Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1183results about "Polarisation multiplex systems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
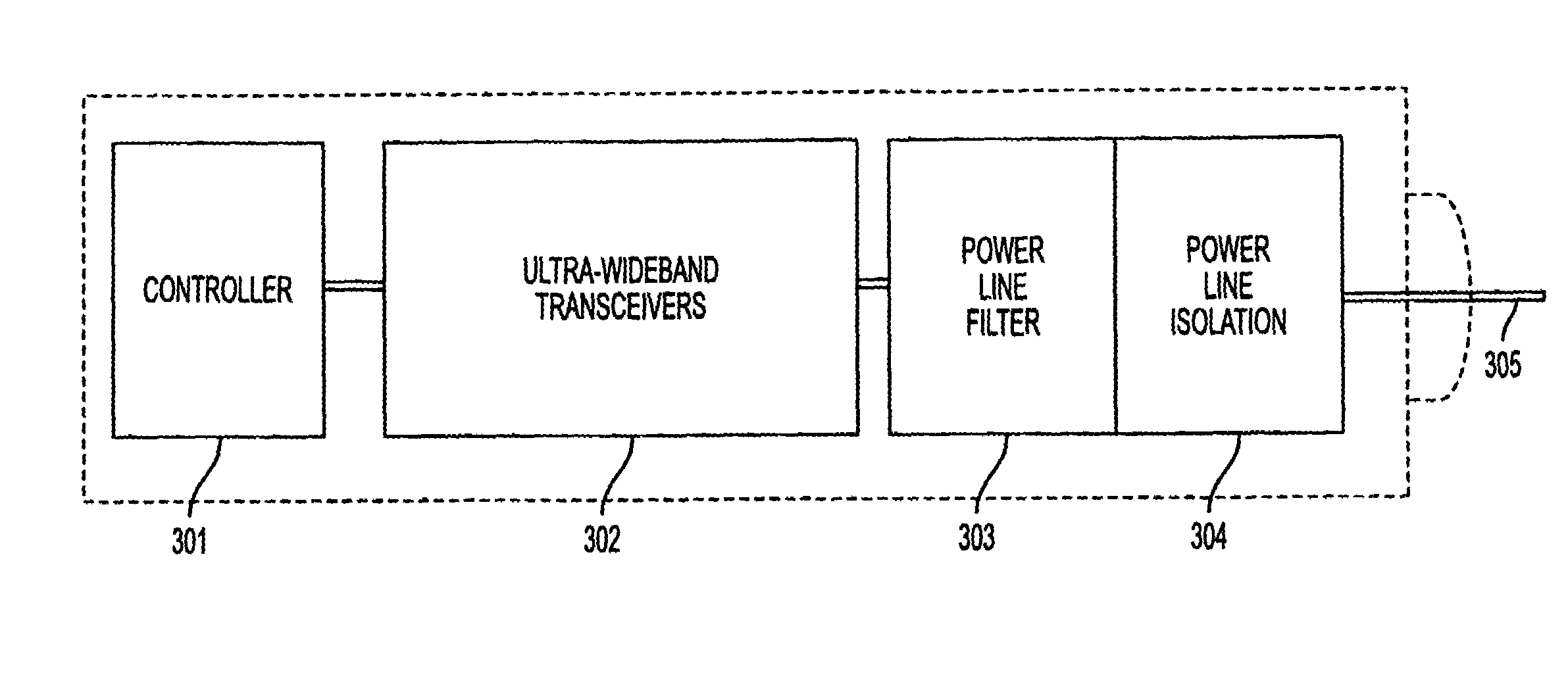
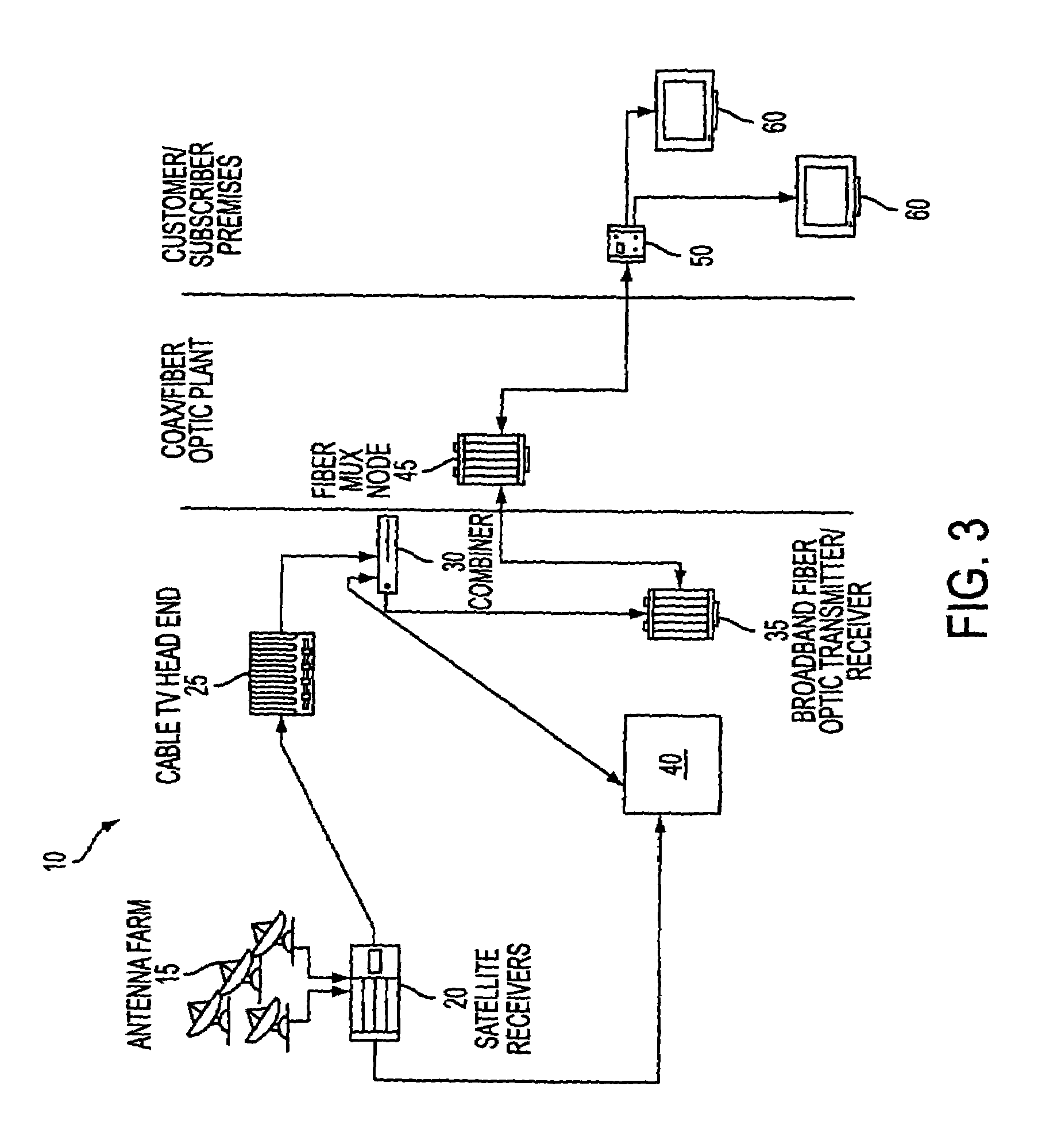
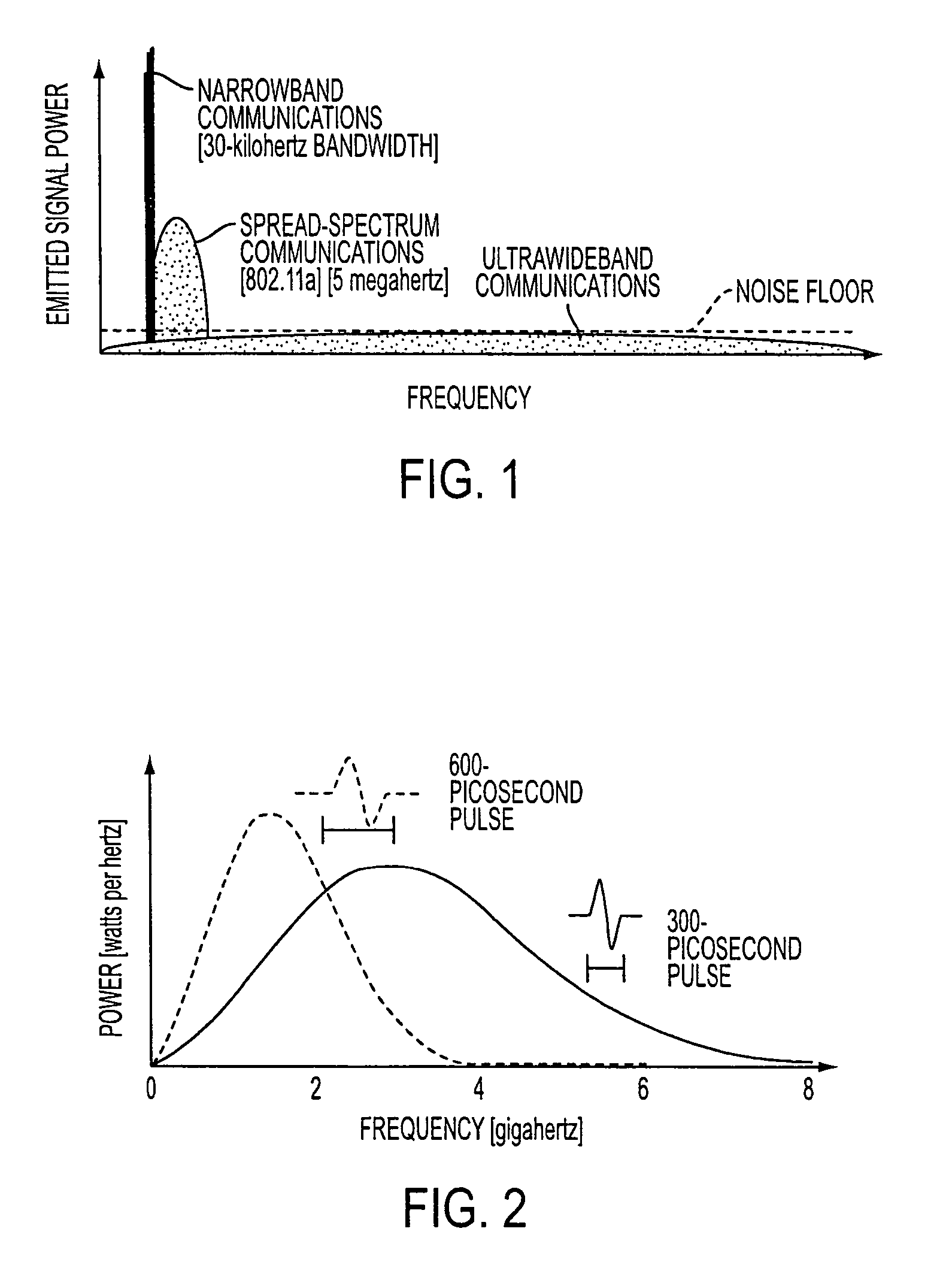
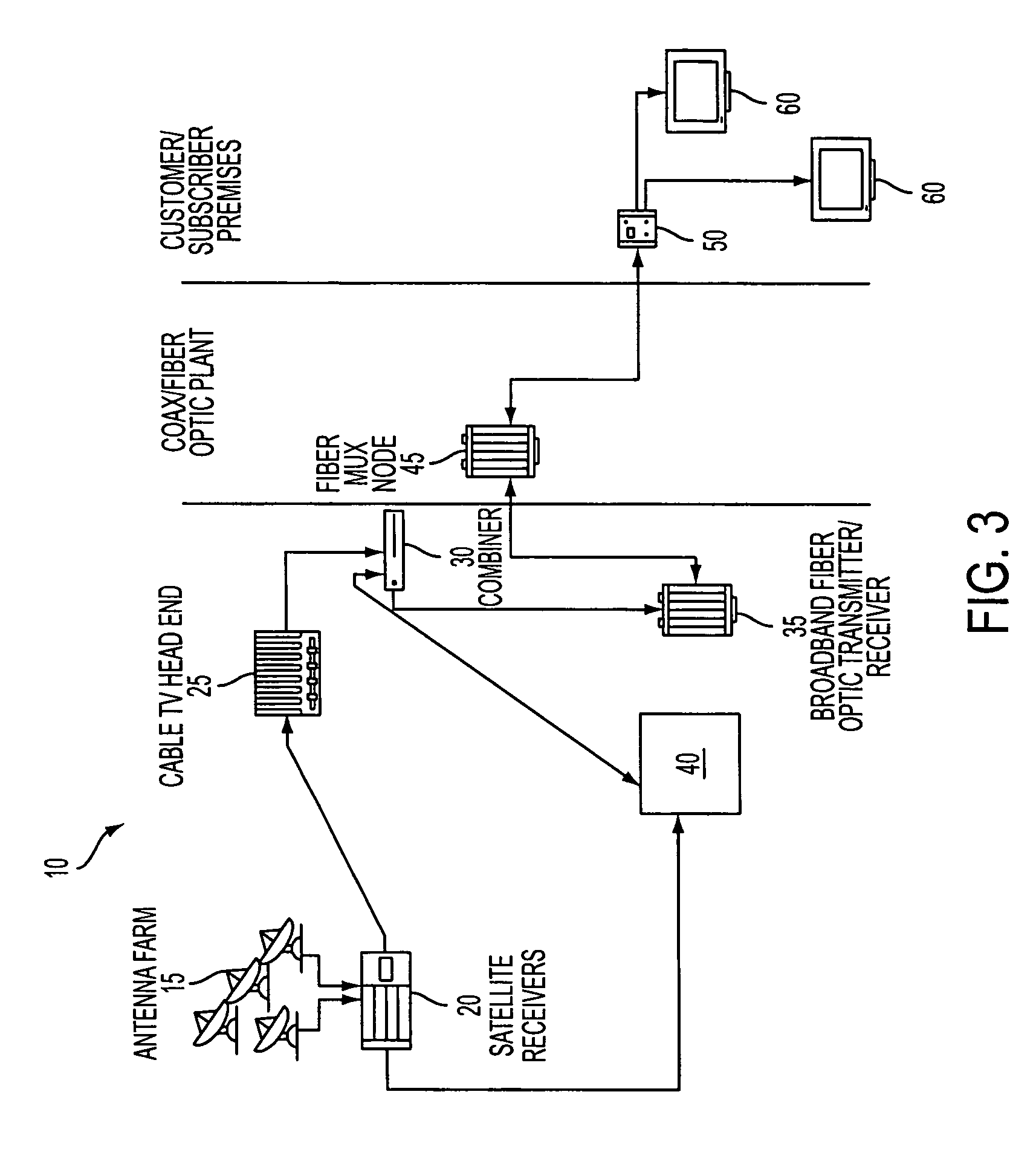
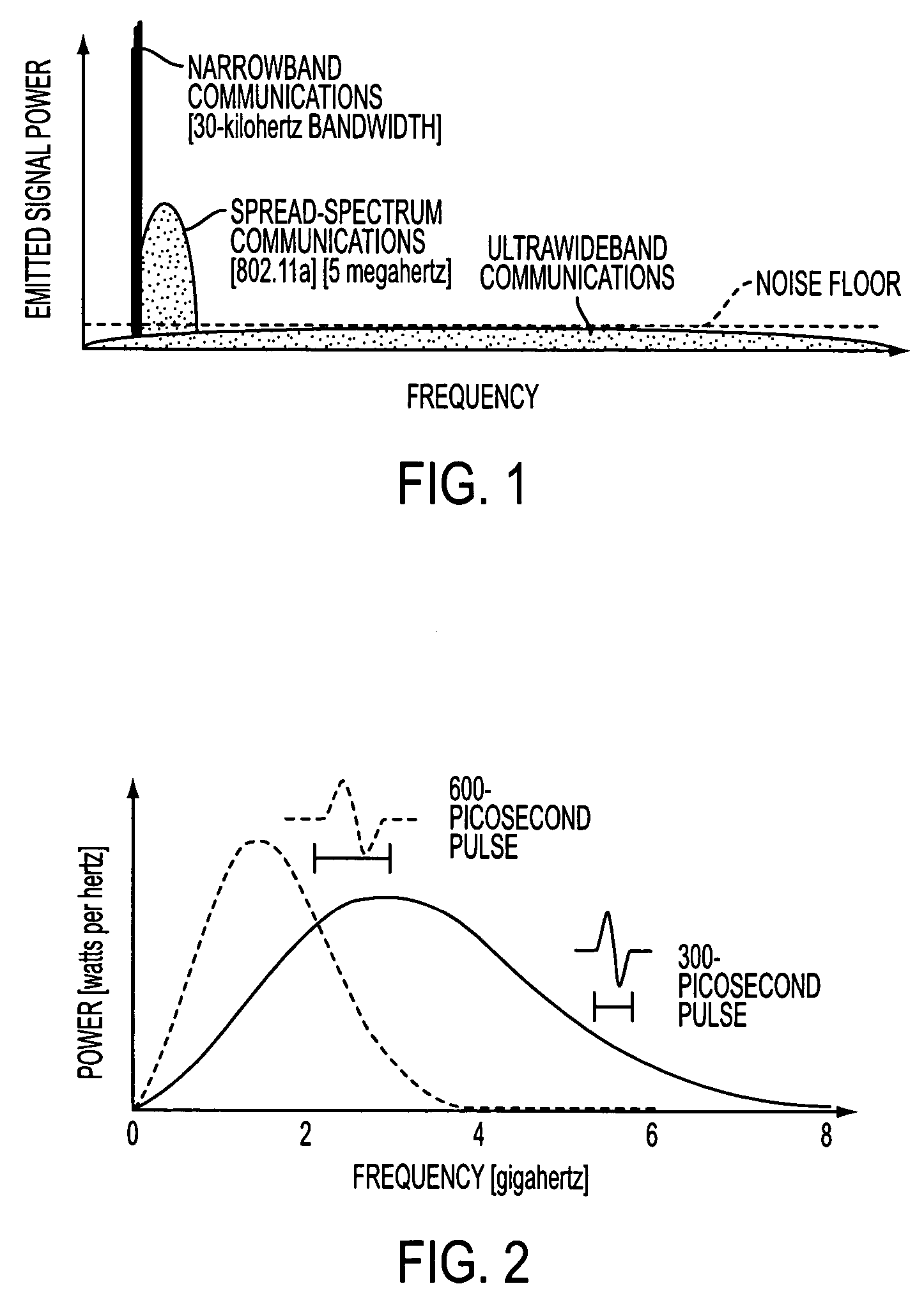
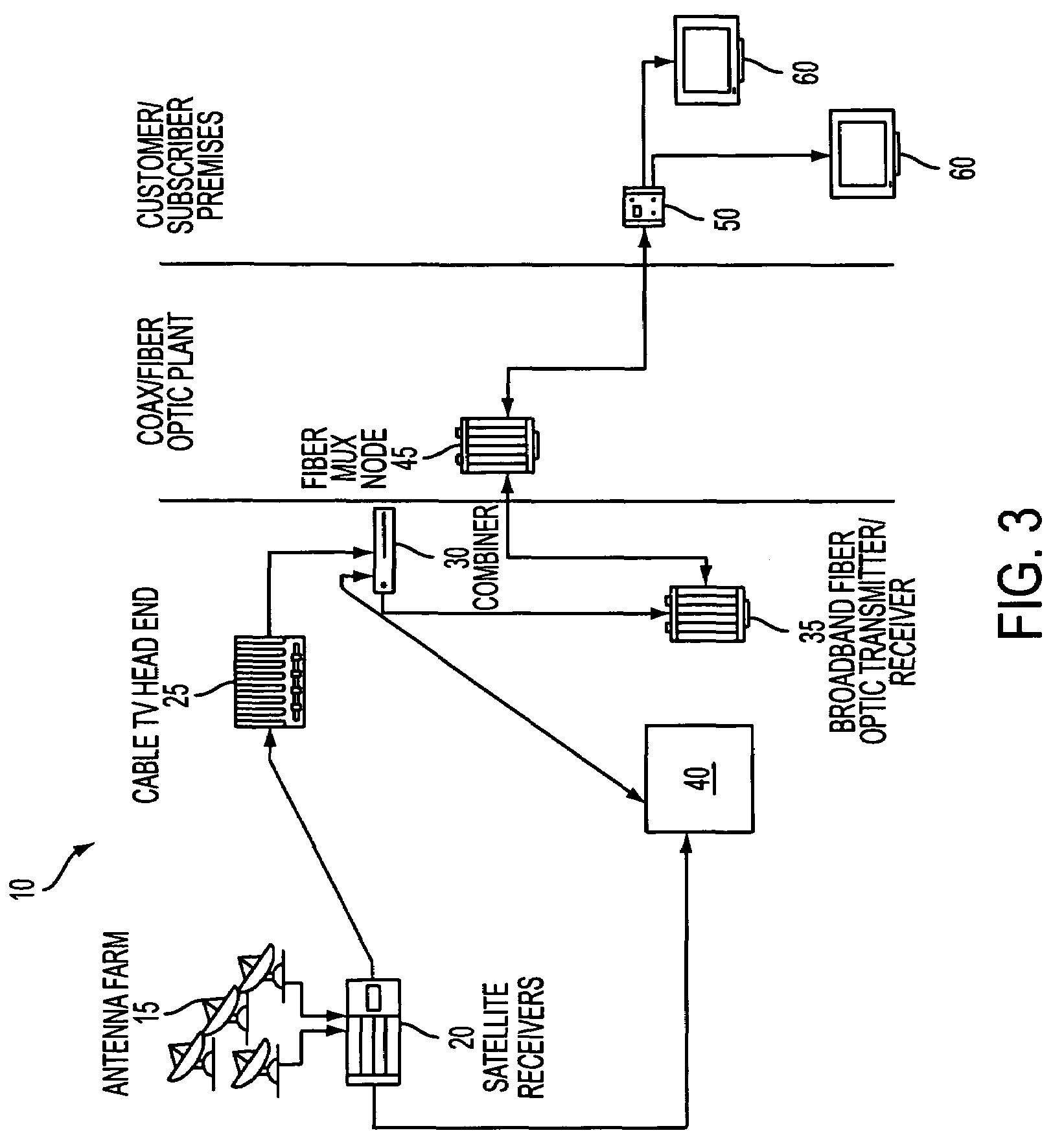
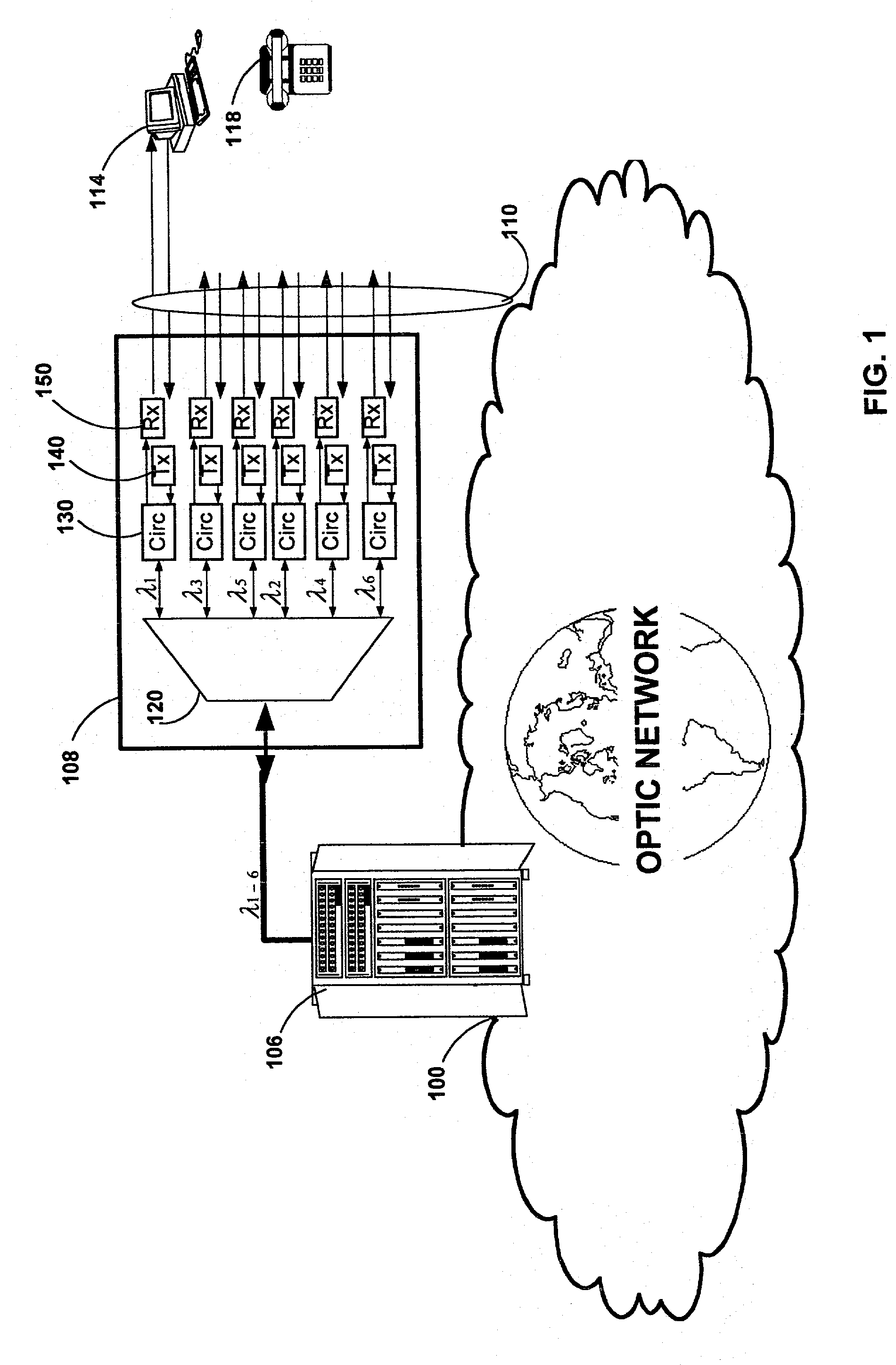
Ultra-wideband communication through local power lines
InactiveUS7027483B2Transmission/receiving by adding signal to waveBroadband local area networksUltra-widebandSubject matter
A system, method and apparatus structured to transmit a plurality of ultra-wideband pulses through an electric power medium is provided. One embodiment of the method comprises an ultra-wideband transmitter structured to transmit the plurality of ultra-wideband pulses through the electric power medium and an ultra-wideband receiver structured to receive the plurality of ultra-wideband pulses from the electric power medium. Another embodiment of the present invention comprises a power supply that provides ultra-wideband communications to devices that obtain power from the power supply. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement rules that allow a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure contained herein. This Abstract is submitted with the explicit understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
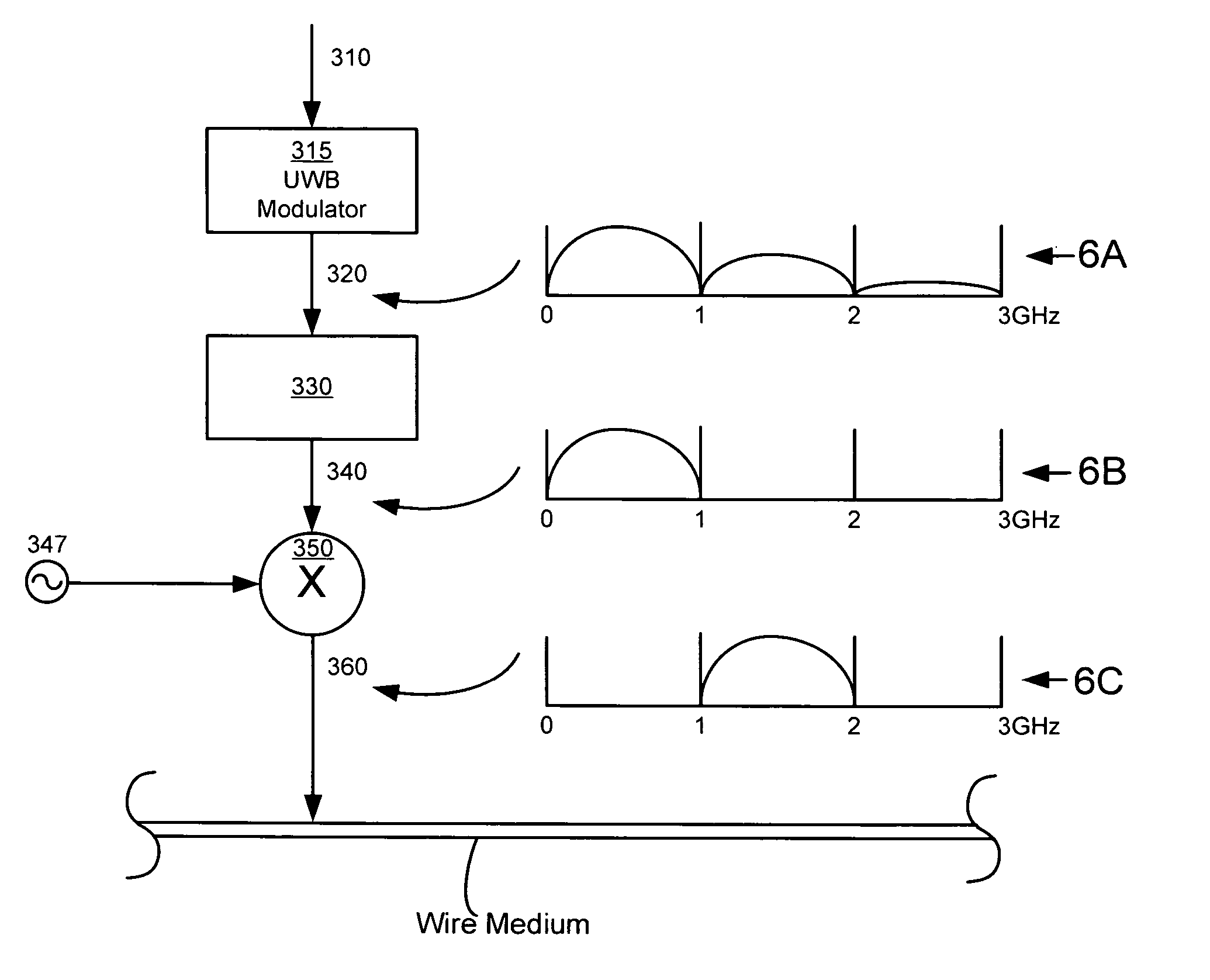
Ultra-wideband communication through a wire medium
InactiveUS7099368B2High bandwidthImprove rendering capabilitiesTransmission/receiving by adding signal to wavePolarisation multiplex systemsUltra-widebandSubject matter
Methods and apparatus for creating, transmitting and receiving ultra-wideband pulses through wire media are presented. One embodiment of the present invention transmits ultra-wideband pulses that occupy radio frequencies that are not used by other electromagnetic signals present in a wire medium of interest. Other embodiments of the invention may create, transmit, and receive ultra-wideband pulses that use radio frequency(s) that are not used by other signals present on wire media within a wire network of interest. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement rules that allow a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure contained herein. This Abstract is submitted with the explicit understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HLDG 73
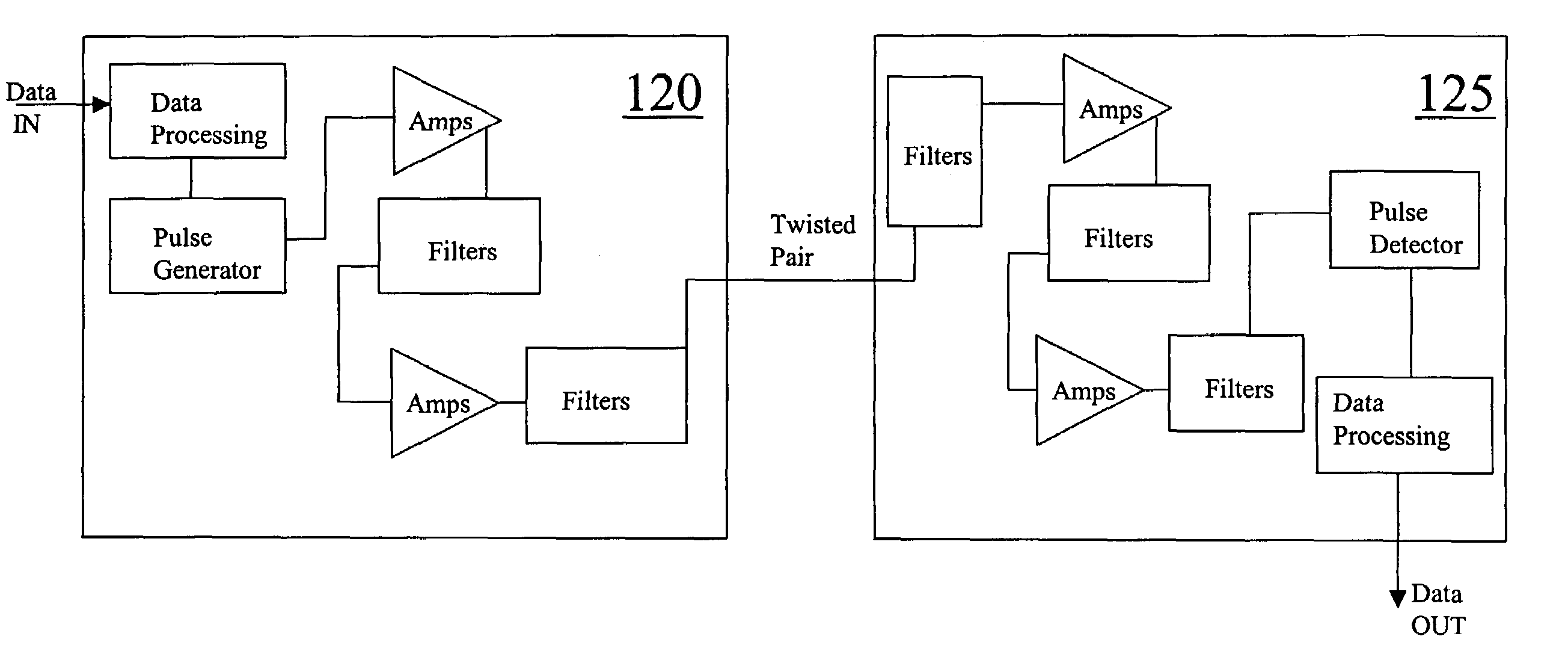
Ultra-wideband communication through twisted-pair wire media
InactiveUS7167525B2Transmission/receiving by adding signal to waveBroadband local area networksUltra-widebandBroadband pulse
Methods and apparatus that transmit ultra-wideband pulses through twisted-pair wire media are provided. One method includes transmitting an ultra-wideband pulse through the twisted-pair wire media at dissimilar time periods. Another method includes transmitting an ultra-wideband pulse through the twisted-pair wire media at dissimilar radio frequencies. Yet another method includes transmitting an ultra-wideband pulse through the twisted-pair wire media at dissimilar time periods and at dissimilar radio frequencies. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement rules that allow a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure contained herein. This Abstract is submitted with the explicit understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HLDG 73
Optical transceivers for use in fiber optic communication networks
ActiveUS20110255870A1Simplify channel impairment compensation algorithmMinimizes sizeModulated-carrier systemsPolarisation multiplex systemsTransceiverFrequency spectrum
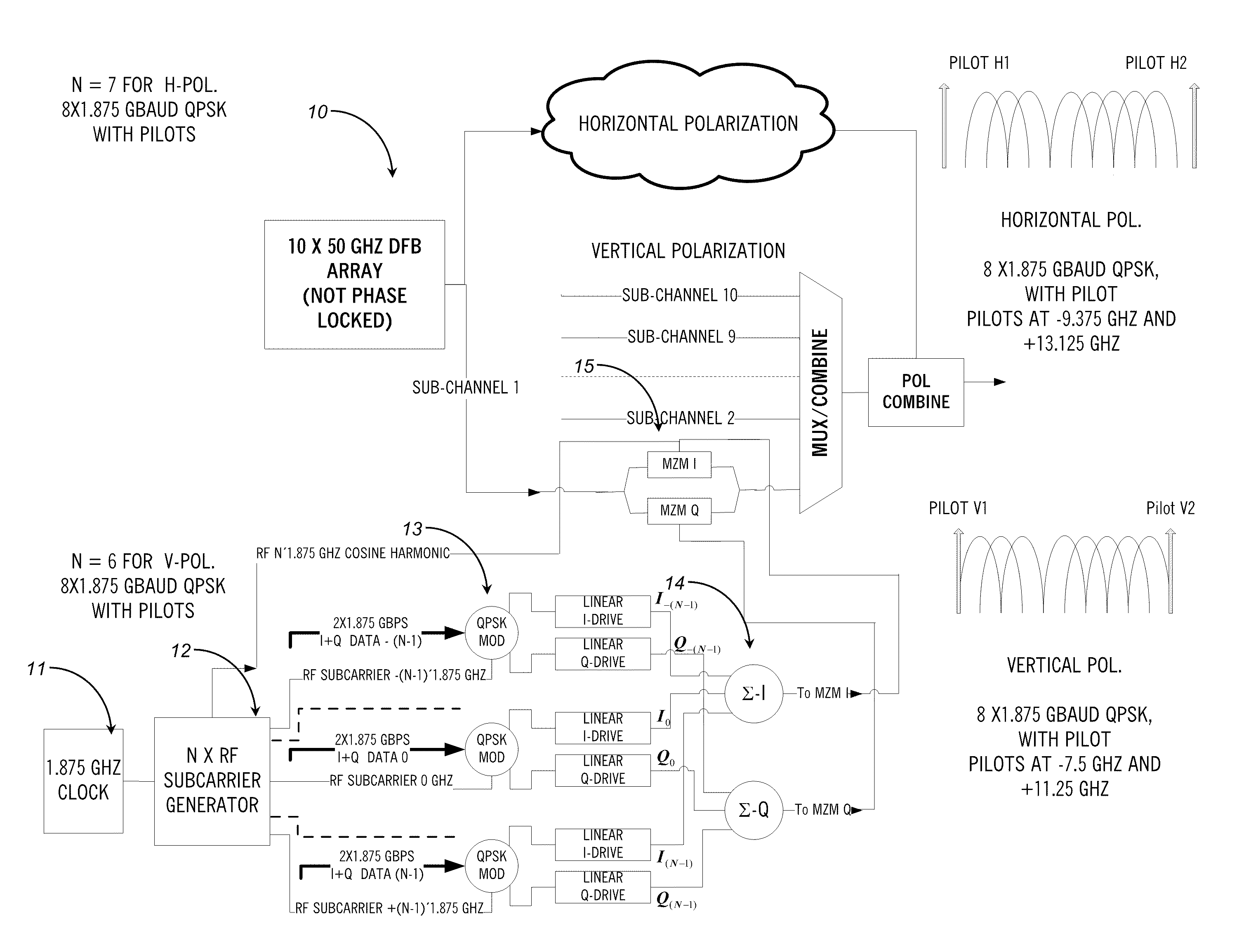
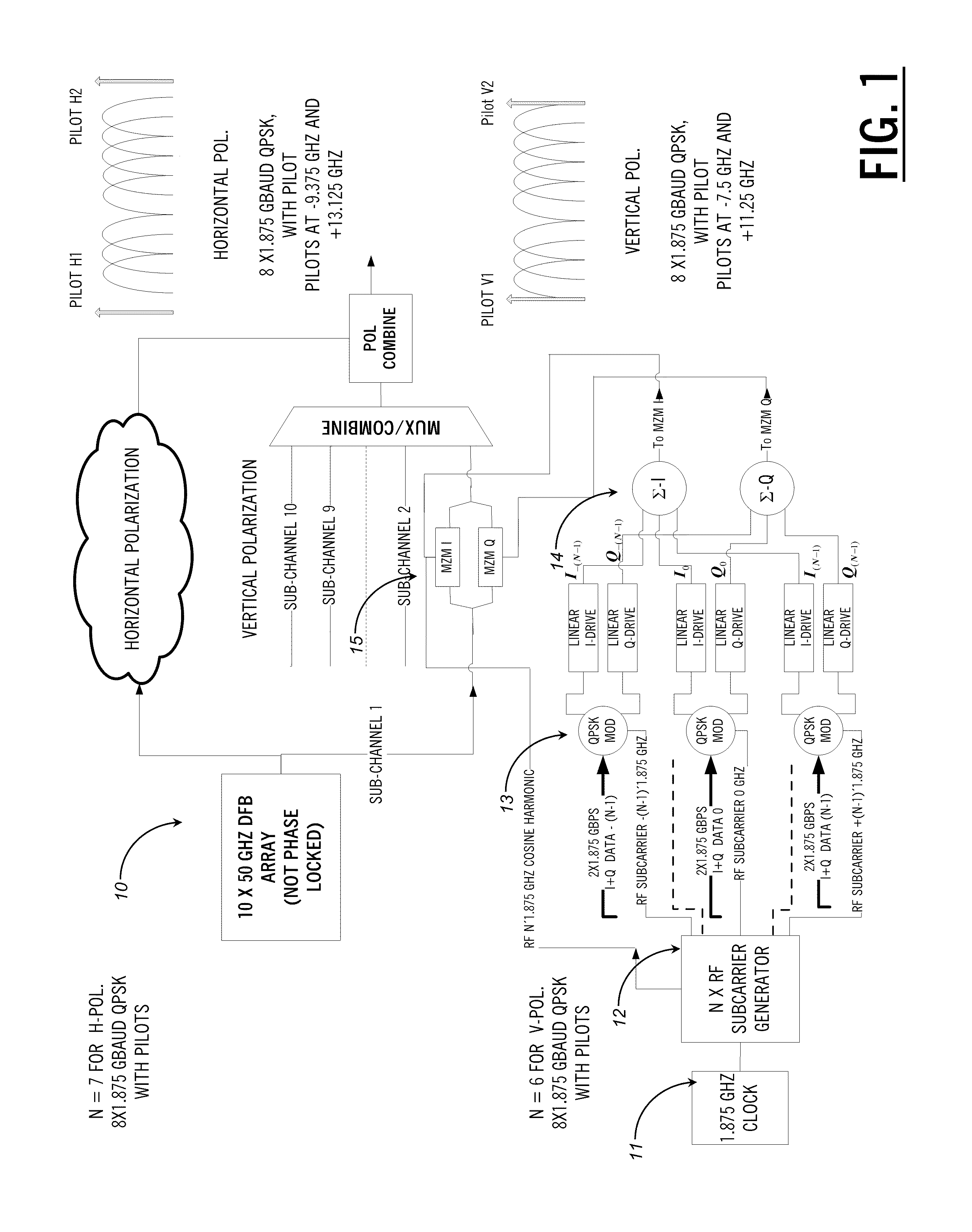
The present disclosure provides a polarization multiplexed transceiver, including: a transmitter; a receiver; circuitry within the transmitter configured to insert pilot tones as a reference state of polarization for a polarization multiplexed signal; and circuitry within the receiver configured to de-multiplex the polarization multiplexed signal using the pilot tones. The transmitted signal is constructed in such a manner as to facilitate the division of the receiver processing between the analog and digital domains such that the implementation may be simultaneously both highly spectrally efficient and power efficient.
Owner:CIENA
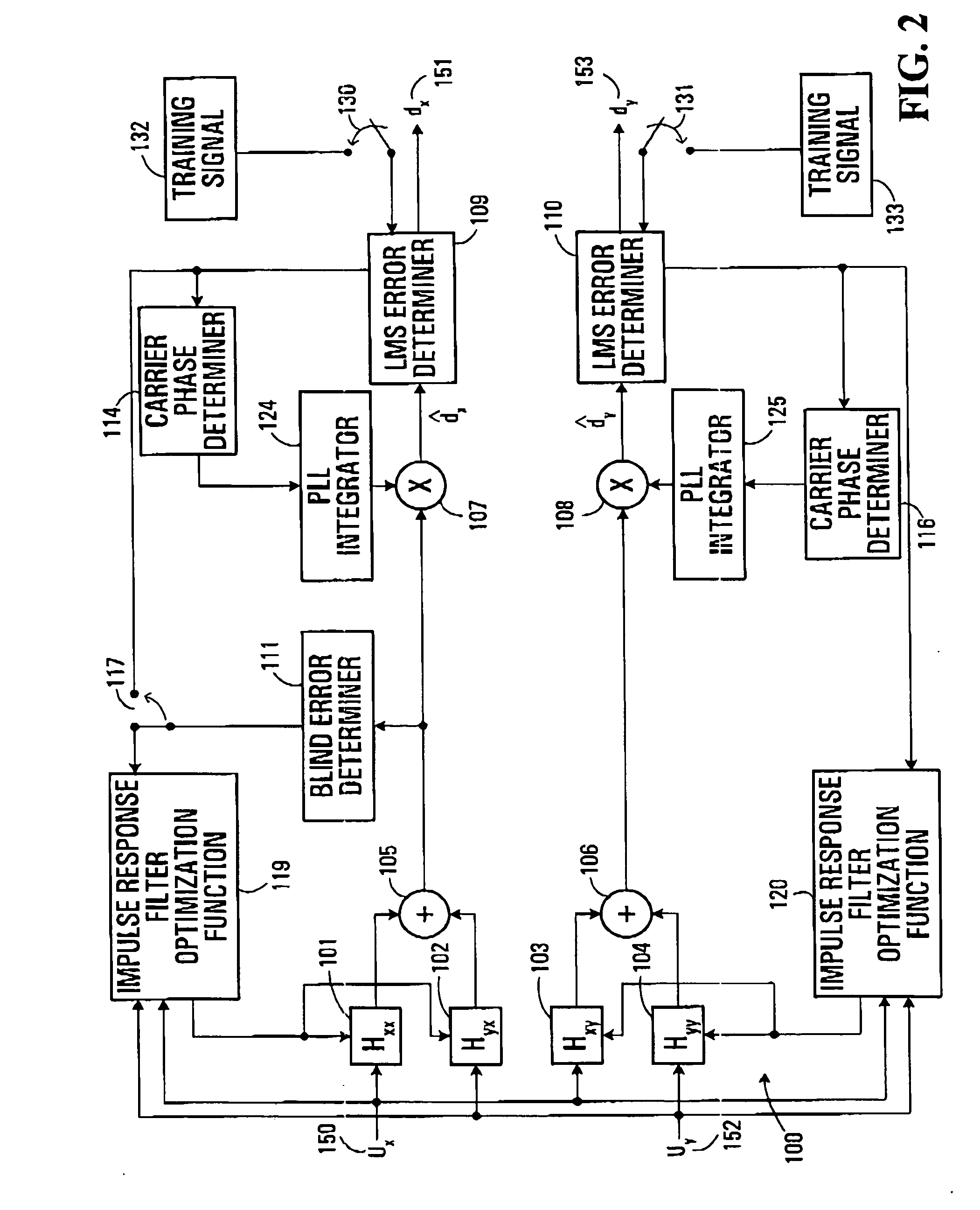
Equalization strategy for dual-polarization optical transport system
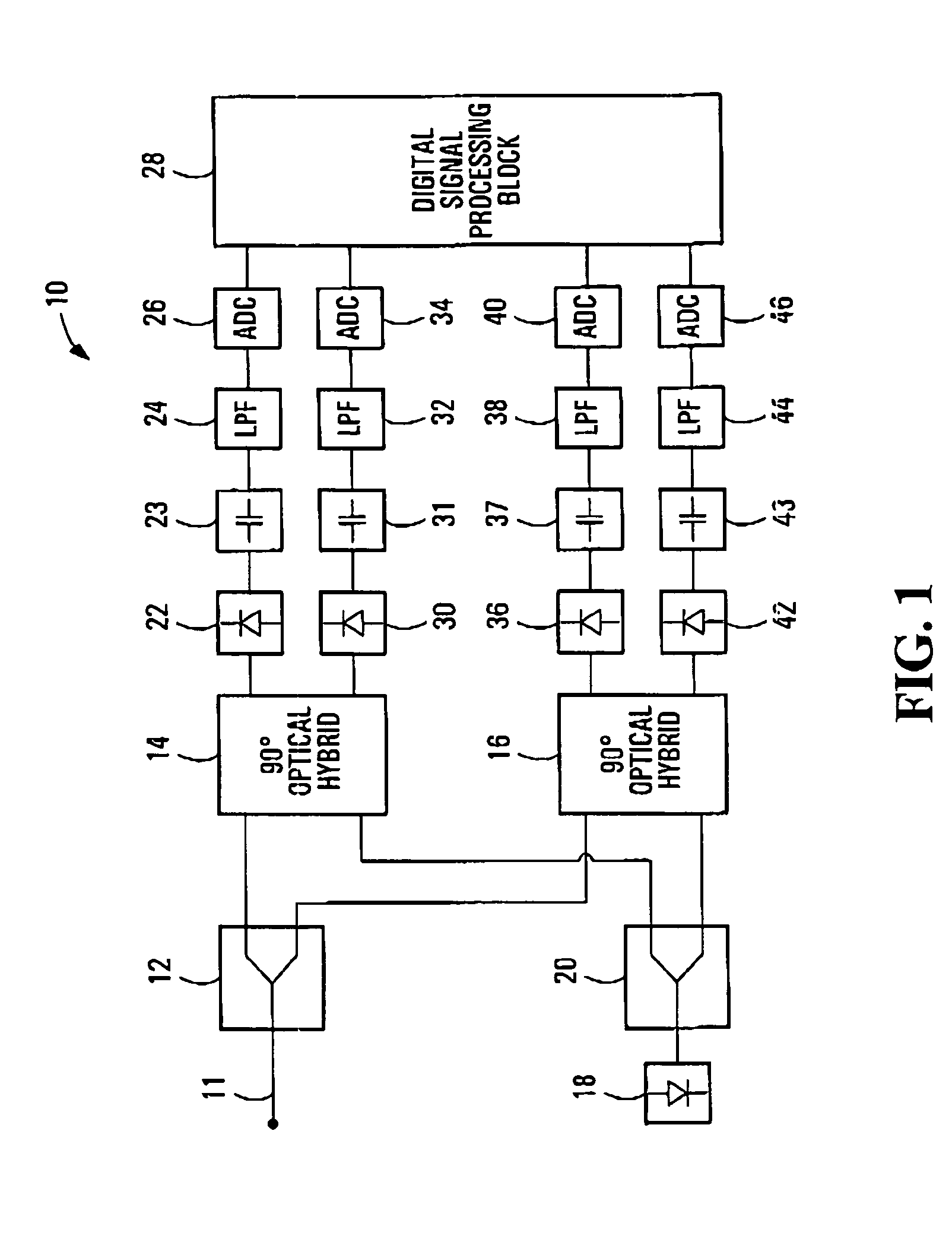
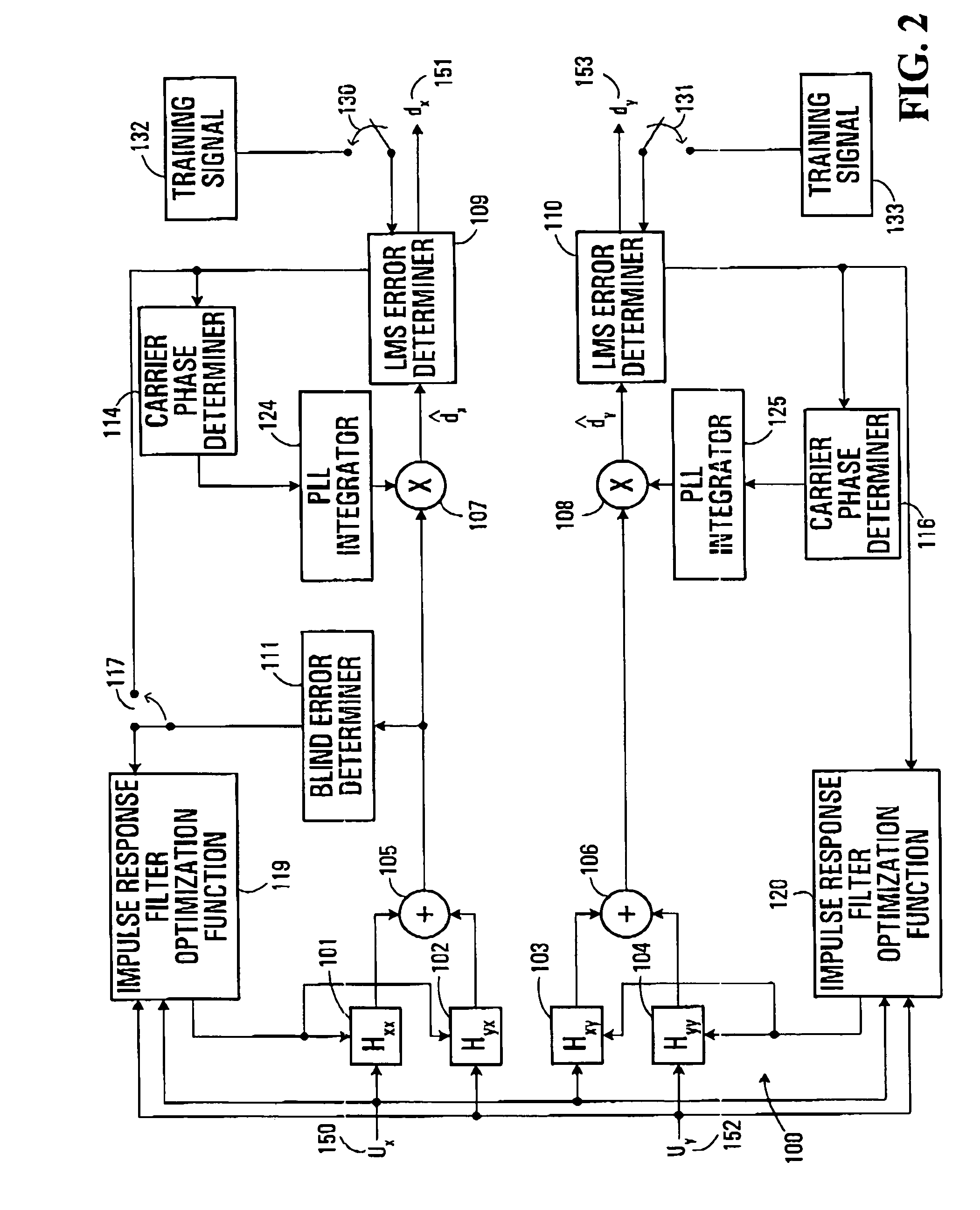
ActiveUS20050196176A1Avoid convergencePrevent degradationMultiple-port networksError preventionDigital signal processingSelf recovery
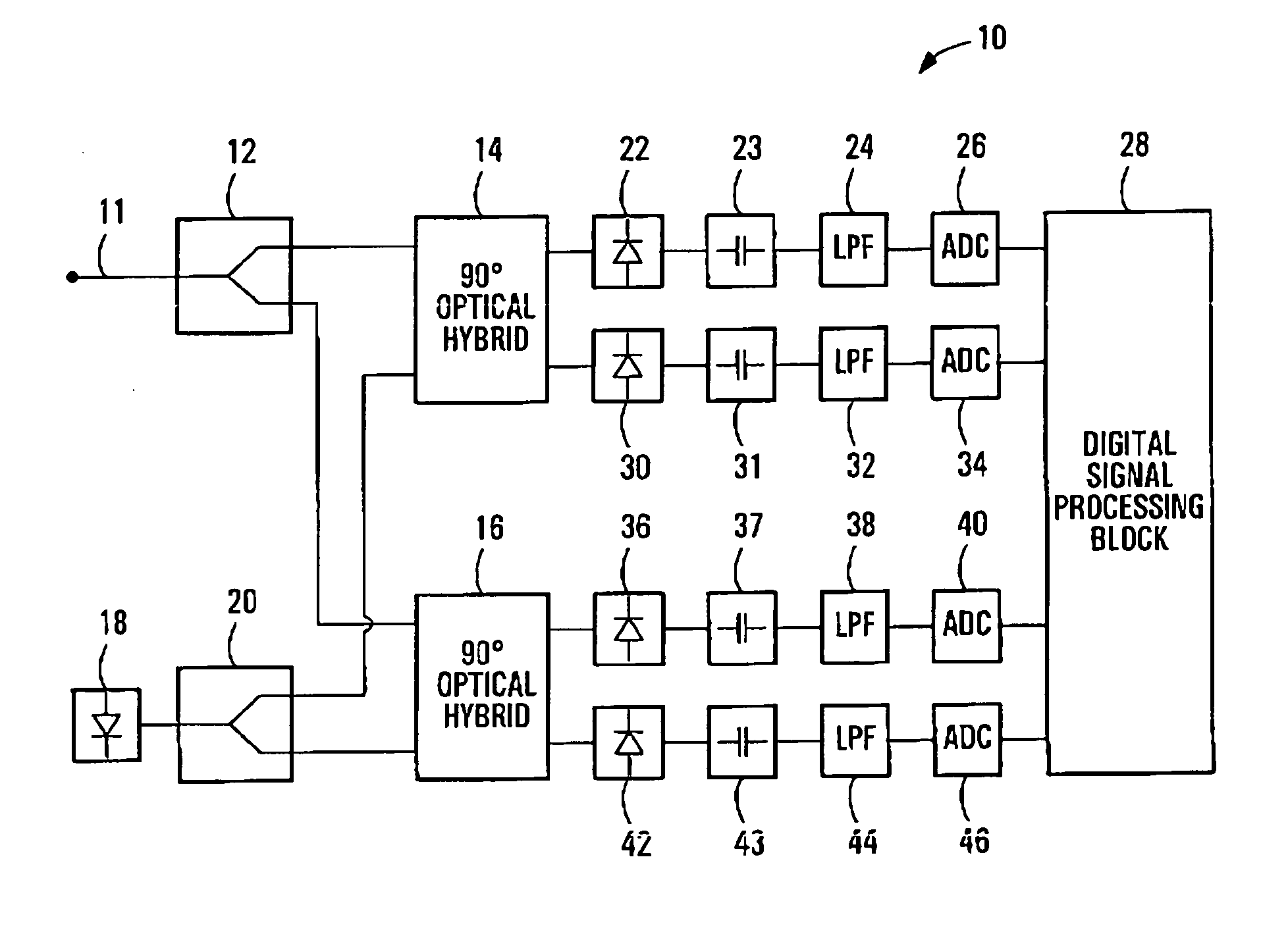
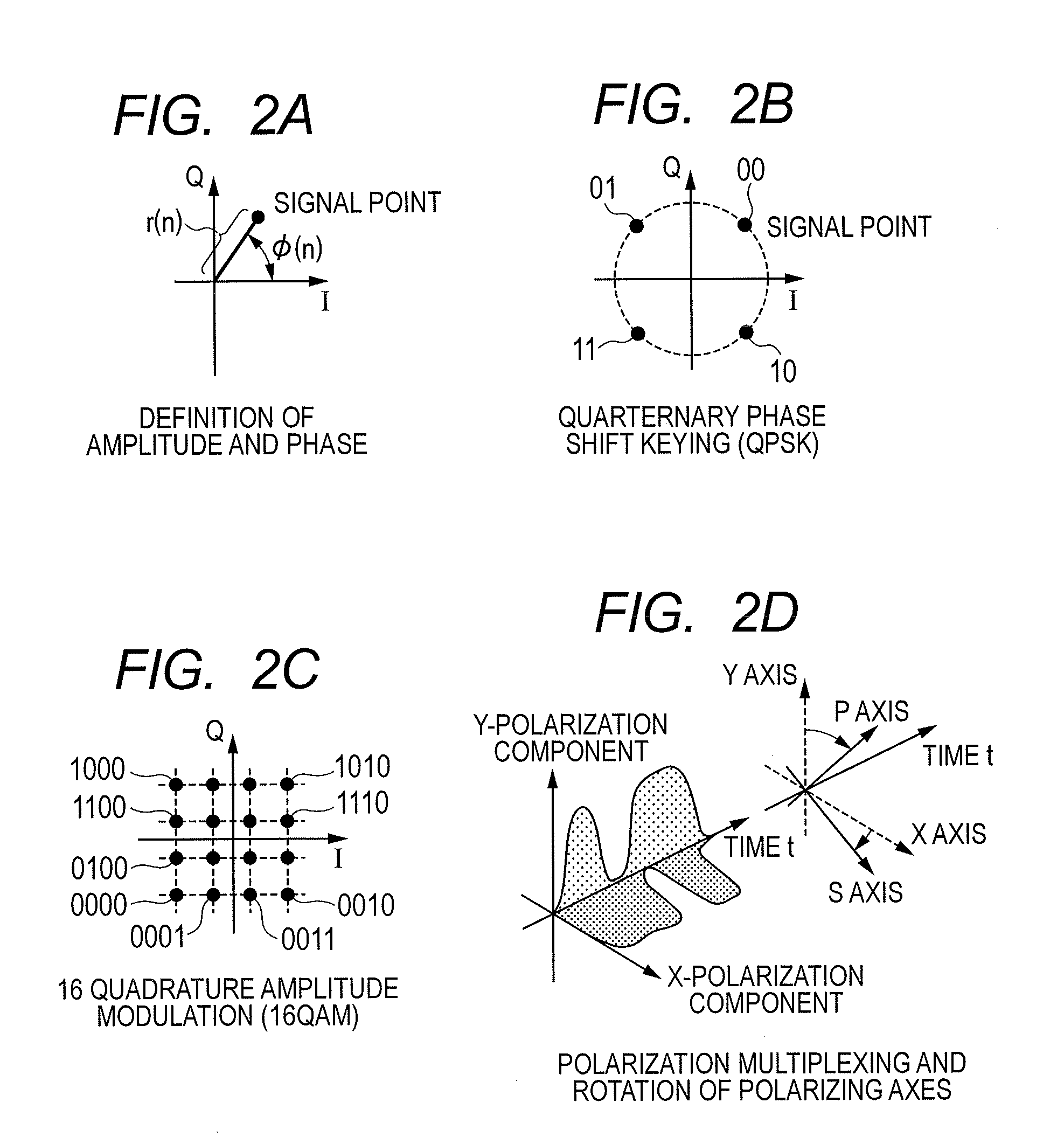
A method is provided for an equalization strategy for compensating channel distortions in a dual-polarization optical transport system wherein the received signal includes a complex signal of a first transmitted polarization component and a complex signal of a second transmitted polarization component. In a first step, a blind self-recovery mode used a blind adaptation algorithm in calculating and modifying multiple complex equalizer transfer function coefficients to enable recovery of only the complex signal of the first transmitted polarization component. By recovering only a single polarization component in the first step the degenerate case of recovering only a single transmitted signal at both polarization component outputs of an equalizer is prevented. In a second step, equalization is performed in a training mode for calculating and modifying the multiple complex equalizer transfer function coefficients to enable recovery of the complex signals of the first and second transmitted polarization components. In a third step, equalization is performed in a data directed mode for continuing to calculate and modify the multiple complex equalizer transfer function coefficients to ensure continued recovery of the complex signals of the first and second transmitted polarization components. The method is suited for a digital signal processing implementation in a coherent receiver when a modulation scheme used on a transmitted signal is quadriphase-shift keying (QPSK). In other embodiments, the method can be used with modulation schemes such as binary PSK, M-ary PSK where M>4, or Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM).
Owner:CIENA
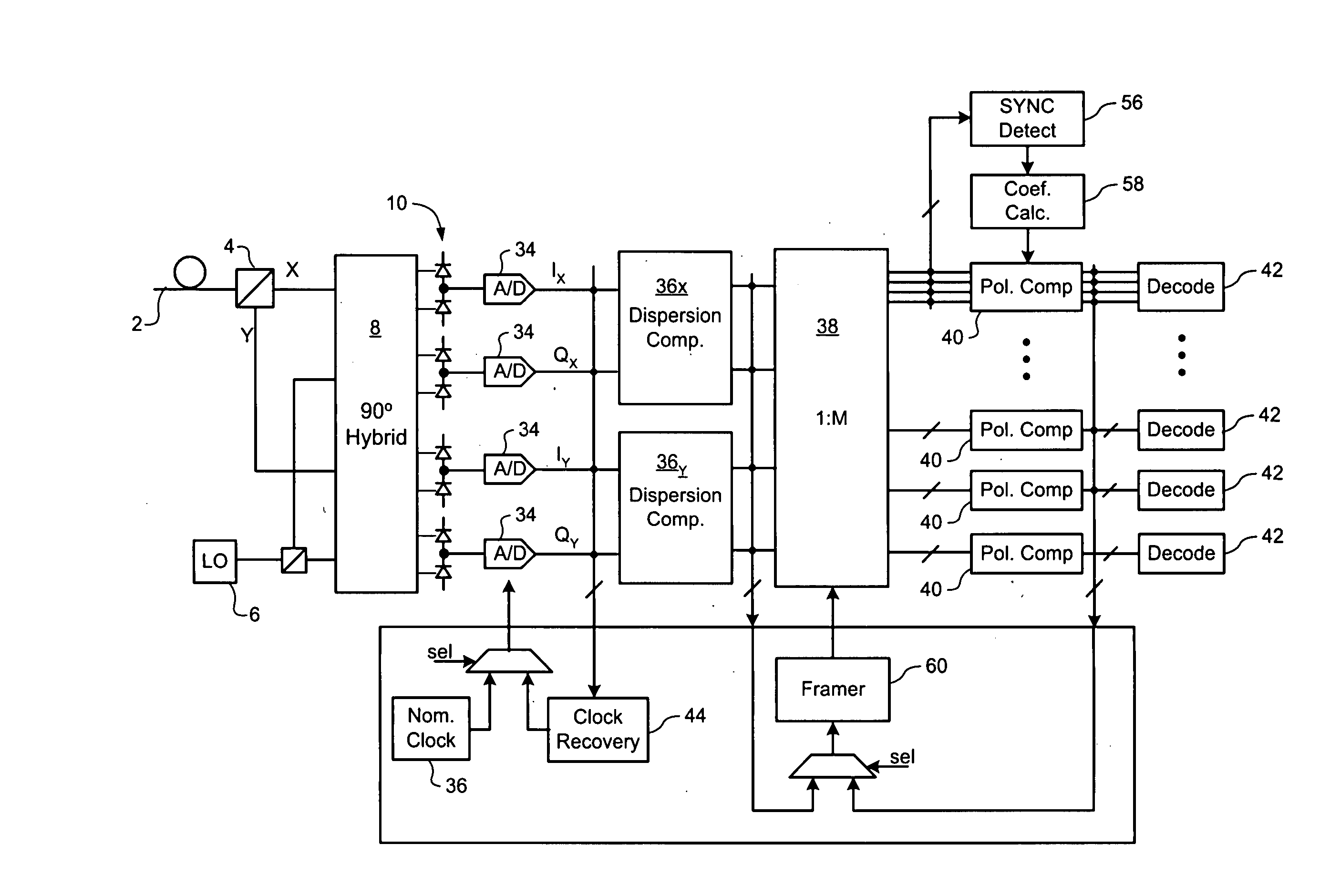
Efficient data transmission and training of data processing functions
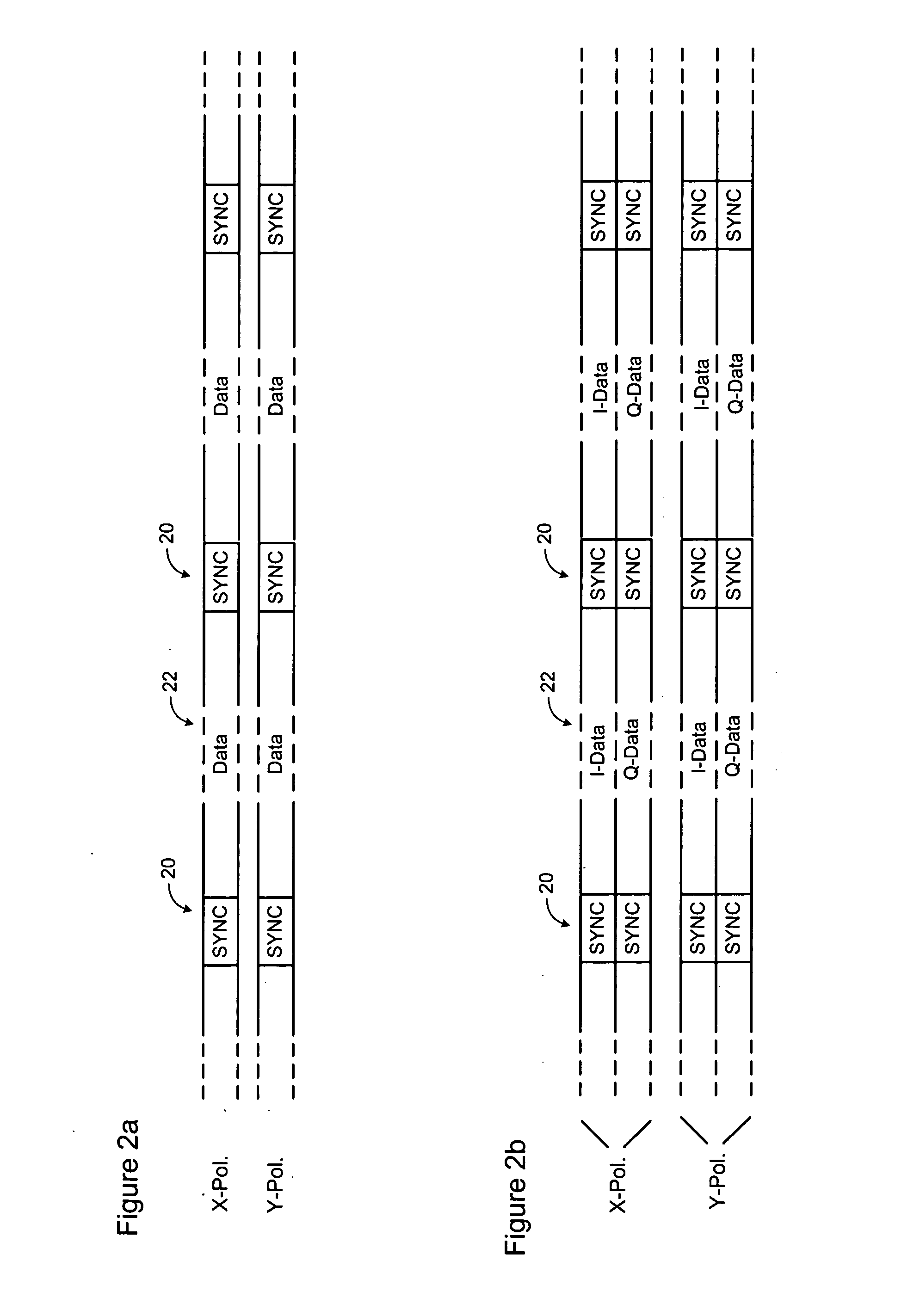
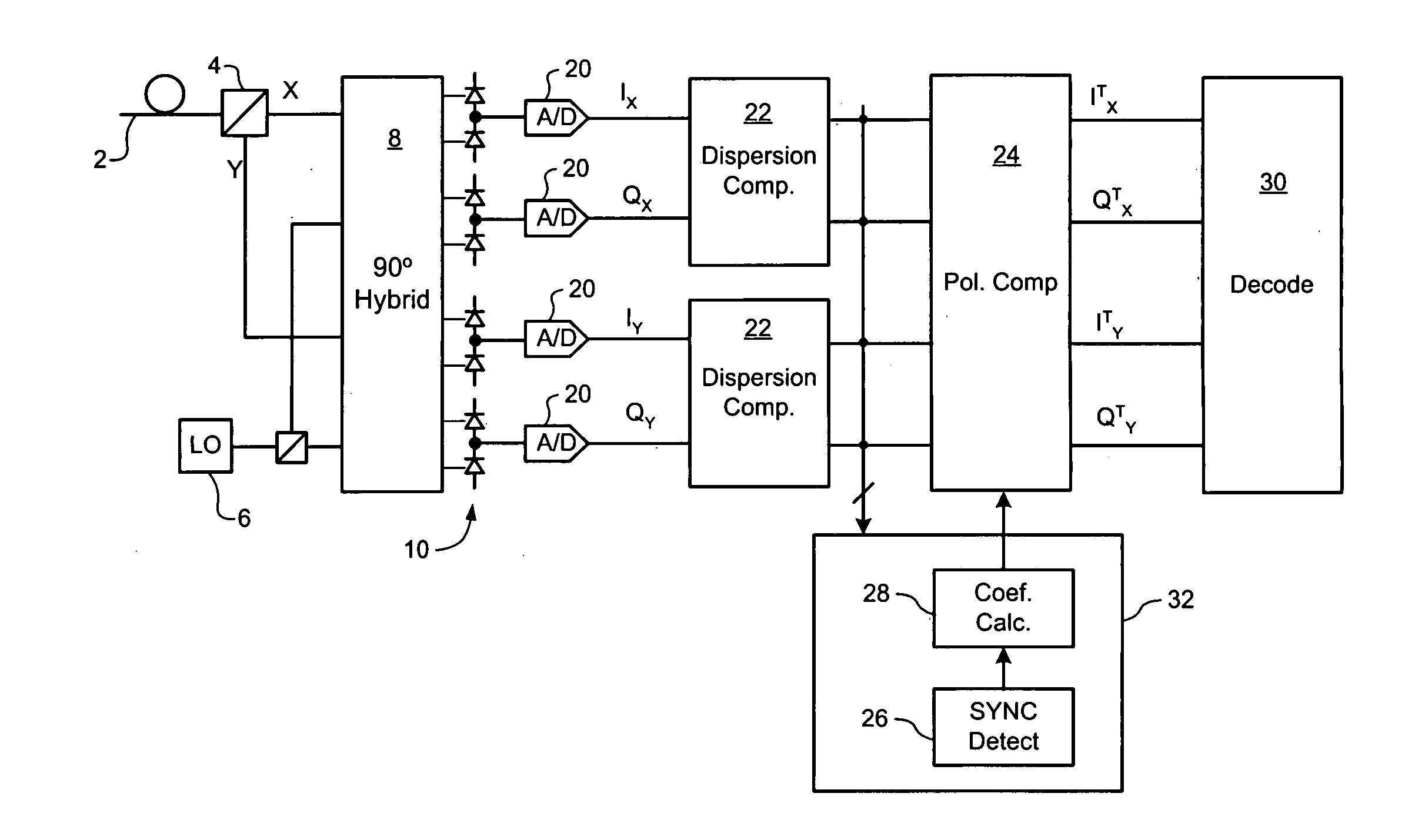
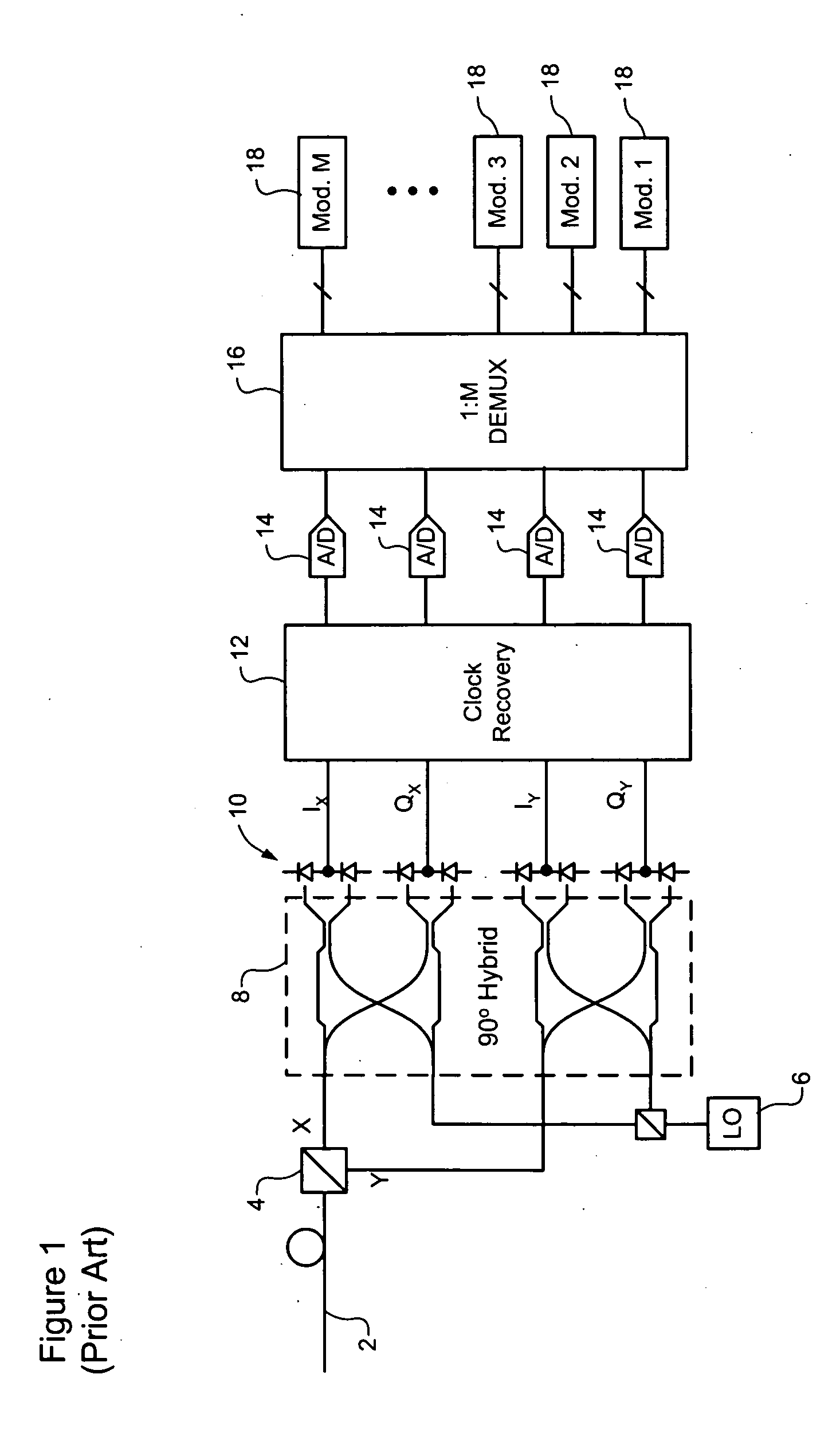
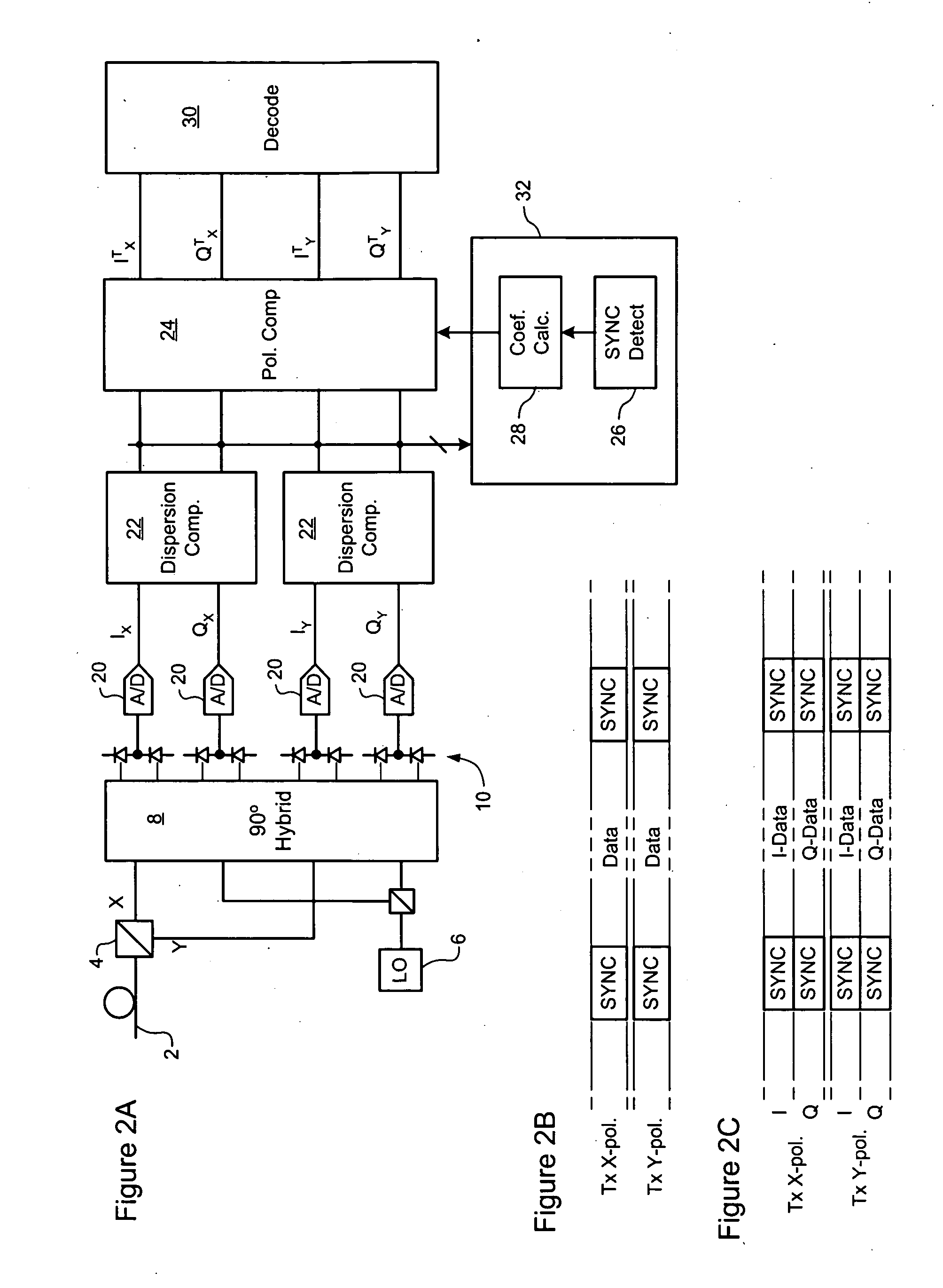
InactiveUS20070092260A1Efficient data transferCost-effectivePolarisation multiplex systemsTime-division multiplexComputer hardwareCommunications system
A method of a conveying data through an optical communications system. An optical signal is received through the optical communication system, the optical signal comprising data symbols and SYNC bursts, each SYNC burst having a predetermined symbol sequence. The received optical signal is oversampled to generate a multi-bit sample stream. The sample stream is partitioned into blocks of contiguous samples, wherein each block of samples partially overlaps at least one other block of samples and encompasses at least one SYNC burst and a plurality of data symbols. Each block of samples is independently processed to detect a value of each data symbol.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
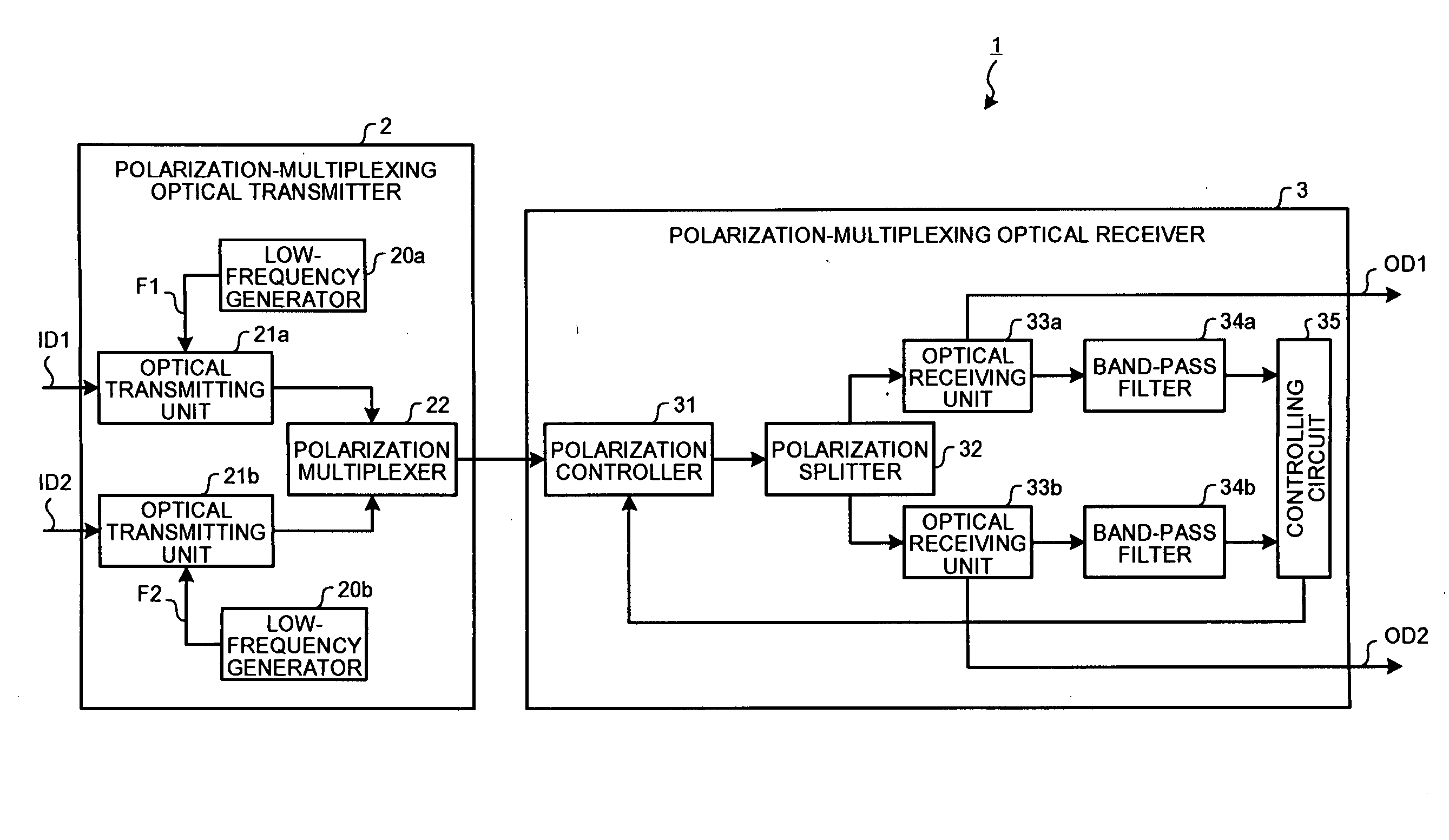
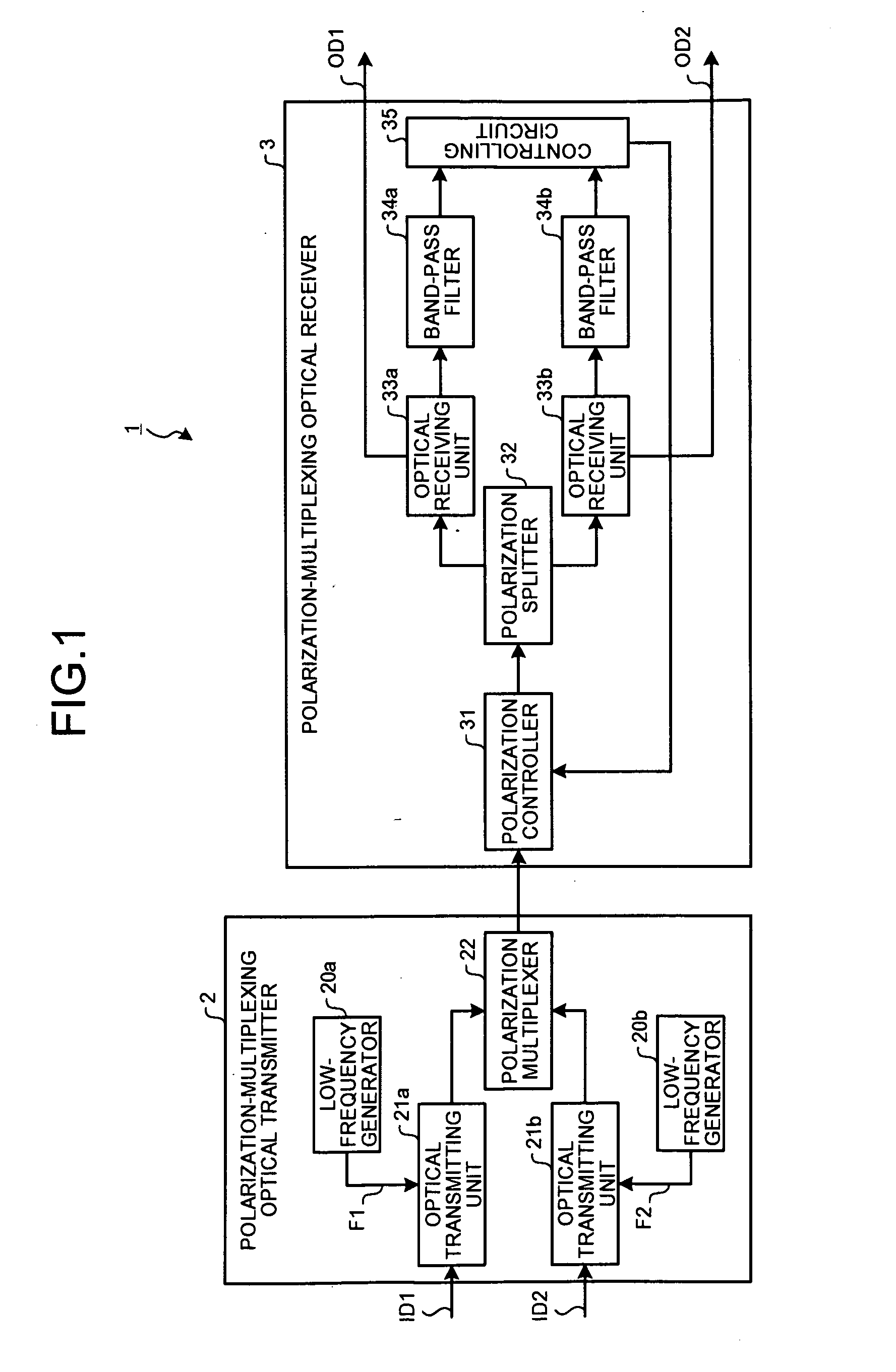
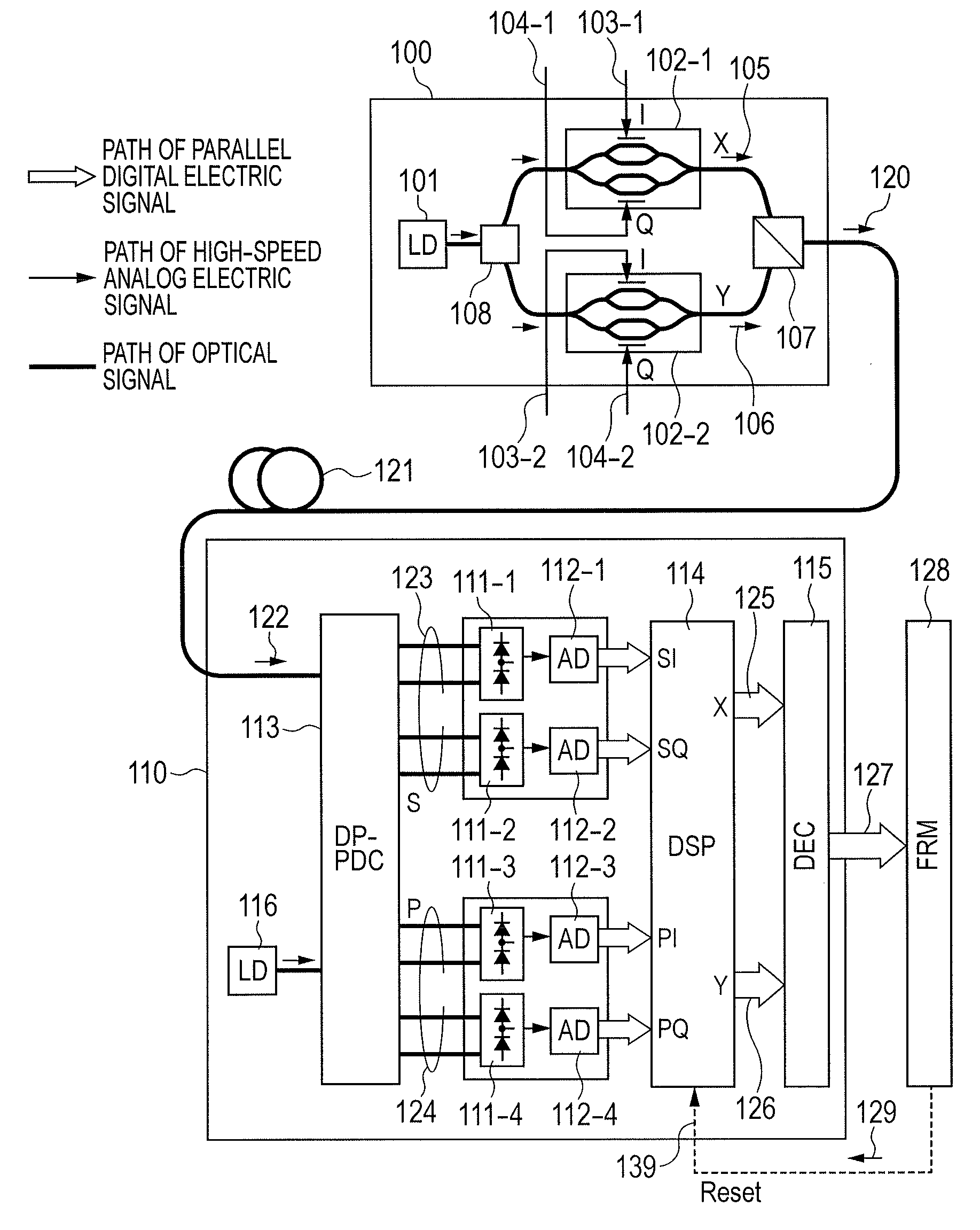
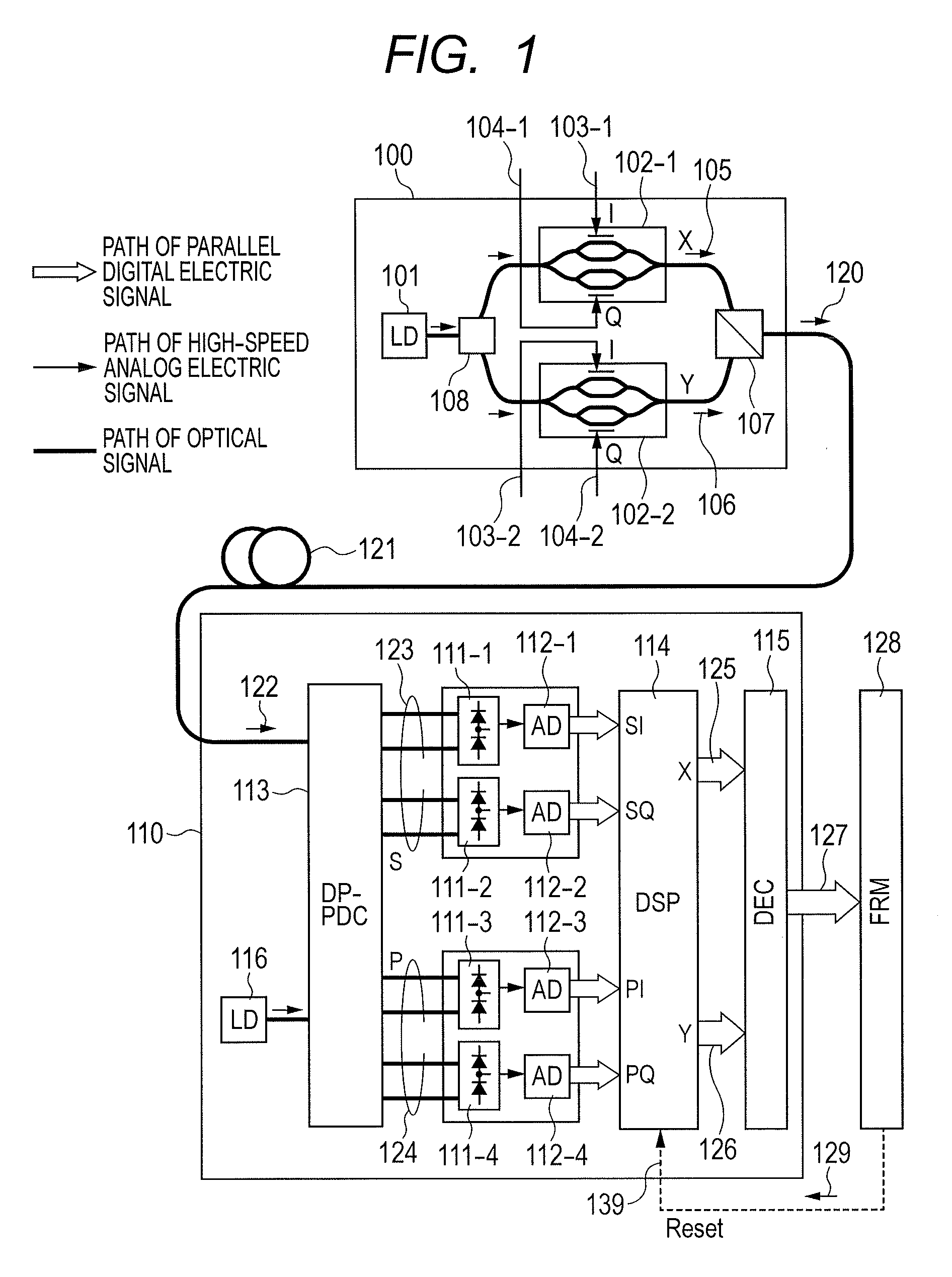
Polarization-multiplexing optical transmitter polarization-multiplexing optical receiver, polarization-multiplexing optical transceiving system, and controlling method thereof
InactiveUS20080232816A1Minimizes valueMaximizing and minimizing outputPolarisation multiplex systemsOptical mode multiplex systemsPolarization multiplexedCarrier signal
By using low-frequency signals, an optical transmitting unit modulates one of a wavelength, a transmission timing, and an intensity of light as a carrier wave. A polarization multiplexer synthesizes the output light signals, modulated by the optical transmitting unit, in polarization states orthogonal to each other and generates polarization-multiplexing signals. A polarization splitter splits by extracting two orthogonal polarization components from the polarization-multiplexing signals. The polarization states of the polarization-multiplexing signals are controlled by a polarization controller in an optical receiving unit. A band-pass filter extracts components transmitting through passbands from output signals of the optical receiving unit and outputs an intensity of the components. Based on the intensity output from the filter, a controlling circuit generates feedback control signals for maximizing a ratio of the components of the low-frequency signals and by using the feedback control signals, the polarization controller controls the polarization states of the optical multiplexing signals.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
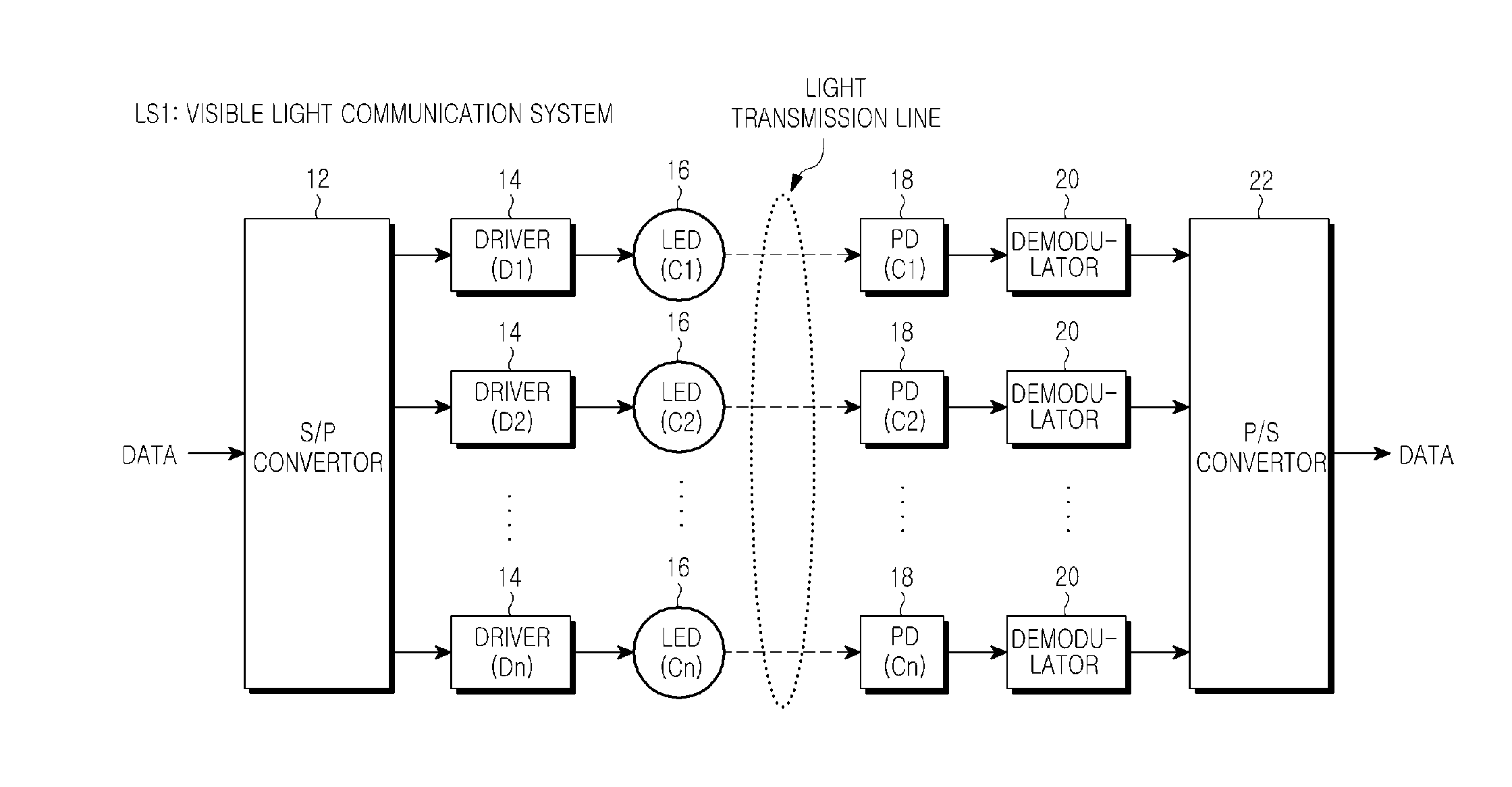
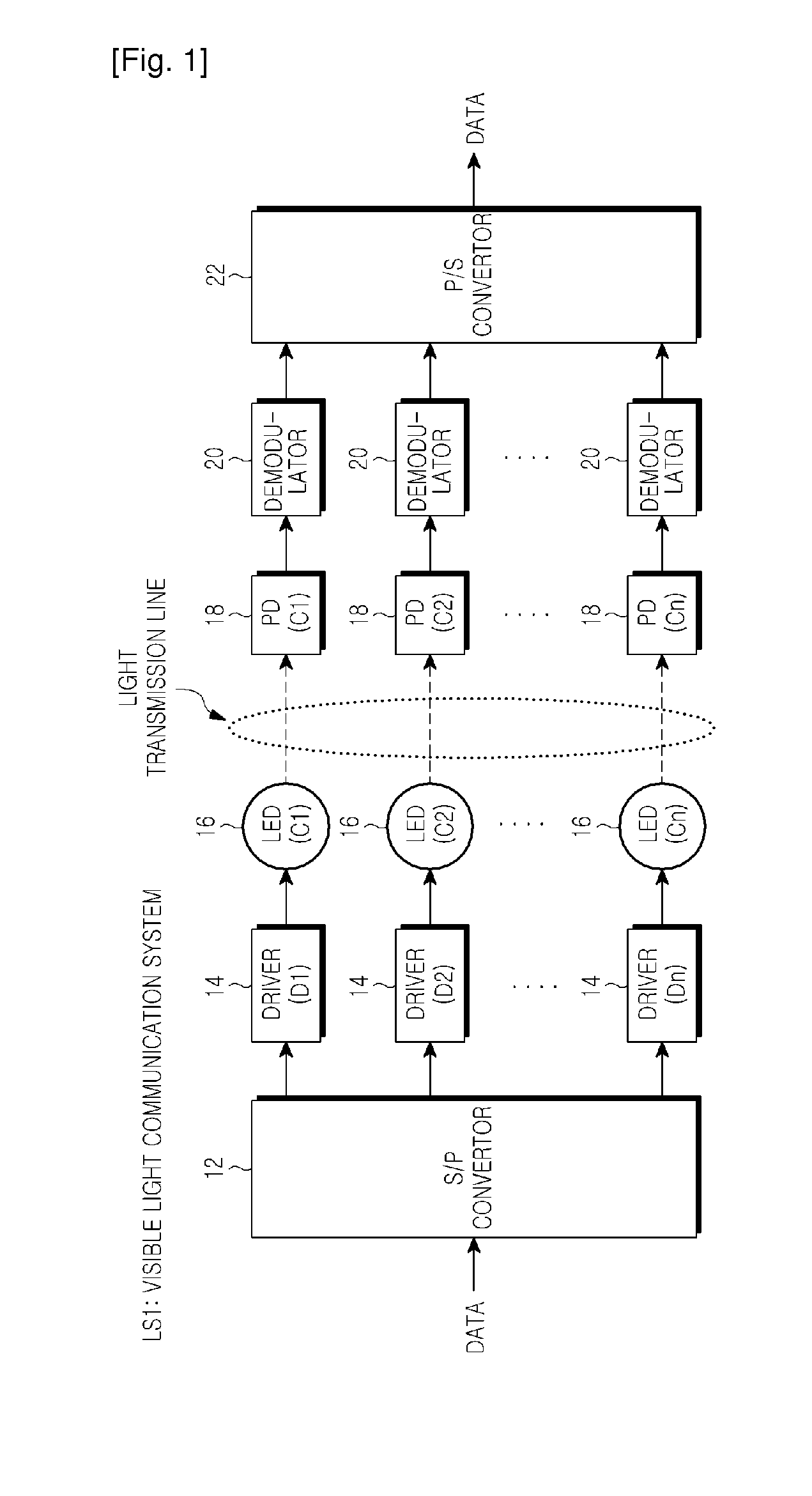
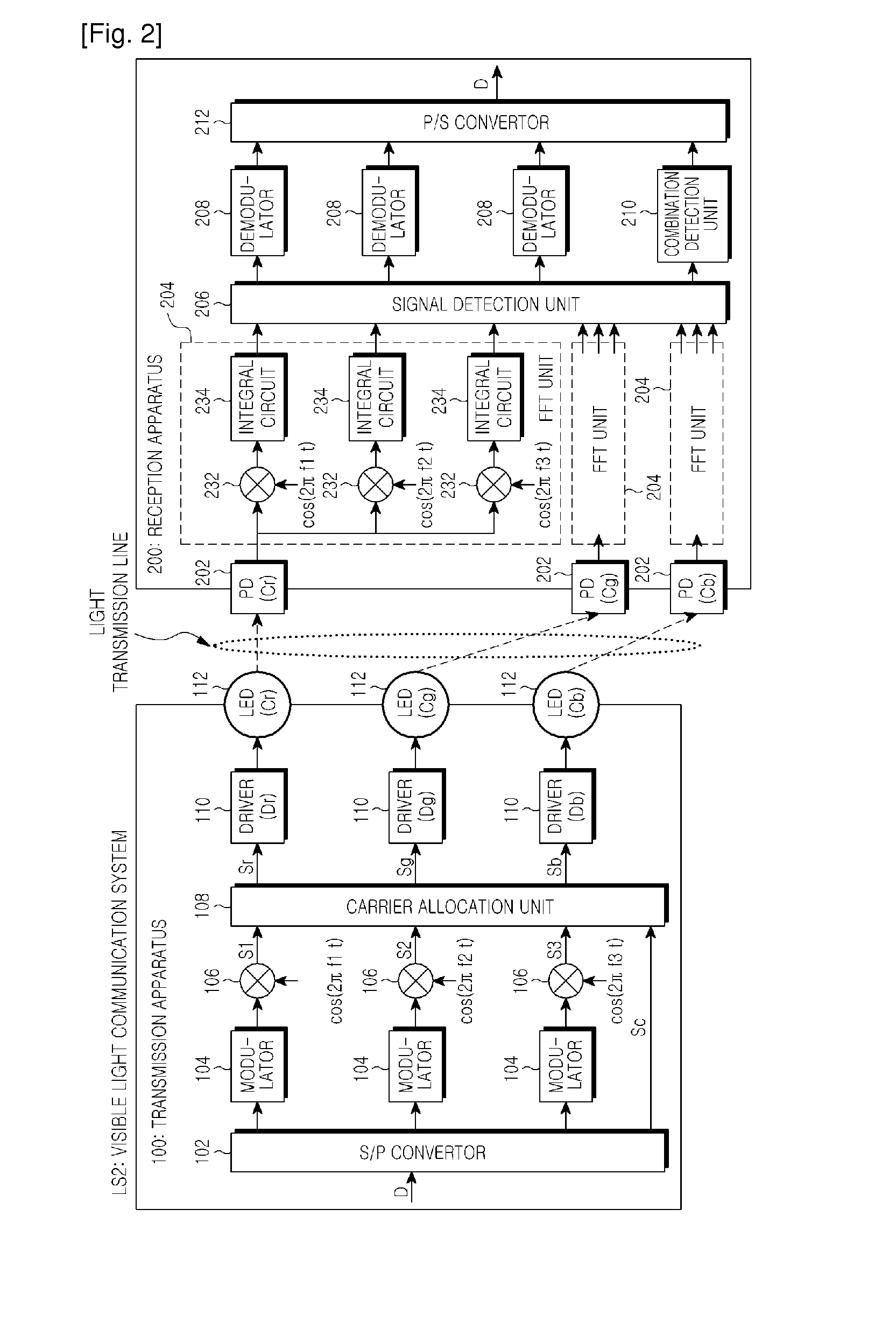
Visible ray communication system and method for transmitting signal
ActiveUS20110229147A1Improve communication qualityMore transmissionPolarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCommunication qualityCommunications system
A visible ray communication system and method that improve transmission rate and remove an influence of inter-color interference to improve the communication quality. A transmission apparatus included in the visible ray communication system allocates each carrier signal component of an OFDM signal, which is modulated into transmission information, to a plurality of LEDs of different colors. The information is added to a combination of a carrier frequency and an LED wavelength, when a carrier signal is allocated to an, in addition to each carrier signal being modulated into the information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
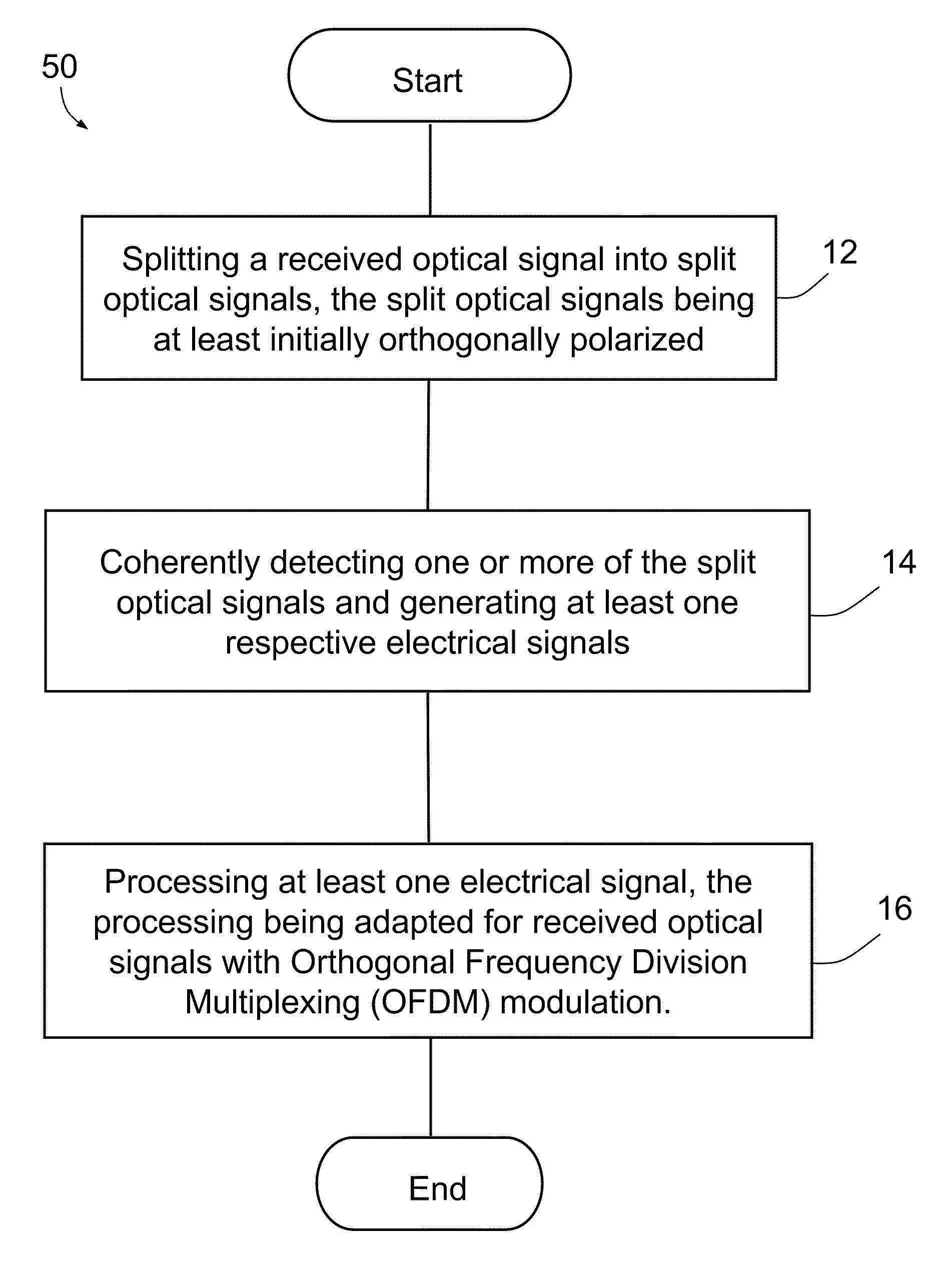
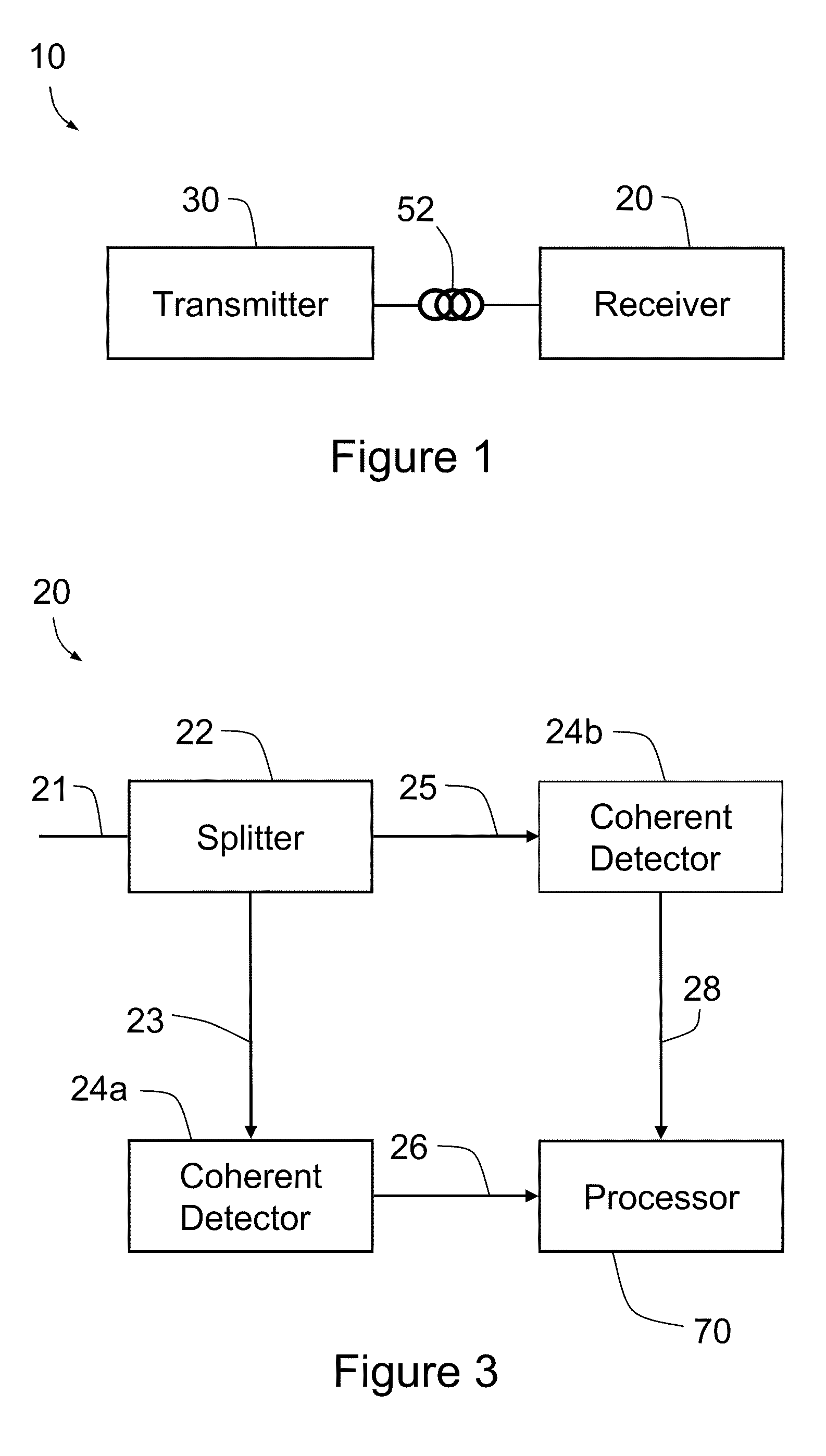
Method and system for polarization supported optical transmission
InactiveUS20100021163A1Compensation effectDoubling capacityPolarisation multiplex systemsElectromagnetic receiversTransfer systemOptical polarization
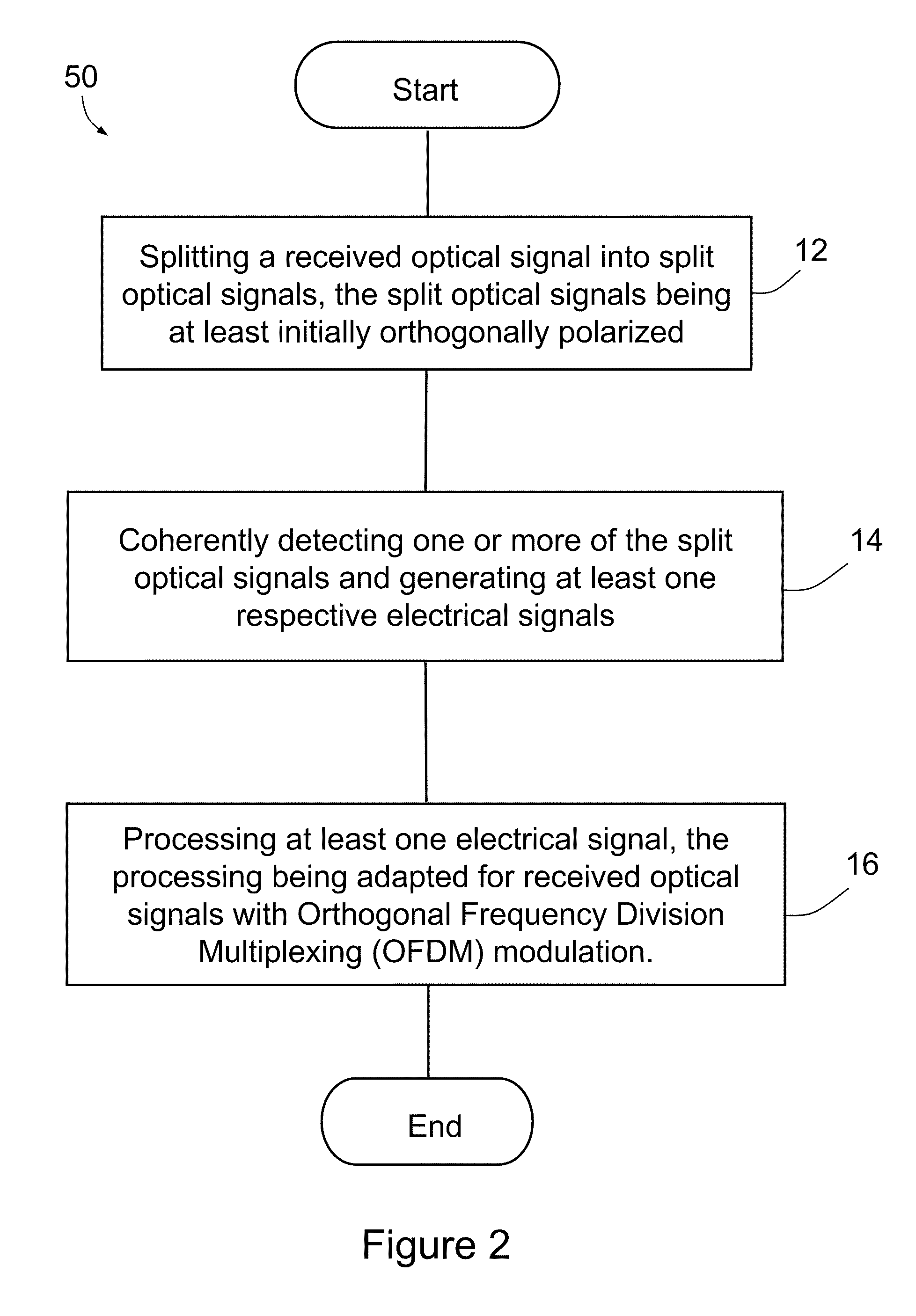
A method comprising splitting a received optical signal into split optical signals, the split optical signals being at least initially orthogonally polarized, coherently detecting at least one of the split optical signals and generating an electrical signal indicative thereof, and processing said electrical signal, the processing being adapted for received optical signals with orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) modulation. A transmission system, a transmitter and a receiver are also provided.
Owner:OFIDIUM PTY LTD
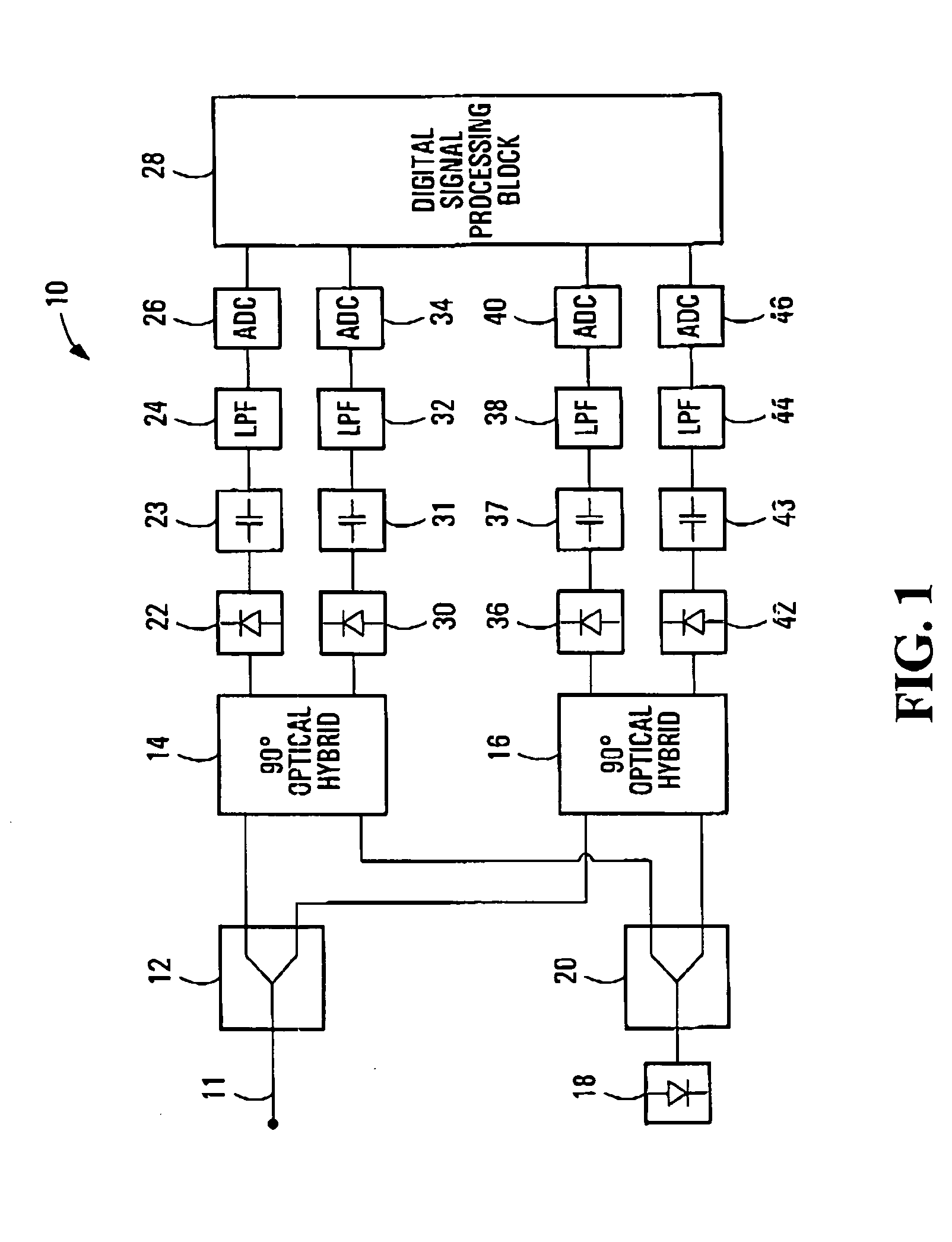
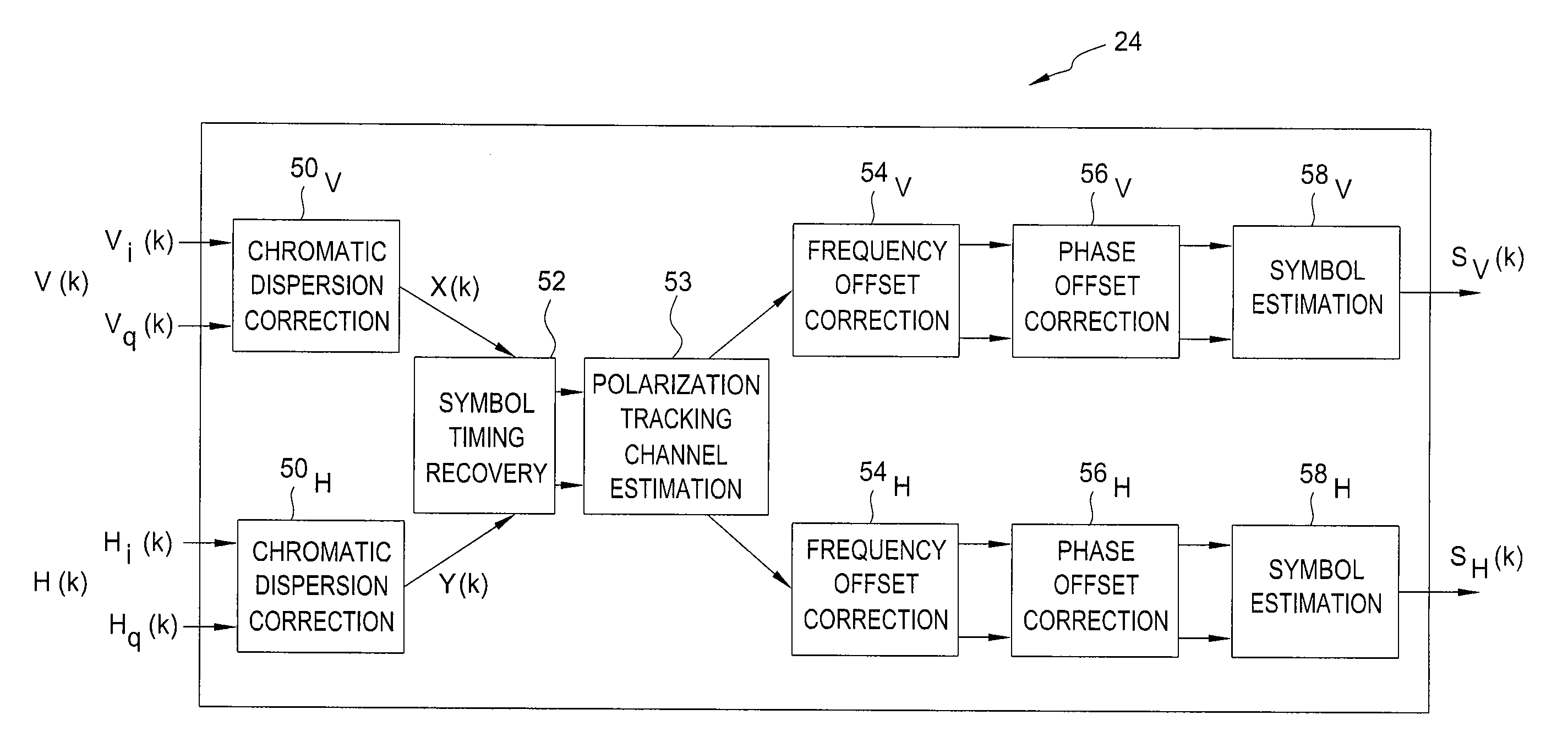
Symbol Timing Recovery in Polarization Division Multiplexed Coherent Optical Transmission System
ActiveUS20100329677A1Polarisation multiplex systemsElectromagnetic receiversDigital signal processingMultiplexing
A method, apparatus and system for providing clock and data recovery in a receiver for receiving a high speed coherent polarization division multiplexed optical signal using a digital signal processing block including a spectral domain spatial combiner are provided.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method and apparatus for filtering an optical beam
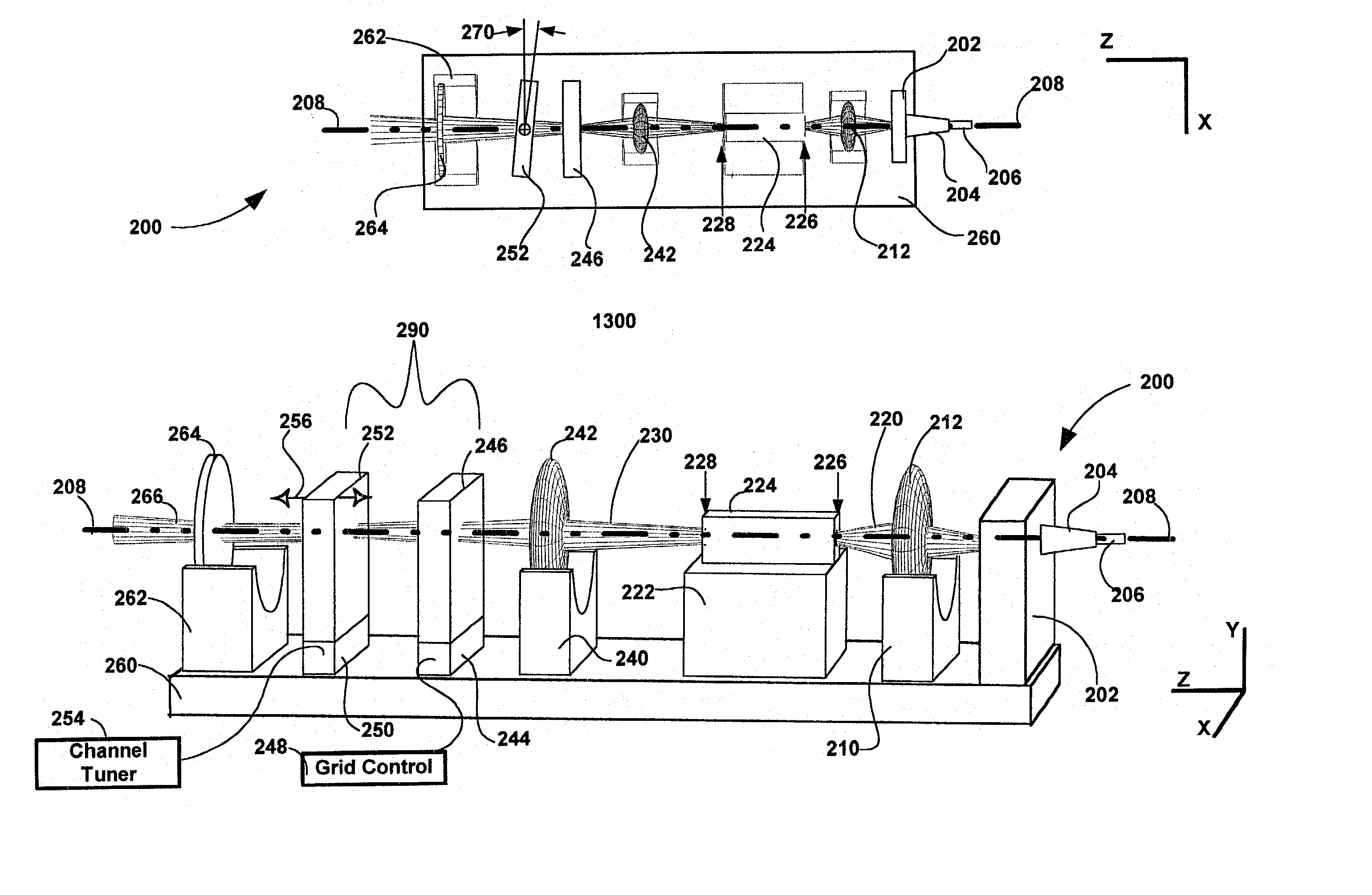
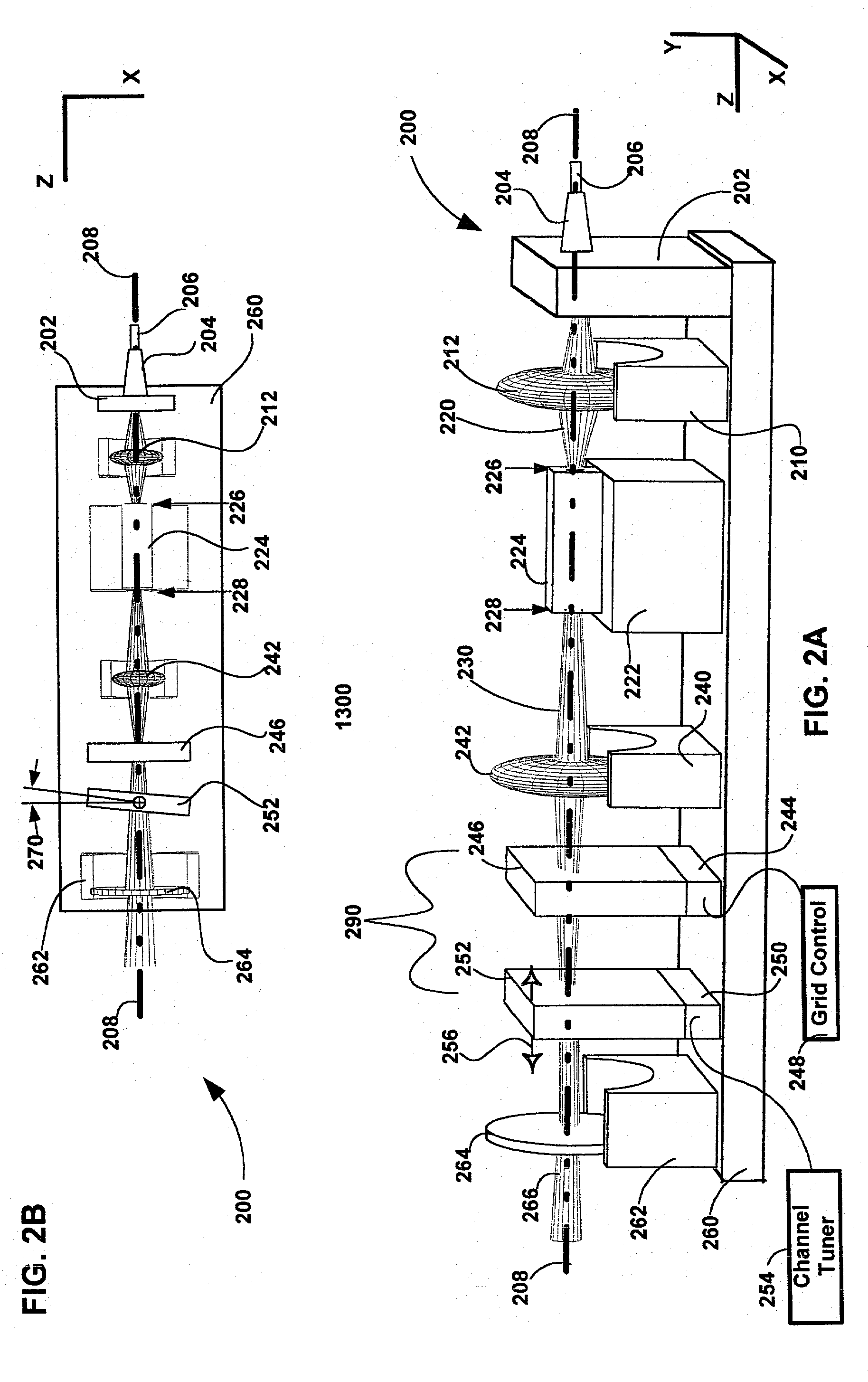
InactiveUS20020126345A1Compact form factorEasy to tuneLaser optical resonator constructionPolarisation multiplex systemsExternal cavity laserMesh grid
The invention pertains to wavelength-agile optical filters suitable for wavelength-division-multiplexed (WDM) optical communications networks. More particularly, the invention pertains to optical filters with a wavelength reference that can be remotely switched to arbitrarily selectable channels on a standard grid, and to re-configurable optical communications networks employing same. The present invention provides a communication apparatus with a tunable filter which may be used in a wide range of applications including tuning an external cavity laser (ECL), selecting a wavelength for an add / drop multiplexer and providing channel selection and feedback for a wavelength locker. The filter may be utilized as a discrete component or in combination with circulators, wavelength lockers and gain medium. The filter may be implemented in whole or in part as part of a gain medium. The tunable filter exhibits a compact form factor and precise tuning to any selected wavelength of a predetermined set of wavelengths comprising a wavelength grid. The tunable filter may thus be utilized in telecom applications to generate the center wavelengths for any channel on the ITU or other optical grid.
Owner:INTEL CORP
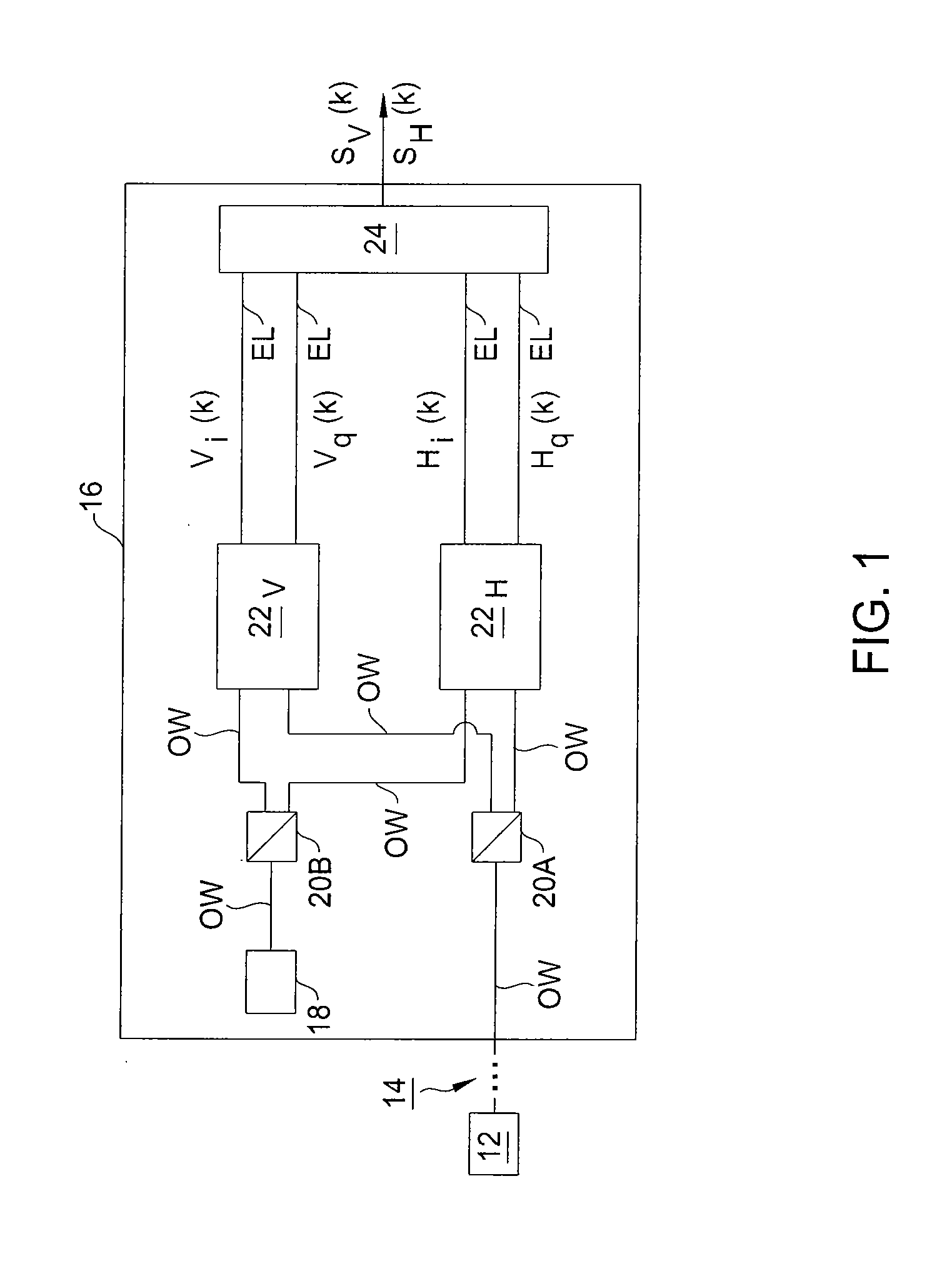
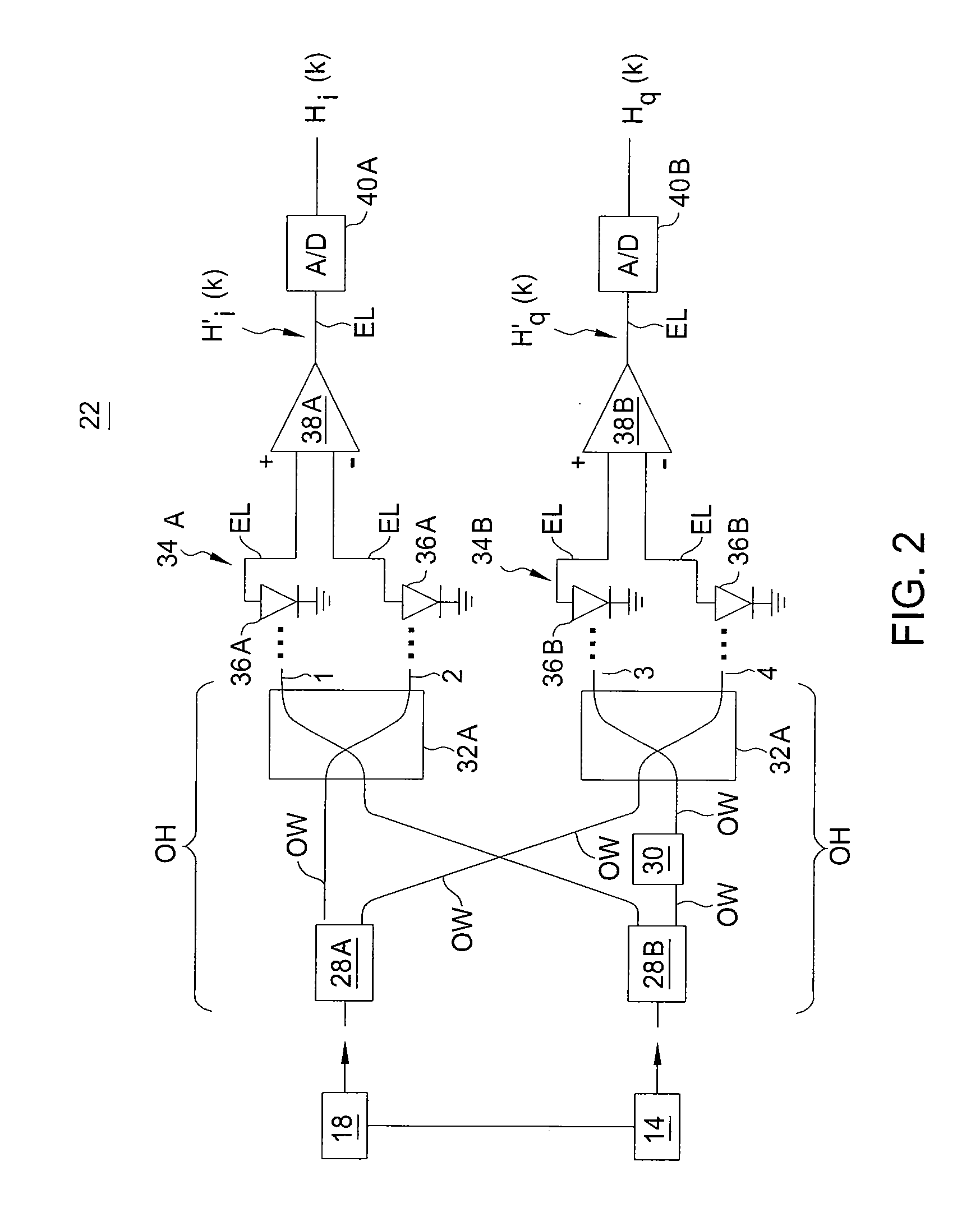
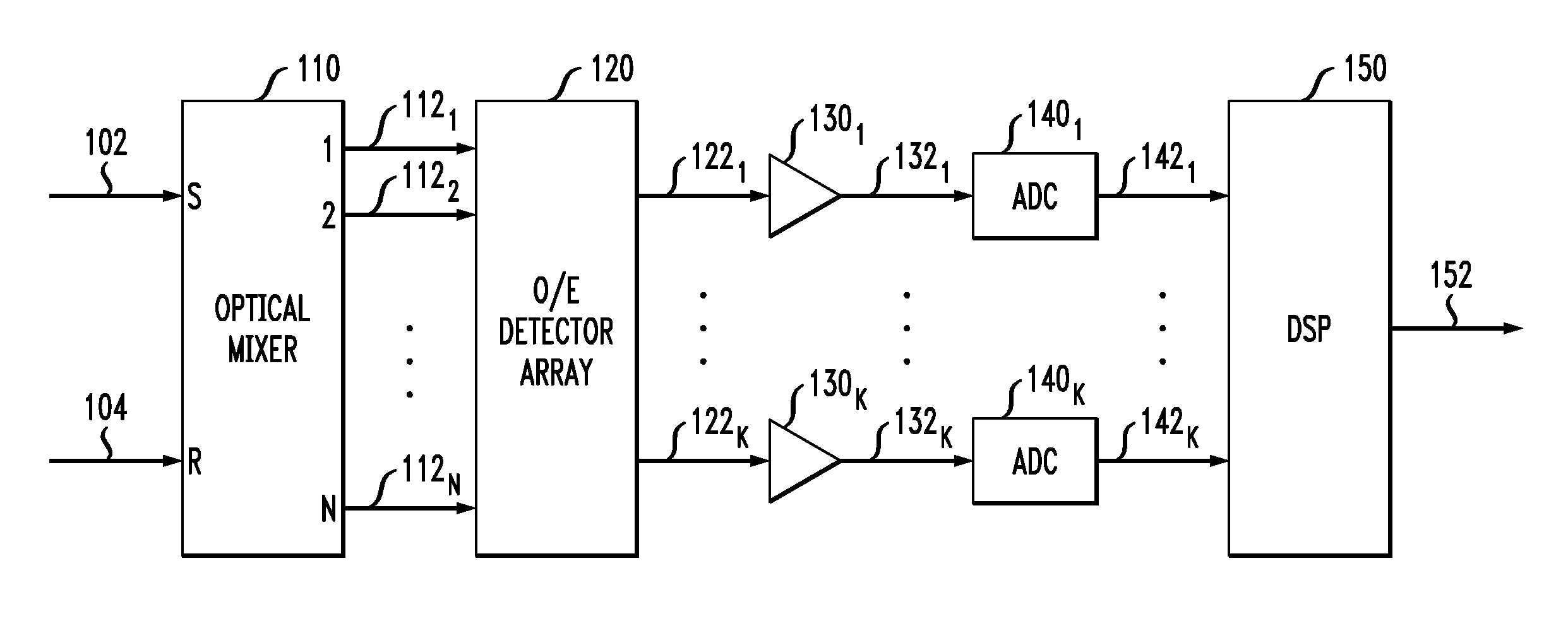
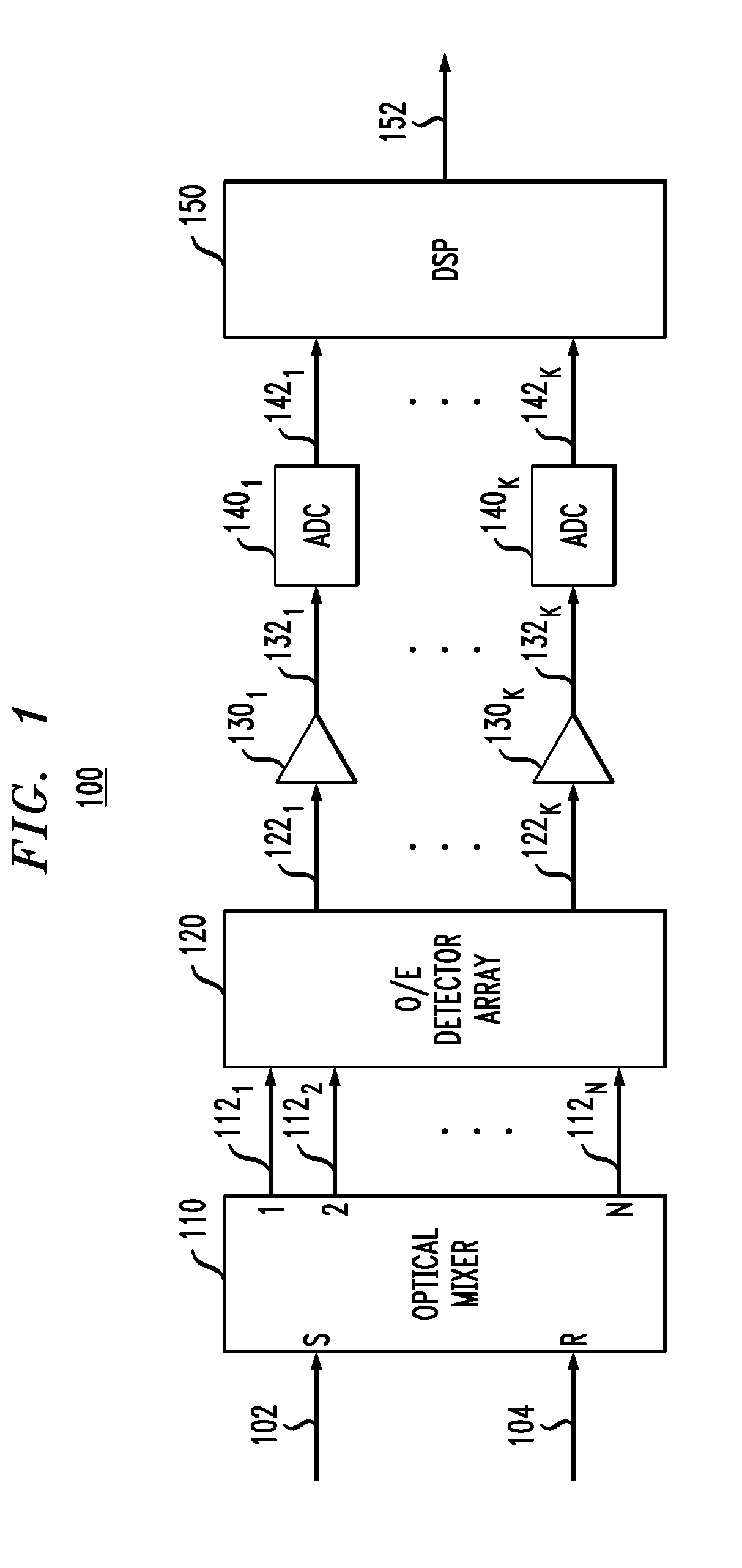
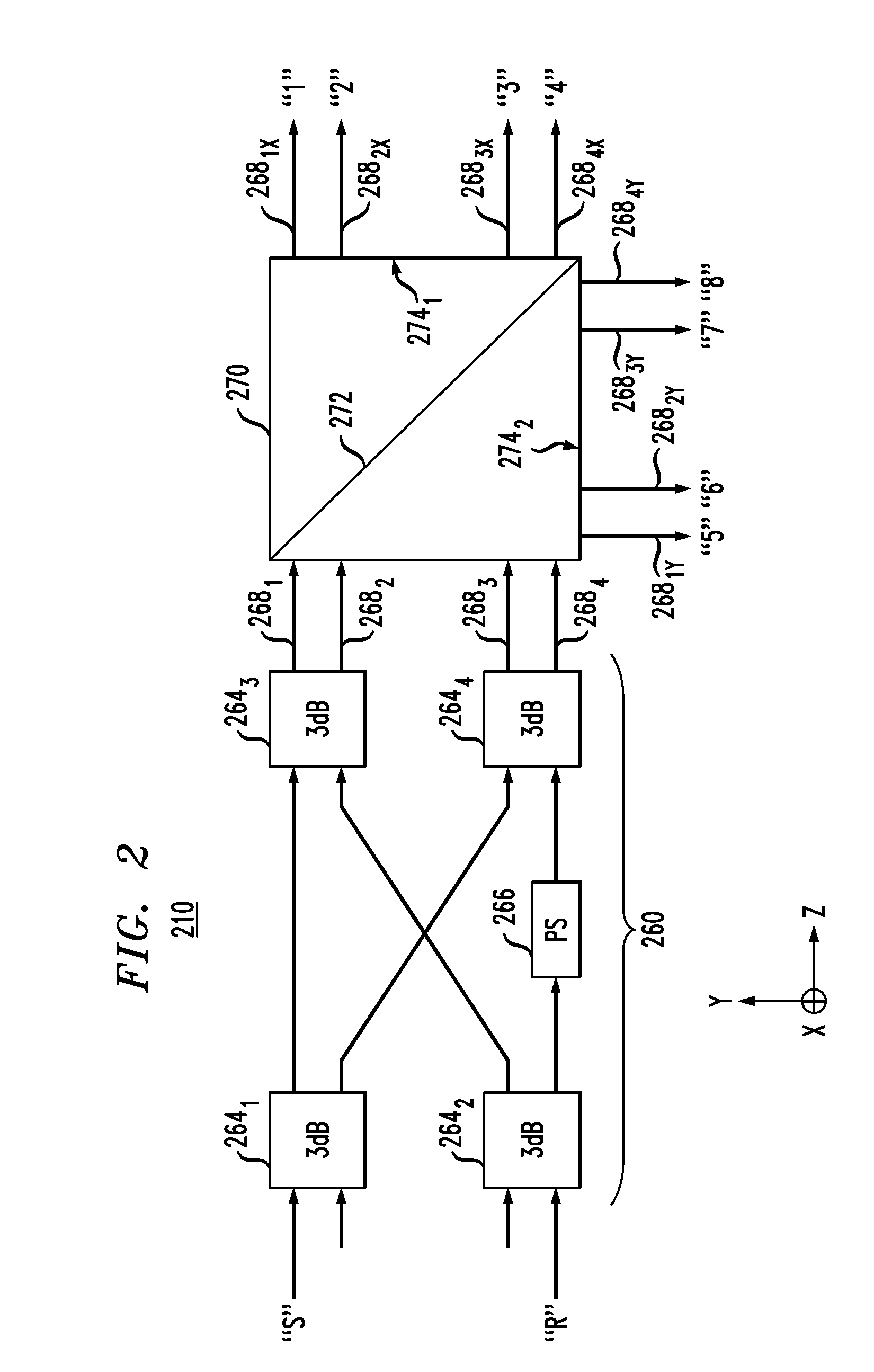
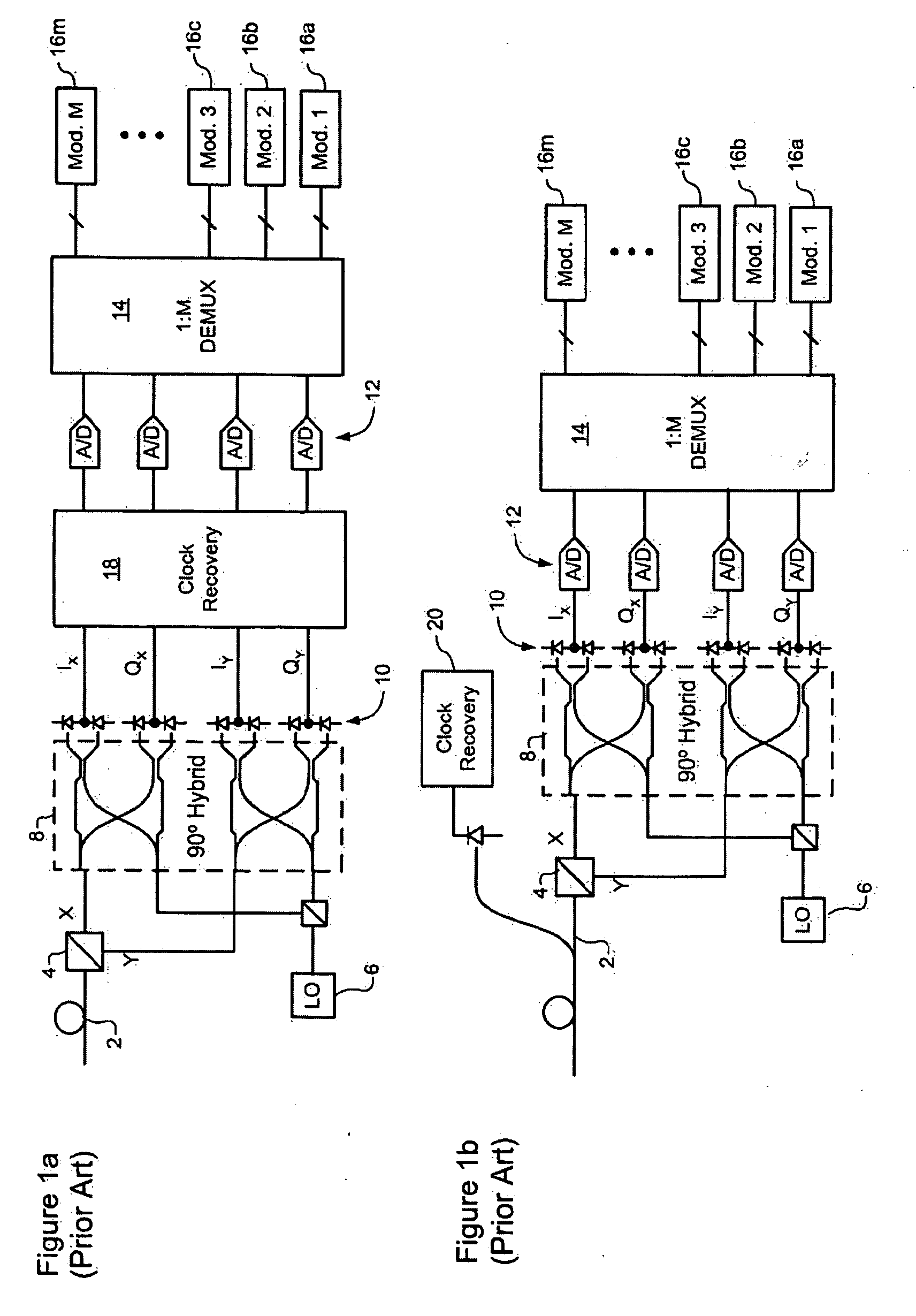
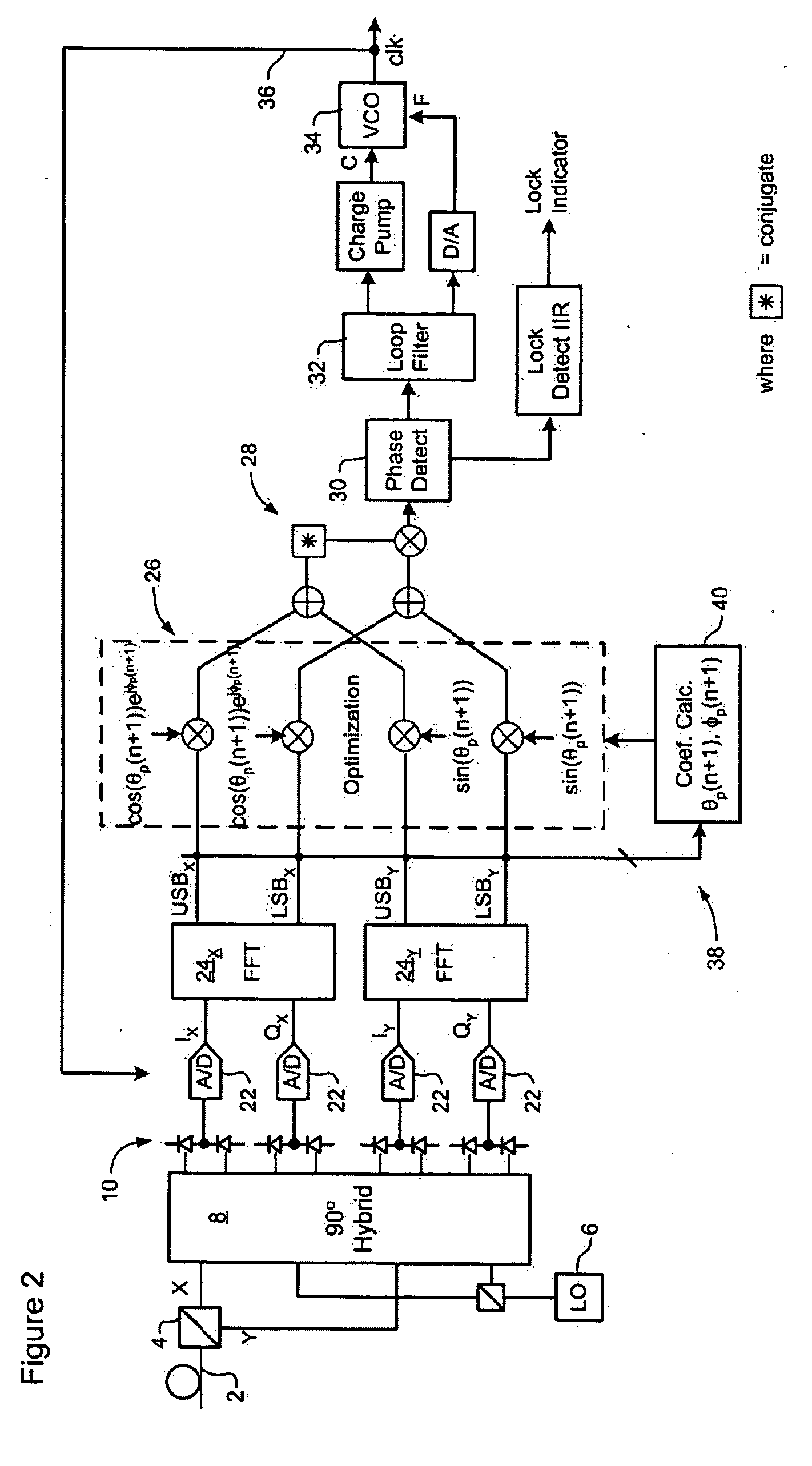
Optical mixer for coherent detection of polarization-multiplexed signals
InactiveUS20100158521A1Data recoveryPolarisation multiplex systemsElectromagnetic receiversLocal oscillator signalBeam splitter
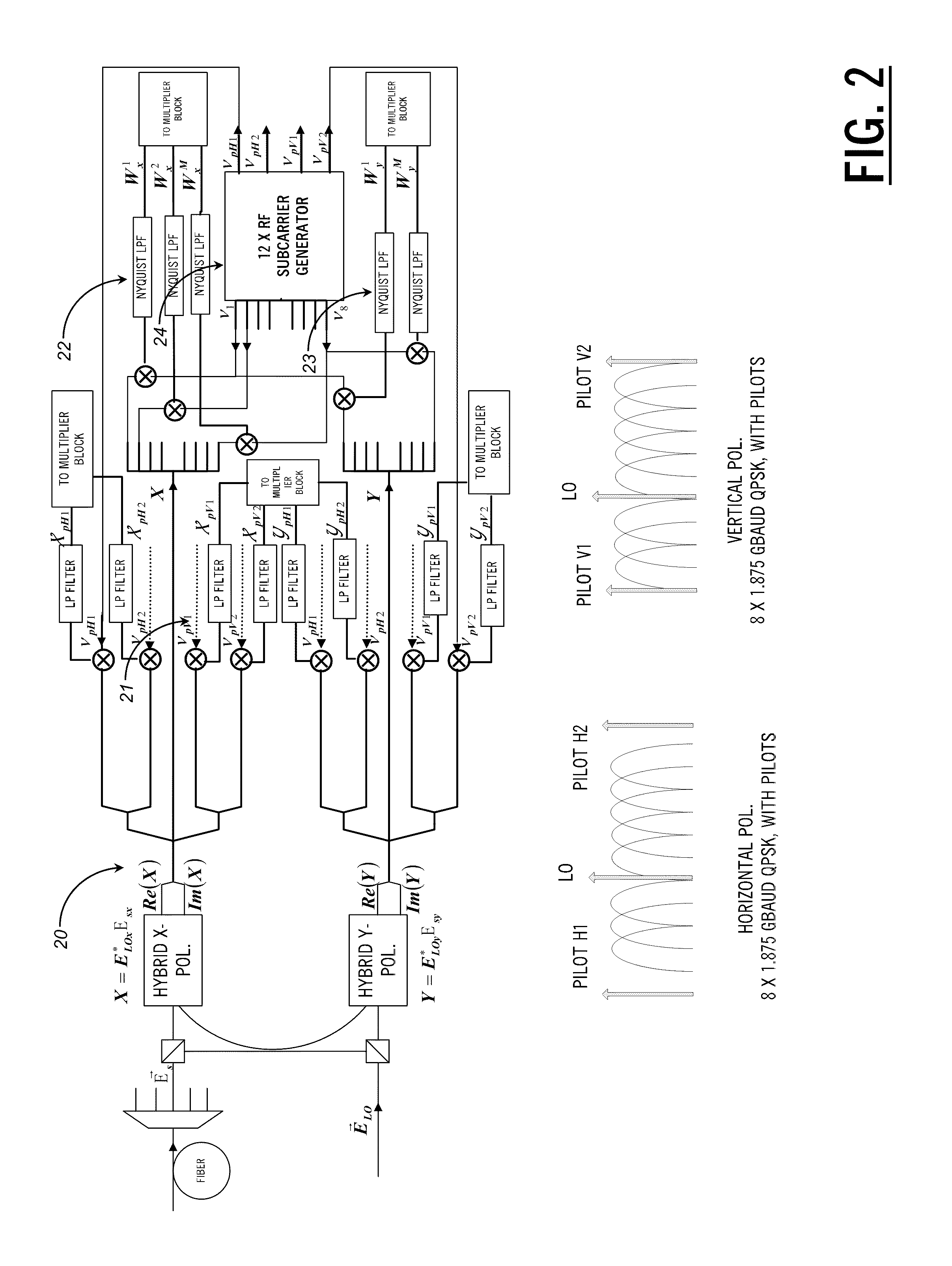
An optical mixer that, in one embodiment, has a single optical hybrid optically coupled to a single polarization beam splitter. The optical hybrid mixes a polarization-multiplexed optical communication signal and a local-oscillator signal to generate four mixed signals, each corresponding to a different relative phase shift between the communication and local-oscillator signals. The polarization beam splitter separates each of the mixed signals into two polarization components, subsequent processing of which enables an optical receiver employing the optical mixer to recover the data carried by the communication signal.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Polarization-Multiplexed Optical Transmission System, Polarization-Multiplexed Optical Transmitter, and Polarization-Multiplexed Optical Receiver
InactiveUS20120134676A1Preventing signal quality degradationReliable polarizationPolarisation multiplex systemsOptical mode multiplex systemsDigital signal processingPolarization diversity
There is a need to prevent two receivers from converging on a state of receiving the same polarization state, fast start receivers, and ensure highly reliable operations. A polarization-multiplexed transmitter previously applies frequency shifts of frequencies +Δf and −Δf to X-polarization and Y-polarization digital information signals to be transmitted. Optical field modulators modulate and polarization-multiplex the signals. As a result, a frequency difference of 2Δf is supplied to X-polarization and Y-polarization components. A polarization diversity coherent optical receiver 215 receives the signal. A frequency estimation portion in a digital signal processing circuit detects a frequency difference signal in both polarization components. This signal is used to a polarization splitting circuit in the digital signal processing circuit.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Coherent receiver having an interleave-chirped arrayed waveguide grating
ActiveUS20110038631A1Accurate representationPolarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsWavelength demultiplexerComputational physics
An optical coherent detector that employs an interleave-chirped arrayed waveguide grating (AWG). The AWG has a periodic chirp pattern that enables the AWG to function as an optical 90-degree hybrid. If the AWG is implemented using a birefringent material, then the AWG can also function as a polarization demultiplexer. In one embodiment, the AWG is designed to simultaneously function as a wavelength demultiplexer, a polarization demultiplexer for each wavelength-division-multiplexed (WDM) signal component, and a 90-degree hybrid for each polarization-division-multiplexed component of each WDM signal component.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
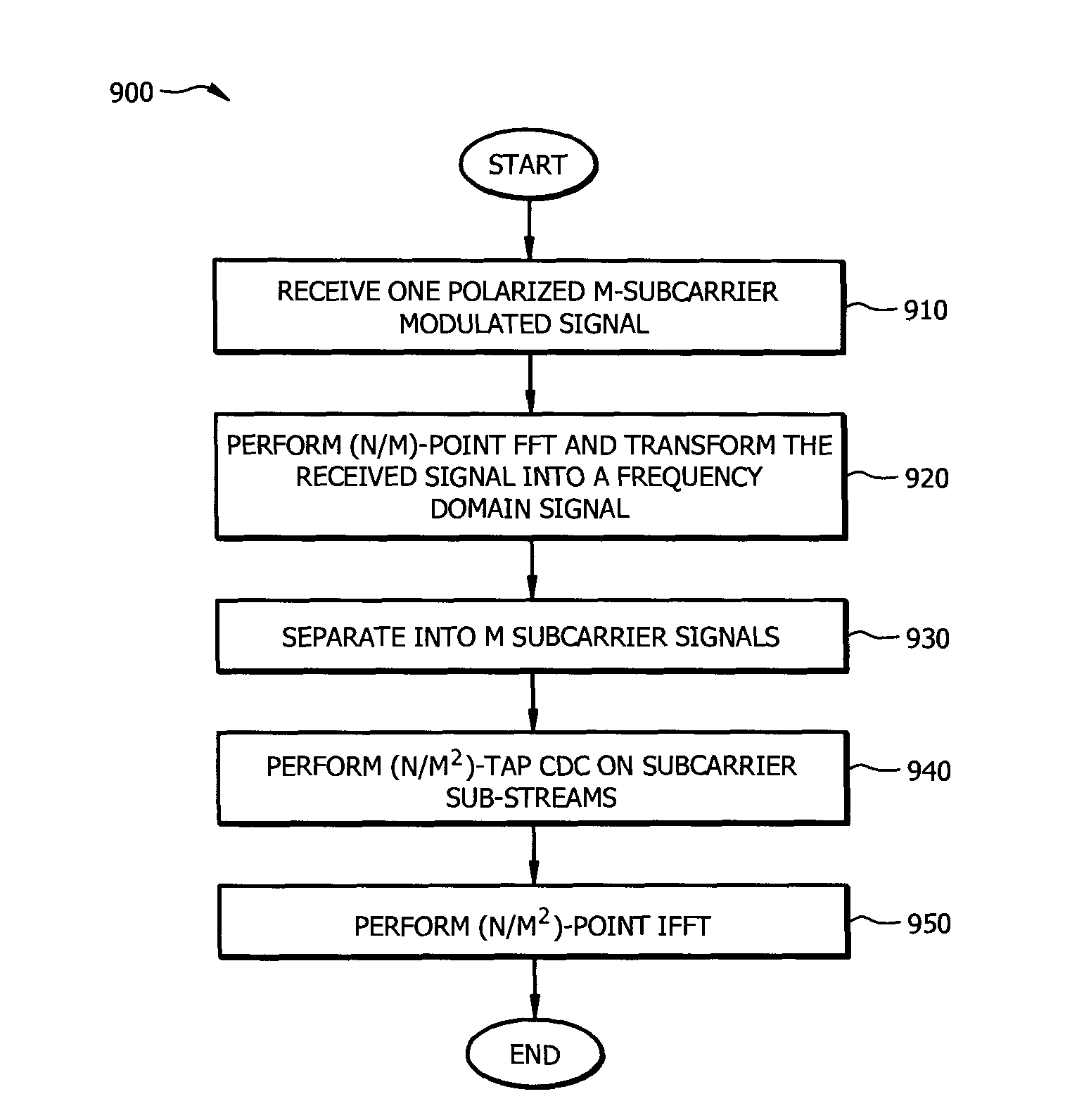
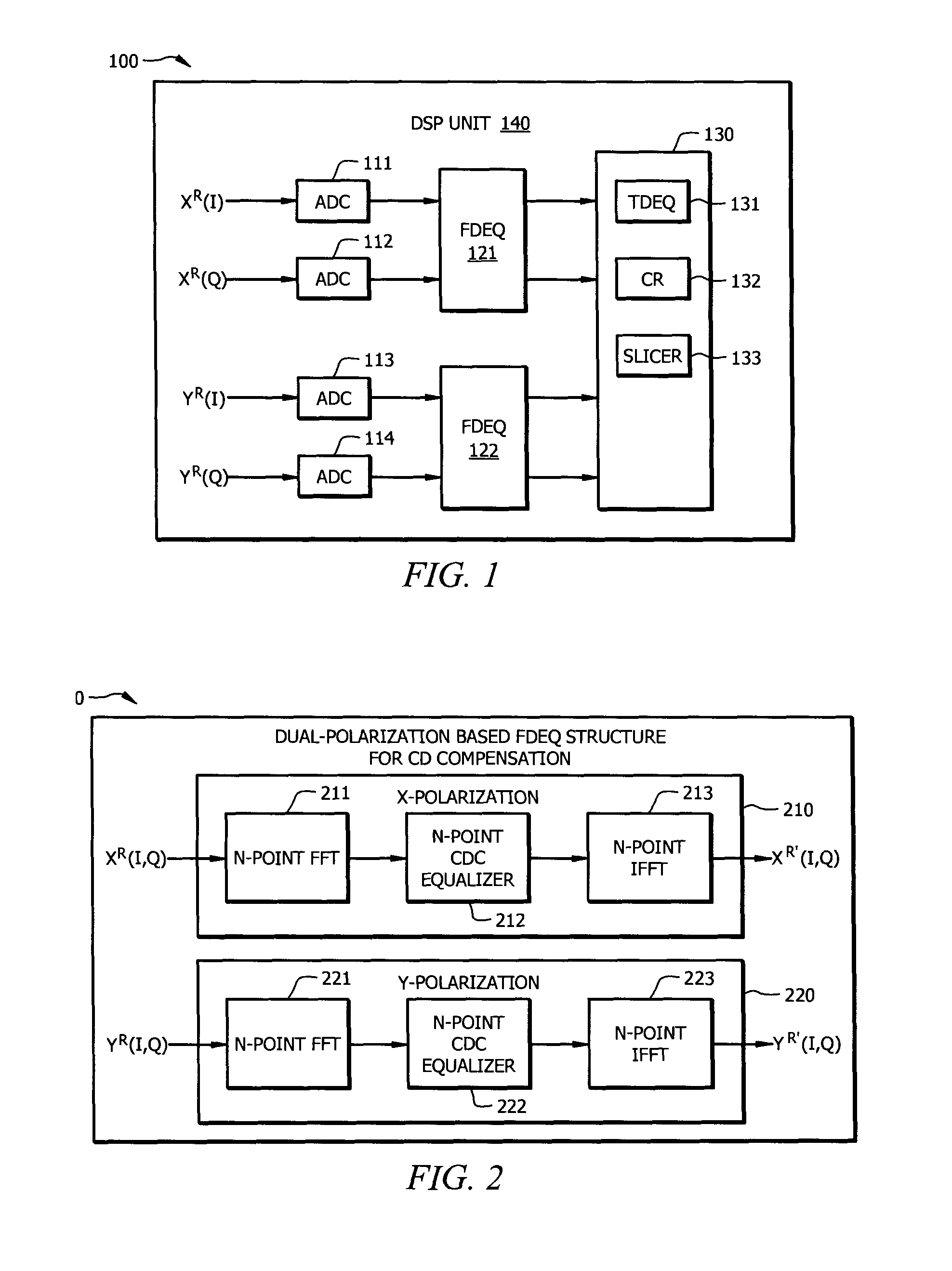
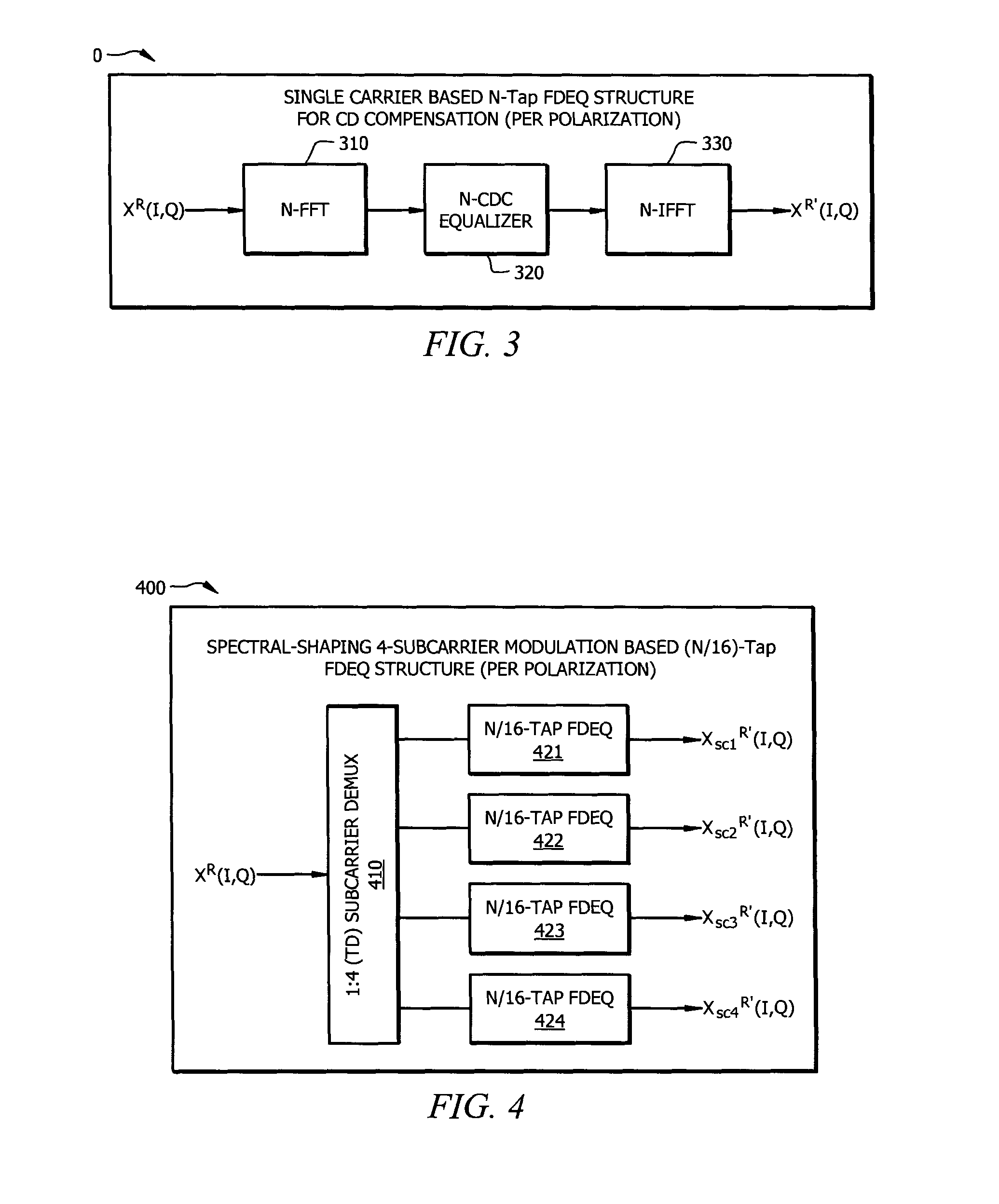
Resource-Efficient Digital Chromatic Dispersioin Compensation in Fiber Optical Communication Using Spectral-Shaping Subcarrier Modulation
ActiveUS20140099116A1Polarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberFrequency spectrum
An optical receiver comprising a frontend configured to receive an optical signal and convert the optical signal into a plurality of digital electrical signals comprising a plurality of spectrally shaped subcarrier signals carrying symbol mapped data information, and a digital signal processor (DSP) unit coupled to the frontend and configured to receive the digital signals from the frontend, demulitplex the digital signals into the subcarrier signals, and compensate chromatic dispersion (CD) for each of the subcarrier signals by applying an equalizer, wherein each of the subcarrier signals is associated with a unique tone frequency and a unique spectral shape. Also disclosed is an optical transmitter comprising a digital signal processor (DSP) unit configured to map data symbols onto a plurality of electrical subcarrier signals that are non-overlapping and spectrally shaped in a frequency domain.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexed communications with nonlinearity compensation
InactiveUS20090190929A1Improve throughputImprove performancePolarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsInformation recoveryEngineering
The present invention discloses a transmitter and receiver for optical communications system, which provide compensation of the optical link nonlinearity. M-PSK modulating is used for data embedding in an optical signal in each WDM channel using orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) technique. At the receiver side electrical output signals from a coherent optical receiver are processed digitally with the link nonlinearity compensation. It is followed by the signal conversion into frequency domain and information recovery from each subcarrier of the OFDM signal. At the transmitter side an OFDM encoder provides a correction of I and Q components of a M-PSK modulator driving signal to compensate the link nonlinearity prior to sending the optical signal to the receiver.
Owner:CELIGHT
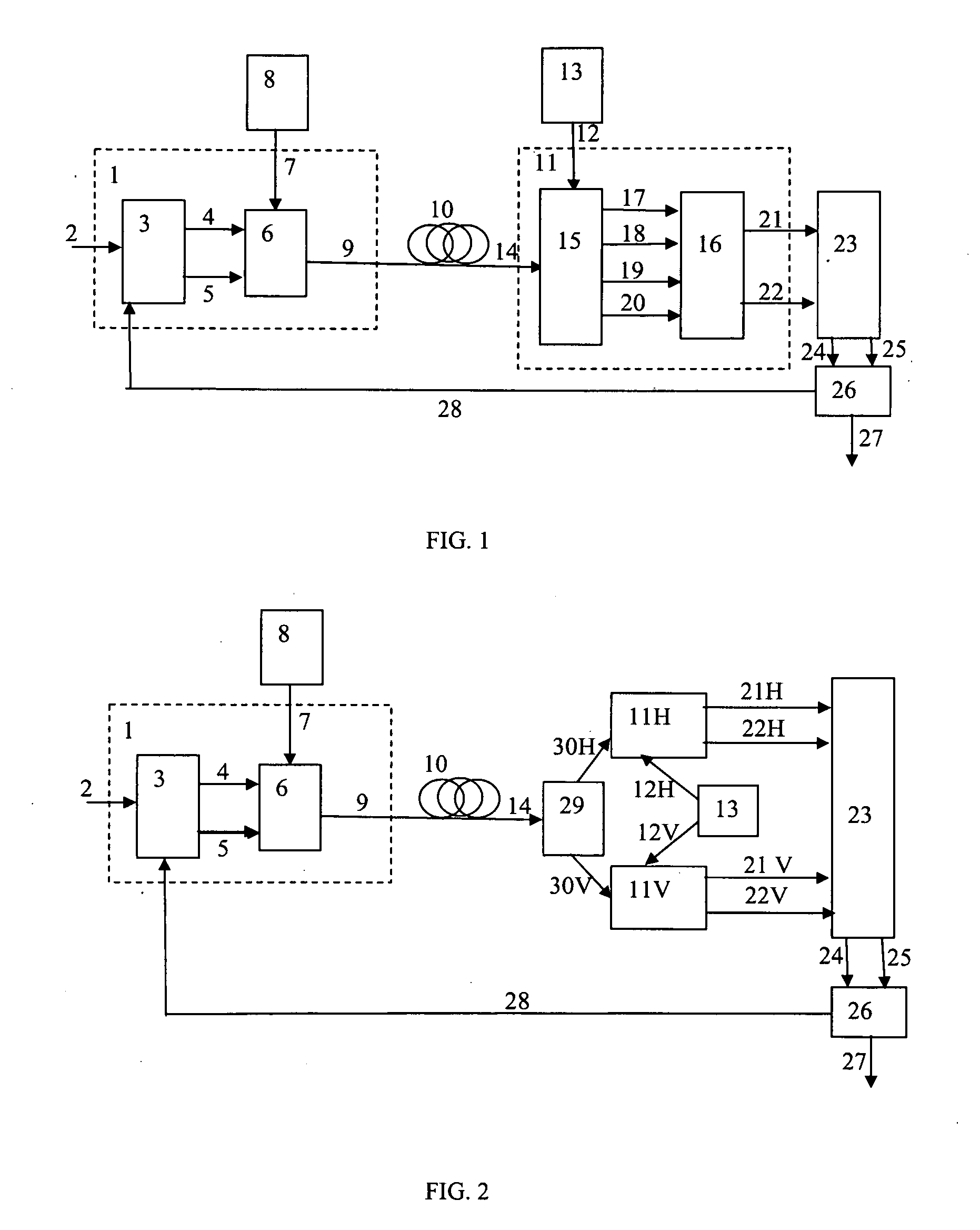
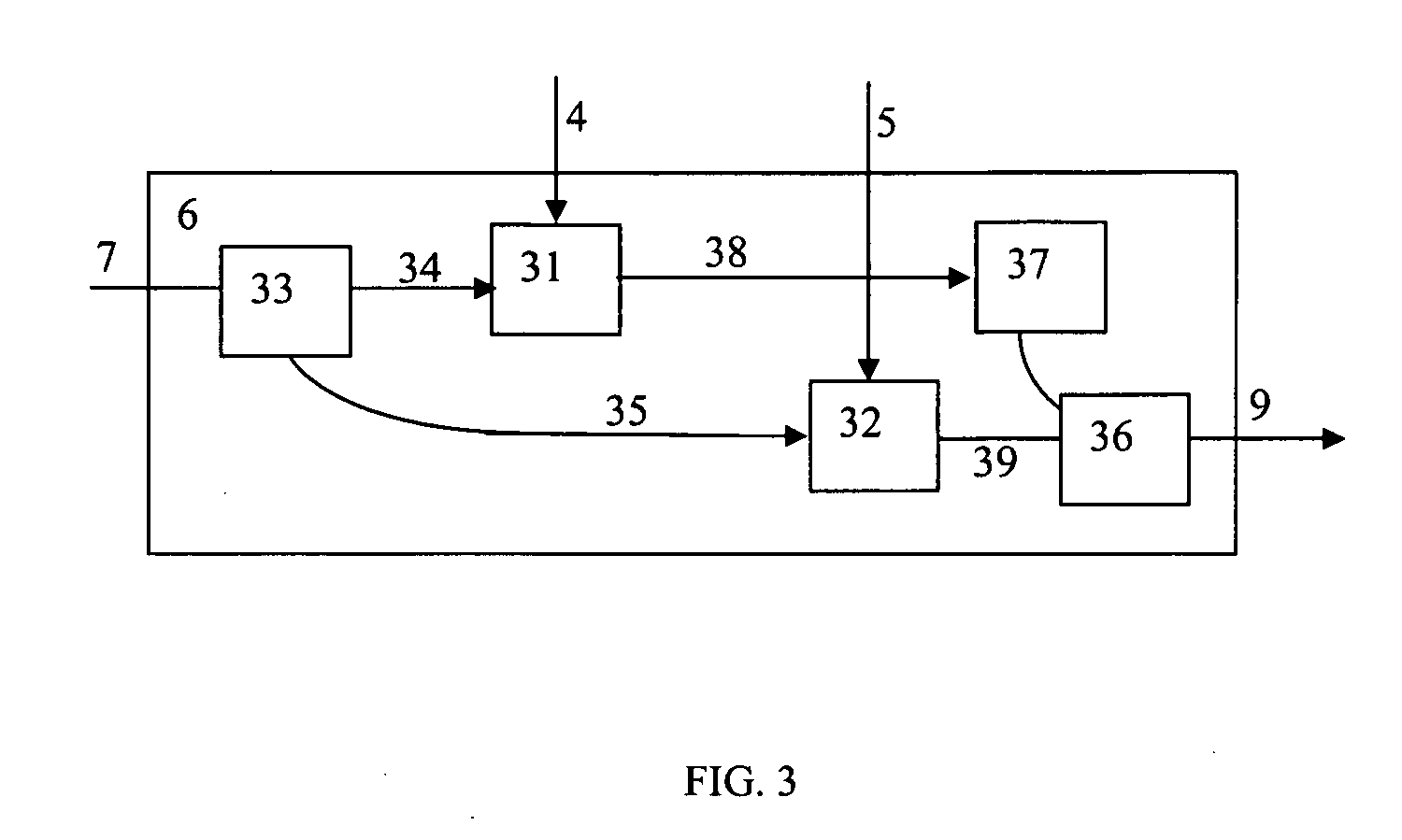
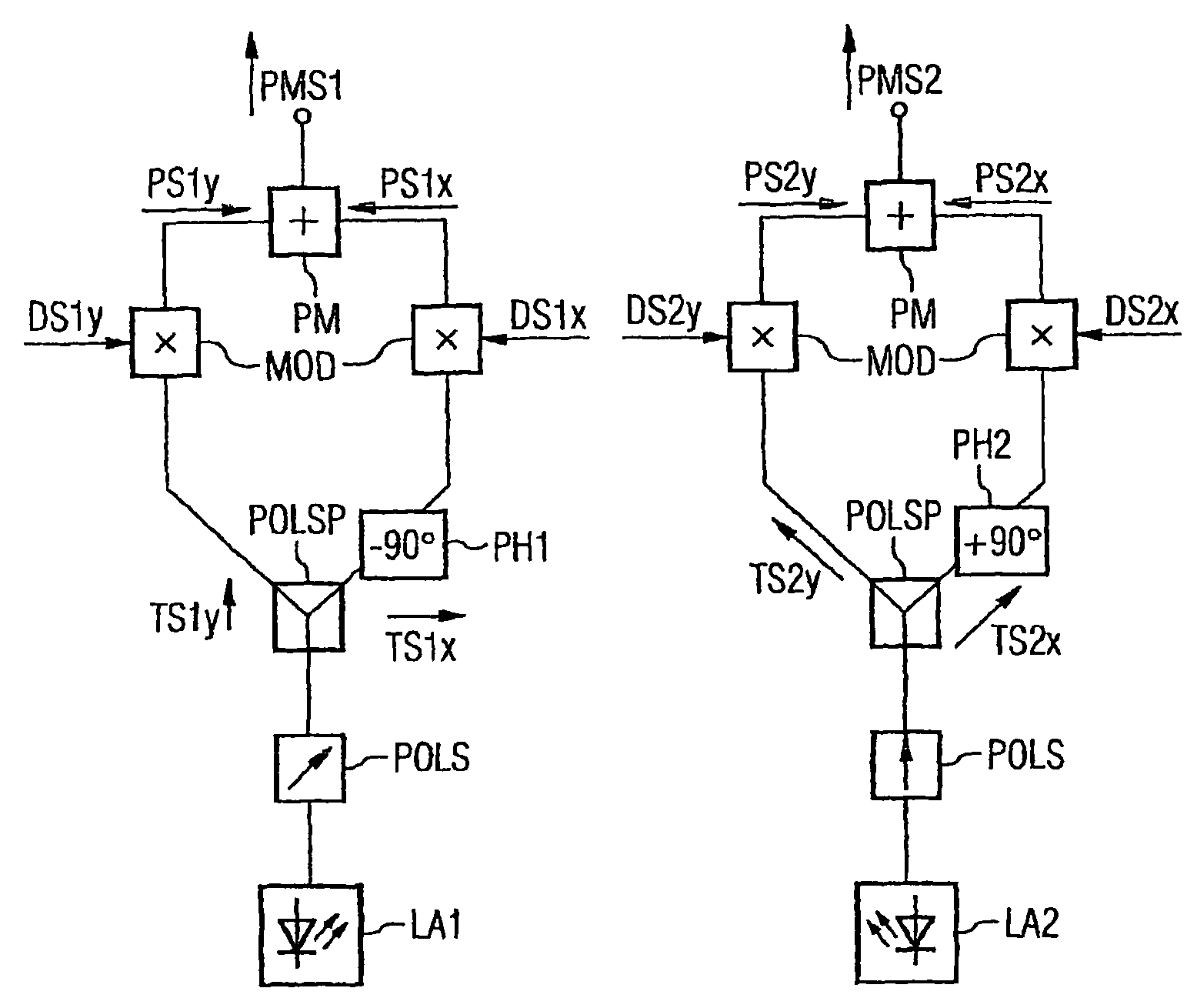
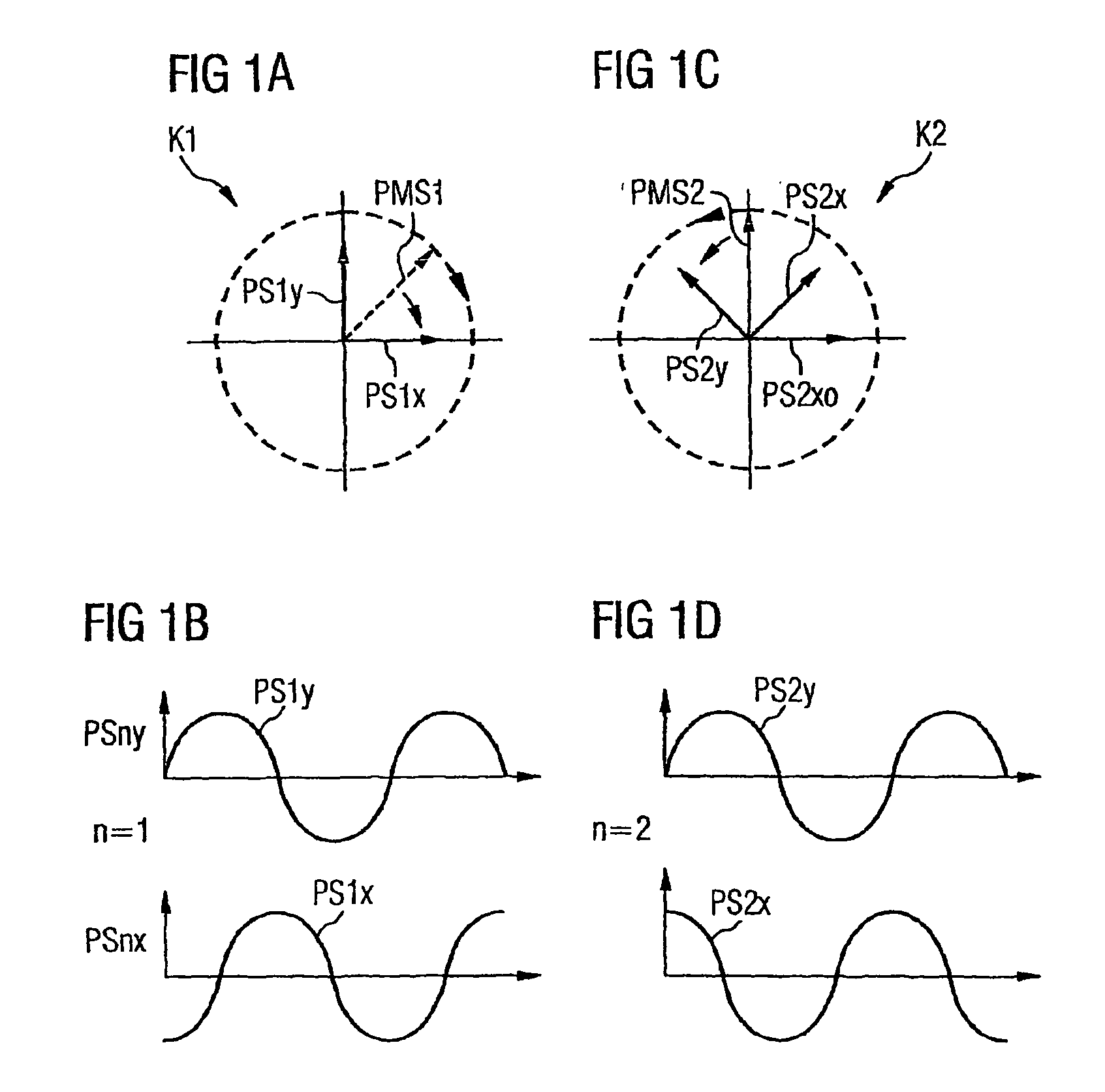
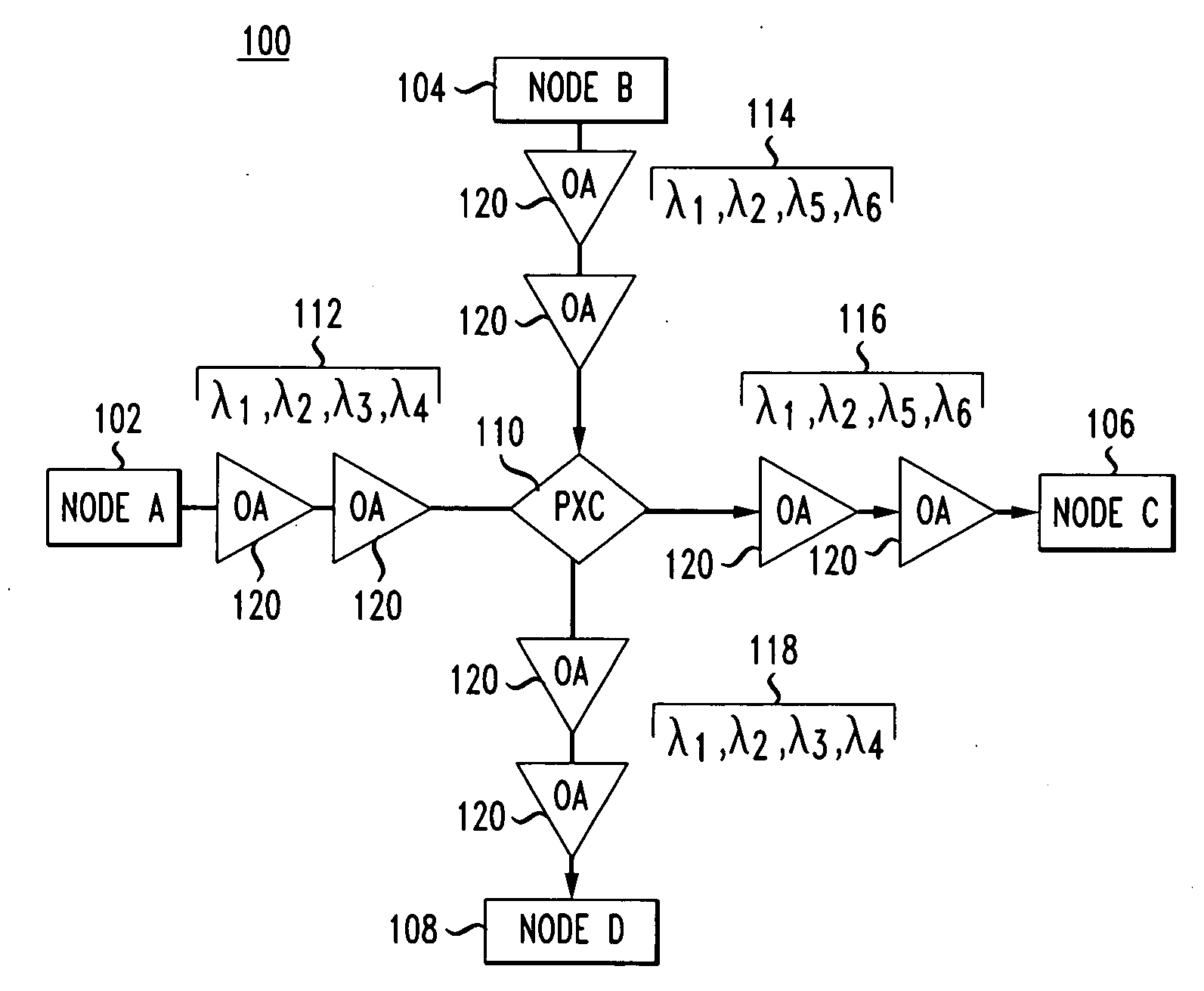
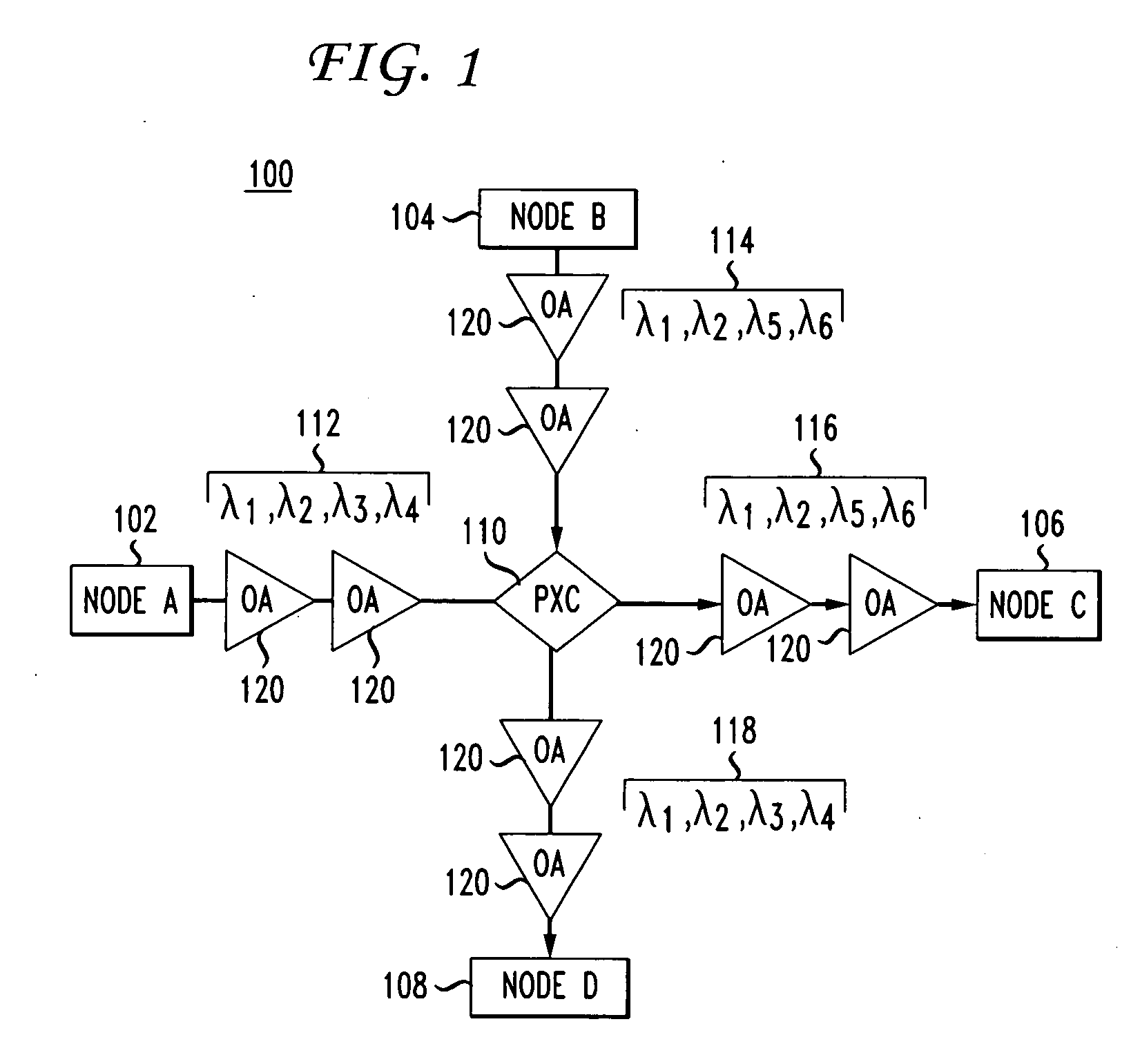
Methods for the optical transmission of polarization multiplex signals
InactiveUS7865080B2Reduce interactionStrong mutual interferencePolarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsPhysicsPolarization plane
In order to reduce mutual interferences between POLMUX and signals, the signals are transmitted with differed to each other carrying signals, thereby making it possible to obtain the circular polarization of each resulting POLMUX signal. Each second POLMUX signal is transmissible with an opposite circular polarization. In order to reduce also interferences when only one modulated data signal is transmitted through a POLMUX channel, a polarization plane of modulated data signals of each second POLMUX channel is turned at 45°. In a variant, polarization multiplex signals are produces and the resulting polarizations thereof in adjacent channels are perpendicular to each other.
Owner:XIEON NETWORKS SARL
Multiplexer and Modulation Arrangements for Multi-Carrier Optical Modems
ActiveUS20120251119A1Polarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsSuper-channelModem device
Consistent with the present disclosure, data, in digital form, is received by a transmit node of an optical communication, and converted to analog signal by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) to drive a modulator. The modulator, in turn, modulates light at one of a plurality of wavelengths in accordance with the received data forming a plurality of corresponding carriers. The plurality of carriers are then optically combined with a fixed spacing combiner to form a superchannel of a fixed capacity. Accordingly, the number of carriers are selected according to a modulation format and symbol rate to realize the fixed capacity, for example. The superchannel is then transmitted over an optical communication path to a receive node. At the receive node, the superchannel is optically demultiplexed from a plurality of other superchannels. The plurality of carriers are then supplied to a photodetector circuit, which receives additional light at one of the optical signal carrier wavelengths from a local oscillator laser. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) is provided in the receive node to convert the electrical signals output from the photodetector into digital form. The output from the ADC is then filtered in the electrical domain, such that optical demultiplexing of the carriers is unnecessary.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
High speed polmux-ofdm using dual-polmux carriers and direct detection
InactiveUS20100086303A1Low costSame spectrum efficiencyPolarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingTransmission system
A polarization multiplexing, orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (POMUX) transmission system utilizing direct detection.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA
Equalization strategy for dual-polarization optical transport system
ActiveUS7315575B2Avoid convergencePrevent degradationMultiple-port networksError preventionDigital signal processingTransport system
Owner:CIENA
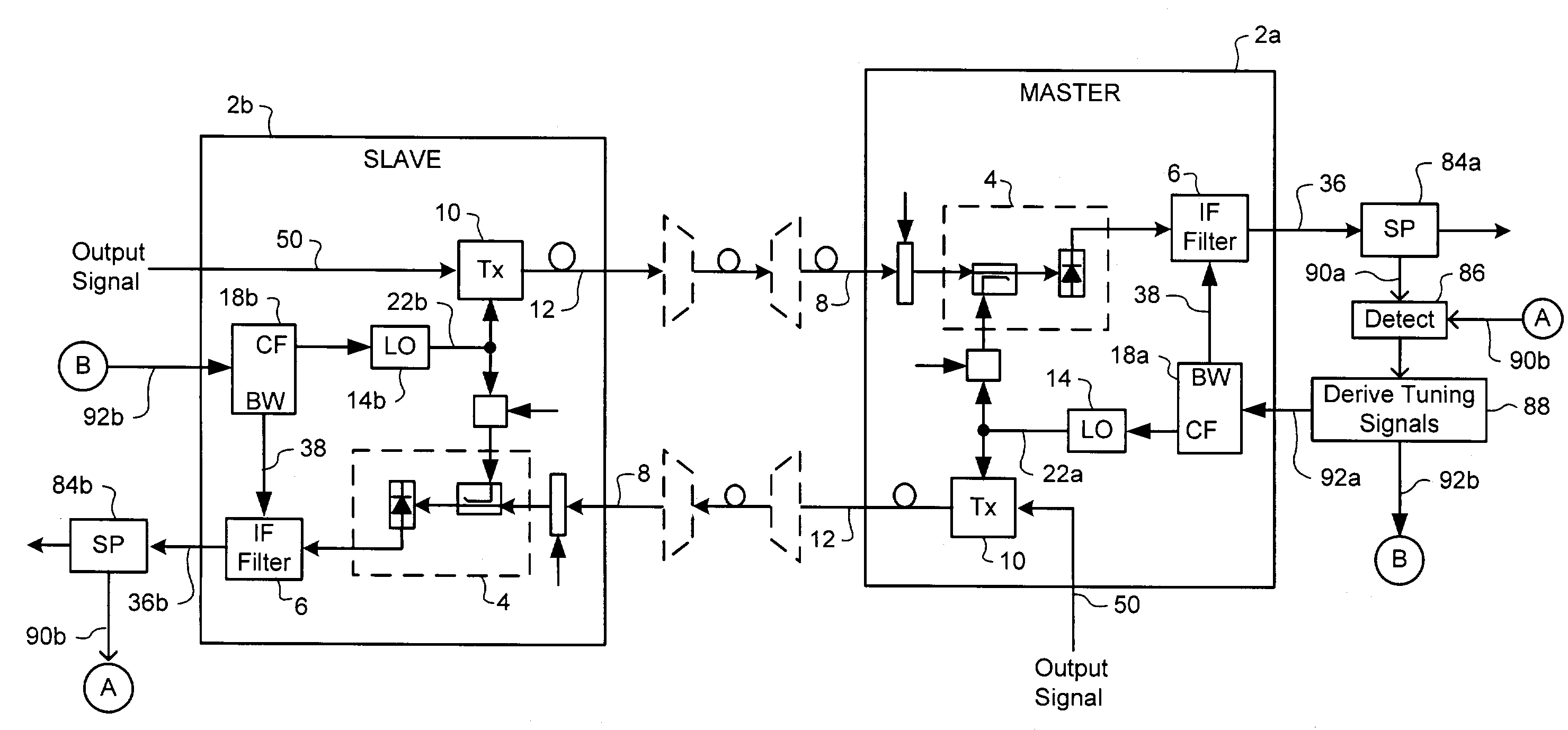
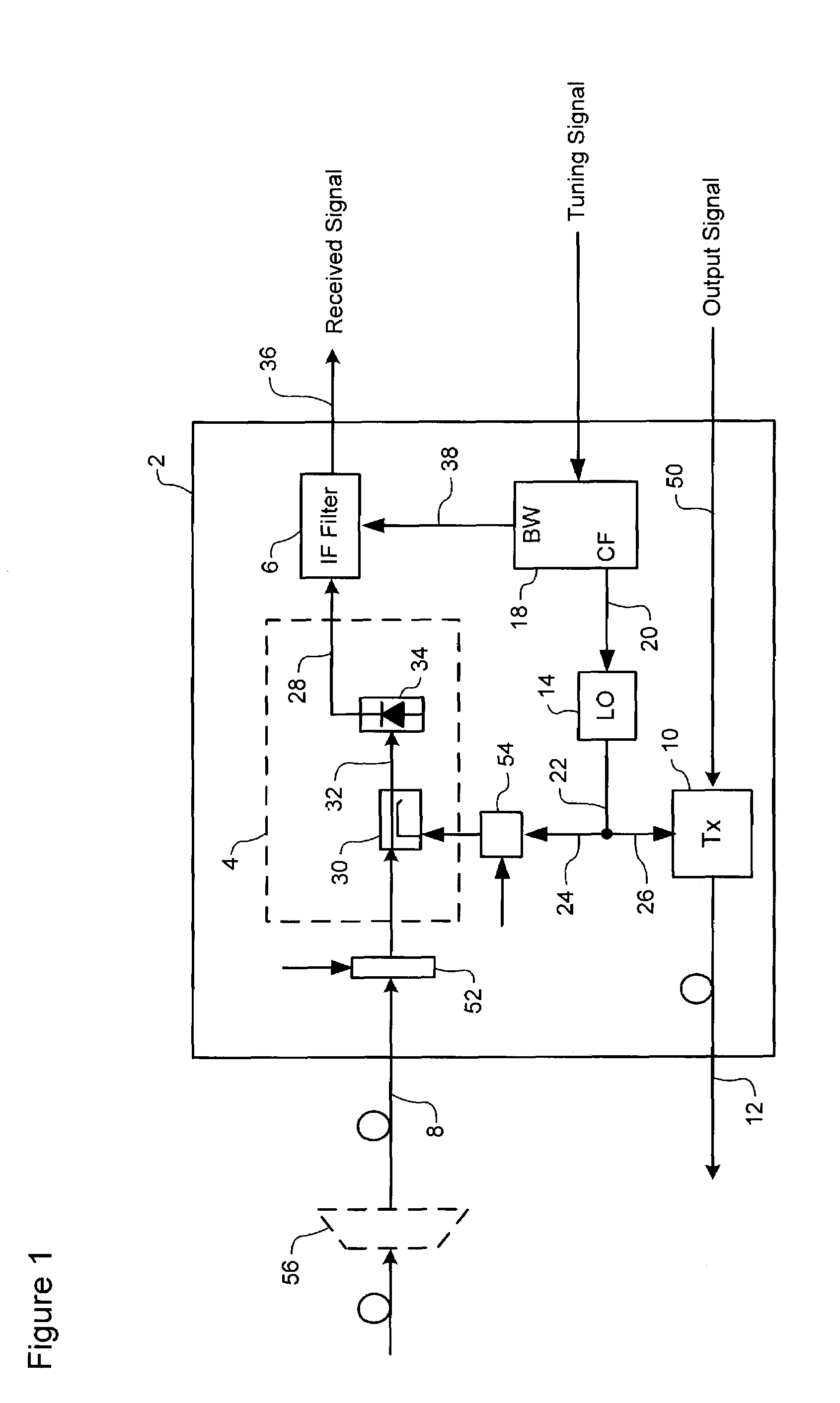
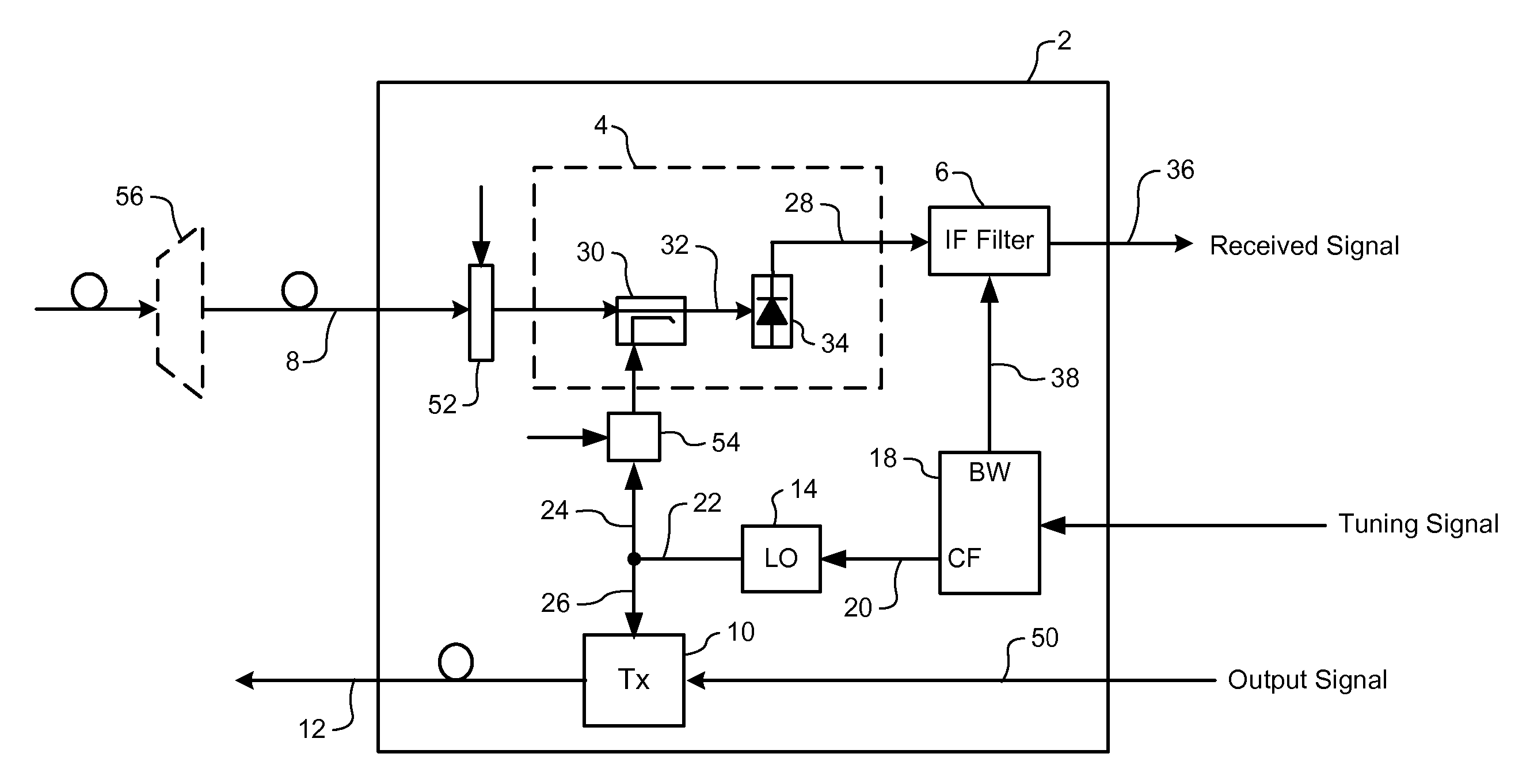
Frequency agile transmitter and receiver architecture for DWDM systems
ActiveUS7209664B1Polarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransceiverLocal oscillator
A frequency-agile optical transceiver includes a shared local oscillator (LO), a coherent optical receiver and an optical transmitter. The LO operates to generate a respective LO optical signal having a predetermined LO wavelength. The coherent optical receiver is operatively coupled to the LO, and uses the LO signal to selectively receive traffic of an arbitrary target channel of an inbound broadband optical signal. The optical transmitter is also operatively coupled to the LO, and uses the LO to generate an outbound optical channel signal having a respective outbound channel wavelength corresponding to the LO wavelength.
Owner:CIENA
Optical switch and optical waveform monitoring device utilizing optical switch
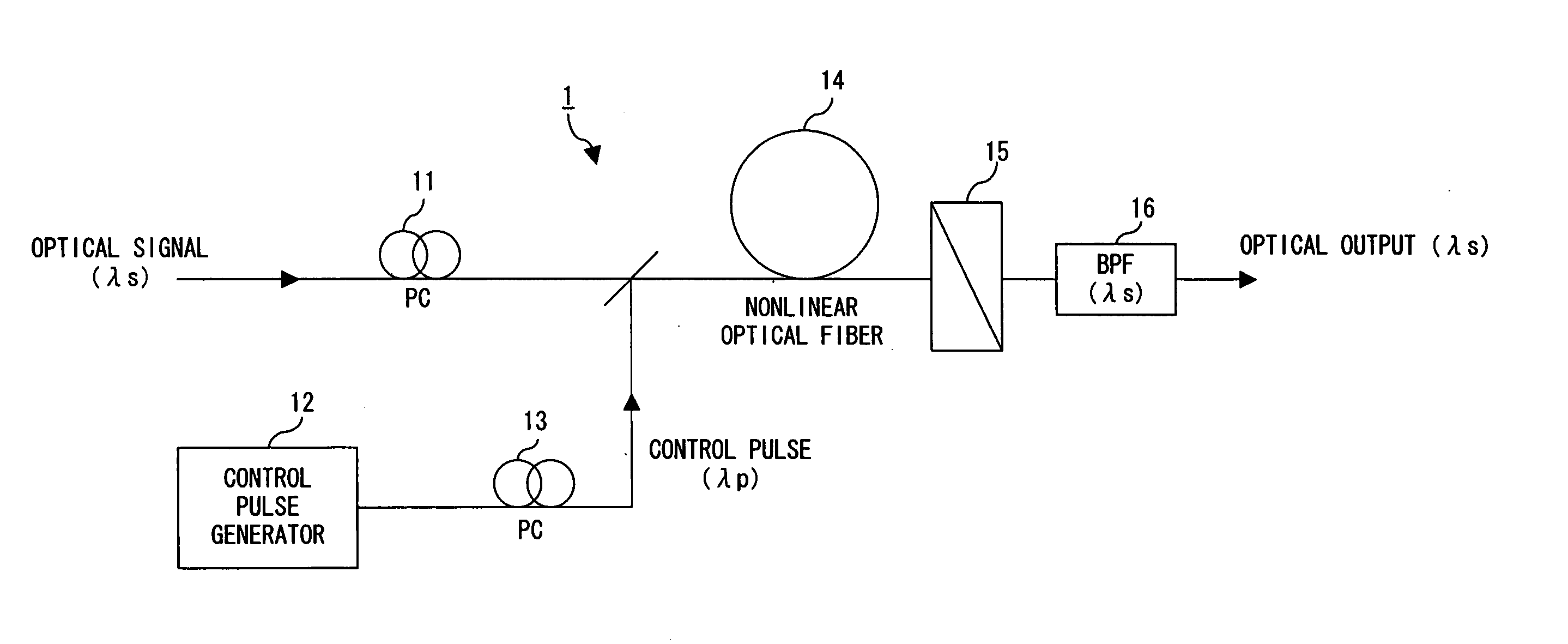
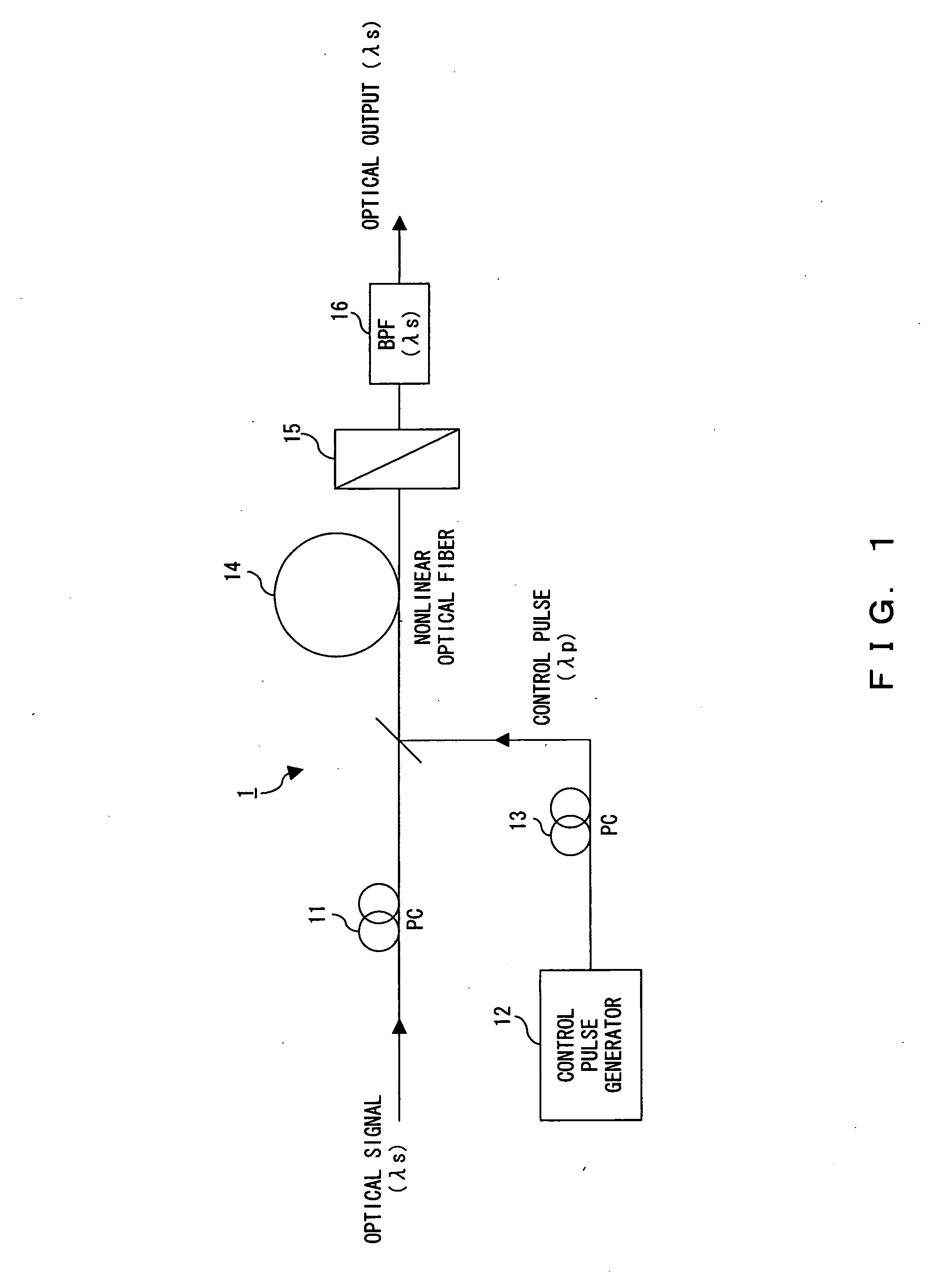
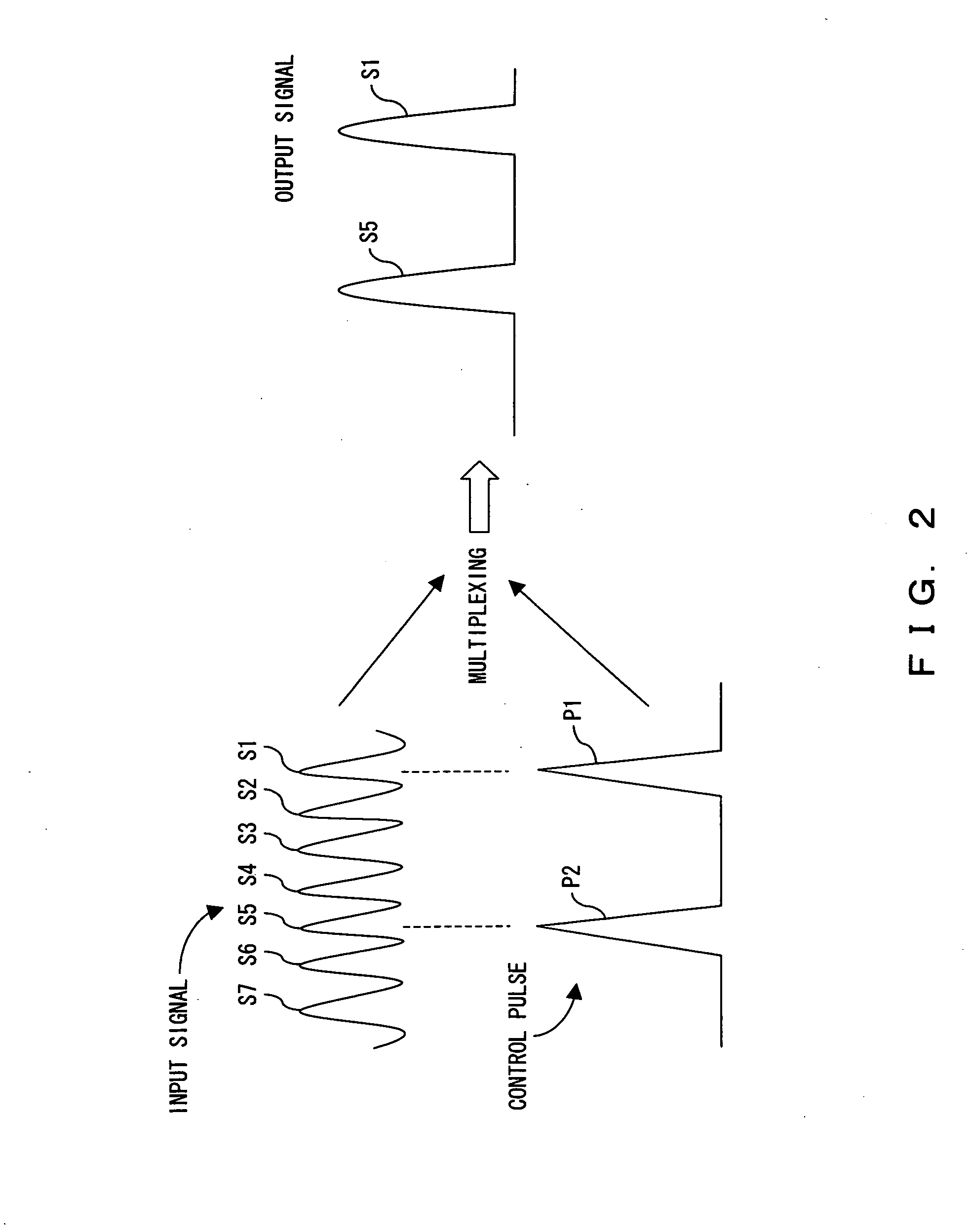
ActiveUS20060051100A1Improve switching efficiencyExcellent optical S/N ratioLaser detailsPolarisation multiplex systemsPolarizerLength wave
The polarization direction of an optical signal is changed by a polarization controller so as to be orthogonal to a main axis of a polarizer. A control pulse generator generates control pulses from control beam with a wavelength which is different from the wavelength of the optical signal. The optical signal and the control pulse are input to a nonlinear optical fiber. In the nonlinear optical fiber, the optical signal, during a time period in which the optical signal and the control pulse coincide, is amplified with optical parametric amplification around a polarization direction of the control pulse. The optical signal, during the time period in which the optical signal and the control pulse coincide, passes through the polarizer.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical communication system using wdma and CDMA
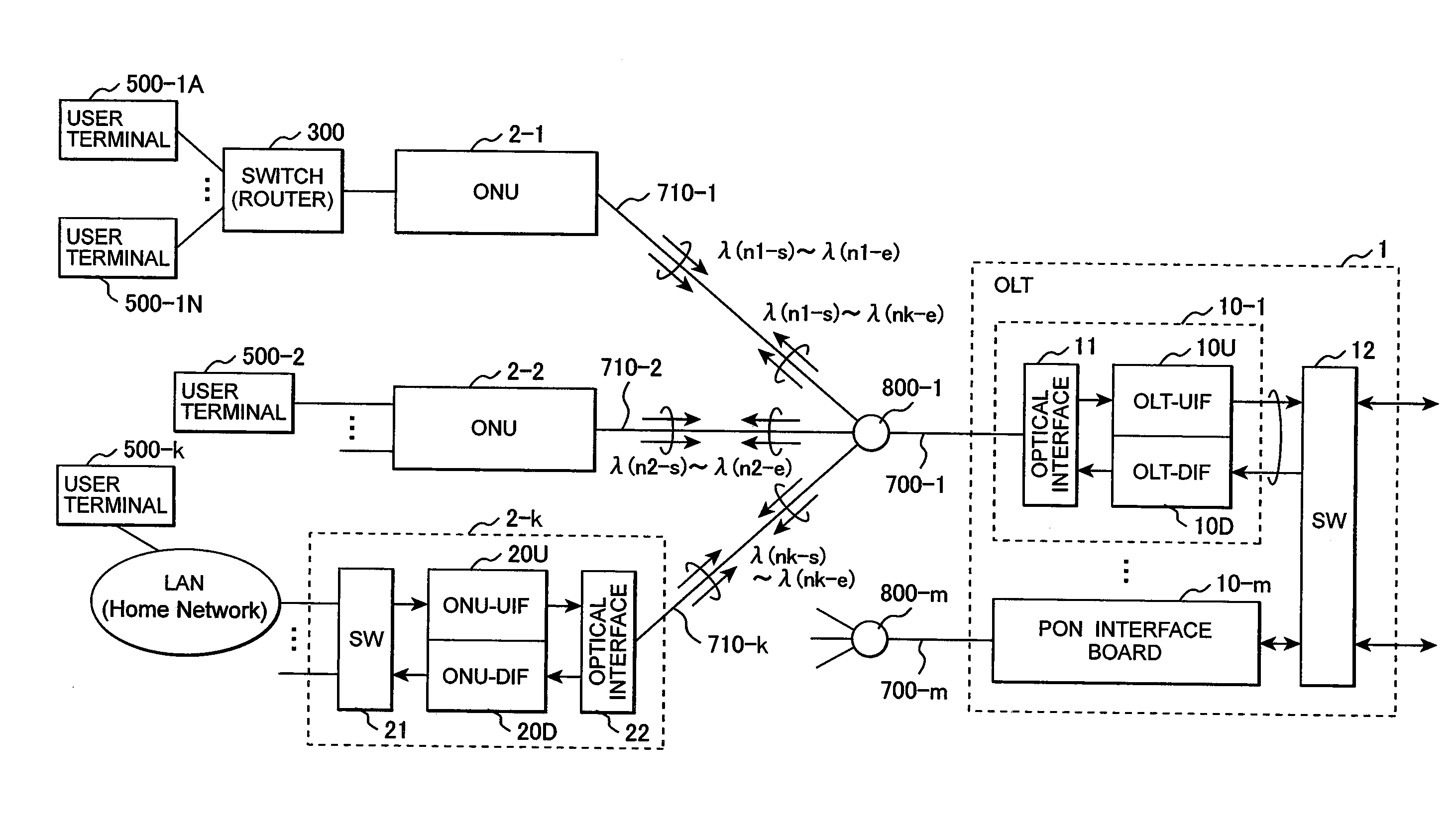
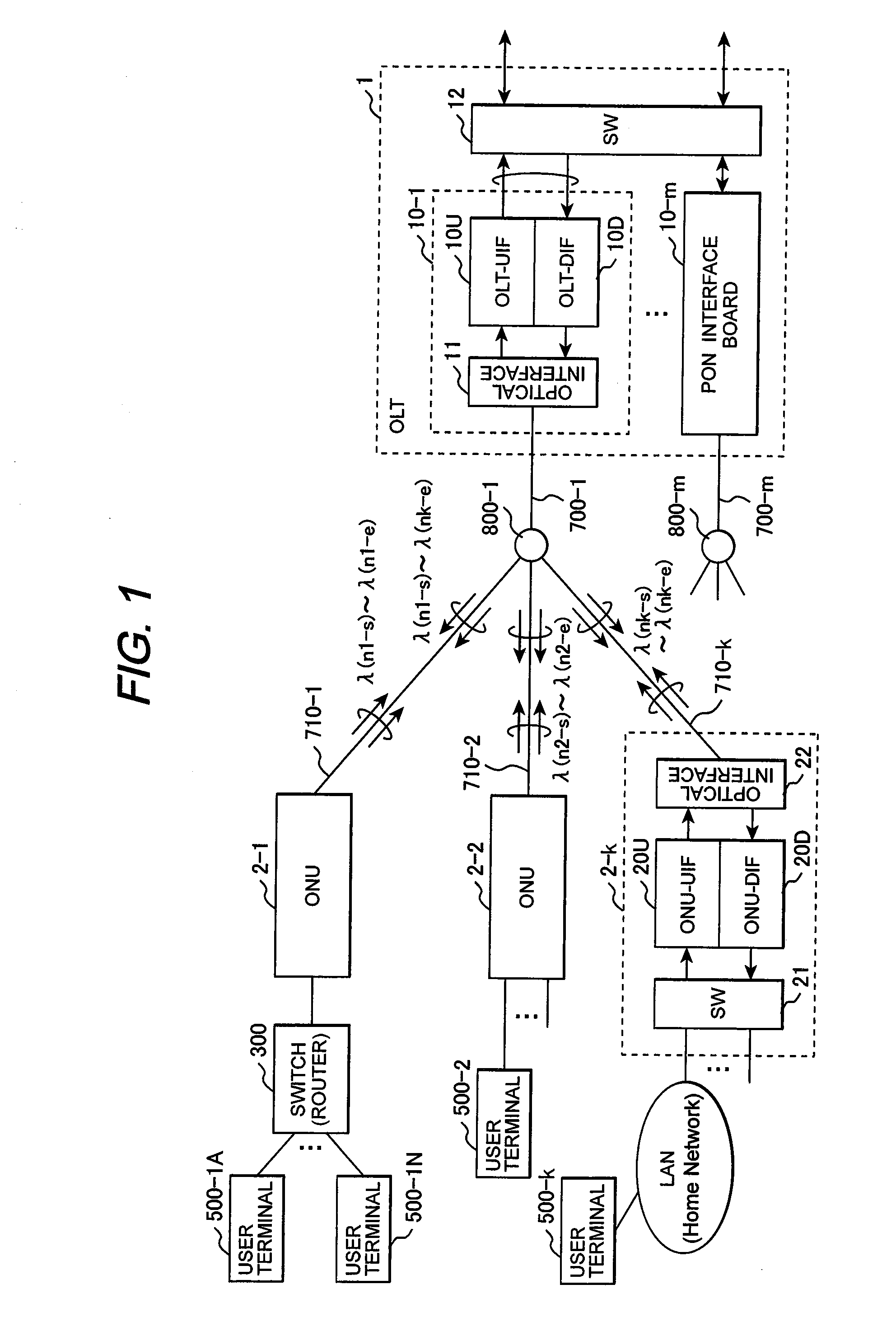
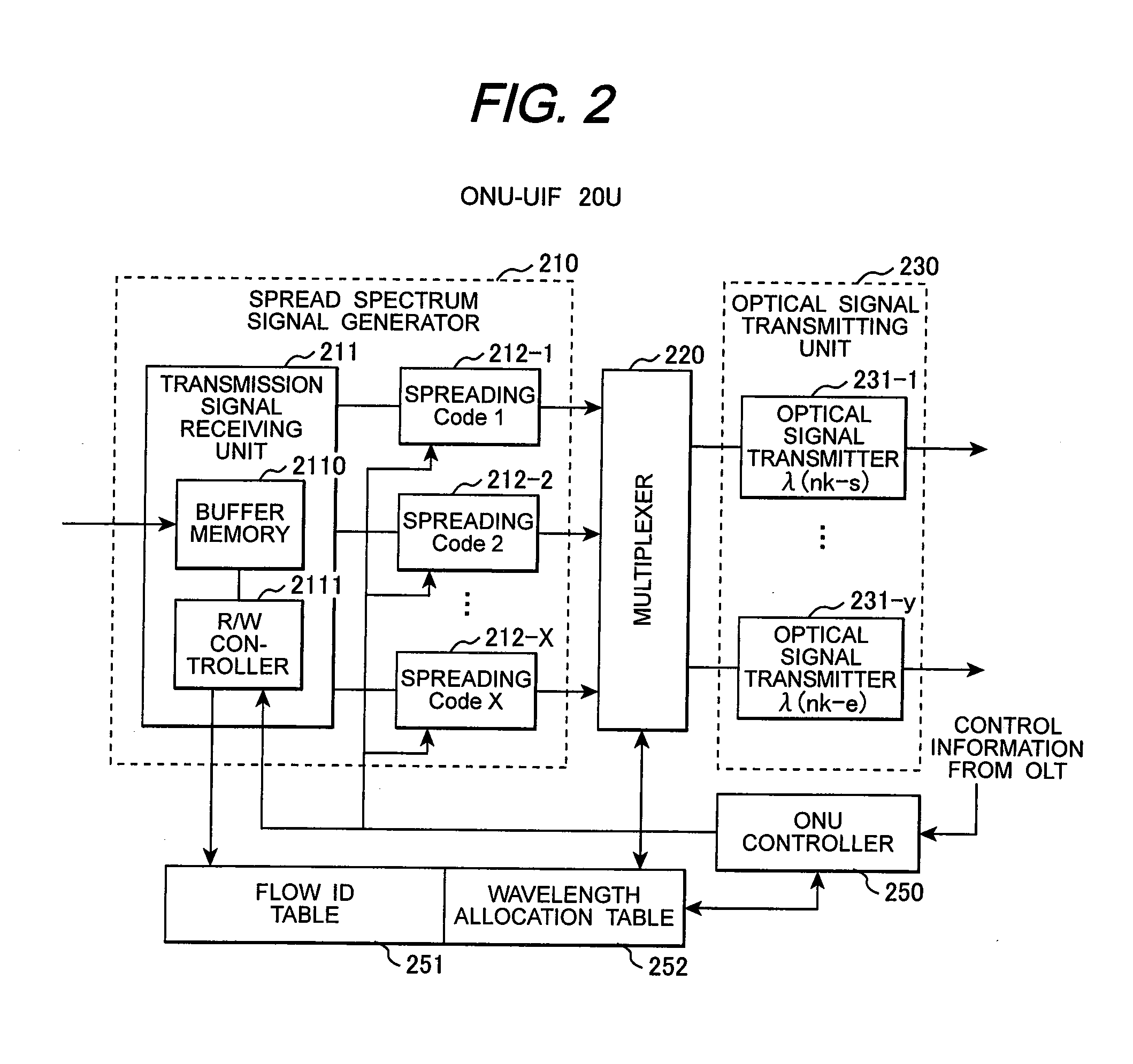
InactiveUS20080304828A1Avoid interferenceEasy to useMultiplex system selection arrangementsPolarisation multiplex systemsCarrier signalData channel
In a PON system, an OLT periodically transmits a channel resource information block specifying a carrier wavelength and a spreading code on a first downstream channel to which a spread-spectrum spreader having a first spreading code is applied; one of ONUs receives the channel resource information block with a spread-spectrum despreader having the first spreading code and transmits a connection request to the OLT, using the carrier wavelength and the spreading code specified by the channel resource information block; the OLT having received the connection request transmits a new channel resource information block specifying a carrier wavelength and a spreading code to be used on an upstream data channel to the requester ONU through the first channel; and the requester ONU transmits data, using the carrier wavelength and the spreading code specified by the new channel resource information block.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Clock recovery from an optical signal with polarization impairments
ActiveUS20060285855A1Pulse automatic controlPolarisation multiplex systemsCommunications systemClock recovery
A method of recovering a clock signal from an optical signal received through an optical communications system. A digital sample stream is processed to generate a dispersion compensated signal. The dispersion compensated signal is then tapped to obtain upper side band and lower side, band signals of each received polarization of the optical signal. The upper side band sand lower side band signals are then processed to compensate polarization dependent impairments and the clock recovered from the resulting optimized.
Owner:CIENA
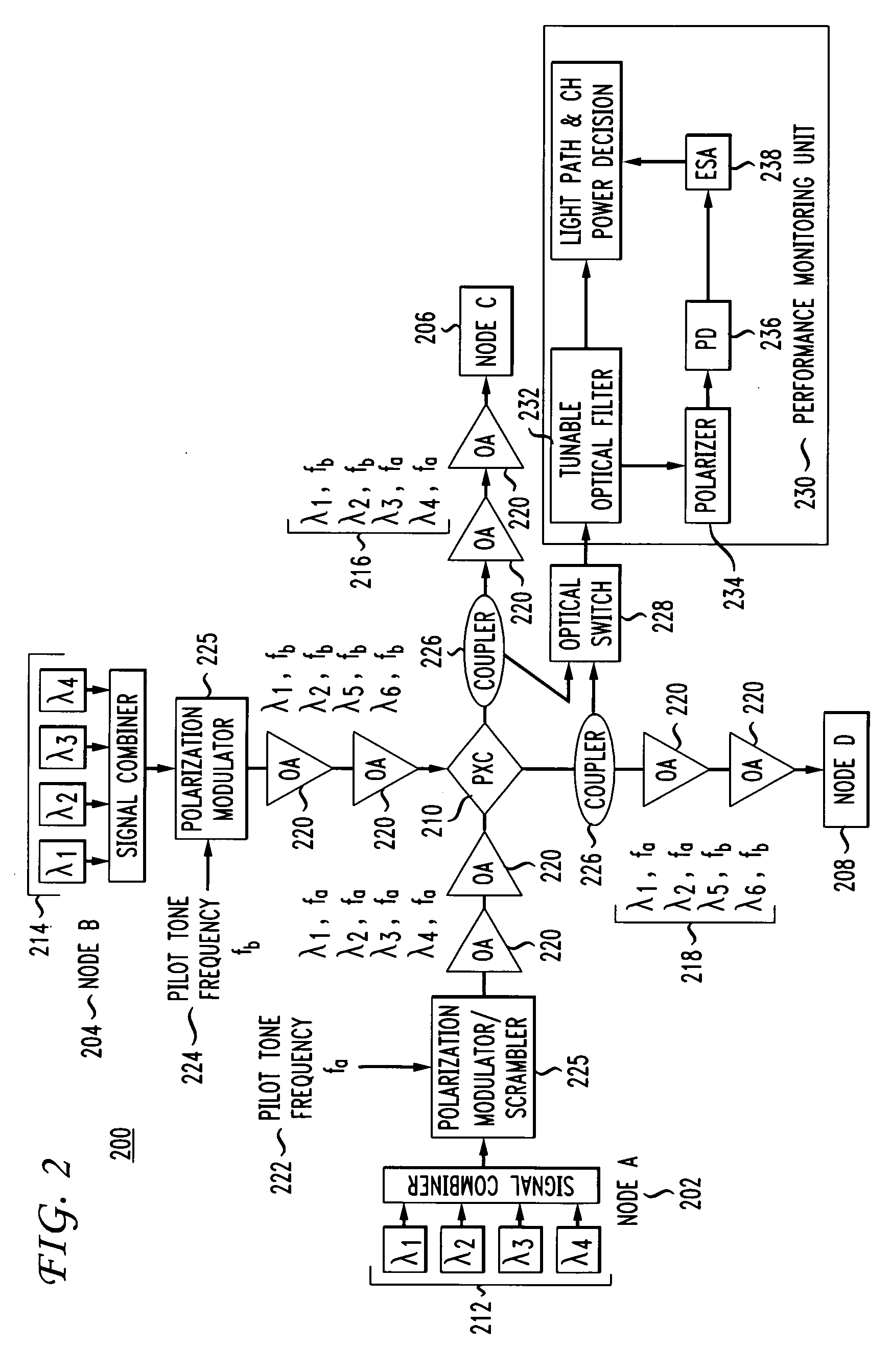
Method for lightpath monitoring in an optical routing network
ActiveUS20090196603A1Polarisation multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringSignal onSingle polarization
A method and system for enabling lightpath monitoring in an optical network is disclosed. A single polarization modulator / scrambler introduces a pilot tone signal as an overlay on a plurality of optical signals on a source node and a performance monitoring unit detects the pilot tone signal to enable light path monitoring and identification through the optical network.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Polarization compensation in a coherent optical receiver
ActiveUS20070092259A1Polarisation multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationPolarization dependentOptical receivers
A method of processing a stream of digital samples of an optical signal received by a coherent optical receiver. The digital sample stream is processed to generate a dispersion compensated sample stream. The dispersion compensated sample stream is then processed to compensate polarization dependent impairments of the optical signal.
Owner:CIENA
Frequency agile transmitter and receiver architecture for dwdm systems
InactiveUS20070154221A1Polarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransceiverLocal oscillator
A frequency-agile optical transceiver includes a shared local oscillator (LO), a coherent optical receiver and an optical transmitter. The LO operates to generate a respective LO optical signal having a predetermined LO wavelength. The coherent optical receiver is operatively coupled to the LO, and uses the LO signal to selectively receive traffic of an arbitrary target channel of an inbound broadband optical signal. The optical transmitter is also operatively coupled to the LO, and uses the LO to generate an outbound optical channel signal having a respective outbound channel wavelength corresponding to the LO wavelength.
Owner:CIENA
Communication through multiplexed one-dimensional optical signals
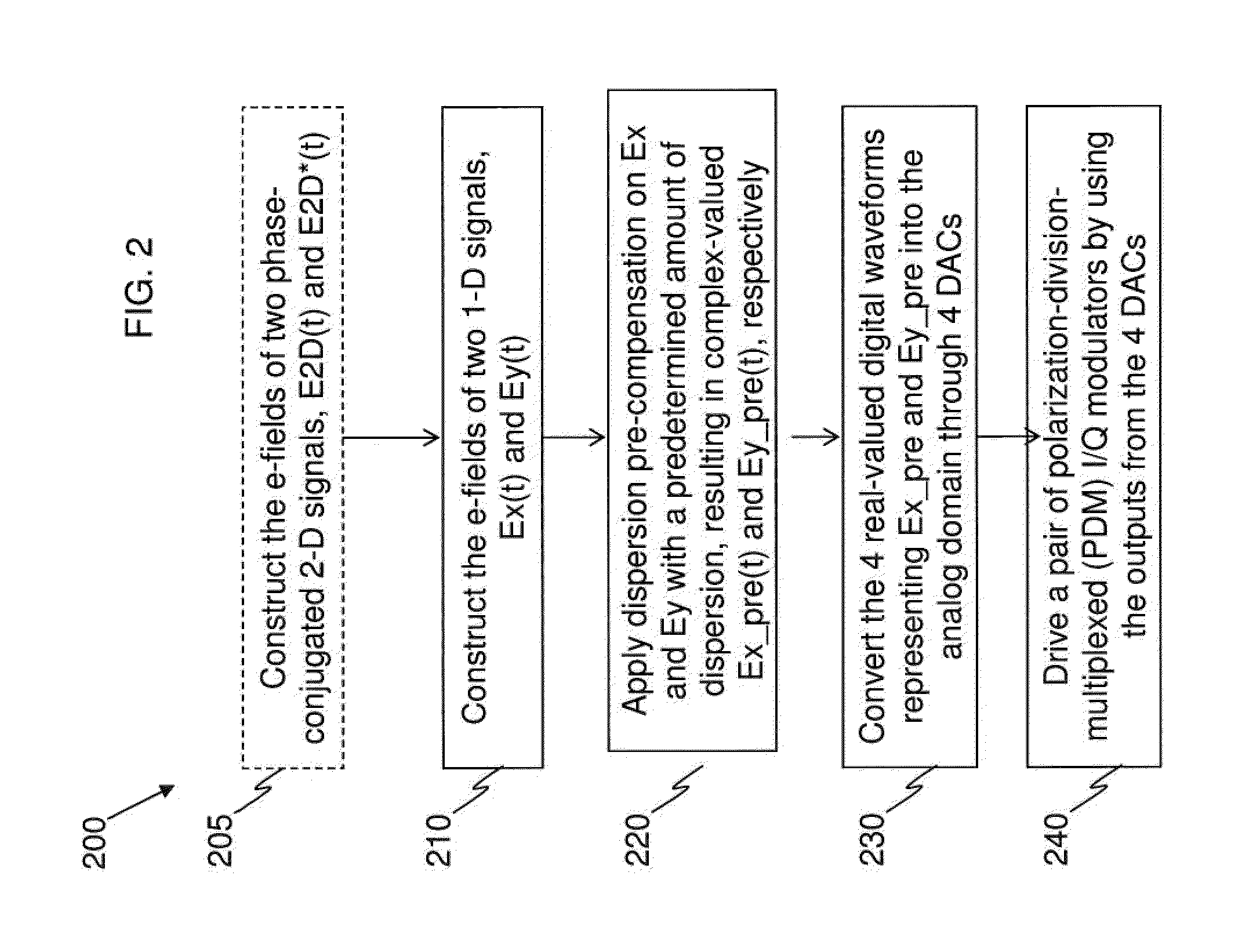
ActiveUS20130136449A1Effectively cancellingImprove signal qualityPolarisation multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationMultiplexingCarrier signal
An example apparatus comprises an optical transmitter which includes a first processor and at least two optical modulators. The first processor is configured to generate a first electronic representation for each of at least two optical signals for carrying payload data modulated according to a one-dimensional (1-D) modulation format, and to induce on respective ones of the first electronic representations an amount of dispersion that depends on a power-weighted accumulated dispersion (ADPW) of a transmission link through which the at least two optical signals are to be transmitted thereby generating complex-valued electronic representations of pre-dispersion-compensated optical signals. Each of the at least two optical modulators modulate a respective analog version corresponding to a respective one of the complex-valued electronic representations onto a polarization of an optical carrier.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
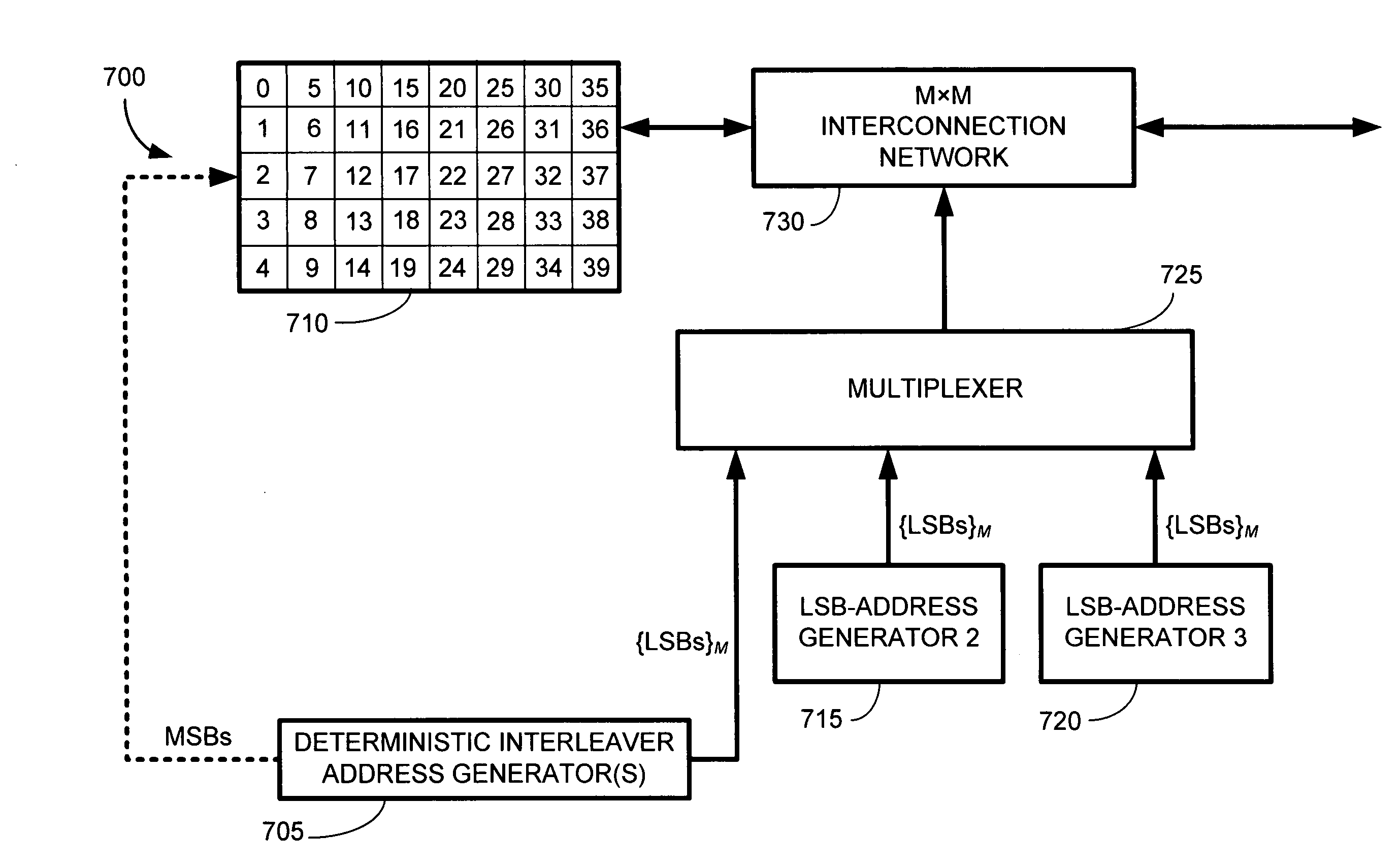
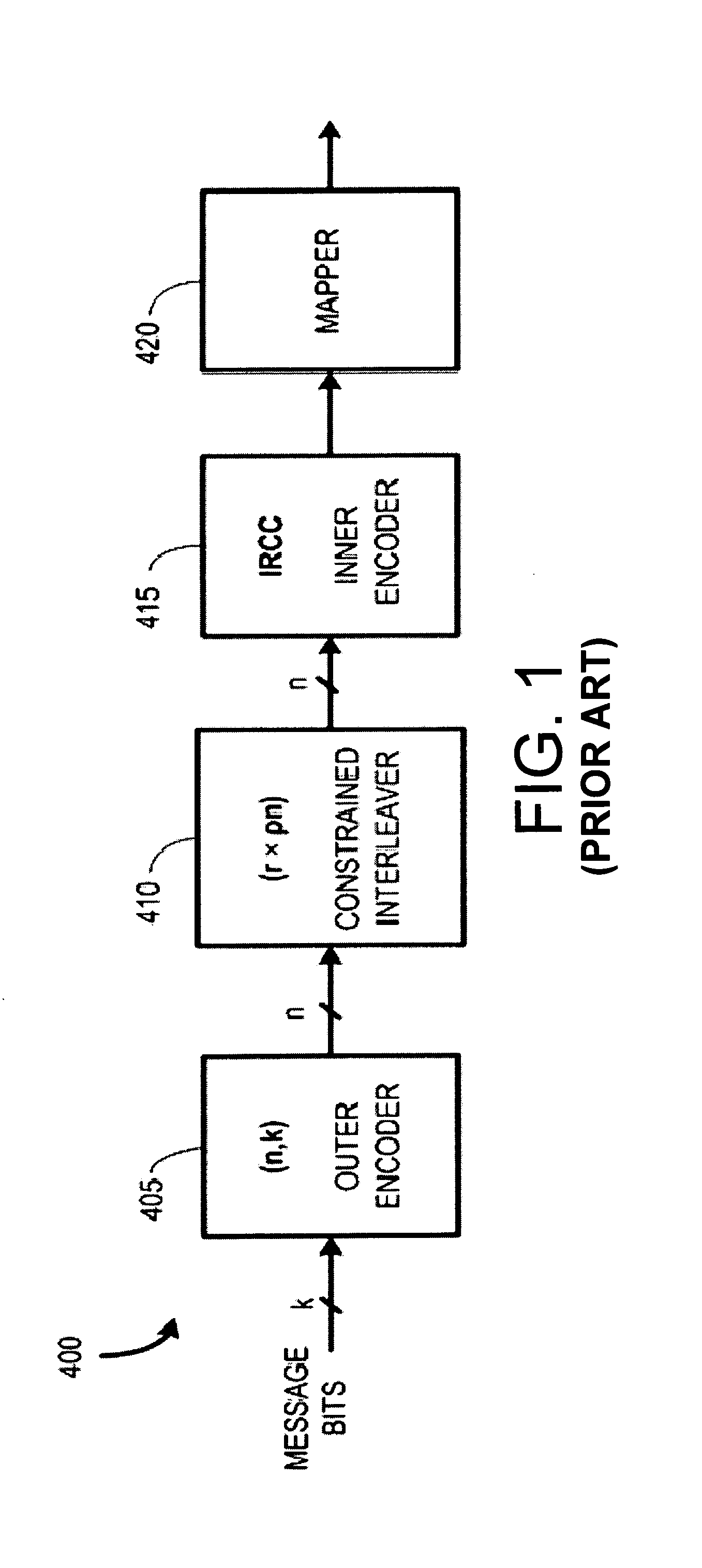
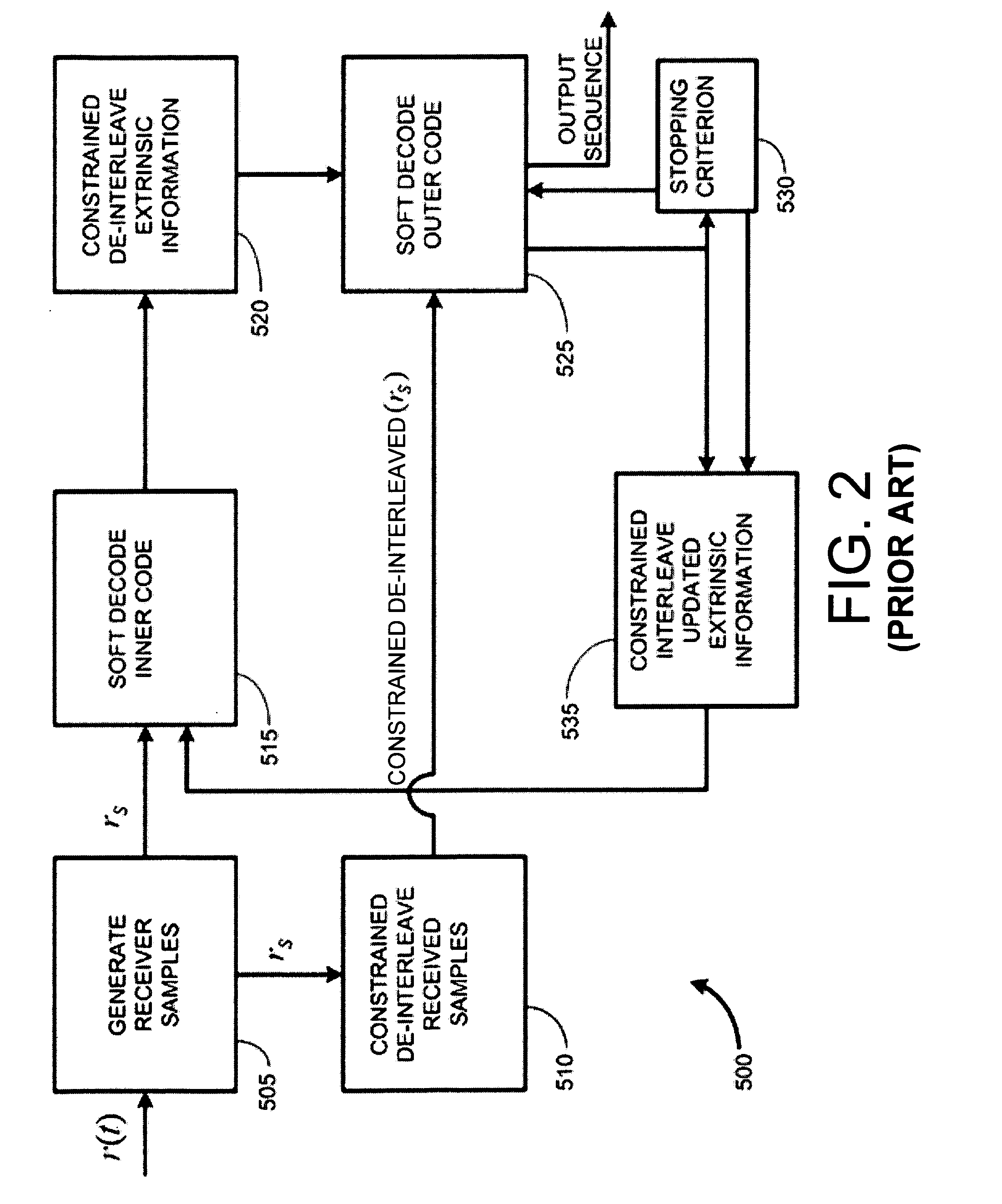
Constrained interleaving for 5G wireless and optical transport networks
InactiveUS20160352419A1Increase data rateIncrease performance rateSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation multiplex systemsCommunications systemAlgorithm
The present invention provides a design framework that is used to develop new types of constrained turbo block convolutional (CTBC) codes that have higher performance than was previously attainable. The design framework is applied to design both random and deterministic constrained interleavers. Vectorizable deterministic constrained interleavers are developed and used to design parallel architectures for real time SISO decoding of CTBC codes. A new signal mapping technique called constrained interleaved coded modulation (CICM) is also developed. CICM is then used to develop rate matching, spatial modulation, and MIMO modulation subsystems to be used with CTBC codes and other types of codes. By way of example, embodiments are primarily provided for improved 5G LTE and optical transport network (OTN) communication systems. Detailed descriptions of embodiments are also provided that combine aspects of MIMO and spatial modulation systems to improve bandwidth efficiency. Such embodiments are applicable to multi-antenna and single antenna MIMO systems as well as multichannel systems, OFDM systems, and TDM systems.
Owner:FONSEKA JOHN P +1
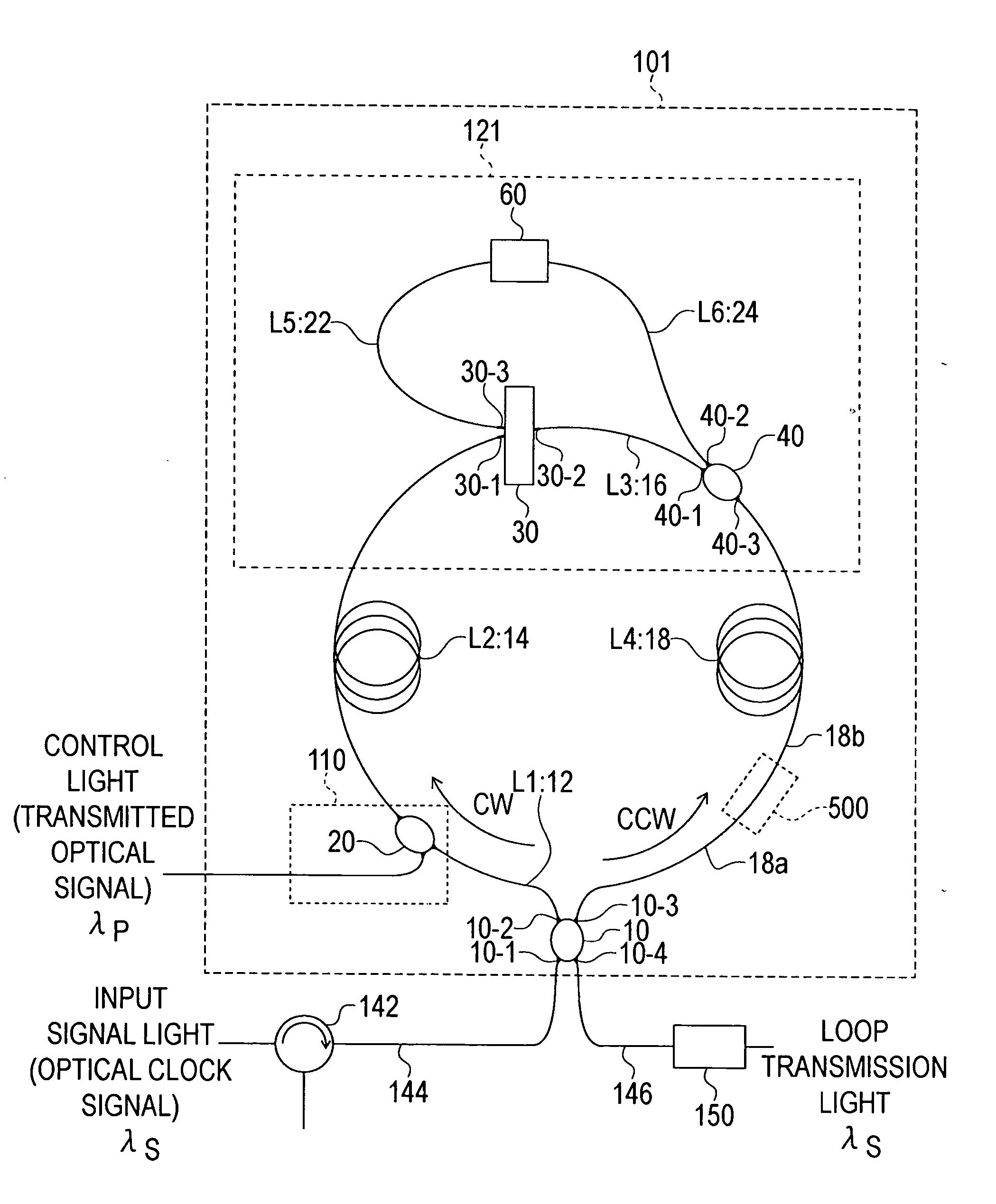
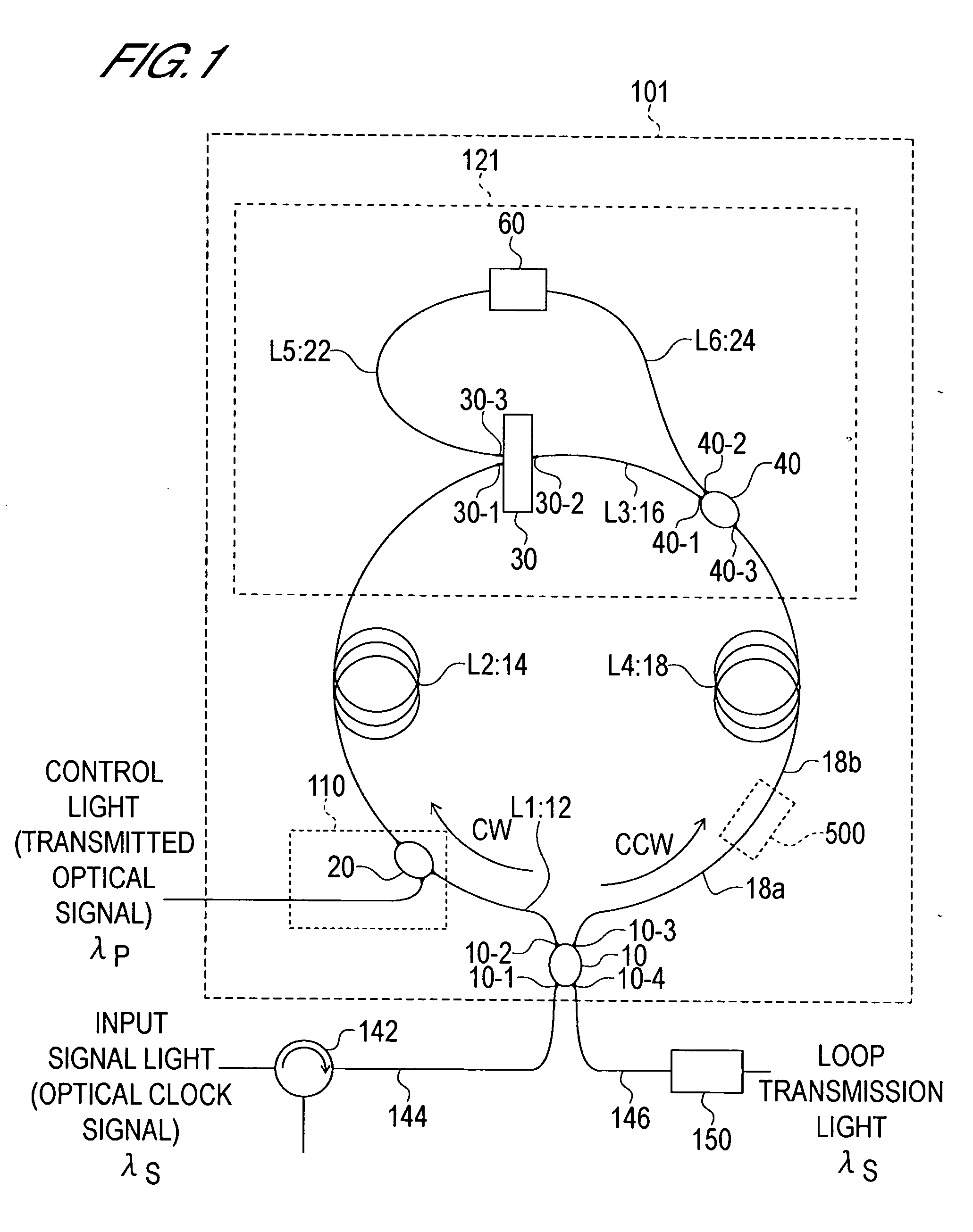
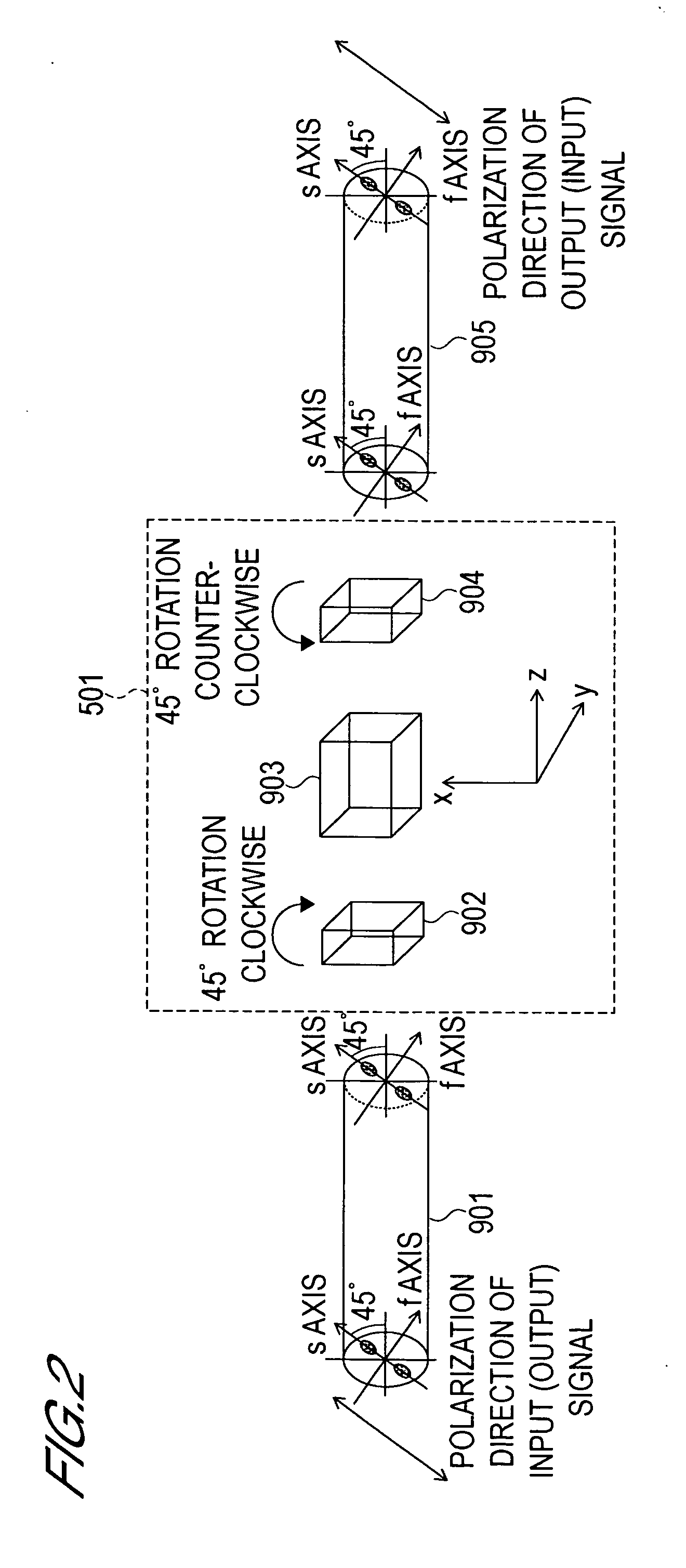
Optical Switch
InactiveUS20060045536A1Guaranteed uptimeLighting is limitedPolarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsWavelengthWaveguide
The present invention provides an optical switch in which a switching operation is not affected even when the polarization state of a control light varies. The optical switch comprises a loop-form optical waveguide loop circuit formed from an optical nonlinear medium, control light input means of phase control means for inputting the control light into the optical waveguide loop circuit, a wavelength demultiplexing / multiplexing circuit, and a phase bias circuit. The optical waveguide loop circuit is constituted by an optical path formed from a first polarization-maintaining single-mode fiber extending from an optical demultiplexer / multiplexer to the control light input means, an optical path formed from a second polarization-maintaining single-mode fiber extending from the control light input means to the wavelength demultiplexing / multiplexing circuit, and an optical path formed from a fourth polarization-maintaining single-mode fiber extending from the wavelength demultiplexing / multiplexing circuit and returning to the optical demultiplexer / multiplexer. The wavelength demultiplexing / multiplexing circuit is formed as a loop-form optical waveguide loop circuit by a third polarization-maintaining single-mode fiber connecting a wavelength demultiplexer and a multiplexer, a fifth polarization-maintaining single-mode fiber connecting the wavelength demultiplexer and a polarization plane rotation portion, and a sixth polarization-maintaining single-mode fiber connecting the polarization plane rotation portion and the multiplexer. The phase bias circuit is inserted at a point on any one of the first through fourth polarization-maintaining single-mode fibers.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com