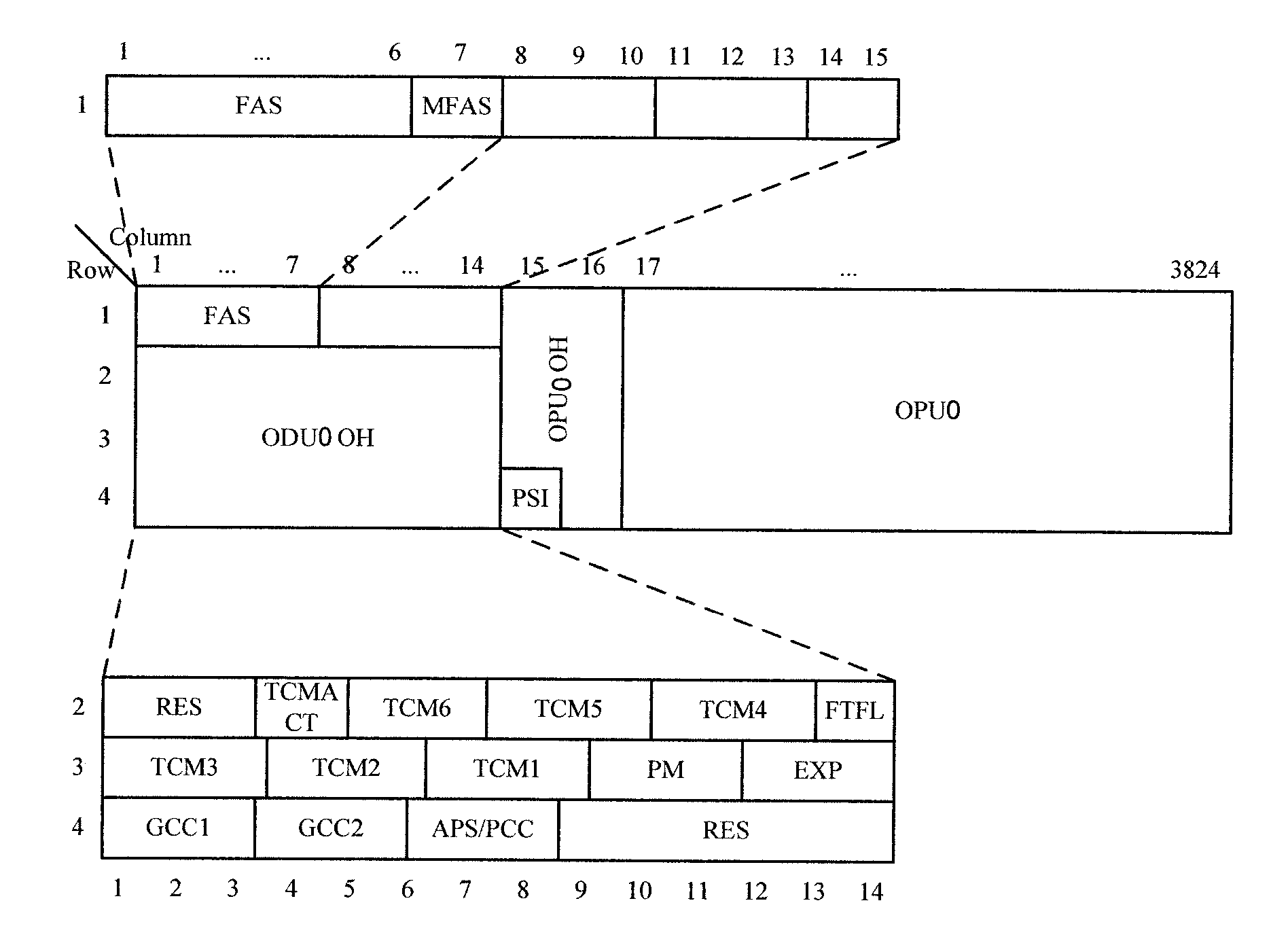
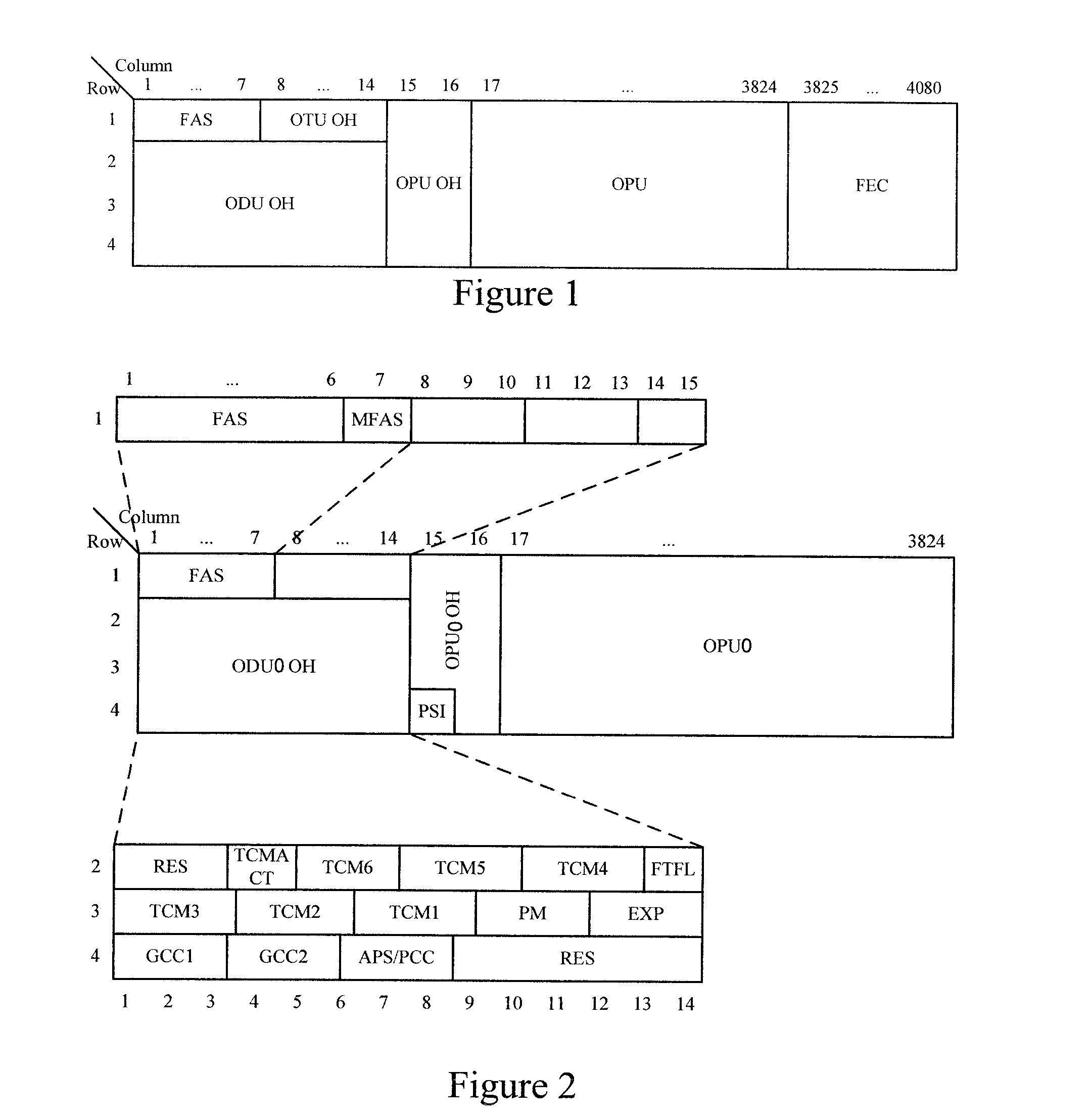
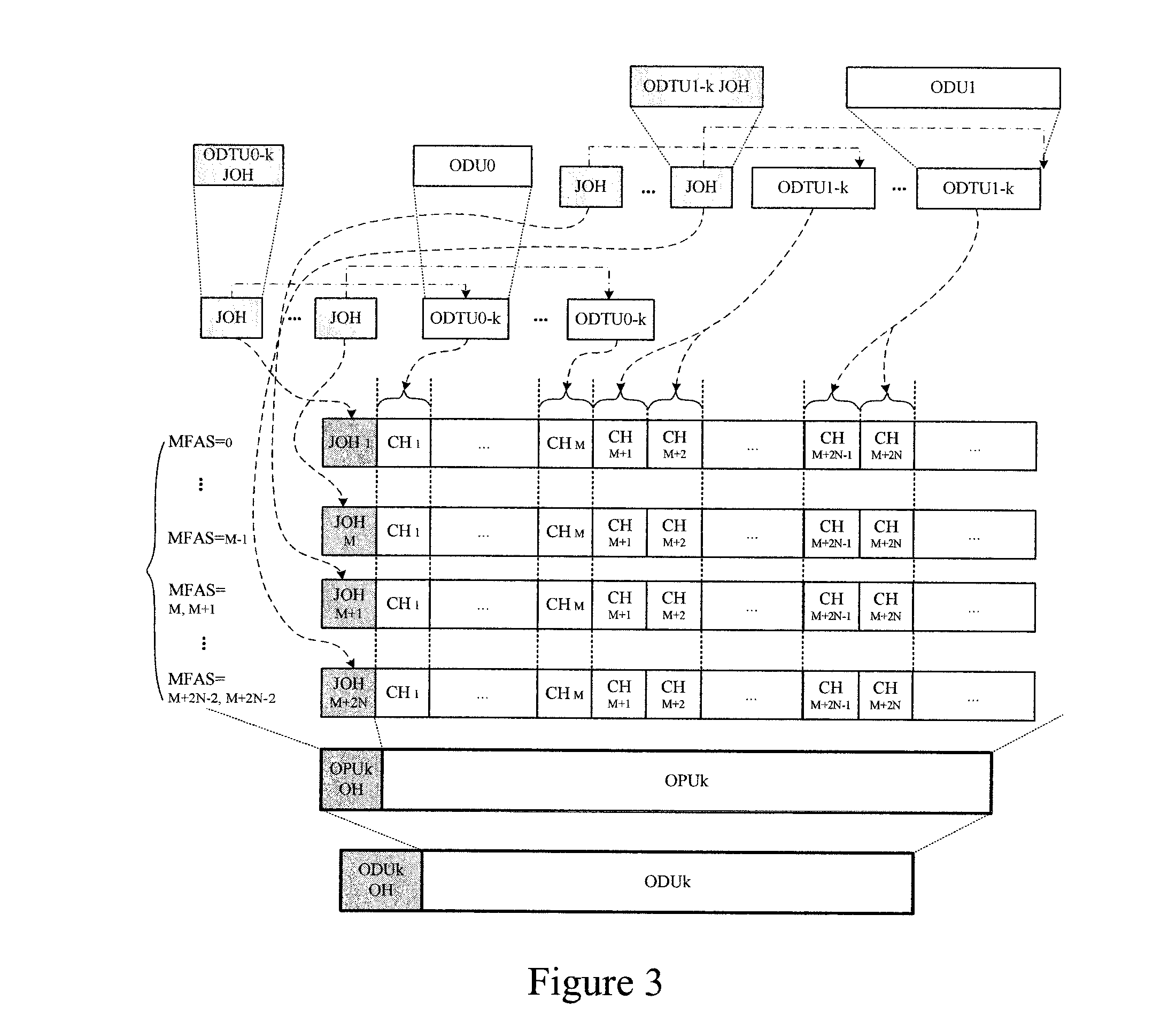
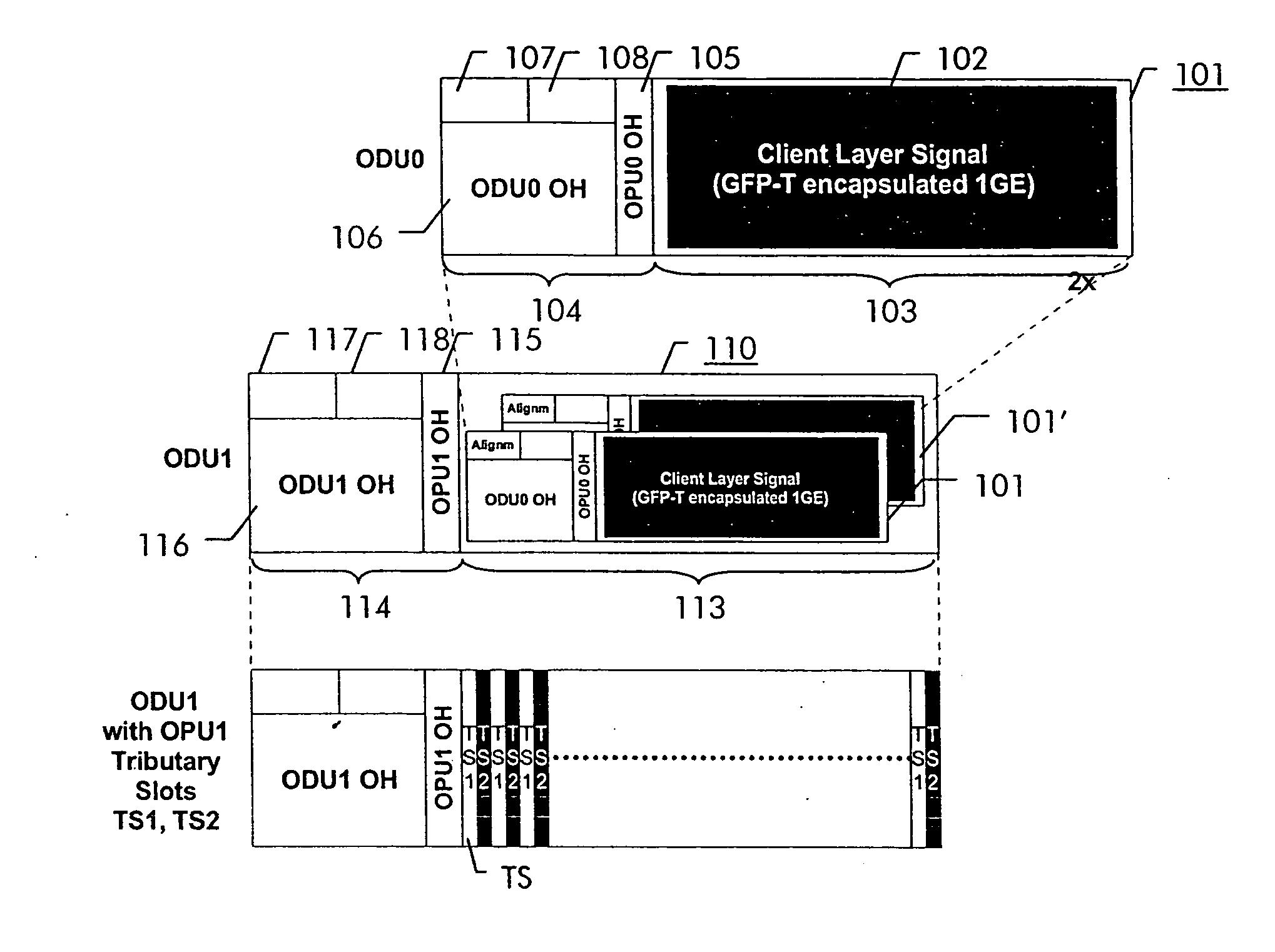
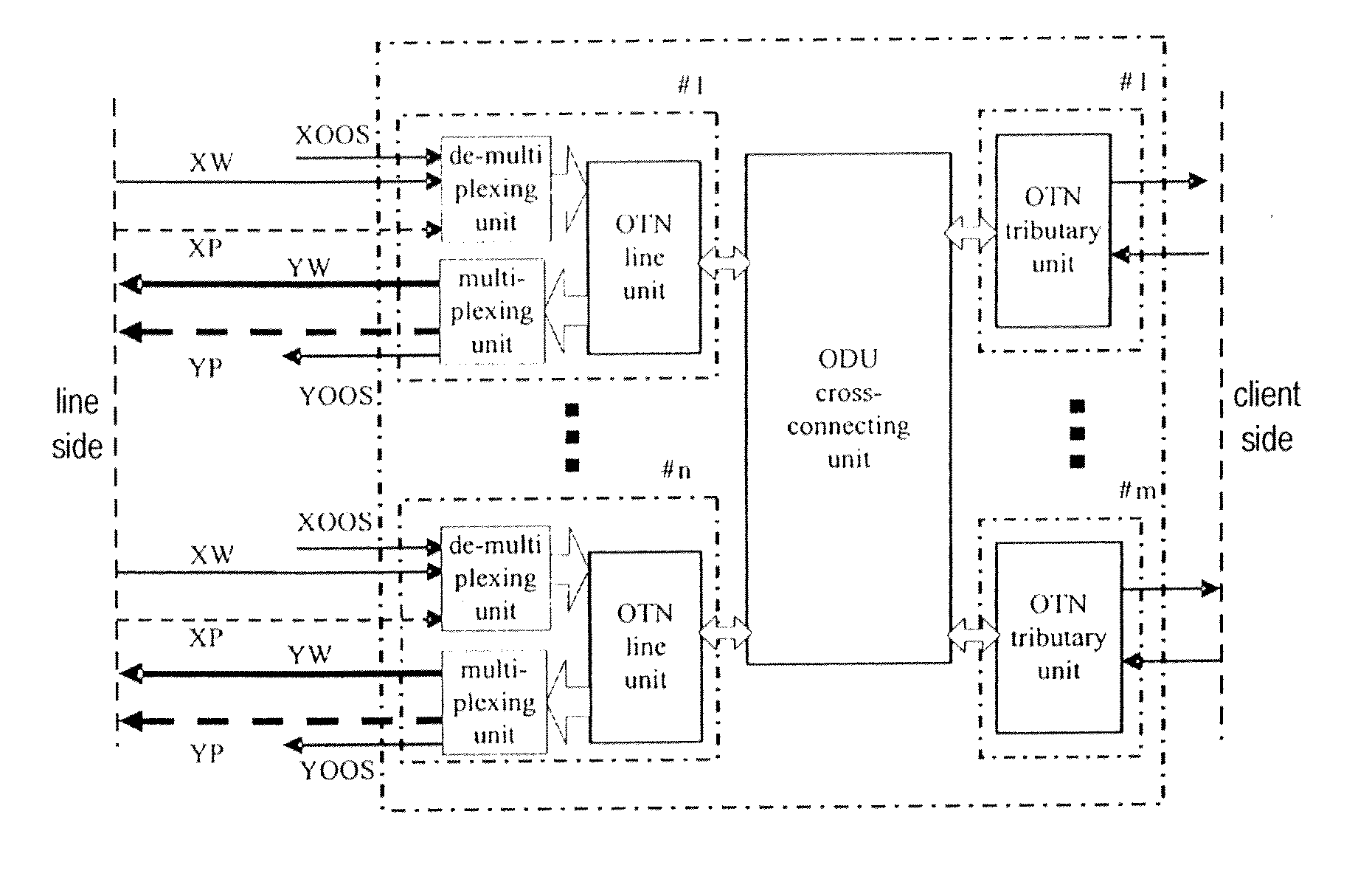
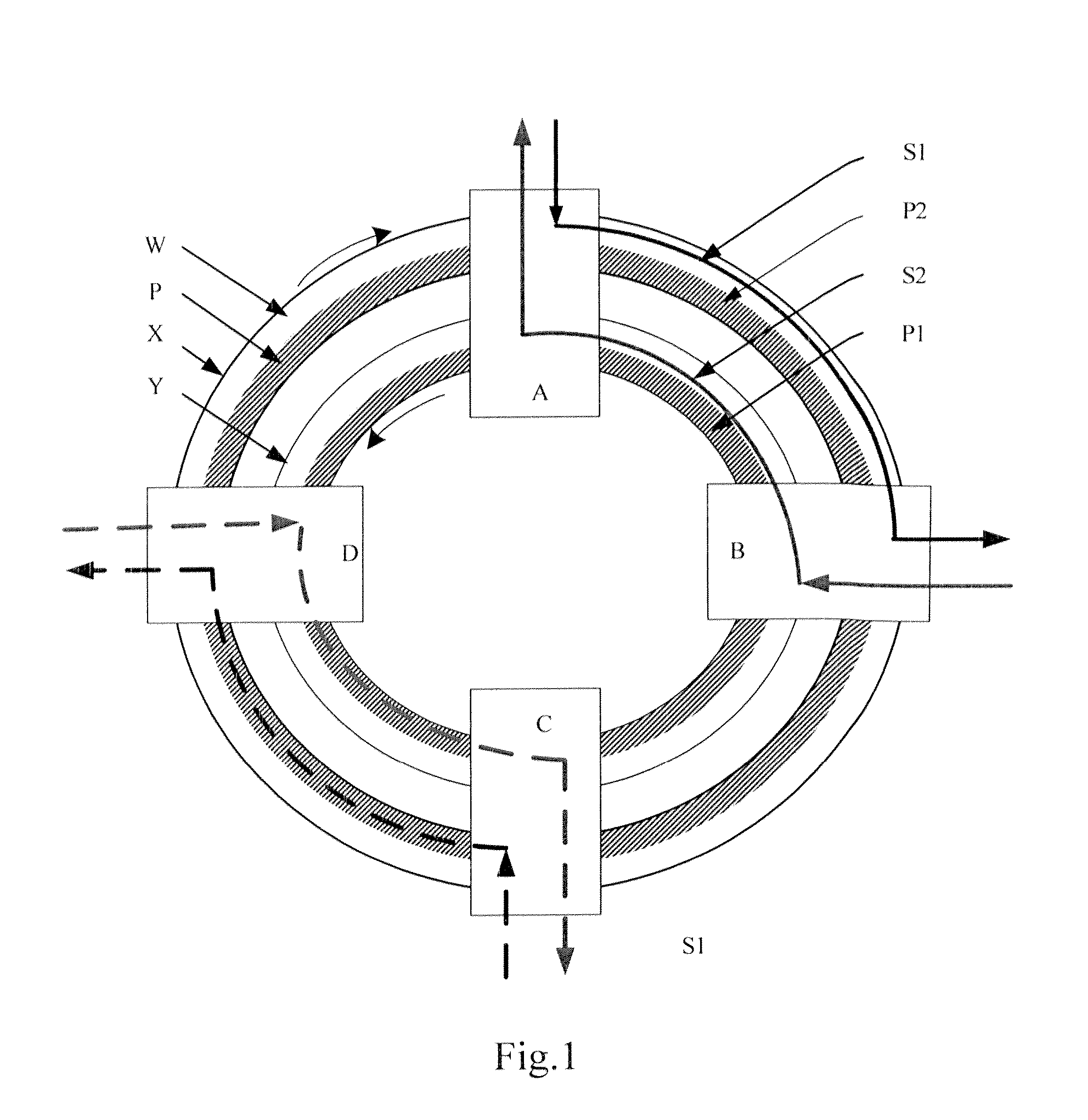
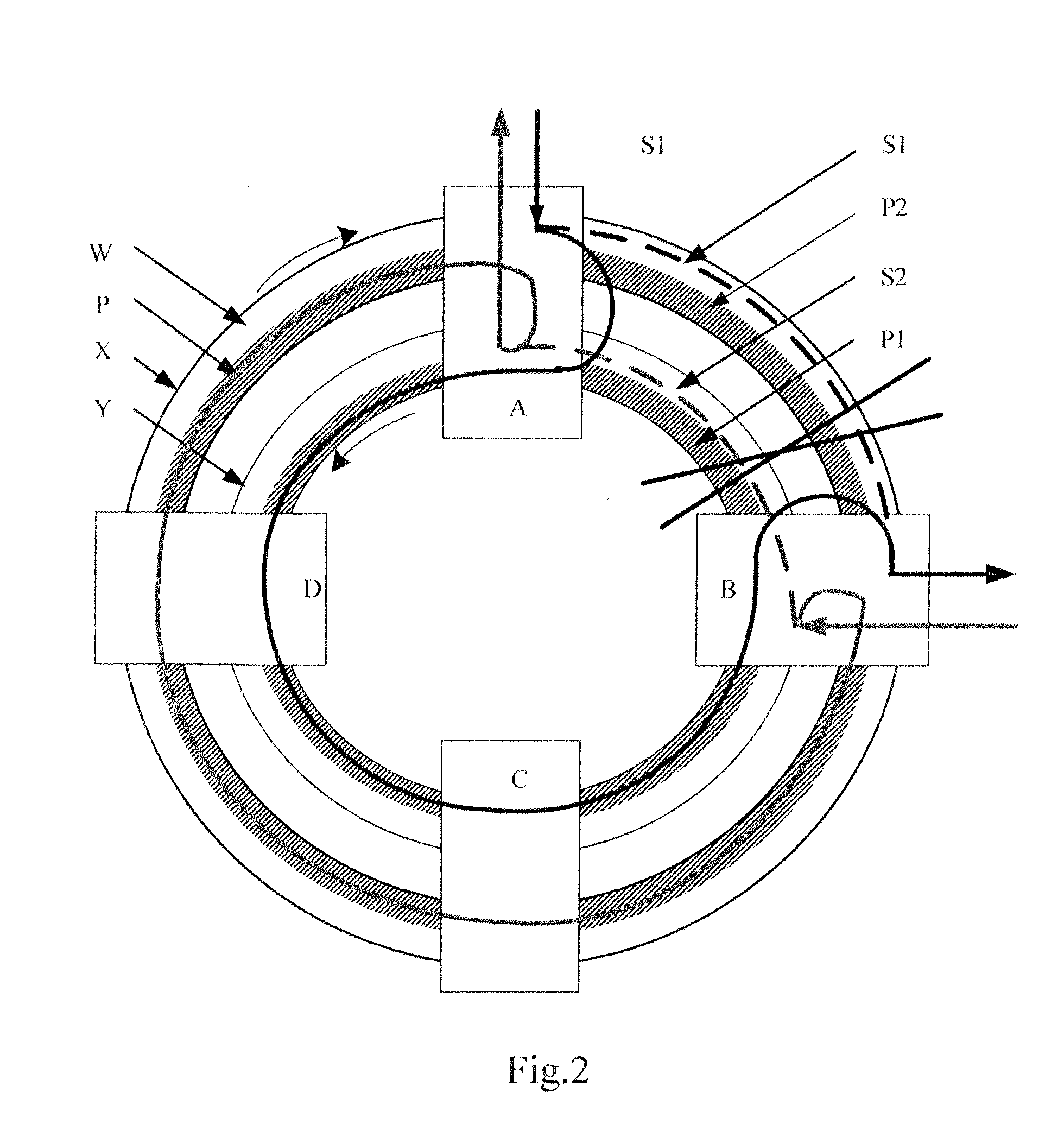
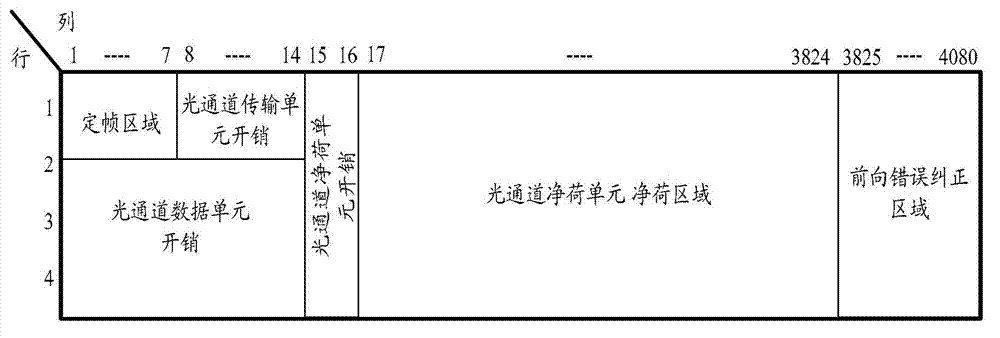
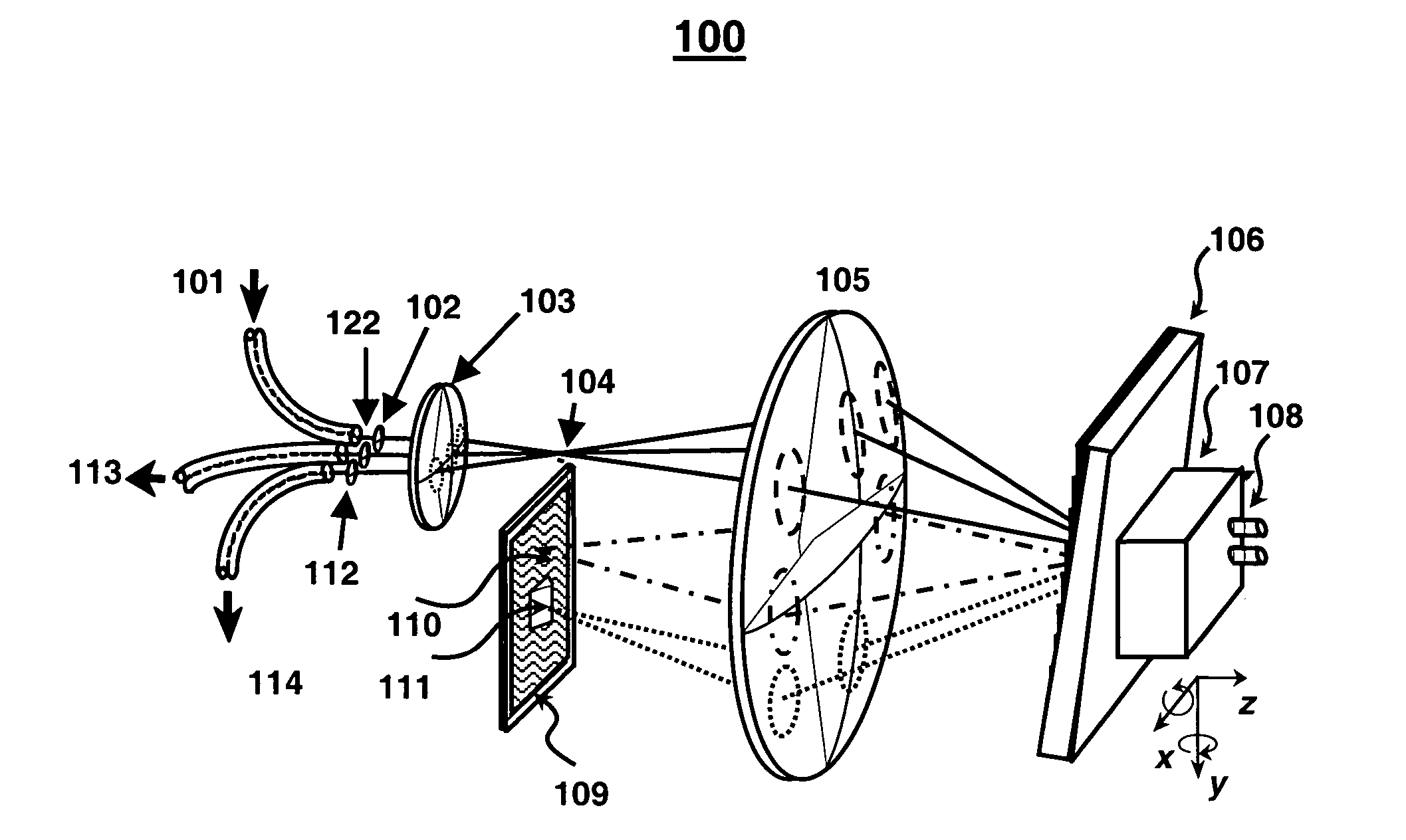
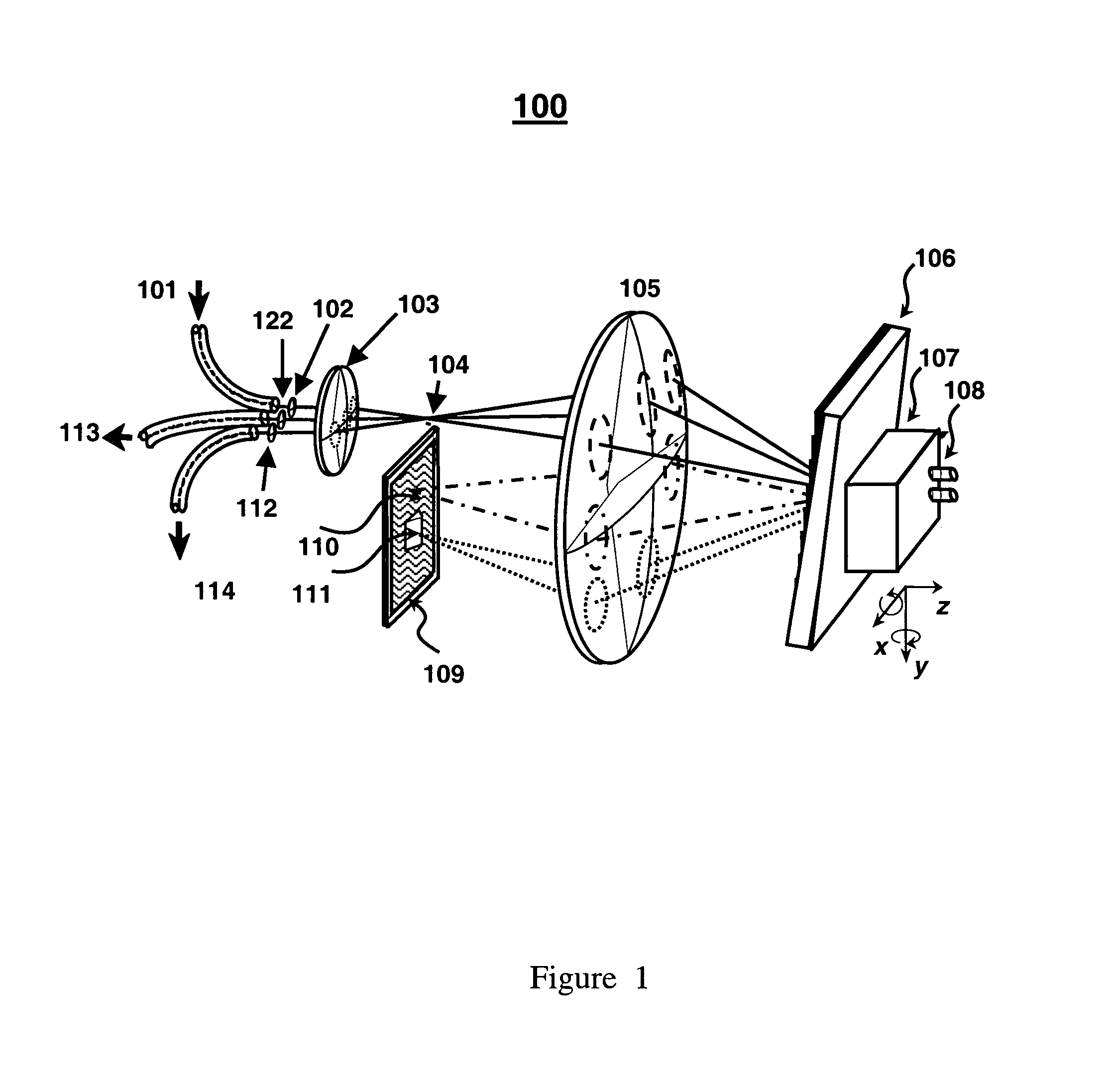
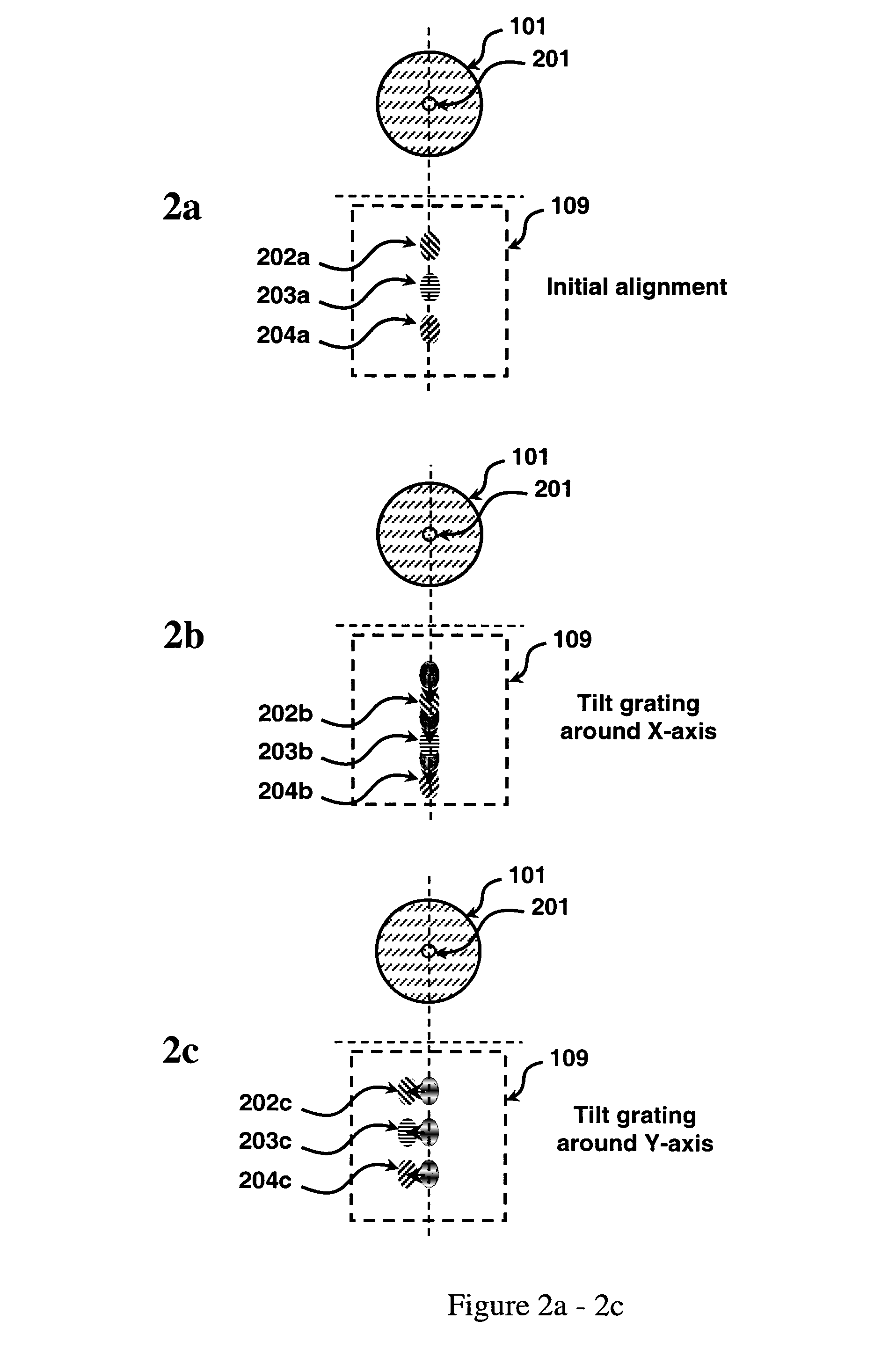
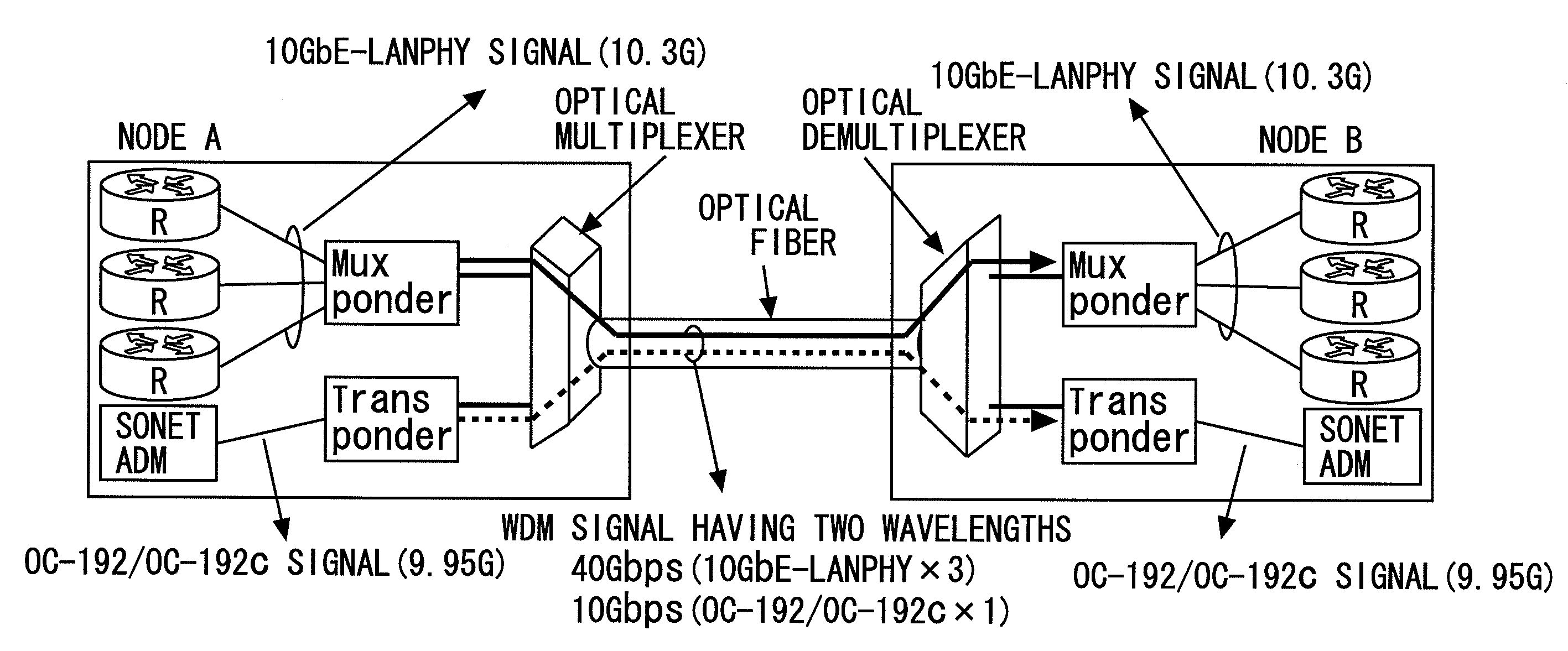
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
986 results about "Optical Transport Network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
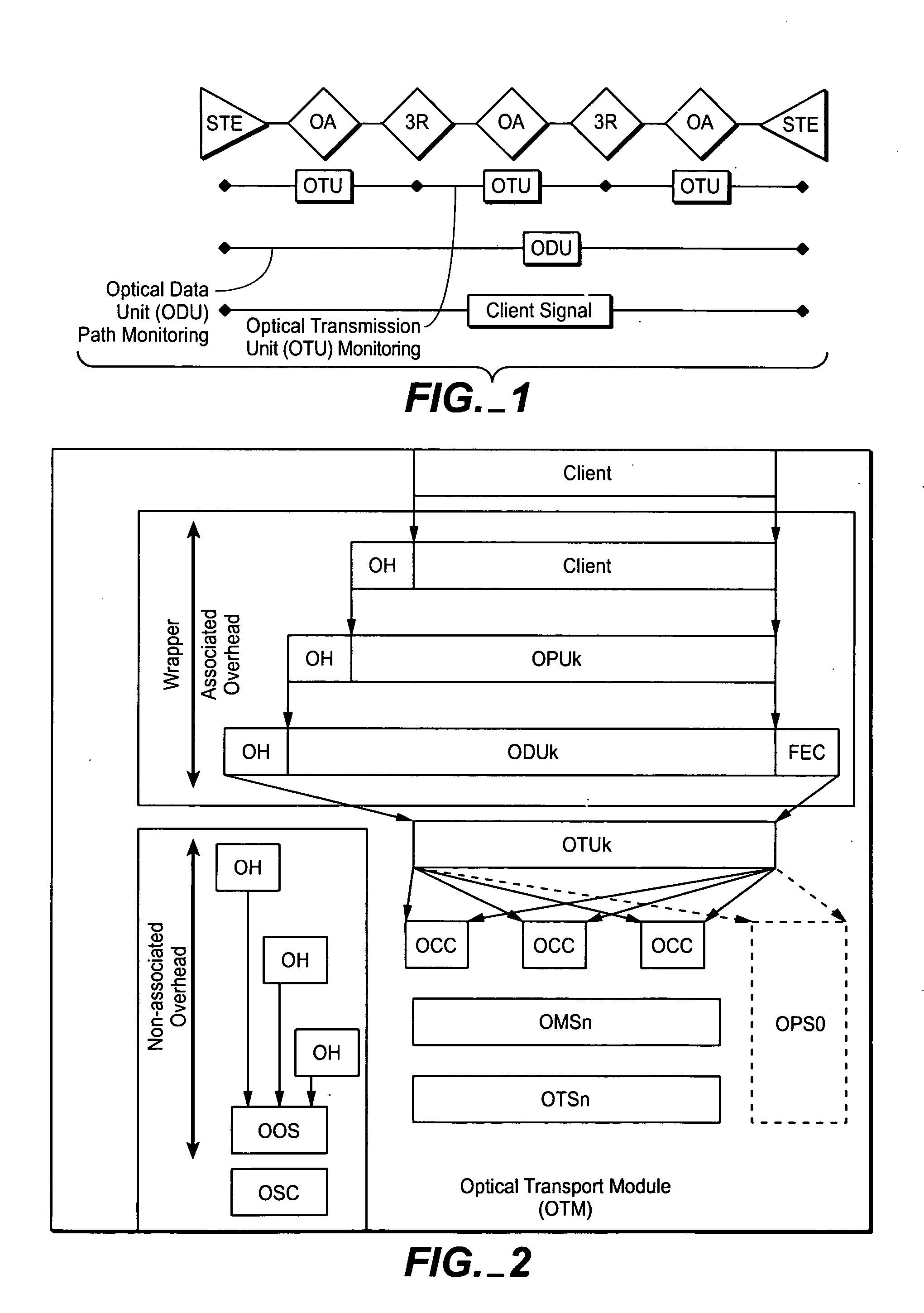
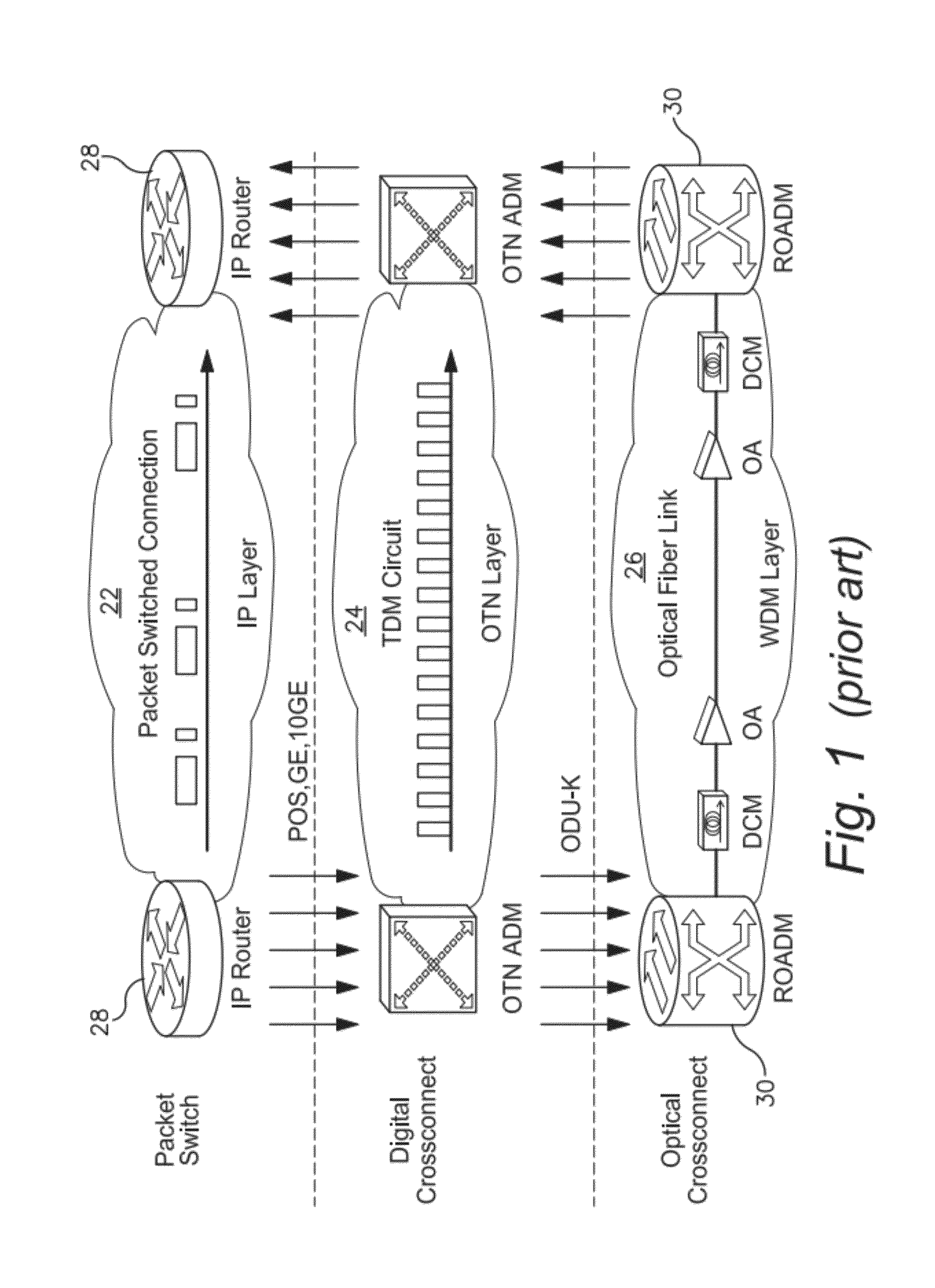
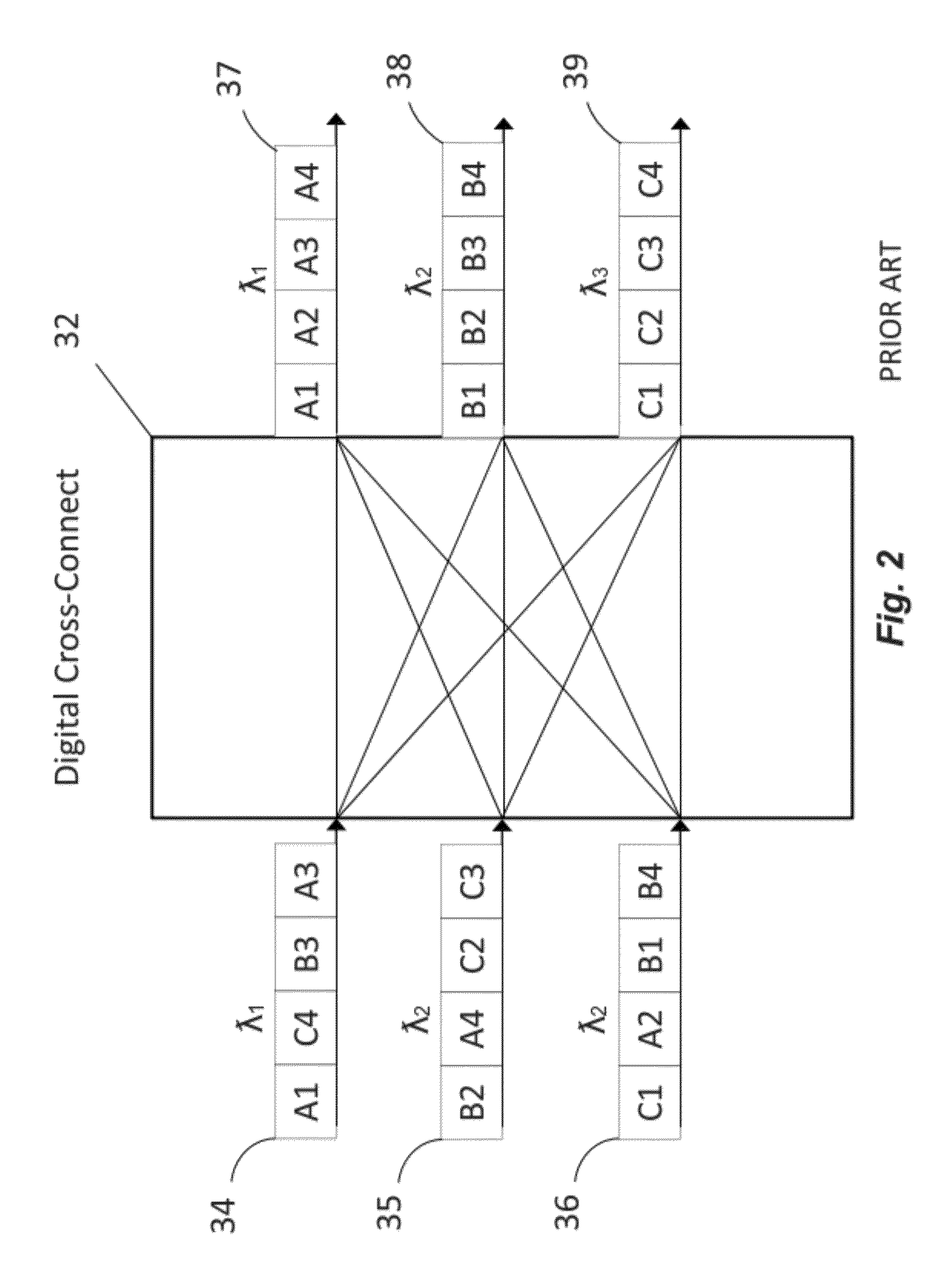
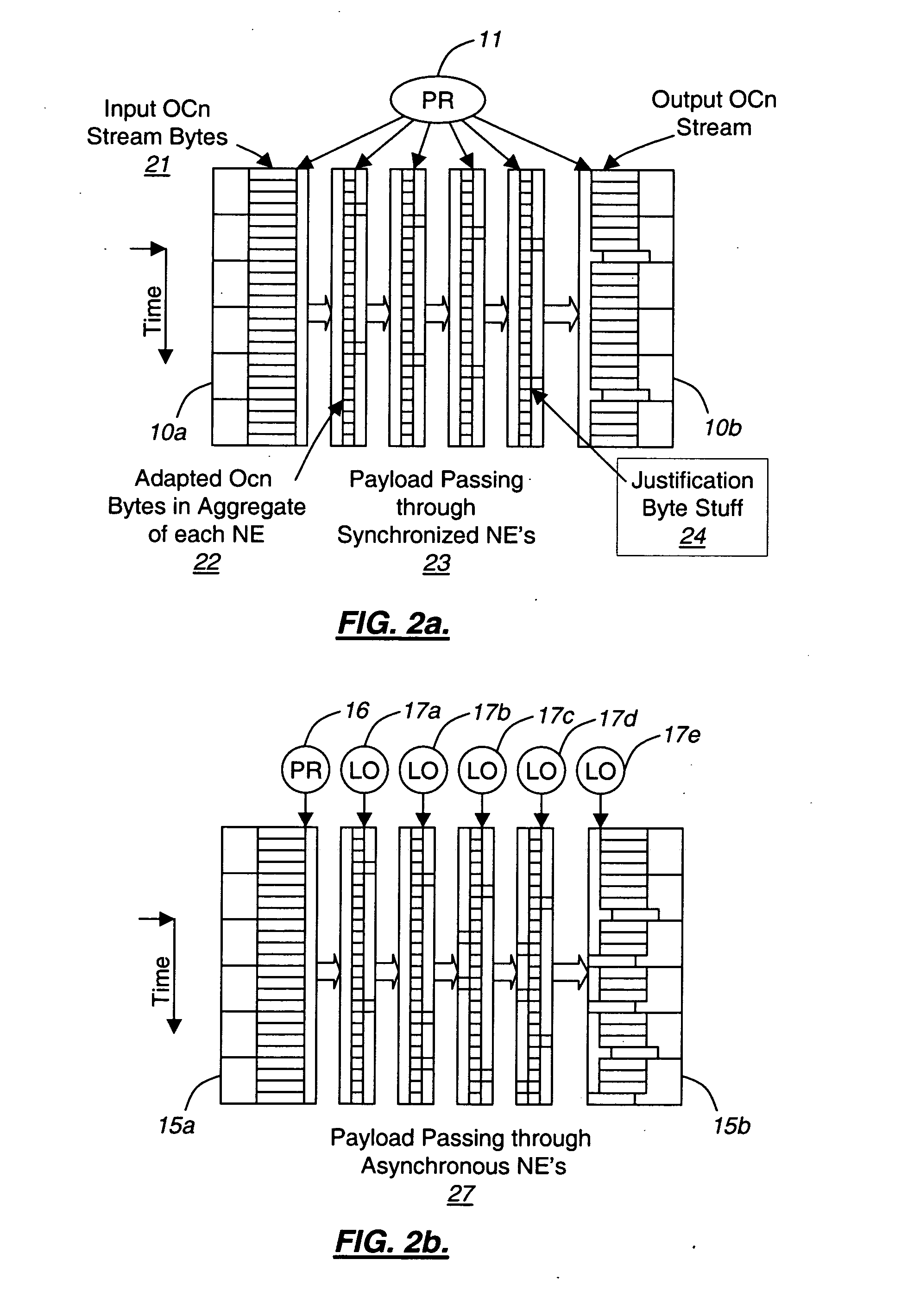
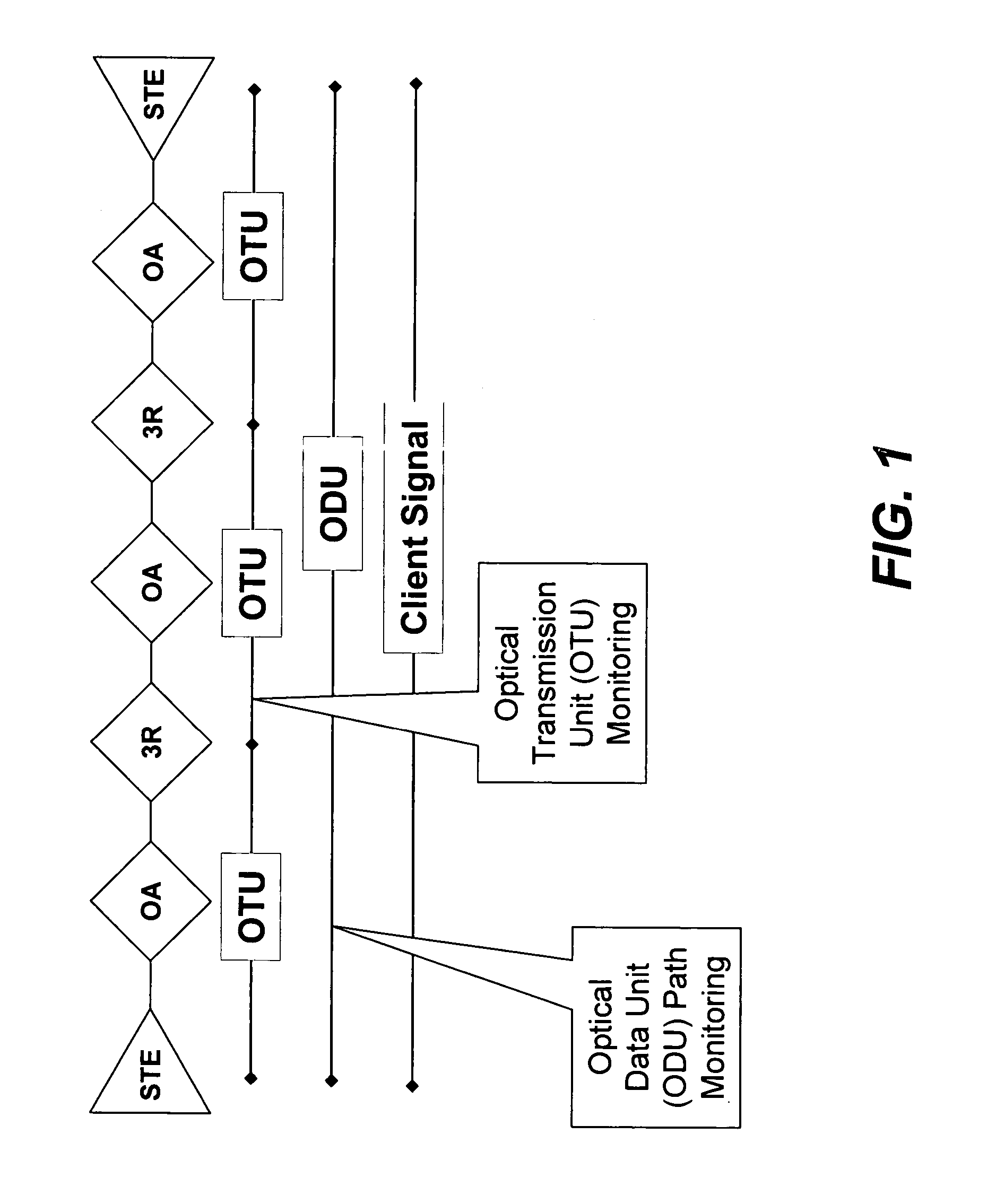
ITU-T defines an Optical Transport Network (OTN) as a set of Optical Network Elements (ONE) connected by optical fiber links, able to provide functionality of transport, multiplexing, switching, management, supervision and survivability of optical channels carrying client signals. An ONE may Re-time, Re-Amplify, Re-shape (3R) but it does not have to be 3R – it can be purely photonic.
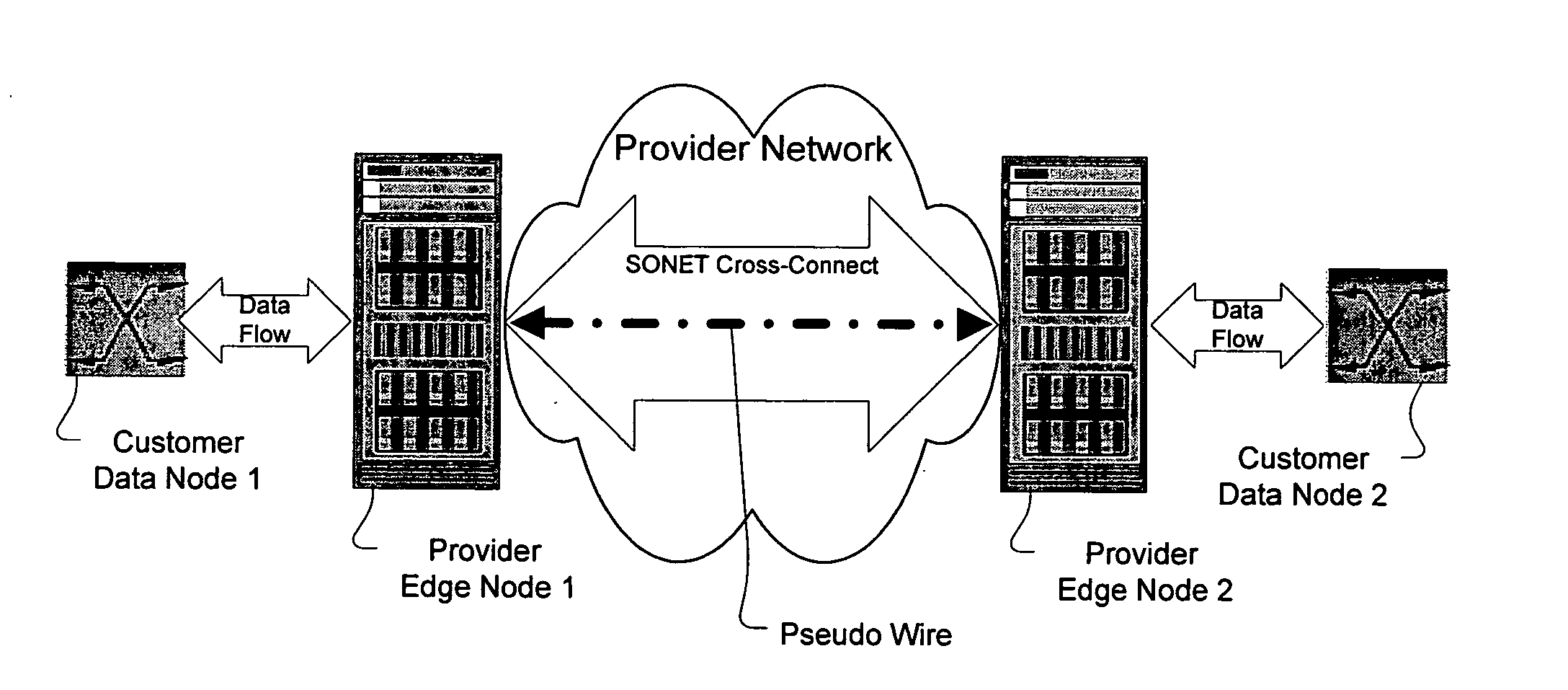
Method and apparatus for performing data flow ingress/egress admission control in a provider network
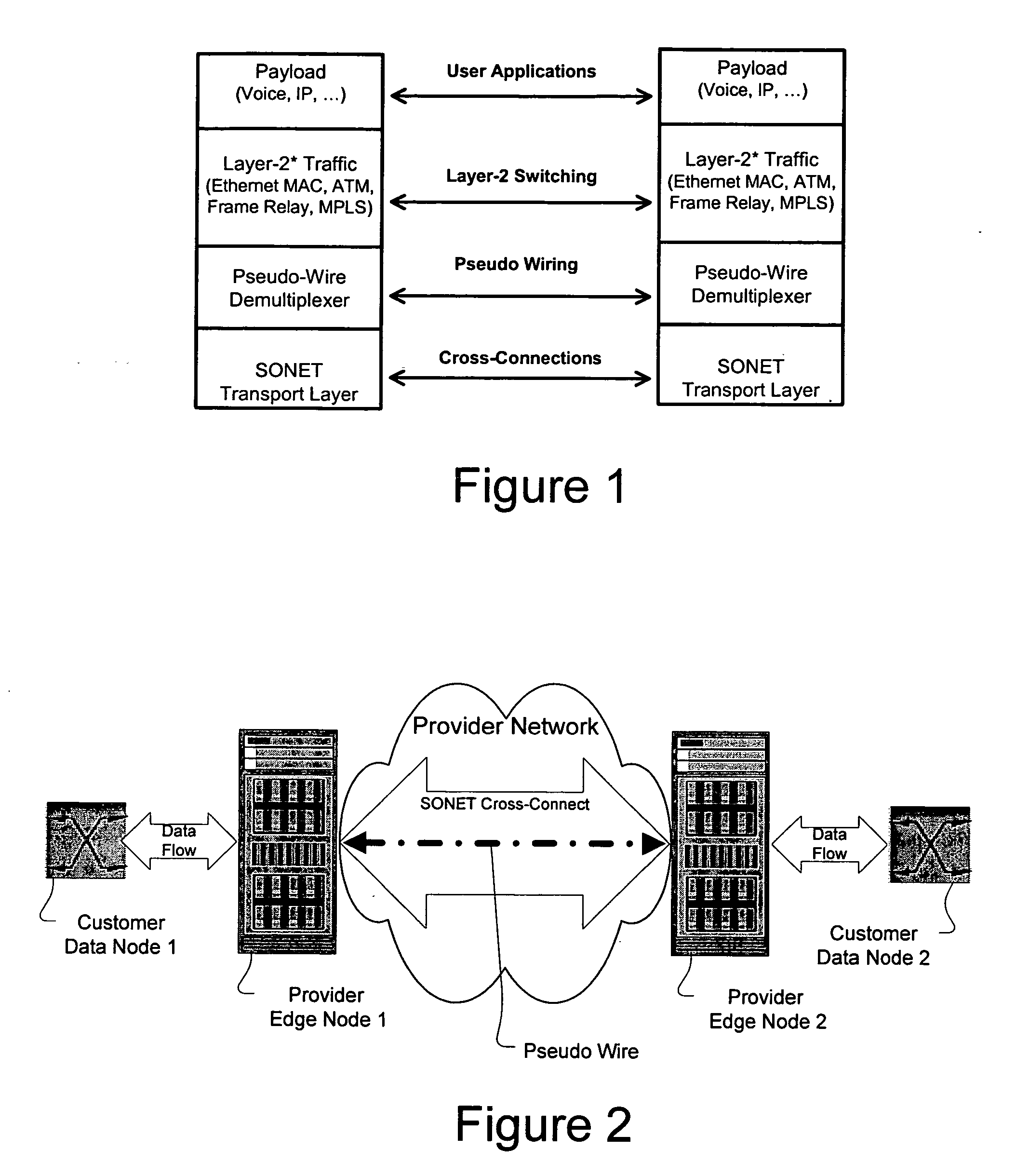
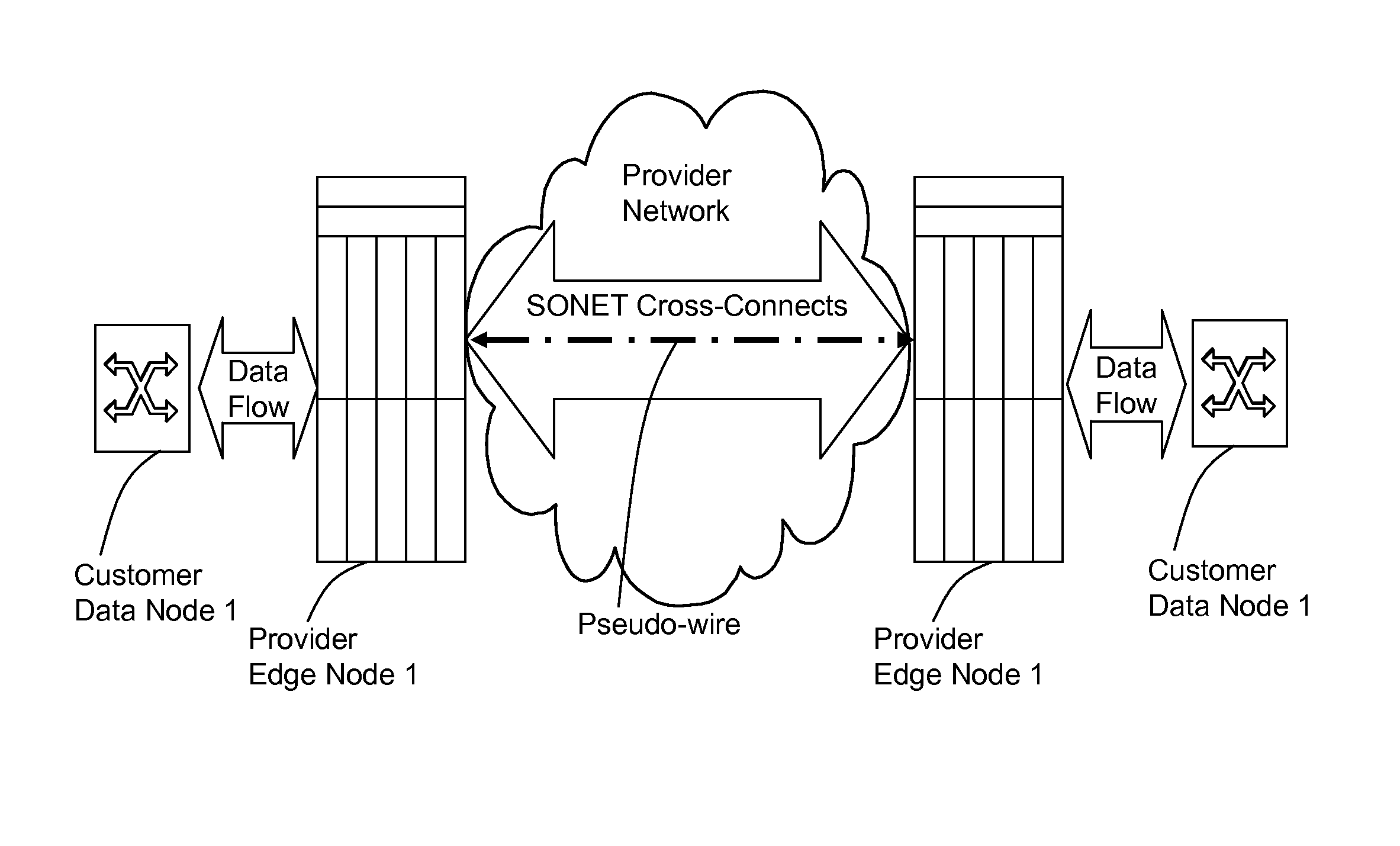
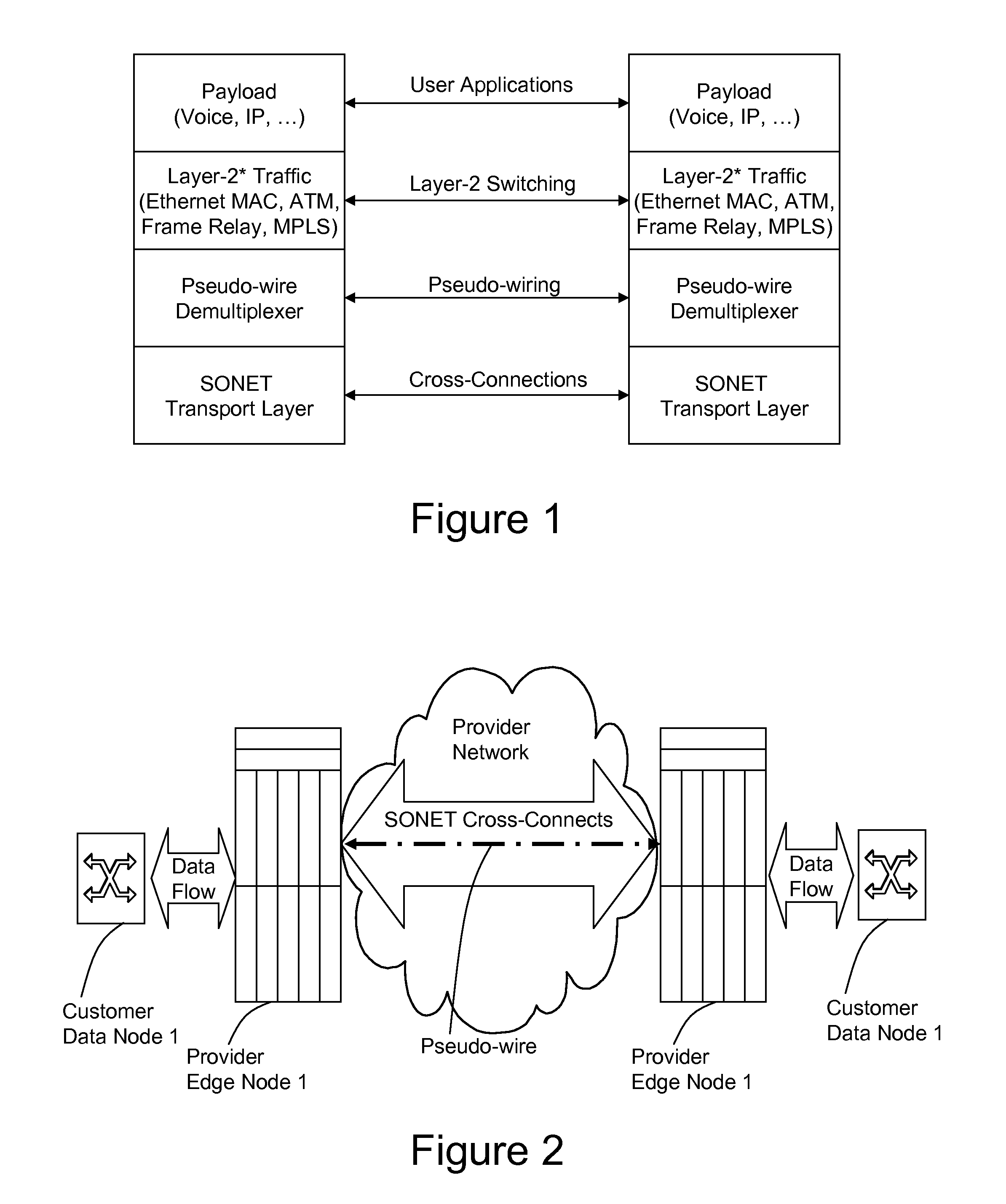
A method, apparatus and network for transporting layer-2 frames, such as Ethernet MAC, ATM AAL5, and Frame Relay, over MPLS, SONET / SDH, or OTN optical transport networks as well as electrical transport networks is disclosed. The method establishes "pseudo-wires" between, for example, routers, Layer-2 packet switches, or SONET / SDH switches. Inter-related ingress and egress resource tables may be used by provider edge nodes to negotiate consistently managed data tunnels across a provider network on behalf of data flowing from / to a diverse base of customer edge nodes. Detailed network resource information particular to each of the data flows is exchanged between provider edge nodes during the creation of pseudo-wires. Admission control algorithms are applied at the ingress and egress points in order to manage the data flows into a provider network and exiting from a provider network to customer equipment. By applying pseudo-wire shuffling and preemption techniques, the providers can make better use of their network resources by admitting more pseudo-wires.
Owner:CIENA
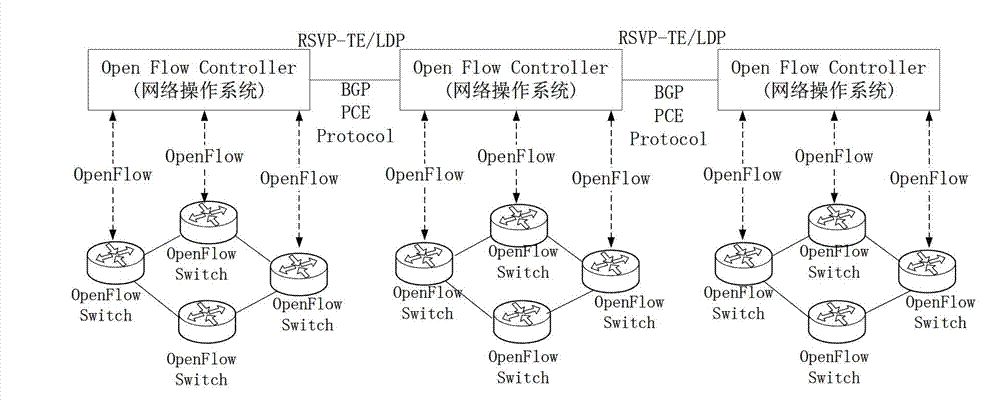
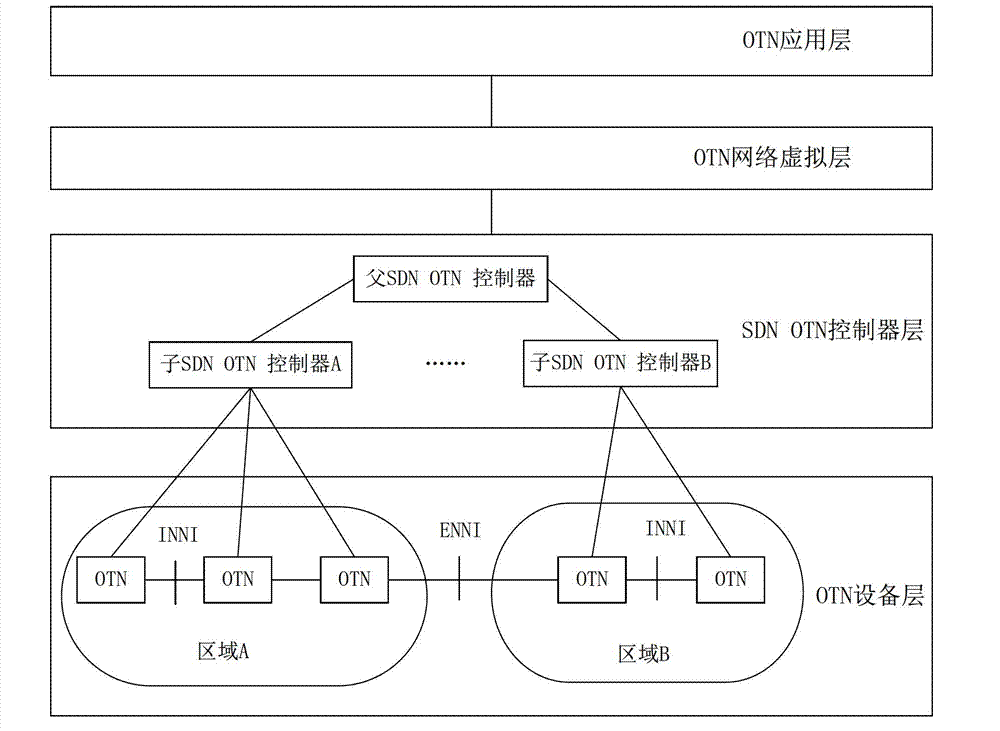
Framework system of grade software defined network software controller and implementation method thereof
ActiveCN103051565AResolve resource conflictsAvoid asyncData switching networksStructure of Management InformationNetwork control
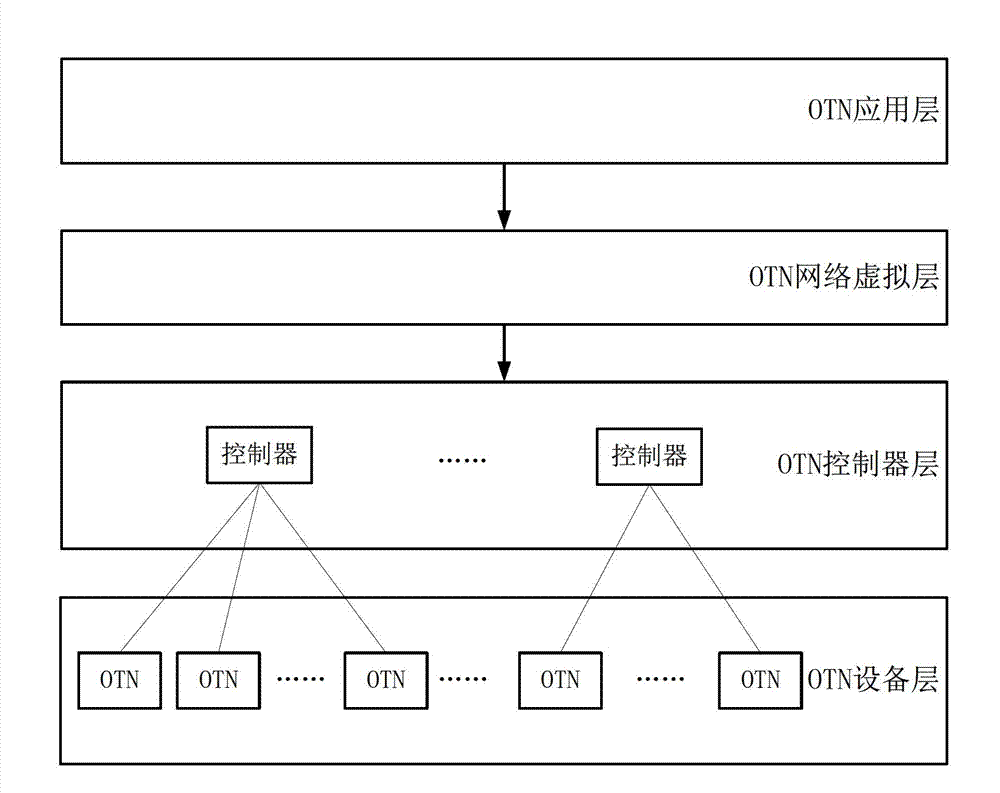
The invention discloses a framework system of a grade software defined network software controller and an implementation method thereof. The framework system and the implementation method are applied in a multi-domain optical transport network (OTN); an inter-domain mapping relation of a whole network view and a physical device network is established according to whole network topologic information by a primary (SDNOTN) controller; an inter-domain mapping processing request of the whole network view and the physical device network in each domain is sent to each auxiliary SDNOTN; and the domain mapping relation of the whole network view and the physical device network is established by the auxiliary SDNOTN controllers. Grade structures of the primary SDNOTN controller and the auxiliary SDNOTN controllers are arranged in the framework system, so that the mapping relation of the multi-domain whole network view and the overall physical device network in real sense is realized, and a whole network resource optimizing algorithm is realized in the real sense, so that the problem that the inter-domain link resource conflict occurs in a cross-domain service connection signaling process can be thoroughly solved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Universal digital framer architecture for transport of client signals of any client payload and format type
ActiveUS20050286521A1Reduce the required sizeReduce capacityError preventionTransmission systemsClient-sideByte
Client signals to be transported in a transmission network, particularly an optical transmission network, may have different payload envelope rates and are digitally mapped on the client egress side into first transport frames (also referred to as iDTF frames, or intra-node or internal digital transport frames), at the client side for intra-transport within terminal network elements (NEs) and further digitally mapped into second transport frames (also referred to as DTFs or digital transport frames) for inter-transport across the network or a link which, through byte stuffing carried out in the first transport frames so that they always have the same frame size. As a result, the system of framers provides for a DTF format to always have a uniformly universal frame rate throughout the network supporting any client signal frequency, whether a standard client payload or a proprietary client payload, as long as its rate is below payload envelope rate of the client signal. At the client signal ingress side, the signal are digitally demapped from the second transport frames (DTF format) into the first transport frames where the stuff bytes are removed and accordingly processed at an intermediate node element before further transport, or digitally demapped from the first transport frames (iDTF format) to reproduce or reassemble the client signal or signals comprising the client payload at the client payload envelope rate for reception at the client's equipment. Among various features disclosed, two predominate features are (1) a single channel or network rate for transport of all signals between network elements (NEs) and end terminal network elements and (2) the digitally wrapping of different types of payloads into N client side or first frames using stuff bytes to render each client side frame size equal to a predetermined value. Then the stuffed first frames are wrapped into line side or second frames for transport over the network at the same high speed line rate for all digitally wrapped client signals. The client side framers may be, for example, running at the lowest signal rate encountered, to digitally wrap then into parallel N client signals or digitally wrap a client signal multi-sected into N parts, where these two different client signals have different payload rates.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Method and apparatus for performing data flow ingress/egress admission control in a provider network
A method, apparatus and network for transporting layer-2 frames, such as Ethernet MAC, ATM AAL5, and Frame Relay, over MPLS, SONET / SDH, or OTN optical transport networks as well as electrical transport networks is disclosed. The method establishes “pseudo-wires” between, for example, routers, Layer-2 packet switches, or SONET / SDH switches. Inter-related ingress and egress resource tables may be used by provider edge nodes to negotiate consistently managed data tunnels across a provider network on behalf of data flowing from / to a diverse base of customer edge nodes. Detailed network resource information particular to each of the data flows is exchanged between provider edge nodes during the creation of pseudo-wires. Admission control algorithms are applied at the ingress and egress points in order to manage the data flows into a provider network and exiting from a provider network to customer equipment. By applying pseudo-wire shuffling and preemption techniques, the providers can make better use of their network resources by admitting more pseudo-wires.
Owner:CIENA
Method and Device for Transmitting Low Rate Signals Over an Optical Transport Network
ActiveUS20070248121A1Increase ratingsImprove transmission efficiencyTime-division multiplexOptical multiplexChannel dataMultiplexing
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method for transmitting low rate signals over an optical transport network, including: adapting the low rate signals into low rate optical channel data units of the same rate level with the low rate signals; asynchronously mapping each of the low rate optical channel data units into a low rate optical channel data tributary unit respectively, and generating justification overhead used for rate adaptation for each of the low rate optical channel data units; and forming a higher order optical channel data unit with at least one low rate optical channel data tributary unit and justification overhead corresponding to the low rate optical channel data tributary unit. The present invention enables the optical transport network to support mapping, multiplexing and highly efficient transmission of low rate signals.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for transporting a client layer signal over an optical transport network (OTN)
InactiveUS20060104309A1Solve the financial burdenDoubling capacityTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationMultiplexingChannel data
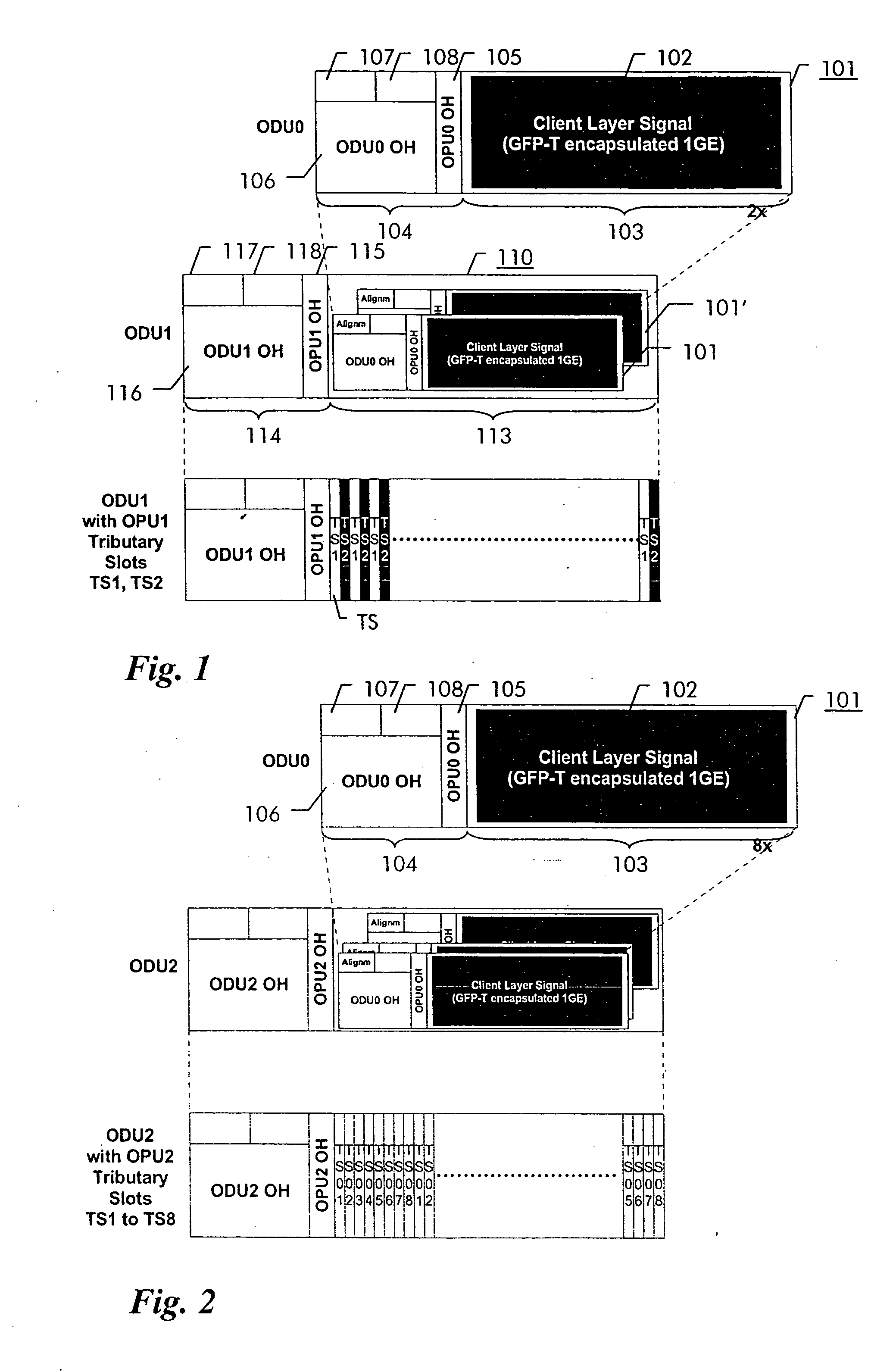
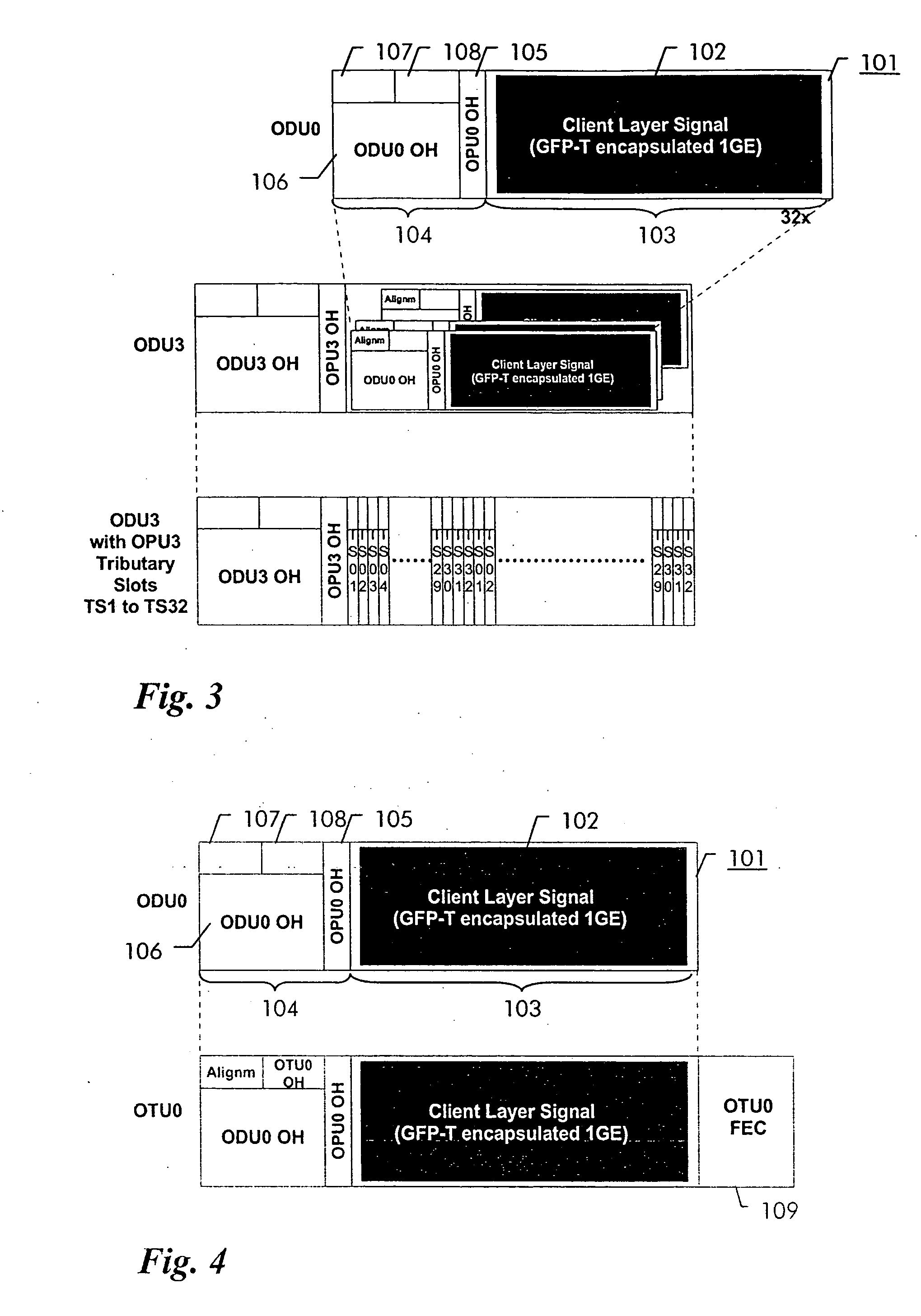
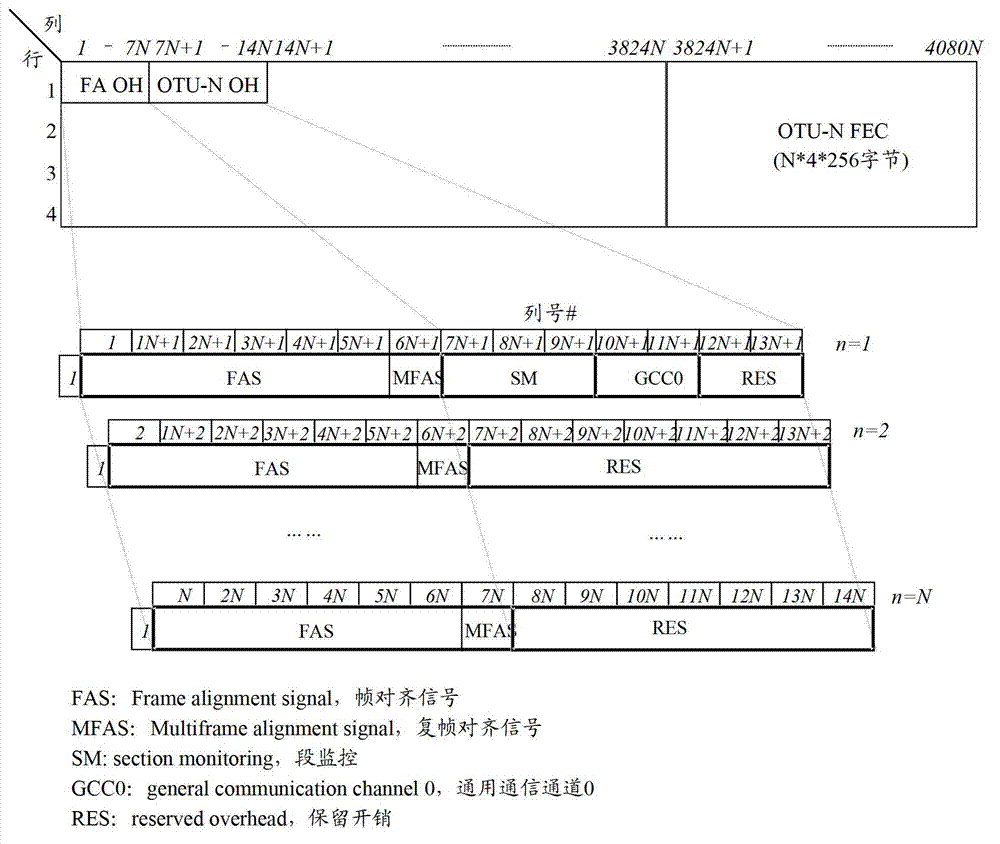
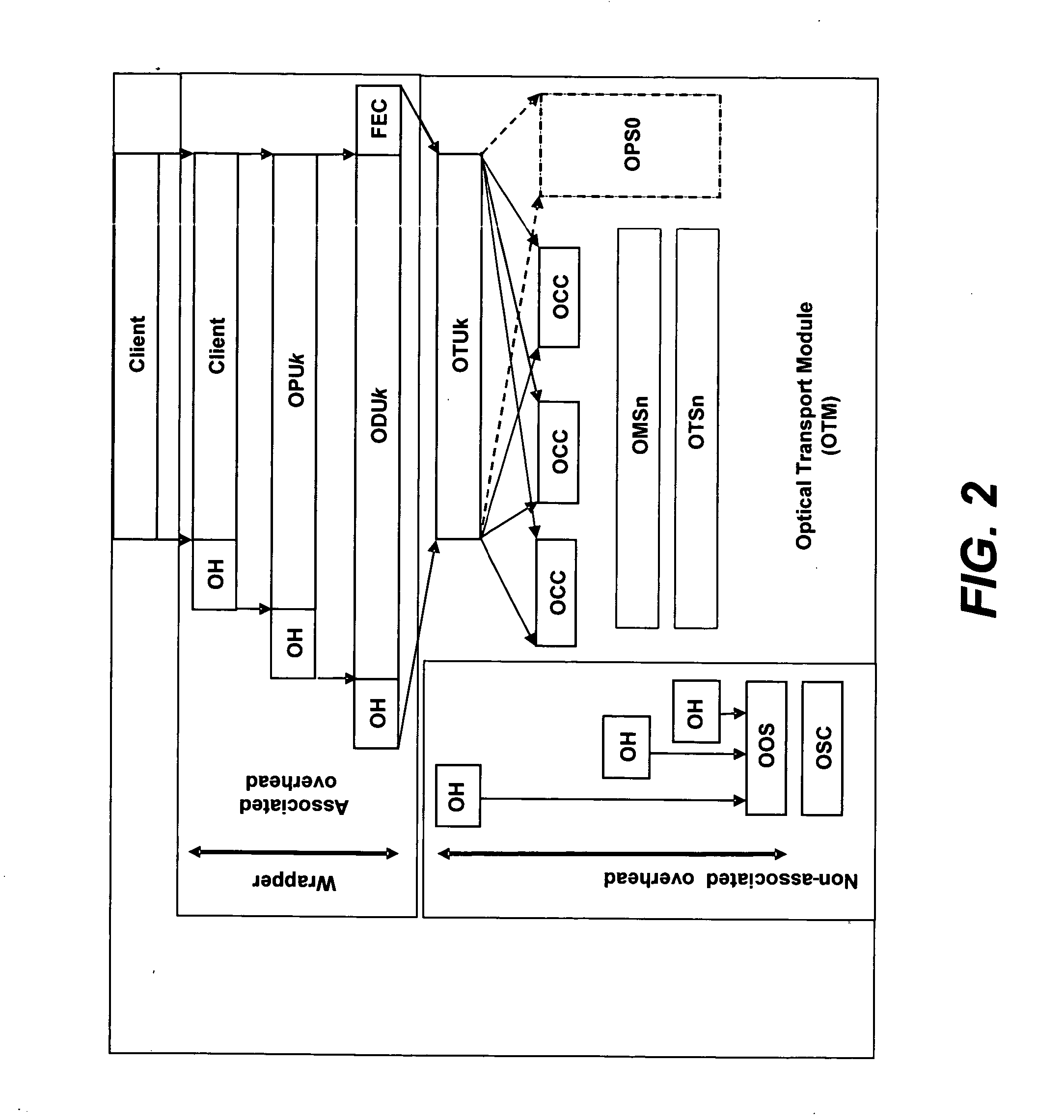
In order to facilitate the transport of 1 Gbit / s Ethernet signals over an Optical Transport Network using the Optical Transport Hierarchy as specified by ITU-T G.709, a new OTH entity referred to as Optical Channel Data Unit-0 (ODU0, 101) with a capacity of approximately 1.22 Gbit / s is defined. This new entity fits perfectly into the existing OTH multiplexing structure, allowing the transport of two times a 1 Gbit / s Ethernet client layer signal within the capacity of one ODU1 (110), while being individually switchable. A 1 Gbit / s Ethernet signal (102) can be mapped into the ODU0 payload (103) using the Transparent Generic Framing Procedure (GFP-T) encapsulation technique as specified in Rec. G.7041.
Owner:RPX CORP
Device and method for transmitting data traffic in optical transport network
InactiveUS20070104485A1Avoid overheadImprove bandwidth utilizationTime-division multiplexOptical multiplexData trafficOptical Transport Network
A device and a method for transmitting data traffic in an OTN are disclosed. First, all the time slots in the payload area of an OTN frame are allocated to sub-domains with certain bandwidth; then, the sub-domains are grouped into sub-domain groups to carry data traffic based on the bandwidth demand of various data traffic. The device and method provided in the present invention map the data directly on the OTN frame after encapsulating the data traffic so as to effectively avoid the redundant overhead and processing in the intermediate network hierarchies; and the bandwidth utilization is increased as much as possible by means of sub-domain and bandwidth allocation in the payload area of the OTN frame.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for multi-antenna signal transmission in rf long-distance wireless bs
InactiveUS20070160012A1Reduce networking costsSimplify system complexitySpatial transmit diversityTime-division multiplexControl signalEngineering
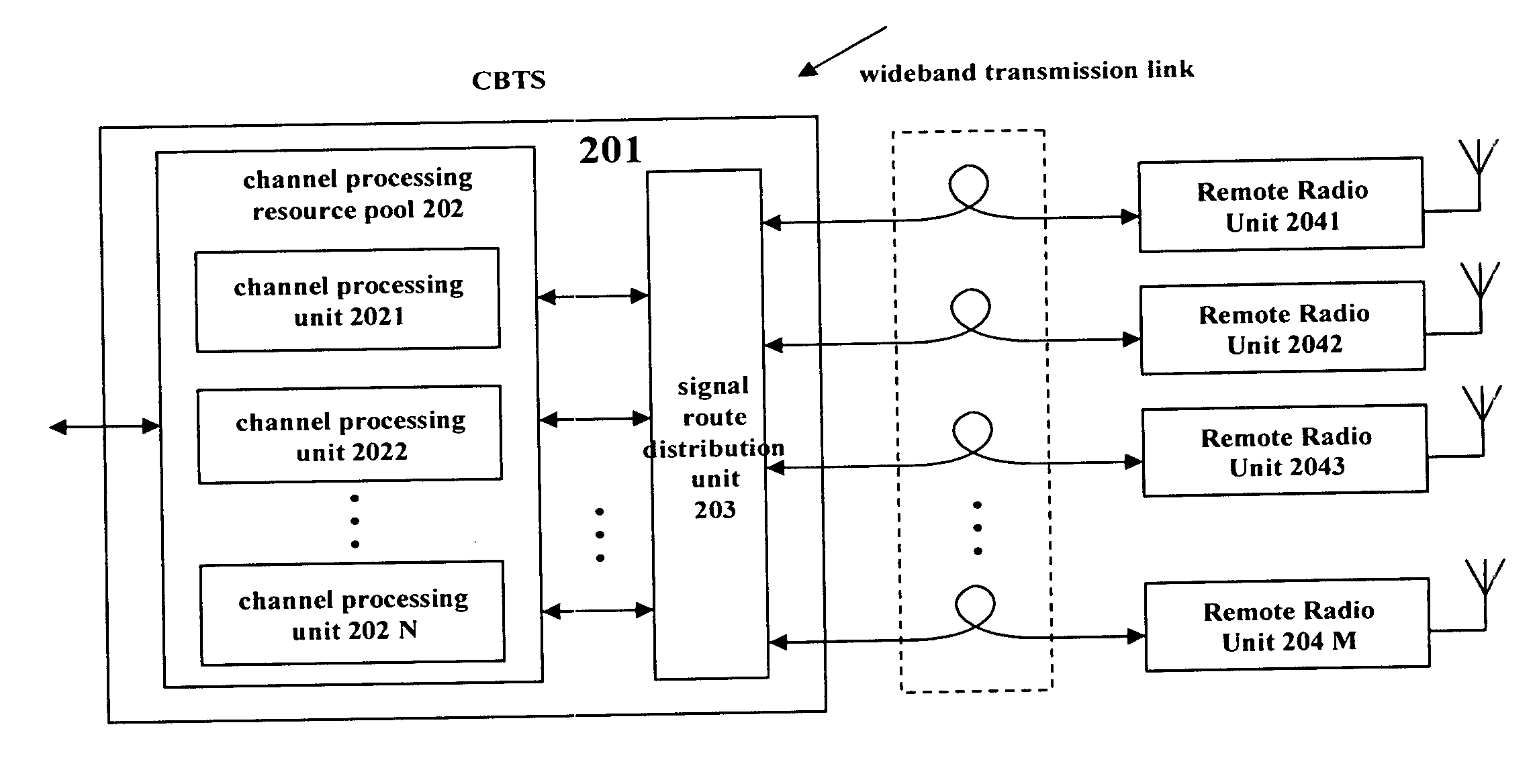
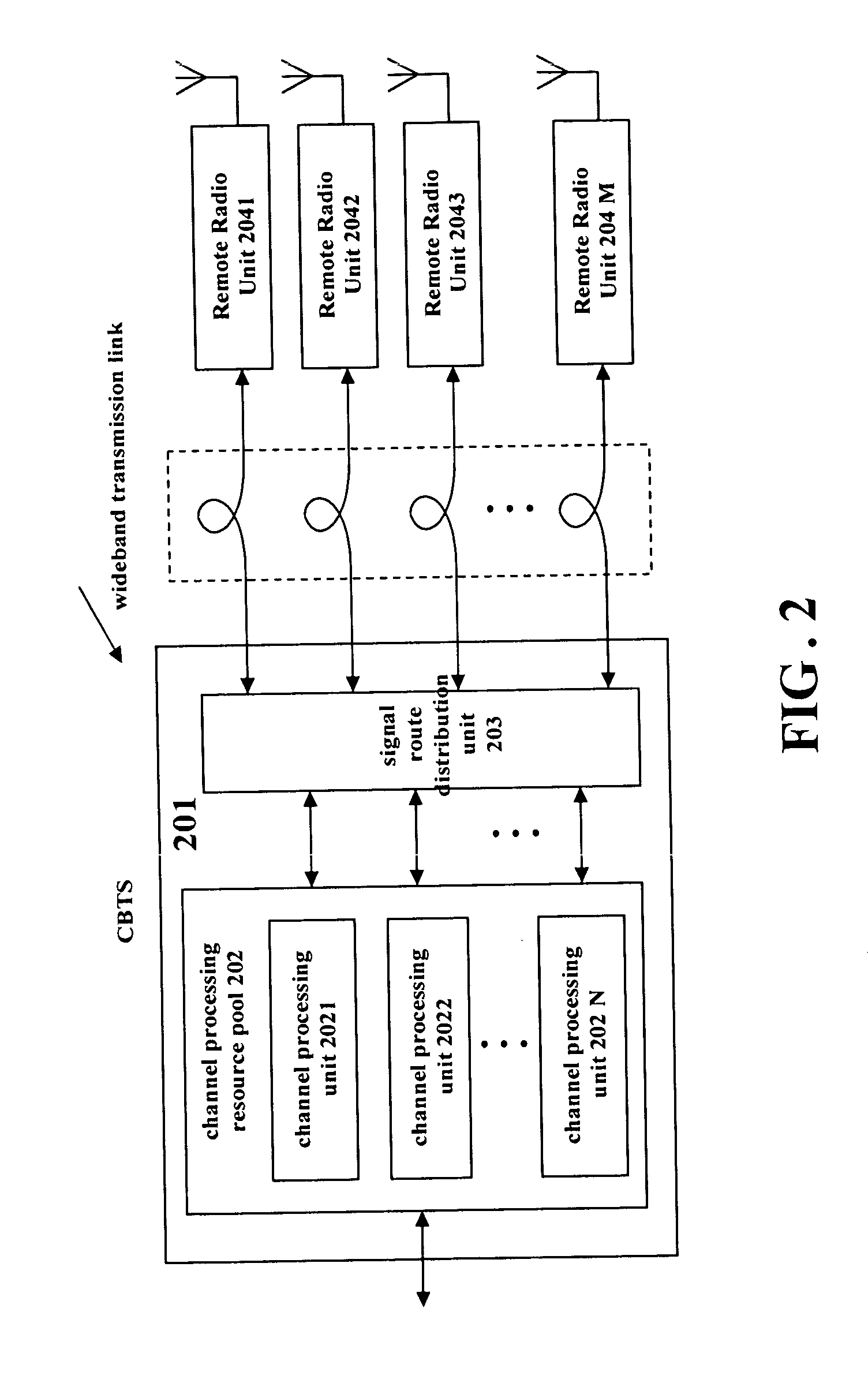
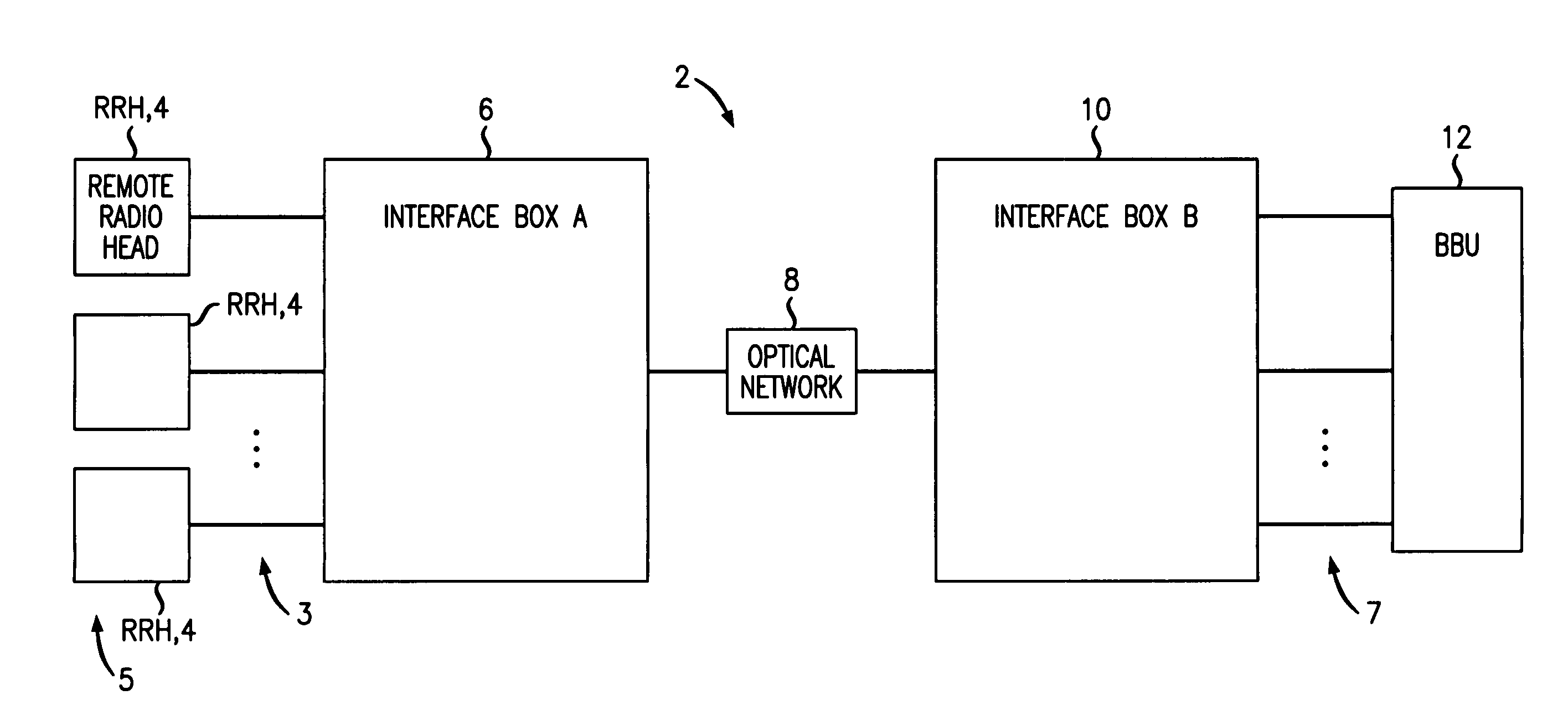
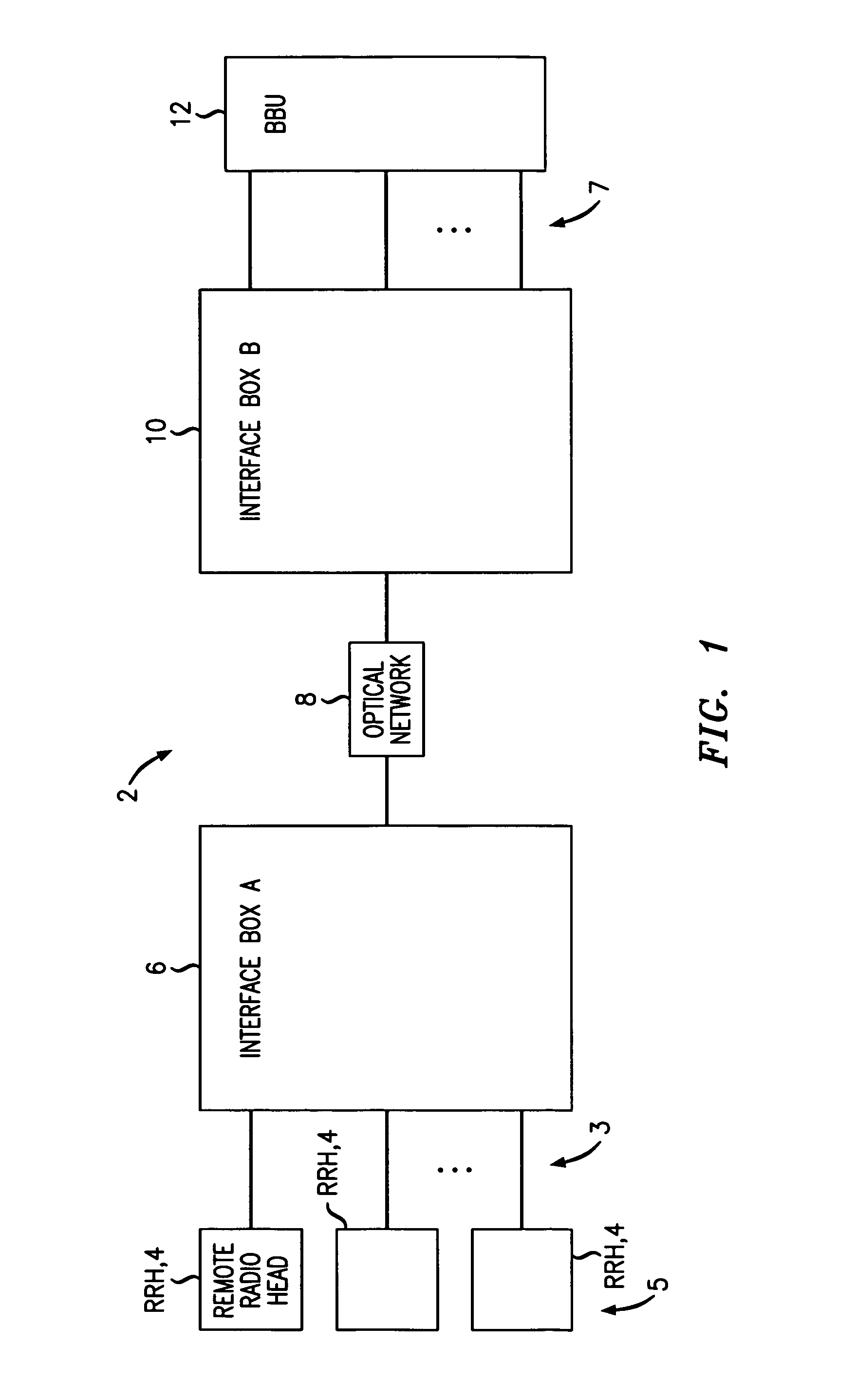
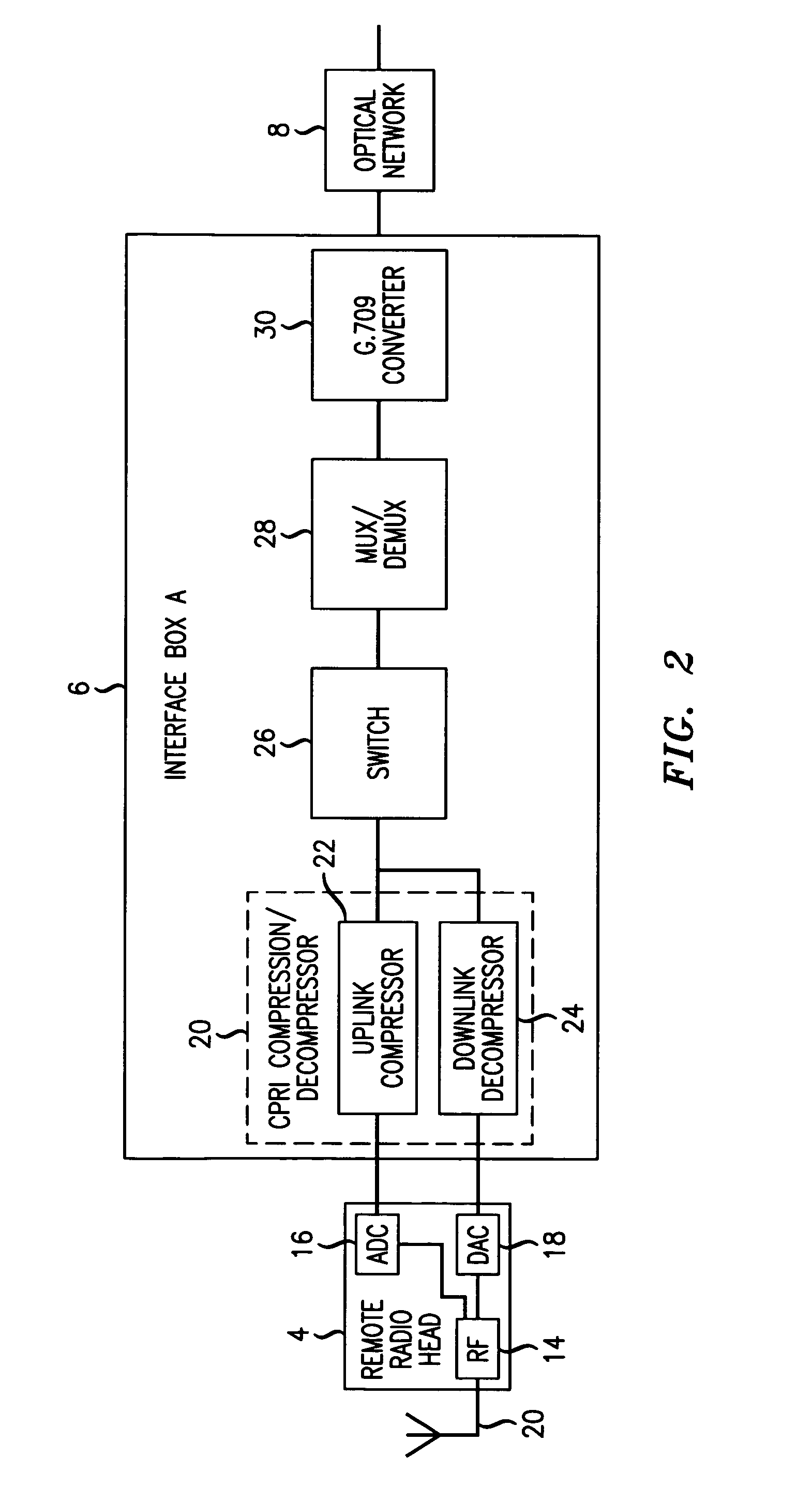
The invention relates to a method for transmitting a plurality of antenna signals in a wireless Base Transceiver Station (BTS) using Remote Radio Head (RRH) technology and the corresponding system. The method includes the steps of: transmitting signals over the transmit channel using Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) / Optical Transmission Network (OTN), multiplexing the plurality of antenna signals adopting the manners of time division multiplex or GFP frame-level multiplex; forming the multiplexed antenna signal stream and in-band control signaling stream into Generic Framing Procedure (GFP) frame; or forming the plurality of antenna signals and the plurality of respective control signals on the in-band control signaling channel into a plurality of respective GFP frames in parallel; and further mapping the GFP frames to STM-N / OTM-n frames, therefore multiplexing the plurality of antenna signals and the in-band control signaling stream to realize the SDH / OTN-based transmission. According to the invention, in the circumstance of using a plurality of antennas for transmitting signals, the strict time and phase relations between various antenna signals can be ensured, and also system complexity can be simplified, the transmission delays from various antenna signals to CBTS are totally the same.
Owner:UTSTARCOM TELECOM CO LTD +1
Digital subcarrier optical network utilizing digital subcarrier cross-connects with increased energy efficiency
ActiveUS20120269510A1Reduce power consumptionReduce energy consumptionEnergy efficient ICTModulated-carrier systemsFrequency spectrumSpectral efficiency
The present invention provides reduced power dissipation and other benefits at the optical transport network layer by utilizing a digital subcarrier optical network comprising multiple digital subcarrier cross-connect switches. This offers several advantages for optical networks, including spectral efficiency and robustness against signal corruption and consumption of less energy than traditional TDM-based electric switches (OTN / SONET / SDH).
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
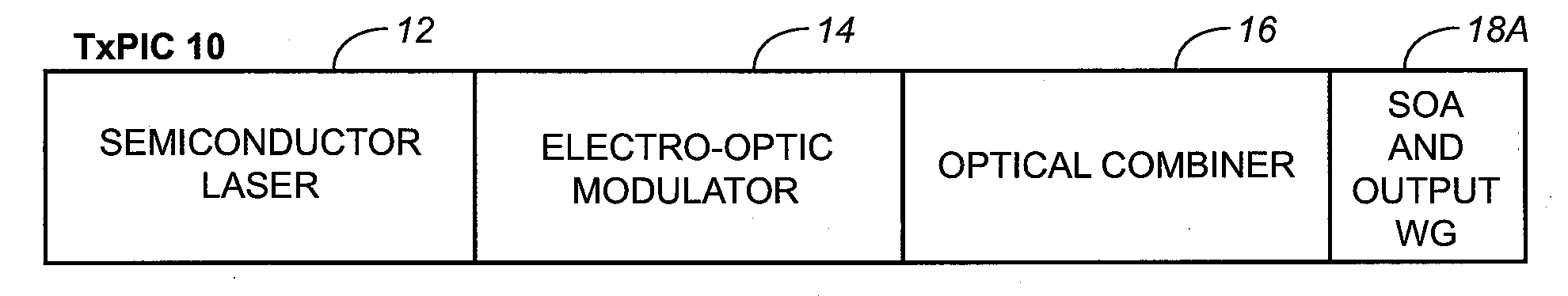
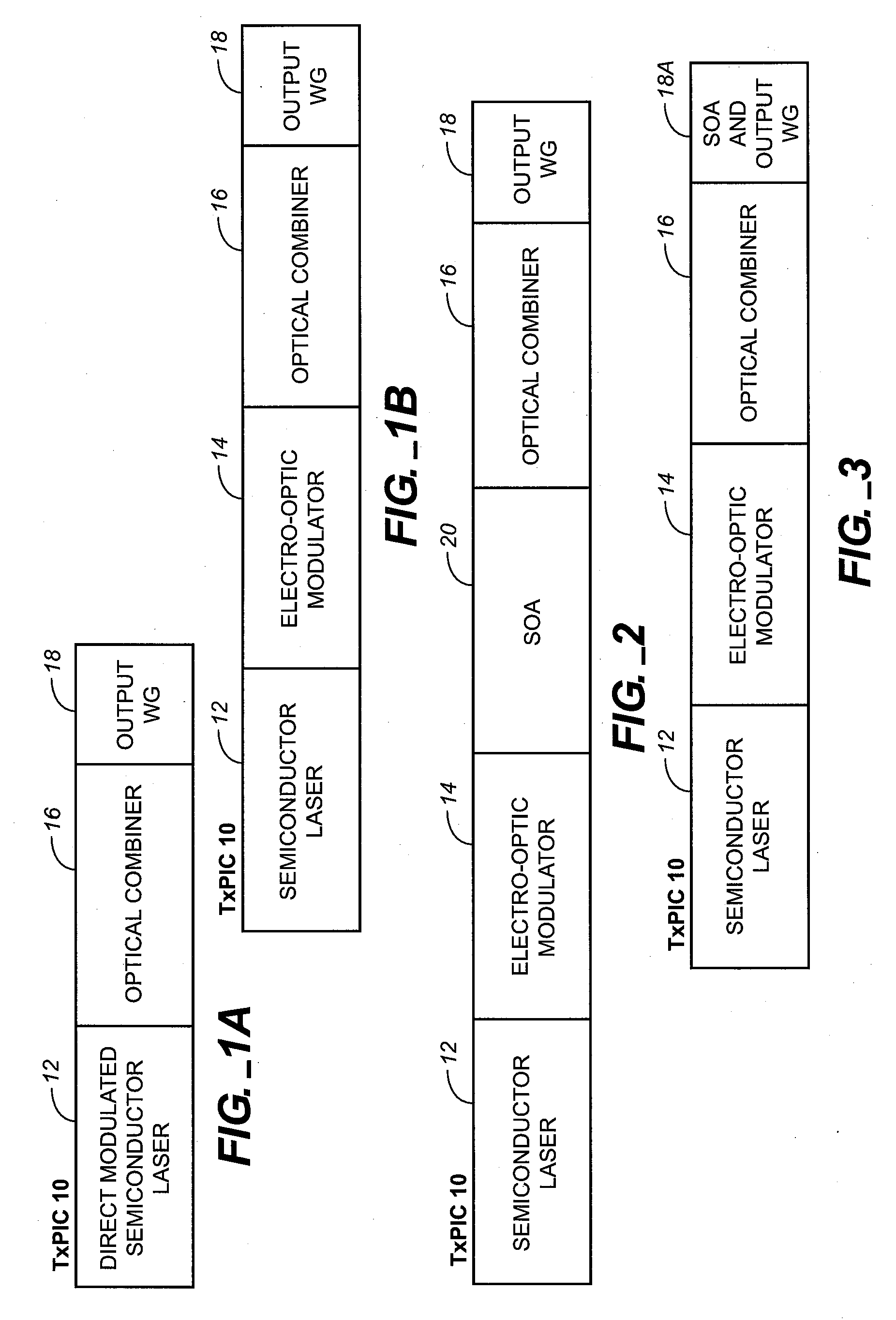
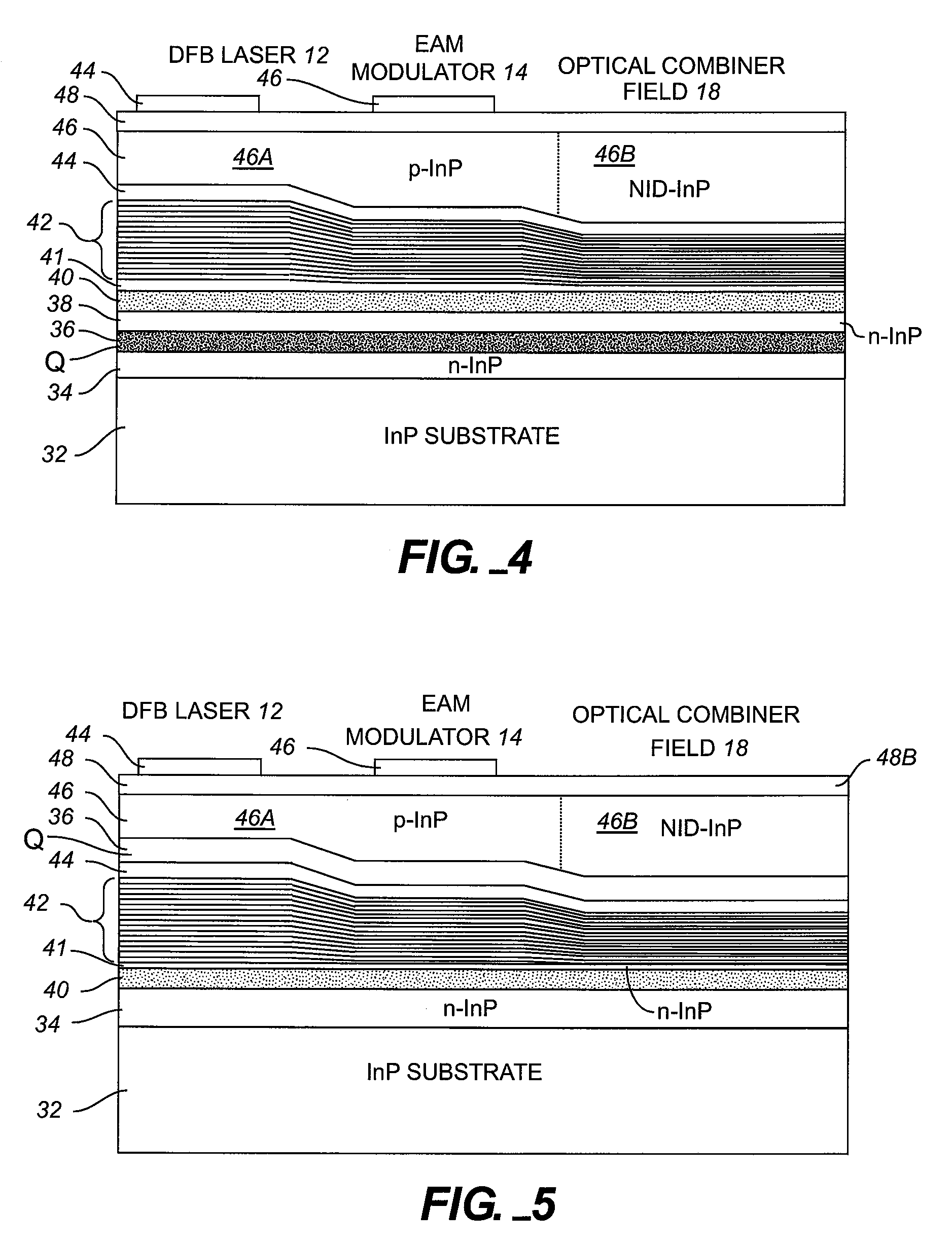
TRANSMITTER PHOTONIC INTEGRATED CIRCUITS (TxPICs) AND OPTICAL TRANSPORT NETWORK SYSTEM EMPLOYING TxPICs
InactiveUS20080044128A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical waveguide light guideSignal onOpto electronic
A photonic integrated circuit (PIC) chip comprising an array of modulated sources, each providing a modulated signal output at a channel wavelength different from the channel wavelength of other modulated sources and a wavelength selective combiner having an input optically coupled to received all the signal outputs from the modulated sources and provide a combined output signal on an output waveguide from the chip. The modulated sources, combiner and output waveguide are all integrated on the same chip.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Constrained interleaving for 5G wireless and optical transport networks
InactiveUS20160352419A1Increase data rateIncrease performance rateSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation multiplex systemsCommunications systemAlgorithm
The present invention provides a design framework that is used to develop new types of constrained turbo block convolutional (CTBC) codes that have higher performance than was previously attainable. The design framework is applied to design both random and deterministic constrained interleavers. Vectorizable deterministic constrained interleavers are developed and used to design parallel architectures for real time SISO decoding of CTBC codes. A new signal mapping technique called constrained interleaved coded modulation (CICM) is also developed. CICM is then used to develop rate matching, spatial modulation, and MIMO modulation subsystems to be used with CTBC codes and other types of codes. By way of example, embodiments are primarily provided for improved 5G LTE and optical transport network (OTN) communication systems. Detailed descriptions of embodiments are also provided that combine aspects of MIMO and spatial modulation systems to improve bandwidth efficiency. Such embodiments are applicable to multi-antenna and single antenna MIMO systems as well as multichannel systems, OFDM systems, and TDM systems.
Owner:FONSEKA JOHN P +1
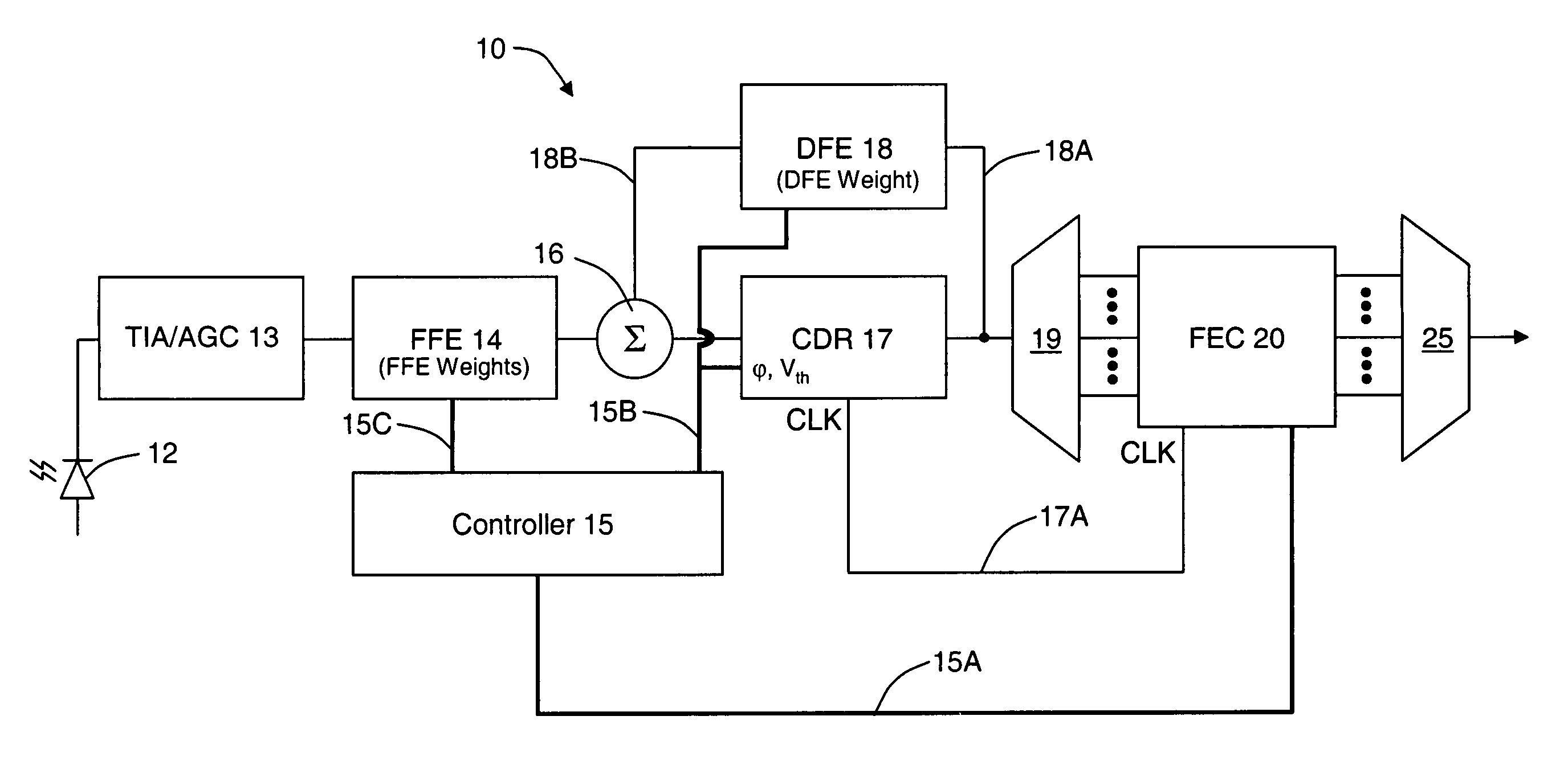
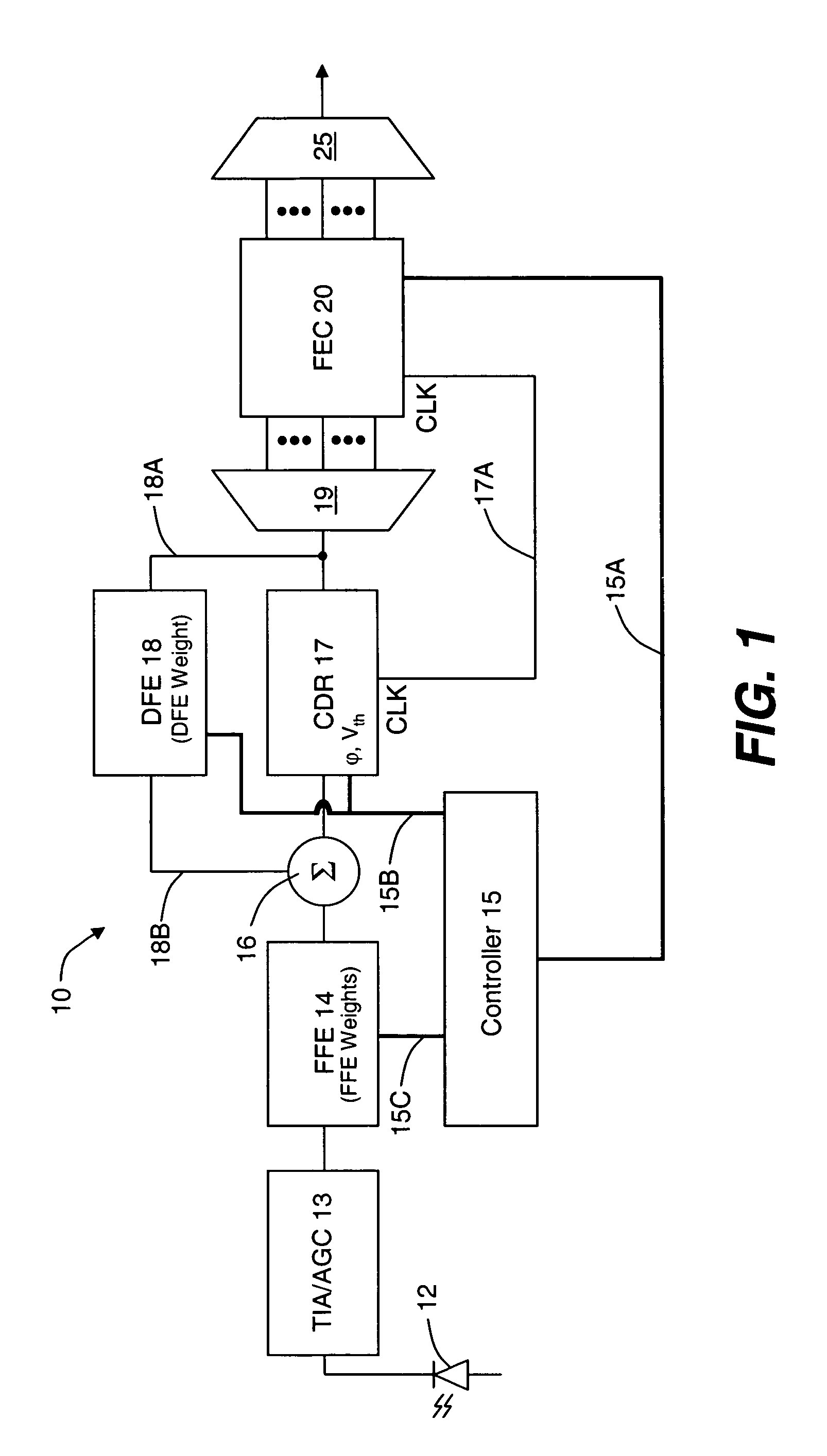
Pattern-dependent error counts for use in correcting operational parameters in an optical receiver
ActiveUS7574146B2Accurate methodReduce manufacturing costMultiple-port networksError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorWeight coefficientSemiconductor chip
An optical transmission network includes an optical transmitter photonic integrated circuit (TxPIC) chip, utilized in an optical transmitter and has a plurality of monolithic modulated sources integrated for multiple signal channels on the same semiconductor chip is provided with channel equalization at the optical receiver side of the network that permits one or more such integrated modulated sources in the TxPIC chip to be out of specification thereby increasing the chip yield and reducing manufacturing costs in the deployment of such TxPIC chips. FEC error counts at the FEC decoder on the optical receiver side of the network includes counters that accumulate a plurality of bit pattern-dependent error counts based on different N-bit patterns in the received data bit stream. The accumulated counts of different N-bit patterns are utilized to provide for corrections to threshold and phase relative to the bit eye pattern as well as provided for weight coefficients for the optical receiver equalization system. The deployment of this type of equalization in a digital OEO REGEN network substantially reduces, if not eliminates, the need for dispersion compensating fiber (DCF) or EDFAs in an optical link of the network and enhances the optical receiver tolerance to chromatic dispersion (CD) so that an increase in chip yield is realized for TxPIC chips not operating with acceptable operational parameters, particularly with a desired frequency chirp parameter relative to at least one of the TxPIC modulated sources.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Method for time slot partition and overhead processing of optical payload unit in light transmission network
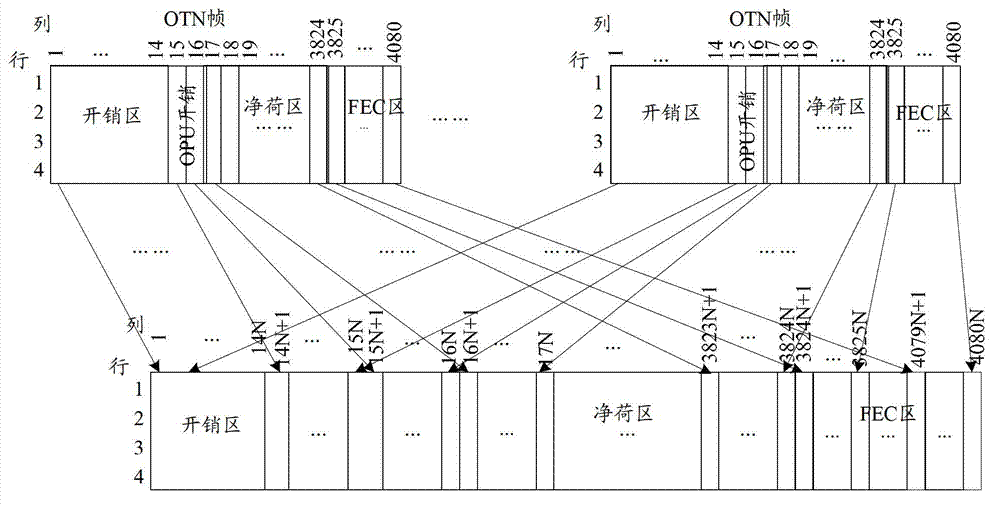
ActiveCN101155016AImprove effectivenessIncrease flexibilityError preventionTime-division multiplexMultiple frameComputer compatibility
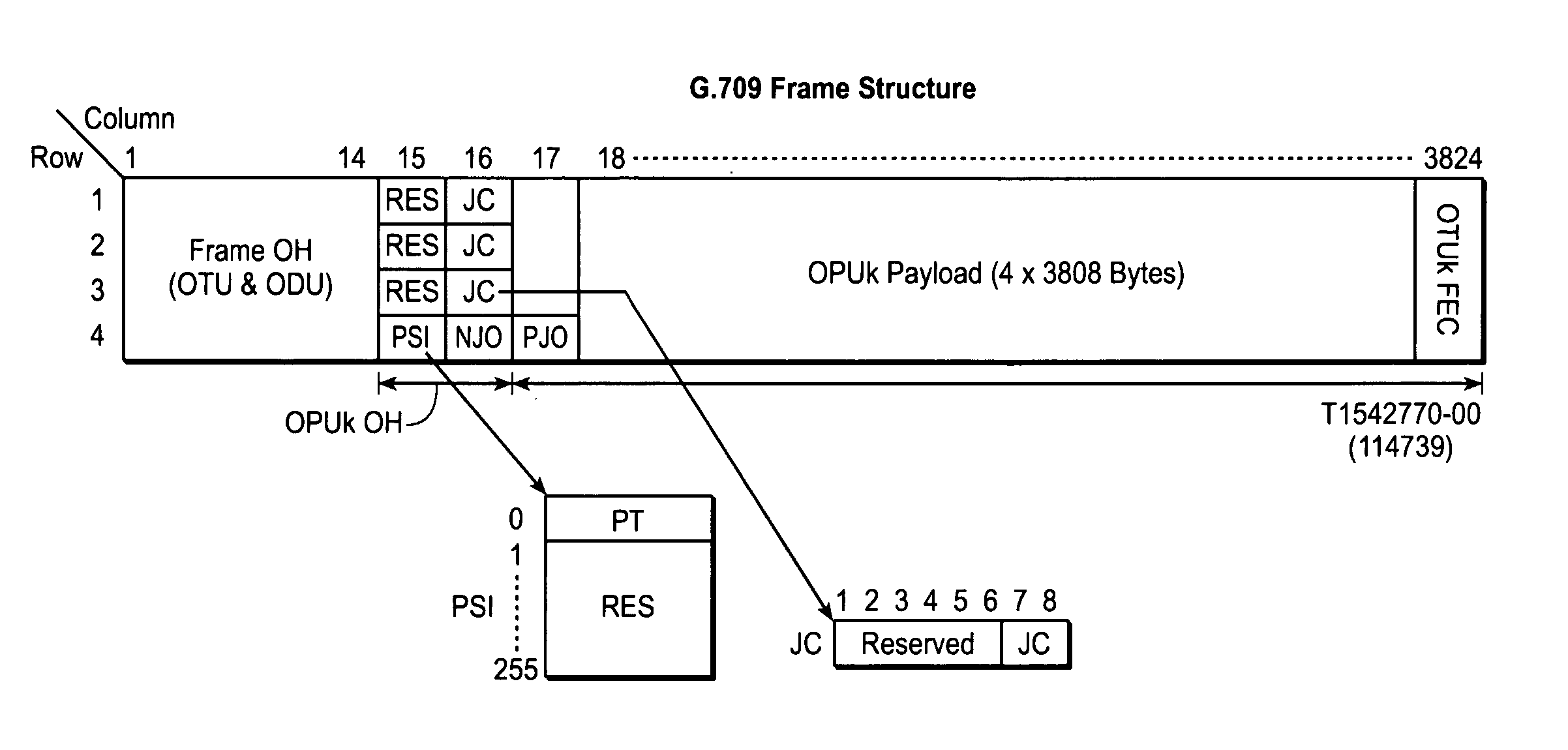
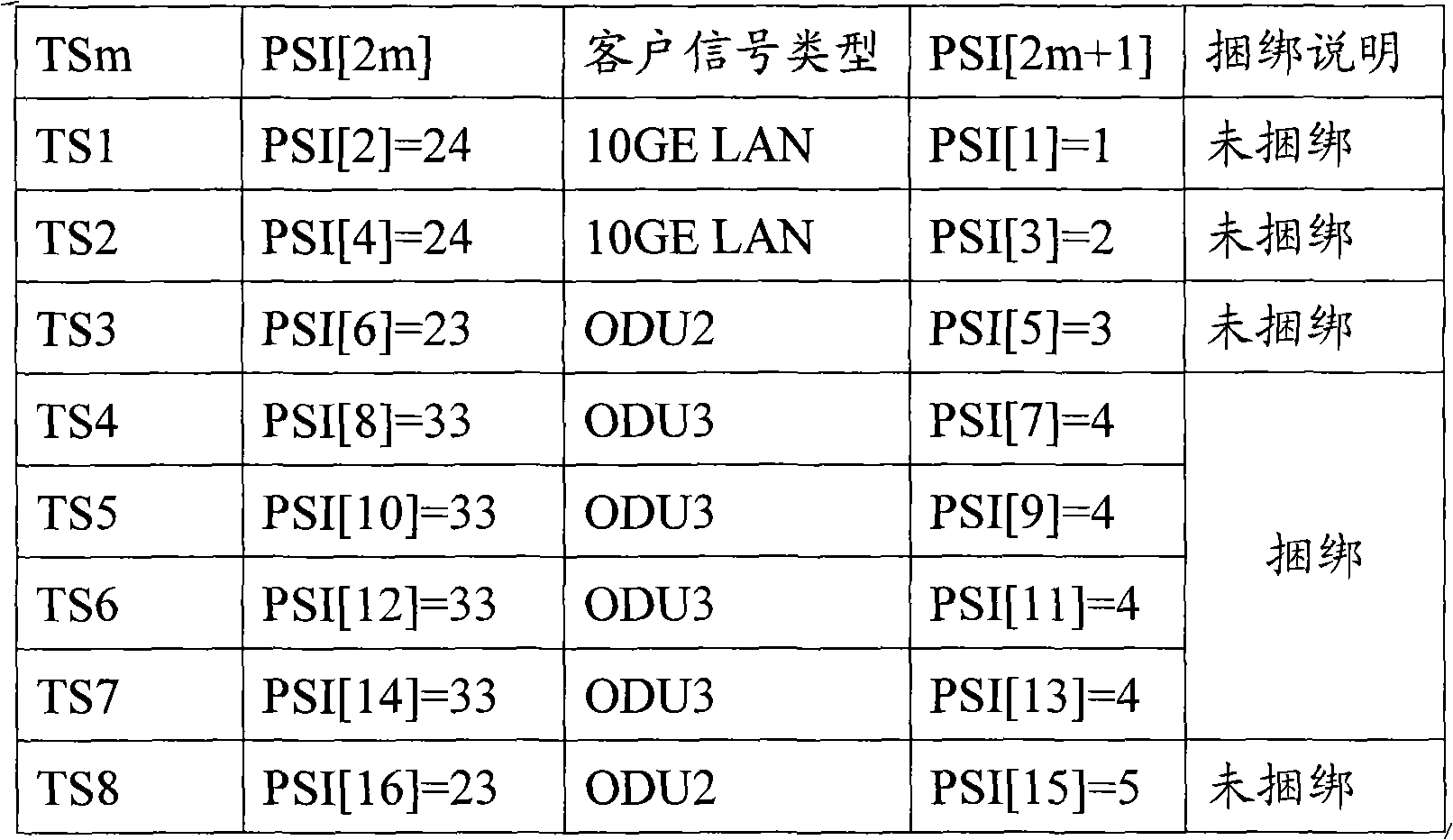
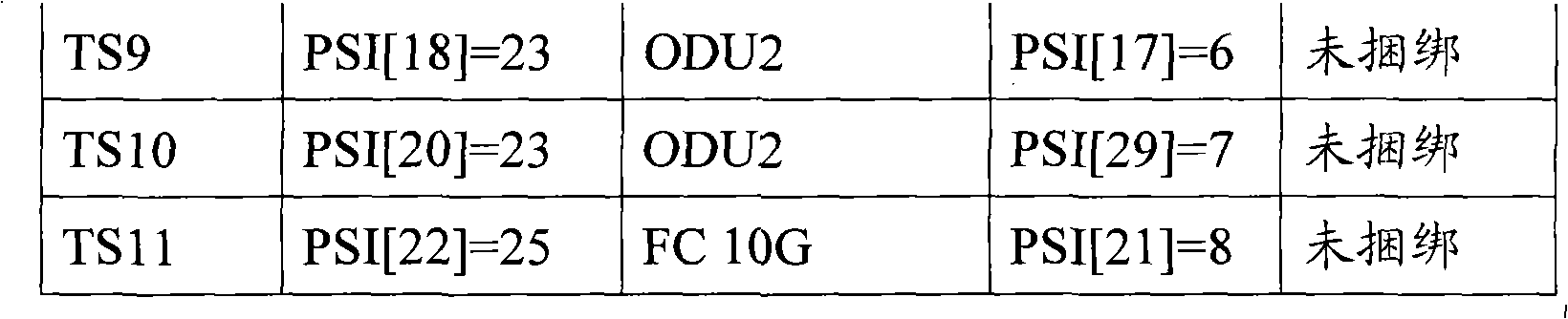
The present invention relates to a method for dividing the time slot and treating the spending of optical payload unit in the optical transport network, which comprises the steps of: A. confirming the time slot number of the optical payload unit in the payload area according to the character of the business signal, doing time slot division to the payload area and confirming the mapping mode of corresponding business of each time slot; B. expending the value of the payload structure identifying byte in the spending of the optical payload unit according to the dividing condition of the time slot, saving the mapping structure, time slot number, and the branch line port number and mapping mode corresponding to each time slot in the payload structure identifying byte; C. representing the undefined first to sixth bit assignment value as the multi-frame and distributing the spending loop spend by the optical payload unit in the spending of the optical payload unit. The invention increases the availability of band width and the flexibility of the mapping mode by redefining the spending byte in the original specification, increasing the relevant portion divided by the time slot with a low cost, and the invention has a better compatibility.
Owner:NANJING ZHONGXING XIN SOFTWARE CO LTD
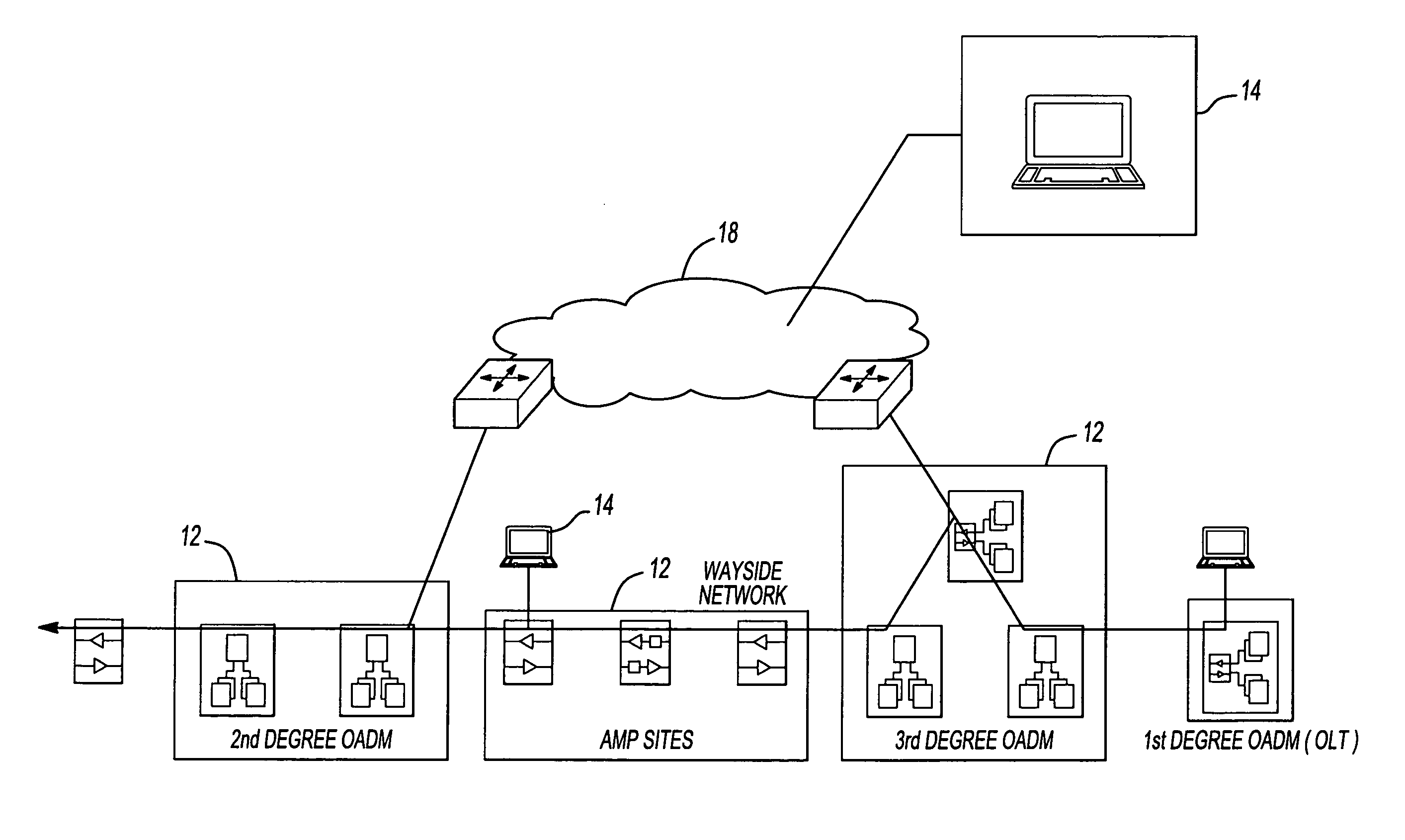
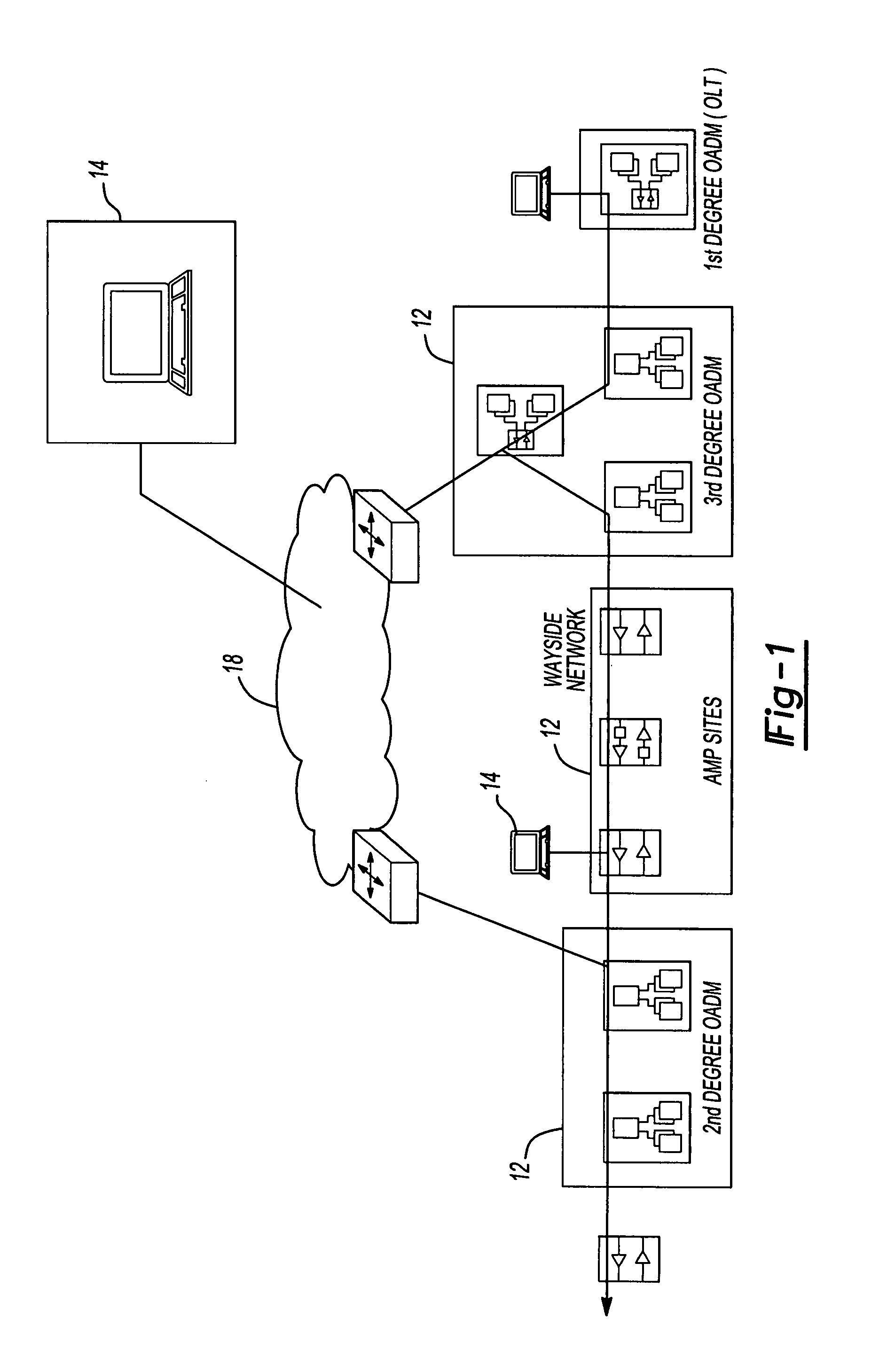
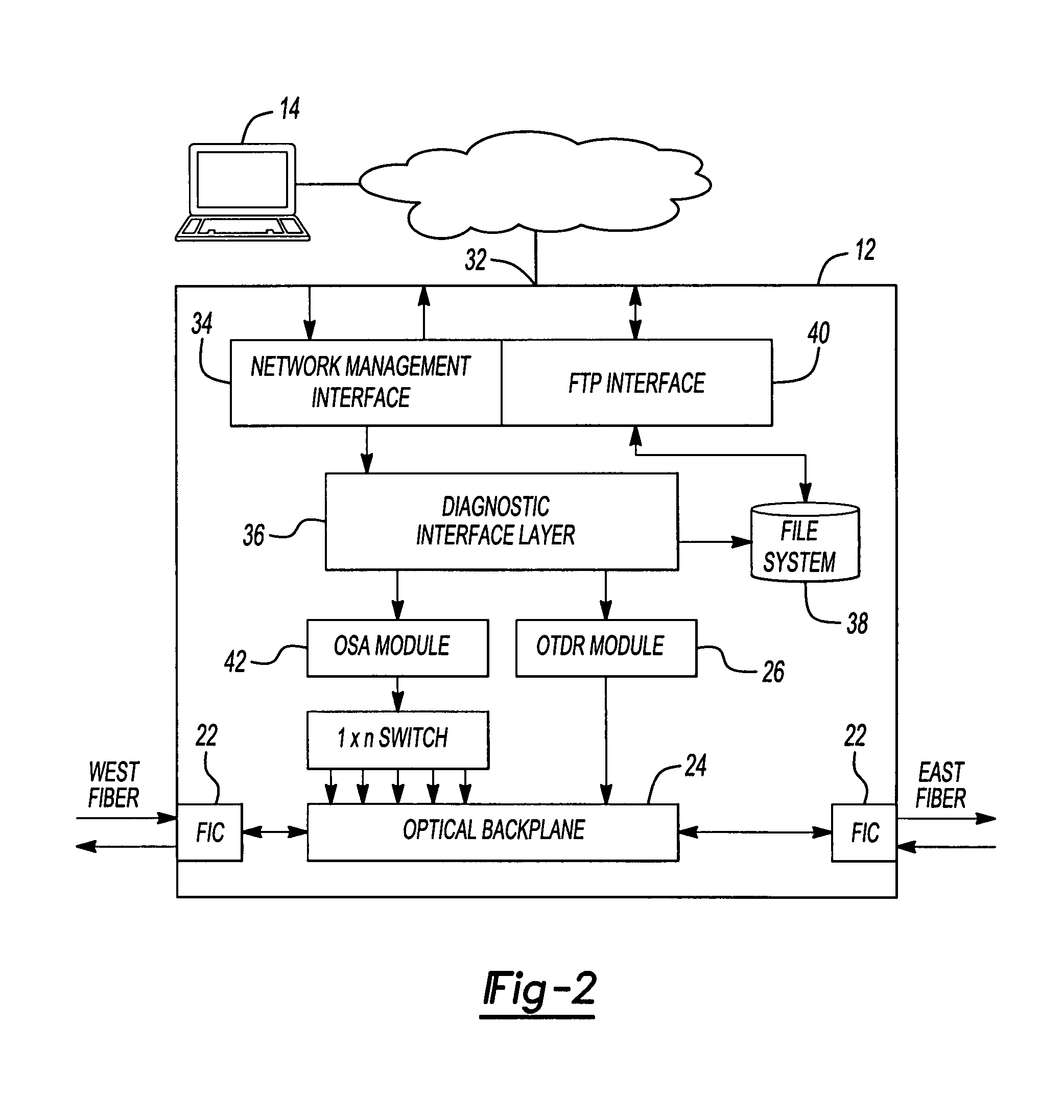
Network diagnostic tool for an optical transport network
InactiveUS7242862B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringEngineeringDiagnostic system
A network diagnostic system is provided for an optical transport network having a plurality of network elements. The network diagnostic system includes at least one network element having a network diagnostic operation integrated therein and operable to perform the network diagnostic operation, thereby determining a network performance characteristic associated with the optical transport network; a wayside communication subsystem interconnecting the network elements residing in the optical transport network; and a network diagnostic device in data communication with the at least one network element and operable to initiate the network diagnostic operation at the network element.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
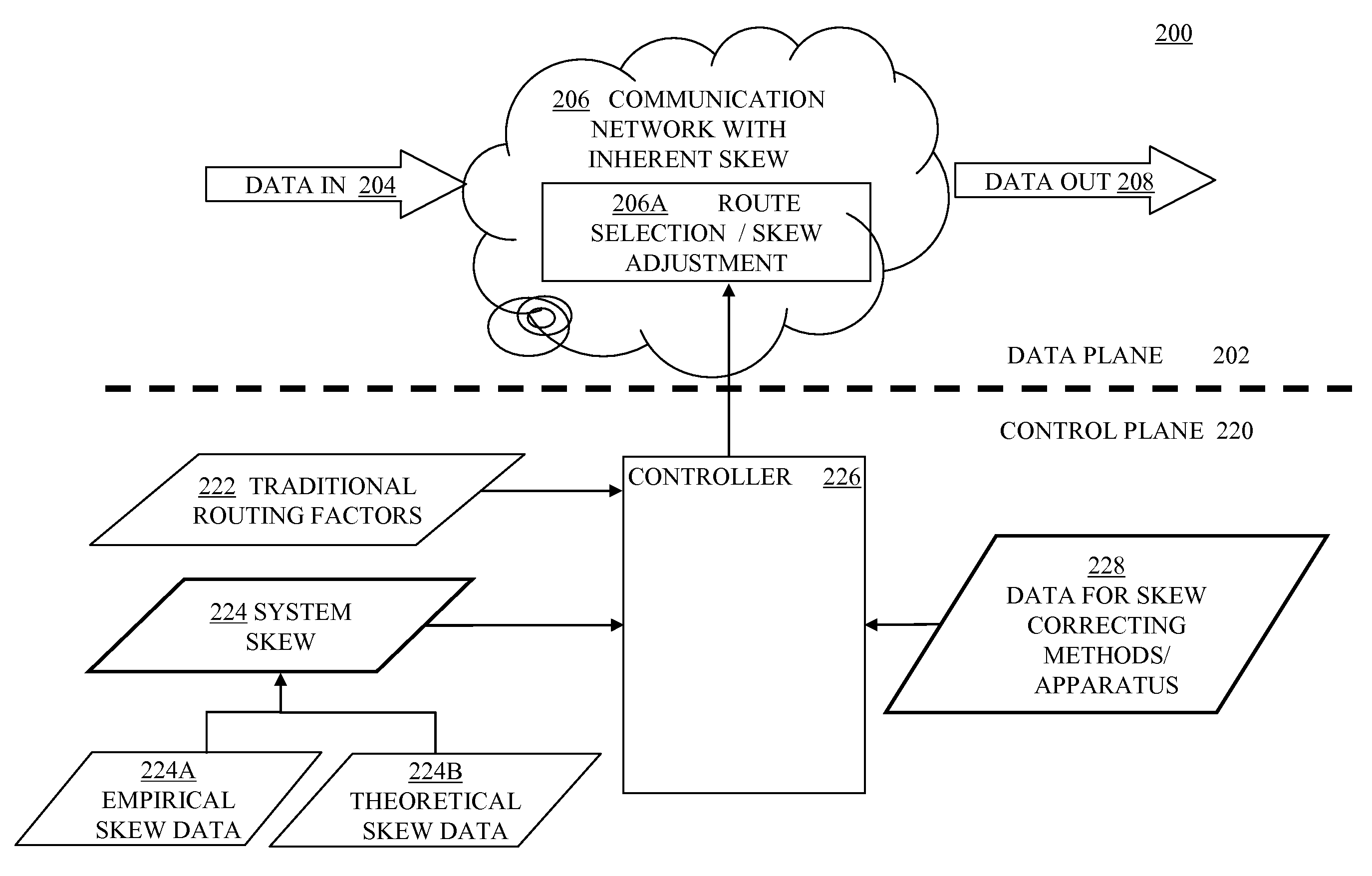
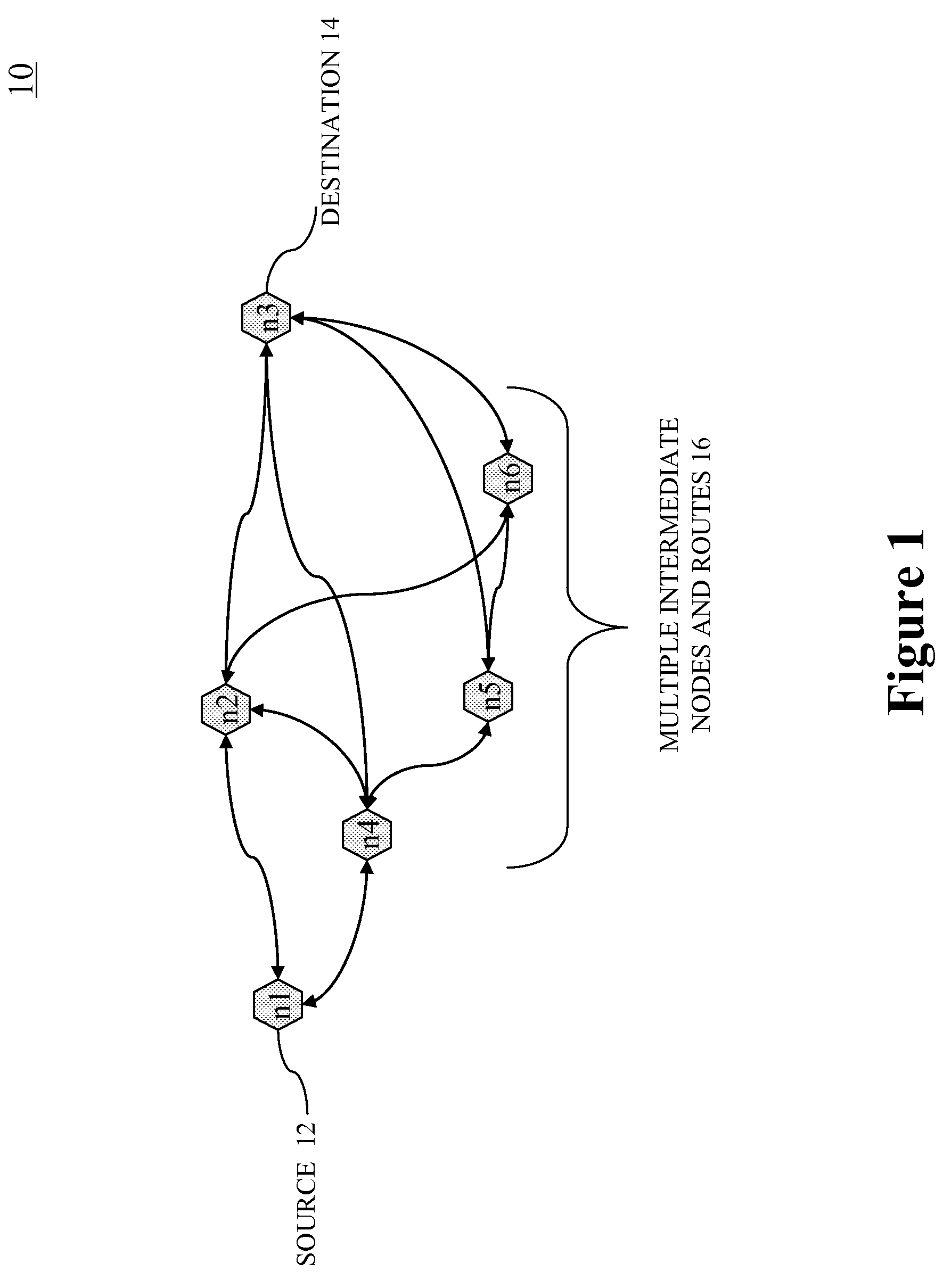
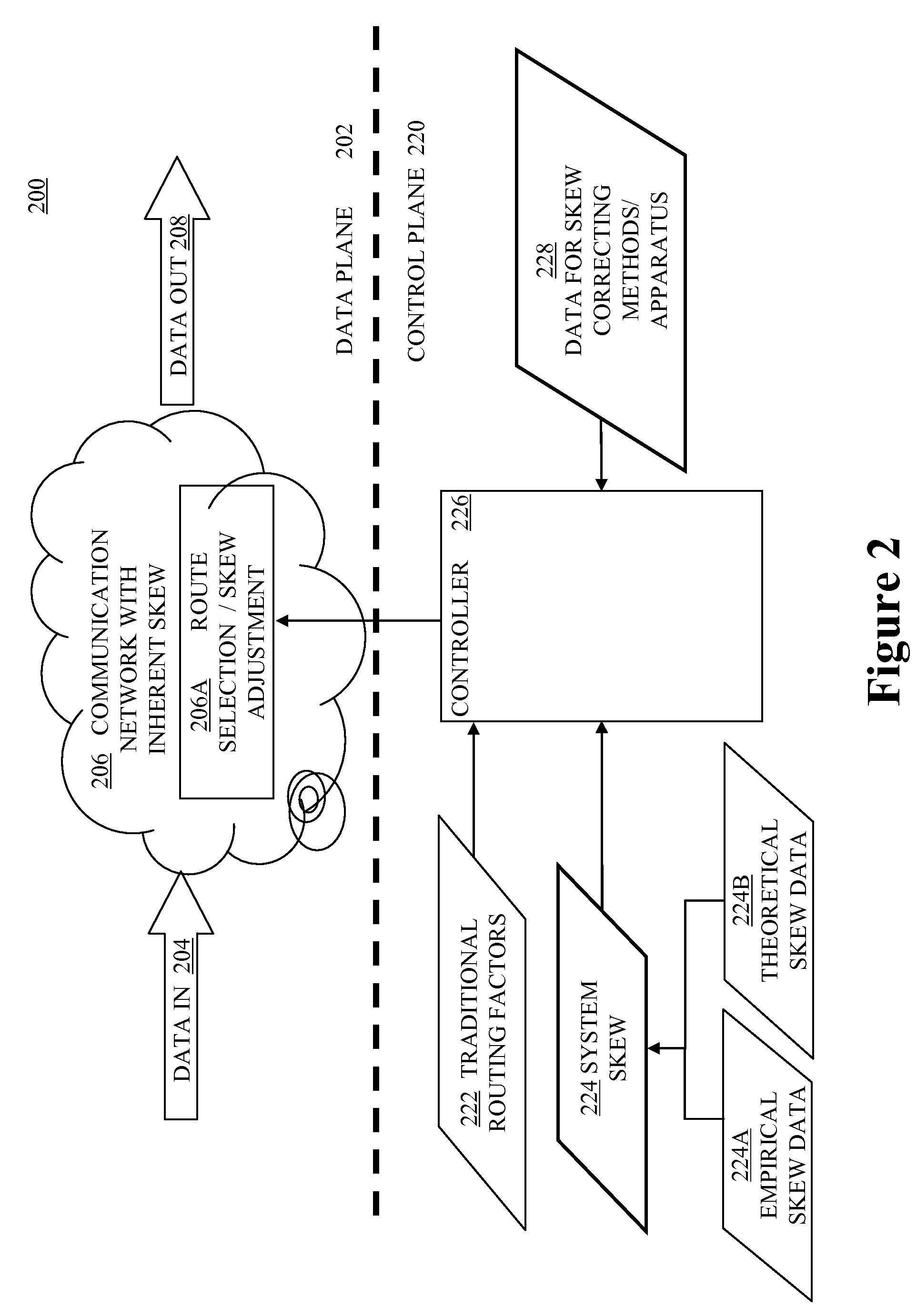
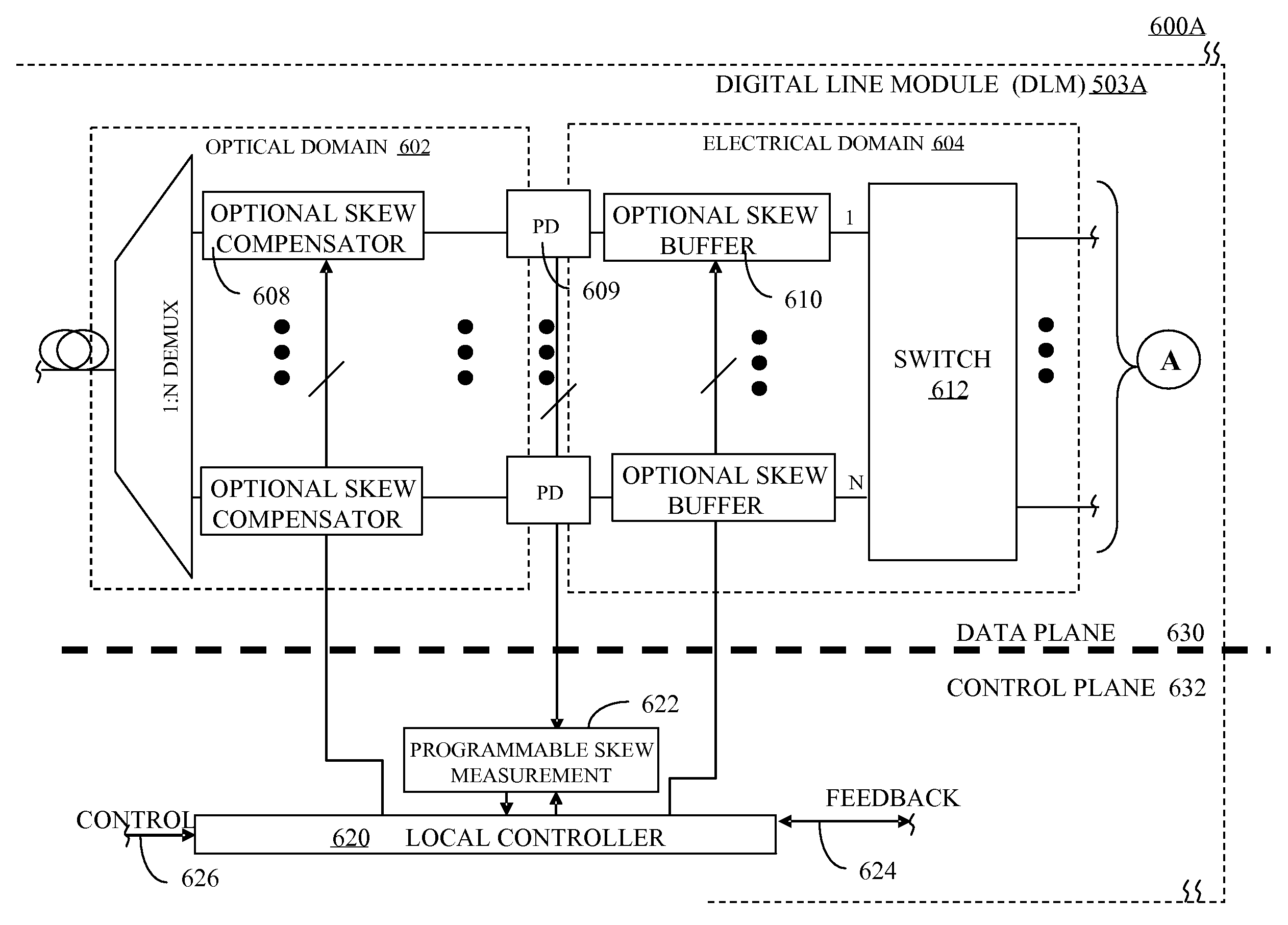
Communication Network with Skew Path Monitoring and Adjustment
ActiveUS20080175590A1Beneficial network operationGuaranteed uptimeWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionFiberCarrier signal
Embodiments of the present invention route a WDM signal across multiple communication paths using skew characteristics of at least some of the communication paths. The network is an optical transport network, using either circuit or packet based switching, and wavelength division multiplexed wavelengths and / or optical carrier groups (“OCGs”) over a fiber link to another node in the network. The plurality of communication paths involves different signal and path attributes such as a plurality of carrier wavelengths, optical carrier groups, physical communication paths (different nodes, different fibers along a same path, or any combination of the foregoing), or any other differentiating factors between two paths.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
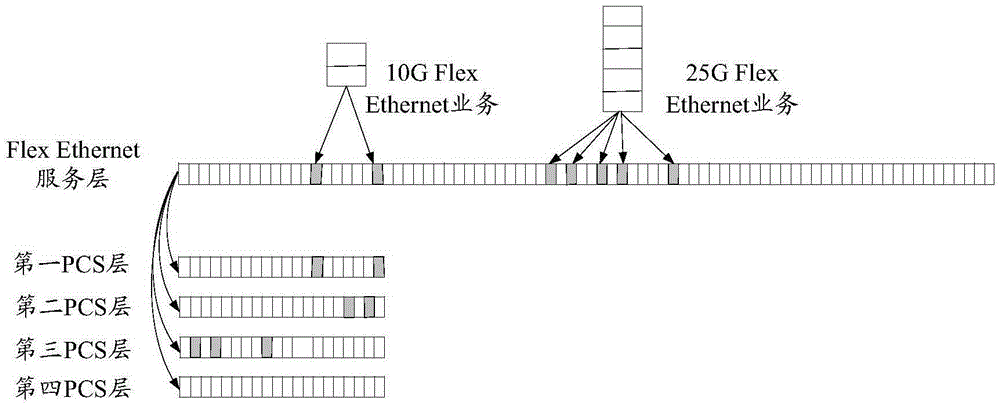
Flexible Ethernet business's optical transport network carrying method and apparatus
ActiveCN106788855AEasy to handleIncrease profitTime-division multiplexData switching networksChannel dataTransport network
The embodiments of the invention disclose a flexible Ethernet business's optical transport network carrying method and an apparatus wherein the method comprises: extracting a flexible Ethernet business from a flexible Ethernet service layer; performing data division to the flexible Ethernet business to obtain at least two data queues with each data queue carrying a queue identification; mapping each data queue to an optical transport network container which comprises an optical channel data unit k container or a flexible optical channel data unit container; and transporting the various optical transport network containers to the optical transport network. With the embodiments of the invention, the utilization efficiency of the band width could be raised and the optical transport network building cost is reduced.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
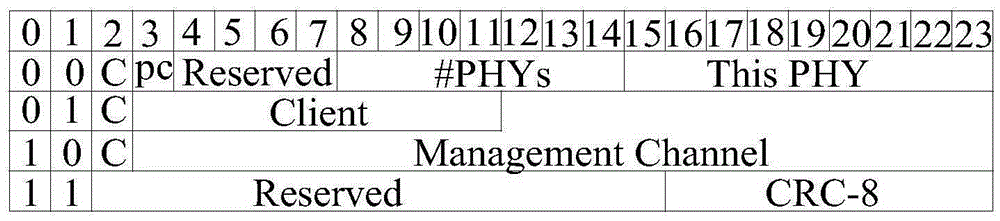
Method and apparatus for using stuffing bytes over a g.709 signal to carry multiple streams
Methods and apparatus for allowing containers in an optical transport network to be shared between users are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, a first network element that is a part of an optical transport network includes a frame generator and an output arrangement. The frame generator creates a frame with a fixed stuff area that includes a first set of bits that provide channel identification information, a second set of bits that provide justification information, and a third set of bits that indicate either or both payload type information and client signal fail information. The output arrangement places the frame within a container for transport through the optical transport network. The bandwidth of the container is arranged to be utilized by a plurality of network elements including the first network element.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Flexible ethernet and multi link gearbox mapping procedure to optical transport network
ActiveUS20160119075A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsTime-division multiplexTransport systemMulti link
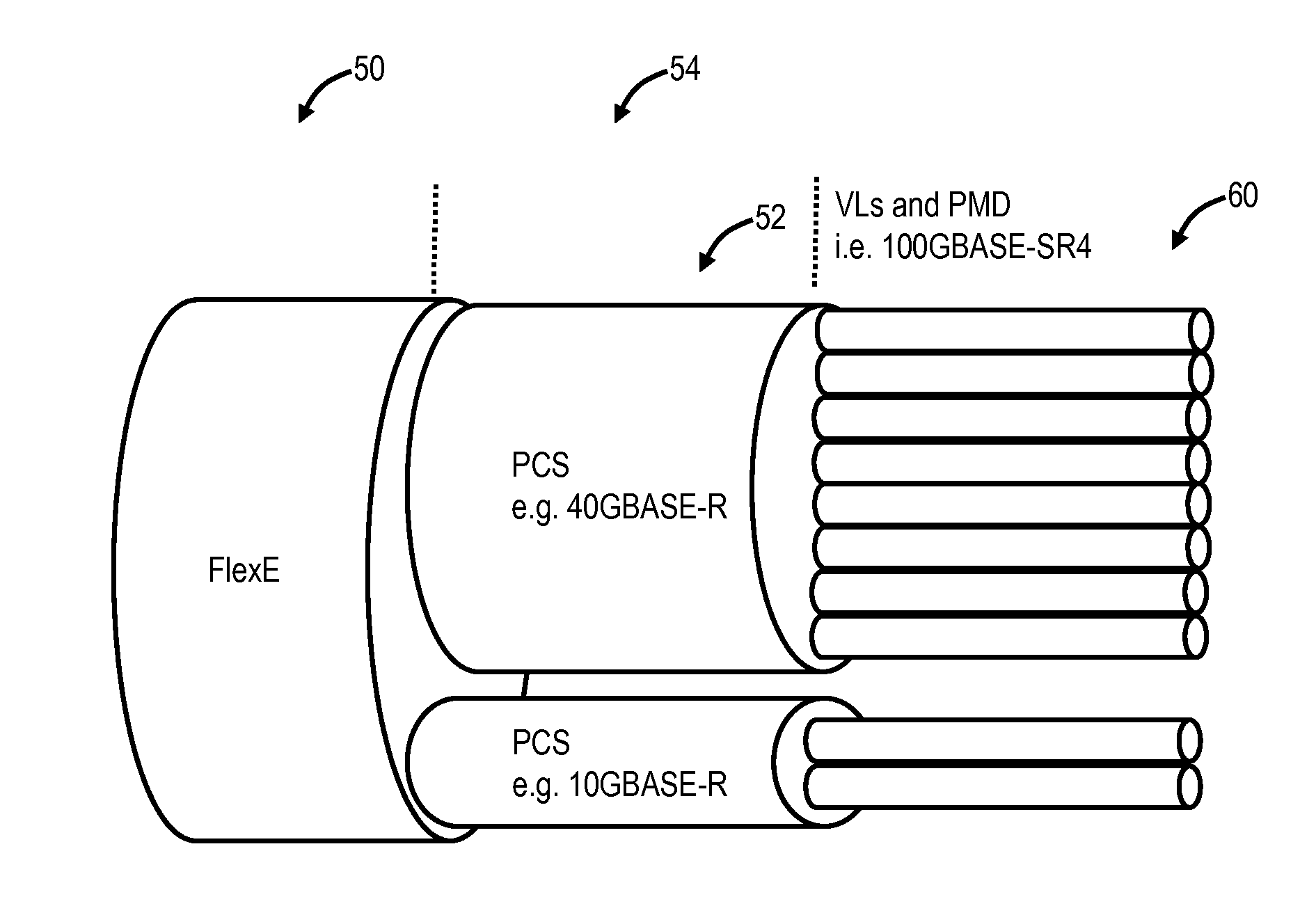
A flexible mapping method to map a Physical Coding Sublayer (PCS) structure from Flexible Ethernet and / or Multi Link Gearbox (MLG) to Optical Transport Network (OTN), includes receiving one or more Virtual Lanes; and mapping each of the one or more Virtual Lanes into a Tributary Slot, wherein a rate and number of the Tributary Slot(s) in OTN is set based on a rate and number of the one or more Virtual Lanes. A transport system and a flexible de-mapping method are also described. The systems and methods map the generalized MLG-style group of lanes (virtual PHYs / PMDs) into an OPUflex Tributary Slot (TS) structure, keeping PCS structures intact, and creates a single ODUflex container with a matching rate of FlexE for end-to-end flow.
Owner:CIENA
A method of processing a digital signal for transmission, a method of processing an optical data unit upon reception, and a network element for a telecommunications network
InactiveUS20140355991A1Conducive to poolingWavelength-division multiplex systemsTime-division multiplexDigital dataTelecommunications link
A method of processing a digital signal for transmission is provided comprising digital data frames, by compressing the digital data frames; and generating an optical data unit for transmission comprising multiple of the compressed digital data frames. The optical data unit is configured for transport by an Optical Transport Network, OTN.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Customer signal transmission method in optical transmitting network and related equipment
ActiveCN101291179AIncrease profitImprove flexibility and adaptabilityError preventionTime-division multiplexChannel dataComputer network
The embodiment of the invention provides a client signal transmission method in an optical transport network and relevant equipment, wherein the embodiment of the method comprises the steps of: obtaining the client signal and mapping the client signal to a tributary unit which is preset in the payload area of the optical-channel payload unit OPUk; respectively marking the corresponding tributary unit of each client signal; marking the tributary unit number of the payload area of the OPUk; marking the type of the mapped client signal in the tributary unit; and sending the optical-channel data unit ODUk including OPUk to the OTN network. The embodiment of the invention is capable of establishing transmission channels suitable for client signal rate, thereby improving the utilization ratio of the transmission channels in the process of the CBR transparent transmission and strengthening the flexible adaptability of the OTN equipment to the access service.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and Node Apparatus for Traffic Protection in Optical Transport Network
ActiveUS20070292129A1Improve transmission reliabilitySimplify network configurationLaser detailsTime-division multiplexFiberEngineering
Disclosed is a method and node apparatus for traffic protection of Optical Transport Network (OTN), including: setting a part of channels in one fiber as working channels used for carrying traffic in need of protection, and setting a part of channels in the other fiber with a reverse transmission direction as protection channels, the number of which is equal to that of the working channels, to form a one-to-one protection for the working channels; when a failure in an optical line of OTN is detected, determining a bridging node and a switching node in accordance with pre-designated protection strategy, bridging and switching the traffic to be transmitted through the failed optical line between the working channels and the protection channels at the determined bridging node and switching node. This invention can realize OTN protection based on two-fiber OMS shared protection ring, and improve the transmission reliability of optical networks.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and device for transmitting and receiving client signal in optical transport network
ActiveCN102820951AEasy to configureError preventionTime-division multiplexFrequency spectrumReference rate
The inventive embodiment provides a method and a device for transmitting and receiving a client signal in optical transport network, belonging to the field of optical transport network. The transmitting method comprises: mapping the received client signal to a container OTU-N with a variable rate, which is N times the preset reference rate grade, wherein N is a configurable positive integer according to requirement; dividing the container OTU-N with the variable rate into N photon channel transmission units OTUsub according to columns, the rate of each OTUsub being equal to the reference rate grade; modulating the N photon channel transmission units OTUsub to a one-channel or multi-channel optical carrier; and transmitting the one-channel or multi-channel optical carriers on the same optical fiber. The method provided by the invention is adaptive to the change in spectral bandwidth of an optical layer by mapping the client signal to the container OTU-N with the variable rate and by transmitting the OTU-N through the same optical fiber, thereby realizing optimized configuration of the bandwidth resources of the optical transport network.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Externally synchronized optical transport network systems and associated methods
ActiveUS20070116061A1Less jitterLess wander build-upTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationExternal referenceNoise margin
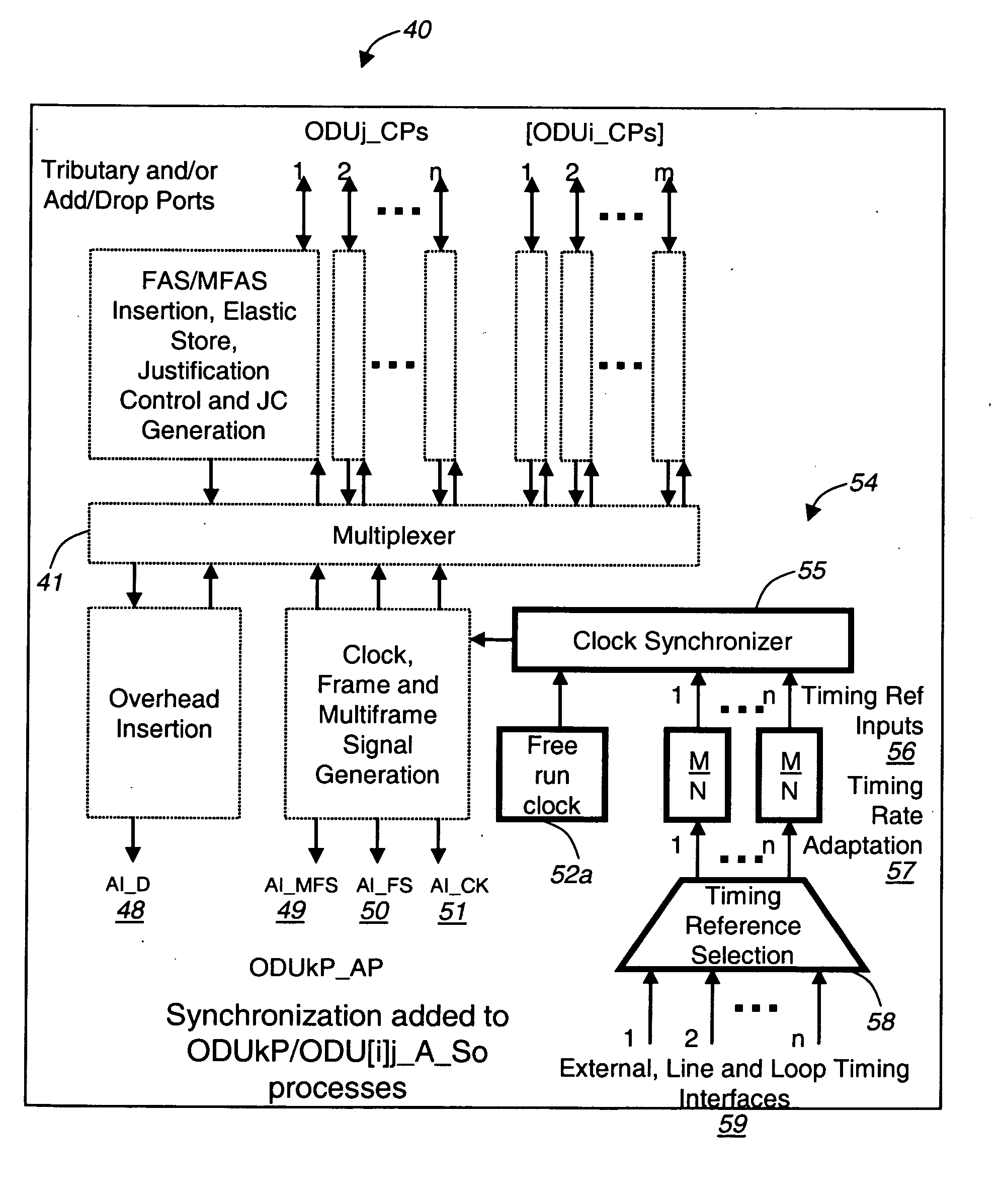
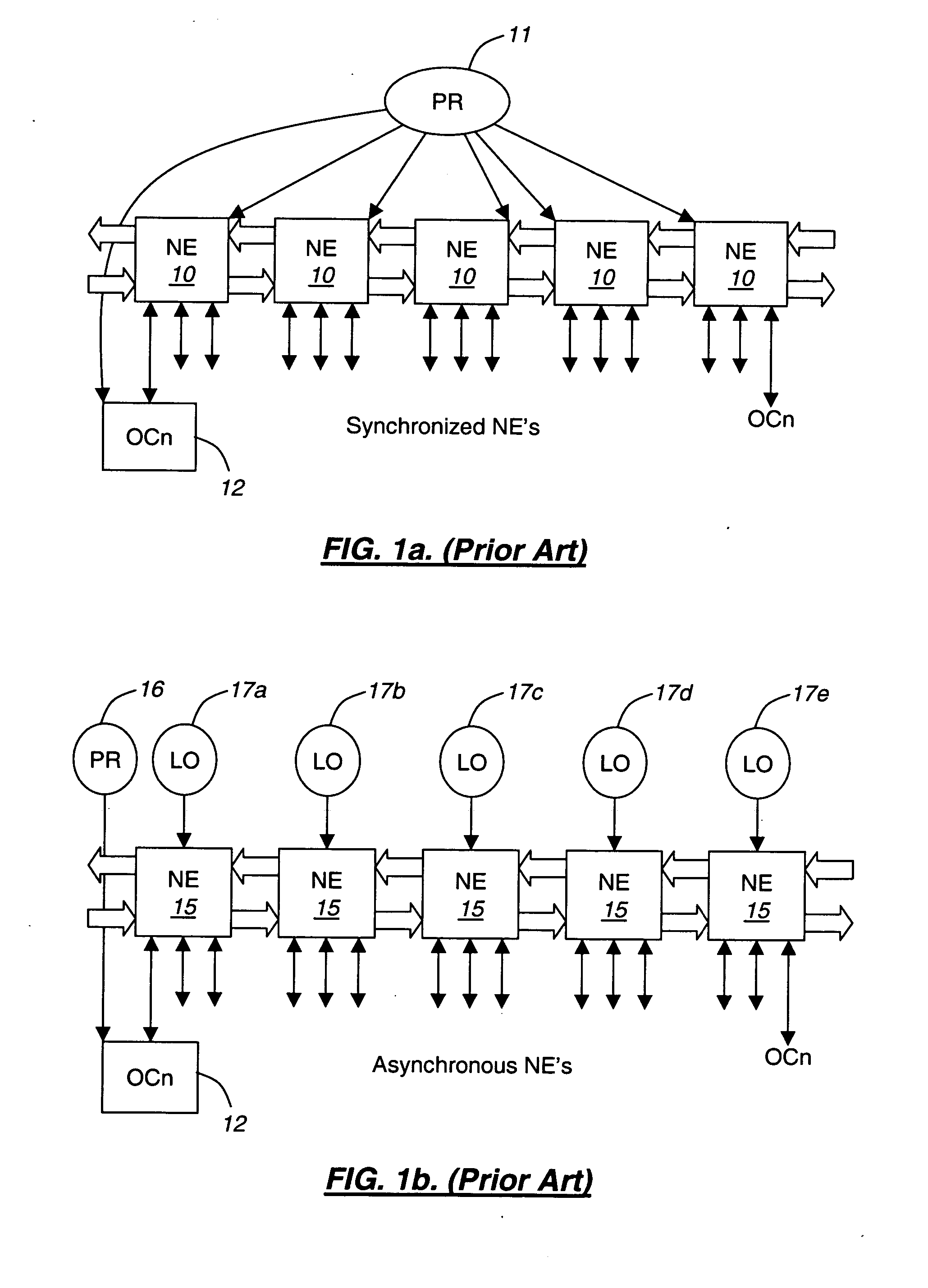
The present invention utilizes external synchronization to generate a completely standardized or functionally standardized optical transmission unit of level k (OTUk[V]) signal providing less jitter and wander build-up through a network of optical transport network (OTN) elements. This increases noise margins of transported signals and payloads. The present invention provides stratum-level synchronization utilizing a standards-based approach. In one embodiment of the present invention, rate adapters are included to provide m / n scaling of OTUk[V] signals to rates common in SONET and SDH synchronizers to provide line and loop distribution of timing through OTUk[V] signals. The present invention provides a choice of external synchronization sources including building integrated timing source (BITS), line, and loop timing sources. In another exemplary embodiment, the present invention provides multiple external references and automated timing protection switching for redundancy and reliability.
Owner:CIENA
Communication Network with Skew Compensation
Embodiments of the present invention compensate for skew across a wavelength division multiplexed network. The network is a wavelength division multiplexed optical transport network. The skew compensation can be performed electrically or optically. It can be performed on the transmission side of the network, the receiver side of the network or at any intermediary node on the network.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Spectral plane method and apparatus for wavelength-selective optical switching
We describe a variable bandwidth tunable optical spectral filtering device and associated method for selectively directing a portion of a wavelength multiplexed input signal, entering through one or more optical fibers, into one or more output signals provided to one or more optical fibers and / or electronic outputs. The optical filtering is accomplished using free-space diffractive wavelength de-multiplexing optics combined with a fixed (permanent) patterned structure located in the spectrally dispersed image plane. The structure can direct a selected spectral portion of the optical signal to one or more separate outputs, such as an optical fiber or power detector. A single active element in the optical path is used to spatially shift, or steer, the entire input spectrum at the dispersed spectral image plane, to control the portion of the input spectrum illuminating specific features on the permanent patterned structure. In one preferred embodiment, a device with a fixed selective area triangular shaped tilted reflective facet on a flat reflective surface is constructed such that the light reflected off the flat reflective surface and off the triangular reflective facet are selectively multiplexed back and directed to different output fiber ports. Inputs at different angles of incidence on the reflective structures may be deflected by the same structures to different output port fiber ports. A reconfigurable variable-bandwidth tunable optical add / drop multiplexing device is constructed using such a filtering device and an application of such an add / drop multiplexing in a optical transport network is demonstrated.
Owner:WILSON GORDON +1
Optical network system
InactiveUS20080080860A1Reduced resourceEasy to operateWavelength-division multiplex systemsTime-division multiplexMultiplexingLength wave
An optical transponder includes a mapping unit mapping, out of multiple types of signals including a first client signal and a second client signal that transmission rates are different from each other, the first client signal having a lower transmission rate to a Generic Framing Procedure (GFP) frame defined in ITU-T Recommendations; a coding unit applying 64B / 66B coding to the first client signal mapped to the GFP frame; and a multiplexing unit multiplexing the first client signal to which the 64B / 66B coding has been applied and the second client signal in a frame conforming to an Optical Transport Network (OTN) defined in ITU-T Recommendations; in which the first client signal and the second client signal are accommodated in an identical frame in a mixed manner and transmitted as an optical signal having one wavelength.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
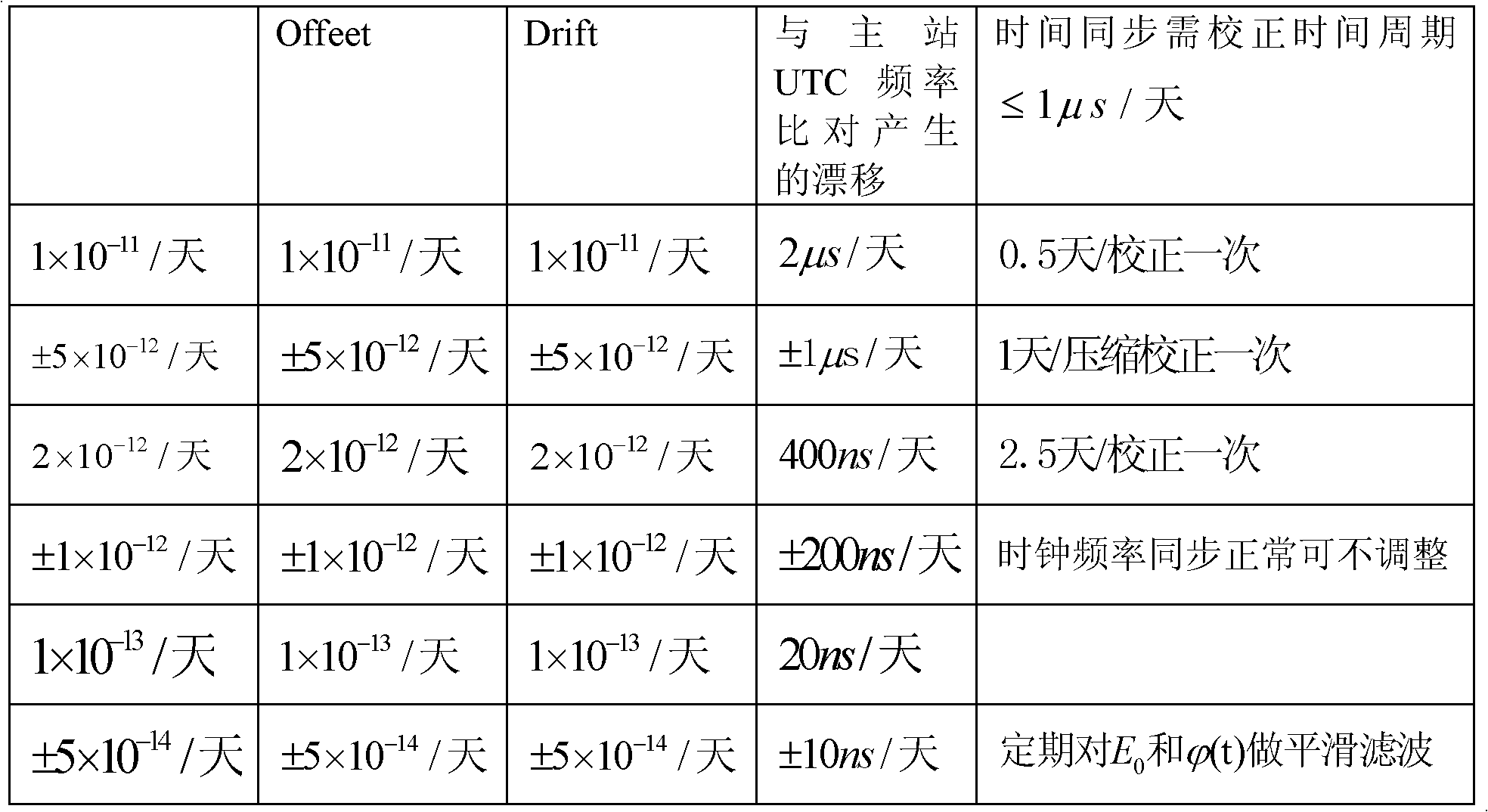
UTC high-precision time synchronization method based on optical transmission network
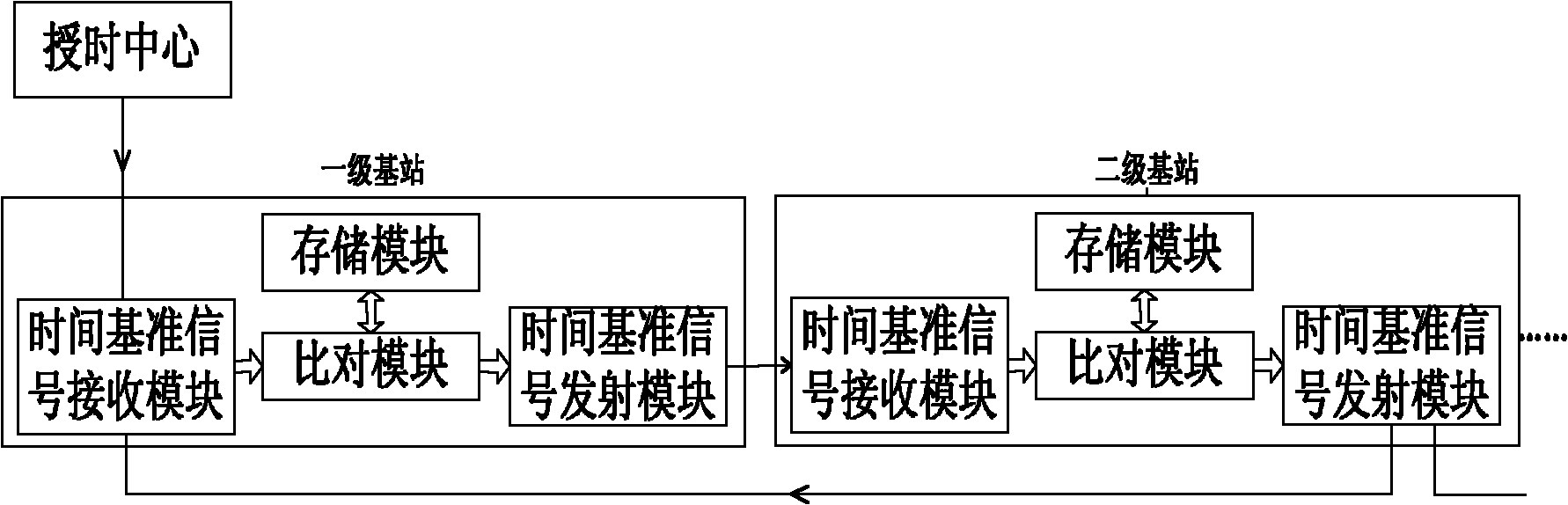
ActiveCN101902292AImprove accuracyImprove stability and reliabilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexPrimary stationThird generation
The invention discloses a UTC high-precision time synchronization method based on an optical transmission network. In the invention, time base signals are transmitted by the optical transmission network between a primary station between a secondary station: firstly, the time base is transmitted to the secondary station by the primary station, and then time interval deviation is calculated by the secondary station based on time shown by a local clock of the secondary station and the time base; secondly, the local clock of the secondary station is corrected by the secondary station based on thetime interval deviation and a checked time base is returned to the primary station by the secondary station; and finally, the time base originally sent to the secondary station is corrected by the primary station based on the checked time base and the time shown by a local clock of the primary station and the corrected time base is sent to the secondary station again by the primary station. When the time base is transmitted between the primary station and the secondary station, two-way comparison is conducted between the primary station and the secondary station to precisely measure transmission delay asymmetry of a transmission loading network, accurately judge and standardize time and frequency synchronization scope of the secondary station, and provide 3G / 4G communication networks withthe high-precision time synchronization method based on the integration of time and frequency, thereby realizing higher-precision time and frequency synchronization.
Owner:DATANG TELECOM TECH CO LTD
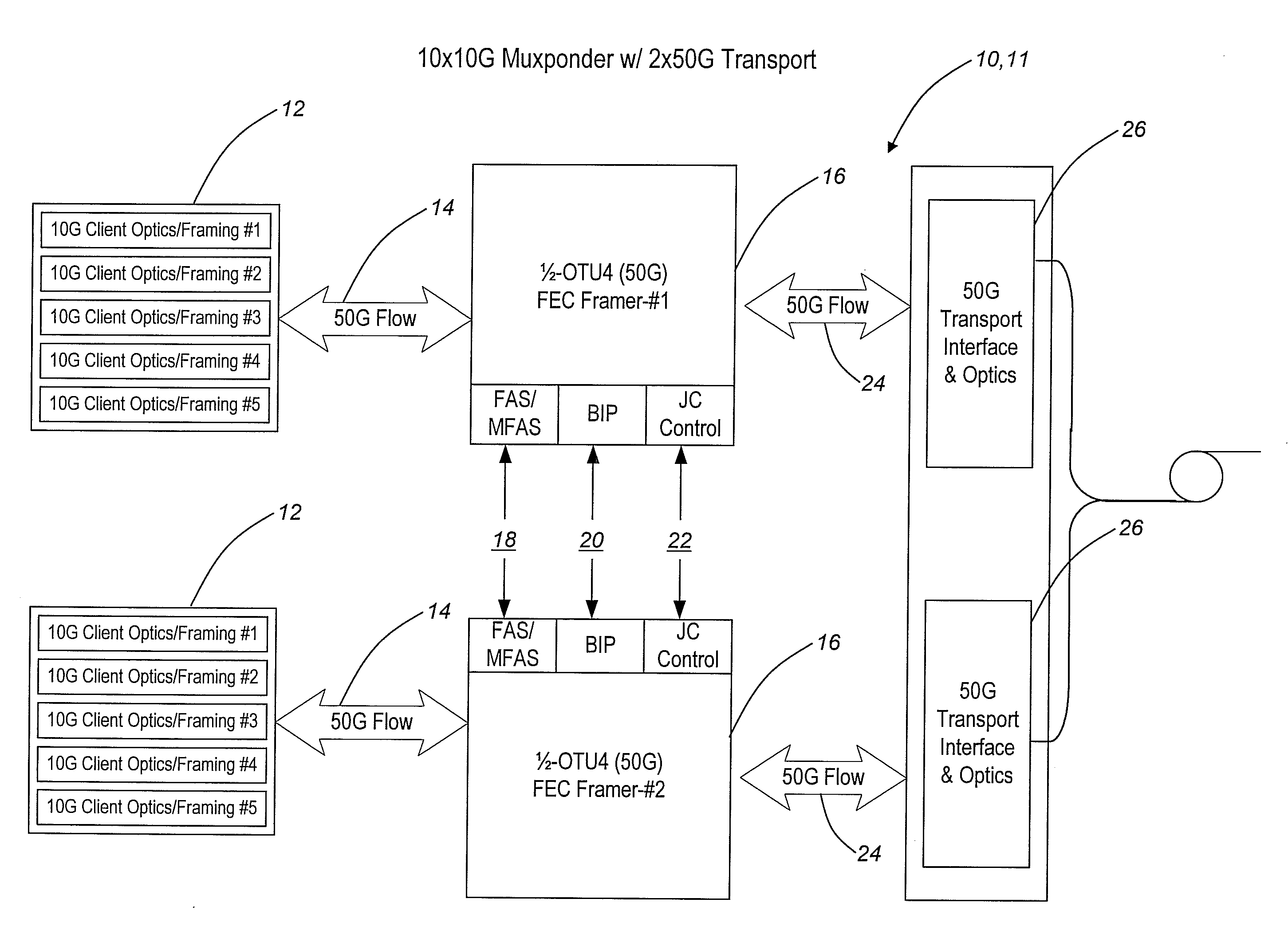
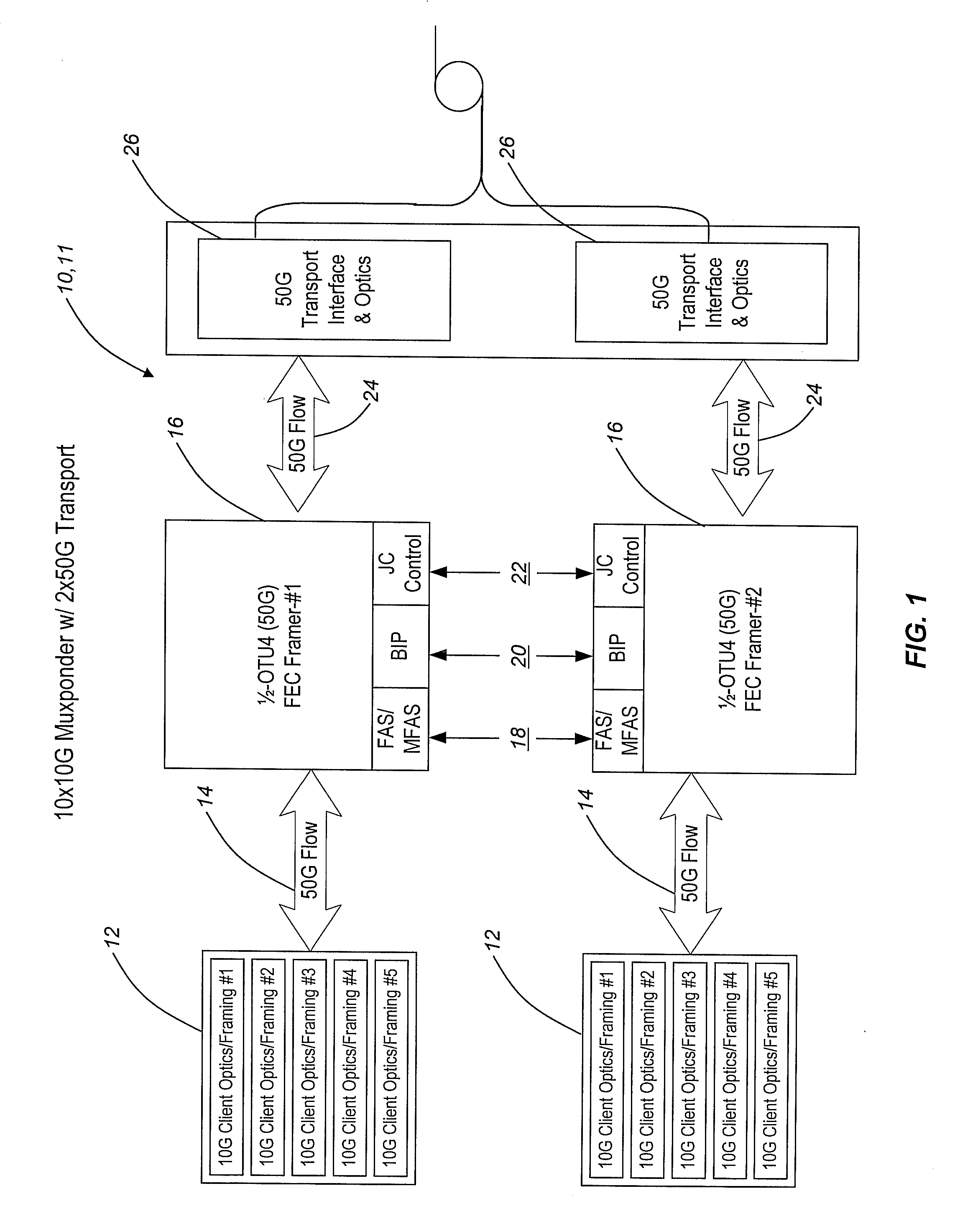
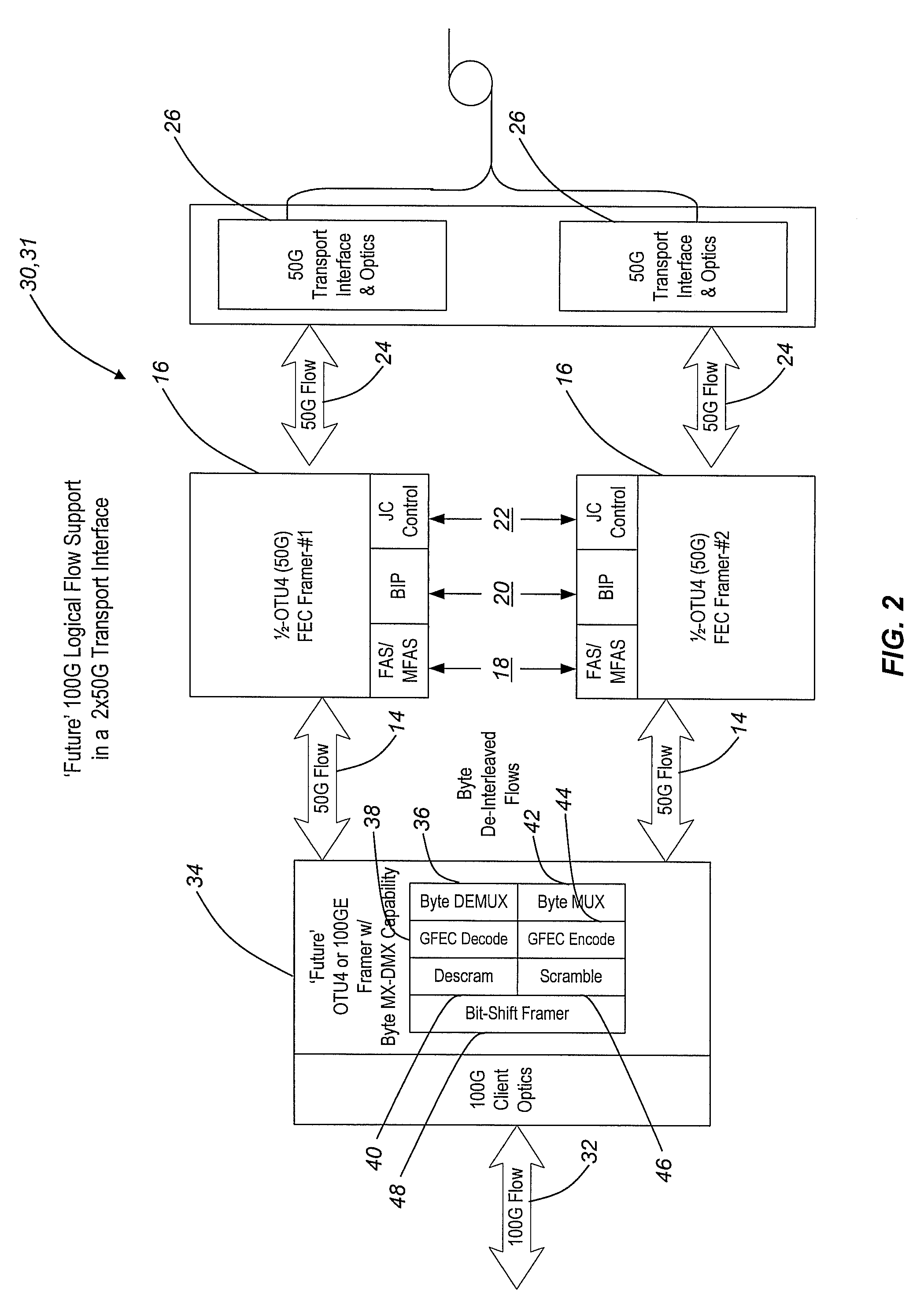
Byte-interleaving systems and methods for 100g optical transport enabling multi-level optical transmission
ActiveUS20090169217A1Useful and efficient and cost-effectiveTime-division multiplexElectromagnetic transmittersMultiplexingForward error correction
The present invention provides byte-interleaving systems and methods for Optical Transport Unit N (OTUN) (i.e. Optical Transport Unit 4 (OTU4)) and 100 Gb / s (100 G) optical transport enabling multi-level optical transmission. The byte-interleaving systems and methods of the present invention support the multiplexing of sub-rate clients, such as 10 Gb / s (10 G) clients, 40 Gb / s (40 G) clients, etc., into two 50 Gb / s (50 G) logical flows, for example, that can be forward error correction (FEC) encoded and carried on a single wavelength to provide useful, efficient, and cost-effective 100 G optical transport today. Signaling format support allows these two 50 G logical flows to be forward compatible with an evolving OTU4 and 100 G signaling format without waiting for optical and electronic technology advancement. Signaling format support also allows an evolving standard 100 G logical flow (i.e. OTU4, 100 Gb / s Ethernet (100 GbE), etc.) to be carried as 2×50 G logical flows, 4×25 G logical flows, or other lower rate formats on a single wavelength.
Owner:CIENA
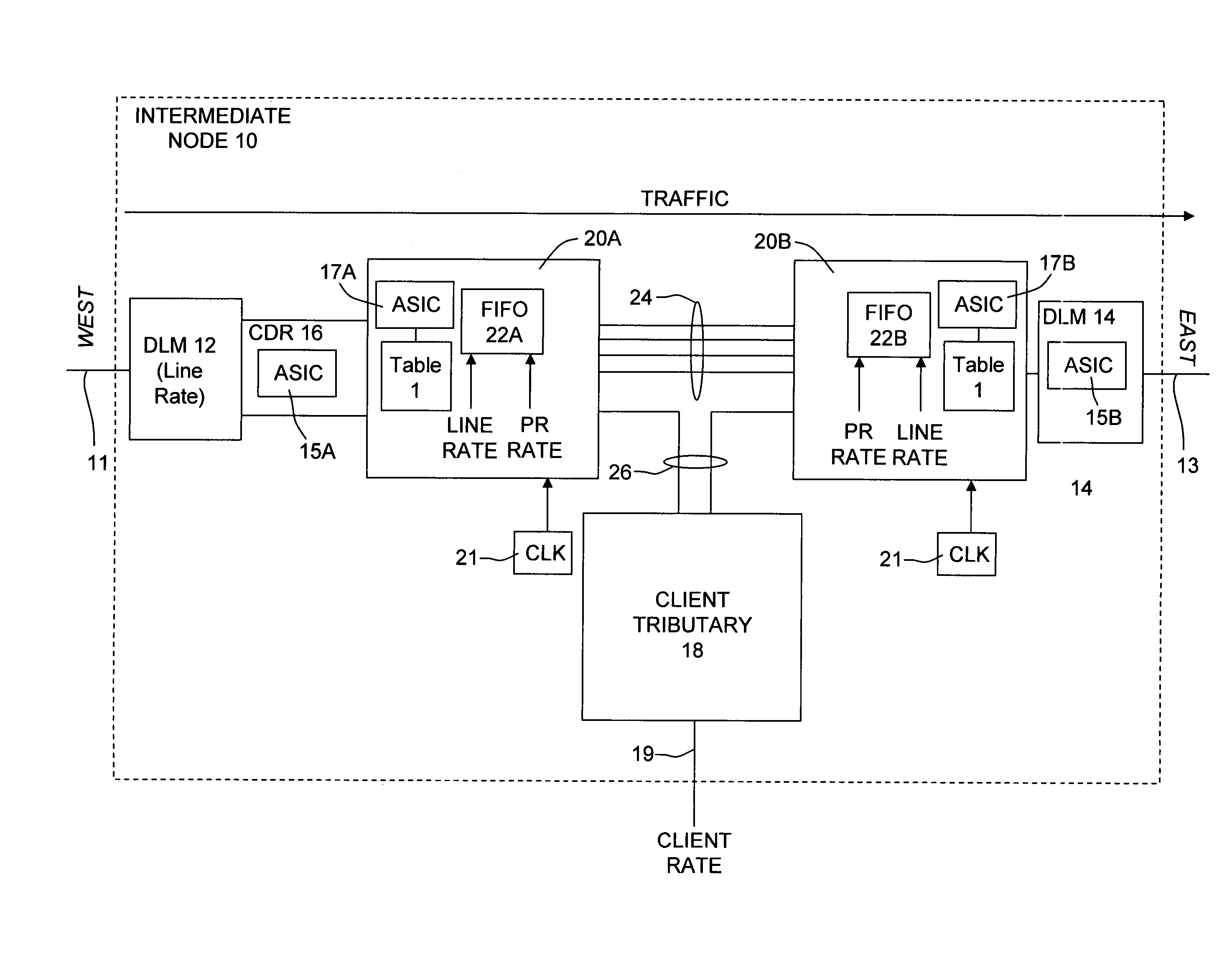
Optical transmission network with asynchronous mapping and demapping and digital wrapper frame for the same
ActiveUS7286487B2Reduce manufacturing costLow costError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission protocolLine rate
An optical transmission network is inherently asynchronous due to the utilization of a variable overhead ratio (V-OHR). The network architecture makes extensive use of OEO regeneration, i.e., deals with any electronic reconditioning to correct for transmission impairments, such as, for example, FEC encoding, decoding and re-encoding, signal reshaping, retiming as well as signal regeneration. The optical transmission network includes a plesiochronous clocking system with intermediate nodes designed to operate asynchronously with a single local frequency clock without complicated network synchronization schemes employing high cost clocking devices such as phase locked loop (PLL) control with crystal oscillators and other expensive system components. The asynchronous network operation provides for asynchronous remapping or remapping of any client signal utilizing any type of transmission protocol where the line side rate or frequency is always the same frequency for the payload signal and the local frequency at an intermediate node is set to a local reference clock in accordance with the payload type and its overhead ratio, i.e., the overhead ratio is varied to meet the desired difference between the line rate or frequency and the desired client signal payload rate or frequency for the particular client signal payload type.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
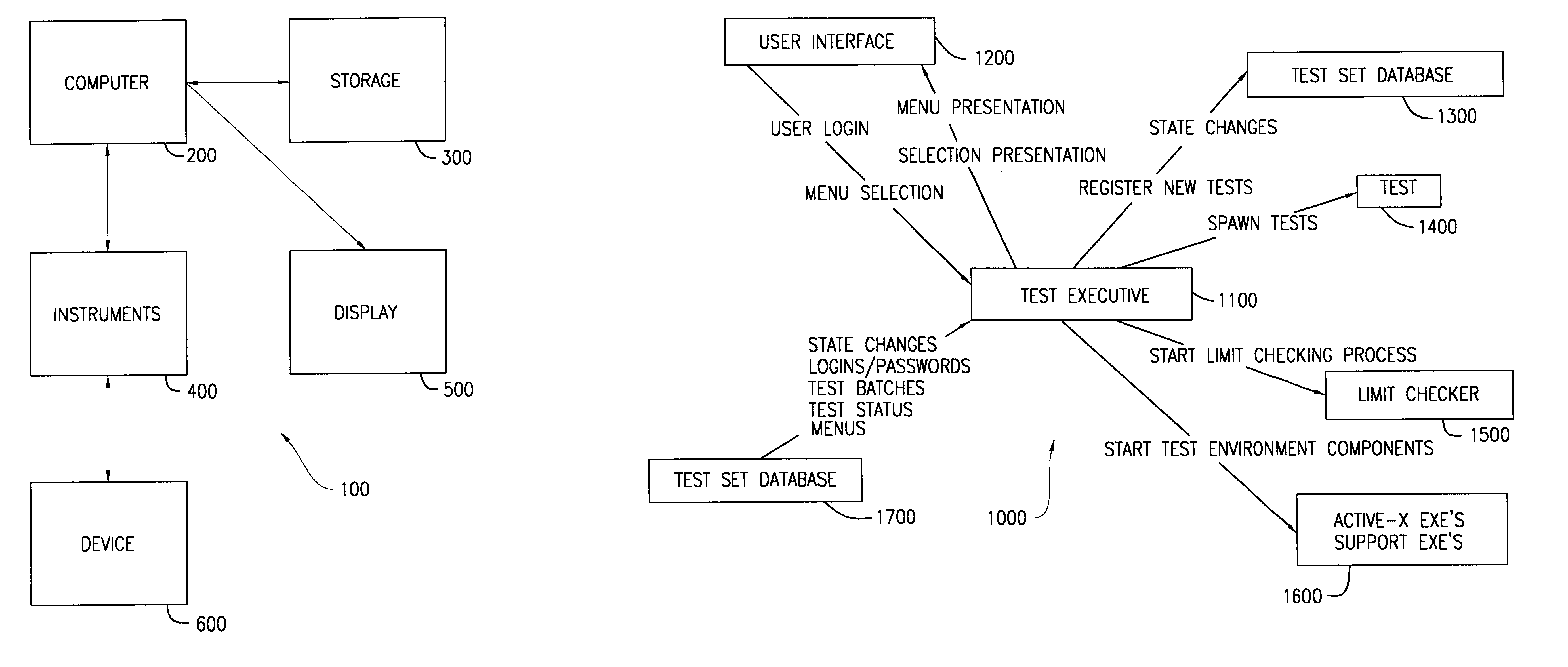
Method for limit checking
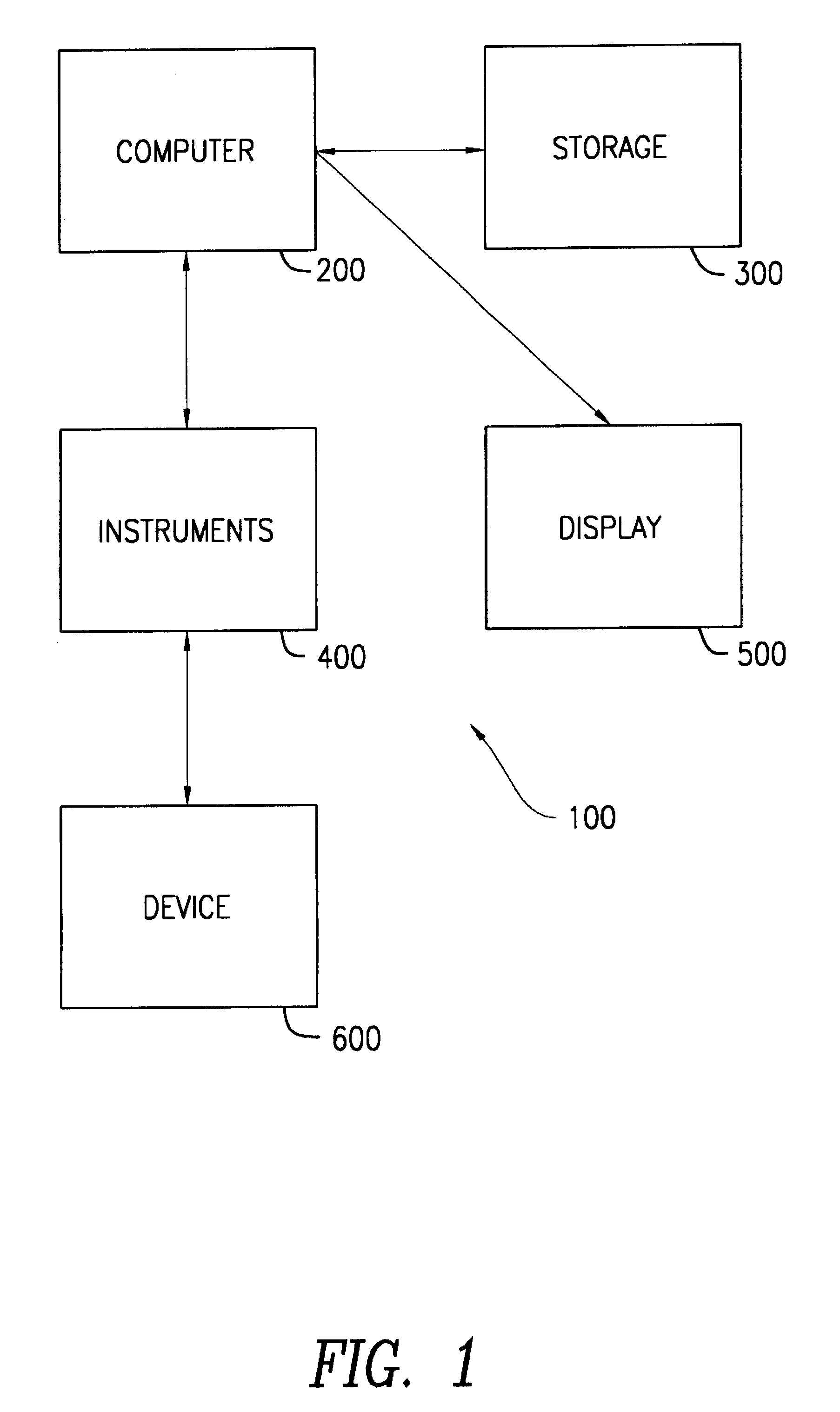
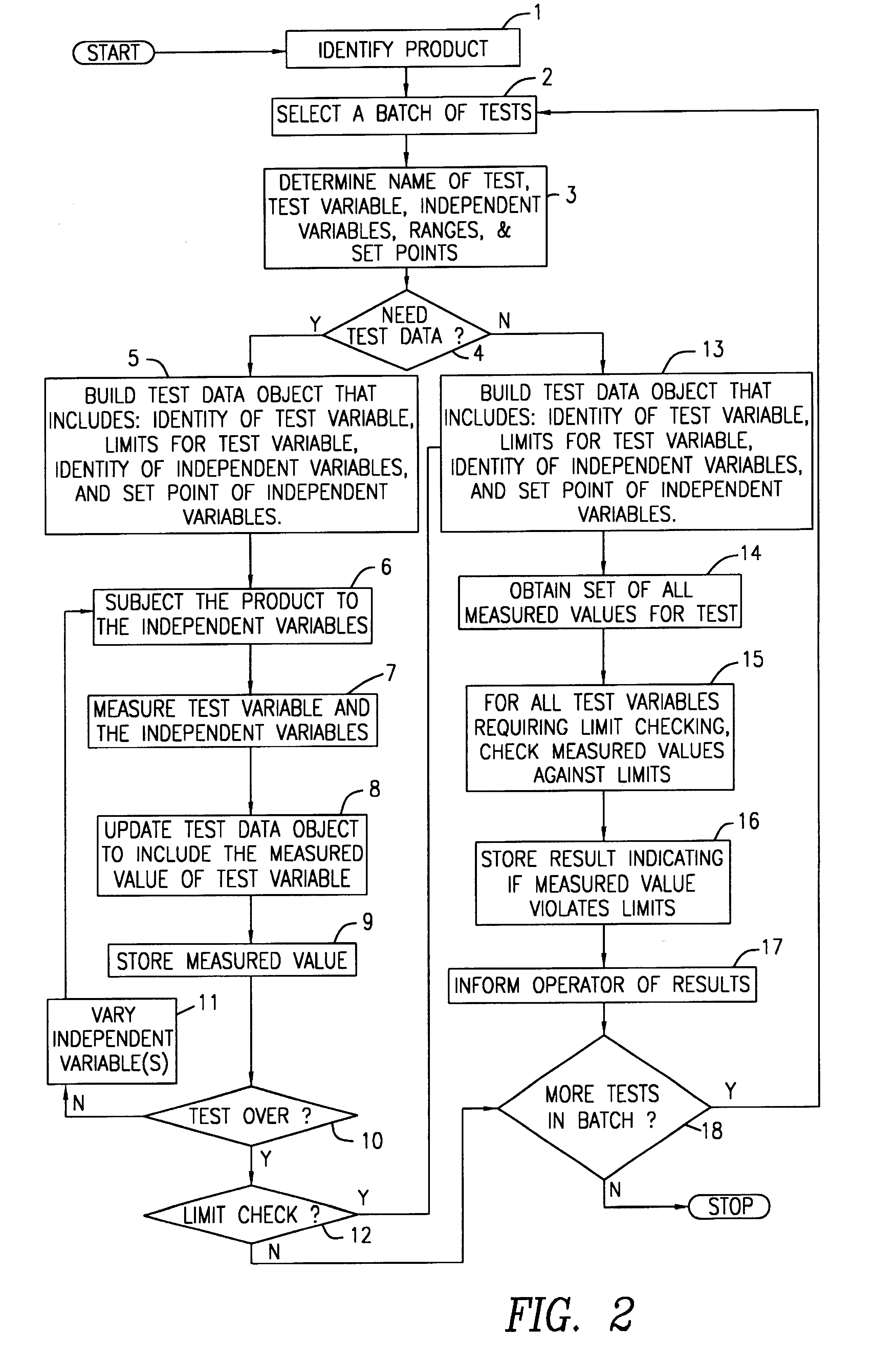
InactiveUS6415246B1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsComputer hardwareTest measurement
A device and method is provided for automatically validating test measurements of an optical entity in an optical transmission network. The method includes creating an object in a database that includes a test variable. In addition, a limit relating to the test variable value is included. The method further includes comparing the test variable value against the limit and indicating if the test variable violates the limit. The device includes a computer memory containing data that relates to performance testing. The data comprises a test identifier, a test variable identifier and a plurality of independent variable identifiers.
Owner:SUBCOM LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com