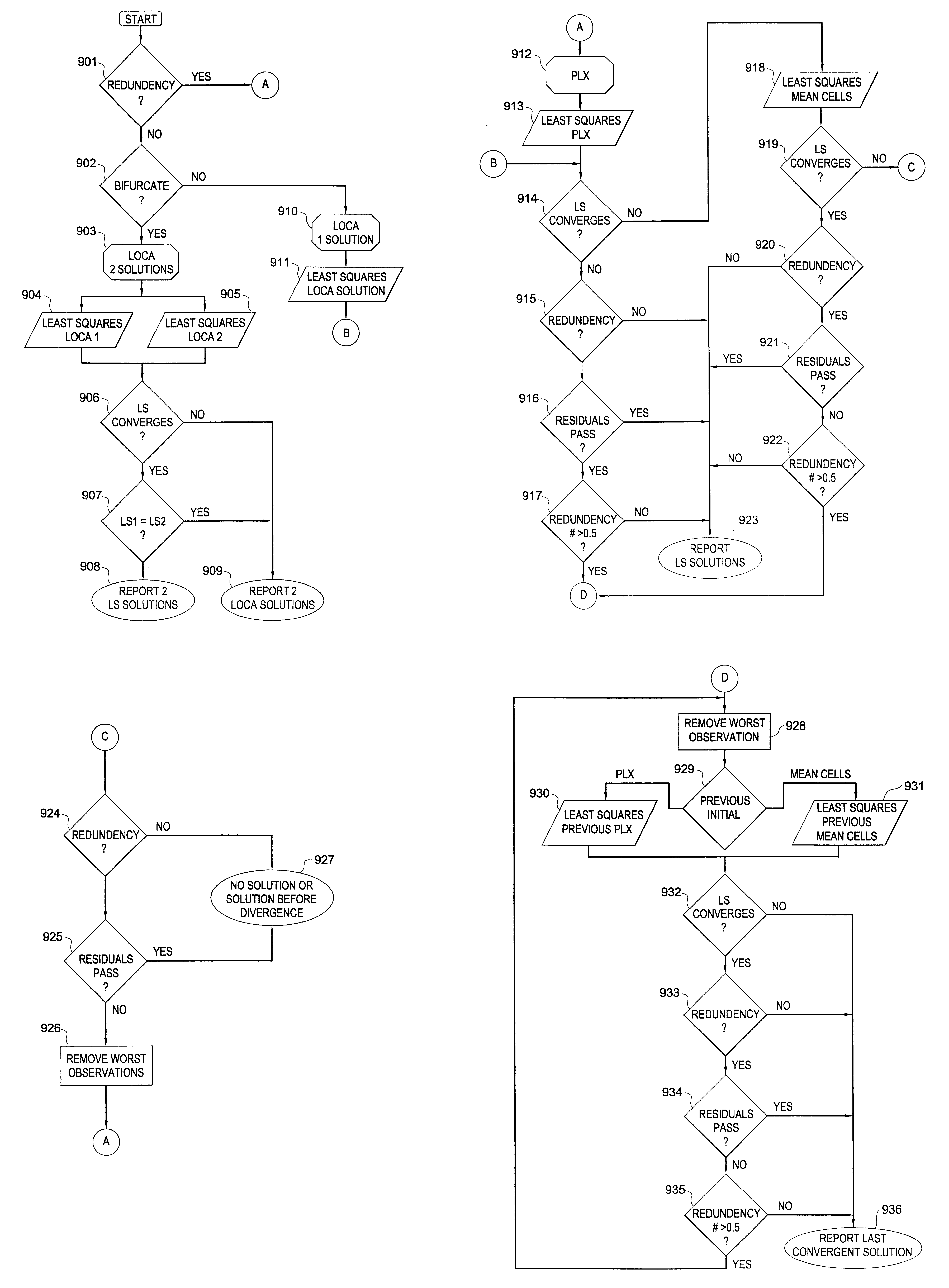
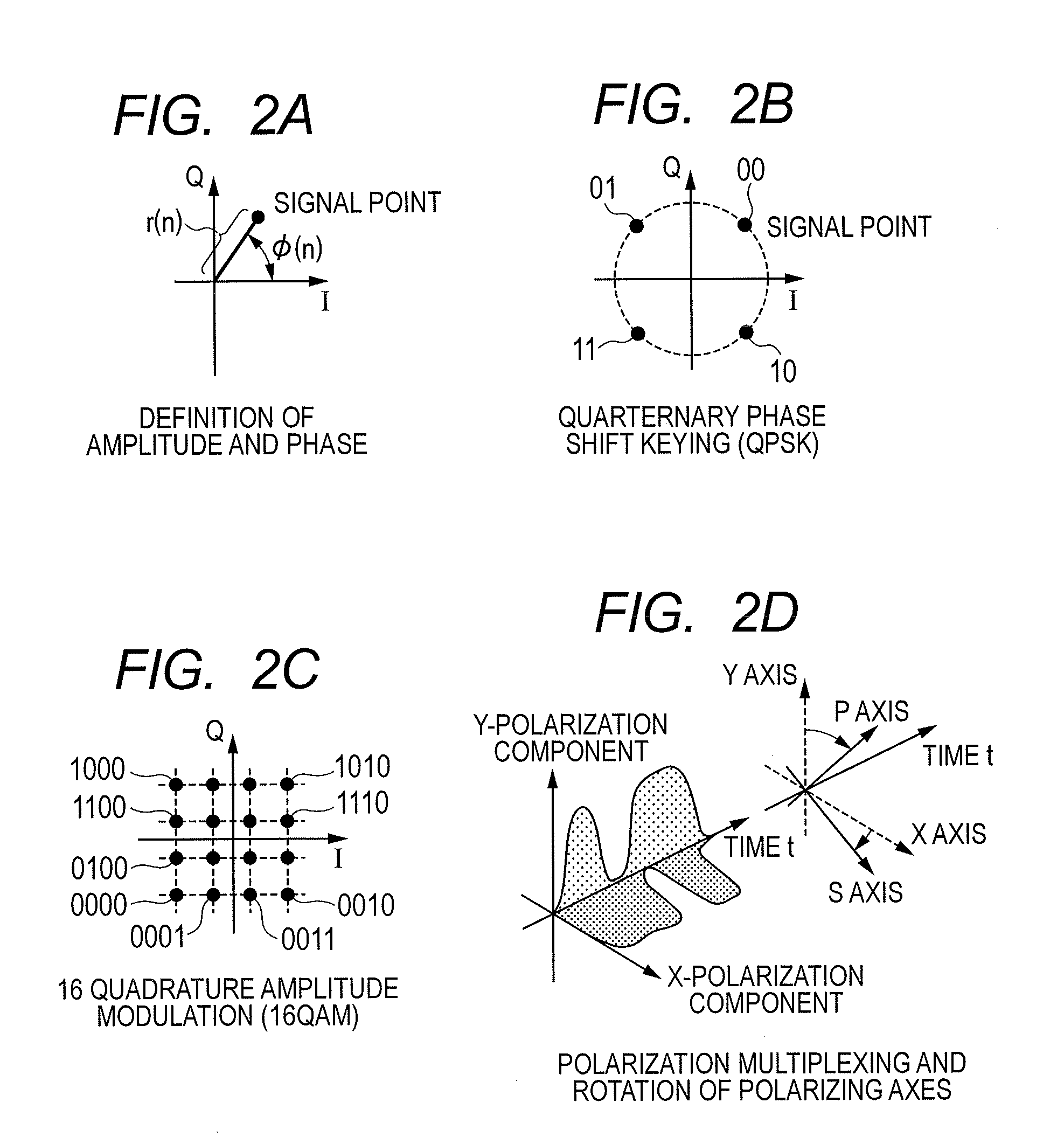
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2427 results about "Frequency difference" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
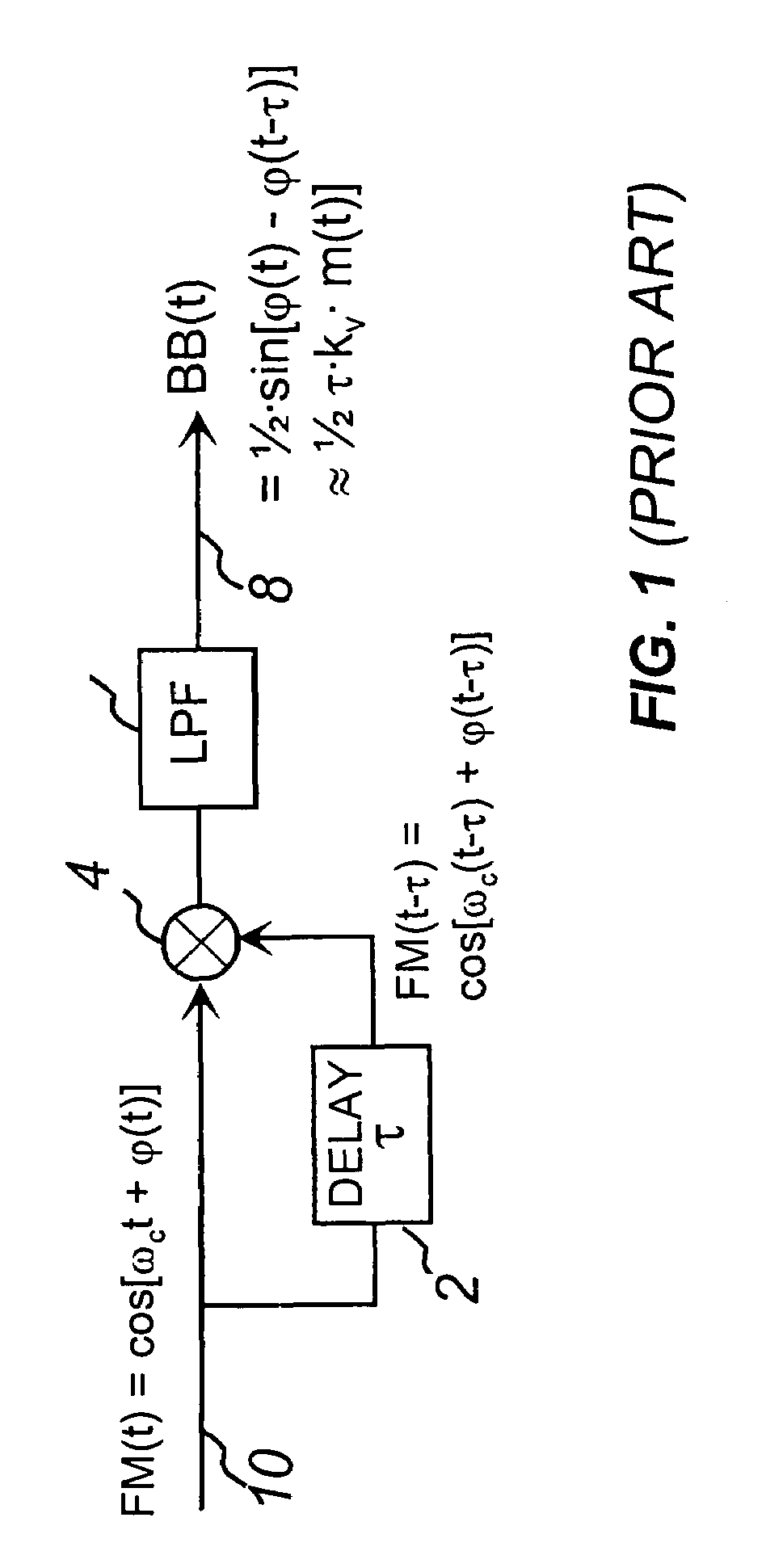
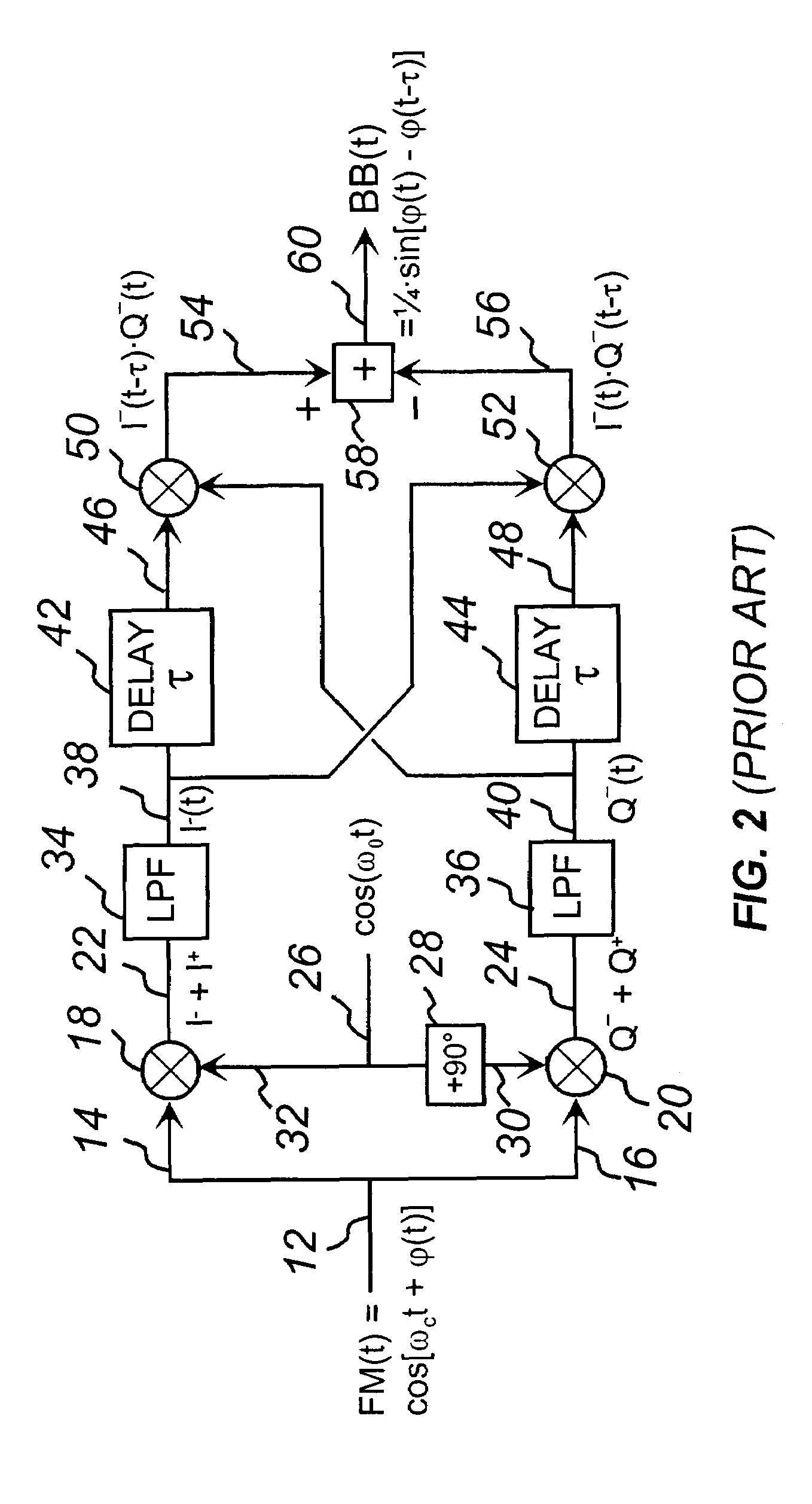
Frequency difference is the difference in speeds between your clock and the NTP clock (effectively deemed to be perfect). If you clock gains a minute every hour (compared to the NTP server clock), that's the frequency difference. It's also called drift.
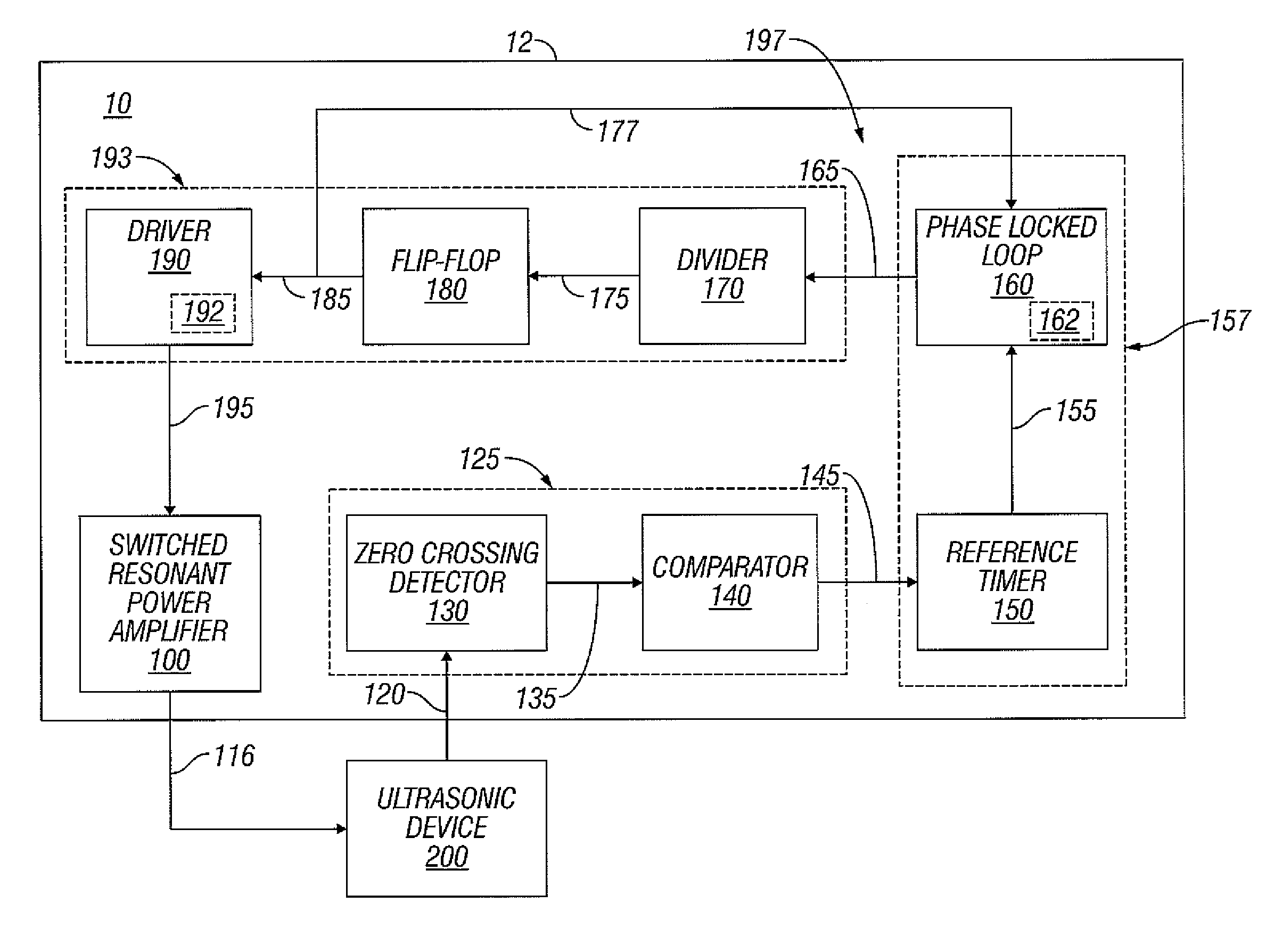
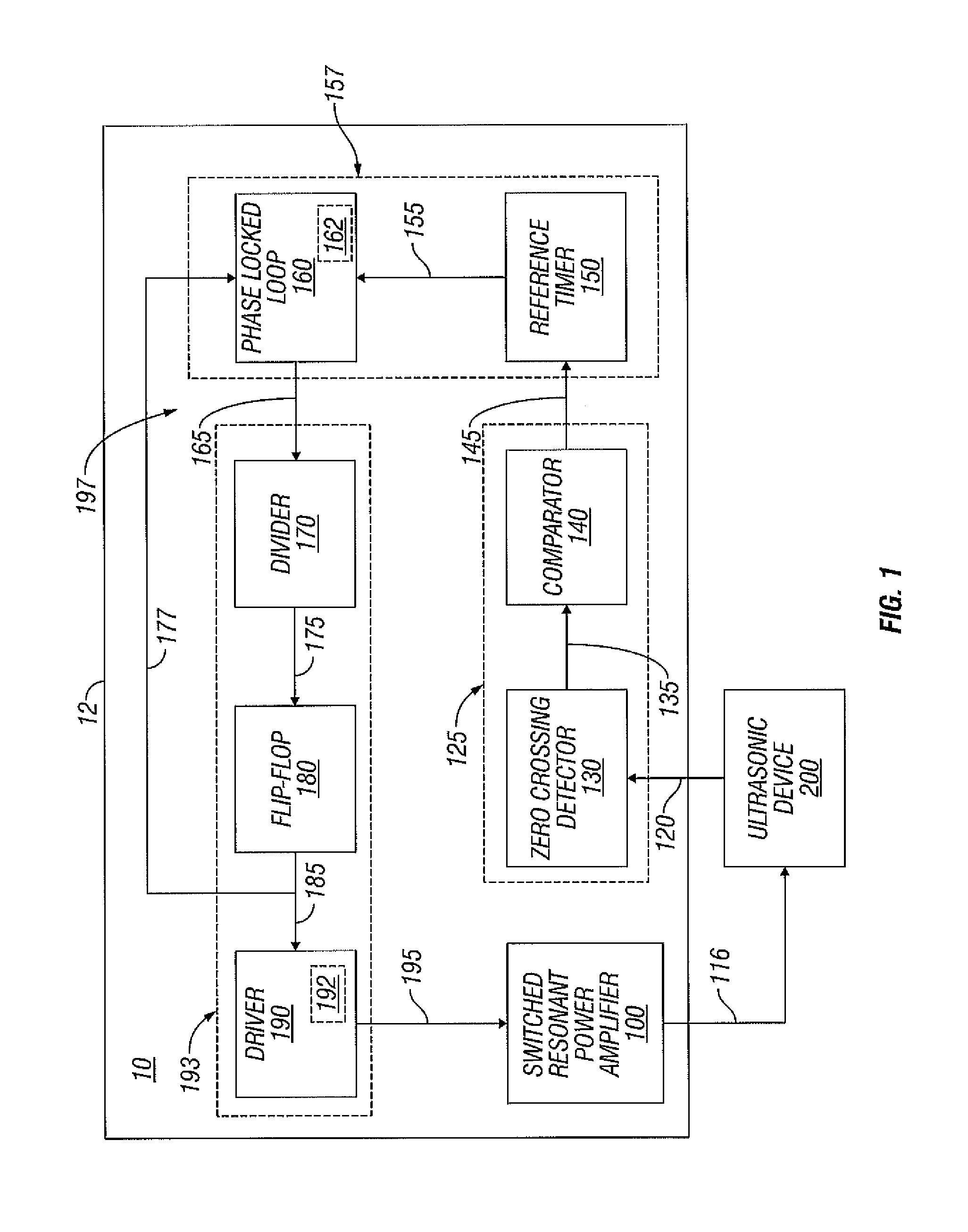
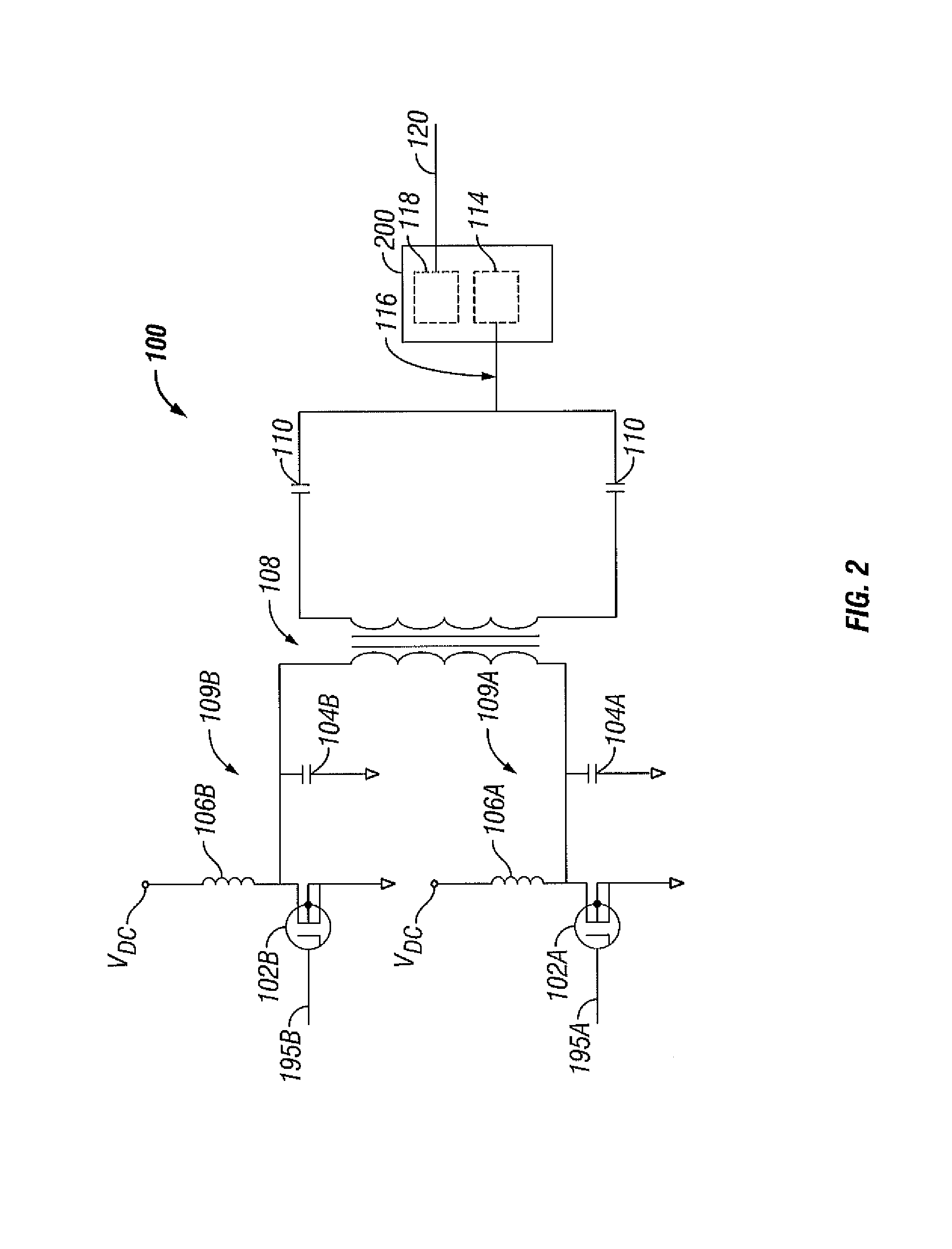
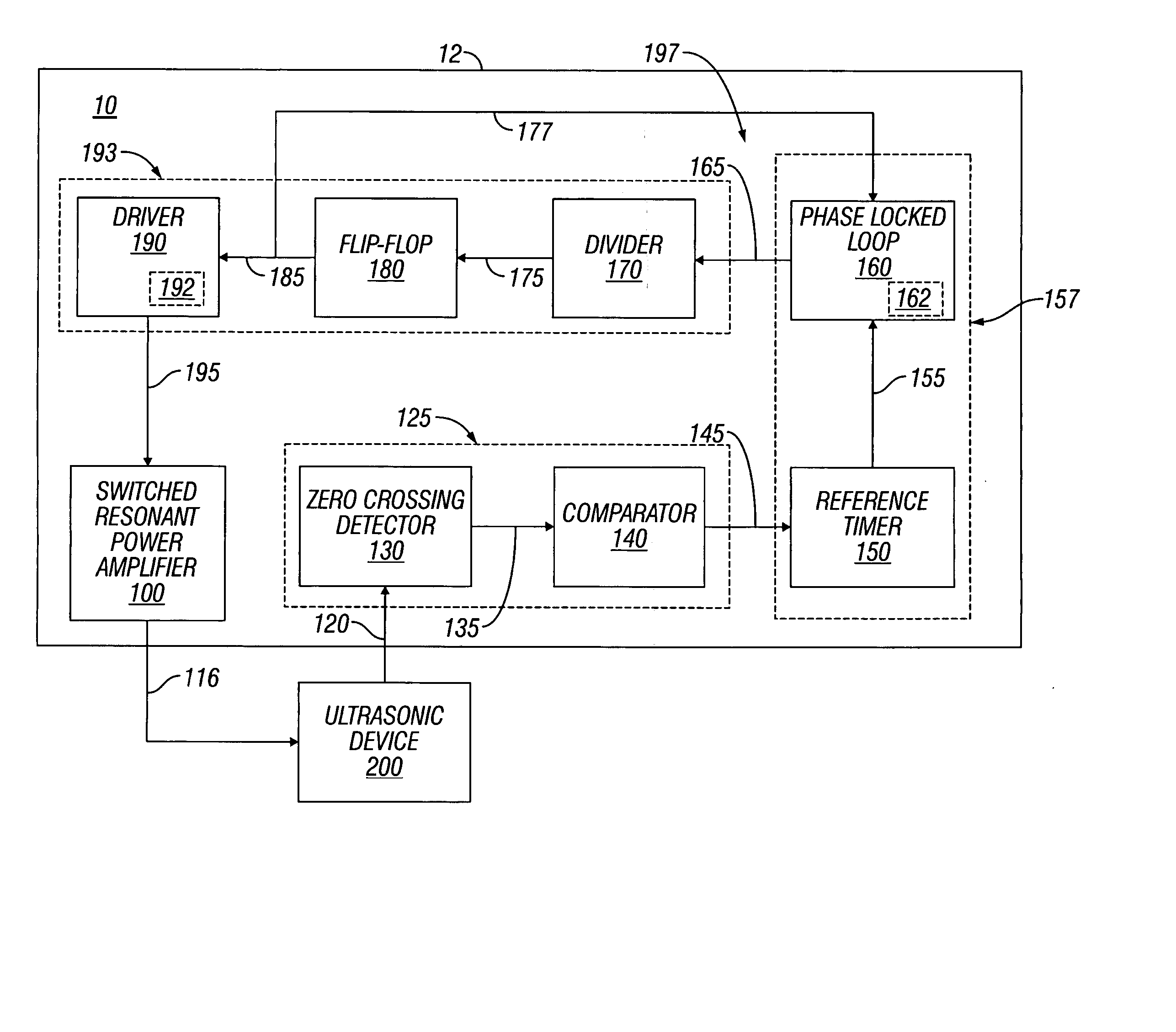
Switched resonant ultrasonic power amplifier system
ActiveUS7396336B2Operation efficiency can be improvedSmall footprintUltrasound therapyAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyHemt circuitsControl ultrasound
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
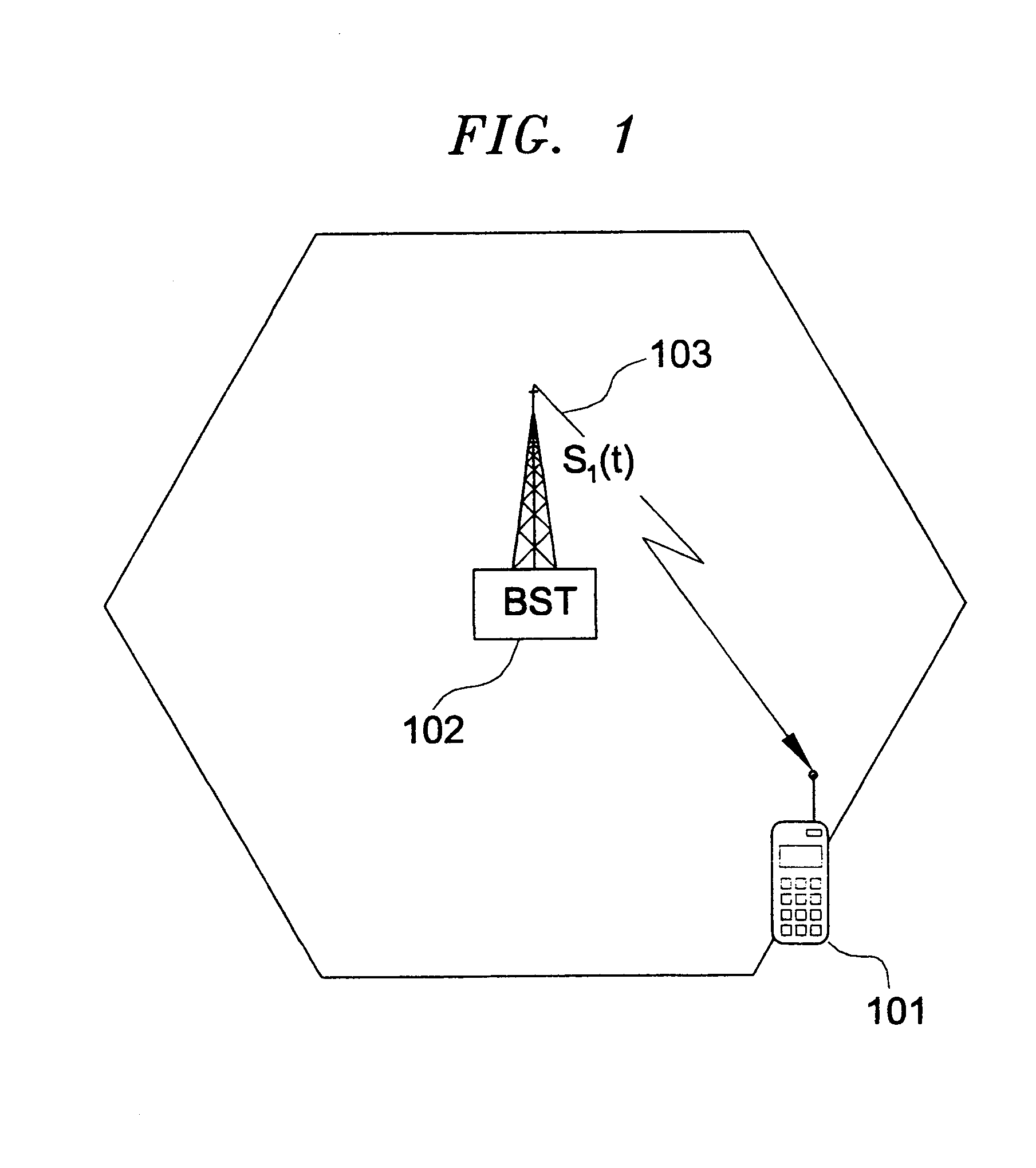
Methods and apparatus to position a mobile receiver using downlink signals part IV
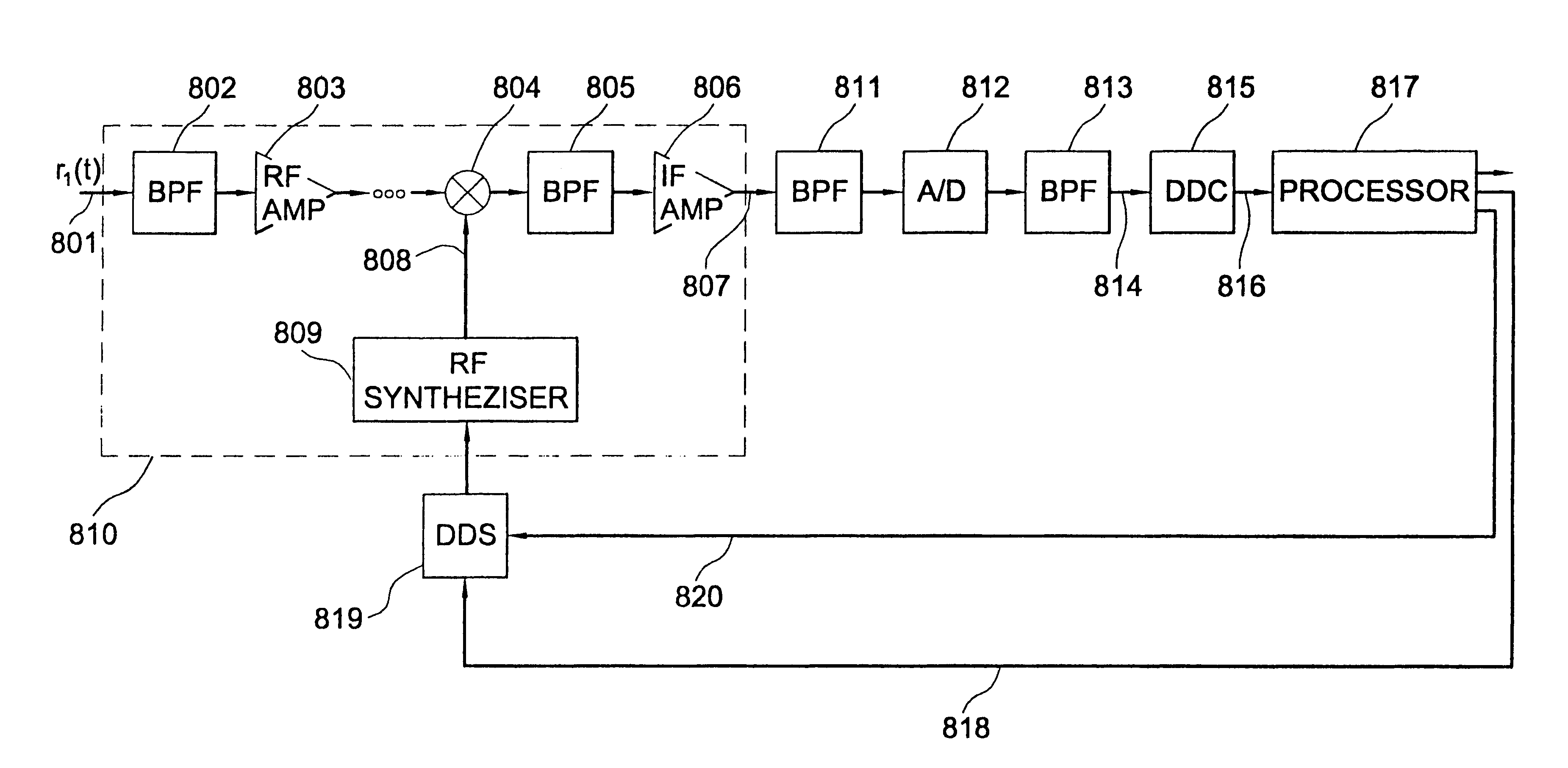
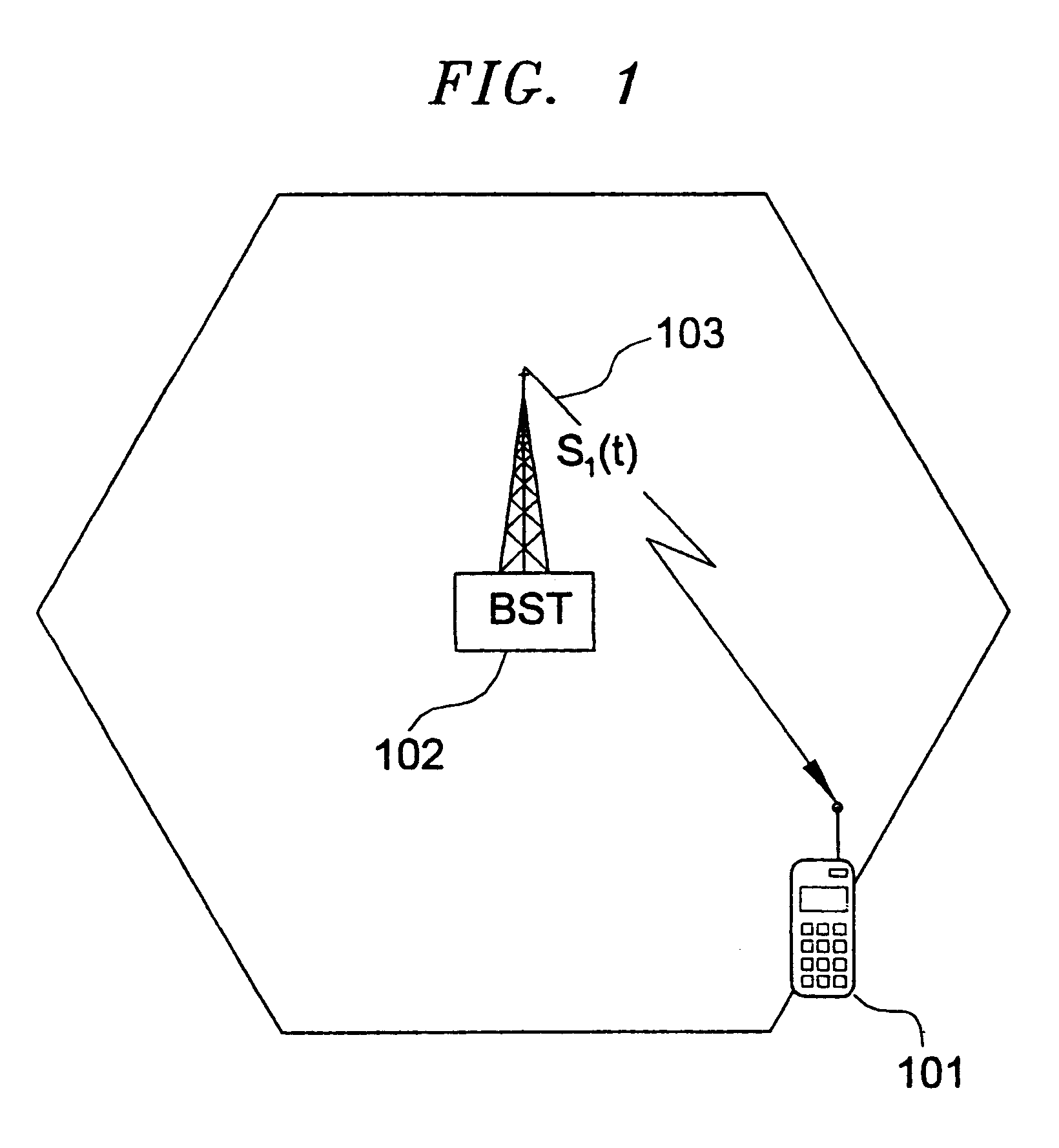
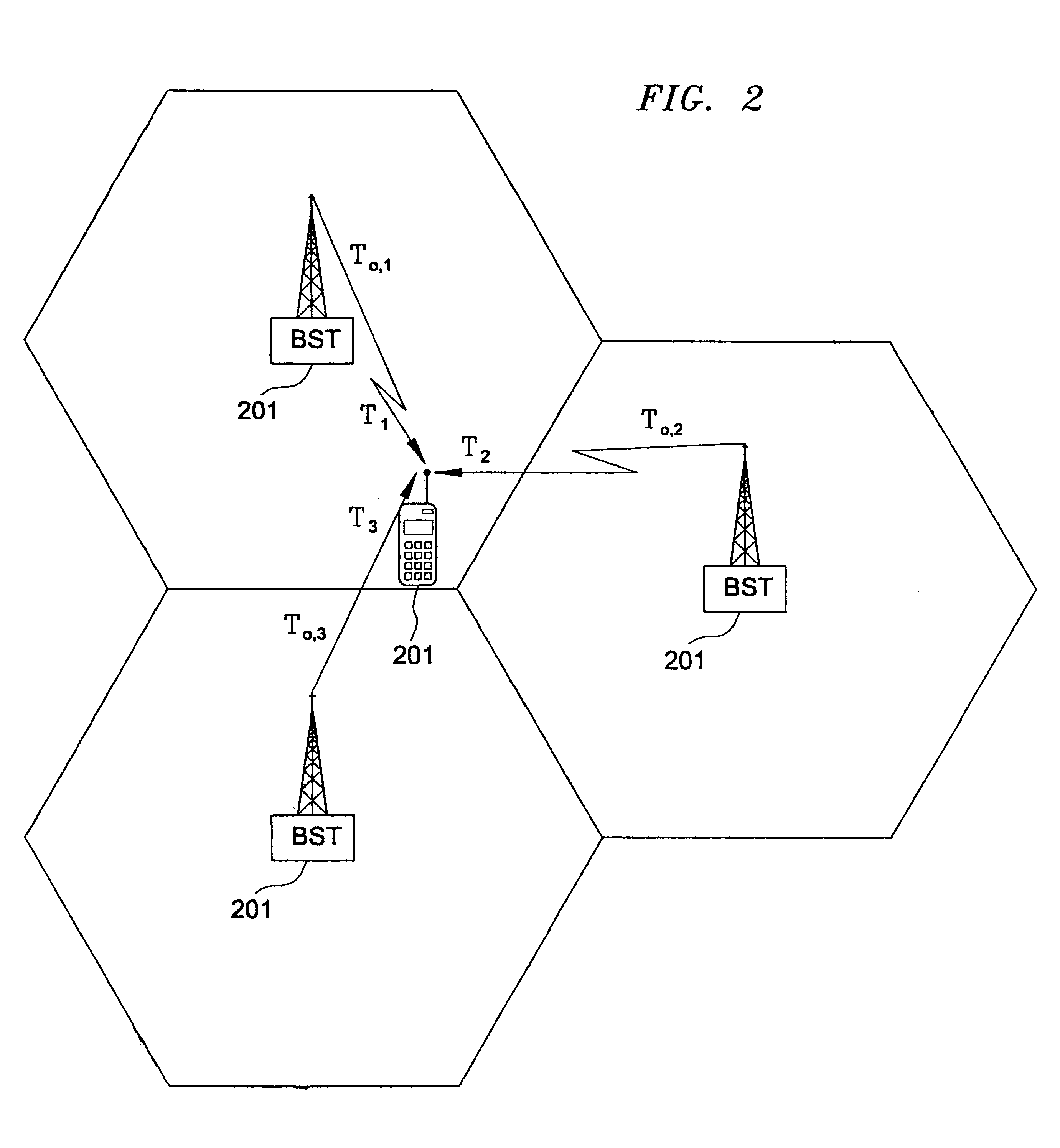
The invention consists of methods and apparatus to estimate the position and velocity of a Mobile Receiver (MR) using either the Time Of Arrival (TOA) of signals received by the MR, their Phase Of Arrival (POA), their Strength Of Arrival (SOA), their Frequency Of Arrival (FOA), or a combination thereof, with respect to a reference produced by a Reference Receiver (RR) of known location. In order to solve for the coordinates of the MR, the invention uses either hyperbolic multilateration based on Time Difference Of Arrival (TDOA), or linear multiangulation based on Phase Difference Of Arrival (PDOA), or both. In order to solve for the velocity of the MR, the patent uses FOA based on Frequency Difference Of Arrival (FDOA).
Owner:CELL LOC LOCATION TECH
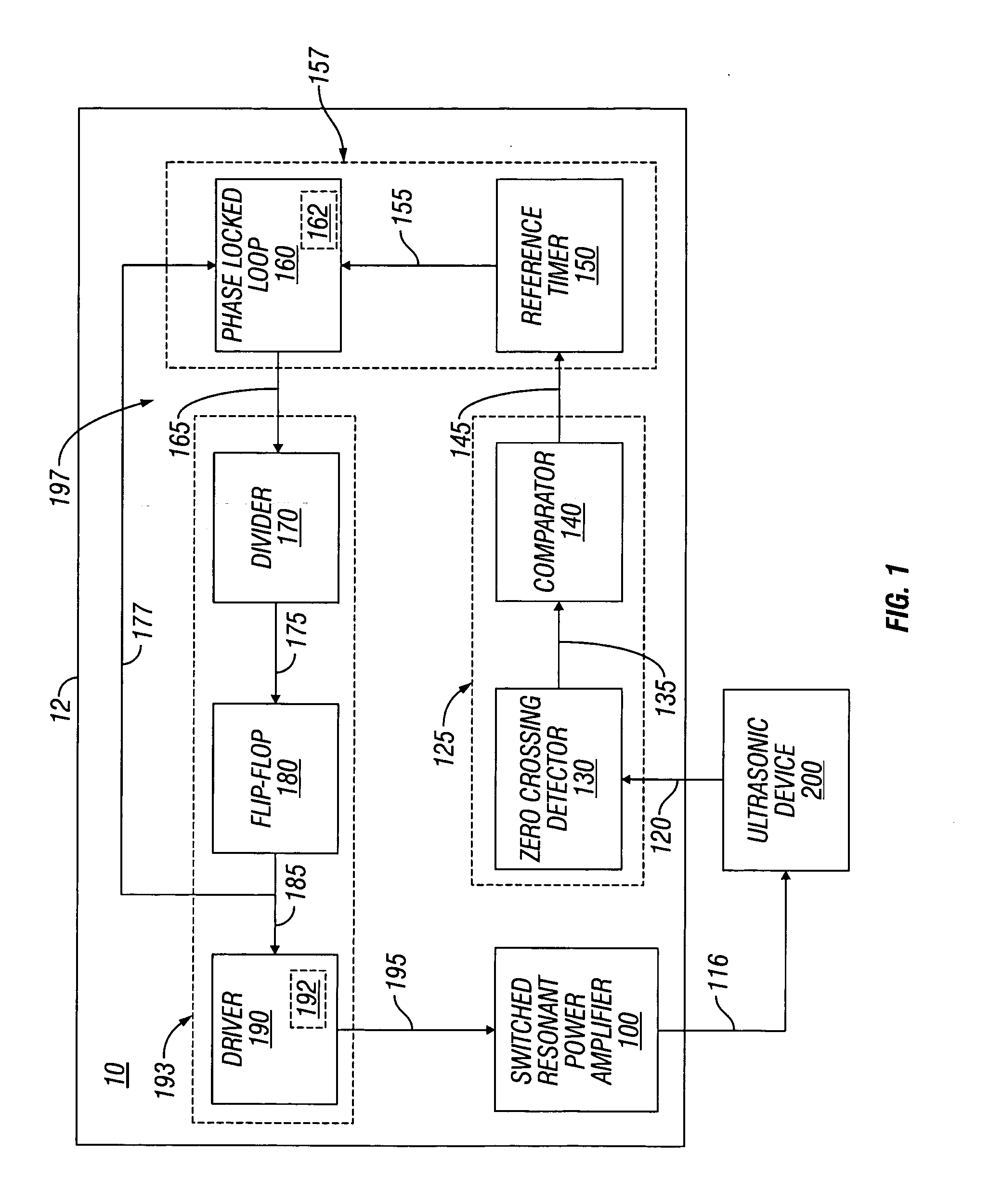
Switched resonant ultrasonic power amplifier system
ActiveUS20050149151A1Reduce frequencyControl outputUltrasound therapyAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencySonificationAudio power amplifier
A switched resonant power amplifier system for ultrasonic transducers is disclosed. The system includes an amplifier that receives and processes a driver output signal for generating a drive signal that is provided to an ultrasonic device for controlling output of the ultrasonic device. An output control circuit receives and processes a signal related to a feedback signal generated by the ultrasonic device and a divider reference signal, and generates a compensated clock signal that is adjusted for at least one of phase and frequency differences between the received feedback signal and the divider reference signal. A compensated drive circuit receives and processes the compensated clock signal for generating the divider reference signal, and for generating the driver output signal.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
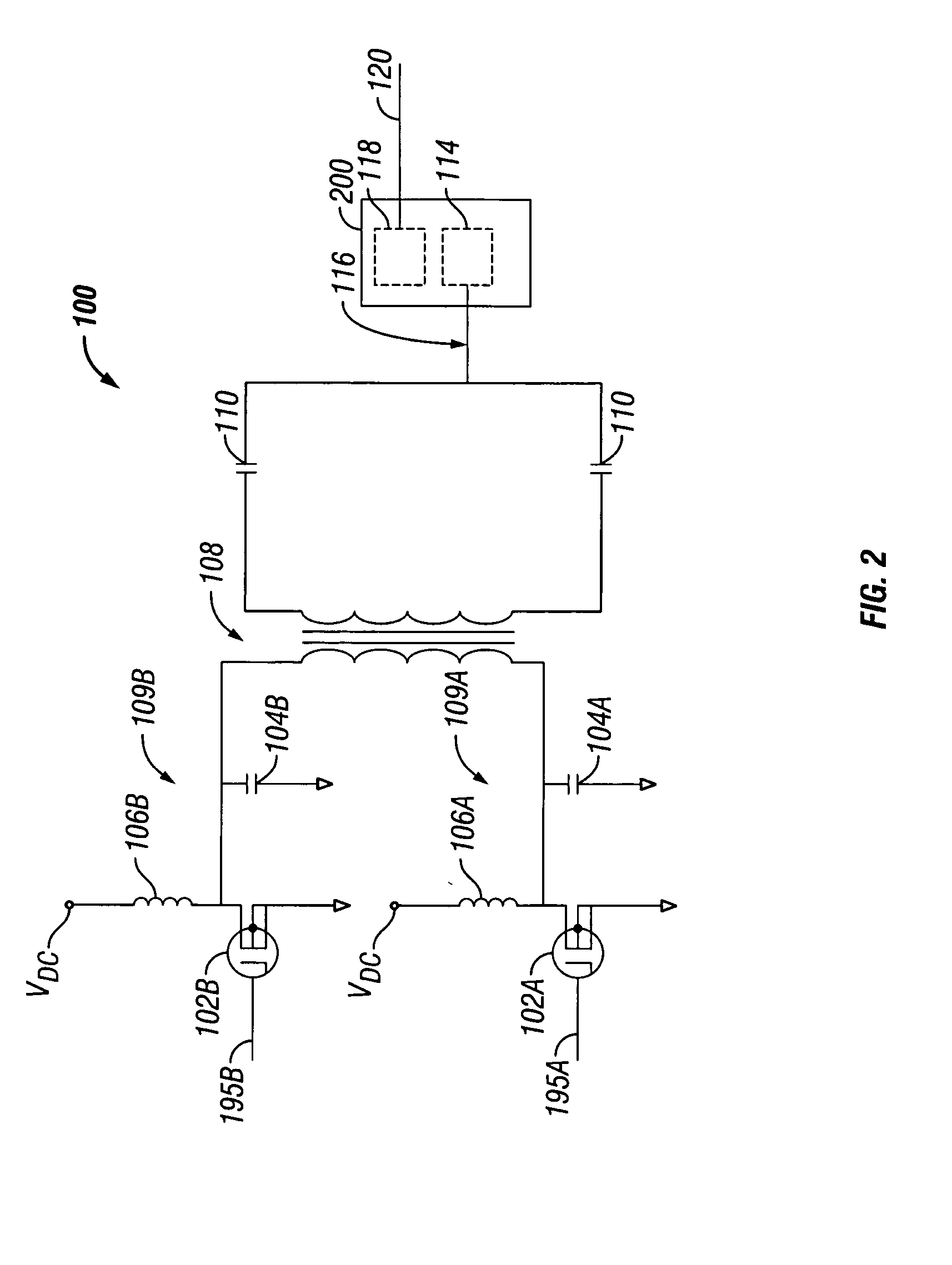
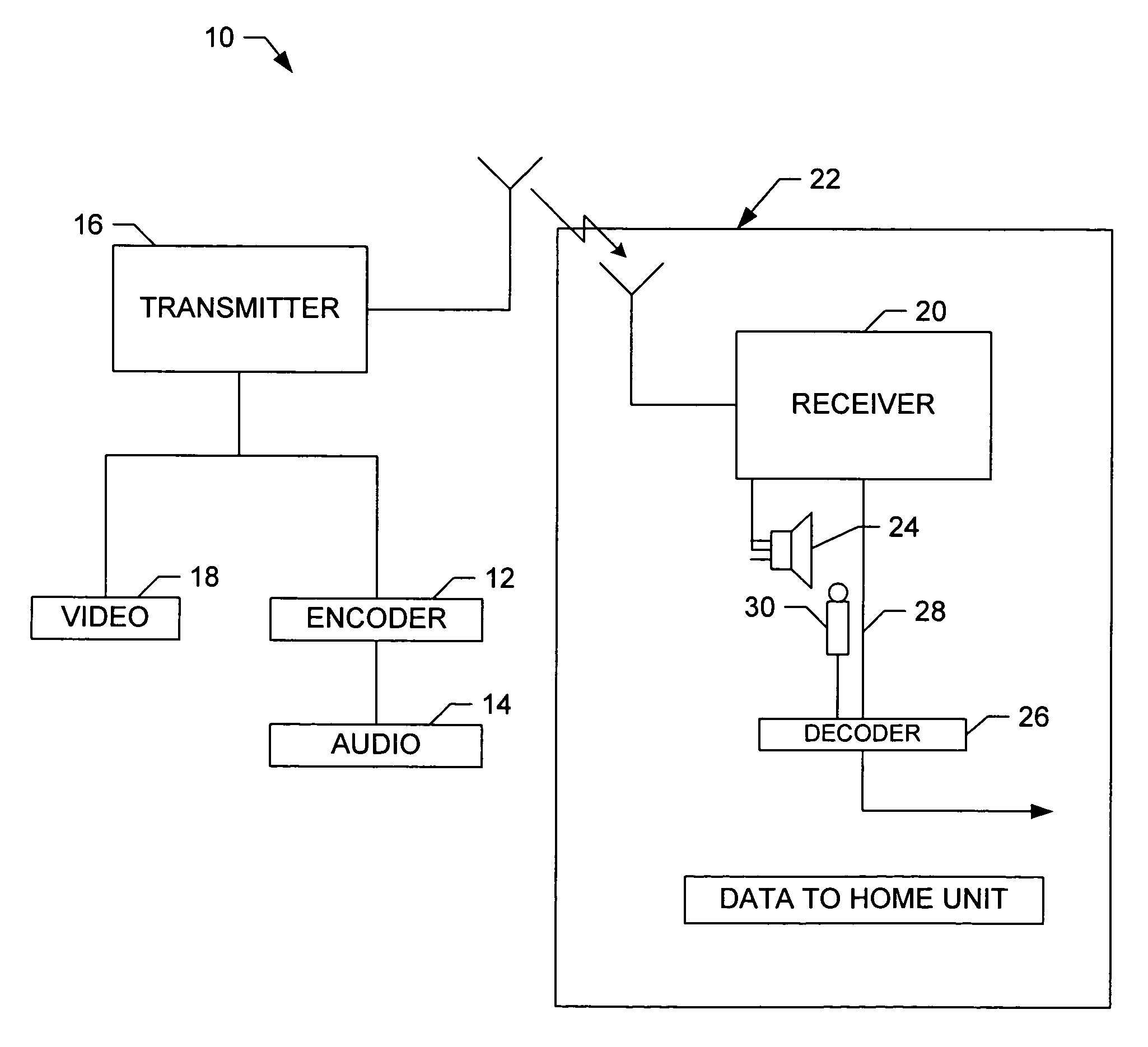
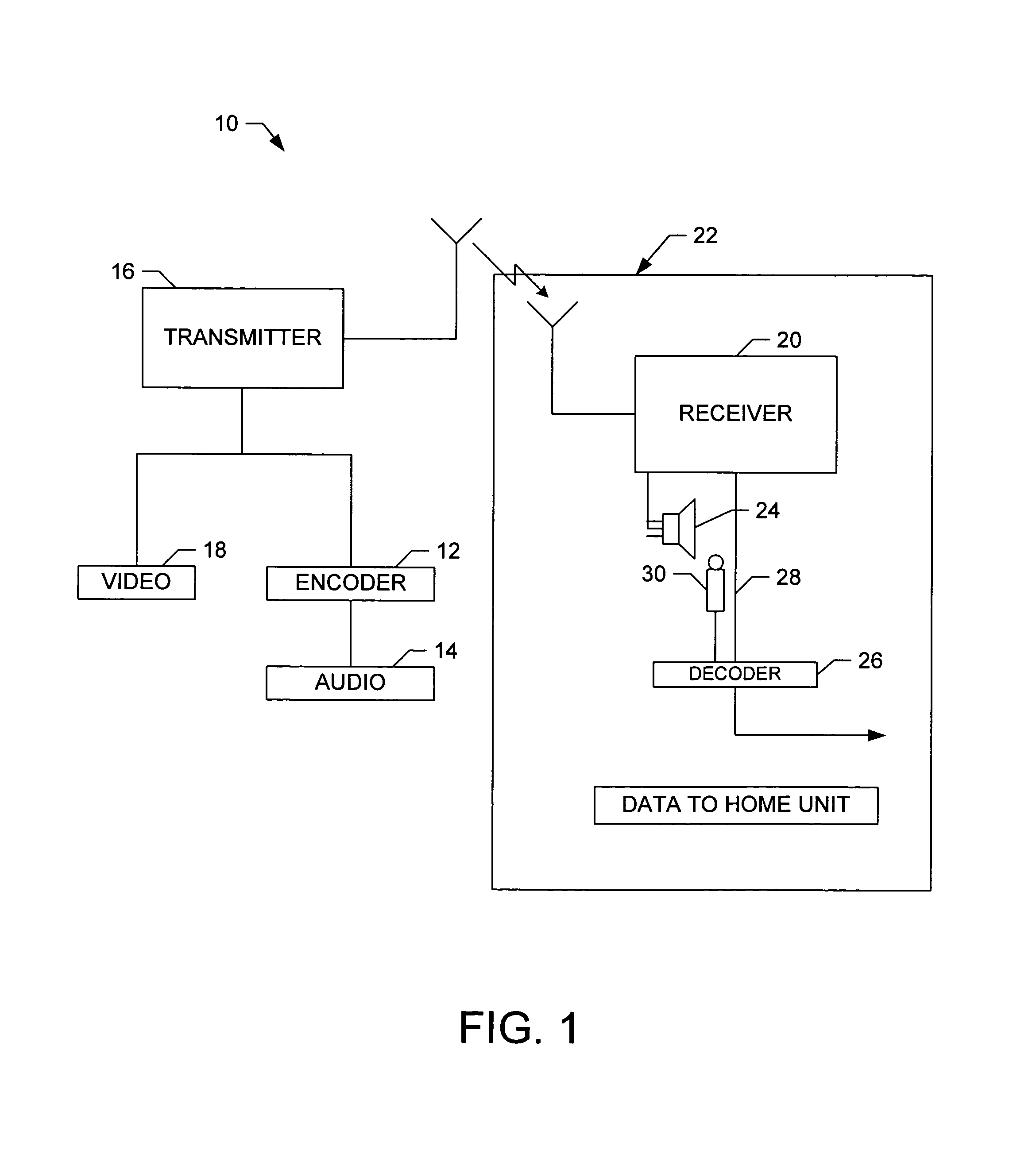
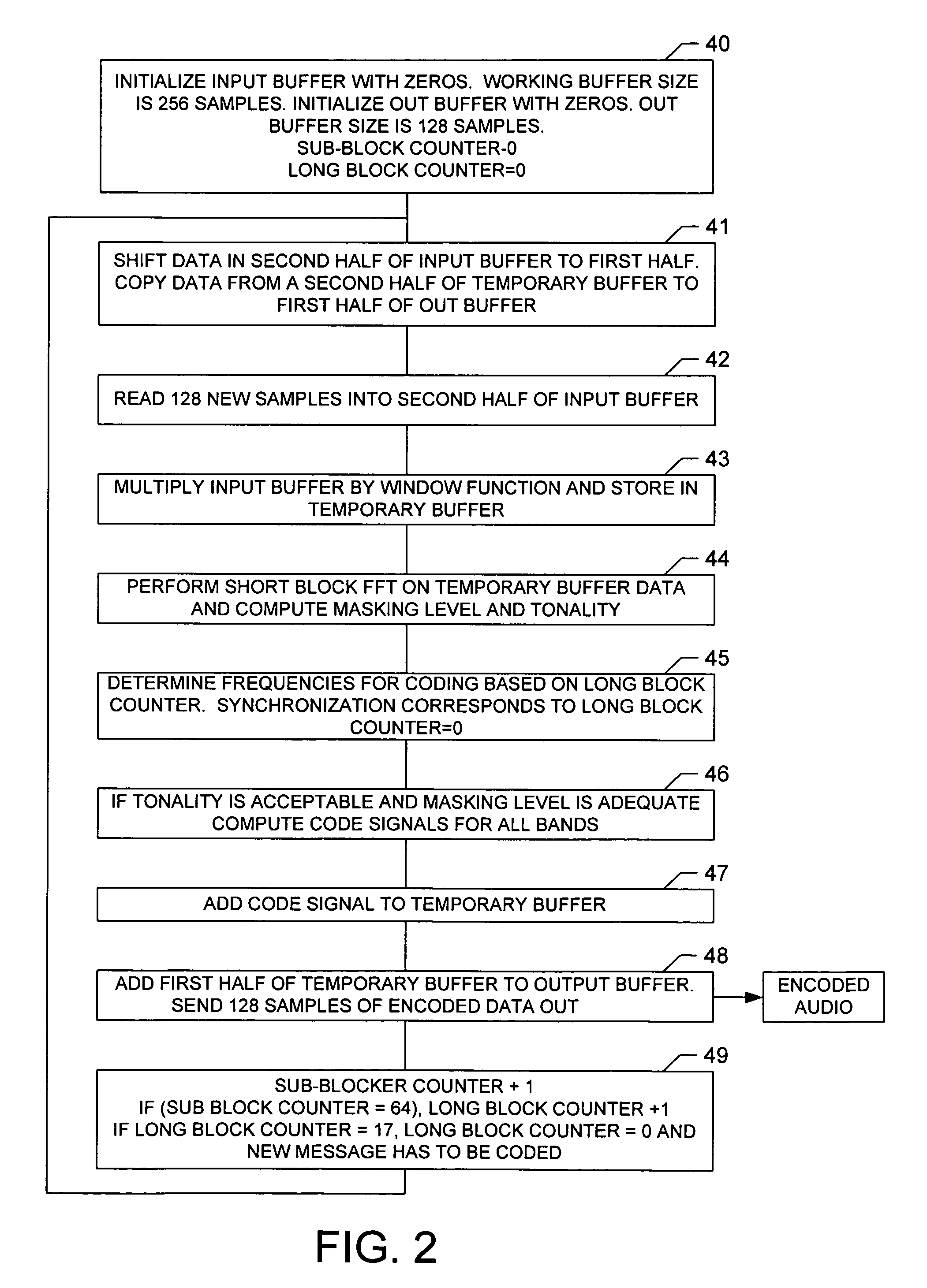
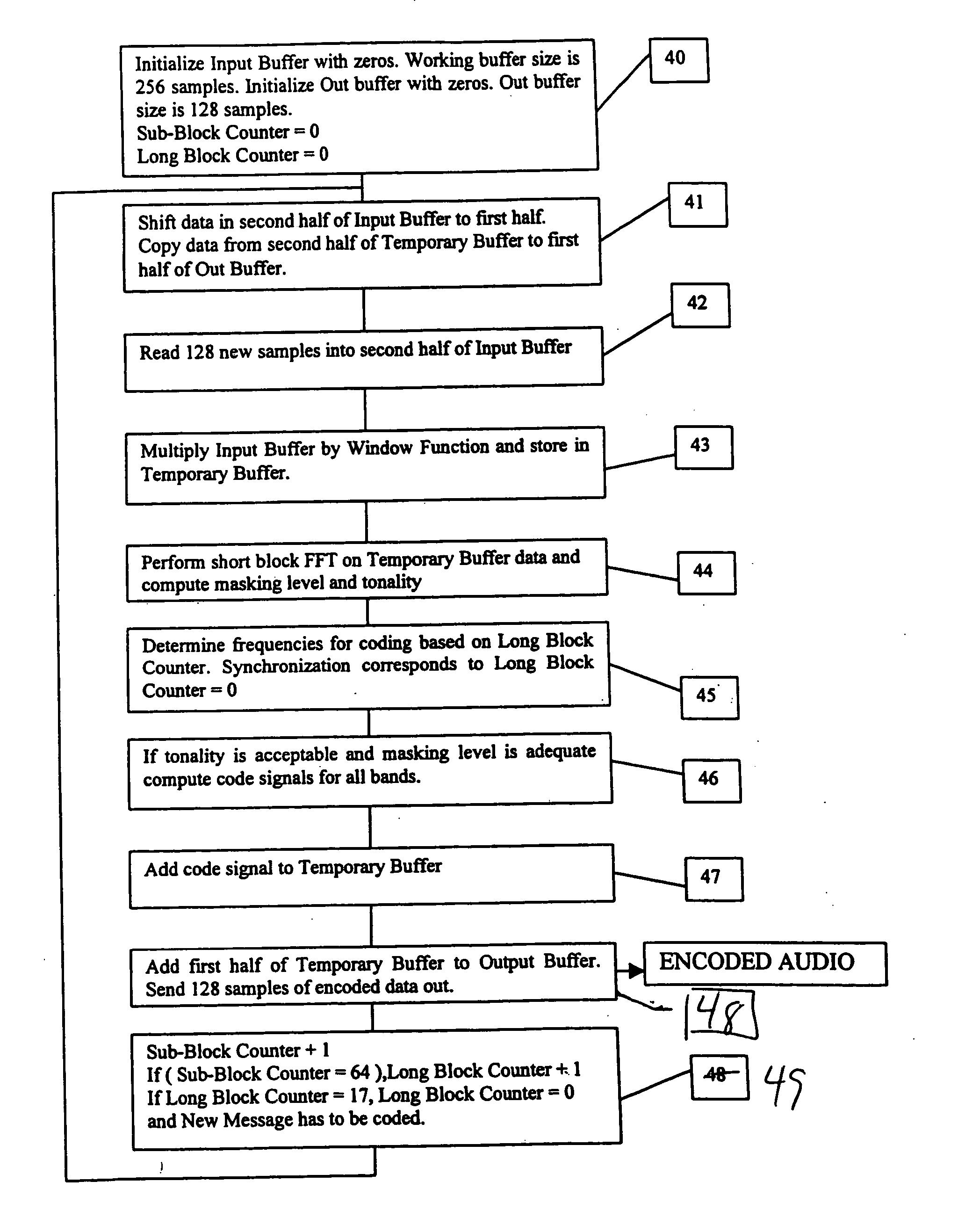
Multi-band spectral audio encoding
An encoder includes a sampler that samples an audio signal and that generates from the samples a plurality of short blocks of sampled audio. Each of the short blocks has a duration less than a minimum audibly perceivable signal delay. A processor combines the plurality of short blocks into a long block. The long block is transformed into a frequency domain signal having a plurality of independently modulatable frequency indices. The frequency difference between adjacent indices is determined by the minimum duration and the sampling rate of the sampler. A neighborhood of frequency indices is selected so that the frequency difference between a lowest index and a highest index within the neighborhood is less than a predetermined value. Two or more of the indices are modulated in the neighborhood so as to make a selected one of the indices an extremum while keeping the total energy of the neighborhood constant. A plurality of frequency bands are so coded. A decoder decides that a bit or bits have been received if, in a majority of the frequency bands, the decoder detects a modulated index.
Owner:NIELSEN COMPANY US LLC THE A DELAWARE LIMITED LIABILITY
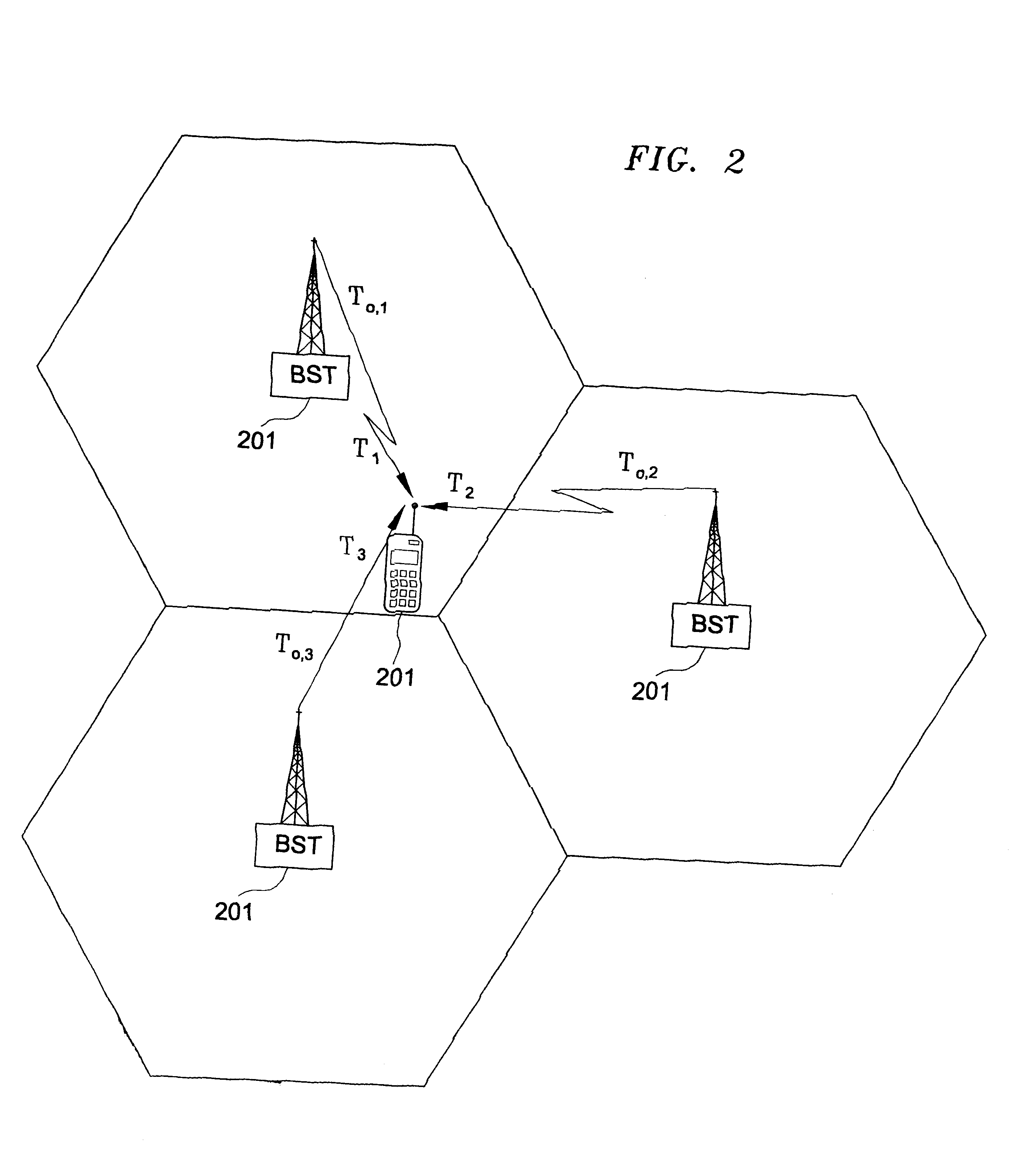
Methods and apparatus to position a mobile receiver using downlink signals, part I
InactiveUS6208297B1Reduce the impactReduce impactDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationPhase differenceImage resolution
The invention comprises of methods and apparatus to estimate the position and velocity of a Mobile Receiver (MR) using either the Time Of Arrival (TOA) of signals received by the MR, their Phase Of Arrival (POA), their Strength Of Arrival (SOA), their Frequency Of Arrival (FOA), or a combination thereof, with respect to a reference produced by a Reference Receiver (RR) of known location. In order to solve for the coordinates of the MR, the invention uses either hyperbolic multilateration based on Time Difference Of Arrival (TDOA), or linear multiangulation based on Phase Difference Of Arrival (PDOA), or both. In order to solve for the velocity of the MR, the patent uses FOA based on Frequency Difference Of Arrival (FDOA). An important contribution of this invention is the way the MR receives, processes and combines available signals for location purposes. Another important contribution of this invention is the way the RR receives, processes and combines available signals for reference purposes. Yet another important contribution of the invention is the application of Super-Resolution (SR) techniques at both the MR and the RR to increase the resolution of the estimated TOAs, POAs, SOAs, or FOAs.
Owner:CAPITOL ENERGY RESOURCES INC +1
Device communications of an implantable medical device and an external system
An implantable medical device, external unit, and method for establishing communication between them are disclosed. The external unit learns the frequencies of transmission and reception for the implant. The transmit frequency of the implant is learned by the external unit measuring a difference between the transmit frequency of the implant and the external unit's receive frequency. The receive frequency of the implant is learned by the measured difference between its transmit frequency and the receive frequency of the external unit when the implant has a fixed transmit and receive frequency difference. Otherwise, the receive frequency is learned by the implant measuring the difference between its receive frequency and the transmit frequency of the external unit and by sending an indication of the difference to the external unit through the return signal. The external unit may anticipate a beginning of the implant's preset communication period based on its internal clock.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method and apparatus for interferometry
InactiveUS20110235045A1High measurementImprove scanning accuracyRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryHelical computed tomographyEngineering
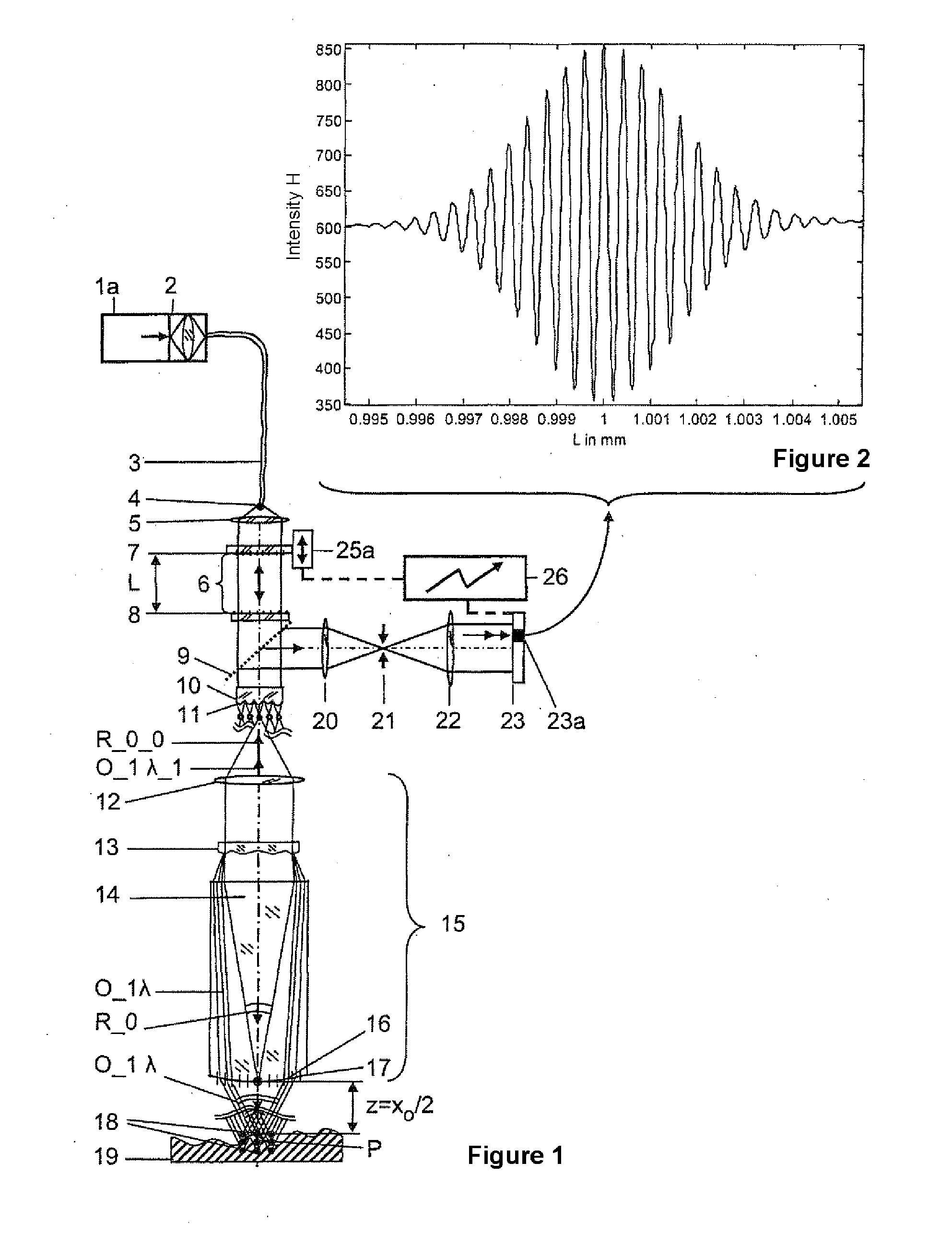
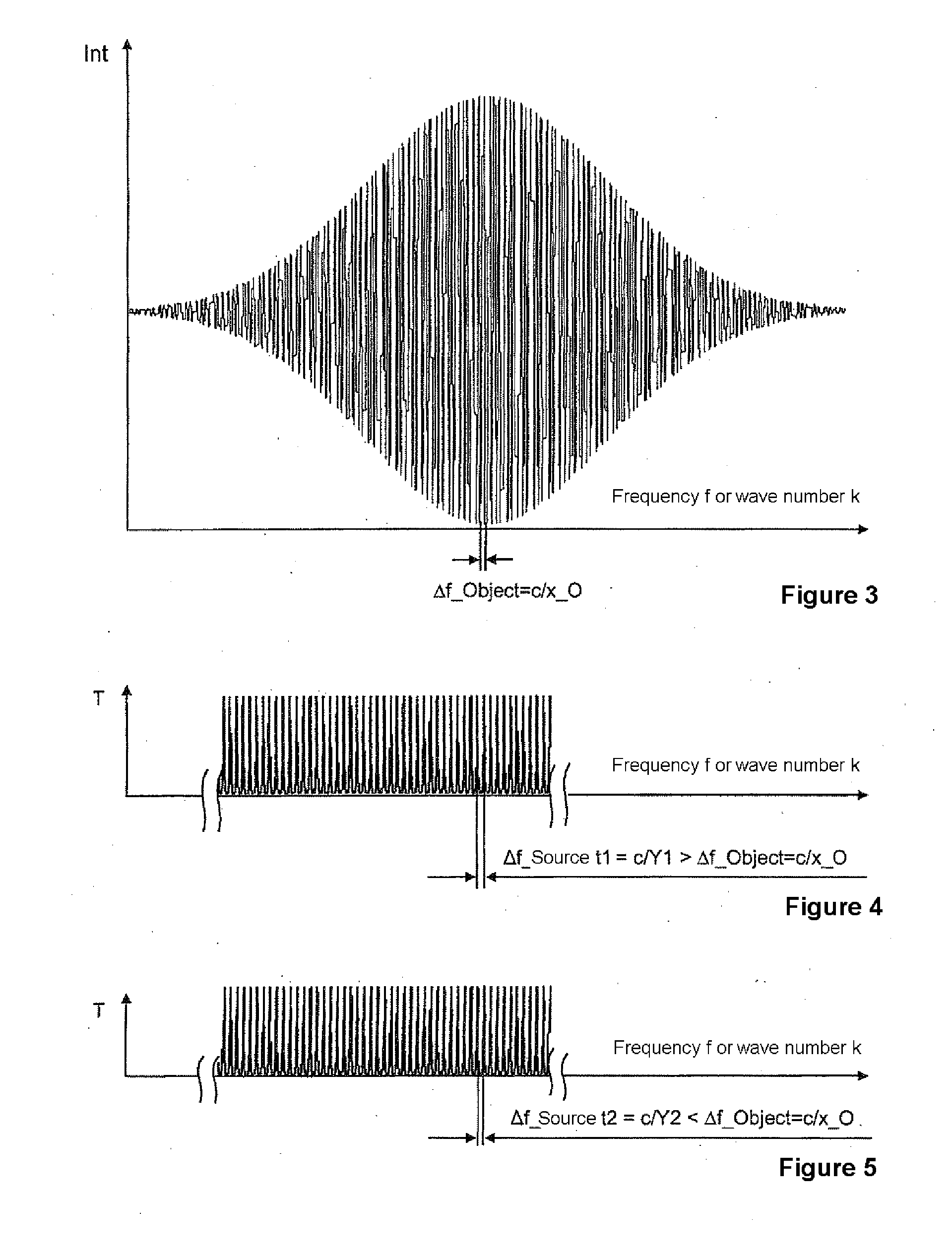
A method and an arrangement are provided for scalable confocal interferometry for distance measurement, for 3-D detection of an object, for OC tomography with an object imaging interferometer and at least one light source. The interferometer has an optical path difference not equal to zero at each optically detected object element. Thus, the maxima of a sinusoidal frequency wavelet, associated with each detected object element, each have a frequency difference Δf_Objekt. At least one spectrally integrally detecting, rastered detector is arranged to record the object. The light source preferably has a frequency comb, and the frequency comb differences Δf_Quelle are changed in a predefined manner over time in a scan during measuring. In the process, the frequency differences Δf_Quelle are made equal to the frequency difference Δf_Objekt or equal to an integer multiple of the frequency differences Δf_Objekt at least once for each object element.
Owner:UNIV STUTTGART
Methods and apparatus to position a mobile receiver using downlink signals, part II
InactiveUS6204812B1Use minimizedLow costDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationPhase differenceMultilateration
The invention consists of methods and apparatus to estimate the position and velocity of a Mobile Receiver (MR) using either the Time Of Arrival (TOA) of signals received by the MR, their Phase Of Arrival (POA), their Strength Of Arrival (SOA), their Frequency Of Arrival (FOA), or a combination thereof, with respect to a reference produced by a Reference Receiver (RR) of known location. In order to solve for the coordinates of the MR, the invention uses either hyperbolic multilateration based on Time Difference Of Arrival (TDOA), or linear multiangulation based on Phase Difference Of Arrival (PDOA), or both. In order to solve for the velocity of the MR, the patent uses FOA based on Frequency Difference Of Arrival (FDOA). An important contribution of this invention is the way the MR receives, processes and combines available signals for location purposes. Another important contribution of this invention is the way the RR receives, processes and combines available signals for reference purposes.
Owner:CELL LOC LOCATION TECH
Temperature compensation mechanism for a micromechanical ring resonator
InactiveUS6859113B2Additional requirementAcceleration measurement using interia forcesImpedence networksVIT signalsAtomic physics
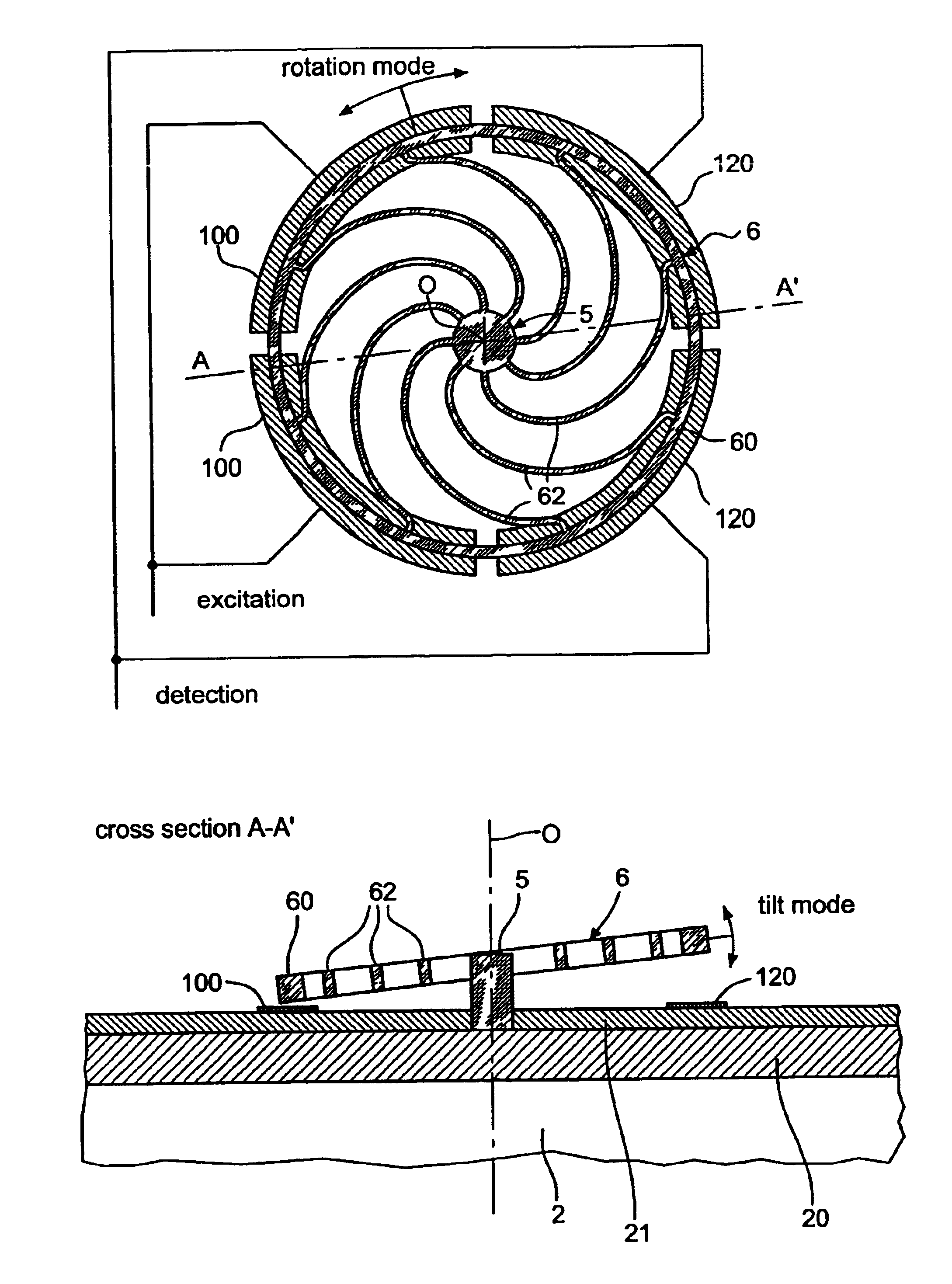
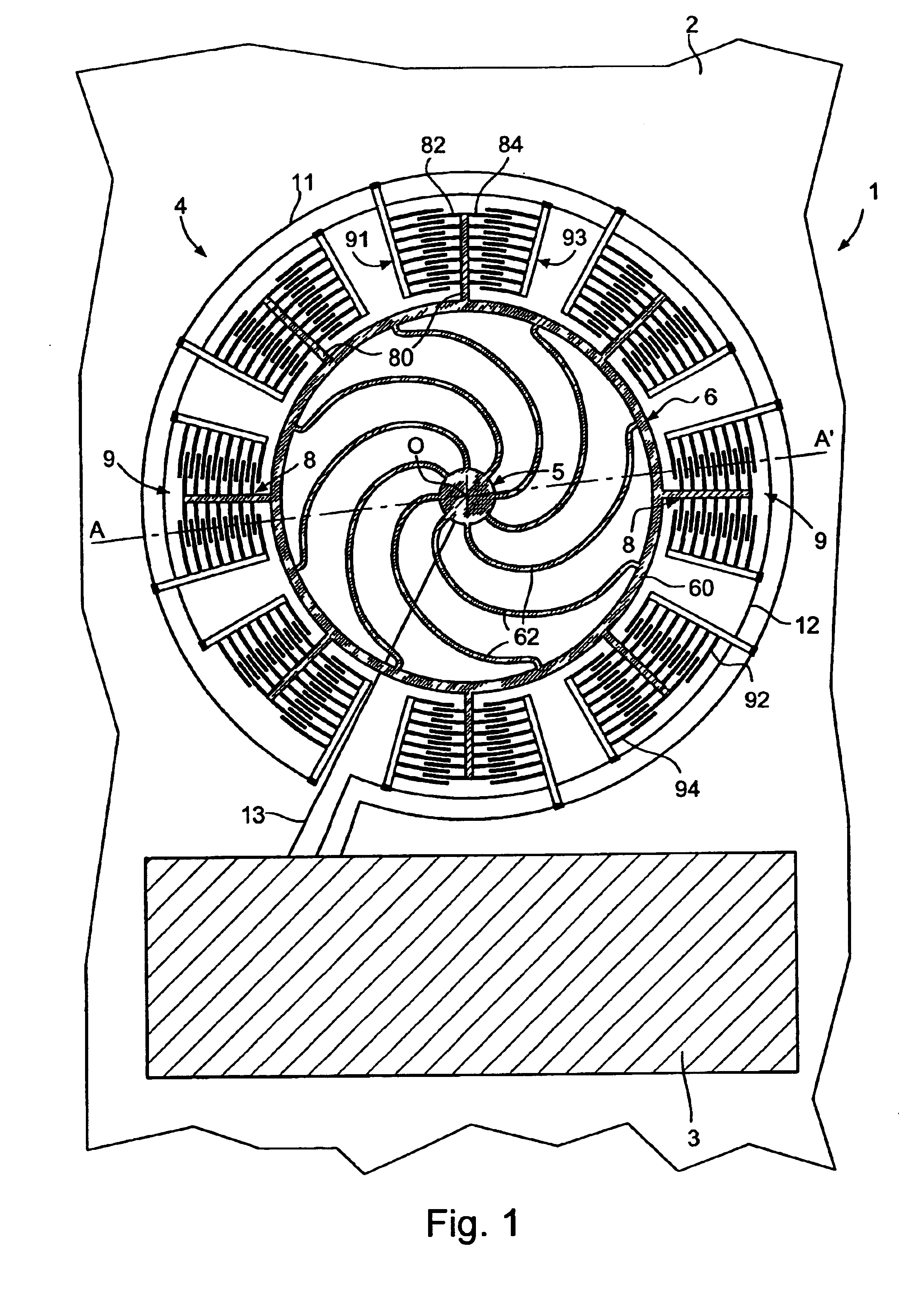
A time base including a resonator (4) and an integrated electronic circuit (3) for driving the resonator into oscillation and for producing, in response to the oscillation, a signal having a determined frequency. The resonator is an integrated micromechanical ring resonator supported above a substrate (2) and adapted to oscillate in a first oscillation mode. The ring resonator includes a free-standing oscillating structure (6). Electrodes (100, 120; 130, 150) are positioned under the free-standing oscillating structure in such a way as to drive and sense a second oscillation mode in a plane substantially perpendicular to the substrate and having a resonant frequency which is different from the resonant frequency of the first oscillation mode, a frequency difference between the resonant frequencies of both oscillation modes being used for compensating for the effect of temperature on the frequency of the signal produced by the time base.
Owner:ETA SA MFG HORLOGERE SUISSE
Droop control system for grid-connected synchronization
InactiveUS20130073109A1Minimizes voltage fluctuationGood effectMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlProcess moduleElectric power system
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Polarization-Multiplexed Optical Transmission System, Polarization-Multiplexed Optical Transmitter, and Polarization-Multiplexed Optical Receiver
InactiveUS20120134676A1Preventing signal quality degradationReliable polarizationPolarisation multiplex systemsOptical mode multiplex systemsDigital signal processingPolarization diversity
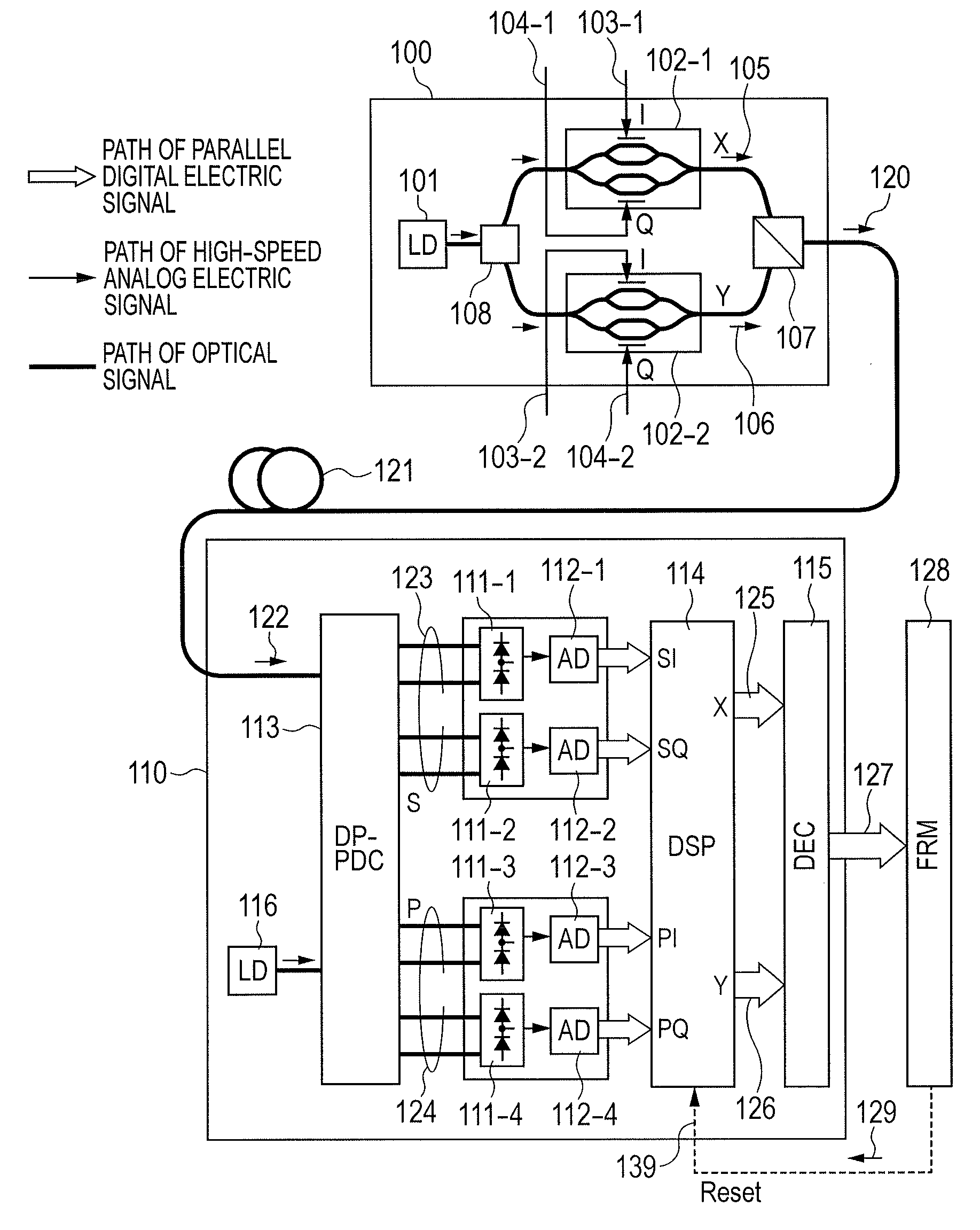
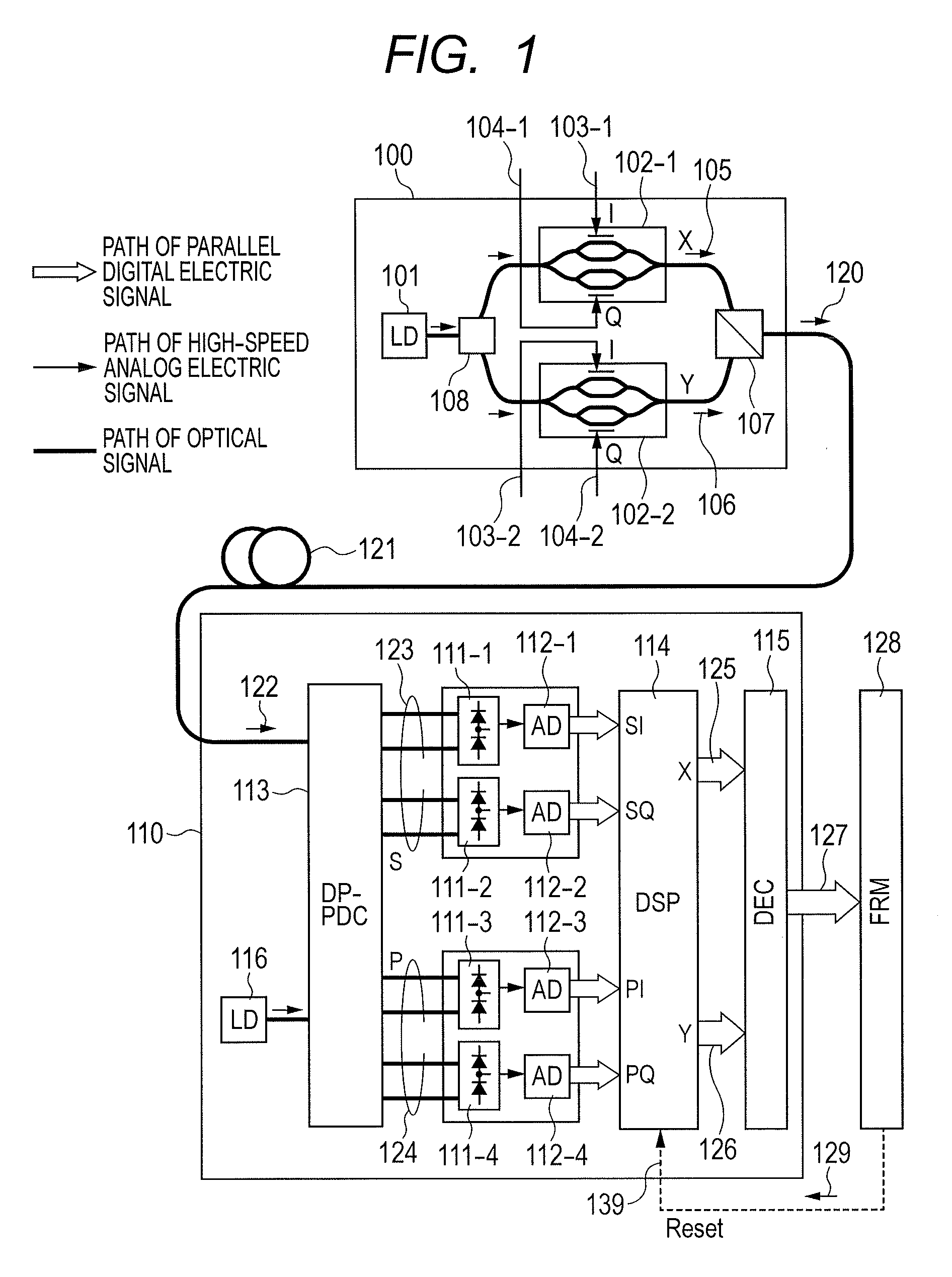
There is a need to prevent two receivers from converging on a state of receiving the same polarization state, fast start receivers, and ensure highly reliable operations. A polarization-multiplexed transmitter previously applies frequency shifts of frequencies +Δf and −Δf to X-polarization and Y-polarization digital information signals to be transmitted. Optical field modulators modulate and polarization-multiplex the signals. As a result, a frequency difference of 2Δf is supplied to X-polarization and Y-polarization components. A polarization diversity coherent optical receiver 215 receives the signal. A frequency estimation portion in a digital signal processing circuit detects a frequency difference signal in both polarization components. This signal is used to a polarization splitting circuit in the digital signal processing circuit.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
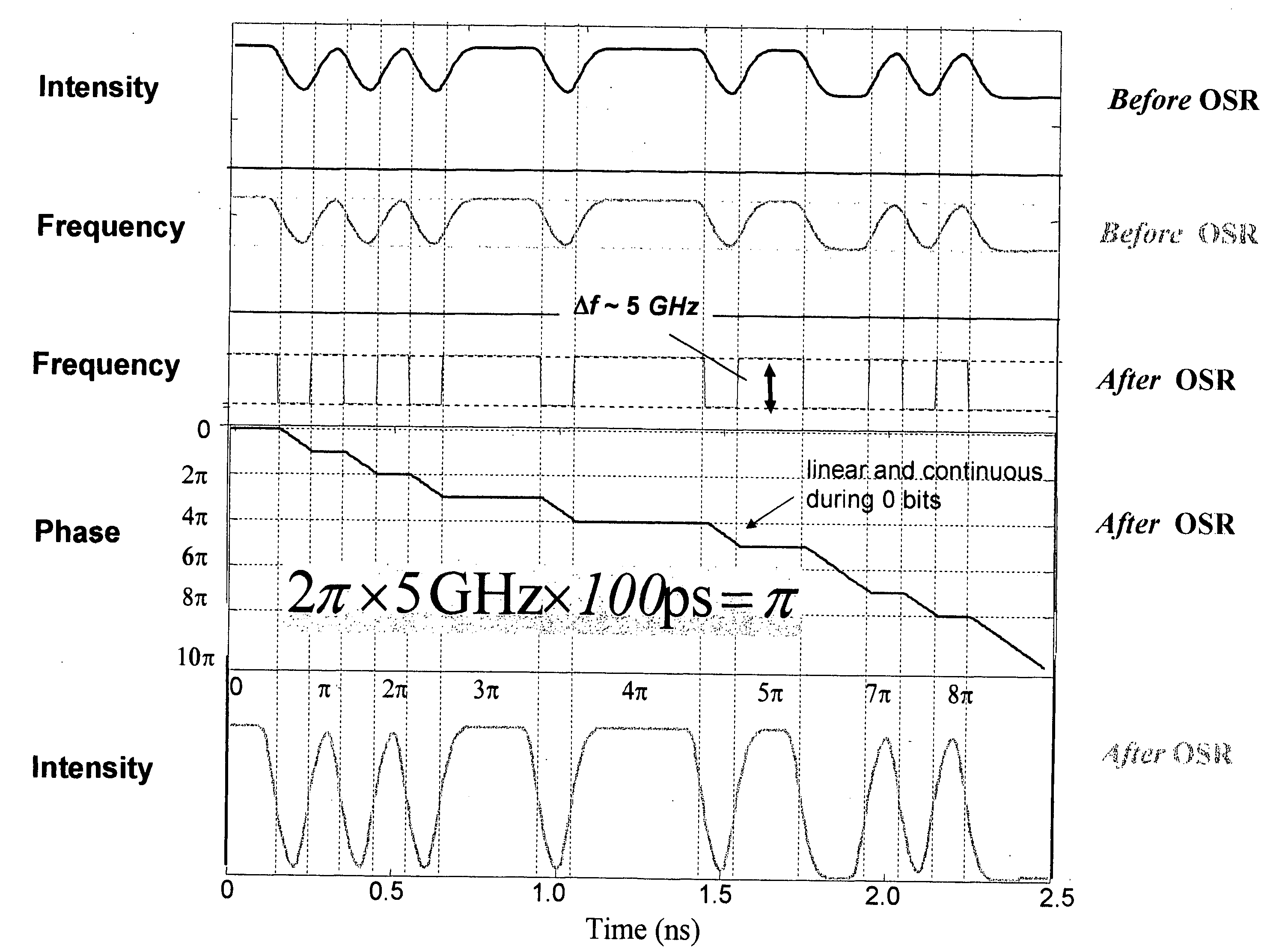
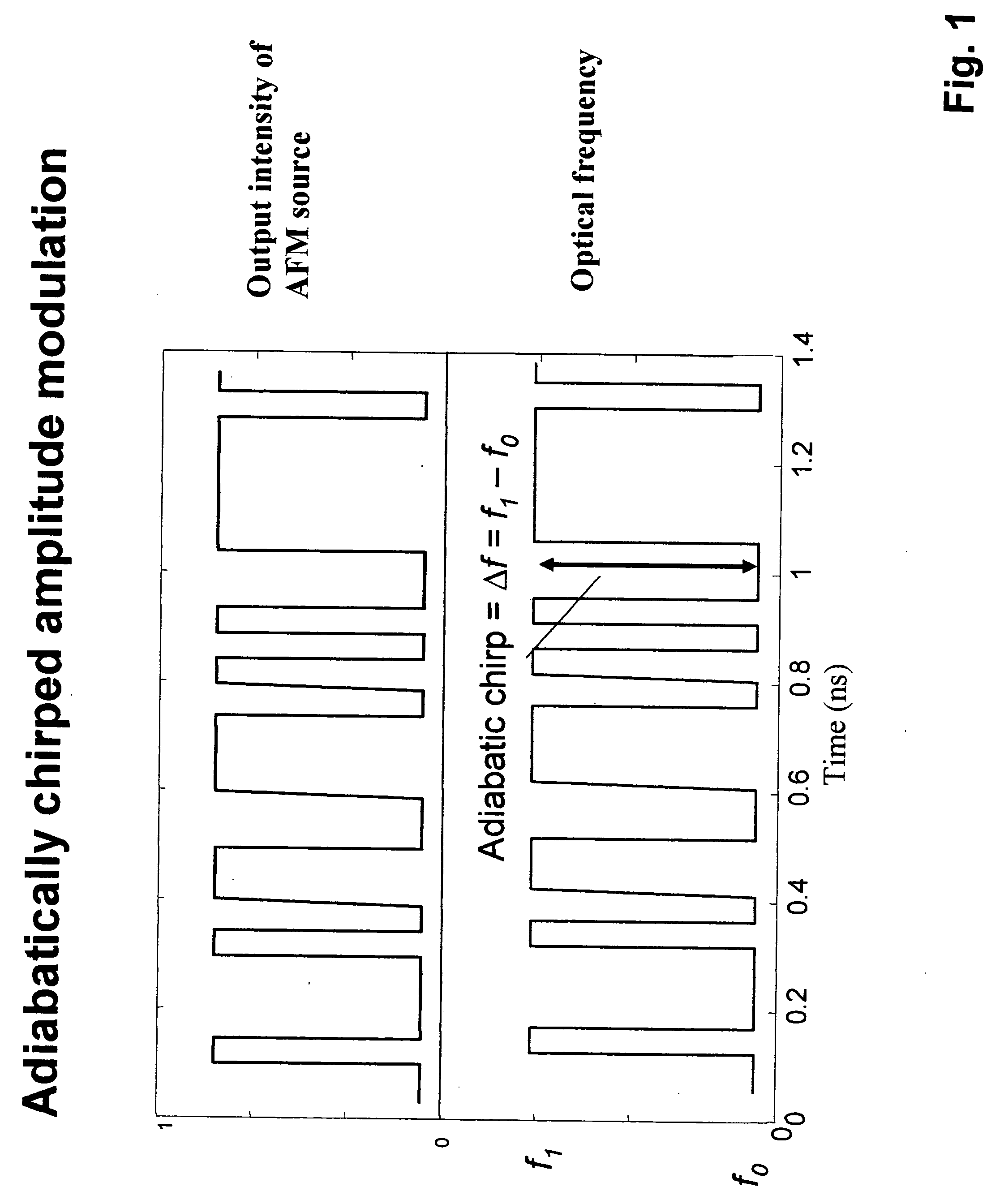
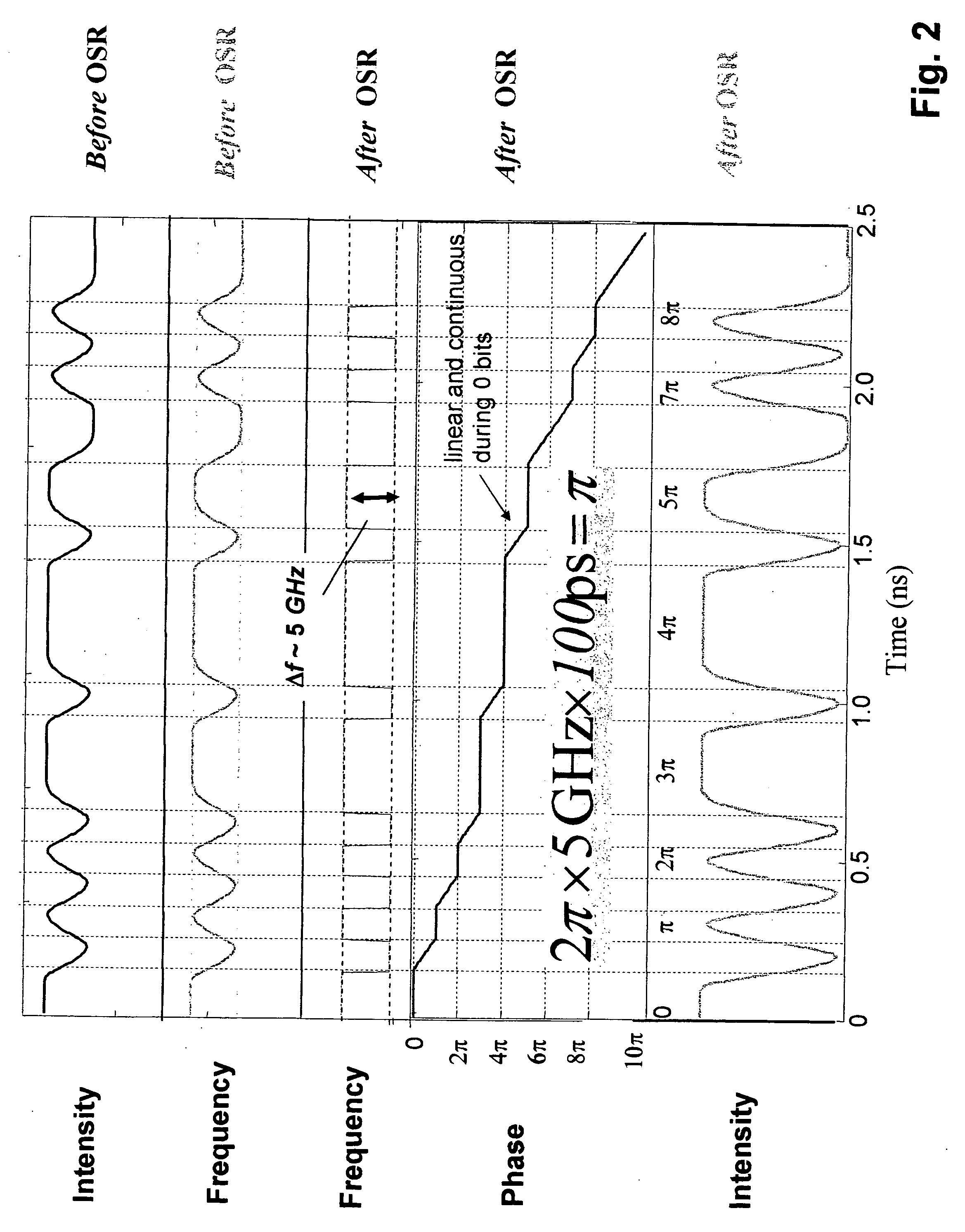
Method and apparatus for transmitting a signal using simultaneous FM and AM modulation
There is provided method for transmitting binary data contained in respective successive time cells, the data being in the form of an optical signal obtained by amplitude modulation and frequency modulation of an optical carrier wave, with a 0 bit data value having a 0 bit mean amplitude having a 0 bit amplitude time duration and a 0 bit frequency having a 0 bit frequency duration, and a 1 bit data value having a 1 bit mean amplitude having a 1 bit amplitude time duration and a 1 bit frequency having a 1 bit frequency duration; the improvement wherein: independently adjusting the 0 bit mean amplitude relative to the 1 bit mean amplitude; independently adjusting the 0 bit frequency relative to the 1 bit frequency; and independently adjusting time duration of the frequency profile of the 1 bit relative to the time duration of the amplitude profile of the 1 bit, whereby to extend the error-free propagation of the optical signal though a dispersive optical fiber beyond the dispersion limit. There is provided a method for transmitting Non-Return-To-Zero (NRZ) binary data contained in respective successive time cells, the data being in the form of an optical signal obtained by amplitude modulation and frequency modulation of an optical carrier wave, with a 0 bit data value having a 0 bit mean amplitude having a 0 bit amplitude time duration and a 0 bit frequency having a 0 bit frequency duration, and a 1 bit data value having a 1 bit mean amplitude having a 1 bit amplitude time duration and a 1 bit frequency having a 1 bit frequency duration; the improvement wherein: the phase across each 1 bit data value is substantially constant, and the phase of the carrier changes across each and every 0 bit by an amount equal to the product of the frequency difference between the 1 bit and the 0 bit and the duration of the 0 bit; whereby to extend the error-free propagation of the optical signal though a dispersive optical fiber beyond the dispersion limit. In accordance with one form of the present invention, there is provided a method for transmitting binary data contained in respective successive time cells, the data being in the form of an optical signal obtained by amplitude modulation and frequency modulation of an optical carrier wave, with a 0 bit data value having a 0 bit mean amplitude having a 0 bit amplitude time duration and a 0 bit frequency having a 0 bit frequency duration, and a 1 bit data value having a 1 bit mean amplitude having a 1 bit amplitude time duration and a 1 bit frequency having a 1 bit frequency duration; the improvement wherein: the amplitude profile of the 1 bit is substantially bell-shaped, and the frequency profile of the 1 bit is substantially square-shaped, with steeper rise and fall time and a wider flat top region; whereby to extend the error-free propagation of the optical signal though a dispersive optical fiber beyond the dispersion limit.
Owner:AZNA +1
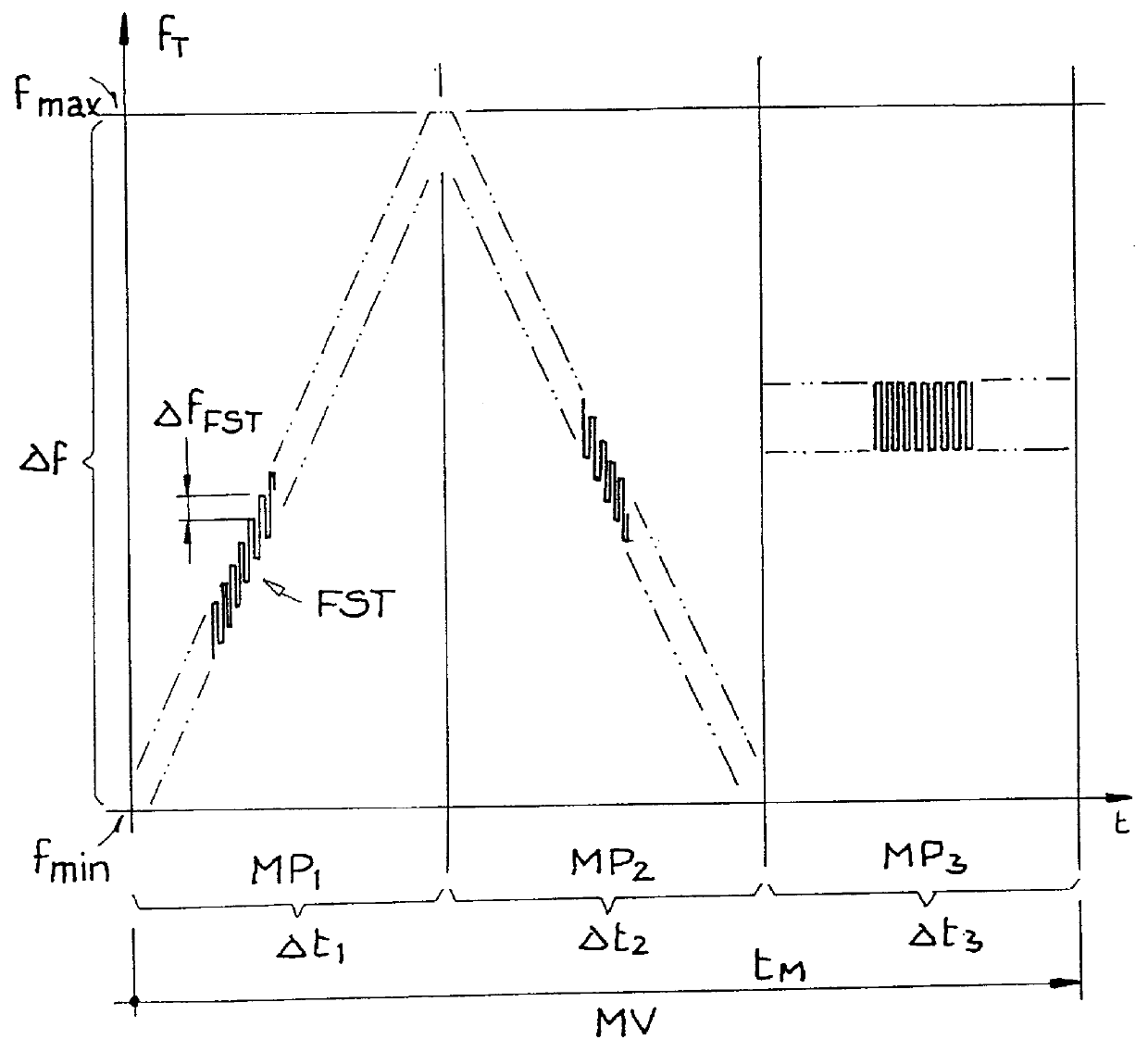
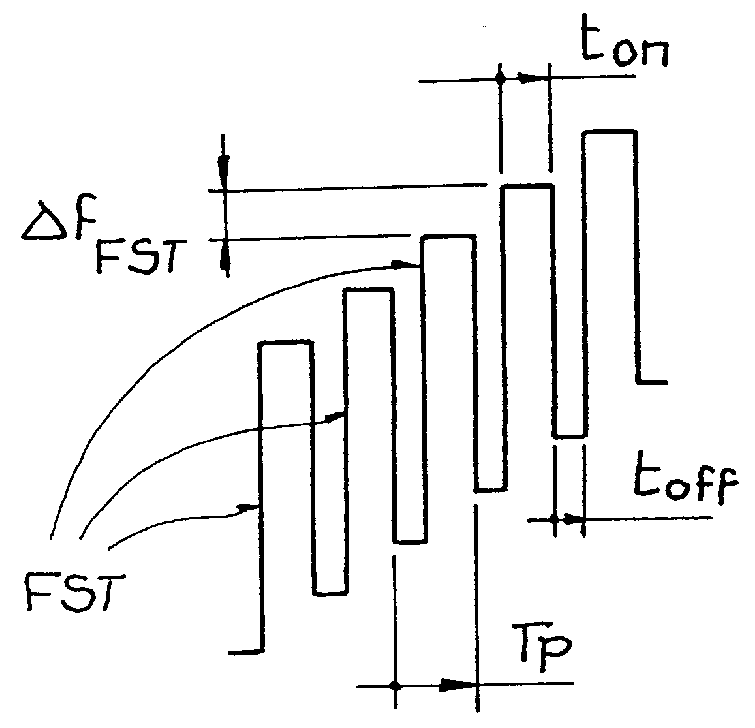
Method for operating a radar system
InactiveUS6147638AAvoid disadvantagesLow costRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsPhase difference
In a method for operating a radar system, the object is to determine by simple means and at low cost the distance and / or the radial velocity of at least one target object with high resolution. For this purpose, in each measuring phase of the measurement process in the "pulse FMCW radar system", switchover between a transmission mode and a receiving mode is effected a multiple number of times and at short intervals of time. In the transmission mode, all receiving units of the radar system are switched off, while a pulse-shaped (frequency-modulated) transmission signal with time-successive transmission pulses having a specific pulse-on time and a specific carrier frequency is emitted from at least one transmitter unit of the radar system. In receiving mode, all transmitter units are switched off in the pulse-off times of the transmission pulses, while from at least one receiver unit all reflection signals originating from the last emitted transmission pulse are detected as received signal from the entire observation range before emission of the next transmission pulse. The distance and / or the radial velocity of the reflection objects is determined indirectly by the signal processing unit of the radar system by evaluation of the frequency difference and / or phase difference between the transmission signal and the received signal.
Owner:AUTOMOTIVE DISTANCE CONTROL SYST
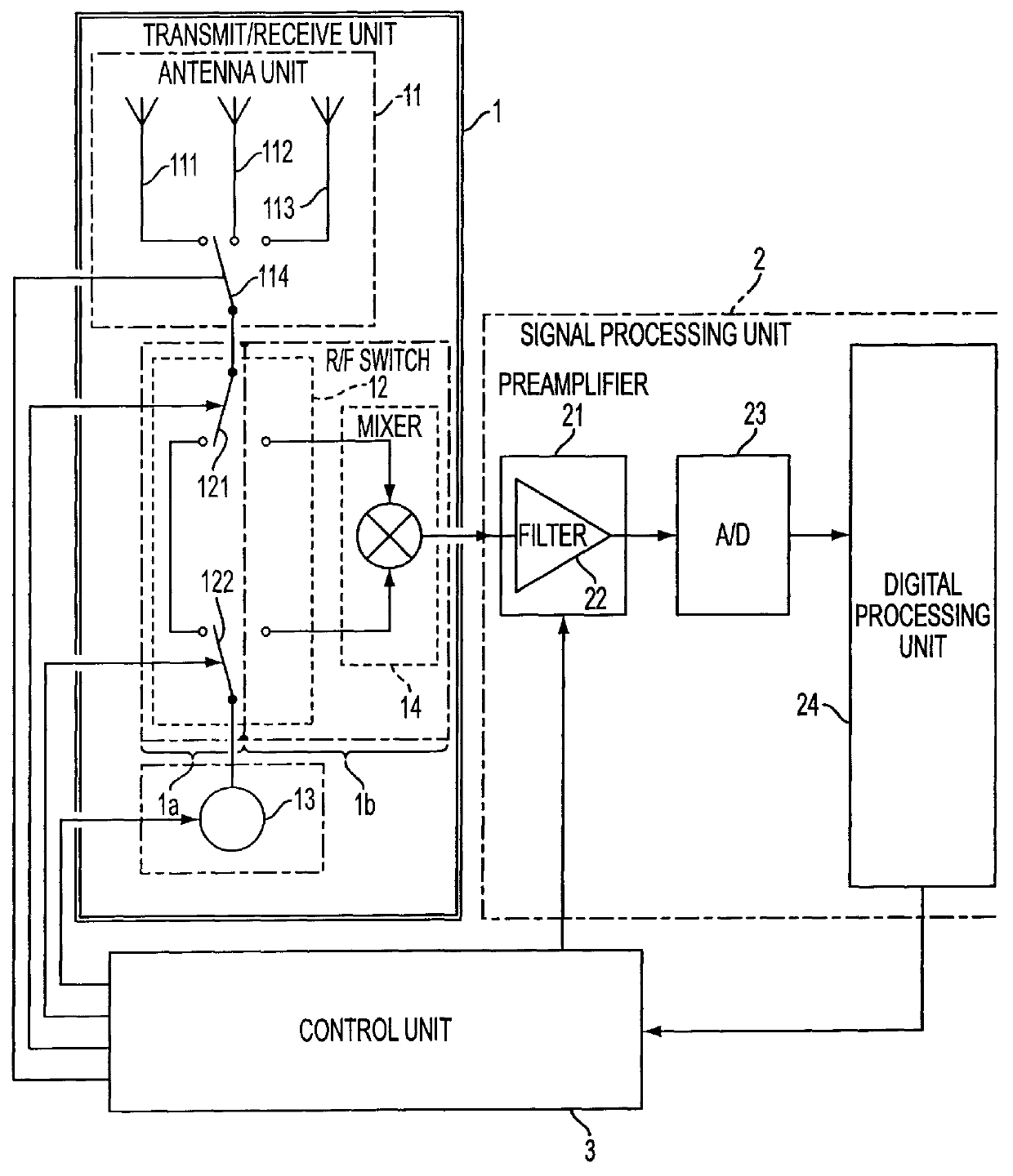
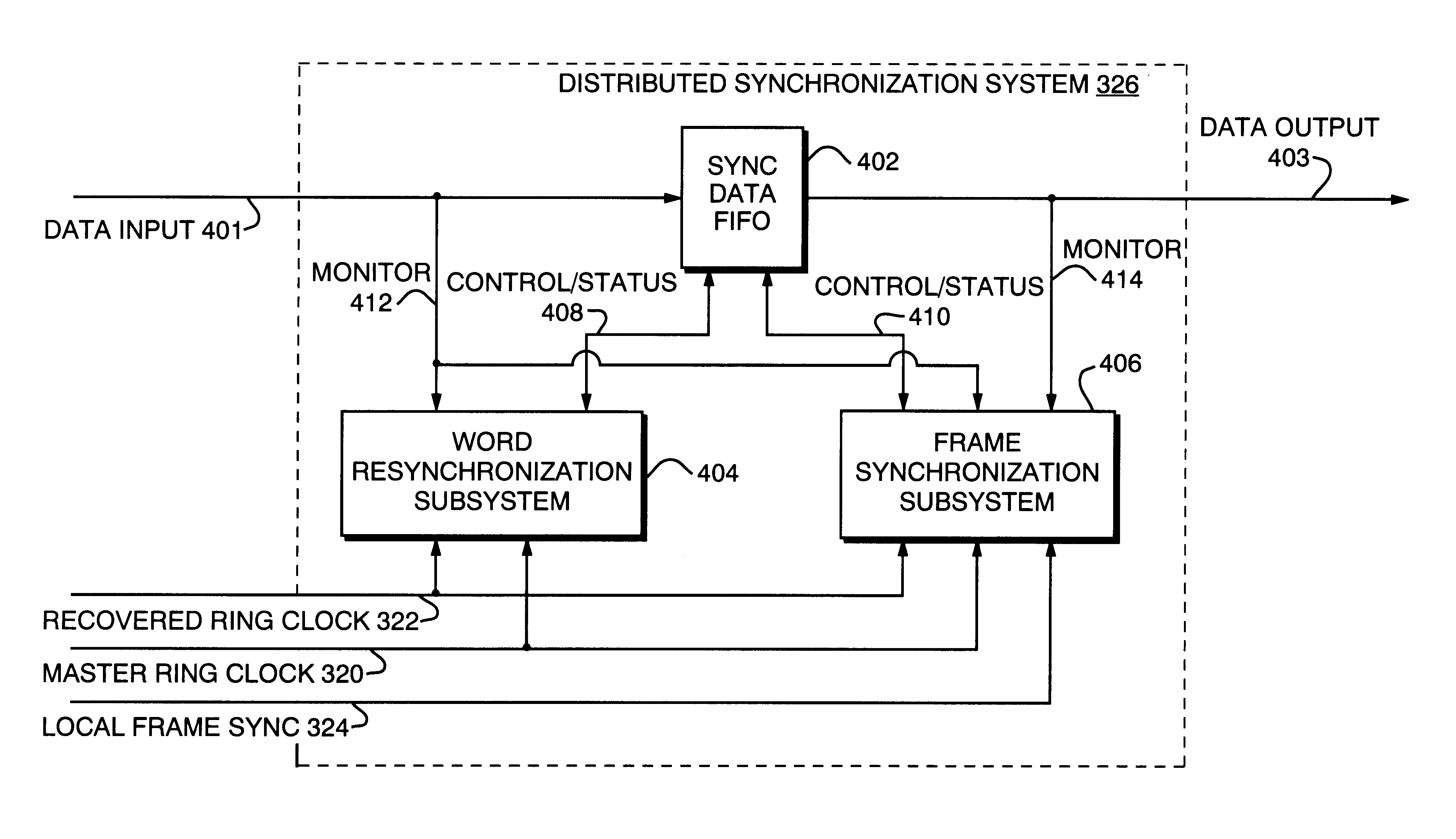
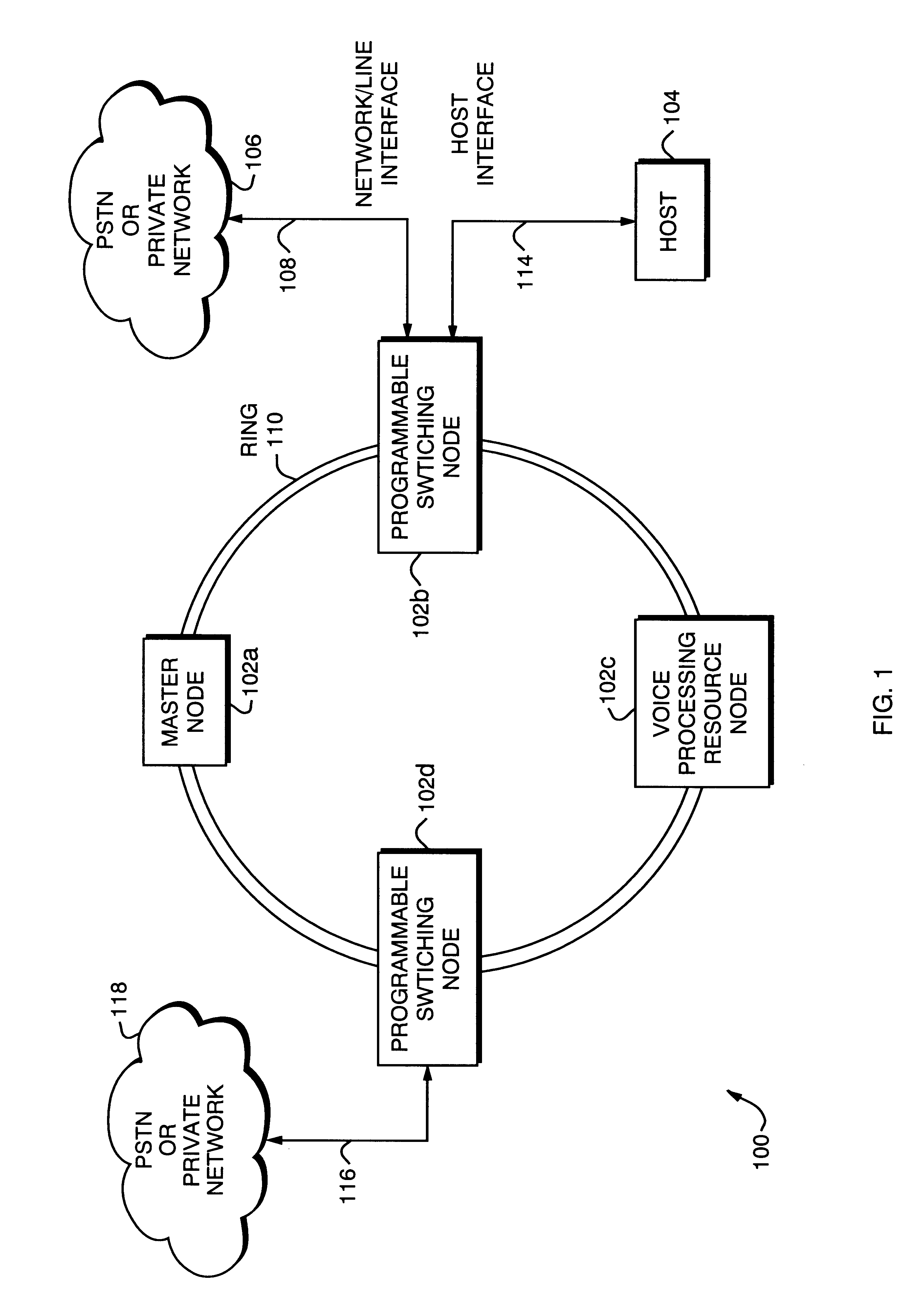
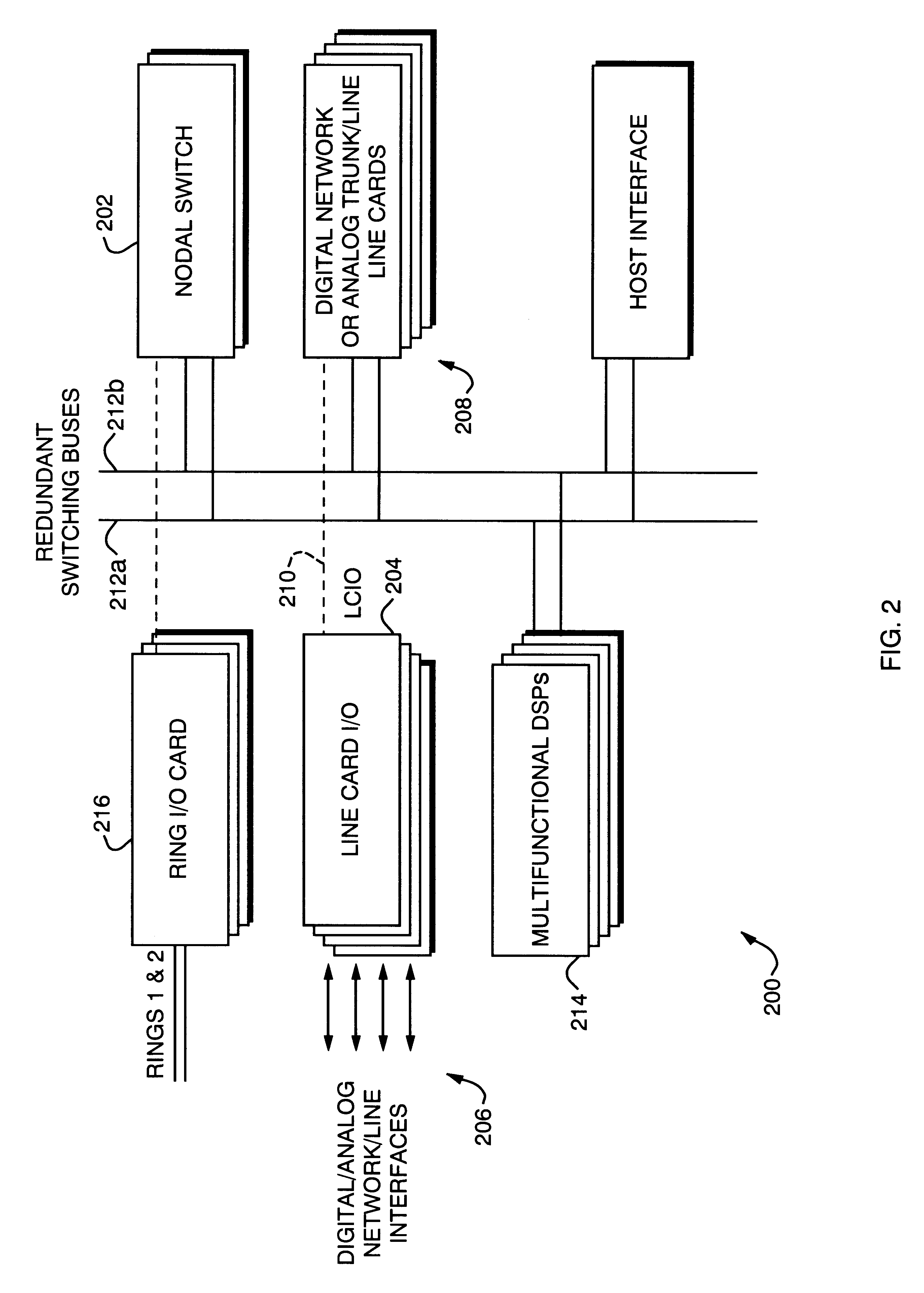
Distributed network synchronization system
InactiveUS6278718B1Effective absorptionOptimization rangeTime-division multiplexLoop networksAsynchronous communicationTelecommunications network
A distributed synchronization system for use in each node of a distributed asynchronous telecommunications network system that continually monitors and controls the flow of data through an implementing node to prevent dataflow errors due to phase and frequency differences in source and destination nodal clocks, and to control inter-nodal network latency so as to support the transmission of synchronous data. A synchronization data FIFO buffers predetermined fields or portions of fields of a unique frame packet received from a source node before retransmission to a destination node on the network. The frame packet includes a frame synchronization field indicating the beginning of a new frame packet; a payload field containing valid data; and a dead zone field providing bandwidth during which the present invention performs synchronization functions. A frame synchronization subsystem, implemented in a designated master node, guarantees that a frame is released at the beginning of an independently-determined frame regardless of network latency. A word resynchronization subsystem manages the flow of data through the data FIFO of each non-master node, receiving and storing data at the source node's clock rate and transmitting the data according to its own clock, thereby guaranteeing the efficient receipt and transmission of data between asynchronously-communicating nodes.
Owner:EXCEL SWITCHING
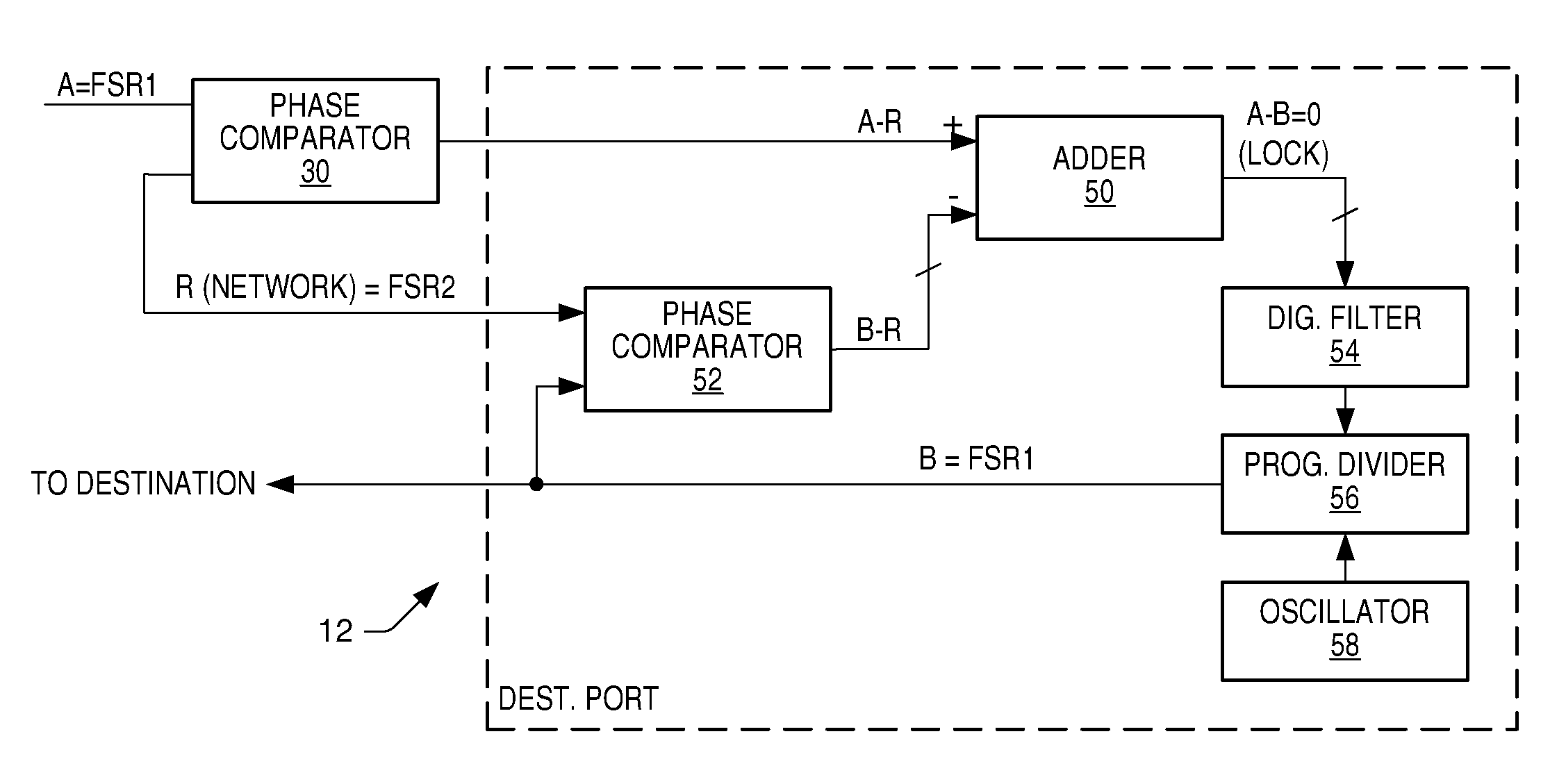
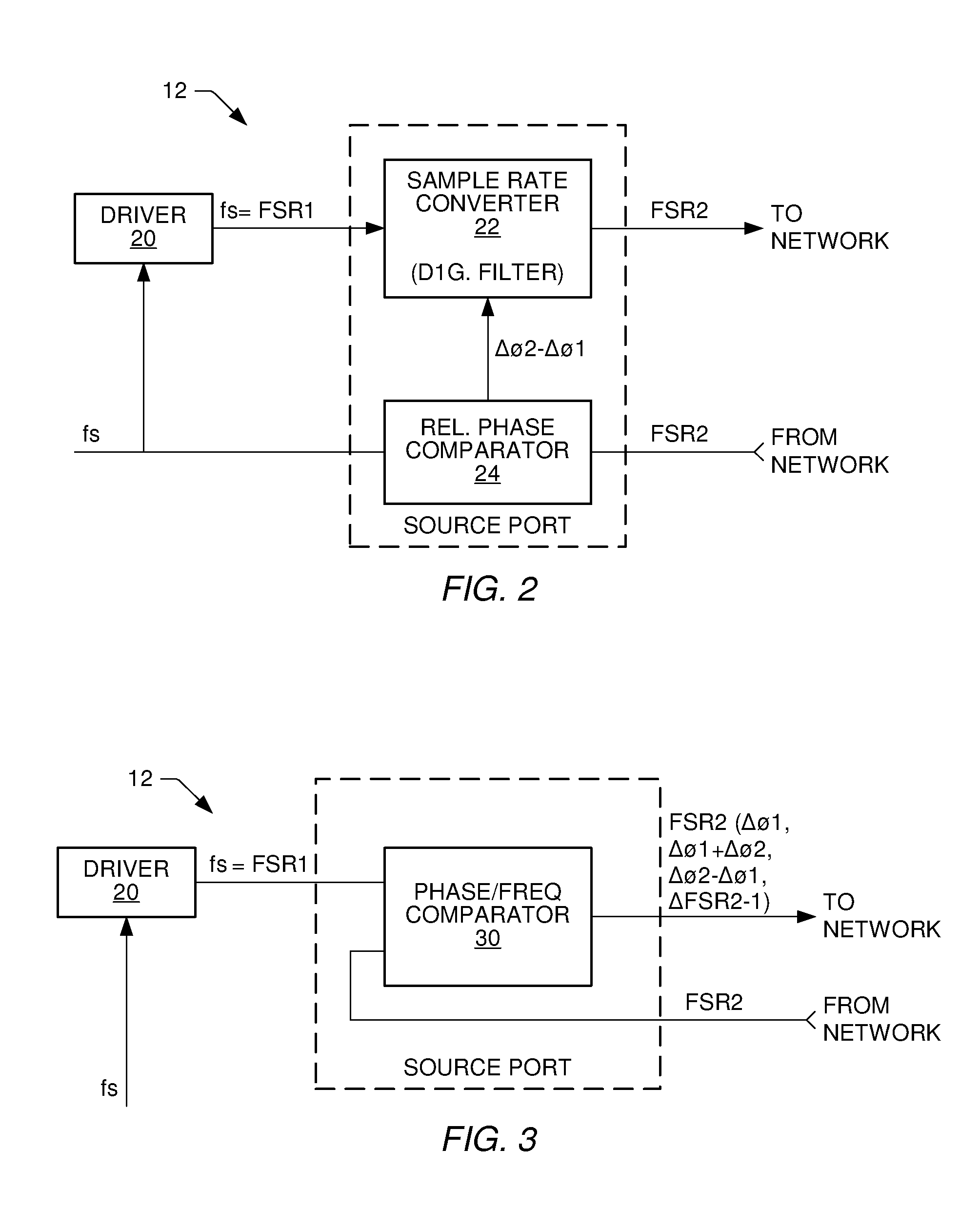
Communication system and method for sample rate converting data onto or from a network using a high speed frequency comparison technique
ActiveUS7106224B2High resolutionImprove accuracyTime-division multiplexIndividual digits conversionSample rate conversionPhase difference
A communication system, source and destination ports of the communication system, and methodology is provided for transporting data in one of possibly three different ways. Data is transported across the network at a frame sample rate that can be the same as or different from the sample rate or master clock within the source port or the destination port. If the sample rate of the source port is known, the sample rate of the destination port can be created using a PLL within the destination port and simply employing a phase comparator in the source port. The phase comparator forwards the phase or frequency difference of the network transfer rate and the source sample rate to the destination port, which then generates a local clock equivalent to the source which then compiles audio data being played at the same rate in which it was sampled at the source. Where economically feasible, sample rate conversion can be used at the source. However, sample rate conversion at the destination is preferred if the source sample rate is forwarded across the network relative to the frame transfer rate of the synchronous network. The sample rate converter simply produces a play rate from the transmitted information at the destination. Again, however, sample rate conversion compares relative phase difference changes similar to the phase difference compared in the digital PLL mode. As a further alternative, sample rates within the source and destination ports can be derived from the network frame rate using fractional dividers in the source and destination ports.
Owner:STANDRD MICROSYSTEMS CORPORATION
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing synchronization
Embodiments are directed to first and second OFDM pilot symbols. The first and second pilot symbols may have first and second sets, respectively, of allowed, forbidden, and active carrier frequencies. The second sets of carrier frequencies may be formed by frequency shifting the respective first sets by a predetermined frequency, such as the frequency difference between adjacent carriers. An embodiment is directed to frequency translating part of a first received pilot symbol by one carrier interval in a first direction, frequency translating part of a second received pilot symbol by one carrier interval in a second direction that is opposite from the first direction, and forming a correlation by multiplying the frequency translated parts of the first and second pilot symbols by complex conjugates of parts of the pilot symbols upon which frequency translation has not been performed, and summing the multiplication results.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
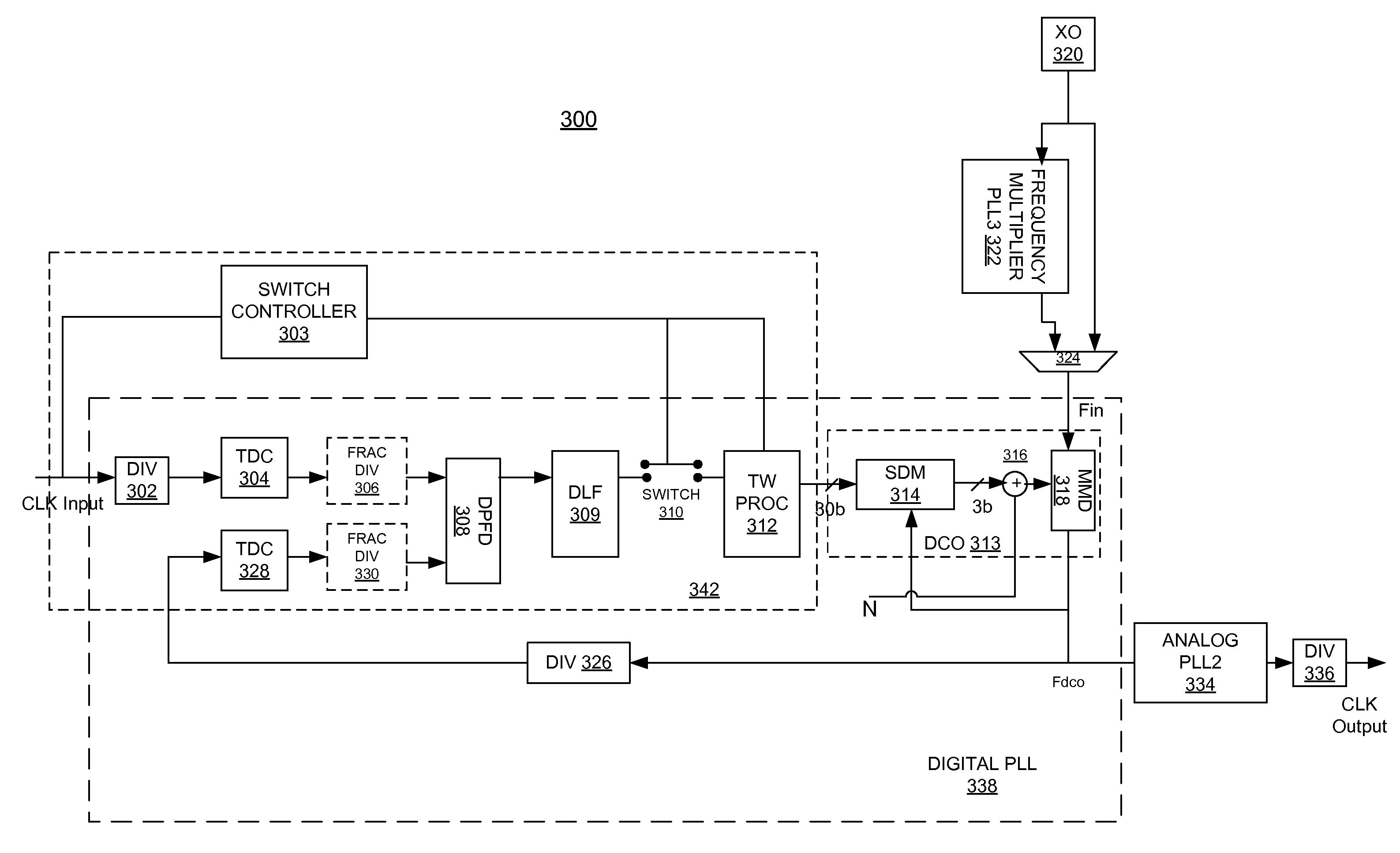
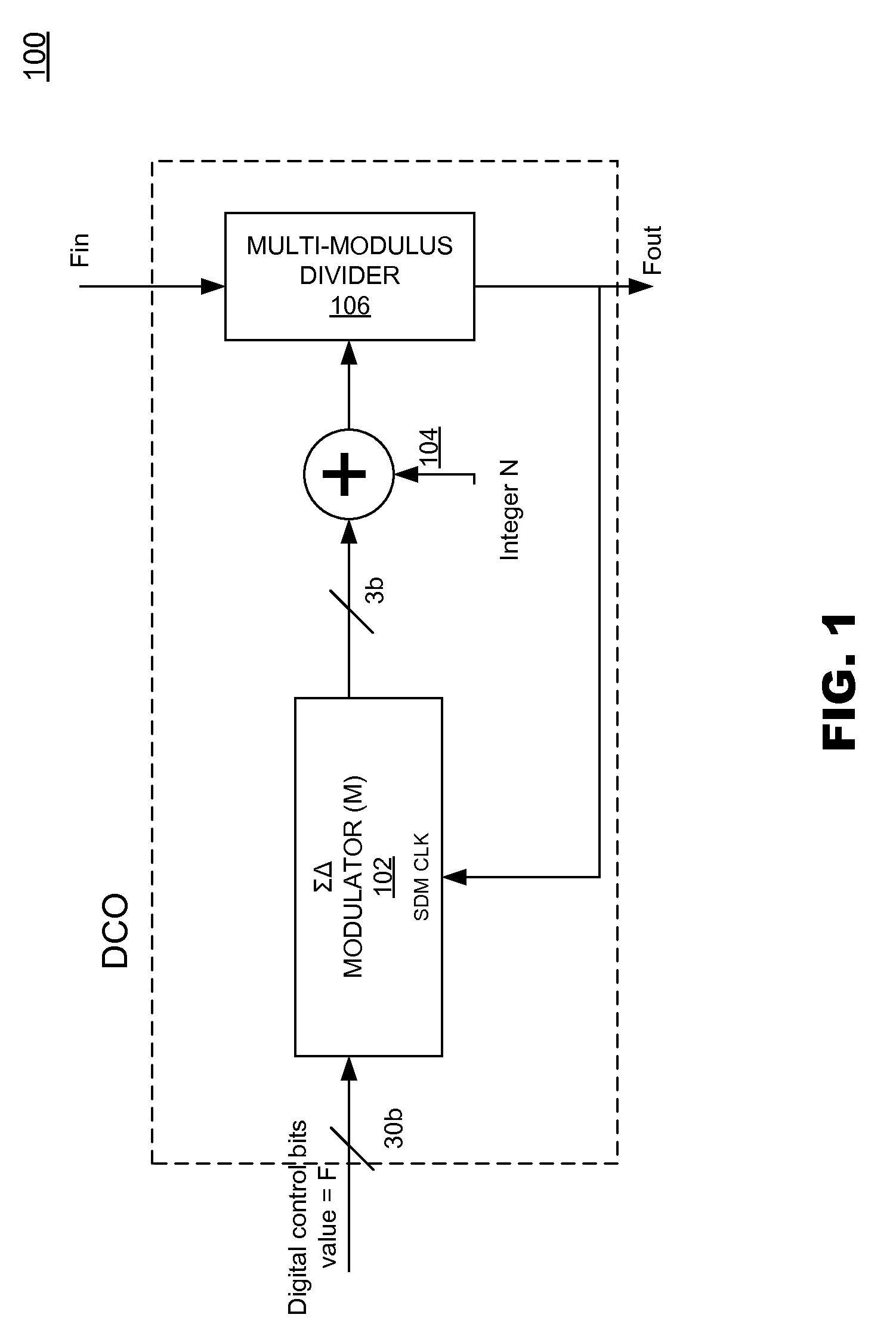
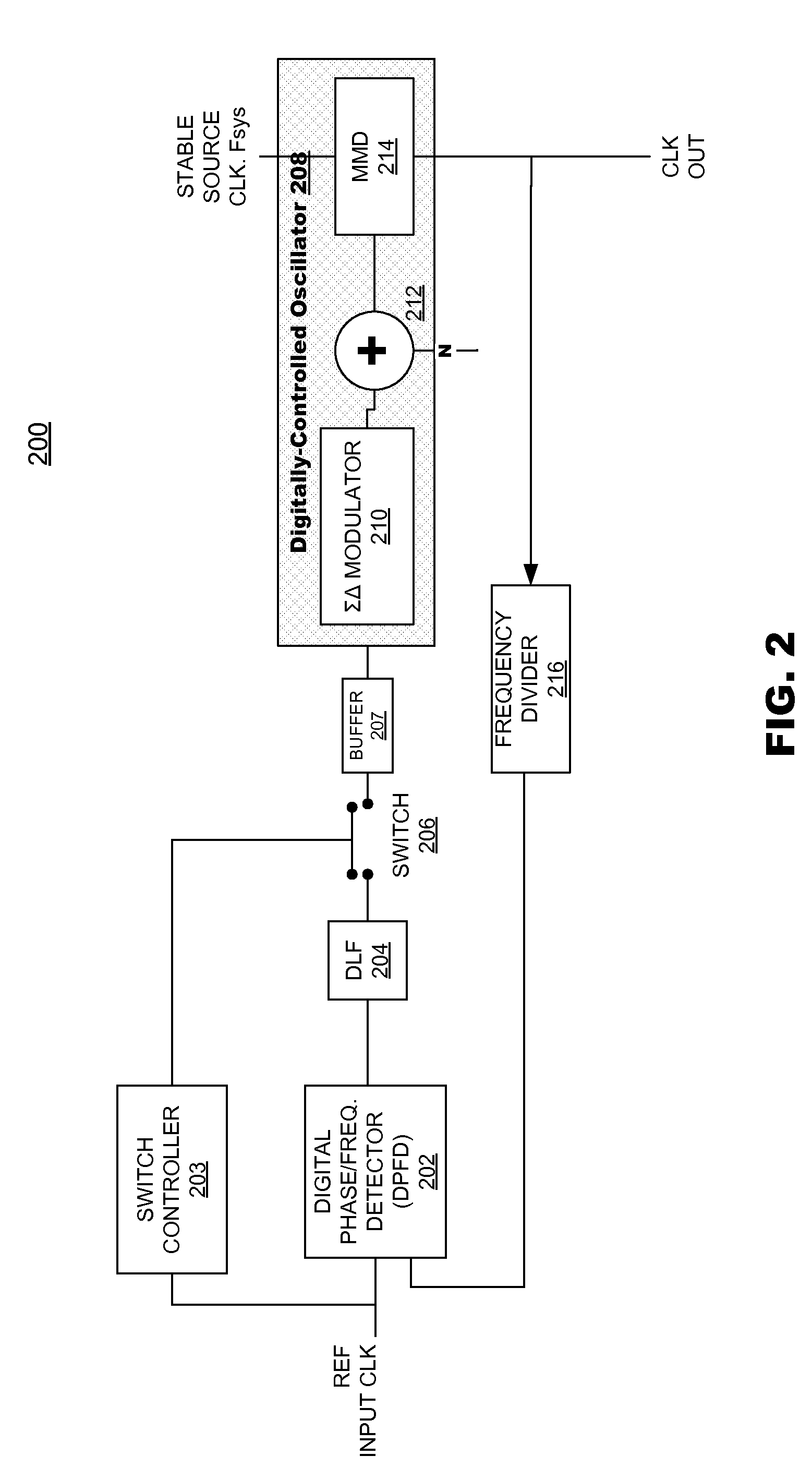
Digital Phase-Locked Loop Clock System
A clock system includes a digital phase / frequency detector (DPFD), a buffer, a digitally-controlled oscillator (DCO) including a sigma-delta modulator (SDM), an adder, a first frequency divider. The DPFD may have a first input for a reference input clock and a second input for a feedback signal, and outputting a difference signal representing a phase and / or frequency difference between the reference input clock and the feedback signal. The buffer may be coupled to the DPFD for accumulating the difference signal over time. The sigma-delta modulator (SDM) may have a control input coupled to the buffer. The adder may have inputs coupled to the (SDM) and a source of an integer control word. The first frequency divider may have an input for a clock signal and a control input coupled to the adder, the DCO generating an output clock signal having an average frequency representing a frequency of the input clock signal divided by (N+F / M), wherein N is determined by the integer control word and F / M is determined by an output of the SDM. The system clock also may include a phase-locked loop (PLL) including a phase / frequency detector that has a first input coupled to the output of the DCO and a second input that is phase-locked to the first input, and a second frequency divider coupled from the second input of the PLL to the second input of the DPFD.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
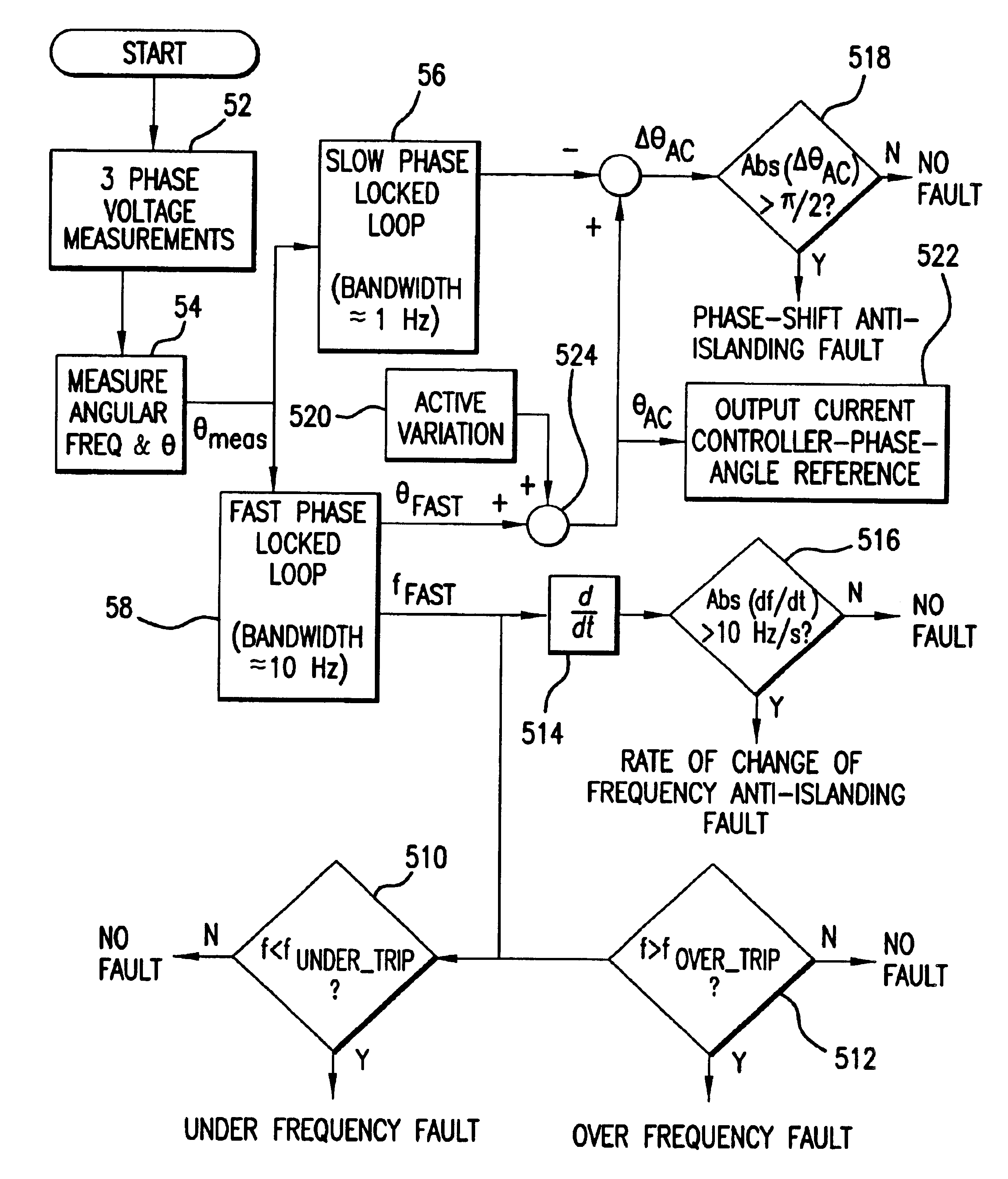
Detection of islanded behavior and anti-islanding protection of a generator in grid-connected mode
InactiveUS6864595B2Single network parallel feeding arrangementsGas turbine plantsIslandingElectric power system
A method of controlling a generator system connected to an electric power system in which the output frequency characteristic of the generator system is measured, a first phase angle and frequency of the measured frequency characteristic is estimated using a first phase locked loop having a first bandwidth, and a second phase angle and frequency of the measured frequency characteristic is estimated using a second phase locked loop having a second bandwidth greater than the first bandwidth. Further, the method calculates a frequency difference between the first and second estimated frequencies, and an angle variation that is proportional to the calculated frequency difference. The estimated second phase angle is then added to the calculated angle variation so as to form an output current phase angle reference, and an output current phase angle of the generator system is controlled to be aligned with the output current phase angle reference. The method also determines whether or not the generator system is within a generation island based on the measured frequency characteristic.
Owner:CAPSTONE TURBINE
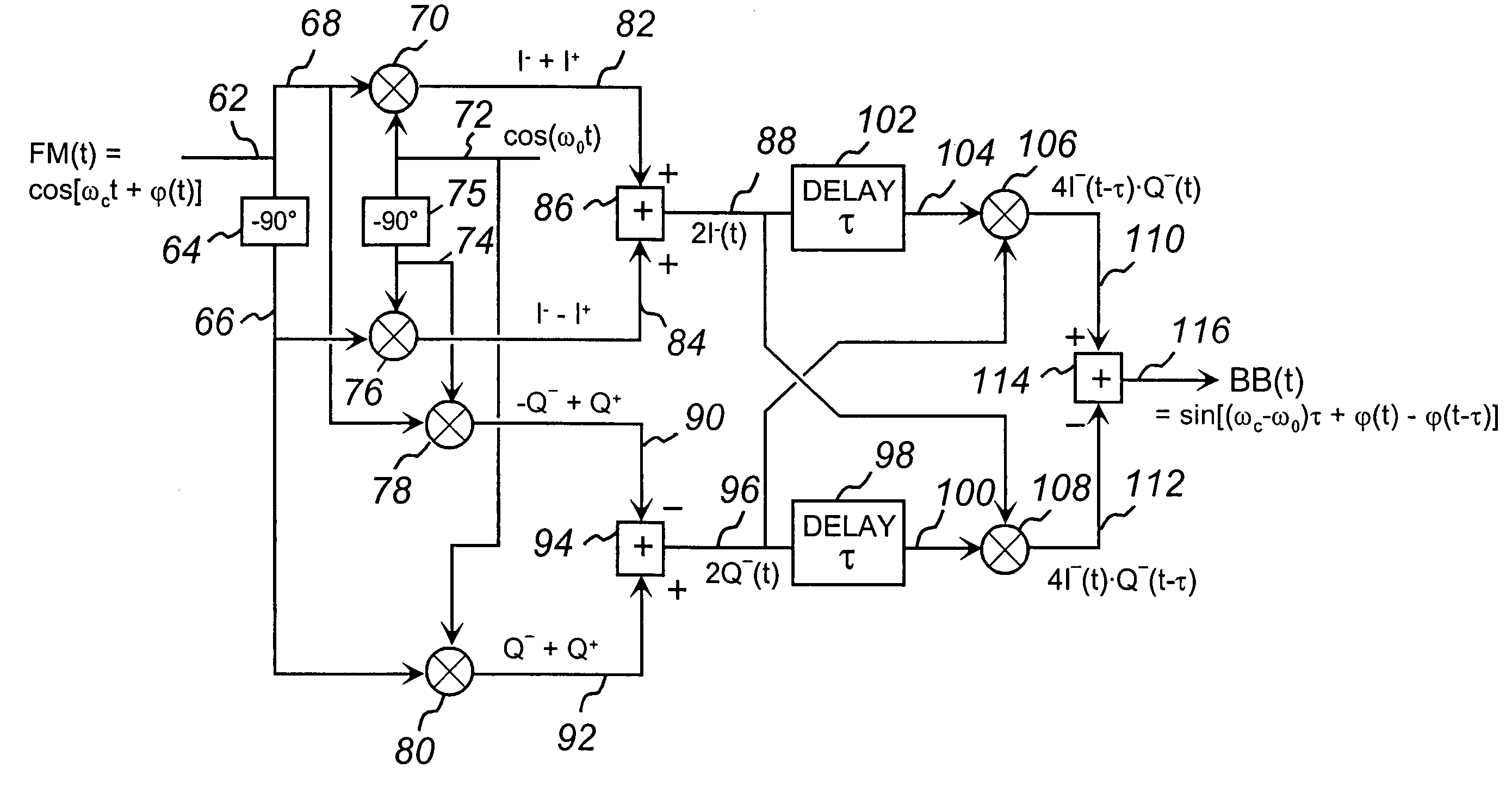
High frequency low noise phase-frequency detector and phase noise reduction method and apparatus
The present invention discloses a new type of extremely low-noise phase-frequency detector (PFD) 500, broadband from DC to multi-GHz RF frequencies for PLL synthesizer applications. Free of any feedback mechanisms, thus inherently fast, it operates close to transition frequency fT of IC processes or frequency limits of discrete mixers. The PFD 500 utilizes complex SSB conversion in both the in-phase and quadrature arms, delaying the in-phase arm in 530, beating the delayed signal 124 with the un-delayed quadrature signal 122 in mixer 126. The output 128 contains both the frequency difference and the phase difference information between the two signals 118 and 520, providing both the frequency-discrimination (FD) and the phase detection (PD) functions. Utilizing standard mixers the PFD 500 can achieve superior CNRs of 180 dBc / Hz at multi-GHz RF. Additionally, utilizing the FD / FM demodulation capability, the present invention improves phase noise of various signals and linearity of FM modulators.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Base station, receiving device, mobile terminal, and frequency sharing method
InactiveUS20090088083A1Many problemEnergy efficient ICTPower managementCommunications systemEngineering
A disclosed base station is used in a first wireless communication system using a first frequency band that is the same as or adjacent to a second frequency band used by a second wireless communication system, and includes a propagation loss estimation unit configured to estimate propagation loss of a signal in the first frequency band when the signal arrives at a receiving device of the second wireless communication system; a frequency difference calculation unit configured to calculate a frequency difference between the first frequency band and the second frequency band; a maximum transmission power determining unit configured to determine maximum transmission power based on the estimated propagation loss and the calculated frequency difference; and a transmission control unit configured to transmit a signal with transmission power less than or equal to the maximum transmission power determined by the maximum transmission power determining unit.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
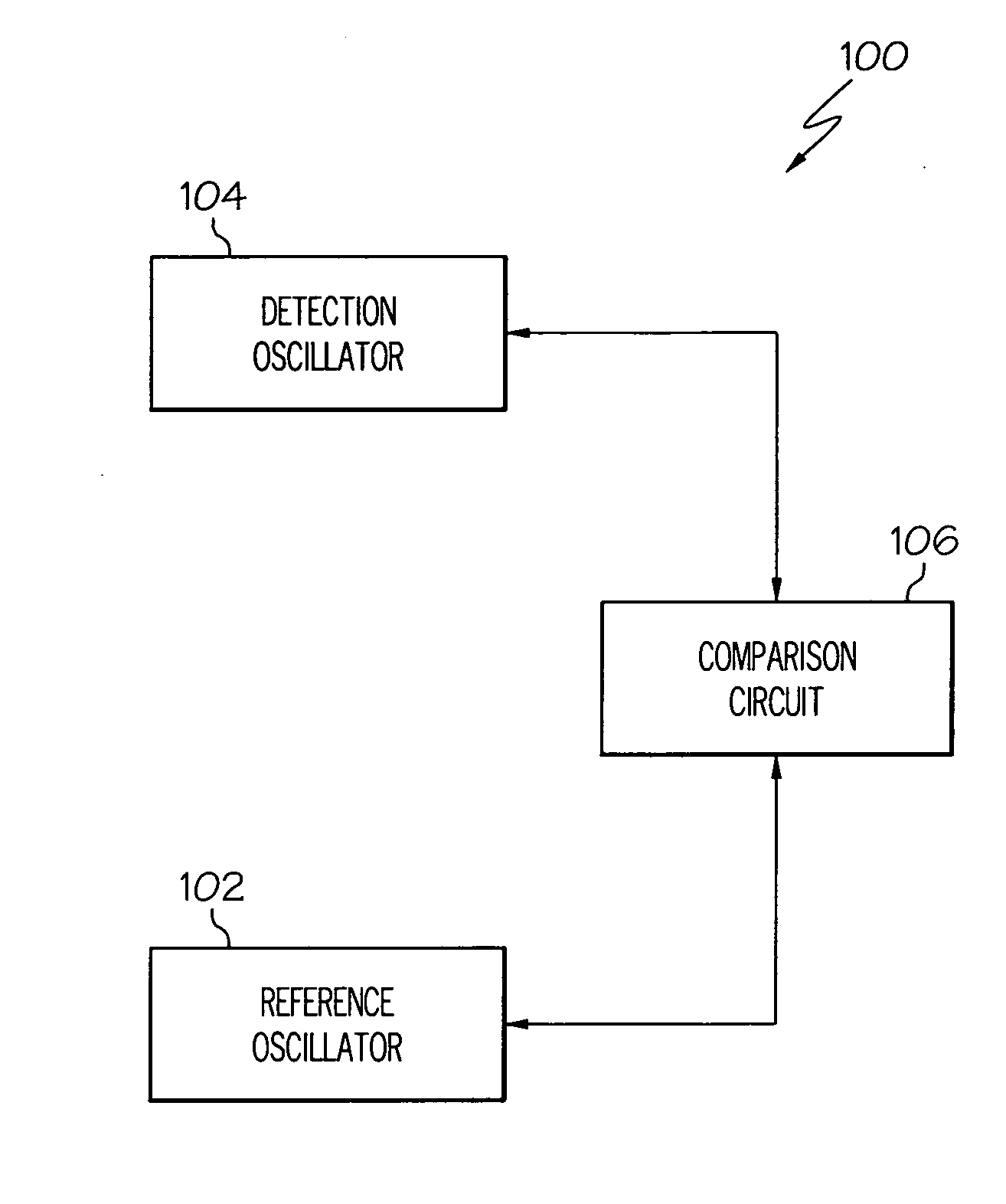
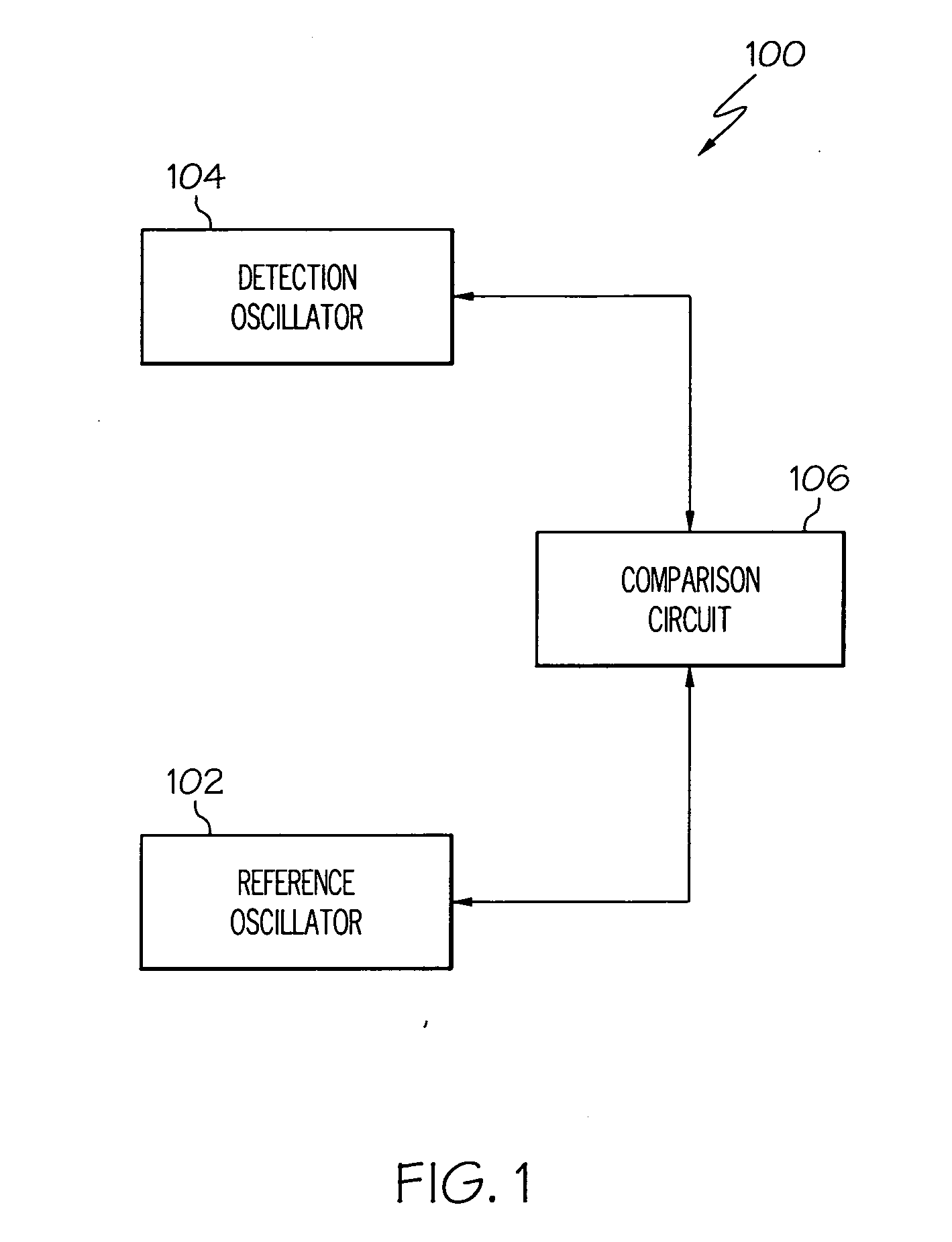
Tamper monitor circuit
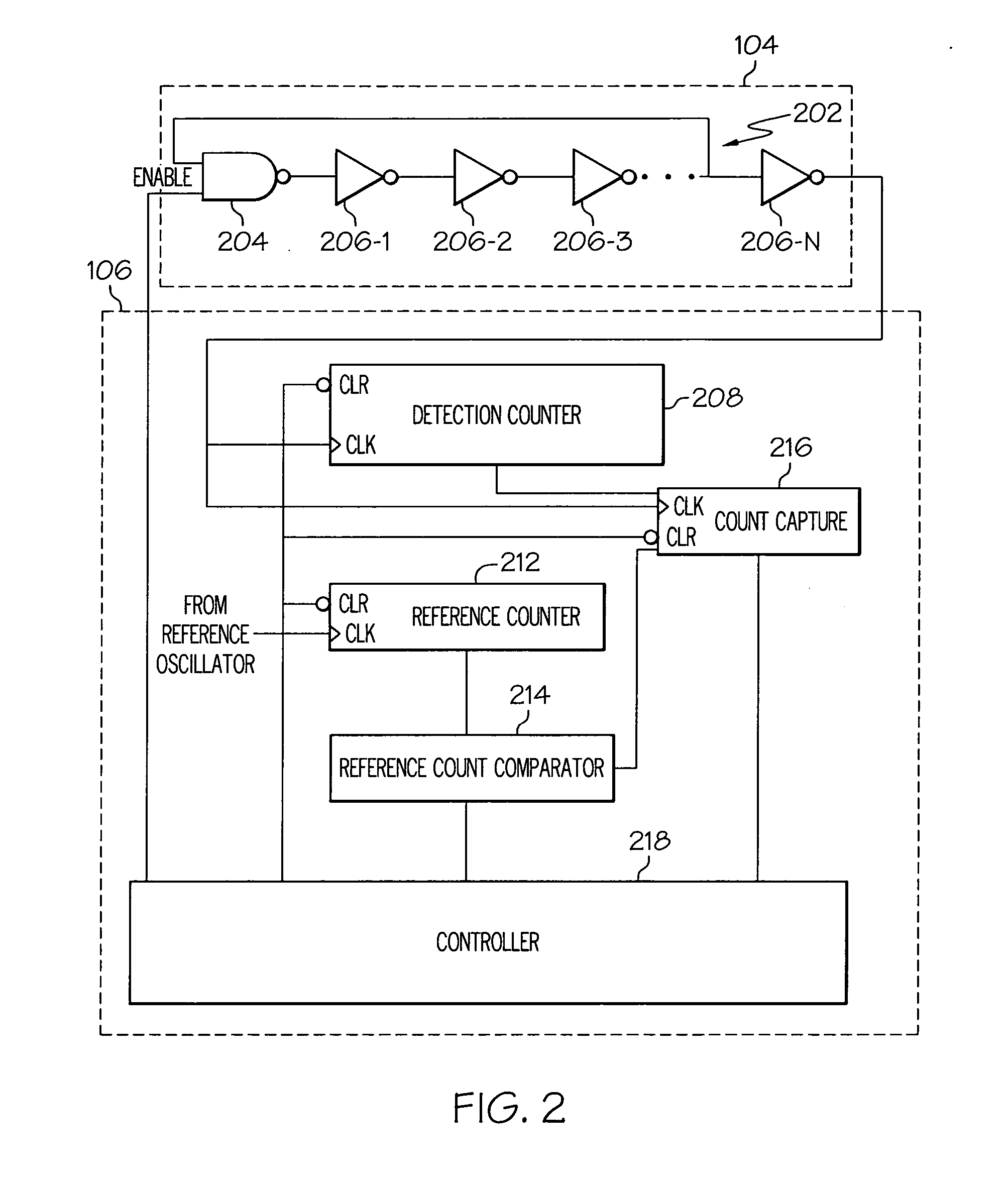
ActiveUS20070069875A1Signalling system detailsInternal/peripheral component protectionEngineeringCLOCK
A tamper monitor circuit detects voltage, temperature, and / or clock variations that may be associated with a circuit tampering technique, and triggers an appropriate tamper response. The tamper monitor circuit includes a reference oscillator, a detection oscillator, and a comparison circuit. The reference oscillator supplies a reference signal having a reference frequency. The detection oscillator operates at a circuit temperature and is energized with a supply voltage, and supplies a detection signal having a frequency that varies with variations in the circuit temperature, variations in the supply voltage, or both. The comparison circuit receives the reference signal and the detection signal and, in response to the reference signal, selectively determines the frequency of the detection signal, determines a frequency difference between two or more of the determined frequencies, and supplies a tamper detect signal if the determined frequency difference exceeds a predetermined difference threshold.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Clock synchronization circuit and operation method thereof
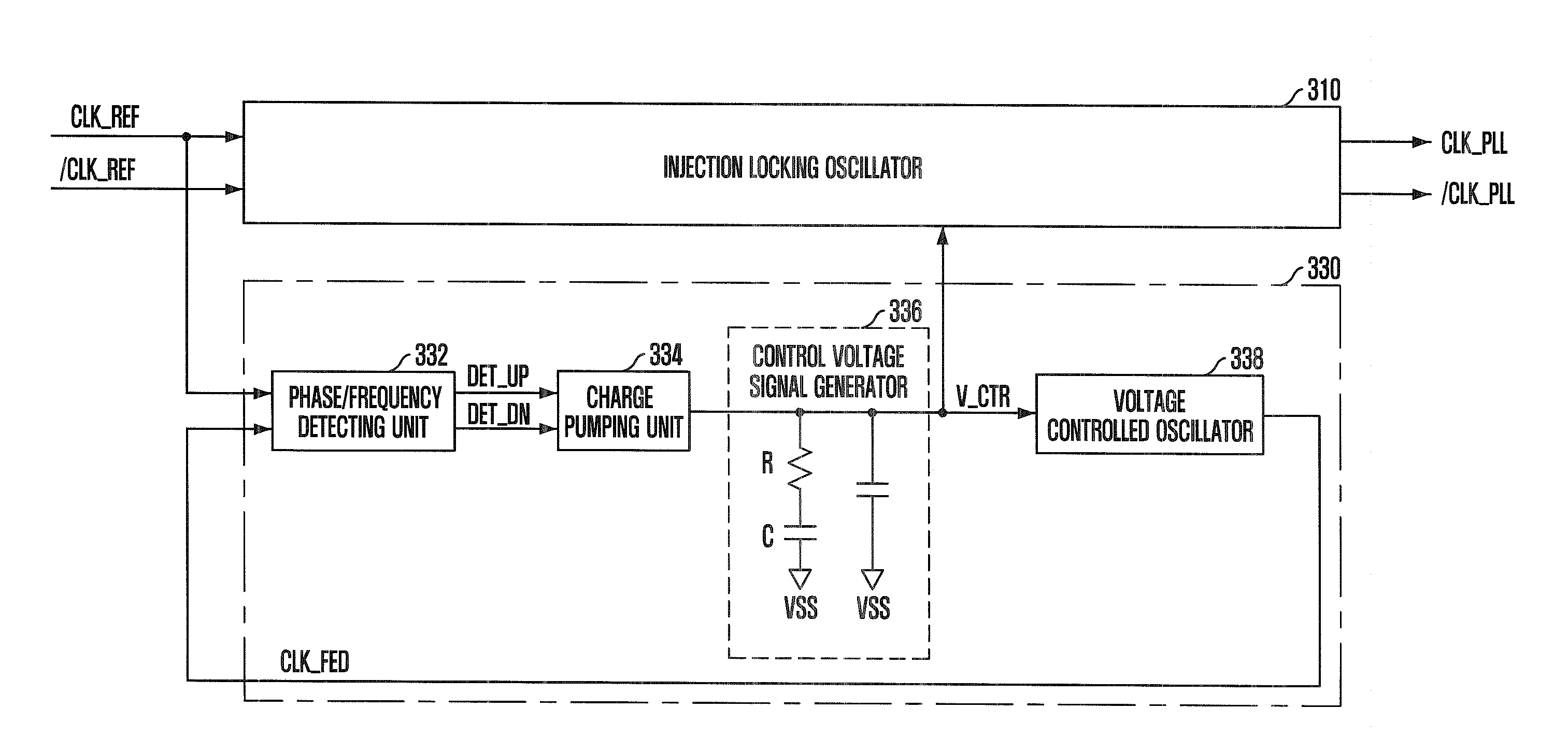
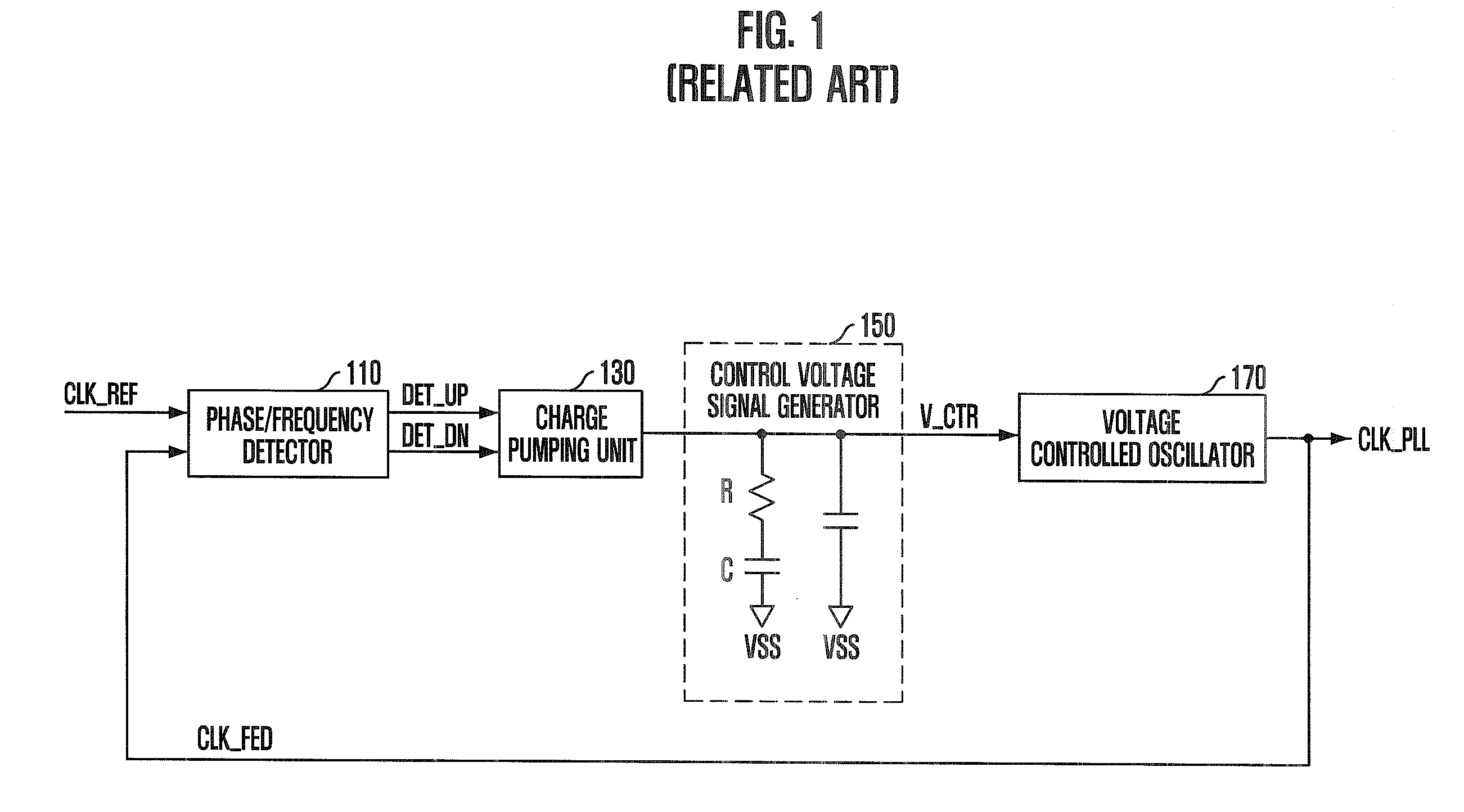
InactiveUS20090175116A1Improve operating characteristicsStable phase/frequency locking operationPulse automatic controlDigital storageInjection lockedPeak value
A semiconductor memory device with a clock synchronization circuit capable of performing a desired phase / frequency locking operation, without the jitter peaking phenomenon and the pattern jitter of an oscillation control voltage signal using injection locking. The device includes a phase-locked loop that detects a phase / frequency difference between a feedback clock signal and a reference clock signal to generate an oscillation control voltage signal corresponding to the detected phase / frequency difference, and generates the feedback clock signal corresponding to the oscillation control voltage signal. An injection locking oscillation unit sets up a free running frequency in response to the oscillation control voltage signal and generates an internal clock signal which is synchronized with the reference clock signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Quantum processing device
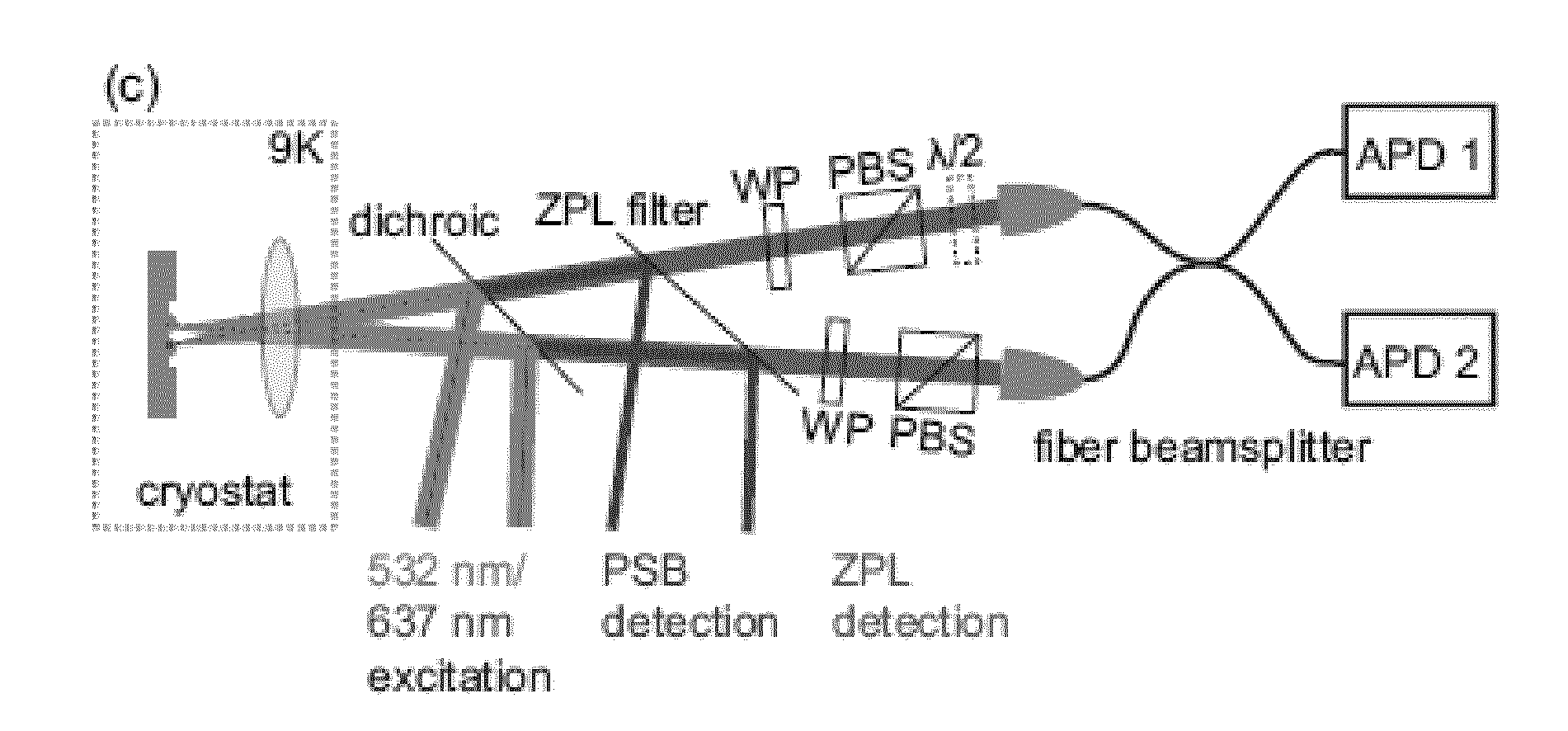
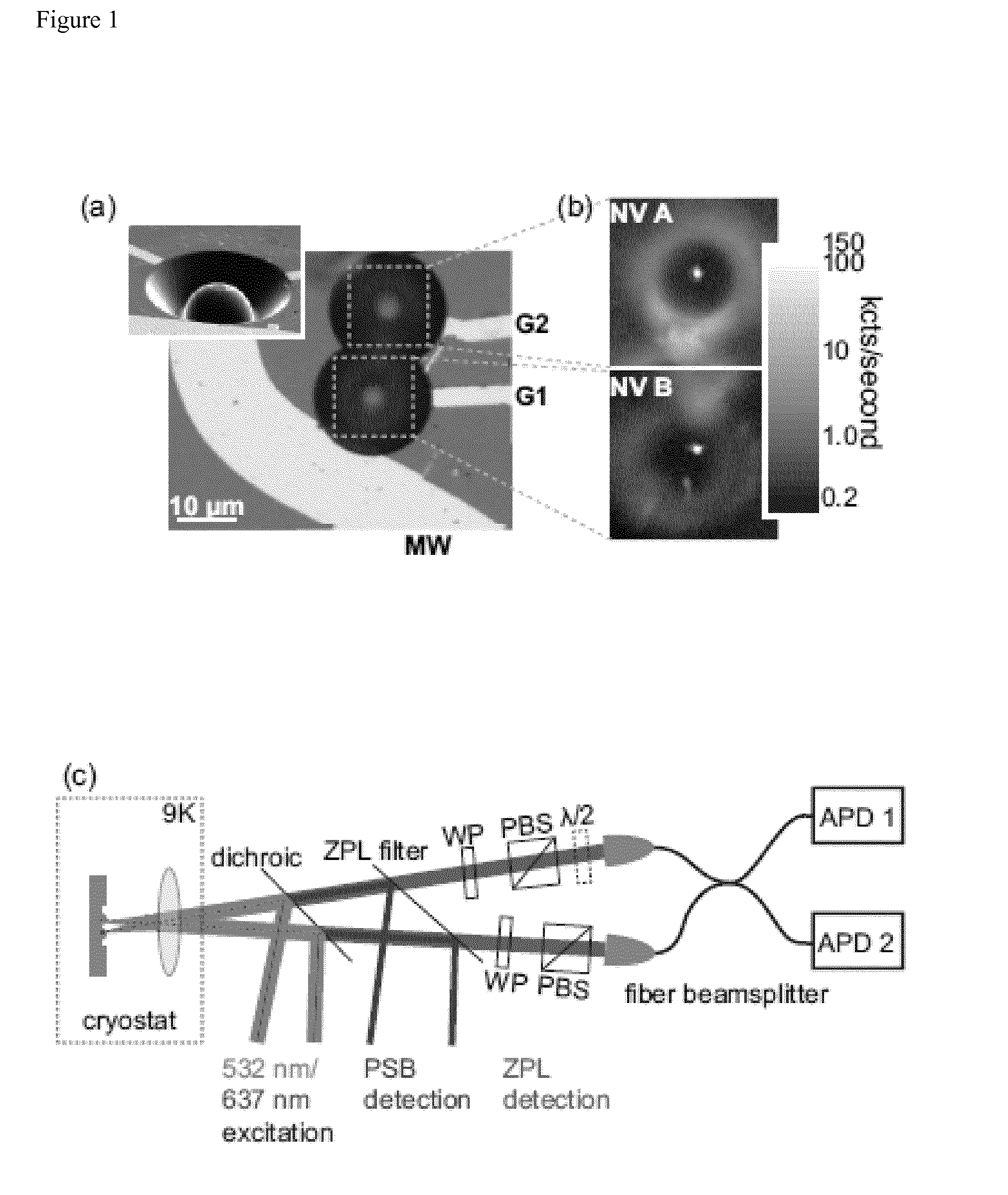
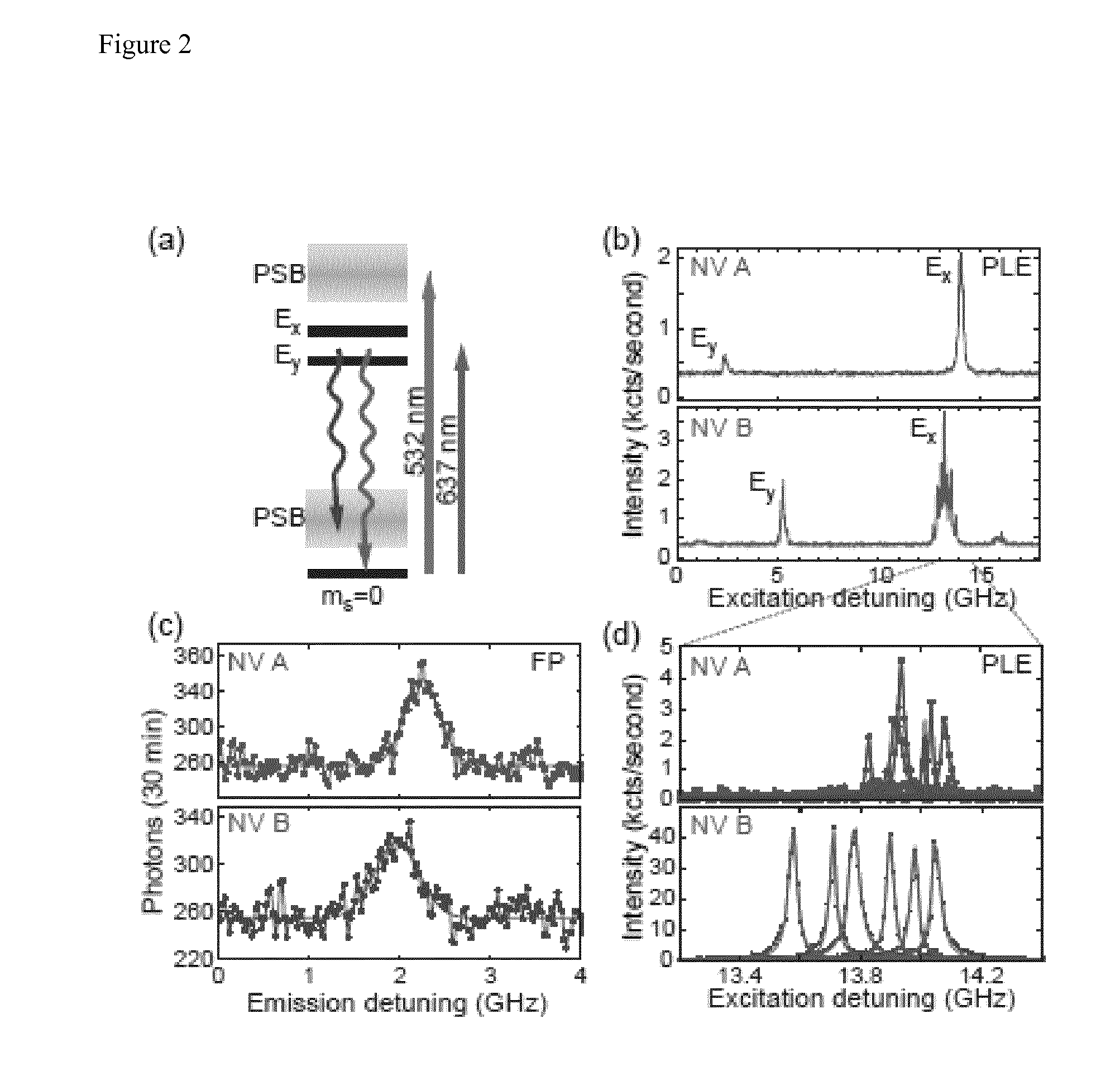
ActiveUS20140291490A1High efficiency in photon collectionAttenuation bandwidthQuantum computersNanoinformaticsPhoton emissionPhoton detection
A device for achieving multi-photon interference, said device comprising: at least two solid state photon emitters, each solid state photon emitter comprising nuclear and electron spin states coupled together, each solid state photon emitter being configured to produce photon emission comprising a photon emission peak, wherein the photon emission peaks from different solid state photon emitters have a first frequency difference between peak intensities, and wherein the electron spin states of each solid state photon emitter are resolvable; an excitation arrangement configured to individually address the at least two solid state photon emitters; a plurality of optical out coupling structures wherein each solid state photon emitter is provided with an associated optical out coupling structure; a tuning arrangement configured to reduce the first frequency difference between the peak intensities of the photon emission peaks from the at least two solid state photon emitters to a second frequency difference which is smaller than the first frequency difference; a photon interference arrangement configured to overlap photon emissions from the at least two solid state emitters after tuning; and a detector arrangement configured to detect photon emissions from the at least two solid state emitters after tuning and passing through the photon interference arrangement, wherein the detector arrangement is configured to resolve sufficiently small differences in photon detection times that tuned photon emissions from the at least two solid state emitters are quantum mechanically indistinguishable resulting in quantum interference between indistinguishable photon emissions from different solid state photon emitters.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX TECH LTD
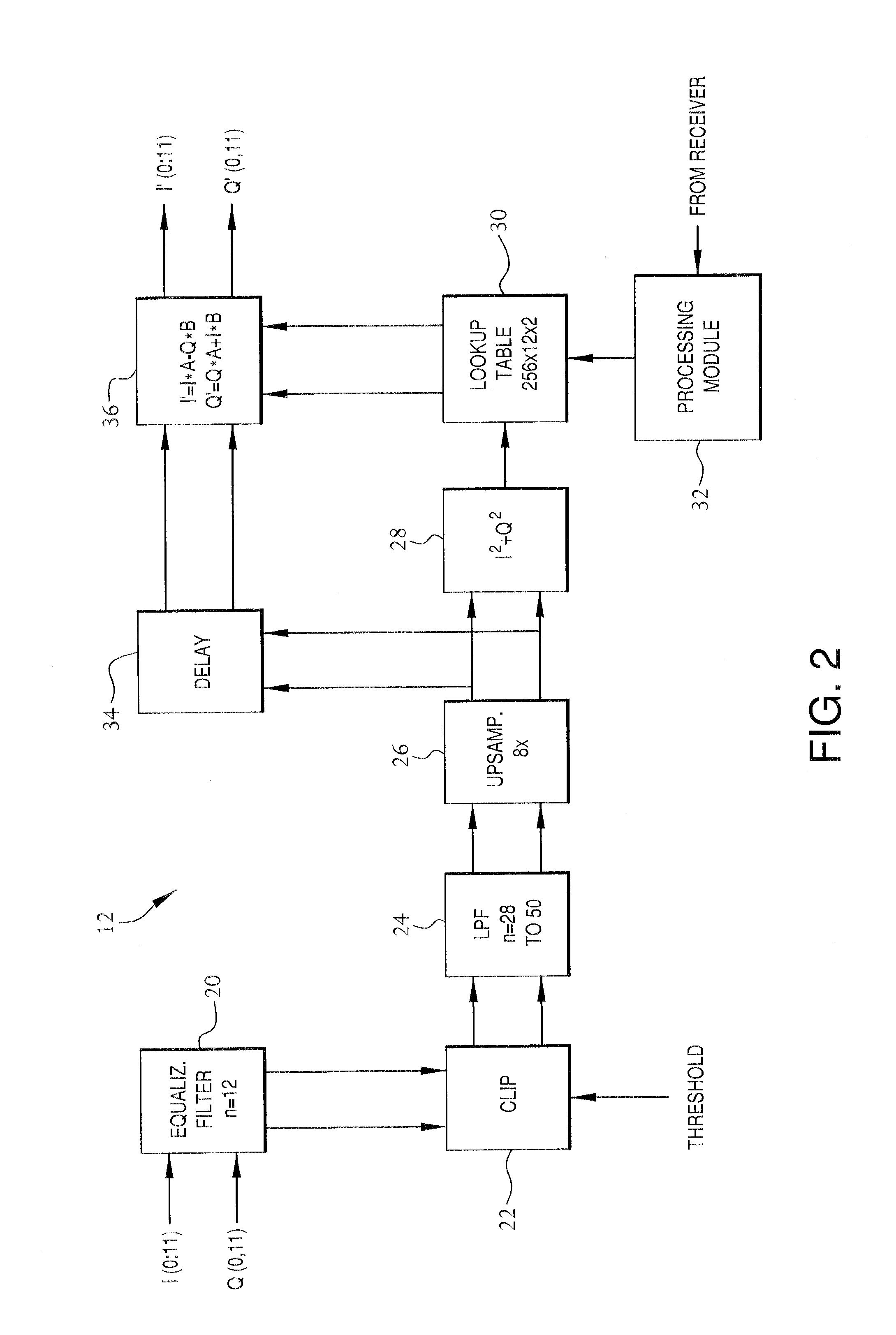
Frequency-dependent phase pre-distortion for reducing spurious emissions in communication networks
InactiveUS7248642B1Spurious emission can be reducedEmission reductionModulated-carrier systemsSecret communicationPhase differenceSpurious emission
A frequency-dependent phase pre-distortion technique is applied to an input signal in order to reduce spurious emissions resulting from subsequent amplification of the signal. In preferred embodiments, the frequency-dependent phase pre-distortion of the present invention is implemented in combination with the (frequency-independent) magnitude and phase pre-distortion technique described in U.S. patent application Ser. No. 09 / 395,490 (“the '490 application”), where one or more frequency-dependent phase pre-distortion signals are either advanced or delayed relative to the main pre-distorted signal generated in accordance with the '490 application. Each frequency-dependent phase pre-distortion signal is preferably based on a 180° phase difference between a pair of (critical) frequencies located outside (e.g., one on each side) of the signal channel. The magnitude of the frequency difference between the pair of critical frequencies dictates the magnitude of the desired advancement or delay in time of the frequency-dependent pre-distortion signal relative to the main pre-distorted signal. Embodiments of the present invention may be implemented in either the baseband domain or the RF domain. Implementations may also be based on look-up tables that are adaptively updated to ensure optimal performance over time.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Electrostatic Ion Trap
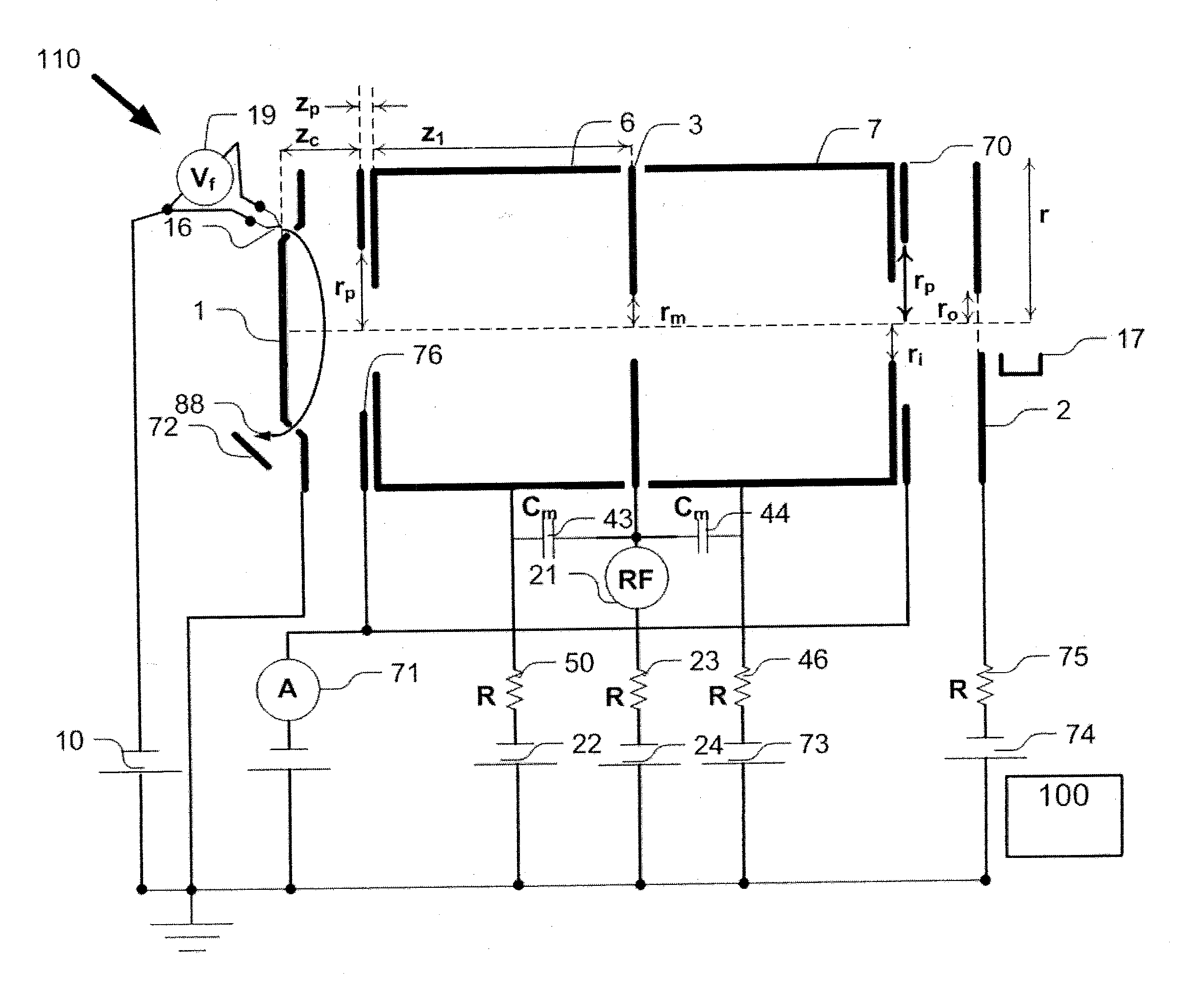
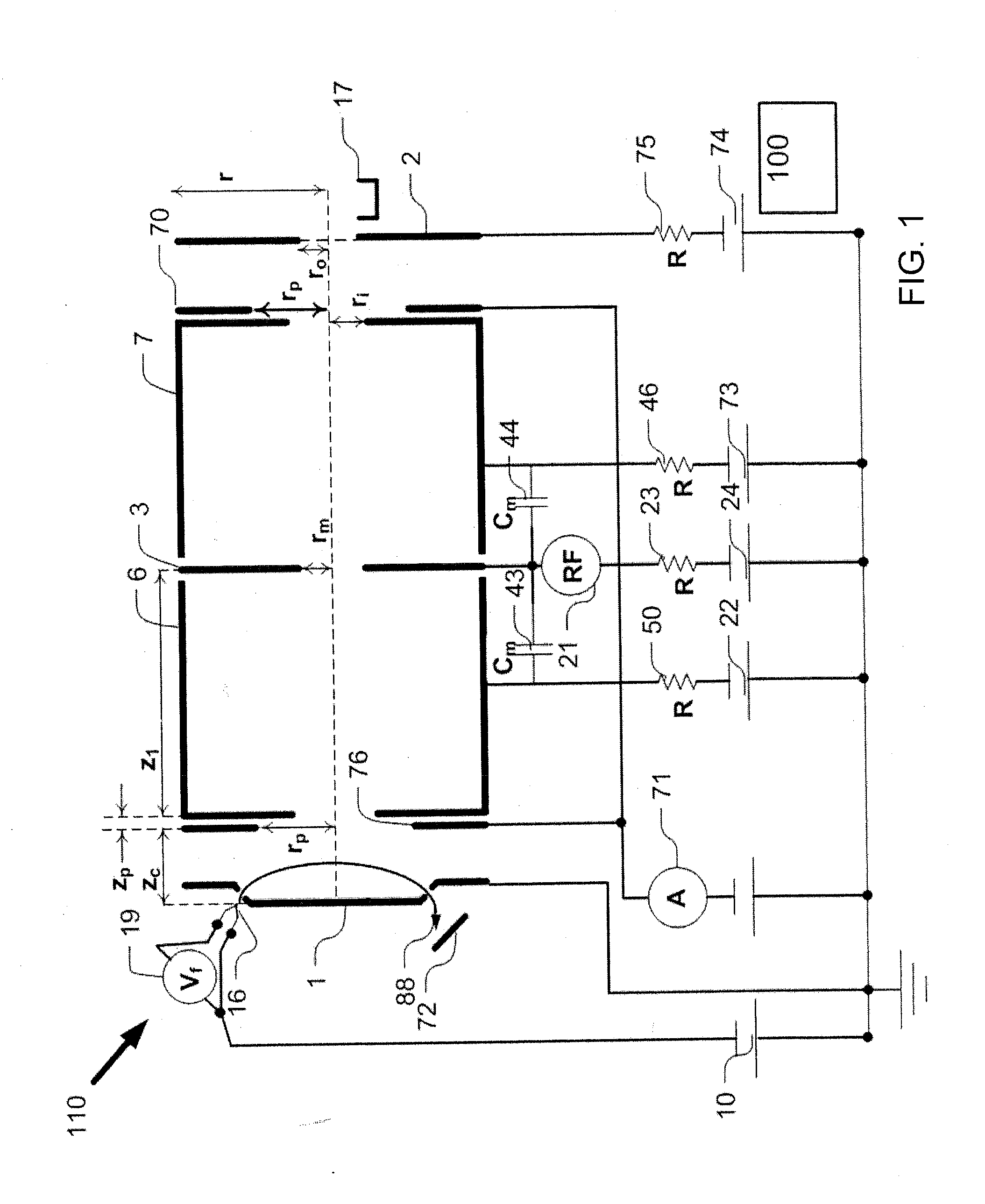
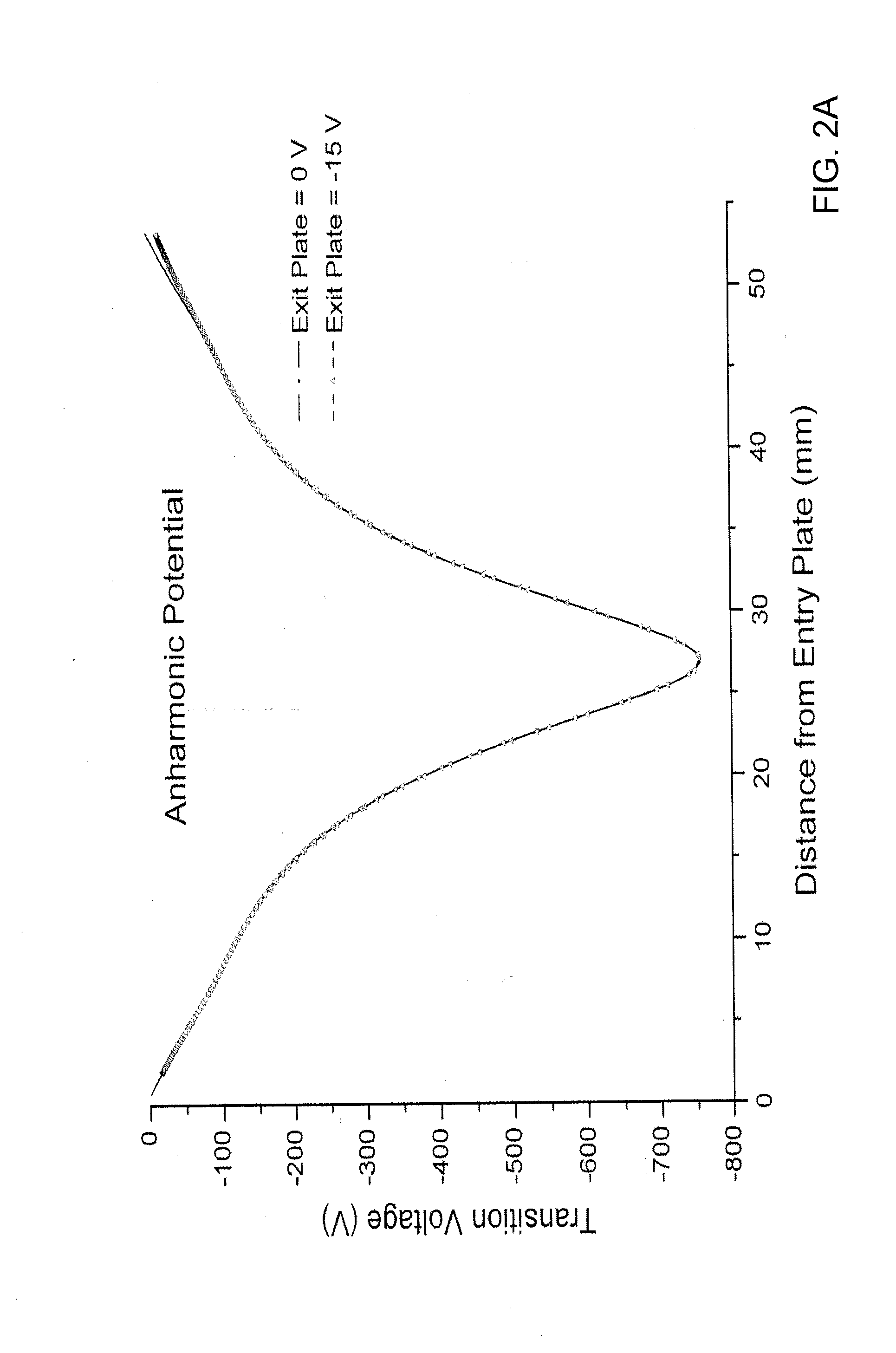
ActiveUS20120112056A1Quality improvementReduction from baselineStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIon trap mass spectrometryHarmonic
An ion trap includes an electrode structure, including a first and a second opposed mirror electrodes and a central lens therebetween, that produces an electrostatic potential in which ions are confined to trajectories at natural oscillation frequencies, the confining potential being anharmonic. The ion trap also includes an AC excitation source having an excitation frequency f that excites confined ions at a frequency of about twice the natural oscillation frequency of the ions, the AC excitation frequency source preferably being connected to the central lens. In one embodiment, the ion trap includes a scan control that mass selectively reduces a frequency difference between the AC excitation frequency and about twice the natural oscillation frequency of the ions.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Frequency synthesizer and high-speed automatic calibration device therefor
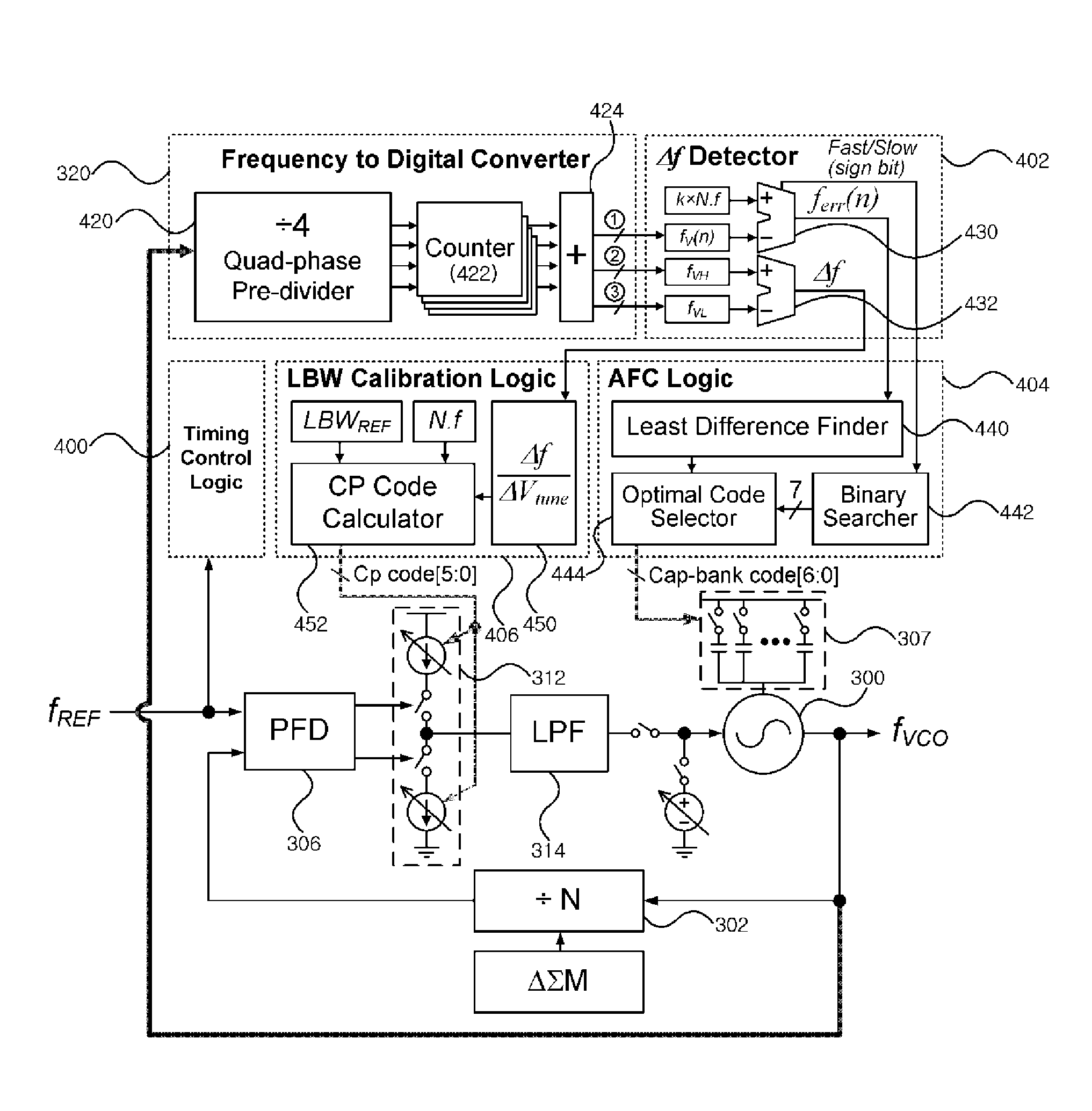
ActiveUS8008956B1Reduce frequency calibration timeConstantPulse automatic controlOptimal controlLoop bandwidth
A frequency synthesizer and an automatic calibration device are disclosed. An automatic calibration device for a phase-locked loop based frequency synthesizer includes: a frequency-to-digital converter for converting a frequency of a signal outputted from a voltage controlled oscillator into a first digital value; a frequency difference detector for calculating a difference between the first digital value outputted from the frequency-to-digital converter and a second digital value corresponding to a target frequency; an automatic frequency calibration logic for selecting an optimal control code for a capacitor bank such that an output frequency of the voltage controlled oscillator is closer to the target frequency; and a loop bandwidth calibration logic for tuning a charge pump gain such that a loop bandwidth is kept constant in the optimal control code using the frequency-to-digital converter. Thus, the calibration speed can be increased, and the loop bandwidth can be kept constant within the output frequency range.
Owner:KWANGWOON UNIV IND ACADEMIC COLLABORATION FOUND
Inter-clock domain data transfer FIFO circuit
InactiveUS20110320854A1Reduce the number of gatesGenerating/distributing signalsData conversionClock rateData transmission
The inter-clock domain data transfer FIFO circuit provides a circuit that transfers data between two clock domains of unrelated frequencies. The gate count is kept relatively low, thereby allowing data transfer between the two clock domains at one data item per cycle of the lower of the two frequencies. Depending on the frequency difference between the data producer and consumer, the initial latency could be as low as a fraction of a cycle and no more than two cycles of the consumer's clock. The operation of the data transfer FIFO circuit has been verified using gate-level simulations for several ratios of clock frequencies.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Two-optical signal generator for generating two optical signals having adjustable optical frequency difference
InactiveUS6674969B1Laser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsInjection lockedOptical frequencies
A two-optical signal generator is provided for generating two optical signals, where a difference between optical frequencies or optical wavelength of the two optical signals can be adjusted. A first optical modulator modulates a single-mode optical signal generated by a first light source according to an inputted signal, and outputs a modulated optical signal including predetermined specific two optical signals having a predetermined optical frequency difference, while a second light source generates a multi-mode optical signal including predetermined two further optical signals having substantially the same wavelengths as those of the predetermined specific two optical signals of the modulated optical signal, respectively. Then an optical injection device optically injects the modulated optical signal into the second light source, and the predetermined specific two optical signals of the modulated optical signal are injection-locked into the predetermined two further optical signals of the multi-mode optical signal, so that the second light source generates an injection-locked predetermined specific two optical signals.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
High precision speed-measuring distance-measuring radar system and method
ActiveCN101236253AImprove electro-optic efficiencyReduce power consumptionElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadar systemsLocal oscillator
The invention relates to a high precision speed and distance measuring laser radar system and a speed and distance measuring method. The basic principle of the invention is as follows: linear chirp modulation and pseudo-random code modulation of lasers are performed; most lasers after modulation are taken as outgoing lasers and transmitted by a telescope; a small part of the lasers is taken as local oscillator beams and used for coherent detection; laser echo signals are divided into two parts; distance information is obtained after related operation of one part of the laser echo signals and original pseudo-random codes; the frequency difference of the local oscillator beams and echo signal beams is obtained after coherent detection of the other part of the laser echo signals and the local oscillator beams and pulse compression, and simultaneously comprises the distance information and Doppler shift; the Doppler shift is obtained through mathematical manipulation, thereby speed information is obtained. The high precision speed and distance measuring laser radar system and a speed and distance measuring method of the invention is characterized in that the speed information and the distance information of a target can be obtained with high precision.
Owner:HANGZHOU ZHONGKE TIANWEI TECH
Multi-band spectral audio encoding
An encoder includes a sampler that samples an audio signal and that generates from the samples a plurality of short blocks of sampled audio. Each of the short blocks has a duration less than a minimum audibly perceivable signal delay. A processor combines the plurality of short blocks into a long block. The long block is transformed into a frequency domain signal having a plurality of independently modulatable frequency indices. The frequency difference between adjacent indices is determined by the minimum duration and the sampling rate of the sampler. A neighborhood of frequency indices is selected so that the frequency difference between a lowest index and a highest index within the neighborhood is less than a predetermined value. Two or more of the indices are modulated in the neighborhood so as to make a selected one of the indices an extremum while keeping the total energy of the neighborhood constant. A plurality of frequency bands are so coded. A decoder decides that a bit or bits have been received if, in a majority of the frequency bands, the decoder detects a modulated index.
Owner:NIELSEN MEDIA RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com