Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
117results about How to "Compensation delay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
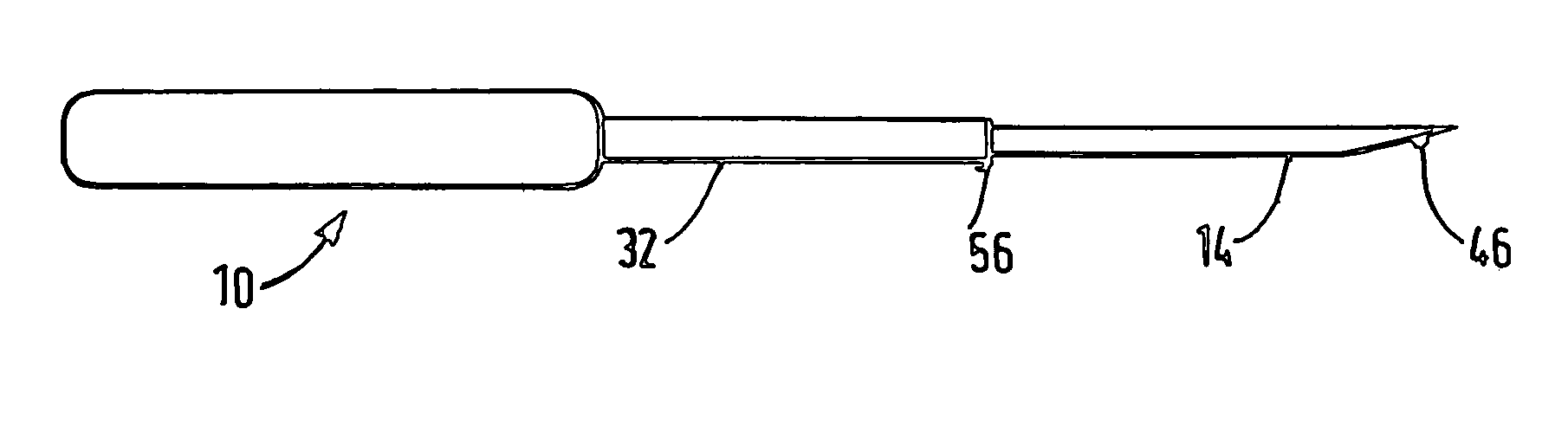
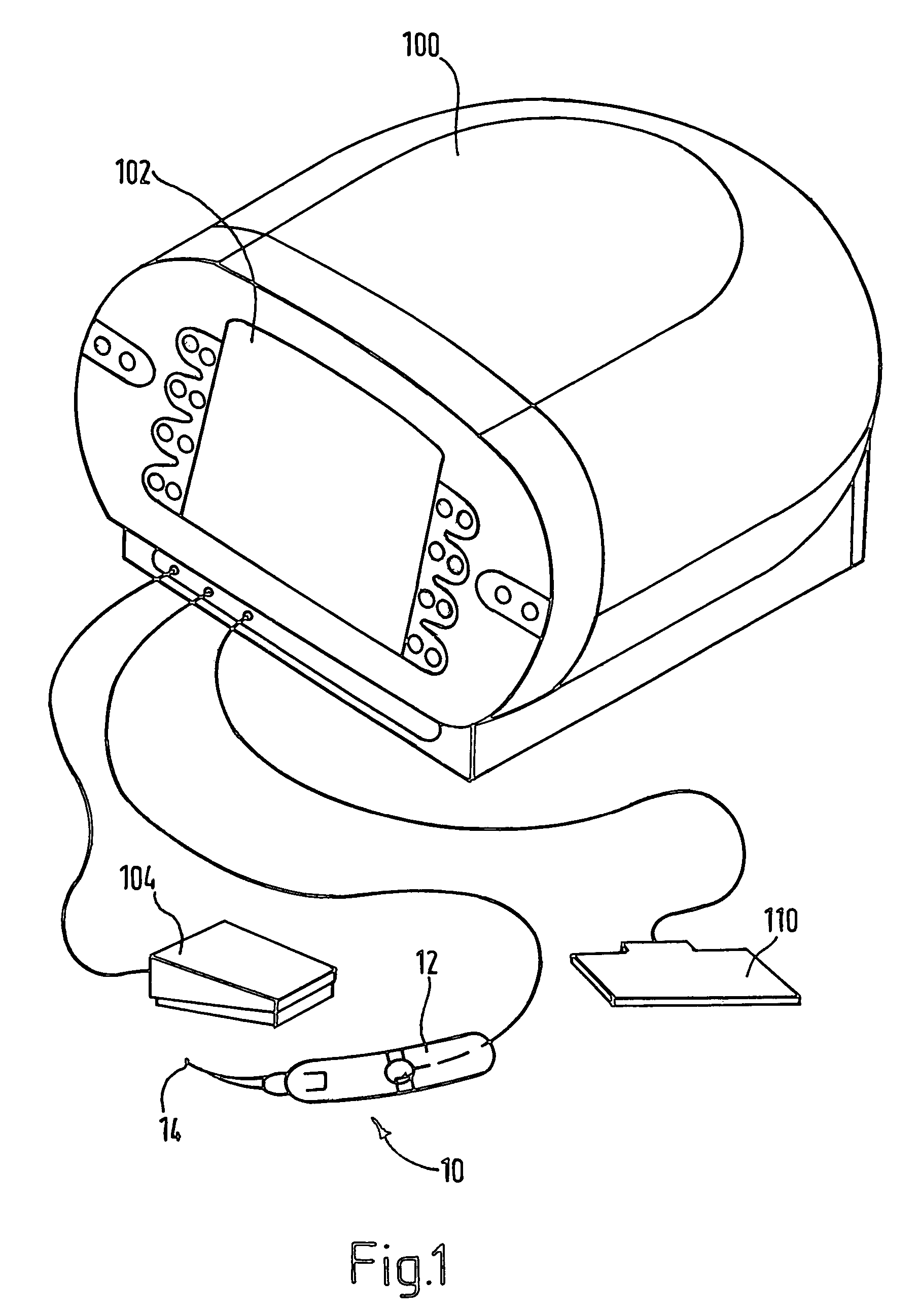
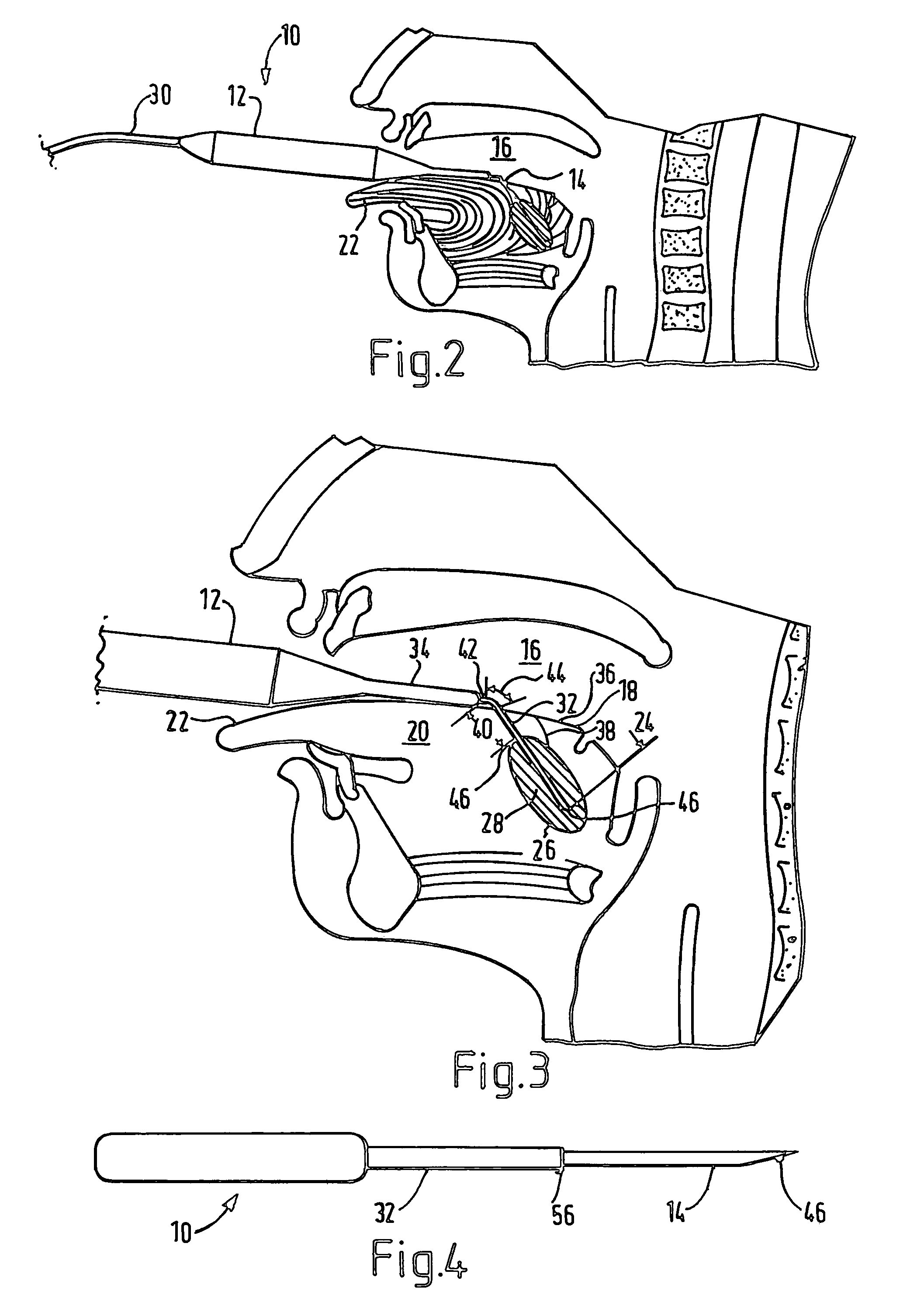
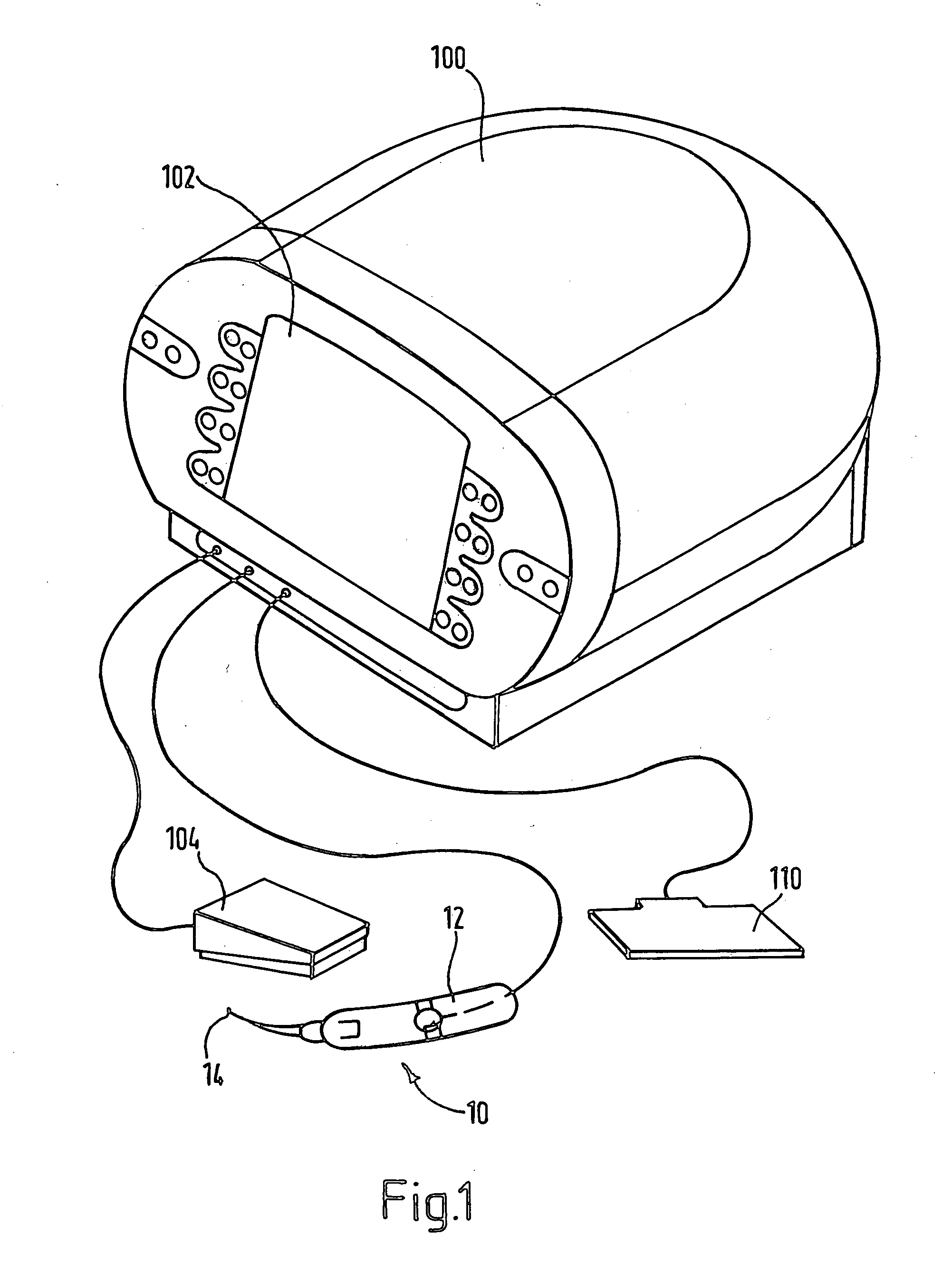
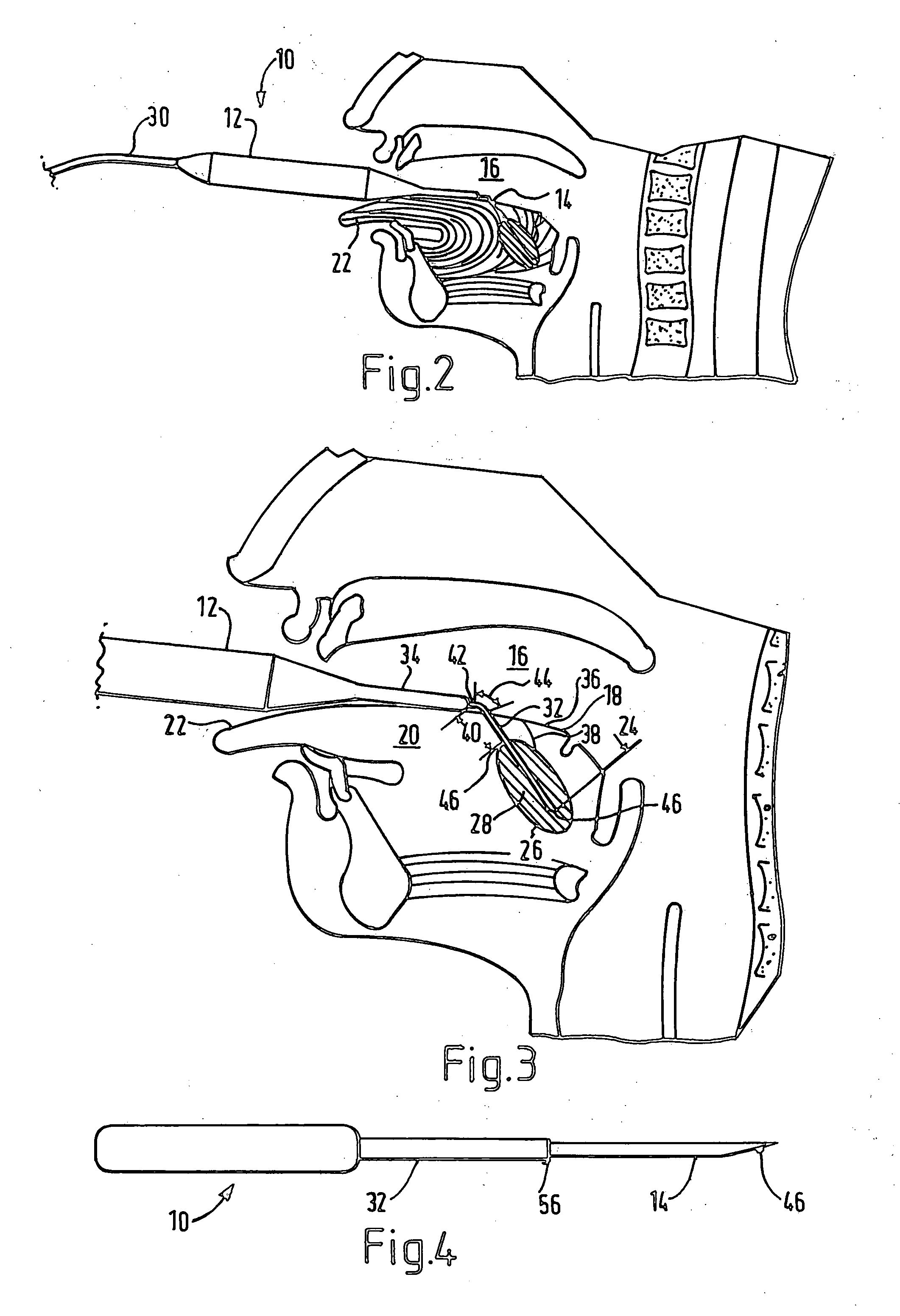
Electrosurgical method and apparatus
ActiveUS7377918B2Compensation delayIncrease temperatureSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingThreshold temperatureRadio frequency
Owner:GYRUS ENT
Electrosurgical method and apparatus
ActiveUS20050251128A1Compensation delayIncrease temperatureSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingEngineeringRadio frequency
Apparatus for forming a lesion in body tissue includes a probe having an active region with an electrode for contacting tissue to be treated, and an inactive region including an insulative sleeve around a portion of the electrode. The temperature of the inactive region is monitored using a temperature sensor. A controller supplies radio frequency energy to the electrode and samples signals from the temperature sensor. By performing a calculation using the sampled signals and a predetermined inactive region threshold temperature, and by adjusting the supplied radio frequency power, the inactive region of the probe can be maintained at or below an inactive region maximum temperature whilst the controller continues to supply radio frequency energy to the electrode. The probe has a second temperature sensor, mounted at a distal end of the electrode, the controller being configured to reduce the supplied radio frequency power when the electrode temperature reaches a predetermined maximum electrode temperature.
Owner:GYRUS ENT
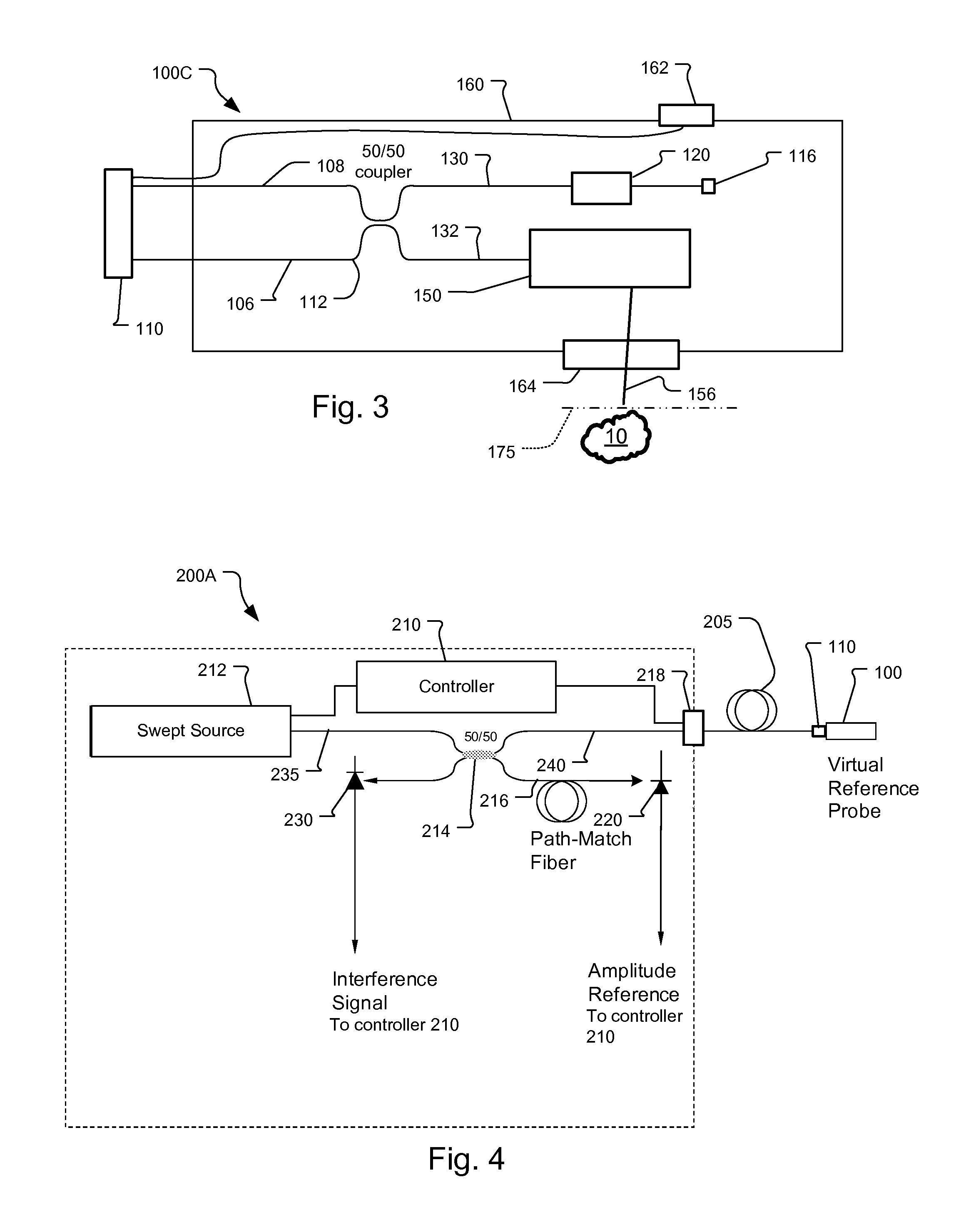
OCT Combining Probes and Integrated Systems
ActiveUS20090284749A1Noise minimizationInterference minimizationInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansSystems designLaser source
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) probe and system designs are disclosed that minimize the effects of mechanical movement and strain to the probe to the OCT analysis. It also concerns optical designs that are robust against noise from the OCT laser source. Also integrated OCT system-probes are included that yield compact and robust electro-opto-mechanical systems along with polarization sensitive OCT systems.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
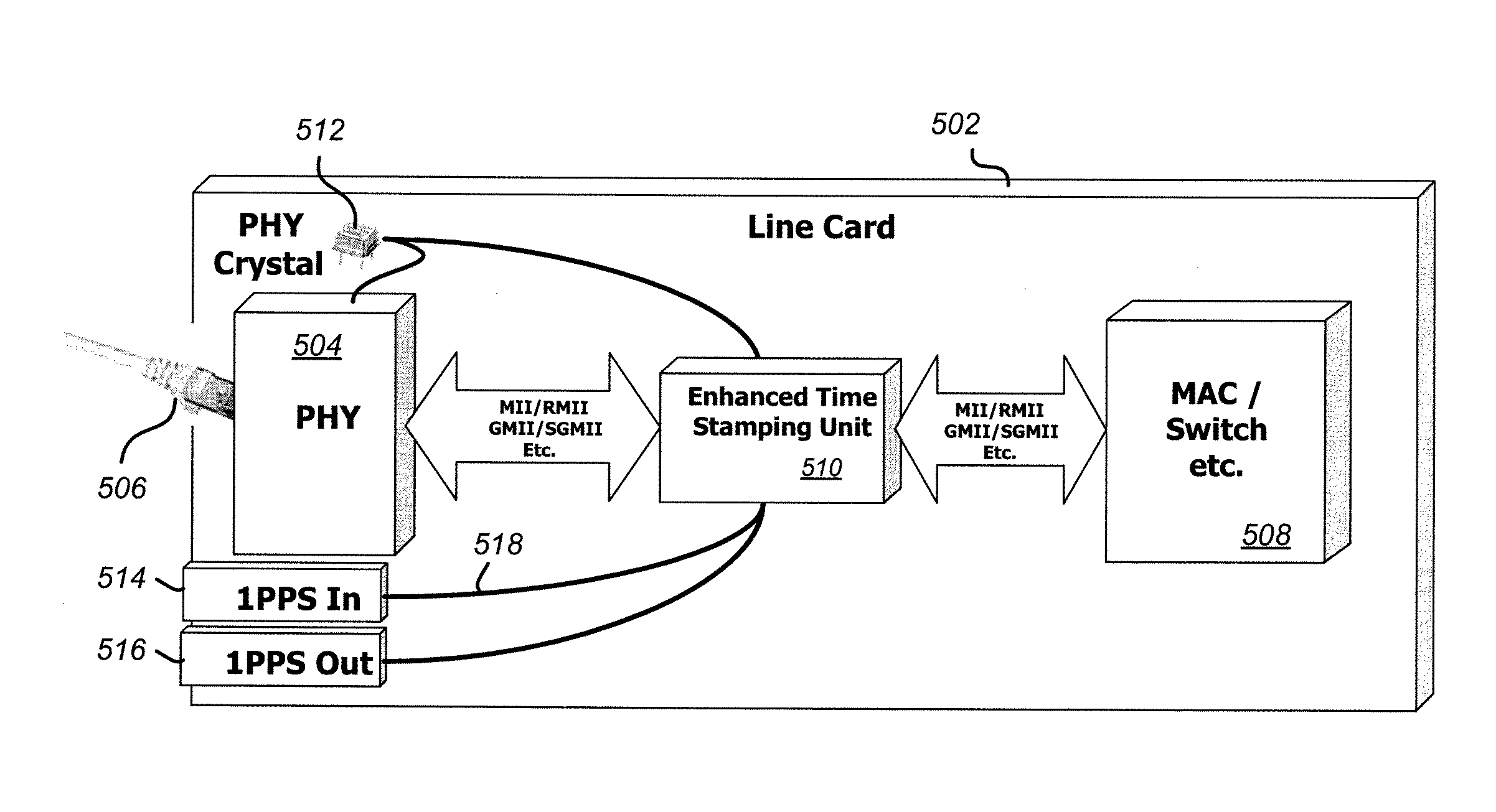
Measurement and adjustment of real-time values according to residence time in networking equipment without access to real time
InactiveUS20110051754A1Easy to applyCompensation delayTime-division multiplexNetwork elementResidence time
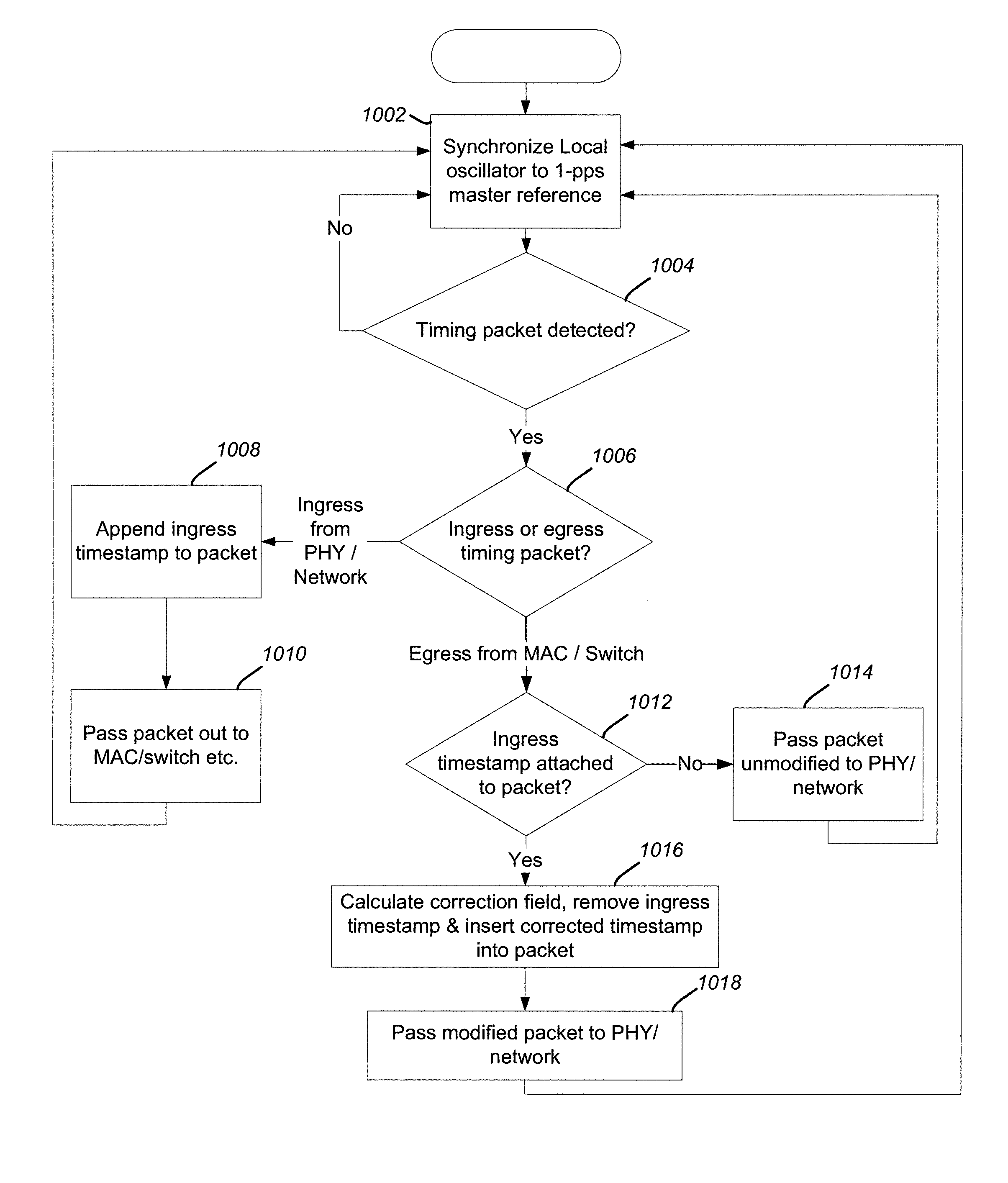
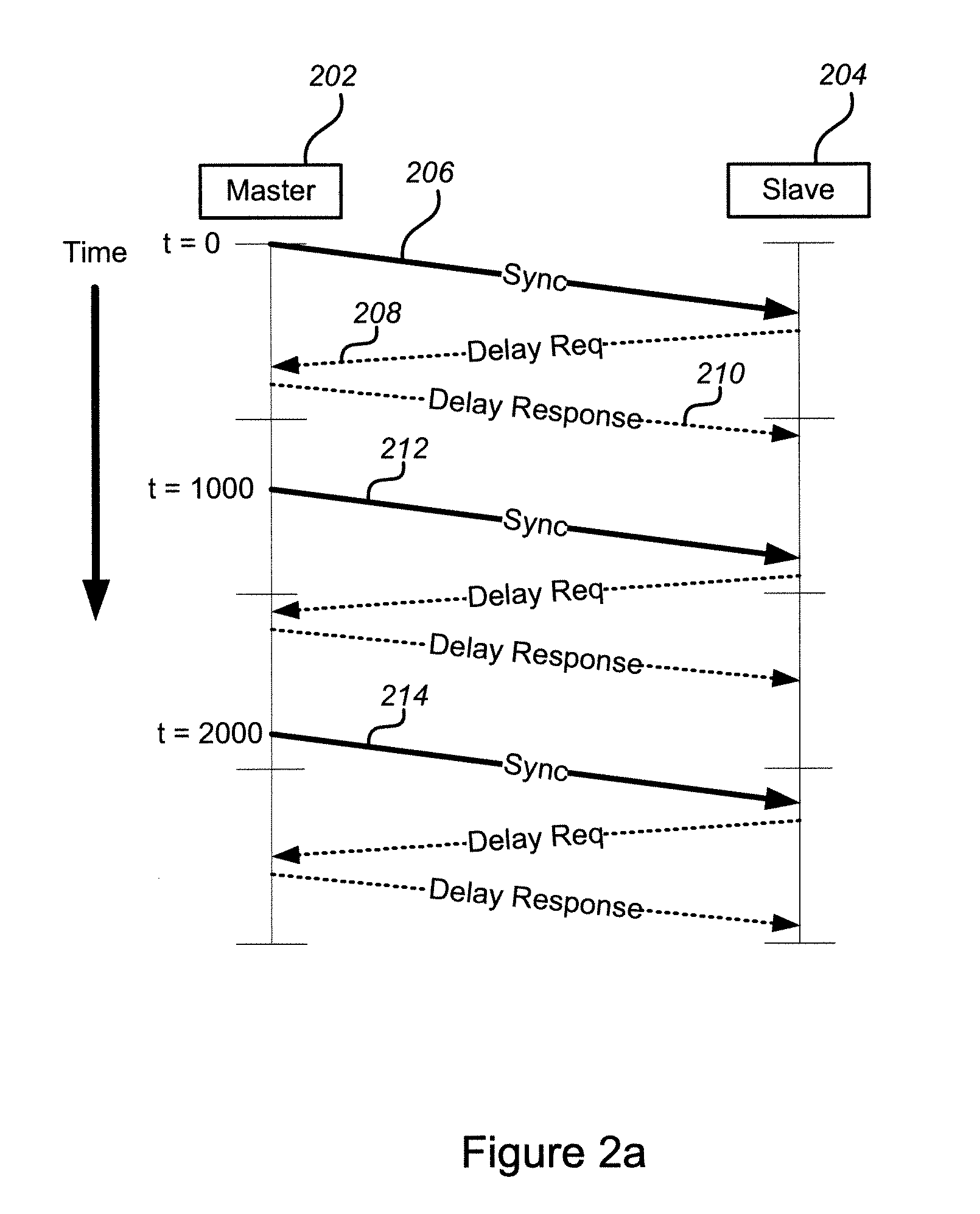
A system and method of synchronizing clocks in a distributed network is disclosed. A simple 1-pulse-per-second timing pulse is routed to time-stamping units in each network device and utilized to measure traffic-dependent synchronization packet residence delays within network elements. Synchronization messages are updated to reflect the measured residence times, thus creating transparent clocks that can readily be synchronized across the network. The simple timing pulse architecture allows the method to be applied readily both to new designs and to retrofit existing hardware.
Owner:SEMTECH CORP
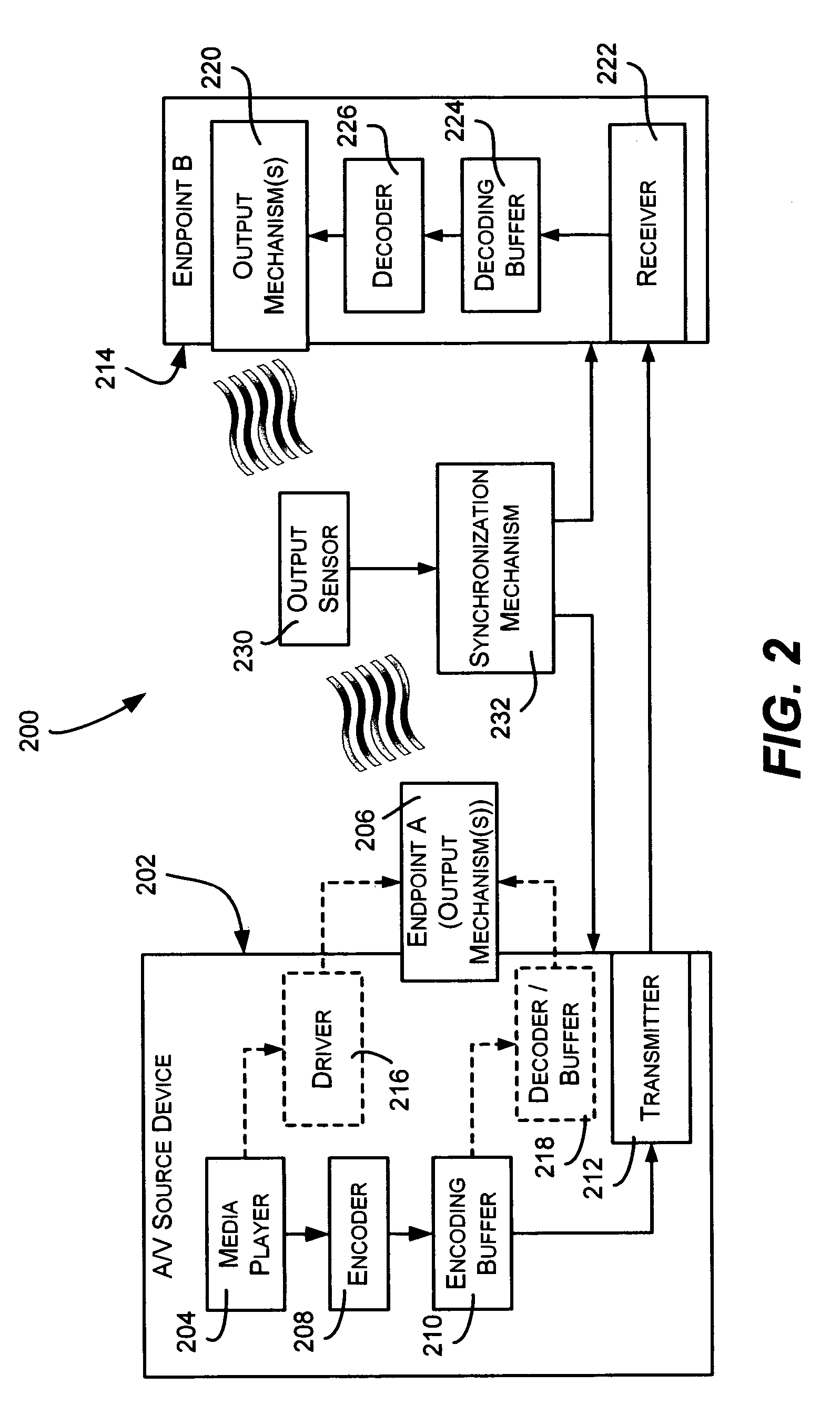
Audio and video buffer synchronization based on actual output feedback
ActiveUS20060161835A1Compensation delayCarrier indexing/addressing/timing/synchronisingSelective content distributionDigital dataPattern matching
A method and system for keeping endpoints such as speakers and displays synchronized via feedback based on the actual output of the endpoints. A source of audiovisual content transmits corresponding digital data to one or more endpoints, such as over a home network, where it may be buffered and / or decoded for playback. Microphones or the like sense actual (post-buffering / decoding) output from one or more endpoints and feed it back to a synchronization mechanism. The synchronization mechanism employs pattern matching or similar techniques to determine whether and how to adjust the timing of endpoints to synchronize their actual outputs. Synchronization may be accomplished by controllably delaying transmission and / or other processing, by controllably changing the rate of advancing in a buffer, and / or by jumping ahead in a buffer. The synchronization mechanism may adjust multiple endpoints, e.g., when limited buffer size limits the amount of adjustment a single device can provide.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
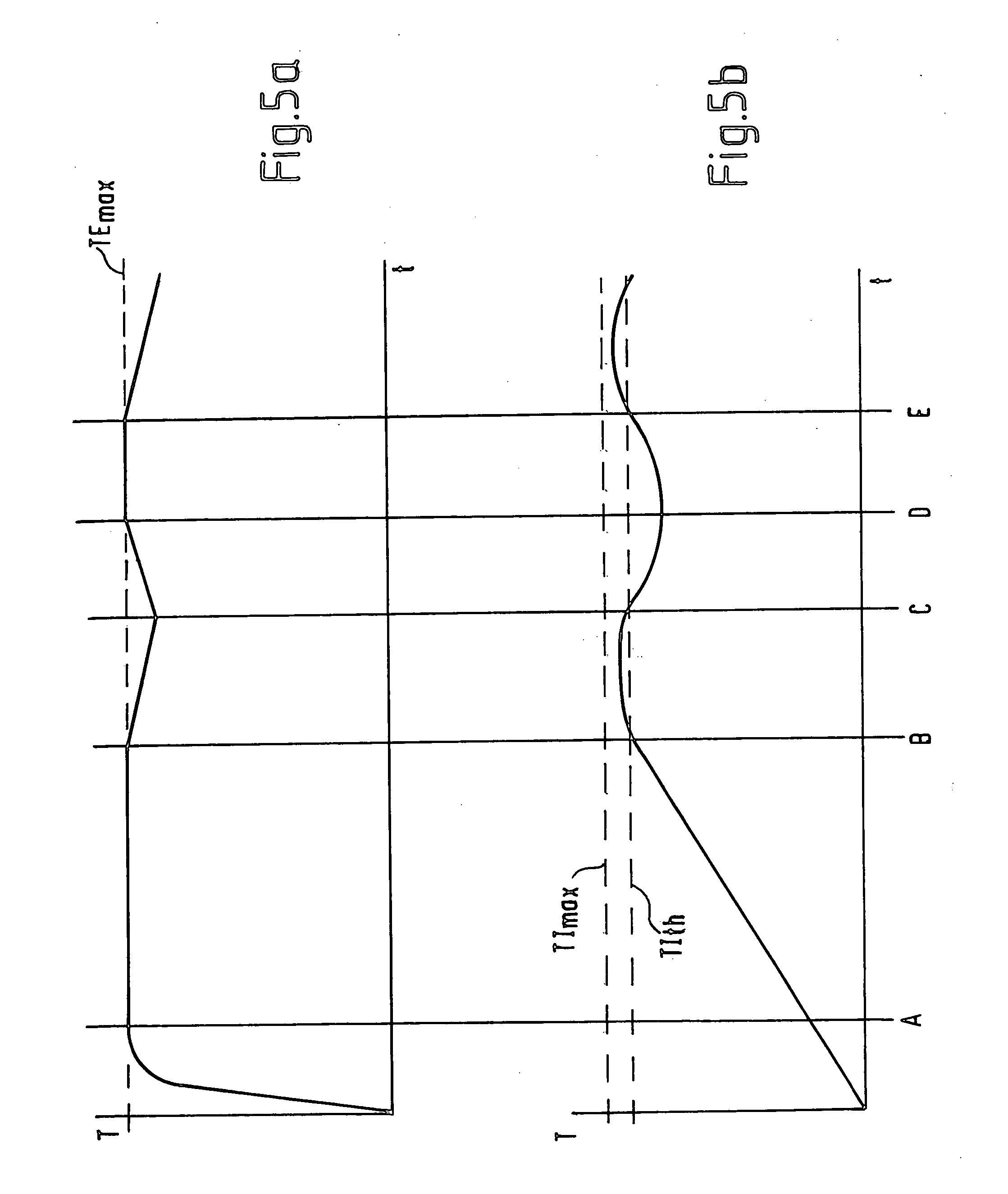
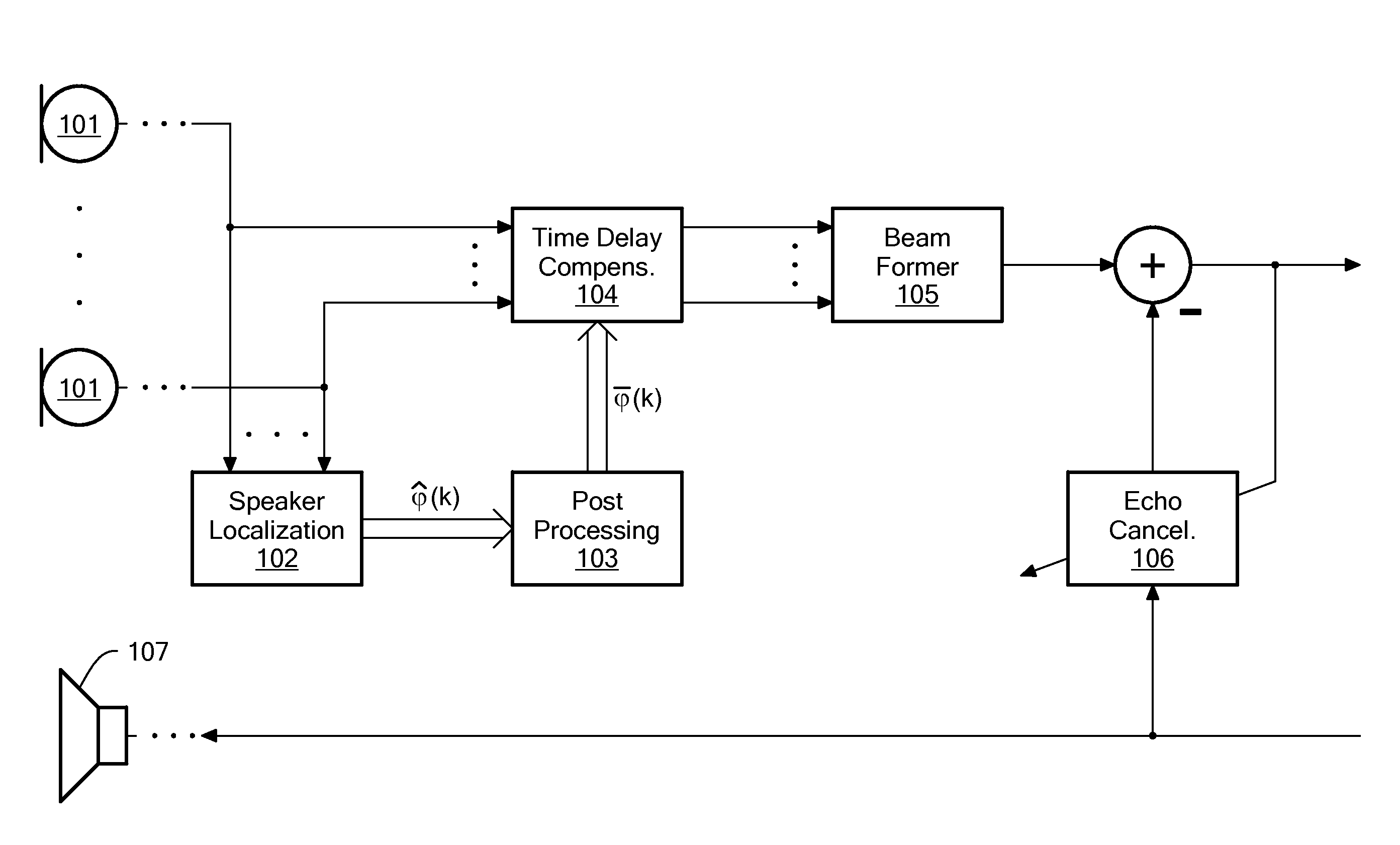
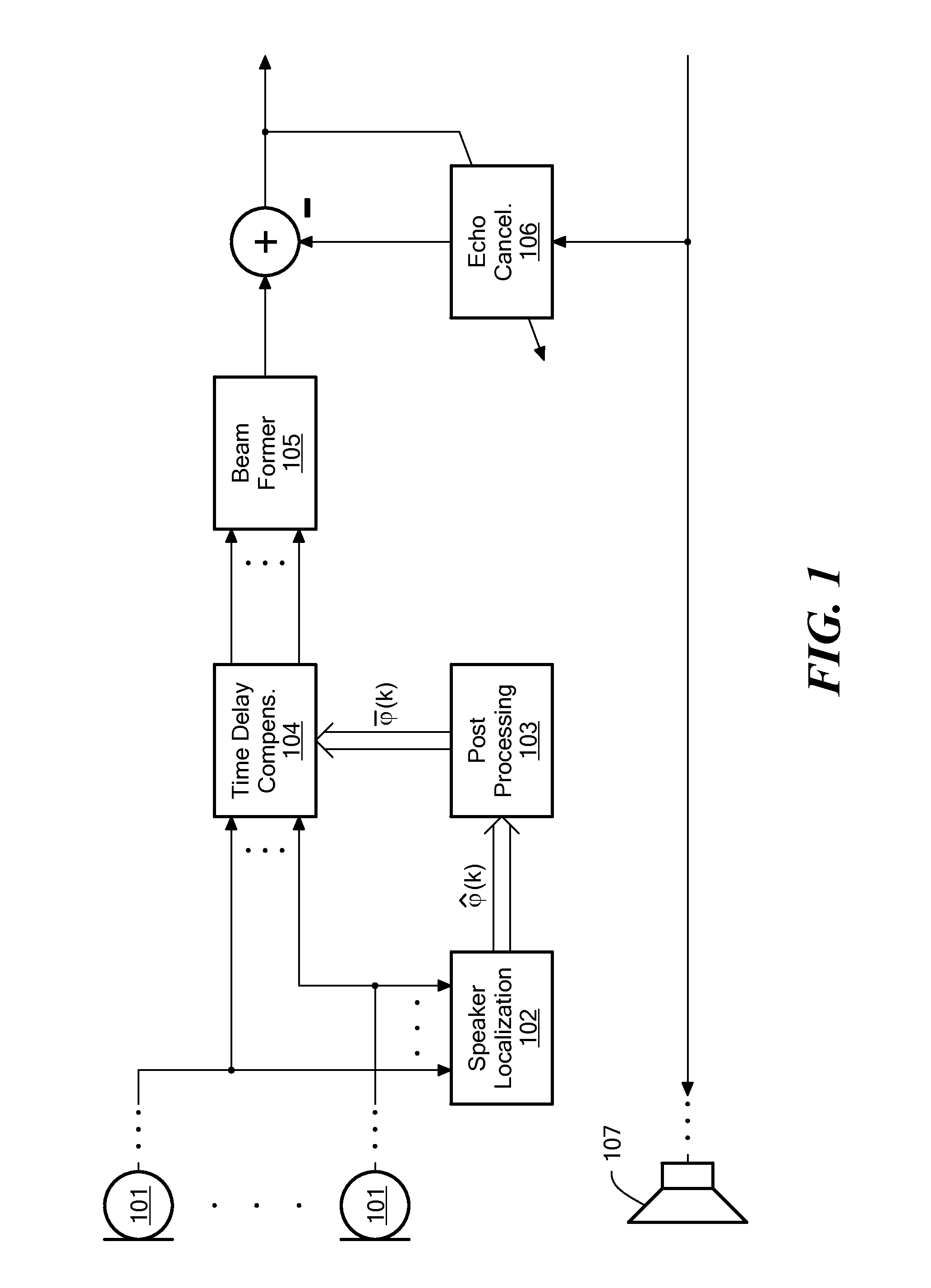
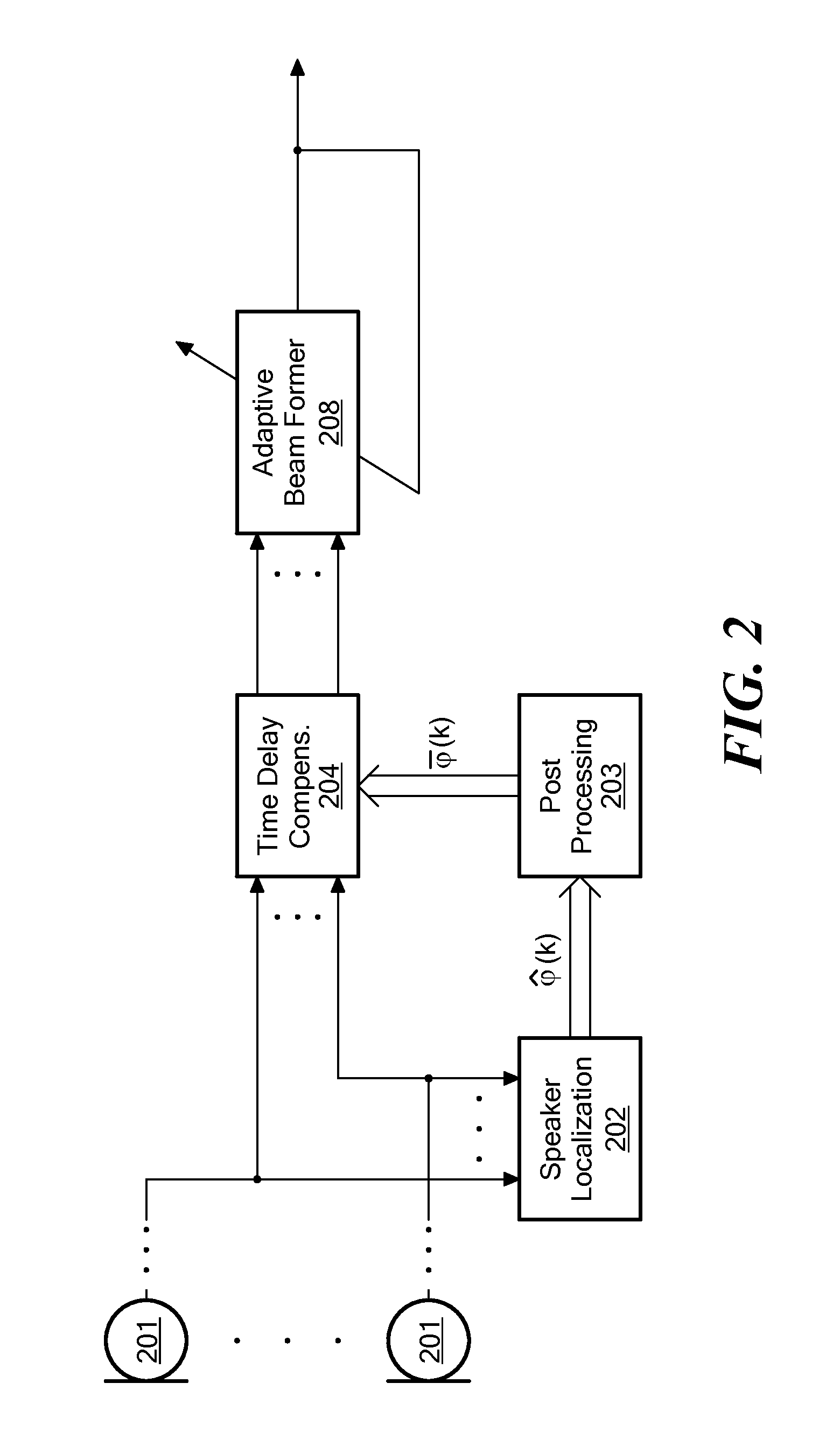
Method for Determining a Time Delay for Time Delay Compensation
ActiveUS20100150364A1Time delay compensationCompensation delayMicrophonesInterconnection arrangementsSound sourcesTime delays
The invention provides a computer-implemented method for determining a time delay for time delay compensation of a microphone signal from a microphone array in a beamformer arrangement. For a given time, an instantaneous estimate of a position of a wanted sound source and / or of a direction of arrival of a signal originating from the wanted sound source is determined. The computer system then determines whether the instantaneous estimate deviates from a preset estimate of a position of the wanted sound source and / or of a direction of arrival of a signal originating from the wanted sound source according to a predetermined criterion. The predetermined criterion comprises a check whether the instantaneous estimate deviates from the preset estimate by at least a predetermined deviation threshold. If the predetermined criterion is fulfilled, the instantaneous estimate for the given time is set by the computer system as the preset estimate, and the computer system determines the time delay for time delay compensation of the microphone signal based on the instantaneous estimate.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
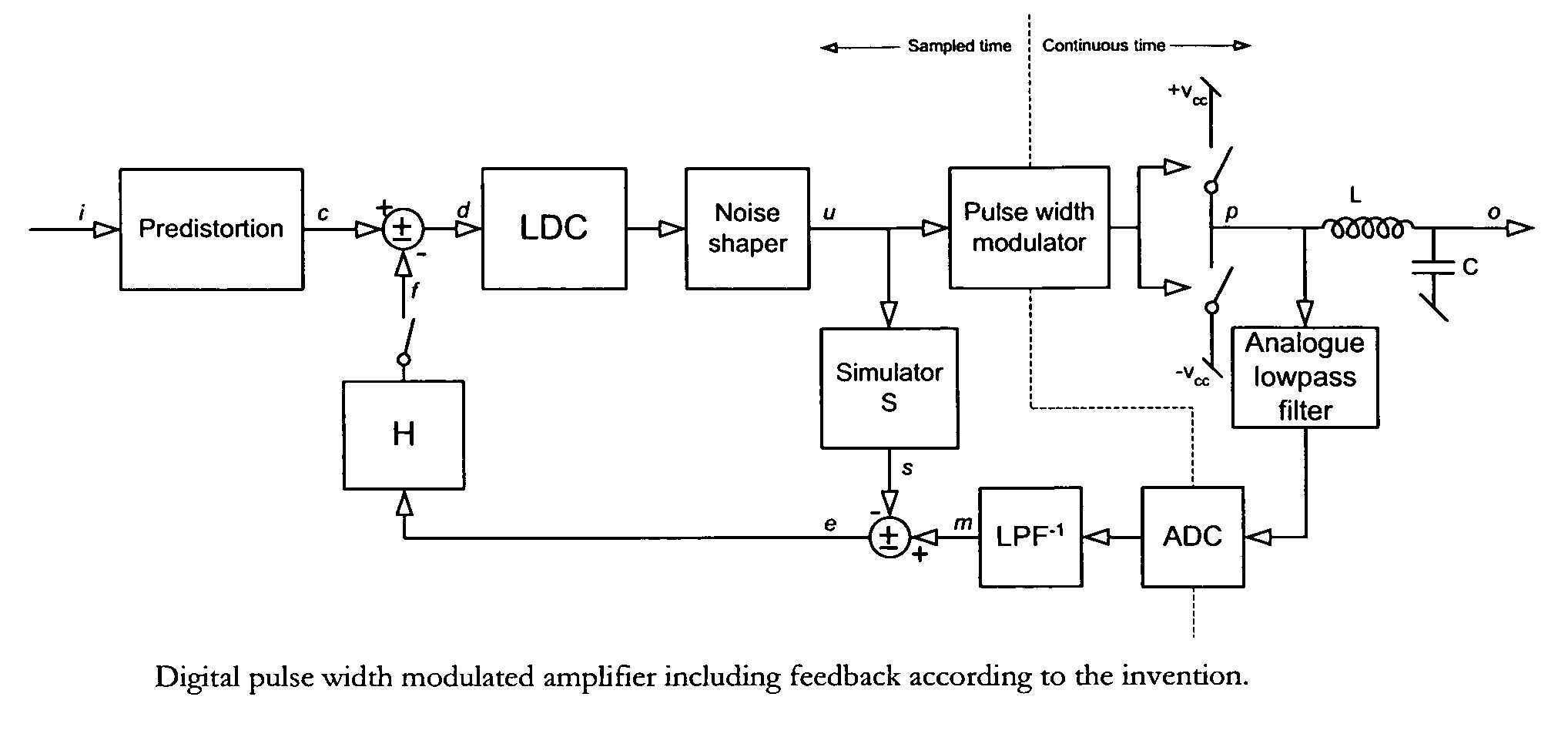
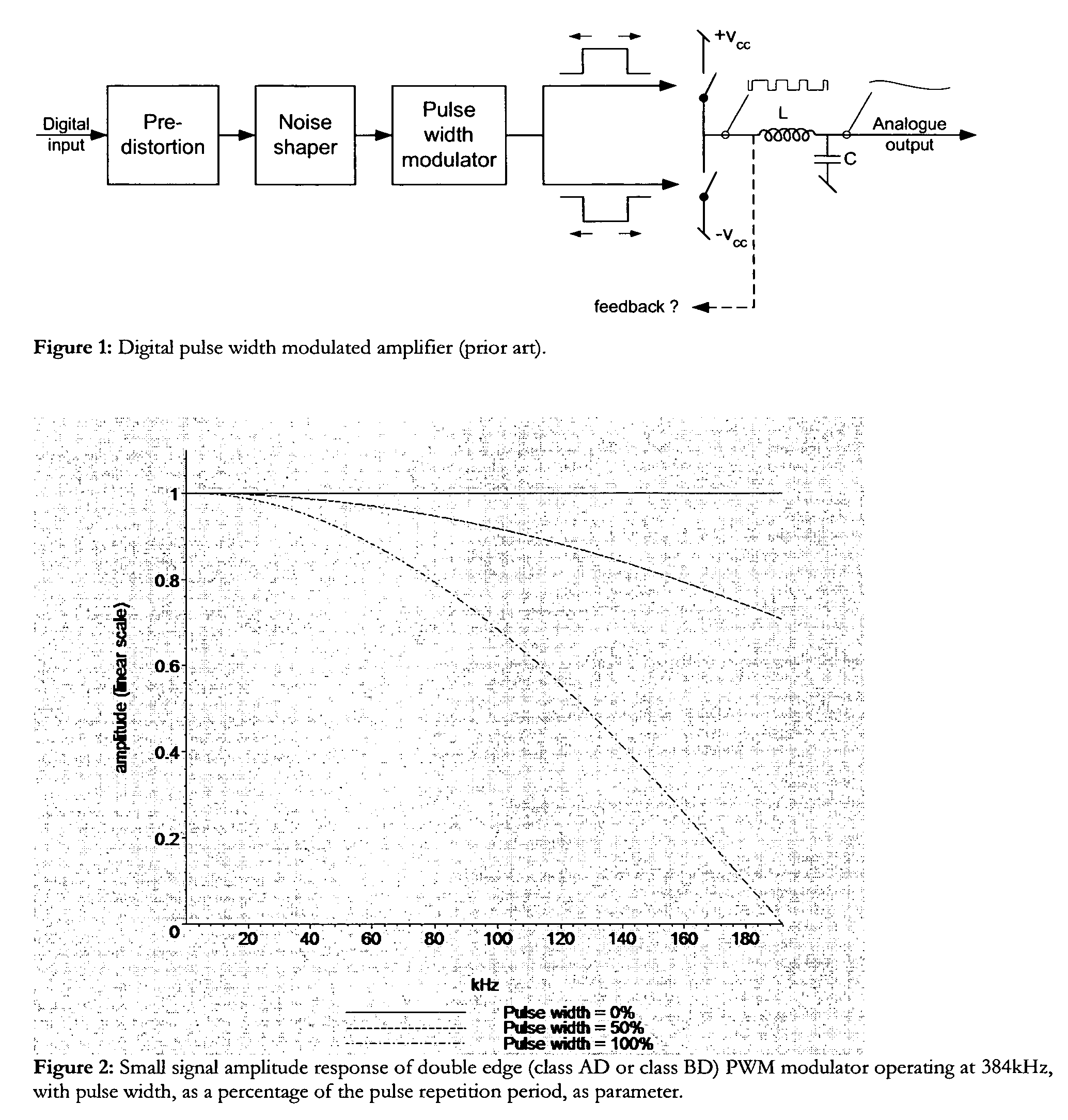
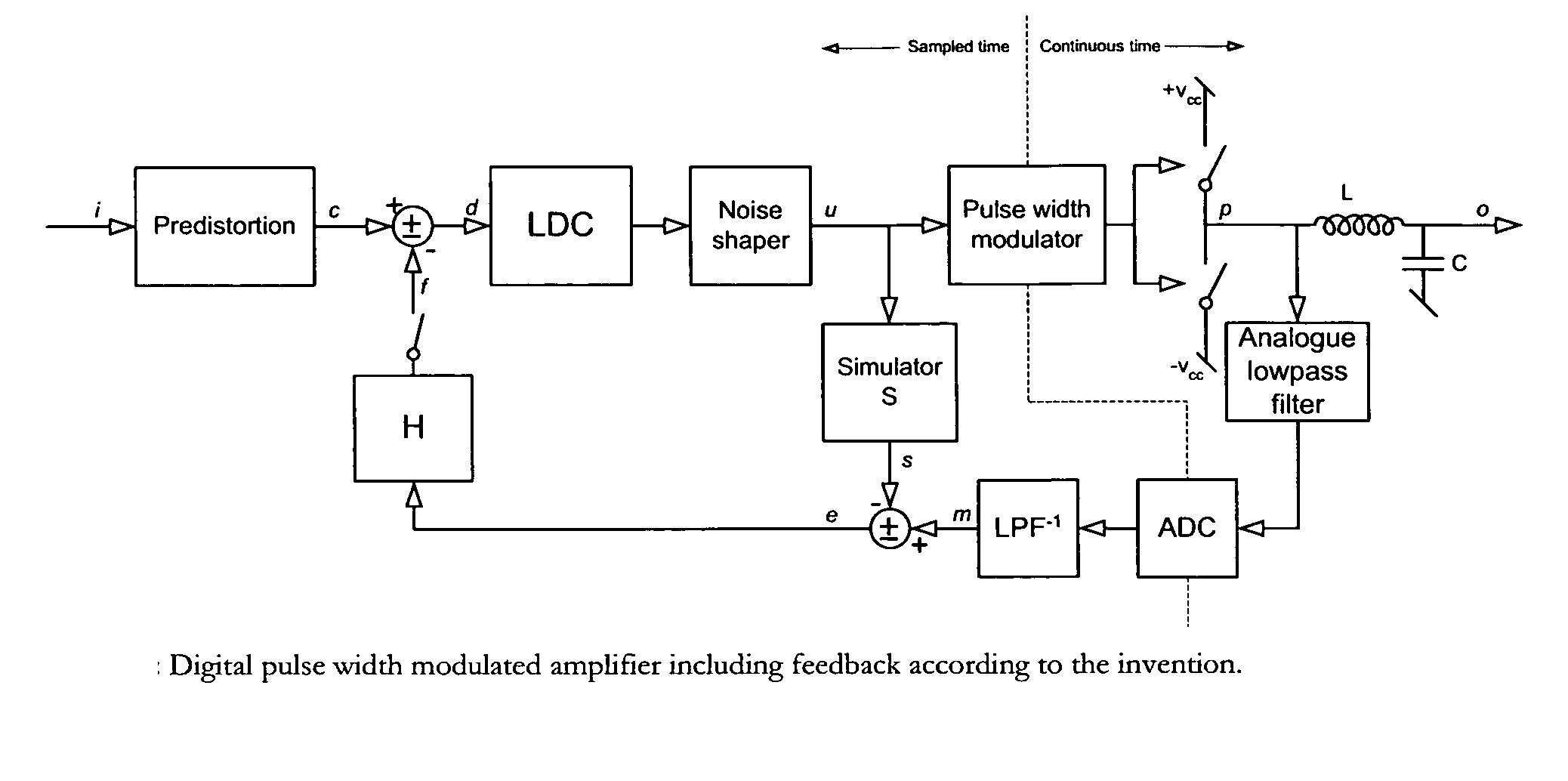
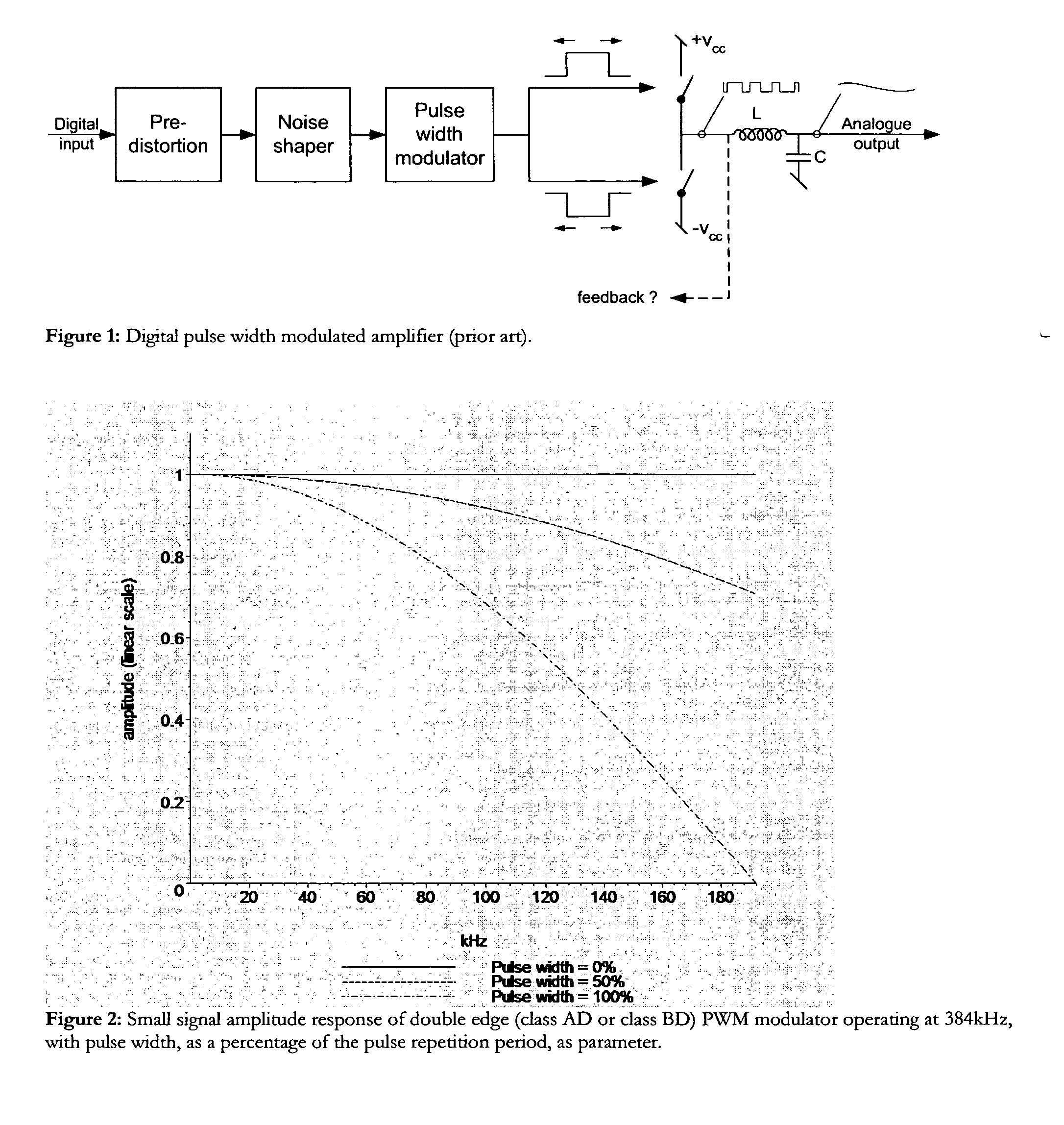
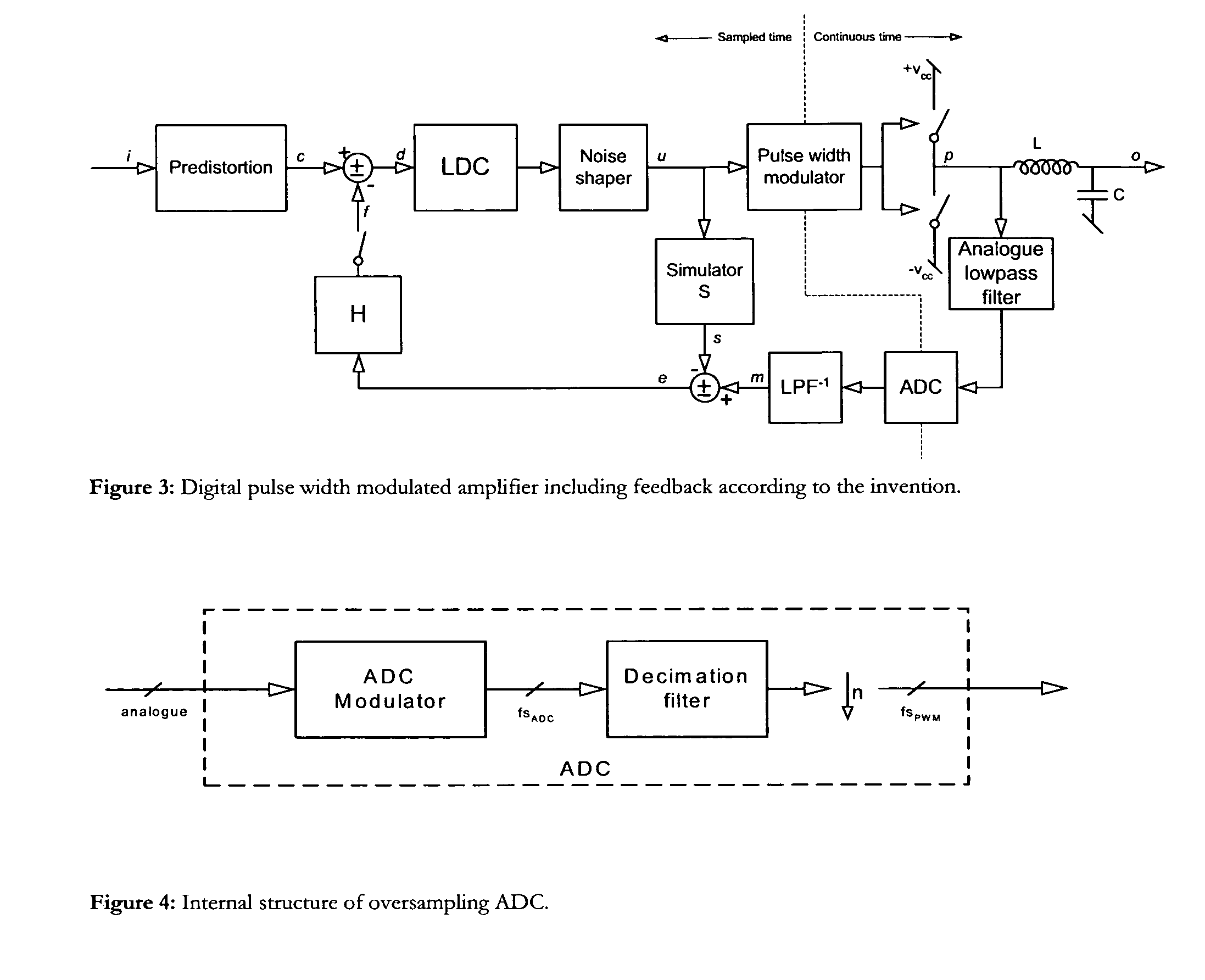
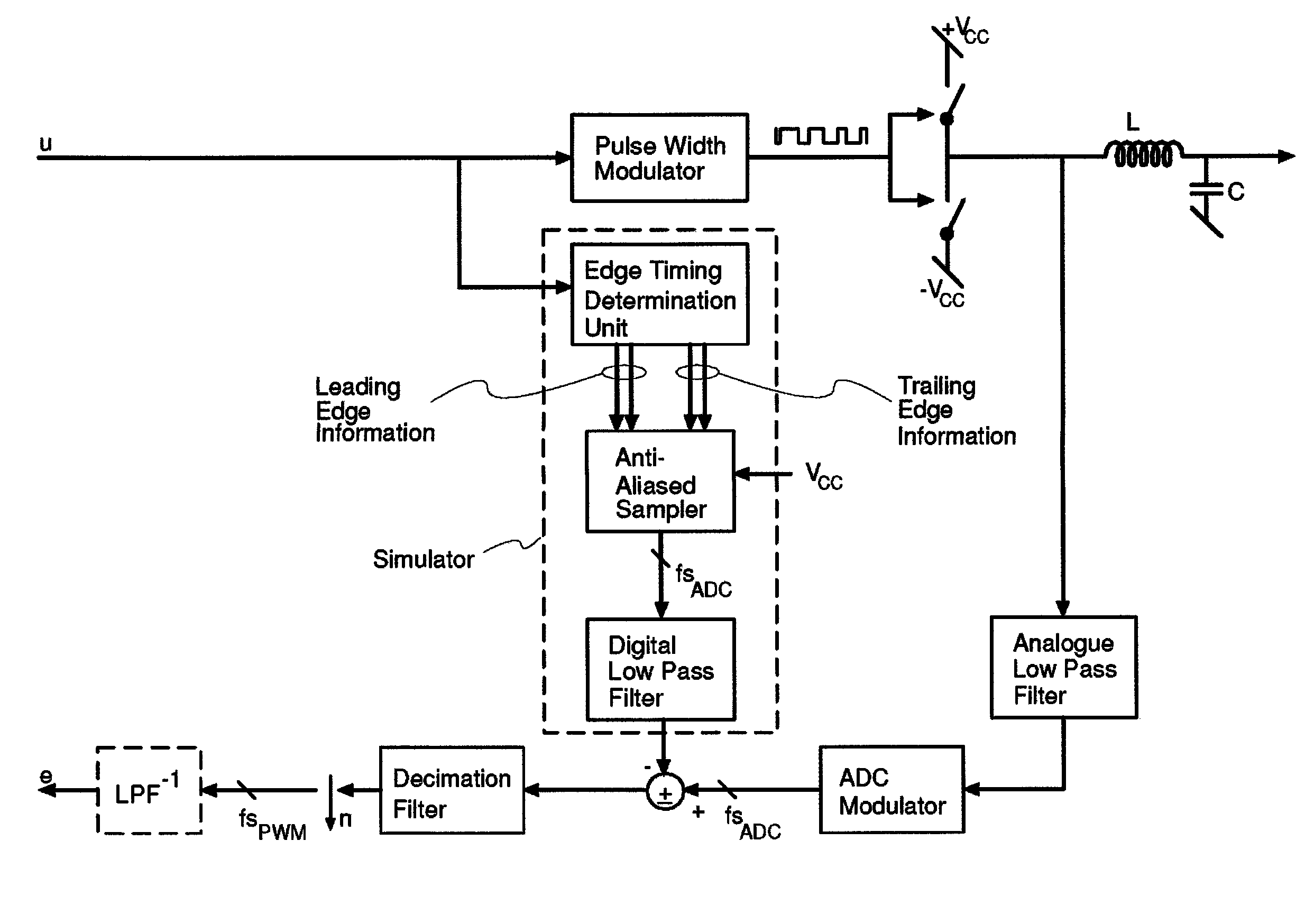
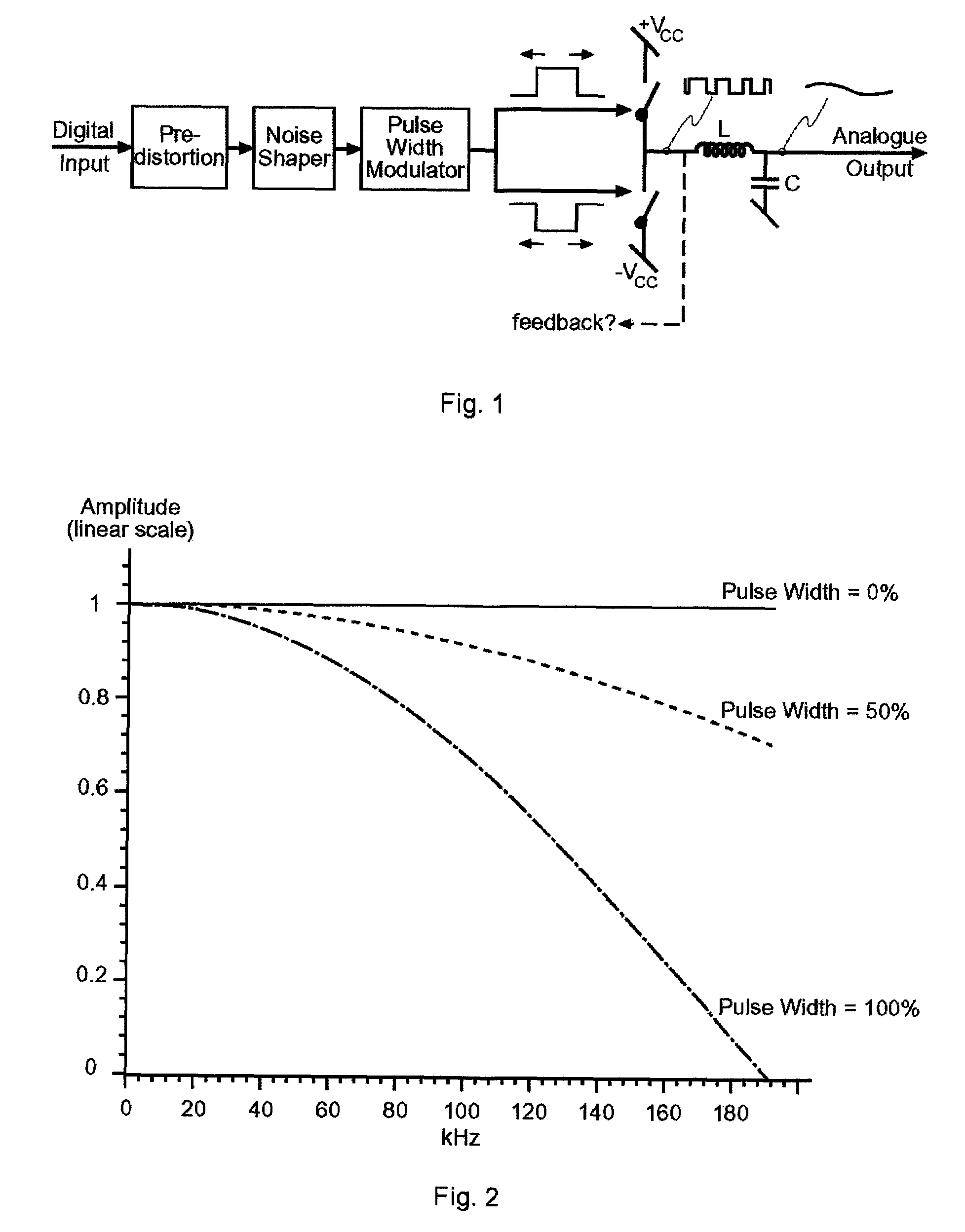
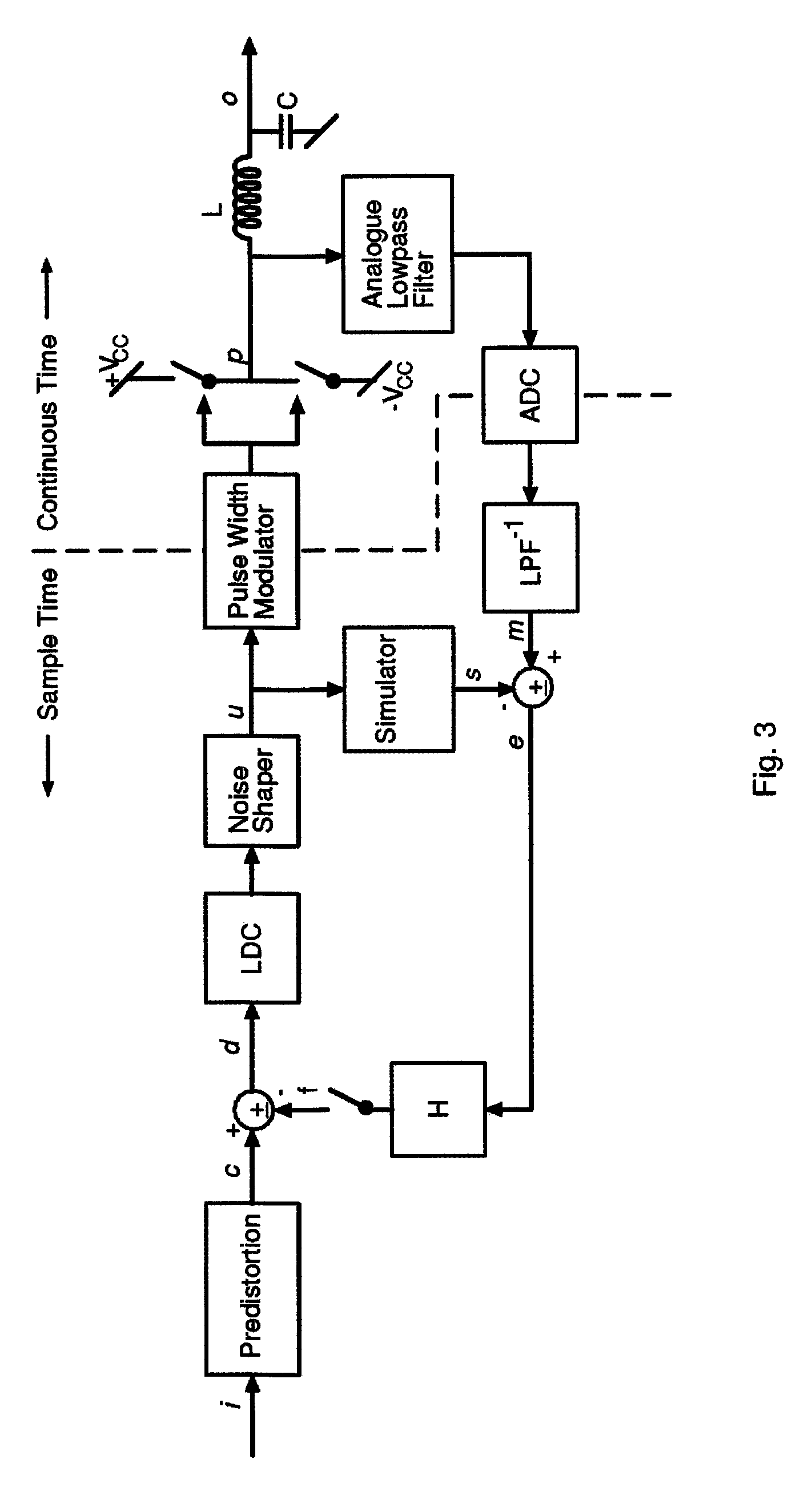
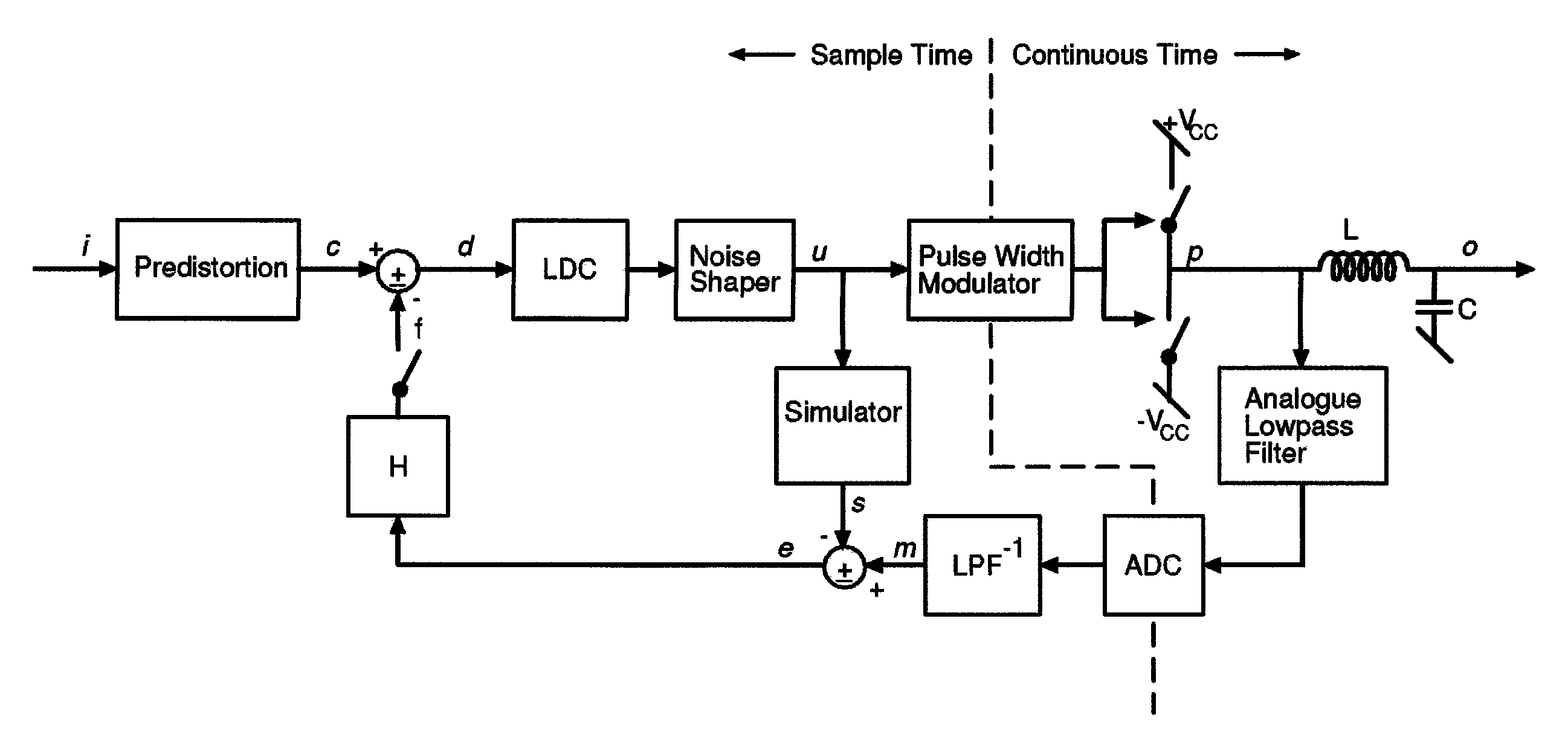
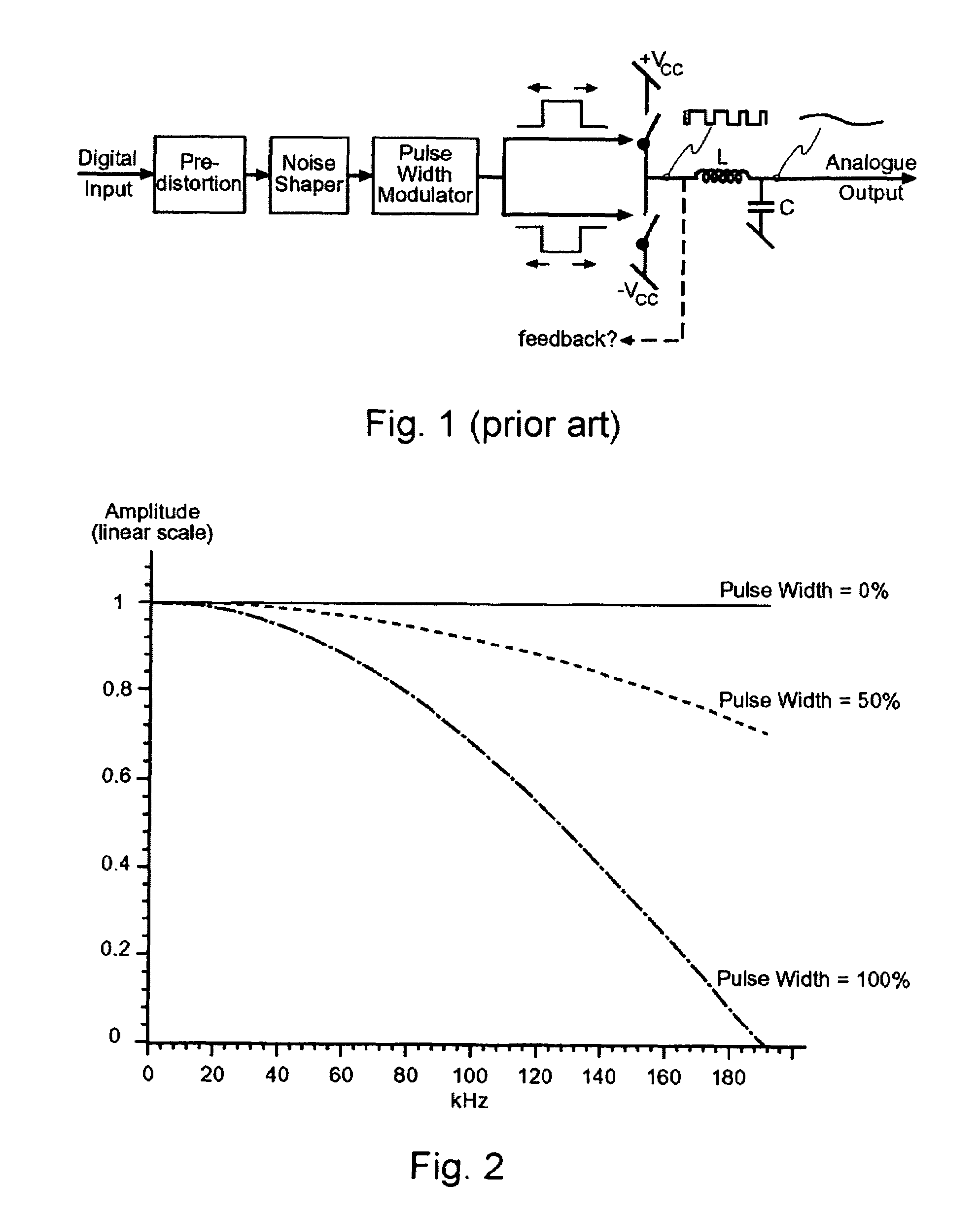
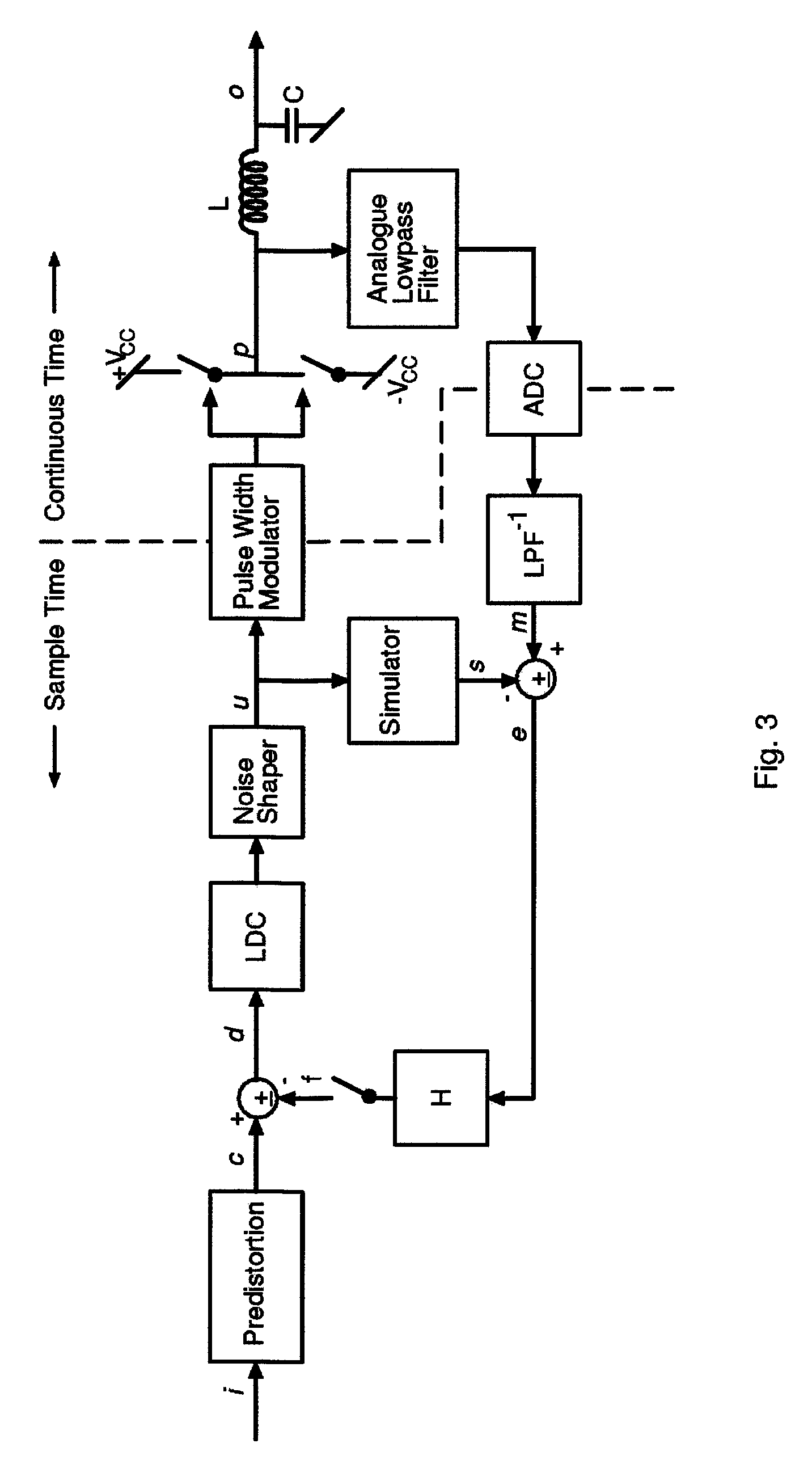
Digital PWM amplifier with simulation-based feedback
InactiveUS7286009B2Compensation delayAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierNoise shaping
Systems and methods for performance improvements in digital switching amplifiers using simulation-based feedback. In one embodiment, a digital pulse width modulation (PWM) amplifier includes a signal processing plant configured to receive and process an input audio signal. The amplifier also includes a simulator configured to model processing of audio signals by the plant. The outputs of the plant and the simulator are provided to a subtractor, the output of which is then added to the input audio signal as feedback. The plant may consist of a modulator and power switch, a noise shaper, or any other type of plant. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) may be provided to convert the output audio signal to a digital signal for input to the subtractor. Filtering may be implemented before or after the ADC, and a decimator may be placed after the ADC if it is an oversampling ADC.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
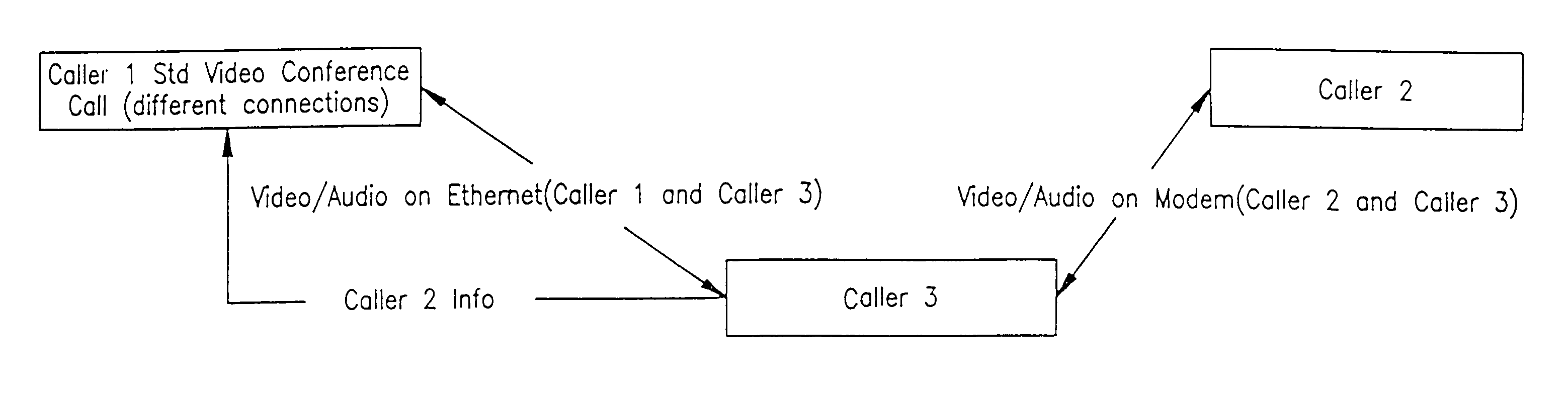
Methods for multiple media digital communication
InactiveUS7075924B2Increase and decrease rateImprove continuitySpecial service provision for substationPulse modulation television signal transmissionMedia typeCommunications system
Methods for media communication in a digital communication system. In one embodiment, the media comprises a plurality of media types (including for example audio, video, and / or data packets), and the system includes a processing apparatus for establishing communication between first and second callers over respective first and second communication mediums, which include one or more packet-switched communication channels. The method comprises using a connection routine of the processing apparatus to enable media type selections by the callers, and transmitting, via the processing apparatus, a plurality of media packets corresponding to each of the selected media types.
Owner:RPX CORP
Digital PWM amplifier with simulation-based feedback
InactiveUS20070152750A1Compensation delayAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlEngineeringAnalog-to-digital converter
Systems and methods for performance improvements in digital switching amplifiers using simulation-based feedback. In one embodiment, a digital pulse width modulation (PWM) amplifier includes a signal processing plant configured to receive and process an input audio signal. The amplifier also includes a simulator configured to model processing of audio signals by the plant. The outputs of the plant and the simulator are provided to a subtractor, the output of which is then added to the input audio signal as feedback. The plant may consist of a modulator and power switch, a noise shaper, or any other type of plant. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) may be provided to convert the output audio signal to a digital signal for input to the subtractor. Filtering may be implemented before or after the ADC, and a decimator may be placed after the ADC if it is an oversampling ADC.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
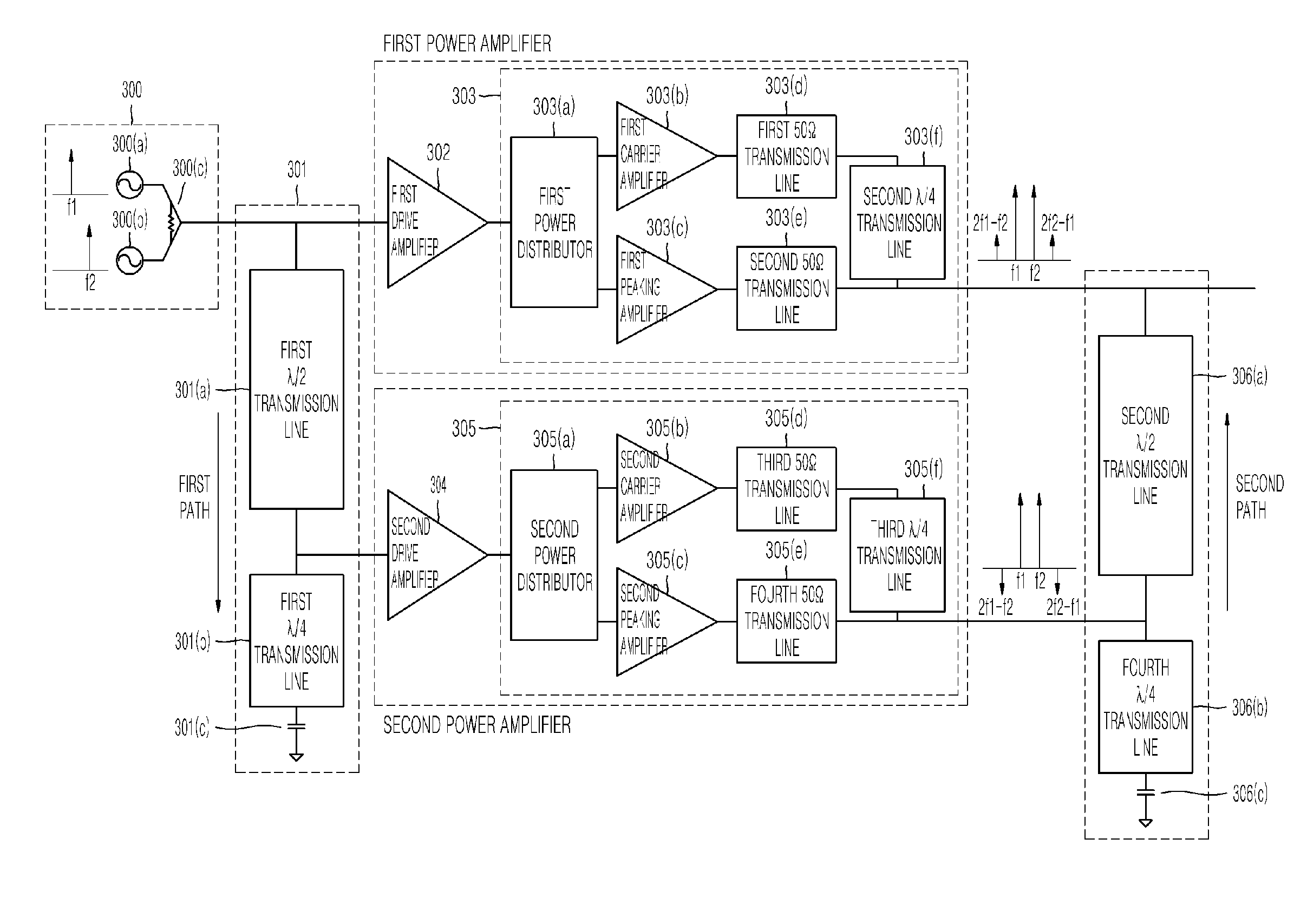
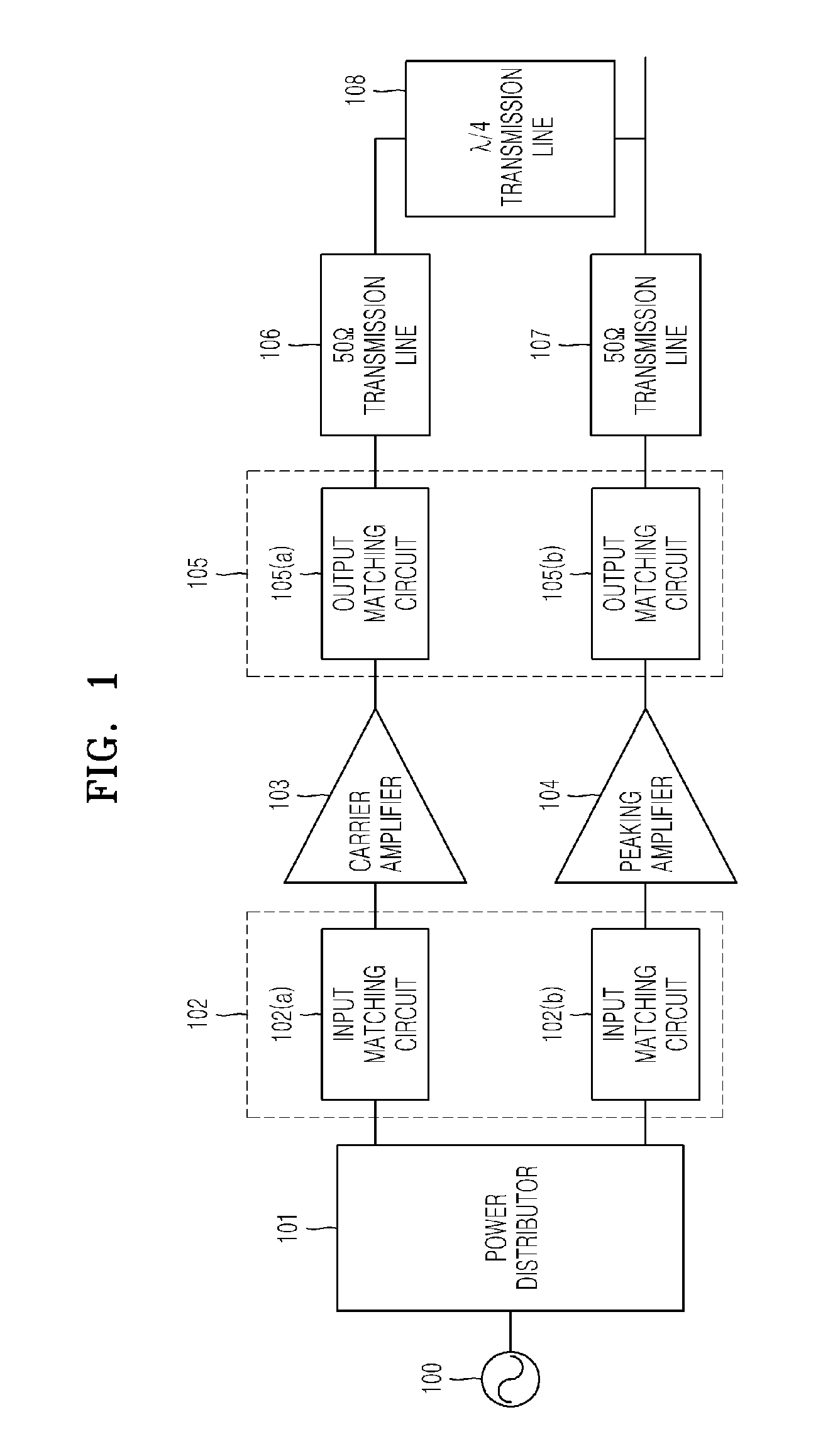
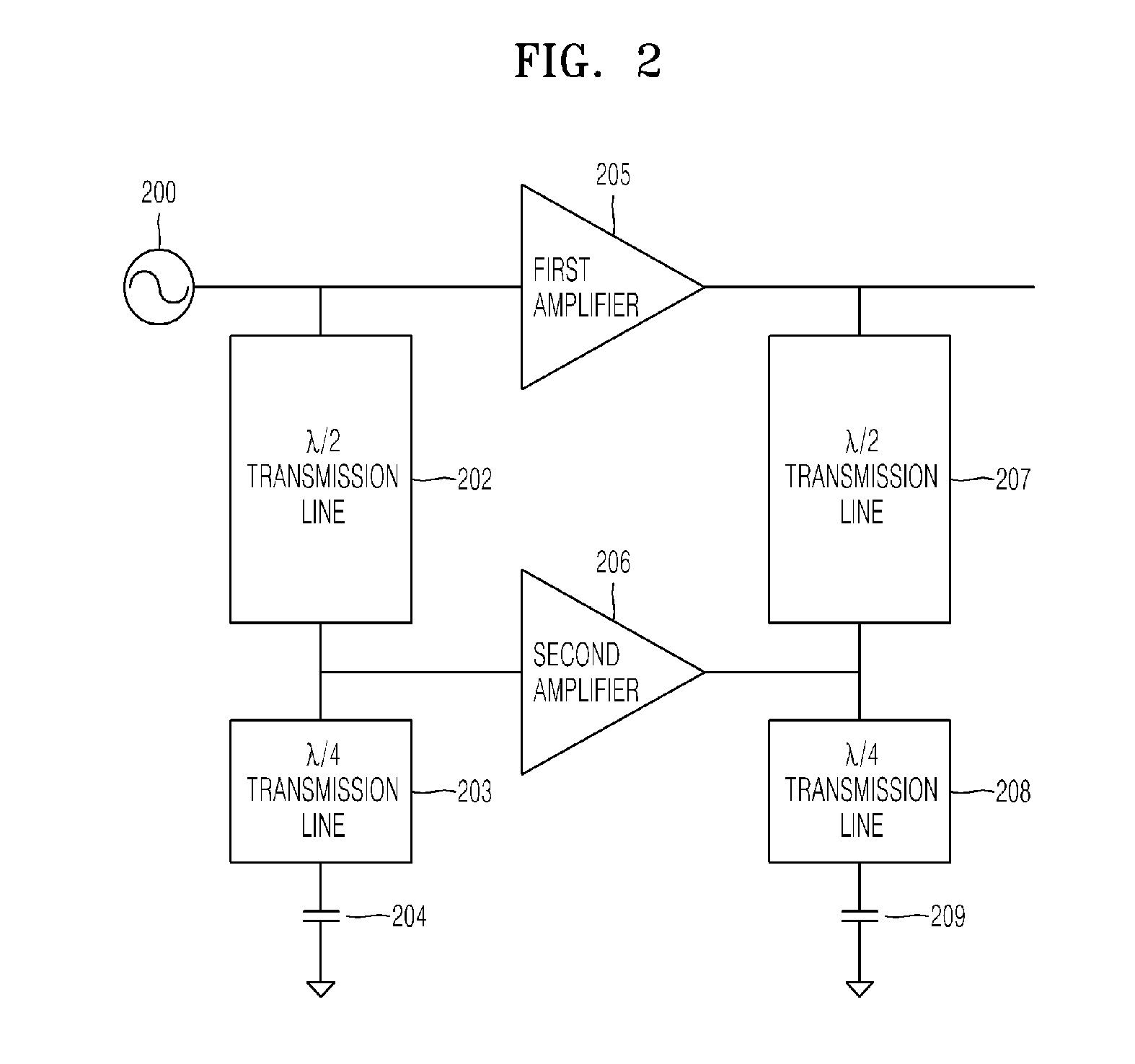
Distributed doherty power amplifier
InactiveUS20110175677A1Prevent leakageCompensation delayPower amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierCarrier signal
Provided is a distributed Doherty power amplifier exhibiting high efficiency and linearity at a wide range of bandwidths, the distributed Doherty power amplifier including a first amplifier; a second amplifier, which is connected to the first amplifier in parallel; a first shifting unit, which is interconnected between the input of the first amplifier and the input of the second amplifier and inverses the phase of the input of the second amplifier; and a second shifting unit, which is interconnected between the output of the first amplifier and the output of the second amplifier and inverses the phase of the output of the second amplifier, wherein the first amplifier and the second amplifier are Doherty power amplifiers, and each of the Doherty power amplifiers includes a carrier amplifier and a peaking amplifier, which are connected in parallel.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
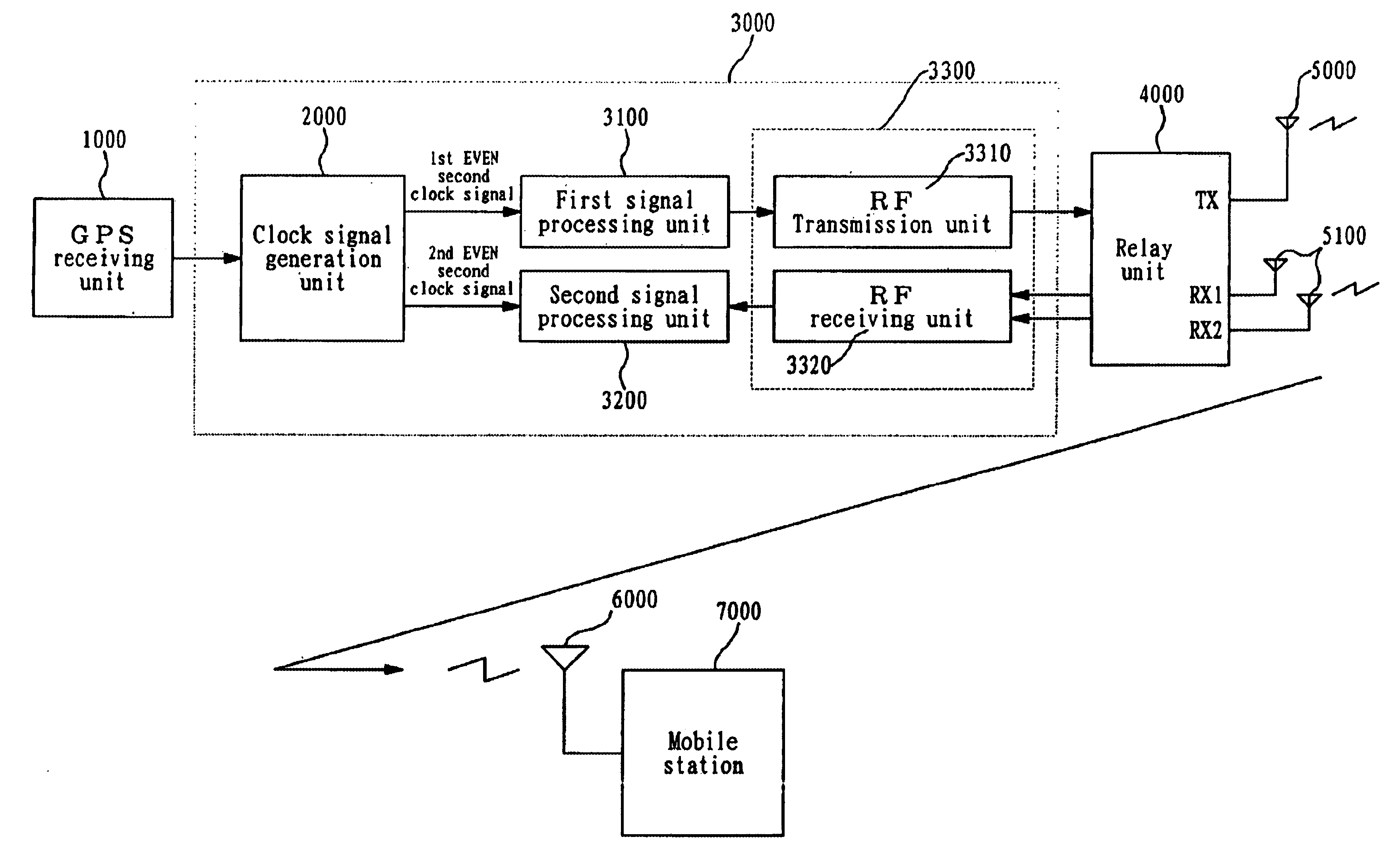
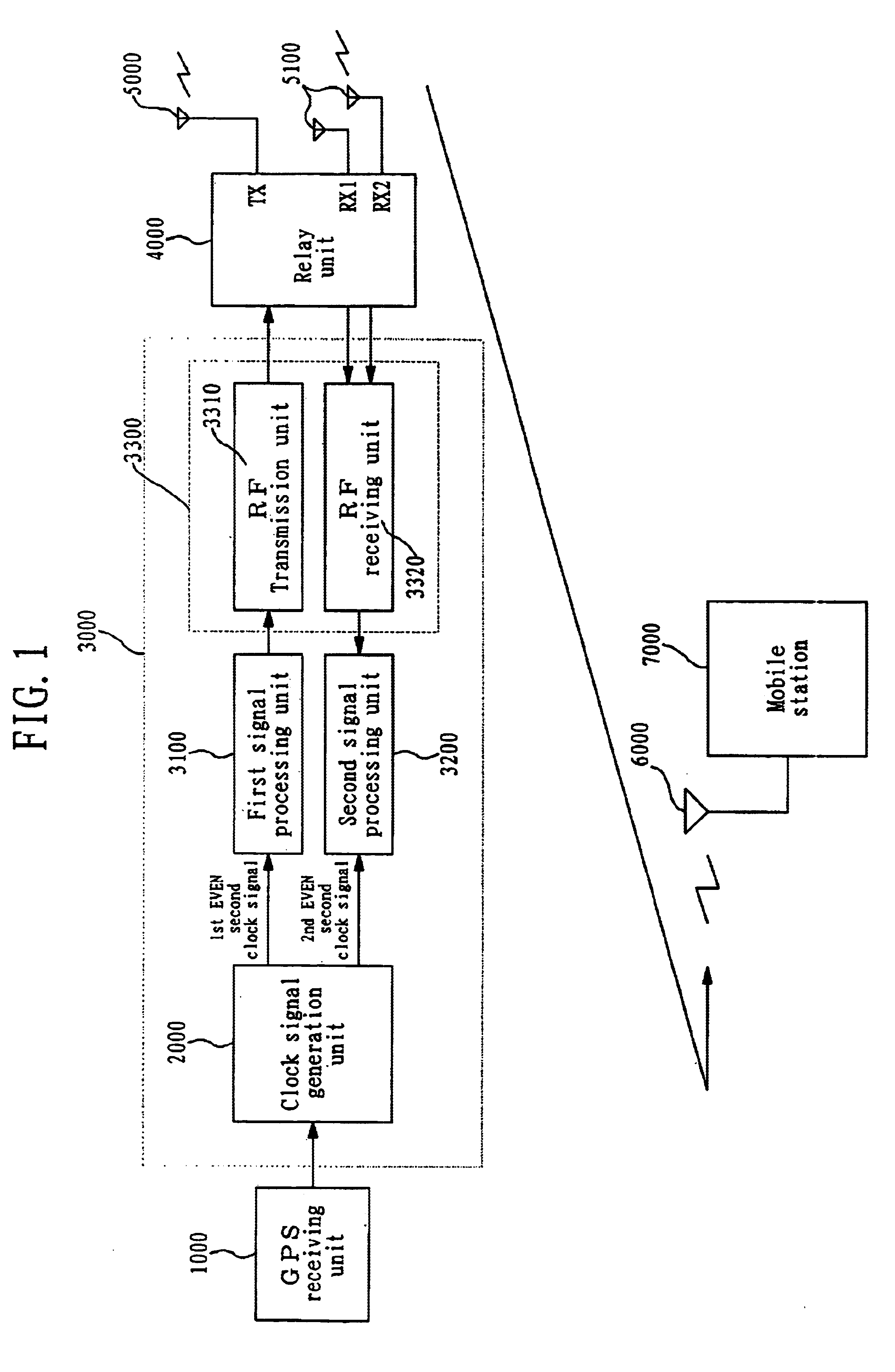
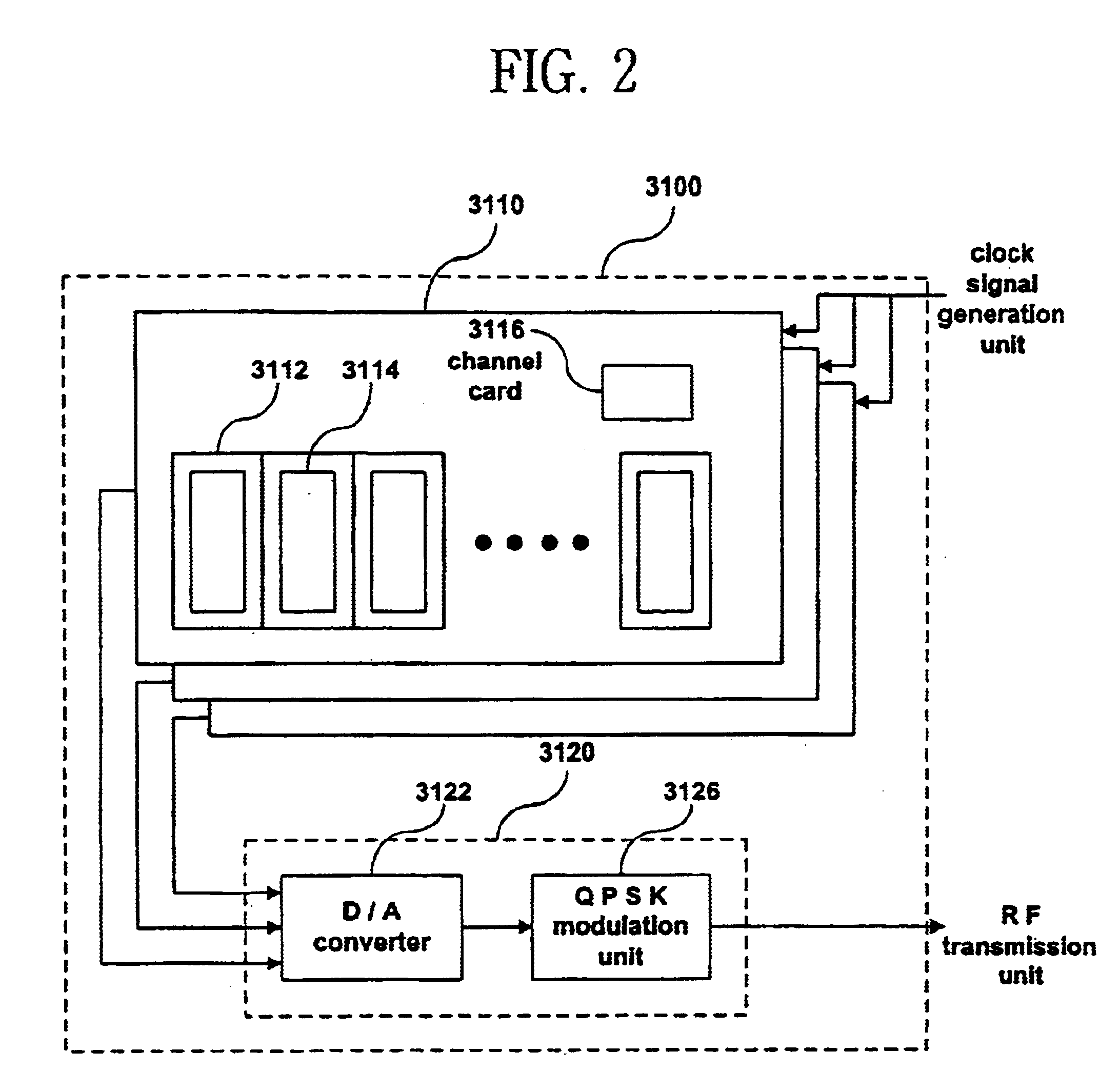
Base station for compensating route delay between bases station and mobile station of CDMA mobile communication system and operation method thereof
InactiveUS6885647B1Decrease of cell communicationReduce communicationTime-division multiplexCode division multiplexPropagation delayCommunications system
A base station for compensating a fixed route delay between a base station and a mobile station of a CDMA mobile communication system and an operation method thereof are disclosed. This base station includes a clock signal generation unit for receiving a 10 MHz, TOD and 1 PPS signal from a GPS receiving unit and generating a 1st even second clock signal in synchronization with the 1 PPS and a 2nd even second clock signal which is obtained by delaying the 1st even second clock signal by a maximum bidirectional propagation delay time between a base station and a relay unit, a first signal processing unit for receiving the 1st even second clock signal from the clock signal generation unit and modulating a forward link channel from the base station to a mobile station in synchronization with the 1st even second clock signal, and a second signal processing unit for receiving the 2nd even second clock signal from the clock signal generation unit and demodulating a backward link channel from the mobile station to the base station in synchronization with the 2nd even second clock signal, for thereby compensating a decrease of a cell communication radius due to a fixed route delay factor on a communication route between a base station and a mobile station.
Owner:USRCOM KOREA
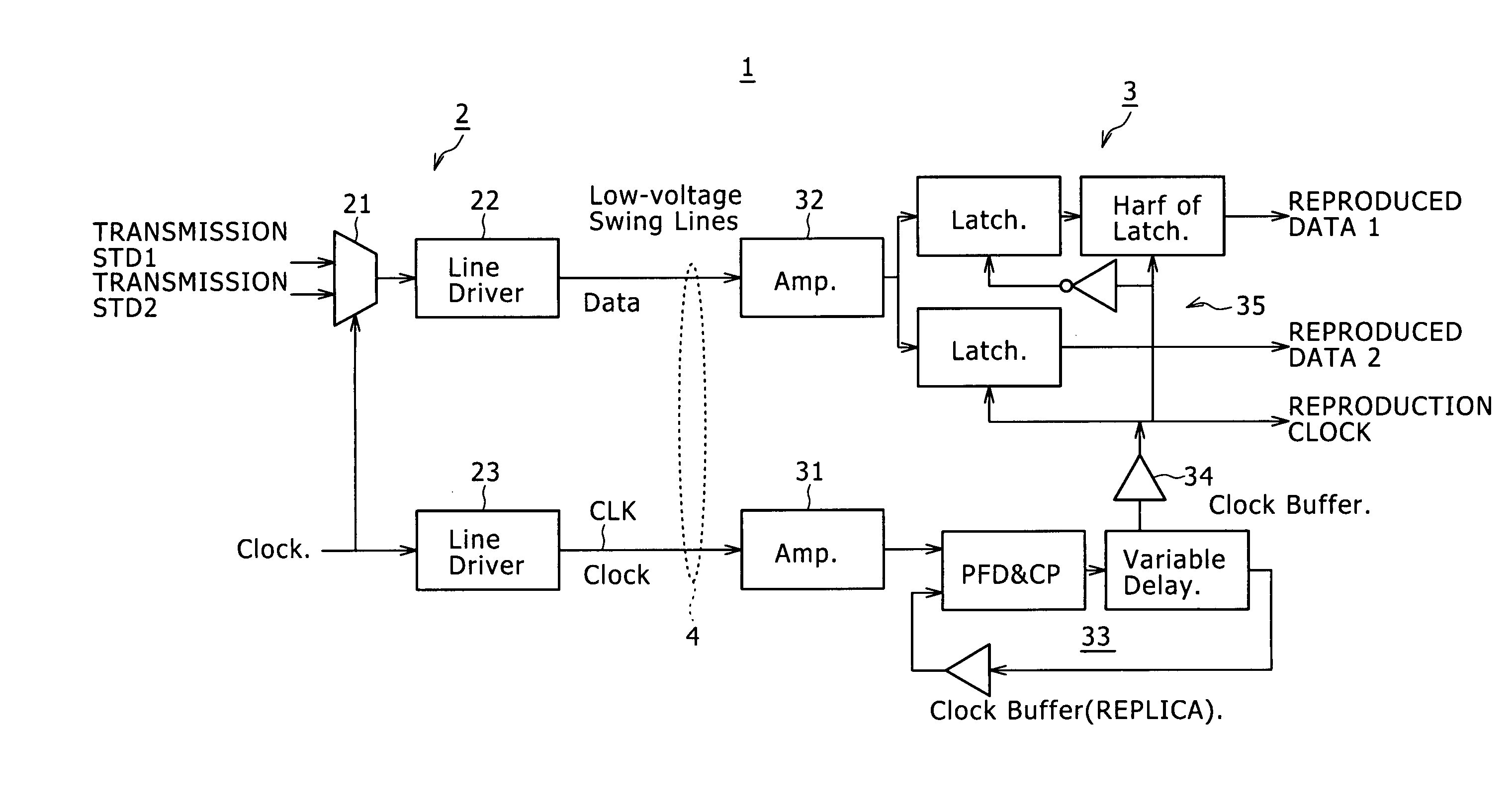
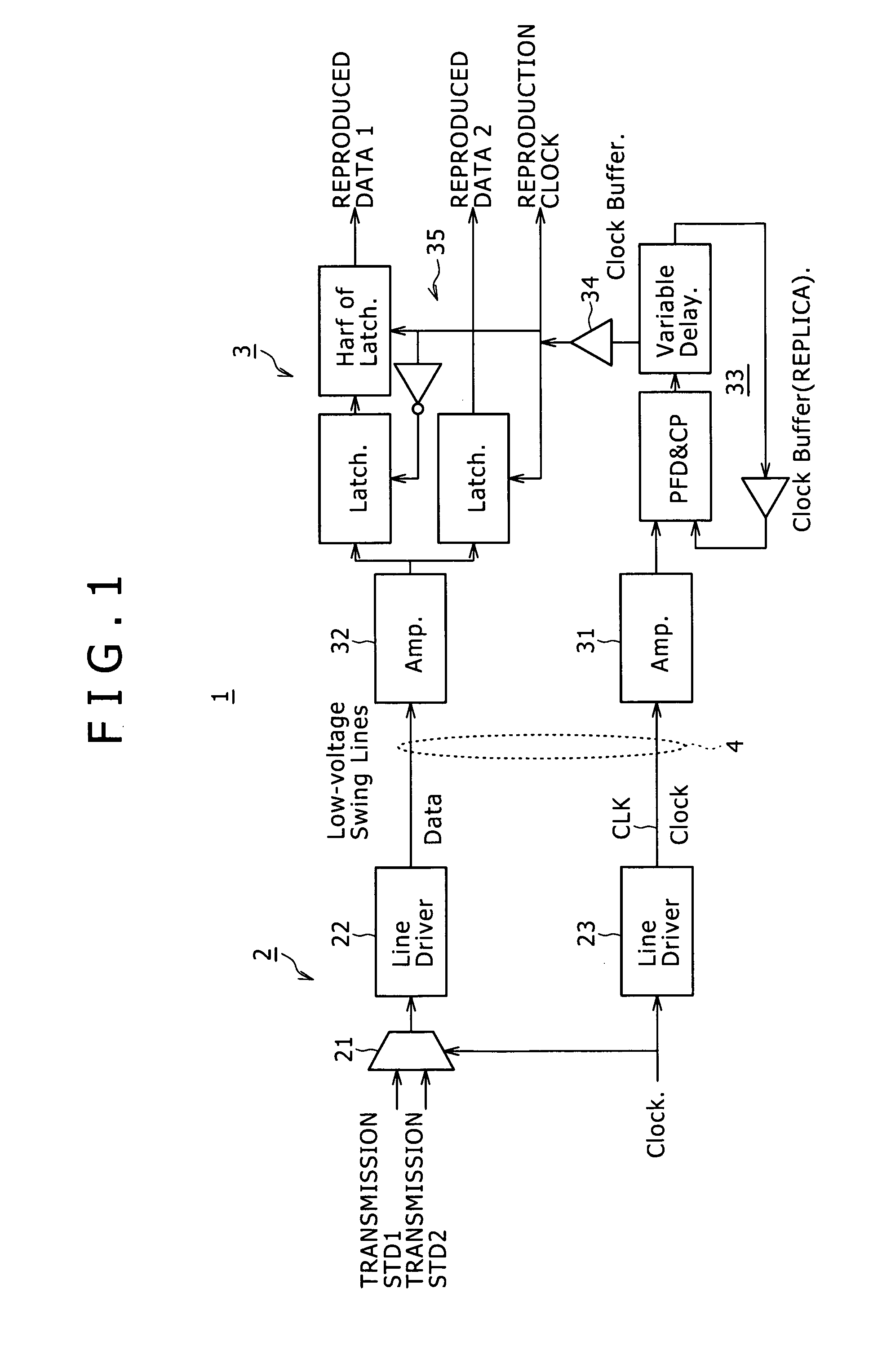
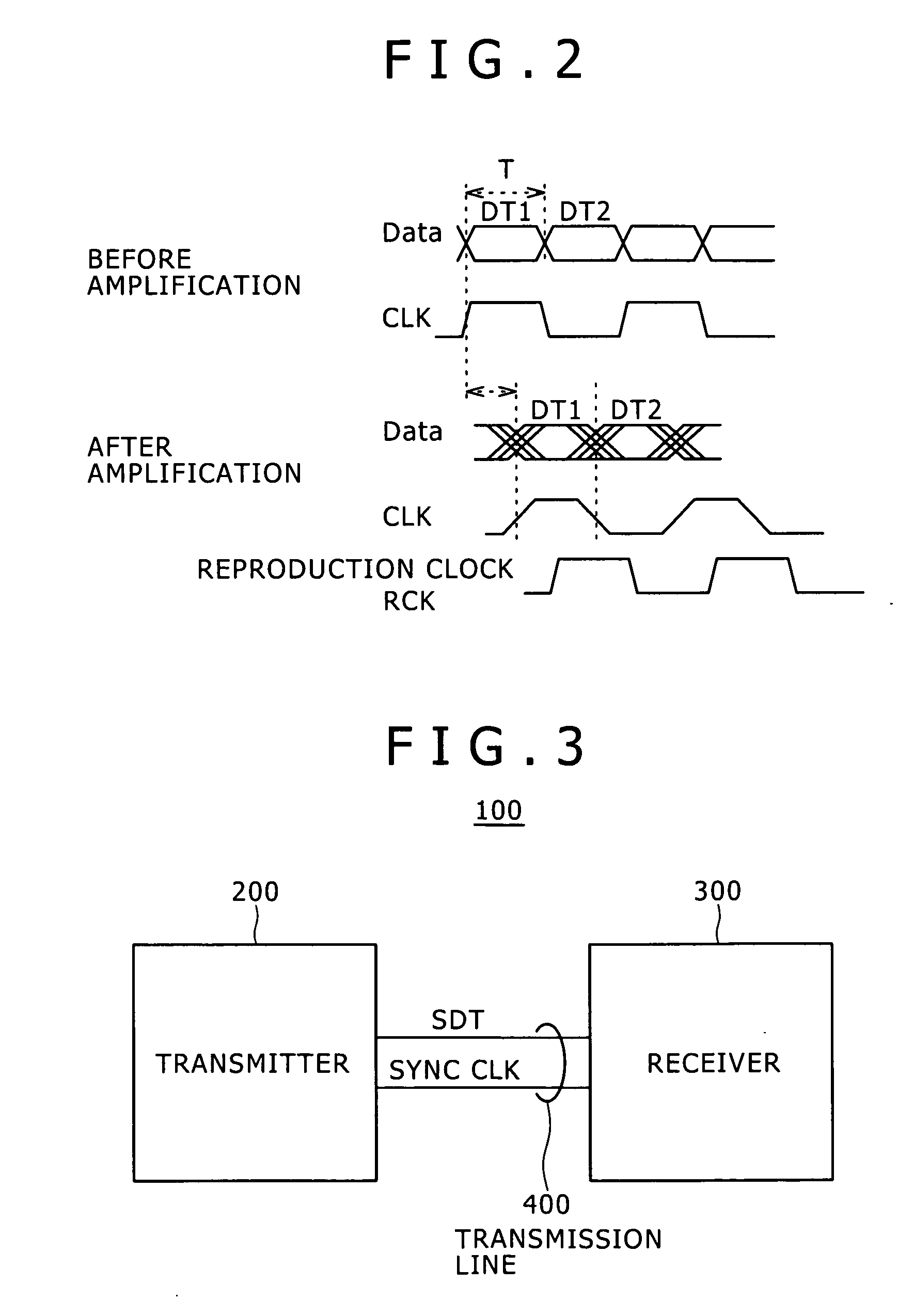
Communication system, receiver and reception method
InactiveUS20090232250A1Compensation delayImprove accuracySynchronisation information channelsError preventionClock recoverySynchronism
A communication system includes: a transmitter adapted to transmit a synchronizing clock and serial data synchronous with the synchronizing clock over a line at low amplitude; and a receiver adapted to receive the serial data and synchronizing clock from the transmitter. The receiver includes an amplifier adapted to amplify the received synchronizing clock of low amplitude to restore the clock to its original amplitude, a latched comparator adapted to latch the received serial data in synchronism with a reproduction clock, and a phase-locked circuit.
Owner:SONY CORP
Transmitting device, receiving device, and transceiving method thereof
ActiveUS20140204962A1Compensate lossCompensation delayTime-division multiplexTransmissionBroadcastingGenerating unit
A transmitting device which transmits a plurality of streams is provided. The transmitting device comprises: a first multimedia data consisting of multimedia contents; a first synchronization information for synchronization of a second multimedia data consisting of multimedia contents; a first transmitting data including a first signaling data for the first multimedia data and a second signaling data for the second multimedia data, a data generating unit generating a second transmitting data including a second synchronization information for synchronization of the second multimedia data and the first multimedia data, a first transmitting unit transmitting the first transmitting data supplied from the data generating unit to a receiving device through a broadcasting network, and a second transmitting unit transmitting the second transmitting data supplied from the data generating unit to the receiving device through an IP network.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
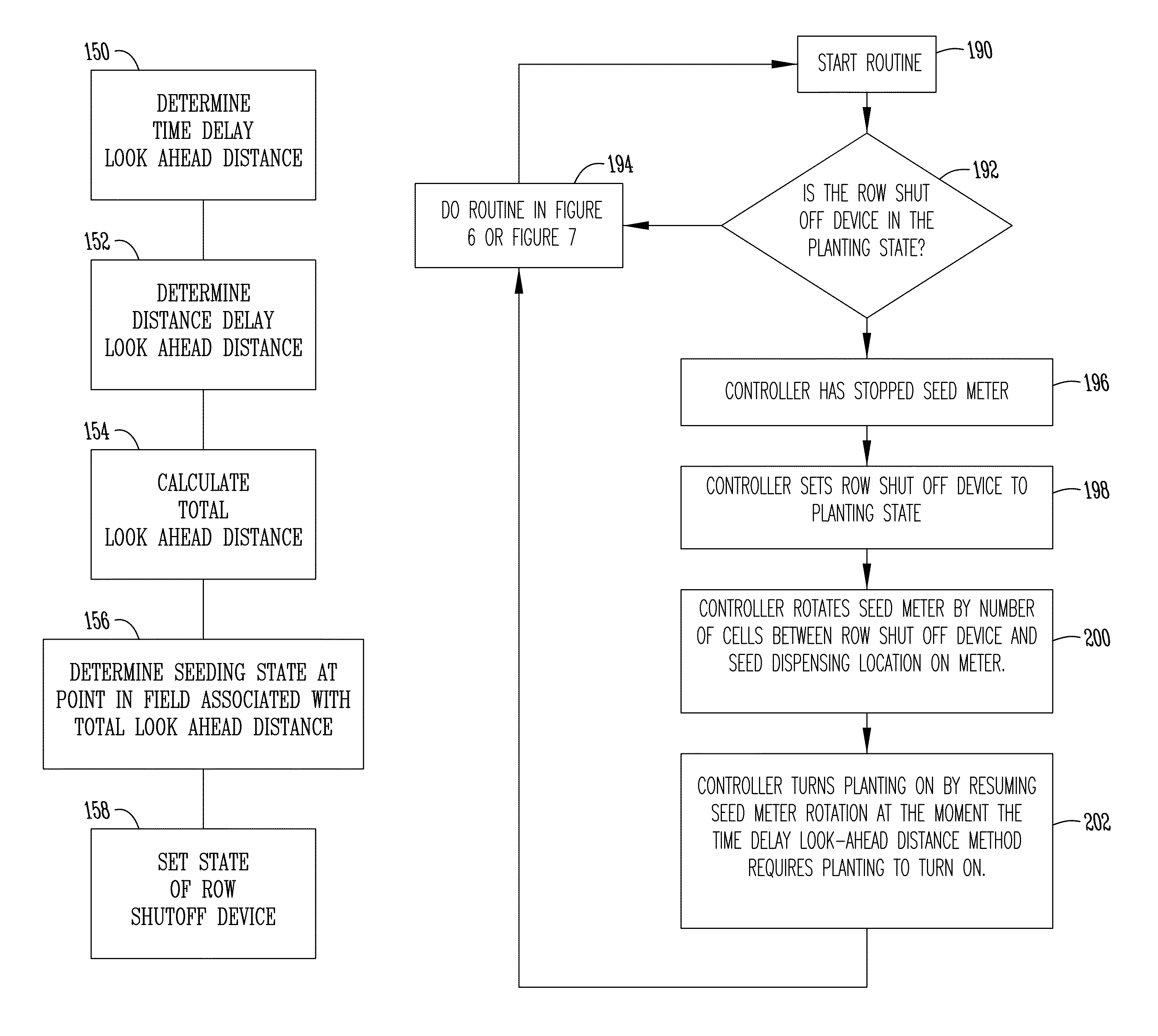
Compensation method for planter shut off delay
ActiveUS8600629B2Compensation delayImprove stateAnalogue computers for trafficFertiliser distributersControl systemIntelligent control
Owner:LEADER TECH
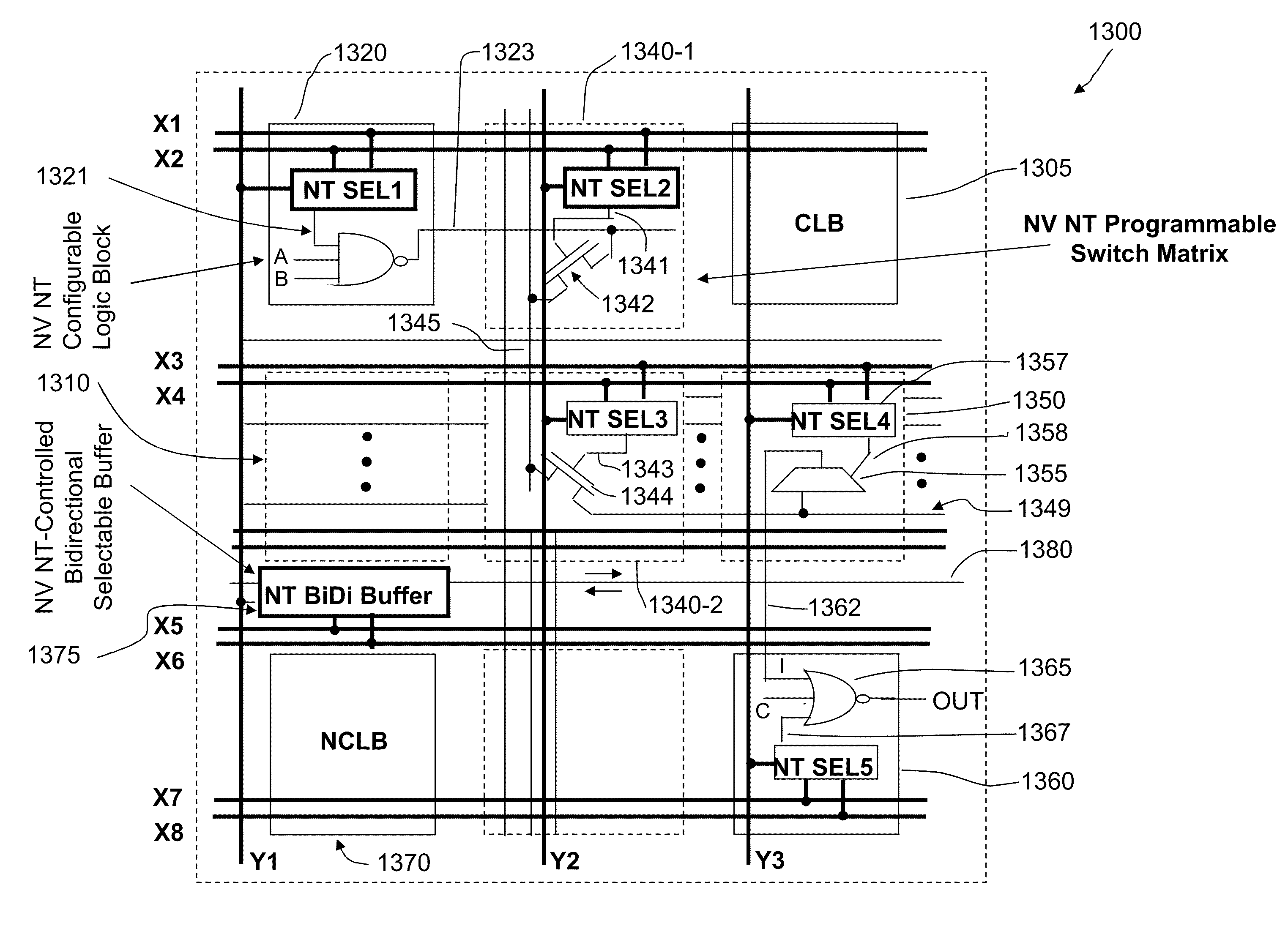
Nonvolatile nanotube programmable logic devices and a nonvolatile nanotube field programmable gate array using same
ActiveUS20100039138A1Compensation delayEasy accessNanoinformaticsDigital storageProgrammable logic deviceCMOS
Field programmable device (FPD) chips with large logic capacity and field programmability that are in-circuit programmable are described. FPDs use small versatile nonvolatile nanotube switches that enable efficient architectures for dense low power and high performance chip implementations and are compatible with low cost CMOS technologies and simple to integrate.
Owner:NANTERO
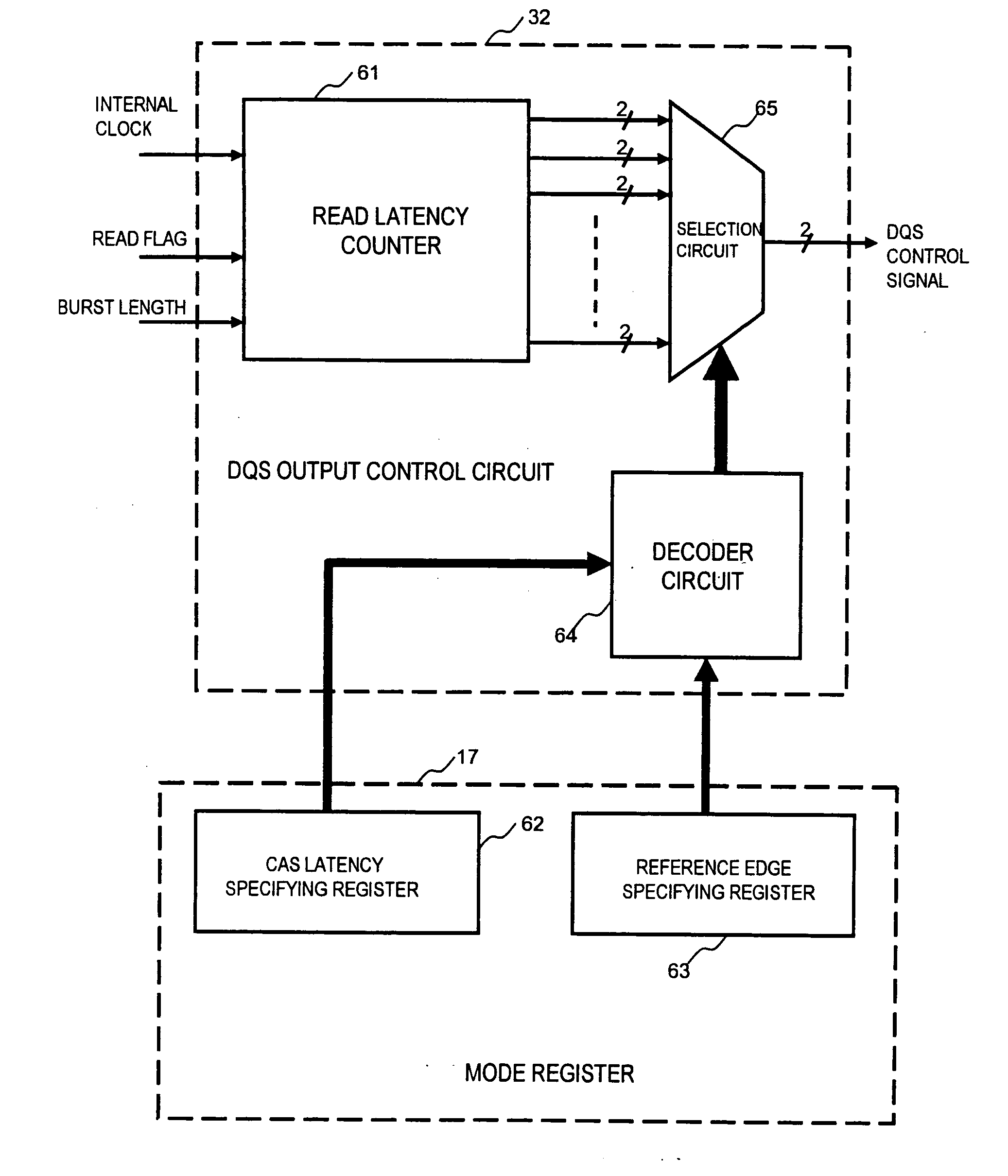
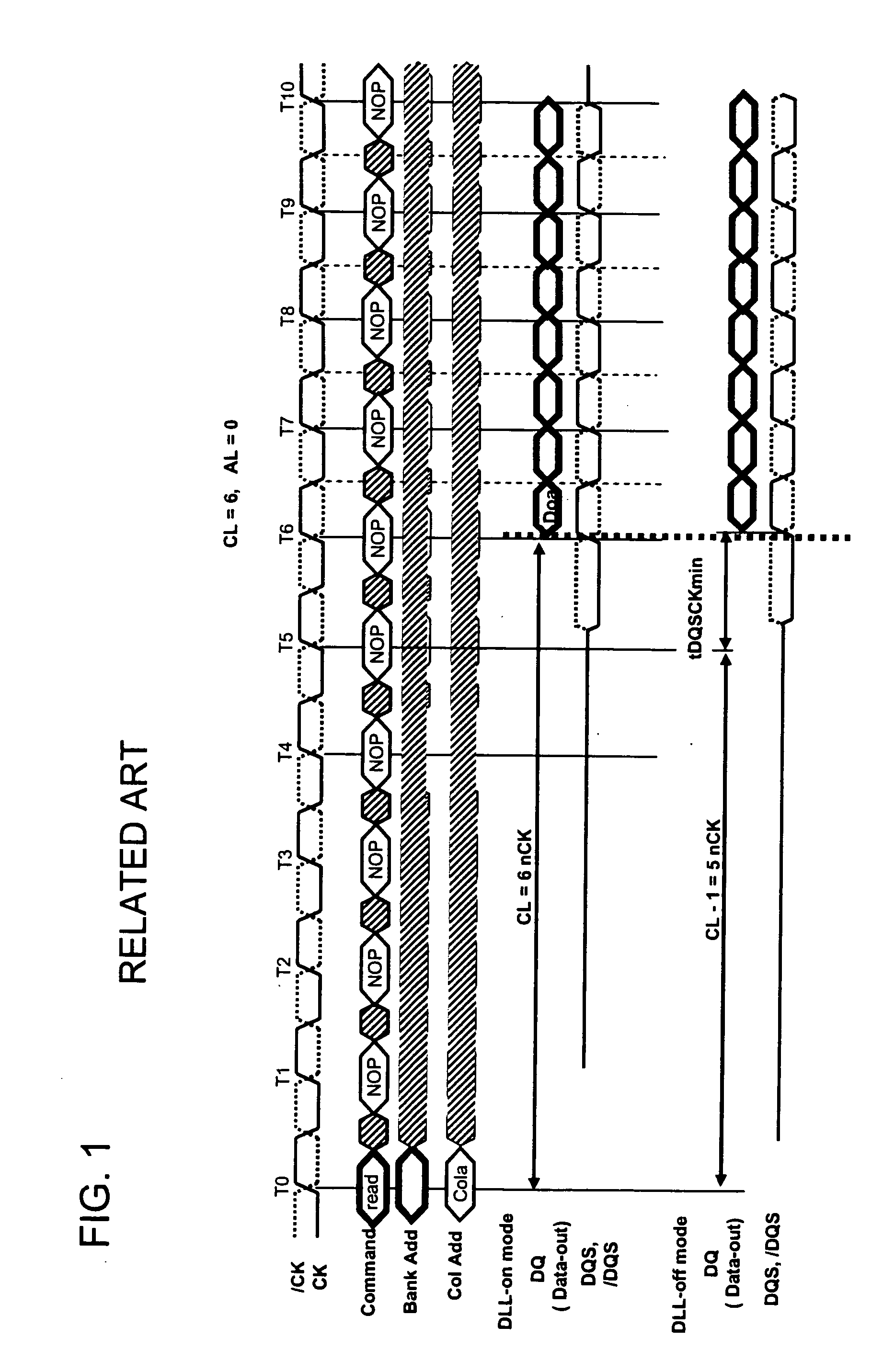
Semiconductor memory device and read wait time adjustment method thereof, memory system, and semiconductor device
InactiveUS20100182856A1Improve latencyShorten the timeDigital storageProcessor registerPhase deviation
A semiconductor memory device operates in synchronization with a system clock, without using a synchronous circuit such as a DLL or a PLL. The semiconductor memory device includes a synchronous circuit for generating output signals phase aligned with the system clock, a synchronous circuit selection circuit that performs switching between a synchronous circuit selection mode and a synchronous circuit non-selection mode, and a reference edge specifying register that specifies an edge of an internal clock which serves as a reference for outputting read data in the synchronous circuit non-selection mode. In the synchronous circuit selection mode, the read data is output by adjusting a phase deviation of the internal clock with respect to the system clock, using the synchronous circuit. In the synchronous circuit non-selection mode, the read data is output in synchronization with the internal clock, without using the synchronous circuit. For a delay of the internal clock with respect to the system clock, the edge of the internal clock used as the reference is adjusted by the reference edge specifying register. Then, even if the synchronous circuit is not used, a large timing deviation does not thereby occur.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
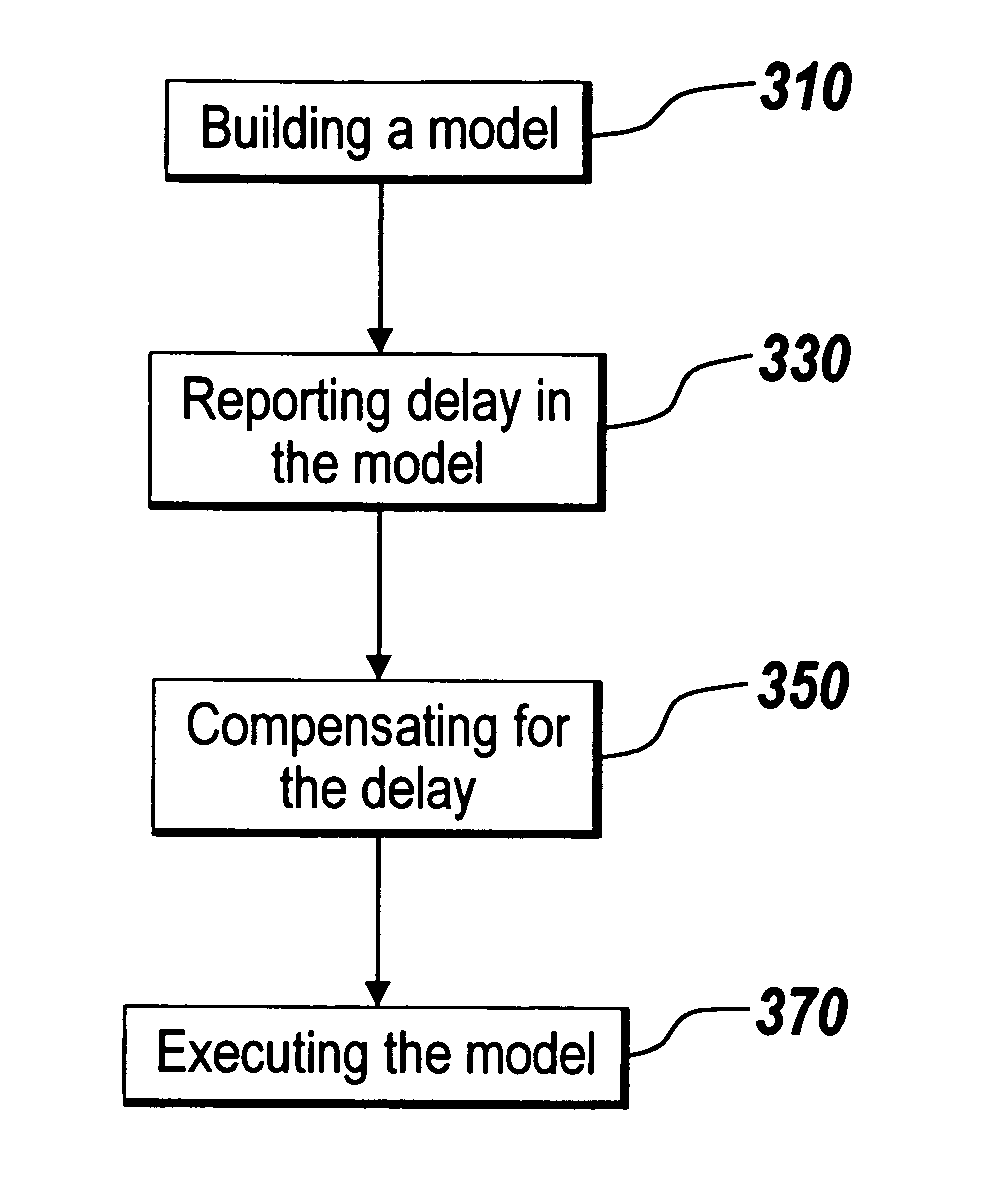
Compensating for delay in modeling environments
InactiveUS7460984B1Compensation delayComputation using non-denominational number representationComputer aided designComputer scienceExecution model
Methods and systems for automatically reporting delay incurred in a model is disclosed. The delay may be incurred in a part or in an entire portion of the model. Delay incurred in each component of the model is determined and reported to users before executing the model. The delay of each component of the model may be determined based on intrinsic information of the component. If the intrinsic information of the component does not provide information on the delay of the component, the component may be simulated to determine the delay of the components. The model may be automatically compensated for the delay. The delay is reported prior to the execution of the model, and compensated for without executing the model.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
Measurement and adjustment of real-time values according to residence time in networking equipment without access to real time
A system and method of synchronizing clocks in a distributed network is disclosed. A simple 1-pulse-per-second timing pulse is routed to time-stamping units in each network device and utilized to measure traffic-dependent synchronization packet residence delays within network elements. Synchronization messages are updated to reflect the measured residence times, thus creating transparent clocks that can readily be synchronized across the network. The simple timing pulse architecture allows the method to be applied readily both to new designs and to retrofit existing hardware.
Owner:SEMTECH CORP
Efficient pulse laser light generation and devices using the same
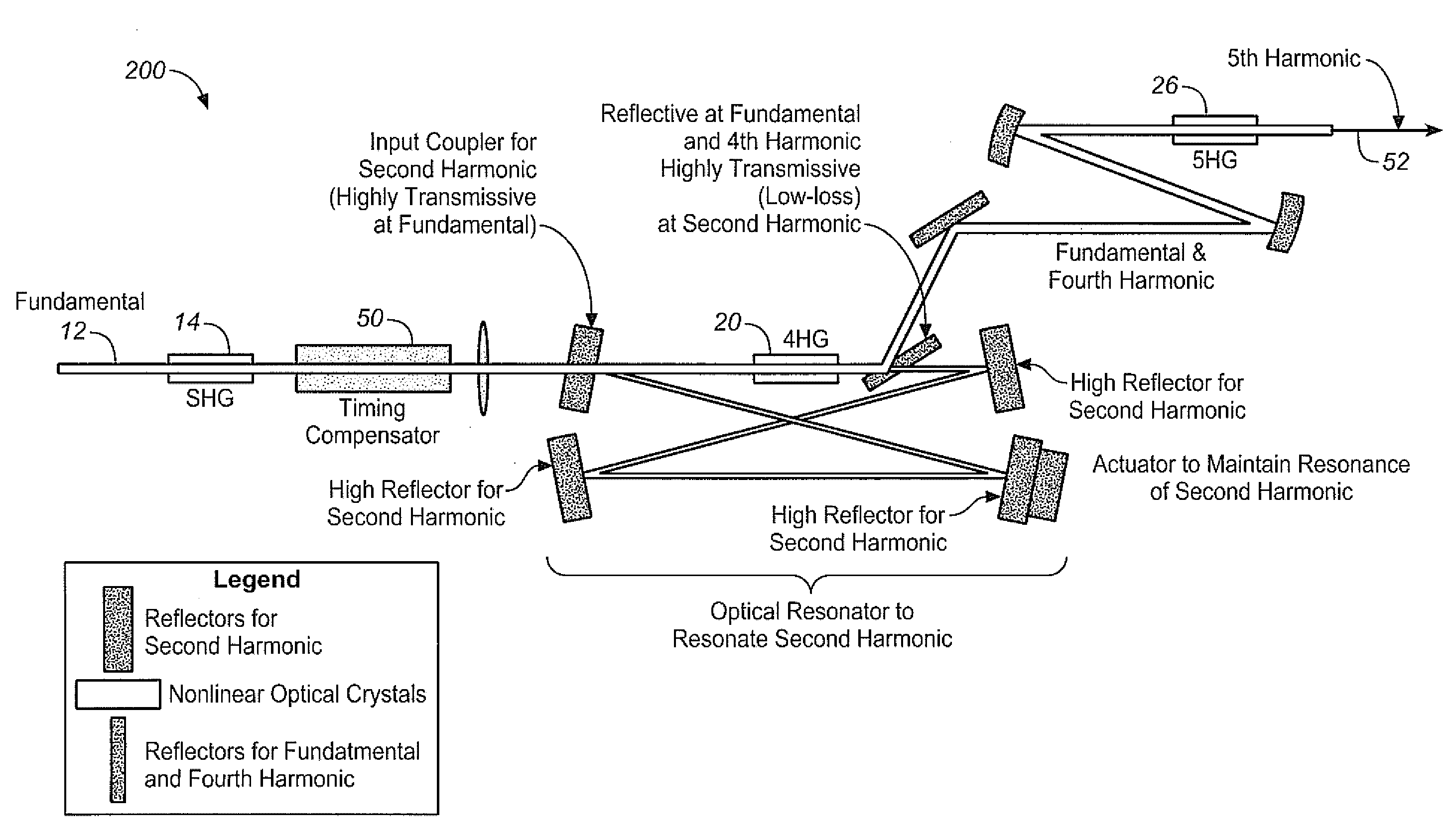
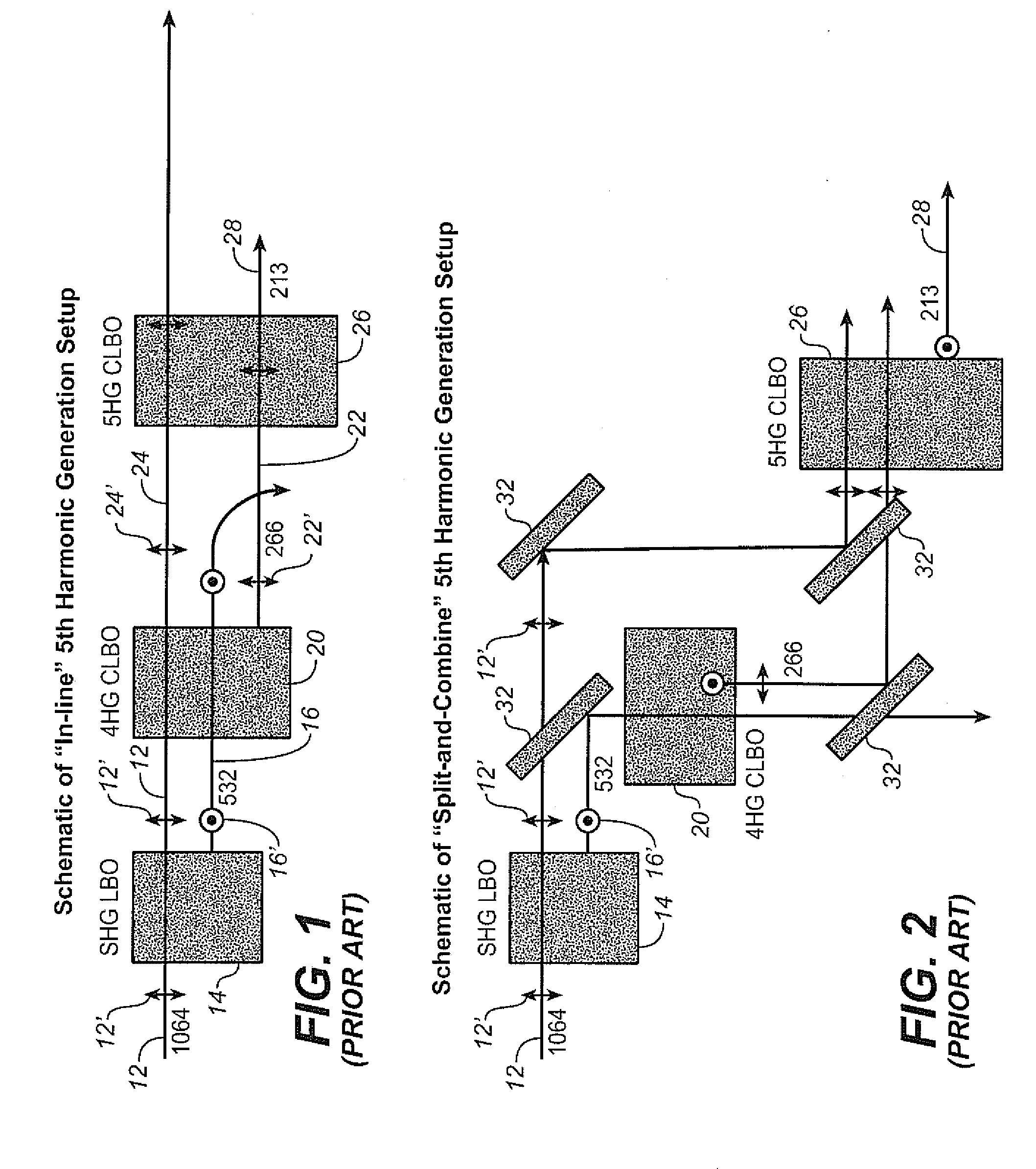
A time delay is introduced in the optical path of the light pulse at fundamental wavelength relative to that for the fourth harmonic light pulse in a set up for generating the 5th harmonic, to compensate for at least a portion of the time delay of the fourth harmonic relative to the fundamental wavelength caused by 4HG generation. In one embodiment, this is achieved by introducing a time delay of the fundamental relative to the second harmonic wavelength, such as preferably by means of a timing compensator in the optical paths of the second harmonic and the fundamental wavelength. Preferably, any further delay of the fourth harmonic relative to the fundamental wavelength caused by other optical components can also be compensated for in this manner.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA +1
Motion control servo loop apparatus
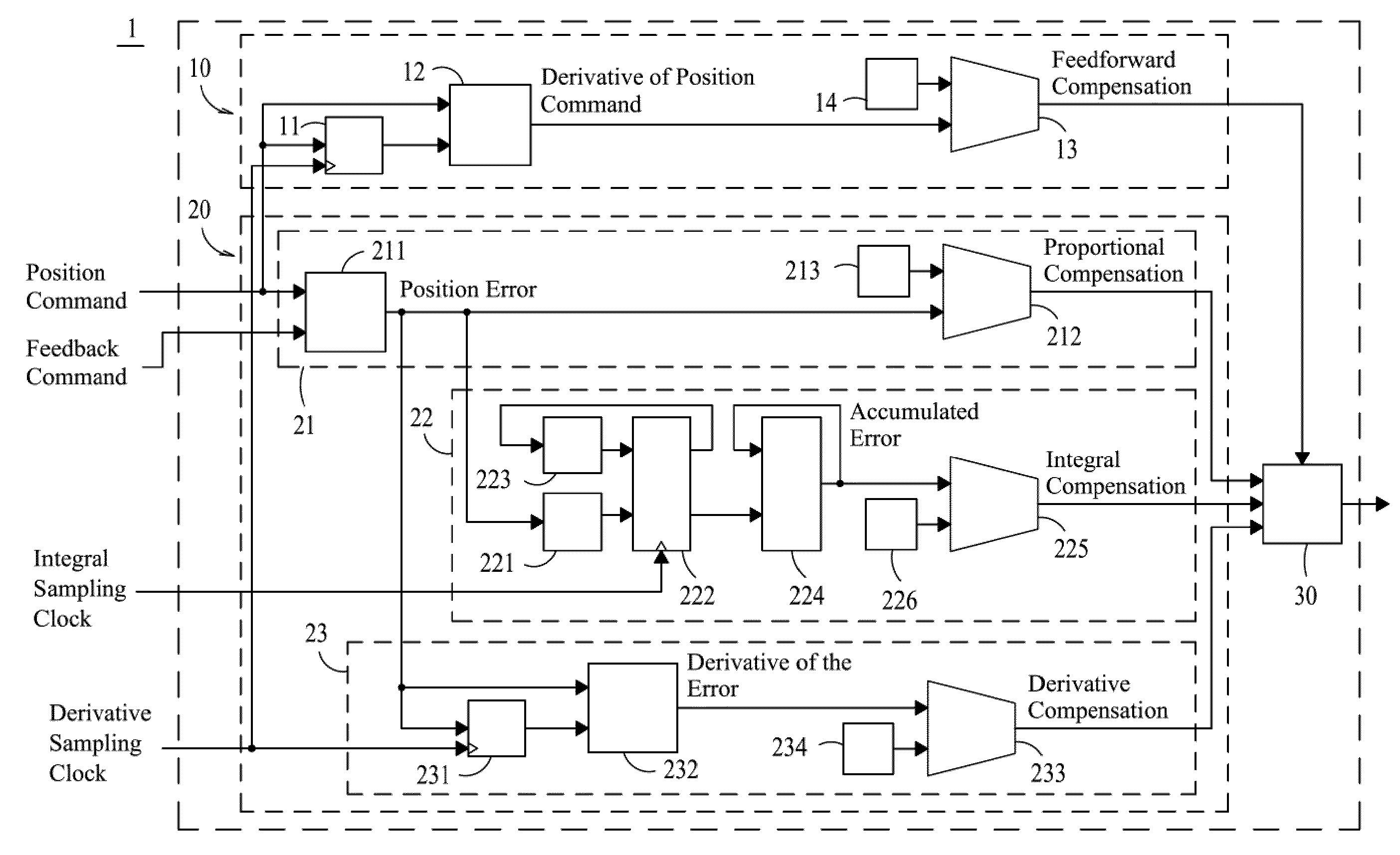
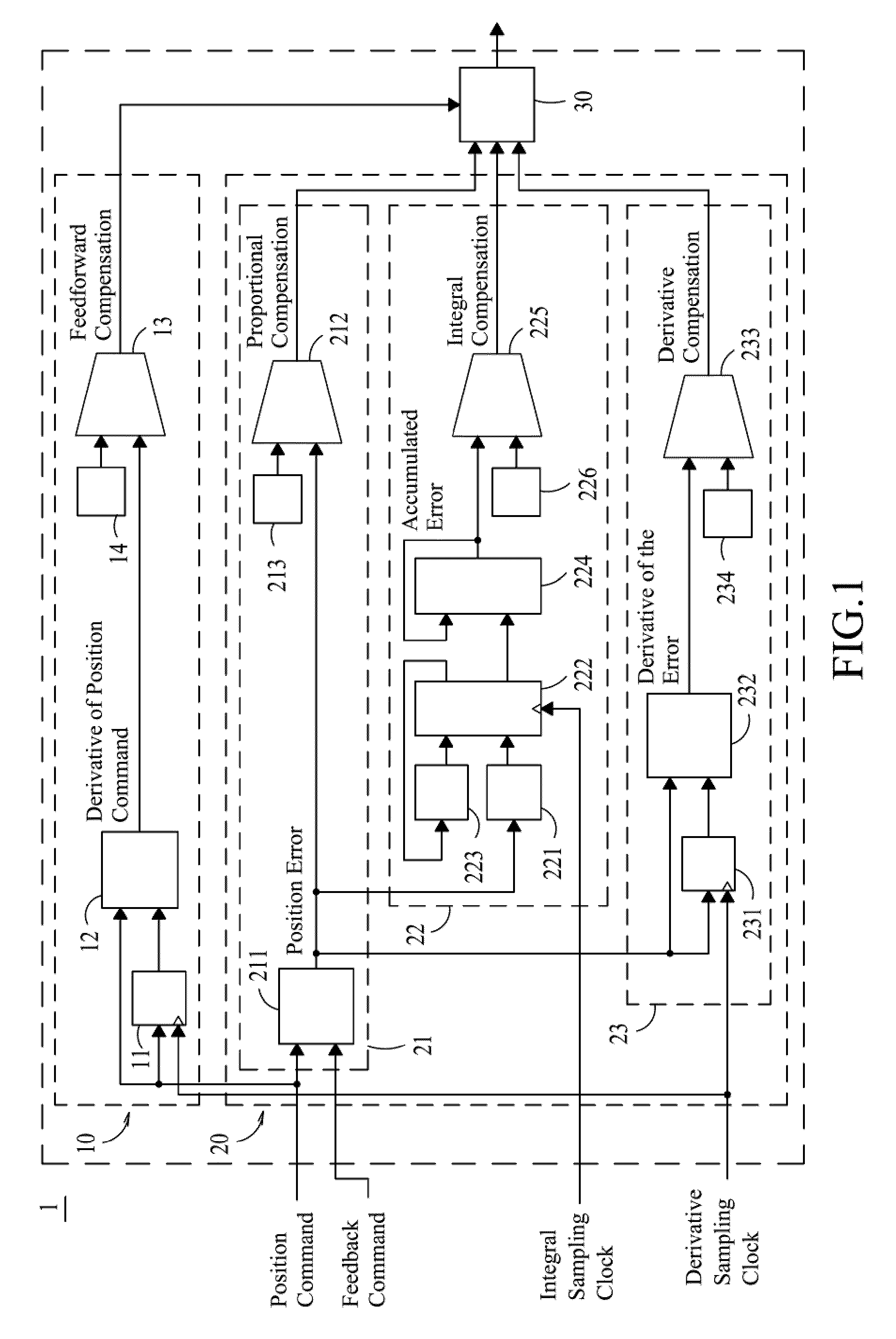
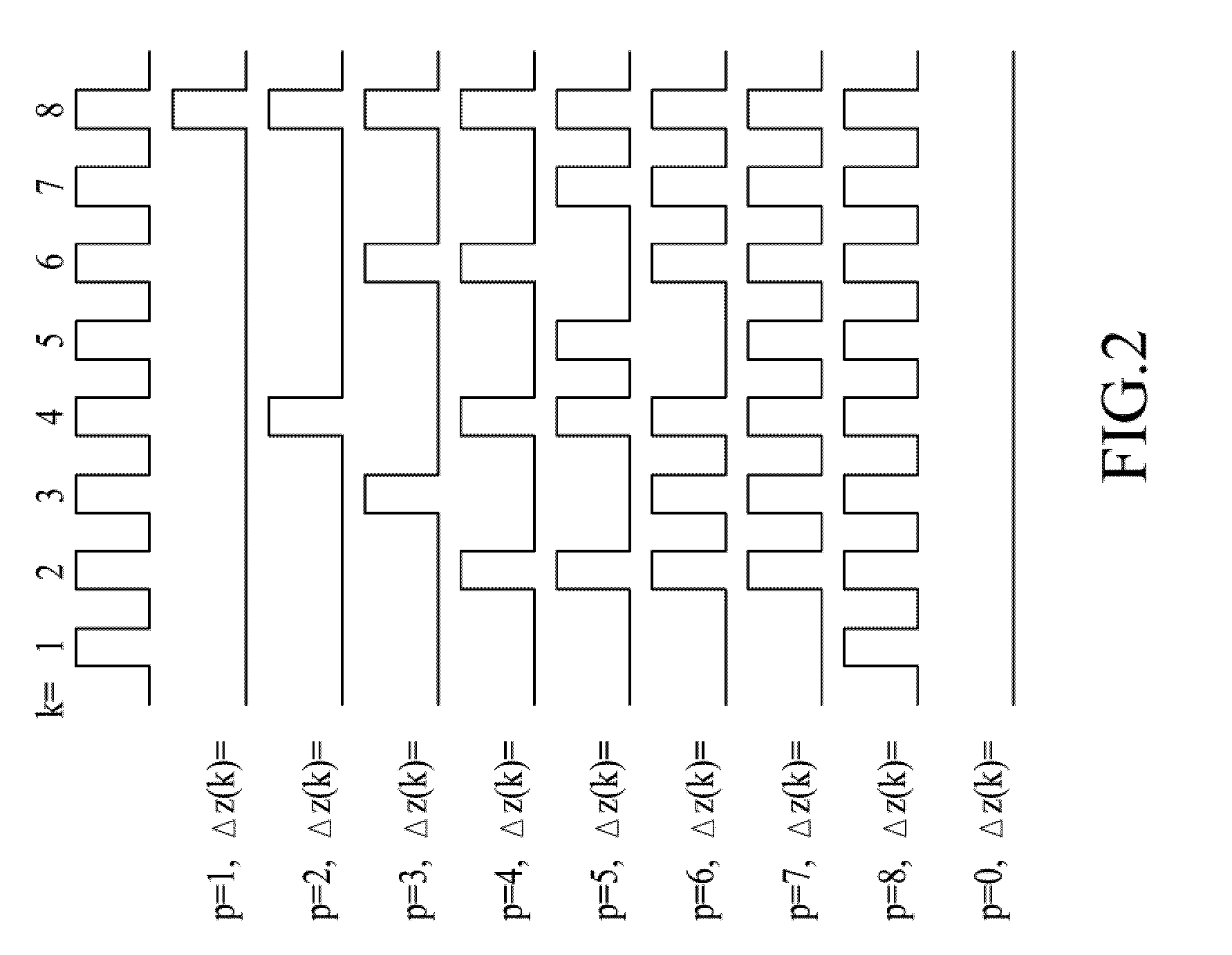
ActiveUS20100152868A1Improve response speedEliminate errorsProgramme controlDynamo-electric converter controlProportional controlDigital differential analyzer (graphics algorithm)
A motion control servo loop apparatus, comprising: a feed-forward control module, and a proportional-integral-derivative (PID) control loop and a compensation adder. The feed-forward control module is capable of generating a feed-forward compensation. The PID control loop further comprises: a proportional control module, an integral control module and a derivative control module. The proportional control module is capable of generating a proportional compensation. The derivative control module is capable of generating a derivative compensation. The integral control module uses a digital differential analyzer (DDA) algorithm to perform integration for accumulated errors with respect to each sampling clock at each DDA pulse and thus output an accumulated error, which is then processed to generate an integral compensation. Thereafter, the compensation adder receives the feed-forward compensation, the proportional compensation, the integral compensation and the derivative compensation to calculate a position error compensation for a motor driver.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
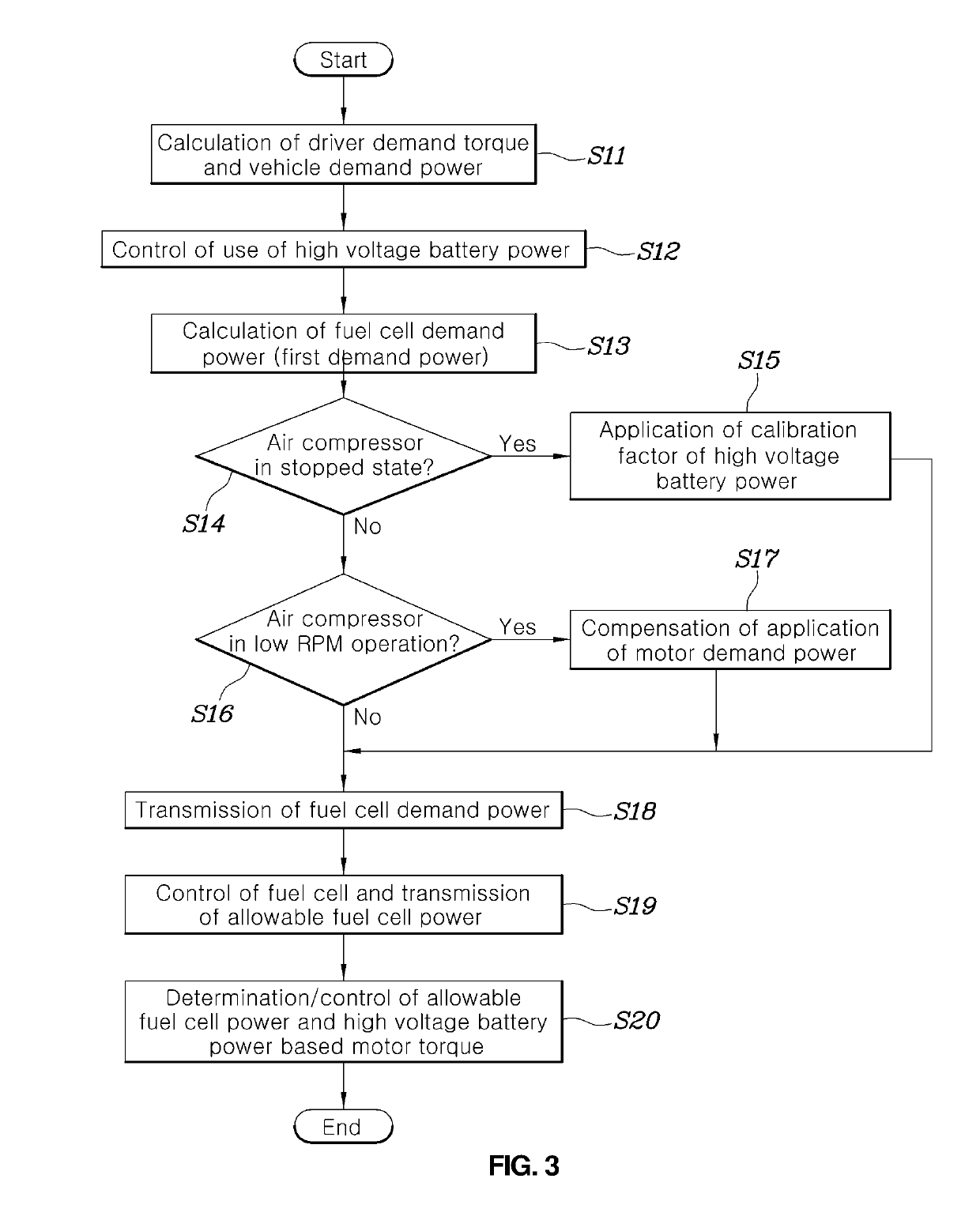
Apparatus and method for power demand distribution in fuel cell vehicle
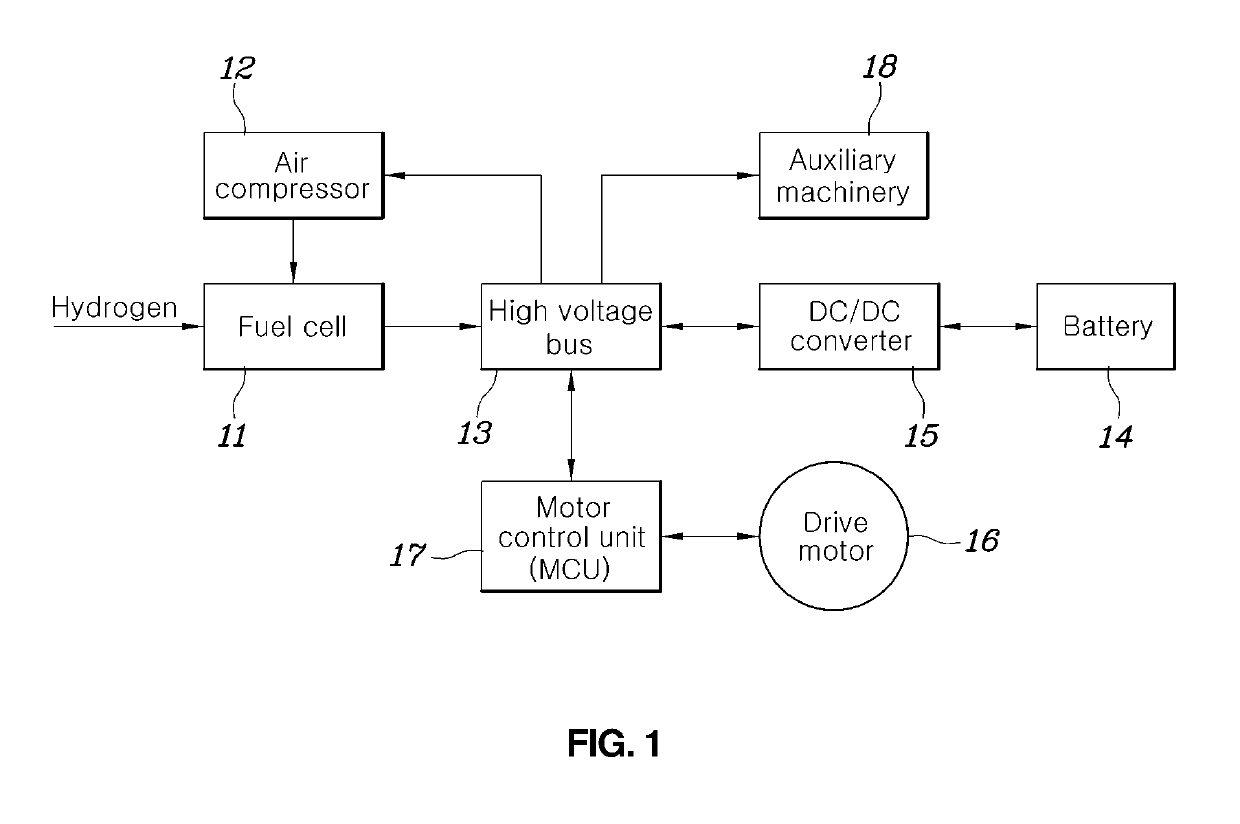
ActiveUS20190160963A1Efficient supplyReduced dynamic performanceHybrid vehiclesReactant parameters controlFuel cellsDrive motor
An apparatus for power demand distribution in a fuel cell vehicle includes: a battery management system calculating an allowable battery power that a battery can supply; a power demand distribution controller configured to derive a vehicle demand power including a drive motor demand power required by the drive motor, and determine a value corresponding to a vehicle demand power minus the allowable battery power being scaled down or the drive motor demand power, as a fuel cell demand output; and a fuel cell controller configured to drive the air compressor feeding the air to the fuel cell to enable a fuel cell to generate the fuel cell demand output calculated by the power demand distribution controller.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Apparatus for multiple media digital communication
InactiveUS7050425B2Increase and decrease rateImprove continuitySpecial service provision for substationPulse modulation television signal transmissionComputer hardwareMedia type
Apparatus for media communication in a communication system. In one embodiment, the apparatus comprises: a processor; and a routine running on the processor for negotiating with the remote processing machine a selection of at least one media type using a media type selection protocol that supports the description of a plurality of media types including audio, video and data, and to configure, according to the selection, the apparatus to process media data packets received from and to be transmitted to the remote processing machine over a packet switched network.
Owner:RPX CORP
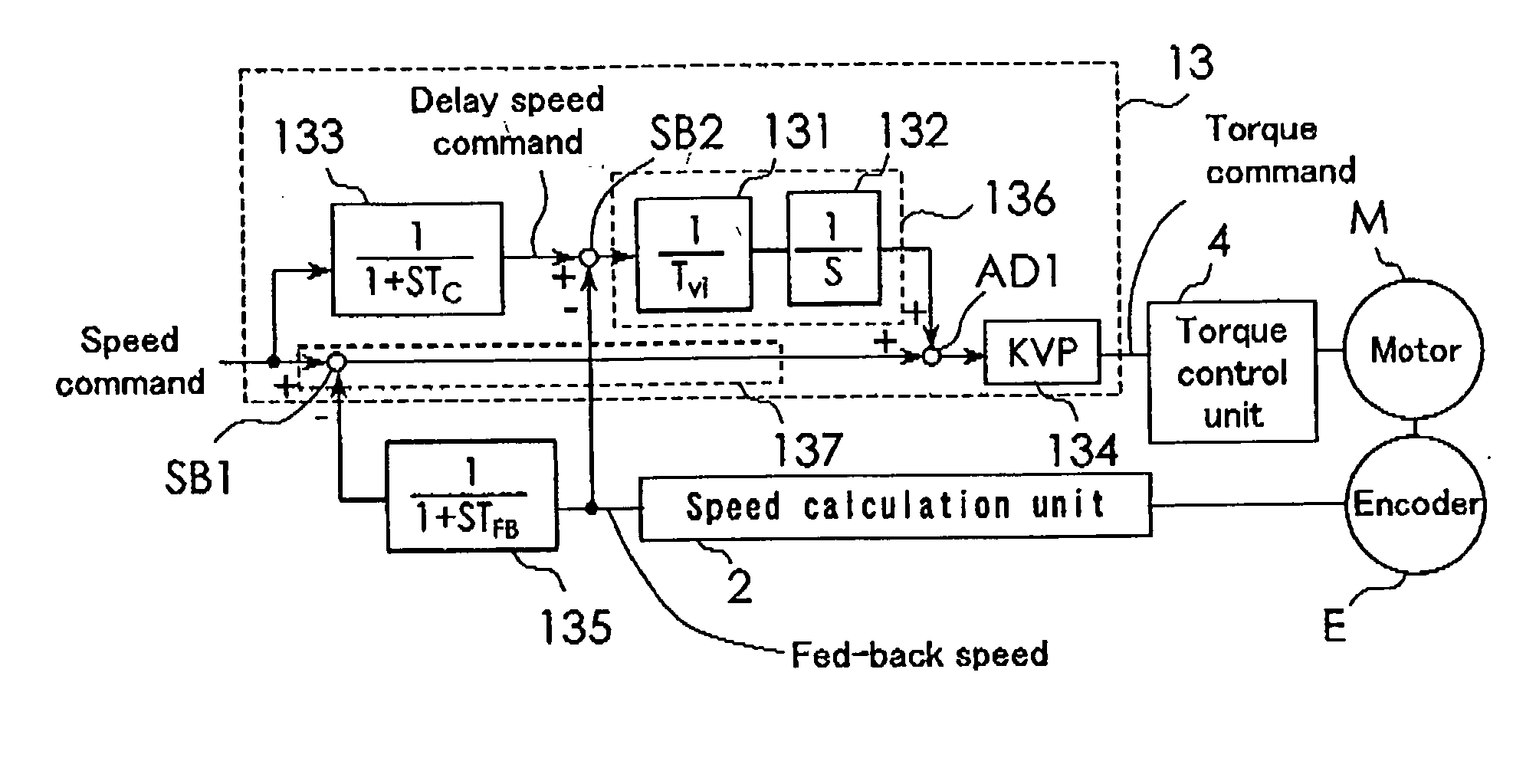
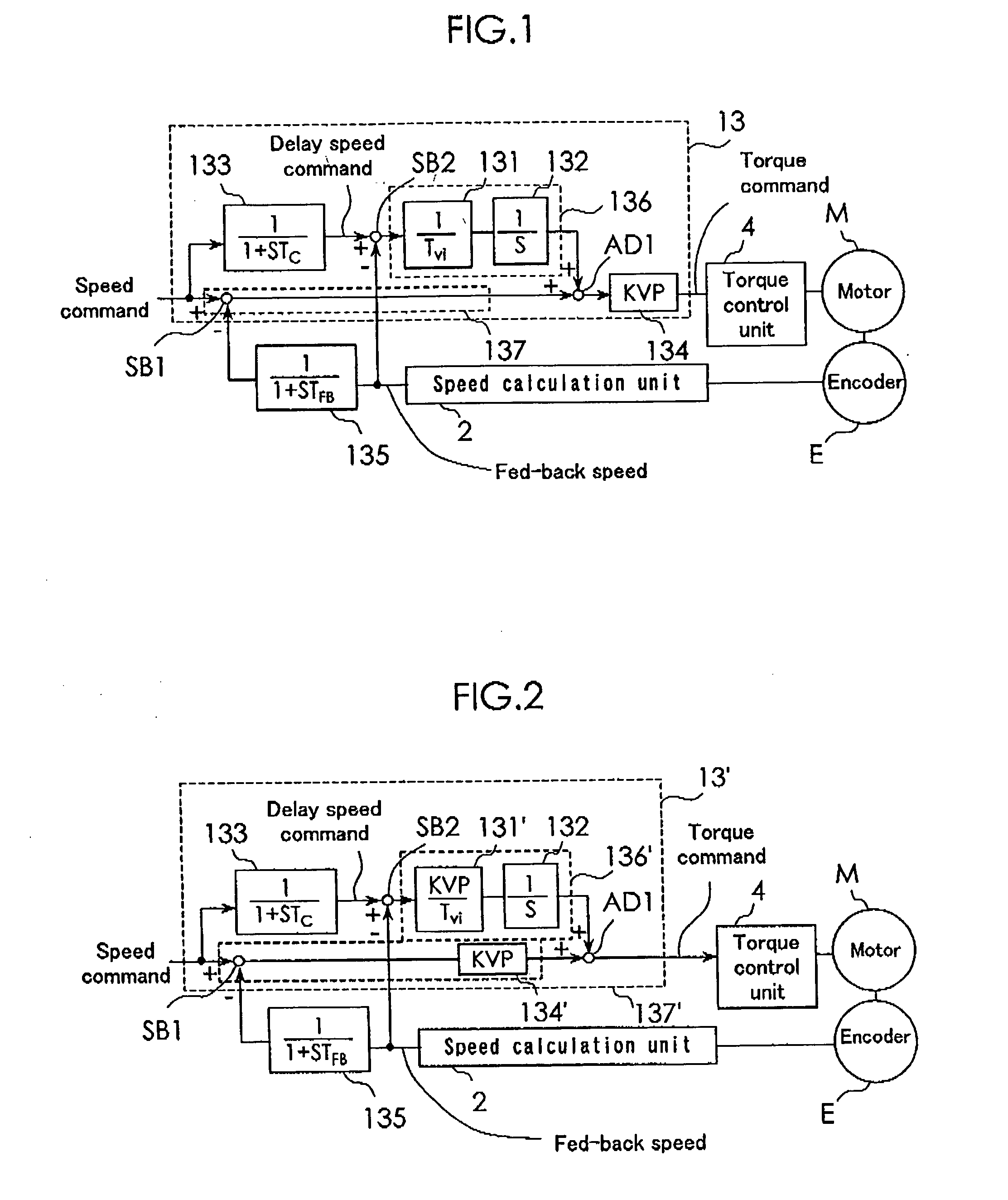
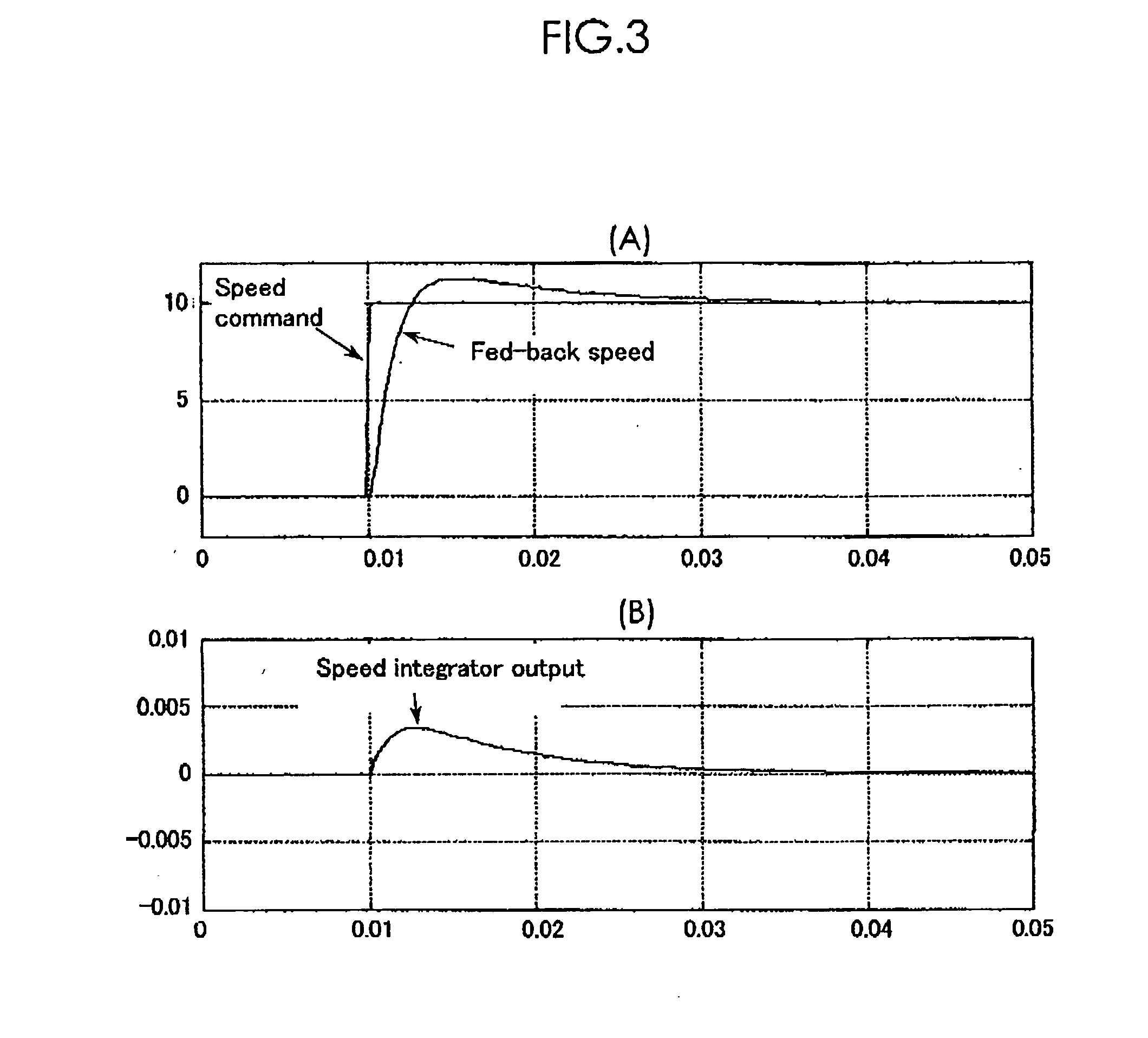
Motor control device
ActiveUS20060208683A1Eliminate rippleShorten speedSingle-phase induction motor startersElectronic commutation motor controlIntegratorSpeed control system
A speed controller includes a speed integration compensation low-pass filter, an integral control system, a proportional control system, and a multiplication device 134. The speed integration compensation low-pass filter has a transfer function corresponding to a delay of a speed control system. The integral control system 136 is multiplied by an integral gain by a multiplier and integrated by a speed integrator before being supplied to an adder. The adder adds an output of the proportional control system and an output of the integral control system and outputs the result to the multiplier, which in turn multiplies the output of the adder by a proportional gain and outputs the result as a torque command. The multiplication means multiplies the output of the integral control system and the output of the proportion control system by a speed proportional gain and outputting the value of the torque command.
Owner:SANYO DENKI CO LTD
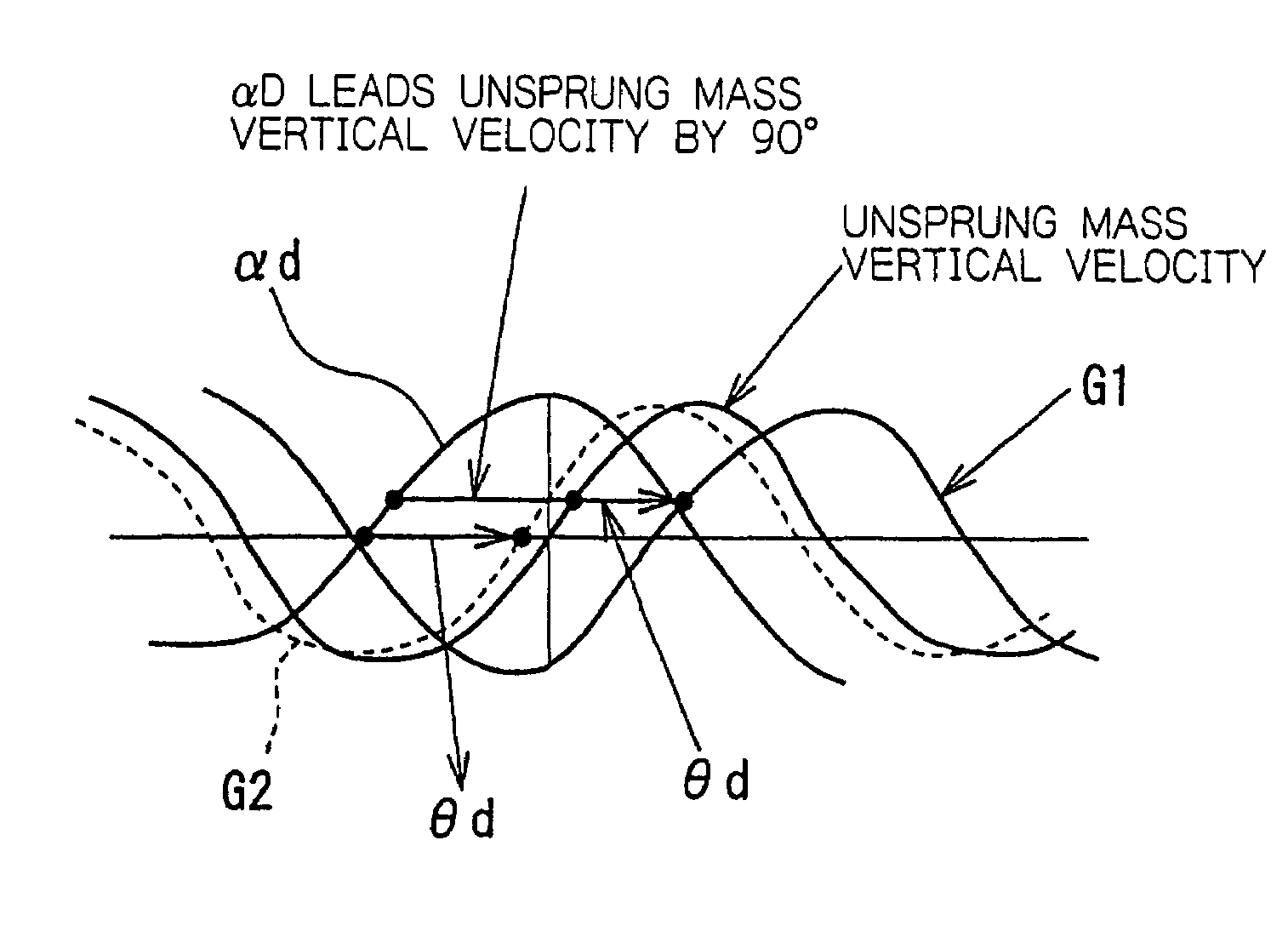
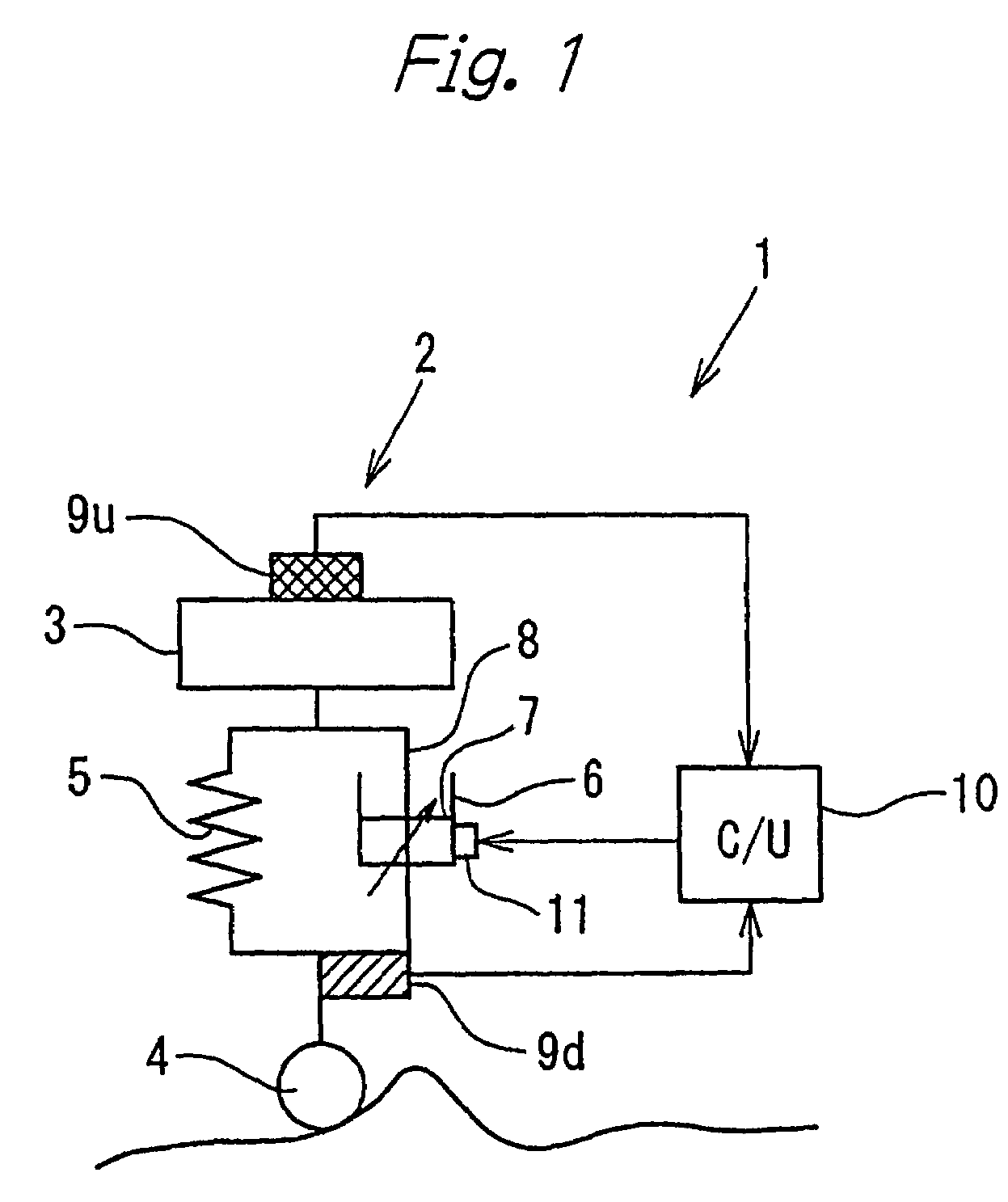
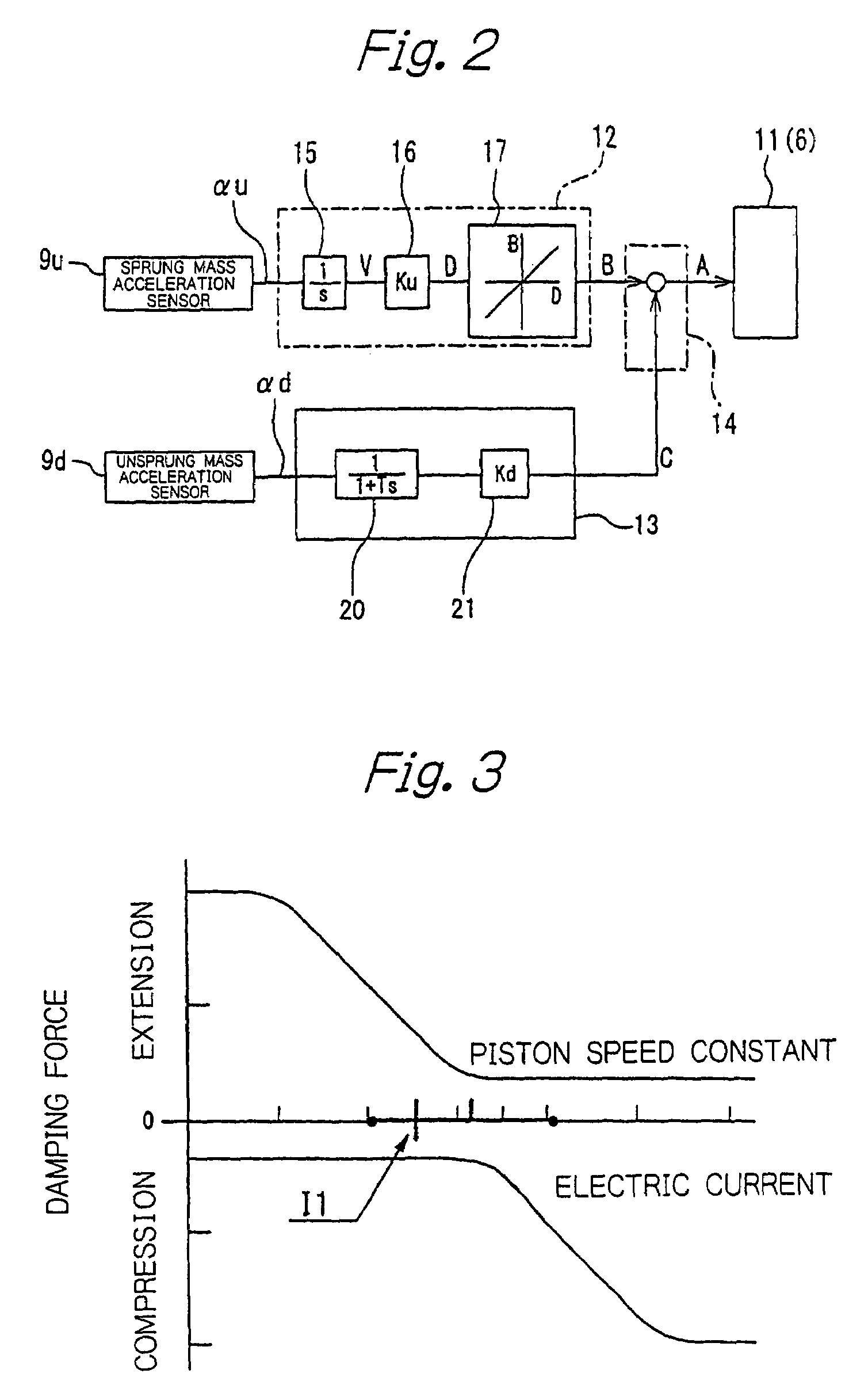
Suspension control apparatus
InactiveUS7333882B2Improve efficiencyCompensation delayPortable framesDigital data processing detailsControl systemControl signal
In a suspension control system a sky-hook command signal (B) obtained from velocity data obtained by integrating a sprung mass acceleration (αu) from a sprung mass acceleration sensor (9u) and an unsprung mass vibration damping command signal (C) obtained on the basis of an unsprung mass acceleration (αd) detected by an unsprung mass acceleration sensor (9d) are added together to obtain a control signal (A) for a damping characteristic inverting type shock absorber (6). The control signal (A) reflects the unsprung mass acceleration (αd) that leads in phase by 90° the piston speed. Accordingly, it is possible to compensate for a response delay due to an actuator (11), etc.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
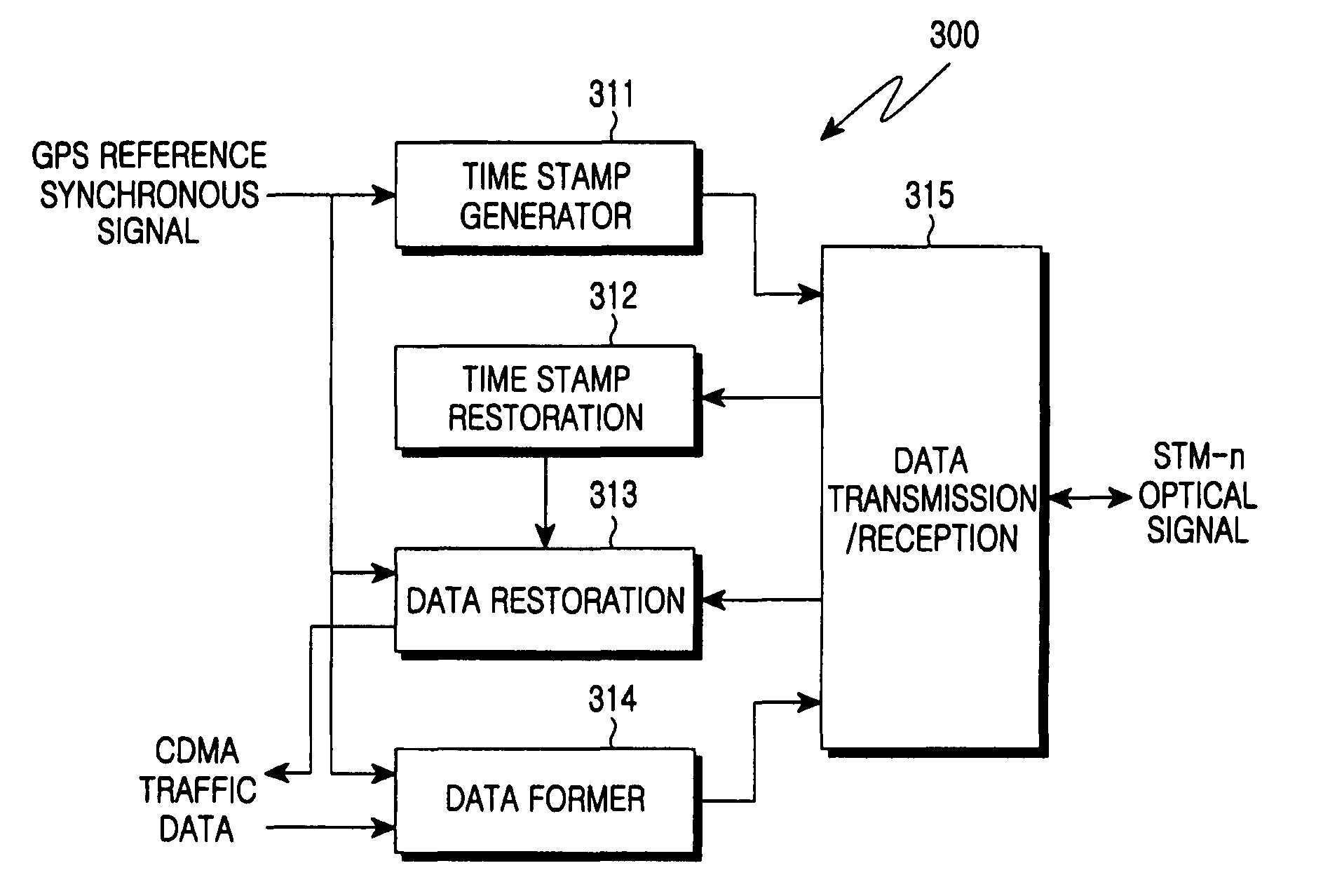
Apparatus for controlling data transmission/reception between main system and remote system of BTS in mobile communication system
ActiveUS7359346B2Overcome problemsGuaranteed reliabilitySynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexData transmissionOptical path
An apparatus for controlling data transmission / reception between a main system and a remote system of a base transceiver station (BTS) in a mobile communication system to improve reliability of data without the limitation of signal transmission distance between a main system and a remote system. The apparatus has: a time stamp generator for generating a time stamp signal indicating start of a Synchronous Transfer Mode STM) frame using a reference synchronous signal; a data former for receiving and being synchronized with the reference synchronous signal, and converting received traffic data into STM frame data; and a data transmitter for receiving and mapping the output data of the time stamp generator with a data communication channel (DCC), receiving output data of the data former, mapping the output data of the data former with a frame transmission channel, converting data mapped with the channels into an optical signal for transmission on an optical path.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Low-noise, low-distortion digital PWM amplifier
InactiveUS7728658B2Compensation delayNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceLow noiseLow distortion
Systems and methods for performance improvements in digital switching amplifiers using low-pass filtering to reduce noise and distortion. In one embodiment, a digital pulse width modulation (PWM) amplifier includes a signal processing plant configured to receive and process an input audio signal. The amplifier also includes a low-pass filter configured to filter audio signals output by the plant. The filtered output of the plant is added to the input audio signal as feedback. The plant may consist of a modulator and power switch, a noise shaper, or any other type of plant. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) may be provided to convert the output audio signal to a digital signal. Filtering may be implemented before or after the ADC, and a decimator may be placed after the ADC if it is an oversampling ADC.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
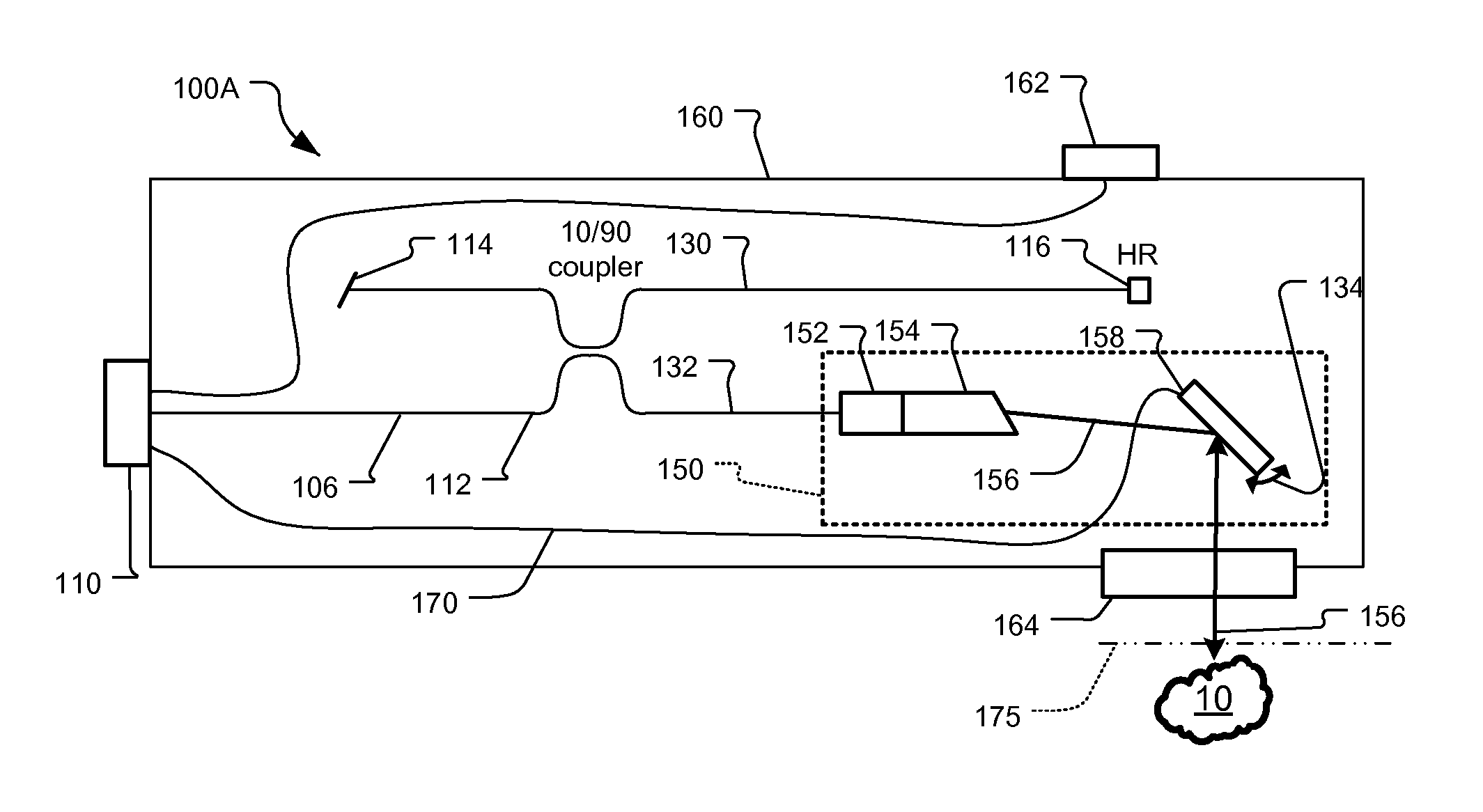
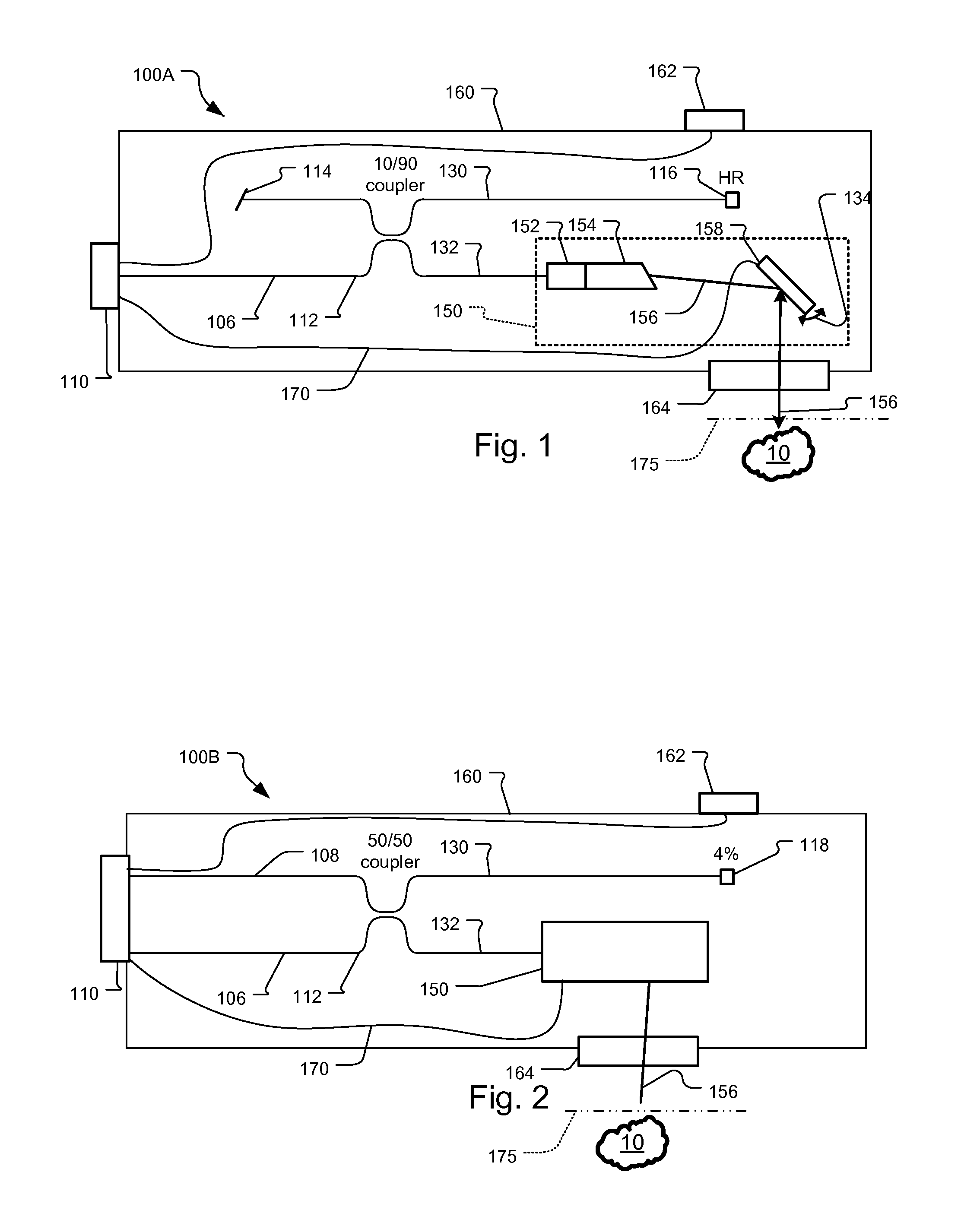
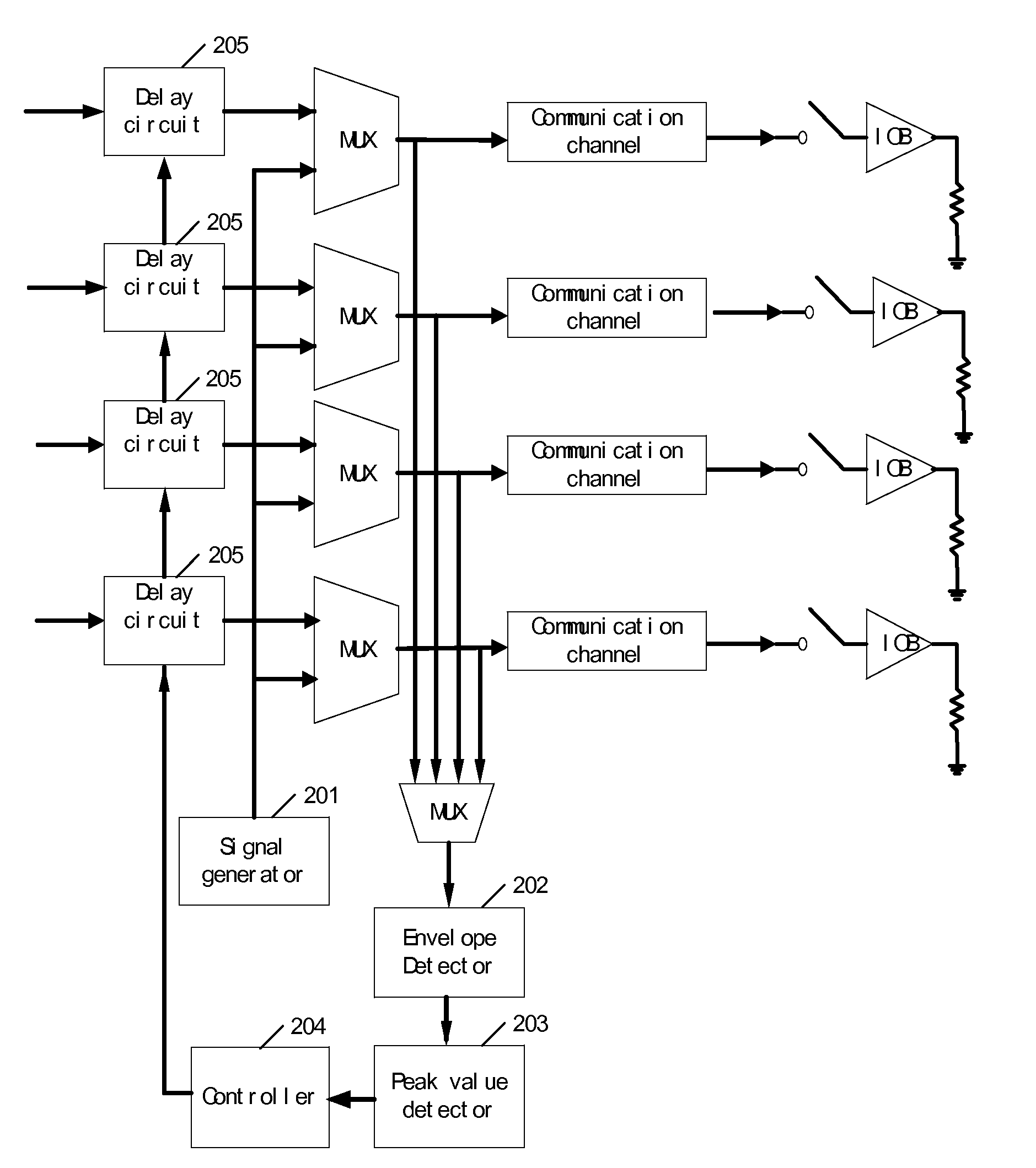
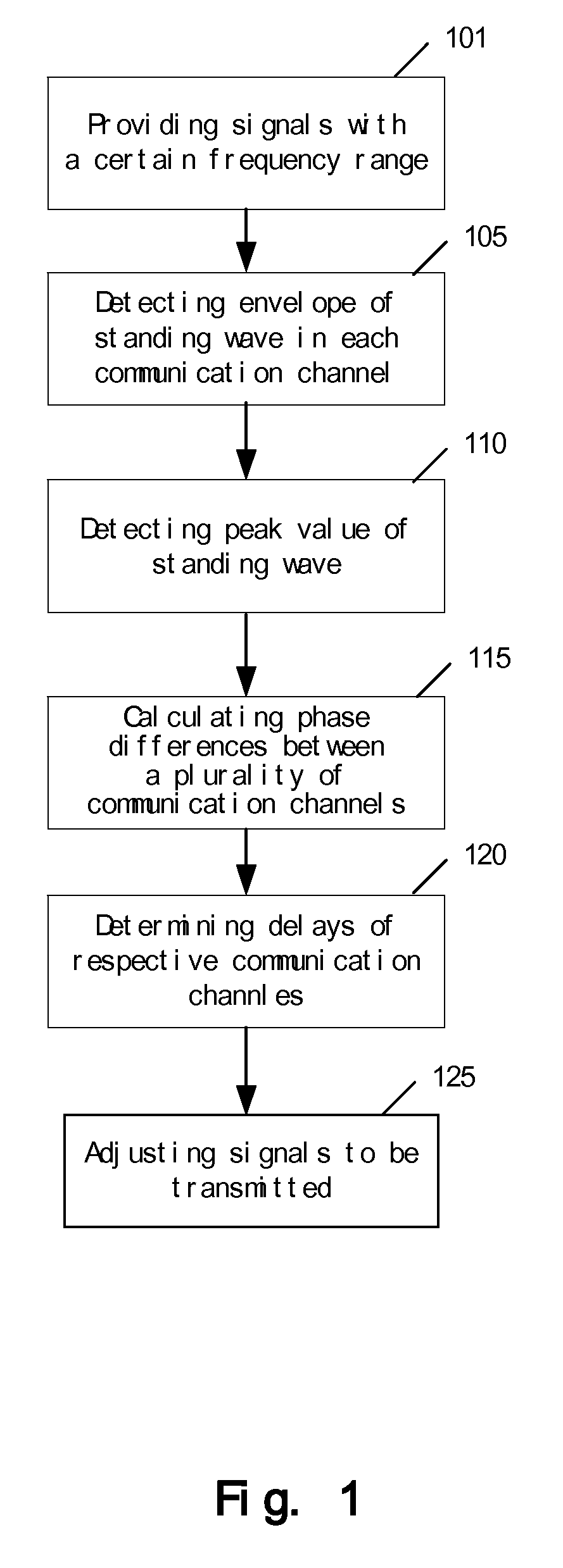
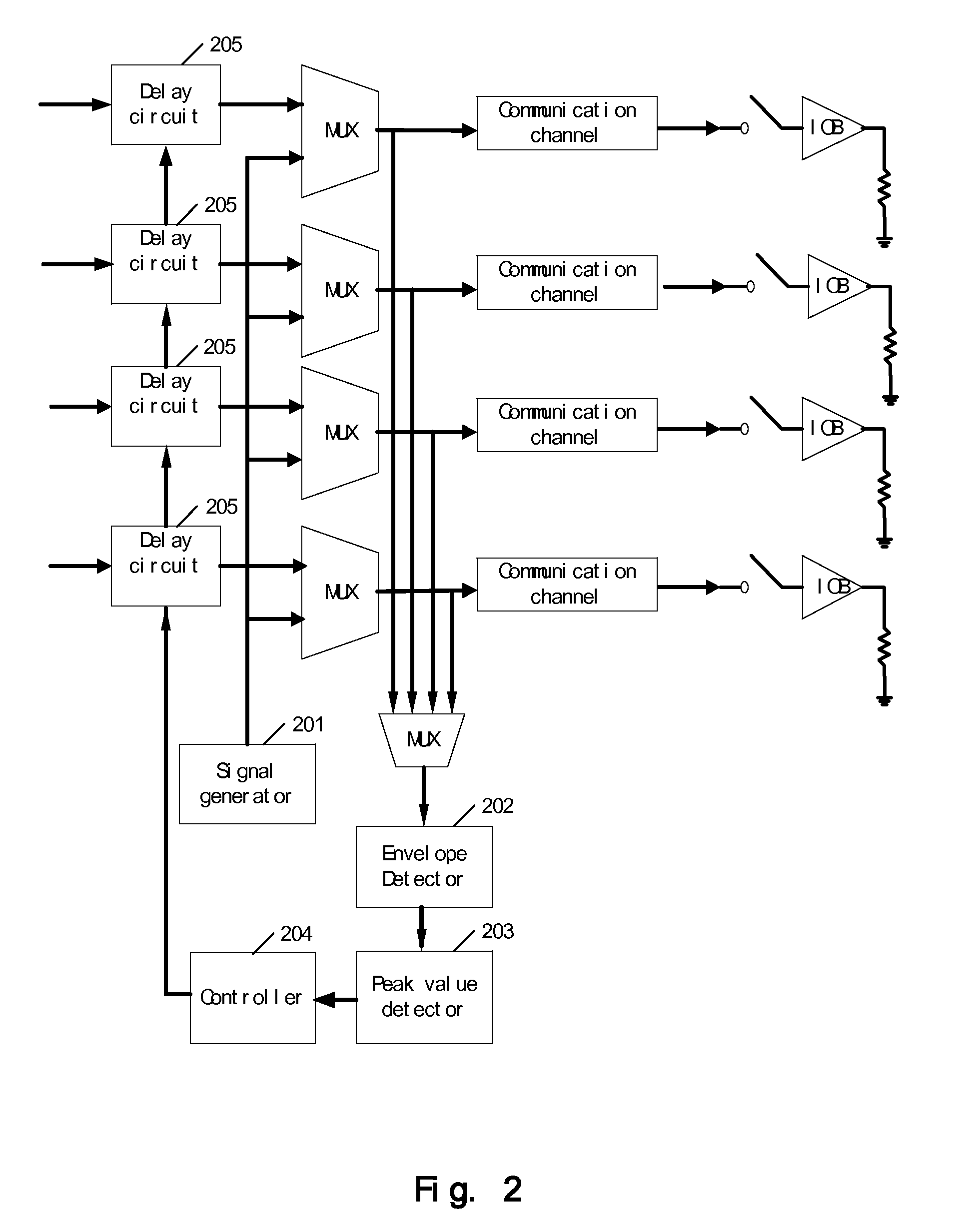
Method and device for compensating for delays of a plurality of communication channels
InactiveUS20080205439A1Simple structureReduce power consumptionTime-division multiplexBaseband systemsPhase differencePeak value
A device and method for compensating for delays of a plurality of communication channels, provides signals with a certain frequency range, wherein the signals form standing waves in the plurality of communication channels; calculates phase differences between the plurality of communication channels according to the signal frequencies at the peak values of the standing waves; and determines the delay of each communication channel according to the above phase differences. The device and method may be applied to the communication channels of high speed parallel connection to eliminate the delays of the communication channels and realize length matching. Since the device and method determine the delays of communication channels by means of the phase differences, even when the delay difference exceeds a clock cycle, it can calculate the phase differences properly.
Owner:IBM CORP
Digital PWM amplifier having a low delay corrector
InactiveUS7576606B2Compensation delayGain controlDc amplifiers with modulator-demodulatorDigital down converterAudio power amplifier
Systems and methods for performance improvements in digital switching amplifiers using a low delay corrector. In one embodiment, a digital pulse width modulation (PWM) amplifier includes a signal processing plant configured to receive and process an input audio signal. The amplifier also includes a low delay corrector configured to receive signals output by the plant. The output of the low delay corrector is added to the input audio signal as feedback. The plant may consist of a modulator and power switch, a noise shaper, or any other type of plant. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) may be provided to convert the output audio signal to a digital signal. Filtering may be implemented before or after the ADC, and a decimator may be placed after the ADC if it is an oversampling ADC.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
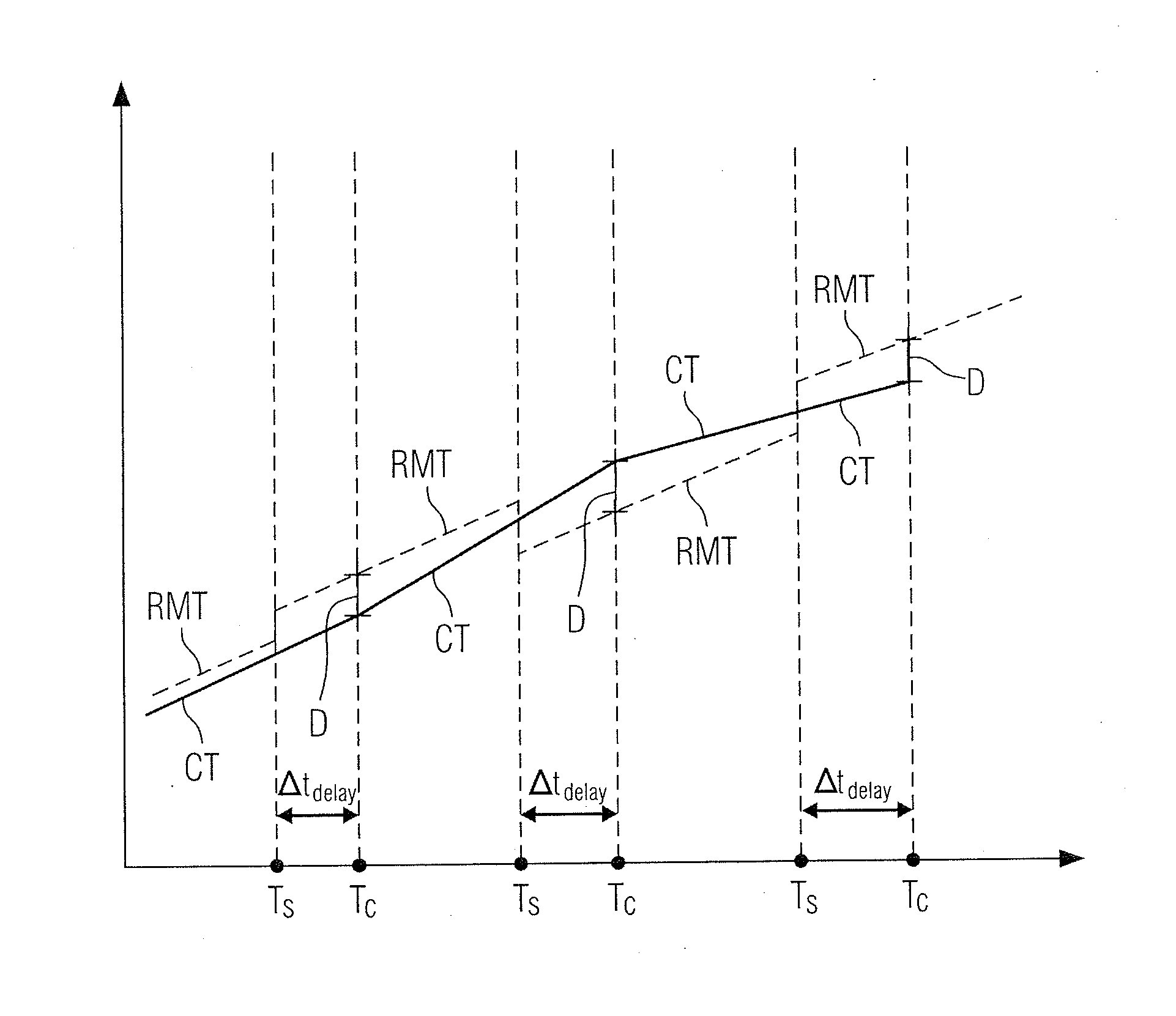
System and Method for Time Synchronization in a Communication Network
InactiveUS20120051374A1Good estimateFree from jumpTime-division multiplexSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlClock timeReal-time computing
A system and method for time synchronization in a communication network. The communication network includes a plurality of network nodes each having a respective internal clock, and a reference node having a reference clock and each configured transmits synchronization messages within the communication network. At least one network node is configured to determine an estimated reference clock time discretely upon arrival of a synchronization message at the at least one network node. To that end, the at least one network node includes a controller for determining a controlled time comprising a time-continuous estimate of the discreetly estimated reference clock time. The controller is configured to determine the controlled time based on an input that is extrapolated to an execution time instant of the controller, where the execution time instant is separated from the time instant of arrival of the synchronization message by a delay (Δtdelay).
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Phase lock evoked response audiometer
InactiveUS6406439B1Strong evoked potentialStronger evoked potentialsElectroencephalographyAudiometeringEngineeringAudiometer
An evoked response audiometer method and apparatus in which a patient receives an auditory stimulus signal comprising a carrier frequency which is periodically amplitude modulated and frequency modulated whereby the stimulus is at least substantially frequency specific, the brain potential signals of the patient evoked by the auditory signal being sampled to determine whether phase locking to the modulated auditory signal has occurred, the auditory signal being selectively controlled to advance or delay one modulation with respect to the other modulation to cause enhancement of the evoked response to the auditory stimulus.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com