Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
103 results about "Path gain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
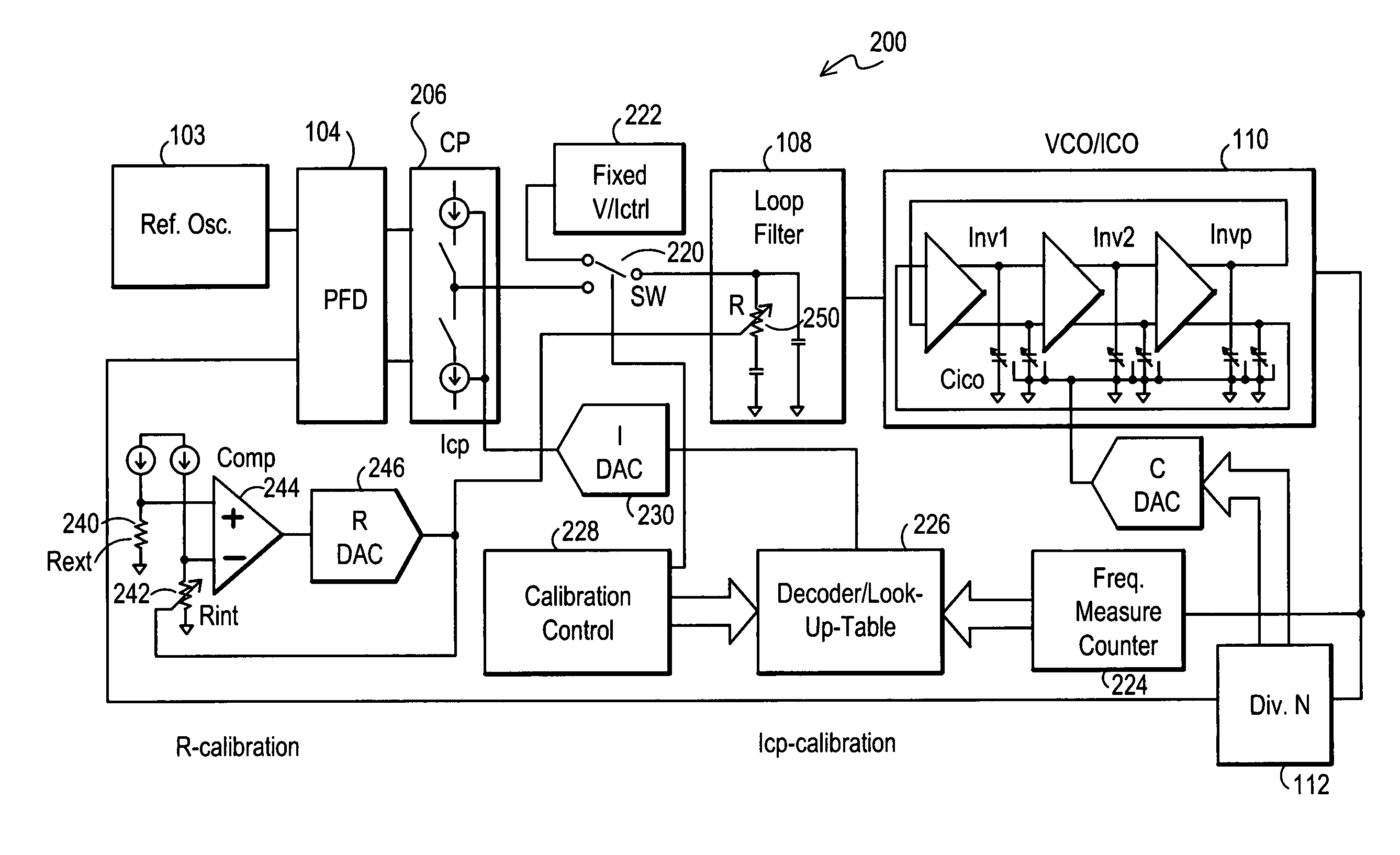
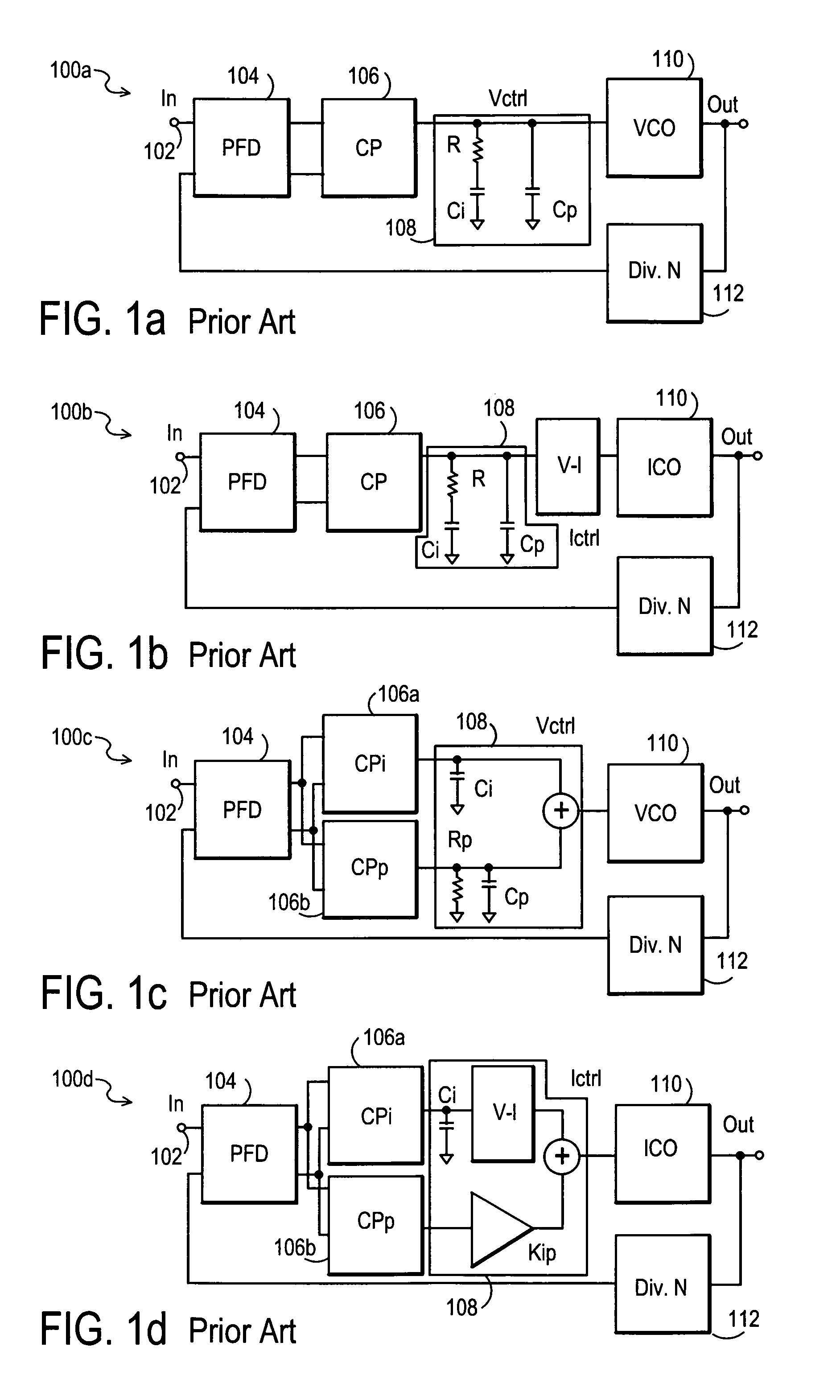
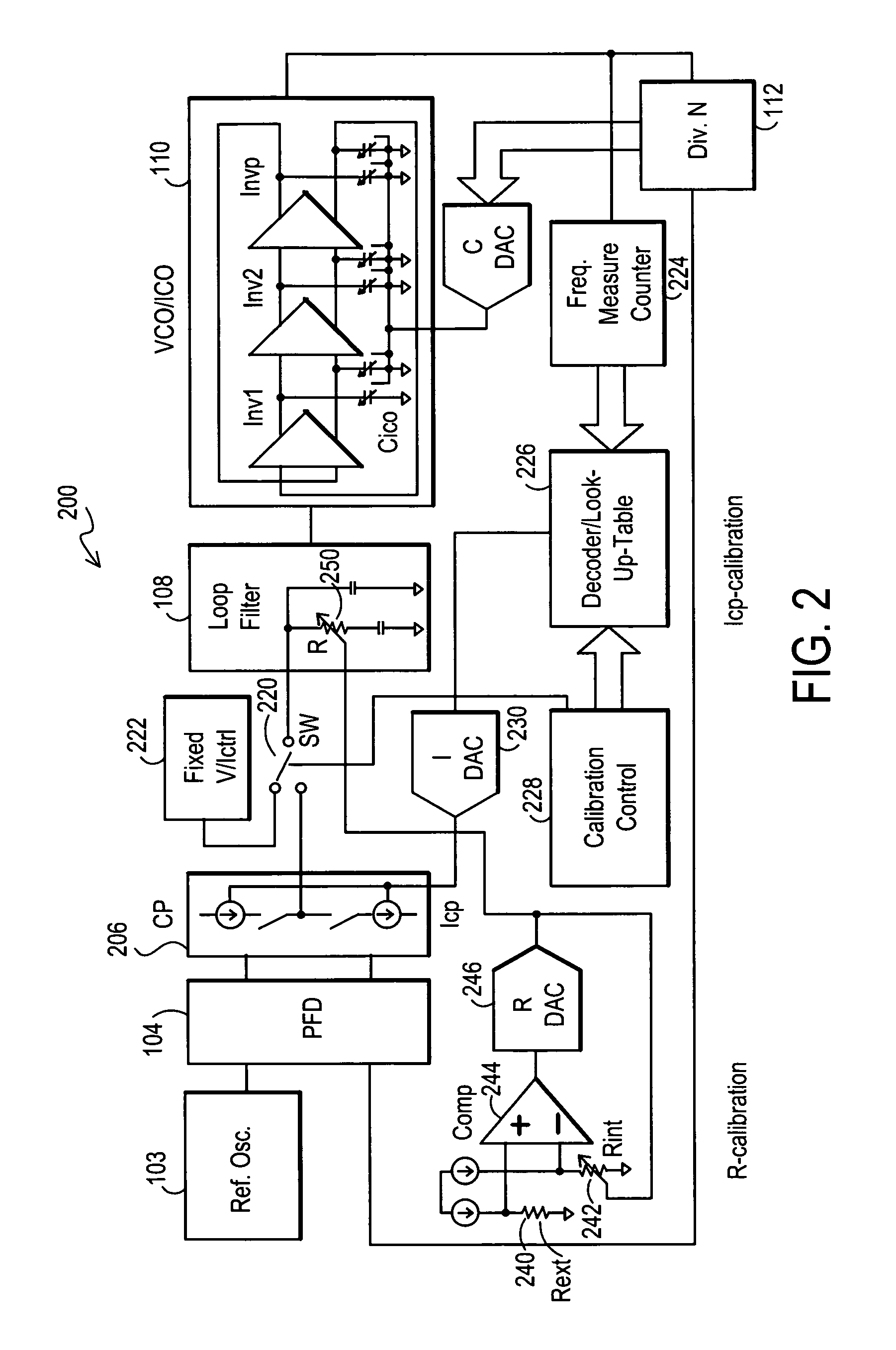
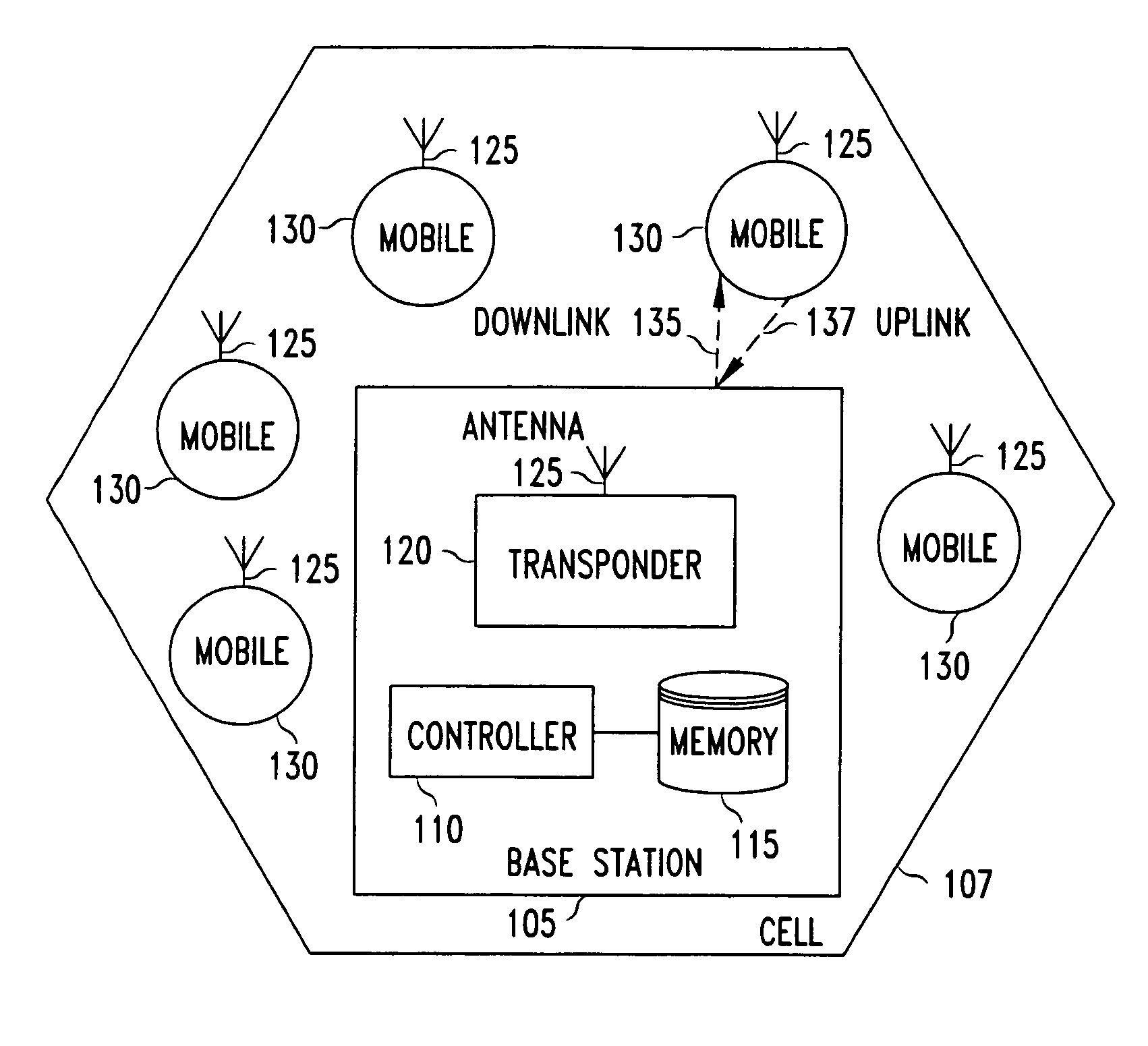
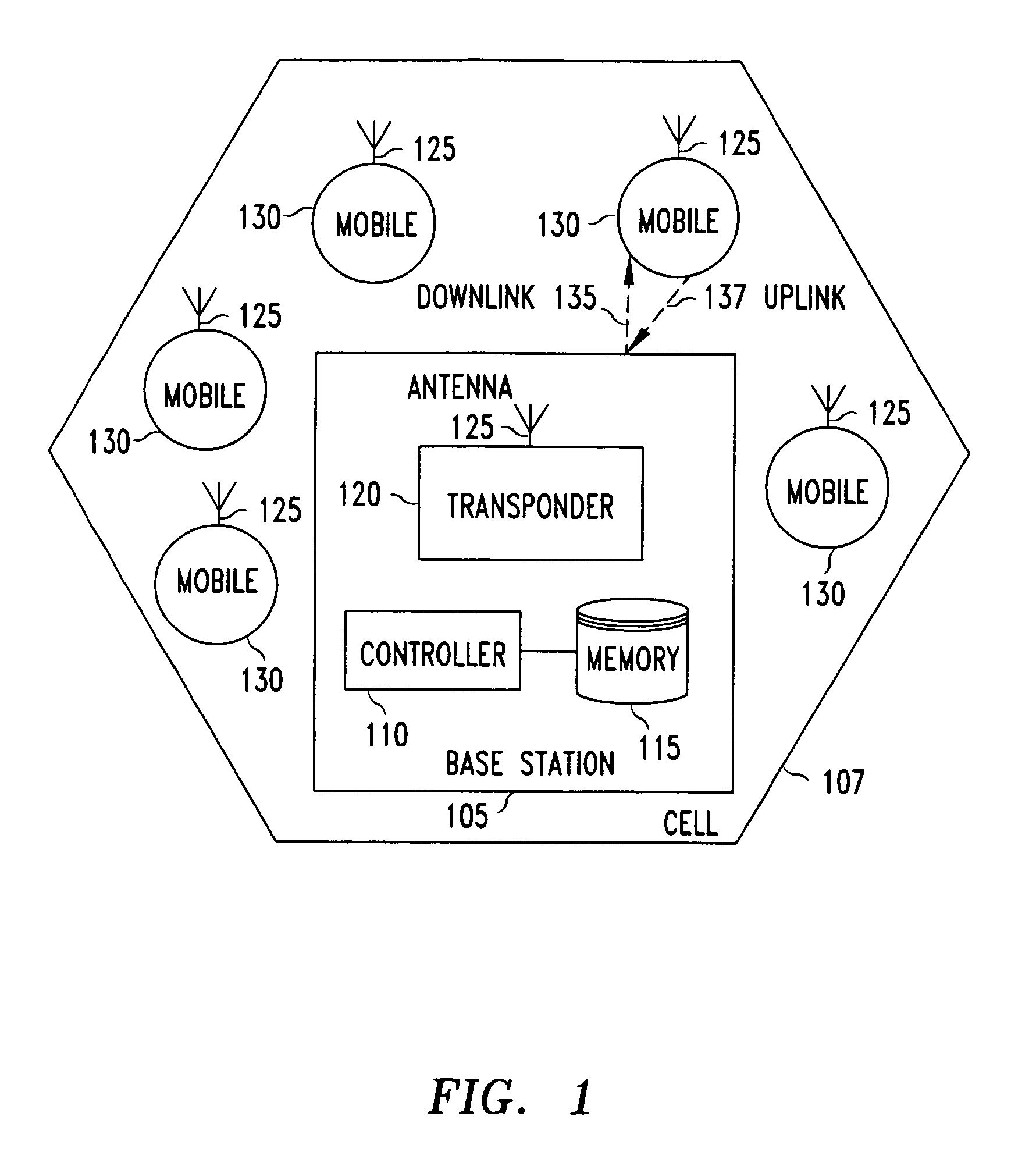
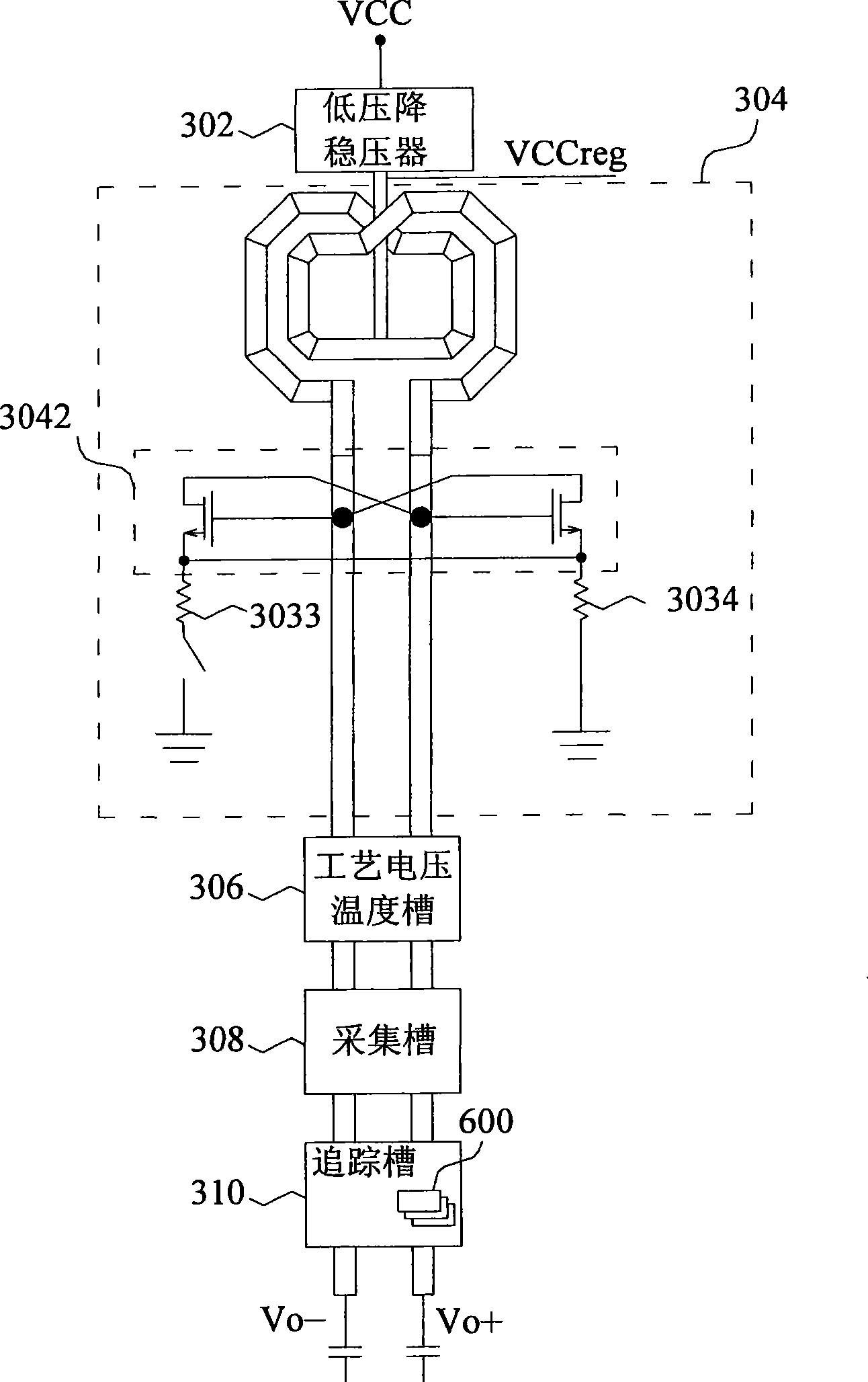
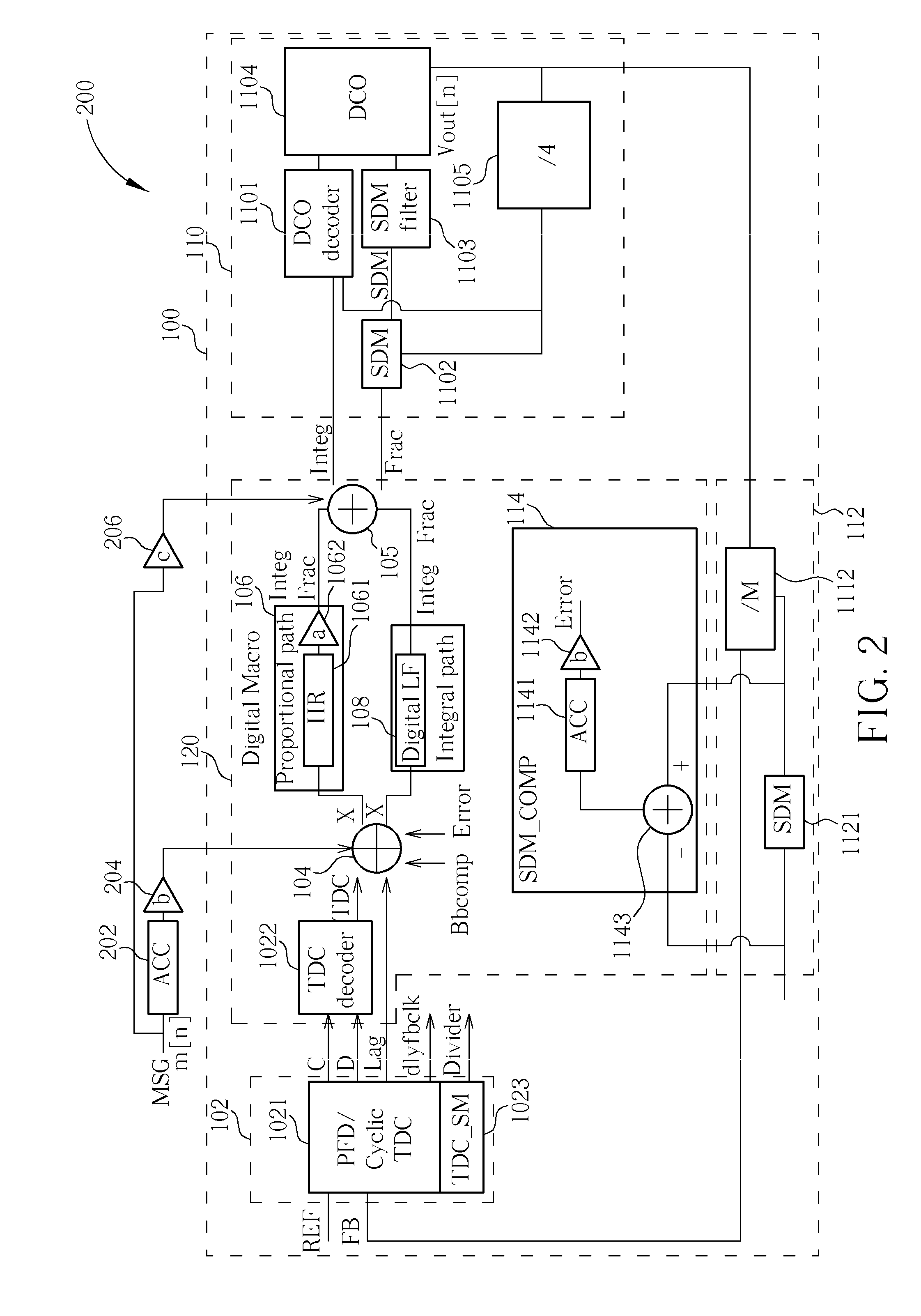
Method and apparatus to achieve a process, temperature and divider modulus independent PLL loop bandwidth and damping factor using open-loop calibration techniques
InactiveUS7095287B2Reduce complexityImprove accuracyPulse automatic controlFrequency analysisDamping factorProportional control
Several open-loop calibration techniques for phase-locked-loop circuits (PLL) that provide a process, temperature and divider modulus independence for the loop bandwidth and damping factor are disclosed. Two categories of open-loop techniques are presented. The first method uses only a single measurement of the output frequency from the oscillator and adjusts a single PLL loop element that performs a simultaneous calibration of both the loop bandwidth and damping factor. The output frequency is measured for a given value of the oscillator control signal and the charge-pump current is adjusted such that it cancels the process variation of the oscillator gain. The second method uses two separate and orthogonal calibration steps, both of them based on the measurement of the output frequency from the oscillator when a known excitation is applied to the open loop signal path. In the first step the loop bandwidth is calibrated by adjusting the charge-pump current based on the measurement of the forward path gain when applying a constant phase shift between the two clocks that go to the phase frequency detector, while the integral path is hold to a constant value. During the second step the damping factor is calibrated by adjusting the value of the integral loop filter capacitor based on the measurement of the oscillator output frequency when excited with a voltage proportional with the integral capacitor value, while the proportional control component is zeroed-out.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
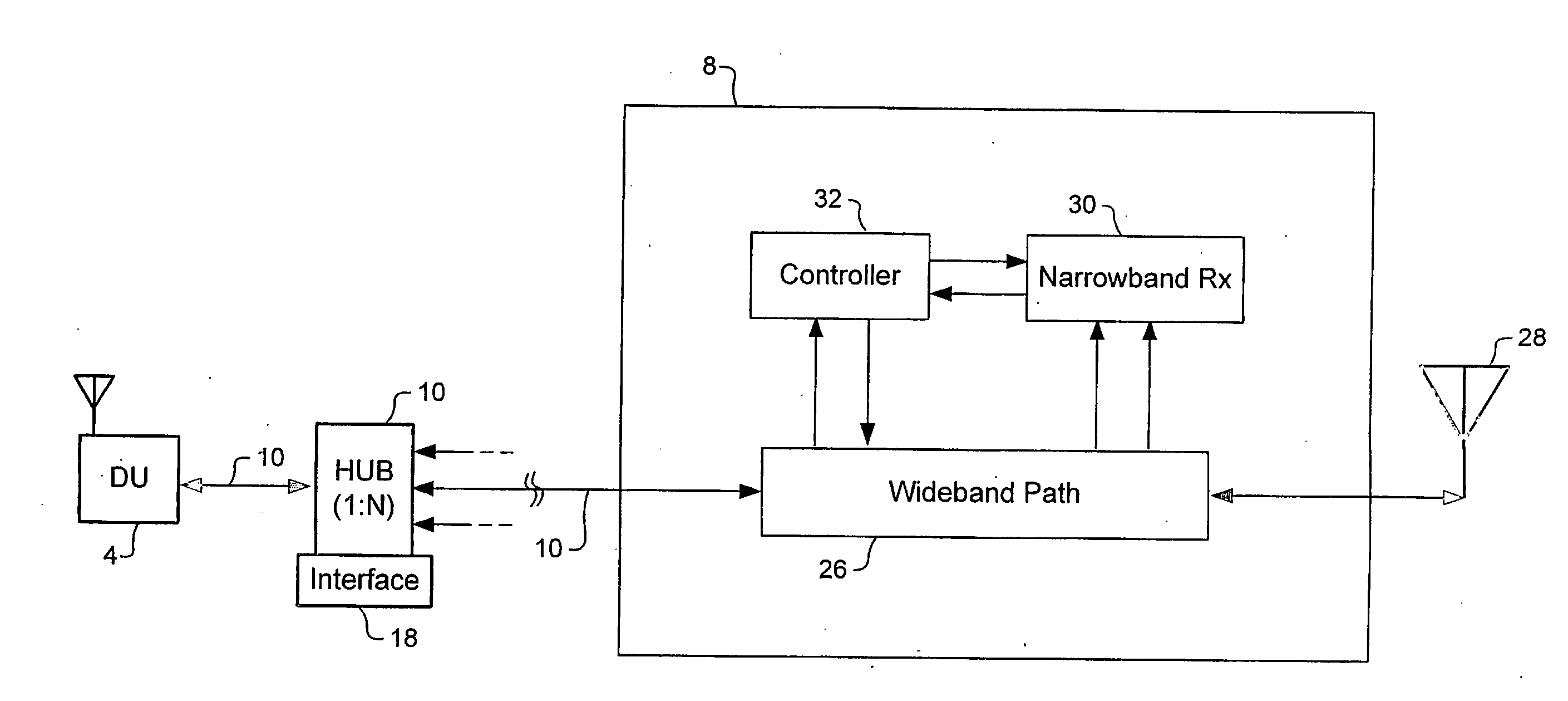
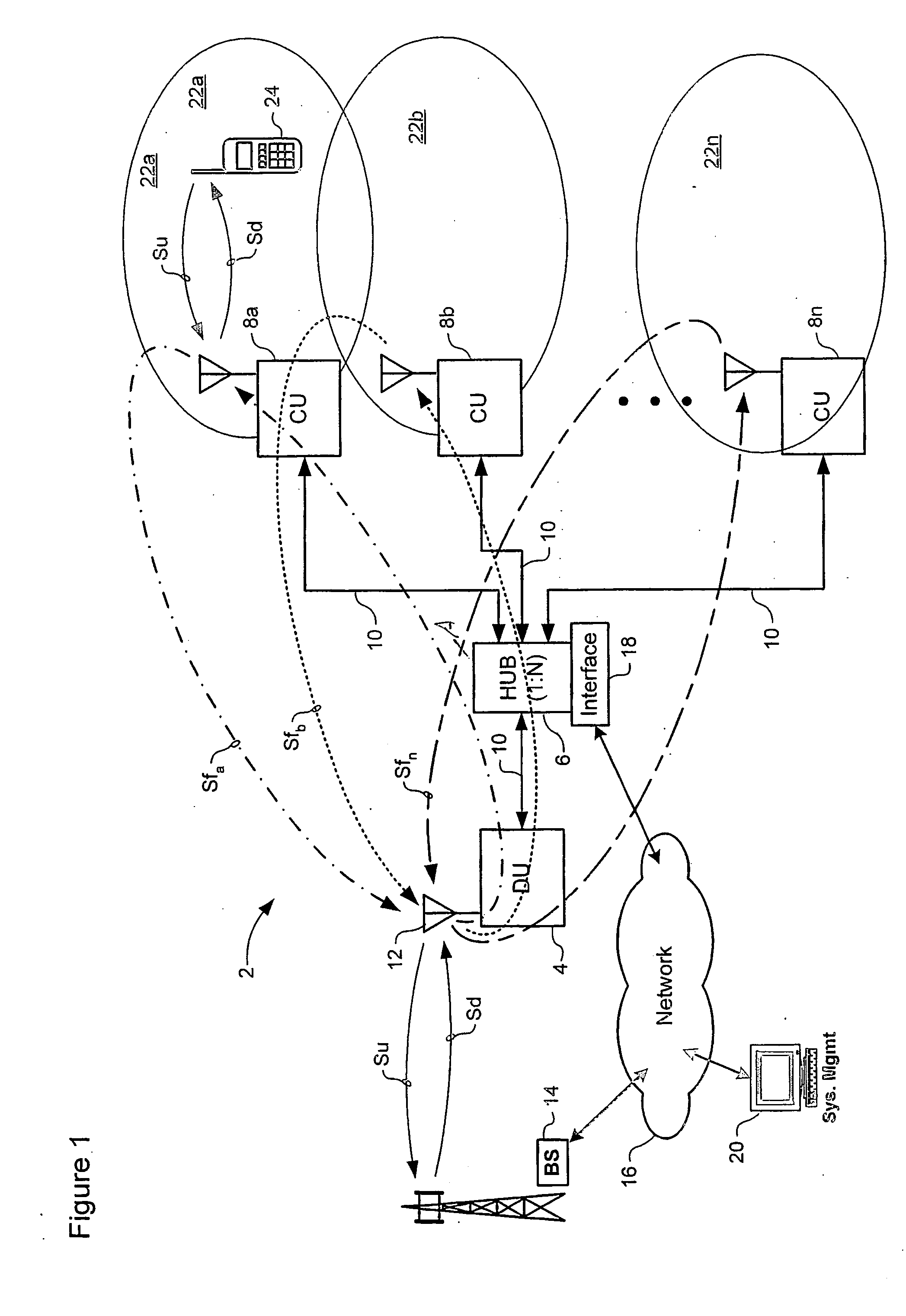
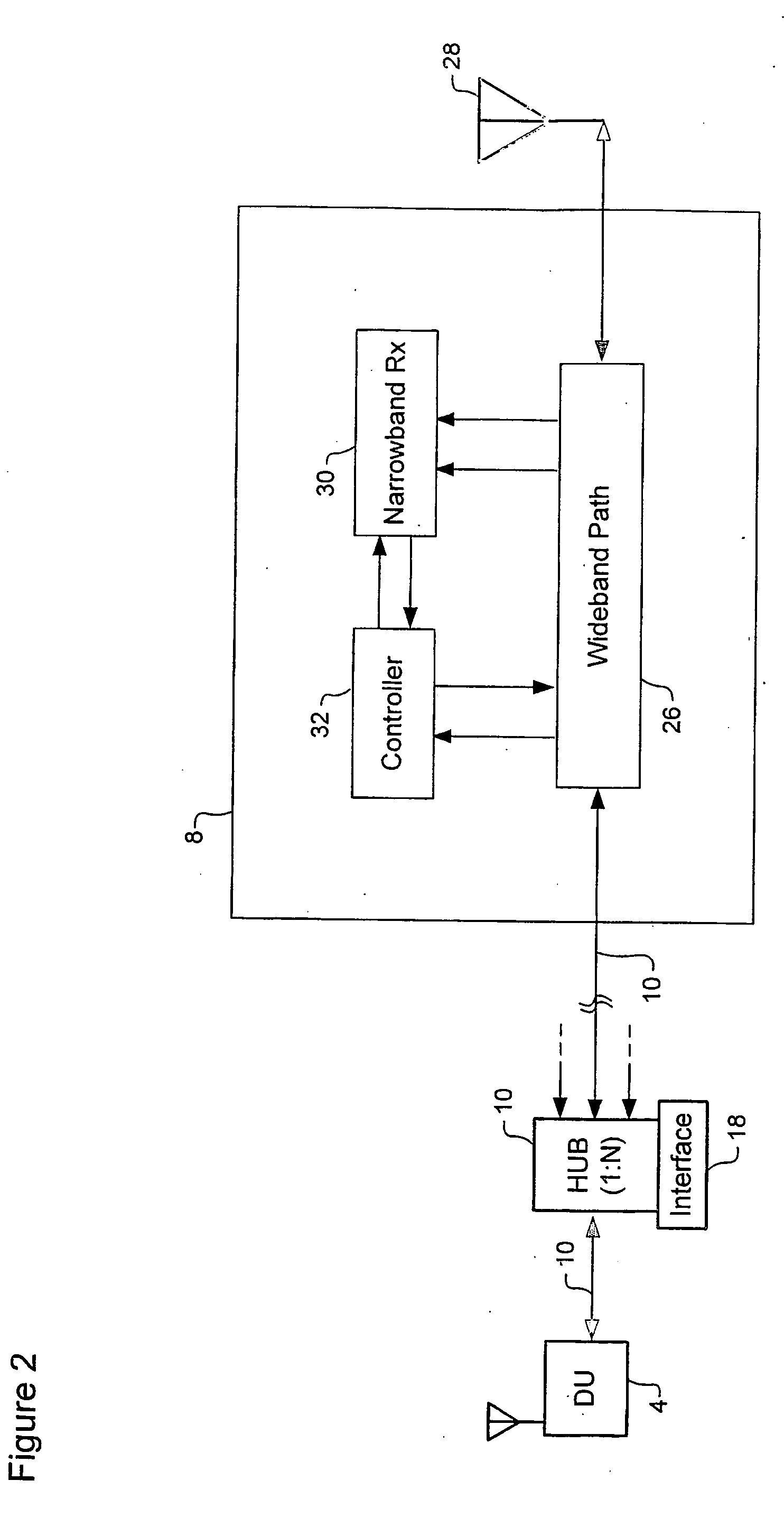
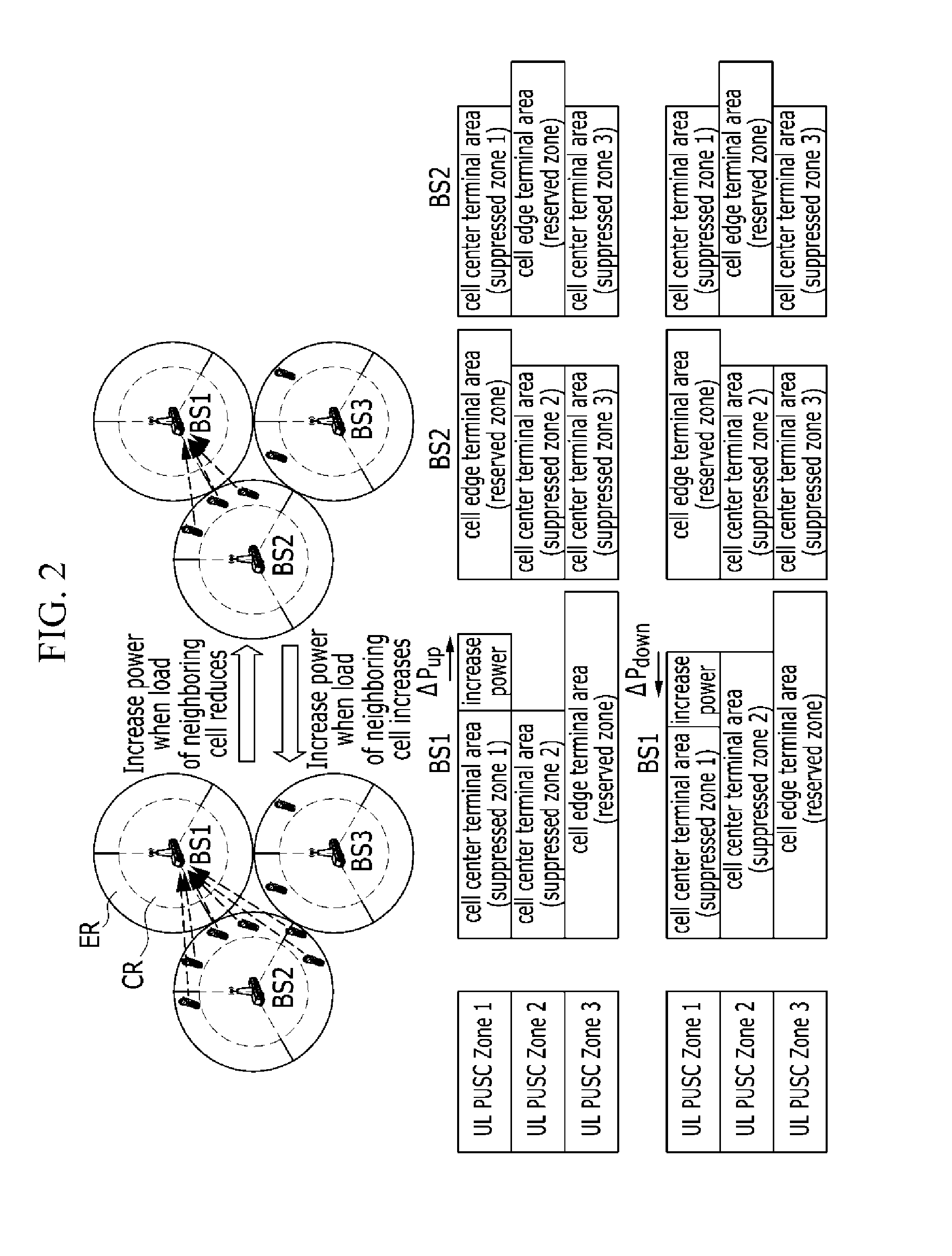
Distributed adaptive repeater system
A distributed adaptive repeater system includes a donor unit, two or more coverage units (CUs), and an intelligent hub. The donor unit operates to maintain bidirectional wireless communication with a base station of a wireless communications network. Each coverage unit maintains bidirectional wireless communication with transceivers located within a respective coverage area, and is further adapted to independently control a signal path gain to ensure stability of a respective feedback loop to the donor unit. Finally, the intelligent hub is operatively coupled between the donor unit and the coverage units, and adapted to monitor a status of each coverage unit.
Owner:SPOTWAVE WIRELESS INC
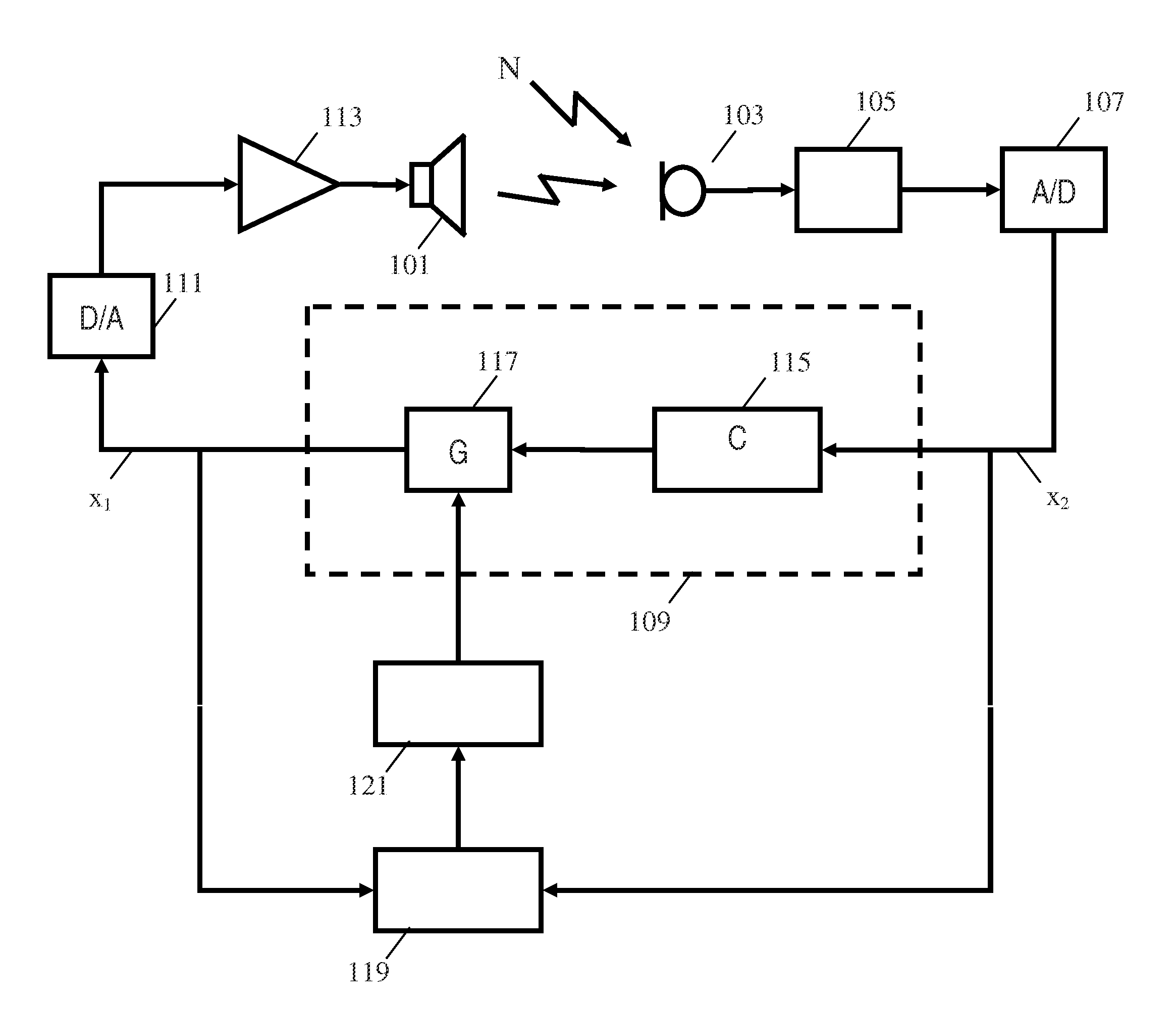
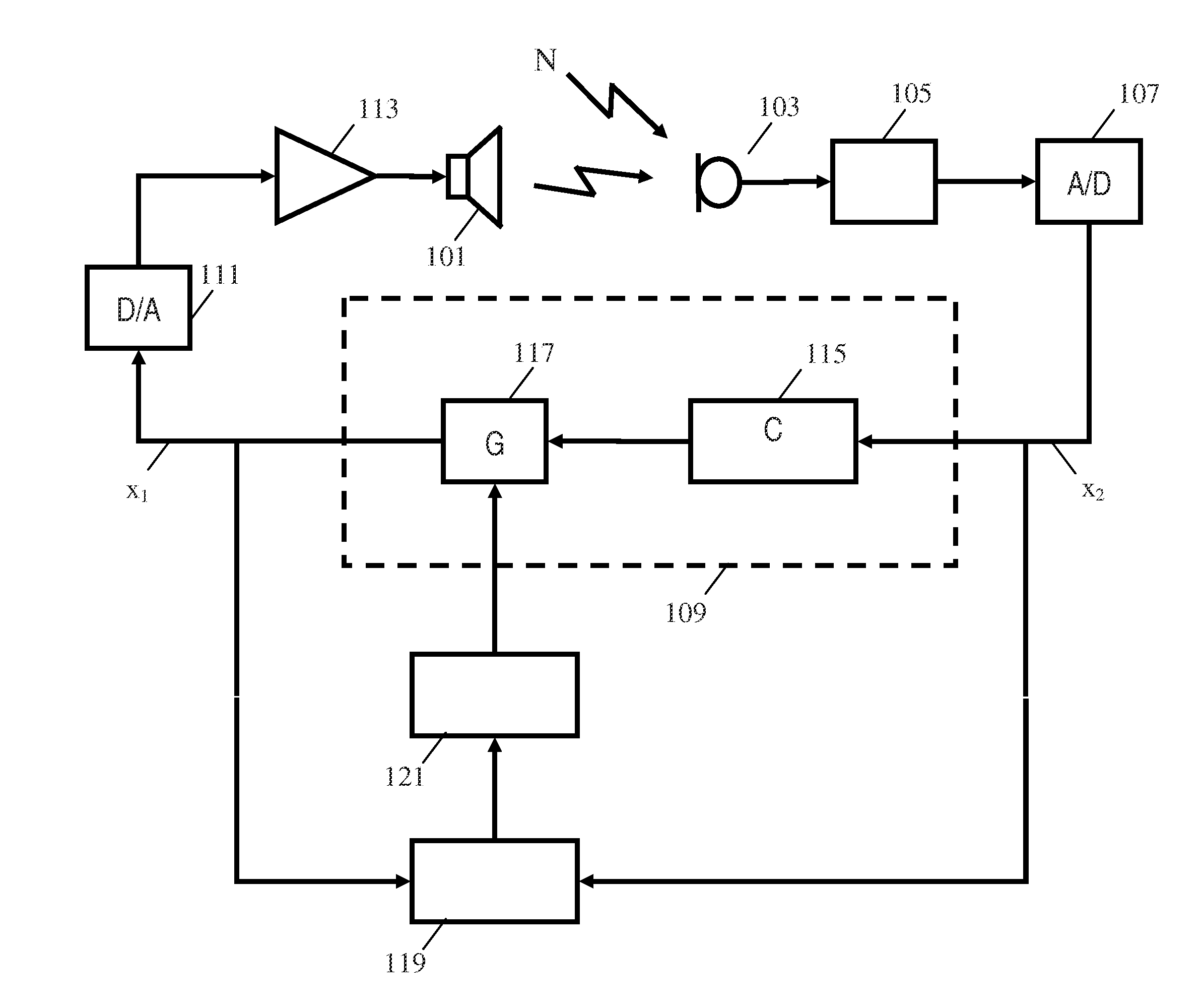
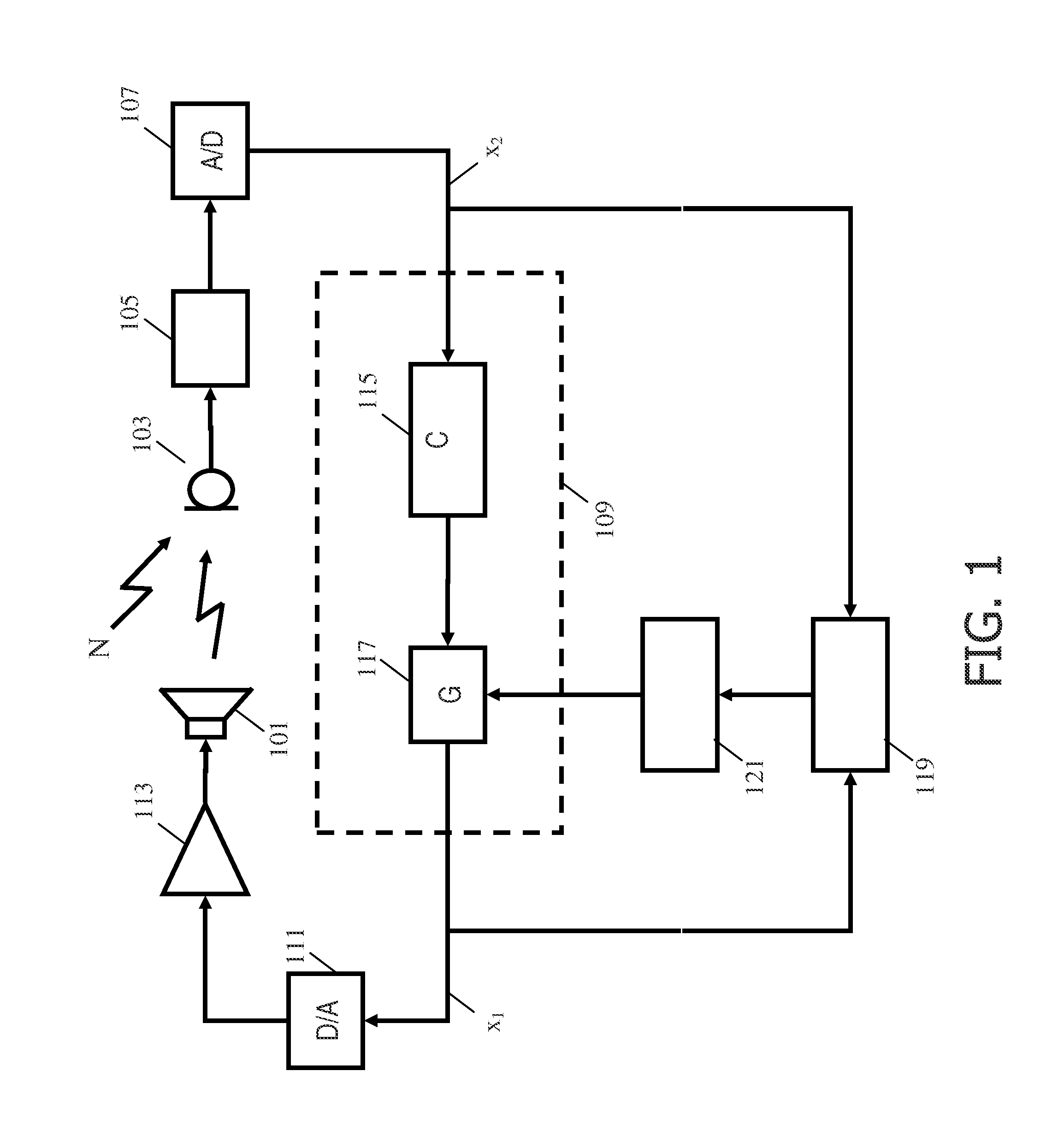
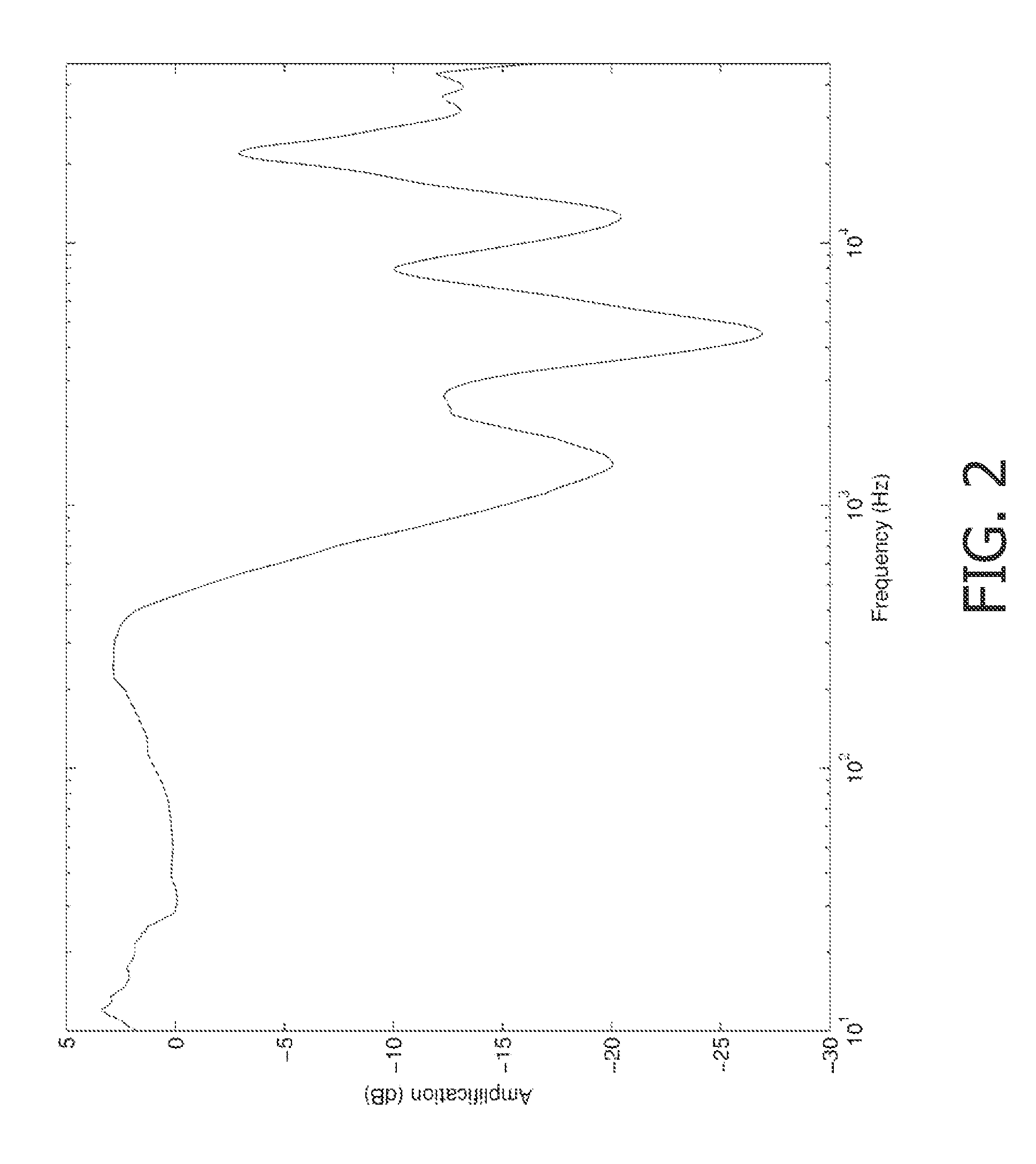
Active audio noise cancelling
ActiveUS20110249826A1Good compensationImprove performanceEar treatmentSpeech analysisTransducerEngineering
A noise canceling system comprises a microphone (103) generating a captured signal and a sound transducer (101) radiating a sound canceling audio signal in the audio environment. A feedback path (109) from the microphone (103) to the sound transducer (101) comprises a non-adaptive canceling filter (115) and a variable gain (117) and receives the captured signal and generates a drive signal for the sound transducer (101). A gain detector determines a secondary path gain for at least part of a secondary path of a feedback loop. The secondary path may include the microphone (103), the sound transducer (101), and the acoustic path therebetween but does not include the non-adaptive canceling filter (115) or the variable gain (117). A gain controller (121) adjusts the gain of the variable gain (117) in response to the secondary path gain. The system uses simple gain estimation and control to efficiently compensate for variations in the secondary path to provide improved stability and noise canceling performance.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
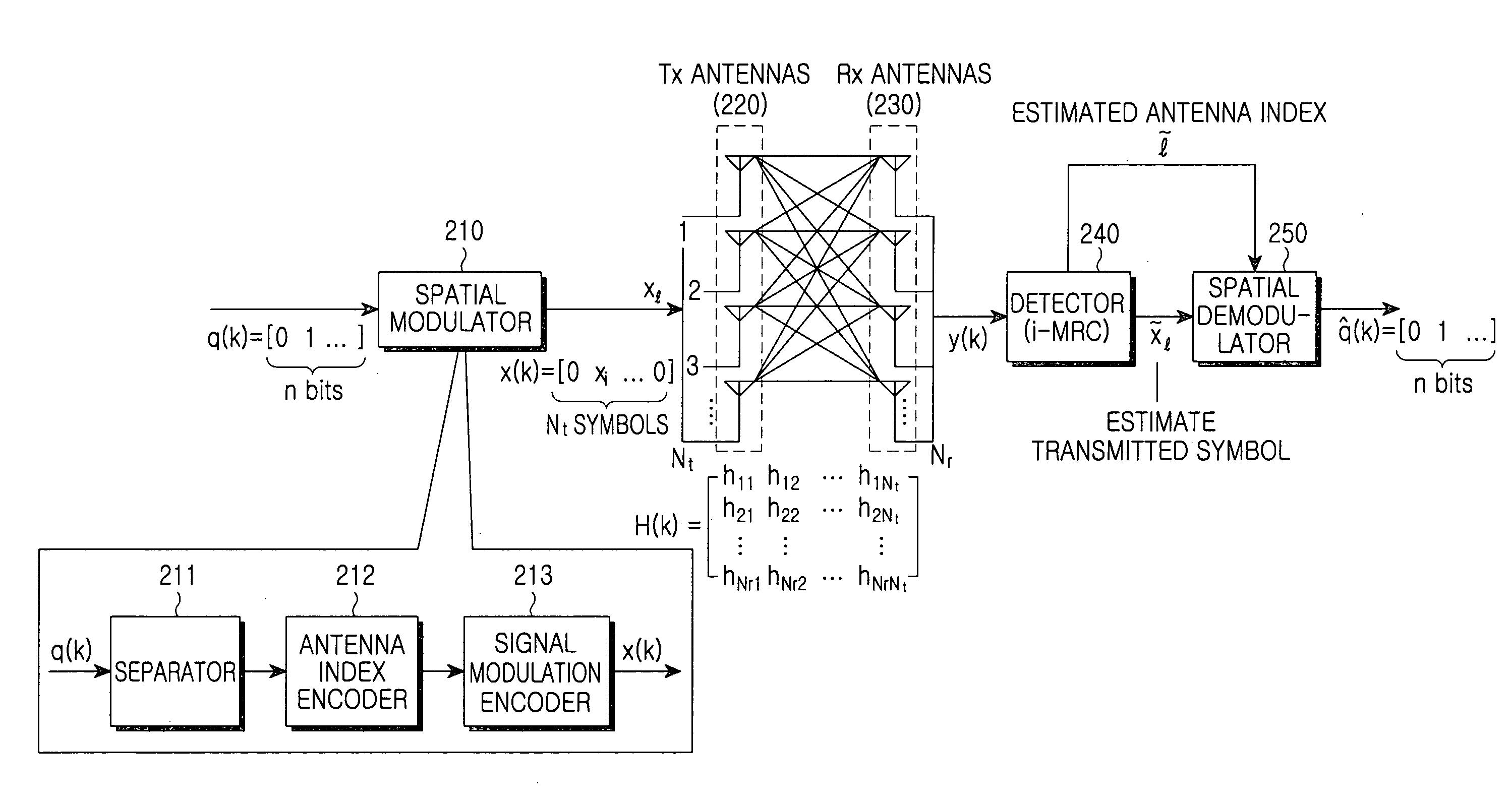
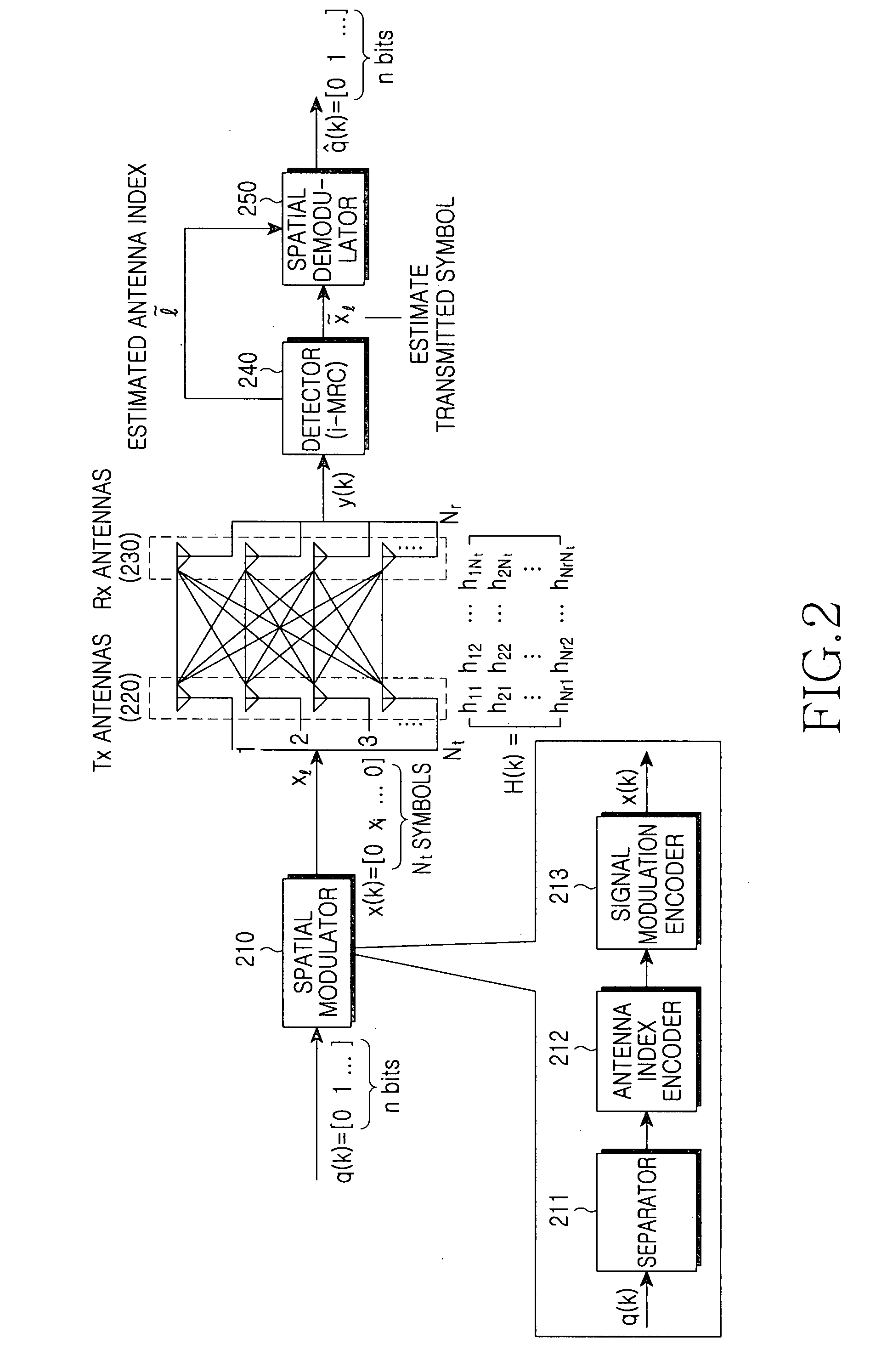
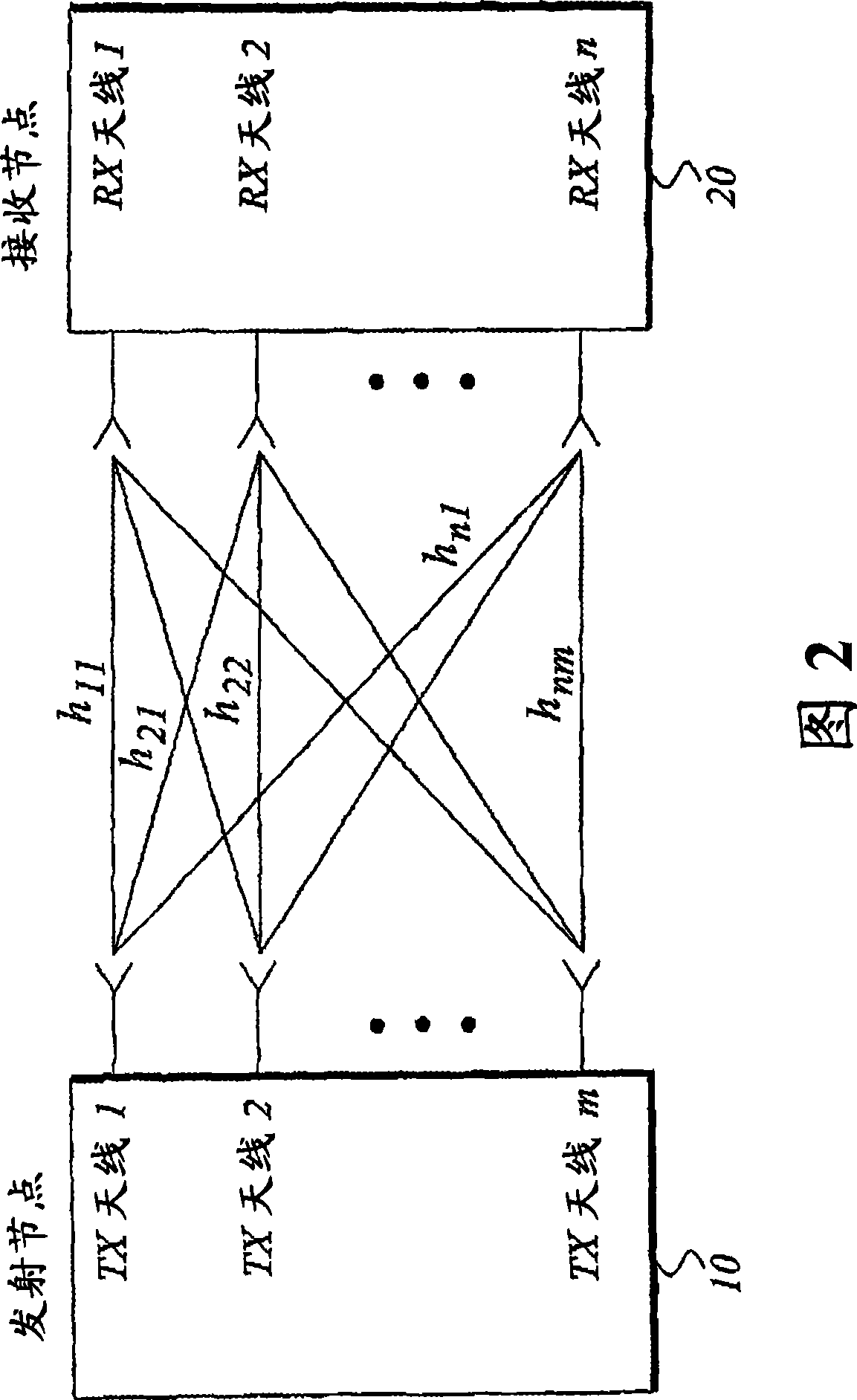
Spatial modulation method and transmitting and receiving apparatuses using the same in a multiple input multiple output system
ActiveUS20080037673A1Eliminate needImprove transmission efficiencyDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationMultiple inputSignal modulation
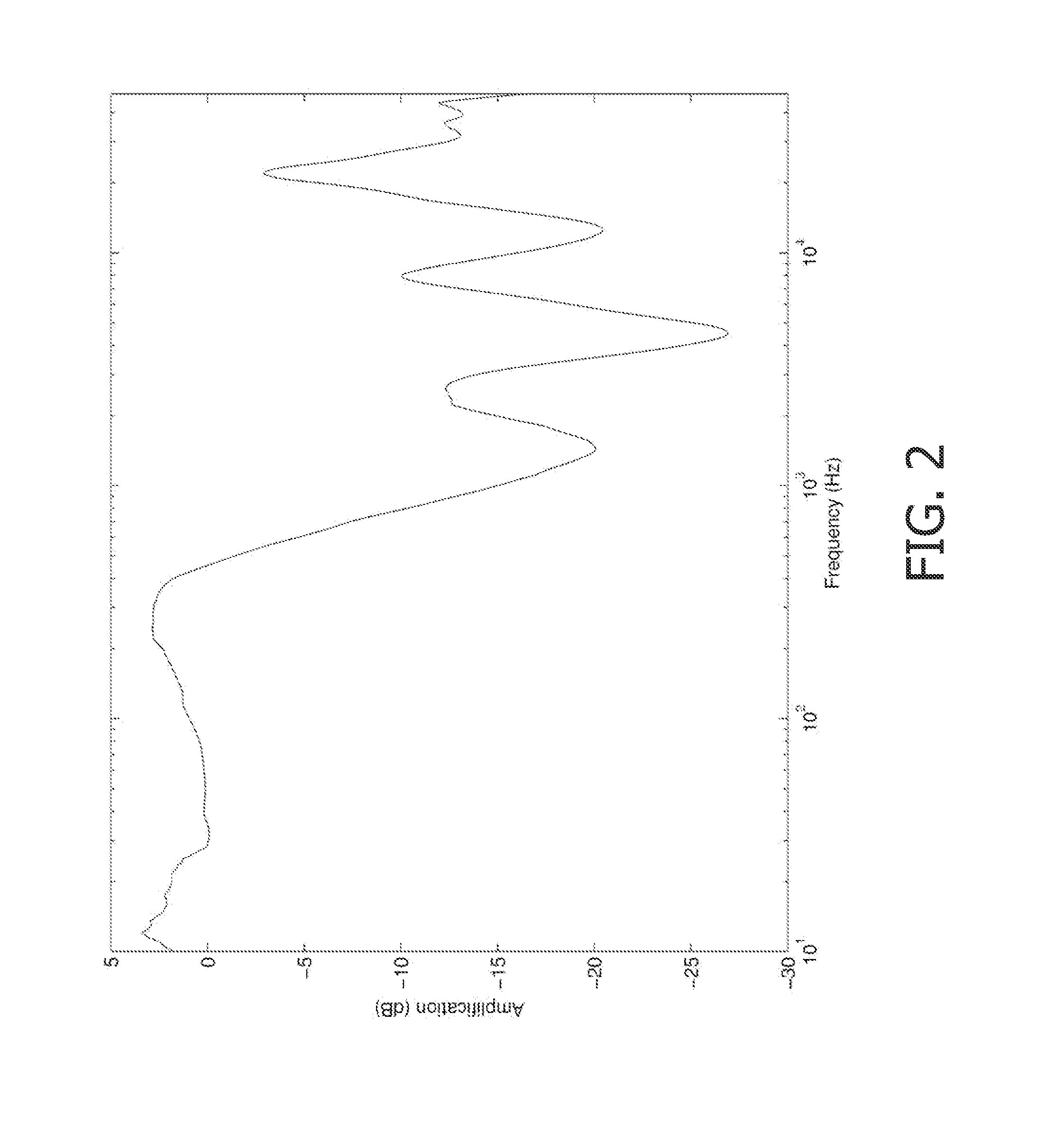
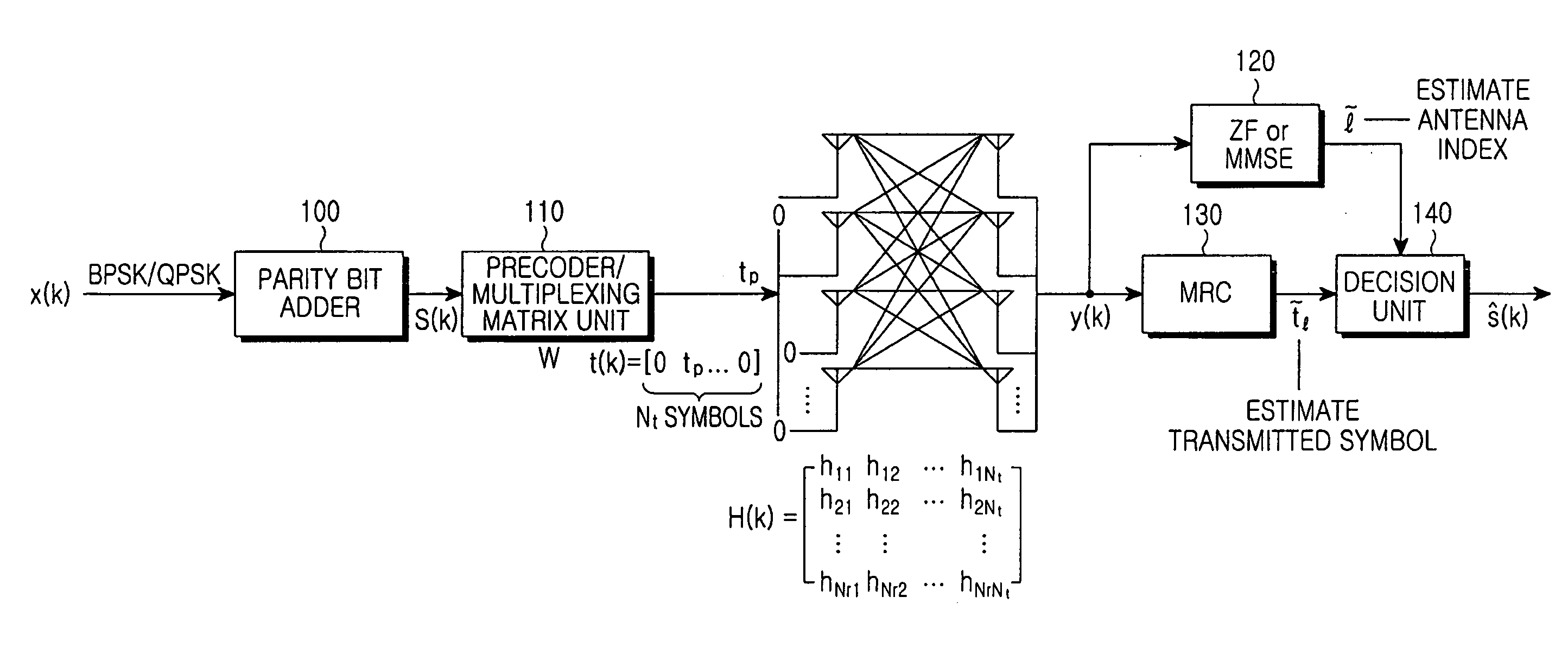
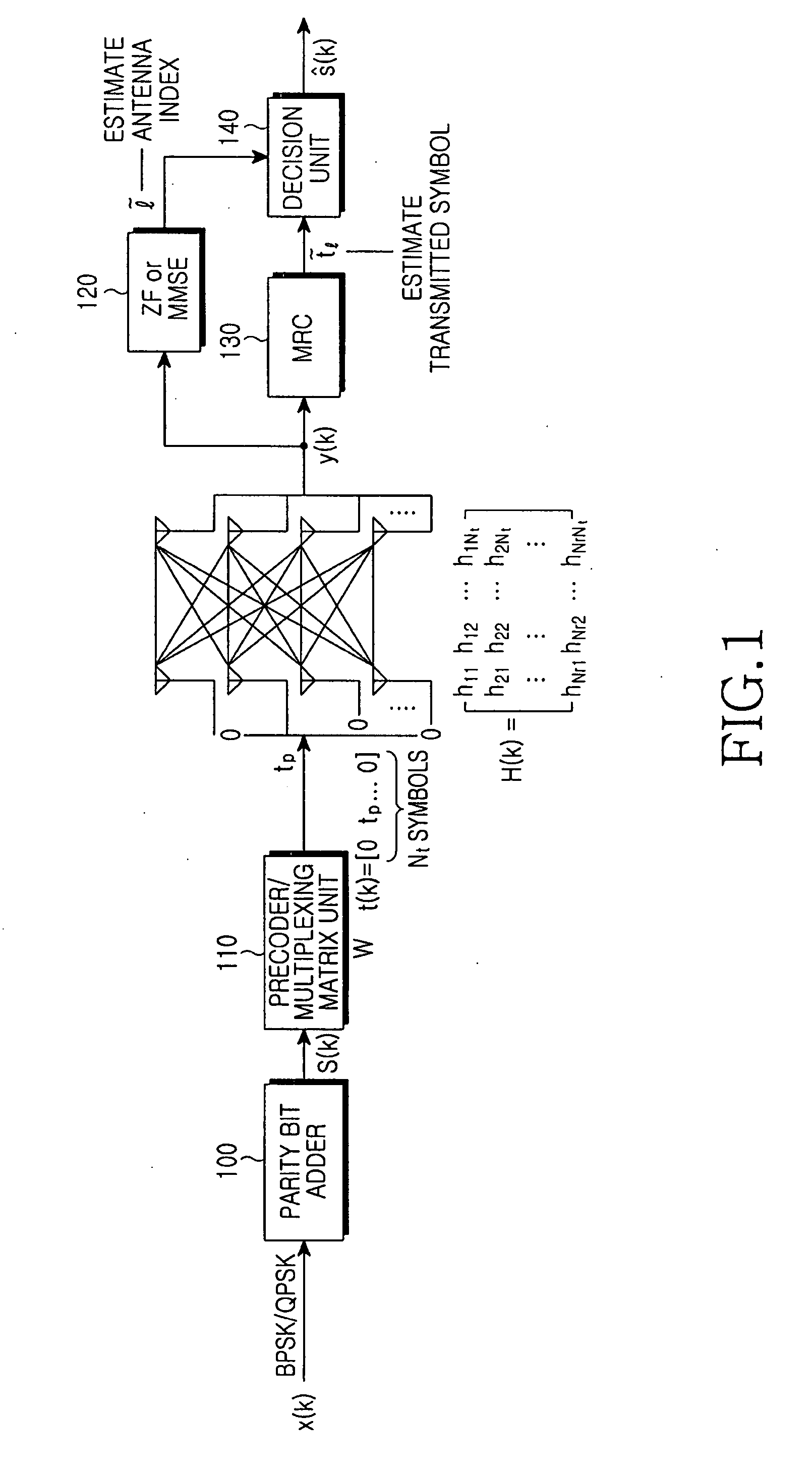
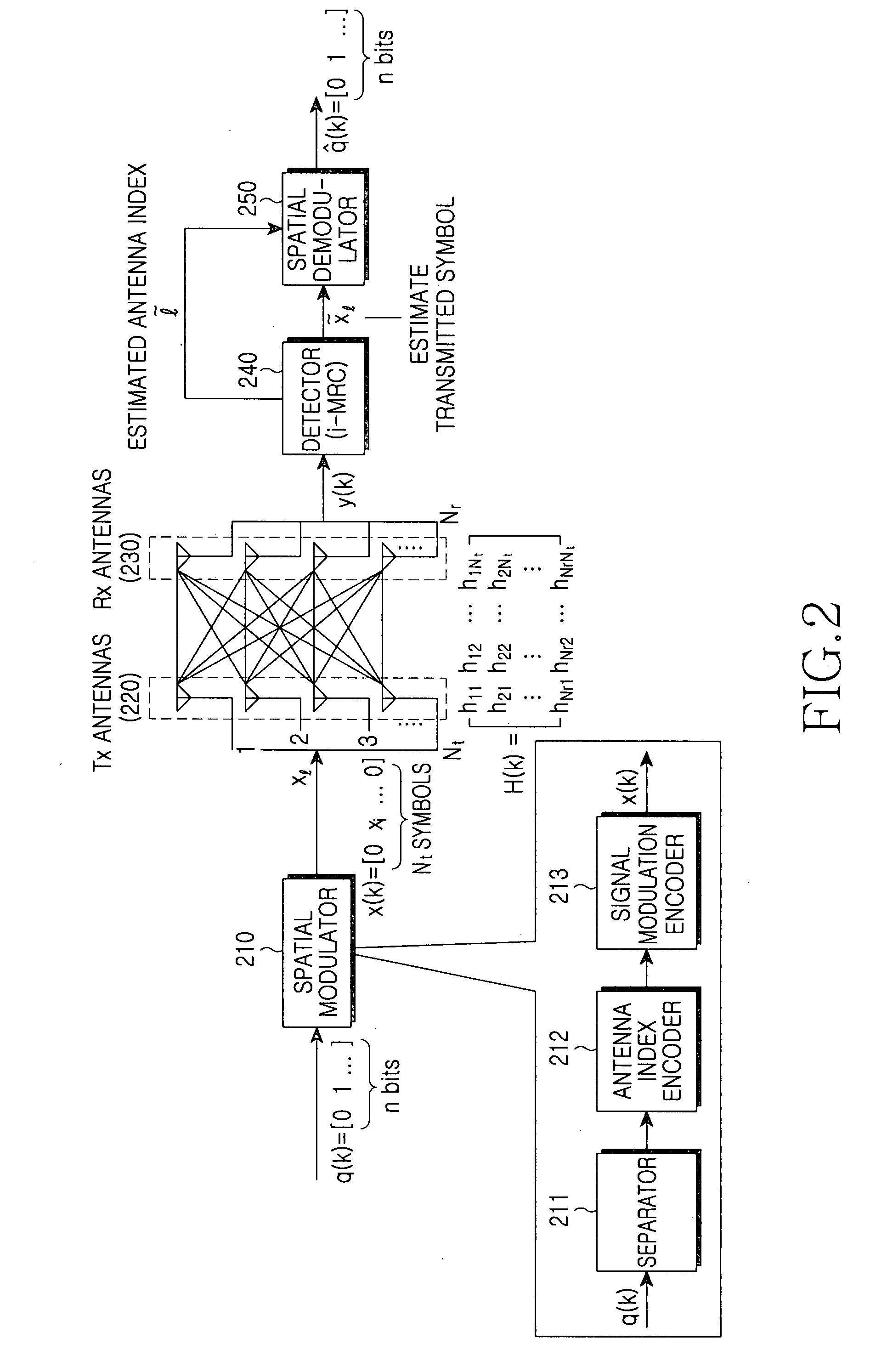
A spatial modulation method and transmitting and receiving apparatuses using the spatial modulation method in a MIMO system are provided. The spatial modulation method uses an index of an activated antenna and a signal modulation constellation as an information source. The spatial modulation method is applied to the transmitting apparatus. The receiving apparatus uses a spatial modulation detection method in which a channel path gain is repeatedly multiplied to detect the spatially modulated signal efficiently.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
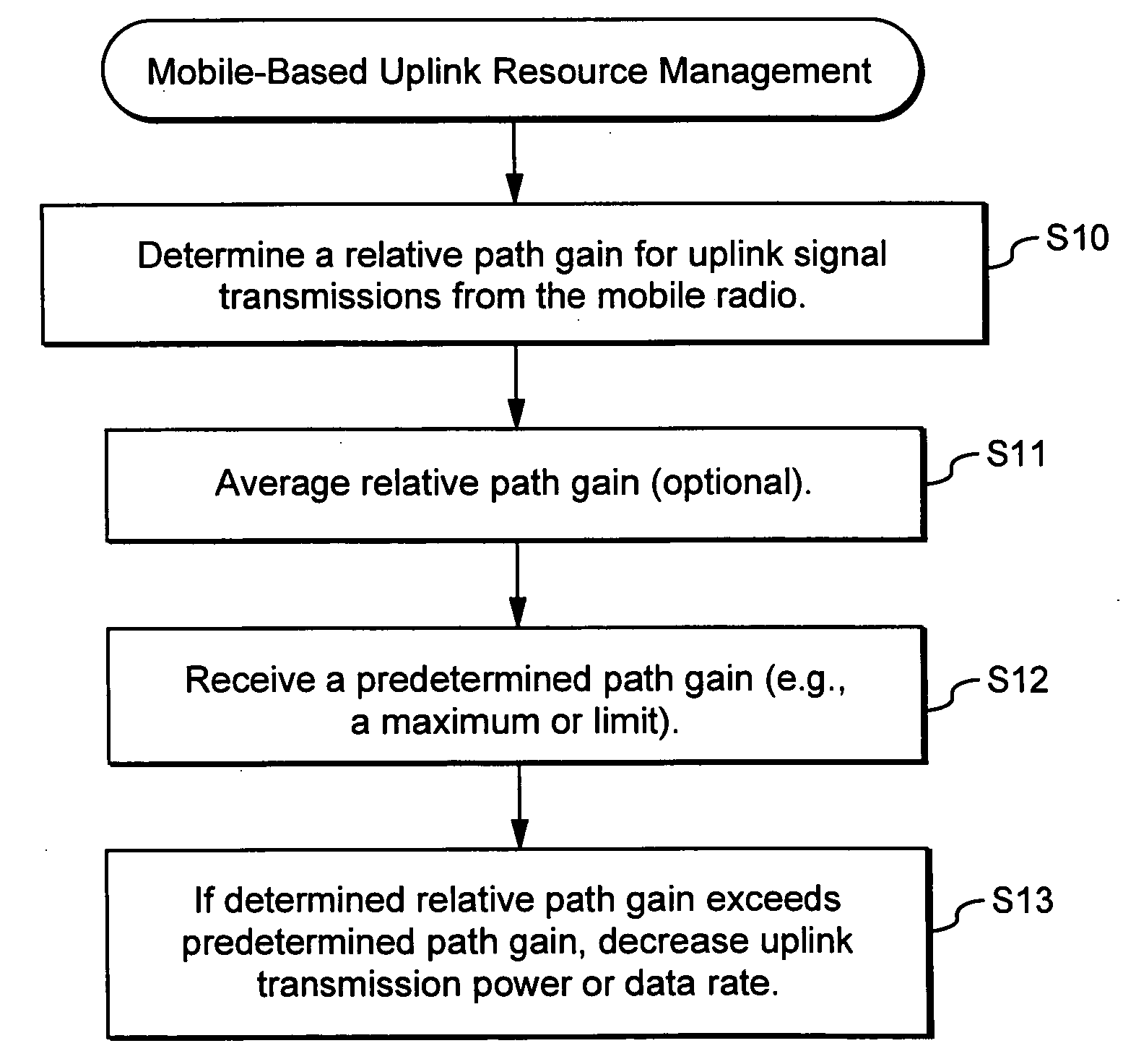
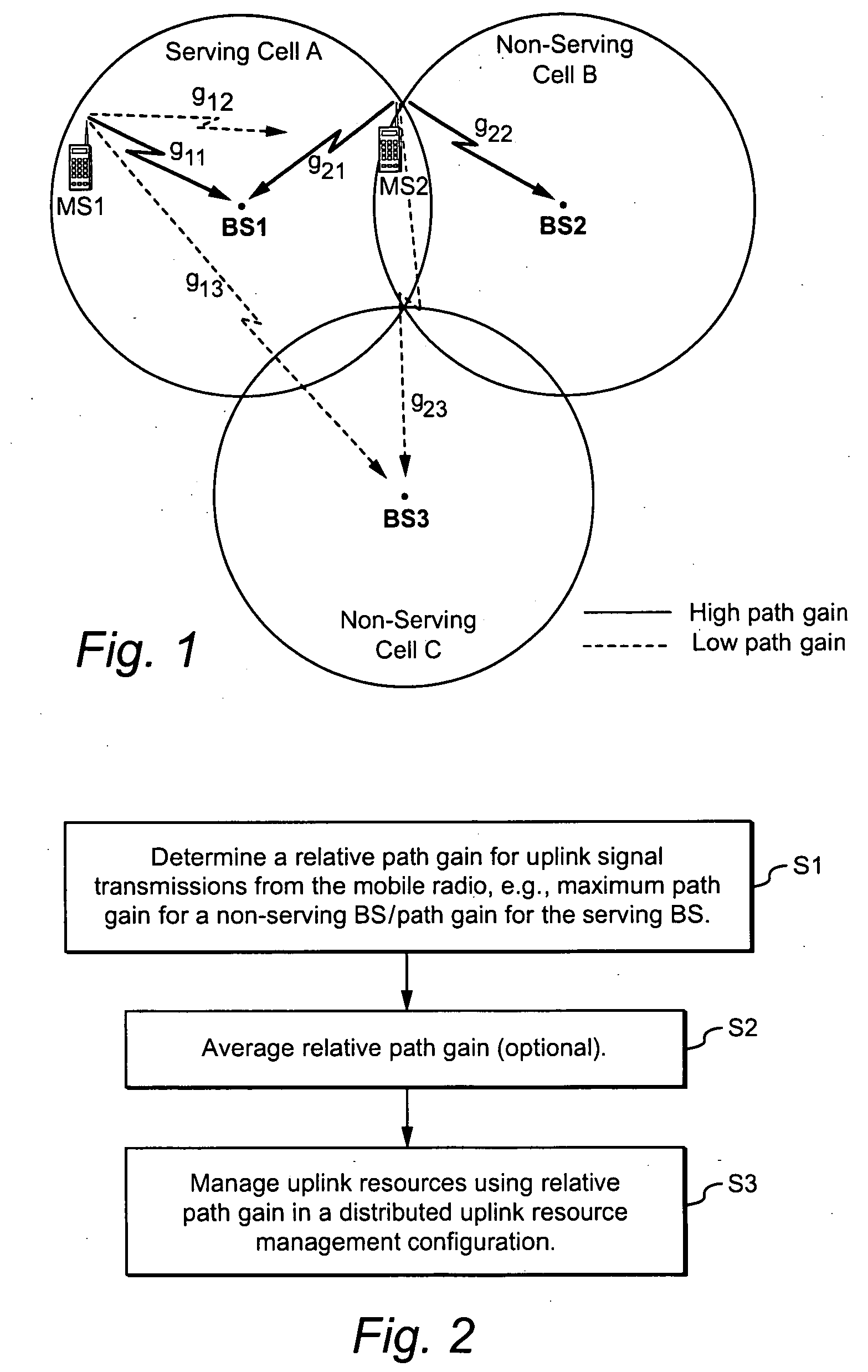
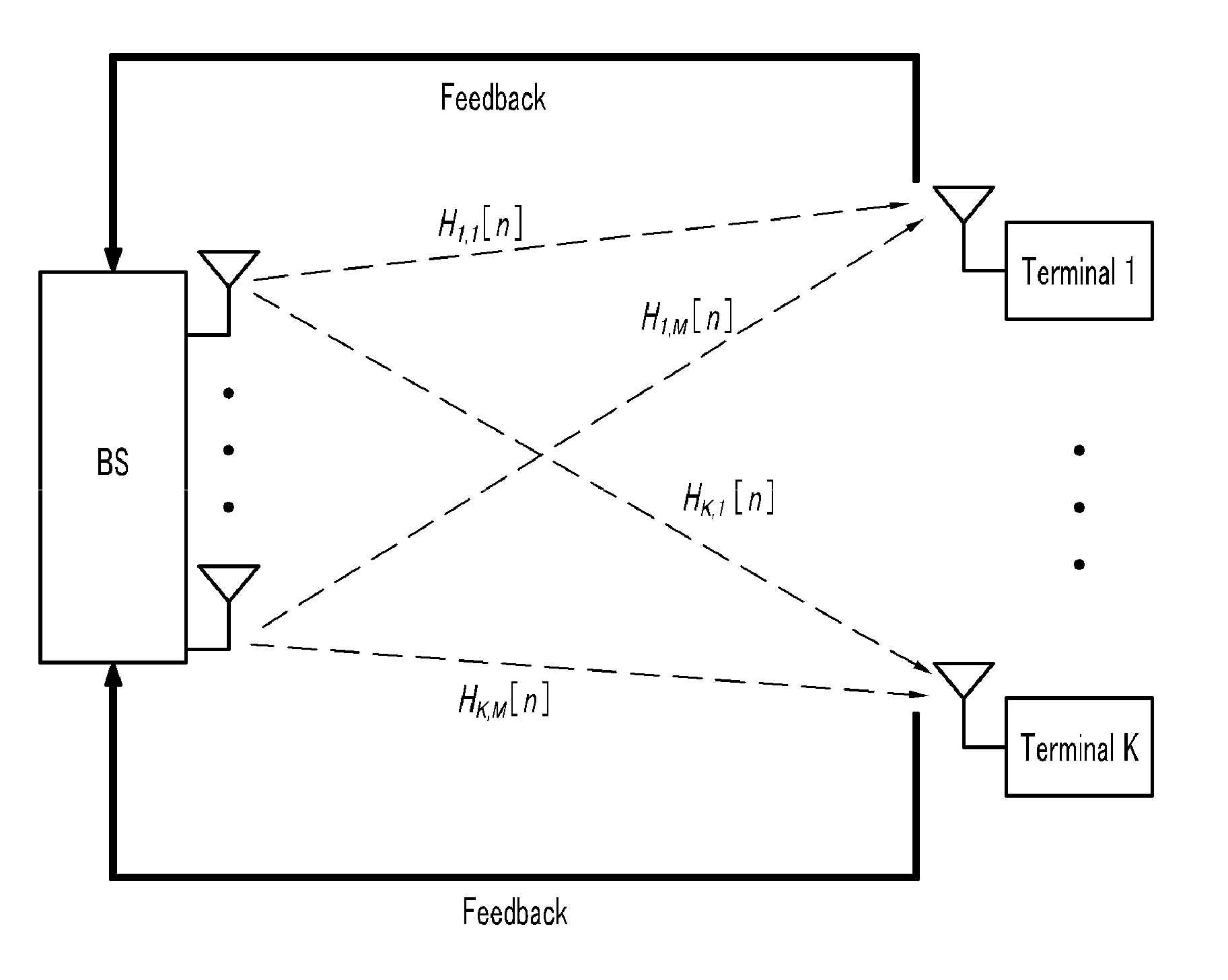
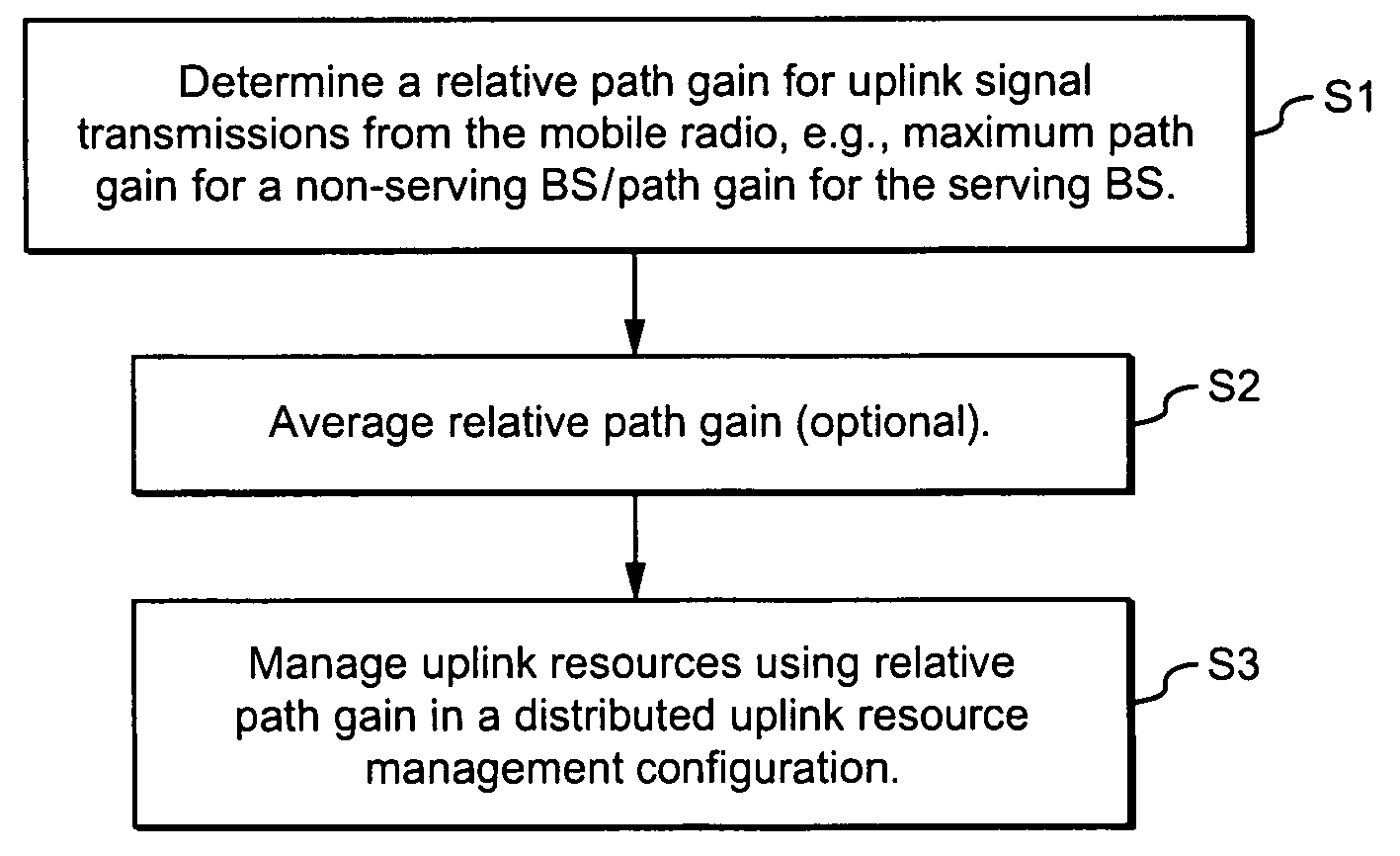
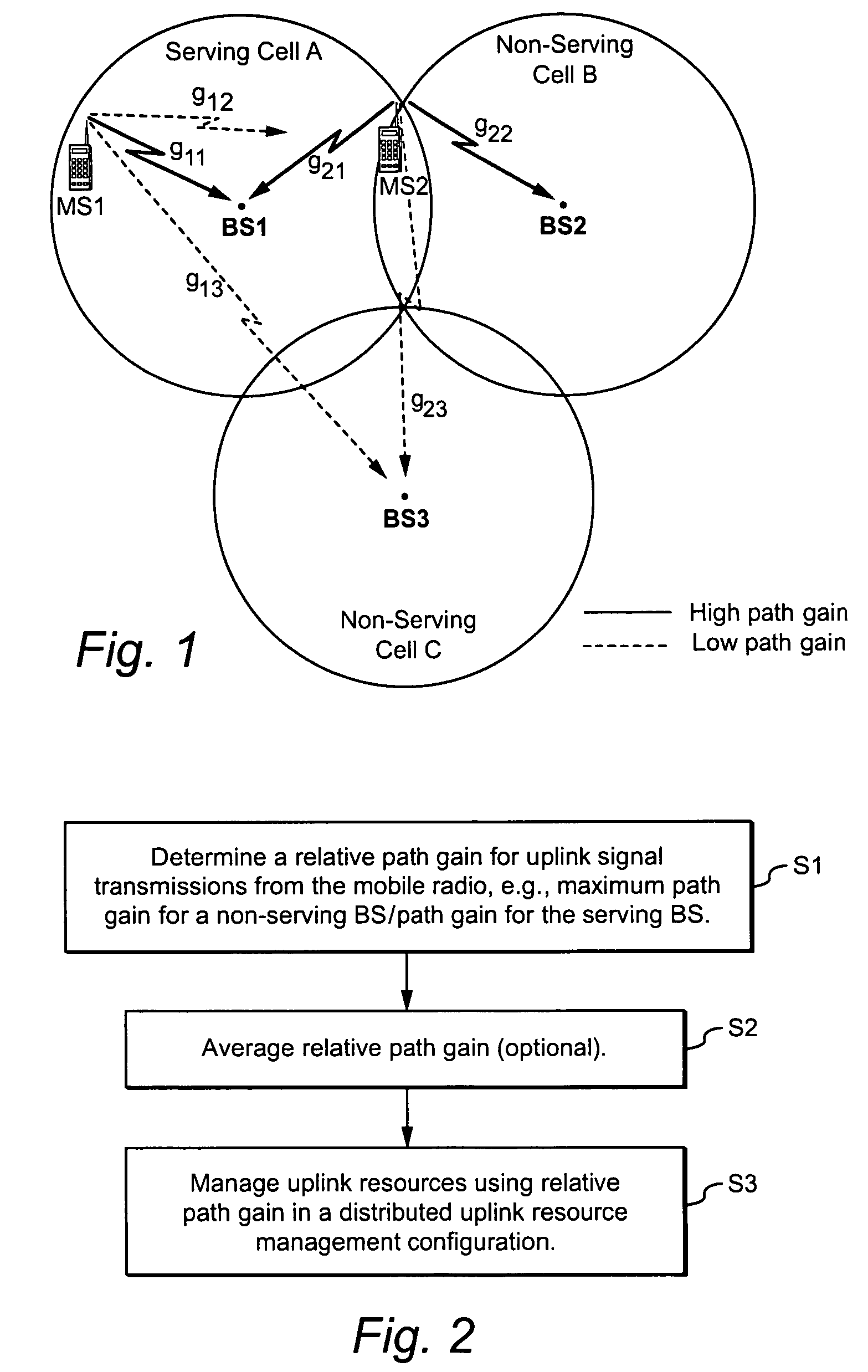
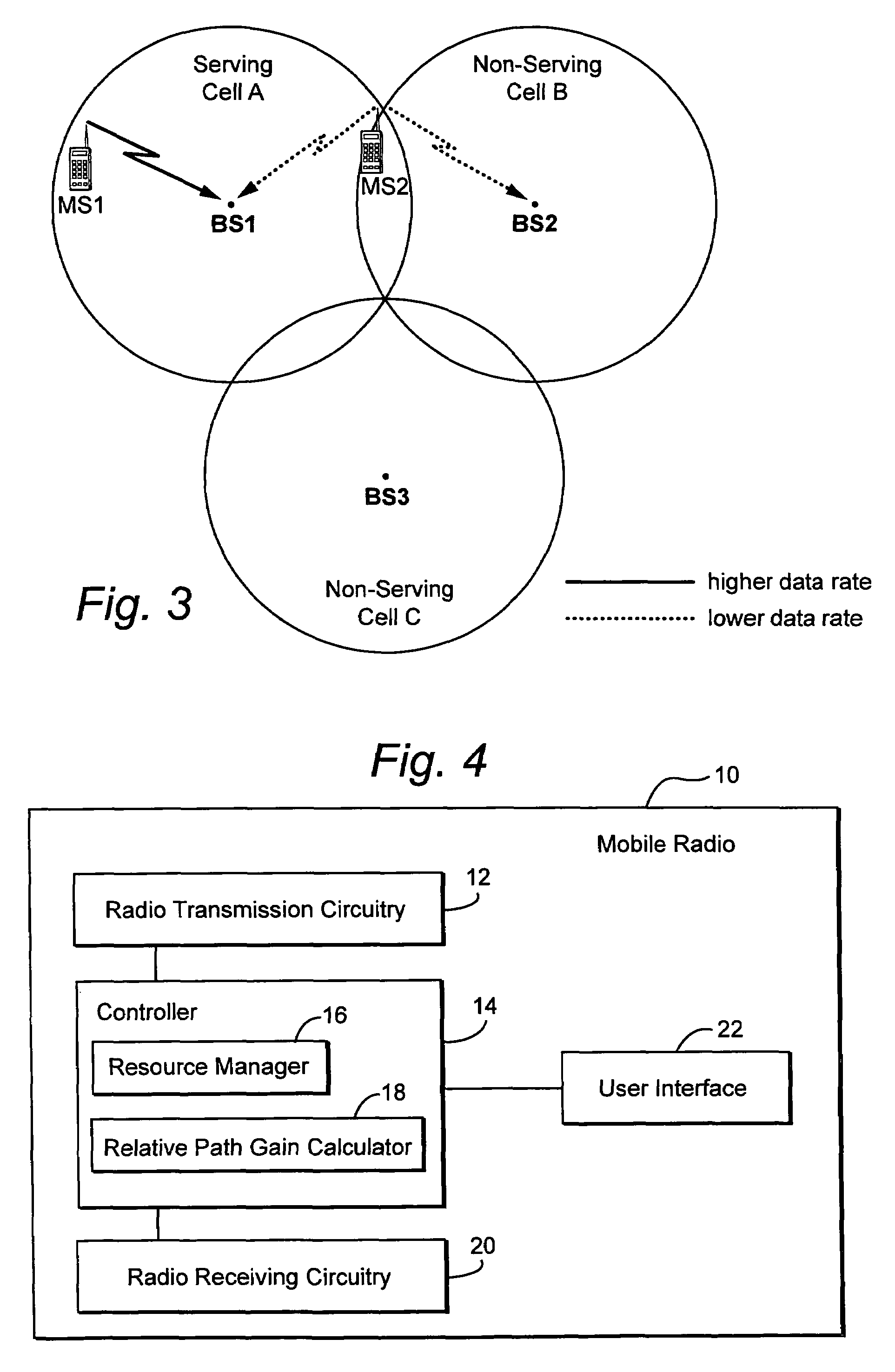
Using uplink relative path gain related measurements to support uplink resource management
ActiveUS20060194546A1Reduce adverse effectsImprove uplink resource managementPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementResource managementMobile station
A cellular system includes a first cell associated with a first base station, a second cell associated with a second base station, and a mobile radio currently served by the first base station. Distributed resource control may be used in which the first base station alone or in combination with the mobile station makes resource management decisions without having to involve a central controller. In ad-hoc networking, access points can manage resources in a distributed fashion. Relative path gain is determined for an uplink signal from the mobile radio. Relative path gain is based on a comparison of a first path gain related quantity for a mobile uplink signal to the second base station with a second path gain related quantity for the mobile uplink signal to the second base station. Uplink resources in the first cell are managed based on the relative path gain related quantity.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
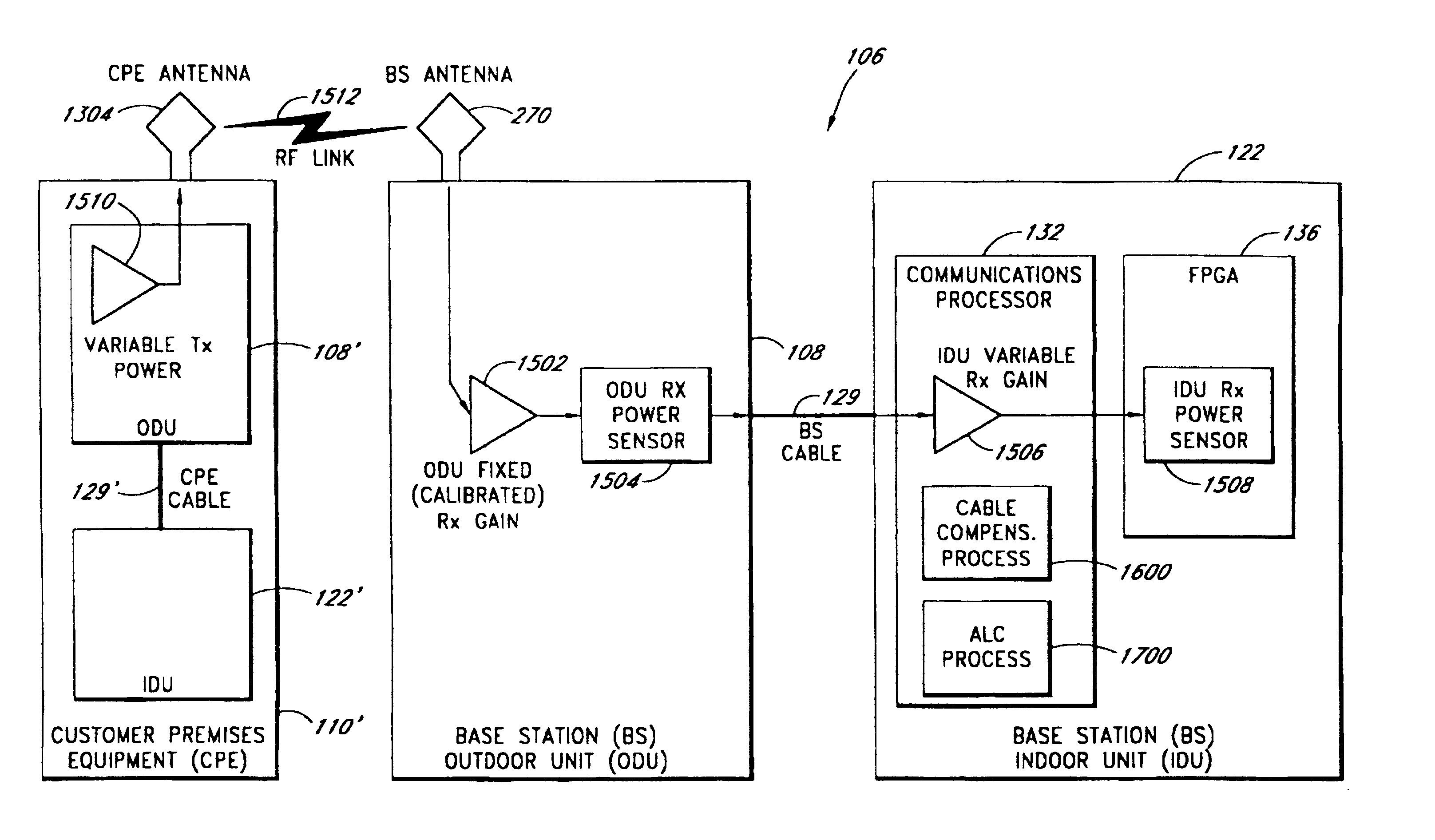
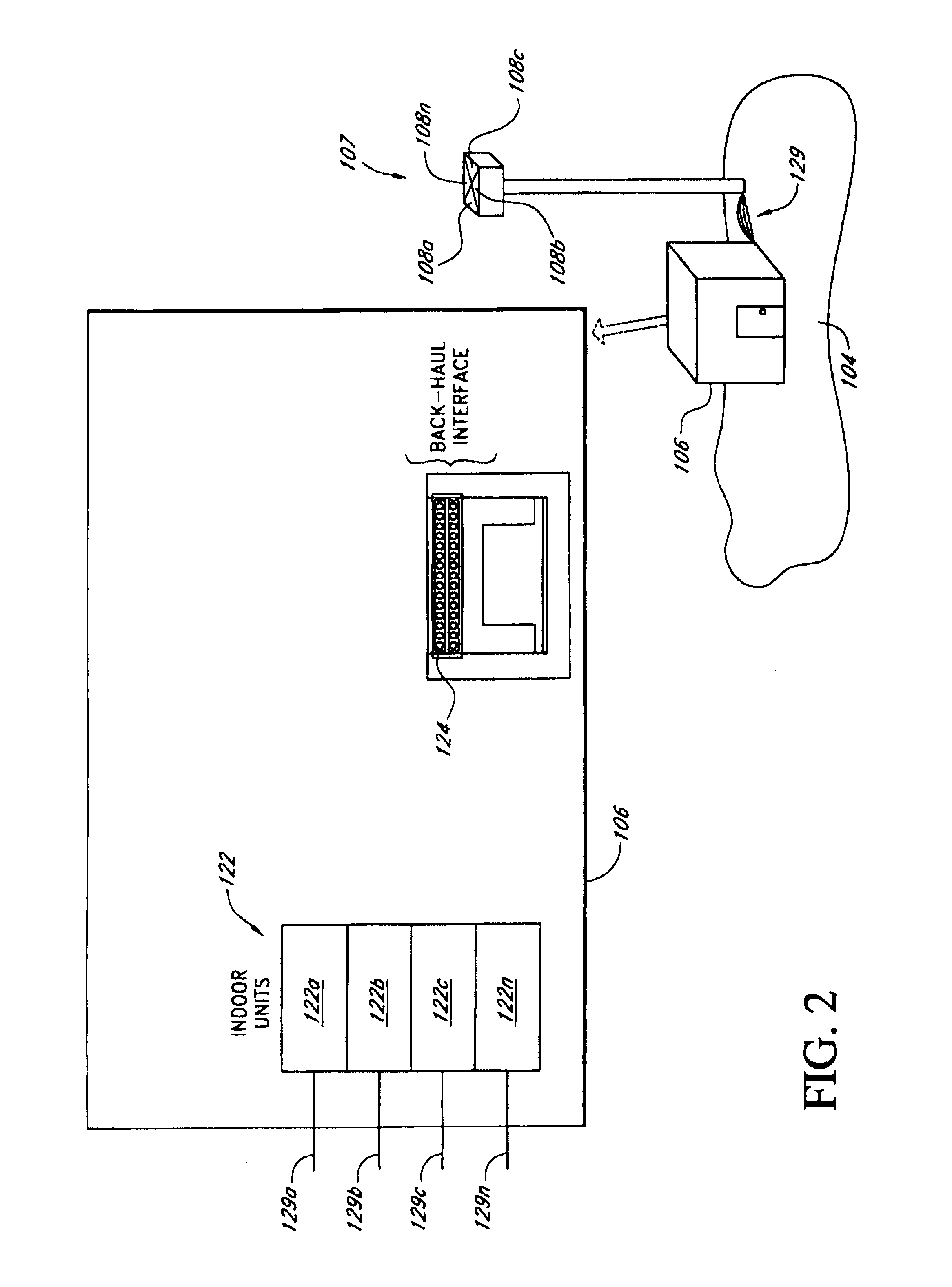
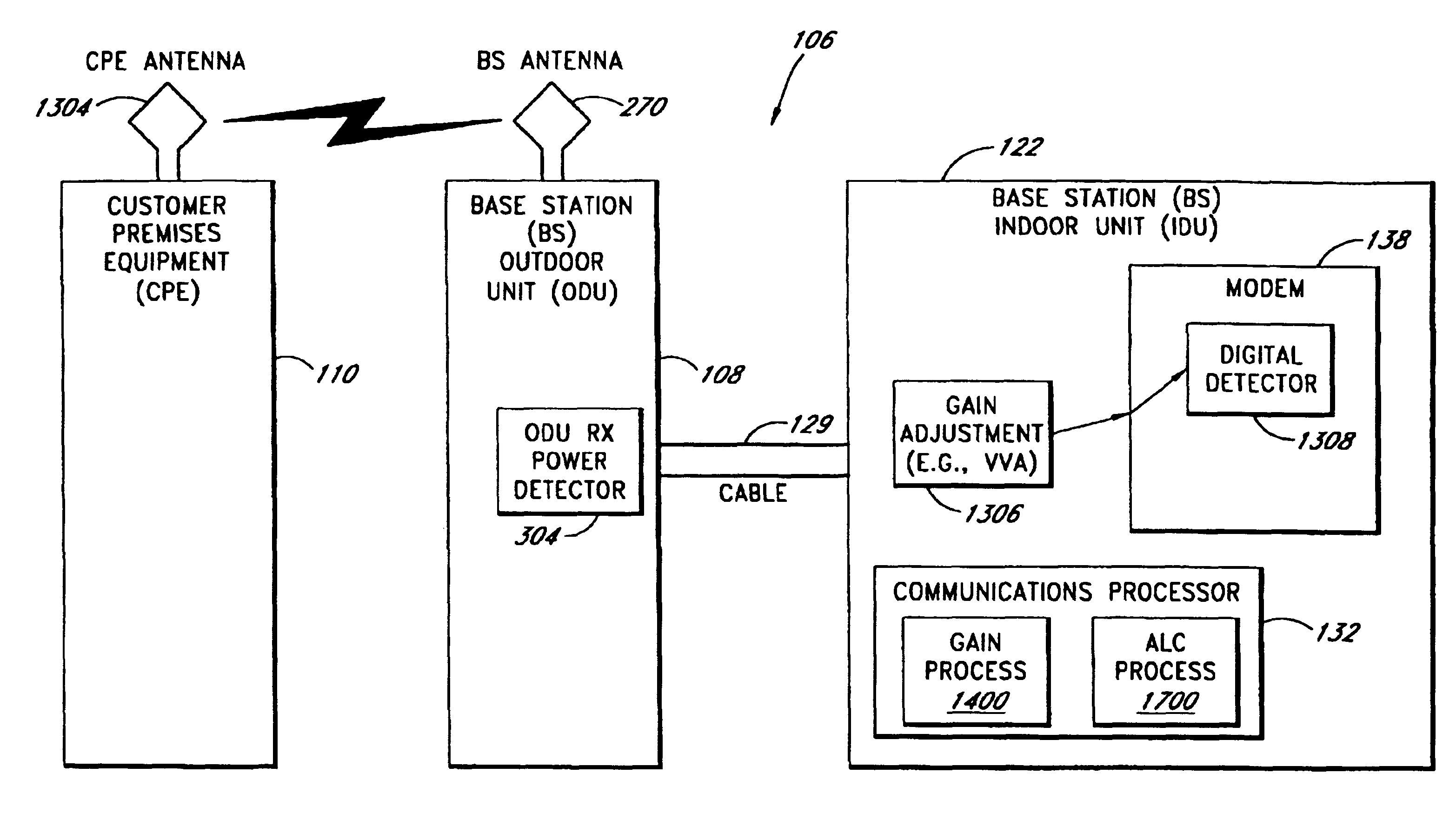
System and method of automatically calibrating the gain for a distributed wireless communication system
InactiveUSRE41655E1Increase receive path gainPower managementTransmission control/equalisingCable transmissionCommunications system
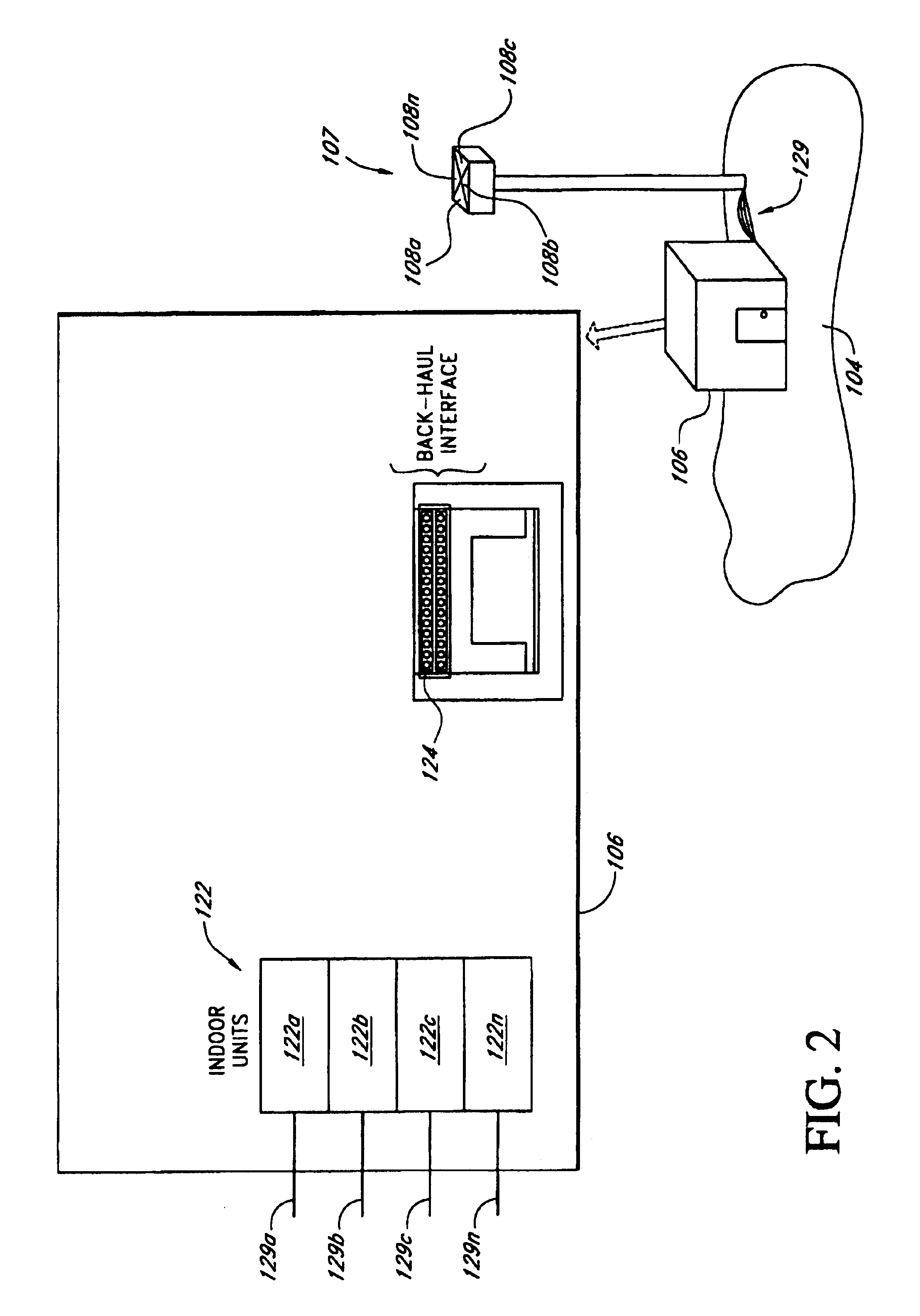
A system and method providing a wireless broadband connection between base stations and customer sites. The system includes indoor units, within the base stations and customer sites, that communicate across cables to outdoor units. The indoor units link to routers, switches and other devices and services. The outdoor units transmit and receive wireless data and send it to the indoor units. The indoor units control the functioning of the outdoor units by transmitting digital messages along the interface cables. The outdoor units report various detector values to the indoor units, which allows the indoor units to tune and adjust several functions within the outdoor units. Several embodiments for automatically calibrating the receive path gain in the base stations to compensate for the base station cable between the indoor unit and outdoor unit are described. In addition, anAn improved transmit power control technique which is not affected by modulation type, is also described.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES FUND 83 LLC
Method and system for integrated link adaptation and power control to improve error and throughput performance in wireless packet networks
InactiveUS7502340B1Improve throughputPower managementMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsKaiman filterComputer terminal
The invention provides a system that implements an algorithm for integrated link adaptation and power control to achieve specified error rates and to improve an overall throughput for real-time applications in wireless packet networks. The system initially divides wireless terminals into groups according to their signal path gains. Afterwards, the system can periodically adapt transmissions (i.e., link adaptations) based on the required error rates, actual error statistics and average transmission power for each wireless terminal group. Furthermore, transmission power can be adjusted by an enhanced Kalman-filter method to ensure successful reception.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
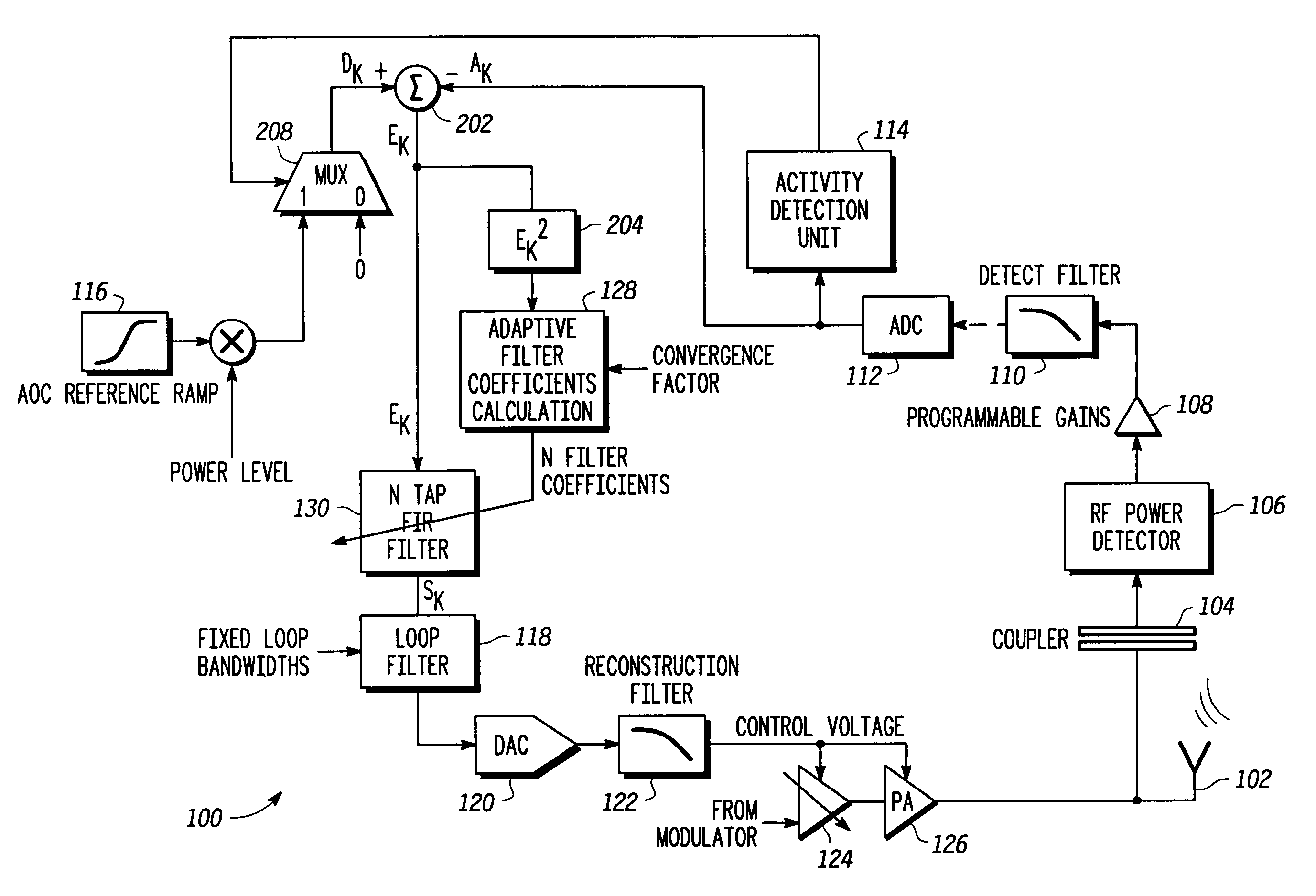
Adaptive transmit power control system
InactiveUS20050122166A1Resonant long antennasTransmission systemsDigital signal processingPower control system
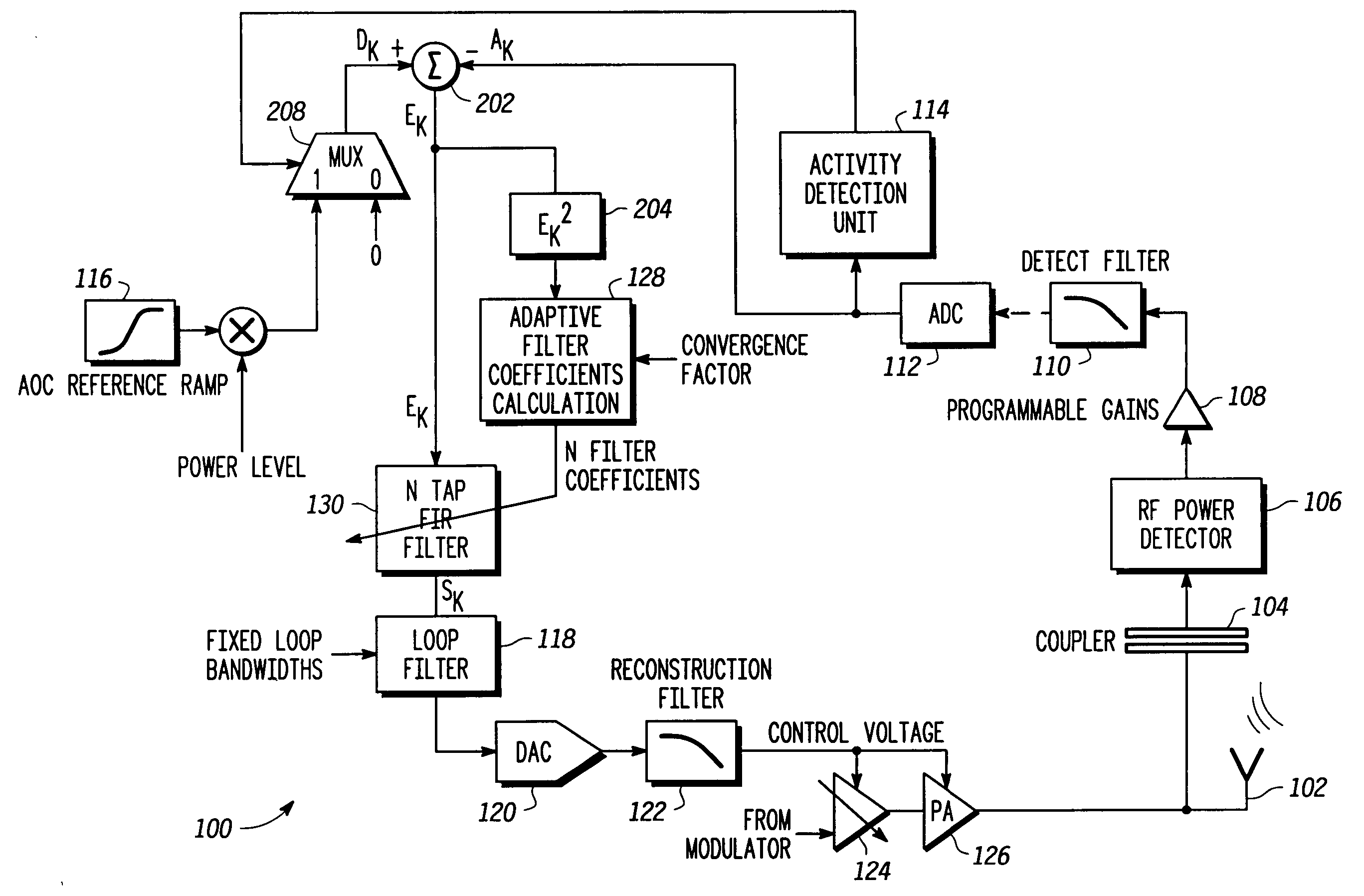
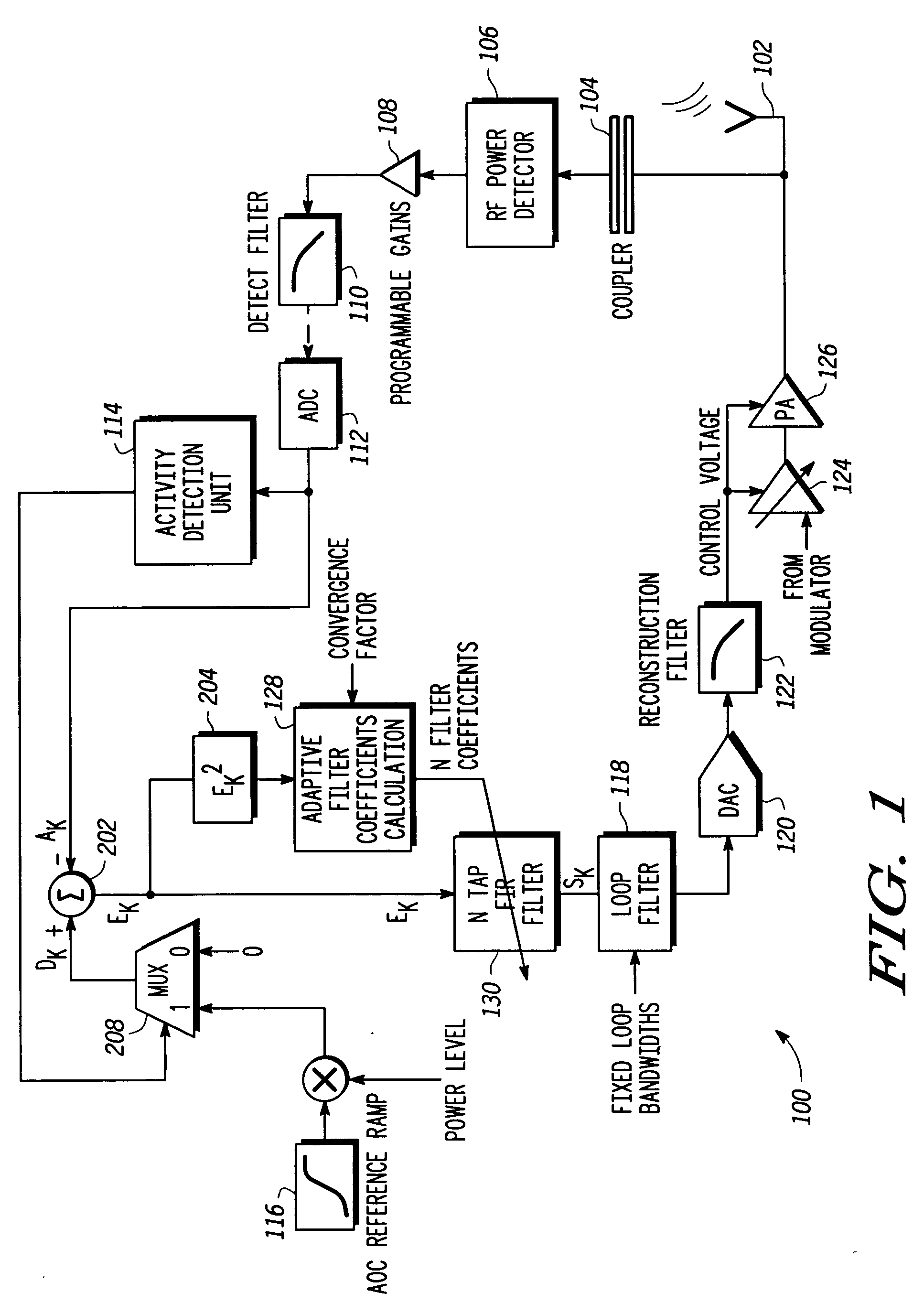
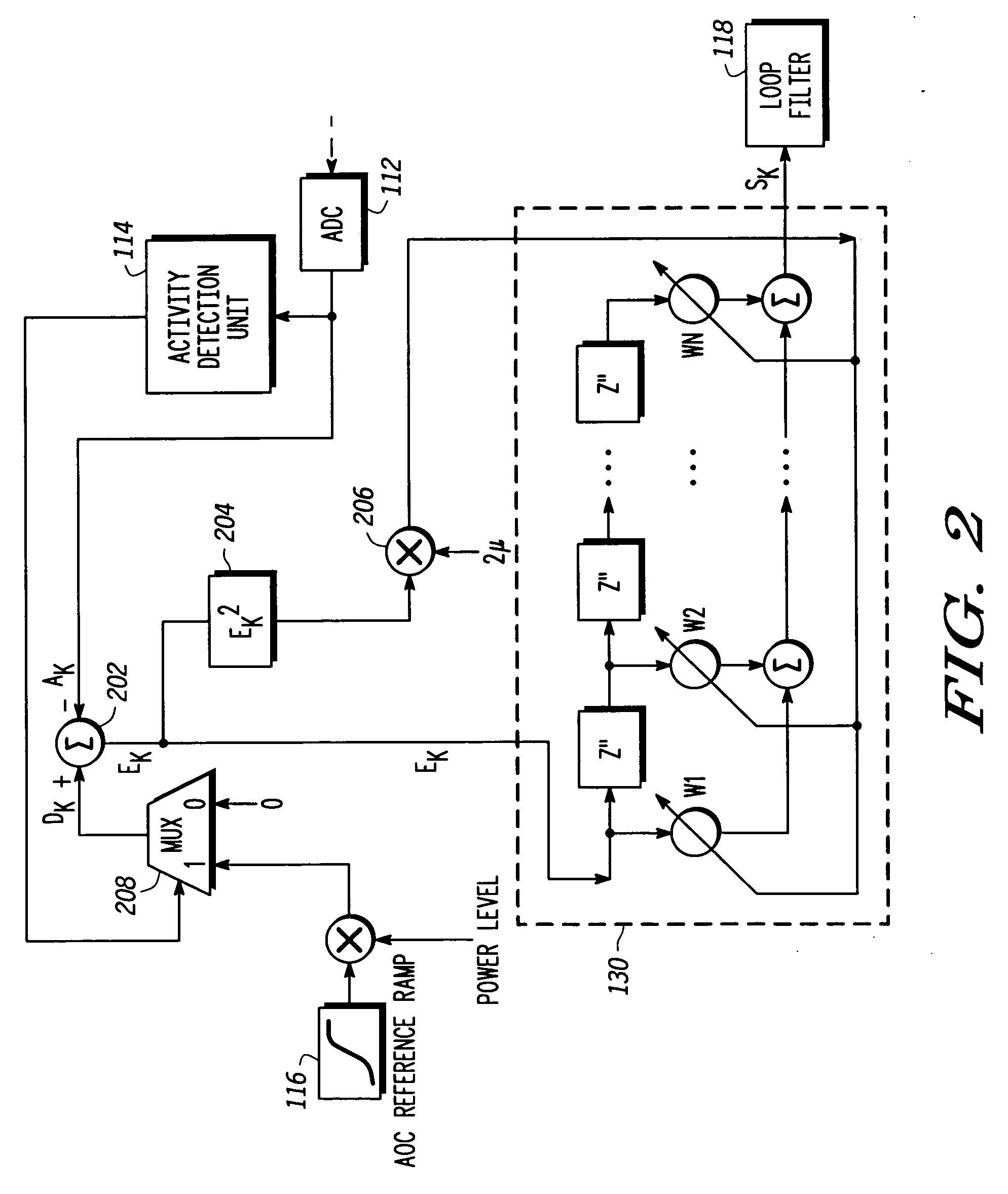
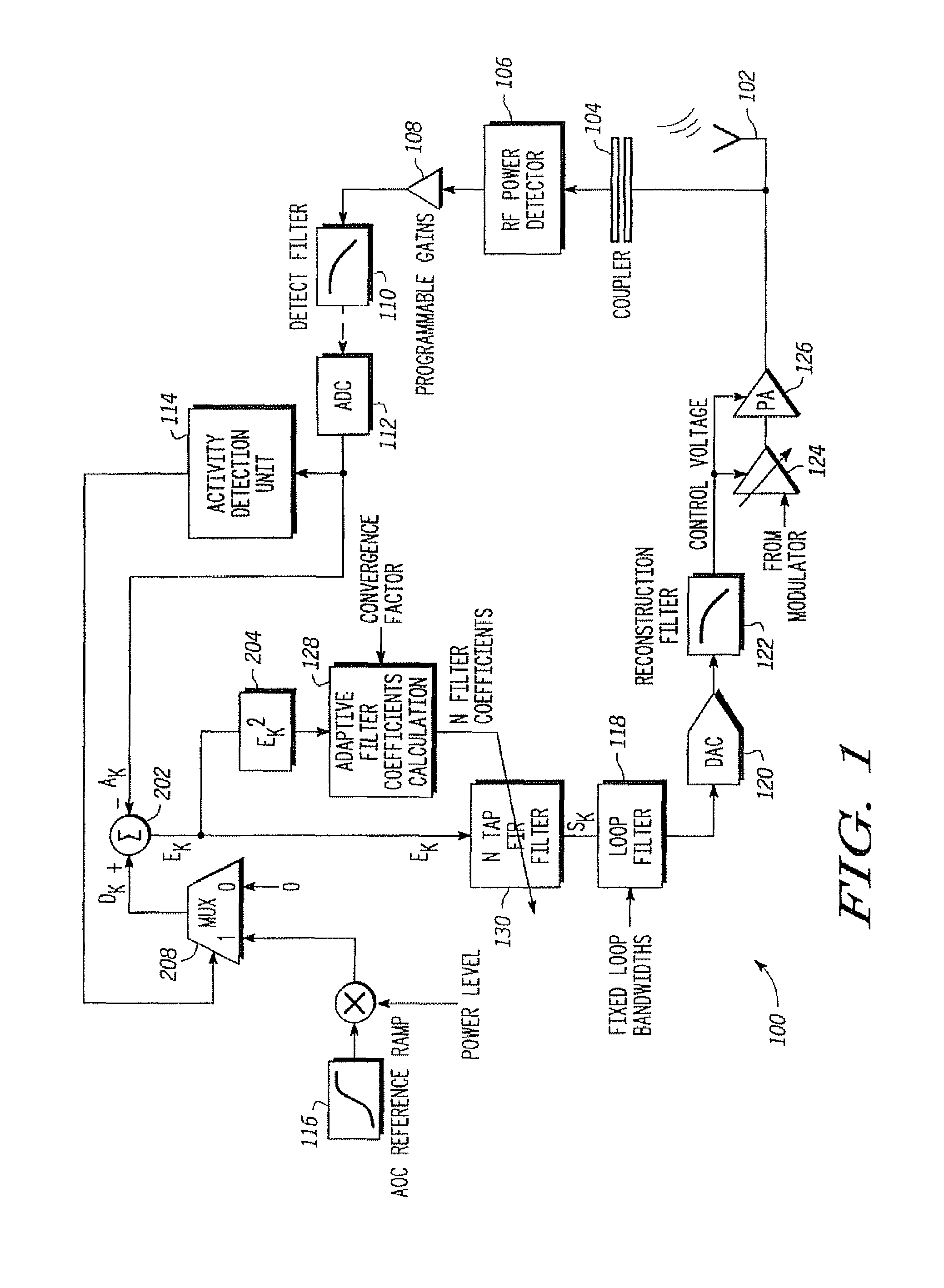
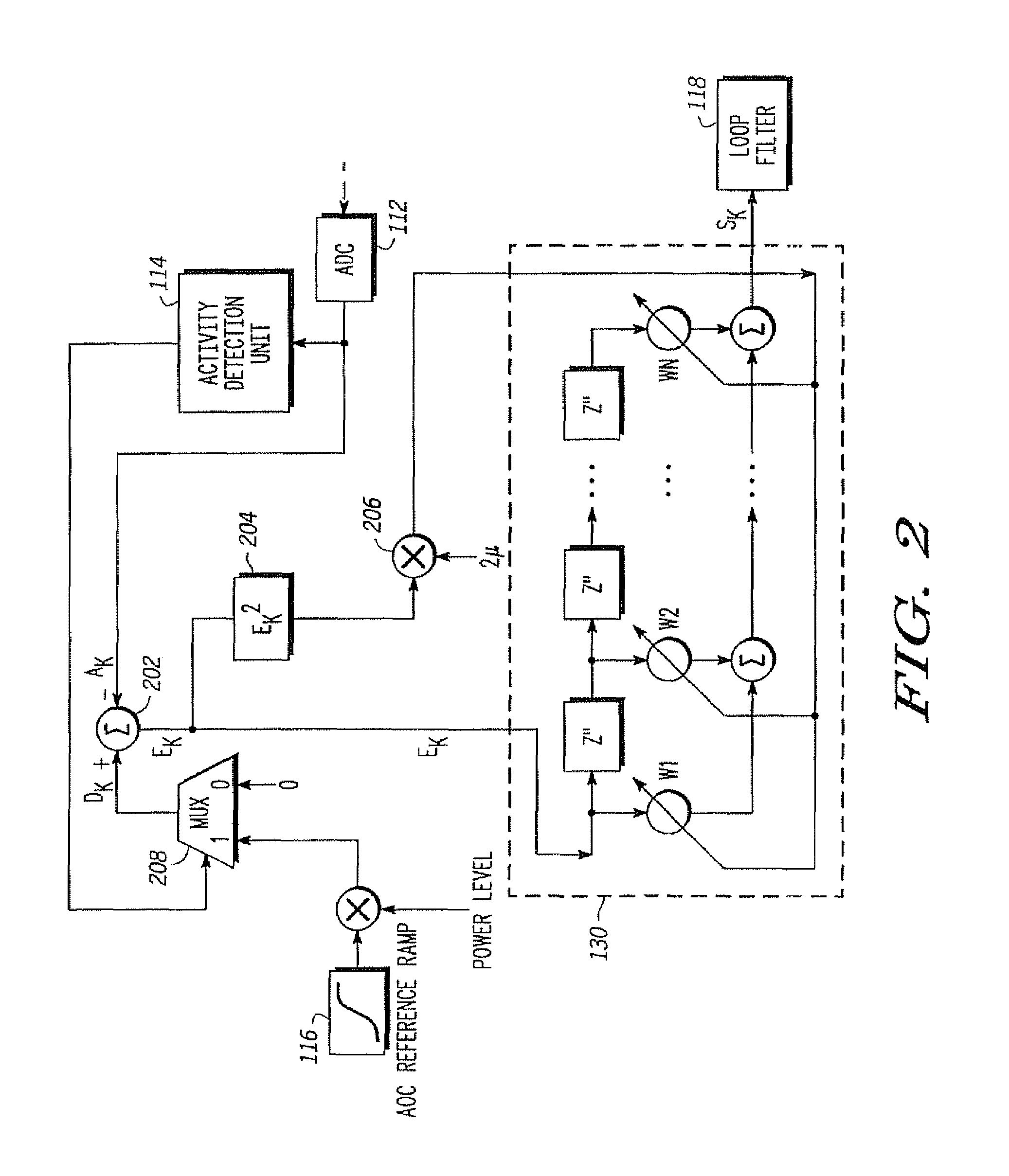
An adaptive closed loop transmit power control system which does not require extensive factory calibration of power control loop bandwidths and feedback detect path gain settings over the power transition ranges, frequency bands of operation, temperature, and supply voltage is disclosed. The system automatically compensates for any gain or slope variations in the analog feedforward and feedback paths to maintain system stability and meet performance specifications. The system achieves this by using an adaptive digital signal processing (DSP) system architecture within the feedback path of this closed loop power control system. The system eliminates the need for extensive factory calibration of such parameters as loop bandwidths and feedback detect path gain settings over power transition ranges, frequency bands of operation, temperature, and supply voltage.
Owner:APPLE INC
Transmission power control method for a wireless communication system
InactiveUS20080014980A1Preventing increase in average transmission powerReduce capacityPower managementEnergy efficient ICTCommunications systemControl data
Transmission power relative to a propagation path having a variation in gain is controlled to increase communication channel capacity, and a data rate is controlled in accordance with the variation of the increased communication channel capacity. In order to increase the communication channel capacity, the transmission power is determined so that the sum of noise power (=received noise power / propagation path gain) converted into one at a transmitter and the transmission power becomes constant. As a result, contrary to the background art, the transmission power is controlled to be reduced when the propagation path gain decreases and to be increased when the propagation path gain increases.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and apparatus for controlling power for uplink
ActiveUS20110141933A1Effectively reducing interference amountEfficient reductionPower managementError preventionPower parameterPower control
A method and apparatus for controlling power for uplink are provided. When a base station is moving or unable to communicate with others, at least one interference amount is estimated for a neighboring base station based on a path gain between a terminal and the neighboring base station and a transmission power of each encoding packet size and transmission format included in a candidate group related to scheduling transmission power parameters. A target interference amount is determined based on an interference amount control value and an initial target interference amount according to a processing load of a serving base station, and one interference amount is selected from estimated interference amounts based on the target interference amount. The terminal determines the transmission power based on an encoding packet size and a transmission format corresponding to the selected interference amount.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
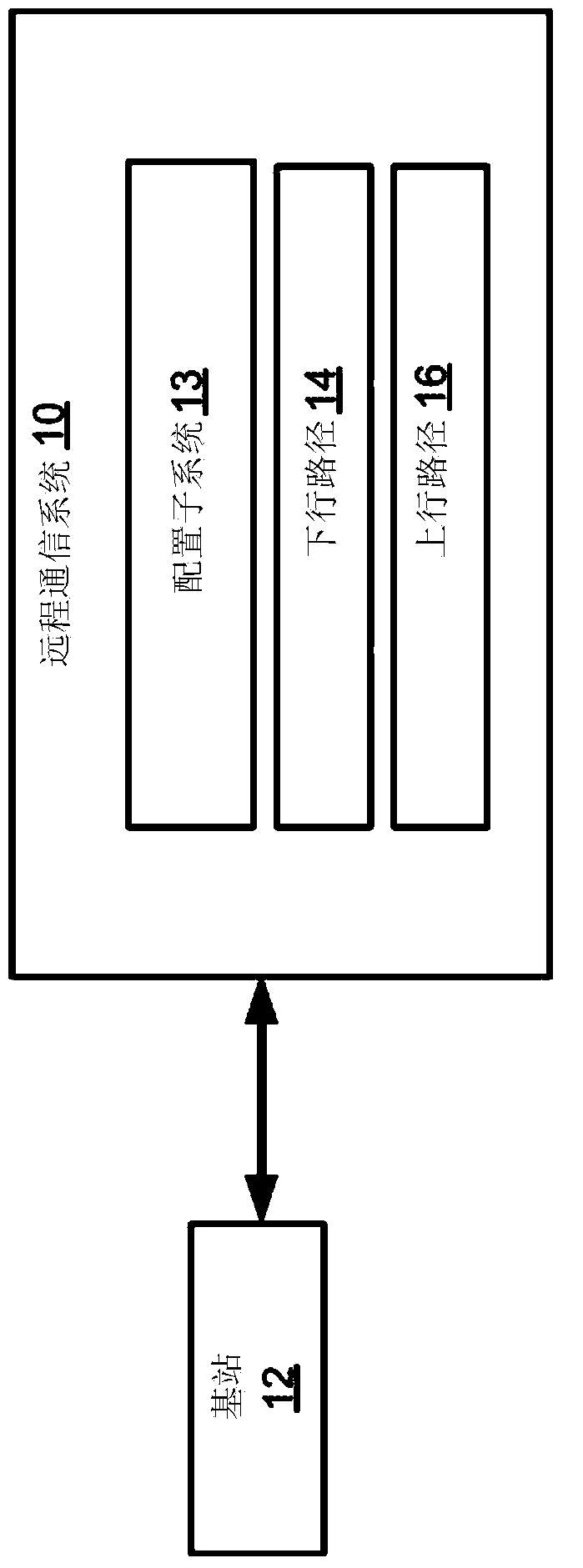
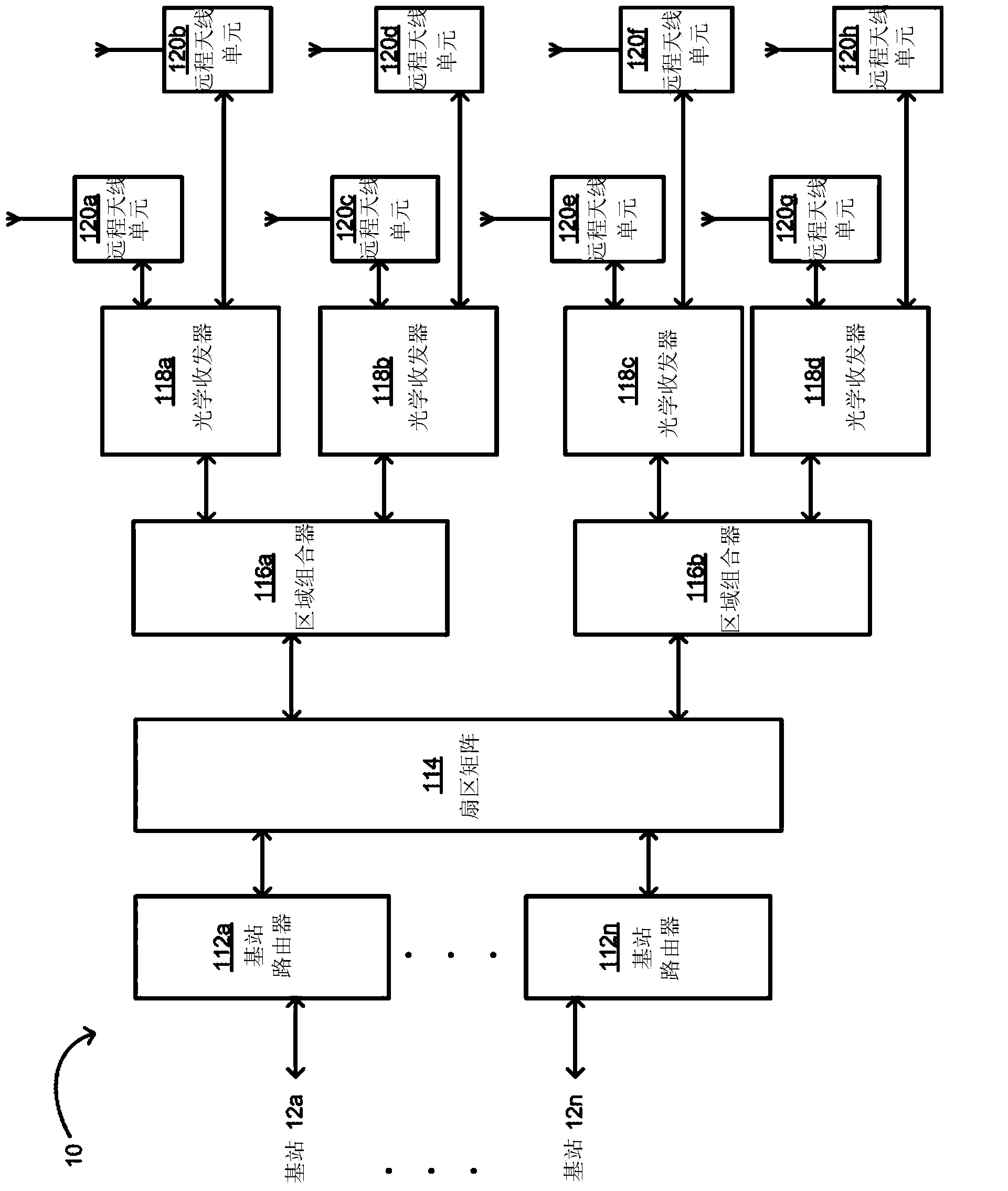
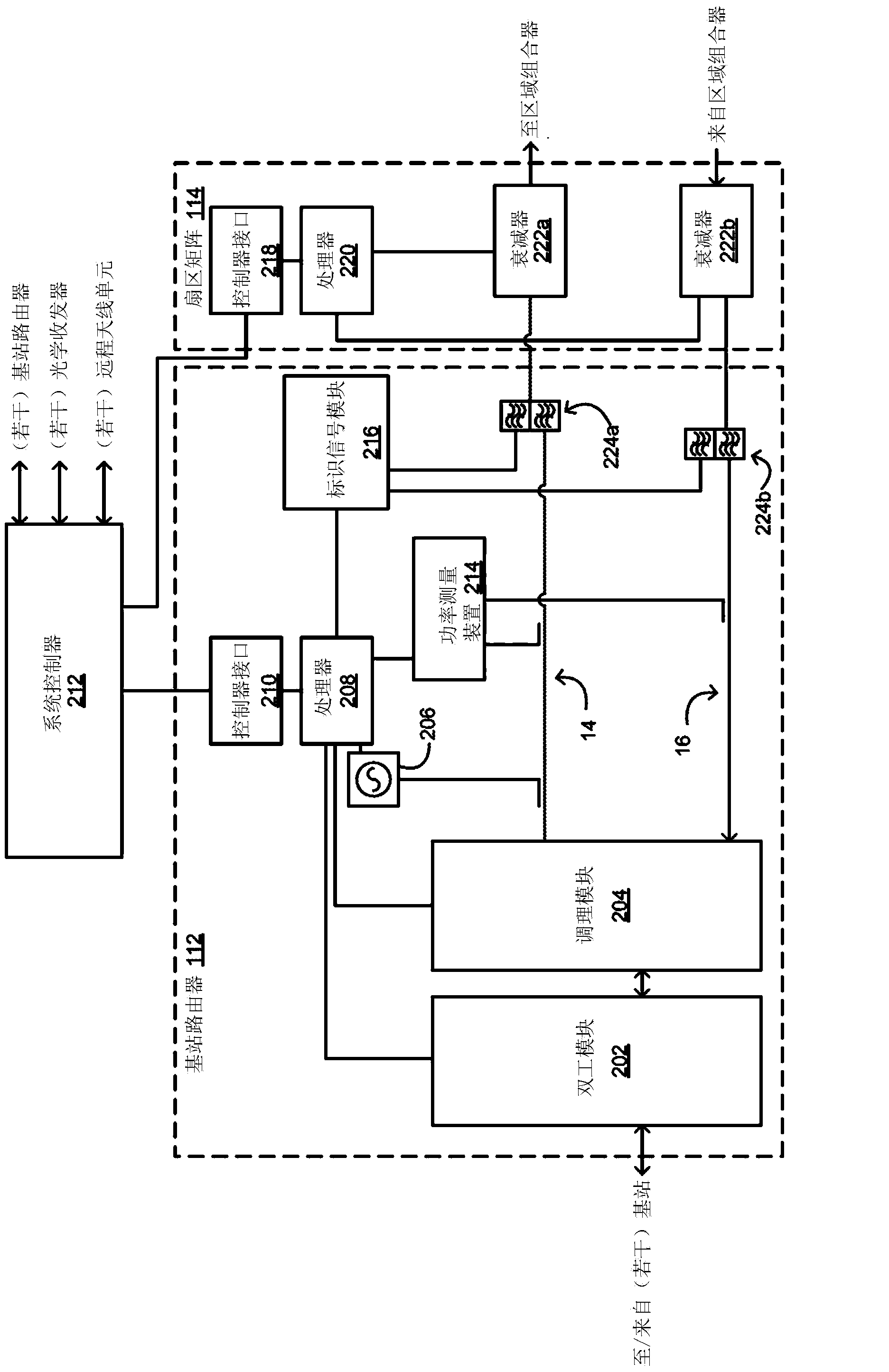
Configuration sub-system for telecommunication systems
Certain aspects are directed to a configuration sub-system for telecommunication systems. The configuration sub-system can include a test signal generator, a power measurement device, at least one additional power measurement device, and a controller. The test signal generator can be integrated into components of a telecommunication system. The test signal generator can provide a test signal to a signal path of the telecommunication system. The power measurement device and the additional power measurement device can respectively be integrated into different components of the telecommunication system. The power measurement device and the additional power measurement device can respectively measure the power of the test signal at different measurement points in the signal path. The controller can normalize signals transmitted via the telecommunication system by adjusting a path gain for the signal path based on measurements from the power measurement device and the additional power measurement device.
Owner:ANDREW WIRELESS SYST GMBH
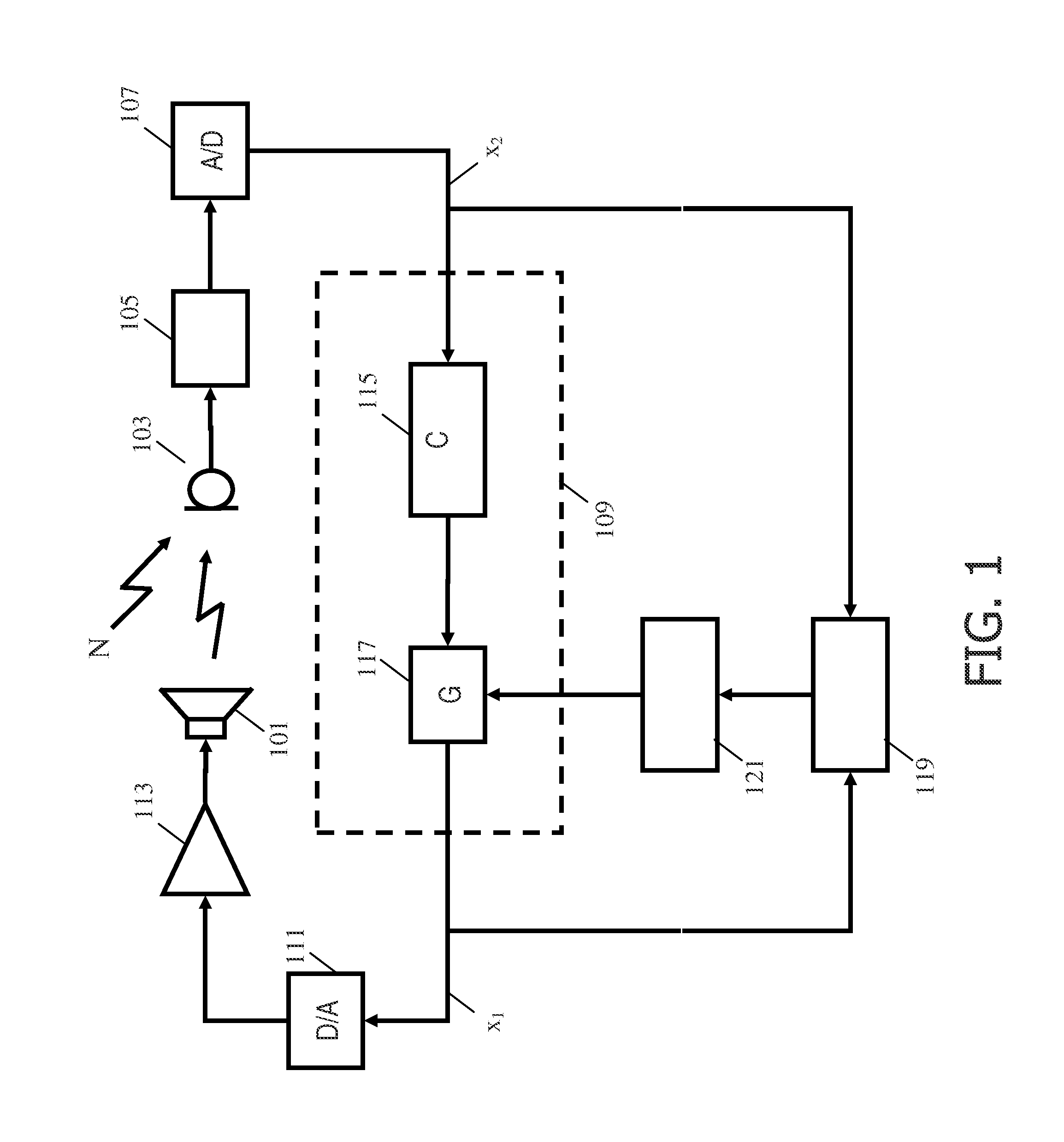
Active audio noise cancelling
ActiveUS8948410B2Improve performanceReduce complexityEar treatmentSpeech analysisTransducerEngineering
A noise canceling system comprises a microphone generating a captured signal and a sound transducer radiating a sound canceling audio signal in the audio environment. A feedback path from the microphone to the sound transducer includes a non-adaptive canceling filter and a variable gain and receives the captured signal and generates a drive signal for the sound transducer. A gain detector determines a secondary path gain for at least part of a secondary path of a feedback loop. The secondary path may include the microphone, the sound transducer, and the acoustic path therebetween but does not include the non-adaptive canceling filter or the variable gain. A gain controller adjusts the in of the variable gain in response to the secondary path gain. The system use simple gain estimation and control to efficiently compensate for variations in the secondary path to provide improved stability and noise canceling performance.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Adaptive transmit power control system
InactiveUS7215972B2Resonant long antennasTransmission systemsDigital signal processingPower control system
An adaptive closed loop transmit power control system which does not require extensive factory calibration of power control loop bandwidths and feedback detect path gain settings over the power transition ranges, frequency bands of operation, temperature, and supply voltage is disclosed. The system automatically compensates for any gain or slope variations in the analog feedforward and feedback paths to maintain system stability and meet performance specifications. The system achieves this by using an adaptive digital signal processing (DSP) system architecture within the feedback path of this closed loop power control system. The system eliminates the need for extensive factory calibration of such parameters as loop bandwidths and feedback detect path gain settings over power transition ranges, frequency bands of operation, temperature, and supply voltage.
Owner:APPLE INC
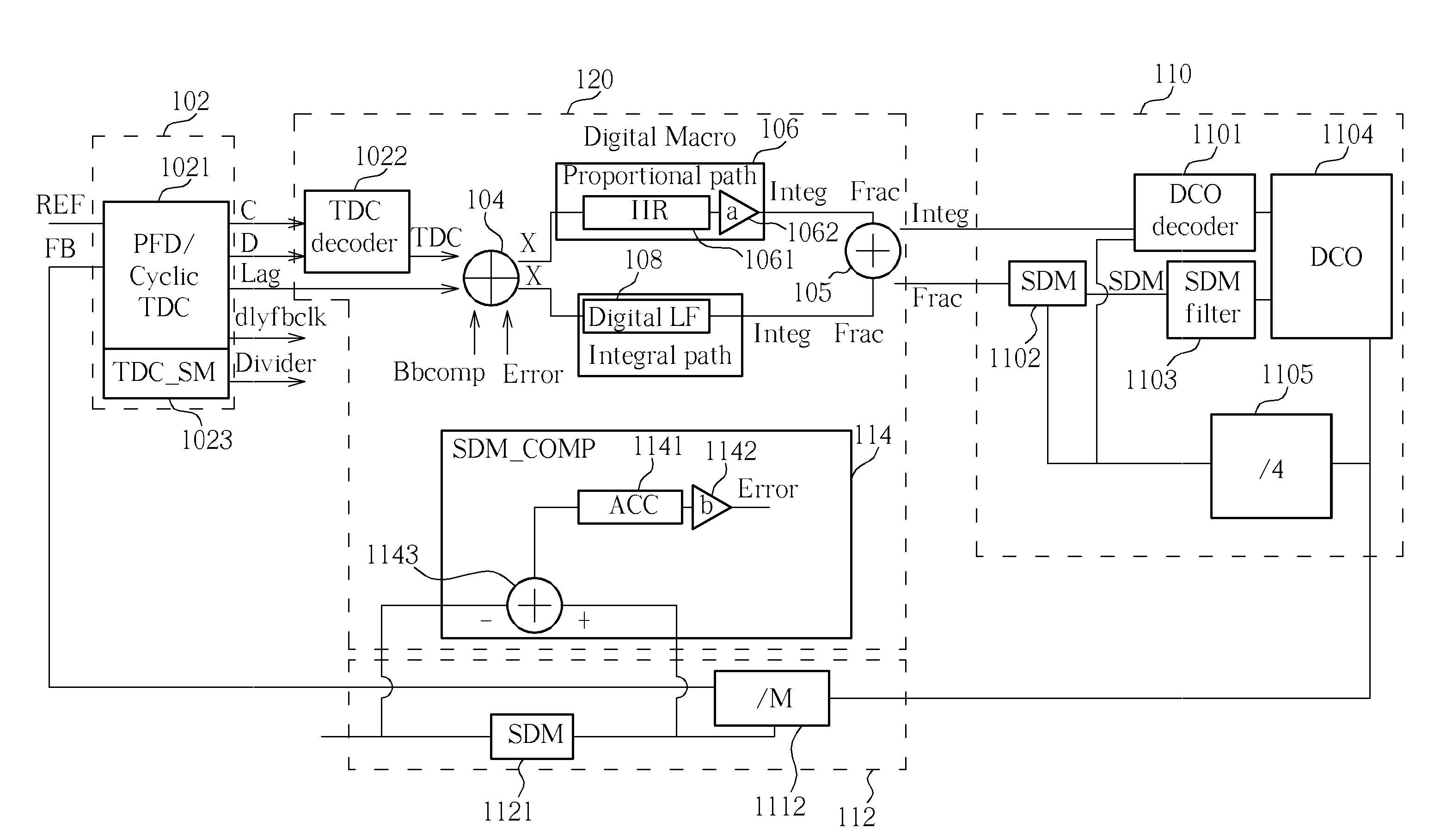
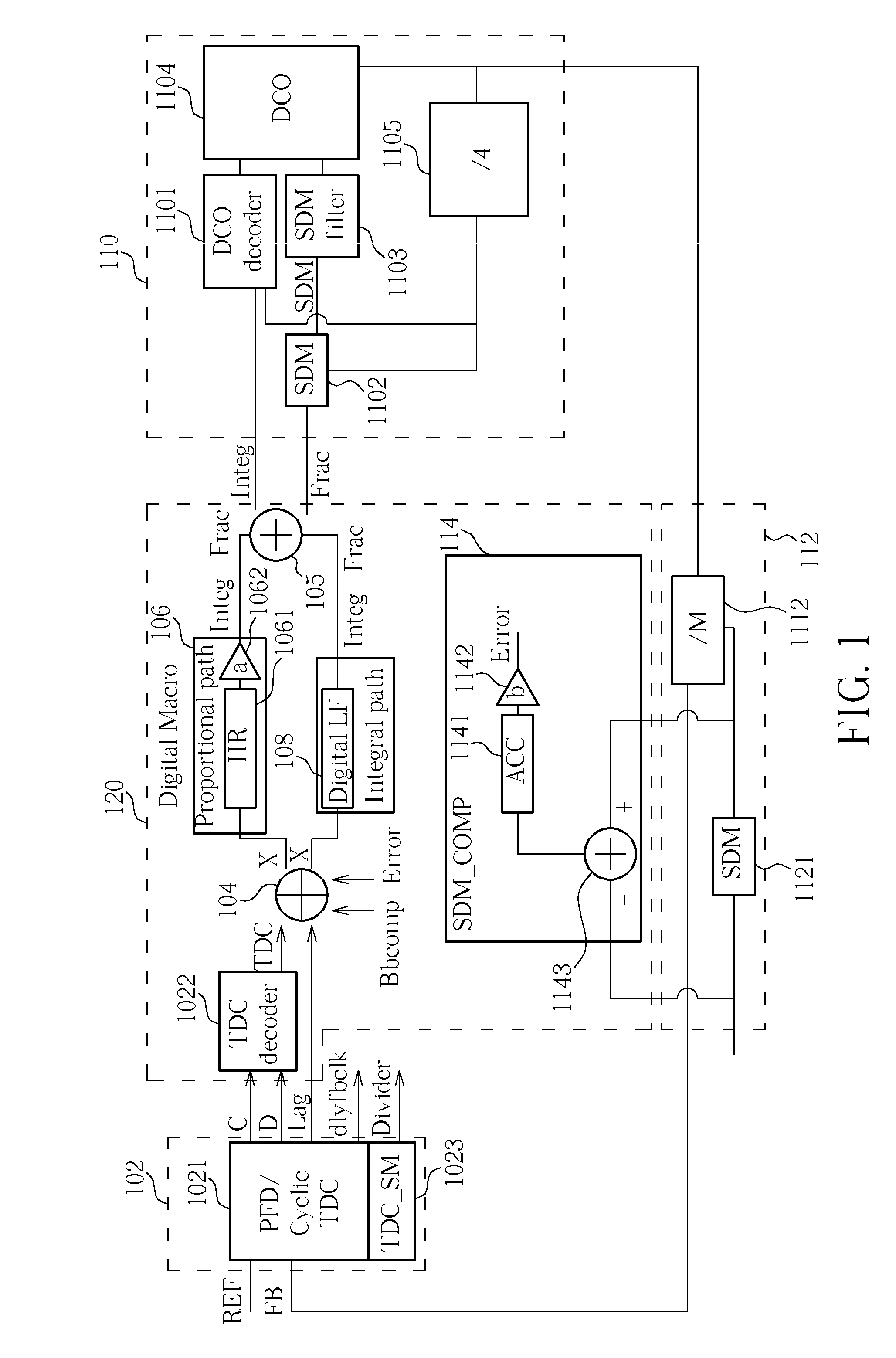
Error protection method, tdc module, ctdc module, and calibration method thereof
InactiveCN101414821AReduce errorsCorrection errorAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsLoop bandwidthDigital converter
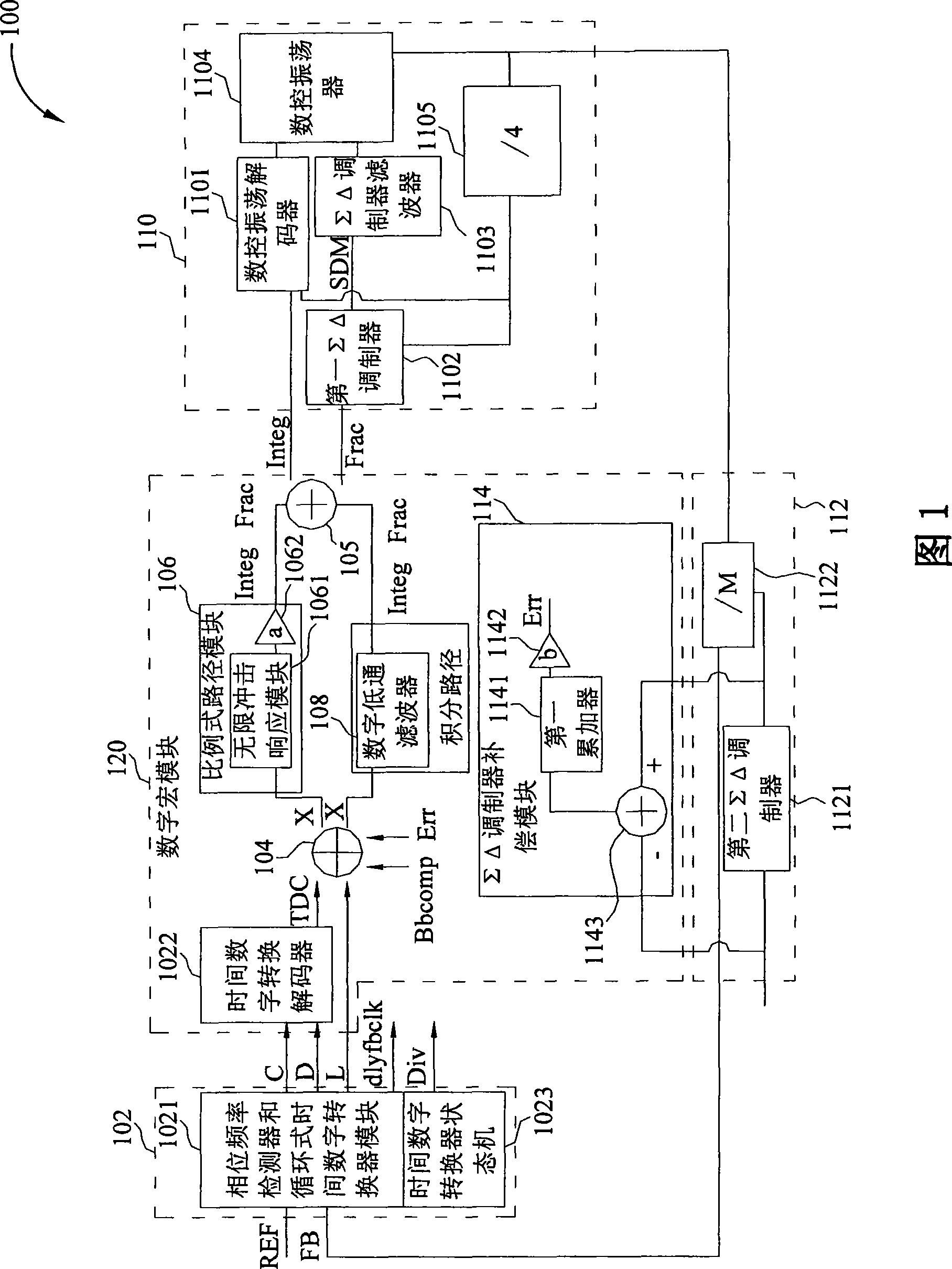
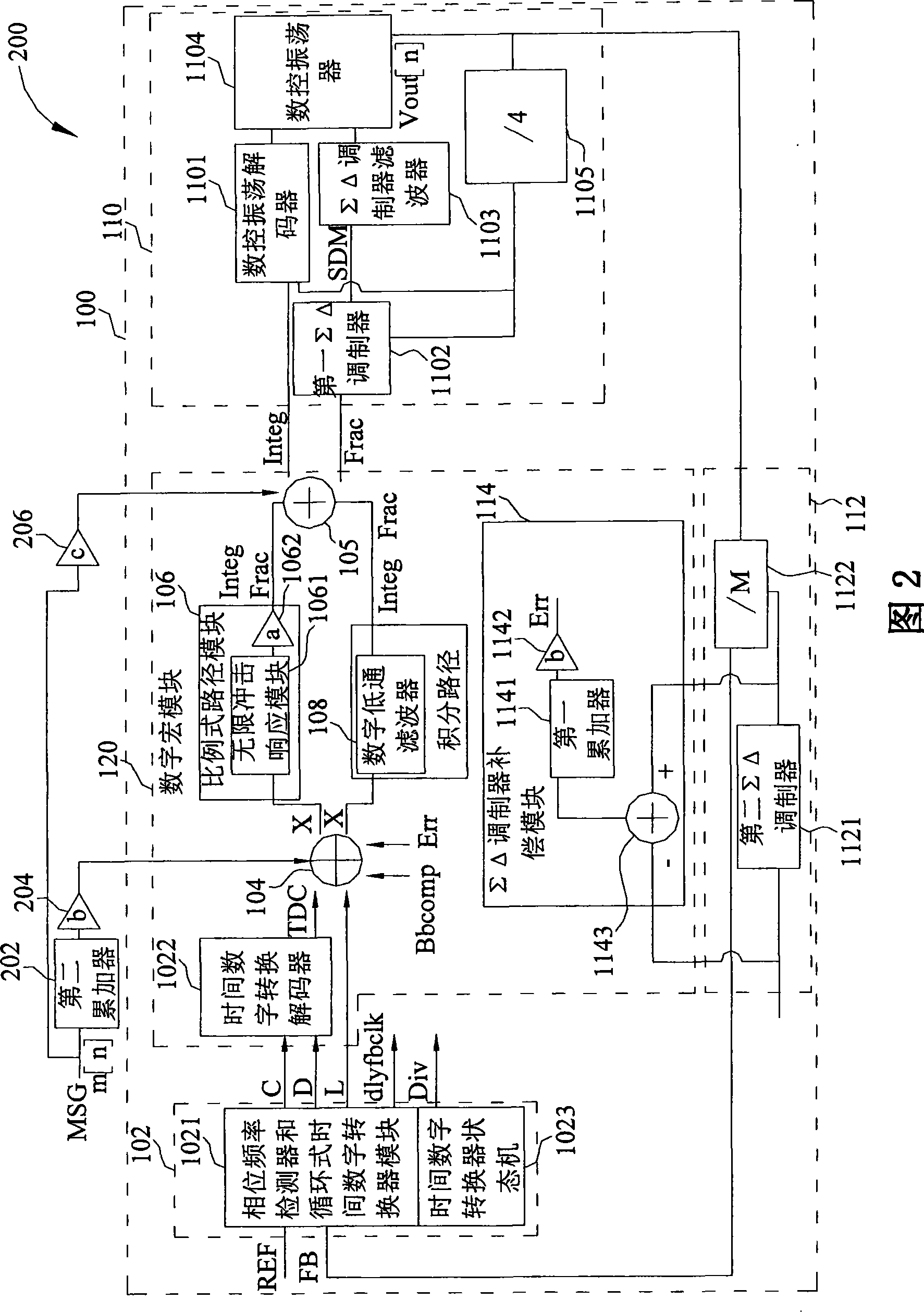
For decreasing errors within an analog phase-locked loop, an all-digital phase-locked loop (ADPLL) with digital components and digital operations is used. The ADPLL may also be used for direct frequency modulation (DFM). By defining a proportional path gain of an ADPLL by a bandwidth and a reference frequency of the ADPLL, by a TDC gain, a DCO gain, a dividing ratio of a frequency divider, a gain of an amplifier or a combination thereof, the gain of the amplifier may be adjusted so that an optimal loop bandwidth of the ADPLL may be well calibrated. For achieving the aim of entirely digital of the ADPLL, the gains of the TDC and the DCO may be further adjusted in a digital manner.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
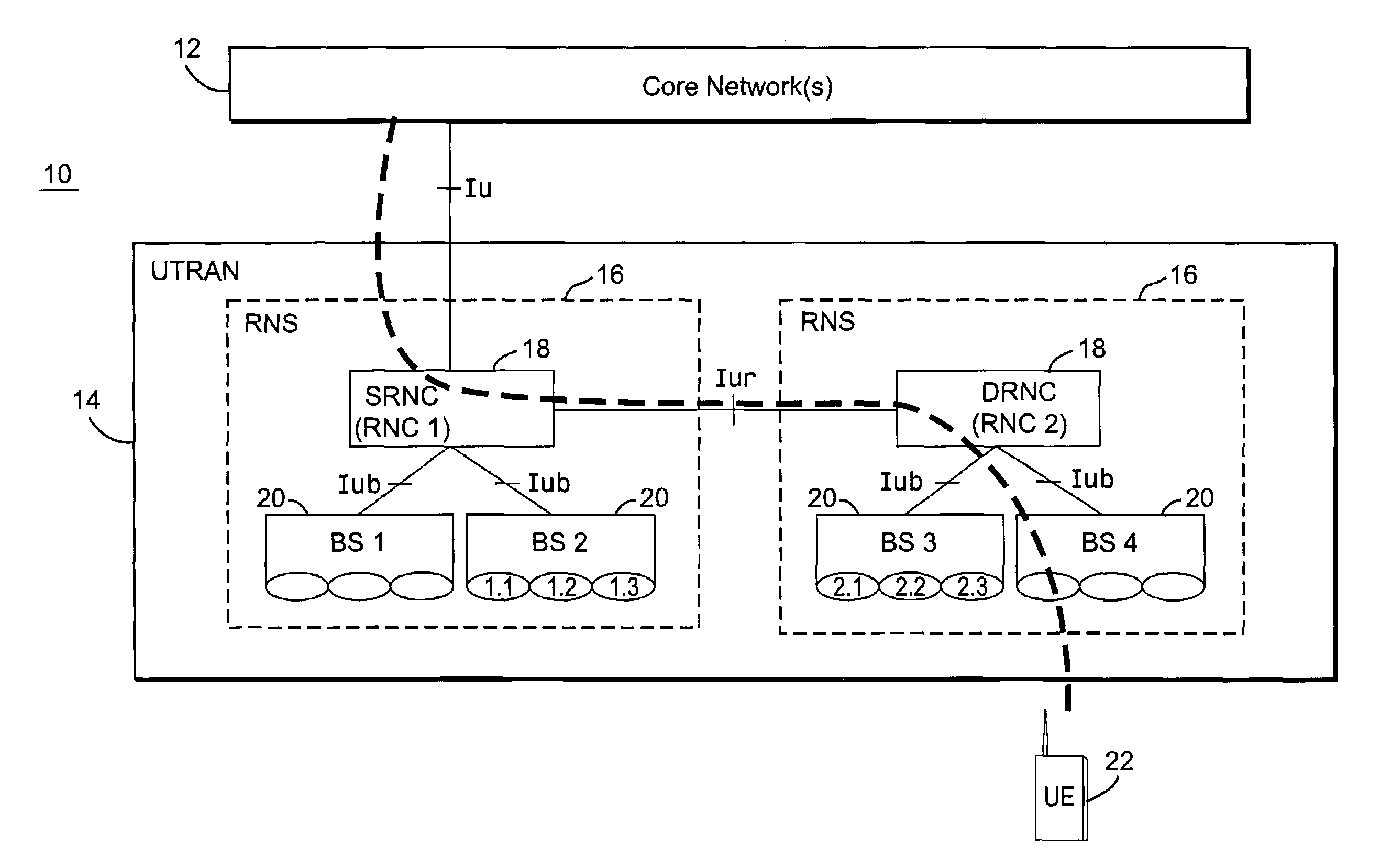
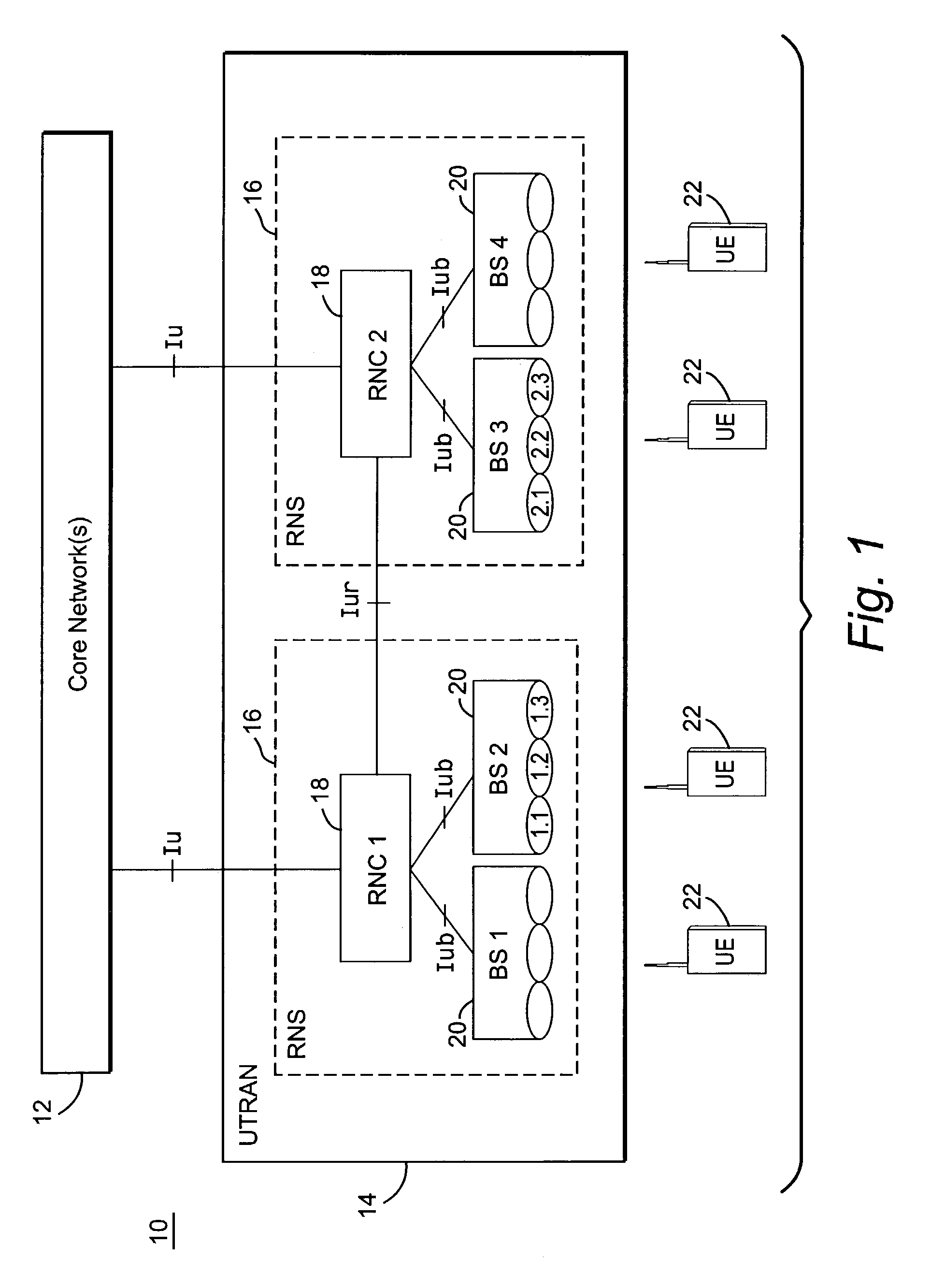
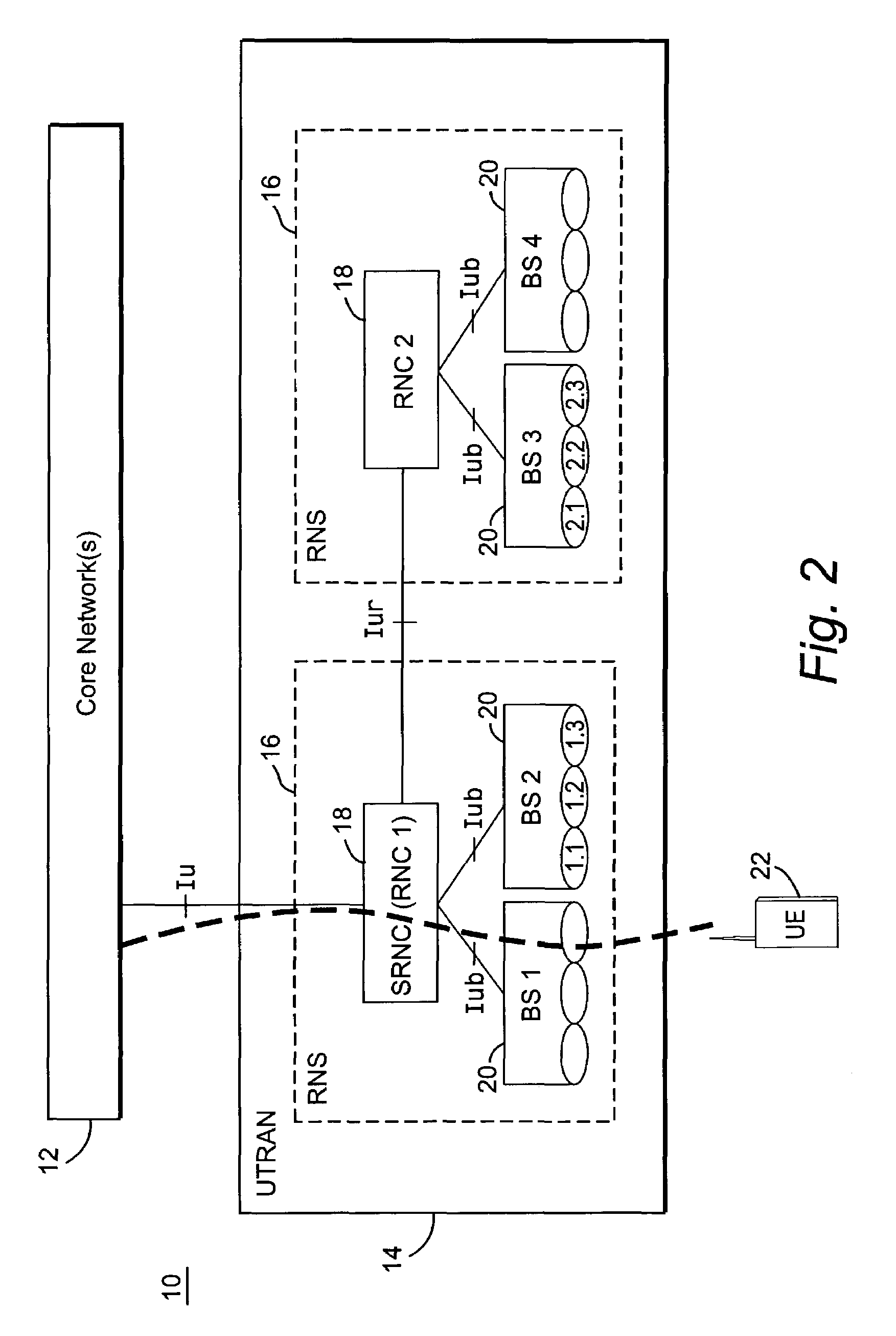
Uplink load determination and signaling for admission and congestion control
InactiveUS7146175B2Effective approachNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunicationsUplink transmission
A serving RNC signals the load contribution of all mobiles for which it is the serving RNC to all cells controlled by another RNC that are affected by the uplink transmissions of those mobiles. This allows the other RNC to determine the contribution of those mobiles to the total uplink interference in its cells. In one example, the uplink load maybe estimated using mobile-based path gain measurements.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
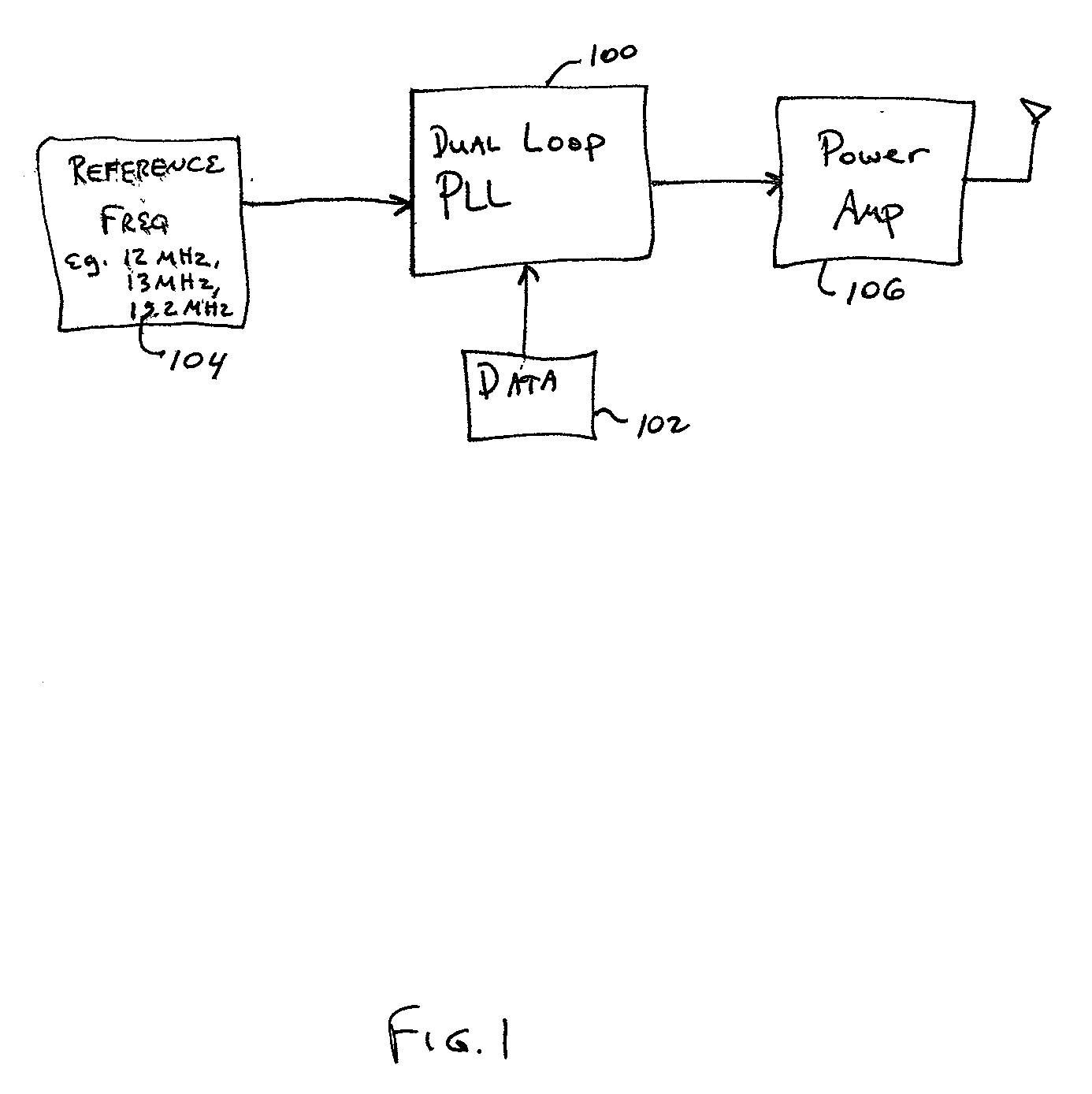
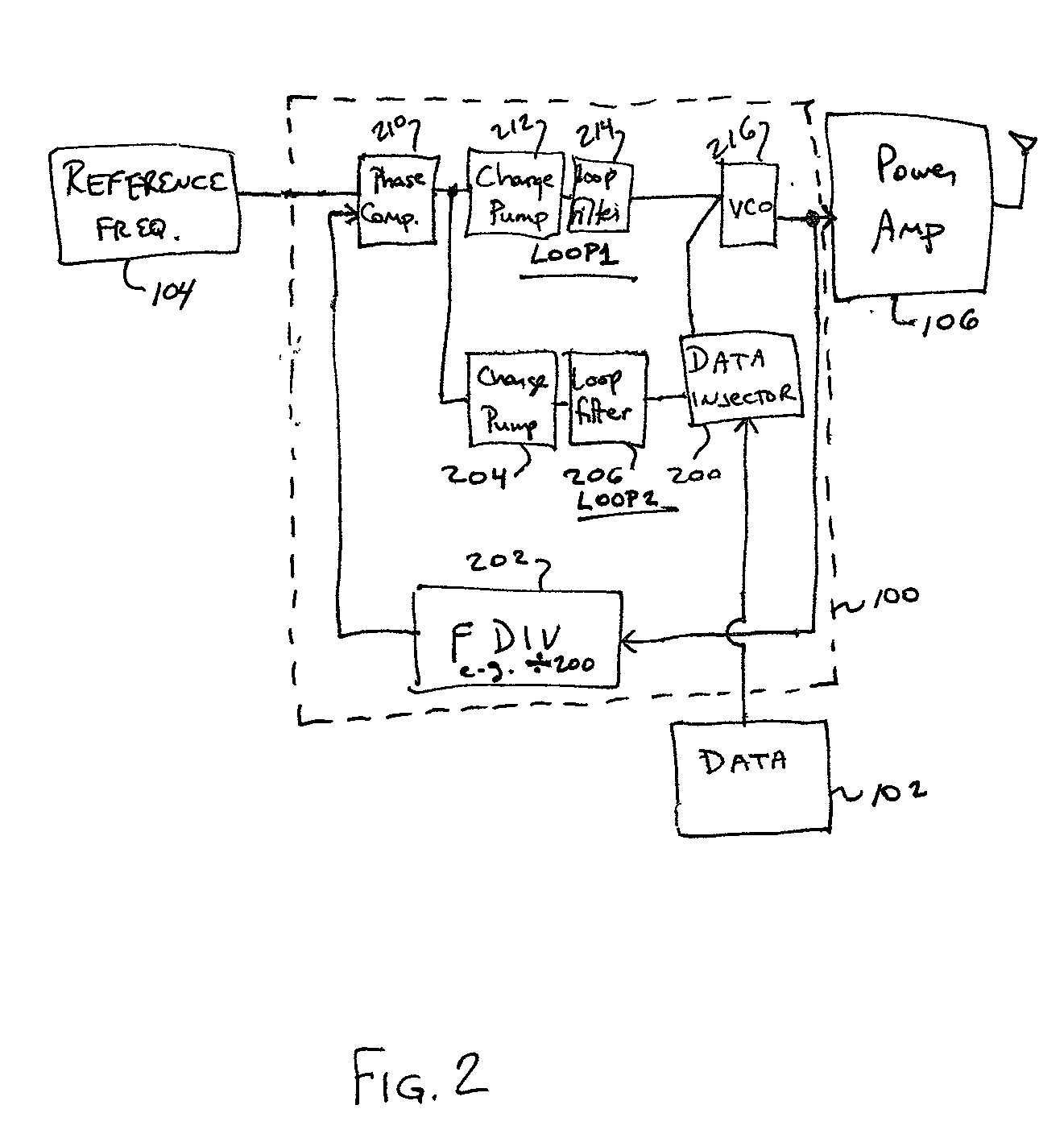
Accurate gain direct modulation (KMOD) using a dual-loop PLL
InactiveUS20030203724A1Automatic scanning with simultaneous frequency displayPulse automatic controlBluetooth piconetsFrequency synthesizer
The present invention provides a baseband RF clock synthesizer having particular use in a BLUETOOTH piconet device, which has the capability of providing simple and accurate calibration of modulation path gain (KMOD) by introducing a dual-loop phase locked loop (PLL) in the RF clock signal synthesizer. The disclosed technique and apparatus controls the maximum frequency deviation by the difference of two locked frequencies, one frequency in each path of the dual-path PLL. Once the PLL is locked within some frequency error, the present technique and apparatus calibrates for the deviation of amplitude of the modulation due to the modulation path. Accordingly, modulation gain (KMOD) calibration is provided by adding an auxiliary loop to a PLL in an RF frequency synthesizer.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
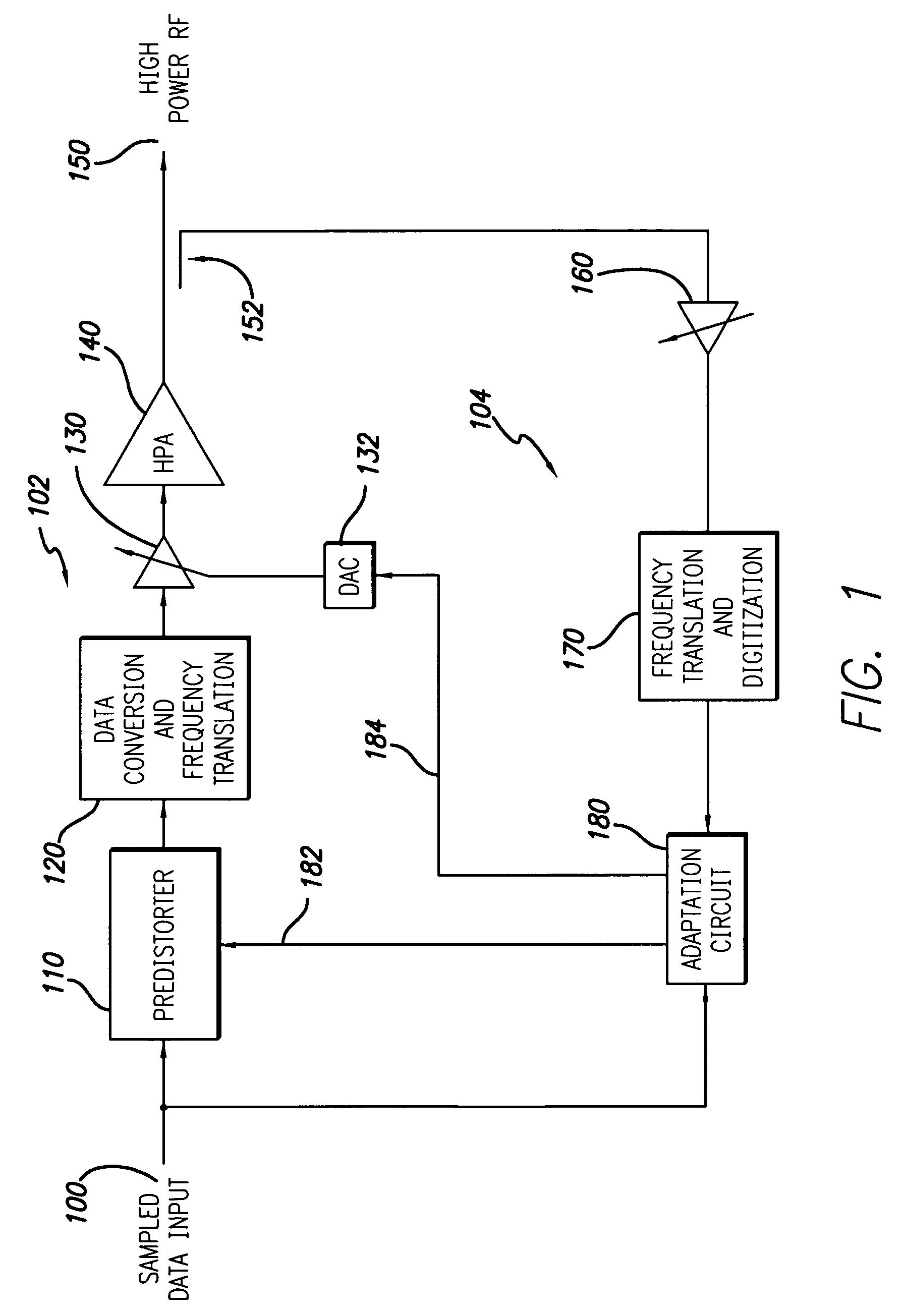
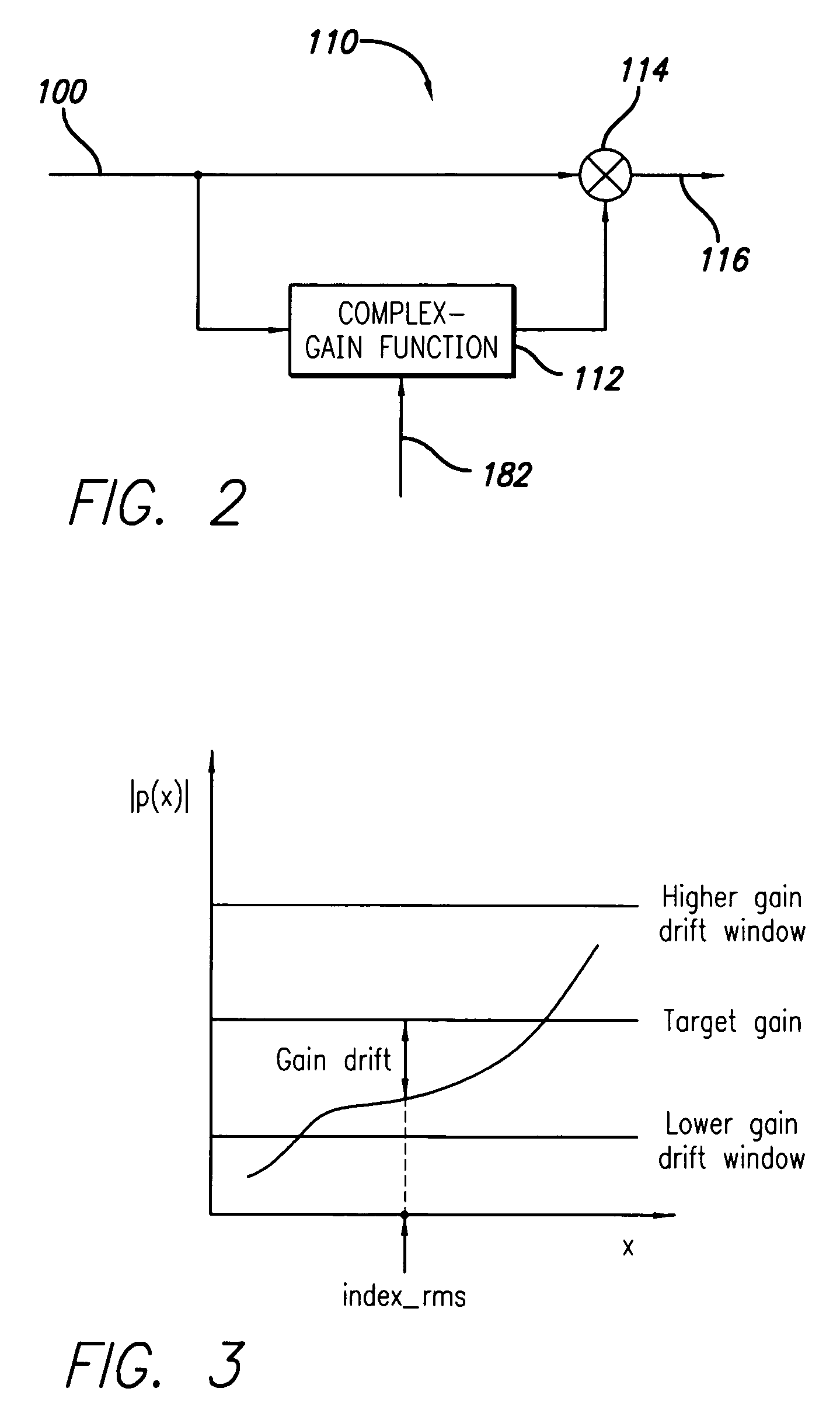
System and method for forward path gain control in a digital predistortion linearized transmitter
InactiveUS20060098758A1Multiple-port networksResonant long antennasTransmitted powerVariable Characteristic
A system and method for controlling the gain in the forward signal path of a digital predistortion linearizer is disclosed. The loop gain of the predistortion system is driven to unity, where a separately controlled constant-gain observation path allows accurate gain control of the forward path. This is divided into digital gain from the predistortion function and analog gain from a Voltage Variable Attenuator (VVA) in the transmitter. The invention balances the distribution between these two domains in order to maximize dynamic range and minimize noise in the forward signal path. In order to distribute the forward path gain accurately, the characteristic of the VVA must be well known. Since these devices tend to be non-linear, with variable characteristic over temperature and batch, the invention compensates for this non-linear behavior by tracking the varying transfer characteristic of the VVA, giving a predictable local characteristic. Another aspect of the disclosed invention is the ability to operate with very low transmit power and loop gain levels, allowing accurate gain control during such scenarios as cell initialization, that require operation over a wide dynamic range.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Hearing aid and method of estimating dynamic gain limitation in a hearing aid
ActiveUS20090067654A1Increase volumeEar treatmentHearing aids signal processingTransducerEngineering
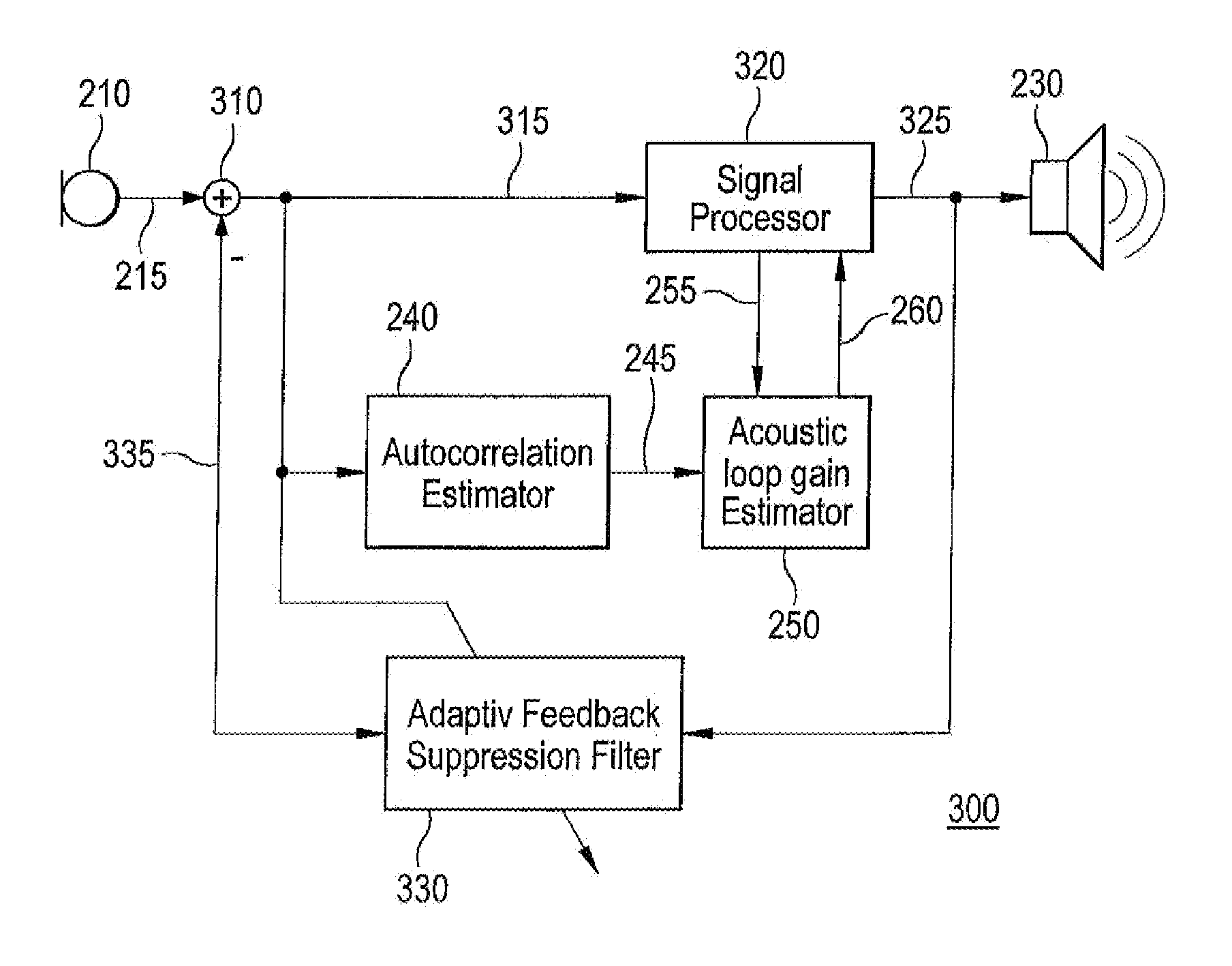
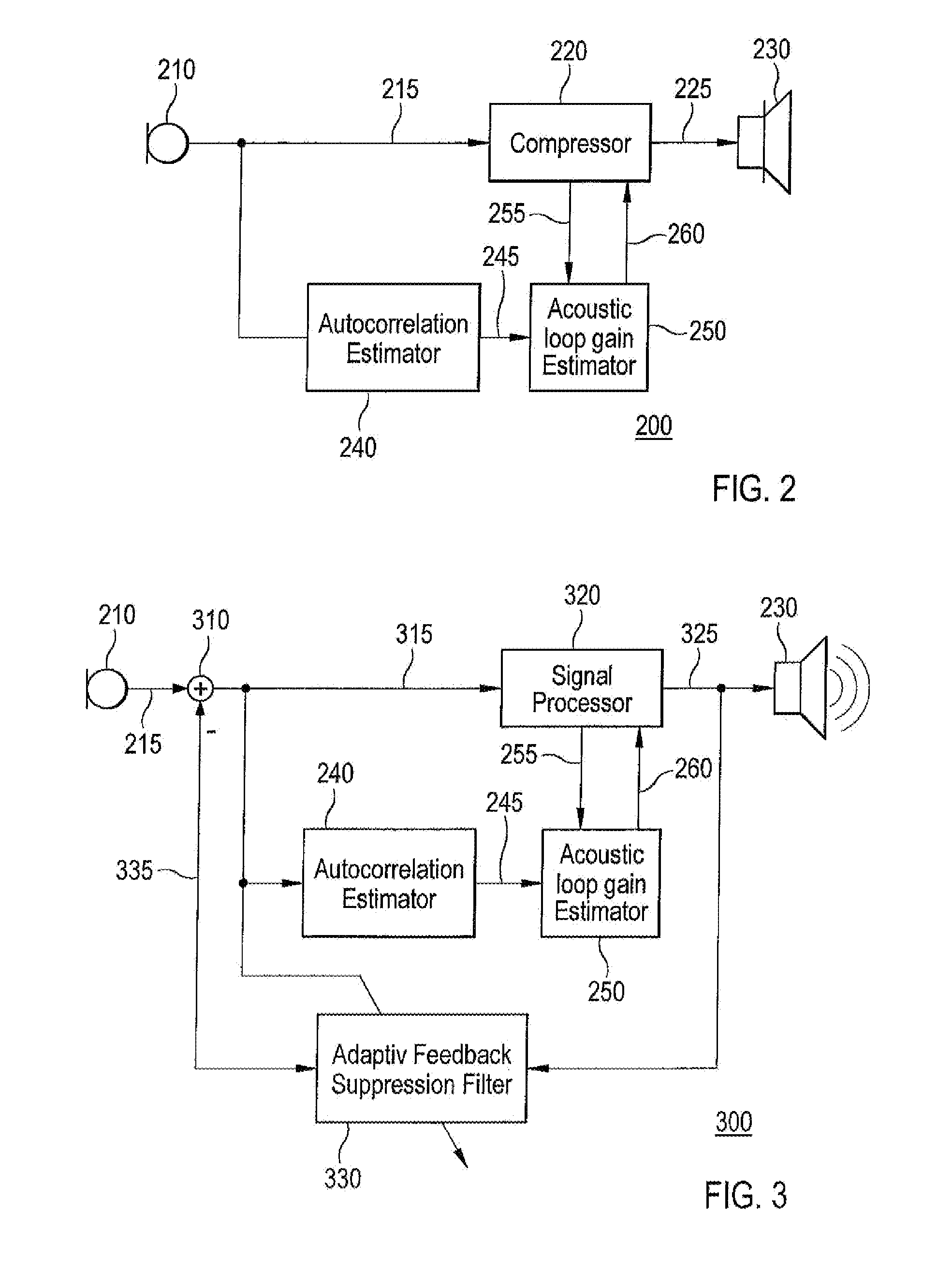
There is presented a hearing aid that comprises an input transducer for transforming an acoustic input signal into an electrical input signal, a compressor for generating an electrical output signal from the electrical input signal, an output transducer for transforming the electrical output signal into an acoustic output signal, an autocorrelation estimator for calculating an autocorrelation estimate of the electrical input signal, and an acoustic loop gain estimator for determining a dynamic gain limit from the autocorrelation estimate and an instantaneous gain level of the signal processor. The invention further provides a method of adjusting signal path gain in a hearing aid, and a system for providing increased stability in a hearing aid.
Owner:WIDEX AS
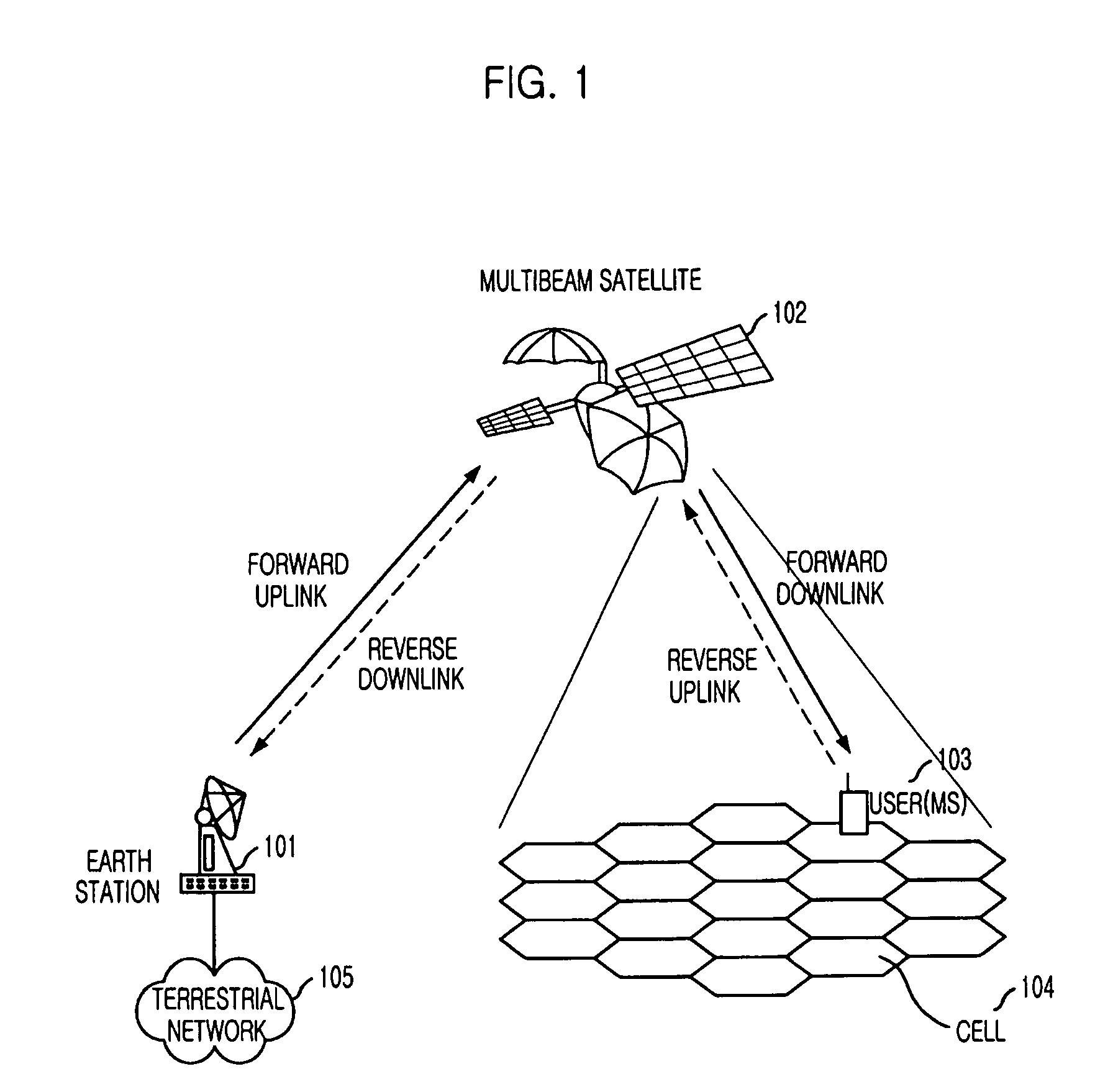
Adaptive packet transmission method for transmitting packets in multibeam satellite communication system
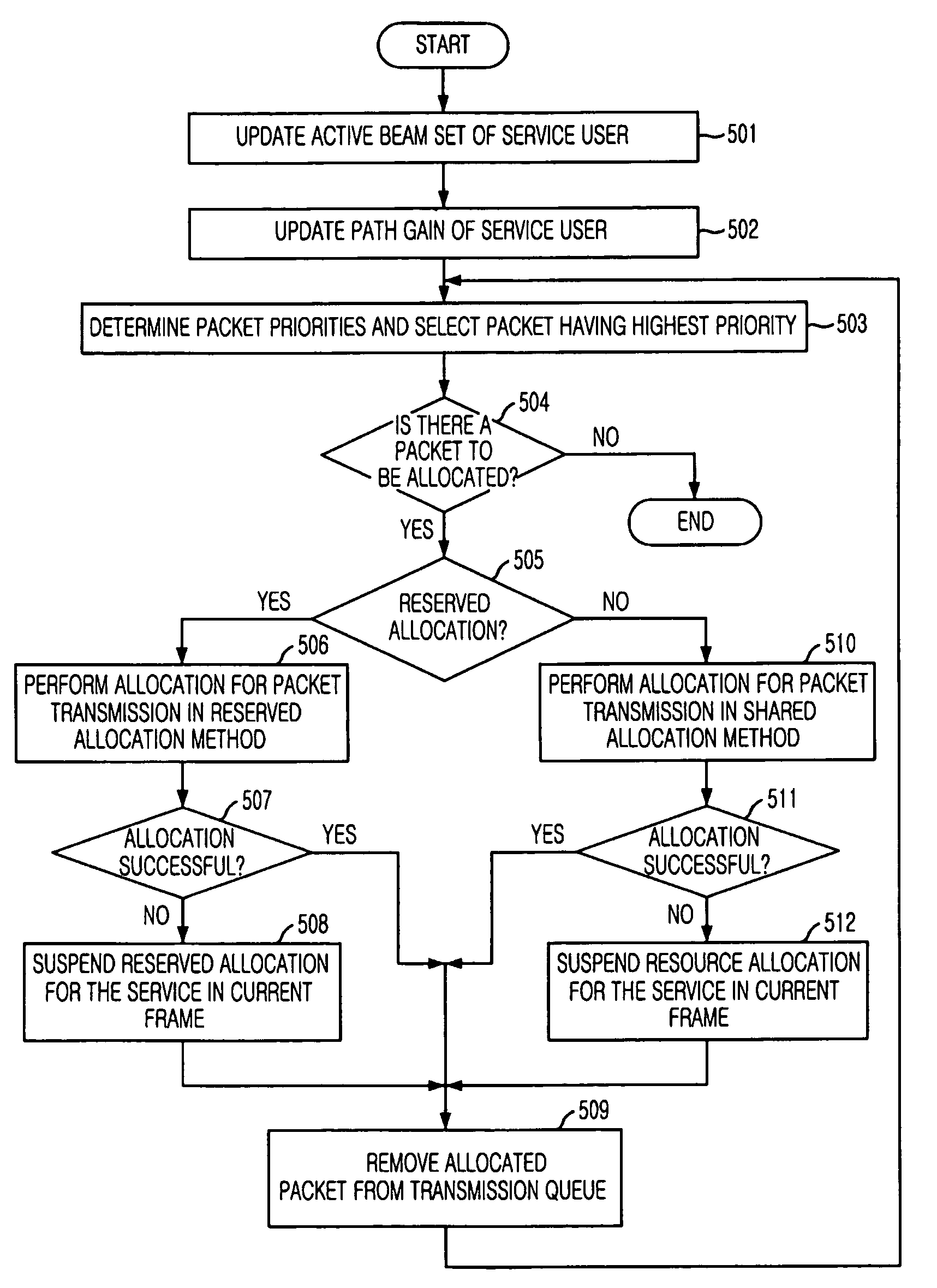
InactiveUS7554937B2Interference minimizationEfficient use ofEnergy efficient ICTPower managementMobile stationPacket transmission
Provided is an adaptive packet transmission method in a cellular mobile communication system using a multibeam satellite. The method includes the steps of: a) being periodically reported, from mobile stations, of average receiving power levels of beam pilot signals transmitted in a plurality of beams; b) estimating a path gain between beams and the mobile station based on the reported average power levels of beam pilot signals; c) determining priorities for packets to be transmitted to each of the mobile stations; d) selecting a beam requiring the lowest transmission power for transmitting the packet having the highest priority, and allocating the lowest power required for satisfying a predetermined packet reception quality when the packet is transmitted in the selected radio resource, by using the path gain estimated for each of the mobile stations; and e) if the radio resources and / or the transmission power that can be used are not sufficient or if there is a packet to be allocated, performing the step c).
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Traffic controlling method based on layered roadline calculating
InactiveCN1948912AImprove operational efficiencyReduce search sizeInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsShort path algorithmTraffic network
The invention relates to traffic control method based on layered route computing. It uses layer strategy to divide traffic network into different layer, gains the path from the low layer network to high by preparing algorithm, and combines it with the optimal path gained in the high layer network to gain whole network optimal path. The invention solves the defect of the pure shortest path algorithm which only can gain space or time shortest path, selects the meaning optimal path for traveling car.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
Spatial modulation method and transmitting and receiving apparatuses using the same in a multiple input multiple output system
ActiveUS8094743B2Eliminate needImprove transmission efficiencyDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationEngineeringMultiple input
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Estimation and compensation method for iq imbalance
InactiveUS20100329397A1Improve convenienceEffectivenessError preventionFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationTime domainEngineering
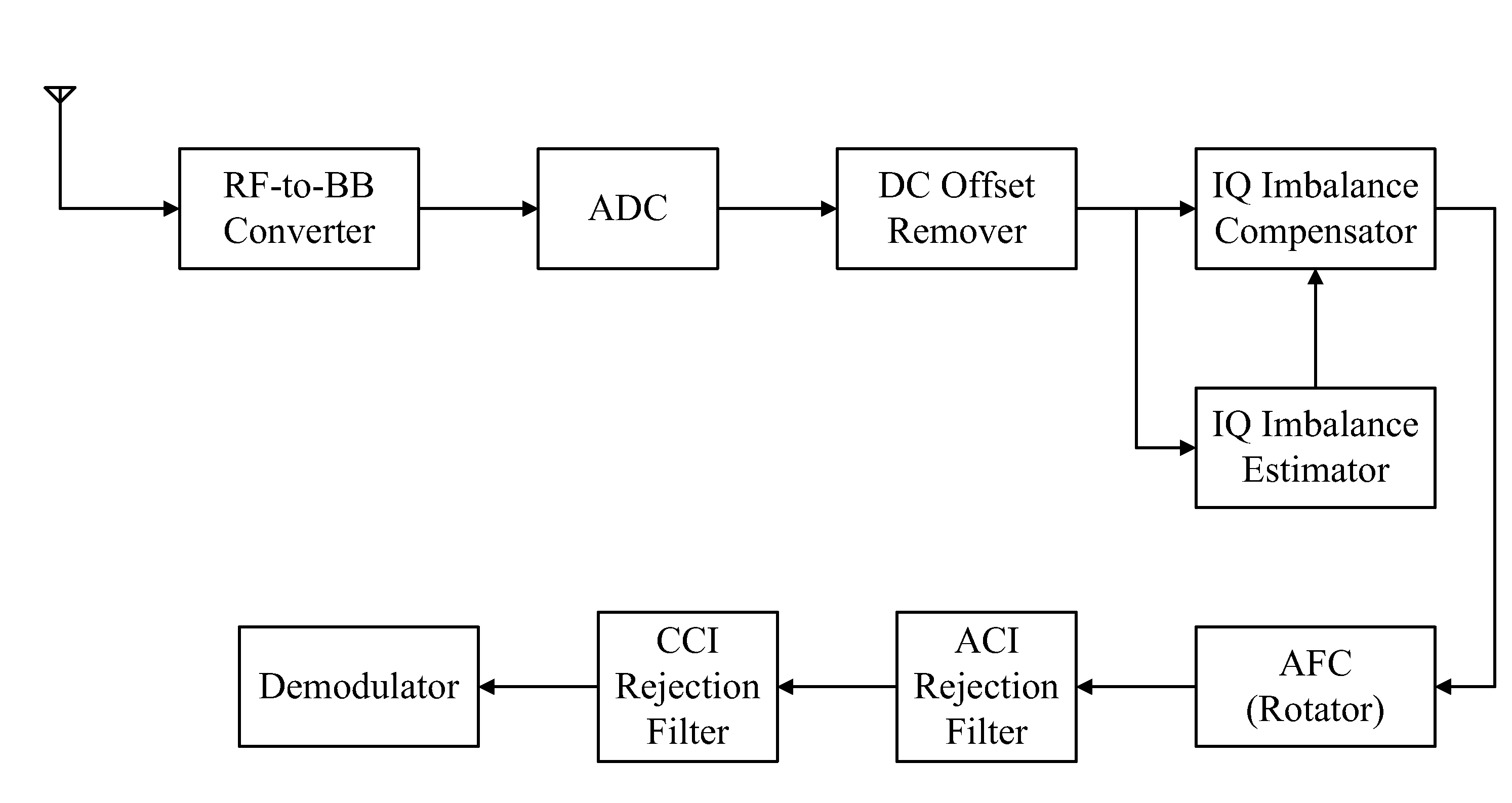
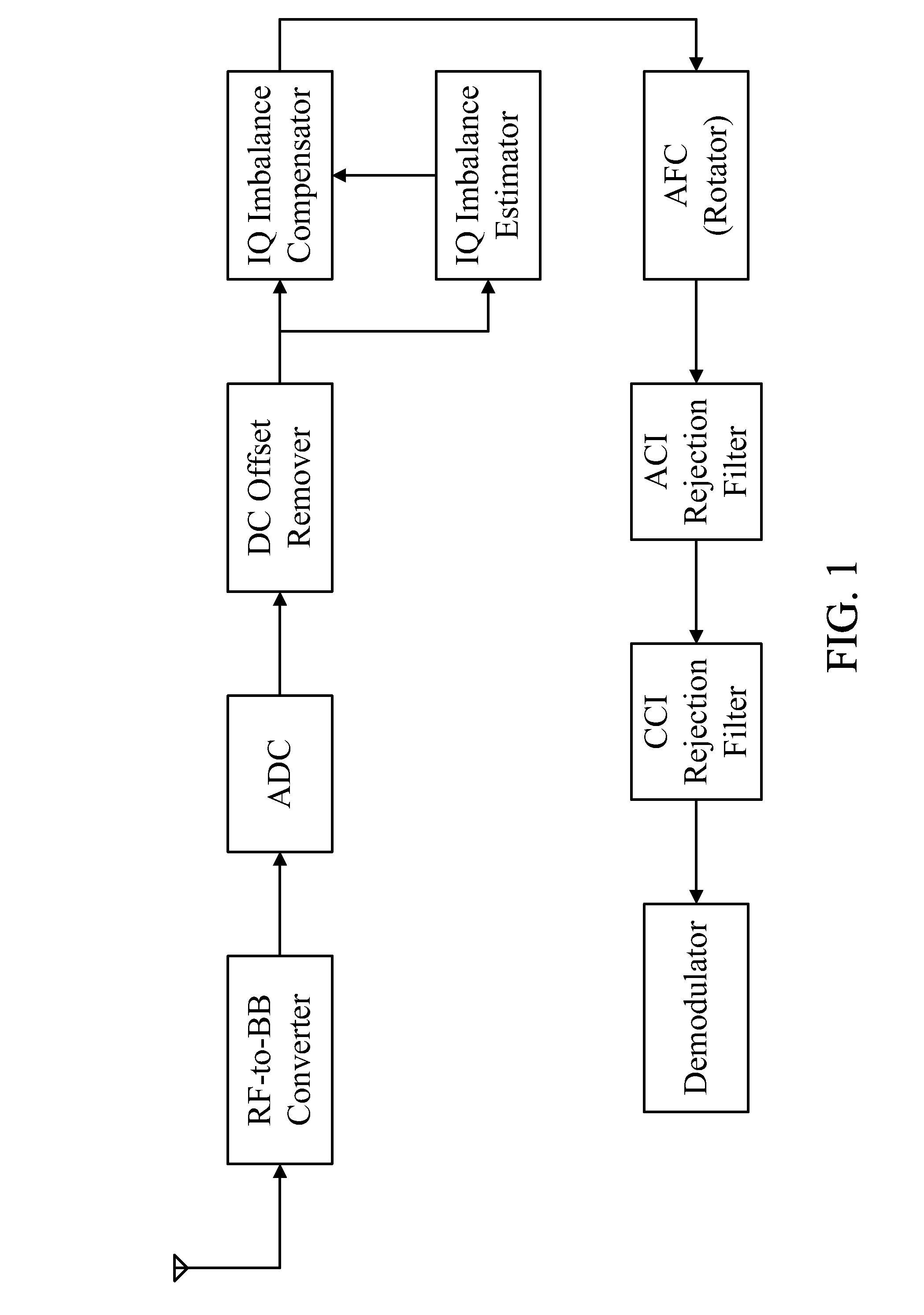
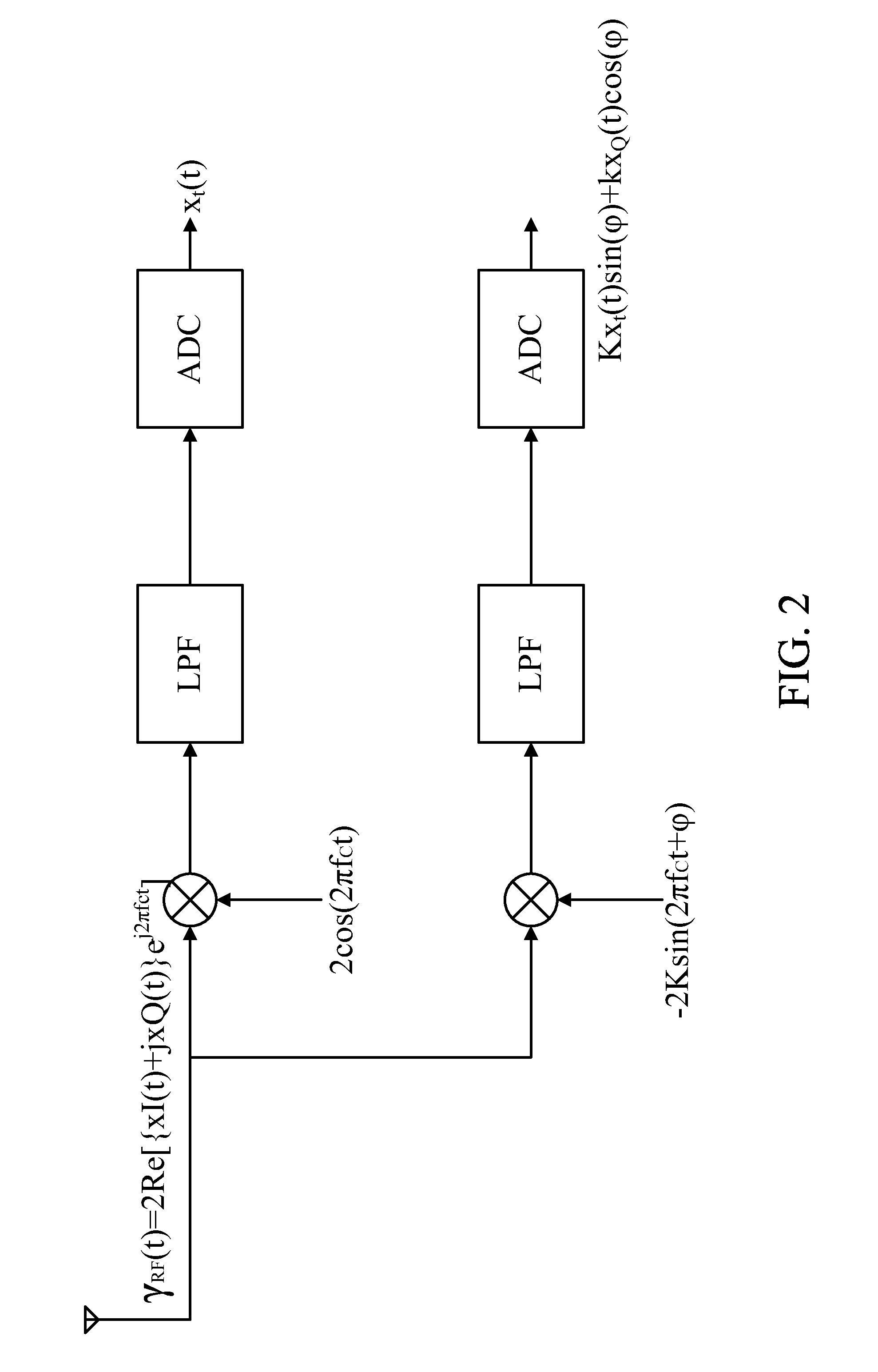
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for estimating and compensating IQ imbalance of a baseband sampling digital communication receiver in digital time domain. Specifically, after an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) in the baseband sampling system, a structure including a crosstalk gain estimator, a Q-path gain estimator, an IQ imbalance compensator, and a lock detector is utilized to execute IQ imbalance estimation and compensation. In contrast to real-time frequency domain estimator / compensator, the present invention requires very little or no additional memory and delay processing, and therefore provides the estimation apparatus and method with convenience.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICON KOREA INC
Power control in a wireless system having multiple interfering communication resources
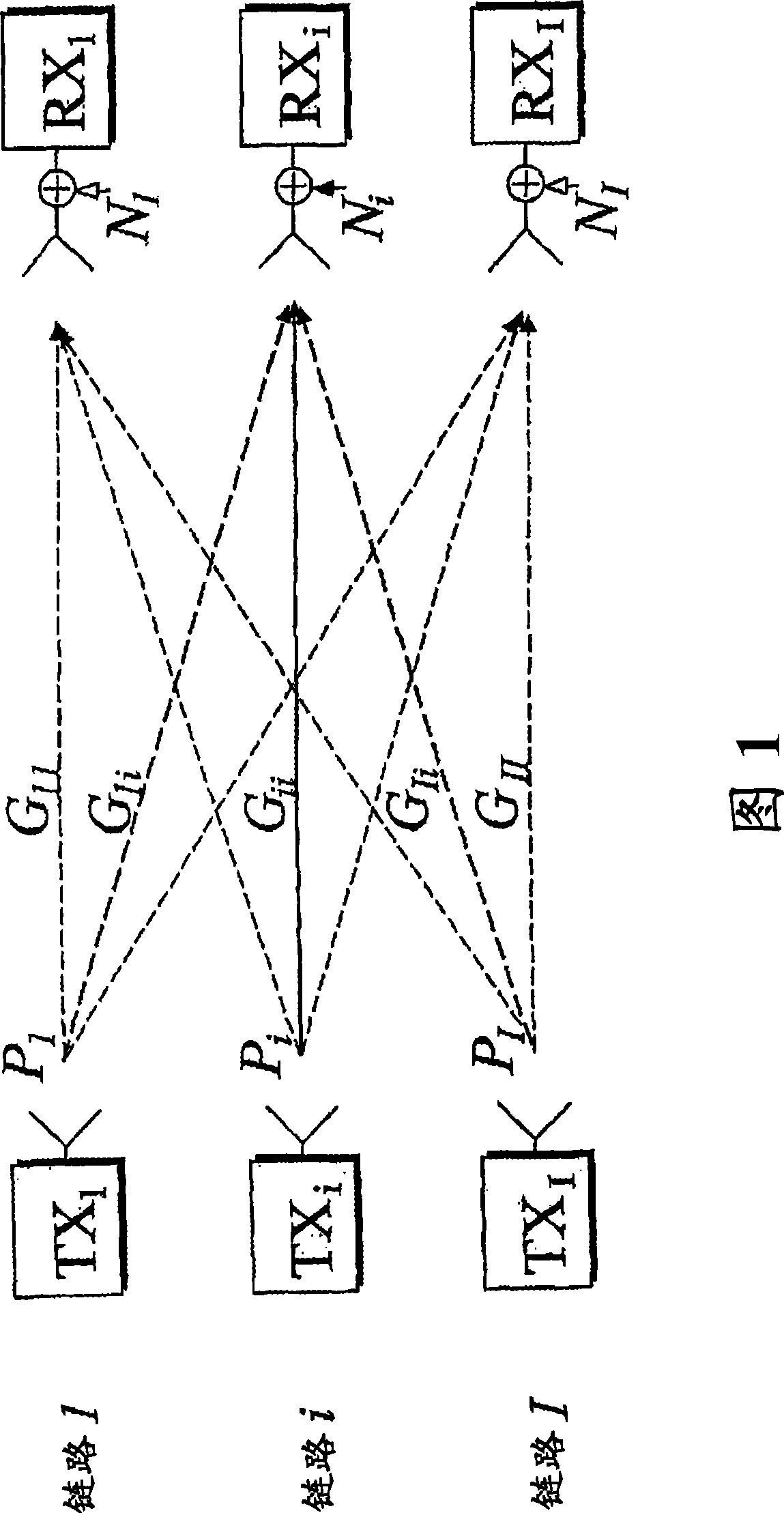
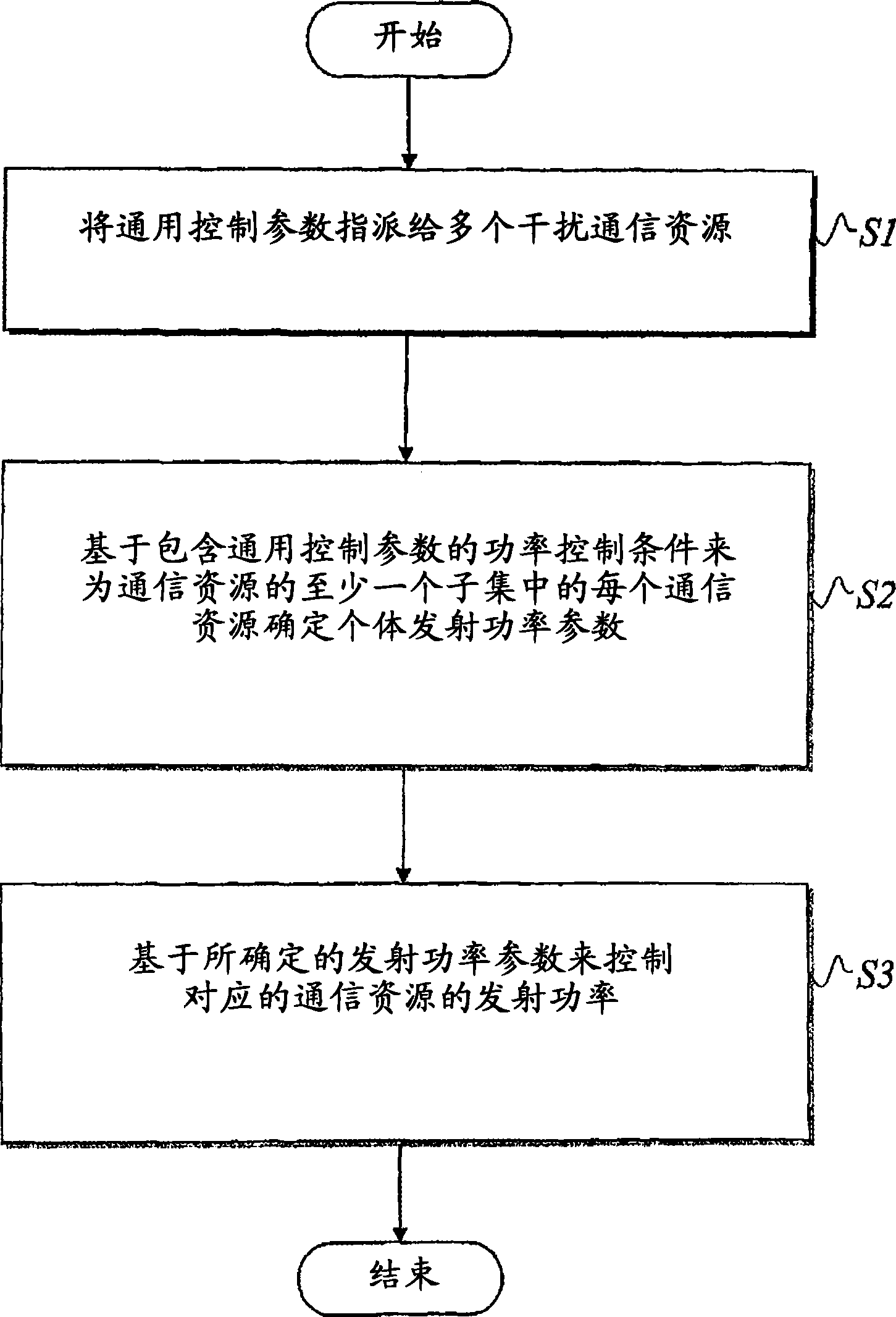
InactiveCN101427479ASpeed maximizationMaximize throughputPower managementTransmission control/equalisingCommunications systemTransmitted power
A wireless communication system having multiple interfering communication resources is considered. A power control procedure is based on assigning (Sl) a common control parameter to the considered communication resources, and using the control parameter together with a unique power control condition (S2) for determining the individual transmit power parameters of the communication resources. In particular, the idea is to determine, for each one of at least a subset of said communication resources, an individual transmit power parameter based on a power control condition implying that the total received power divided with the path gam of the communication resource should correspond to the common control parameter (S2). The determined transmit power parameters are then used for controlling (S3) the transmit powers of the corresponding communication resources. By using the proposed power control condition when determining the transmit power parameters, and then adapting the transmit data rates according to the resulting link quality, it is possible to maximize aggregate data rate for any given amount of total invested power.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
All-digital phase-locked loop, loop bandwidth calibration method, and loop gain calibration method for the same
ActiveUS20090096538A1Pulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsAudio power amplifierLoop bandwidth
For decreasing errors within an analog phase-locked loop, an all-digital phase-locked loop (ADPLL) with digital components and digital operations is used. The ADPLL may also be used for direct frequency modulation (DFM). By defining a proportional path gain of an ADPLL by a bandwidth and a reference frequency of the ADPLL, by a TDC gain, a DCO gain, a dividing ratio of a frequency divider, a gain of an amplifier or a combination thereof, the gain of the amplifier may be adjusted so that an optimal loop bandwidth of the ADPLL may be well calibrated. For achieving the aim of entirely digital of the ADPLL, the gains of the TDC and the DCO may be further adjusted in a digital manner.
Owner:XUESHAN TECH INC
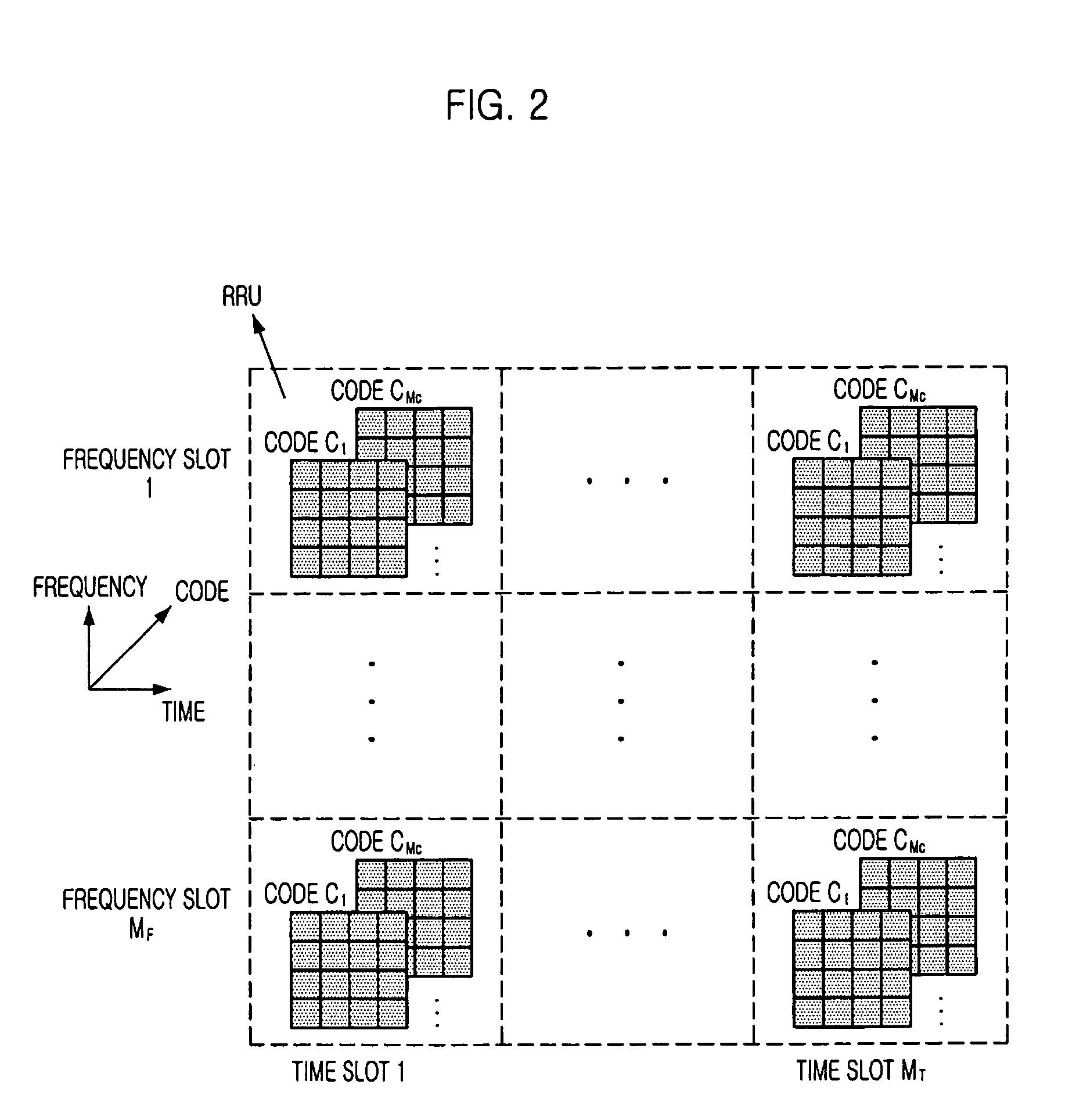
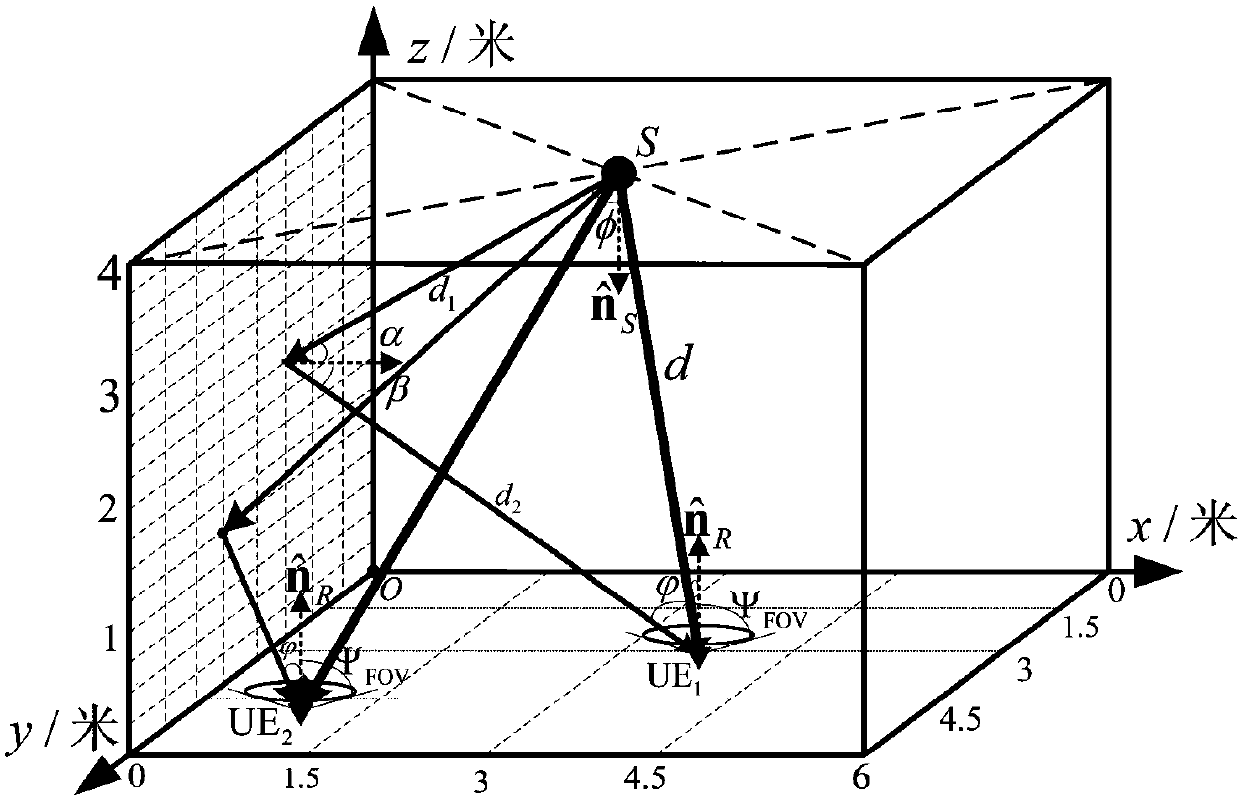
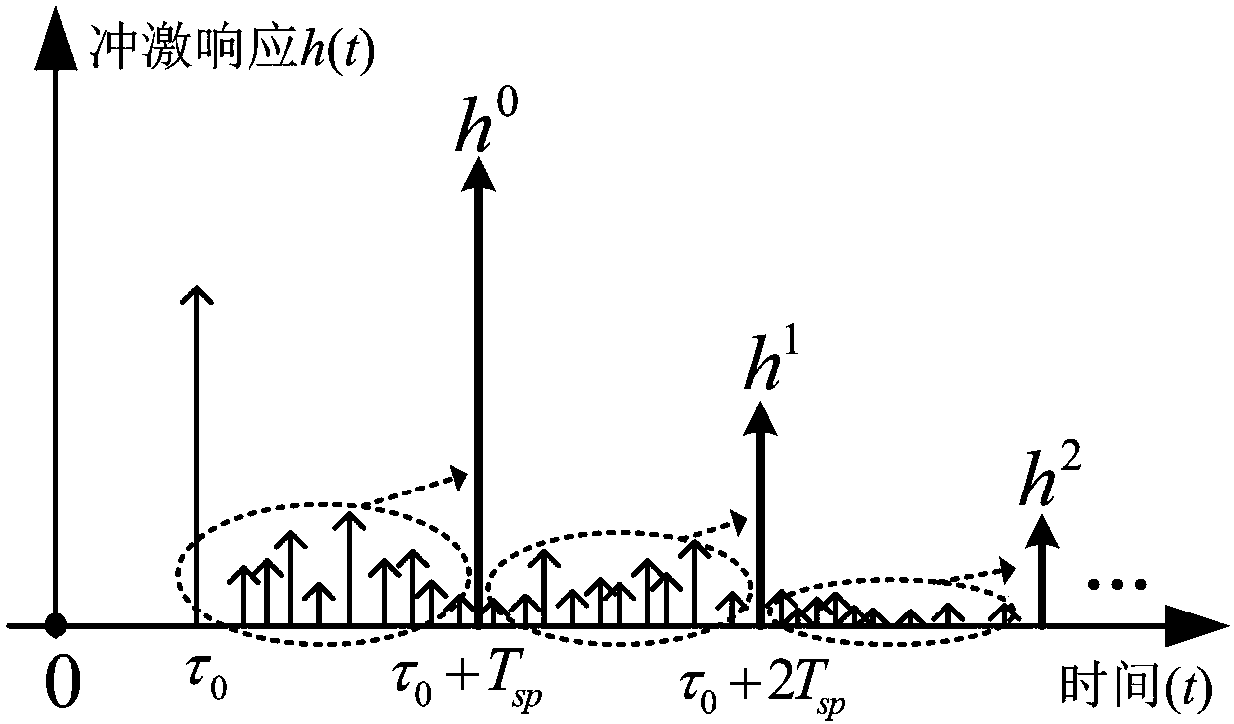
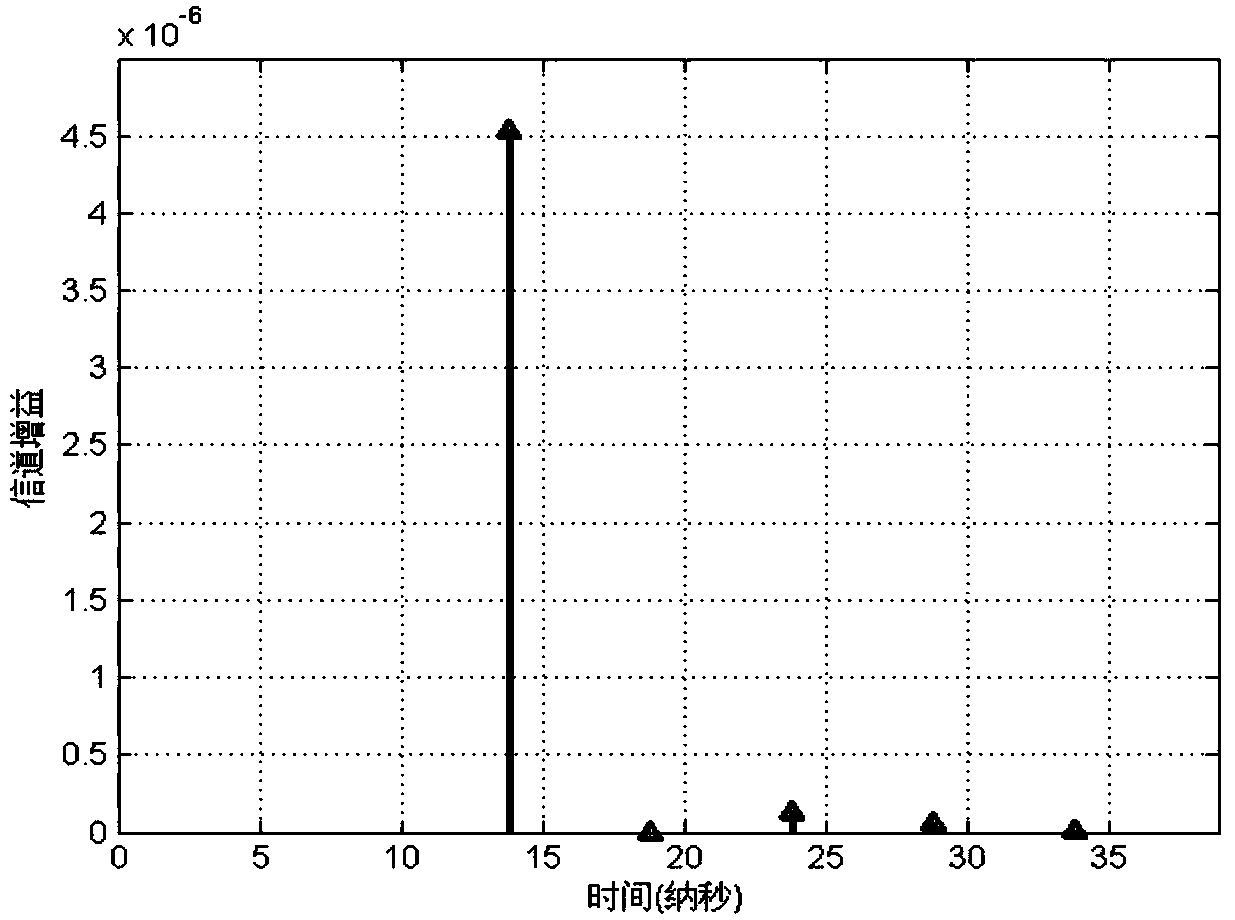
Multipath fading channel modeling method of indoor visible light MIMO communication system
InactiveCN105939177AIgnoring temporal dispersionTime dispersion cannot be ignoredTransmission monitoringModulation bandwidthTime domain
The invention discloses a multipath fading channel modeling method of an indoor visible light MIMO communication system, and aims at building a calculation method which is applicable to an indoor visible light MIMO communication system, can combine LED modulation bandwidth with a multipath channel model, can solve a multipath fading channel modeling method when a transmitting end has time dispersivity and provides each path gain of a multipath channel. The multipath fading channel modeling method comprises the steps of (1) calculating time domain pulse response of each pair of an LED and a PD in a VLC-MIMO system by adopting an iteration method; (2) replacing a practical LOS (Light of Sight) channel by using an equivalent LOS channel to realize channel modeling synchronization as time dispersivity exists when a path difference between the LOS channels is great; (3) obtaining a symbol sampling speed of a receiving end based on the modulation bandwidth of the LED, providing definition of inter-symbol interference and accordingly determining an integral time section of each path gain of the multipath channel; and (4) integrating the pulse response in the integral time section of each path gain so as to obtain each path gain of the multichannel.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for channel state feedback by quantization of time-domain coefficients
ActiveUS20090185607A1Efficient collectionReduce amountReceivers monitoringSignal allocationTime domainChannel state information
The present invention relates to a channel state transmission method using time domain coefficient quantization. A terminal measures channel information in the time domain and transmits it to a base station. In this instance, a multipath frequency selective fading channel is displayed in a tapped delay line format configured with a per-path path delay value and a path gain in the time domain, differentiates a quantization level for each path gain for more efficient transmission, quantizes the same, and transmits it to a transmitter. Therefore, while the amount of bandwidths required for transmitting state information from the terminal to the base station is reduced, the base station can efficiently acquire channel state information on the entire bandwidths. Also, the base station transmits signals to many terminals through beamforming by using the acquired reliable channel state information, thereby increasing the terminal's signal receiving performance.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +2
Using uplink relative path gain related measurements to support uplink resource management
A cellular system includes a first cell associated with a first base station, a second cell associated with a second base station, and a mobile radio currently served by the first base station. Distributed resource control may be used in which the first base station alone or in combination with the mobile station makes resource management decisions without having to involve a central controller. In ad-hoc networking, access points can manage resources in a distributed fashion. Relative path gain is determined for an uplink signal from the mobile radio. Relative path gain is based on a comparison of a first path gain related quantity for a mobile uplink signal to the second base station with a second path gain related quantity for the mobile uplink signal to the second base station. Uplink resources in the first cell are managed based on the relative path gain related quantity.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
System and method of automatically calibrating the gain for a distributed wireless communication system
InactiveUSRE41936E1Power managementTransmission control/equalisingCable transmissionCommunications system
A system and method providing a wireless broadband connection between base stations and customer sites. The system includes indoor units, within the base stations and customer sites, that communicate across cables to outdoor units. The indoor units link to routers, switches and other devices and services. The outdoor units transmit and receive wireless data and send it to the indoor units. The indoor units control the functioning of the outdoor units by transmitting digital messages along the interface cables. The outdoor units report various detector values to the indoor units, which allows the indoor units to tune and adjust several functions within the outdoor units. Several embodiments for automatically calibrating the receive path gain in the base stations to compensate for the base station cable between the indoor unit and outdoor unit are described. In addition, anAn improved transmit power control technique which is not affected by modulation type, is also described.
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
Clock and data recovery circuit with jitter tolerance enhancement
ActiveUS20180198597A1Improve toleranceSynchronisation error correctionPulse automatic controlBang bangLoop bandwidth
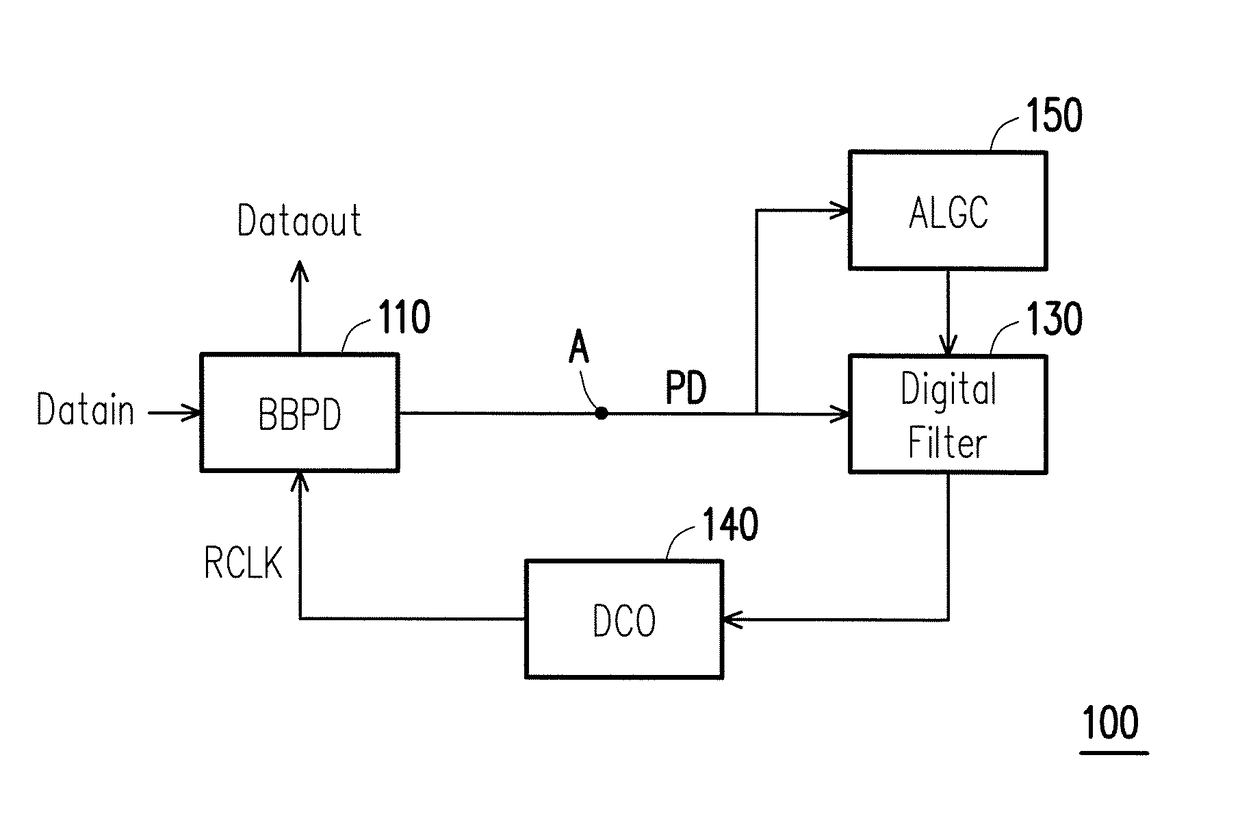
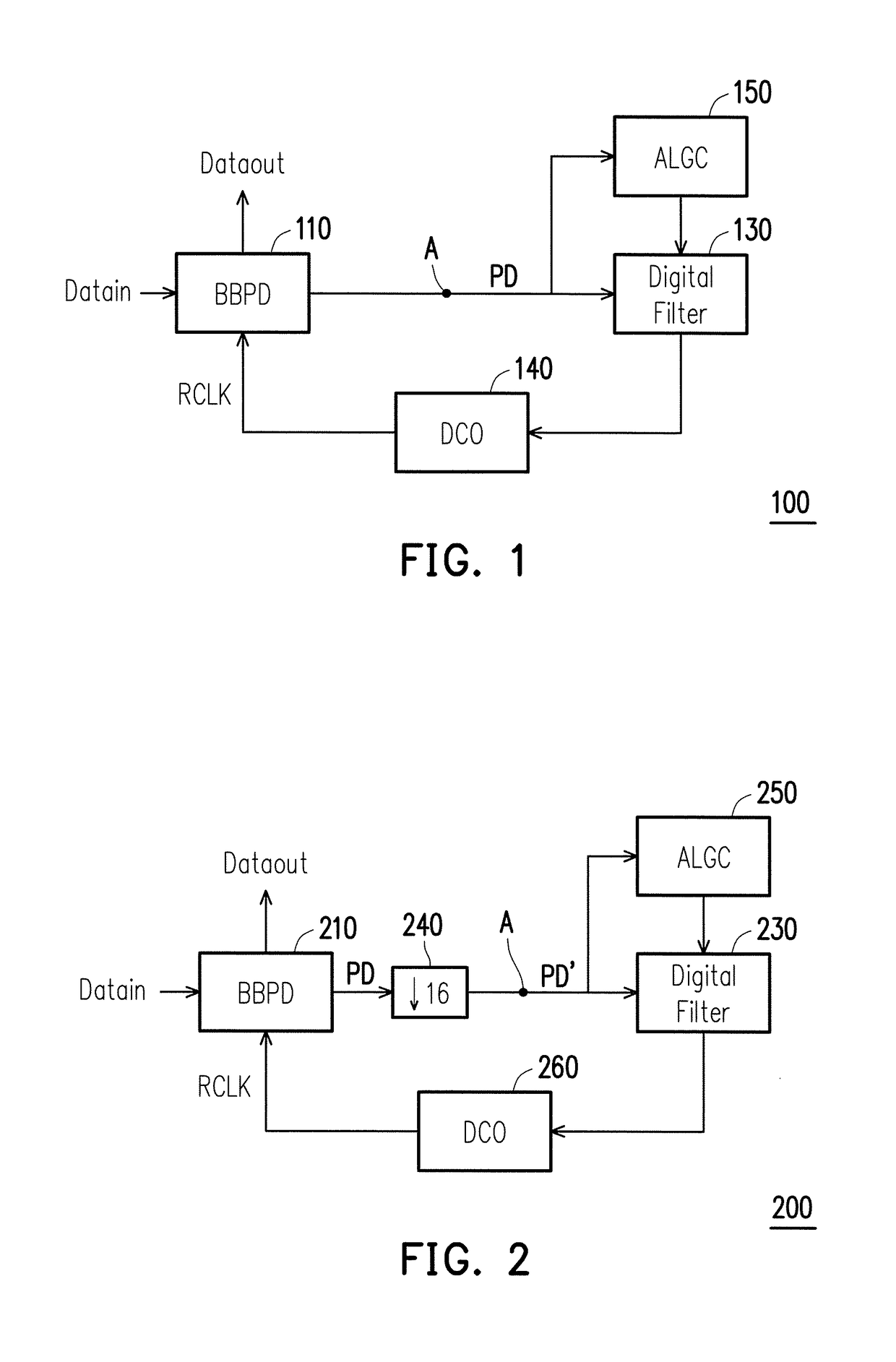
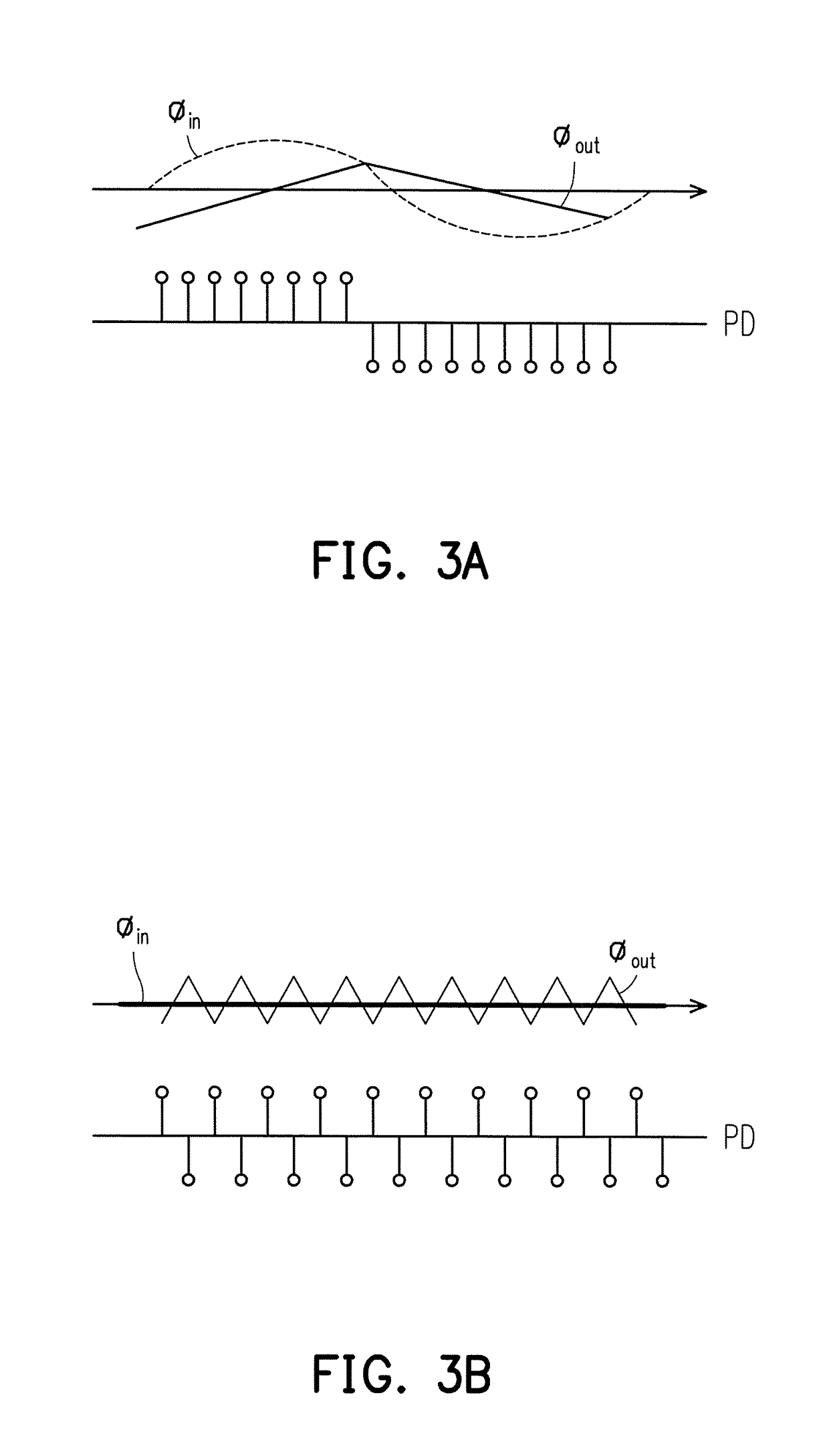
A clock and data recovery circuit with jitter tolerance enhancement is provided. The CDR circuit includes: a bang-bang phase detector, a digital filter, a digitally controlled oscillator, and an adaptive loop gain control circuit. The CDR circuit detects a loop bandwidth variation and adjusts the loop bandwidth of CDR circuit by adjusting proportional path and integral path gain factors of the digital filter of the CDR circuit. The loop gain controller uses two methods to adjust the loop gain in CDR circuit: bang-bang adjusting method and linear adjusting method.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Multi-path channel modeling method of indoor single light source visible light communication system
InactiveCN107332615ASolve the synchronization problem of multipath channel modelingThe starting point of time is not easy to determineClose-range type systemsTransmission monitoringStart timeTime delays
The invention relates to a multi-path channel modeling method of an indoor single light source visible light communication system. In view of a small angle of view of an actual photoelectric detector (PD), the invention provides the multi-path channel modeling method according to an LED modulation symbol period. The method comprises a first step of giving a size of an indoor communication room, and characteristics of an LED and a PD, and calculating, by using an iteration method, time domain impulse responses of line of sight and multiple reflection signals between the LED and the PD in the single light source visible light communication system; a second step of determining a starting time point of multi-path channel modeling; a third step of giving a definition of inter-code interference, and determining a symbol sampling period of a receiving terminal; a fourth step of using a sum of impulse responses between sampling intervals as a gain of each path of the multi-path channel; and a fifth step of relative to the starting time point of modeling, dividing the sampling period by time delay of a finally received optical signal, and rounding up to an integer of a result of the previous division operation so as to be used as a total number of paths of the multi-path channel.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com