Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3296results about "Diagnostic markers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
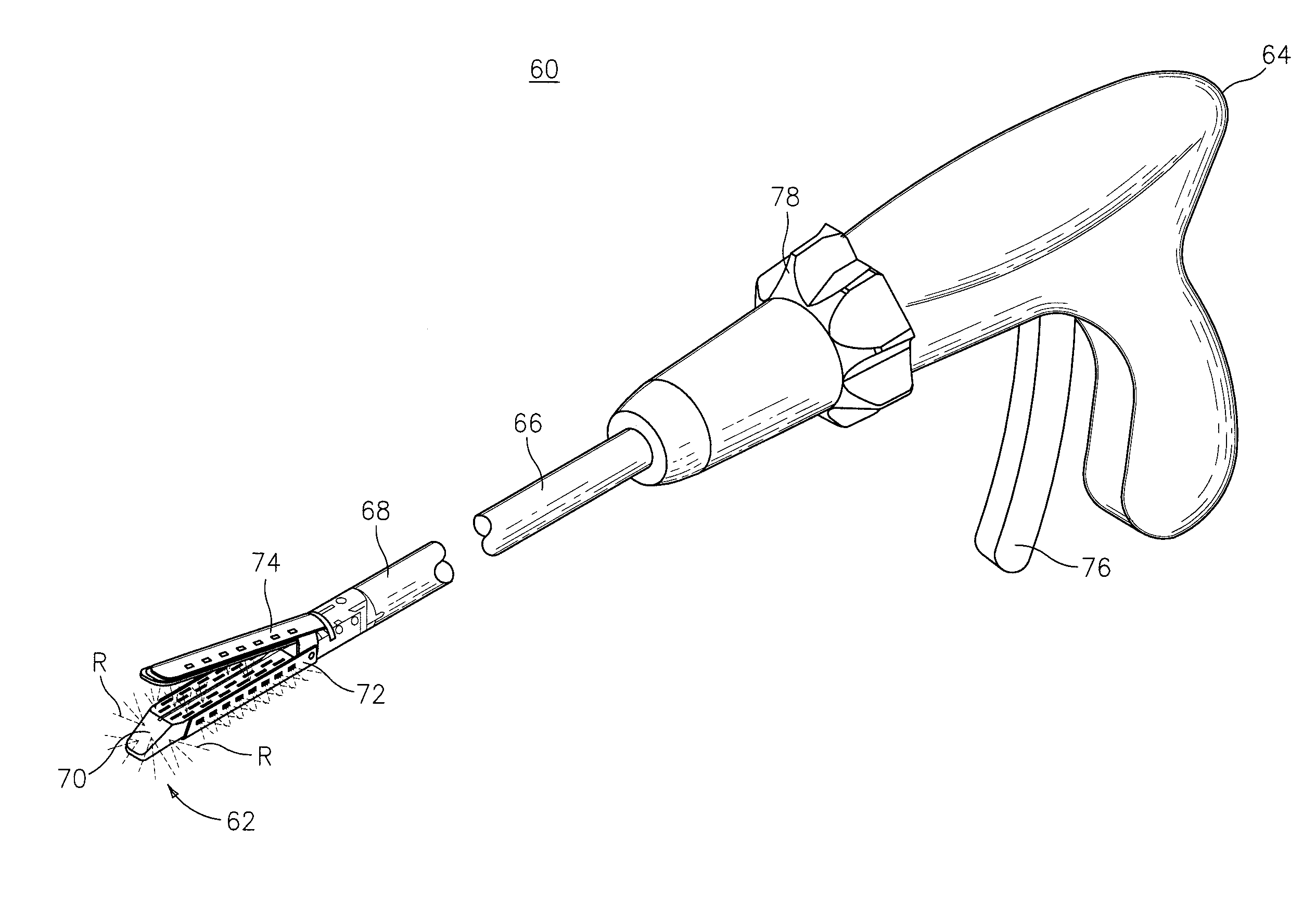
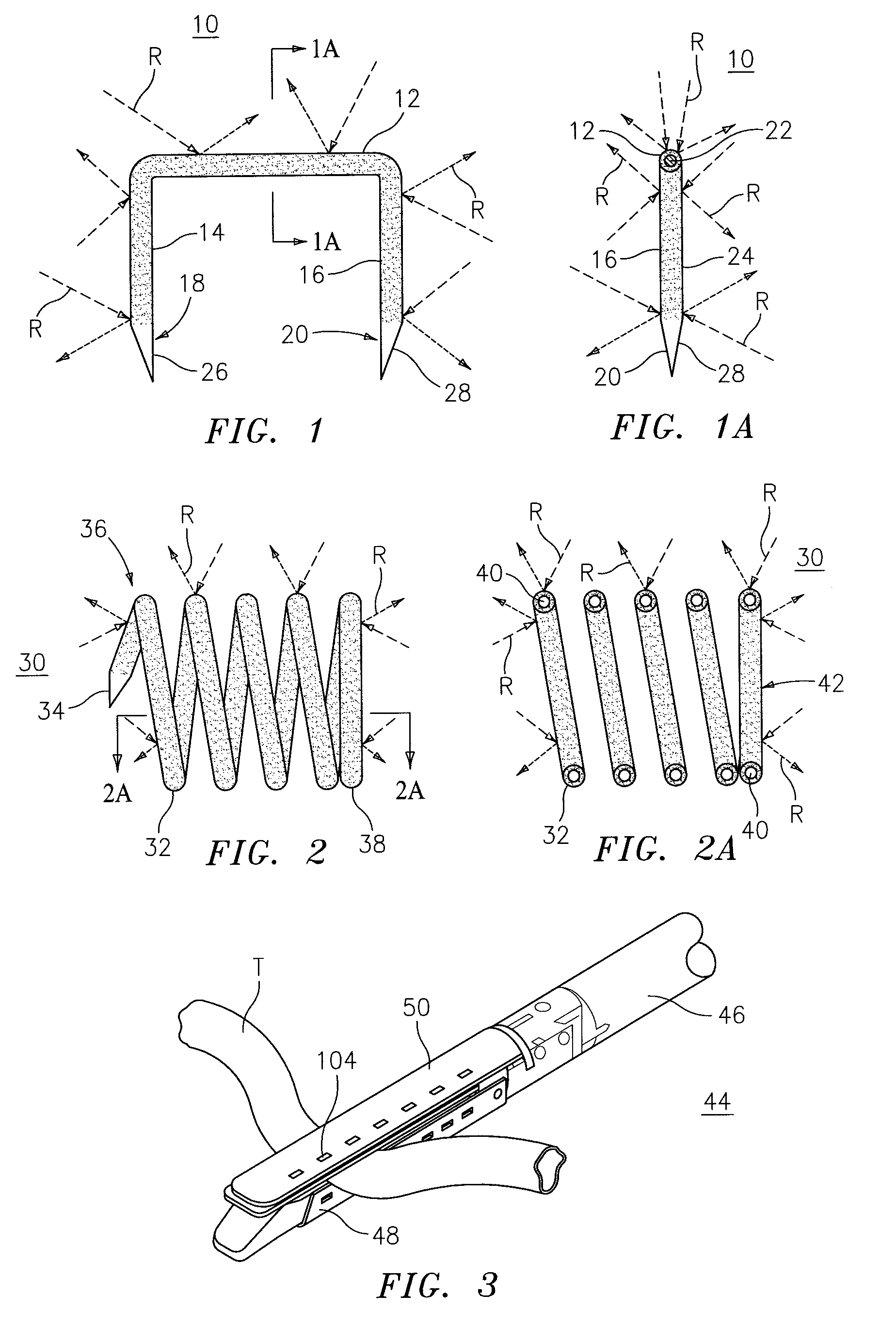
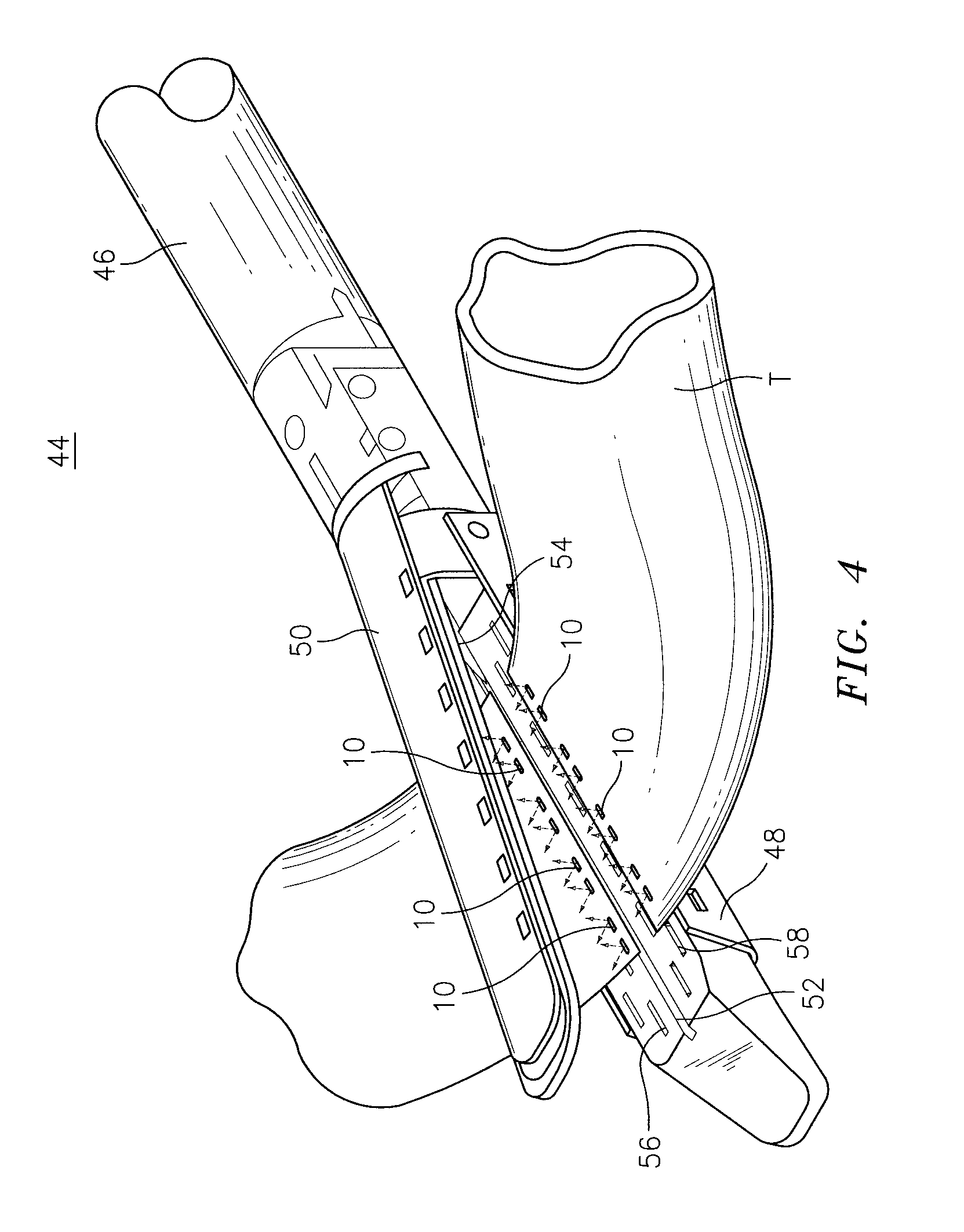
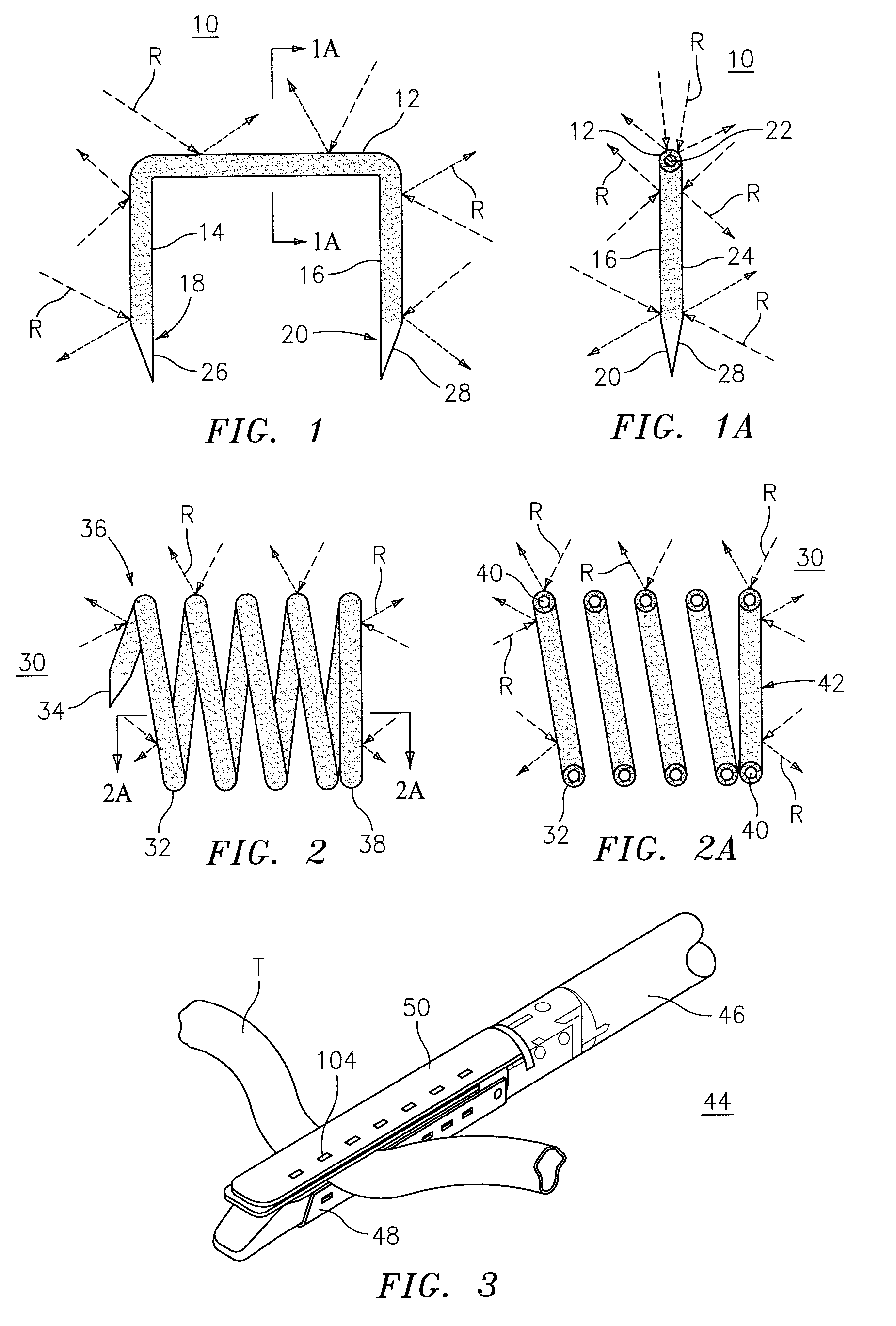
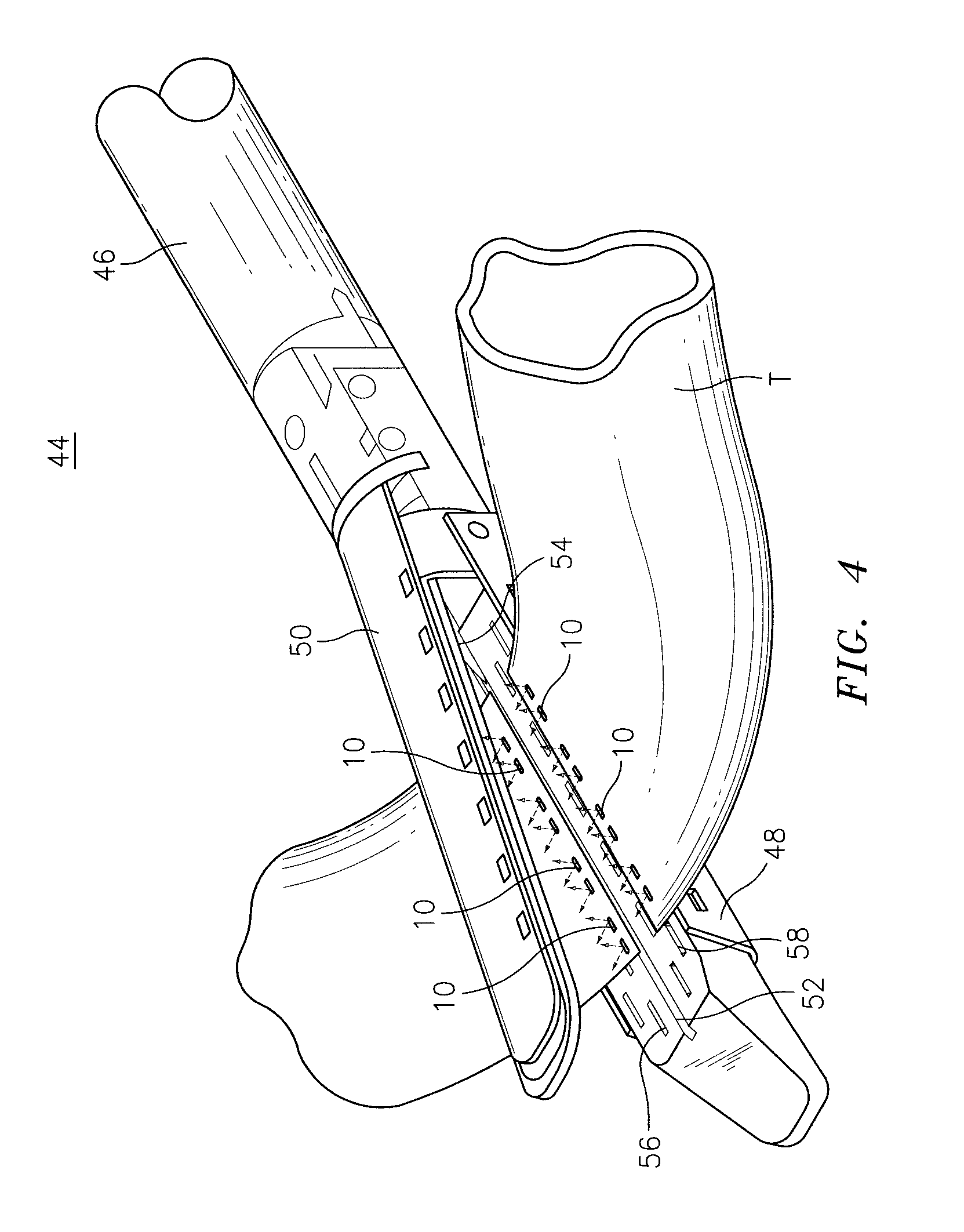
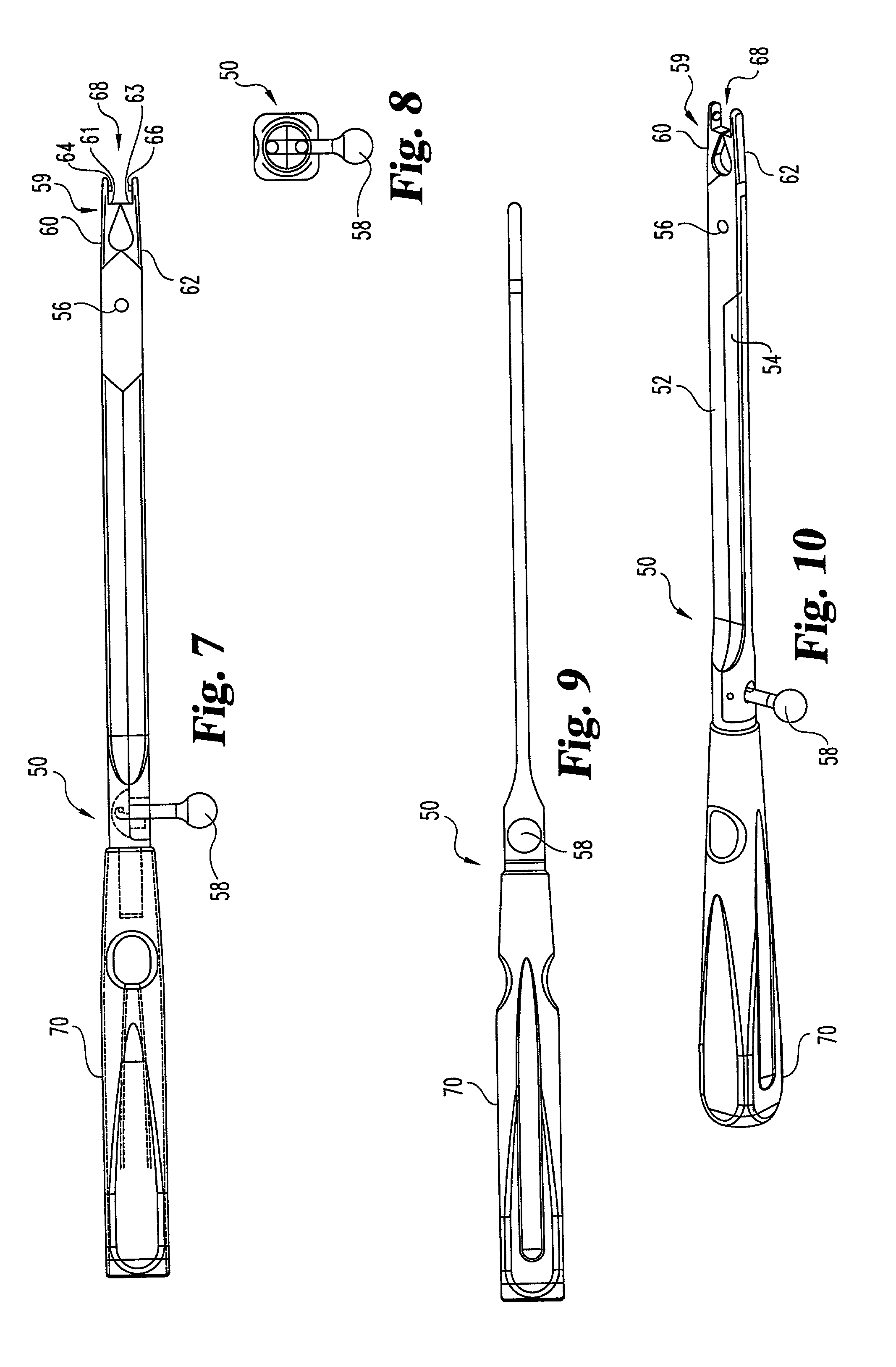
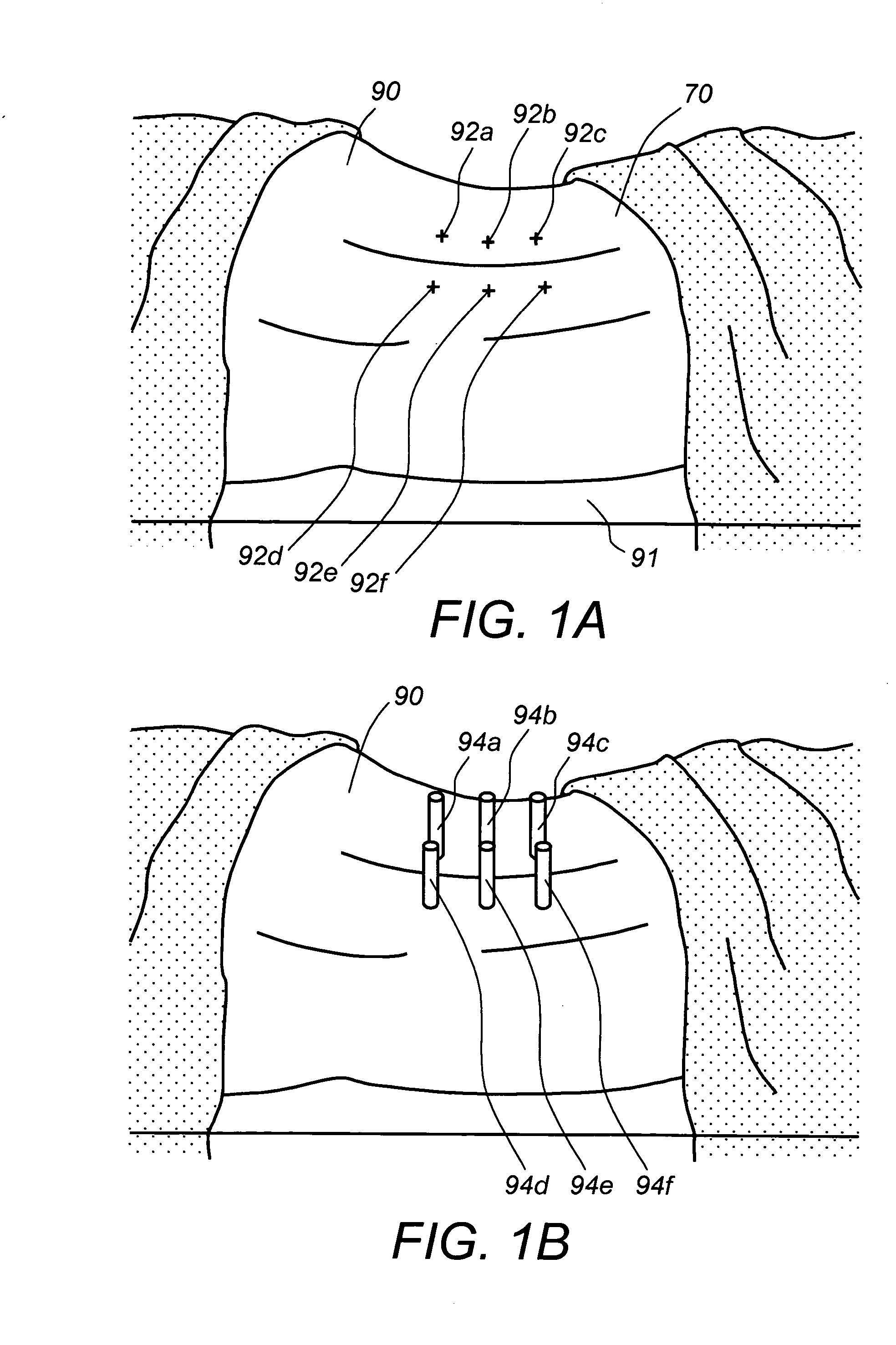
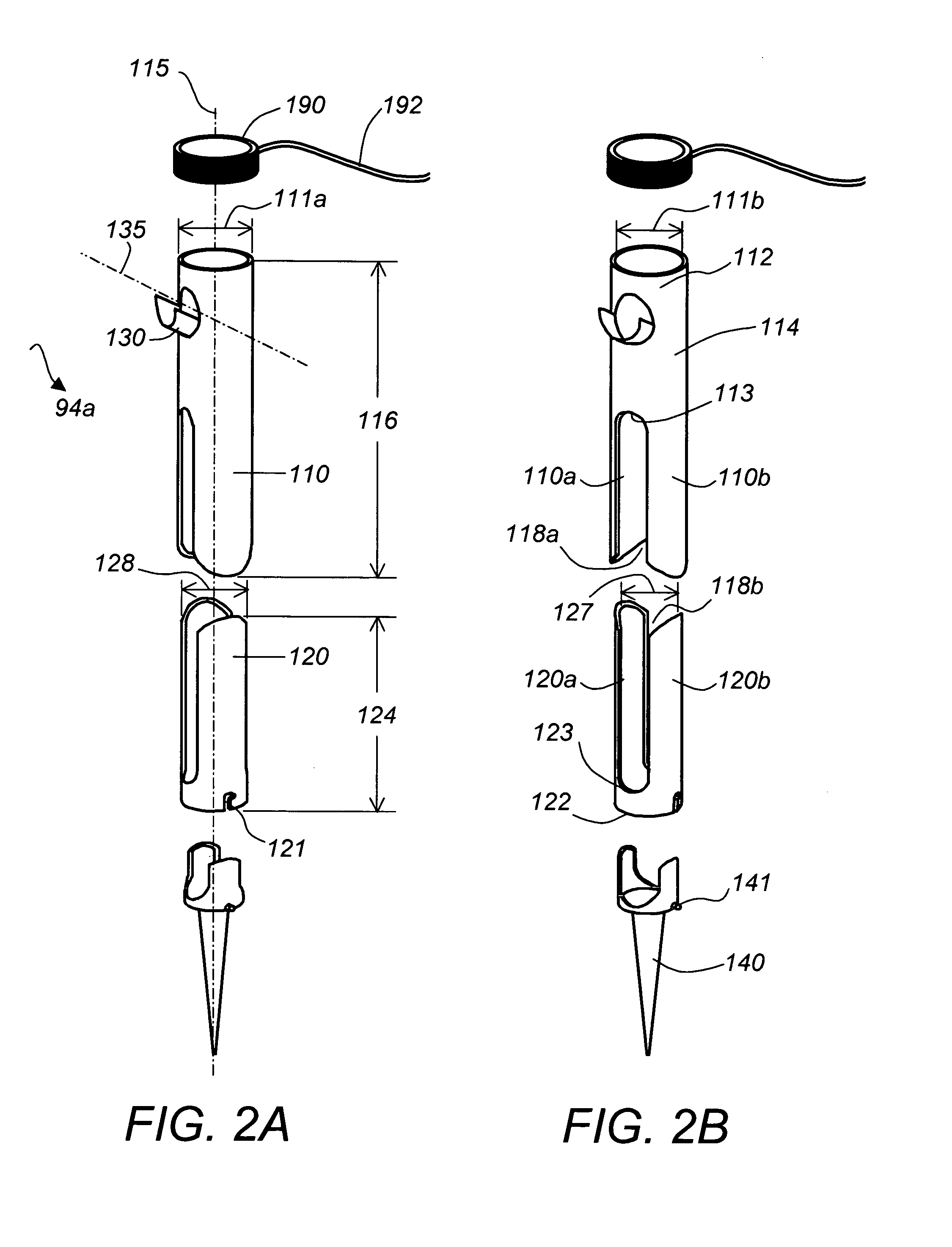
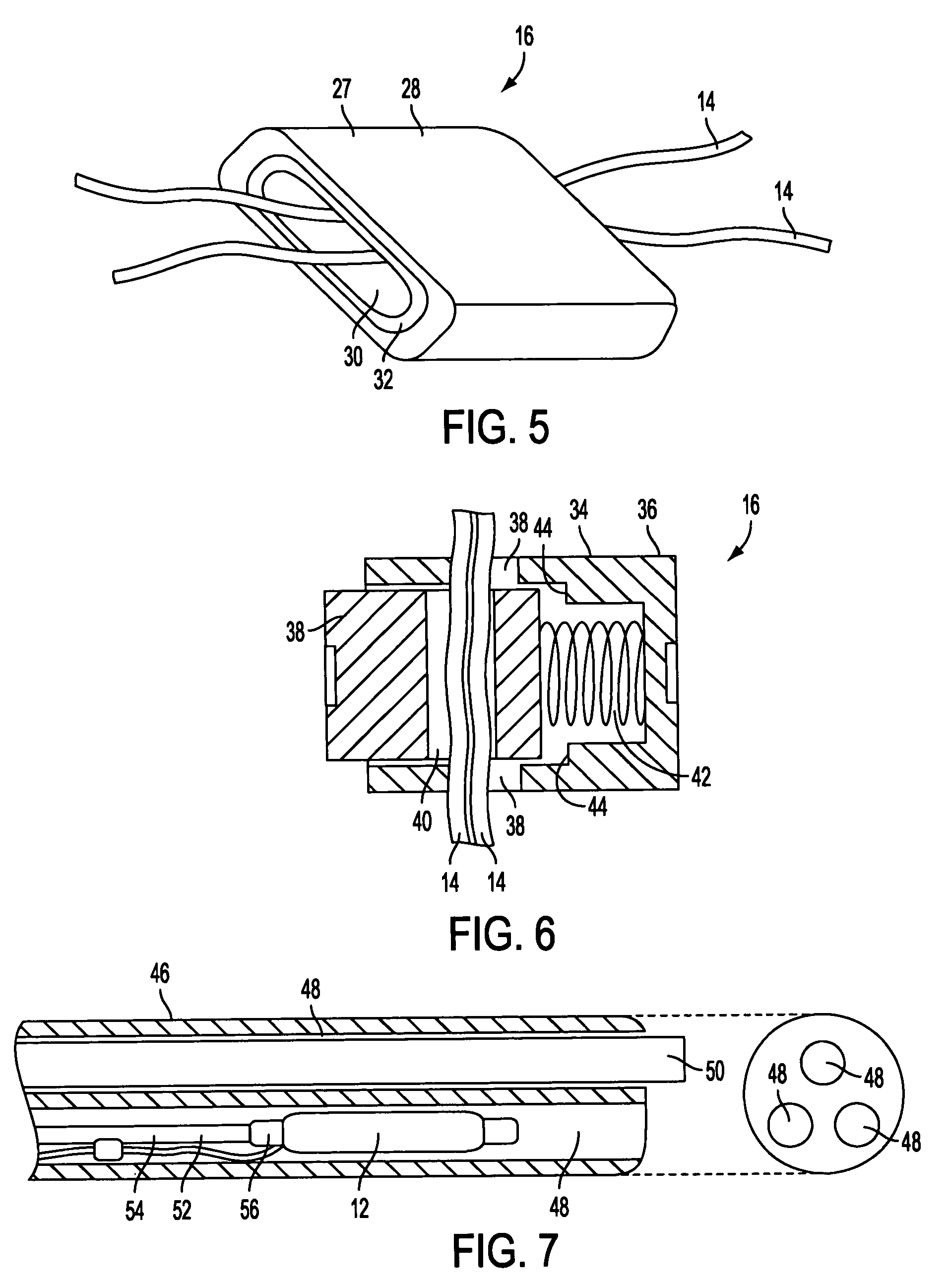
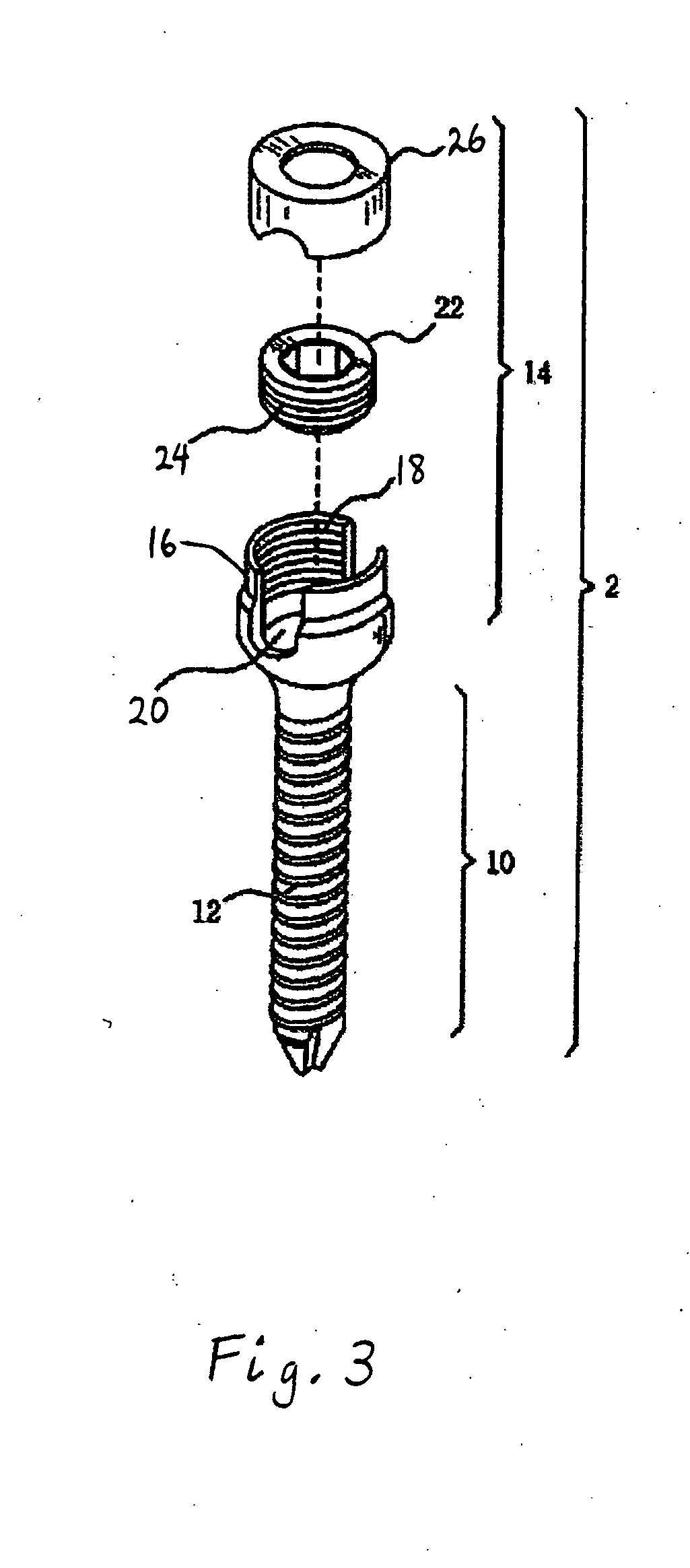
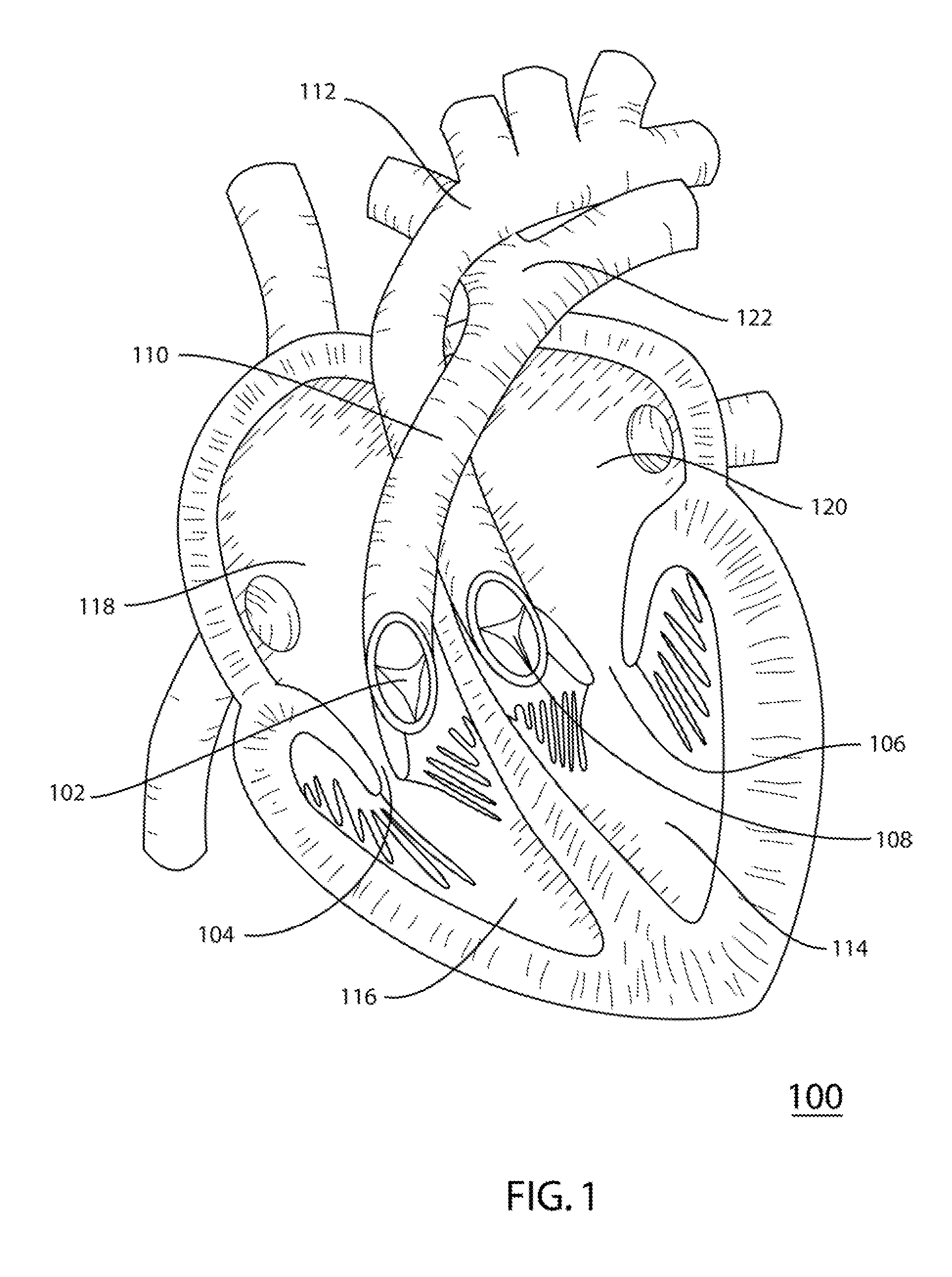
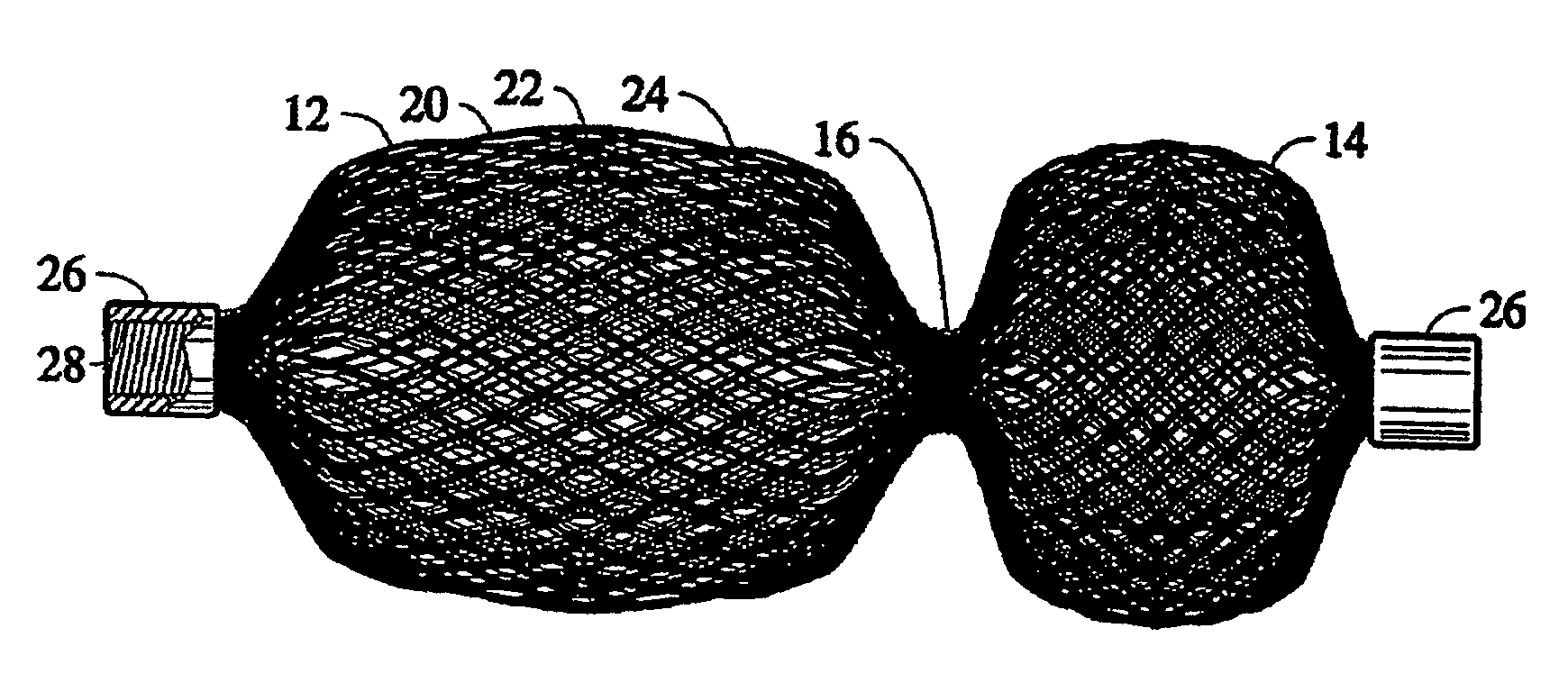
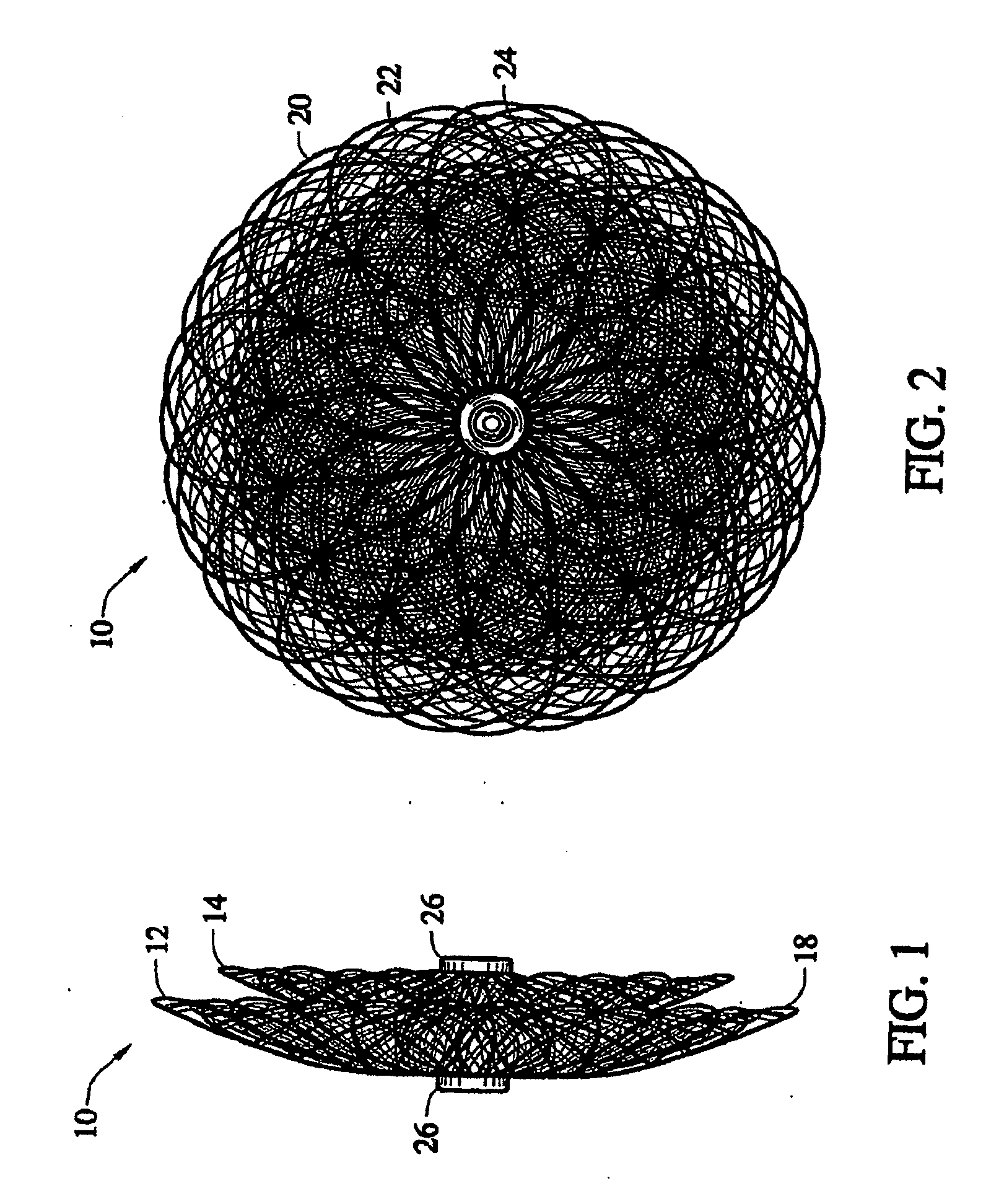
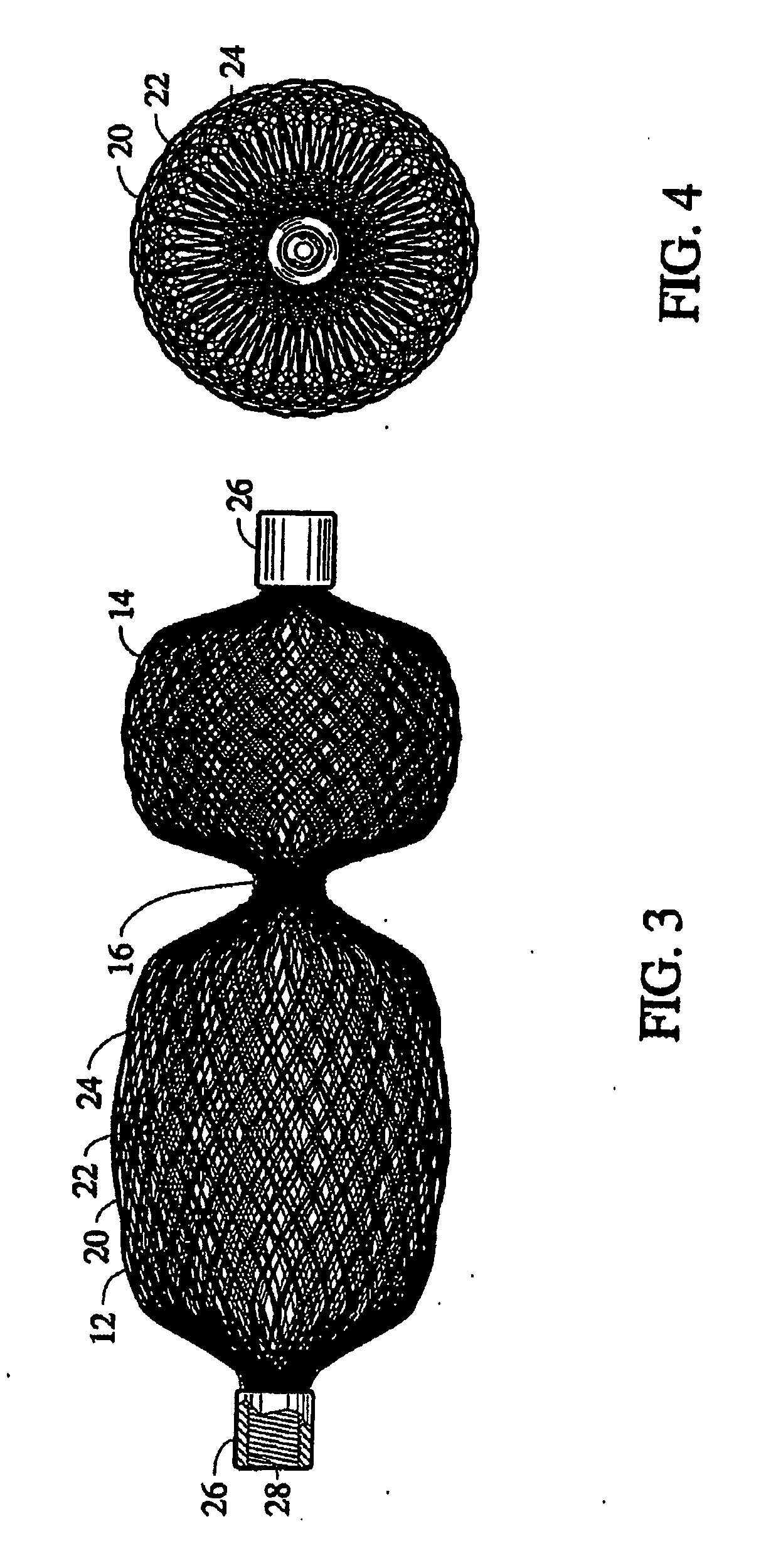
Coated surgical staples and an illuminated staple cartridge for a surgical stapling instrument
InactiveUS7954687B2Increase awarenessReduce reflectivitySuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleEngineering
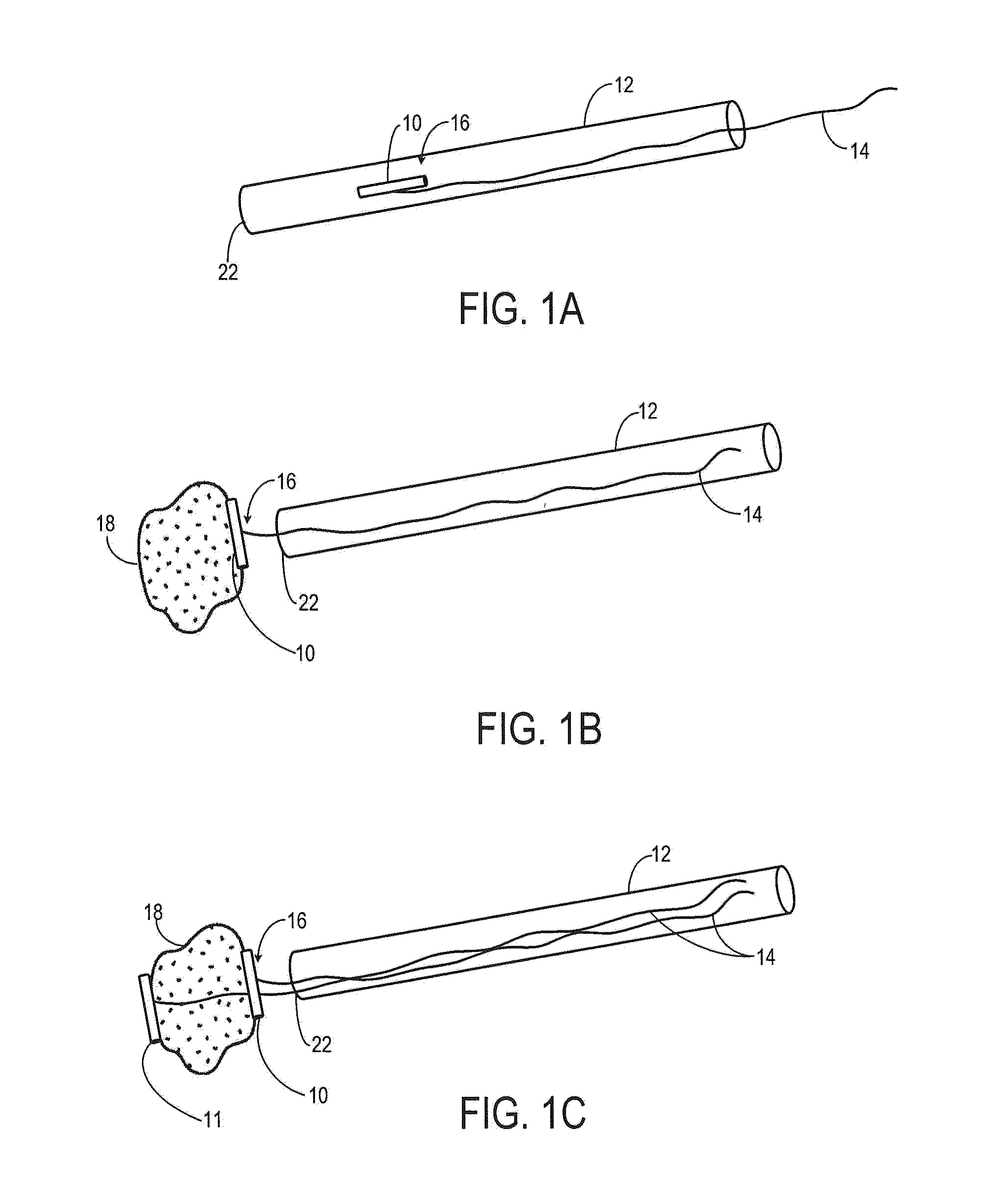
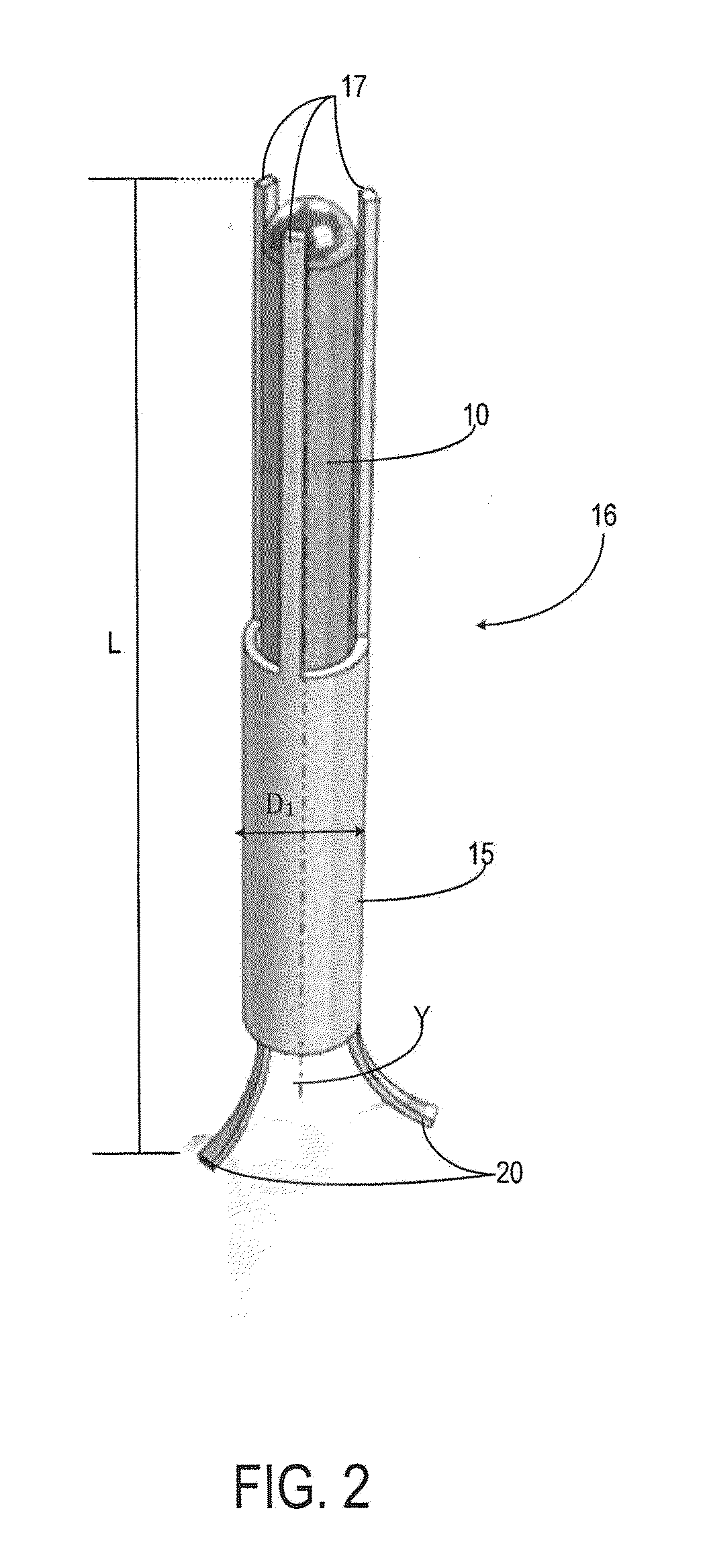
A coated surgical fastener is provided for an easy visualization within tissue. The coated surgical fastener includes a core and a relatively non-reflective coating applied about the core. There is also disclosed an illuminated staple cartridge for use with a surgical stapling device having a light source. The illuminated staple cartridge includes a transparent insert and a relatively nontransparent U-shaped outer channel at least partially surrounding the transparent insert. Windows formed in sides of the U-shaped outer channel allow defined amounts of light to project from the sides of the illuminated staple cartridge.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
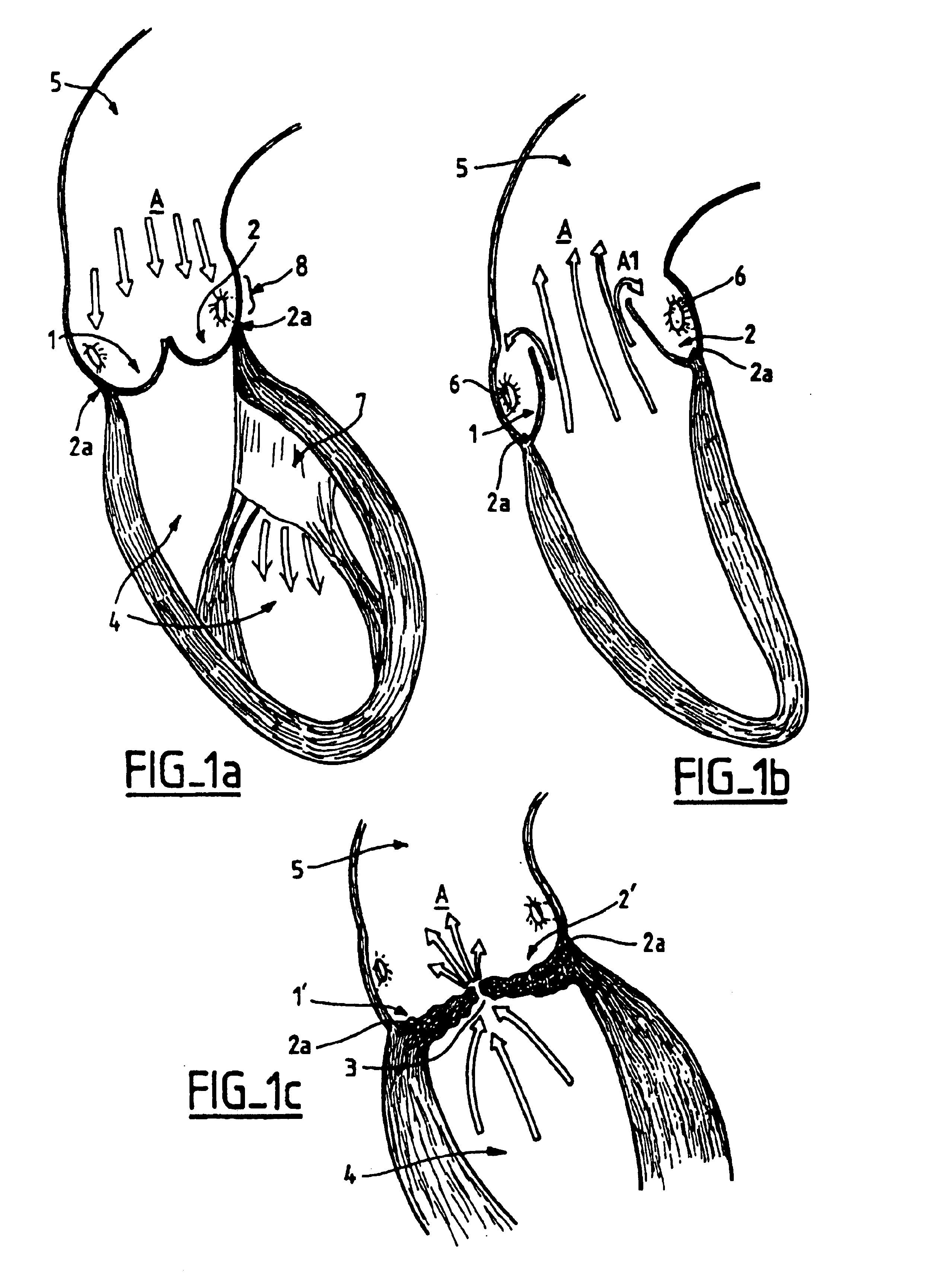
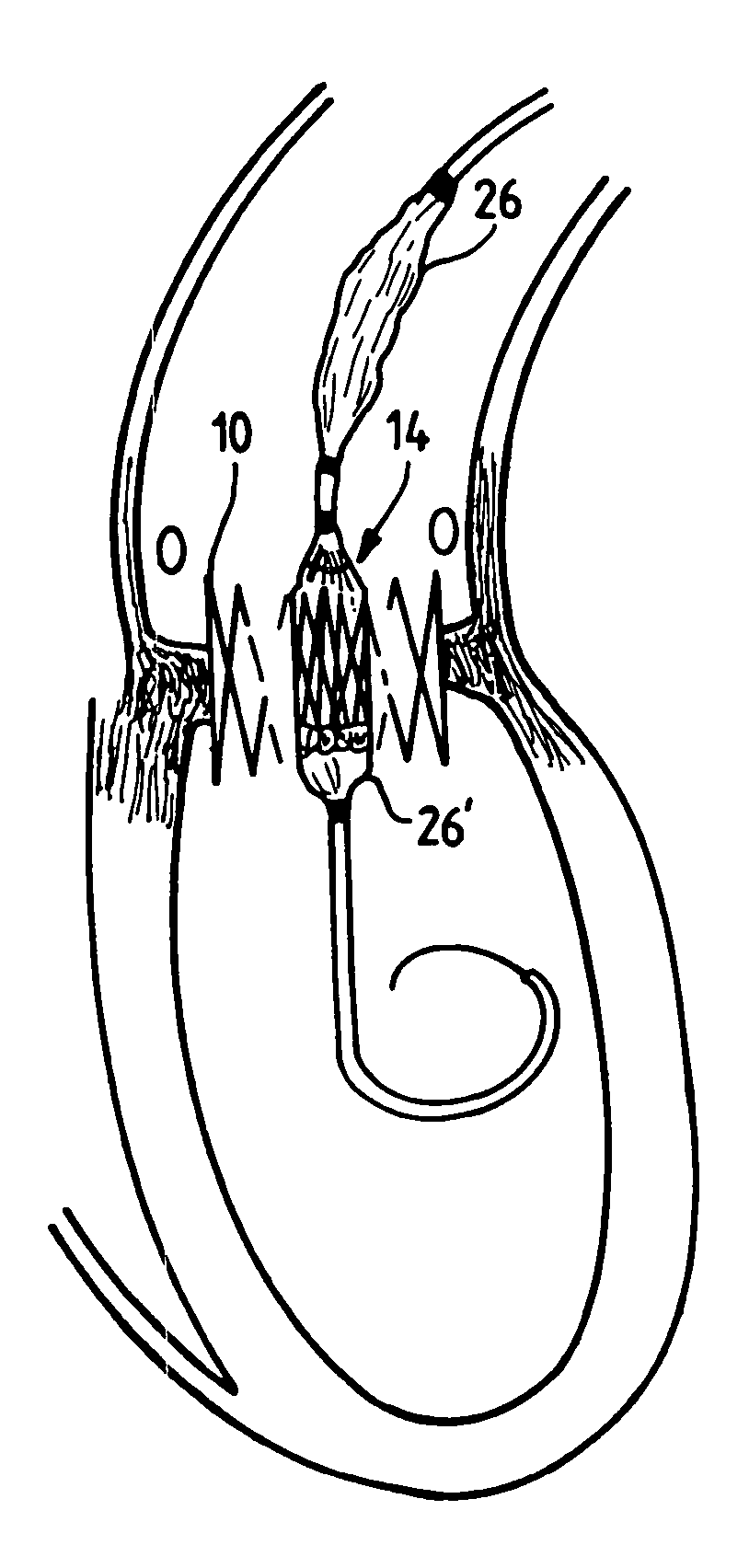
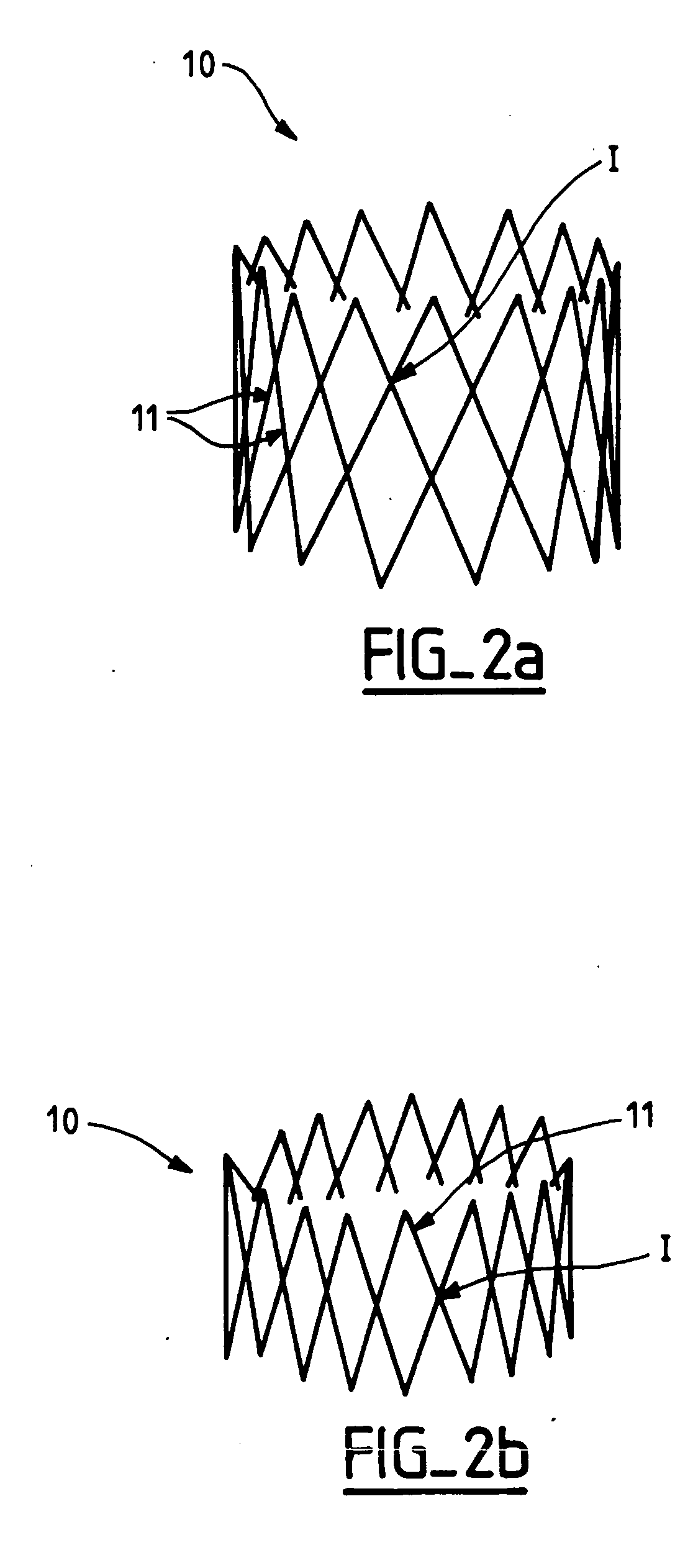
Value prosthesis for implantation in body channels
A valve prosthesis which is especially useful in the case of aortic stenosis and capable of resisting the powerful recoil force and to stand the forceful balloon inflation performed to deploy the valve and to embed it in the aortic annulus, comprises a collapsible valvular structure and an expandable frame on which said valvular structure is mounted. The valvular structure is composed of physiologically compatible valvular tissue that is sufficiently supple and resistant to allow the valvular structure to be deformed from a closed state to an opened state. The valvular tissue forms a continuous surface and is provided with strut members that create stiffened zones which induce the valvular structure to follow a patterned movement in its expansion to its opened state and in its turning back to its closed state.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI PVT
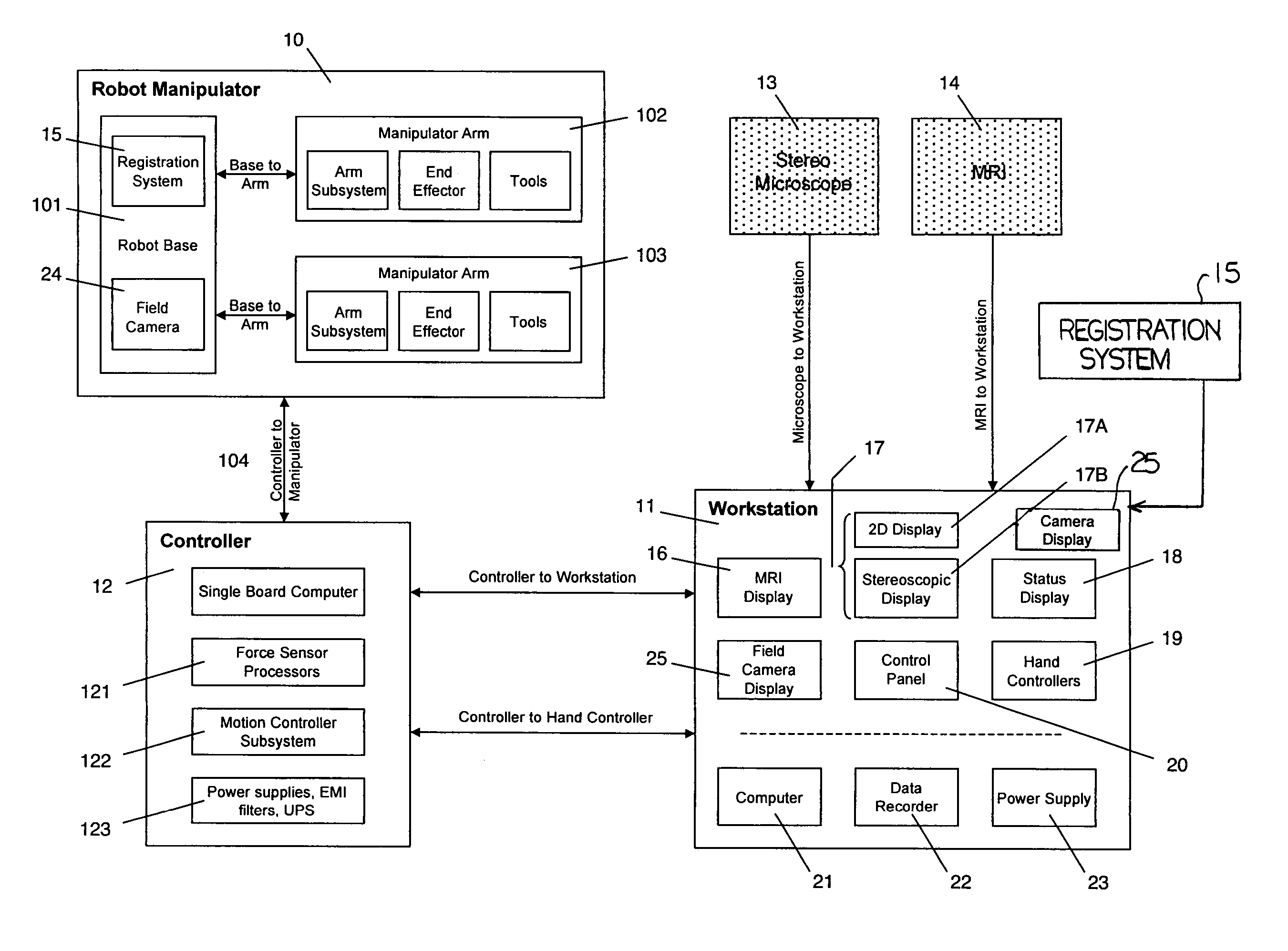
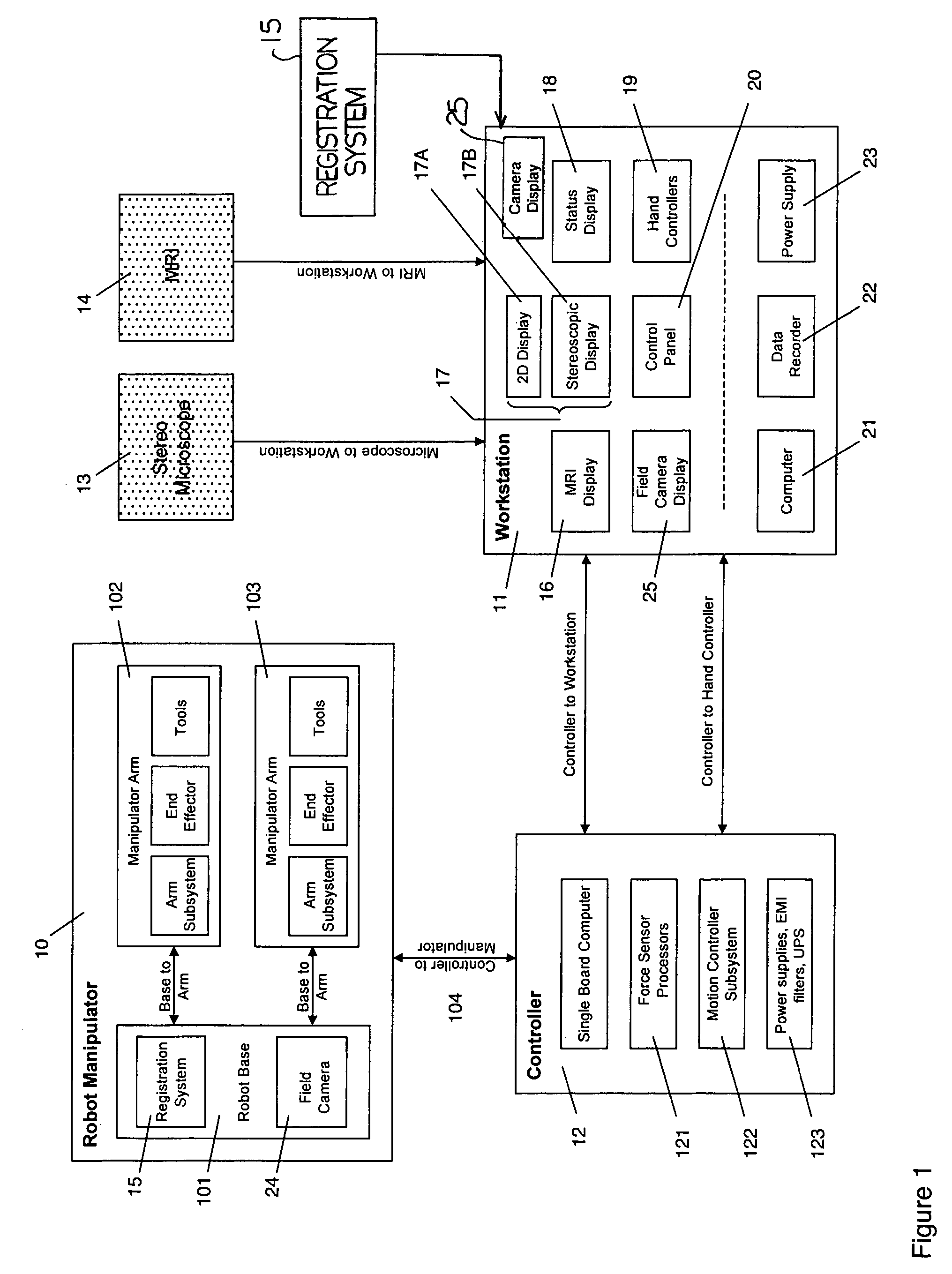
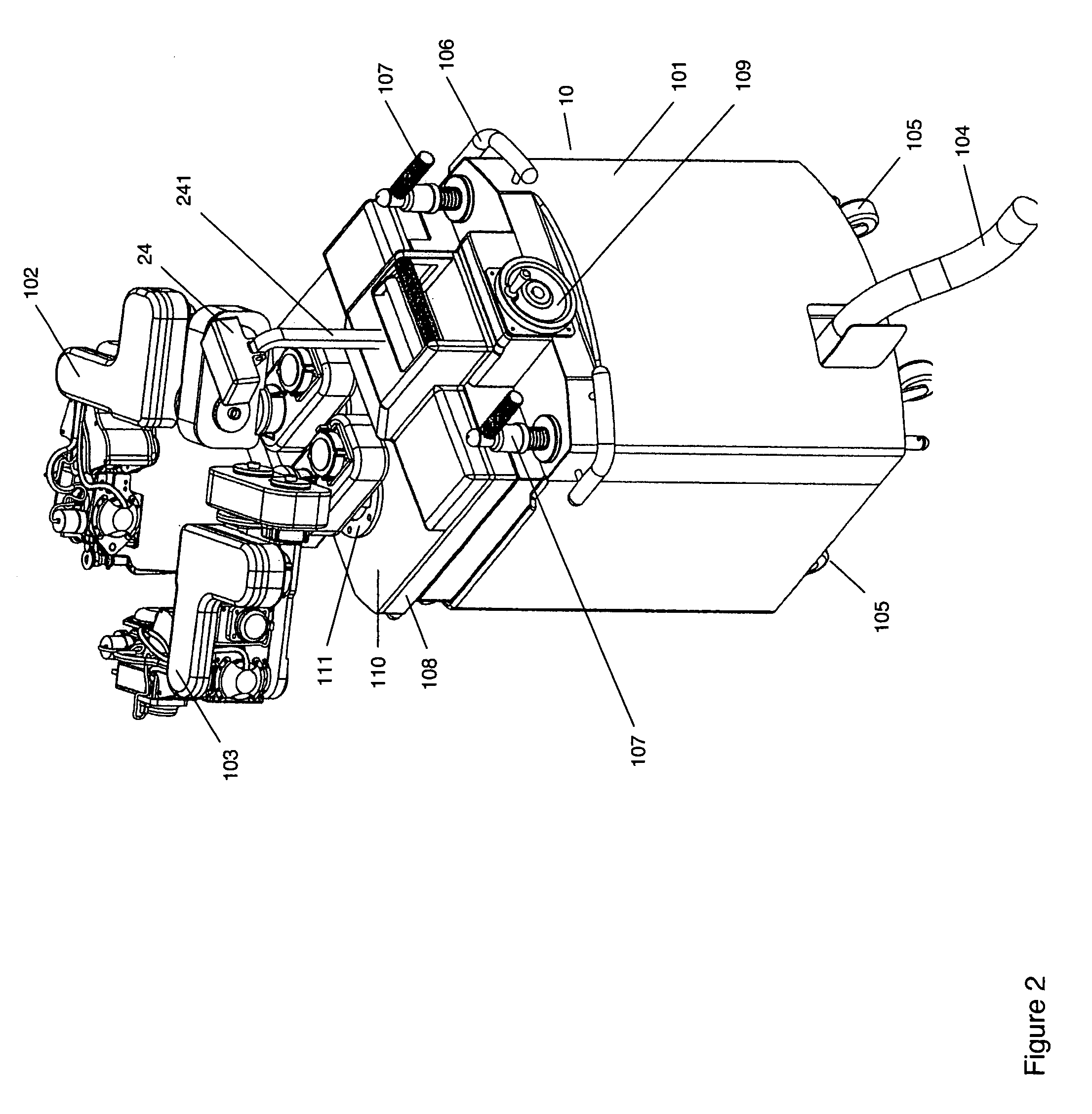
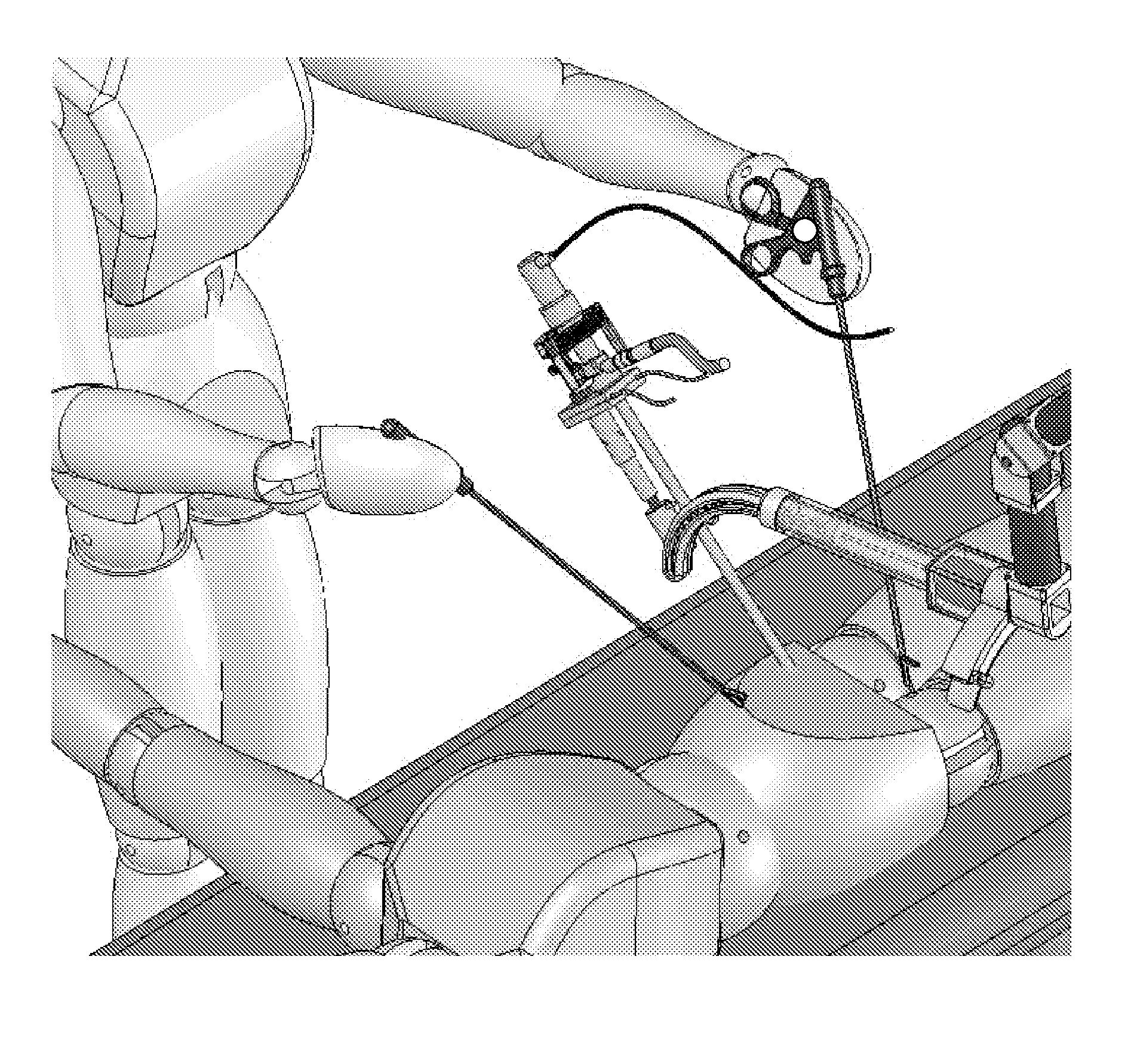
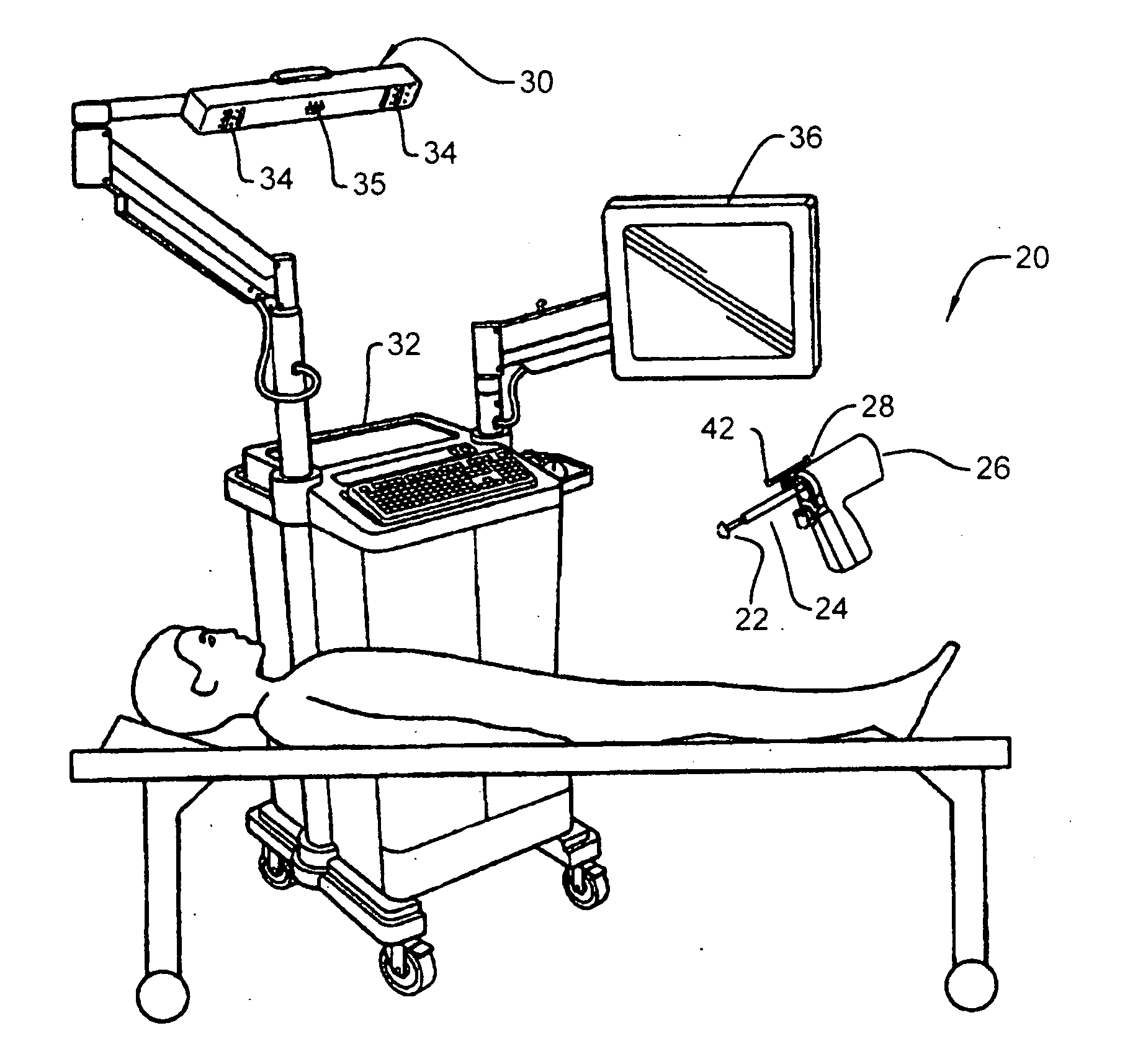
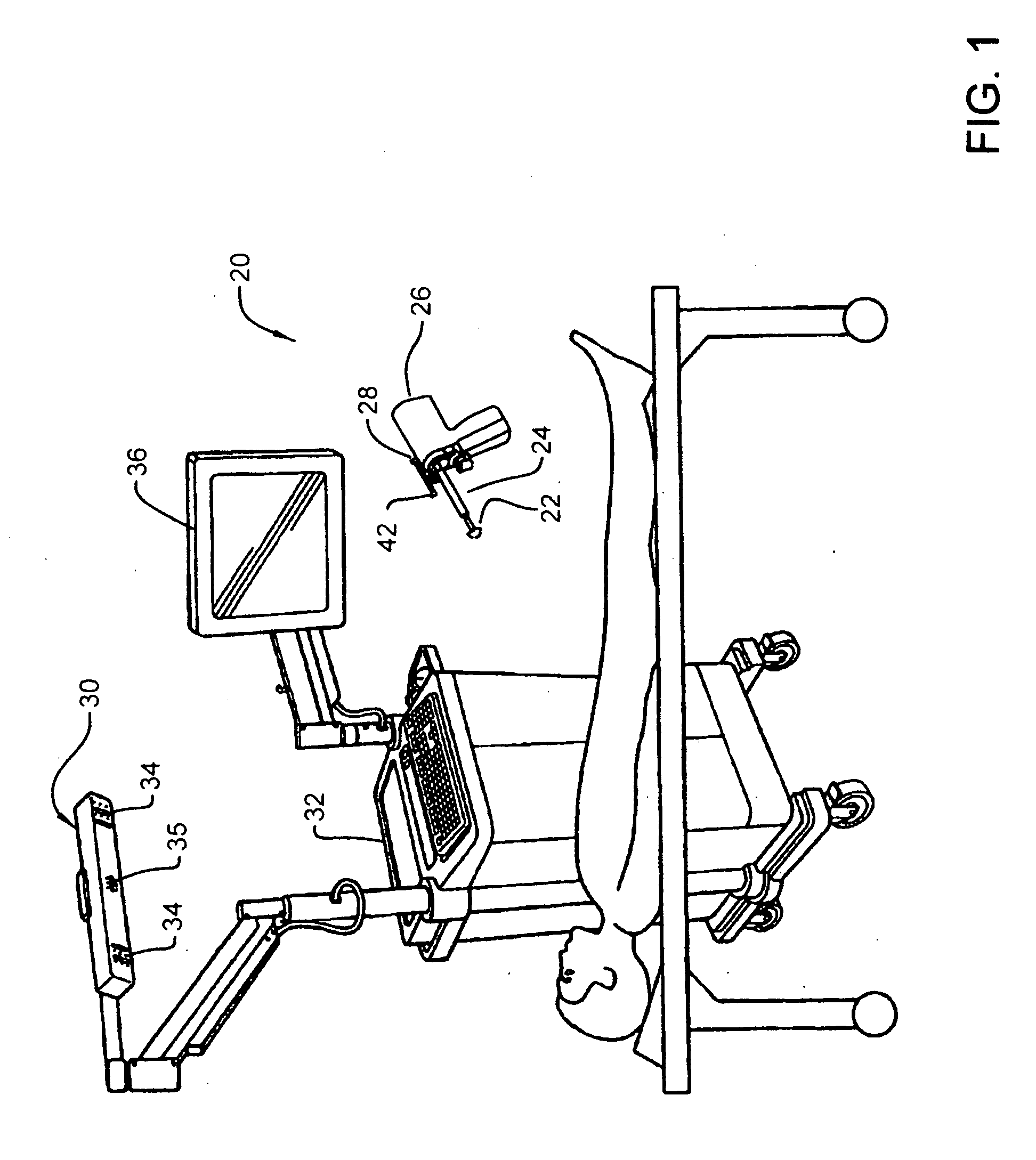
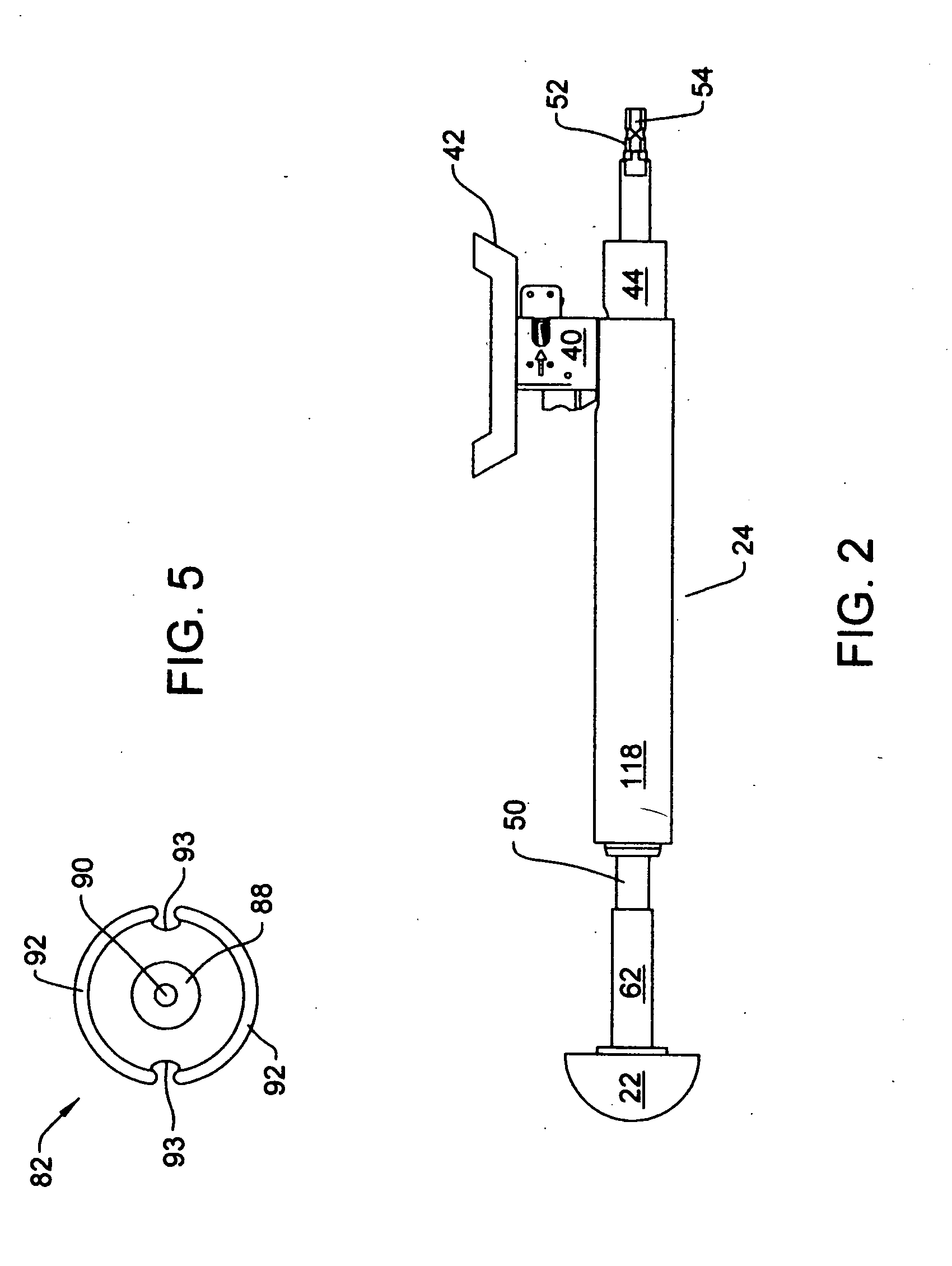
Microsurgical robot system
ActiveUS7155316B2Minimize patient riskComplete efficientlyProgramme-controlled manipulatorEndoscopesMicroscopic observationDisplay device
A robot system for use in surgical procedures has two movable arms each carried on a wheeled base with each arm having a six of degrees of freedom of movement and an end effector which can be rolled about its axis and an actuator which can slide along the axis for operating different tools adapted to be supported by the effector. Each end effector including optical force sensors for detecting forces applied to the tool by engagement with the part of the patient. A microscope is located at a position for viewing the part of the patient. The position of the tool tip can be digitized relative to fiducial markers visible in an MRI experiment. The workstation and control system has a pair of hand-controllers simultaneously manipulated by an operator to control movement of a respective one or both of the arms. The image from the microscope is displayed on a monitor in 2D and stereoscopically on a microscope viewer. A second MRI display shows an image of the part of the patient the real-time location of the tool. The robot is MRI compatible and can be configured to operate within a closed magnet bore. The arms are driven about vertical and horizontal axes by piezoelectric motors.
Owner:DEERFIELD IMAGING INC
Apparatus and methods for delivering a closure device
An apparatus for delivering a clip to close an opening through tissue includes a sheath and a carrier assembly including a clip therein that is slidable on the sheath. An actuator assembly is connectable to the sheath, and telescoping actuator members extend from the handle that are connectable to the carrier assembly for advancing the carrier assembly along the sheath. An obturator on the actuator assembly includes splines that may be deployed beyond a distal end of the sheath, and expanded to a transverse expanded configuration for positioning the sheath before deploying the clip. The actuator members include cooperating detents that selectively release the actuator members as the carrier assembly reaches predetermined positions along the sheath for deploying the clip from the carrier assembly, and that collapse the splines to allow removal of the apparatus after deploying the clip.
Owner:INTEGRATED VASCULAR SYST
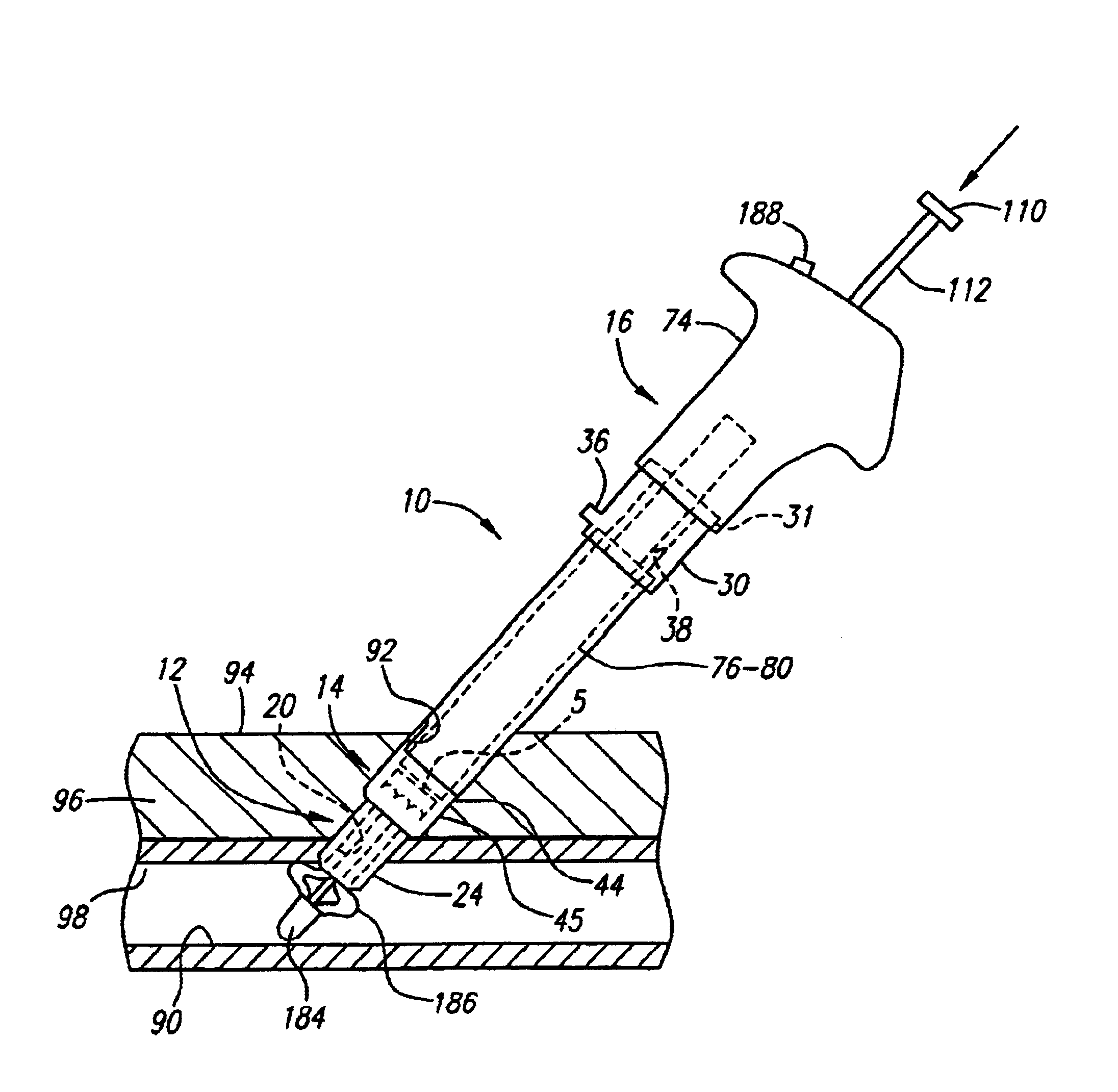
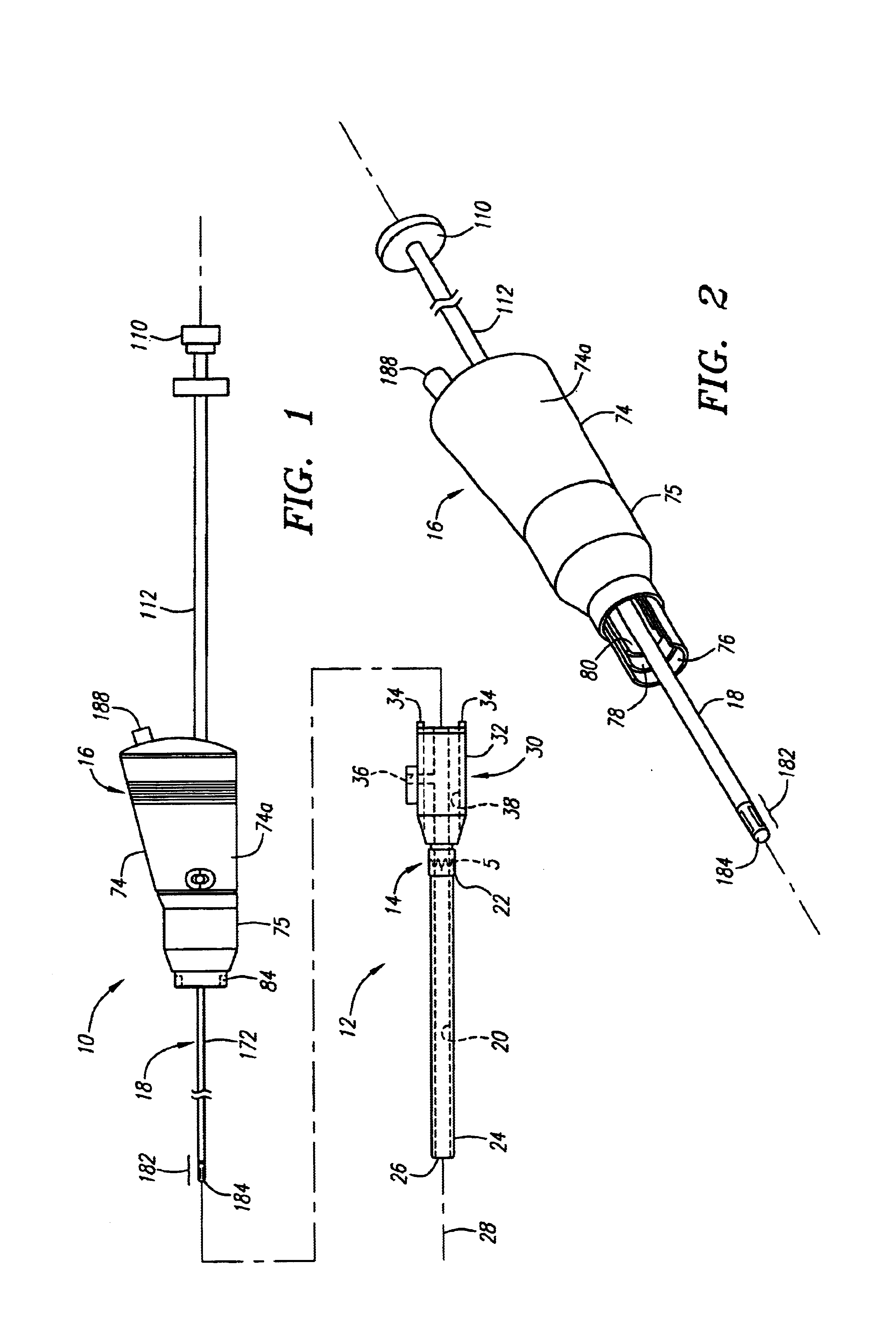
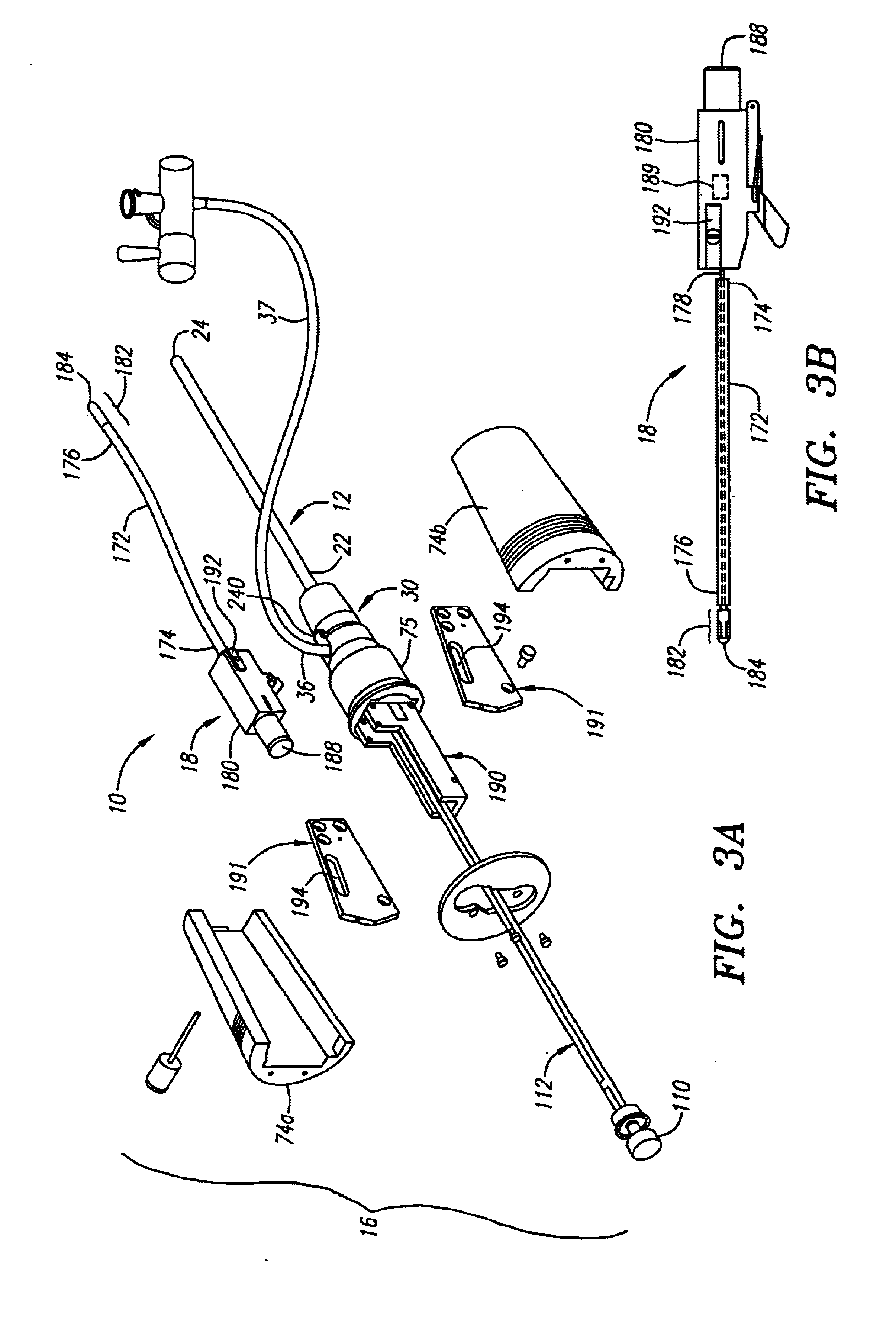
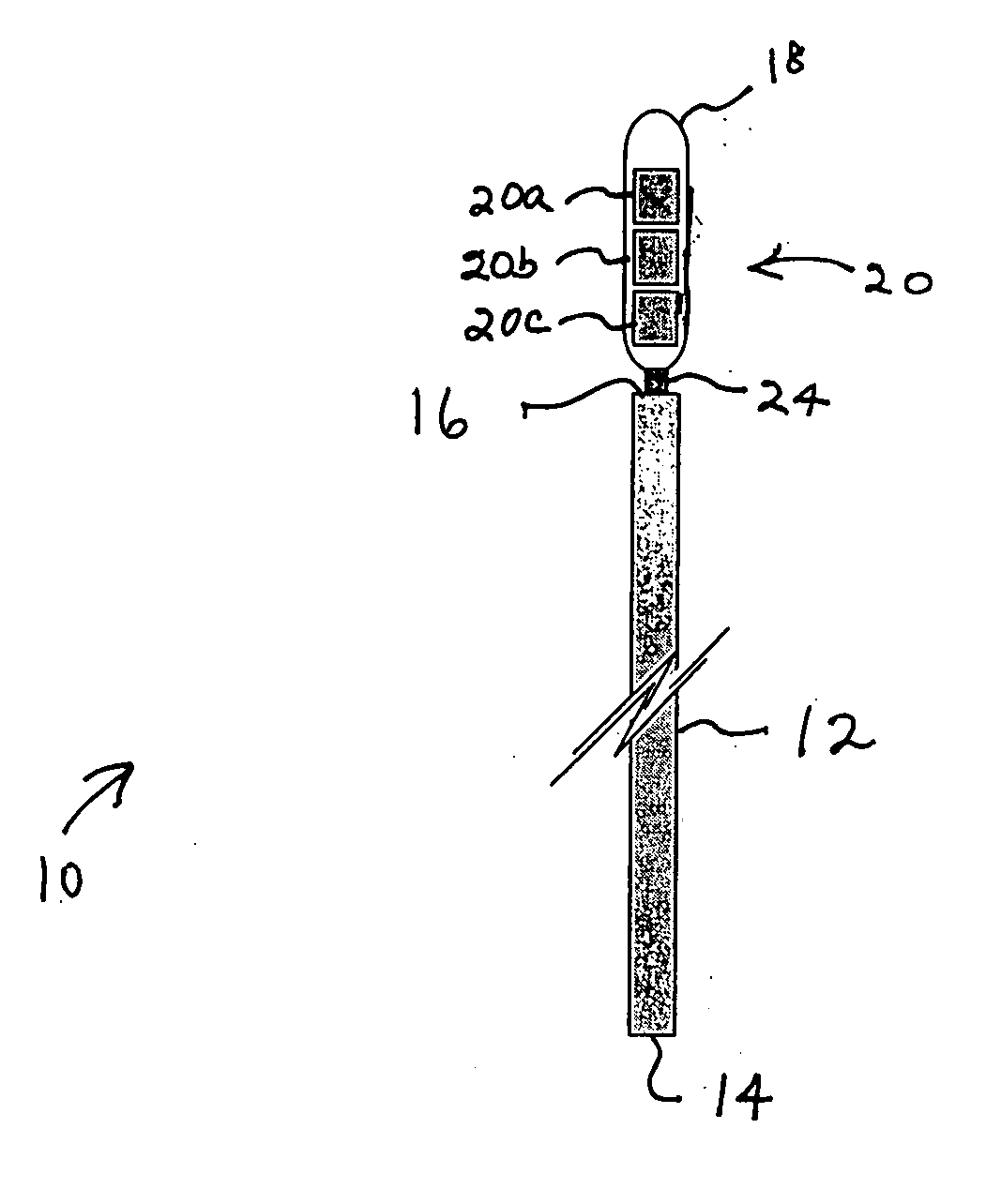
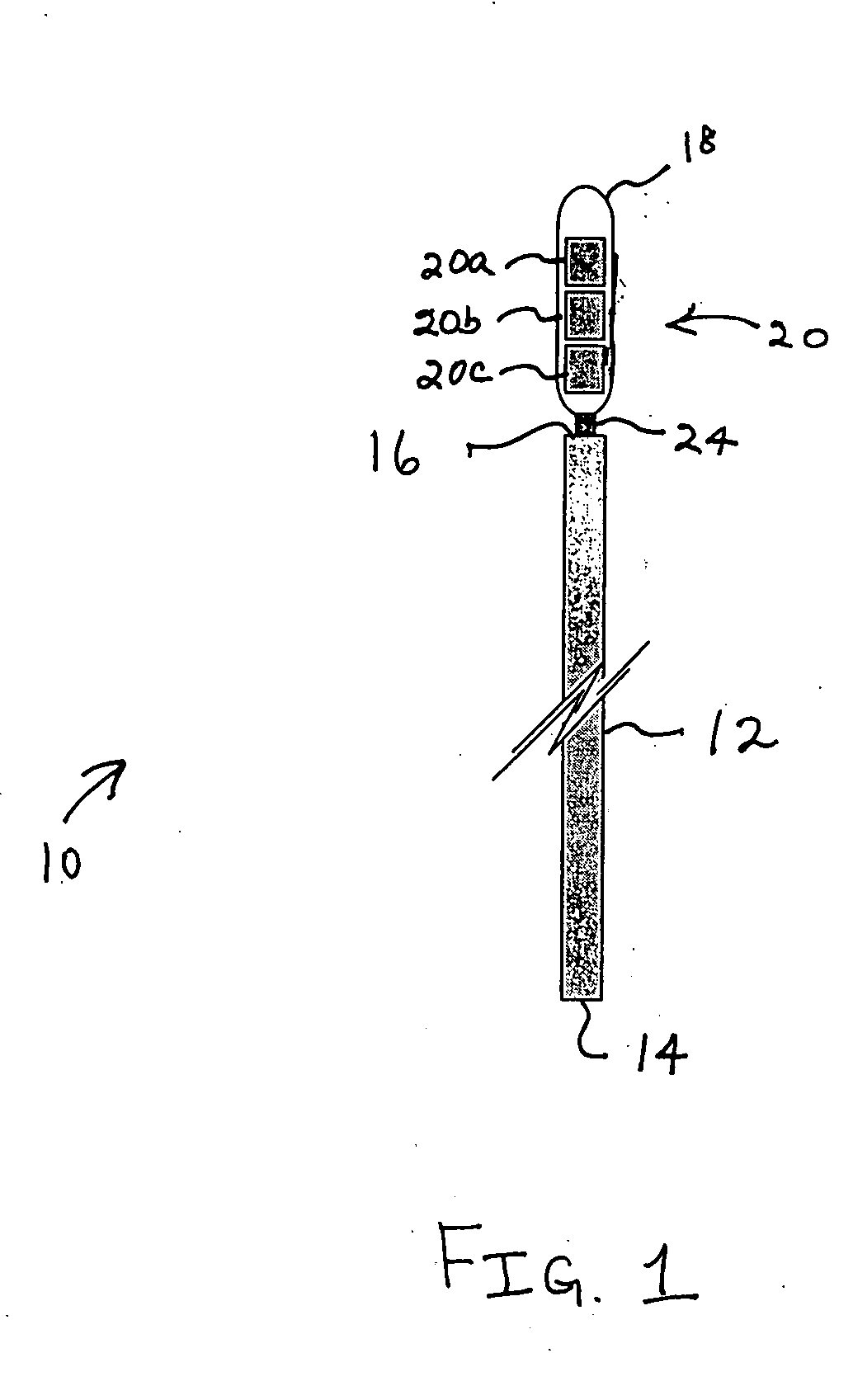
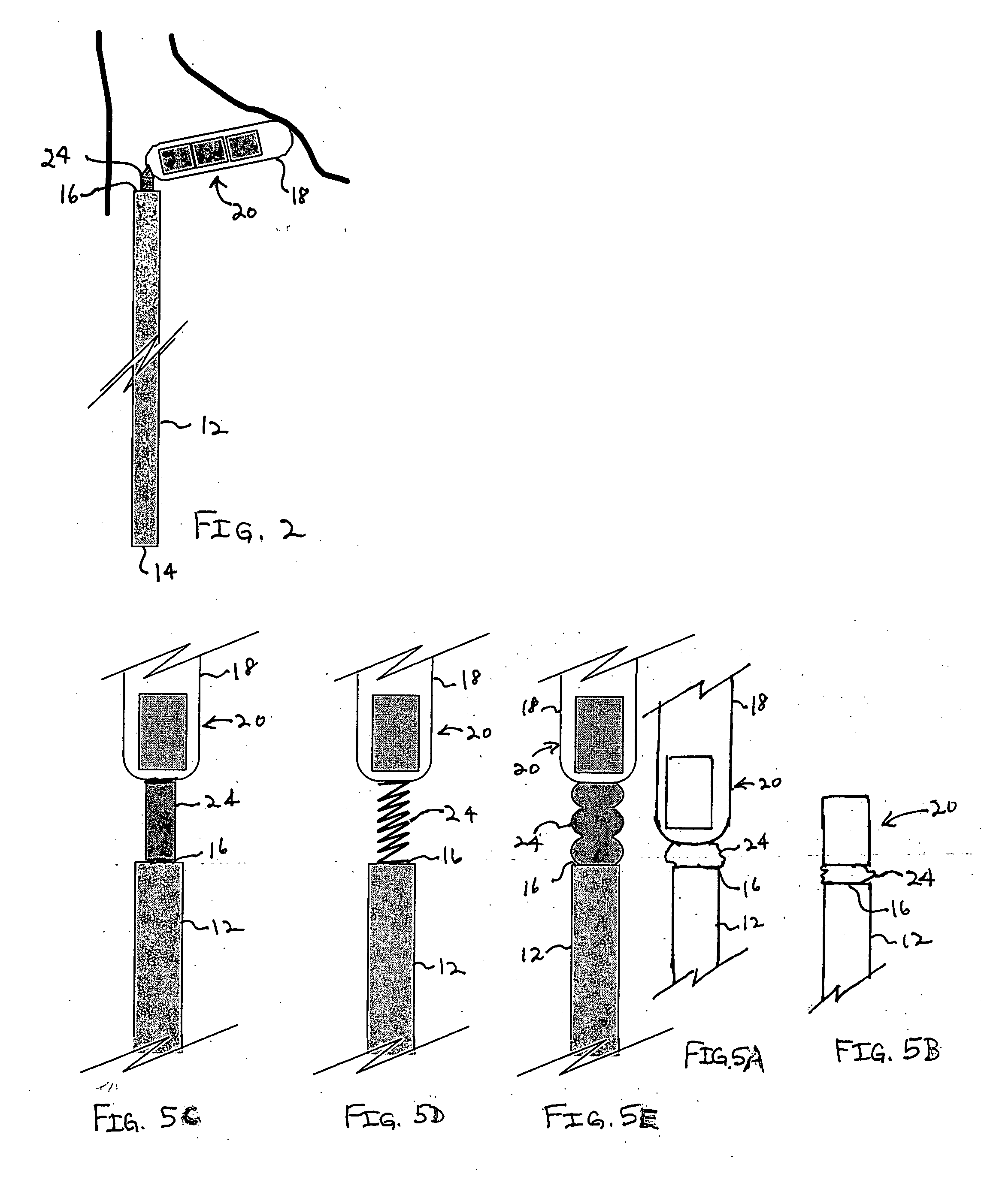
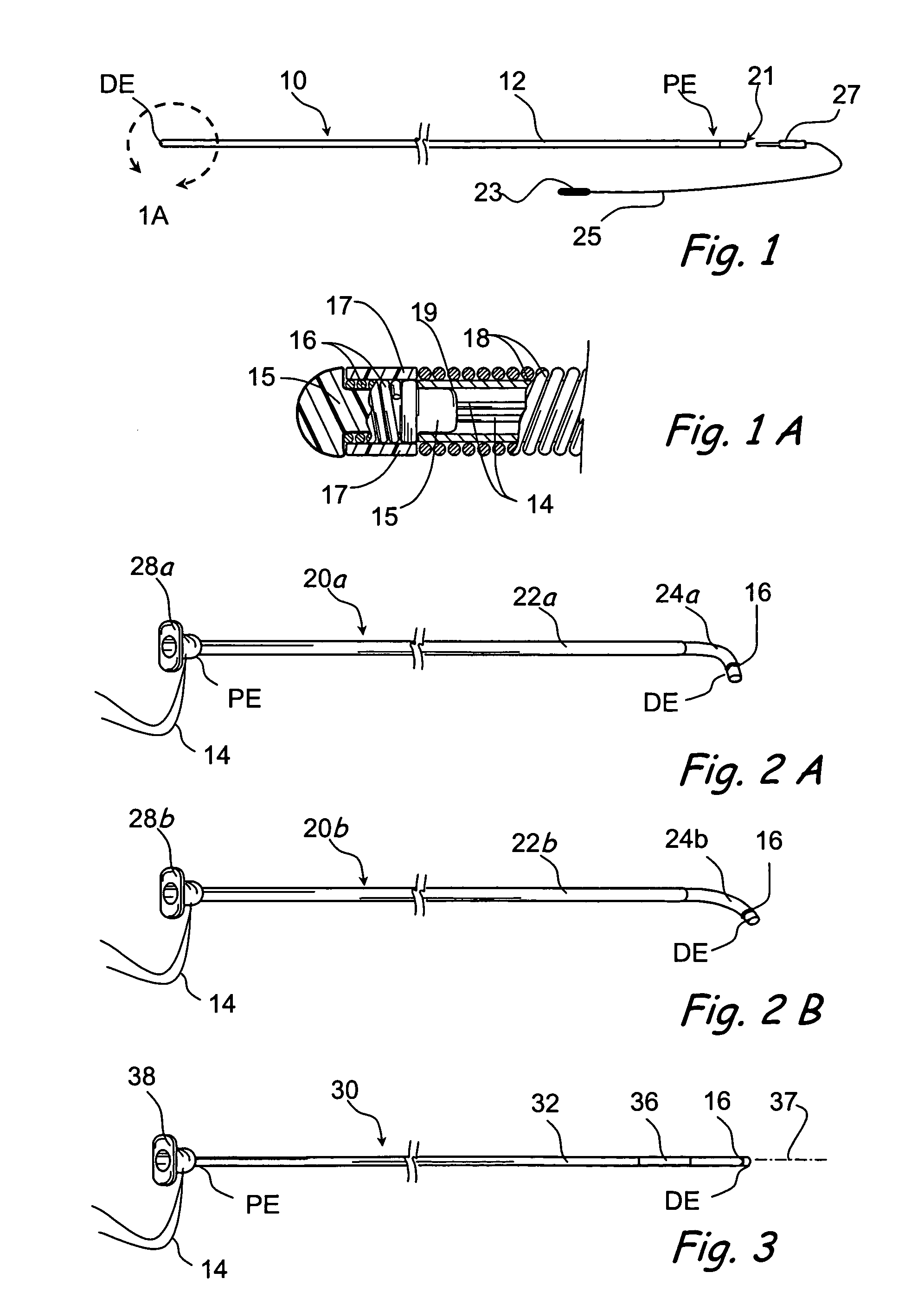
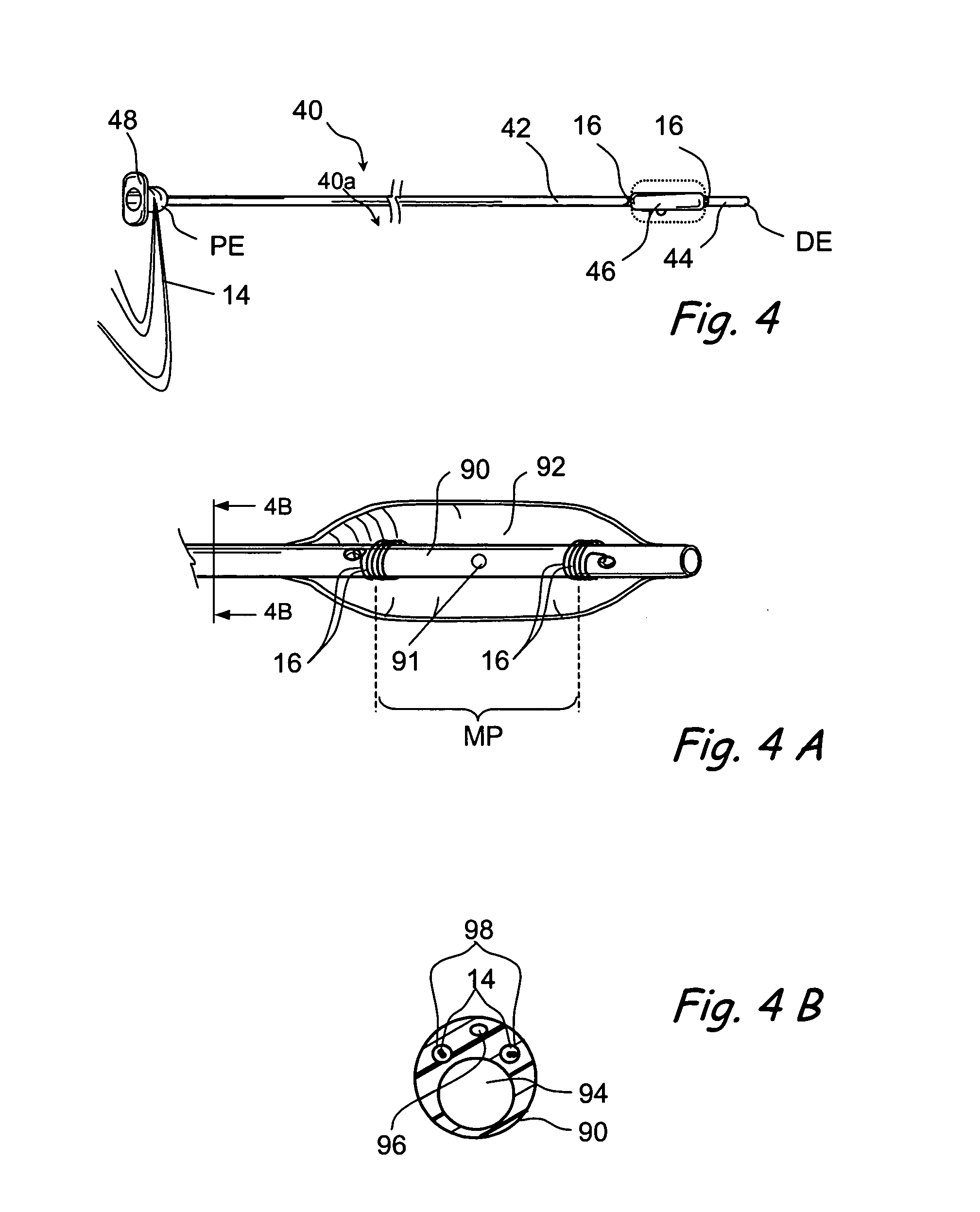
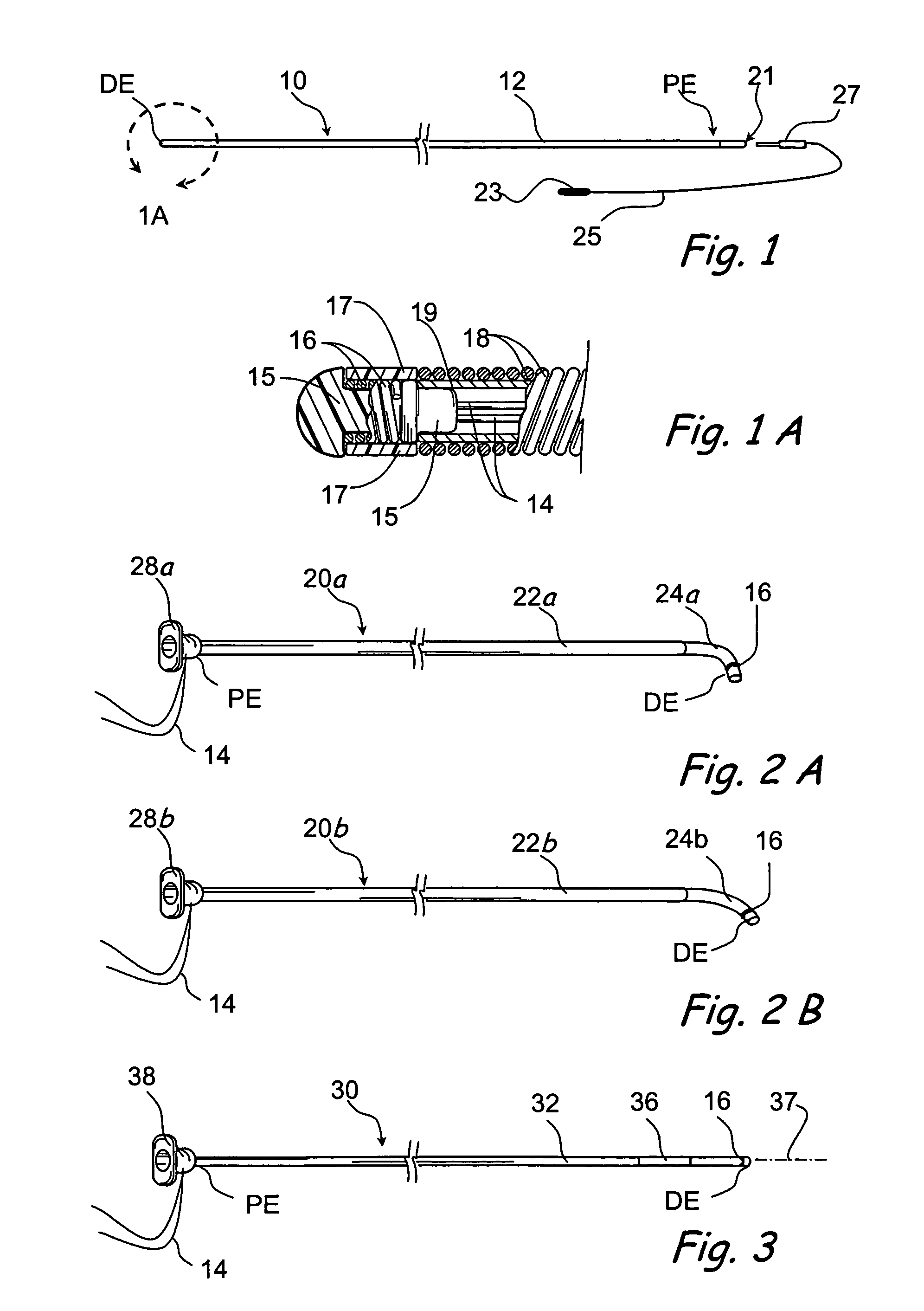
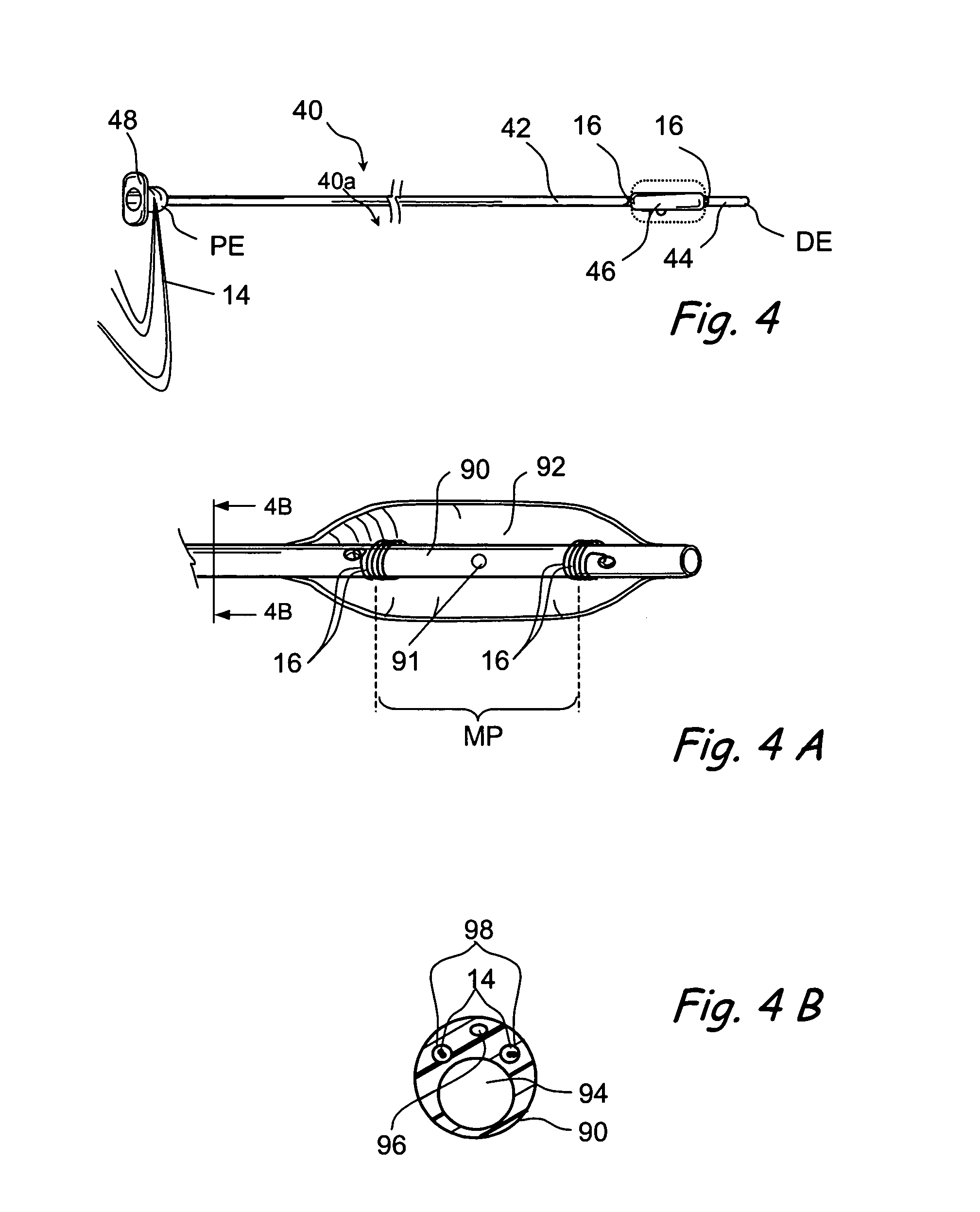
Method and apparatus for indicating an encountered obstacle during insertion of a medical device
A technique for detecting and indicating an internal anatomical obstacle encountered during insertion of a medical device into the body of a patient, comprising an elongated member such as a tube, catheter, guidewire, or other device, having a location indicating element, such as a permanent magnet, flexibly coupled to its distal end, and an external detector that tracks and displays the location and orientation of the location indicating element. The flexible coupling has sufficient stiffness to maintain the orientation of the location indicating element against the forces from both gravity and flowing blood within a patient's vasculature, but allows the location indicating element to change orientation if it encounters an obstacle during insertion. The medical caregiver monitors the detector's display and determines encounters with obstacles by observing changes in the orientation of the location indicating element.
Owner:LUCENT MEDICAL SYST
Tissue biopsy and treatment apparatus and method
InactiveUS6869430B2Improve clinical outcomesPrecise positioningSurgical needlesControlling energy of instrumentSensor arrayTissue biopsy
An embodiment of the invention provides a tissue biopsy and treatment apparatus that comprises an elongated delivery device that is positionable in tissue and includes a lumen. A sensor array having a plurality of resilient members is deployable from the elongated delivery device. At least one of the plurality of resilient members is positionable in the elongated delivery device in a compacted state and deployable with curvature into tissue from the elongated delivery device in a deployed state. At least one of the plurality of resilient members includes at least one of a sensor, a tissue piercing distal end or a lumen. The sensor array has a geometric configuration adapted to volumetrically sample tissue at a tissue site to differentiate or identify tissue at the target tissue site. At least one energy delivery device is coupled to one of the sensor array, at least one of the plurality of resilient members or the elongated delivery device.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Automatic tool marking
Owner:GYRUS ACMI INC (D B A OLYMPUS SURGICAL TECH AMERICA)
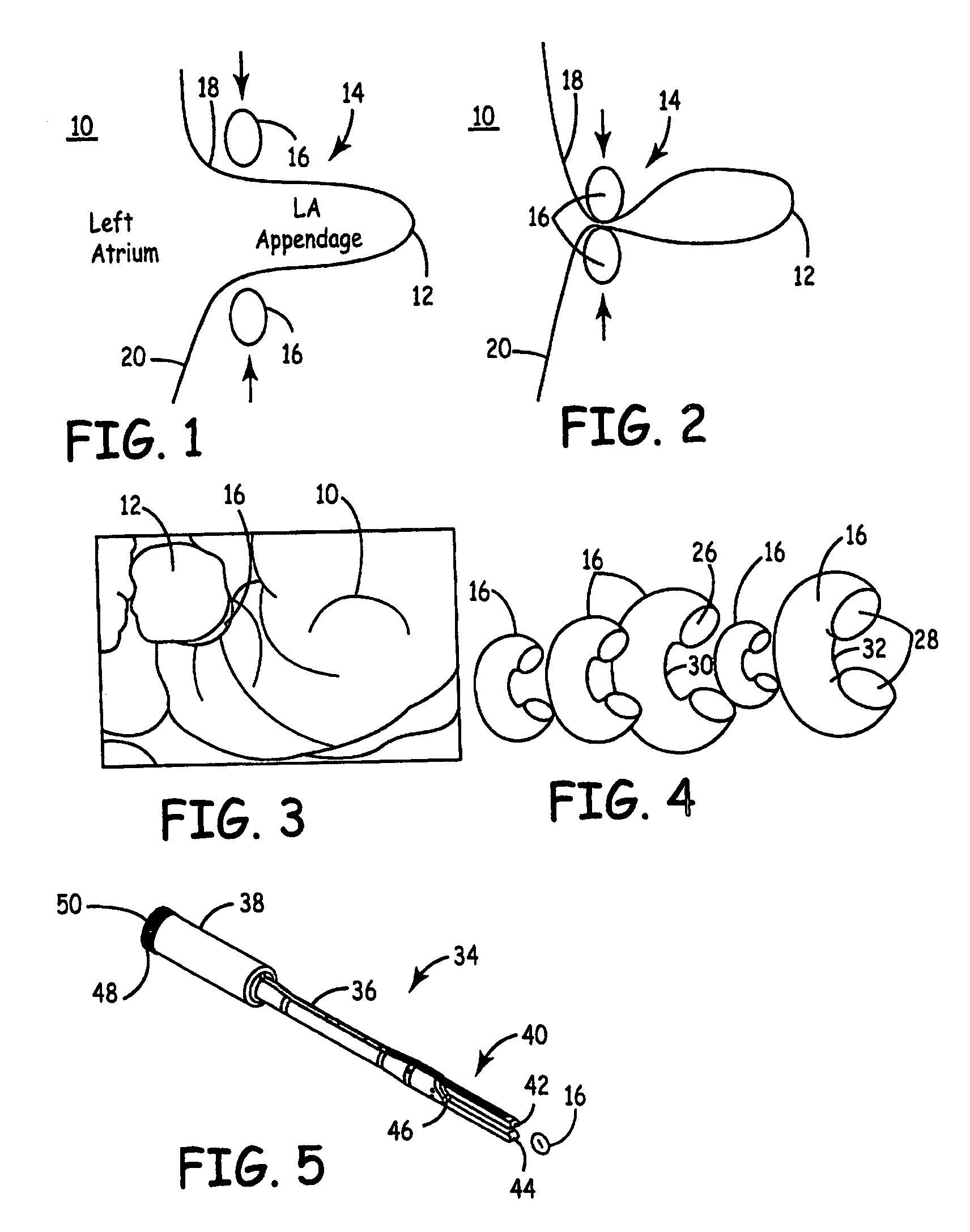
Device for occlusion of a left atrial appendage
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and method for a tissue resection margin measurement device
ActiveUS20160192960A1Minimally invasiveCompensation for deformationMedical imagingSurgical needlesMeasurement deviceVisual perception
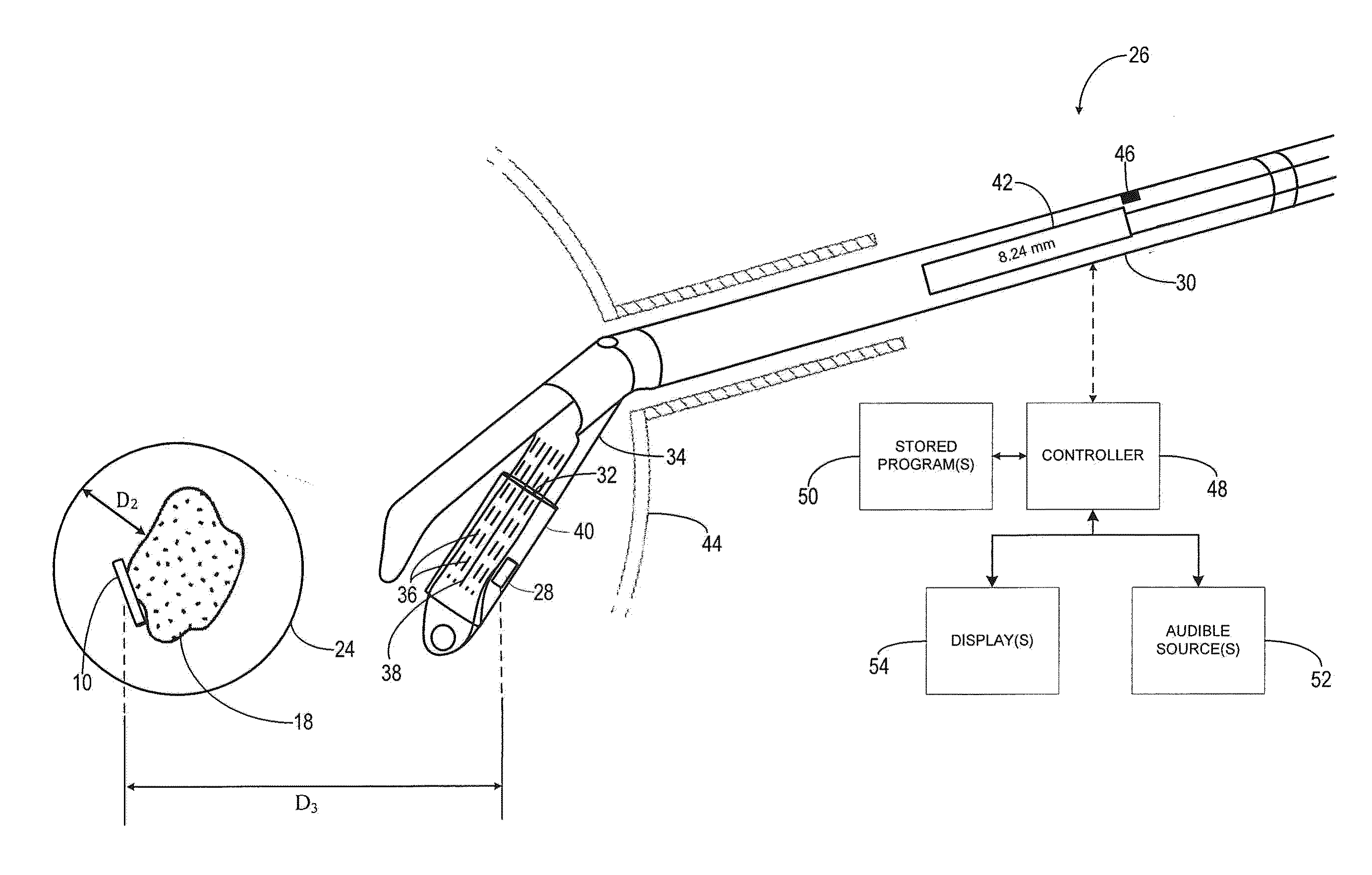
Embodiments of the invention provide a system and method for resecting a tissue mass. The system for resecting a tissue mass includes a surgical instrument and a first sensor for measuring a signal corresponding to the position and orientation of the tissue mass. The first sensor is dimensioned to fit insider or next to the tissue mass. The system also includes a second sensor attached to the surgical instrument configured to measure the position and orientation of the surgical instrument. The second sensor is configured to receive the signal from the first sensor. A controller is in communication with the first sensor and / or the second sensor, and the controller executes a stored program to calculate a distance between the first sensor and the second sensor. Accordingly, visual, auditory, haptic or other feedback is provided to the clinician to guide the surgical instrument to the surgical margin.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
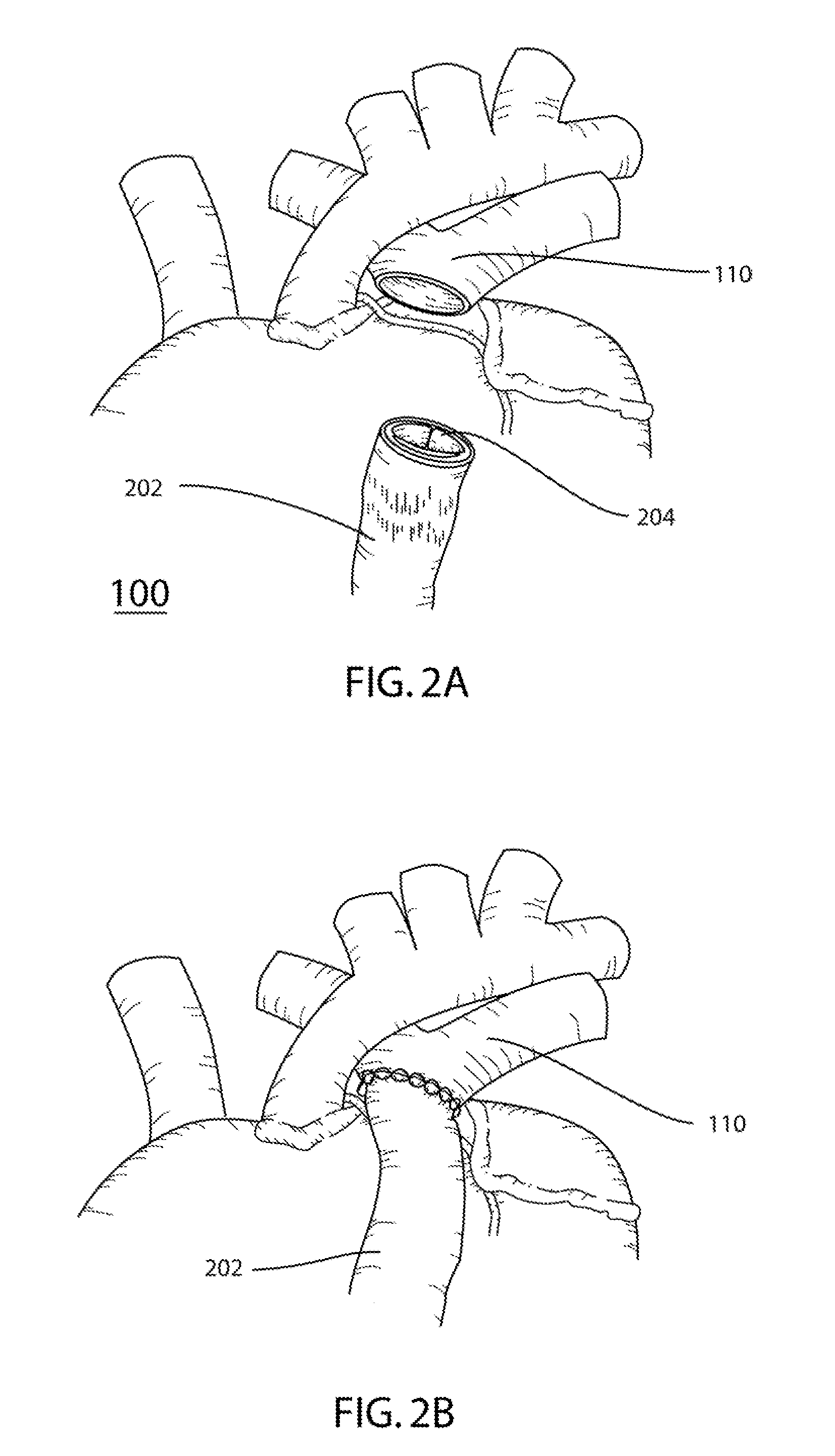
Coated Surgical Staples and an Illuminated Staple Cartridge for a Surgical Stapling Instrument
ActiveUS20090114701A1Increase awarenessReduce reflectivitySuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical stapleEngineering
A coated surgical fastener is provided for an easy visualization within tissue. The coated surgical fastener includes a core and a relatively non-reflective coating applied about the core. There is also disclosed an illuminated staple cartridge for use with a surgical stapling device having a light source. The illuminated staple cartridge includes a transparent insert and a relatively nontransparent U-shaped outer channel at least partially surrounding the transparent insert. Windows formed in sides of the U-shaped outer channel allow defined amounts of light to project from the sides of the illuminated staple cartridge.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Interbody fusion grafts and instrumentation
InactiveUS7479160B2Maintain disc heightMaintain distractionInternal osteosythesisBone implantMedicineDonor bone
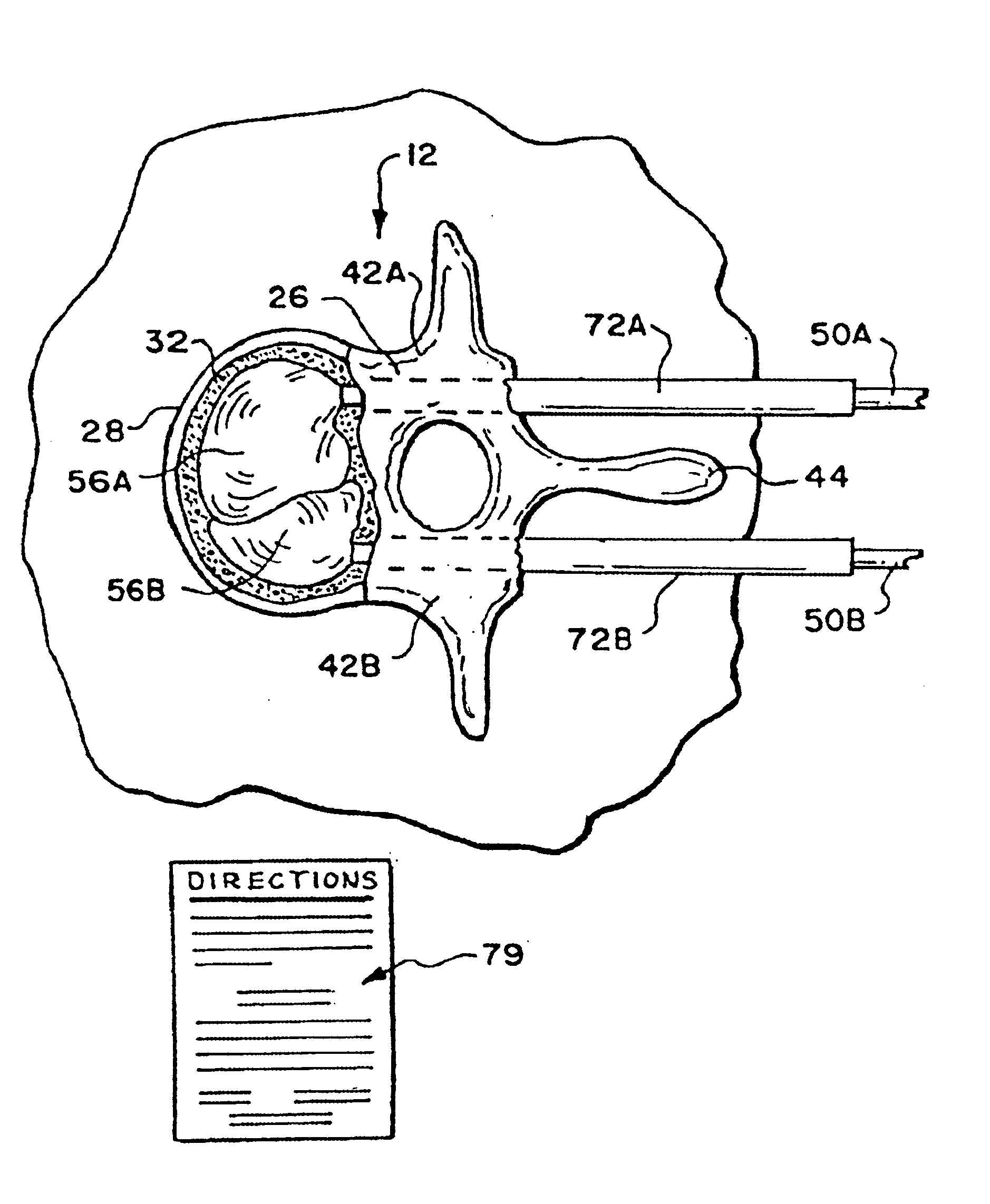
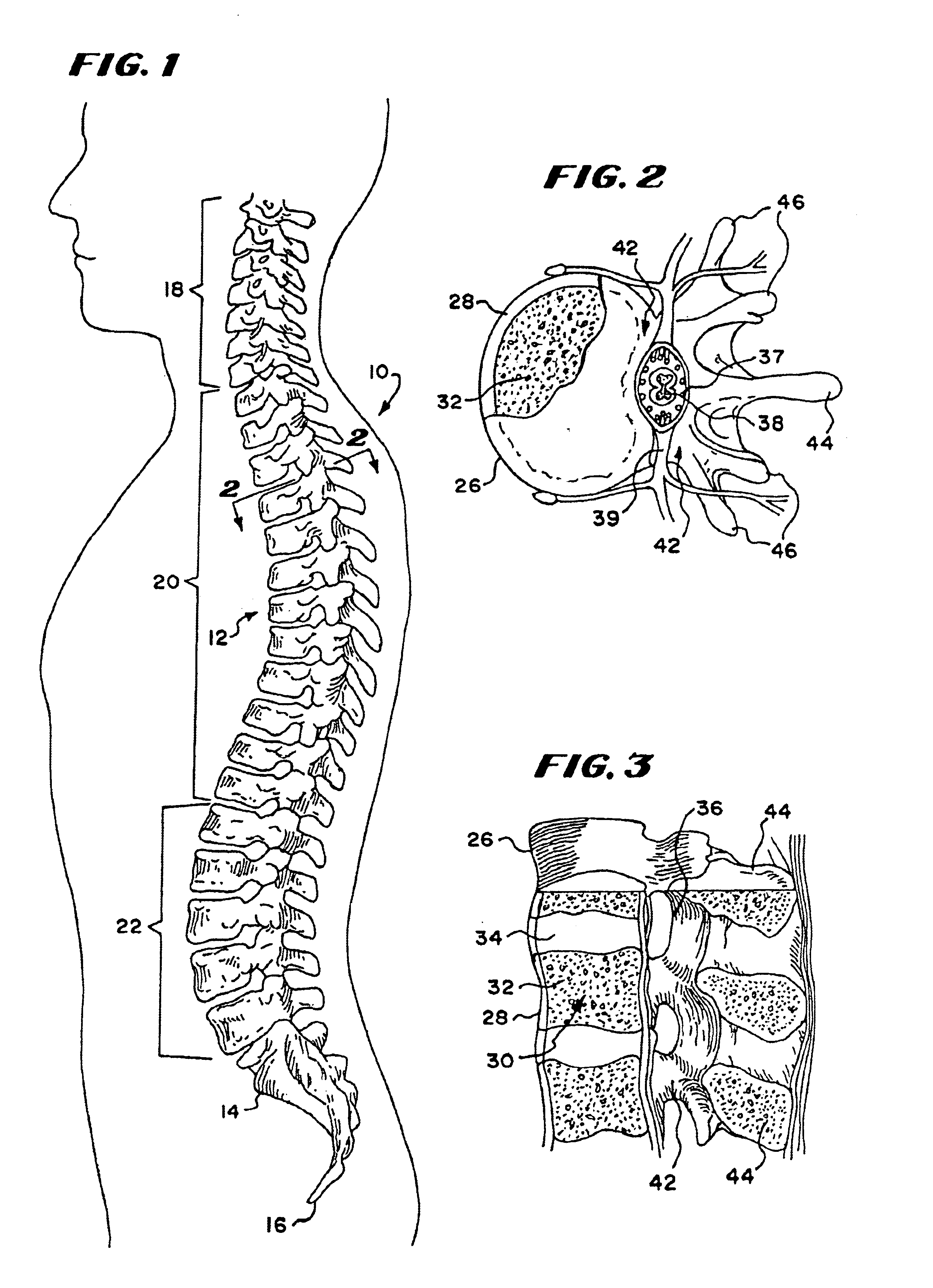
This invention relates to implants formed from donor bone for use in lumbar interbody fusion procedures and instruments for performing such procedures. The implants are formed to include a concave surface formed from a portion of the medullary canal of a long bone. The concaved surface defines a recess in the implant that serves as a depot for osteogenic material. Specific instruments for inserting the implants prepared according to this invention and for preparing the intervertebral space to receive the implants are also provided.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
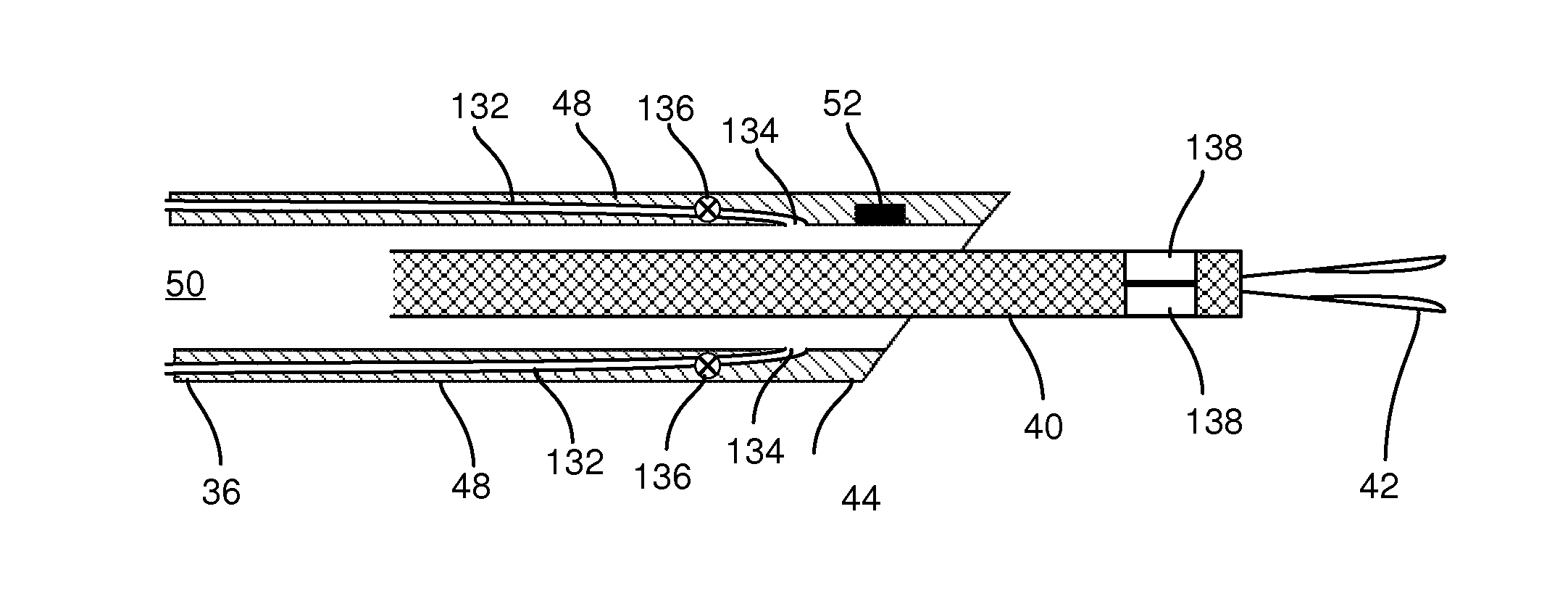
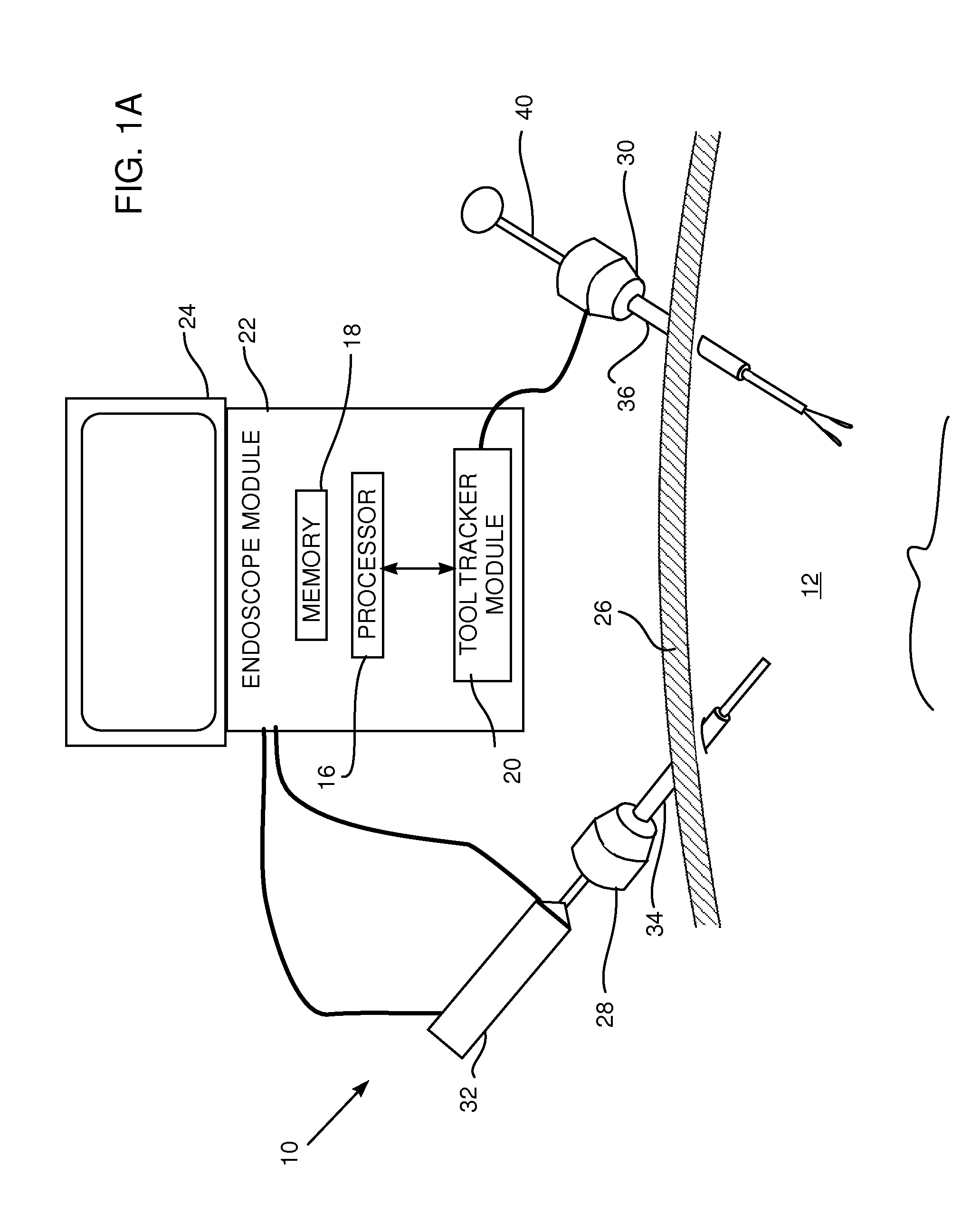
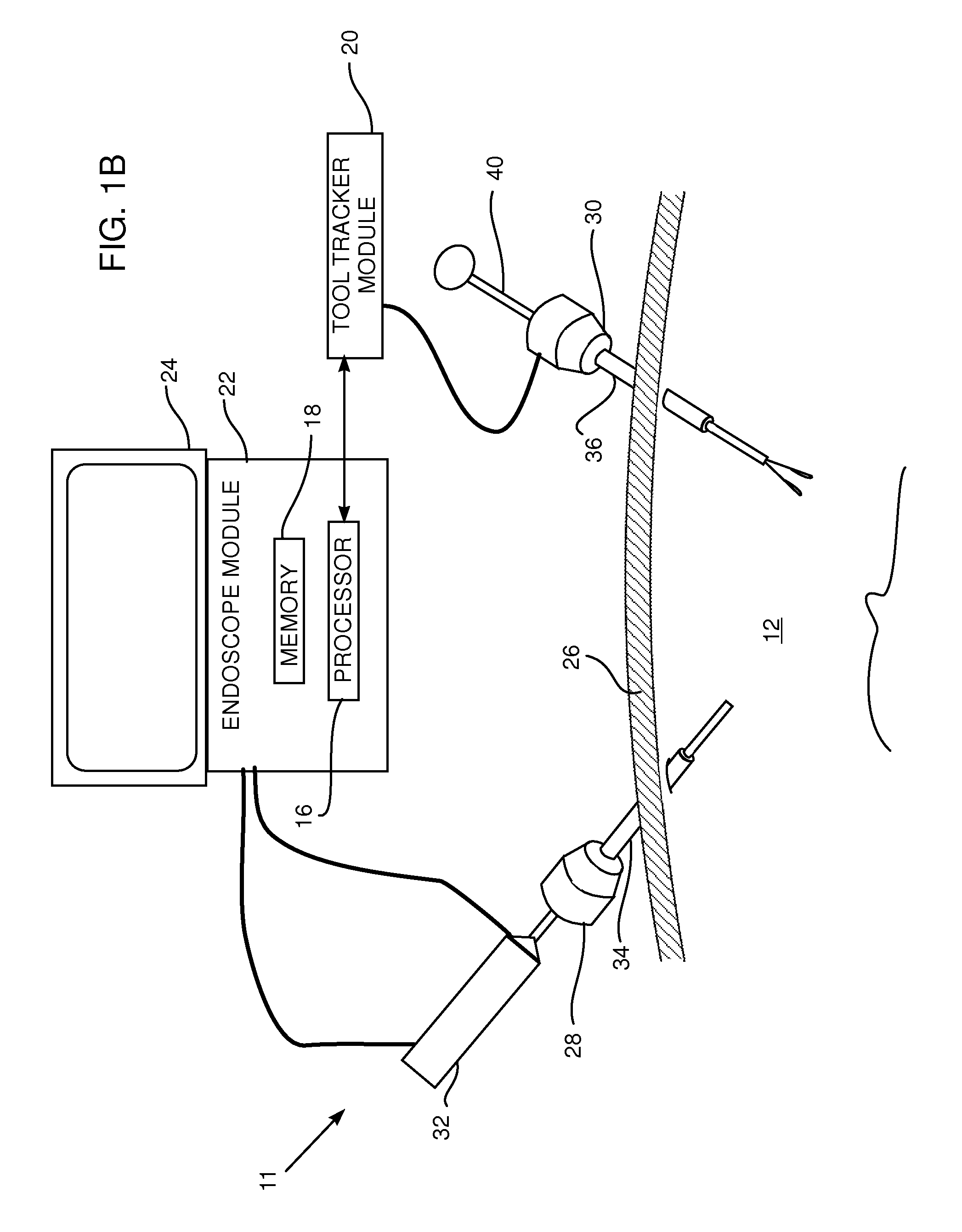
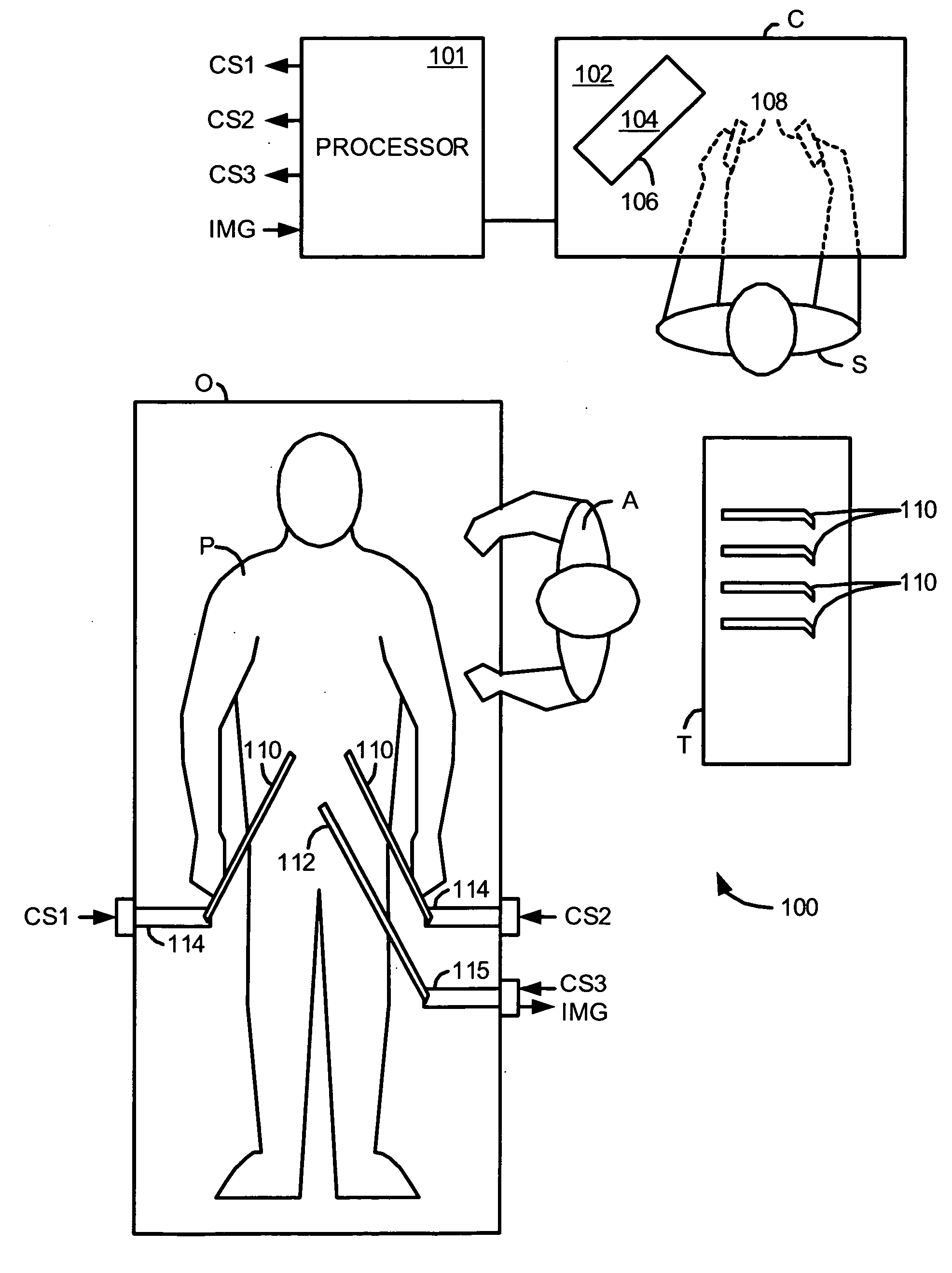
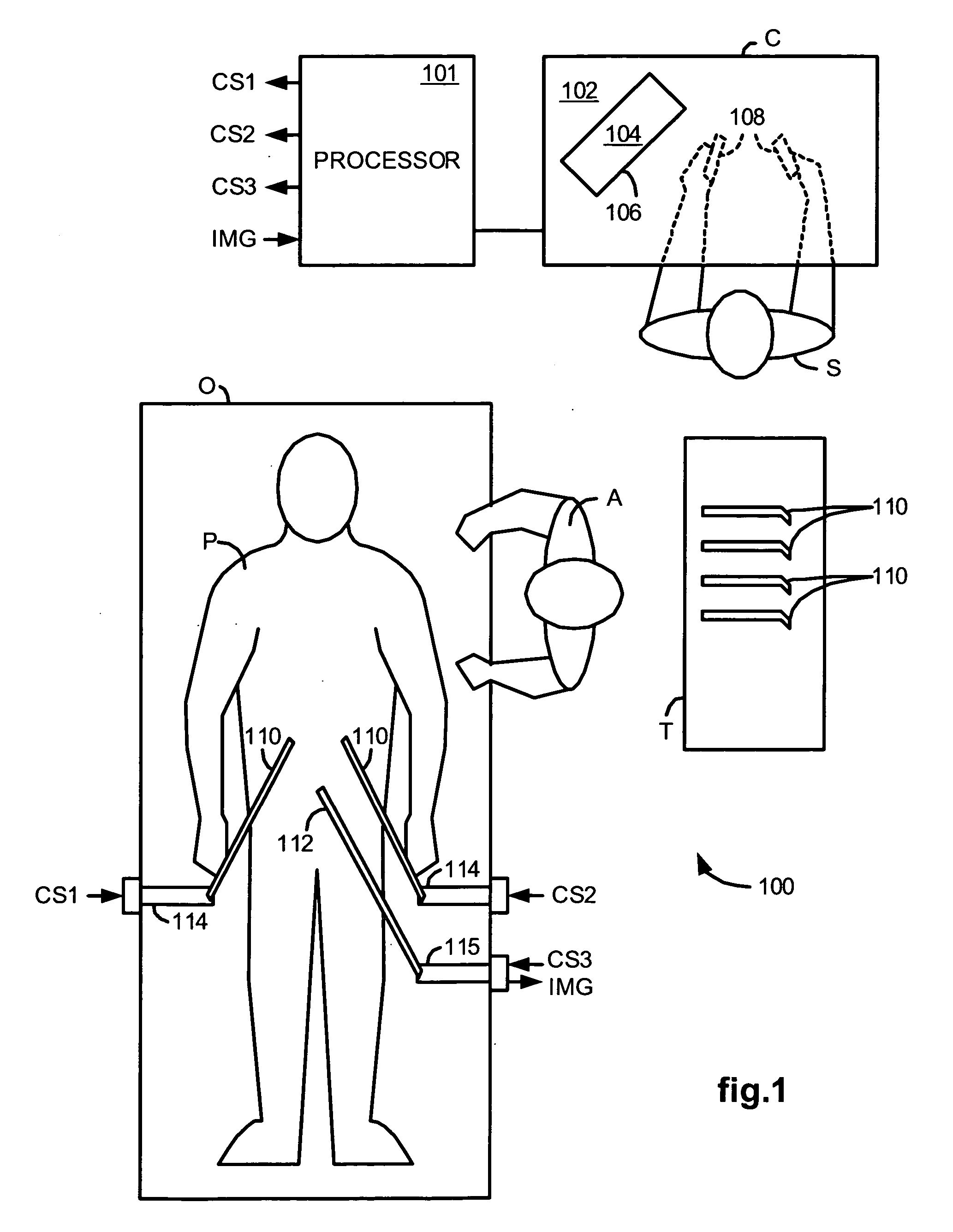
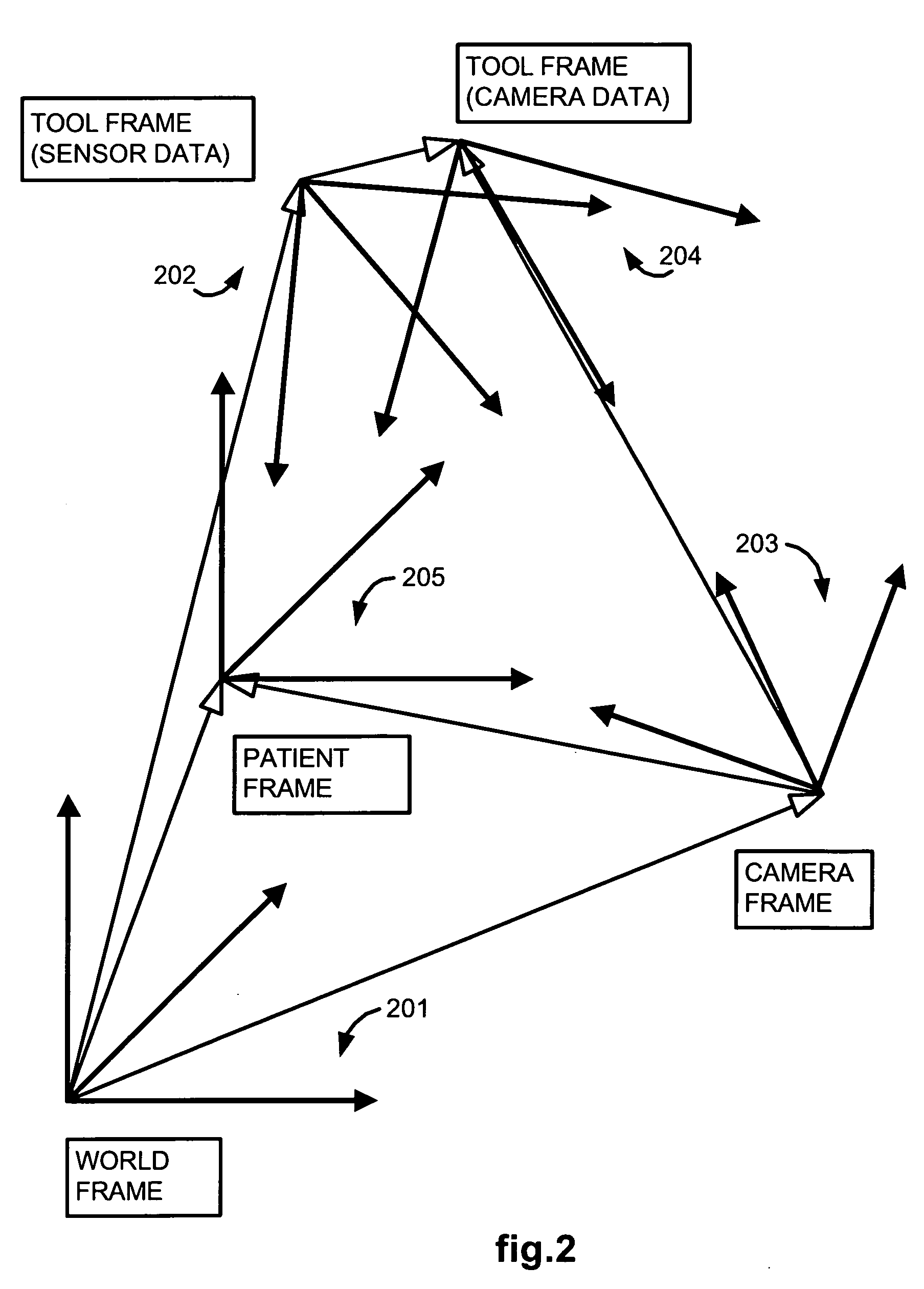
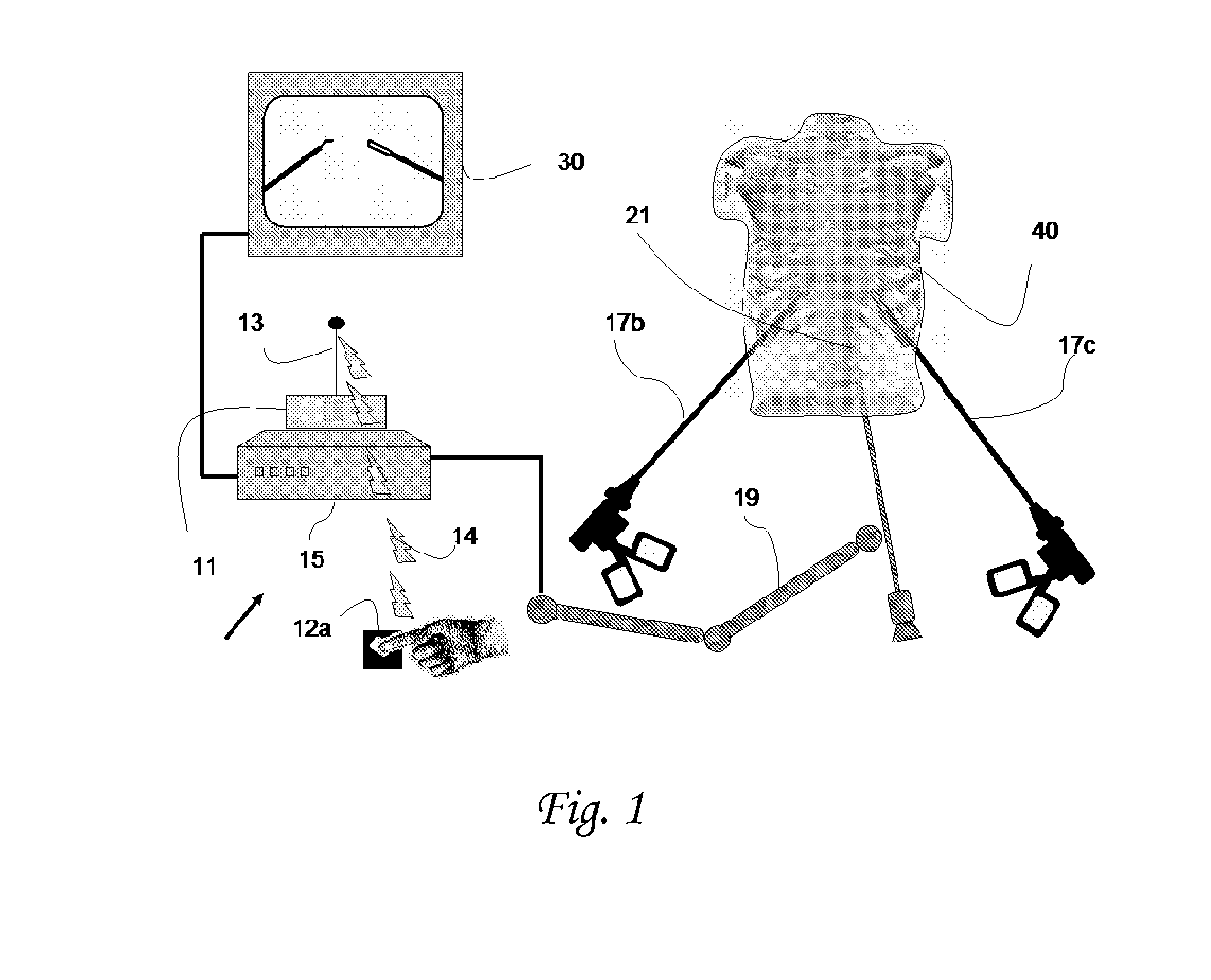
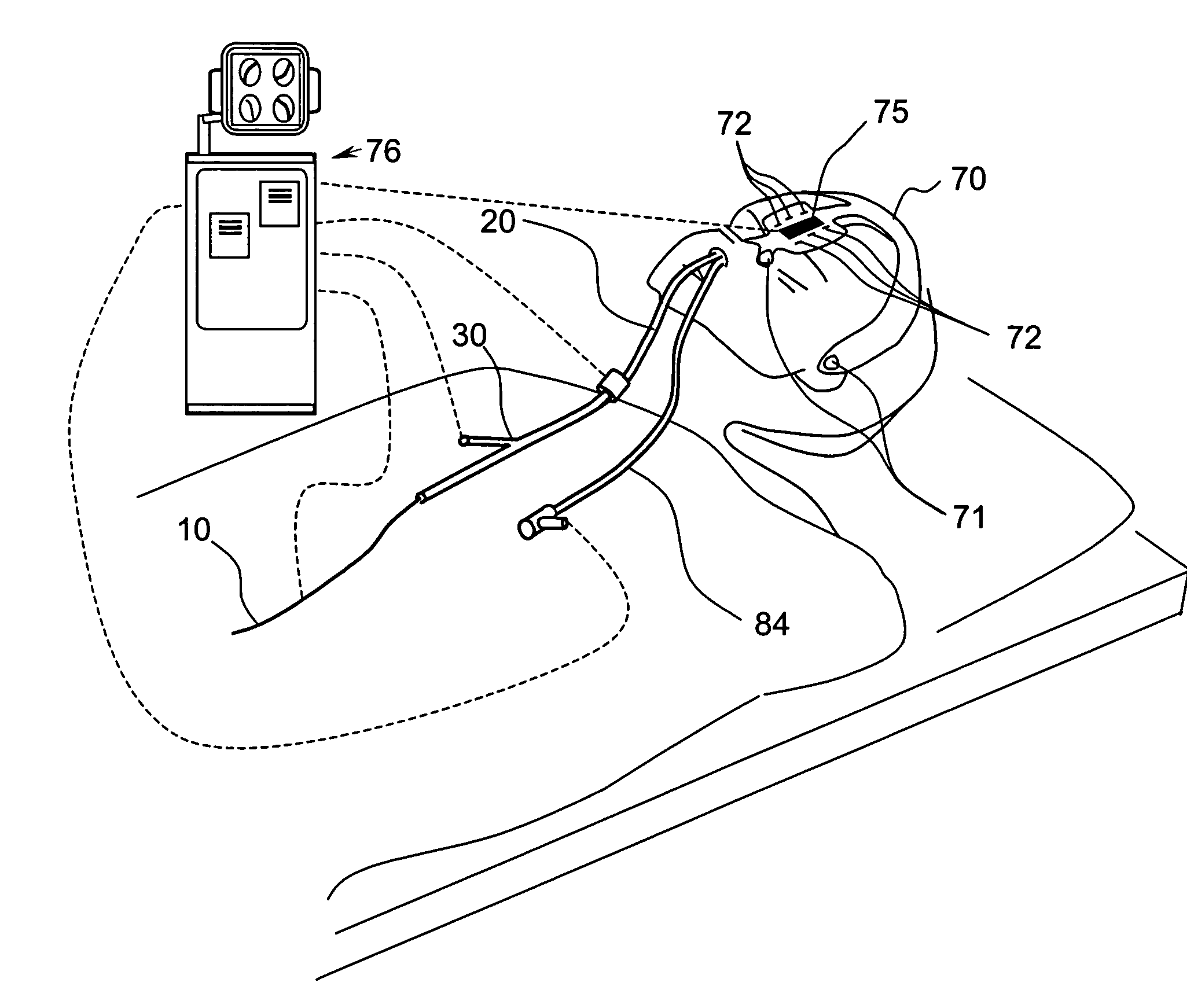
Methods and system for performing 3-D tool tracking by fusion of sensor and/or camera derived data during minimally invasive robotic surgery
ActiveUS20060258938A1Easy to distinguishFacilitate communicationSurgical navigation systemsLaproscopesTriangulationExternal camera
Methods and system perform tool tracking during minimally invasive robotic surgery. Tool states are determined using triangulation techniques or a Bayesian filter from either or both non-endoscopically derived and endoscopically derived tool state information, or from either or both non-visually derived and visually derived tool state information. The non-endoscopically derived tool state information is derived from sensor data provided either by sensors associated with a mechanism for manipulating the tool, or sensors capable of detecting identifiable signals emanating or reflecting from the tool and indicative of its position, or external cameras viewing an end of the tool extending out of the body. The endoscopically derived tool state information is derived from image data provided by an endoscope inserted in the body so as to view the tool.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Methods and devices for performing procedures within the ear, nose, throat and paranasal sinuses
Devices, systems and methods for performing image guided interventional and surgical procedures, including various procedures to treat sinusitis and other disorders of the paranasal sinuses, ears, nose or throat.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
Methods and devices for improving percutaneous access in minimally invasive surgeries
ActiveUS20050065517A1Reduce the difficulty of operationReduce riskInternal osteosythesisCannulasLess invasive surgeryPost operative
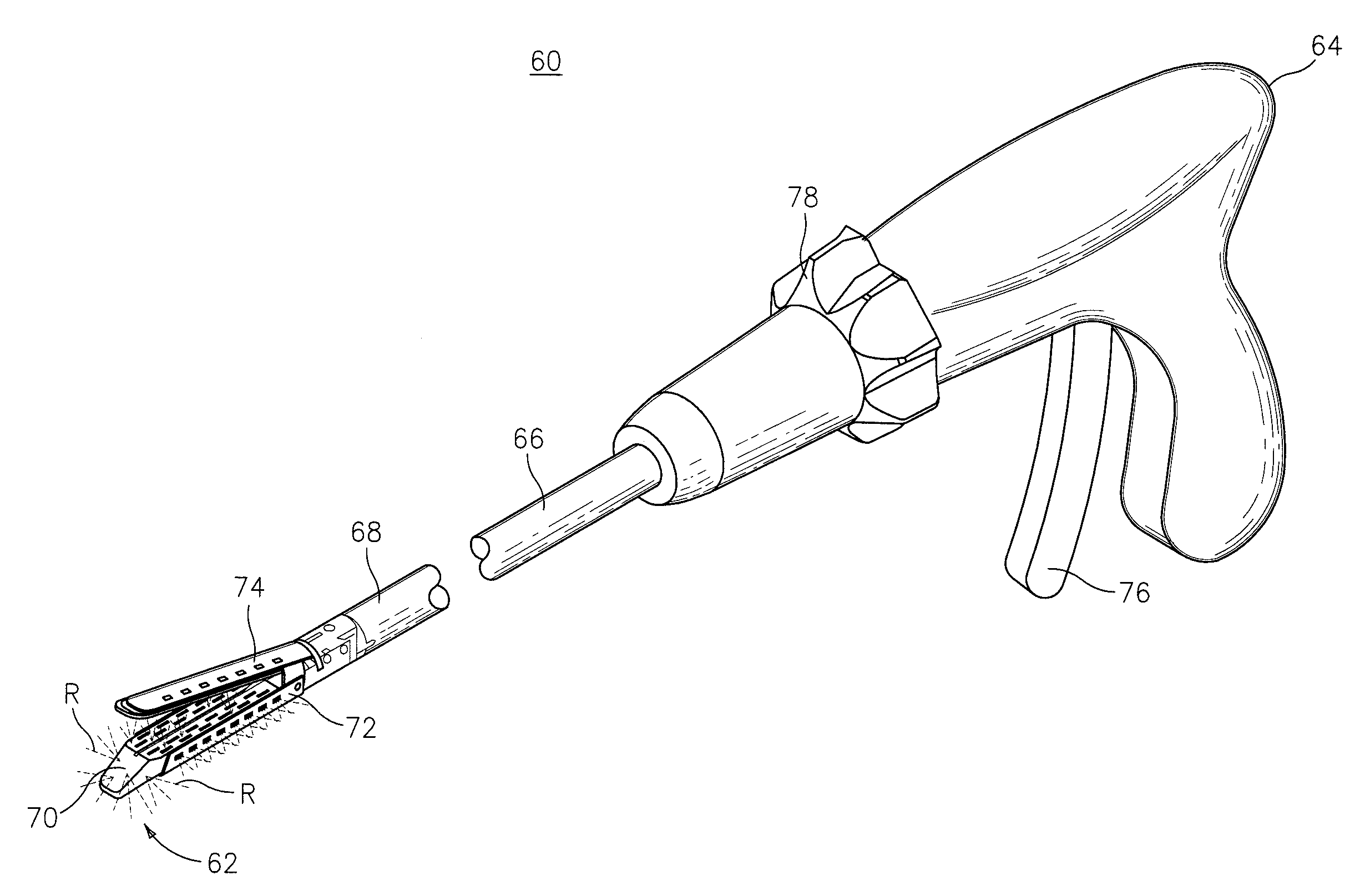
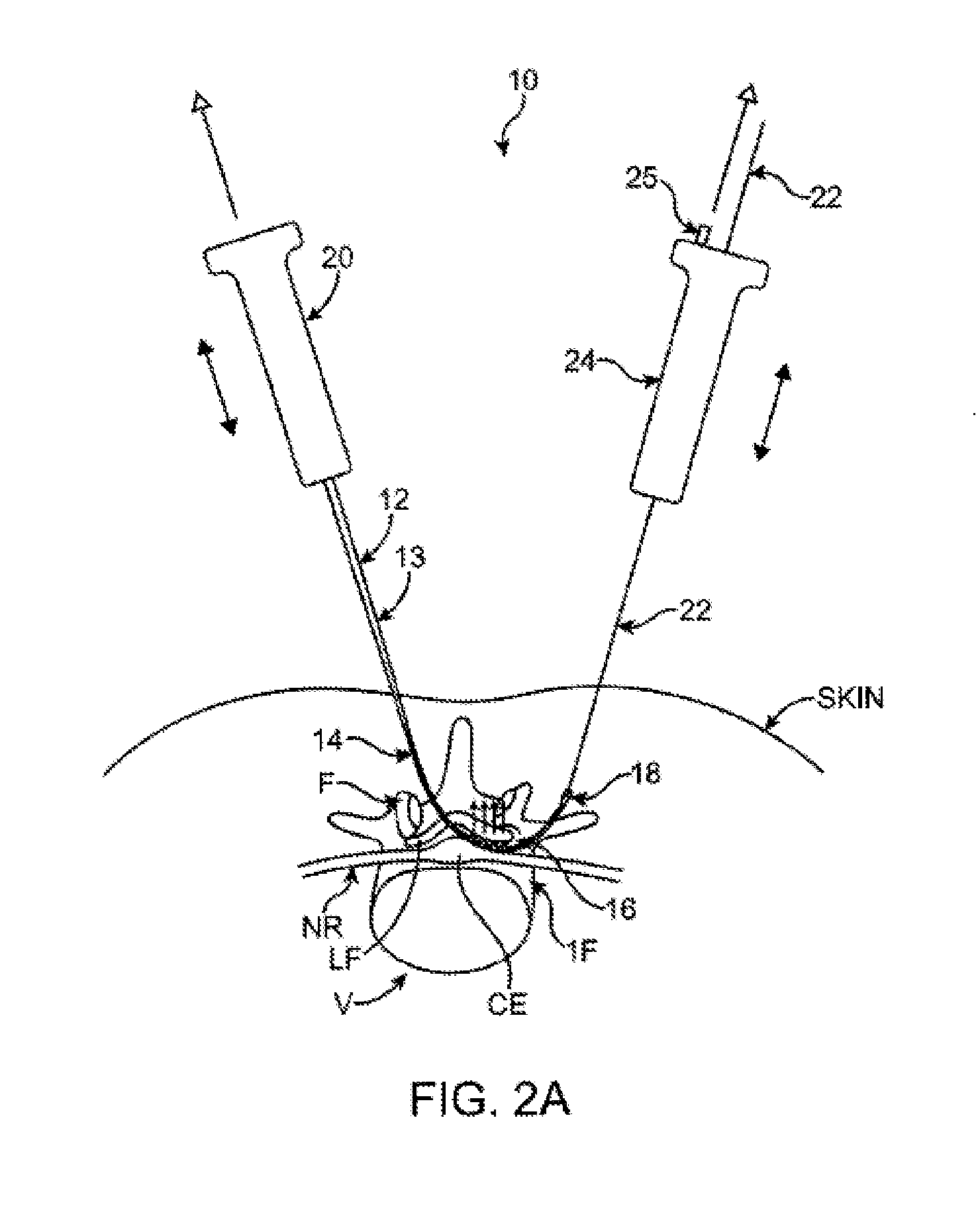
A device for use as a portal in percutaneous minimally invasive surgery performed within a patient's body cavity includes a first elongated hollow tube having a length adjusted with a self-contained mechanism. The first elongated tube includes an inner hollow tube and an outer hollow tube and the inner tube is adapted to slide within the outer tube thereby providing the self-contained length adjusting mechanism. This length-adjustment feature is advantageous for percutaneous access surgery in any body cavity. Two or more elongated tubes with adjustable lengths can be placed into two or more adjacent body cavities, respectively. Paths are opened within the tissue areas between the two or more body cavities, and are used to transfer devices and tools between the adjacent body cavities. This system of two or more elongated tubes with adjustable lengths is particularly advantageous in percutaneous minimally invasive spinal surgeries, and provides the benefits of minimizing long incisions, recovery time and post-operative complications.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Device and method for assisting laparoscopic surgery - rule based approach
InactiveUS20140228632A1Prevent movementConstant field of viewUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesImaging processingControl system
The present invention provides a surgical controlling system, comprising: a. at least one endoscope adapted to provide real-time image of surgical environment of a human body; b. at least one processing means, adapted to real time define n element within said real-time image of surgical environment of a human body; each of said elements is characterized by predetermined characteristics; c. image processing means in communication with said endoscope, adapted to image process said real-time image and to provide real time updates of said predetermined characteristics; d. a communicable database, in communication with said processing means and said image processing means, adapted to store said predetermined characteristics and said updated characteristics; wherein said system is adapted to notify if said updated characteristics are substantially different from said predetermined characteristics.
Owner:TRANSENTERIX EURO SARL
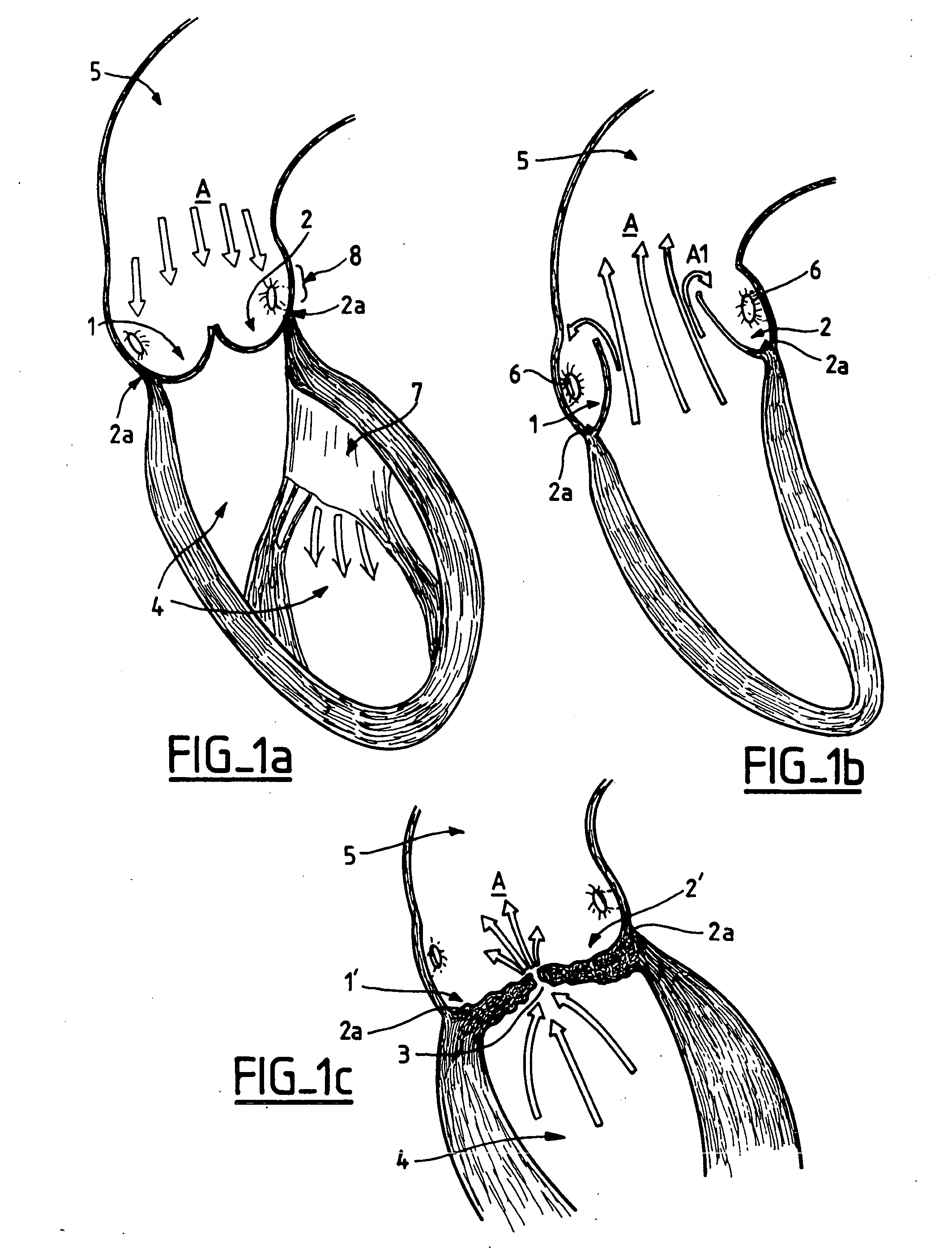
Device, system, and method for aiding valve annuloplasty
A device comprising a reference ring that may be temporarily disposed in abutment with the inferior perimeter surface of a heart valve to aid non-optical visualization of the valve annulus. The reference ring is elastically transformable between a straight delivery configuration and a generally circular or helical deployment configuration. The reference ring may include an inflatable portion that can be temporarily expanded on the inferior side of the valve annulus to deform the valve annulus into a temporary ledge or shelf for apposition with an annuloplasty ring. A system comprising a delivery catheter including a lumen with an exit port, the reference ring being slidably positionable within the lumen and being extendable from the exit port.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
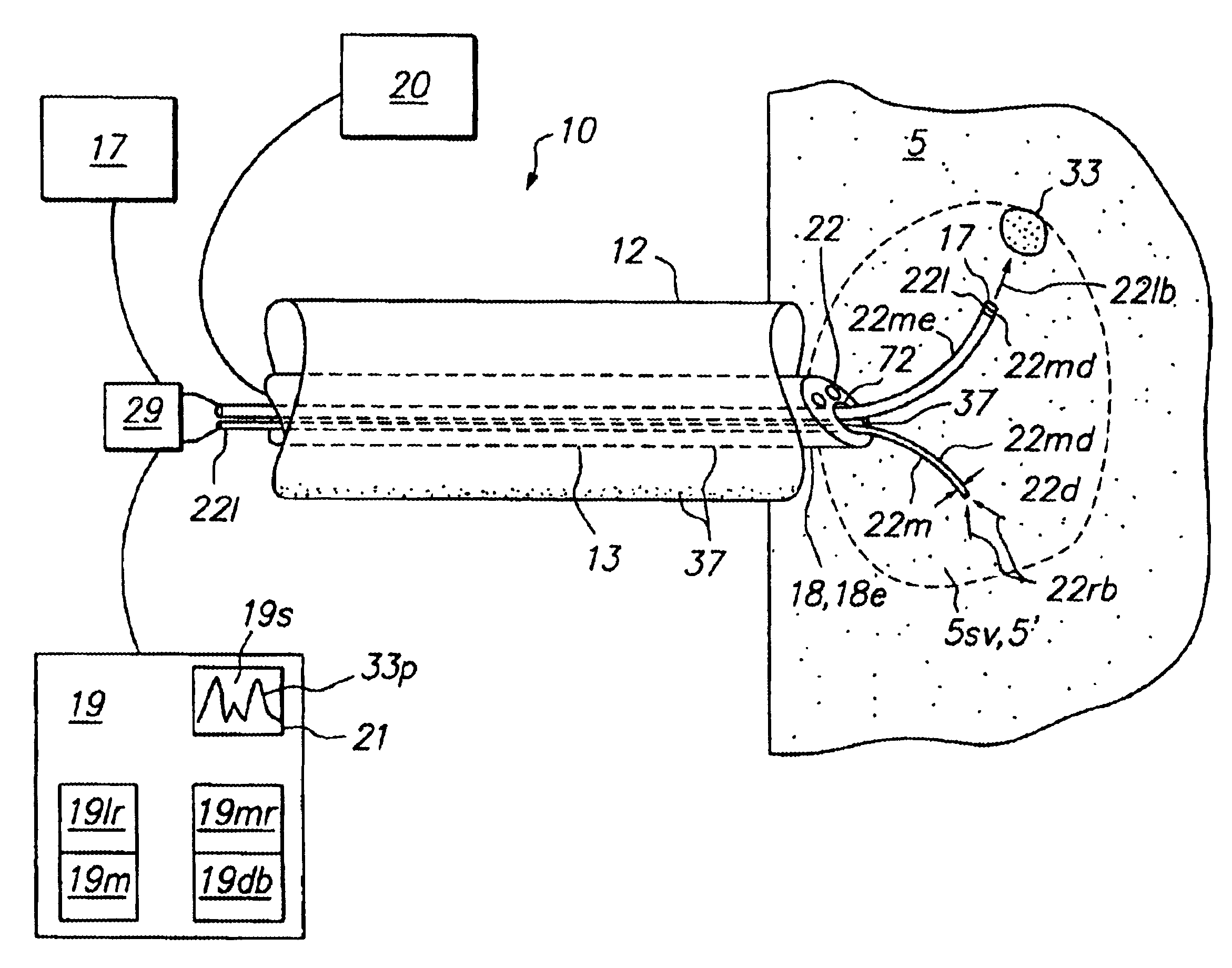
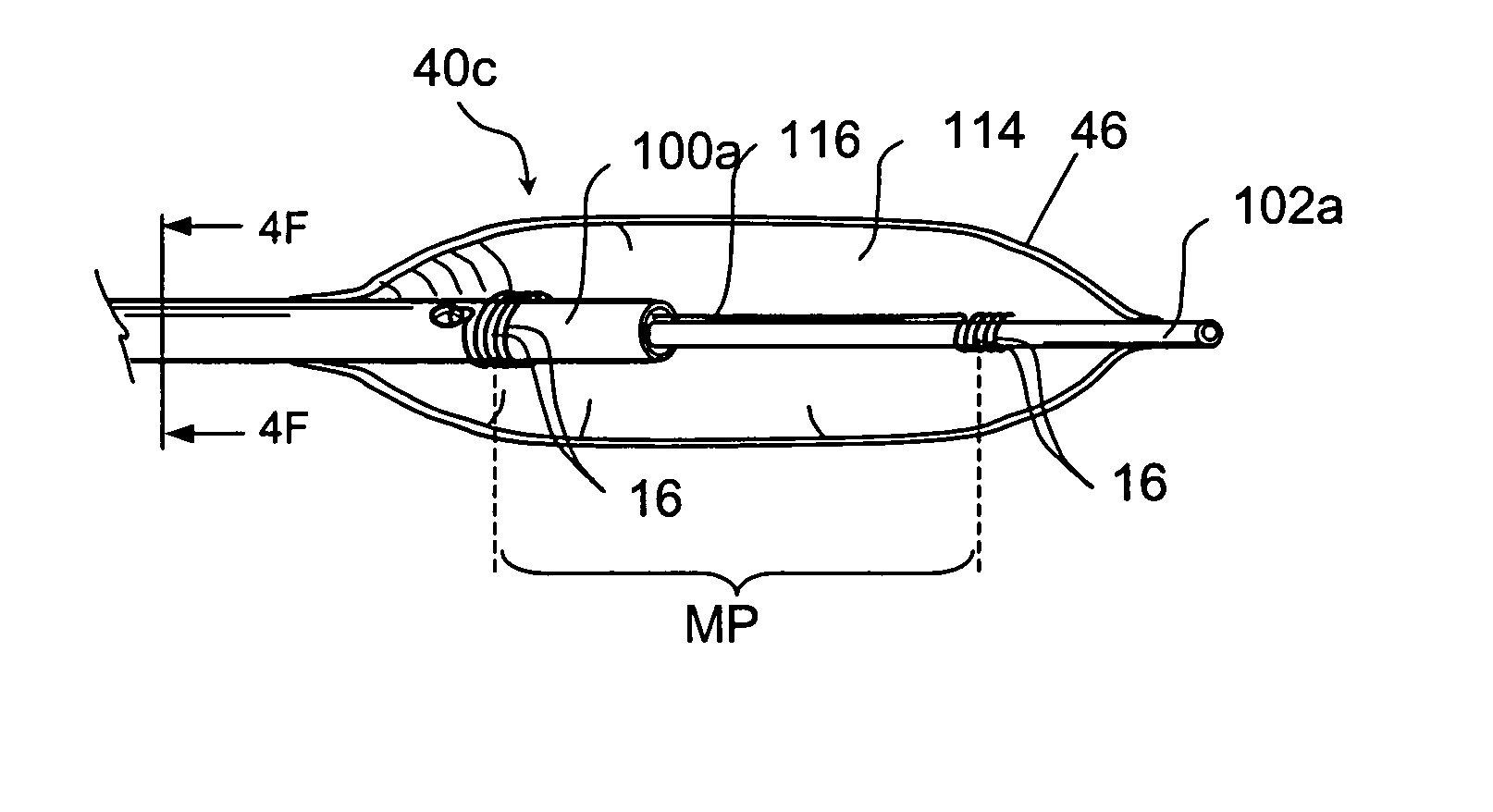
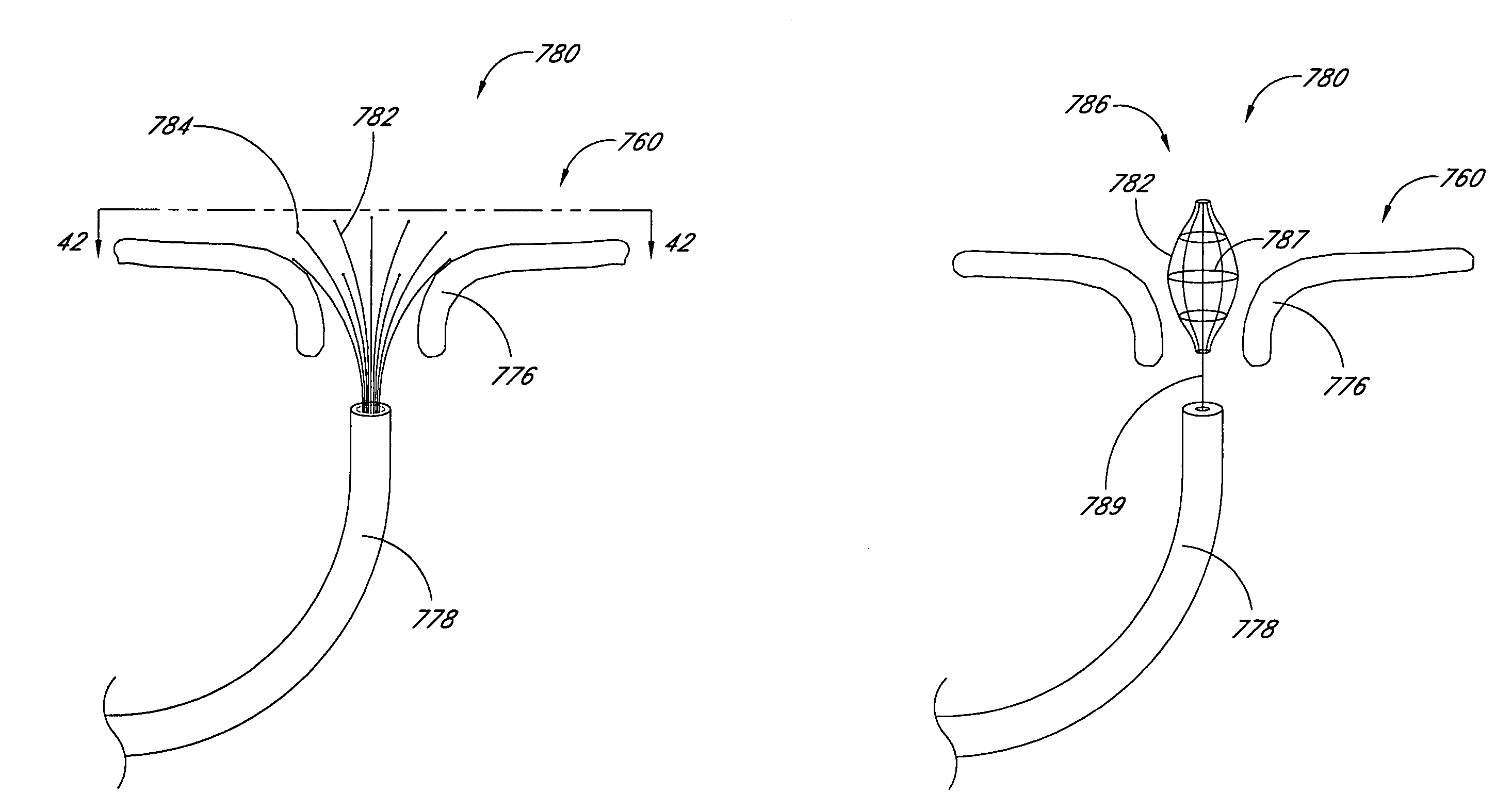
Heart valve leaflet locator
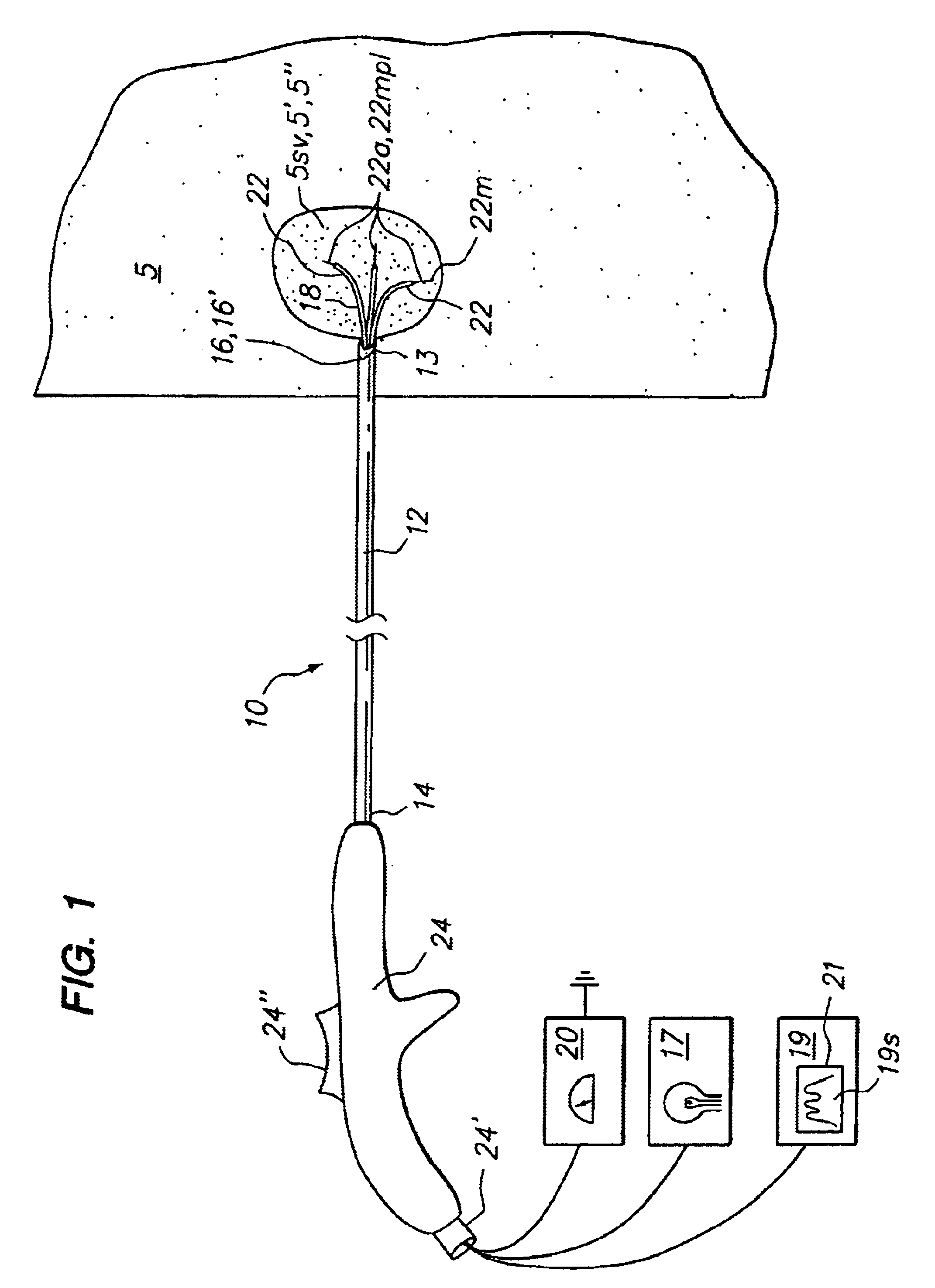
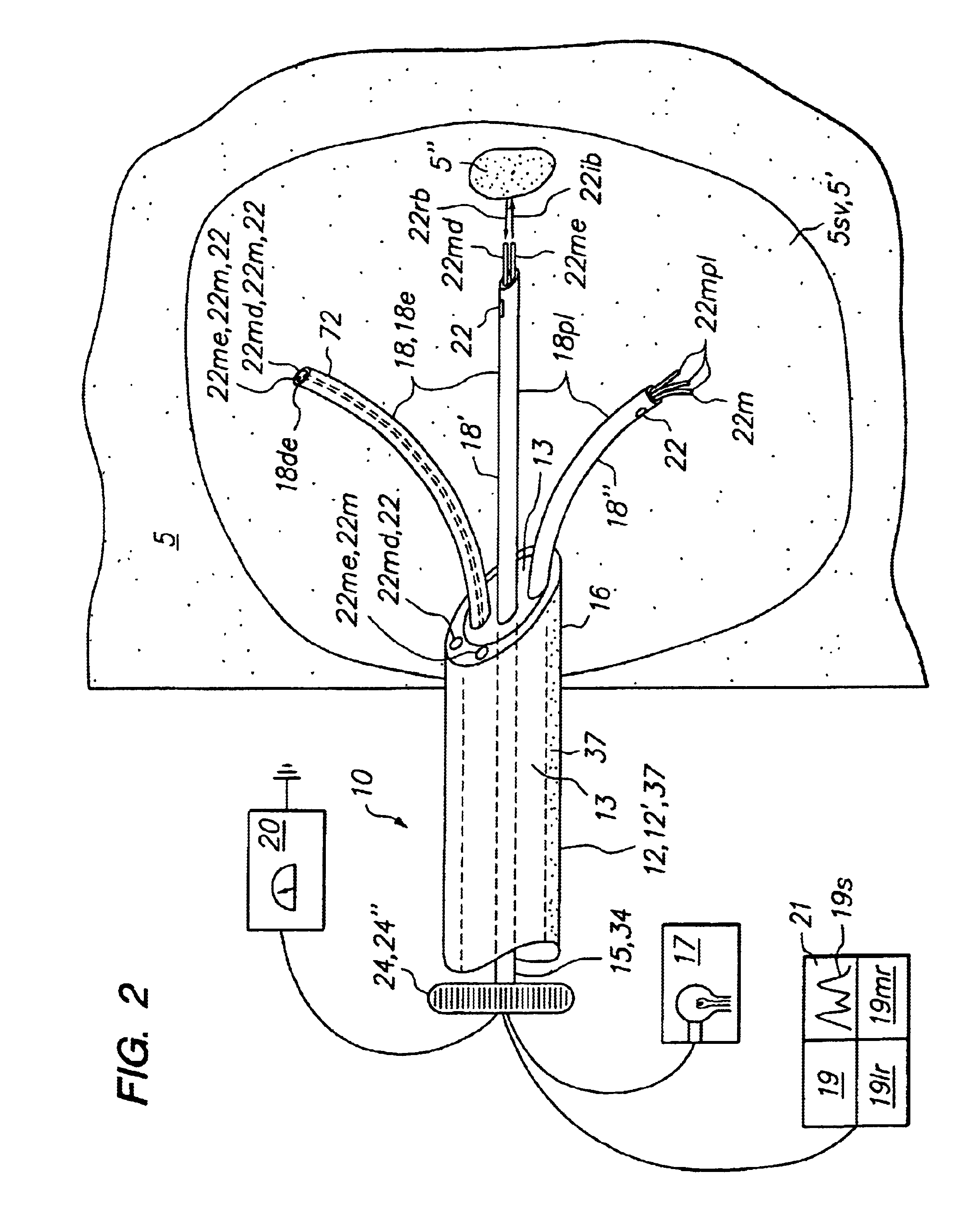
Disclosed are methods and devices for determining valve leaflet orientation. A catheter is provided with a conformable, radiopaque target. The target is deployed within a valve, such as the mitral valve. The conformable target conforms to the coaptation axis in response to closing of the valve leaflets. That coaptation axis may then be visualized, and utilized to determine information about valve operation, or to assist in placement of devices in the vicinity of the valve.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
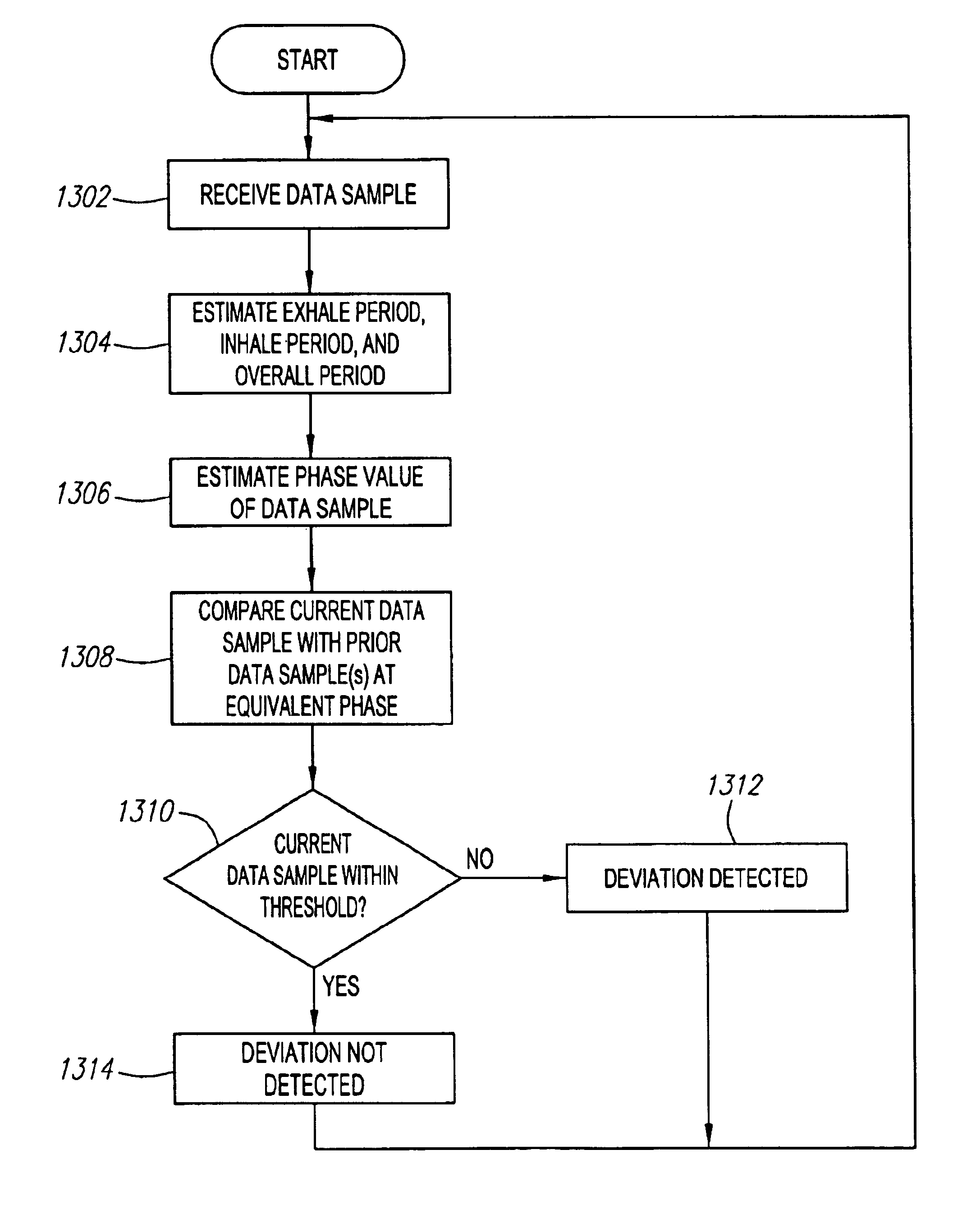
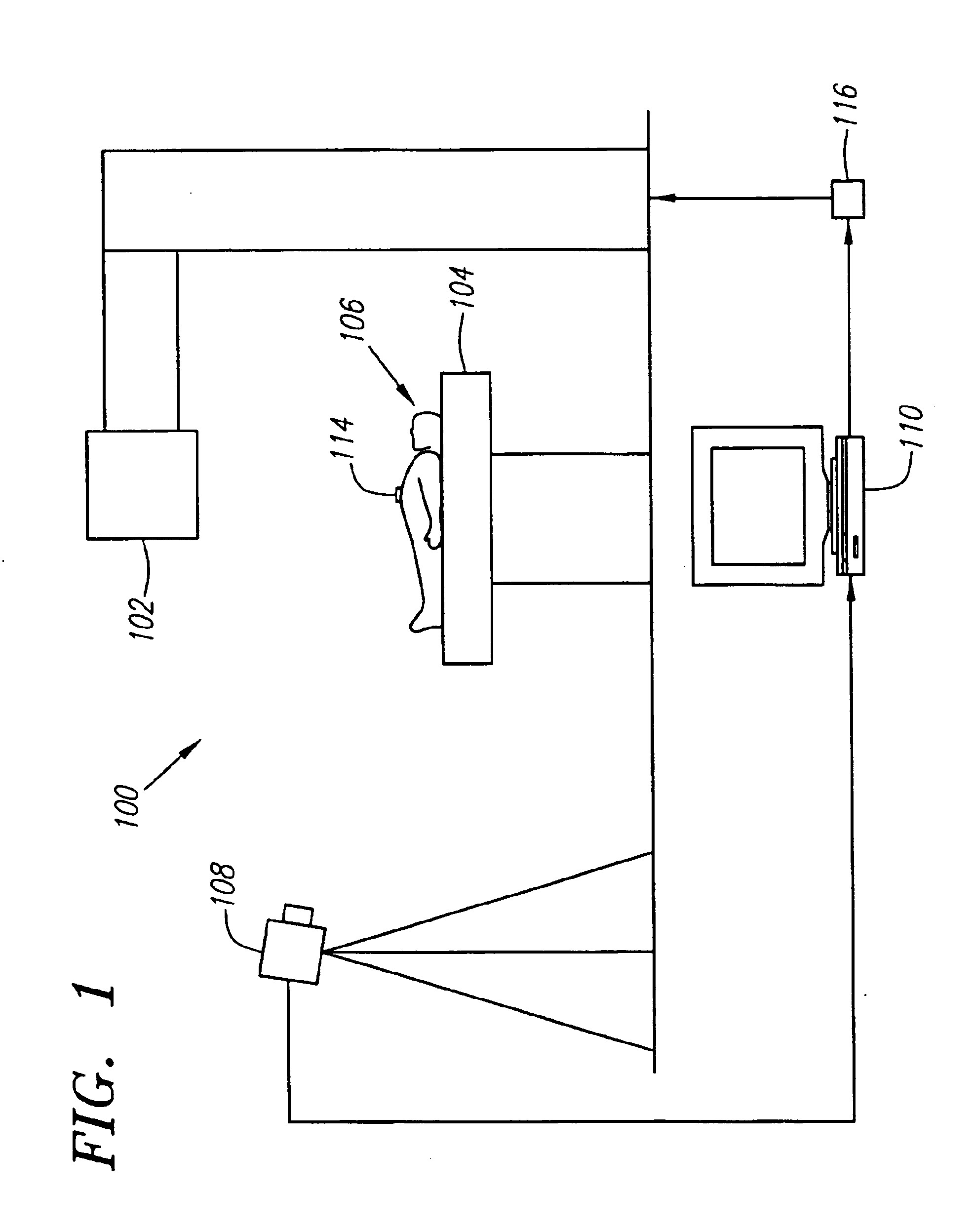
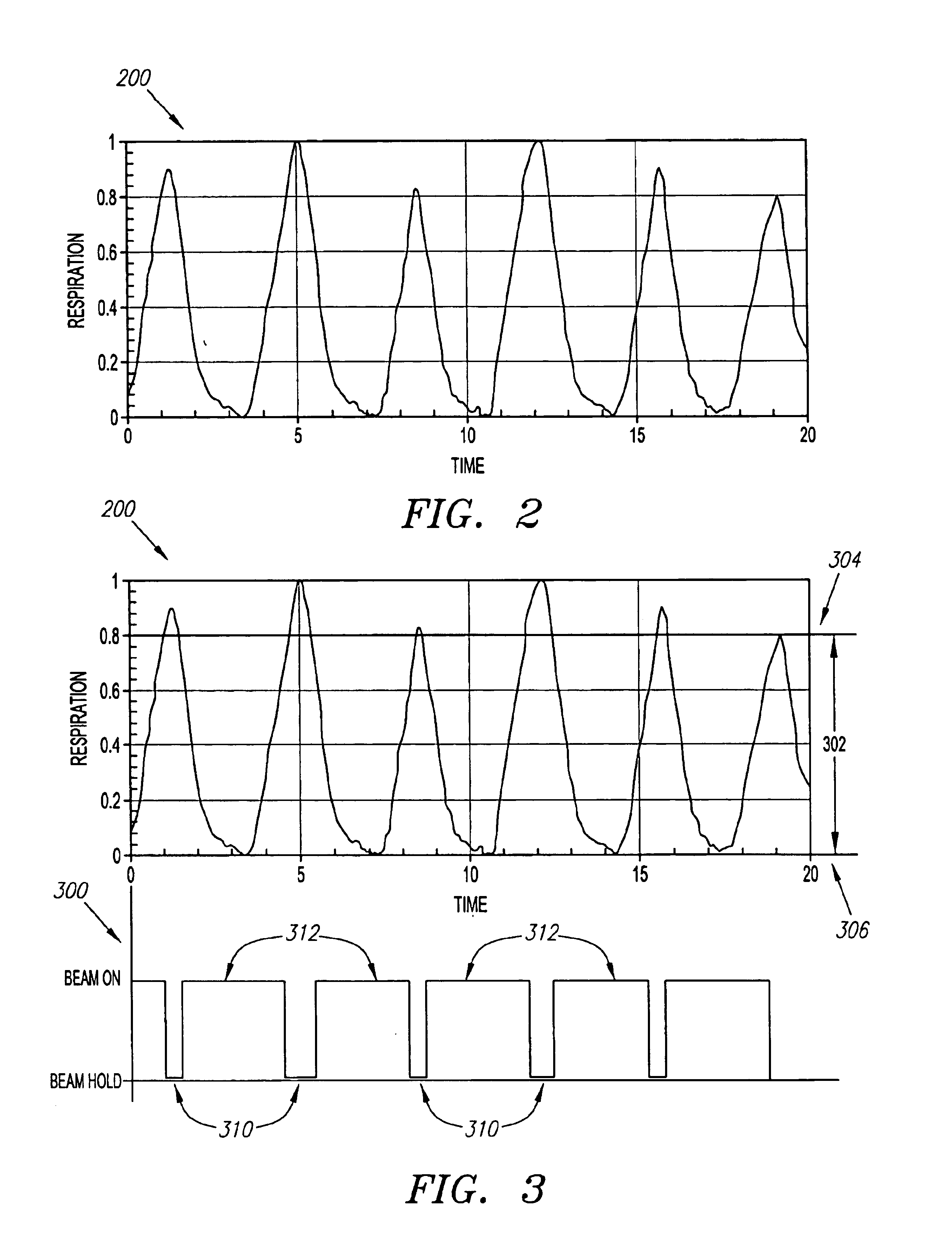
Method and system for predictive physiological gating
InactiveUS6937696B1Consistent positionEasy to FeedbackSurgeryDiagnostic markersComputed tomographyEngineering
A method and system for physiological gating is disclosed. A method and system for detecting and predictably estimating regular cycles of physiological activity or movements is disclosed. Another disclosed aspect of the invention is directed to predictive actuation of gating system components. Yet another disclosed aspect of the invention is directed to physiological gating of radiation treatment based upon the phase of the physiological activity. Gating can be performed, either prospectively or retrospectively, to any type of procedure, including radiation therapy or imaging, or other types of medical devices and procedures such as PET, MRI, SPECT, and CT scans.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
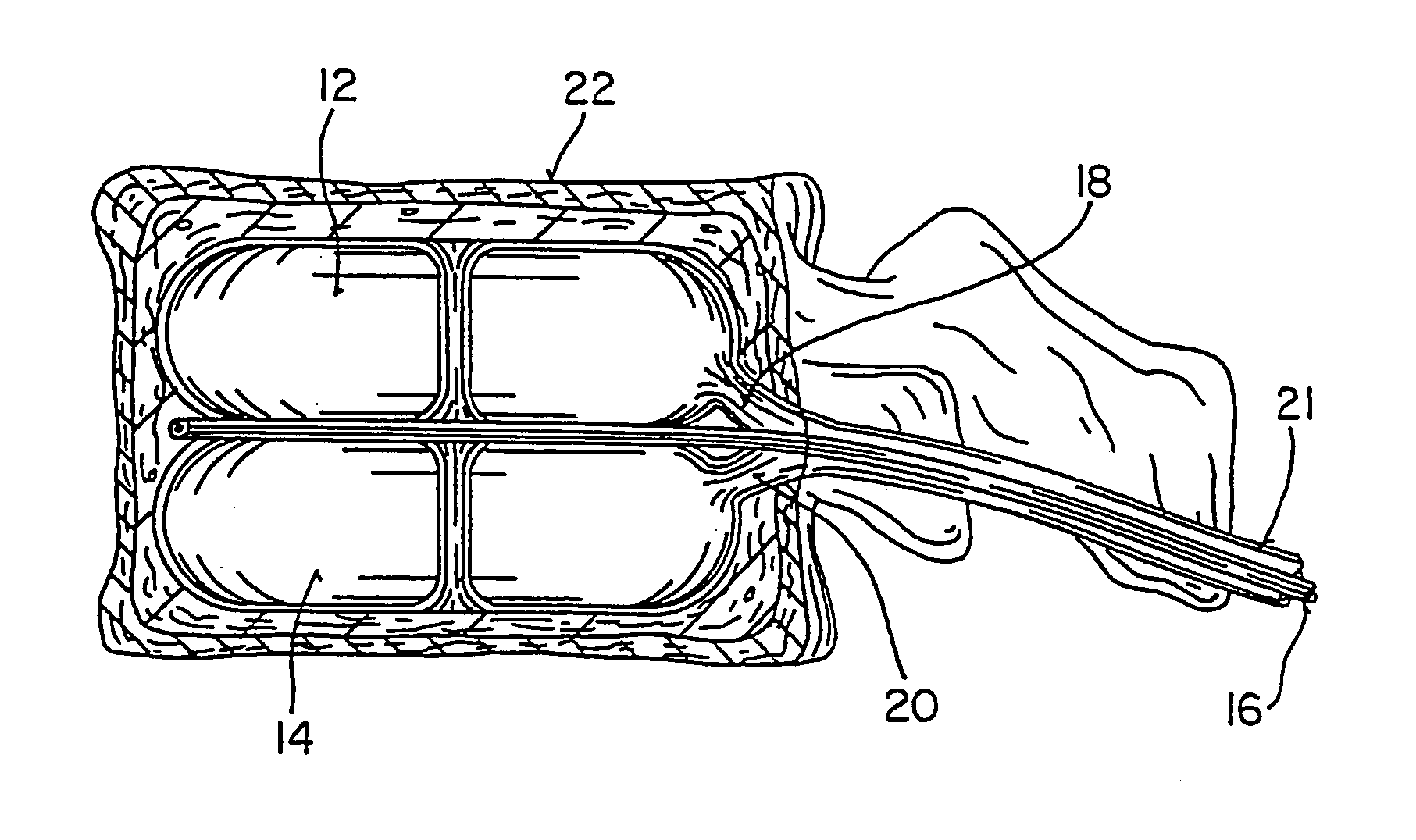
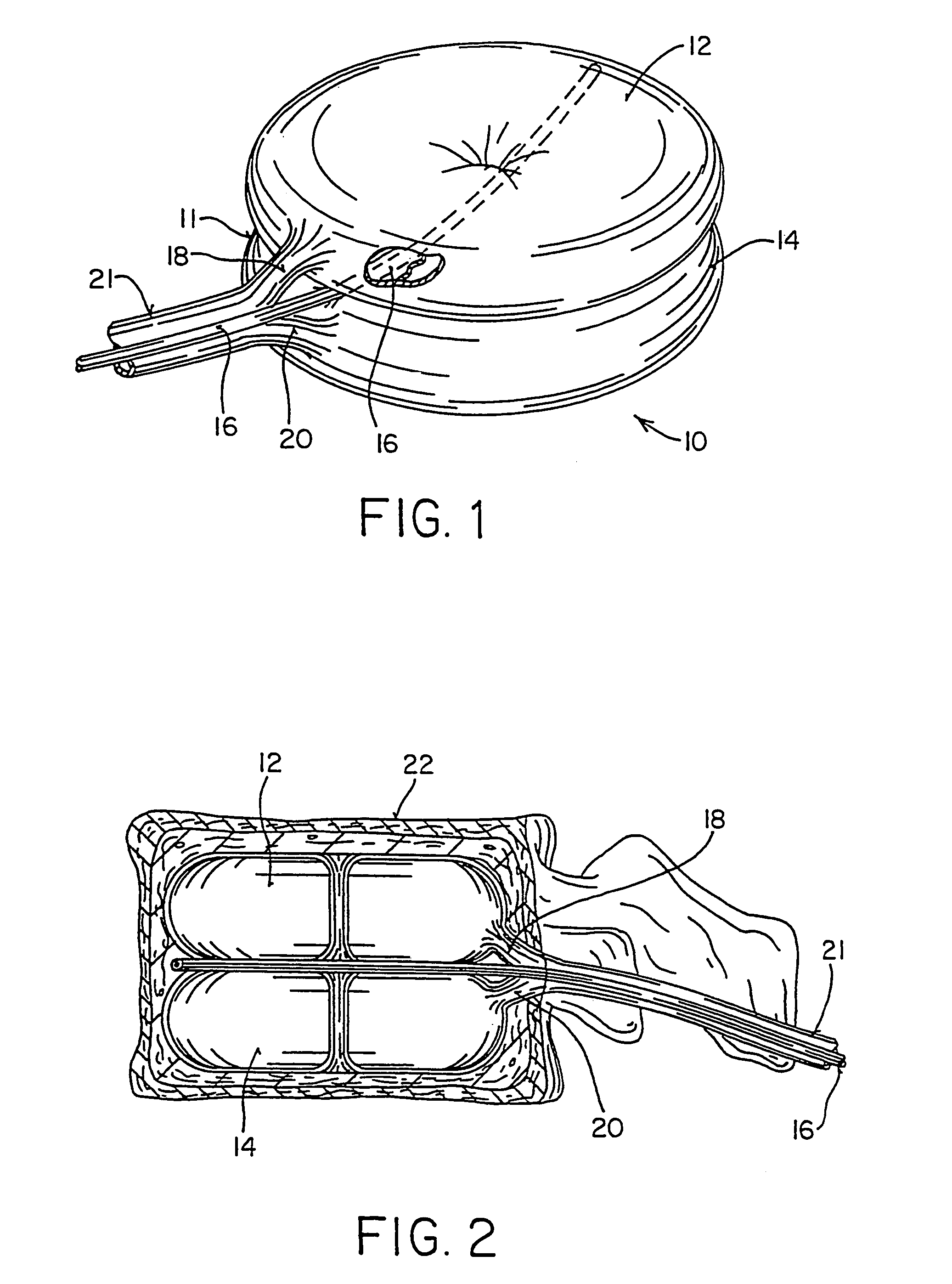
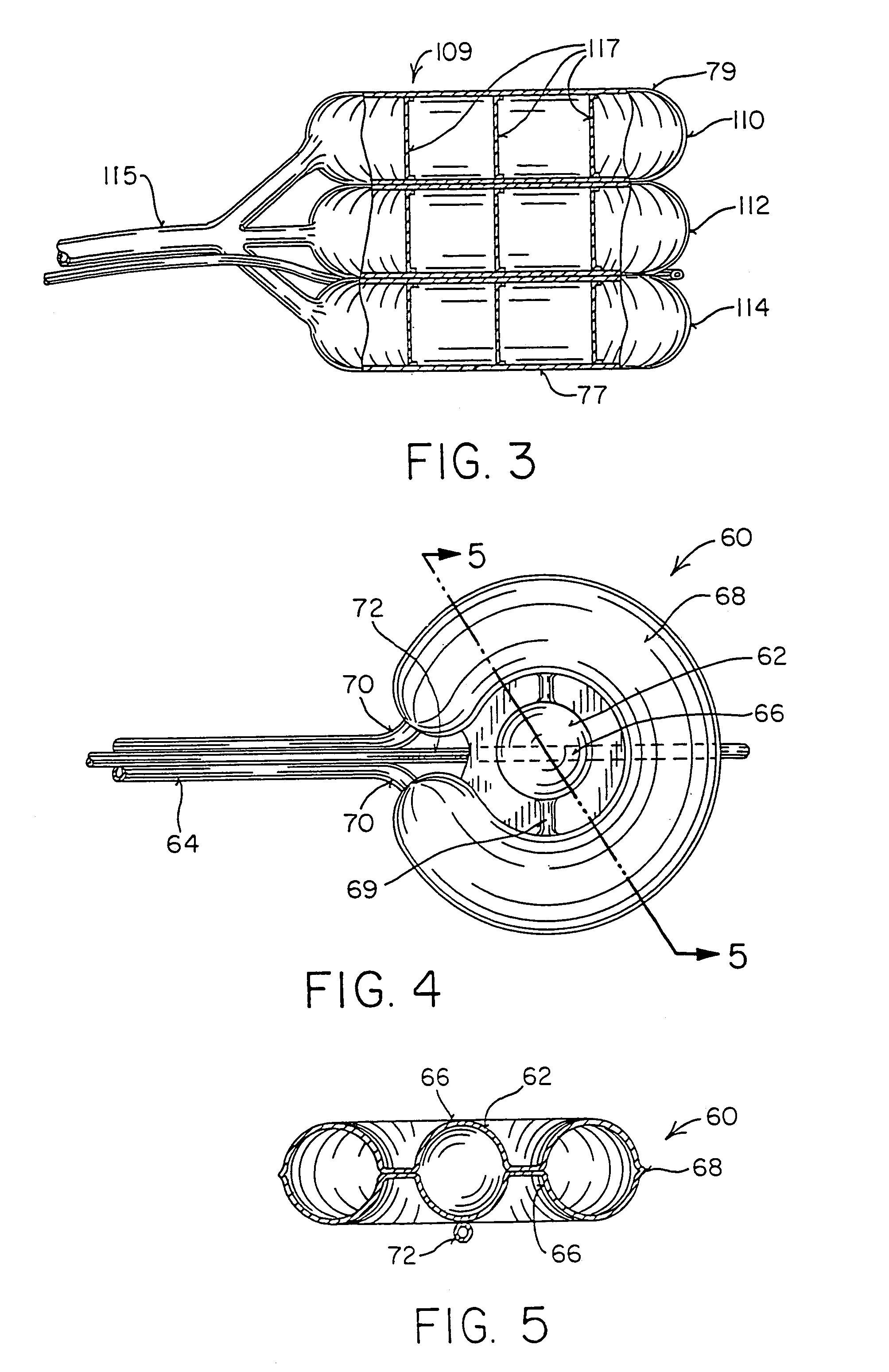
Implantable artificial partition and methods of use
InactiveUS7160312B2Reduce the cross-sectional areaReduce probabilitySuture equipmentsHeart valvesMedicineGastro intestinal
Apparatus and methods are provided for partitioning a gastro-intestinal lumen by intraluminally reducing a local cross-sectional area thereof. The apparatus comprises a plurality of anchors adapted for intraluminal penetration into a wall of the gastro-intestinal lumen to prevent migration or dislodgement of the apparatus, and a partition, which may include a drawstring or a toroidal balloon, coupled to the plurality of anchors to provide a local reduction in the cross-sectional area of the gastro-intestinal lumen.
Owner:USGI MEDICAL
Systems and methods for placing materials into bone
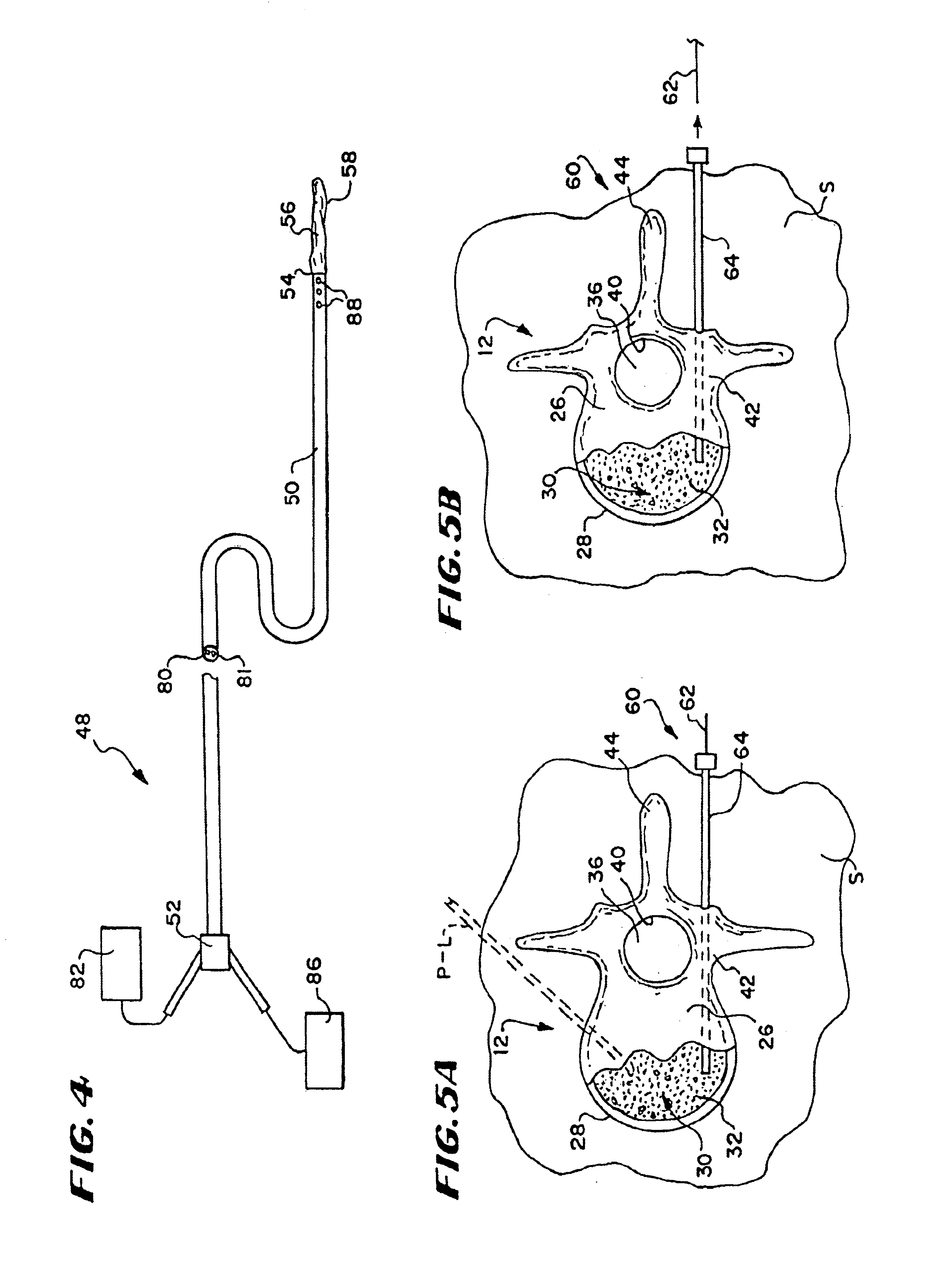
Systems and methods for delivering material into bone deploy a cannula through soft tissue to establish a subcutaneous path into bone. A material is introduced into bone through the cannula. The systems and methods advance a tamping instrument through the cannula to urge material residing in the cannula into bone. The introducing step delivers material at a pressure no greater than about 360 psi.
Owner:ORTHOPHOENIX
Wireless system for providing instrument and implant data to a surgical navigation unit
A system for wirelessly providing data regarding surgical implements such as surgical tools, trial and inserts themselves to a surgical navigation unit. Each implement includes an RFID in which data regarding the implement are stored. The tool used to fit the implement has a first coil positioned to exchange signals with a complementary coil integral with the RFID. The tool also has a prism for receiving a navigation tracker. A second tool coil, in the prism, is connected to the first coil. The second tool coil is also connected to an RFID integral with the tool. The tracker, through the tool coils, reads the data in the implement RFID and the tool RFID. A transmitter in the tracker wirelessly forwards the data to the surgical navigation system. The data are used to facilitate reactive workflow guidance of the procedure and monitor the position of the implement.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
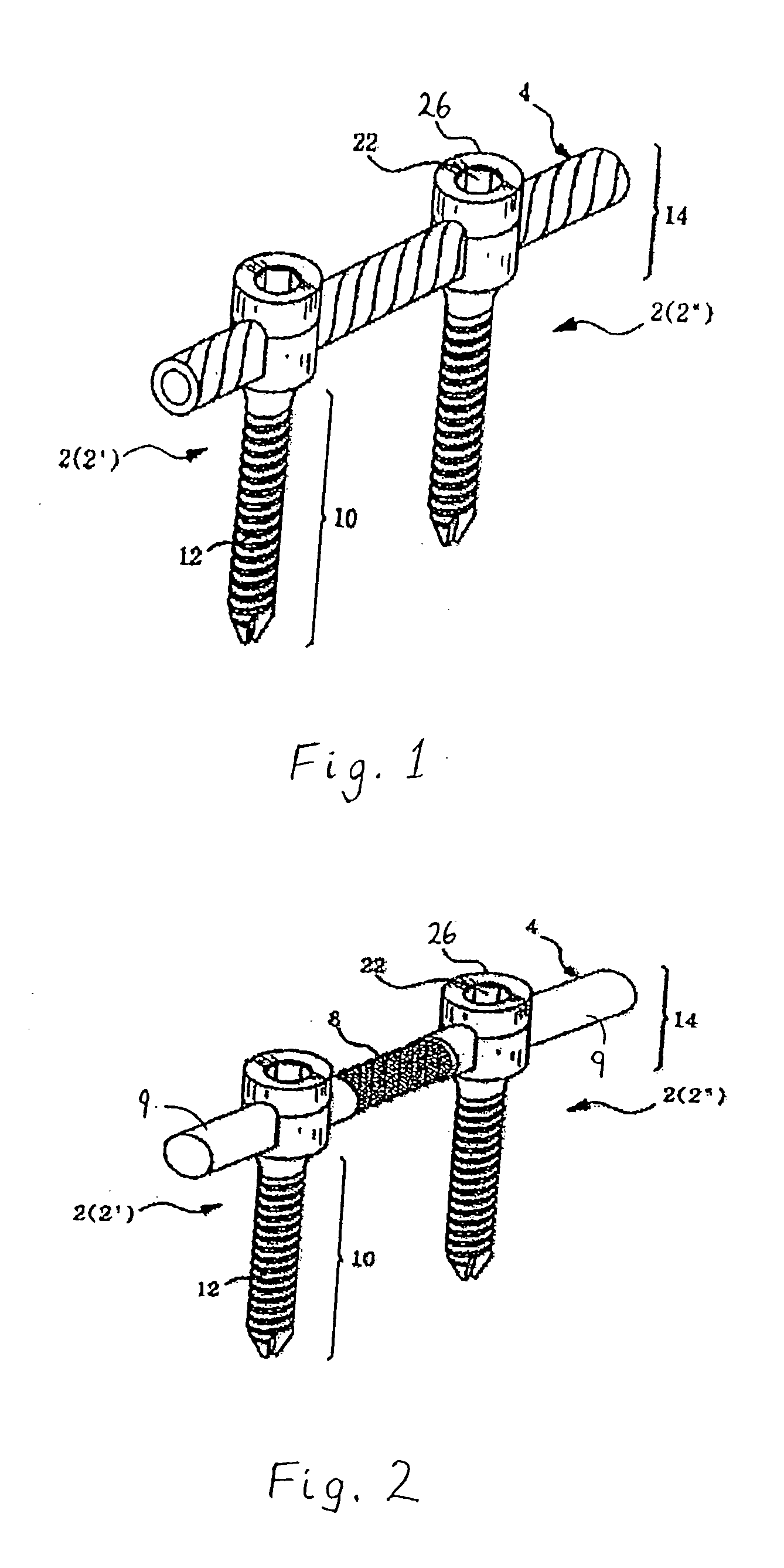
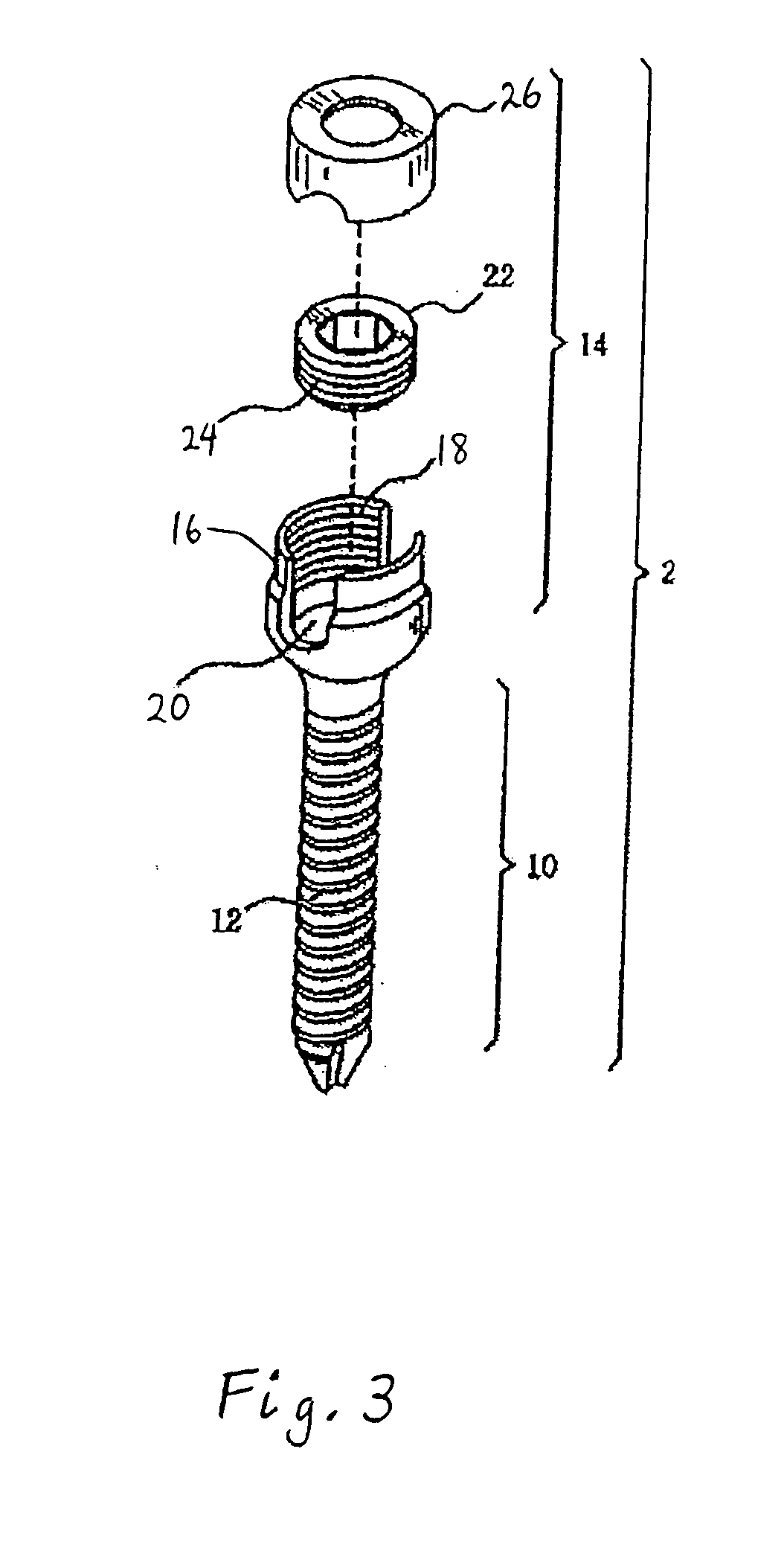
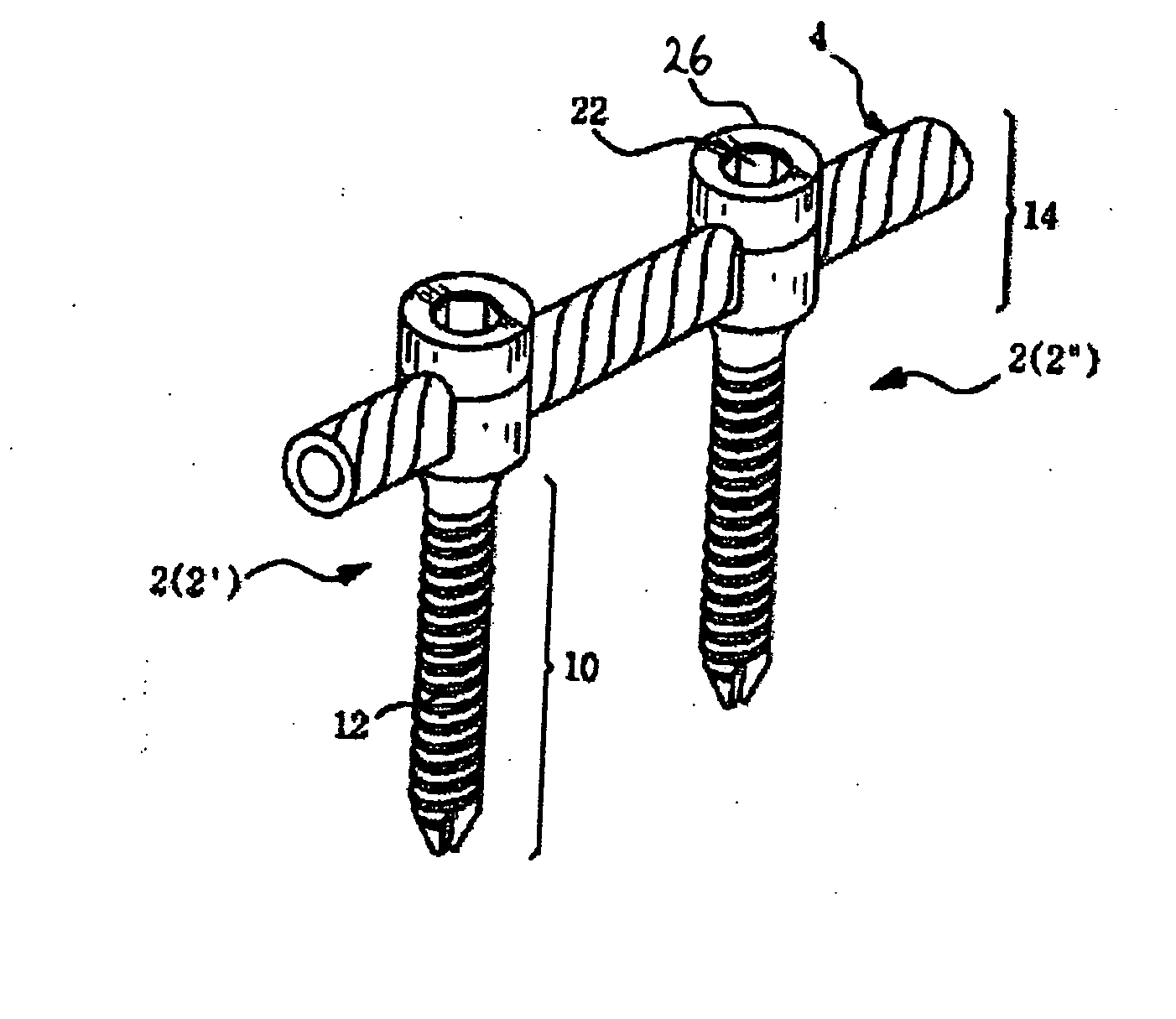
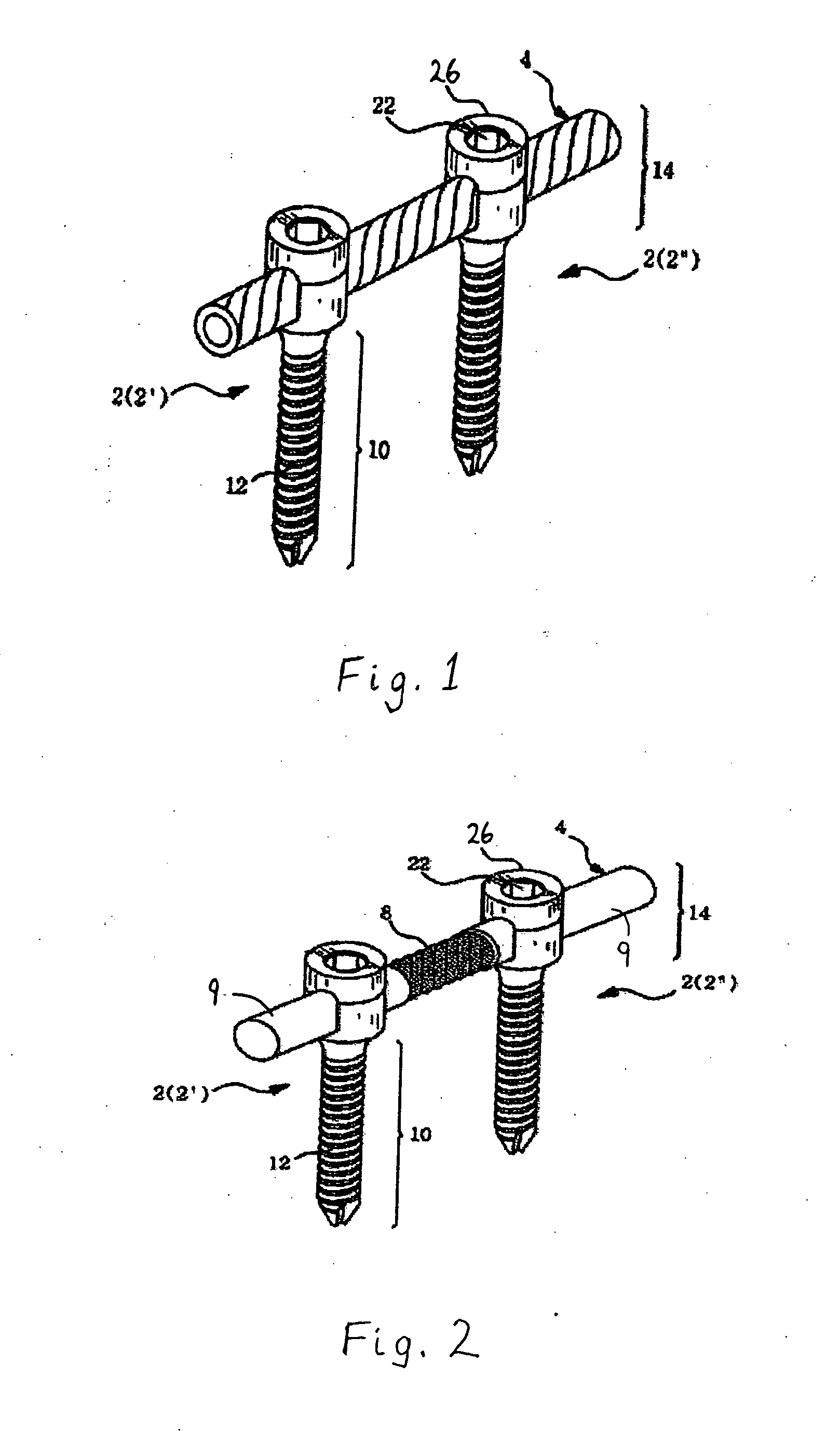
Spinal stabilization device
ActiveUS20050203517A1Easy constructionSimple designInternal osteosythesisEar treatmentEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Method and apparatus for flexible fixation of a spine
InactiveUS20050065516A1Easy constructionSimple designInternal osteosythesisEar treatmentSpinal columnCoupling
A flexible spinal fixation device having a flexible metallic connection unit for non-rigid stabilization of the spinal column. In one embodiment, the fixation device includes at least two securing members configured to be inserted into respective adjacent spinal pedicles, each securing member each including a coupling assembly. The fixation device further includes a flexible metal connection unit configured to be received and secured within the coupling assemblies of each securing member so as to flexibly stabilize the affected area of the spine.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Inflatable device for use in surgical protocol relating to fixation of bone
InactiveUS6981981B2Improve clinical outcomesWorsen conditionSurgical furnitureInternal osteosythesisFilling materialsCancellous bone
Systems for treating a bone, e.g. a vertebral body, having an interior volume occupied, at least in part, by cancellous bone provide a first tool, a second tool, and a third tool. The first tool establishes a percutaneous access path to bone. The second tool is sized and configured to be introduced through the percutaneous access path to form a void that occupies less than the interior volume. The third tool places within the void through the percutaneous access path a volume of filling material. Related methods for treating a bone, e.g. a vertebral body, having an interior volume occupied, at least in part, by cancellous bone provide establishing a percutaneous access path to bone. A tool is introduced through the percutaneous access path and manipulated to form a void that occupies less than the interior volume. A volume of filling material is then placed within the void through the percutaneous access path.
Owner:ORTHOPHOENIX
Valve prosthesis for implantation in body channels
A valve prosthesis which is especially useful in the case of aortic stenosis and capable of resisting the powerful recoil force and to stand the forceful balloon inflation performed to deploy the valve and to embed it in the aortic annulus, comprises a collapsible valvular structure and an expandable frame on which said valvular structure is mounted. The valvular structure is composed of physiologically compatible valvular tissue that is sufficiently supple and resistant to allow the valvular structure to be deformed from a closed state to an opened state. The valvular tissue forms a continuous surface and is provided with strut members that create stiffened zones which induce the valvular structure to follow a patterned movement in its expansion to its opened state and in its turning back to its closed state.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI PVT
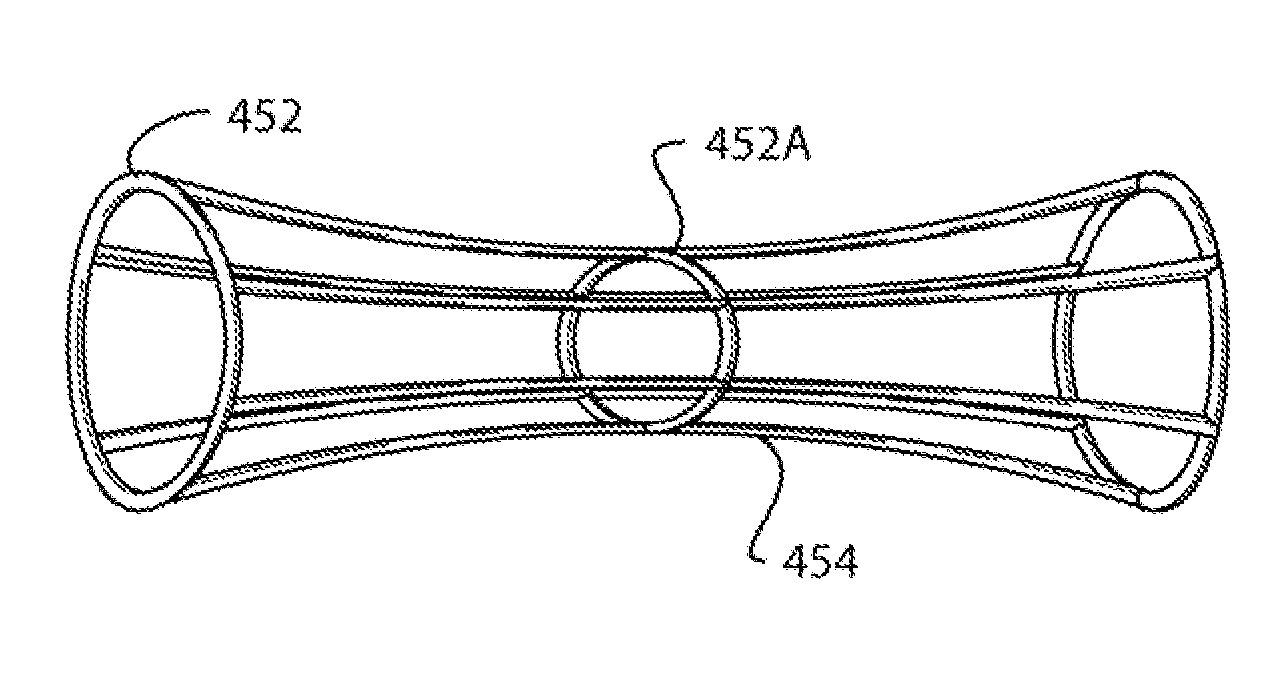
Prosthetic Conduit With Radiopaque Symmetry Indicators
A system and method for treating a vascular condition includes a conduit having an elongate tubular member with an outer surface and an inner surface, the inner surface defines a conduit lumen. The system further includes at least one symmetry indicator attached to the elongate tubular member and a replacement valve device. The replacement valve device includes a prosthetic valve connected to an expandable support structure. The replacement valve device is positioned within the conduit lumen adjacent the inner surface.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
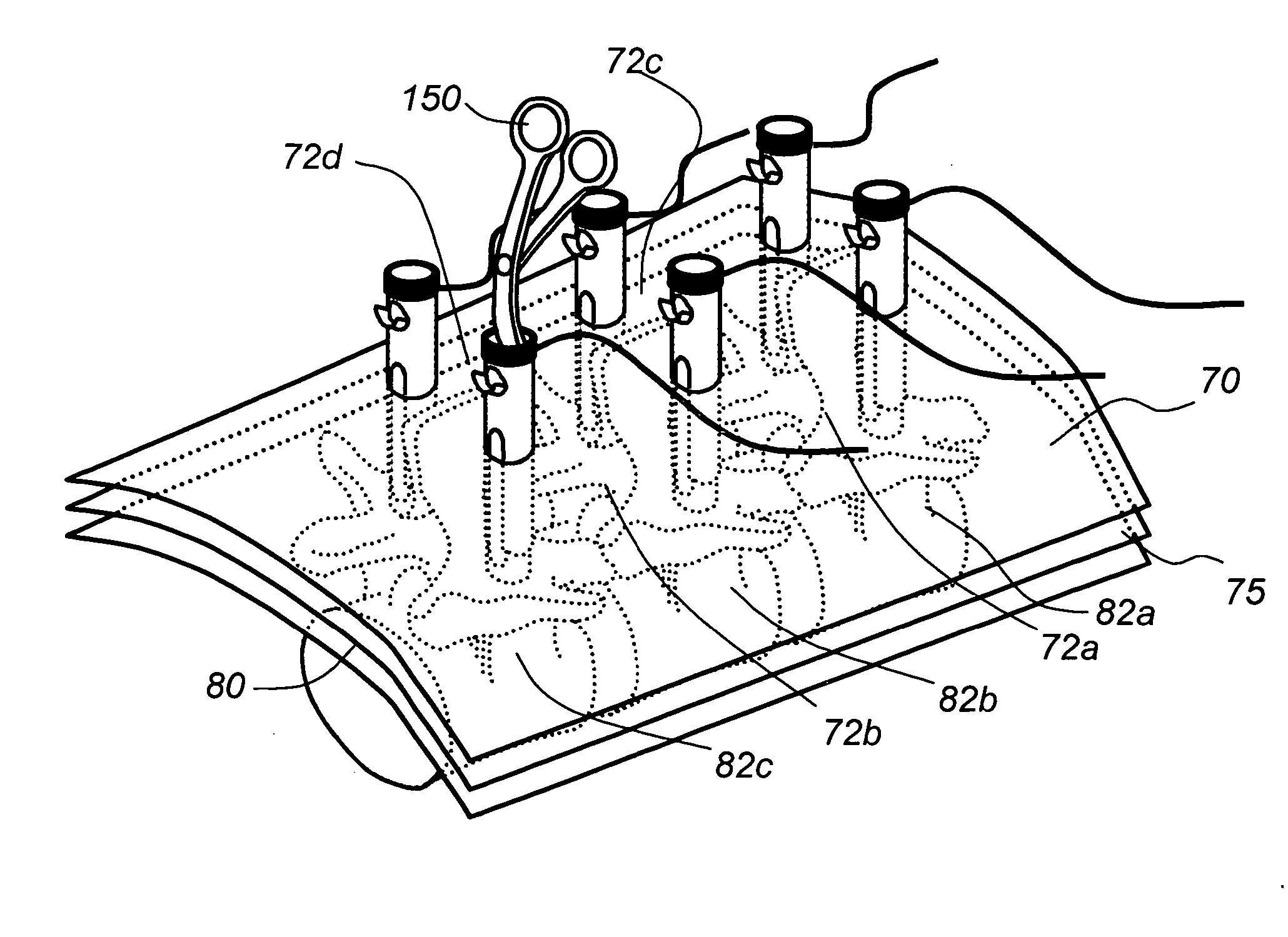
Access and tissue modification systems and methods
Described herein are methods and systems for precisely placing and / or manipulating devices within the body by first positioning a guidewire or pullwire through the body from a first location, around a curved pathway, and out of the body through a second location, so that the distal and proximal ends of the guidewire extend from the body, then pulling a device into position using the guidewire. The device to be positioned within the body is coupled to the proximal end of the guidewire, and the device is pulled into the body by pulling on the distal end of the guidewire that extends from the body. The device may be bimanually manipulated by pulling the guidewire distally, and an attachment to the device that extends proximally, allowing control of both the proximal and the distal ends. In this manner devices (and particularly implants such as innerspinous distracters, stimulating leads, and disc slings) may be positioned and / or manipulated within the body. Devices to modify tissue may also be positioned or manipulated so that a target tissue within the body is modified.
Owner:BAXANO
Systems and methods for treating fractured or diseased bone using expandable bodies
Systems and methods treat fractured or diseased bone by deploying more than a single therapeutic tool into the bone. In one arrangement, the systems and methods deploy an expandable body in association with a bone cement nozzle into the bone, such that both occupy the bone interior at the same time. In another arrangement, the systems and methods deploy multiple expandable bodies, which occupy the bone interior volume simultaneously. Expansion of the bodies form cavity or cavities in cancellous bone in the interior bone volume.
Owner:ORTHOPHOENIX
Device for occluding vascular defects
A multi-layer occluder for treating a target site within the body is provided. The occluder may include first and second layers. For example, the first layer may include braided strands of metallic material, and the second layer may include braided strands of polymeric material. At least one of the first or second layers may be configured to facilitate thrombosis.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Methods and devices for performing procedures within the ear, nose, throat and paranasal sinuses
Devices, systems and methods for performing image guided interventional and surgical procedures, including various procedures to treat sinusitis and other disorders of the paranasal sinuses, ears, nose or throat.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com