Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3310 results about "Timestamping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
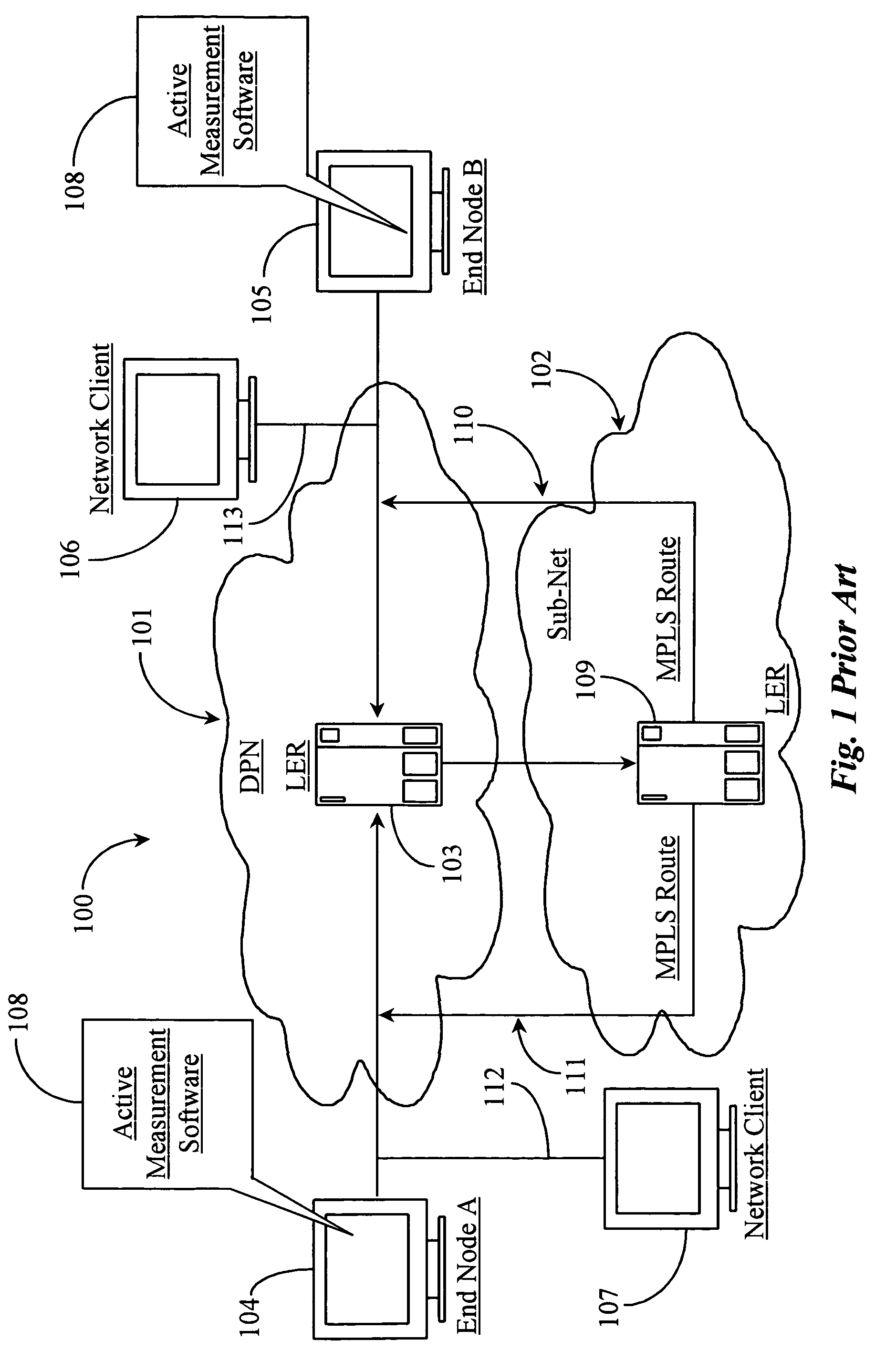
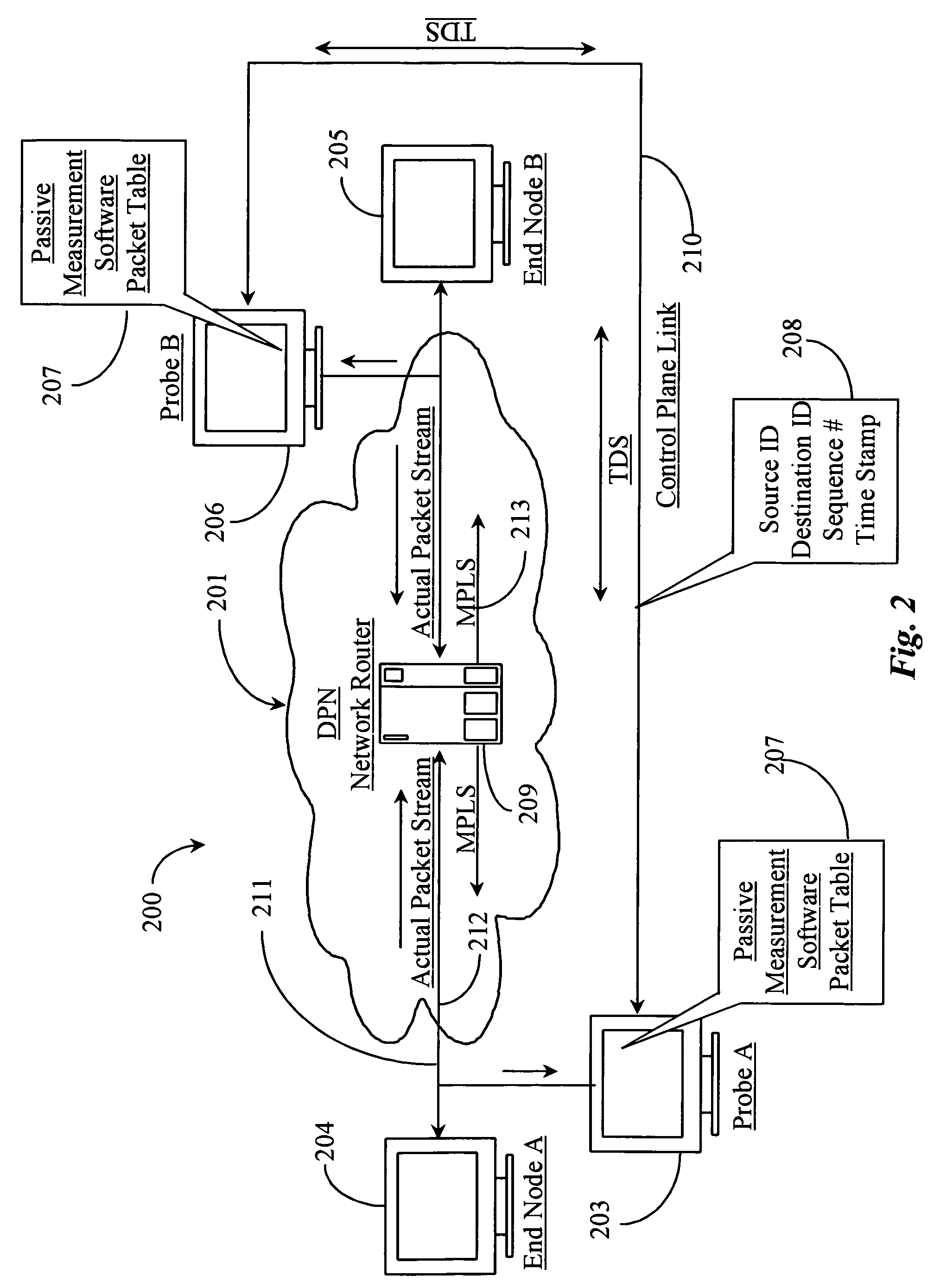
In computing timestamping refers to the use of an electronic timestamp to provide a temporal order among a set of events. Timestamping techniques are used in a variety of computing fields, from network management and computer security to concurrency control. For instance, a heartbeat network uses timestamping to monitor the nodes on a high availability computer cluster.
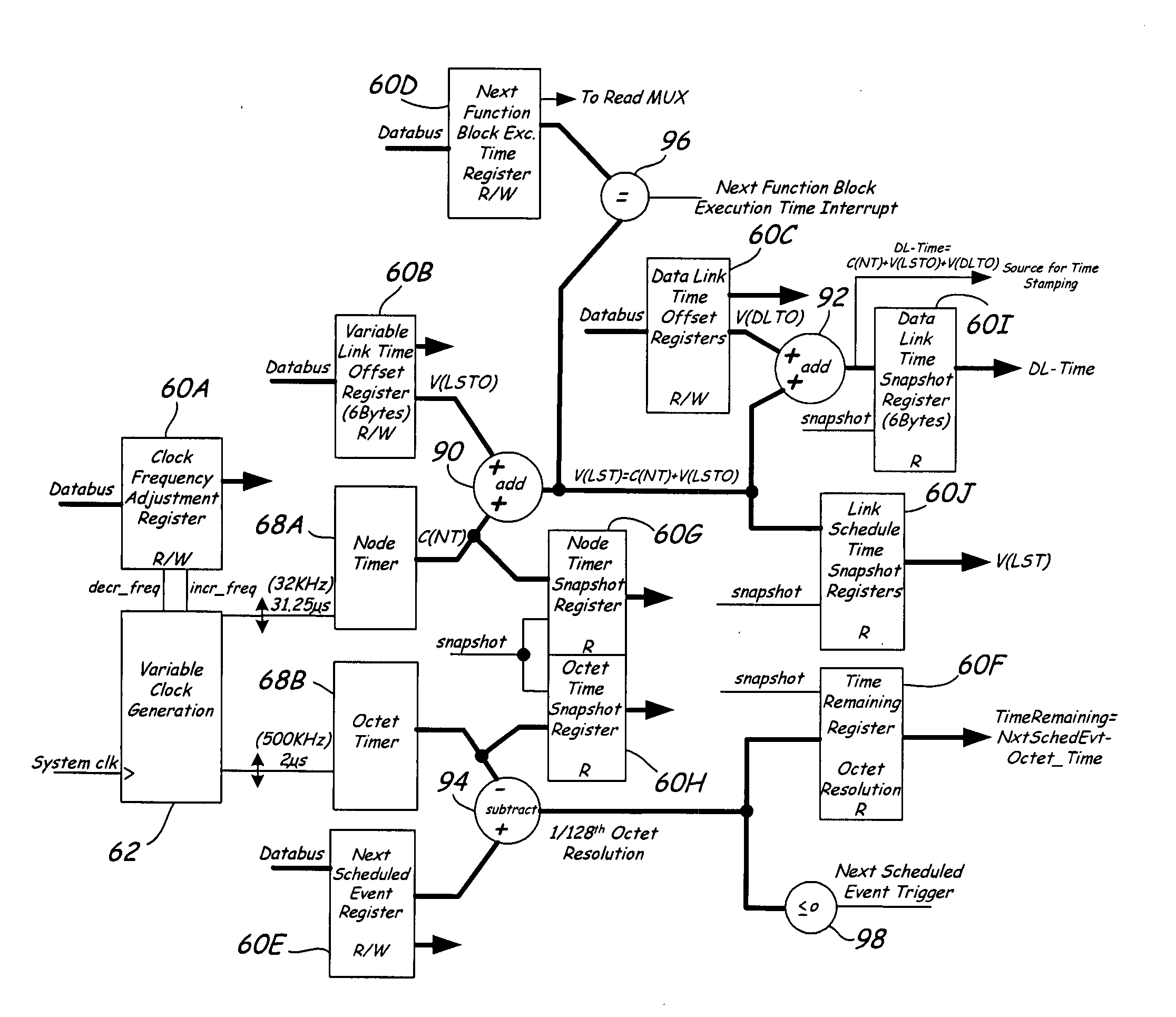
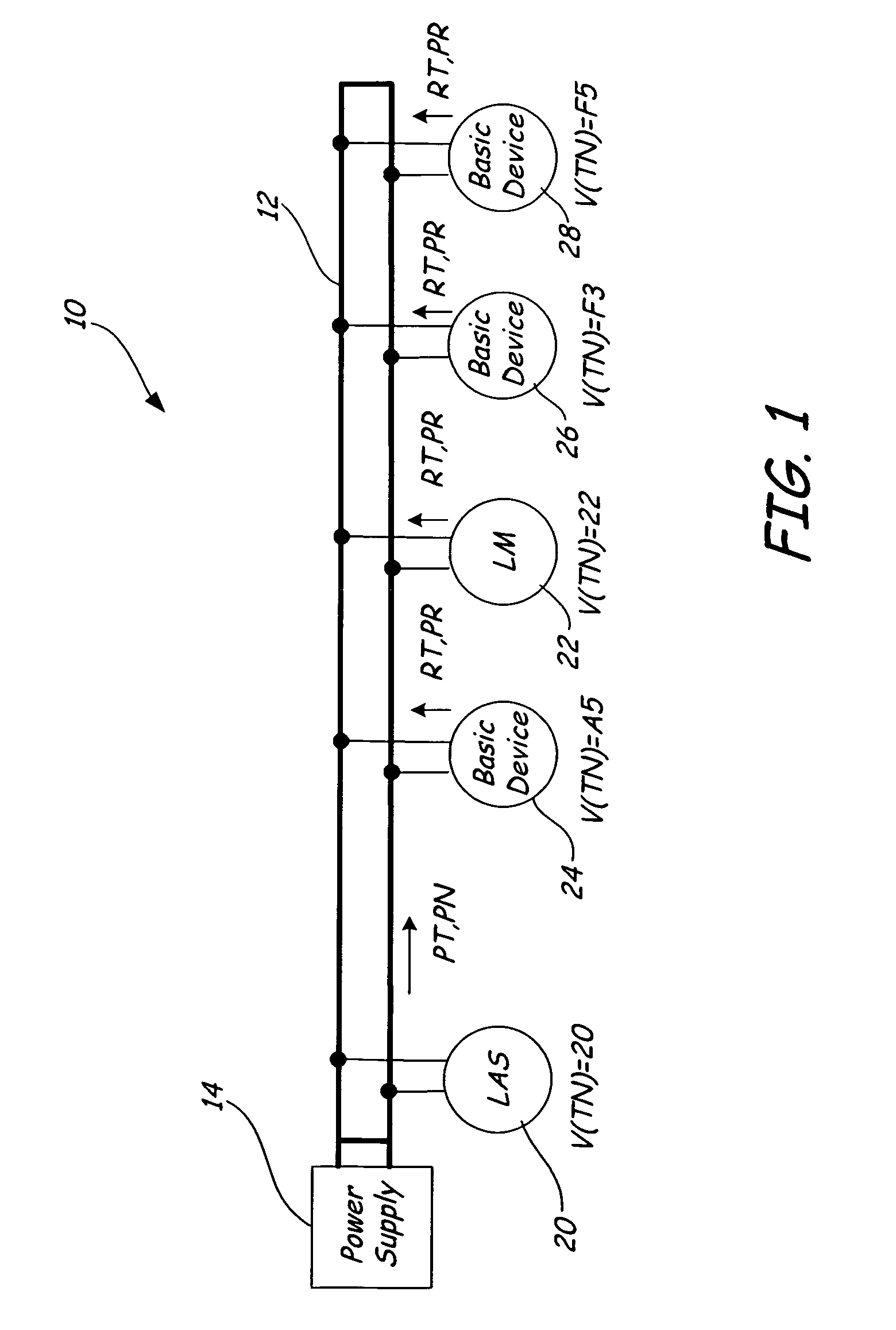
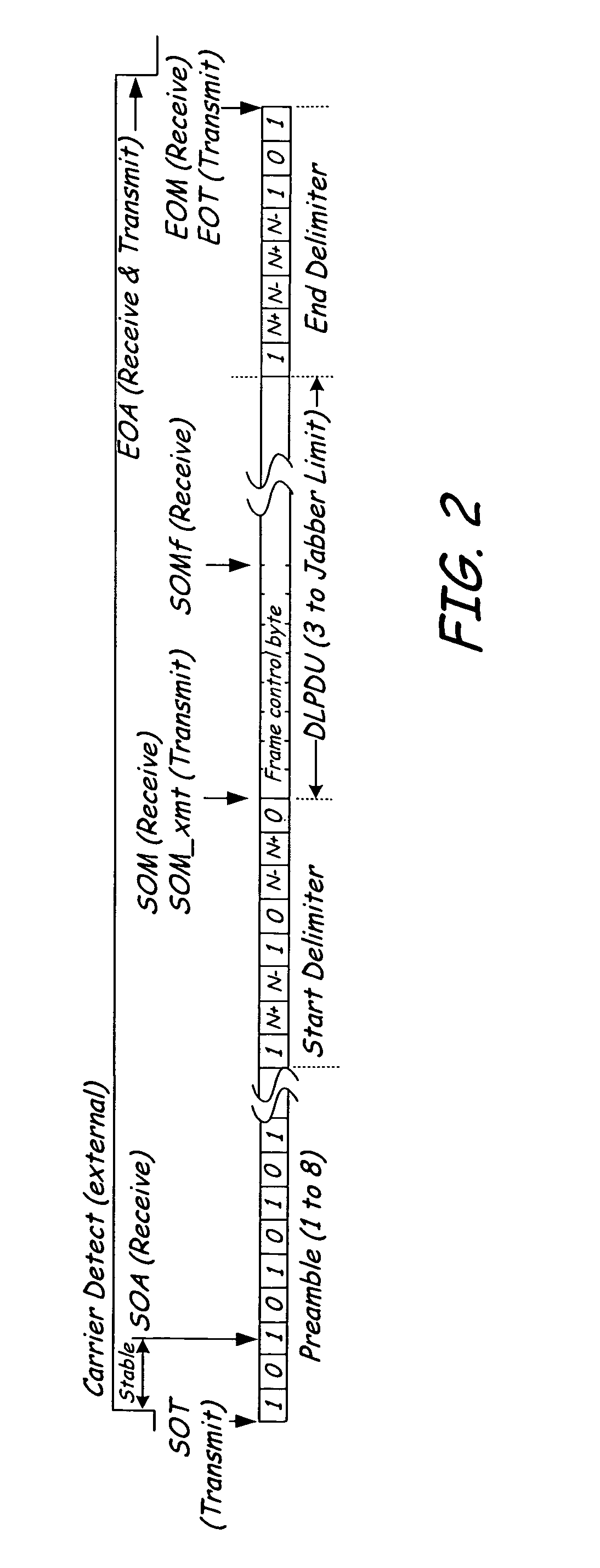
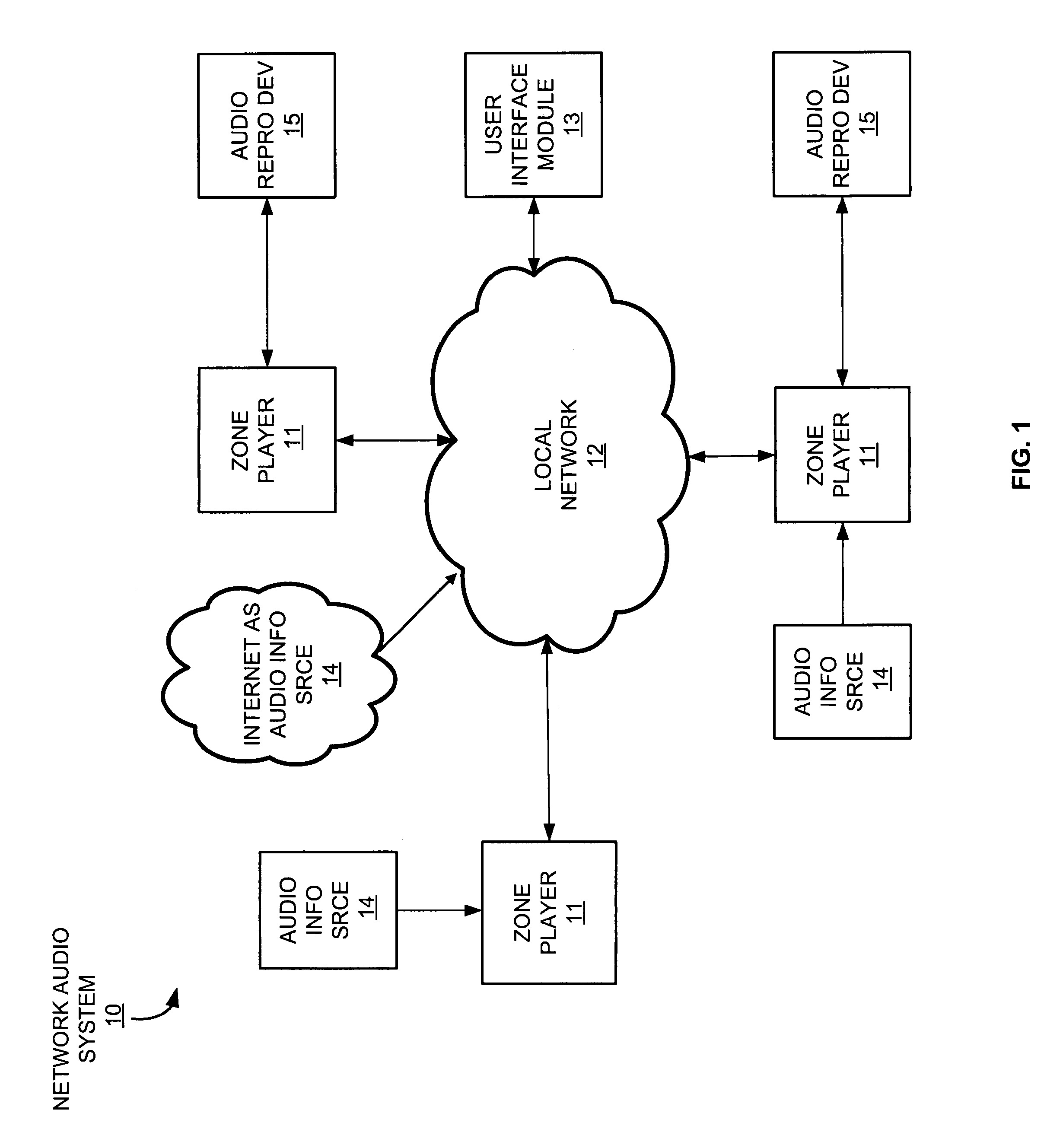
Communication controller with automatic time stamping
ActiveUS20060026314A1Programme controlInput/output to record carriersControl systemCommunication control
Devices in a process control system communicate by data messages over a communication medium segment. Each device includes a communication controller that automatically time stamps events associated with received and transmitted messages.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
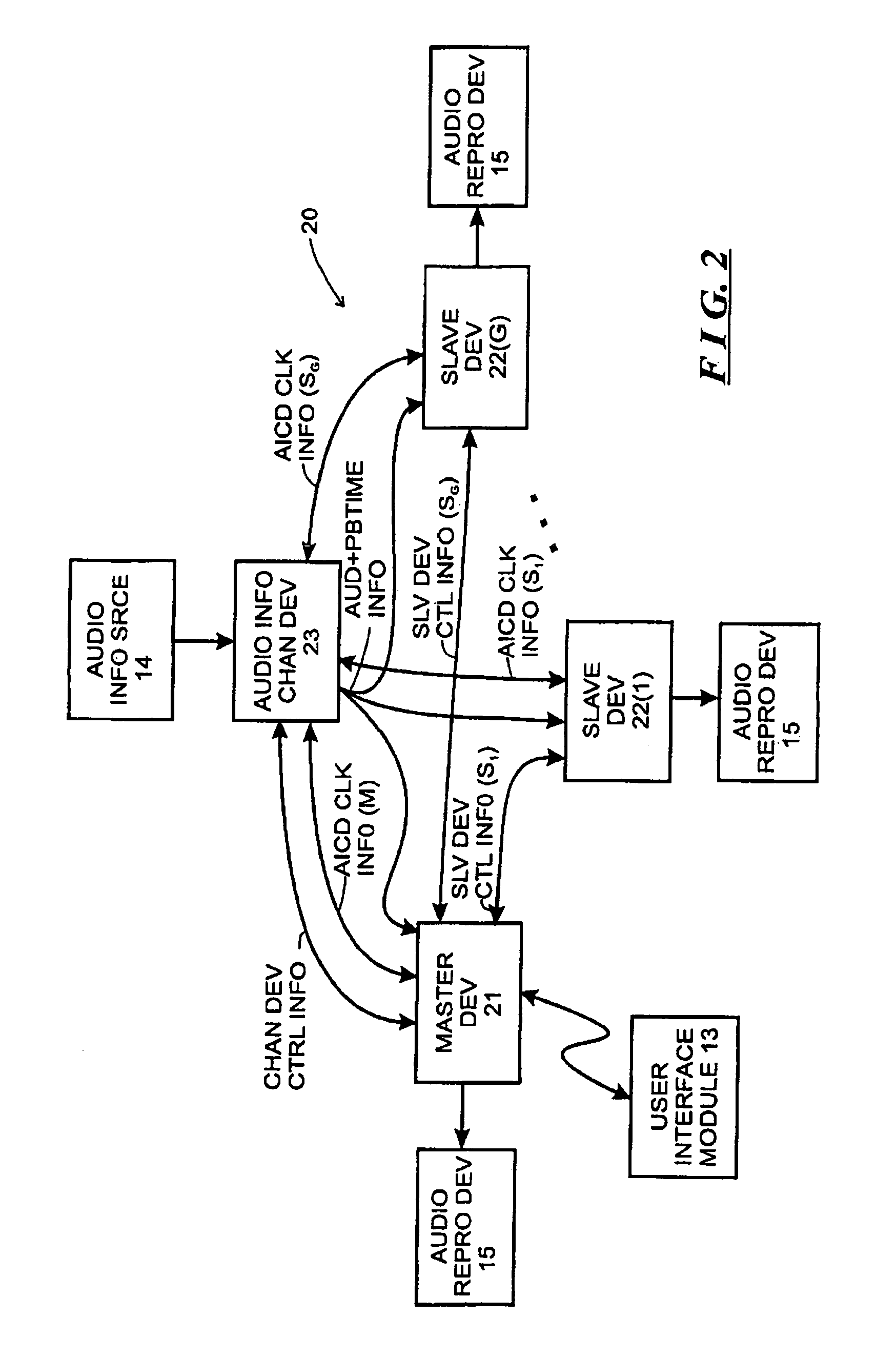
Systems and methods for synchronizing operations among a plurality of independently clocked digital data processing devices without a voltage controlled crystal oscillator
ActiveUS20120029671A1Television system detailsDigital data processing detailsDigital dataEngineering
Owner:SONOS
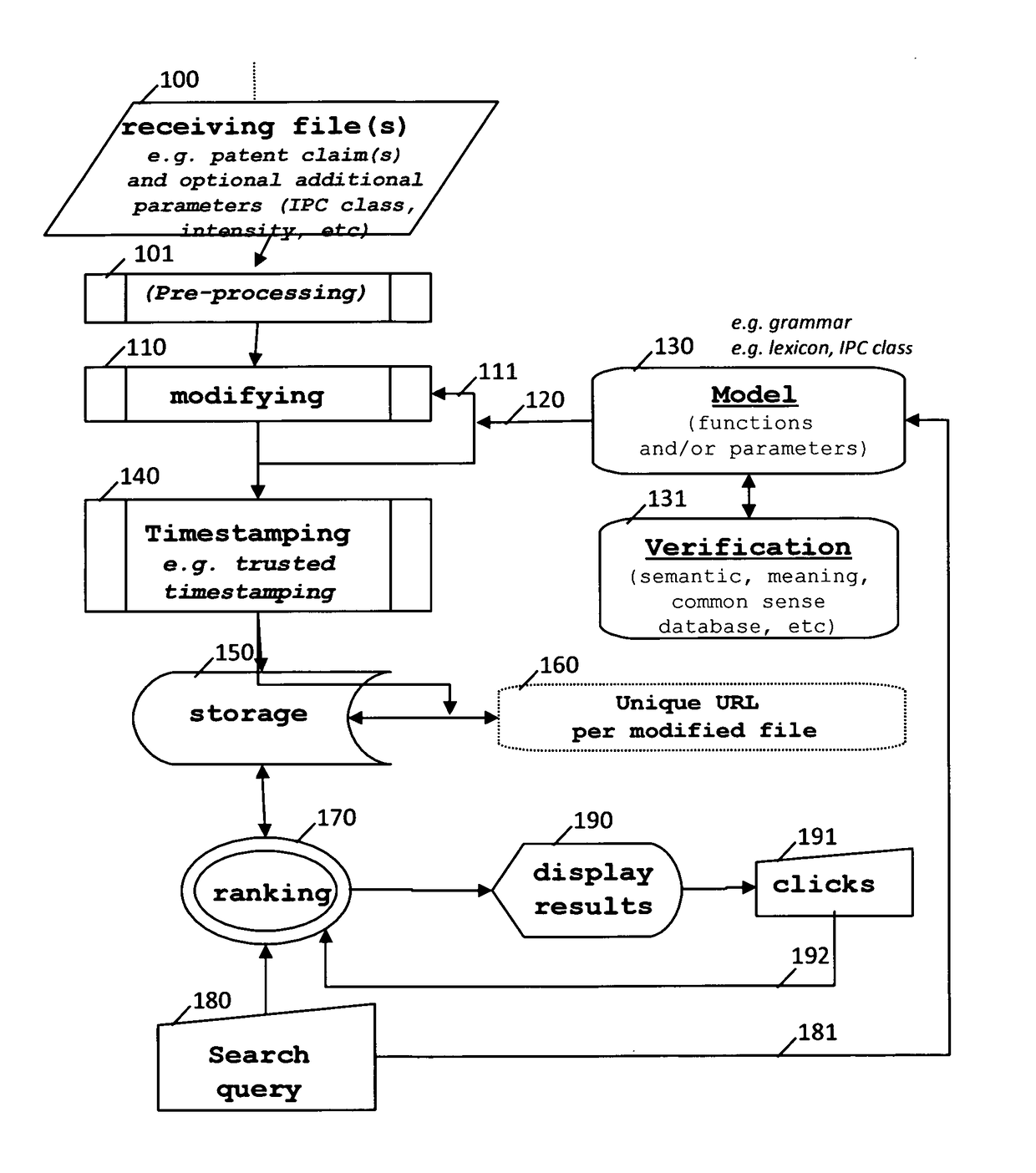
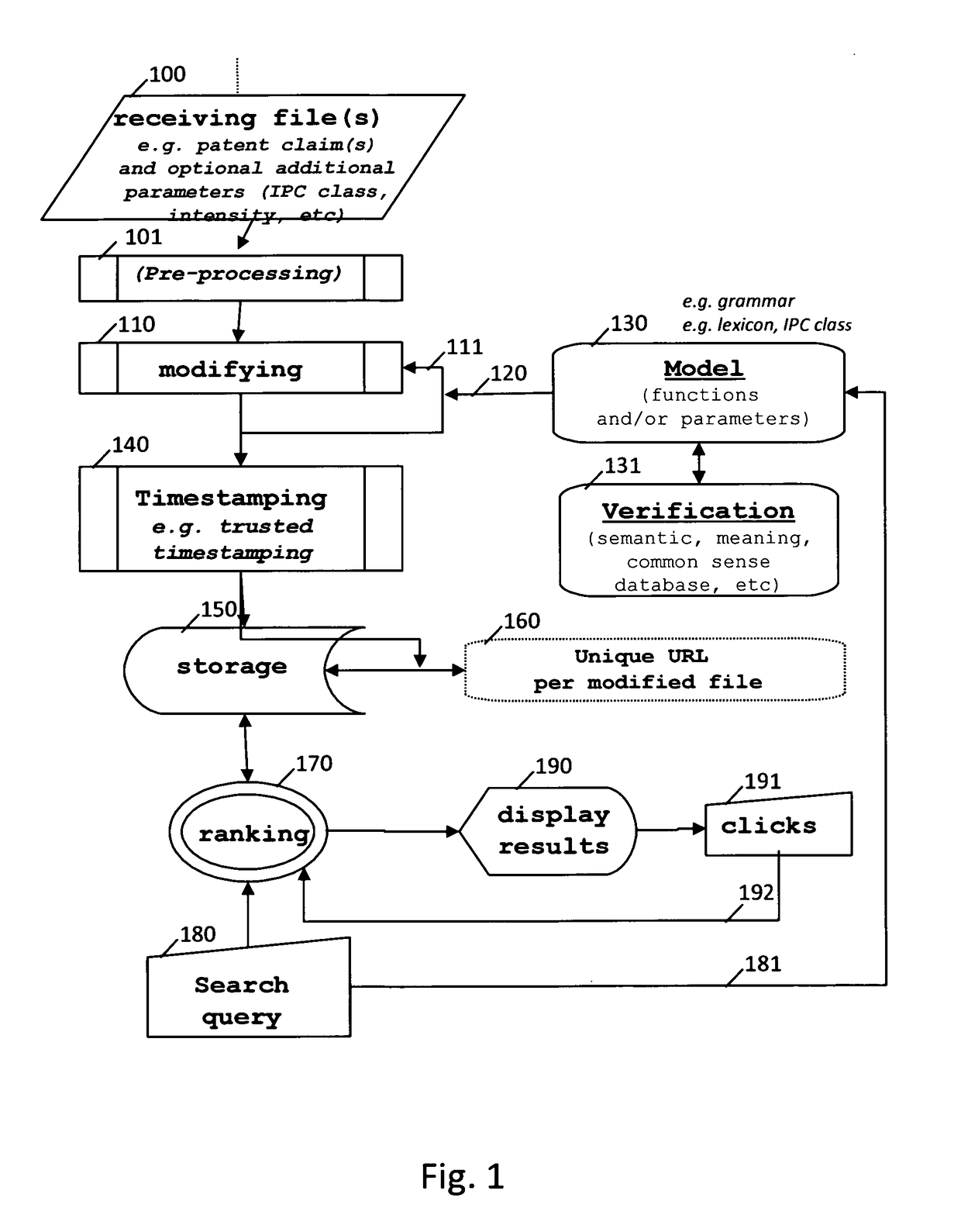
Methods and systems of handling patent claims
InactiveUS20170075877A1Increase in numberImproved accessNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsNatural languagePatent classification
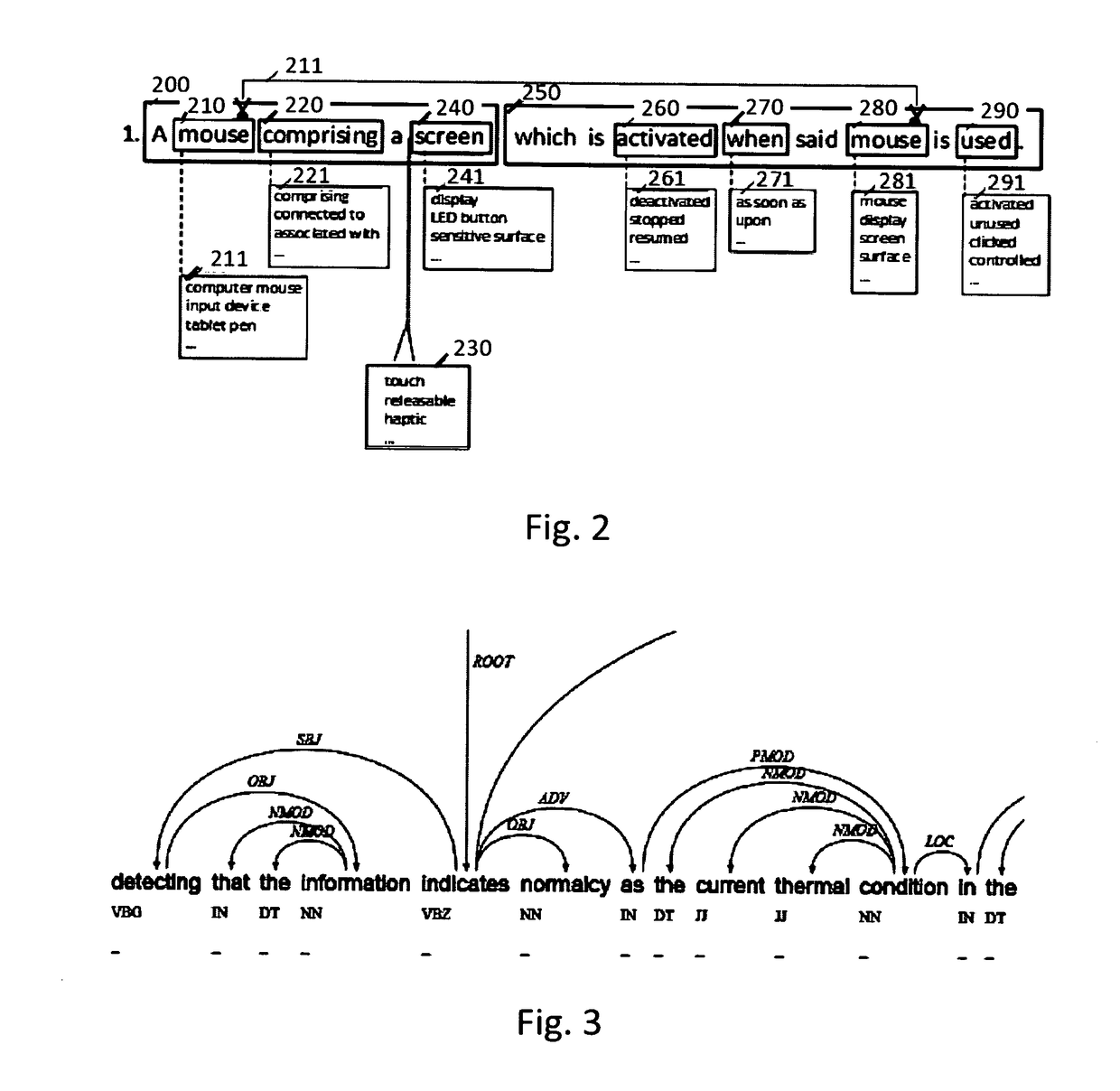
There is disclosed a computer-implemented method of handling a text expressed in a natural language comprising creating a second text or patent claim sentence from a first text or patent claim sentence and timestamping said second text or patent claim sentence. Developments comprise the creation of a plurality of texts or patent claim sentences, the use of trusted and / or trustless timestamping, the use of grammatical texts, the use of a parser and / or of a tagger, modification operations such as addition, insertion and deletion, injection of definitions of words, the use of a thesaurus (synonym, hyponym, hyperonym, holonym, antonym of a word, etc), the use of a unique and optionally persistent web address, making the second text or patent claim available to the public (or not), the use of lexical directions such as a patent classification indication and the use of crowdsourcing techniques.
Owner:LEPELTIER MARIE THERESE
Method and system for authorizing a client computer to access a server computer
InactiveUS7089585B1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsAuthorization certificateHash function
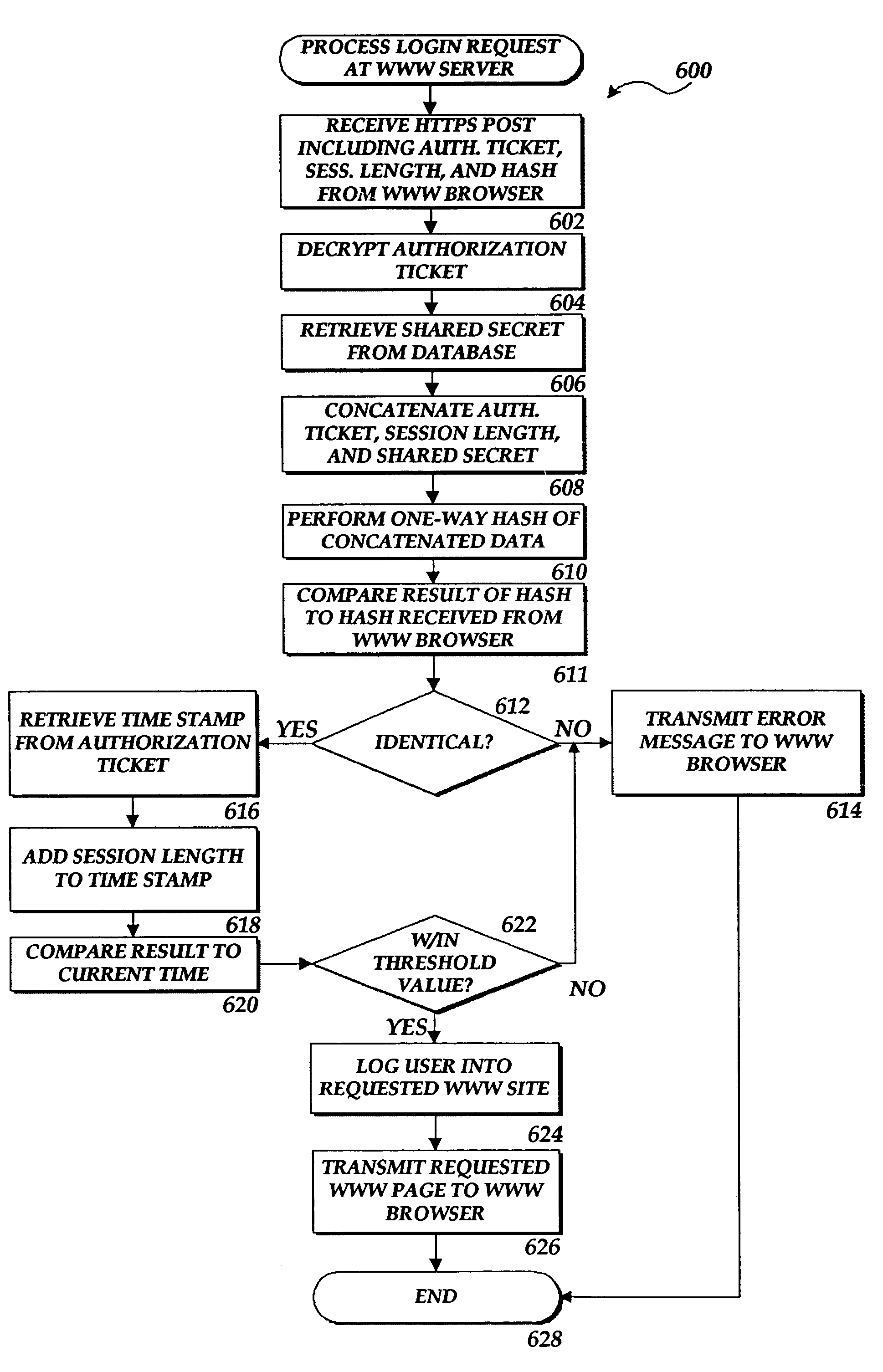
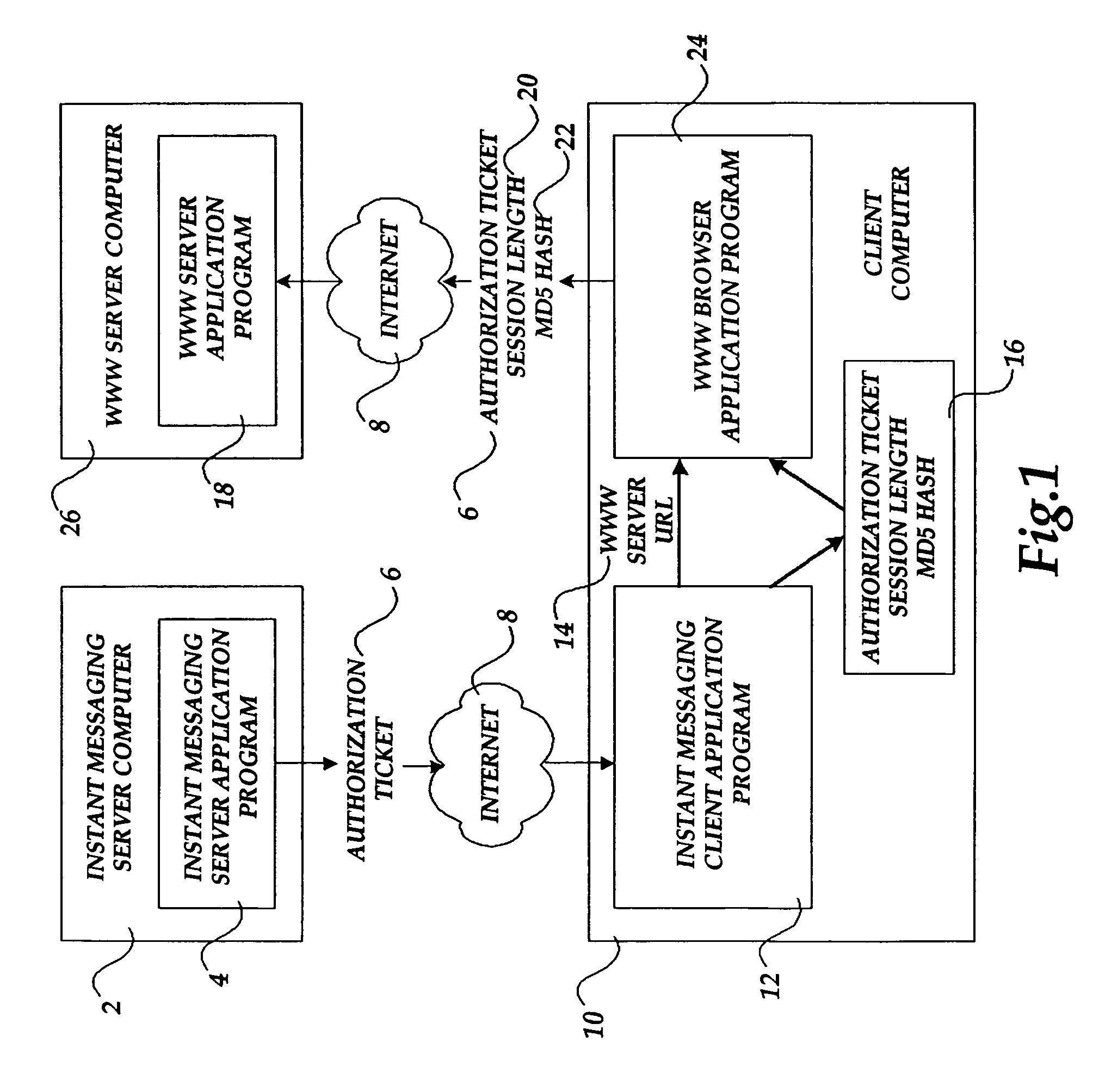
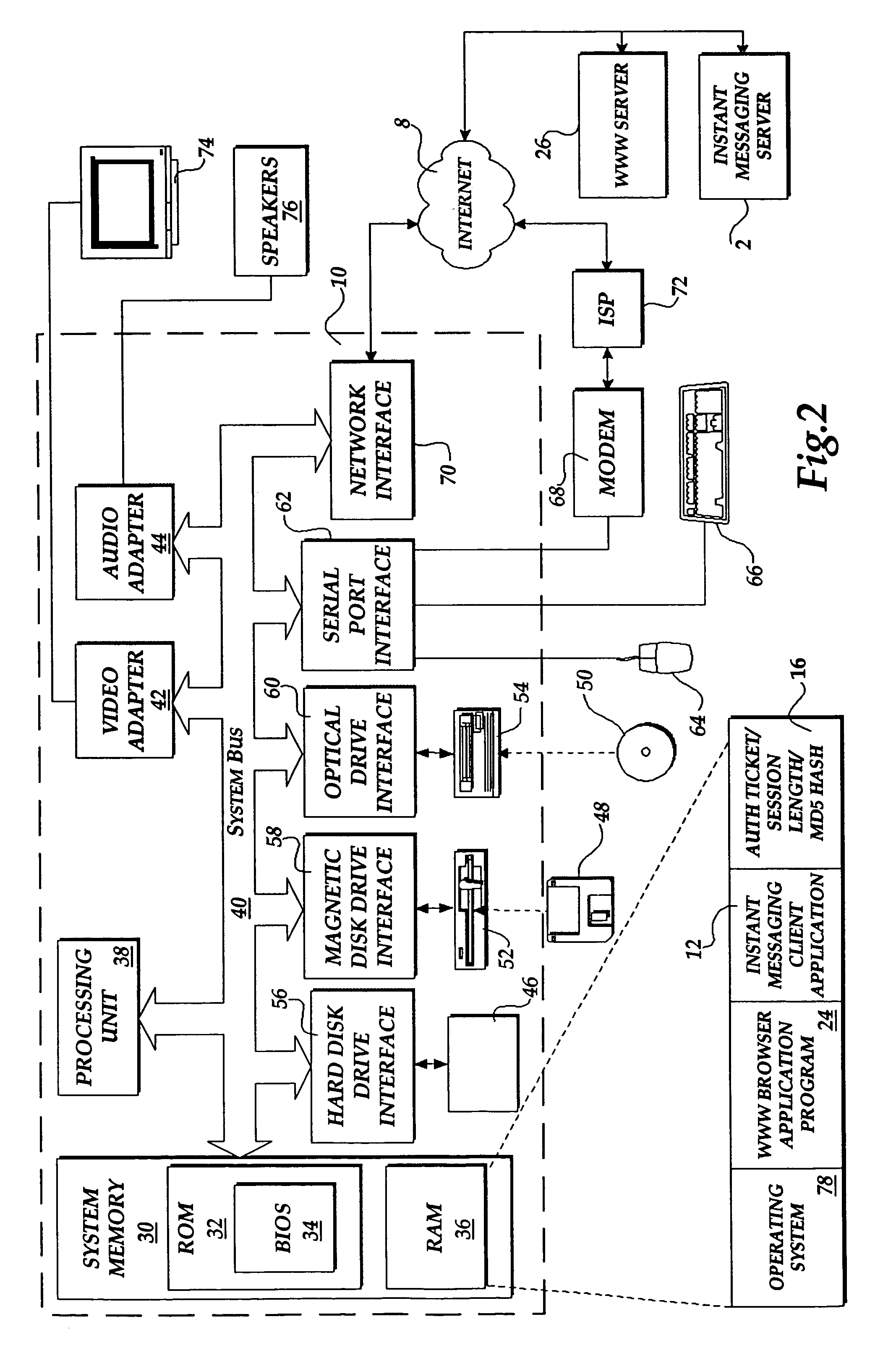
The present invention includes a client computer, a first server computer, and a second server computer. The first server provides an authorization ticket containing a time stamp to the client computer when the client computer is authorized to access the first server. An elapsed time counter is started at the client computer when access is provided to the first server. When a request is received at the client computer to access the second server, the client computer determines the session length based upon the elapsed time counter. The client computer calculates a hash value for the authorization ticket, the session length, and a secret shared with the second server computer. The client computer transmits a login request to the second server including the authorization ticket, the session length, and the hash. The second server decrypts the authorization ticket and retrieves a copy of the shared secret. The second server executes a hash function on the authorization ticket, the session length, and the shared secret. The second server then compares the computed hash to the hash value received from the second client application. If the two hash values are identical, the second server retrieves the time stamp from the authorization ticket and adds the session length to the time stamp. The second server then compares the resulting value to the current time. If the resulting value and the current time are within a preset threshold value, the client computer is provided.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
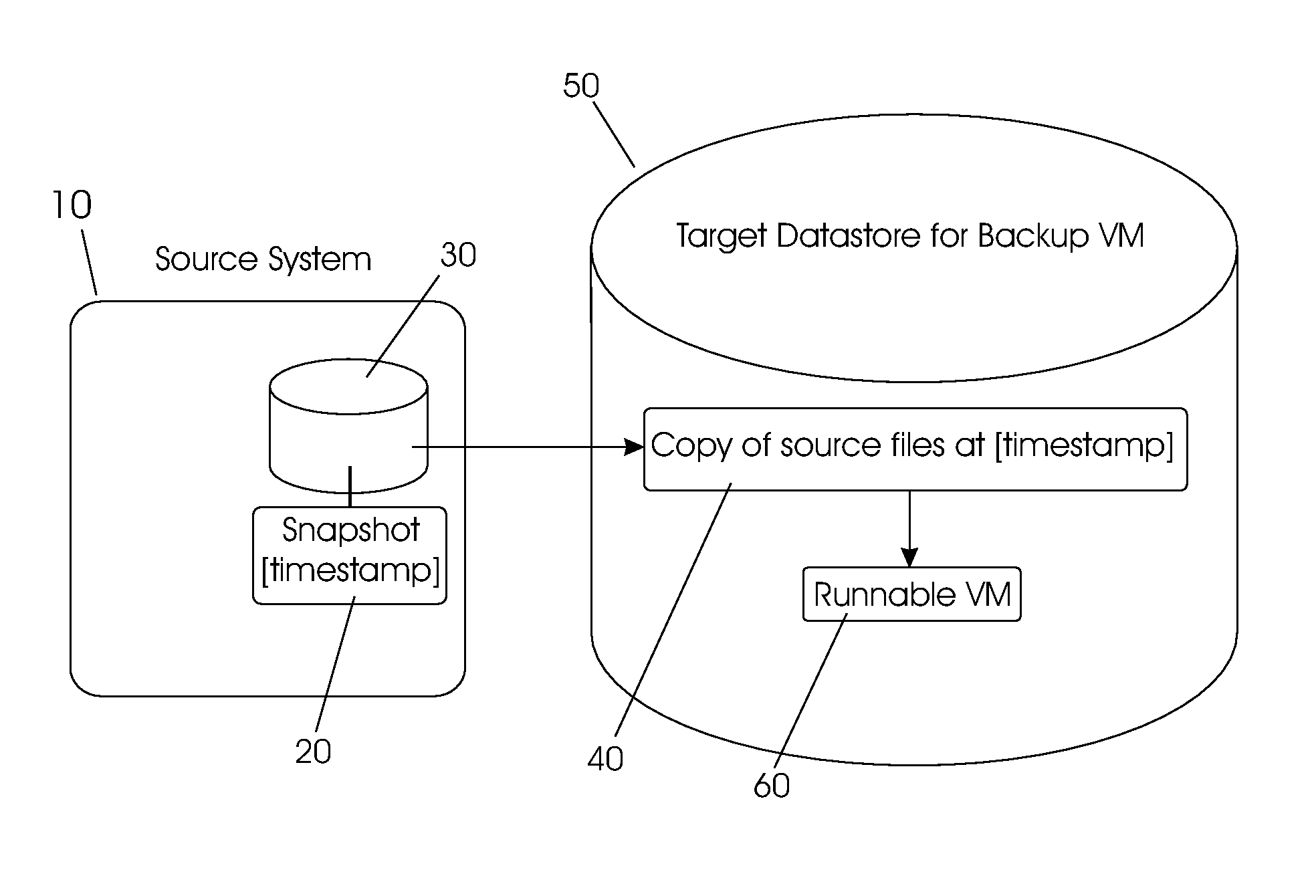
Managing backups using virtual machines
ActiveUS8037032B2Digital data processing detailsError detection/correctionTimestampIncremental backup
One embodiment is a method for providing incremental backups for a source computing machine, the method including: (a) creating a first backup snapshot including a virtual machine (VM) snapshot of an initial copy of a source computing machine volume, wherein said VM snapshot includes a timestamp and a first redo log file; (b) reconfiguring and customizing said first backup snapshot to create a first bootable VM, writing changes associated with said reconfiguring and customizing into said first redo log file, then creating a first bootable snapshot including a VM snapshot of said first bootable VM, wherein said VM snapshot of said first bootable VM includes a timestamp for said first bootable VM and a redo log file; (c) performing an incremental update of said first backup snapshot or a subsequent backup snapshot, then creating a subsequent backup snapshot including a VM snapshot of said incremental update, wherein said VM snapshot of said incremental update includes a timestamp for said incremental update and a redo log file; and (d) reconfiguring and customizing said subsequent backup snapshot to create a subsequent bootable VM, then creating a subsequent bootable snapshot including a VM snapshot of said subsequent bootable VM, wherein said VM snapshot of said subsequent bootable VM includes a timestamp for said subsequent bootable VM and a redo log file.
Owner:VMWARE INC
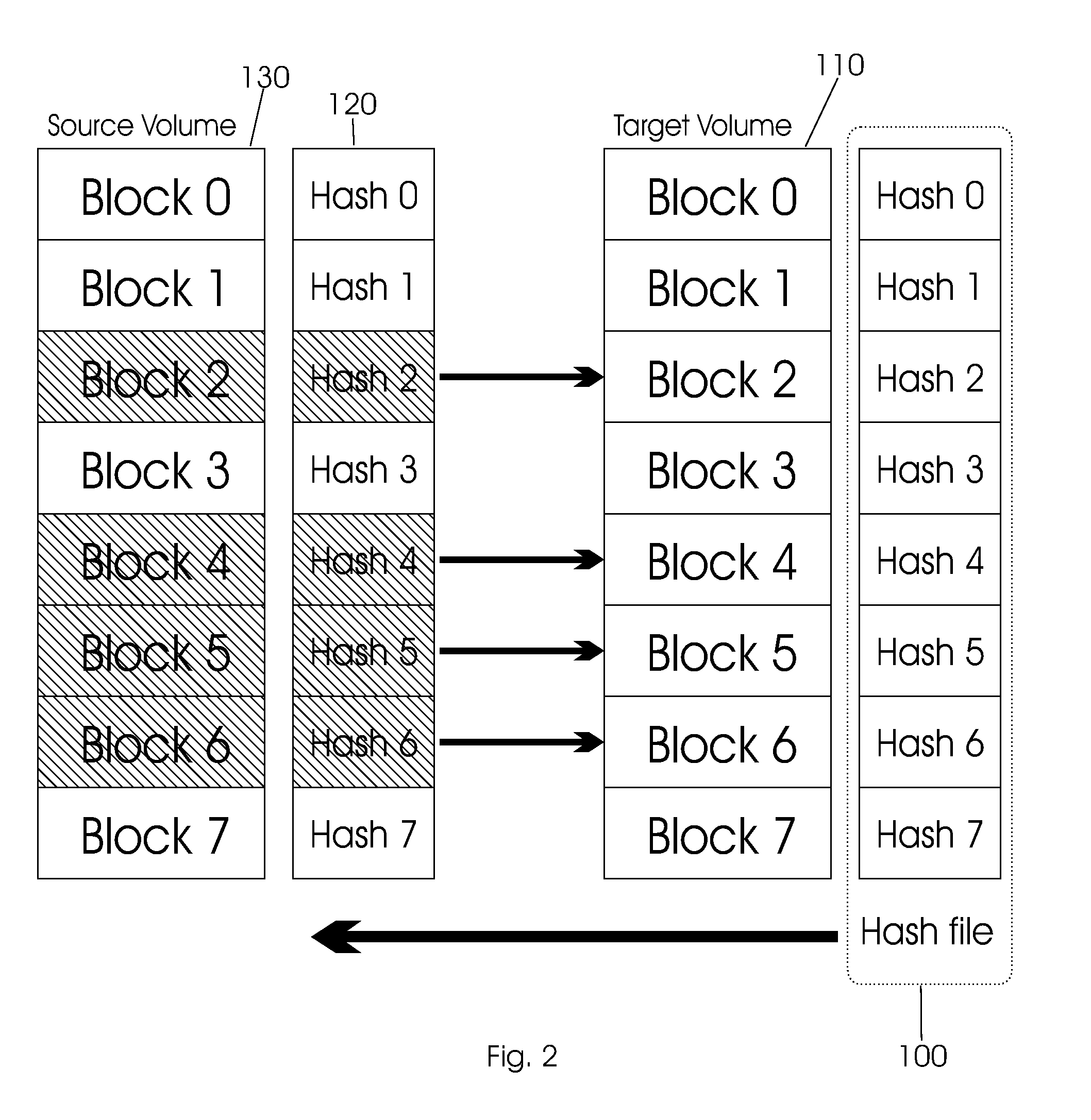
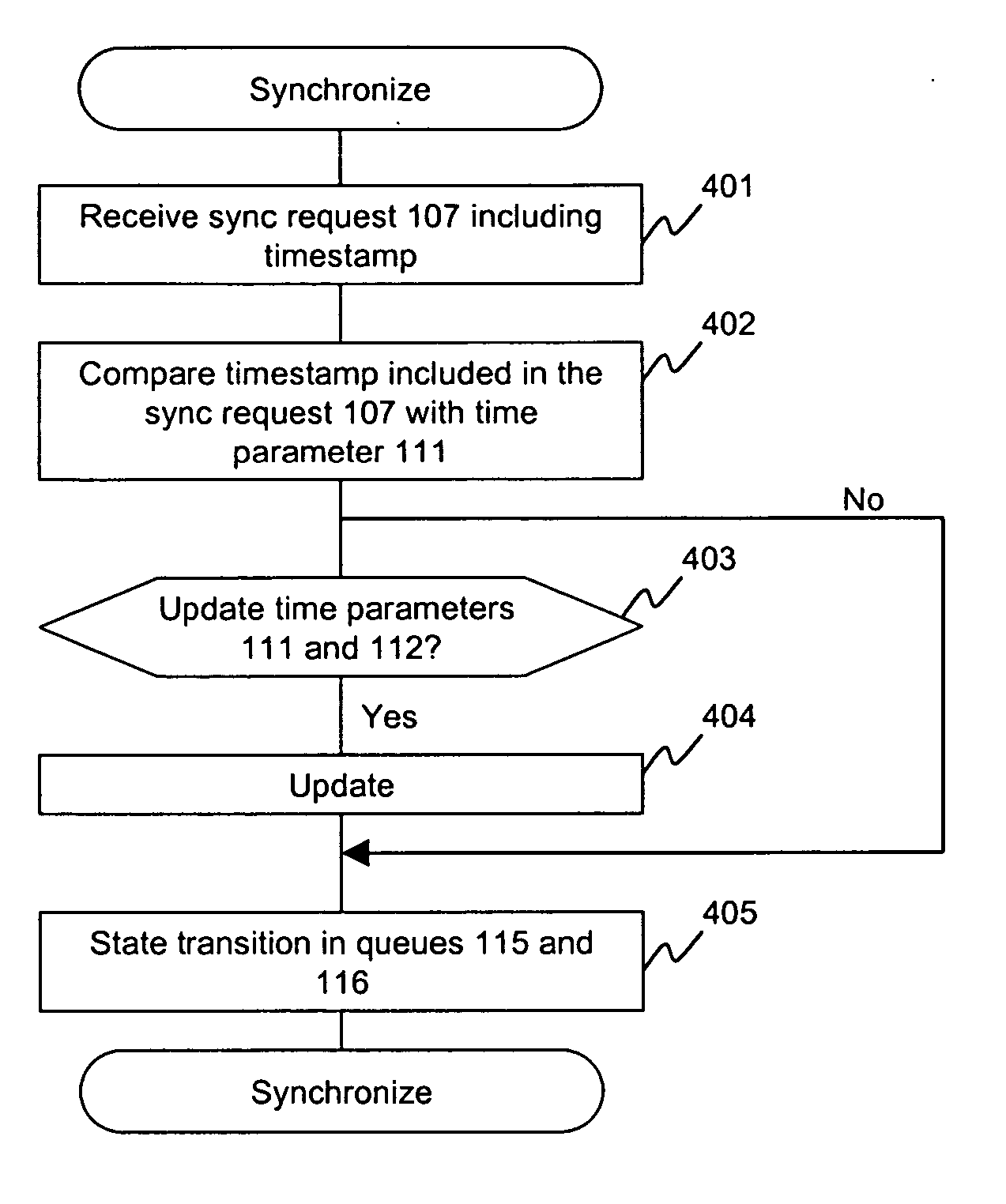
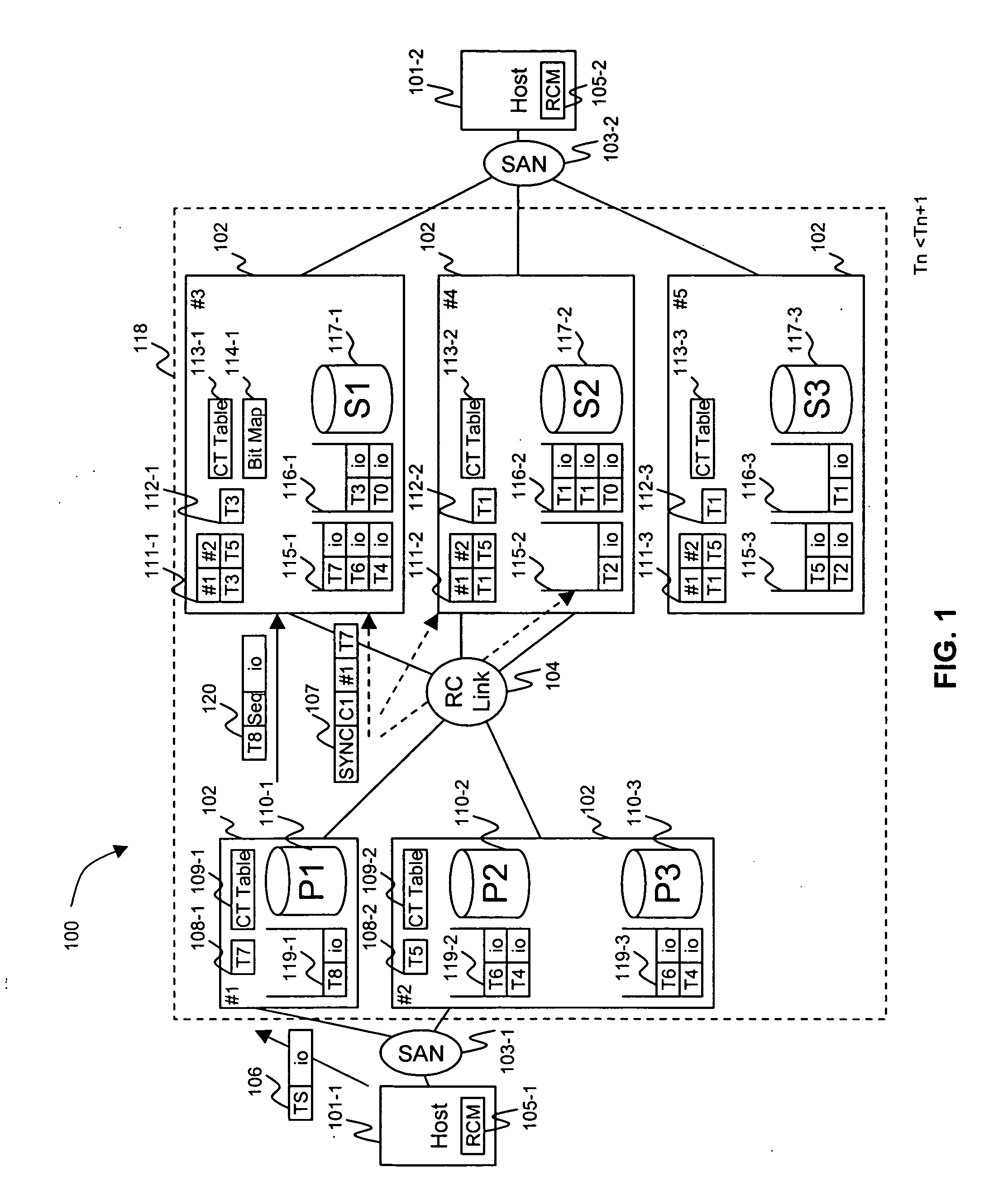
Method and apparatus of remote copy for multiple storage subsystems
A system and method for synchronizing remote copies within a multiple storage network apparatus, incorporates the steps of receiving a plurality of timestamps, comparing the timestamps with a plurality of timestamps stored in a remote copy table, updating a synchronize time value stored by a synchronized time parameter, and receiving a synchronized time stamp, wherein the value associated with the received timestamp is ulterior to the value of the synchronized time stored by the synchronized time parameter. Further, a system and method for synchronizing secondary storage subsystems, incorporates the steps of collecting a plurality of synchronous timestamps from a plurality of secondary storage subsystems, comparing the plurality of collected synchronous timestamps with a synchronize time parameter, updating a remote copy time table, issuing a remote copy queue request, receiving status information about a secondary storage subsystem starting host, and synchronizing the secondary storage subsystem.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
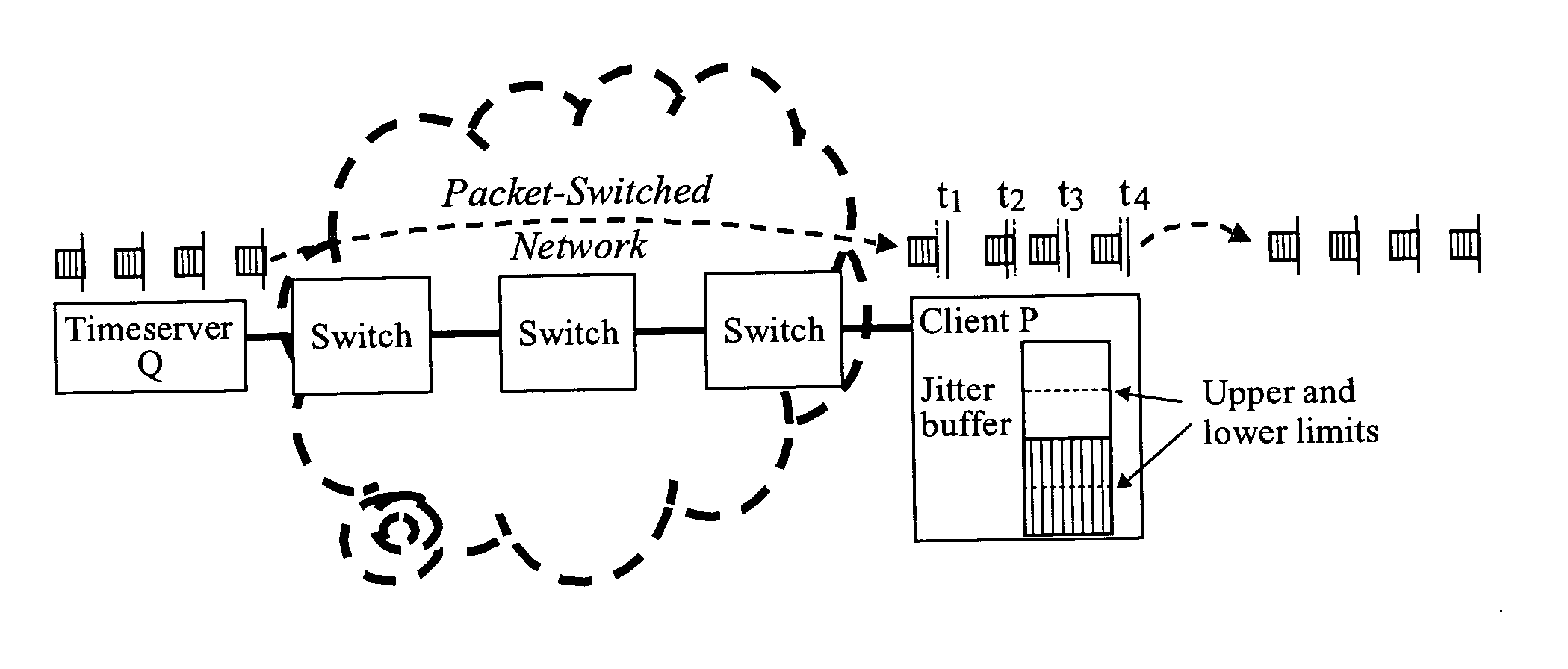
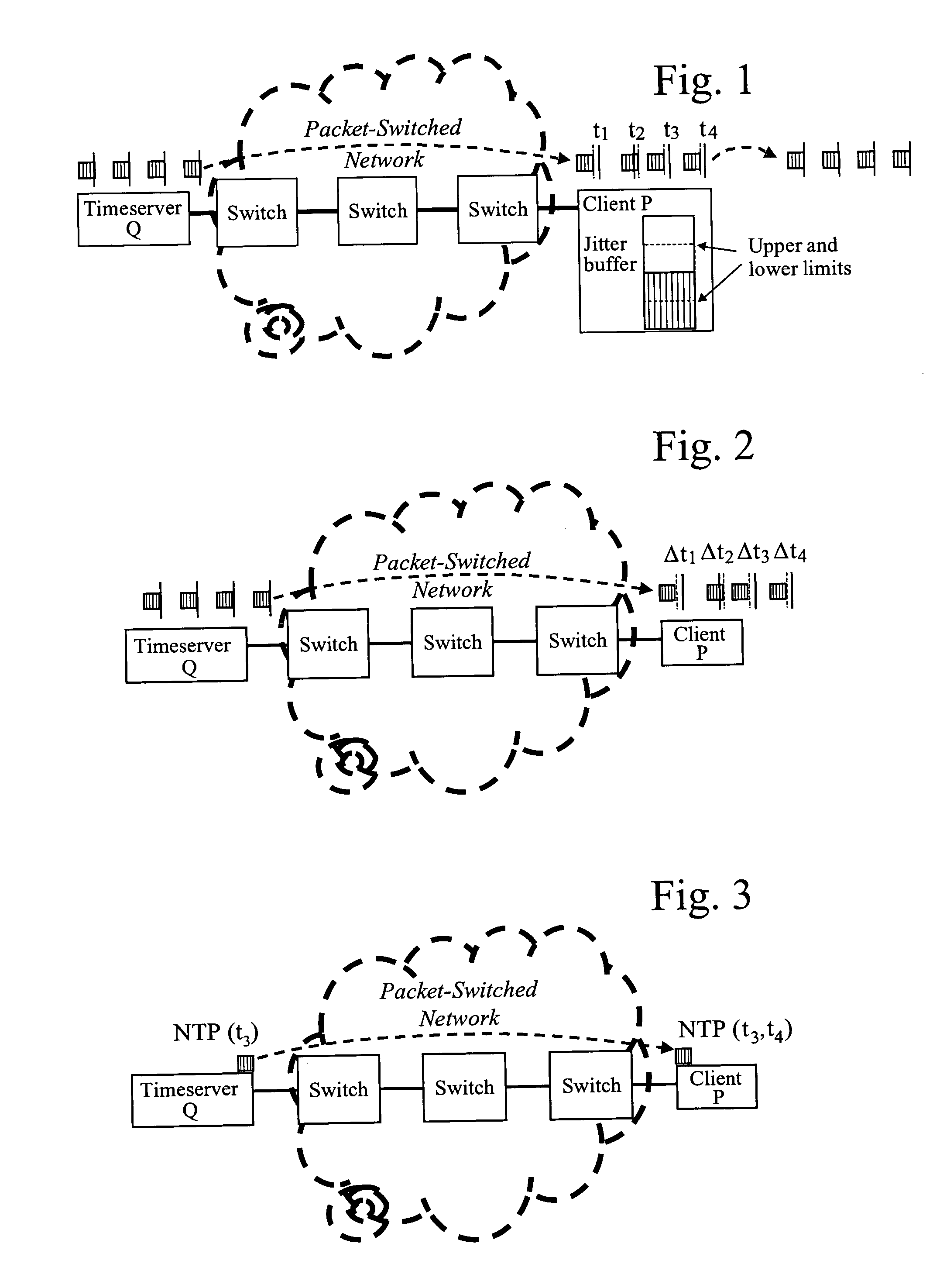
Remote synchronization in packet-switched networks
ActiveUS20050041692A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTimestampTime synchronization
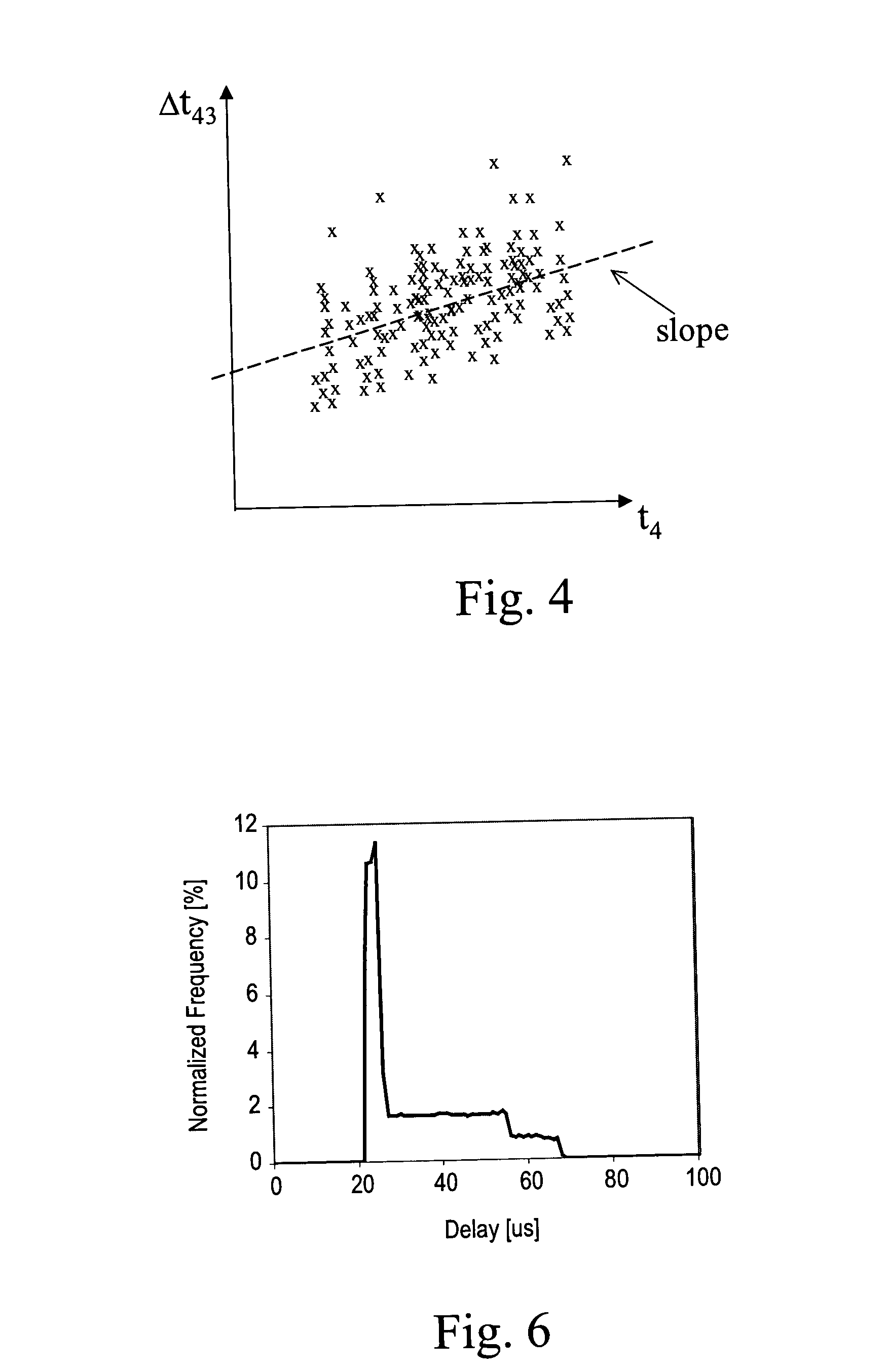
Remote frequency synchronization is achieved between two or more nodes in a packet-switched network using differential timestamps. A line is fit to multiple differential time values using a minimum delay principle. Frequency synchronization and / or absolute time synchronization between the two nodes may be achieved using one or both of uplink and downlink differential time values and fitting one or both of first and second lines to differential time values by different means of the minimum delay principle.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Integrating external and cluster heat map data
ActiveUS20120072578A1Well formedError detection/correctionMultiple digital computer combinationsTimestampHeat map
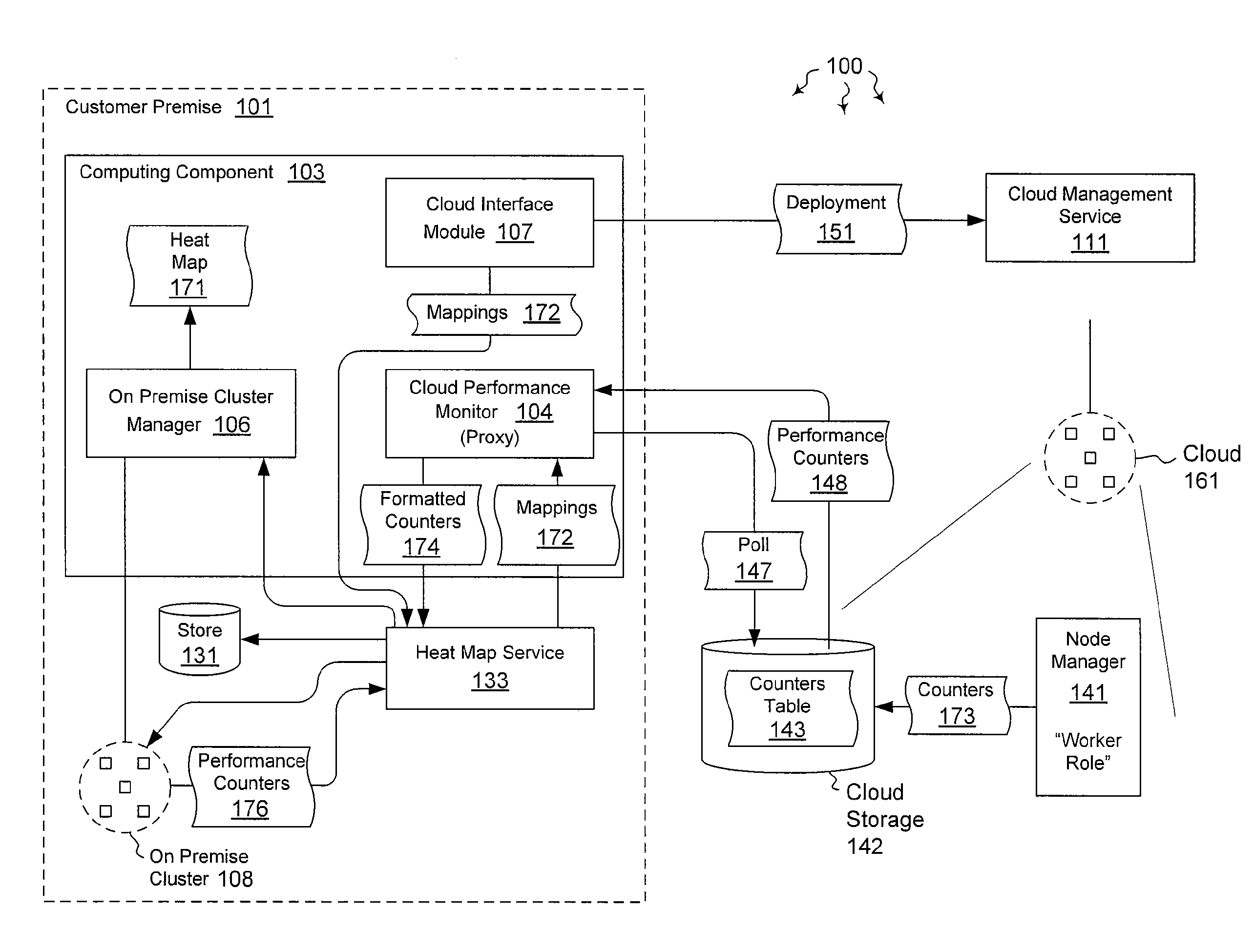
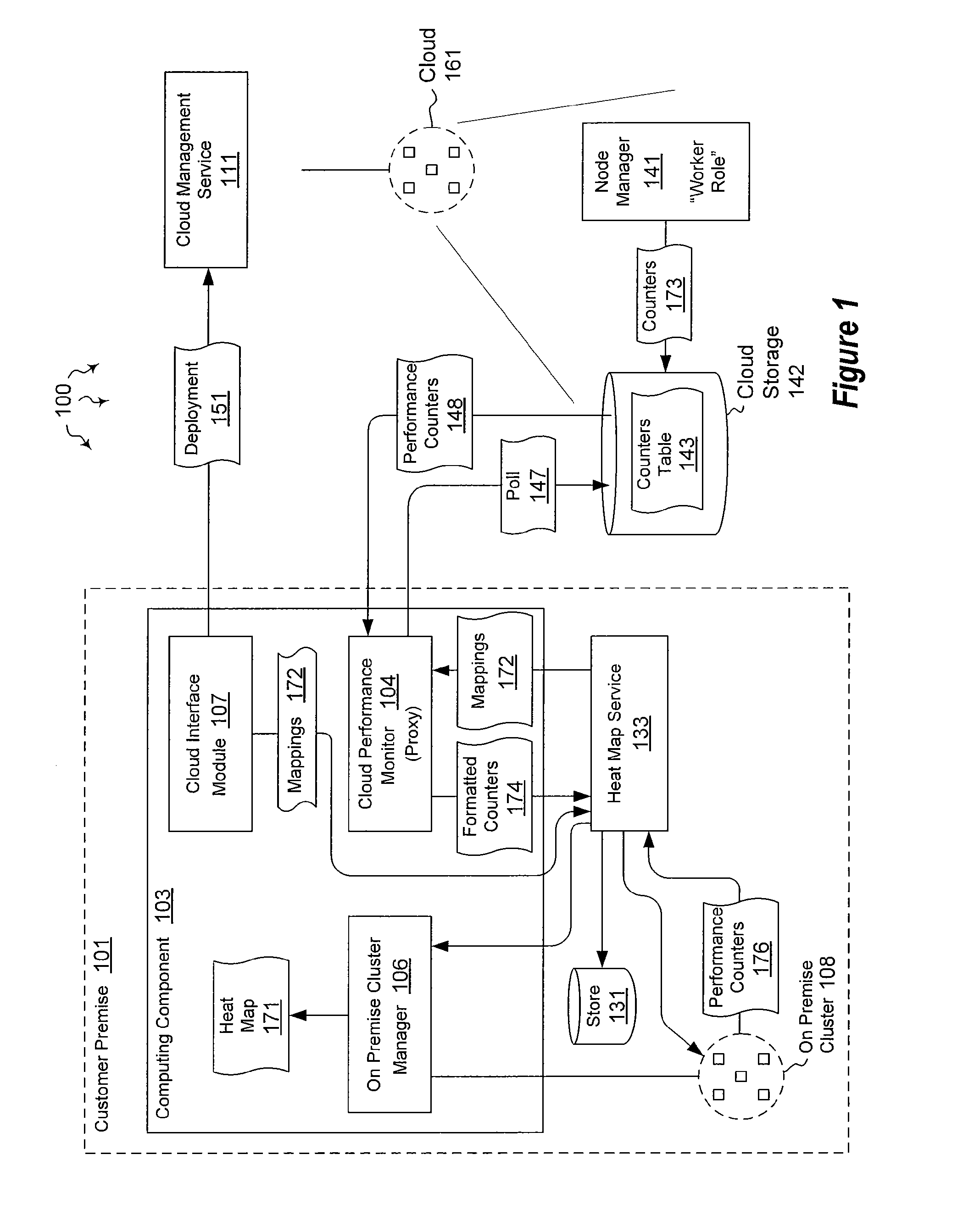
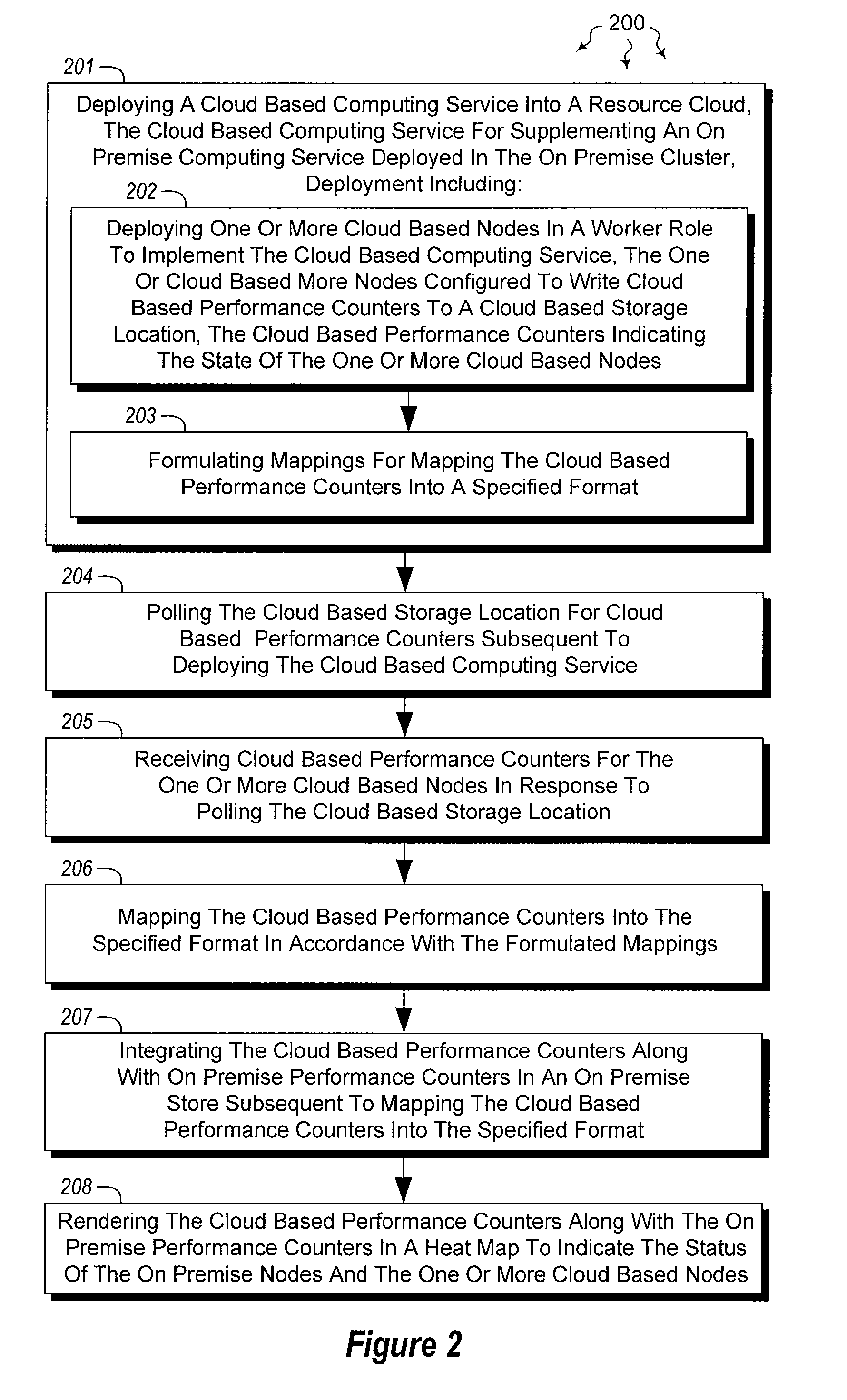
The present invention extends to methods, systems, and computer program products for integrating external and cluster heat map data. Embodiments of the invention include a proxy service that manages (e.g., asynchronous) communication with cloud nodes. The proxy service simulates packets to on-premise services to simplify the integration with an existing heat map infrastructure. The proxy maintains a cache of performance counter mappings and timestamps on the on-premise head node to minimize the impact of latency into heat map infrastructure. In addition, data transfer is minimized by mapping a fixed set of resource based performance counters into a variable set of performance counters compatible with the on premise heat map infrastructure.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
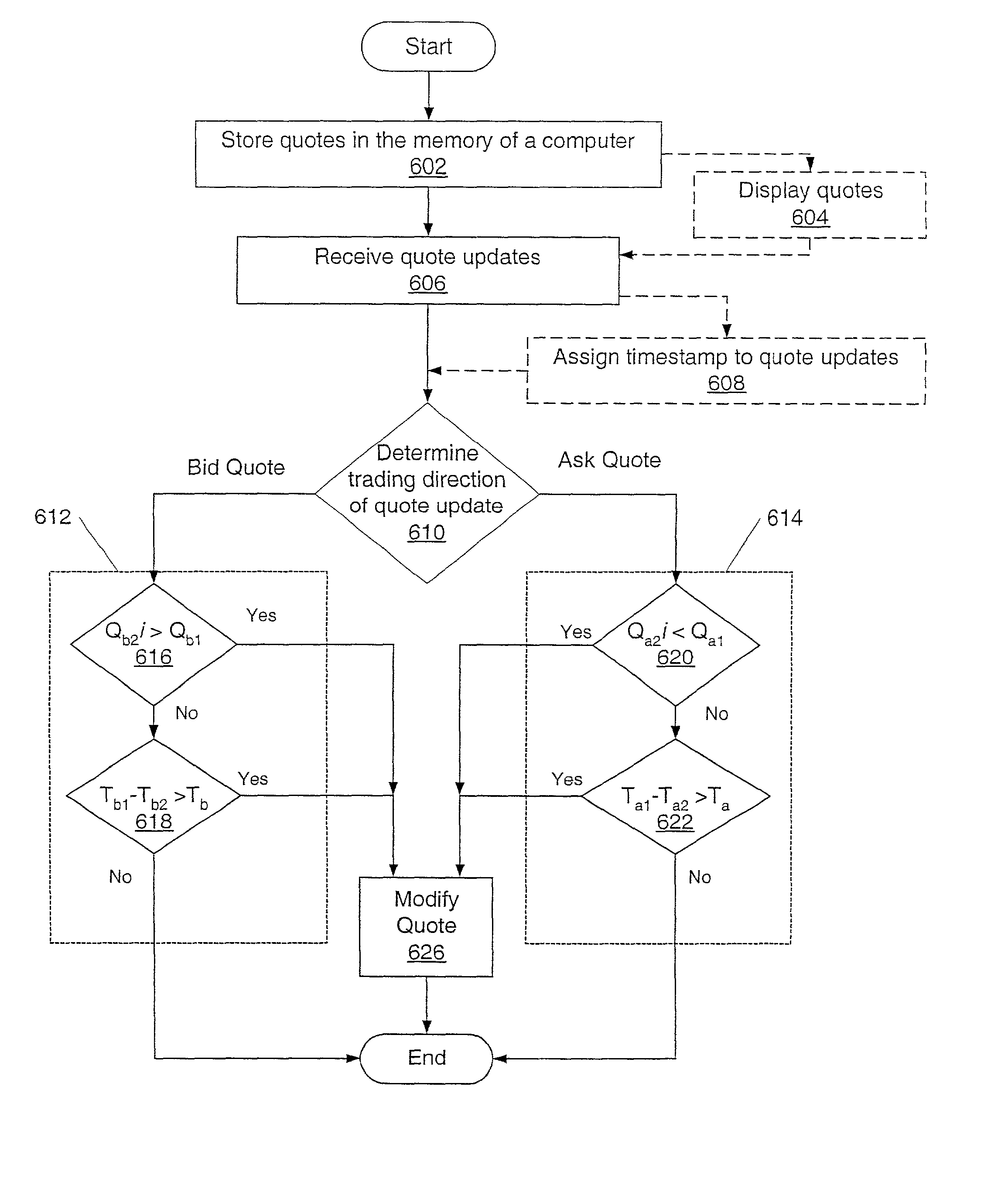
Methods and systems for suppression of stale or invalid data in a securities quotation display
Methods and systems for displaying information related to securities to a user are provided. In an embodiment, a method may include storing securities quotes in a memory of a computer. The method may include receiving quote updates information. The received quote update information and the quotes stored in the memory of the computer may be compared via one or more criteria. For bid quotes, a first criterion may include determining if a quote stored in the memory of the computer is greater than the price of a quote update. For ask quotes, the first criterion may include determining if a quote stored in the memory of the computer is less than the price of a quote update. A second criterion may include determining if a timestamp associated with the quote update minus a timestamp associated with the quote stored in the memory of the computer is greater than a predetermined threshold time. If one or more of the criteria are met, the method may modify the quote in the memory of the computer. Modifying the quote may include, but is not limited to: changing a display color, changing a font style, inhibiting the quote from being displayed, and deleting the quote from the memory of the computer.
Owner:INSTINET GRP INC +2
Method and apparatus for monitoring latency, jitter, packet throughput and packet loss ratio between two points on a network
InactiveUS7961637B2Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCorrect operation testingPacket lossWaiting time
Owner:SPIRENT COMM
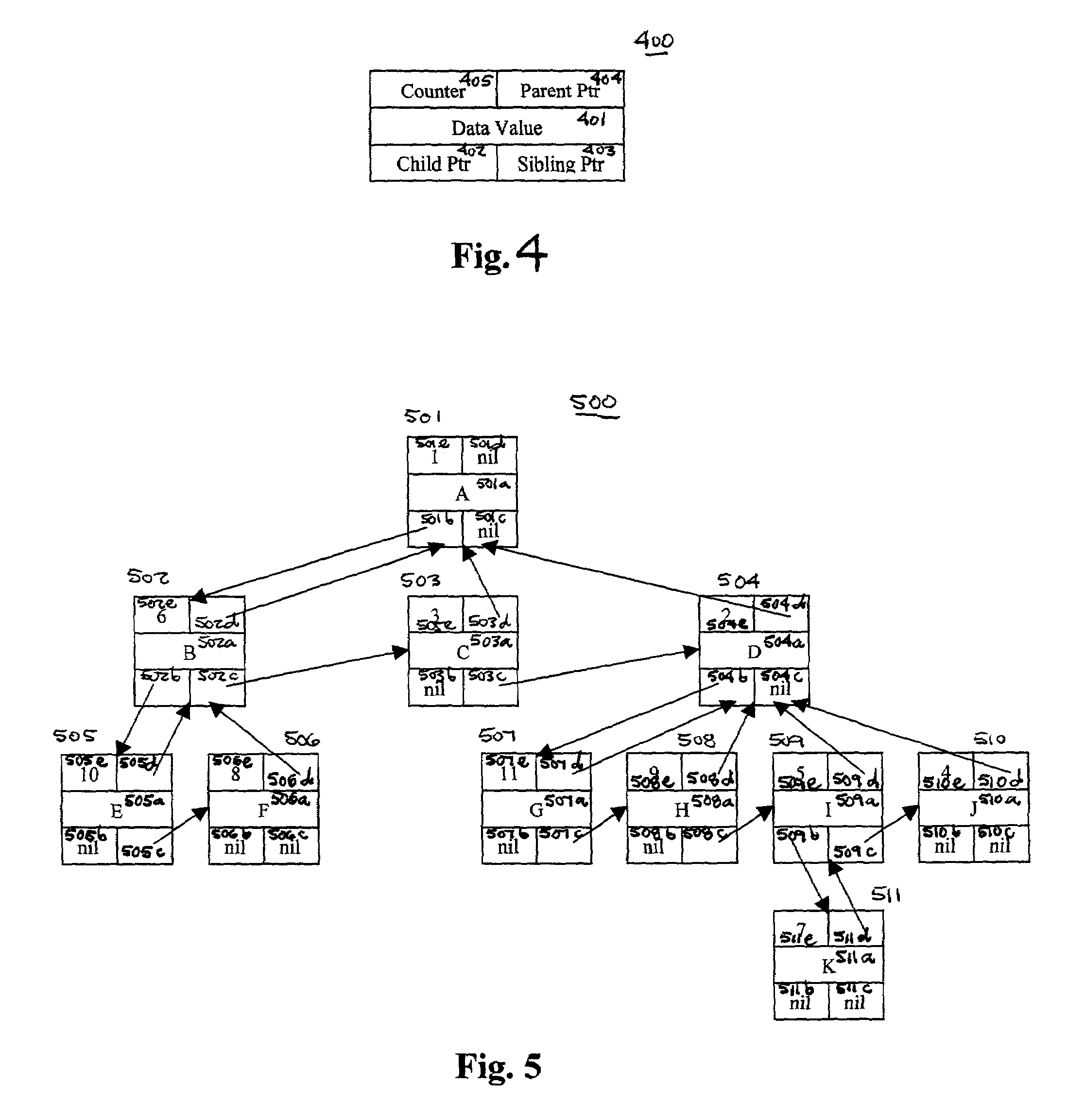
Mechanism for continuable calls to partially traverse a dynamic general tree
ActiveUS6978271B1Data processing applicationsFile access structuresTheoretical computer scienceTree (data structure)
Mechanisms and methods for traversing trees are disclosed. A novel data structure for modeling a node that includes a unique node counter also is described. In certain embodiments of the inventions the unique node counter is a timestamp of sufficient granularity to render each timestamp in the tree unique. A node counter, in conjunction with the lineage of a specified continuation node may be used to locate an appropriate starting point within a tree in a continuation call when the specified continuation node no longer exists in the tree.
Owner:UNISYS CORP
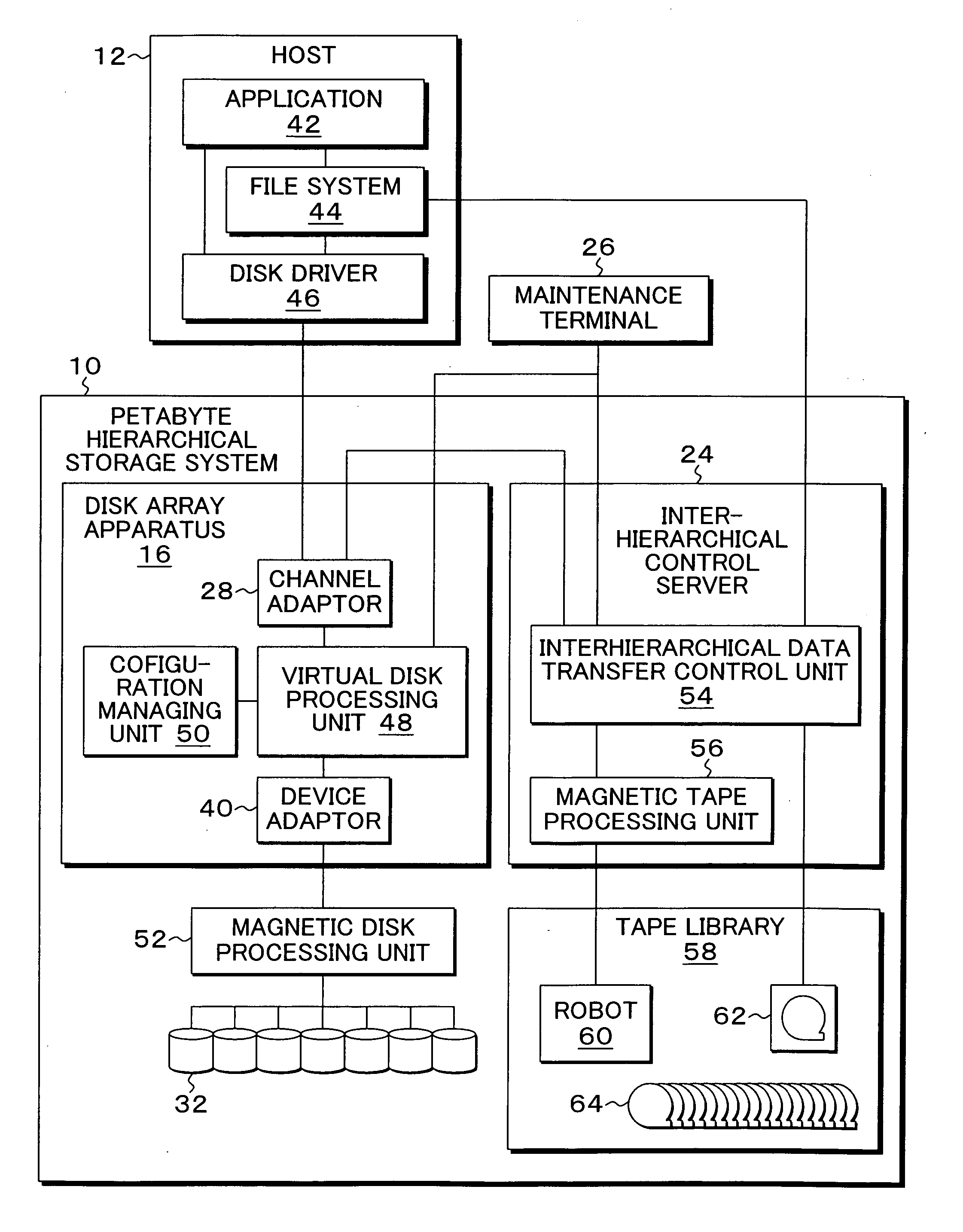
Hierarchical storage system, and control method and program therefor
InactiveUS20070078901A1Shorten the timeTimely processingSpecial data processing applicationsInput/output processes for data processingProcessing elementTime zone
At power-on again, a restore processing unit restores block information tables from a primary storage to a volatile memory. After classifying the block information tables into group-specific links of a plurality of time zones, a first sort processing unit connects the group-specific links to form a group classification link. Then, a second sort processing unit sequentially retrieves the block information tables of the group classification link from the earliest time stamp side for insertion in a position so as to achieve a time-stamp ascending order, thereby reconfiguring the links.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Wireless LANs and neighborhood capture
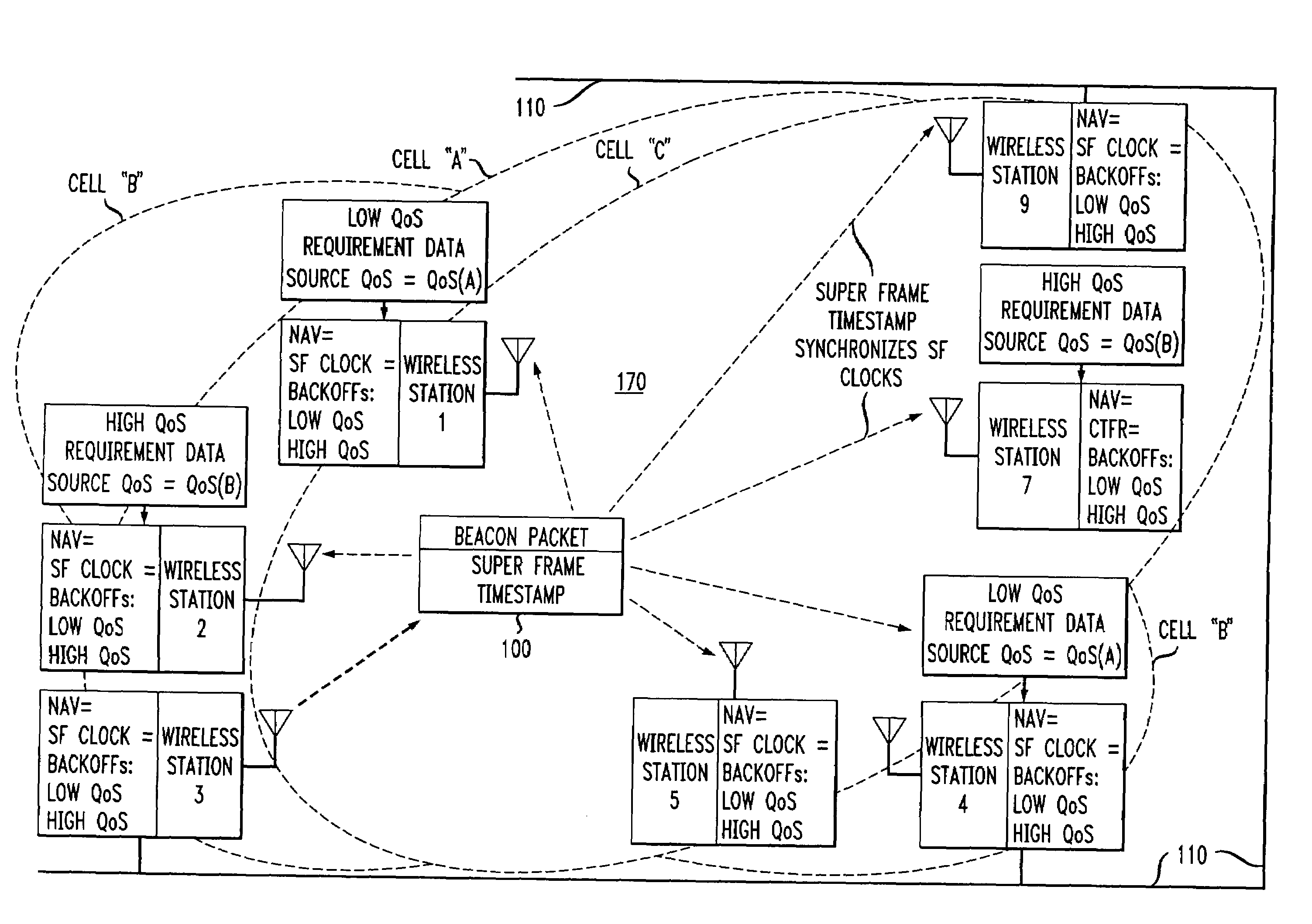
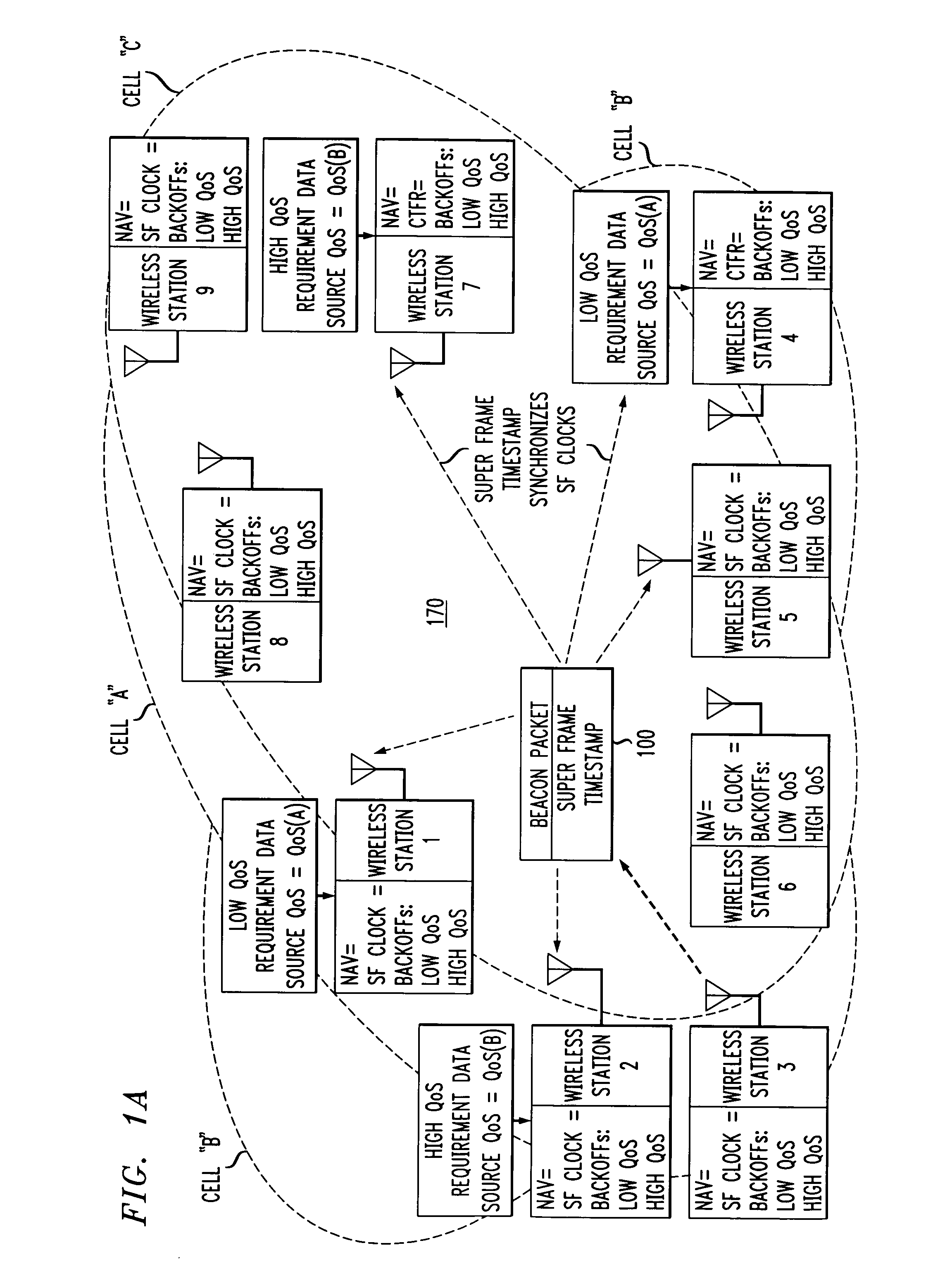
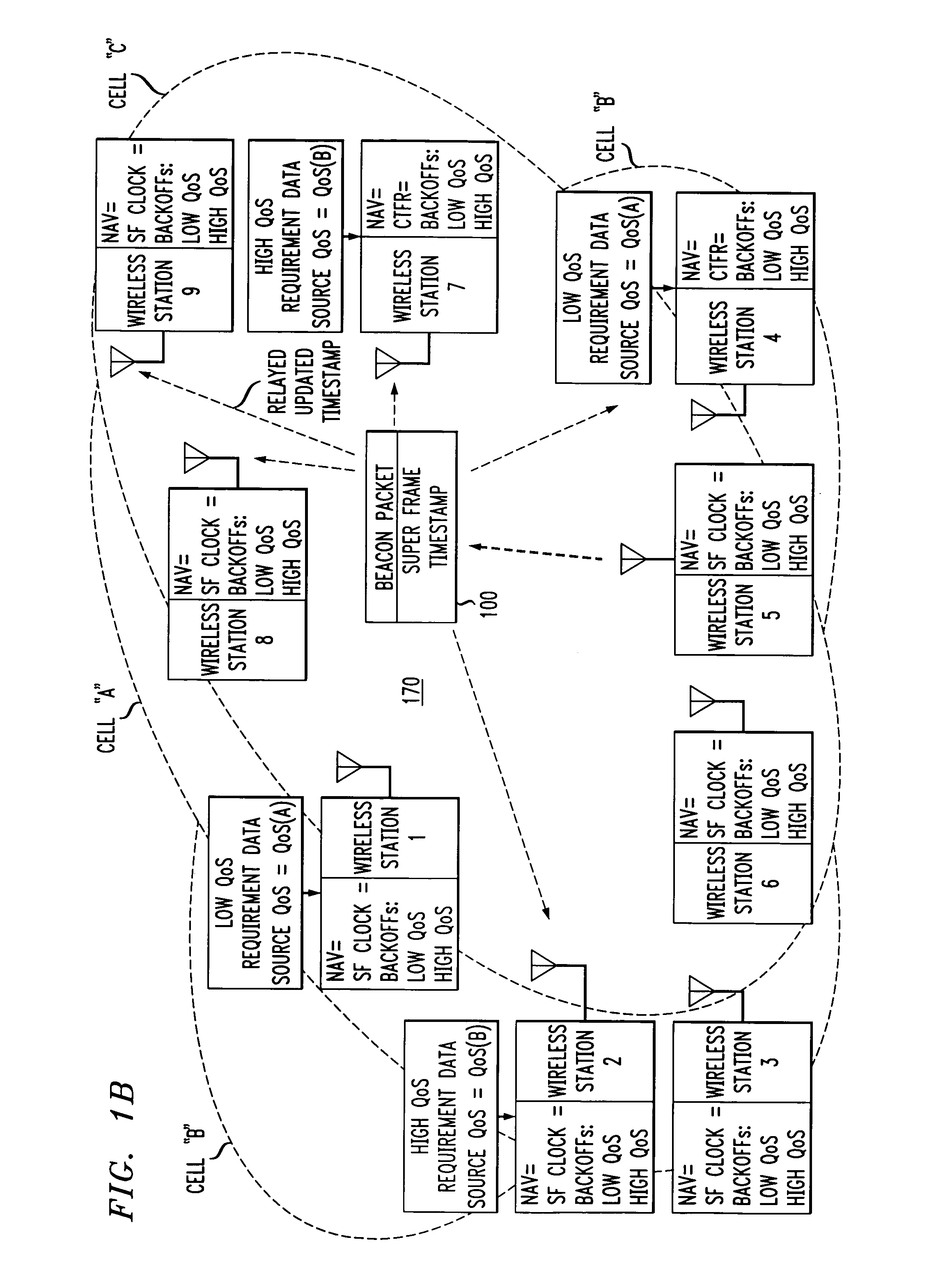
ActiveUS7280517B2Eliminates unfairnessReduce decreaseSynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesTimestampAccess method
Overlapped wireless LAN cells in a medium have an equal chance at establishing a session on the medium. A first member station in the first cell transmits a timing packet containing a timestamp value, which is received at a second member station in the second cell. This synchronizes member stations in the first and second cells to interrupt transmissions at a global channel release instant corresponding to the timestamp value. The member stations in the first and second cells then have the opportunity to contend for access to the medium following the global channel release instant, using a slotted CSMA / CA access method. Each of the member stations in the first and second cells has a superframe clock that is synchronized based on the timestamp value, thereby establishing a periodic global channel release instant during each of a plurality of periodic superframes. The member stations can then periodically interrupt transmissions at the periodic global channel release instant to contend for the medium. The periodic global channel release instant occurs at intervals that are sufficiently close to meet delay and jitter restrictions for time-critical voice and video applications.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
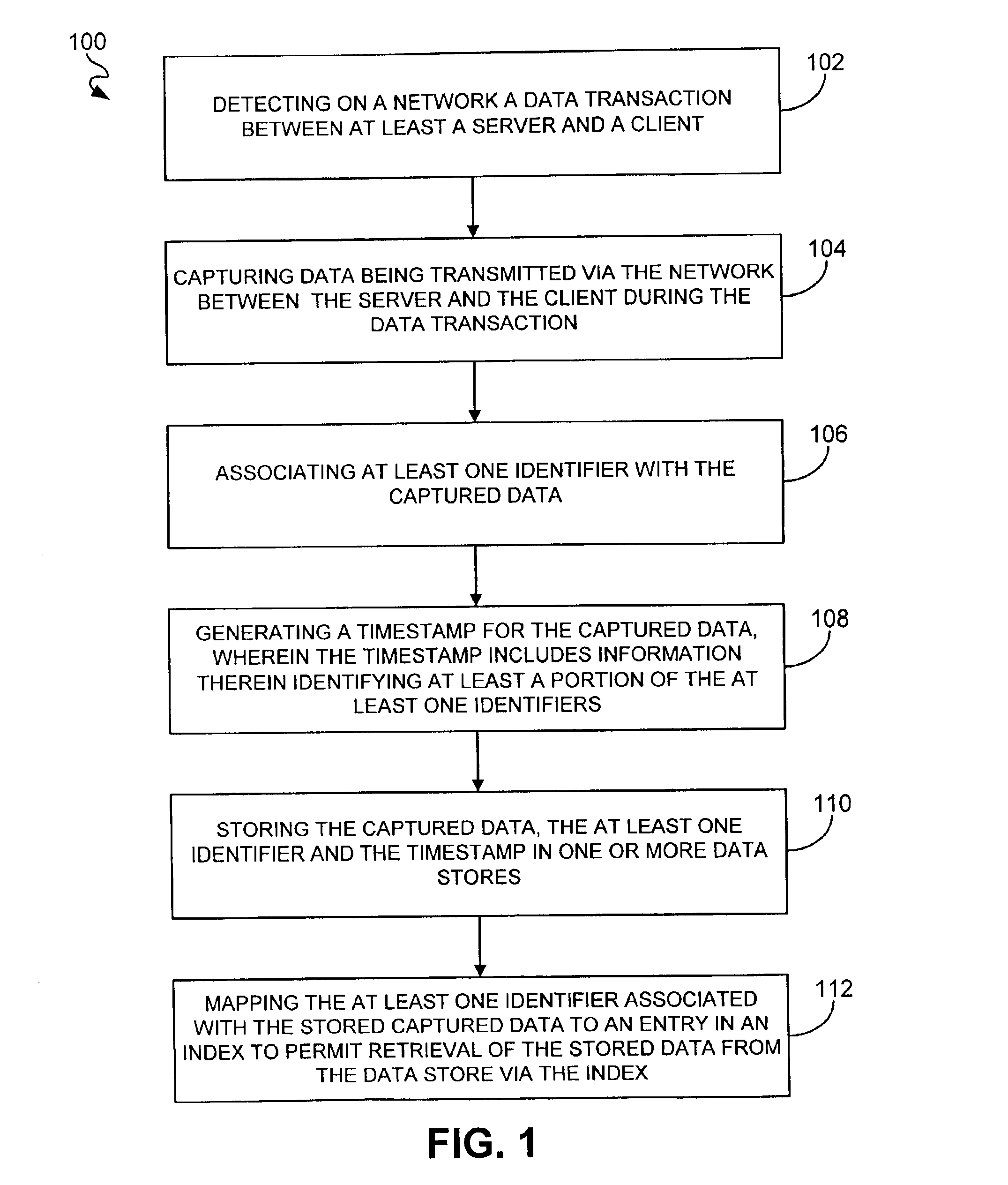
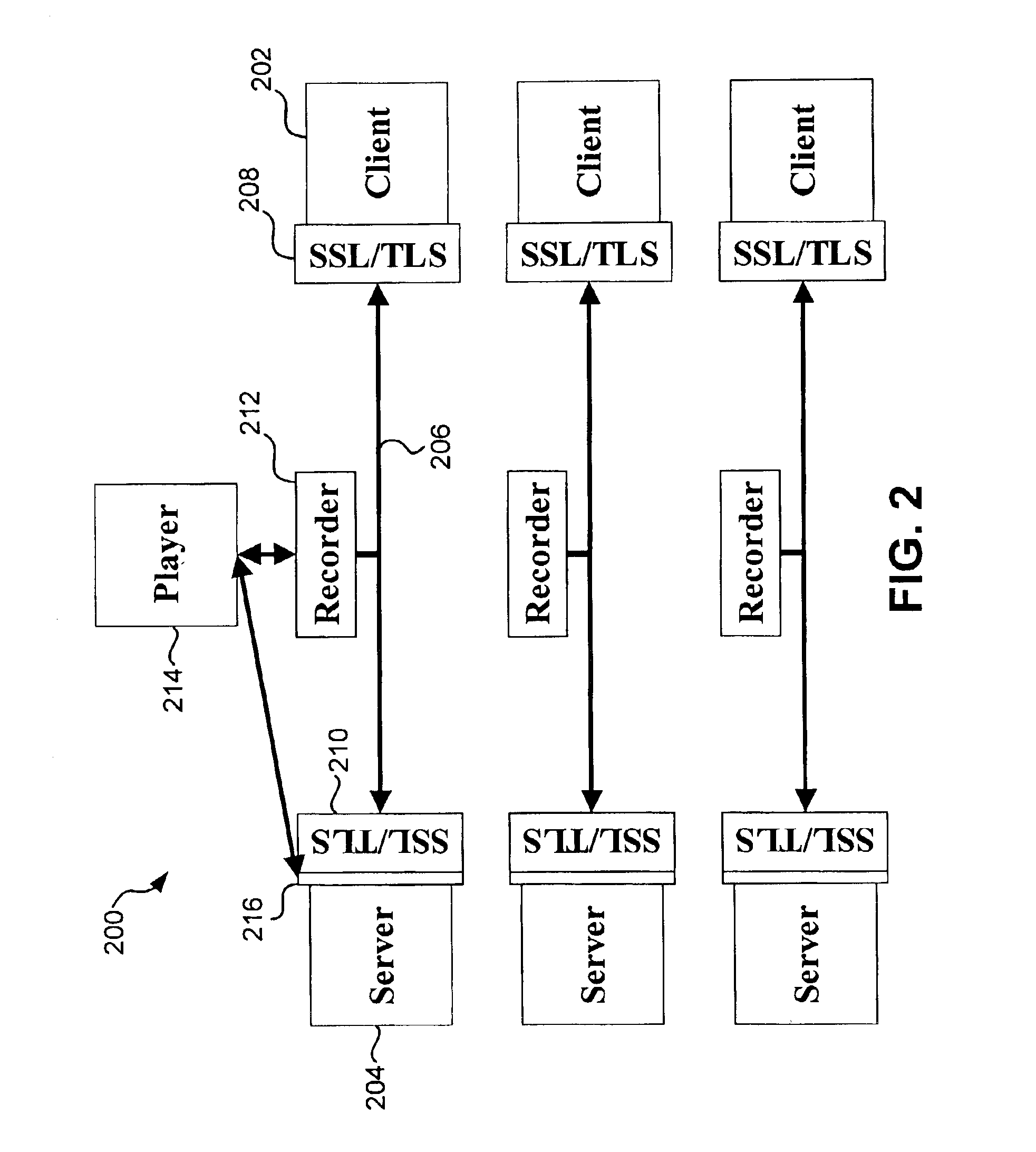
System, method and computer program product for guaranteeing electronic transactions
InactiveUS6874089B2Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationTimestampClient-side
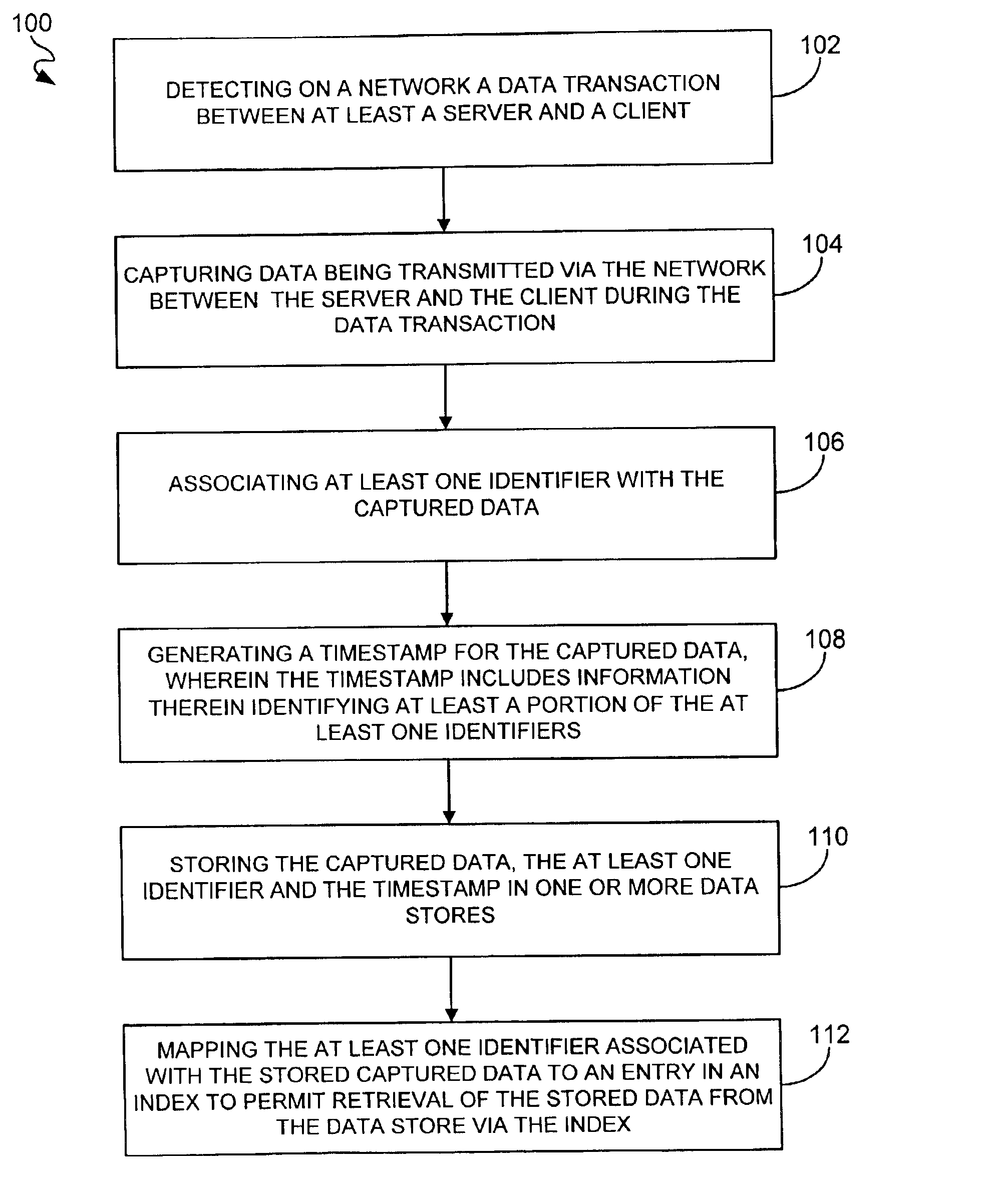
A system, method and computer program product for guaranteeing a data transaction over a network are disclosed. When a data transaction between at least a server and a client is detected on a network, data transmitted via the network between the server and client during the data transaction is captured. At least one identifier is associated with the captured data. A timestamp is also generated for the captured data. The timestamp includes information therein identifying at least a portion of the identifier(s). The captured data, the identifier(s) and the timestamp are stored in one or more data stores. The identifier(s) associated with the stored captured data is also mapped to an entry in an index to permit retrieval of the stored data from the data store via the index.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
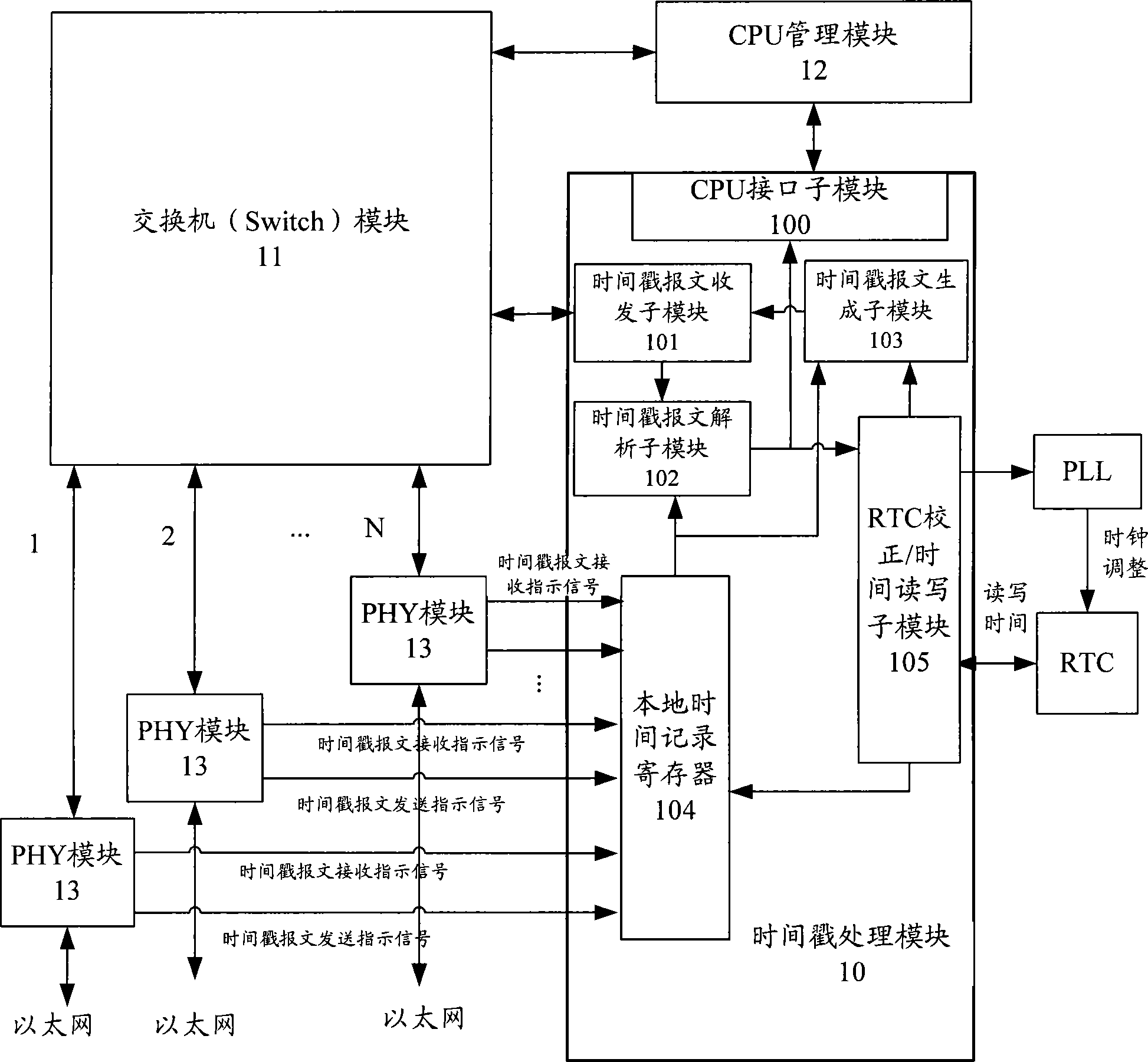
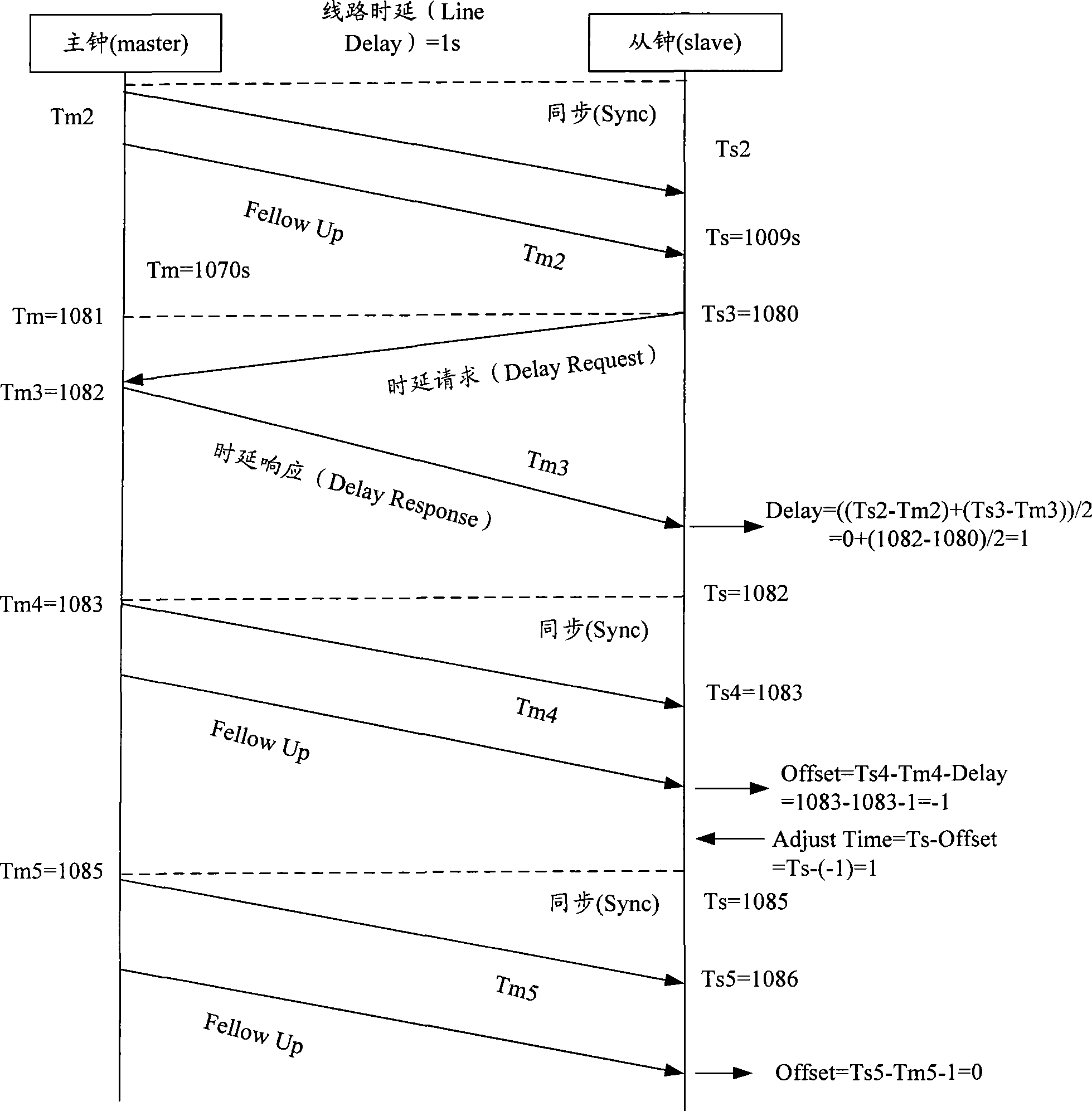
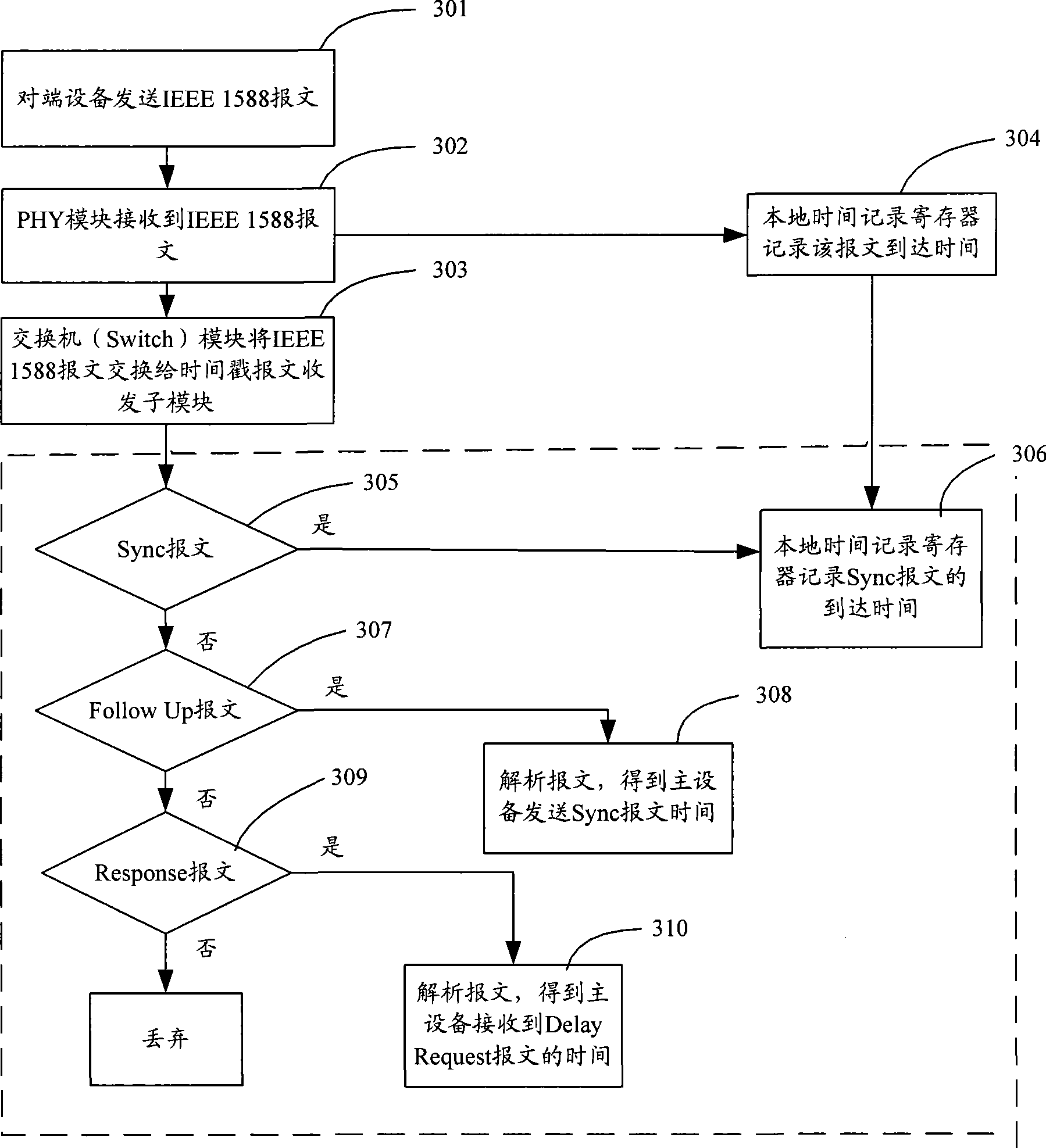
IEEE 1588 time synchronization system and implementation method thereof
ActiveCN101447861ASynchronized High Precision TimeGuaranteed real-timeTime-division multiplexSynchronising arrangementTime informationPHY
The invention discloses an IEEE 1588 time synchronization system. By adding a time-stamp processing module, a time-stamp message transceiving sub module, a time-stamp message resolving sub module, a time-stamp message generating sub module, a local time recording register, and an RTC correction / time read-write module in the module are used for combining peripheral components such as a switch module, a PHY and a real-time clock (RTC) module to form a hardware system. When in use, the high precision time synchronization requested by an IEEE 1588v2 protocol can be implemented by using the modes of one-to-one or one-to-many of master-slave synchronization. The invention also discloses a method for implementing the IEEE 1588 time synchronization, which can implement the function of the time synchronization system by processing the time information of master-slave devices in real time. The invention plays an active role in promoting Ethernet construction.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Measurement and adjustment of real-time values according to residence time in networking equipment without access to real time
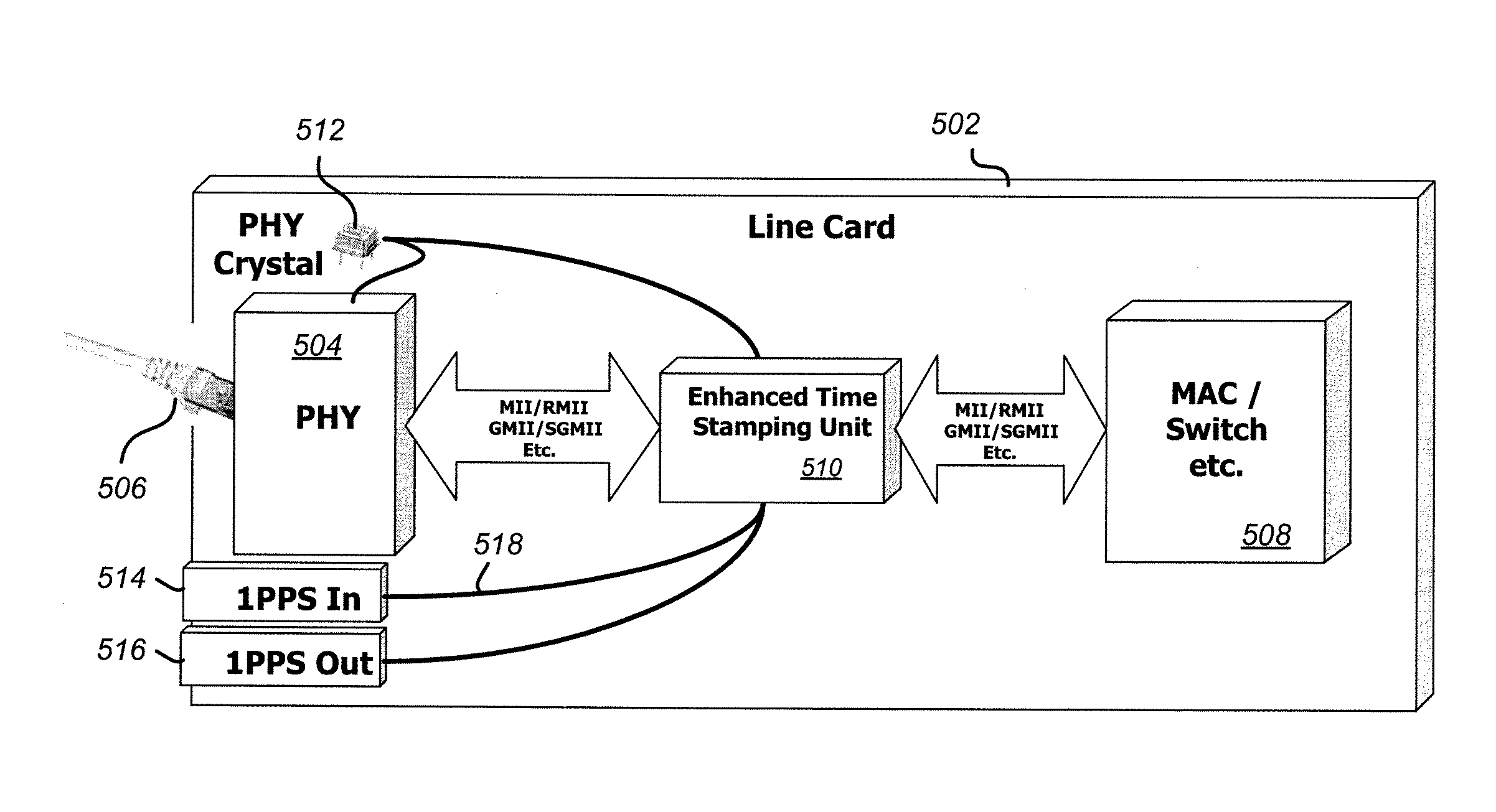
InactiveUS20110051754A1Easy to applyCompensation delayTime-division multiplexNetwork elementResidence time
A system and method of synchronizing clocks in a distributed network is disclosed. A simple 1-pulse-per-second timing pulse is routed to time-stamping units in each network device and utilized to measure traffic-dependent synchronization packet residence delays within network elements. Synchronization messages are updated to reflect the measured residence times, thus creating transparent clocks that can readily be synchronized across the network. The simple timing pulse architecture allows the method to be applied readily both to new designs and to retrofit existing hardware.
Owner:SEMTECH CORP
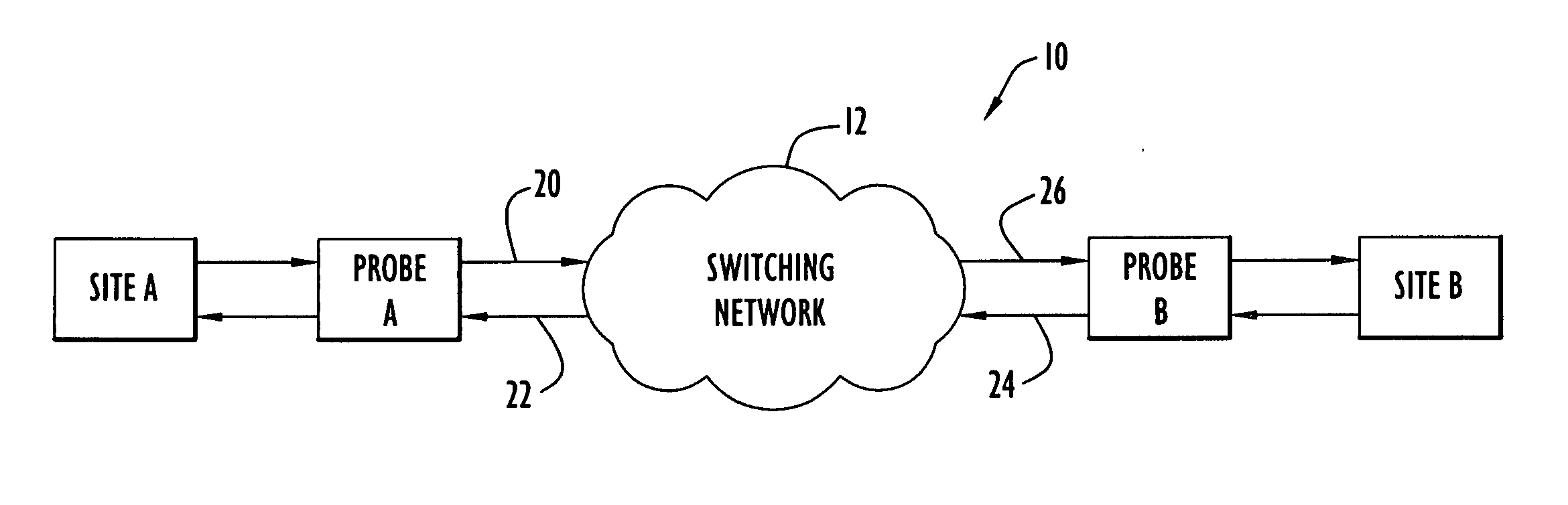
Methods and apparatus for non-intrusive measurement of delay variation of data traffic on communication networks
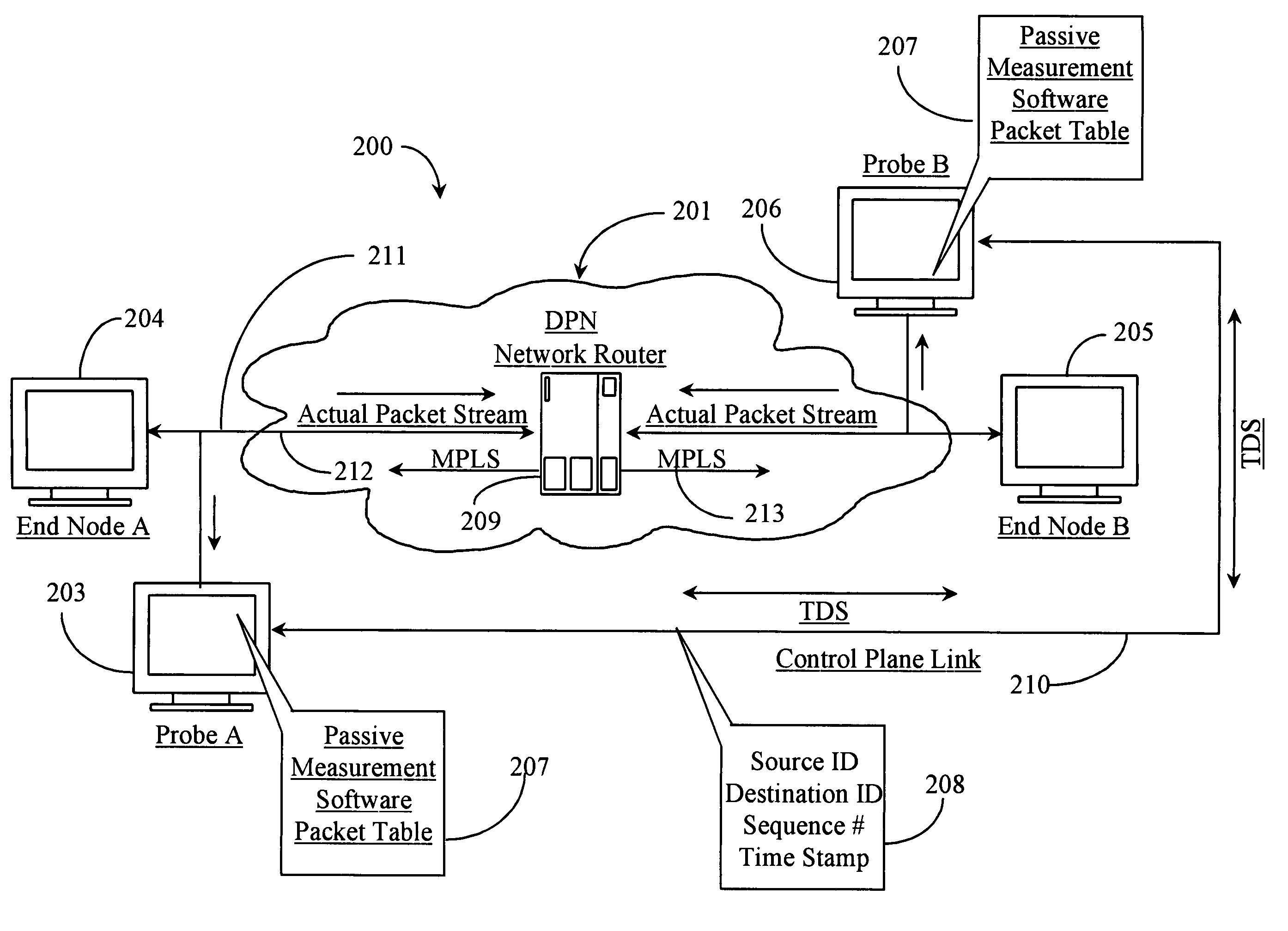
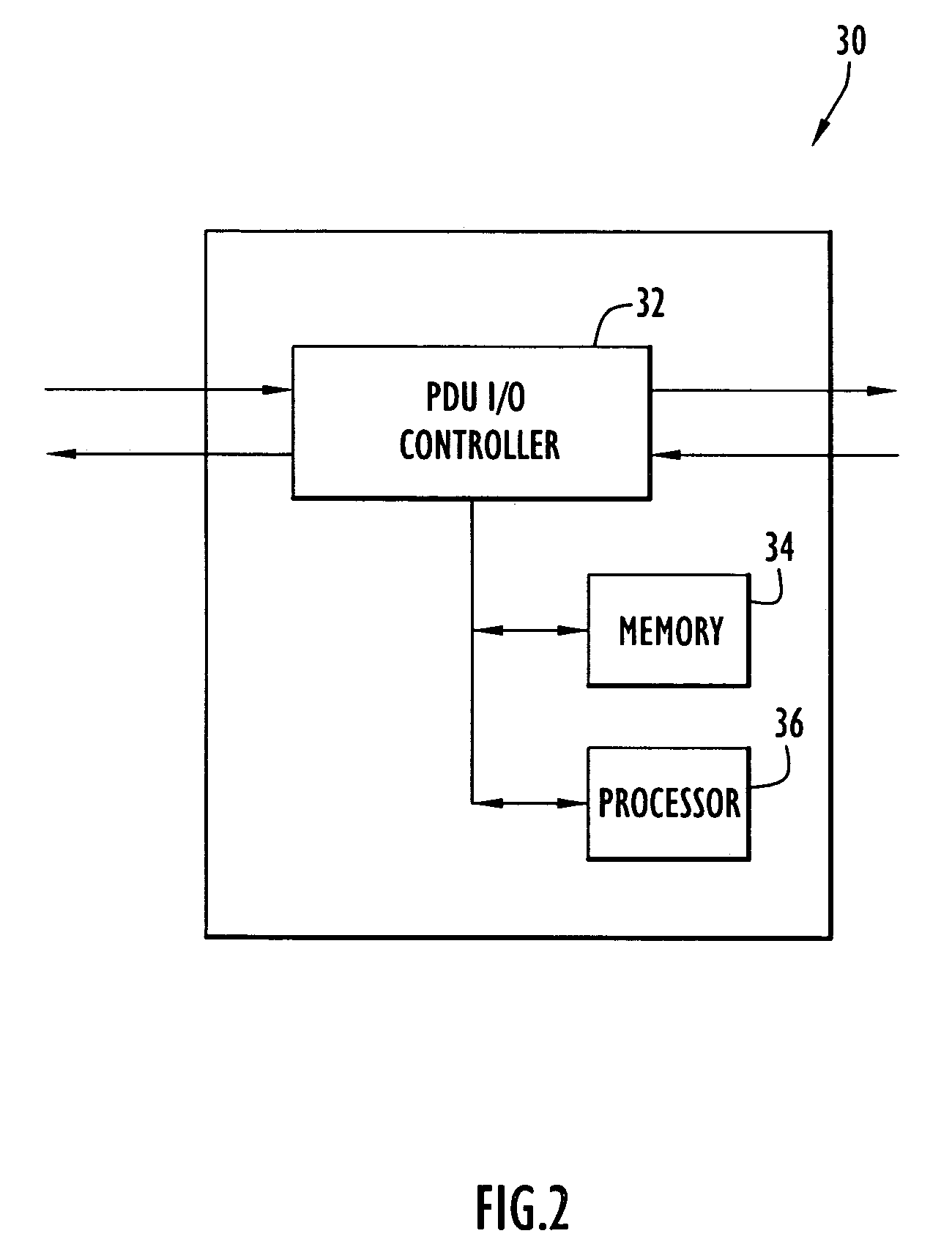
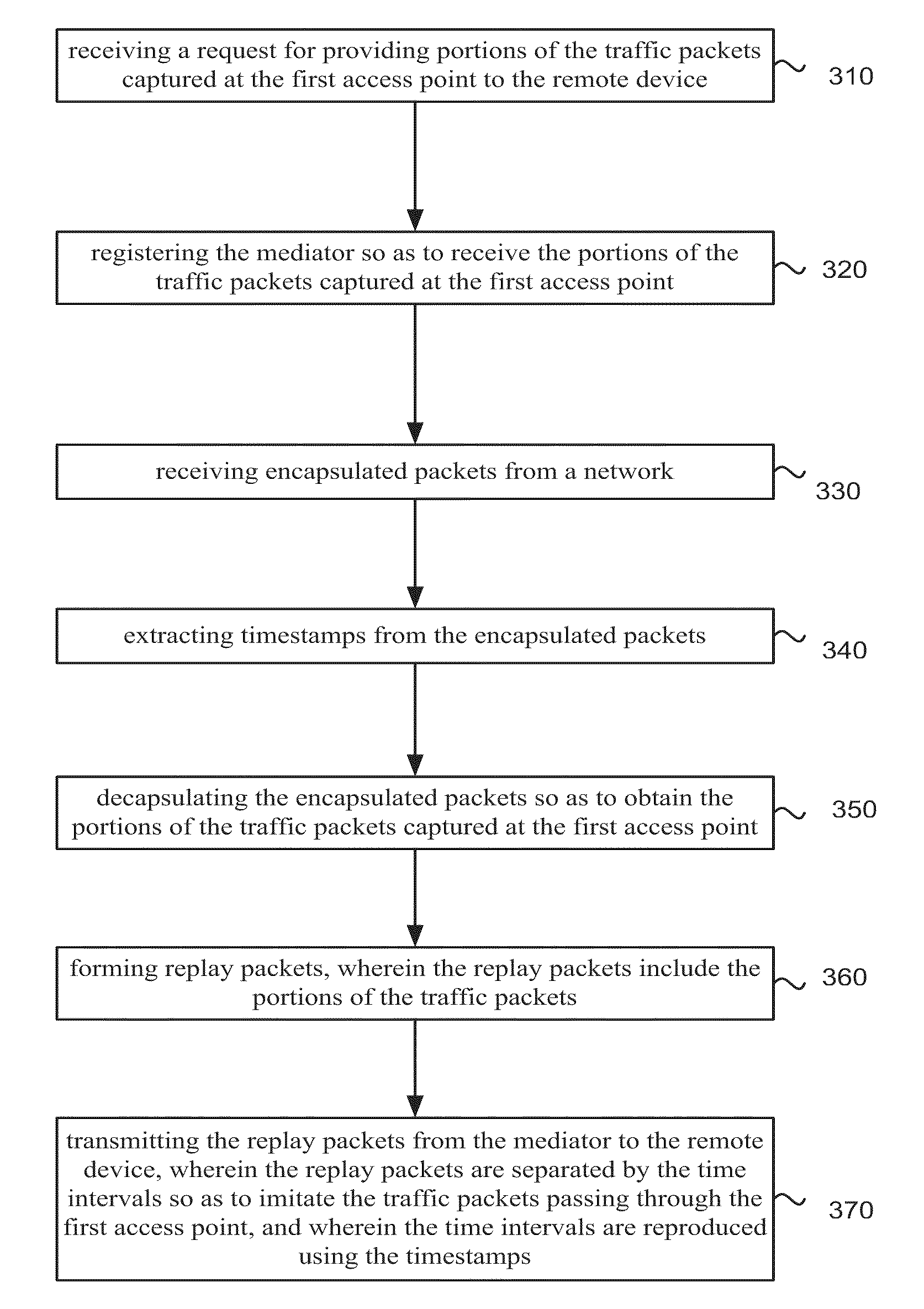
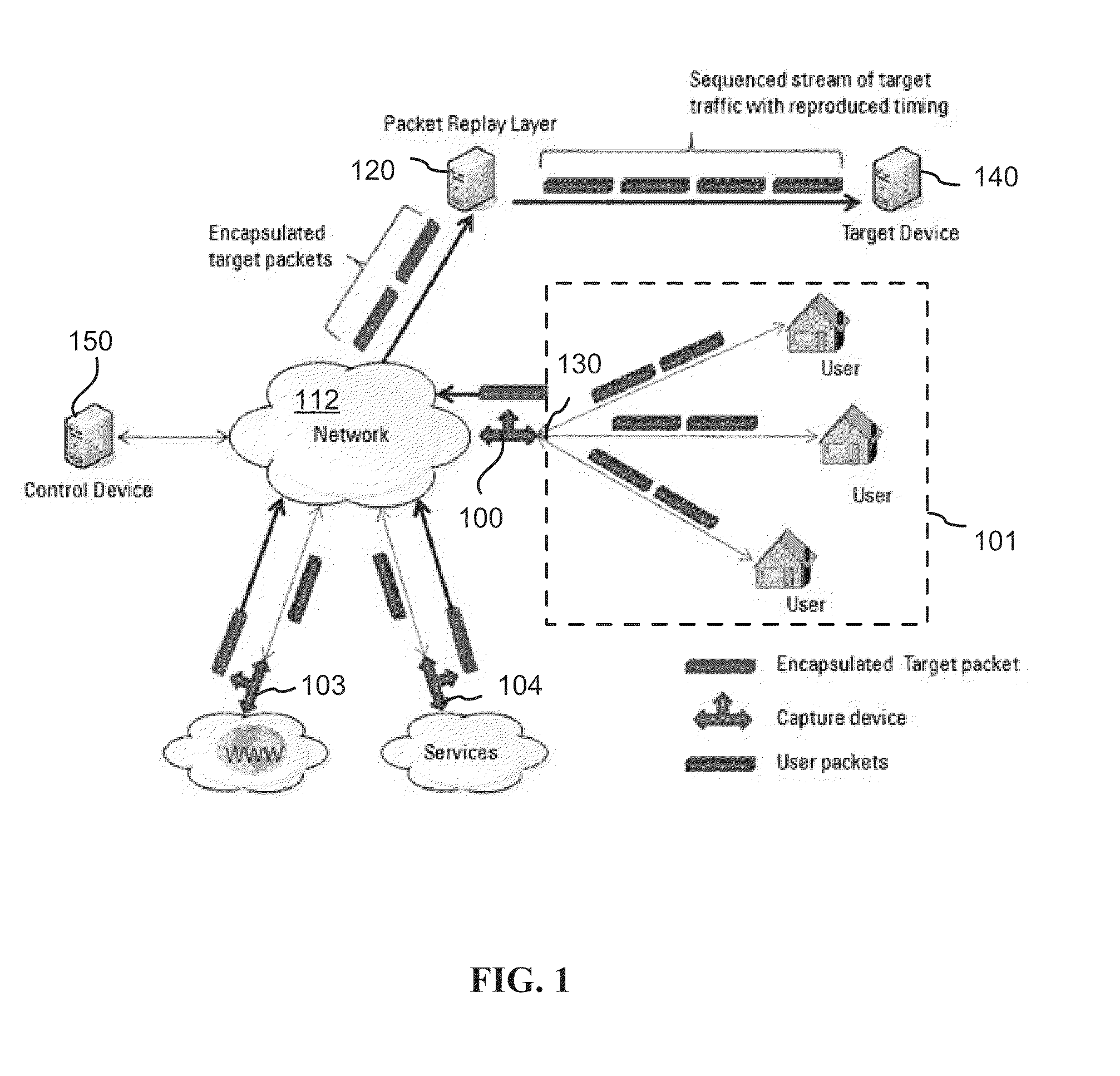
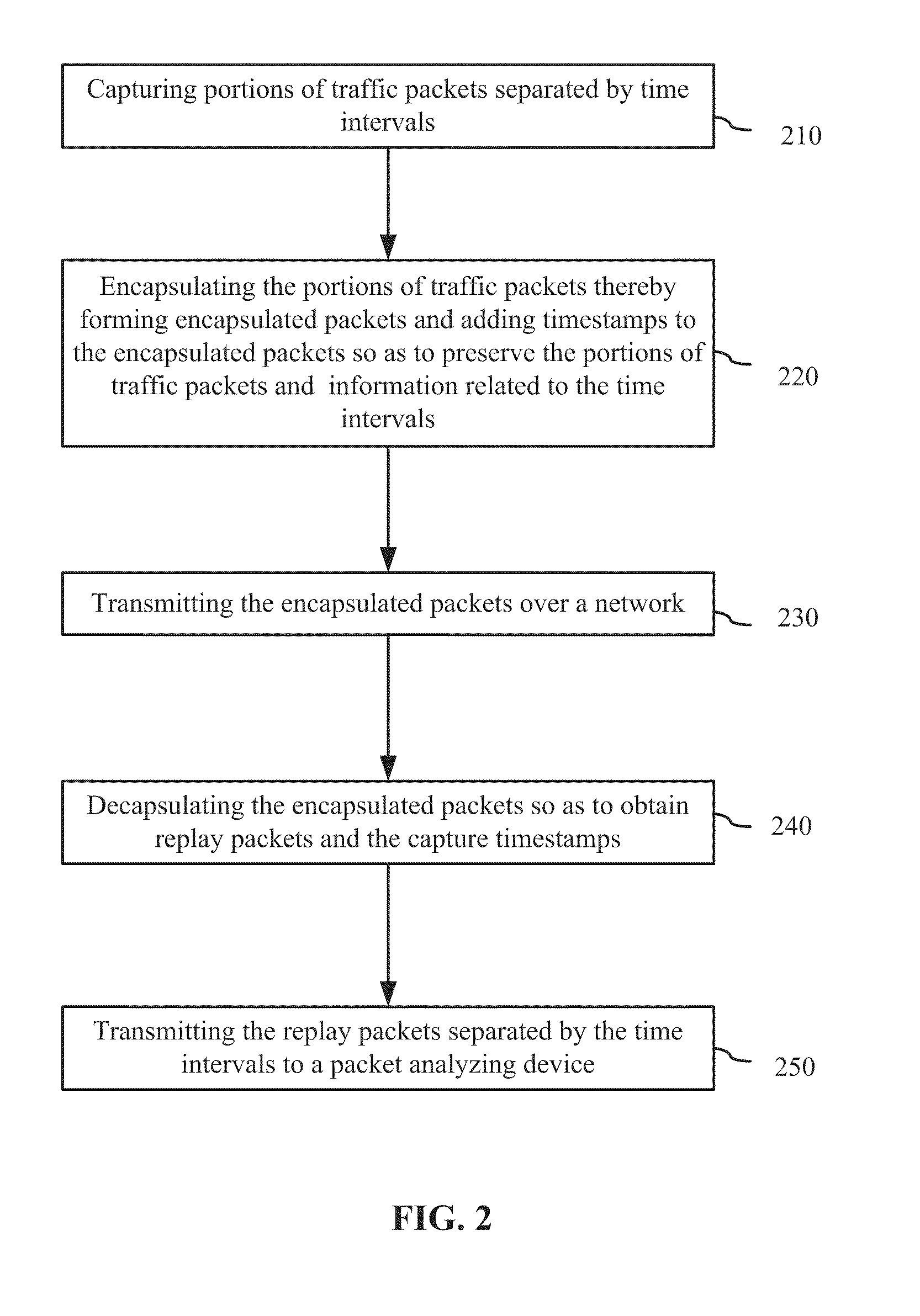
A technique for measuring delay variation (jitter) of data traffic (protocol data units (PDUs)) traversing a communication network involves: generating first PDU identifiers of PDUs observed at a first point and corresponding first timestamps indicating observation times of the PDUs at the first point; generating second PDU identifiers of PDUs observed at a second point and corresponding second timestamps indicating observation times of the PDUs at the second point; and computing, from first and second timestamps having matching PDU identifiers, a measure of variation indicating a delay variation of PDUs between the first and second points. The computation can include computing first time differences between observation times of the PDUs at the first point from the first timestamps, computing second time differences between observation times of the PDUs at the second point from the second timestamps, and computing differences between corresponding first and second time differences having matching PDU identifiers.
Owner:VISUAL NETWORKS OPERATIONS
Method of replicating data between computing devices
InactiveUS20050021571A1Minimizes bandwidth requirementSave considerable memory spaceEnergy efficient ICTDatabase distribution/replicationWireless computingElectronic mail
Resource constrained wireless computing devices (e.g. mobile telephones) are given a replication capability for database records (e.g. to enable backing up contacts, e-mails, photographs etc. onto a remote server). This operates without undue processing burden, using low bandwidth unreliable wireless connections. This is achieved by not including a time stamp in each database record, but instead time stamping only a change log record; this approach saves considerable memory space on the wireless device since there is no need to time stamp every database record, as is usually done in the prior art. The change log defines what data is to be replicated; it alone has to be sent to a main server which hosts a master copy of the database and hence has to be kept up to date. Because the change log is compact, far less data has to be sent for data replication purposes—typically only the field which has changed, how it was be changed and when it was changed on the wireless computing device. Prior art systems typically send an entire record, even though that will contain data that has not changed.
Owner:COGNIMA
Method for time aware inline remote mirroring
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
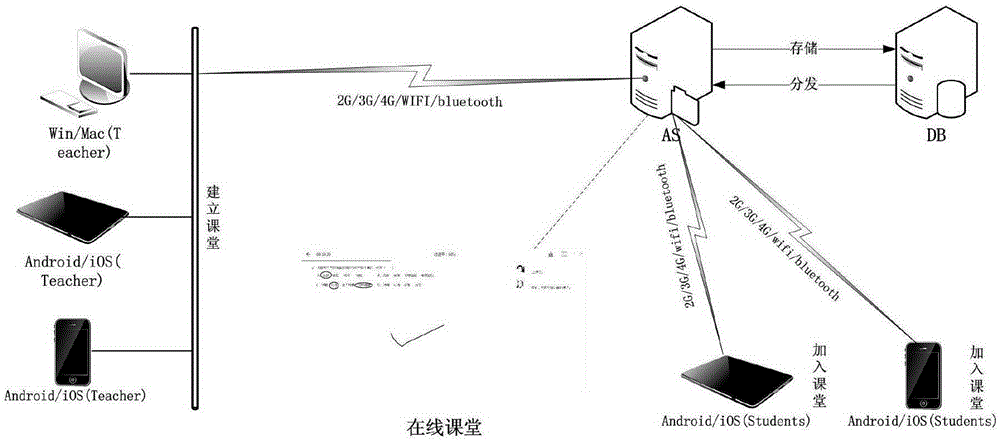
Online teaching recording and playing method and system
ActiveCN105306861AEasy to recordSave bandwidthTelevision system detailsTelevision conference systemsData streamWhiteboarding
The invention provides an effective recording and playing method and system. The recording and playing method and system are characterized in that in an online teaching process or an online meeting, operation of functions of multimedia whiteboard by a user, speech / voice of the user, communication voice with other users and / or tutoring voice and the like are recorded to respectively form different data streams; and a united timestamp can be generated by an online teaching system to mark various data streams rather than completely recording the whole event in a form of streaming media so that network users can conveniently download various data steams which need to be played via a network from a Cloud server or a local area network server anytime anywhere; after obtaining the data streams, clients of user terminals can obtain the data streams on line according to the timestamp and organically combine and play the data streams to the users, thus finishing the on-demand browsing.
Owner:SHENZHEN EAGLESOUL TECH CO LTD
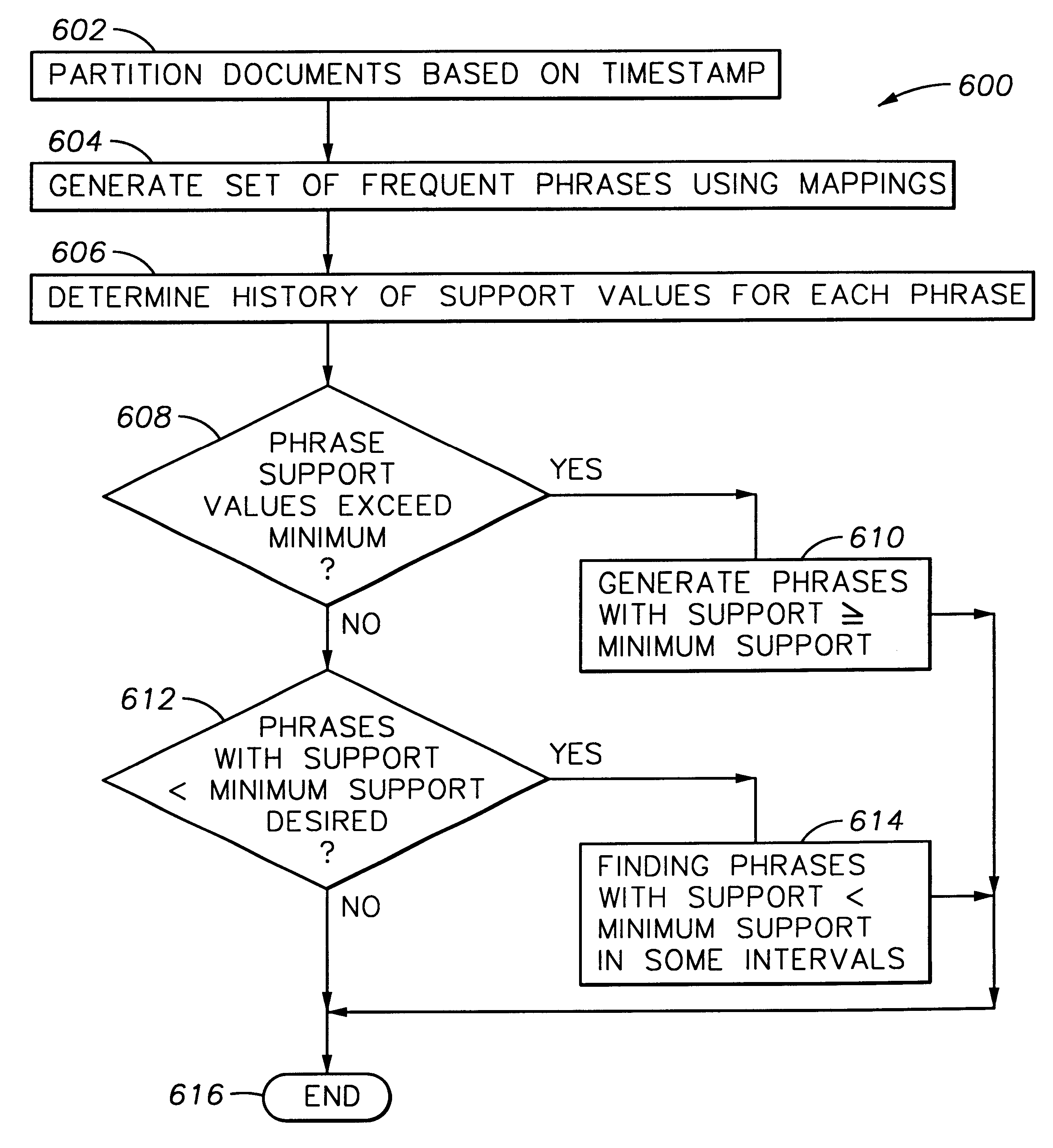
Method and apparatus for partitioning a database upon a timestamp, support values for phrases and generating a history of frequently occurring phrases
A method and apparatus for mining text databases, employing sequential pattern phrase identification and shape queries, to discover trends. The method passes over a desired database using a dynamically generated shape query. Documents within the database are selected based on specific classifications and user defined partitions. Once a partition is specified, transaction IDs are assigned to the words in the text documents depending on their placement within each document. The transaction IDs encode both the position of each word within the document as well as representing sentence, paragraph, and section breaks, and are represented in one embodiment as long integers with the sentence boundaries. A maximum and minimum gap between words in the phrases and the minimum support all phrases must meet for the selected time period may be specified. A generalized sequential pattern method is used to generate those phrases in each partition that meet the minimum support threshold. The shape query engine takes the set of phrases for the partition of interest and selects those that match a given shape query. A query may take the form of requesting a trend such as "recent upwards trend", "recent spikes in usage", "downward trends", and "resurgence of usage". Once the phrases matching the shape query are found, they are presented to the user.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Communications interconnection network with distributed resequencing
InactiveUS6907041B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationTimestampMerge sort
Methods and apparatus for forwarding packets in a multistage interconnection network are provided which timestamp packets using a substantially system-wide timing reference and a merge sorting variant to restore packets to the proper order, using the timestamp information carried in the packets. One implementation determines when packets passing along different paths in the network can be safely forwarded, even when no packets have recently been received on some of the paths, by forwarding status messages along otherwise idle paths. The status messages provide information that can be used by downstream components to allow them to determine when packets passing over other paths can safely be forwarded. One implementation simultaneously resequences packets being delivered to all n outputs of the multistage interconnection network. The resequencing operations are distributed among a plurality of switching elements making up the interconnection network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC +1
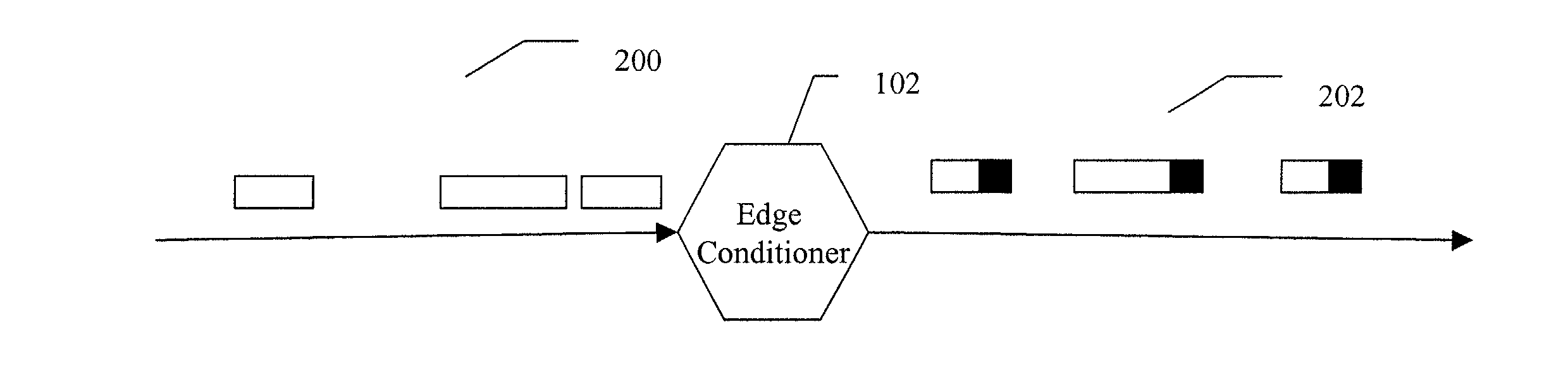
Method and apparatus for packet scheduling using virtual time stamp for high capacity combined input and output queued switching system
InactiveUS20020129158A1Large capacityError preventionTransmission systemsLarge capacityReal-time computing
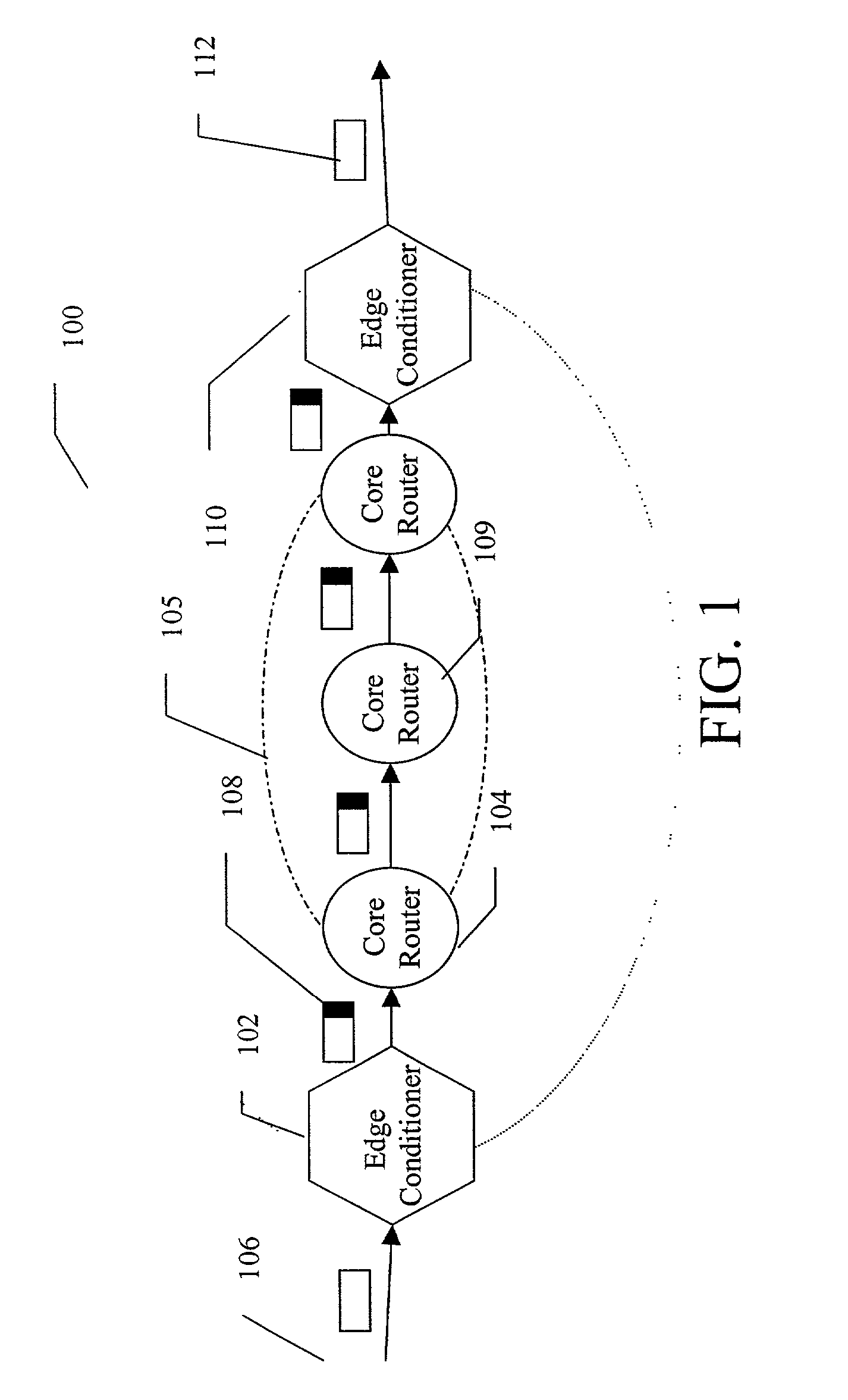
A method and apparatus for packet scheduling using a virtual time stamp for a high capacity combined input and output queued switching system. A network employs a virtual time reference system (VTRS) to generate packet virtual time stamps associated with each packet traversing the network. The VTRS includes edge conditioners located at the edge of the network that receive unregulated packet traffic and generate regulated packet traffic for a given flow. The edge conditioners also add a packet virtual time stamp to each incoming packet. Core routers within a network core reference the packet virtual time stamps to schedule packet flow. The core routers also update the packet virtual time stamps using virtual delays. The packet virtual time stamps are removed from the packets when the packets leave the network core through an edge conditioner.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Computerized notetaking system and method
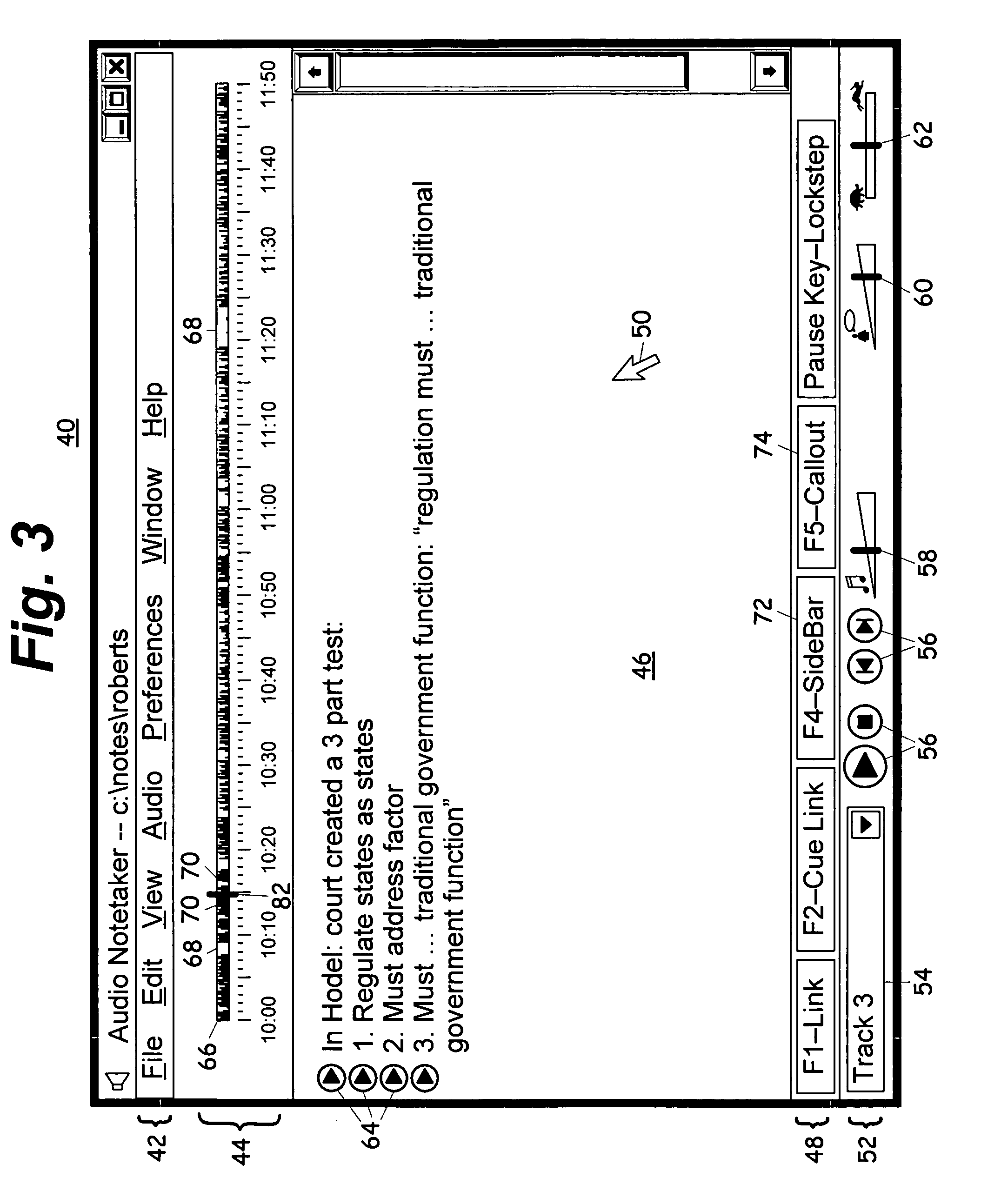
InactiveUS20060075347A1Improve experienceImprove user experienceSound input/outputSpeech recognitionTimestampProbable Case
A computerized notetaking system that records audio and links notes to the audio and has enhancements such as: Always-on audio recording and external timestamp button that work even when the system is turned off. A “next-topic” command that prepares and timestamps a new paragraph while allowing the user to complete the current paragraph. Commands for creating callouts and sidebar boxes in the user notes. A choice of audio filters. Speech recognition for searching through and navigating an audio recording. Speech recognition accuracy enhancement based upon typed notes. Playback, including lockstep playback, that prefers starting and stopping at word boundaries without overlap when possible. A self-adjusting preplay parameter. A “repeat slower” command that replays a few seconds of audio and then resumes at normal speed. Integrated background audio that plays music or white noise when notes-related audio is not being played. Several other enhancements are disclosed.
Owner:REHM PETER H
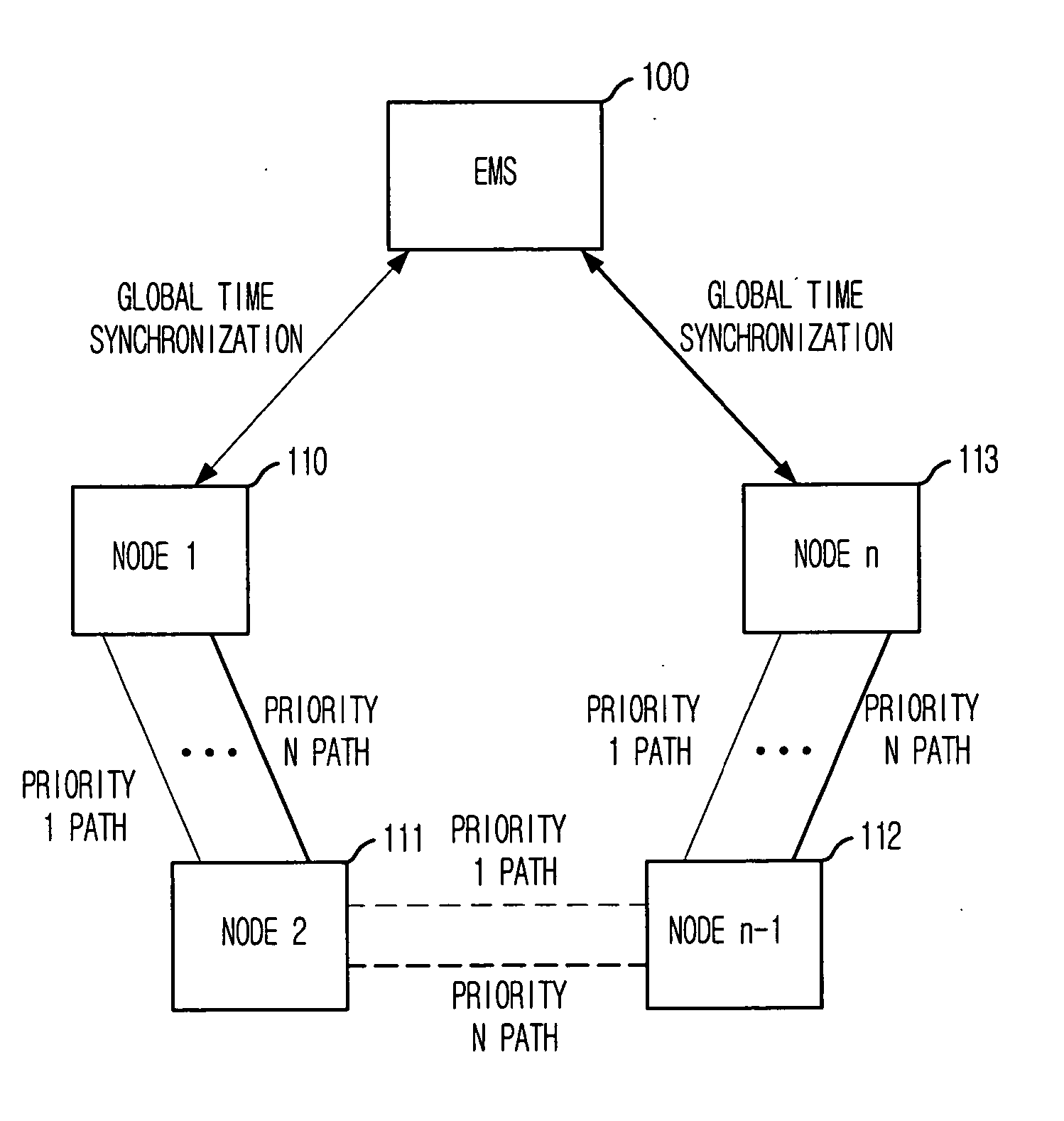
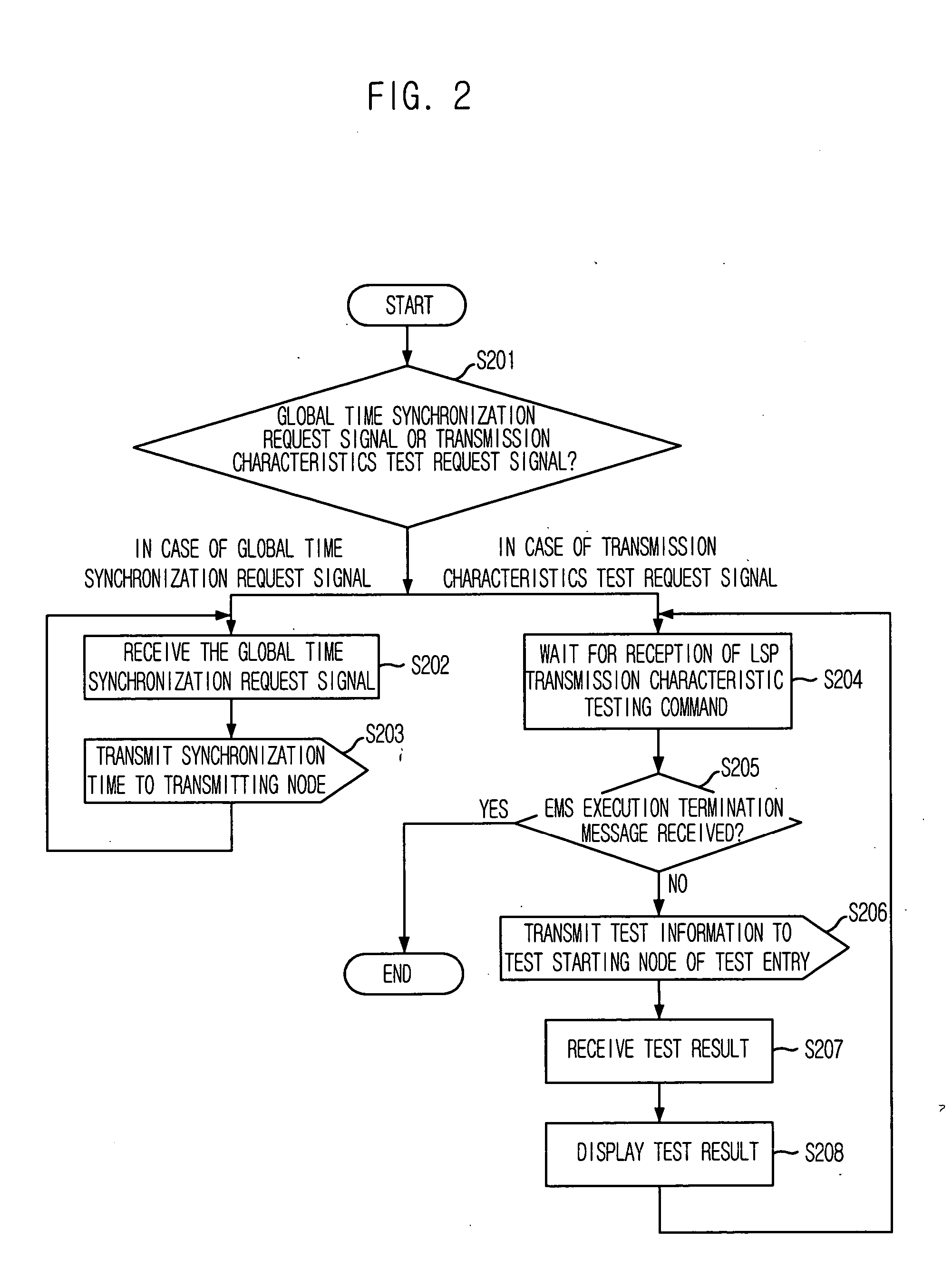
Method for measuring characteristics of path between nodes by using active testing packets based on priority
Provided are a method for measuring characteristics of a path between nodes by using active testing packets based on priority, i.e., an inter-node path characteristic measuring method, which can measure and provide characteristics of a generated node, when an inter-node data transmission path is generated based on Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) to provide a path with satisfactory transmission delay, jitter and packet loss that are required by a user, and to provide a computer-readable recording medium for recording a program that implement the method. The method includes the steps of: a) synchronizing system time of the nodes with a global standard time; b) forming each testing packet; c) registering frame sequence and the global standard time during transmission; and d) calculating transmission delay time, jitter and packet loss by using time stamp and packet sequence information of a frame received by the destination node and transmitting the result to the management system.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
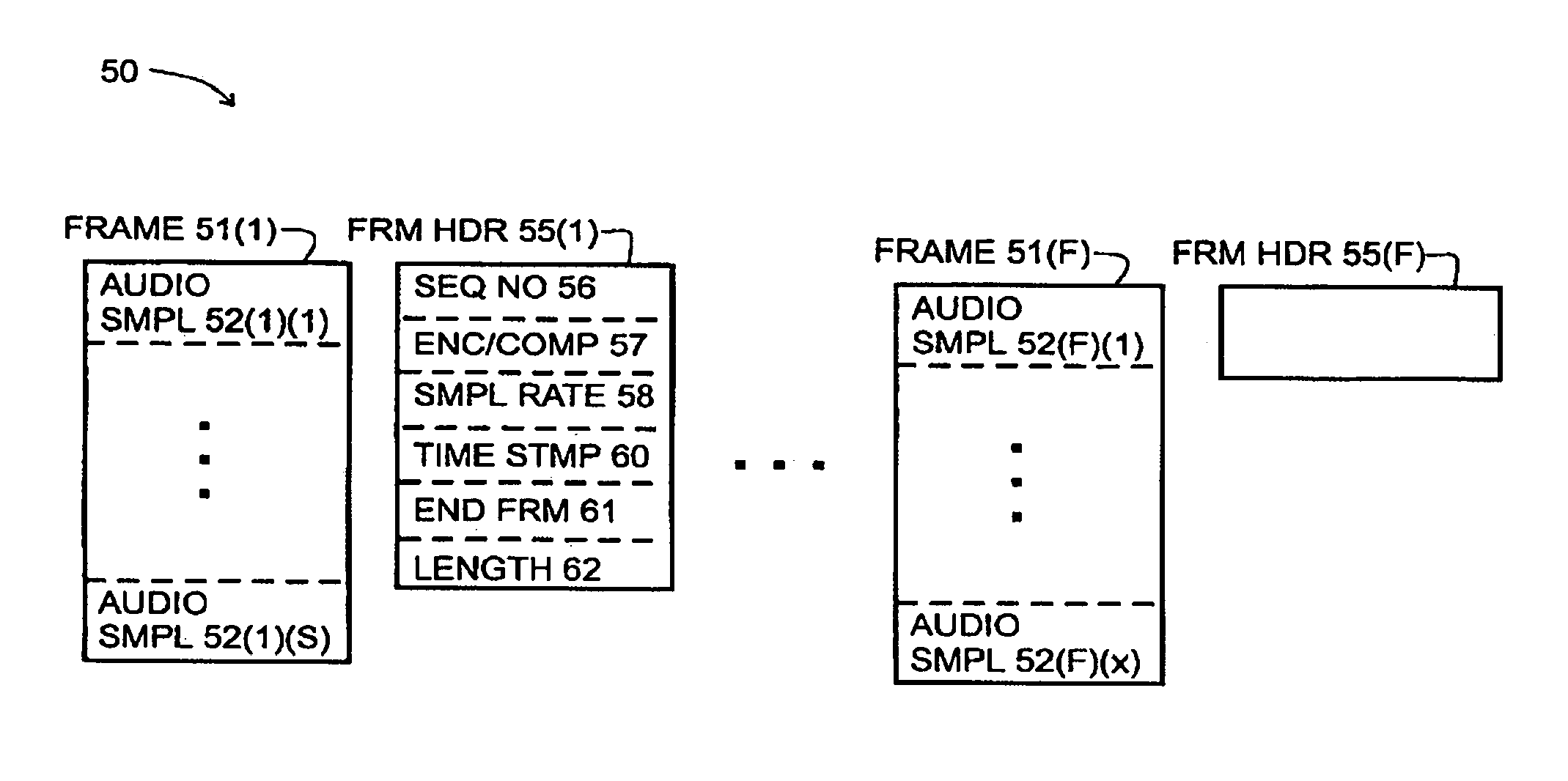
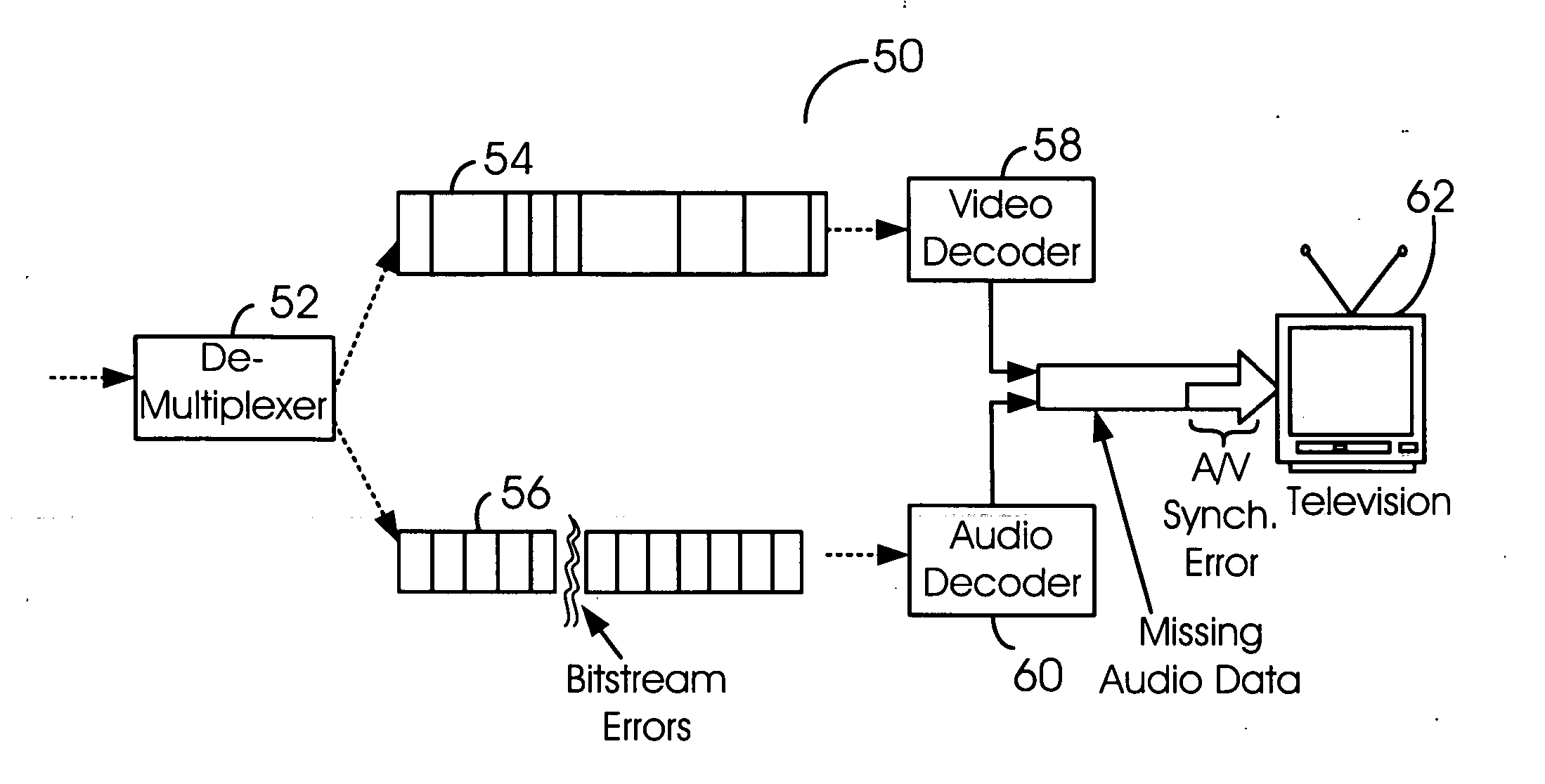
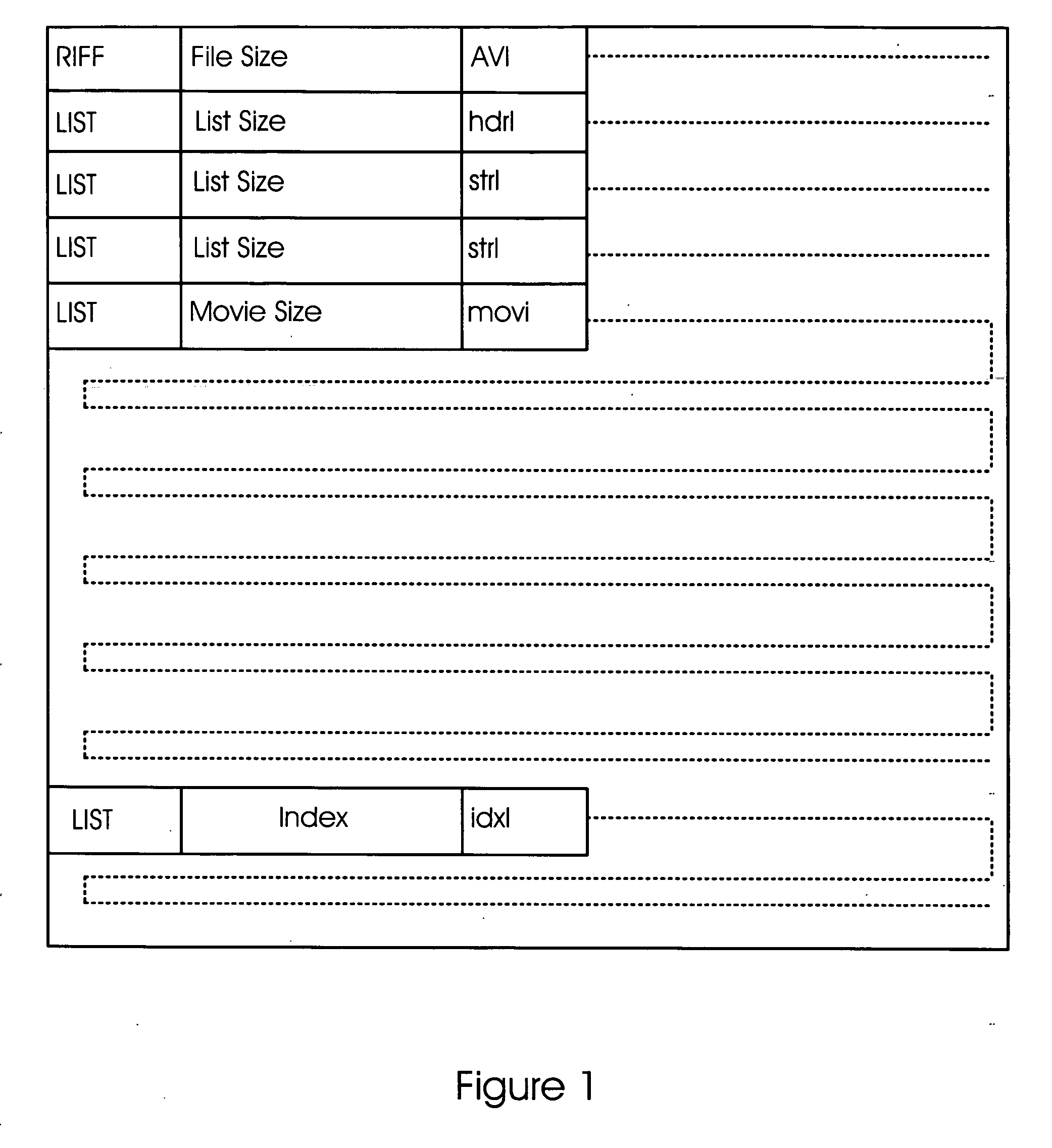
Accurate and error resilient time stamping method and/or apparatus for the audio-video interleaved (AVI) format
InactiveUS20070067472A1Raise the possibilityImprove service qualityMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionData signalEngineering
An apparatus comprising a first circuit and a second circuit. The first circuit may be configured to embed one or more timestamp chunks into a compressed bitstream in response to one of a video data signal and an audio data signal. The second circuit may be configured to generate an output signal in response to decoding the compressed bitstream. Each of the one or more timestamp chunks comprises an error correction mechanism configured to detect and correct errors on the compressed bitstream prior to decoding the compressed bitstream.
Owner:LSI CORPORATION
Coherency of replicas for a distributed file sharing system
ActiveUS7500020B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalTimestampDistributed computing
A plurality of data objects may be replicated across a plurality of computing nodes coupled to a network. The network may include a first node operable to initiate an update operation to update a plurality of replicas of a first object. If one or more of the replicas are not reachable then the update operation may update a subset (e.g., a quorum) but not all of the replicas. For each node on which one of the replicas was updated in the update operation, the node may add the object to a list of incoherent objects. The list of incoherent objects may subsequently be used to bring the lagging replicas in sync with the replicas that were updated. In another embodiment, a plurality of replicas of an object may be stored on a plurality of nodes, similarly as described above. A first node that stores a replica of the object may store a first timestamp associated with the replica on the first node. The timestamp may be used to ensure that the replica on the first node is coherent with respect to one or more other replicas by periodically communicating with the one or more other replicas when a threshold amount of time has passed without the replica on the first node receiving an update.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
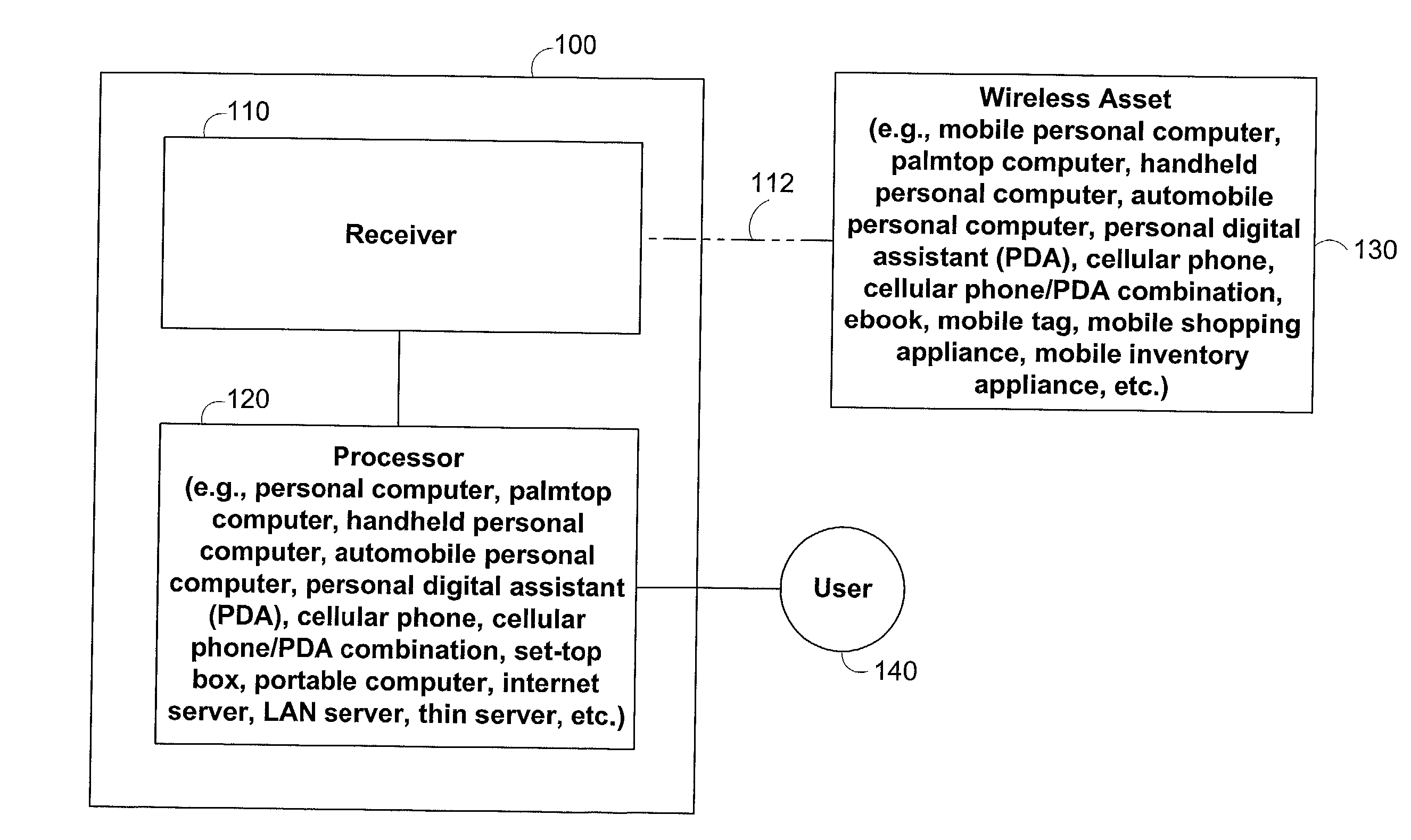
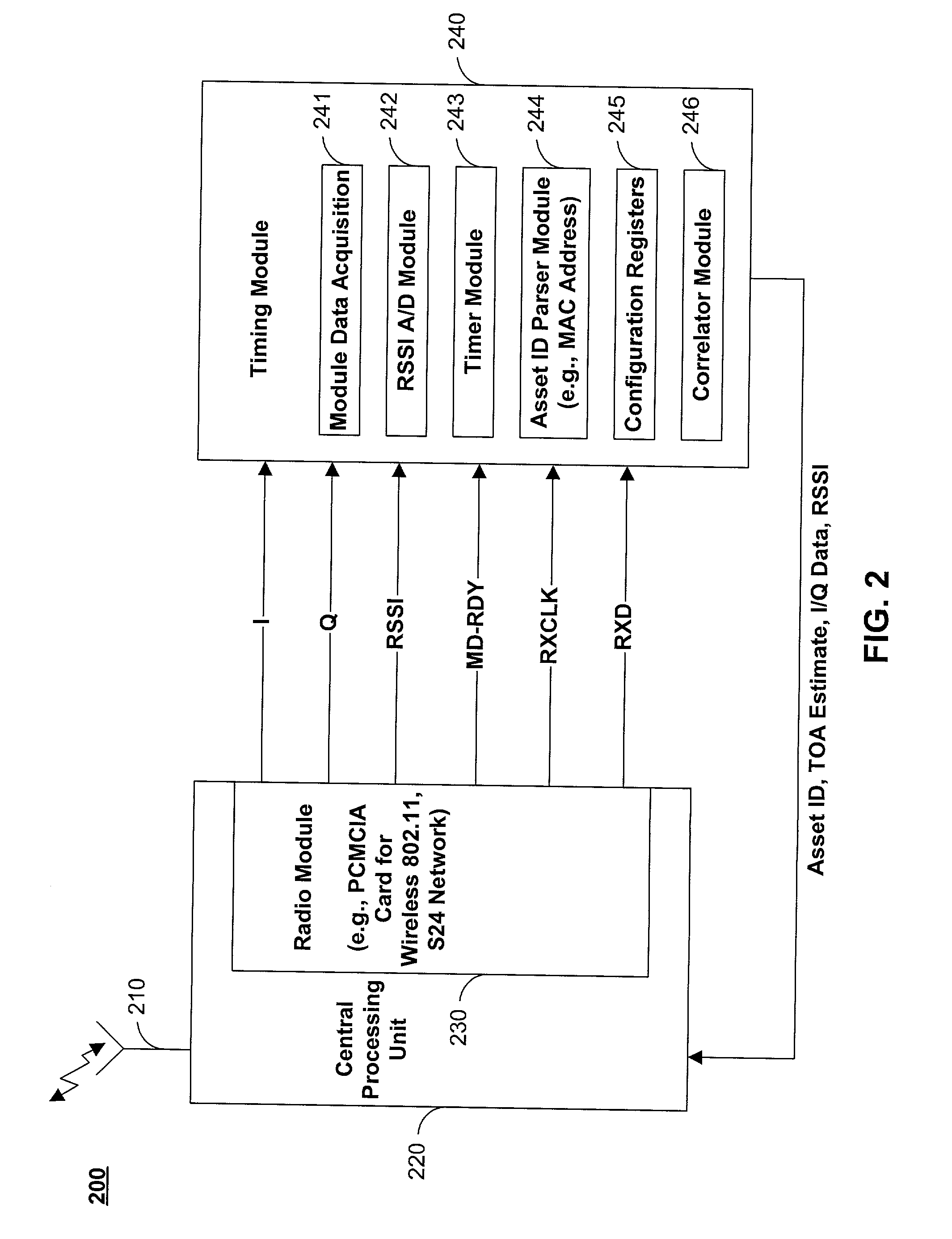
Methods and apparatus for identifying asset location in communication networks
ActiveUS20020097182A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionTelevision system scanning detailsRadio frequencyTime difference
The location of unmodified wireless assets in a wireless communication network may be identified using time differences of arrivals of a communication sequence at different network receivers. Time-stamping devices may include correlator circuits in parallel with signal decoders to time-stamp communication sequences. Cellular wireless networks may be frequency-multiplexed to increase spatial time-stamping density. Tags may be attached to passive assets to provide location identification information to network devices. Locations of assets broadcasting standard 802.11 radio frequency structures may be identified. Noise inherent in correlating a communication sequence may be reduced by using a selected correlation function.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
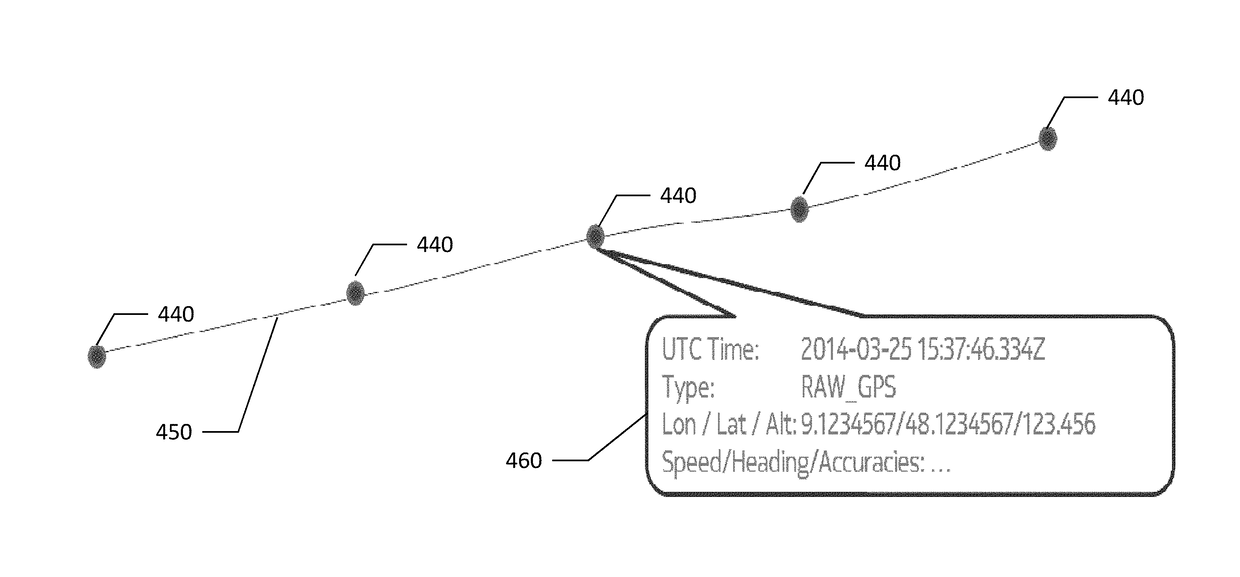
Method, apparatus, and computer program product for processing sensor data
PendingUS20170358204A1Instruments for road network navigationRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesTimestampComputer science
A method is provided that includes: receiving a plurality of estimated position points, each estimated position point including a timestamp, where each estimated position point is an estimate of a position of a vehicle at a time respective timestamp; receiving on or more path events, where each of the one or more path events includes a timestamp and data from at least one sensor of the vehicle; generating a path from the plurality of estimated position points, where the estimated position points are arranged in order of ascending time represented by the respective timestamp; and interpolating between two of the estimated position points to determine a location corresponding to one of the one or more path events, where the timestamp of the one of the one or more path event corresponds to a time that is between the times represented by the timestamps of the two estimated position points.
Owner:HERE GLOBAL BV
Correlation and enrichment of telephone system call data records
InactiveUS6891938B1Easy to detectImprove Billing AccuracyTelephonic communicationTraffic capacityCommunications system
Methods to correlate call data records in a telephone or other communication system. A combination of parameter values in the data records and timestamps associated with some of the parameters can be used for such correlation. The information available within a single call record has limitations due to the fact that critical routing information may be (a) missing or (b) incorrect. Correlation of call detail records obtained from various communication segments provides the ability to mutually enrich the records so as to increase billing accuracy, as well as to enhance the detection of call mis-routing and perform traffic analysis.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com