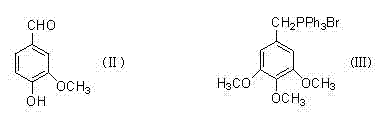Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
353 results about "Bromate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The bromate anion, BrO⁻₃, is a bromine-based oxoanion. A bromate is a chemical compound that contains this ion. Examples of bromates include sodium bromate, (NaBrO₃), and potassium bromate, (KBrO₃). Bromates are formed many different ways in municipal drinking water.
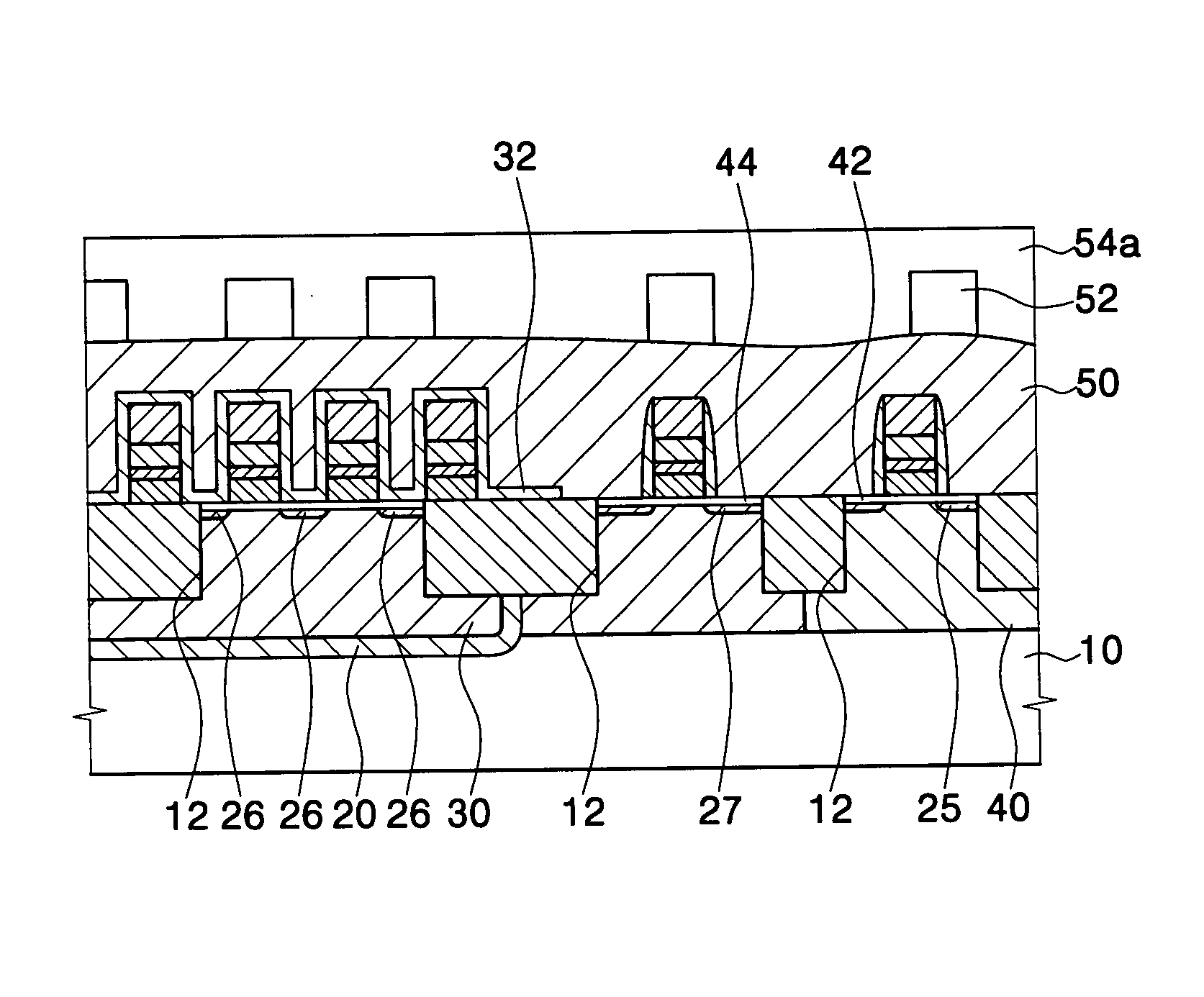
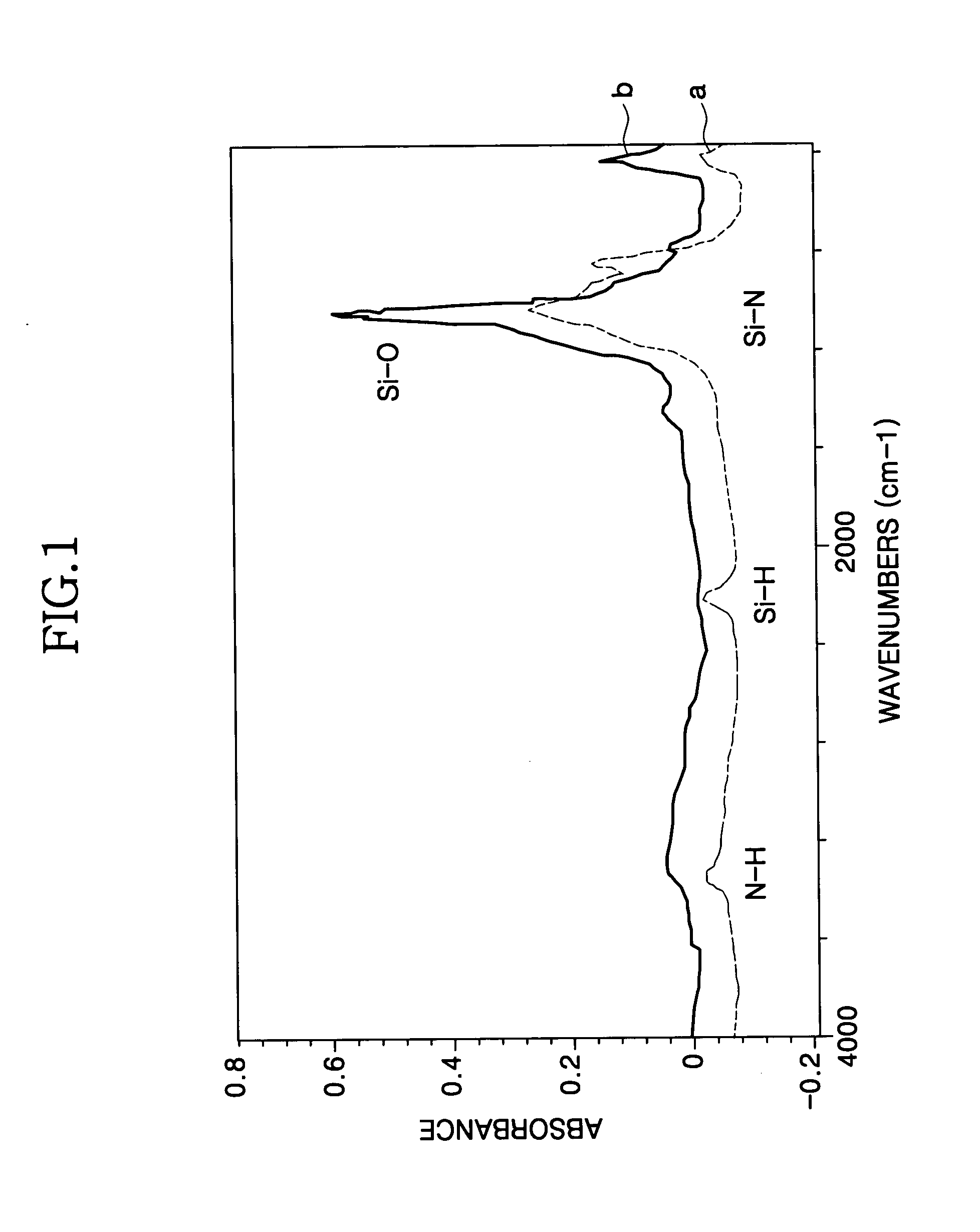
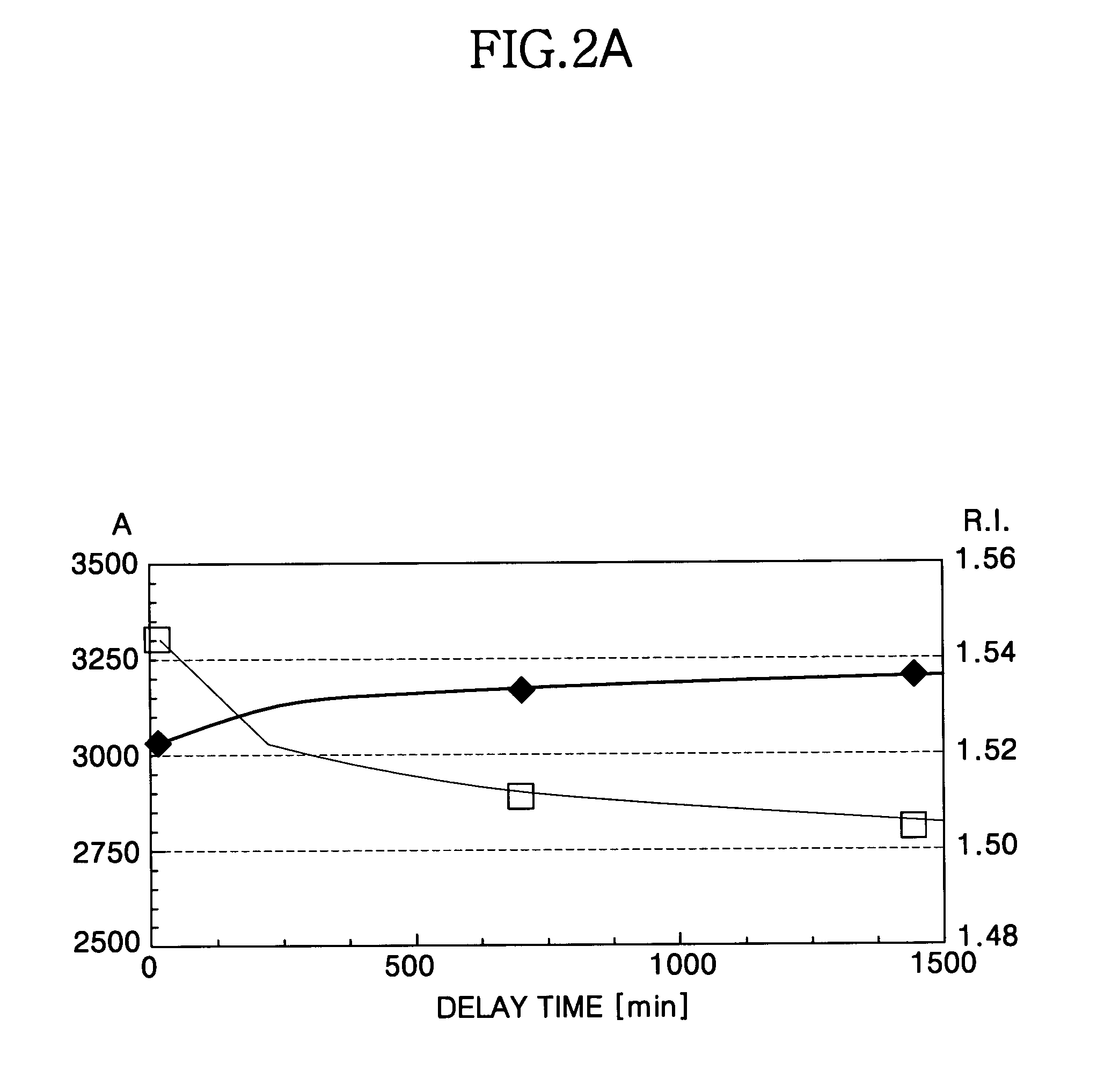
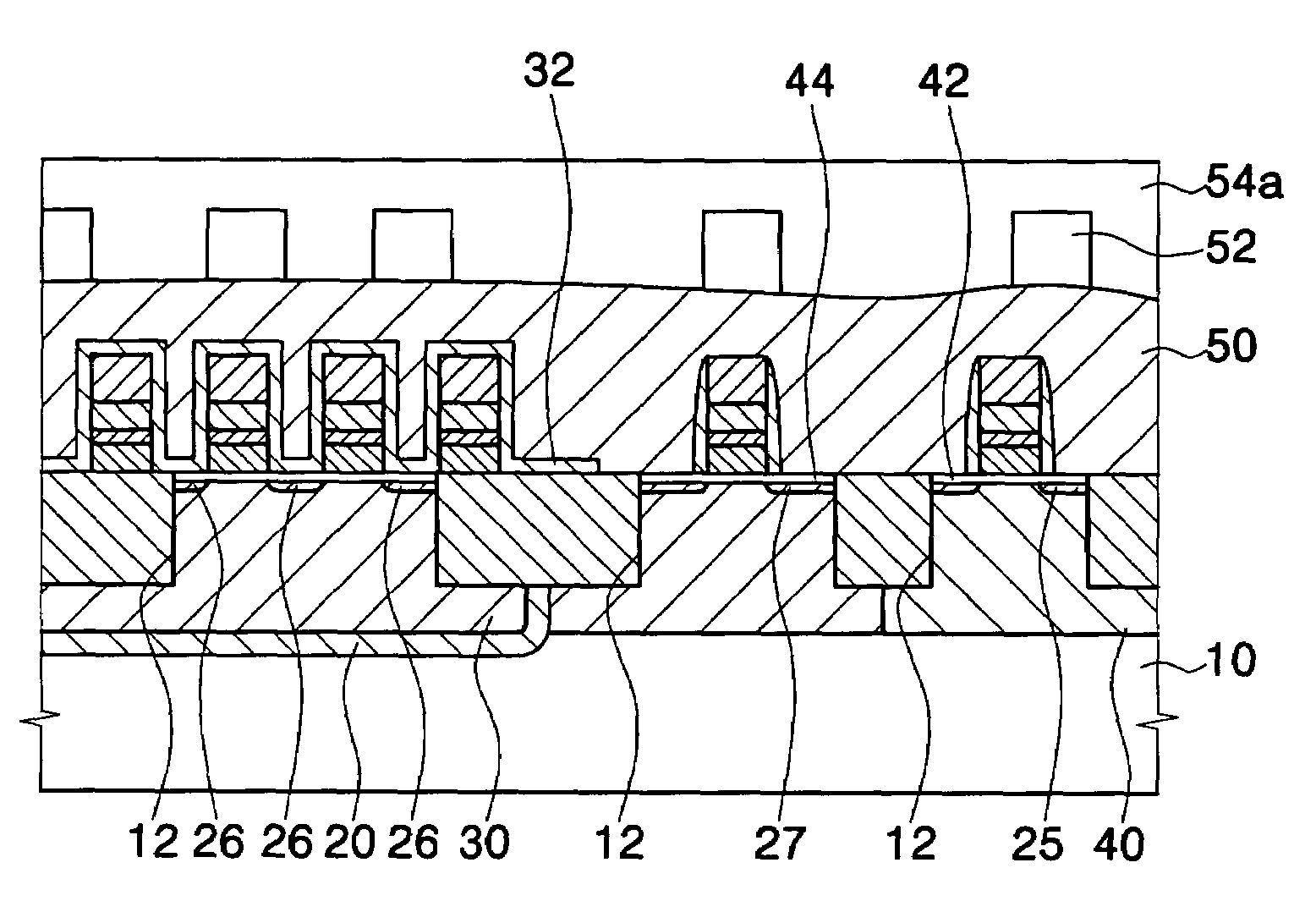
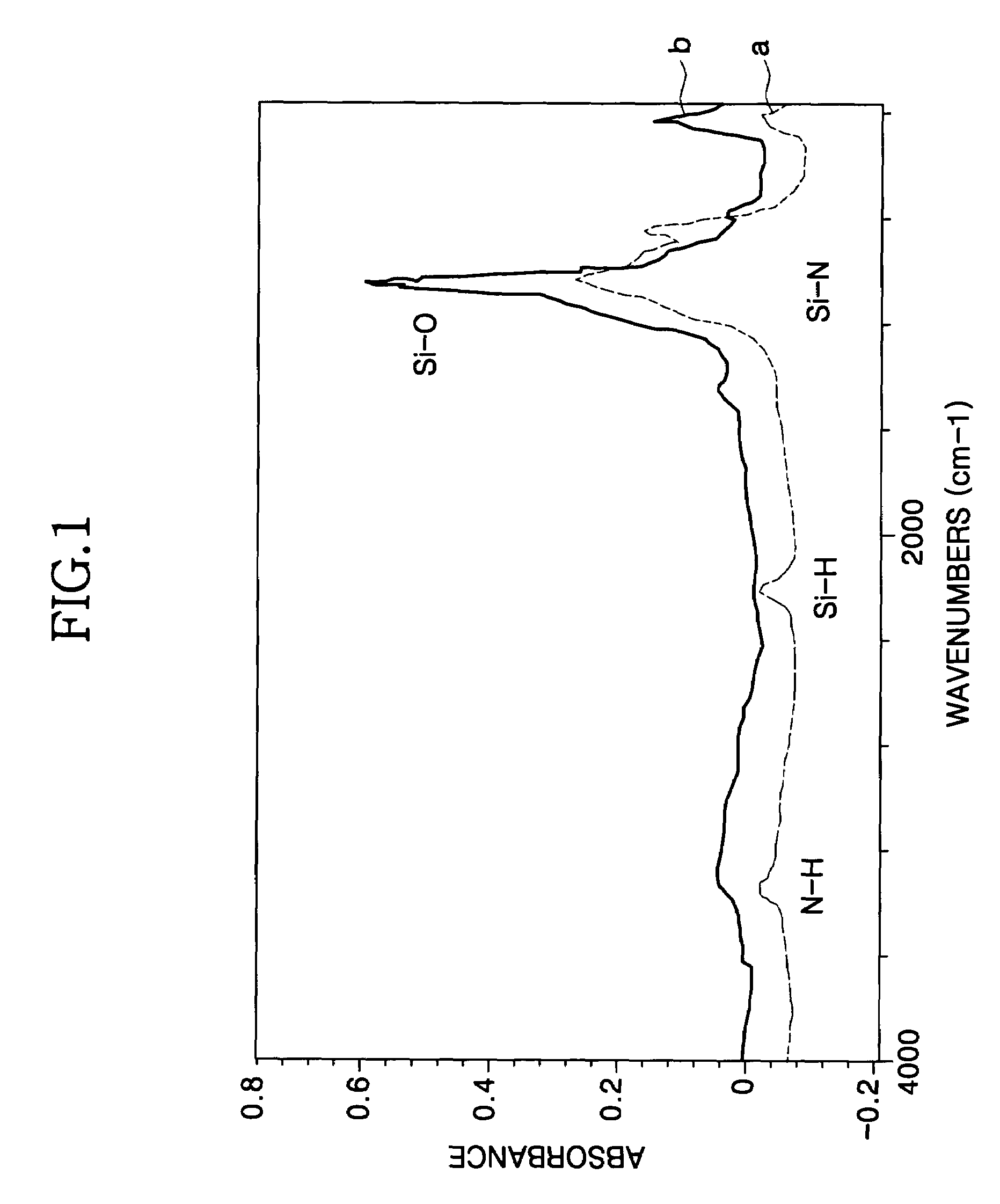
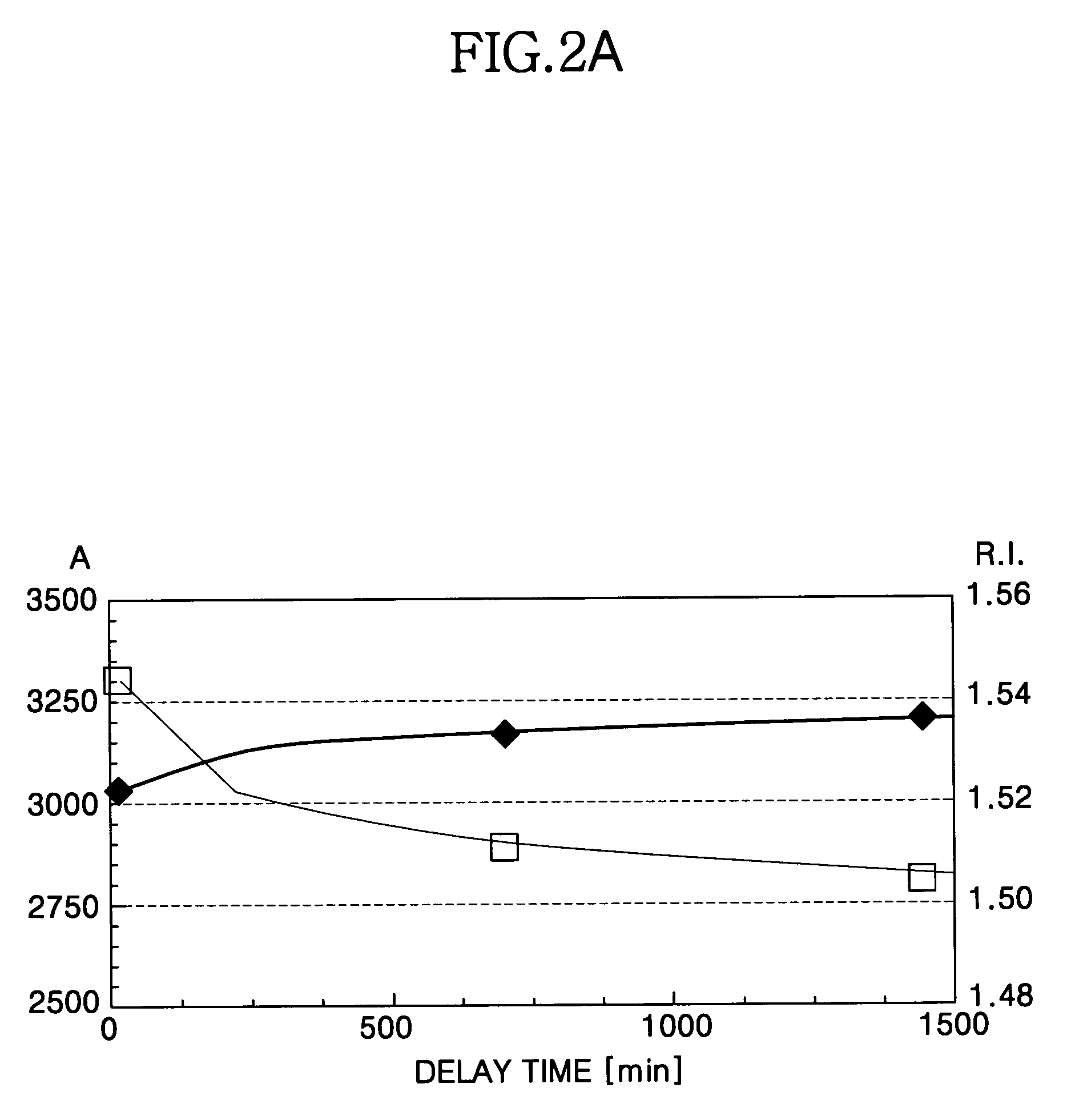
Method for forming a silicon oxide layer using spin-on glass
A method is provided for forming silicon oxide layers during the processing of semiconductor devices by applying a SOG layer including polysilazane to a substrate and then substantially converting the SOG layer to a silicon oxide layer using an oxidant solution. The oxidant solution may include one or more oxidants including, for example, ozone, peroxides, permanganates, hypochlorites, chlorites, chlorates, perchlorates, hypobromites, bromites, bromates, hypoiodites, iodites, iodates and strong acids.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Color stabilized antimicrobial polymer composites
A polymer composite comprising a melt-processed polymer compounded with a color stabilizer comprising a bromate or iodate ion, and a silver-based antimicrobial agent. The specified color stabilizers are particularly superior in inhibiting undesirable darkening or discoloration of melt-processed polymers compounded with silver-based antimicrobial agents containing a grain-size controlling additive.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
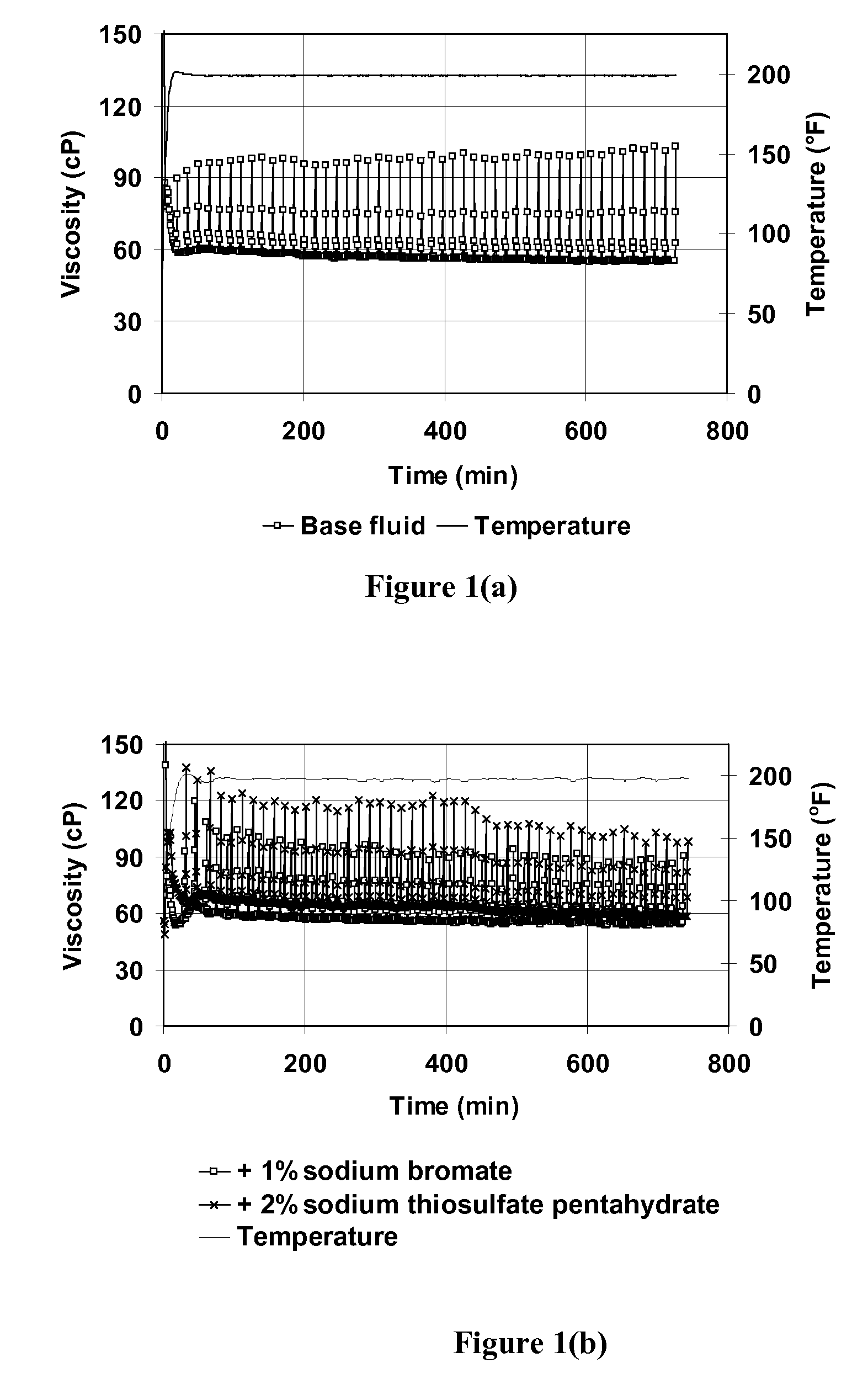
Oxidative Internal Breaker System With Breaking Activators for Viscoelastic Surfactant Fluids
Compositions and methods are given for delayed breaking of viscoelastic surfactant gels inside formation pores, particularly for use in hydraulic fracturing. Breaking inside formation pores is accomplished without mechanical intervention or use of a second fluid. Bromate oxidizing agents are used along with selected breaking activators for the bromate breaking compounds. Useful bromate breaking activators include acid-generating breaking activators, oxidizing sulfur containing breaking activators, and reducing agent breaking activators.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method for removing organic pollutant in water by catalysis ozonation
InactiveCN101327985APromote decompositionSolve the remaining problemsWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by oxidationBromateHuman health
The invention relates to a catalytic ozonation method for removing the organic pollutant, which solves the problems that in the prior art both the residual hydrogen peroxide from the homogeneous catalysis ozonation using hydrogen peroxide as catalyst and the byproduct bromate produced by the heterocatalysis ozonation using metal oxide as catalyst play a bad impact on human health and cause secondary pollution of water. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: a. laying the catalyst in a reactor; b. adding ozone and hydrogen peroxide; c. controlling the contacting time of the ozone and the hydrogen peroxide, that is, finishing the removal of the organic pollutant in water. The method of the invention dissolves the problem of residual hydrogen peroxide, reduces the formation of the bromate without causing the secondary pollution of water and affecting human health, which is suitable to apply in the real water treatment process as a drinking water advanced treatment technology.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Gradient Ozone Catalytic Oxidation Method for Degrading Organic Pollutants in Water
ActiveCN102276095AAchieving Gradient OxidationControl contentMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by oxidationNitrosoCatalytic oxidation
The invention relates to a method for degrading organic pollutants in water by gradient ozone catalytic oxidation, and relates to a gradient ozone catalytic oxidation combination method for degrading organic pollutants in water. By the method, the problem that the conventional advanced oxidation technology has defects during individual use, the problem that the organic pollutants in the water cannot be removed efficiently, the problem that the influence of the pH value and temperature of the water on the method is large, and the problem that high-toxicity byproducts are formed are solved. In the method, water treatment is realized by combining two or three of a process for treating O3 individually, an enhanced catalytic oxidation process for O3 and an O3 / ultraviolet (UV) process sequentially. By the reasonable optimizing and gradient combination of the three treatment modes, the method is suitable for wide pH values and a wide temperature range, the pollutants with intermediate toxicity are controlled to be formed, the toxicity of the pollutants is reduced, the pollutants in the water is degraded efficiently and completely, and the content of oxidative species in effluent is controlled. An efficient oxidation treatment effect is kept at low temperature, and the generation of bromate, nitroso dimethylamine, chlorate, perchlorate, iodate and periodate can be controlled greatly.
Owner:哈尔滨工投环保产业有限公司
Color stabilized antimicrobial polymer composites
Owner:SANDFORD DAVID W +1
Explosive composition and its use
InactiveUS6984274B2Improve structural strengthLess-expensive productionBelt retractorsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementNitro compoundPorosity
An explosive composition comprises a porous fuel and an oxidizer. The porous fuel is a solid with a structure size measuring between about 2 nm and 1000 nm and has a porosity that lies between 10% and 98%. The oxidizer is solid or liquid at room temperature and is incorporated into the pores of the porous fuel. The oxidizer is selected, in an amount of at least 50% by weight relative to a total quantity of the oxidizer, from the group consisting of hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl ammonium nitrate, organic nitro compounds or nitrates, alkali metal nitrates or earth alkali metal nitrates as well as metal nitrites, metal chlorates, metal perchlorates, metal bromates, metal iodates, metal oxides, metal peroxides, ammonium perchlorate, ammonium nitrate and mixtures thereof.
Owner:TRW AIRBAG SYST
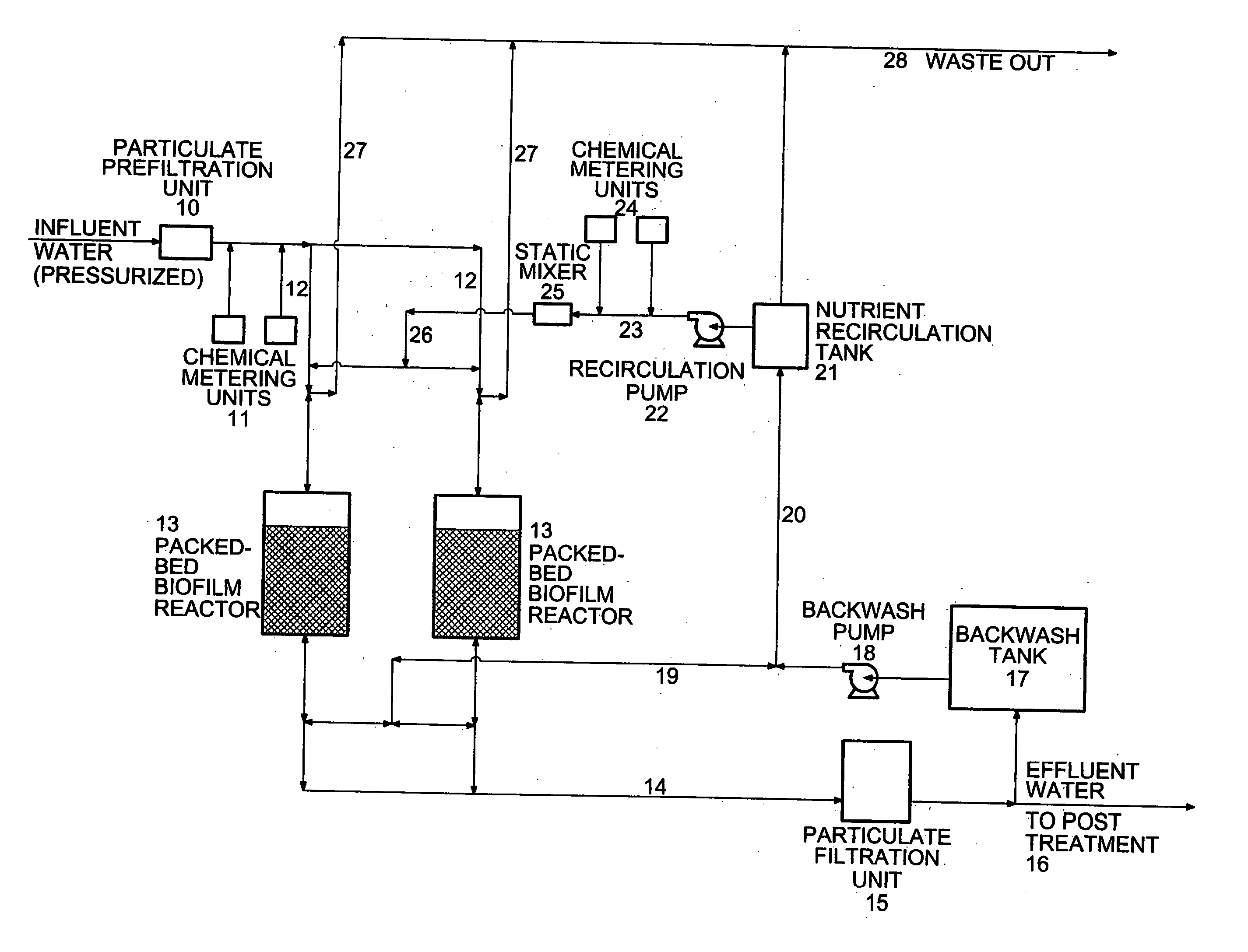
Inorganic contaminant removal from water
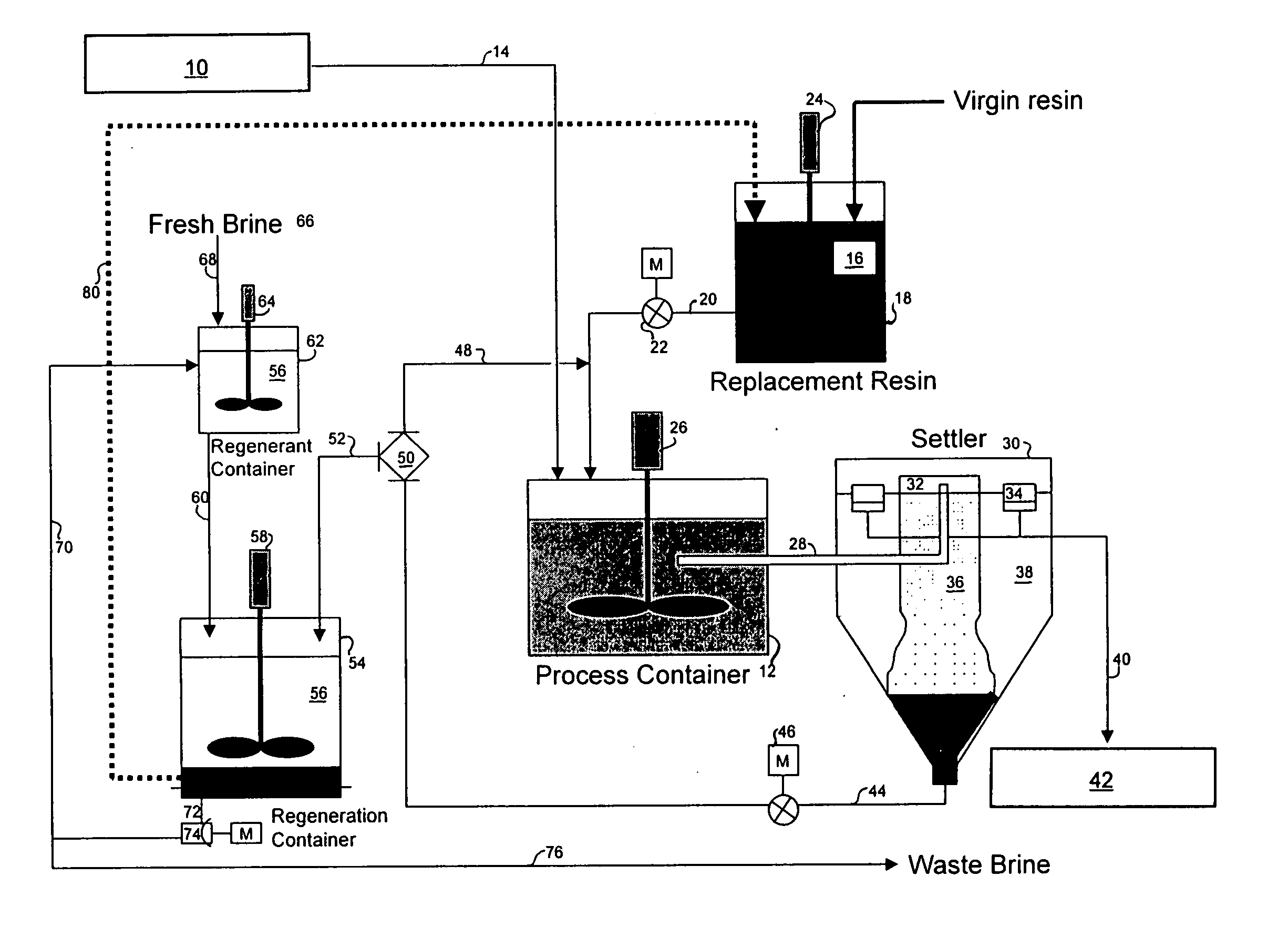
A method is provided for removing an inorganic ionic species or organometallic ion contaminant, or combination contaminants, including such as arsenic, chromium, bromide, bromate, perchlorate, and / or others from water which contains an unacceptably high concentration of the contaminant(s). The method includes treating the water with an ion exchange resin, preferably a magnetic ion exchange resin such as MIEX® Resin, which is capable of adsorbing the inorganic ionic species contaminant(s), and regenerating and recycling the ion exchange resin back to the process. The method produces potable water from ground water containing such contaminants and eliminates breakthrough and chromatographic peaking problems observed with conventional ion exchange systems.
Owner:IXOM OPERATIONS
Inorganic contaminant removal from water
ActiveUS20060011550A1Organic anion exchangersIon-exchanger regenerationHigh concentrationPotable water
A method is provided for removing an inorganic ionic species or organometallic ion contaminant, or combination contaminants, including such as arsenic, chromium, bromide, bromate, perchlorate, and / or others from water which contains an unacceptably high concentration of the contaminant(s). The method includes treating the water with an ion exchange resin, preferably a magnetic ion exchange resin such as MIEX® Resin, which is capable of adsorbing the inorganic ionic species contaminant(s), and regenerating and recycling the ion exchange resin back to the process. The method produces potable water from ground water containing such contaminants and eliminates breakthrough and chromatographic peaking problems observed with conventional ion exchange systems.
Owner:IXOM OPERATIONS
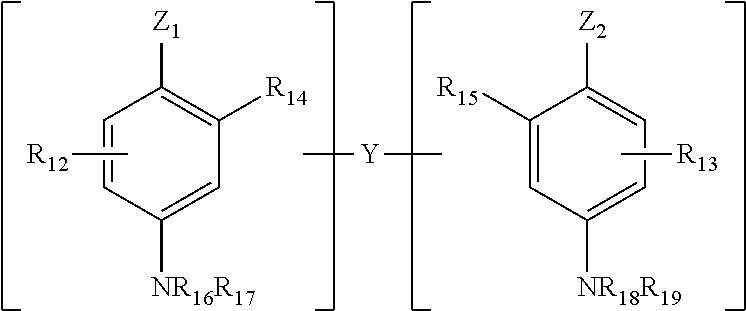
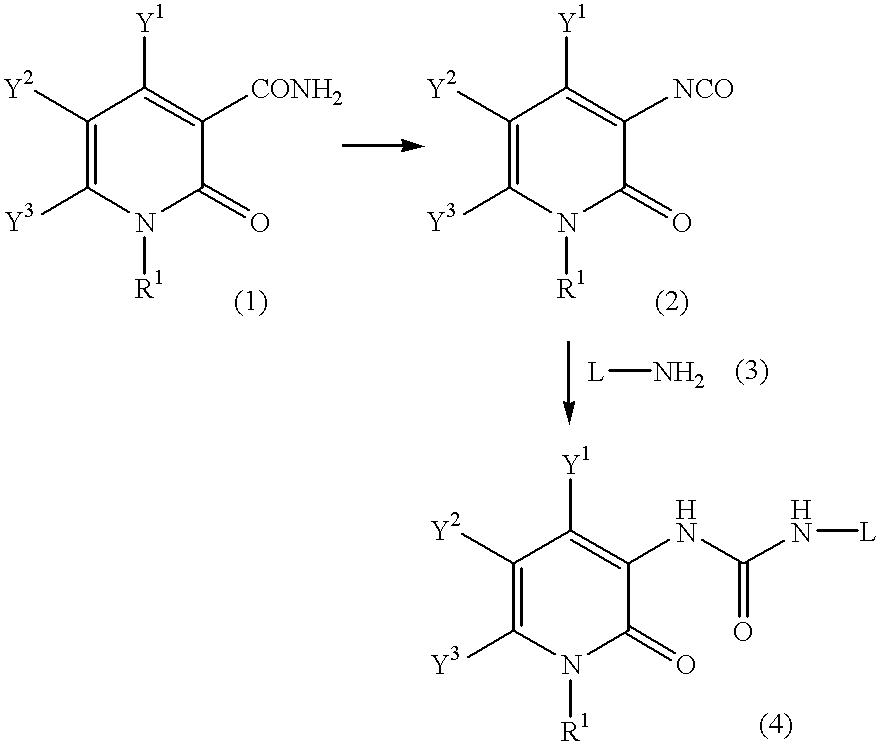
Pyridone derivatives and process for preparing the same
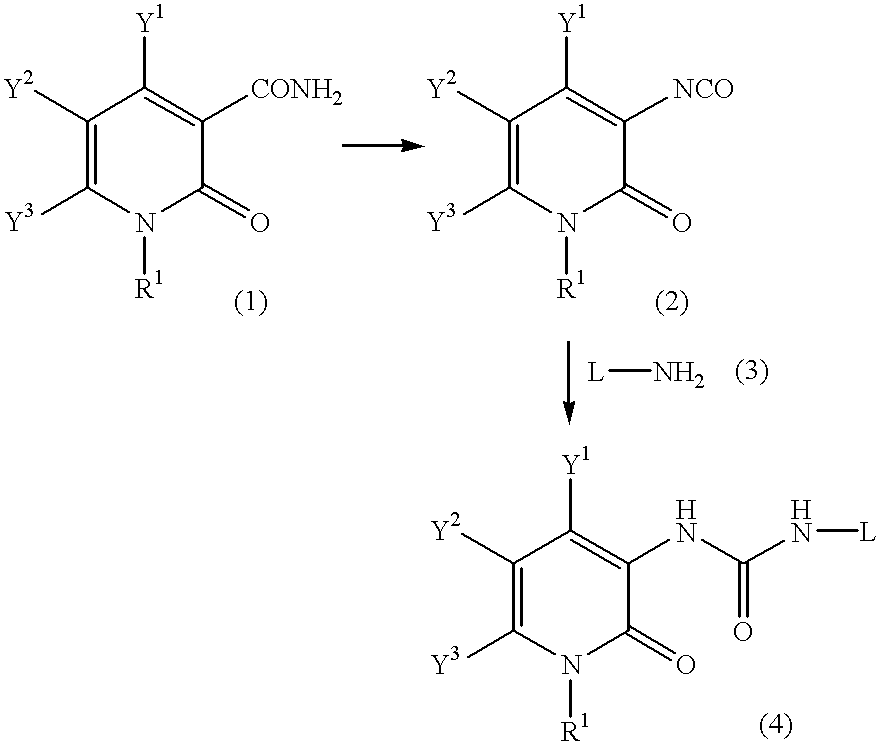
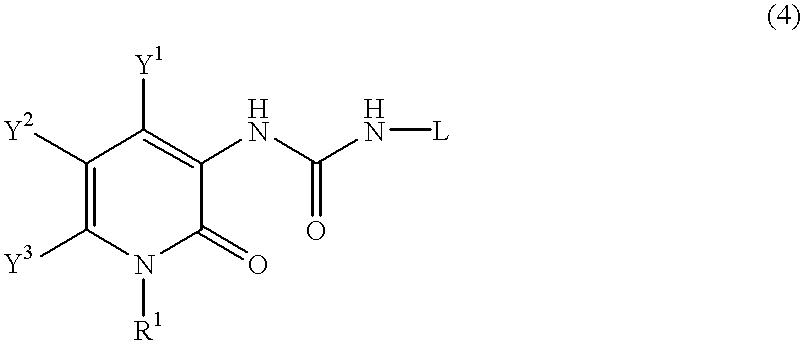
A process for preparing a pyridone derivative (4), which comprises reacting the compound (1) with a hypochlorite or a hypobromite or with lead tetraacetate to give the compound (2), and reacting the compound (2) with the compound (3). Said process is preferably especially from the standpoint of safety. wherein R1 is hydrogen, alkyl, substituted alkyl, etc.; Y1 is hydrogen, alky, substituted alky, etc.; Y2 and Y3 are indenpently hydrogen, halogen, etc.; and L is alkyl, substituted alkyl, etc.
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD
Method for forming a silicon oxide layer using spin-on glass
A method is provided for forming silicon oxide layers during the processing of semiconductor devices by applying a SOG layer including polysilazane to a substrate and then substantially converting the SOG layer to a silicon oxide layer using an oxidant solution. The oxidant solution may include one or more oxidants including, for example, ozone, peroxides, permanganates, hypochlorites, chlorites, chlorates, perchlorates, hypobromites, bromites, bromates, hypoiodites, iodites, iodates and strong acids.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Improvement method for preparing canthaxanthin
The invention provides a method for preparing canthaxanthin. The method comprises that: in water and organic solvent immiscible with the water, under the action of hydrogen peroxide catalyst, alkali metal chlorate or bromate and beta-carotene are subjected to oxidation reaction, wherein the oxidation reaction is carried out by adding hydrogen peroxide into a mixture containing the beta-carotene, the water, metal iodide, the organic solvent immiscible with the water and the alkali metal chlorate or the alkali metal bromate to obtain reaction mixed solution. The method can efficiently produce the canthaxanthin in an industrialized mode in short time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEDICINE CO LTD XINCHANG PHAMACEUTICAL FACTORY
Method and system for treating oxidized contaminant-containing matrix
InactiveUS20060292684A1Reduce maintenanceHigh degreeWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsSulfurElectron donor
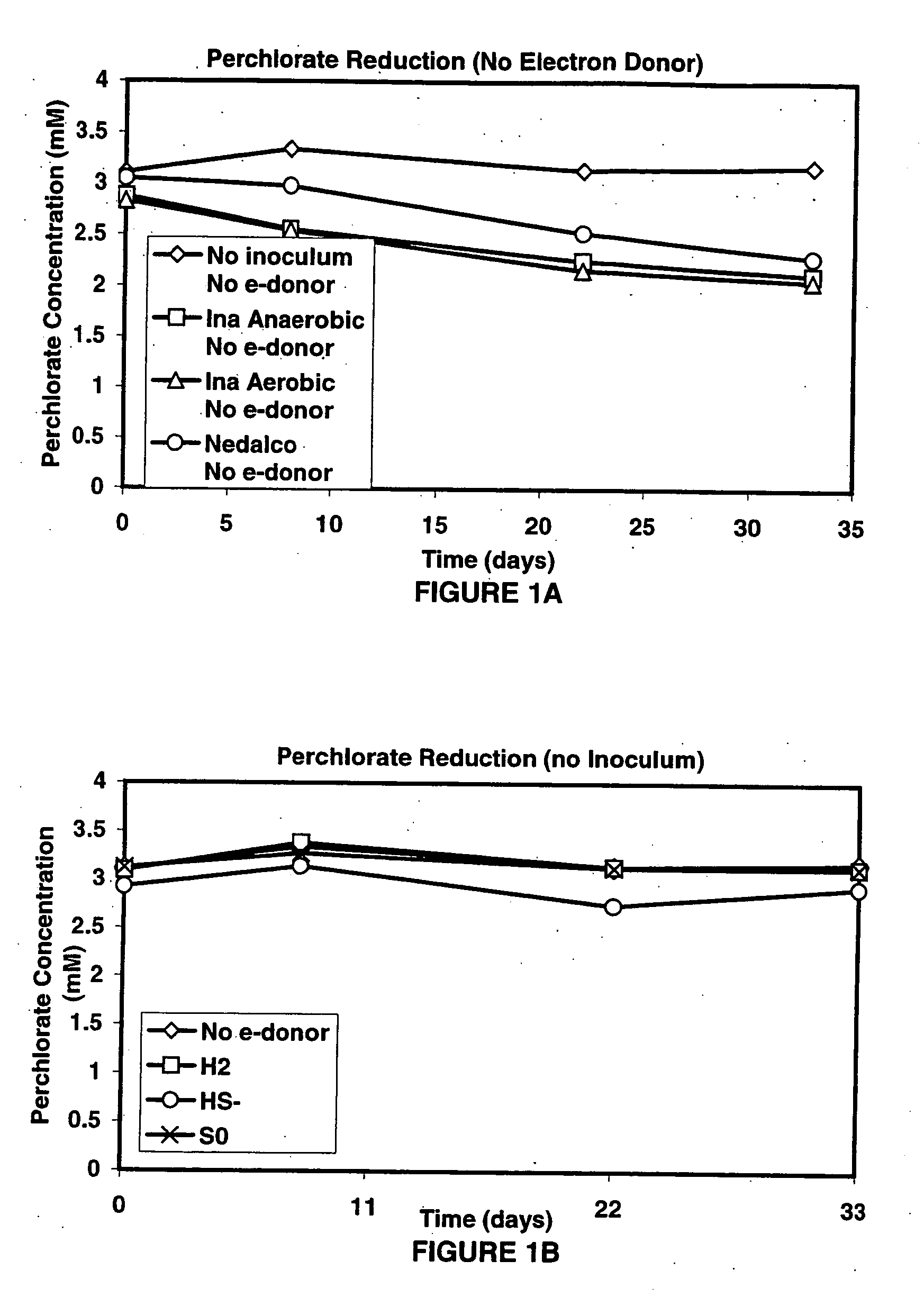
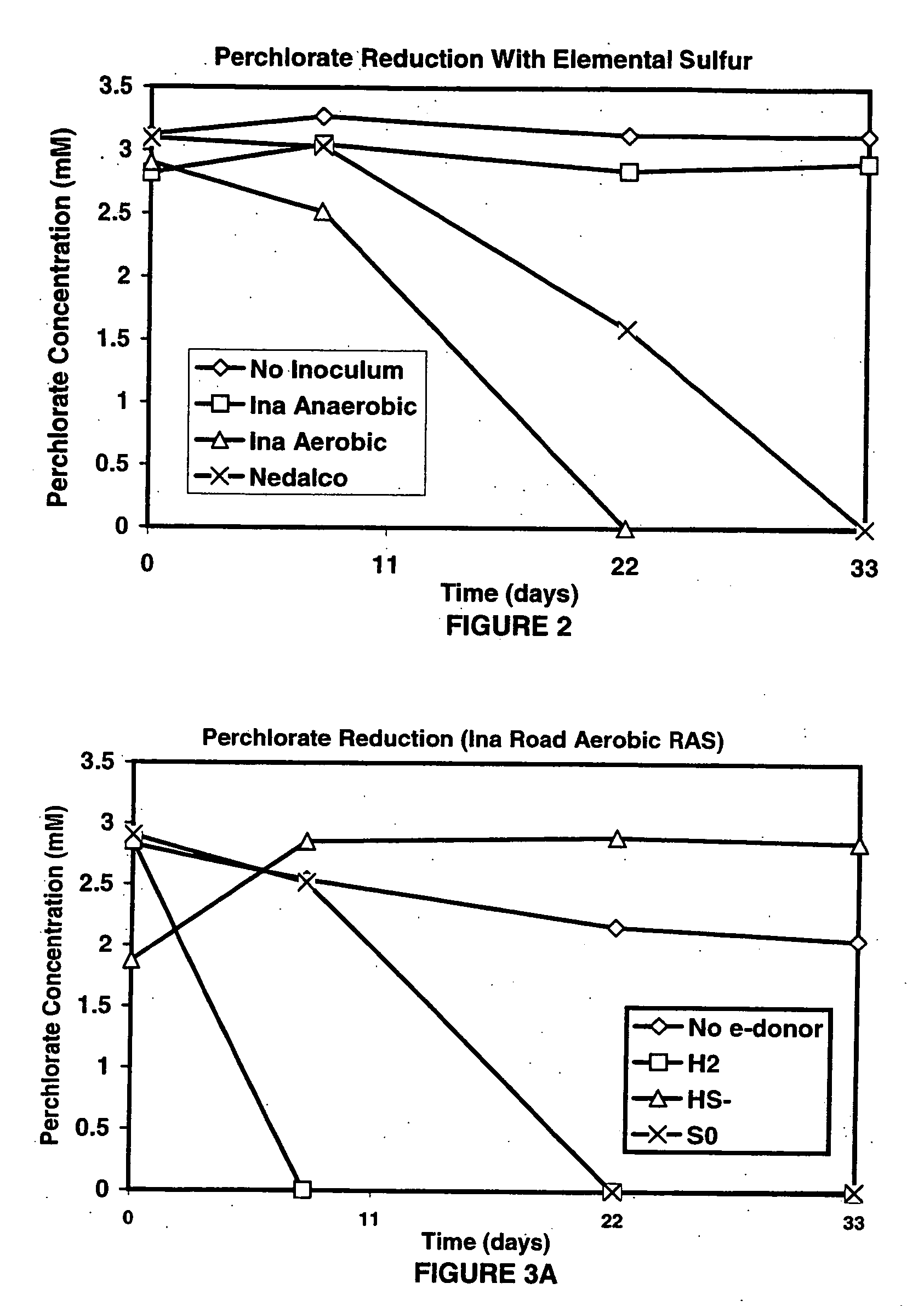
A new and useful way of treating oxidized-contaminant-containing water, soil, rock, other geological or non-geological matrix formation (such as a landfill) is provided. A bioreactor is provided that includes elemental sulfur and a microbial population capable of oxidizing sulfur and reducing pertechnate (TcO4−), arsenate (H2AsO4−), chromate (CrO42−), bromate (BrO3−), chlorite (ClO2−), chlorate (ClO3−), perchlorate (ClO4−), and uranium(VI) oxide, with biological reduction of these oxidized contaminants in the matrix containing the oxidized contaminant performed by the bioreactor, with the elemental sulfur as the electron donor.
Owner:HYDRO GEO CHEM
K3B6O10 Br nonlinear optical crystal, preparation and use
ActiveCN101498040APolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsNonlinear optical crystalBromine
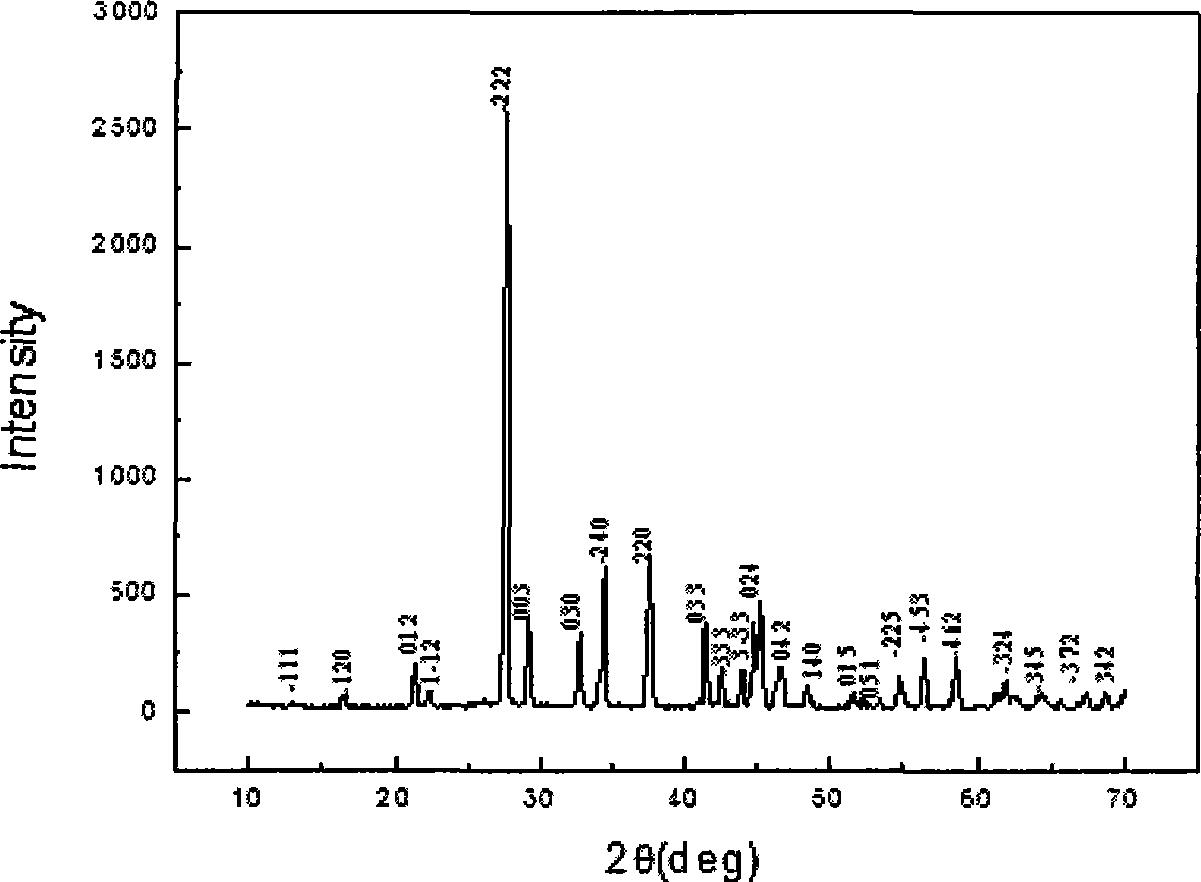
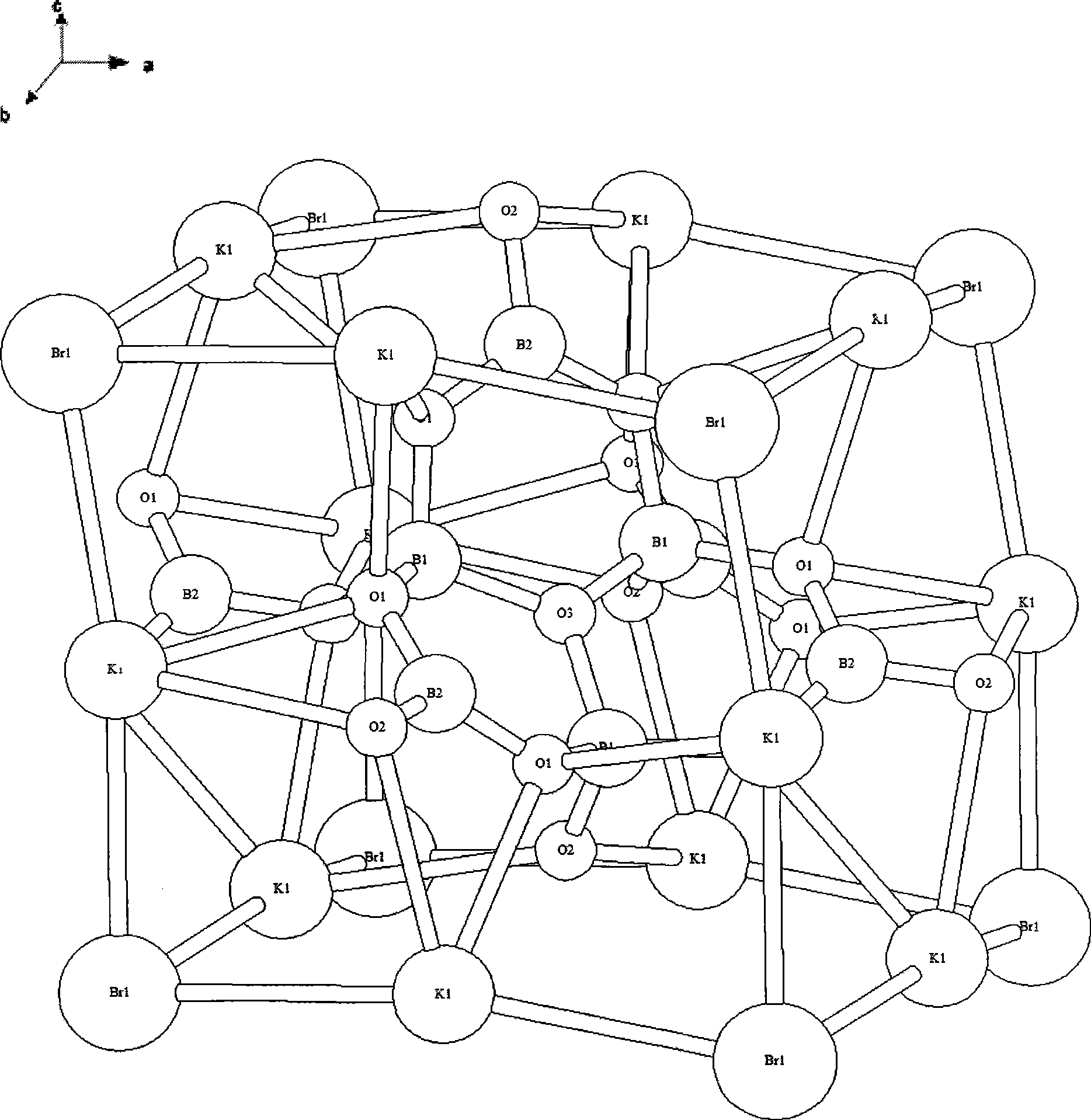
The invention relates to a nonlinear optical bromine-contained kalium borate bromate crystal, a preparation method and applications thereof. The crystal has a molecular formula of K3B6O10Br, belongs to a trigonal system, and has a space group of R3m, a molecular weight of 422.07 and a perovskite structure. The crystal adopts a high-temperature solution method, mixes and heats a kalium borate bromate compound and flux and stabilizes the temperature of a mixture which is cooled to a saturation temperature to obtain a mixed solution; a corundum rod bound with Pt wire is put in the mixed solution which is cooled to the saturation temperature to obtain the needed crystal, and the crystal is extracted out of a liquid level and is cooled to a room temperature so as to obtain the nonlinear optical crystal kalium borate bromate. The crystal is twice the nonlinear optical effect of a KDP crystal and has a light-transmitting band of 210nm to 3000nm, is non-deliquescent in air, has short growth period, is easy to cut, polish, process and store and is suitable for making nonlinear optical devices. The nonlinear optical crystal is widely applicable to nonlinear optical devices such as frequency multiplication converters, optical parameter oscillators, and the like.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
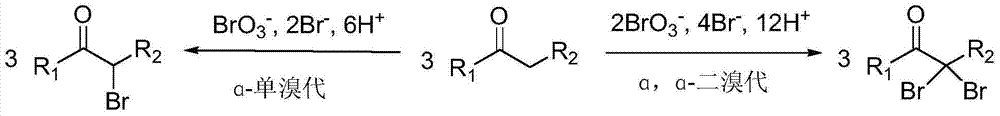
Method for preparing alpha-monobrominated ketone and alpha, alpha-dibrominated ketone compounds by selectively brominating ketone compounds
InactiveCN104119211AIncrease profitHigh selectivity for brominationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationKetoneSolvent
The invention discloses a method for preparing alpha-monobrominated ketone and alpha, alpha-dibrominated ketone compounds by selectively brominating ketone compounds. The method comprises the steps of by taking ketone compounds as reactants, taking bromated and metal bromides in the presence of bromic acid or inorganic acid as brominating reagents and taking alcohol as a solvent, selectively brominating the ketone compounds into corresponding alpha-monobrominated ketone. The reaction has effects of high brominating selectivity, gentle reaction condition, high reaction velocity and high yield; the selected brominating reagents are cheap, easily available and low in toxicity; moreover, the method is high in bromine rate which is close to requirements of green chemistry, and therefore, the method is easy for industrial production and has good application prospect.
Owner:HUANGSHAN UNIV
Compositions and methods for altering the appearance of hair
ActiveUS20140326270A1Minimizes problemMinimize damageCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsSulfateMedicine
Disclosed are methods and compositions for altering the color of hair, comprising treating the hair with a pre-alkalizing composition and then treating the hair with a color-altering composition comprising at least one first oxidizing agent chosen from peroxides, persulfates, perborates, percarbonates, peracids, bromates, their salts and mixtures thereof, and further optionally comprising at least one fatty substance and / or thickening agent, and / or at least one second oxidizing agent. The methods may further optionally comprise applying onto the hair a coloring composition comprising, in a cosmetically acceptable carrier, at least one dye compound chosen from oxidative dye precursors, and direct dye compounds.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Preparation of non-hazardous brominating reagents
InactiveUS6740253B2Easy to handleStable storageDispersed particle filtrationOrganic compound preparationAqueous sodium hydroxideBromate
The present invention relates to a non-hazardous brominating reagent from an aqueous alkaline bromine byproduct solution obtained from bromine recovery plant and containing 25 to 35% bromine dissolved in aqueous lime or sodium hydroxide containing alkali bromide and alkali bromate mixture having bromide to bromate stoichiometric ratio in the range of 5:1 to 5.1:1 or 2:1 to 2.1:1 and a pH ranging between 8-12 and also relates to a method for borminating aromatic compounds by using the above brominating agent.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Pyridone derivatives and process for preparing the same
InactiveUS6452008B2Potent ACAT inhibitory activityProcess stabilityOrganic chemistryHalogenHypochlorite
A process for preparing a pyridone derivative (4), which comprises reacting the compound (1) with a hypochlorite or a hypobromite or with lead tetraacetate to give the compound (2), and reacting the compound (2) with the compound (3). Said process is preferably especially from the standpoint of safety.wherein R1 is hydrogen, alkyl, substituted alkyl, etc.; Y1 is hydrogen, alky, substituted alky, etc.; Y2 and Y3 are indenpently hydrogen, halogen, etc.; and L is alkyl, substituted alkyl, etc.
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD
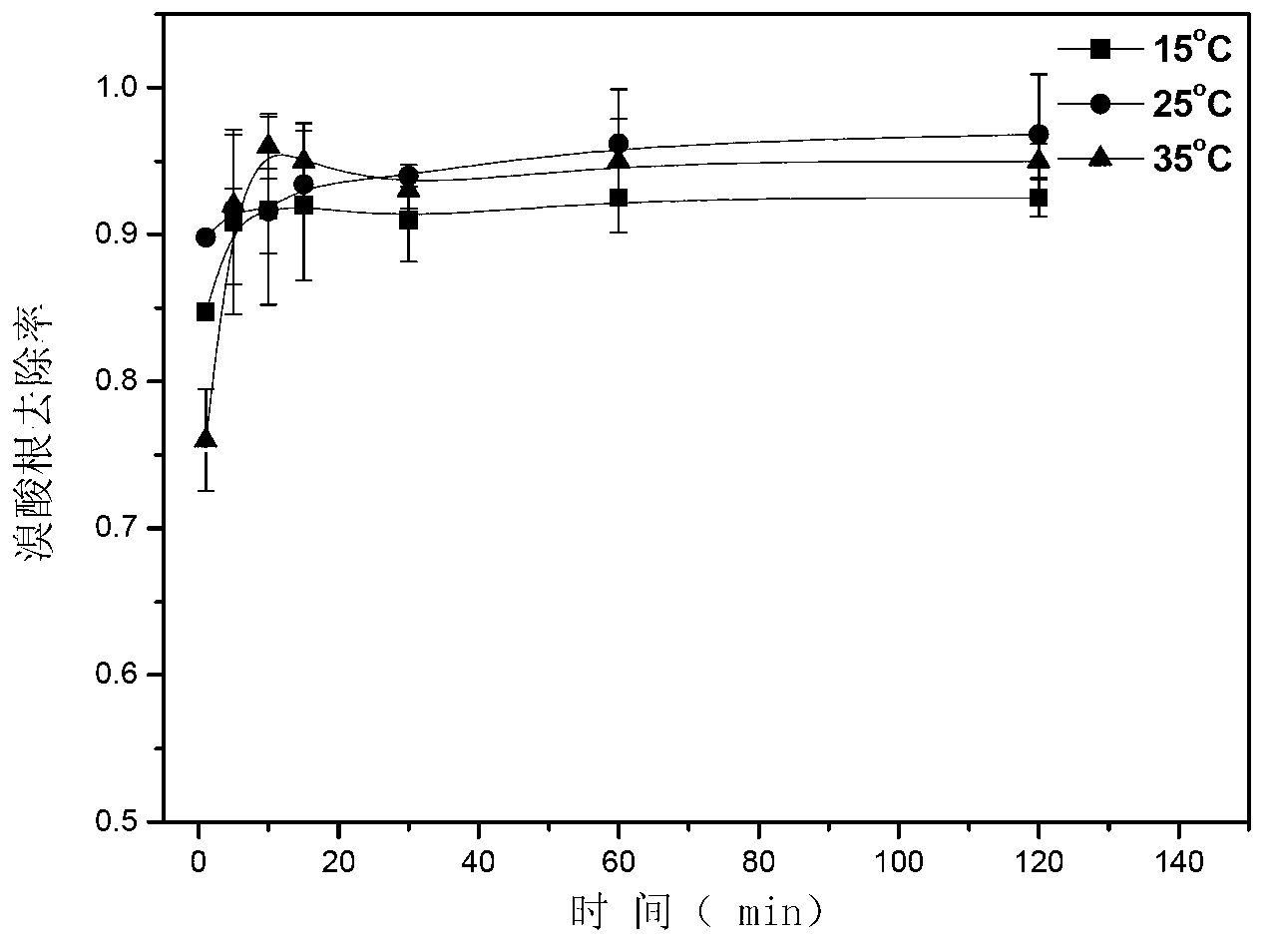
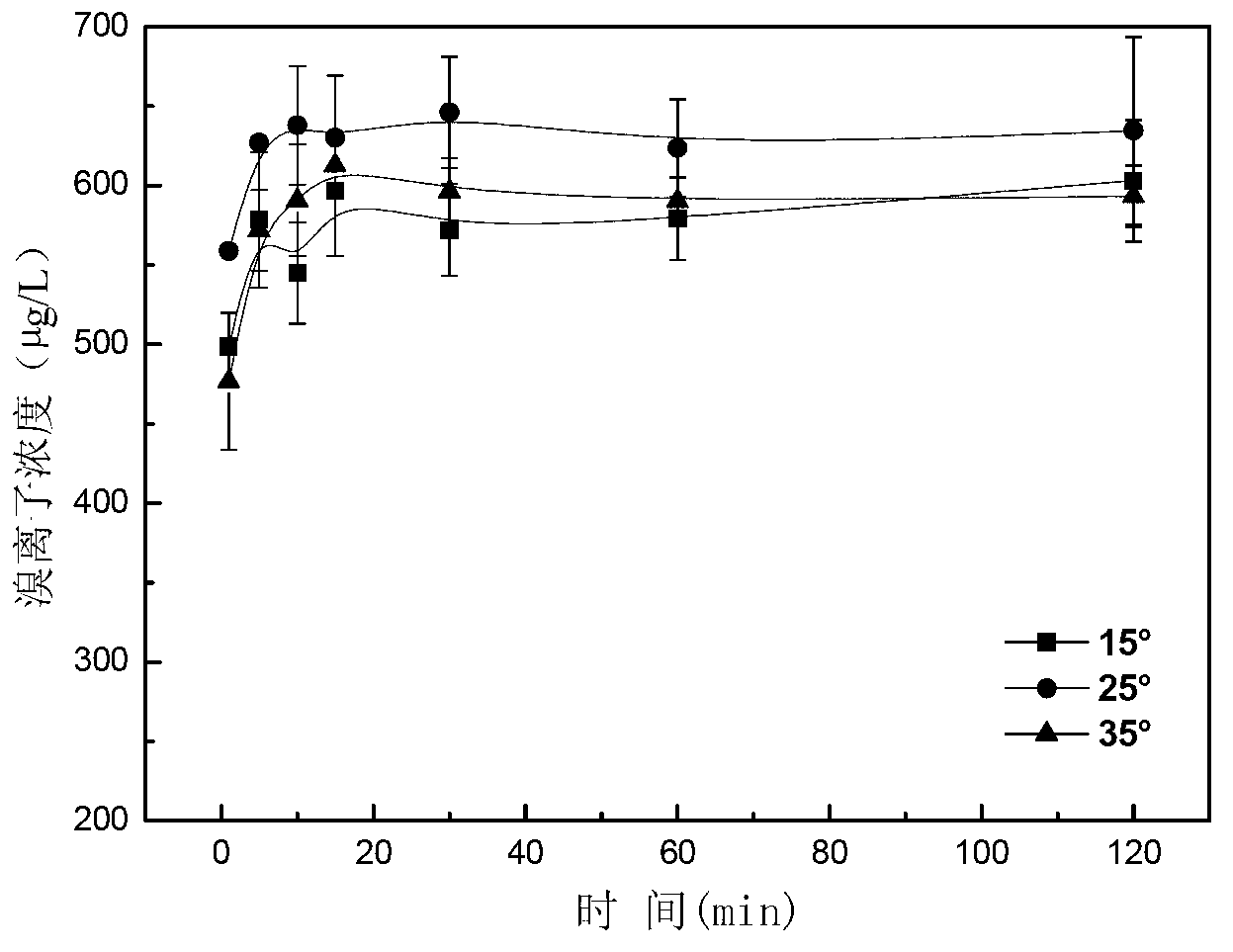
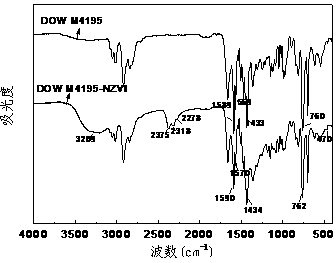
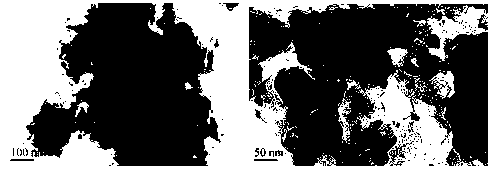
Method for removing bromate through ordered mesoporous carbon loaded nanoscale zero-valent iron material
InactiveCN103232125AImprove reducibilityEfficient reductionWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater bathsHydrogen
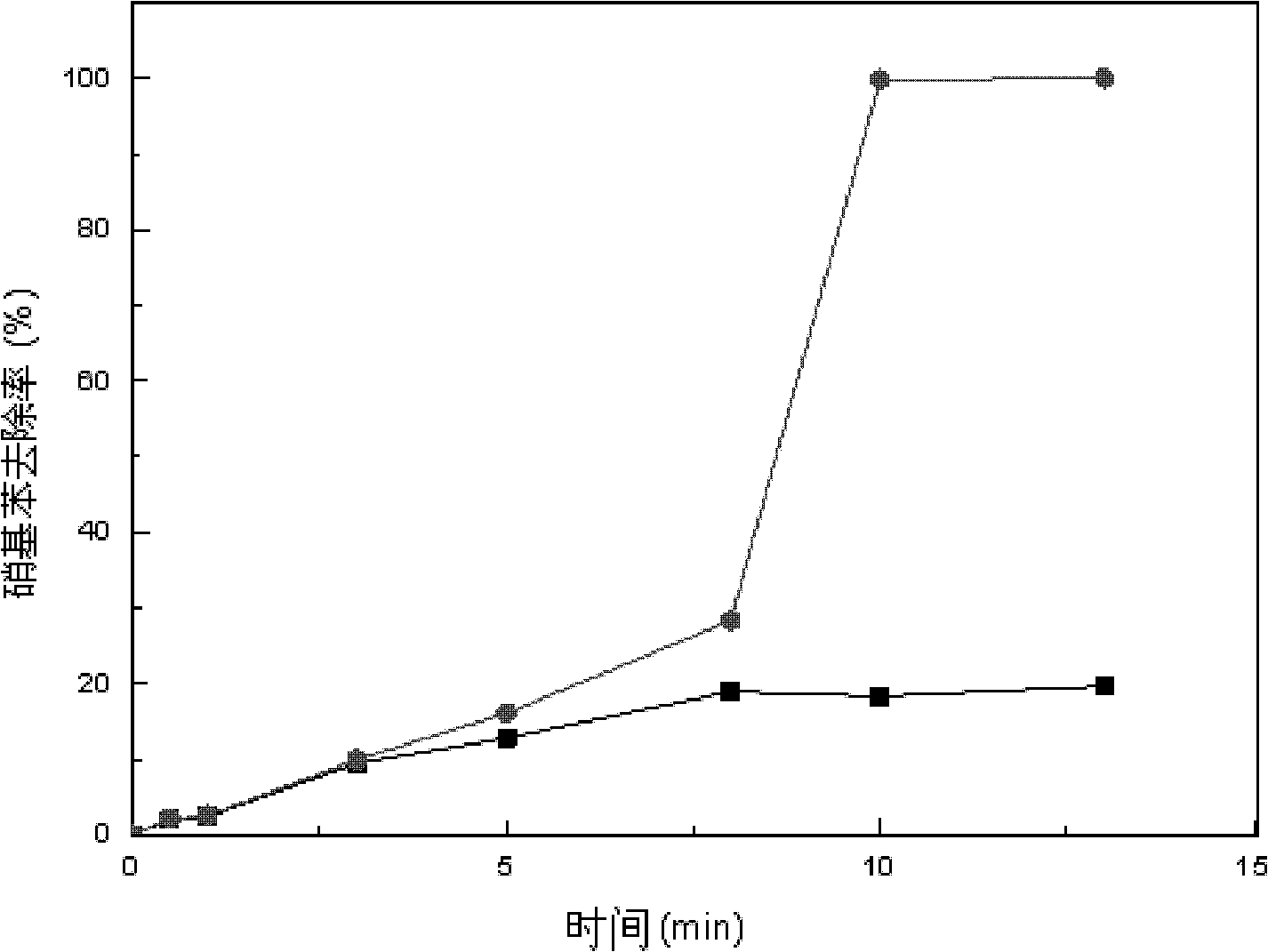
The invention provides a method for removing bromate through an ordered mesoporous carbon loaded nanoscale zero-valent iron material. The method comprises the following steps of: adjusting pH (Potential Of Hydrogen) of a BrO3-solution at initial concentration of 1 to 10mg / L to 3 to 10; adding0.35g of an ordered mesoporous carbon loaded nanoscale zero-valent iron composite material with load rate being 25% to 1L of the BrO3<->solution; and reacting the mixed solution for 1 to 120 minutes at an oscillating speed of 200 rotations per minute in a constant-temperature water bath oscillator at 15 to 35 DEG C. The method can be performed under various conditions, can effectively remove BrO3<-> out of water, and has the characteristics of simple and convenient process, high reducing and removing efficiency and fast removing; the removal rate can be more than 90% after reacting for 5 minutes; and the total iron amount in the water is not detected. Therefore, the method has a good application prospect in purification of bromate ions in the drinking water.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
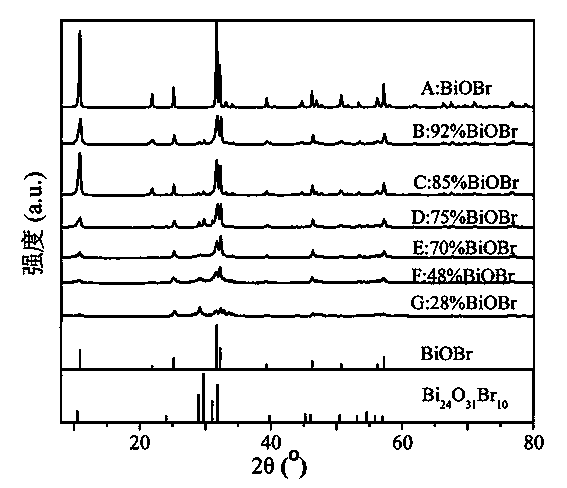
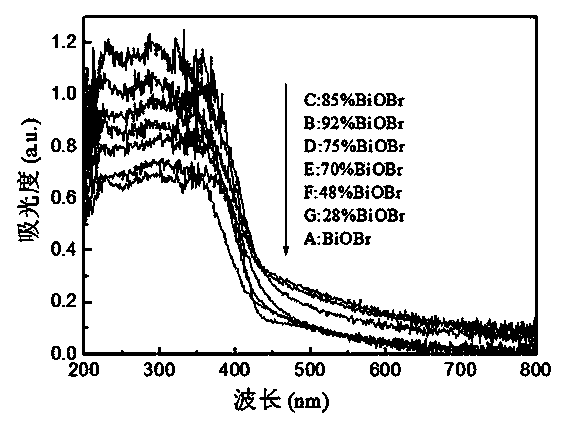
Visible-light catalytic activity BiOBr-based heterojunction and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104190445AOvercomes the drawback of needing to add water to form a solutionEfficient separationPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationTetramethylammonium bromideHydrobromide
The invention discloses a visible-light catalytic activity BiOBr-based heterojunction material which is prepared from BiOBr and Bi24O31Br10 at a mass ratio of (28%-100%):(0%-72%). A preparation method of the BiOBr-based heterojunction material comprises the following steps: (1) mixing bismuth nitrate, urea, and one or more than one of tetramethyl ammonium bromide, tetraethyl ammonium bromide, 2-bromoethylamine hydrobromide and 3-bromopropylamine hydrobromide at a mass ratio of 1:(0.1-1.0):(0.1-1.0) to obtain a mixture, and heating the mixture until melting so as to obtain an ionic liquid; (2) heating the ionic liquid obtained in the step (1) until burning; and (3) collecting a solid generated after complete burning in the step (2), and cooling and grinding the solid to obtain the BiOBr-based heterojunction material. The preparation method is simple without requiring complicated equipment, and is short in time, high in yield, low in cost and suitable for industrial large-batched production.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
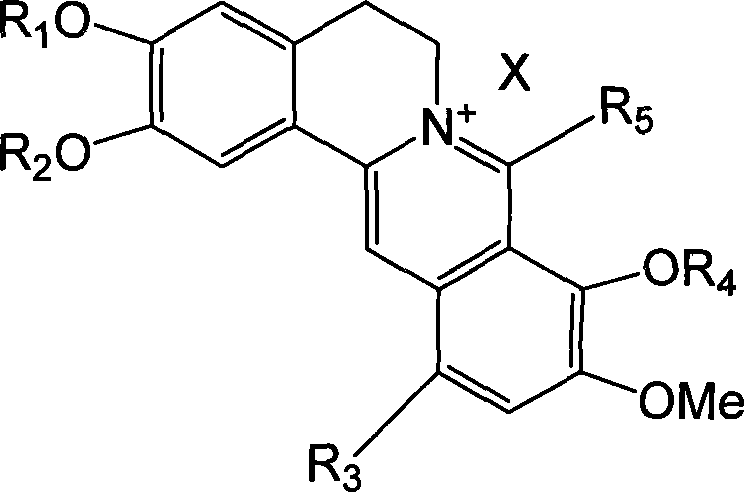
Long chain alkyl berberine salt derivative, synthetic method and use
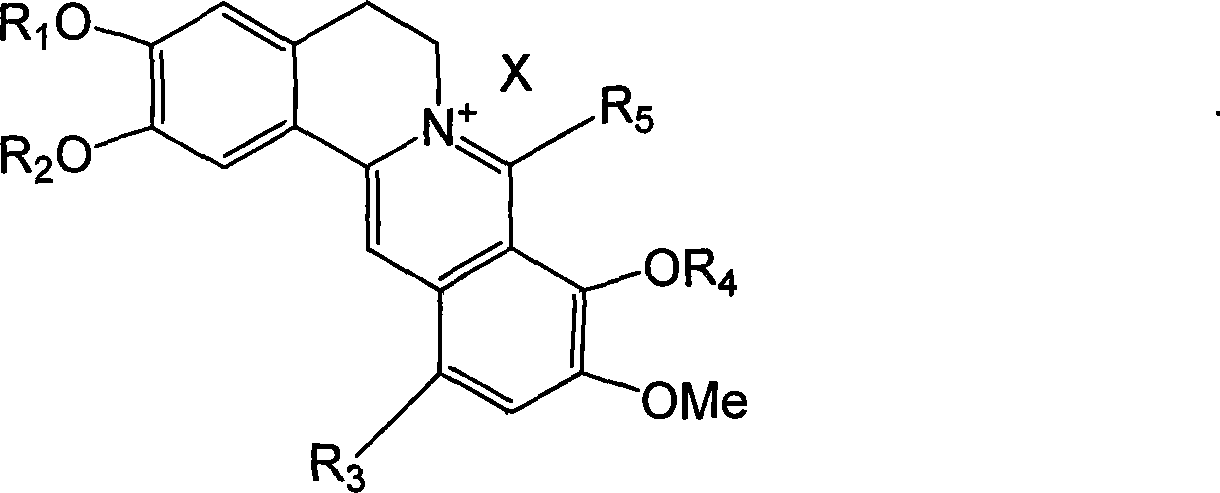
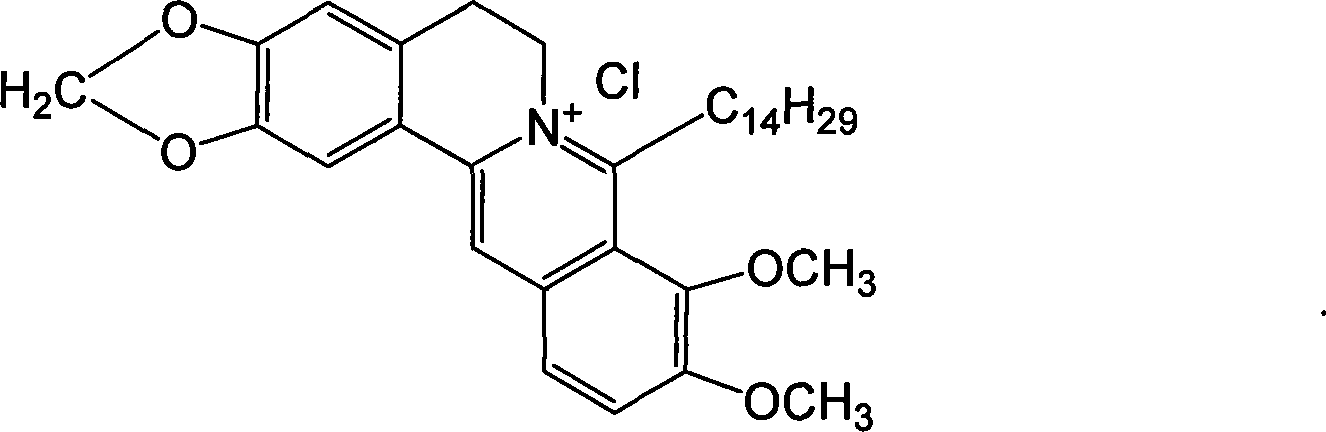
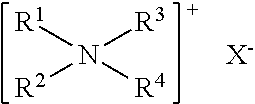
The present invention relates to a class of chemically named long chain alkyl berberine salt derivatives (hydrochloride or Bromate or iodate or hydrofluoric acid salt), and the molecular structural formula is stated above, wherein, X is equal to F-, Cl-, Br-, I-, SO42-, NO3-, PO43-, citric acid radical, acetic acid radical or lactic acid radical. R1, R2, R3, R4, R5 see table above. The class of the substances is provided with obvious hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activities which are significantly higher than that of berberine salt, so that the invention is a very promising new compound with hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic medicinal values.
Owner:重庆神农投资(集团)股份有限公司
Method for controlling generation quantity of bromic acid radicle in treating procedure for oxidizing drinking water by ozone
InactiveCN101050036AGeneration of controlInhibitionMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processCatalytic oxidationWater quality
This invention relates to a method for controlling the quantity of bromate ions produced during treatment of ozone-oxidized drinking water. The method solves the problems of consuming residual chlorine, eroding pipes and meshes, and generating toxic substances by present techniques. The method controls the quantity of bromate ions by introducing cerium oxide, transition metal oxide-doped cerium oxide or supported cerium oxide catalyst for catalytic oxidation. The quantity of produced bromate ions is decreased by 80% when the bromic ions concentration is 100-200 mu.g / L and the consumption of cerium oxide is 100 mg / L. The method has a high efficiency in inhibiting the generation of bromate ions, and the yield of byproducts is 20-30% lower than that produced by pure ozone oxidation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for preparing 3,4,5-trimethoxy-3'-hydroxy-4'-alkoxy diphenylethane
InactiveCN103539642AImprove protectionSignificant technological progressOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationPalladium on carbonBenzaldehyde
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Film treating agent for treatment before electro-coating of die-cast aluminum alloy workpiece and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101665934ASave energyElectrophoretic coatingsMetallic material coating processesHydrofluoric acidHazardous substance
Owner:DALIAN SANDAAOKE CHEM
Tungsten polishing solution
InactiveUS7132058B2Other chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChlorate ionBromate
A tungsten CMP solution for planarizing semiconductor wafers includes a primary oxidizer having a sufficient oxidation potential for oxidizing tungsten metal to tungsten oxide; and the tungsten CMP solution has a static etch rate for removing the tungsten metal. A secondary oxidizer lowers the static etch rate of the tungsten CMP solution. The secondary oxidizer is selected from the group consisting of bromates and chlorates. Optionally the tungsten CMP contains 0 to 50 weight percent abrasive particles; and it contains a balance of water and incidental impurities.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Method for removing bromate ion in drinking water
InactiveCN101456617ACause secondary pollutionImprove stabilityWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeNitrateFiltration
The invention relates to a method for removing bromate ions in drinking water and belongs to the technical filed of drinking water purifying treatment. The method removes the bromate ions in the drinking water by using an ion exchange principle of inorganic lamellar compounds. The key points of the method comprise: mixing a certain amount of a divalent metal oxide and a certain amount of a trivalent metal oxide according to a molar mass ratio of 3:1 or 3:2, pressing the mixed powder into sheets or columns and sintering the sheets or the columns at 1,300 to 1,600 DEG C for 8 to 12 hours; grinding a product of the sintering into fine grains and placing the fine grains into a saturated solution of a divalent metal chloride or a nitrate with magnetic stirring for 48 hours for complete reaction; and then carrying out filtration, drying and grinding to obtain a lamellar compound. The lamellar compound is filled in a filled column of the prior filtering device as a filtering and absorbing material. After the drinking water containing bromate ions is treated by the filled column, 87 to 97 percent of the bromate ions in the drinking water are removed.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Compositions and methods for altering the appearance of hair
ActiveUS20140305464A1Altering appearance of hairMinimize damageCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsPersulfateSulfate
Disclosed are methods and compositions for altering the color of hair, comprising treating the hair with a pre-alkalizing composition and then treating the hair with a color-altering composition comprising at least one lift-enhancing agent, at least one oxidative dye precursor, at least one oxidizing agent chosen from peroxides, persulfates, perborates, percarbonates, peracids, bromates, their salts and mixtures thereof, and optionally, at least one direct dye.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Long-service-life high-speed acid environment protection bright chemical nickel plating additive and use method thereof
InactiveCN101851752AImprove performanceStable speedLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingGlutaric acidThiourea
The invention relates to a long-service-life high-speed acid environment protection bright chemical nickel plating additive and a use method thereof. A complexing agent in the additive is a mixture of three kinds or more than three kinds of materials in lactic acid, malic acid, citric acid, glycine, glycollic acid and salicylic acid through being mixed according to any proportion. A stabilizing agent is a composite stabilizing agent prepared from thiosemicarbazone derivatives and oxygenated chemicals according to a mass ratio of 1 / 10 to 30, and the oxygenated chemicals are iodate or molybdateor bromate, an accelerating agent is one kind of materials in glutaric acid or adipic acid. A buffering agent is prepared from either boric acid or sodium tetraborate and either acetic acid or sodiumacetate according to a mass ratio of 1 / 2 to 5. The chemical nickel plating additive of the invention can realize the mass production. When being used, the chemical nickel plating additive is directlyadded into water to be diluted according to the proportion for use, and the operation is simple. After the use for 8 to 10 periods, the plating layer performance and the speed are still stable, the stability of plating liquid is good, nickel is not separated out from the wall of a tank, the phosphorus content of the plating layer is stabilized ranged from 5 to 8 percent, and the plating layer is bright.
Owner:济南德锡科技有限公司
Nitrogen ligand chelate resin nanoscale zero-valent iron-loaded composite material and method thereof for reduction of bromate in water
InactiveCN102976471APromote reductionImprove reduction efficiencyWater/sewage treatment by reductionNitrogenFixed bed
The present invention discloses a nitrogen ligand chelate resin nanoscale zero-valent iron-loaded composite material and application thereof for reduction of bromate in water, and belongs to the field of drinking water advanced treatment. The structure of the composite material is that: (1) the carrier of the composite material is the chelate resin having a pyridyl group, and (2) inner and outer surfaces of the carrier loads nanoscale zero-valent iron, wherein the preparation of the zero-valent iron includes guiding Fe3+ or Fe2+ by chelation into the inner and outer surfaces of the resin, reducing to zero-valent iron by using sodium borohydride, and vacuum drying to obtain the zero-valent iron composite material. The step of bromate reduction in water includes: passing a bromated-containing solution through a fixed bed adsorption column loaded with the nitrogen ligand chelate resin nanoscale zero-valent iron-loaded composite material. Treated by the present invention, the BrO3- concentration at the adsorption column outlet can be reduced to below 10 [mu]g / L. The composite material overcomes the problem that the reduction efficiency of ordinary iron element is low, and the release of iron ions is excessive during the reduction of pollutants, realizes the reduction of bromate well, and is a highly efficient and rapid material for pollutant degradation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
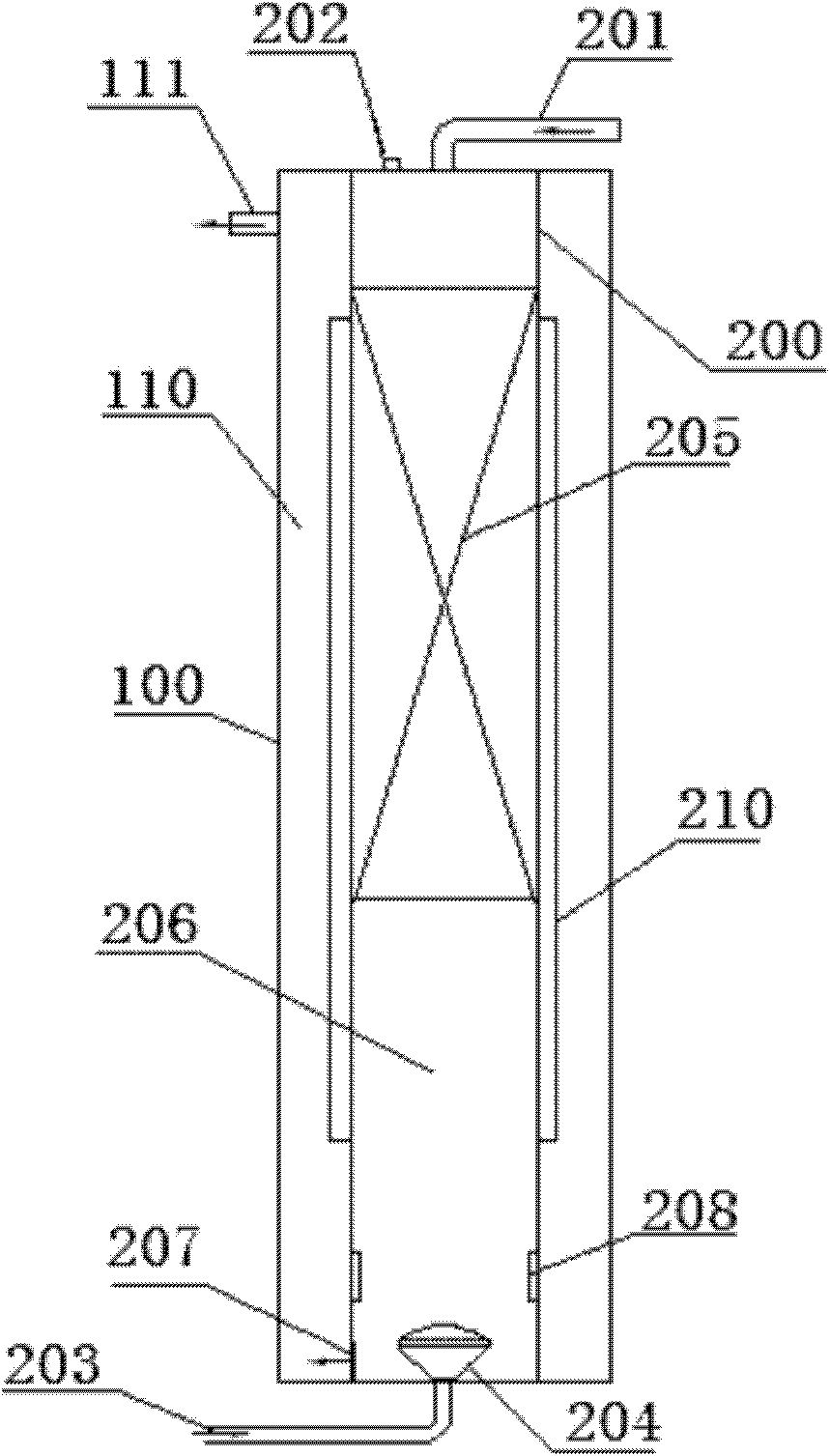
Device and method with ultrasonic ozone and ultraviolet synergized for water treatment
InactiveCN102491451AImprove solubilityIncrease contact areaWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsUltrasonic sensorWastewater
The invention discloses a device and a method with ultrasonic ozone and ultraviolet synergized for water treatment. The device comprises an outer cylinder and an inner cylinder positioned inside the outer cylinder, an ultraviolet treatment area is formed between the outer cylinder and the inner cylinder, and a water outlet is arranged on the upper portion of the wall of the outer cylinder. An ultraviolet lamp is arranged on the outer wall of the inner cylinder, an air inlet pipe and an air escape valve are arranged at the top of the inner cylinder, and an ozone inlet pipe is arranged at the bottom of the inner cylinder and connected with an ozone aerator. A padding layer is arranged on the inner upper of the inner cylinder, an ultrasonic reaction area is arranged below the padding layer, and a water outlet valve and an ultrasonic transducer are disposed on the inner wall of the ultrasonic reaction area. Using the device to treat slightly-polluted waste water enables quality of discharged water to reach the primary standard of national emission standards, and the problem of bromate during ozonization of brominated waste water can be solved. In addition, the device and the method have the advantages of simple flow, no pollution and low cost.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com