Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
524 results about "Feedback capacitor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
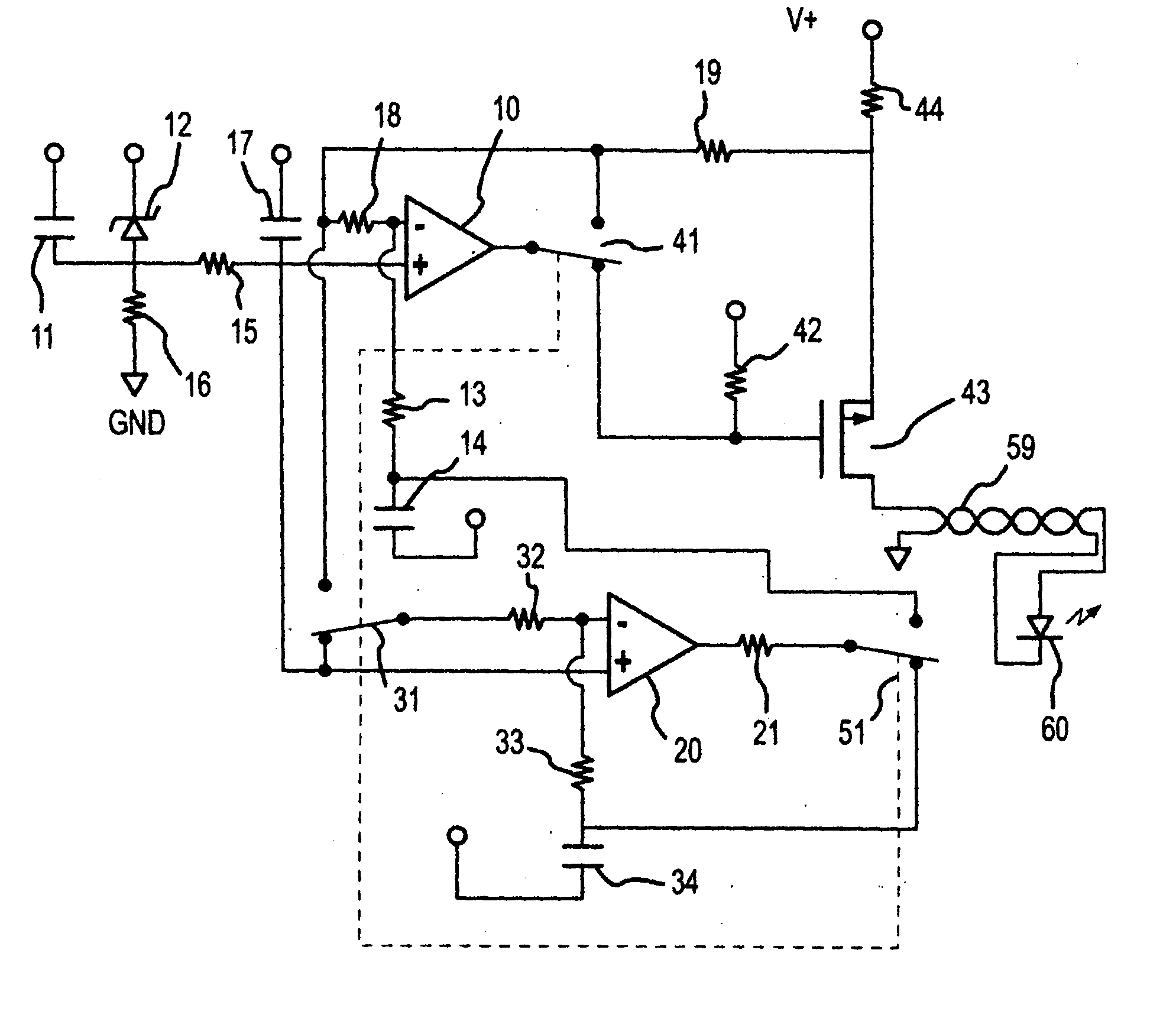
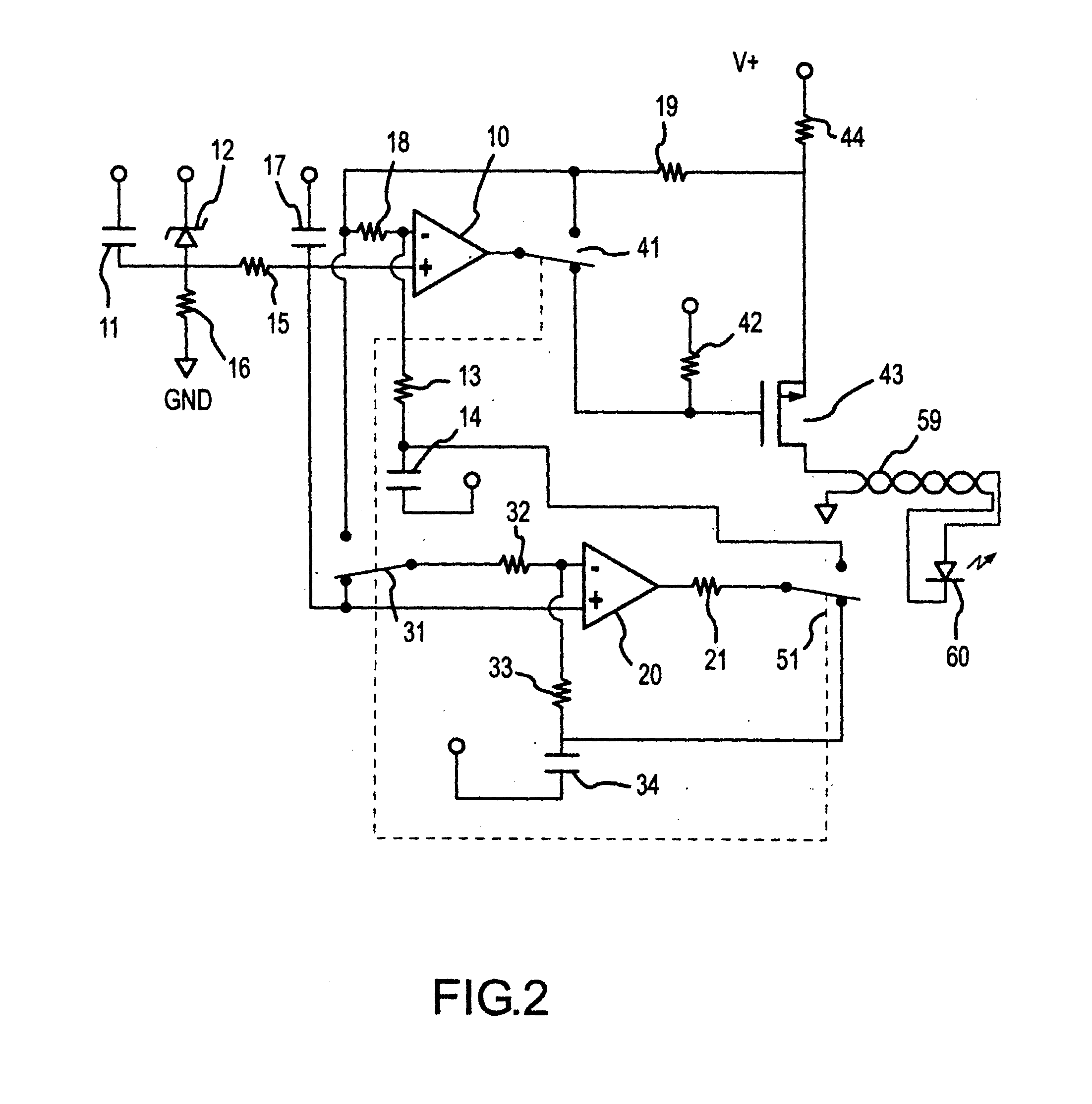
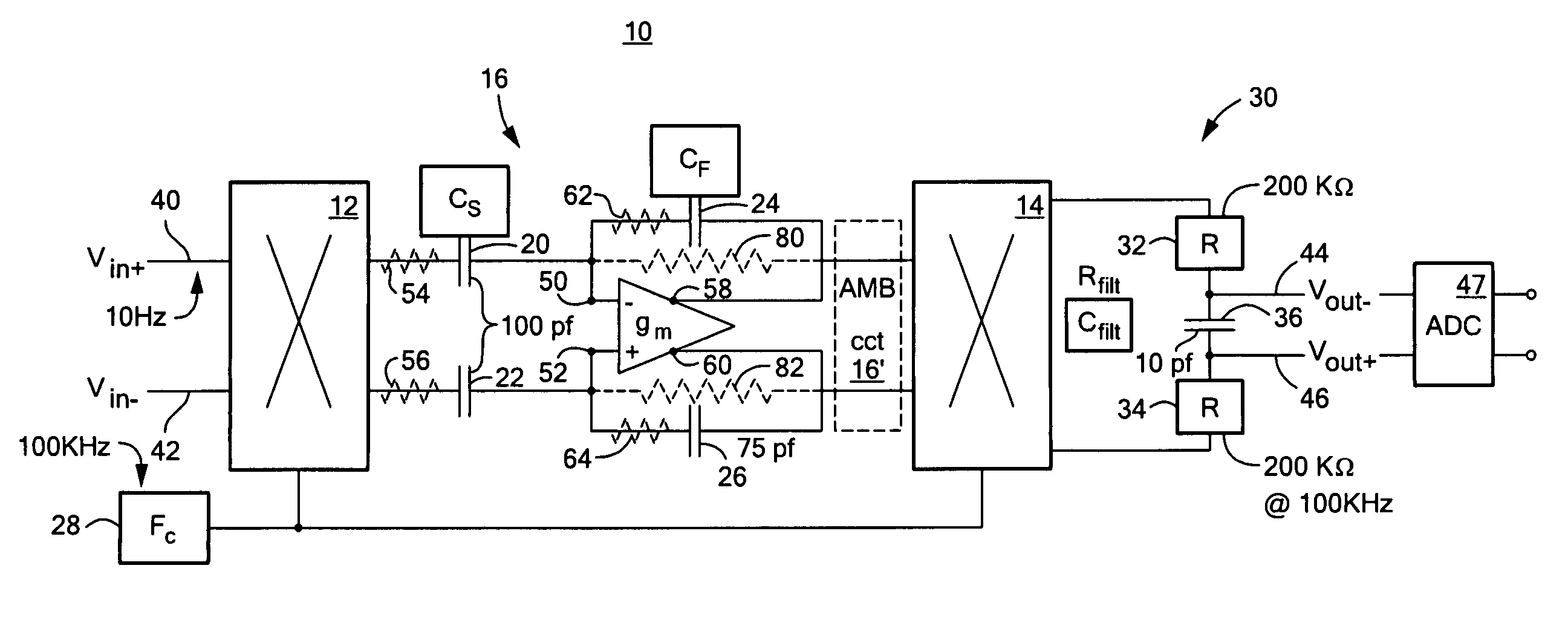
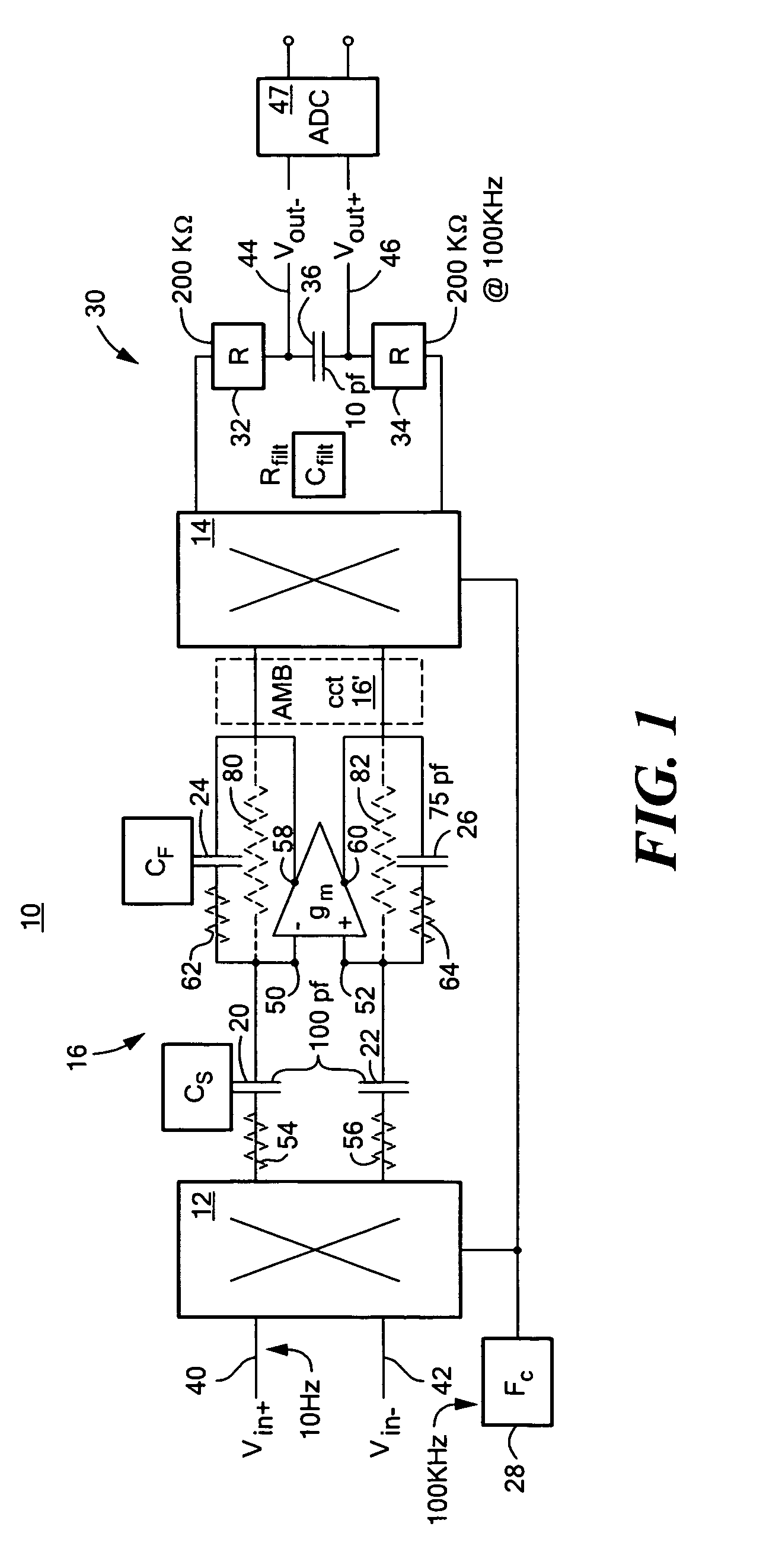
Oximeter with nulled op-amp current feedback
InactiveUS6720734B2Eliminating low frequency driftEasy to detectElectric light circuit arrangementDiagnostic recording/measuringDriving currentLight flashes
A method of producing a diode drive current in an oximeter includes sensing at least a part of a current passing through the diode and converting the sensed current to a sensed voltage, inputting the sensed voltage to a feedback amplifier for stabilizing the current passing through the diode, and eliminating an offset voltage across inputs of the feedback amplifier. A pulse oximeter includes a diode for emitting light flashes, a feedback amplifier having inputs, a feedback capacitor, and an output, the feedback amplifier stabilizing a current passing through the diode, a nulling amplifier having inputs, a nulling capacitor, and an output, the nulling amplifier charging and discharging the feedback capacitor until the inputs of the feedback amplifier are at a same voltage. The operation may include synchronizing an elimination of input offset voltages of the feedback and nulling amplifiers with on or off state of diode current.
Owner:DATEX OHMEDA
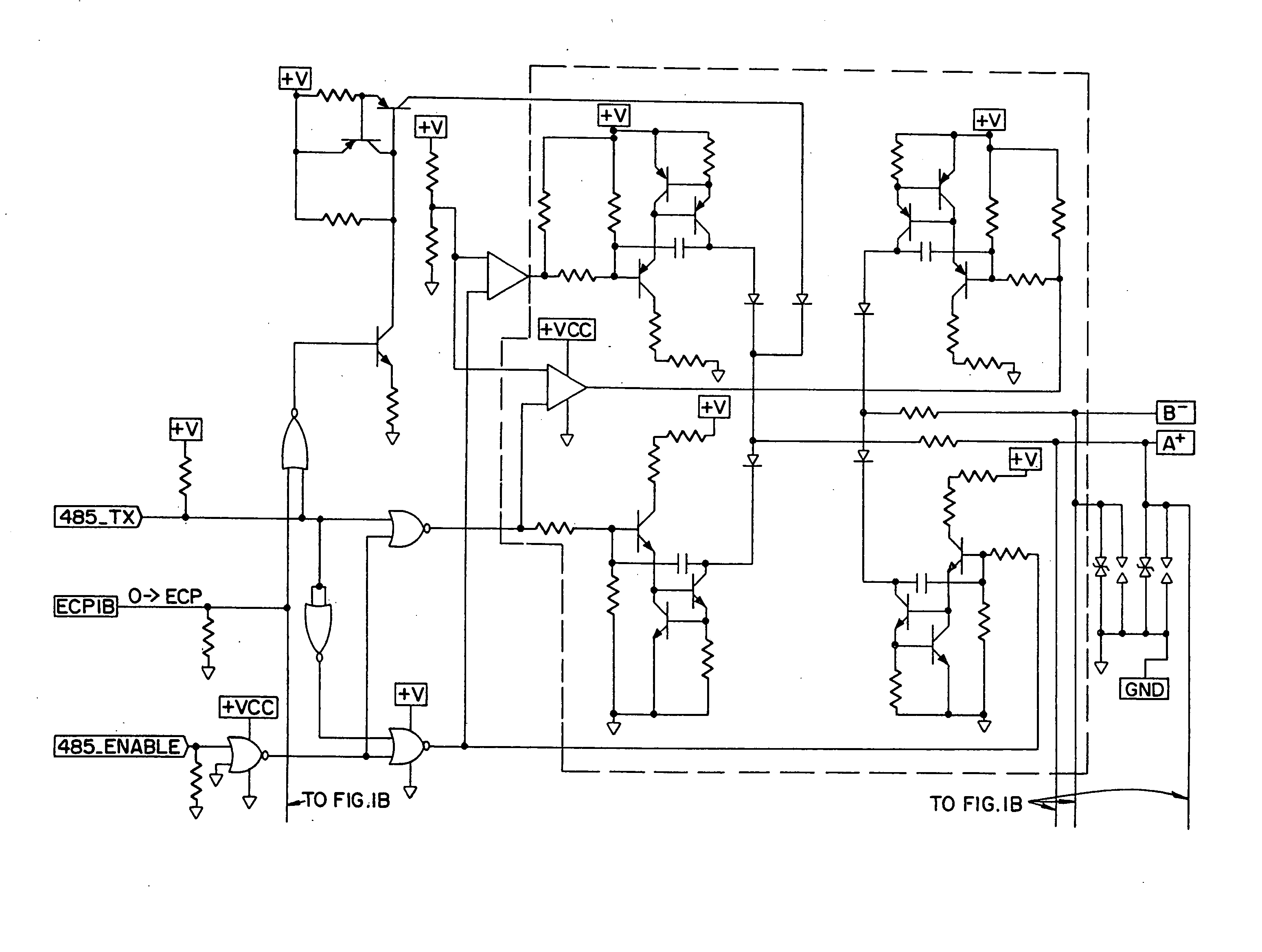
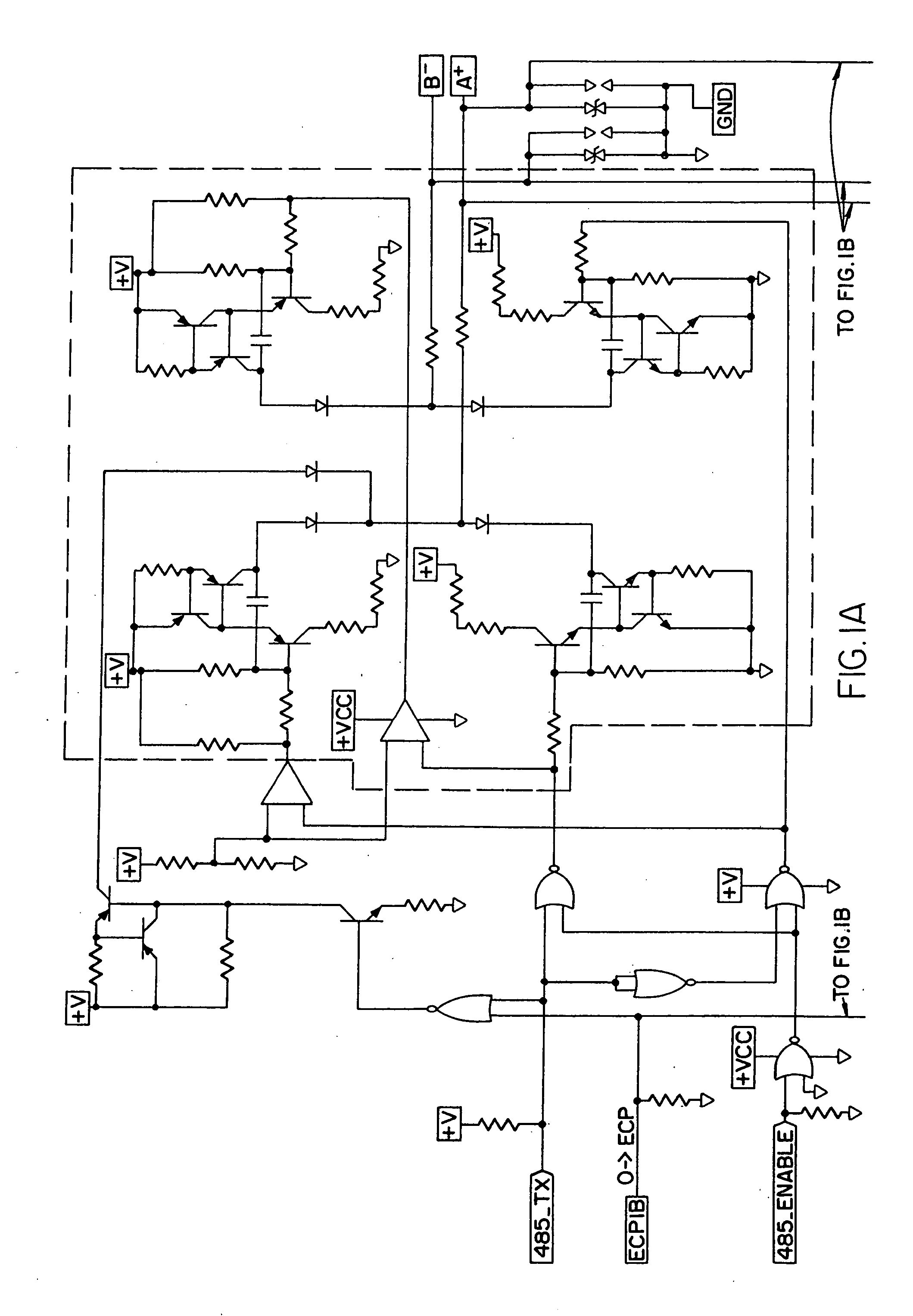
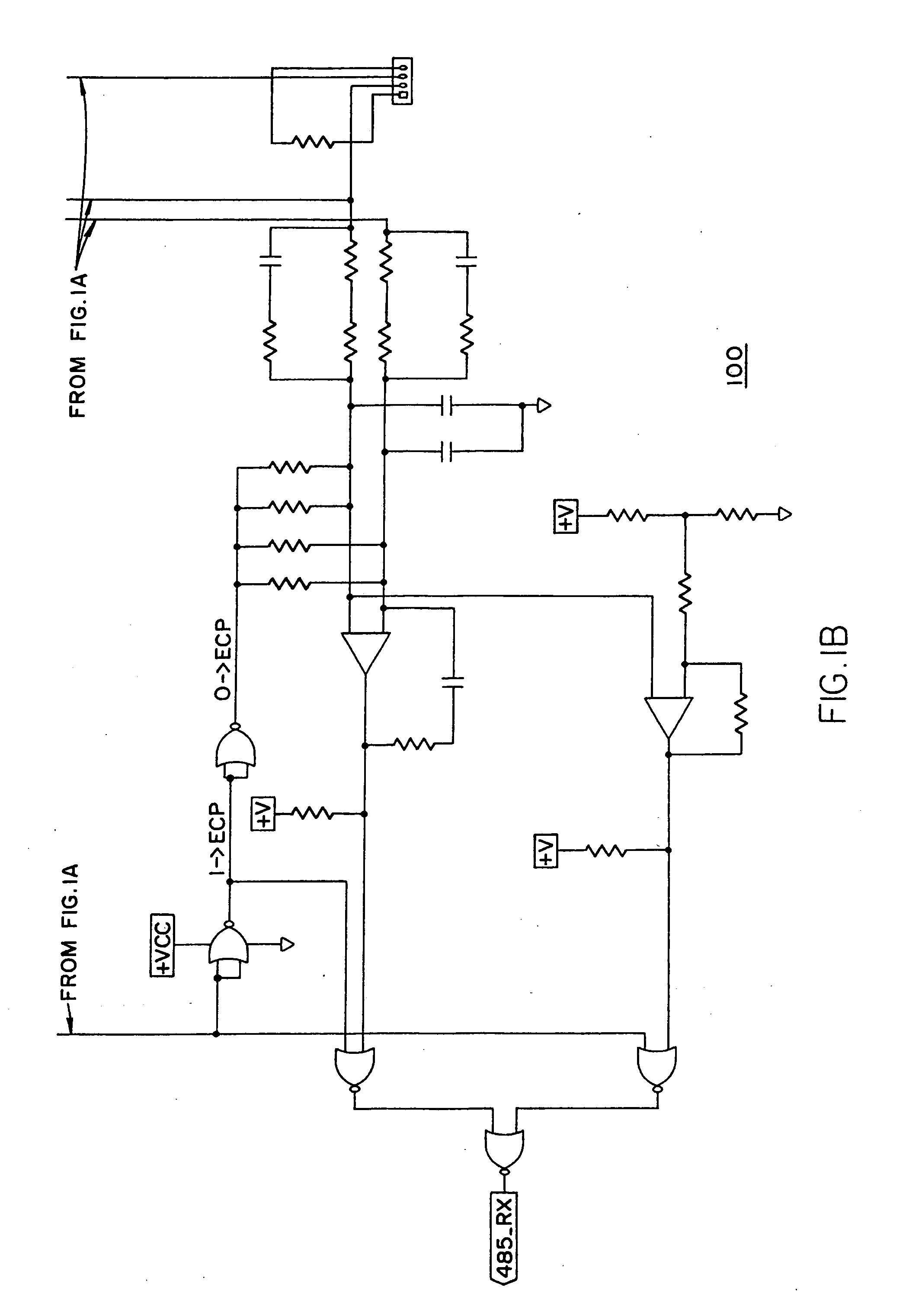
Feedback circuit for line load compensation and reflection reduction
InactiveUS20070164779A1Reduce reflectionReliability increasing modificationsElectronic switchingElectrical resistance and conductanceCapacitance
Line load compensation and reflection reduction in a signal transmitting circuit is provided using feedback capacitors. The feedback capacitor serially coupled with a resistance generates an RC rise / fall time that is independent of the line load. Additionally, by selecting a capacitor that yields a rise / fall time of approximately ⅓ of the maximum bit transmission time, signal reflection on the signal line can be reduced. Accordingly, by incorporating the feedback capacitor with a differential drive circuit, such as the IB 485 driver, variations in line load can be compensated for while also reducing signal reflection due to un-terminated or improperly terminated signal lines, thus allowing a free topology implementation.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
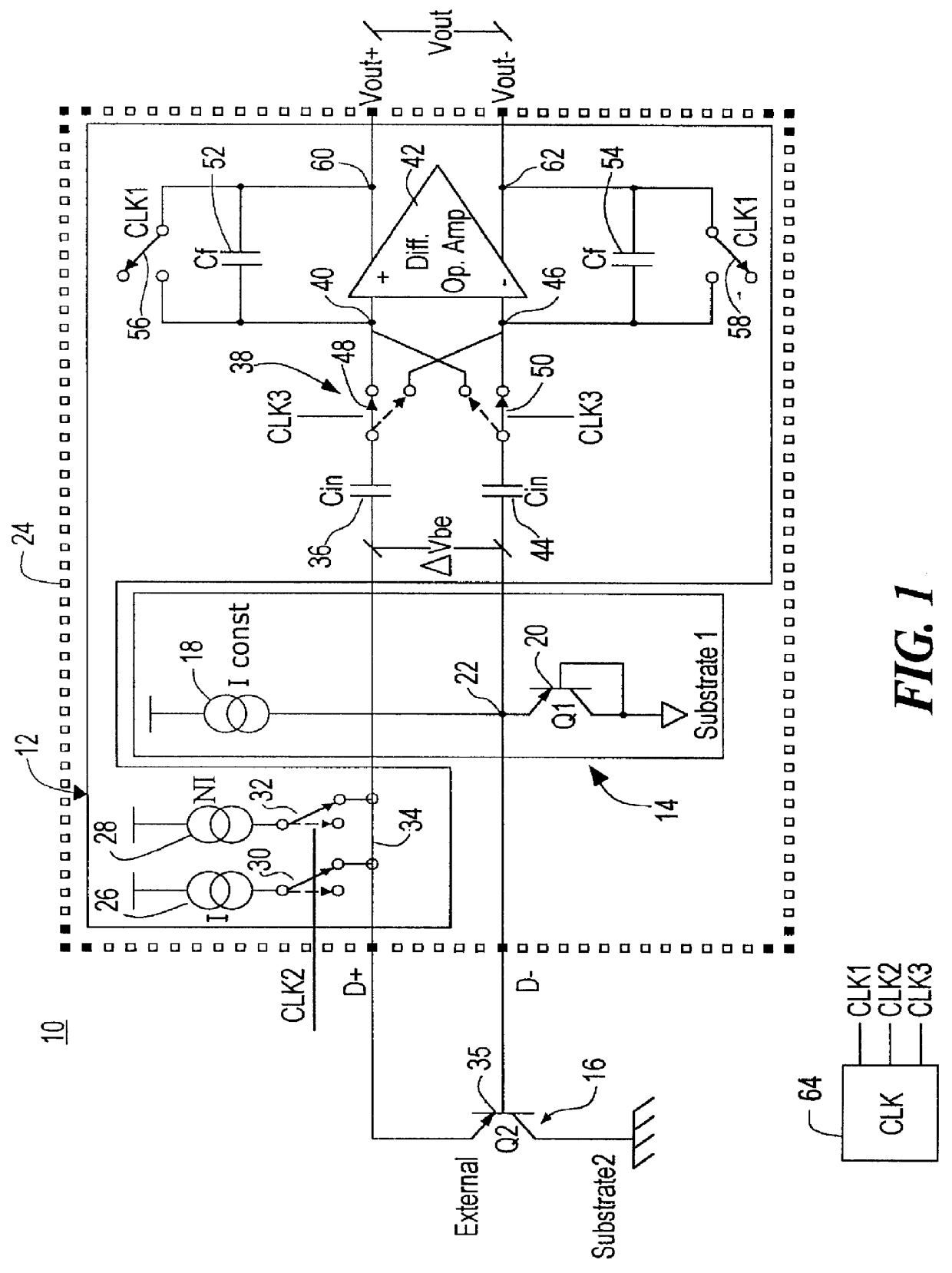
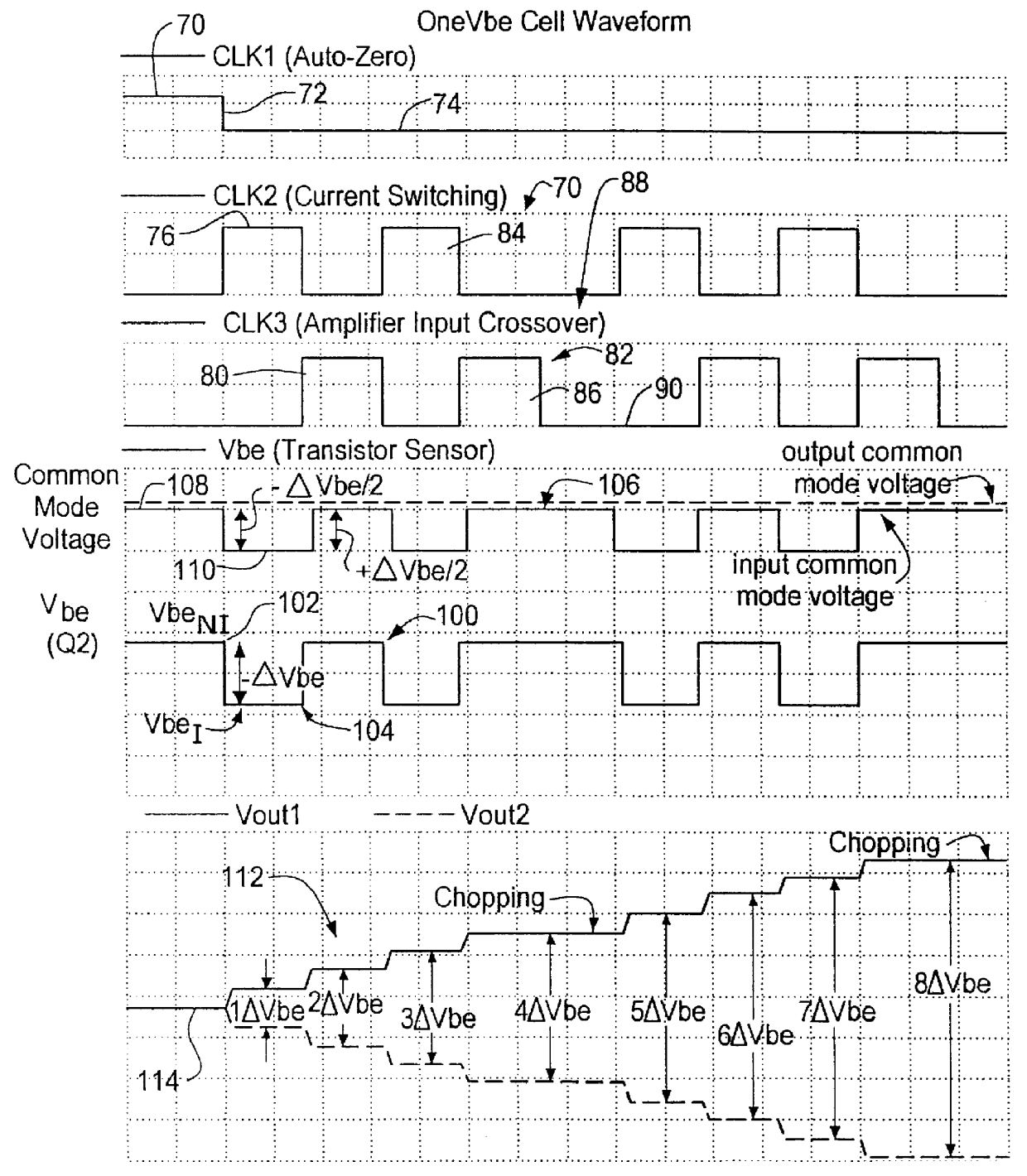
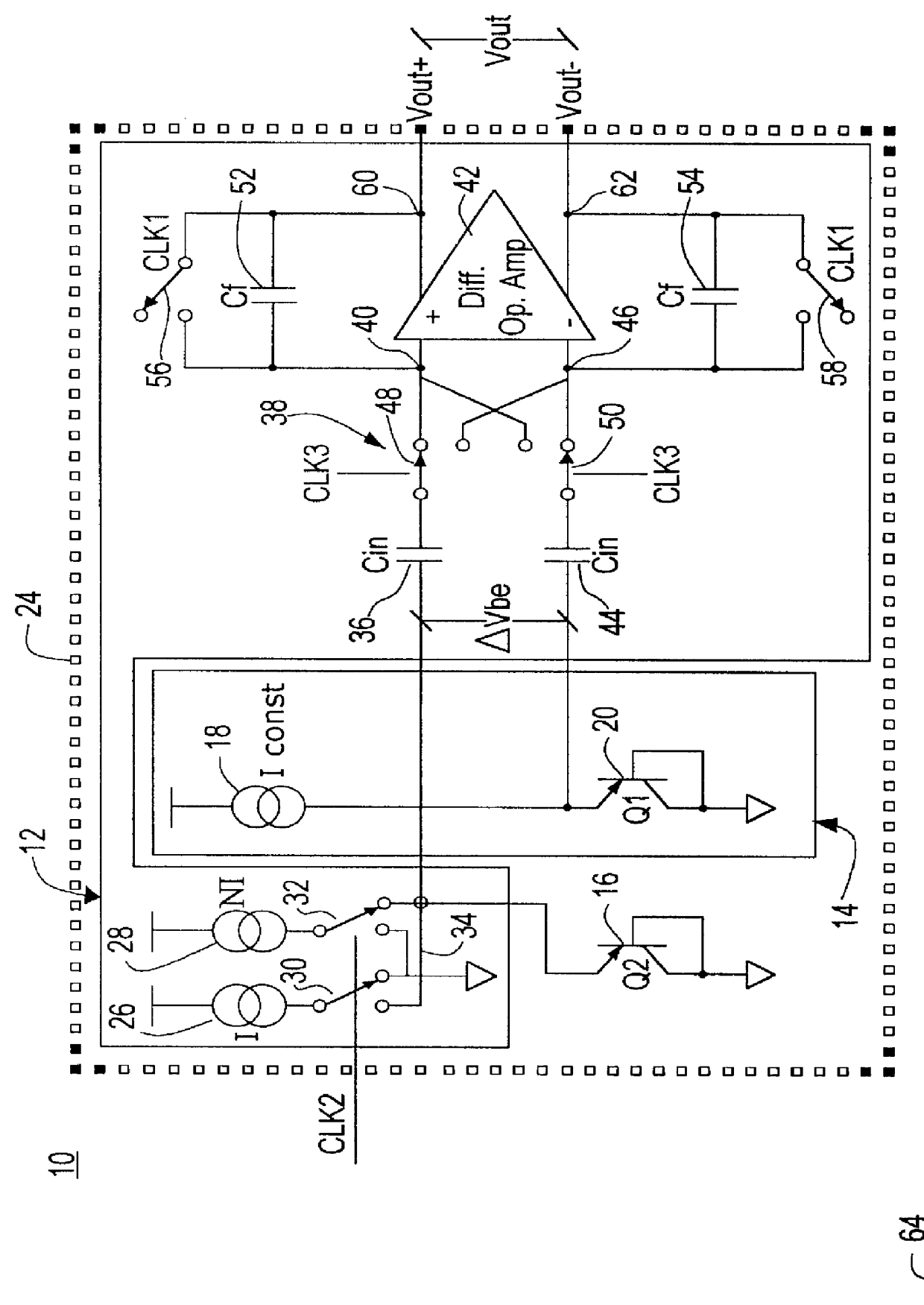
Decoupled switched current temperature circuit with compounded DELTA V be
InactiveUS6097239AThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsElectronic switchingDelta-vAudio power amplifier
A decoupled switched current temperature circuit with compounded DELTA Vbe includes an amplifier having an inverting input with corresponding non-inverting output and a non-inverting input with a corresponding inverting output; a PN junction connected to the non-inverting input through a first input capacitor and a voltage reference circuit is connected to the inverting input through a second input capacitor; a current supply includes a low current source and a high current source; a switching device applies the high current source to the PN junction and applies the low current source to the PN junction for providing the DELTA Vbe of the PN junction to the first capacitor; a first feedback capacitor is interconnected between the inverting output and the non-inverting input and a second feedback capacitor is interconnected between the non-inverting output and inverting input of the amplifier to define the gain on each of the inputs to produce a differential voltage across the outputs representative of the temperature of the PN junction; first and second reset switching devices discharge the first and second feedback capacitors, respectively, and a multi-phase switched device alternately interchanges the connection of the first and second input capacitors with the amplifier inputs for compounding the single DELTA Vbe .
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
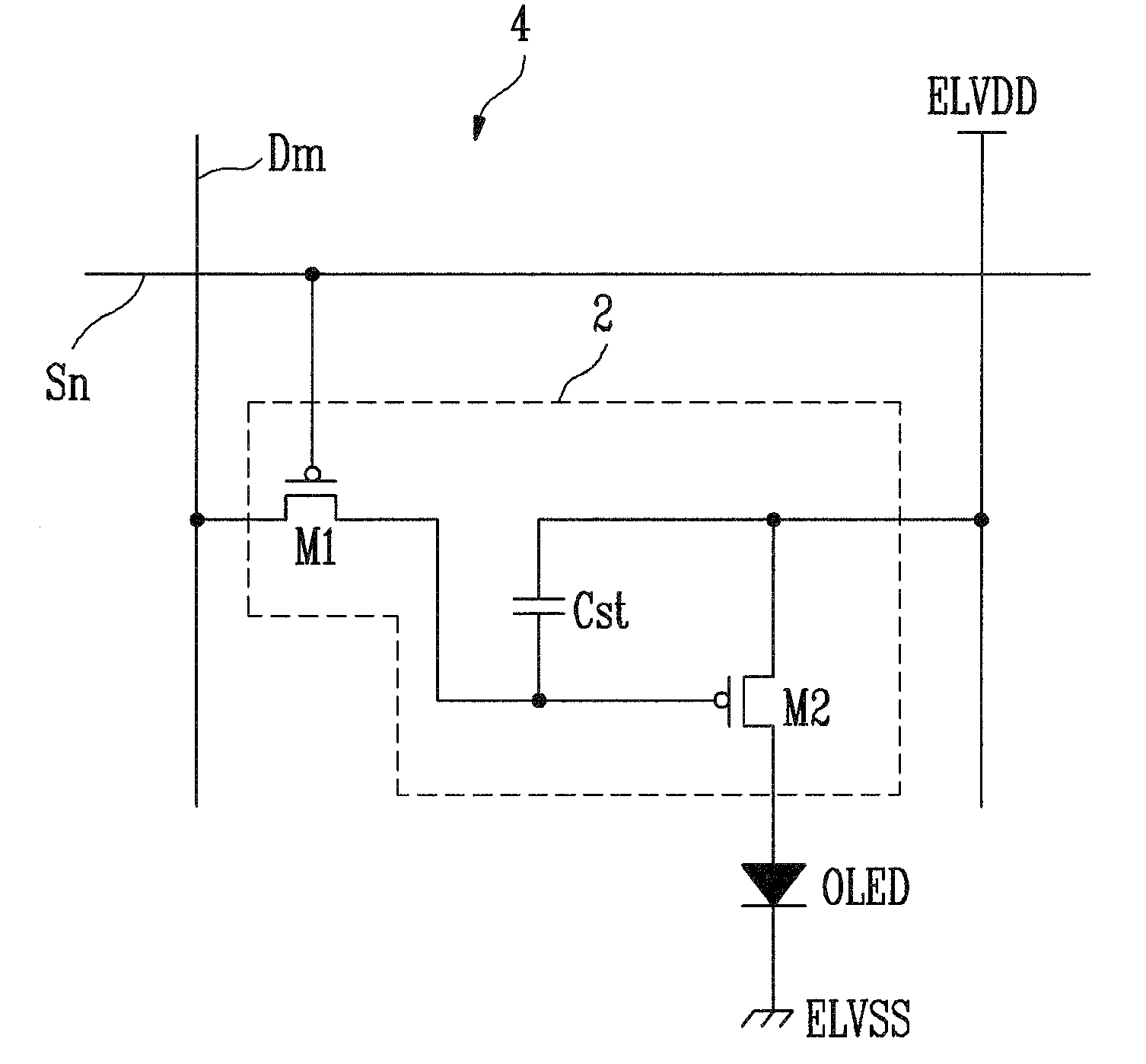
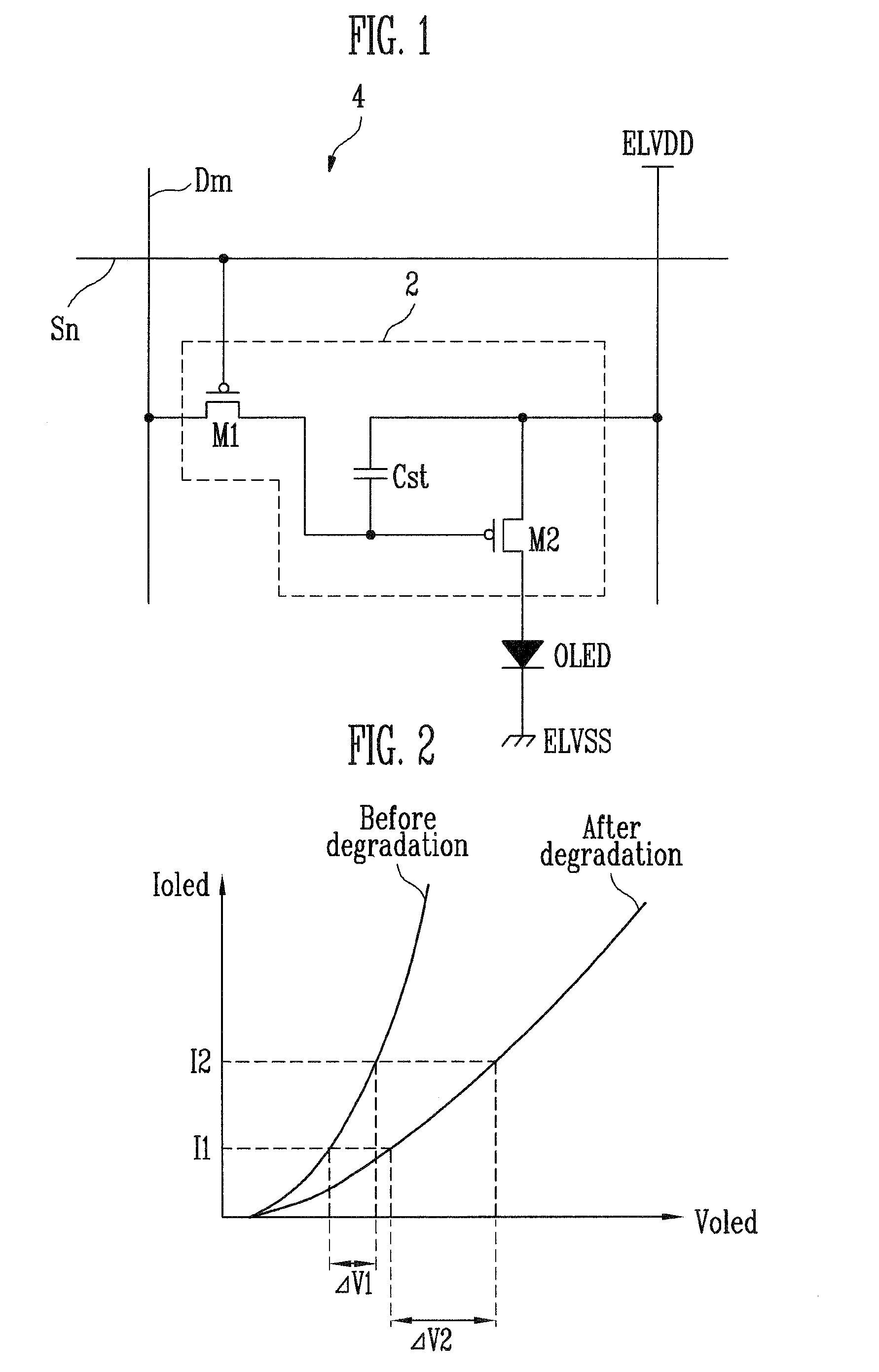
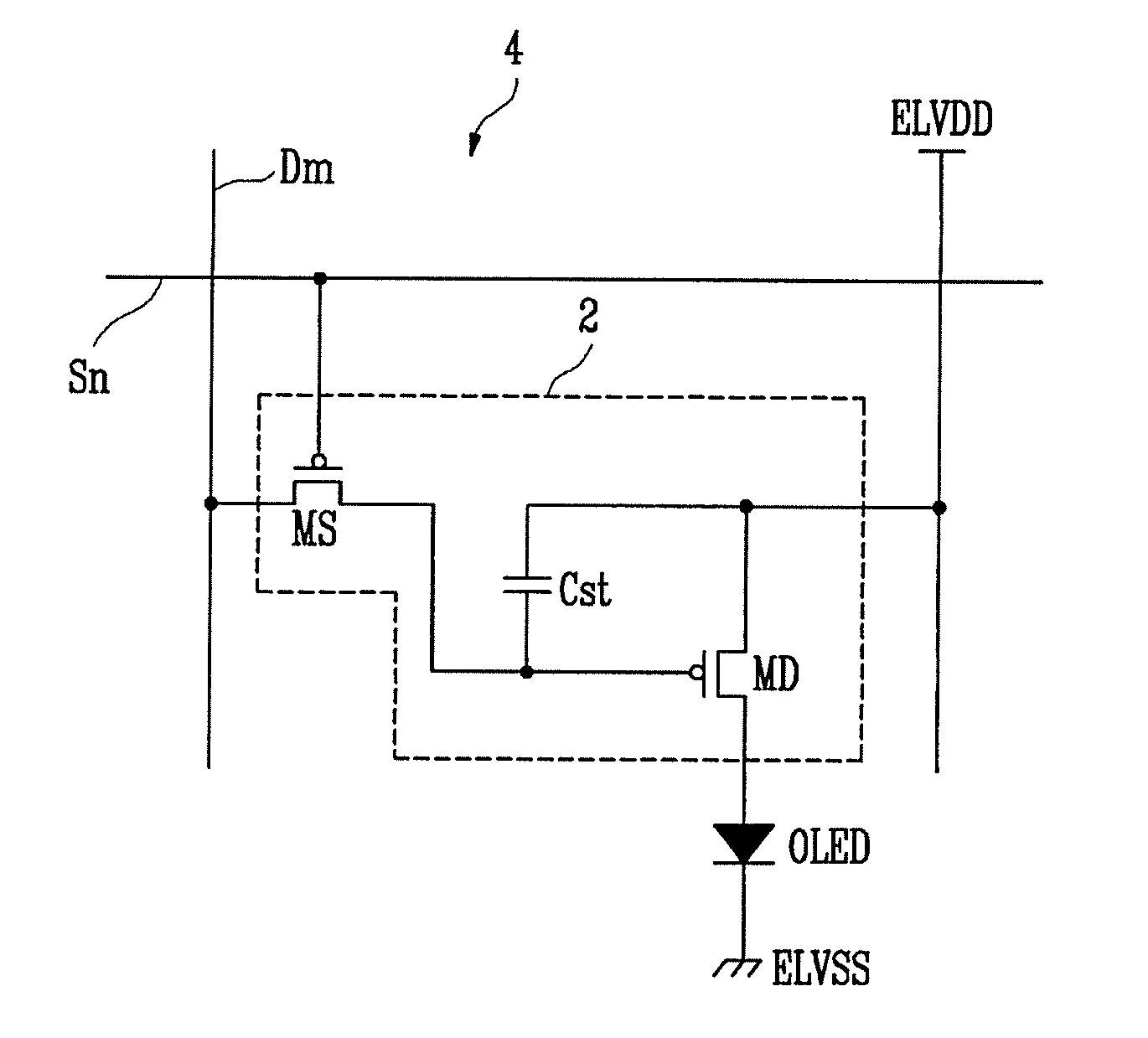
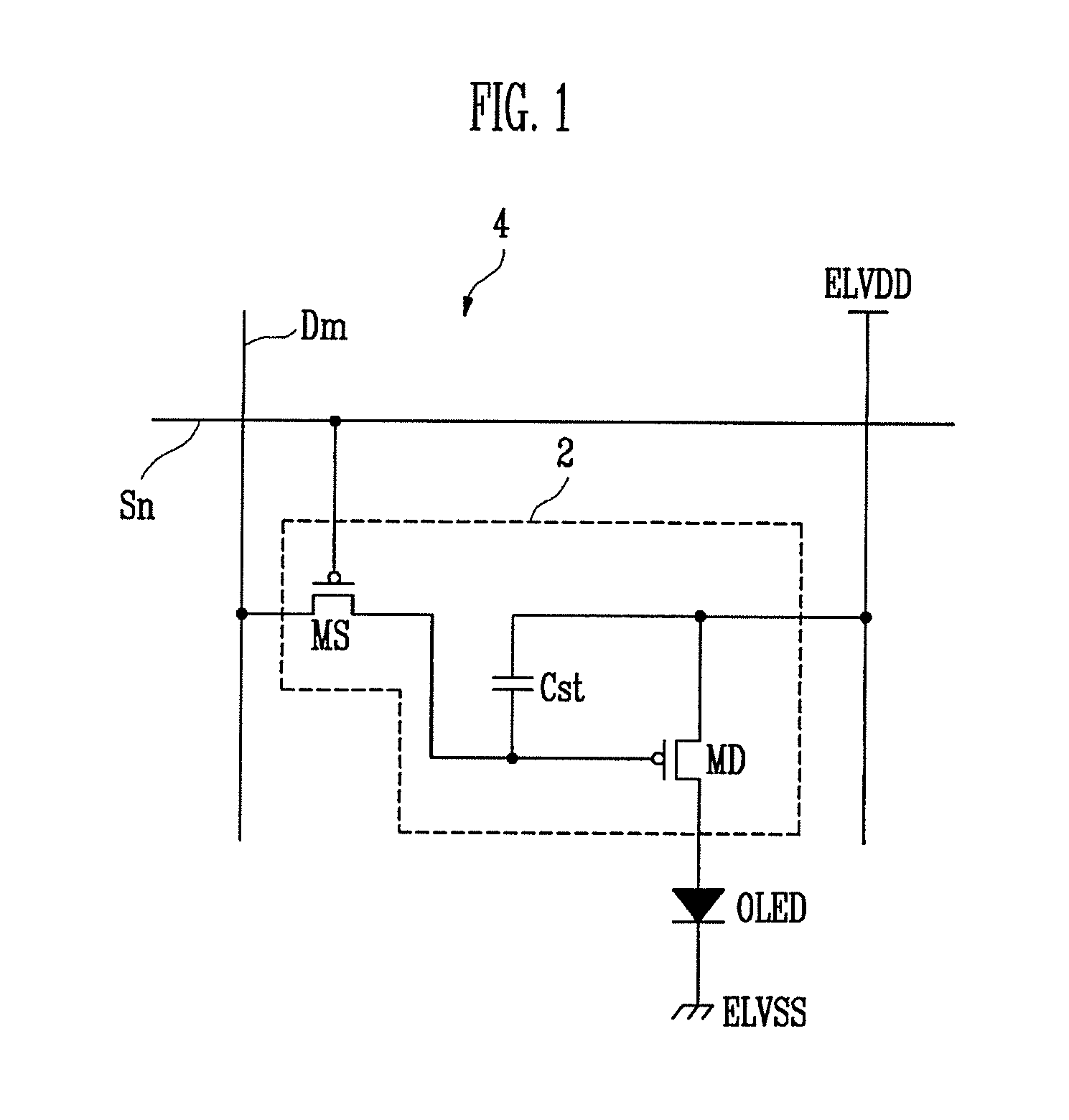
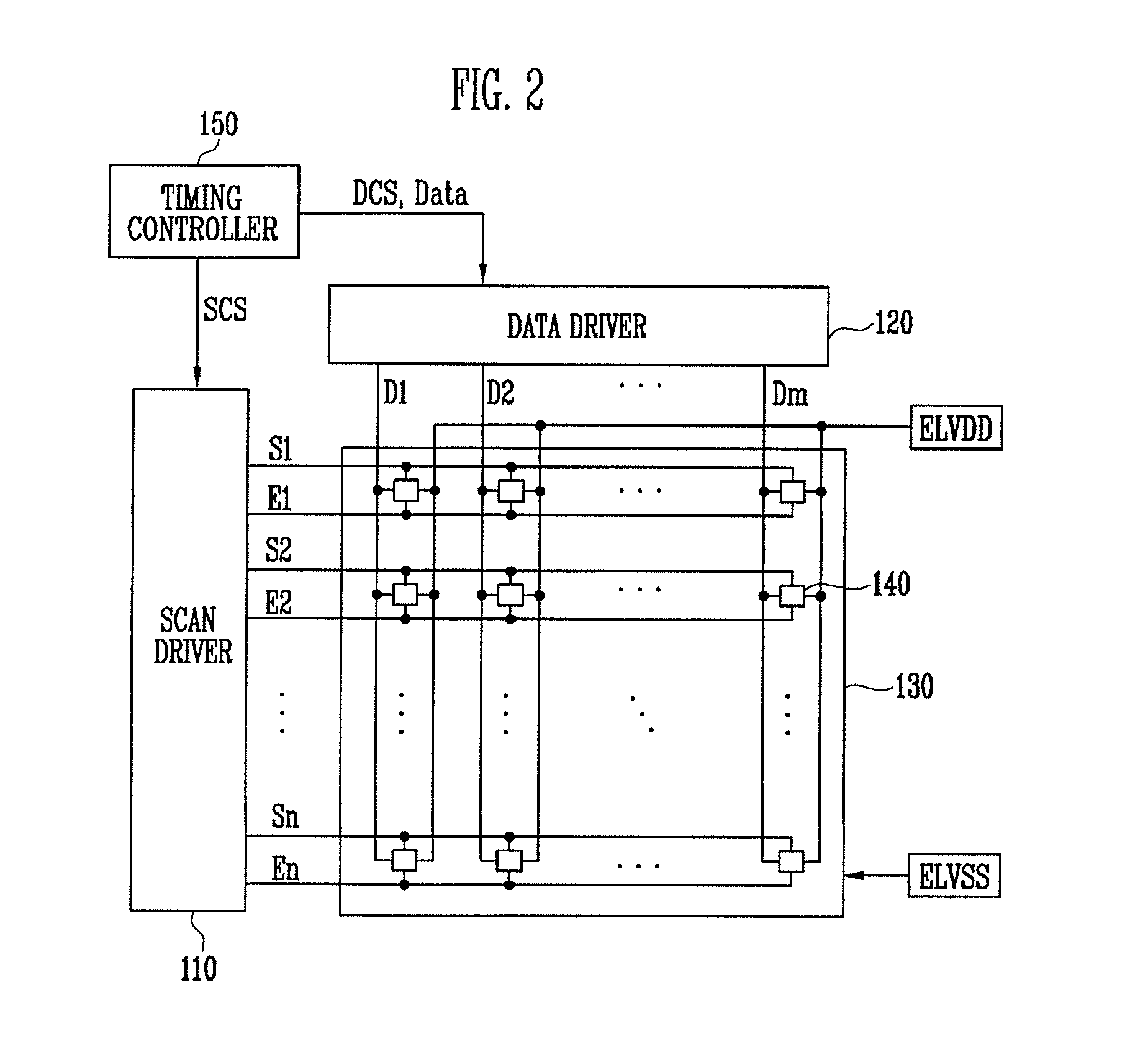
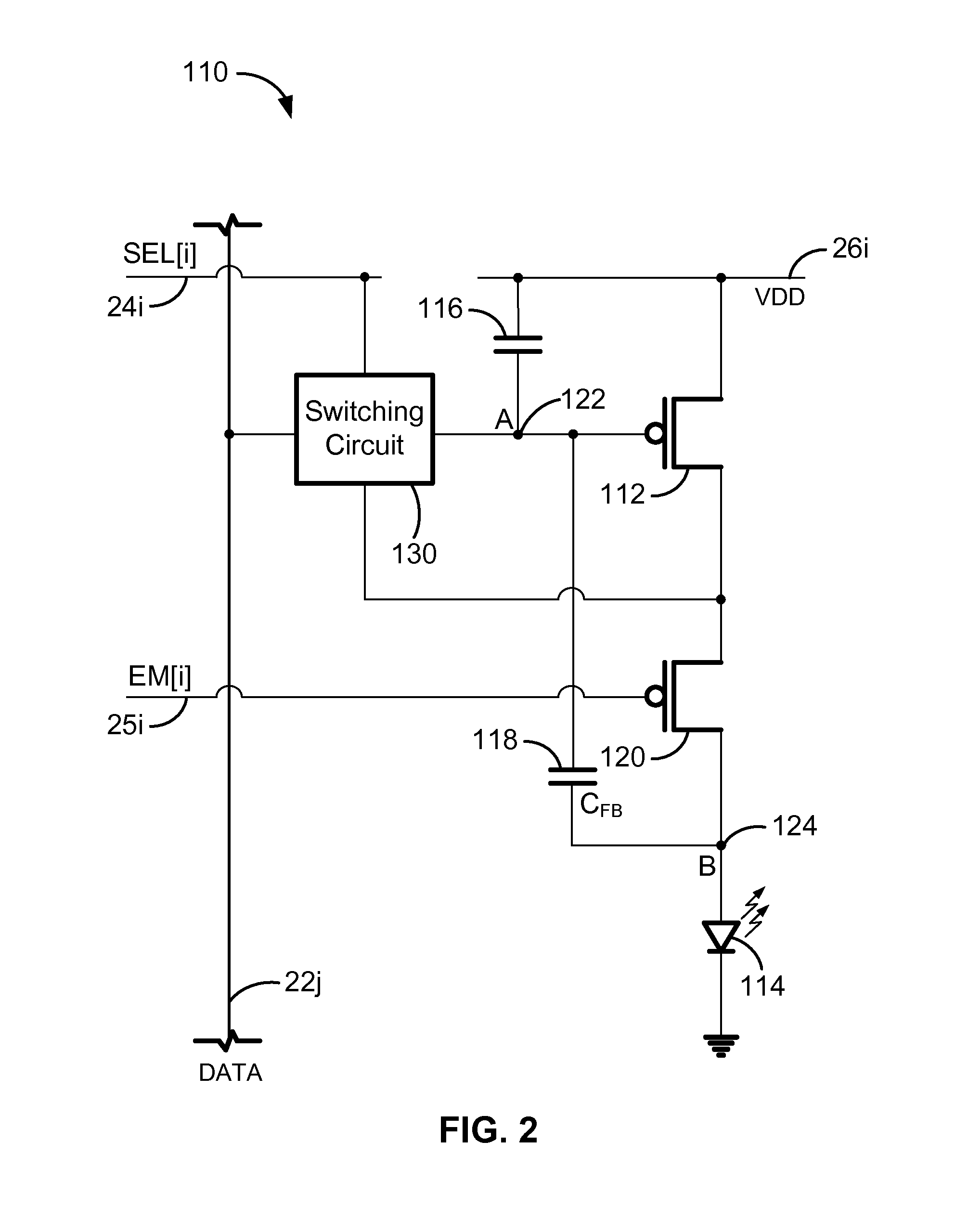
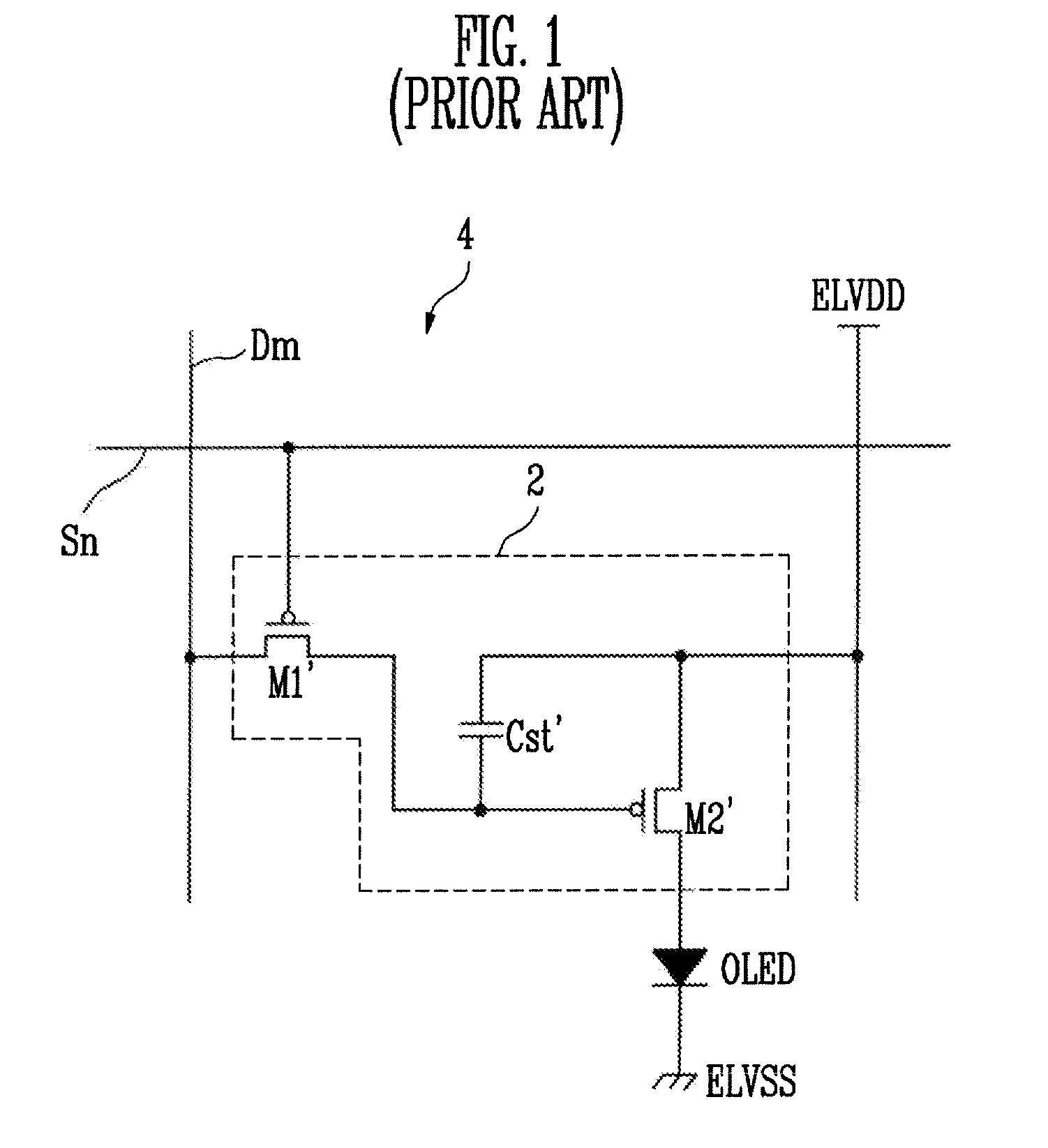
Pixel and organic light emitting display using the same
A pixel capable for compensating for the degradation of an organic light emitting diode. The pixel includes an organic light emitting diode; a pixel circuit including a driving transistor for controlling an electric current capacity flowing from a first power source to a second power source via the organic light emitting diode; and a compensation unit for controlling a voltage of a gate electrode of the driving transistor to correspond to a degradation of the organic light emitting diode. The compensation unit includes first and second feedback capacitors coupled in series between an anode electrode of the organic light emitting diode and the gate electrode of the driving transistor and a switching transistor coupled between a common node of the first and second feedback capacitors and a reset power source and for turning on when a control signal is supplied to a control line coupled to the switching electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Capacitive fingerprint sensor with improved sensing element
ActiveUS9152841B1Parasitic influence is reducedReduce impactCapacitance measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityParasitic capacitance
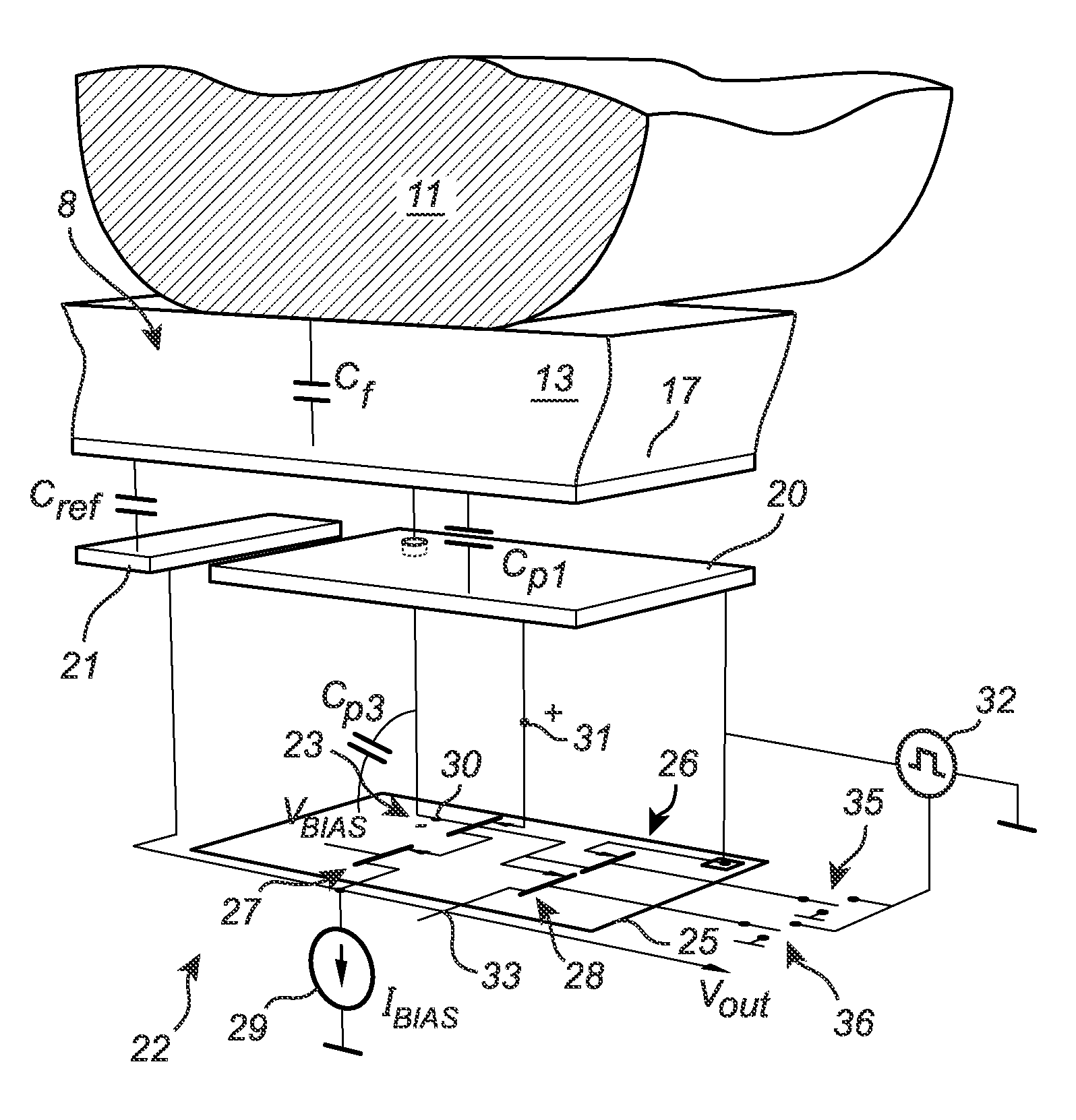
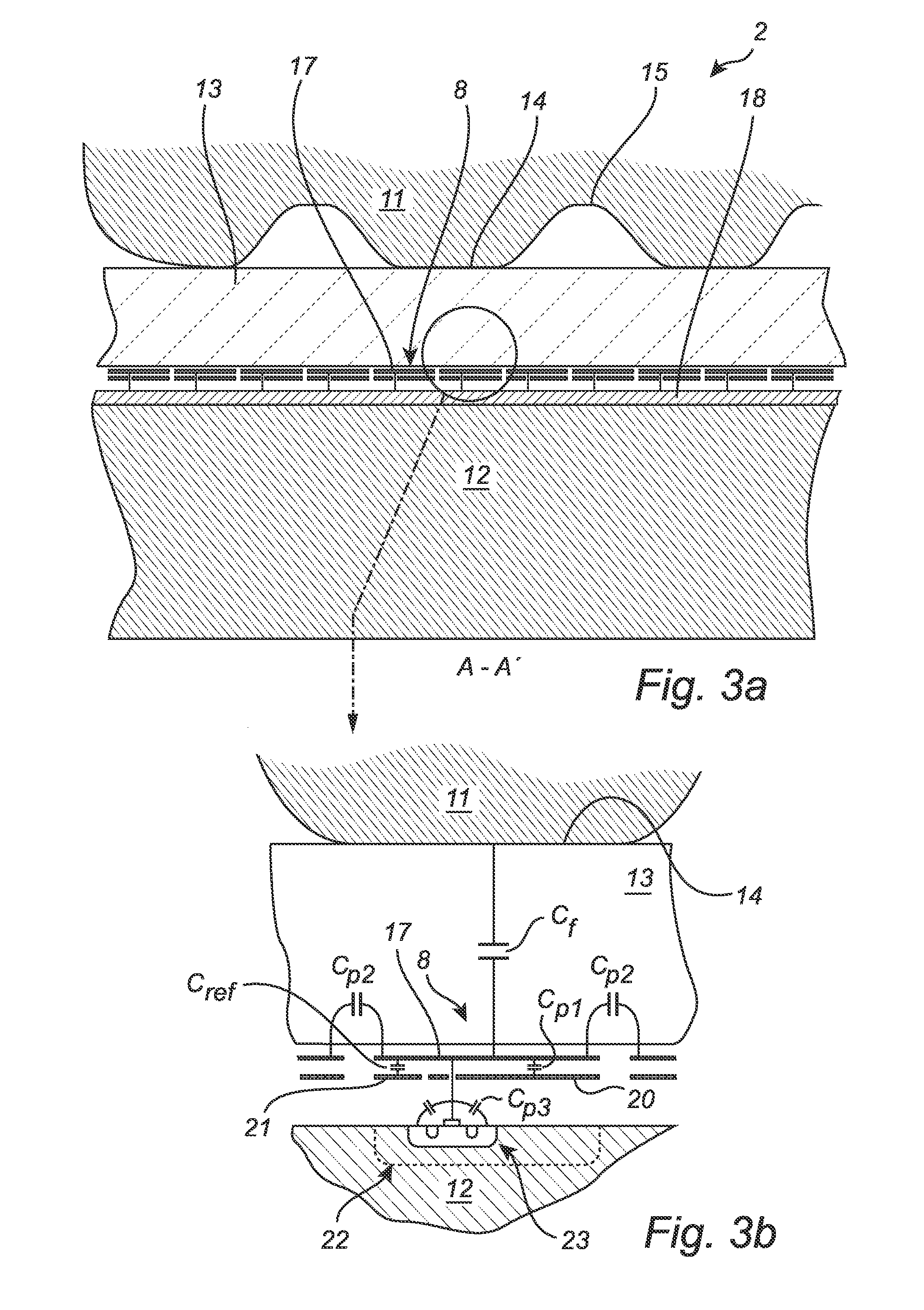
The present invention relates to a capacitive fingerprint sensing device comprising a semiconductor substrate; and an array of sensing elements formed on the semiconductor substrate. Each of the sensing elements comprises a protective dielectric top layer; a sensing structure arranged underneath the top layer; and a charge amplifier connected to the sensing structure. The charge amplifier comprises a negative input connected to the sensing structure; a positive input; an output providing a sensing signal; a feedback capacitor; and a sense transistor having a gate constituting the negative input. The sense transistor is formed in an insulated well in the semiconductor substrate. The fingerprint sensing device further comprises excitation signal providing circuitry connected to the positive input of the charge amplifier and the well for changing electric potentials of the sensing structure and the well, to thereby reduce the influence of parasitic capacitances in the sensing element.
Owner:FINGERPRINT CARDS ANACATUM IP AB
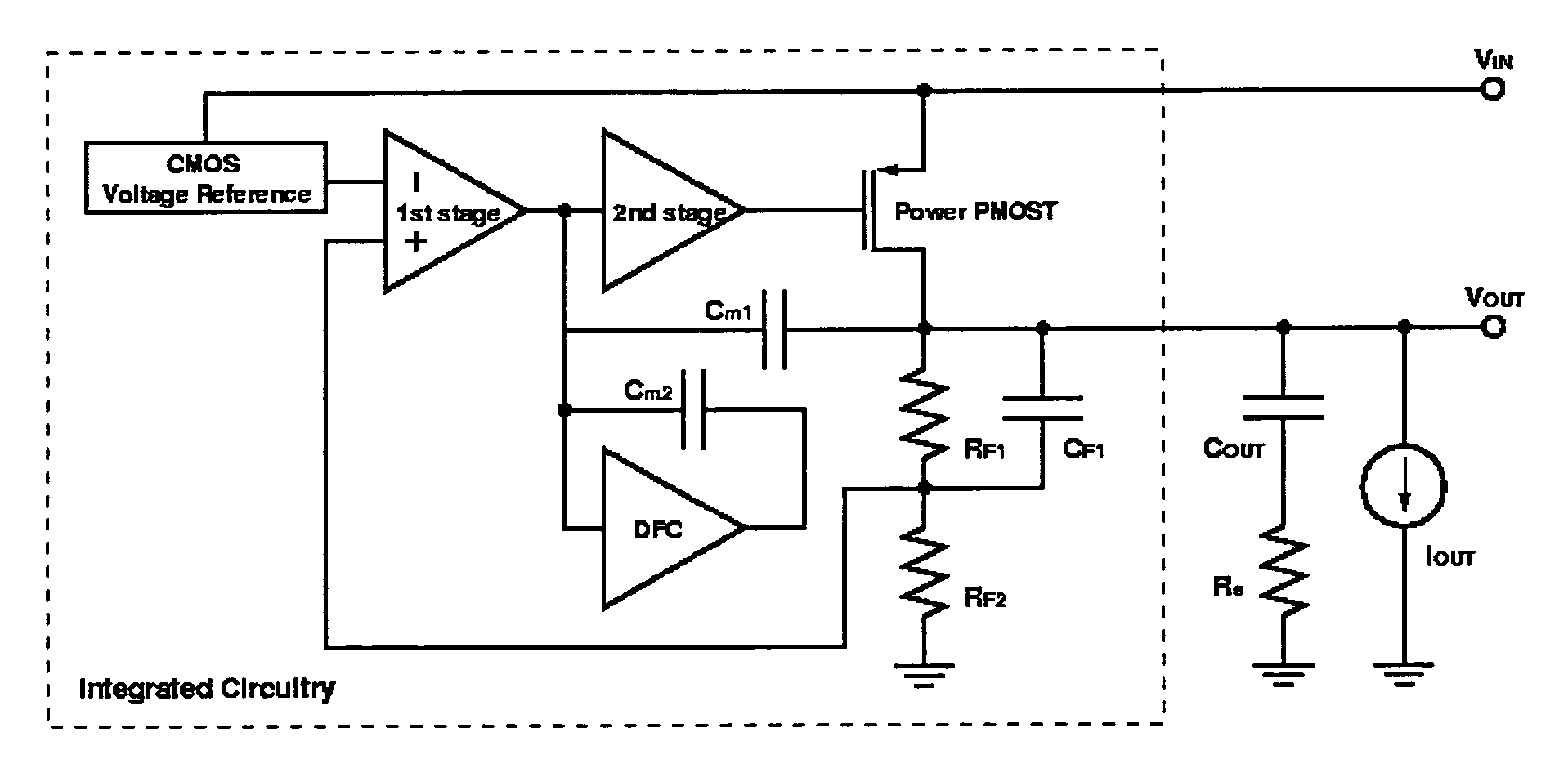
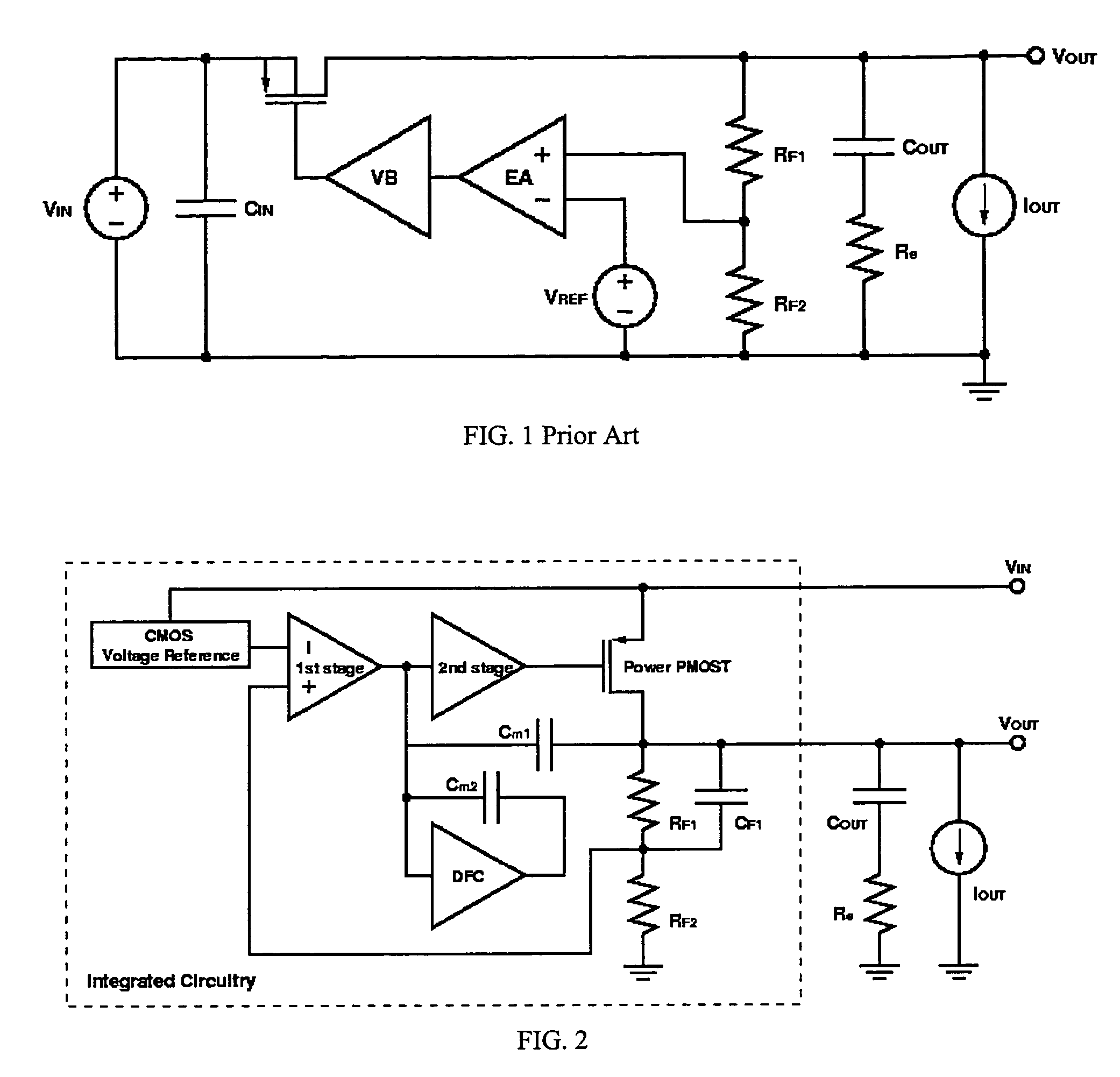
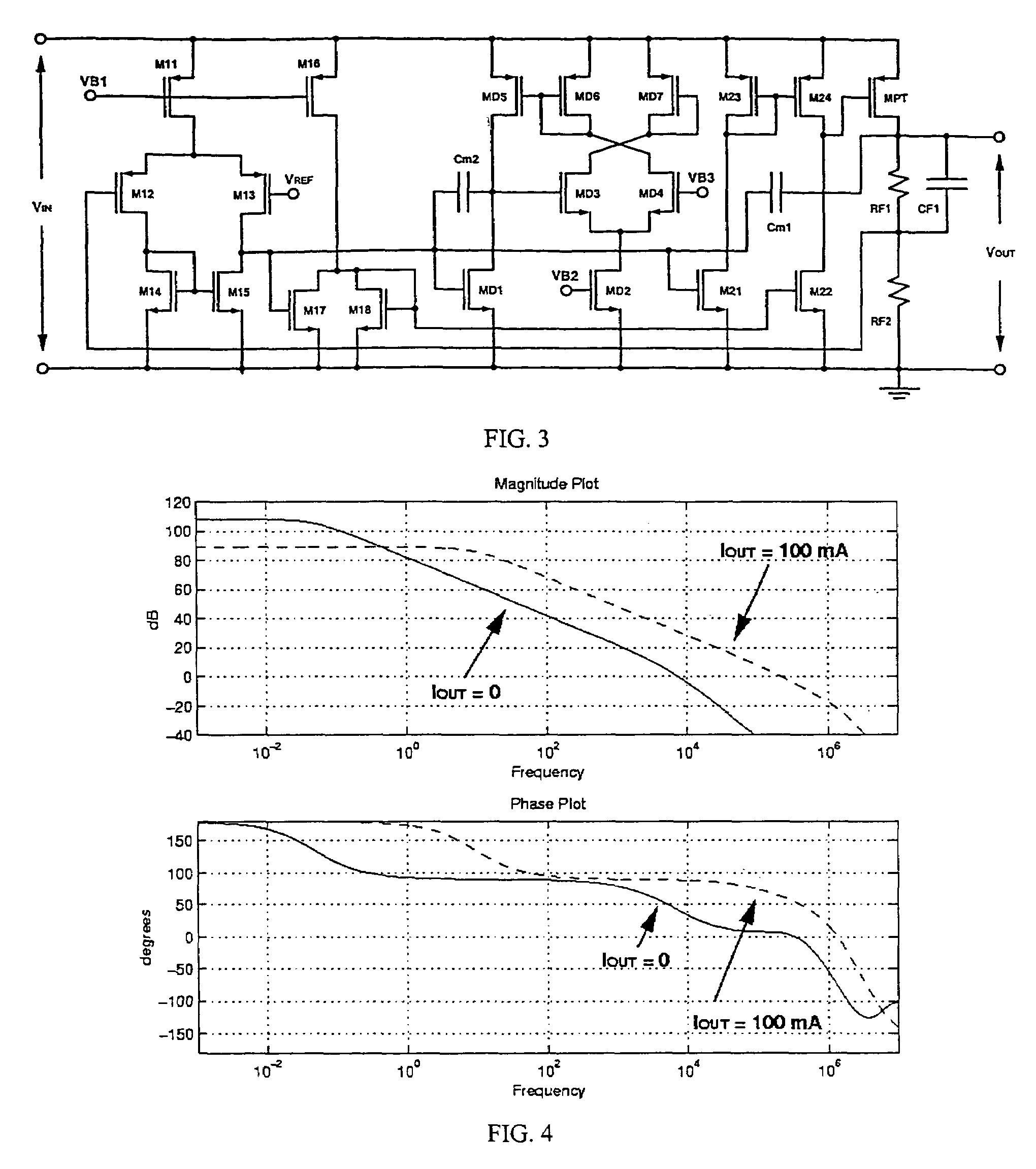
Low dropout regulator capable of on-chip implementation
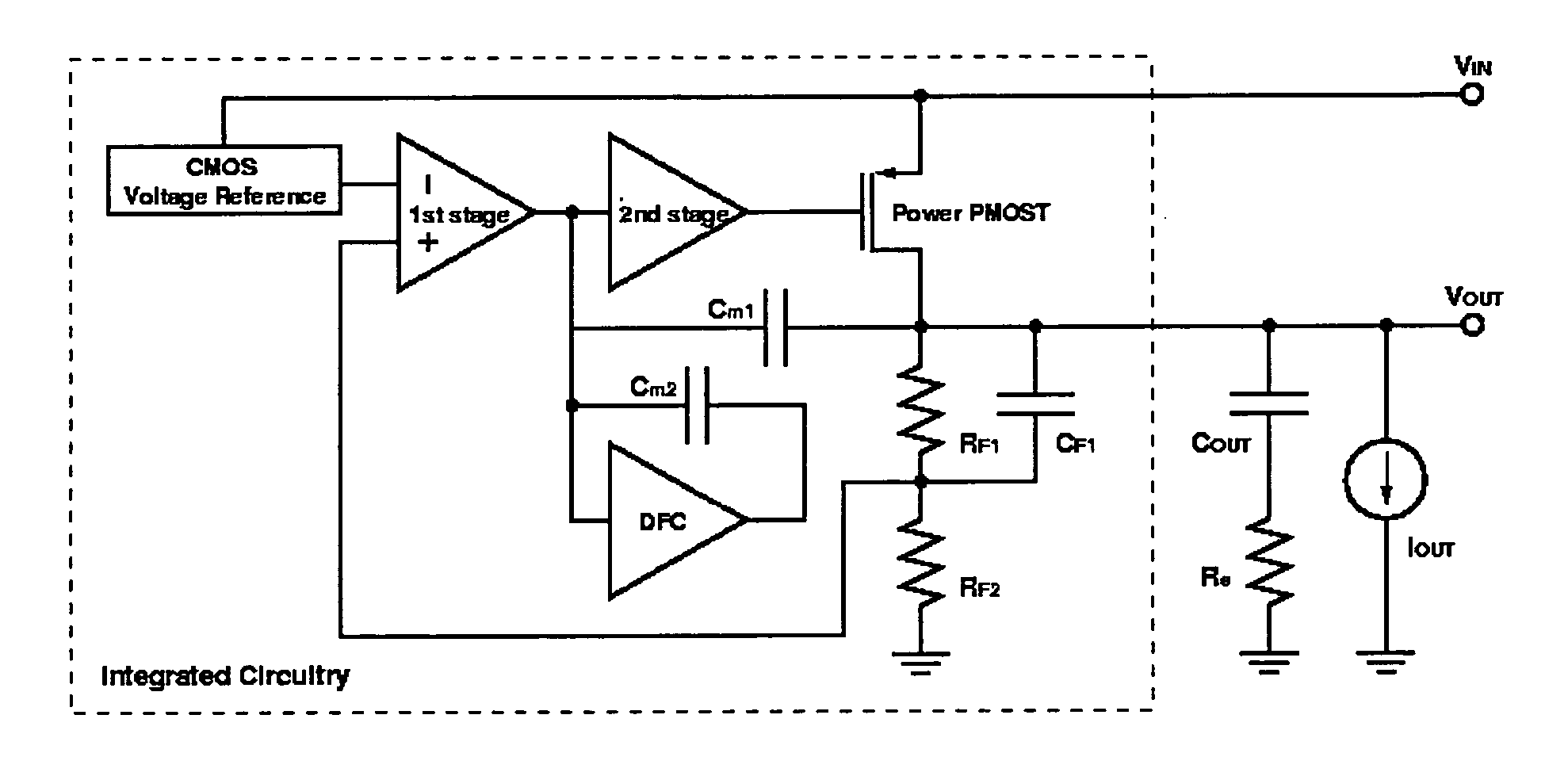
A low-dropout regulator comprises a high-gain error amplifier having a differential input stage and a single-ended output, a high-swing high-positive-gain second stage with input connecting to the output of the error amplifier and a single-ended output, a p-type MOS transistor with gate terminal connecting to the output of the second stage, source terminal connecting to the supply voltage, and drain terminal to the output of the low-dropout regulator. A first-order high-pass feedback network connects the output of the low-dropout regulator and the positive input of the error amplifier, and a damping-factor-control means comprising a negative gain stage with a feedback capacitor connects the input and output of this gain stage. A capacitor is connected between the output of the error amplifier and the output of the low-dropout regulator, while a voltage reference connects to the negative input of the error amplifier. The regulator does not require an off-chip capacitor for stability and has improved load transient response and power supply rejection ratio.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Over current protection circuit and method
InactiveUS7558037B1Efficient and reliableDc-dc conversionArrangements responsive to excess currentCapacitanceVoltage converter
Circuit and method for providing over-current and overloading protection with a single additional pin. A converter controller circuit is provided that includes a voltage controlled oscillator and outputs upper and lower gating signals for driving the upper and lower driving transistors in a voltage converter, for example, in an inductor-inductor capacitor half-bridge circuit topology. A current sense input pin of the circuit receives a voltage corresponding to the current flowing in the half-bridge circuit. A feedback input pin has an external capacitor coupled to it and receives a voltage from an output voltage sensor at the output terminals. Over-current protection is provided by sensing the voltage at the current sense input pin with no external components needed. Overload protection is provided by utilizing the external feedback capacitor and the feedback input pin during overload conditions. Methods for providing over-current and overload protection are disclosed.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Pixel, organic light emitting display using the same, and associated methods
A pixel including an organic light emitting diode, a second transistor controlling a current supplied to the organic light emitting diode, a pixel circuit configured to compensate a threshold voltage of the second transistor; and a compensating unit controlling a voltage of a gate electrode of the second transistor in order to compensate for deterioration of the organic light emitting diode. The compensating unit includes seventh and eighth transistors coupled in series between the organic light emitting diode and a first power source, the seventh and eight transistors being commonly connected to a fourth node therebetween, first and second feedback capacitors coupled in series between the fourth node and a second node, the second node being coupled to the gate electrode of the second transistor, and a ninth transistor coupled between a predetermined voltage source and a fifth node that is common to the first and second feedback capacitors.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Switched capacitor amplifier with higher gain and improved closed-loop gain accuracy
ActiveUS20080186093A1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier combinationsCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
A switched capacitor CMOS amplifier uses a first stage non-inverting CMOS amplifier driving a second stage inverting CMOS amplifier. The first stage amplifier is provided with positive feedback to substantially increase the gain of the first stage amplifier. In the described examples, the positive feedback is provided either by connecting a capacitor from the output to the input of the first stage amplifier or by connecting a shunt transistor in parallel with an input transistor and driving the transistor from the output of the first stage amplifier. The substantially increased gain resulting from the positive feedback allows the gain of the switched capacitor amplifier to be set by the ratio of the capacitance of an input capacitor to the capacitance of a feedback capacitor. The amplifier also includes switching transistors for periodically discharging the input capacitor and the feedback capacitor.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Pixel and organic light emitting display using the same
ActiveUS20110102403A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDriving currentPower flow
A pixel capable of compensating for the deterioration of an organic light emitting diode (OLED). The pixel includes an OLED coupled between first and second power sources, a pixel circuit including a driving transistor coupled between the first power source and the OLED and having a gate electrode coupled to a first node so that driving current corresponding to a voltage applied to the first node is supplied to the OLED, and a compensation circuit for controlling the voltage of the first node in accordance with deterioration of the OLED to compensate for the deterioration of the OLED. The compensation circuit includes first and second transistors coupled between the OLED and a third power source, first and second feedback capacitors coupled between the first node and a second node that is between the first transistor and the second transistor, and a third transistor coupled to the third power source.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
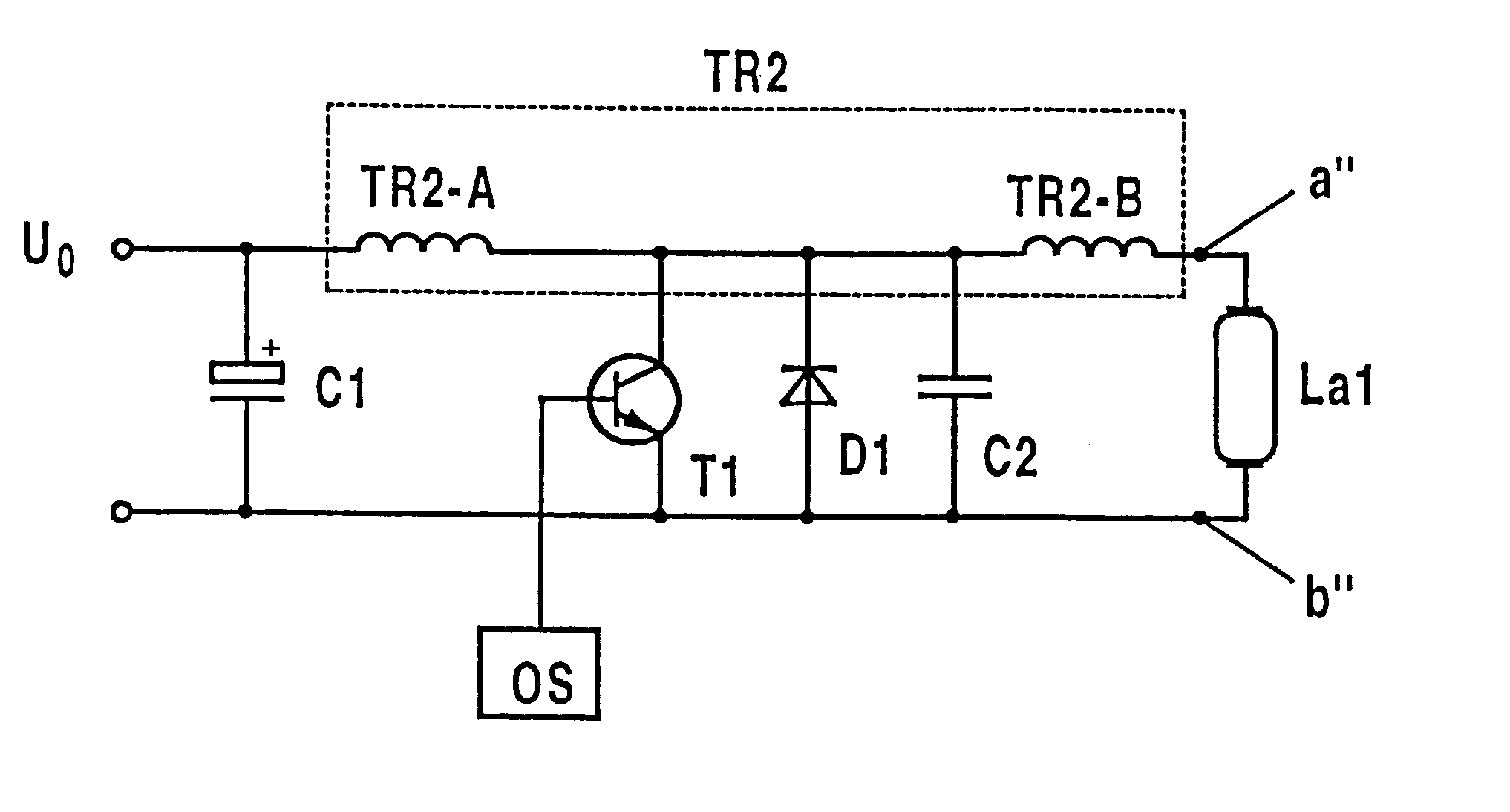
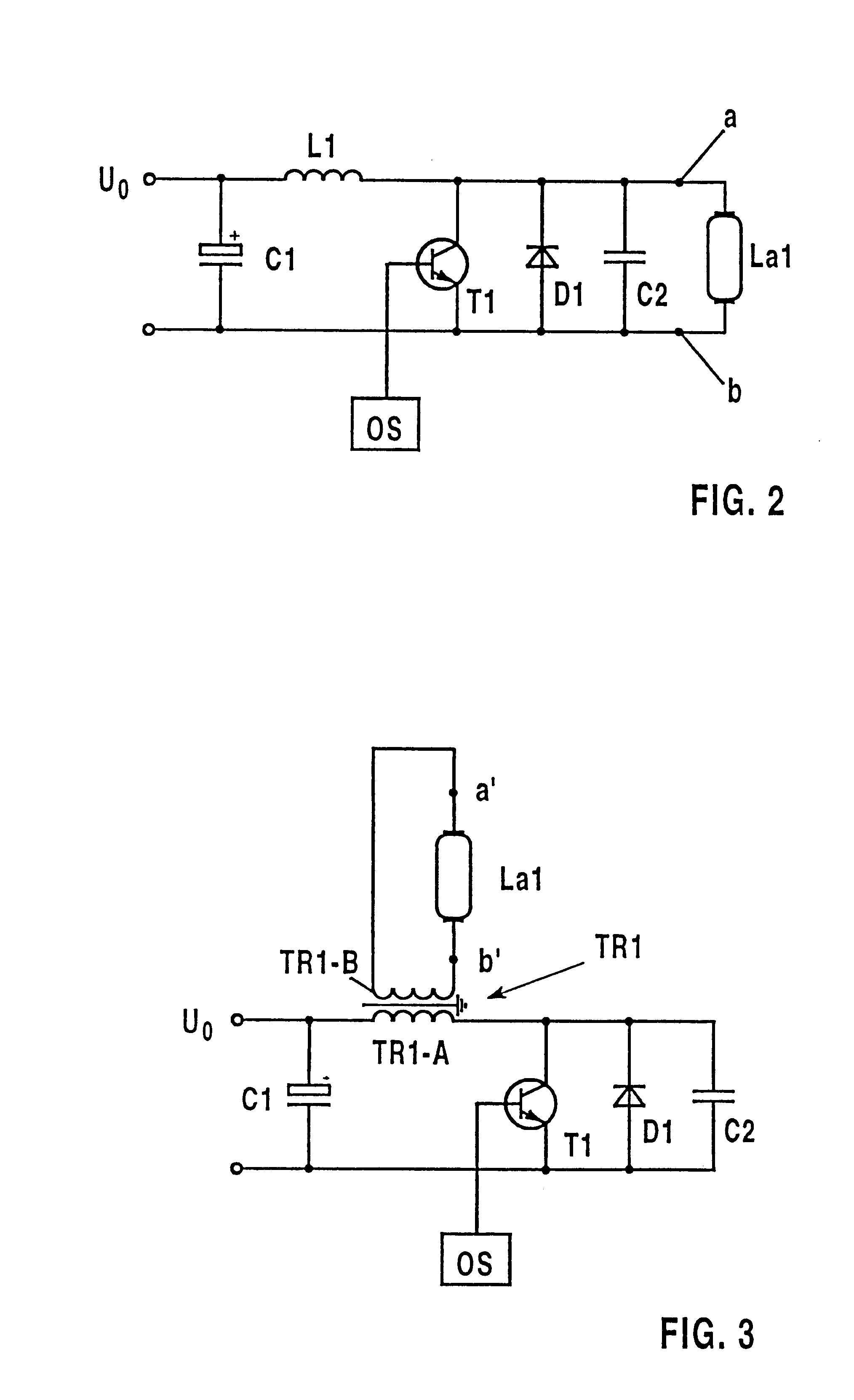
Process for generating voltage pulse sequences and circuit assembly therefor
InactiveUS6323600B1Electric light circuit arrangementGas discharge lamp usageCapacitanceAutotransformer
An electrical circuit arrangement for producing pulsed-voltage sequences for the operation of discharges which are impeded dielectrically comprises a series circuit formed from a tuned circuit inductance (TR2-A) and a controlled switch (T1), a pulse generator (OS) which drives the switch (T1), an electrical valve (D1) which is connected in parallel with the switch (T1), a tuned circuit capacitance (C2) which is likewise connected in parallel with the switch (T1), a means (TR2-B, a'', b'') for coupling a lamp (La1) to at least one electrode which is impeded dielectrically, and, optionally, a buffer and feedback capacitor (C1) which is connected in parallel with the series circuit formed by the tuned circuit inductance (TR2-A) and the switch (T1). The means for coupling a lamp comprises in particular two connections (a'', b'') and the secondary winding (TR2-B) of an autotransformer (TR2), which is connected between a first pole of the switch (T1) and the corresponding connection (a''), the primary winding (TR2-A) of the autotransformer (TR2) acting as the tuned circuit inductance. The second connection (b') is connected to the second pole of the switch (T1). In operation, the switch (T1) opens and closes alternately in time with the drive signal of the pulse generator (OS), as a result of which a sequence of voltage pulses, which are separated by pauses, is produced at the electrodes, which are impeded dielectrically, of a lamp (La1) which is connected to the connections (a'', b'').
Owner:PATENT TREUHAND GESELLSCHAFT FUR ELECTRIC GLUEHLAMPEN MBH
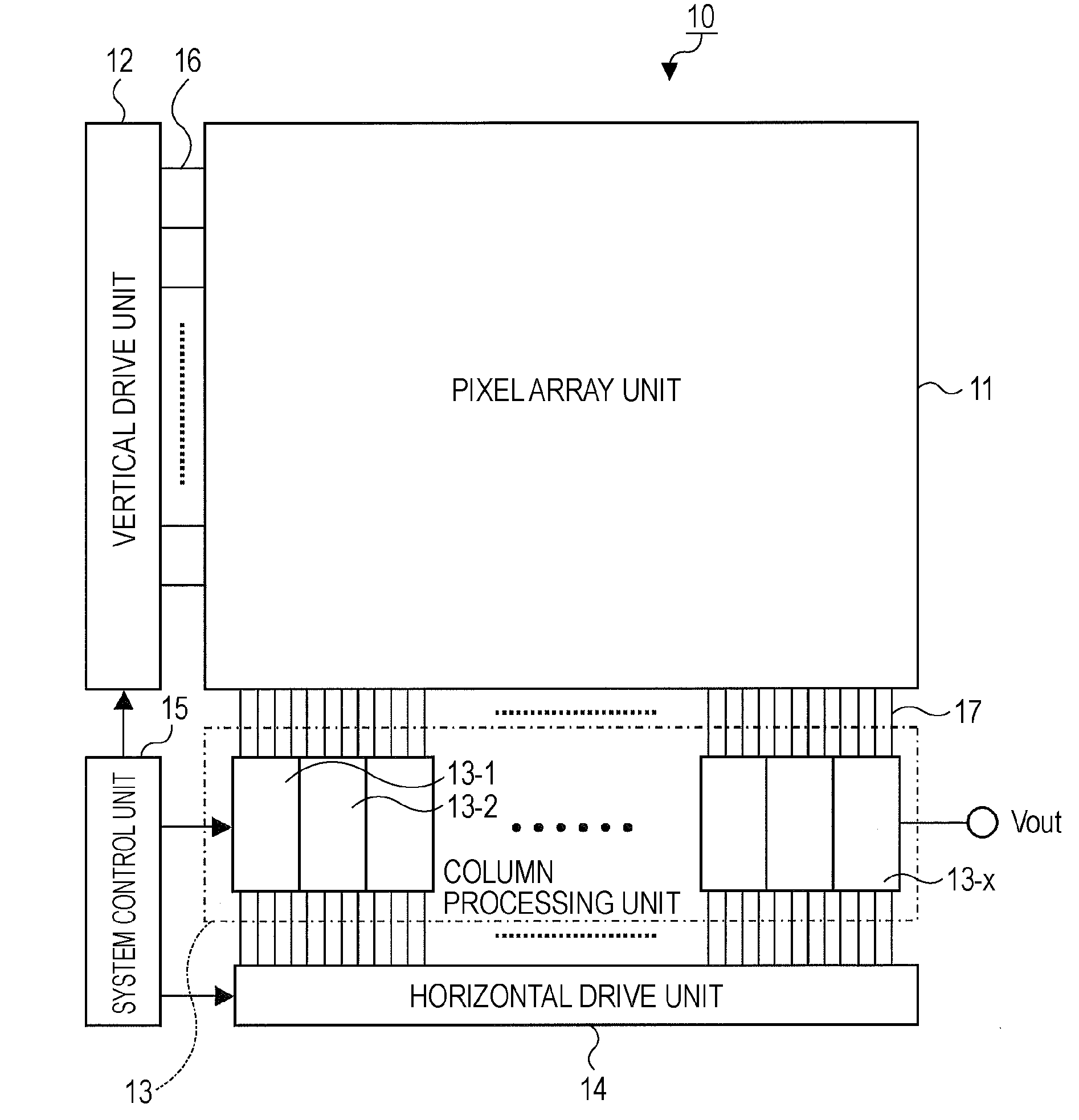
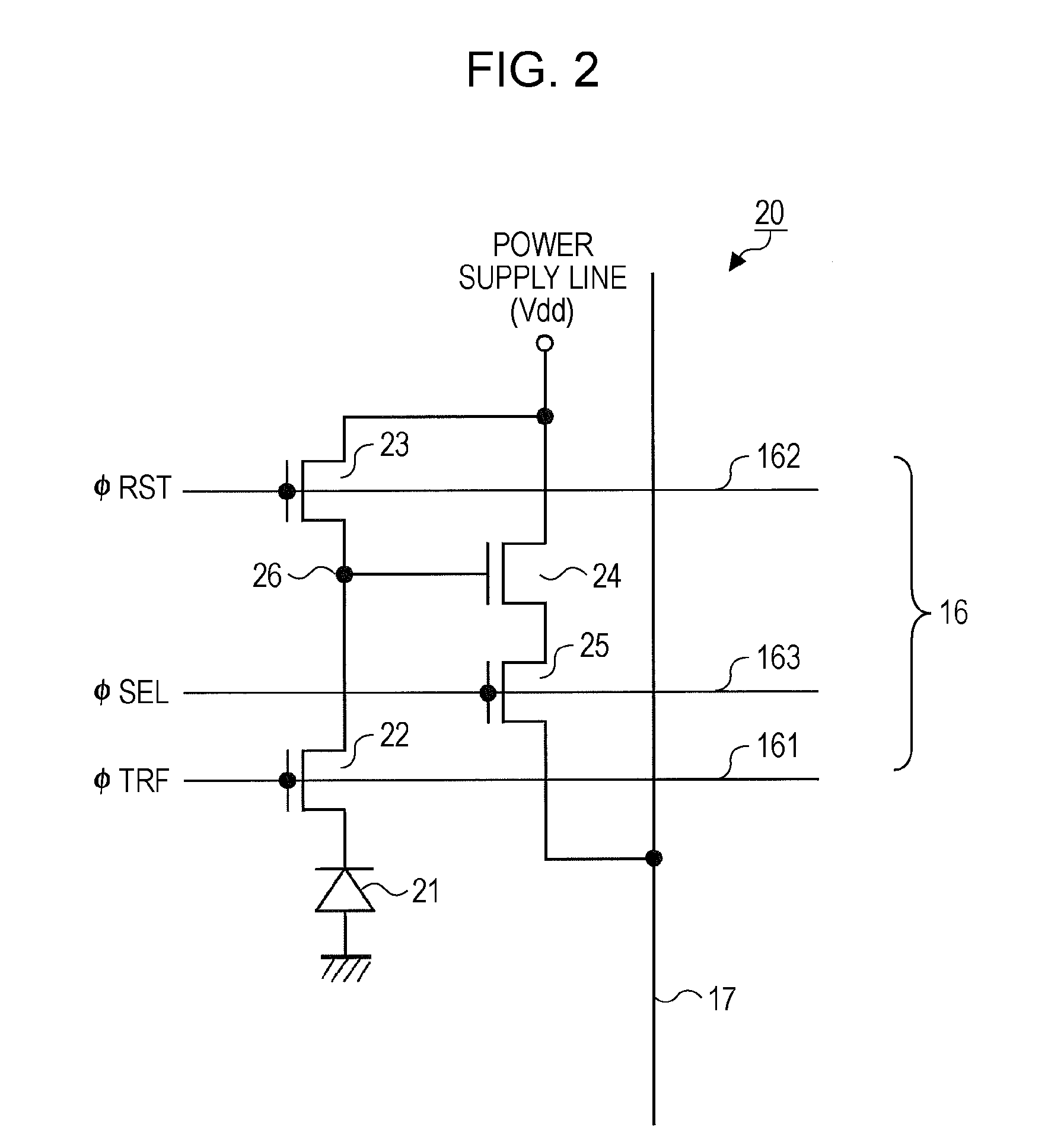
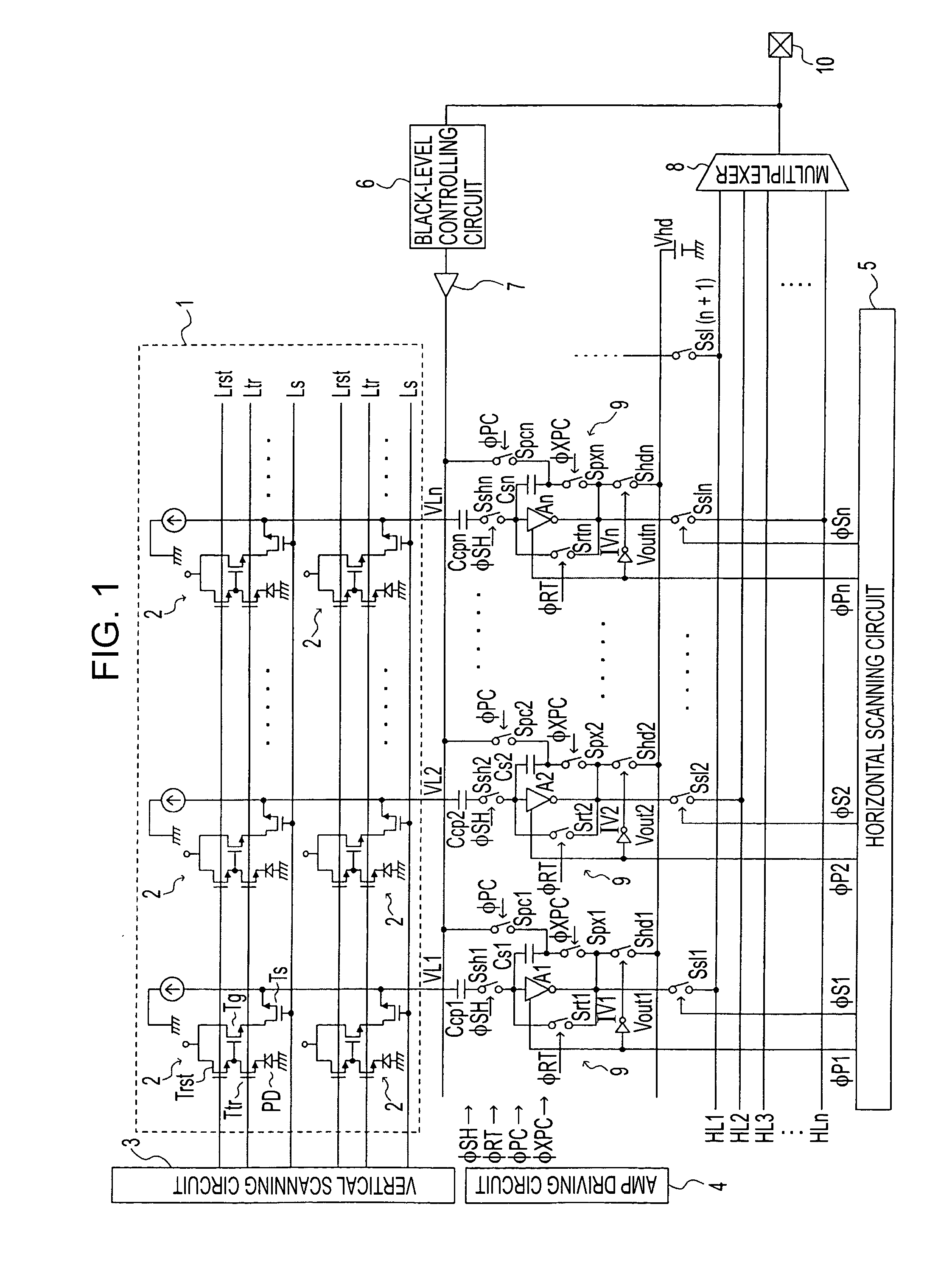
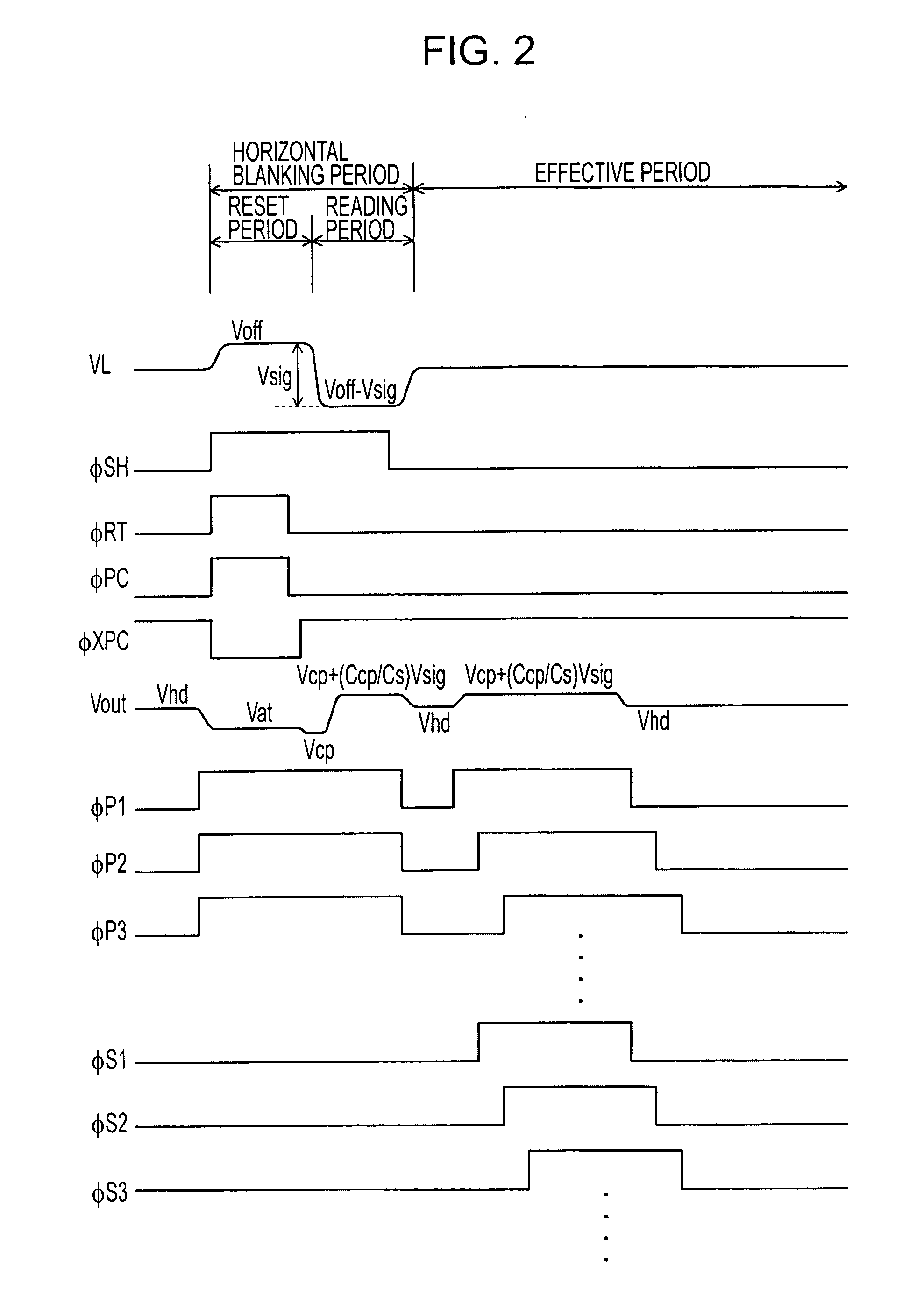
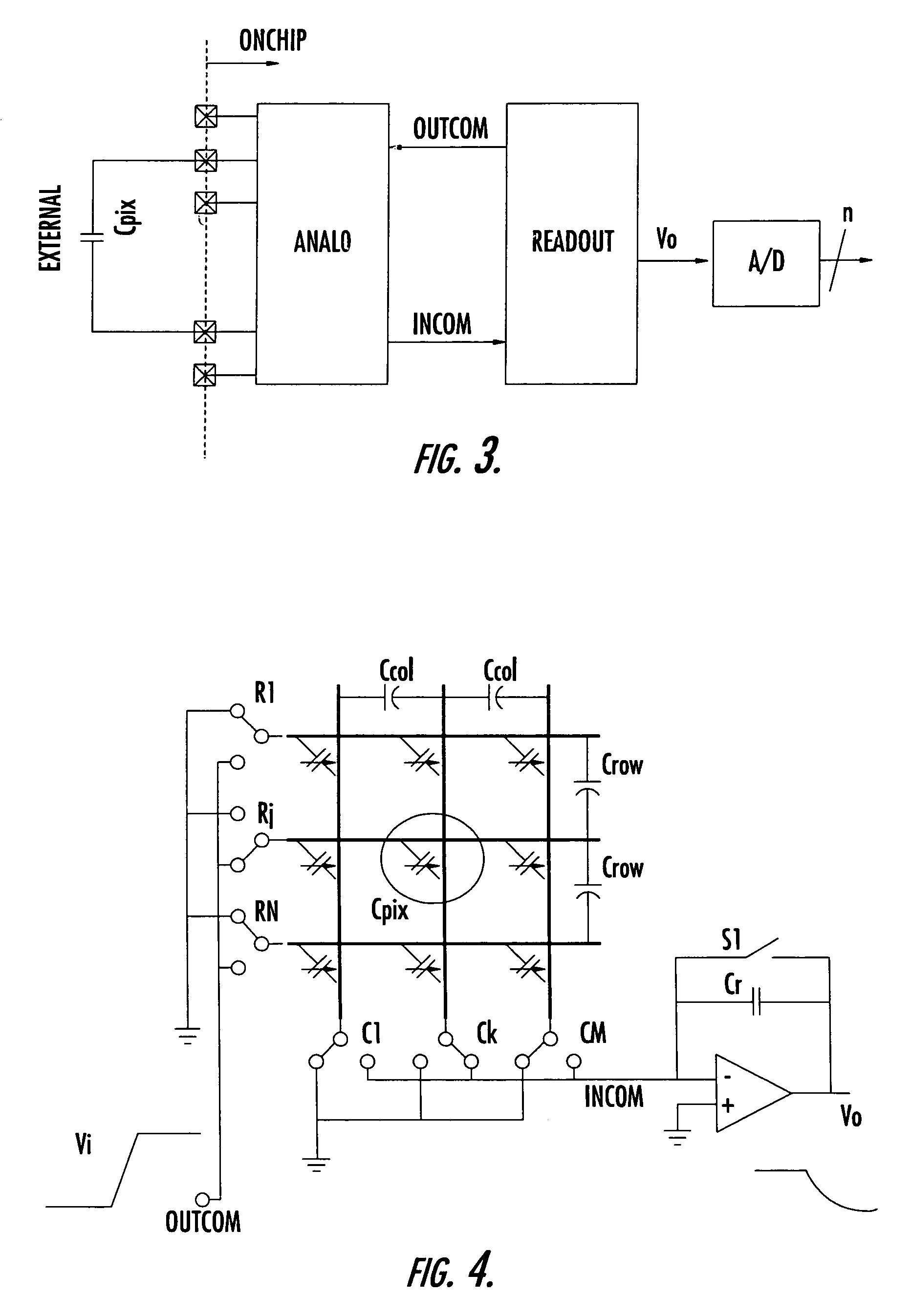
Solid-state image sensing device, method for reading signal of solid-state image sensing device, and image pickup apparatus
ActiveUS20090190018A1Reduce circuit areaReduce chip sizeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
An image sensor includes a pixel array having vertical signal lines, each interconnected to one of columns of the pixel array, and a column processor including a unit readout circuit provided for each of sets of a predetermined number of columns. The unit readout circuit includes input switches, each connected to a corresponding one of the vertical signal lines and being sequentially turned on and off, an input capacitor having one end commonly connected to the input switches, a reference switch for selectively providing a reference voltage to the input capacitor, an operational amplifier connected to the other end of the input capacitor, a reset switch for selectively providing a short-circuit between input and output ends of the operational amplifier, and a feedback circuit provided for each of the columns and including a feedback switch and a feedback capacitor connected in series between the two ends of the operational amplifier.
Owner:SONY CORP
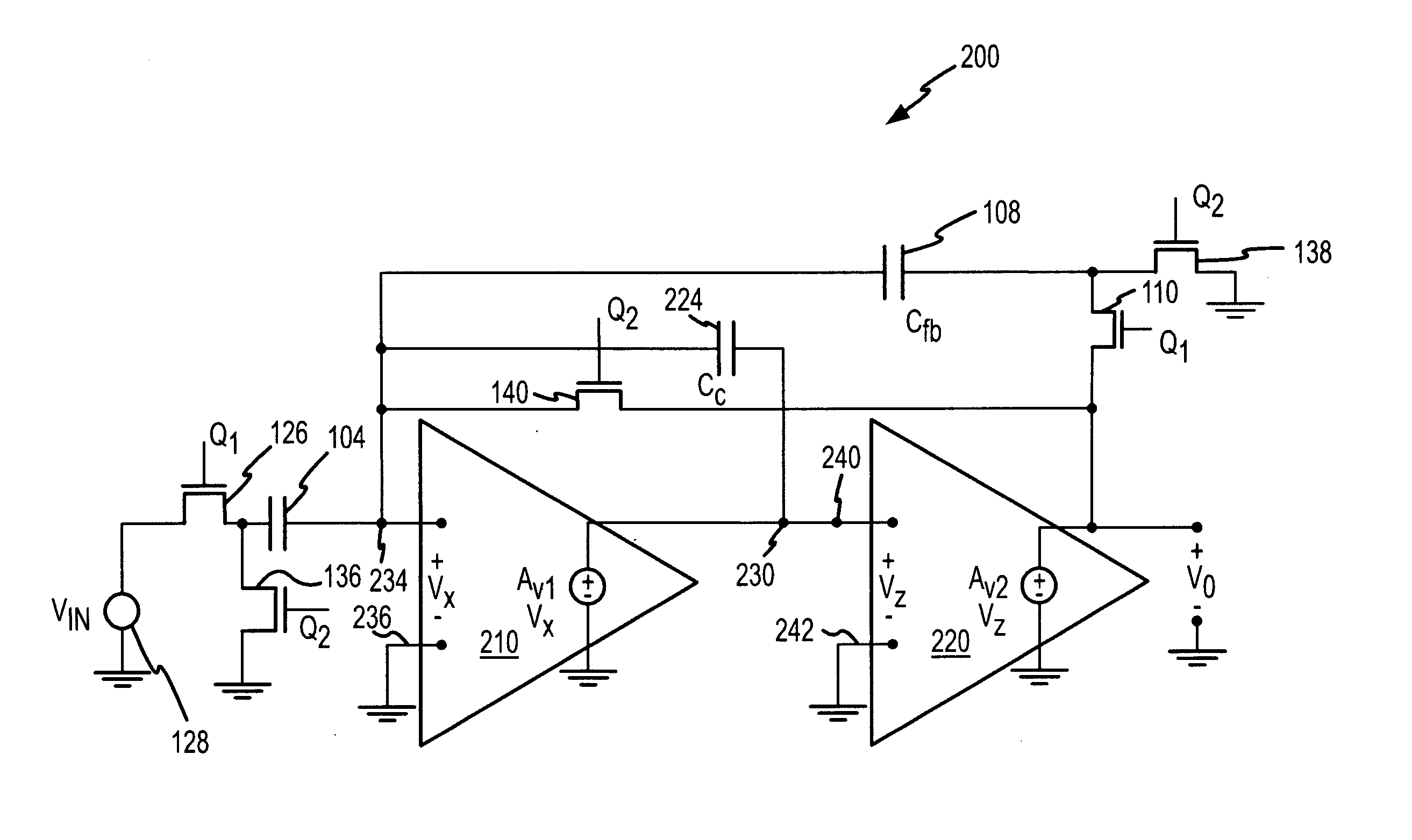
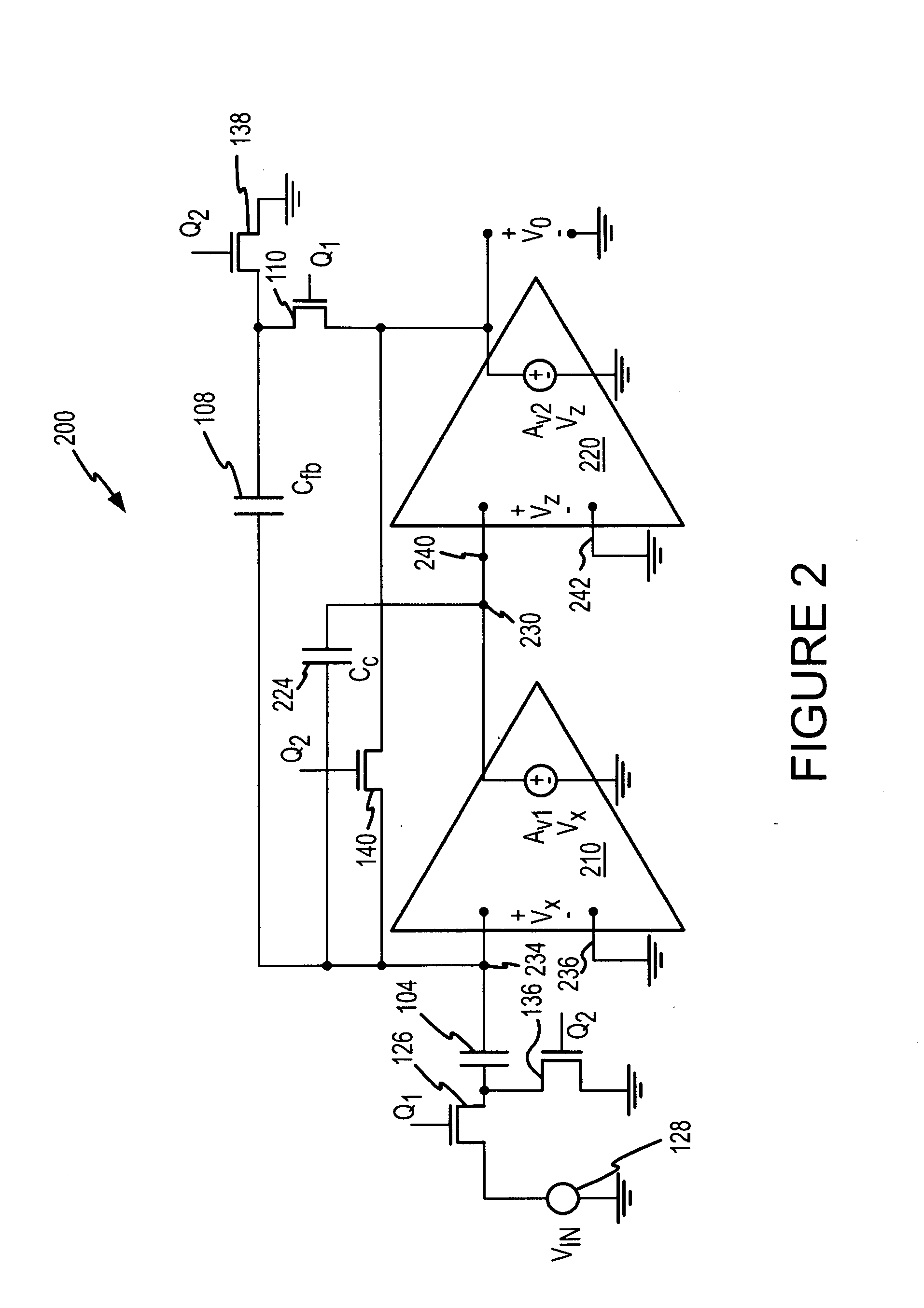
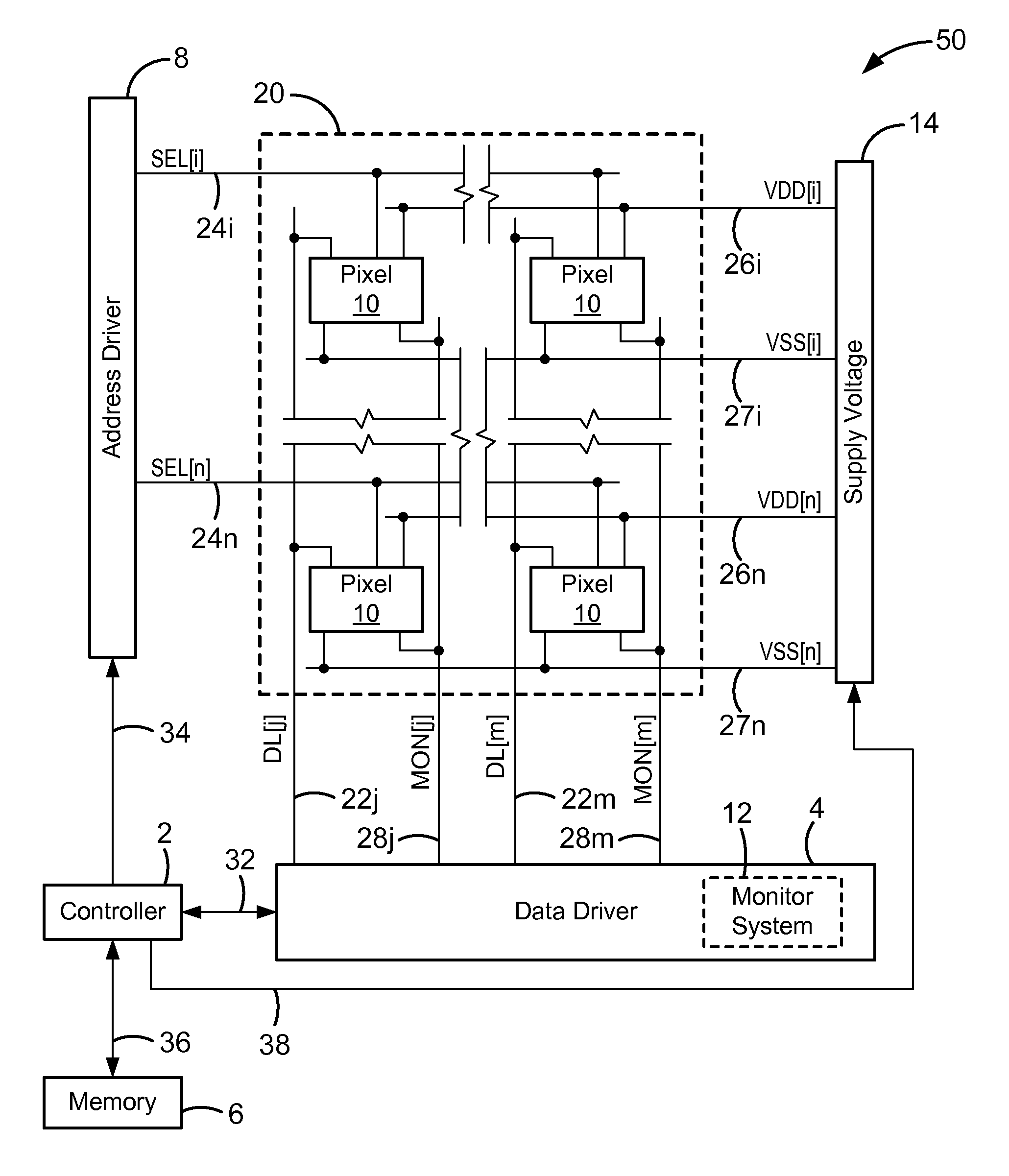
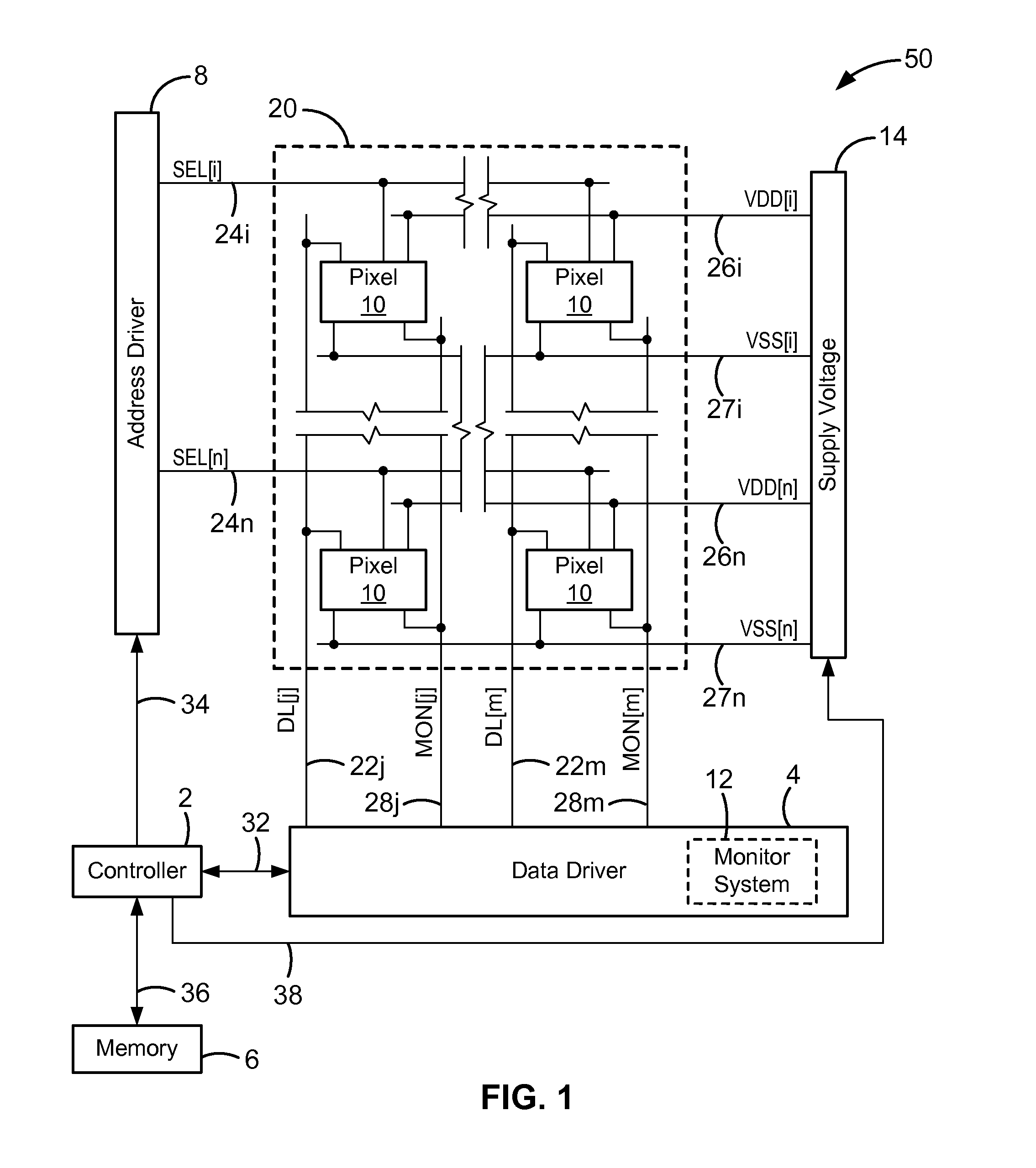
Pixel circuits including feedback capacitors and reset capacitors, and display systems therefore
ActiveUS20130300724A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingCapacitancePower flow
A display with a pixel circuit for driving a current-driven emissive element includes a feedback capacitor in series between the emissive element and a programming node of the pixel circuit. During driving, variations in the operating voltage of the emissive element due to variations in the current conveyed through the emissive element by a driving transistor are accounted for. The feedback capacitor generates voltage adjustments at the programming node that correspond to the variations at the emissive element, and thus reduces variations in light emission. A reset capacitor connected to a select line is selectively connected to the gate terminal of the driving transistor and resets the driving transistor prior to programming. The select line adjusts the voltage on the gate terminal to reset the driving transistor by the capacitive coupling of the select line to the gate terminal created by the reset capacitor.
Owner:IGNIS INNOVATION
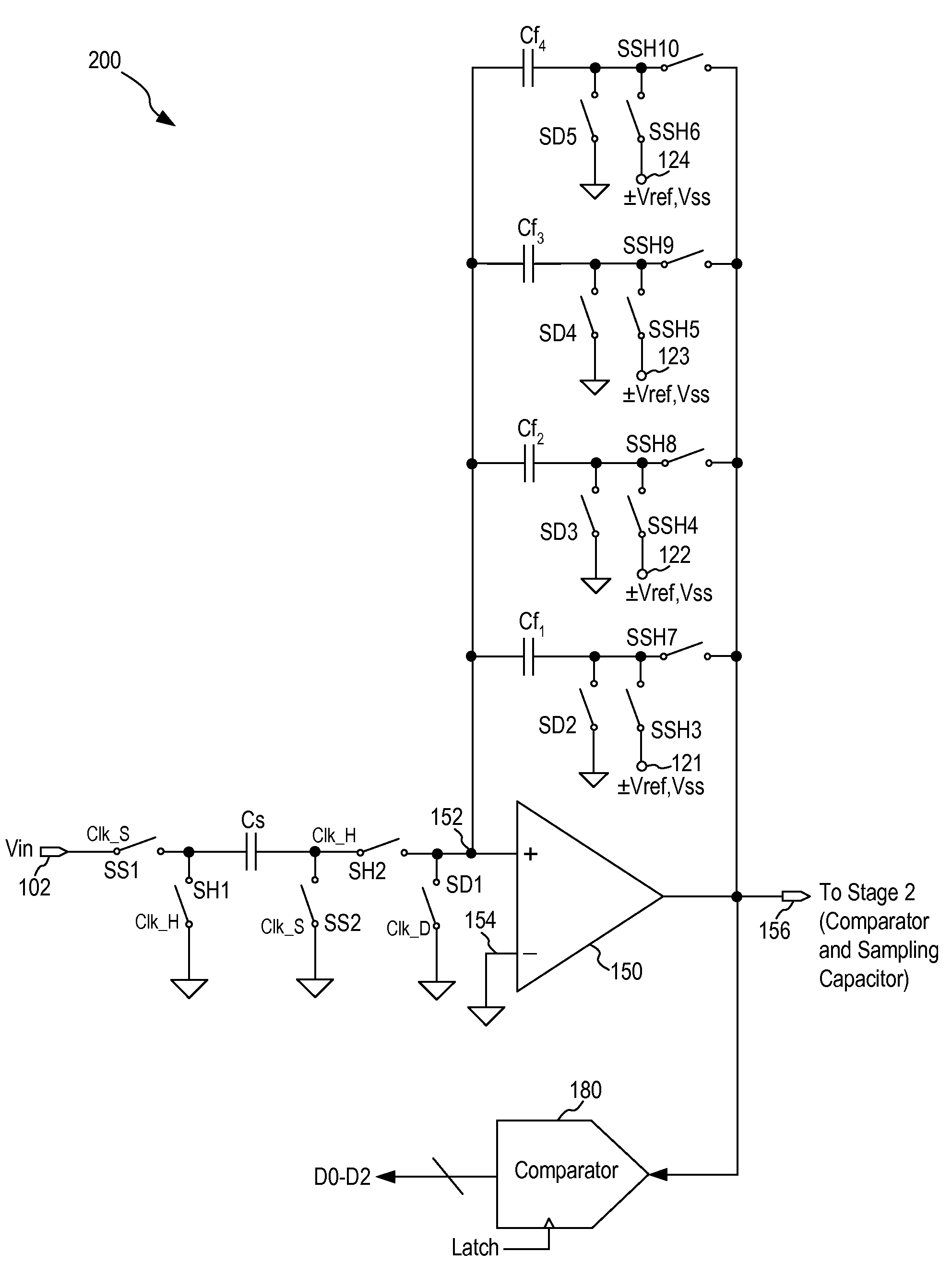
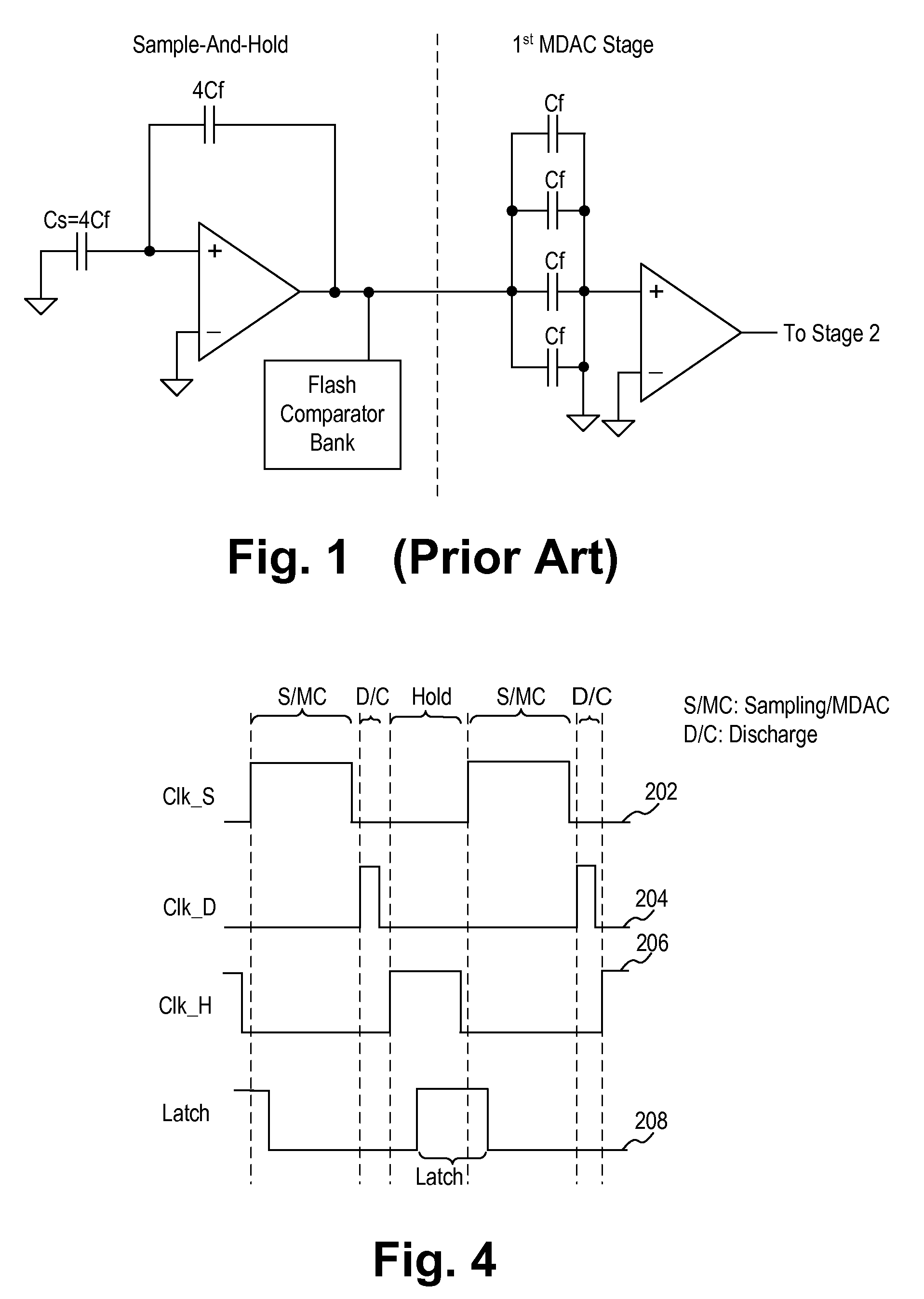
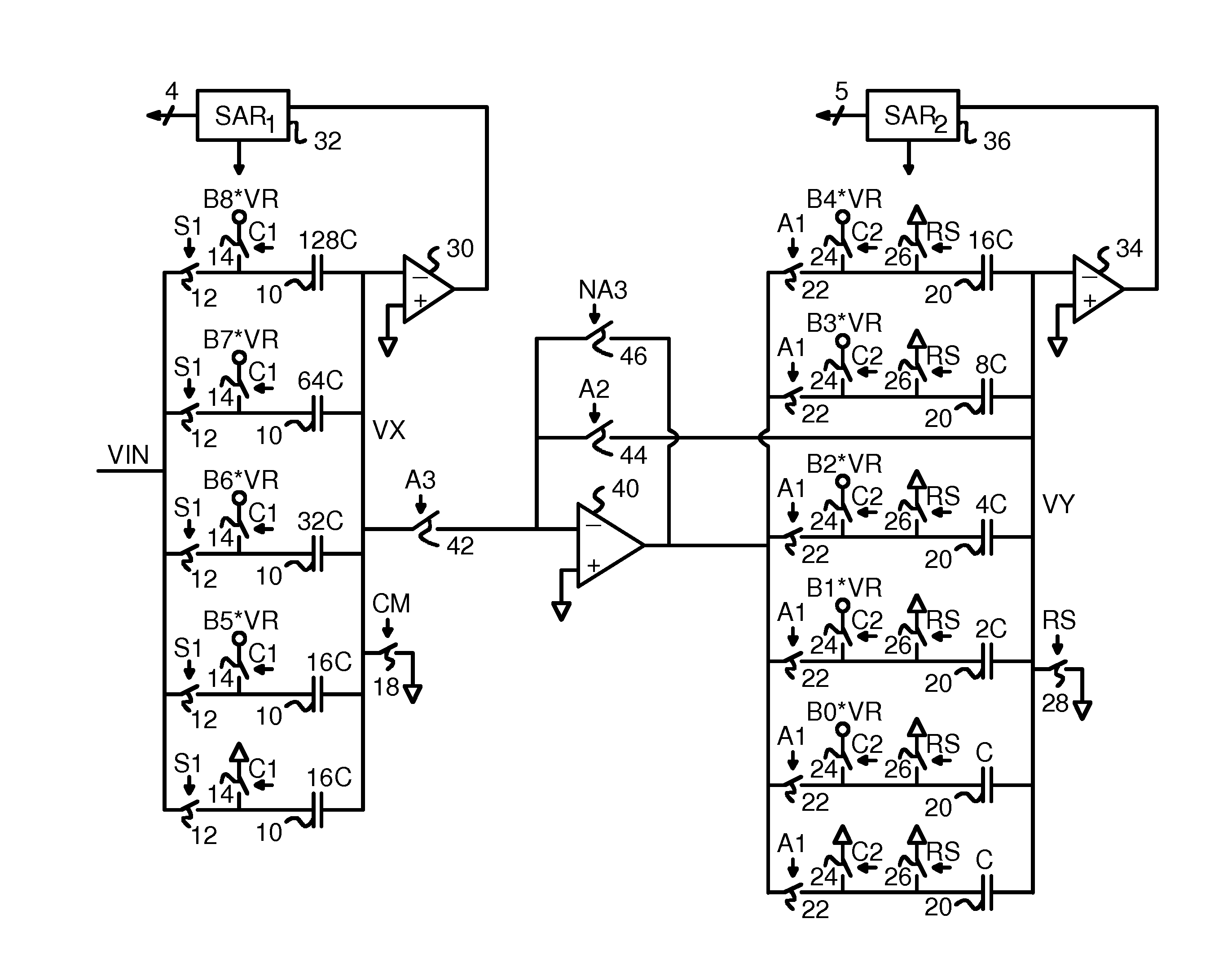
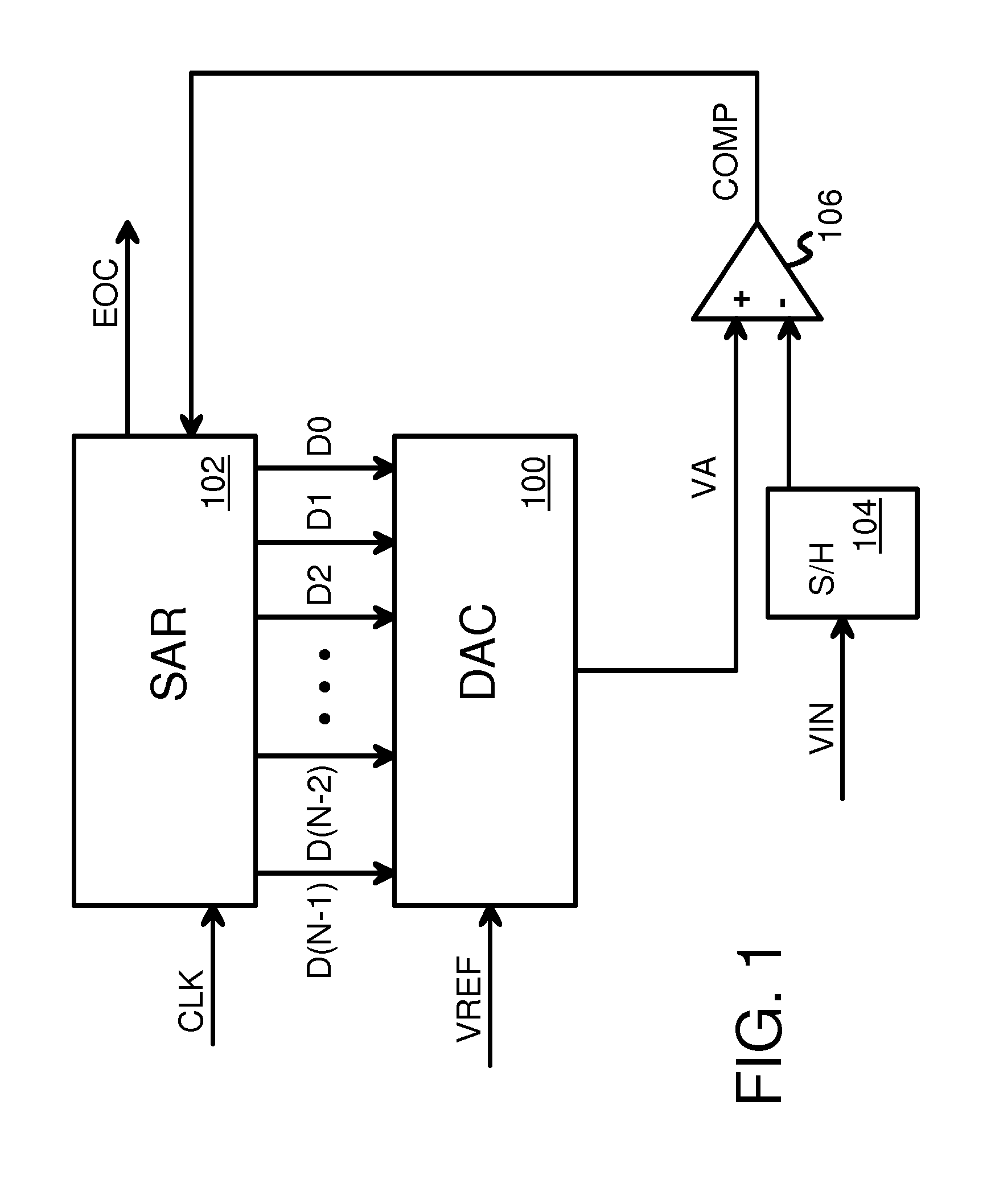
Opamp and capacitor sharing scheme for low-power pipeline ADC
ActiveUS7265705B1Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsAudio power amplifierAnalog-to-digital converter
A first stage circuit for a high-speed, high-resolution pipeline analog-to-digital converter (ADC) implements operational amplifier (opamp) sharing and capacitor sharing to combine the sample-and-hold (SAH) and the MDAC (multiplying digital to analog converter) functions in the first residue stage of the pipeline ADC. In one embodiment, the first stage circuit includes a sampling capacitor, an amplifier, a feedback capacitor array and a comparator. The sampling capacitor and the feedback capacitor array are configured by switches to operate in a sampling / MDAC mode, a discharge mode and a hold mode. In this manner, the sample-and-hold operation and the MDAC operation are merged into the first stage circuit of the pipeline ADC to achieve low power and high speed of operation.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
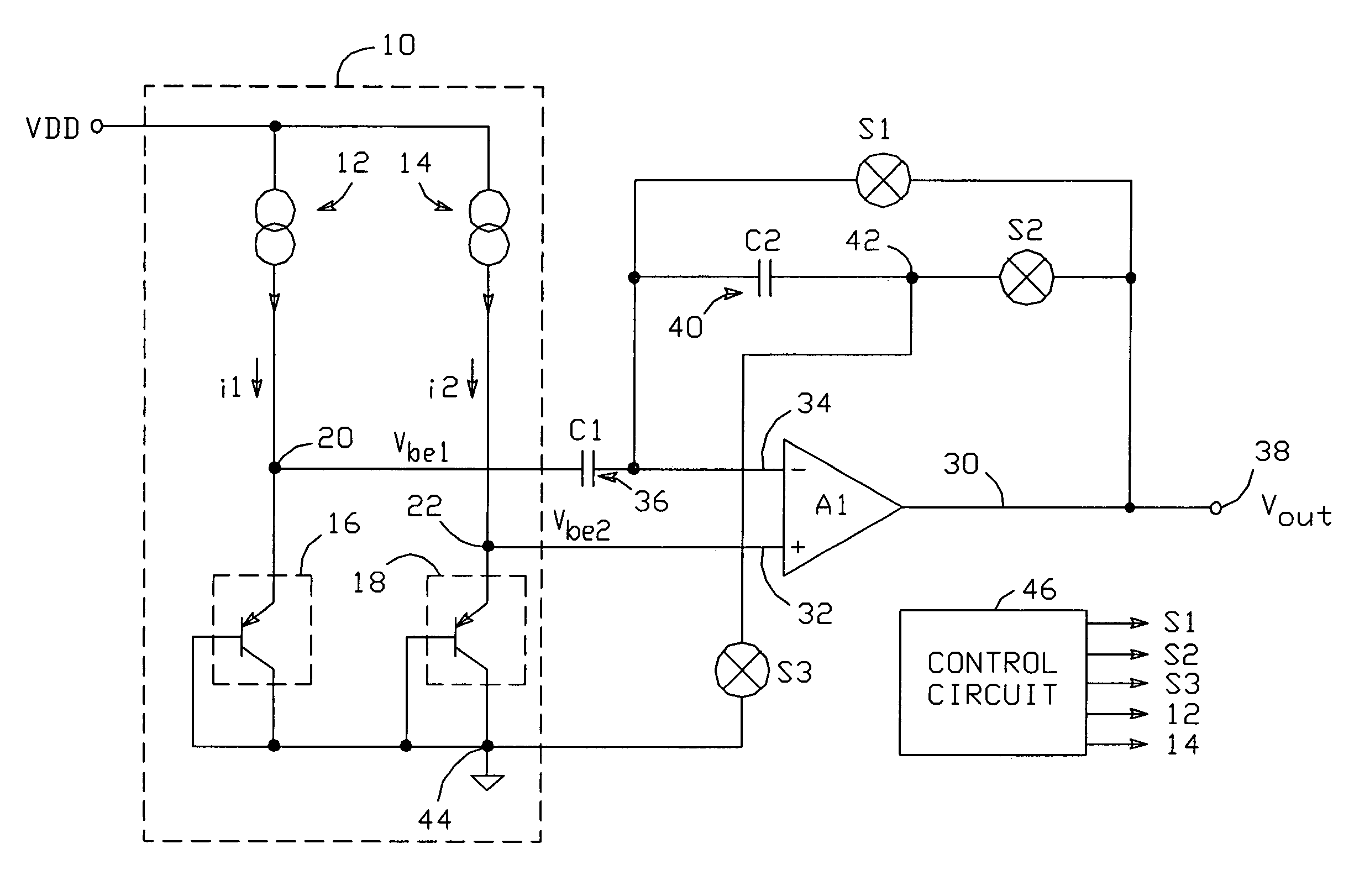
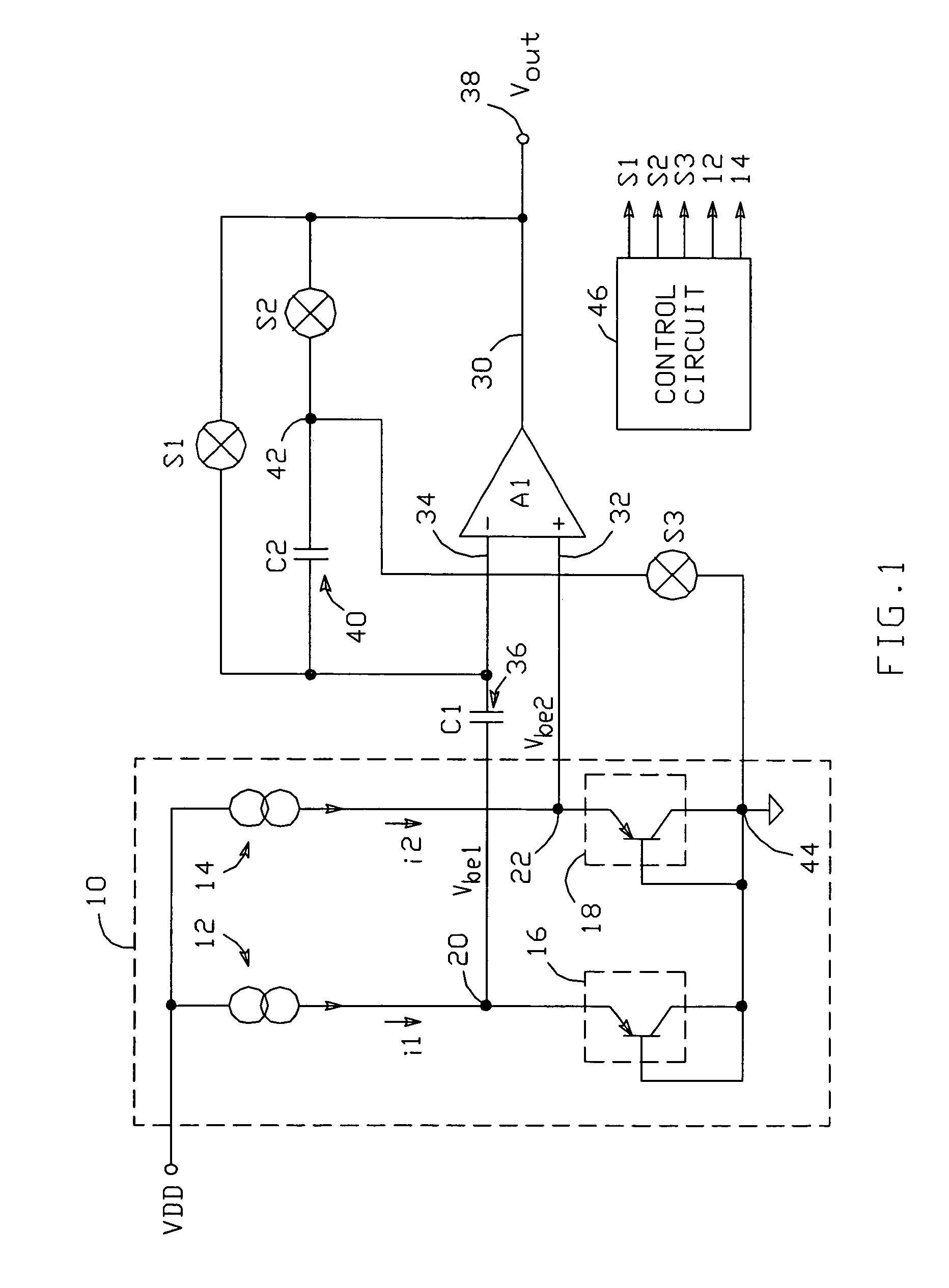
Voltage source circuit with selectable temperature independent and temperature dependent voltage outputs
ActiveUS7112948B2Increase flexibilityImprove performanceConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
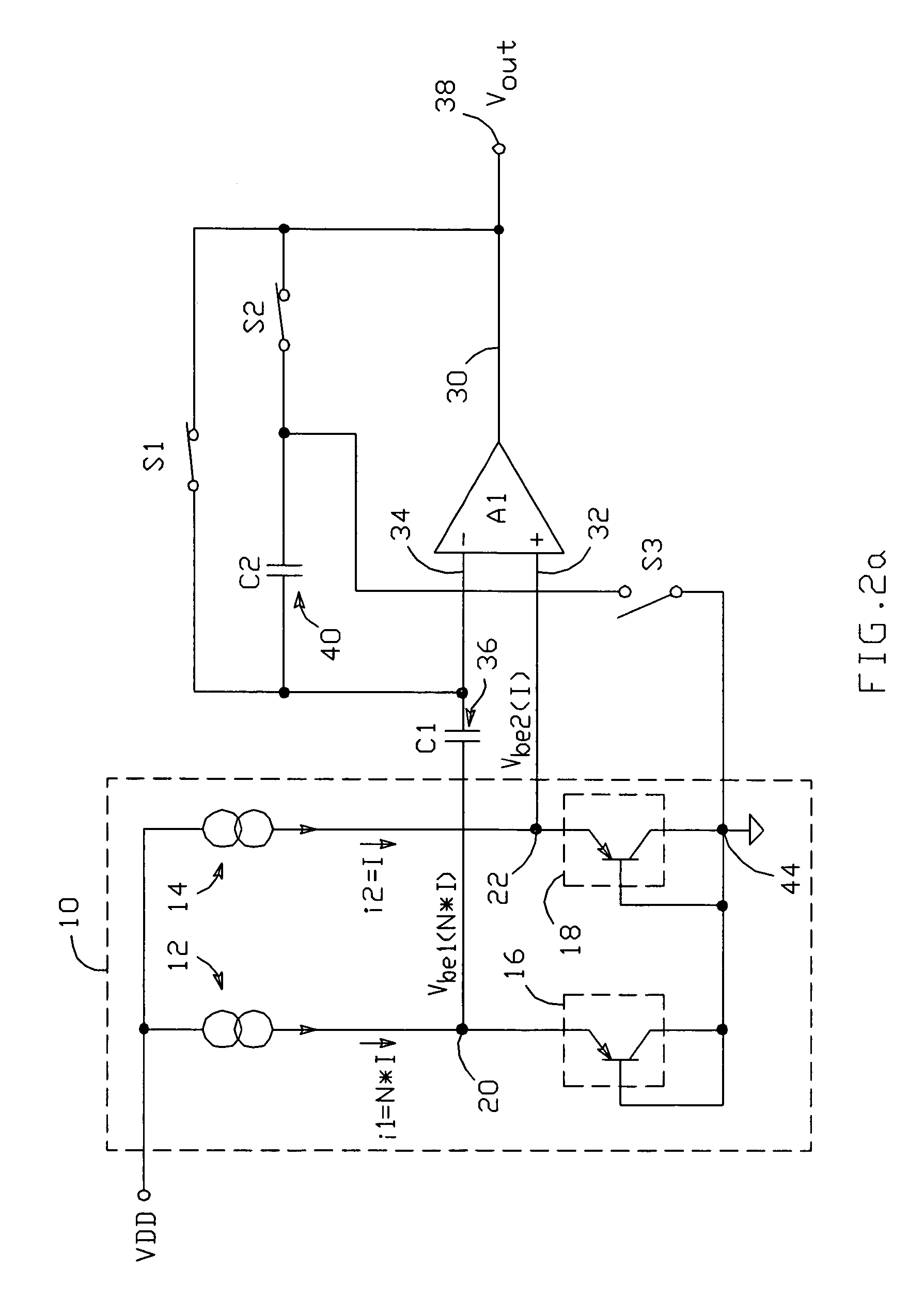
A voltage source includes first and second pn junctions which conduct the outputs of respective current sources to establish respective base-emitter voltages Vbe1 and Vbe2 at respective nodes; Vbe1 and Vbe2 can each be generated with a current I or a current N*I. An amplifier A1 has its non-inverting input connected to the second node and its inverting input connected to the first node through an input capacitor; a feedback capacitor is connected between the inverting input and a third node. Switches are connected between A1's inverting input and A1's output, between the third node and A1's output, and between the third node and a circuit common point. A control circuit operates the switches and current sources during first and second operating phases to selectively produce a temperature independent output voltage or a temperature dependent output voltage.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
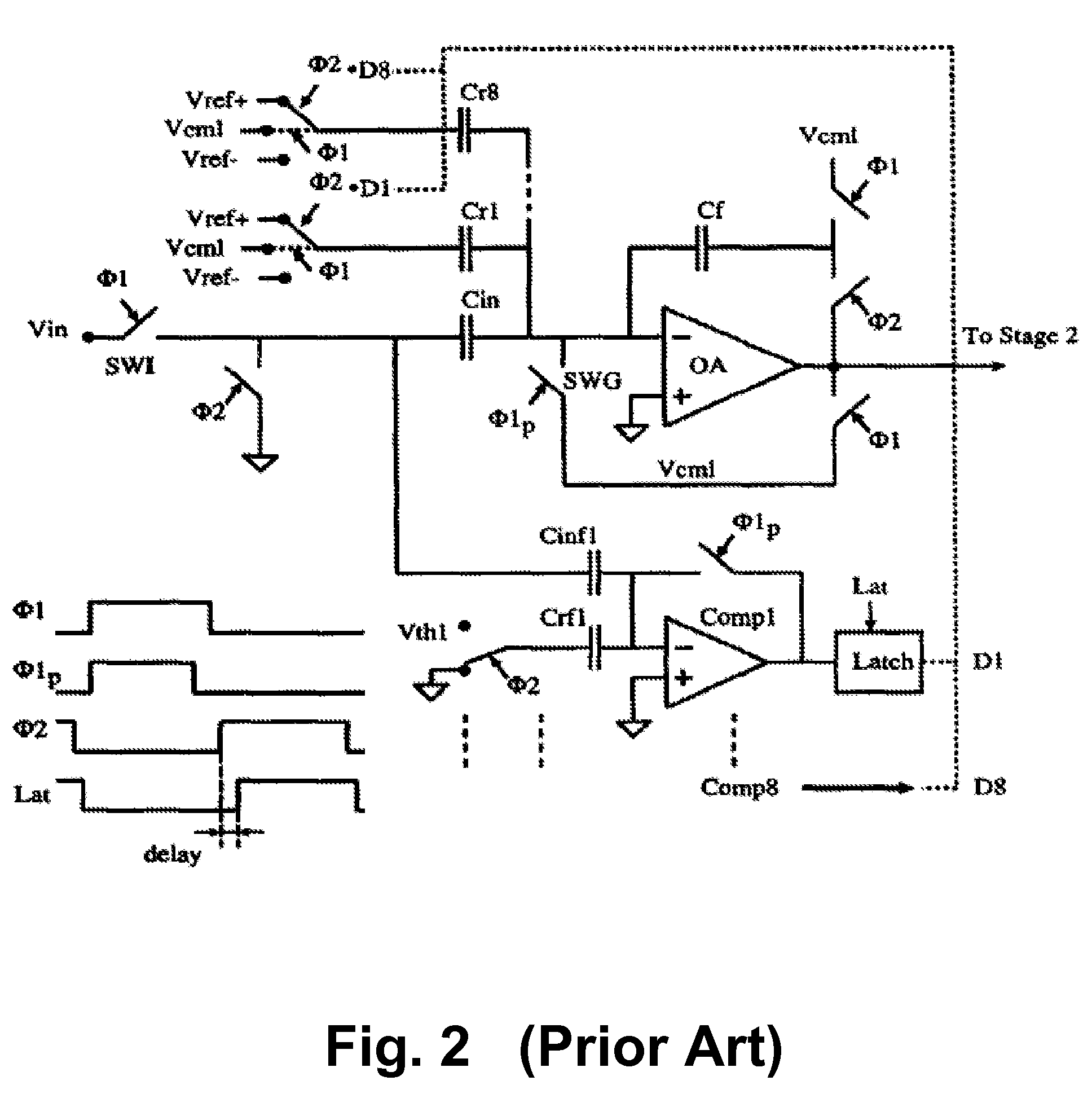
Sample hold circuit, and pipeline ad converter using the circuit
InactiveCN101040441AOperating current variableLower operating average currentElectric signal transmission systemsCharge amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
A switched capacitor sample hold circuit using a source-earthed input operation amplifier. This operation circuit is provided with a feed forward circuit or a feedback circuit, which is connected with a feedback capacitor of the operation amplifier through a switch. An input common voltage or the middle point voltage of an output is detected to precharge the feedback capacitor beforehand with the difference from a reference voltage thereby to suppress fluctuations in an output operation point at the time of amplifying the operation amplifier.
Owner:SONY CORP
Low power, low noise amplifier system
ActiveUS7795960B2Improve noiseLow powerAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDifferential amplifiersLow noiseAudio power amplifier
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Solid-state imaging apparatus
ActiveUS8711259B2Television system detailsMultiple input and output pulse circuitsCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
Owner:CANON KK
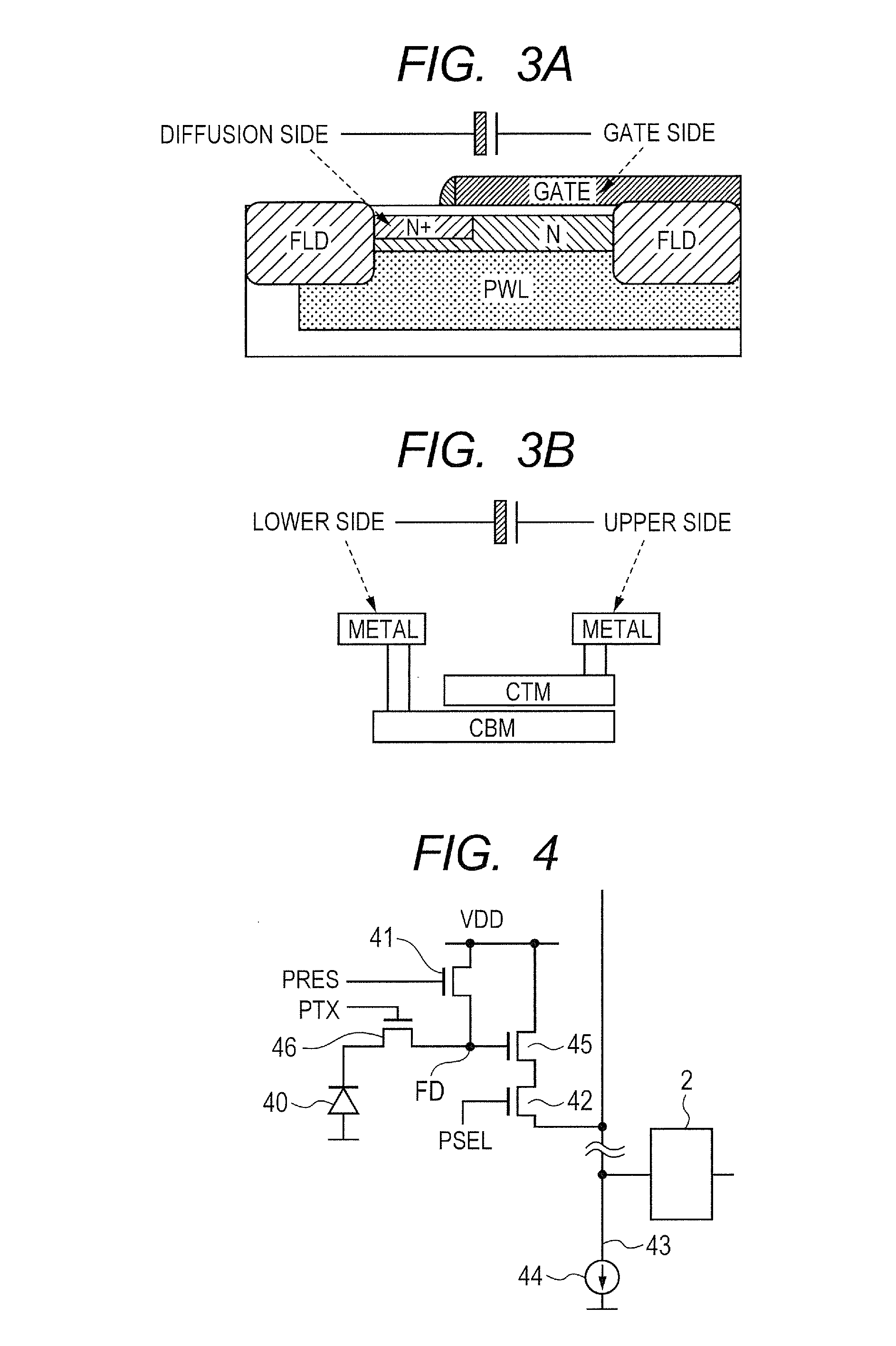
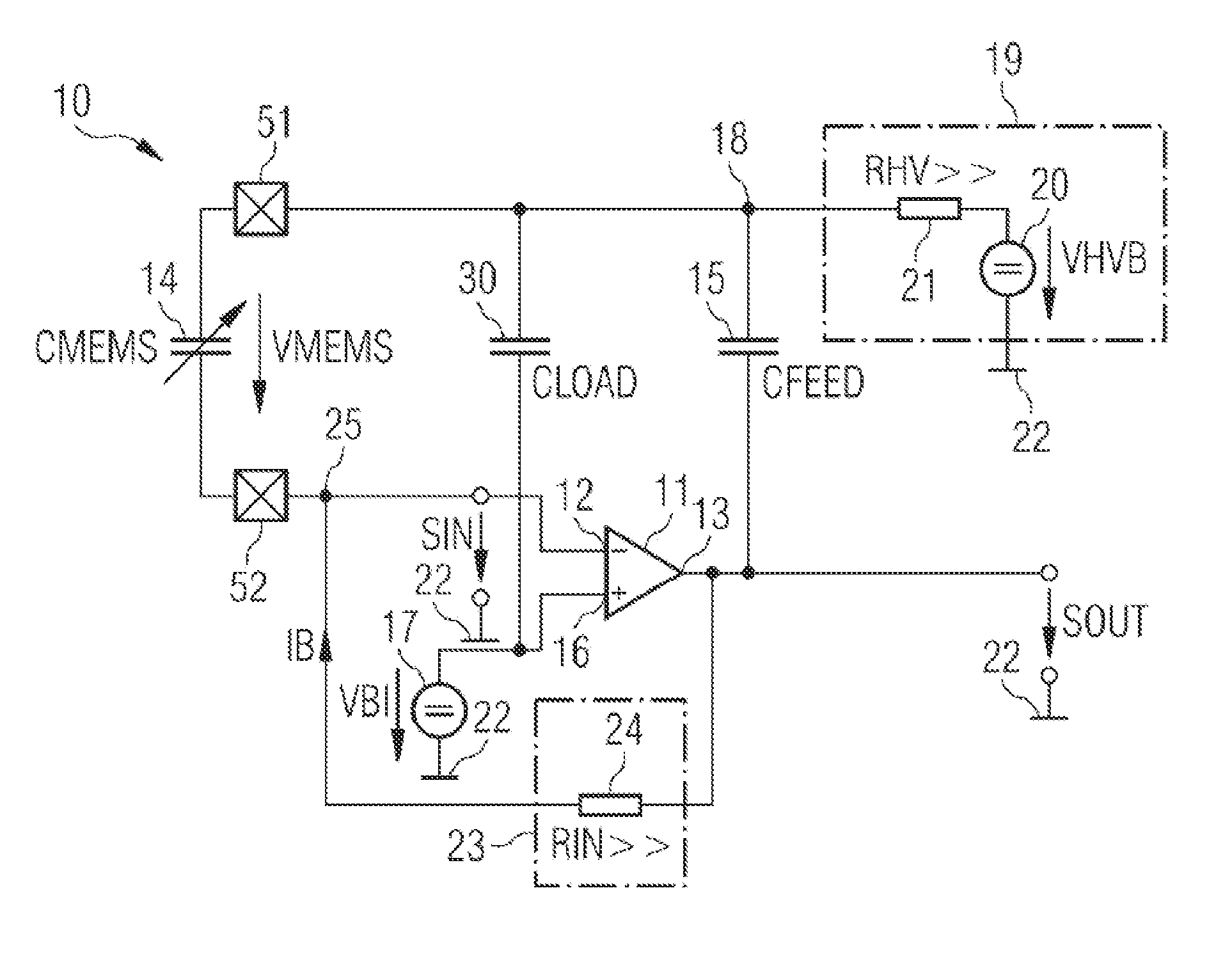
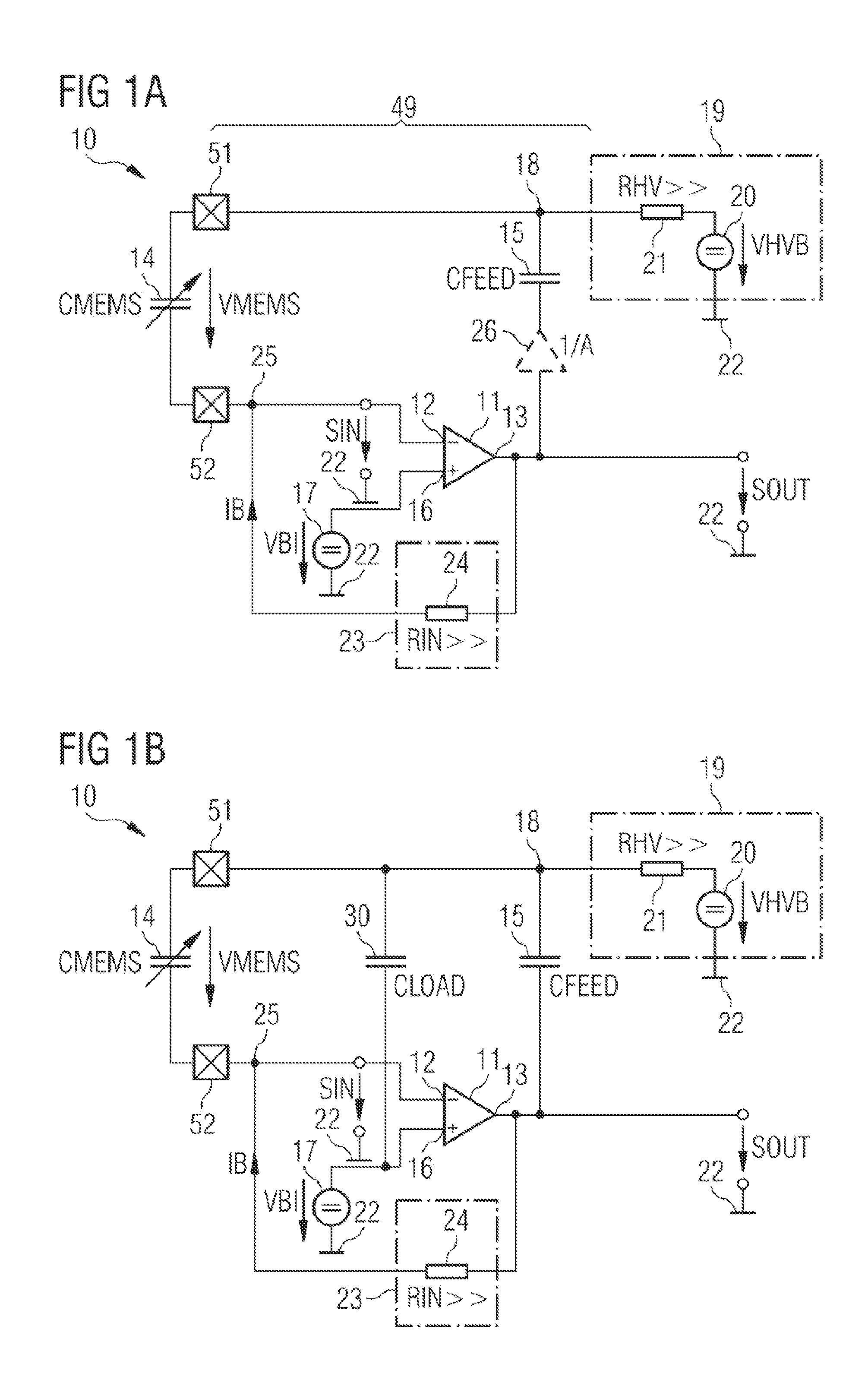
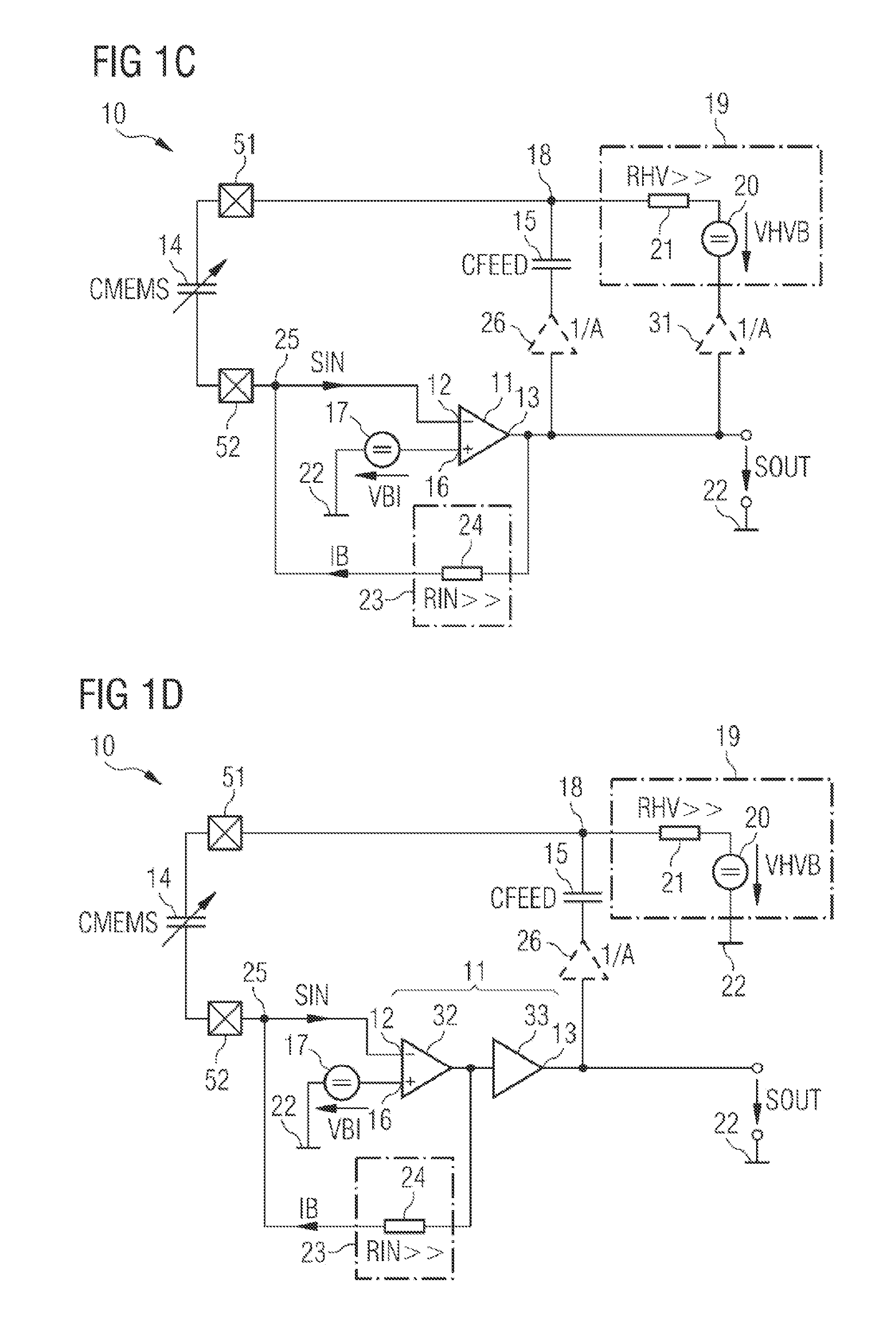
Sensor arrangement and method for generating an amplified sensor signal
ActiveUS20150137834A1Generate lotImprove efficiencyNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsCapacitance measurementsAudio power amplifierEngineering
A sensor arrangement (10) comprises an amplifier (11) having a signal input (12) to receive an input signal (SIN) and a signal output (13) to provide an amplified sensor signal (SOUT) that is an inverted signal with respect to the input signal (SIN). Furthermore, the sensor arrangement (10) comprises a feedback path connecting the signal output (13) to the signal input (12), wherein the feedback path comprises a series connection of a capacitive sensor (14) and a feedback capacitor (15). A voltage source arrangement (19) of the sensor arrangement (10) is connected to a feedback node (18) between the capacitive sensor (14) and the feedback capacitor (15).
Owner:AMS AG
Efficient charge transfer using a switched capacitor resistor
InactiveUS7006813B2Low powerExtend battery lifeModulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesTransmission noise suppressionLow noiseCapacitance
The application of a non-zero voltage offset to rotating capacitors 1111 and 1112 permit the use of a single positive voltage supply. However, the precharging of the rotating capacitors 1111 and 1112 is power inefficient. A power efficient and low-noise precharging operation is realized through the sharing of the charge on a feedback capacitor 1075 and 1080 that is significantly larger than the rotating capacitors 1111. Once a precharging operation is complete, the charge on the feedback capacitor 1075 and 1080 is refreshed from its residual charge level (rather than zero charge level) to a desired charge level.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
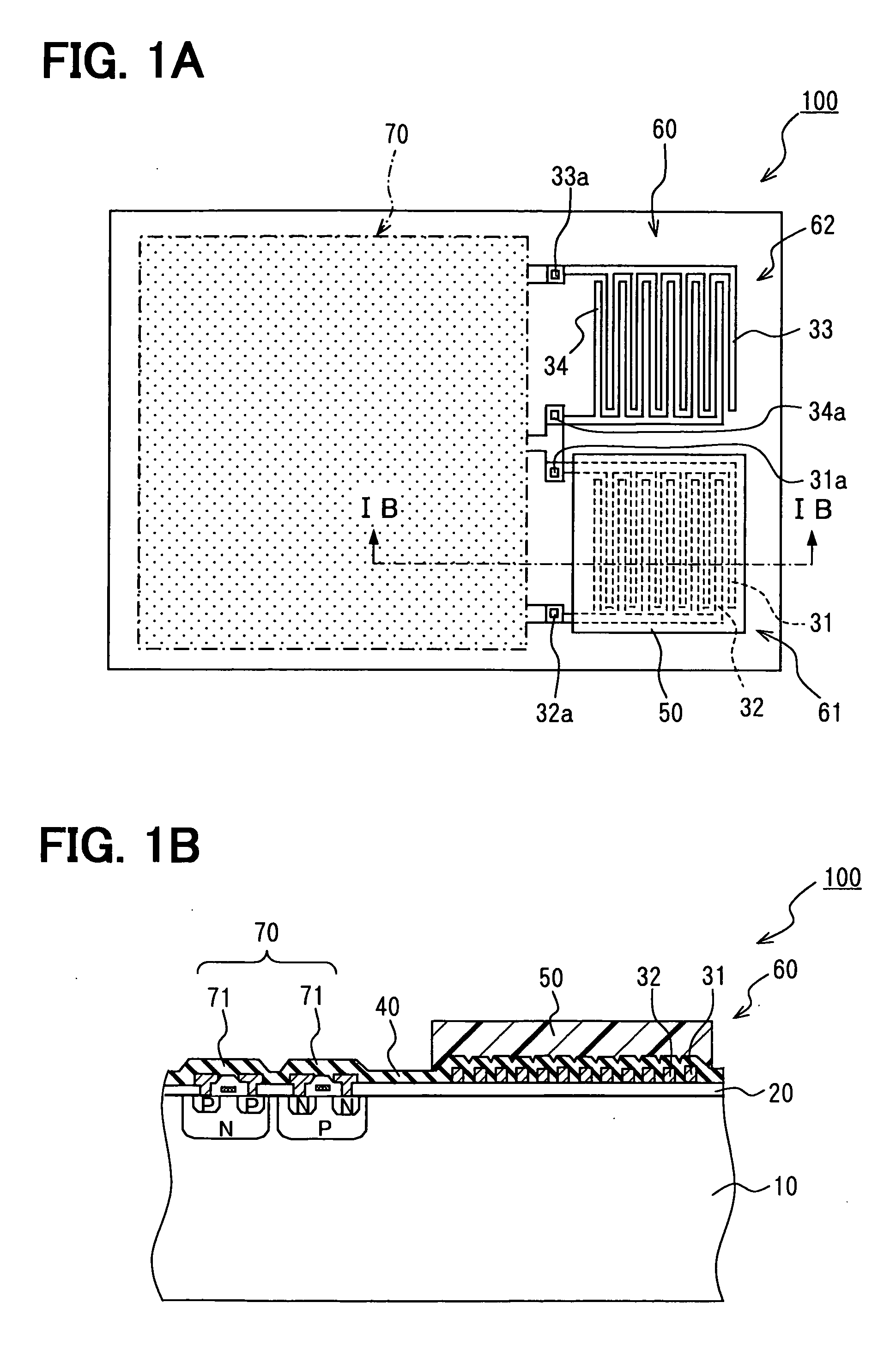
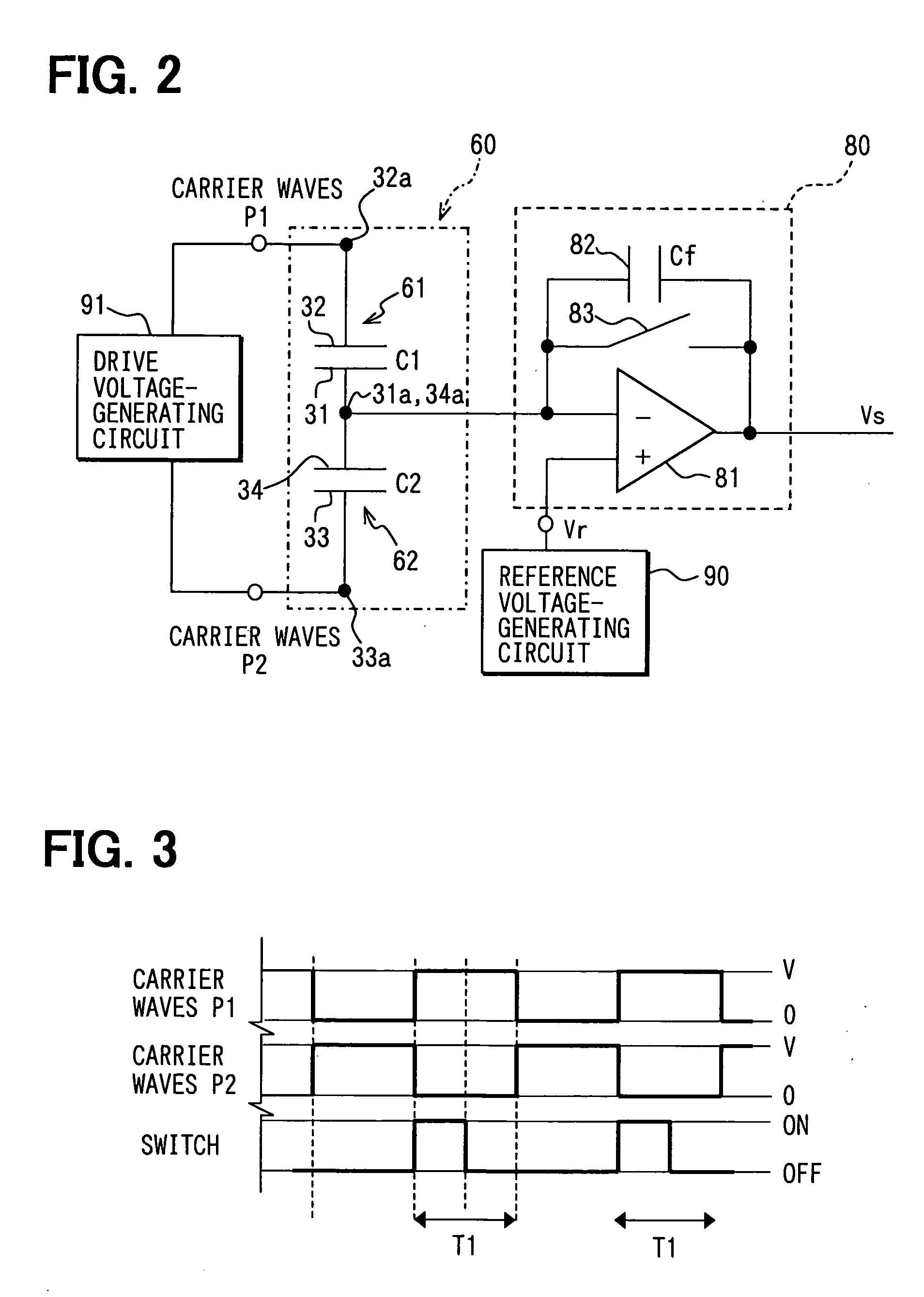
Capacitance type physical quantity detector
InactiveUS20060037393A1Change capacitanceLow costResistance/reactance/impedenceUsing mechanical meansCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
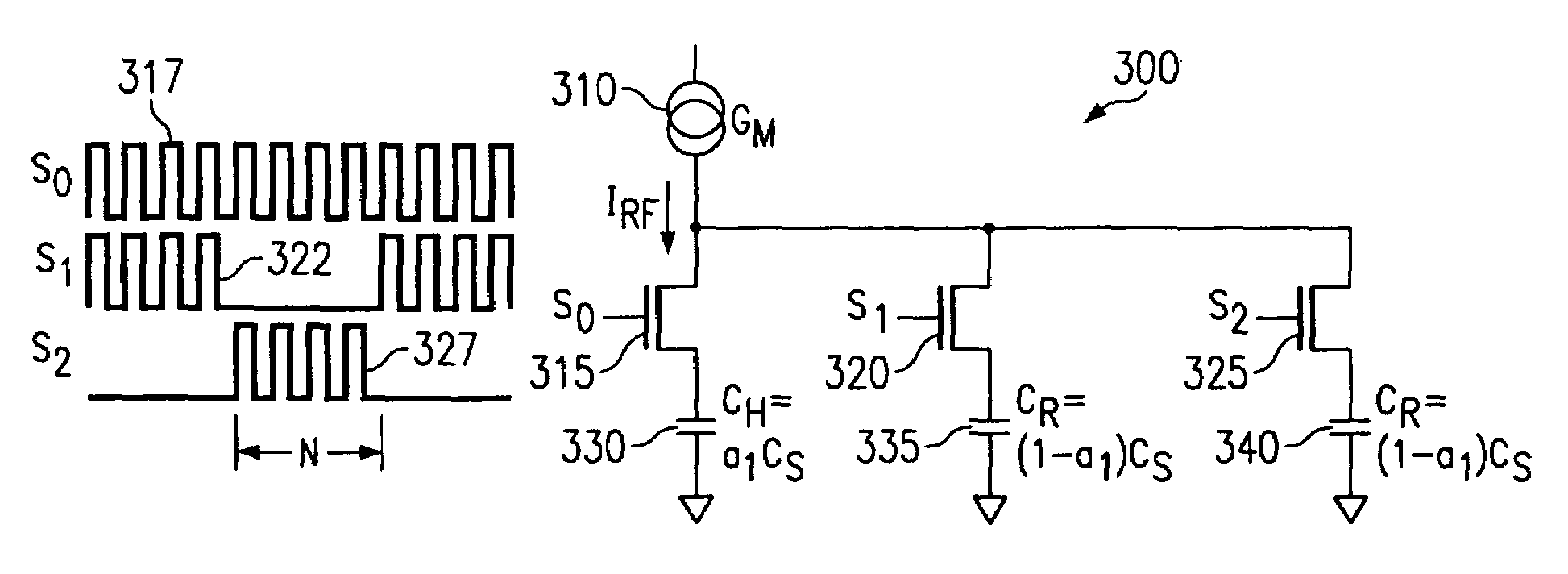
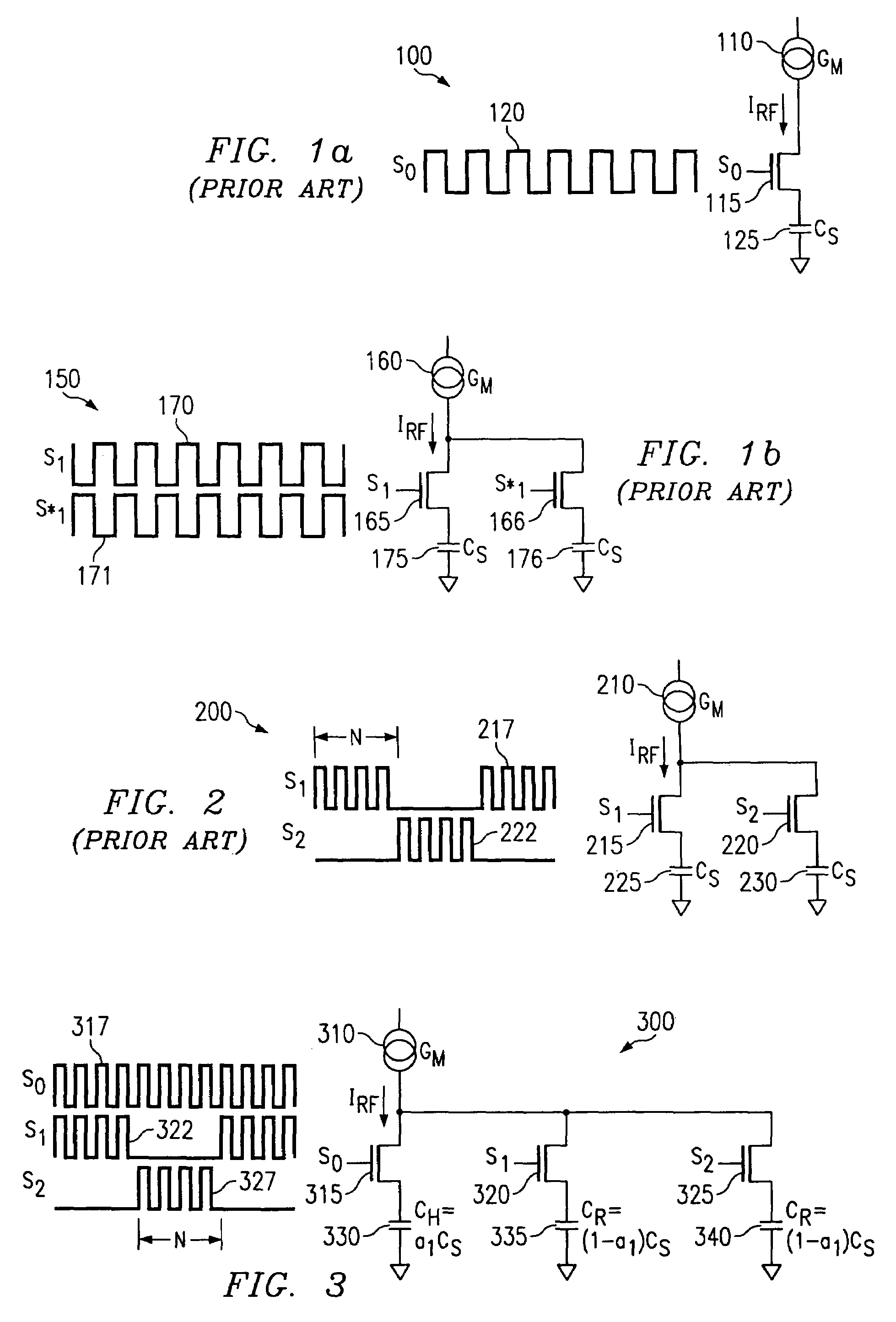
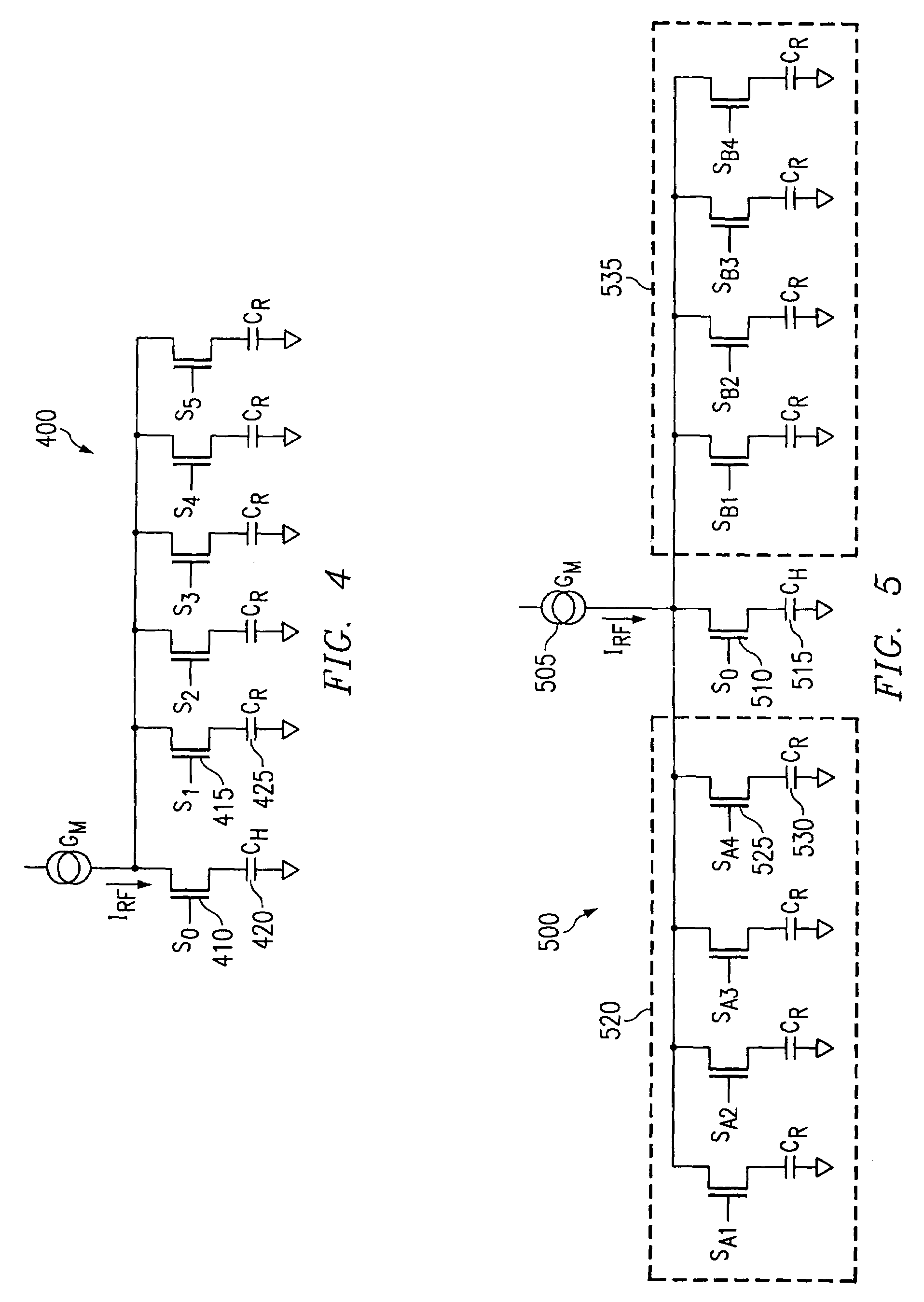
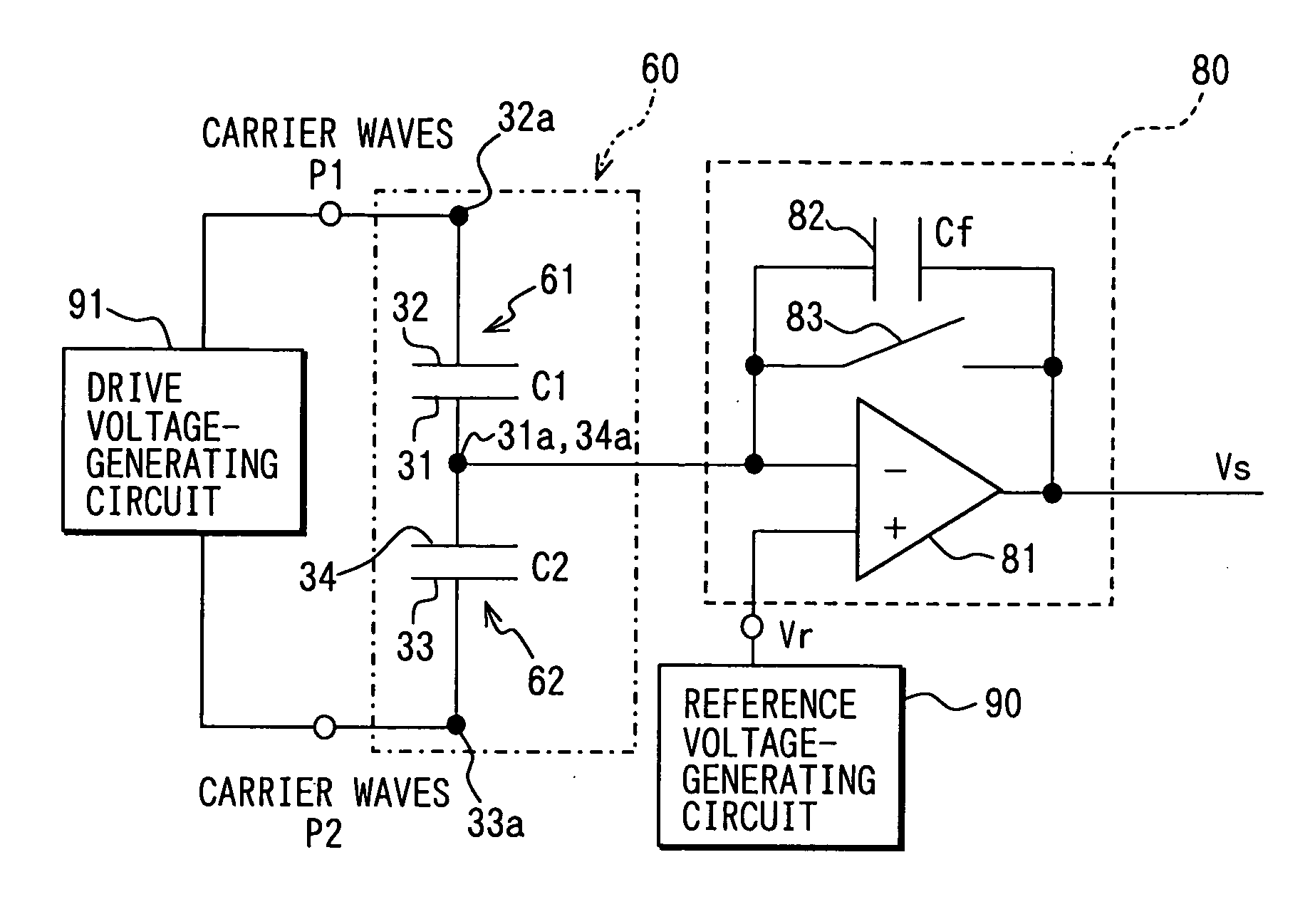
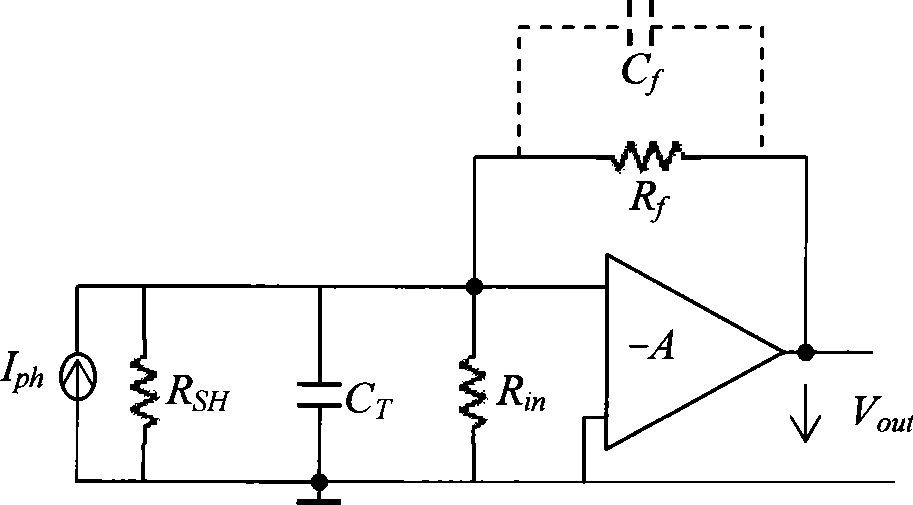
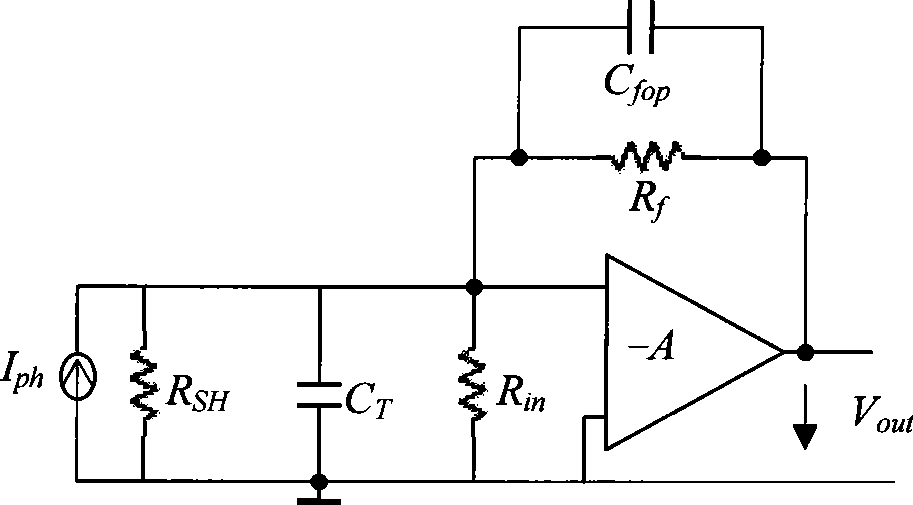
A capacitance type physical quantity detector includes a sensor unit of which the capacitance varies depending upon a change in the physical quantity and a C-V converter unit which converts a change in the capacitance of said sensor unit into a voltage. The C-V converter unit includes an operational amplifier, a feedback capacitor, switching means connected in parallel with said feedback capacitor, a reference voltage-generating circuit for applying a reference voltage to the operational amplifier, and a drive voltage-generating circuit for applying a drive voltage to said sensor unit. At least any one of the feedback capacitance of said feedback capacitor, the reference voltage formed by said reference voltage-generating circuit or the drive voltage formed by said drive voltage-generating circuit varies depending upon the temperature to correct temperature characteristics of the sensor unit.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
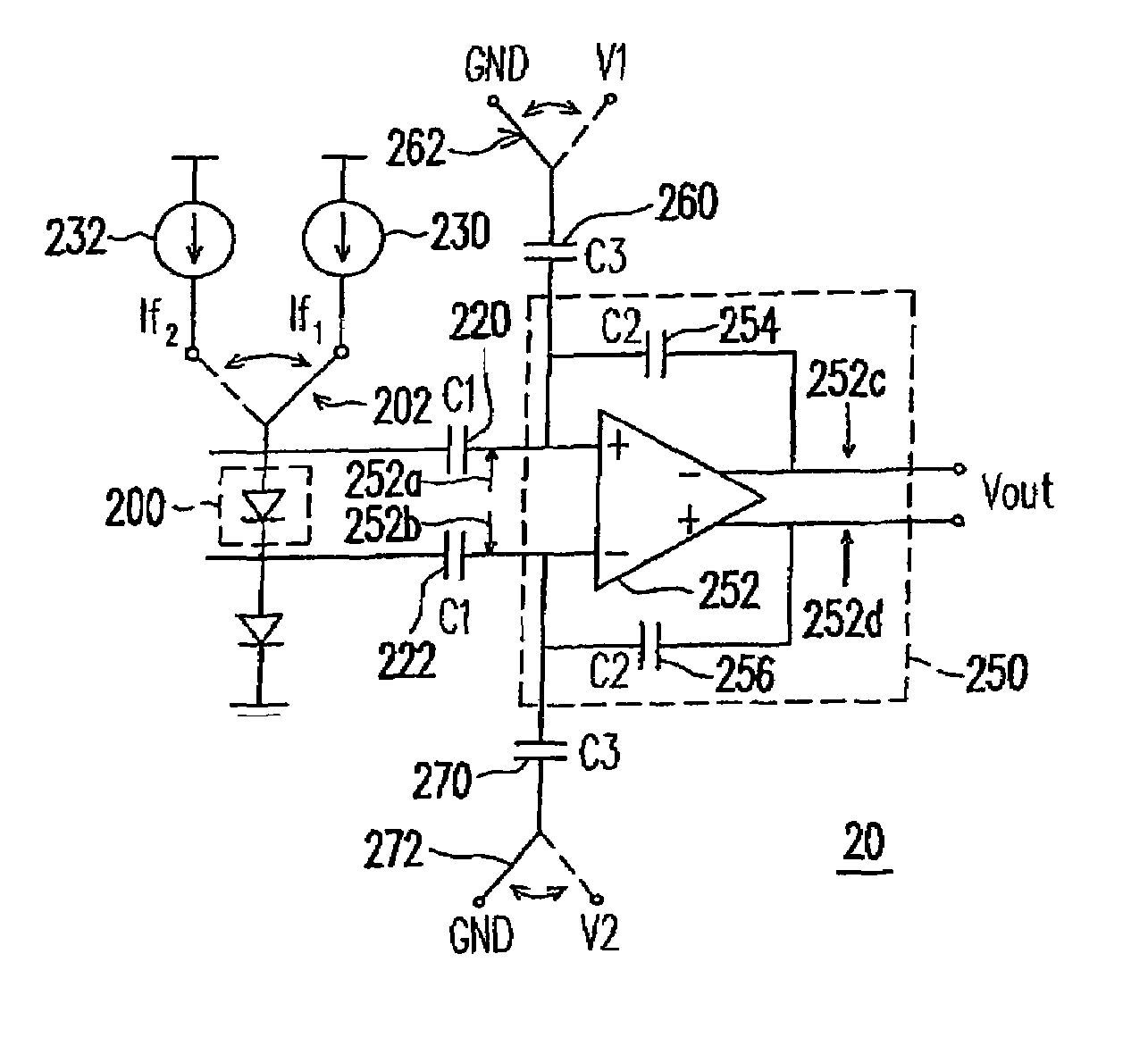
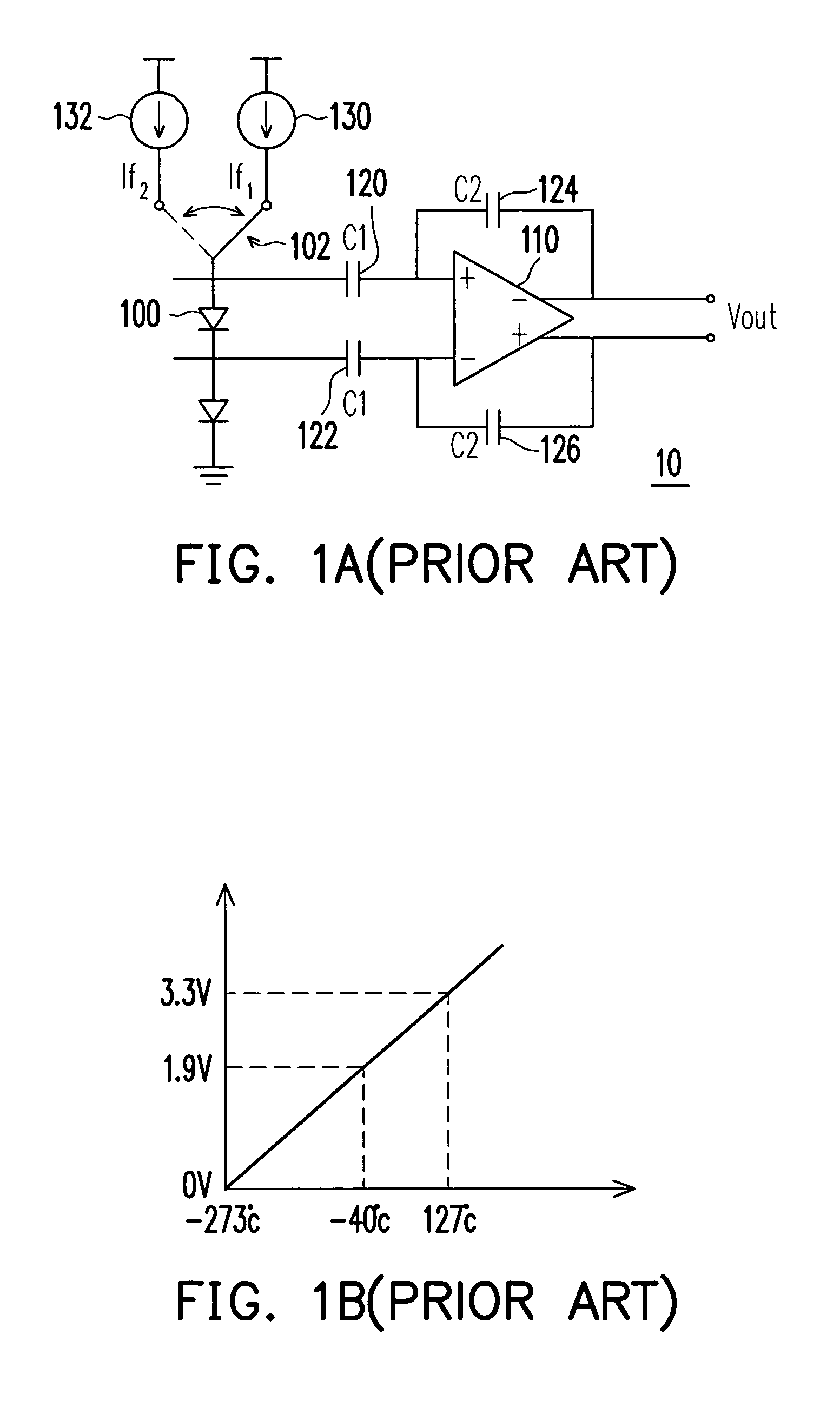
Temperature sensor
InactiveUS7312648B2Improve precisionRaise the ratioThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansFeedback capacitorSwitched capacitor
A temperature sensor, which comprises a temperature-dependent element, a comparator unit, first / second capacitors and first / second switching capacitors, is provided. The temperature-dependent element has an input terminal selectively coupled to one of a first current source and a second current source, and has an output terminal. The comparator unit comprises a comparator and first / second feedback capacitors. One end of the first switching capacitor is coupled to the first comparator input terminal, and another end of the first switching capacitor is selectively coupled to one of two different voltages. One end of the second switching capacitor is coupled to the second comparator input terminal, and another end of the second switching capacitor is selectively coupled to one of two different voltages.
Owner:HIMAX TECH LTD
High-power supply noise restraint low-voltage difference voltage regulator
InactiveCN101271344AImproved noise suppressionEnhanced inhibitory effectElectric variable regulationLow voltageEngineering
Owner:WUXI ZGMICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
ActiveUS7295143B2Improve uniformityTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
There is a need for providing a variable amplifier circuit suited for a semiconductor integrated circuit and a high-performance camera preprocessing LSI using the variable amplifier circuit. At first timing, a first input capacitor acquires a first signal. An amplifier circuit amplifies a second signal acquired to the second input capacitor according to a gain corresponding to a capacity ratio between the second input capacitor and a feedback capacitor composed of a variable capacitor device. At second timing, the second input capacitor acquires a second signal. The amplifier circuit amplifies the first signal according to a gain corresponding to a capacity ratio between the first input capacitor and the feedback capacitor. A variable gain amplifier circuit interleavingly amplifies the first signal and the second signal in synchronization with the first timing and the second timing.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Solid-state imaging device, pixel-signal processing method, analog-signal transferring device, and analog-signal transferring method
InactiveUS20050083420A1Easy transferReduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAutomatic controlAudio power amplifier
From a pixel array where imaging pixels are arranged, pixel signals of respective columns on a selected row are read in parallel in a horizontal blanking period of a horizontal period. The pixel signals of the respective columns are output to horizontal signal lines in an effective period of the horizontal period via charge integrating amps provided respectively for the columns, i.e., provided respectively for vertical signal lines, and are thereby transferred horizontally. In the charge integrating amps, it is possible to enter a standby state while holding the pixel signals by a holding voltage. Furthermore, in the charge integrating amps, a reference potential for precharging feedback capacitors for amps at the time of a reading operation is automatically controlled based on a black level. Furthermore, pixel signals from the respective charge integrating amps are horizontally transferred in parallel using a plurality of horizontal signal lines.
Owner:SONY CORP
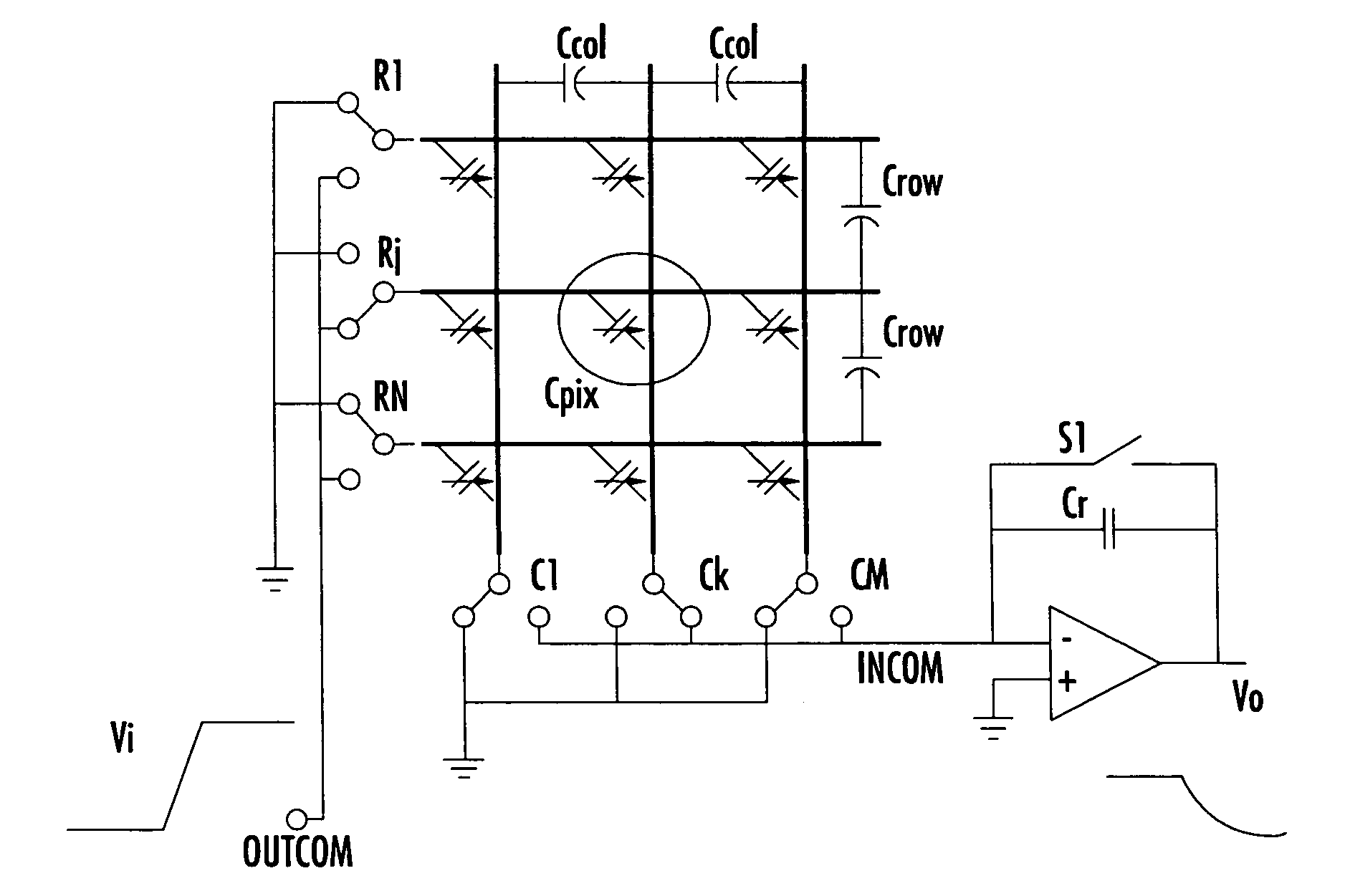
Method of reading a capacitive sensor and related integrated circuit
ActiveUS7755683B2Low costOvercome problemsTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAudio power amplifierVoltage reference
The method is for reading a capacitive sensor and may be implemented by a circuit for biasing and reading capacitances that includes circuits for selecting a column line and a row line, and a charge amplifier producing an output voltage representing the capacitance of the selected capacitor intercepted by the selected column and row lines. The method includes preliminarily resetting the output voltage of the charge amplifier, connecting all the deselected row and column plates of the array to a reference voltage and connecting a feedback capacitor and the selected capacitor to an inverting input of the amplifier, applying a step voltage on the capacitor that is connected to the inverting input of the amplifier, and reading the output voltage at steady-state.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Loading-free multi-stage SAR-assisted pipeline ADC that eliminates amplifier load by re-using second-stage switched capacitors as amplifier feedback capacitor
ActiveUS9219492B1Power saving provisionsElectric signal transmission systemsCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
A multi-stage Successive-Approximation Register (SAR) pipeline Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) has an amplifier between two switched capacitor networks, each controlled by a SAR. The load capacitance of the amplifier is magnified due to the amplifier's gain. This magnified load capacitance can disproportionately increase power consumption. The back plates of the second-stage switched capacitors are connected to the amplifier input using a feedback switch during an amplification phase, so that the second-stage switched capacitors are connected between the input and output of the amplifier as a feedback capacitor, rather than a load capacitor. Reset switches are added to drive both plates of the second-stage switched capacitors to ground during a reset phase before the amplification phase. Thus the second-stage switched capacitors function as both the feedback capacitor and as the switched capacitors controlled by the second SAR. Amplifier power is reduced since there is no separate load capacitor during the amplification phase.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Low dropout regulator capable of on-chip implementation
A low-dropout regulator comprises a high-gain error amplifier having a differential input stage and a single-ended output, a high-swing high-positive-gain second stage with input connecting to the output of the error amplifier and a single-ended output, a p-type MOS transistor with gate terminal connecting to the output of the second stage, source terminal connecting to the supply voltage, and drain terminal to the output of the low-dropout regulator. A first-order high-pass feedback network connects the output of the low-dropout regulator and the positive input of the error amplifier, and a damping-factor-control means comprising a negative gain stage with a feedback capacitor connects the input and output of this gain stage. A capacitor is connected between the output of the error amplifier and the output of the low-dropout regulator, while a voltage reference connects to the negative input of the error amplifier. The regulator does not require an off-chip capacitor for stability and has improved load transient response and power supply rejection ratio.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Pixel and organic light emitting display
InactiveUS20090146987A1Compensation for Threshold Voltage VariationsElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesControl lineVoltage reference
A pixel at an ith pixel row (i is a natural number) includes an organic light emitting diode (OLED); a driving transistor for supplying a current to the OLED and a storage capacitor between a gate electrode of the driving transistor and an (i−1)th emission control line; and a compensating unit for controlling a voltage of the gate electrode of the driving transistor to compensate for deterioration of the OLED. The compensating unit includes: a first compensating unit transistor and a second compensating unit transistor between the OLED and a first power source; first and second feedback capacitors between a second node between the first and second compensating unit transistors and a first node between the gate electrode of the driving transistor and the storage capacitor; and a third compensating unit transistor coupled between a third node between the first and second feedback capacitors and a reference voltage source.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Trans-impedance amplifier with low noise and high gain-bandwidth product
ActiveCN101505140AWide signal bandwidthIncrease signal gainAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifiers controlled by lightCapacitanceLow noise
The invention provides an optical-receiver preamplifier for receiving analog or digital optical signals. The preamplifier comprises a high-gain amplifier A1, an input circuit, a negative-feedback impedor Zf, a low-gain amplifier A2 adjustable in gain and a feedback capacitor Cff, wherein the input circuit takes a photoelectric converter as a main component; the negative-feedback impedor Zf is connected with the reverse input end and the output end of the A1; the feedback capacitor Cff connects the output end of the A2 with the reverse input end of the A1; and the output end of the A1 can be directly connected with the input end of the A2 or can be connected with the input end of the A2 through a buffer. Output signals of the preamplifier are taken out from the output end of the A1 or the output end of the buffer, and can be directly subjected to subsequent signal processing or be further amplified and then subjected to subsequent signal processing.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com