Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
850 results about "Damping factor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
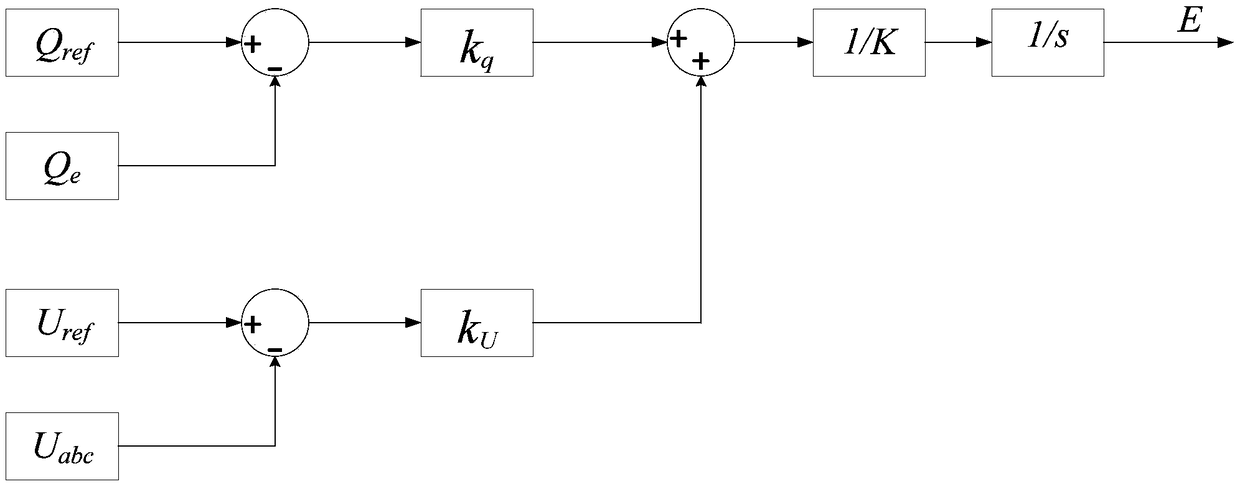
In an audio system, the damping factor gives the ratio of the rated impedance of the loudspeaker to the source impedance. Only the resistive part of the loudspeaker impedance is used. The amplifier output impedance is also assumed to be totally resistive. The source impedance (that seen by the loudspeaker) includes the connecting cable impedance. The load impedance Zₗₒₐd (input impedance) and the source impedance Zₛₒᵤᵣcₑ (output impedance) are shown in the diagram.
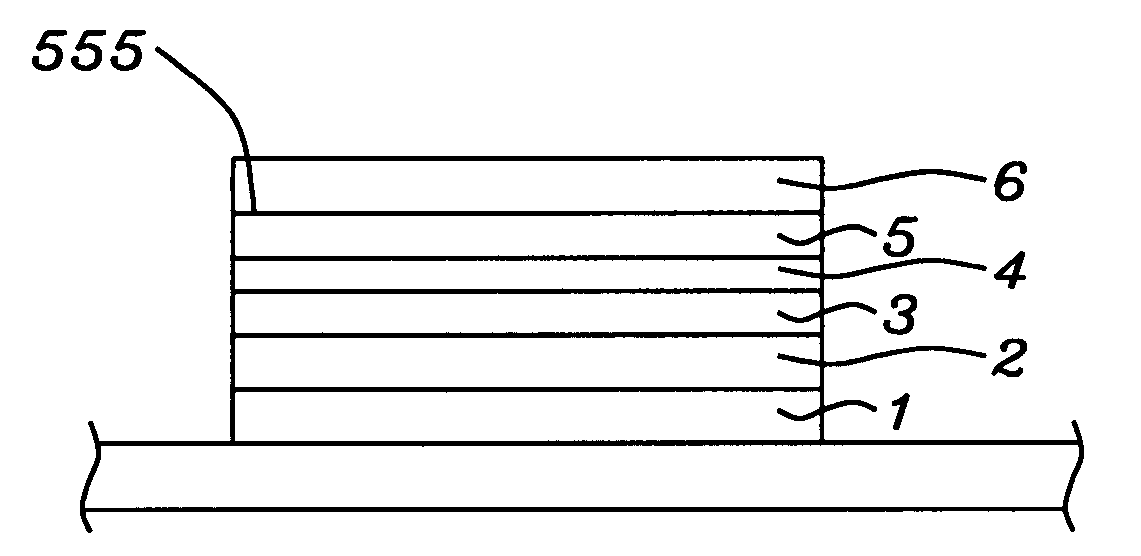
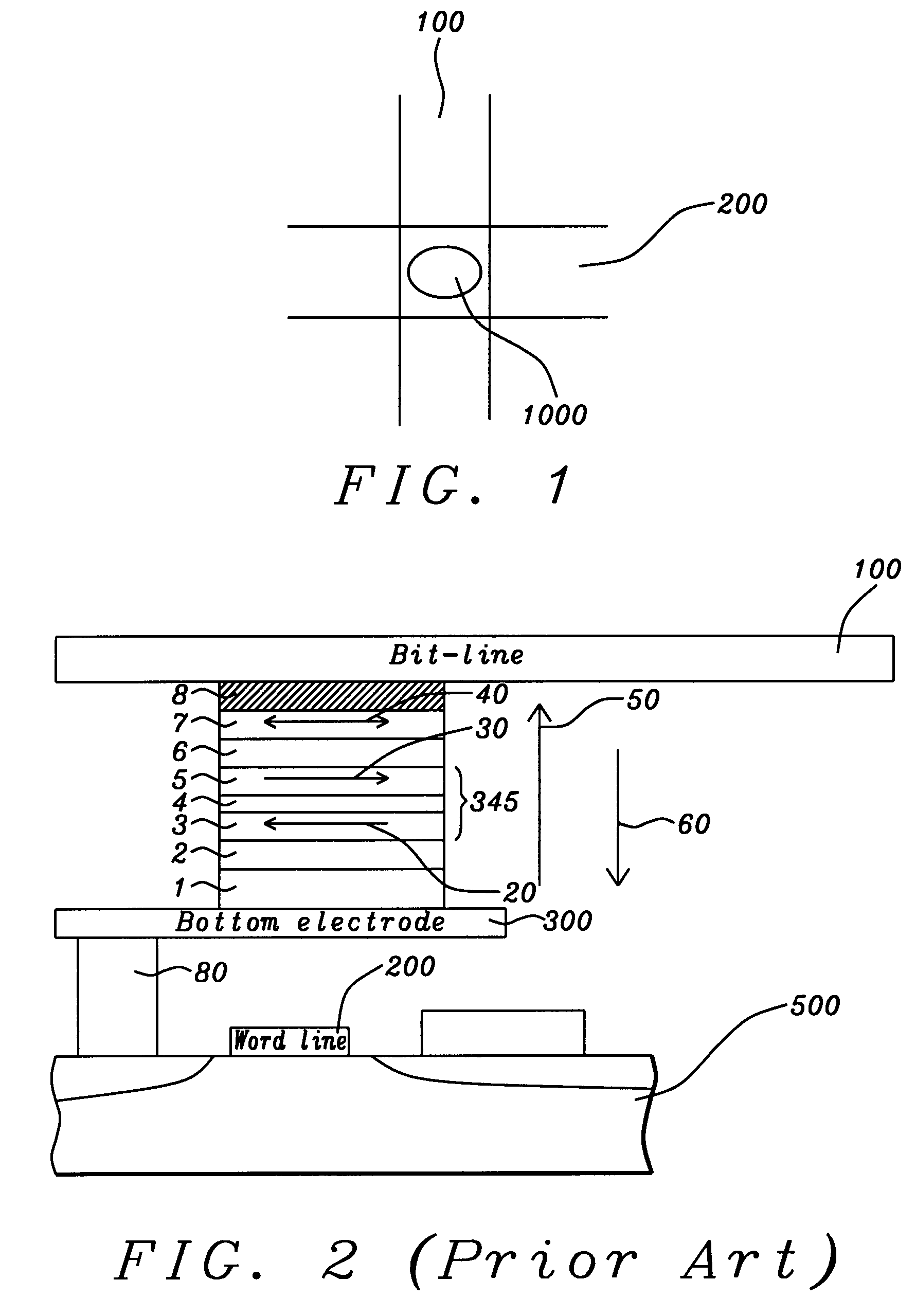
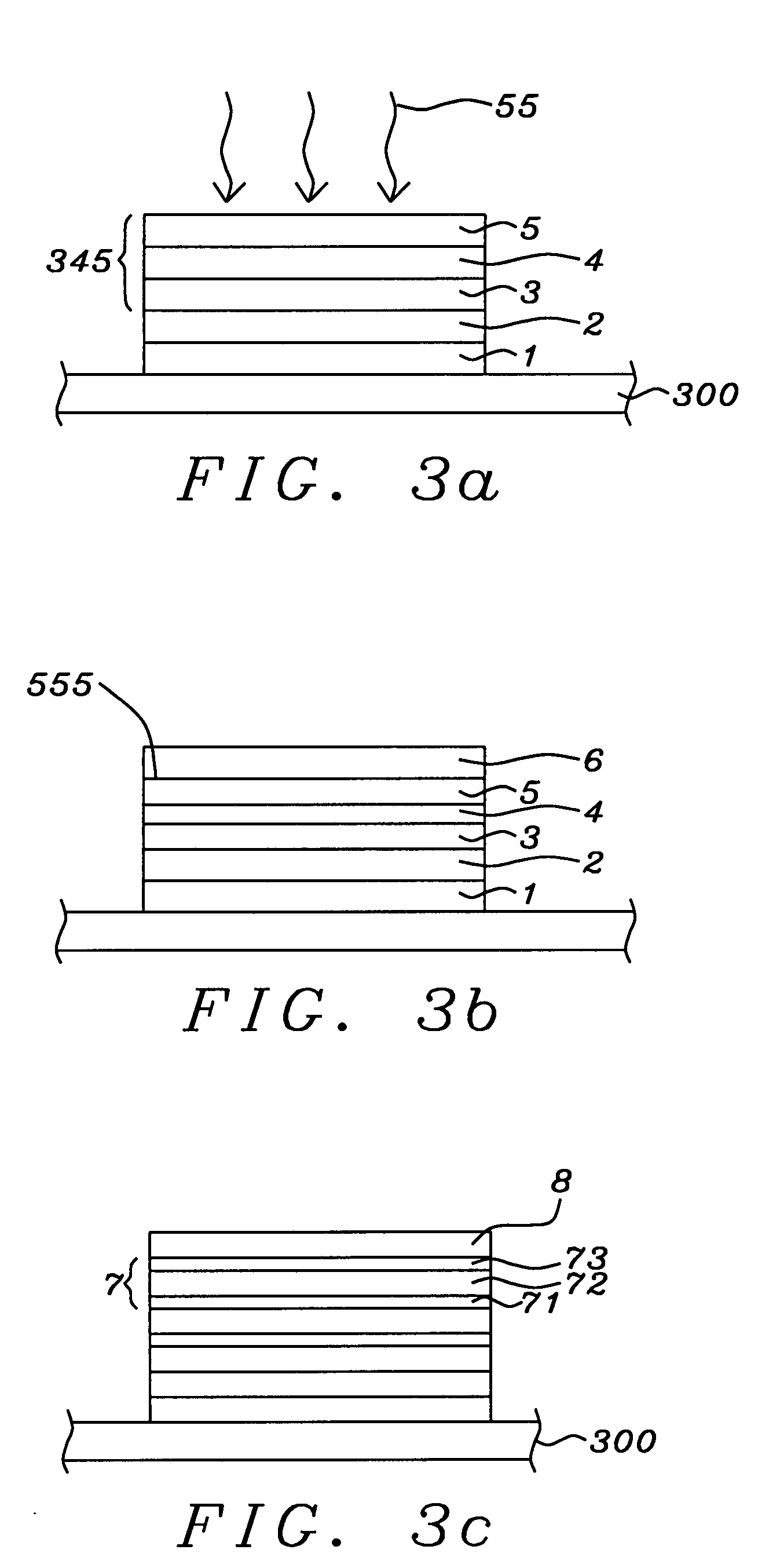
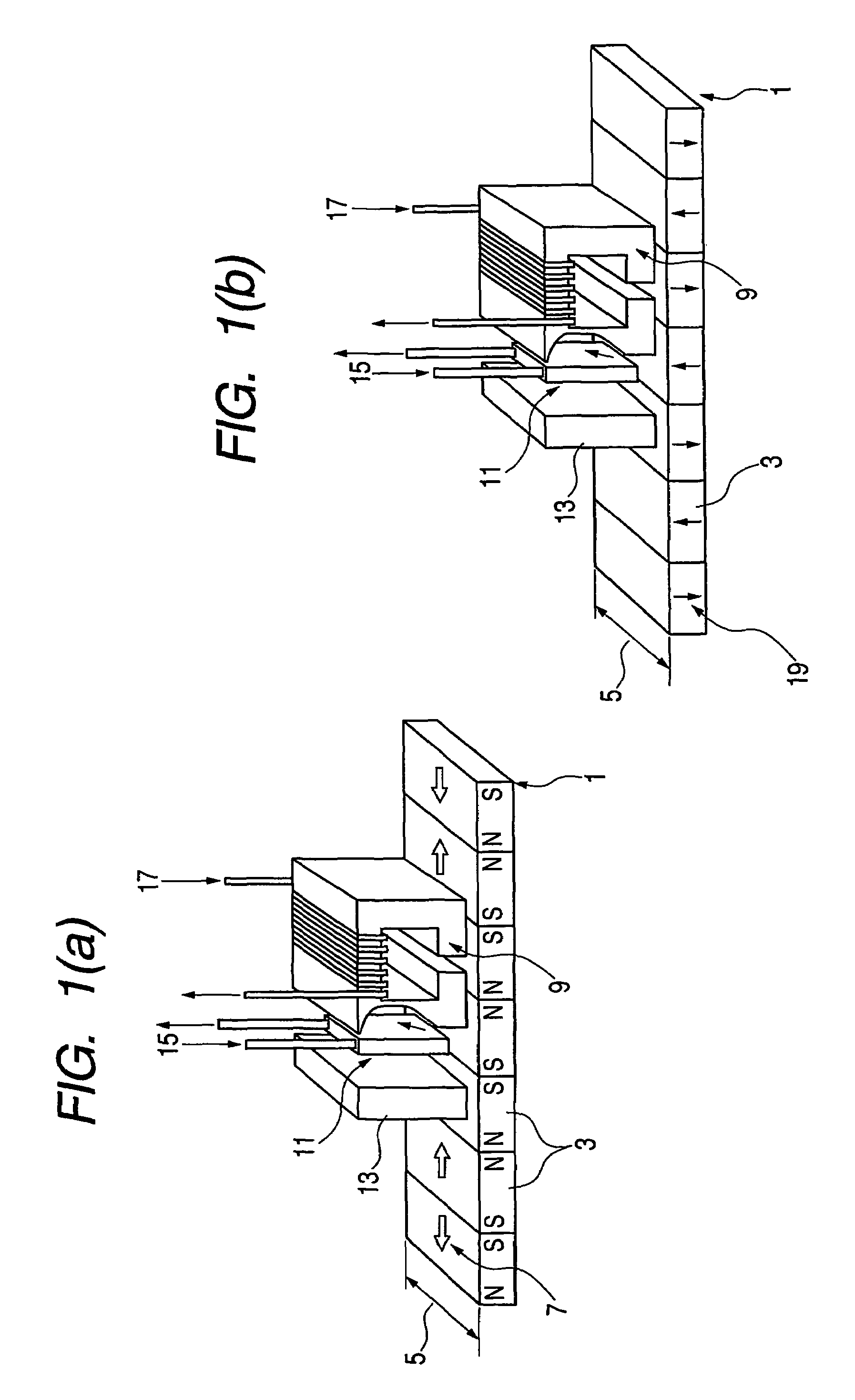
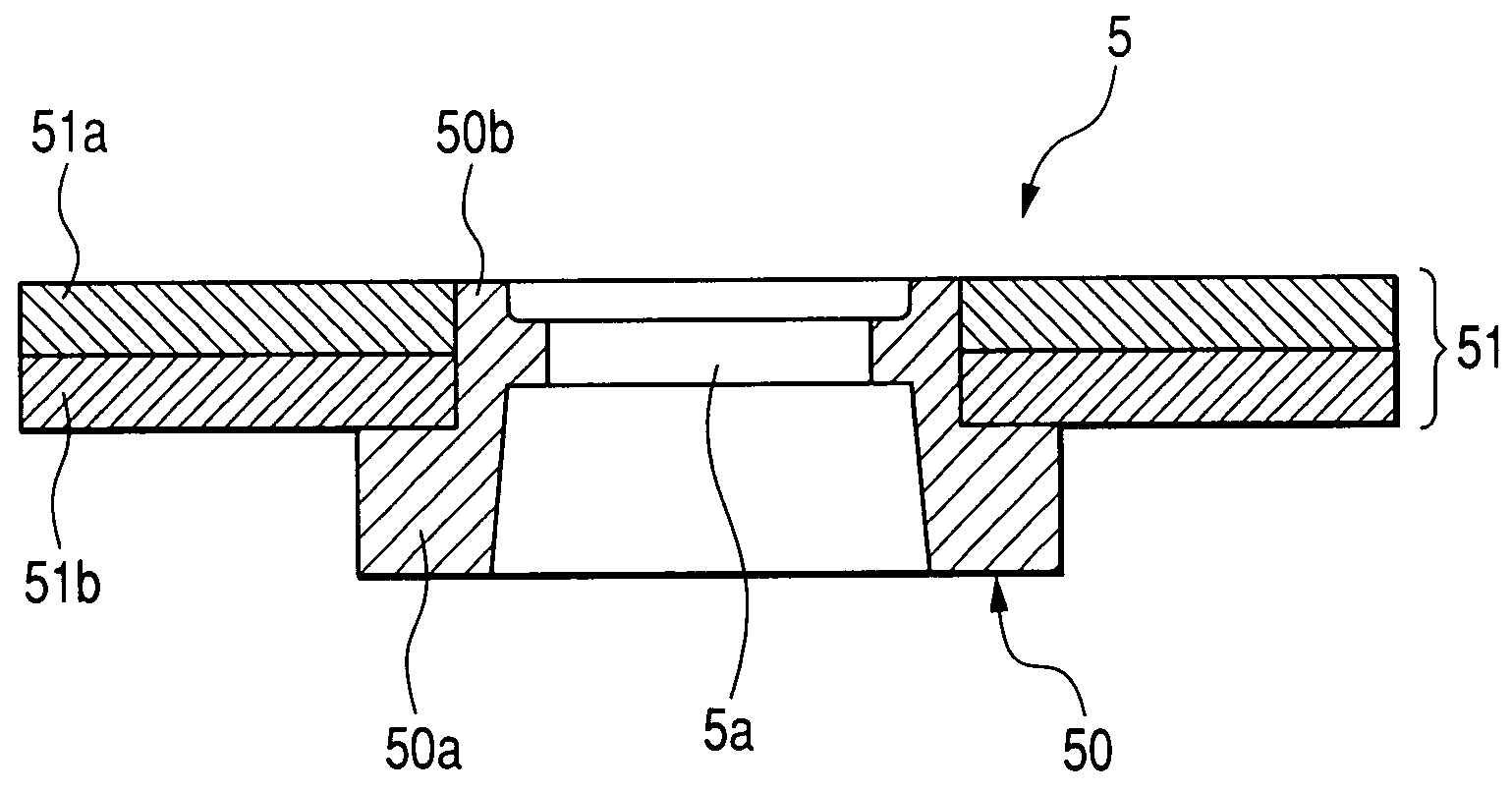
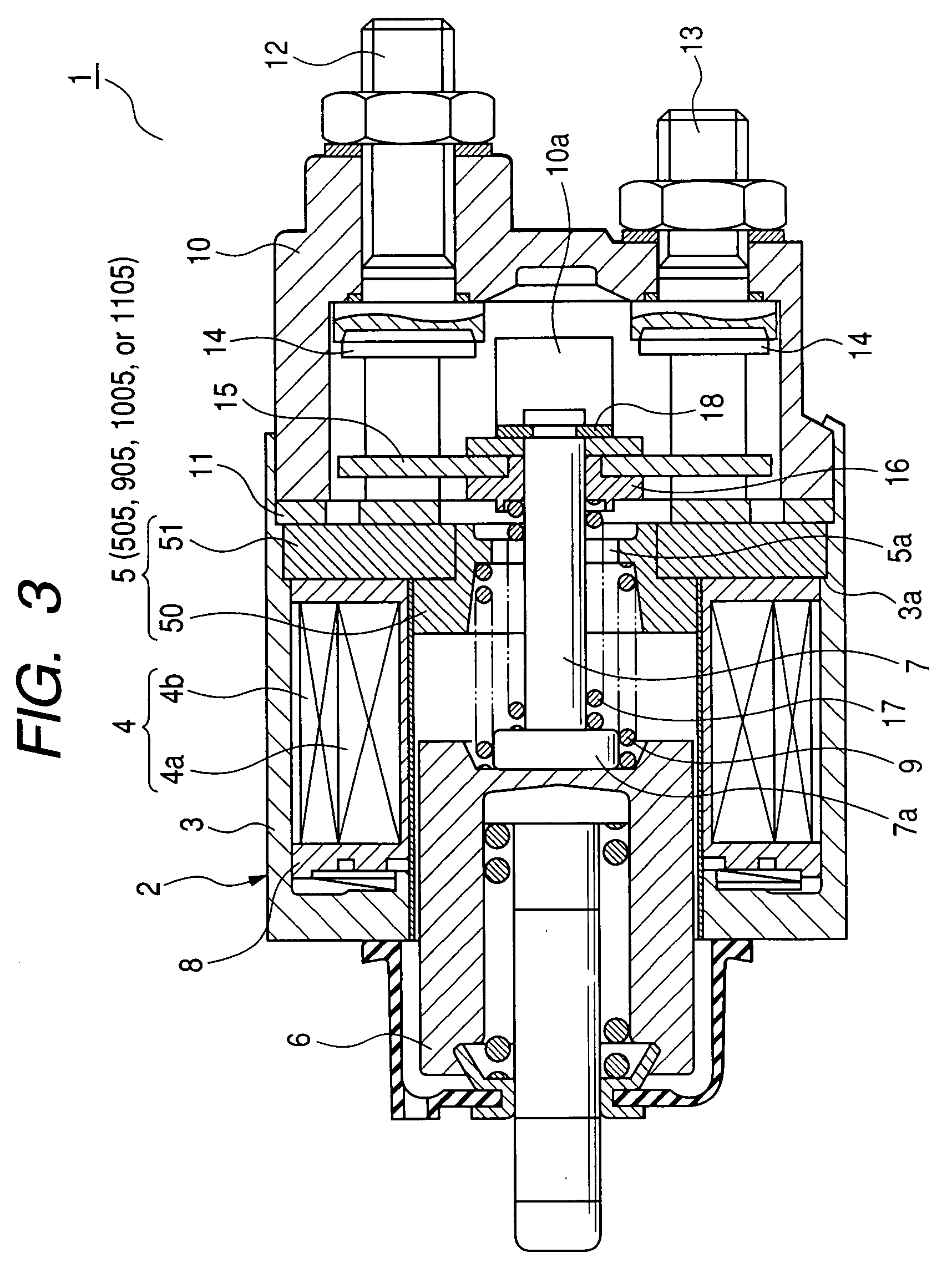
High performance MTJ element for STT-RAM and method for making the same
ActiveUS20090027810A1Low angular dispersionEasy to operateNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpin angular momentum of lightDamping factor
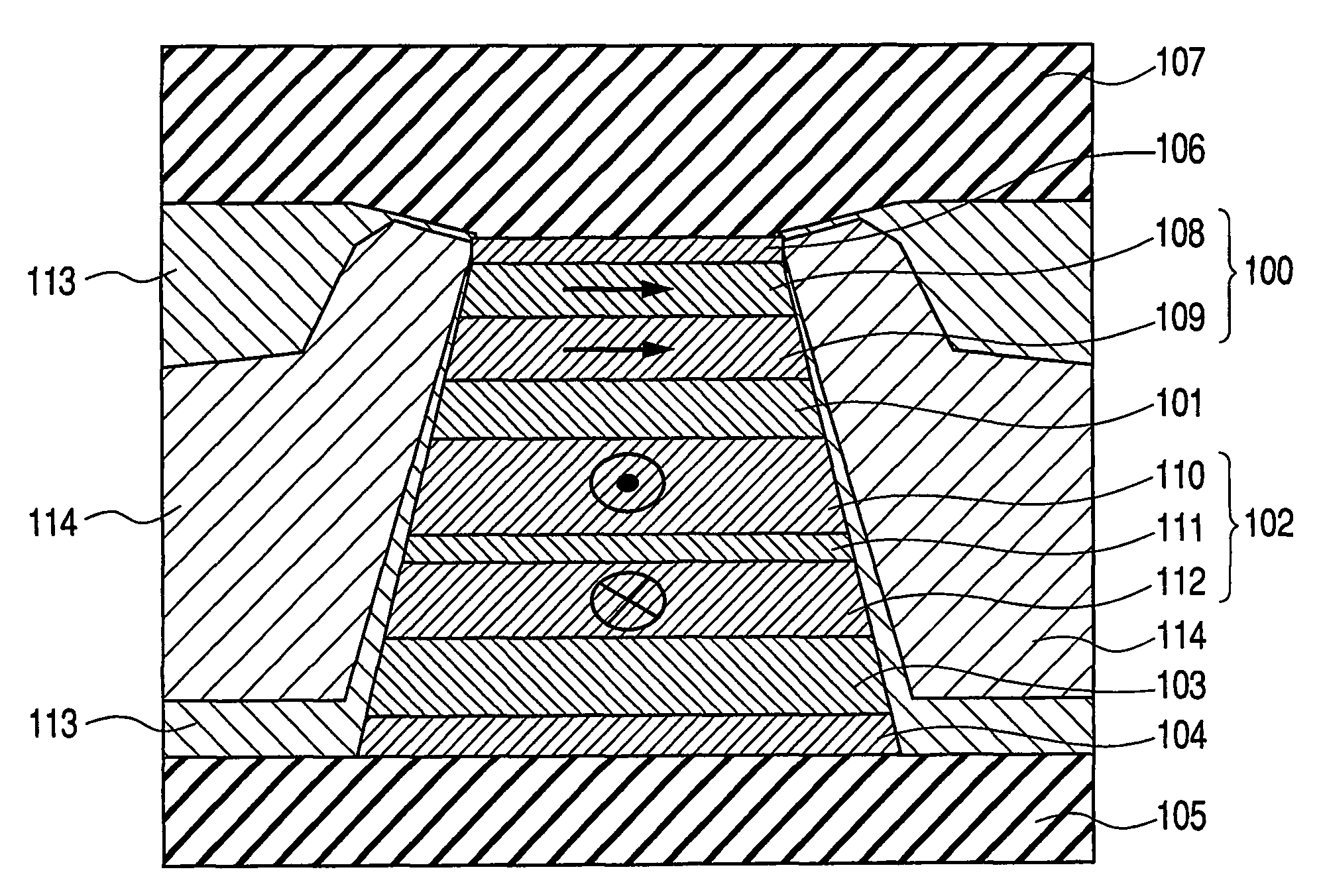
We describe the structure and method of forming a STT-MTJ MRAM cell that utilizes transfer of spin angular momentum as a mechanism for changing the magnetic moment direction of a free layer. The device includes an IrMn pinning layer, a SyAP pinned layer, a naturally oxidized, crystalline MgO tunneling barrier layer that is formed on an Ar-ion plasma smoothed surface of the pinned layer and, in one embodiment, a free layer that comprises an amorphous layer of Co60Fe20B20. of approximately 20 angstroms thickness formed between two crystalline layers of Fe of 3 and 6 angstroms thickness respectively. The free layer is characterized by a low Gilbert damping factor and by very strong polarizing action on conduction electrons. The resulting cell has a low critical current, a high dR / R and a plurality of such cells will exhibit a low variation of both resistance and pinned layer magnetization angular dispersion.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
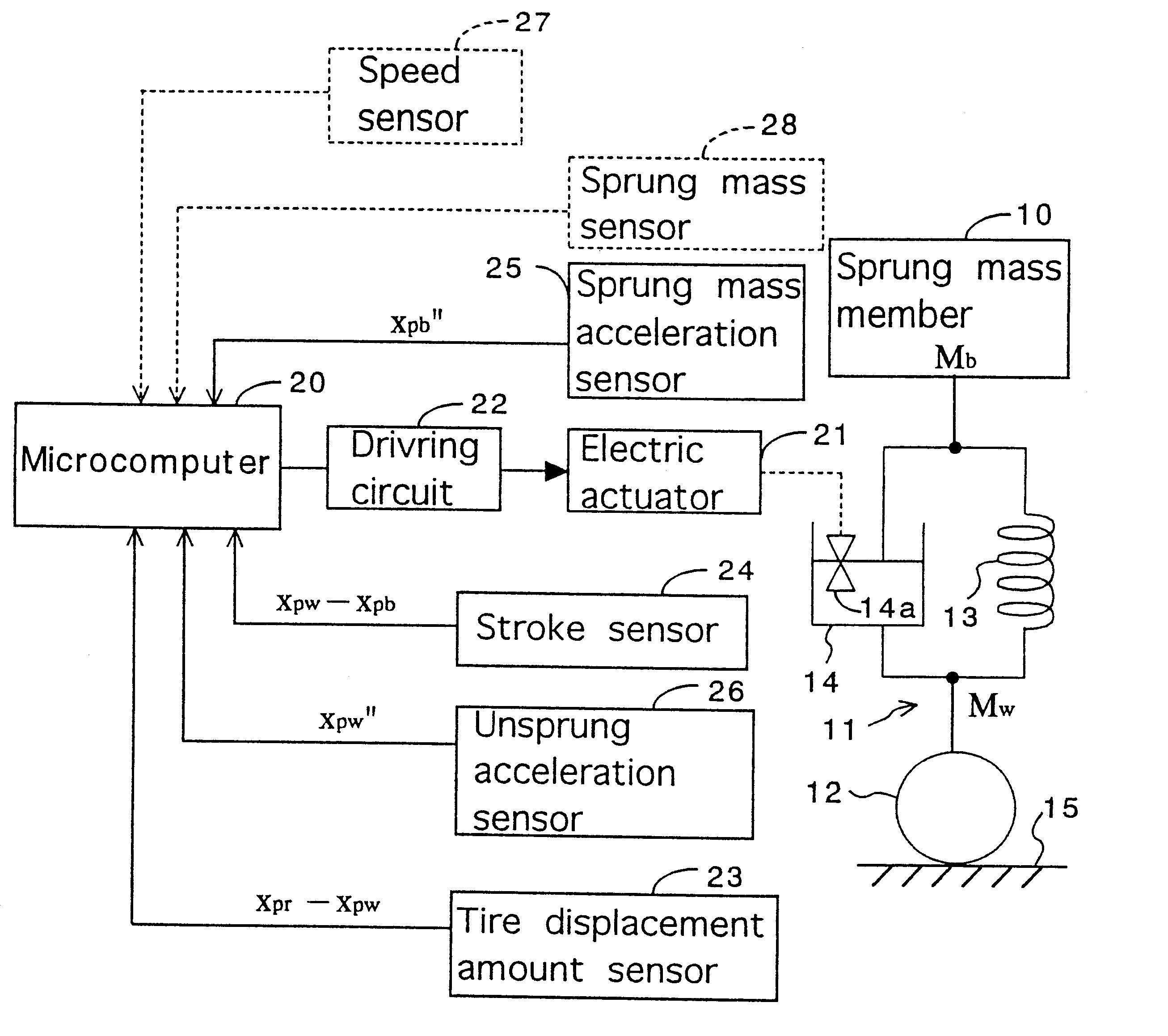
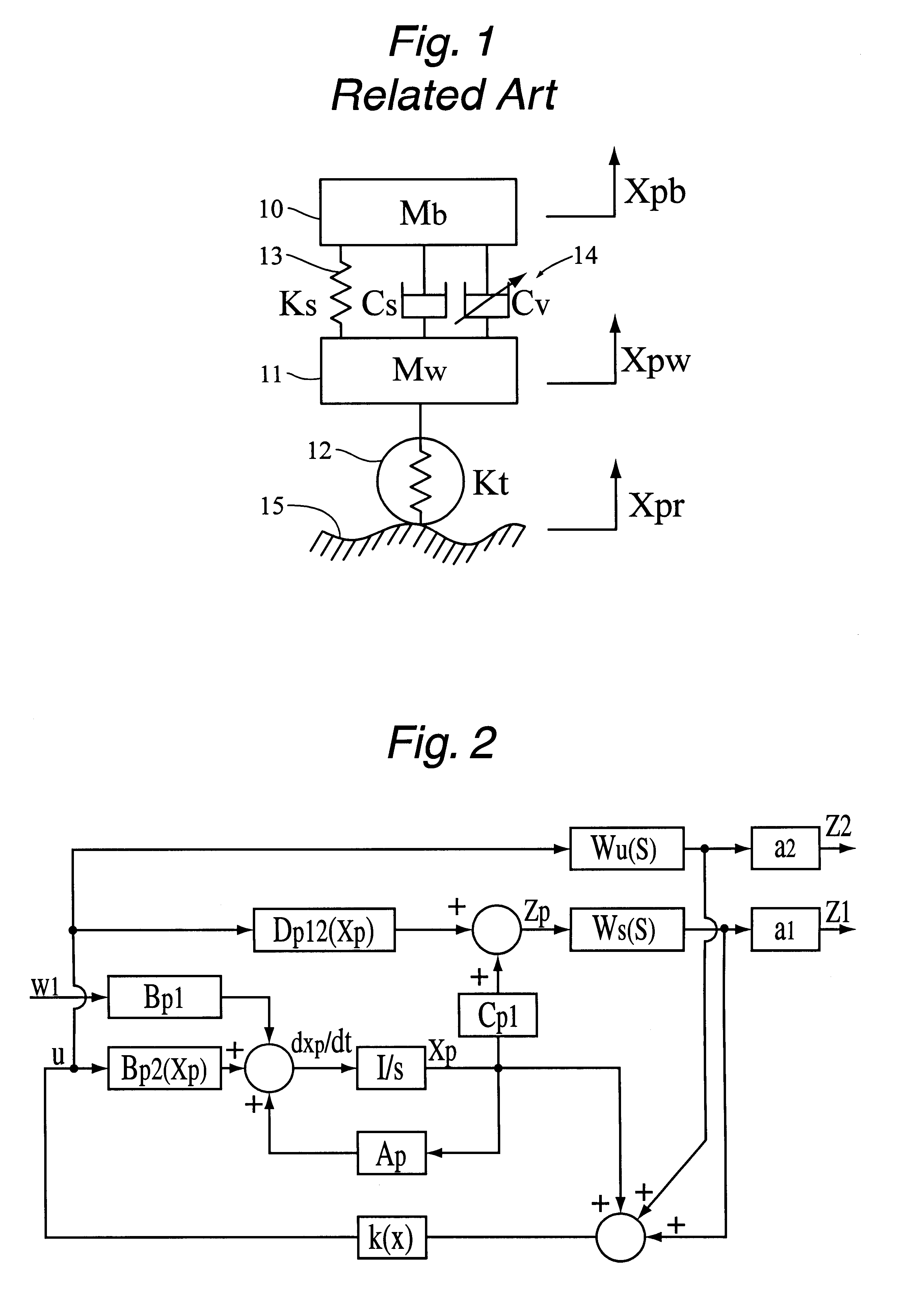
Control system for resilient support mechanism such as vehicle suspension mechanism
InactiveUS6314353B1Continuous changeEnhance running stability and comfortDigital data processing detailsNon-rotating vibration suppressionDamping factorRelative displacement
A control system for a resilient support mechanism such as a suspension mechanism of a wheeled vehicle including a damper disposed between an unsprung mass member and a sprung mass member of the vehicle, wherein a damping coefficient of the damper is divided into a linear portion and a nonlinear portion, and wherein the nonlinear portion of the damping coefficient is defined as a control input u and applied with a frequency weight Wu(s), while a vertical velocity of the sprung mass member, a relative velocity of the sprung mass member to the unsprung mass member and a vertical acceleration of the sprung mass member are defined as an evaluation output zp and applied with a frequency weight Ws(s). In the control system, a nonlinear Hinfin control theory is applied to a generalized plant to obtain a positive definite symmetric solution P and to calculate a target damping force based on the positive definite symmetric solution P and a state amount such as the vertical velocity of the sprung mass member, a relative displacement of the sprung mass member to the unsprung mass member or the like.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
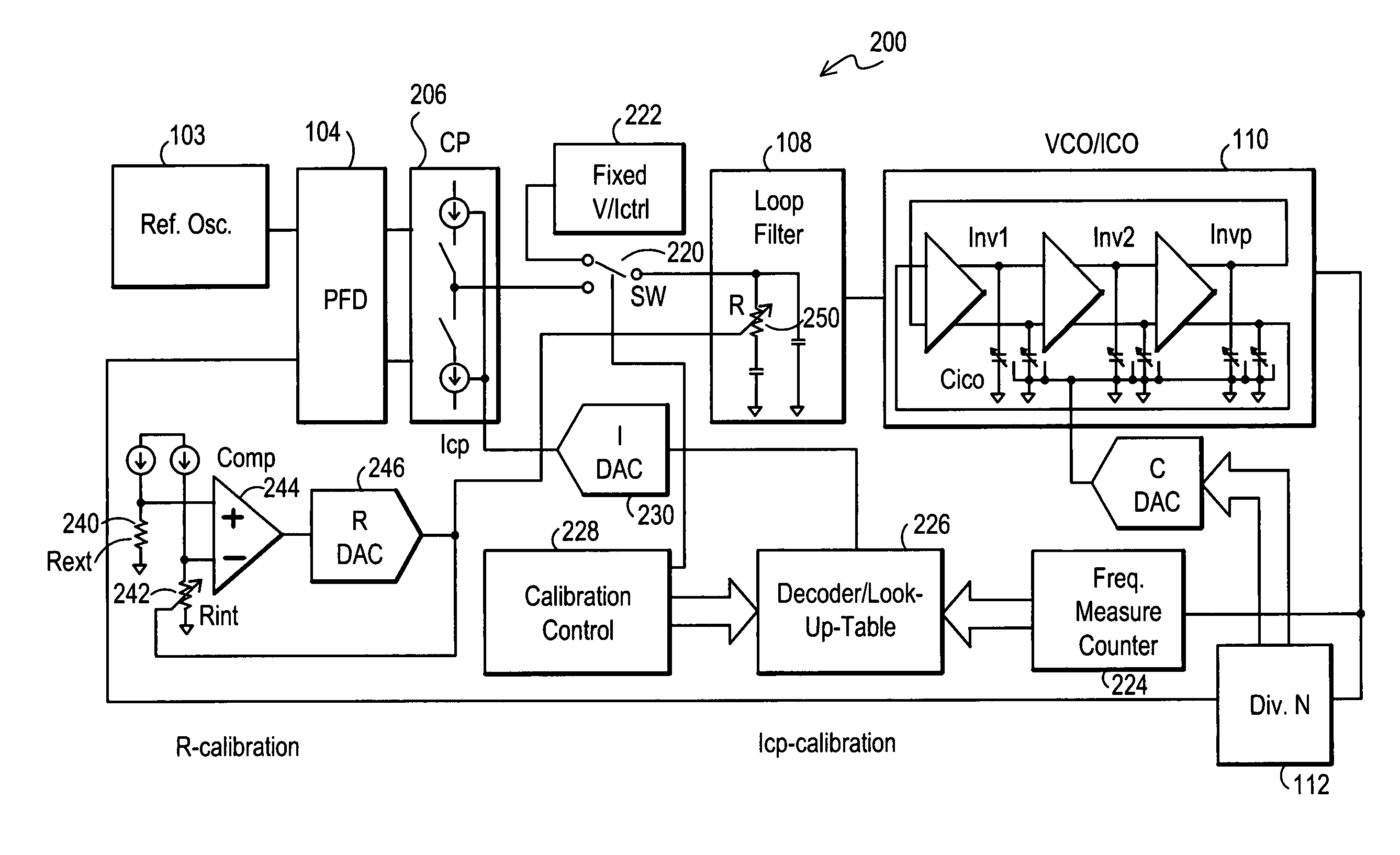
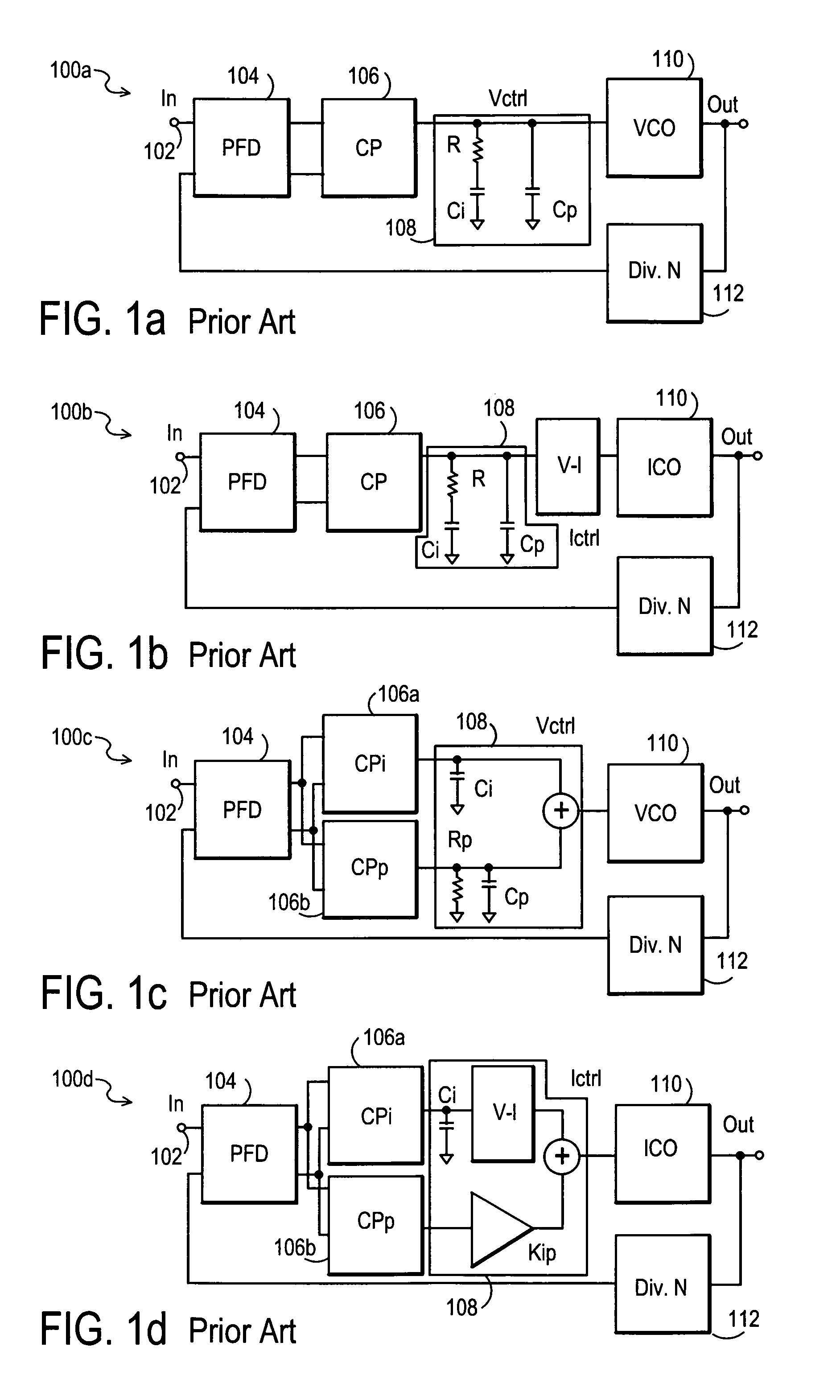
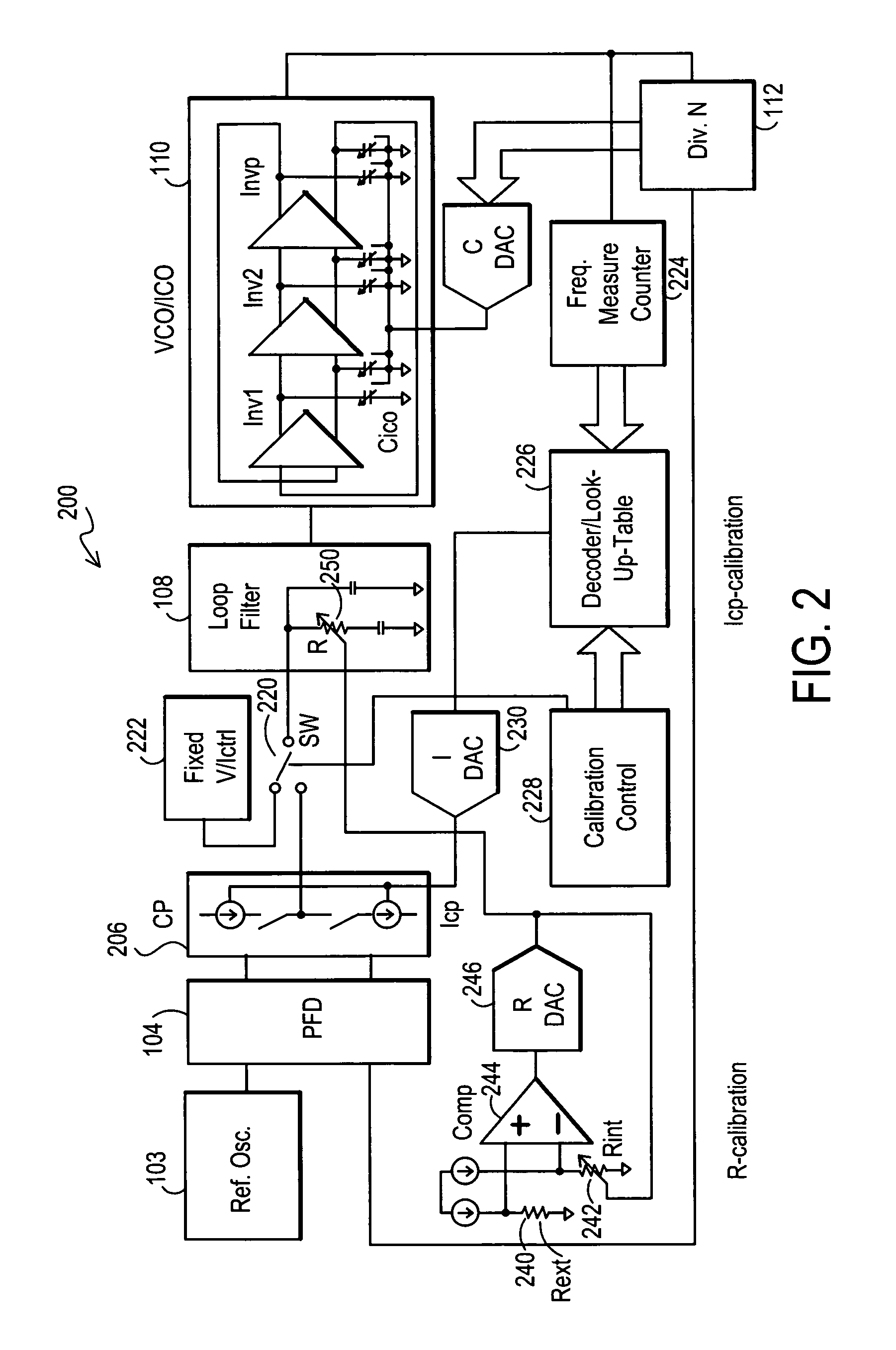
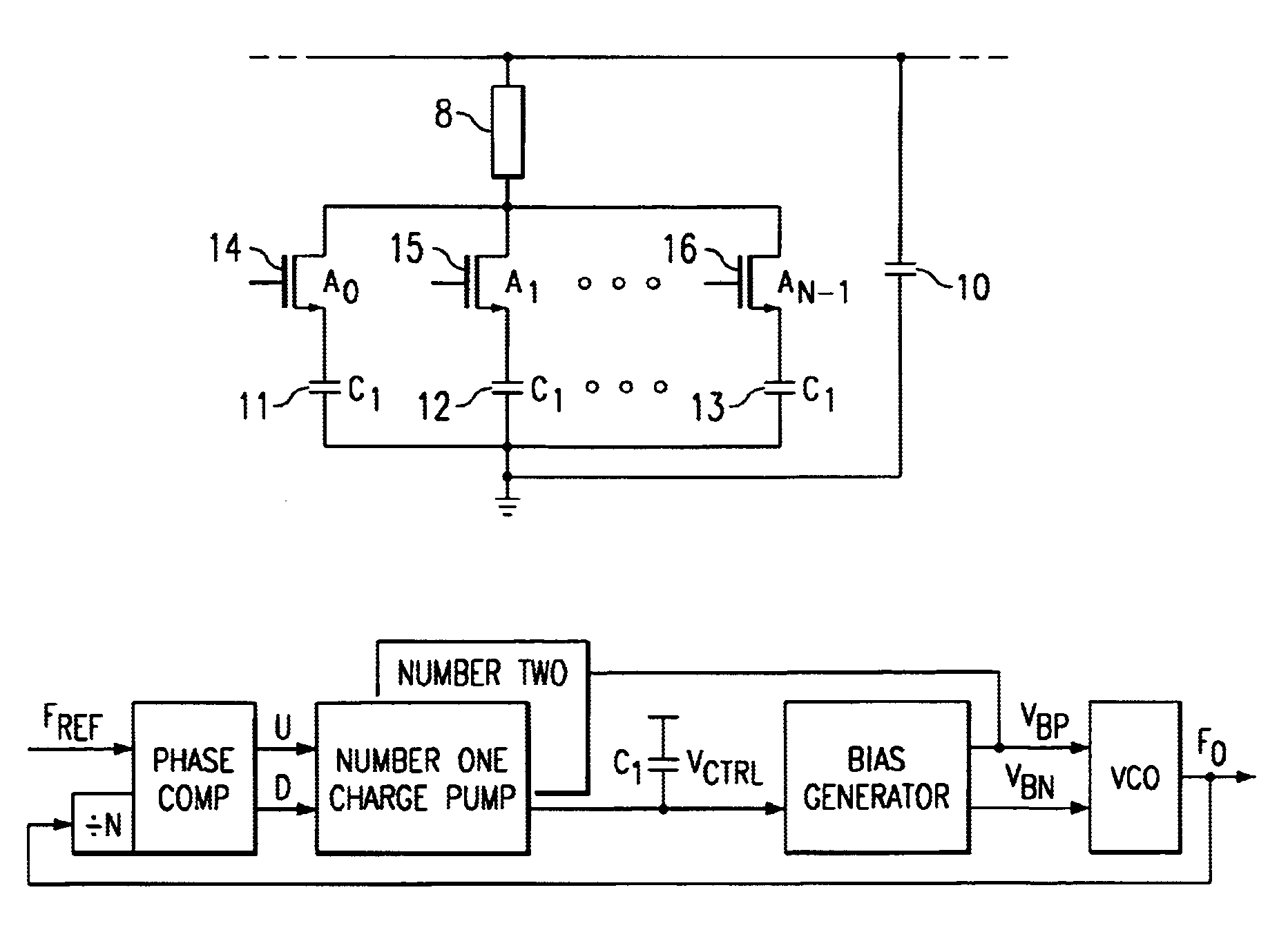
Method and apparatus to achieve a process, temperature and divider modulus independent PLL loop bandwidth and damping factor using open-loop calibration techniques
InactiveUS7095287B2Reduce complexityImprove accuracyPulse automatic controlFrequency analysisDamping factorProportional control
Several open-loop calibration techniques for phase-locked-loop circuits (PLL) that provide a process, temperature and divider modulus independence for the loop bandwidth and damping factor are disclosed. Two categories of open-loop techniques are presented. The first method uses only a single measurement of the output frequency from the oscillator and adjusts a single PLL loop element that performs a simultaneous calibration of both the loop bandwidth and damping factor. The output frequency is measured for a given value of the oscillator control signal and the charge-pump current is adjusted such that it cancels the process variation of the oscillator gain. The second method uses two separate and orthogonal calibration steps, both of them based on the measurement of the output frequency from the oscillator when a known excitation is applied to the open loop signal path. In the first step the loop bandwidth is calibrated by adjusting the charge-pump current based on the measurement of the forward path gain when applying a constant phase shift between the two clocks that go to the phase frequency detector, while the integral path is hold to a constant value. During the second step the damping factor is calibrated by adjusting the value of the integral loop filter capacitor based on the measurement of the oscillator output frequency when excited with a voltage proportional with the integral capacitor value, while the proportional control component is zeroed-out.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
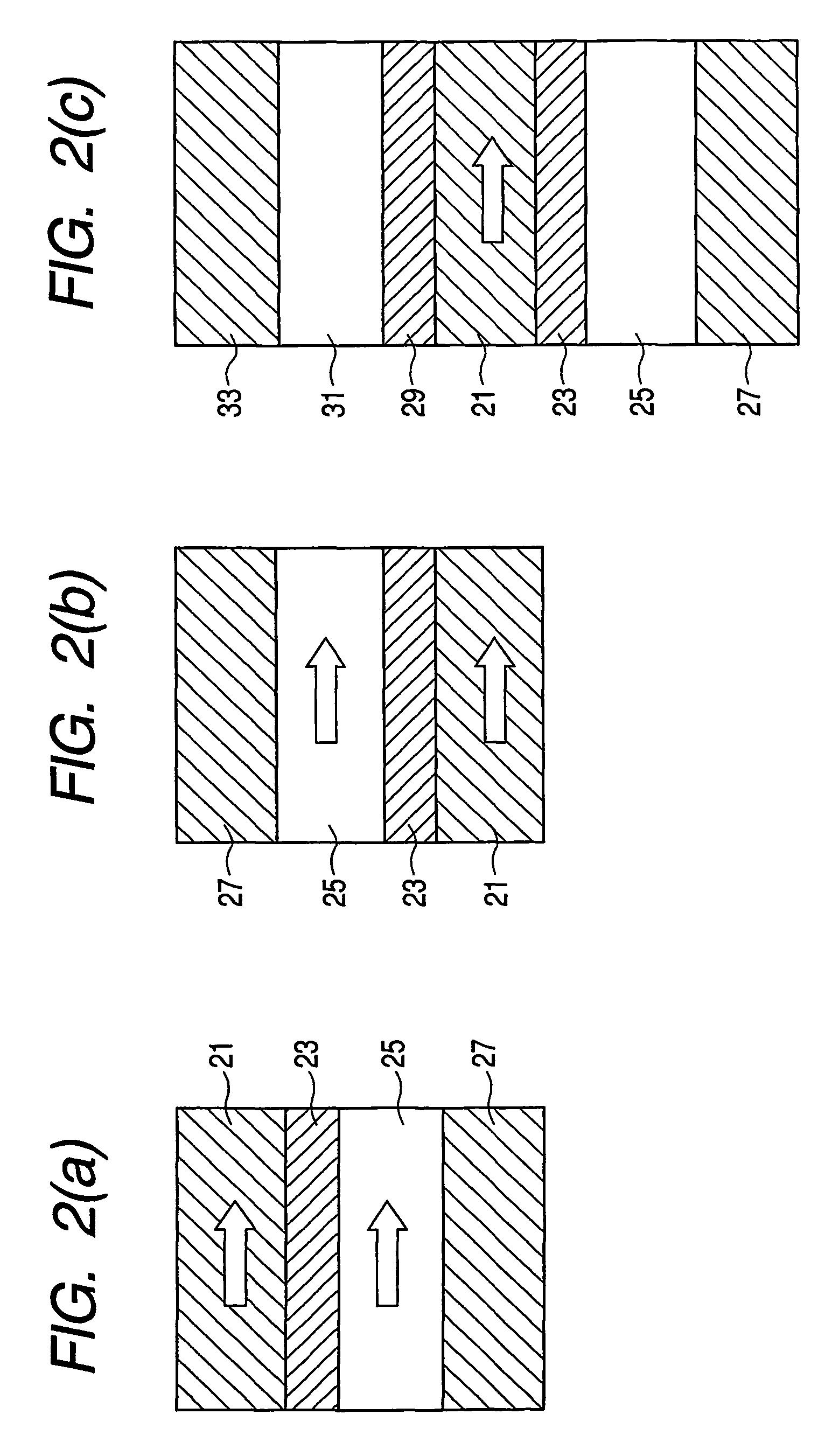
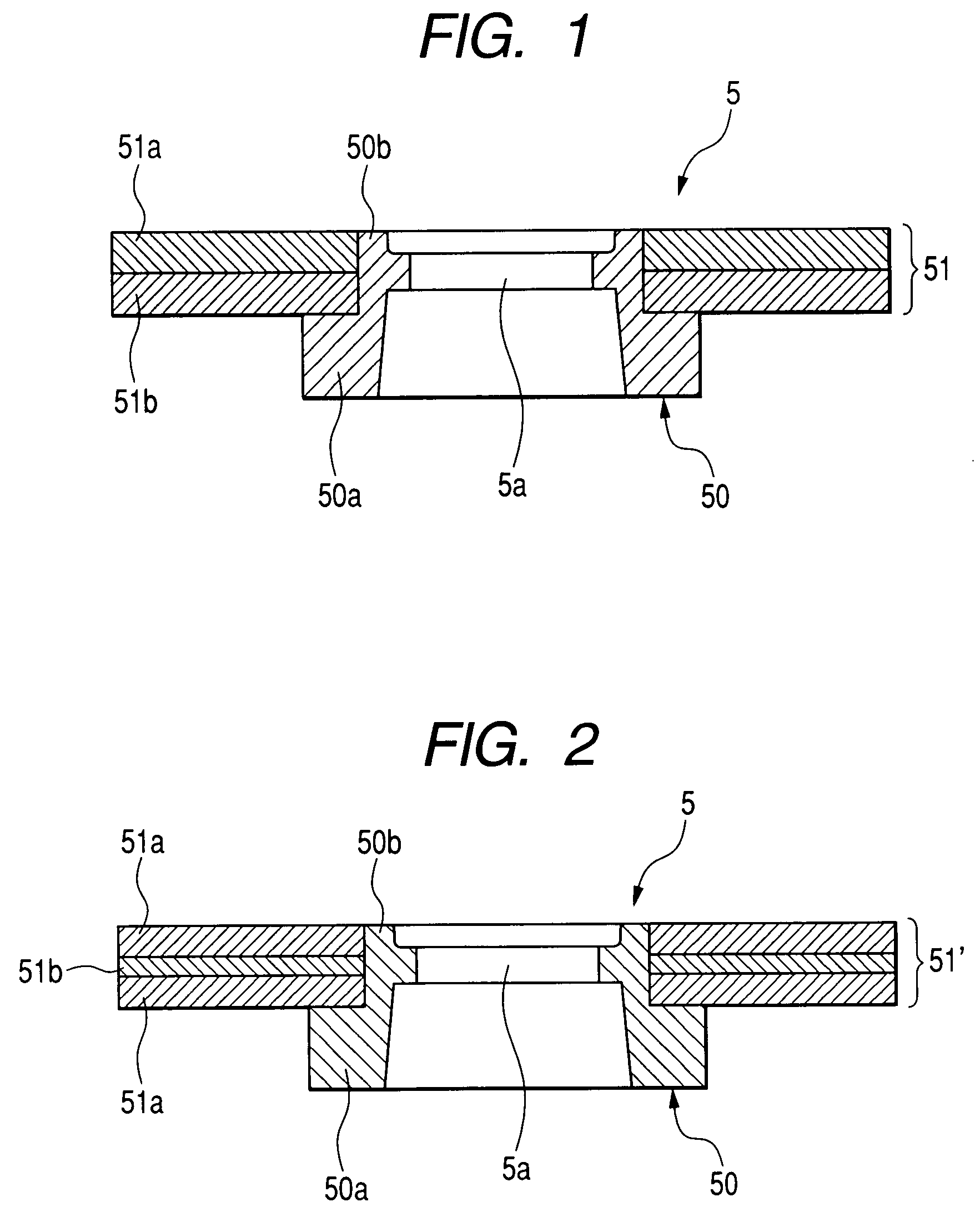
High performance MTJ element for STT-RAM and method for making the same
ActiveUS7750421B2Easy to operateLow dispersionNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpin angular momentum of lightDamping factor
A STT-MTJ MRAM cell that utilizes transfer of spin angular momentum as a mechanism for changing the magnetic moment direction of a free layer includes an IrMn pinning layer, a SyAP pinned layer, a naturally oxidized, crystalline MgO tunneling barrier layer that is formed on an Ar-ion plasma smoothed surface of the pinned layer and, in one embodiment, a free layer that comprises an amorphous layer of Co60Fe20B20 of approximately 20 angstroms thickness formed between two crystalline layers of Fe of 3 and 6 angstroms thickness respectively or on a single such layer. The free layer is characterized by a low Gilbert damping factor and by very strong polarizing action on conduction electrons. The resulting cell has a low critical current, a high dR / R and a plurality of such cells will exhibit a low variation of both resistance and pinned layer magnetization angular dispersion.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
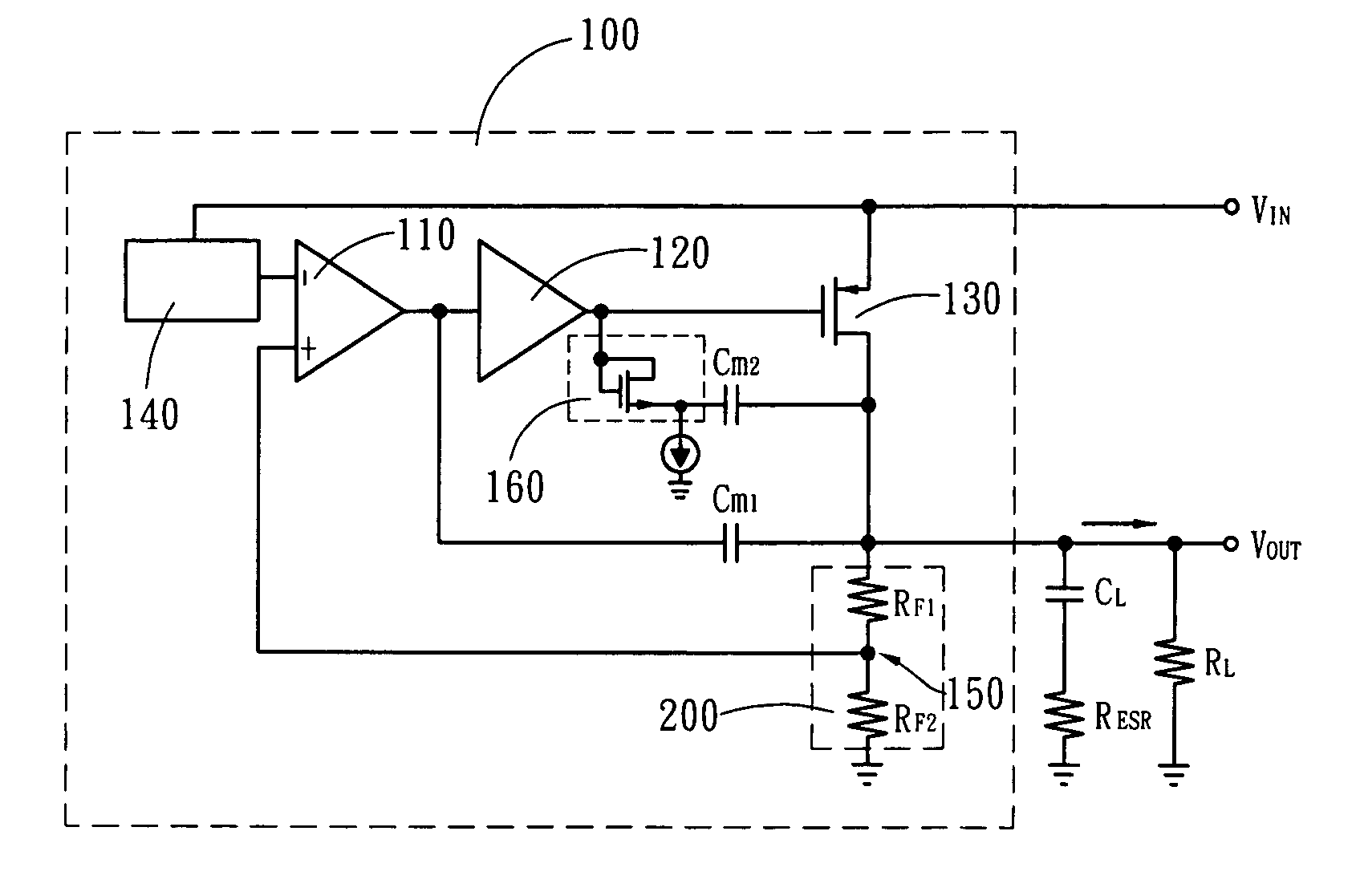
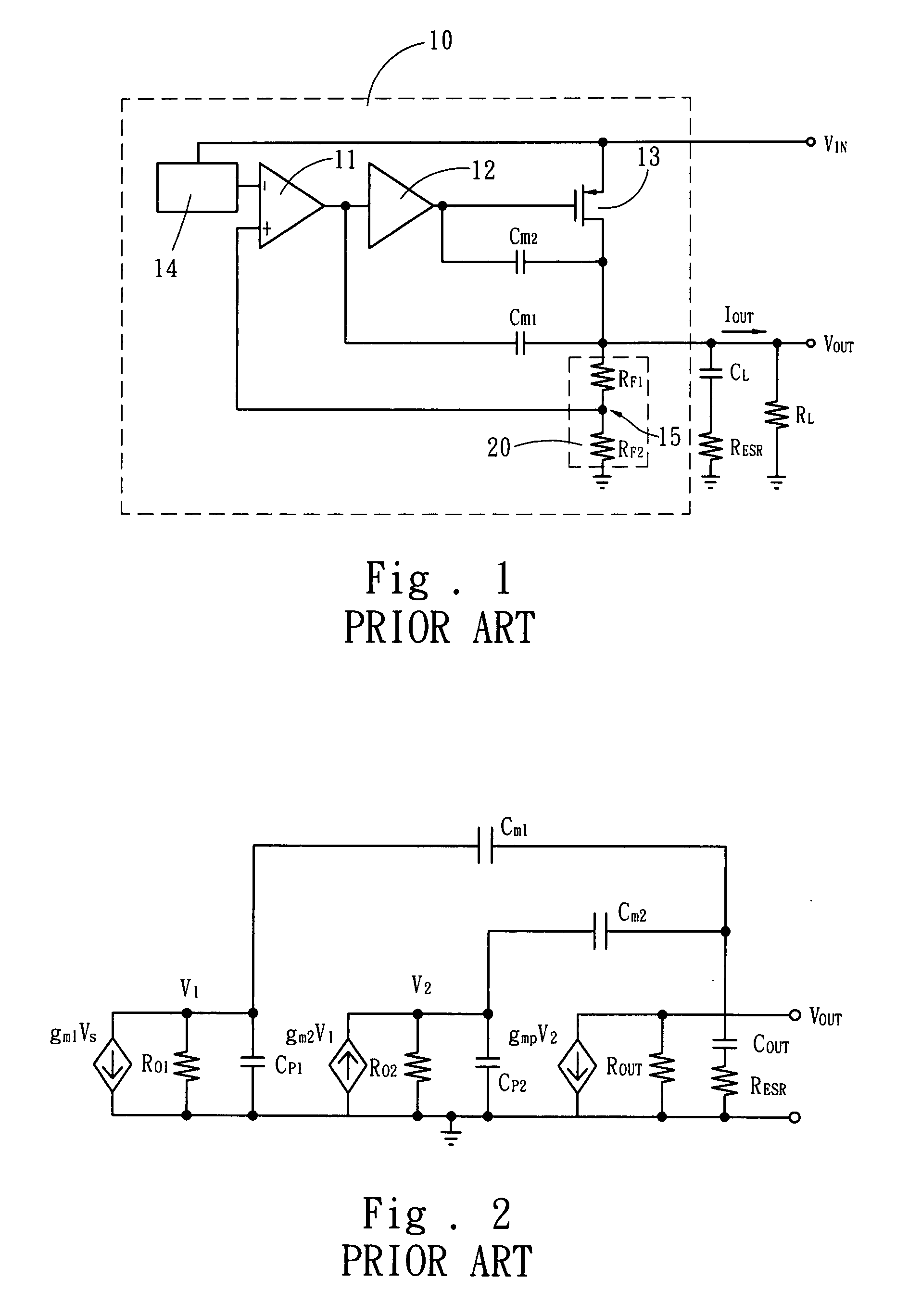
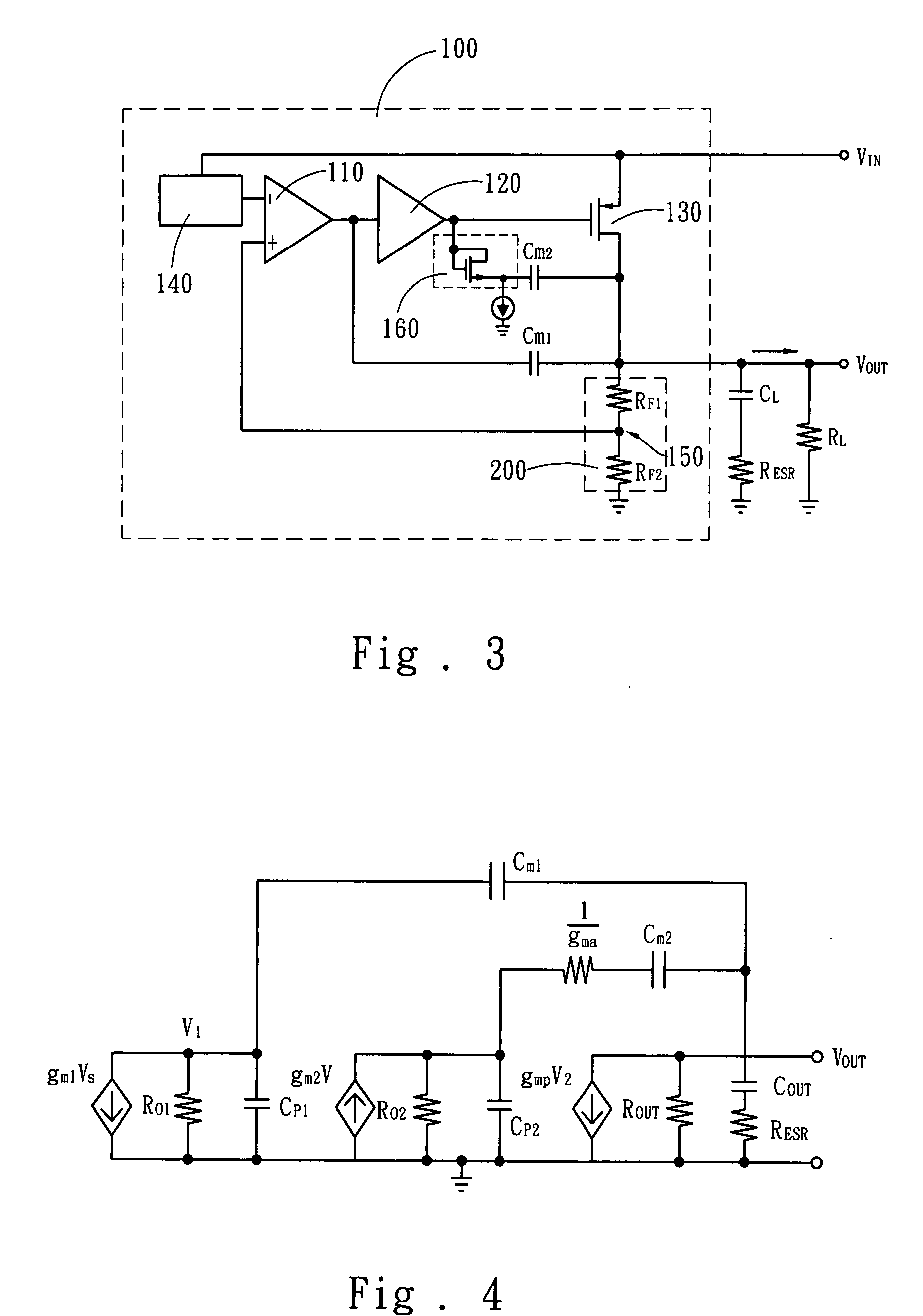
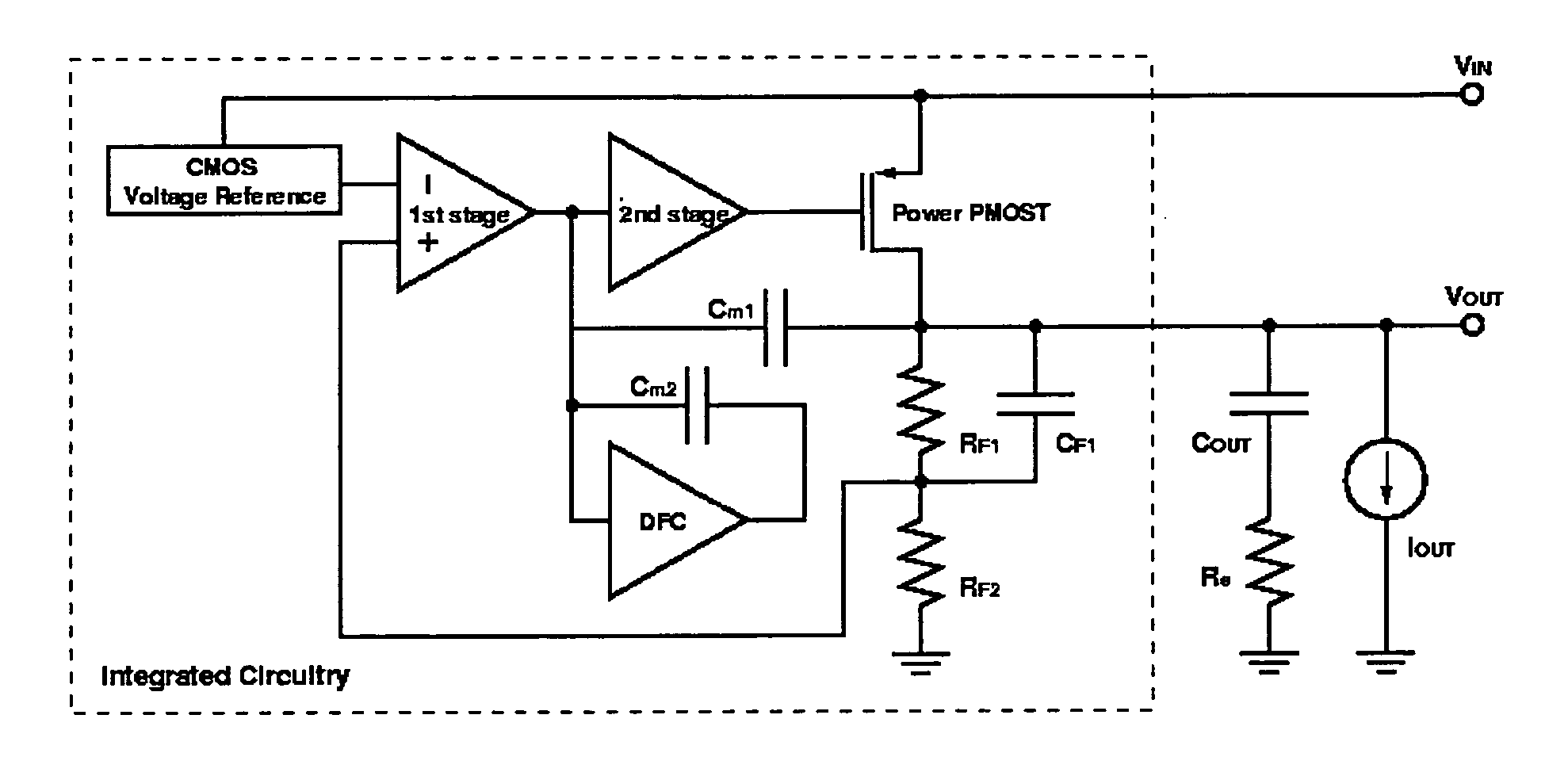
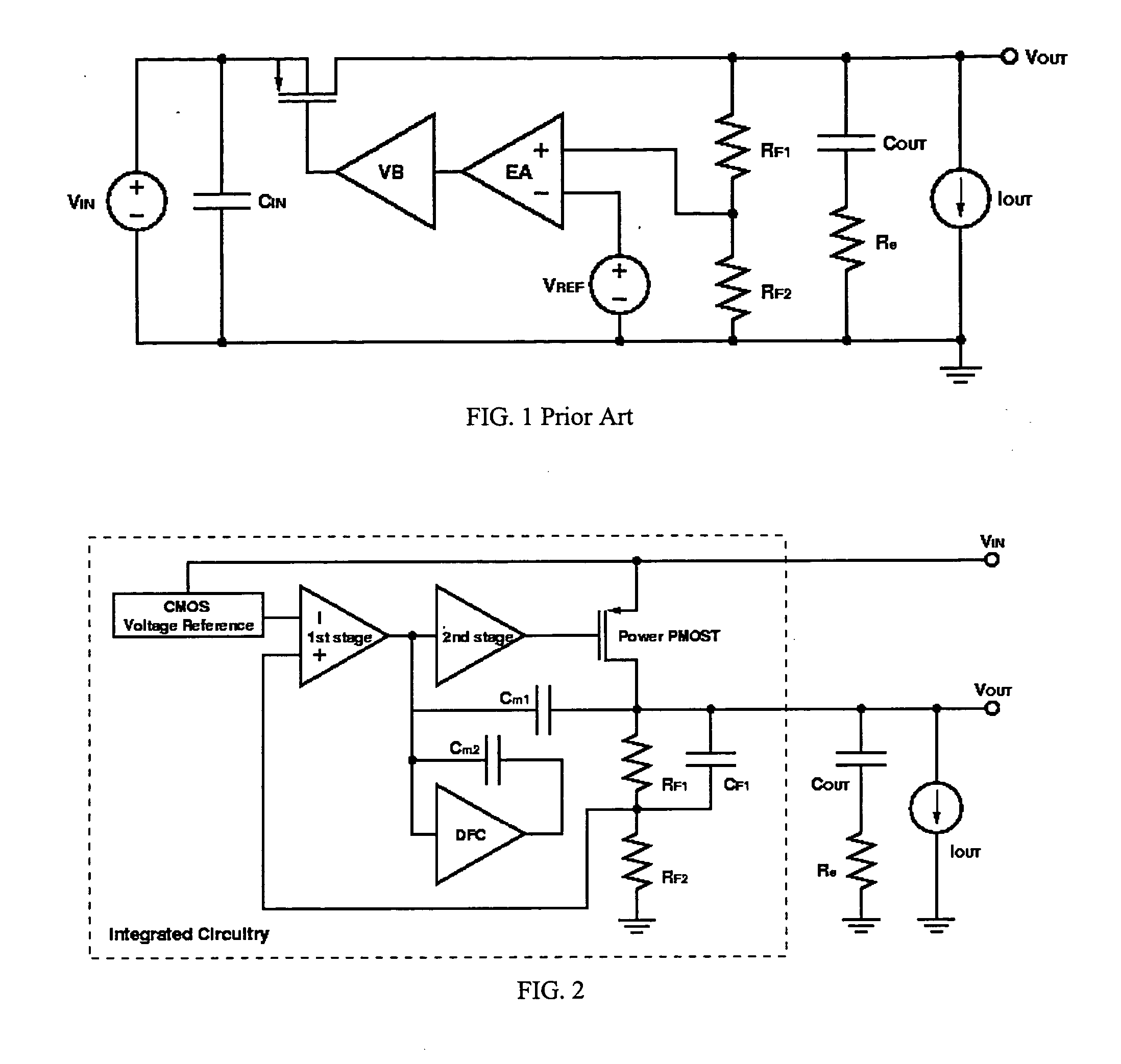
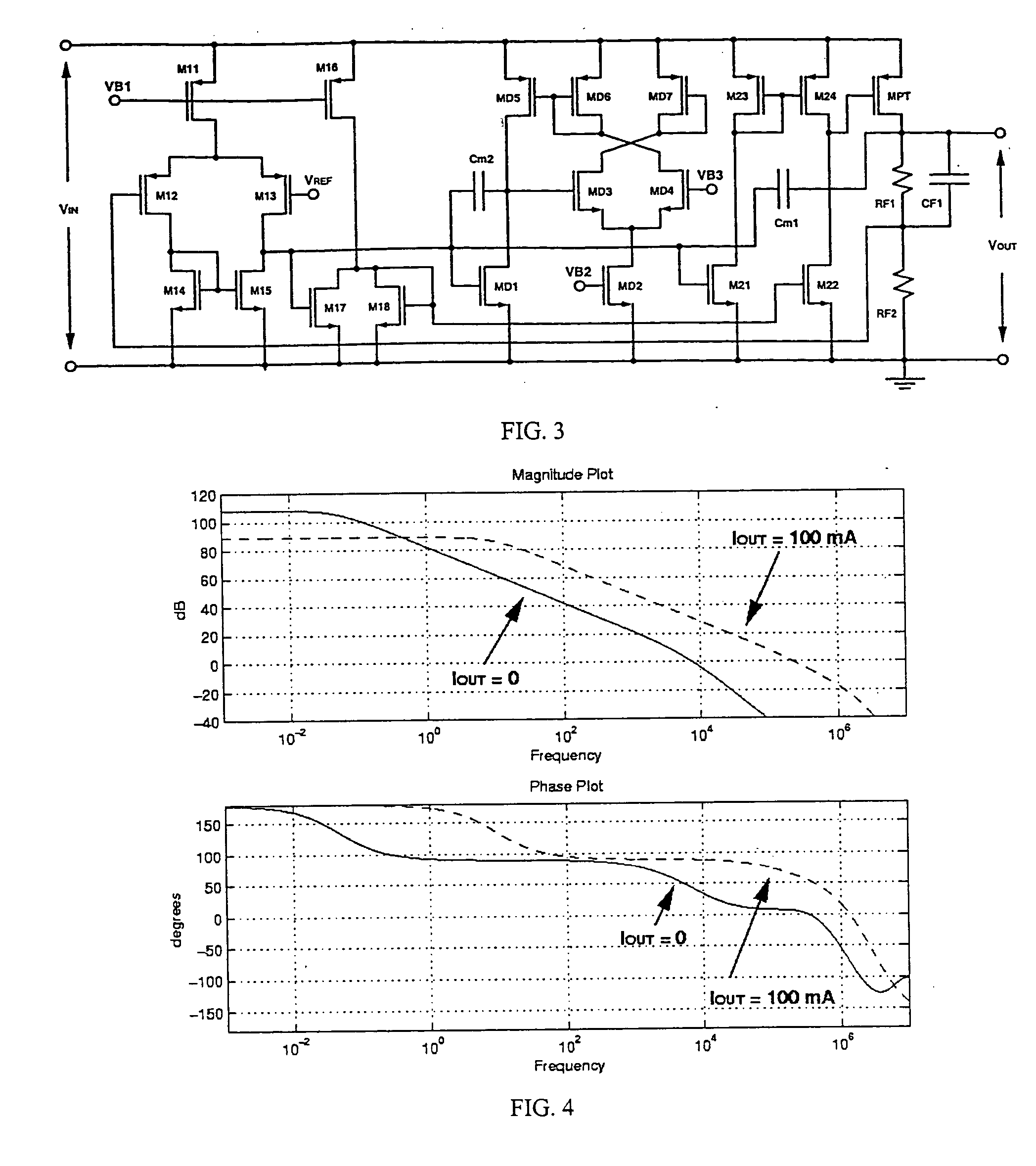
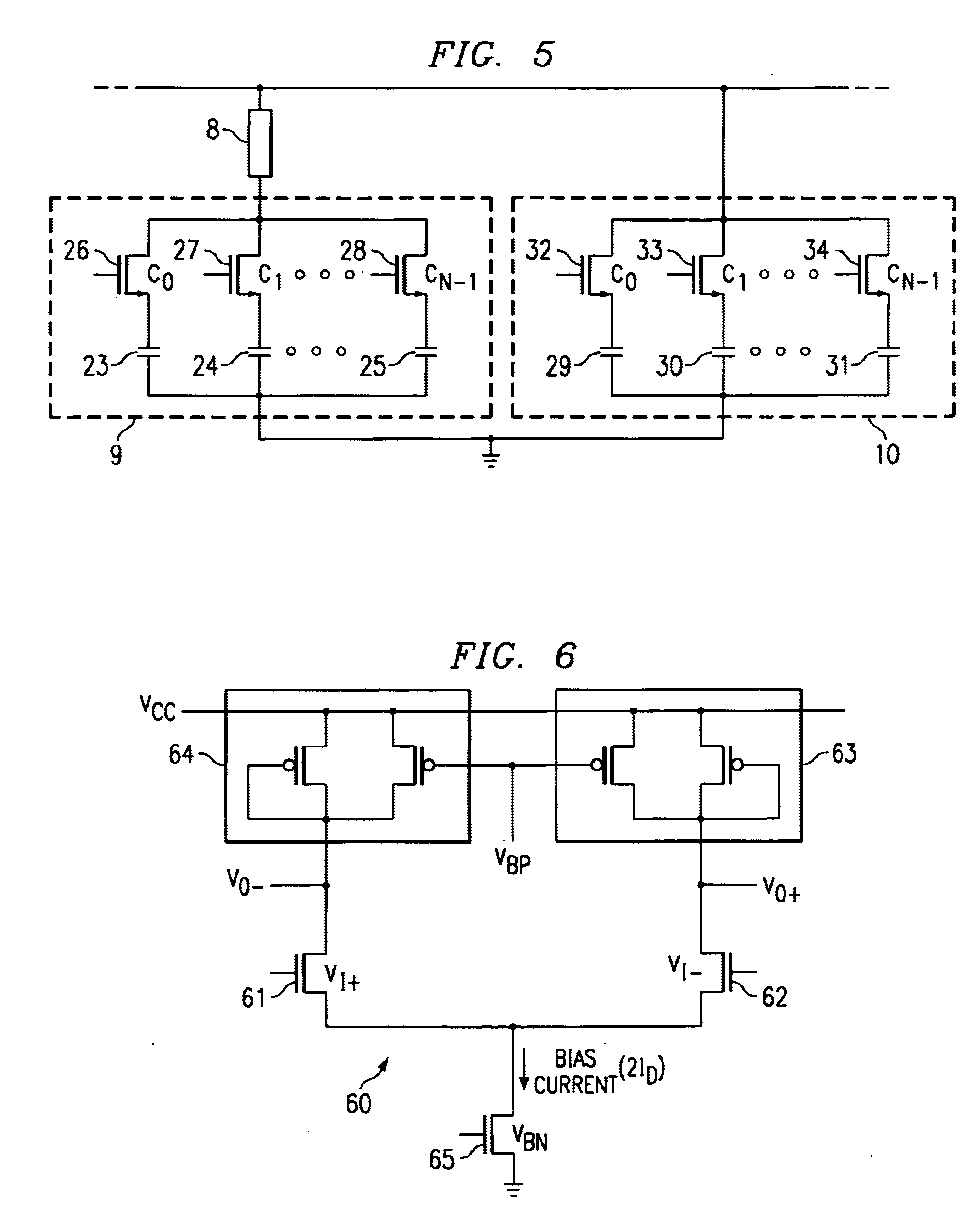
Low dropout linear voltage regulator
InactiveUS20090001953A1Sufficient phase-angle marginIncrease capacitanceNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifiers with impedence circuitsLinear regulatorCapacitance
The present invention discloses an LDO (Low DropOut) linear voltage regulator, which is based on an NMC (Nested Miller Compensation) architecture and can be capacitor-free, wherein an active resistor is added to the feedback path of the Miller compensation capacitor to increase the controllability of the damping factor, solve the problem of extensively using the output capacitor with a parasitic resistance, and solve the problem that a compromise must be made between the damping factor control and the system loop gain. Further, the present invention utilizes a capacitor-sharing technique to reduce the Miller capacitance required by the entire system and accelerate the stabilization of output voltage without influencing stability.
Owner:SITRONIX TECH CORP
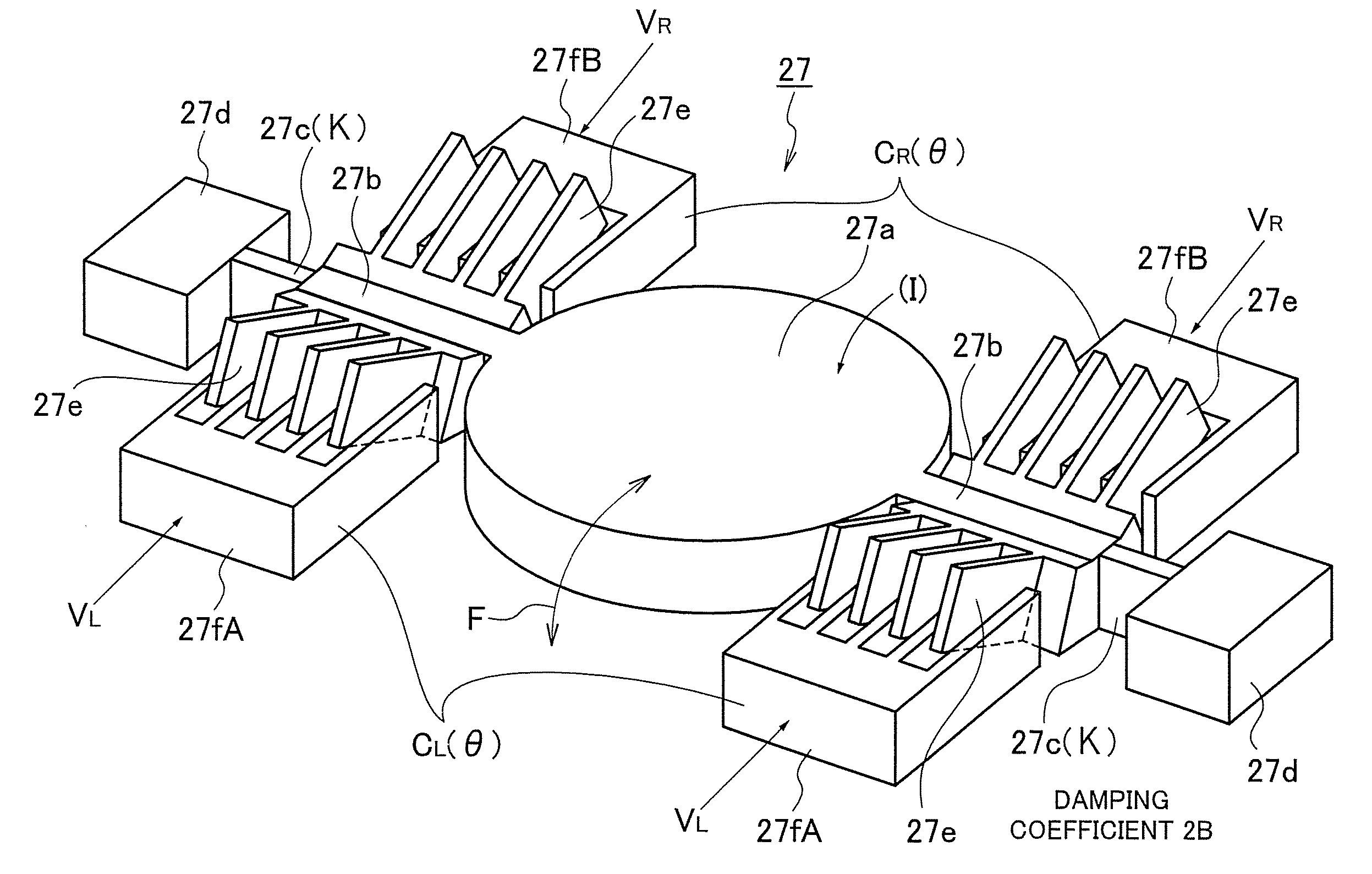
Method of driving MEMS mirror scanner, method of driving MEMS actuator scanner and method of controlling rotation angle of MEMS actuator
InactiveUS20090244668A1Simple planQuickly determine parameterOptical elementsDamping factorMoment of inertia
A method of driving a MEMS mirror scanner having an electrostatic actuator, comprising a step of driving the electrostatic actuator according to an input signal in accordance with a driving waveform obtained by the following equation,whenC+′(θ)≠0VV(t)=1C+′(θ)I[-C-′(θ)IVB+-(1ICL(θ)θ)(1ICR(θ)θ)VB2+C+′(θ)I(θ¨+2BIθ.+κIθ)]whenC+′(θ)=0VV(t)=θ¨+2BIθ.+κIθ2C-′(θ)IVBwhere, B / I, κ / I, (1 / I)·dCL(θ) / dθ and (1 / I)·dCR(θ) / dθ are parameters for obtaining the driving waveform, θ(t) is a desired mirror angle response, I is a moment of inertia of a moving part including a mirror, 2B is a damping factor (damping coefficient), κ is a spring constant, CL(θ) and CR(θ) are angle dependencies of an electric capacitance, VB is a constant bias voltage in differential driving, and C+′(θ) and C−′(θ) are ½ of the sum and the difference of the first order derivative of CL(θ) and CR(θ) with respect to θ, respectively, which are represented by defined equations.
Owner:KK TOPCON
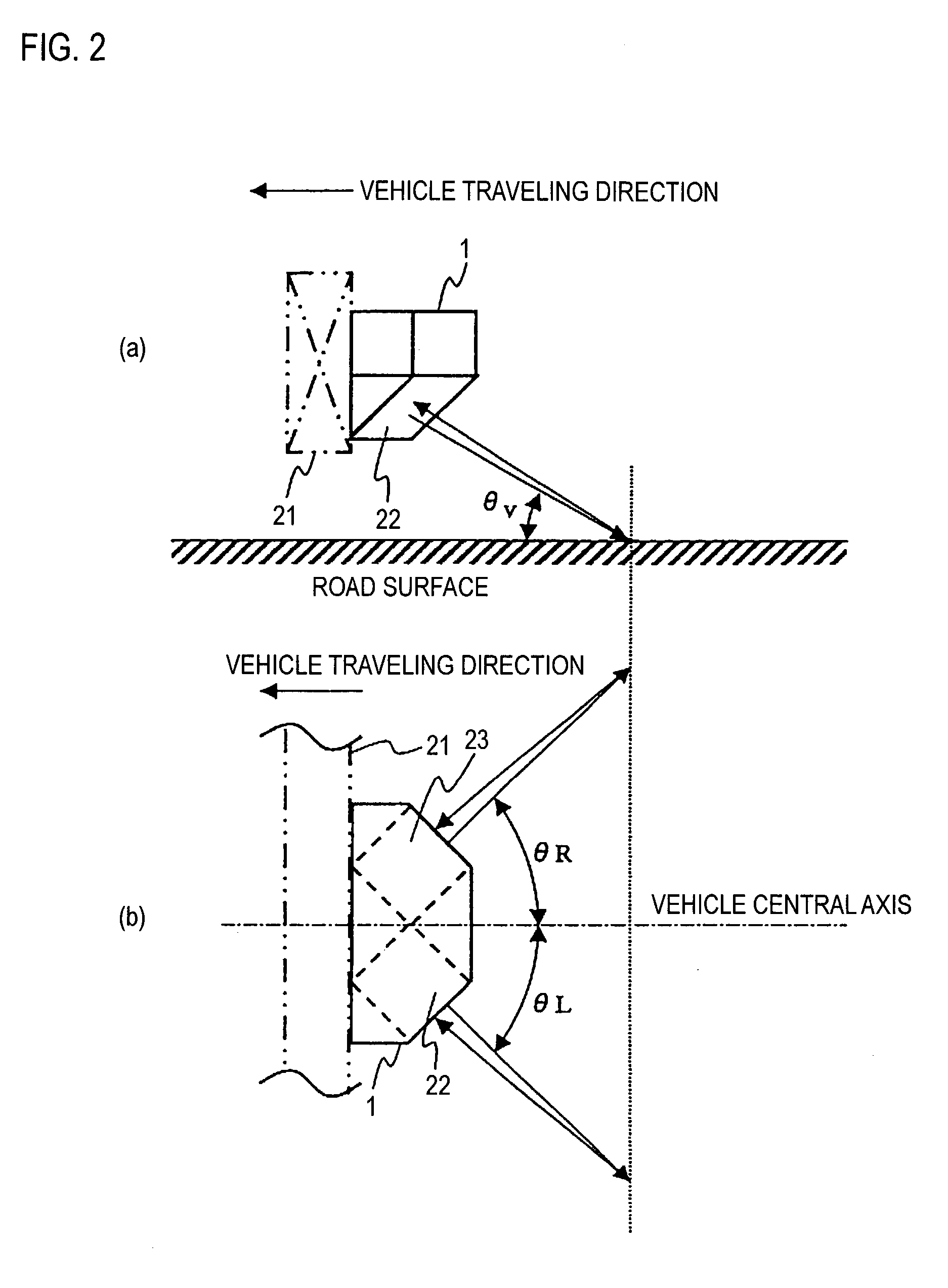
Vehiclar travel control device
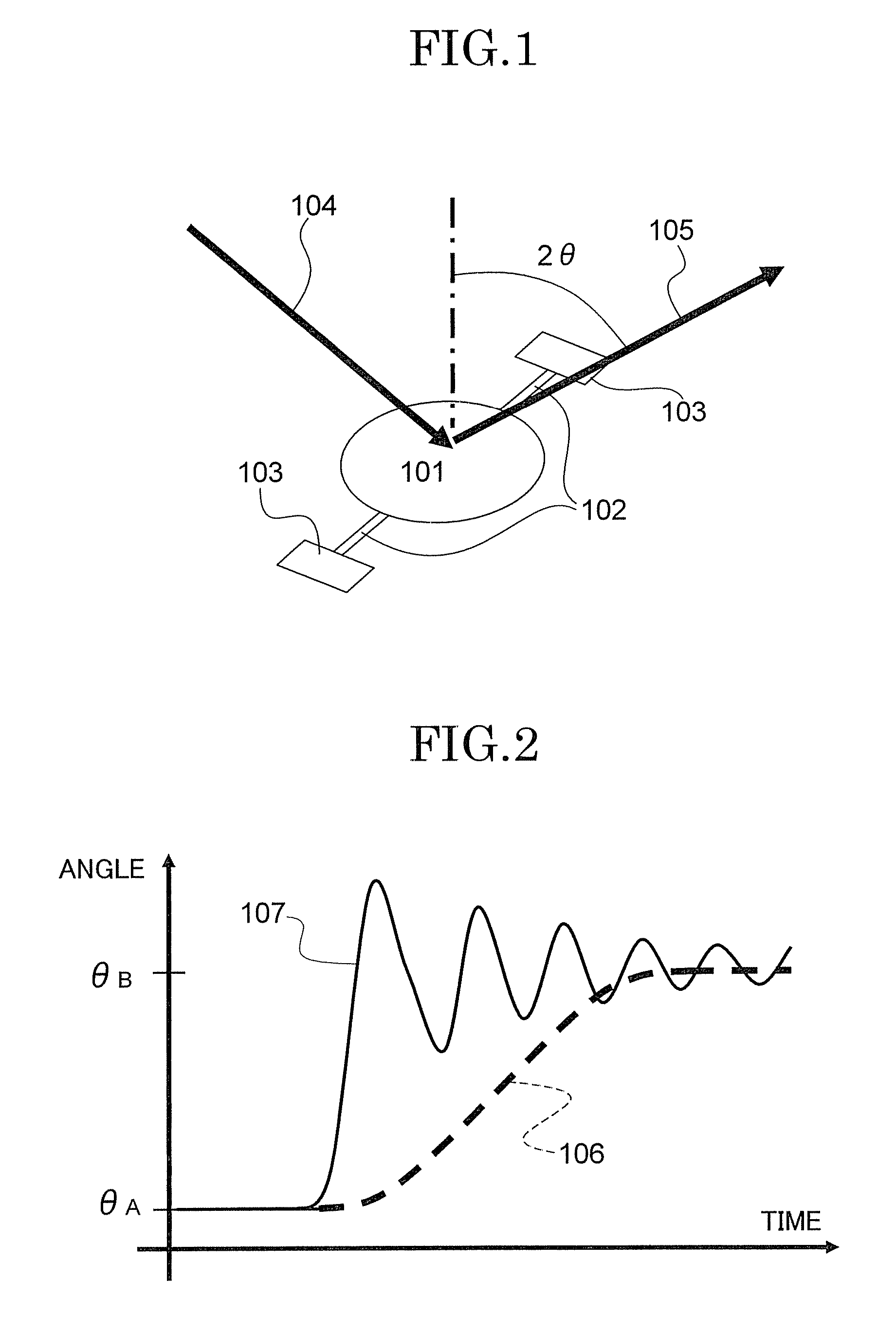
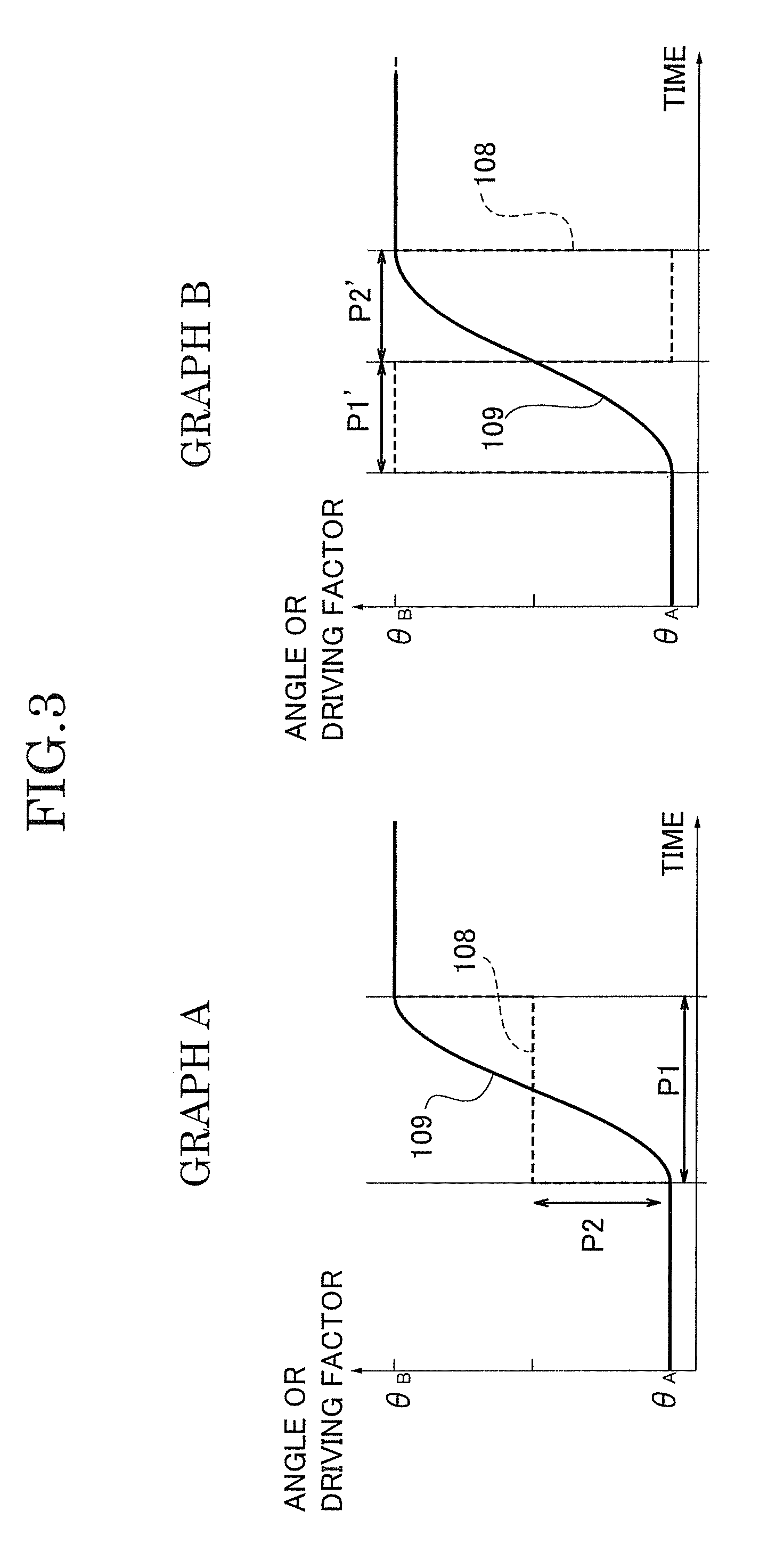
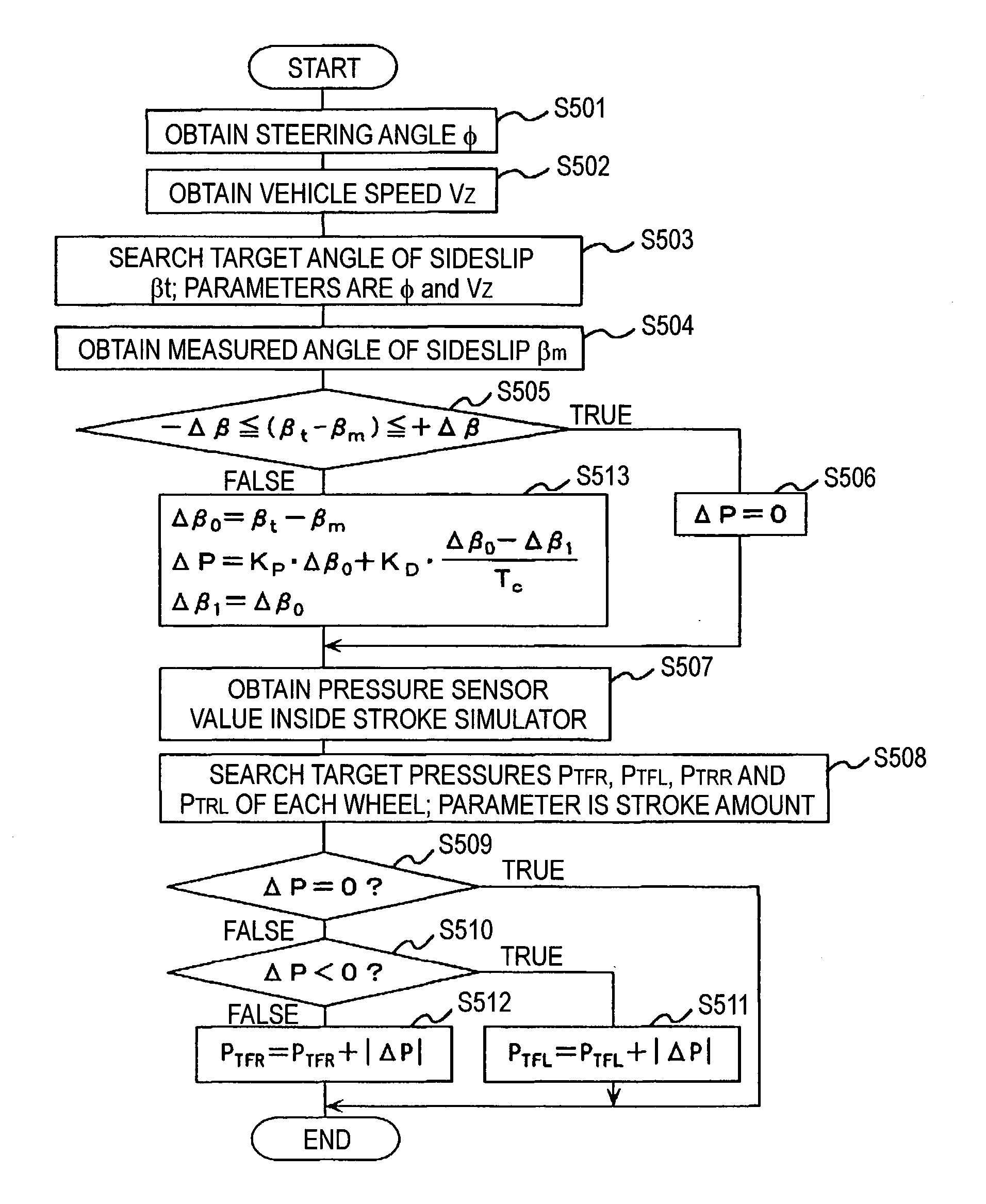
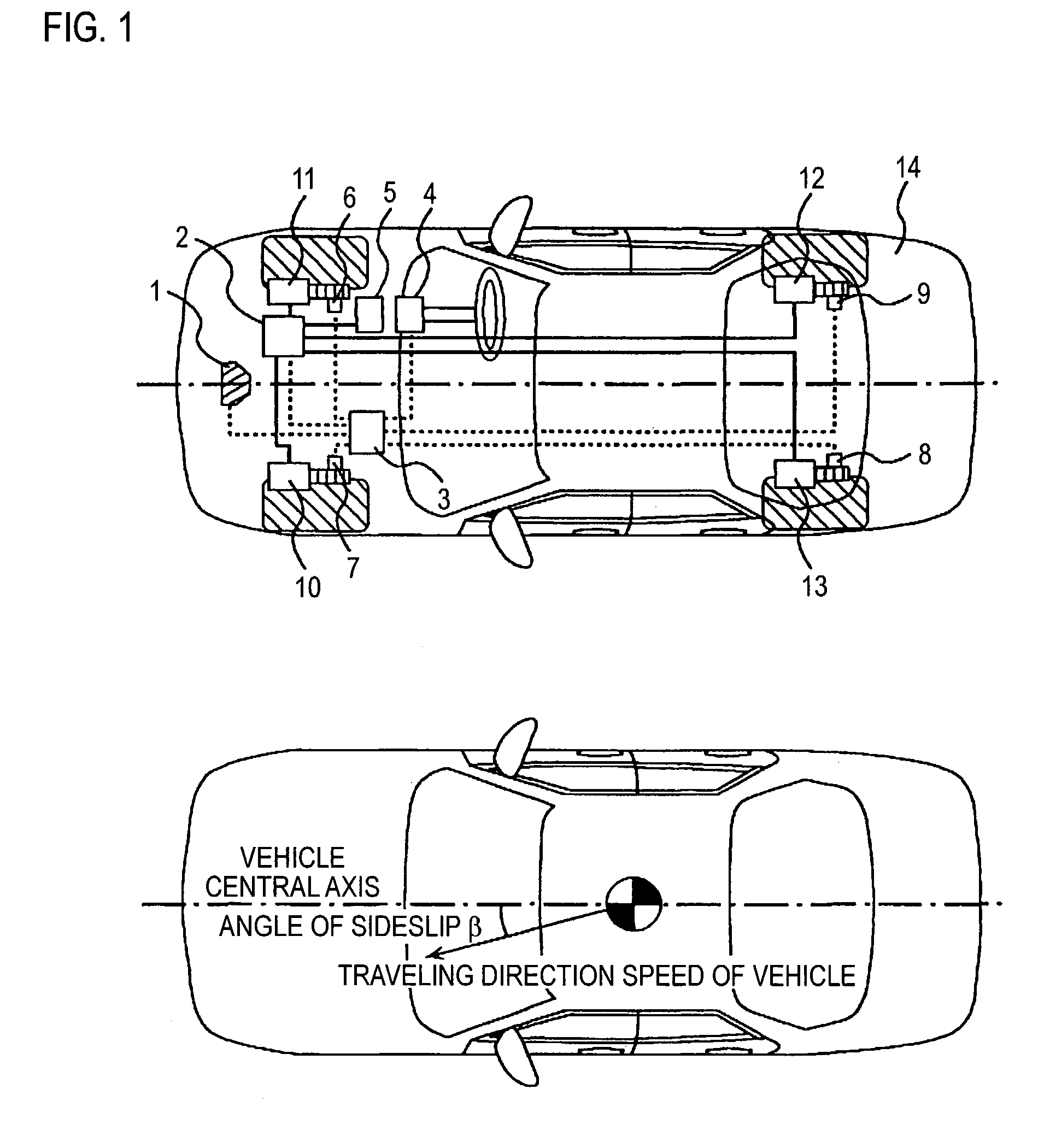
InactiveUS20040138802A1Analogue computers for trafficComputations using stochastic pulse trainsDamping factorRadar
In a vehicular control device, it is necessary to measure or calculate six physical quantities-forward-reverse speed, left-right speed, vertical speed, pitch angle, roll angle, and angle of sideslip-representing vehicular movement and to control the braking force of each wheel and / or the damping coefficient of each suspension shock absorber in order to further shorten braking distance particularly at the time of braking and to prevent spin at that time. In this case, it is necessary to furnish sensors to measure speed and angle directly. In the present invention, four radar sensors are used in order to directly measure the forward-reverse speed and the left-right speed. Also, the vertical speed, the pitch angle, the roll angle, and the angle of sideslip are indirectly measured from the output of the radar sensors. By using three or four radar sensors, six physical quantities-the forward speed, the left-right direction speed, the vertical speed, the angle of sideslip, the pitch angle, and the roll angle-can be measured. Also, by using two radar sensors, three physical quantities-the forward speed, the left-right speed, and the angle of sideslip-can be measured.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
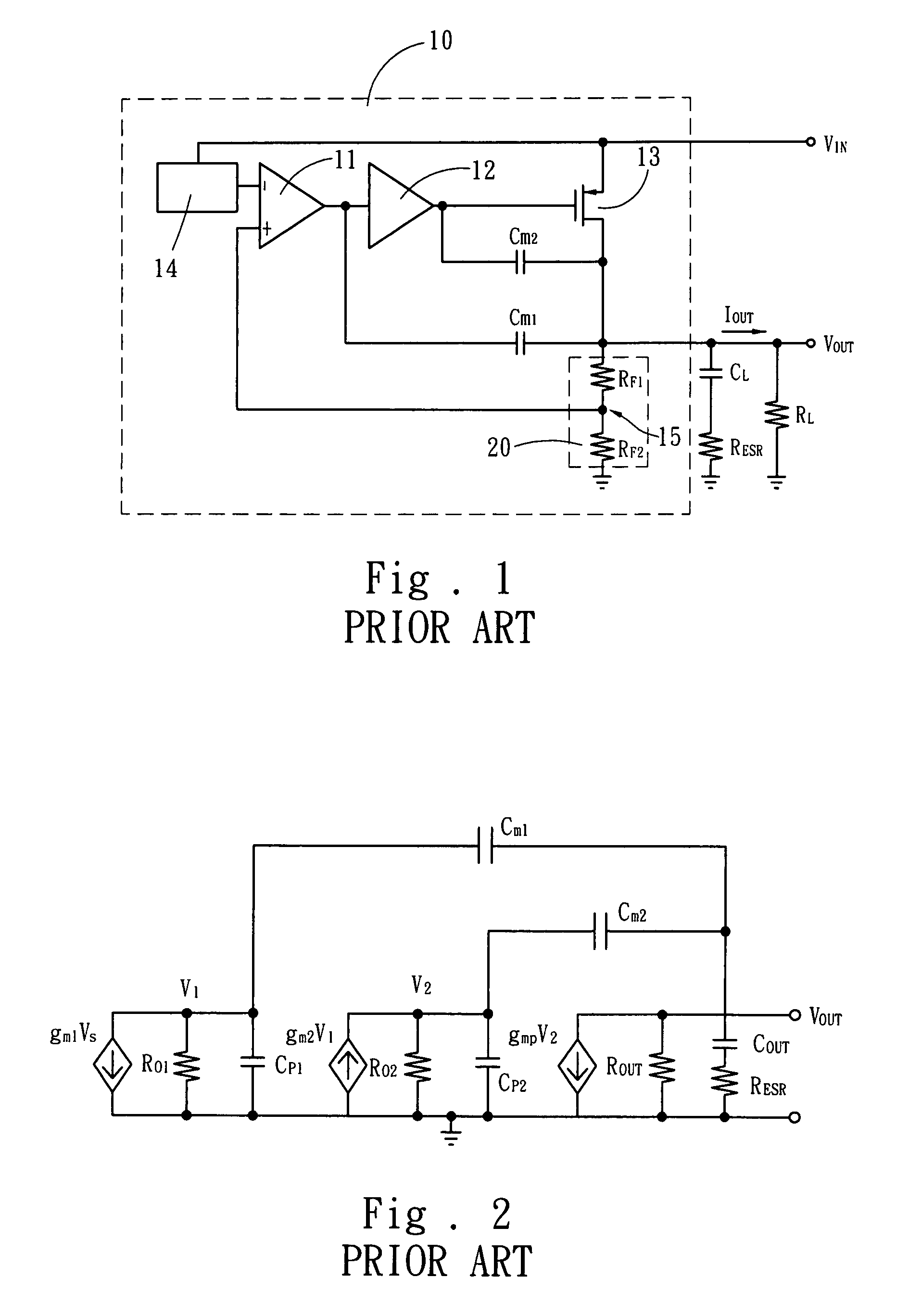
Low dropout regulator capable of on-chip implementation
A low-dropout regulator comprises a high-gain error amplifier having a differential input stage and a single-ended output, a high-swing high-positive-gain second stage with input connecting to the output of the error amplifier and a single-ended output, a p-type MOS transistor with gate terminal connecting to the output of the second stage, source terminal connecting to the supply voltage, and drain terminal to the output of the low-dropout regulator. A first-order high-pass feedback network connects the output of the low-dropout regulator and the positive input of the error amplifier, and a damping-factor-control means comprising a negative gain stage with a feedback capacitor connects the input and output of this gain stage. A capacitor is connected between the output of the error amplifier and the output of the low-dropout regulator, while a voltage reference connects to the negative input of the error amplifier. The regulator does not require an off-chip capacitor for stability and has improved load transient response and power supply rejection ratio.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
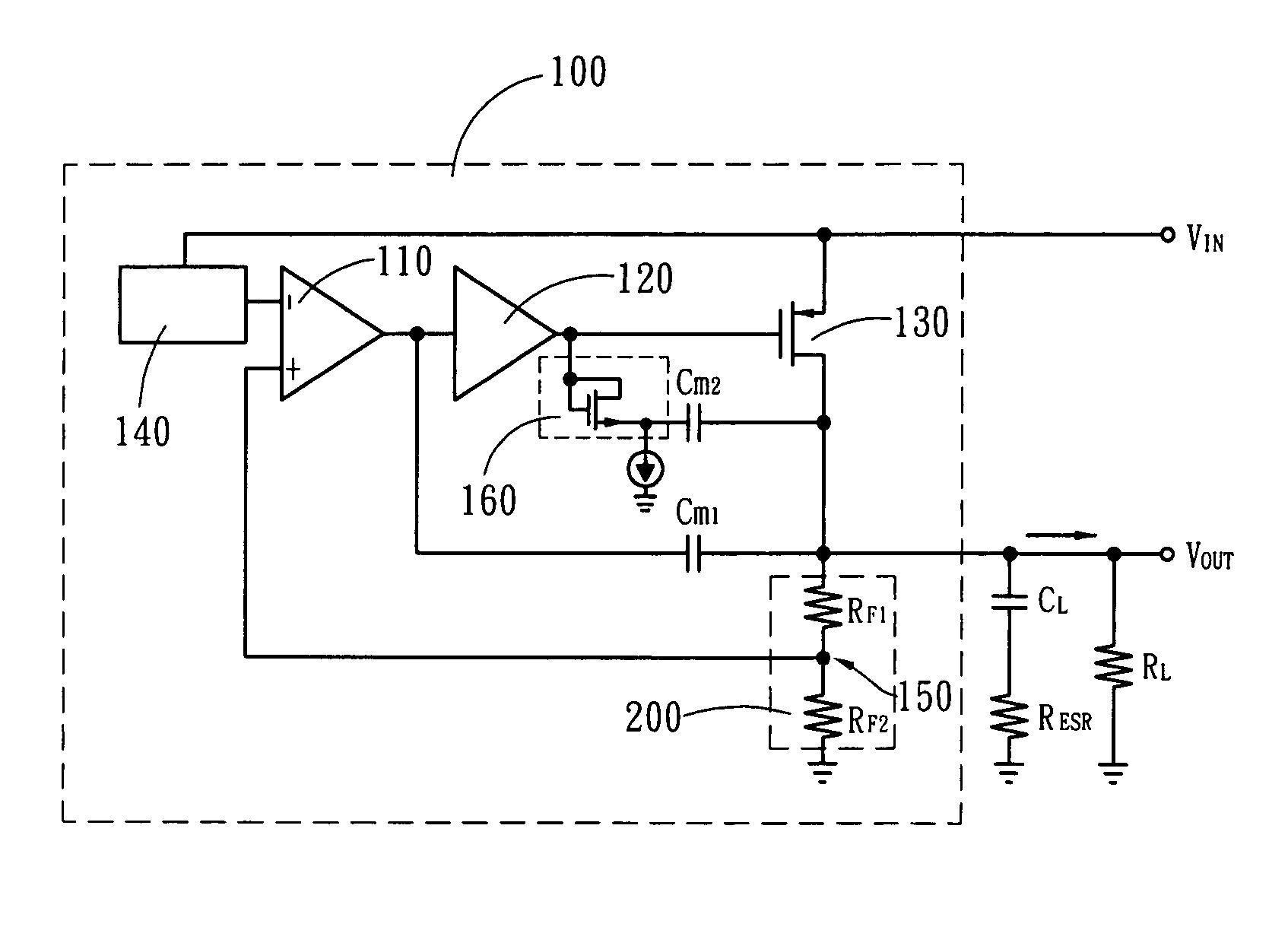
Frequency compensation techniques for low-power multistage amplifiers
InactiveUS6208206B1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceDamping factorCapacitance
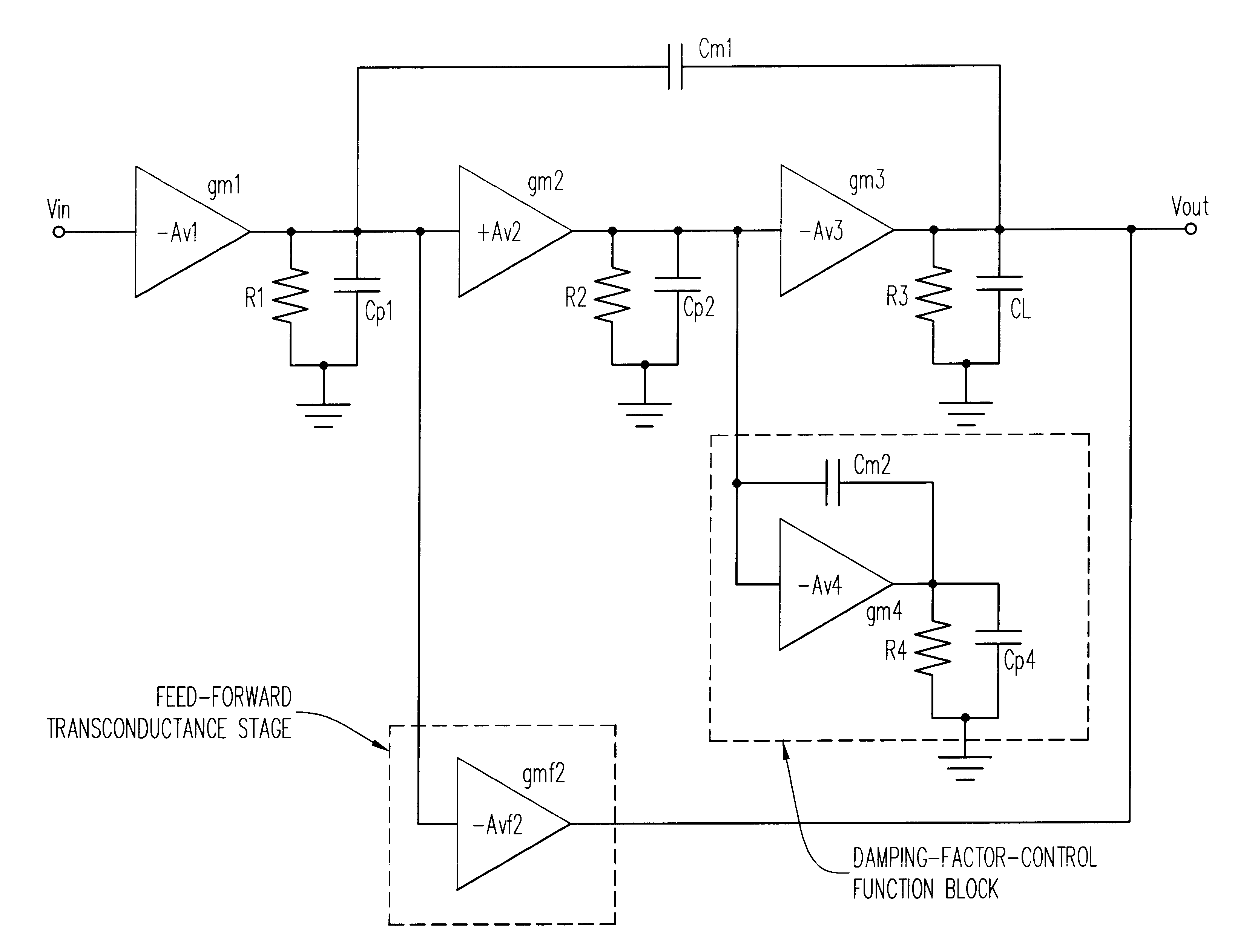
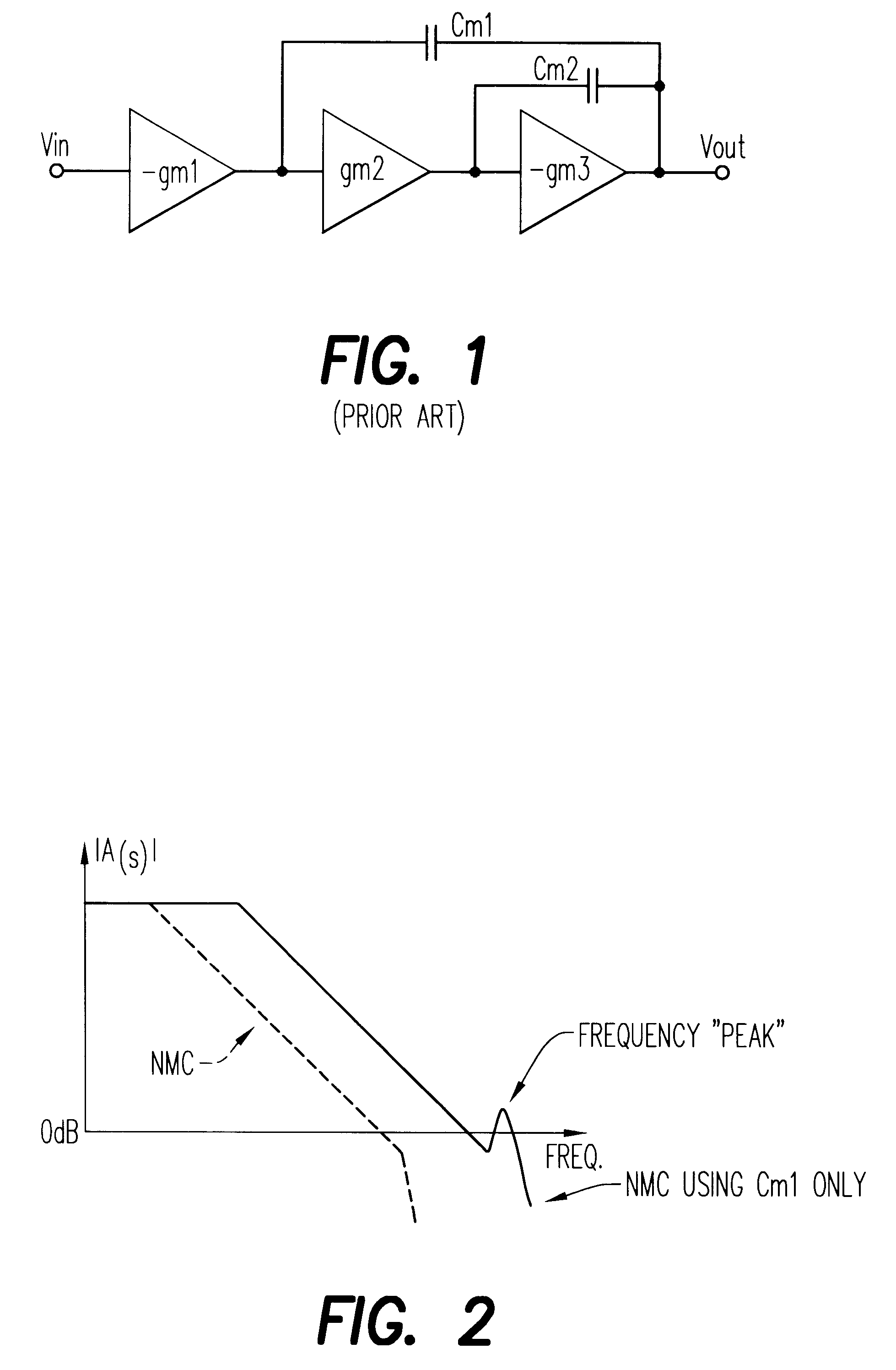
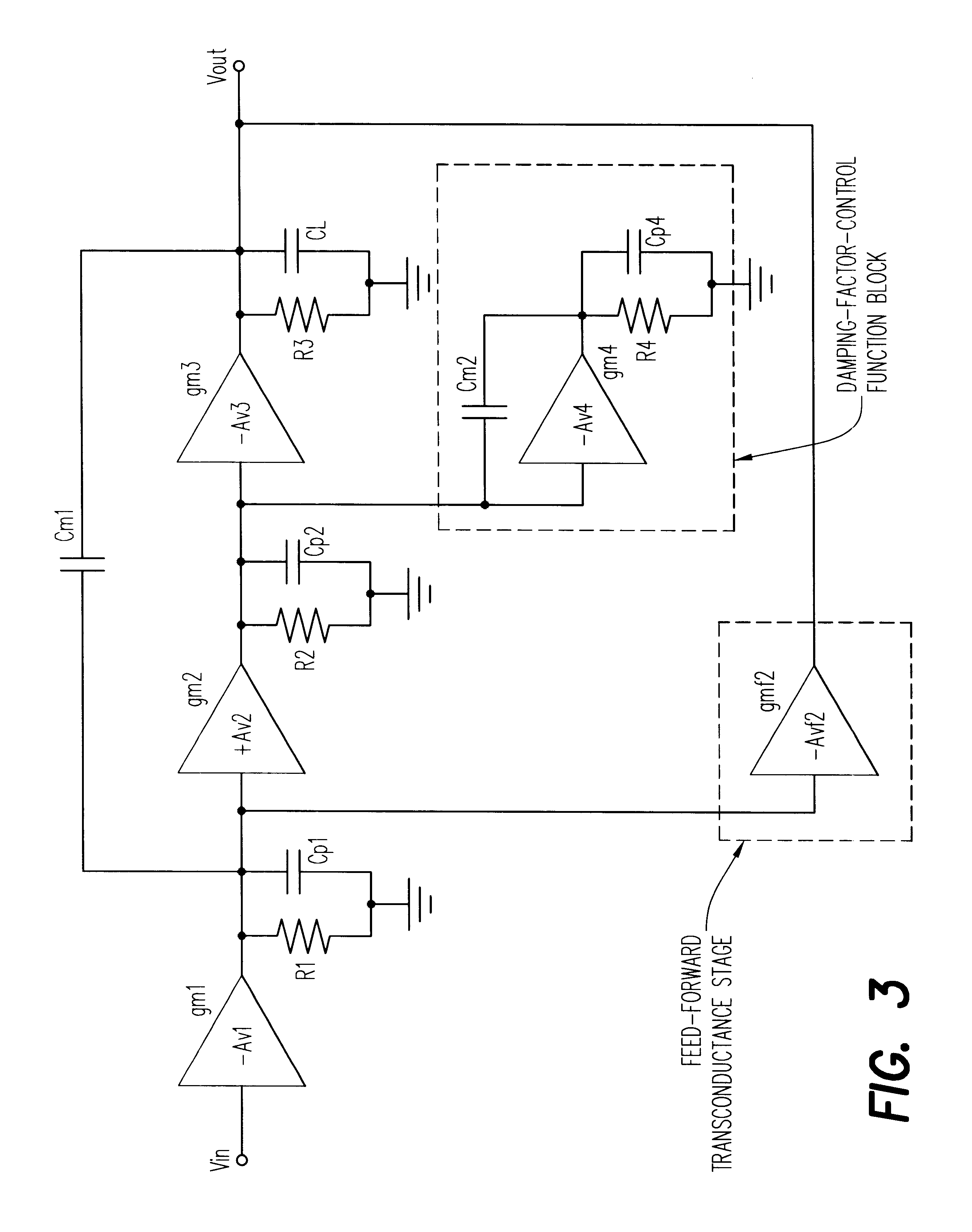
A three stage amplifier is disclosed provided with a novel frequency compensation technique. Only a single feedback loop with a single compensation capacitance is provided. Instead of a conventional nested compensation technique, damping factor control is provided by means of a fourth gain stage in order to stabilize the amplifier. The resulting amplifier is particularly useful to drive large capacitive loads for low-voltage low-power applications.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Composite free layer for stabilizing magnetoresistive head
A magnetoresistive read head includes a spin valve having at least one free layer spaced apart from at least one pinned layer by a spacer. The free layer includes a cobalt compound as a thin film including at least one of Co—X, CoFe—X and CoNi—X, where X is an element from the lanthanoid family (a 4-f element). The content of Co is higher than 80 percent, and the content of the lanthanoid element is less than 10 percent. The film may comprise the entire free layer, or be positioned adjacent to one or more conventional free layer films. The pinned layer is a conventional single layer, or a synthetic multi-layered structure having a spacer between sub-layers. Because the spin valve structure has a high exchange stiffness and damping factor, spin transfer effect is reduced and a high-speed dynamic response is provided.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
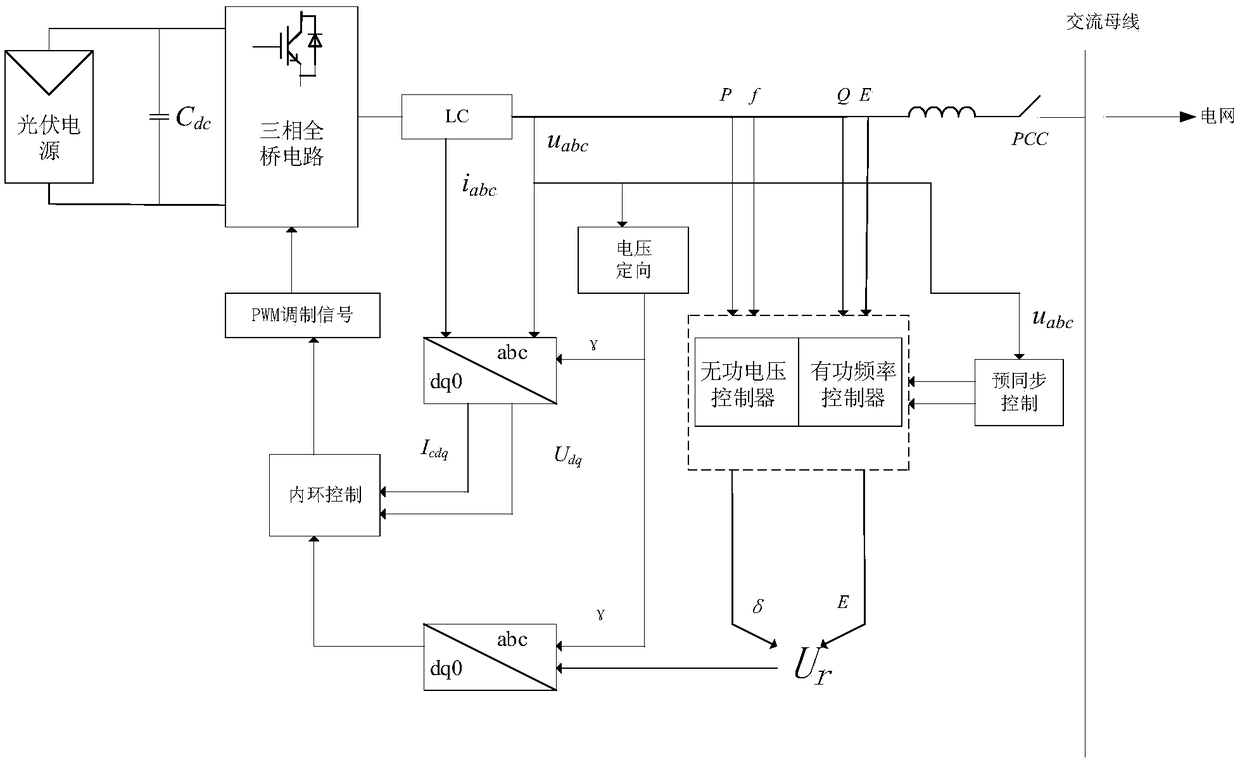
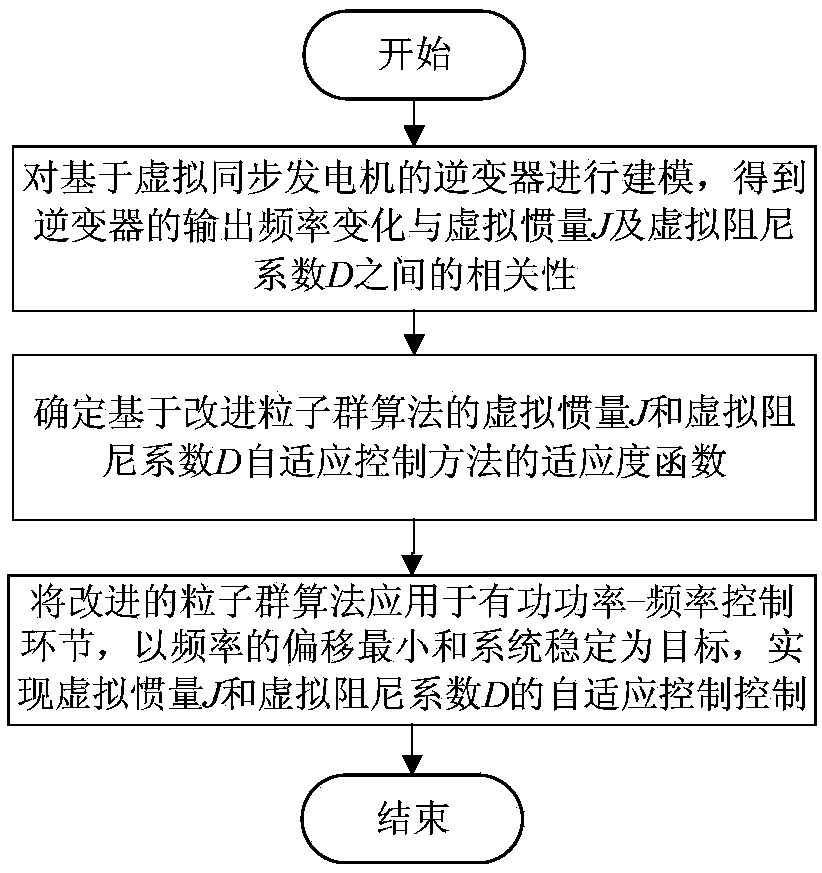
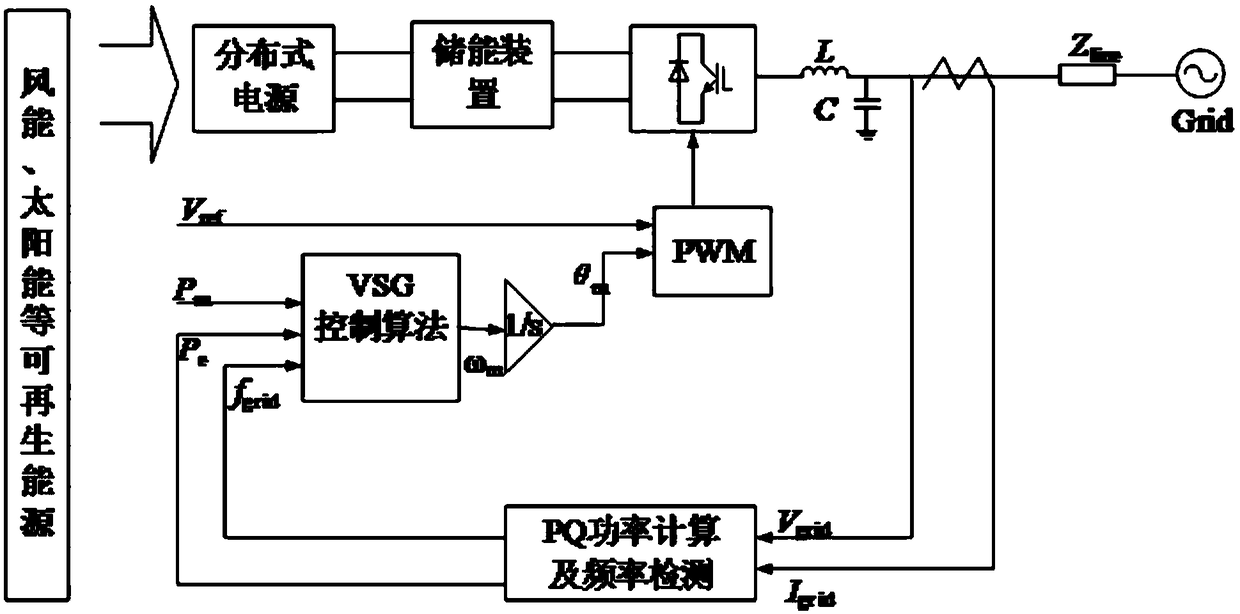
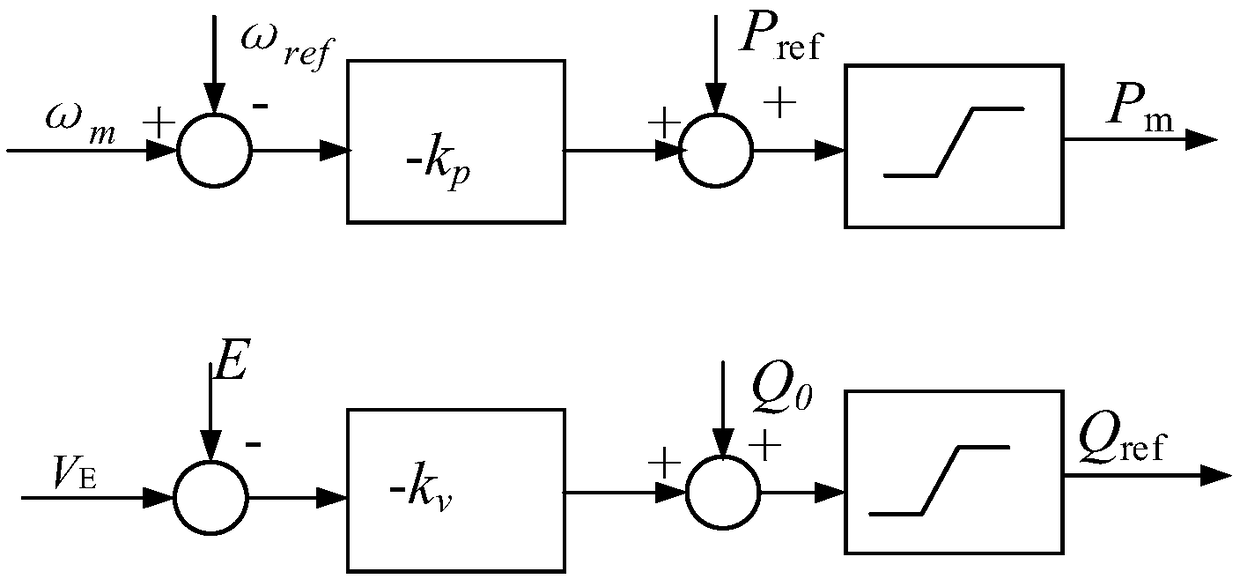
Virtual synchronous generator virtual inertia and virtual damping coefficient adaptive control method
ActiveCN109256801AAchieving Active Power-Frequency ControlIncrease dampingSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionDamping factorVirtual synchronous generator
The invention provides a virtual synchronous generator virtual inertia and virtual damping coefficient adaptive control method, which relates to the technical field of smart grid and intelligent algorithms. Firstly, the inverter based on the virtual synchronous generator is modeled, and the correlation between the output frequency of the inverter and the virtual inertia J and the virtual damping coefficient D is obtained. Then the fitness function of the adaptive control method of virtual inertia J and virtual damping coefficient D based on the improved particle swarm optimization algorithm isdetermined. Finally, the improved particle swarm optimization algorithm is applied to the active power. In the frequency control part, the real-time adaptive control of virtual inertia J and virtualdamping coefficient D is realized in order to minimize the frequency deviation and stabilize the system. The invention provides a virtual synchronous generator virtual inertia and virtual damping coefficient real-time adaptive control method, which fully utilizes the characteristics of the virtual inertia and introduces the virtual damping coefficient, so that the inverter is more stable and the frequency offset is smaller.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Appliance comprising polyurethane foam
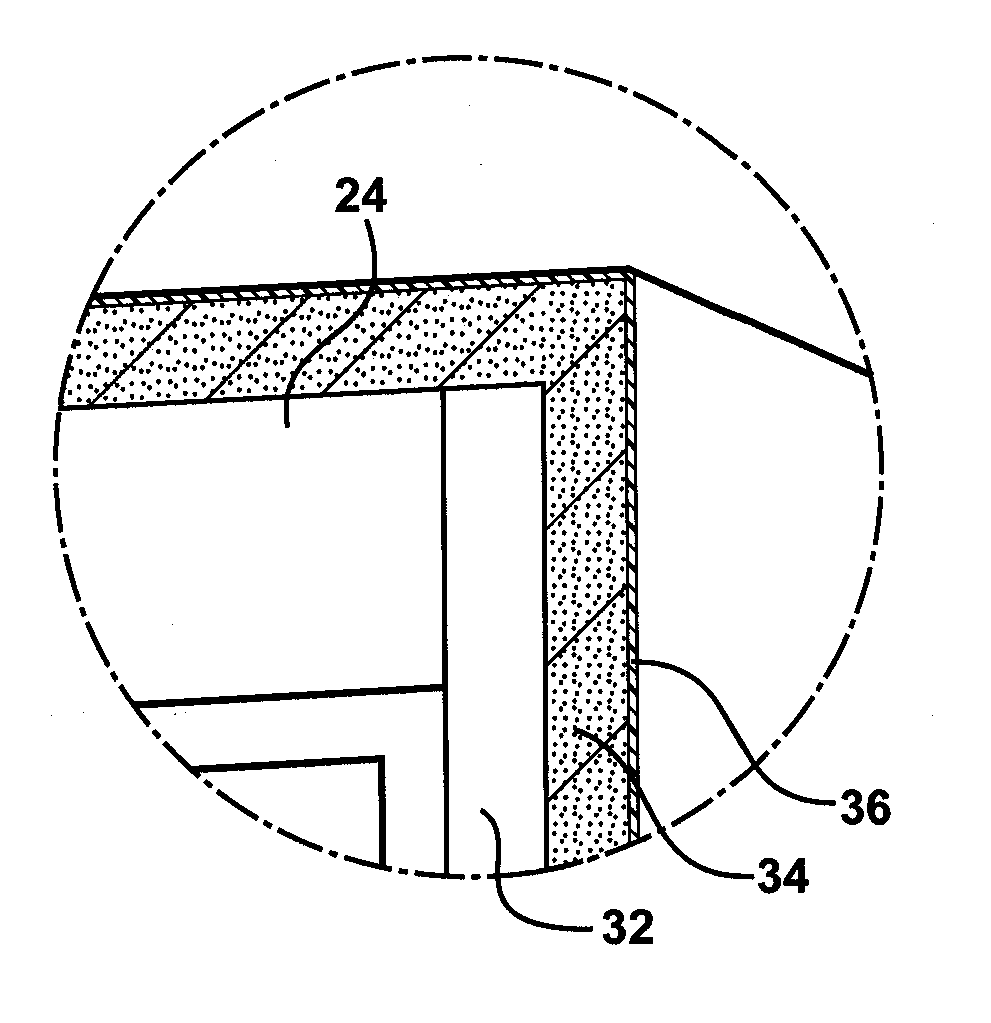
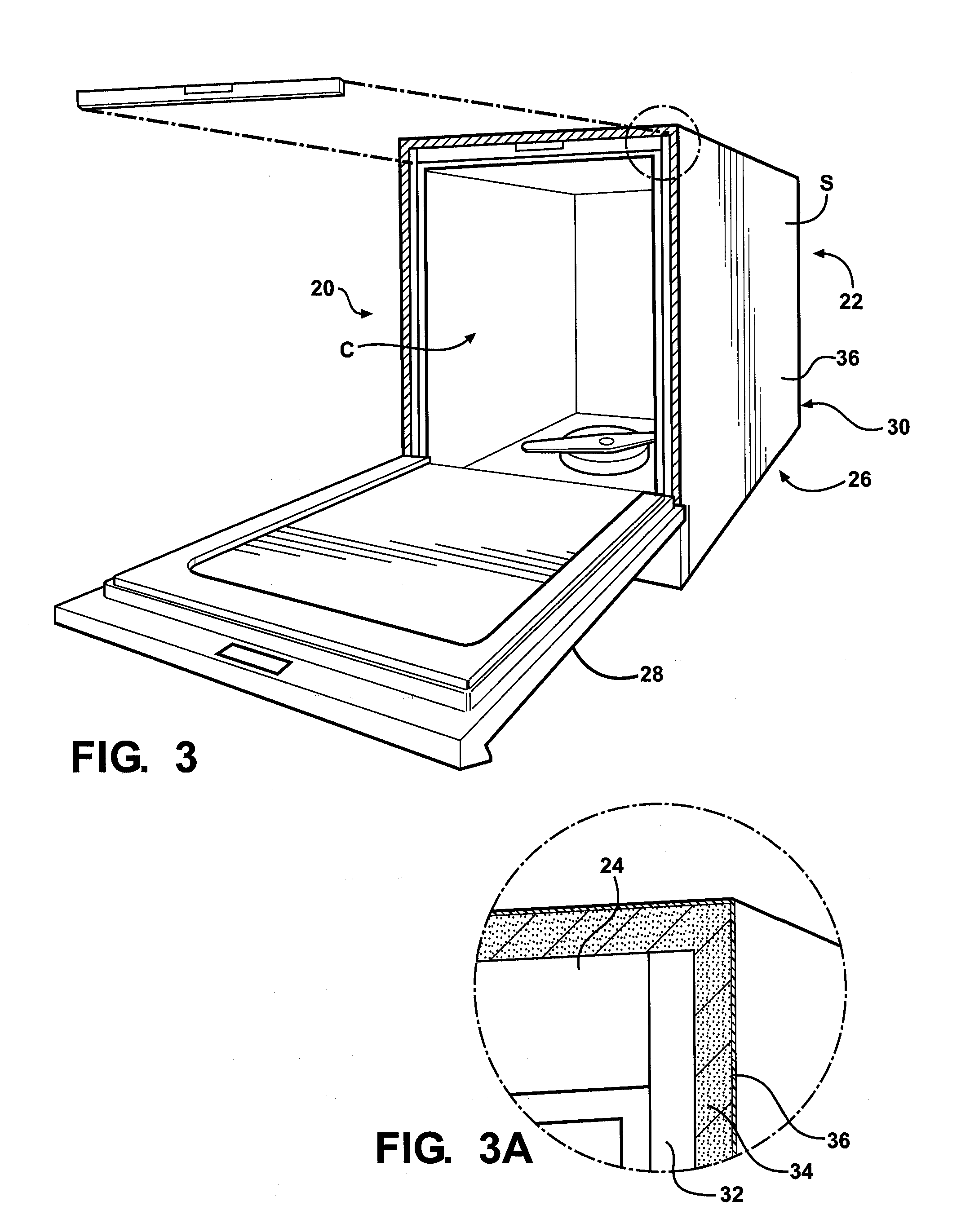
InactiveUS20110168217A1Reduce noiseReduce vibrationTableware washing/rinsing machine detailsLayered productsDamping factorEngineering
An appliance includes a housing having top and bottom panels disposed opposite each other and a plurality of walls connected to the top and bottom panels. The top and bottom panels and the plurality of walls define a cavity of the appliance. The housing also has an outermost surface about which a polyurethane foam is disposed. The polyurethane foam reduces noise and vibrations emitted from the appliance during use and has a density of from 20 to 50 pounds per cubic foot (pcf). The polyurethane foam also has a damping factor of at least 0.2 measured at a temperature of from 40° C. to 60° C. Furthermore, the polyurethane foam has a k-factor of less than 2.0 btu-in / hr-ft2-° F. which reduces an amount of energy required to operate the appliance. The appliance is formed by applying the polyurethane foam to at least one of the top panel, bottom panel, and plurality of walls.
Owner:BASF AG
Vibrating diaphragm and micro acoustic generator equipped with vibrating diaphragm
ActiveCN105933831AImprove rigidityStrong heat resistancePolymeric diaphragmsNon-planar diaphragms/conesDamping factorTotal harmonic distortion
The invention discloses a vibrating diaphragm and a micro acoustic generator equipped with the vibrating diaphragm, and relates to the technical field of electroacoustic products. The vibrating diaphragm has a multilayer composite structure which comprises thermoplastic elastomer layers and adhesive film layers which are alternately stacked together. According to the vibrating diaphragm and the micro acoustic generator equipped with the vibrating diaphragm, the technical problems in the prior art that a micro loudspeaker has poor F0 stability and high total harmonic distortion can be solved. The vibrating diaphragm and the micro acoustic generator equipped with the vibrating diaphragm are low in total harmonic distortion and damping coefficient, higher in F0 stability and high in sound quality so that the requirements of people for the high sound quality of electronic equipment can be met.
Owner:GOERTEK INC
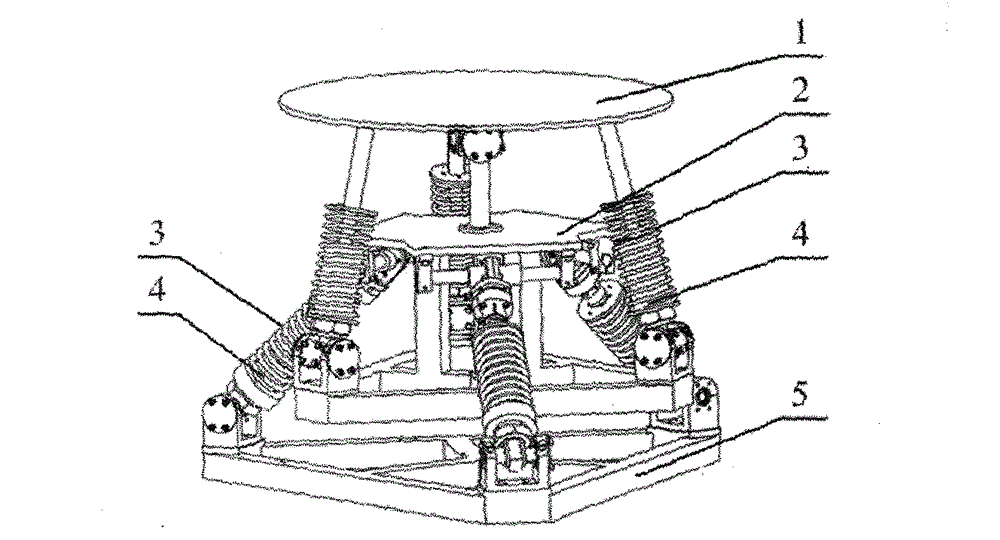
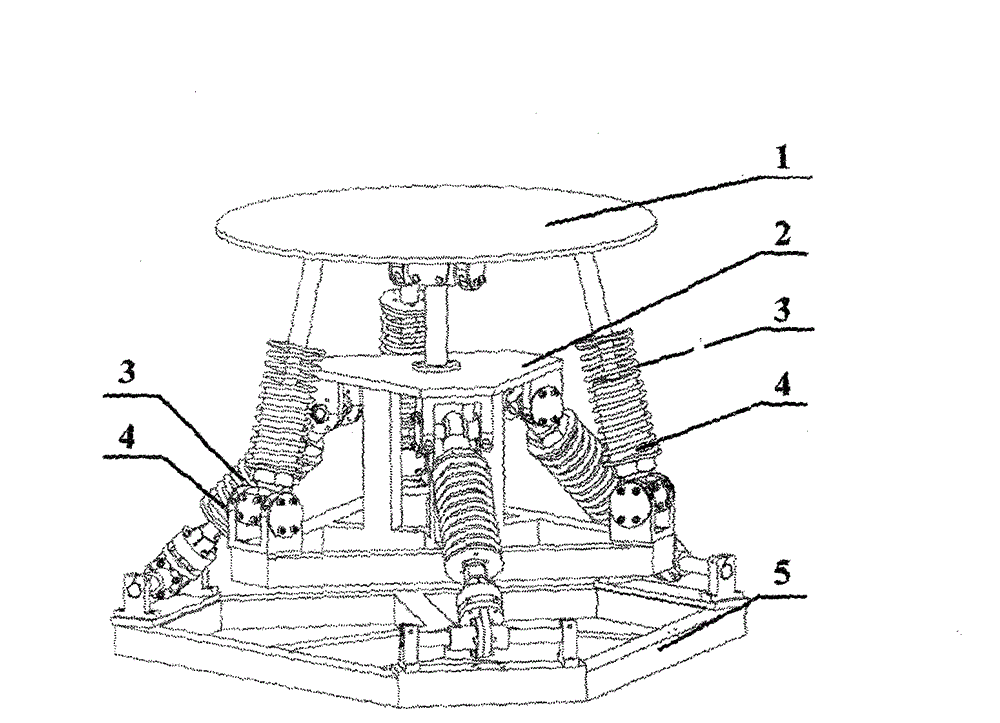
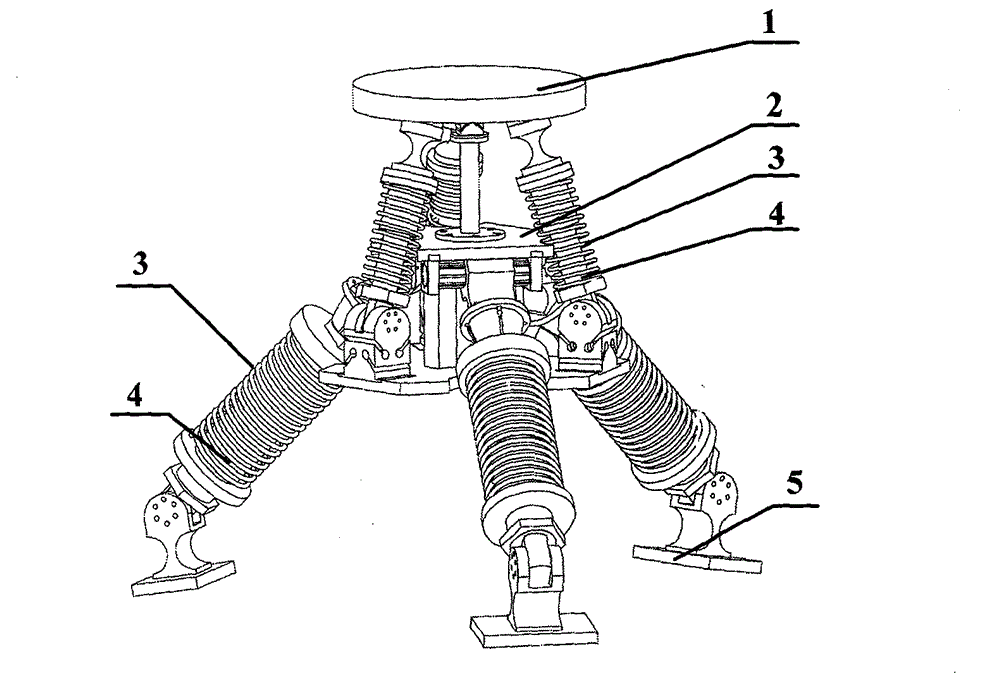
Hybrid mechanism-based five-dimensional vibration isolation platform
ActiveCN102865328AImprove the dynamic environmentImprove working environmentNon-rotating vibration suppressionDamping factorEngineering
The invention relates to a five-dimensional vibration isolation device which is suitable for equipment arranged on a dynamic carrier. Aiming at the problem of five-dimensional vibration of the equipment on the dynamic carrier, one hybrid mechanism-based vibration isolation platform is arranged between an equipment mounting platform and a carrier connecting platform to realize five-dimensional vibration isolation. The vibration isolation platform consists of the equipment mounting platform (1), a middle platform (2), the carrier connecting platform (5), six branched chains comprising vibration isolation subsystems and a constraint branch containing no vibration isolation subsystem, so that vibration isolation along spatial three-movement two-rotation directions can be realized. Each vibration isolation subsystem in each branched chain is formed by connecting a linear spring (3) and a magneto-rheological damper (4) in parallel; and control over the entire platform is realized by changing a damping coefficient of the magneto-rheological damper. Since the movement and the rotation of a hybrid mechanism are fully decoupled, the control of the system is relatively simple. Experiments prove that the vibration isolation platform using the five-dimensional vibration isolation device enables that a vibration signal transferred to the equipment by the carrier is obviously weakened, so that the vibration isolation platform has the advantage of effectively and reliably improving the dynamic environment of the equipment of the dynamic carrier.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
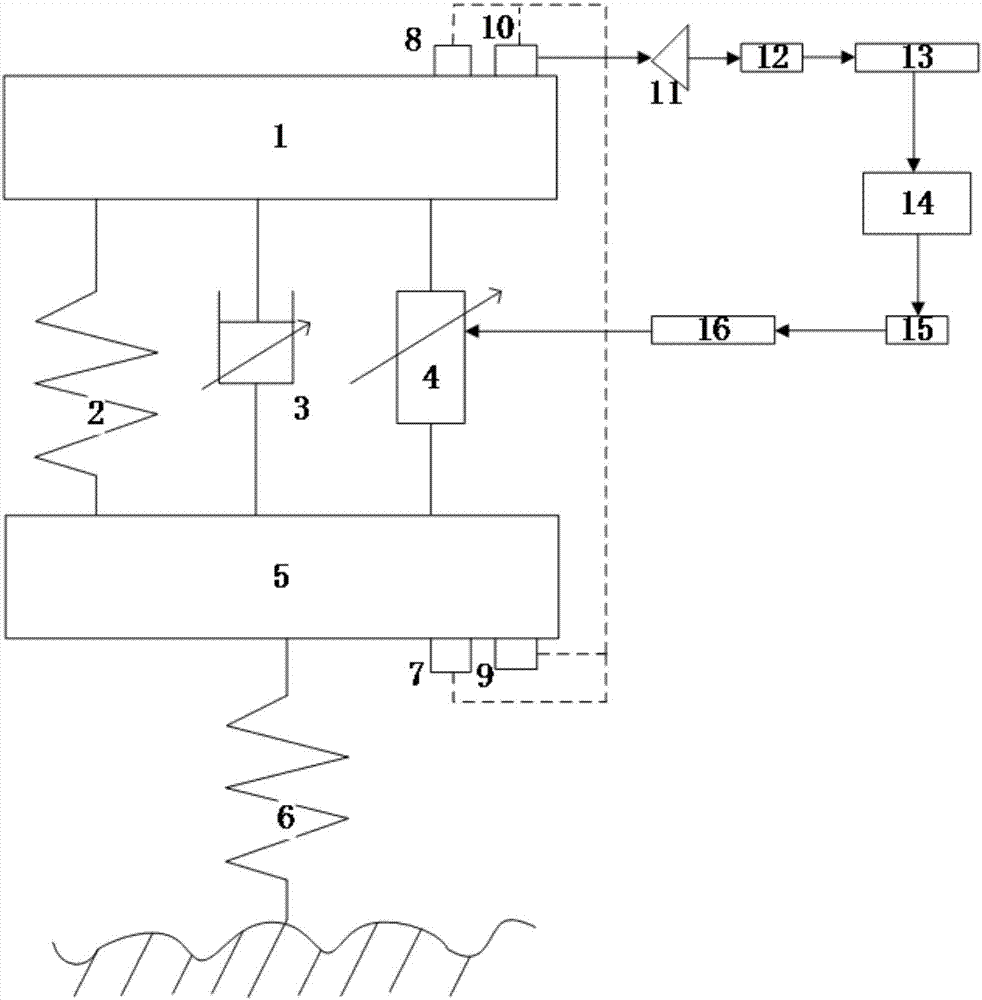
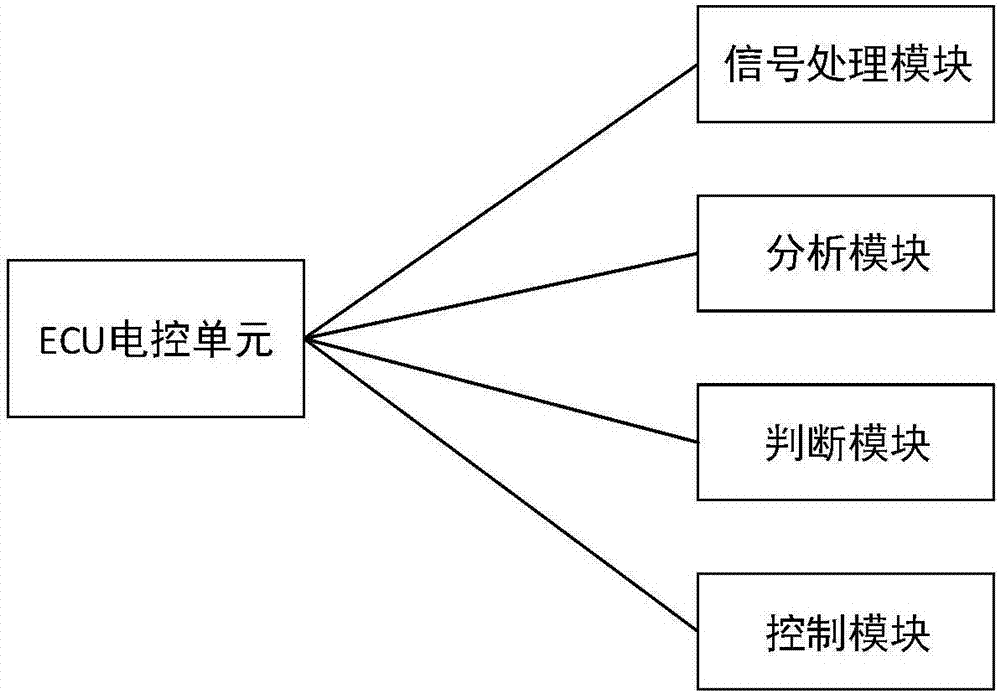
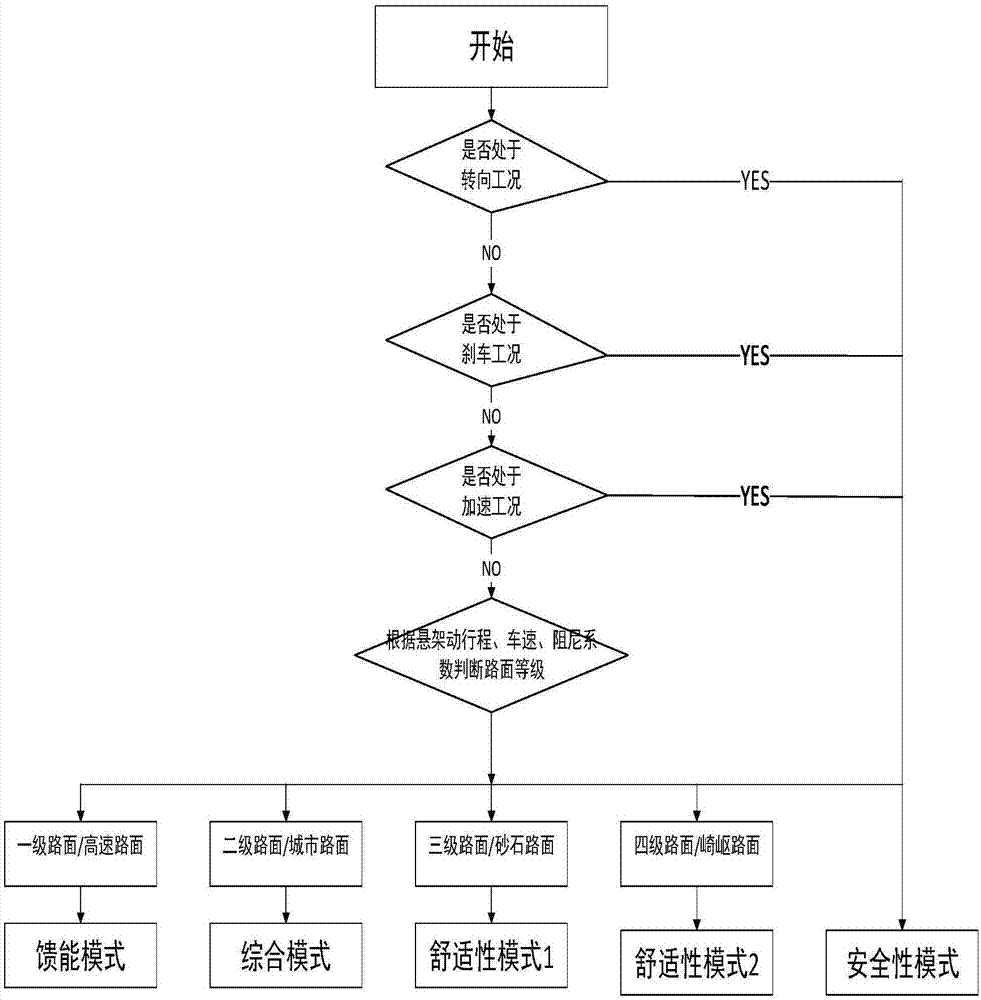
Vehicle pavement identification system and suspension mode switching method
ActiveCN106985627AImprove ride comfort performanceImprove driving safetyResilient suspensionsDamping factorRoad surface
The invention relates to a vehicle pavement identification system and a suspension mode switching method and belongs to the field of automobile safety and comfort. A suspension mainly comprises sprung mass, an elastic element, a damper, a linear motor, unsprung mass, an acceleration sensor A, an acceleration sensor B, a displacement sensor A, a displacement sensor B, a current amplifier, an A / D converter, a signal storage unit, an ECU, a power amplifier and a D / A converter. The ECU (14) comprises a signal processing module, an analysis module, a judgment module and a control module, receives displacement signals and acceleration signals, measured by the vehicle sensors, of the sprung mass and the unsprung mass, grades road conditions by combining the vehicle speed and the damping coefficient and meanwhile controls the suspension by combining vehicle working conditions and switching different modes to meet the requirements of safety and comfort. According to the vehicle pavement identification system and the suspension mode switching method, the linear motor is adopted as an actuator, brake energy of the suspension can be recovered under good road conditions for supplying to other systems for using, and energy feedback performance is achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
System and method for damping vibrations in elevator cables
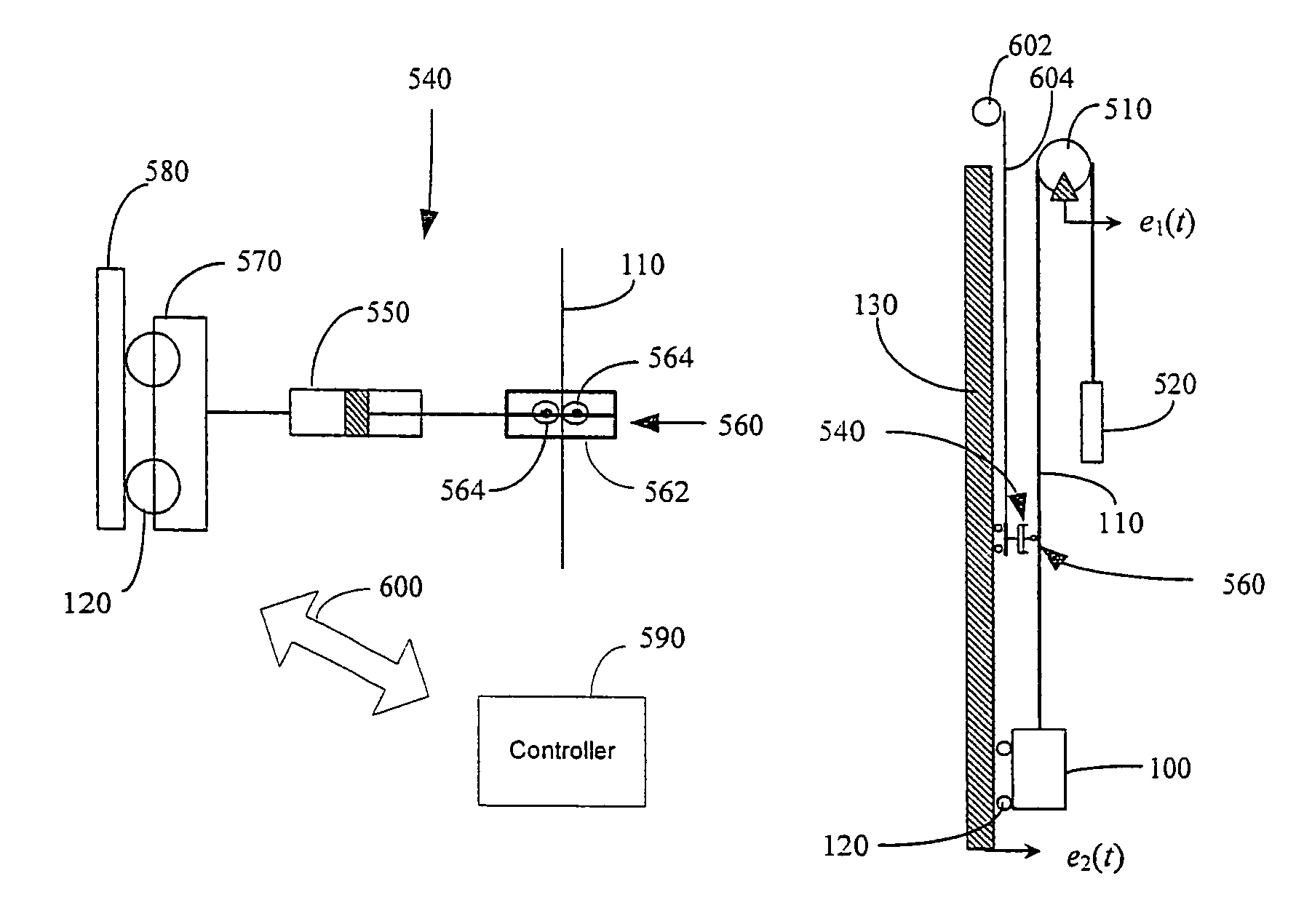
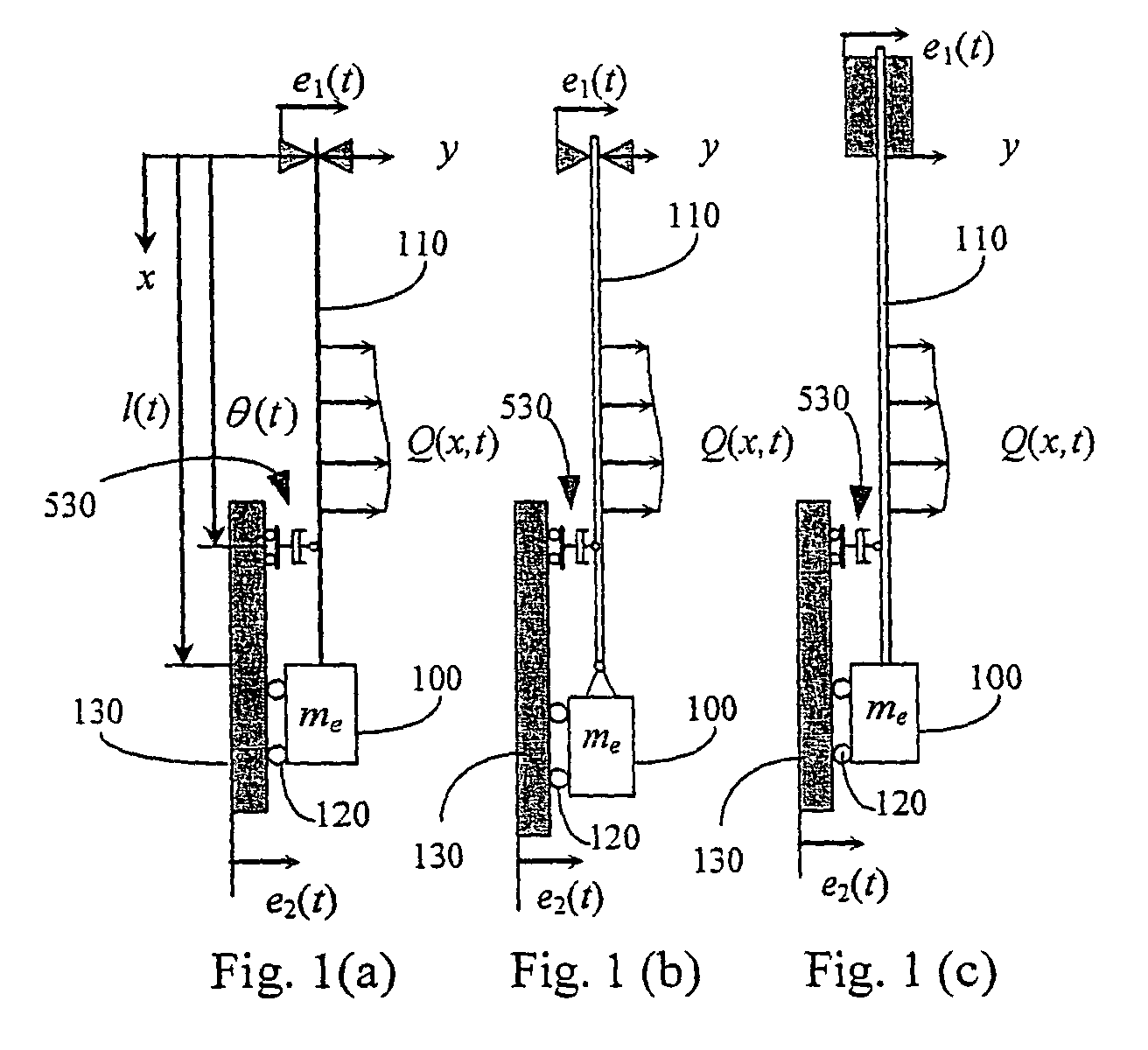
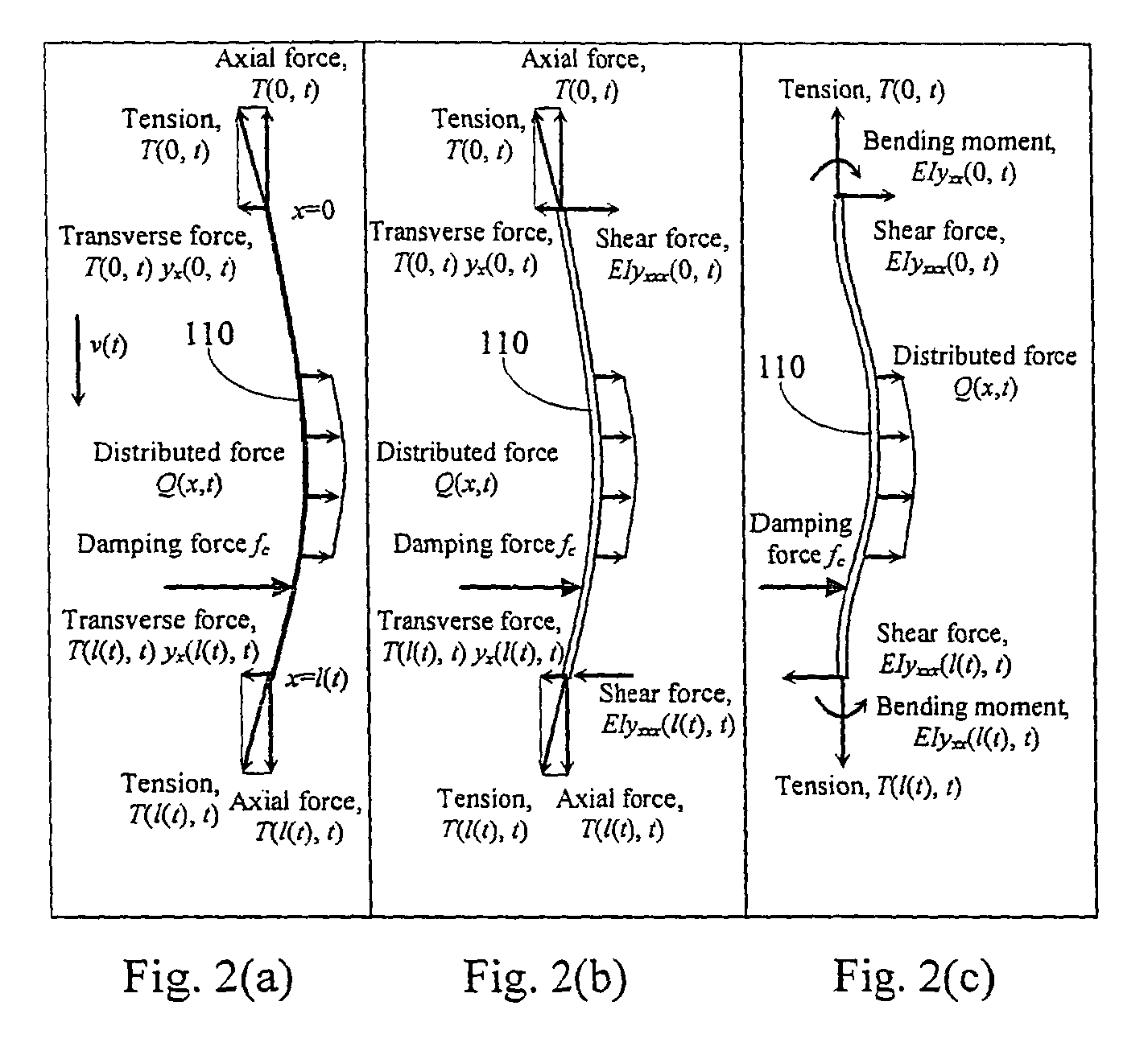
A vibration damped elevator system is provided that includes a damper or dampers attached to the elevator cable. The damping coefficients of the damper or dampers are chosen to provide optimum dissipation of the vibratory energy in the elevator cable. A method of determining the optimum placement of the damper or dampers and their respective damping coefficients is also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
Electromagnetic switch
InactiveUS20070194867A1Reduce its spring constantIncrease its damping (or its attenuation) coefficientWindingsMagnetic circuitDamping factorEngineering
In an electromagnet switch, a stationary iron core is composed mainly of a base part and a disk part. The base part is faced to a plunger and the disk part is forcedly inserted and fixed to a boss part formed in the base part. The disk part is composed of a metal plate of ferromagnetic substance (iron plate) and another substance plate (made of resin or rubber and the like, for example,) of a smaller spring constant or a larger damping coefficient than that of the metal plate. The metal plate and another substance plate are laminated. Another substance plate absorbs or reduces the impact force when the plunger is electromagnetically attracted toward and collides with the base part. The propagation of a large impact noise or crashing sound is thereby suppressed, and as a result the impact noise can be reduced.
Owner:DENSO CORP
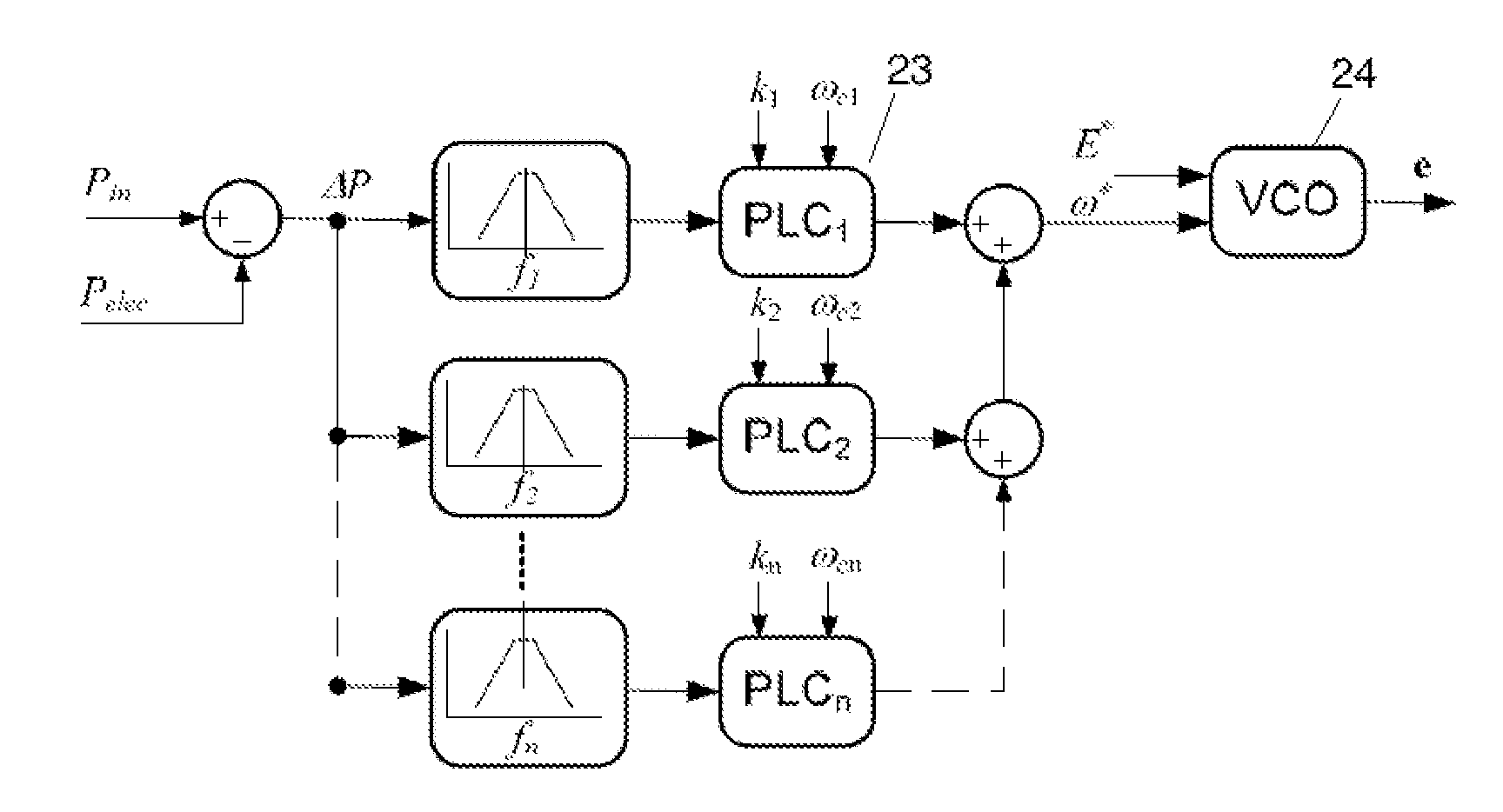
Virtual controller of electromechanical characteristics for static power converters
InactiveUS20140067138A1Good flexibilityReduce inertiaMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlDamping factorPower grid
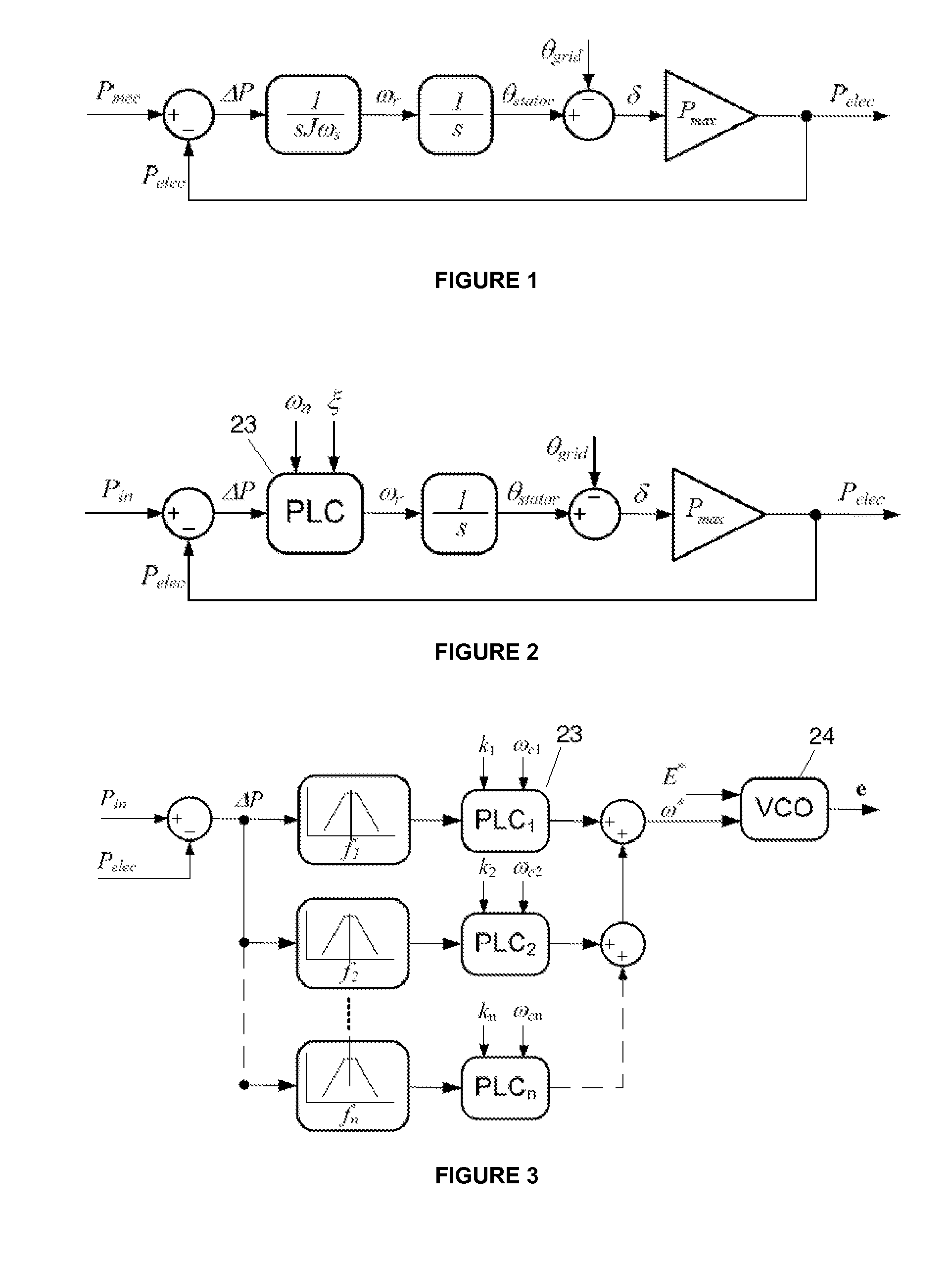
The invention relates to a virtual controller of electromechanical characteristics for a static power converter that includes a PLC (23) (power loop controller), which receives, at the input thereof, the power difference (ΔP) between the input power (Pin) (power delivered to the converter by the primary source) and the power delivered to the grid (Pelec) and is able to modify online the parameters of the virtual inertia coefficient and the damping factor as a function of the desired response and of the grid conditions for different frequency ranges.
Owner:ABENGOA SOLAR NEW TECH SA
Hearing protection device with damped material
ActiveUS20060162992A1High glass transition temperatureLower transition temperatureStethoscopeEarplugsDamping factorElastomer
The invention provides a hearing protection device having an attenuating body composed of an elastomer with an increased glass transition temperature and a reduced glass-to-rubber transition temperature such that the damping factor of the material peaks at a higher temperature and, resultantly, the damping factor is increased over a range of temperatures and frequencies typically experienced by the device during usage. The increased damping results in higher sound attenuation provided by the hearing protection device.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Molded soft elastomer/hard polyester composition with noise damping properties
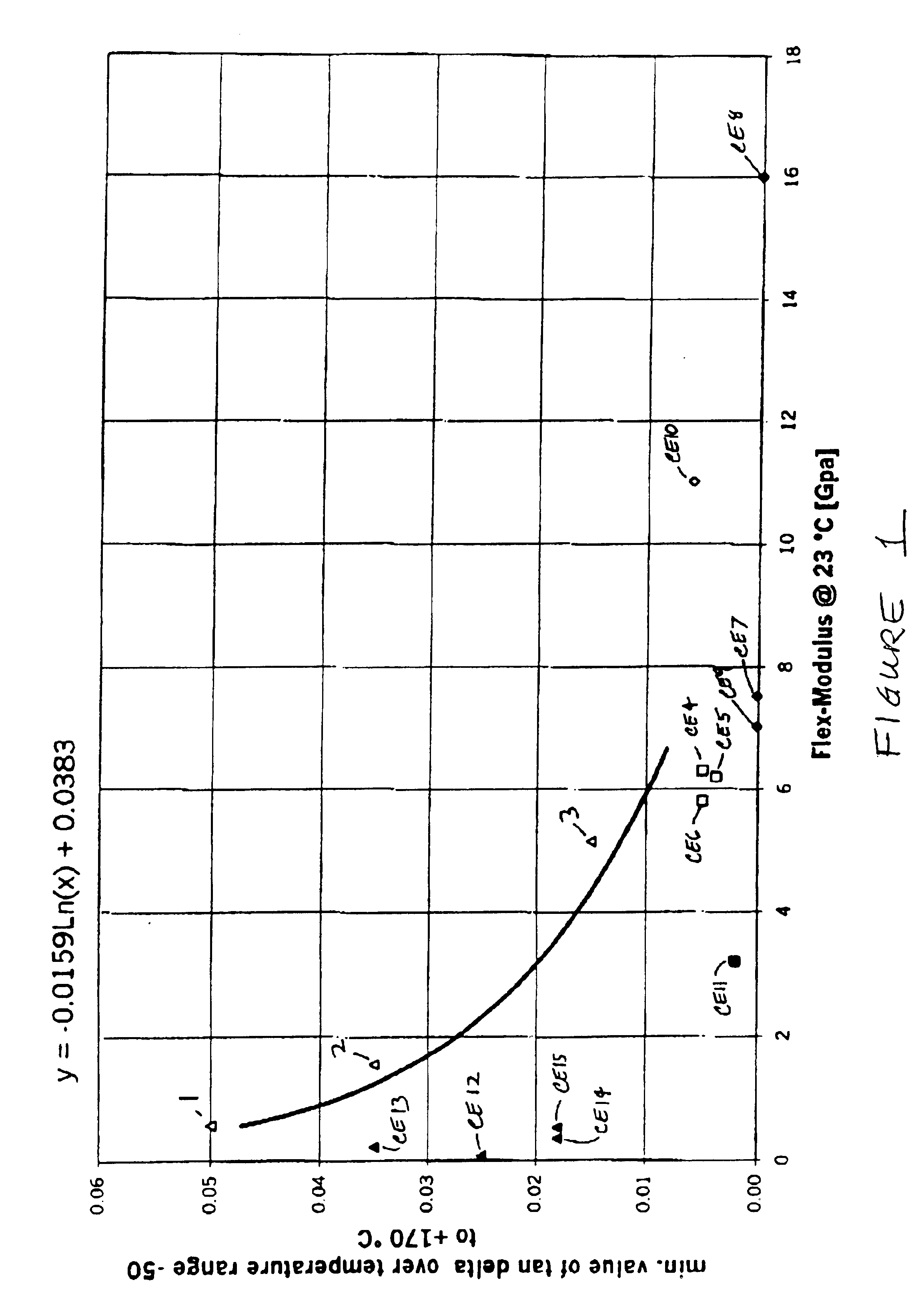
The invention provides a molded composition having improved noise damping properties, made of a blend of a soft thermoplastic polyether elastomer and a hard polyester resin reinforced with a fibrous or particulate filler, the molded composition having an inhomogeneous structure comprising a surface part which is rich in elastomer and depleted in the polyester resin and the reinforcing filler compared to its inner part, obtained by monocomponent injection molding of a blend of the soft and the hard polyester resin wherein only the polyester resin contains the reinforcing particulate filler. The molded composition has a flex modulus Fm in the range 0.5 to 10 GPa, and maintains a sufficient minimum tan delta damping factor t_ over a temperature range of −50° C. to 170° C.
Owner:TE CONNECTIVITY GERMANY GMBH
Method for preparing polymer-based damping composite material capable of being designed into alternate laminar structure
The invention discloses a method for preparing a polymer base damping composite material, the structure of which can be designed like an alternating layer, comprising the steps as follows: two polymer materials are respectively put into two extruding machines of a microbedding coextrusion device to be fused and plasticized, the two fused mass are laminated into two layers at a merging device, after the cutting and laminating of a splitting device comprising n splitting units, the composite material with 2<(n+1)> layers can be obtained. The two polymers distribute like alternating layers along the extrusion direction, the number of layers and the ratio of layers and thickness are respectively determined by the number of the splitting units and the rotating speed ratio of the extruding machine, so that the structure of the composite material has designability. Compared with the traditional preparation method, the polymer base damping composite material prepared by the invention has the characteristics of high damping factor, wide effective damping temperature zone and high elongation at break. The devices used in the invention are easily available, the raw material is commercially available without compounding other chemicals, in addition, the operation is simple, the production cost is low, and the efficiency is high.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
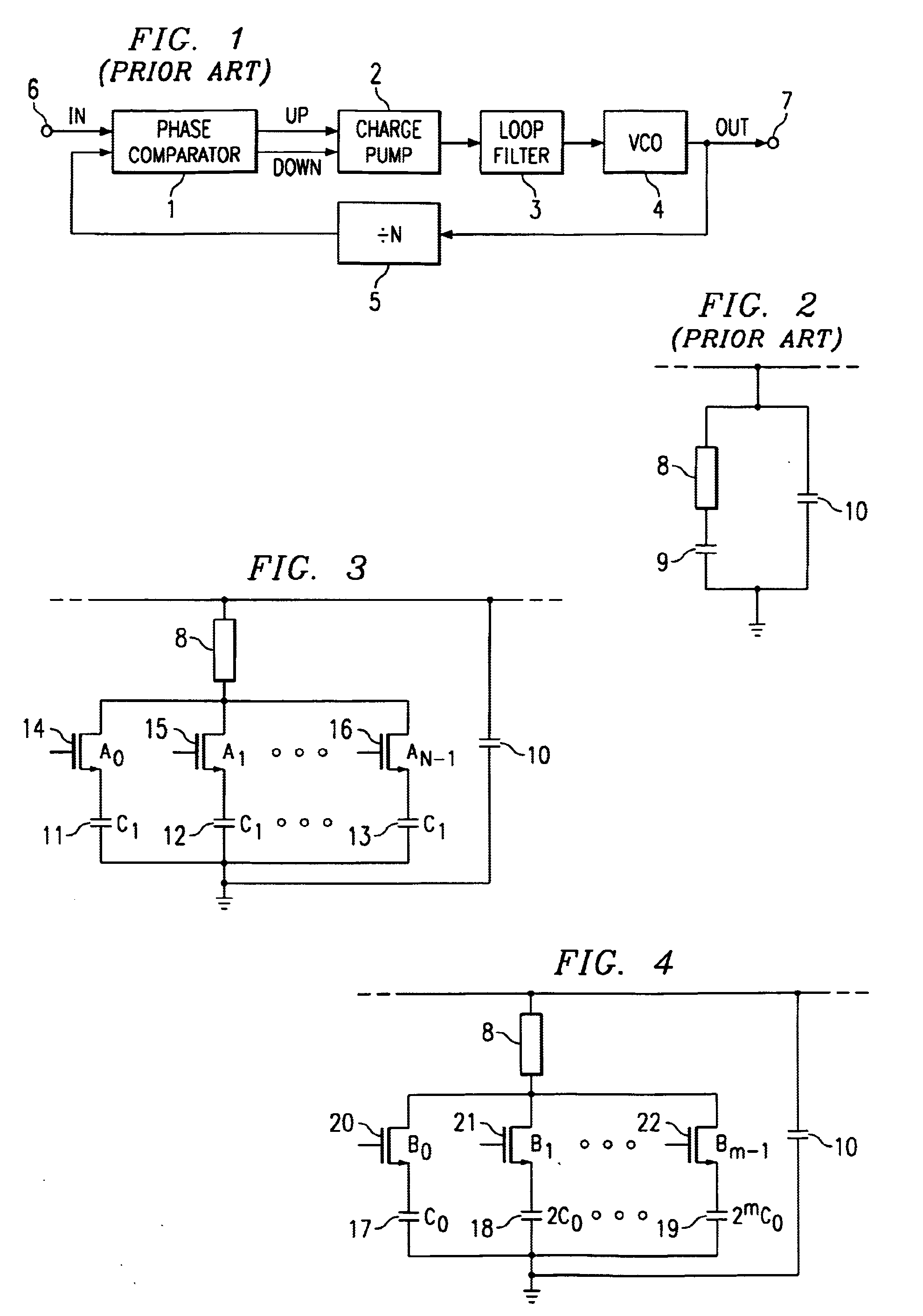
Use of configurable capacitors to tune a self biased phase locked loop
InactiveUS6873214B2Pulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsCapacitanceDamping factor
A phase locked loop (PLL) comprising an input, an output, a charge generator, a low pass filter 3, an oscillator 4 and a frequency divider 5. The frequency divider 5 has an input coupled to the output of the PLL and an output coupled to an input of the charge generator. The frequency at the output of the frequency divider 5 is equal to the frequency at the input of the frequency divider divided by a selectable divider ratio N. The PLL has a damping factor z and a bandwidth to compare frequency ratio ω3 / ωref. The low pass filter 3 has a first capacitor for integrating the charge produced by the charge generator. The capacitance of that first capacitor is arranged to be proportional to the divider ratio N so that the damping factor z and the bandwidth to compare frequency ratio ω3 / ωref are substantially independent of the divider ratio N.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
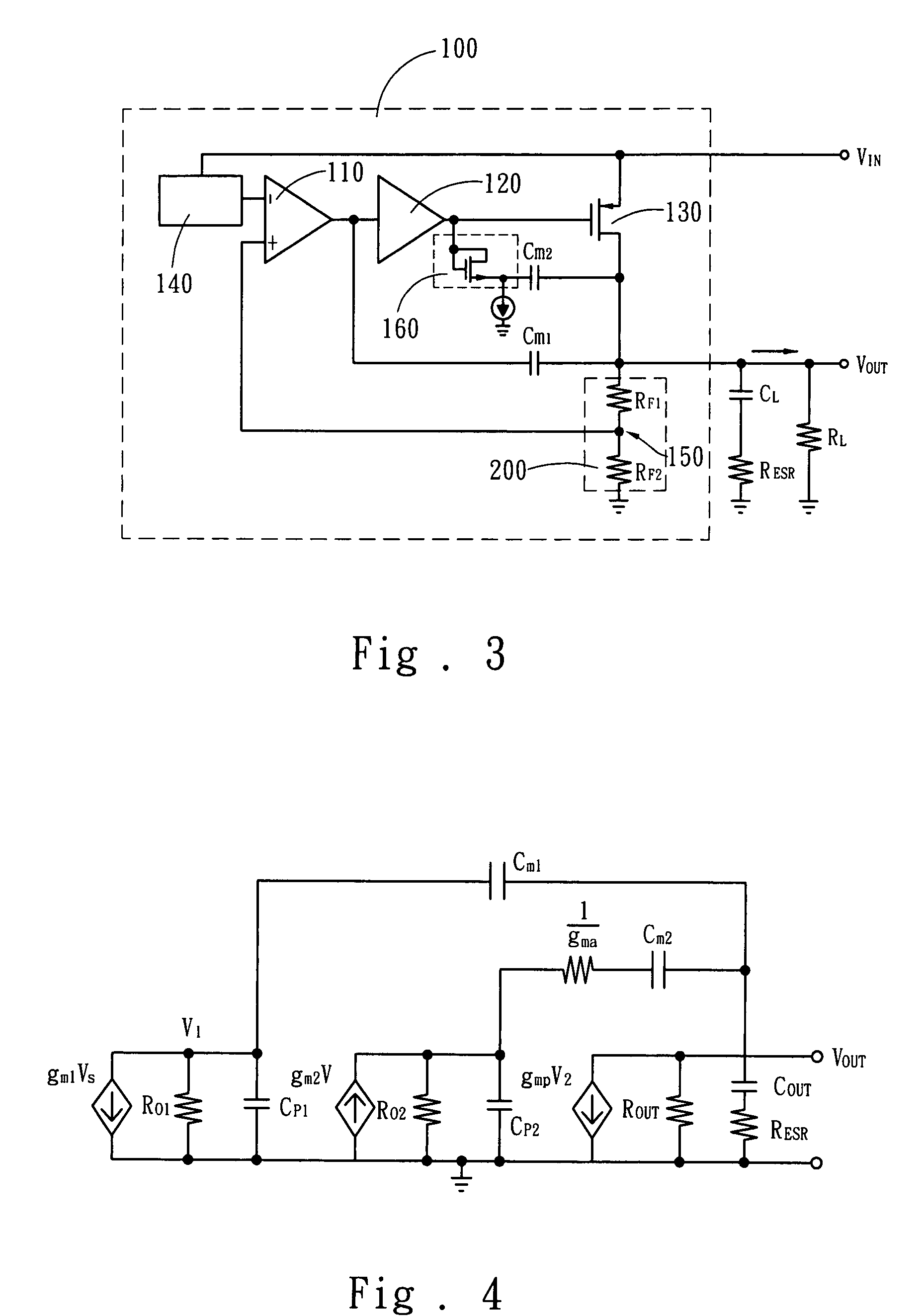
Low dropout linear voltage regulator with an active resistance for frequency compensation to improve stability
InactiveUS7710091B2Improve controllabilityImprove stabilityNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifiers with impedence circuitsDamping factorCapacitance
The present invention discloses an LDO (Low DropOut) linear voltage regulator, which is based on an NMC (Nested Miller Compensation) architecture and can be capacitor-free, wherein an active resistor is added to the feedback path of the Miller compensation capacitor to increase the controllability of the damping factor, solve the problem of extensively using the output capacitor with a parasitic resistance, and solve the problem that a compromise must be made between the damping factor control and the system loop gain. Further, the present invention utilizes a capacitor-sharing technique to reduce the Miller capacitance required by the entire system and accelerate the stabilization of output voltage without influencing stability.
Owner:SITRONIX TECH CORP
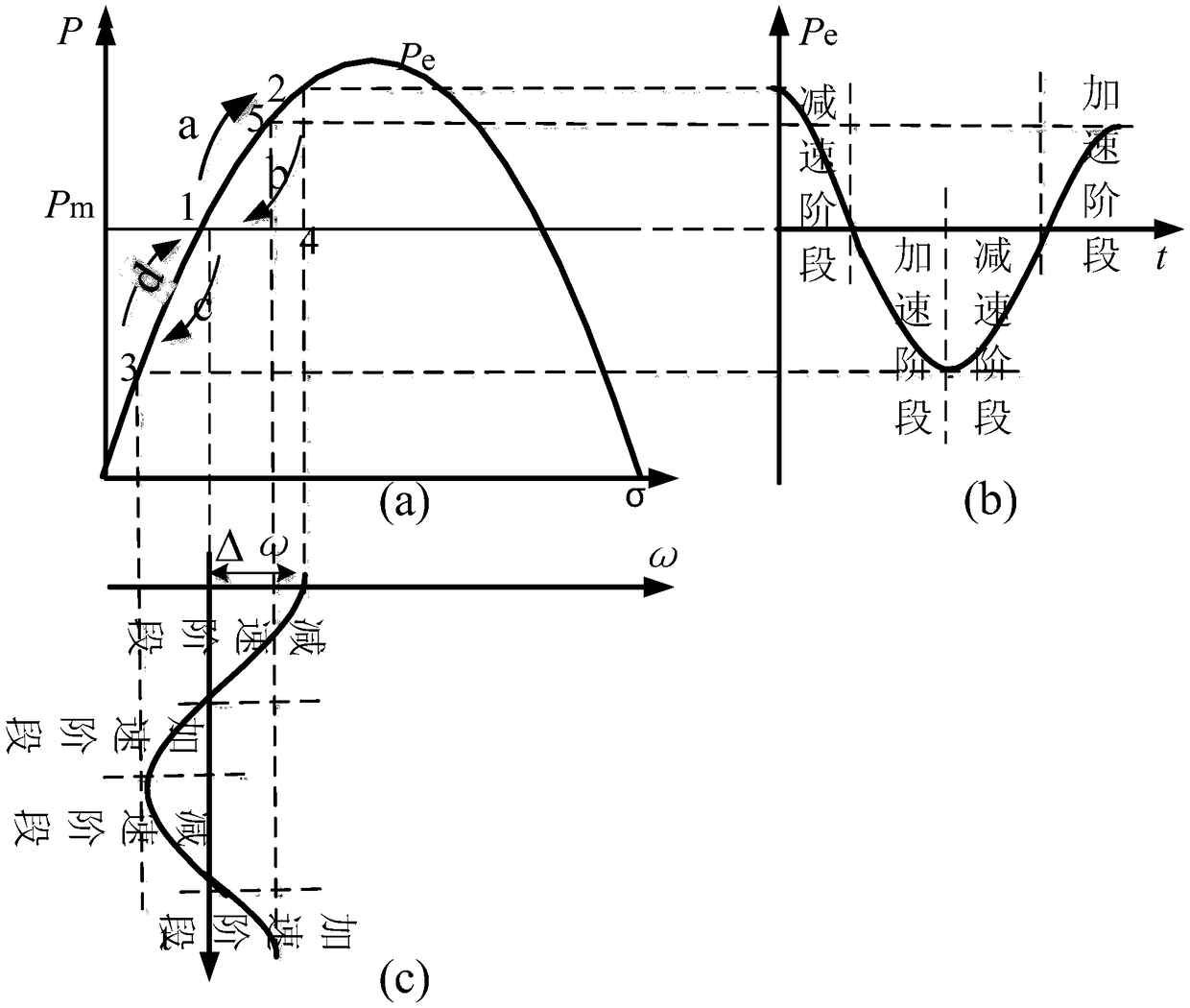
A transient adaptive parameter control strategy for microgrid based on VSG
ActiveCN109149605ASimple structureImprove dynamic stabilityPower oscillations reduction/preventionDamping factorMicrogrid
The invention discloses a microgrid transient adaptive parameter control strategy based on VSG, belonging to the field of microgrid frequency control. The invention comprises the following steps: a dynamic model of a microgrid system based on VSG is constructed; The virtual inertial torque and virtual damping factor of the system model are controlled adaptively. The stability of the system energyfunction is evaluated. Matlab / simulink software is used to simulate and analyze the numerical example. By analyzing the frequency oscillation process, the method of the invention establishes the dynamic relationship between the system inertia and the system frequency offset, and changes the virtual inertia factor in real time according to the frequency change, thereby effectively suppressing the frequency oscillation, enabling the system to better cope with the transient disturbance and providing the system frequency stability.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
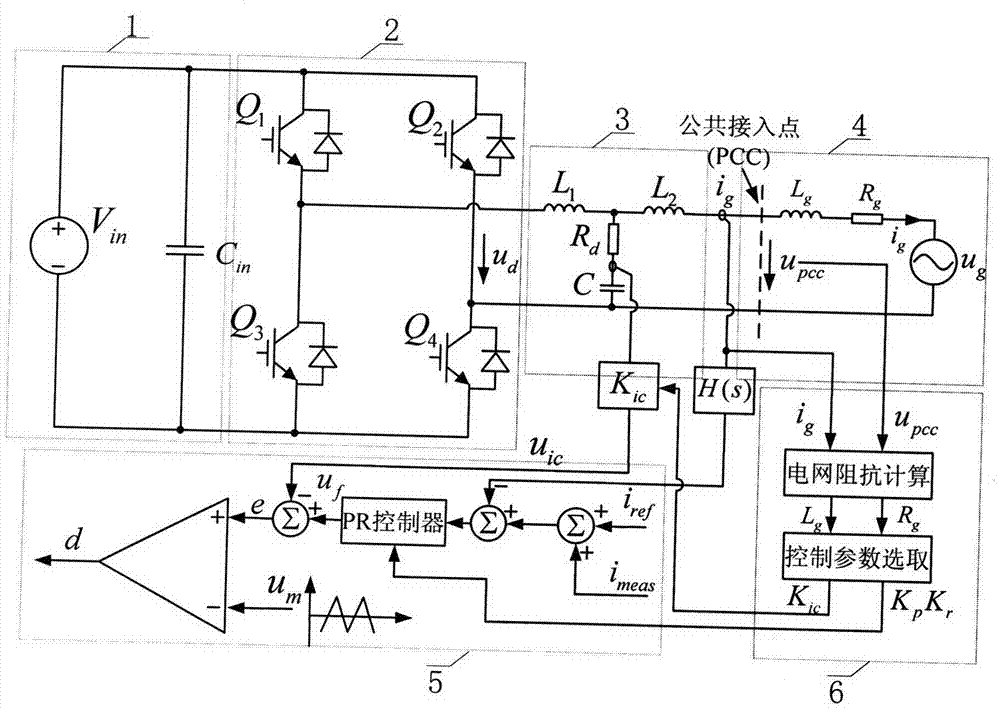
Method for adaptively controlling hybrid damping of grid-connection inverter applicable to weak grid access conditions
ActiveCN103545838AReasonable frequency characteristicsPR parameter increaseAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsDamping factorGrid impedance
The invention relates to a method for adaptively controlling hybrid damping of a grid-connected inverter applicable to weak grid access conditions. Most existing methods are used for optimally controlling fixed impedance of grids at present, but grid access conditions of grid-connected inverters are dynamic and varied, so that adaptive control under different grid impedance conditions has high application value. The method includes measuring impedance information of a weak grid by a harmonic injection process; enabling a controller to adaptively modify loop parameters and active damping coefficients; ensuring a wide stability margin and a proper control bandwidth of a control system. The method has the advantages that the novel method for adaptively controlling the hybrid damping is based on real-time measurement on impedance of the grid, and optimal control parameters in a DSP (digital signal processor) are automatically selected, so that the control bandwidth and a phase margin of the inverter under different grid impedance access conditions can be guaranteed, and the grid-connected inverter can safely and reliably run under the various grid impedance conditions.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS +1
Attitude controller for quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle with dynamic characteristics being unknown and method
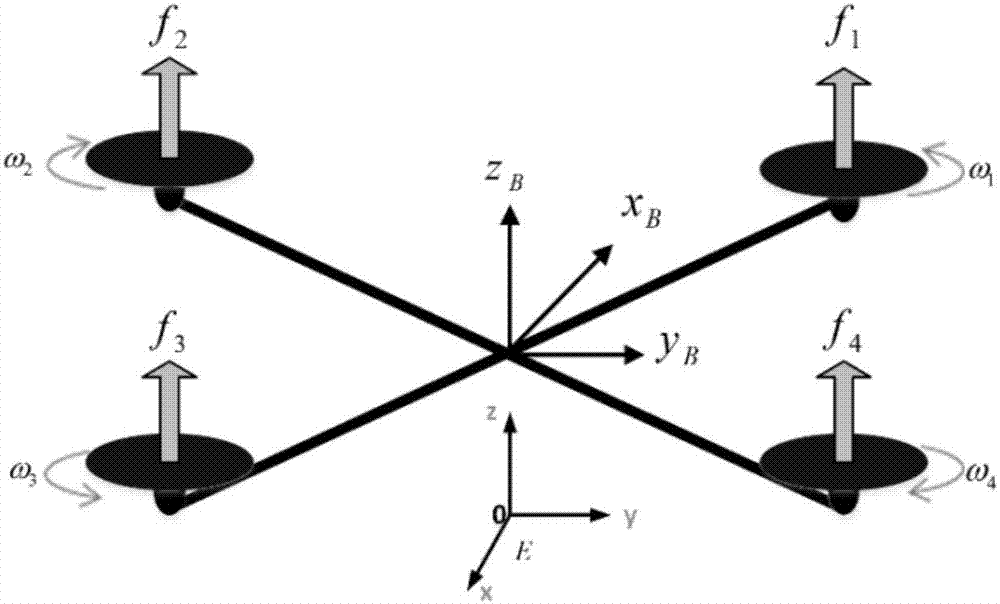
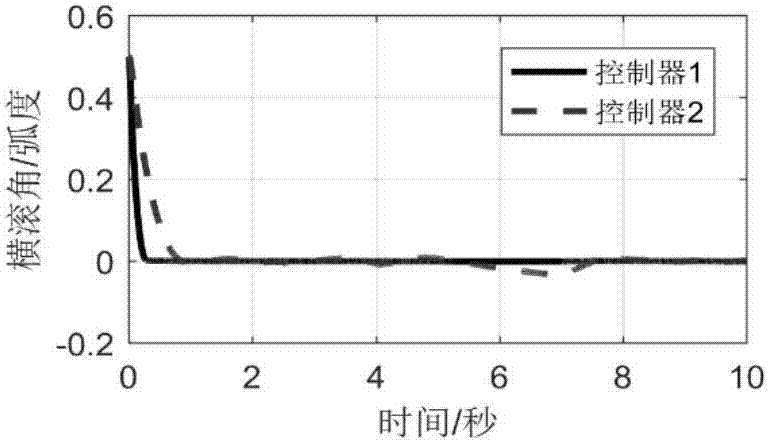
ActiveCN107479567AFast convergenceImprove robustnessAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsDamping factorAttitude control
The invention discloses an attitude controller for a quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle with dynamic characteristics being unknown and a method. It is assumed that quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle model parameters such as the moment of inertia and the air damping coefficient are unknown, and bounded disturbance suffered by the system is time-varying and always exists in the system. In allusion to the unknown model parameters, the invention designs a corresponding differential estimator to perform online estimation on a position parameter. Based on a parameter estimation value, an improved adaptive nonsingular terminal sliding mode controller is designed to complete stable control for the attitude of the quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle. In addition, an adaptive disturbance compensator is further designed to perform effective compensation on the bounded disturbance. Simulation and experimental results show that the control algorithm can well accomplish stable control for the attitude of the quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle and has high robustness for the unknown dynamic characteristics and disturbance of the system.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Magnetorheological torsional vibration damper for engine
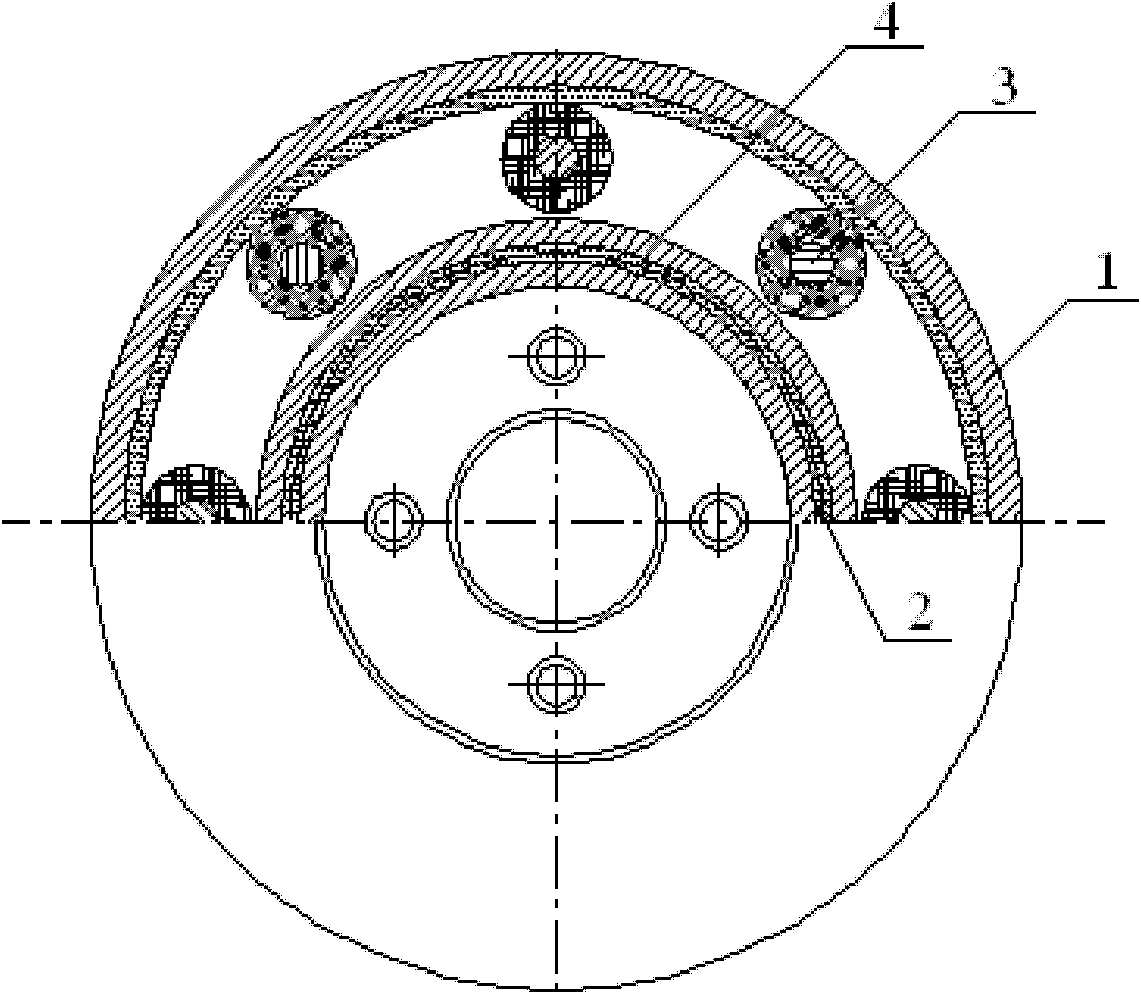
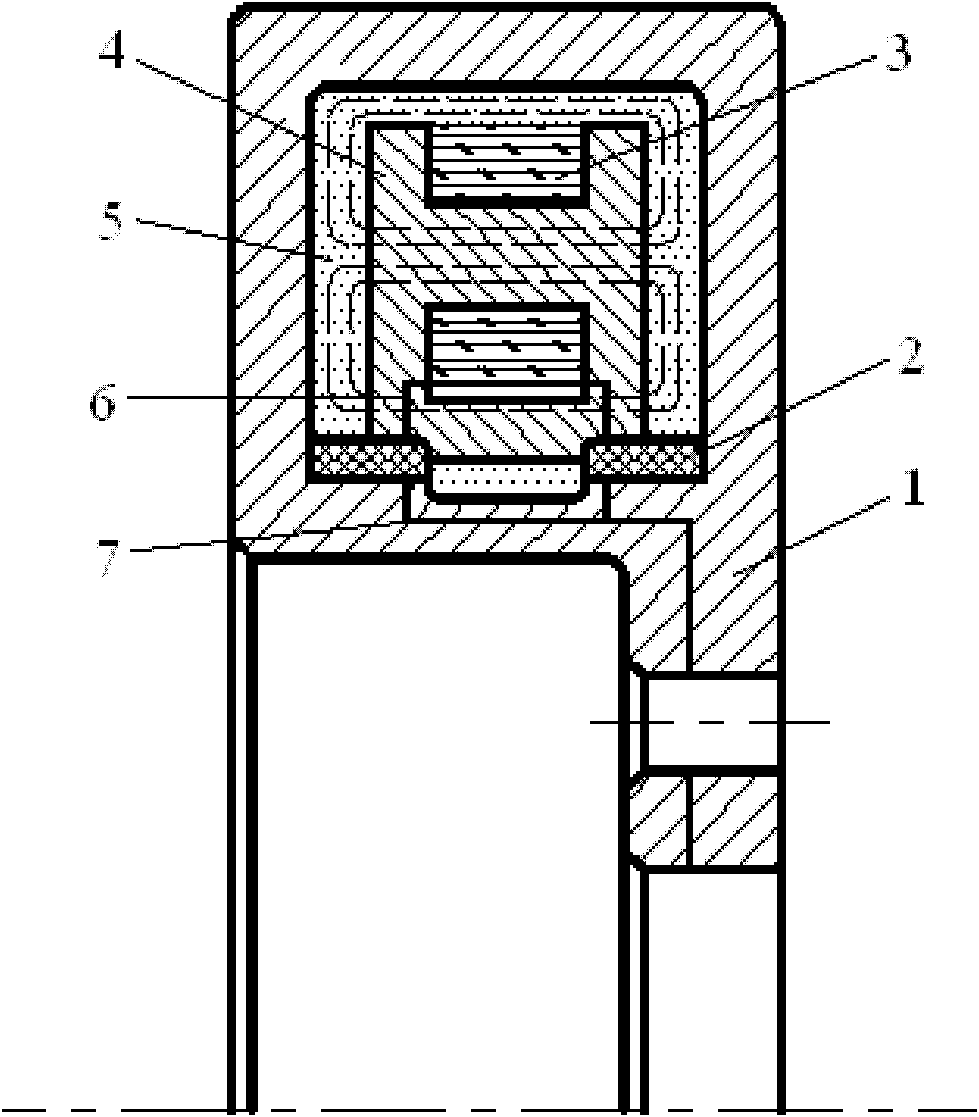
InactiveCN102168736AWon't leakImprove sealingNon-rotating vibration suppressionDamping factorPower flow
The invention discloses a magnetorheological torsional vibration damper for an engine. The damper is characterized in that: an inertia disc is arranged in an annular shell; an antifriction lining is arranged at the outer end of the inner circumference of the annular shell, and the inertia disc can rotate freely around the antifriction lining in the annular shell; a conductive coil is arranged in the inertia disc; magnetorheological fluid is filled in a gap between the annular shell and the inertia disc; a lead wire is connected with the antifriction lining; and the lead wire is exported from the center of the damper through an insulating conduit of the annular shell. By utilizing the characteristic that the conductive coil is electrified and generates a magnetic field to control flowing of the magnetorheological fluid, the rotation damping force of the damper can be adjusted, so that the defect that the damping coefficient of the traditional silicone oil torsional vibration damper can only be a single damping coefficient is overcome. The external magnetic force is changed by changing the volume of current, so that the damping characteristic of the magnetorheological fluid is changed. Therefore, the magnetorheological torsional vibration damper has excellent damping effect when a crankshaft is resonant, and has better damping effect than that of the silicone oil damper under other frequencies.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Vehicle hydraulic damper with actively adjustable damping for semiactive suspension
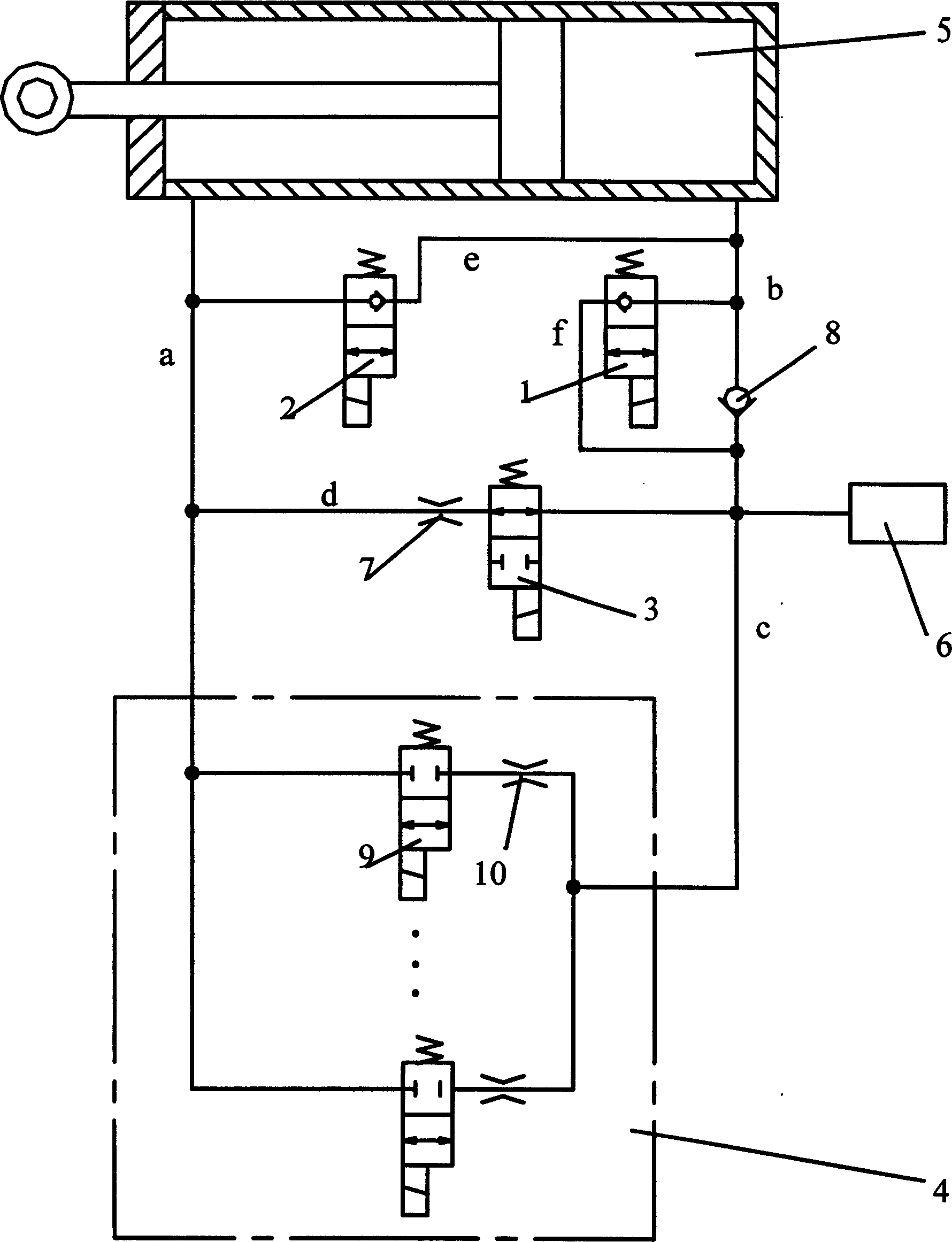
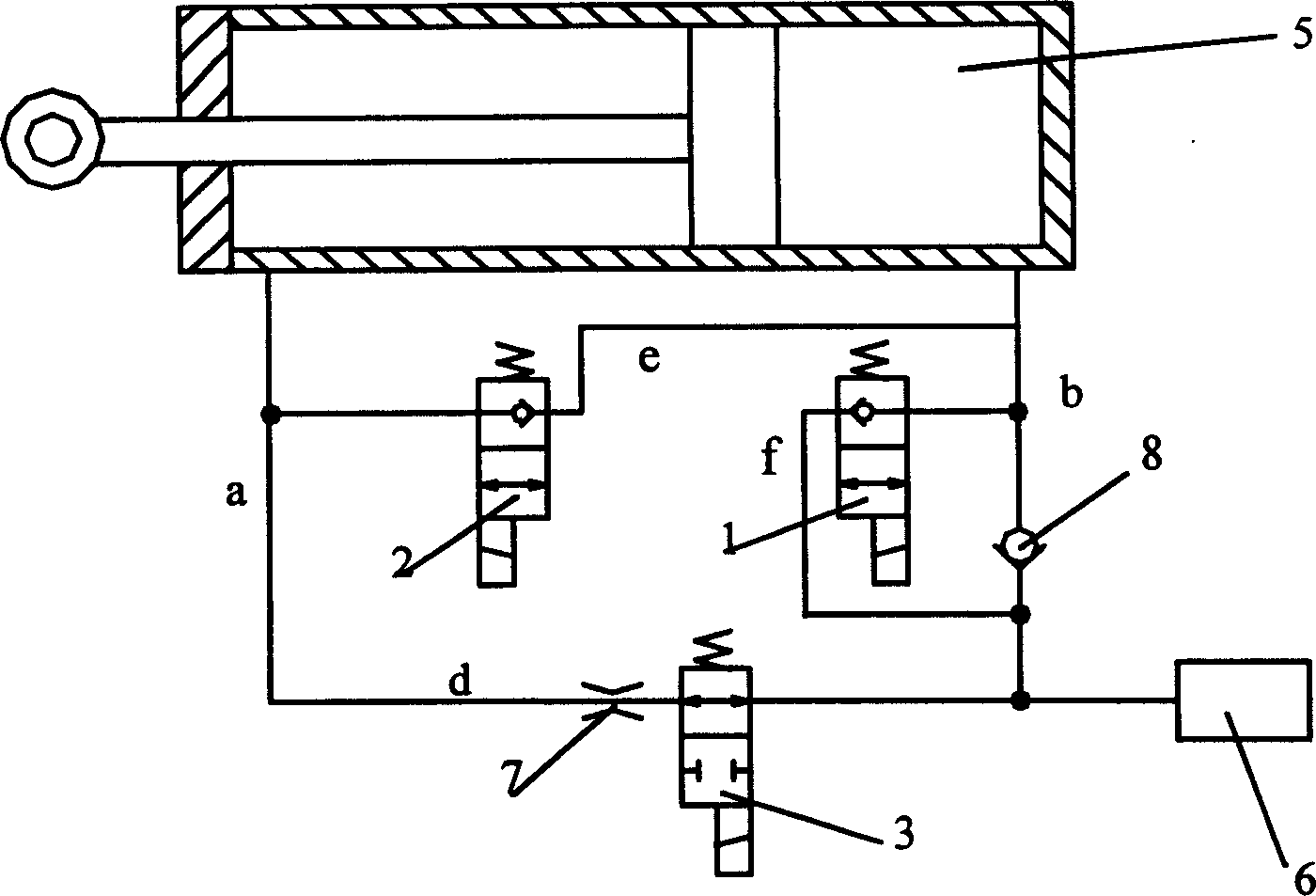
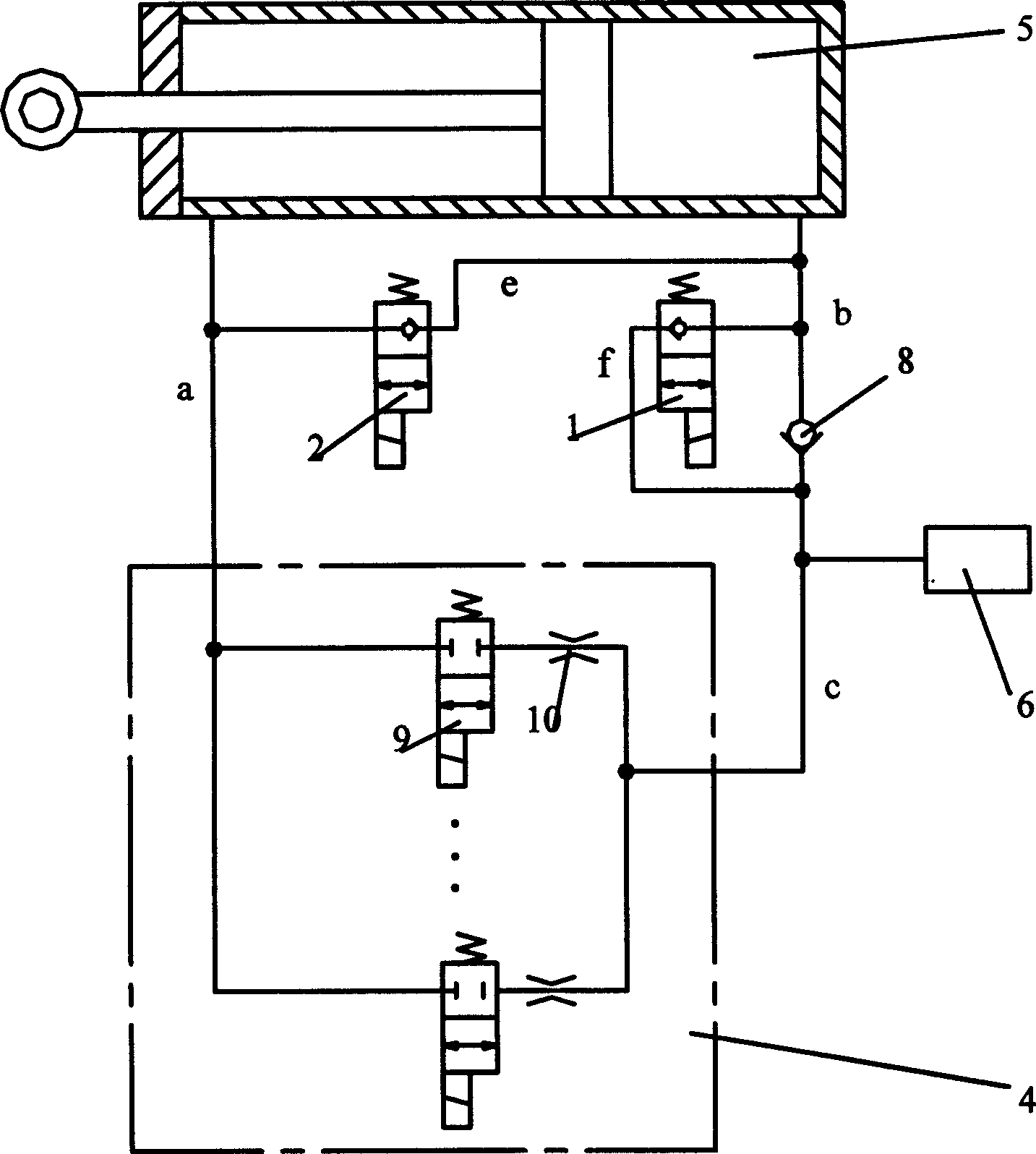
The invention discloses a liquid control valve with adjustable damp which comprises: a damping control unit that is constructed by high speed electro-magnetism switch valve and fixing damp connected in row, several damp control units joint in parallel forms the liquid damper control valve with adjustable damp, one of its end oil line is connected with the right chamber of the damping vibration cylinder via the oil tank, one end of the third electro-magnetism valve, one end of single direction valve and oil line b; the other end of the first electro-magnetism valve is connected with oil line c via the oil line f; the other end of the liquid control valve with adjustable damp is connected with one end of the fixing damp, one end of the second electro-magnetism valve, the left chamber of the damping vibration cylinder via oil line a; the other end of the fixing damper is connected with the other end of the third electro-magnetism valve and the other end of the second electro-magnetism valve is connected with oil b via oil e. The invention can get the corresponding damp coefficient with the different requirement of the system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
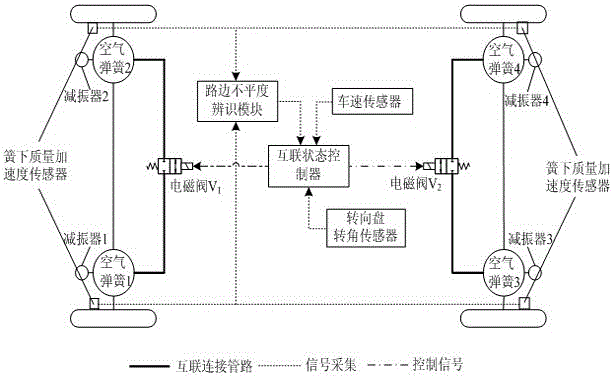
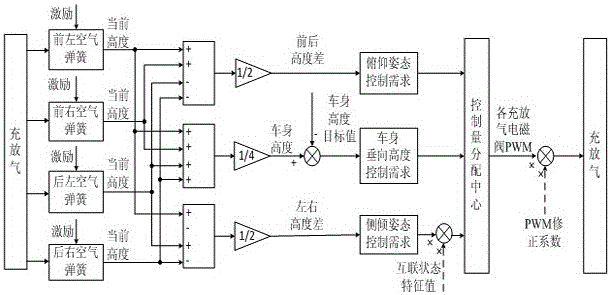
Cooperative control system and method for damping-adjustable and vehicle body height-adjustable interconnection air suspension
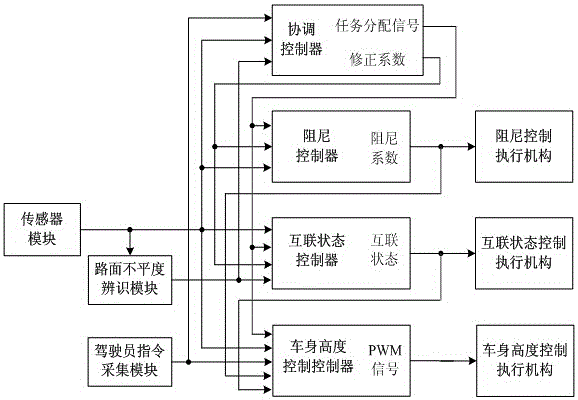
InactiveCN105082920AWork coordinationImprove performanceResilient suspensionsDamping factorControl system
The invention discloses a cooperative control system and method for a damping-adjustable and vehicle body height-adjustable interconnection air suspension. The cooperative control system comprises a sensor module, a road unevenness recognition module, a driver instruction collection module, a coordination controller, an interconnection state controller, an interconnection state control execution mechanism, a damping controller, a damping control execution mechanism, a vehicle body height controller and a vehicle body height control execution mechanism. First, an interconnection state control strategy, a vehicle body height control strategy and a damping control strategy are made; then, the coordination controller is built, the working sequence of the controllers is determined according to current driving conditions, specific control sentences are corrected, vehicle body height control is corrected according to the interconnection state and the damping coefficient, and interconnection state control and damping control are corrected according to correction coefficients provided by the coordination controller. By means of the cooperative control system and method, an interconnection state control system, a vehicle body height control system and a damping control system can be effectively coordinated, and therefore the overall performance of the damping-adjustable and vehicle body height-adjustable interconnection air suspension can be obviously improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
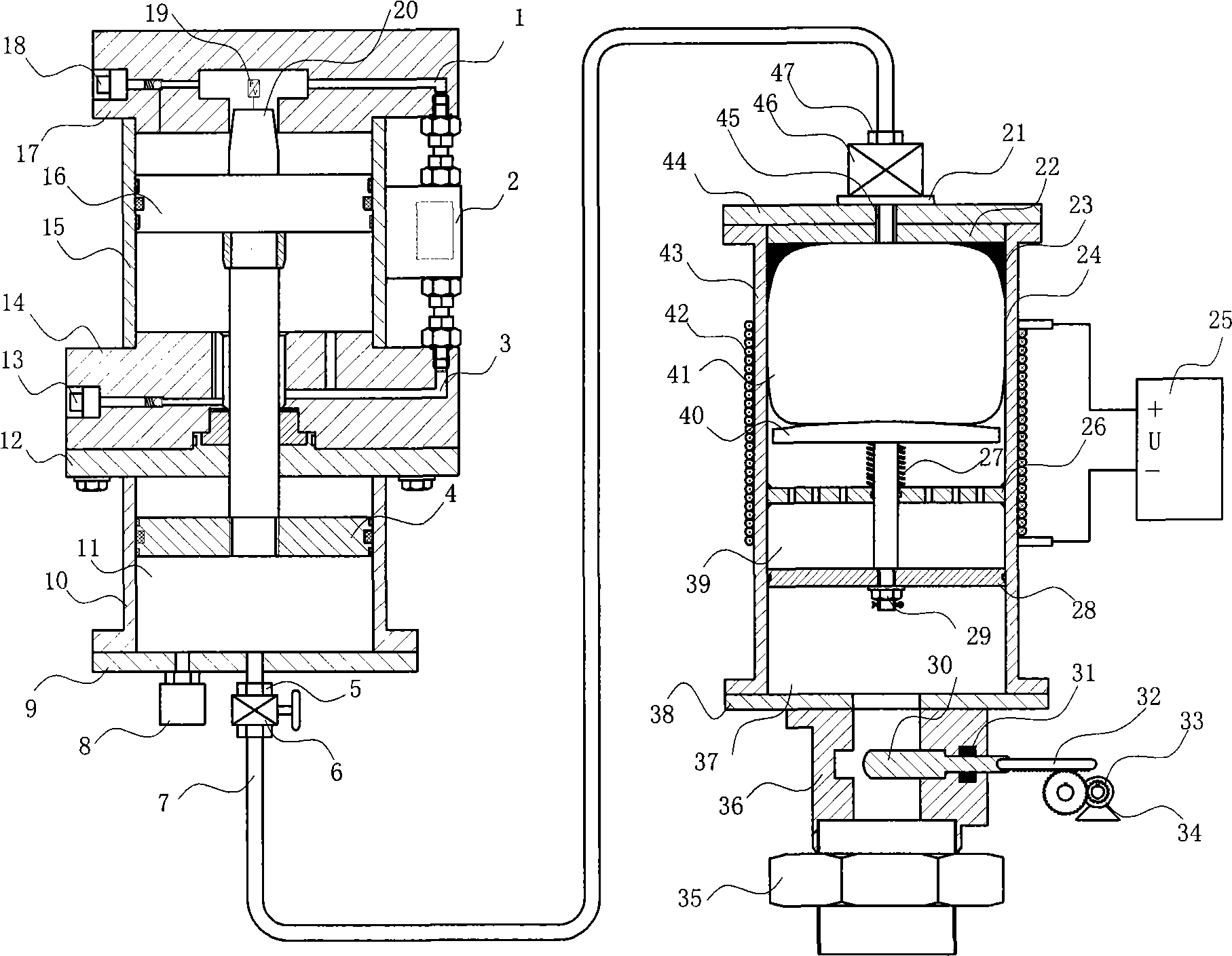
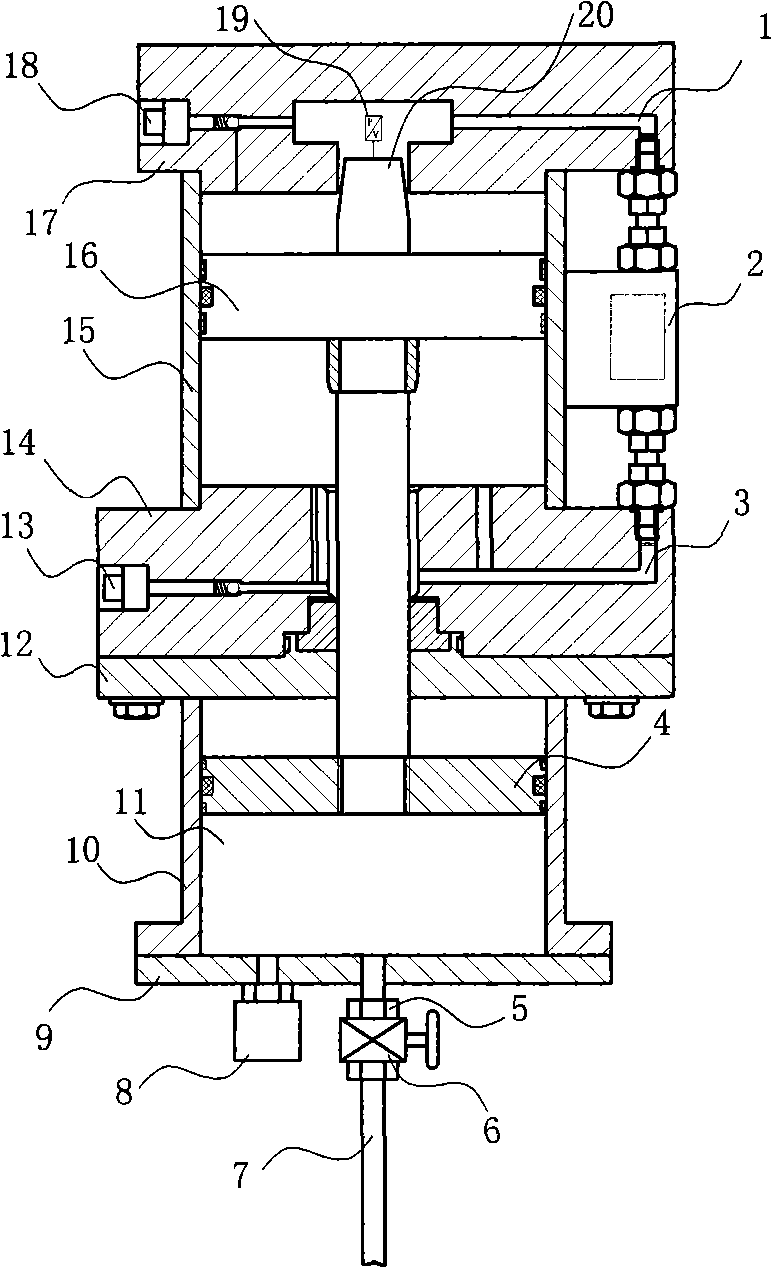
Parameter self-adapting and regulation leather bag type hydraulic accumulator
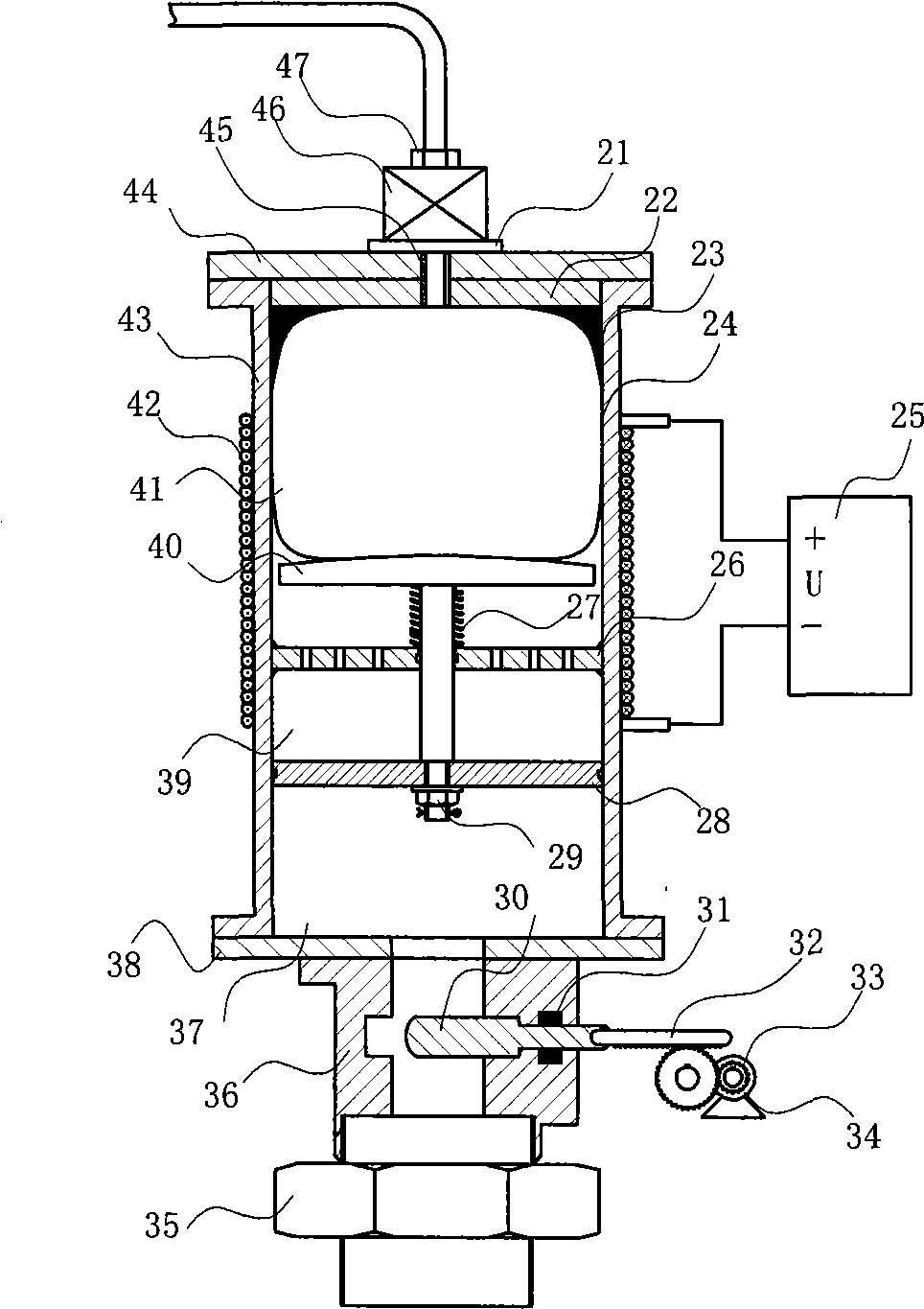
InactiveCN101476571AChange the application statusImprove air tightnessMechanical apparatusDamping factorSolenoid valve
The invention discloses a parameter adaptive adjustment bag type accumulator. A second air cavity (41) of a parameter variable accumulator device is communicated with a first air cavity (11) of an online adjustment accumulator through a high-pressure electromagnetic valve (46) and a high-pressure gas pipeline (7), and a filling valve cover (36) of the parameter variable accumulator device is communicated with a hydraulic system through a filling valve cover (35). The parameter adaptive adjustment bag type accumulator adopts a valve control hydraulic cylinder to control the air cavity volume and the gas pressure, and a DSP control center to calculate proper parameters so as to achieve automatic adjustment and overcome the defects that the prior accumulator parameter selection is inaccurate and the adjustment is impossible once the accumulator parameter is determined. Because an electromagnetic coil is adopted to adjust the size of the magnetic field in a magnetorheological fluid cavity and a step motor is adopted to control the size of the oil-passing area of an oil inlet, the damping coefficient of the accumulator can be changed dynamically, thus not only the requirement on the speedability and the stability of the compression shock and pulsation of an absorption system is met, but also the requirement on various functions of the same accumulator is met.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com