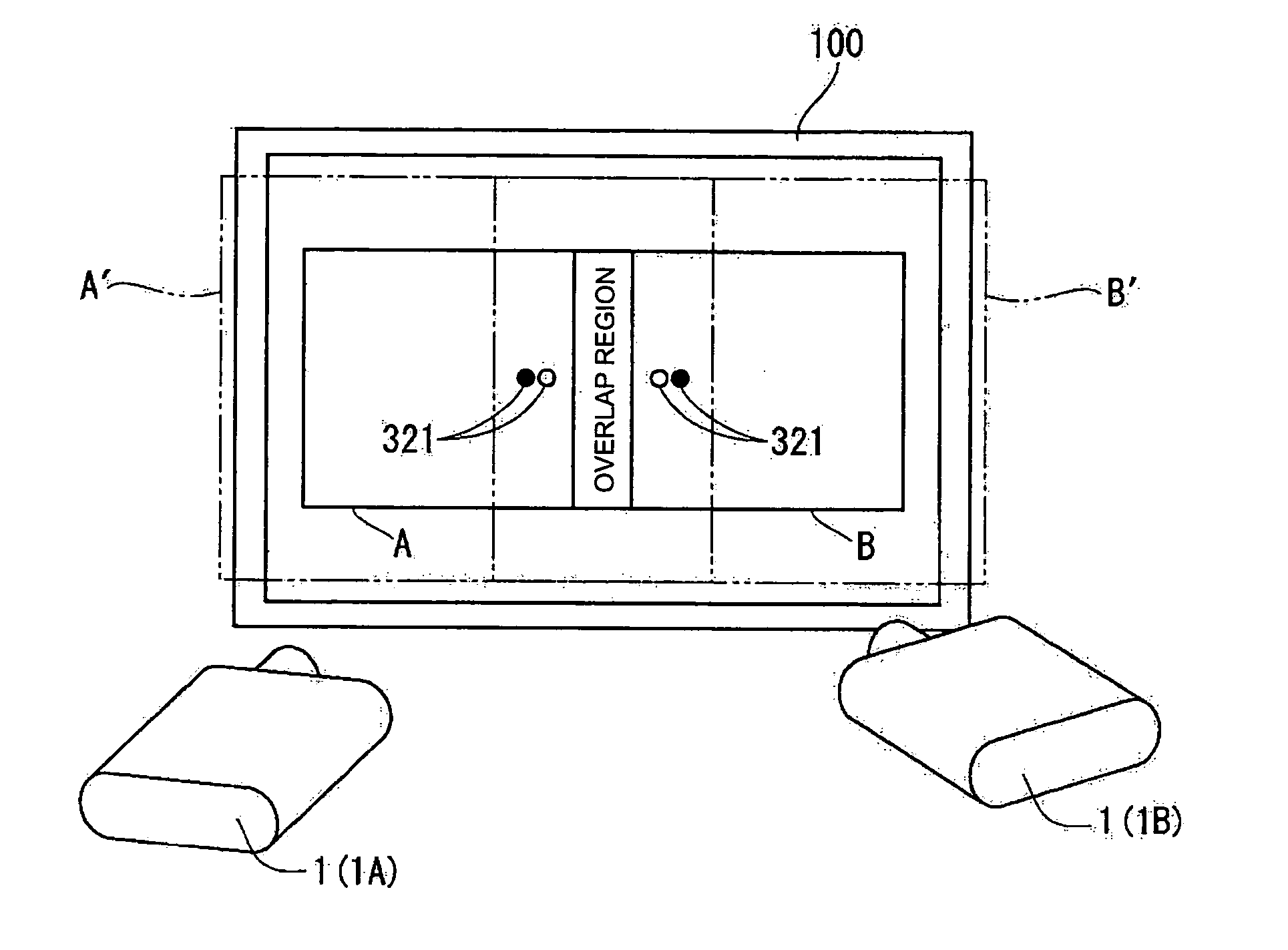
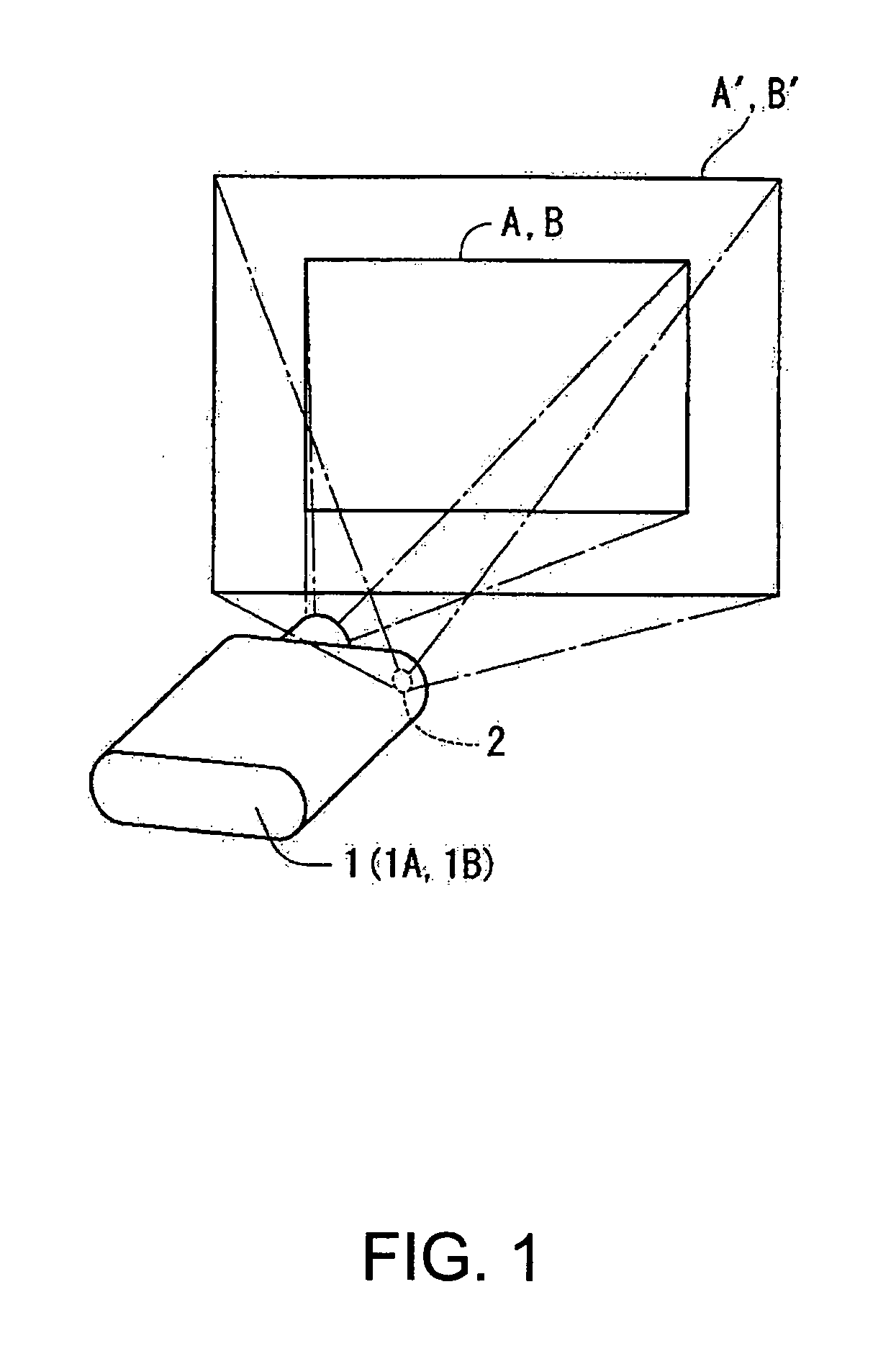
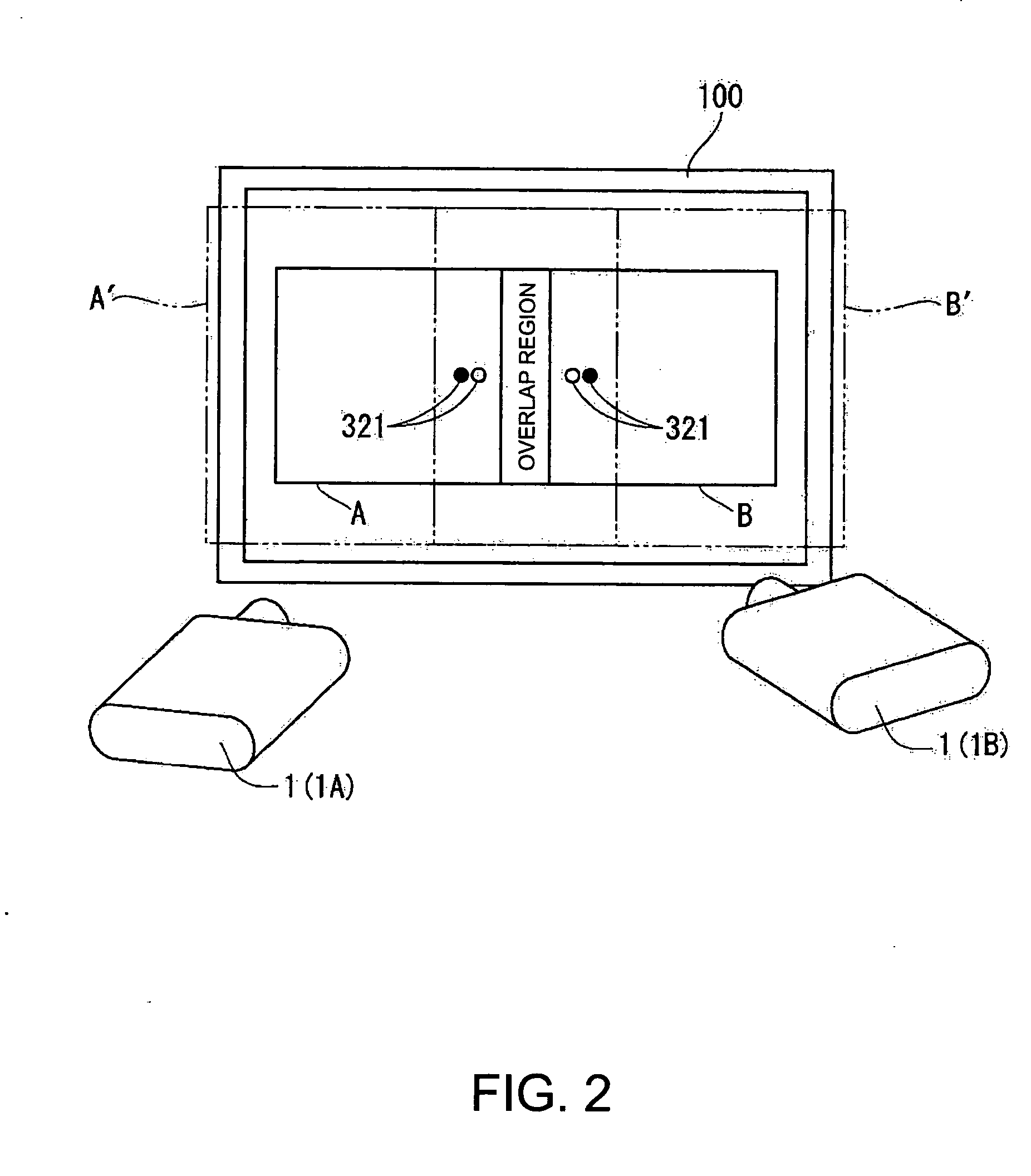
Super-resolution overlay in multi-projector displays
InactiveUS20040239885A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsProgram codeFourier transform
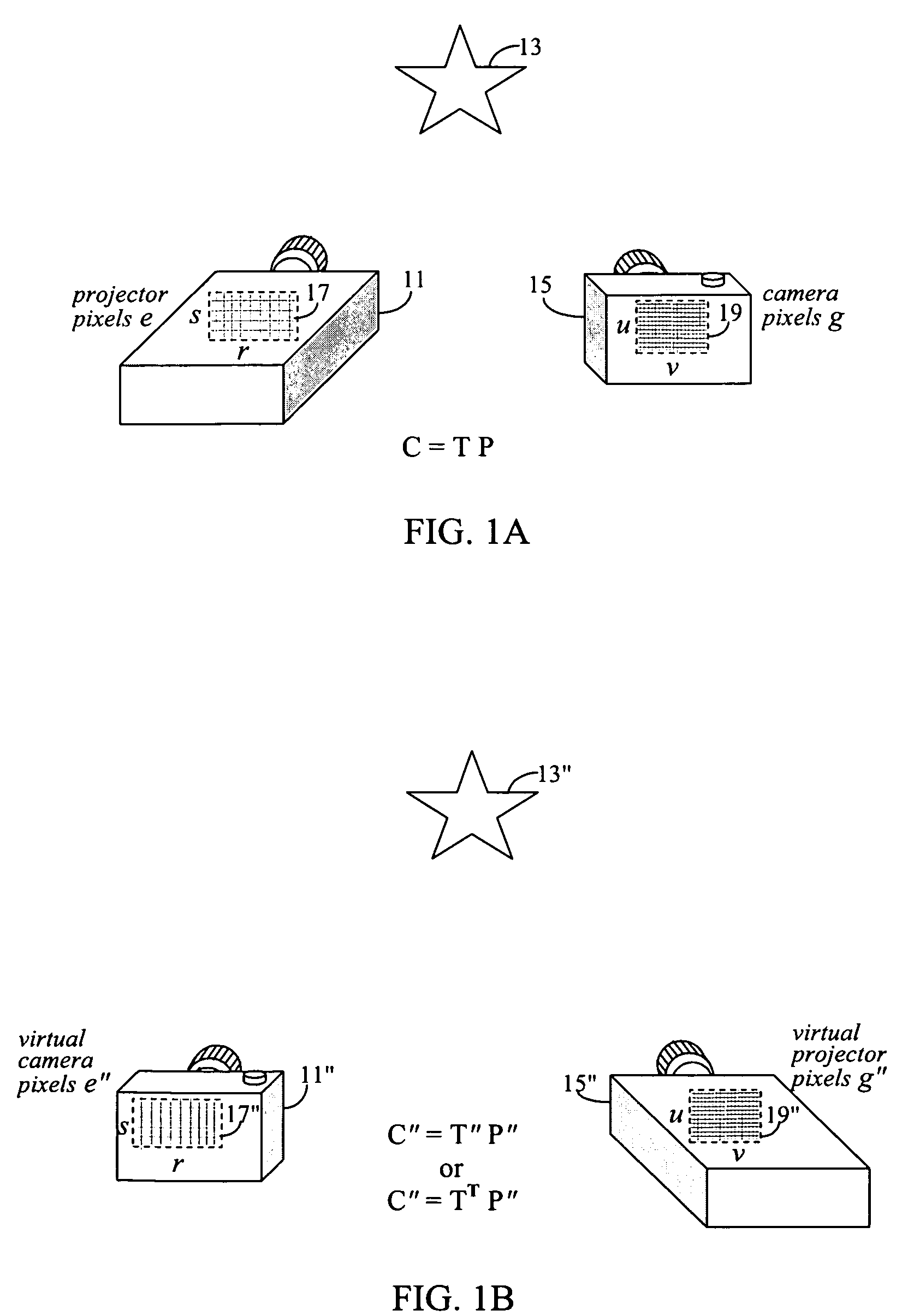
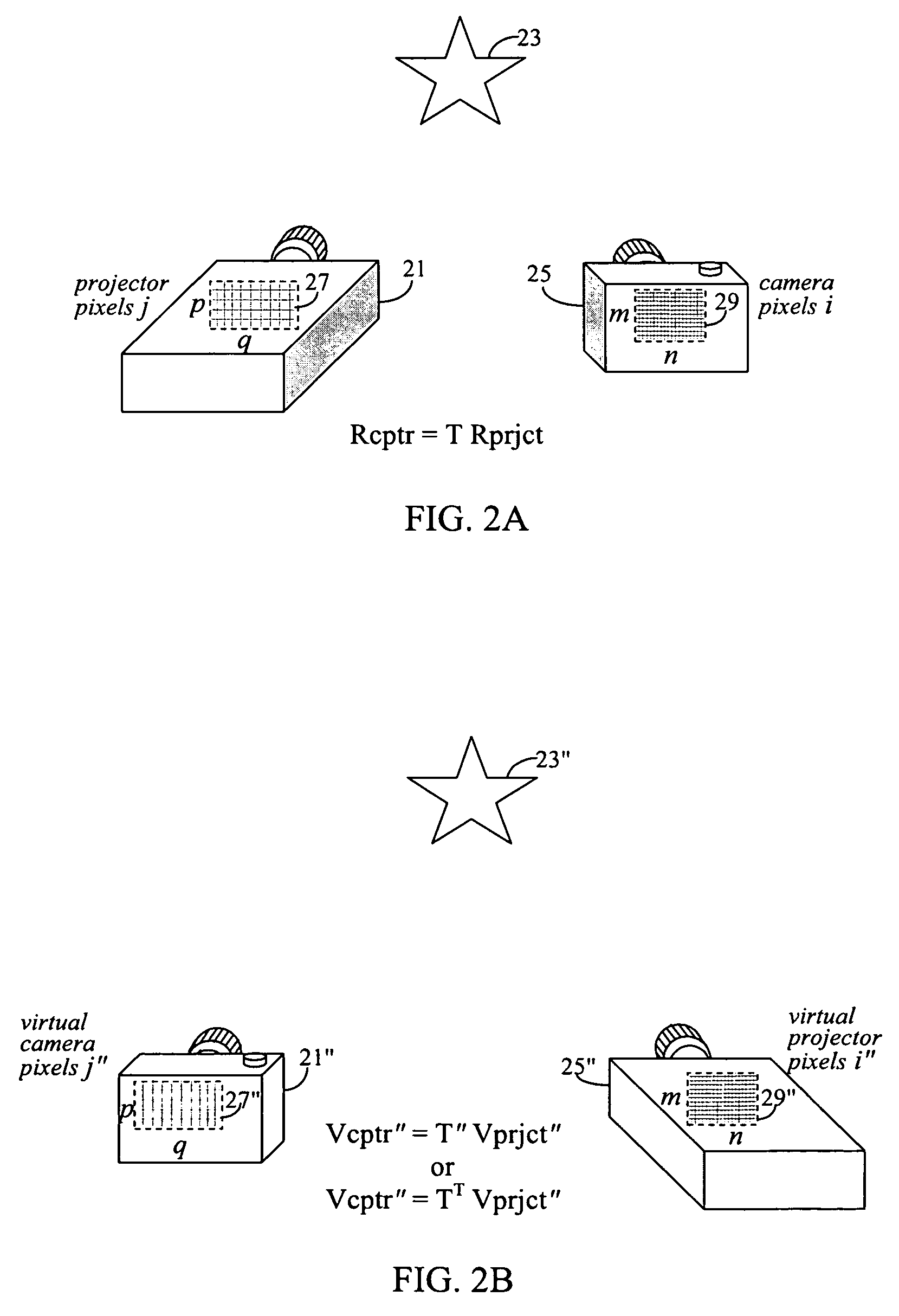
A technique, associated system and computer executable program code, for projecting a superimposed image onto a target display surface under observation of one or more cameras. A projective relationship between each projector being used and the target display surface is determined using a suitable calibration technique. A component image for each projector is then estimated using the information from the calibration, and represented in the frequency domain. Each component image is estimated by: Using the projective relationship, determine a set of sub-sampled, regionally shifted images, represented in the frequency domain; each component image is then composed of a respective set of the sub-sampled, regionally shifted images. In an optimization step, the difference between a sum of the component images and a frequency domain representation of a target image is minimized to produce a second, or subsequent, component image for each projector. Here, a second set of frequency domain coefficients for use in producing a frequency domain representation of the second component image for each projector is identified. Taking the inverse Fourier transform of the frequency domain representation of the second component image, converts the information into a spatial signal that is placed into the framebuffer of each component projector and projected therefrom to produce the superimposed image.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Small memory footprint light transport matrix capture
ActiveUS8106949B2Easy to shipEasy to implementTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging processingProjection image
A projection system uses a transformation matrix to transform a projection image p in such a manner so as to compensate for surface irregularities on a projection surface. The transformation matrix makes use of properties of light transport relating a projector to a camera. A display pipeline of user-supplied image modification processing modules are reduced by first representing the processing modules as multiple, individual matrix operations. All the matrix operations are then combined with, i.e., multiplied to, the transformation matrix to create a modified transformation matrix. The created transformation matrix is then used in place of the original transformation matrix to simultaneously achieve both image transformation and any pre and post image processing defined by the image modification processing modules.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
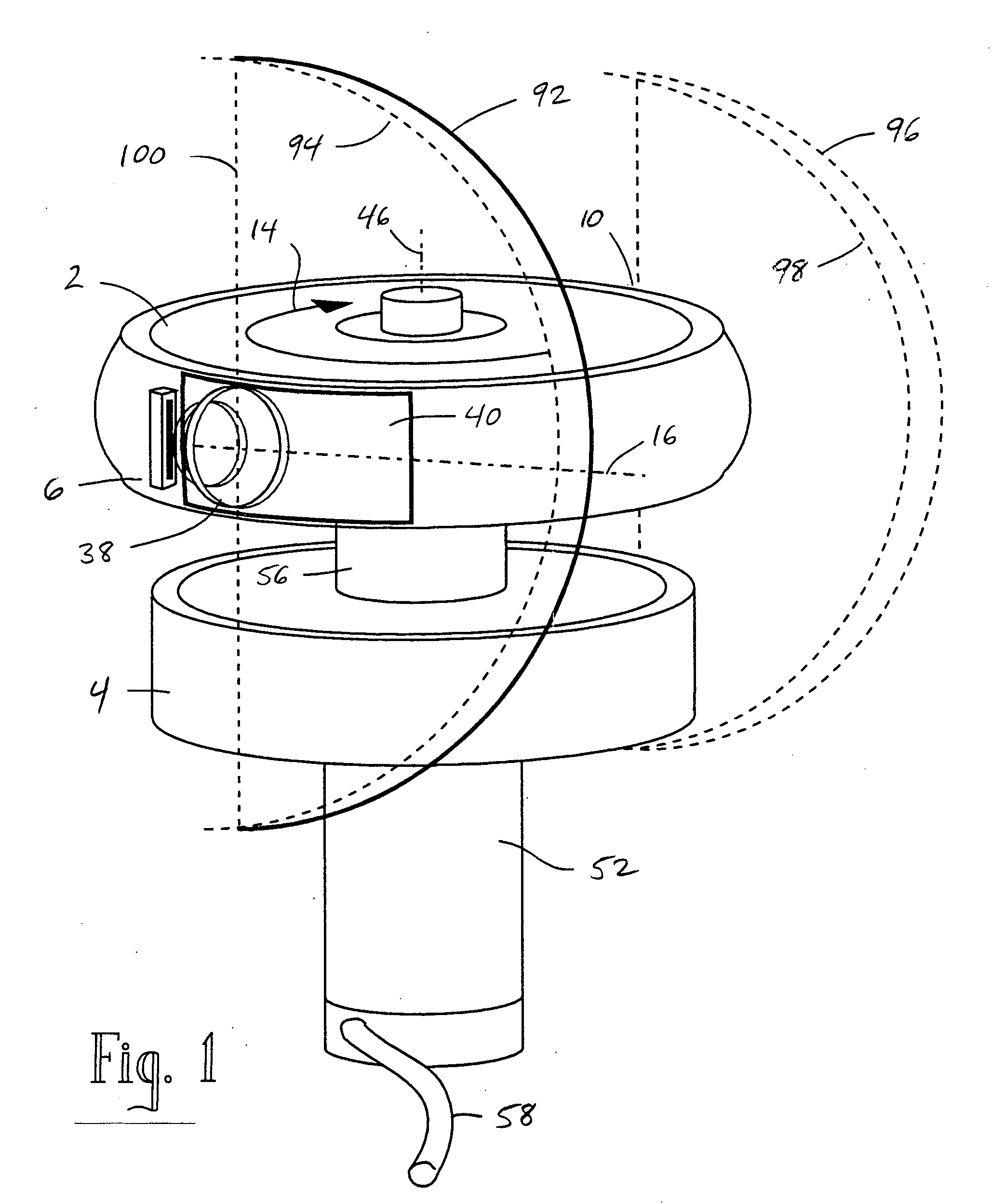
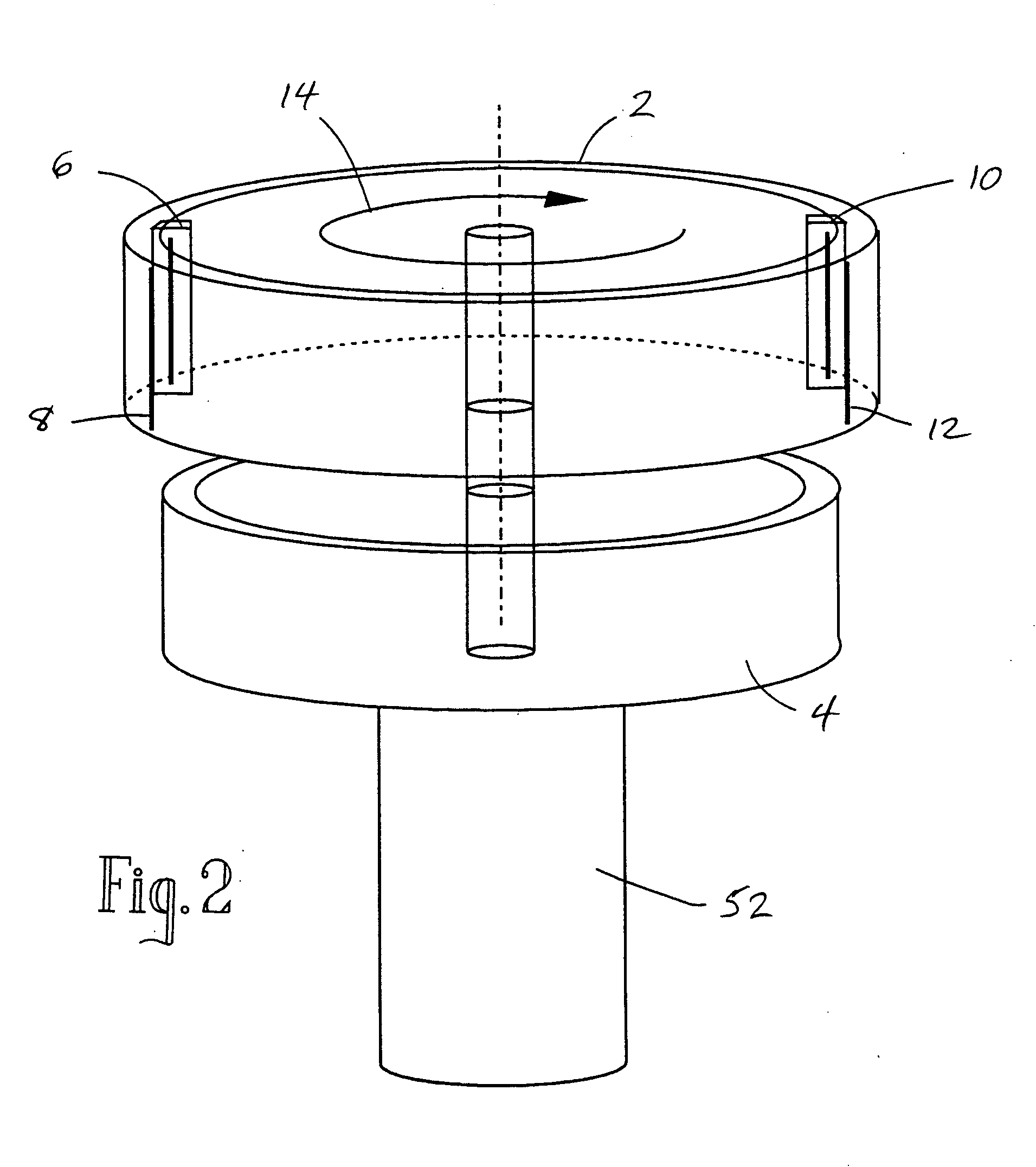
Rotating scan camera
InactiveUS20060072020A1High resolutionHigh light sensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsViewpointsRapid rotation
A scanning camera with a rotating drum has one or more sensors characterized by a non-radial optical axis. With two sensors on opposite sides of the drum and facing in substantially the same direction, stereoscopic recording of a panorama is accomplished as the drum rotates. The adjustment of convergence between stereoscopic viewpoints is described that improves the viewing and interpretation of stereoscopic images. Rapid rotation of the scanning camera produces panoramic motion picture recording, with the final frame speed dependent on the sensitivity and speed of the sensor, the resolution desired, and the capabilities of the recording device. The preferred embodiment employs rotating fisheye lenses for a substantially full-sphere field of view. Additional sensors in the same arrangement are used to increase resolution and light sensitivity through multiplexed or additive recording of the image data. Recording image information using film, either internal or external to the camera drum, is also described as a cost-effective alternative to digital media storage.
Owner:IMMERSIVE LICENSING
Projector
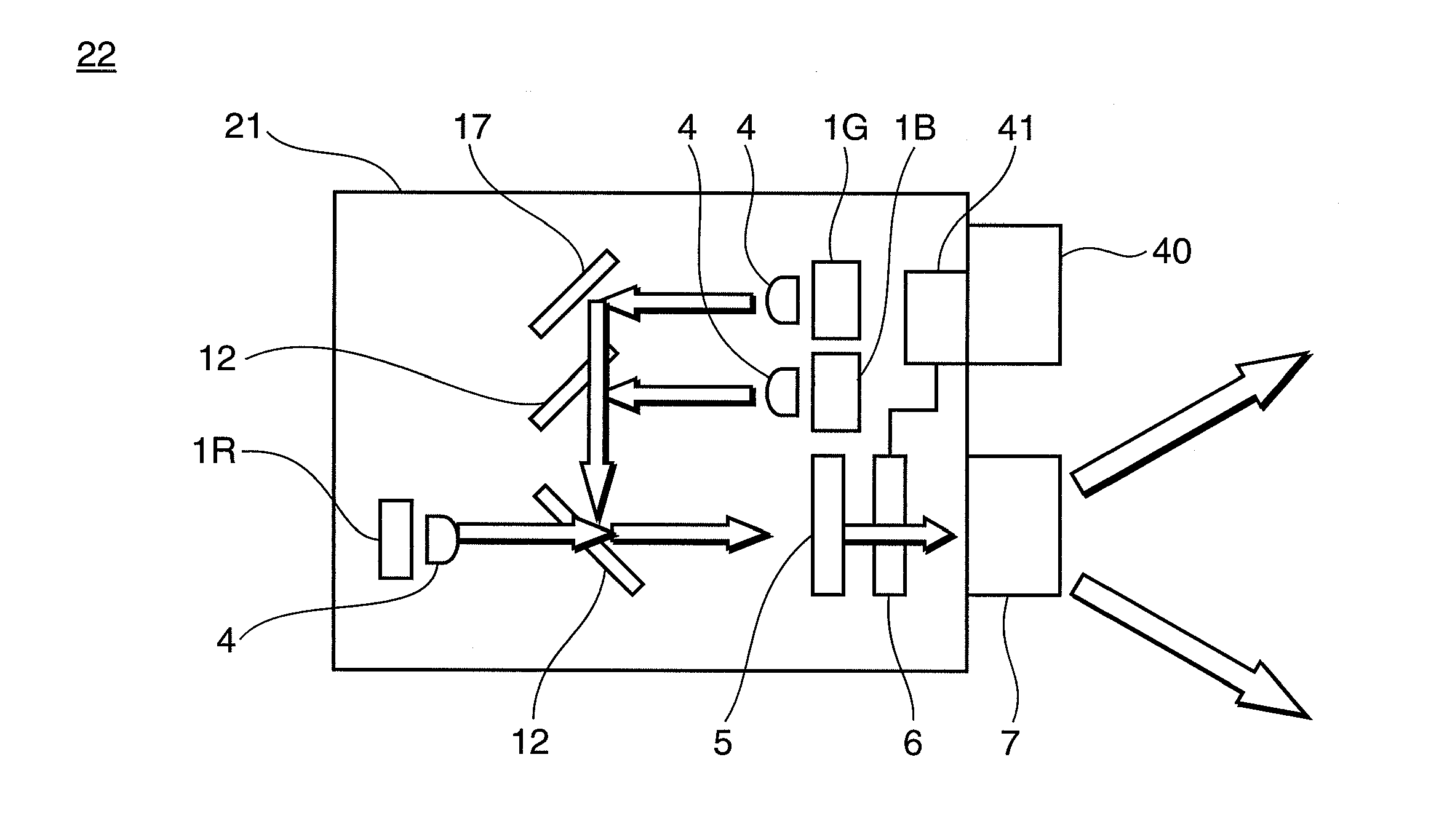
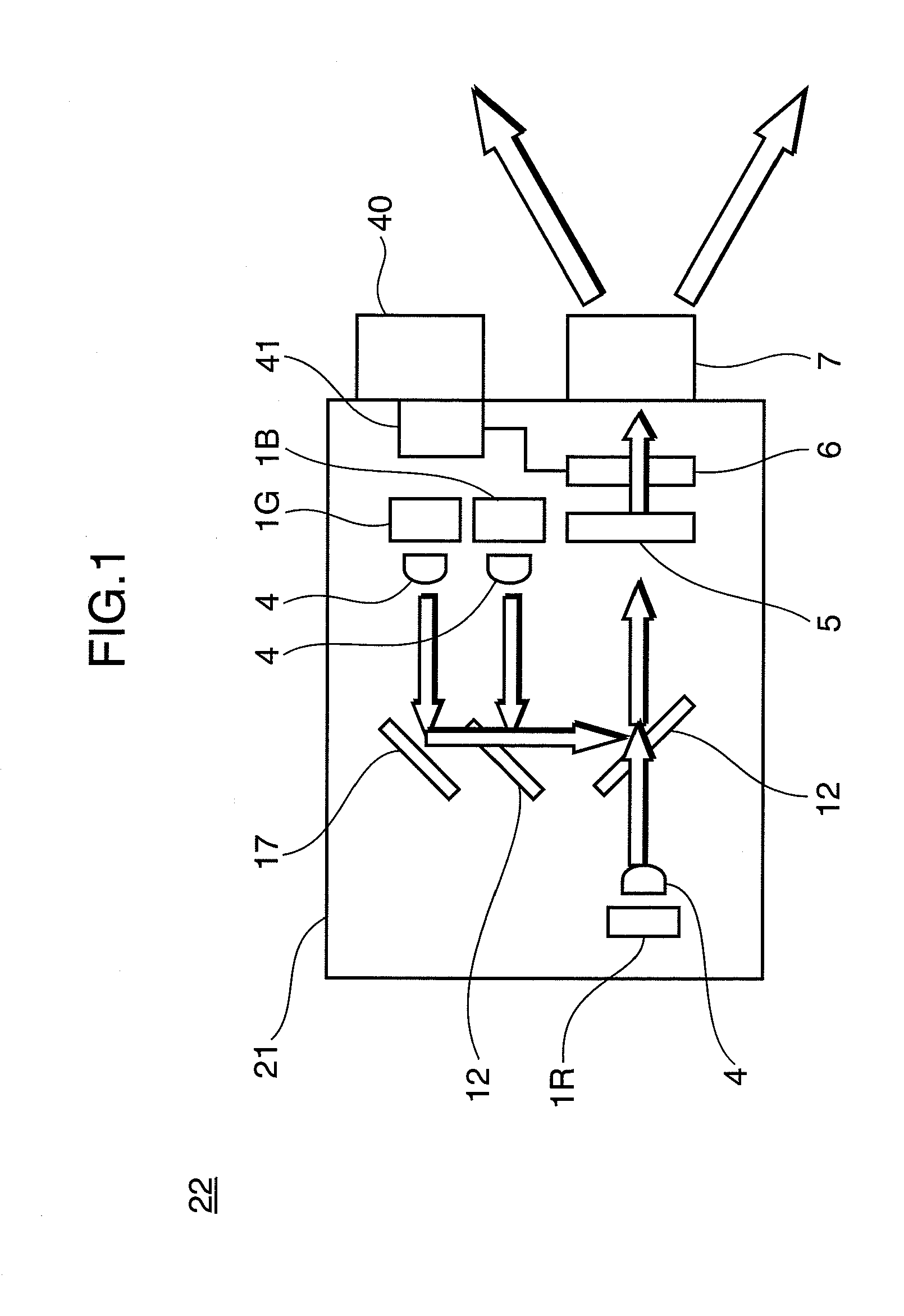
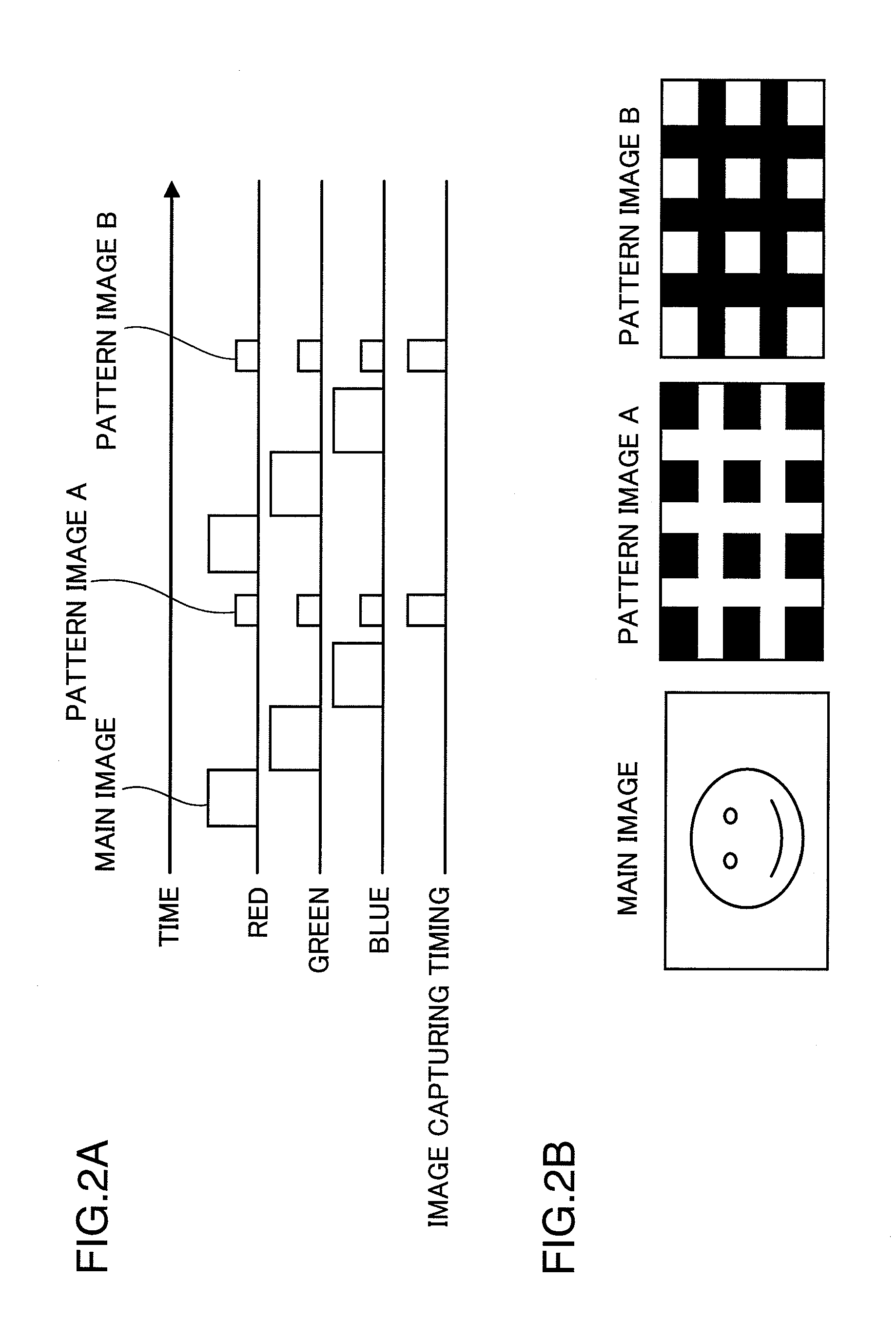
ActiveUS20100201894A1Simple configurationInhibit deteriorationTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImage signalVisual perception
A projector has: light source (1R, 1G, 1B); a light modulation unit (6) that modulates a light emitted from the light source based on image signals; a display control unit (41) that outputs the image signals including main cyclic image signals to the light modulation unit, and controls the display thereof; a projection unit (7) that projects the image based on the light modulated by the light modulation unit; and an imaging unit (40) that captures an image to be displayed based on the light projected from the projection unit, and the display control unit inserts a correction image signal for projecting a correction image, which is visually recognized as a uniform white or gray screen when time integration is performed, between the cyclic main image signals.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
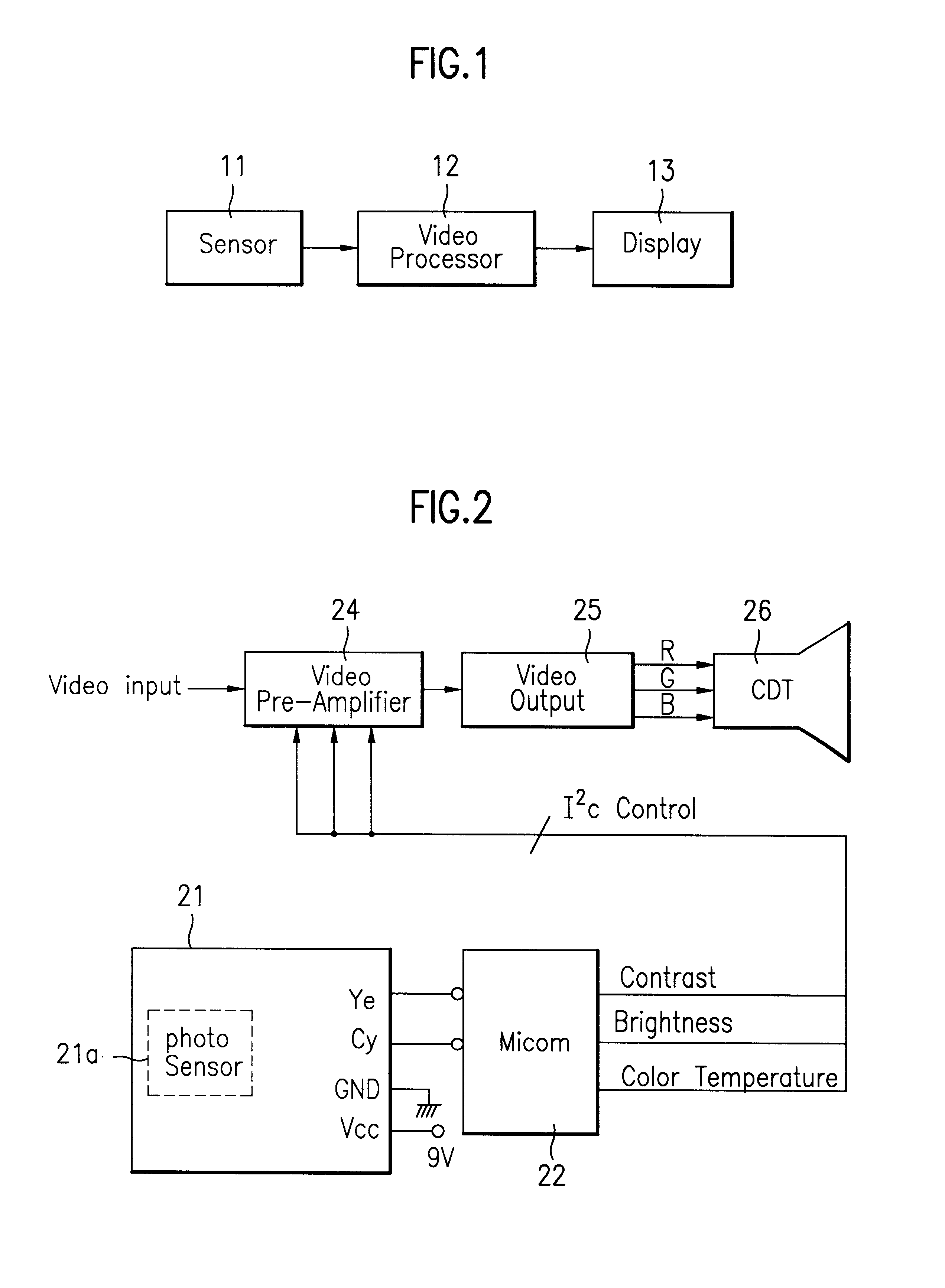
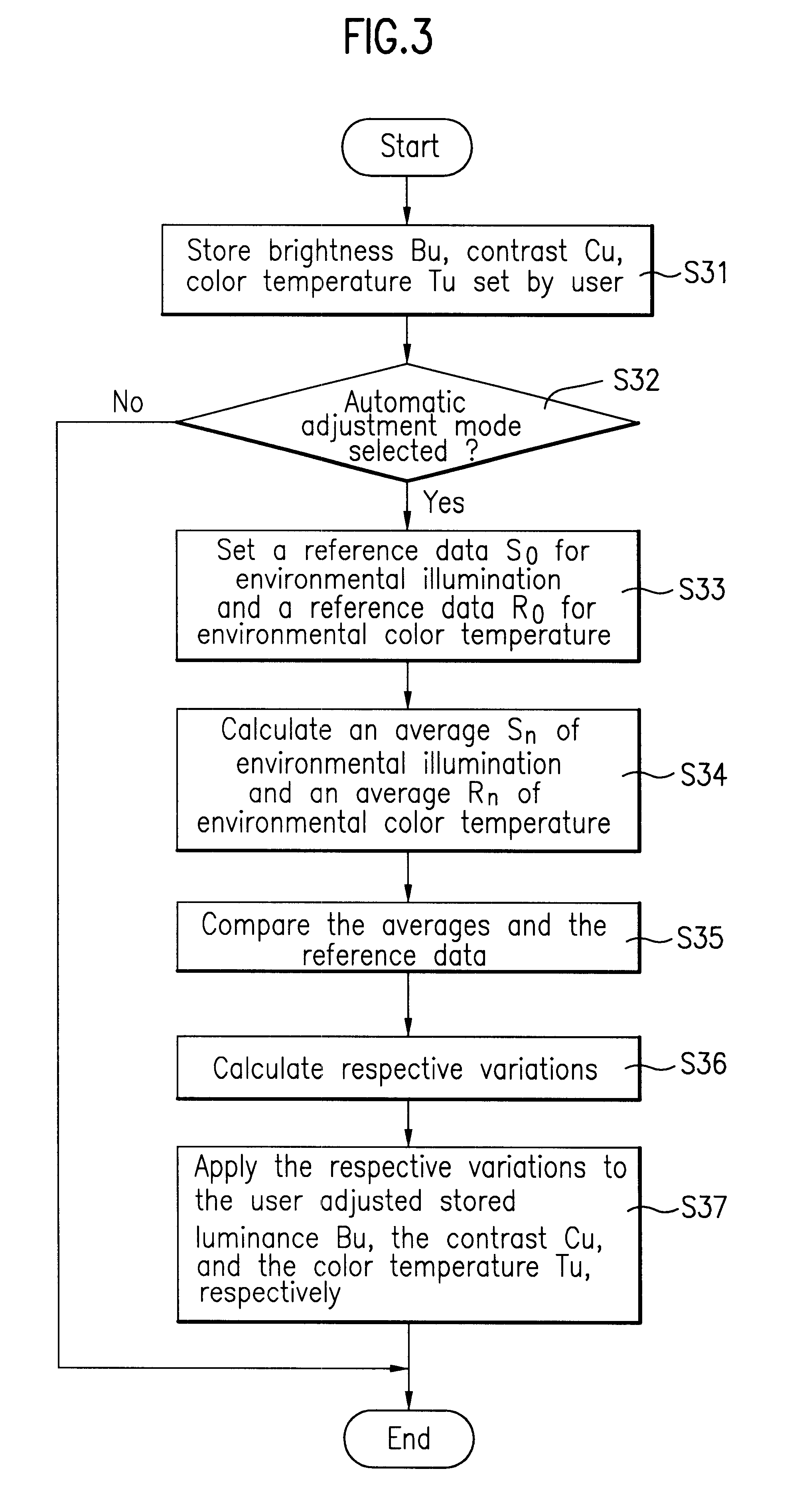
Device and method for auto-adjustment of image condition in display using data representing both brightness or contrast and color temperature
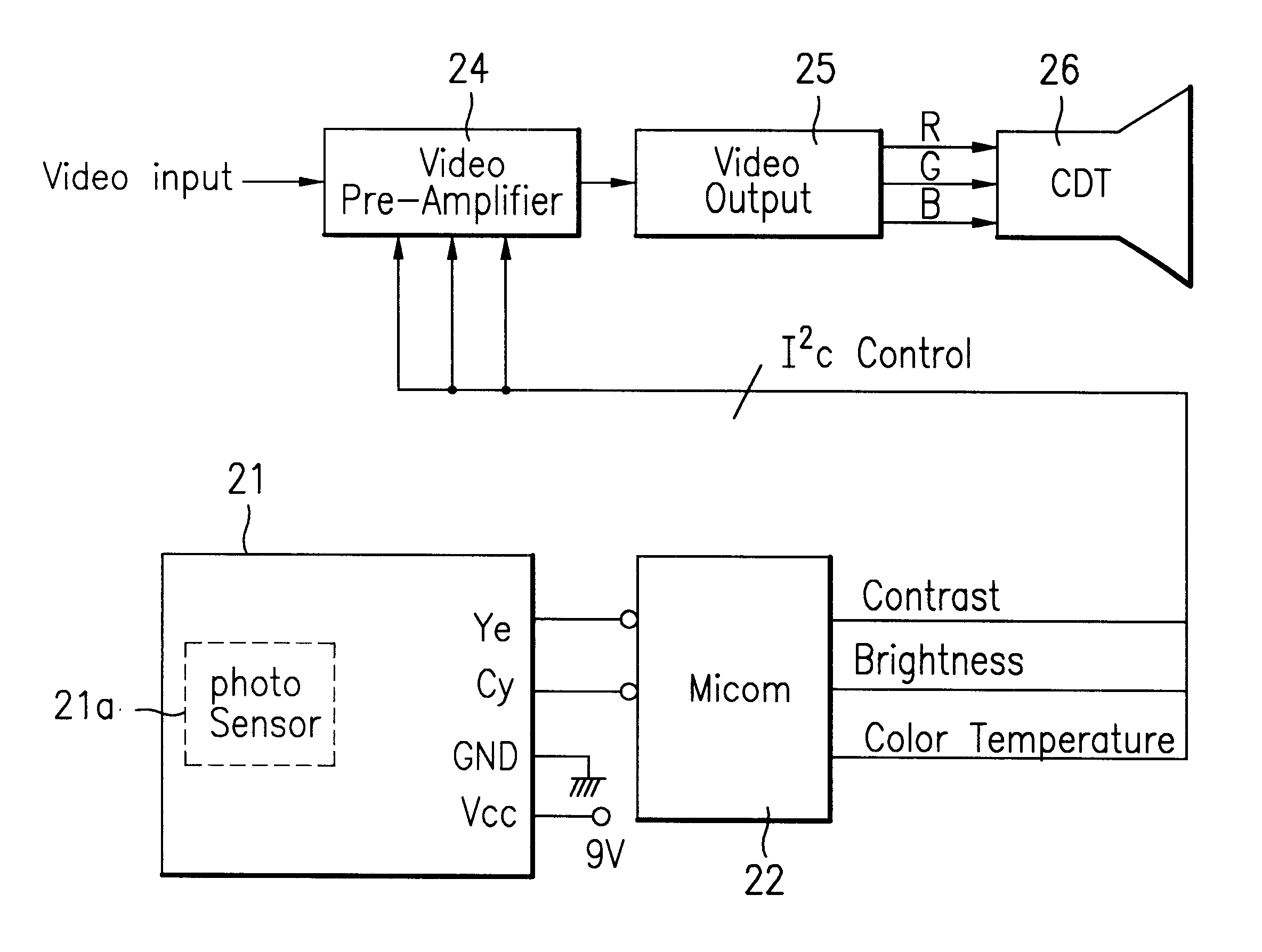
InactiveUS6292228B1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsImaging conditionDisplay device
A device and method for automatically adjusting an image condition in a display is, disclosed. The present device and method optimizes the image condition of a display according to individual preferences by taking into account the brightness and color temperature set initially by a user. Particularly, the present invention includes a photo sensor to detect the environmental illumination and a micro processor utilizing the detected data to appropriately adjust the image condition with respect to a user <CUSTOM-CHARACTER FILE="US06292228-20010918-P00001.TIF" ID="CUSTOM-CHARACTER-00001"> preference.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
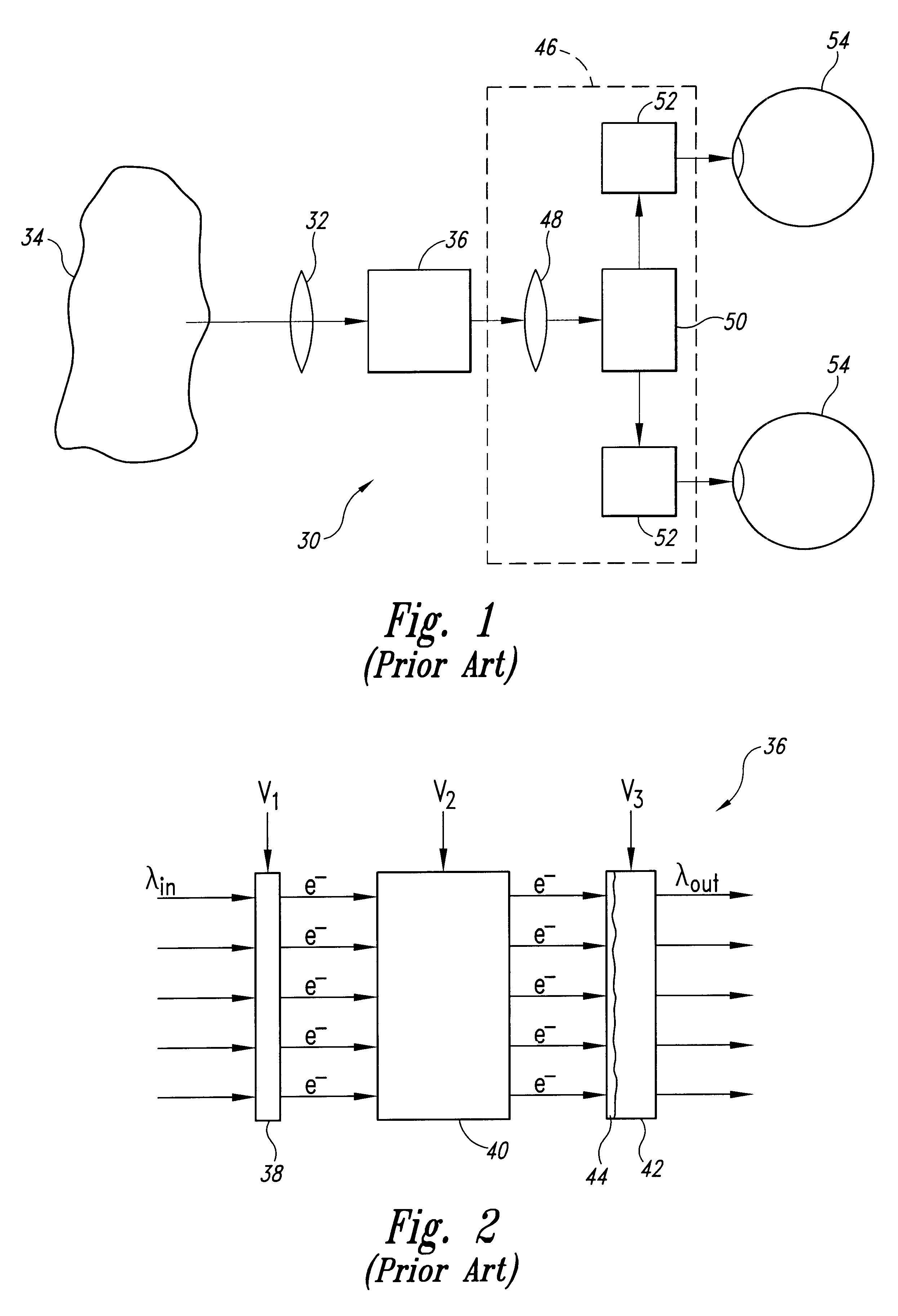
Compensating for the chromatic distortion of displayed images
A graphics system comprises pixel calculation units and a sample buffer which stores a two-dimensional field of samples. Each pixel calculation unit selects positions in the two-dimensional field at which pixel values (e.g. red, green, blue) are computed. The pixel computation positions are selected to compensate for image distortions introduced by a display device and / or display surface. Non-uniformities in a viewer's perceived intensity distribution from a display surface (e.g. hot spots, overlap brightness) are corrected by appropriately scaling pixel values prior to transmission to display devices. Two or more sets of pixel calculation units driving two or more display devices adjust their respective pixel computation centers to align the edges of two or more displayed images. Physical barriers prevent light spillage at the interface between any two of the display images. Separate pixel computation positions may be used for distinct colors to compensate for color distortions.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Multimode system for calibrating a data strobe delay for a memory read operation
InactiveUS6889334B1Allow in applicationAllow in useElectronic circuit testingCode conversionComputer moduleMemory controller
A system for coordinating the timing of a data strobe with data supplied by a memory module to the memory controller read data FIFO of a processor-based system, providing multiple calibration modes. A calibration PDL (programmable delay line) is used to reiteratively test the time taken for a test data strobe to traverse a portion of the memory controller circuit, and to generate a calibration value based upon the time taken. The calibration procedure may be initiated in any one of several modes, including: according to a predetermined schedule; implemented in software; in response to changes in environmental factors such as temperature or voltages sampled at one or more locations; in response to a software-driven trigger; or in response to a user-initiated trigger, communicated to a system of the invention either by input via a user interface to the processor-based system or by a software command.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Method and system for calibrating projectors to arbitrarily shaped surfaces with discrete optical sensors mounted at the surfaces
InactiveUS20050030486A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDisplay deviceOptical coupling
A system determines correspondence between locations on a display surface and pixels in an output image of a projector. The display surface can have an arbitrary shape and pose. Locations with know coordinates are identified on the display surface. Each location is optically coupled to a photo sensor by an optical fiber installed in a throughhole in the surface. Known calibration patterns are projected, while sensing directly an intensity of light at each location for each calibration pattern. The intensities are used to determine correspondences between the of locations and pixels in an output image of the projector so that projected images can warped to conform to the display surface.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC INFORMATION TECH CENT AMERICA ITA
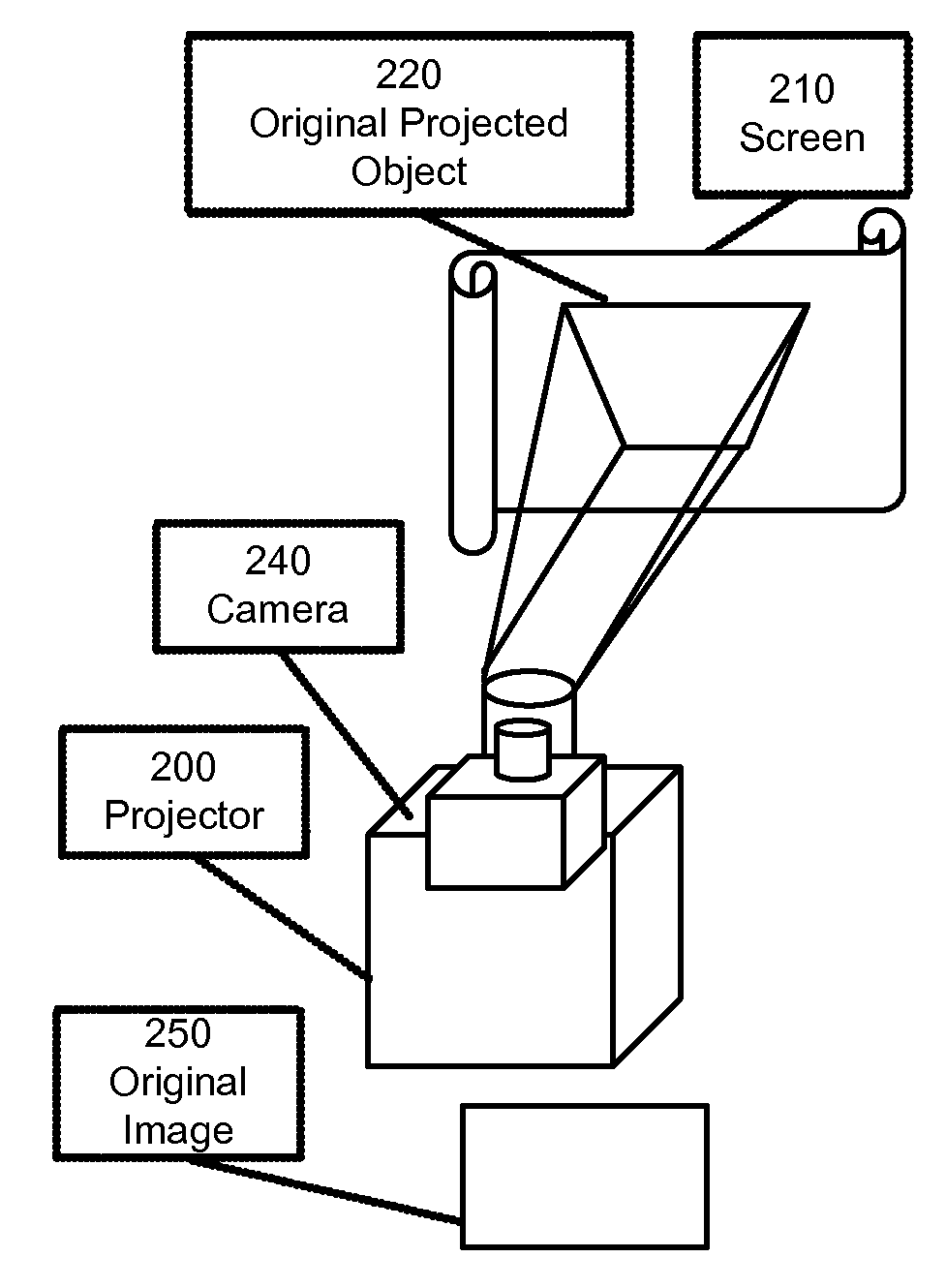
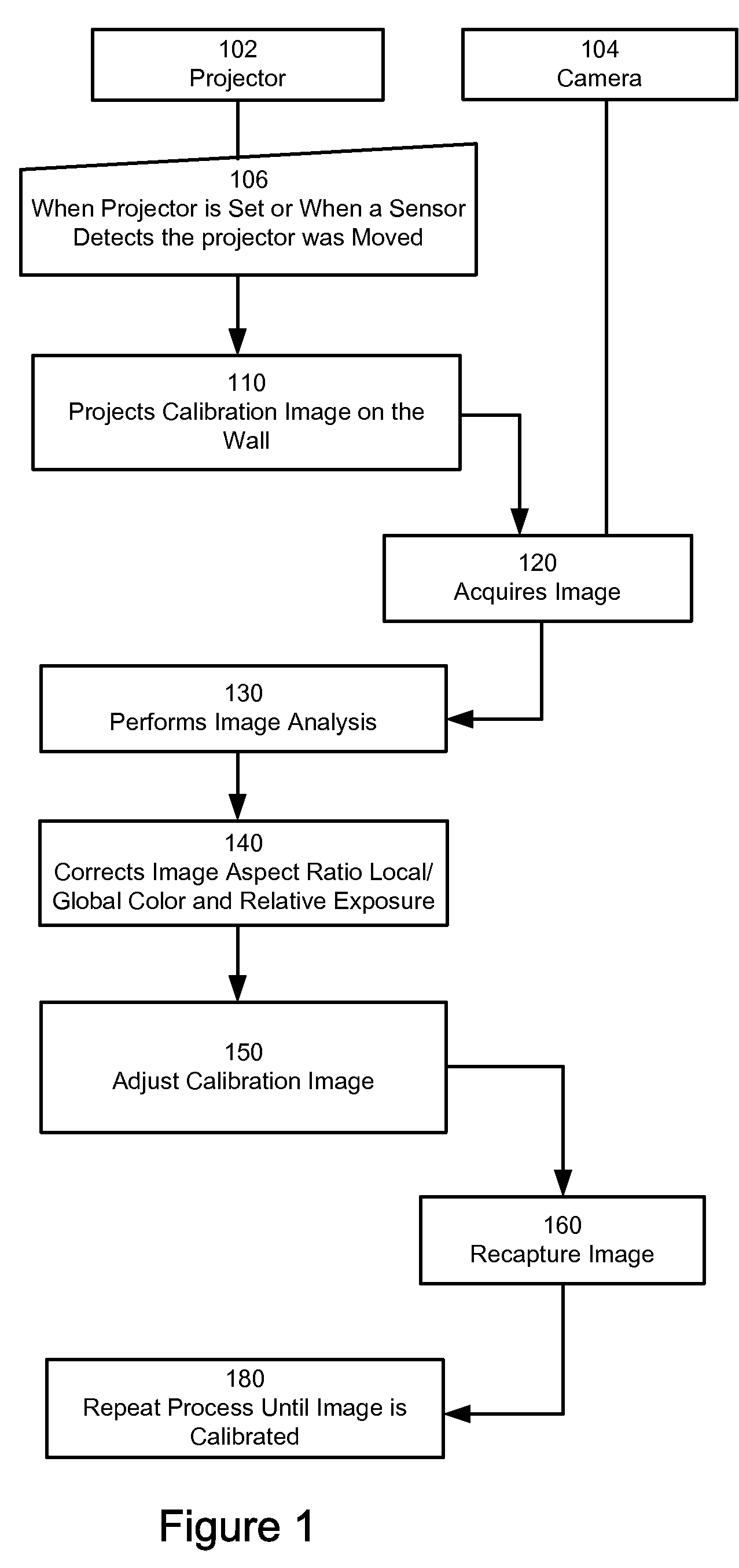
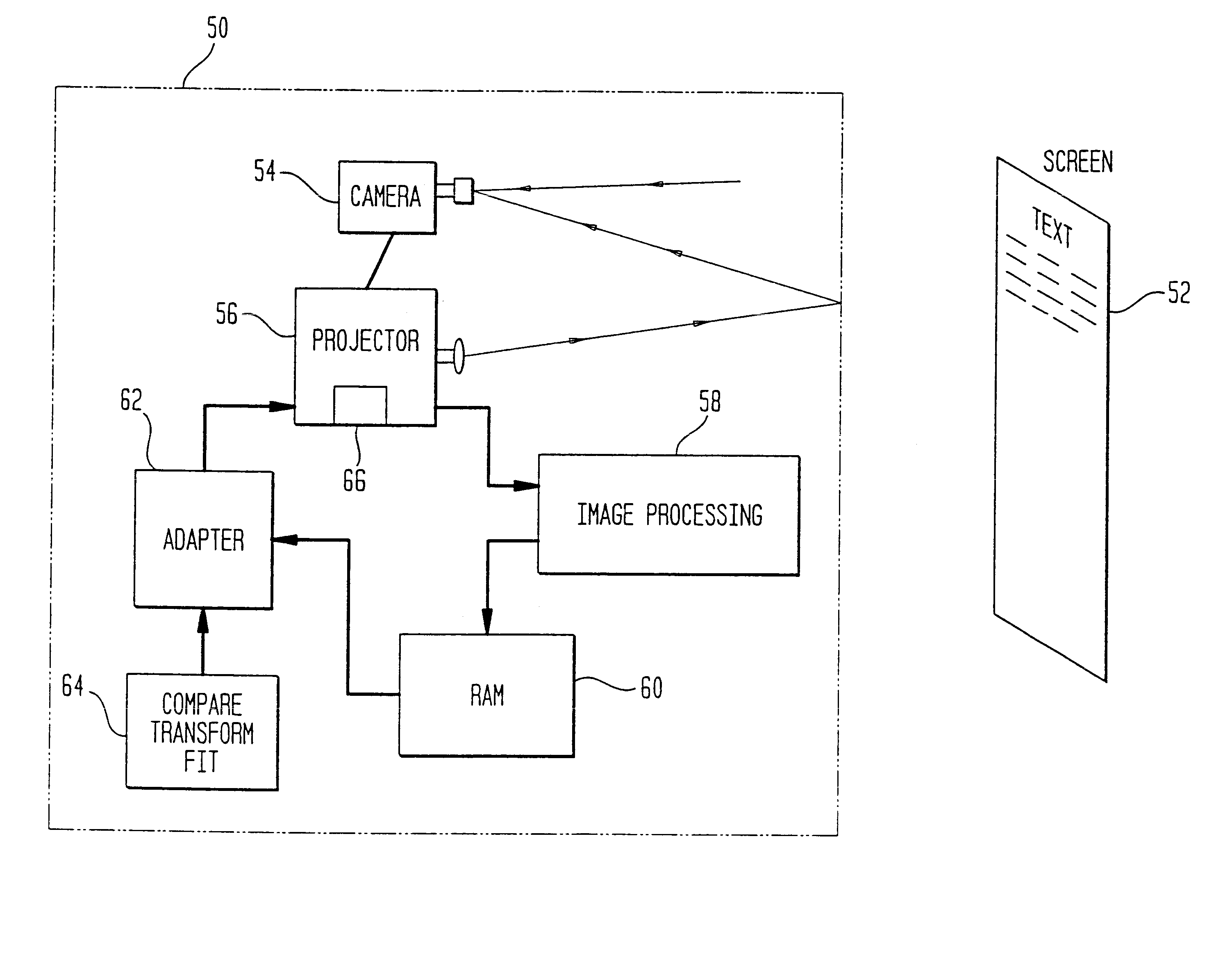
Camera Based Feedback Loop Calibration of a Projection Device
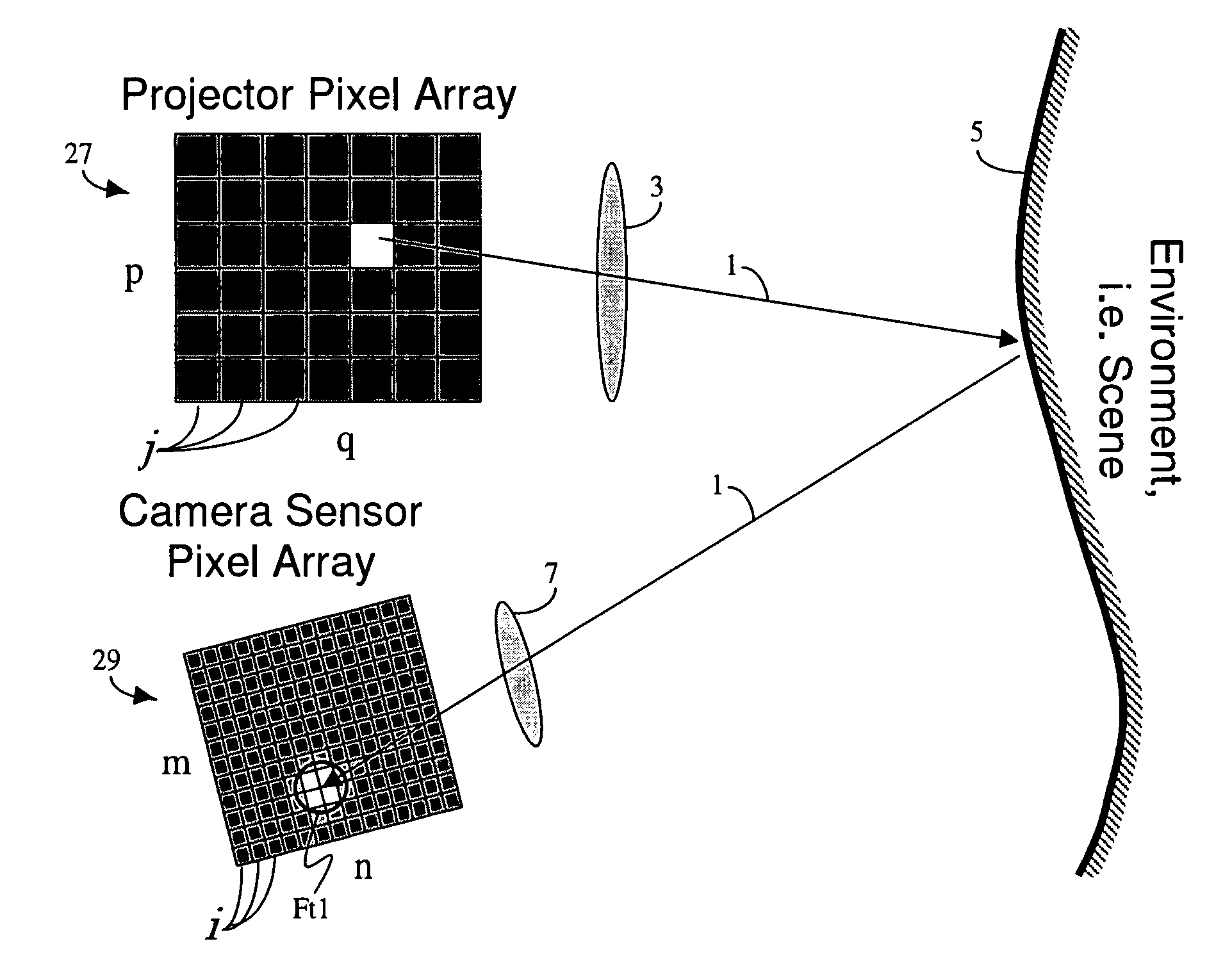
InactiveUS20090115915A1Television system scanning detailsPulse generatorComputer visionDigital image
A system is provided for projecting a calibrated image. The system includes a projector to project an uncalibrated image. A processor-based digital image acquisition device is in communication with the projector and is disposed to acquire the projected, uncalibrated image. The device is also programmed to compensate for one or more parameters of viewing quality, and to communicate calibration information to the projector to project a first calibrated image.
Owner:DIGITALPTICS EURO
Method and system for calibrating projectors to arbitrarily shaped surfaces with discrete optical sensors mounted at the surfaces
InactiveUS7001023B2Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsOptical couplingPhysics
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC INFORMATION TECH CENT AMERICA ITA
Resolution Scalable View Projection
InactiveUS20100245684A1Simplified generationEasy to useTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsProjection imageImage resolution
A projection system uses a transformation matrix to transform a projection image p in such a manner so as to compensate for surface irregularities on a projection surface. The transformation matrix makes use of properties of light transport relating a projector to a camera. If the resolution a camera is lower than that of a projector within said projection system, then the transformation matrix will have holes where image data corresponding to a projector pixel will have been lost. In this, case, new image are generated to fill-in the holes.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Scanned beam display
A display apparatus includes first and second IR or other light sources that produce light at respective first and second non-visible wavelengths. The light is modulated according to a desired image. The modulated light is then applied to a wavelength selective phosphor that converts each component of the light to a respective visible wavelength. In one embodiment, the image source is a scanned light beam display that scans an IR light beam onto a screen that carries the phosphor.
Owner:MICROVISION
Matching the edges of multiple overlapping screen images
A graphics system comprises pixel calculation units and a sample buffer which stores a two-dimensional field of samples. Each pixel calculation unit selects positions in the two-dimensional field at which pixel values (e.g. red, green, blue) are computed. The pixel computation positions are selected to compensate for image distortions introduced by a display device and / or display surface. Non-uniformities in a viewer's perceived intensity distribution from a display surface (e.g. hot spots, overlap brightness) are corrected by appropriately scaling pixel values prior to transmission to display devices. Two or more sets of pixel calculation units driving two or more display devices adjust their respective pixel computation centers to align the edges of two or more displayed images. Physical barriers prevent light spillage at the interface between any two of the display images. Separate pixel computation positions may be used for distinct colors to compensate for color distortions.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
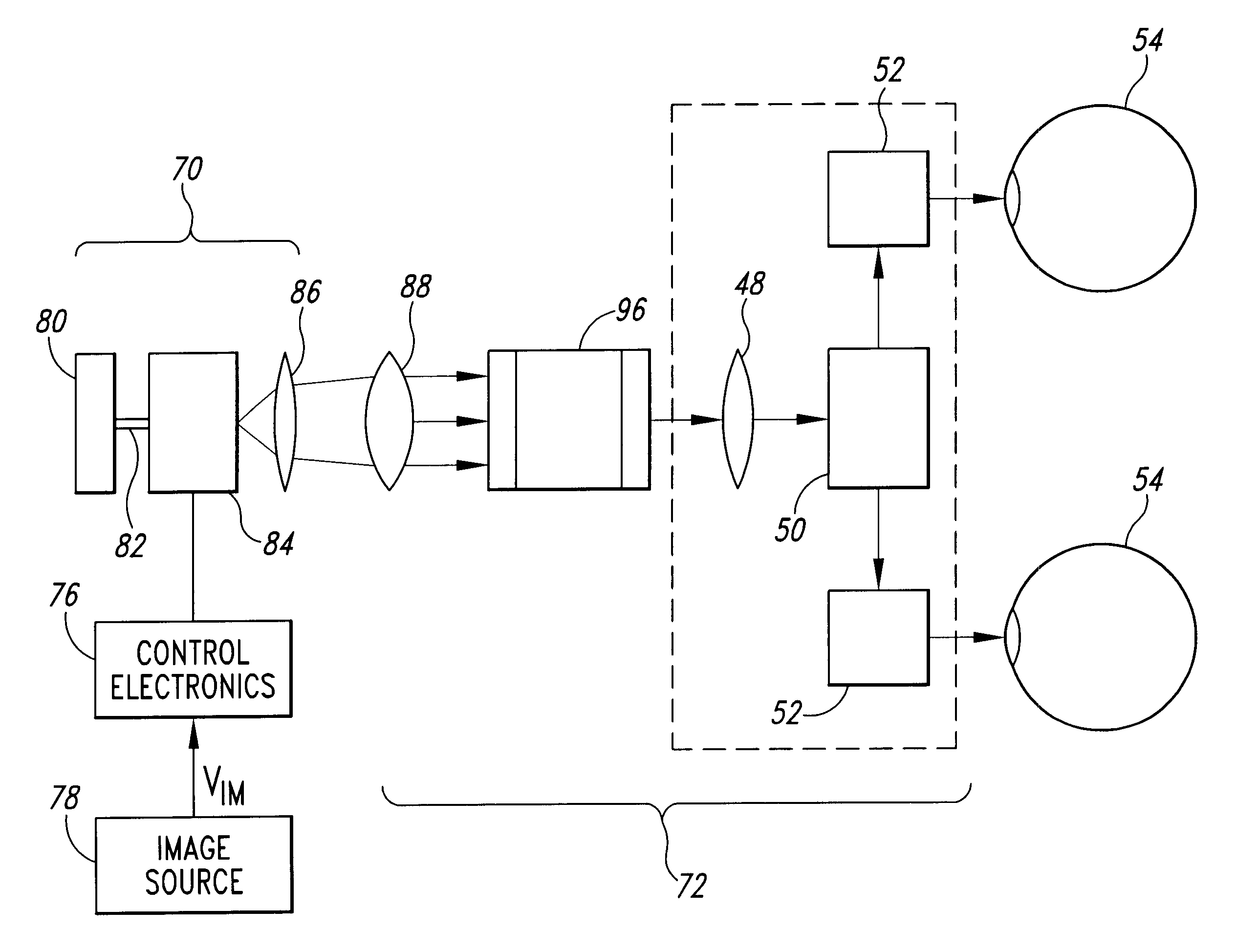
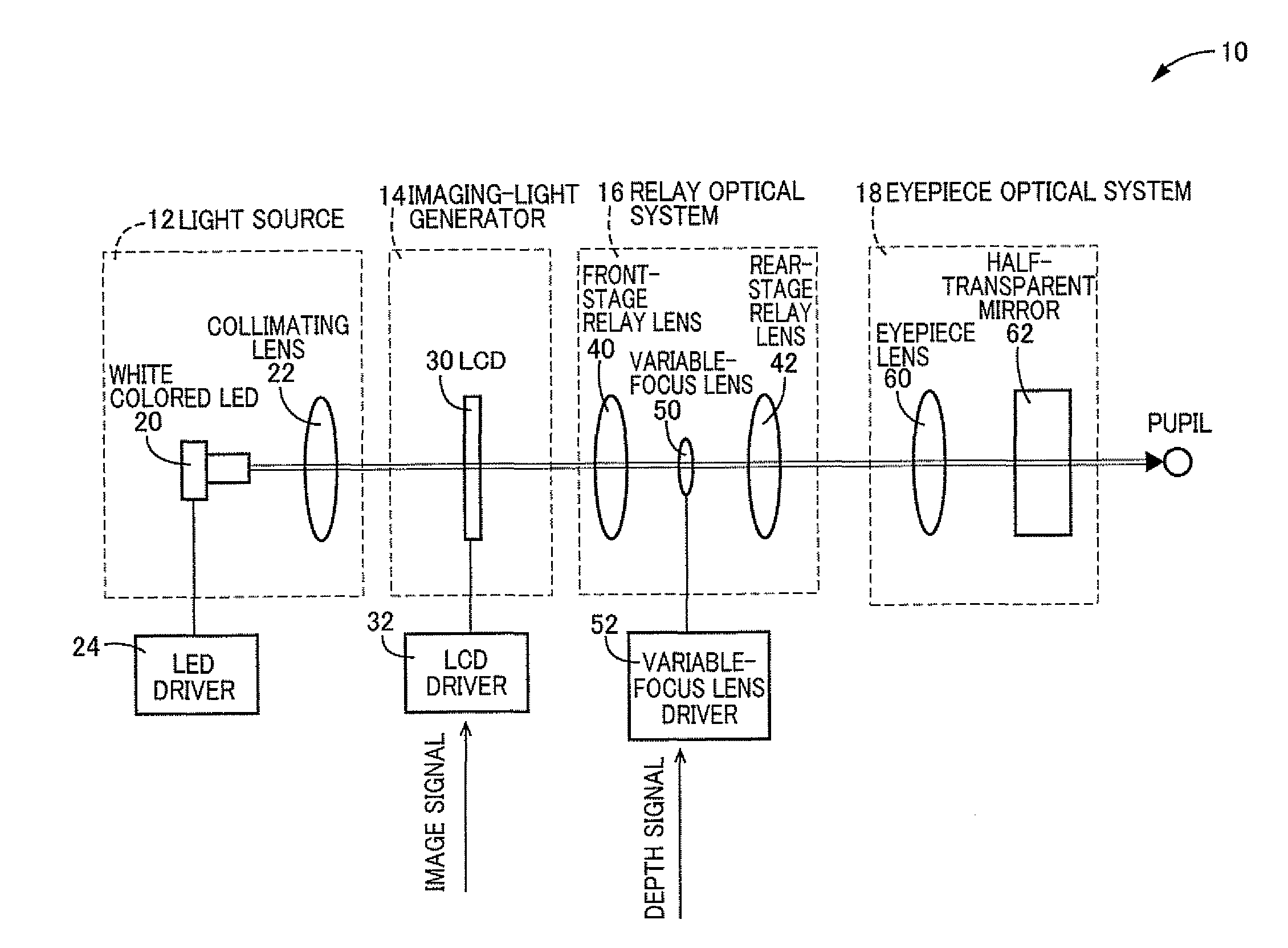
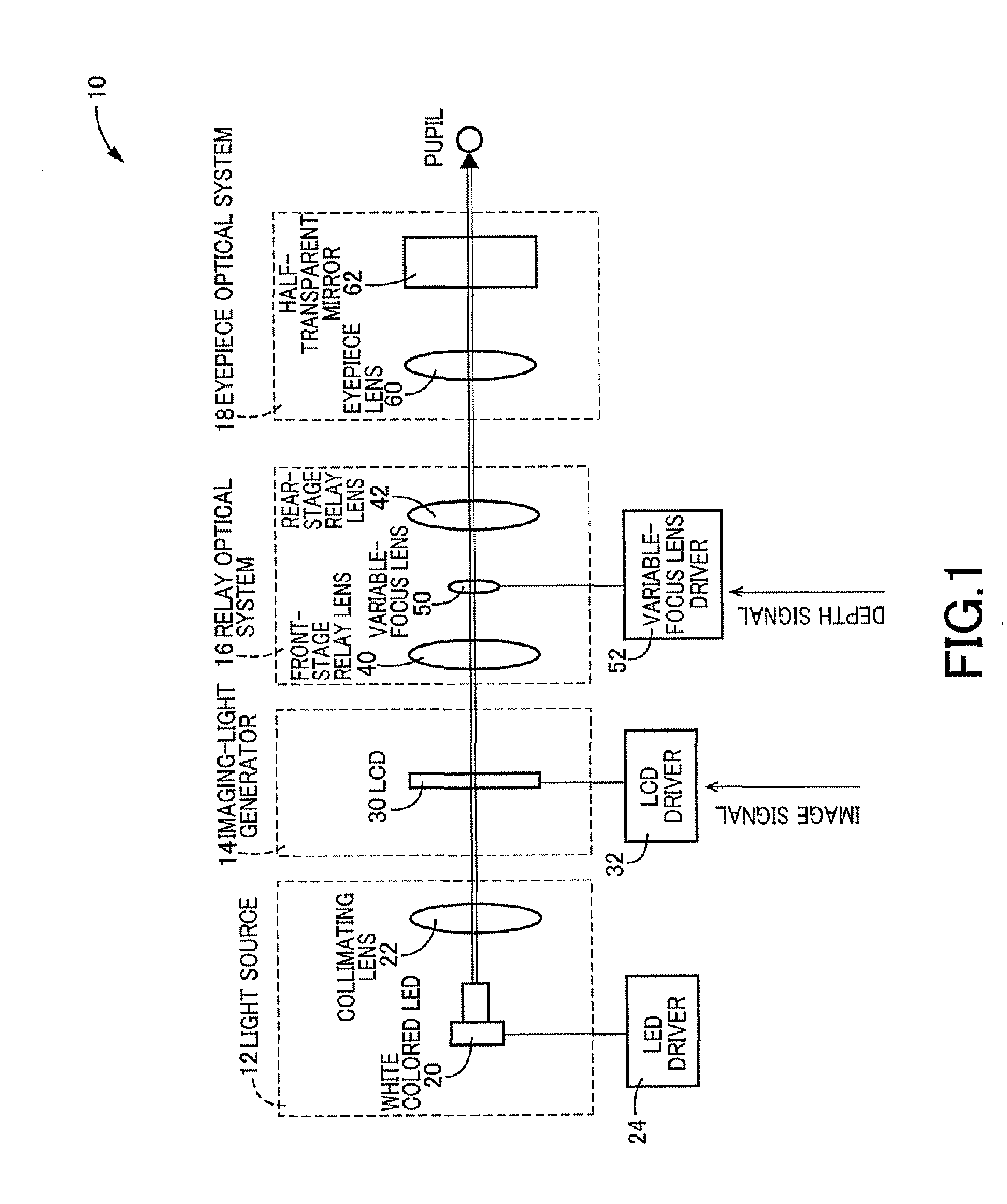
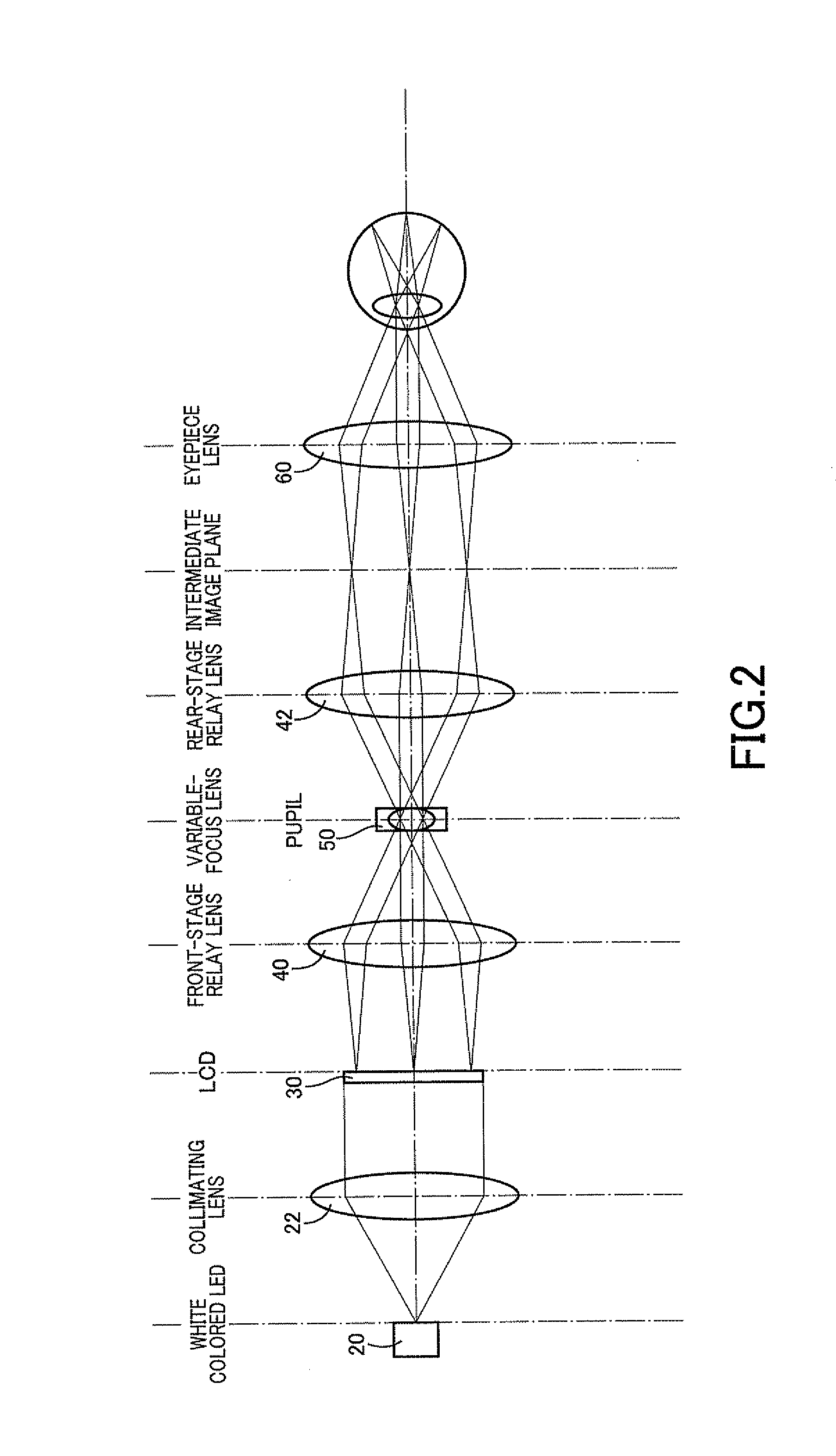
Image display device using variable-focus lens at conjugate image plane
An image display device for optically displaying an image is disclosed. This device includes: a light source; an imaging-light generator converting light emitted from the light source, into imaging light representative of the image to be displayed, to thereby generate the imaging light; a relay optical system focusing the imaging light emitted from the imaging-light generator, on an image plane which is located at an optically conjugate position to the imaging-light generator, the relay optical system defining a pupil through which the imaging light passes, within the relay optical system; a variable-focus lens disposed at a position generally coincident with the pupil, the variable-focus lens having a varying focal length; and a wavefront-curvature adjuster configured to vary the focal length by operating the variable-focus lens, to thereby adjust a wavefront curvature of the imaging light emitted from the relay optical system.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
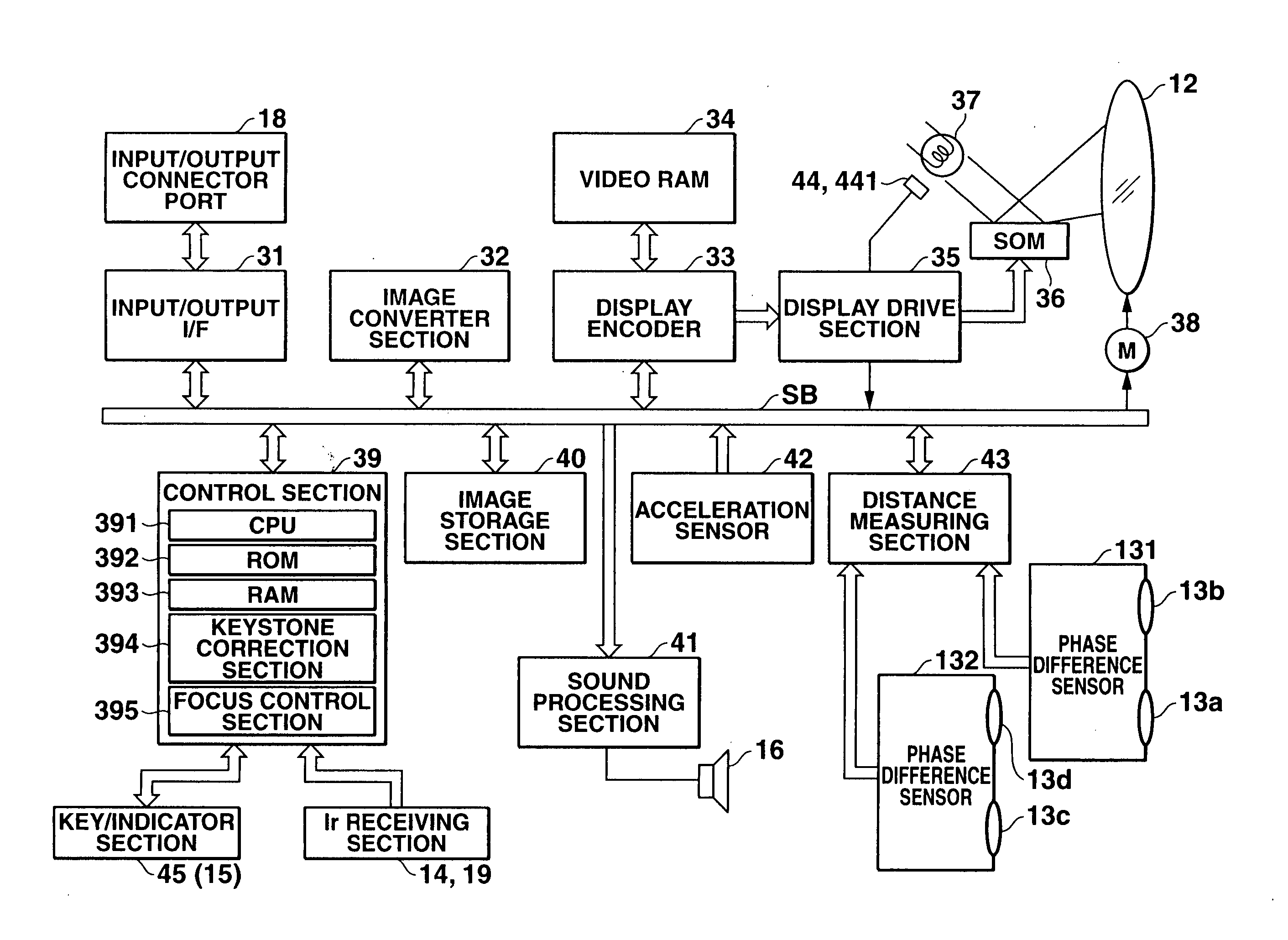
Projection apparatus, projection method and recording medium recording the projection method
ActiveUS20050046803A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsProjection imageImage formation
A projection apparatus comprising a projection section for projecting an image corresponding to an input image signal, a distance measuring section for measuring each distance of several positions on an image projection plane made by the projection section, a focus control section for making keystone correction on an image projected by the projection section so that a projection image is formed into a rectangular shape having a proper aspect ratio based on each distance obtained by the distance measuring section while controlling a focus position of the image projected by the projection section, and a control section for instructing to carry out processing by the focus control section.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
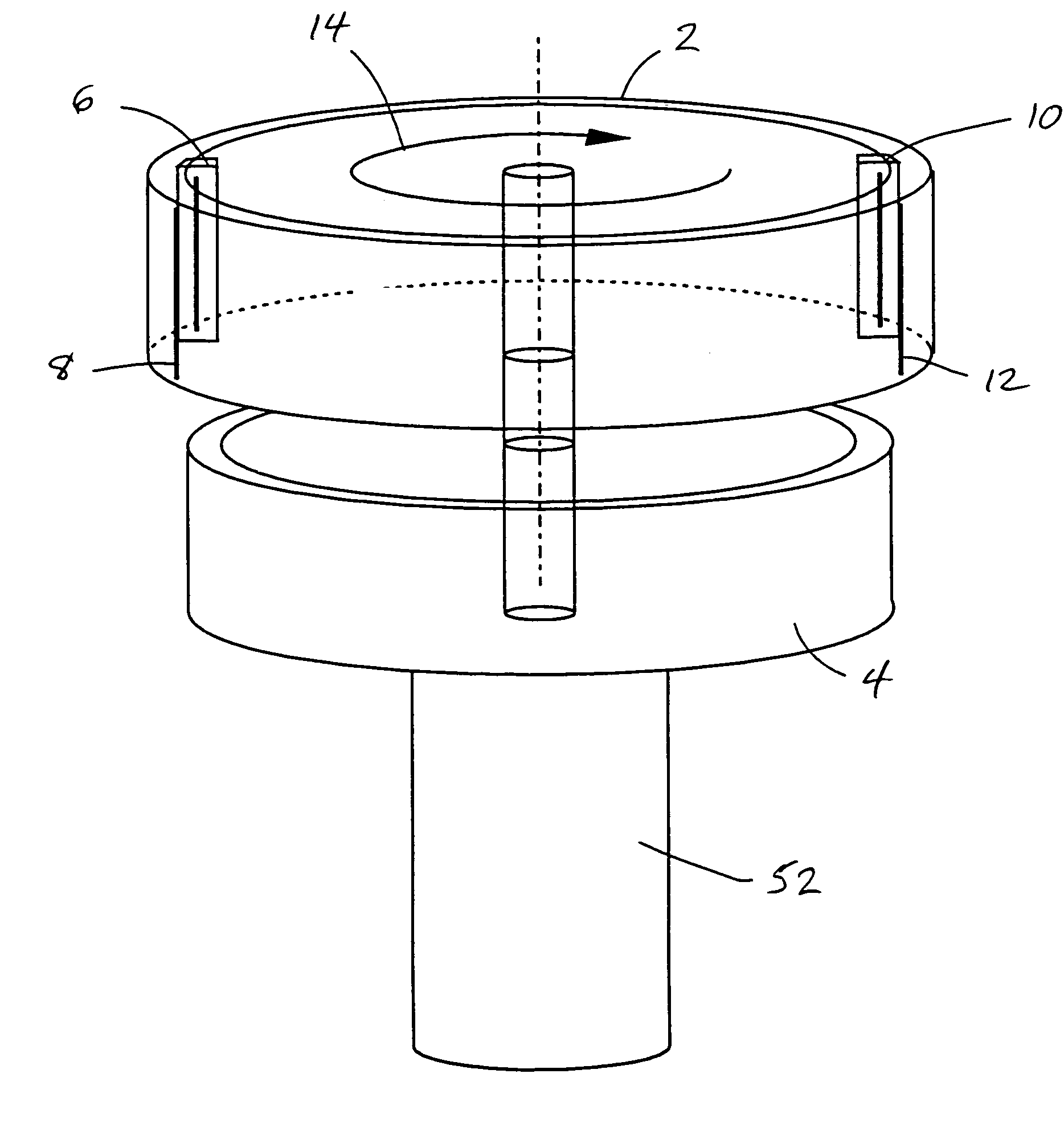
Shift register and image display apparatus using the same
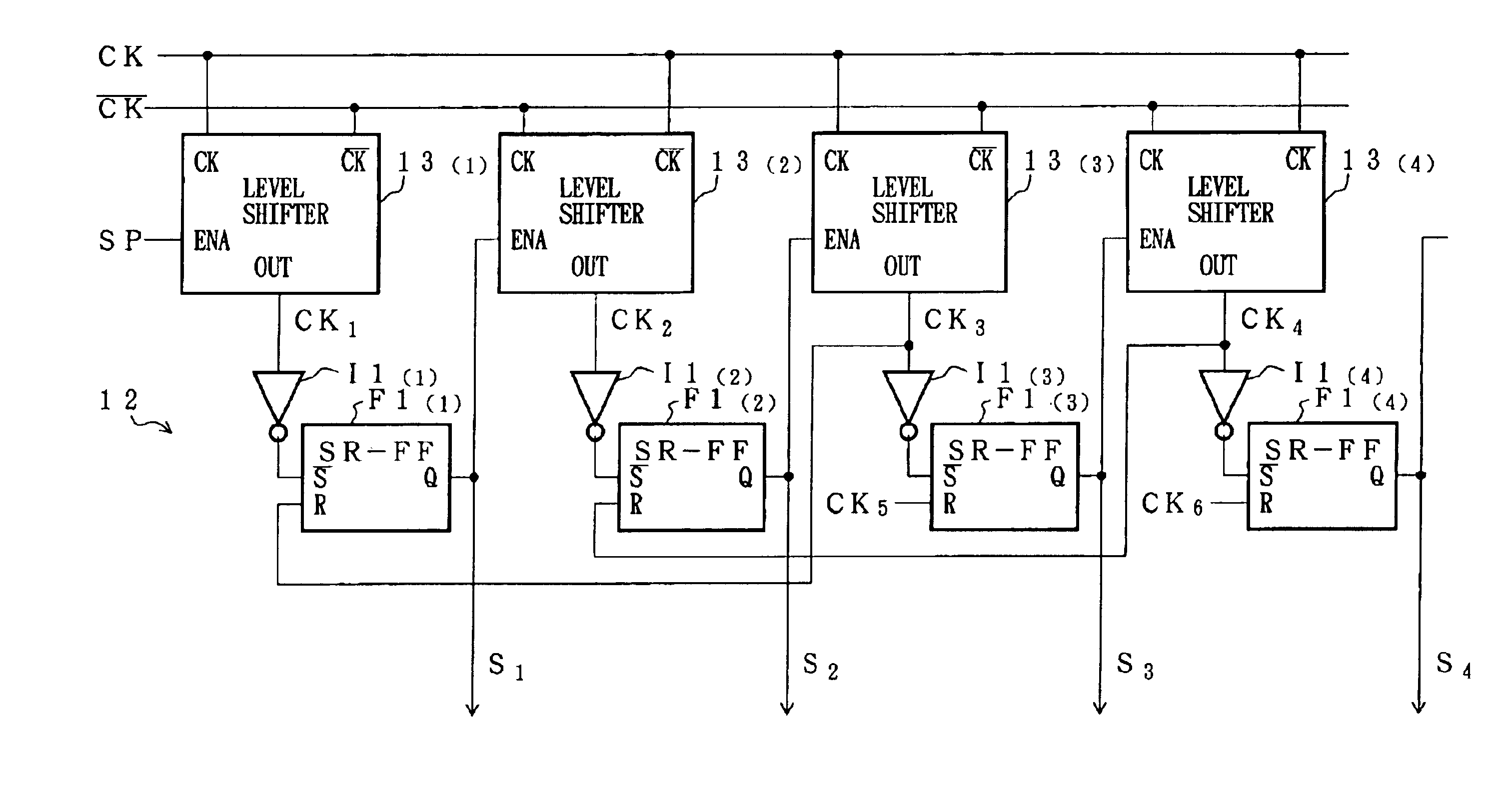
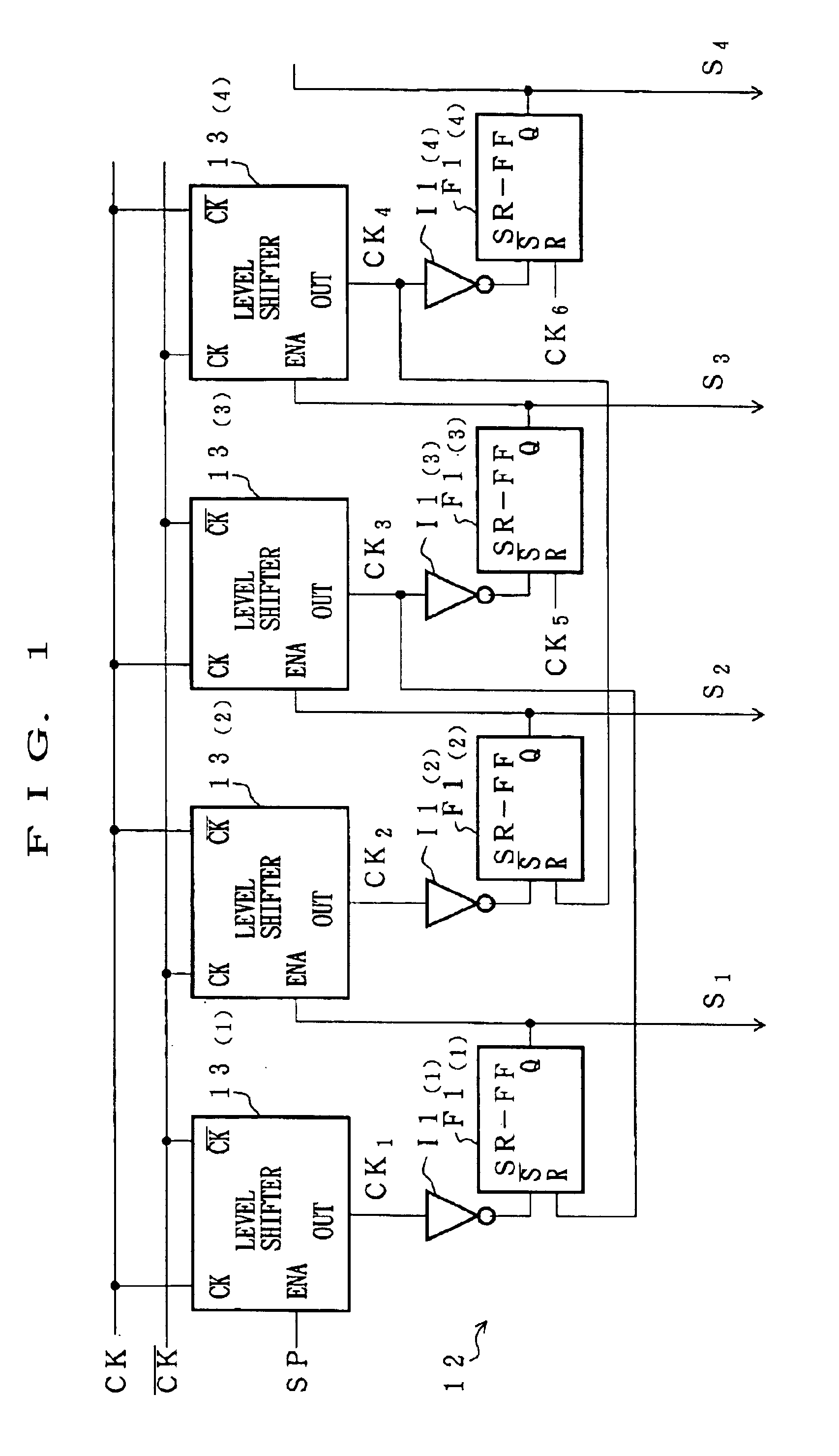
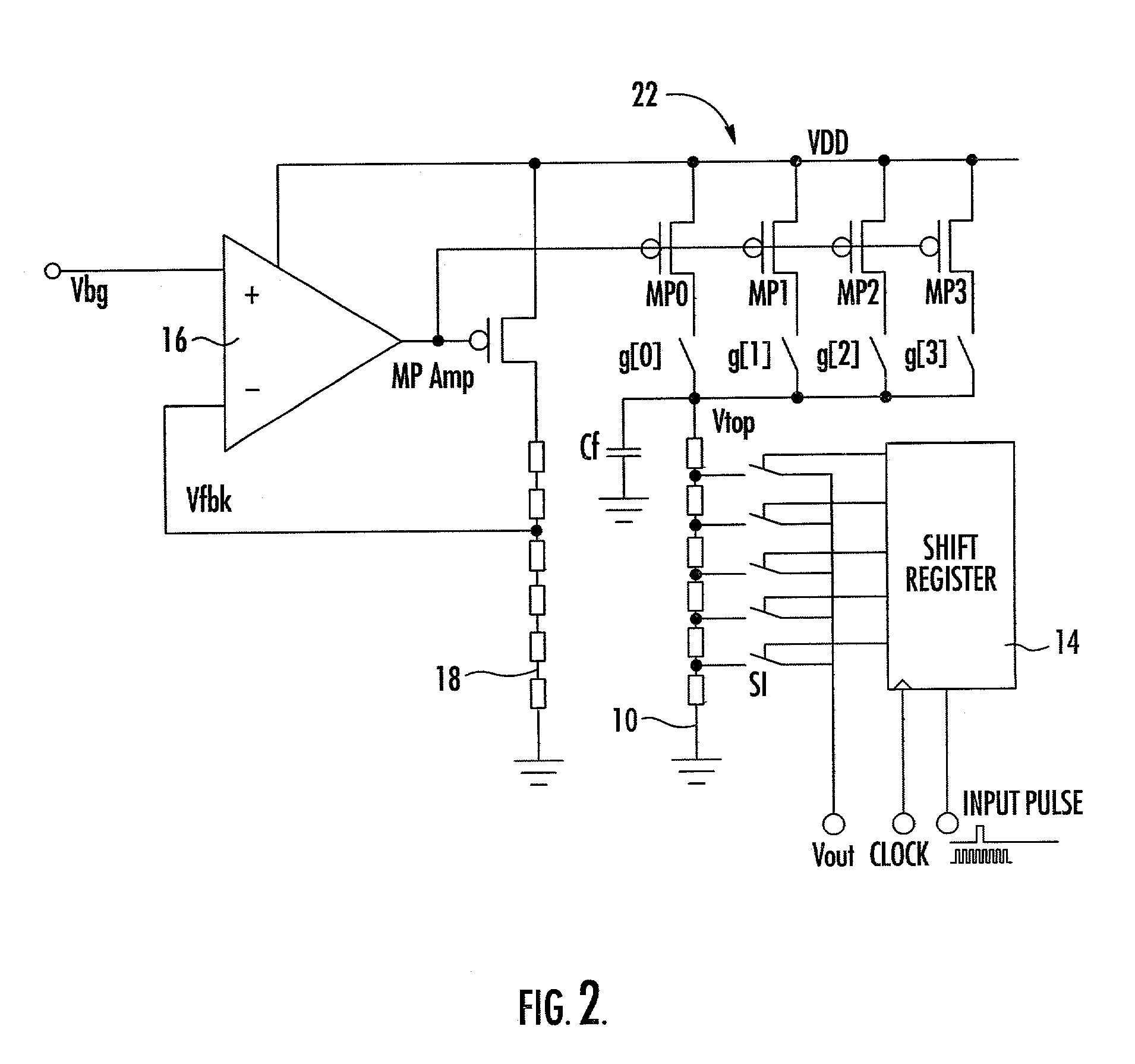
InactiveUS6909417B2Reduce distanceReduce load capacityPulse generatorPulse automatic controlShift registerEngineering
A level shifter 13 is provided for each of SR flip flops F1 constituting a shift register 11. The level shifter 13 increases a voltage of a clock signal CK. This arrangement reduces a distance for transmitting a clock signal whose voltage has been increased, as compared with a construction in which a voltage of a clock signal is increased by a single level shifter and the signal is transmitted to each of the flip flops; consequently, a load capacity of the level shifter can be smaller. Furthermore, each of the level shifters is operated during a pulse output of the previous level shifter 13, and the operation is suspended at the end of the pulse output. Thus, the level shifters 13 can operate only when it is necessary to apply a clock signal CK to the corresponding SR flip flop F1. As a result, even when an amplitude of a clock signal is small, it is possible to reduce power consumption of the shift resister under normal operation.
Owner:SHARP KK
Matching the edges of multiple overlapping screen images
InactiveUS7079157B2Large latency of a frame buffer may be avoidedSignificant latencyImage enhancementImage analysisGraphicsGraphic system
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
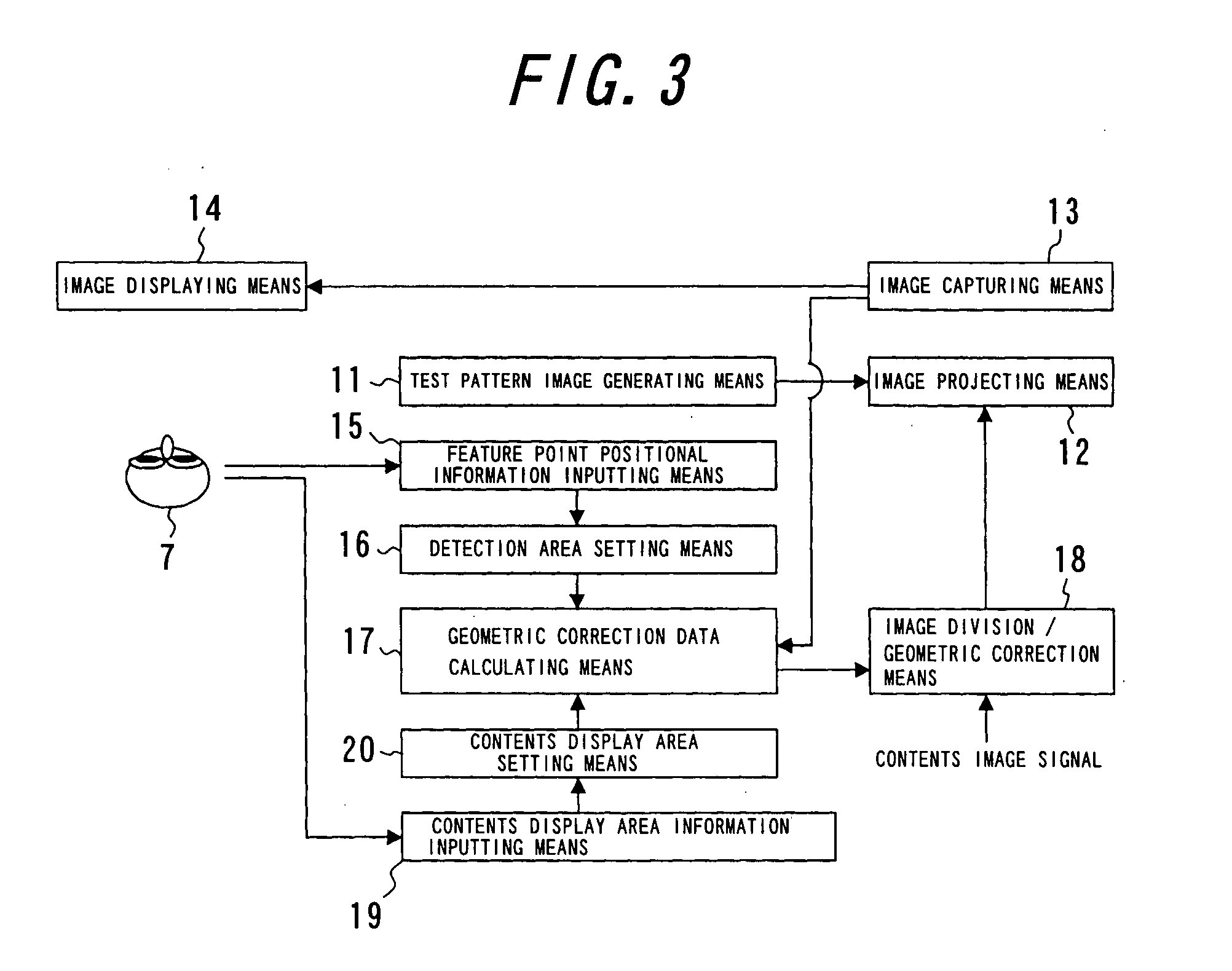
Geometric Correction Method in Multi-Projection System
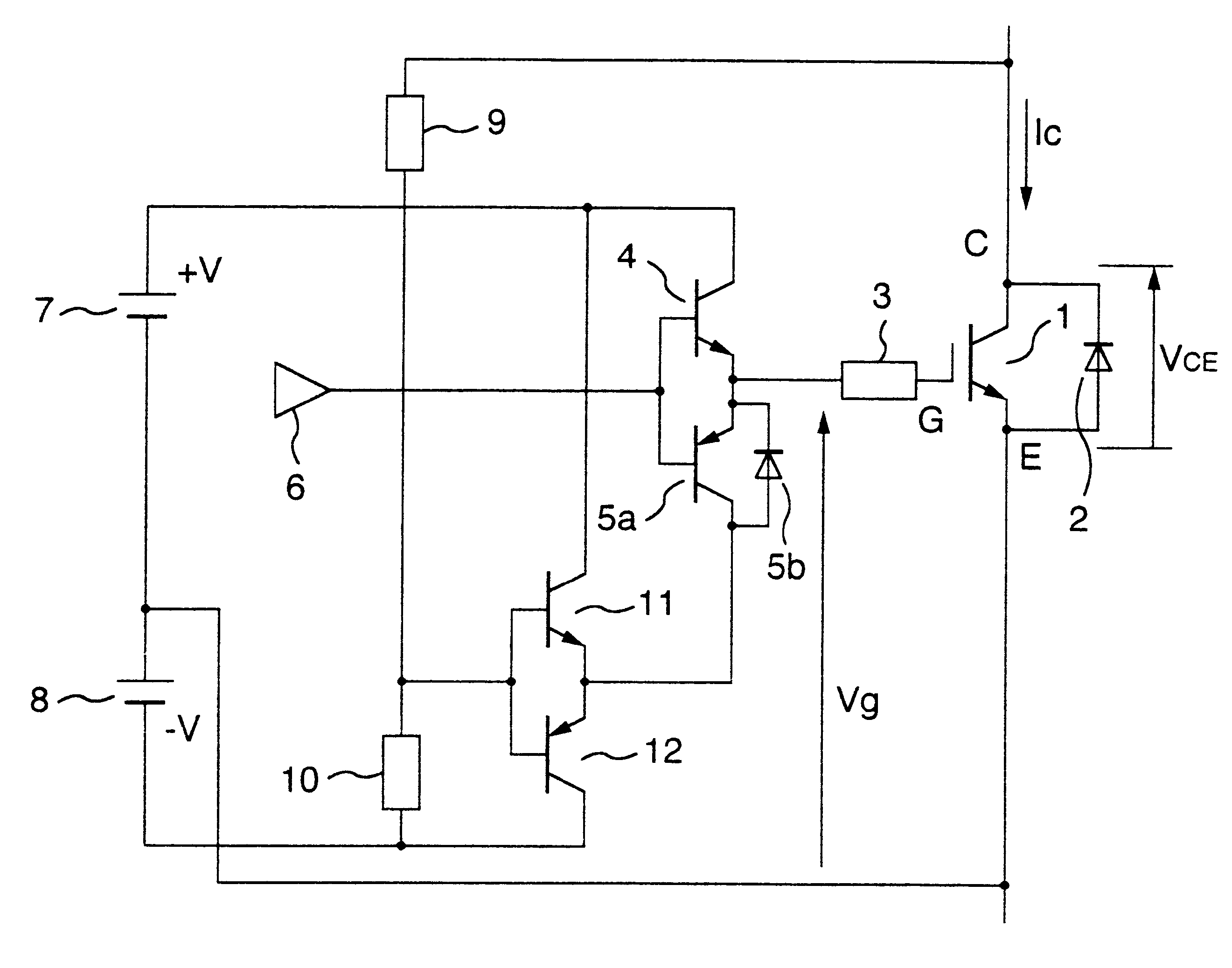
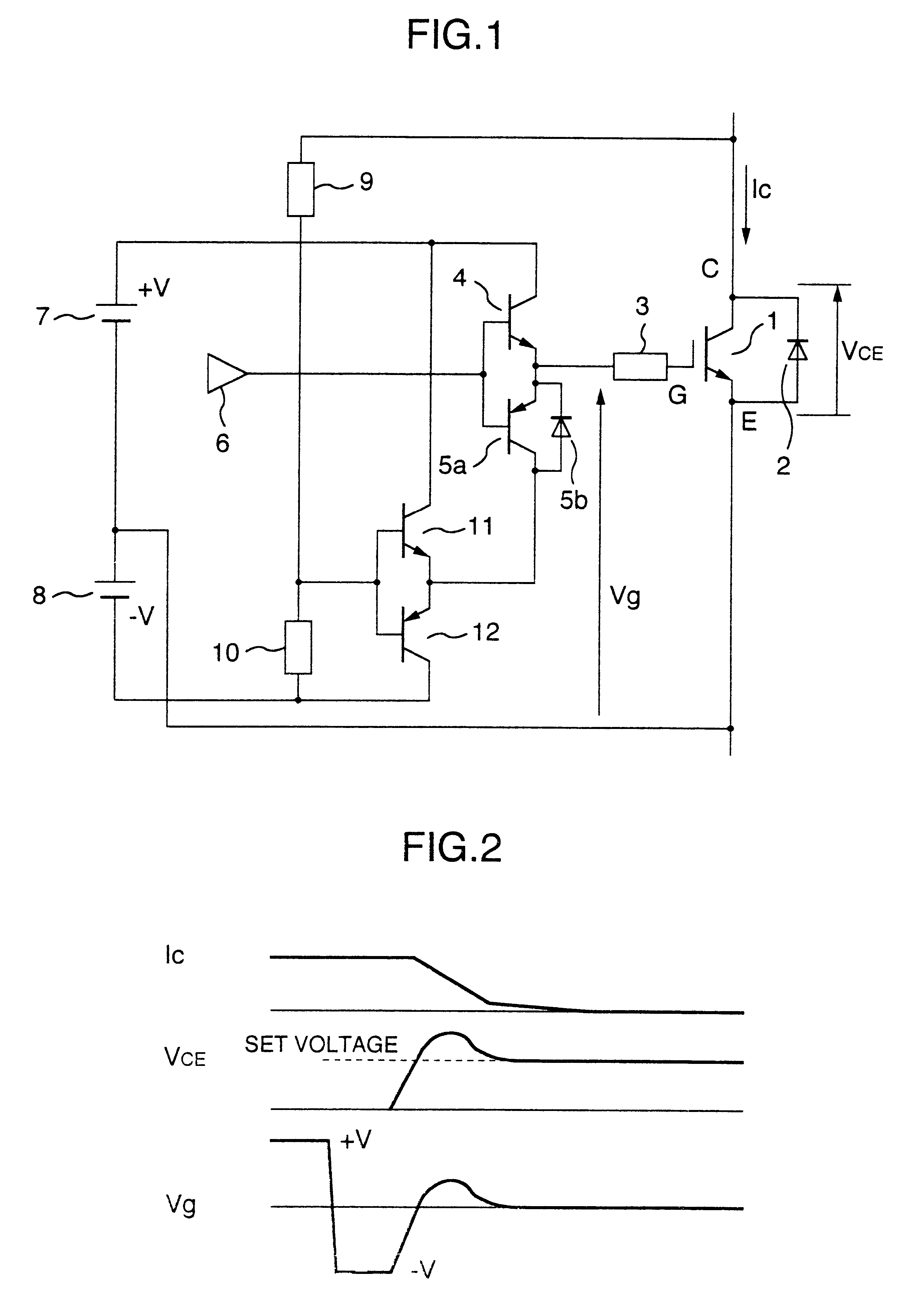
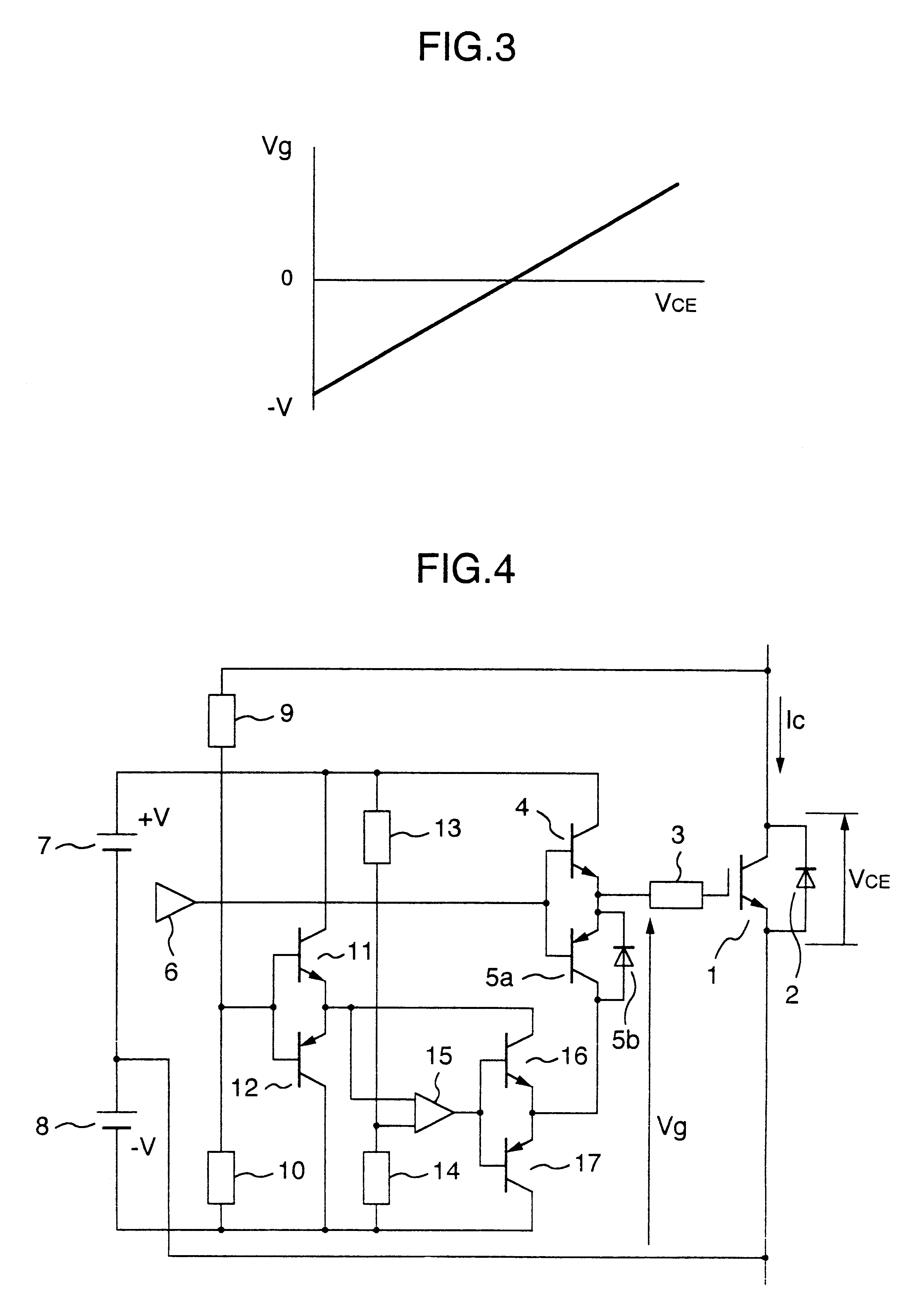
InactiveUS20080136976A1Simply and accurately carriedSimplified and convenient operationTelevision system scanning detailsPulse generatorImage correctionProjection system
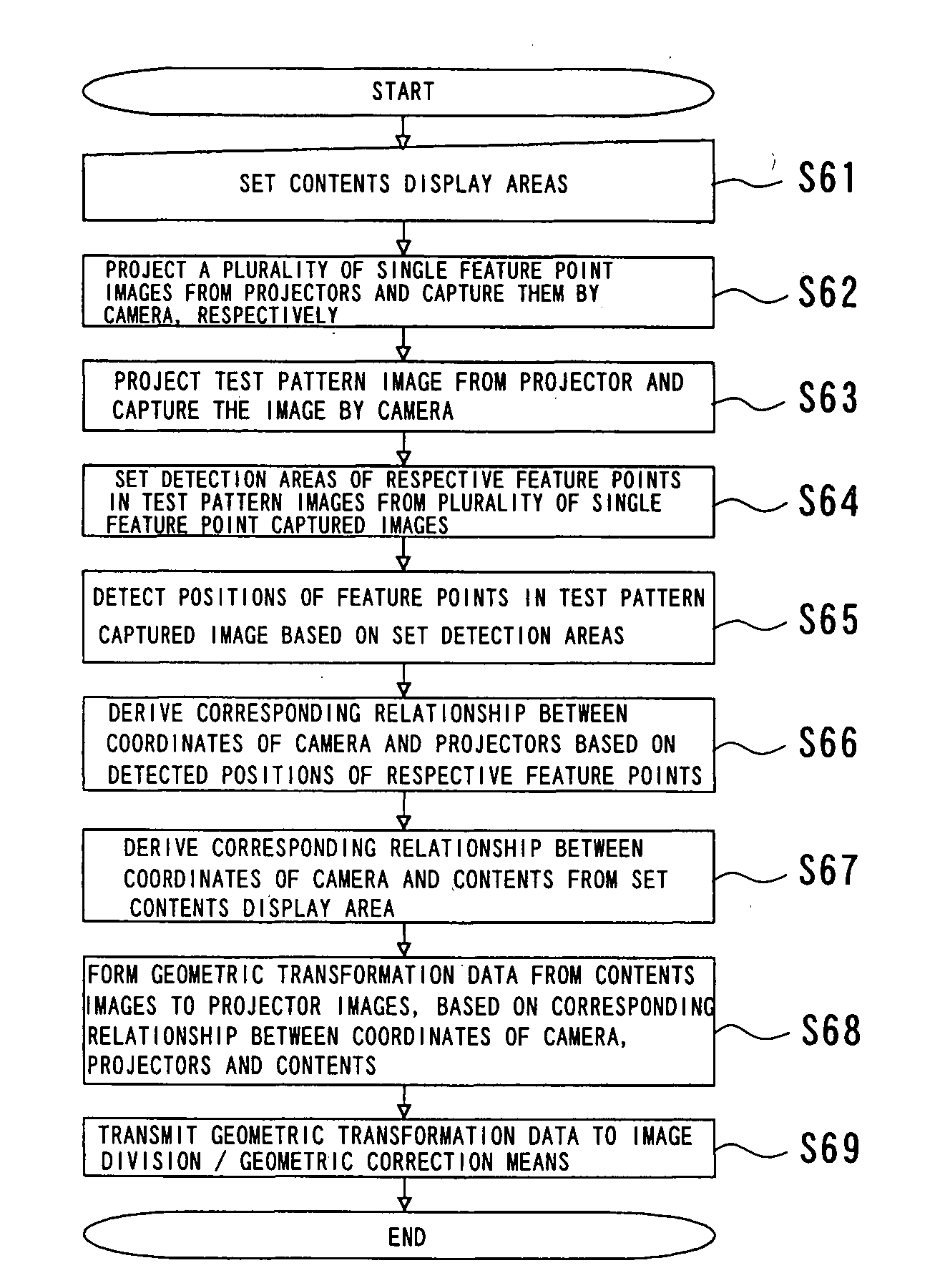
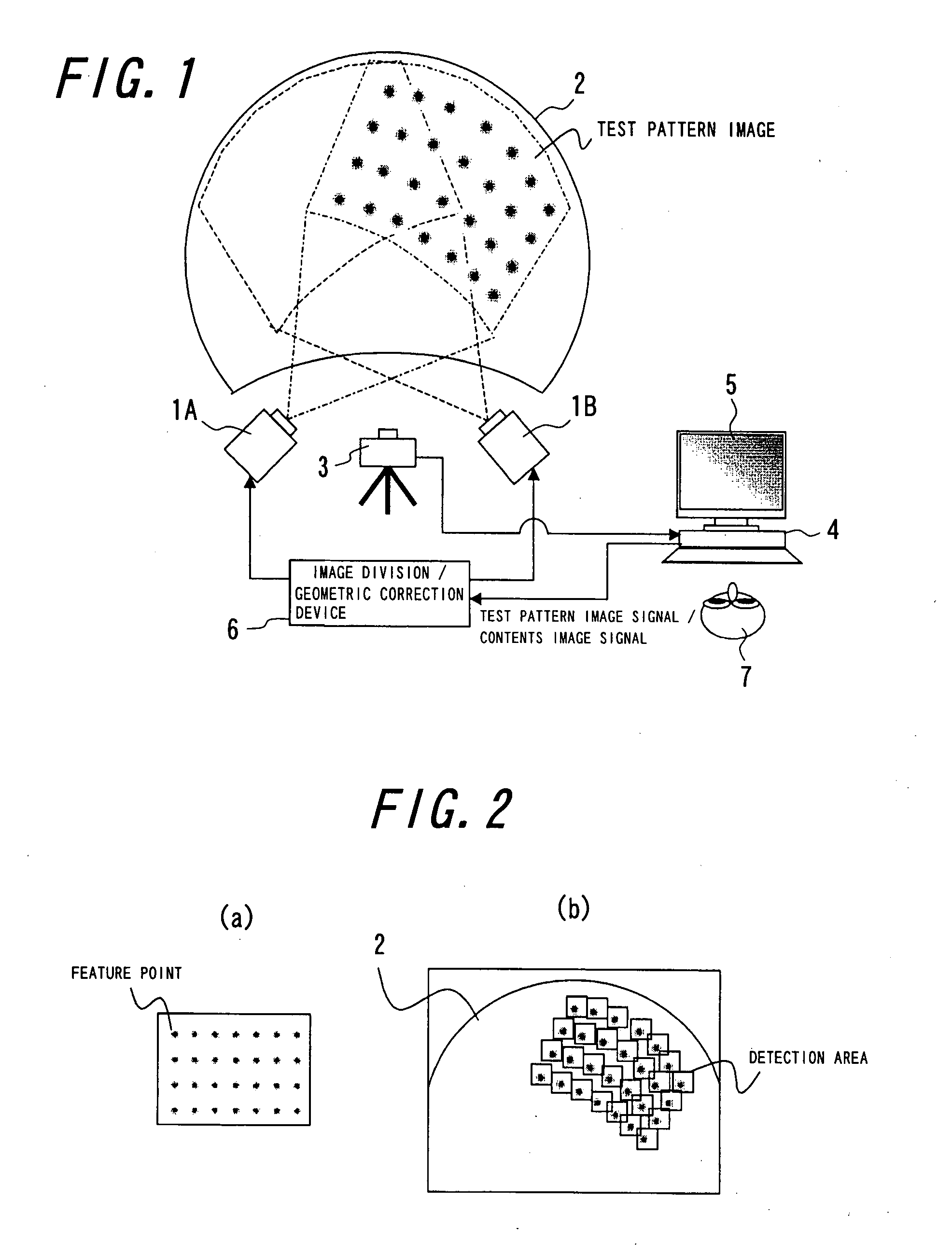
A geometrical correcting method allowing geometrical correction to be performed simply, accurately and in short a time, even in a multi-projection system including a screen of complex shape and projectors complexly arranged, for significantly improving the maintenance efficiency. Test pattern images having feature points are projected by respective projectors, and captured and displayed on a monitor, approximate positions of the feature points are designated and input while referring to the displayed test pattern captured image, and the accurate positions of the feature points in the test pattern images are detected according to the approximate position information. An image correction data for aligning the images projected by the projectors is calculated from the detected positions based on the feature points, the coordinate information of the feature points in a predetermined test pattern image, and the coordinate position relationship between a separately predetermined contents image and the test pattern captured image.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
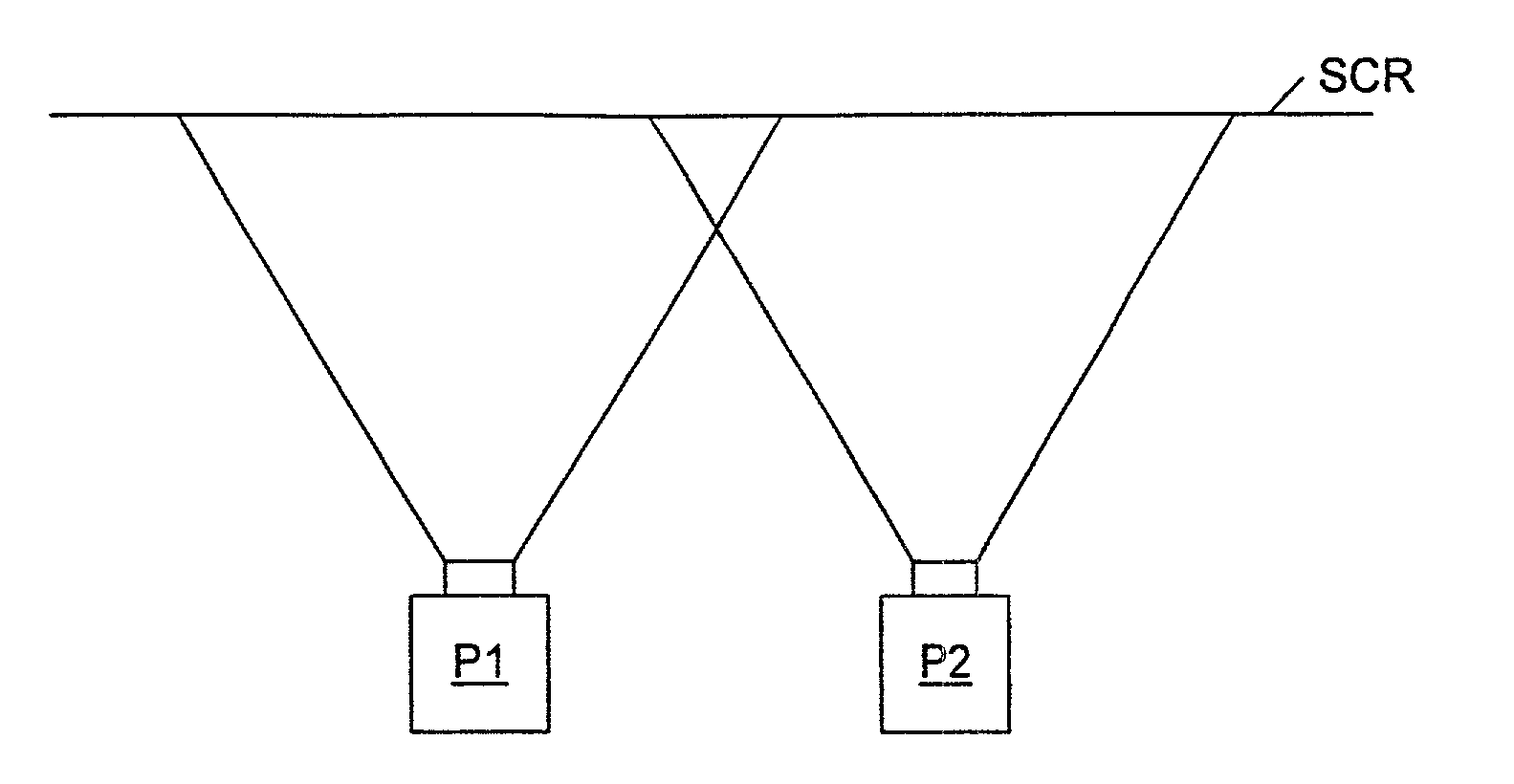
System for the automatic adaptation of projector images and a method for the implementation thereof
InactiveUS6597410B1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsComputer graphics (images)Projector
A computerized projector system which automatically adapts projected images emanating from projectors to fit the size and conditions of screens on which the images are displayed. Moreover, disclosed is a novel method of utilizing a computerized projector system which automatically adapts projected images to a shape and condition in correlation with the size and configuration of the screens onto which the images are projected.
Owner:IBM CORP
Projection system and method including spatial light modulator and compact diffractive optics
ActiveUS20070058143A1Reduce weightLow costTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSpatial light modulatorLight beam
A method and apparatus for a projection display system includes a spatial light modulator and a volume illumination hologram. The spatial light modulator comprises a digital micromirror device, and the projection system includes a laser light source to produce a sequence of collimated, colored, light beams for the illumination hologram. Waste light produced by the spatial light modulator is transmitted to the illumination hologram, and the illumination hologram emits waste light from at least one of its edges. Waste light emitted from an edge of the illumination hologram is absorbed by a light sensor to control the intensity of the light beams. A projection focusing element is mounted proximate a side of the illumination hologram to focus the image beam from the spatial light modulator for viewing. A projection hologram is interposed between the side of the illumination hologram and the projection focusing element to manage waste light.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
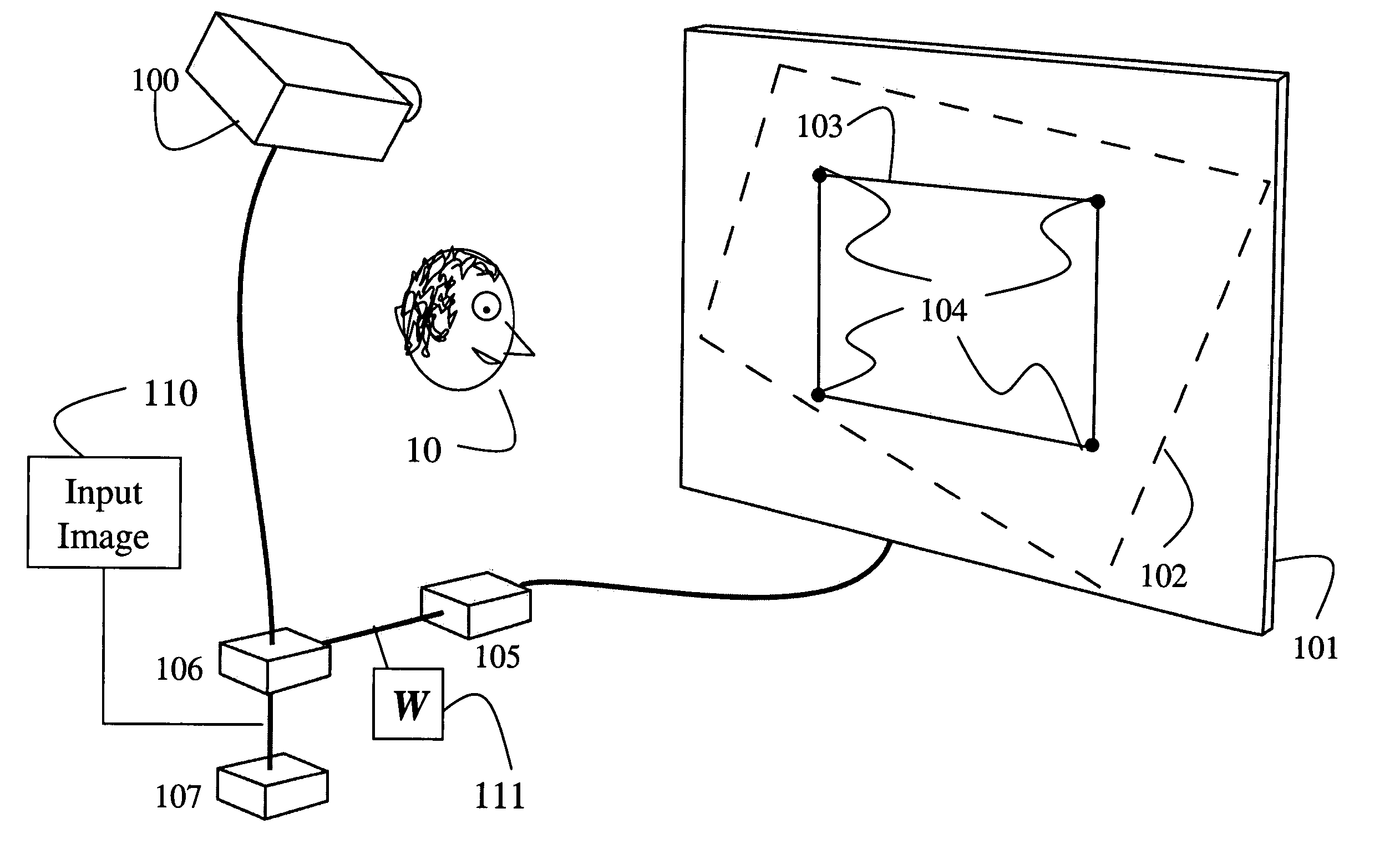
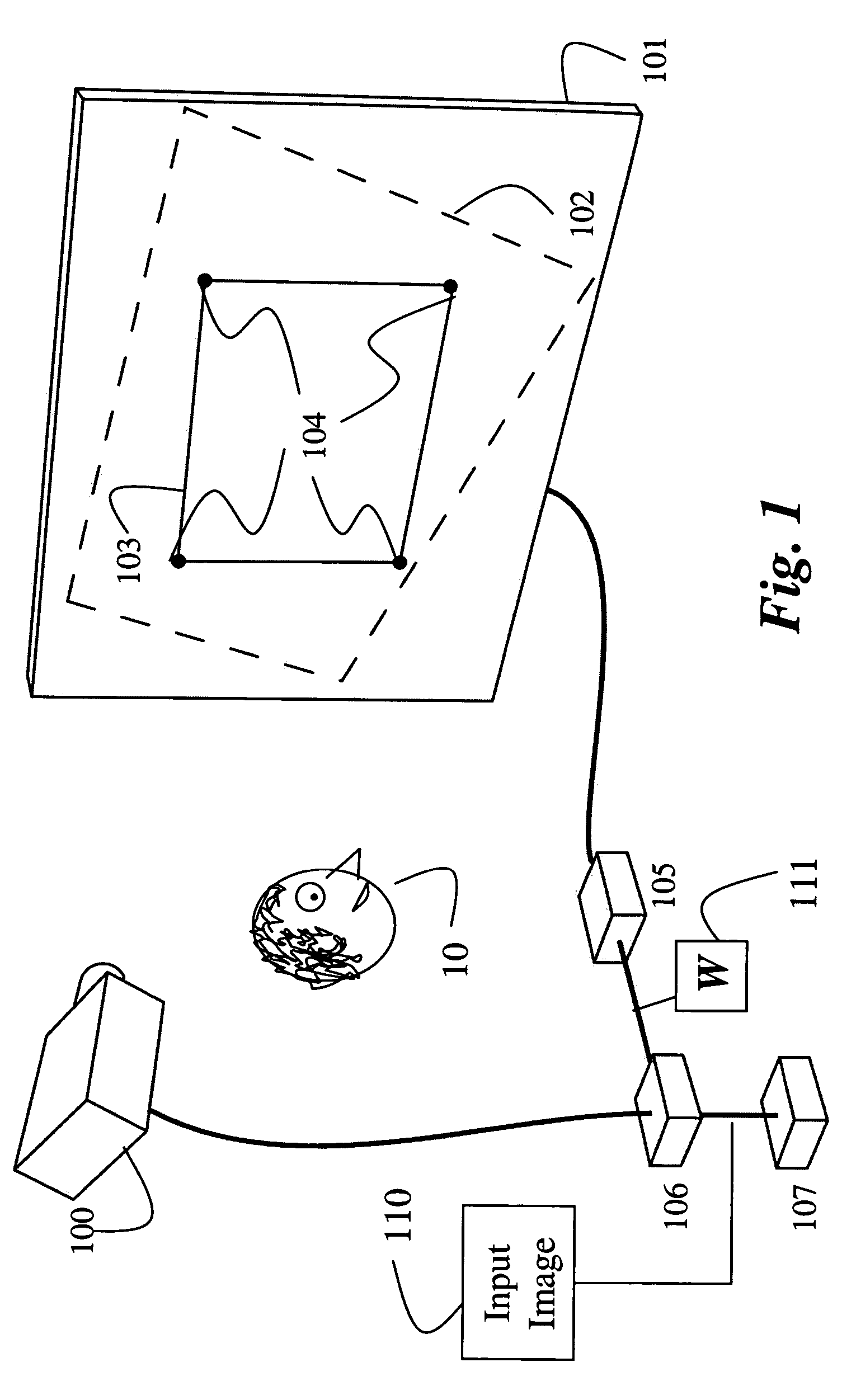
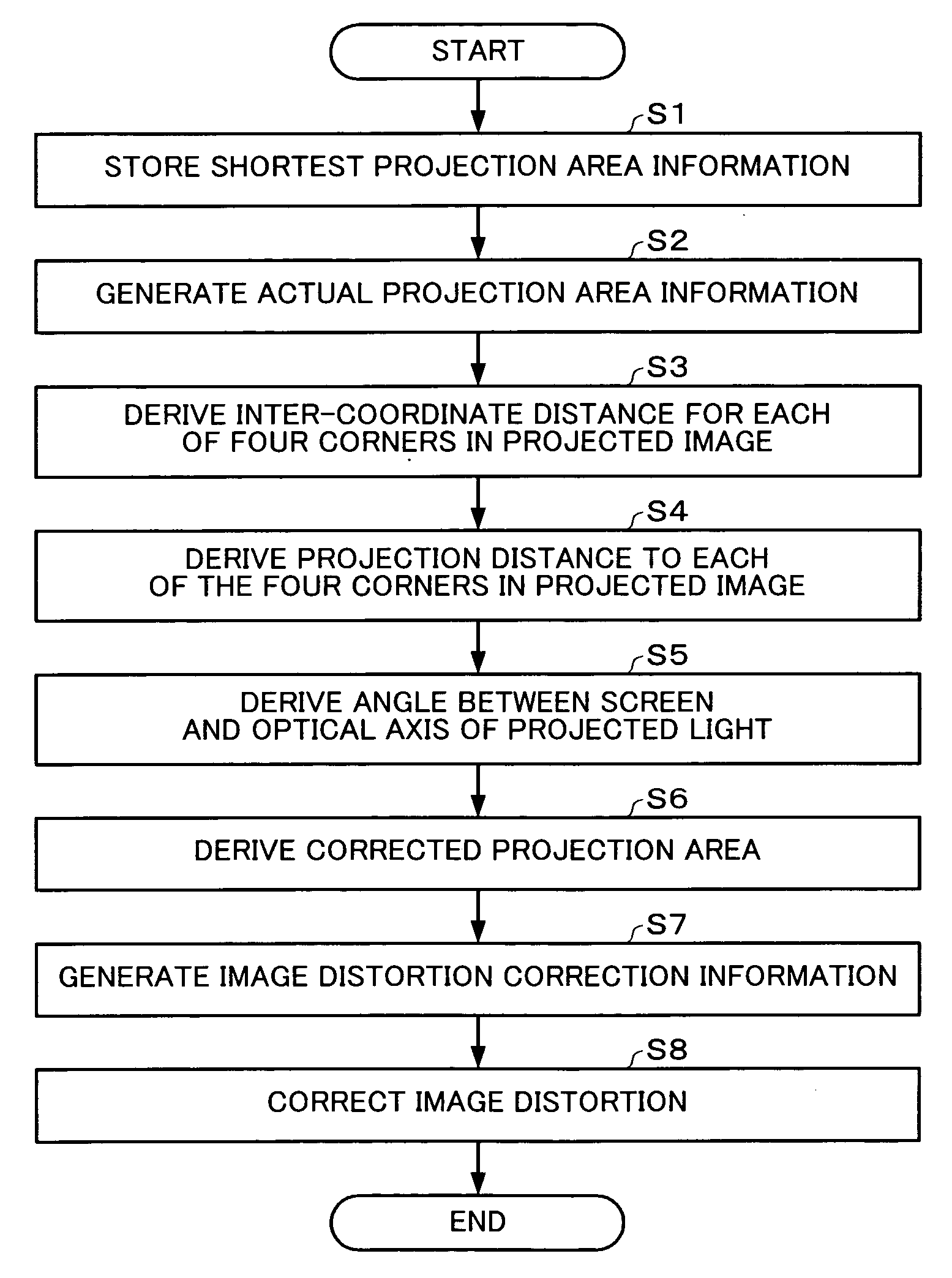
Image processing system, projector, program, information storage medium and image processing method
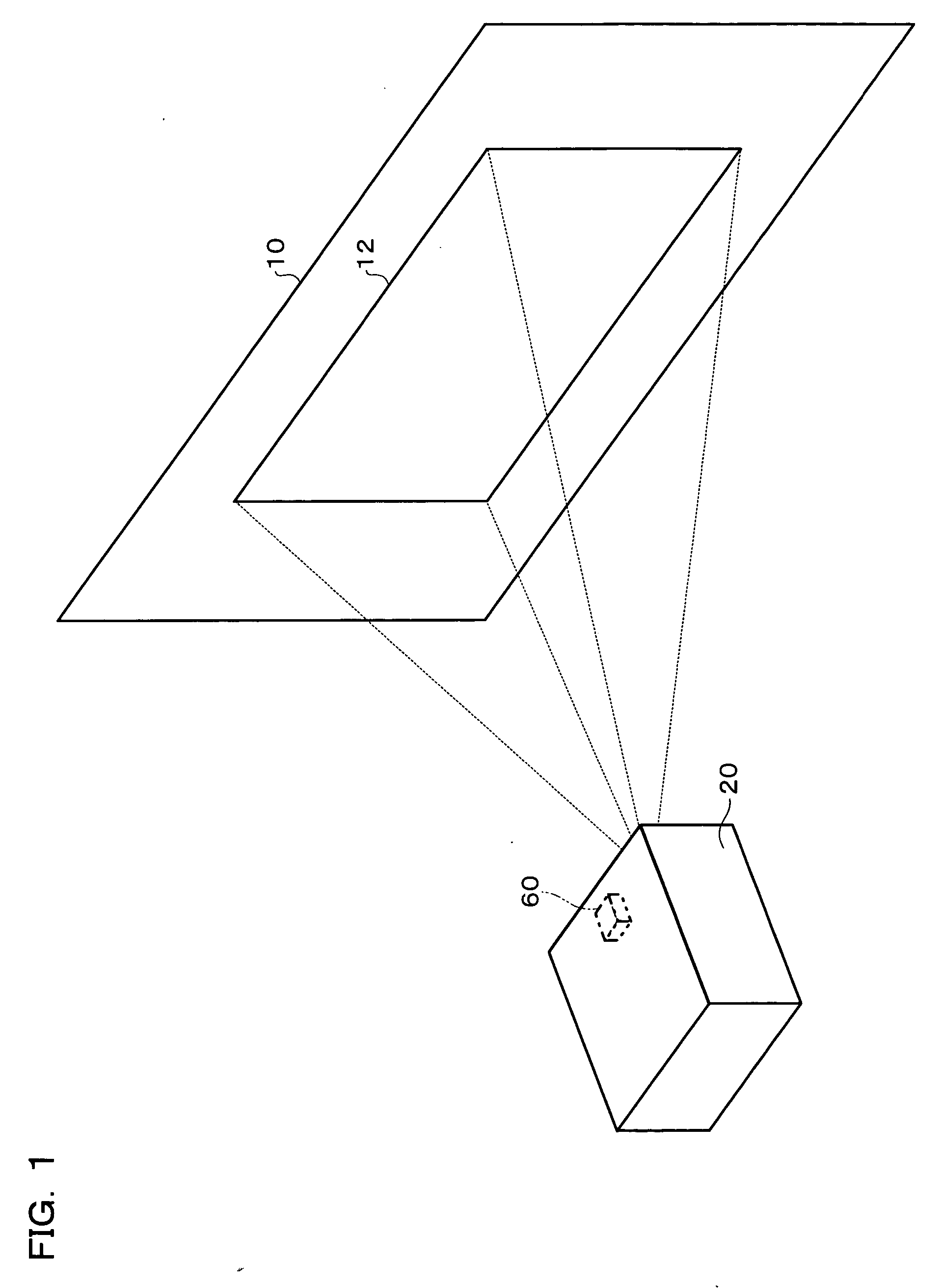
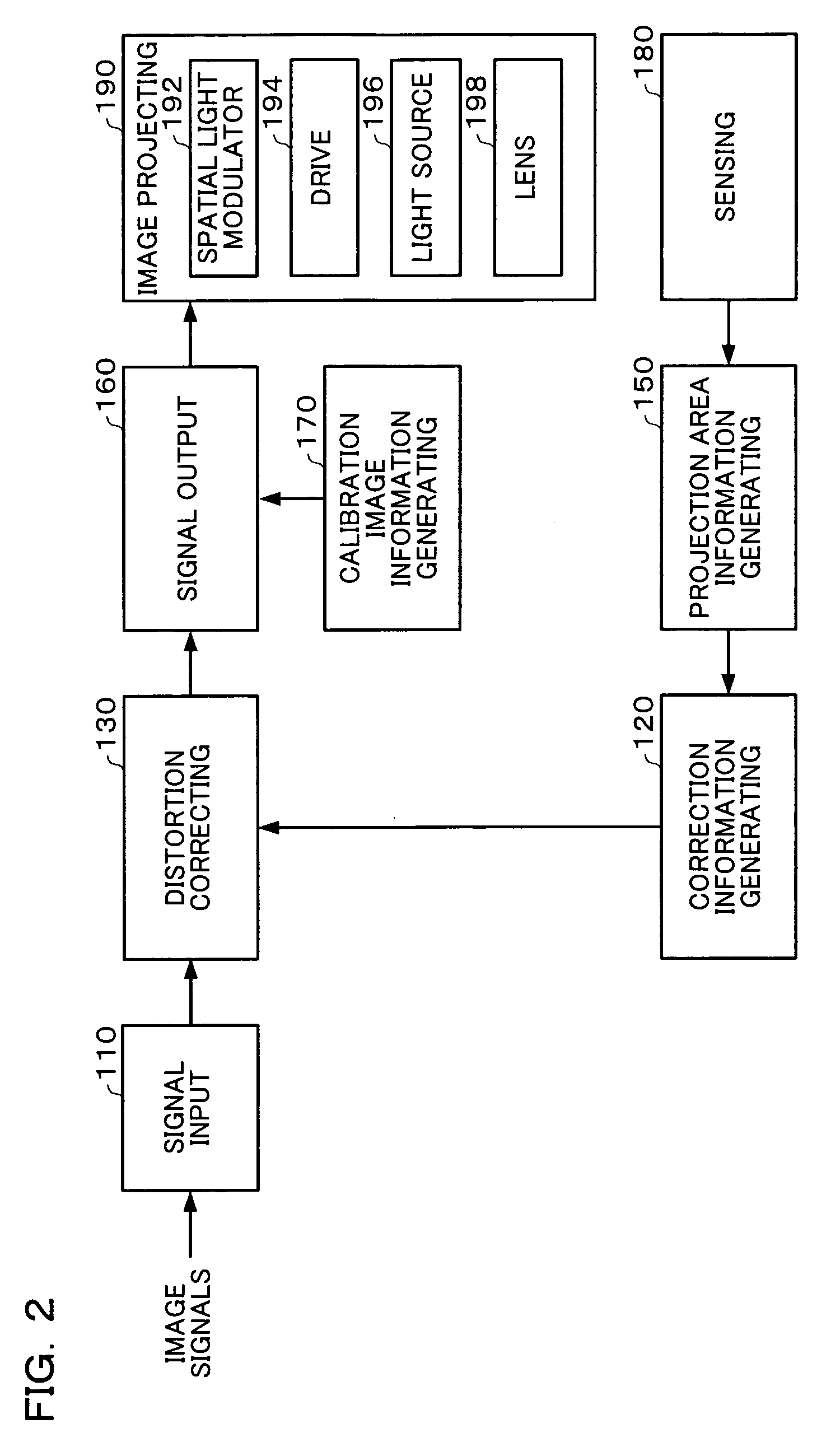
InactiveUS20050036117A1Correct distortionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging processingShortest distance
To provide an image processing system and the like which can correct a distortion of a projected image through only a single sensor, a projector has a calibration image information generating section which generates image information used to display a rectangular calibration image; an image projection section which projects the calibration image onto a projection target, based on the image information; a sensing section which senses a region including the projected calibration image plane and generates sensing information; a projection area information generating section which generates shortest-distance projection area information based on the sensing information in such a state that a distance between the projection section and the projection target is different from the distance in an actual operating condition, and generates actual projection area information based on the sensing information in the actual operating condition; and a correction information generating section which generates image distortion correction information, based on the shortest-distance projection area information and actual projection area information.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
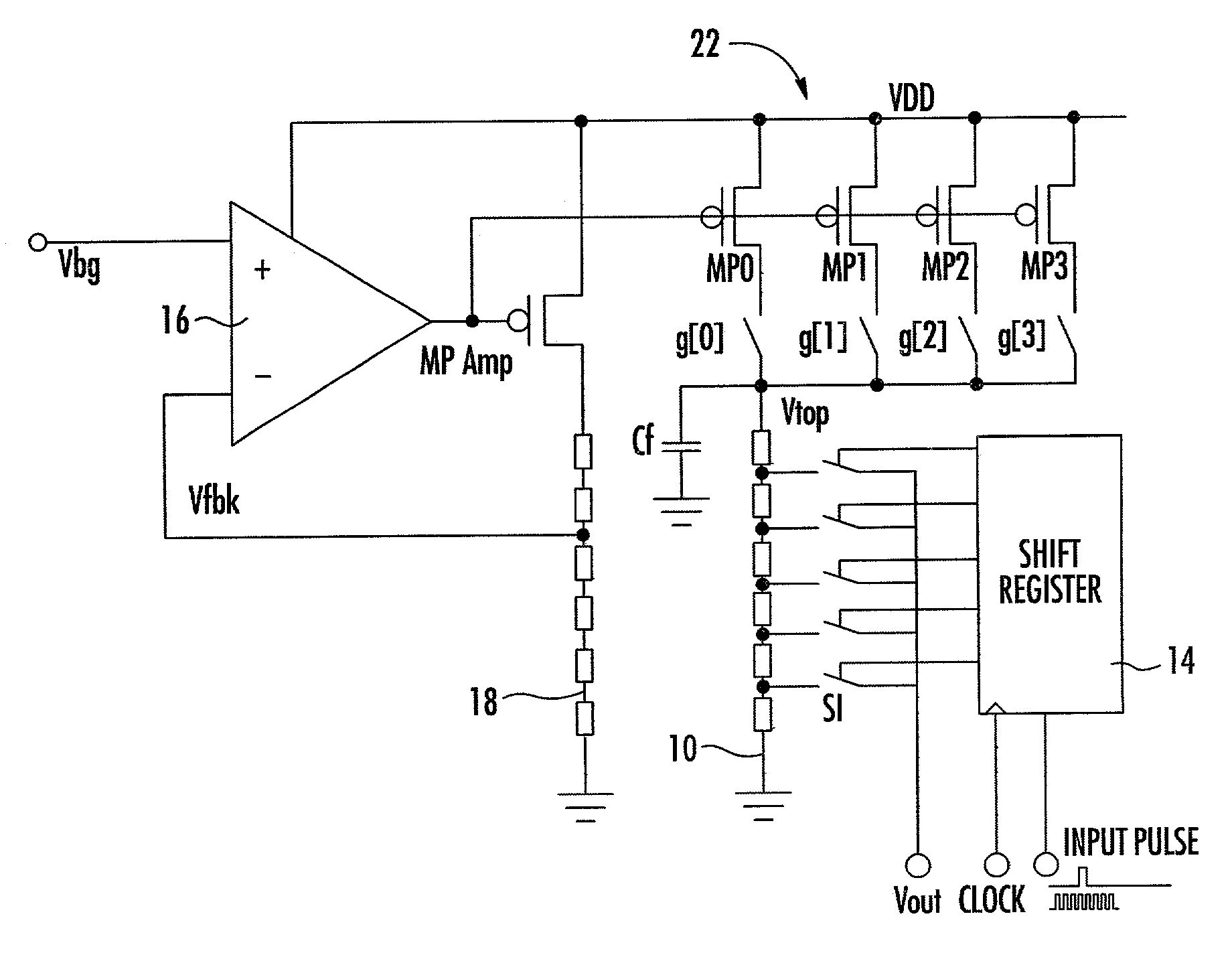
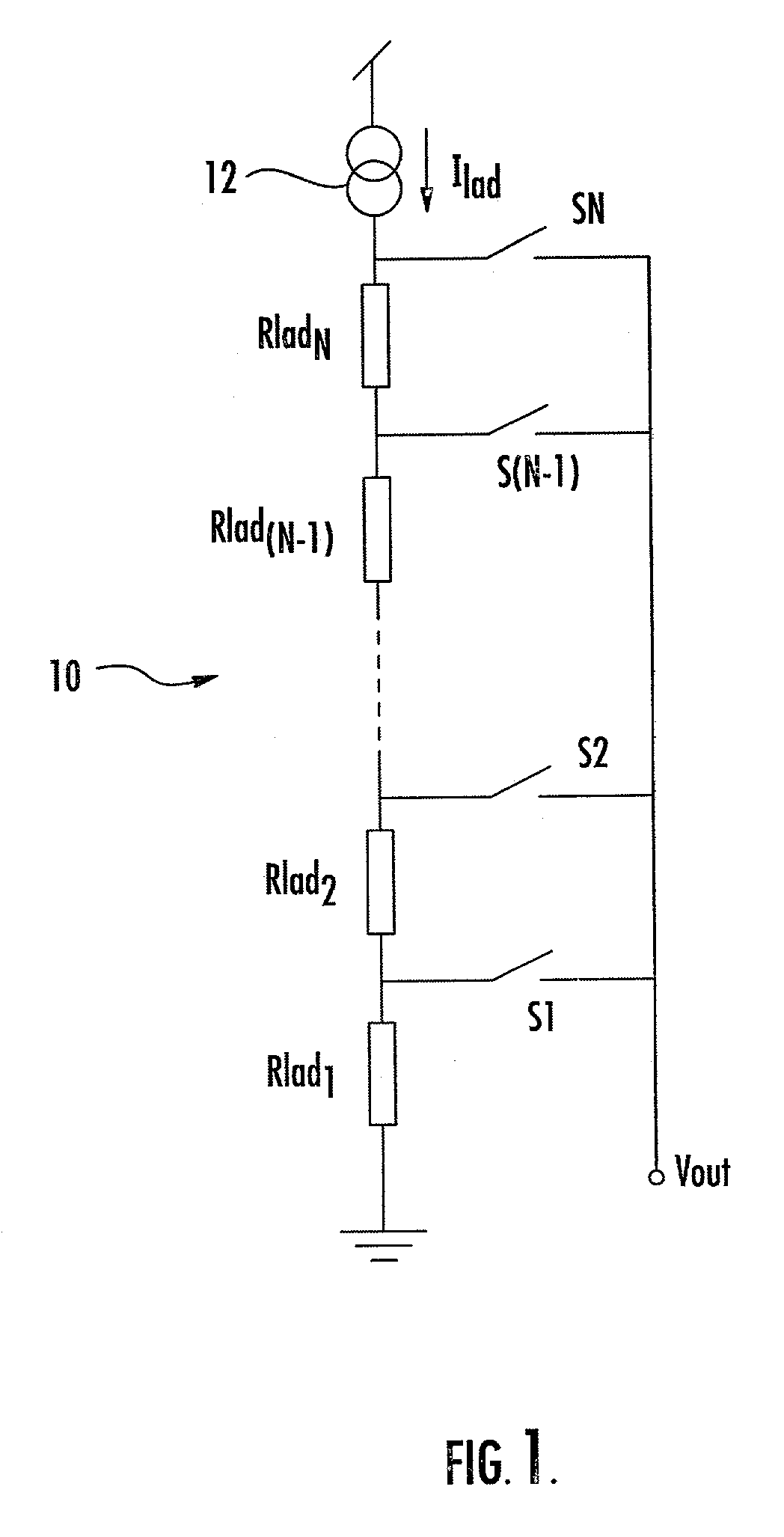
Ramp generator for image sensor ADC
A ramp generator includes a resistance ladder supplied with a constant current. Switches are closed in sequence by a shift register to provide a stepped ramp output. The constant current is controlled by referencing an on-chip bandgap voltage that is used as an input to a feedback circuit controlling current through a reference resistor ladder.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS LTD
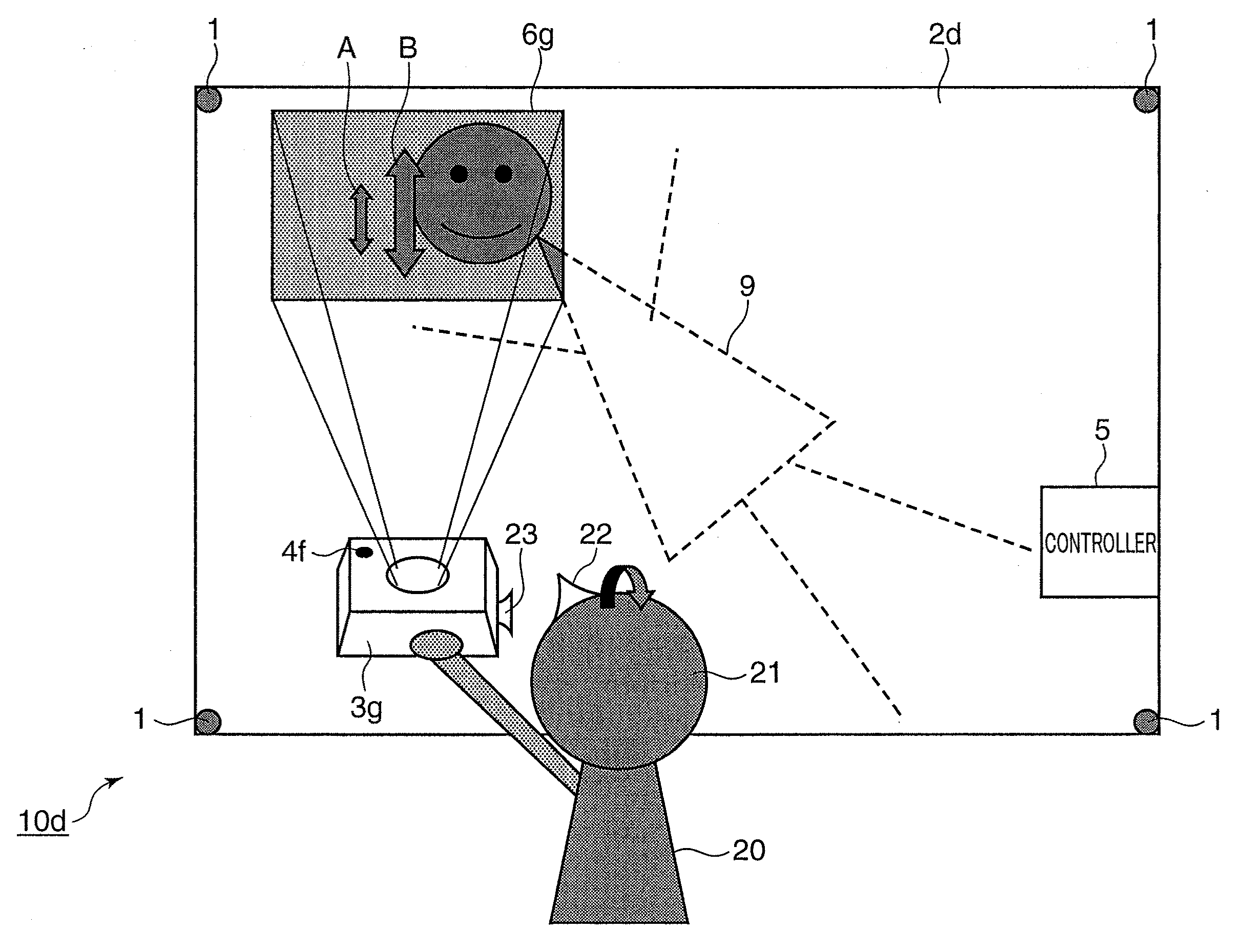
Projector system and video projection method
ActiveUS20090207322A1Television system scanning detailsColor signal processing circuitsLocation detectionComputer graphics (images)
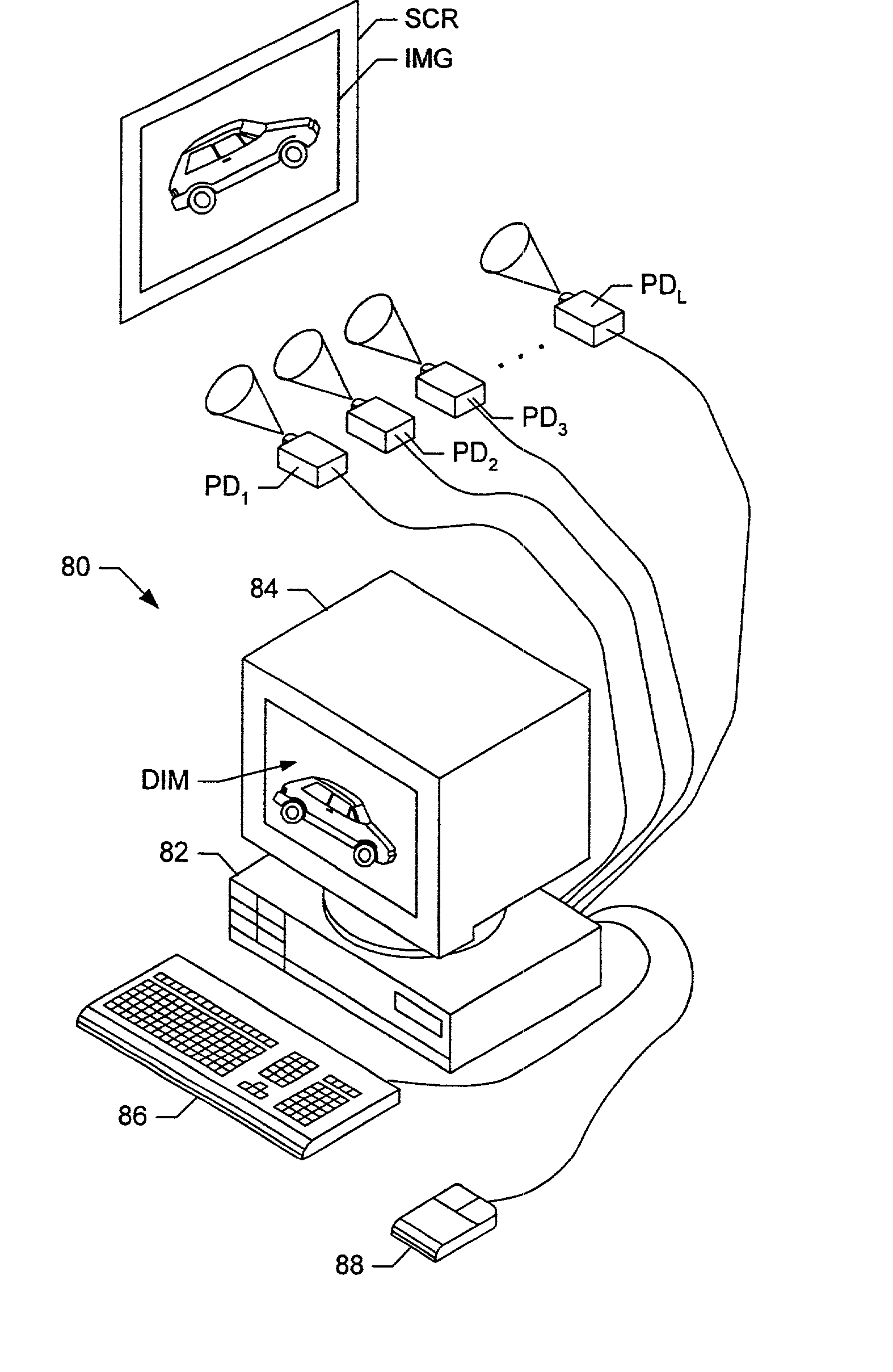
A projector system is provided with at least one projector mobile in a specified space and adapted to project a video to a projection area included in the specified space in accordance with inputted video information, a plurality of position sensors each including a position detecting section for detecting a positional relationship of the projector with the projection area and arranged in a specified positional relationship with the specified space, and a controller for controlling a video to be projected from the projector to the projection area based on detection results by the position detecting sections of the plurality of position sensors.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Projector, method of controlling the projector, program for controlling the projector, and recording medium storing the program
InactiveUS20060181685A1Achieve effectEasy to useTelevision system scanning detailsPulse generatorProjection imageImage capture
A projector includes an image capture device that captures an image in a capture region larger than a projection region of a projection image; an image determining unit that compares and determines the projection image projected by the corresponding projector with another projection image projected in the capture region on the basis of capture information acquired from the image capture device; a transmission image display unit that projects and displays a transmission image indicating that the corresponding projector is ready to perform a tiling projection when the image determining unit determines that the projection image projected by the corresponding projector is the same as the another projection image; a transmission image determining unit that determines whether or not another projector projecting the another projection image has projected the transmission image; and a process parameter creating unit that creates a process parameter which processes display information of the projection image on the basis of a determination result of the transmission image determining unit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Recording a stereoscopic image of a wide field of view
InactiveUS7525567B2Improve stabilityEliminate the problemTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsRapid rotationRotating drum
A scanning camera with a rotating drum has one or more sensors characterized by a non-radial optical axis. With two sensors on opposite sides of the drum and facing in substantially the same direction, stereoscopic recording of a panorama is accomplished as the drum rotates. Rapid rotation of the scanning camera produces panoramic motion picture recording, with the final frame speed dependent on the sensitivity and speed of the sensor, the resolution desired, and the capabilities of the recording device. The preferred embodiment employs rotating fisheye lenses for a substantially fill-sphere field of view. Streamlining of the lens elements on the drum surface is described for quiet operation of the camera, even at high rotation speeds. The rapid rotation of the drum characteristic of motion picture frame rates can improve both the stability and portability of the camera. The gyroscopic effect of the rotating weight of the drum can increase the stability of the camera, and the apparent weight of the camera can be reduced by the lifting effect of aerodynamic elements such as rotors added to the rotating drum. The adjustment of convergence are described that improve the viewing of stereoscopic images. Additional sensors in the same arrangement are used to increase resolution through multiplexed recording of the image data. Recording image information using film, either internal or external to the camera drum, is also described as a cost-effective alternative to digital media storage.
Owner:IMMERSIVE LICENSING
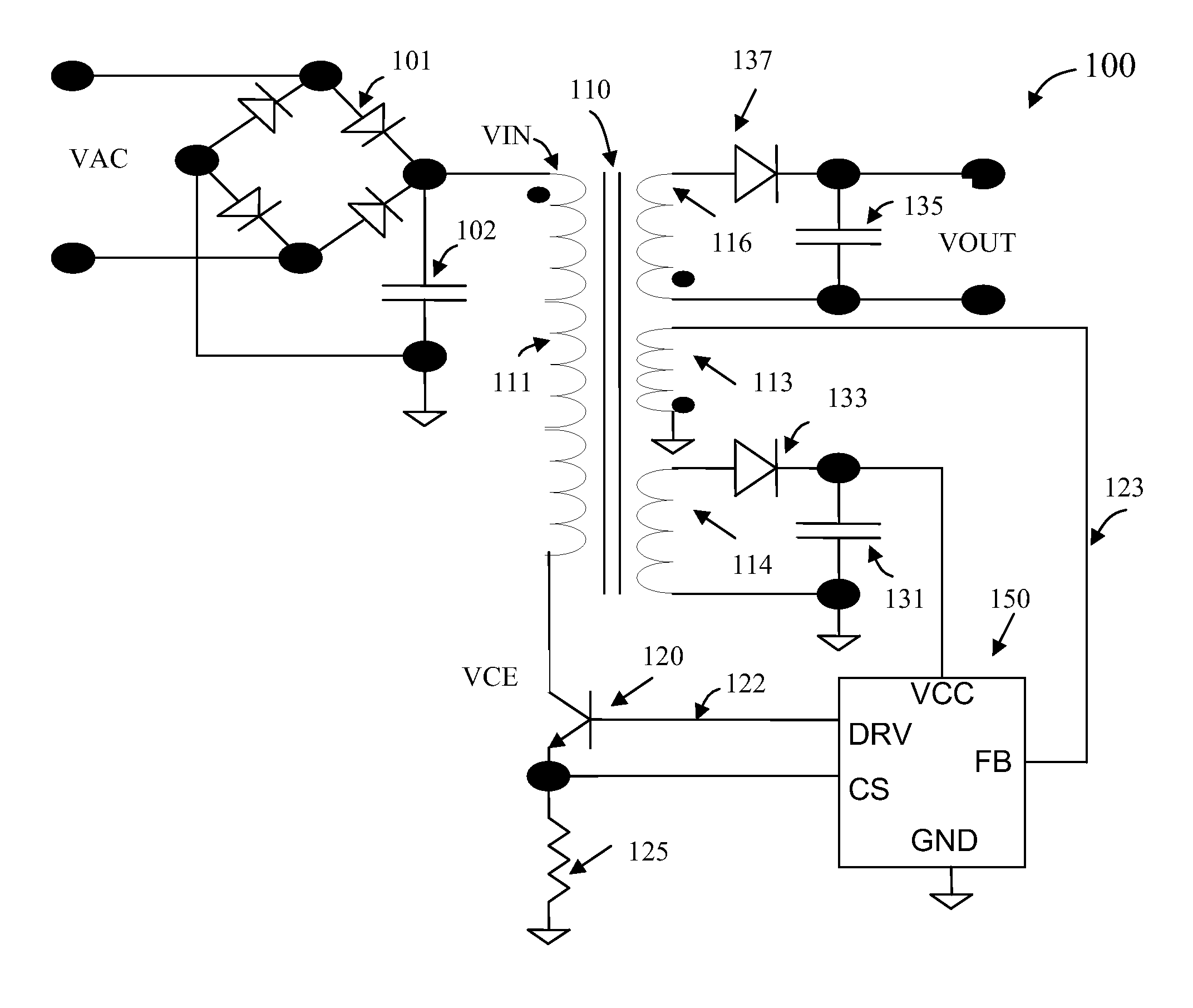
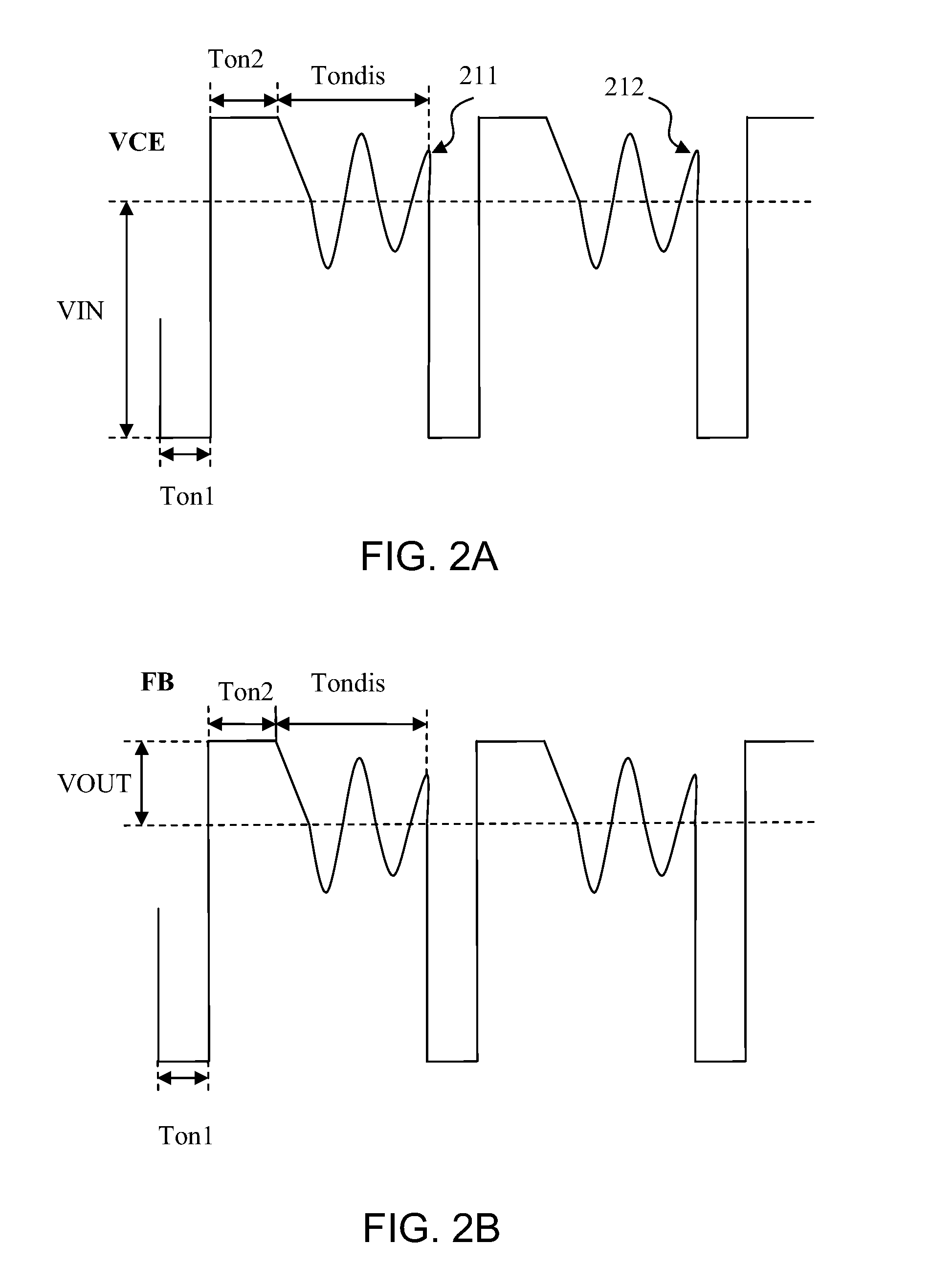
Method and system for pulse frequency modulated switching mode power supplies
ActiveUS20080310191A1Reduce conversion lossSolve the power is smallPulse generatorDc-dc conversionControl signalElectromagnetic interference
A pulse frequency modulation (PFM) controller for controlling a switching mode power supply. The controller includes an output terminal for providing a control signal to turn on and off a current in the power supply to regulate an output of the power supply. A first input terminal receives a feedback signal related to the output of the power supply, the feedback signal exhibiting a ringing waveform when the current in the power supply is turned off. The controller also includes a control circuit configured to provide the control signal in response to the feedback signal. The control signal is adapted to turn on the current in the power supply when the feedback signal is substantially at a valley of the ringing waveform of the feedback signal. In an embodiment, such a PFM controller can reduce turn-on transition loss in a power supply and provides frequency dithering to reduce electromagnetic interference.
Owner:BCD SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor power converting apparatus
InactiveUS6380796B2Increase rate of changeEliminate the effects ofPulse generatorElectronic switchingReverse biasGate voltage
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Real-Time Geometry Aware Projection and Fast Re-Calibration
InactiveUS20110176007A1Reduce restrictionsImage enhancementImage analysisHat matrixProjector camera systems
Aspects of the present invention include systems and methods for recalibrating projector-camera systems. In embodiments, systems and methods are able to recalibrate automatically the projector with arbitrary intrinsic and pose, as well as render for arbitrarily desired viewing point. In contrast to previous methods, the methods disclosed herein use the observing camera and the projector to form a stereo pair. Structured light is used to perform pixel-level fine reconstruction of the display surface. In embodiments, the geometric warping is implemented as a direct texture mapping problem. As a result, re-calibration of the projector movement is performed by simply computing the new projection matrix and setting it as a camera matrix. For re-calibrating the new view point, the texture mapping is modified according to the new camera matrix.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
View Projection for Dynamic Configurations
InactiveUS20090073324A1Easy to shipSimple processTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsHat matrixProjection image
A method and system for compensating for a moving object placed between a projector and a projection scene is shown. The method / system dividing a movement pattern of the moving object into N discrete position states, and for each of said N position states determining a corresponding view projection matrix. While projecting an image within any of the N position states, multiplying a desired projection image by the corresponding view projection matrix.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Graphics system configured to perform distortion correction
A graphics system comprises pixel calculation units and a sample buffer which stores a two-dimensional field of samples. Each pixel calculation unit selects positions in the two-dimensional field at which pixel values (e.g. red, green, blue) are computed. The pixel computation positions are selected to compensate for image distortions introduced by a display device and / or display surface. Non-uniformities in a viewer's perceived intensity distribution from a display surface (e.g. hot spots, overlap brightness) are corrected by appropriately scaling pixel values prior to transmission to display devices. Two or more sets of pixel calculation units driving two or more display devices adjust their respective pixel computation centers to align the edges of two or more displayed images. Physical barriers prevent light spillage at the interface between any two of the display images. Separate pixel computation positions may be used for distinct colors to compensate for color distortions.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com