Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
89 results about "Fourth harmonic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
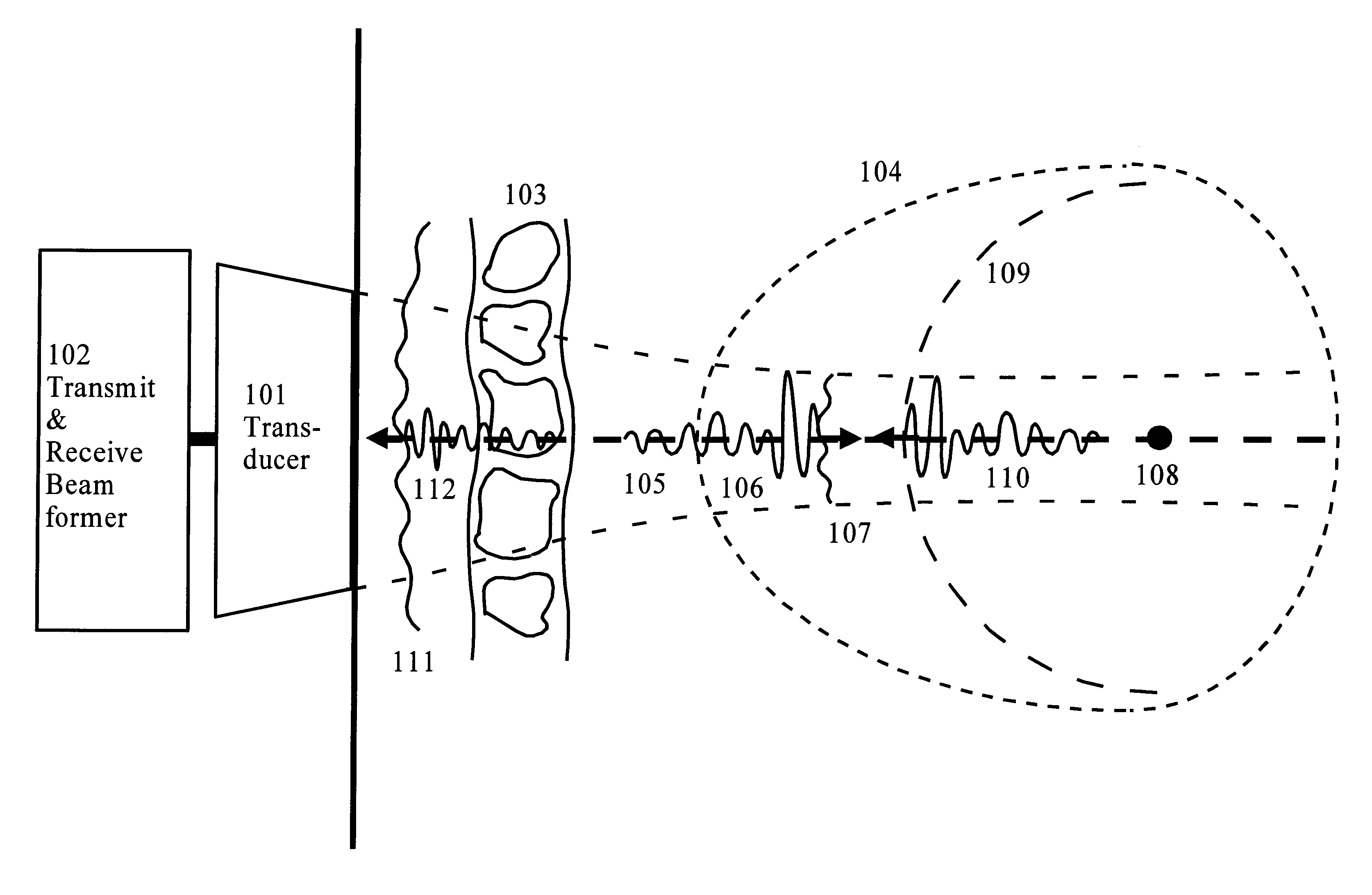
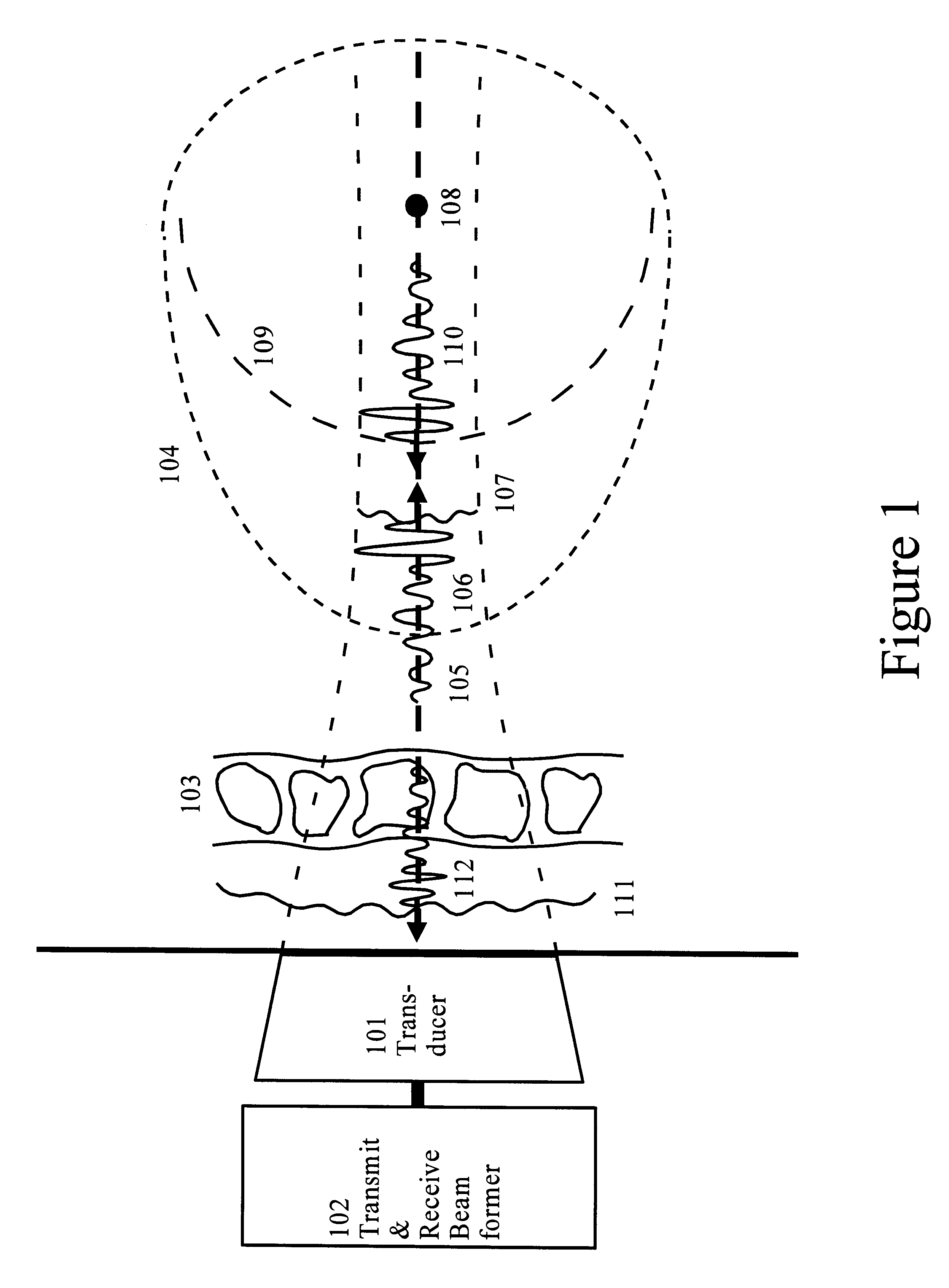
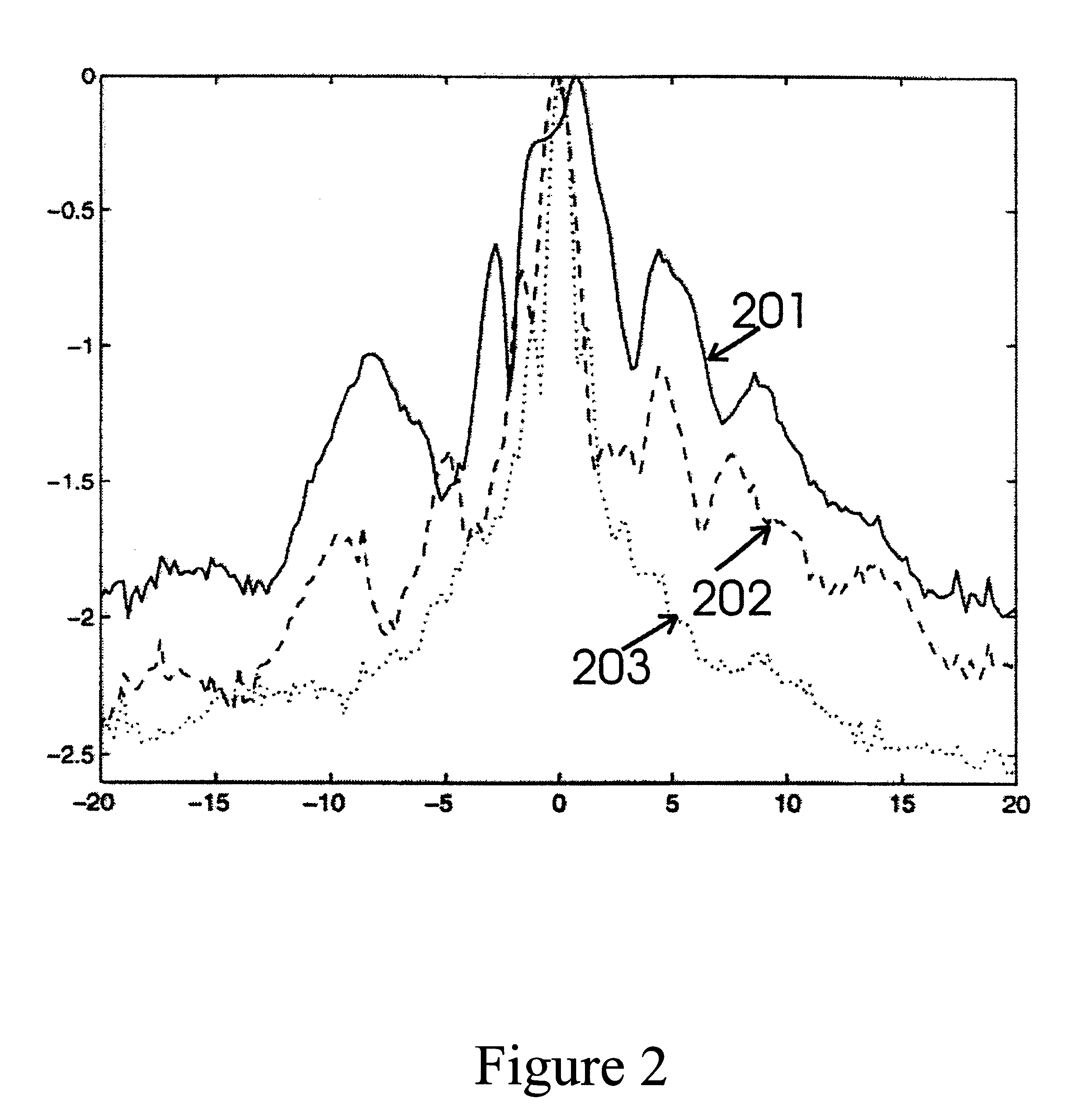
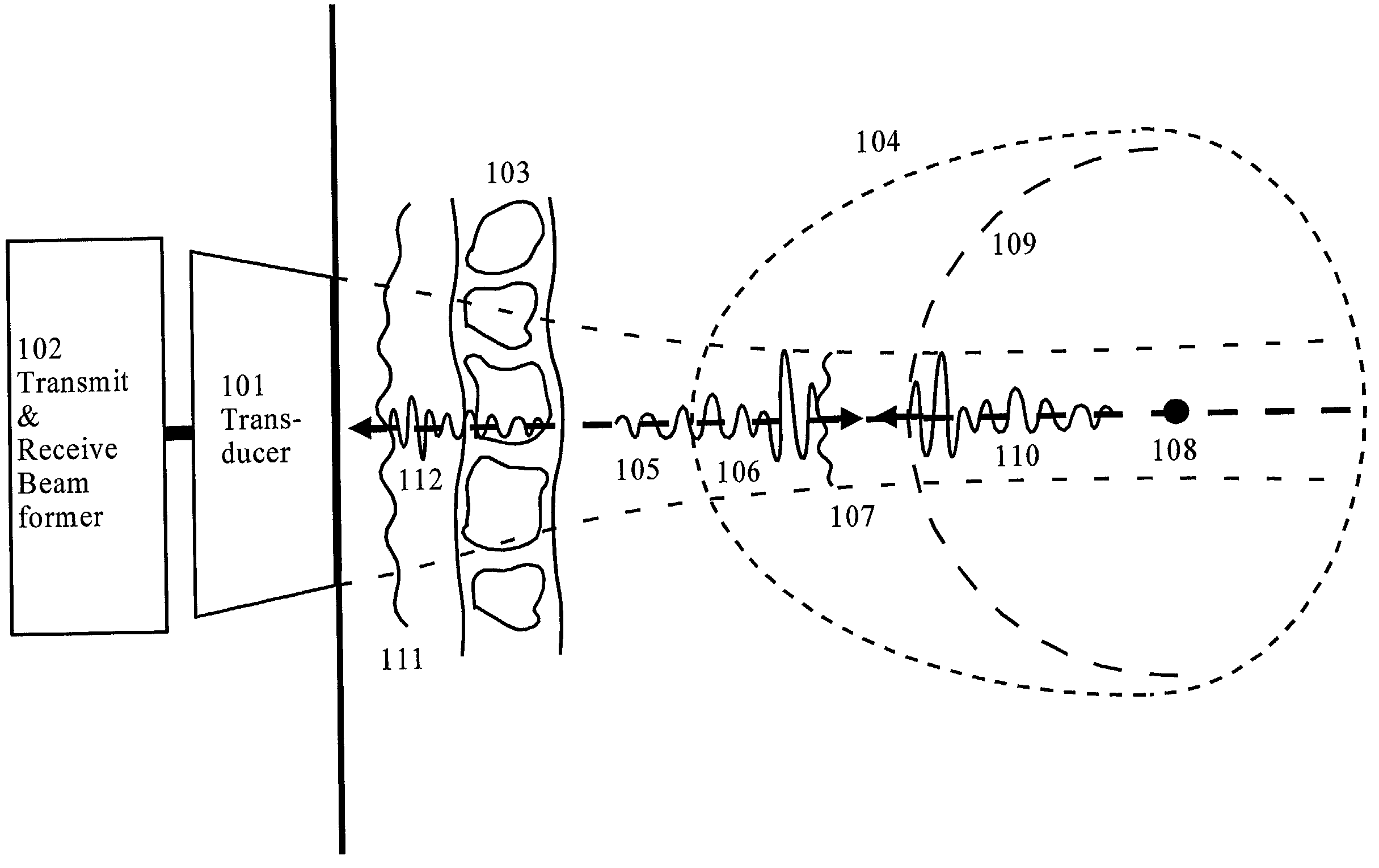
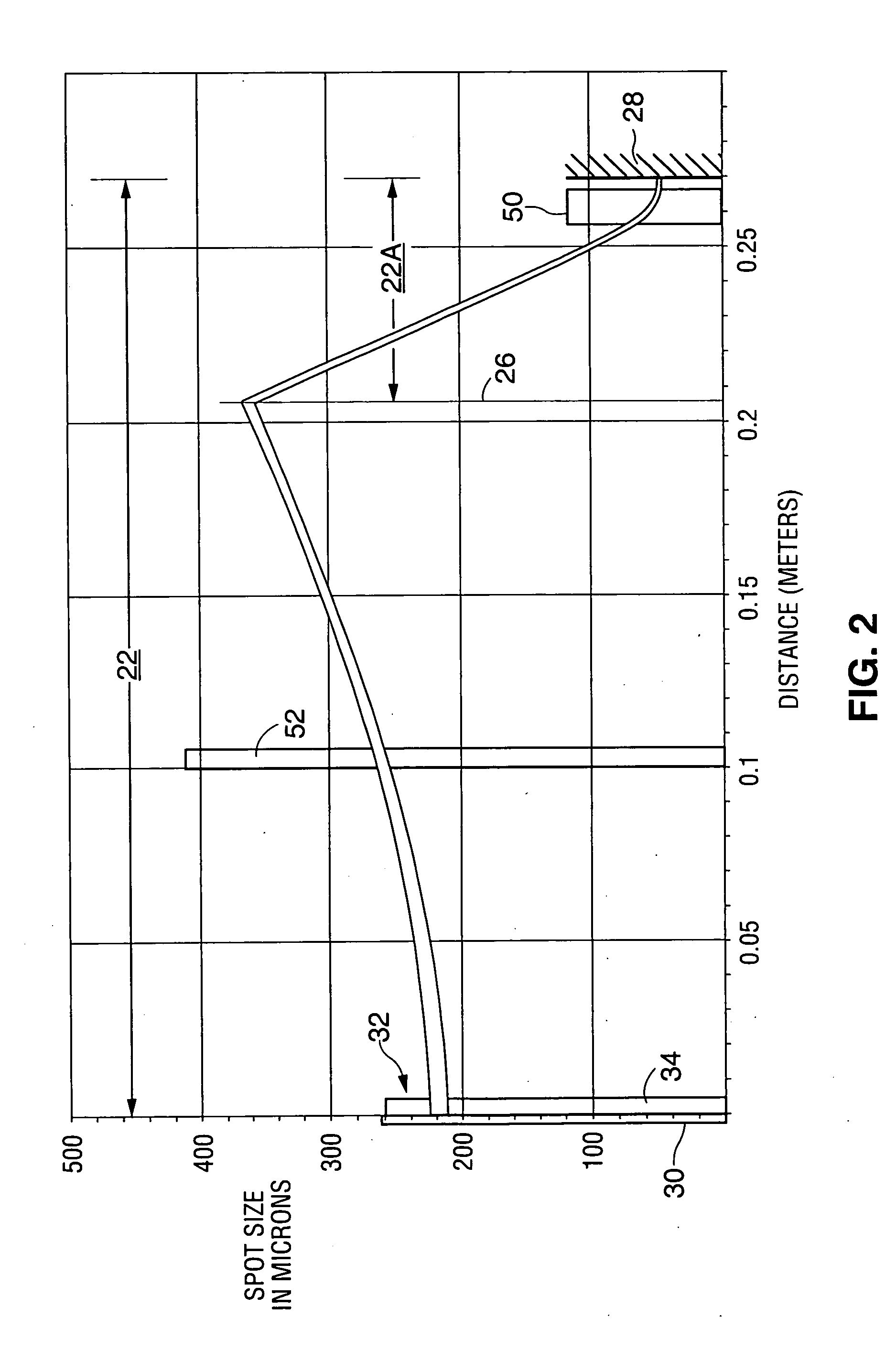
Correction of phasefront aberrations and pulse reverberations in medical ultrasound imaging
InactiveUS6485423B2Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasound imagingUltrasonography
Owner:ANGELSEN BJORN A J +1
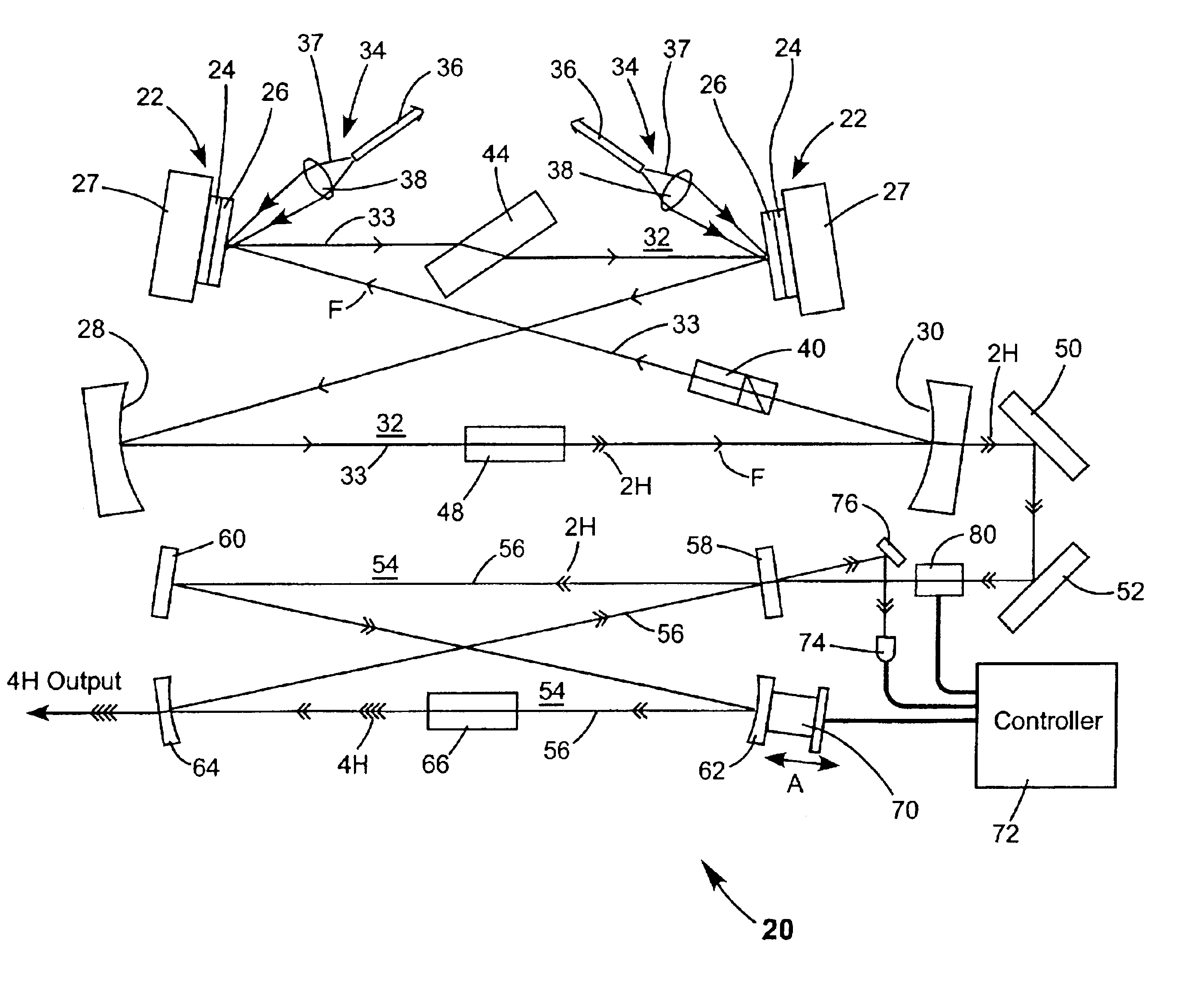
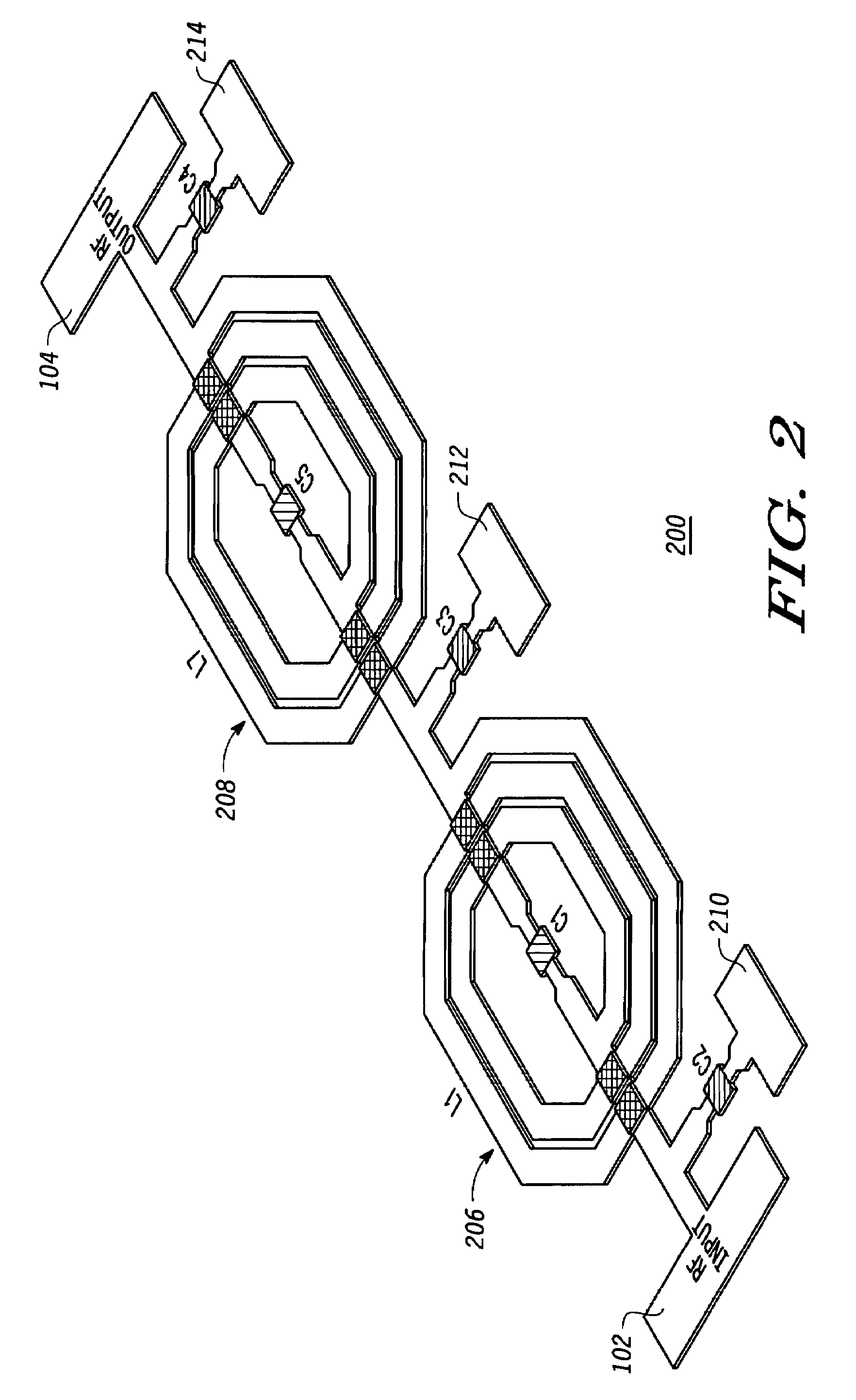
Optically pumped semiconductor ring laser
InactiveUS6940880B2Doubling frequencyLaser optical resonator constructionExcitation process/apparatusFourth harmonicOptical pumping
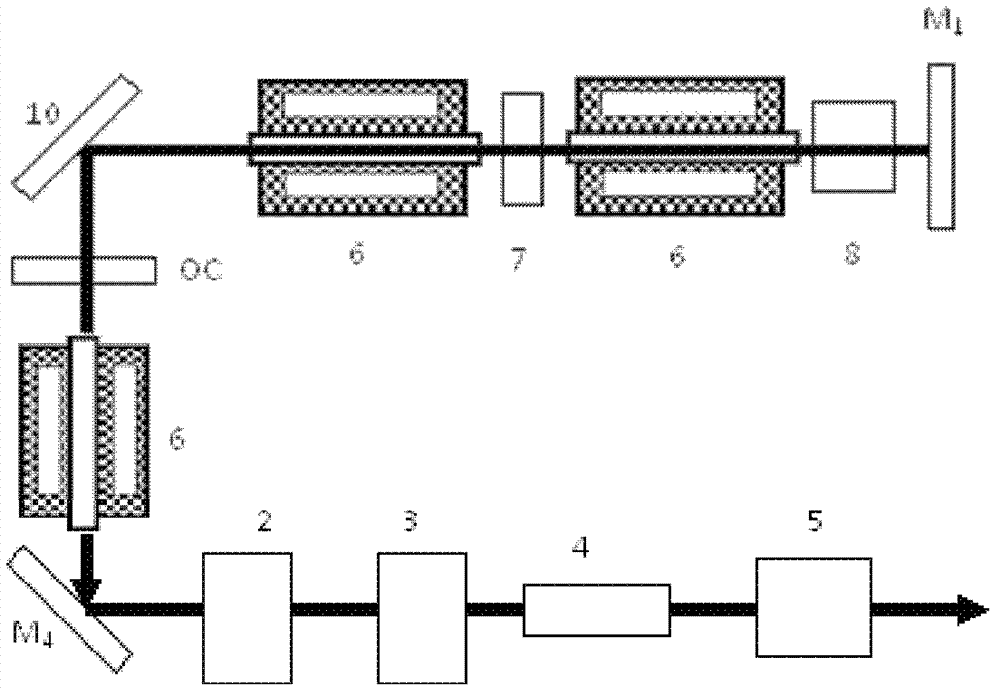
An optically pumped semiconductor laser includes an active ring-resonator having two or more optically pumped semiconductor (OPS) structures each including a mirror-structure and a multilayer gain-structure. The mirror-structures serve as fold mirrors for the resonator axis. An optically nonlinear crystal may be included in the ring-resonator for generating second-harmonic radiation from fundamental radiation generated in the resonator. Another optically nonlinear crystal may be provided for generating third-harmonic or fourth-harmonic radiation from the second-harmonic radiation. In one example, including a third-harmonic generating crystal, a passive ring-resonator partially coaxial with the active ring-resonator is provided for circulating second-harmonic radiation to provide resonant amplification of the second-harmonic radiation for enhancing third-harmonic conversion. Apparatus for automatically maintaining the passive ring-resonator in a resonant condition for the second-harmonic radiation is disclosed.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Radiation source apparatus and duv beam generation method
ActiveUS20120026578A1Improve efficiencyLaser detailsOriginals for photomechanical treatmentFourth harmonicLength wave
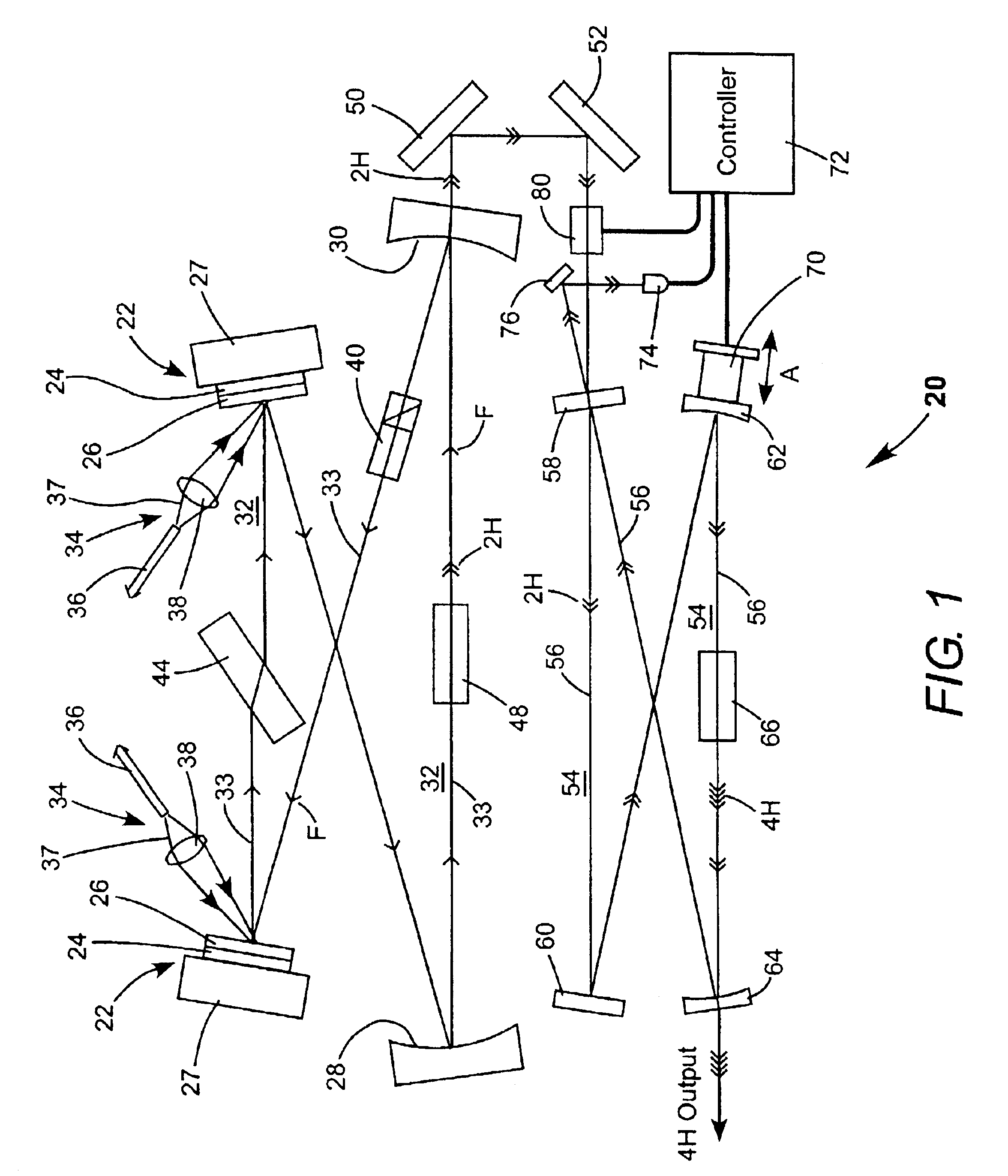
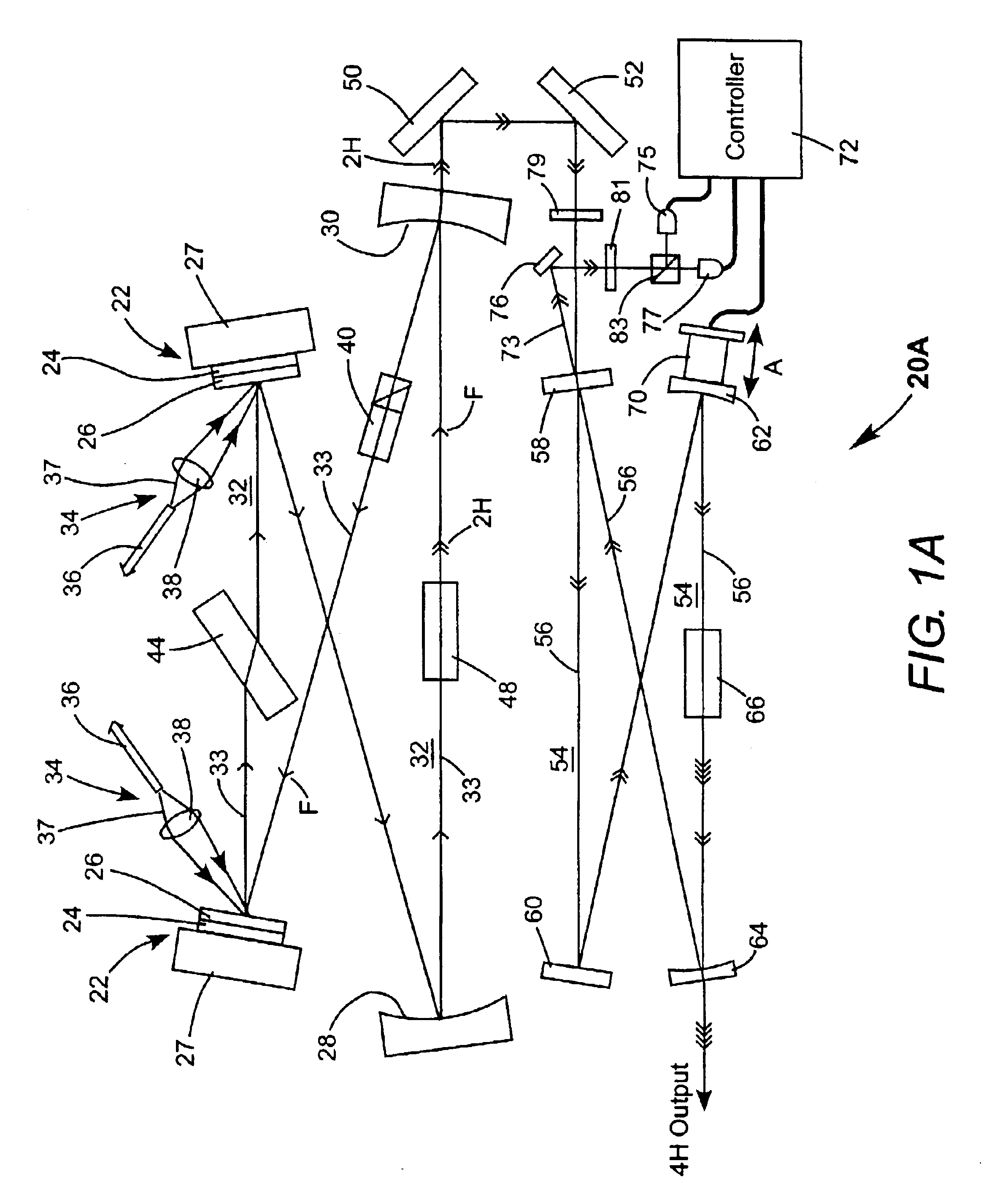
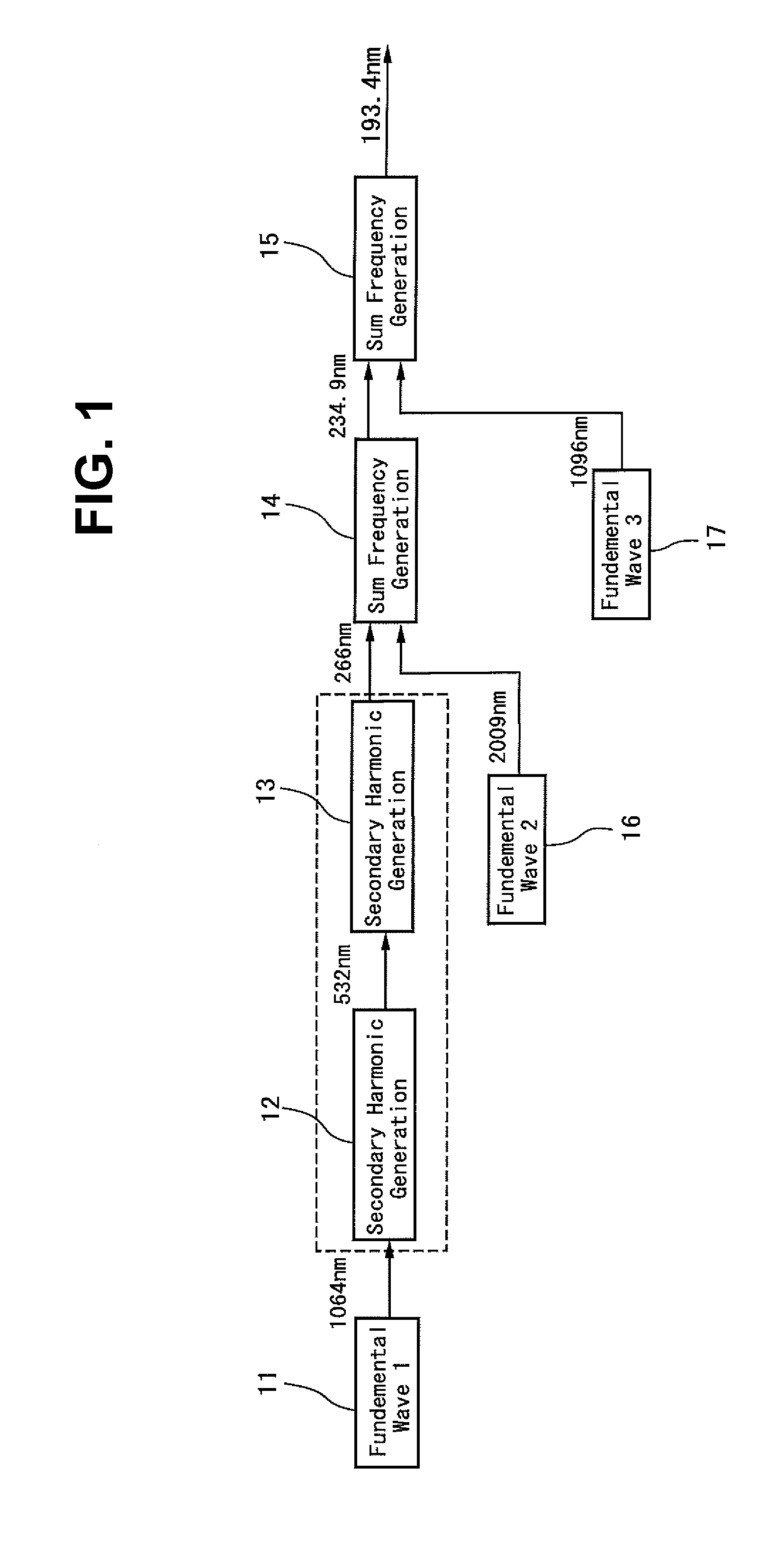
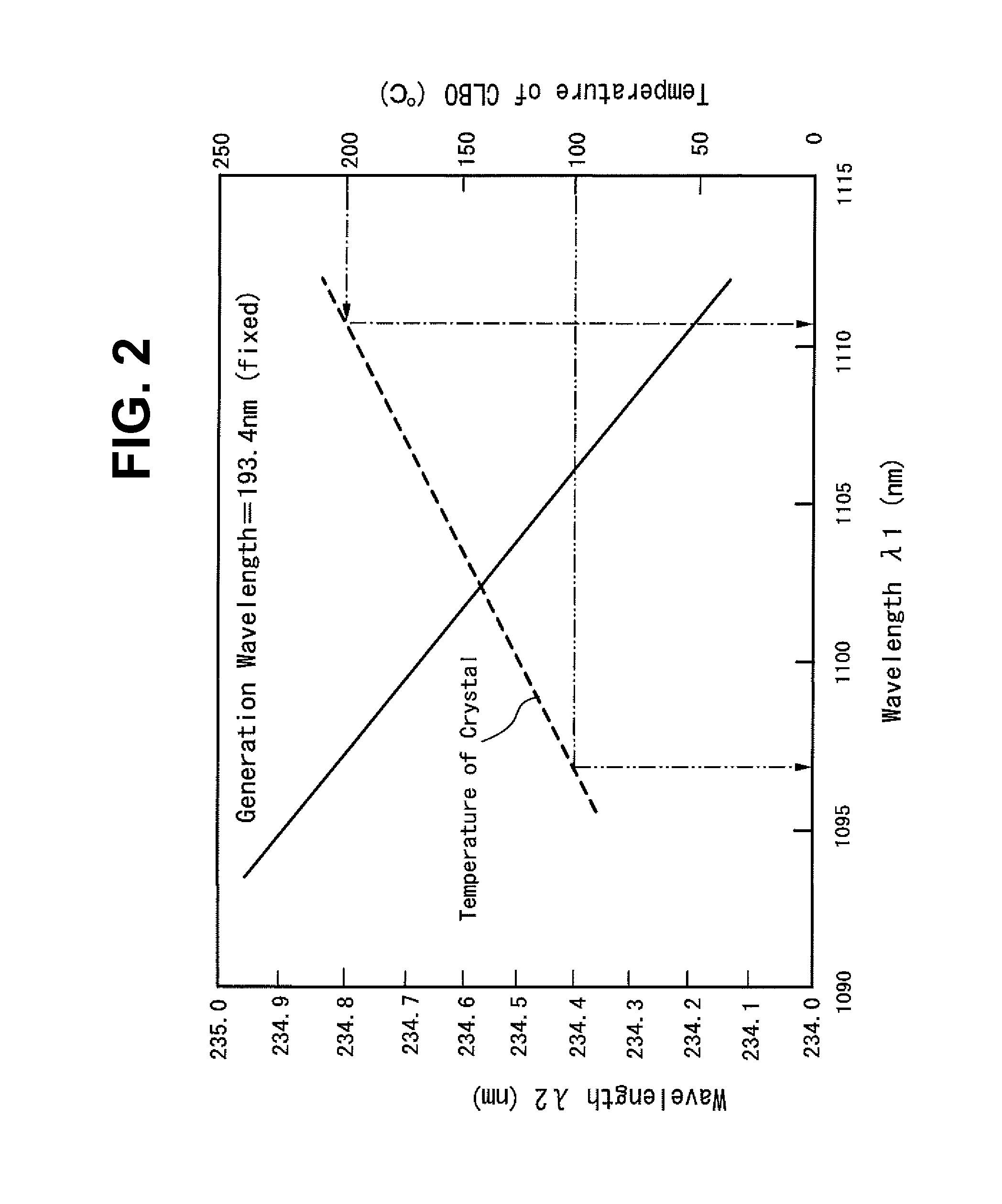
The present invention provides a radiation source apparatus which can generate a DUV radiation beam having a wavelength of 193.4 nm efficiently. The radiation source apparatus according to the invention has first wavelength conversion means arranged to receive a first laser beam of a first fundamental wavelength and to generate a fourth-harmonic wavelength of the first fundamental wavelength, second wavelength conversion means arranged to receive the beam of the fourth-harmonic wavelength of the first fundamental wavelength (266 nm) and a second laser beam of a second fundamental wavelength and to sum-frequency mix the fourth-harmonic with the second fundamental wavelength radiation to generate a beam of second DUV radiation having a wavelength between approximately 232 nm and 237 nm, and third wavelength conversion means arranged to receive the beam of second DUV radiation and the third laser beam of a third fundamental wavelength and to sum-frequency mix the second DUV radiation with the third fundamental wavelength radiation to generate third DUV radiation having a wavelength between approximately 192.5 nm and 194.5 nm.
Owner:LASERTEC CORP
Correction of phasefront aberrations and pulse reverberations in medical ultrasound imaging
InactiveUS20020002333A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSurgeryUltrasonographyUltrasound imaging
A method of correcting for phasefront aberrations in ultrasound imaging uses highly spaced apart point scatterers artificially placed in the tissue being imaged. The point scatterers reflect the transmitted sound and are individually differentiated to provide singular reference points for correction of signals reflected from the surrounding tissue. The differentiation is performed by comparison of the third or fourth harmonic frequencies of the reflected signals. To ensure the necessary high dispersal of the point scatterers, high amplitude pulses of the transmitted signal destroy point scatterers in selected image regions. In an alternate embodiment, correction is performed by stochastic analysis of signals reflected from the highly dispersed point scatterers. A reference signal is compared to the second harmonic of the reflected signal to reduce noise.
Owner:ANGELSEN BJORN A J +1
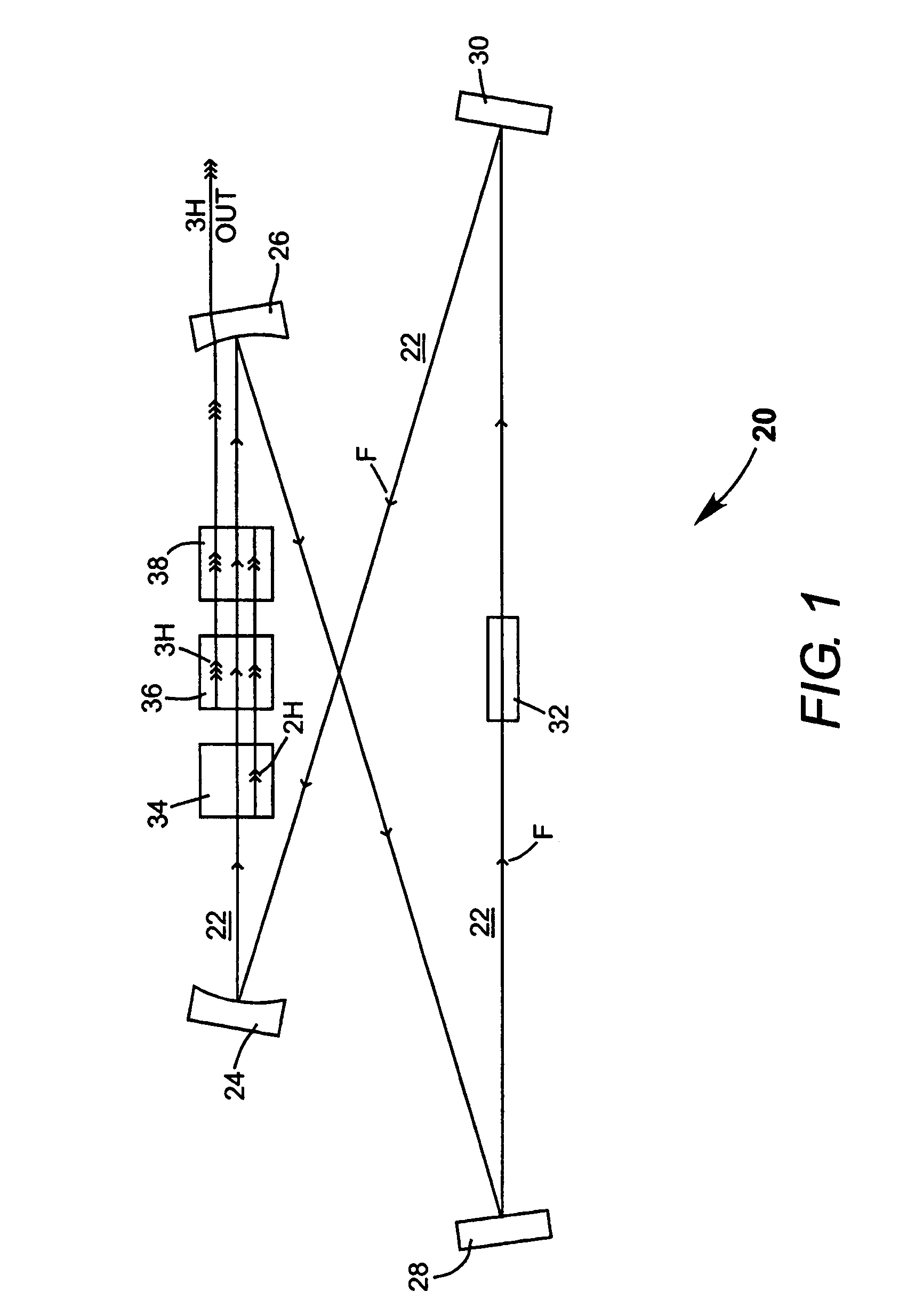
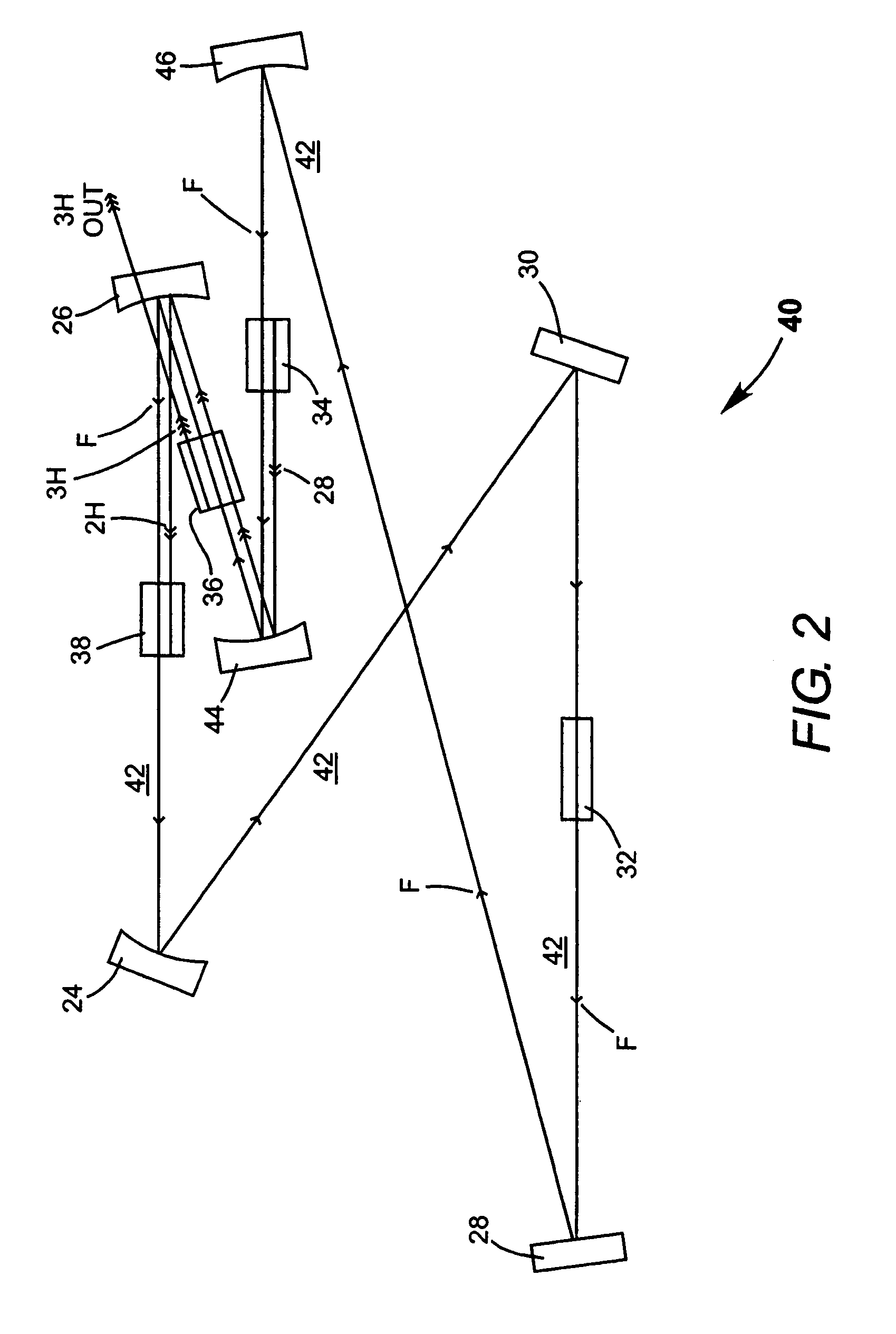
Intracavity frequency-tripled CW laser with traveling-wave ring-resonator
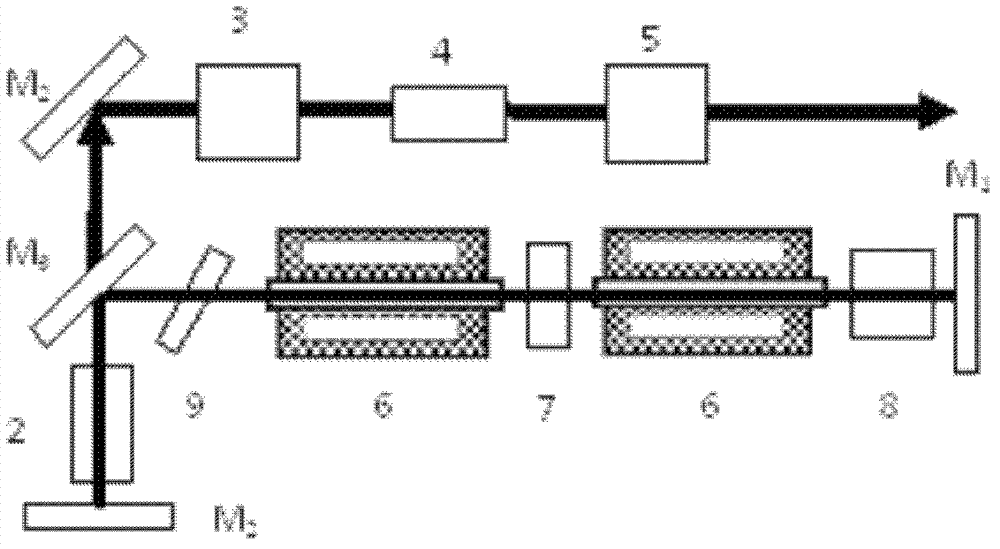
InactiveUS7130321B2Improve efficiencyIncrease volumeLaser optical resonator constructionLaser output parameters controlFourth harmonicThird harmonic
Owner:COHERENT INC
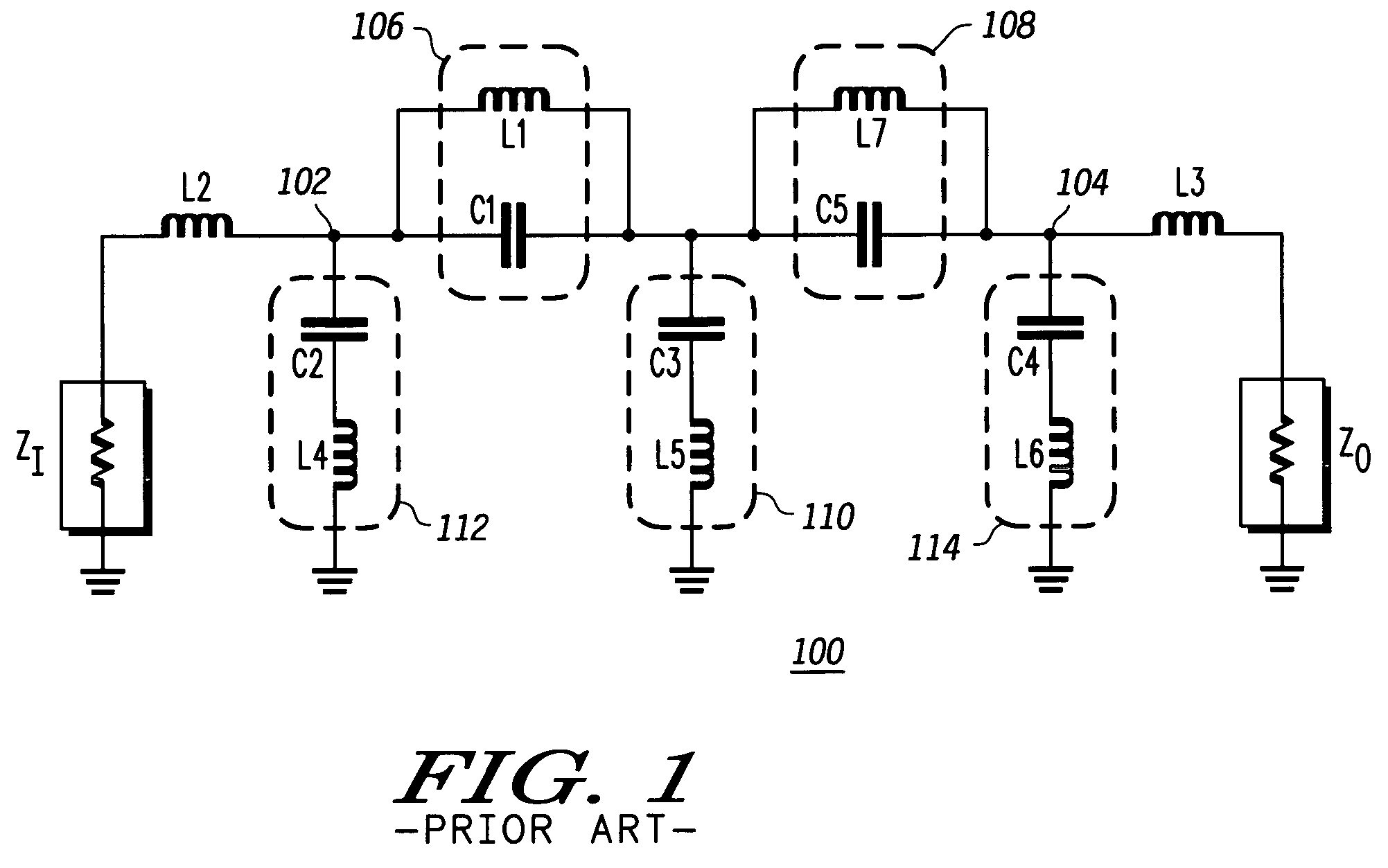
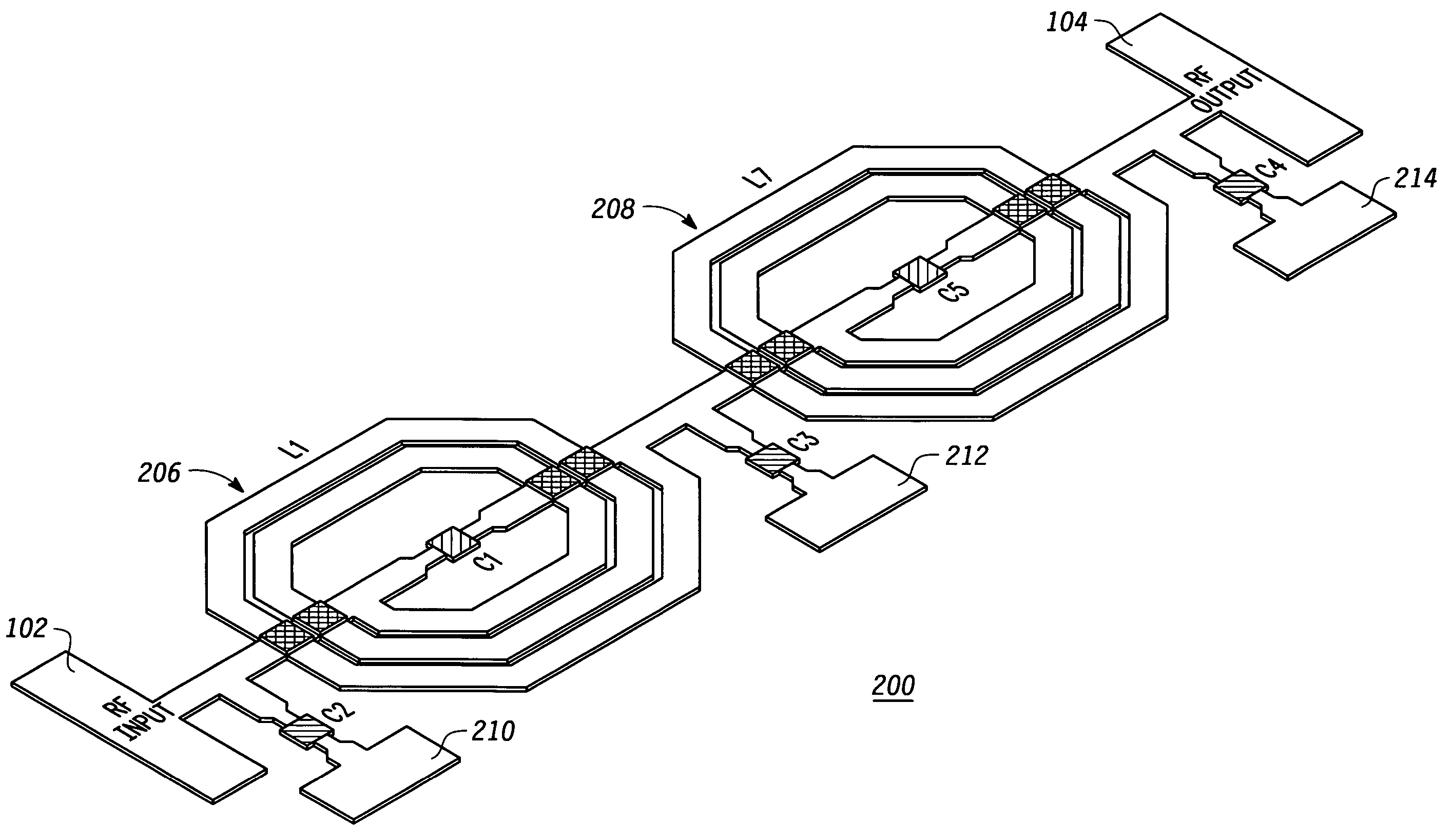
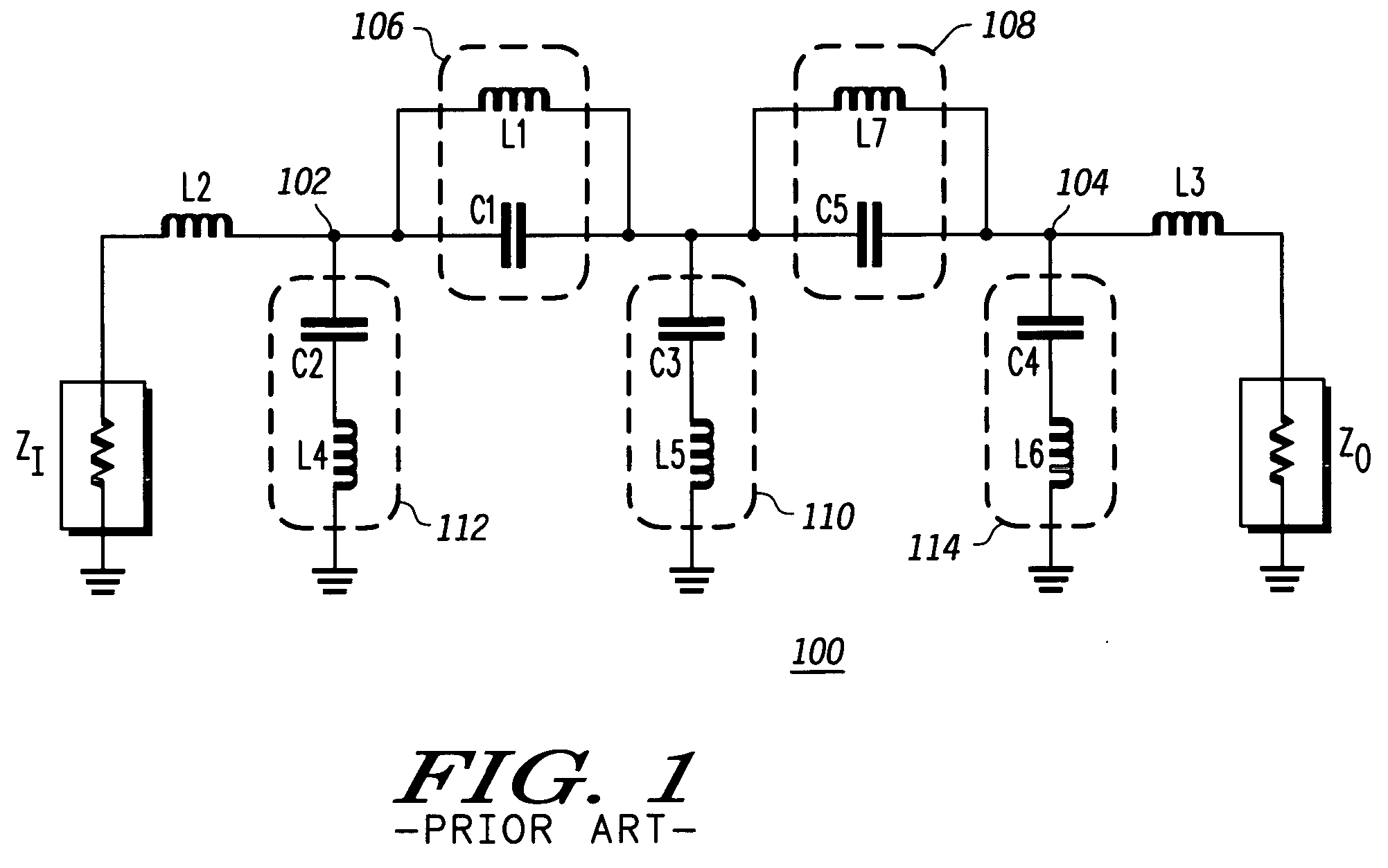
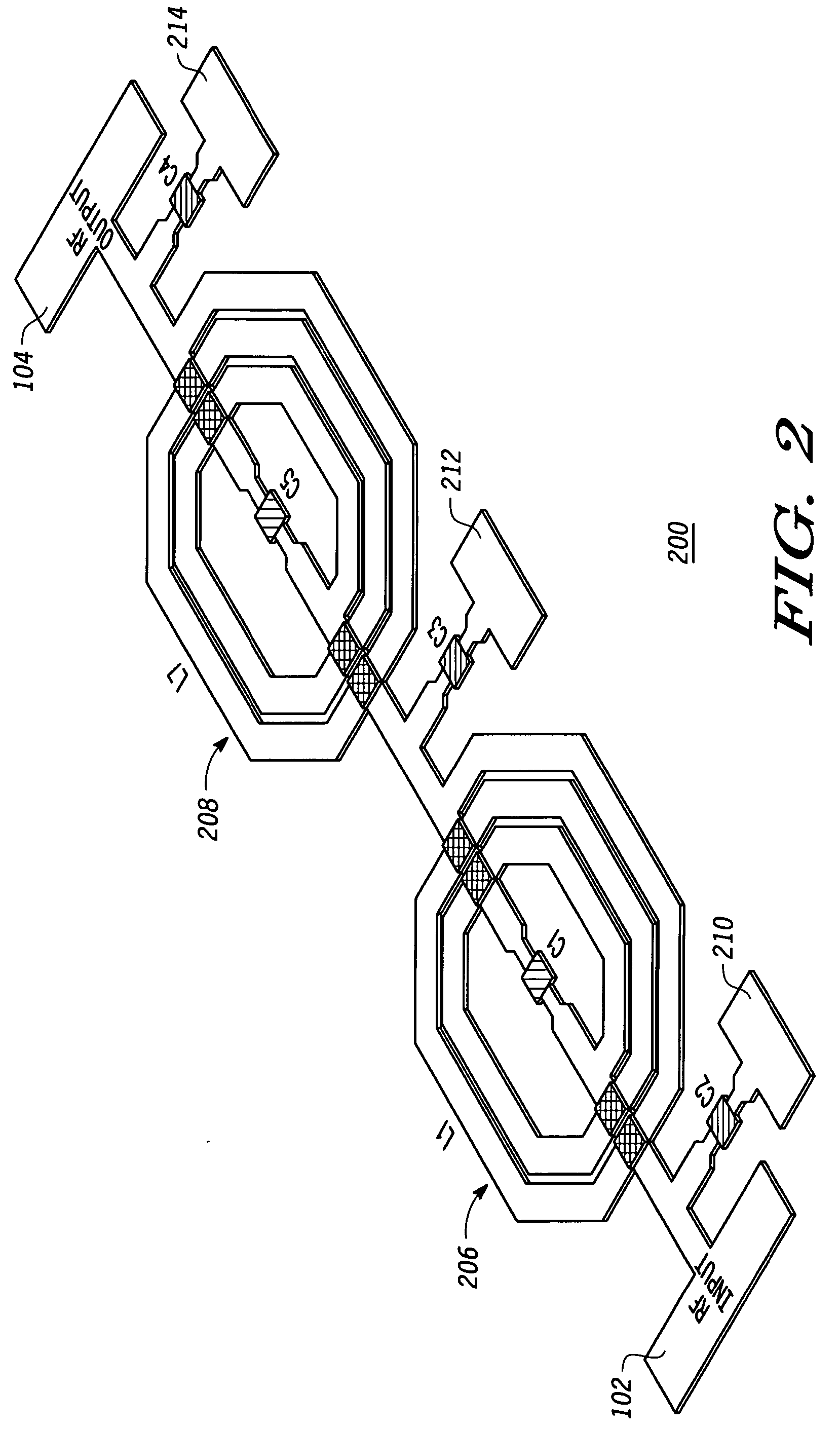
Compact radio frequency harmonic filter using integrated passive device technology
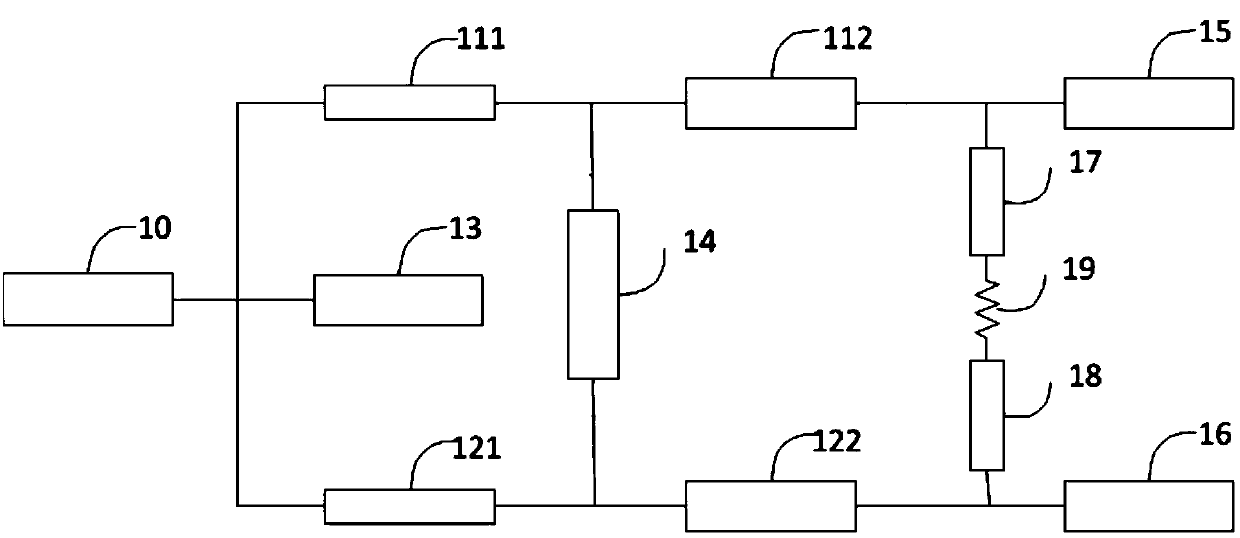
ActiveUS7418251B2Reducing overall size and packaging requirementReduce equipment footprintMultiple-port networksTransmissionFourth harmonicThird harmonic
A radio frequency (“RF”) harmonic filter circuit as disclosed herein is fabricated using integrated passive device (“IPD”) technology. The RF harmonic filter circuit is configured to provide second, third, and fourth harmonic rejection while providing good input and output impedance matching. The RF harmonic filter circuit employs only one IPD loop inductance (preferably used for a second harmonic resonance circuit), which results in a significant die / package size reduction. The RF harmonic filter circuit also employs a combined circuit that performs input and / or output impedance matching and third harmonic rejection.
Owner:NXP USA INC
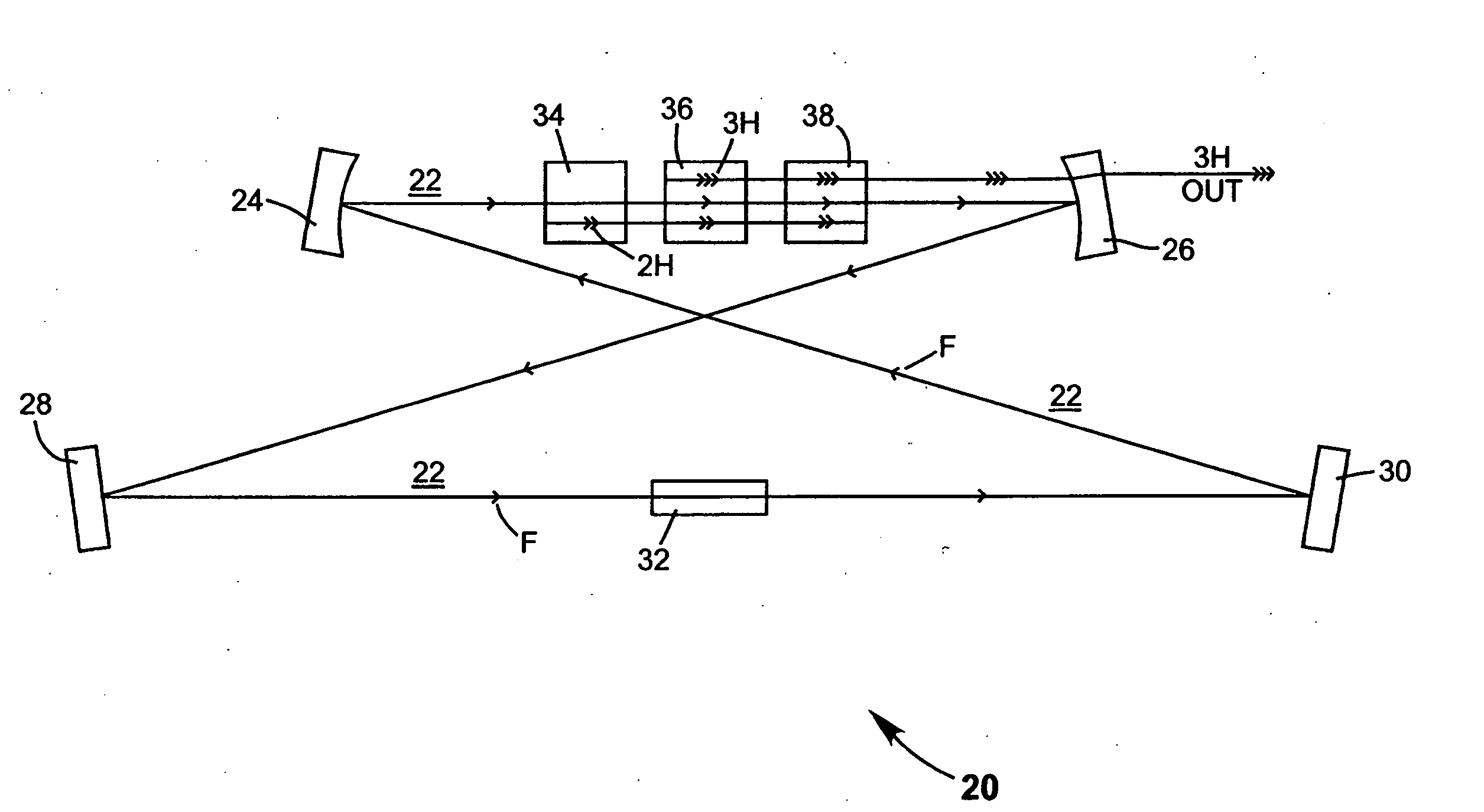
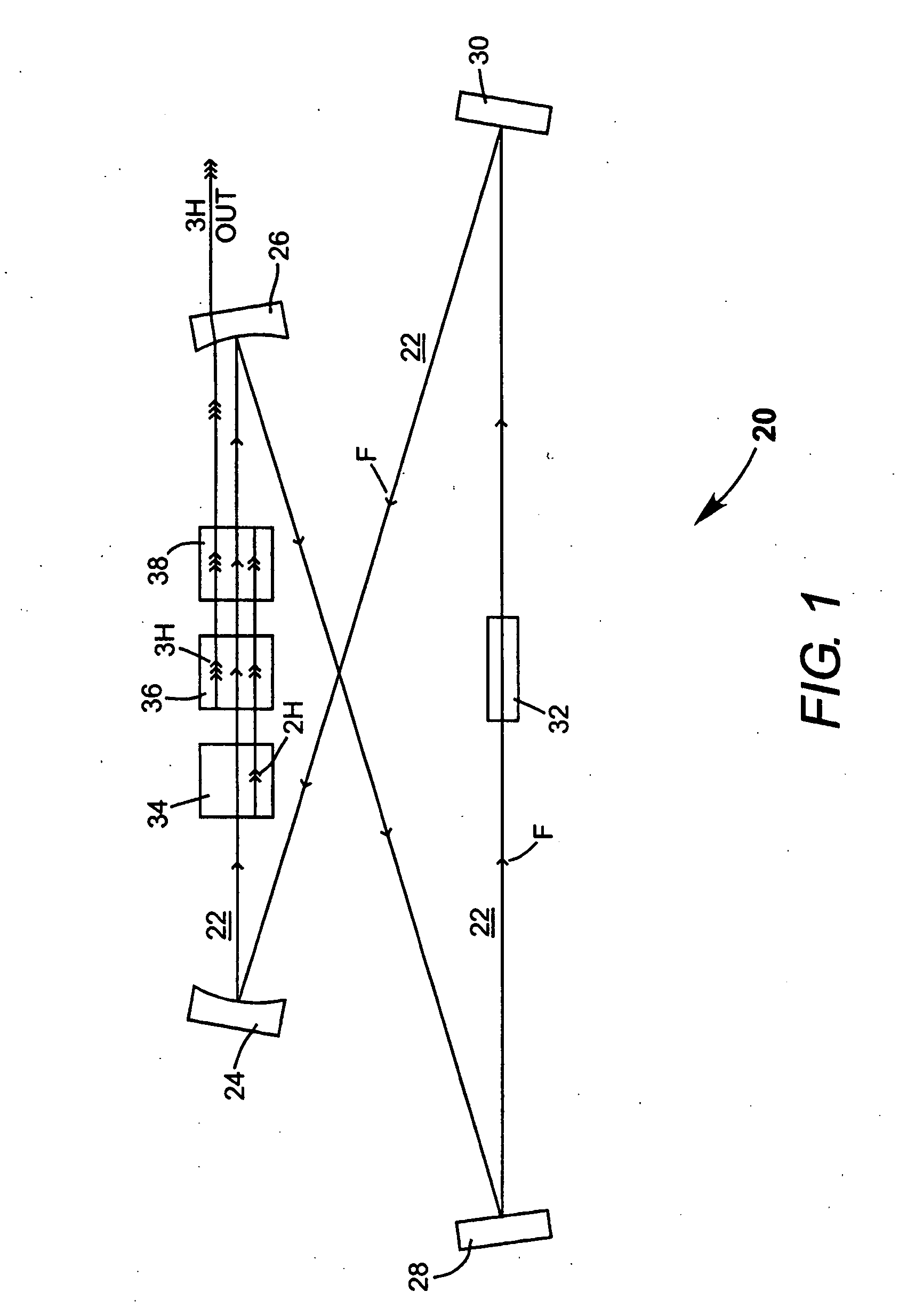
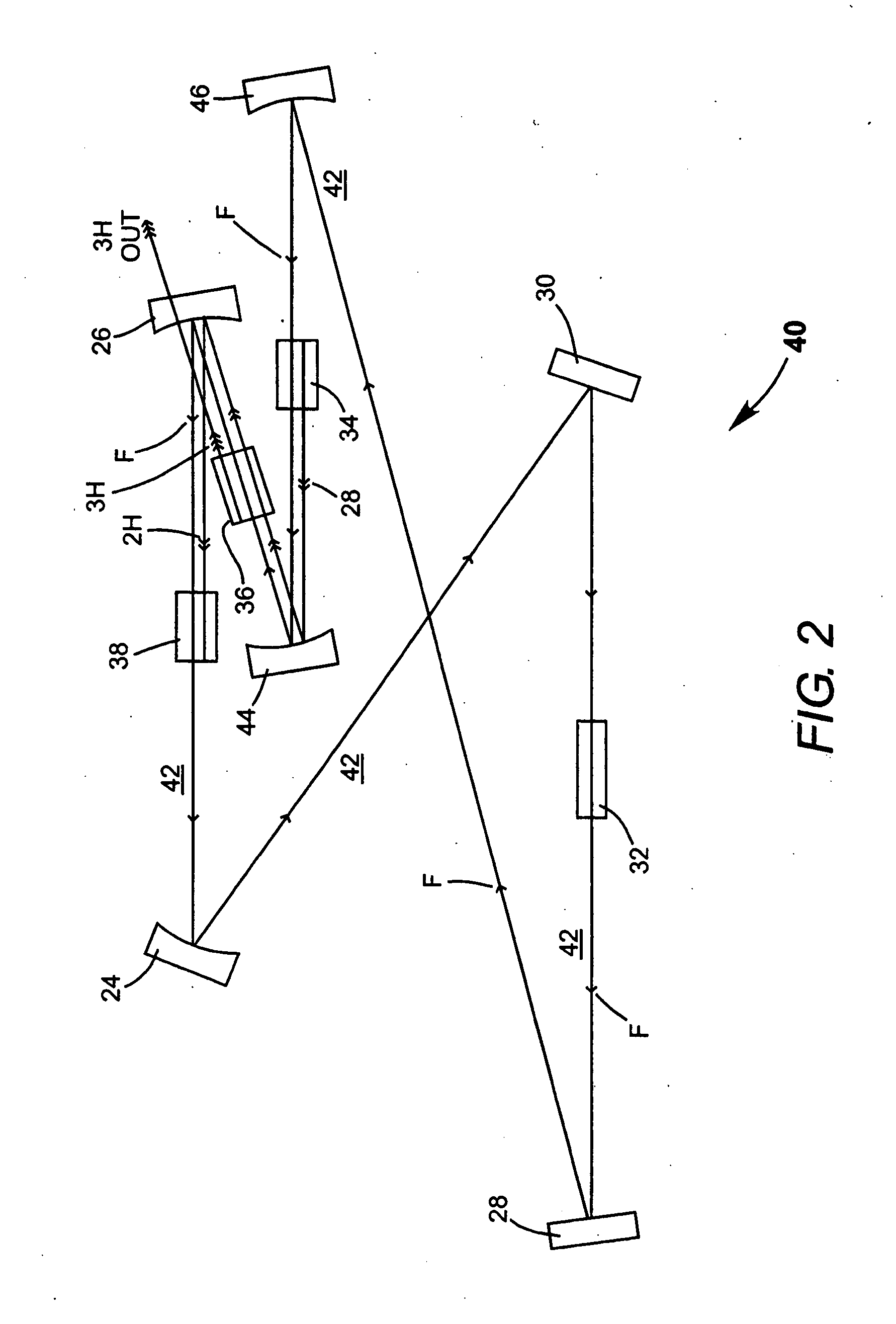
Intracavity frequency-tripled CW laser with traveling-wave ring-resonator
InactiveUS20050163187A1Improve efficiencyIncrease volumeLaser optical resonator constructionLaser output parameters controlFourth harmonicThird harmonic
A traveling-wave ring laser resonator includes one or more gain-elements for generating fundamental radiation and three optically nonlinear crystals. A portion of the fundamental radiation is converted to second-harmonic radiation in a first of the crystals. Remaining fundamental radiation and the second-harmonic radiation traverse a second of the optically nonlinear crystals where a portion of each is converted to third-harmonic radiation. Fundamental and second-harmonic radiation pass through the third of the optically nonlinear crystals where most of the second-harmonic radiation is converted back to fundamental radiation. The third-harmonic radiation can be delivered from the resonator as output radiation or mixed with the fundamental radiation in a fourth optically nonlinear crystal to generate fourth harmonic radiation. An optical parametric oscillator arrangement is also disclosed.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Compact radio frequency harmonic filter using integrated passive device technology
ActiveUS20060141978A1Small sizeReduced packaging requirementsMultiple-port networksTransmissionFourth harmonicThird harmonic
A radio frequency (“RF”) harmonic filter circuit as disclosed herein is fabricated using integrated passive device (“IPD”) technology. The RF harmonic filter circuit is configured to provide second, third, and fourth harmonic rejection while providing good input and output impedance matching. The RF harmonic filter circuit employs only one IPD loop inductance (preferably used for a second harmonic resonance circuit), which results in a significant die / package size reduction. The RF harmonic filter circuit also employs a combined circuit that performs input and / or output impedance matching and third harmonic rejection.
Owner:NXP USA INC
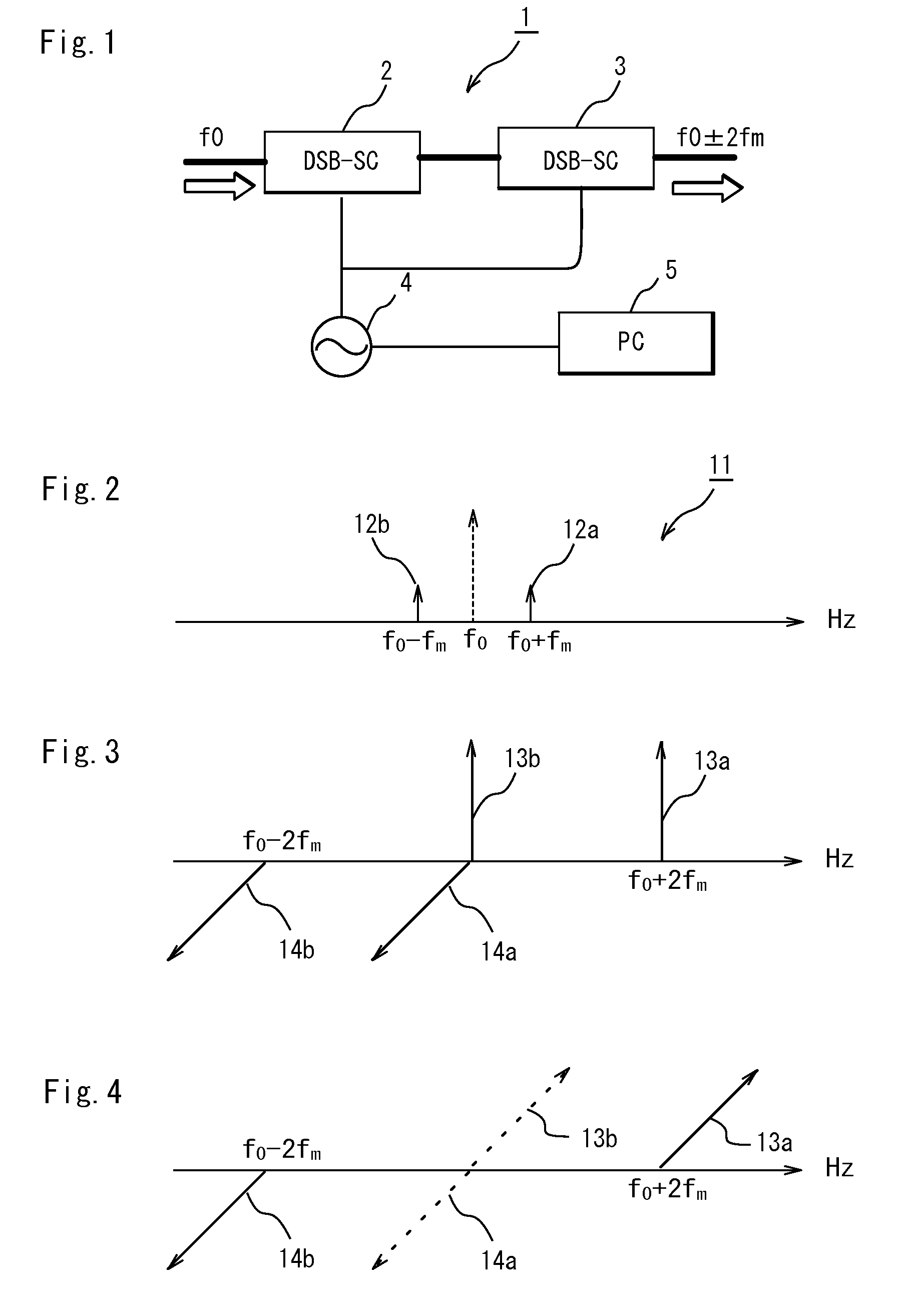
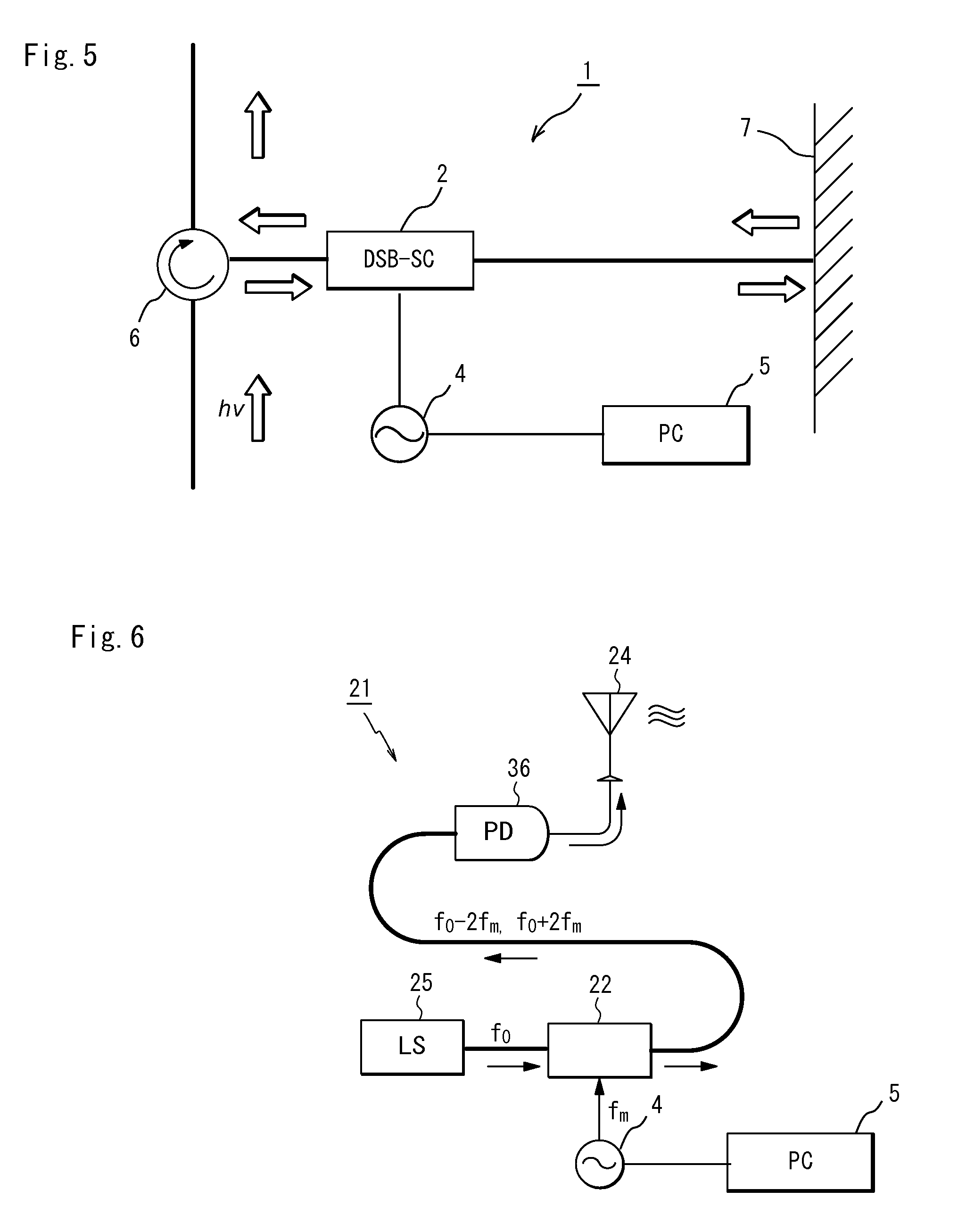
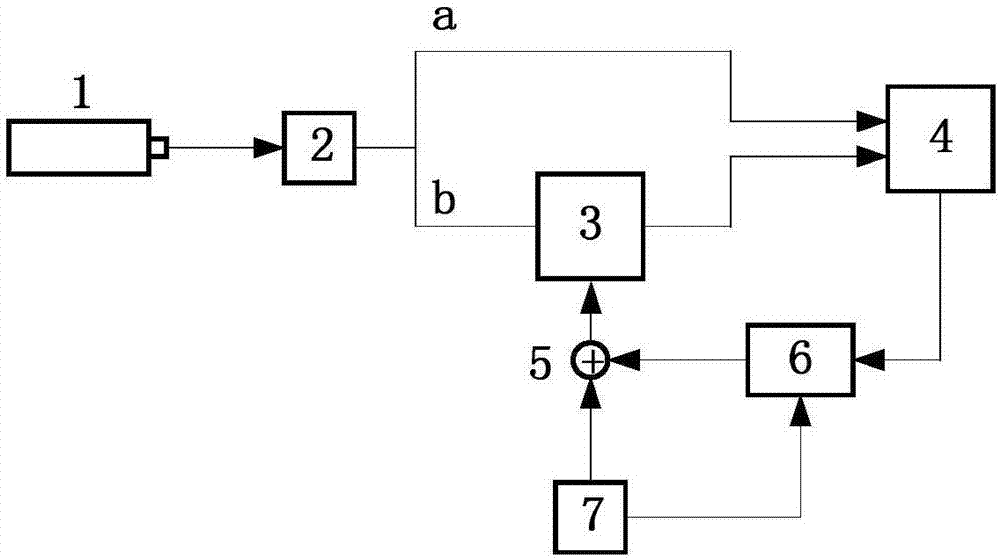
Fourth harmonic generating system using optical double side-band suppressed carrier modulator
InactiveUS20090103924A1Promote generationOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsFourth harmonic generationFourth harmonic
The present invention is to provide an optical modulating system for generating a signal of a frequency (f0+2fm) and a signal of a frequency (f0−2fm) and suppressing a signal of a frequency (f0) by a DSB-SC modulator.A fourth harmonic generating system for solving the above problem comprises a first DSB-SC modulator (2) a second DSB-SC modulator (3) and a signal control section (5) for controlling a modulating signal from a signal source (4) for generating modulating signals applied to the first and second DSB-SC modulators (2,3) so that a lower side-band signal (f0) generated by modulating the upper side-band signal of the DSB-SC modulator (2) by the DSB-SC modulator (3) and an upper side-band signal (f0) generated by modulating the lower side-band signal of the DSB-SC modulator (2) by the DSB-SC modulator (3) cancel each other.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
Radiation source apparatus and DUV beam generation method
ActiveUS8503068B2Improve efficiencyLaser detailsOriginals for photomechanical treatmentFourth harmonicLight beam
The present invention provides a radiation source apparatus which can generate a DUV radiation beam having a wavelength of 193.4 nm efficiently. The radiation source apparatus according to the invention has first wavelength conversion means arranged to receive a first laser beam of a first fundamental wavelength and to generate a fourth-harmonic wavelength of the first fundamental wavelength, second wavelength conversion means arranged to receive the beam of the fourth-harmonic wavelength of the first fundamental wavelength (266 nm) and a second laser beam of a second fundamental wavelength and to sum-frequency mix the fourth-harmonic with the second fundamental wavelength radiation to generate a beam of second DUV radiation having a wavelength between approximately 232 nm and 237 nm, and third wavelength conversion means arranged to receive the beam of second DUV radiation and the third laser beam of a third fundamental wavelength and to sum-frequency mix the second DUV radiation with the third fundamental wavelength radiation to generate third DUV radiation having a wavelength between approximately 192.5 nm and 194.5 nm.
Owner:LASERTEC CORP
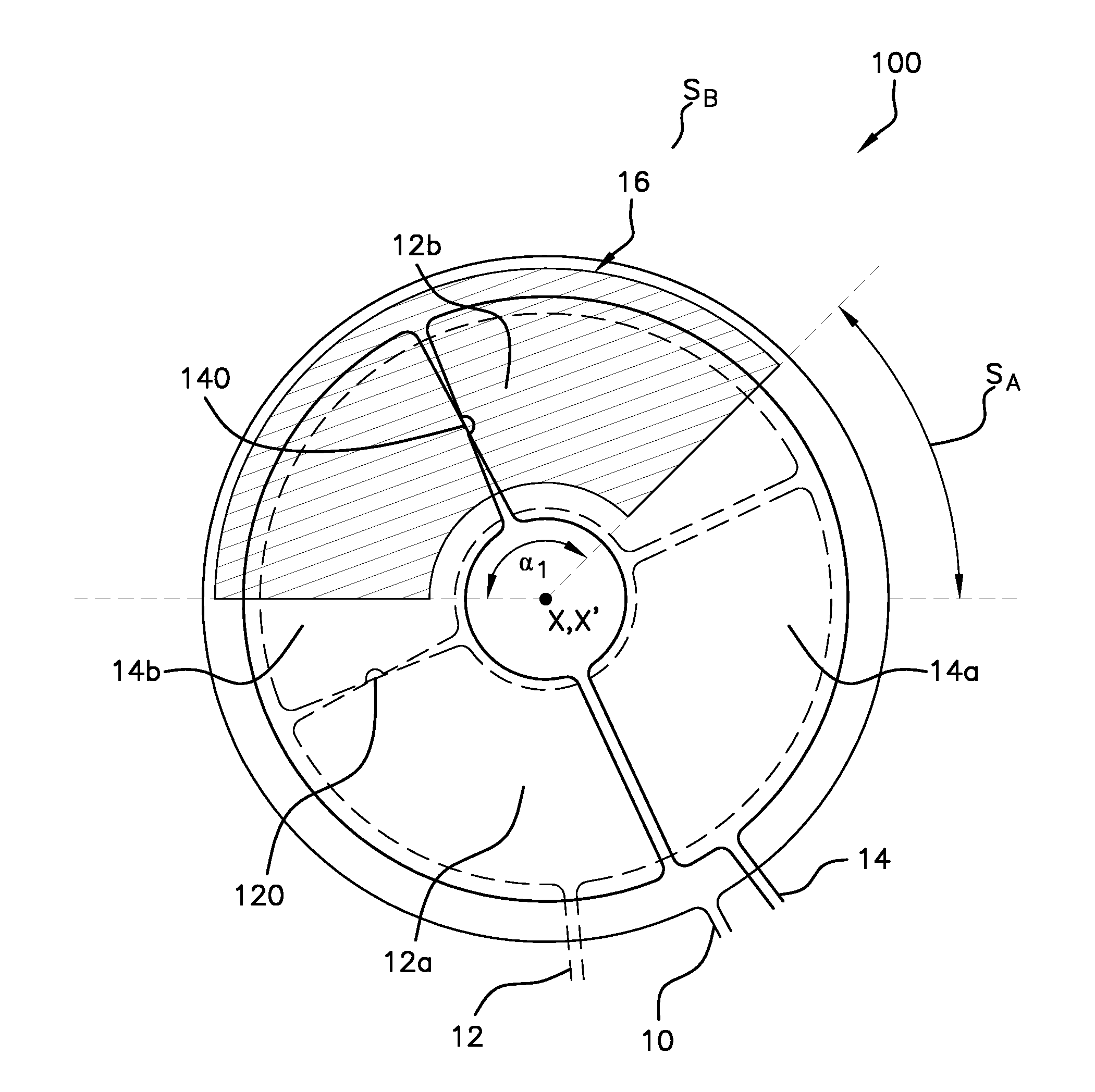
Inductive sensor for angular measurement of the position of a moving part and measuring method using such a sensor
ActiveUS20140167788A1Improve linearityReducing angular openingResistance/reactance/impedenceUsing electrical meansFourth harmonicClassical mechanics
An inductive sensor includes a primary winding, two secondary windings and a moveable target, the primary winding being centered about a central axis and carrying a high-frequency alternating current which can induce a voltage in secondary windings, the secondary windings also being centered about the central axis and made up of a number k of substantially identical loops, which are successively crossed and arranged opposite the primary winding. In this case, the target is made up of a part having p=1 angular sector with an angular opening. The opening of the angular sector of the target is less than that of a loop of secondary winding with a deviation calculated such as to eliminate the fourth harmonic of the linearity deviation Fourier decomposition, between the measured angular value and real angular value for the position of the target over the measurement course.
Owner:VITESCO TECH GERMANY GMBH
Deep ultraviolet laser apparatus
InactiveUS20070064749A1Generate efficientlyIncrease productionLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersFourth harmonicAudio power amplifier
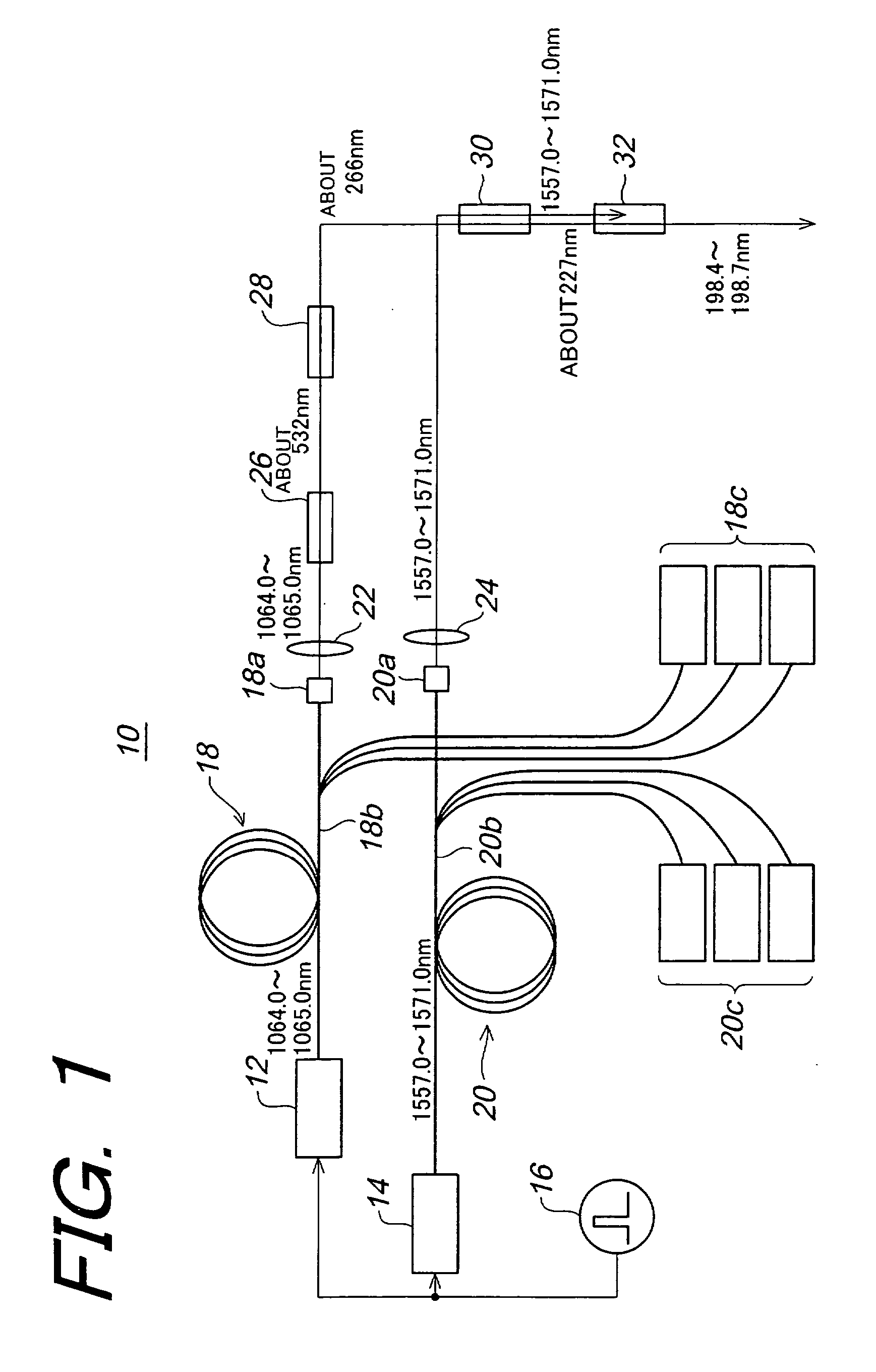
In order to generate efficiently a deep ultraviolet laser beam having a wavelength in a deep ultraviolet region and to make the generated laser beam to be high output, it is arranged in such that a laser beam having about 227 nm wavelength is generated by sum-frequency mixing of fourth harmonic of the laser beams obtained by amplifying semiconductor laser beams having 1064.0 to 1065.0 nm wavelengths by means of an optical fiber amplifier, and the laser beams obtained by amplifying semiconductor laser beams having 1557.0 to 1571.0 nm wavelengths by means of another optical fiber amplifier; and further laser beams having 198.4 to 198.7 nm wavelengths are generated by sum-frequency mixing of the above sum-frequency mixed laser beam and the above-described semiconductor laser beams having 1557.0 to 1571.0 nm wavelengths.
Owner:ADVANCED MASK INSPECTION TECH +1
Bass boosting processing method and device
InactiveCN1801611ASimple structureGood bass boostElectrophonic musical instrumentsStereophonic circuit arrangementsBandpass filteringFourth harmonic
Owner:SHENZHEN LANGUANG ELECTRONICS INDAL CORP
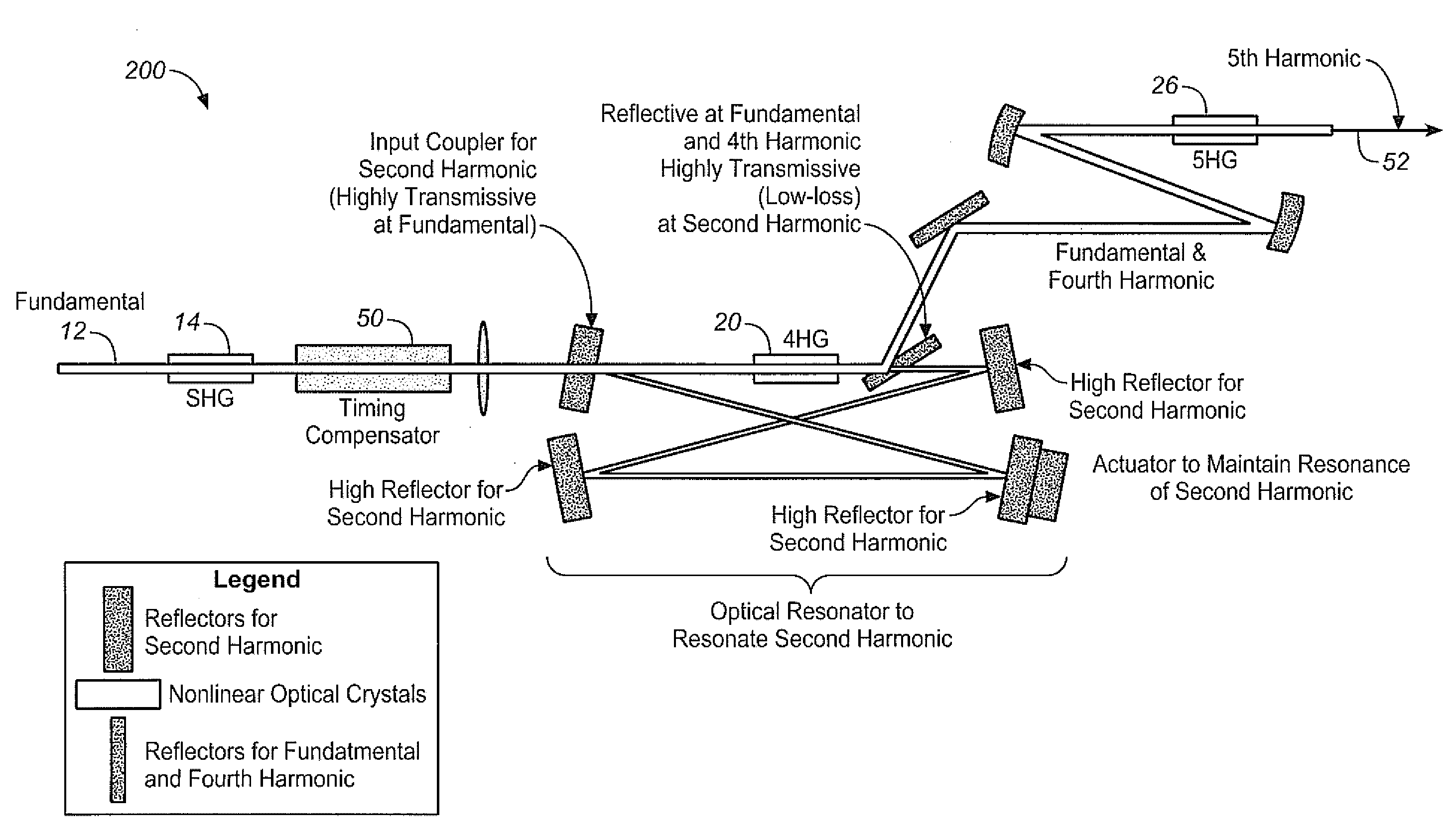
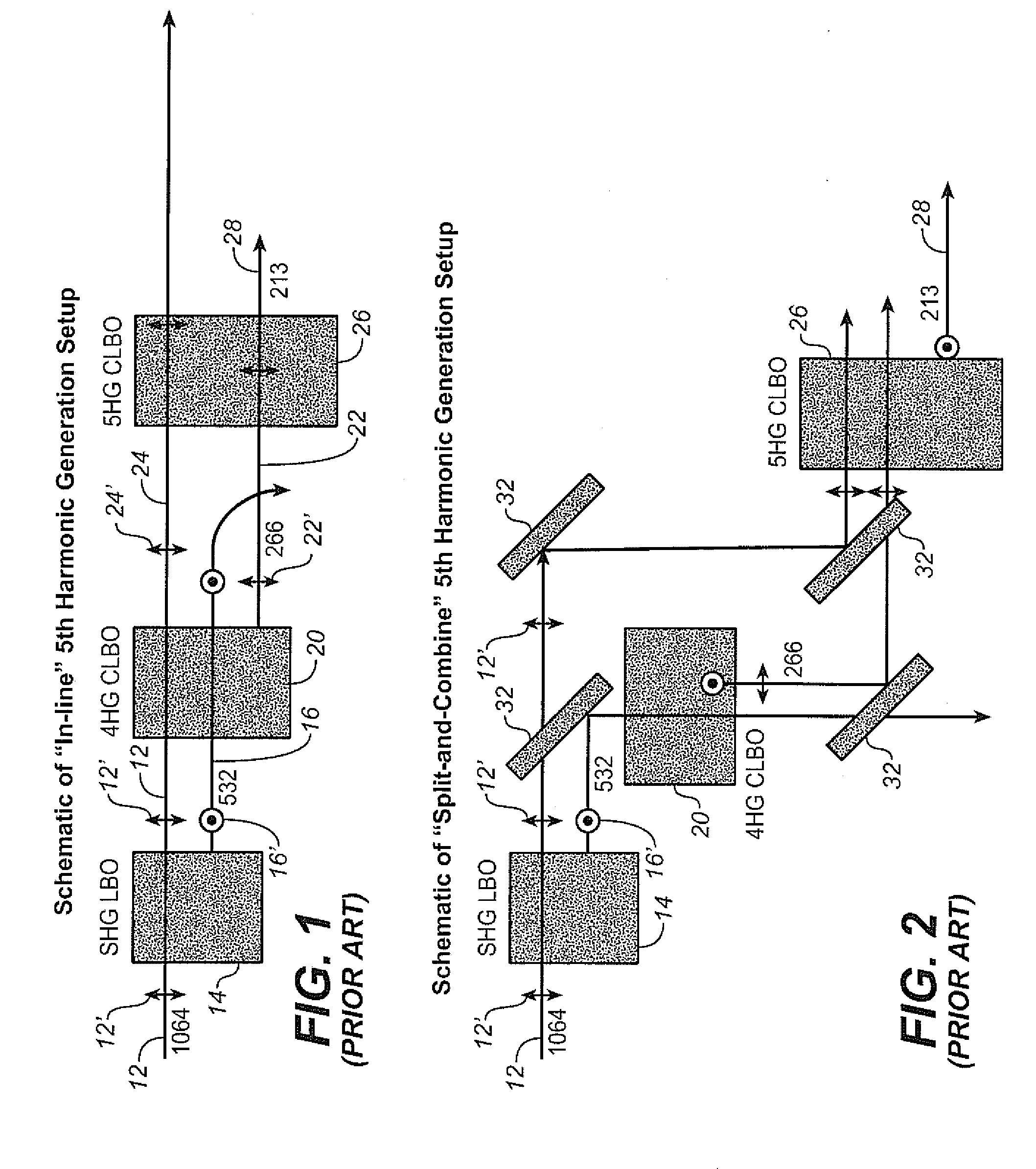
Efficient pulse laser light generation and devices using the same
A time delay is introduced in the optical path of the light pulse at fundamental wavelength relative to that for the fourth harmonic light pulse in a set up for generating the 5th harmonic, to compensate for at least a portion of the time delay of the fourth harmonic relative to the fundamental wavelength caused by 4HG generation. In one embodiment, this is achieved by introducing a time delay of the fundamental relative to the second harmonic wavelength, such as preferably by means of a timing compensator in the optical paths of the second harmonic and the fundamental wavelength. Preferably, any further delay of the fourth harmonic relative to the fundamental wavelength caused by other optical components can also be compensated for in this manner.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA +1
Method and apparatus for reducing capacitively coupled radio frequency energy between a semiconductor device and an adjacent metal structure
ActiveUS7204701B1Reduce radiationMaximize absorptionCross-talk/noise/interference reductionPrinted circuit aspectsCapacitanceFourth harmonic
A bolster plate apparatus, used to secure a semiconductor device intermediate a printed circuit board and a heat sink apparatus, includes either an indentation or an open aperture into which a radio frequency absorptive material may be disposed. The absorptive material may be a ferrite material specifically selected to absorb frequencies in the range of the second to fourth harmonic of the processor clock signal frequency. The type of the ferrite material implanted in the bolster plate is selected to maximize the absorption of radio frequency energy, particularly that emitted at the pad vias on the underside of the printed circuit board, without affecting the signal integrity of the other pad connections. The shape of the cutout or aperture is also defined by the arrangement of RF emitting pads on the underside of the printed circuit board. The open aperture, without any absorptive material, effectively increases the distance between the source of the radio frequency energy and the metal body of the bolster plate, thereby reducing the amount of radio frequency energy absorbed by the bolster plate and the electromagnetic interference generated thereby. Also disclosed is a method for reducing the radiated emission from an adjacent semiconductor device by selectively removing pads from the undersurface of the PCB board to effectively reduce the sources of the radio frequency energy, and, therefore the amount of RF energy capacitively coupled with RF energy metal body of the bolster plate.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
All-solid-state short wave ultraviolet laser source
InactiveCN103199429AIncrease powerHigh beam qualityActive medium materialNon-linear opticsNonlinear optical crystalFourth harmonic
The invention discloses an all-solid-state short wave ultraviolet laser source which comprises a near-infrared base frequency laser, a second harmonic frequency non-linear optical crystal, a light beam matching regulator control system, a fourth harmonic frequency non-linear optical crystal and a light beam splitting collimation reshaping system, wherein the second harmonic frequency non-linear optical crystal, the light beam matching regulator control system, the fourth harmonic frequency non-linear optical crystal and the light beam splitting collimation reshaping system are sequentially arranged along the laser output direction of the near-infrared base frequency laser. The near-infrared base frequency laser outputs a near-infrared laser, a second harmonic frequency laser is generated through the second harmonic frequency non-linear optical crystal and enters the fourth harmonic frequency non-linear optical crystal through the light beam matching regulator control system, a high-efficiency fourth harmonic frequency laser is generated, and output of a short wave ultraviolet laser with high power and high light beam quality is achieved through the light beam splitting collimation reshaping system. According to the all-solid-state short wave ultraviolet laser source, output of the high-efficiency near-infrared base frequency laser is achieved through precise wavelength choice technology and low-gain laser oscillation amplification technology, output of the high-efficiency second harmonic frequency laser is achieved through the non-linear optical crystal, then generation of the high-efficiency fourth harmonic frequency laser is achieved through the non-linear optical crystal, and therefore the output of the short wave ultraviolet laser with the high power and the high light beam quality is achieved.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-power external-cavity optically-pumped semiconductor lasers
InactiveUS20050220165A1Temperature safetyLarge fundamental mode-sizeLaser optical resonator constructionExcitation process/apparatusFourth harmonicWavelength
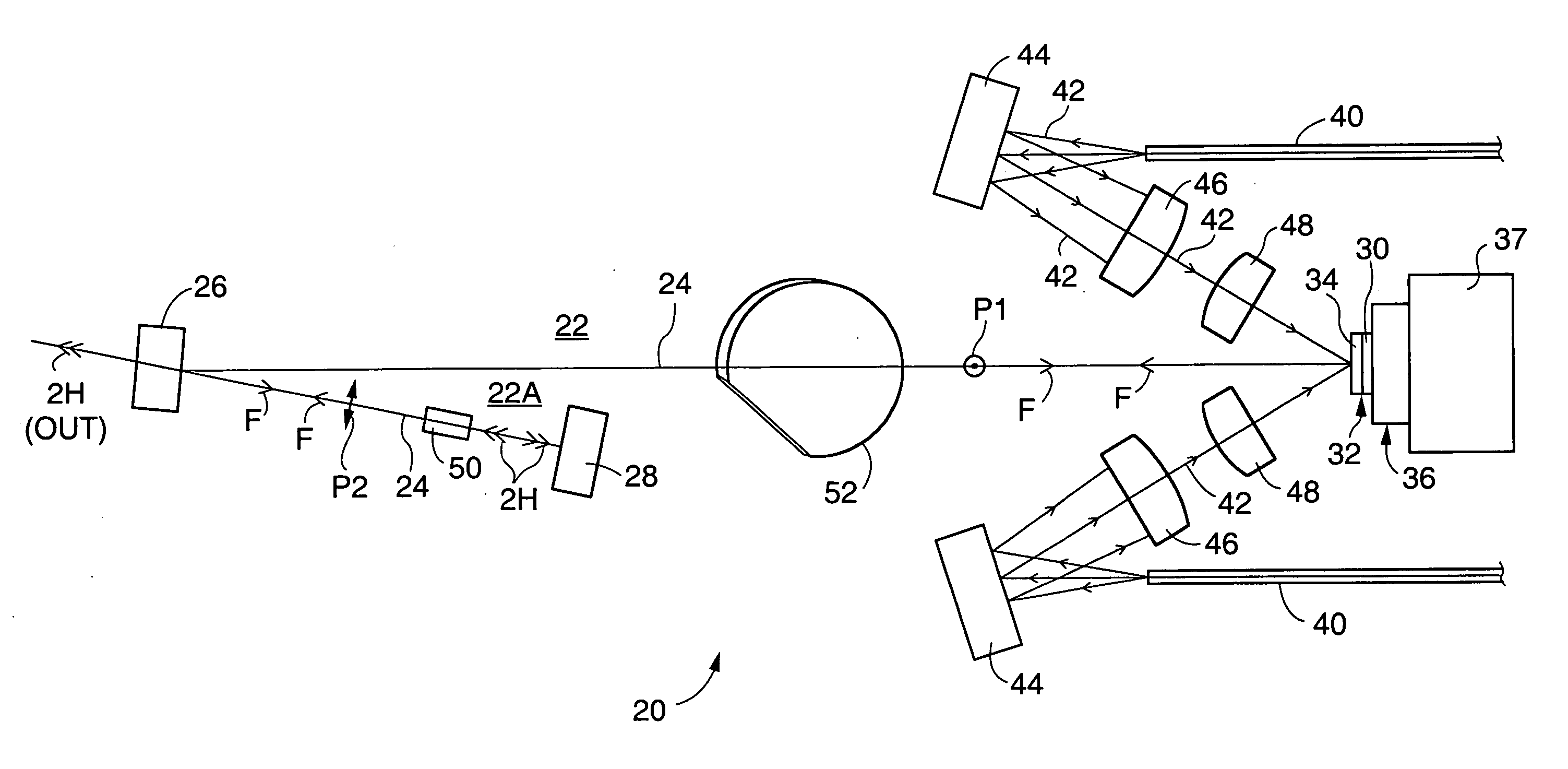
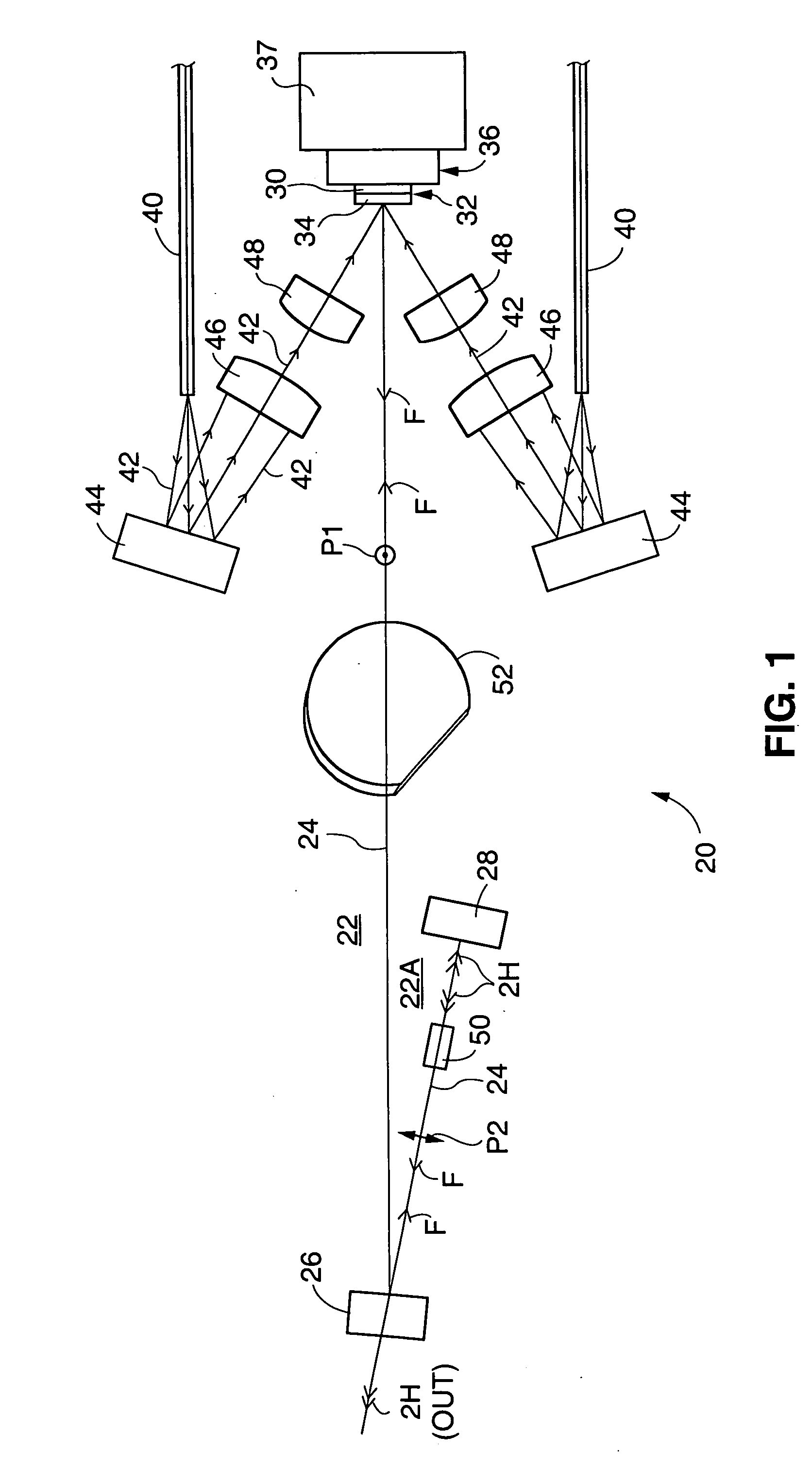
External-cavity optically-pumped semiconductor lasers (OPS-lasers) including an OPS-structure having a mirror-structure surmounted by a surface-emitting, semiconductor multilayer (periodic) gain-structure are disclosed. The gain-structure is pumped by light from diode-lasers. The OPS-lasers can provide fundamental laser output-power of about two Watts (2.0 W) or greater. Intracavity frequency-converted arrangements of the OPS-lasers can provide harmonic laser output-power of about one-hundred milliwatts (100 mW) or greater, even at wavelengths in the ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum. These high output powers can be provided even in single axial-mode operation. Particular features of the OPS-lasers include a heat sink-assembly for cooling the OPS-structure, a folded resonator concept for providing optimum beam size at optically-nonlinear crystals used for frequency conversion, preferred selection of optically-nonlinear materials for frequency-conversion, and compound resonator designs for amplifying second harmonic-radiation for subsequent conversion to third or fourth harmonic radiation.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Fourth harmonic generating system using optical double side-band suppressed carrier modulator
InactiveUS7853153B2Promote generationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingFourth harmonic generationFourth harmonic
The present invention is to provide an optical modulating system for generating a signal of a frequency (f0+2fm) and a signal of a frequency (f0−2fm) and suppressing a signal of a frequency (f0) by a DSB-SC modulator.A fourth harmonic generating system for solving the above problem comprises a first DSB-SC modulator (2) a second DSB-SC modulator (3) and a signal control section (5) for controlling a modulating signal from a signal source (4) for generating modulating signals applied to the first and second DSB-SC modulators (2,3) so that a lower side-band signal (f0) generated by modulating the upper side-band signal of the DSB-SC modulator (2) by the DSB-SC modulator (3) and an upper side-band signal (f0) generated by modulating the lower side-band signal of the DSB-SC modulator (2) by the DSB-SC modulator (3) cancel each other.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
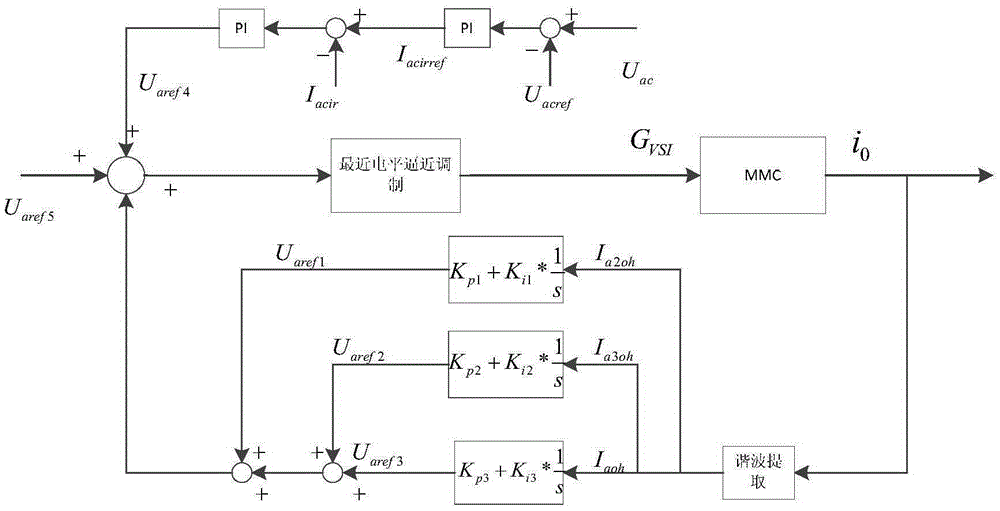
Control method for suppressing modularized multi-level current transformer output current harmonic wave
ActiveCN105406748AGuaranteed equal pressureGuaranteed uptimeDc-ac conversion without reversalNegative feedbackFourth harmonic
The invention discloses a control method for suppressing modularized multi-level current transformer output current harmonic wave. At first, the modularized multi-level output current is detected, a second harmonic component, a third harmonic component, and a fourth harmonic component or above are obtained by a Fourier analysis method and then are compared with 0, and the modulated voltage components of suppressed harmonic wave via a generalized frequency division PI regulator and are added to the modulated component under voltage stabilization control and the modulated component of the output voltage to obtain a total modulated voltage. After the total modulated voltage is obtained, the modulation is carried out by means of a closest level approximation method to obtain modularized multi-level current transformer triggering pulse. By means of the harmonic compensation scheme, the harmonic components, after being detected, of the output current are superposed to a control system through negative feedback, so that the output harmonic wave of the modularized multi-level current transformer can be directly and effectively suppressed.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
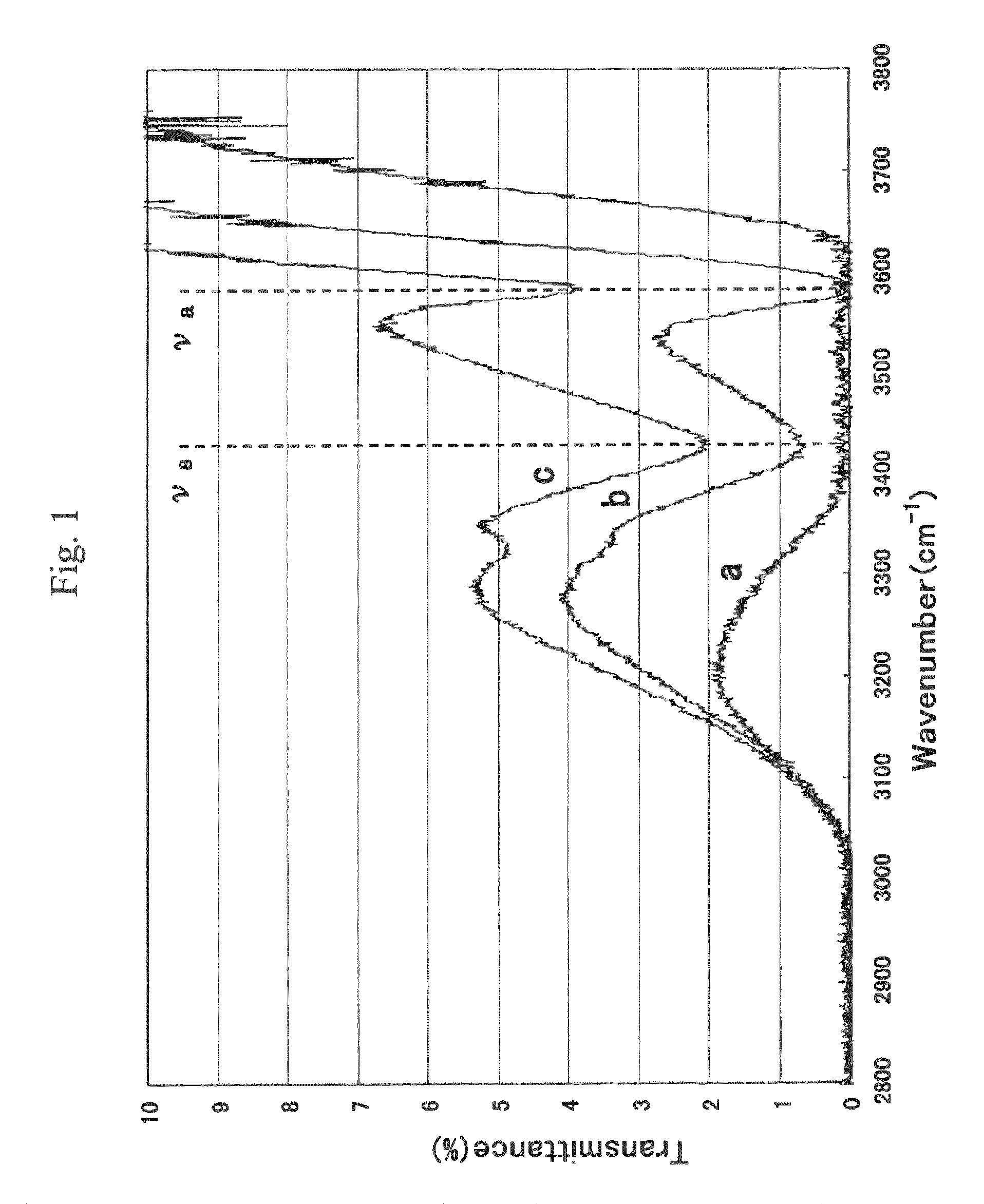
Optical wavelength conversion element having a cesium-lithium-borate crystal
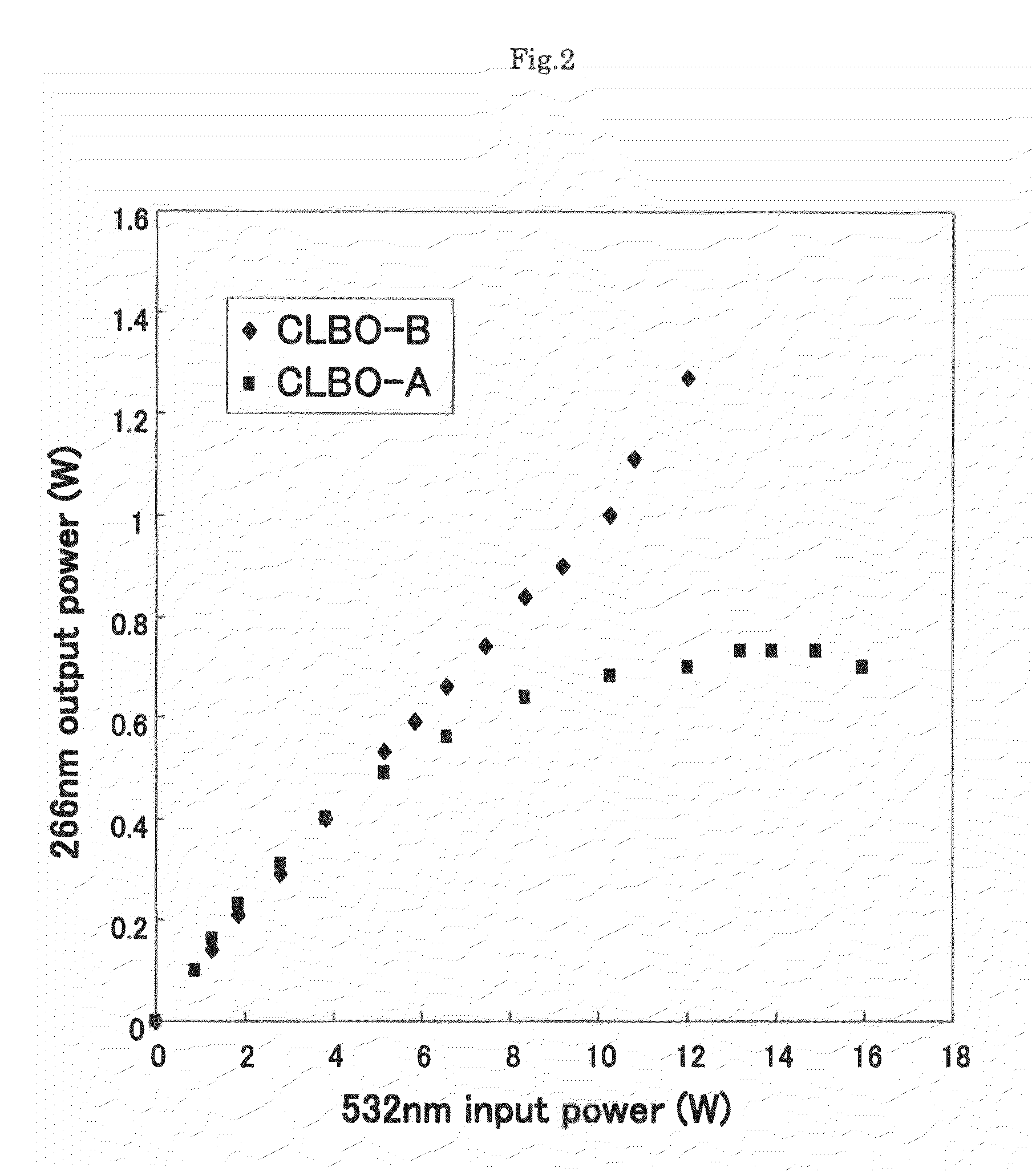
ActiveUS7948673B2Increase output powerImprove performanceLaser detailsLight demodulationFourth harmonicNd:YAG laser
An optical wavelength conversion element includes a cesium-lithium-borate crystal processed into a 10-mm long optical element cut in an orientation that allows a fourth harmonic of a Nd:YAG laser to be generated. A transmittance (Ta) at 3589 cm−1 in an infrared transmission spectrum of the optical element is used as an index that indicates a content of water impurities in the crystal and is independent of a polarization direction. An actual measurement of the transmittance Ta is at least 1%, without taking into account loss at an optically polished surface of the crystal. A wavelength conversion device, a ultraviolet laser irradiation apparatus, a laser processing system, and a method of manufacturing an optical wavelength conversion element are also described.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV +1
Laser system and laser wavelength conversion
InactiveUS20050008047A1Long-termPrevent rotOptical devices for laserNon-linear opticsNonlinear optical crystalComing out
A laser system is enabled to generate laser beam stably for a long term by avoiding the decay of nonlinear optical crystals due to moisture. The fundamental laser wave at a wavelength of 1064 nm is emitted from the pumping chamber unit of the solid-state laser device. The fundamental laser wave enters the first nonlinear optical crystal unit (20). The wavelength of the laser beam is converted into a half by the first nonlinear optical crystal unit (20). The converted laser beam emanates out of the unit. The fundamental laser wave and the second harmonic laser wave are introduced into the second nonlinear optical crystal unit. Each of the laser beams is converted into the third harmonic laser wave (three-time fundamental frequency) or the fourth harmonic laser beam (four-time fundamental frequency) and the laser beam comes out of the exit-window (34). The nonlinear optical crystal units (20), (30) are held in a hermetically sealed cell whose inner surface is treated to be water-repellent. As the dry atmosphere is kept by means of isolating the nonlinear optical crystal from the outer air, the crystals can avoid decay due to moisture and the damage on the crystals can be reduced.
Owner:ORC MFG
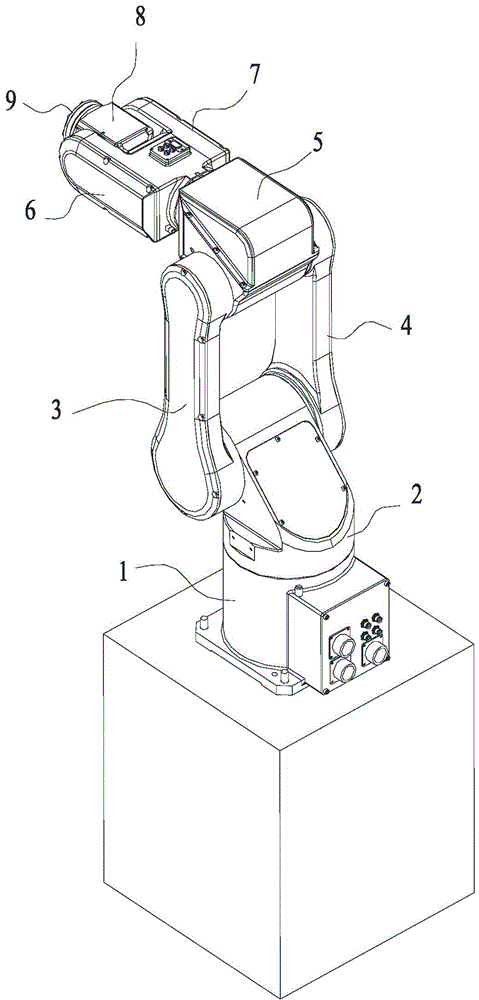
Six-axis robot
InactiveCN104308837AIncrease torquePrevent hogging spaceProgramme-controlled manipulatorFourth harmonicReduction drive
The invention discloses a six-axis robot which comprises a base, a rotating base, supporting big arms, shoulder joints, supporting small arms, wrist joints and a terminal end actuator, wherein a first servo motor is fixedly arranged in the inner cavity in the base, a first harmonic speed reducer is arranged on the lower end of the inner cavity of the rotating base, a second servo motor is fixedly arranged on the upper end of the inner cavity of the rotating base, a second harmonic speed reducer and a third harmonic speed reducer are arranged on the inner cavities of the supporting big arms, a third servo motor and a fourth servo motor are fixedly arranged on the inner cavities of the shoulder joints, a first belt wheel is fixedly connected to the output shaft of the fourth servo motor, a fifth servo motor, a fourth harmonic speed reducer and a fifth harmonic speed reducer are arranged on the inner cavities of the supporting small arms, a second belt wheel is fixedly connected to a soft wheel of the fourth harmonic speed reducer, the second belt wheel is in transmission connection with the first belt wheel through a first synchronization belt, a sixth servo motor and a sixth harmonic speed reducer are arranged on the inner cavities of the wrist joints, and the terminal actuator is fixedly connected with the soft wheel of the sixth harmonic speed reducer. The six-axis robot is good in flexibility and fast in action.
Owner:SHENZHEN DAYUCNC TECH
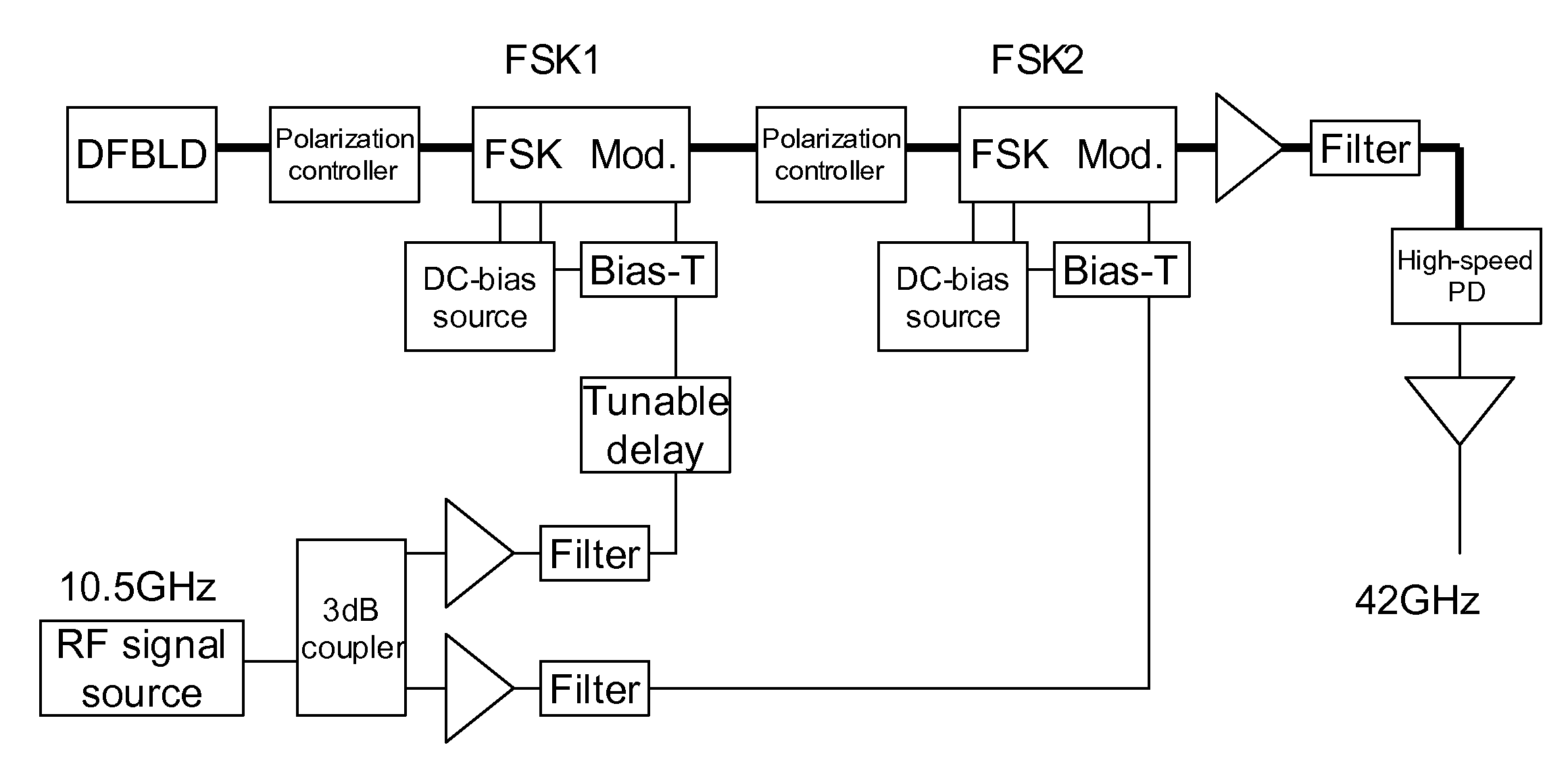
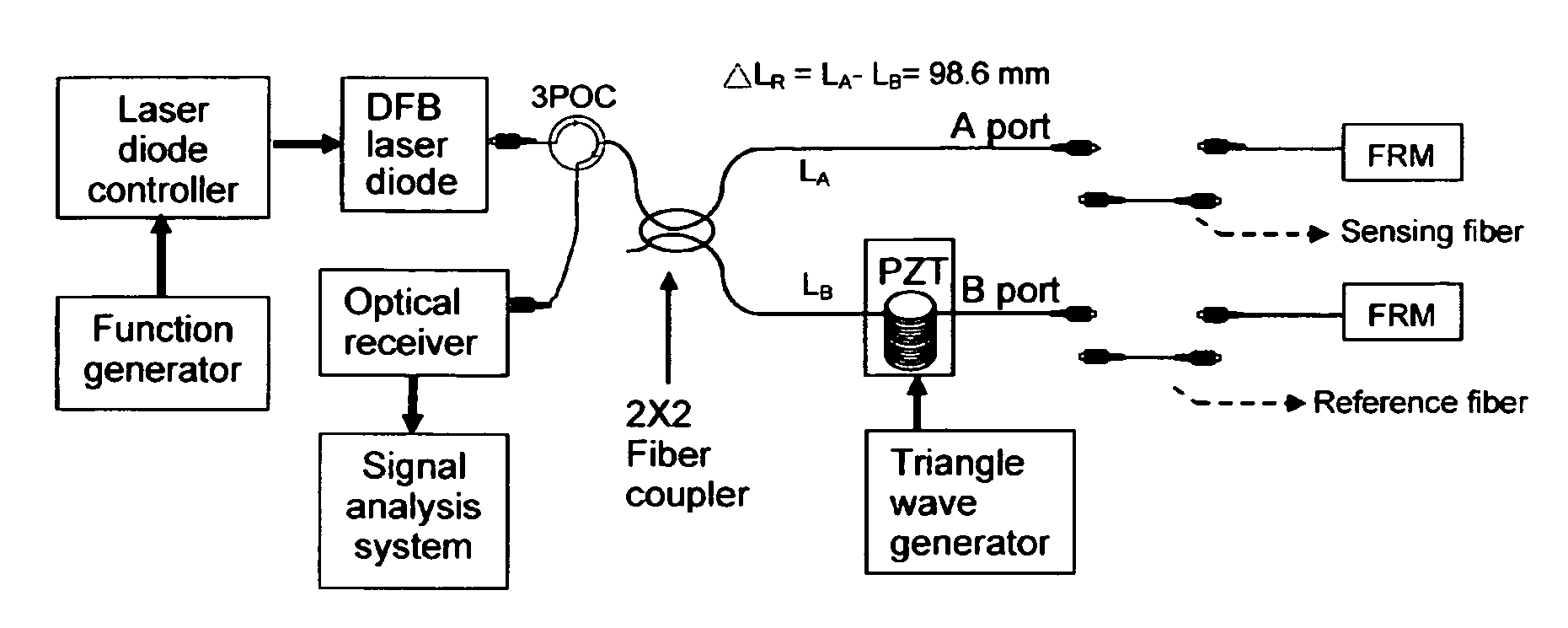
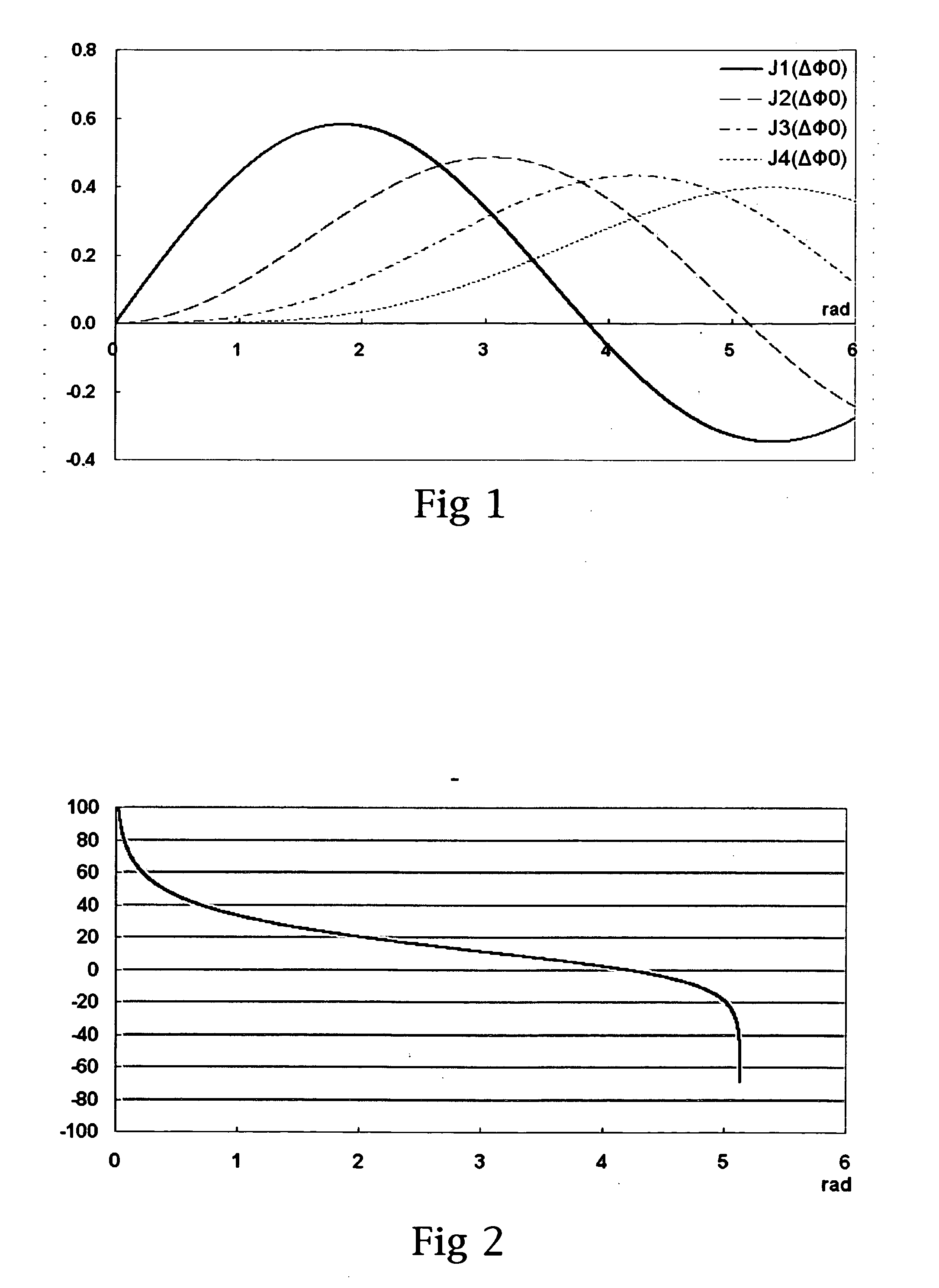
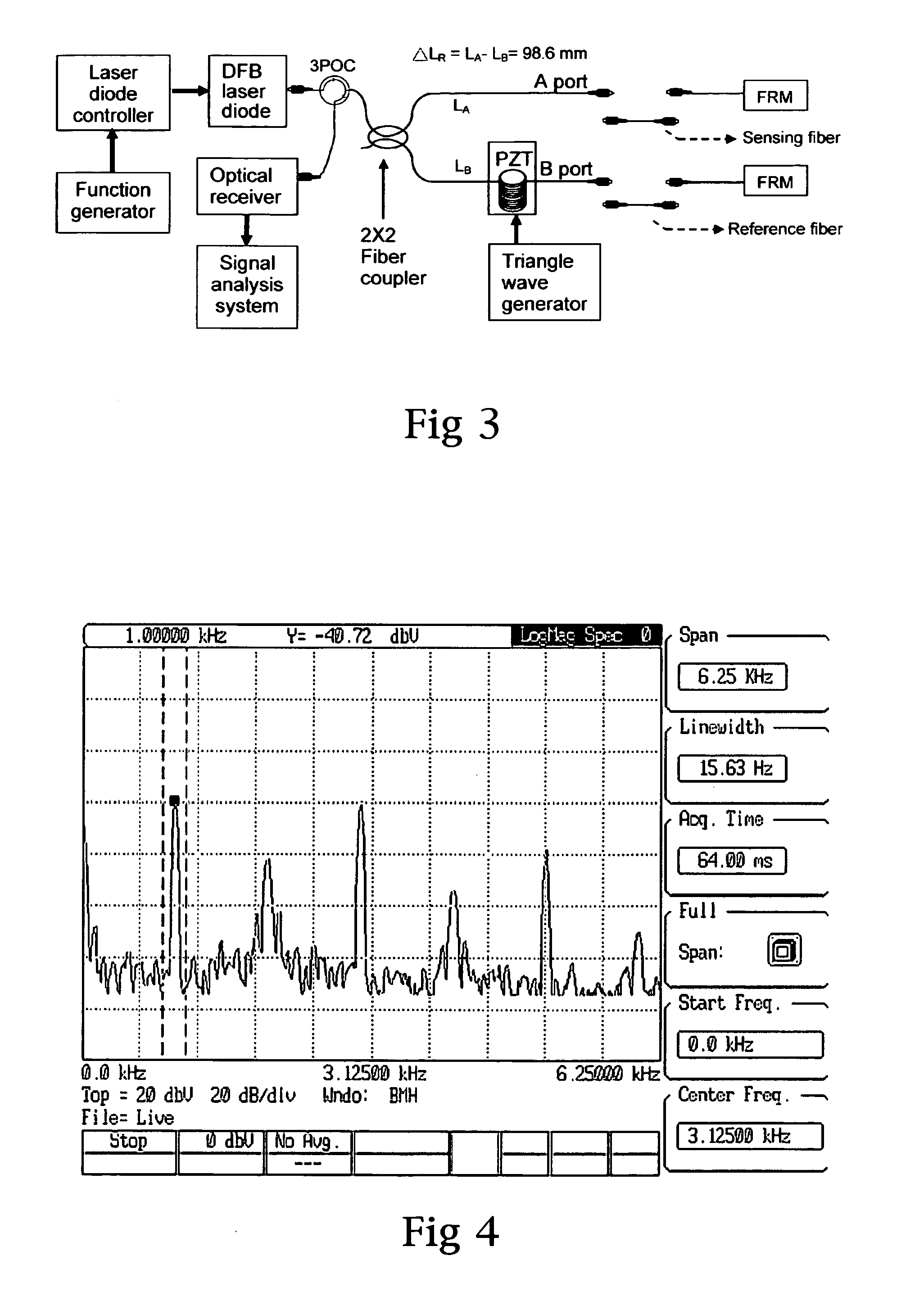
For path imbalance measurement of the two arms fiber optic interferometer
InactiveUS20100171960A1Accurate measurementReduce errorsUsing optical meansFourth harmonicCarrier signal
Path imbalance measurement of the two arms fiber optic interferometer includes employing a current carrier signal to modulate the semiconductor laser light source of the interferometer to let it output interference signals to generate a carrier phase signal through path imbalance of the interferometer. Then, the interference signals are expanded to be the harmonic components of carrier phase signal frequency by Bessel function. Subsequently, we use the specific relation between the second and the fourth harmonic components of the interference signals to develop the theory of path imbalance measurement. The method mentioned above can measure a few decimeters of path imbalance and its accuracy can reach to a millimeter.
Owner:NXTAR FIBER OPTIC SECURITY
Wilkinson power divider with harmonic suppression function
InactiveCN107634298AWith filtering characteristicsWith harmonic suppression functionCoupling devicesFourth harmonicThird harmonic
The invention discloses a Wilkinson power divider with a harmonic suppression function. The Wilkinson power divider with the harmonic suppression function comprises a dielectric layer, wherein one side of the dielectric layer is adhered with a signal metal layer, and the other side of the dielectric layer is adhered with a metal ground layer; and the signal metal layer comprises a microwave transmission branched circuit, a second harmonic suppression branched circuit, a third harmonic suppression branched circuit, a fourth harmonic suppression branched circuit and an isolating resistor. The invention is used for the Wilkinson power divider.
Owner:JIAMUSI UNIVERSITY
Millimeter-wave time division frequency-modulation shipborne multi-target detection collision-proof radar
InactiveCN101661107AIncrease the working distanceAvoid blind distanceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFourth harmonicAcousto-optics
The invention relates to the technical field of radio positioning radars, in particular to a millimeter-wave time division frequency-modulation shipborne multi-target detection collision-proof radar.A quasi-optical dielectric lens antenna annular array is arranged; a DSP cyclically scans wave beams to omni-directionally guard against a target possibly collided on a water surface; the radar receives / emits reference signals with full-phase-coherence, and adopts time division time sequence asynchronous control; signals of a water photographic sensor, a ship speed sensor and a global positioningsystem (GPS) sensor access an MCU control time division circuit to generate n-path modulation frequency and waveform millimeter-wave linear phase-lock frequency modulation, and are emitted through anR / T2, an optical circulator, a beam switch, and an antenna array; back waves are subjected to processing control in the DSP and the MCU through the antenna array, the beam switch, the optical circulator, an R / T1, a low noise high frequency amplifier, a fourth-harmonic mixer, an intermediate frequency amplifier, a time division circuit, and a multi-target signal related matched filter; and when theradar meets multiple targets, the radar inhibits false-alarm and determines azimuth angles, distances and relative speeds thereof through the DSP, displays three-dimensional images and identifies a target closest to the ship through a CRT, performs the audible and visual alarm if the distance of the target is smaller than a safety distance, intelligently avoids a barrier or reduces speed or brakes if the distance of the target is approximate to a danger distance, and controls and references an actual condition of the water surface to combine the speed of the ship and GPS data to make a choice, thereby obviously improving the sailing safety of the ship.
Owner:阮树成
Permanent-magnet rotary electric machine
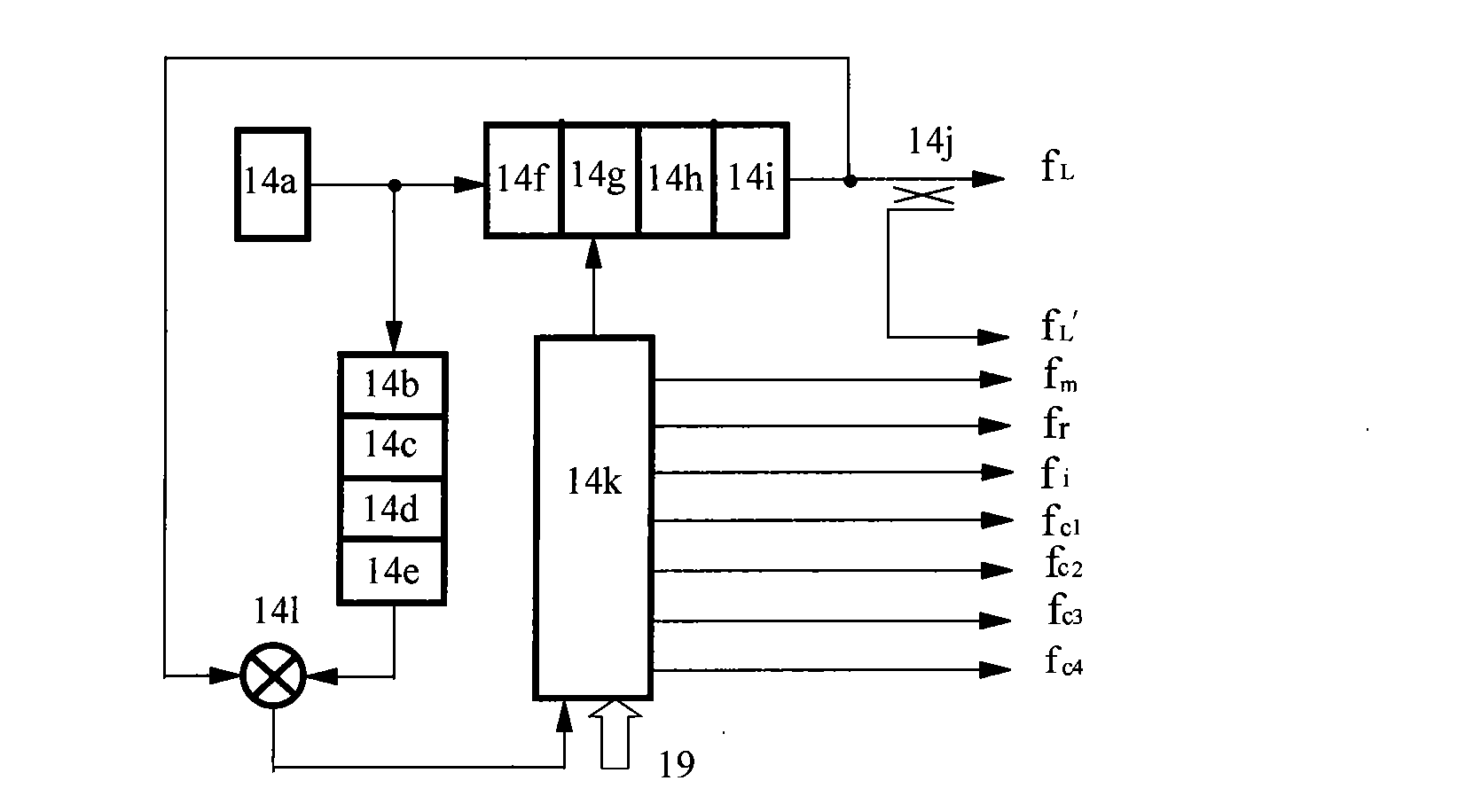
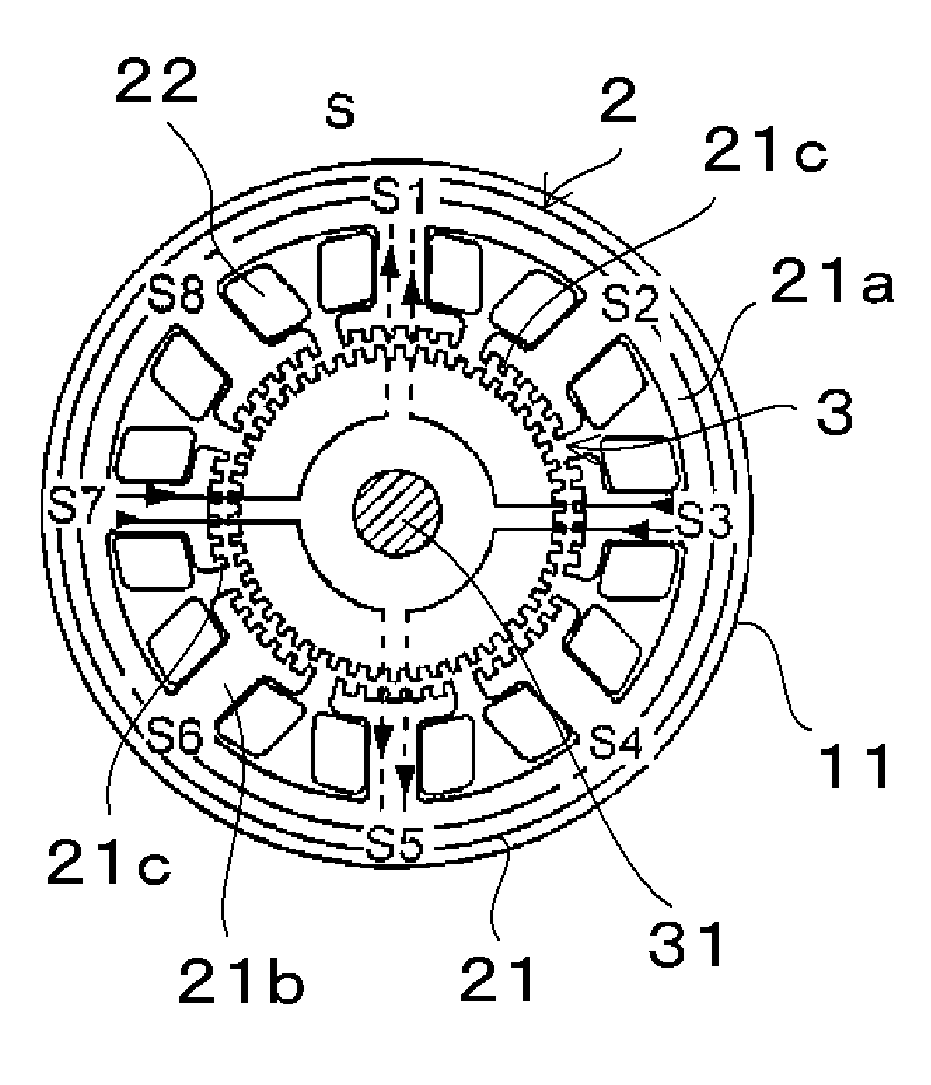
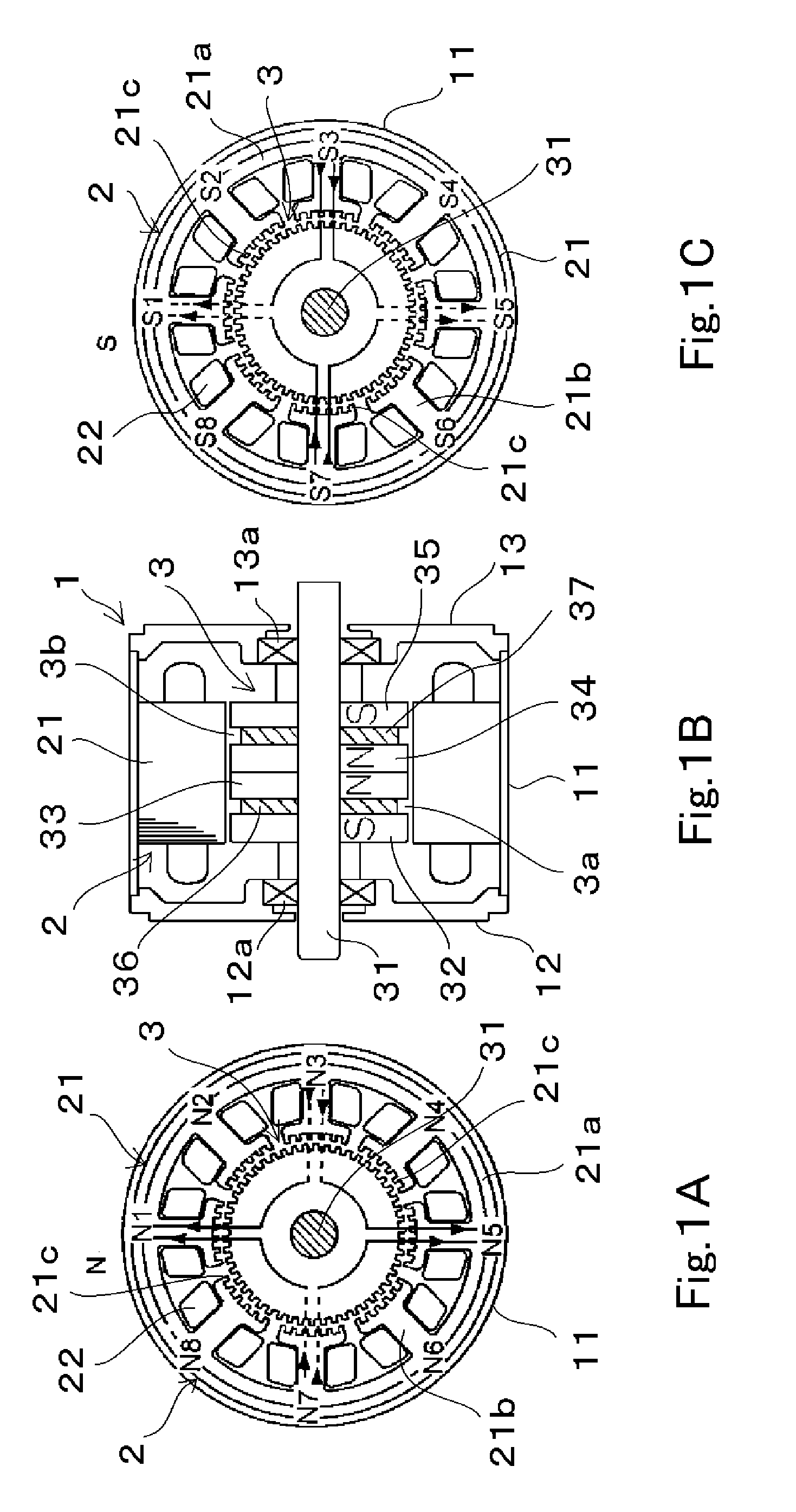
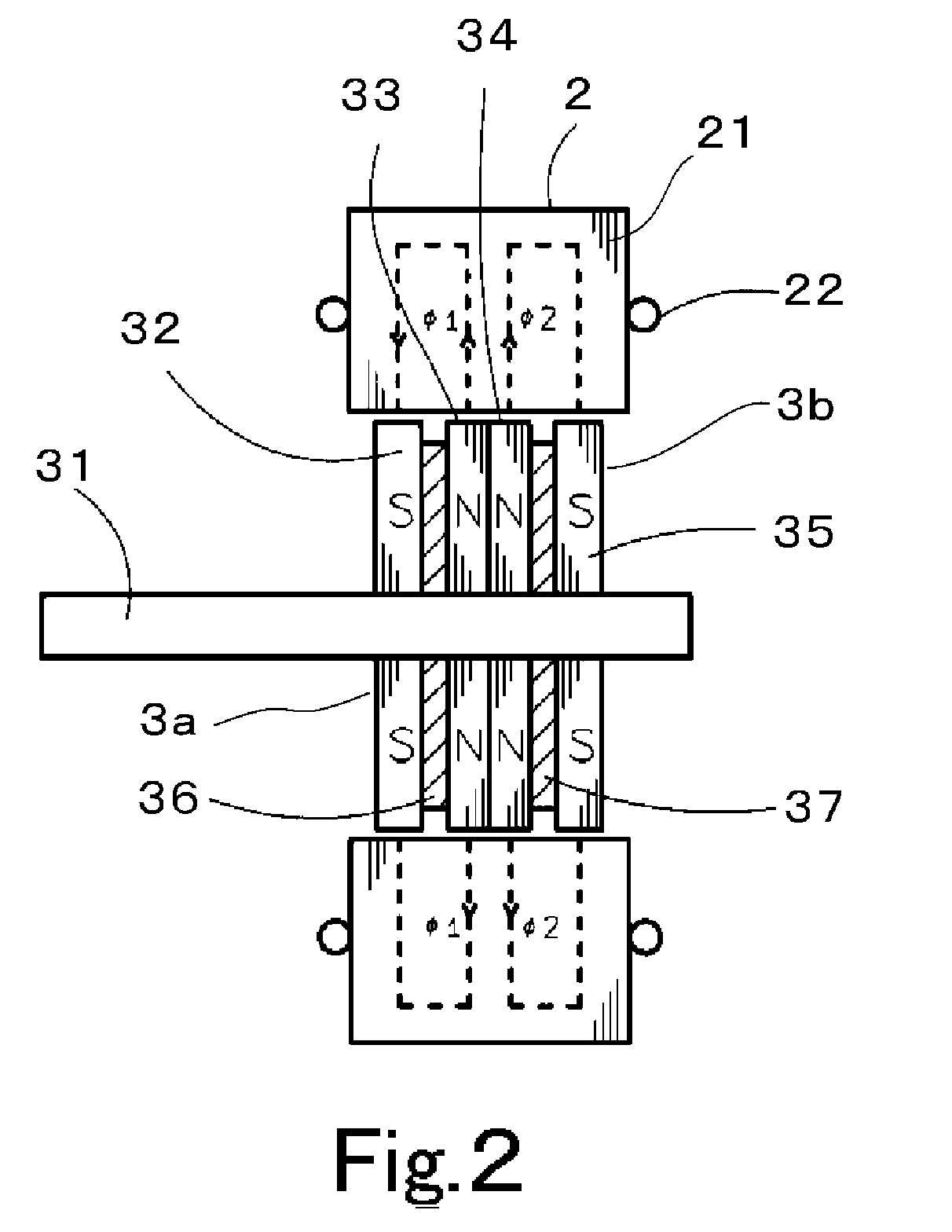
ActiveUS20100133929A1Shorten the length of the magnetic circuitShorten the lengthMaster clocksManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesFourth harmonicElectric machine
A permanent-magnet rotary electric machine preferably includes a stator and a rotor opposed thereto via an air gap. The stator includes a stator core having 4m (m is an integer equal to or larger than 2) main poles each having inductor teeth at a tip thereof. The rotor includes two rotor units adjacent to each other in the axial direction. Each rotor unit includes a pair of rotor magnetic poles and a permanent magnet arranged therebetween. The permanent magnets in the rotor are axially magnetized in opposite directions to each other. Each rotor magnetic pole has magnetic teeth on its outer periphery at a regular pitch. The rotor magnetic poles in each rotor unit are arranged such that the magnetic teeth of one rotor magnetic plate are offset by half a pitch from those of the other rotor magnetic pole, and the magnetic teeth of adjacent rotor magnetic poles are aligned with each other in the axial direction. The tooth pitch of the inductor teeth of each stator main pole is different from that of the magnetic teeth of the rotor magnetic pole to generate a fourth harmonic component of a permeance between the stator and the rotor zero.
Owner:NIDEC SERVO CORP
Optical quadruple frequency millimeter wave optical carrier wireless communication system
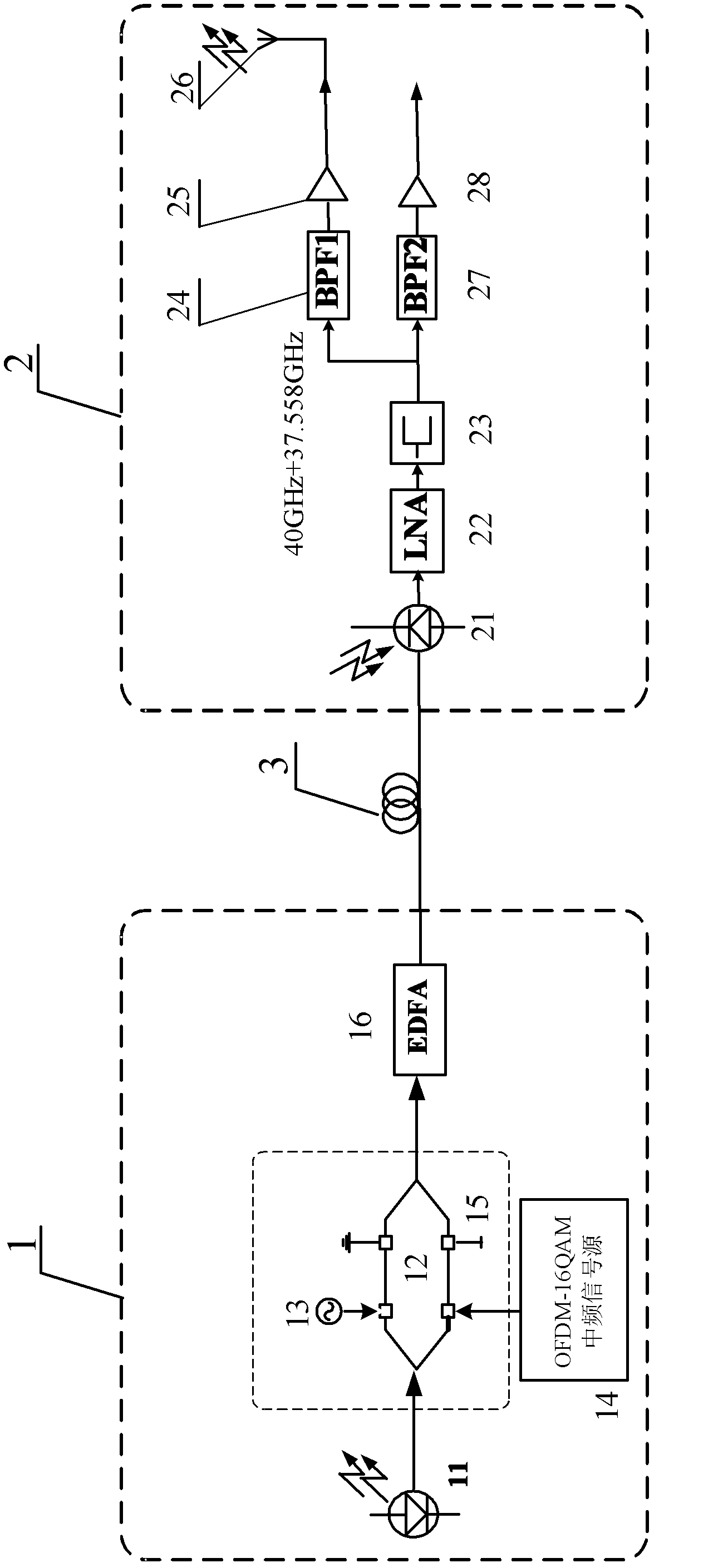
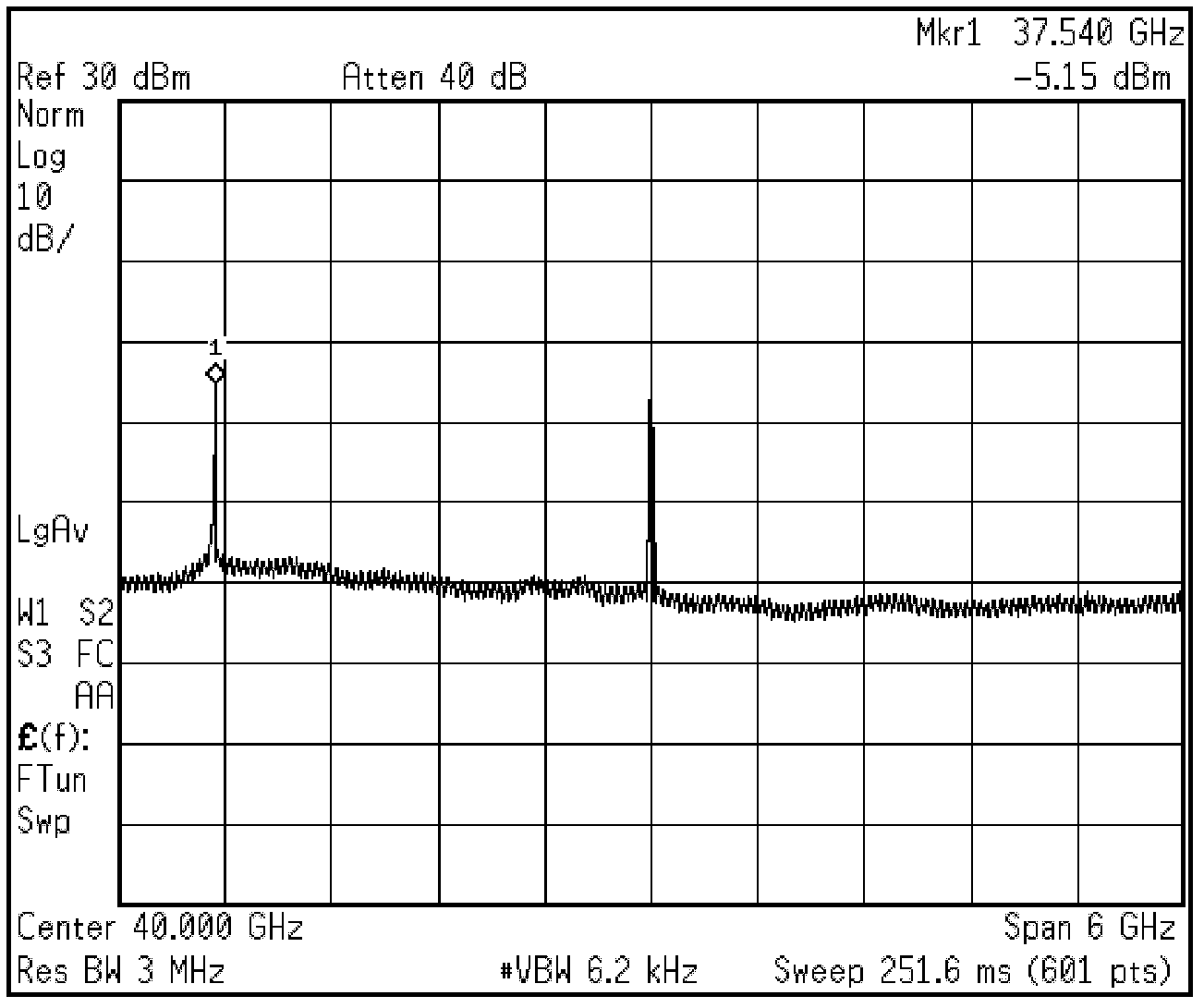
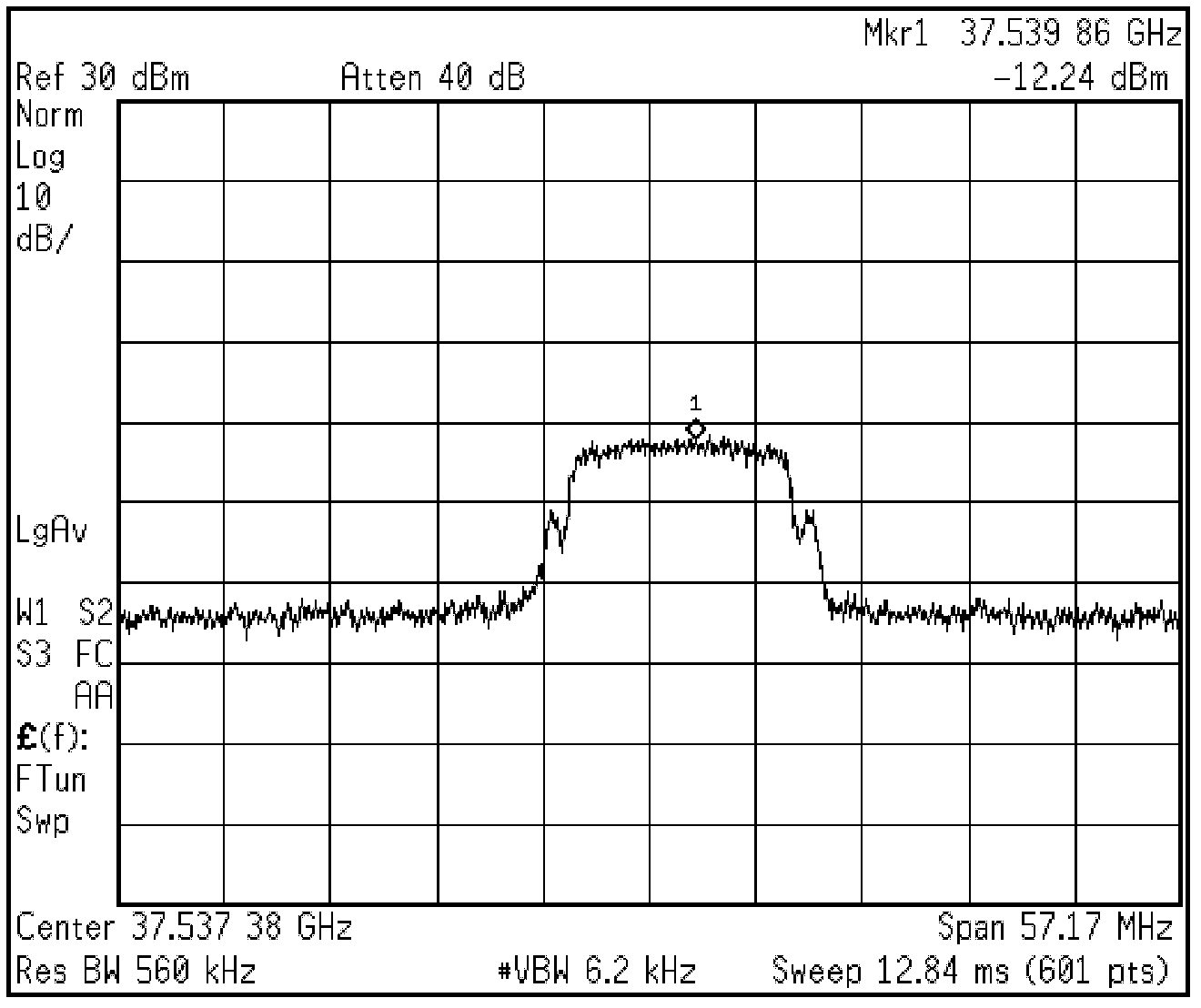
InactiveCN102324979AReduce the oscillation frequencySimple structureMulti-frequency code systemsRadio-over-fibreFourth harmonicData information
The invention relates to an optical quadruple frequency millimeter wave optical carrier wireless communication system which comprises a center station, a base station and a downlink fiber. The center station and the base station are in fiber connection through a down link. The center station comprises a laser, a double-electrode Mach-Zehnder optical modulator and an erbium doped fiber amplifier which are in series connection in order. The double-electrode Mach-Zehnder optical modulator is used for generating a fourth harmonic side frequency component containing a cosine microwave signal, and carrying OFDM-16QAM data information. The base station is used for receiving the fourth harmonic side frequency component containing the cosine microwave signal and carried OFDM-16QAM data information, and through carrying out bias set, filtering and amplification on the received signal, a millimeter wave signal of OFDM-16QAM modulation for antenna emission is obtained. The system in the invention has the characteristics of simple structure, easy realization and low cost.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Measurement method of modulation degree and initial phase used for sinusoidal phase modulating interference measurement
The invention relates to measurement of the modulation degree and the initial phase of sinusoidal phase modulating interference measurement. The object of the invention is to propose a method for overcoming the defect of complicated measuring process of the modulation degree in the sinusoidal phase modulating interference measurement, the method is simple and feasible, and the calculated modulation degree value avoids errors in the principle. According to the technical scheme, the measurement method of the modulation degree and the initial phase of sinusoidal phase modulating interference measurement includes: light splitting of light beams emitted by a laser is performed by employing a light-splitting apparatus to construct a Michelson interferometer, and sine modulation is performed on an interference phase by employing an external modulation technology or an internal modulation technology; and a photoelectric conversion module receives modulated Michelson interference signals, the Michelson interference signals are input to a signal processing module after analog-to-digital conversion, a fourth harmonic amplitude is extracted, and the modulation degree and the initial phase are solved through calculation. The method is mainly applicable to occasions of modulation interference measurement.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
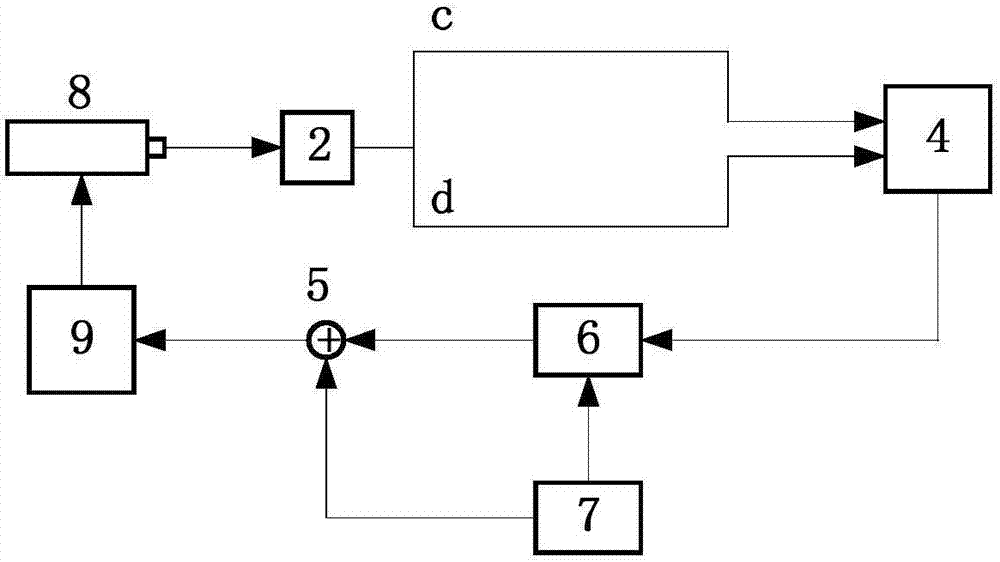
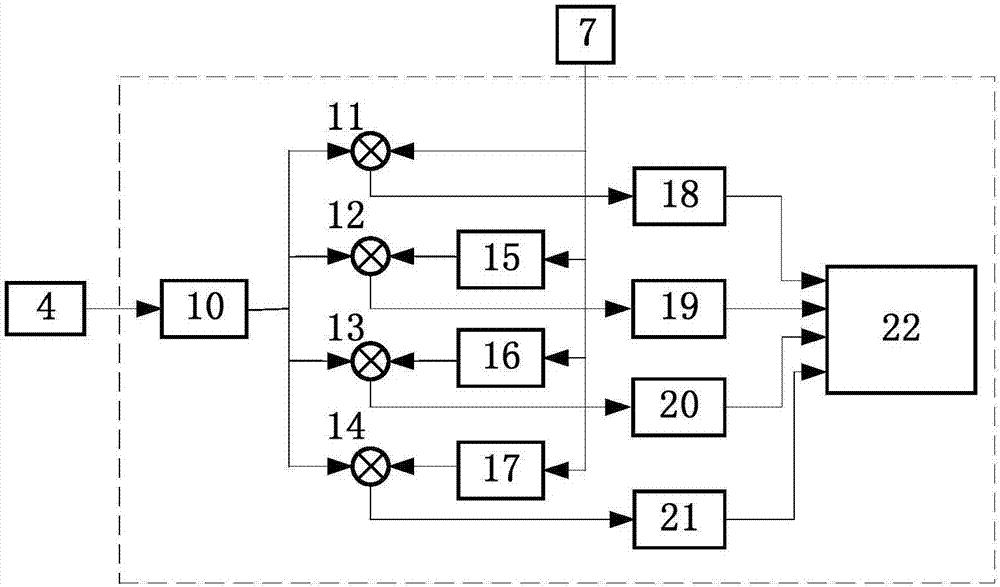
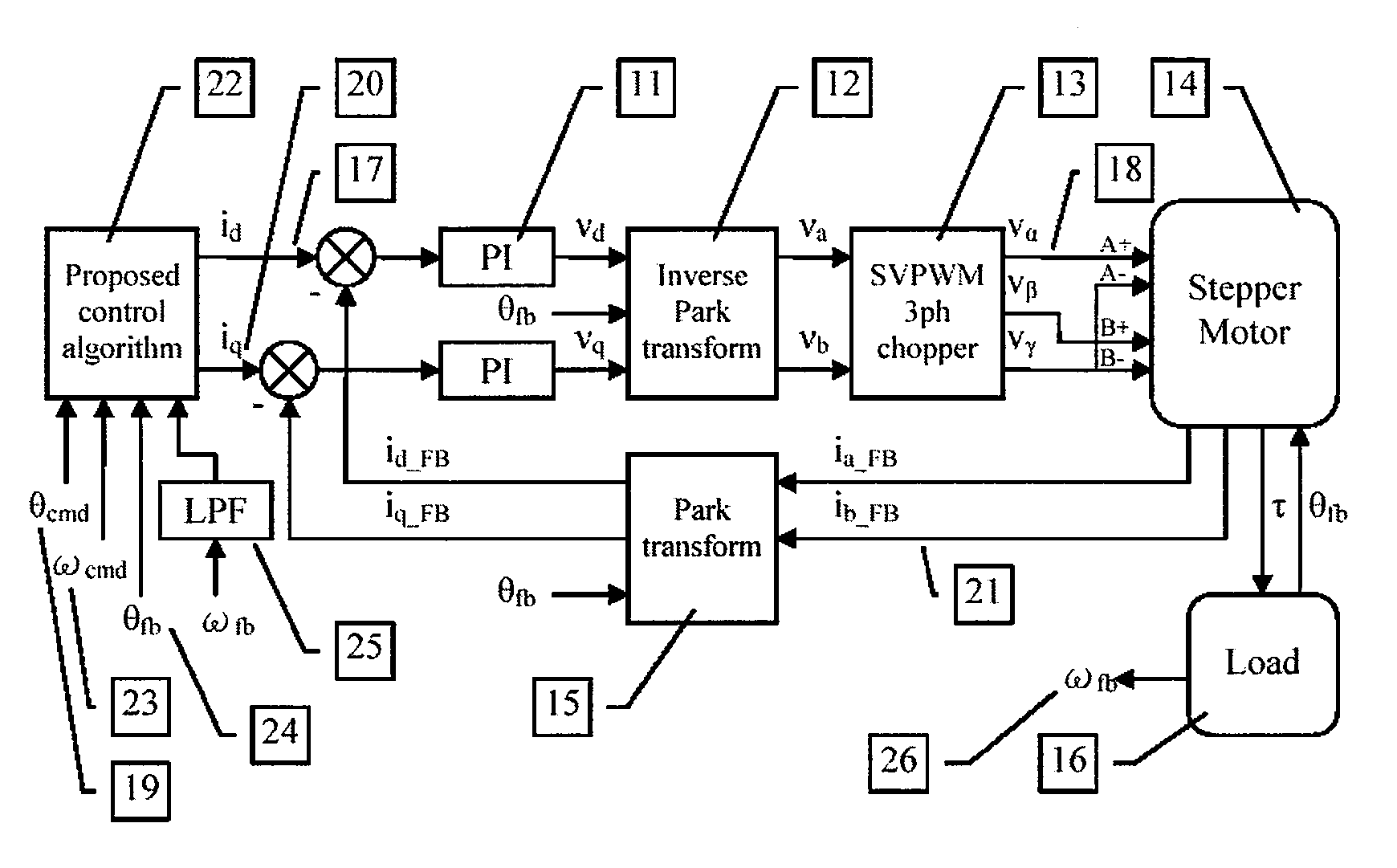
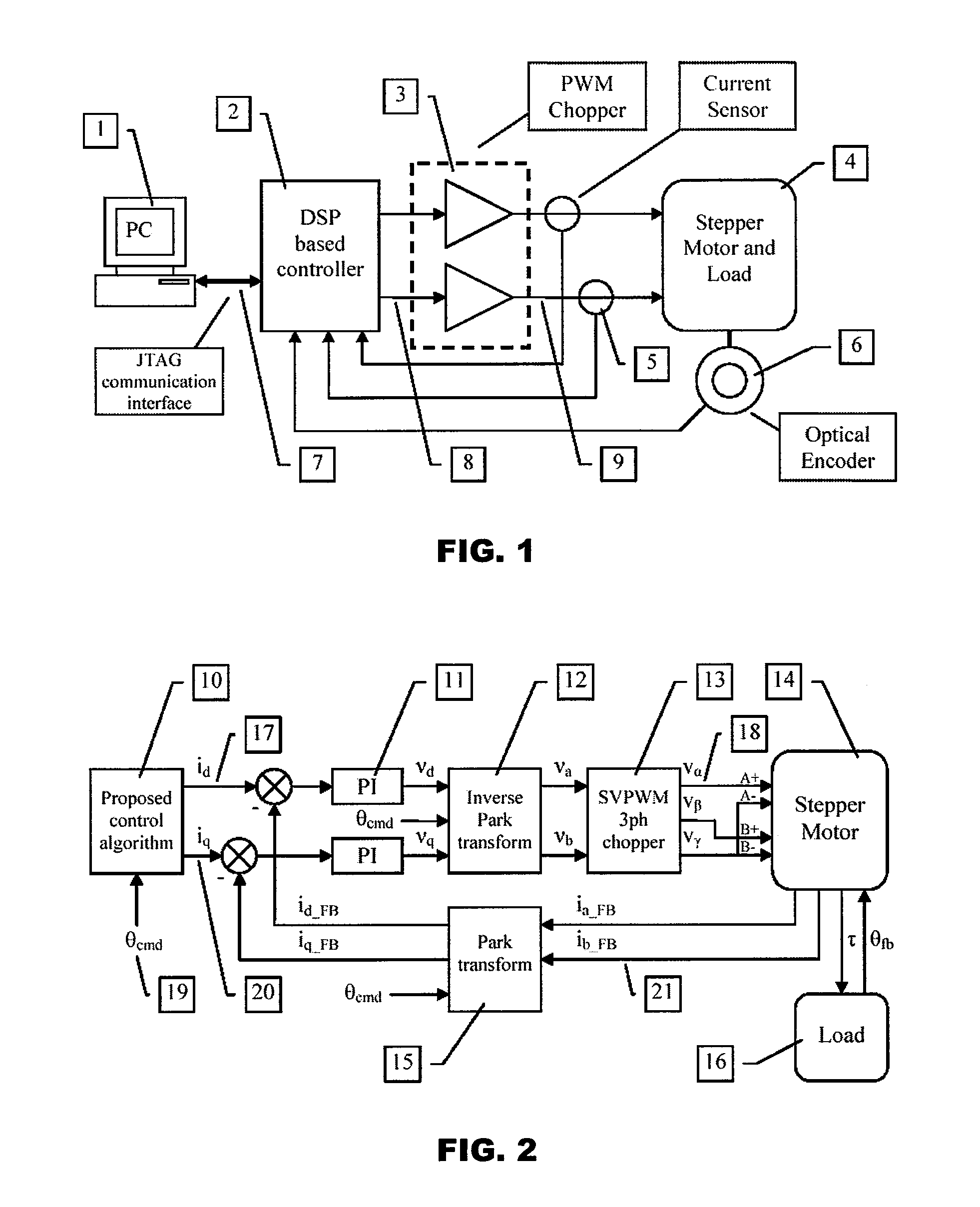
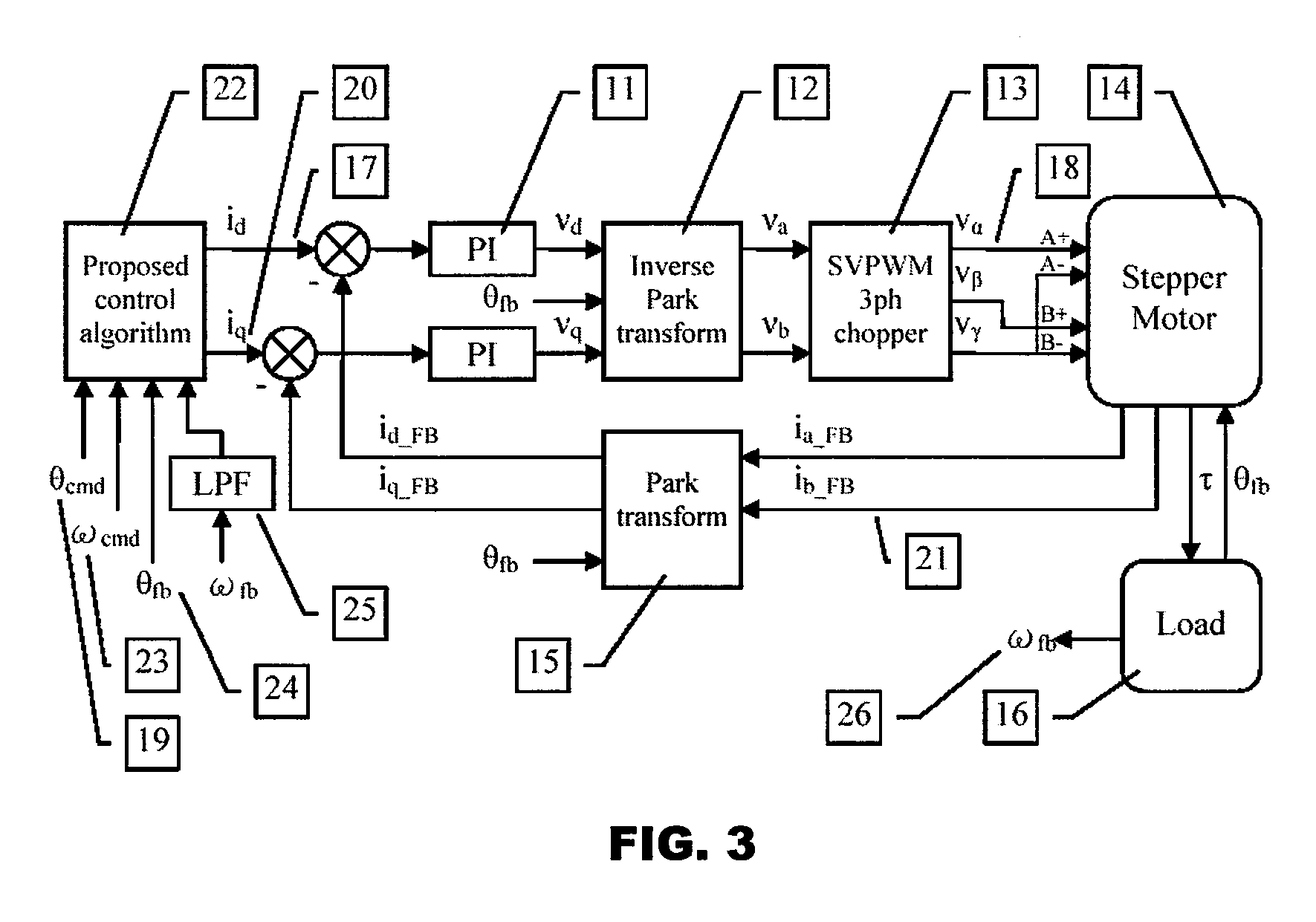
Model-based active electronic damping for stepper motors
ActiveUS7733051B2Efficient and accurateComputer controlTemperatue controlPhase shiftedFourth harmonic
A method for damping vibrations in a stepper motor with micro-stepping control which comprises the steps of identifying the force amplitudes and phase shifts of multiple harmonic detent torques of the stepper motor, such as the first, second and fourth harmonic detent torques, and tuning the stepper motor with different current commands until minimum friction and resistive torque are obtained. Thereafter, a compensating harmonic current derived from said force amplitudes and phase shifts of the said multiple harmonic detent torques is injected into a current command during operation of the stepper motor to compensate for torque ripples.
Owner:ASM ASSEMBLY AUTOMATION LTD
Generation of solid laser with biquadratic harmonic wave
InactiveCN1855648AImprove power densityGuaranteed stabilityLaser detailsFourth harmonicDouble frequency
Owner:HANS LASER TECH IND GRP CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com