Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
596 results about "Optical parametric oscillator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
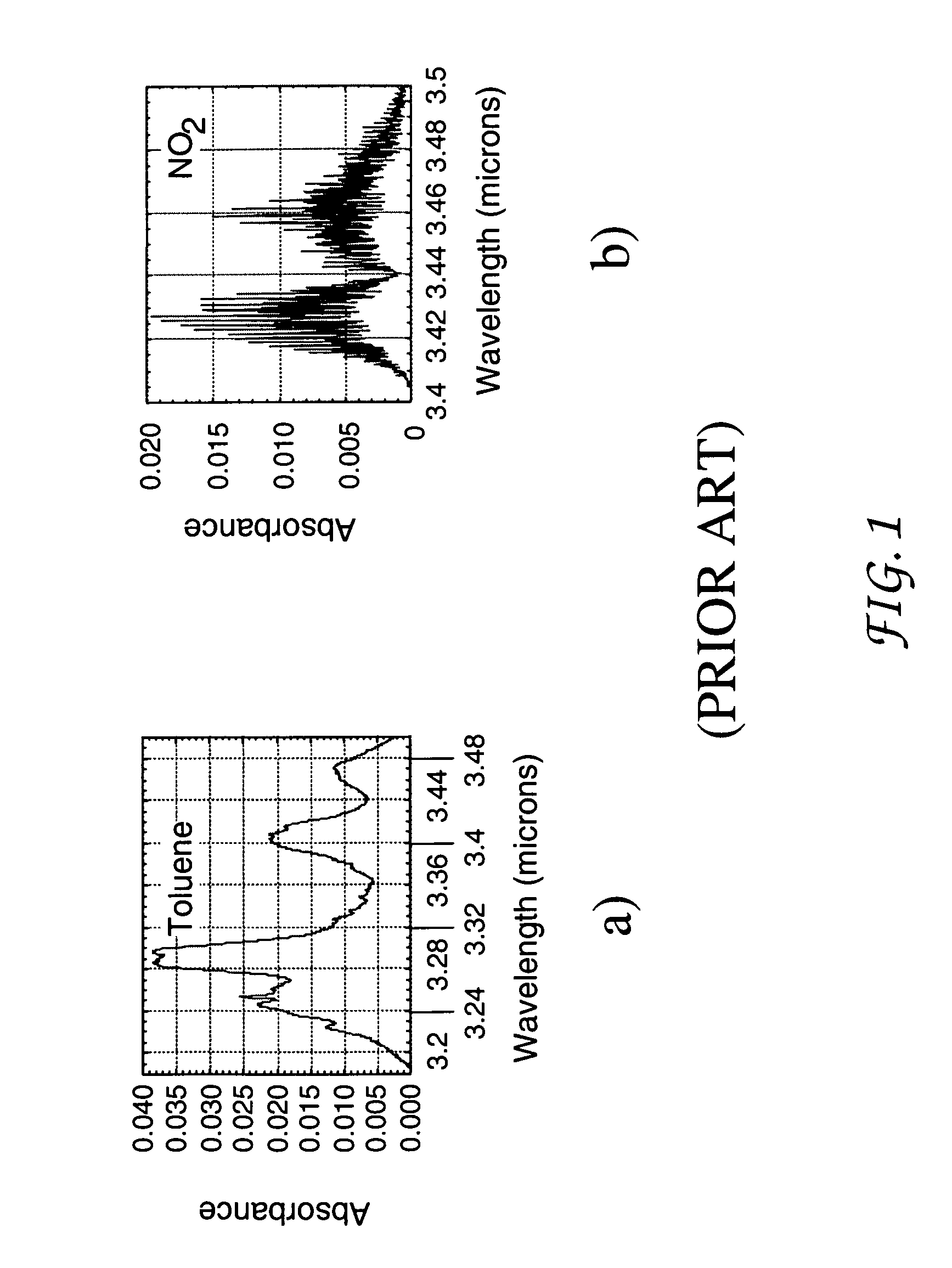
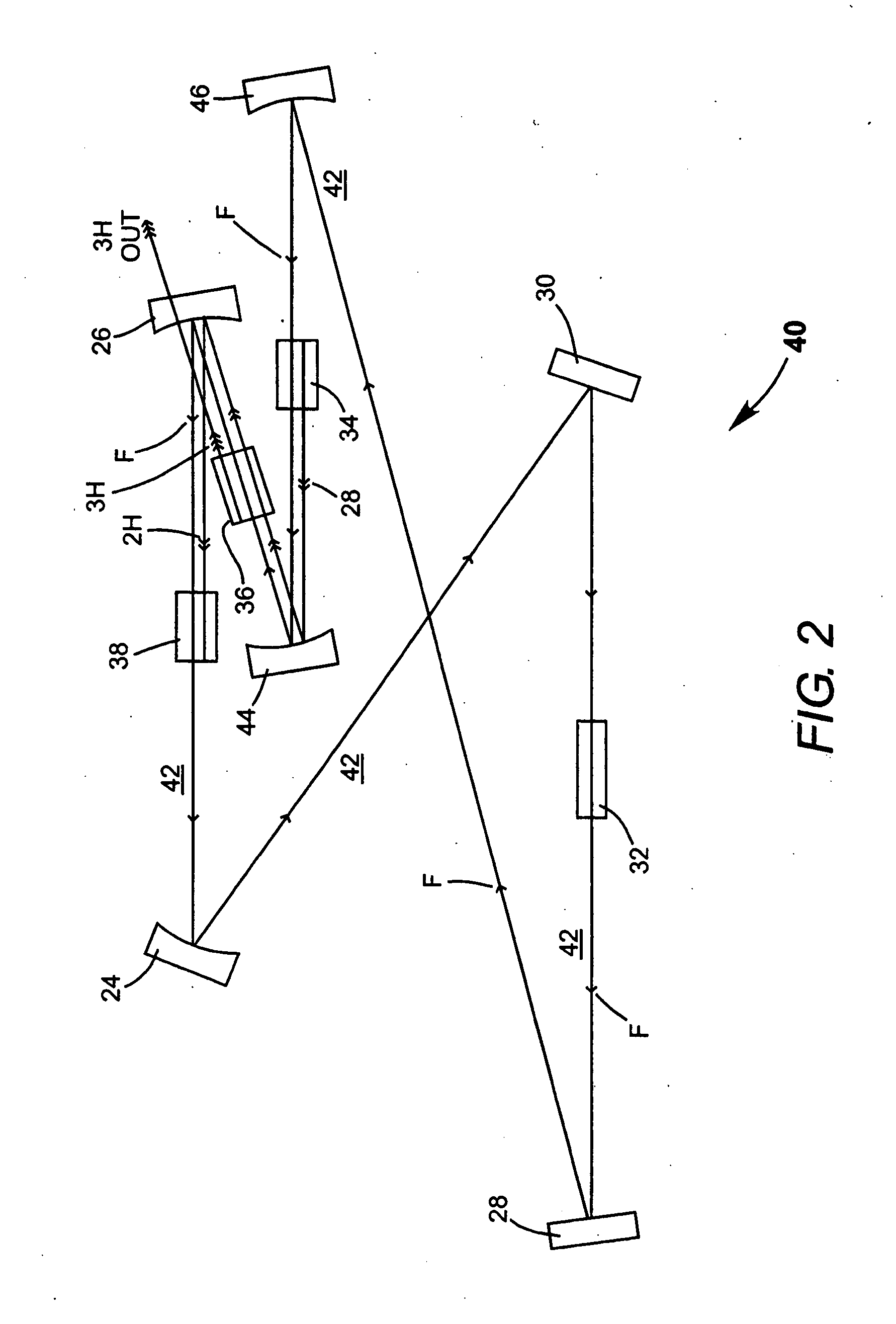
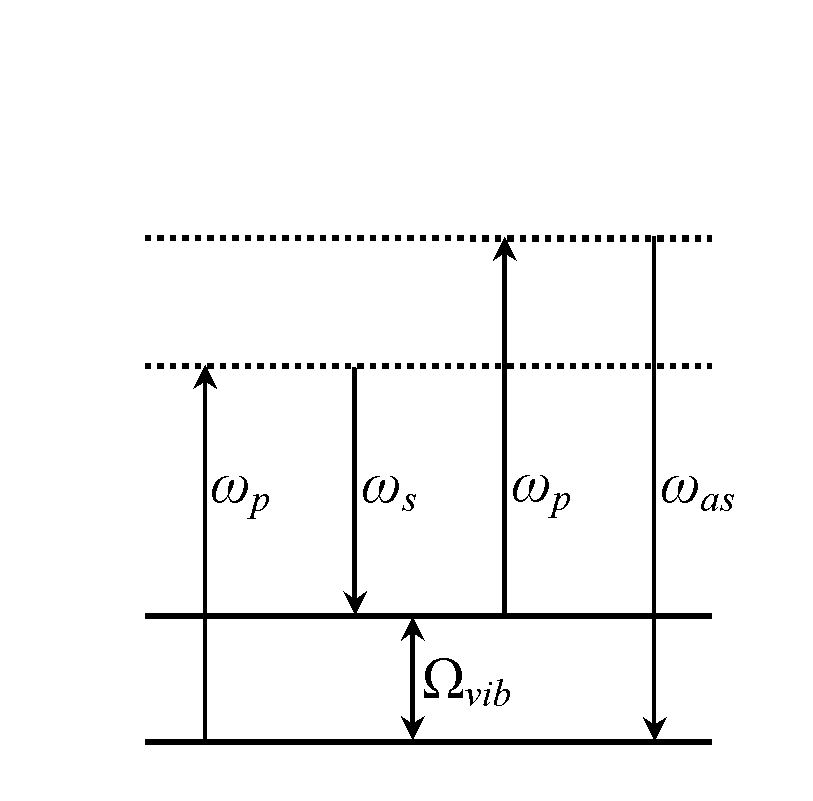
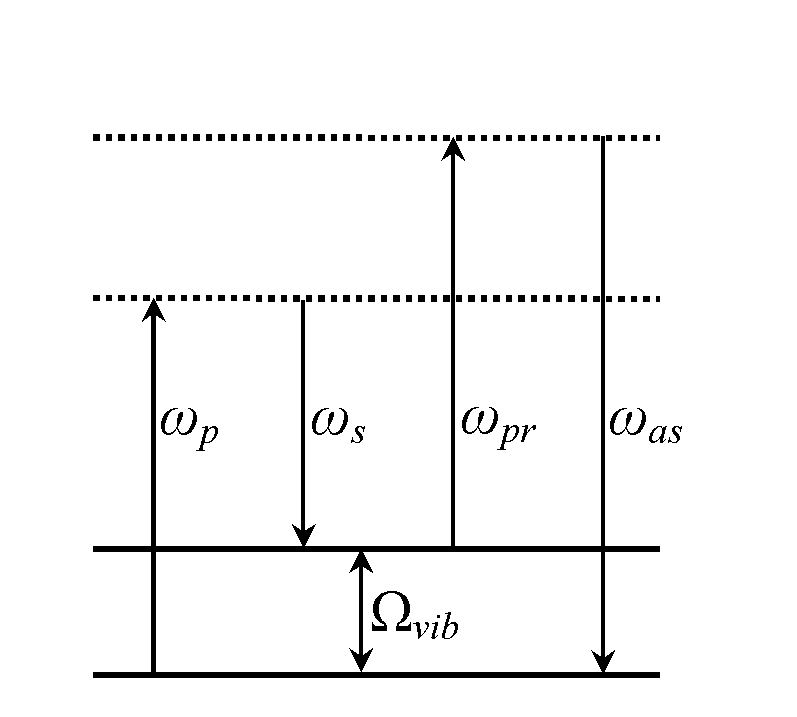
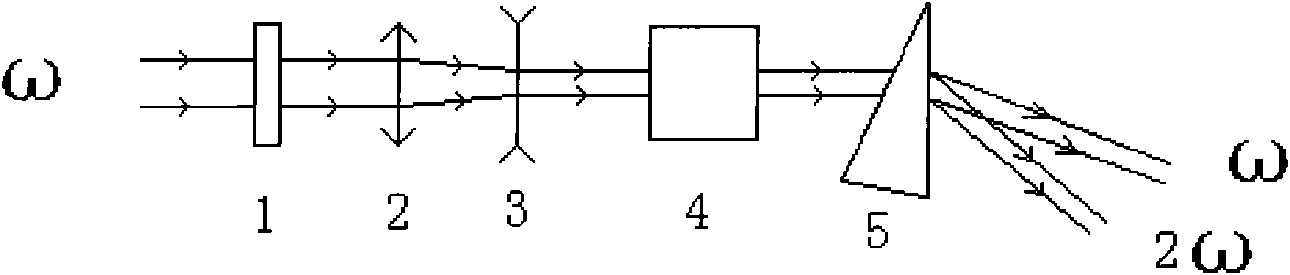
An optical parametric oscillator (OPO) is a parametric oscillator that oscillates at optical frequencies. It converts an input laser wave (called "pump") with frequency ωₚ into two output waves of lower frequency (ωₛ,ωᵢ) by means of second-order nonlinear optical interaction. The sum of the output waves' frequencies is equal to the input wave frequency: ωₛ+ωᵢ=ωₚ. For historical reasons, the two output waves are called "signal" and "idler", where the output wave with higher frequency is the "signal".
Optical System and Assembly Method
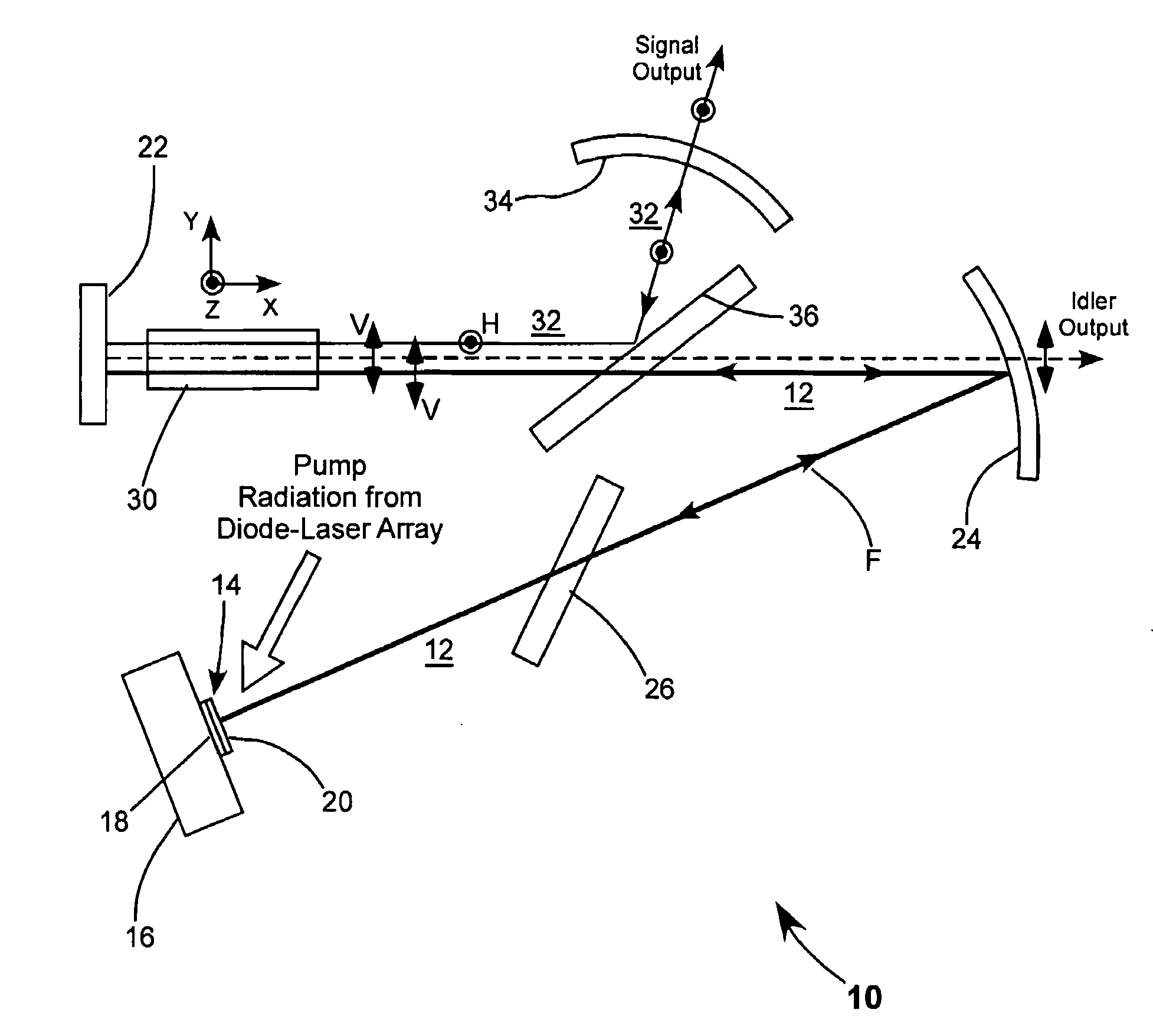
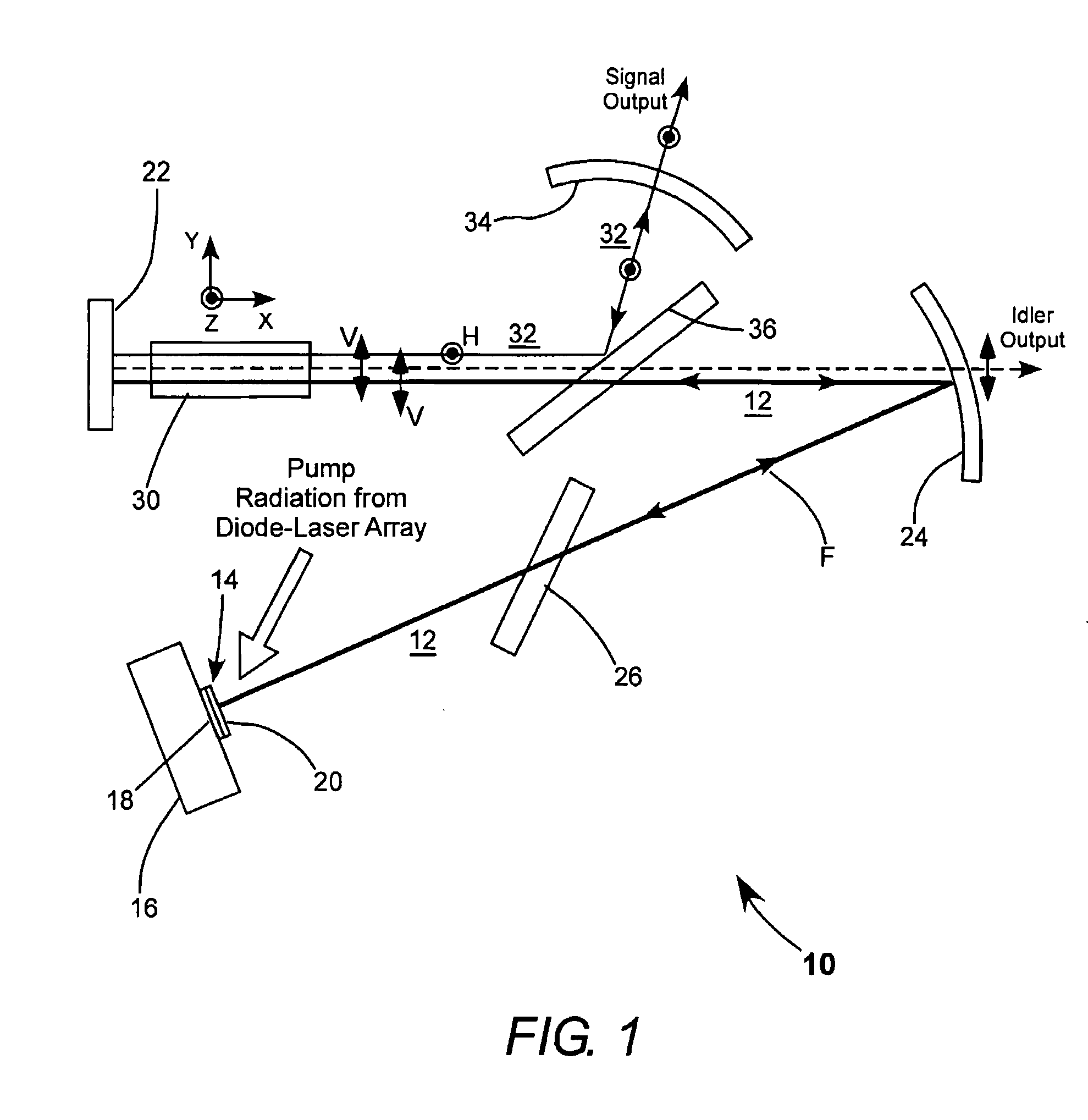
InactiveUS20100253769A1Need long operating lifetimesMethod is feasibleLaser arrangementsColor television detailsSpatial light modulatorDisplay device
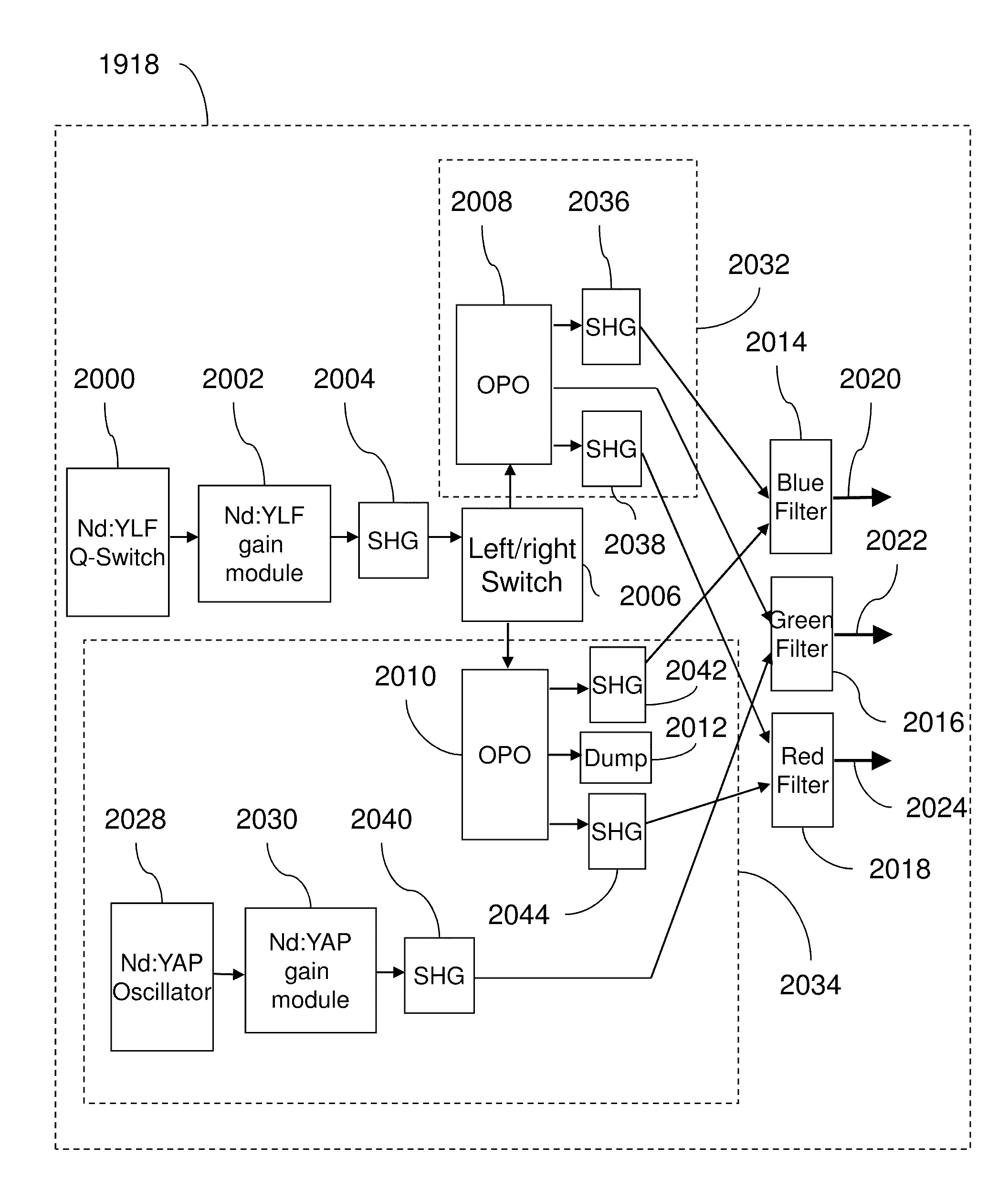
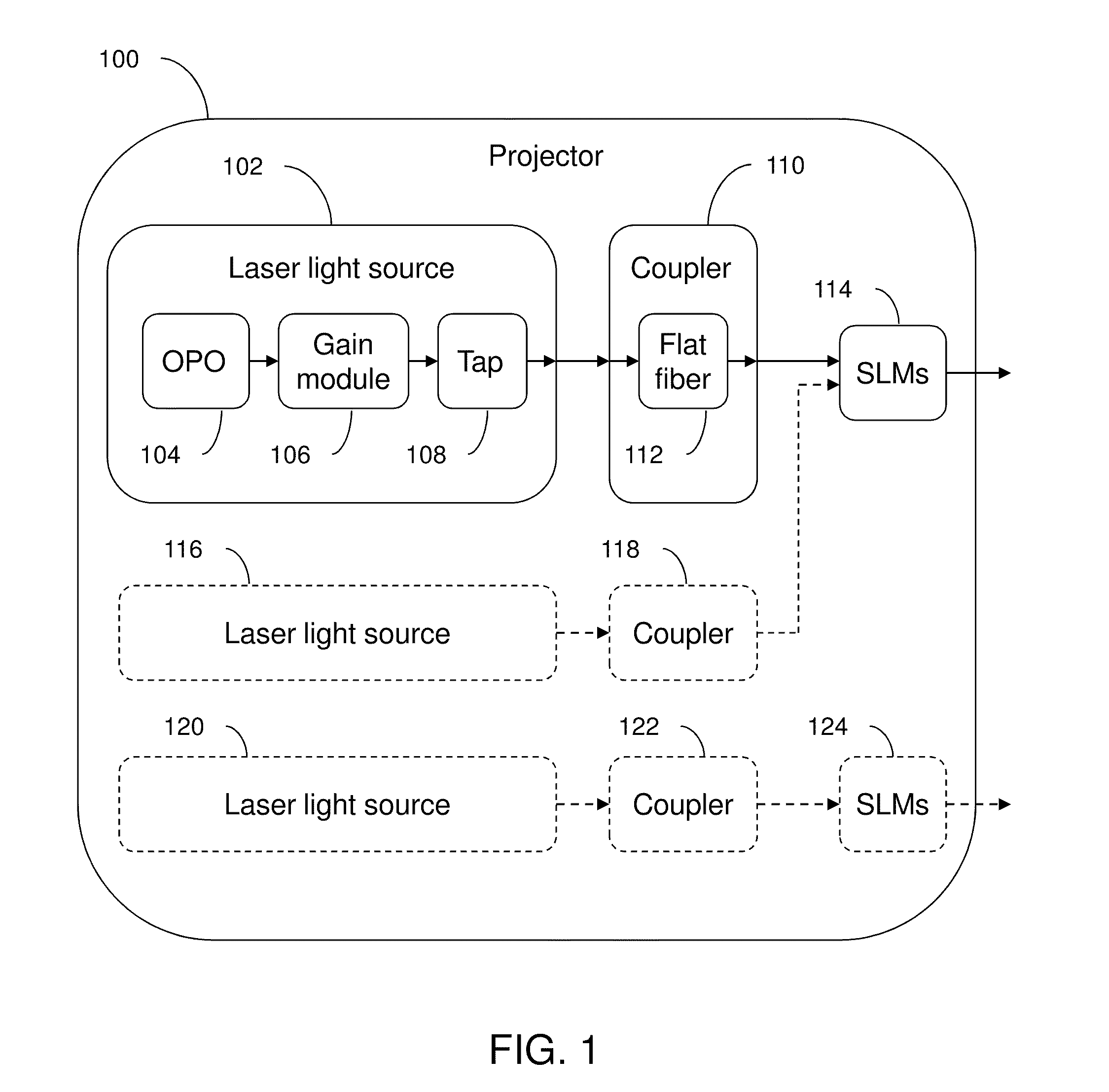
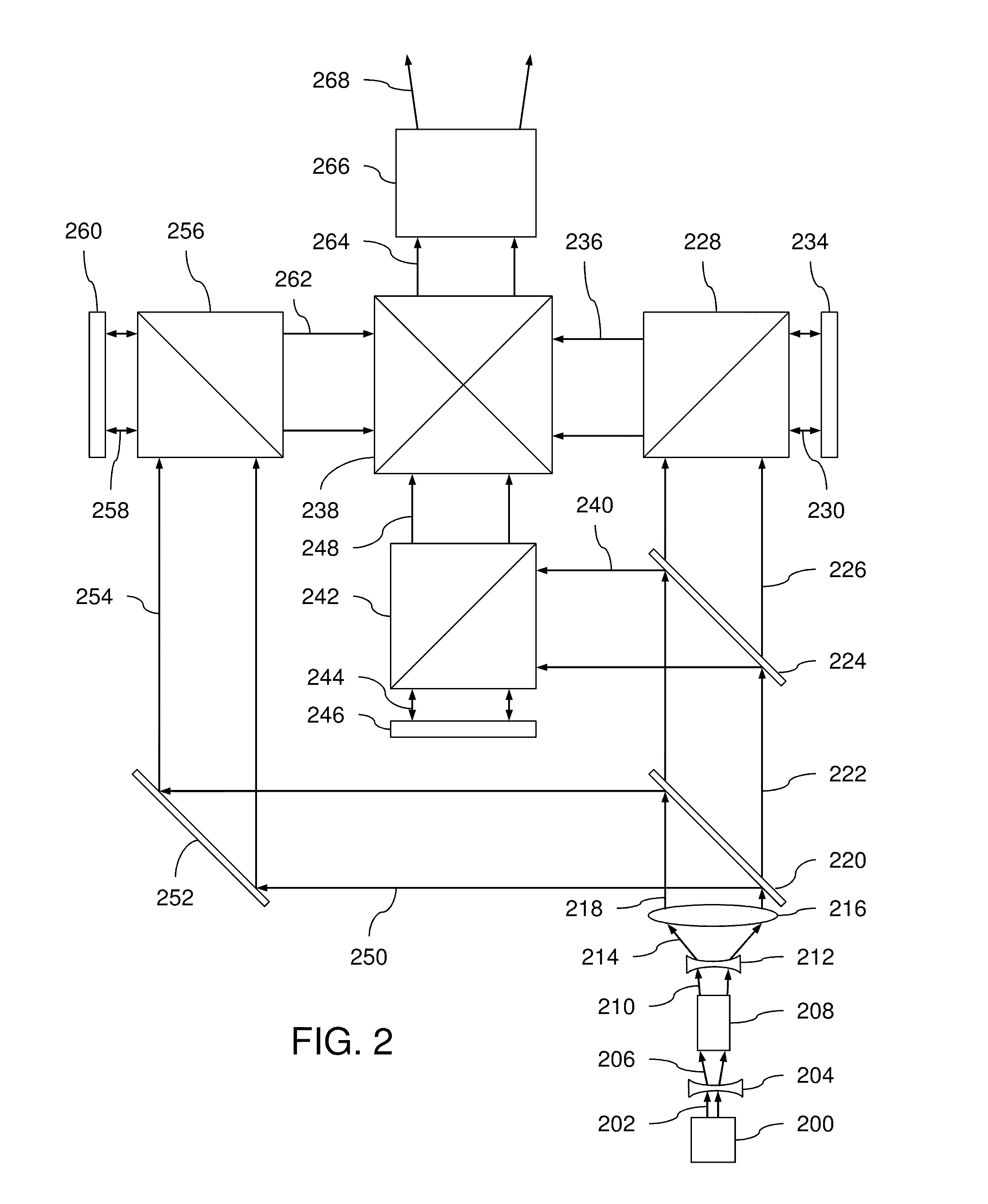
An optical system which includes some or all of the following parts: a laser light source which illuminates a spatial light modulator such that optical characteristics are preserved; a stereoscopic display which has a polarization-switching light source; a stereoscopic display which includes two infrared lasers, two optical parametric oscillators, and six second harmonic generators; two light sources processed by two parts of the same spatial light modulator; a method of assembly using an alignment plate to align kinematic rollers on a holding plate; an optical support structure which includes stacked, compartmented layers; a collimated optical beam between an optical parametric oscillator and a second harmonic generator; a laser gain module with two retroreflective mirrors; an optical tap which keeps the monitored beam co-linear; an optical coupler which includes an optical fiber and a rotating diffuser; and an optical fiber that has a core with at least one flat side.
Owner:PROJECTION VENTURES INC
Tunable light source for use in photoacoustic spectrometers
InactiveUS6975402B2The process is compact and efficientOptical signal transducersColor/spectral properties measurementsFiberFine structure
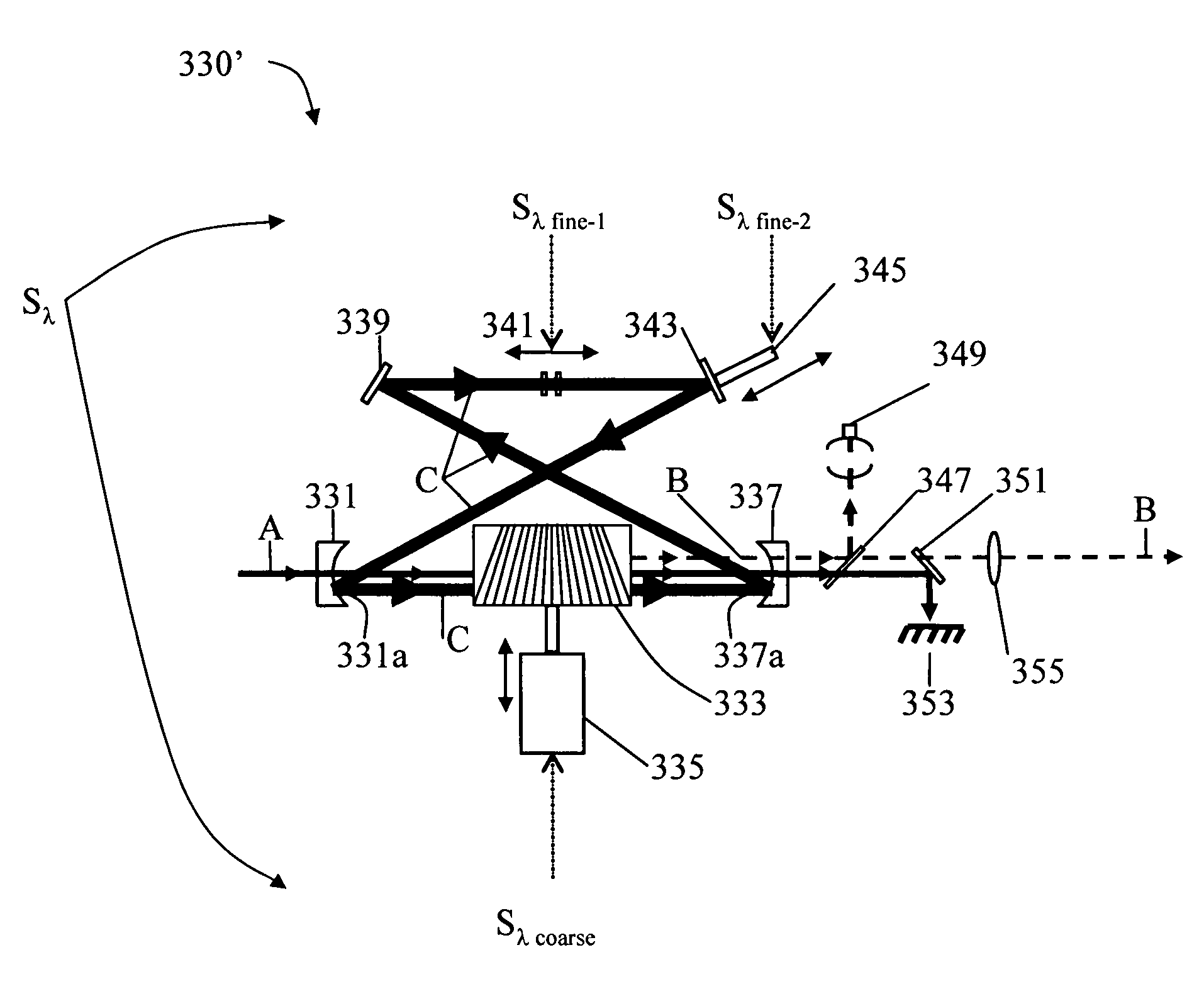
The present invention provides a photoacoustic spectrometer that is field portable and capable of speciating complex organic molecules in the gas phase. The spectrometer has a tunable light source that has the ability to resolve the fine structure of these molecules over a large wavelength range. The inventive light source includes an optical parametric oscillator (OPO) having combined fine and coarse tuning. By pumping the OPO with the output from a doped-fiber optical amplifier pumped by a diode seed laser, the inventive spectrometer is able to speciate mixtures having parts per billion of organic compounds, with a light source that has a high efficiency and small size, allowing for portability. In an alternative embodiment, the spectrometer is scanned by controlling the laser wavelength, thus resulting in an even more compact and efficient design.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
Radio frequency modulation of variable degree and automatic power control using external photodiode sensor for low-noise lasers of various wavelengths
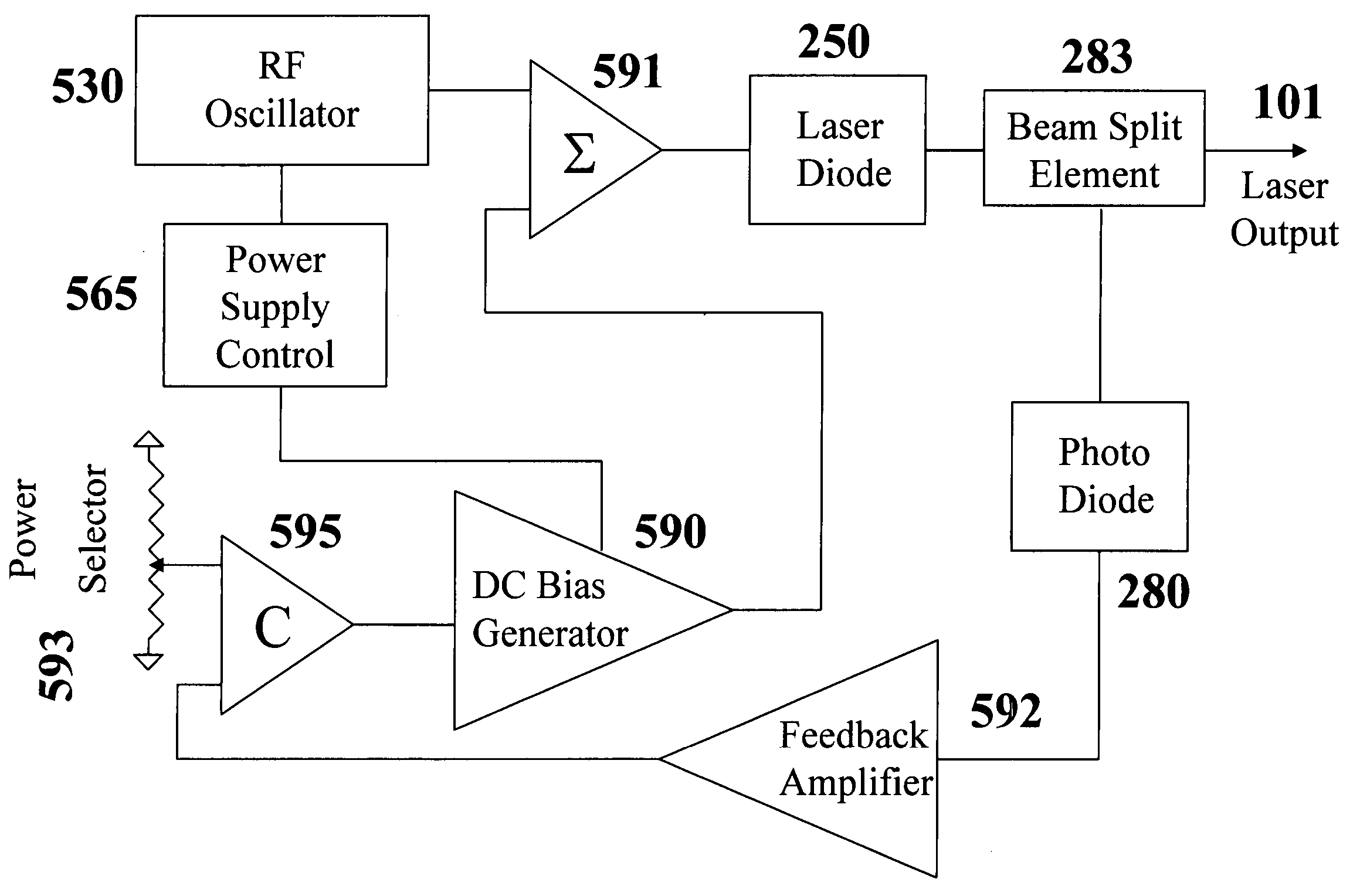
ActiveUS20060215716A1Increase output powerWide wavelength rangeLaser detailsSemiconductor laser optical deviceLow noiseRadio frequency
A low-noise laser diode module comprises a laser diode for emitting light with a wavelength in the range from UV to IR, a drive circuit for injecting electrical current into said diode, and an automatic power control circuit for monitoring and adjusting laser output power using front-facet photodiode external to the laser assembly and a feedback loop. Said drive circuit produces injection current modulated by an RF signal with variable degrees, depending on the wavelength to be stabilized, the desired spectral bandwidths of the laser output, and / or other applications. Said RF signal can be a sine wave, a distorted sine wave, a rectified sine wave, a non-sine wave, a series of narrow pulses, or repetitive shunt. The present invention encompasses a method for producing stable, broadband, and low-coherent laser. The present invention also encompasses a method for producing stable narrowband or single longitudinal mode laser. The present invention further encompasses a compact light source applicable to DPSS lasers, fiber lasers, optical parametric oscillators, low-speckle laser display systems, and seeders, with or without nonlinear frequency conversion processes.
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION
Backscatter absorption gas imaging systems and light sources therefore
ActiveUS7151787B2Low power operationLaser using scattering effectsColor/spectral properties measurementsAudio power amplifierLength wave
The location of gases that are not visible to the unaided human eye can be determined using tuned light sources that spectroscopically probe the gases and cameras that can provide images corresponding to the absorption of the gases. The present invention is a light source for a backscatter absorption gas imaging (BAGI) system, and a light source incorporating the light source, that can be used to remotely detect and produce images of “invisible” gases. The inventive light source has a light producing element, an optical amplifier, and an optical parametric oscillator to generate wavelength tunable light in the IR. By using a multi-mode light source and an amplifier that operates using 915 nm pump sources, the power consumption of the light source is reduced to a level that can be operated by batteries for long periods of time. In addition, the light source is tunable over the absorption bands of many hydrocarbons, making it useful for detecting hazardous gases.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
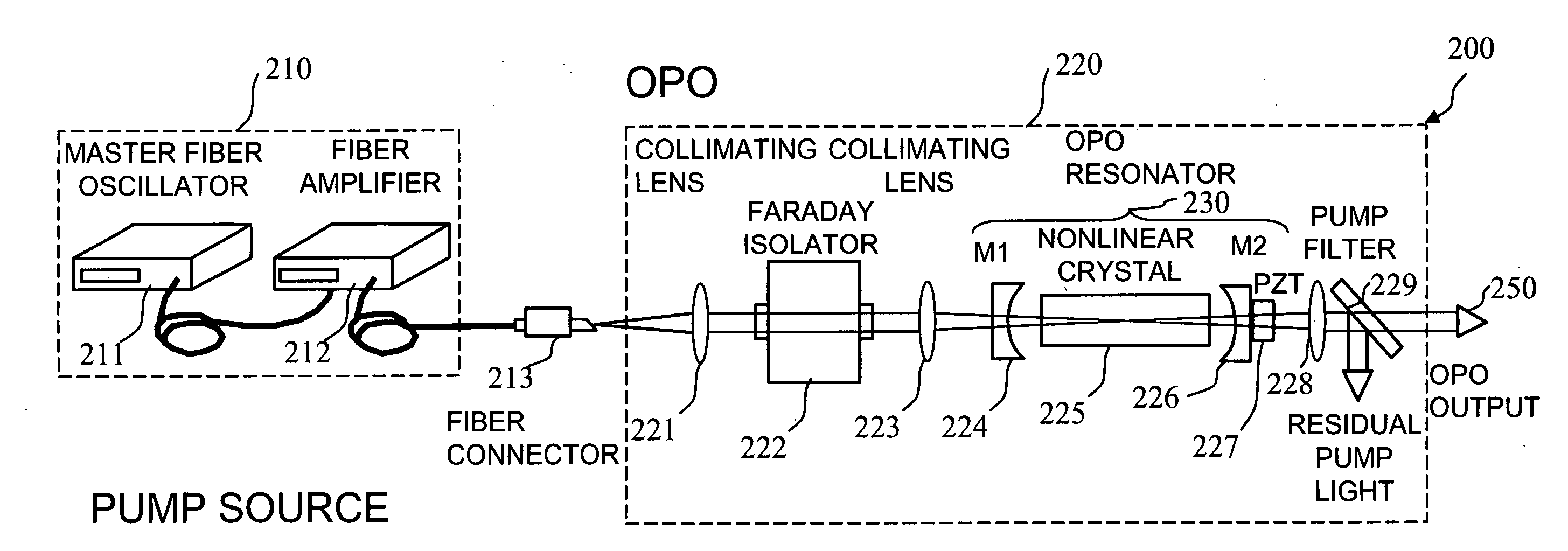
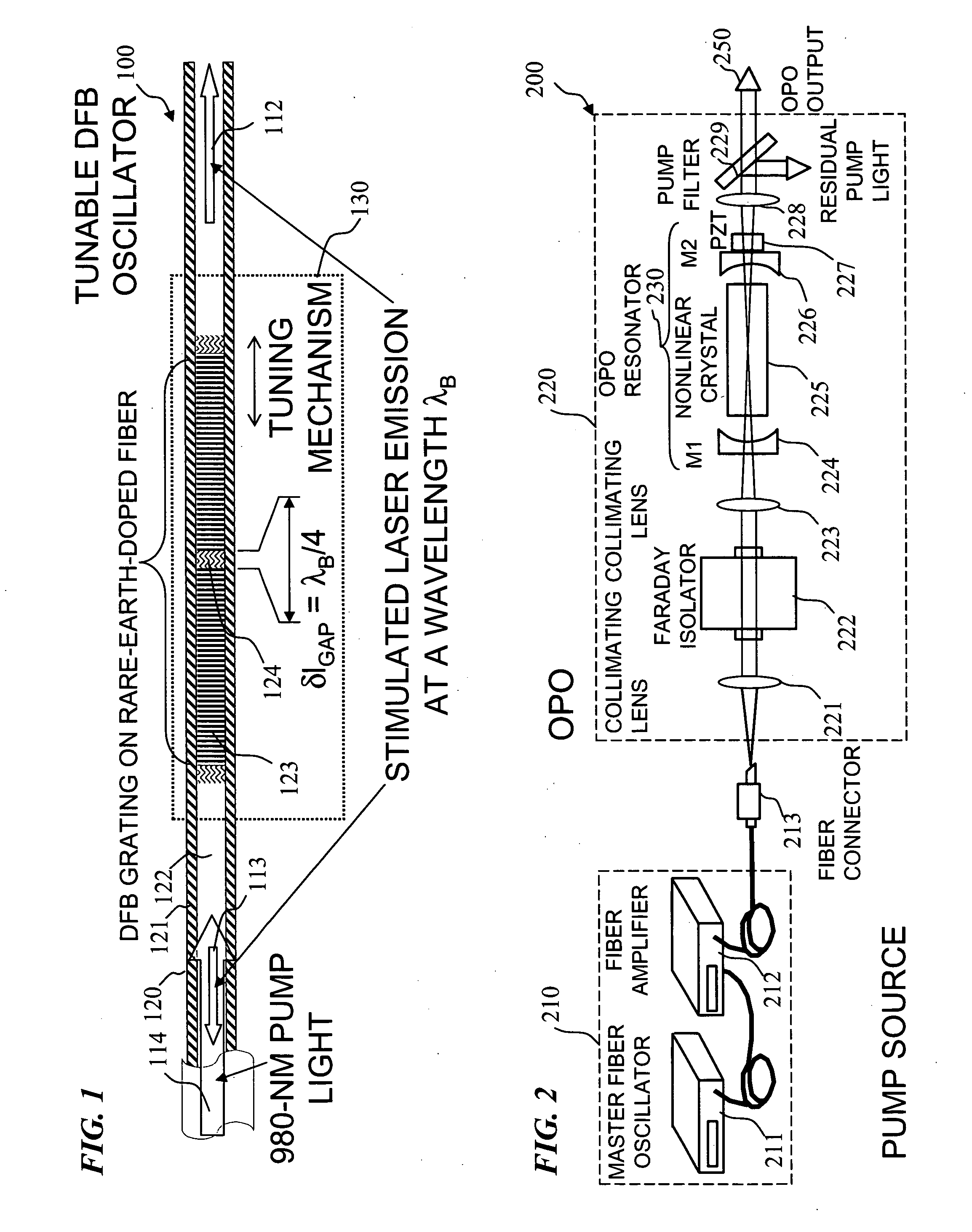
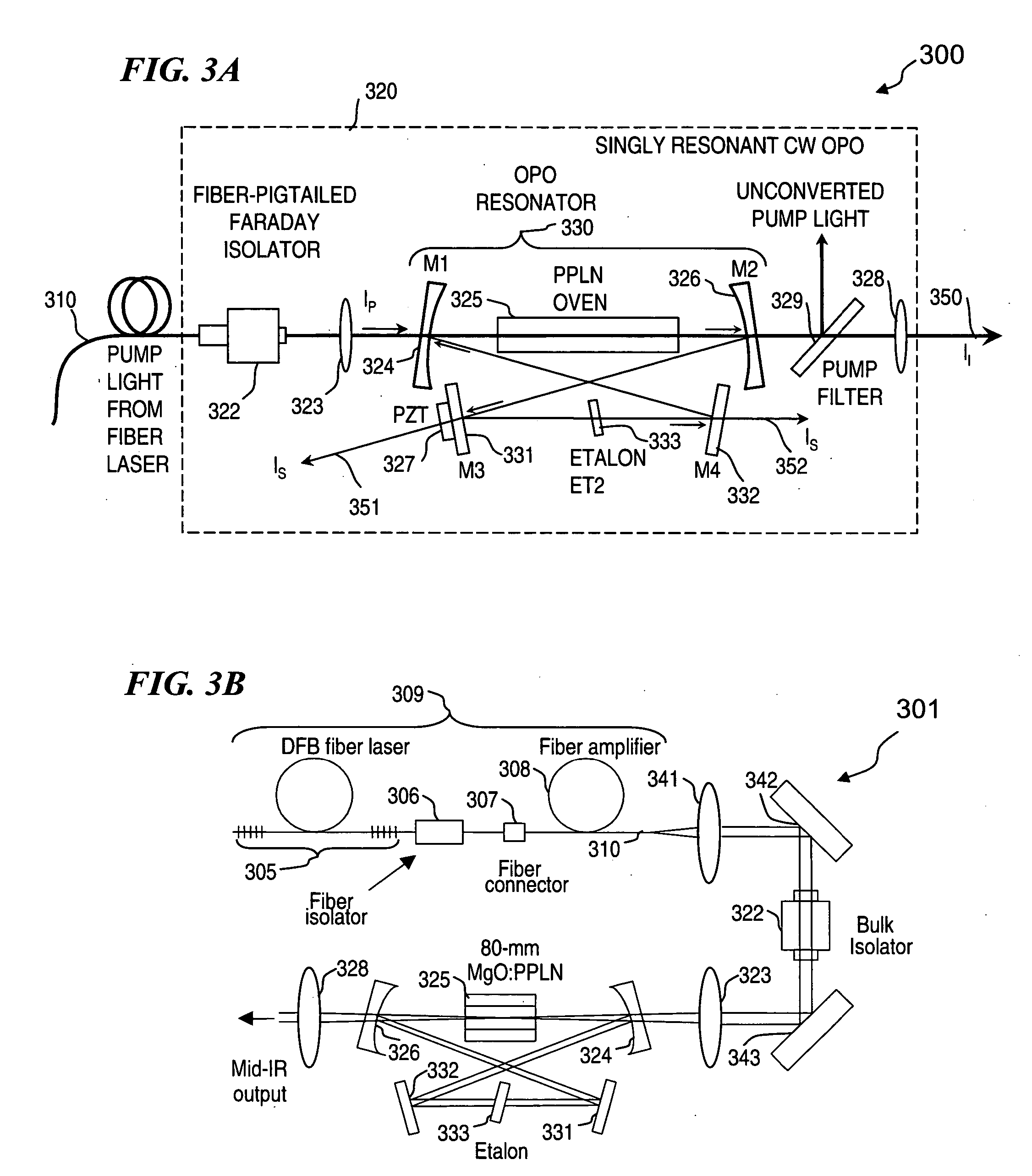
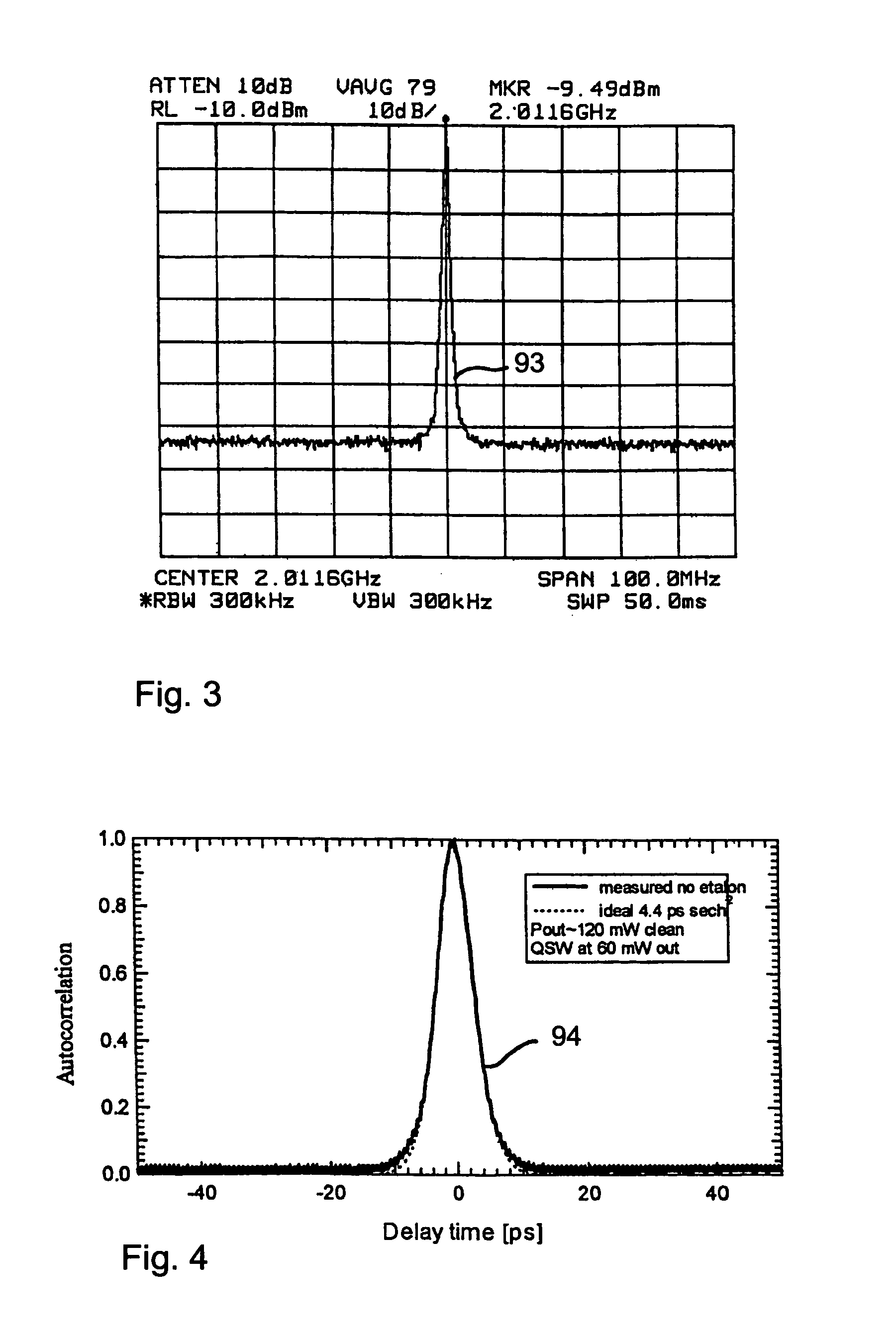
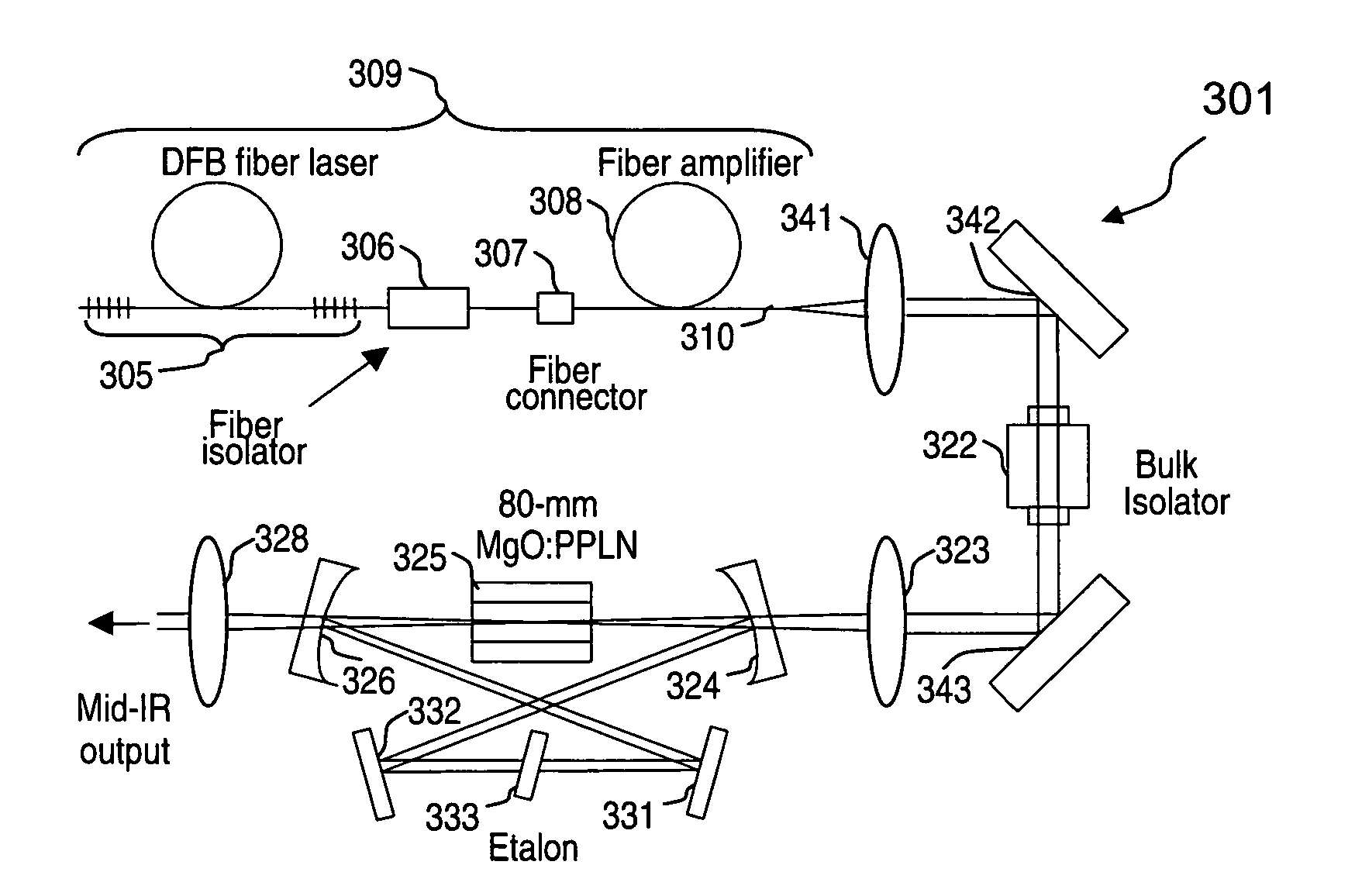
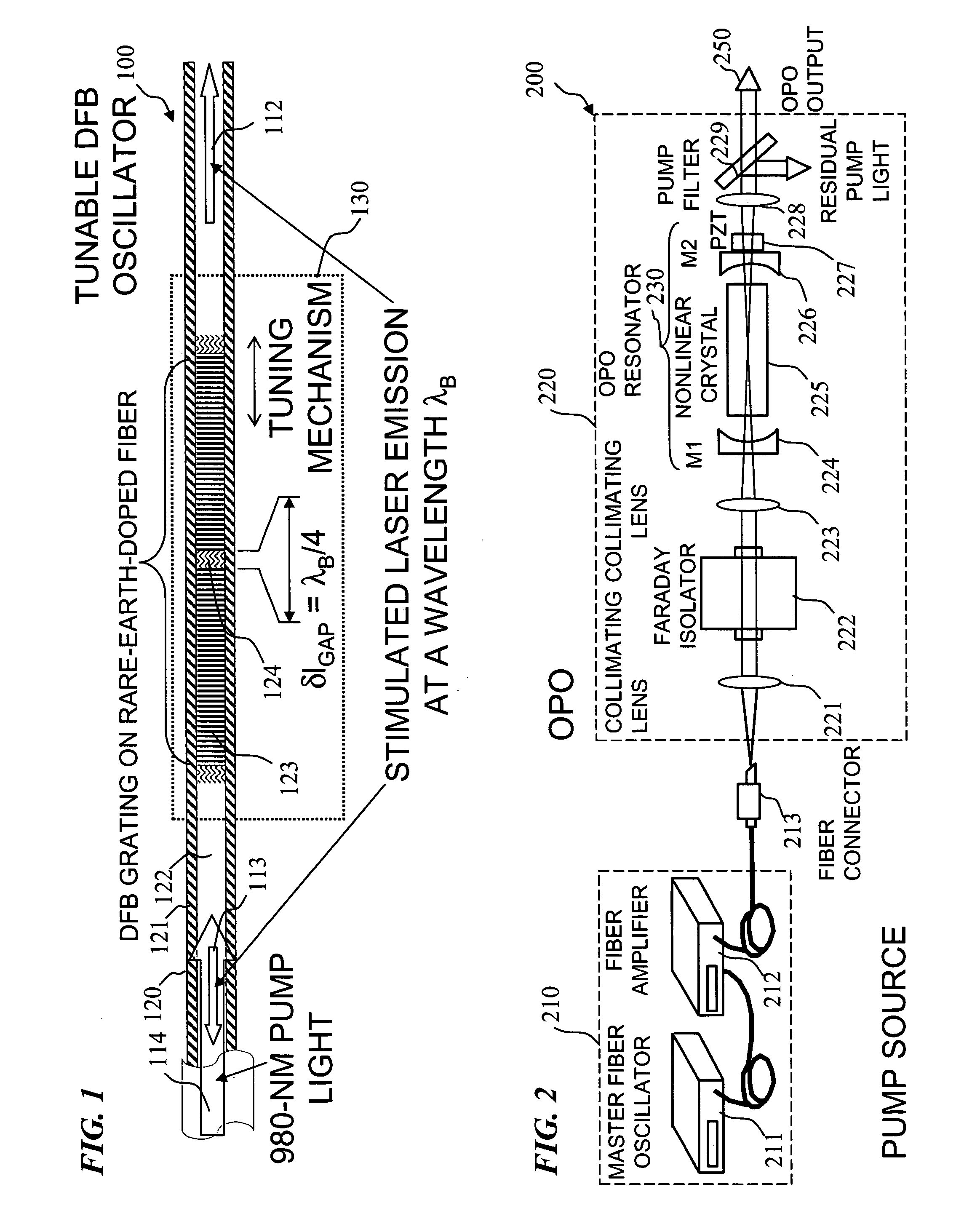
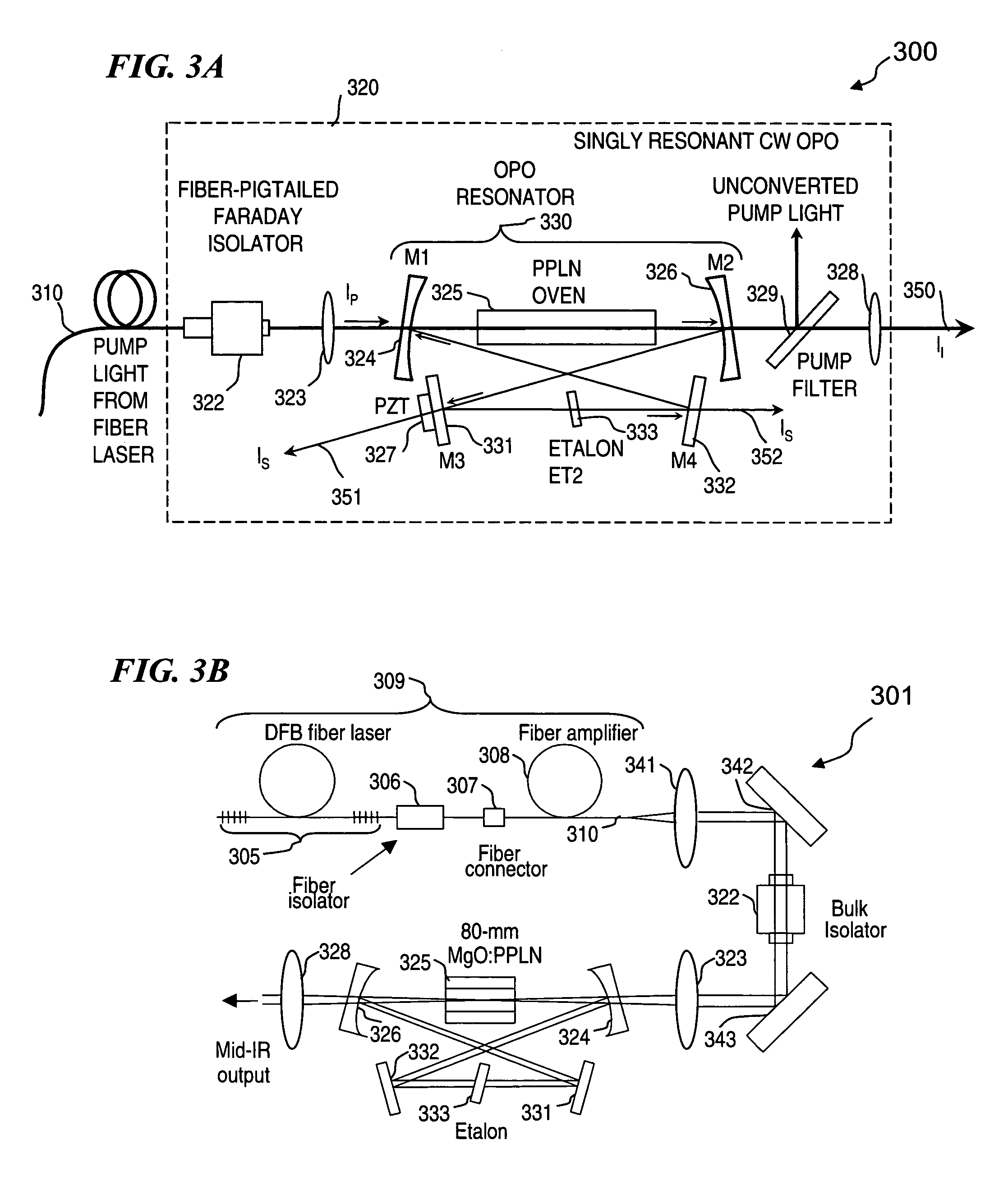
Apparatus and method for pumping and operating optical parametric oscillators using DFB fiber lasers
ActiveUS20070035810A1Reduce pump powerLarge and undesirable buildupLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusInfrared laser beamLithium niobate
An optical parametric oscillator (OPO) is described that efficiently converts a near-infrared laser beam to tunable mid-infrared wavelength output. In some embodiments, the OPO includes an optical resonator containing a nonlinear crystal, such as periodically-poled lithium niobate. The OPO is pumped by a continuous-wave fiber-laser source having a low-power oscillator and a high-power amplifier, or using just a power oscillator). The fiber oscillator produces a single-frequency output defined by a distributed-feedback (DFB) structure of the fiber. The DFB-fiber-laser output is amplified to a pump level consistent with exceeding an oscillation threshold in the OPO in which only one of two generated waves (“signal” and “idler”) is resonant within the optical cavity. This pump source provides the capability to tune the DFB fiber laser by straining the fiber (using an attached piezoelectric element or by other means) that allows the OPO to be continuously tuned over substantial ranges, enabling rapid, wide continuous tuning of the OPO output frequency or frequencies.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
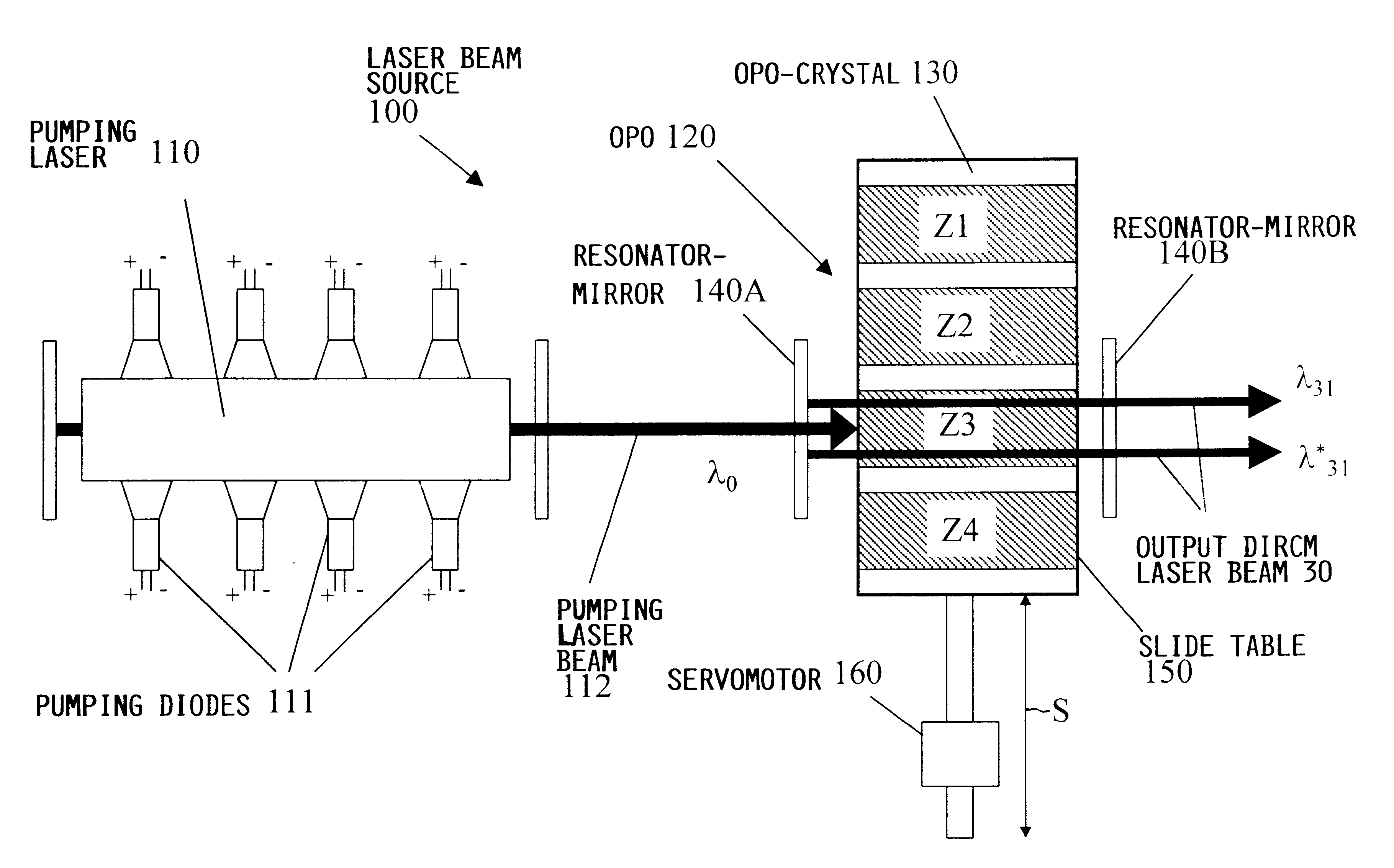
Laser beam source for a directional infrared countermeasures (DIRCM) weapon system
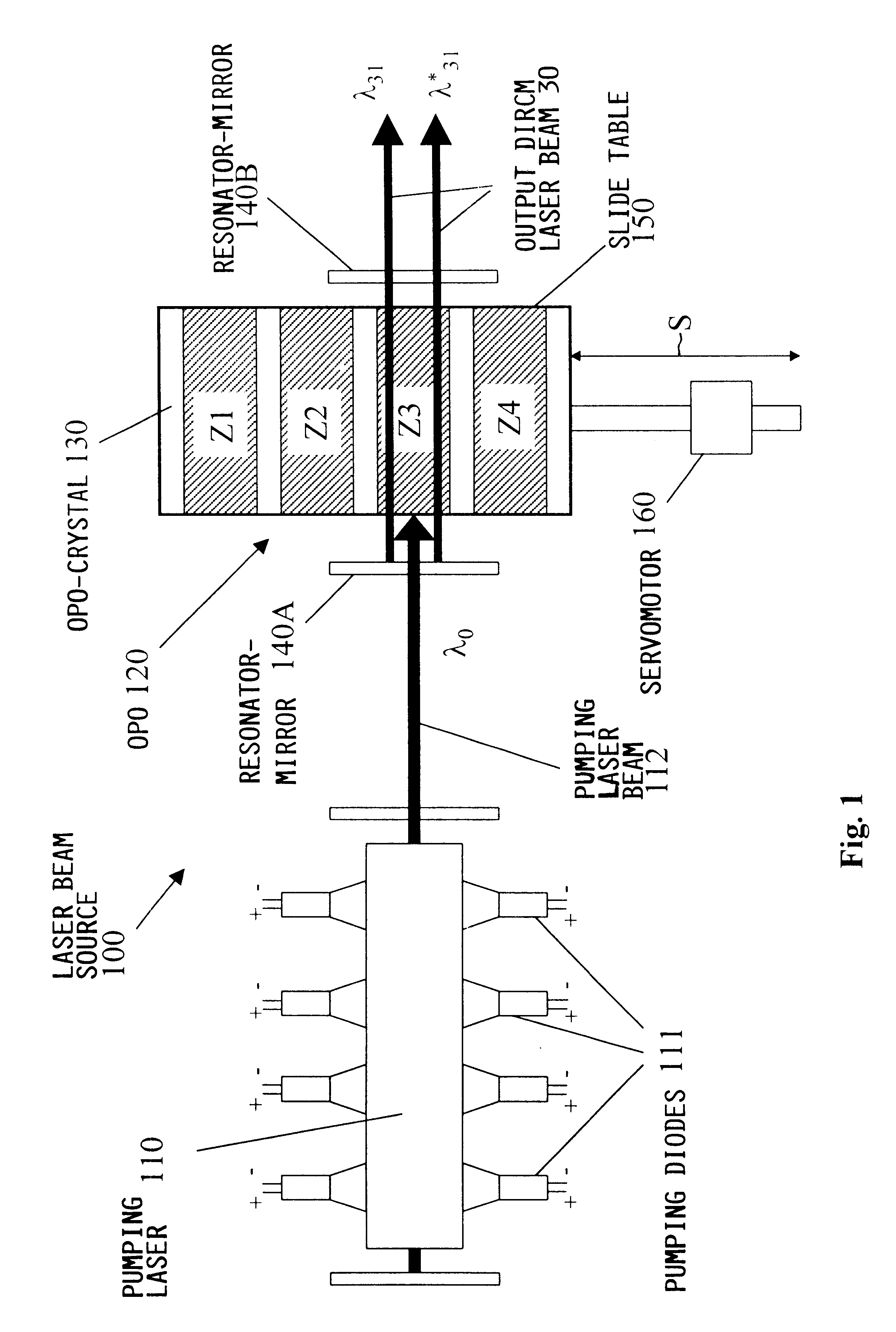
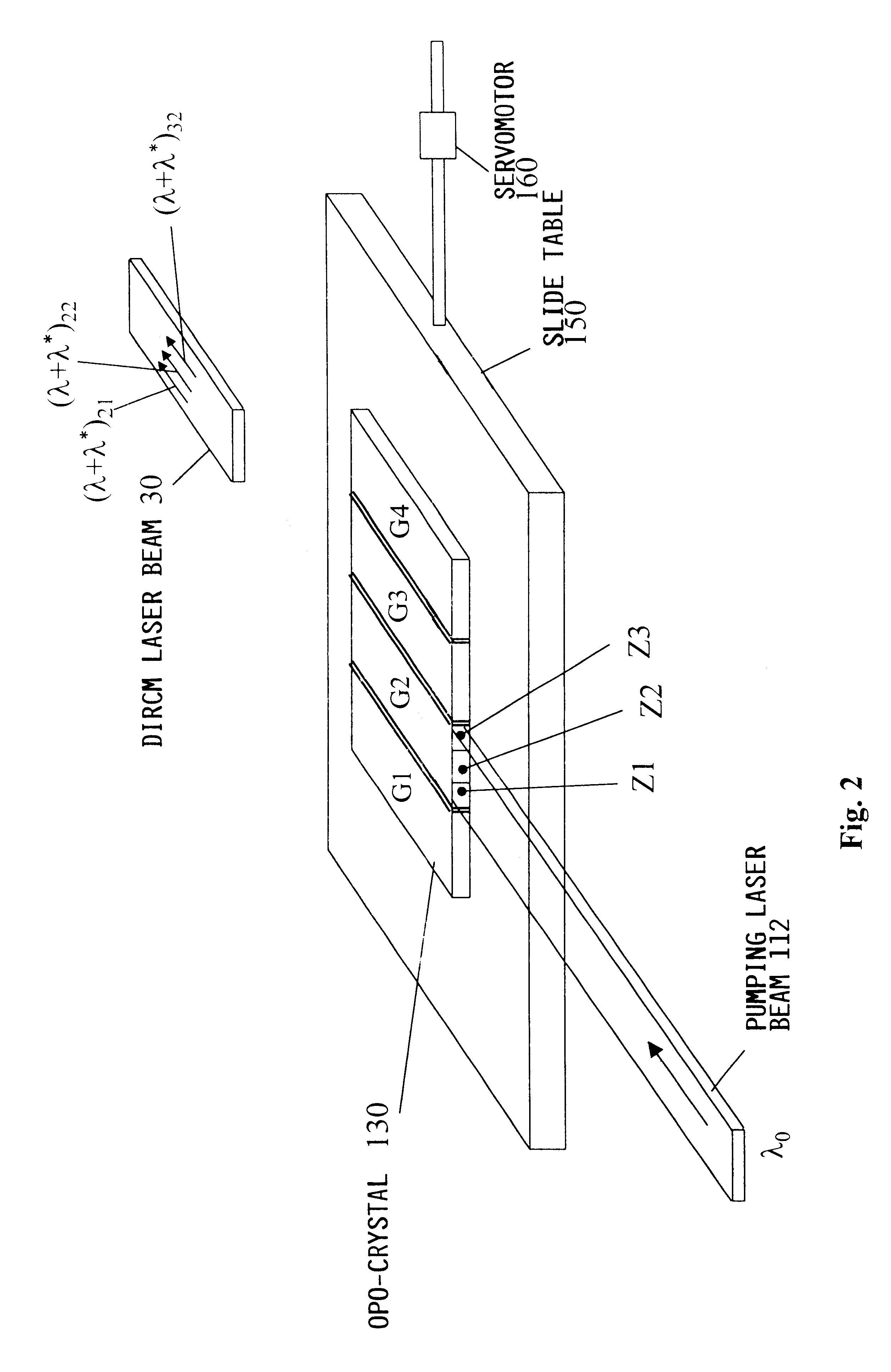
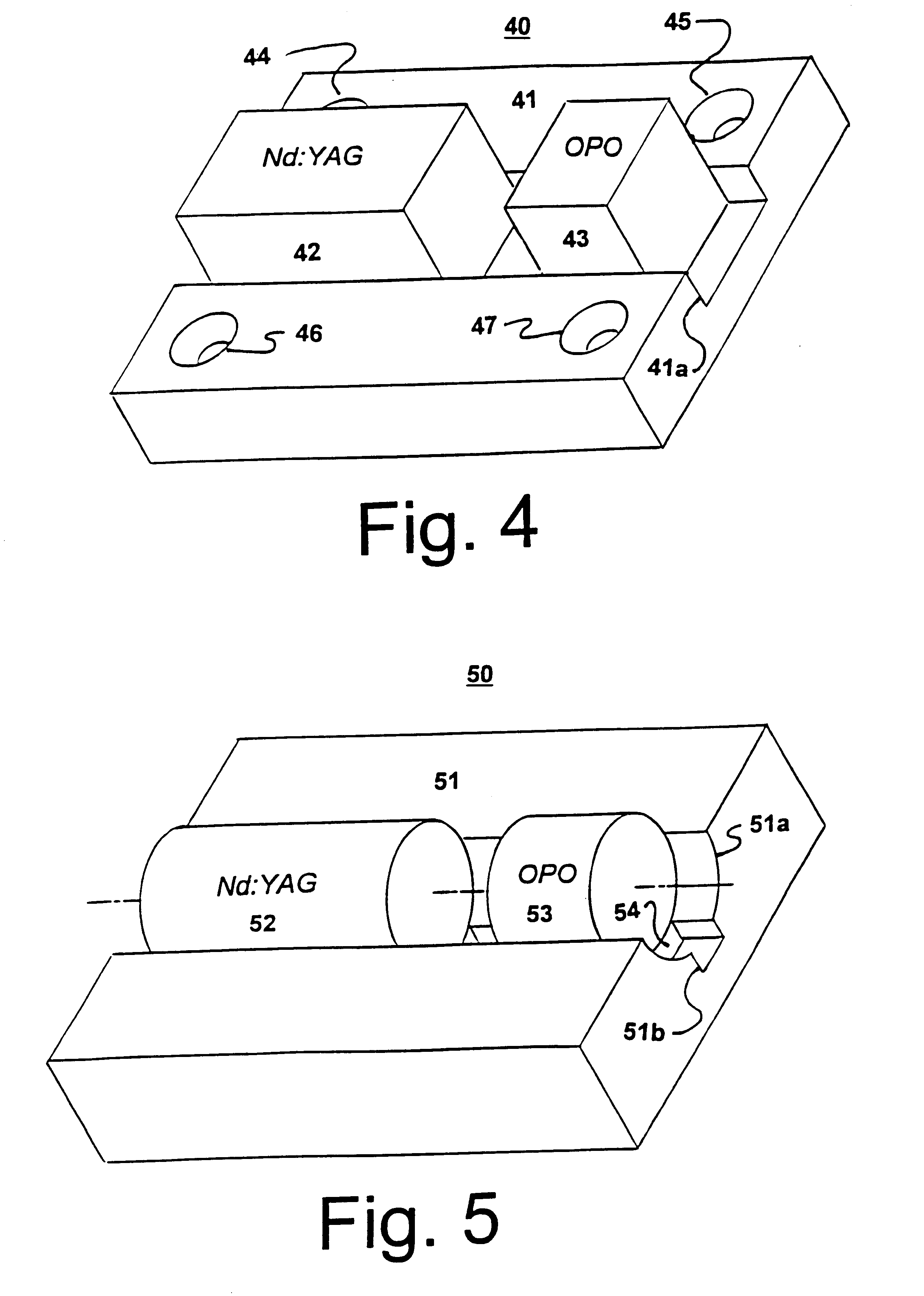
A laser beam source and an operating method thereof is provided for a directional infrared countermeasures (DIRCM) weapon system for defensively countering guided missiles having infrared seeking heads, by directing an infrared laser beam at the guided missile so as to disorient, saturate, or irreversibly destroy the IR detectors and circuitry arranged in the target seeking head. The power, pulse frequency and spectral composition of the laser beam is adjustable and selectable as required to adapt to any particular defensive engagement. To achieve this, the laser beam source comprises an Nd:YAG pumping laser and an optical parametric oscillator including an oscillator crystal arranged in a resonator cavity. The crystal includes a plurality of different periodically polarized crystal zones having different lattice constants. The adjacent zones can be grouped together into selectable crystal zone groups. The beam cross-section of the pumping laser beam corresponds to the cross-section of a single crystal zone or of a crystal zone group encompassing plural zones. The crystal is arranged on a slide table that is slidably displaceable by a servomotor, to move a selected crystal zone or group into the path of the pumping laser beam. Thereby the wavelength components and the relative intensities thereof of the output laser beam can easily be selectively adjusted.
Owner:EADS DEUT GMBH
High-repetition-rate passively mode-locked solid-state laser
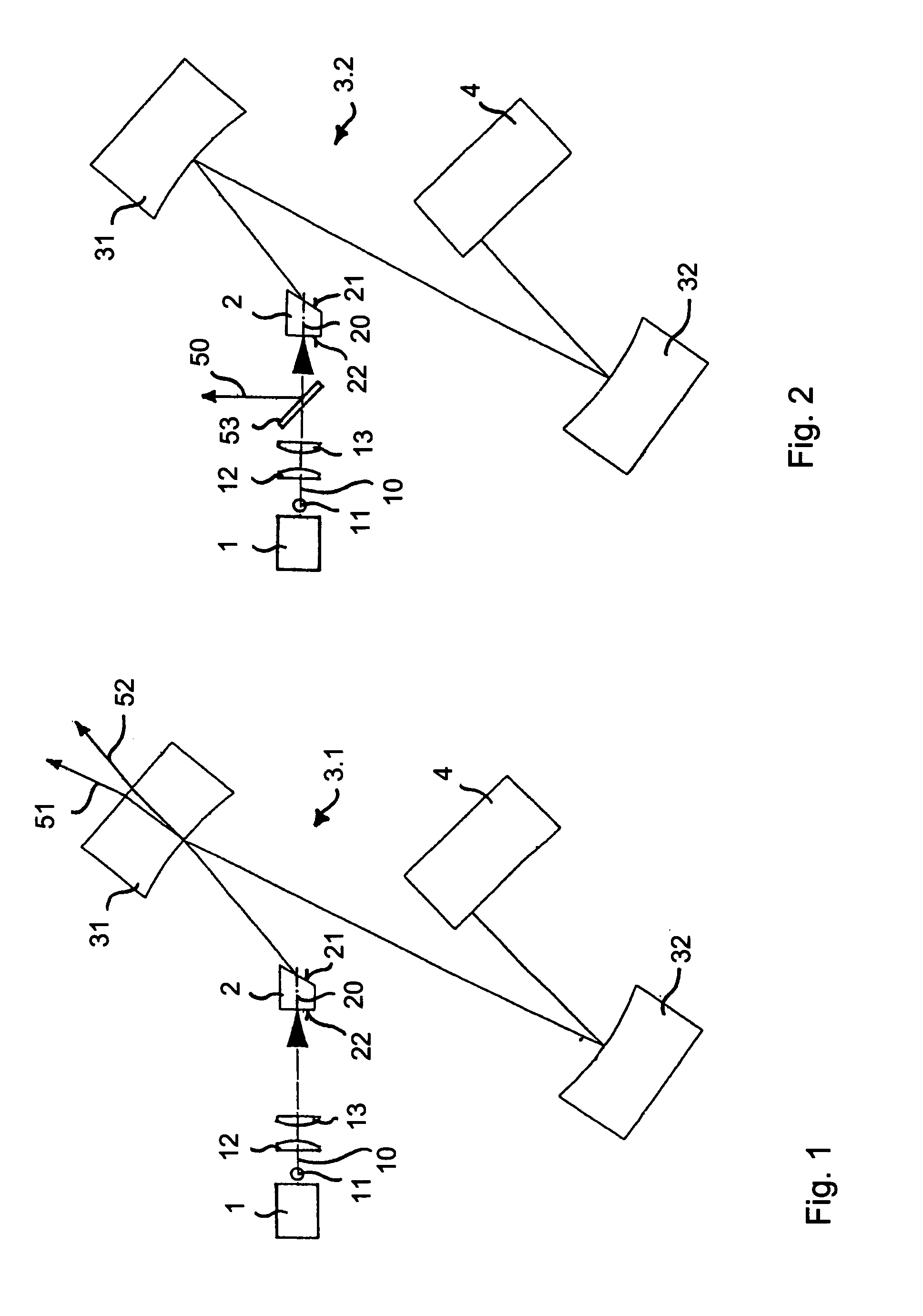
A passively mode-locked solid-state laser is designed to emit a continuous-wave train (51, 52) of electromagnetic-radiation pulses, the fundamental repetition rate of the emitted pulses exceeding 1 GHz, without Q-switching instabilities. The laser includes an optical resonator (3.1), a solid-state laser gain element (2) placed inside the optical resonator (3.1), a device (1) for exciting said laser gain element (2) to emit electromagnetic radiation having the effective wavelength, and a device (4) for passive mode locking including a saturable absorber. The laser gain element (2) is a laser material with a stimulated emission cross section exceeding 0.8×10−18 cm2 at the effective wavelength, and is made of Nd:vanadate. The saturable absorber (4) is preferably a semiconductor saturable absorber mirror (SESAM) device. Even higher repetition rates are achieved by operating the laser in the soliton regime. For use in fiber-optical telecommunication, the laser wavelength is preferably shifted to 1.5 μm by use of an optical parametric oscillator. The laser is simple, robust, compact, efficient, and low-cost. It generates a relatively large average power of 100 mW and higher, which is useful for a number of optical probing and detection applications, in a beam (51, 52) that is substantially a fundamental spatial mode.
Owner:LUMENTUM SWITZERLAND AG
Apparatus and method for pumping and operating optical parametric oscillators using DFB fiber lasers
ActiveUS7620077B2Reduce pump powerLarge and undesirable buildupLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusInfrared laser beamLithium niobate
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
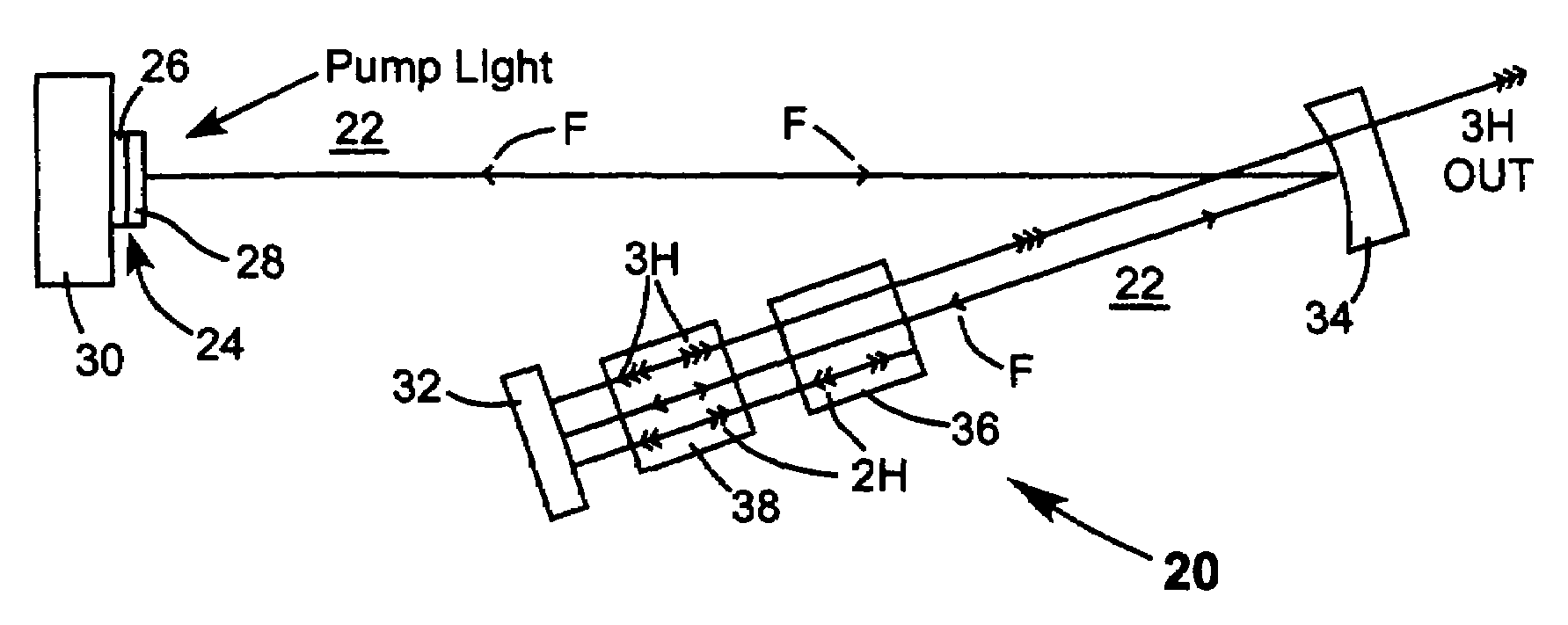
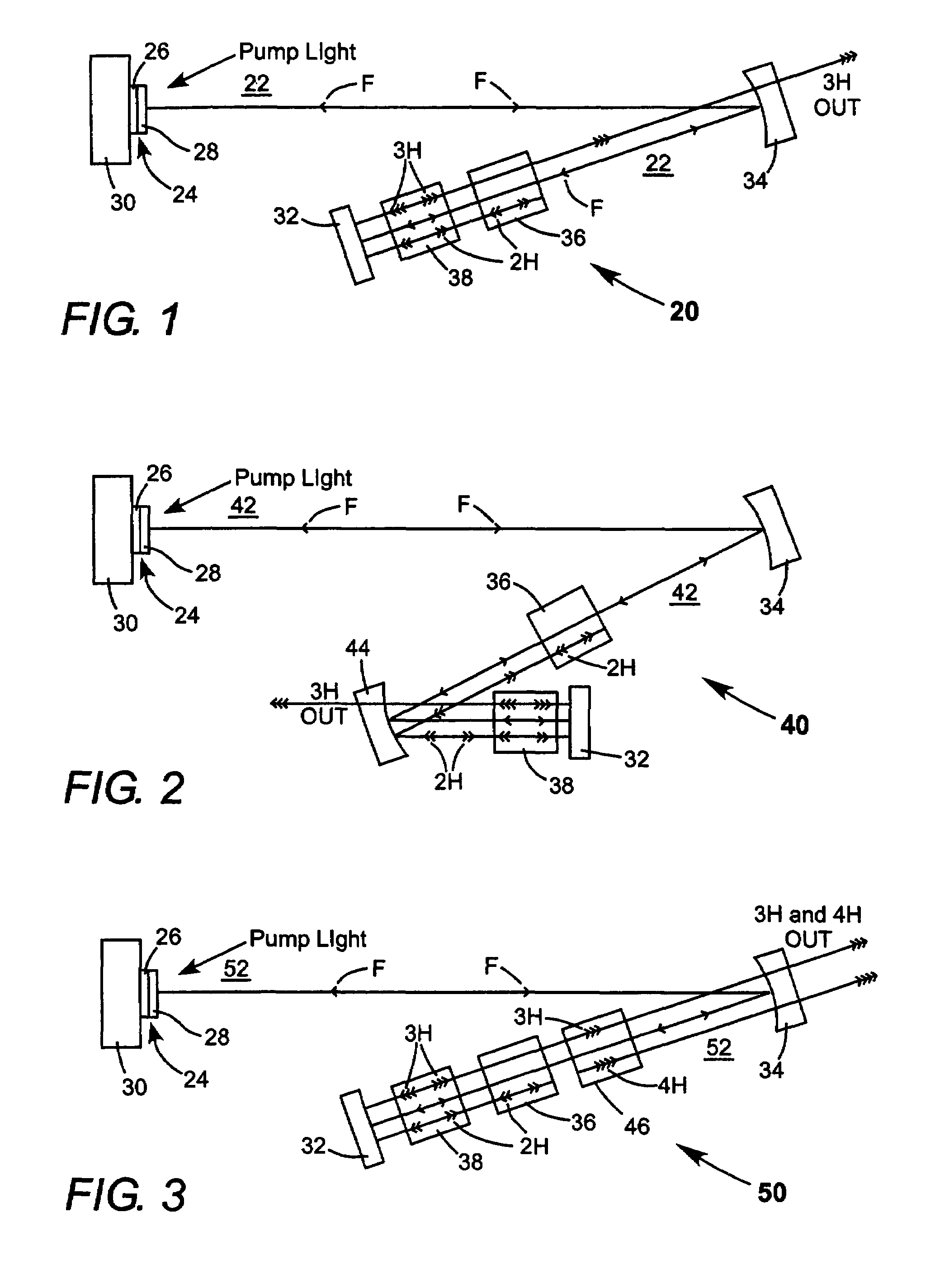
Intracavity frequency-tripled CW laser
InactiveUS20050078718A1High frequencyImprove efficiencyLaser optical resonator constructionExcitation process/apparatusNonlinear crystalsPhysics
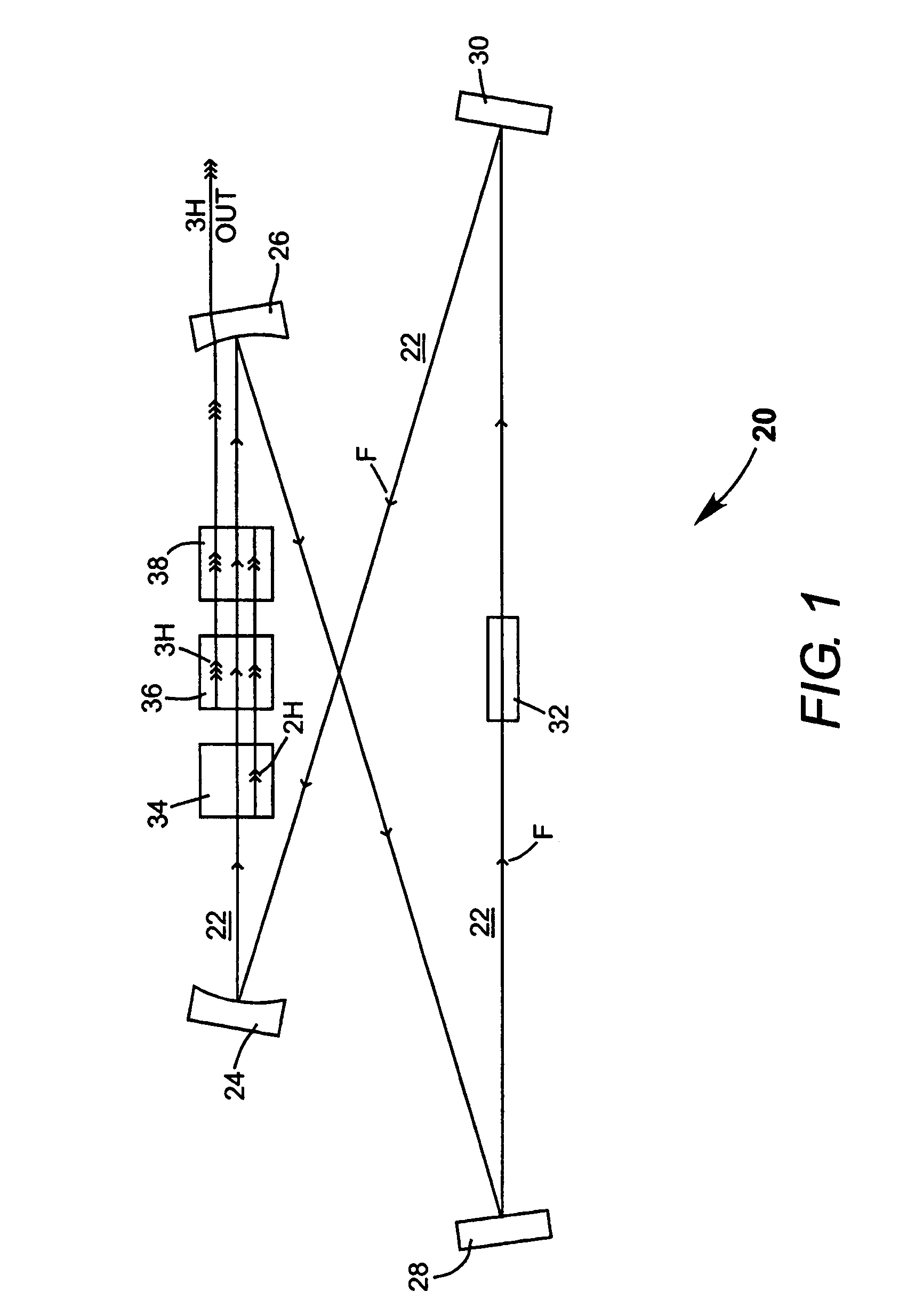
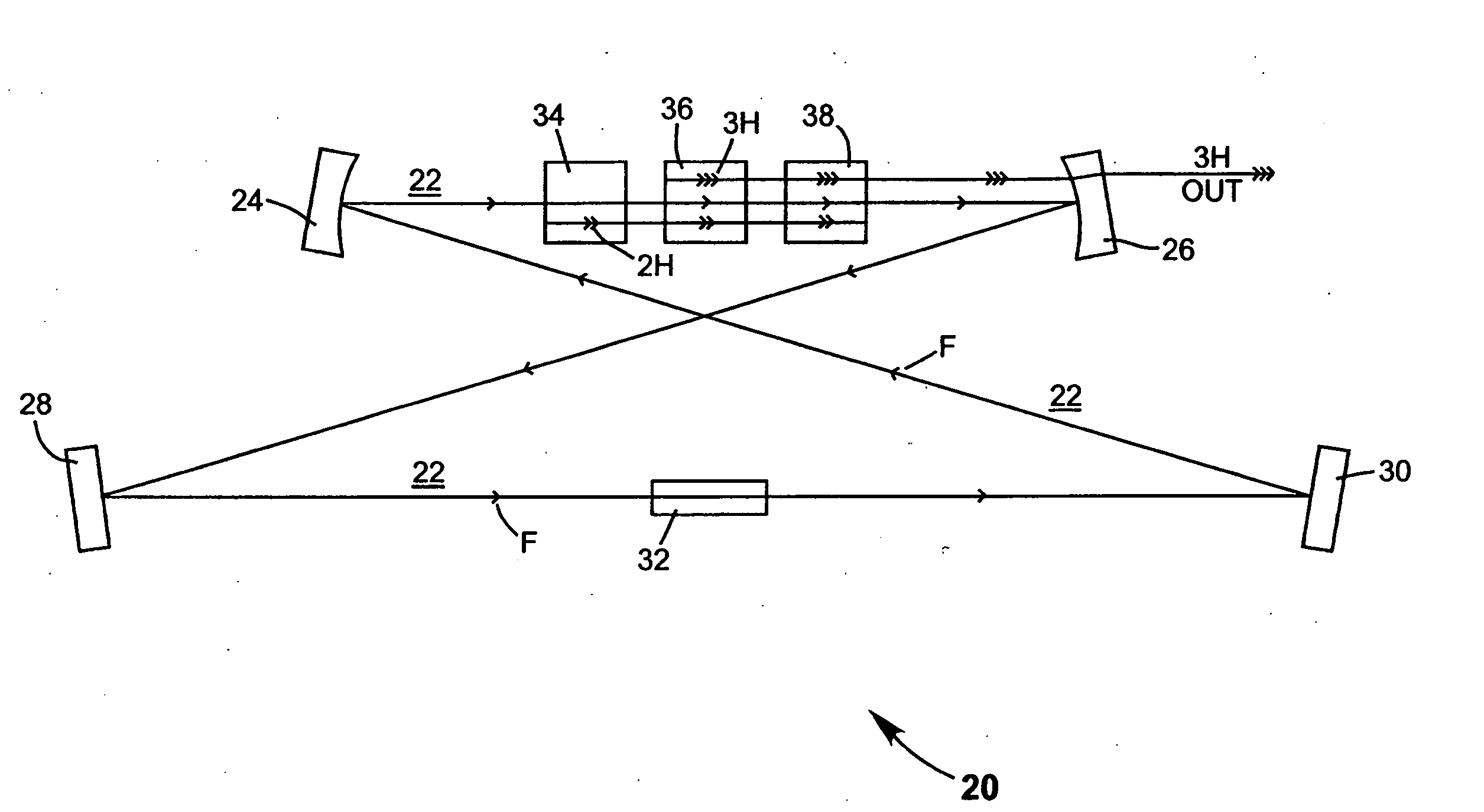
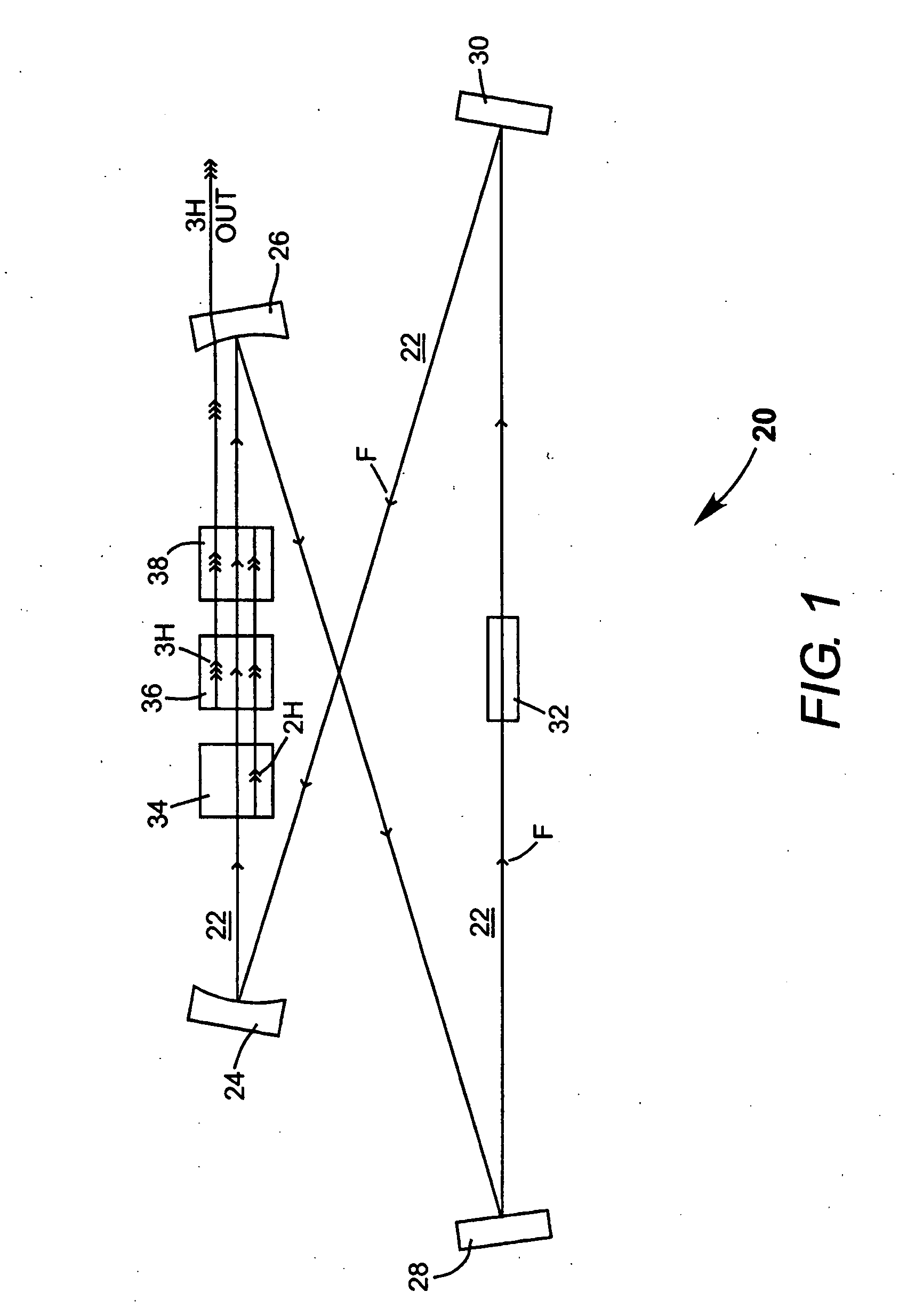
A method of intracavity frequency conversion in a CW laser includes causing fundamental radiation to circulate in a laser resonator. The fundamental radiation makes a first pass through an optically nonlinear crystal where a fraction of the fundamental radiation generates second-harmonic radiation in a forward pass through the crystal. The residual fundamental radiation and the second-harmonic radiation are then sum-frequency mixed in forward and reverse passes through an optically nonlinear crystal such that a fraction of each is converted to third-harmonic radiation. The residual second-harmonic radiation and fundamental radiation from the sum-frequency mixing then make a reverse pass through the second-harmonic generating crystal where the second-harmonic radiation is converted back to fundamental radiation. The third harmonic radiation can be delivered from the resonator as output radiation, or can be used to pump another optically nonlinear crystal in an optical parametric oscillator. Second-harmonic radiation can also be used to pump an optical parametric oscillator.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Method and apparatus for fiber Bragg grating production
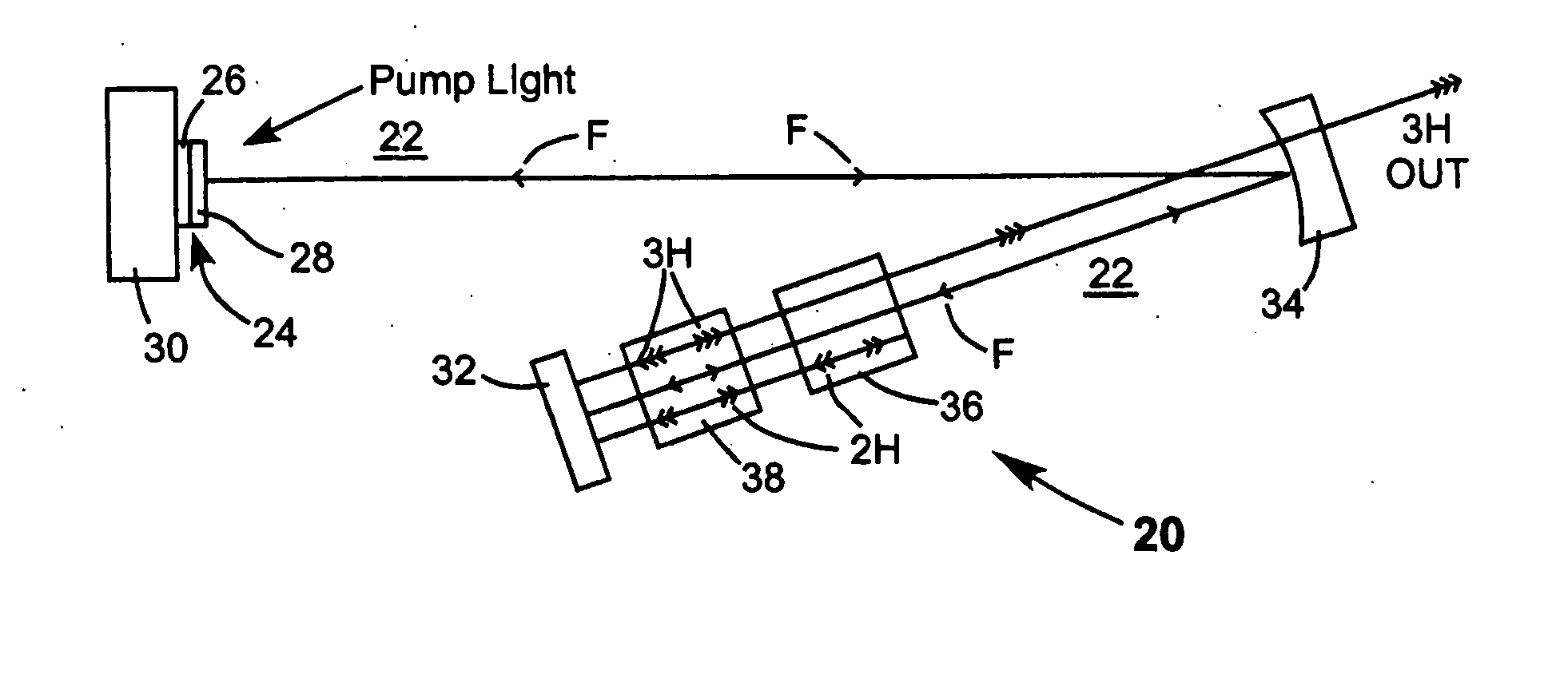
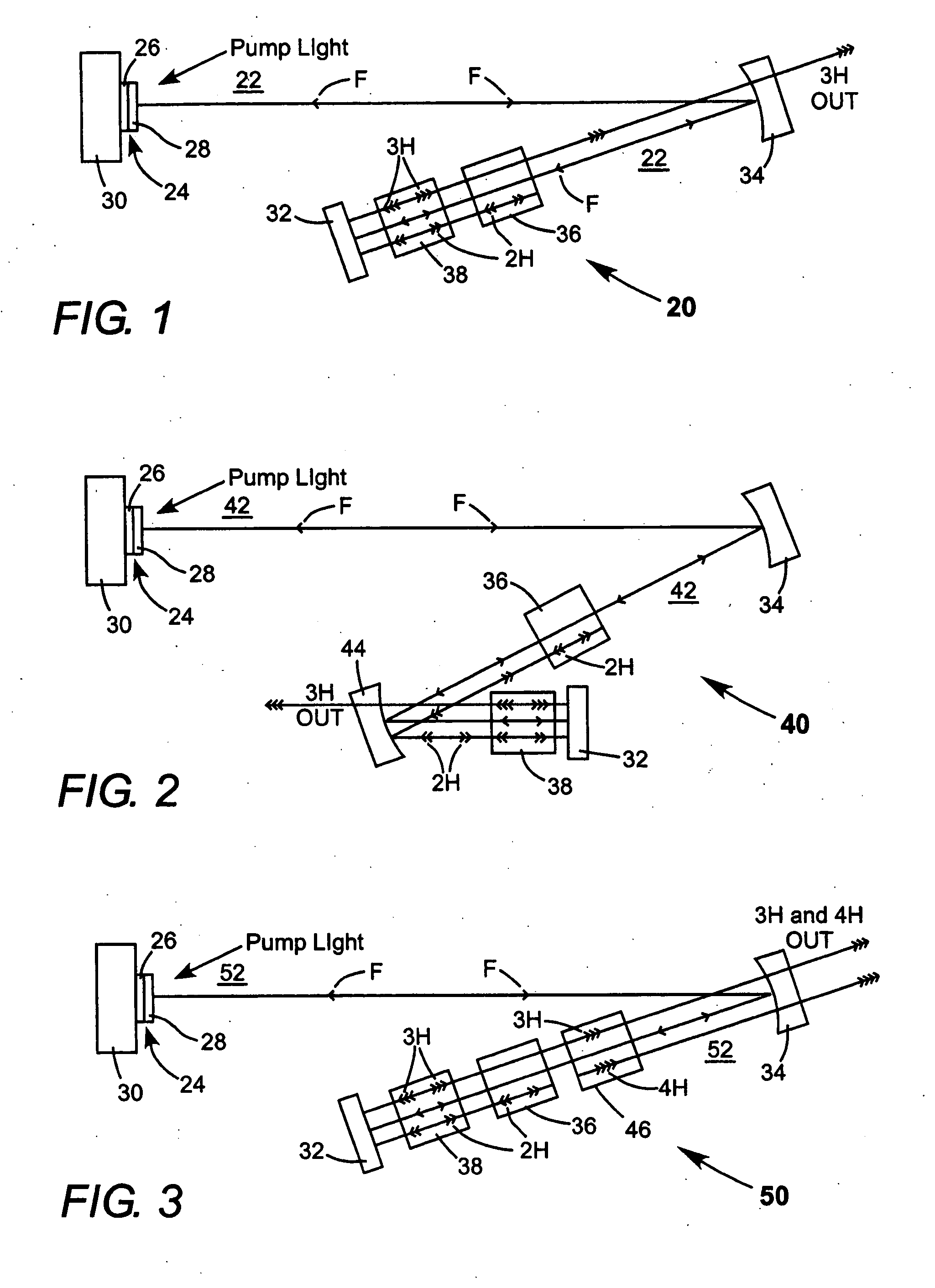
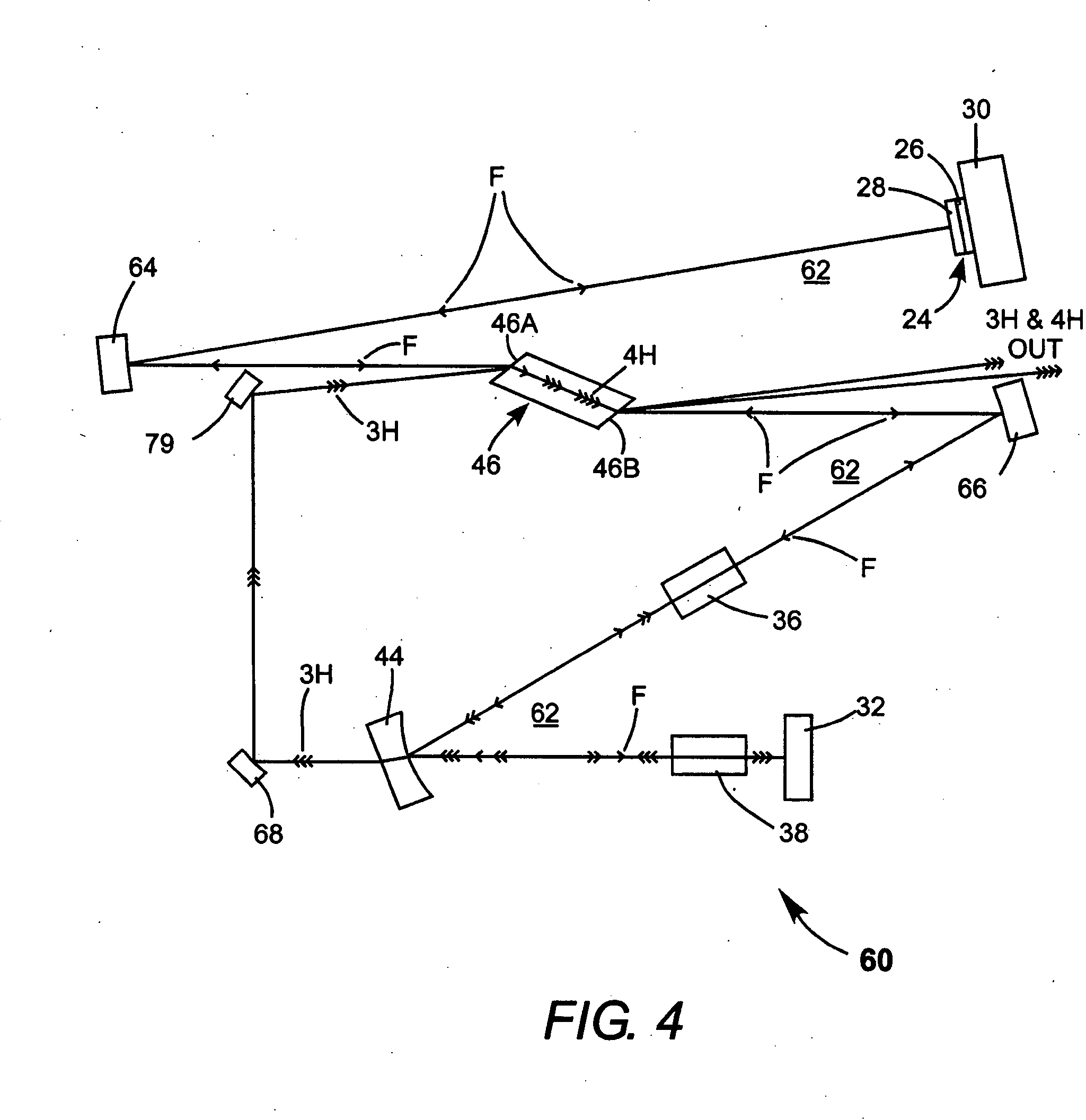
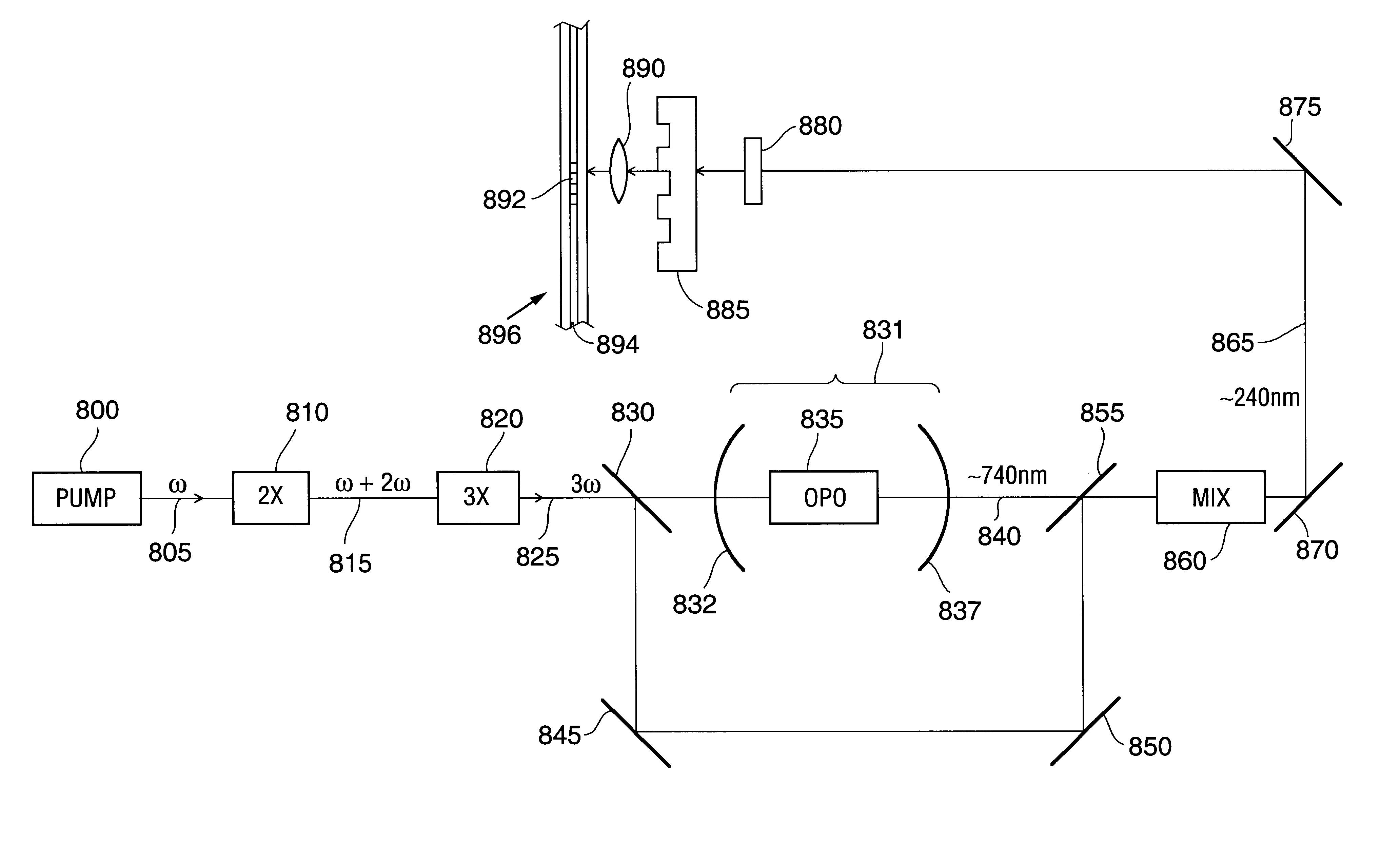
Fiber Bragg writing devices comprising solid state lasers are provided. The solid state lasers comprise optical parametric oscillators and emit moderate peak-power output beams at wavelengths which are suitable for efficient production of fiber Bragg gratings without causing embrittlement of the optical waveguide. These solid state lasers generate output beams with wavelengths of approximately 240 nm, in order to match the primary absorption peak in the ultraviolet range for a typical optical waveguide. Some of these solid state lasers generate tunable wavelength beams using an optical parametric oscillator (“OPO”), then generate harmonics of these tunable beams. Other lasers mix the tunable beam with fixed wavelengths derived from the pump laser to reach the desired output wavelength.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Pseudo-monolithic laser with an intracavity optical parametric oscillator
InactiveUS6373865B1Optical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialOptical axisOptoelectronics
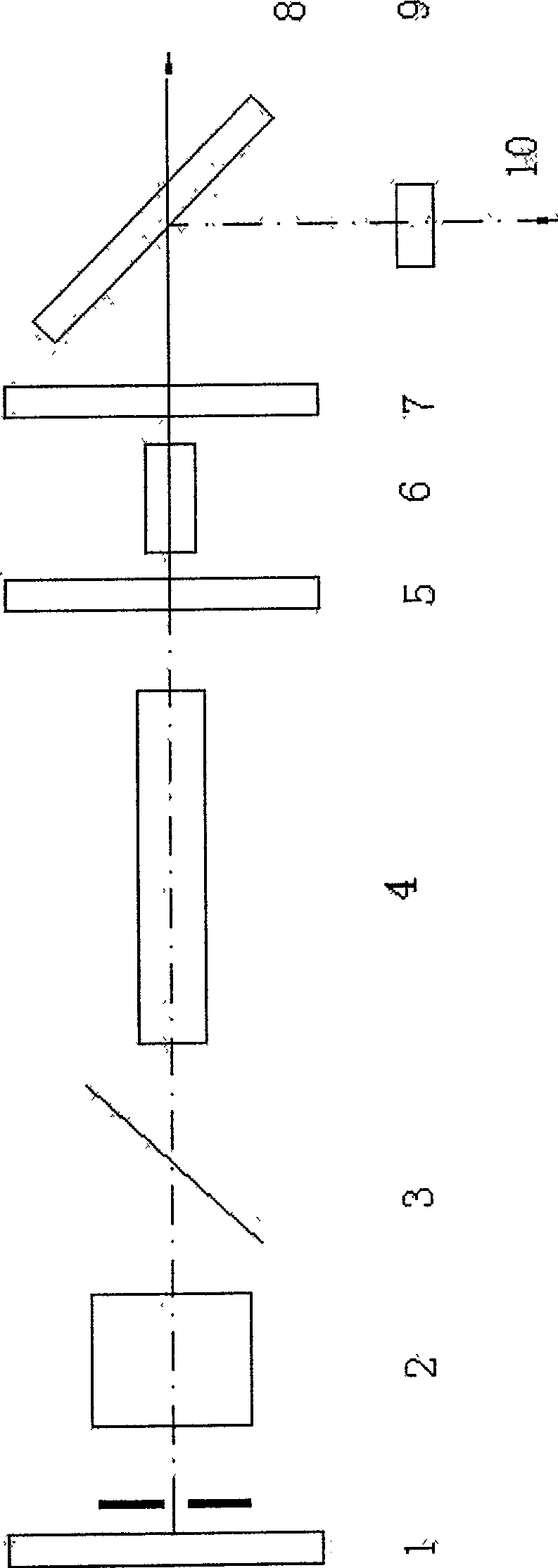
A subassembly for a high powered light pumped, Q-switched and linearly polarized laser with an optical parametric oscillator, the subassembly consisting of two or three rod shaped elements having precisely ground endfaces with selected coatings mounted on a special pallet that at least partially aligns the optical axes of the elements.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Spectral imaging device with tunable light source
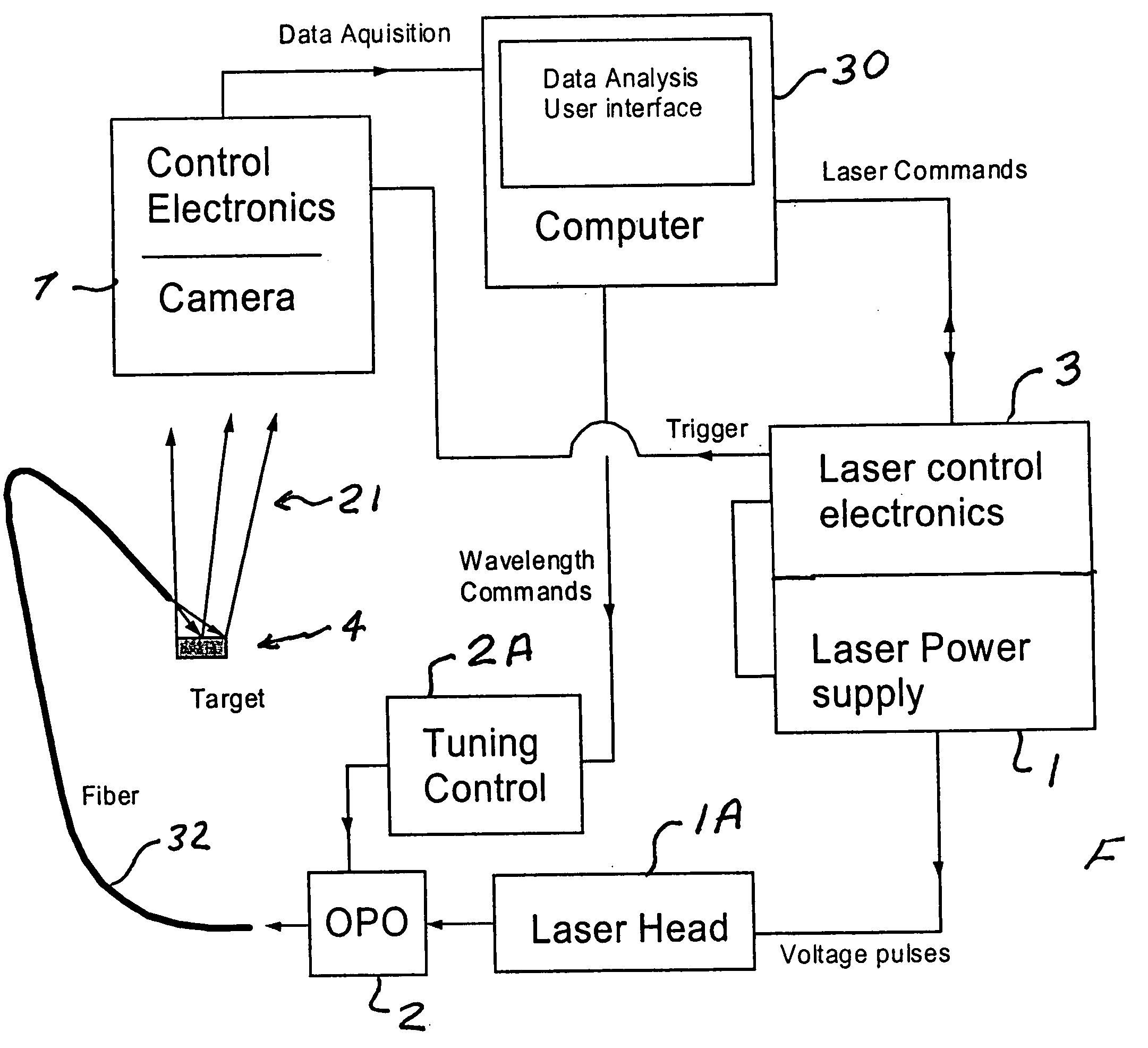
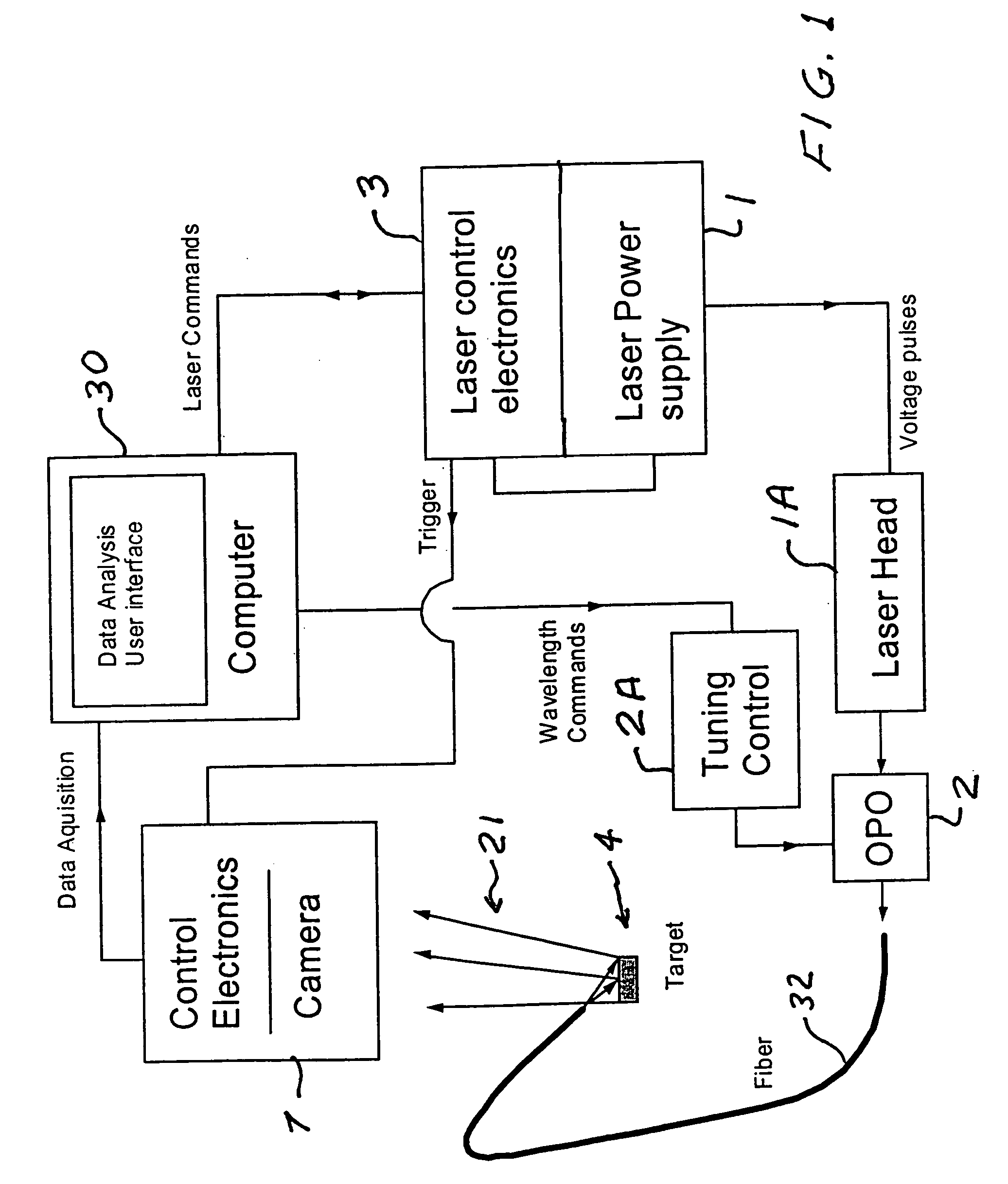
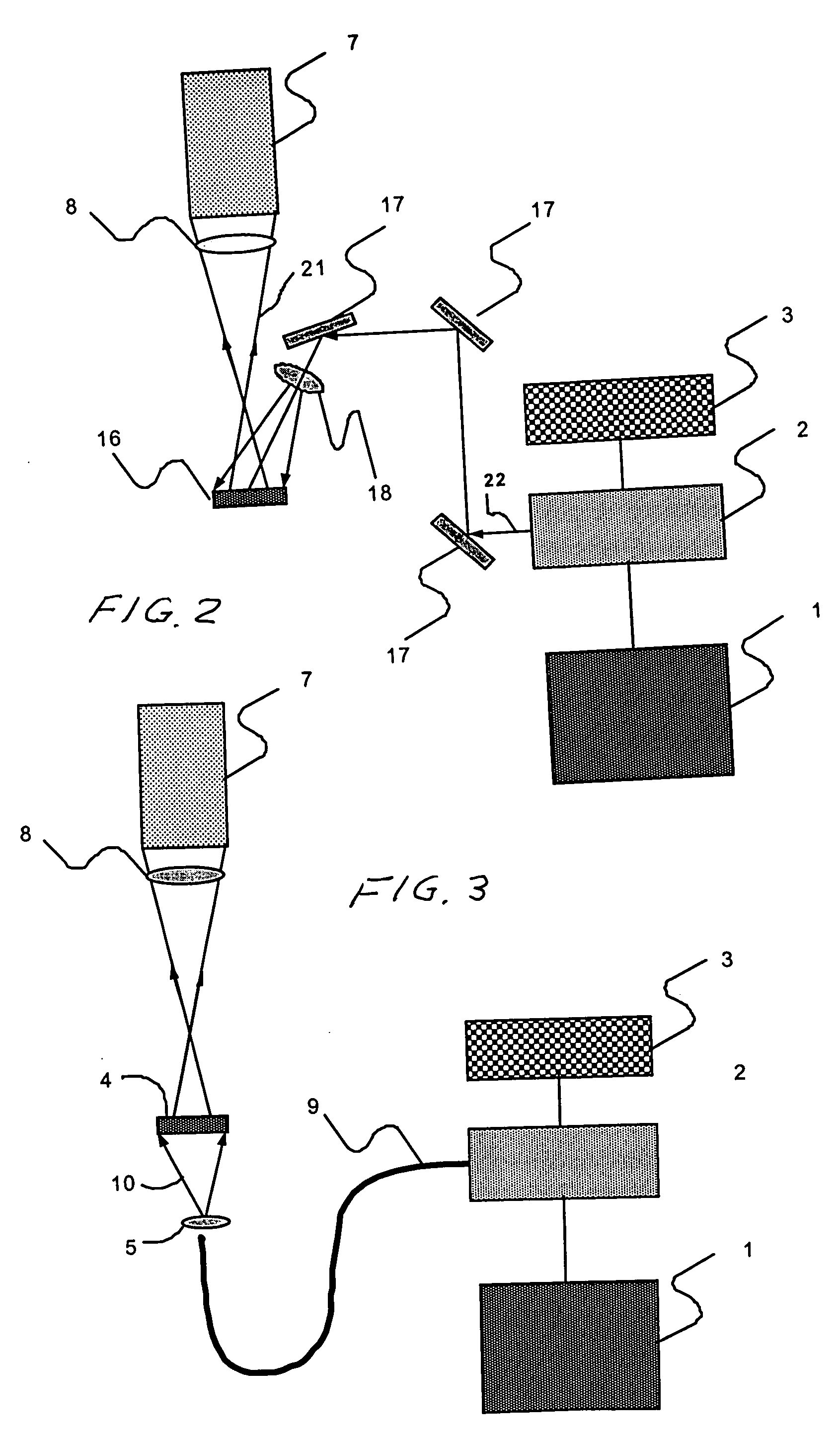
A spectral imaging device with a narrow band spectrally tunable light source. The light source includes an optical parametric oscillator that can be tuned across a wide range of wavelengths while illuminating a target. In a preferred embodiment, a Q-switched YAG laser pumps the OPO. Two-dimensional images of the target may be detected at various wavelengths by a imaging sensor with a many pixel focal plane array to generate data arrays known as hyper-spectral image cubes. These images detecting variations is optical parameters including transmission, reflectivity, and fluorescence of the target can be obtained in various spectral ranges from ultraviolet to infrared for a variety of applications in metrology, agriculture, life sciences, and in the pharmaceutical industry.
Owner:OPOTEK LLC
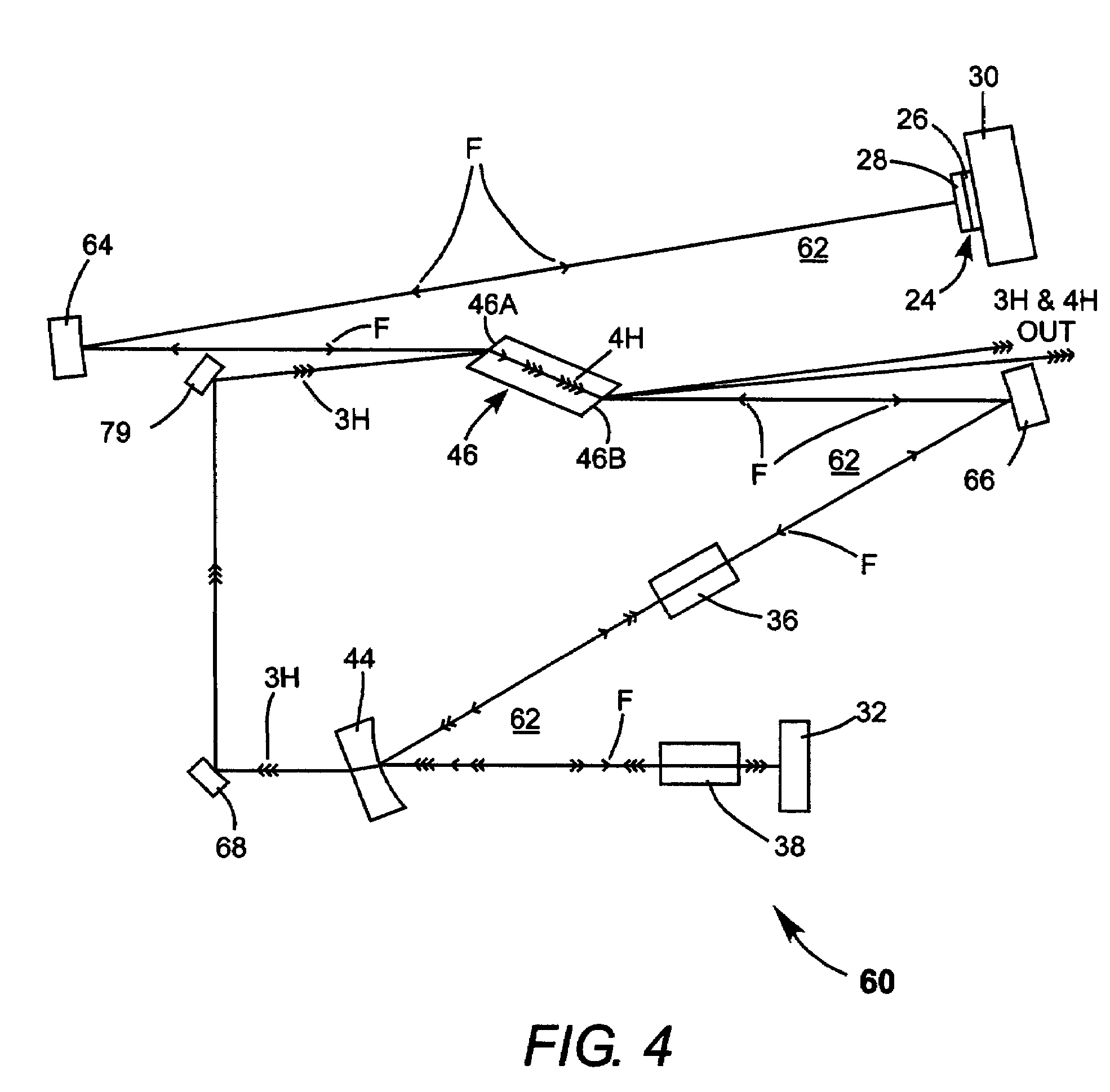
Intracavity frequency-tripled CW laser with traveling-wave ring-resonator
InactiveUS7130321B2Improve efficiencyIncrease volumeLaser optical resonator constructionLaser output parameters controlFourth harmonicThird harmonic
Owner:COHERENT INC
Intracavity frequency-tripled CW laser with traveling-wave ring-resonator
InactiveUS20050163187A1Improve efficiencyIncrease volumeLaser optical resonator constructionLaser output parameters controlFourth harmonicThird harmonic
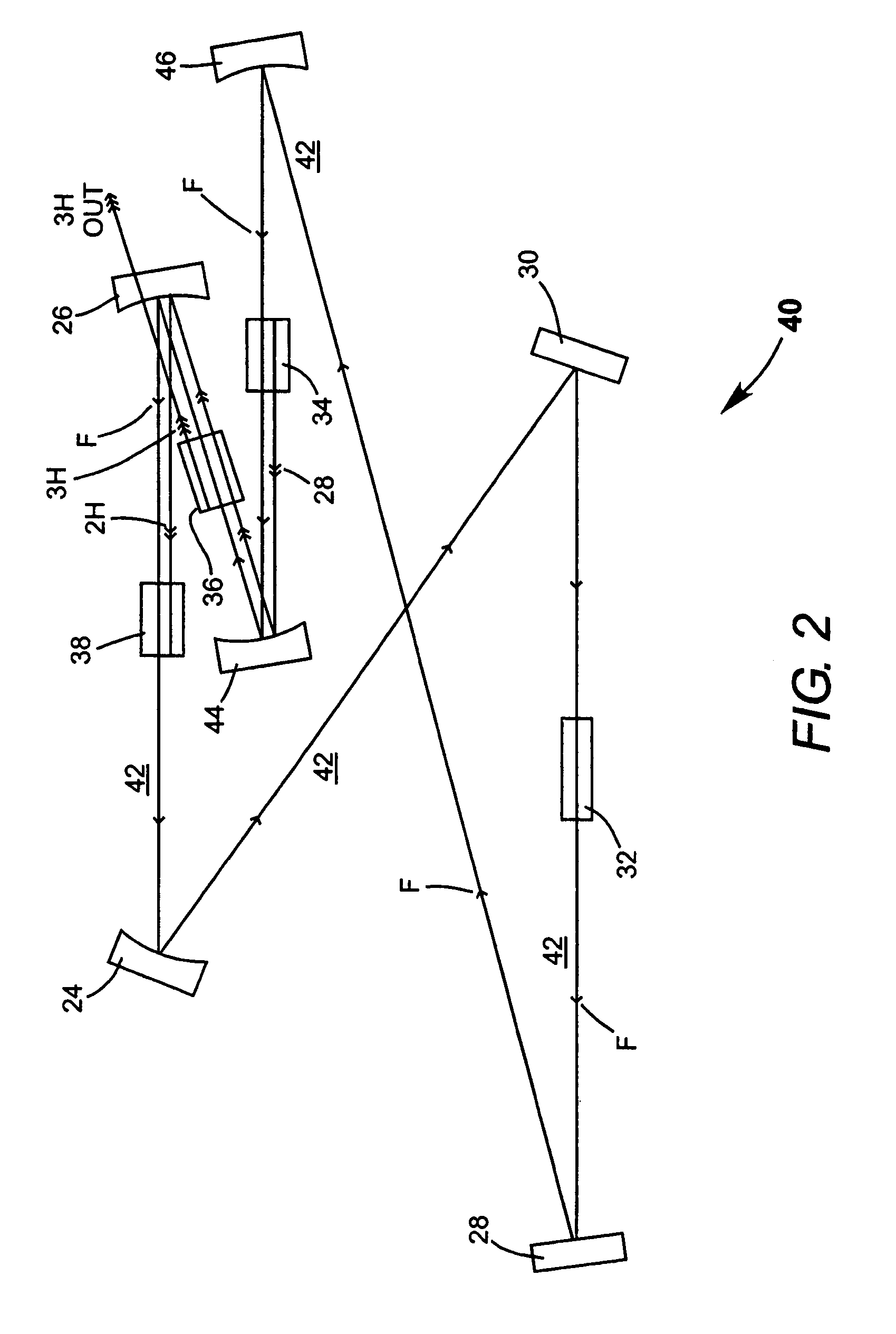
A traveling-wave ring laser resonator includes one or more gain-elements for generating fundamental radiation and three optically nonlinear crystals. A portion of the fundamental radiation is converted to second-harmonic radiation in a first of the crystals. Remaining fundamental radiation and the second-harmonic radiation traverse a second of the optically nonlinear crystals where a portion of each is converted to third-harmonic radiation. Fundamental and second-harmonic radiation pass through the third of the optically nonlinear crystals where most of the second-harmonic radiation is converted back to fundamental radiation. The third-harmonic radiation can be delivered from the resonator as output radiation or mixed with the fundamental radiation in a fourth optically nonlinear crystal to generate fourth harmonic radiation. An optical parametric oscillator arrangement is also disclosed.
Owner:COHERENT INC
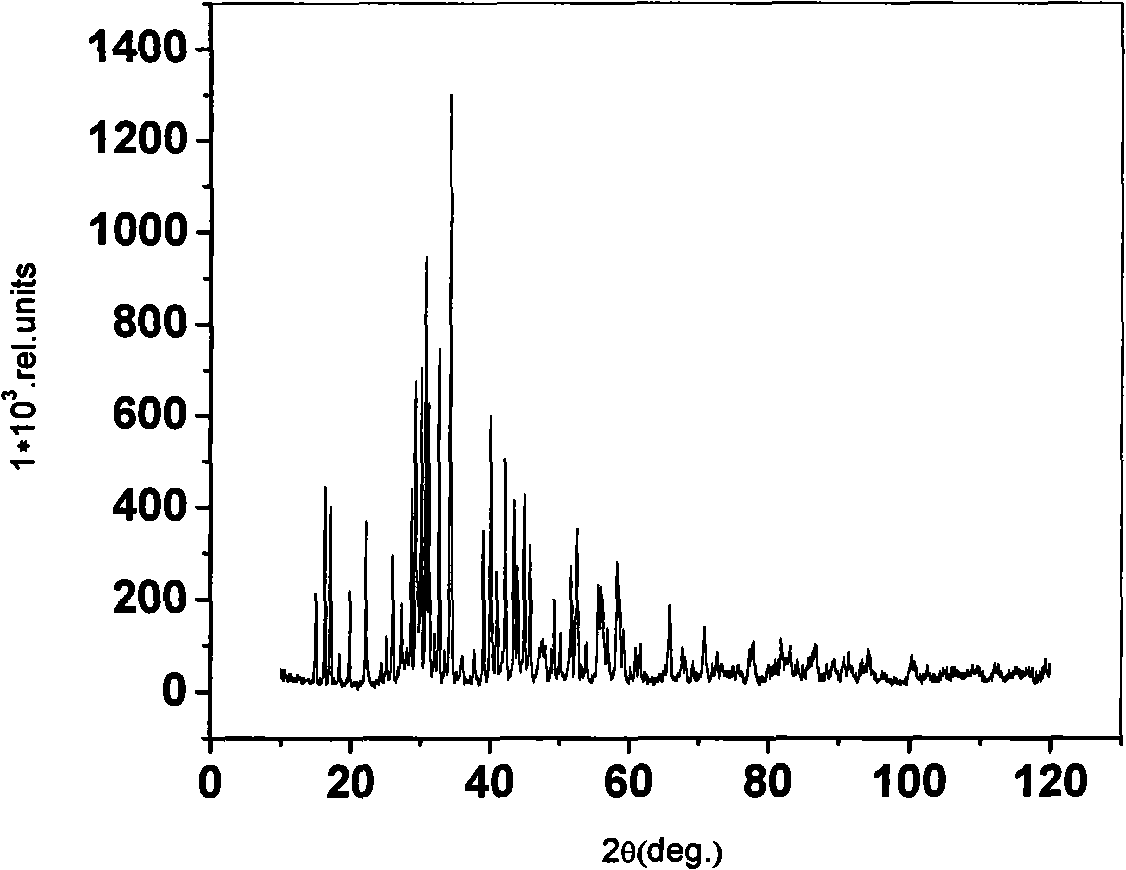
Sulfurized gallium and barium monocrystal as well as growing method and infrared nonlinear optical device thereof
ActiveCN101545141AUnbreakableNot easy to deliquescencePolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsSpace groupSingle crystal
The invention relates to a sulfurized gallium and barium monocrystal as well as a growing method and an infrared nonlinear optical device thereof. A molecular formula of the sulfurized gallium and barium monocrystal is BaGa4S7, the sulfurized gallium and barium monocrystal belongs to the field of rhombic systems, a space group is Pmn21, and a cell parameter is as follows: a=14.755 A, b=6.228 A, c=5.929 A, and alpha=beta=gamma=90 DEG. The nonlinear optical materials are prepared by adopting a crucible decent method to obtain compositions and monocrystals of the same and can be used for manufacturing a secondary harmonic generator, an upper frequency converter, a lower frequency converter and an optical parametric oscillator.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tunable terahertz radiation source based on difference frequency cherenkov effect and modulation method
ActiveCN102386549AOvercoming complexityOvercome rangeSolid masersNon-linear opticsOptical frequenciesPrism
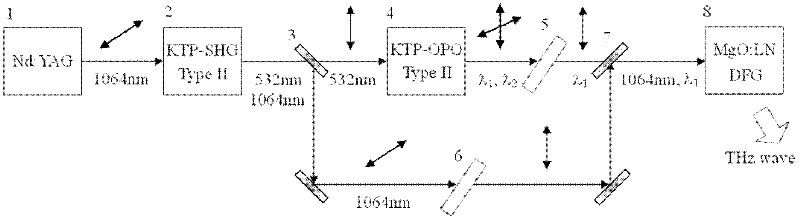
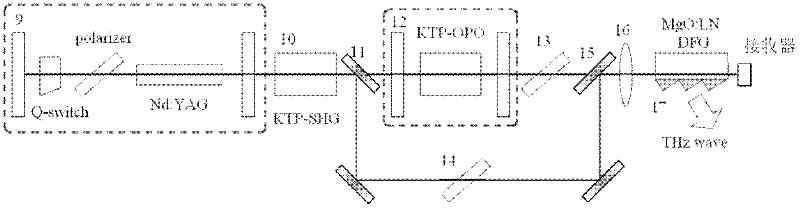
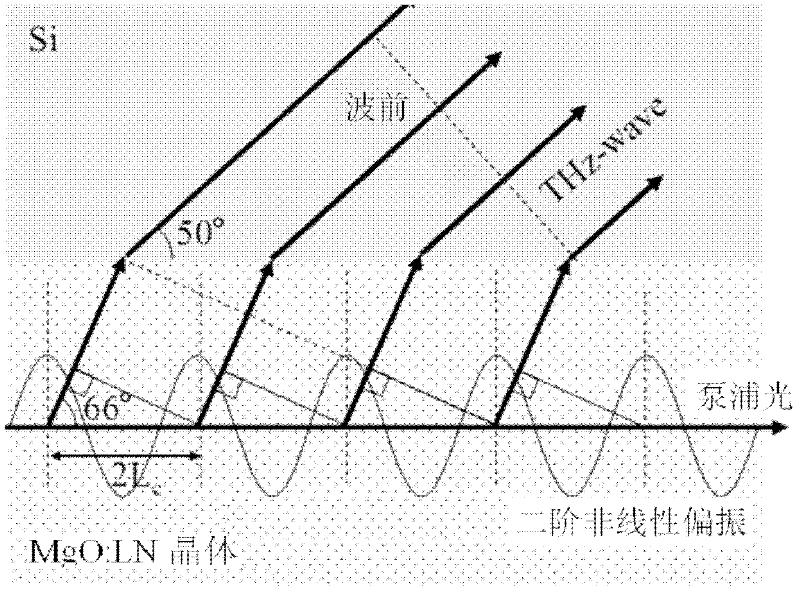
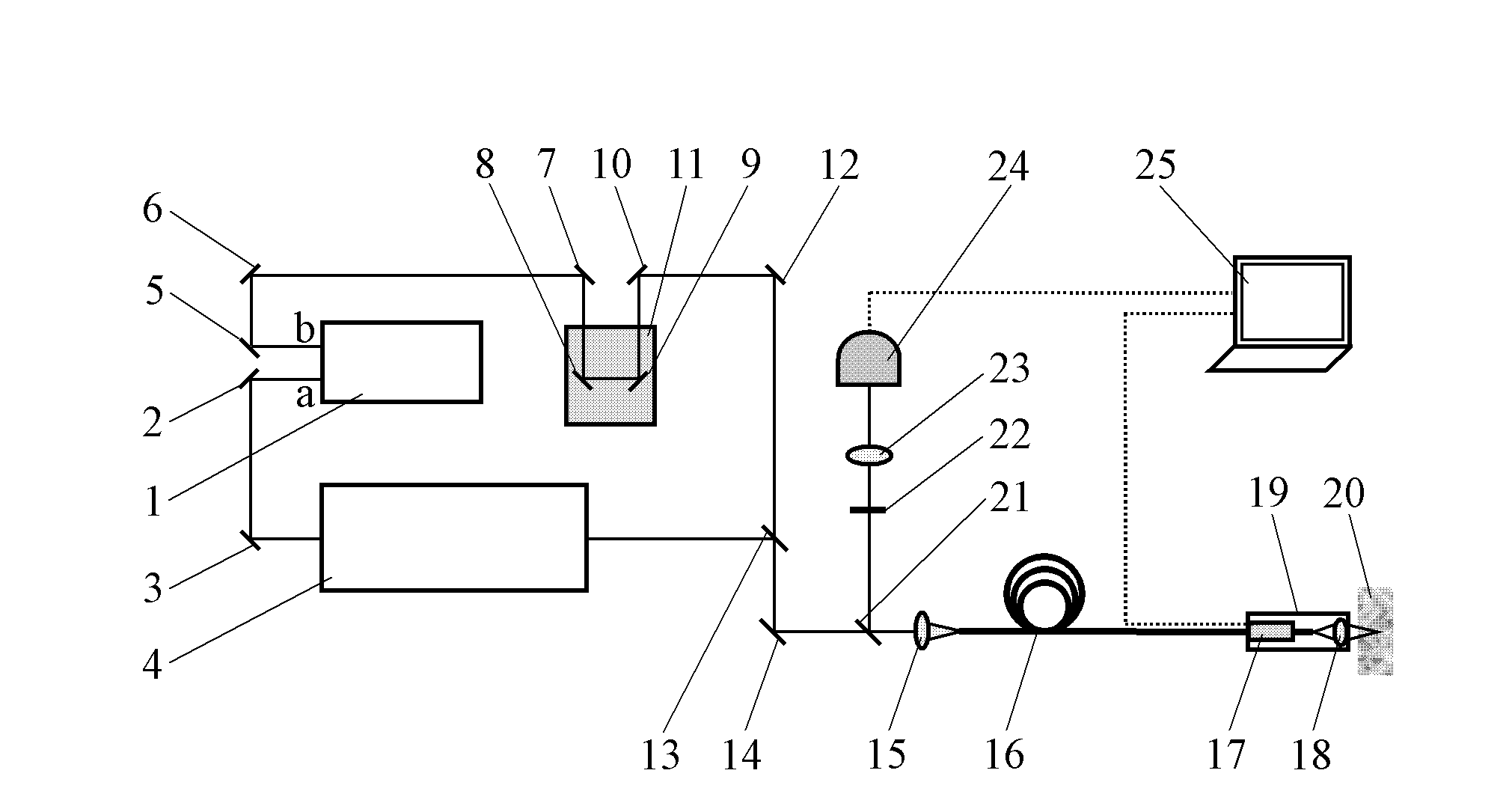
The invention relates to the non linear optical frequency conversion. To realize output of high power THz wave which can be continuously tuned, and stable running at room temperature, the technical scheme used by the invention is that: a tunable terahertz radiation source based on difference frequency cherenkov effect is composed of a laser device, a frequency doubling crystal, a double wavelength parametric oscillator, a harmonic mirror, a polarization filter, a combined beam mirror, a column lens and a difference frequency crystal; the harmonic mirror is placed between the frequency doubling crystal and the double wavelength parametric oscillator; the double wavelength parametric oscillator is II type phase matching KTP (Potassium Titanyl Phosphate) crystal OPO (Optical Parametric Oscillator); the polarization filter, the combined beam mirror and the column lens are arranged between the parametric oscillator and the difference frequency crystal; the difference frequency crystal is amagnesium oxide doped lithium niobate crystal with molecular formula of MgO:LiNbO3 or MgO:LN, and the generated THz wave is coupled and output by an Si prism on the side surface of the difference frequency crystal. The tunable terahertz radiation source based on difference frequency cherenkov effect is mainly applied to the optical frequency conversion.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
System and method for carrying out CARS (Coherent anti-Stokes Raman Scattering) imaging by using four-wave mixing signals generated by optical fiber
The invention relates to a system and method for carrying out CARS (Coherent anti-Stokes Raman Scattering) imaging by using four-wave mixing signals generated by optical fiber. The system comprises a laser source, multiple reflecting mirrors, an optical parametric oscillator, a precise displacement platform, two long-wave-pass dichroscopes, a coupling objective lens, optical fiber, a two-dimensional scanner, a focusing lens, a supporting sleeve, a sample, a band-pass filter, an imaging lens, a detector and a computer. A light beam which is output after the laser source sends a frequency-doubling light beam for pumping the optical parametric oscillator, and a base-frequency light beam sent by the laser source are respectively pumping light and Stokes light for CARS imaging, and the four-wave mixing signals which are excited after the pumping light and the Stokes light are overlapped on time and space and then transmitted in the optical fiber are probe light for CARS imaging. CARS signal light which is generated after the pumping light and the Stokes light are focused on a sample are not overlapped with the frequency of the pumping light and the frequency of the Stokes light and can be separated by the long-wave-pass dichroscopes. Relative to the standard CARS system, the system disclosed by the invention is not newly provided with any device, has no special requirement on the used devices and is simplified in system and saved in cost.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optically pumped semiconductor laser pumped optical parametric oscillator
InactiveUS20070291801A1Laser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionLength waveOptical nonlinearity
An optically pumped semiconductor pumped optical parametric oscillator (OPS-pumped OPO) includes an OPS laser resonator and an OPO resonator A portion the OPS laser resonator axis and the OPO resonator axis are collinear. An optically nonlinear crystal is located in the coaxial portion of the resonators and arranged to frequency divide fundamental radiation generated in the OPS laser resonator into signal and idler radiations. In one arrangement, the OPO laser resonator is also an OPS resonator and is arranged to generate radiation at the wavelength of the signal radiation, with the idler radiation having the difference-frequency wavelength of the signal and fundamental radiations
Owner:COHERENT INC
Backscatter absorption gas imaging systems and light sources therefore
ActiveUS20050053104A1Low power operationLaser using scattering effectsColor/spectral properties measurementsAudio power amplifierHydrocotyle bowlesioides
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
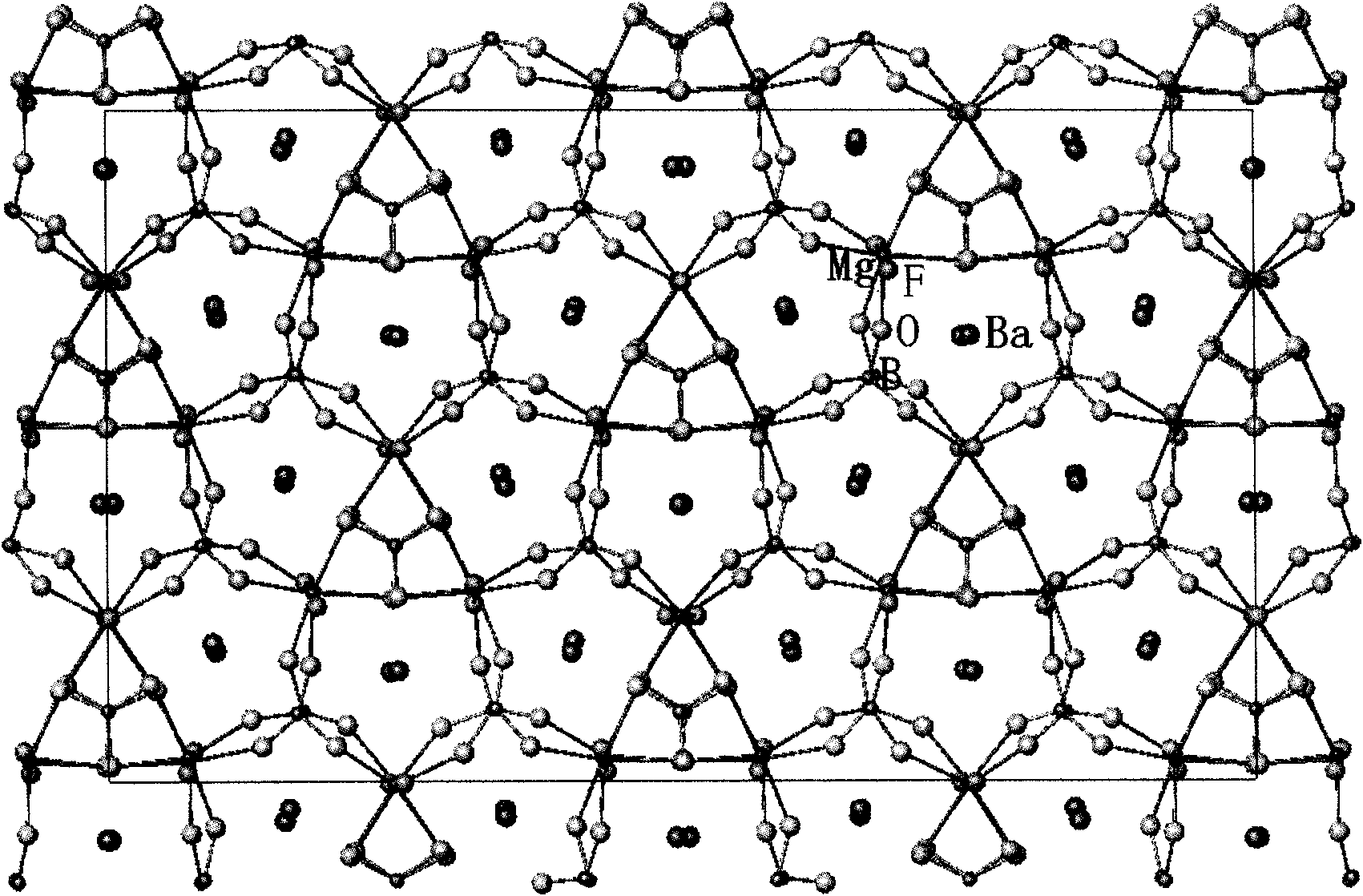
BaMgBO3F non-linear optical crystal, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN101798707AWith nonlinear optical effectChemically stablePolycrystalline material growthFrom melt solutionsRoom temperatureSingle crystal
The invention relates to BaMgBO3F non-linear optical crystal, a preparation method and applications thereof. The crystal has the following cell parameters: a=17.59, b=30.50, c=8.05, alpha=beta=gamma=90, and z=48. Mg2+is coordinated by four Os and two Fs. The solid-solid phase transition temperature is 900+ / -10 DEG C, the low temperature phase has frequency doubling effect, and the ultraviolet or deep-ultraviolet wave band beams are allowed to penetrate. The frequency doubling effect of the high-temperature phase is zero, the decomposing temperature is 1050 DEG C, and the crystal does not generate deliquescence in air, and is not dissolved in the water solution with the pH valve of 2-12 at normal temperature. The method has the following preparation steps of: mixing the BaMgBO3F with a fluxing agent, and heating into a melt body; forming seeds under the temperature of 0.5-5 DEG C above the temperature of the saturation point of the melt body; subsequently, decreasing the temperature to 0-1 DEG C below the temperature of the saturation point, and rotating along with decreasing temperature to grow the crystal; separating the melt body when the crystal is grown to the required size, and decreasing to the room temperature to obtain the BaMgBO3F single crystal. The crystal can be used as the frequency doubling crystal in the optical parametric oscillator or the harmonic generator.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cascaded noncritical optical parametric oscillator
InactiveUS6785041B1Low pumping thresholdImprove efficiencyLight demodulationNon-linear opticsPath lengthMid infrared
Method and system for providing laser light that is tunable over a relatively wide mid-infrared wavelength range, such as 2-17 .mu.m. A first noncritically phase matched nonlinear crystal receives a laser light beam and converts the light to a first cavity beam having a first selected wavelength, using optical parametric oscillation techniques. A second noncritically phase matched nonlinear crystal receives the first cavity beam and converts the light to a second cavity beam having a second selected wavelength. Where the first wavelength is tuned (e.g., by temperature change or effective path length change) over a wavelength range of 2-5 .mu.m, the second wavelength can vary over a higher and broader wavelength range, such as 3-17 .mu.m.
Owner:BLUELEAF LLC
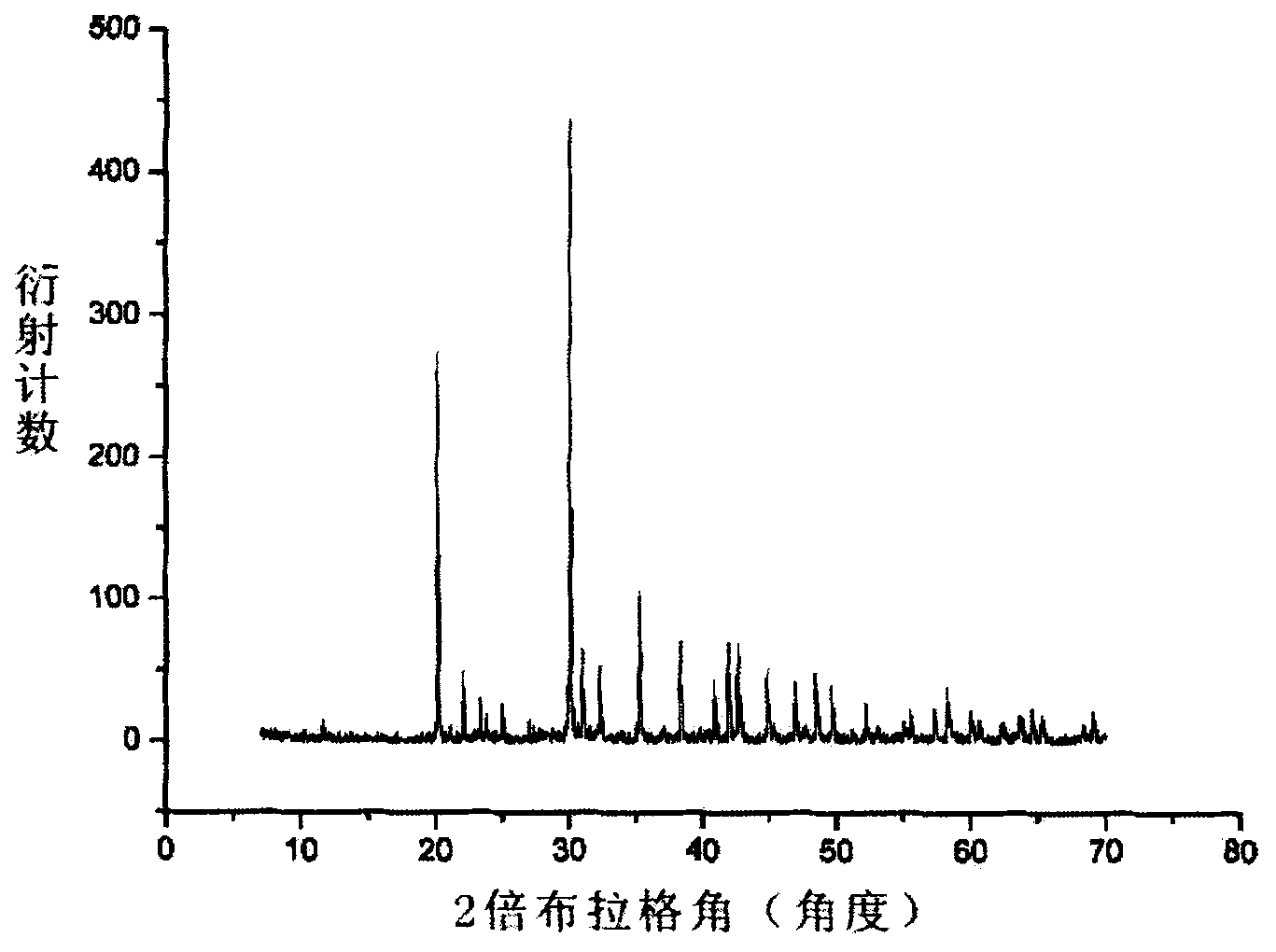
K3B6O10 Br nonlinear optical crystal, preparation and use
ActiveCN101498040APolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsNonlinear optical crystalBromine
The invention relates to a nonlinear optical bromine-contained kalium borate bromate crystal, a preparation method and applications thereof. The crystal has a molecular formula of K3B6O10Br, belongs to a trigonal system, and has a space group of R3m, a molecular weight of 422.07 and a perovskite structure. The crystal adopts a high-temperature solution method, mixes and heats a kalium borate bromate compound and flux and stabilizes the temperature of a mixture which is cooled to a saturation temperature to obtain a mixed solution; a corundum rod bound with Pt wire is put in the mixed solution which is cooled to the saturation temperature to obtain the needed crystal, and the crystal is extracted out of a liquid level and is cooled to a room temperature so as to obtain the nonlinear optical crystal kalium borate bromate. The crystal is twice the nonlinear optical effect of a KDP crystal and has a light-transmitting band of 210nm to 3000nm, is non-deliquescent in air, has short growth period, is easy to cut, polish, process and store and is suitable for making nonlinear optical devices. The nonlinear optical crystal is widely applicable to nonlinear optical devices such as frequency multiplication converters, optical parameter oscillators, and the like.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Intracavity OPO laser
ActiveUS7079557B1High damage thresholdImprove reliabilityLaser detailsLight demodulationReflection lossOptical axis
A laser having an optical parametric oscillator for providing a preselected wavelength beam is provided. A nonlinear crystal cut for phase matching condition preferably cut for noncritical phase matching conditions for the fundamental beam wavelength and the preselected wavelength beam is located in both the optical parametric oscillator cavity and laser resonator cavity.The optical axis of the laser resonator and the optical axis of the optical parametric oscillator cavity are at least partially separate and partially overlap. The laser crystal is located in the laser resonator cavity but not in the optical parametric oscillator cavity. Each end of the OPO nonlinear crystal that intersects the optical axes has a Brewster cut for both the fundamental and preselected wavelength beams so that the fundamental and preselected wavelength beams incident on the nonlinear crystal at approximately the Brewster angle and pass through without substantial reflection loss.The fundamental wavelength beam is directed into the optical parametric oscillator cavity and incidents on nonlinear crystal having a Brewster cut at each end for fundamental and preselected wavelength beam without substantial reflection loss. A portion of the fundamental wavelength beam is partially converted to a preselected wavelength beam. The fundamental beam and the preselected wavelength beams are reflected back through the nonlinear crystal. Preselected wavelength beam is separated from the fundamental wavelength beam.
Owner:PHOTONICS INDS INT
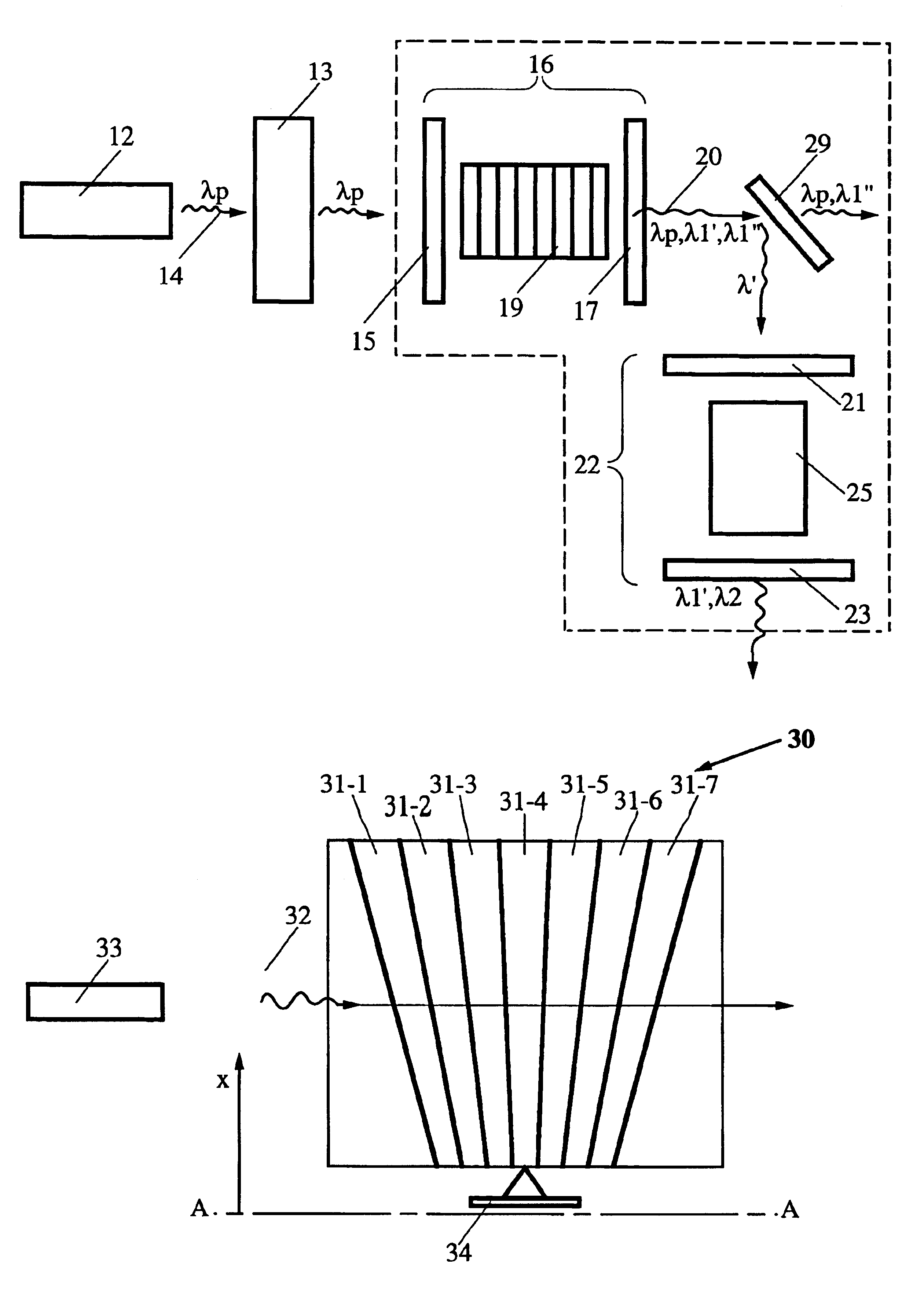
Broadly tunable optical parametric oscillator
ActiveUS20110180729A1Color/spectral properties measurementsOptical devices for laserPicosecond laserLength wave
A novel broadly tunable optical parametric oscillator is described for use in numerous applications including multi-photon microscopy. The optical parametric oscillator includes at least one sub-picosecond laser pump source configured to output a pump signal having a wavelength of about 650 nm or less and at least one type II optical parametric oscillator in optical communication with the pump source and configured to generate a single widely tunable pulsed optical signal. In one application, an optical system is in optical communication with the optical parametric oscillator and configured to direct at least a portion of the optical signal to a specimen, and at least one analyzing device is configured to receive a signal from the specimen in response to the optical signal.
Owner:NEWPORT CORP
Large size barium borate bismuth nonlinear optical crystal and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101302647AFast growthWide band of light transmissionPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltNonlinear optical crystalSpace group
The invention relates to a large-sized bismuth barium borate non-linear optic crystal, which belongs to the orthorhombic system with a space group equal to Pna21 and a molecular formula equal to BaBiBo4. The crystal is made from a mixed system of bismuth barium borate, fluxing agent Bi2O3 and BaB2O4, or BaO and Bi2O3; the nonlinear optical effect of the crystal is approximately five times of that of (KH2PO4) KDP; and the crystal is transparent within a wave band of between 200 and 3,000 nm, and has the large size with 1 to 100mmx1 to 100mmx1 to 100mm. The large-sized bismuth barium borate non-linear optic crystal has the advantages of quick making speed, simple operation, low cost, large-sized and transparent crystal made by the non-linear optic crystal, wide light-transmission wave band, ideal mechanical property, infrequent fragmentation, stable physicochemical properties, no deliquescence and easy processing and preservation; moreover, the non-linear optic crystal can be used to make non-linear optical devices such as a multiple frequency generator, an upper frequency converter or a lower frequency converter and an optical parametric oscillator.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
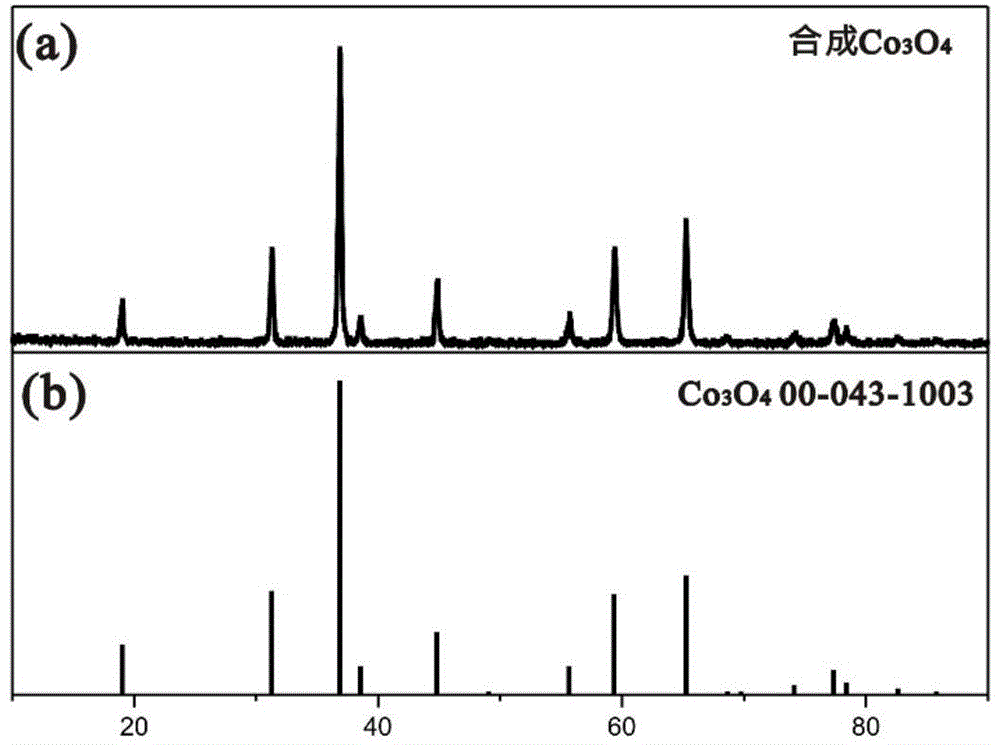
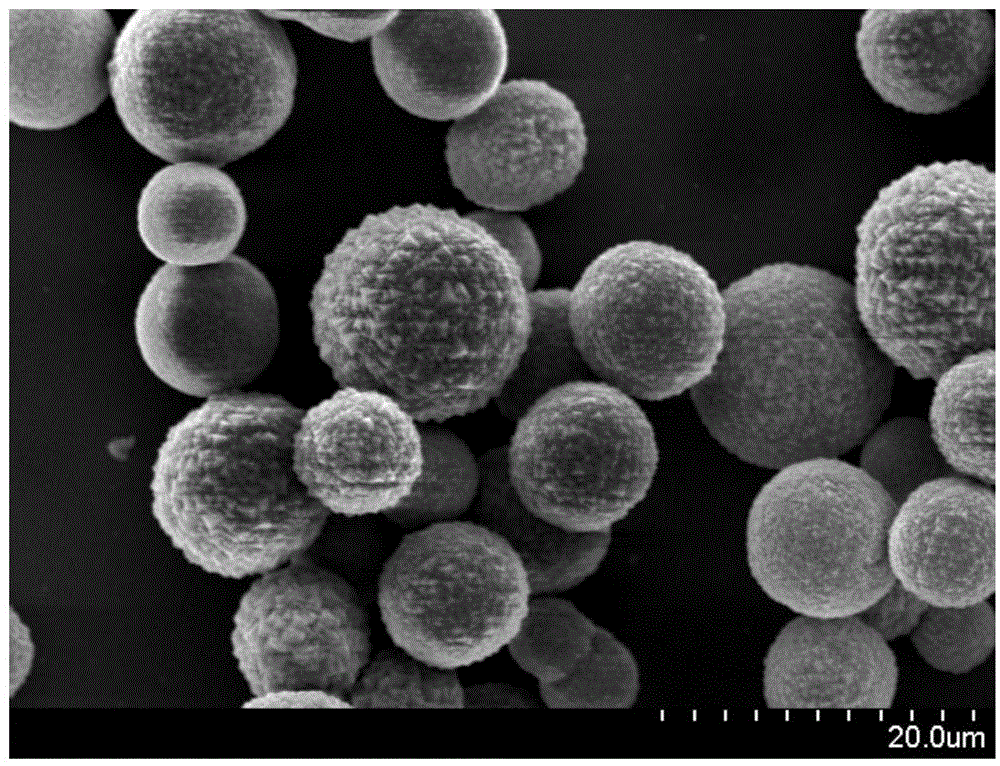
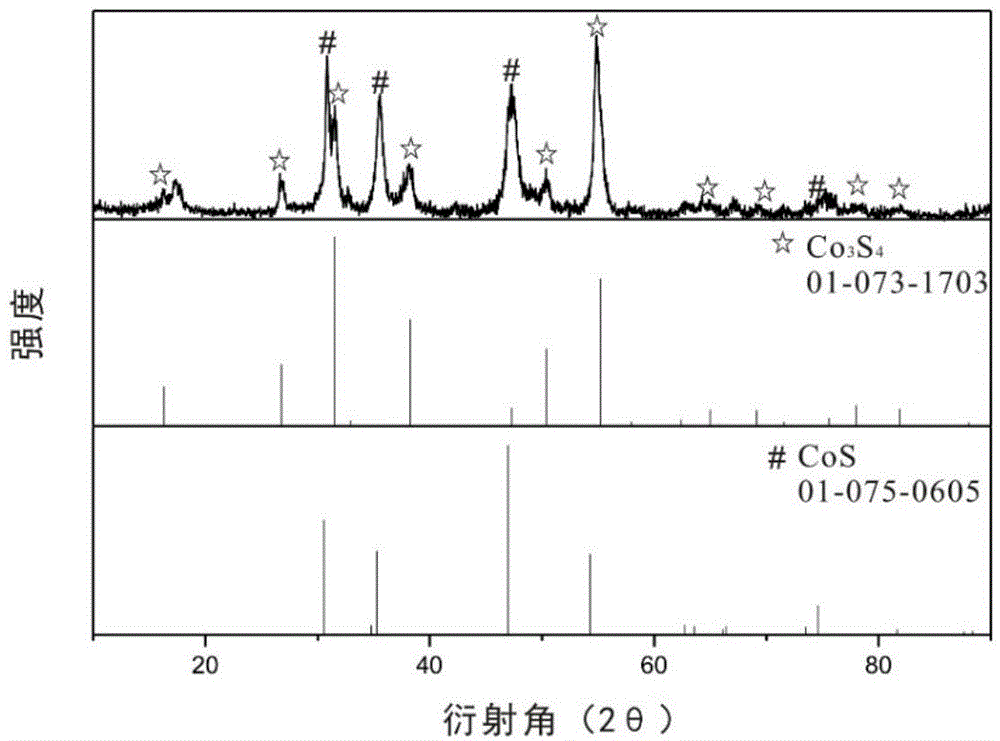
Preparation method and application of cobalt sulfur compound
ActiveCN104993132AWide range of sourcesHigh specific capacityCobalt sulfidesCell electrodesSemiconductor materialsSolar cell
Relating to cobalt sulfur compounds, the invention provides a preparation method and application of a cobalt sulfur compound. The method includes: dissolving a water soluble cobalt source and urea in a mixed solvent to form a solution, carrying out reaction to obtain cobalt carbonate, performing calcinations to obtain a cobalt oxide, and reacting the cobalt oxide with a sulfur source in a reducing atmosphere to obtain a micrometer-scale cobalt sulfur compound. The micrometer-scale cobalt sulfur compound can be spherical cobalt sulfur compound or lamellar square-like cobalt sulfur compound, and the obtained cobalt sulfur compound can be Co9S8, CoS, Co3S4 and CoS2, etc. The cobalt sulfur compound prepared by the preparation method provided by the invention can be applied as an electrode active material in preparation of secondary battery electrodes. According to the invention, specific shape cobalt sulfide can be prepared, is low in synthesis cost and has high tap density, and can be applied to secondary battery electrode materials, optical parametric oscillators, semiconductor materials, solar cells and other aspects.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Large size potassium strontium borate nonlinear optical crystal, preparation and use thereof
InactiveCN101514492AOptical processing accuracy without special requirementsPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsNonlinear optical crystalSpace group
The invention relates to a large size potassium strontium borate nonlinear optical crystal, the preparation and use thereof. The formula of the crystal is: KSr4B3O9, which belongs to rhombic system, the space group is Pna2(1), and the molecular weight is 566.01, and the crystal size is 10-60mmx10-60mmx10-60mm. The preparation contains the following steps of: evenly mixing the potassium strontium borate compound with a fusing assistant, heating, maintaining the constant temperature, cooling to the saturation temperature and obtaining a mixture solution, placing a seed crystal into the mixture solution, lowering the temperature to the saturation temperature to obtain the required crystal, and subsequently extracting the crystal from the liquid level, cooling to room temperature, and finally obtaining the large size potassium strontium borate nonlinear optical crystal. The nonlinear optical effect of the crystal is approximately the same as the KDP, the transparent optical band is 220nm-3000nm. The crystal is simple in operation, low in cost, large in crystal size, short in growth period, less in coating, high in laster damage threshold, good in mechanical property, firm, stable in physicochemical properties, uneasy to deliquescence, convenient for processing and storage, or the like. Accordingly, the nonlinear optical crystal of the invention can be abroadly applied in nonlinear optical devices such as frequency doubler, optical parametric oscillator or the like.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compound barium borofluoride, barium borofluoride non-linear optical crystal, and preparation method and use of the barium borofluoride non-linear optical crystal
ActiveCN102978702APolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltNonlinear optical crystalHardness
The invention discloses a compound barium borofluoride, a barium borofluoride non-linear optical crystal, and a preparation method and a use of the barium borofluoride non-linear optical crystal. The compound barium borofluoride and the barium borofluoride non-linear optical crystal have the same chemical formula of Ba3B6O11F2. The barium borofluoride non-linear optical crystal belongs to a monoclinic system, has a space group P2(1), has cell parameters shown in the patent specification, wherein beta is equal to 101.351(4)deg., and has the molecular weight of 690.88. The powder frequency-doubling effect of the barium borofluoride non-linear optical crystal is 3 times that of KDP (KH2PO4). The compound barium borofluoride is synthesized by a solid-phase reaction method. The barium borofluoride non-linear optical crystal grows by a high-temperature melting method. The barium borofluoride non-linear optical crystal has large mechanical hardness, can be cut, polished and stored easily, and can be widely used in preparation of nonlinear optical devices such as a frequency multiplication generator, an upper frequency converter, a lower frequency converter and an optical parameter resonator.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Intracavity frequency-tripled CW laser
InactiveUS7463657B2High frequencyImprove efficiencyLaser optical resonator constructionExcitation process/apparatusNonlinear optical crystalNonlinear crystals
Owner:COHERENT INC
Thulium laser pumped mid-ir source with broadbanded output
ActiveUS20050286603A1Reduce gainLong pulse widthOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialOptical isolatorRoom temperature
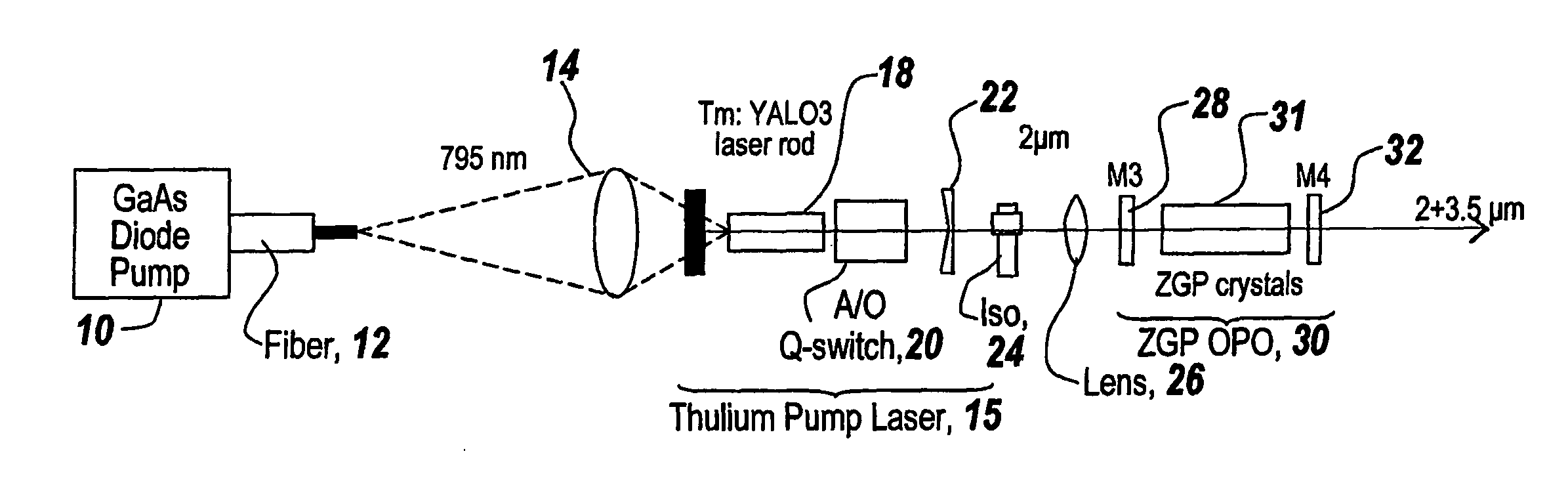
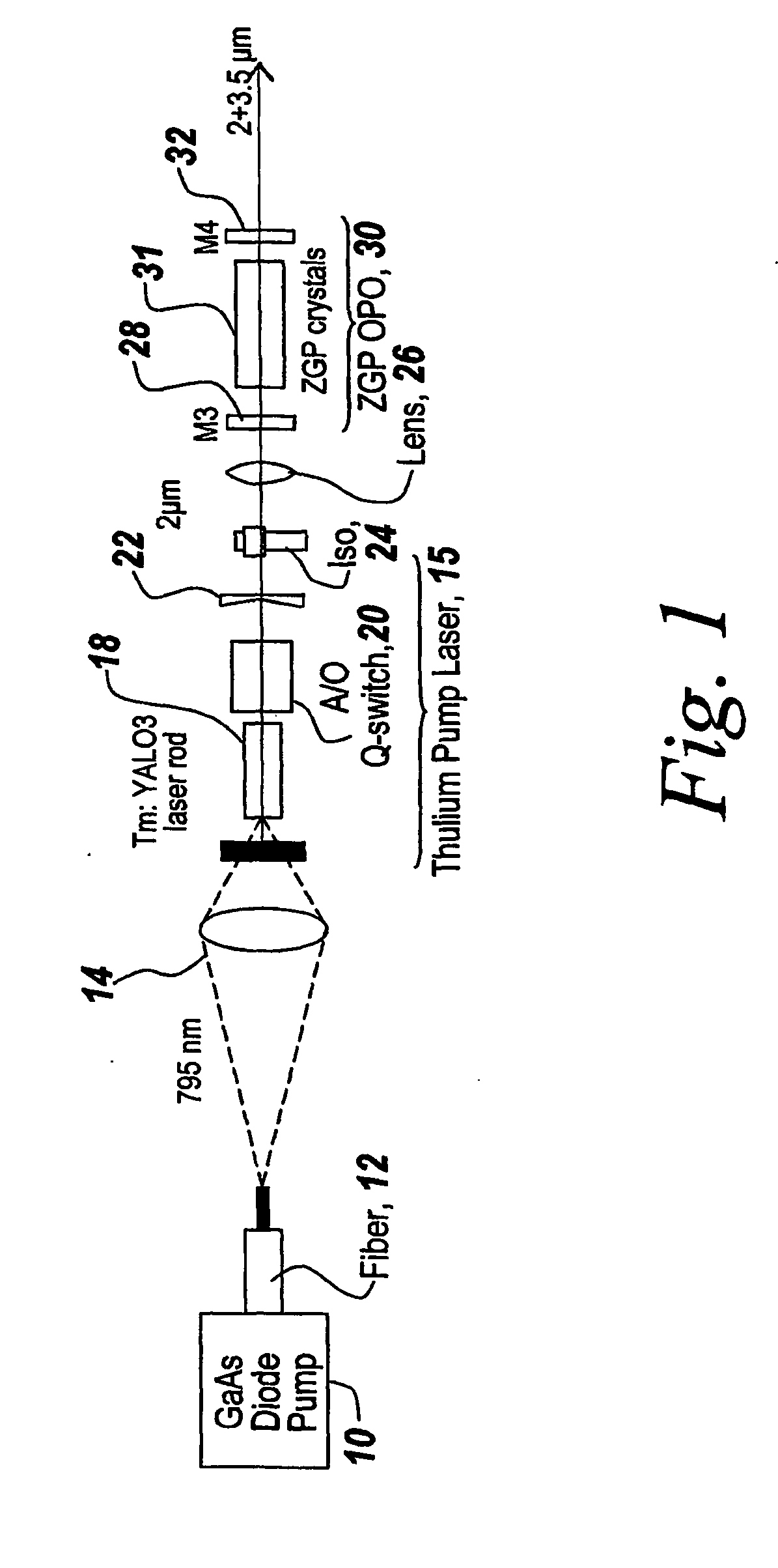
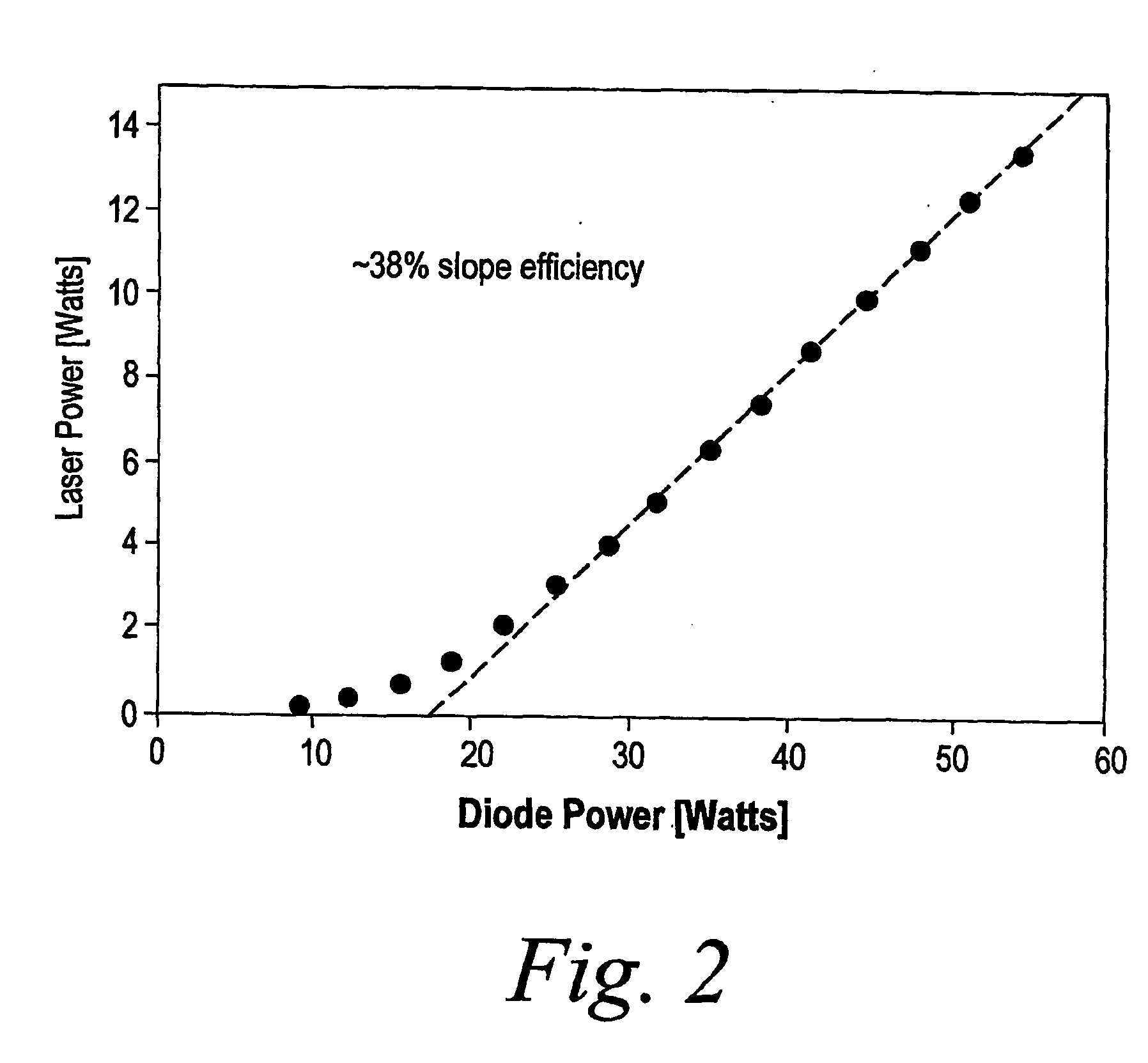
A Thulium laser (15) is used to directly drive a ZnGeP2 optical parametric oscillator (30) with a nominal 2 μm output to generate the 3-5 micron wavelengths. In one embodiment, the ZGP OPO is configured as a linear resonator and in another embodiment the ZGP OPO is configured as a ring resonator. The ring resonator prevents optical feedback to the Thulium laser (15) and eliminates the need for an optical isolator (24). Moreover, the Thulium laser pump (15) is implemented as a Tm:YAlO3 laser in which YAlO is the host for the Thulium YAlO is particularly beneficial as it is a mechanically hard optical material allowing high thermal loading without fracture as well as natural birefringence that can minimize thermal birefringence losses. A longer wavelength transition at 1.99 microns is selected to minimize nonlinear crystal loss. More particularly, a high power, high efficiency Tm:YAlO3 laser repetitively Q-switched at 10 kHz is used to drive a ZnGeP2 OPO. The system is run with room temperature components and achieves over 3 W at 3-5 microns with an efficiency of 5% starting from the pump diode. A two crystal resonator (40, 42) design allows tuning over multiple spectral peaks or alternately as an ultra broad spectral source.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com