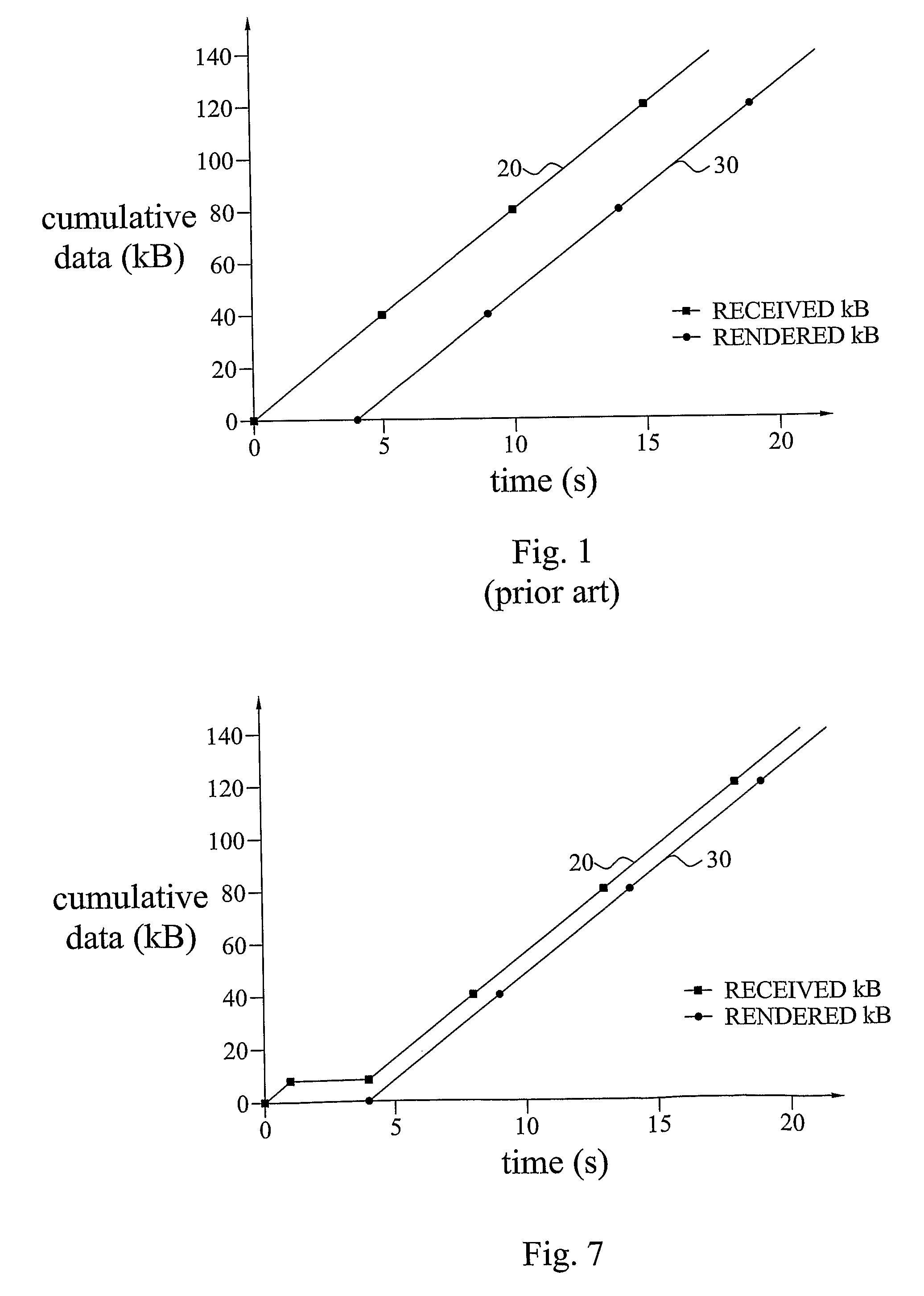Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7795 results about "Transmission delay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
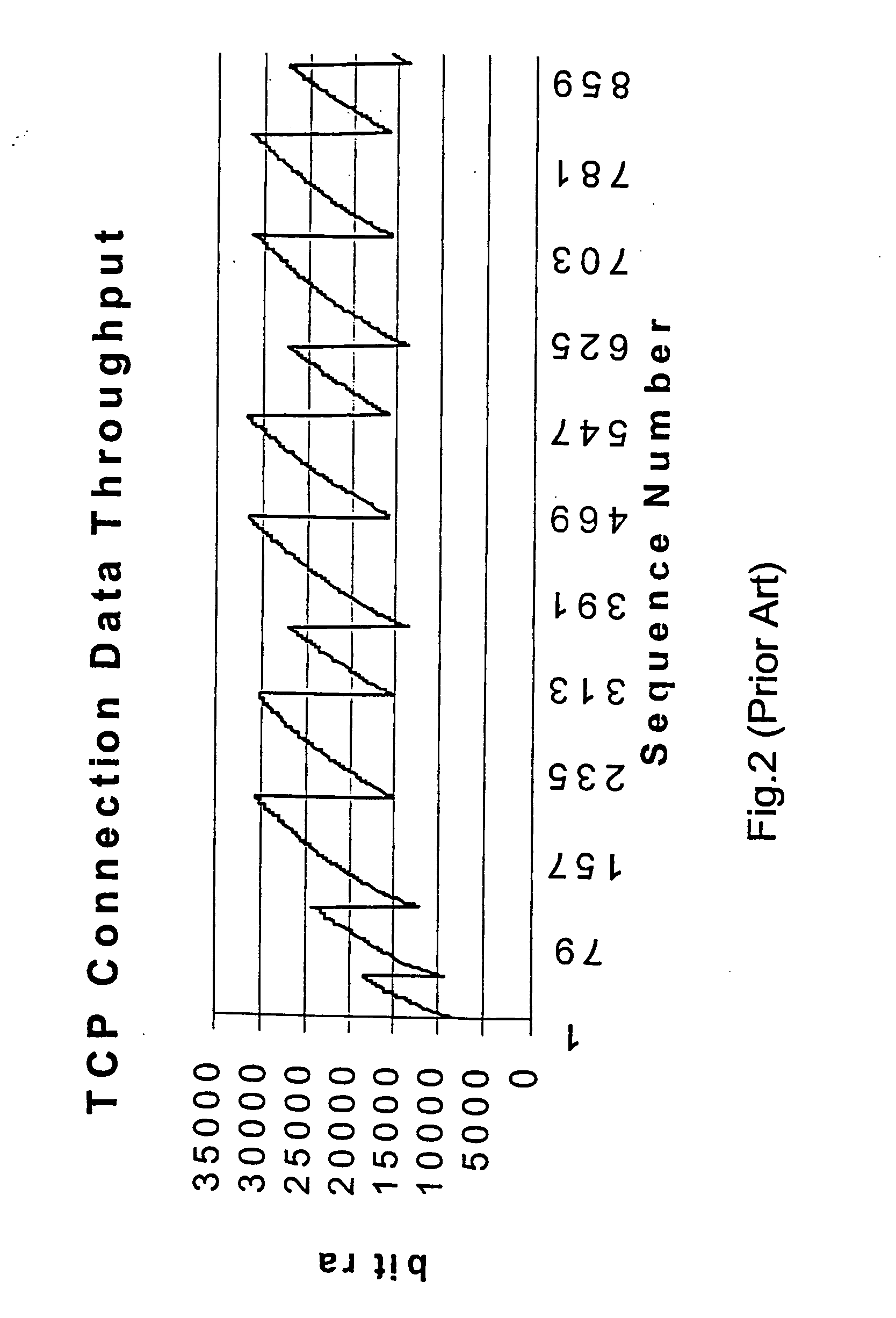
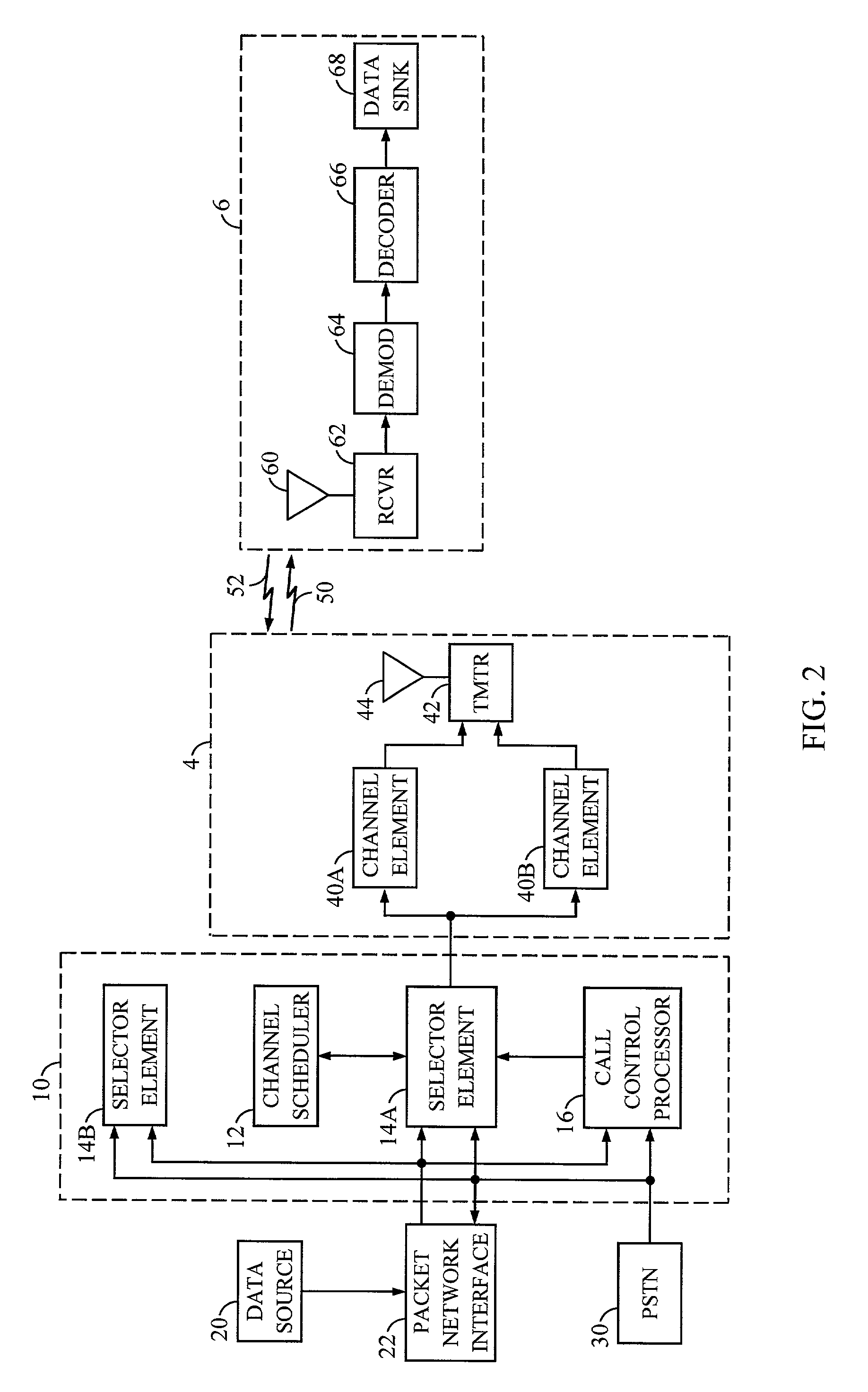
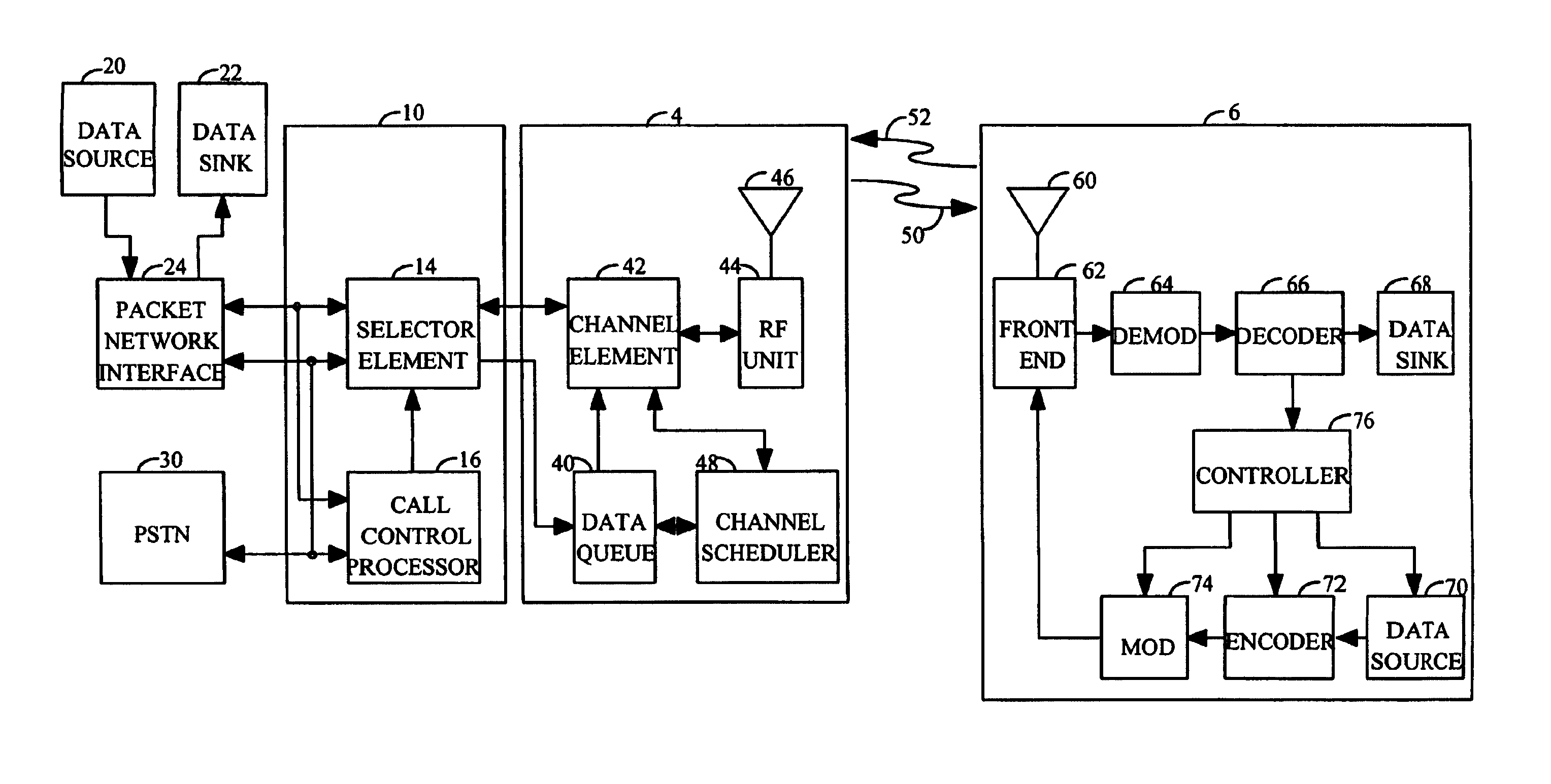
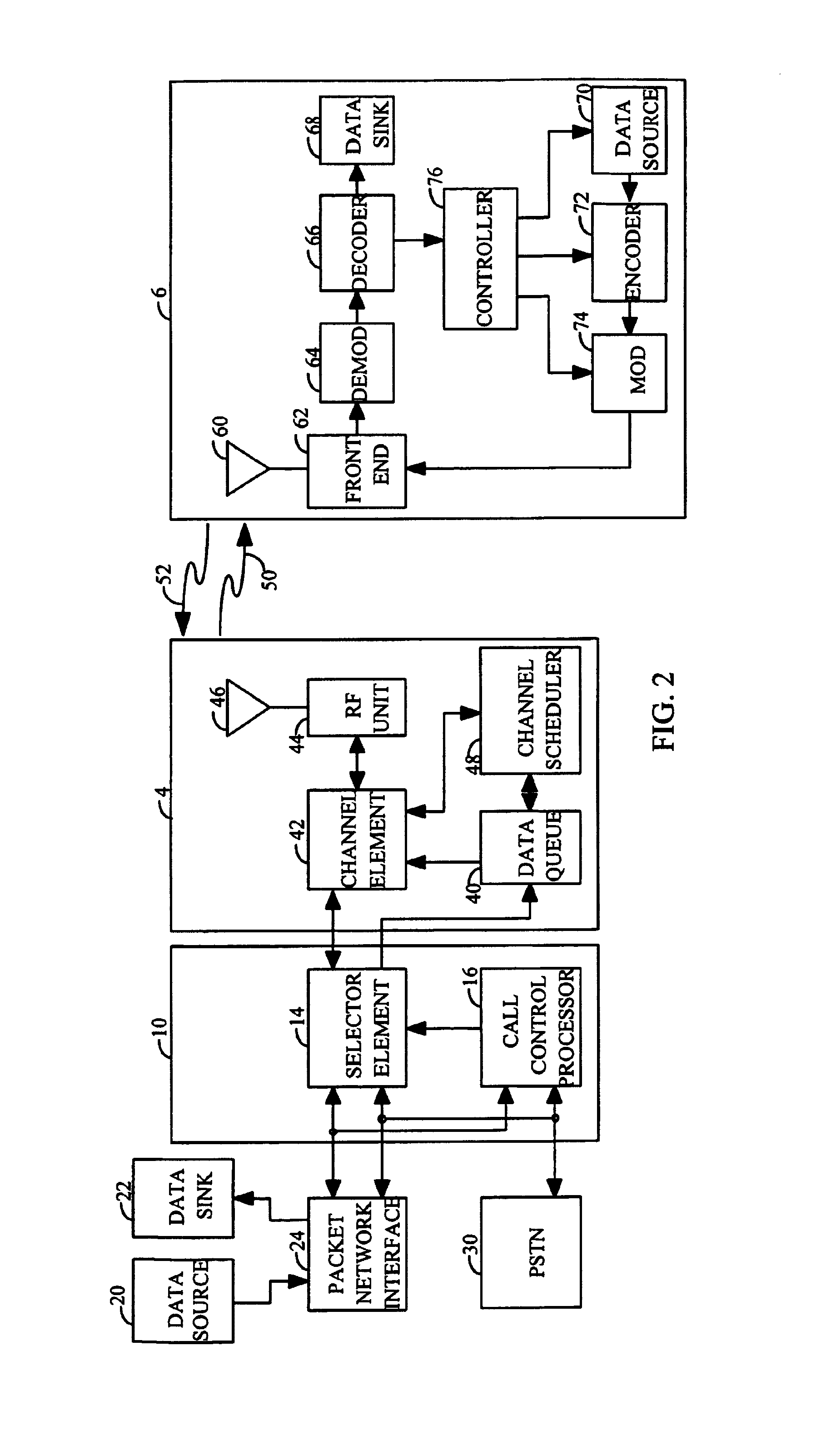
In a network based on packet switching, transmission delay (or store-and-forward delay, also known as packetization delay) is the amount of time required to push all the packet's bits into the wire. In other words, this is the delay caused by the data-rate of the link. Transmission delay is a function of the packet's length and has nothing to do with the distance between the two nodes. This delay is proportional to the packet's length in bits, It is given by the following formula: DT=N/R seconds where DT is the transmission delay in seconds N is the number of bits, and R is the rate of transmission (say in bits per second) Most packet switched networks use store-and-forward transmission at the input of the link.
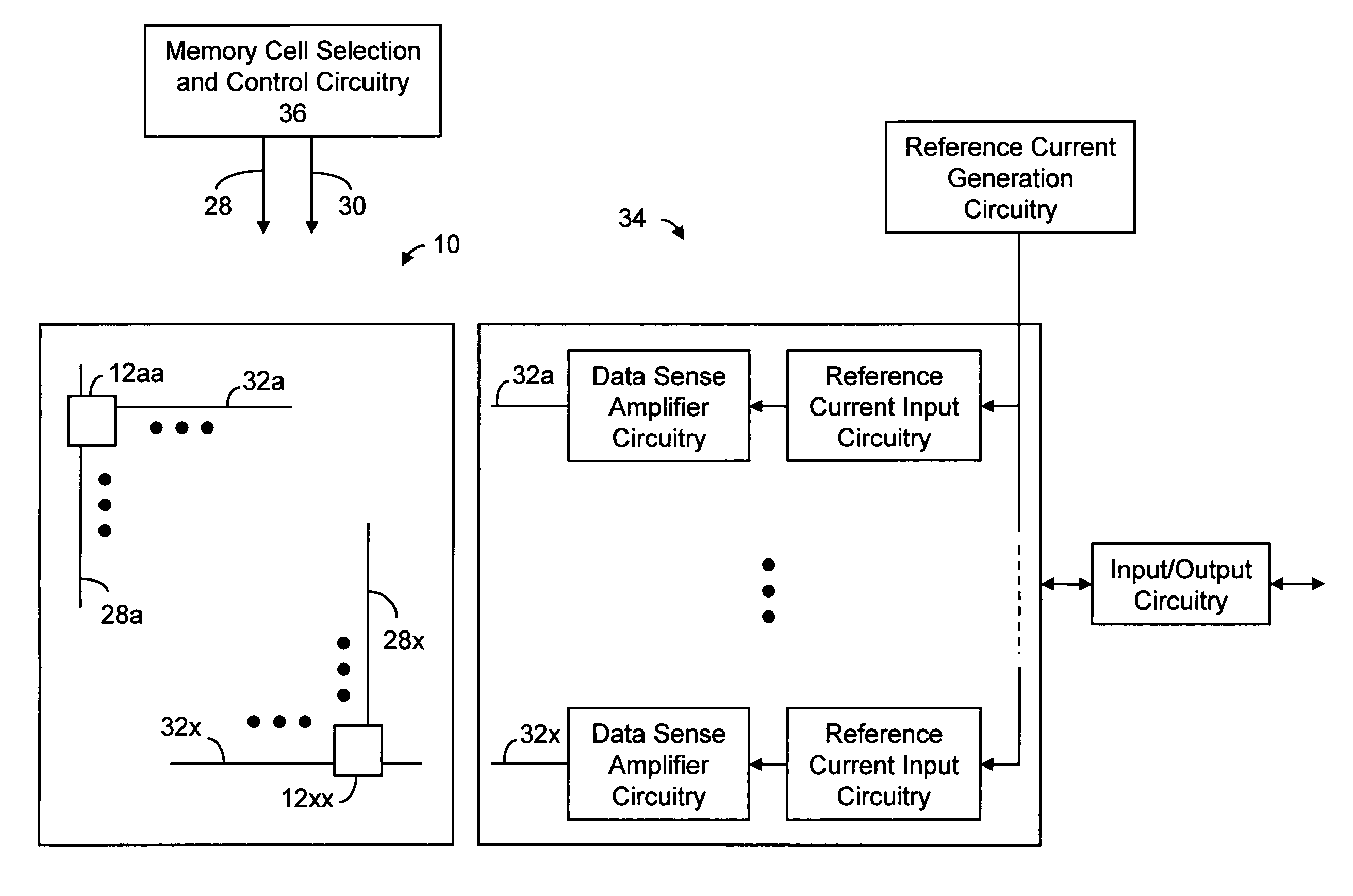
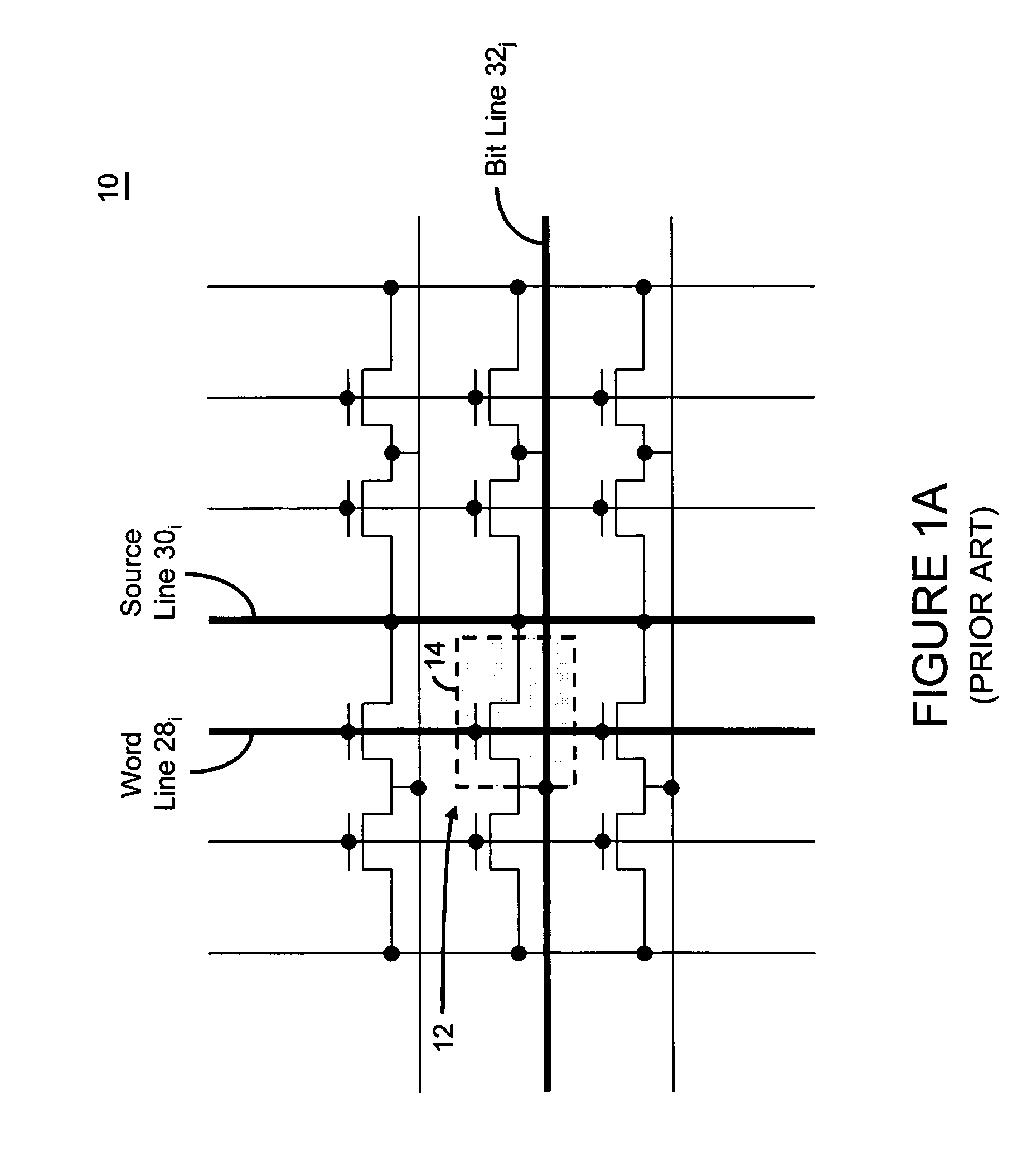
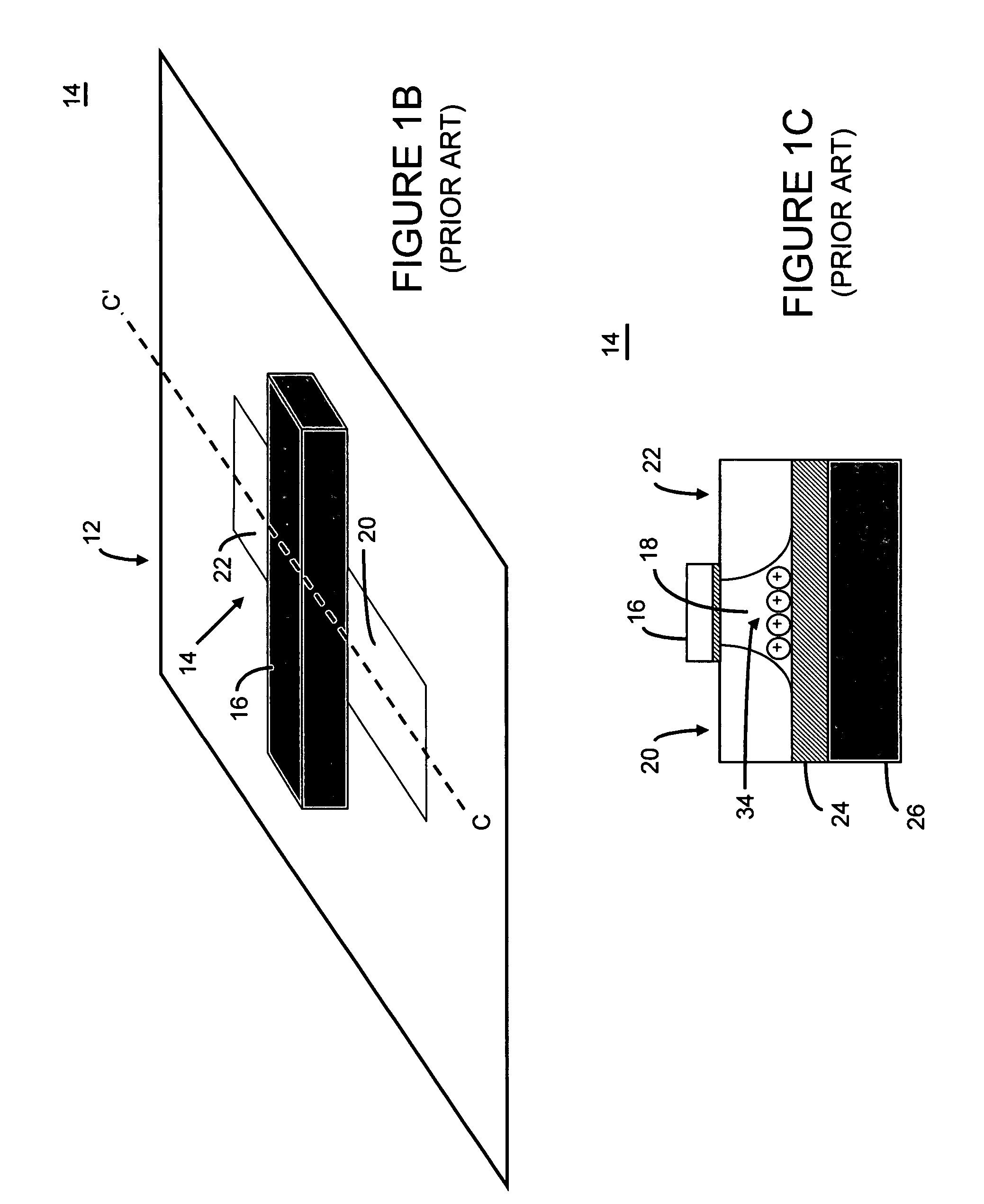
Bipolar reading technique for a memory cell having an electrically floating body transistor
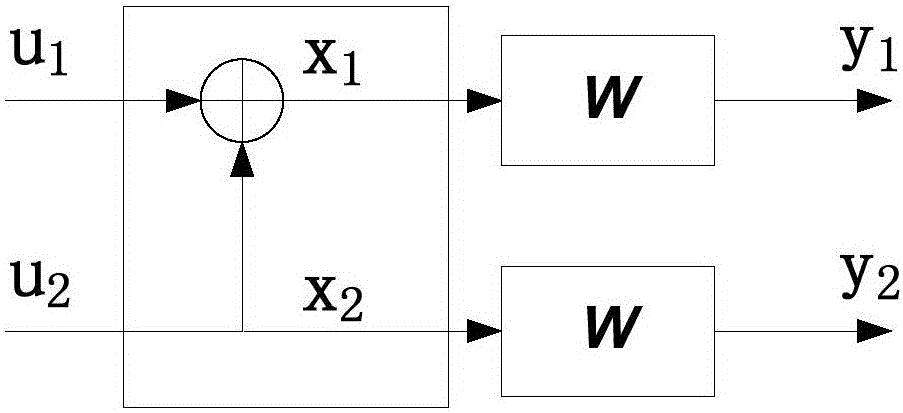
A method and a device for the coding and decoding of an information symbol for transmission over a transmission channel or a received signal value is described and illustrated, whereby a channel symbol used for coding is selected from at least two available channel symbols by means of a pre-calculated expected received signal value. The pre-calculation is achieved, based on the echo properties of the transmission channel and transmission values already sent. A pre-coding method with low receiver-side calculation requirement is thus prepared, whereby the information symbol can be transmitted by means of various channel symbols and thus various transmission values can also be transmitted. The possible selections may be used for minimization of the transmission energy and / or to achieve a minimal disturbance or even a constructive effect through the inter-symbol interference occurring on transmission.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
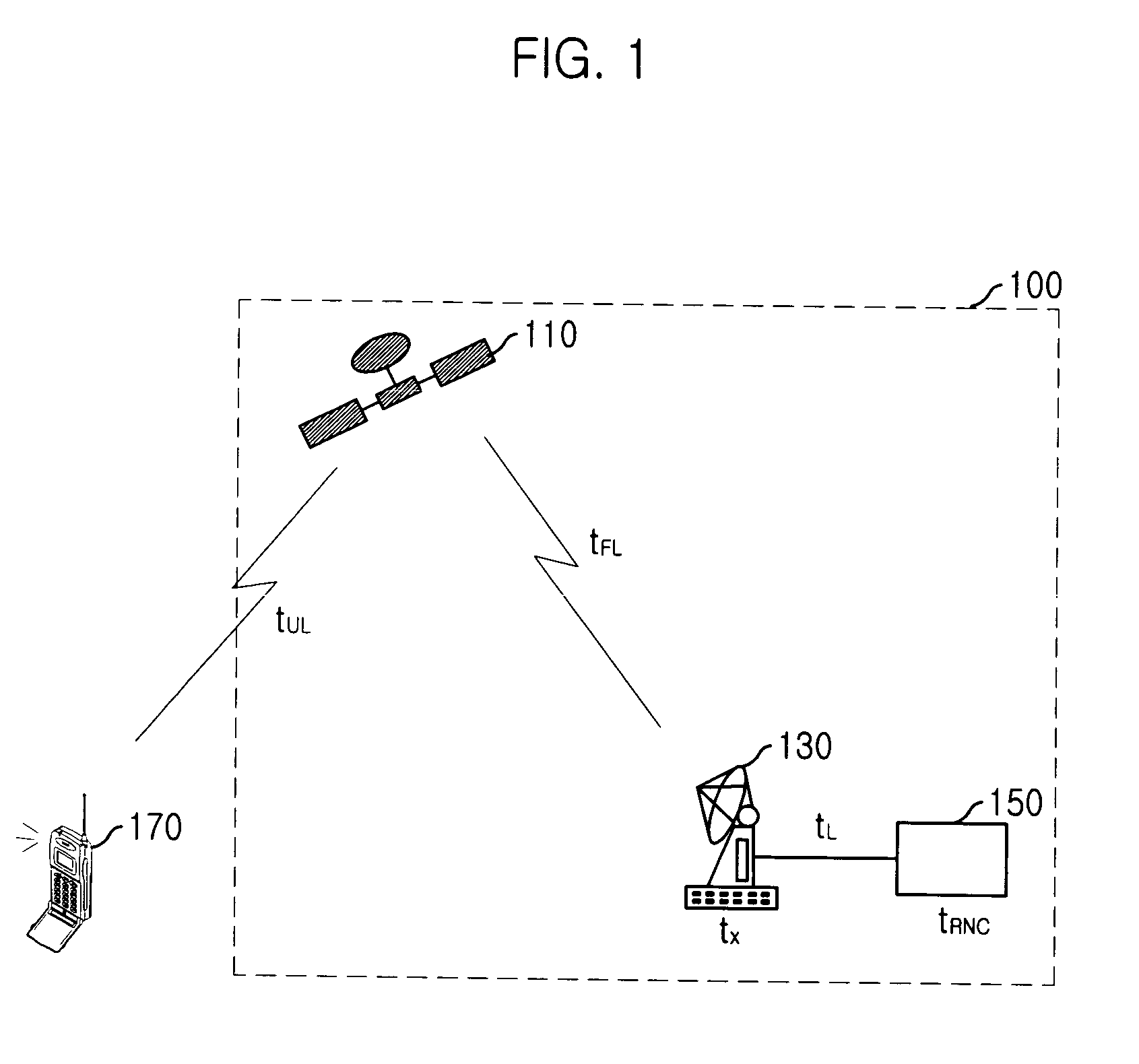
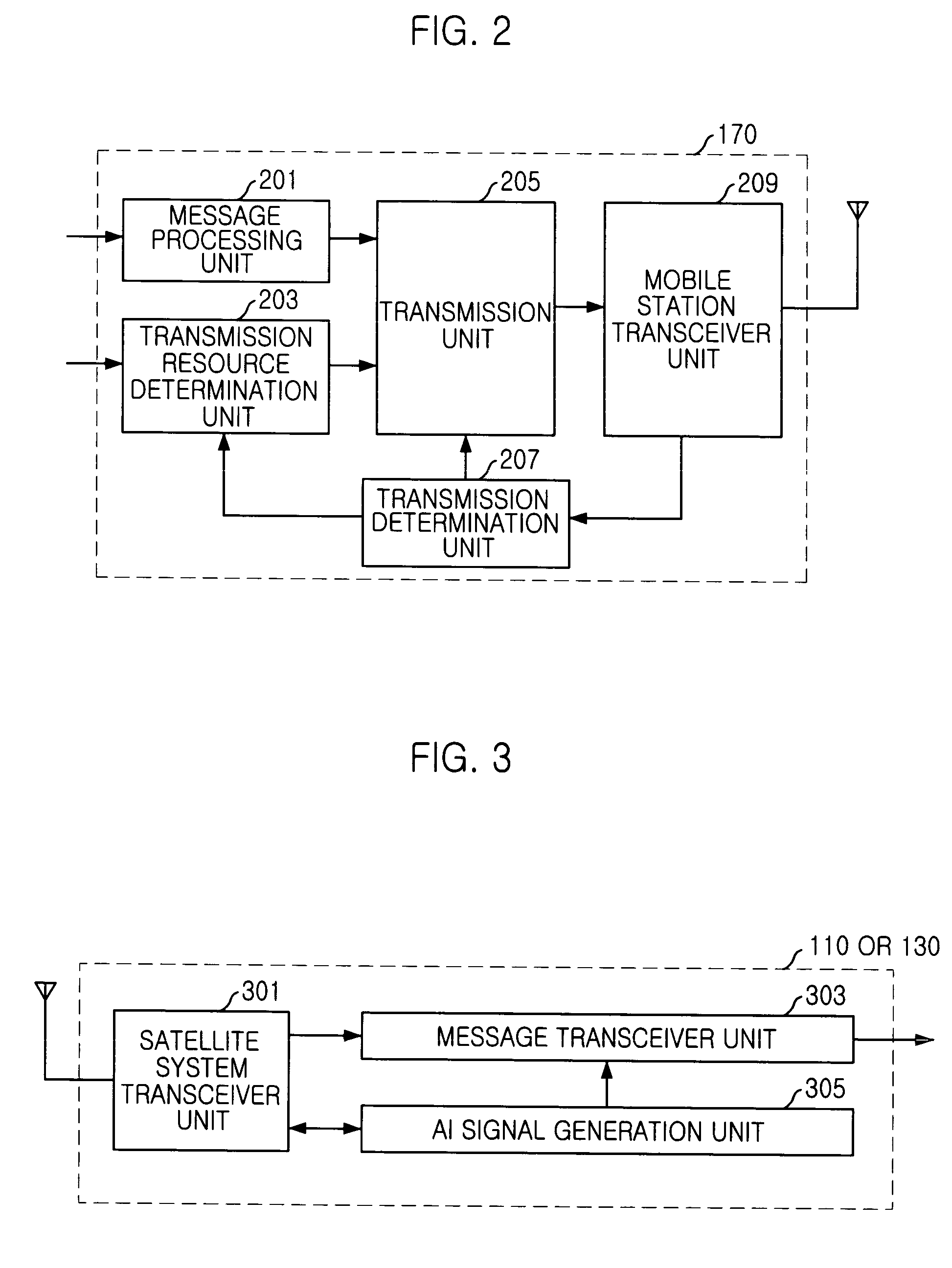
Random access channal access apparatus for mobile satellite communication system and method therefor
ActiveUS20040014452A1Reduce transmission delay timeIncrease probabilityTransmission control/equalisingNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsRandom-access channel
The present invention relates to Random Access Channel (RACH) access apparatus for mobile satellite communication system and method therefor. The method for accessing random access channel (RACH) on satellite system, random access channel (RACH) carrying message from a plurality of mobile stations to the satellite system, the method includes the steps of: receiving preamble and the message, the message successively transmitted with the preamble from the plurality of mobile stations; and transmitting acquisition response signal corresponding to the preamble or the message to the plurality of mobile stations. Accordingly, success of packet reception of satellite system is improved and transmission delay is reduced.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
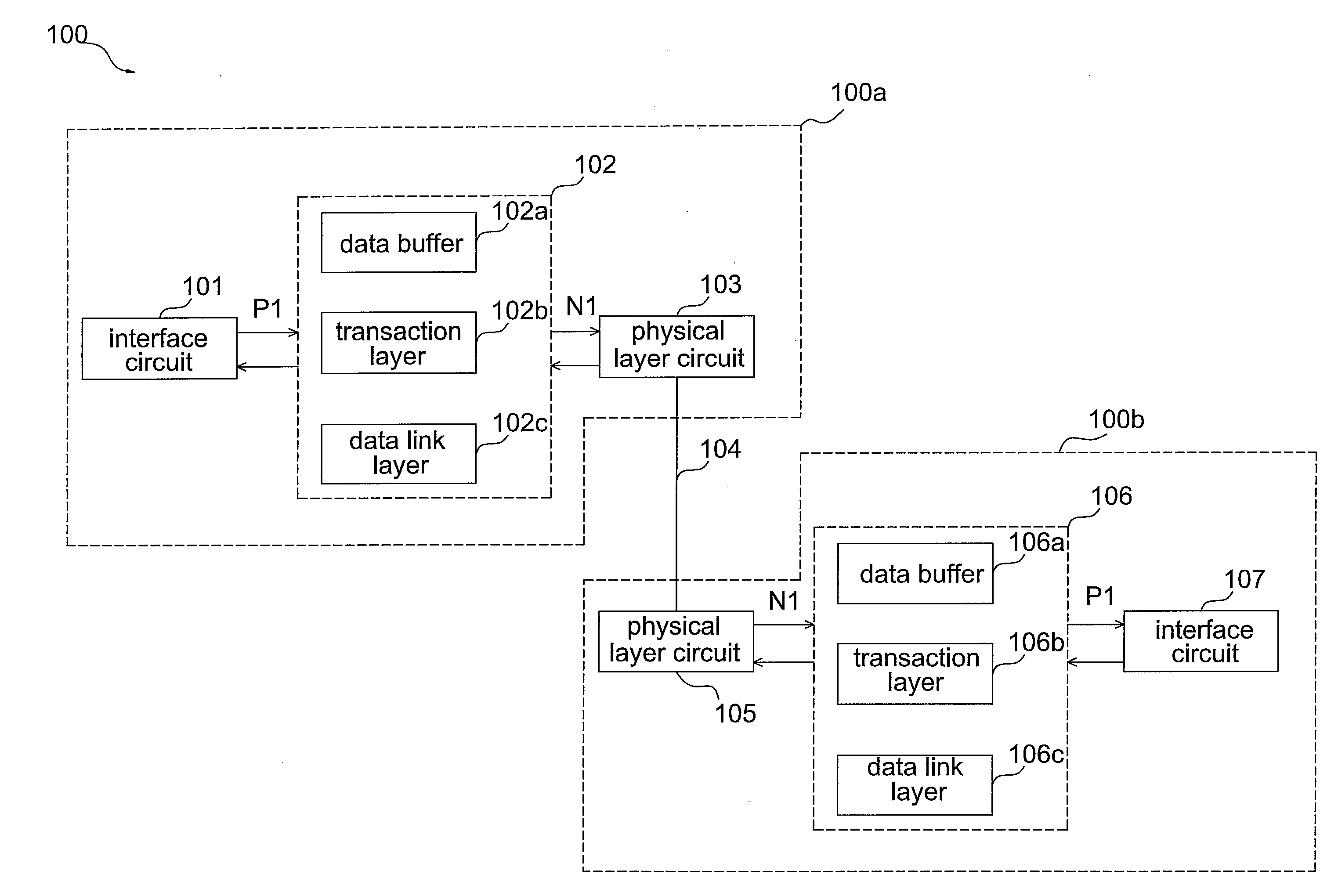
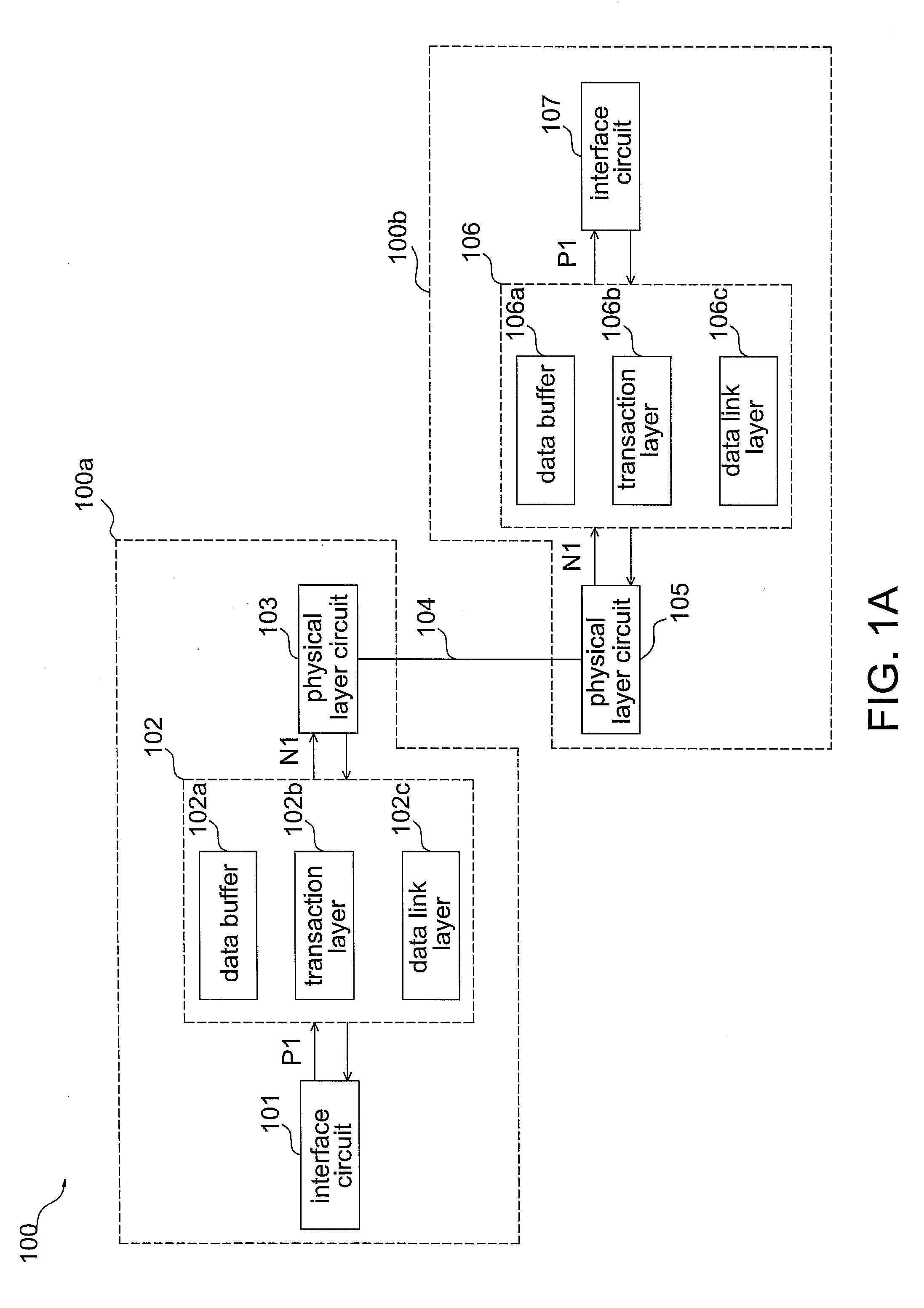
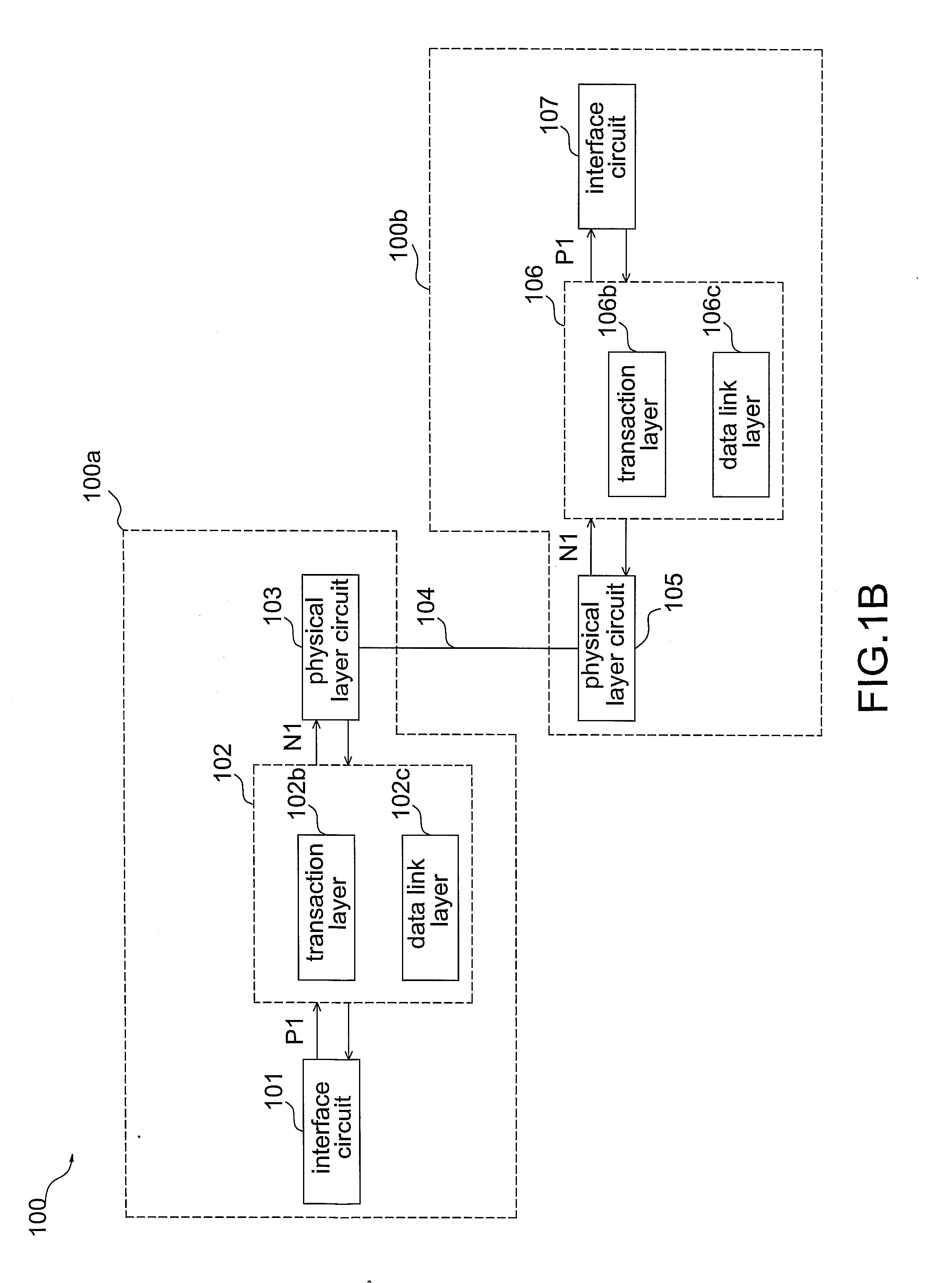
Transmission device and data extended transmission method
InactiveUS20100027559A1Reduce design expenseLow production costNetwork connectionsElectric digital data processingPhysical layerInterface circuits
The invention discloses a transmission device. The transmission device includes an interface circuit, a data converting circuit, at least a physical layer and a transmission medium. The interface circuit is used to receive a PCIe signal or a PCI signal. The data converting circuit is coupled to the interface circuit and used to convert the PCIe signal or the PCI signal into at least a data packet. The physical layer is coupled to the data converting circuit and used to process and transfer the data packet. The transmission medium receives and transfers the data packet.
Owner:ASPEED TECH
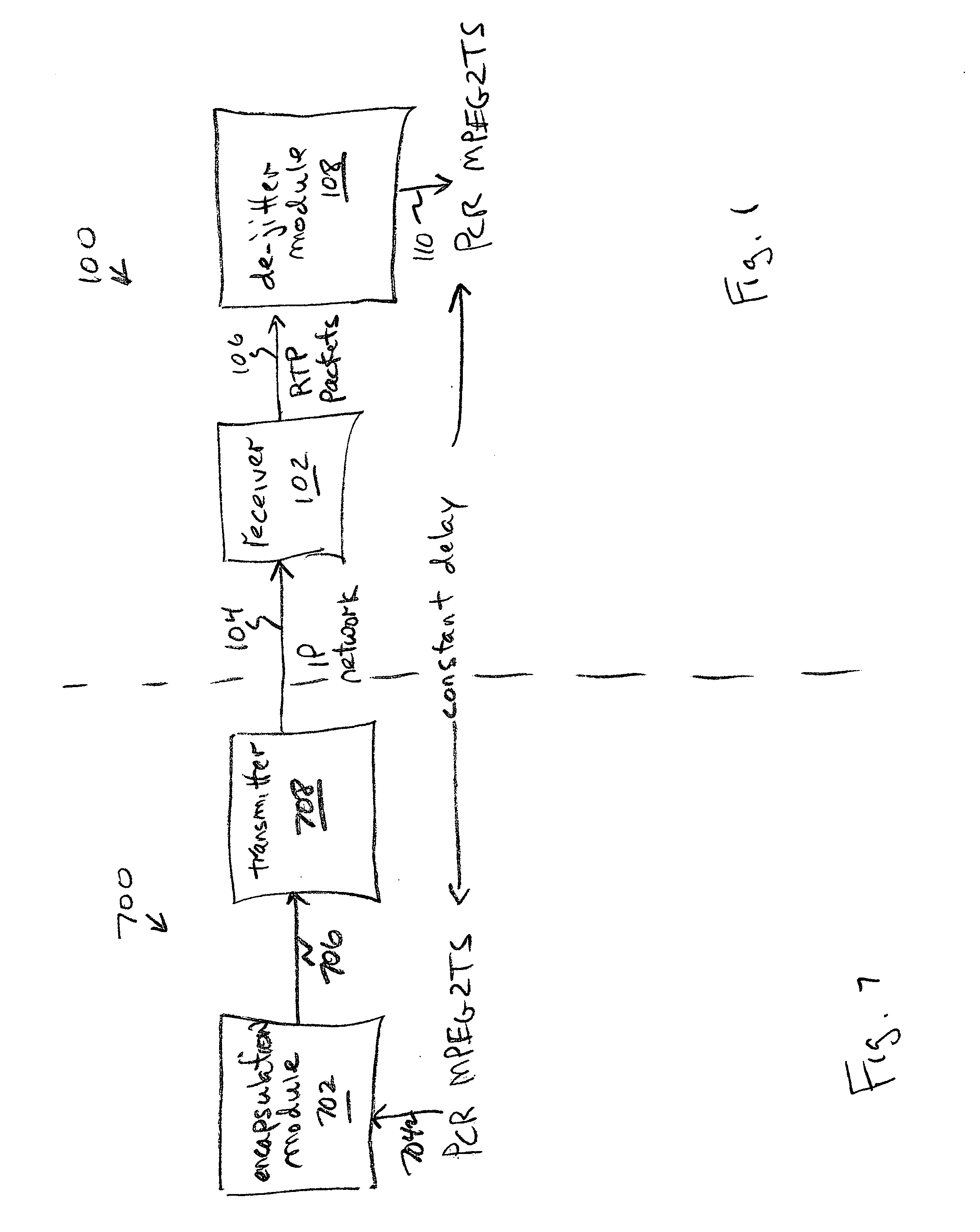
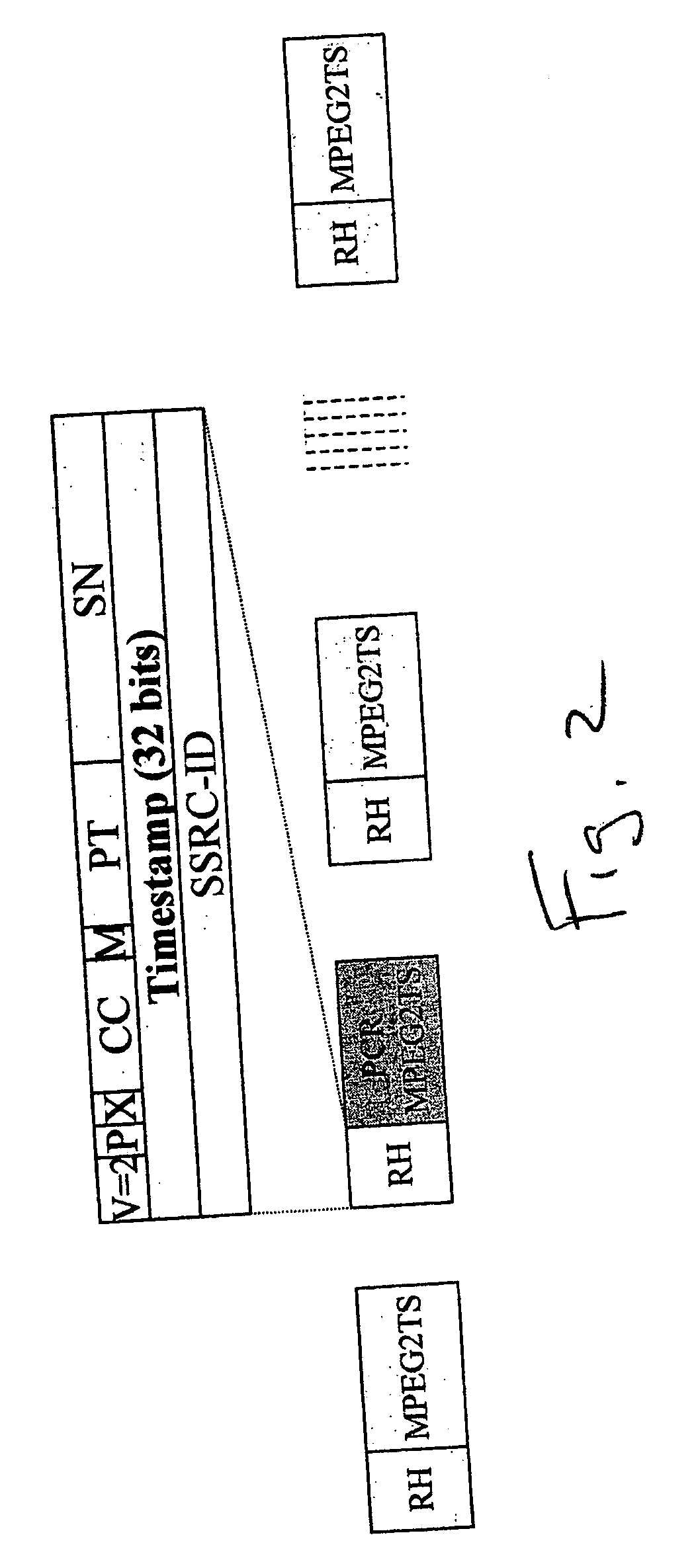
System and method for transporting MPEG2TS in RTP/UDP/IP
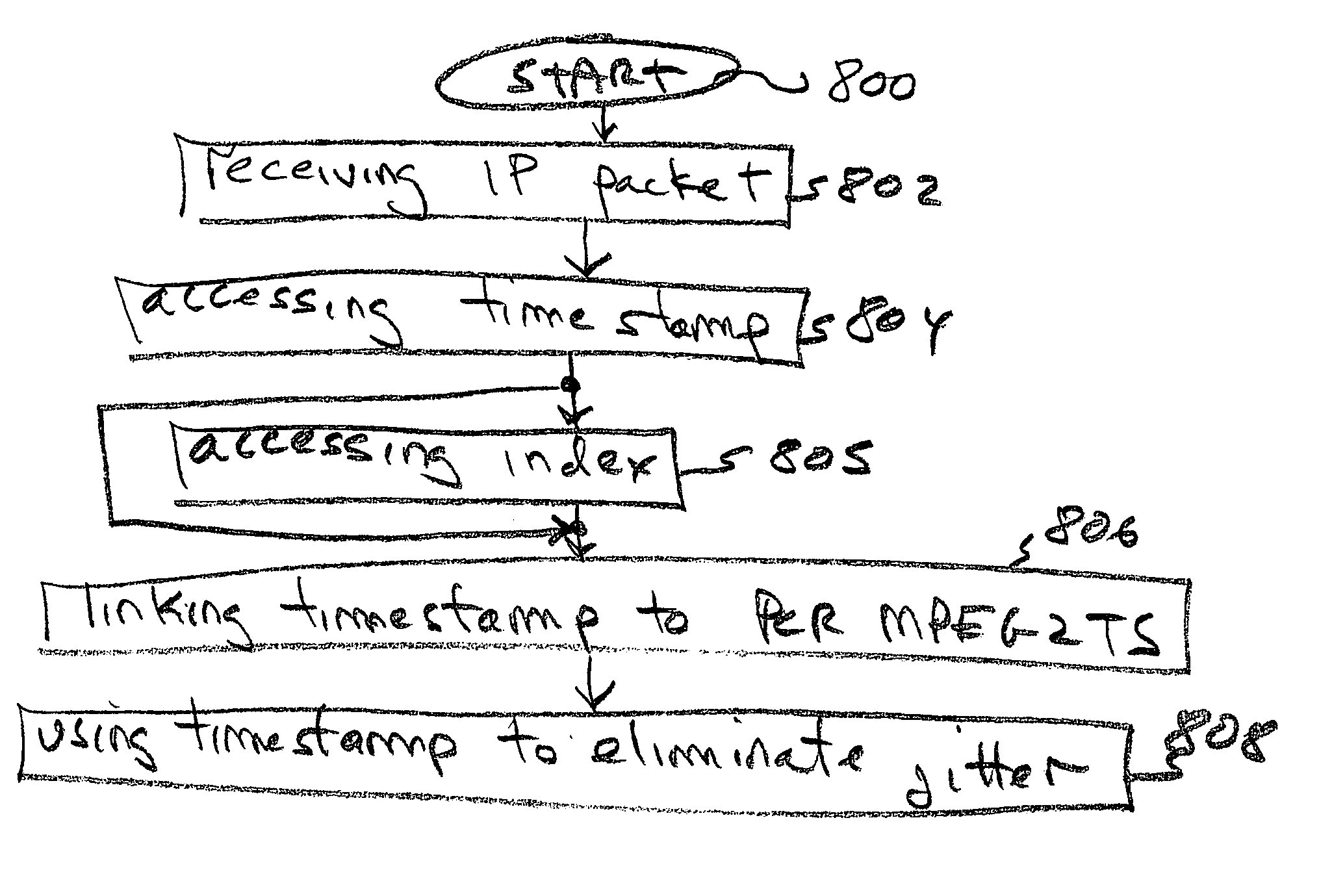
InactiveUS20050177643A1Eliminate variable transmission delay jitterError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsProgram clock referenceNanosecond
Systems and methods are provided for receiving and transmitting an MPEG2 transport stream (TS) in a real-time protocol (RTP) / user datagram protocol (UDP) / Internet protocol (IP) packet. The receiving method comprises: receiving an IP packet via an IP network, having a variable transmission delay; accessing a timestamp carried in a RTP packet; linking the timestamp with a program clock reference (PCR) MPEG2TS carried in the RTP packet payload; and, using the timestamp to eliminate variable transmission delay jitter, associated with the PCR MPEG2TS. In one aspect of the method, the timestamp has a resolution of greater than 500 nanoseconds (ns), so that the variable transmission delay jitter, associated with the PCR MPEG2TS can be reduced to a jitter of less than 500 ns.
Owner:SHARP KK
Touch panel input device
InactiveUS7215329B2Thin thicknessAvoid spreadingInput/output for user-computer interactionTransmission systemsElectricityLoudspeaker
A piezoelectric substrate is fixed to the movable plate or the support substrate directly or through a drive electrode of the piezoelectric substrate. When a pressure on an input operation surface is detected, a drive voltage is impressed on the drive electrodes of the piezoelectric substrate. In response, the piezoelectric substrate vibrates the movable plate or the support substrate, thereby providing tactile feedback to an operator. Because the movable plate or the support substrate directly vibrates without an independent vibrating source, there is no energy loss or transmission delay caused by transmitting the vibration, and finely control of the contraction and expansion of the piezoelectric substrate allows fine control of the vibration. In one embodiment, the drive voltage is modulated with signals dependent on the location of the pressure. In another embodiment, the drive voltage is modulated with audio frequencies to create a speaker.
Owner:SMK CORP
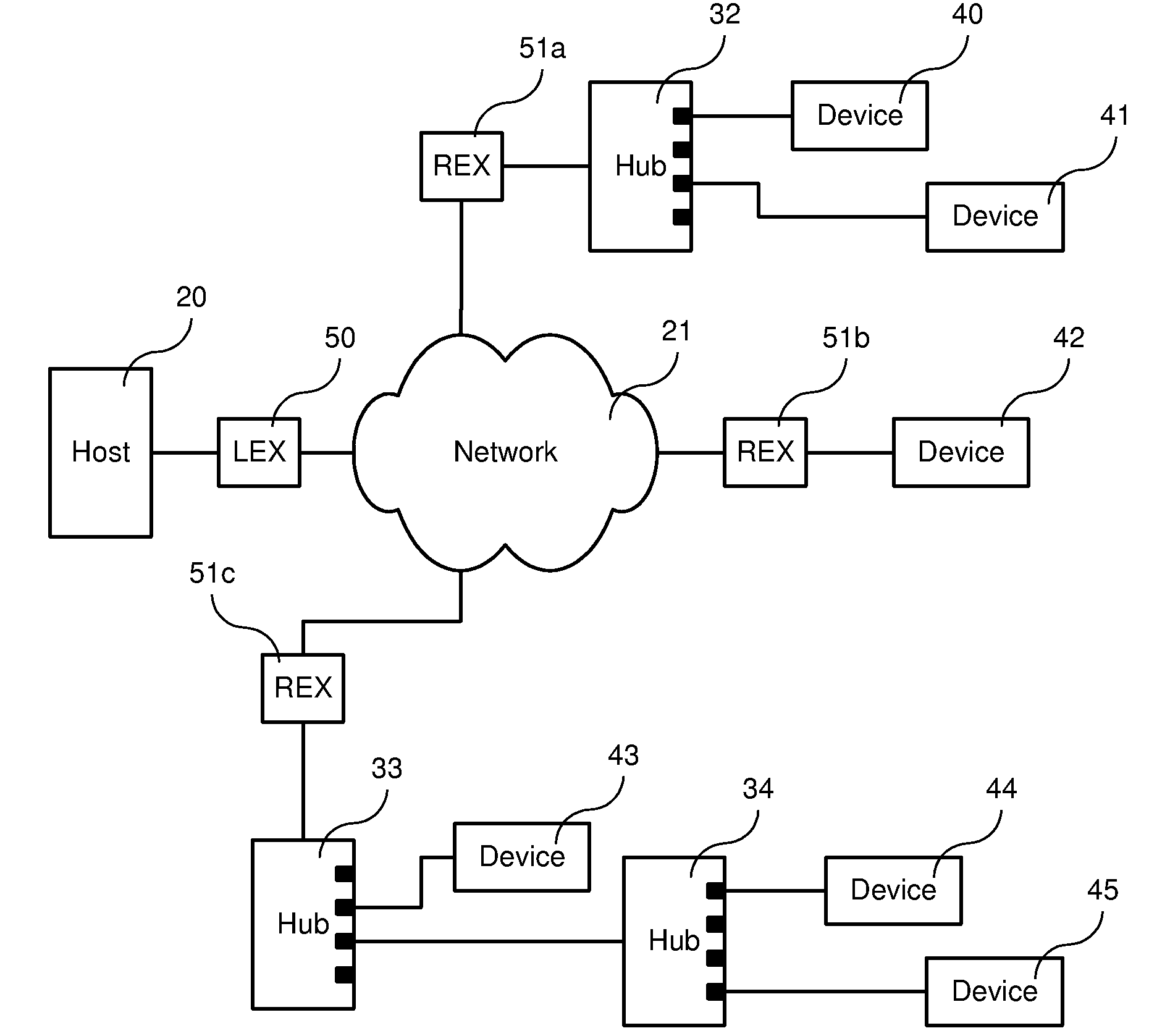
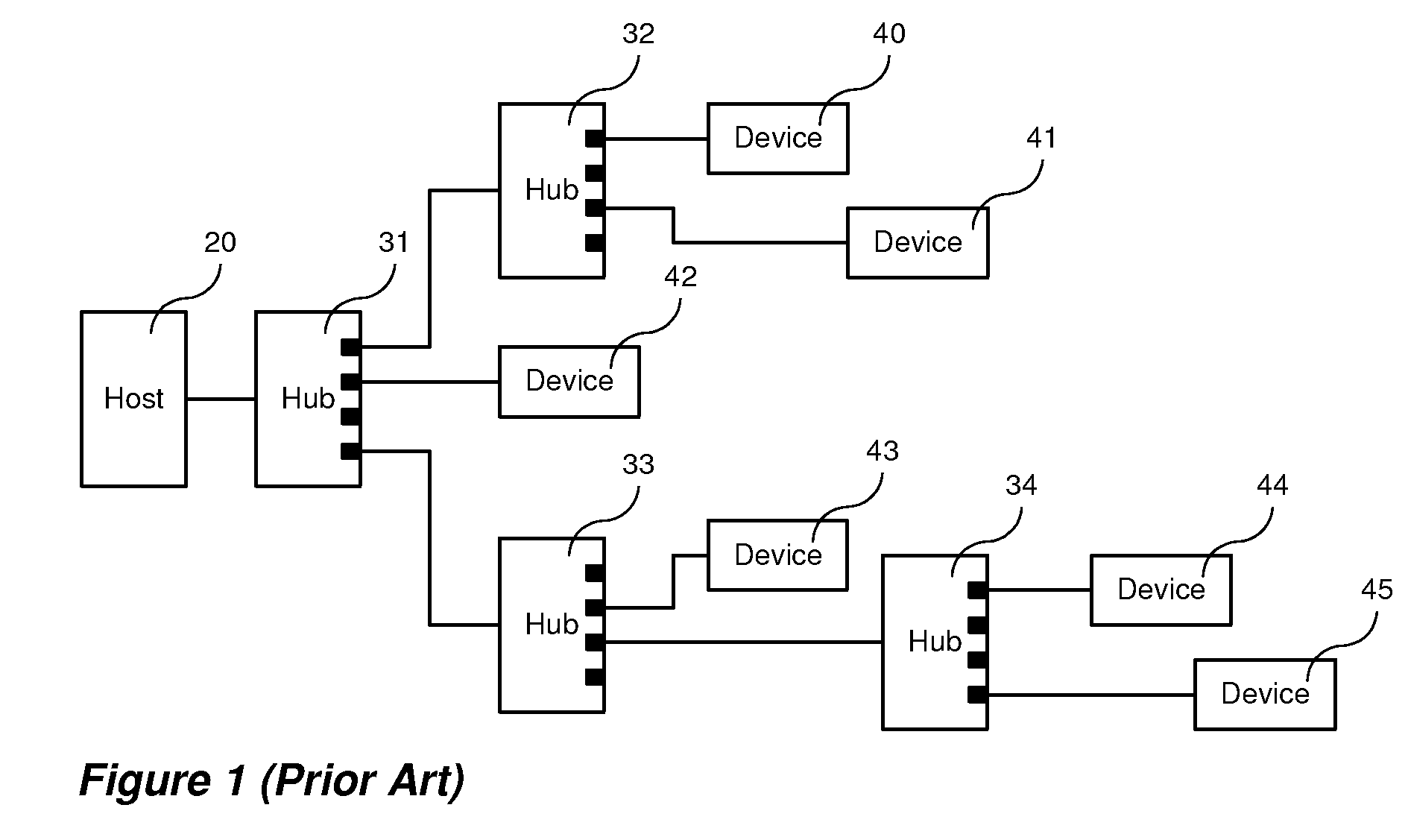
Method and apparatus for distributing USB hub functions across a network
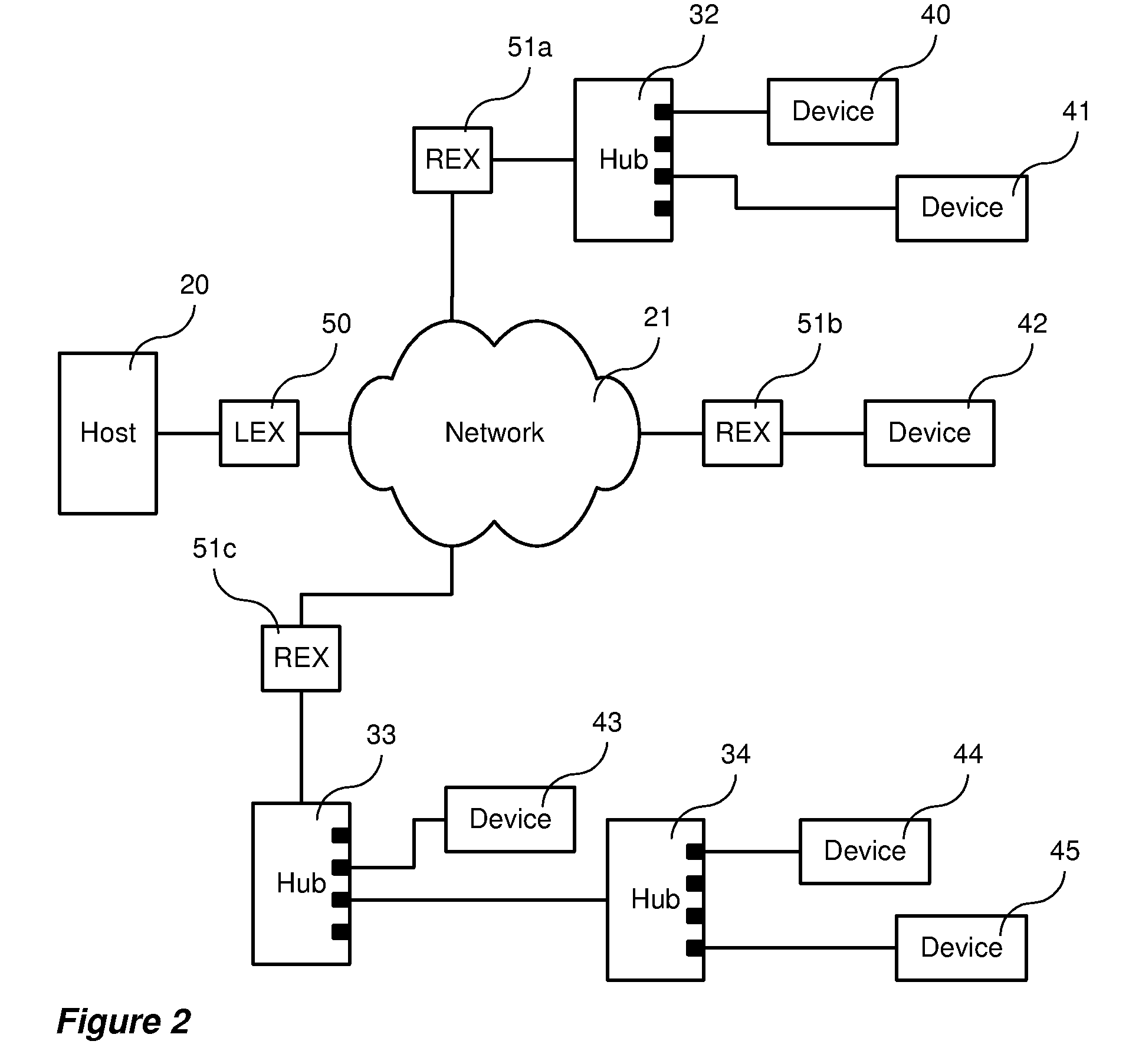
ActiveUS7587536B2Cost effectiveData switching by path configurationElectric digital data processingTime delaysUSB hub
A method and related apparatuses for data transmission between a host computer and one or a plurality of USB compliant peripheral devices over a data communications network is provided which operates in the presence of transmission delays greater than that normally allowed in the USB specification. The host computer is connected to a local extender device which, in turn, is connected to one or a plurality of remote extender devices through the data communications network. The remote extender devices are, in turn, connected to a plurality of conventional USB peripheral devices. Data between the host computer and peripheral devices is stored and processed in the local and remote extender devices in order to allow the host computer and the USB peripheral devices to operate with greater than normally allowed time delays. In particular, the invention is of most utility when the round-trip transmission delay between the host computer and the USB peripheral device exceeds 1 microsecond.
Owner:ICRON TECH
Mechanisms for avoiding problems associated with network address protocol translation
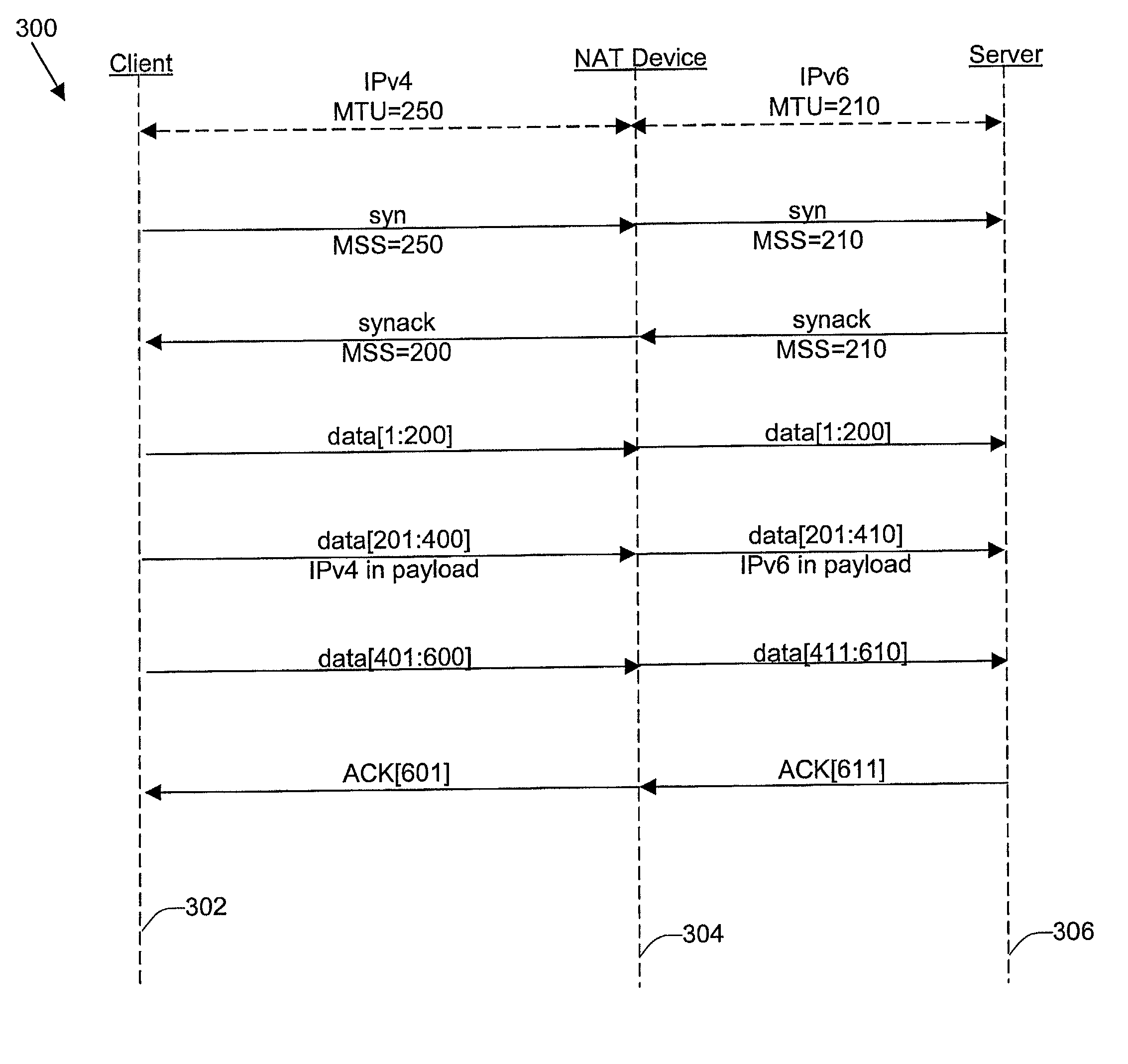
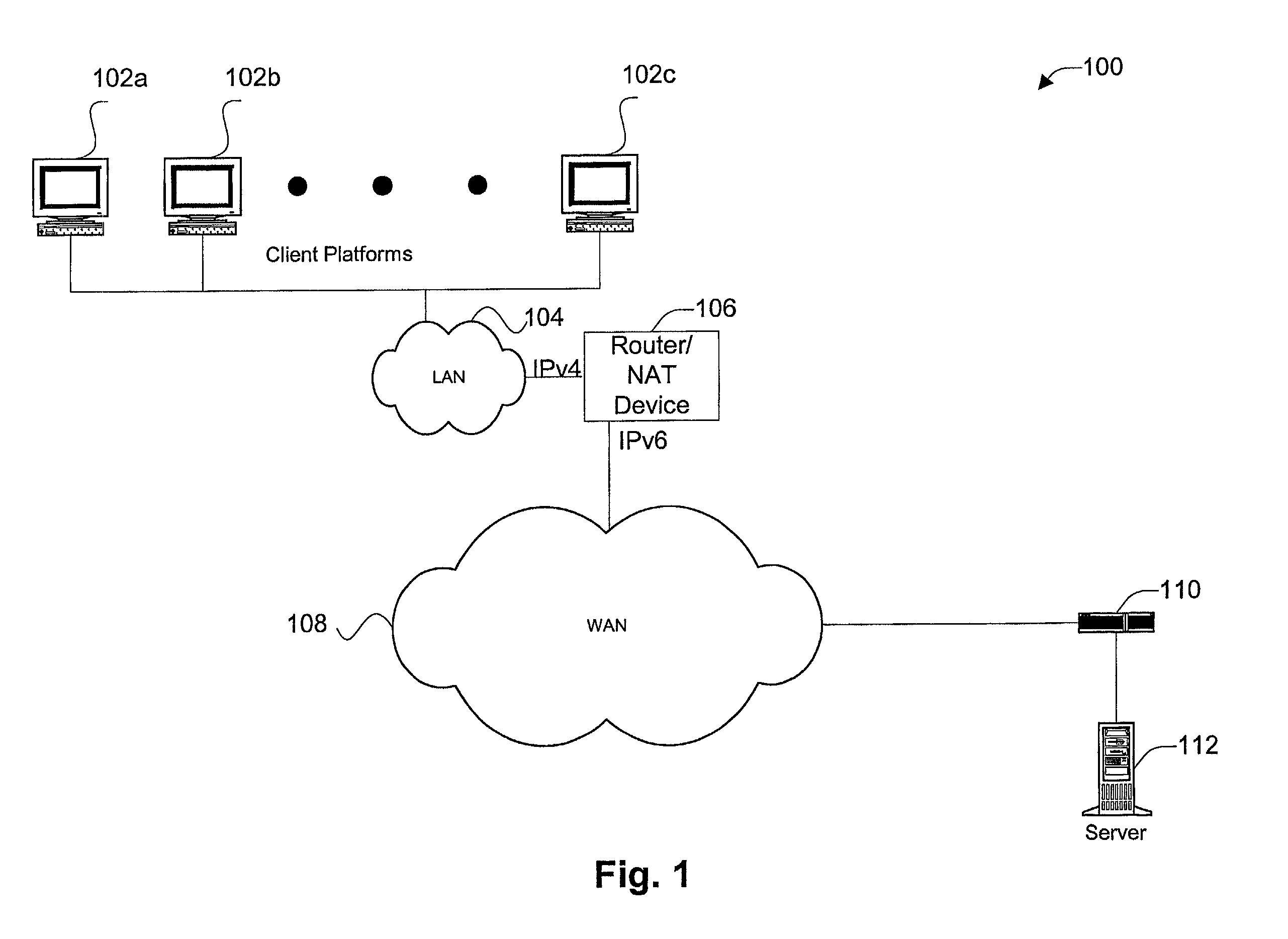
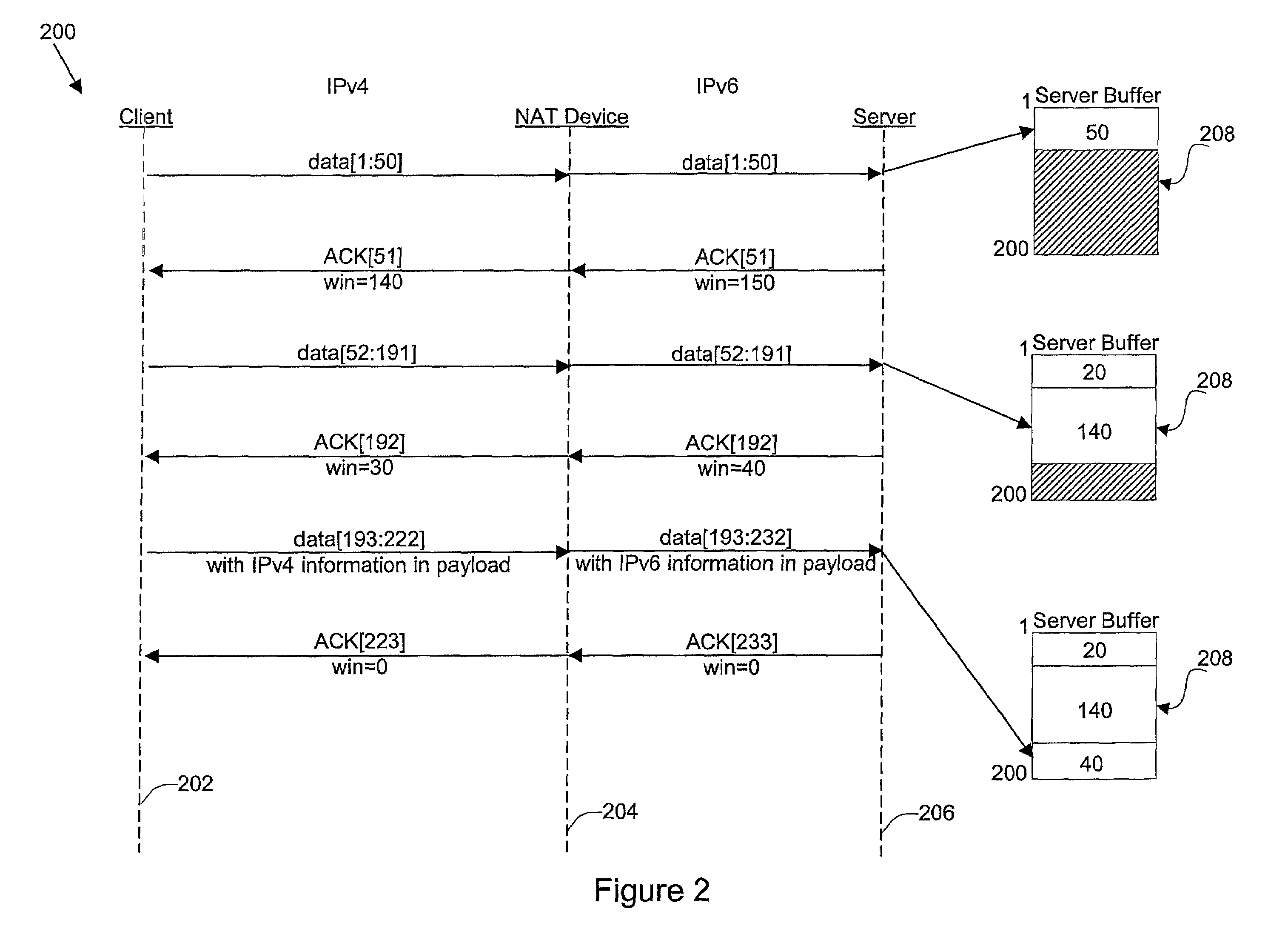
ActiveUS7006526B1Avoid problemsReduce morbidityError preventionTransmission systemsSize differenceSize increase
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for avoiding problems caused by converting between two different protocols, such as IPv4 and IPv6. These problems may include, but are not limited to, fragmentation of packets, dropping of packets, and retransmission of packets. Avoiding these problems will reduce the incidence of transmission delays, bandwidth degradation, and additional processing in the packet's transmission path due to such problems. In general terms, the present invention provides mechanisms for modifying a protocol parameter, such as a TCP or UDP parameter, to avoid problems associated with protocol translation, such as fragmentation. In one implementation, the protocol parameter limits the size of a particular portion of the a packet transmitted by a sending computer node or device. For example, a packet size indicator is communicated to the sending computer node so that the sending computer node sends packets limited by the packet size indicator to thereby avoid associated with the size of such packets. In specific TCP embodiments, the size indicator specifies a window size and / or a maximum segment size. For example, if packets transmitted by a sending node to a receiving node are converted from IPv4 to IPv6 and the window size indicated to the sending node (e.g., by the receiving node) is 512 bytes, the window size is adjusted to 500 bytes before reaching the sending node. The adjustment amount may be based on an estimated size increase resulting from converting from IPv4 to IPv6. In this example, the window size is decreased by 12 bytes since a conversion from IPv4 to IPv6 where one 4 byte IPv4 address is changed to a 16 byte Ipv6 address has an associated size difference of 12 bytes. In a specific embodiment, actual changes in packet size may tracked and the adjusted size indicator may be dynamically based on such tracked changes. In other embodiments, the changes in packet size are predicted, and the adjusted size is preemptively changed as needed.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
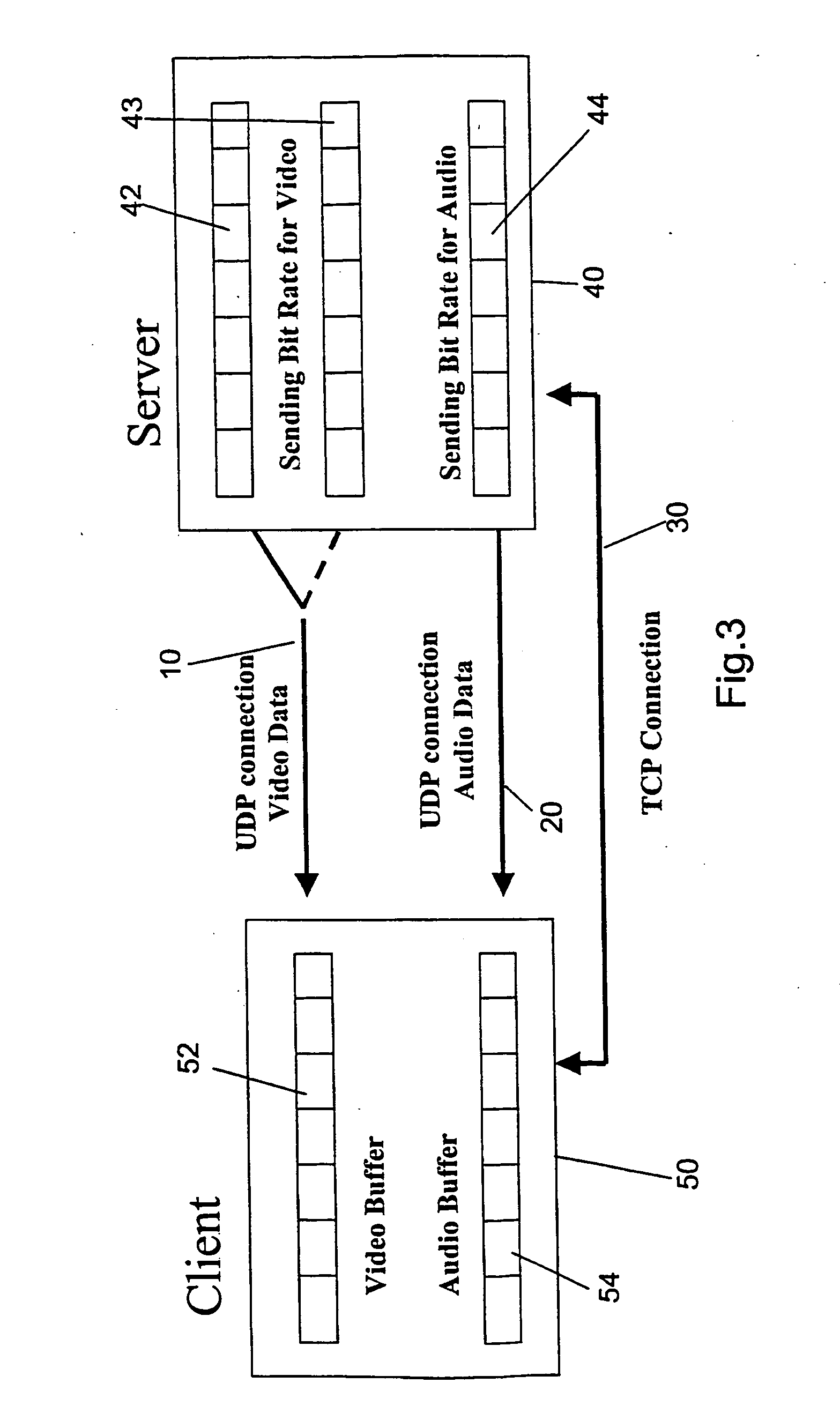
Data communications method and system using buffer size to calculate transmission rate for congestion control
InactiveUS20050021830A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksData streamClient-side
A data transmission method and system is disclosed in which one or more data streams are transmitted at respective transmission rates which are controlled to prevent data buffers in the receiver from overflowing. In some embodiments feedback data concerning the state of each buffer in a receiving client is received at the transmitting server, and used to adapt the sending rates to achieve the effect. Information indicative of the data decode rates or the fill extent of each buffer is communicated to the server as the feedback data. In other embodiments the server makes an open-loop estimate of the remaining space in the buffer, and controls the transmission rate accordingly. A data receiving method and system adapted to receive the data streams is also disclosed.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
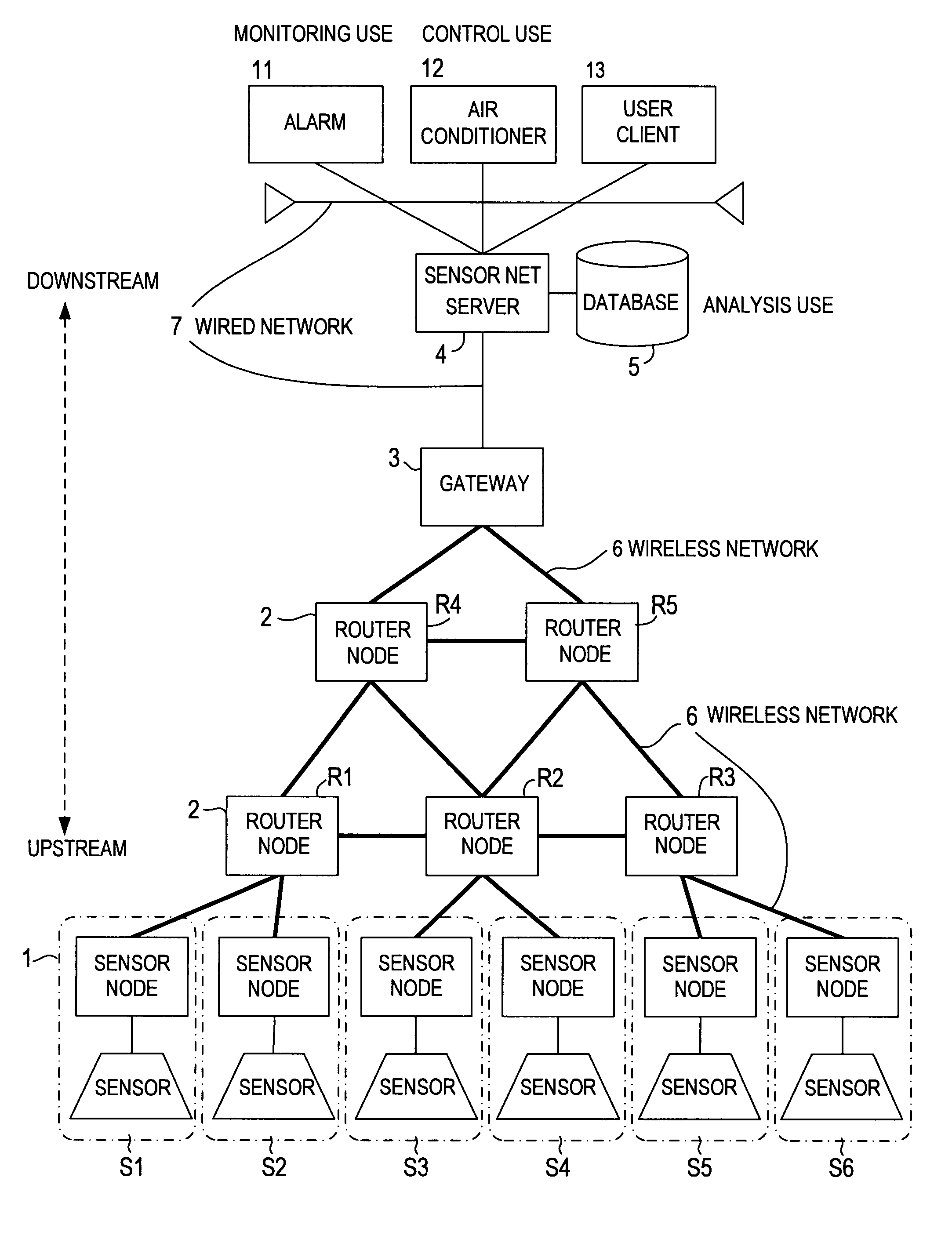
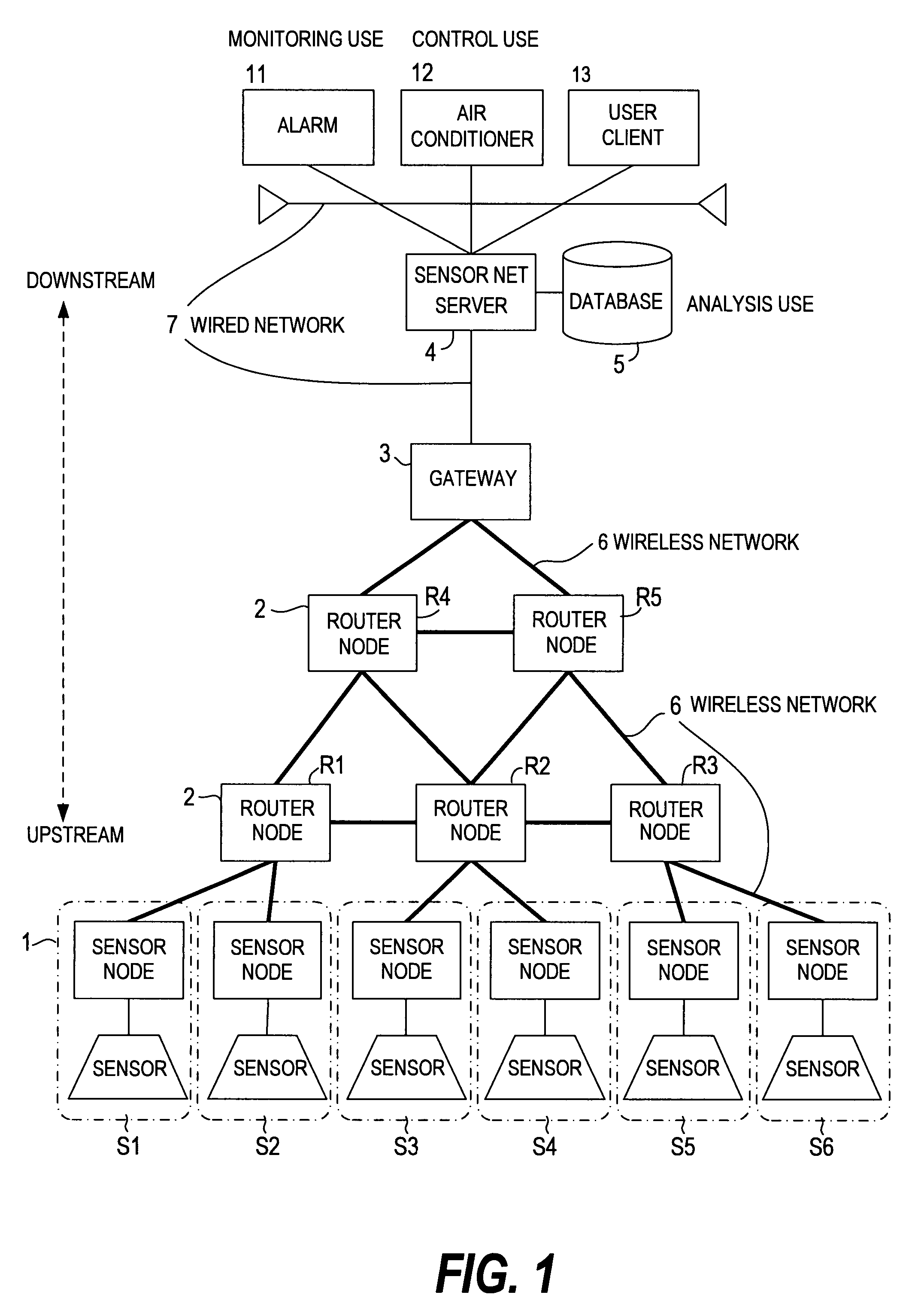
Sensor network system and data processing method for sensor network
InactiveUS8159945B2Prevent overloadEnsures reliability of a sensor net systemError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementSensor nodeReal time transmission
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Variable transmission rate services in a radio access network
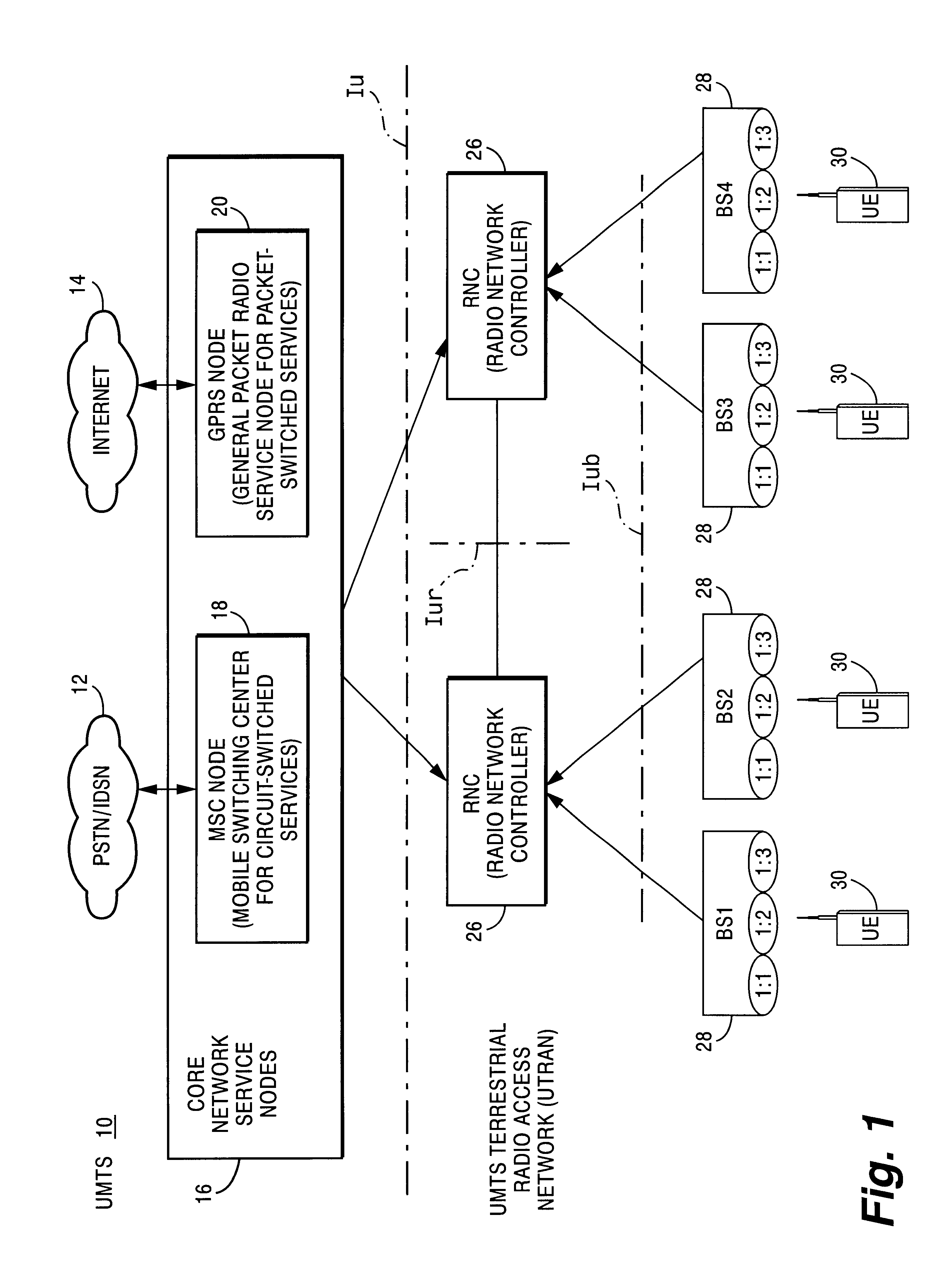
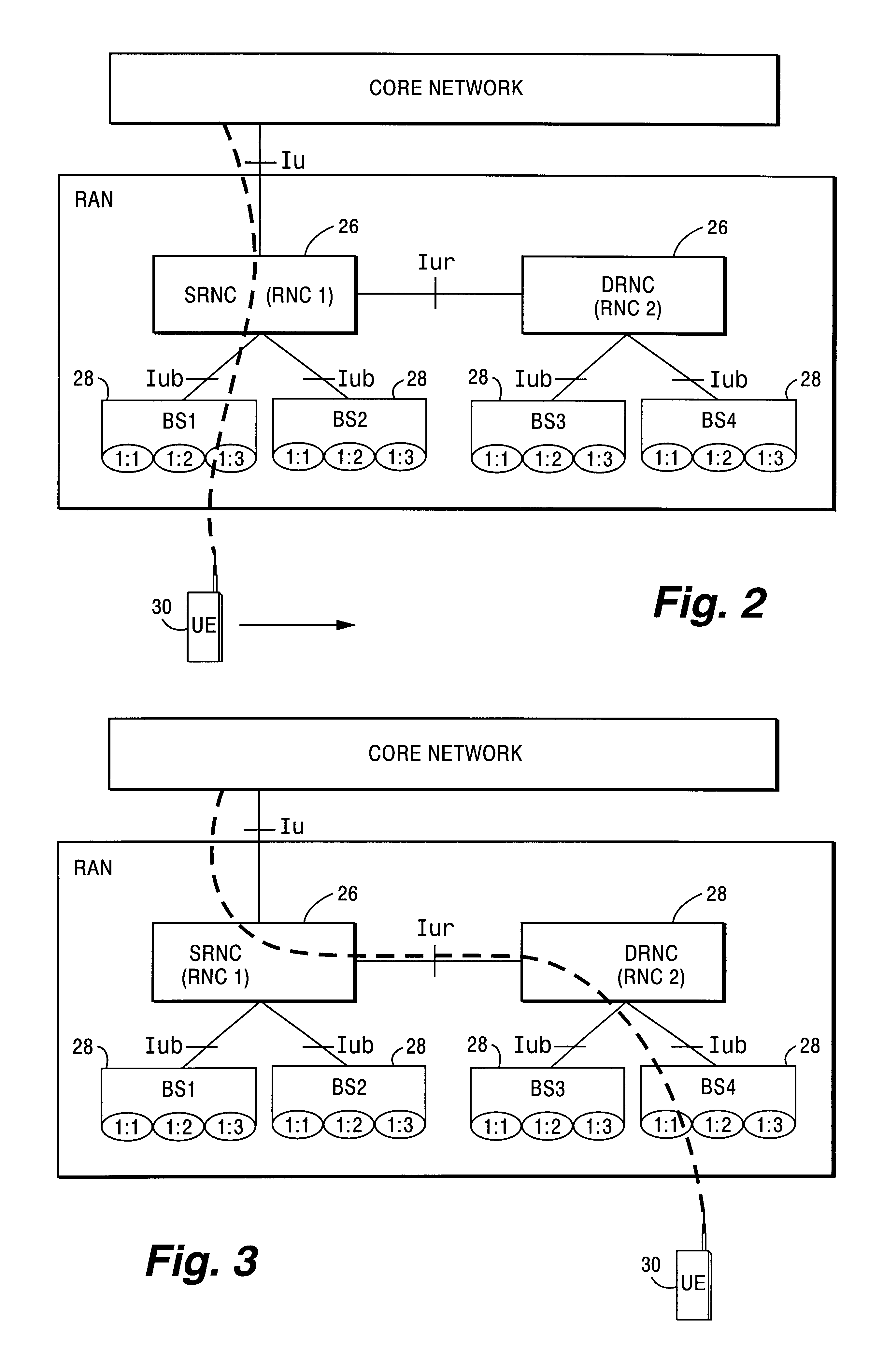
InactiveUS6889050B1Increase capacityNo disruption to callNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationRadio networksTransmission delay
A connection is supported in a radio access network (RAN) between an external network to a UE using a first RAN node and second RAN node. The transmission rate from the first RAN node to the second RAN node is regulated based on a rate control request from the second RAN node. In one example embodiment, the first and second RAN nodes correspond to a serving radio network controller and a drift radio network controller, respectively. In another example embodiment, the first and second RAN nodes correspond to a radio network controller and radio base station, respectively. The rate control request is made based upon a congestion or load condition being monitored by the second RAN node. When the load condition is detected, the second RAN node requests the first RAN node to lower the transmission rate of information. Conversely, when the load condition is relieved, the second RAN node can request that the first RAN node increase the transmission rate of information. The rate control may be applied in both downlink and uplink directions.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
Synchronous shift execution for hybrid transmission
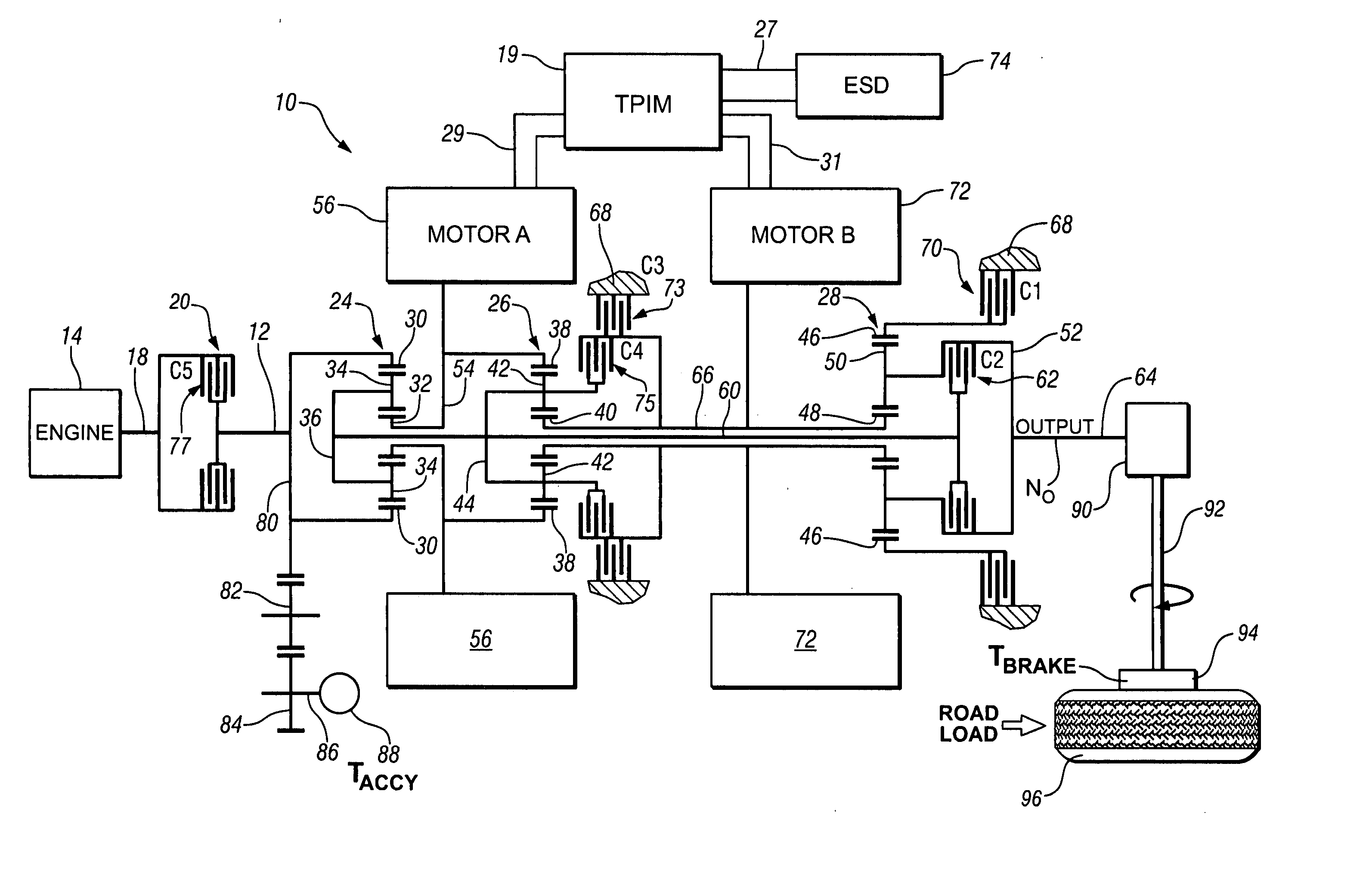
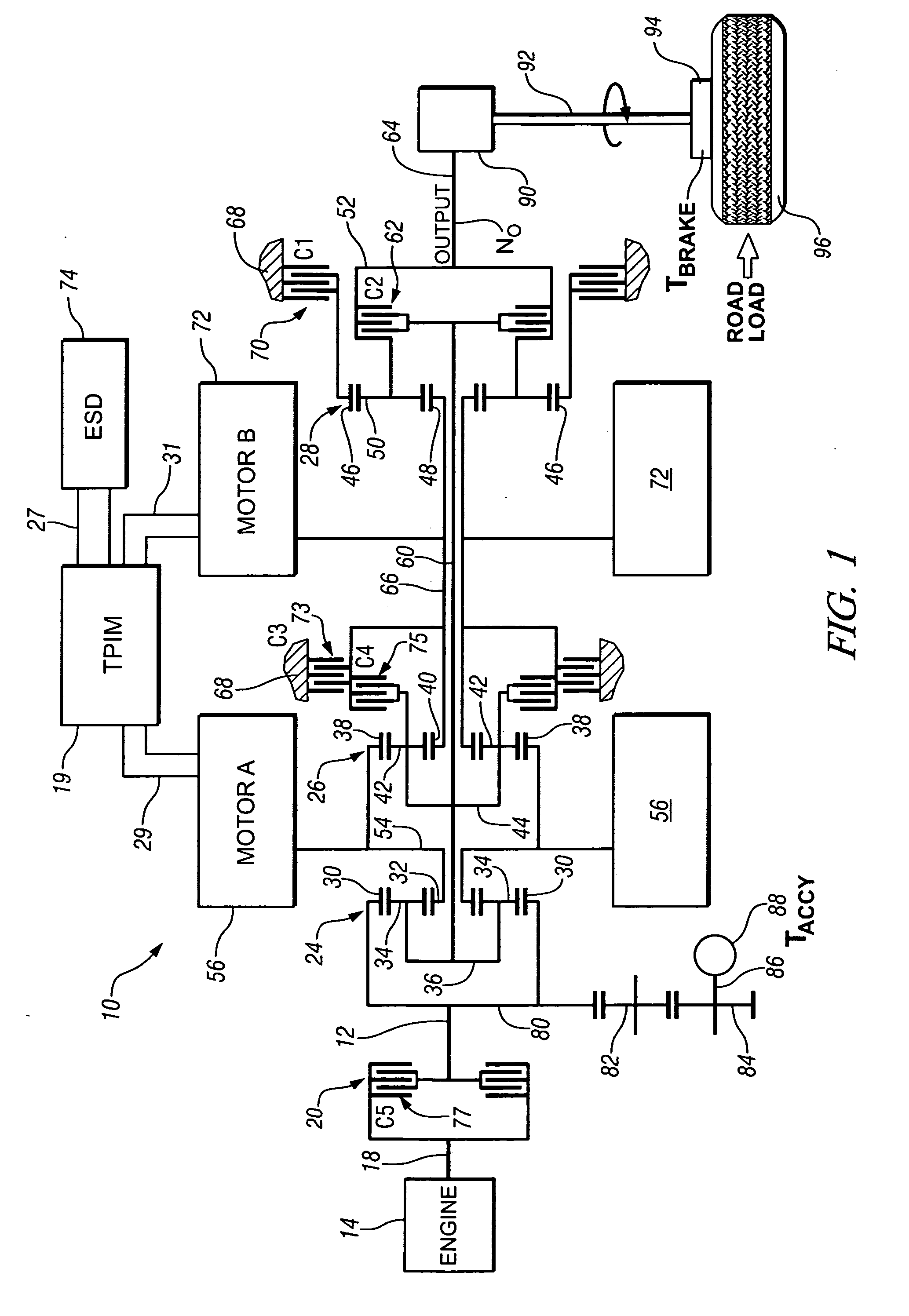
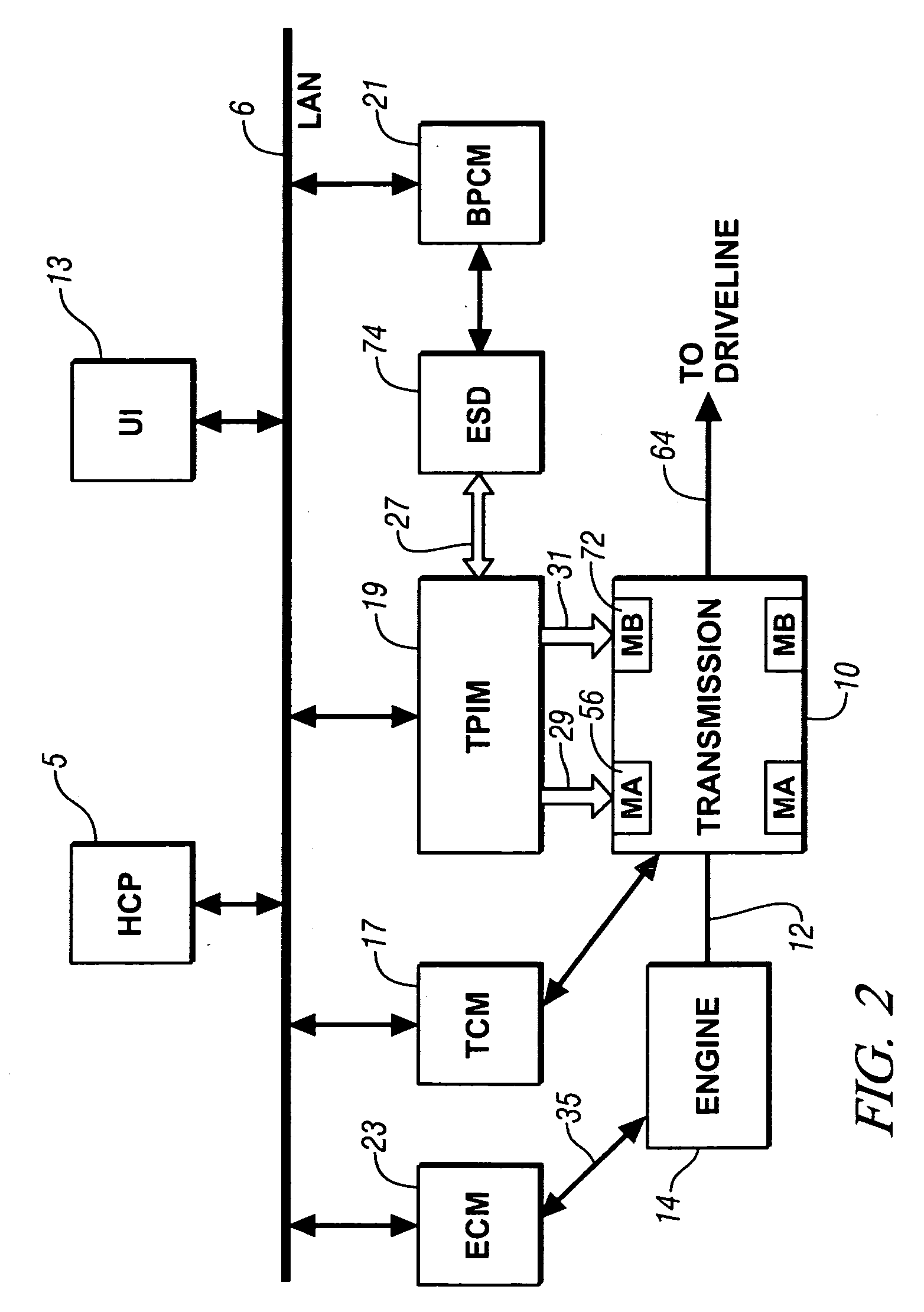
InactiveUS20070260381A1Reduce capacityReducing motive torqueHybrid vehiclesDC motor speed/torque controlControl systemClutch
An apparatus and method are provided to execute synchronous shifting in a powertrain system having multiple torque-generative devices each operable to independently supply motive torque to the transmission device. The exemplary transmission device comprises a two-mode, compound-split, hybrid electromechanical transmission. Operation includes operating in an initial fixed gear ratio, operating the transmission in a mode operation, and, operating the transmission in a final fixed gear ratio. The control system reduces reactive torque of a clutch activating the initial gear, and deactivates the first torque-transfer device when the reactive torque is less than a predetermined value. It determines that speed of an input shaft to the transmission is substantially synchronized with a rotational speed of the second torque-transfer device, and actuates the second torque-transfer device.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
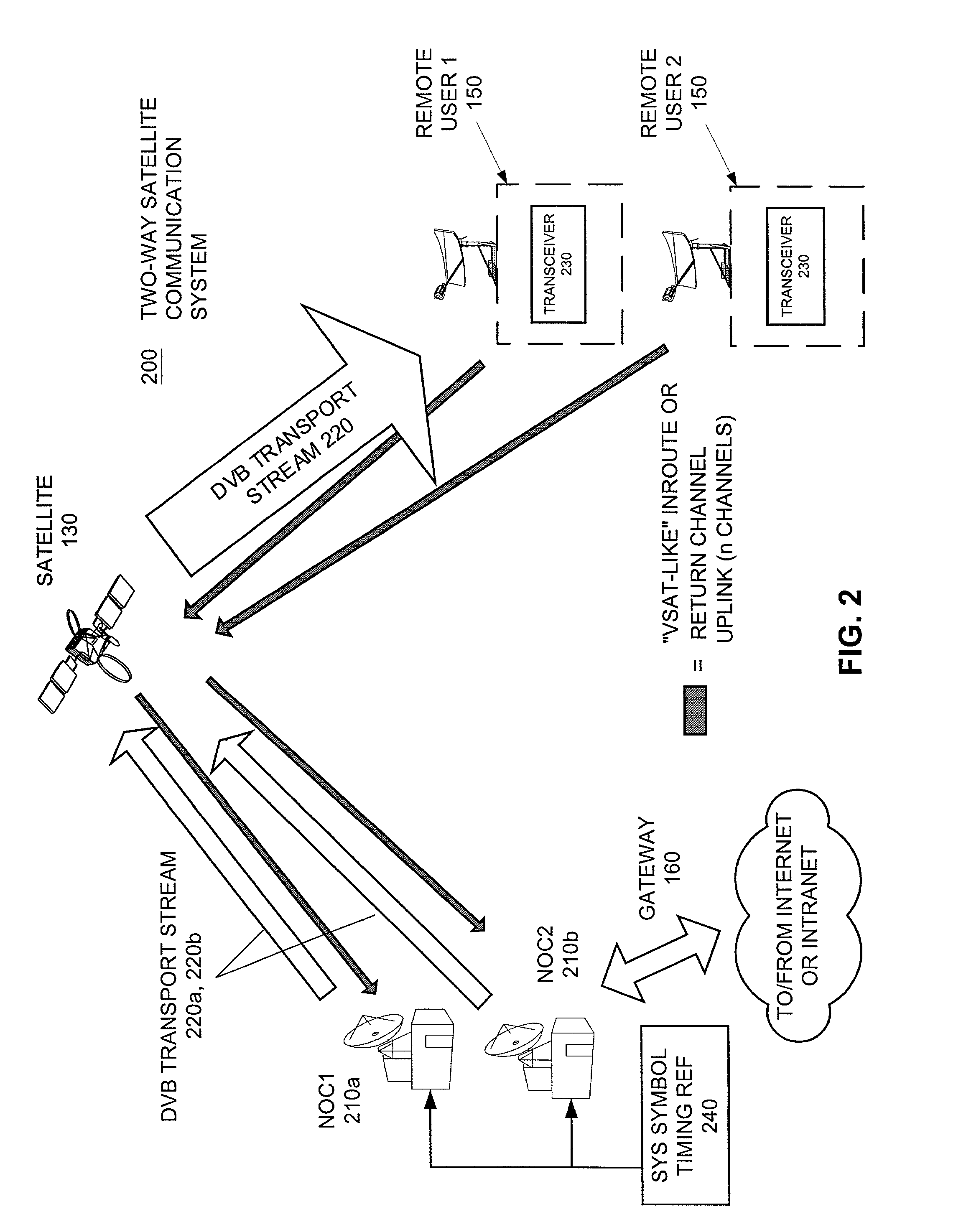
Method and apparatus for deriving uplink timing from asynchronous traffic across multiple transport streams
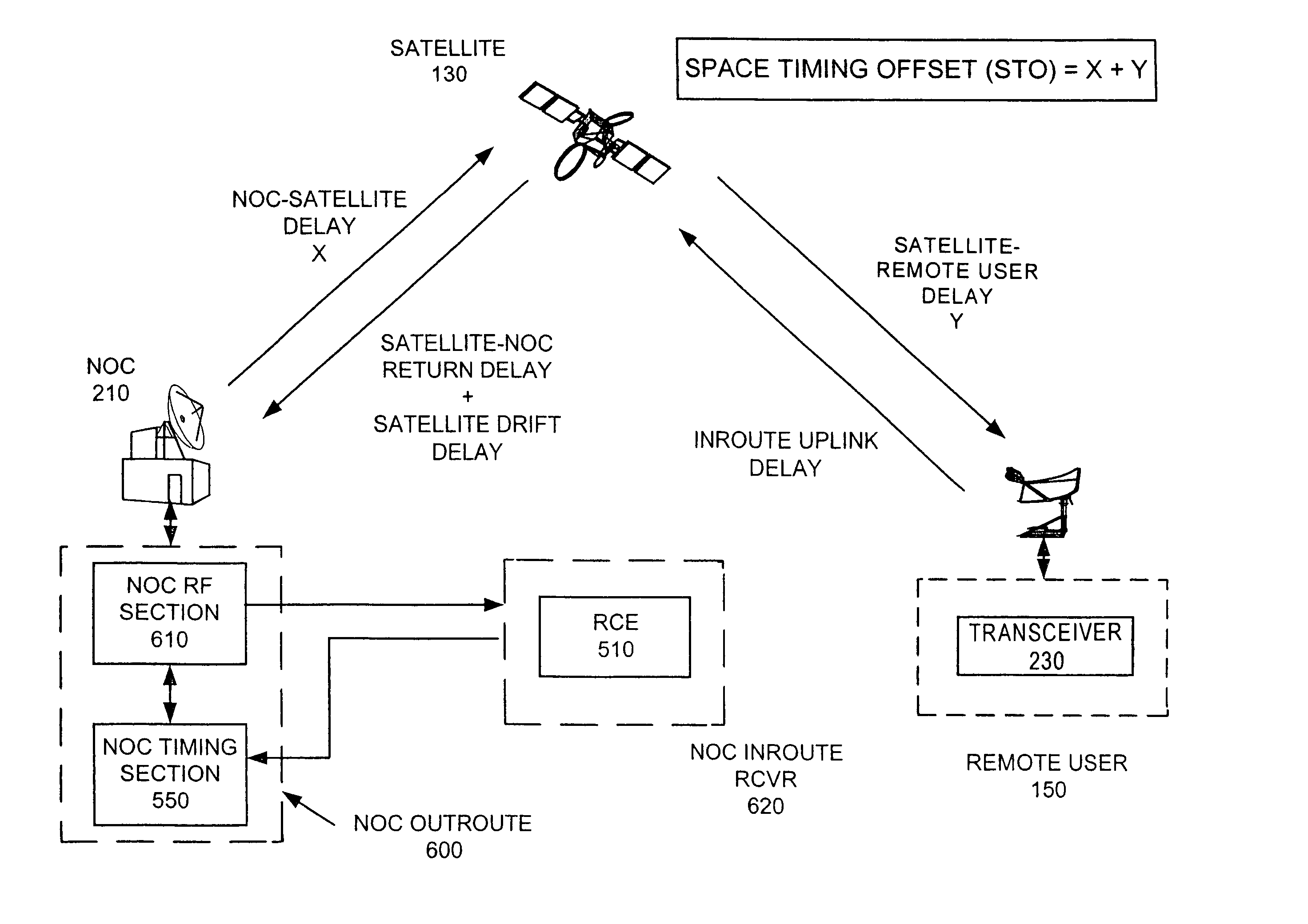
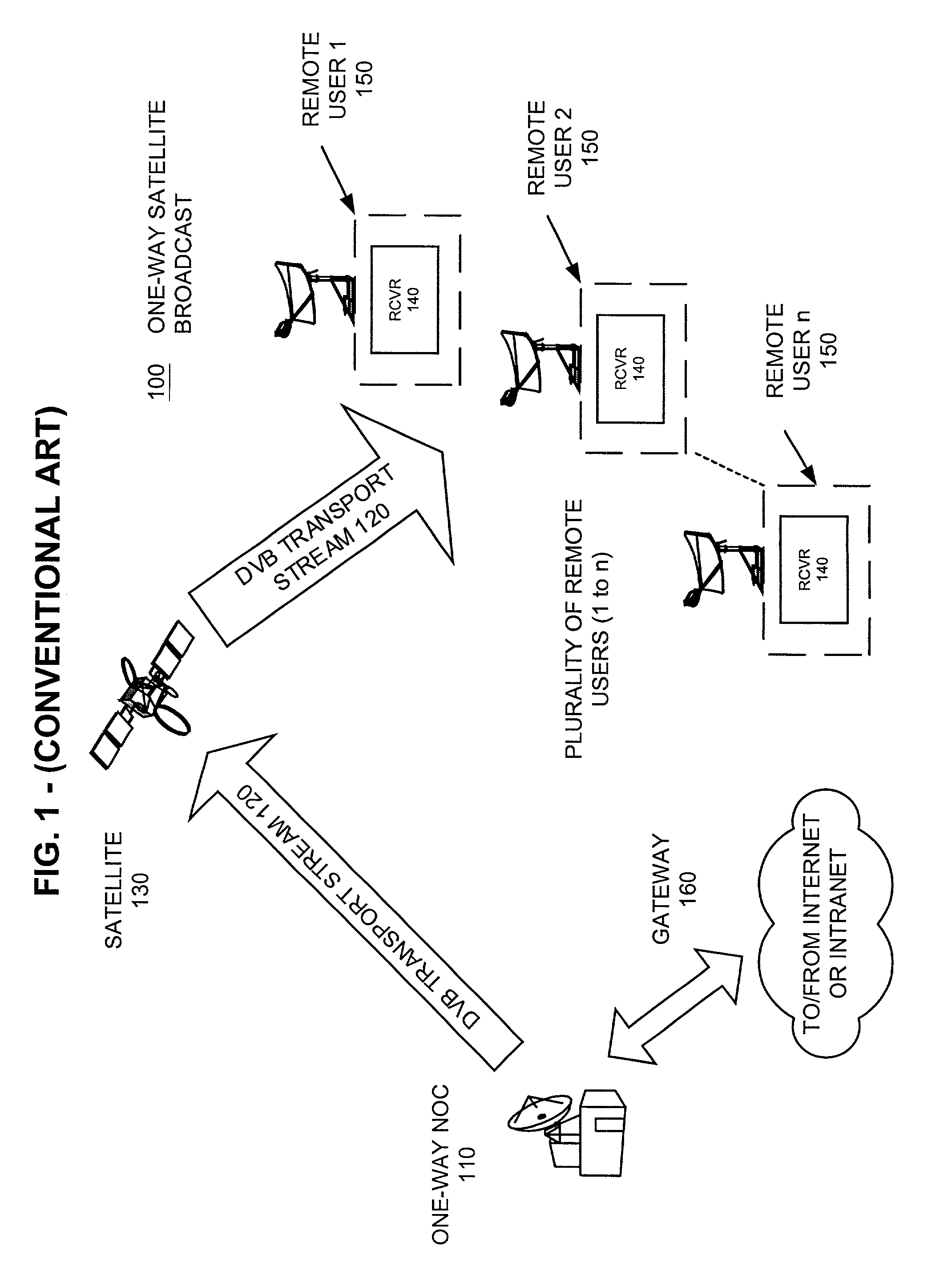
InactiveUS6993009B2Reduce collisionLow-cost and accurateTime-division multiplexRadio transmissionNon real timeData stream
A communication apparatus that shares precise return channel uplink timing information includes a common symbol timing reference and one or more control stations that each transmit independent asynchronous DVB data streams which evenly share the common symbol timing. The control stations each include respective delay trackers to determine broadcast transmission delays associated with the particular control station and transmission path. Each broadcast data stream includes the same non real-time frame marker and a transmission delay message particular to the respective control station. A remote receiver receives one of the broadcast streams and timestamps the non real-time frame marker with a local time of receipt. A timing recovery circuit determines an upcoming return channel frame start time by adjusting the local time of receipt by the particular broadcast transmission delay and a unique receiver offset time. A local transmitter subsequently uplinks a TDMA message in a predetermined time-slot after the return channel frame start time. The method for transmitting a frame synchronized message includes receiving a non real-time frame reference marker in a receiver, timestamping the received frame reference marker with a reception time, and subsequently receiving a control node timing differential at the receiver. The local reception time of the non real-time frame marker is corrected to determine the proper return channel frame transmit start time by applying the control node timing differential and the local offset time. Users then uplink a message during an assigned period after the return channel frame transmit start time.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
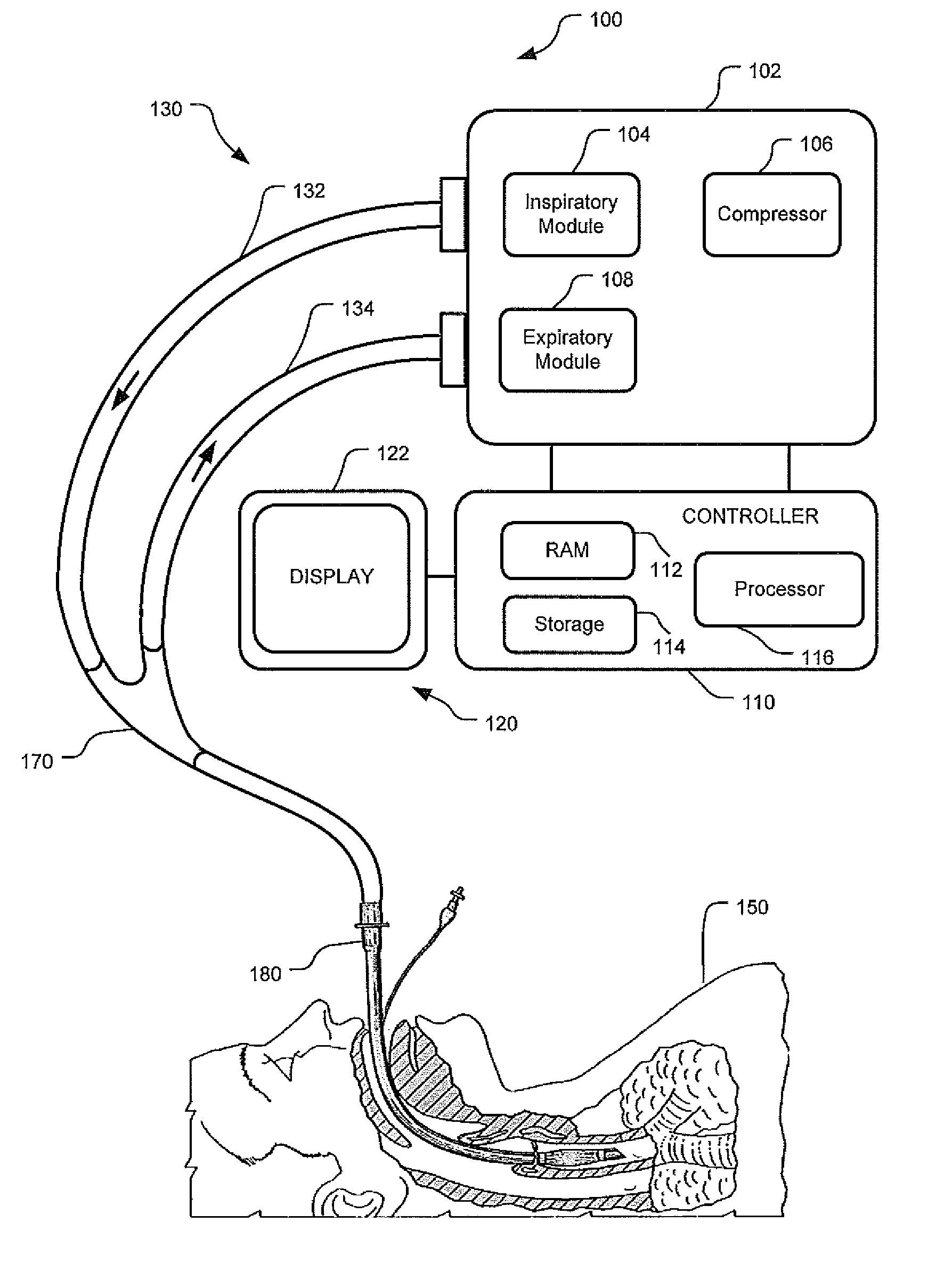
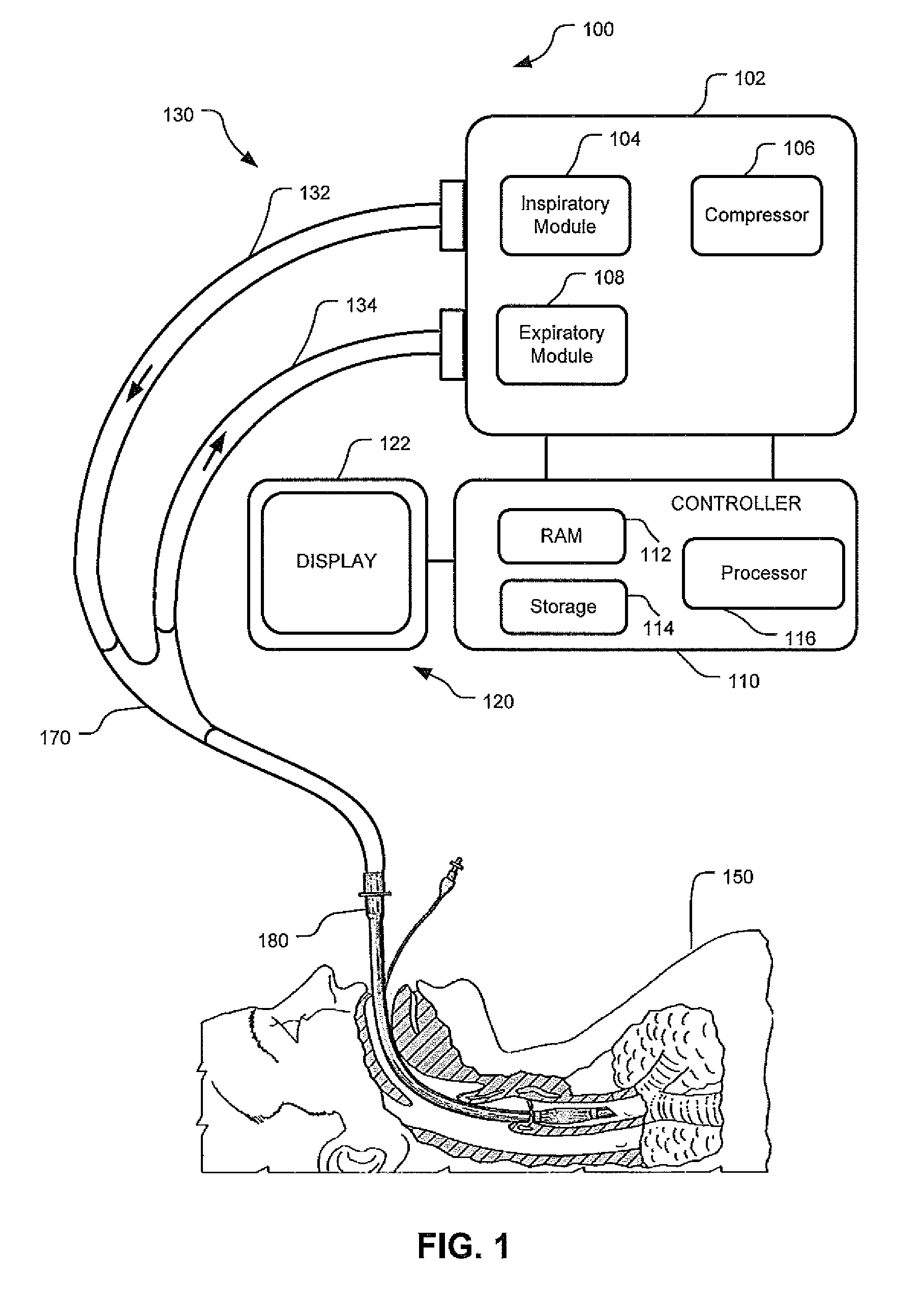
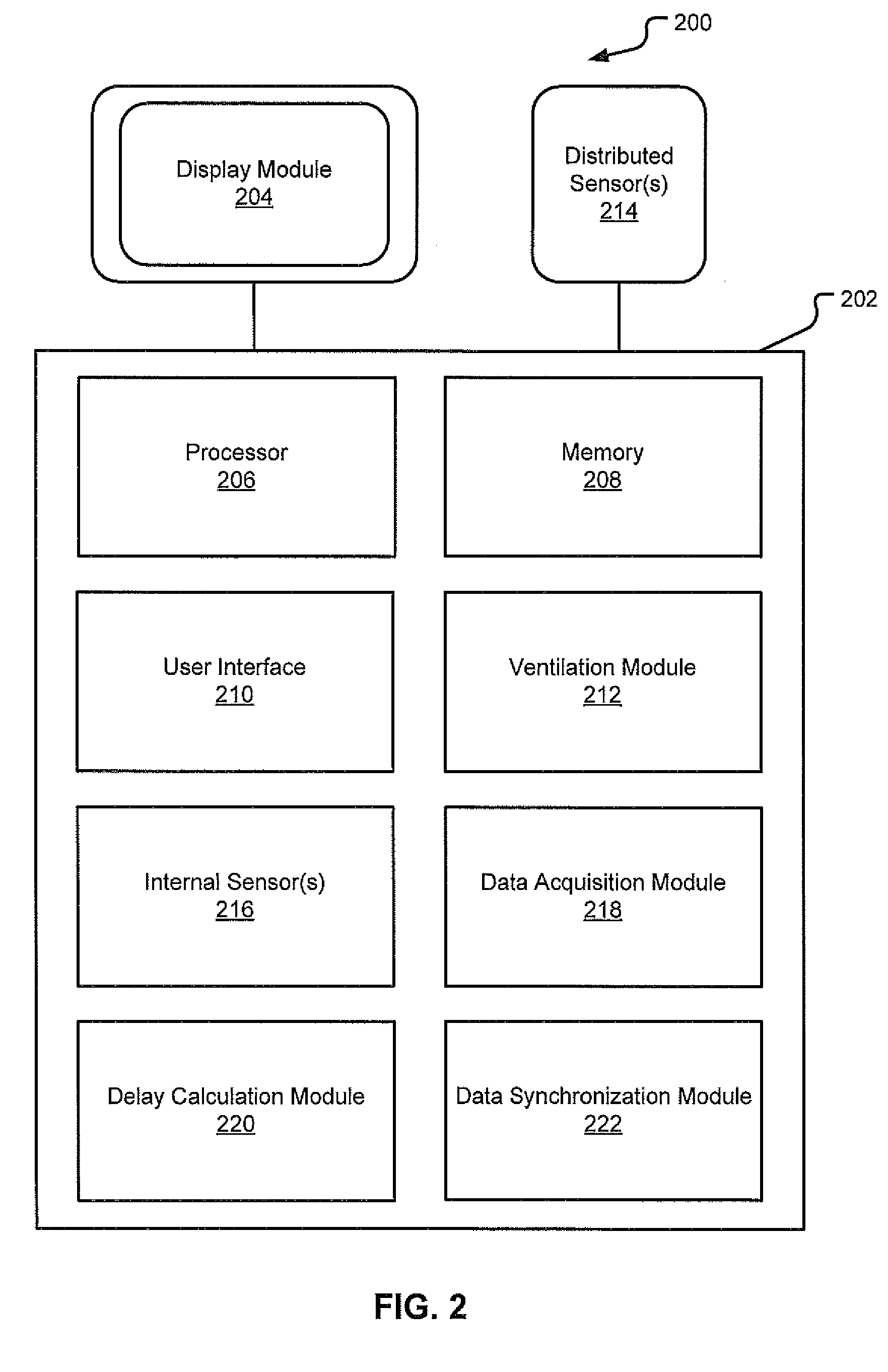
Event-Based Delay Detection And Control Of Networked Systems In Medical Ventilation
ActiveUS20110209704A1Increase flexibilityImprove performanceRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPresent methodNetworked system
This disclosure describes systems and methods for detecting and quantifying transmission delays associated with distributed sensing and monitoring functions within a ventilatory system. Specifically, the present methods and systems described herein define an event-based delay detection algorithm for determining transmission delays between distributed signal measurement and processing subsystems and a central platform that receives data from these subsystems. It is important to evaluate and quantify transmission delays because dyssynchrony in data communication may result in the misalignment of visualization and monitoring systems or instability in closed-loop control systems. Generally, embodiments described herein seek to quantify transmission delays by selecting a ventilator-based defining event as a temporal baseline and calculating the delay between the inception of the defining event and the receipt of data regarding the defining event from one or more distributed sensing devices.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
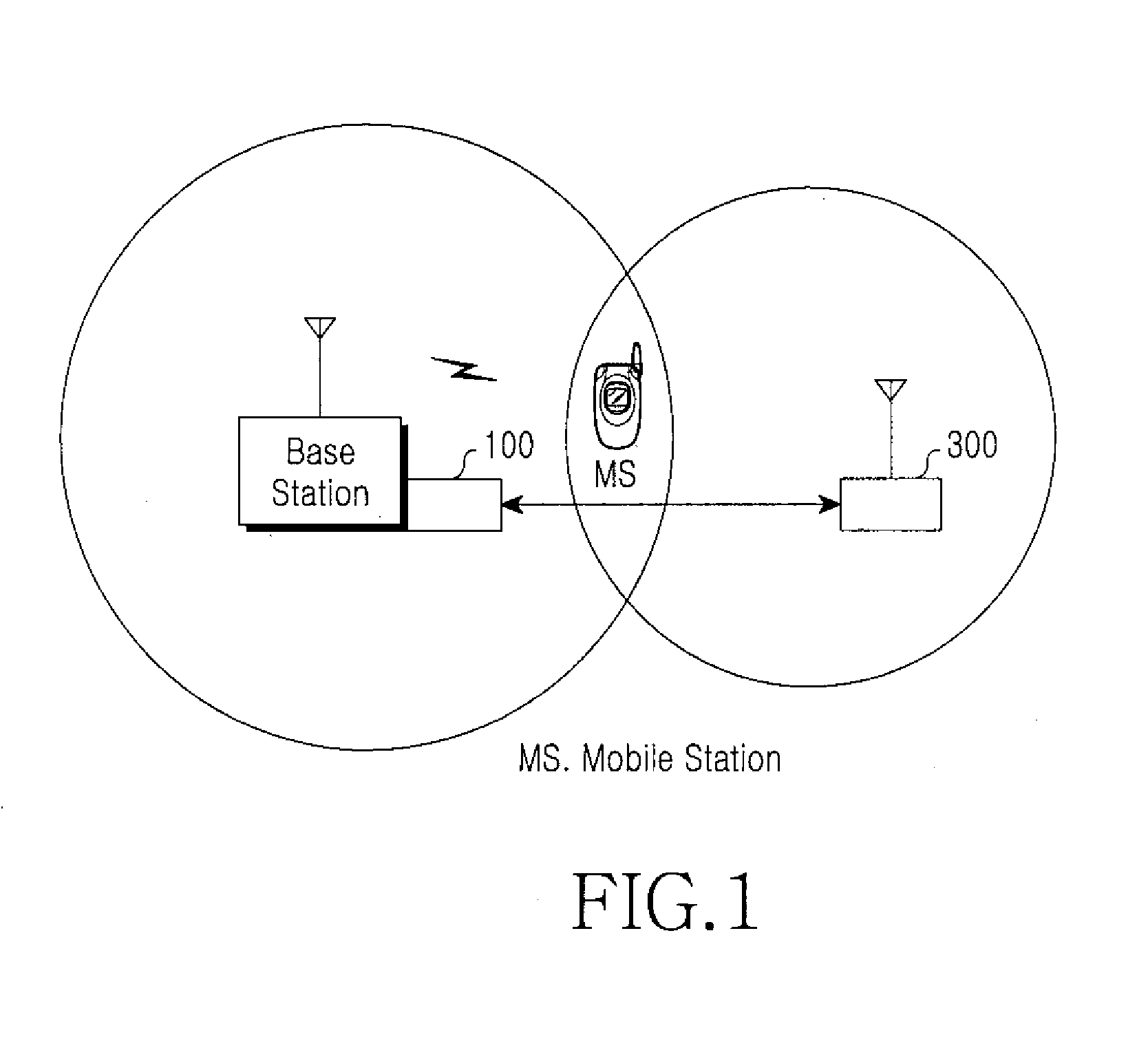
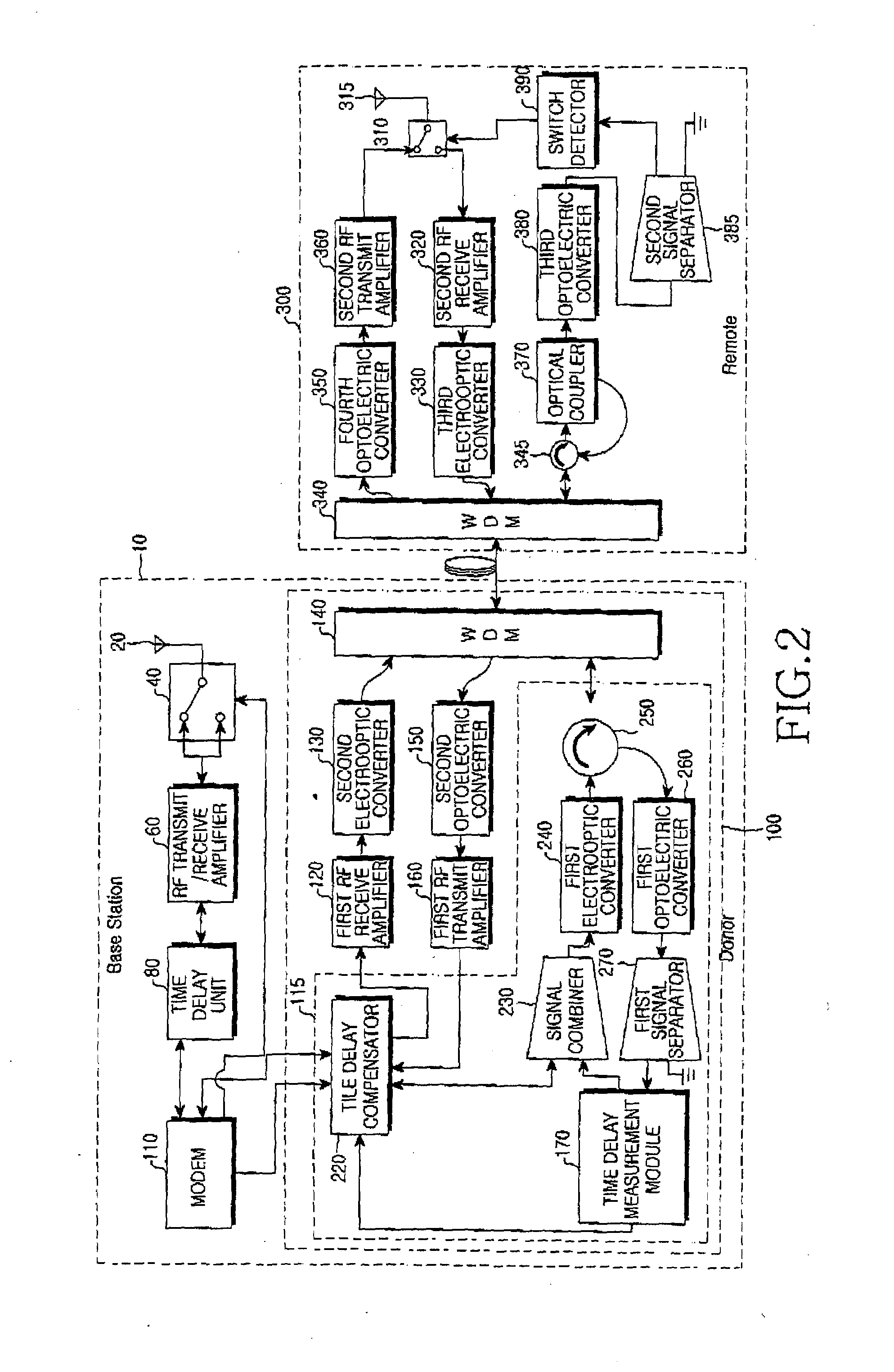
Radio over fiber system and method for controlling transmission time
InactiveUS20080056167A1Improve performanceRadio-over-fibreElectromagnetic repeatersRadio over fiberCommunications system
A radio-over-fiber (RoF) system and method for controlling a transmission time is provided. In a Time Division Duplex (TDD) wireless communication system comprising a Base Station (BS) having a donor and a remote connected thereto via am optical fiber, upstream and downstream Radio Frequency (RF) signals are transmitted and received, and by reliably transmitting a switch control signal to the remote and simultaneously compensating for a transmission time delay occurring in the optical cable, time synchronization of the upstream and downstream RF signals transmitted and received via antennas of the BS and the remote is controlled, thereby efficiently increasing the performance of a TDD wireless service system.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
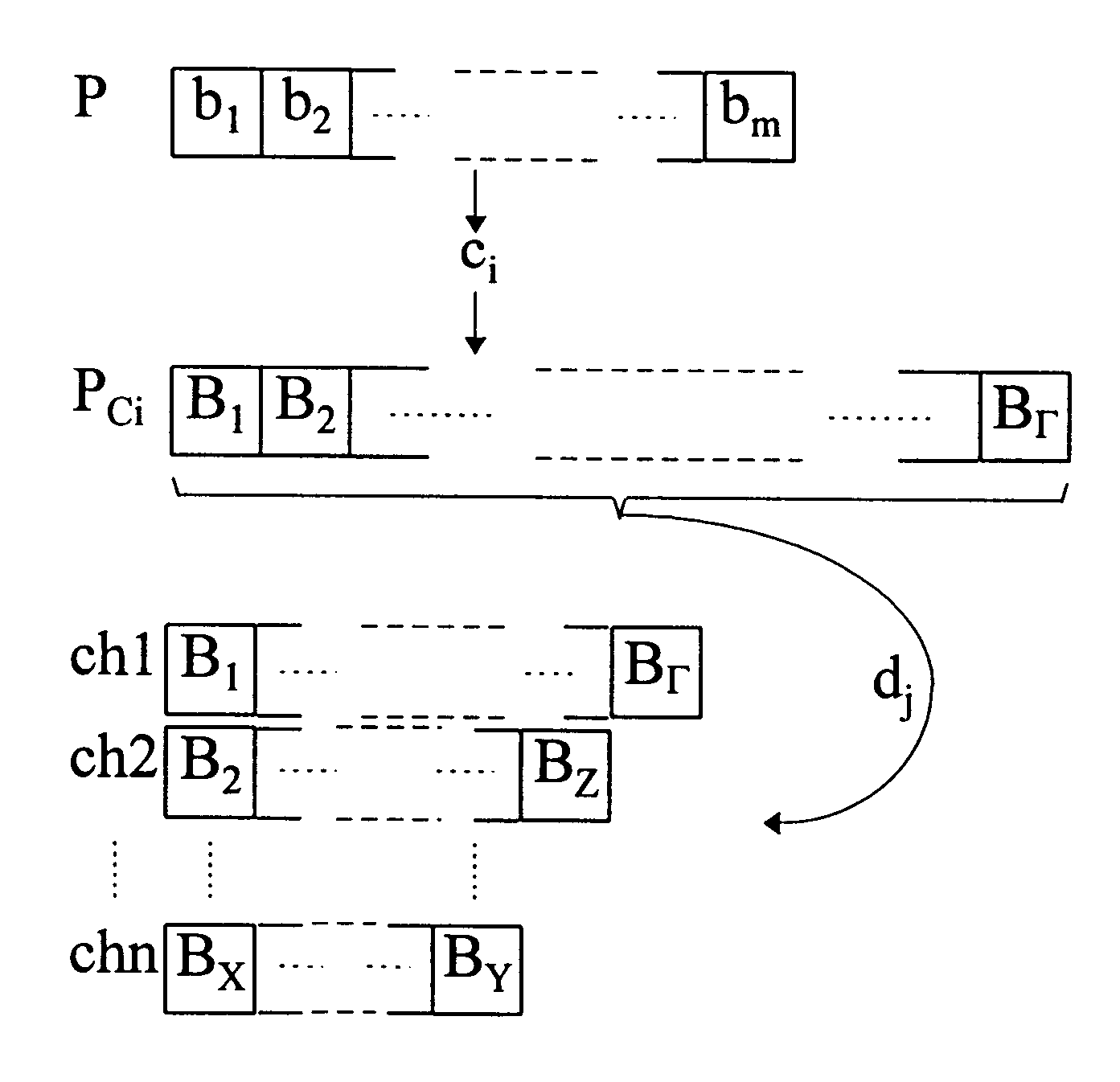
Digital telecommunication system with selected combination of coding schemes and designated resources for packet transmission based on estimated transmission time
InactiveUS6363425B1Quantity minimizationAir interface efficientlyError prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionForward error correctionMajorization minimization
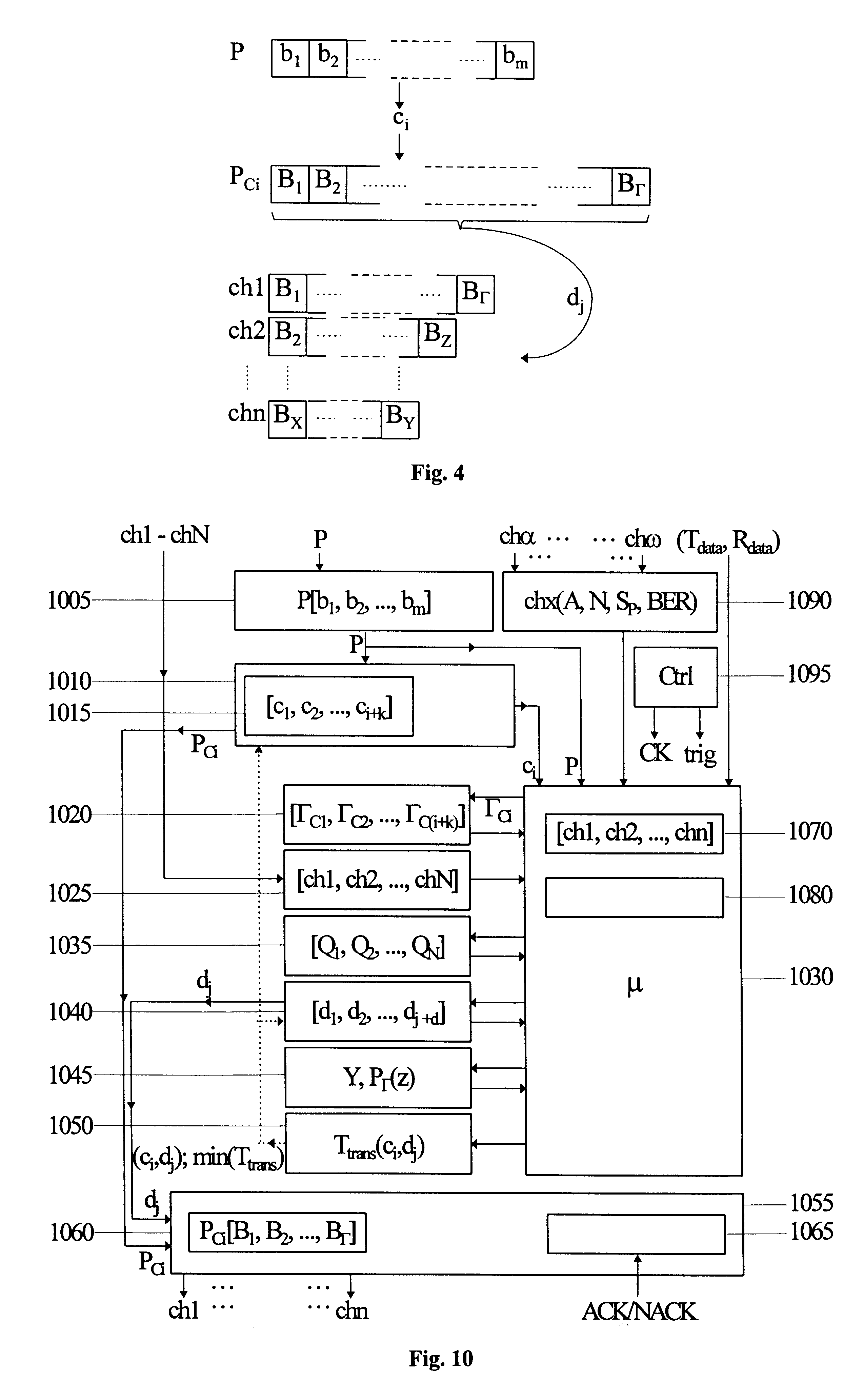
The present invention relates to a method and an arrangement for communicating packet information in a digital telecommunications system. Through the invention is selected a set of designated communication resources (ch1-chn) from an available amount of resources. Every packet (P) is forward error correction encoded into an encoded packet (Pci), via one of at least two different coding schemes (ci), prior to being transmitted to a receiving party, over the designated communication resources (ch1-chn). An estimated transmission time is calculated for all combinations of coding scheme (ci) and relevant distribution (dj) of the encoded data blocks (B1-BΓ), in the encoded packet (Pci) over the set of designated communication resources (ch1-chn), and the combination (ci,dj) is selected, which minimises the estimated transmission time.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Transmission device and transmission method
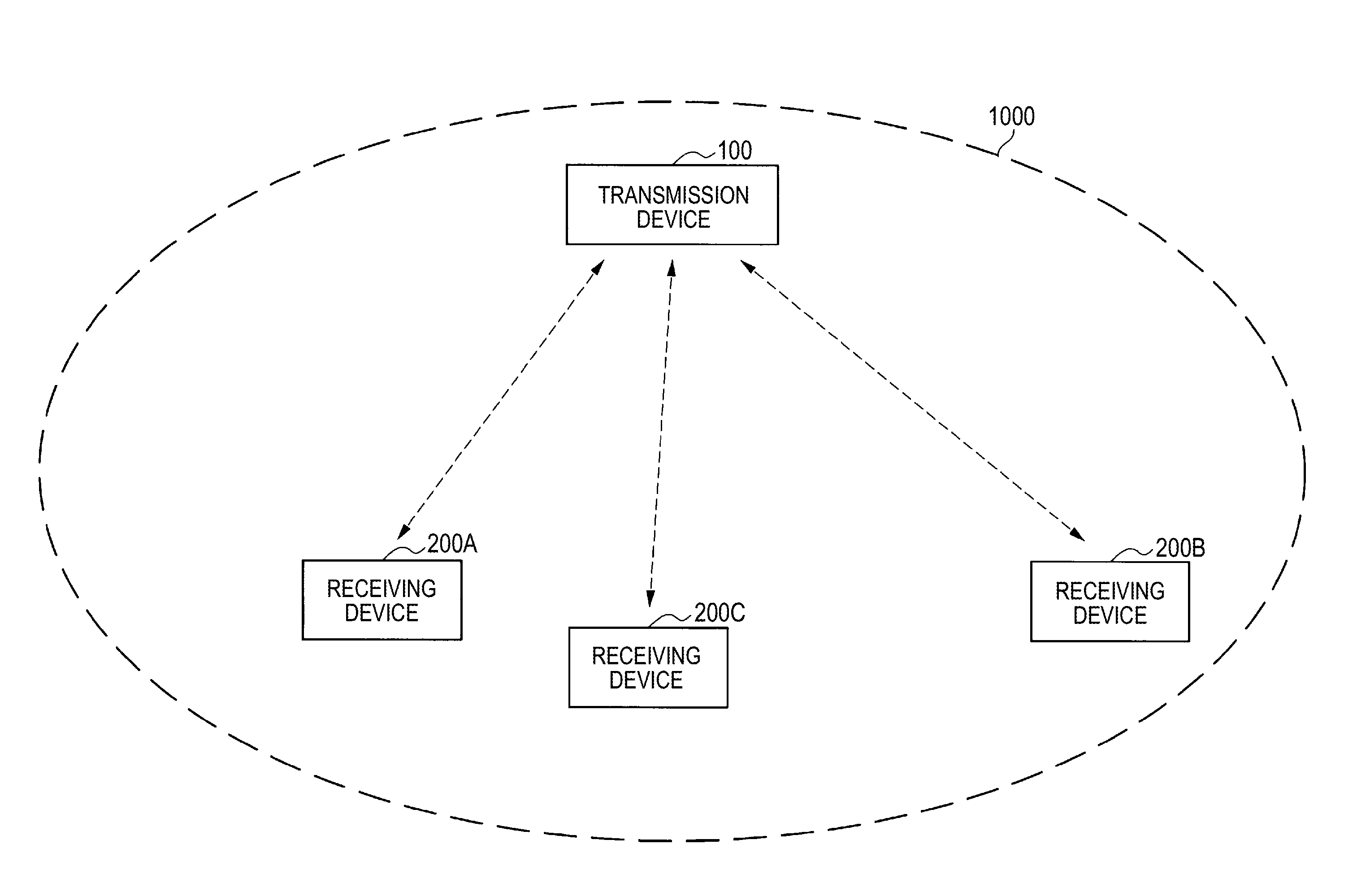
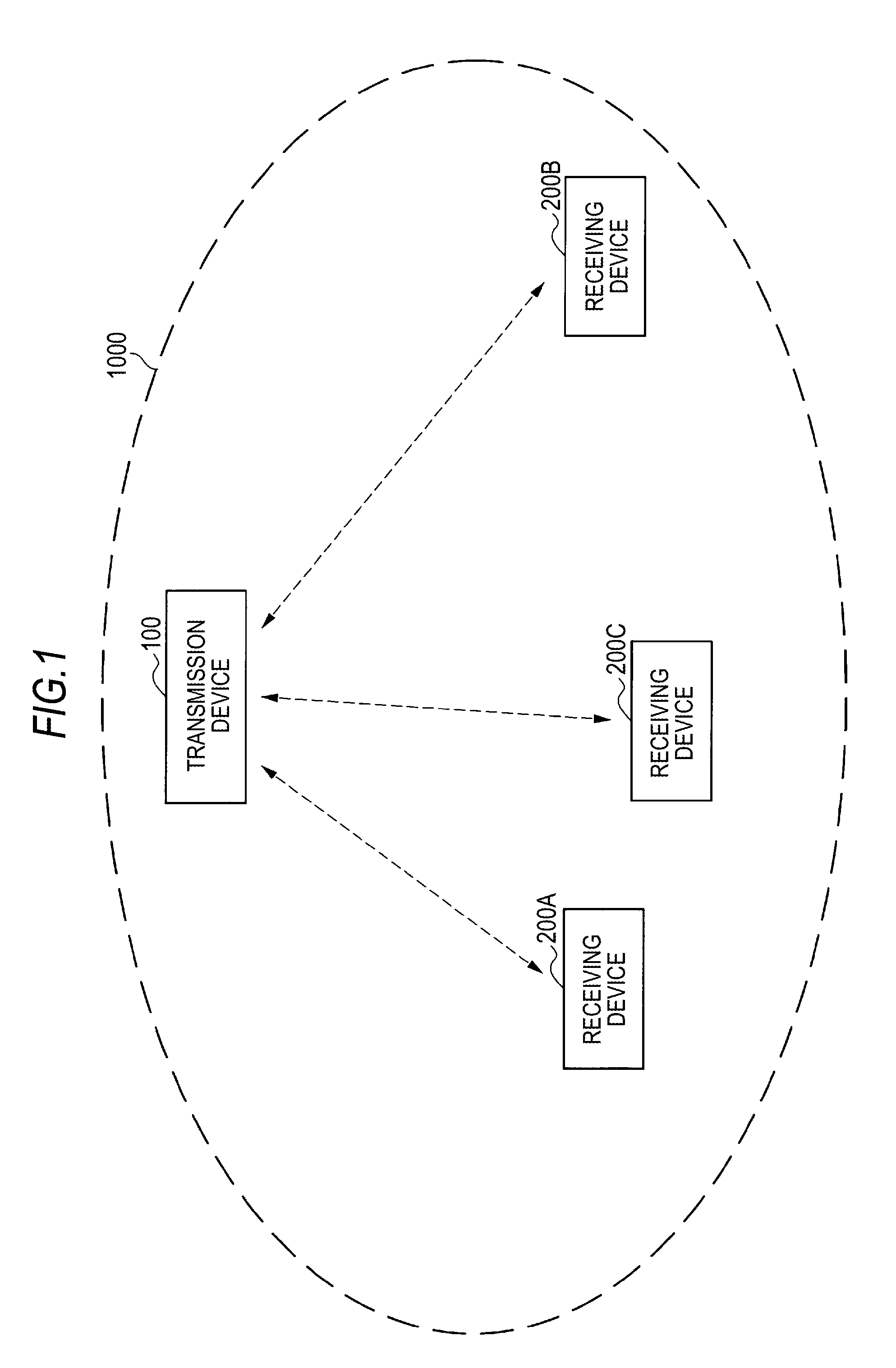
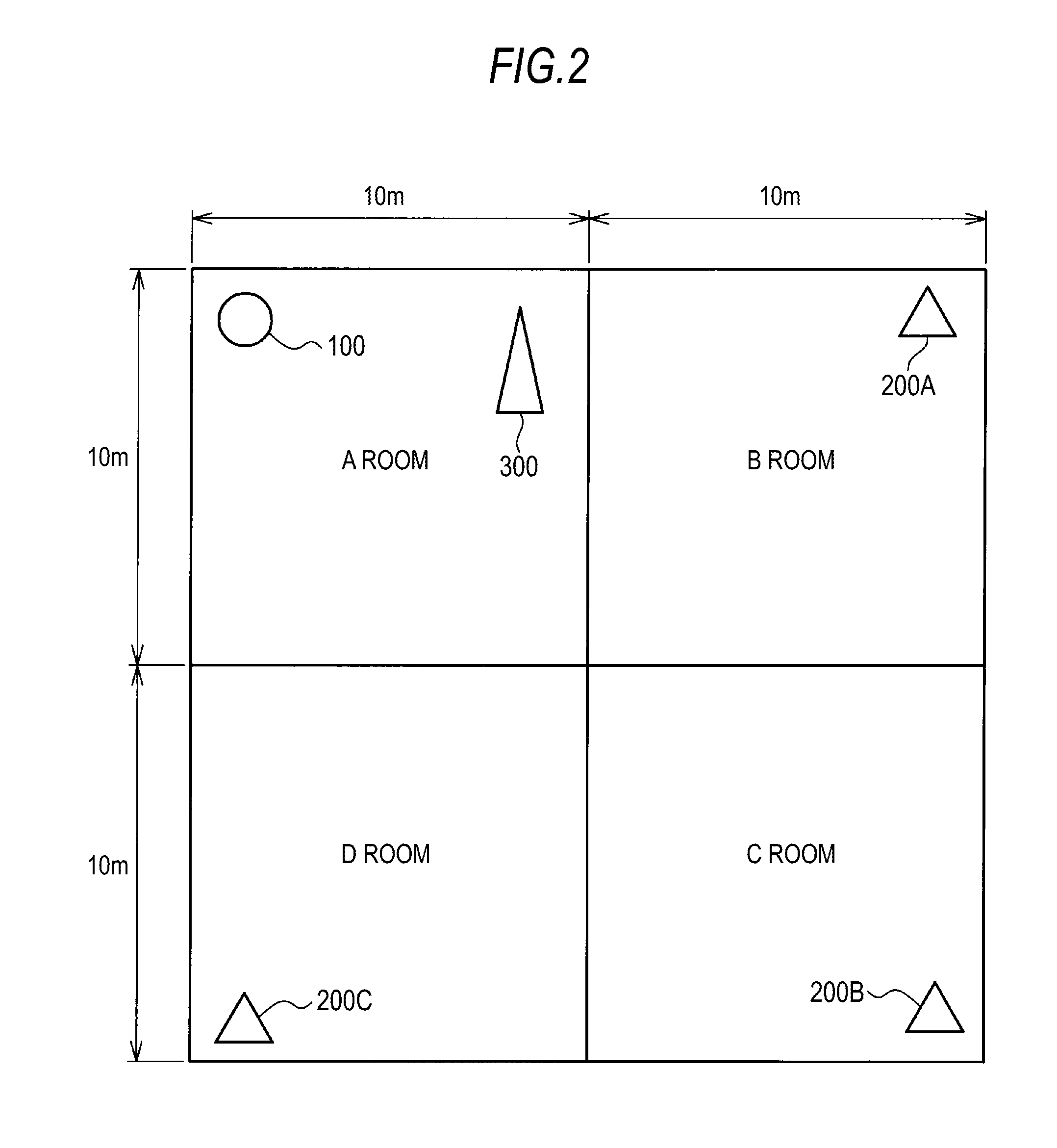
ActiveUS8520870B2Uncomfortable feelingIncrease probabilityNear-field transmissionReceivers monitoringTime informationData set
A transmission device includes: a communication unit performing communication with one or more receiving devices; a distance measurement unit measuring direct distances to the receiving devices; a transmission data setting unit setting transmission data including content data including audio and time information indicating the time when reproduction of content data is started for the receiving devices whose distances are measured based on the measured distances; and a transmission processing unit transmitting transmission data set by the transmission data setting unit to corresponding receiving devices of transmission targets all at once. The transmission data setting unit sets time when the device itself starts reproduction of the content data as a reference time, and sets the time information for synchronizing audio indicated by the content data reproduced in the device itself with audio indicated by the content data reproduced in the receiving devices for each receiving device using the set reference time.
Owner:SONY CORP
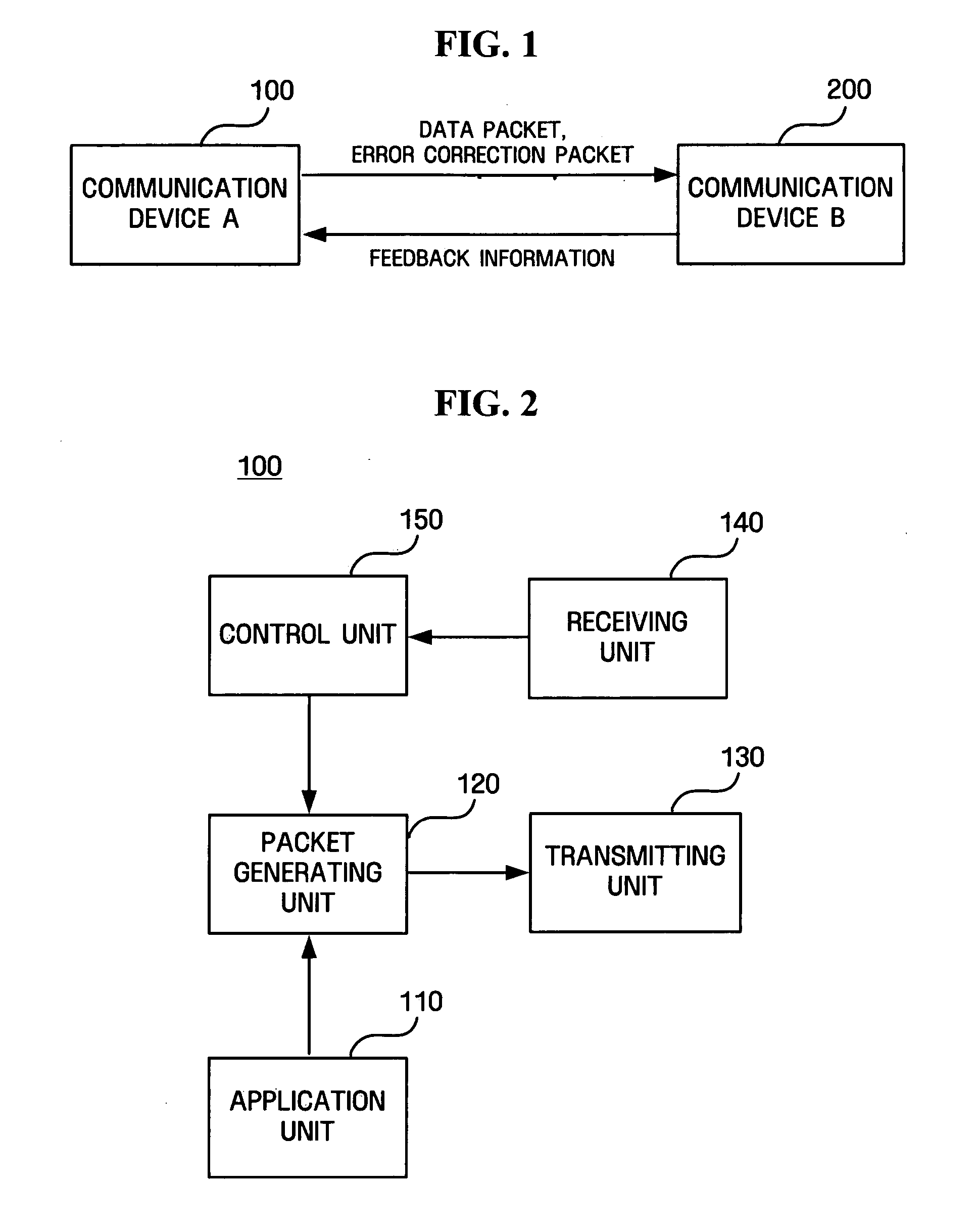
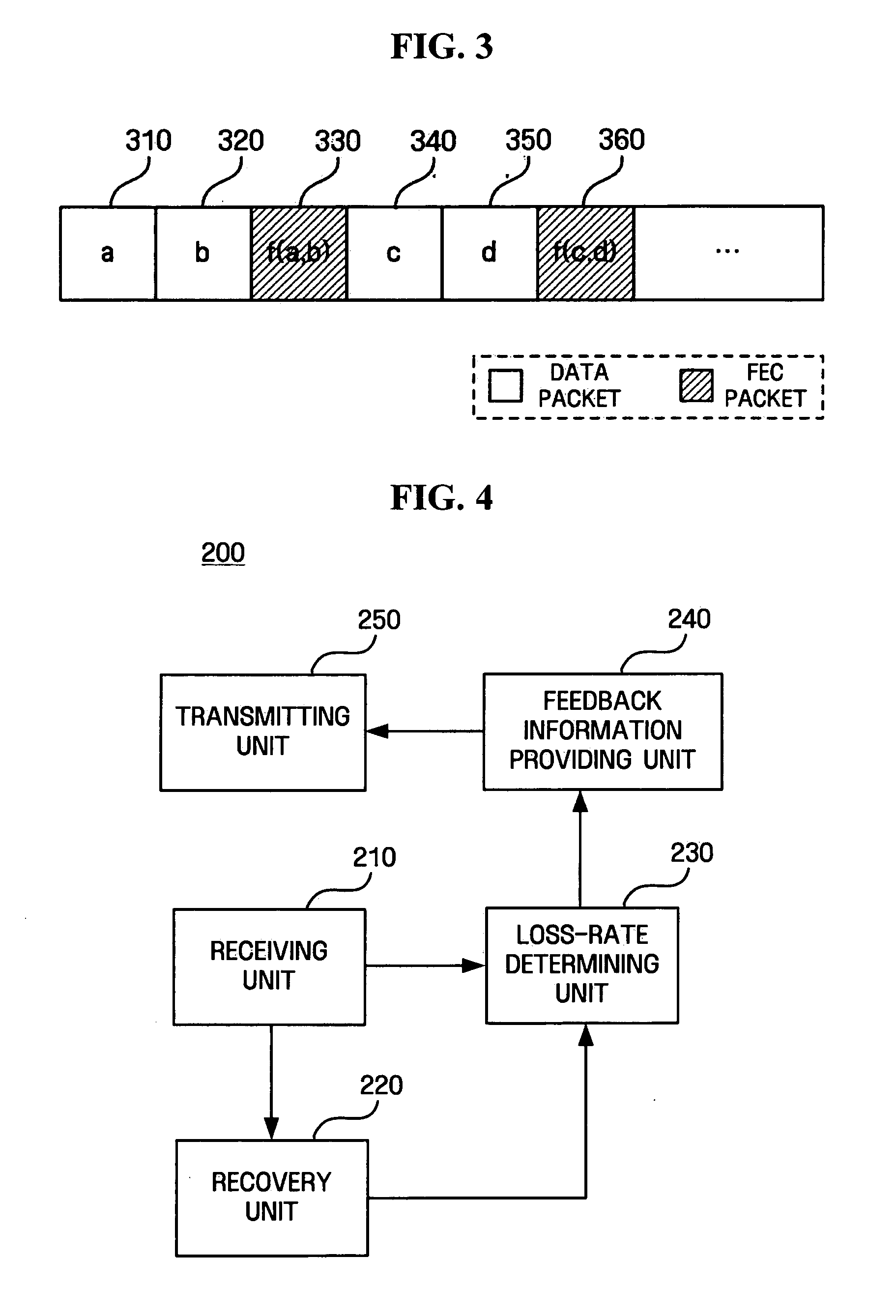
Method of controlling transmission rate by using error correction packets and communication apparatus using the same
ActiveUS20060280205A1Increase percentageReduce percentageEnergy efficient ICTTime-division multiplexCommunication deviceUser Error
A method of controlling transmission rate by using error correction packets and a communication apparatus using the same are provided. According to an embodiment of the present invention, the method of controlling transmission rate by using error correction packets includes transmitting a first packet group composed in a predetermined ratio of data packets and error correction packets, transmitting a second packet group composed of the data packets and the error correction packets in a ratio adjusted based on feedback information about the first packet group, and controlling the transmission rate based on the feedback information about the second packet group.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Deterministically skewing transmission of content streams
ActiveUS20100218231A1Reducing peak bandwidth requirementReduce loadColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer networkTransmission latency
Described are computer-based methods and apparatuses, including computer program products, for deterministically skewing transmission of content streams. A content stream comprising one or more video frames is received. The content stream is buffered in a buffer, wherein the buffer allows simultaneous read access to the content stream at a plurality of locations. One or more video frames of the content stream are transmitted from the buffer to a first device associated with a first subscriber beginning at a first location in the buffer based on a first transmission delay parameter. One or more video frames of the content stream are transmitted from the buffer to a second device associated with a second subscriber beginning at a second location in the buffer based on a second transmission delay parameter.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
Receptacle cover
ActiveUS8668347B2Lower potentialImprove securityTwo pole connectionsLighting support devicesElectricityEngineering
A cover for an electrical receptacle including a faceplate. The cover also includes a first transmission tab configured to be electrically connected to a first power line of the electrical receptacle and a second transmission tab configured to be electrically connected to a second power line of the electrical receptacle. Additionally, the cover includes a device (such as a light source, circuit, port, or sensor) in communication with the first transmission tab and the second transmission tab.
Owner:LIGHTING DEFENSE GRP LLC
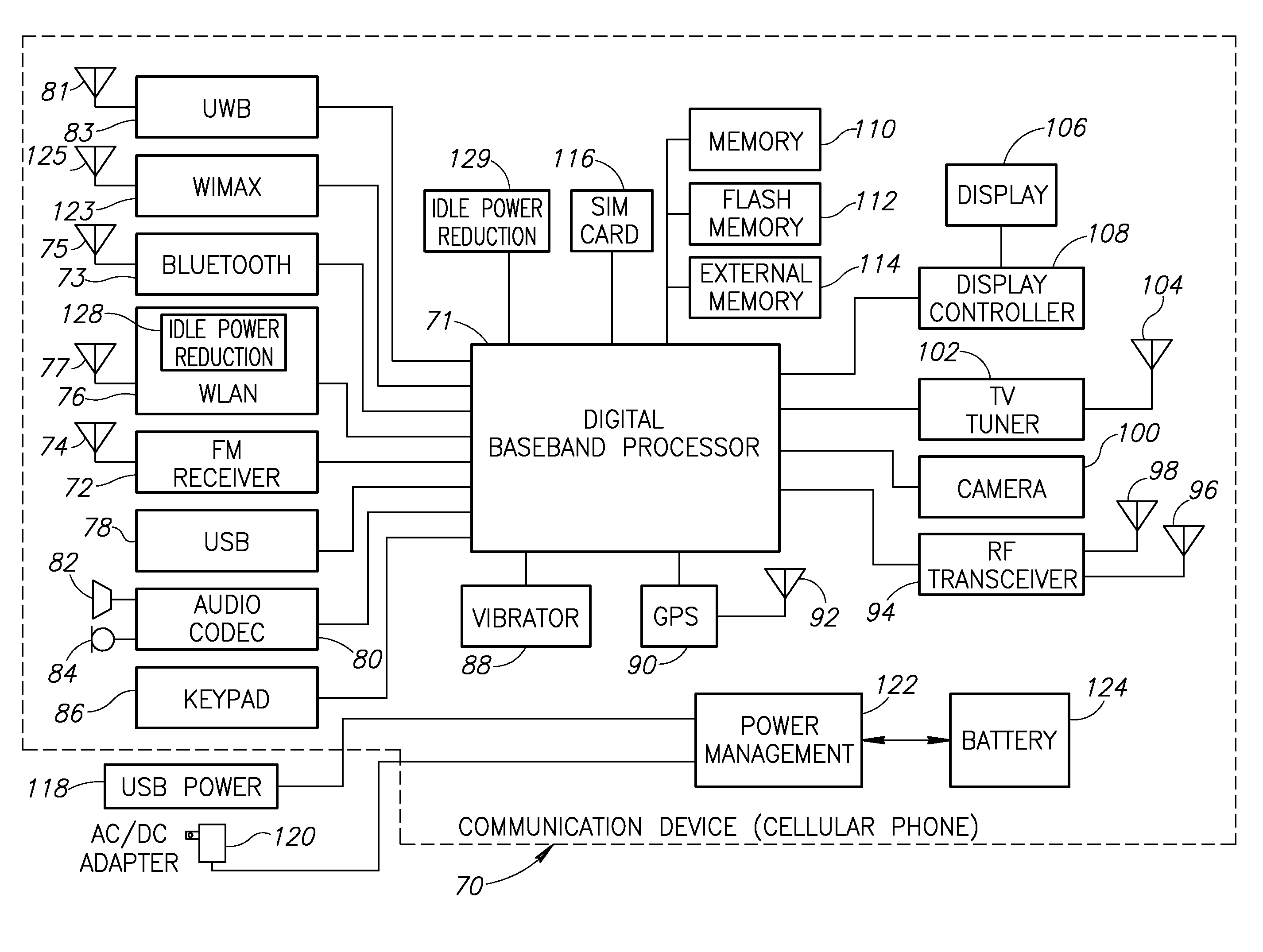
Idle connection state power consumption reduction in a wireless local area network using beacon delay advertisement
ActiveUS20080170551A1Improving idle connection state power consumptionReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTPower managementEngineeringTransmission delay
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of improving idle connection state power consumption in wireless local area network (WLAN) system. Beacon transmission delay information is determined by the access points and advertised to the stations via a Beacon Transmission Delay Information Element. In response, the stations adjust their Wake For Beacon Reception time accordingly to wake up at a time much closer to the actual receipt of the Beacon, thereby reducing power consumption due to the reduced time the receive circuits need to be powered on.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
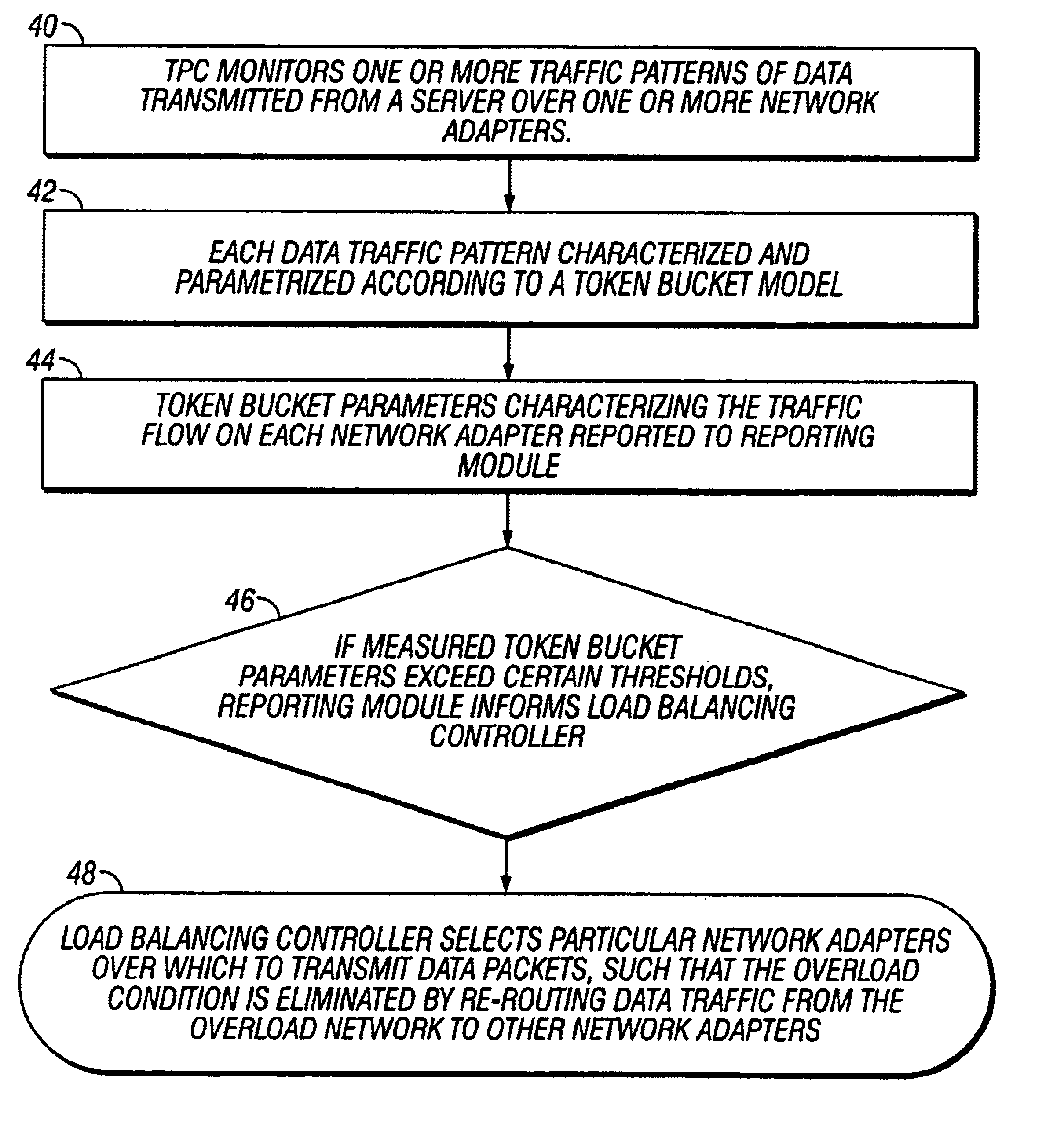
Managing data traffic on multiple ports
InactiveUS6868062B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityData transmission
A traffic pattern of data packets that originate at a traffic source and are transmitted through one of multiple ports is monitored. A parameter value characterizing fluctuations a in a transmission rate of data through the port relative to a transmission rate for the monitored traffic pattern is generated, and data packets from the traffic source are allocated to at least one other port for transmission based on the first parameter value.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and apparatus for forward link rate scheduling
InactiveUS7054293B2Increase profitReduce transmission delayPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementHigh rateCommunications system
In a communication system capable of variable rate transmission, scheduling of high speed data transmission improves utilization of the forward link and decreases the transmission delay in data communication. Each remote station is assigned one primary code channel for the duration of the communication with a cell. Secondary code channels of various types and transmission capabilities can be assigned by a channel scheduler for scheduled transmission of data traffic at high rates. Secondary code channels are assigned in accordance with a set of system goals, a list of parameters, and collected information on the status of the communication network. Secondary code channels can be grouped into sets of secondary code channels. Data is partitioned in data frames and transmitted over the primary and secondary code channels which have been assigned to the scheduled user.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
HARQ (Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request) signal transmitting method and device and receiving method and device based on polar codes
ActiveCN105743621AIncrease the probability of correct decodingLower the average number of sendsError prevention/detection by using return channelError correction/detection using linear codesCommunications systemComputer science
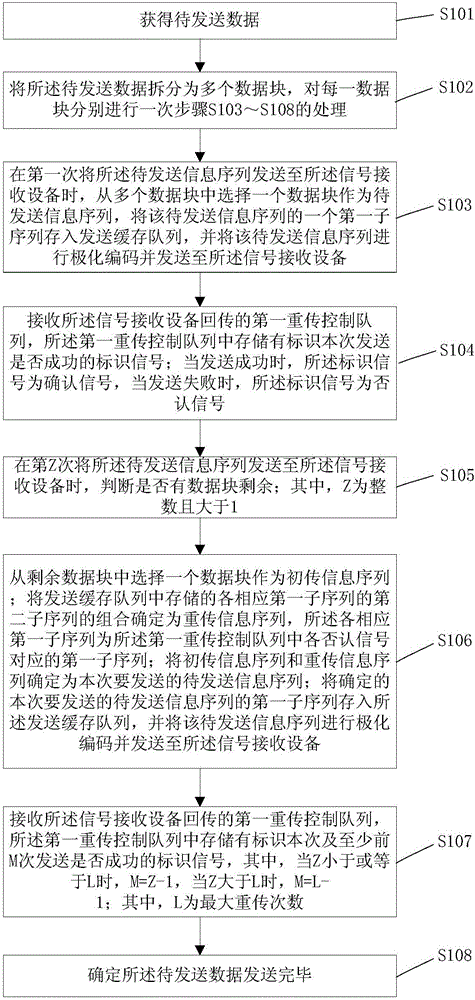
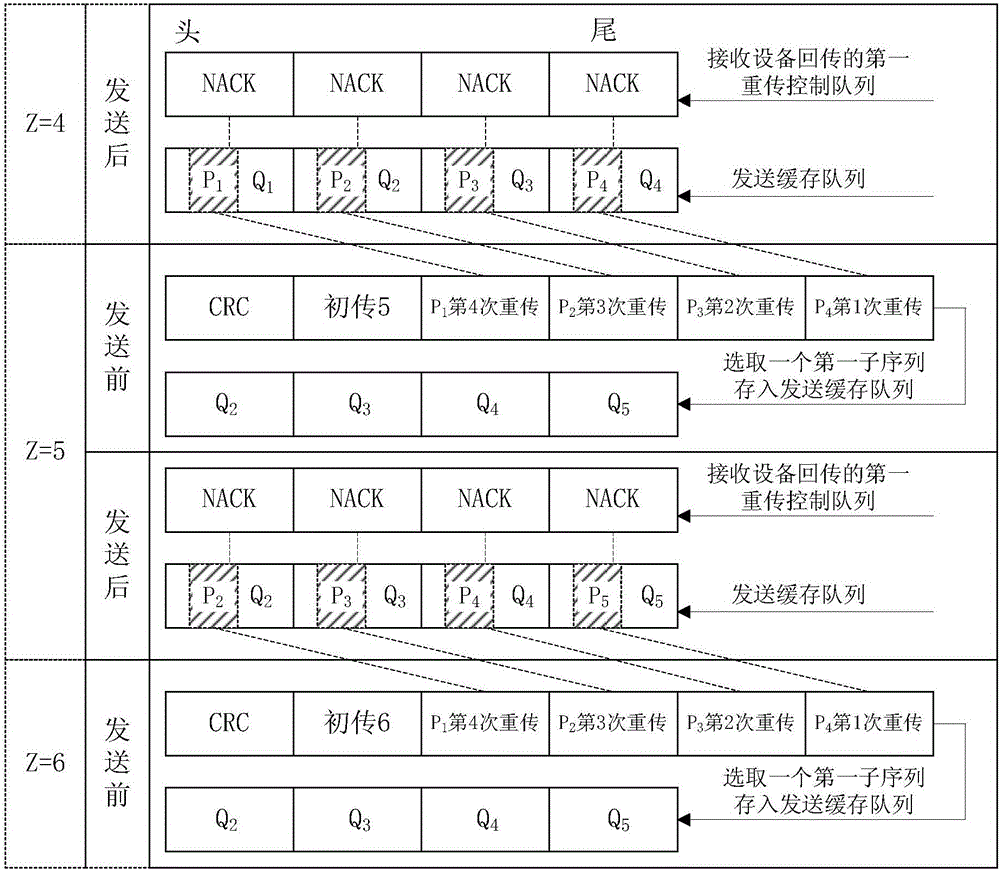
The embodiment of the invention provides an HARQ (Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request) signal transmitting method and device and receiving method and device based on polar codes. When transmitting is carried out at a time, when it is judged that there are surplus data blocks, one data block is selected out from the surplus data blocks as an initial transmitting information sequence; the combination of first sub-sequences and second sub-sequences corresponding to negative acknowledge signals in a first retransmitting control queue is determined as a retransmitting information sequence, wherein the first sub-sequences and the second sub-sequences are stored in a transmitting cache queue; the initial transmitting information sequence and the retransmitting information sequence are determined as to-be-transmitted information sequences; one first sub-sequence of the determined to-be-transmitted information sequences is stored in the transmitting cache sequence; polar coding is carried out to the to-be-transmitted information sequences; and the to-be-transmitted information sequences are transmitted. The accurate decoding probability of the information sequences failed to be transmitted for former M times is improved; therefore, the throughput of the communication system is improved; the average transmitting and receiving times before the accurate decoding is carried out to the to-be-transmitted information sequences is reduced; and therefore, the transmission delay of the communication is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
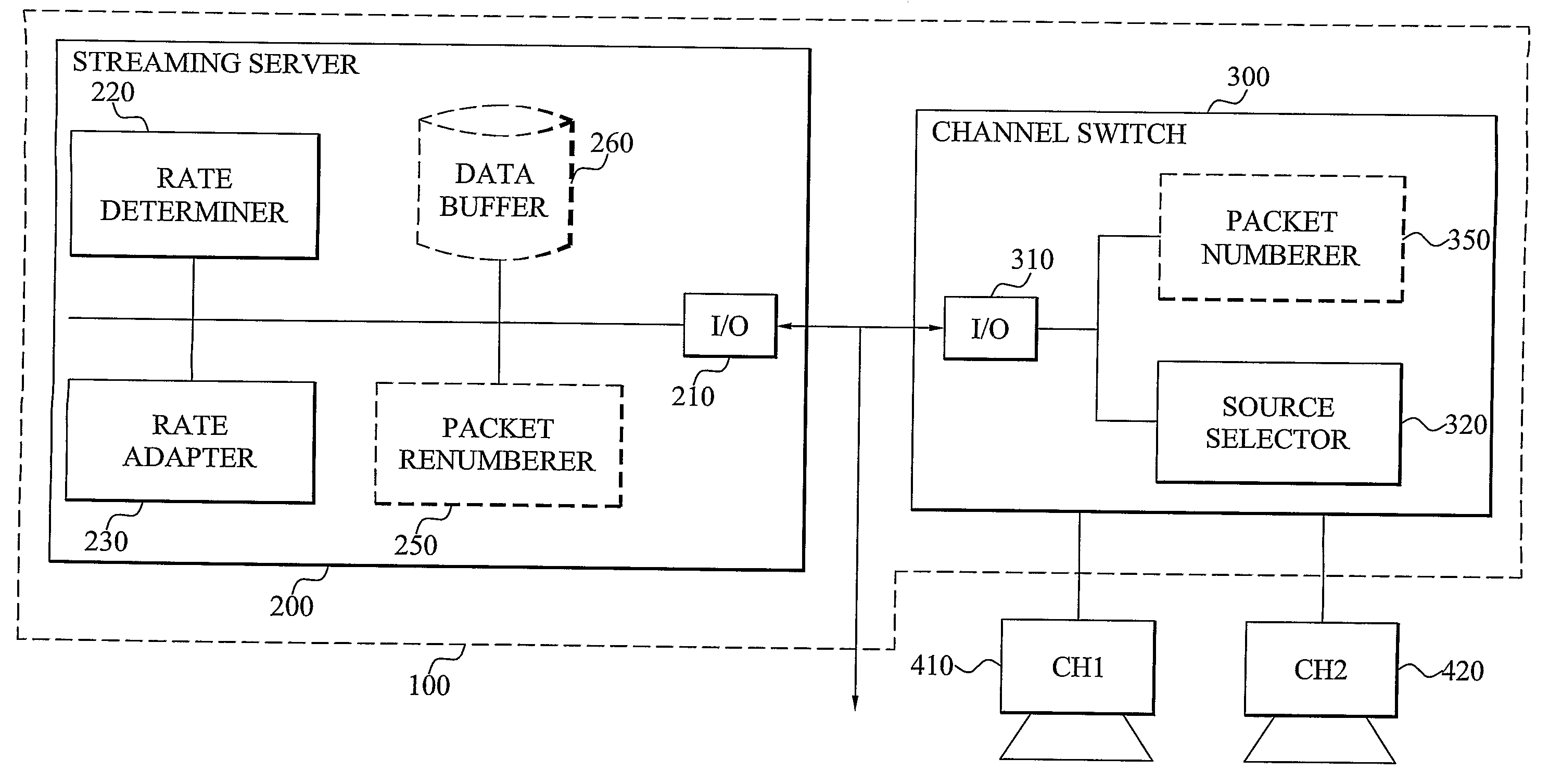
Multimedia Channel Switching
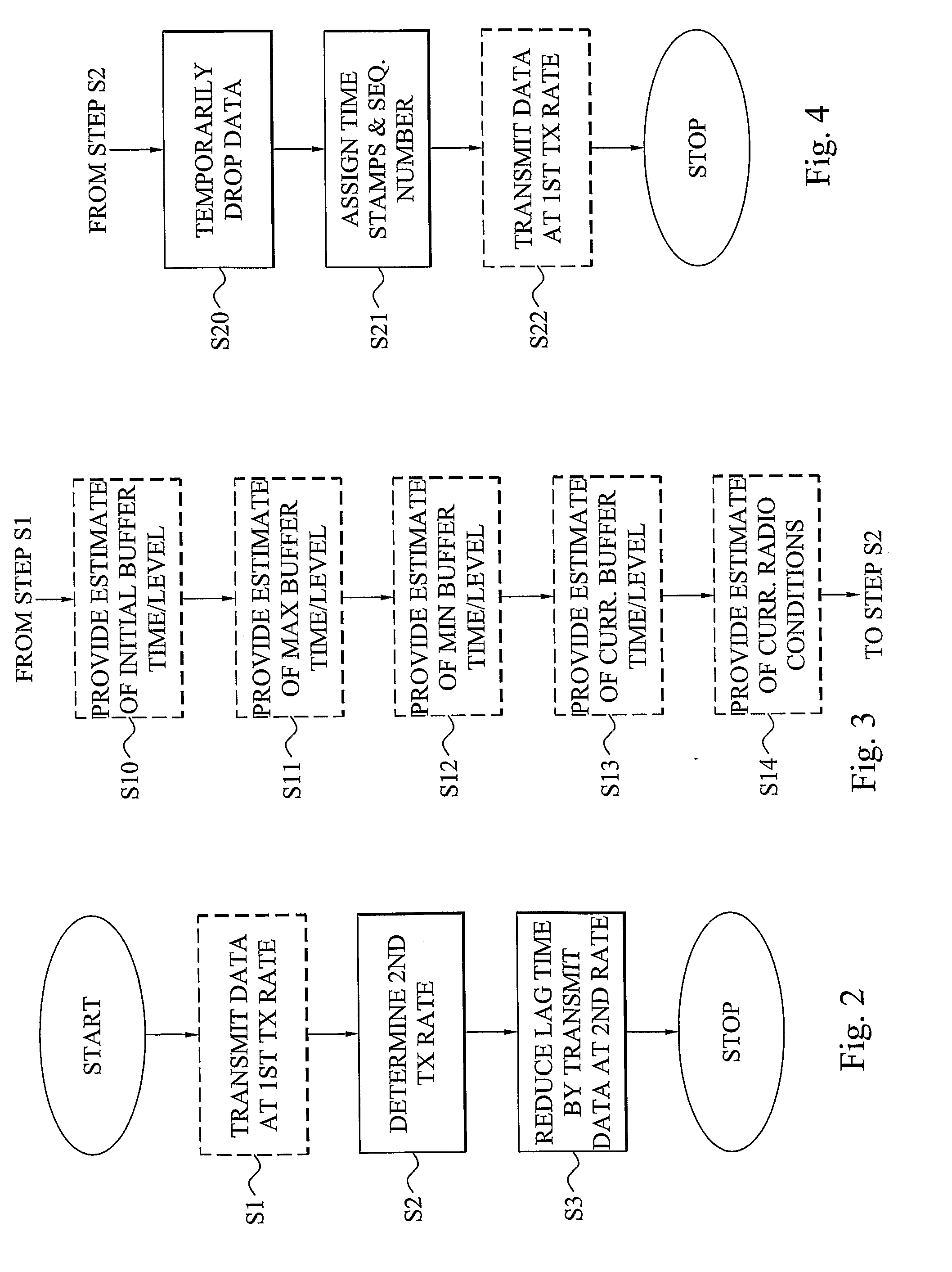
InactiveUS20090222873A1Shorten the timeTime-division multiplexTwo-way working systemsComputer hardwareCommunications system
The invention reduces the user-perceived time of switching multimedia channels in a unicast communications system. This shortening of the switch procedure is obtained by reducing the buffering of the multimedia data in the data buffer of a user terminal. A reduced media buffering results in that multimedia data of the new channel will be rendered in the user terminal in a much shorter period of time. A multimedia provider communicating the multimedia data to the terminal determines a reduced transmission rate that will be temporarily employed for obtaining the buffering reduction. This reduced rate is lower than the normally employed transmission rate and lower than the rendering rate of the media player of the terminal. Consequently, the terminal buffer will be emptying in a faster rate than it is replenished and a buffer level reduction is obtained.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
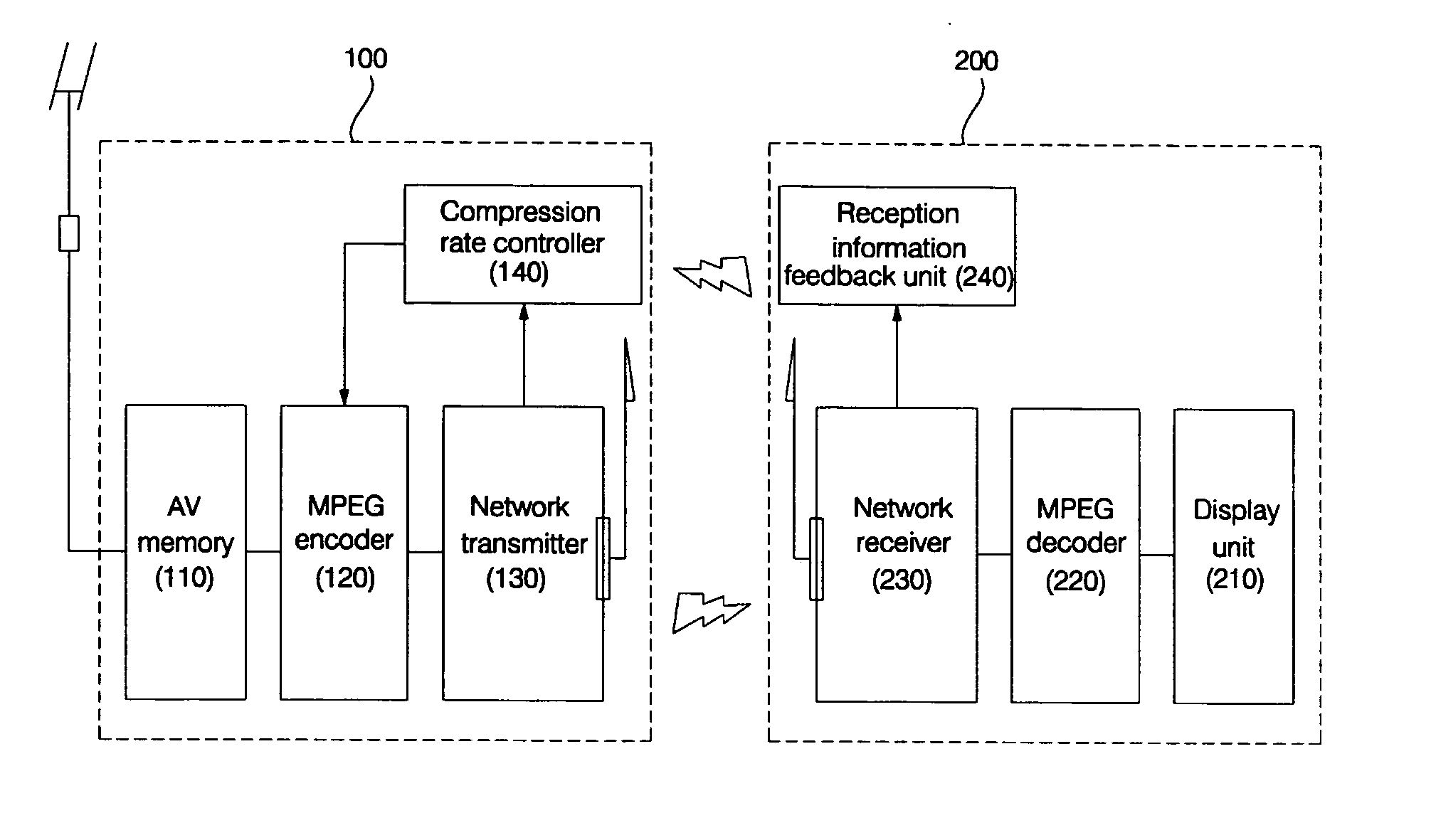
Server system for performing communication over wireless network and operating method thereof
InactiveUS20050210515A1Reduce transmission bandwidthImprove data storage efficiencySpecial service provision for substationPulse modulation television signal transmissionImaging qualityClient-side
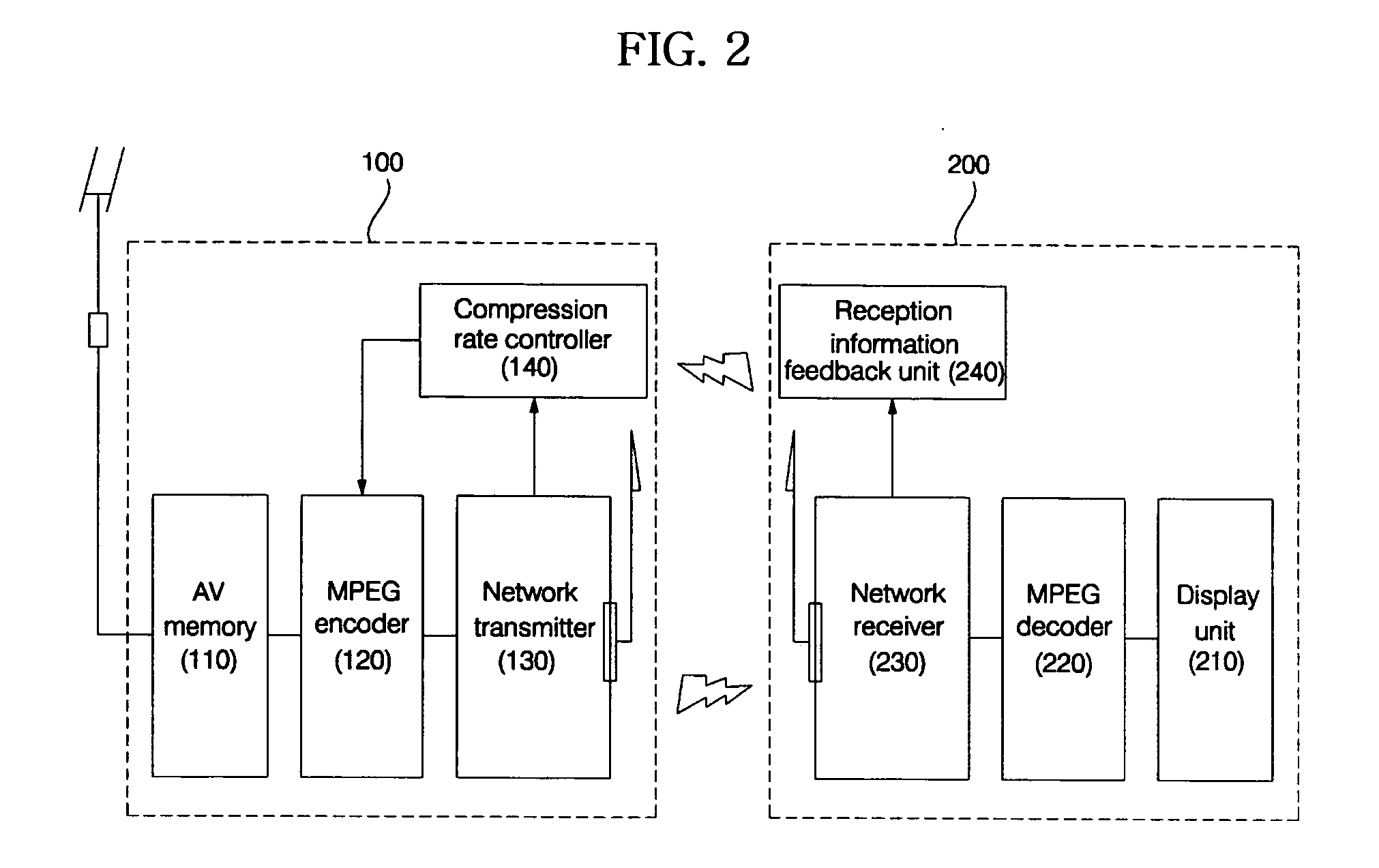
Disclosed are a server system for performing moving picture data communication with a client device over a wireless network, and an operating method thereof. A server device compresses the moving picture data received from an external medium at a variably controlled compression rate according to transmission bandwidth of the current wireless network and an image quality level set by a user in response to a request of the client device. Moreover, the server device transmits the compressed moving picture data to the client device in a wireless fashion. Therefore, transmission delay and playback delay can be avoided and data loss is avoided during a data transmission operation, such that stable data communication can be performed.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Methods, apparatuses and systems facilitating data transmission across bonded communications paths
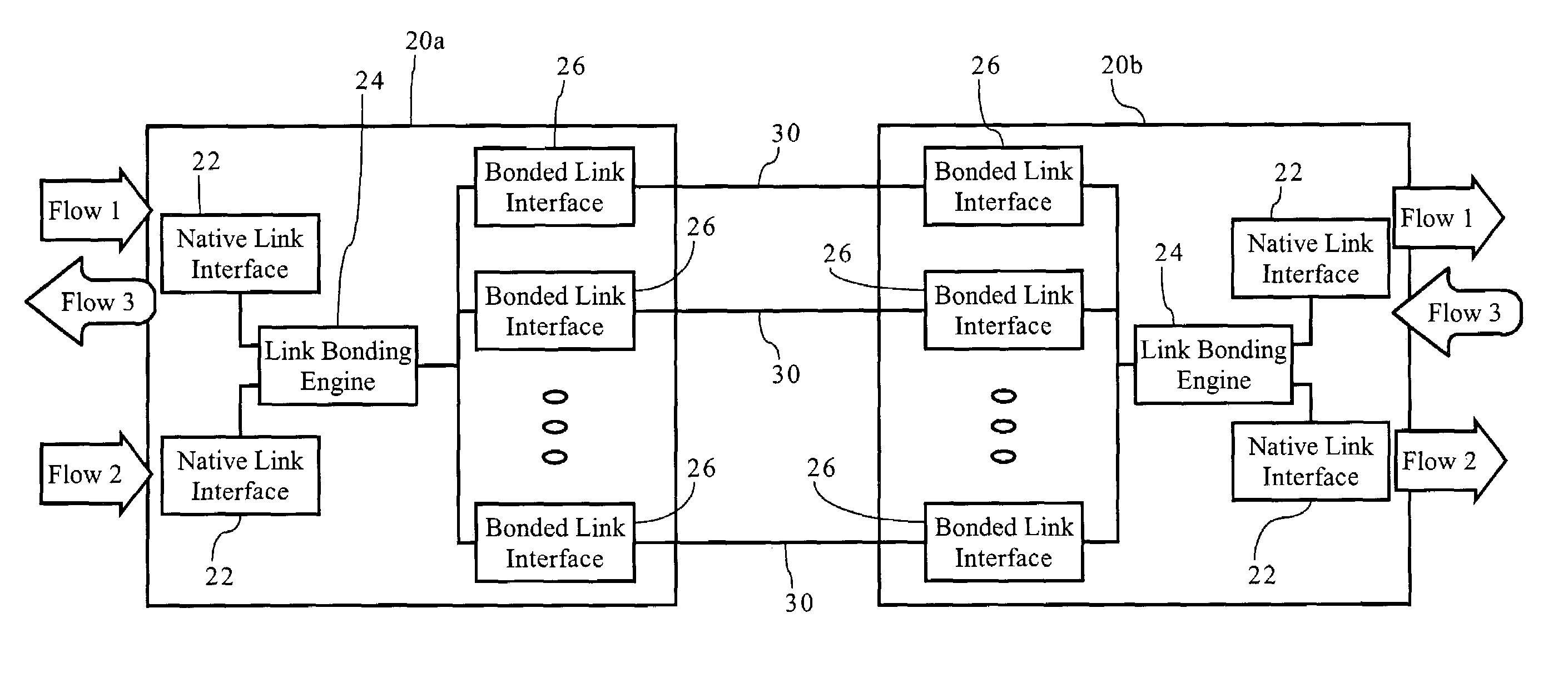
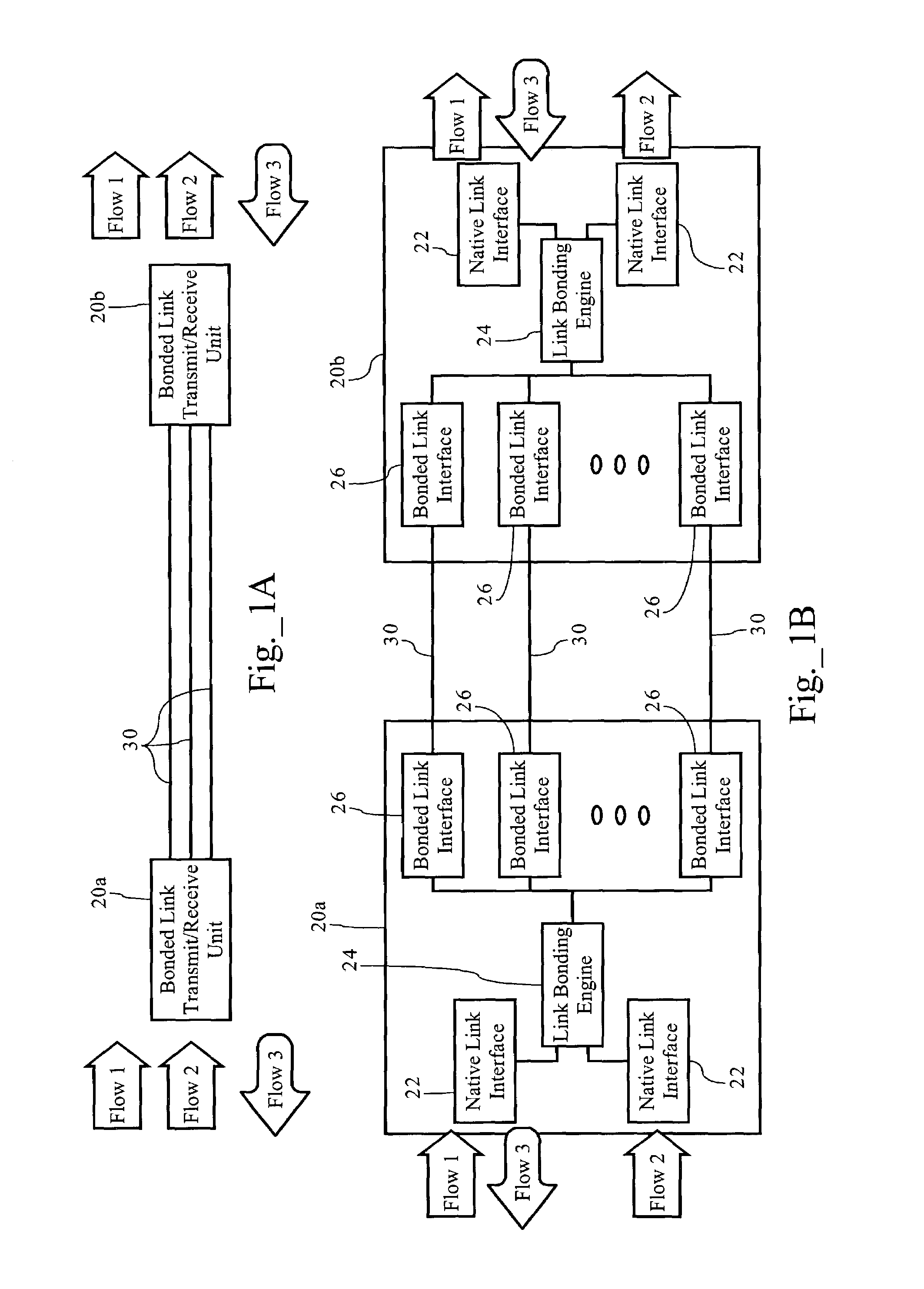
InactiveUS7006500B1Improve data transfer efficiencyLow latency requirementEnergy efficient ICTTelephonic communicationRe sequencingData stream
Methods, apparatuses and systems facilitating the aggregation or bonding of communications paths into a higher-bandwidth, logical communications path. Embodiments of the present invention can be applied to bond different physical links (e.g., xDSL over twisted pairs), different channels on the same physical line, or even different channels or frequencies in a wireless communications network. The present invention further provides methods, apparatuses and systems facilitating the re-sequencing of data flows transmitted across bonded communications paths. In one embodiment, the re-sequencing methodology of the present invention adapts to the transmission delays (both absolute and relative) across the bonded communications path.
Owner:KLAMATH NETWORKS
Method and apparatus for reducing uplink transmission delay in wireless communication system using carrier aggregation
ActiveUS20140016559A1Reduction of uplink transmission delayImprove performancePower managementSynchronisation arrangementCommunications systemUplink transmission
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
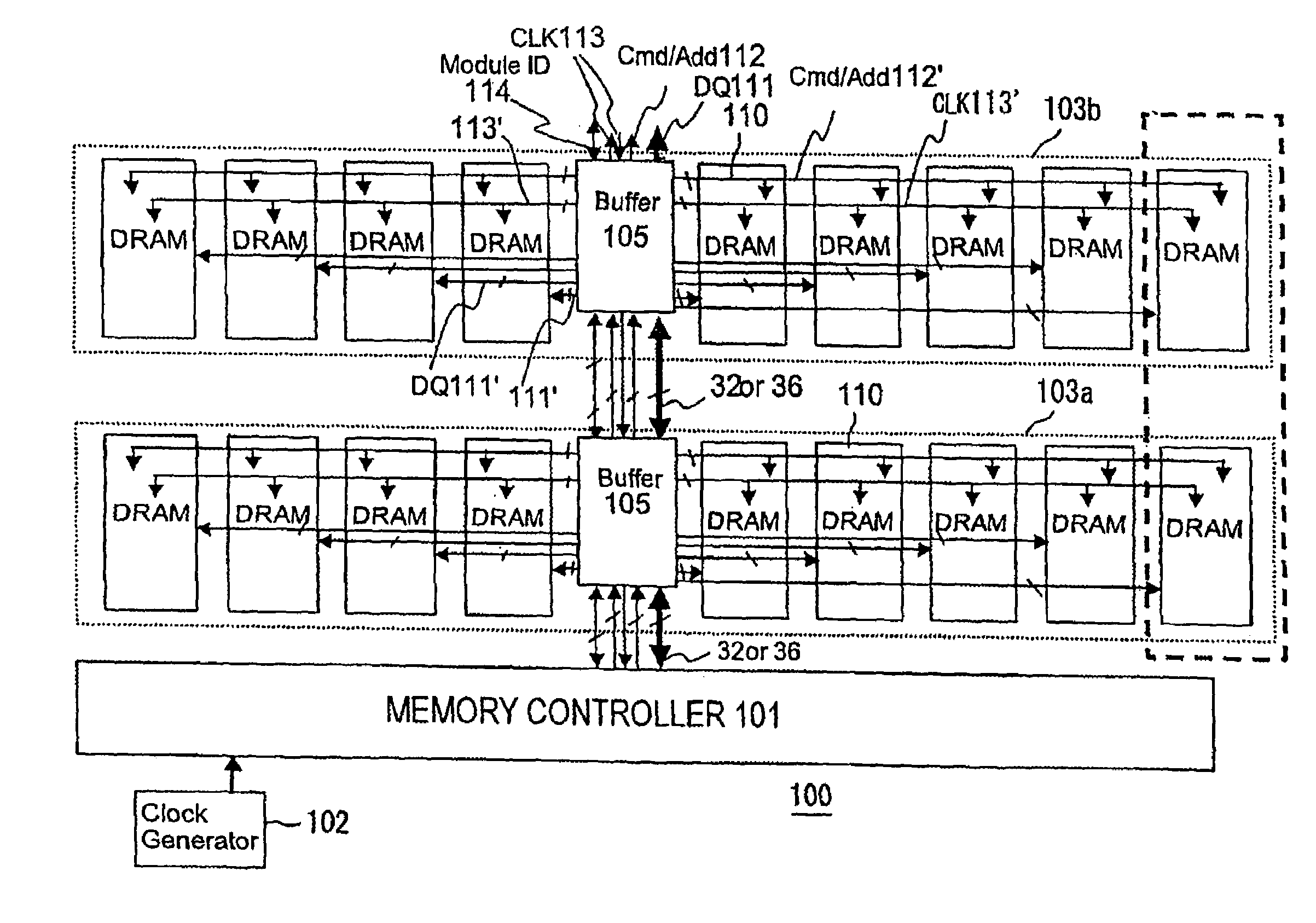
Memory system and data transmission method
ActiveUS7155627B2Easy to adjust at any timeReduce signalingError detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory controllerData transmission
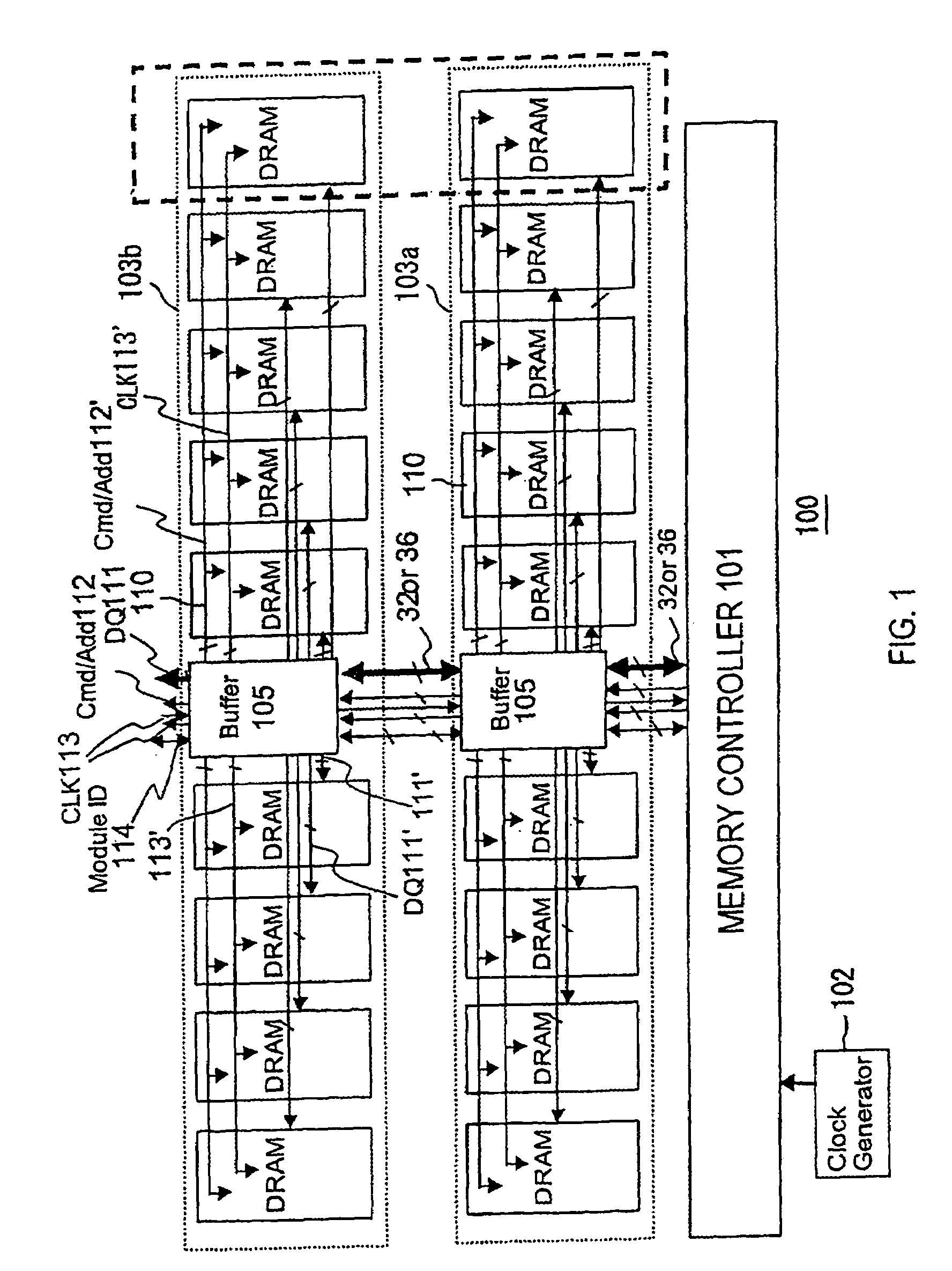
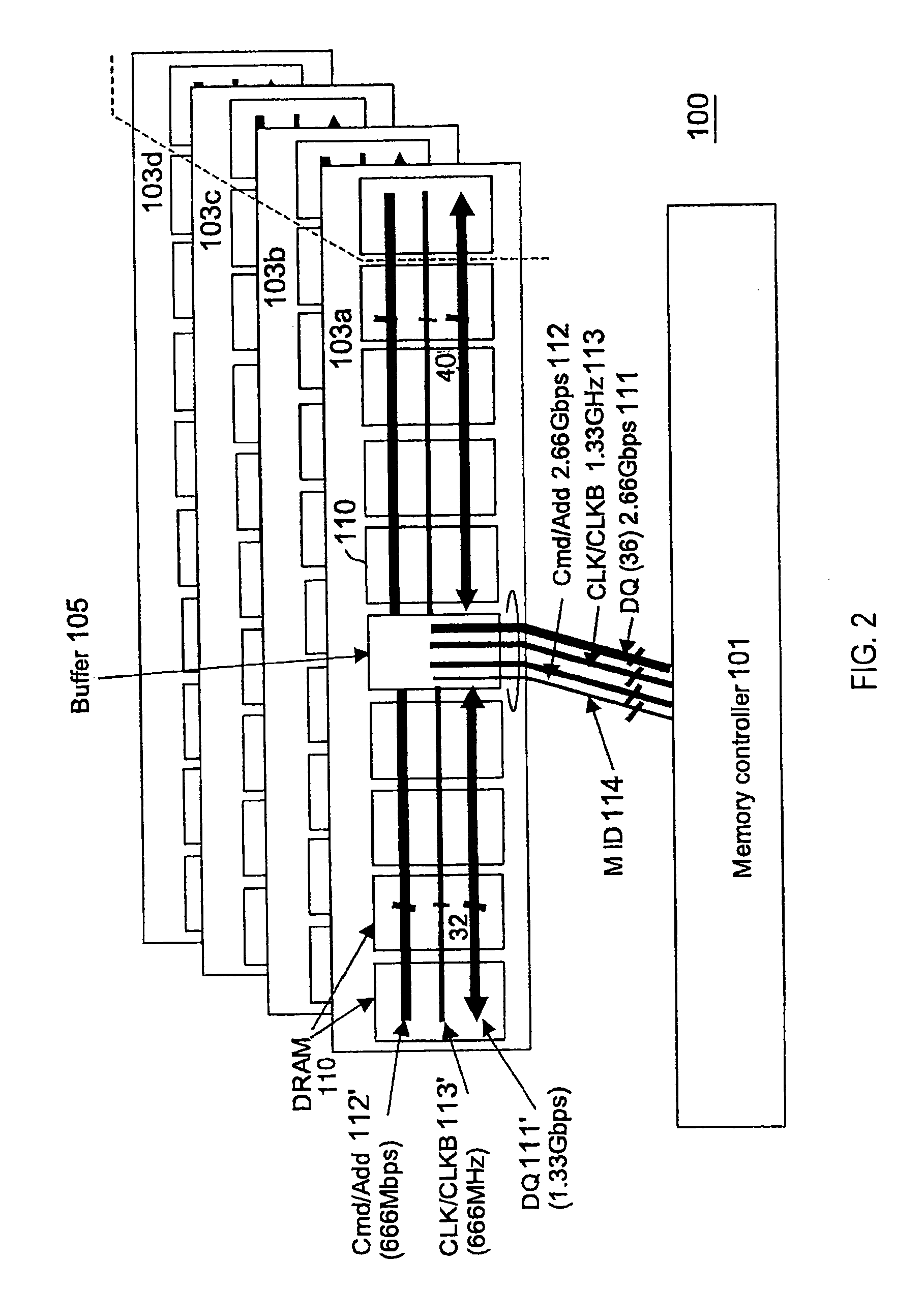
A memory system of a high-speed operation can be realized by reducing an influence of reflection signals etc. caused by branching and impedance mismatching in various wirings between a memory controller and a memory module, and an influence due to transmission delays of data, command / address, and clocks in the memory module. To this end, a memory system comprises a memory controller and a memory module mounted with DRAMs. A buffer is mounted on the memory module. The buffer and the memory controller are connected to each other via data wiring, command / address wiring, and clock wiring. The DRAMs and the buffer on the memory module are connected to each other via internal data wiring, internal command / address wiring, and internal cock wiring. The data wiring, the command / address wiring, and the clock wiring may be connected to buffers of other memory modules in cascade. Between the DRAMs and the buffer on the memory module, high-speed data transmission is implemented using data phase signals synchronous with clocks.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
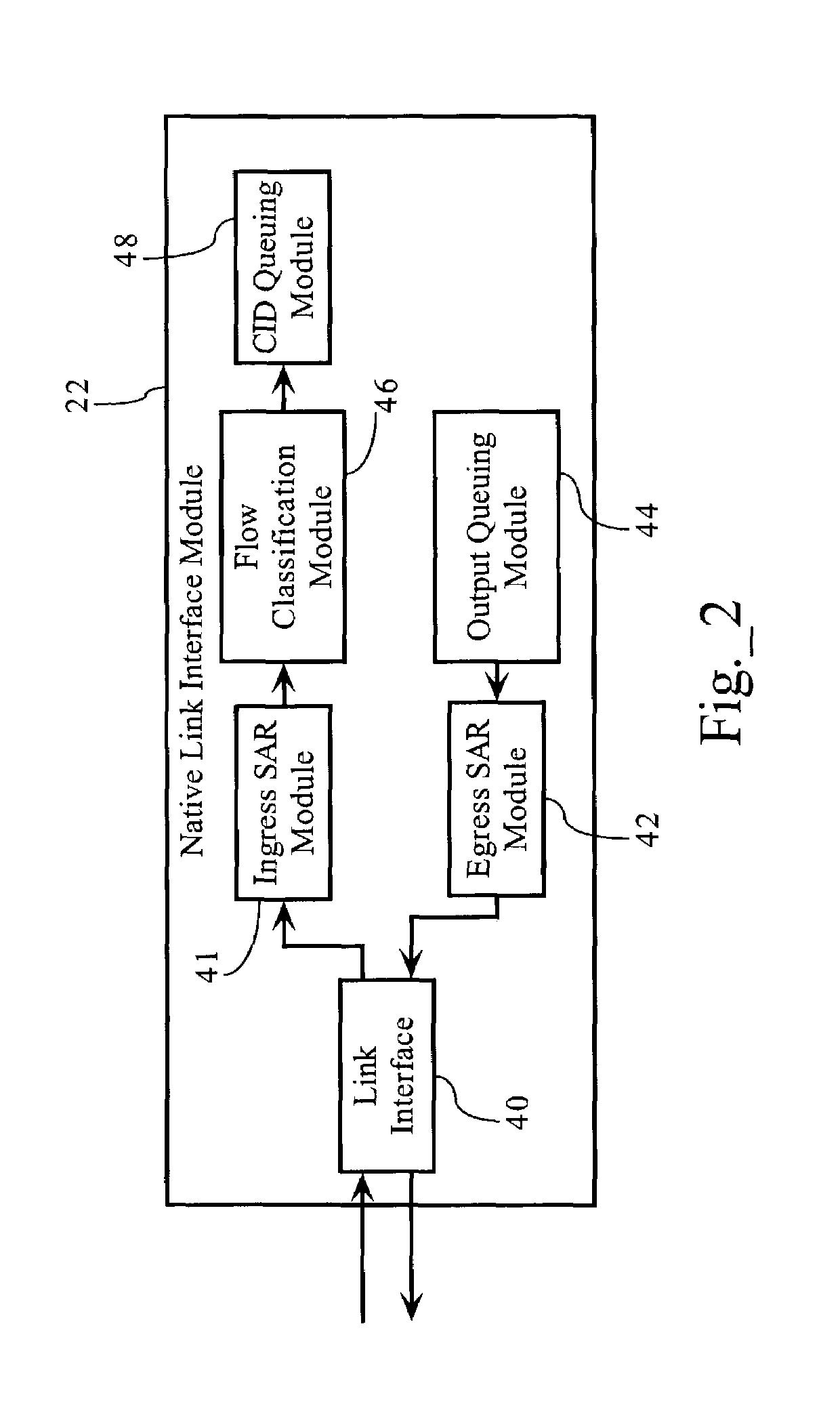
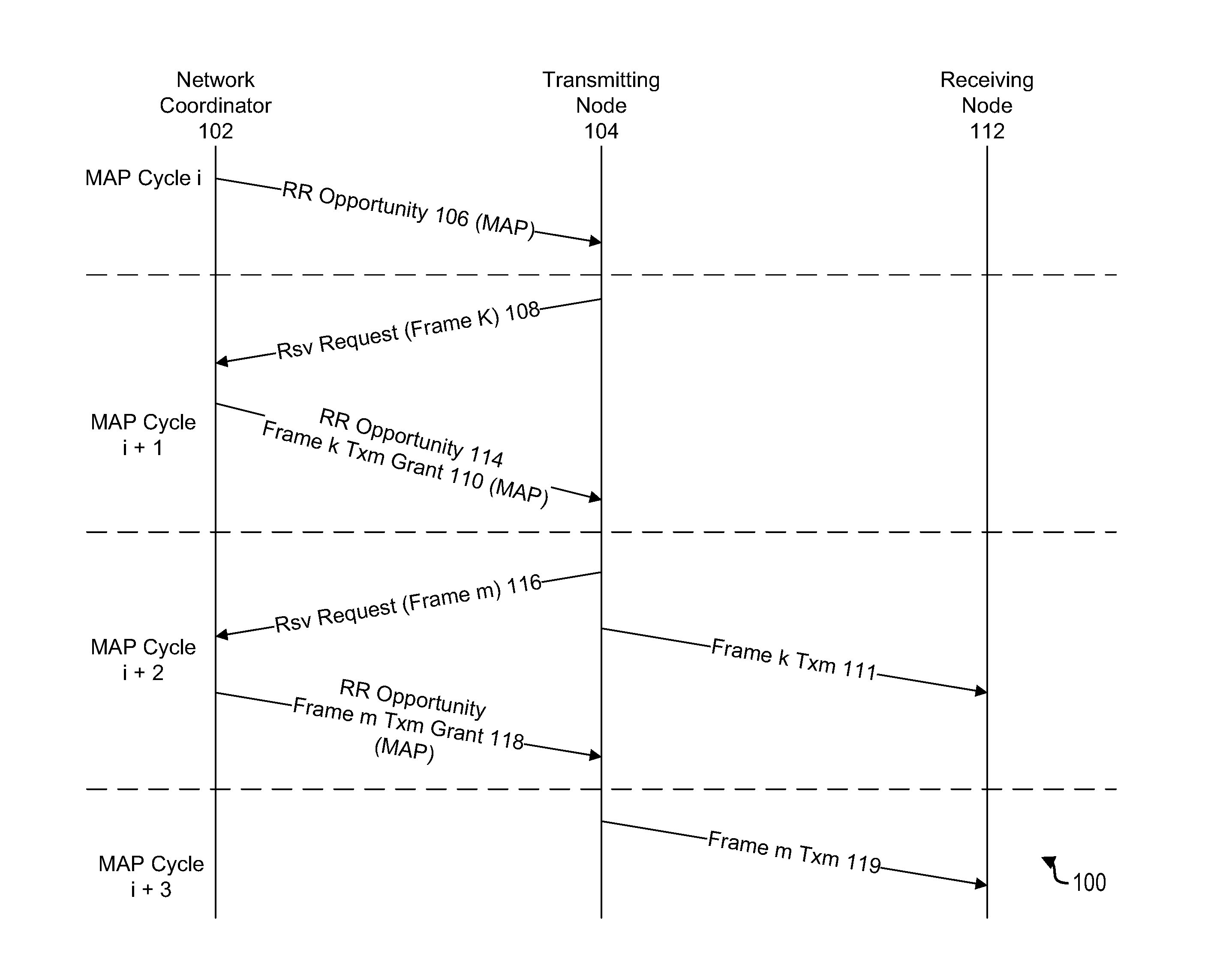
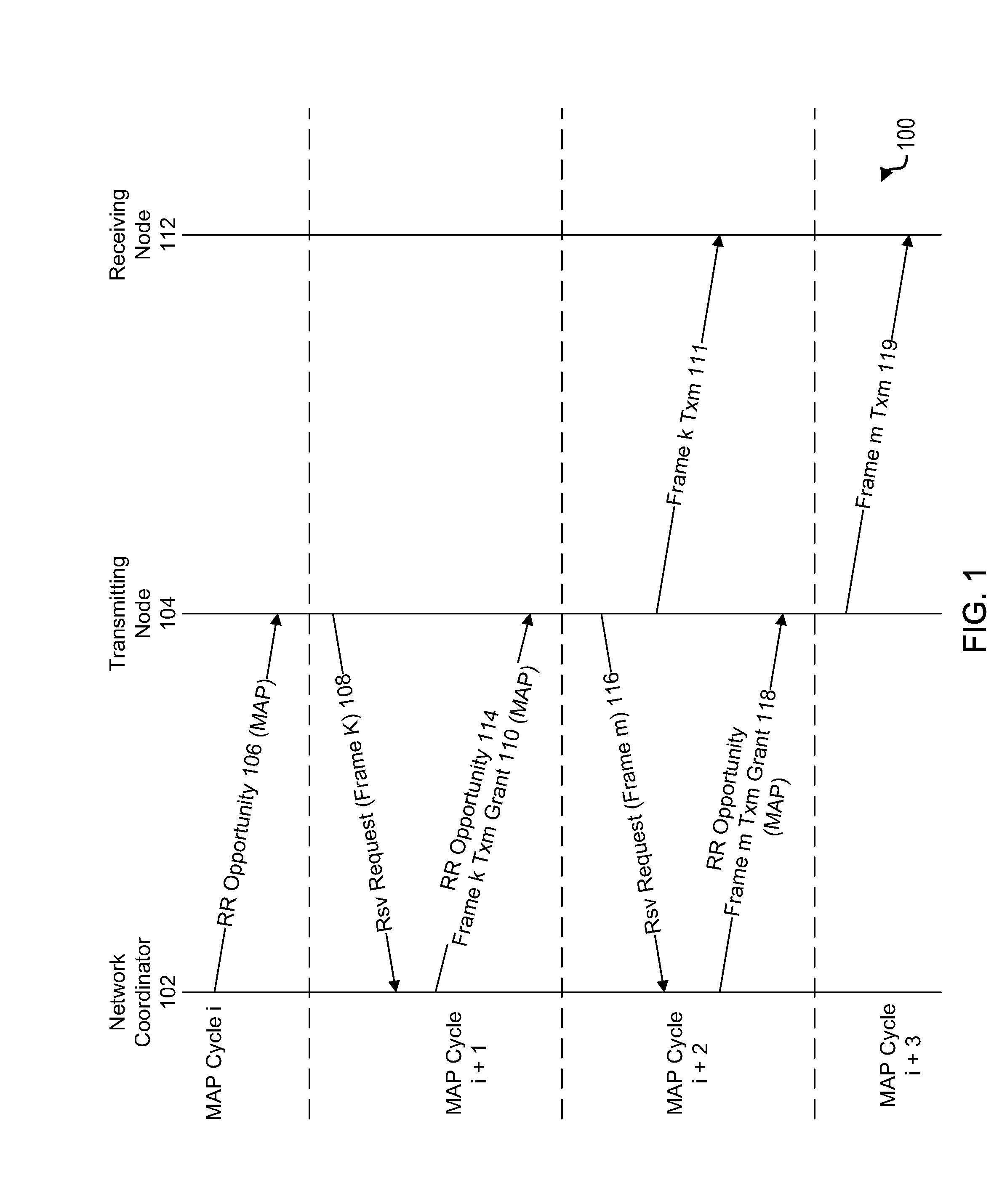
Apparatus and methods for reduction of transmission delay in a communication network
Apparatus and methods for reducing latency in coordinated networks. The apparatus and methods relate to a protocol that may be referred to as the Persistent Reservation Request (“p-RR”), which may be viewed as a type of RR (reservation request). p-RR's may reduce latency, on average, to one MAP cycle or less. A p-RR may be used to facilitate Ethernet audiovisual bridging. Apparatus and methods of the invention may be used in connection with coaxial cable based networks that serve as a backbone for a managed network, which may interface with a package switched network.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
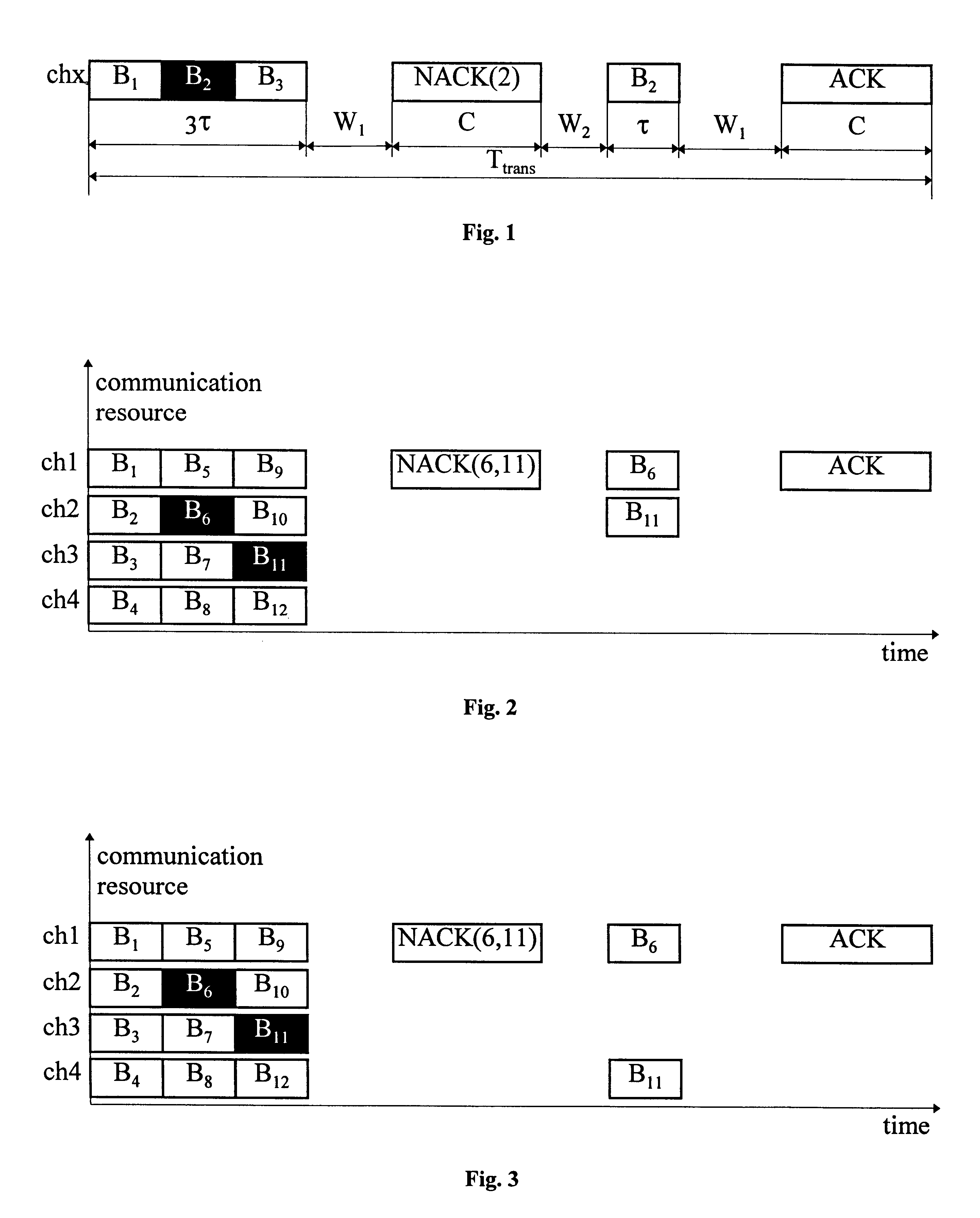
Method and apparatus for high rate packet data transmission
InactiveUS7079550B2Improve efficiencyHigh data transmissionPower managementError prevention/detection by using return channelHigh rateCommunications system
In a data communication system capable of variable rate transmission, high rate packet data transmission improves utilization of the forward link and decreases the transmission delay. Data transmission on the forward link is time multiplexed and the base station transmits at the highest data rate supported by the forward link at each time slot to one mobile station. The data rate is determined by the largest C / I measurement of the forward link signals as measured at the mobile station. Upon determination of a data packet received in error, the mobile station transmits a NACK message back to the base station. The NACK message results in retransmission of the data packet received in error. The data packets can be transmitted out of sequence by the use of sequence number to identify each data unit within the data packets.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com