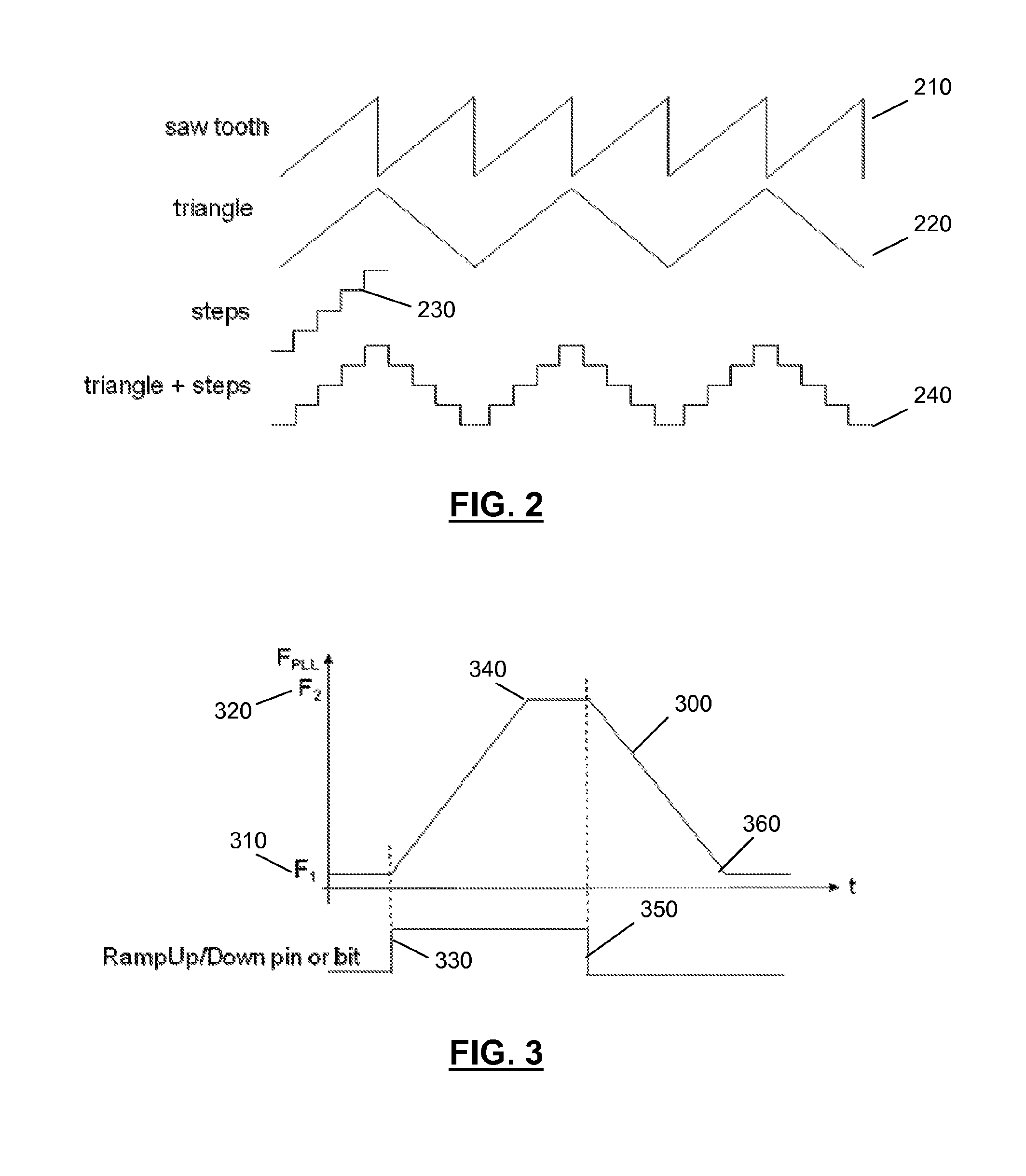
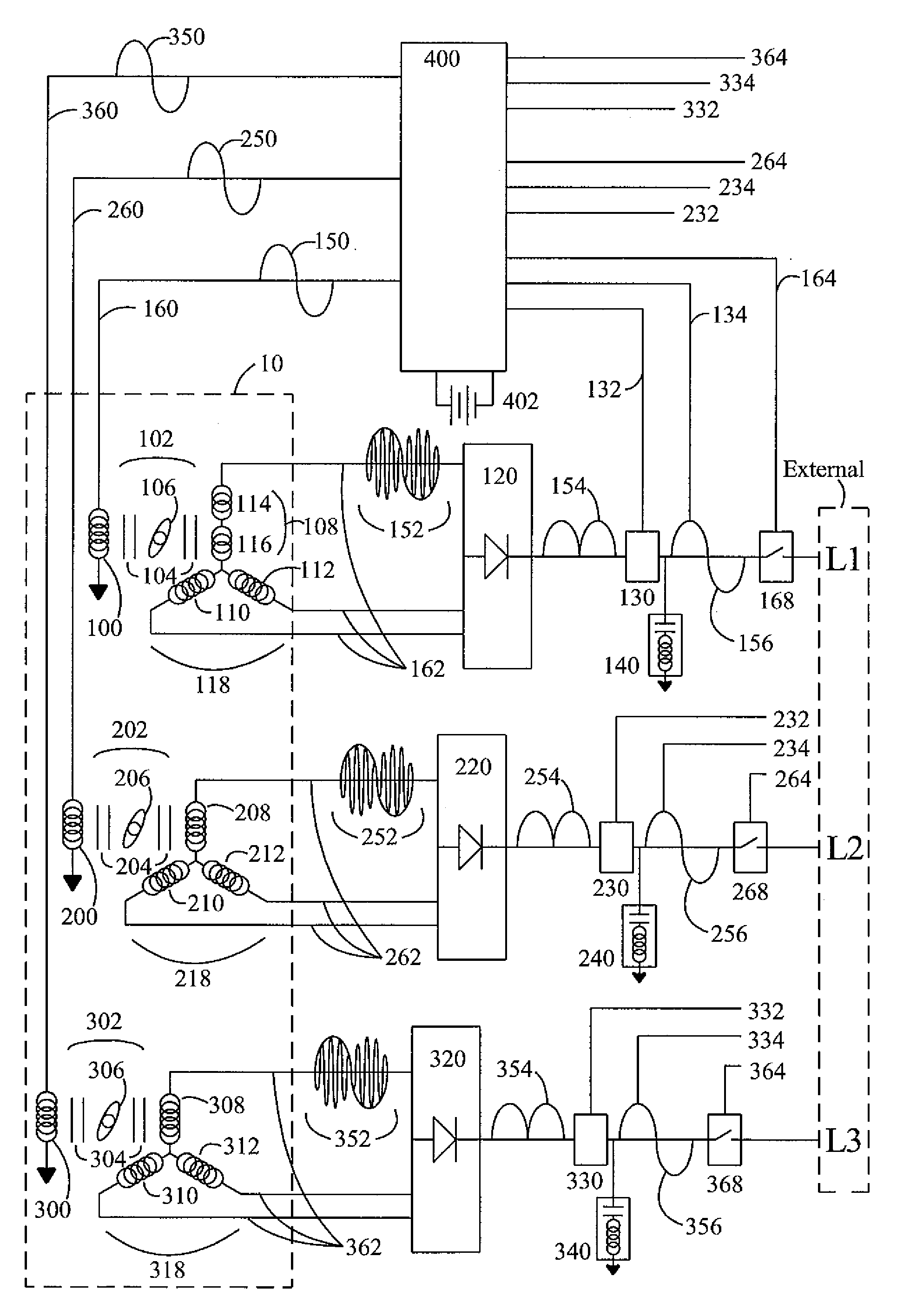
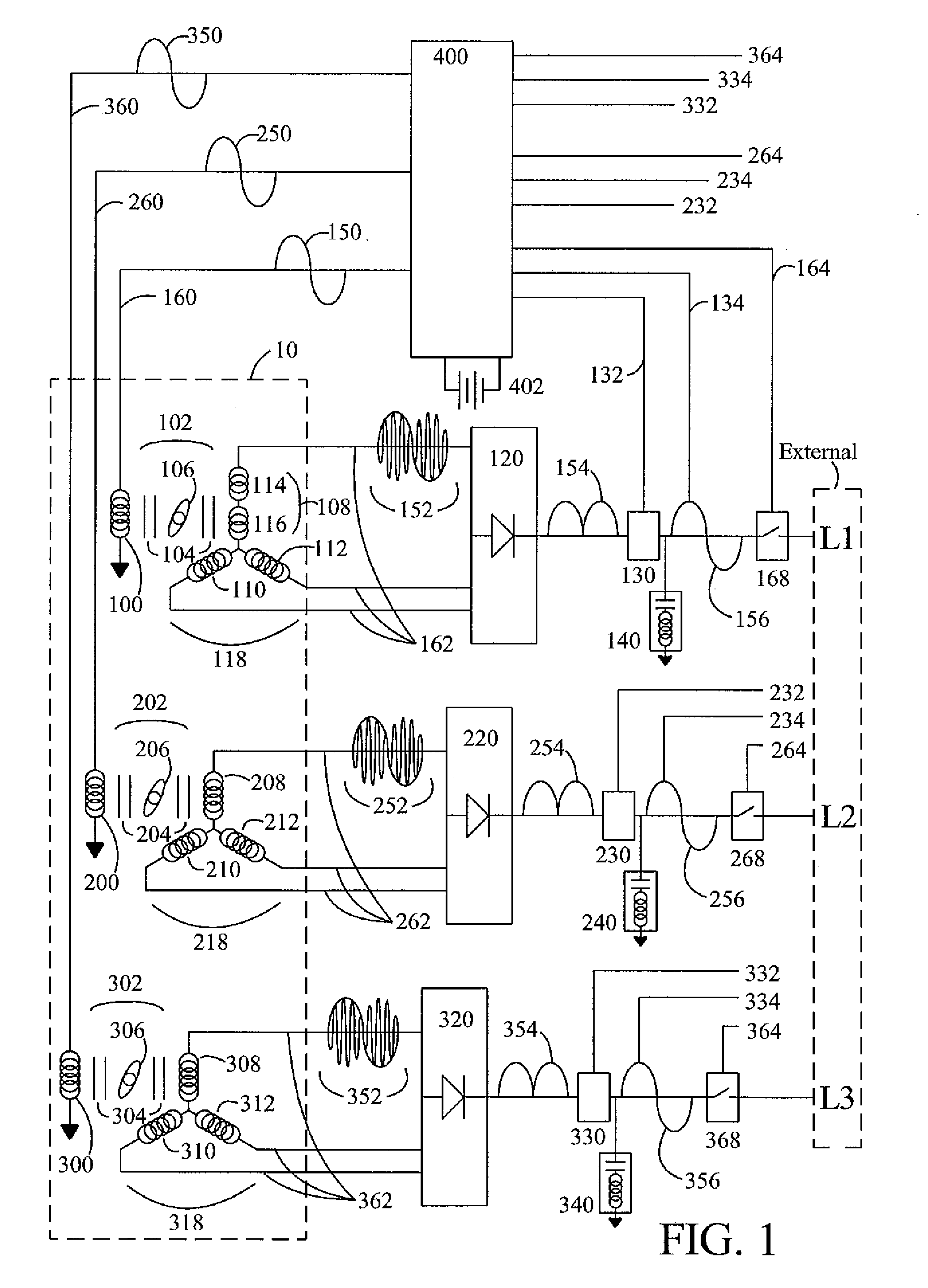
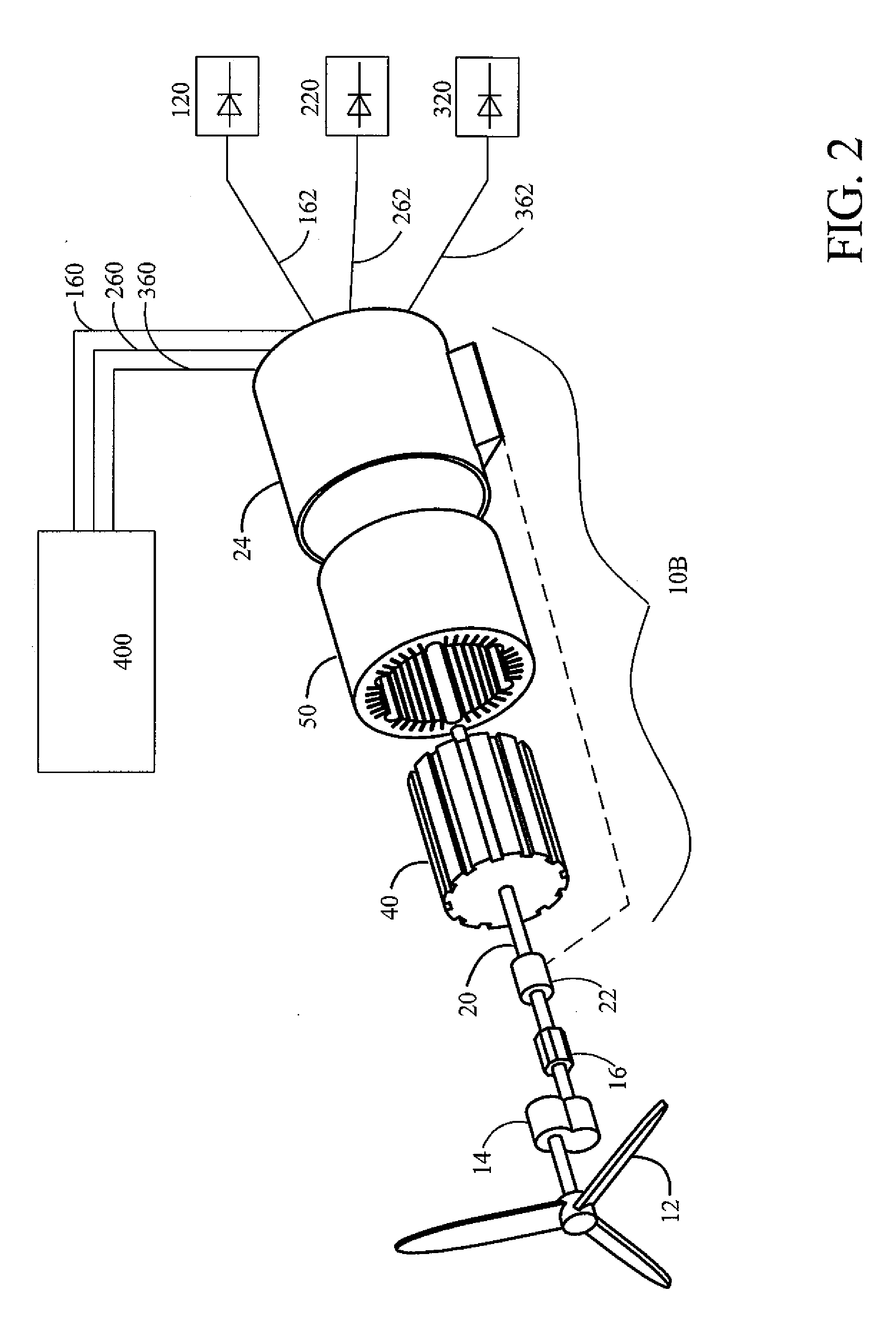
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
624 results about "Frequency generation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
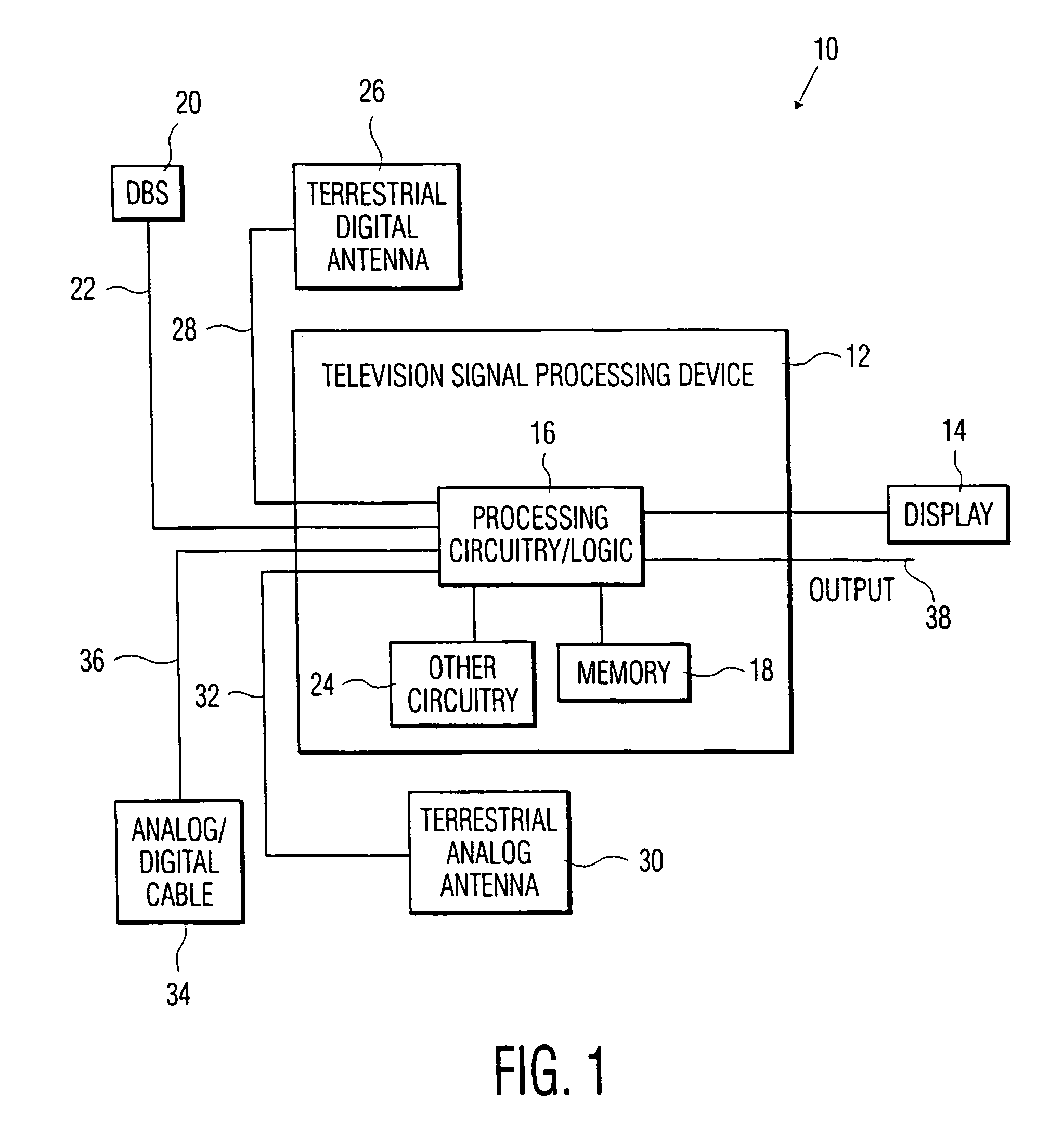
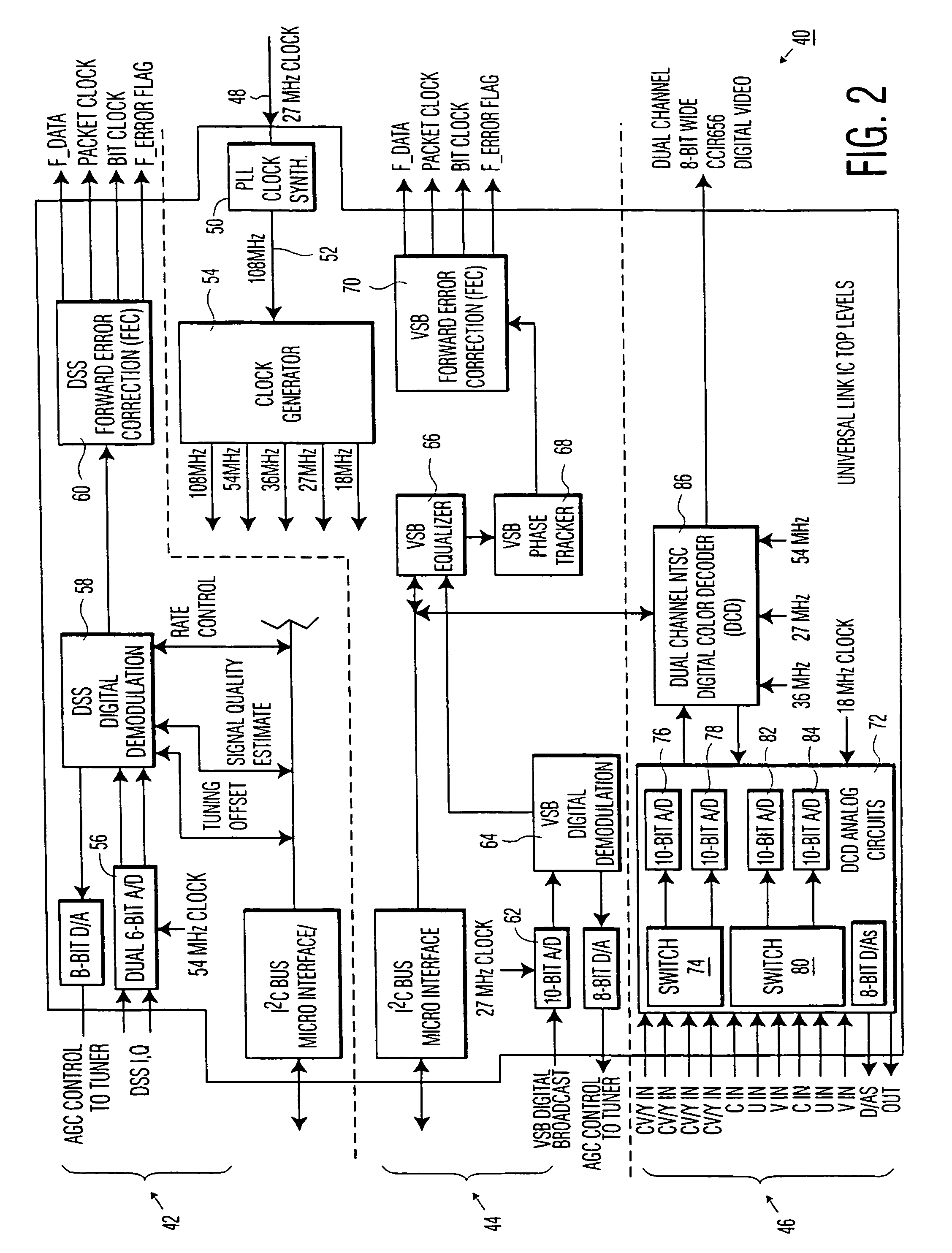
Digital and analog television signal digitization and processing device
InactiveUS7102692B1Easy to processImprove sampling performanceTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsFrequency generationAnalog signal processing
A digital and analog television signal digitization and processing device that performs the digitization and processing functions using a common reference frequency source that is used to generate multiple subclock signals, wherein the reference frequency source is independent of any synchronizing characteristic of the input signal. For dual channel analog signal processing, the common frequency source is not locked to either channel / input signal. Digital signal processing is accomplished based on the same common reference frequency source. Advantageously, the present invention allows all of the analog-to-digital converters and decoder circuitry / logic necessary for simultaneously digitizing and processing several analog and digital television signals to be integrated on a single integrated circuit as well as eliminating duplicate frequency generation circuits.
Owner:MAGNOLIA LICENSING LLC
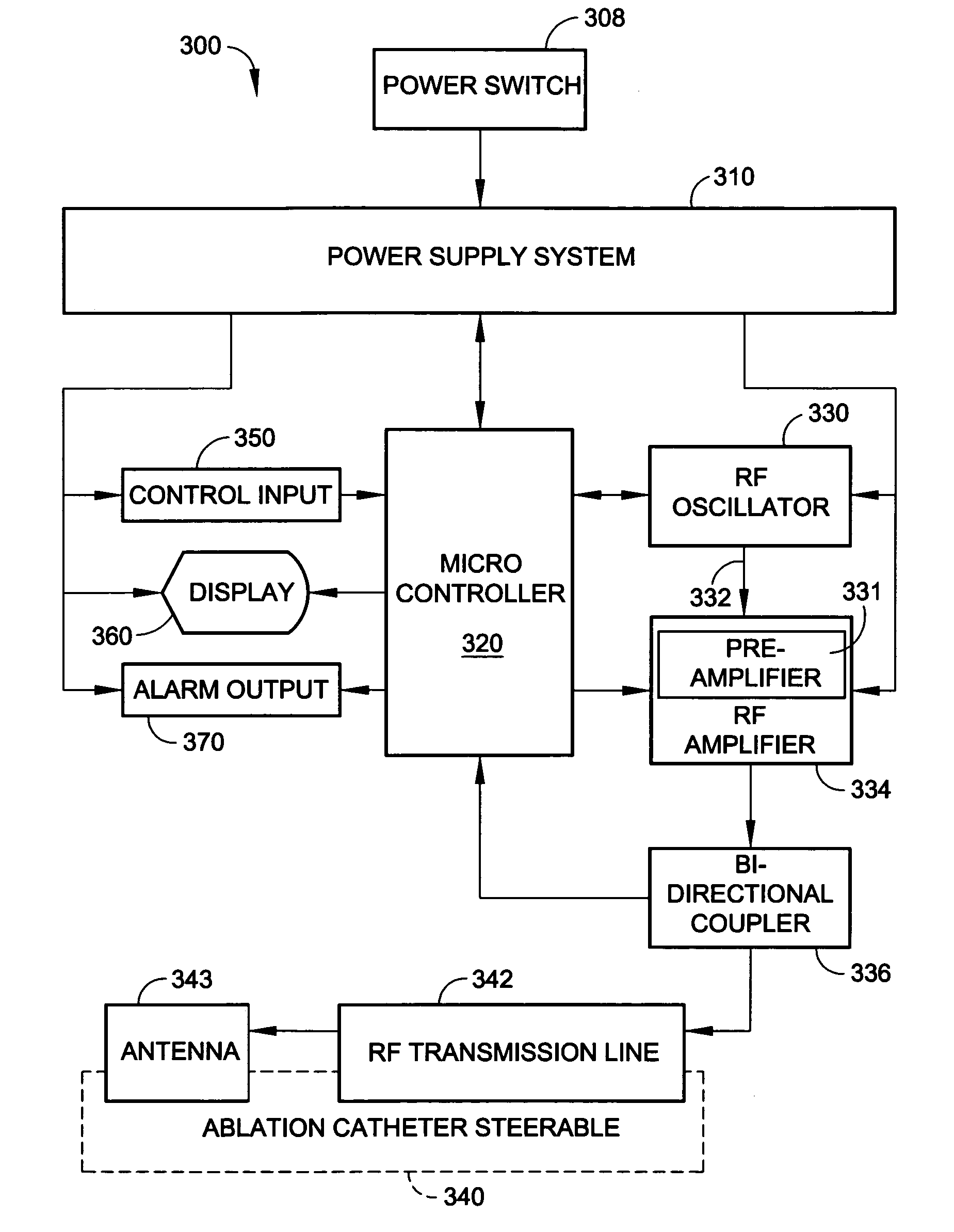
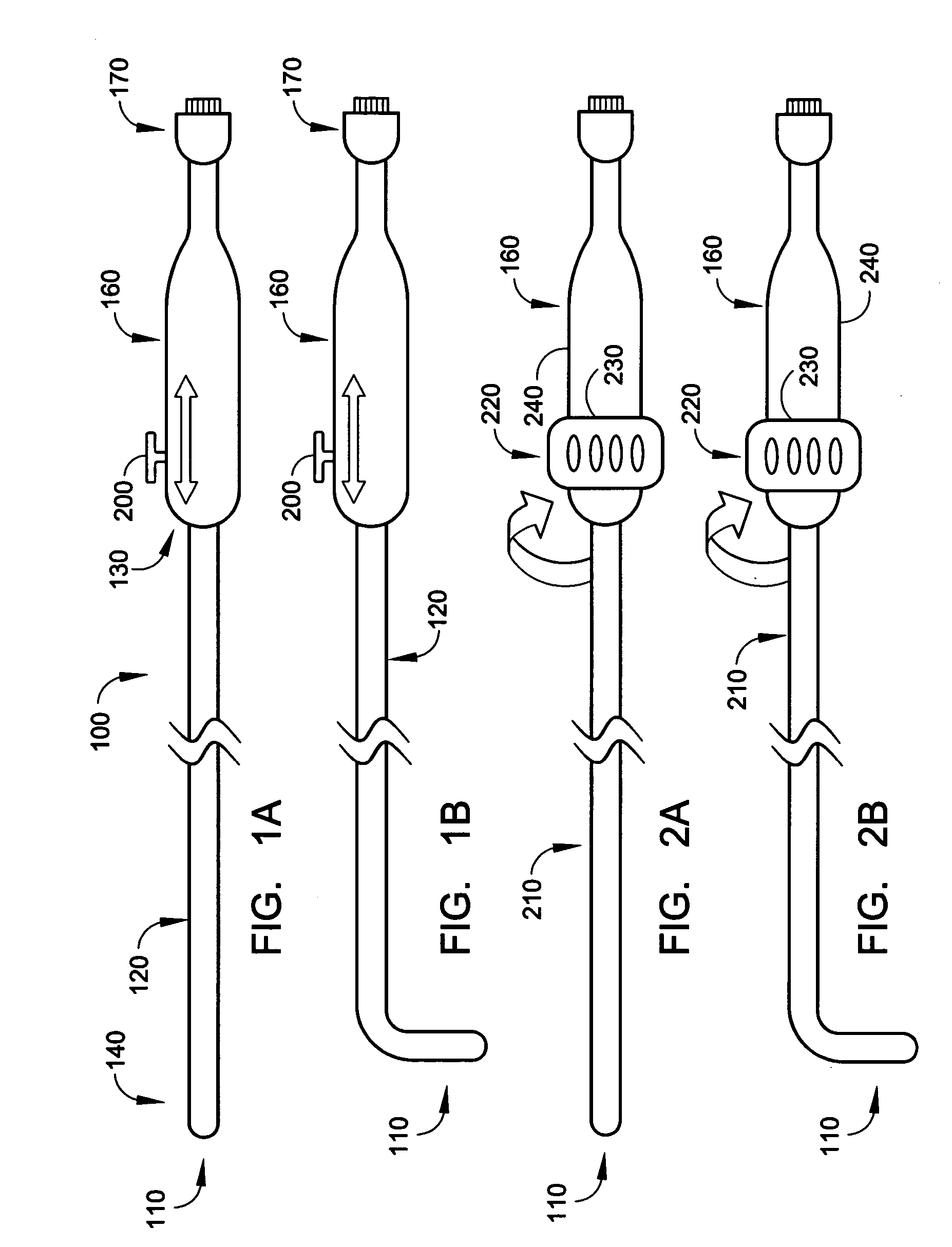
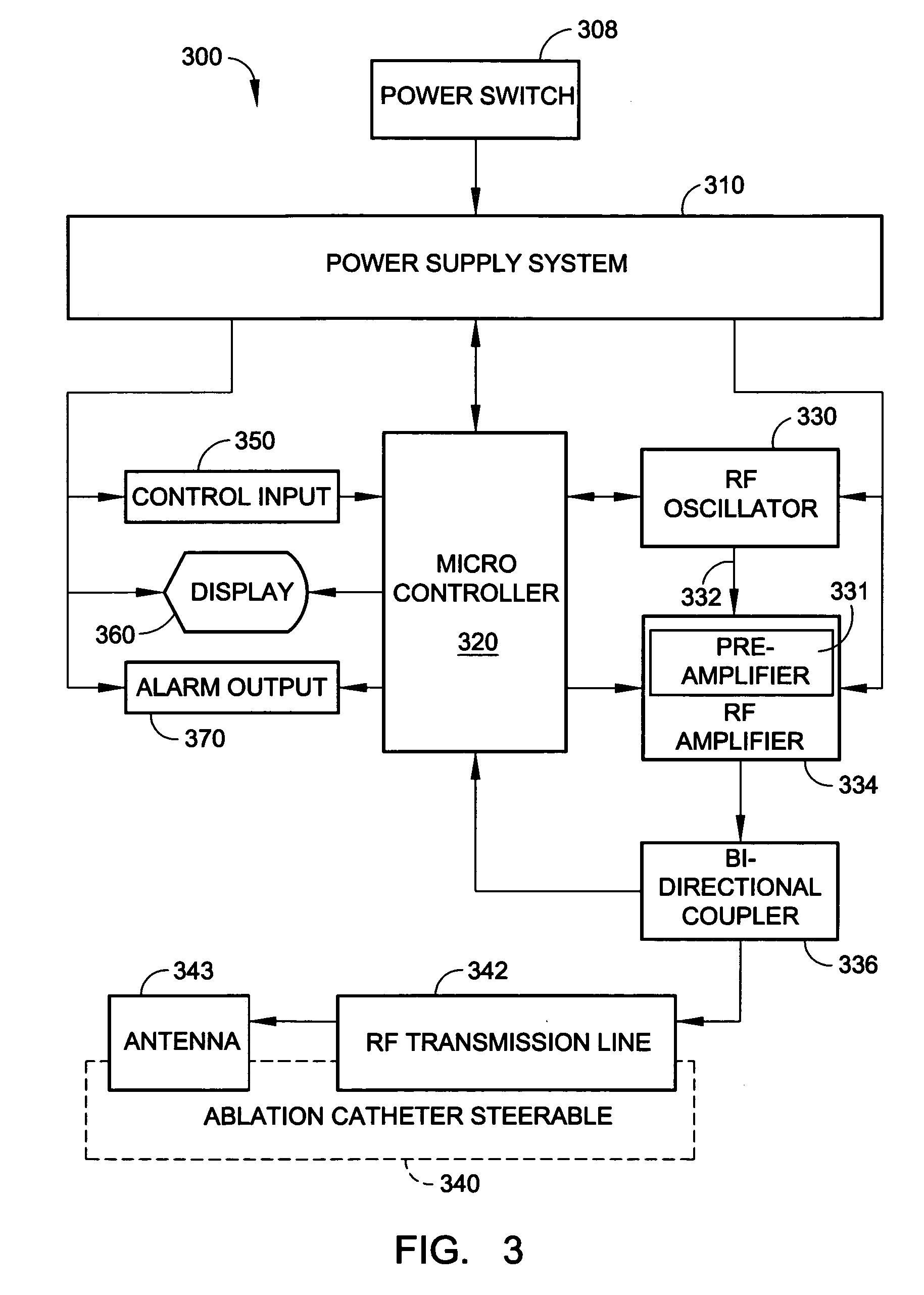
Radio-frequency based catheter system and method for ablating biological tissues
InactiveUS7070595B2Efficient tissue ablationMinimizes power ratioElectrotherapyDiagnostic markersFrequency generationRadio frequency
A method for biological tissue ablation includes shaping a shapeable RF antenna to accommodate the contour of a body vessel adjacent a biological tissue load; generating a train of radio frequency (RF) energy pulses at an output frequency for transmission in a transmission line to the shapeable RF antenna adjacent the biological tissue load; sensing a reflected signal and a forward signal of the RF energy pulses; and adjusting output frequency of the RF energy pulses to effect a substantial match of transmission line impedance with shapeable RF antenna and biological tissue load impedance.
Owner:MEDWAVE INC
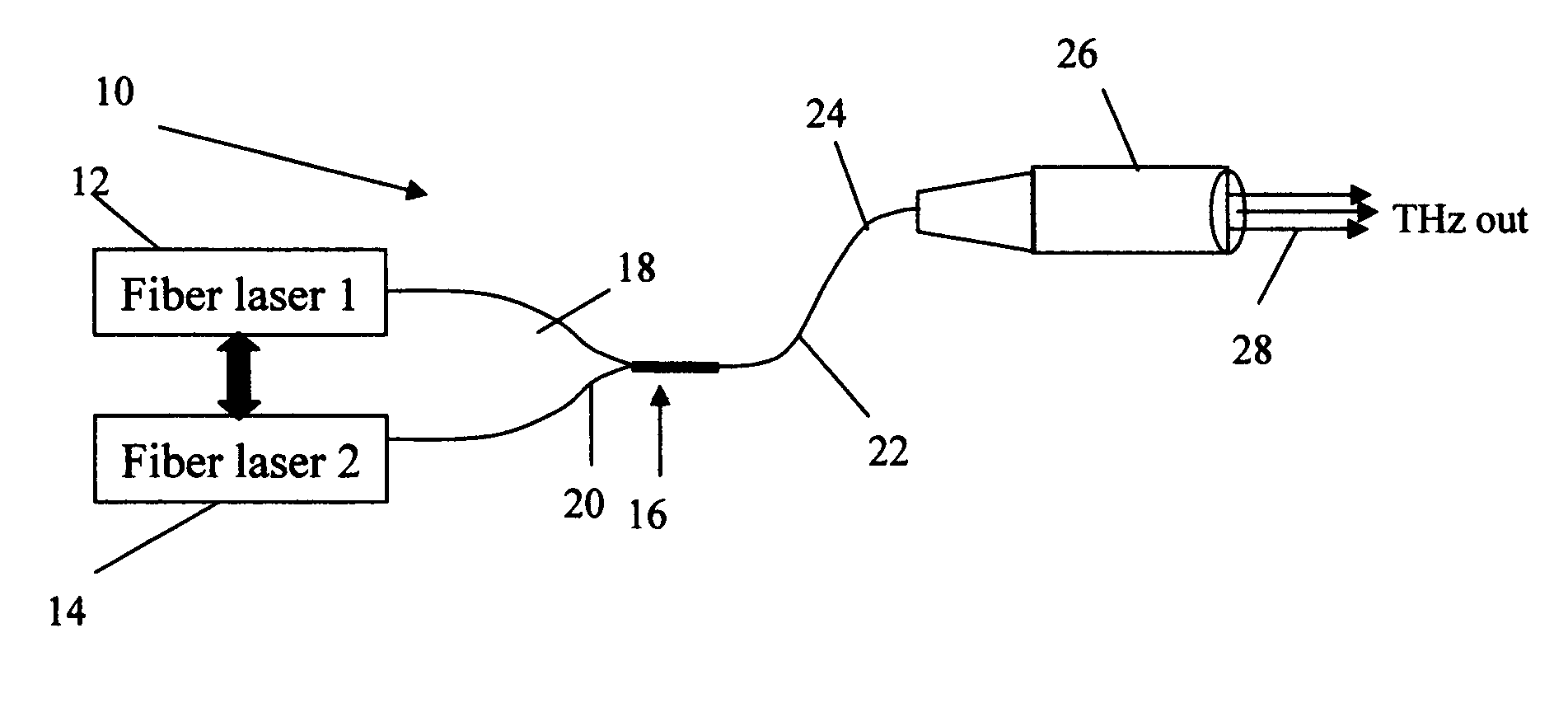
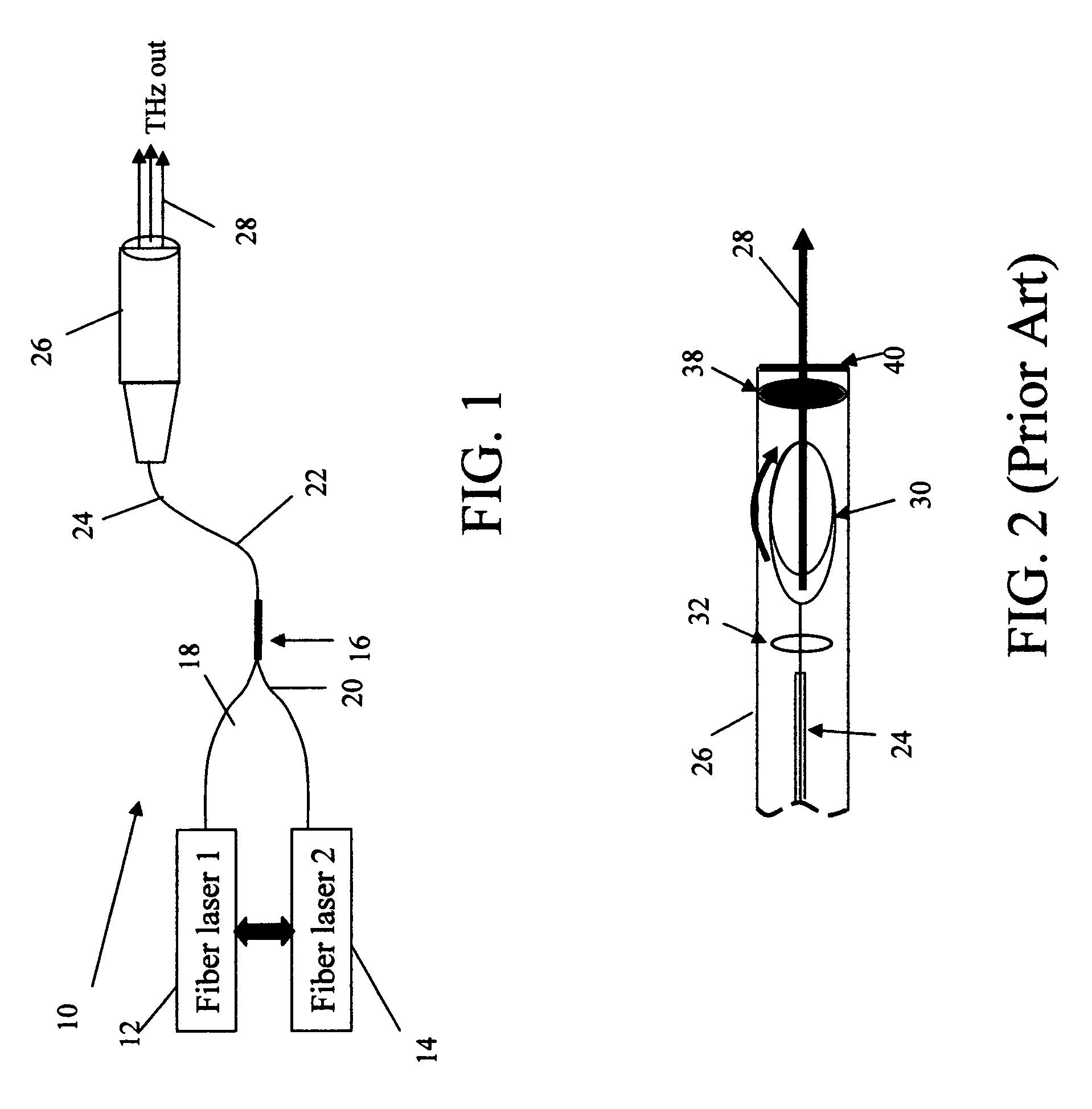
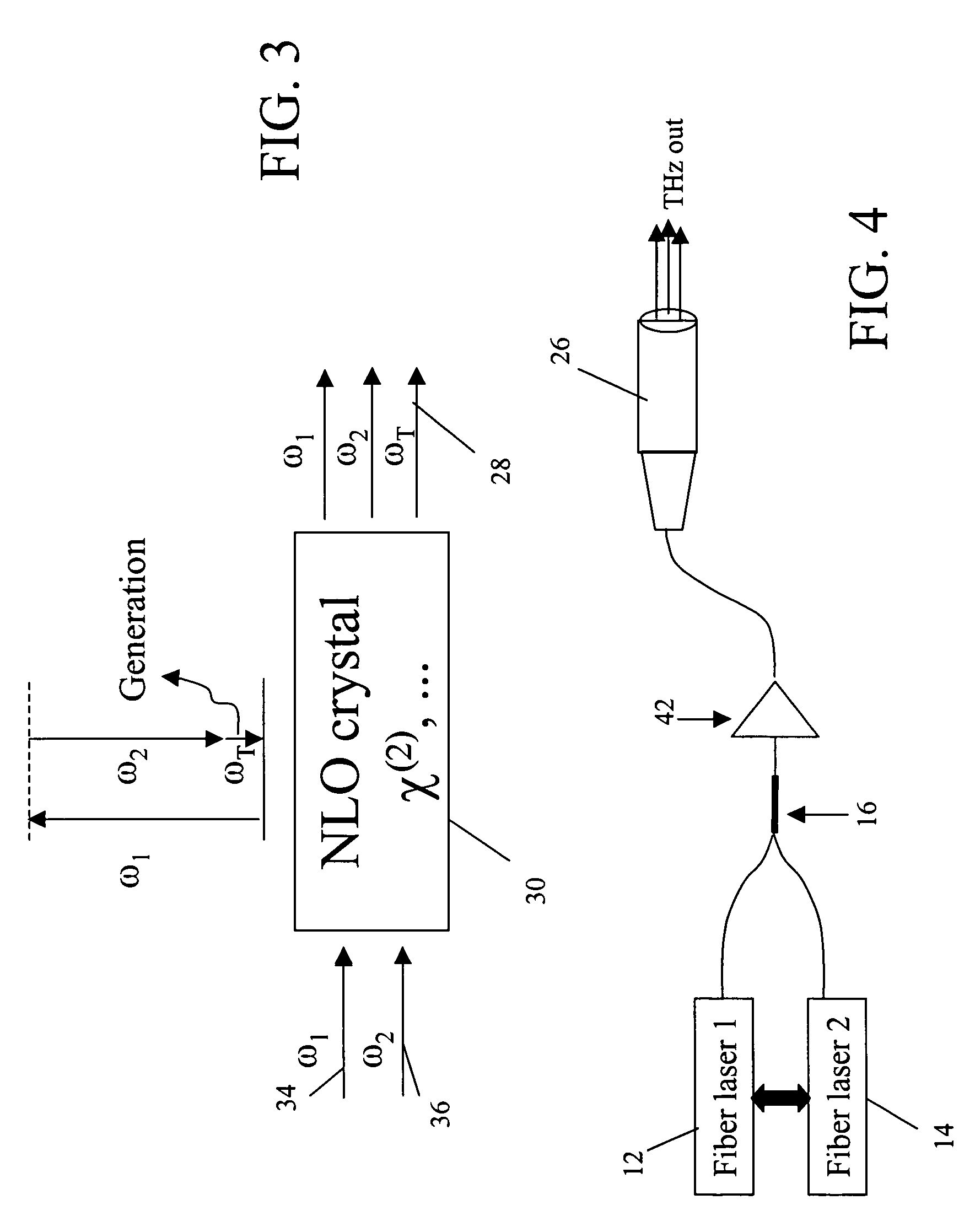
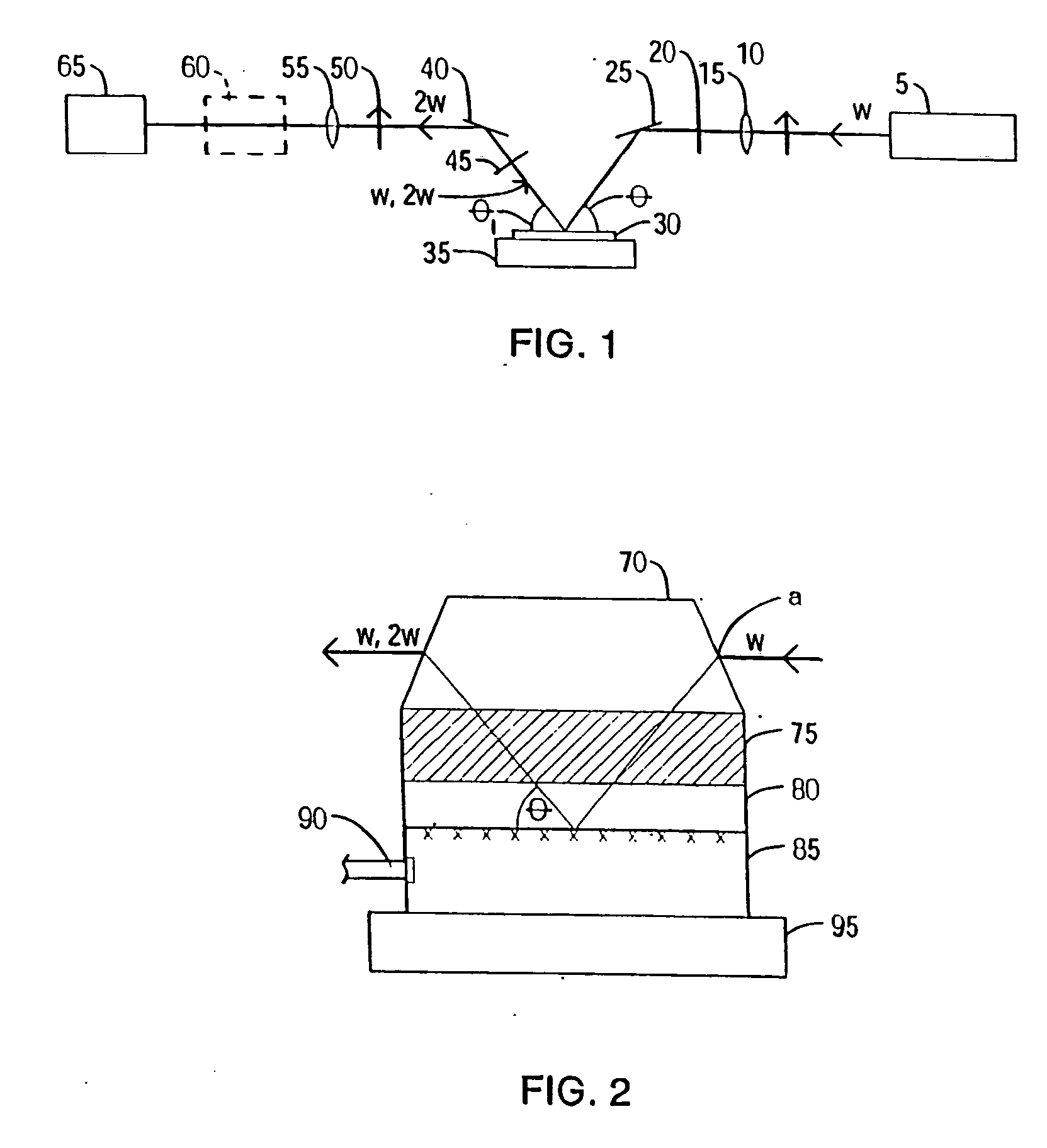
Fiber-laser-based Terahertz sources through difference frequency generation (DFG) by nonlinear optical (NLO) crystals
InactiveUS7054339B1Compact, lightweightCost effectiveLaser detailsNon-linear opticsNonlinear optical crystalFrequency generation
A fiber-laser-based implementation of a Terahertz source through difference frequency generation (DFG) by nonlinear optical (NLO) crystals is compact, tunable and scalable. A pair of fiber lasers (Q-switched, CW or mode-locked) generate single-frequency outputs at frequencies ω1 and ω2. A fiber beam combiner combines the laser outputs and routes the combined output to a THz generator head where a nonlinear interaction process in the NLO crystal generates THz radiation.
Owner:NP PHOTONICS A CORP OF DELAWARE
Method using a nonlinear optical technique for detection of interactions involving a conformational change
InactiveUS20030148391A1No need for labor and time-consuming washing stepLow backgroundCompound screeningMaterial nanotechnologyFrequency generationThird harmonic
A nonlinear optical technique, such as second or third harmonic or sum or difference frequency generation, is used to detect binding interactions, or the degree or extent of binding, that comprise a conformational change. In one aspect of the present invention, the nonlinear optical technique detects a conformational change in a probe due to target binding. In another aspect of the invention, the nonlinear optical technique screens candidate probes by detecting a conformational change due to a probe-target interaction. In another aspect of the invention, the nonlinear optical technique screens candidate modulators of a probe-target interaction by detecting a conformational change in the presence of the modulator.
Owner:BIODESY
Method of detecting proper connection of an endoscope to an endoscope processor
A method detects proper connection of an endoscope to an endoscope processor by measuring pressure pulses applied to the connection point. The method can include measuring for the pressure pulses at a second connection point on the endoscope processor and measuring for a beat frequency produced variations in the frequency of pressure pulses input at each connection point. The method can also include looking for echoes of the pressure pulsations from physical structures within a lumen of the endoscope connected to the connection point.
Owner:ETHICON INC
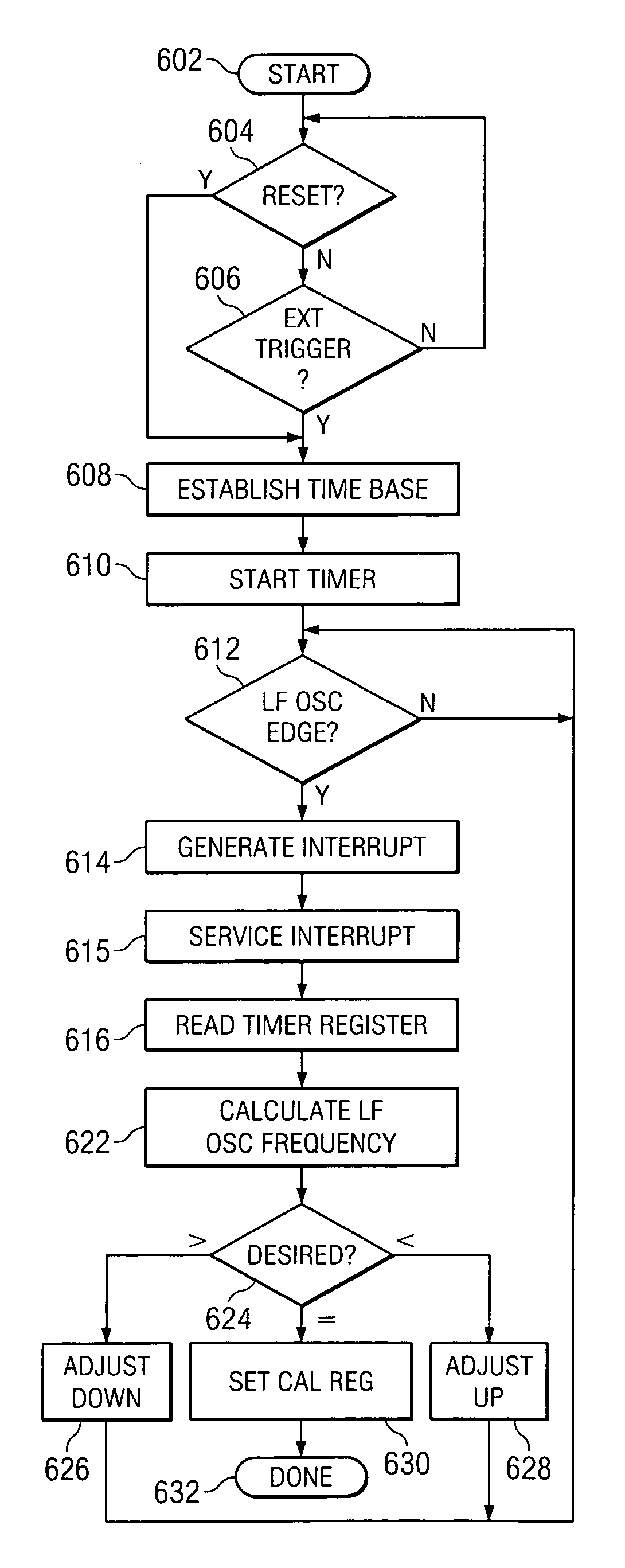
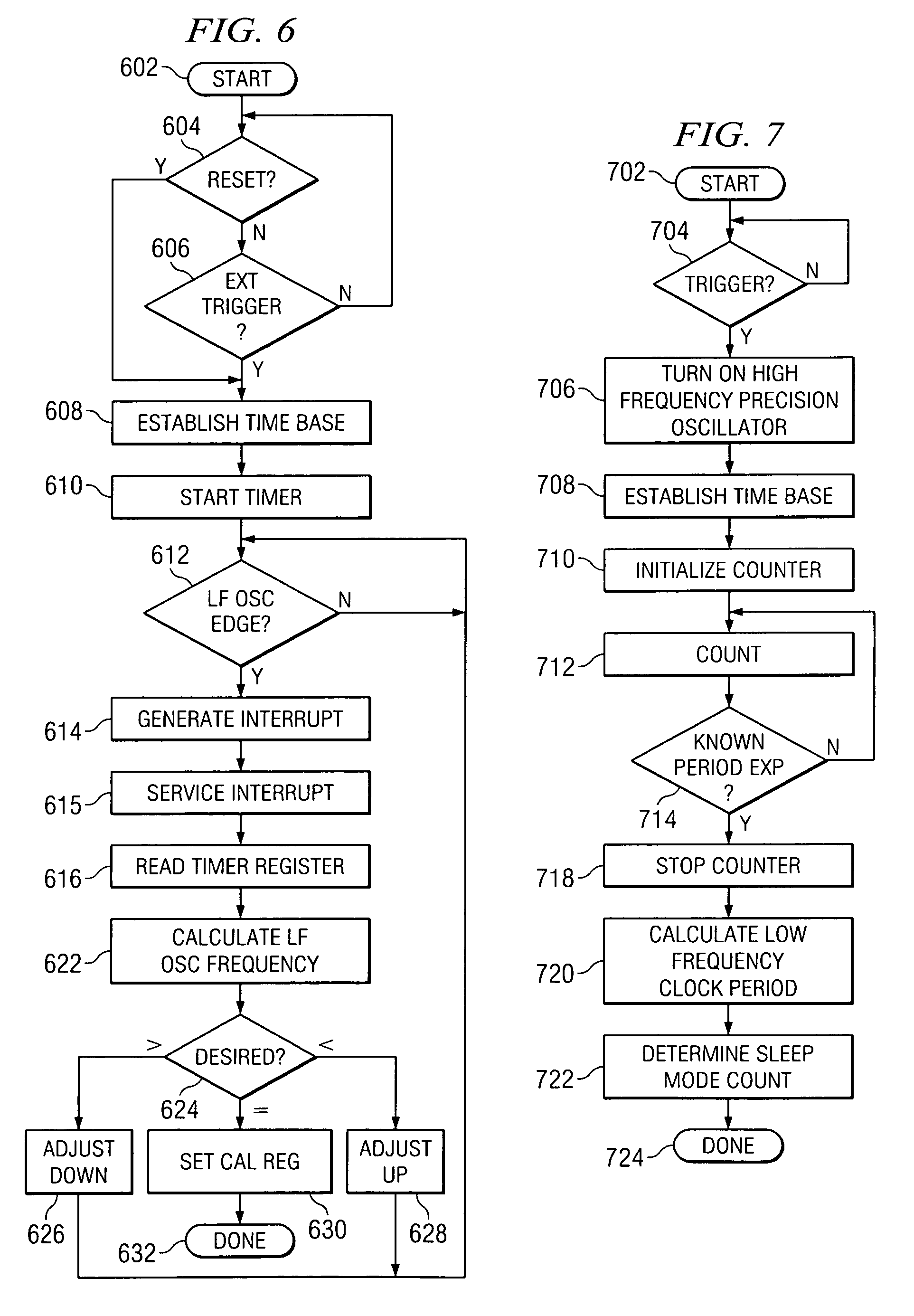
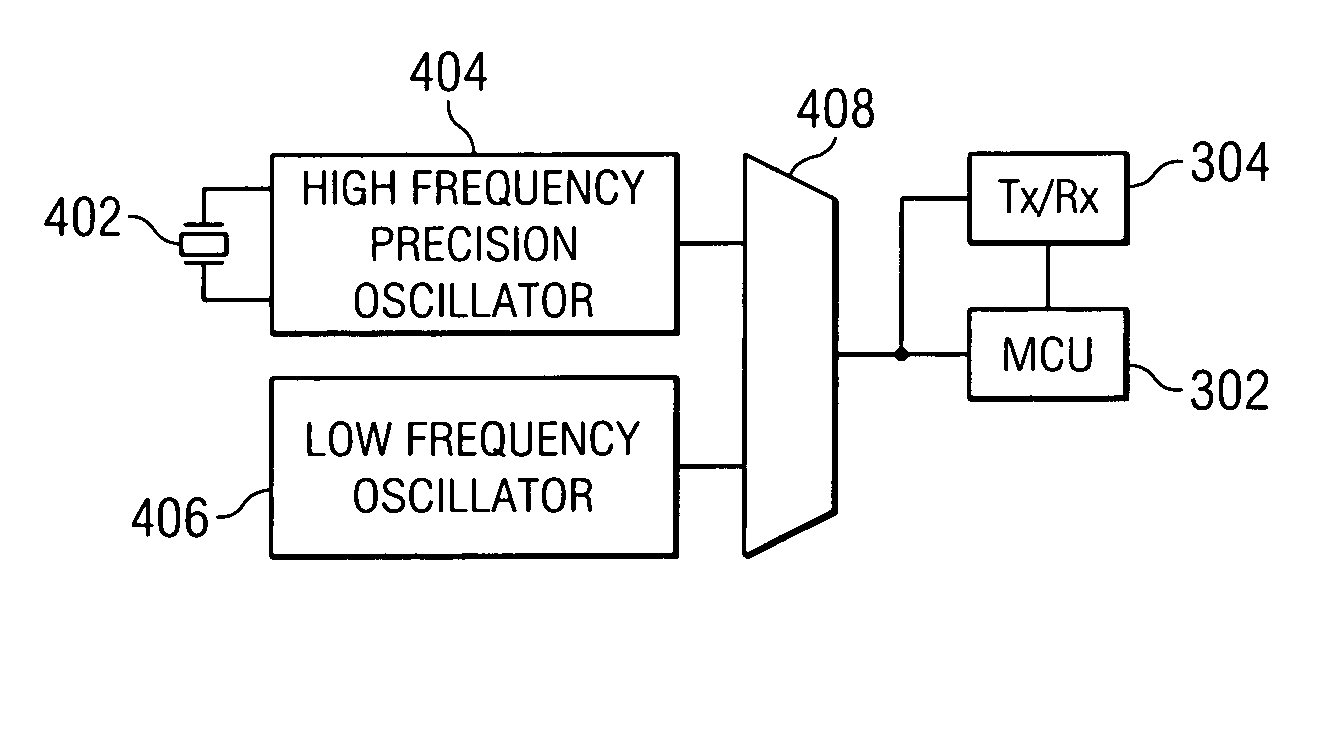
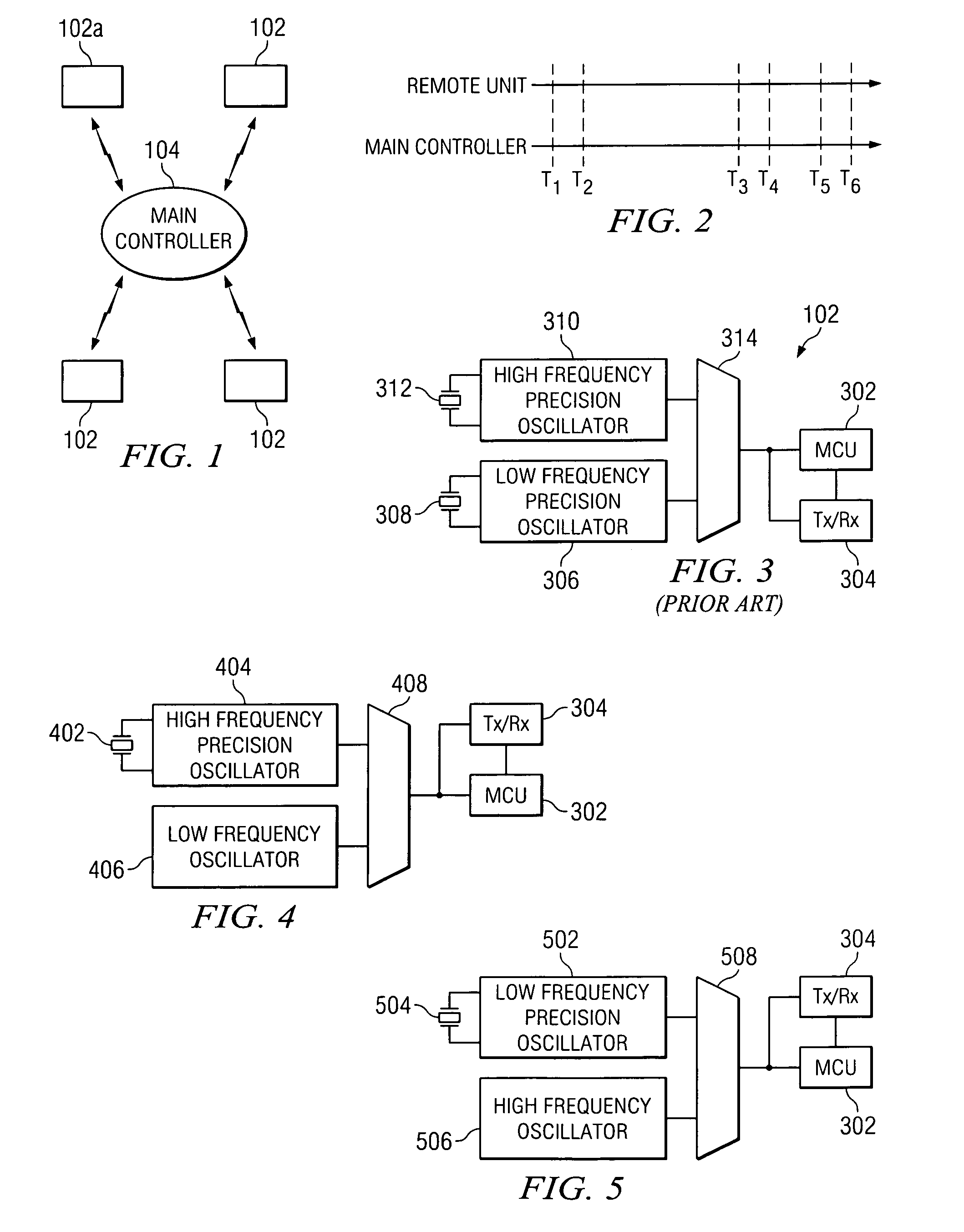
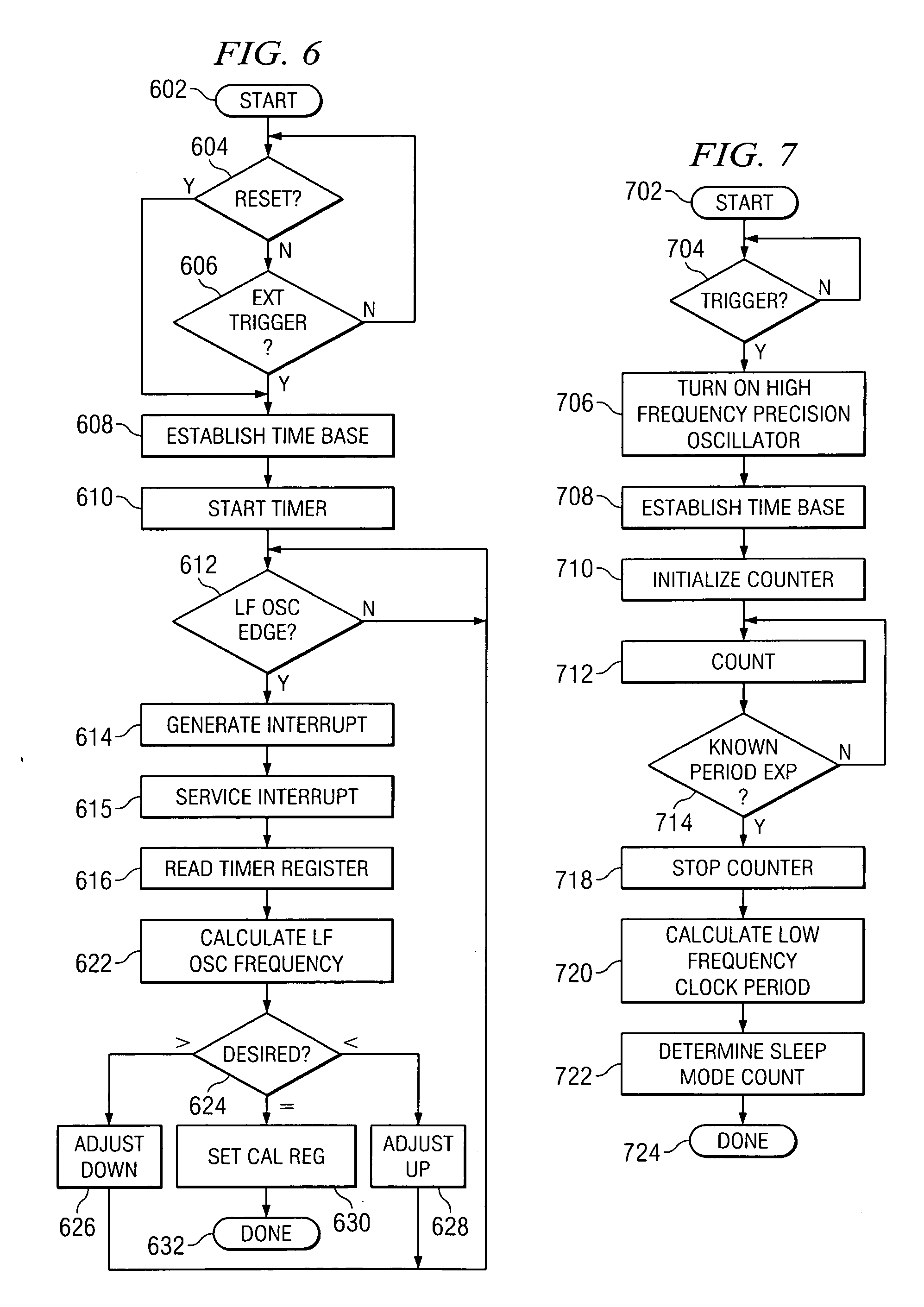
Precise frequency generation for low duty cycle transceivers using a single crystal oscillator
An apparatus and method for calibrating a non-crystal oscillator in a transceiver unit using a crystal-oscillator includes the step of establishing a time base based upon oscillations of the crystal oscillator. A comparison of the number of oscillations for the non-crystal oscillator and the crystal oscillator is made during a known time period is made. An adjustment is determined based upon the established time base and the compared number of oscillations. The transceiving of the transceiver unit is then controlled based upon this adjustment.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Alignment apparatus for x-ray imaging system
A method for aligning a radiation source with a portable image receiver in a radiographic imaging system generates a magnetic field with a predetermined field pattern and with a time-varying vector direction at a predetermined frequency from an emitter apparatus that is coupled to the radiation source, wherein the generated magnetic field further comprises a synchronization signal. Sensed signals from the magnetic field are obtained from a sensing apparatus that is coupled to the image receiver, wherein the sensing apparatus comprises three or more sensor elements, wherein at least two of the sensor elements are arranged at different angles relative to each other and are disposed outside the imaging area of the image receiver. An output signal is indicative of an alignment adjustment according to the amplitude and phase of the obtained sensed signals relative to the synchronization signal.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Method using a nonlinear optical technique for detection of interactions involving a conformational change
InactiveUS20060228725A1No need for labor and time-consuming washing stepLow backgroundCompound screeningMaterial nanotechnologyThird harmonicFrequency generation
A nonlinear optical technique, such as second or third harmonic or sum or difference frequency generation, is used to detect binding interactions, or the degree or extent of binding, that comprise a conformational change. In one aspect of the present invention, the nonlinear optical technique detects a conformational change in a probe due to target binding. In another aspect of the invention, the nonlinear optical technique screens candidate probes by detecting a conformational change due to a probe-target interaction. In another aspect of the invention, the nonlinear optical technique screens candidate modulators of a probe-target interaction by detecting a conformational change in the presence of the modulator.
Owner:BIODESY
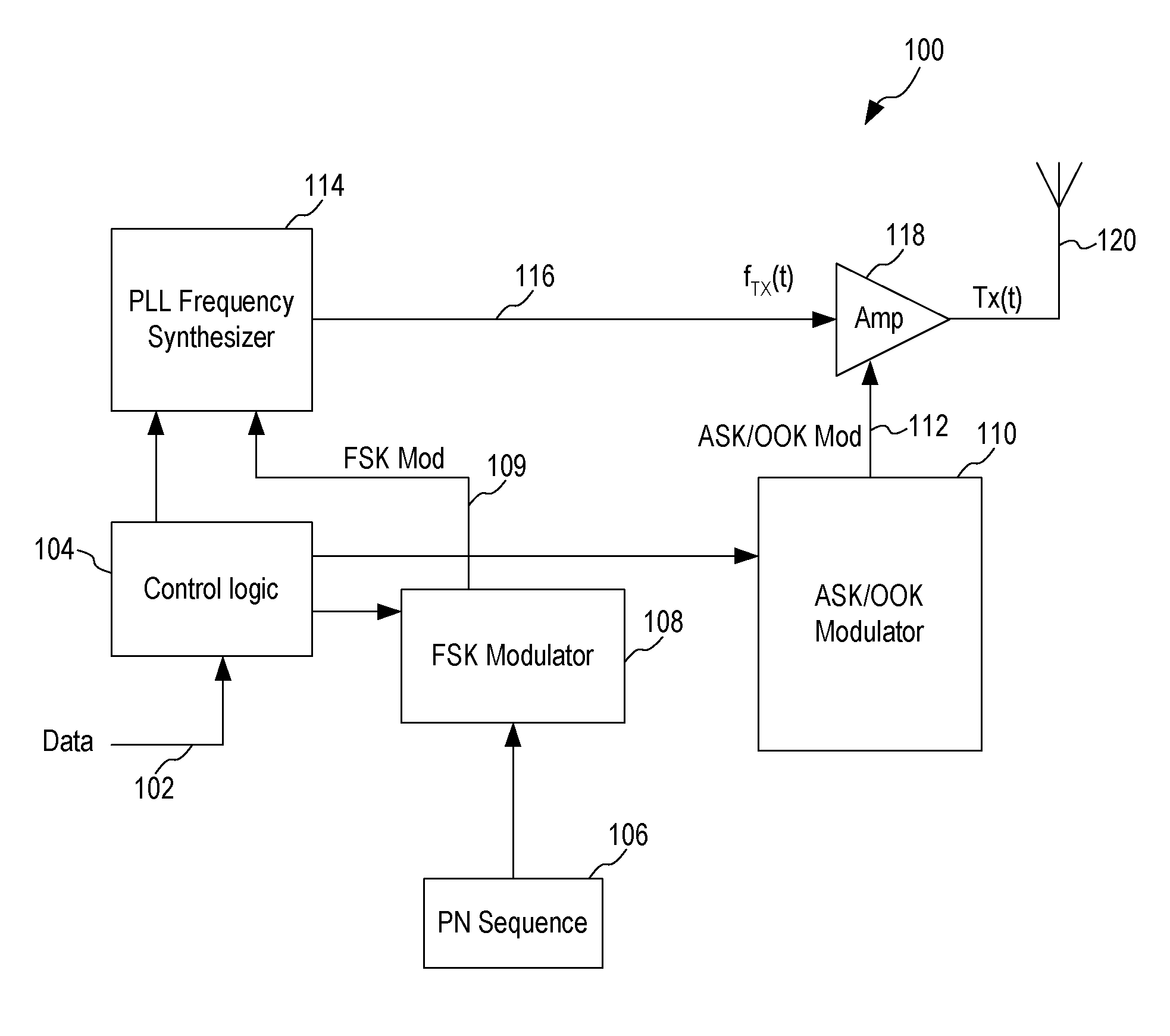
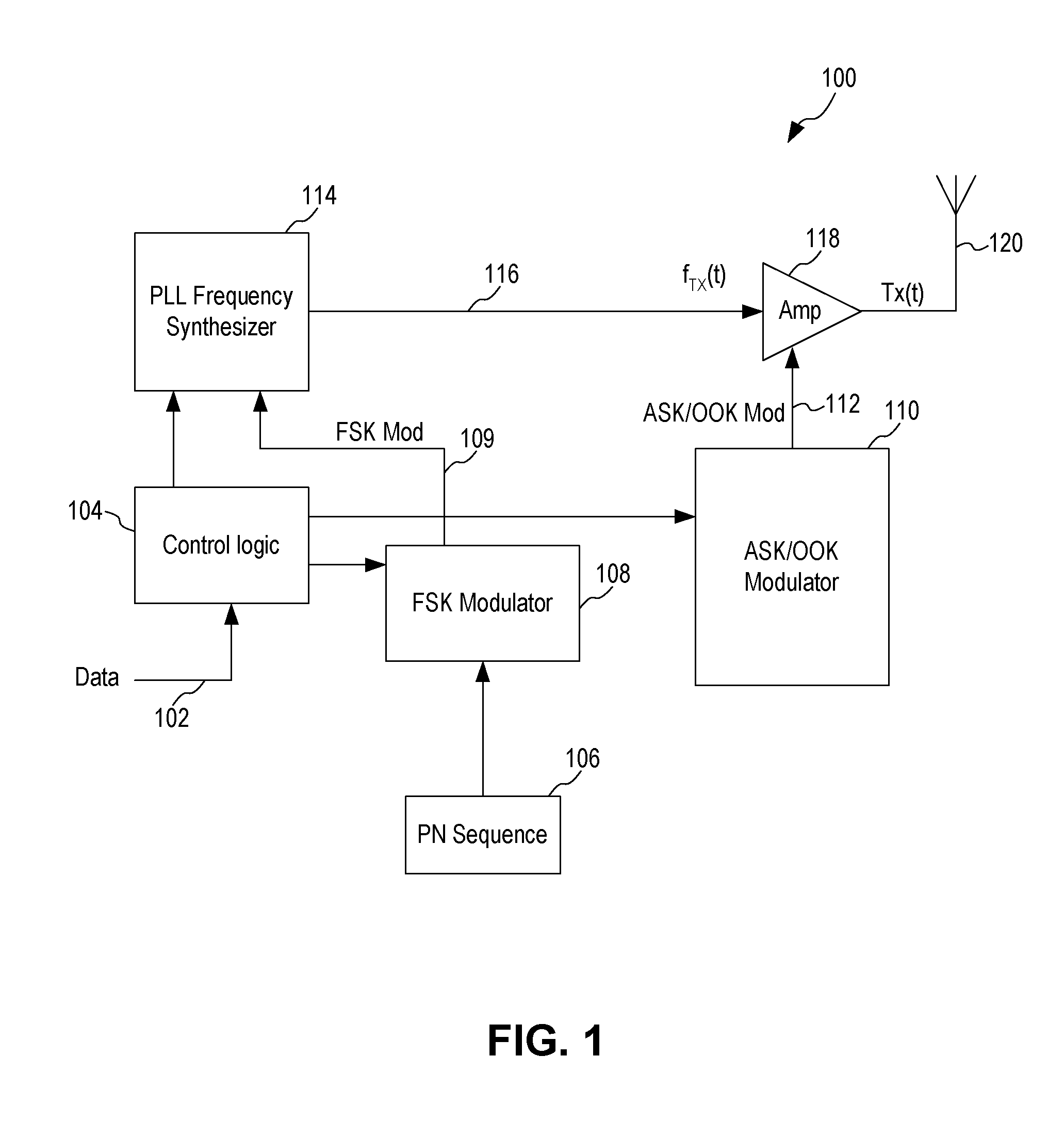
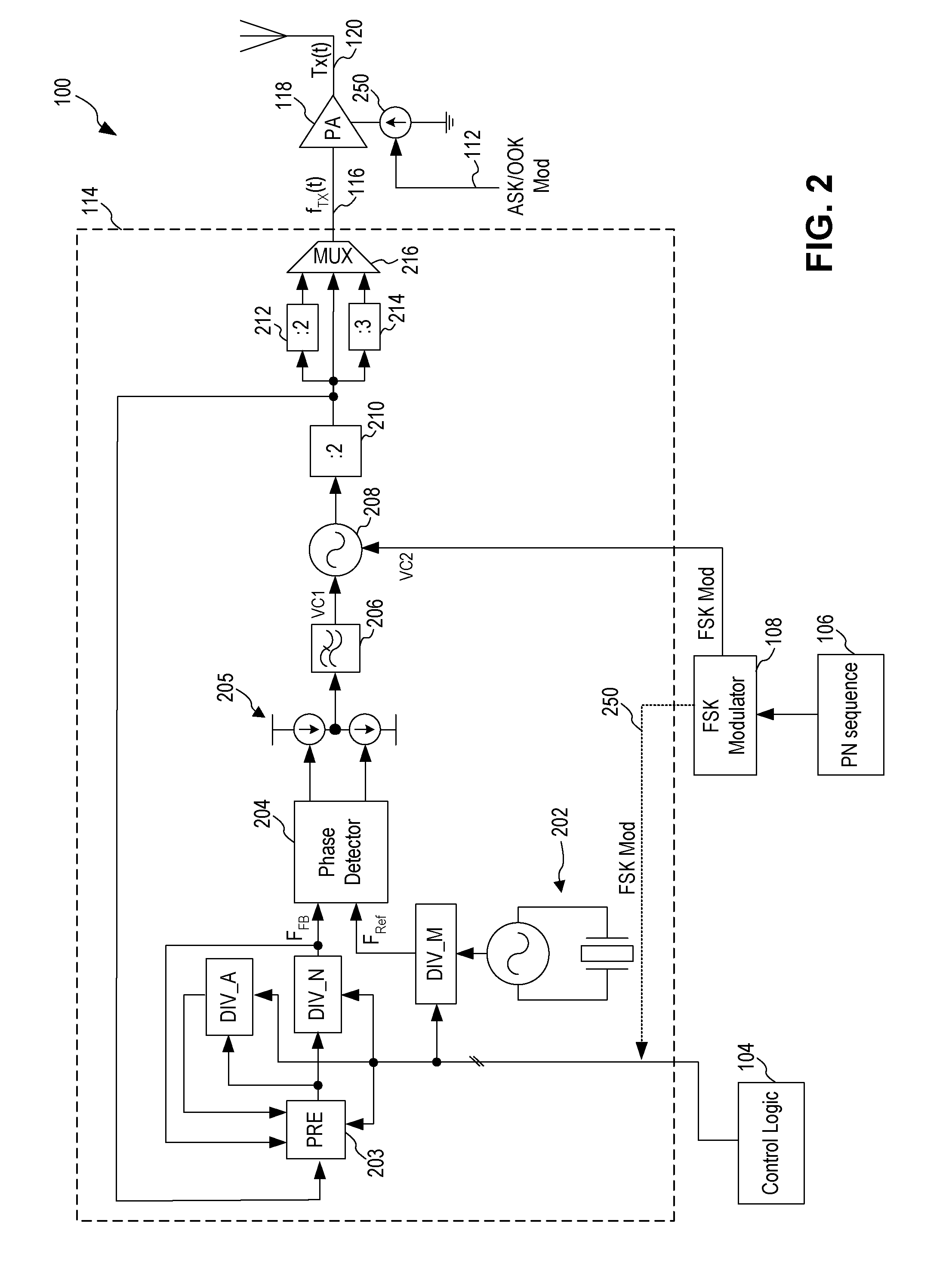
Spread Spectrum ASK/OOK Transmitter
An ASK / OOK transmitter includes a frequency-shift keying (FSK) modulator receiving an input bit sequence and generating a FSK modulation signal indicative of the input bit sequence, a frequency generation circuit receiving the FSK modulation signal and generating a carrier signal having a first frequency where the frequency of the carrier signal is shifted by the FSK modulation signal to form a wideband carrier signal, an amplitude-shift keying (ASK) modulator receiving input data and generating an ASK modulation signal indicative of the input data, and a power amplifier coupled to receive the wideband carrier signal as an input signal and the ASK modulation signal as a control signal. The power amplifier provides a spread spectrum ASK transmission signal where the ASK modulation signal modulates the wideband carrier signal to form the spread spectrum ASK transmission signal.
Owner:MICREL
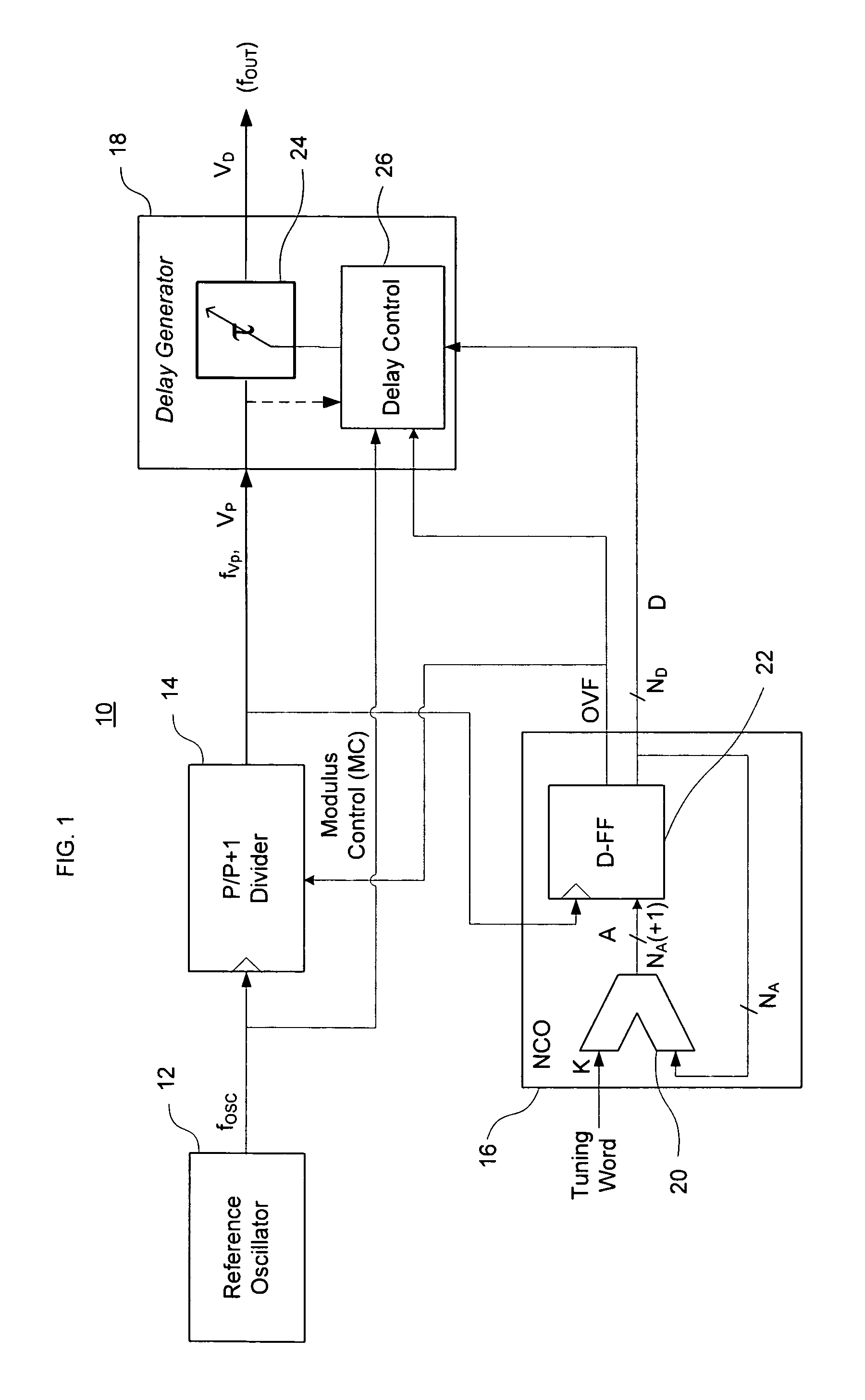
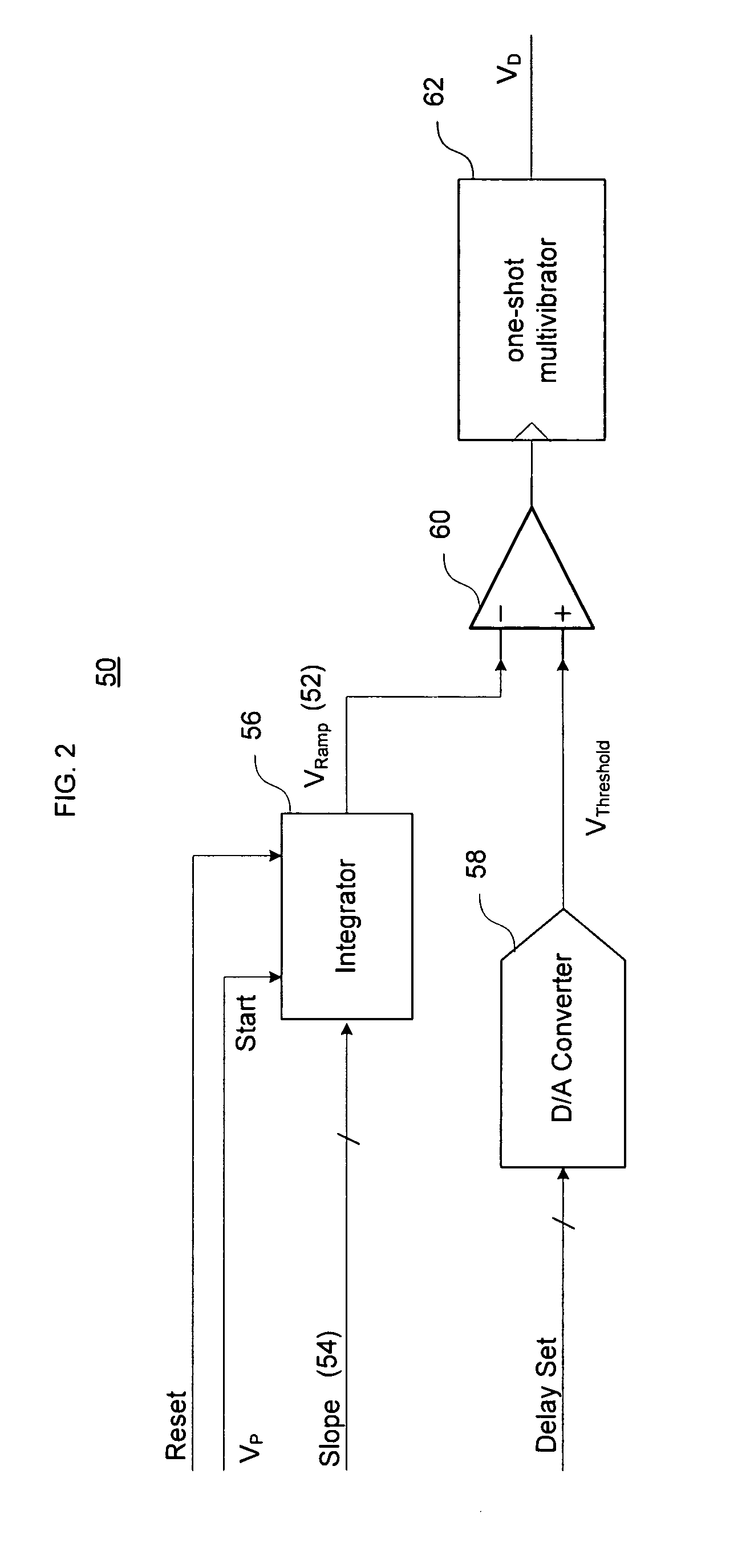
Direct digital synthesizer for reference frequency generation
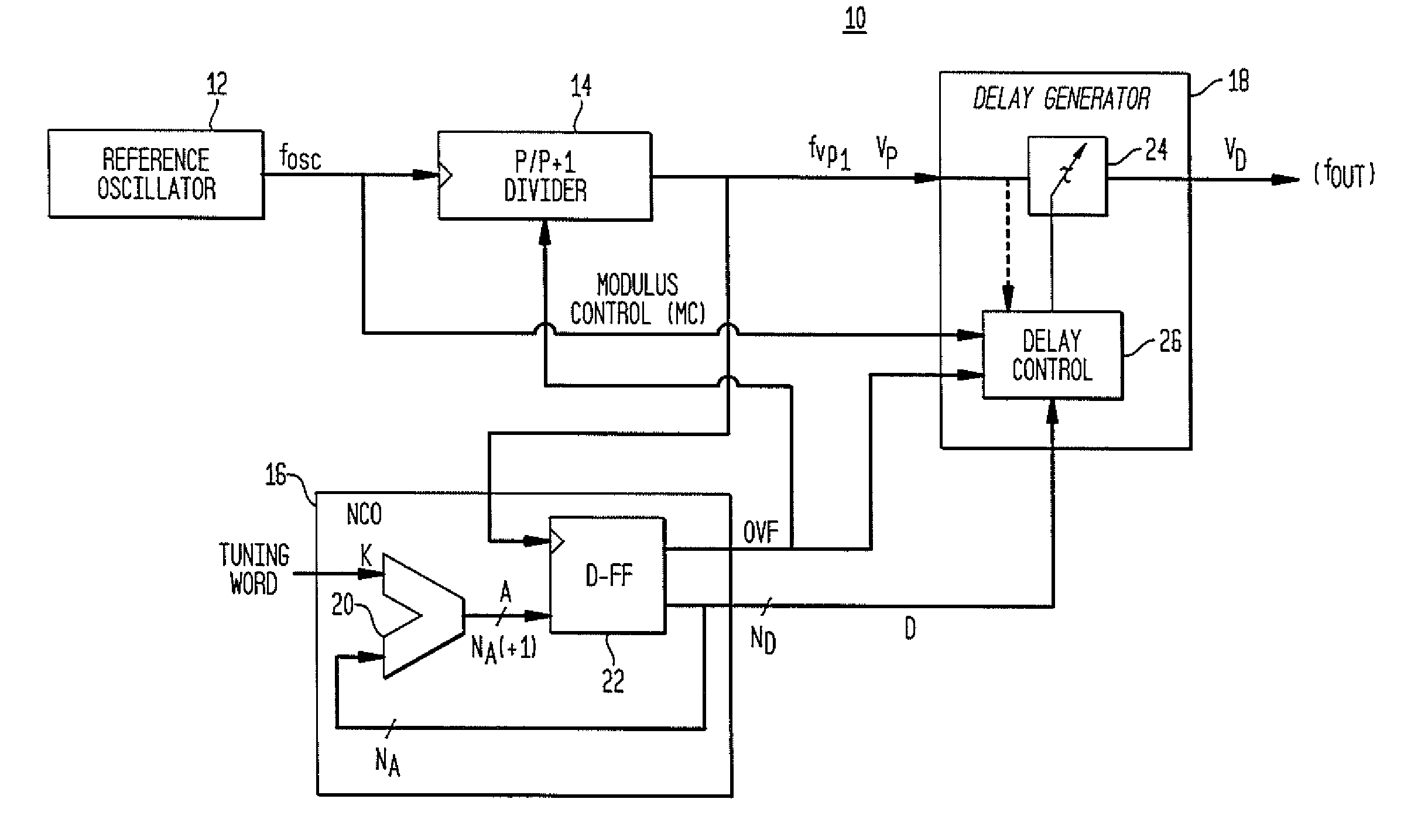
InactiveUS7724097B2Improve noiseImprove performancePulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersFrequency generationDigital controlled oscillator
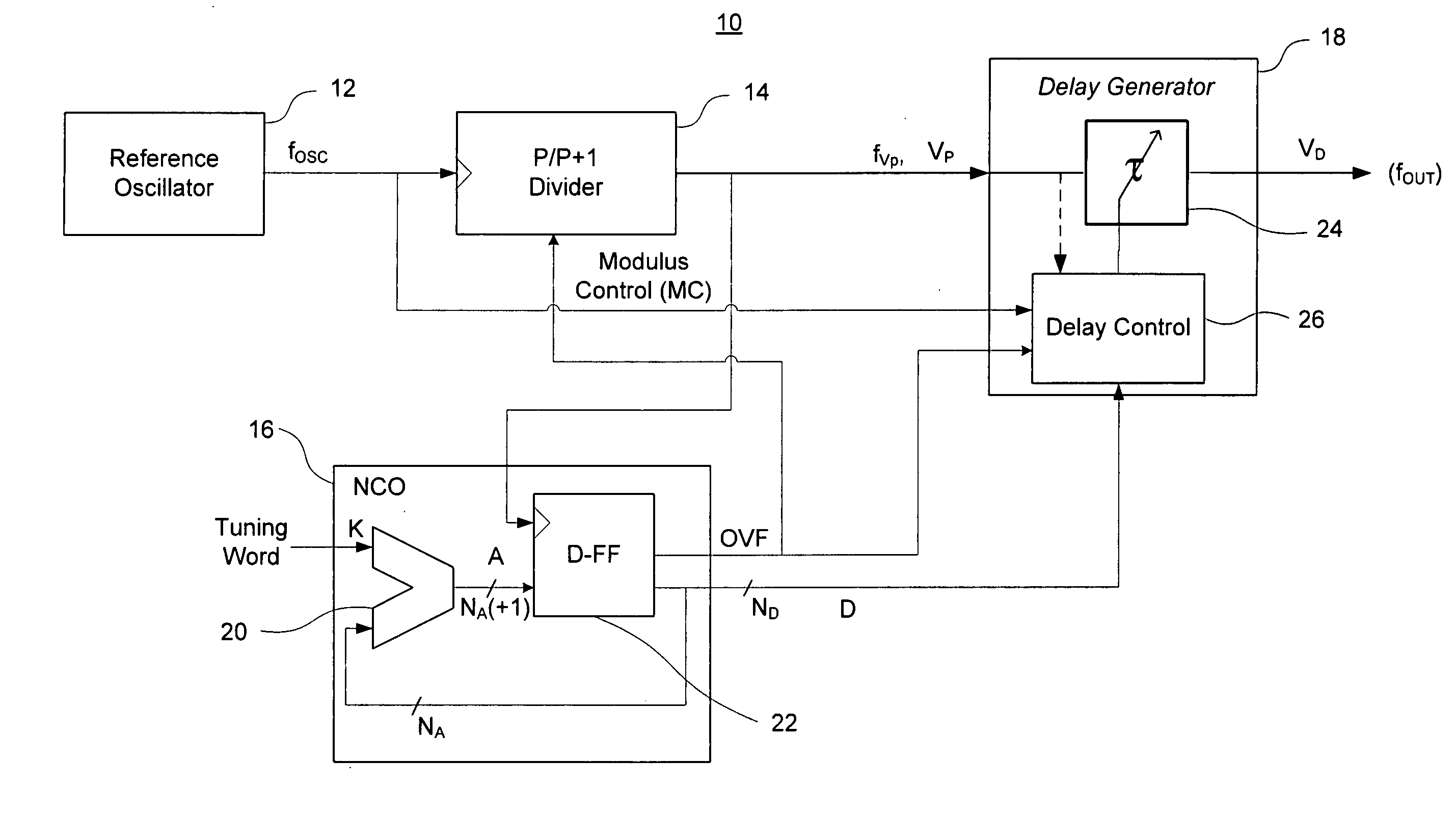
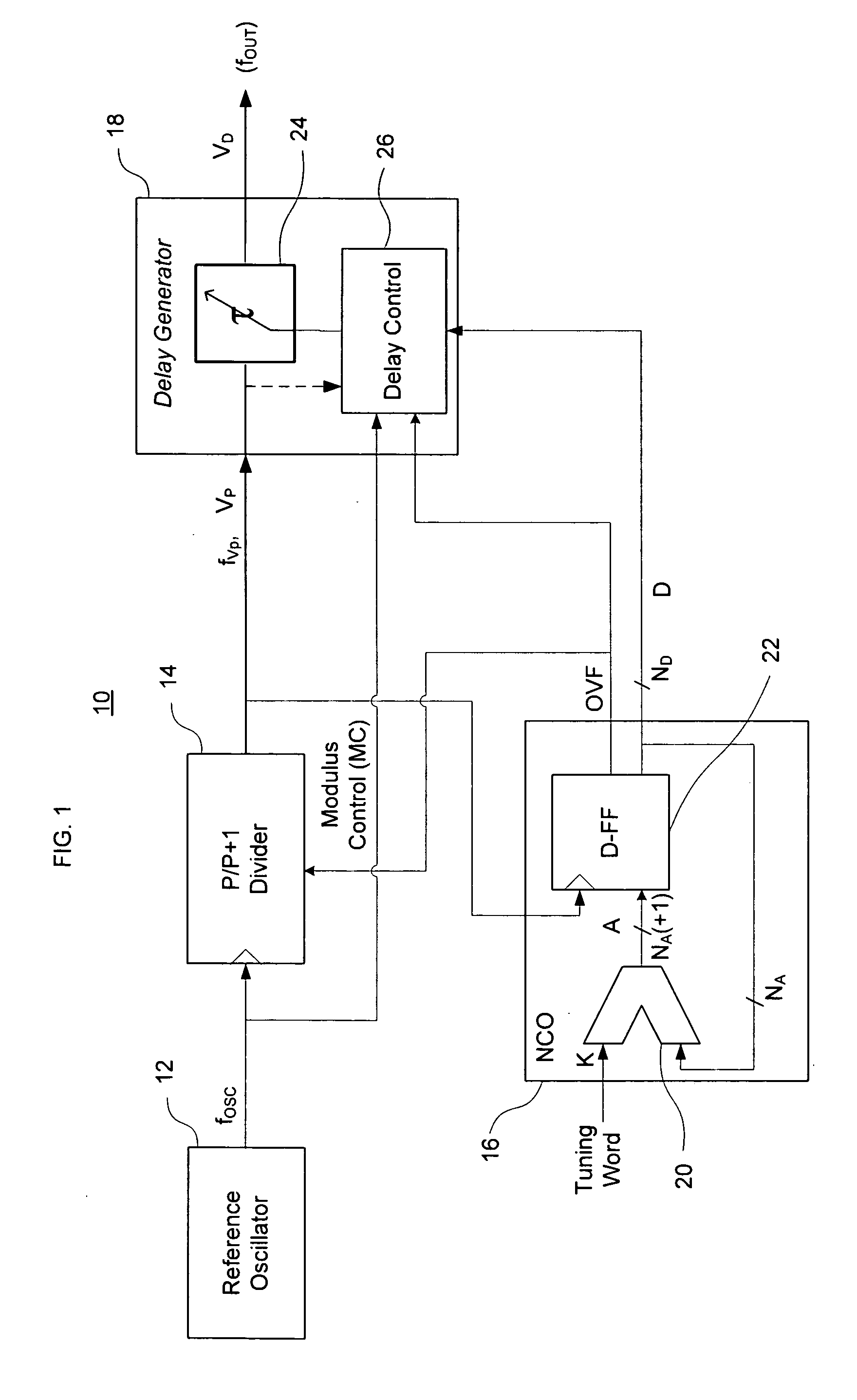
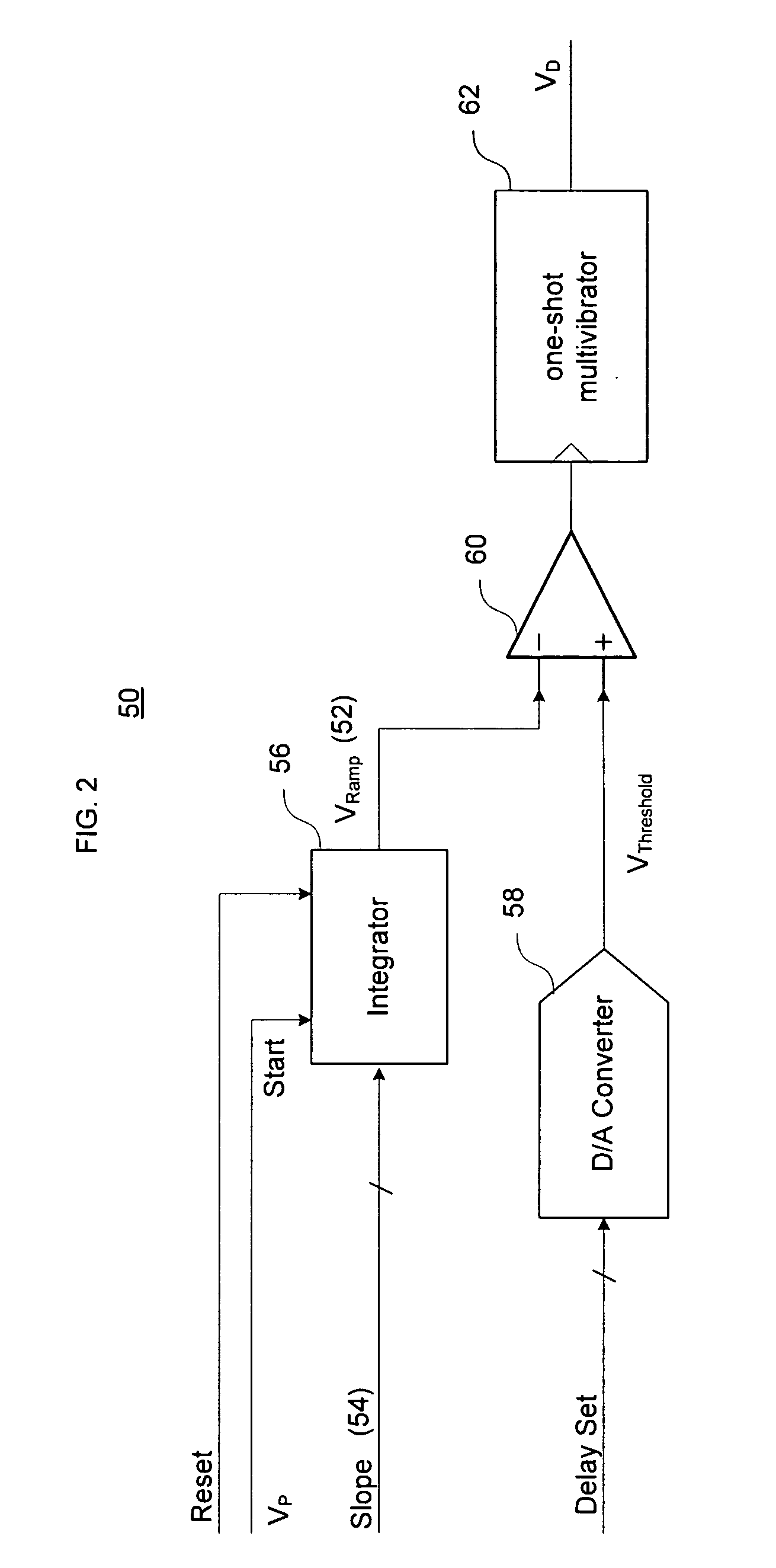
A direct digital frequency synthesizer having a multi-modulus divider, a numerically controlled oscillator and a programmable delay generator. The multi-modulus divider receives an input clock having an input pulse frequency fosc and outputs some integer fraction of those pulses at an instantaneous frequency fVp that is some integer fraction (1 / P) of the input frequency. The multi-modulus divider selects between at least two ratios of P (1 / P or 1 / P+1) in response to a signal from the numerically controlled oscillator. The numerically controlled oscillator receives a value which is the accumulator increment (i.e. the number of divided pulse edges) required before an overflow occurs that causes the multi-modulus divider to change divider ratios in response to receiving an overflow signal. The numerically controlled oscillator also outputs both the overflow signal and a delay signal to the delay generator that further controls the frequency of the multi-modulus divider output signal (Vp) to provide an output signal (VD) with an fout that has improved phase and timing jitter performance over prior art direct digital frequency synthesizer architectures.
Owner:CYMATICS LAB CORP
Magnetic field coupling-type non-contact electric energy transmission device
ActiveCN102315698AReduce volumeImprove transmission efficiencyElectromagnetic wave systemCircuit arrangementsFull bridgeMagnetic field coupling
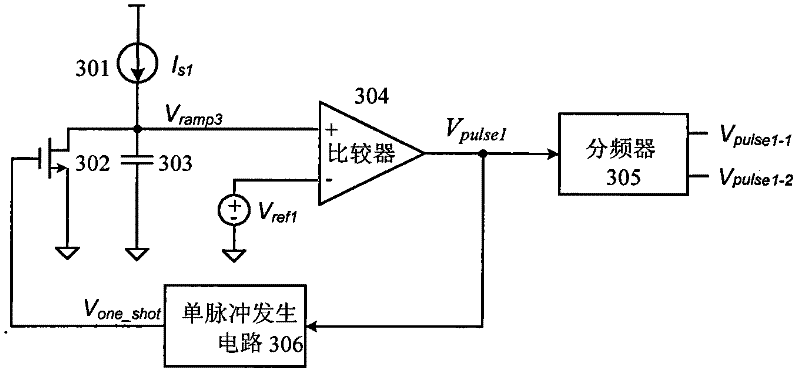
The invention discloses a magnetic field coupling-type non-contact electric energy transmission device, which comprises an electric energy transmitting part and an electric energy receiving part which are independent mutually, wherein a primary full-bridge switch circuit, a sweep frequency generation circuit, a primary switching tube current zero-crossing detection circuit, a primary ramp signal generation circuit, an input current limiting control circuit and a primary PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation) driving control circuit which are in the electric energy transmitting part are integrated in a primary high-power density integrated chip; and a secondary synchronous rectification full-bridge switch circuit, a synchronous rectification control circuit, a secondary switching tube current zero-crossing detection circuit, a secondary ramp signal generation circuit, a constant current / constant voltage control circuit and a secondary PWM driving control circuit which are in the electric energy receiving part are integrated in a secondary high-power density integrated chip. The device captures a resonant frequency point of a system through an automatic scanning process during initial work and ensures that the system always works in a resonance state, and the electric energy transmission efficiency is increased. The magnetic field coupling-type non-contact electric energy transmission device provided by the invention has a single-chip packaging structure and meets the requirements for high efficiency and high stability on the basis of realizing low cost.
Owner:NANJING SILERGY SEMICON TECH CO LTD
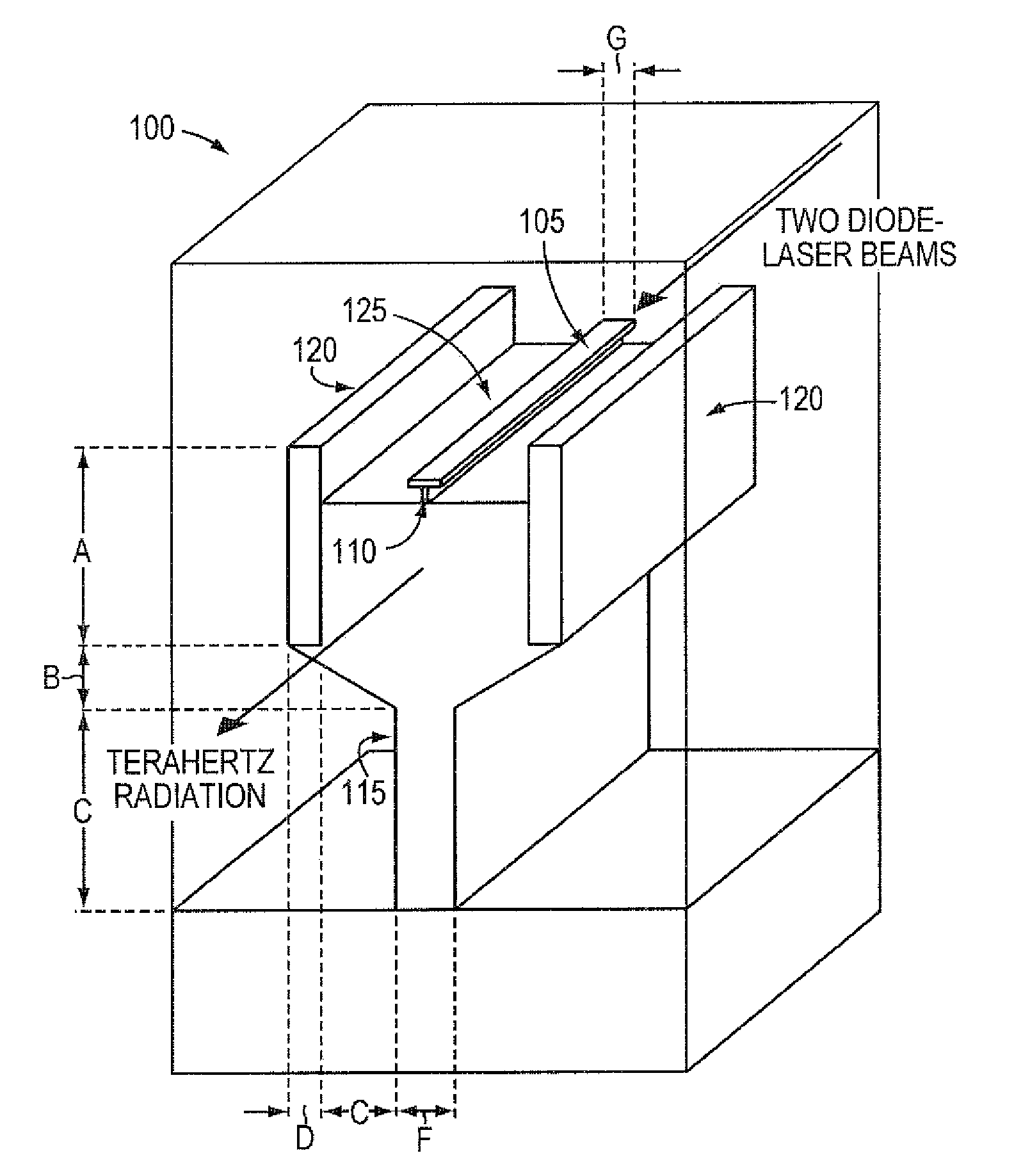
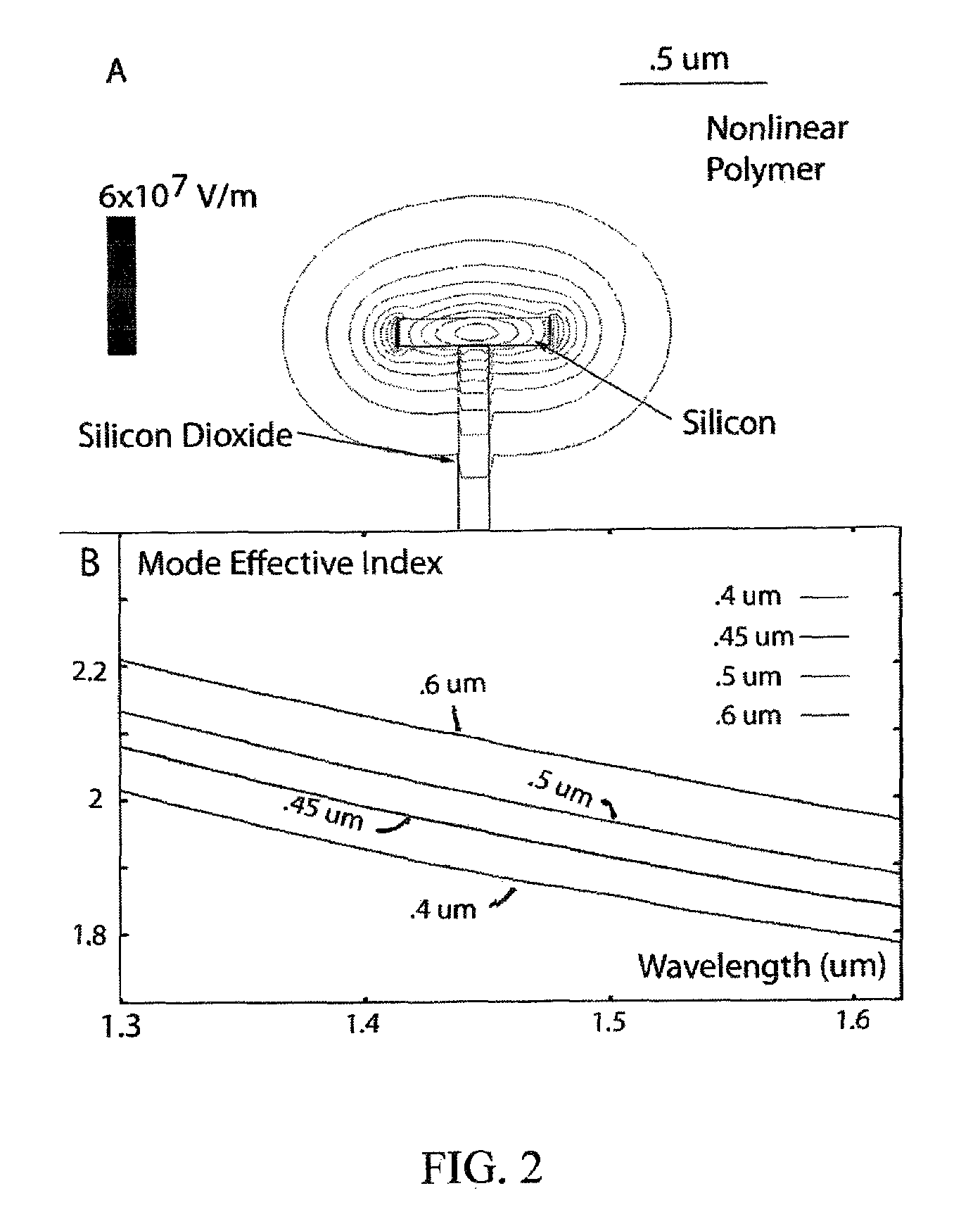
Low loss terahertz waveguides, and terahertz generation with nonlinear optical systems
InactiveUS7480434B2Solid masersOptical waveguide light guideTerahertz radiationNear infrared radiation
A silicon based source for radiation in the 0.5-14 Terahertz regime. This new class of devices will permit continuously tunable, milli-Watt scale, continuous-wave, room temperature operation, a substantial advance over currently available technologies. The Silicon Terahertz Generator (STG) employs a silicon waveguide for near infrared radiation, situated within a metal waveguide for Terahertz radiation. A nonlinear polymer cladding permits two near-infrared lasers to mix, and through difference frequency generation produces Terahertz output. The small dimensions of the design greatly increase the optical fields, enhancing the nonlinear effect. The design can also be used to detect Terahertz radiation.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
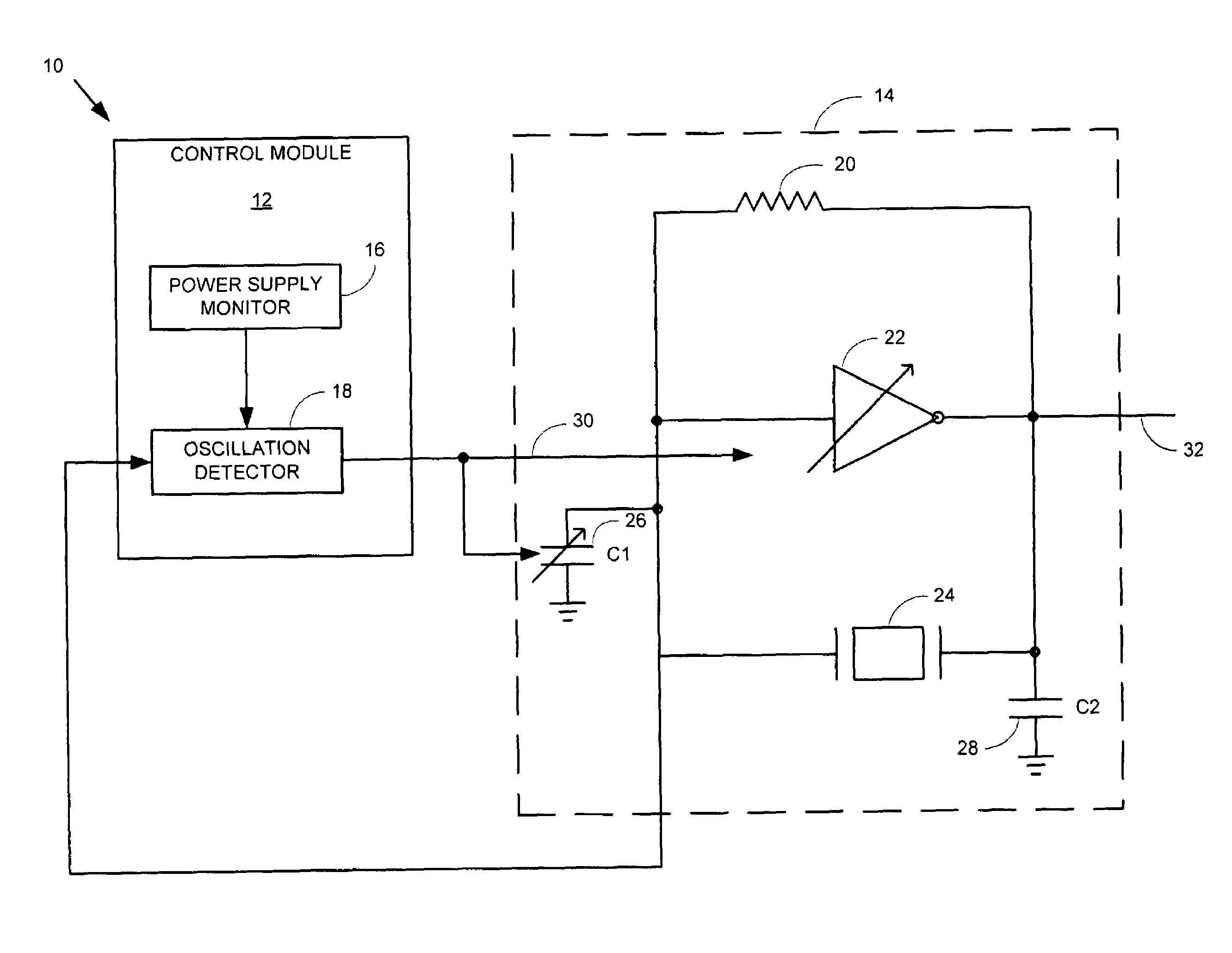
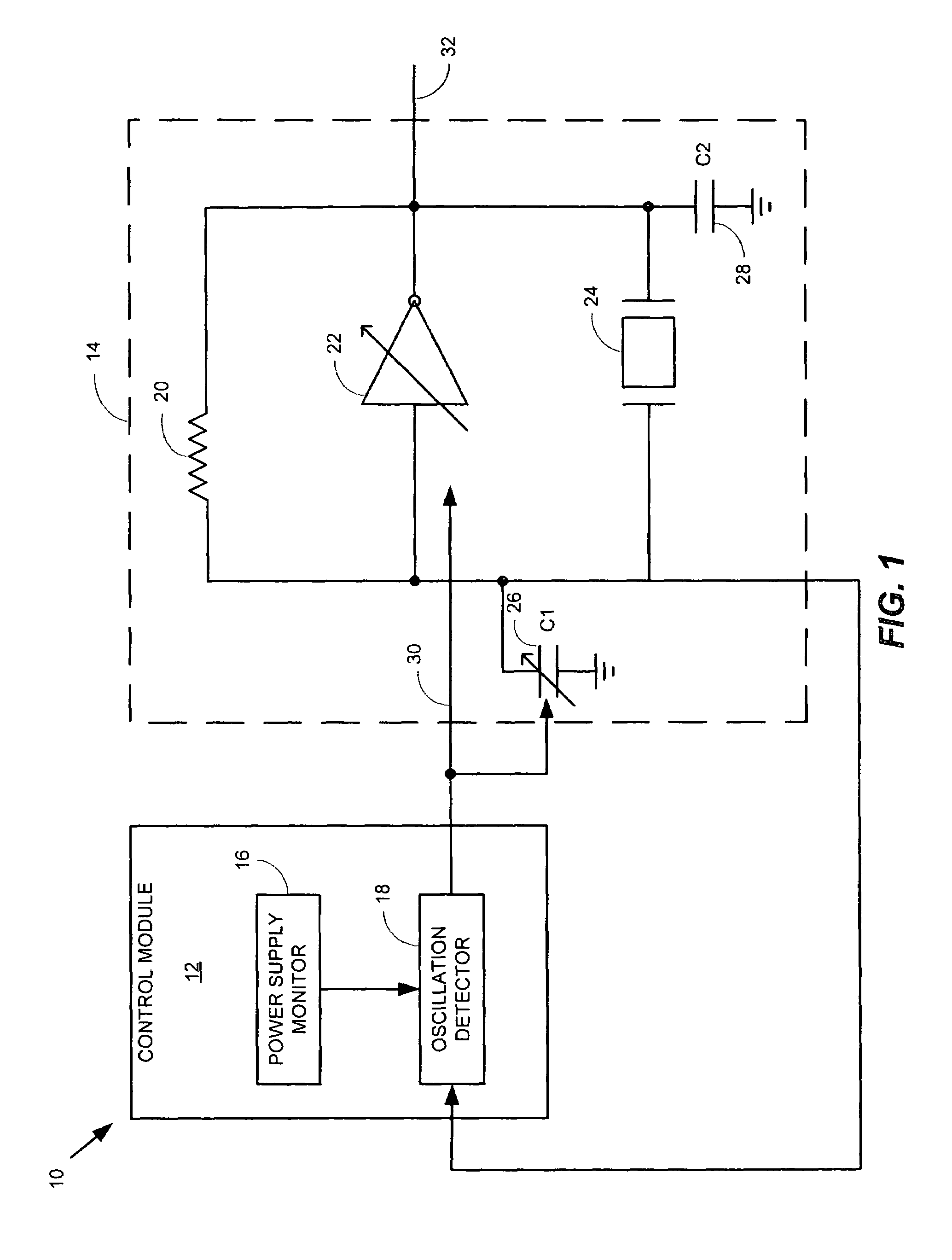
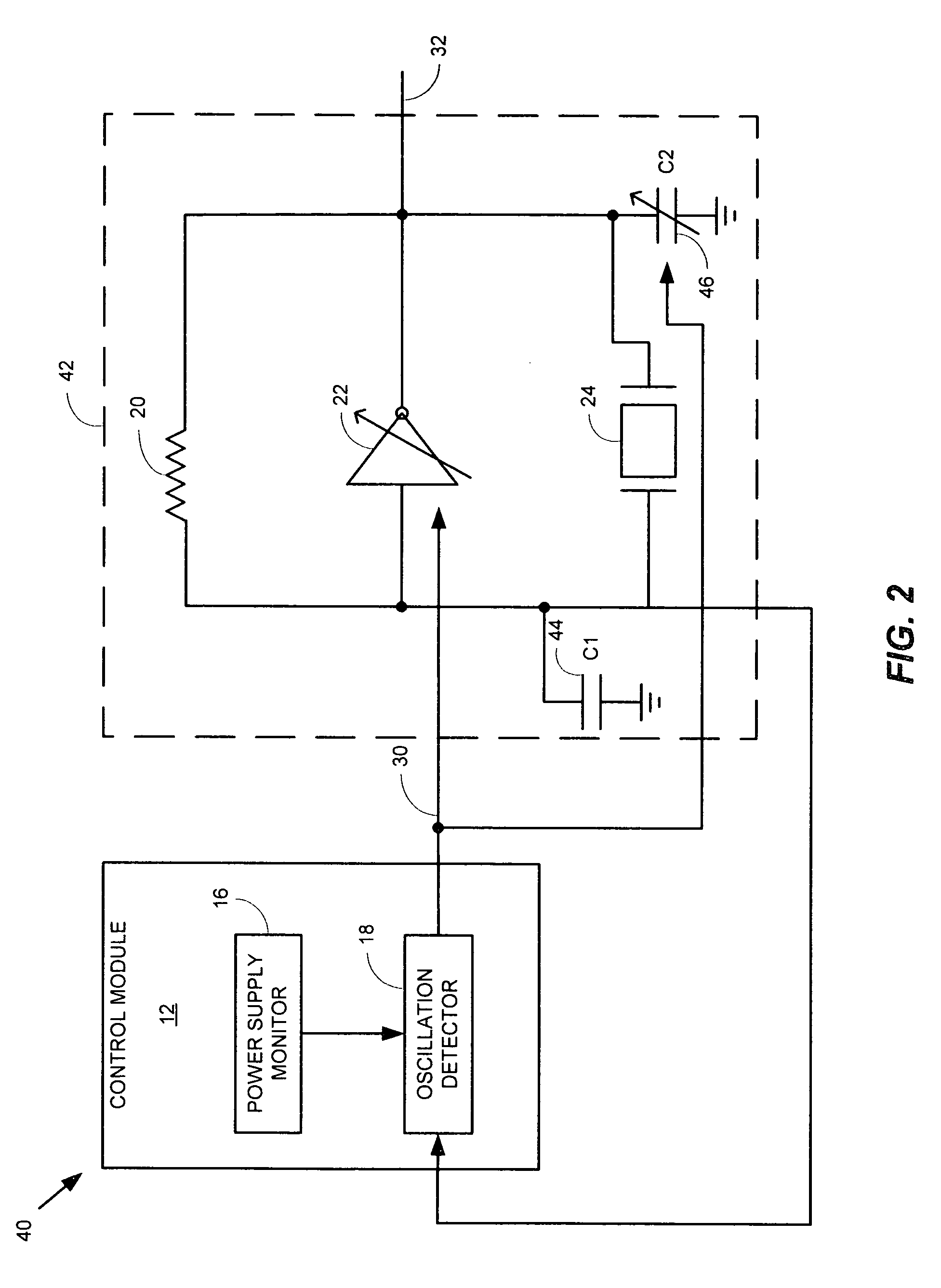
Method and apparatus for a crystal oscillator to achieve fast start-up time, low power and frequency calibration
InactiveUS7348861B1Fast frequency calibrationFast startup timePulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
One embodiment of the present invention includes a frequency generation circuit including a control module, an oscillator circuit coupled to the control module, the oscillator circuit having a start-up time defined by the time required to reach a desired frequency. The oscillator circuit includes an amplifier having an input and an output and being programmably-alterable by the control module, a first capacitor coupled to the input of the amplifier and being programmably-alterable, in capacitance, by the control module, a second capacitor coupled to the output of the amplifier, a crystal resonator coupled to the first and second capacitors for generating an output signal having a desired frequency, wherein fast start-up time is achieved.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Precise frequency generation for low duty cycle transceivers using a single crystal oscillator
An apparatus and method for calibrating a non-crystal oscillator in a transceiver unit using a crystal-oscillator includes the step of establishing a time base based upon oscillations of the crystal oscillator. A comparison of the number of oscillations for the non-crystal oscillator and the crystal oscillator is made during a known time period is made. An adjustment is determined based upon the established time base and the compared number of oscillations. The transceiving of the transceiver unit is then controlled based upon this adjustment.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Phase matching for difference frequency generation and nonlinear optical conversion for planar waveguides via vertical coupling
A high index contrast waveguide based source for radiation. In some embodiments, the radiation is in the 0.5-14 Terahertz regime. Waveguides are provided that permit the generation of radiation at the sum and / or difference frequency of two input beams. In order to control the power level within the waveguide, embodiments in which pluralities of similar or identical waveguide are provided, and the input radiation is divided among the plurality of waveguides. The output radiation can be steered by applying phased array methods and principles.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
Method and device for calibrating phase modulation of spatial light modulators by utilizing heterodyne interference
InactiveCN102109414ALight wave intensity is highLarge degree of phase modulationOptical measurementsTesting optical propertiesSpatial light modulatorPhase difference
The invention discloses a method for calibrating phase modulation degree of spatial light modulators, and the method is used for detecting the phase modulation information by utilizing a heterodyne interference technology. In the method, two beams of coherent optical waves are led to generate a frequency difference by an acousto-optic frequency phase shifter, and the two beams of coherent optical waves are respectively used as a measuring beam and a reference beam; then the effective display area of the spatial light modulator is divided into two parts, a gray value written into one part is 0, and the part is taken as a reference area; the change range of the gray value of the other part is 0-255, and the other part is taken as a test area; the measuring beam is modulated by the spatial light modulators of the reference area and the test area and then interfered with the reference beam; then two photoelectric detectors at an interference field are utilized to respectively detect a reference signal and a measured signal; and the phase difference between the two photoelectric detectors is the phase modulation degree to be measured, therefore, the corresponding relation between the gray value and the phase modulation degree can be established, so that the phase modulation degree of the spatial light modulators can be calibrated.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
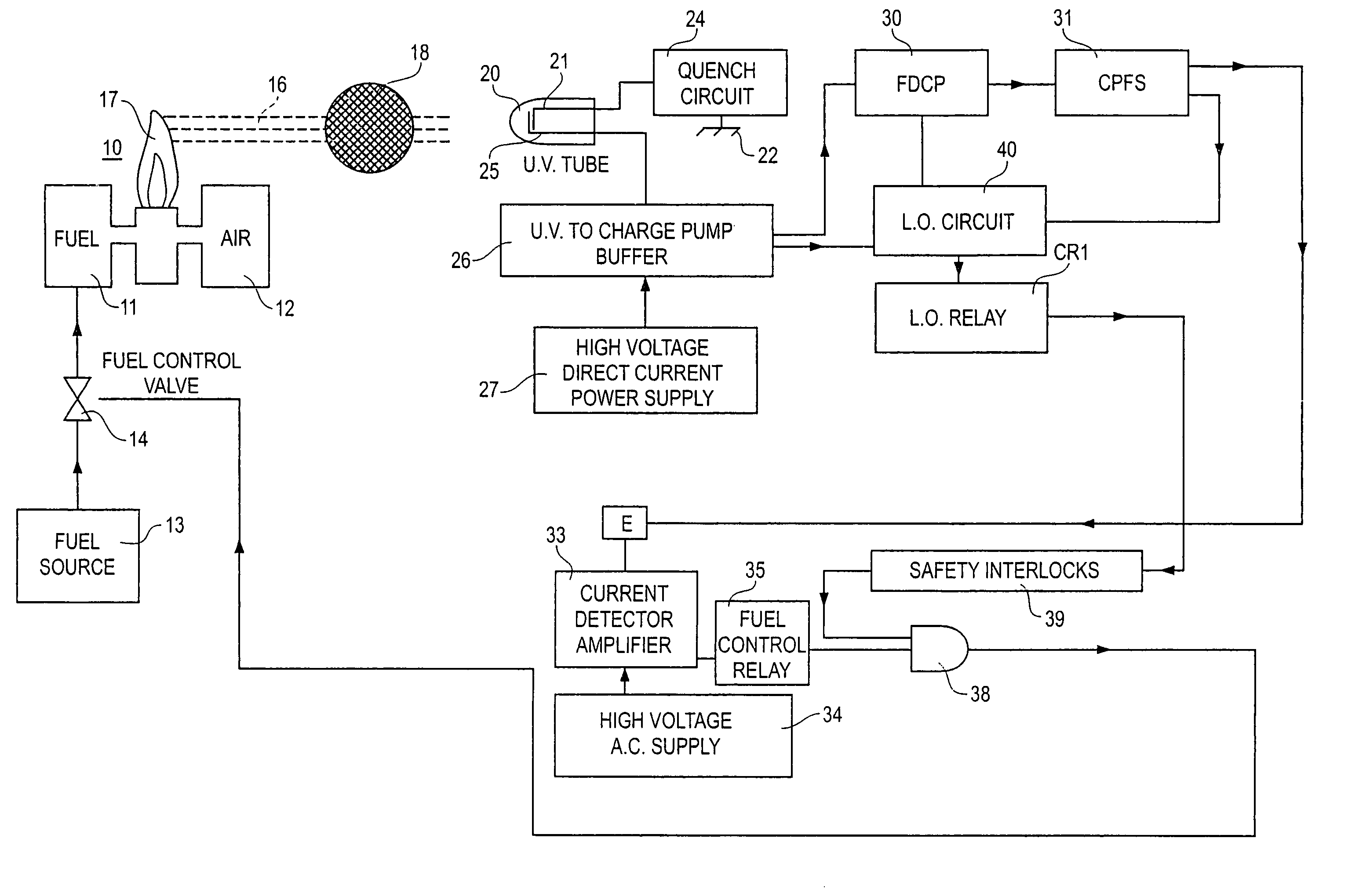
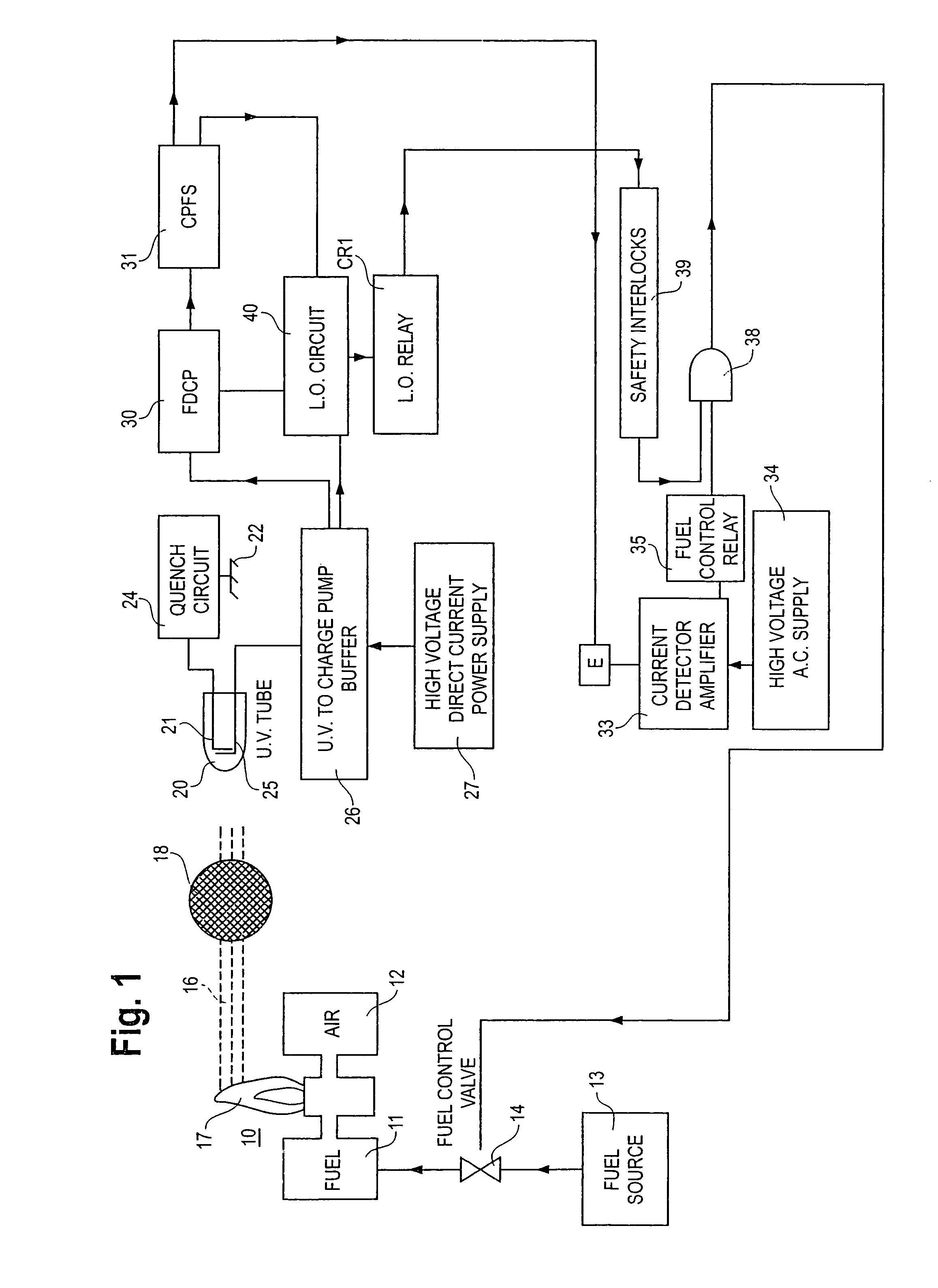
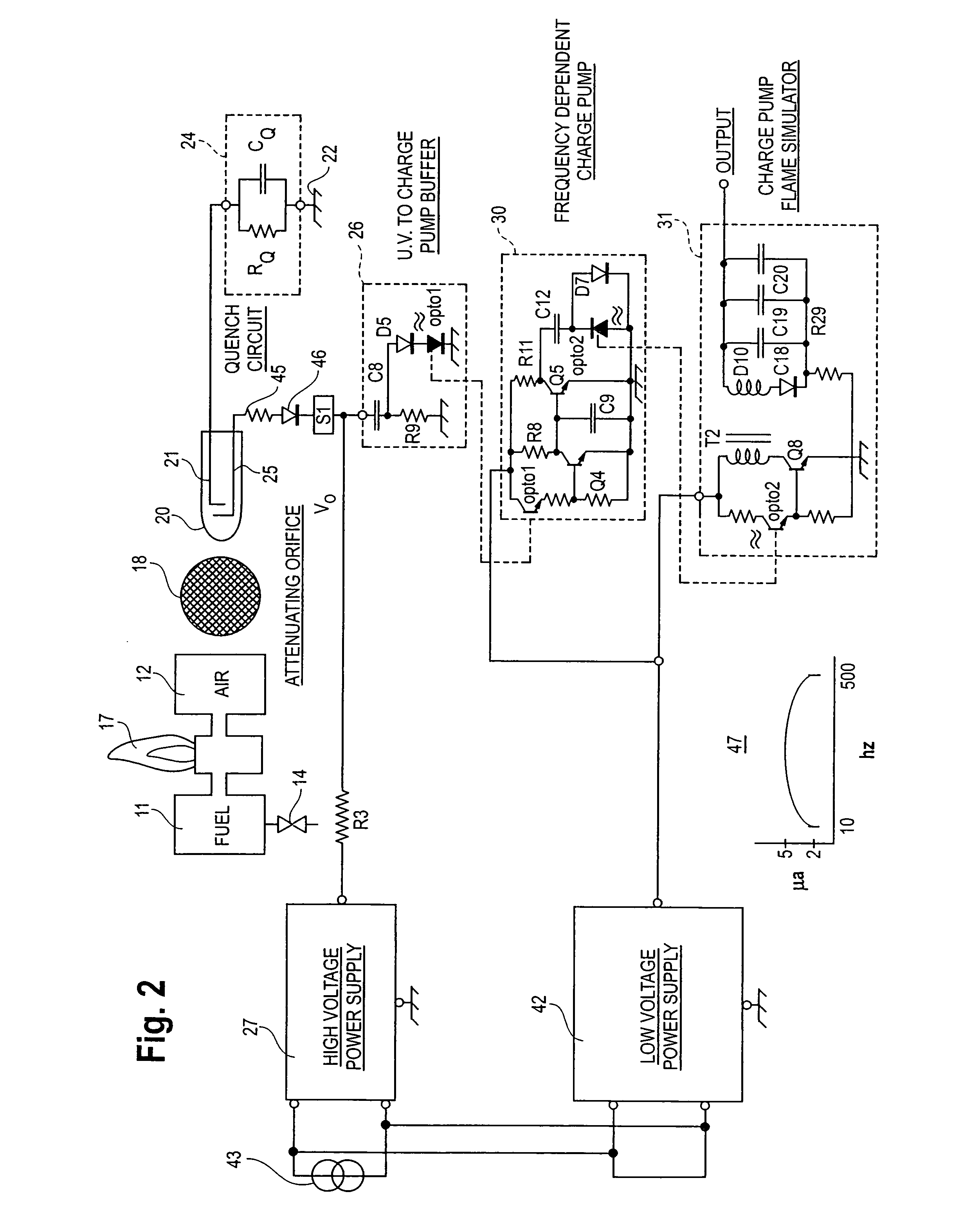
Flame detector, method and fuel valve control
InactiveUS7088253B2Material analysis by optical meansCombustion signal processingFrequency generationCold cathode
A flame detector and burner fuel valve control has an ultraviolet sensitive, cold cathode, gas discharge tube in a DC quench circuit. In the presence of a flame, the circuit generates a pulse signal at a frequency related to the intensity of radiation from the flame. The pulse signal from a contaminated tube is at a higher frequency. A frequency discriminator circuit distinguishes between a flame responsive signal and a contaminated tube signal and controls the burner fuel valve.
Owner:PROTECTION CONTROLS
LED driving circuit package
ActiveUS20130026924A1Electroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesLow voltageFrequency generation
An LED driving circuit package includes a rectification unit to receive an AC power voltage and rectify the AC power voltage to generate a ripple voltage, an LED driving switching unit including a plurality of switch units and a plurality of current control units. The LED driving circuit package further includes a low voltage control unit including a circuit power supply unit to generate low voltage power, a voltage detection unit to detect a magnitude of the ripple voltage, a reference frequency generation unit to generate a reference frequency, and a reference pulse generation unit to generate a reference pulse for controlling the operation of the LED driving switch unit according to the reference frequency and a magnitude of the voltage detected by the voltage detection unit.
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
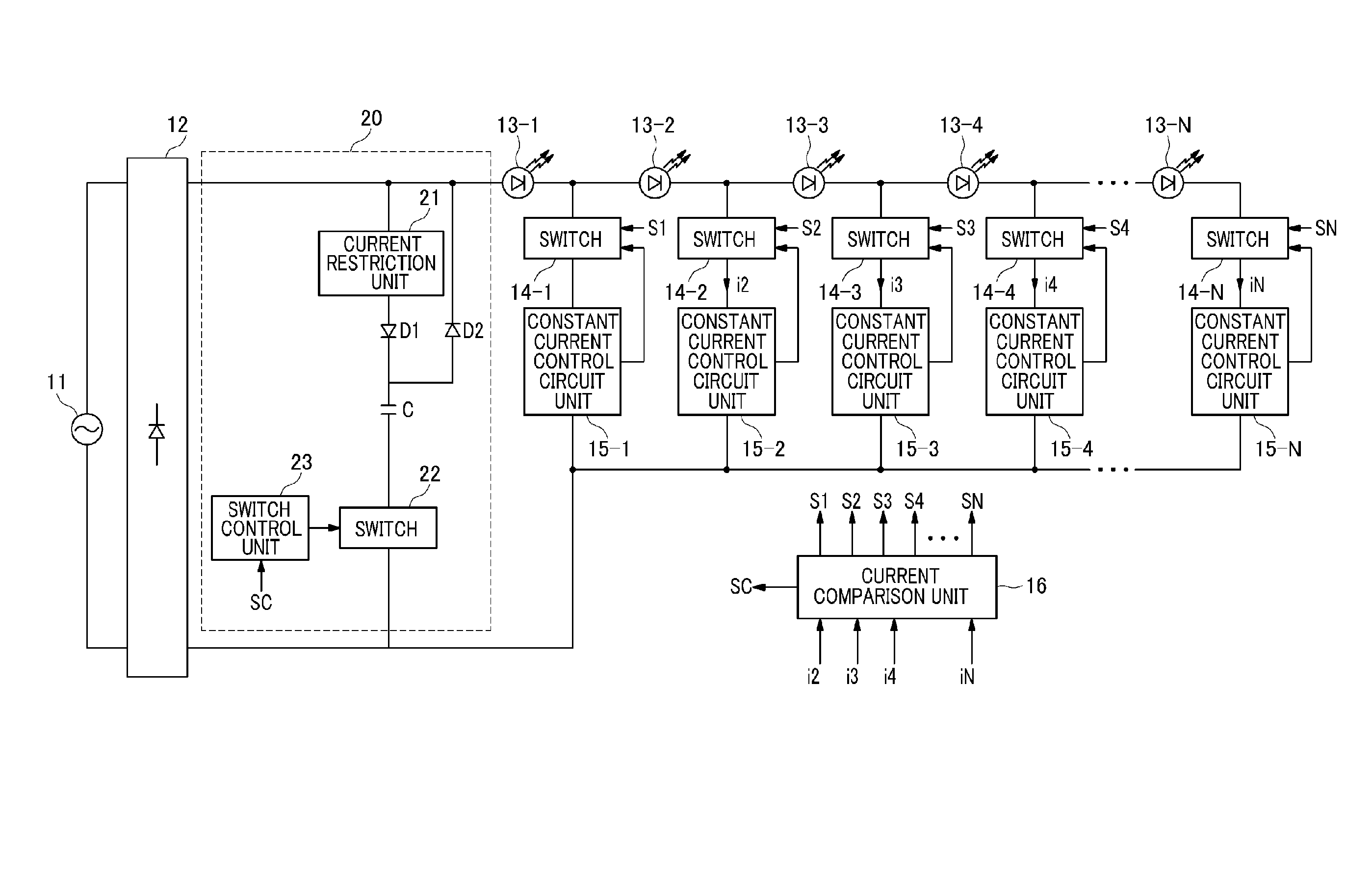
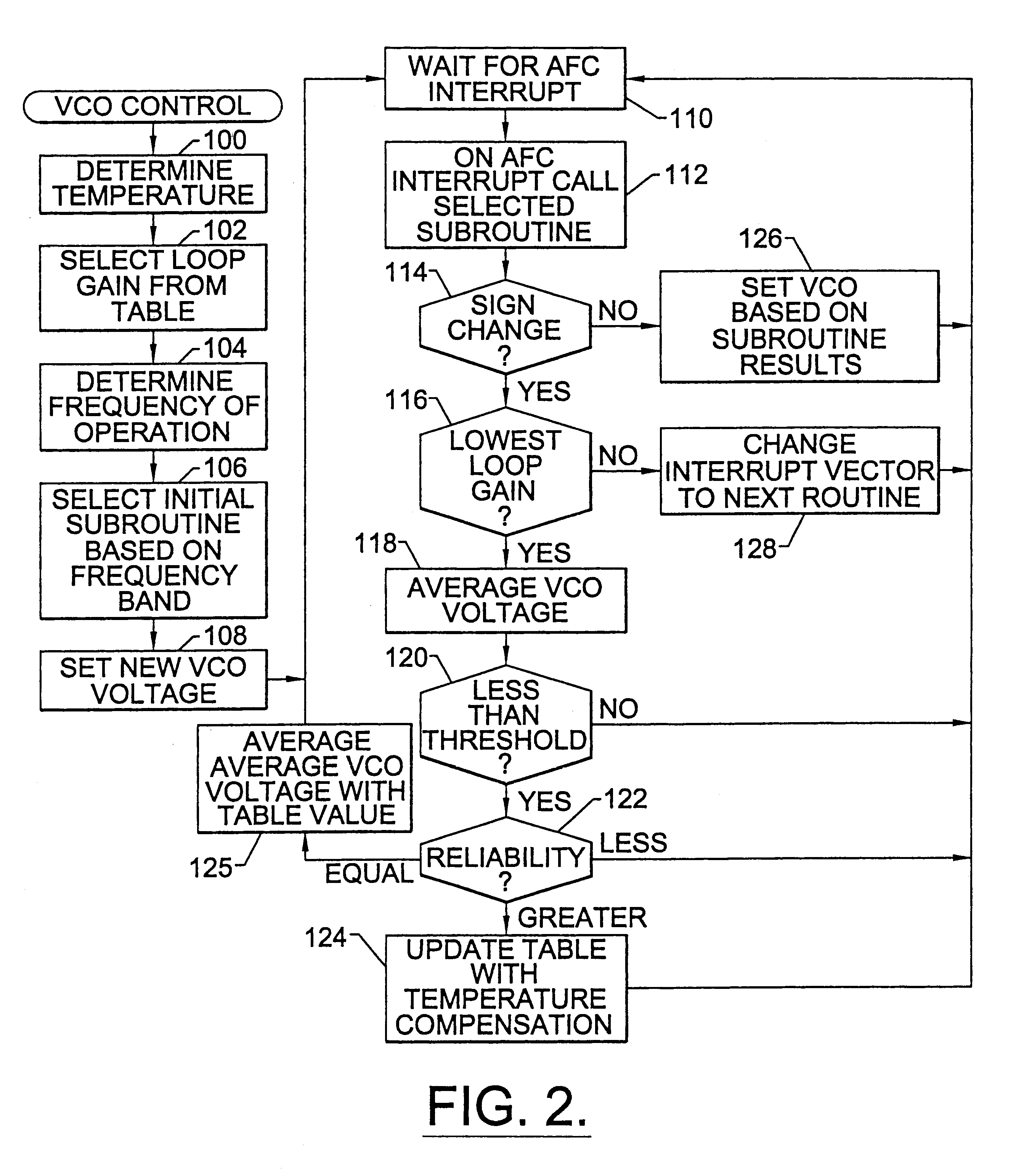
Methods and systems for frequency generation for wireless devices
InactiveUS6278867B1Be consistentPulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationFrequency generationAutomatic frequency control
Methods and systems are provided for frequency generation suitable for use in wireless devices capable of operating at multiple frequencies. Such systems may change the loop gain of an automatic frequency control loop based on the operating frequency of the wireless device. Furthermore, such a frequency dependent loop gain may be carried out by the selection of subroutines with differing loop gains associated with the subroutines. Furthermore, the loop gain may also be temperature compensated based on the temperature of the wireless device and / or the operating frequency of the device.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
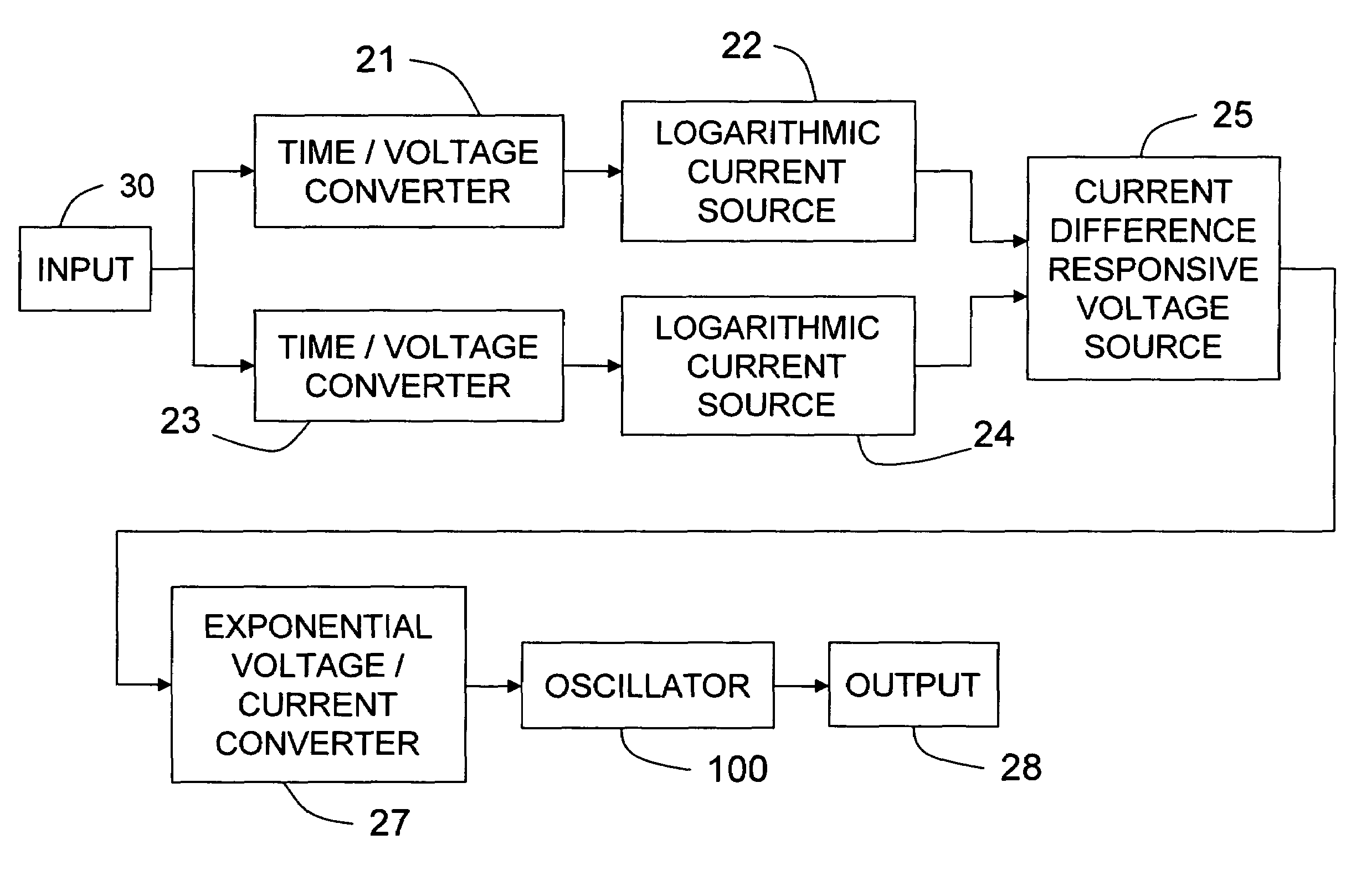
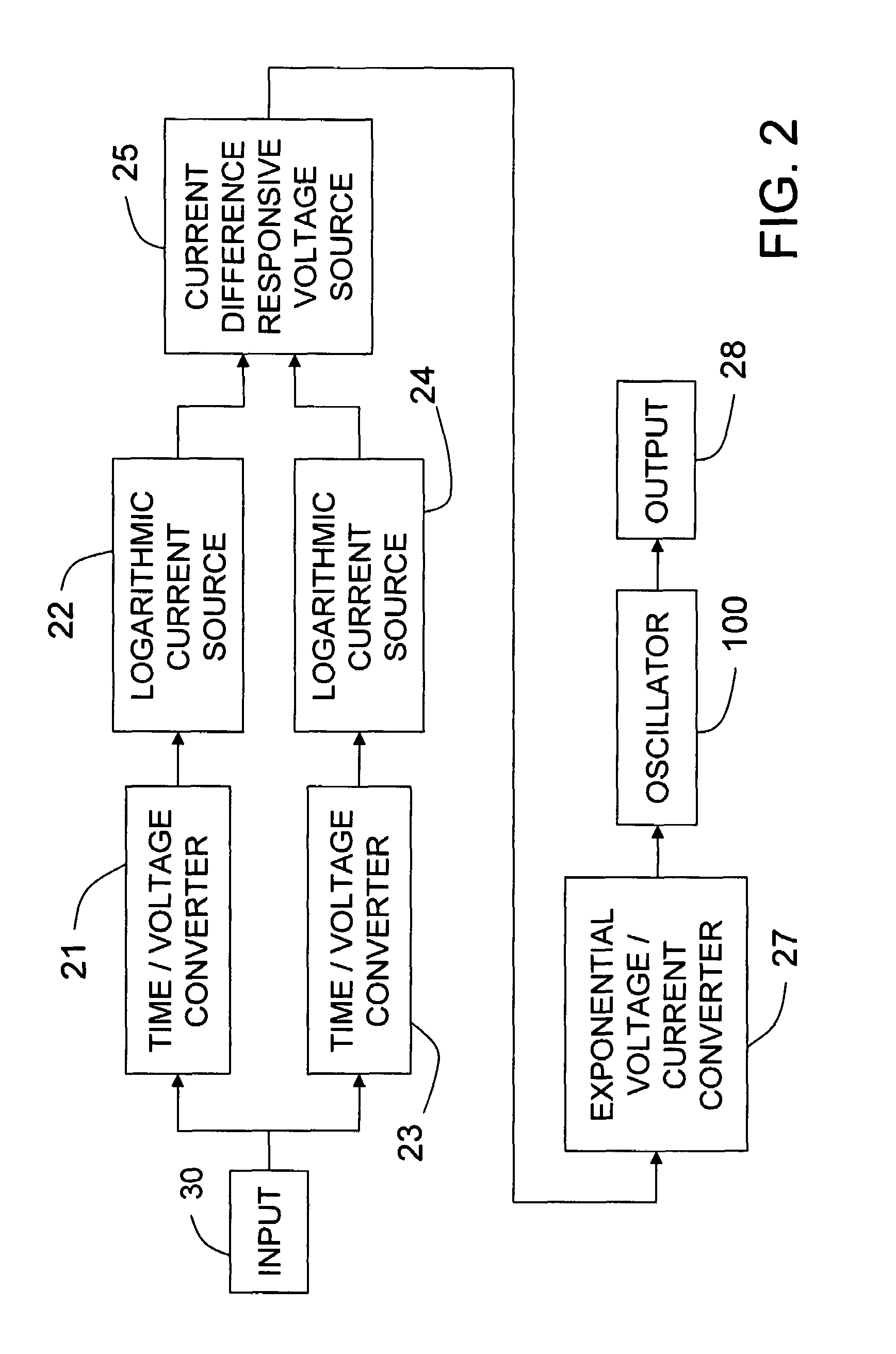
Analog duty cycle replicating frequency converter for PWM signals
ActiveUS7511545B1Low costReduce system costElectric pulse generatorPulse shapingConvertersSoftware engineering
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
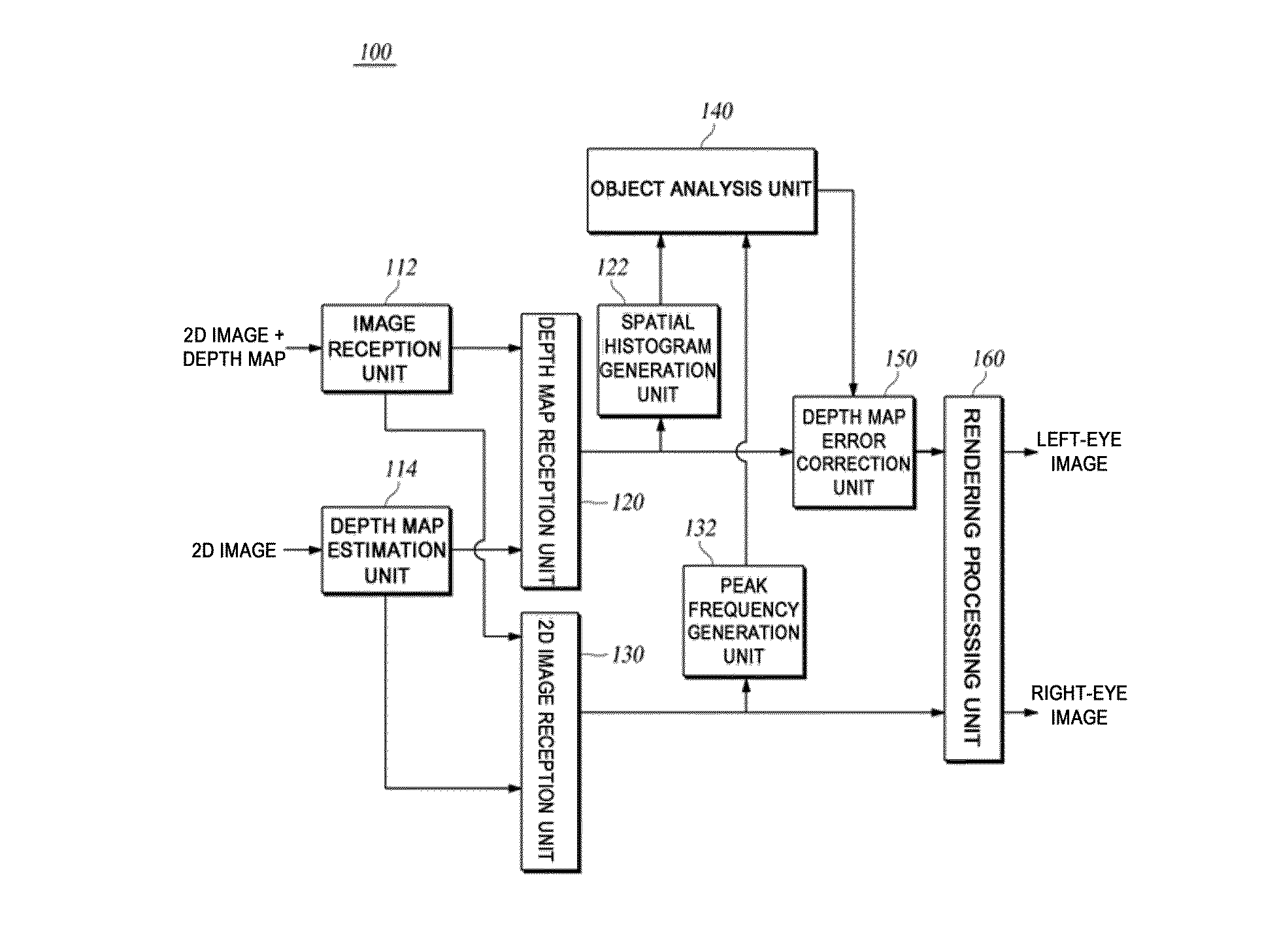
Method and apparatus for correcting errors in stereo images
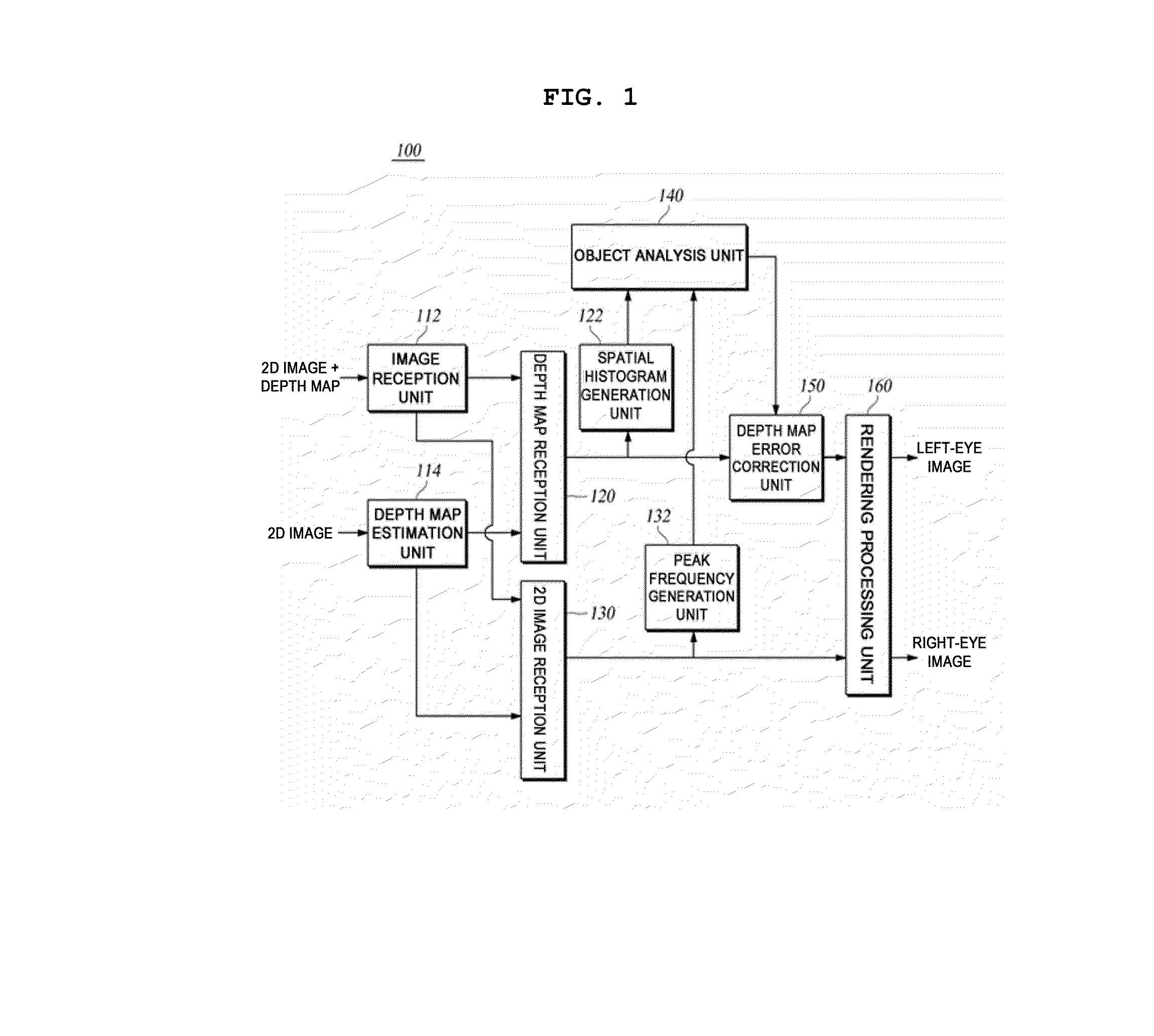
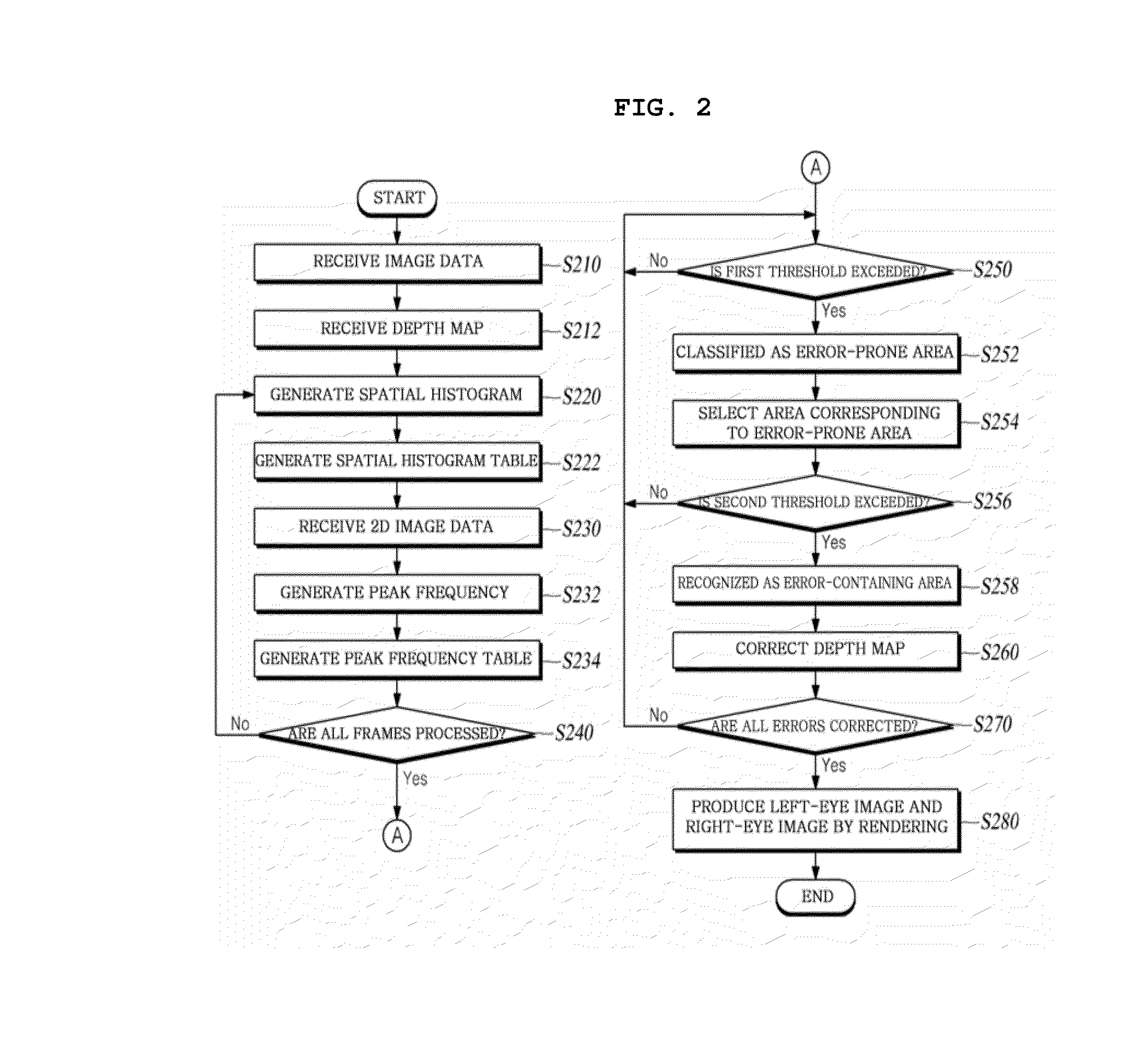
ActiveUS20130009955A1Inhibition effectImproved D effectImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionFrequency generationPeak value
An embodiment of the present invention relates to a method and apparatus for correcting errors in stereo images. The apparatus for correcting errors in stereo images according to an embodiment of the present invention comprises: a space histogram generation unit generating space histogram information using the depth map information on the input image data; a peak frequency generation unit generating a peak frequency using the 2D image data of the input image data; an object analysis unit determining the error in each frame of the input image data on the basis of the space histogram and peak frequency; a depth map error correction unit correcting the depth map information to reduce the error; and a rendering processing unit generating left and right eye images, which are stereo images, by using the corrected depth map information.
Owner:SK PLANET CO LTD
Direct digital synthesizer for reference frequency generation
InactiveUS20110095830A1Reduce power consumptionLow frequency signalPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersFrequency generationRandom noise
A direct digital frequency synthesizer having a multi-modulus divider, a numerically controlled oscillator and a programmable delay generator. The multi-modulus divider receives an input clock having an input pulse frequency fosc and outputs some integer fraction of those pulses at an instantaneous frequency fVp that is some integer fraction (1 / P) of the input frequency. The multi-modulus divider selects between at least two ratios of P (1 / P or 1 / P+1) in response to a signal from the numerically controlled oscillator. The numerically controlled oscillator receives a value which is the accumulator increment (i.e. the number of divided pulse edges) required before an overflow occurs that causes the multi-modulus divider to change divider ratios in response to receiving an overflow signal. The numerically controlled oscillator also outputs both the overflow signal and a delay signal to the delay generator. The delay signal contains phase-dithering noise that is induced by input into the accumulator of an increment generated from a pseudo-random noise generator. The delay signal further controls the frequency of the multi-modulus divider output signal (Vp) to provide an output signal (VD) with an fOUT that has improved phase and timing jitter performance over prior art direct digital frequency synthesizer architectures.
Owner:CYMATICS LAB CORP
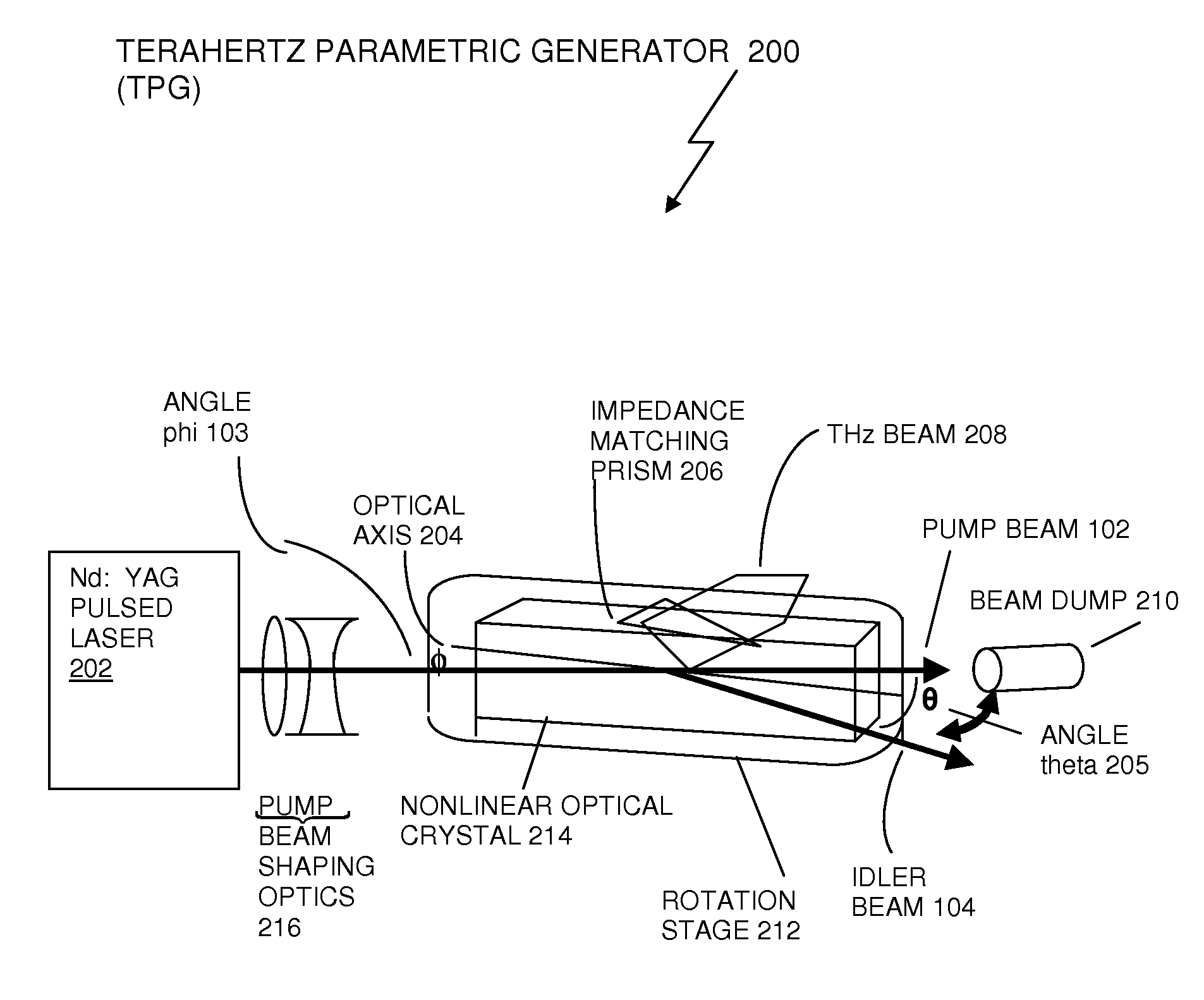
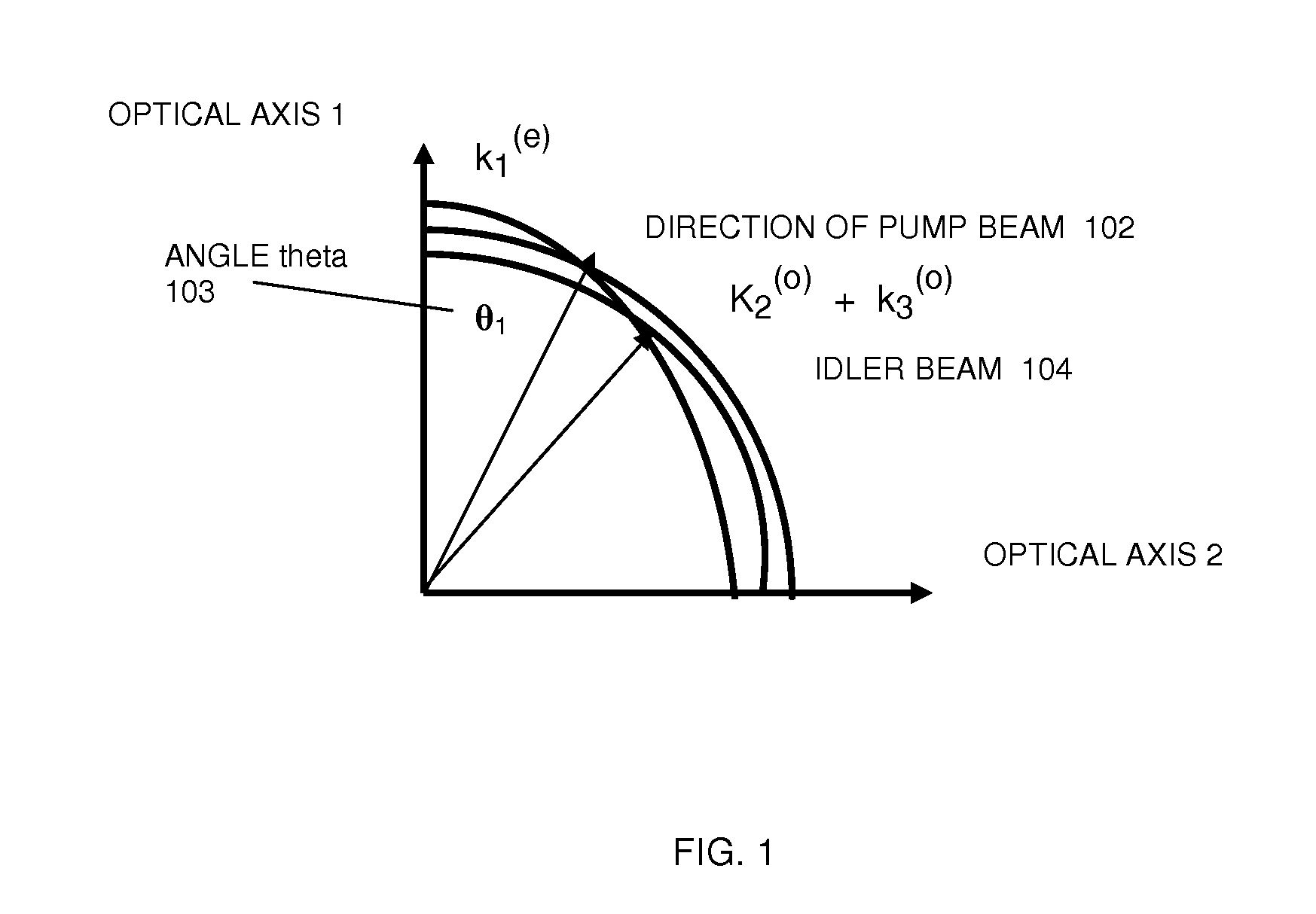
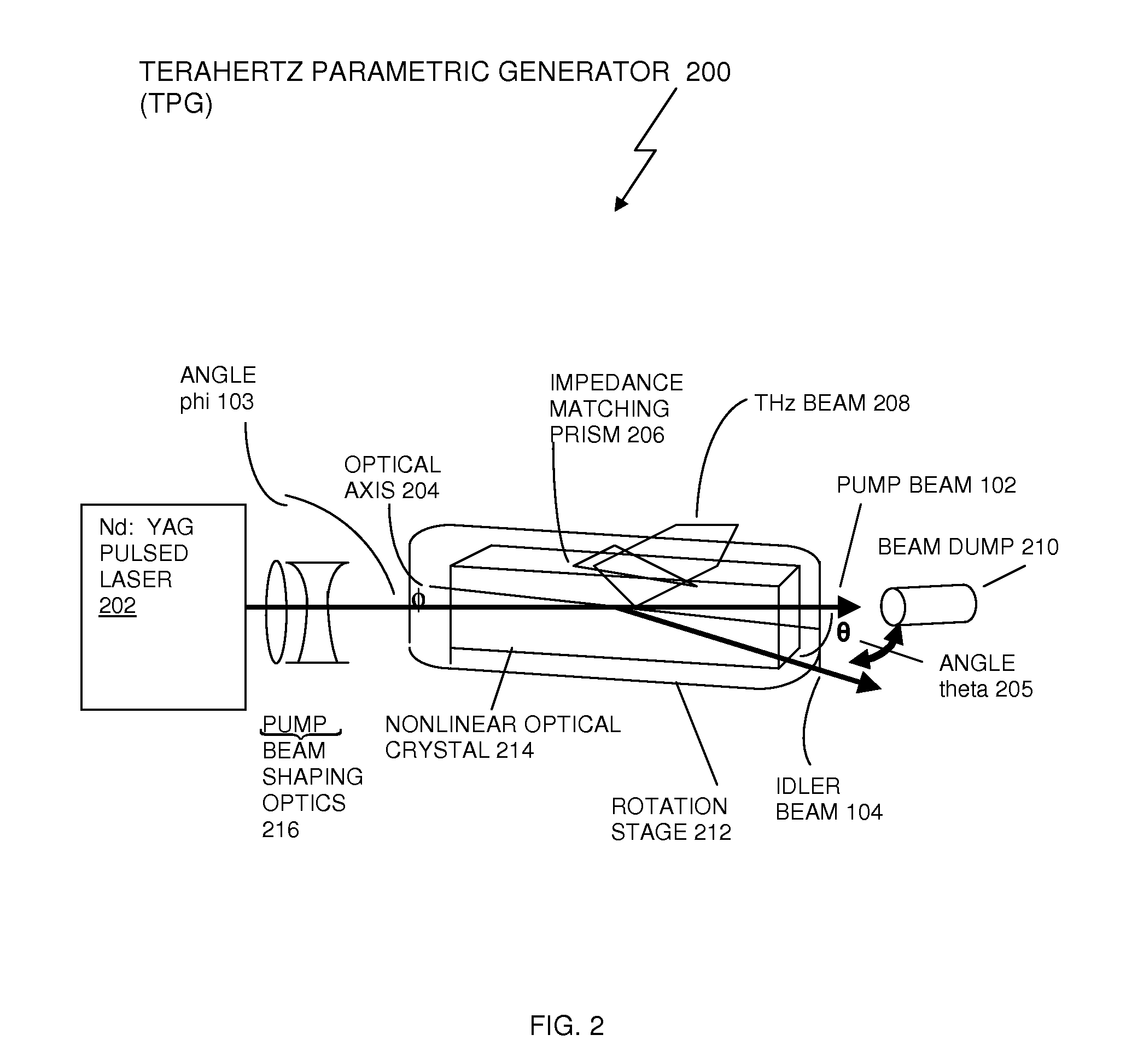
Recycling pump-beam method and system for a high-power terahertz parametric source
InactiveUS20100290487A1Increase output powerHigh repetition rateLaser detailsSolid masersNonlinear optical crystalBeam source
A method and a system are implemented in the fabrication of a portable high power terahertz beam source that can produce a tunable, high power terahertz beam over the frequency from 0.1 THz to 2.5 THz. The terahertz source employs a recycling pump beam method and a beam quality control device. The beam quality control device may or may not be required for a high power terahertz beam generation. In exemplary embodiments, a lithium niobate (LiNbO3) crystal or a lithium niobate crystal doped with 5% magnesium oxide (LiNbO3:MgO) can be used. Other nonlinear optical crystals, including GaSe can be used in place of the LiNbO3 crystal. Through proper alignment of a pump beam, along with recycling a pump beam, high conversion efficiency is achieved, and a high output power beam is produced at terahertz frequencies.
Owner:US GOVT AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY CHIEF OF NAVAL OPERATIONS OFFICE OF COUNSEL ONR NRL CODE OOCCIP
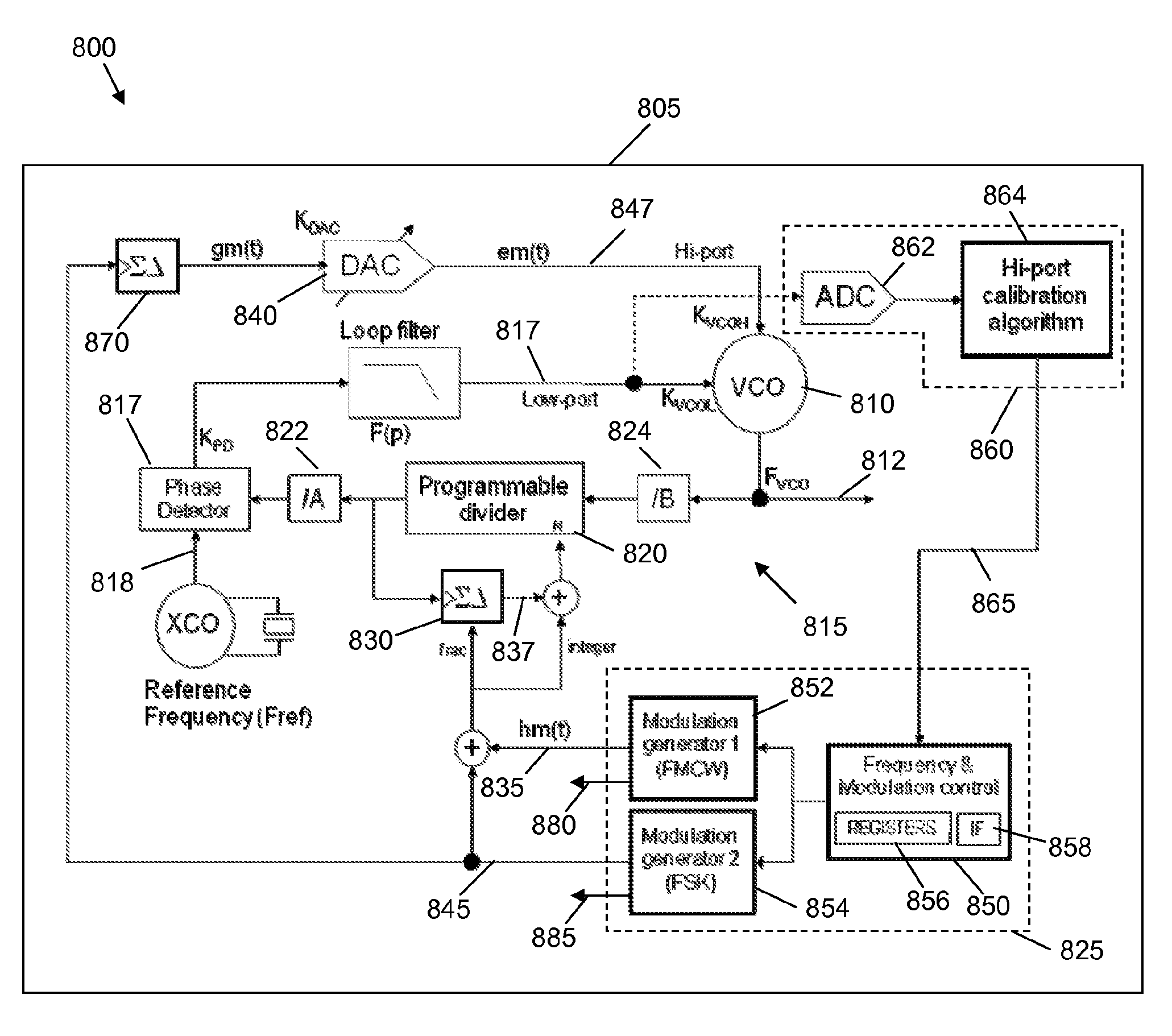
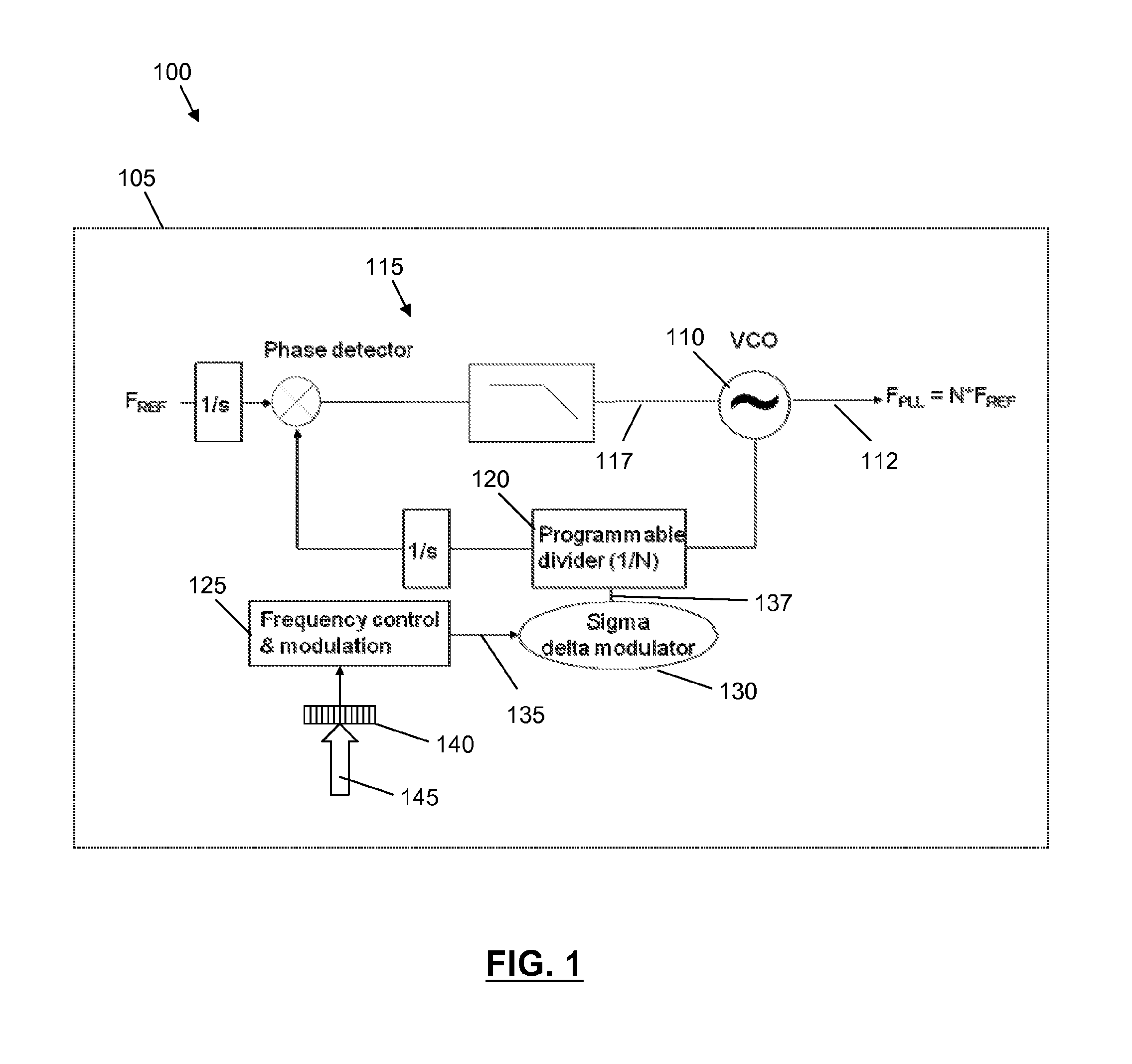
Integrated circuit comprising frequency generation circuitry for controlling a frequency source
An integrated circuit comprises frequency generation circuitry for controlling a frequency source for use in an automotive radar system. The frequency generation circuitry comprises low-path modulation circuitry arranged to generate a first, low-path control signal for providing lower frequency modulation of the frequency source, the low-path modulation circuitry comprising a Phase Locked Loop (PLL) arranged to generate the low-path control signal for controlling the frequency source and a fractional-N divider located within a feedback loop of the PLL, and frequency pattern control module operably coupled to the fractional-N divider and arranged to control the fractional-N divider, by way of at least a first, lower frequency pattern control signal. The frequency generation circuitry further comprises high-path modulation circuitry arranged to generate a second, high-path control signal for providing higher frequency modulation of the frequency source.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Brushless high-frequency alternator and excitation method for dc, single-phase and multi-phase ac power-frequency generation
InactiveUS20100052626A1Minimise currentSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuitAlternating currentConductor Coil
A method is disclosed for arranging and exciting the stator, rotor and various windings of a multi-stage brushless high frequency alternator so that the resulting multiple high frequency sub-phase armature winding outputs can be rectified and commutated into desired phases of power-frequency alternating current (AC) electrical output, including single-phase, split-phase, three-phase and other multiple phase output. Power frequency currents in field windings control output amplitude, output frequency, and output phase. If desired, DC power output can be accommodated as zero power-frequency operation. Devices incorporating this arrangement are suitable of generating fixed frequency electrical power while accommodating variable speed rotation of a generator shaft and offer multiple advantages over existing techniques. The capability to generate speed independent electric power allows natural power sources such as windmills and hydro-power stations to be efficiently coupled to fixed frequency power grids.
Owner:RAVEN ENERGY ALTERNATIVES
Direct digital synthesizer for reference frequency generation
InactiveUS20100052797A1Reduce power consumptionLow frequency signalPulse automatic controlDigital data processing detailsFrequency generationEngineering
A direct digital frequency synthesizer having a multi-modulus divider, a numerically controlled oscillator and a programmable delay generator. The multi-modulus divider receives an input clock having an input pulse frequency fosc and outputs some integer fraction of those pulses at an instantaneous frequency fVp that is some integer fraction (1 / P) of the input frequency. The multi-modulus divider selects between at least two ratios of P(1 / P or 1 / P+1) in response to a signal from the numerically controlled oscillator. The numerically controlled oscillator receives a value which is the accumulator increment (i.e. the number of divided pulse edges) required before an overflow occurs that causes the multi-modulus divider to change divider ratios in response to receiving an overflow signal. The numerically controlled oscillator also outputs both the overflow signal and a delay signal to the delay generator that further controls the frequency of the multi-modulus divider output signal (Vp) to provide an output signal (VD) with an fOUT that has improved phase and timing jitter performance over prior art direct digital frequency synthesizer architectures.
Owner:CYMATICS LAB CORP
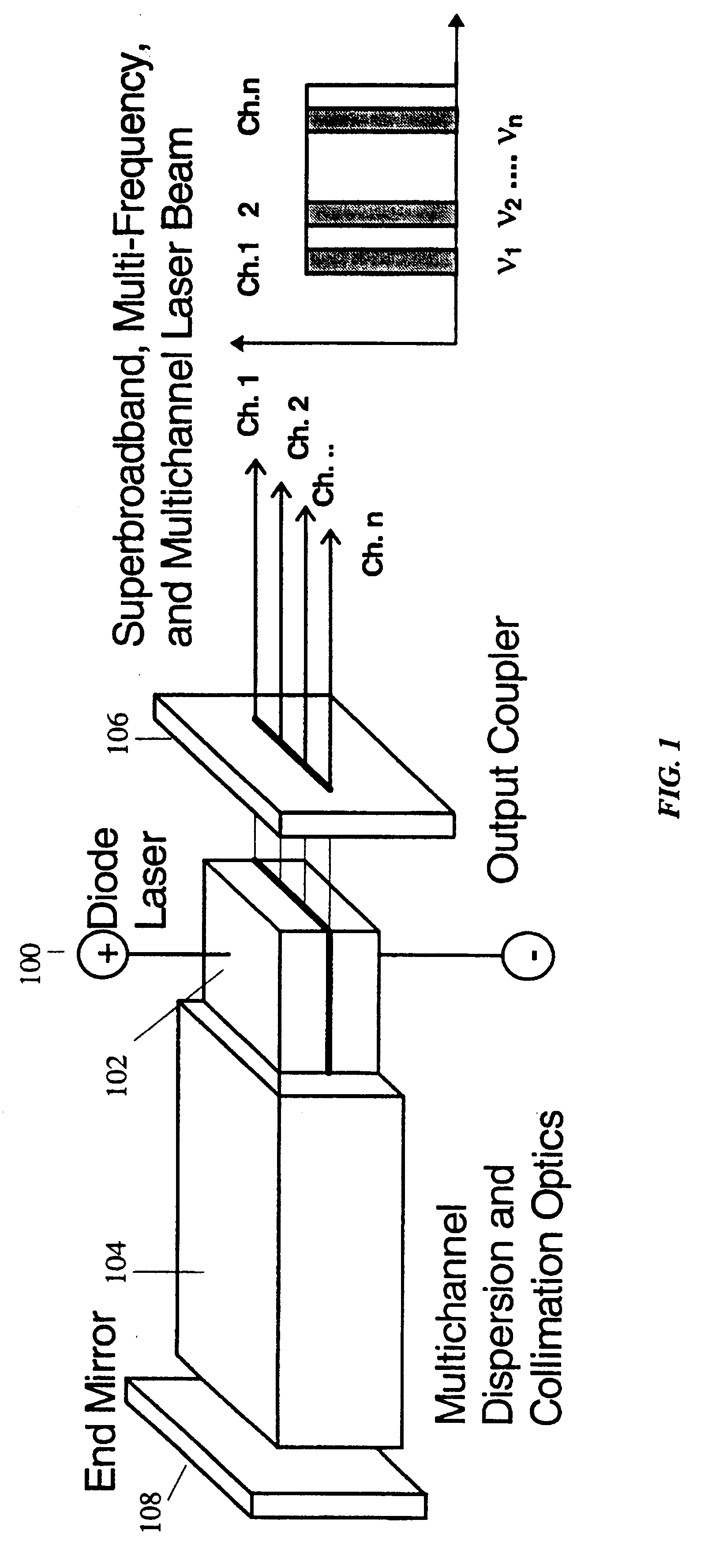
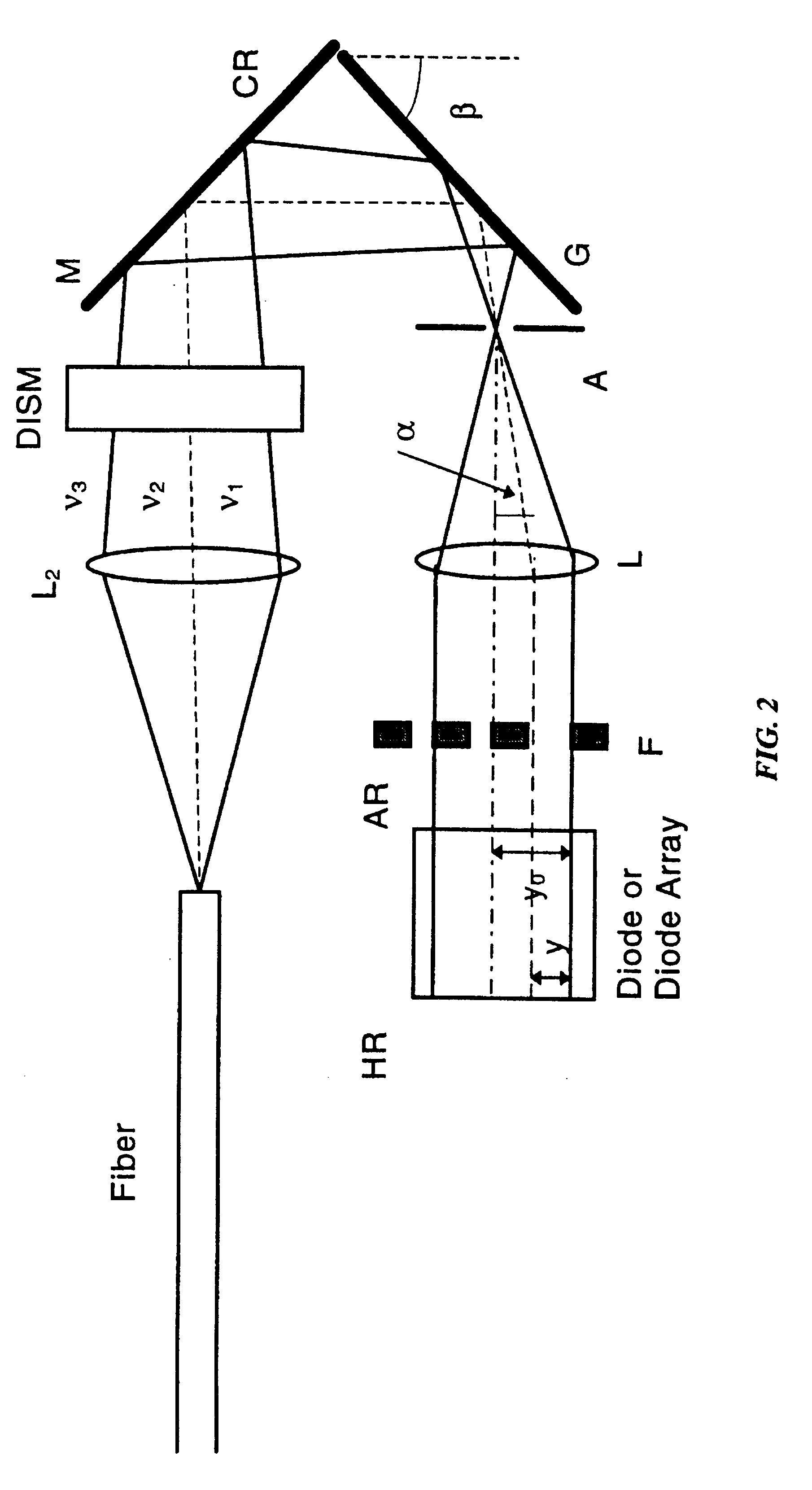
Semiconductor laser with a superbroadband or multiline spectral output
InactiveUS6236666B1Optical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionLaser transmitterFluorescence
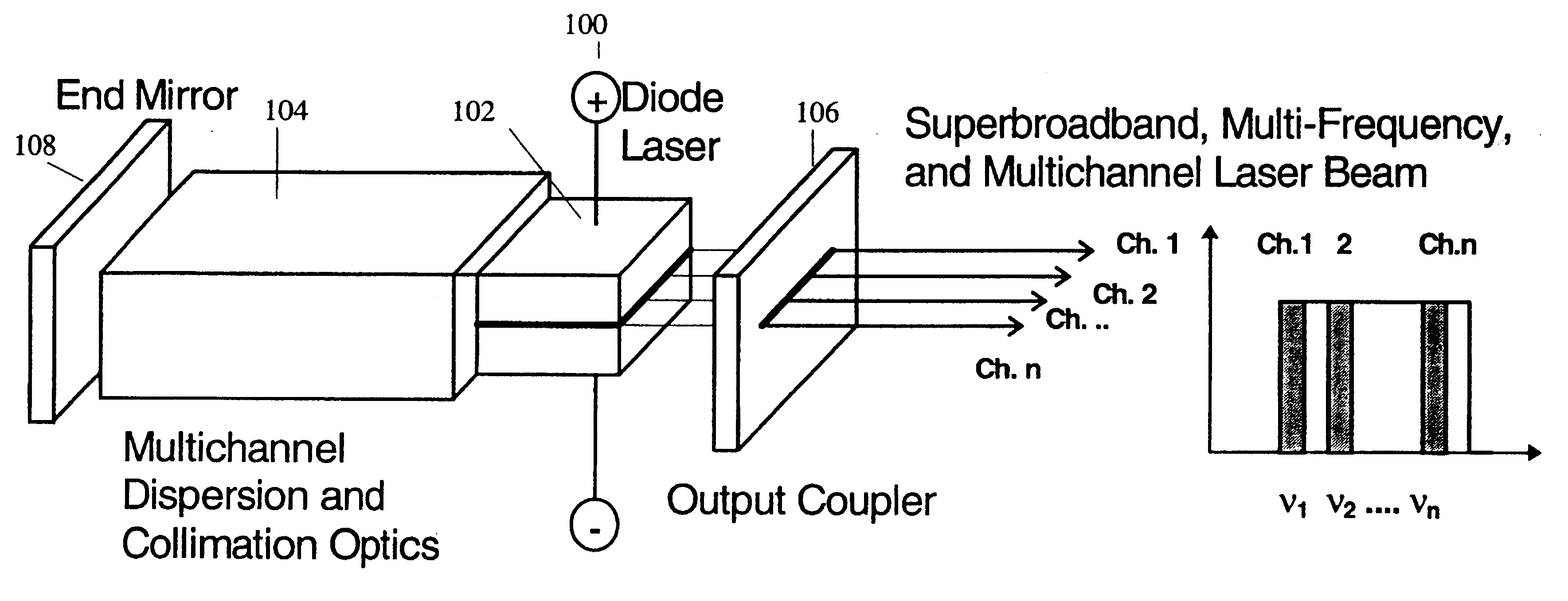
A superbroadband or multiwavelength laser transmitter source for wavelength-division multiplexing, two-wavelength interferometry, differential lidar and optical storage applications. Contrary to conventional tunable laser sources that can switch between different lasing wavelengths in a given wavelength band, the superbroadband laser simultaneously emits at multiple wavelengths. The basic idea of this system is to maintain simultaneous lasing operation in an optical active gain medium at different wavelengths. The system uses a novel dispersive cavity. By designing this cavity structure appropriately, the system creates its own microcavities each lasing at a different wavelength within the fluorescence band of the gain medium. Mode competition in the proposed cavity is absent and spectral range of simultaneous multi-frequency generation is considerably enhanced practically to the spectral width of the active media luminescence spectrum. As a result, the radiation of each mode with its own wavelength is amplified in the active media independently from the simultaneous amplification of the rest of the wavelengths.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Brushless high-frequency alternator and excitation method for three-phase ac power-frequency generation
InactiveUS20080174195A1Minimise currentSynchronous generatorsWindingsAlternating currentConductor Coil
A method is disclosed for arranging and exciting the stator, rotor and various windings of a multi-stage brushless high frequency alternator so that the resulting multiple high frequency sub-phase armature winding outputs can be rectified and commutated into three phase power frequency alternating current (AC) electrical output. Power frequency currents in field windings control output amplitude, output frequency, and output phase. Devices incorporating this arrangement are suitable of generating fixed frequency electrical power while accommodating variable speed rotation of a generator shaft and offer multiple advantages over existing techniques. The capability to generate speed independent electric power allows natural power sources such as windmills and hydro-power stations to be efficiently coupled to fixed frequency power grids.
Owner:RAVEN ENERGY ALTERNATIVES
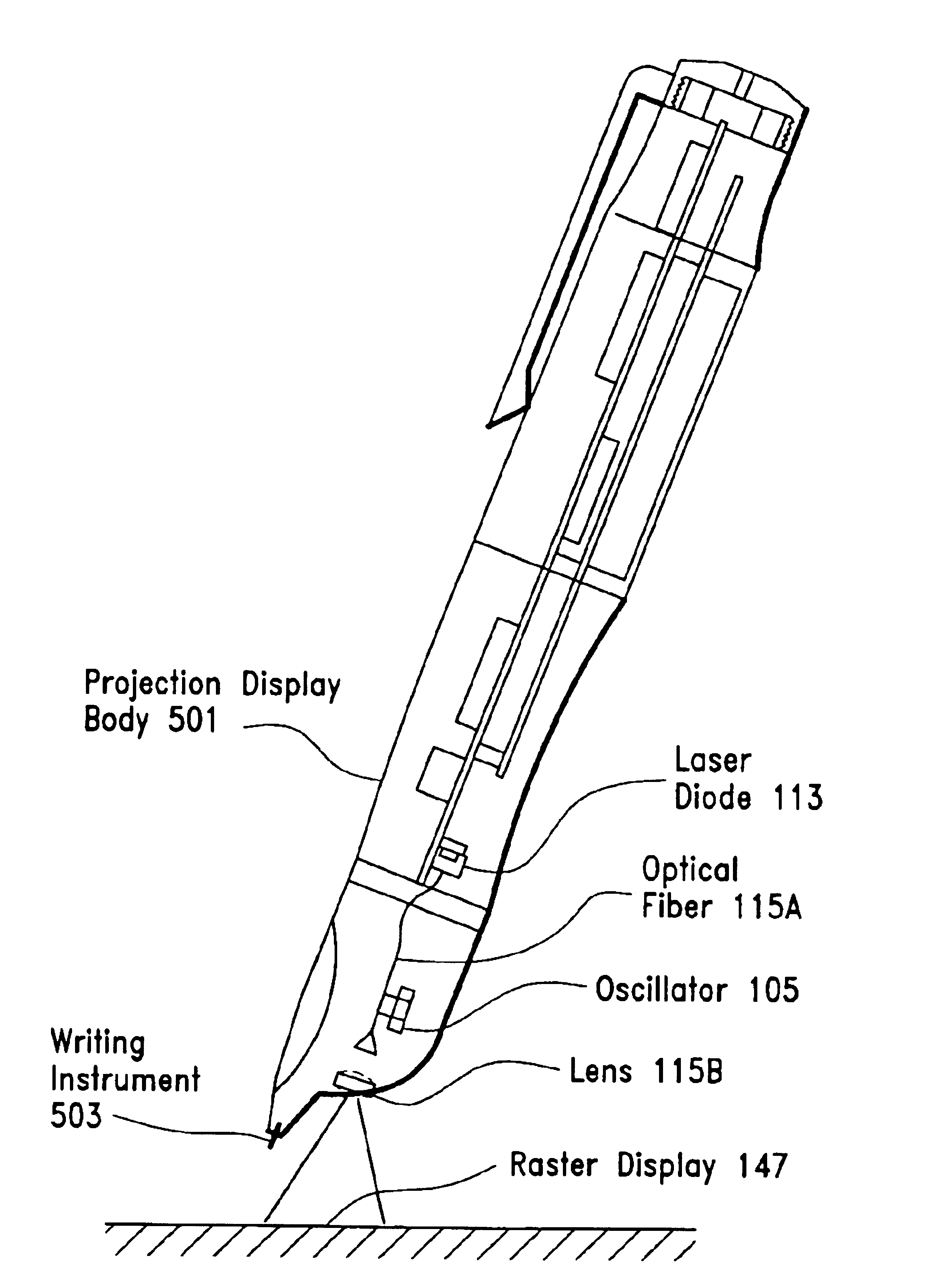
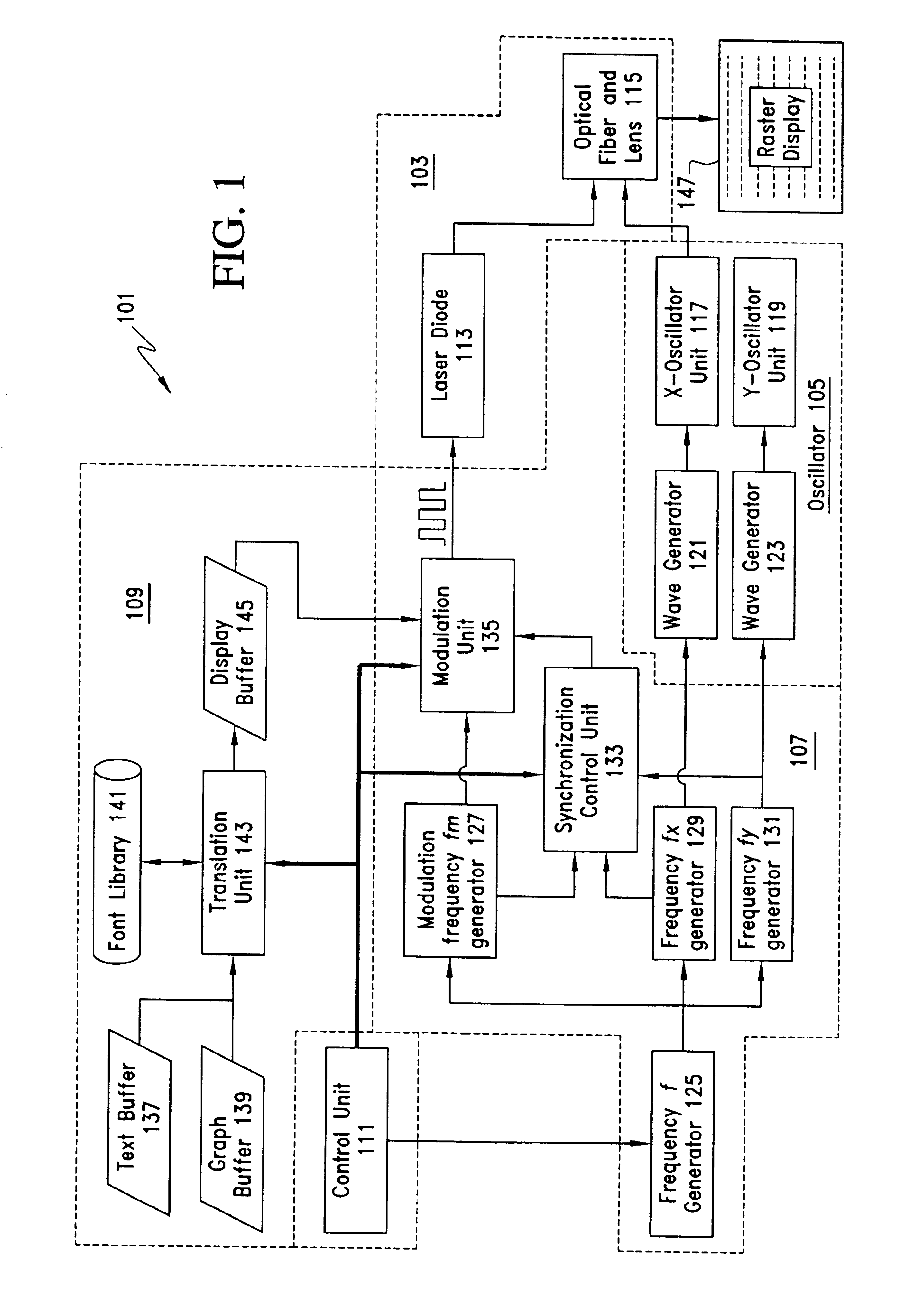
Pen projection display
InactiveUS6964483B2Input/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system scanning detailsGratingDisplay device
The projection display includes a light projector unit for generating and projecting light, an oscillator unit for oscillating light projected from the light projector unit, and a frequency generation and modulation unit. The frequency generation and modulation unit drives the oscillator unit and modulates the light projected by the light projector unit. In turn, the oscillator unit oscillates the light projected by the light projector unit in two dimensions, so that the projected light scans an incident surface in a raster pattern. At the same time, the frequency generation and modulation unit modulates the light produced by the light projector unit in synchronization with the scanning process and image data supplied so that the projected light produces images corresponding to the image data over a scanned area.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Temperature-compensating method for quartz crystal oscillator
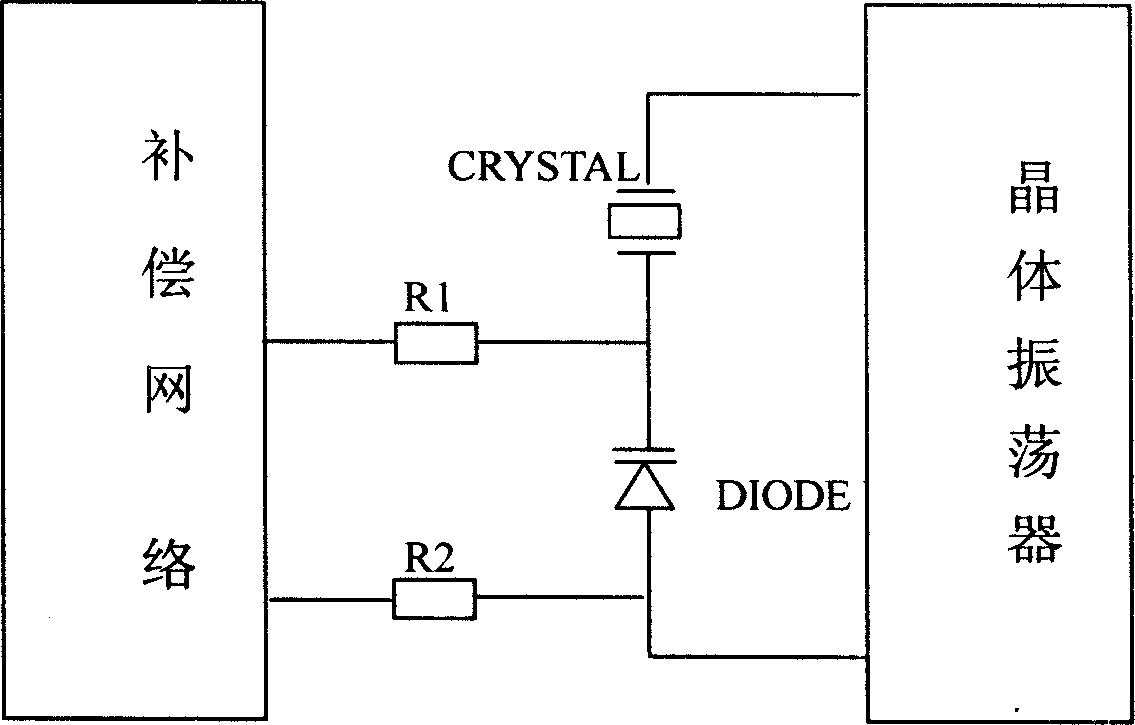
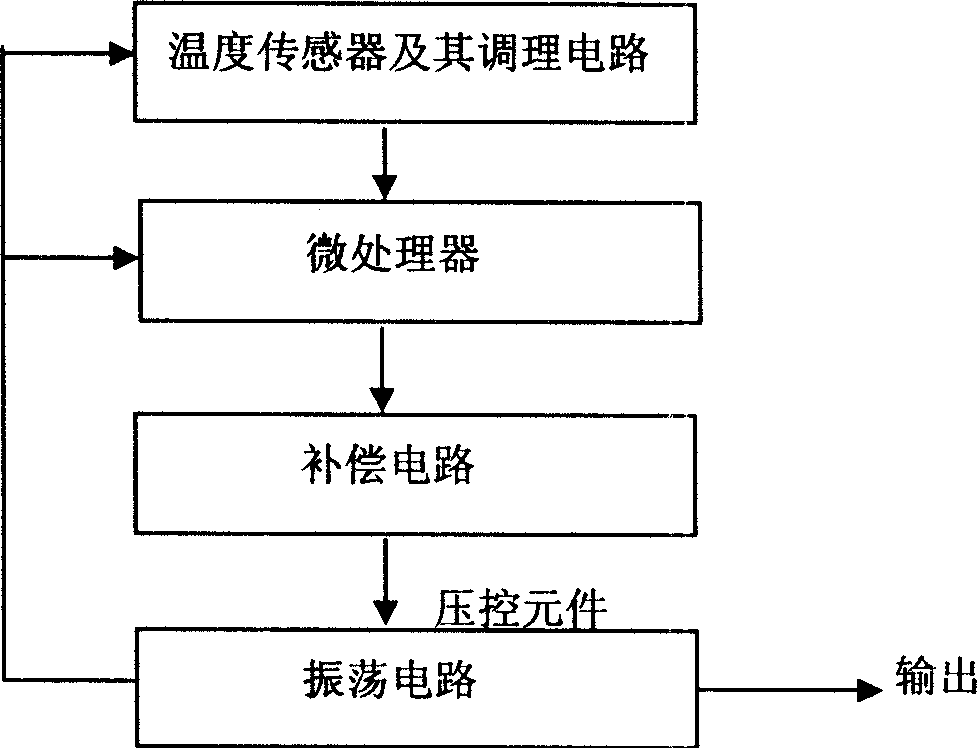
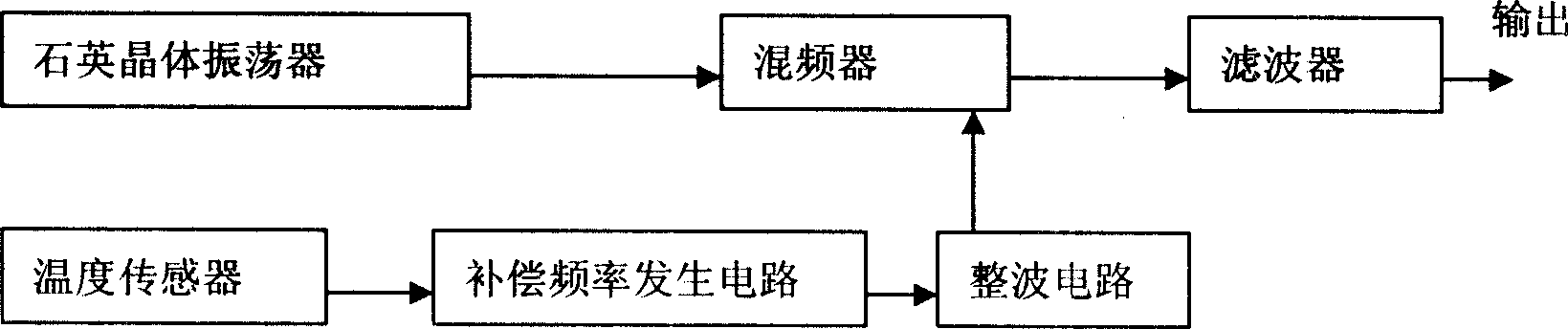
InactiveCN1705222AOvercoming phase jitterTo achieve temperature compensationOscillations generatorsPhase noiseWave shape
A temperature compensation method for quartz crystal oscillator, the temperature sensor and compensation frequency generation circuit producing a compensation frequency signal having equal absolute value and opposite sign with the deviation frequency value produced by uncompensated quartz crystal oscillator, said compensation frequency signal mixed and outputted with the uncompensated frequency signal after wave shaping, obtaining compensated frequency signal after filtering by filter, said invention has low phase noise and can make effective temperature compensation to high frequency overtone quartz crystal oscillator.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com