Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
533 results about "Digitally controlled oscillator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
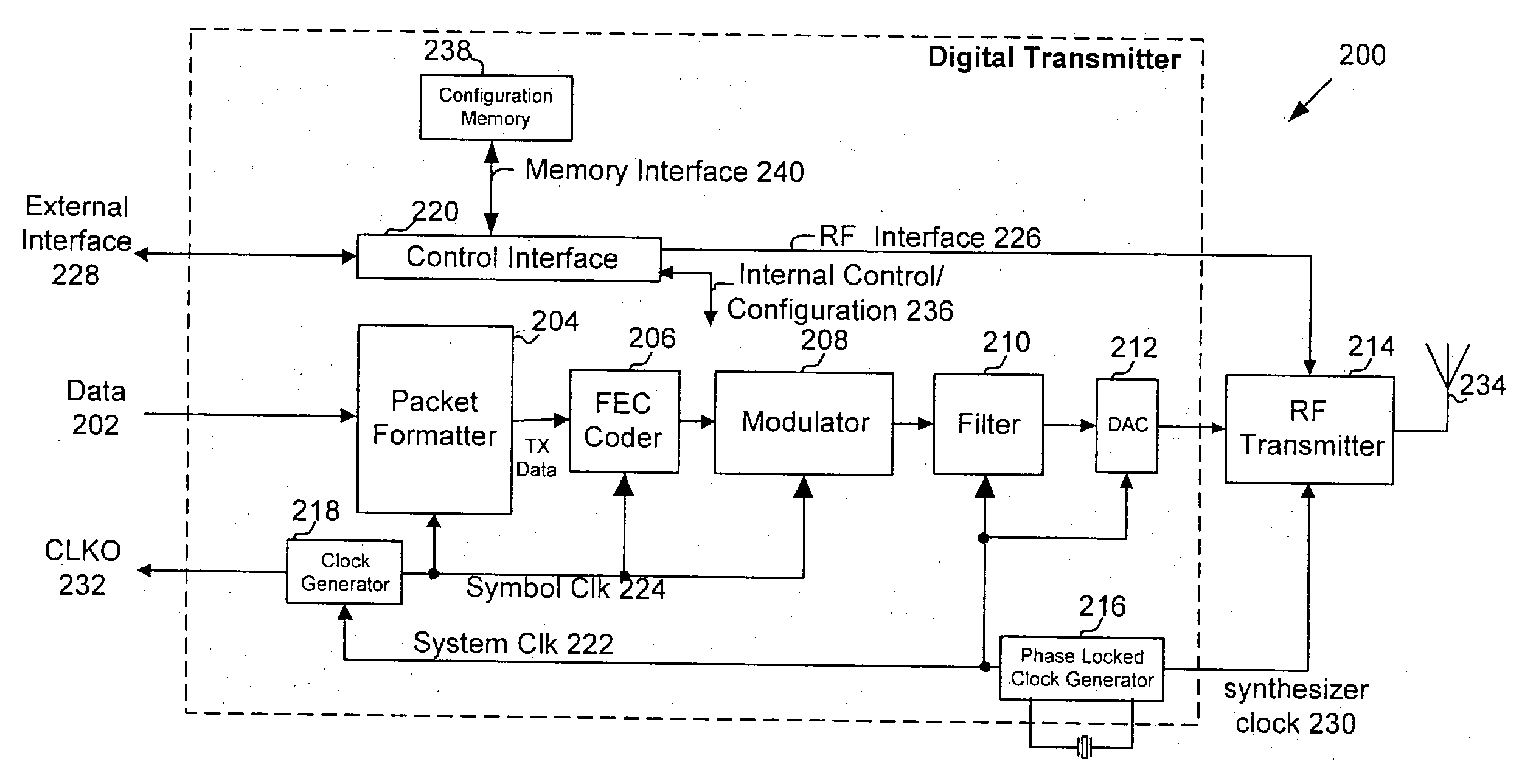
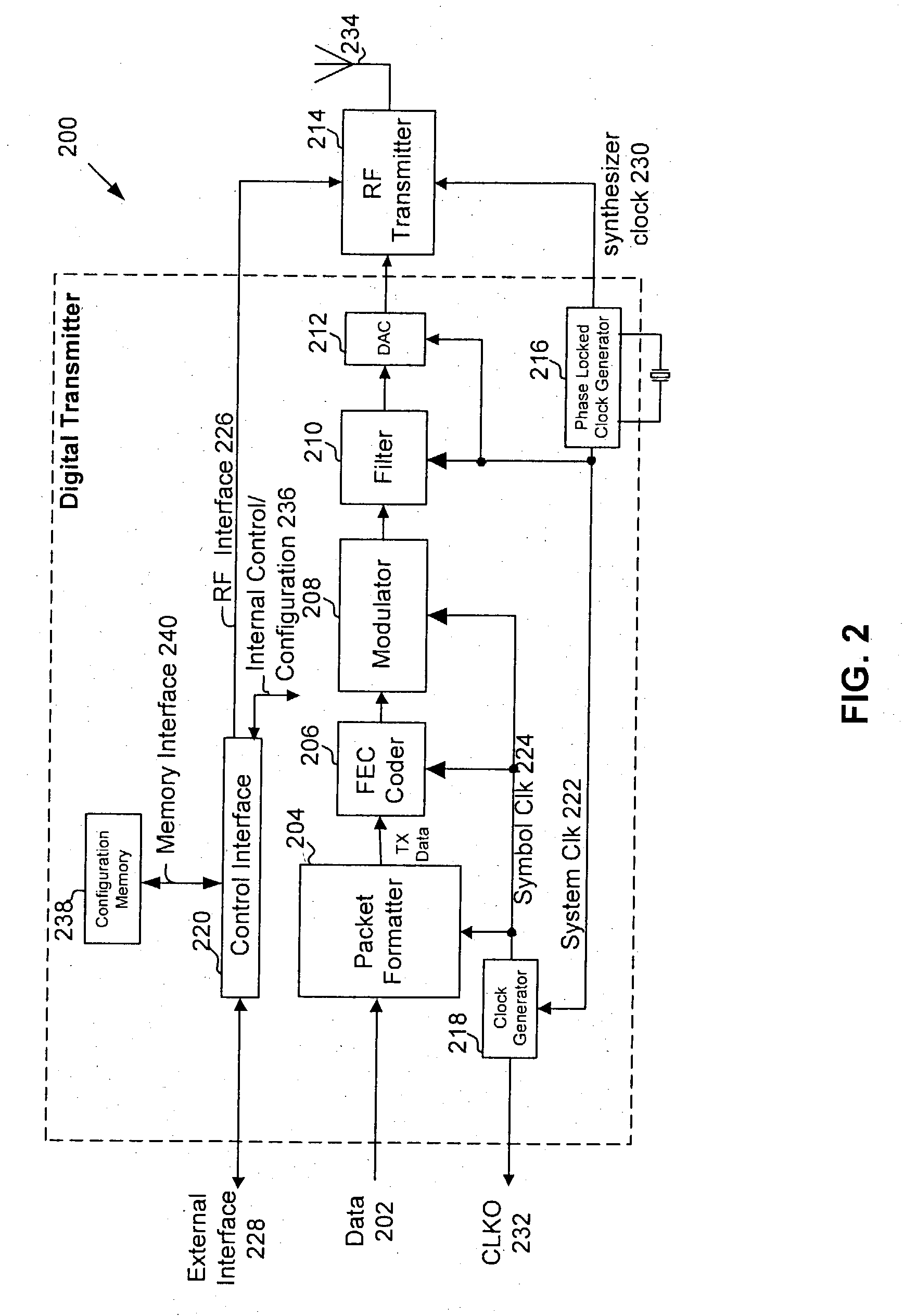
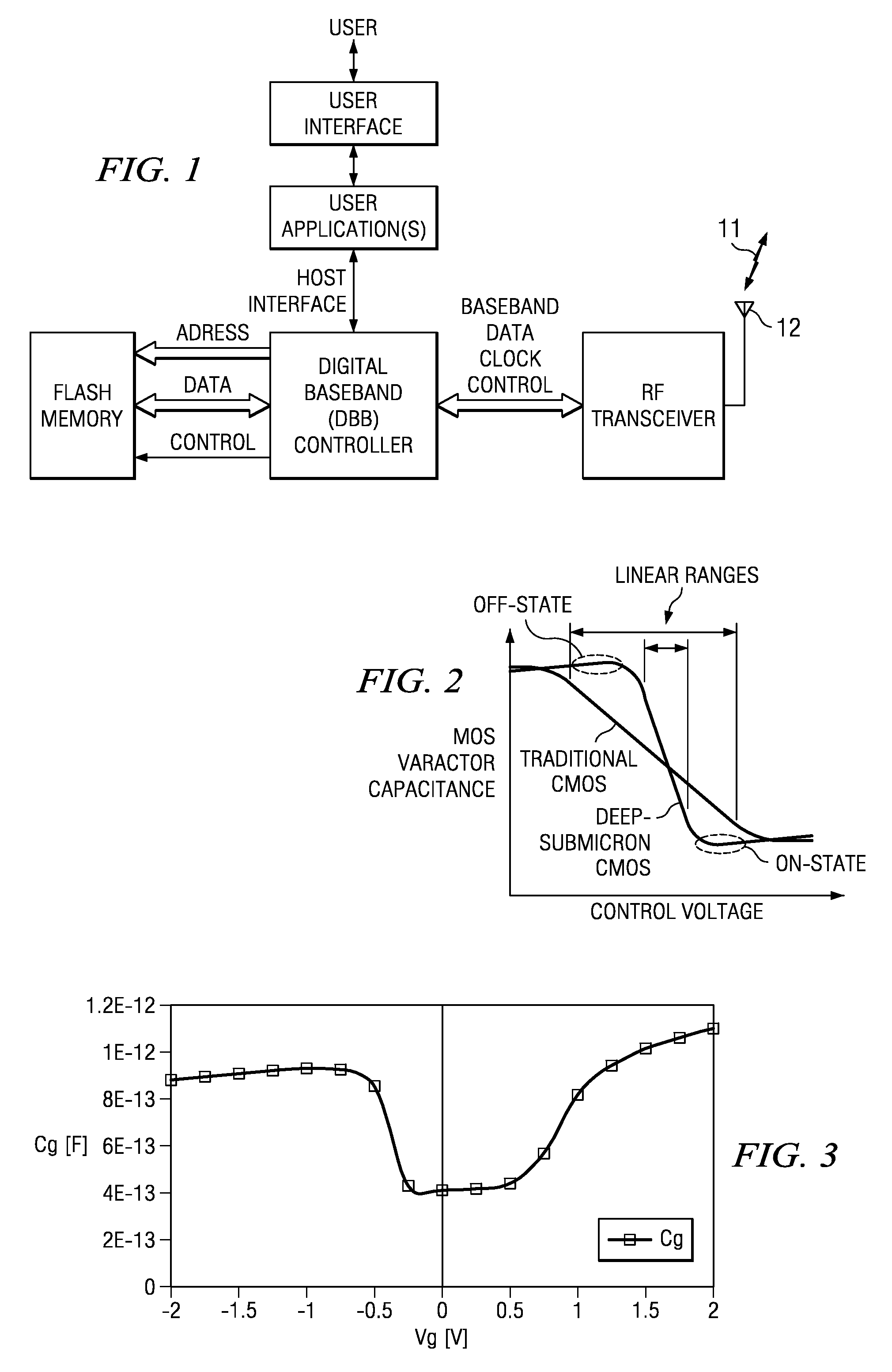
A digitally controlled oscillator or DCO is used in synthesizers, microcontrollers, and software-defined radios. The name is analogous with "voltage-controlled oscillator." DCOs were designed to overcome the tuning stability limitations of early VCO designs. Using a DCO does not make a synthesizer "digital" or "hybrid".
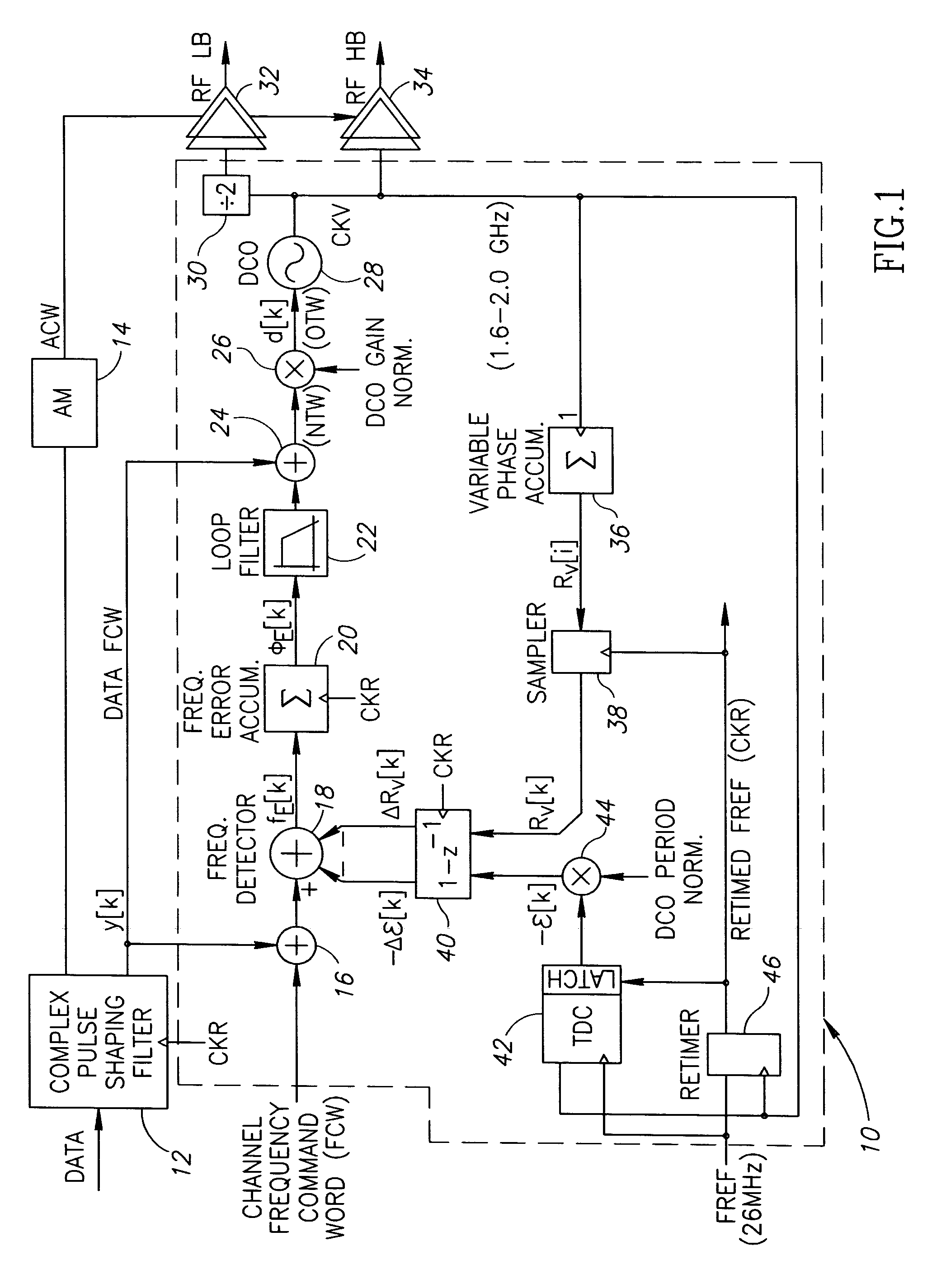
All-digital frequency synthesis with capacitive re-introduction of dithered tuning information
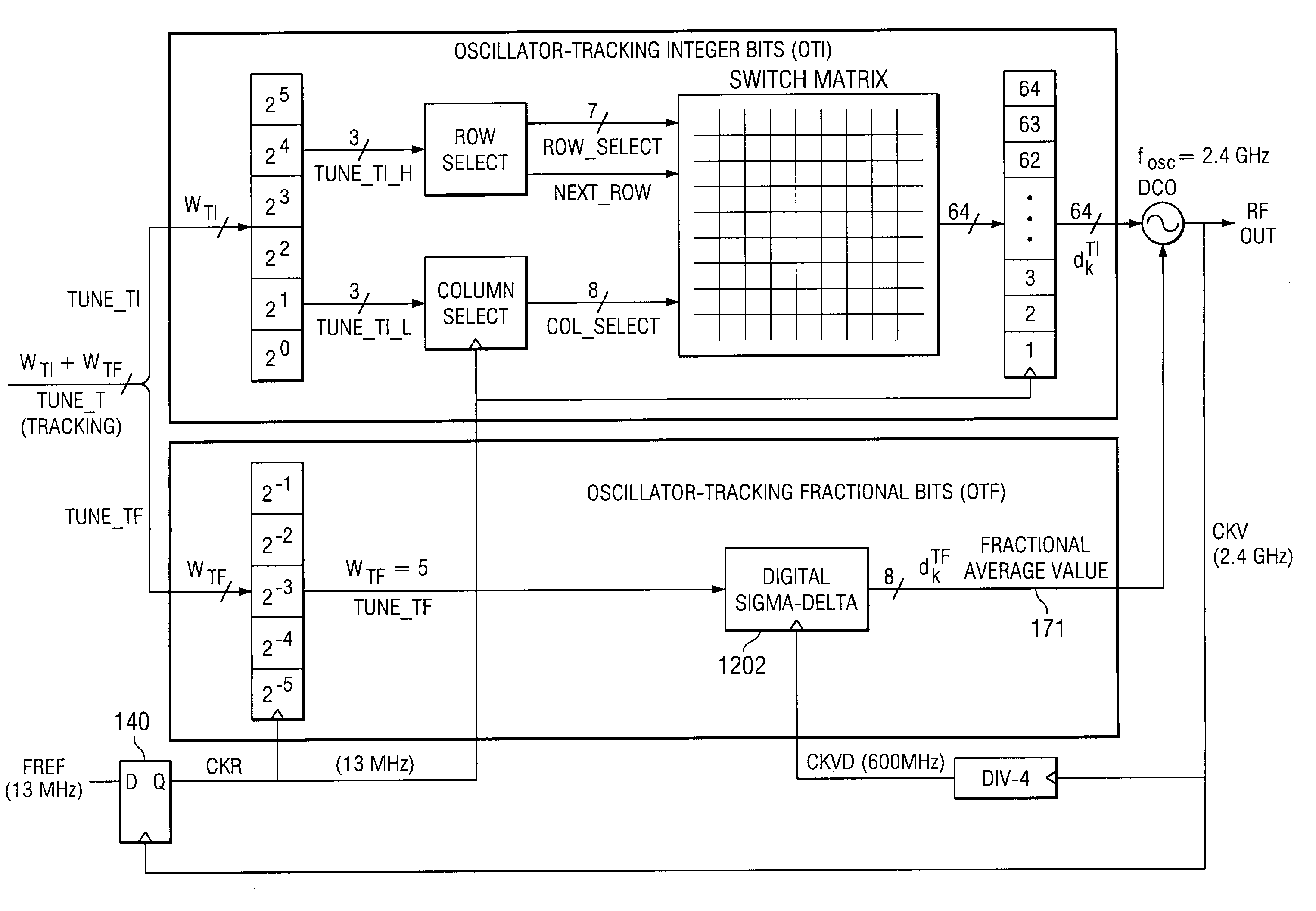
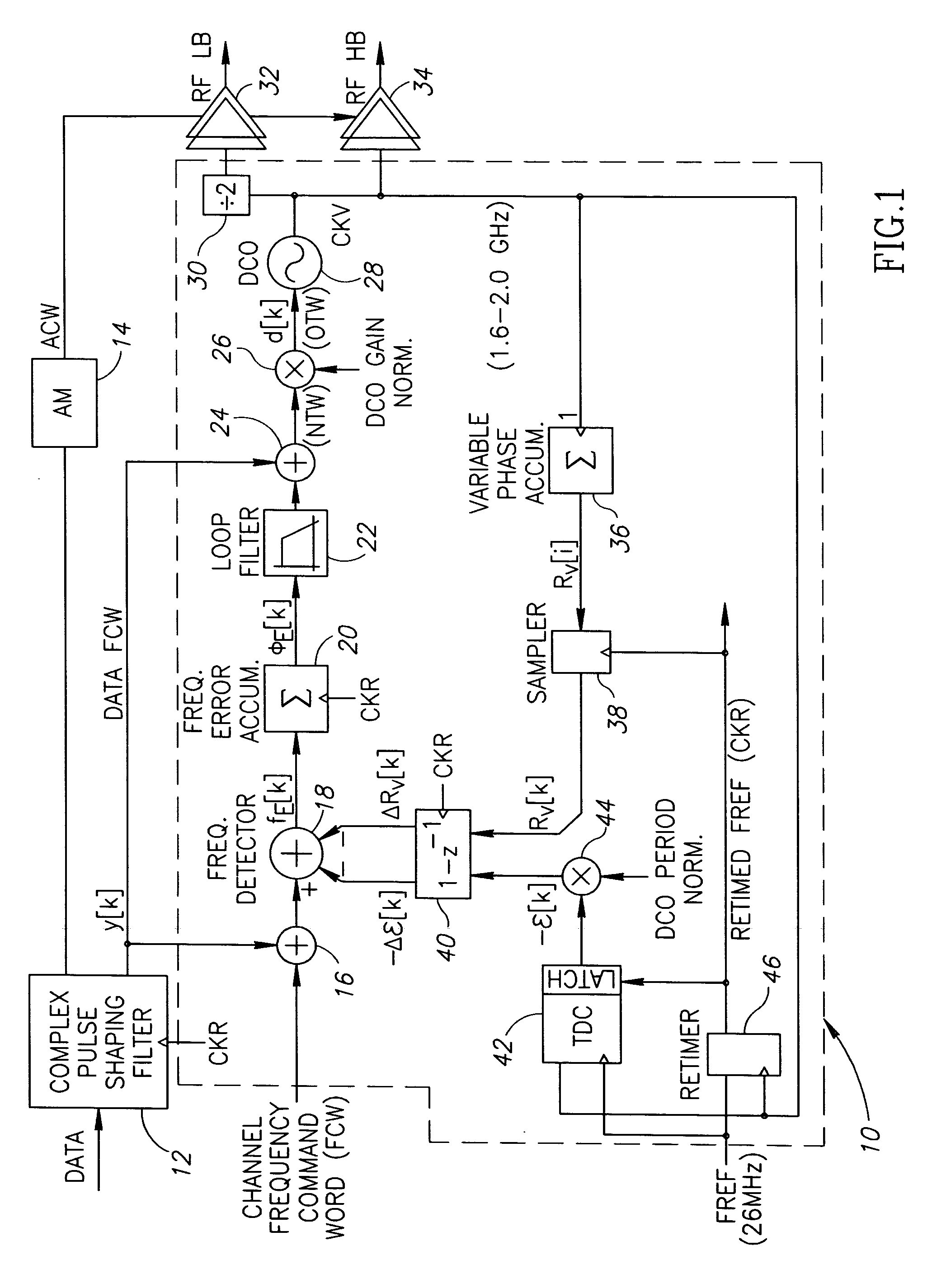
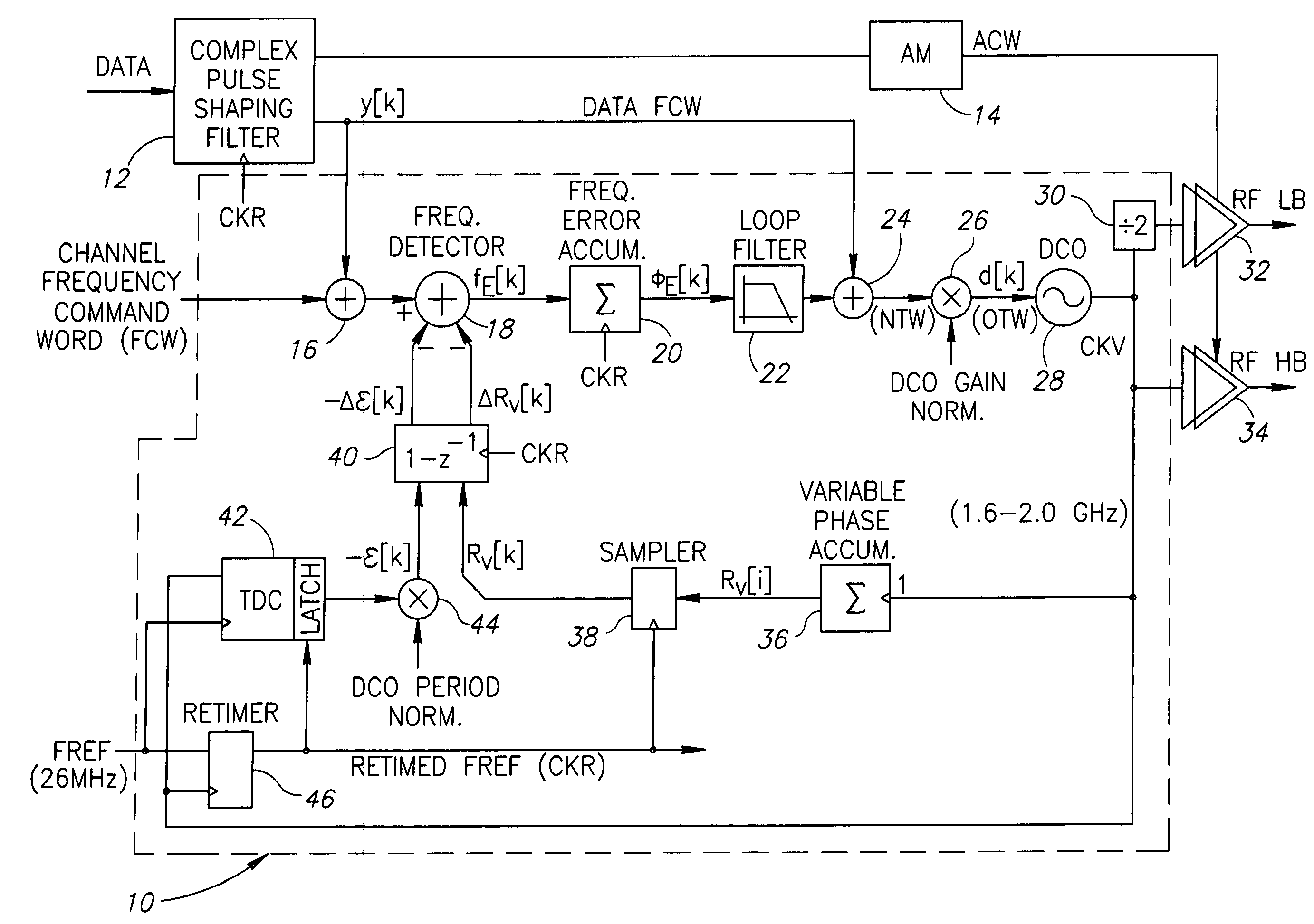
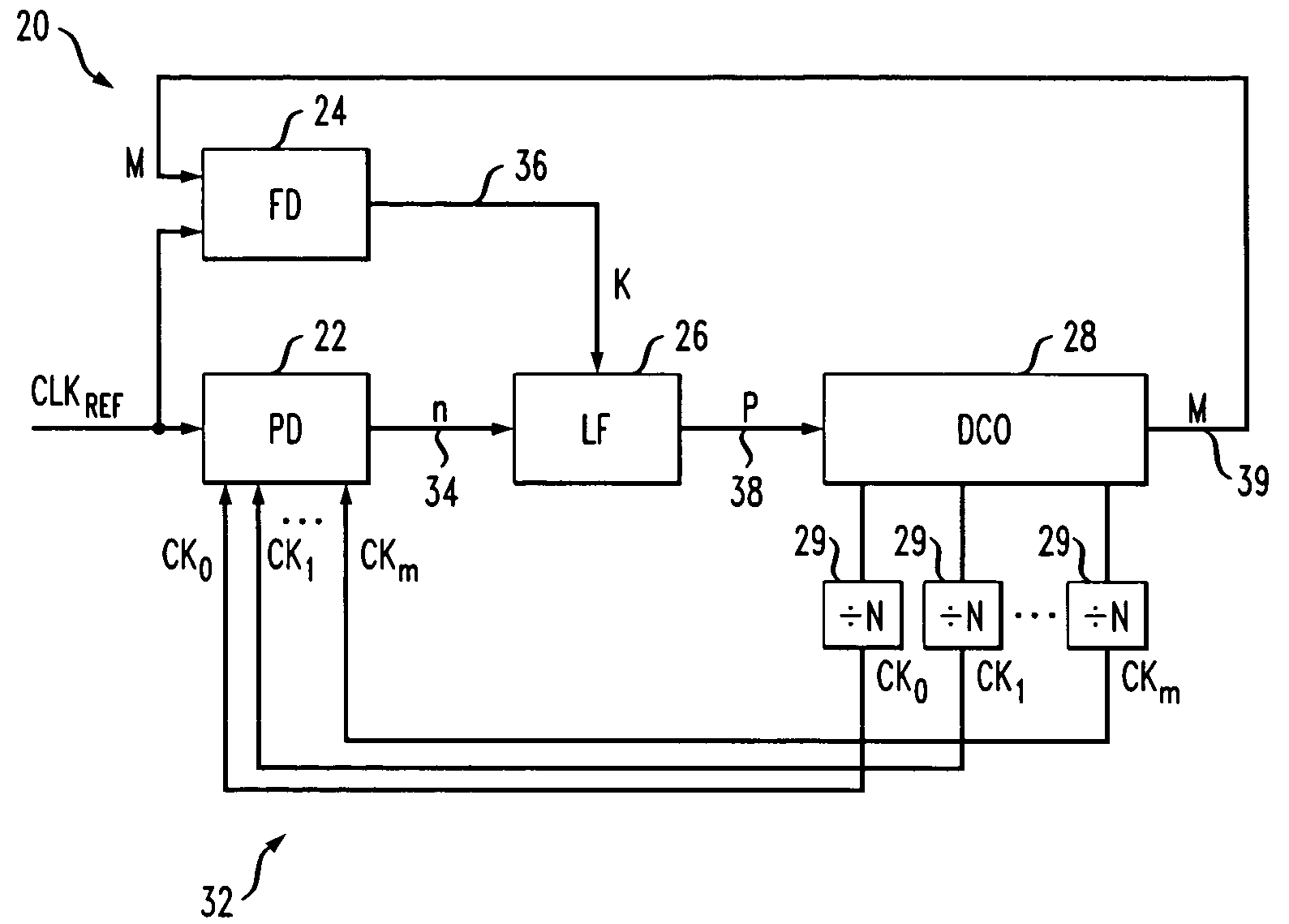
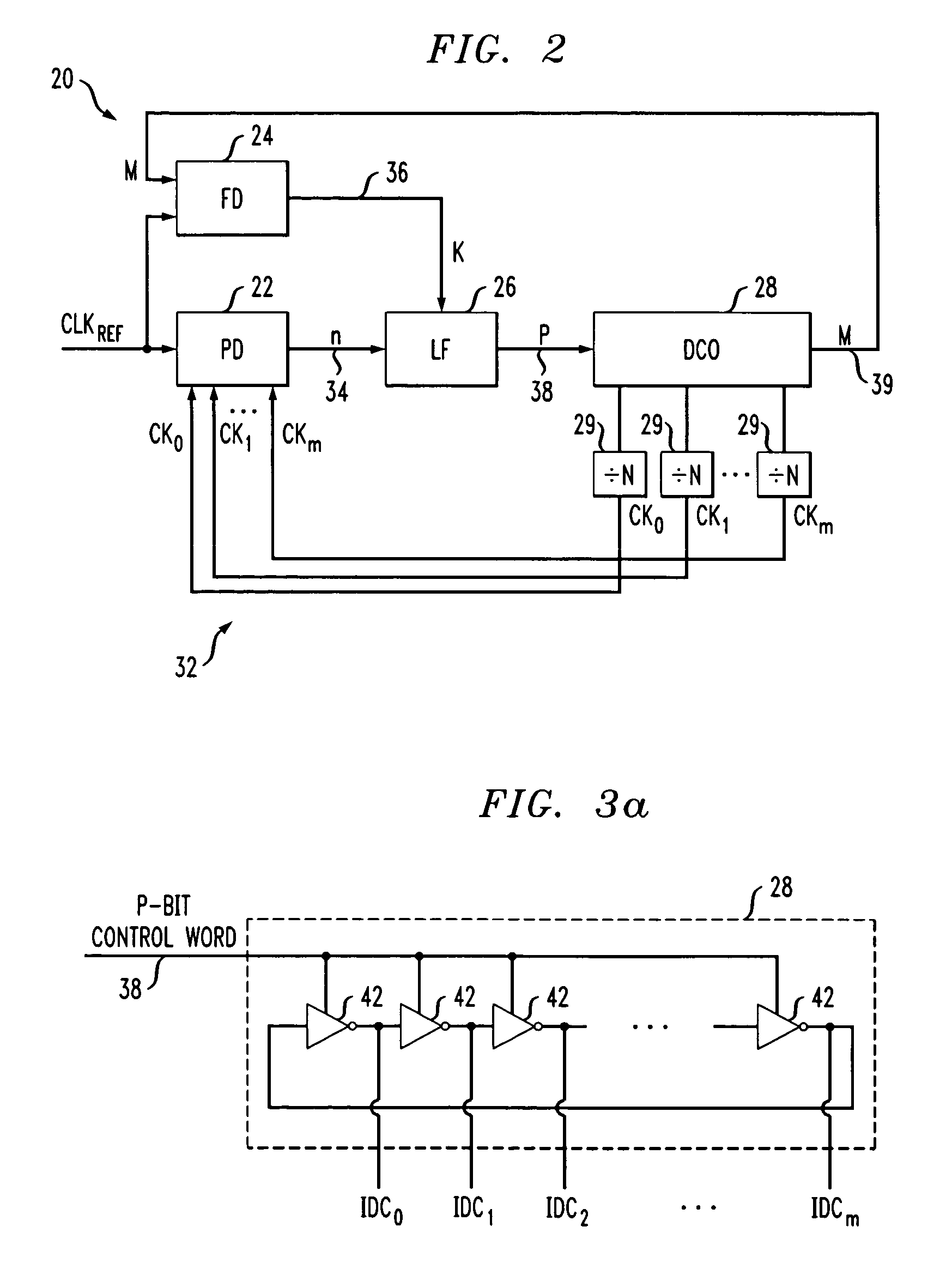
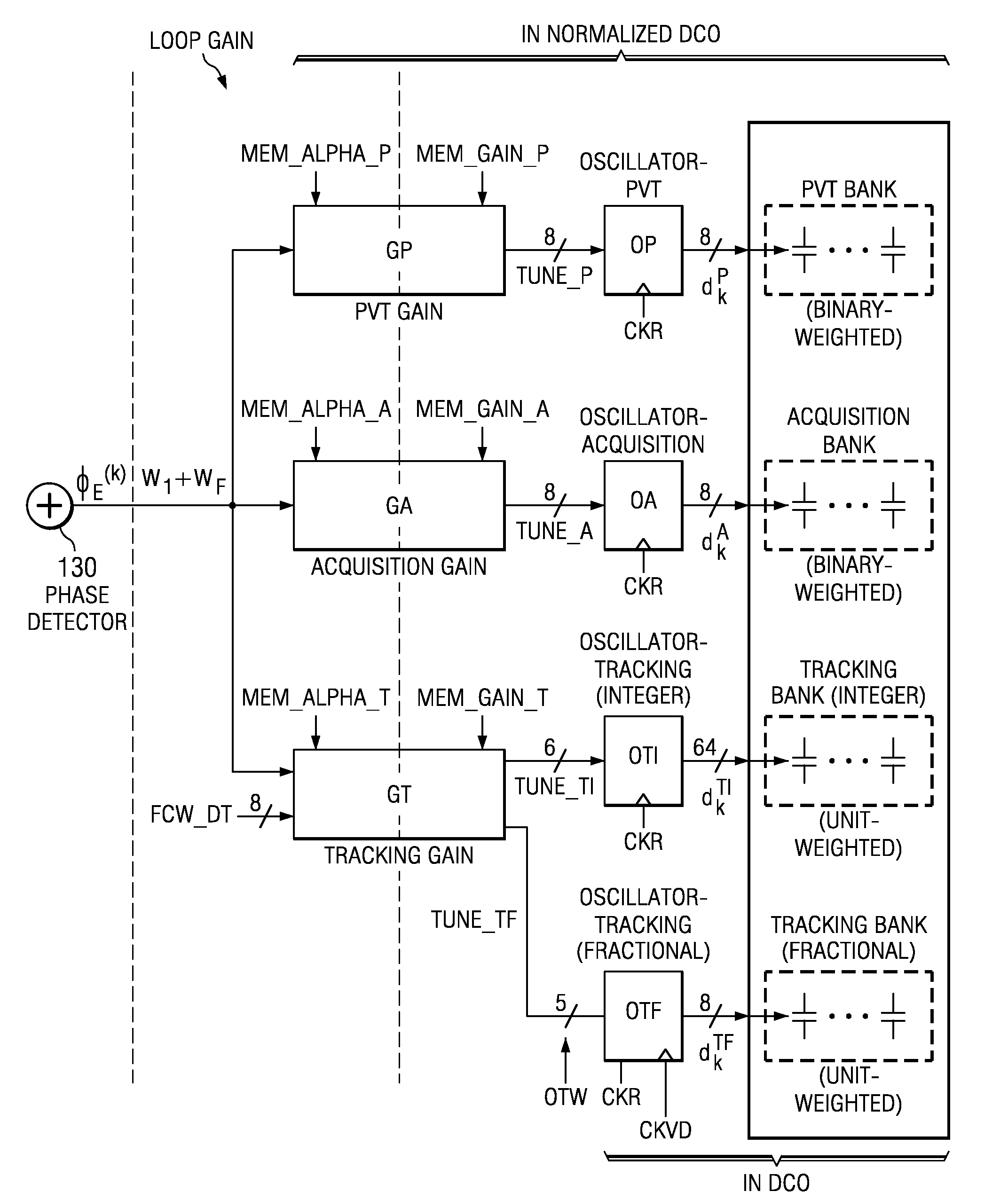
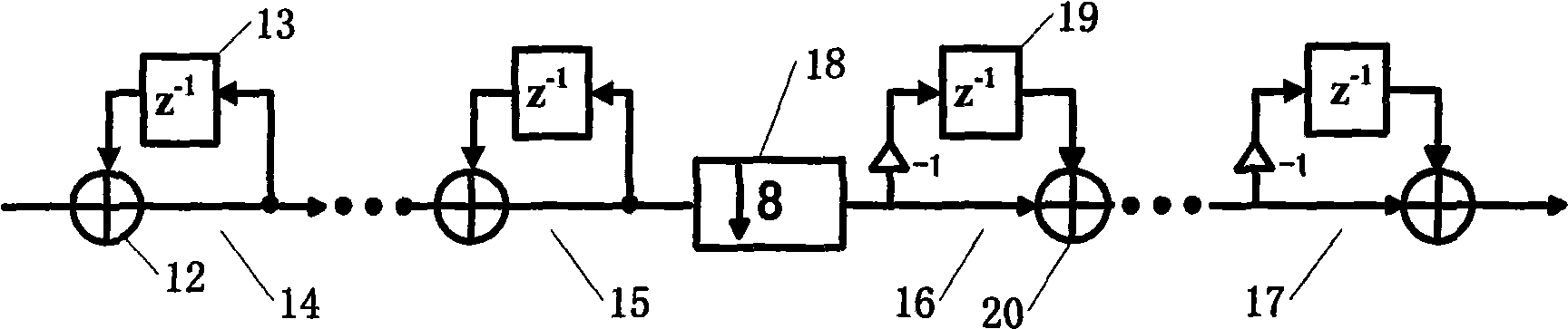
An all-digital frequency synthesizer architecture is built around a digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) that is tuned in response to a digital tuning word (OTW). In exemplary embodiments: (1) a gain characteristic (KDCO) of the digitally controlled oscillator can be determined by observing a digital control word before and after a known change (Δfmax) in the oscillating frequency; and (2) a portion (TUNE_TF) of the tuning word can be dithered (1202), and the resultant dithered portion(dkTF)can then be applied to a control input of switchable devices within the digitally controlled oscillator.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Gain calibration of a digital controlled oscillator
ActiveUS20060033582A1Good estimateImprove performancePulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsSteep descentDigital control oscillator
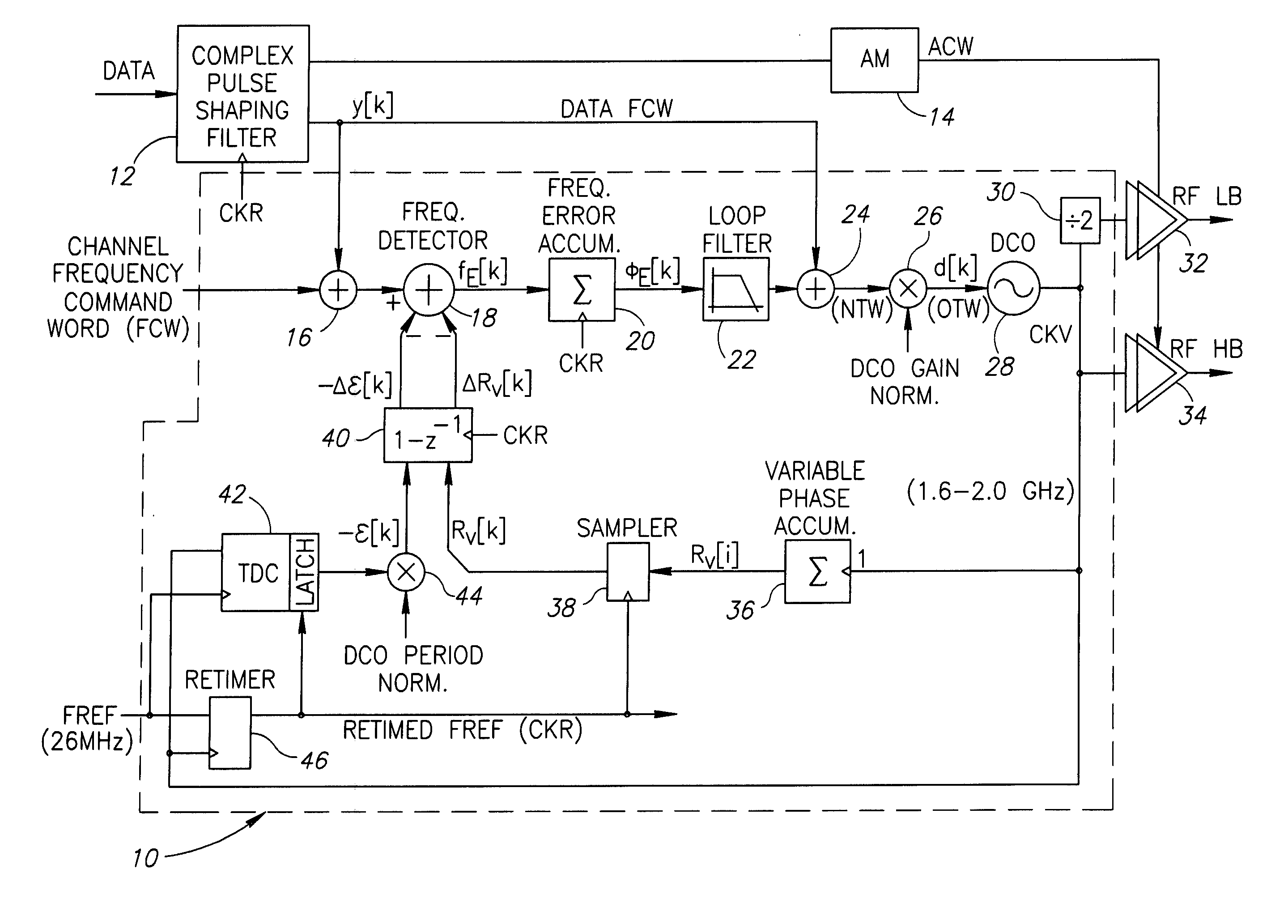
A novel apparatus for and a method of estimating, calibrating and tracking in real-time the gain of a radio frequency (RF) digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) in an all-digital phase locked loop (ADPLL). Precise setting of the inverse DCO gain in the ADPLL modulating path allows direct wideband frequency modulation that is independent of the ADPLL loop bandwidth. The gain calibration technique is based on a steepest descent iterative algorithm wherein the phase ADPLL error is sampled and correlated with the modulating data to generate a gradient. The gradient is then scaled and added to the current value of the DCO gain multiplier.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
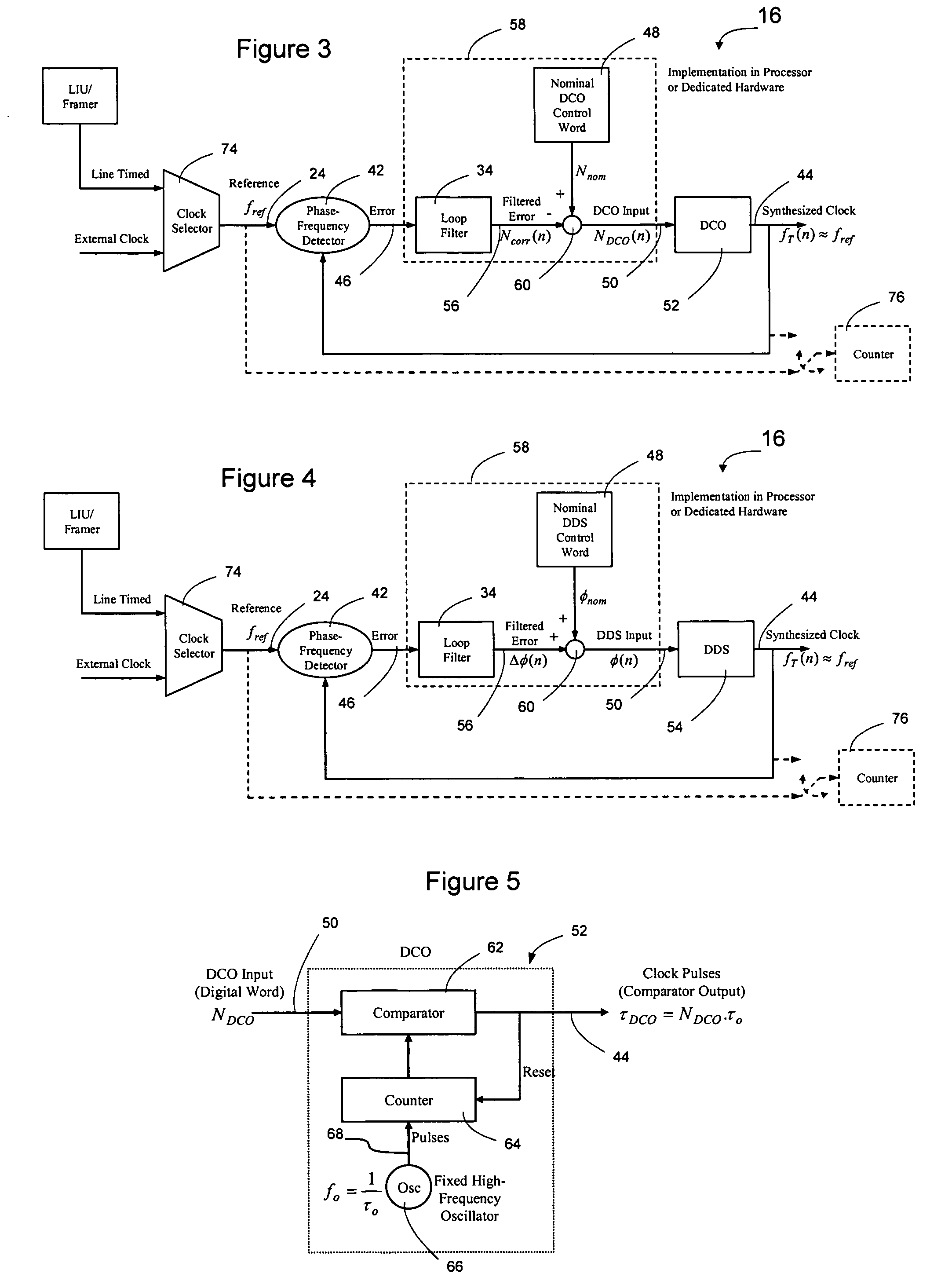
Method and apparatus for synchronizing clock timing between network elements
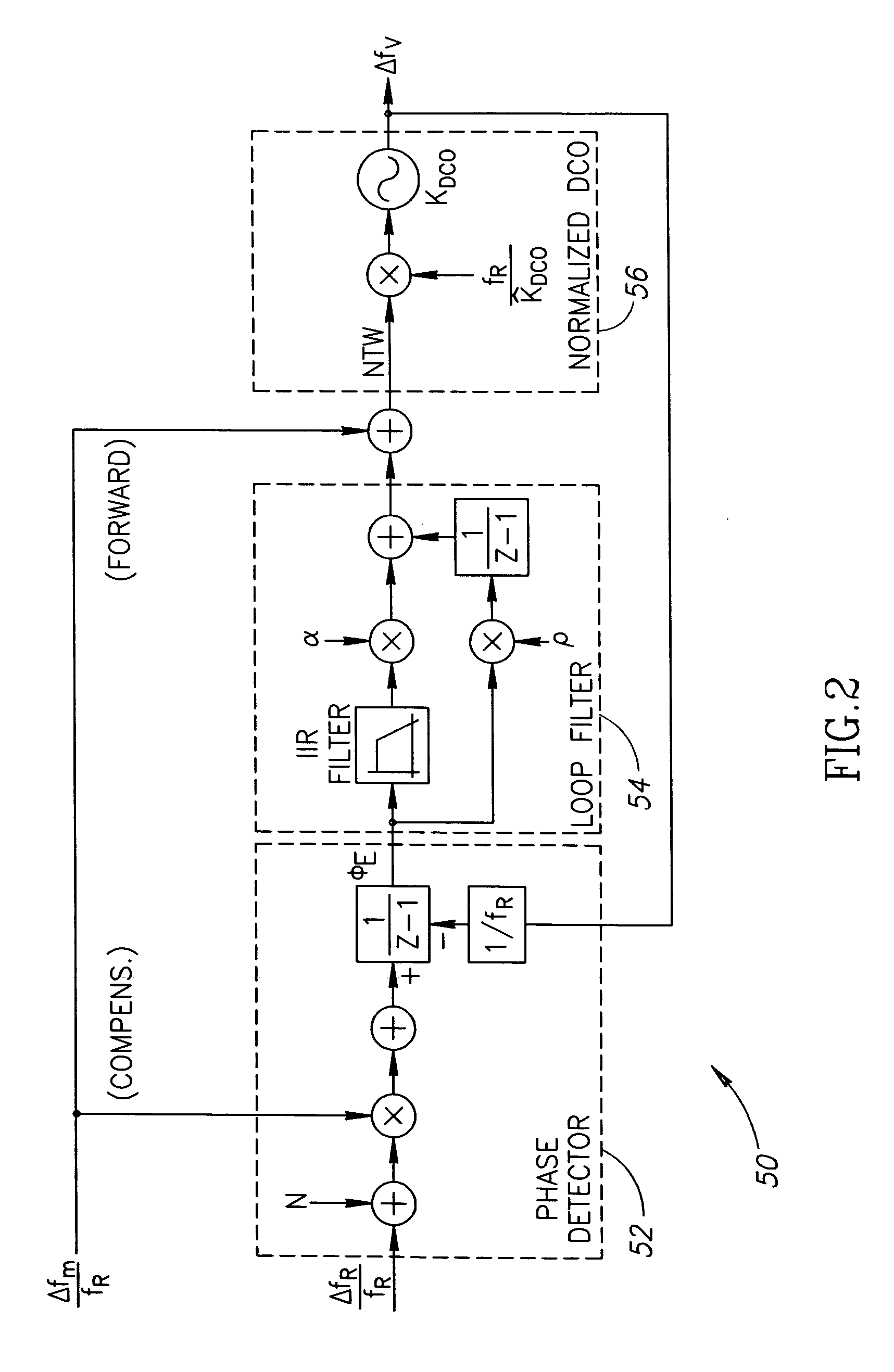
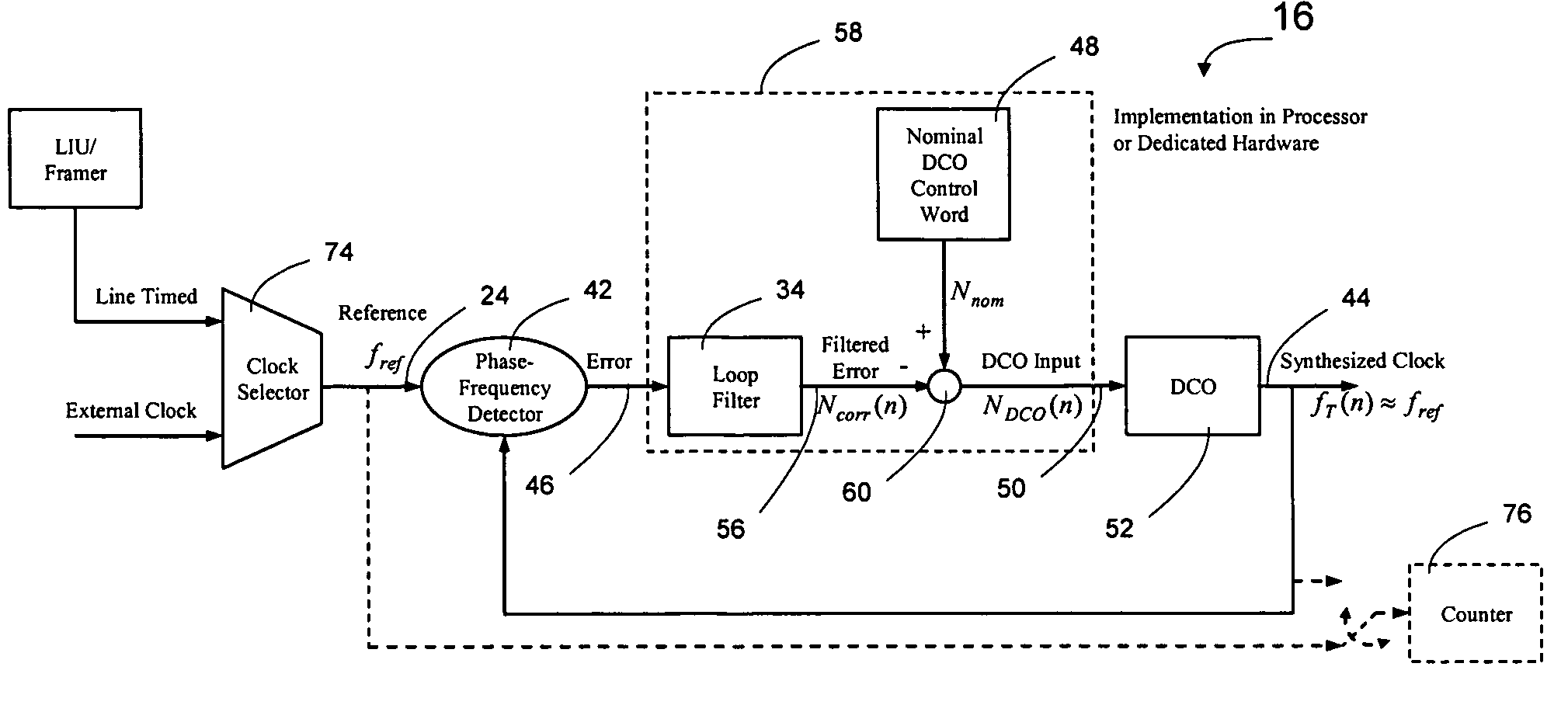
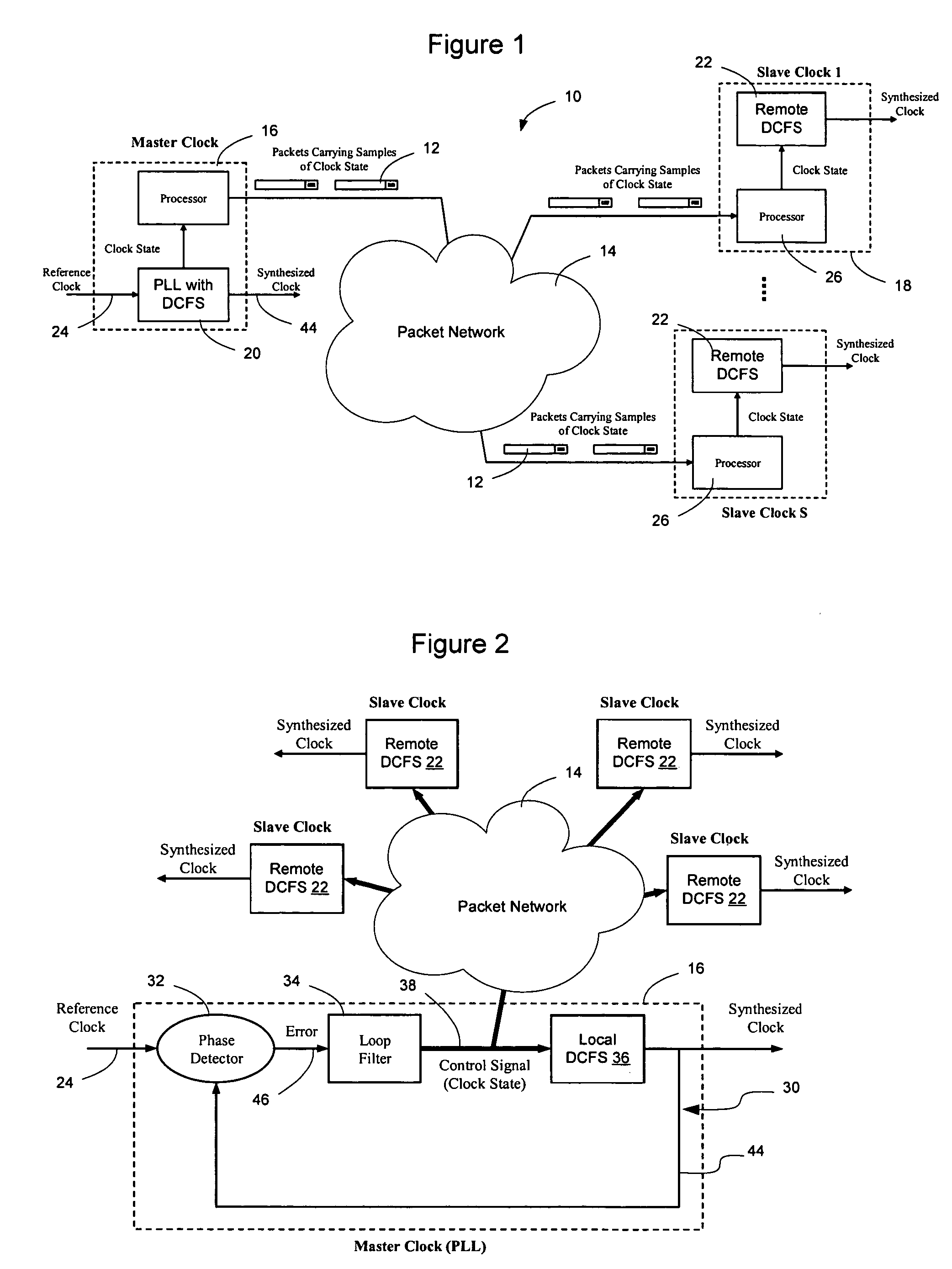
Network elements may be synchronized over an asynchronous network by implementing a master clock as an all digital PLL that includes a Digitally Controlled Frequency Selector (DCFS), the output frequency of which may be directly controlled through the input of a control word. The PLL causes the control word input to the master DCFS to be adjusted to cause the output of the master DCFS to lock onto a reference frequency. Information associated with the control word is transmitted from the master clock to the slave clocks which are also implemented as DCFSs. By using the transmitted information to recreate the master control word, the slaves may be made to assume the same state as the master DCFS without requiring the slaves to be implemented as PLLs. The DCFS may be formed as a digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) or as a Direct Digital Synthesizer (DDS).
Owner:CIENA
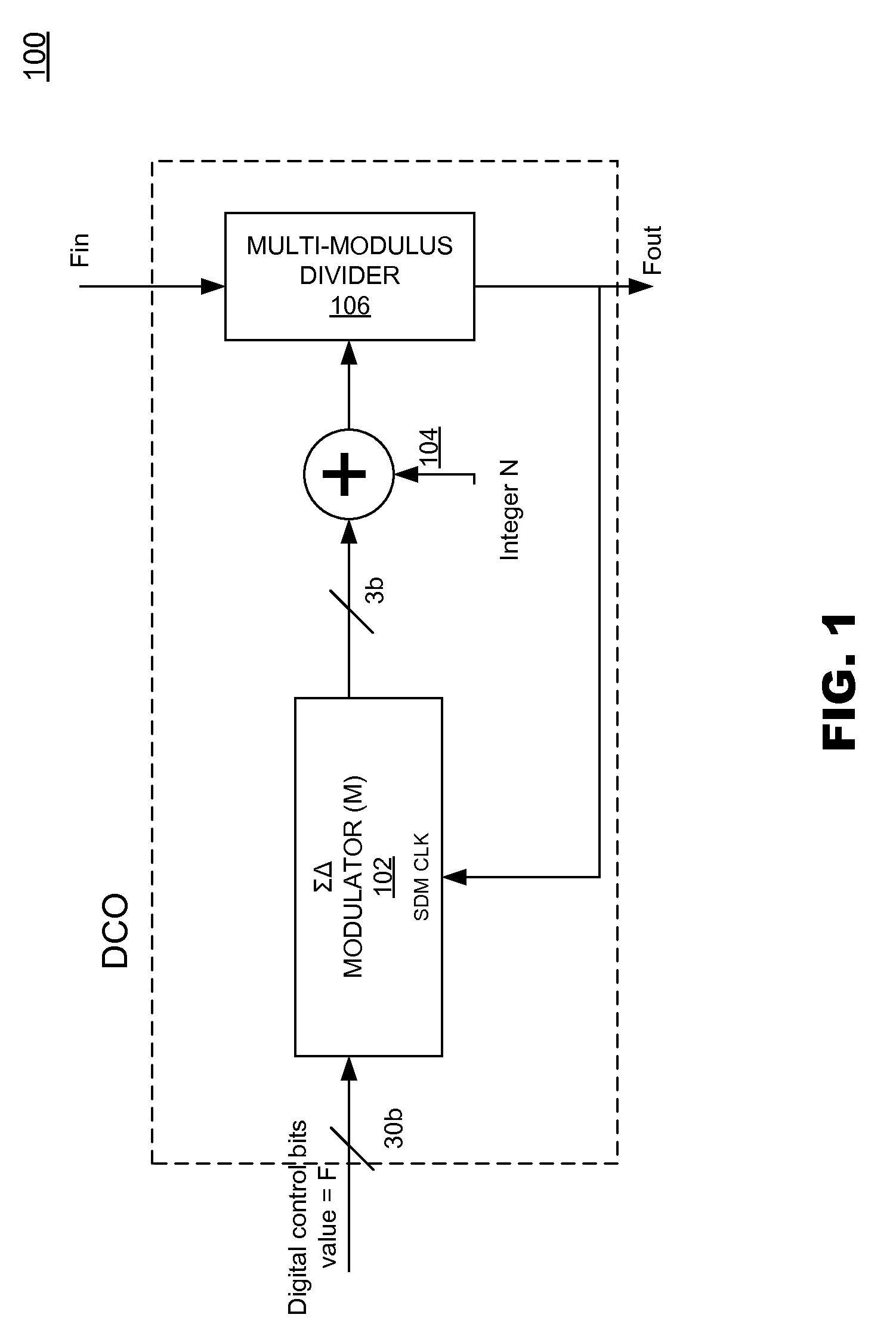
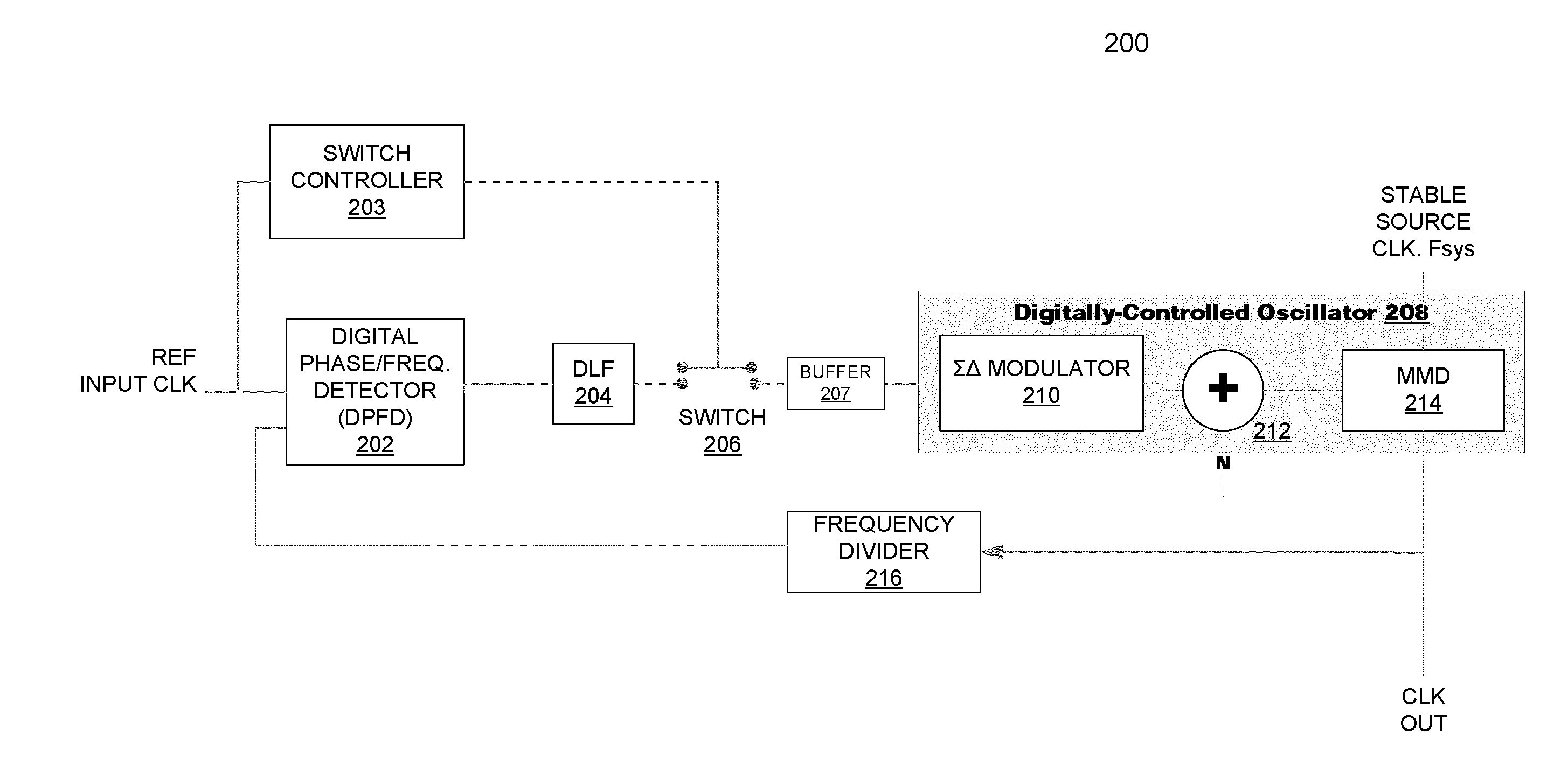
Digital Phase-Locked Loop Clock System
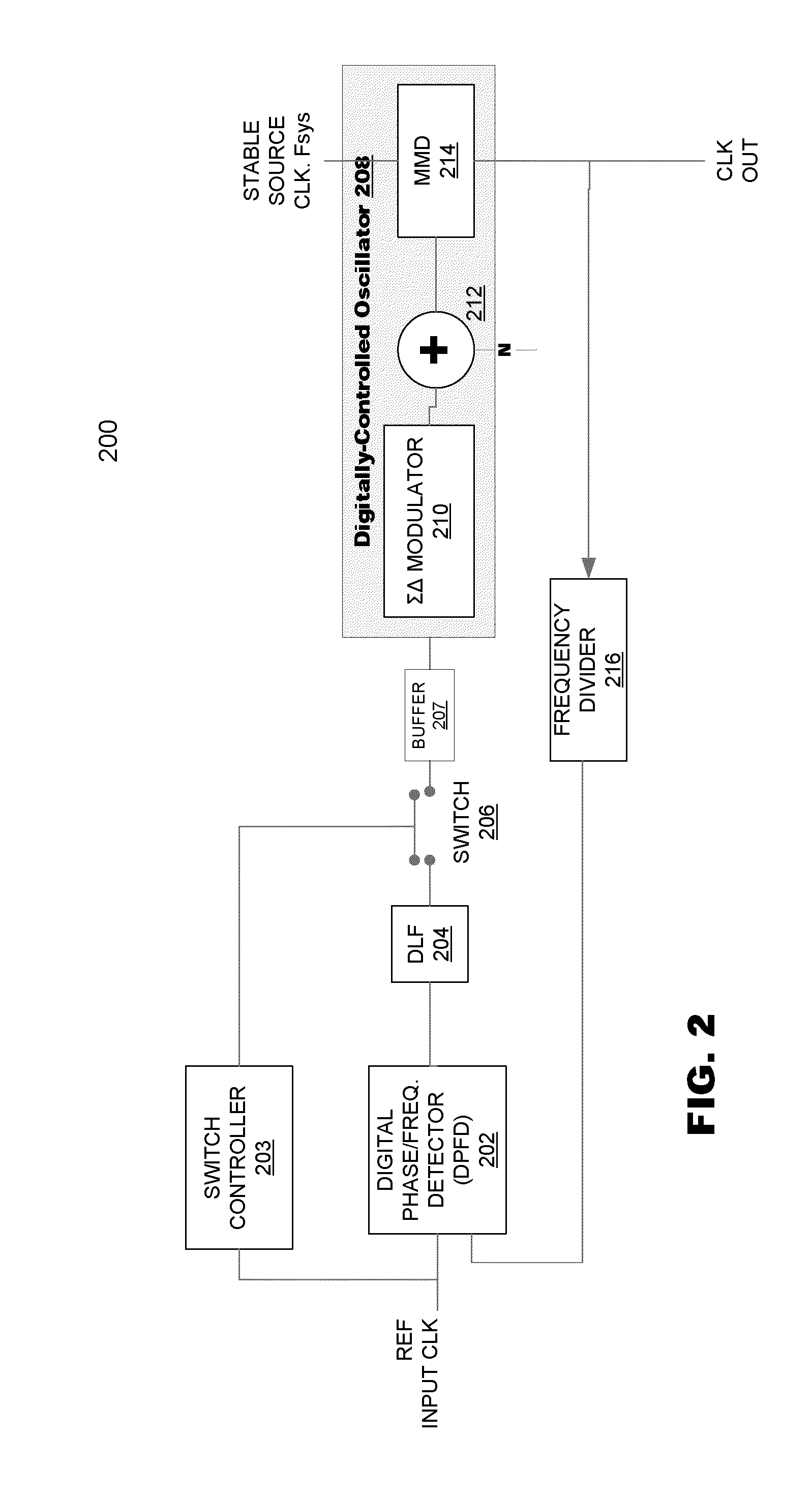
A clock system includes a digital phase / frequency detector (DPFD), a buffer, a digitally-controlled oscillator (DCO) including a sigma-delta modulator (SDM), an adder, a first frequency divider. The DPFD may have a first input for a reference input clock and a second input for a feedback signal, and outputting a difference signal representing a phase and / or frequency difference between the reference input clock and the feedback signal. The buffer may be coupled to the DPFD for accumulating the difference signal over time. The sigma-delta modulator (SDM) may have a control input coupled to the buffer. The adder may have inputs coupled to the (SDM) and a source of an integer control word. The first frequency divider may have an input for a clock signal and a control input coupled to the adder, the DCO generating an output clock signal having an average frequency representing a frequency of the input clock signal divided by (N+F / M), wherein N is determined by the integer control word and F / M is determined by an output of the SDM. The system clock also may include a phase-locked loop (PLL) including a phase / frequency detector that has a first input coupled to the output of the DCO and a second input that is phase-locked to the first input, and a second frequency divider coupled from the second input of the PLL to the second input of the DPFD.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Low complexity synchronization for wireless transmission
ActiveUS20040196926A1Eliminate needInexpensive and low-complexity synchronization for communication systemsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlDigital dataCommunications system
A receiver, system and method for providing symbol timing recovery that allows for inexpensive and low-complexity synchronization for communication systems. A receiver receives a signal including digital data in the form of packets that is transmitted from a transmitter. The receiver uses information contained in each of the packets to align a phase of the receiver clock with a phase of the transmitter clock. The receiver further controls a sampling device such that the in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components are sampled at an optimum sample rate and at an optimum instance of time without requiring a numerically controlled oscillator or voltage controlled oscillator.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Gain calibration of a digital controlled oscillator
ActiveUS7183860B2Good estimatePulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsSteep descentDigital control oscillator
A novel apparatus for and a method of estimating, calibrating and tracking in real-time the gain of a radio frequency (RF) digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) in an all-digital phase locked loop (ADPLL). Precise setting of the inverse DCO gain in the ADPLL modulating path allows direct wideband frequency modulation that is independent of the ADPLL loop bandwidth. The gain calibration technique is based on a steepest descent iterative algorithm wherein the phase ADPLL error is sampled and correlated with the modulating data to generate a gradient. The gradient is then scaled and added to the current value of the DCO gain multiplier.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
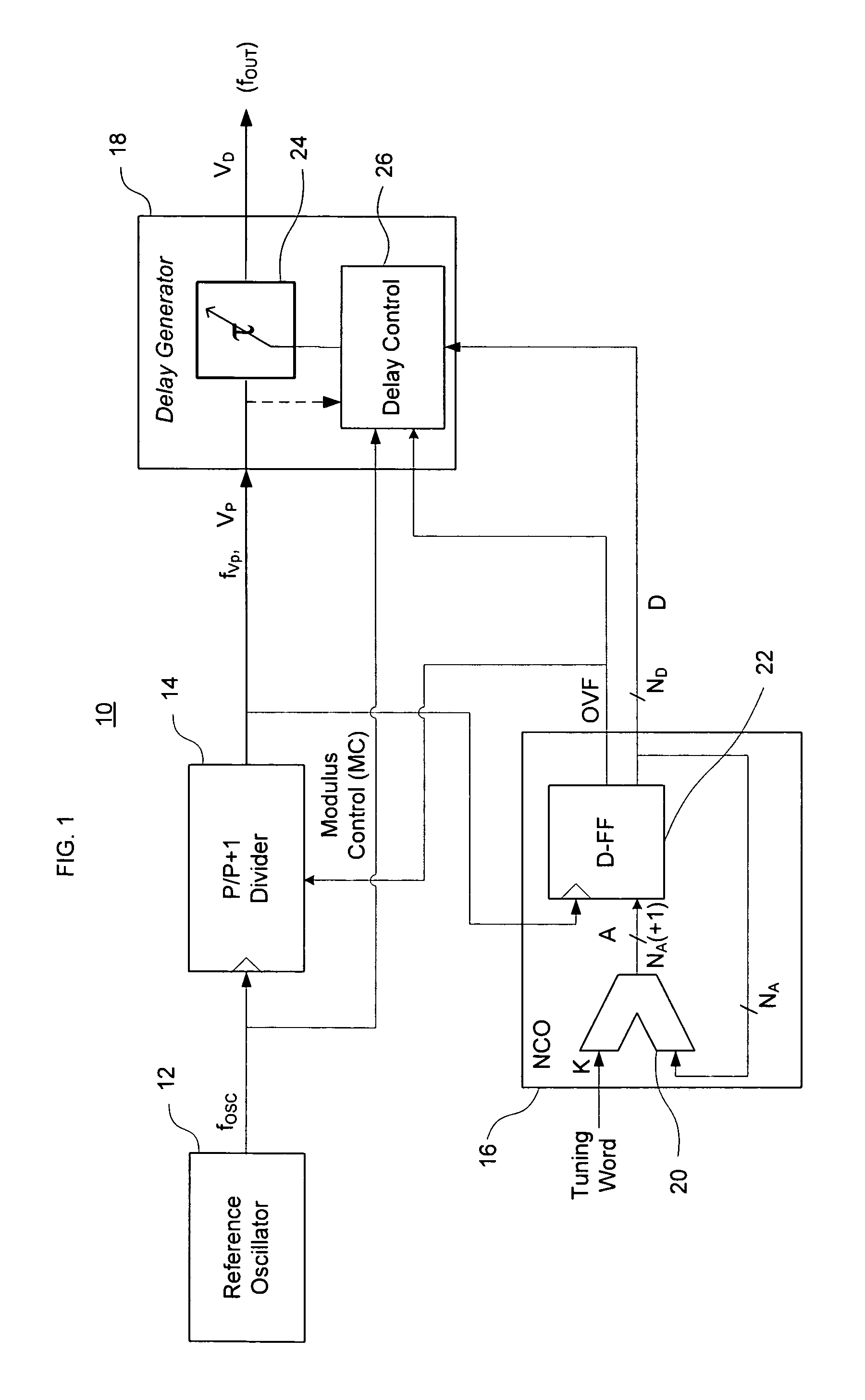
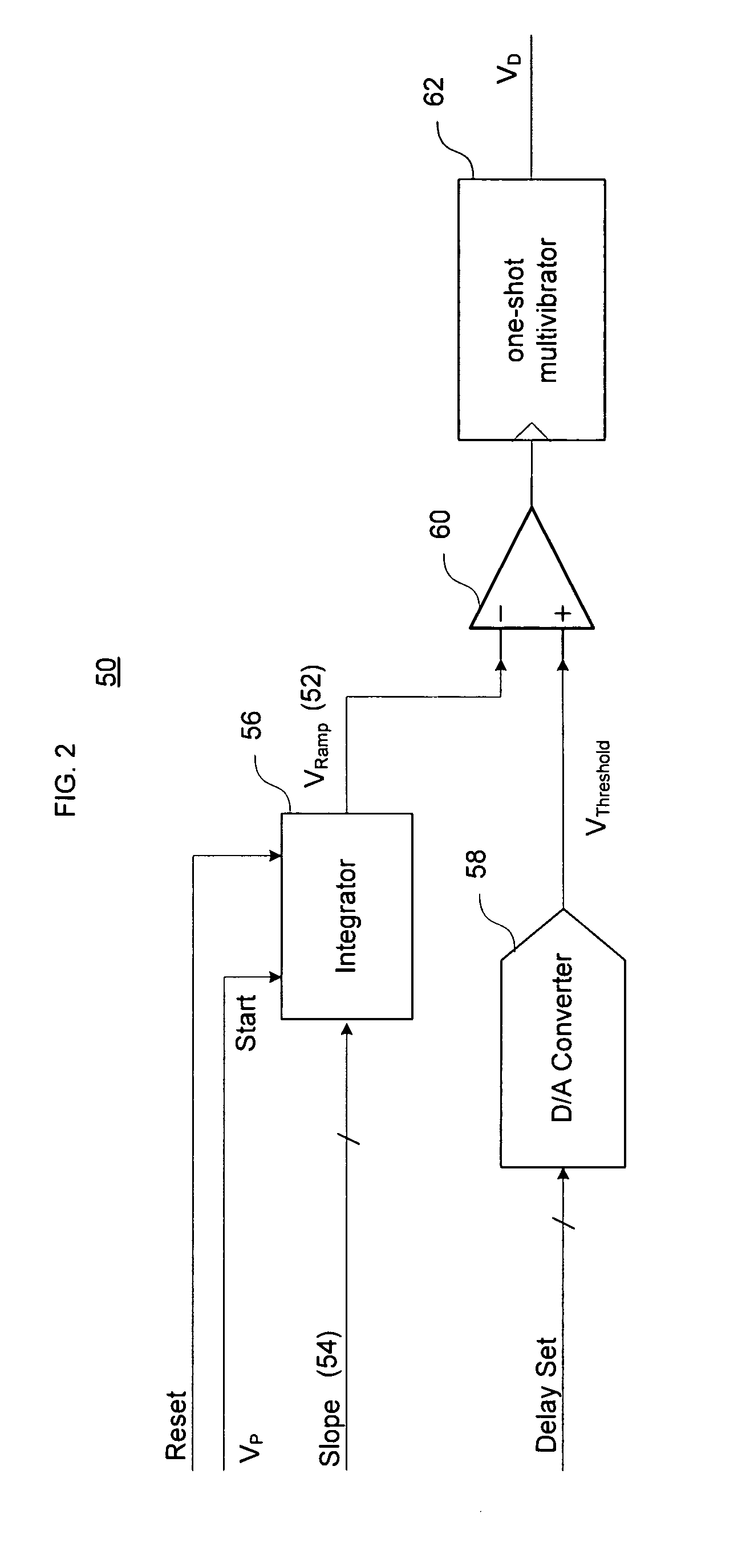
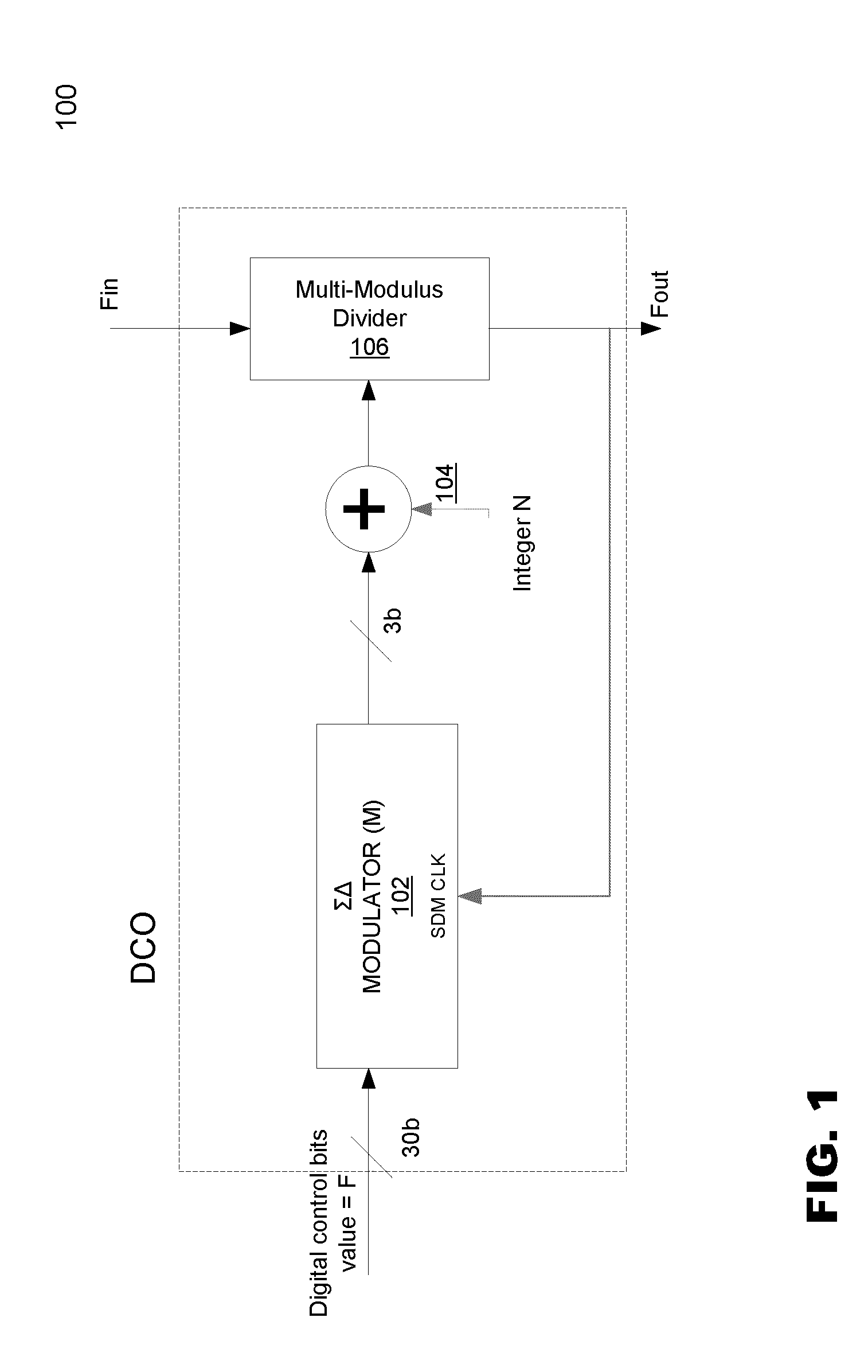
Direct digital synthesizer for reference frequency generation
InactiveUS7724097B2Improve noiseImprove performancePulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersFrequency generationDigital controlled oscillator
A direct digital frequency synthesizer having a multi-modulus divider, a numerically controlled oscillator and a programmable delay generator. The multi-modulus divider receives an input clock having an input pulse frequency fosc and outputs some integer fraction of those pulses at an instantaneous frequency fVp that is some integer fraction (1 / P) of the input frequency. The multi-modulus divider selects between at least two ratios of P (1 / P or 1 / P+1) in response to a signal from the numerically controlled oscillator. The numerically controlled oscillator receives a value which is the accumulator increment (i.e. the number of divided pulse edges) required before an overflow occurs that causes the multi-modulus divider to change divider ratios in response to receiving an overflow signal. The numerically controlled oscillator also outputs both the overflow signal and a delay signal to the delay generator that further controls the frequency of the multi-modulus divider output signal (Vp) to provide an output signal (VD) with an fout that has improved phase and timing jitter performance over prior art direct digital frequency synthesizer architectures.
Owner:CYMATICS LAB CORP
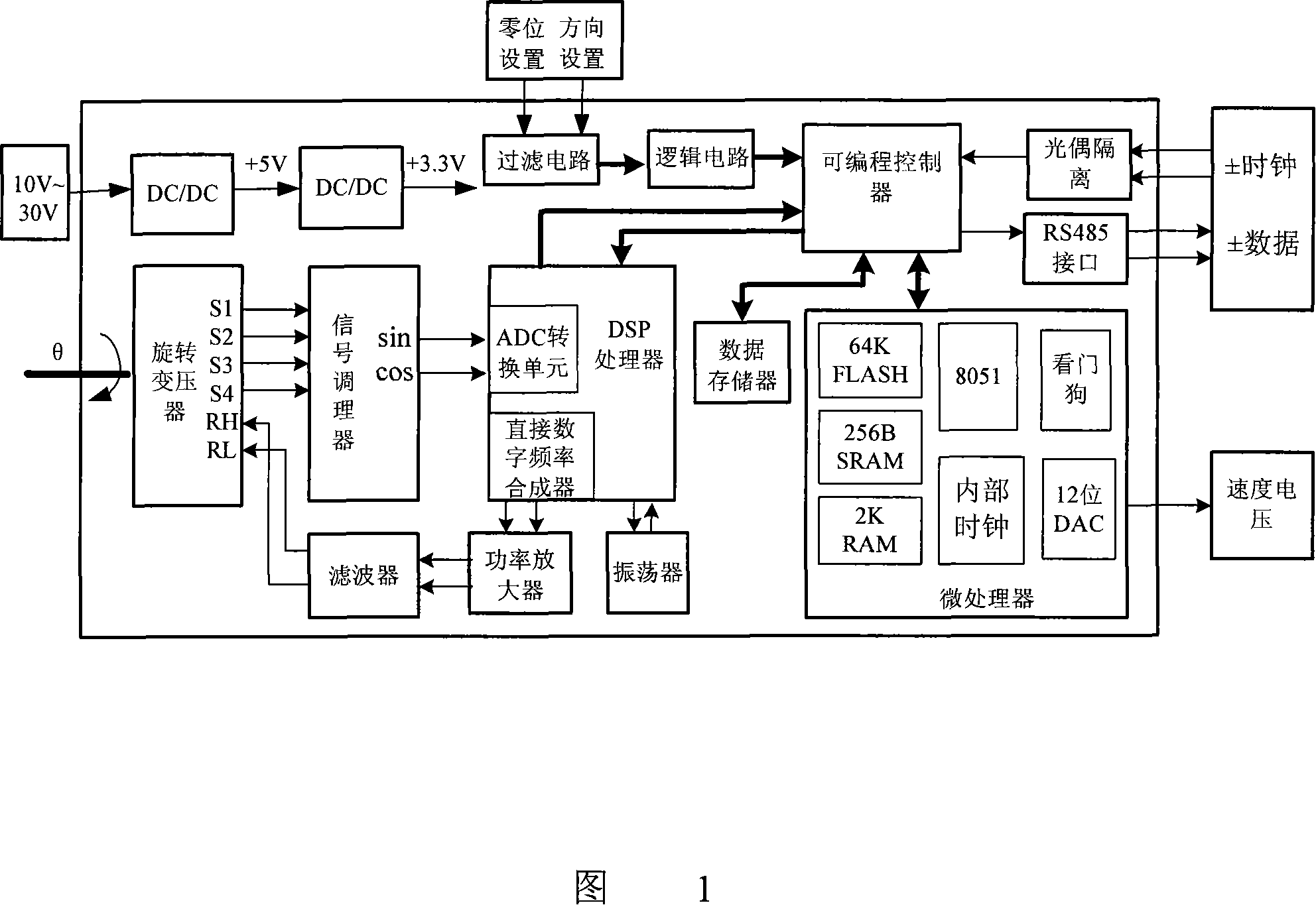
Multiple-loop absolute type rotary encoder based on rotating transformer
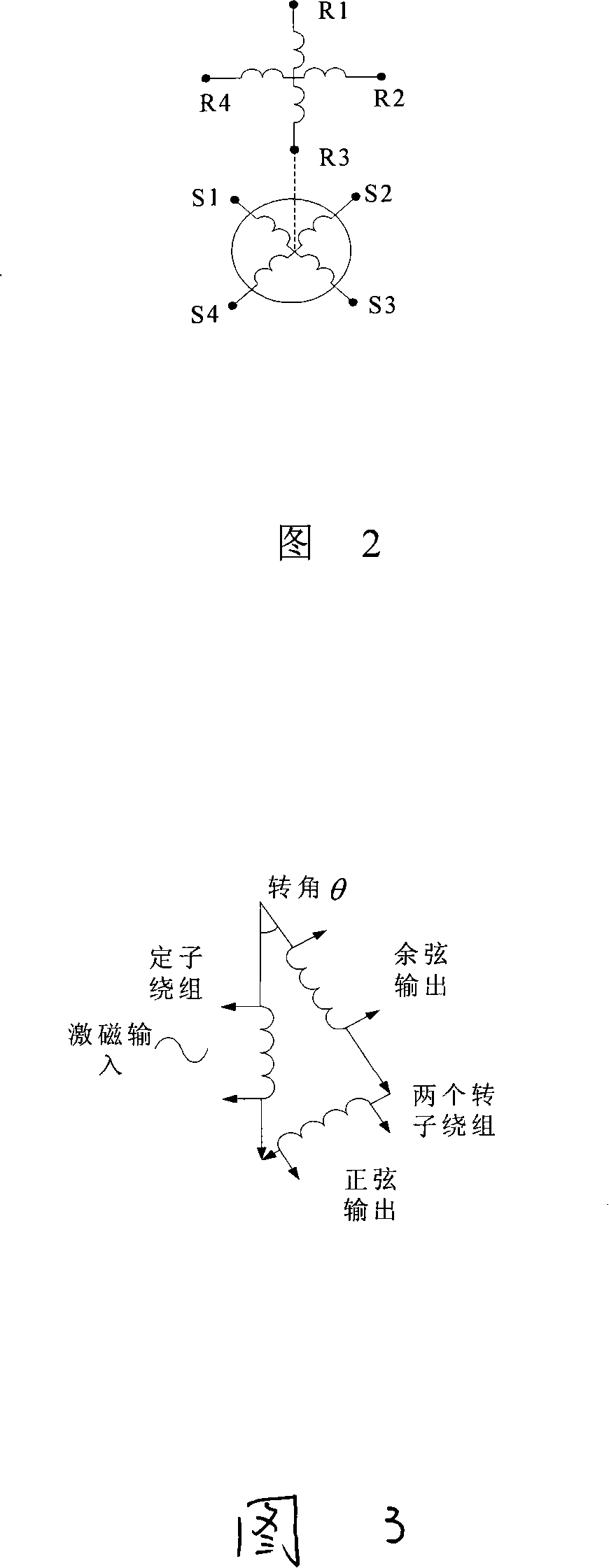
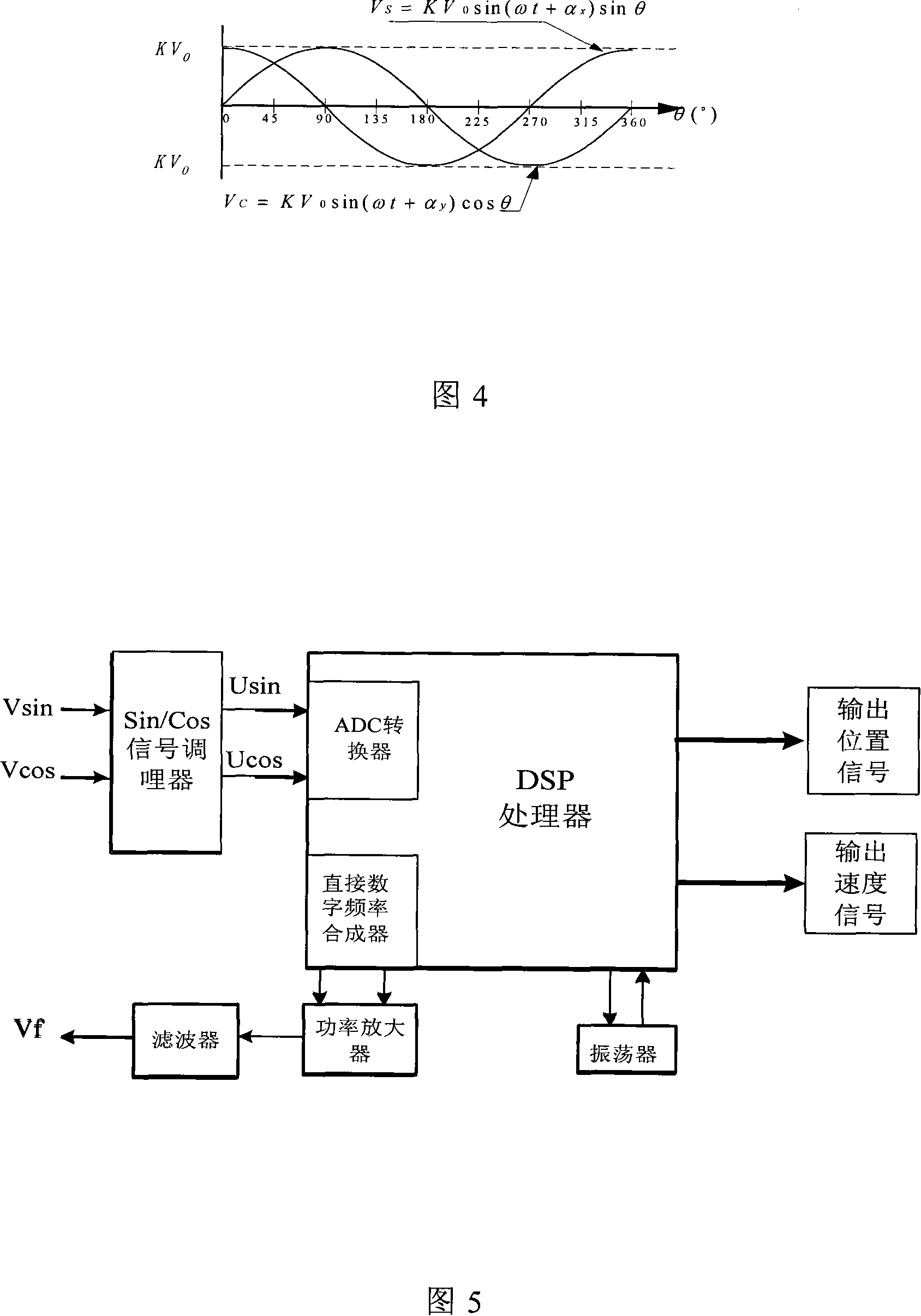
ActiveCN101226066AImprove anti-interference abilityImprove moisture resistanceConverting sensor outputDigital signal processingAxis–angle representation
The invention relates to a multiturn absolute rotary encoder based on a rotary transformer, which is characterized in that: a sensor is displaced by taking the rotary transformer as a shaft angle; a shaft angle decoding circuit can be formed by adopting DSP as a core processor; a sine wave which can be controlled by frequency and phase in the method that the circuit is synthesized by direct digital frequency for the numerical control of an oscillator; and the sine wave is directly taken as an excitation rotary transformer signal via a power amplifier and a filter circuit; the rotary transformer signal is transferred to A / D converter after being run through a matching circuit of electronic transformer; after sampling, digital filtering and digital signal processing, the sine and cosine value for the actual angle of two channels is generated; the angle error change is tracked dynamically by the PI algorithm; the mechanical displacement of the rotating object is converted into digital shaft angle position and speed. The multiturn absolute rotary encoder based on a rotary transformer has the advantages of high tracking speed, high conversion accuracy, high reliability, simple structure, sensitive movement, low environmental condition, strong anti-interference capability, high measuring accuracy and speed voltage output.
Owner:连云港杰瑞电子有限公司
Upstream resource optimization
Systems, methods, and devices are described for scheduling and mapping upstream communications in a satellite communications system. The disclosure includes various channelization and frequency hopping techniques. A gateway is described to perform novel allocation of time slots on upstream frequency channels to allow frequency hopping. A subscriber terminal may perform frequency hopping according to the allocation, and the range may be limited to the transition range of a digitally controlled oscillator unit at the subscriber terminal. A gateway is described to allocate time slots on different upstream frequency channels in a prioritized manner. Subscriber terminals may receive the allocation, and then control the assignment of their upstream traffic to the time slots.
Owner:VIASAT INC
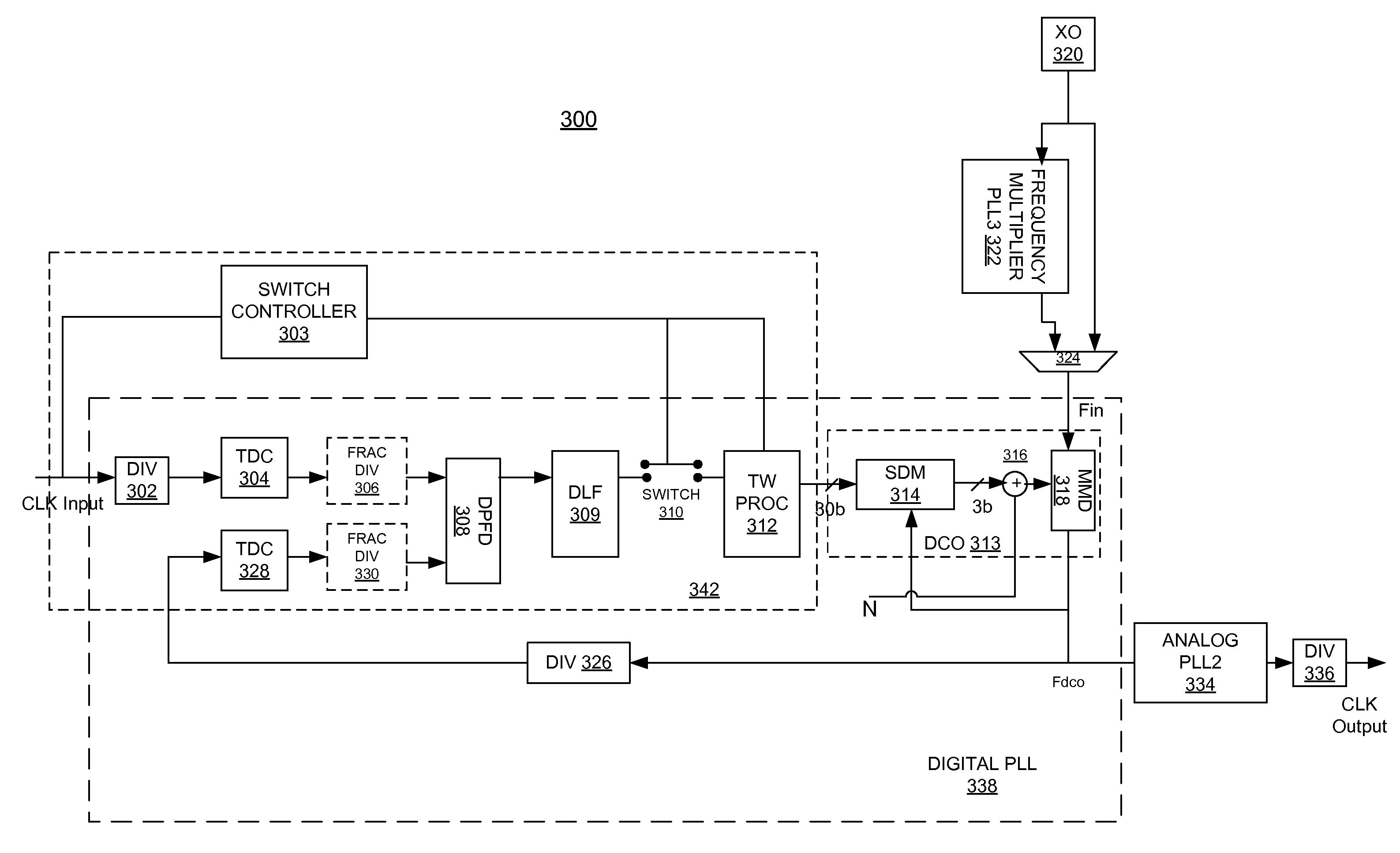
Digital phase-locked loop
Embodiments of the invention include an integrated circuit including a phase-locked loop (PLL). The integrated circuit includes a phase detector, a frequency detector, a loop filter, a digitally-controlled oscillator and a corresponding plurality of frequency dividers. The phase detector generates a first binary output based on a phase comparison of a reference clock signal to a plurality of clock phase inputs. The frequency detector generates a second binary output based on a frequency comparison of the reference clock signal to the clock phase inputs. The loop filter generates a third binary output based on the first binary output and the second binary output. The DCO feeds back the clock phase inputs, via the frequency dividers, to the phase detector based on the third binary output, and feeds back one of the clock phases to the frequency detector based on the third binary output.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
Digital phase locked loop with selectable normal or fast-locking capability
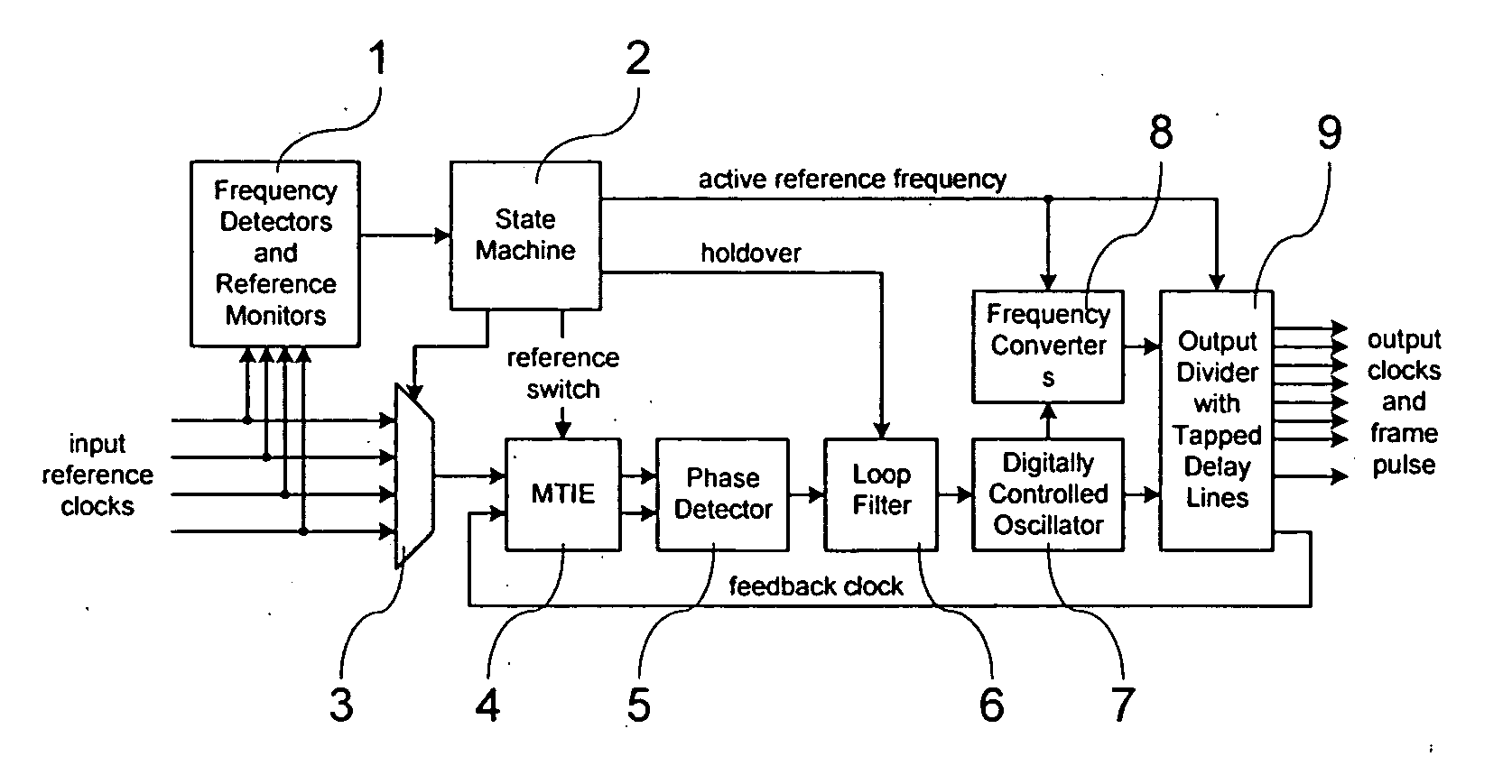
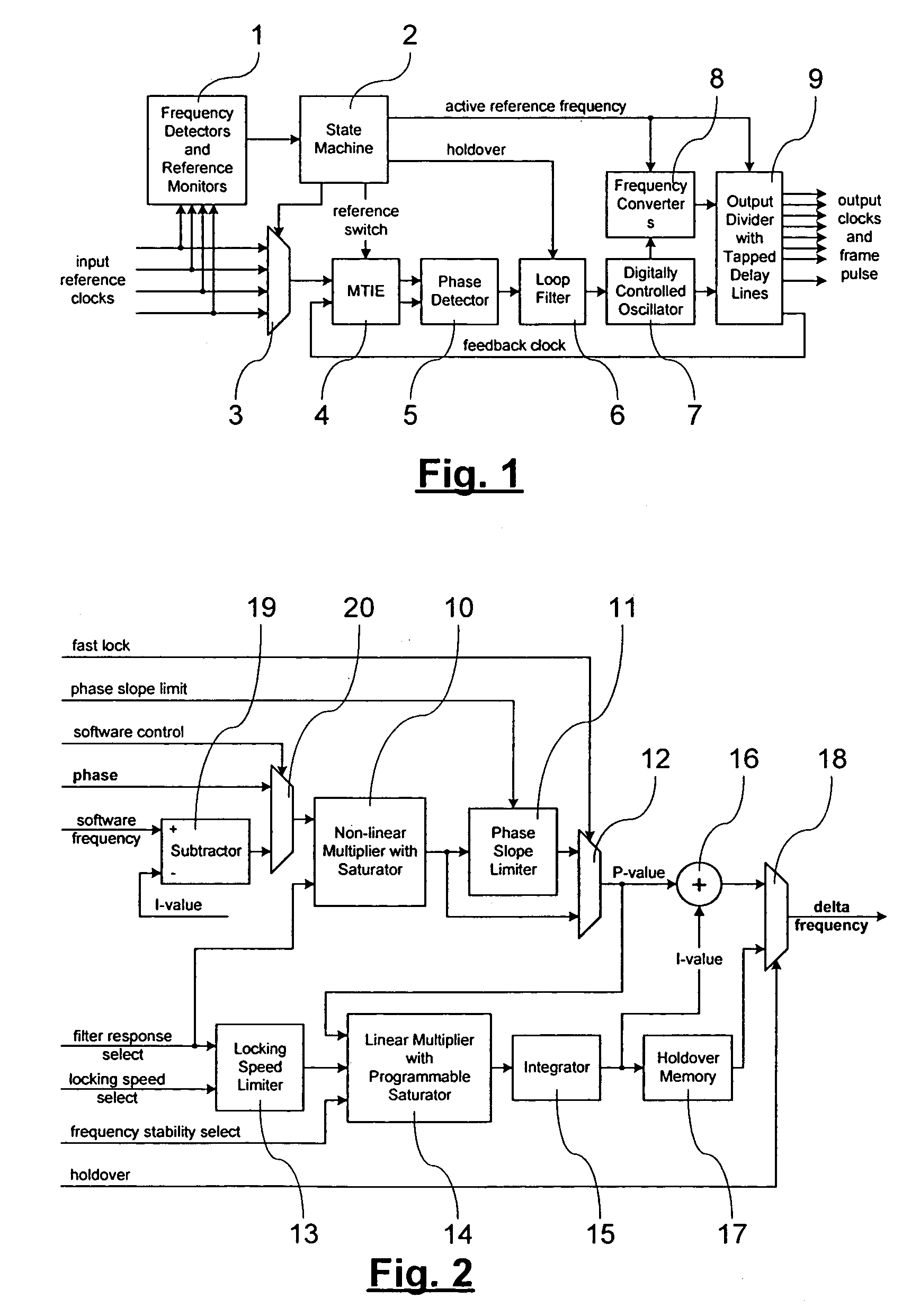
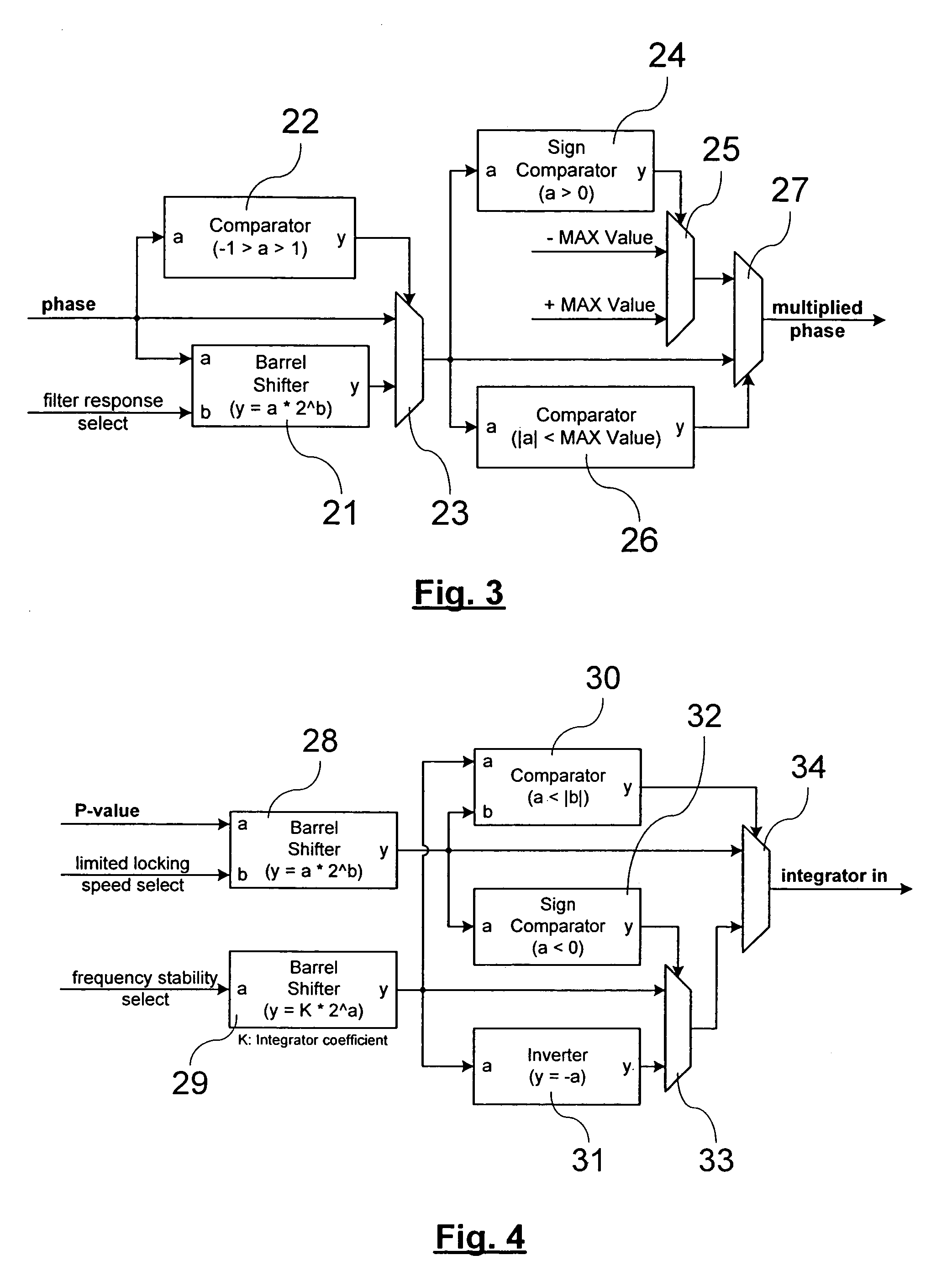
A digital phase locked loop with fast locking capability includes a digitally controlled oscillator for producing an output signal phase locked to an input reference clock, a phase detector for measuring the phase difference between said input reference clock and a feedback clock, and a loop filter for producing a control signal for the digitally controlled oscillator The loop filter includes a proportional circuit for developing a first signal proportional to said phase difference, an integrator for developing a second integrated signal from said first signal, an adder for adding said first and second signals to develop said control signal, and a weighting circuit, preferably a linear multiplier, for selectively adding extra weight to the first signal at an input to the integrator to shorten the locking time of the phase locked loop in a fast locking mode and to rapidly achieve a stable frequency in holdover mode.
Owner:ZARLINK SEMICON LTD
Digitally controlled oscillator and phase locked loop circuit using the digitally controlled oscillator
InactiveUS20090302958A1Pulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsDigitally controlled oscillatorDigital controlled oscillator
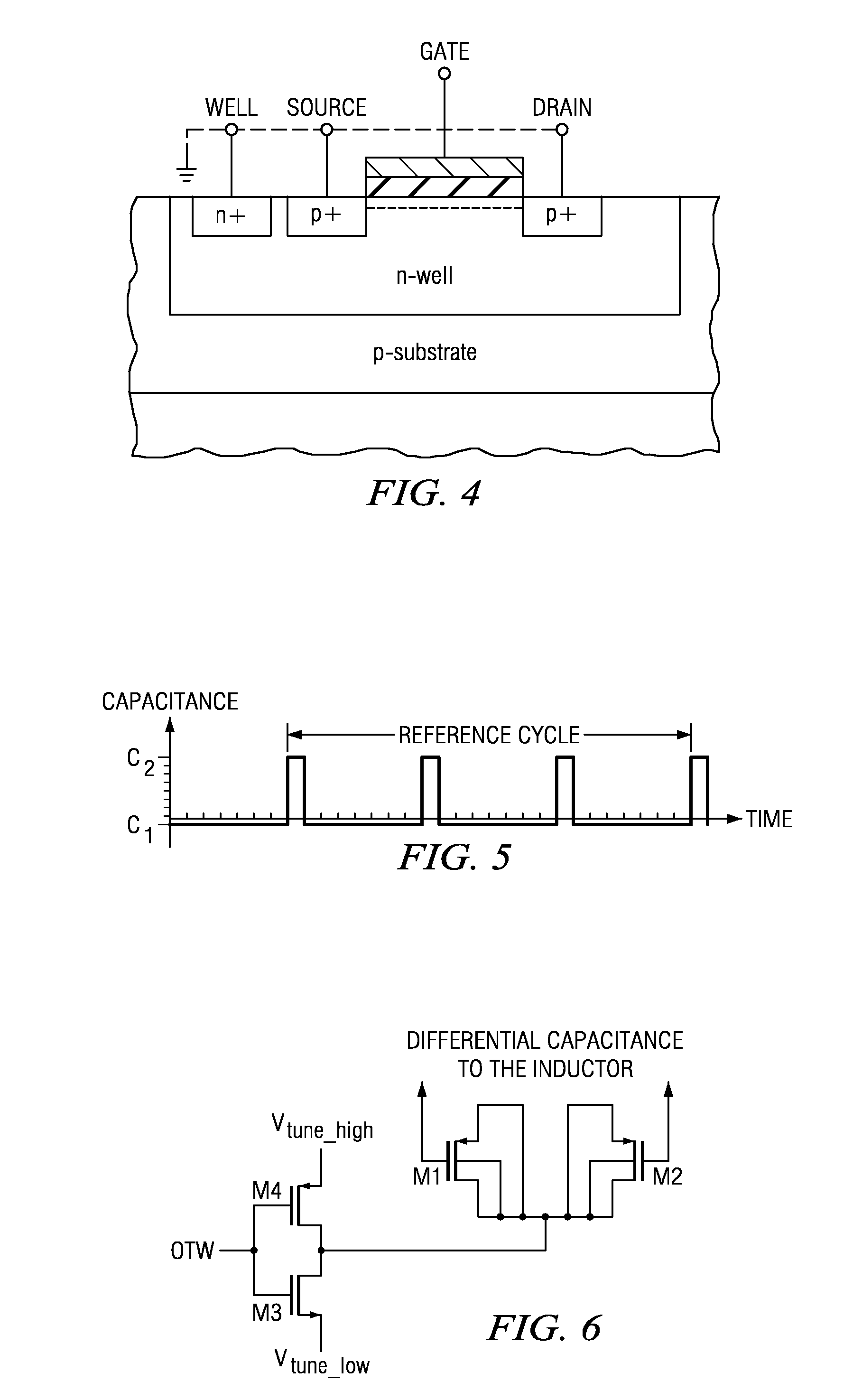
A digitally controlled oscillator includes a differential inductor including a positive terminal which outputs a positive-phase oscillation signal, a negative terminal which outputs a negative-phase oscillation signal, and a center tap, and including a first contact point in an arbitrary position between the positive terminal and the center tap, and a second contact point in a position corresponding to the first contact point between the negative terminal and the center tap, a first variable capacitor bank connected between the positive terminal and the negative terminal and including a plurality of first variable capacitors which switch capacitance between two values according to a first digital control code, and a second variable capacitor bank connected between the first contact point and the second contact point and including a plurality of second variable capacitors which switch capacitance between two values according to a second digital control code.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Gain normalization of a digitally controlled oscillator in an all digital phase locked loop based transmitter
ActiveUS20070085623A1Reduce resolutionHigh multiplication functionPulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsImage resolutionLow complexity
A novel mechanism for gain normalization of a digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) in an all digital phase locked loop (ADPLL)-based transmitter that is operative to split the gain normalization multiplication functionality between a modulating path and a PLL loop. The gain normalization of the modulation loop (referred to as modulation path multiplier) comprises a full bit resolution high precision multiplication function. The gain normalization of the PLL loop, on the other hand, is of significantly lower resolution, hence much lower complexity multiplier logic circuitry is required.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Digitally controlled oscillator and associated method
ActiveUS7330081B1Reduce riskReduce noisePulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationCapacitanceDigital controlled oscillator
A digitally controlled oscillator circuit is provided that comprises a ring oscillator including multiple inverters; multiple digitally controlled capacitors (DCCs), each coupled to apply a digitally controllable amount of capacitance to an output of a different one of the inverters; and control circuitry operable to change an amount of capacitance applied to each inverter during operation of the ring oscillator and to cause the multiple DCCs to apply substantially the same amounts of capacitance to each of the inverter throughout operation of the ring oscillator.
Owner:MARVELL ISRAEL MISL
Harmonic Characterization and Correction of Device Mismatch
A novel apparatus for and method of harmonic characterization and ratio correction of device mismatch between coarse and fine varactor tuning devices within a segmented unified varactor bank of a radio frequency (RF) digitally controlled oscillator (DCO). The DCO uses a single unified bank of varactors that is divided into an MSB bank, LSB bank and sigma-delta (SD-LSB) bank. Any ratio mismatches between MSBs and LSBs are digitally calibrated out using a DCO step-size pre-distortion scheme wherein the LSB steps are adjusted to account for the ratio mismatch between the MSB / LSB step sizes. A harmonic characterization technique is used to estimate the mismatches in the minimal size CMOS tuning varactors of a digitally controlled RF oscillator (DCO), wherein the nominal ratio mismatch between the MSB and LSB devices is estimated using hybrid stochastic gradient DCO gain estimation algorithms. The nominal ratio mismatch and the mismatches in the MSB and LSB banks are used to determine the average MSB / LSB mismatch. The average mismatch value is then used to correct the LSB steps.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Digital pll with automatic clock alignment
One embodiment of the present invention relates to a digital phase locked loop (ADPLL) configured to generate a plurality of time-aligned output clock signals having different frequency values. The ADPLL comprises a digital controlled oscillator configured to generate a variable clock signal that is separated into two signal paths operating according to two separate clock domains. A first signal path is configured to generate a feedback signal that synchronizes the variable clock signal with a reference signal. A second signal path comprises a clock divider circuit configured to synchronously divide the variable clock signal to automatically generate a plurality of time-aligned output clock signals having different frequencies. A clock aligner monitors a phase difference between the variable clock signal and one of the plurality of time-aligned output clock signals and generates a control signal that causes a programmable delay line to automatically time-align the output clock signals with the variable clock signal.
Owner:INTEL CORP
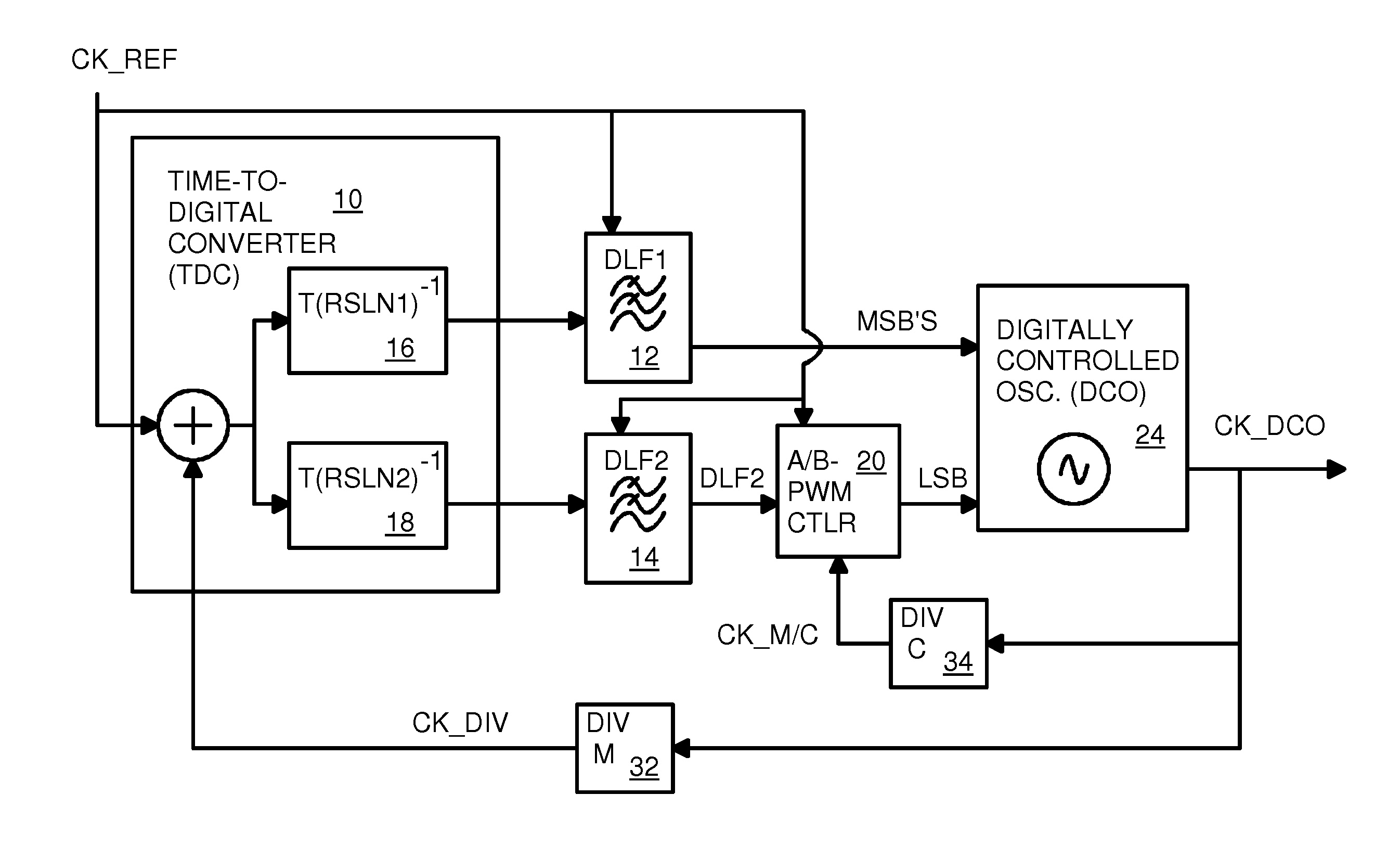
Digital Phase Lock System with Dithering Pulse-Width-Modulation Controller
A Digital Phase-Locked Loop (DPLL) has a digitally-controlled oscillator (DCO) that generates an output clock frequency determined by a digital input with most-significant-bits (MSB's) and a least-significant-bit (LSB). The LSB is generated by a Pulse-Width-Modulation (PWM) controller clocked by a control clock that is the output clock divided by C. A reference clock is compared to a feedback clock that is the output clock divided by M. The PWM controller generates M / C LSB's for each reference clock period and loads them in parallel to a parallel-to-serial shift register that serially delivers the LSBs. The pulse width is determined by a fine digital loop filter that filters phase comparison results using a fine time resolution. A coarse digital loop filter generates the MSB's from phase comparison results using a coarse time resolution. LSB waveforms are dithered by randomly selecting high-going or low-going pulses and randomly adjusting pulse widths.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
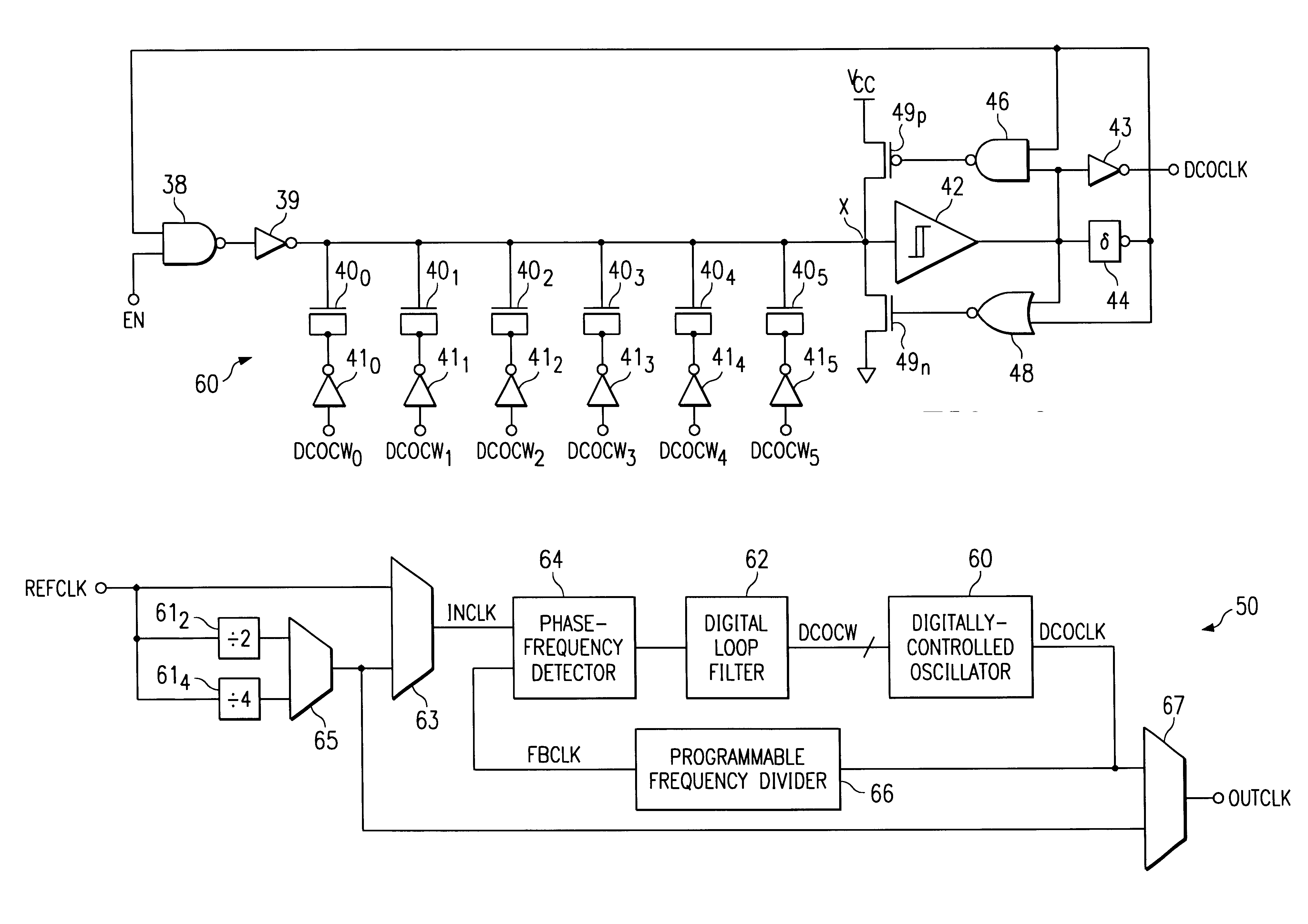
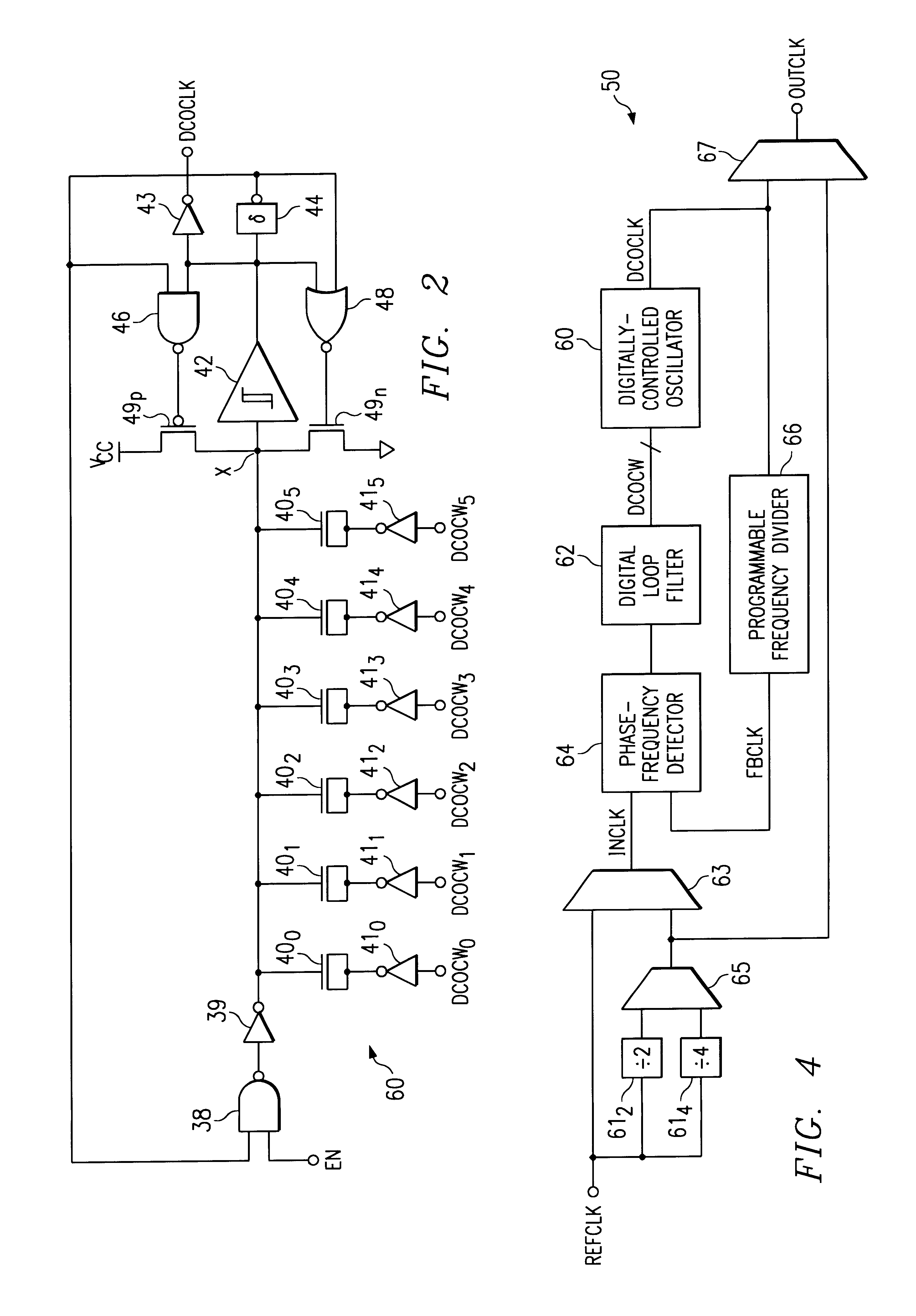
Digitally-controlled oscillator with switched-capacitor frequency selection
InactiveUS6903615B2Low power supply voltageReduce voltageResonant circuit tuningPulse automatic controlCapacitanceEngineering
A digitally-controlled oscillator (DCO) (60), such as may be used in clock generator or clock recovery circuitry in an integrated circuit, is disclosed. The disclosed DCO (60) is a single-stage oscillator including a variable load implemented as a binary-weighted array of switched capacitors (40). Each of capacitors (40) has a plate connected to a common node (X), and a plate that receives a signal corresponding to one bit of a digital control word (DCOCW). The common capacitor node (X) is also connected to the input of a Schmitt trigger (42) that produces the output clock signal (OUTCLK) and a feedback signal that is applied to logic (38, 39) that inverts the common node of the capacitors (40). The switching time at the input of Schmitt trigger (42) depends upon the variable load presented by the array of switched capacitors (40), which is controlled by the digital control word (DCOCW). As a result, the clock signal (OUTCLK) is digitally synthesized by a single stage of the DCO (60). A digital phase-locked loop (PLL) clock generator circuit (50) including a phase detector (64), digital loop filter (62) in combination with the DCO (60), and a programmable frequency divider (66) providing a feedback path from the output of the DCO (60) to the phase detector (64), is also disclosed. The PLL clock generator (50) may be used in an integrated circuit such as a digital signal processor (30) or microprocessor, and is particularly well-suited for use in a battery-powered portable electronic system (200).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Rapid locking method for full digital phase-locked loop
ActiveCN101640533AShort lock timeReduce forecast errorPulse automatic controlDiscriminatorPhase difference
The invention relates to a rapid locking method for a full digital phase-locked loop, which is used for locking the frequency of the full digital phase-locked loop comprising a phase detection discriminator, a time-to-digit converter, a digital filter, a digital controlled oscillator and a frequency divider in a short time. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: finding a control word controlling the frequency of the digital controlled oscillator by a designed algorithm; dividing the frequency of a clock output by the digital controlled oscillator which is controlled bythe control word to obtain a divided-frequency clock with the frequency approximate to a reference clock frequency; and then, controlling the digital controlled oscillator to lock based on a phase difference between the reference clock and the divided-frequency clock which are distinguished by the phase detection discriminator. The full digital phase-locked loop is provided with a rapid frequencycapture loop and a phase-locked loop which alternately work, i.e. firstly, the rapid frequency capture loop finishes frequency capture, and then, the phase-locked loop finishes accurate locking.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Fast hopping frequency synthesizer using an all digital phased locked loop (ADPLL)
ActiveUS20060256910A1Eliminate needReduce power consumptionPulse automatic controlTransmissionPhase shiftedFrequency mixer
A novel and useful fast hopping frequency synthesizer and transmitter associated therewith. The frequency synthesizer and transmitter incorporates a digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) adapted to operate open loop. Instantaneous frequency switching is achieved by changing an oscillator tuning word (OTW) to imitate the three oscillators of a UWB transmitter. In one embodiment, the DCO can change the frequency instantaneously within the 1 / fT of the varactor devices used to construct the DCO. An all digital phase lock loop (ADPLL) is used for offline calibration prior to the start of packet transmission or reception. Any phase shift during the switching is tracked by a digital circuit in the transmitter. In a second embodiment, additional frequency accuracy is provided by use of a numerically controlled oscillator (NCO) that functions to generate a fine resolution complex exponential waveform which effectively shifts the synthesized frequency. A mixer applies the waveform to the I and Q data samples prior to conversion to the digital domain.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Time-to-digital converter and all digital phase-locked loop including the same
ActiveUS20110148490A1Reduce areaReduce noiseAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsLoop filterPhase detector
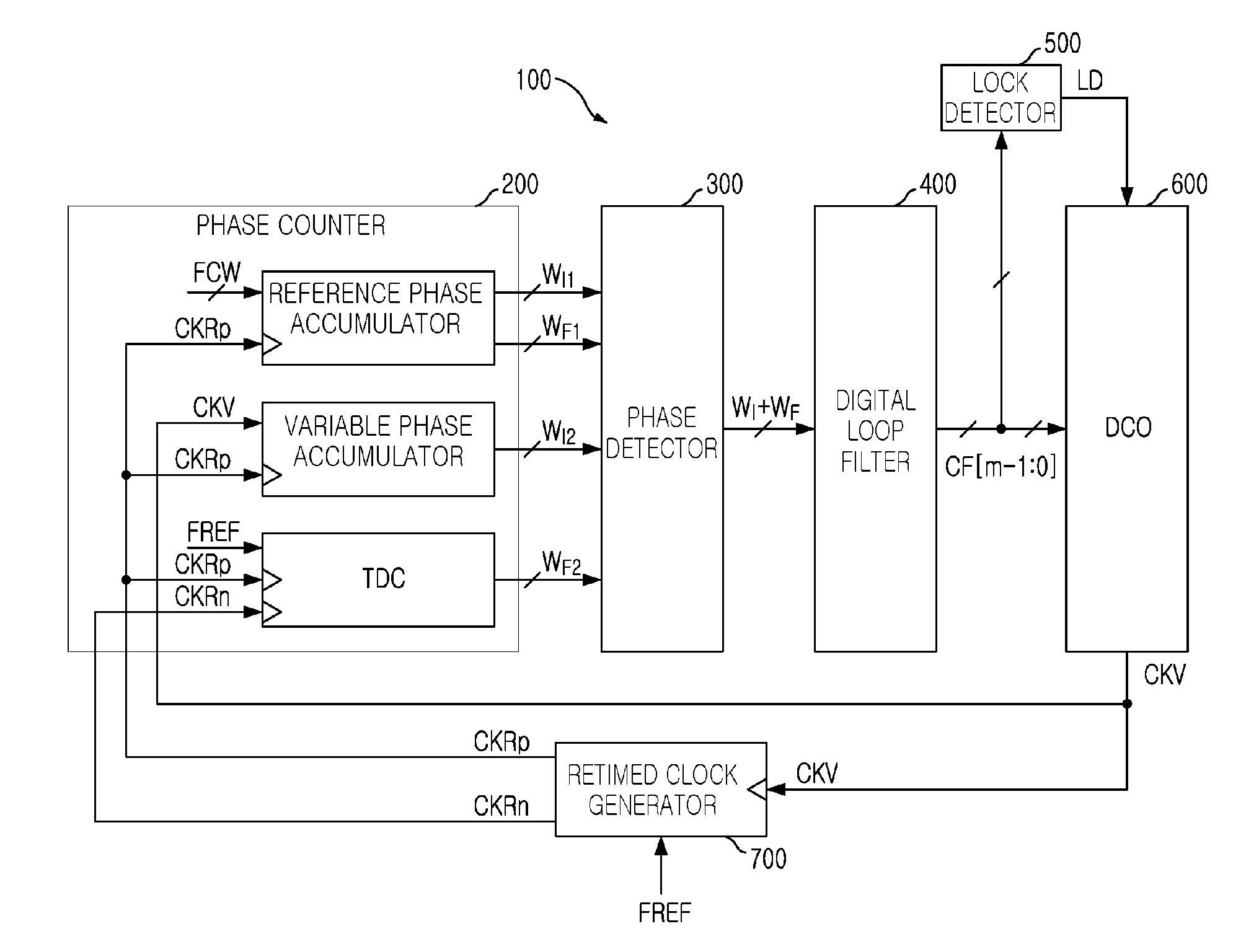
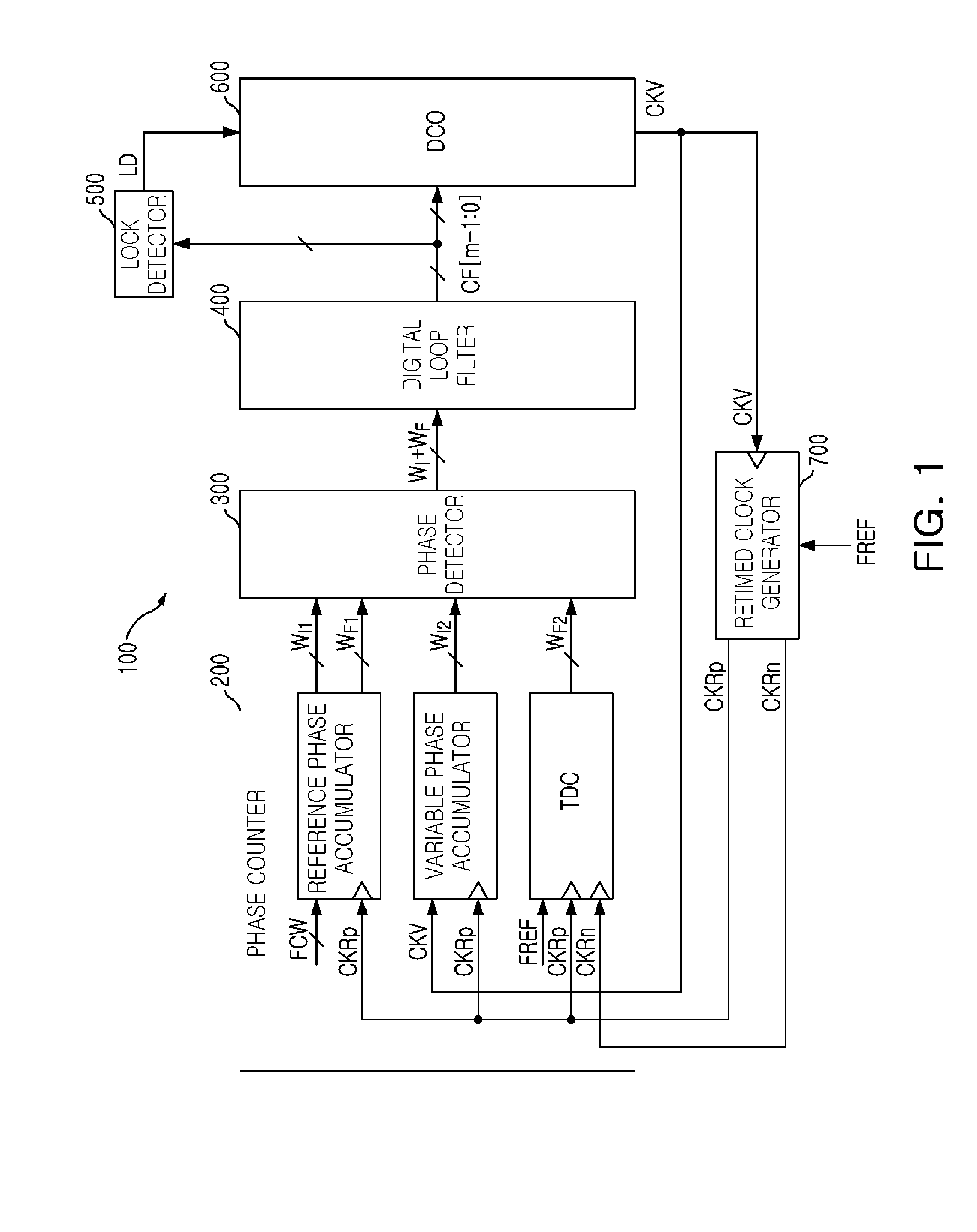
An all digital phase-locked loop (ADPLL) includes: a phase counter accumulating a frequency setting word value and the phase of a digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) clock and detecting a fine phase difference between a reference clock and a retimed clock; a phase detector detecting a digital phase error value compensating for a phase difference between the frequency setting word value and the DCO clock according to the fine phase difference to detect a digital phase error value; a digital loop filter filtering the digital phase error value and controlling PLL operational characteristics; a lock detector generating a lock indication signal according an output of the digital loop filter; a digitally controlled oscillator varying the frequency of the DCO clock according to the output from the digital loop filter; and a retimed clock generator generating the retimed clock by retiming the DCO clock at a low frequency.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
All-digital frequency synthesis with non-linear differential term for handling frequency perturbations
ActiveUS7483508B2Pulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionDigital tuningNumerically controlled oscillator
An all-digital frequency synthesizer architecture is built around a digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) that is tuned in response to a digital tuning word (OTW). In exemplary embodiments: (1) a gain characteristic (KDCO) of the digitally controlled oscillator can be determined by observing a digital control word before and after a known change (Δfmax) in the oscillating frequency; (2) a portion (TUNE_TF) of the tuning word can be dithered (1202), and the resultant dithered portion (dkTF) can then be applied to a control input of switchable devices within the digitally controlled oscillator; and (3) a non-linear differential term (187, 331) can be used to expedite correction of the digitally controlled oscillator when large phase error changes (335) occur.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
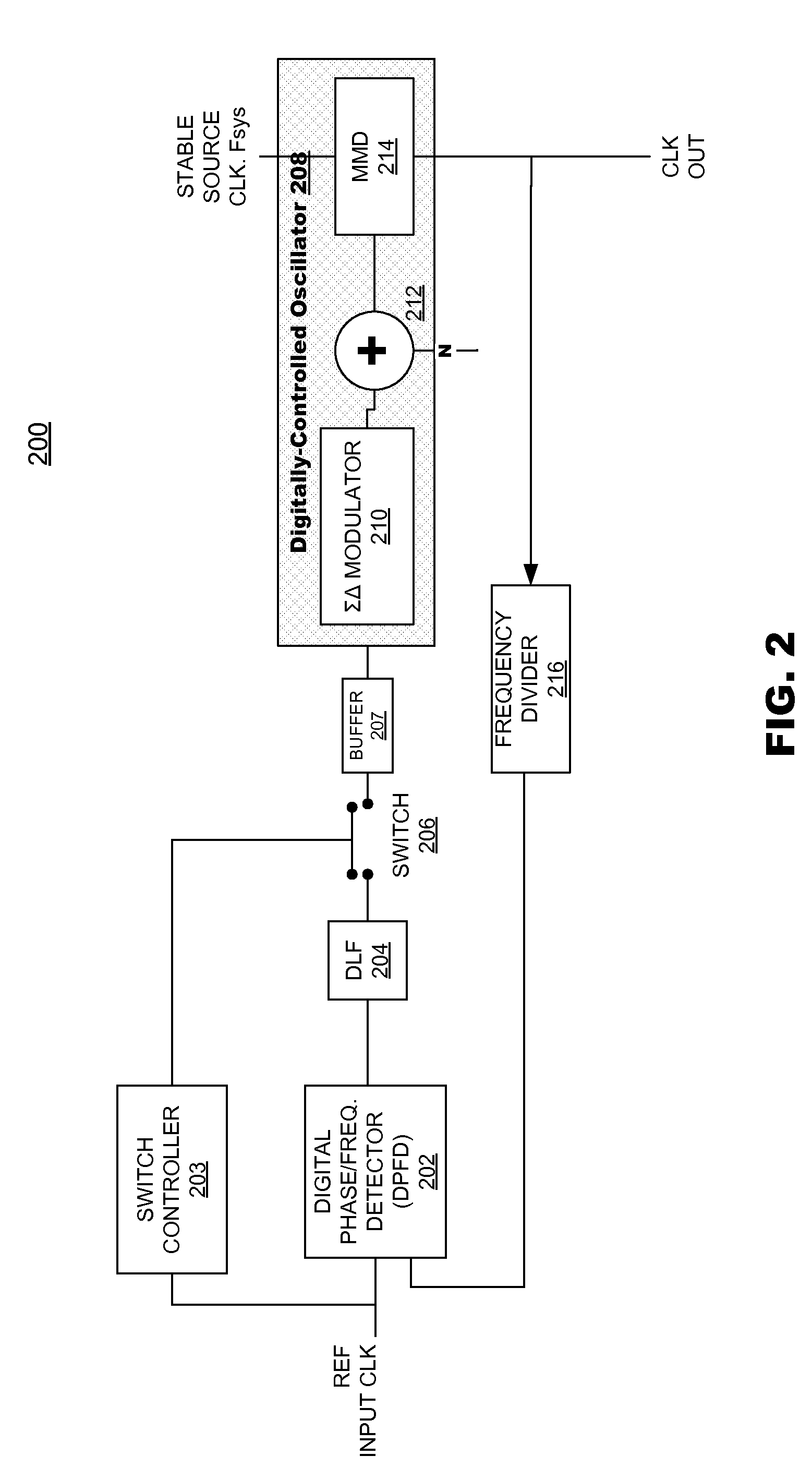
Digital phase-locked loop clock system
A clock system includes a digital phase / frequency detector (DPFD), a buffer, a digitally-controlled oscillator (DCO) including a sigma-delta modulator (SDM), an adder, a first frequency divider. The DPFD may have a first input for a reference input clock, a second input for a feedback signal, the DPFD generating an output representing a difference between the reference input clock and the feedback signal. The buffer may be coupled to the DPFD for accumulating the difference signal over time. The sigma-delta modulator (SDM) may have a control input coupled to the buffer. The adder may have inputs coupled to the (SDM) and a source of an integer control word. The first frequency divider may have an input for a clock signal and a control input coupled to the adder, the DCO generating an output clock signal having an average frequency representing a frequency of the input clock signal divided by (N+F / M), wherein N is determined by the integer control word and F / M is determined by an output of the SDM. The system clock also may include a second frequency divider coupled to the DCO output clock signal outputting the feedback signal to the DPFD.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Wideband Digitally Controlled Injection-Locked Oscillator
A novel and useful digitally controlled injection-locked RF oscillator with an auxiliary loop. The oscillator is injection locked to a time delayed version of its own resonating voltage (or its second harmonic) and its frequency is modulated by manipulating the phase and amplitude of injected current. The oscillator achieves a narrow modulation tuning range and fine step size of an LC tank based digitally controlled oscillator (DCO). The DCO first gets tuned to its center frequency by means of a conventional switched capacitor array. Frequency modulation is then achieved via a novel method of digitally controlling the phase and amplitude of injected current into the LC tank generated from its own resonating voltage. A very linear deviation from the center frequency is achieved with a much lower gain resulting in a very fine resolution DCO step size and high linearity without needing to resort to oversampled noise shaped dithering.
Owner:SHORT CIRCUIT TECH LLC
Adc-based mixed-mode digital phase-locked loop
InactiveUS20110090998A1Increase costReduce noisePulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationDigital tuningVoltage amplitude
A Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) includes a Phase-to-Digital Converter (PDC), a programmable digital loop filter, a Digitally-Controlled Oscillator (DCO), and a loop divider. Within the PDC, phase information is converted into a stream of digital values by a charge pump and an Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC). The stream of digital values is supplied to the digital loop filter which in turn supplies digital tuning words to the DCO. A number of types of ADCs can be used for the ADC including a continuous-time delta-sigma oversampling Digital ADC and a Successive Approximation ADC. The voltage signal on the charge pump output is a small amplitude midrange voltage signal. The small voltage amplitude of the signal leads to numerous advantages including improved charge pump linearity, reduced charge pump noise, and lower supply voltage operation of the overall PLL.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Phase-locked loop circuits and methods implementing pulsewidth modulation for fine tuning control of digitally controlled oscillators
InactiveUS20100013531A1Wide continuous tuning rangePulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionControl signalPhase locked loop circuit
PLL (phase locked loop) circuits and methods are provided in which PWM (pulse width modulation) techniques are to achieve continuous fine tuning control of DCO (digitally controlled oscillator) circuits. In general, pulse width modulation techniques are applied to further modulate dithered control signals that are used to enhance the frequency tuning resolution of the DCO such that the dithered control signals are applied to the fractional tracking control port of the DCO for a selected fraction of a full clock signal based pulse width modulation applied.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method and device for phase error correction
InactiveCN101345886AEliminate long-term accumulationEliminate phase stepsBrightness and chrominance signal processing circuitsDiscriminatorNumerical control
One embodiment of the invention discloses a device and a method of phase error correction, comprising: a phase discriminator, used for latching a controlled phase position sent by the numerical controlled oscillator when a line synchronizing signal and a field synchronizing signal arrive, and comparing with the moment reference phase position, and outputting phase error; a loop filter, used for receiving the phase error sent by the phase discriminator, performing low-pass filtering, and obtaining a frequency control word signal; a numerical controlled oscillator, used for receiving the frequency control word signal sent by the loop filter, generating controlled phase signal, wherein, the phase signal is transmitted to the phase discriminator, and the high position part of the phase signal is transmitted to the lookup table; a lookup table, used for obtaining a quantized value of corresponding sine and cosine functions according to the high position part of the phase signal. The invention eliminates long term accumulation of DDS to frequency quantized error in a complex video signal coder, cuts the phase error with large granularity into uniform phase error with small granularity, and distributes the phase error uniformly on the time.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
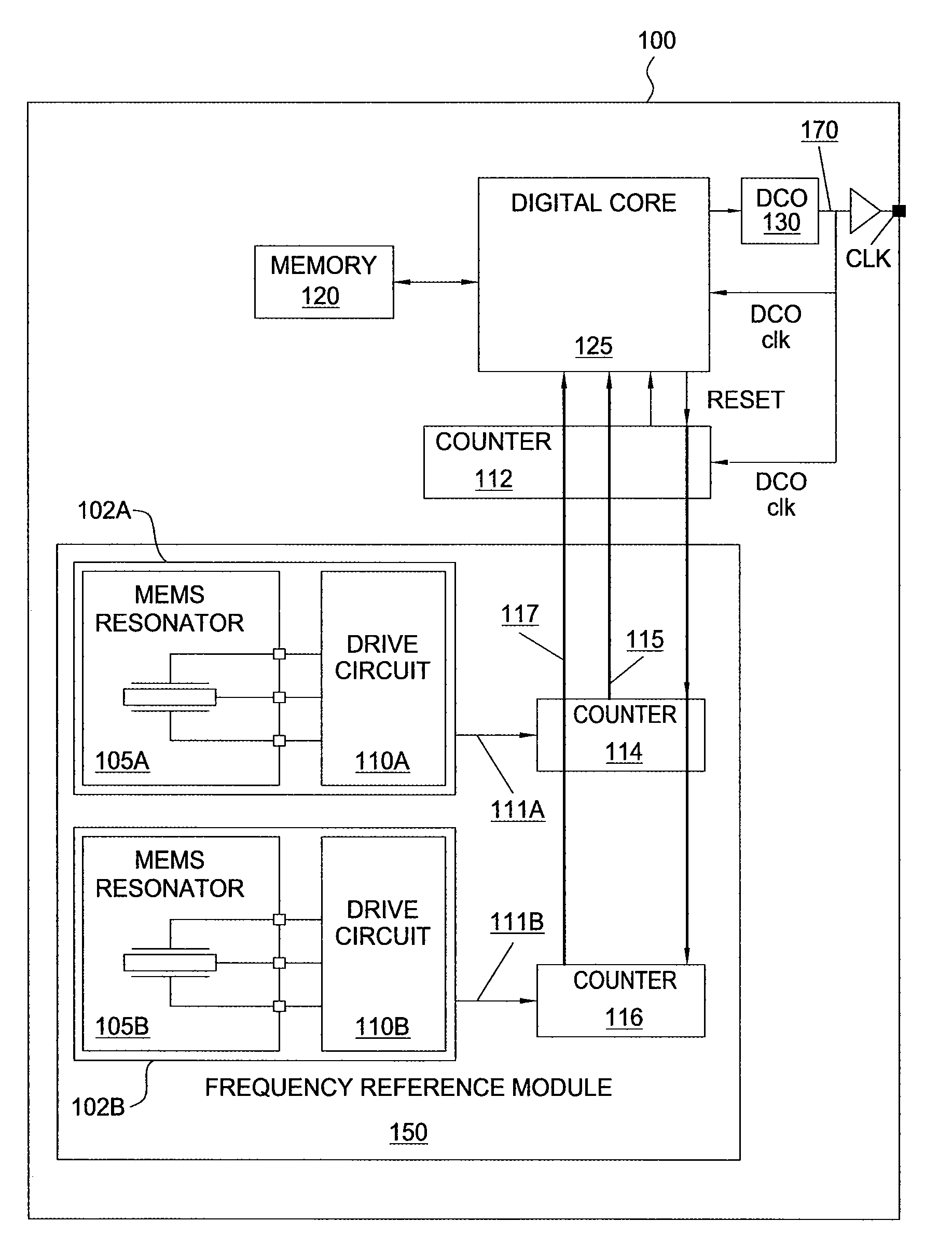
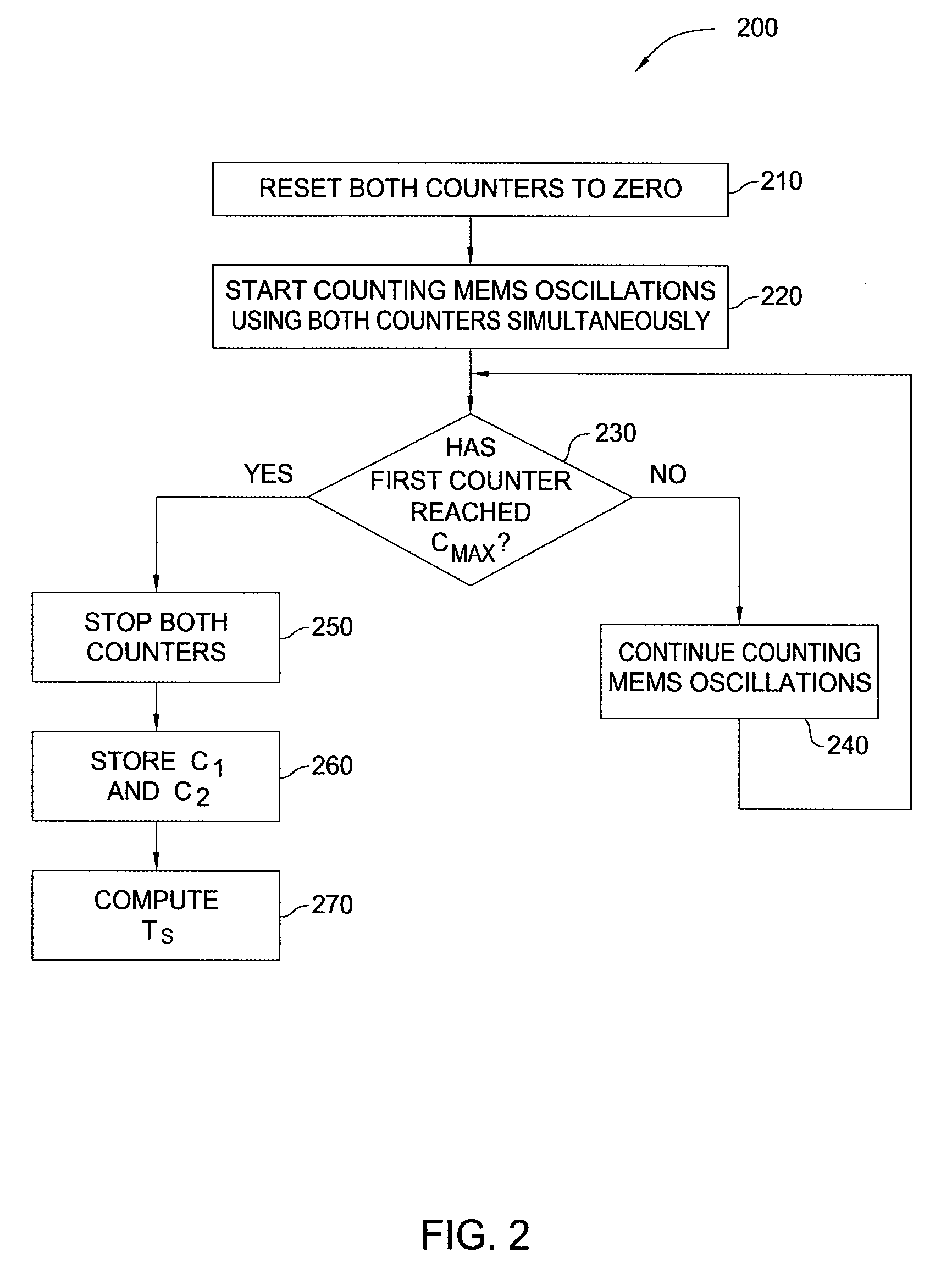
Dynamic temperature compensation for a digitally controlled oscillator using dual MEMS resonators
ActiveUS7545228B1Accurate temperature compensationThermometer detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesDigital controlled oscillatorComputer science
A method for generating a temperature-compensated timing signal that includes counting, within an update interval, a first number of oscillations of a first micro-electromechanical (MEMS) resonator, a second number of oscillations of a second MEMS resonator and a third number of oscillations of a digitally controlled oscillator (DCO), computing a target DCO count based on the first number and second number of oscillations, computing a loop error signal based on the target DCO count and the third number of oscillations, and modifying an output frequency of a temperature-dependent (DCO) timing signal based on the loop error signal. The duration of the update interval may also be modified based on temperature conditions, and the update interval may also be interrupted and the output frequency immediately adjusted, if a significant temperature change is detected. Thus, dynamic and precise temperature compensation is achieved that accommodates constant, slowly changing, and rapidly changing temperature conditions.
Owner:SITIME
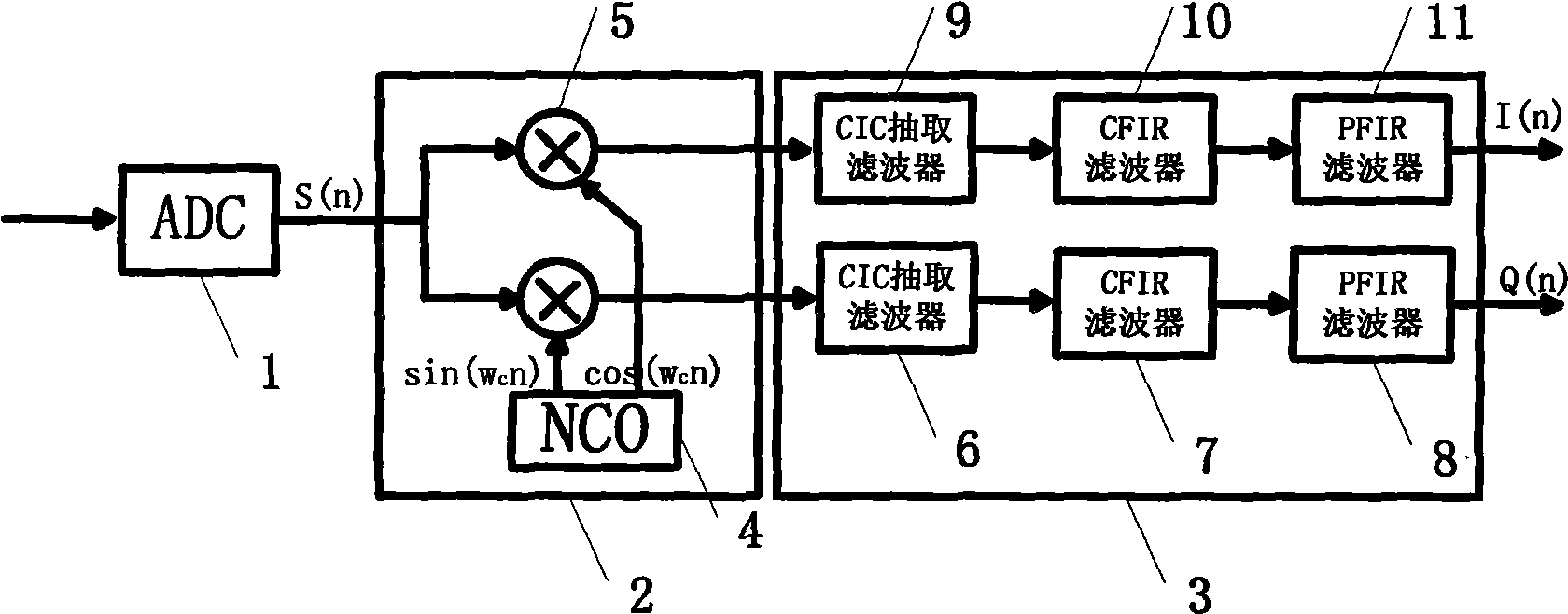
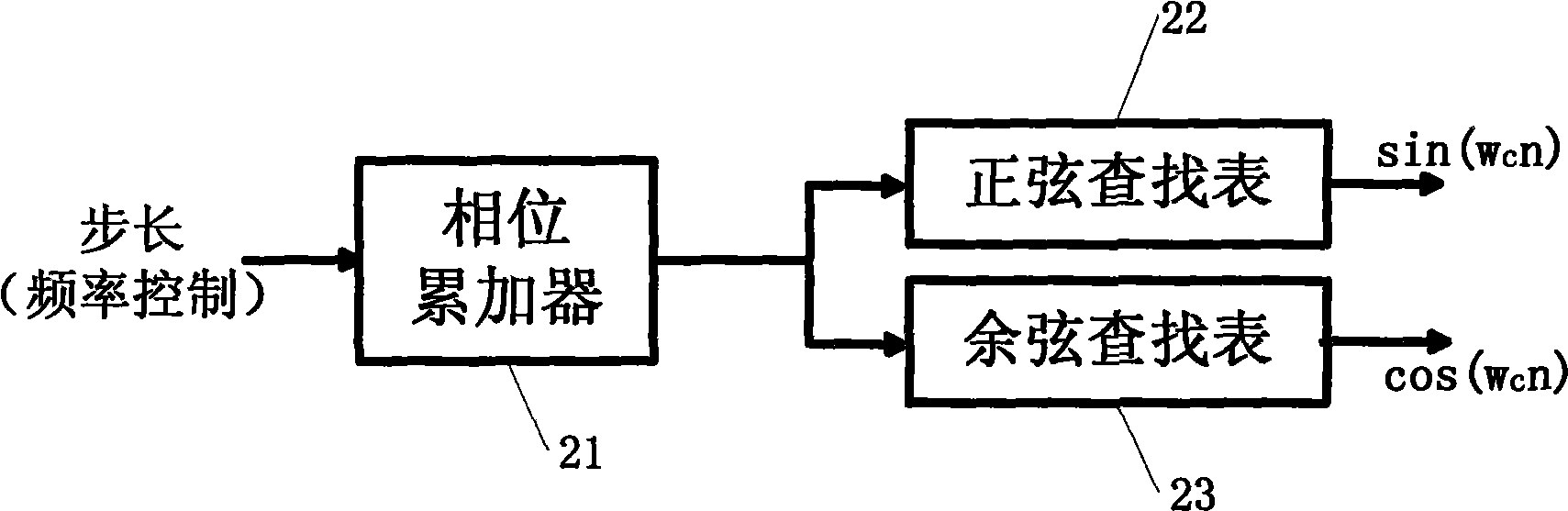
Digital signal down variable frequency processing system based on MIMO real time test platform
InactiveCN101510756AEasy to implementProcessing speedDigital technique networkTransmitter/receiver shaping networksDigital signal processingNumerically controlled oscillator
The invention discloses a digital signal down-conversion processing system based on an MIMO real-time testing platform, pertaining to the technical field of digital signal processing. The system comprises four DDC modules and each DDC module consists of four independent digital signal down-conversion processing channels. Each channel consists of an analog-to-digital converter, a digital quarter mixer and a digital decimation filter set. The digital quarter mixer consists of a digital controlled oscillator and two paths of multipliers, and the digital controlled oscillator is respectively connected with the two multipliers; the digital decimation filter set consists of two groups of filters with complete same parameters and each filter group respectively comprises a CIC decimation filter, a CFIR compensation filter and a PFIR matched filter which are connected in sequence. The system has good expansibility and modularization and can meet the requirements of real-time and high-speed performance.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for realizing integrated time stamp clock synchronous phase-locked loop
InactiveCN101083523AGuaranteed validityPulse automatic controlSynchronising arrangementLoop filterRing circuit
The invention involves a method of digital phase-locked loop for timestamp clock synchronization and equipment. Firstly, the server sends a value, which includes the message S (t) to timestamp, as the input synchronized signal. Take the time on which timestamp the server sent arriving at phase-locked loop as the recording time R (t) of local time. Then take the local timestamp according to the local clock frequency as reference input signal. The numerically controlled adjusts the output frequency according to ring circuit signal by filter. Lastly, the timestamp creater / recorder output the signal as the local clock frequency according to the output signal created by DOC. Under the condition that the invention use larger drift mobility and the lower stability oscillator, the system can provide high accuracy time synchronism.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com