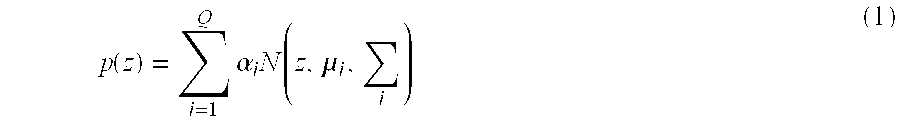Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2780 results about "Fundamental frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The fundamental frequency, often referred to simply as the fundamental, is defined as the lowest frequency of a periodic waveform. In music, the fundamental is the musical pitch of a note that is perceived as the lowest partial present. In terms of a superposition of sinusoids, the fundamental frequency is the lowest frequency sinusoidal in the sum. In some contexts, the fundamental is usually abbreviated as f₀ (or FF), indicating the lowest frequency counting from zero. In other contexts, it is more common to abbreviate it as f₁, the first harmonic. (The second harmonic is then f₂ = 2⋅f₁, etc. In this context, the zeroth harmonic would be 0 Hz.)
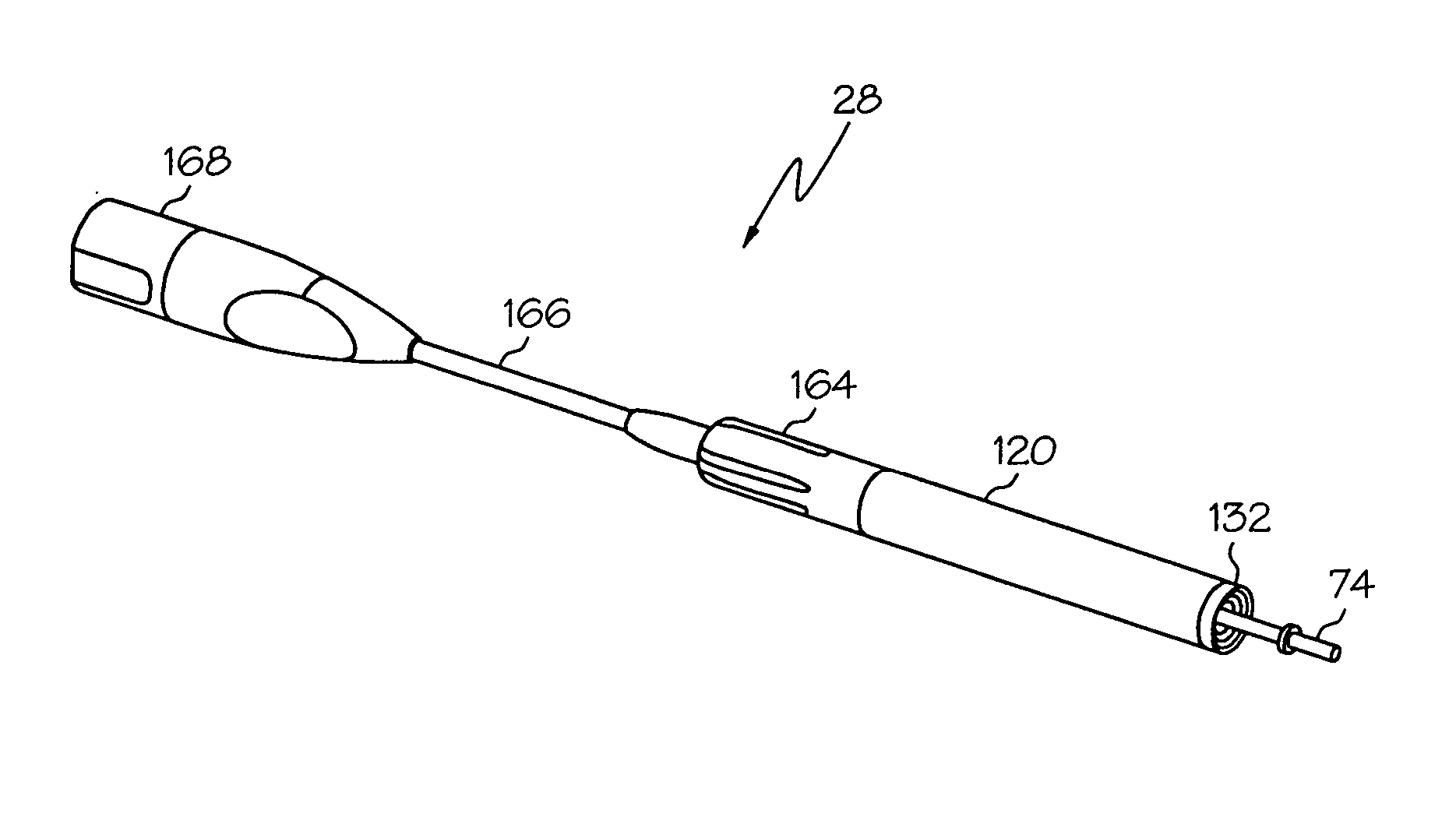
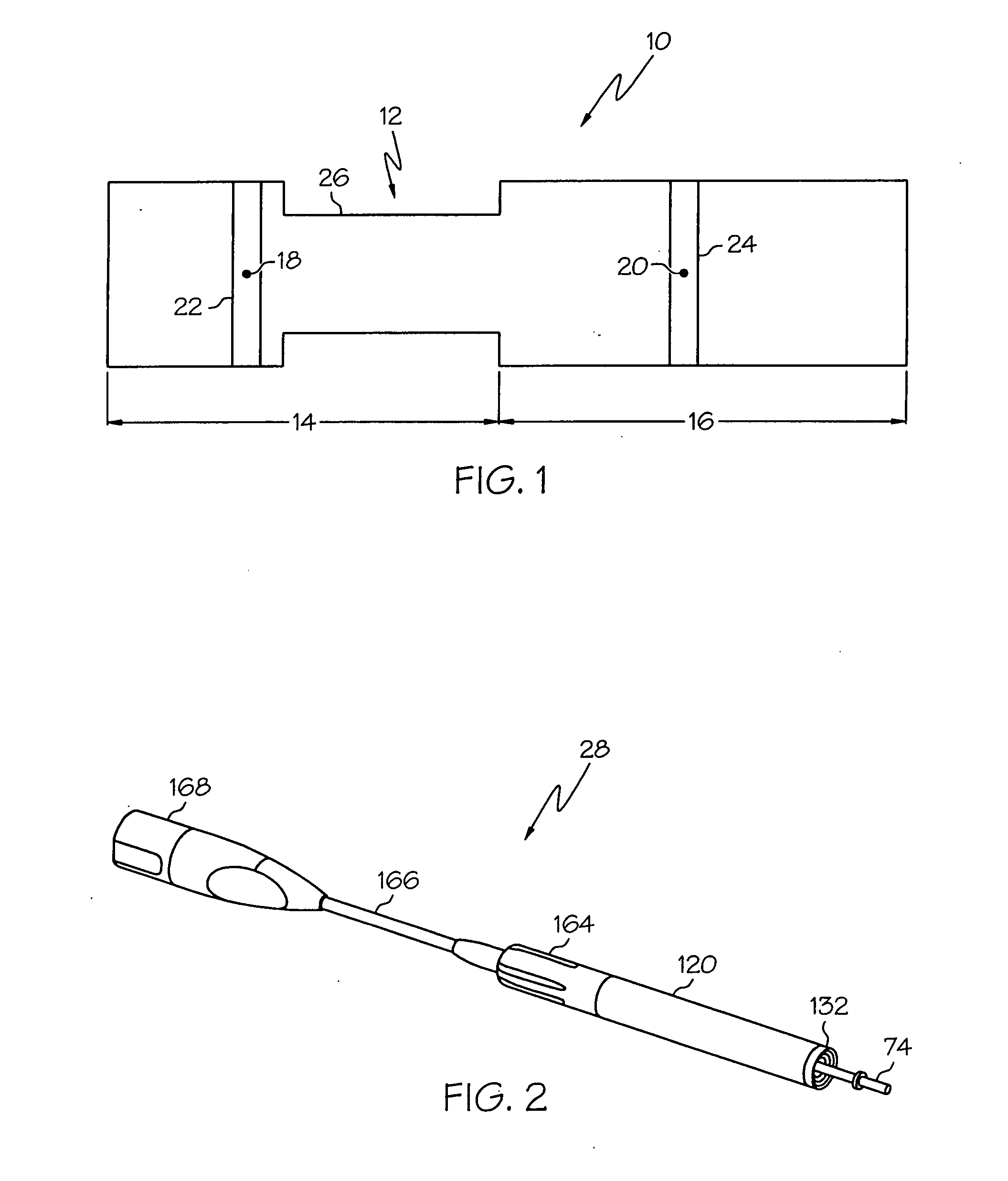
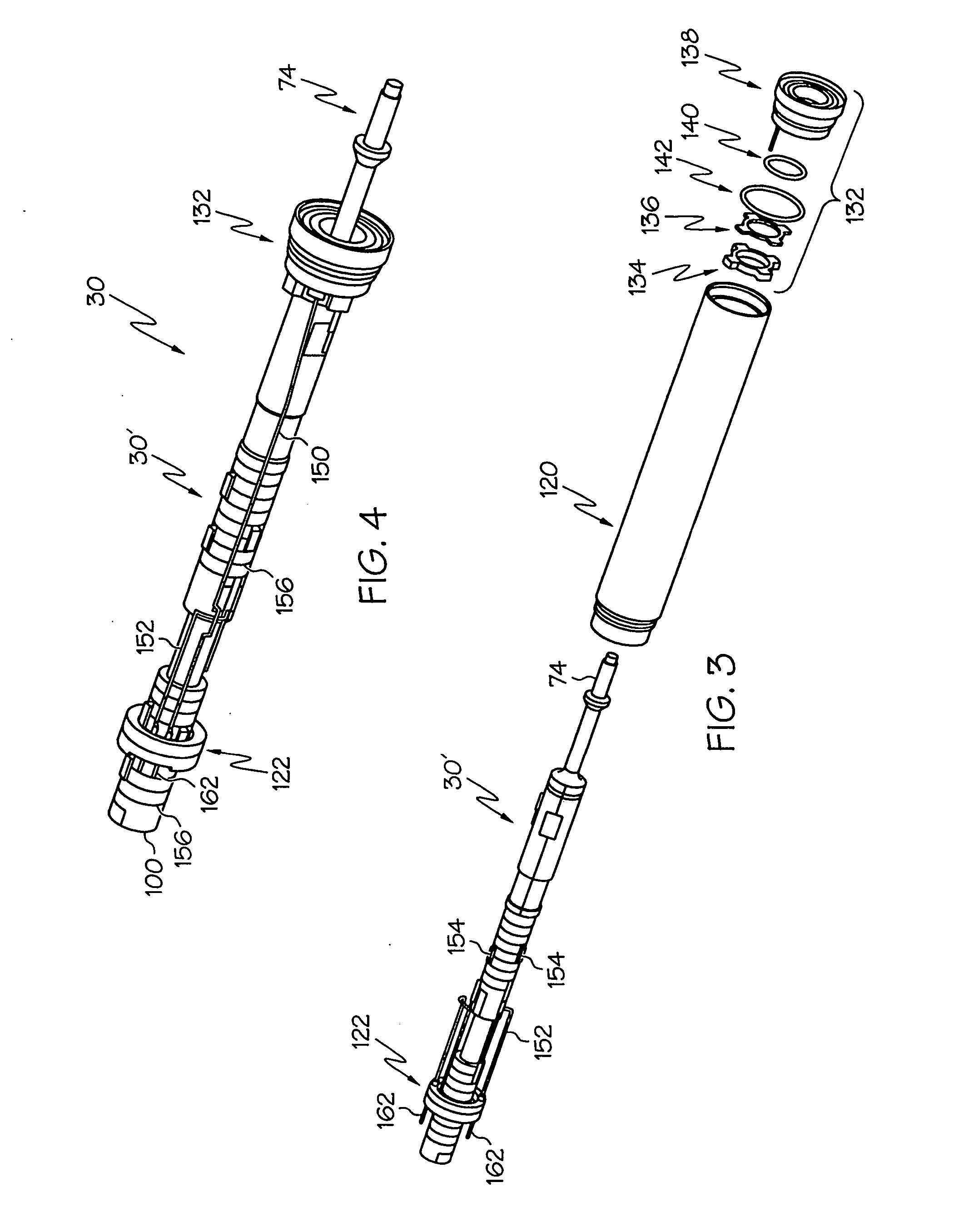
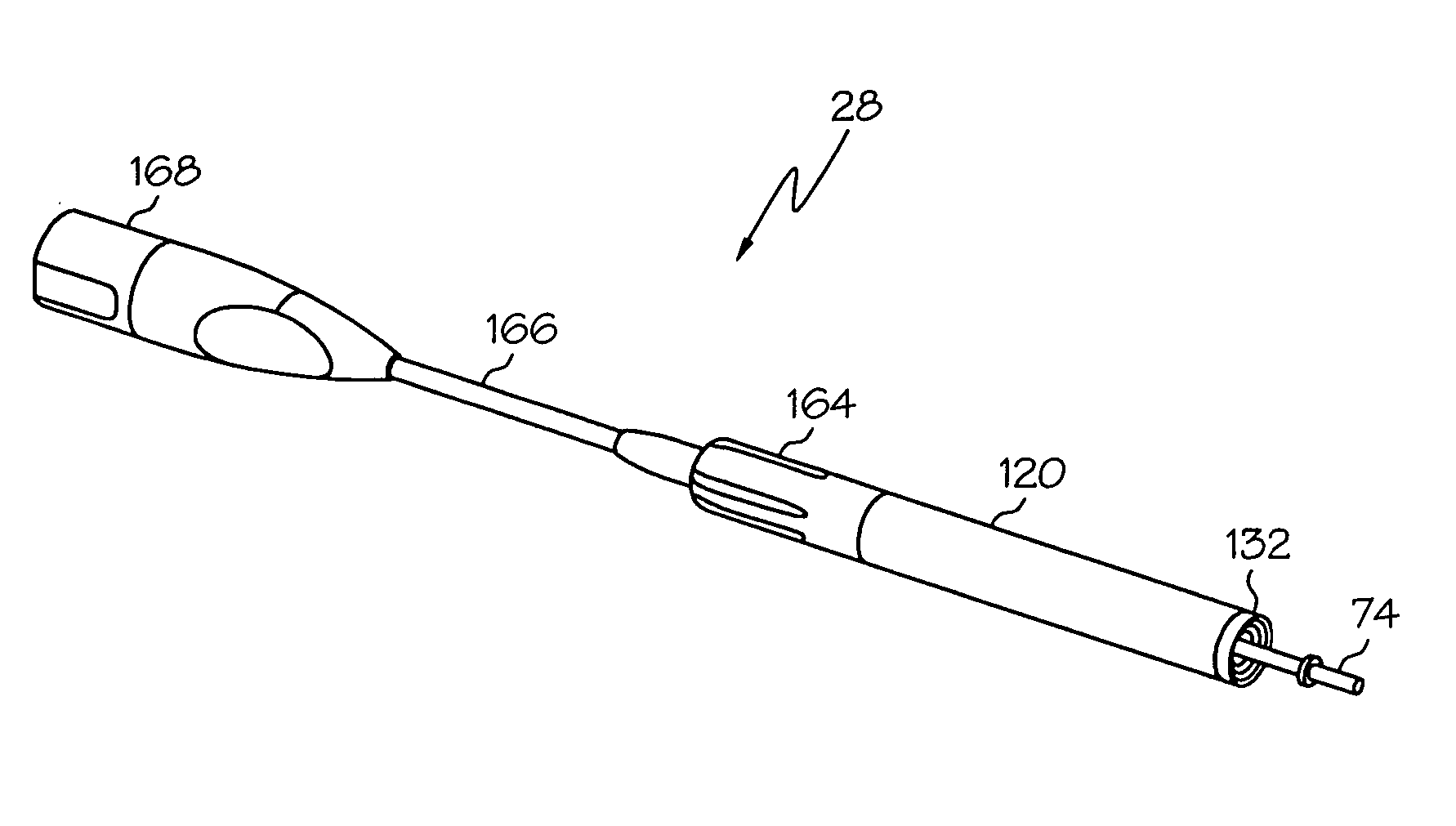
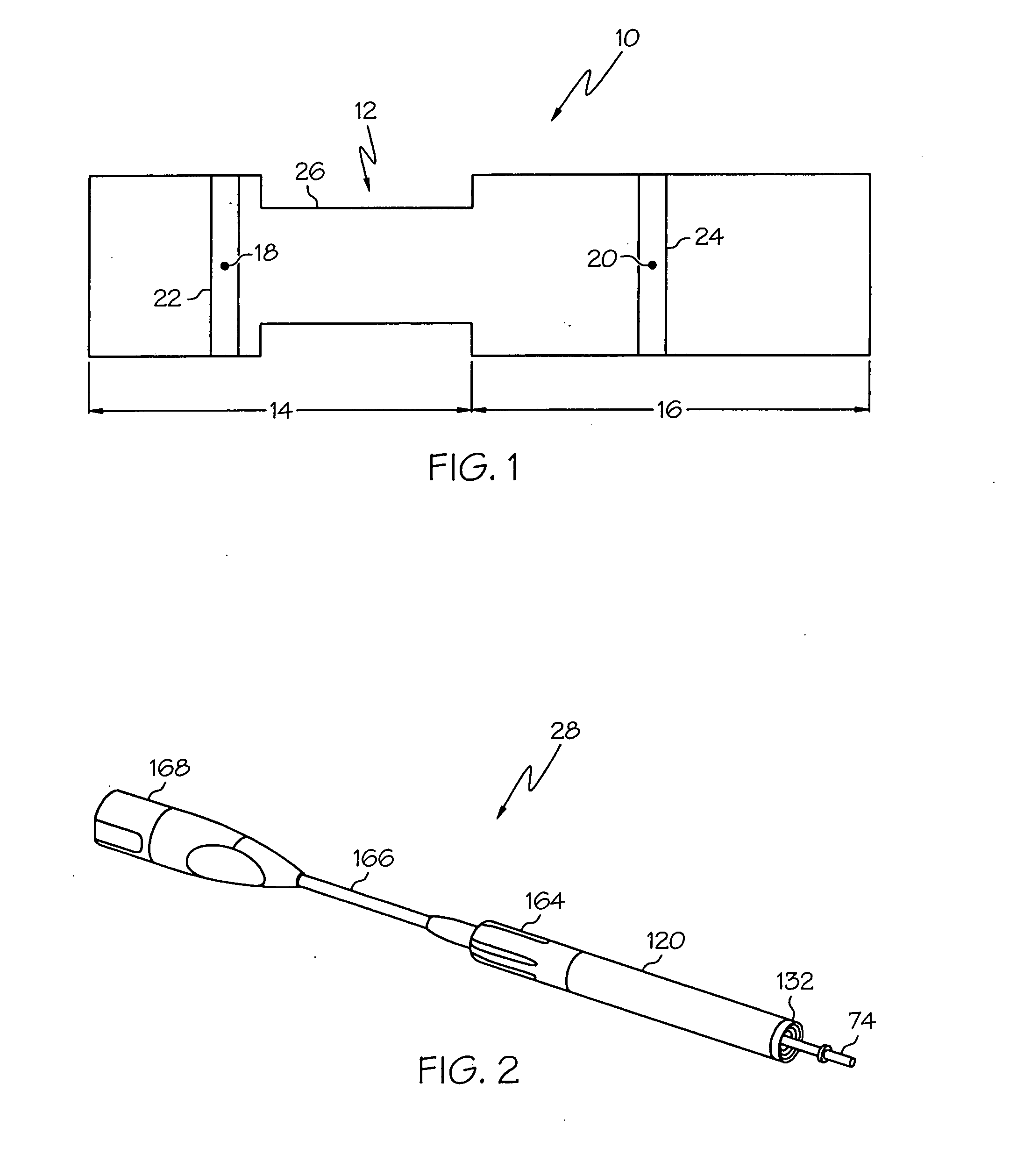
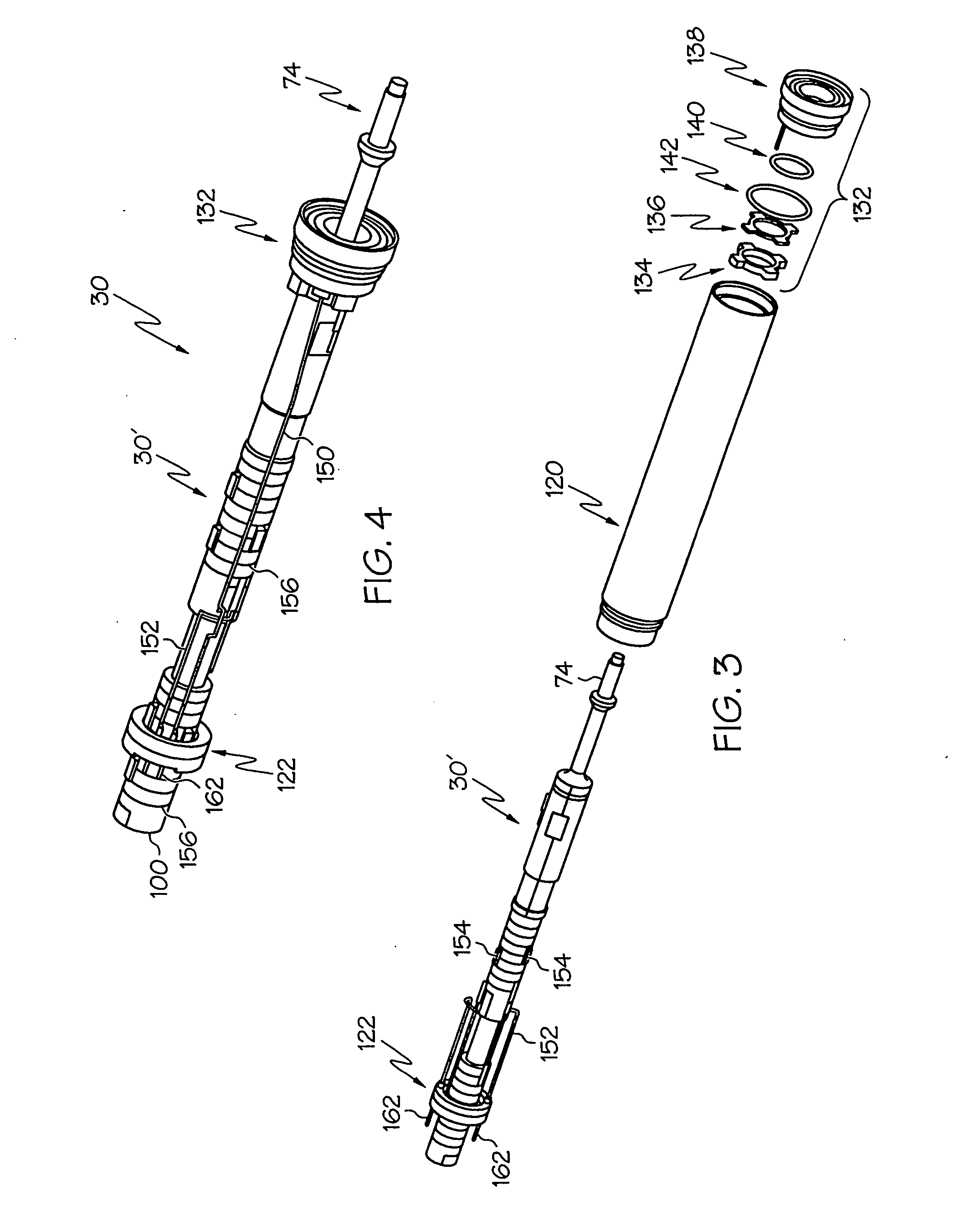
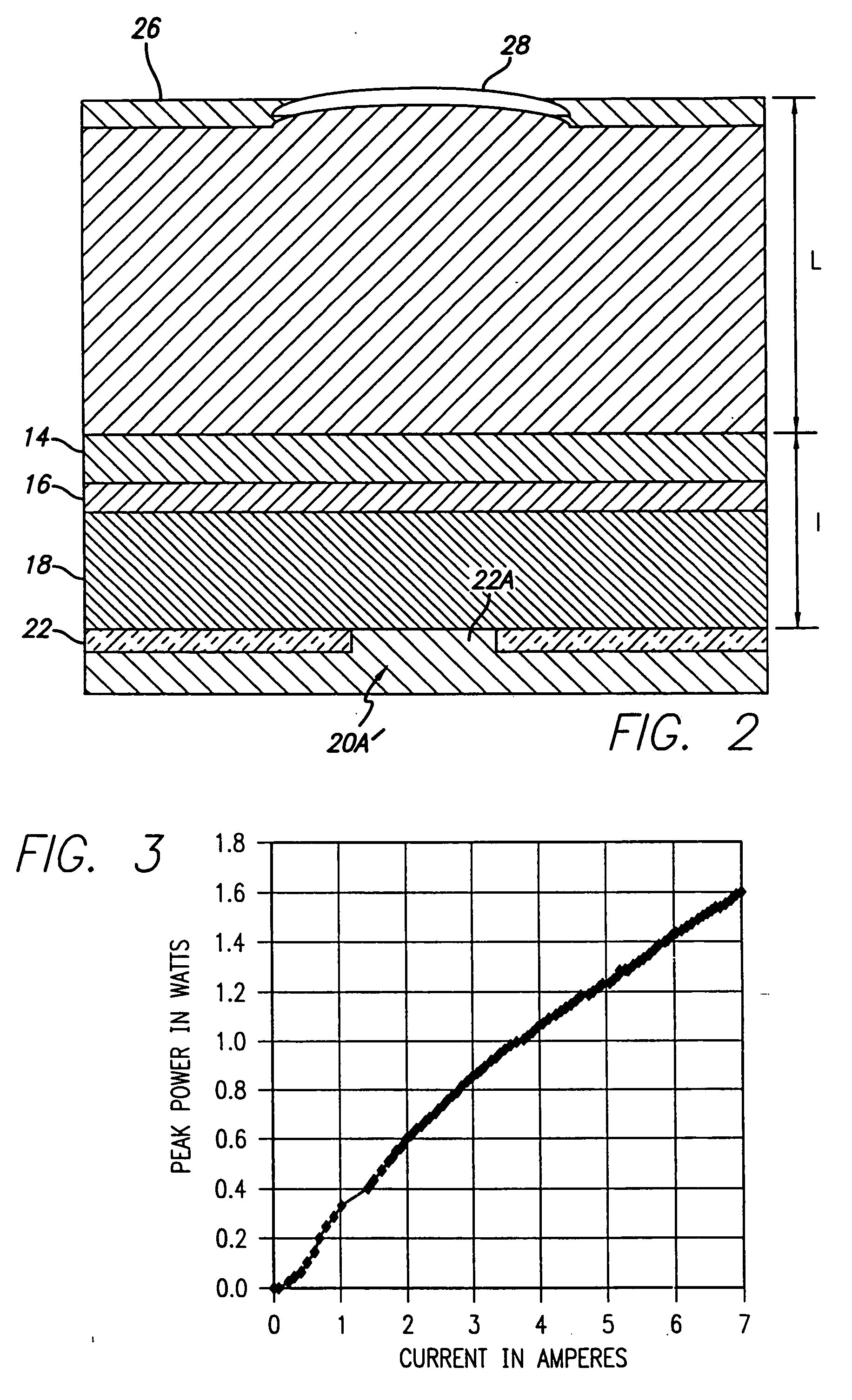
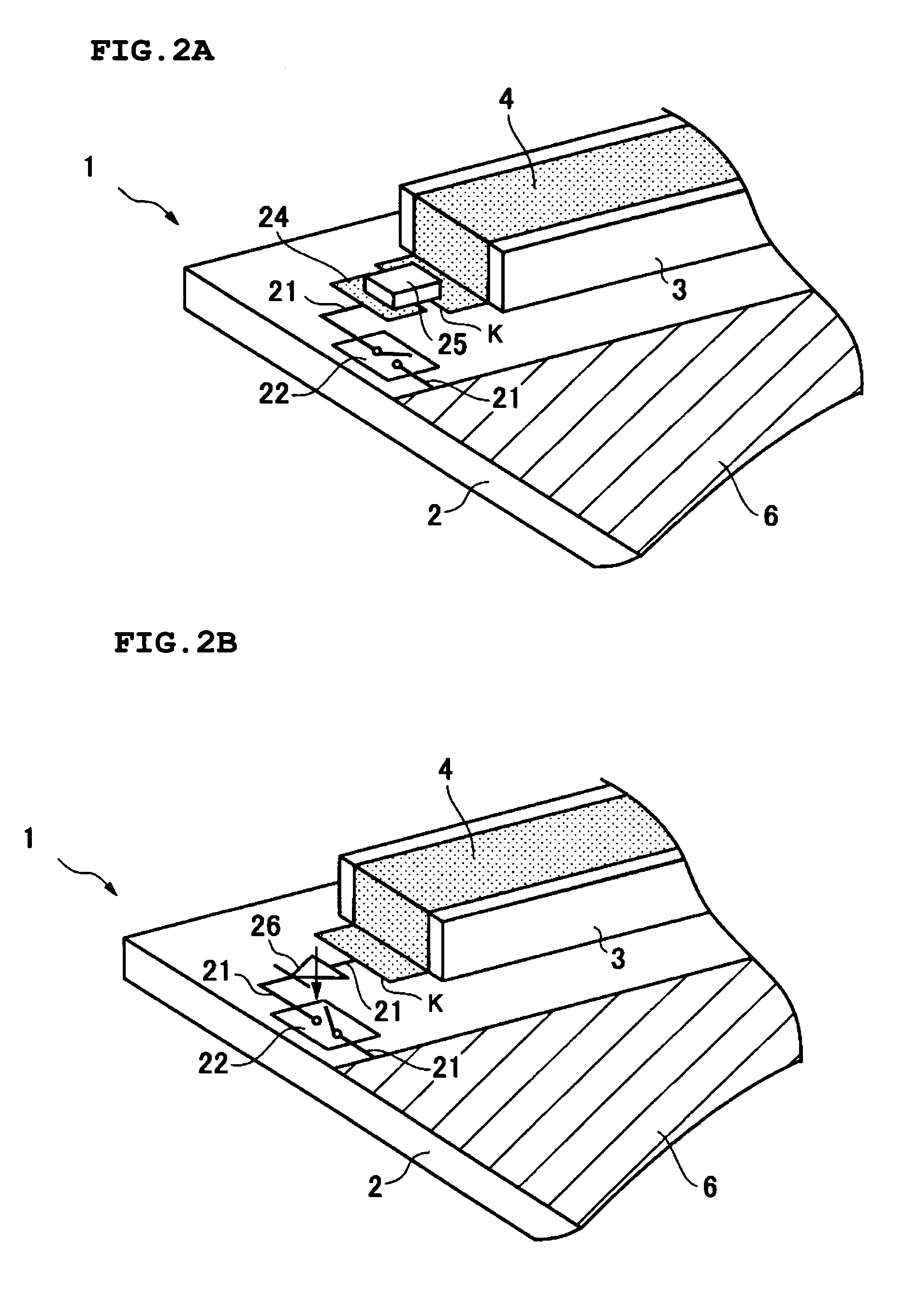
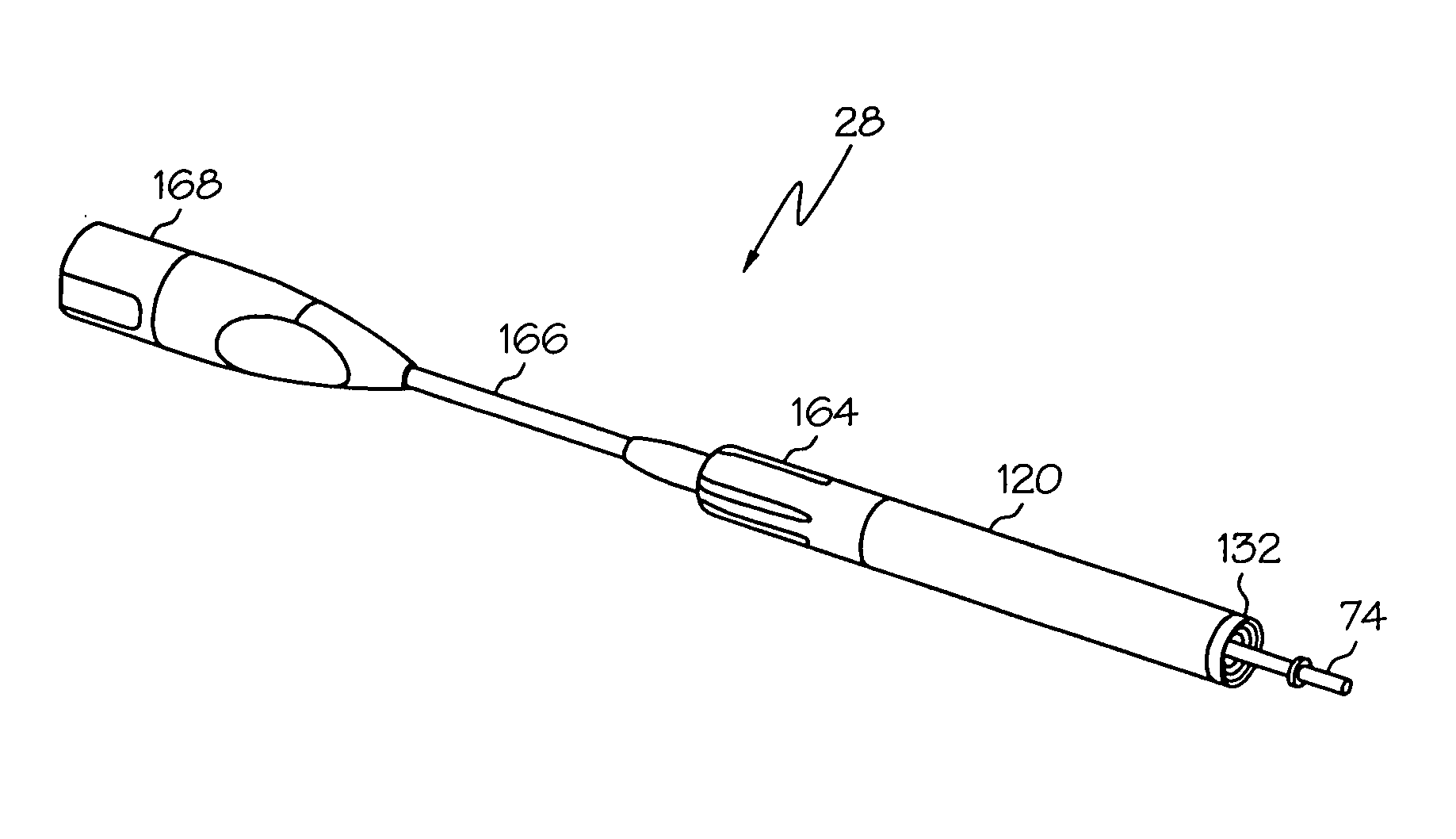
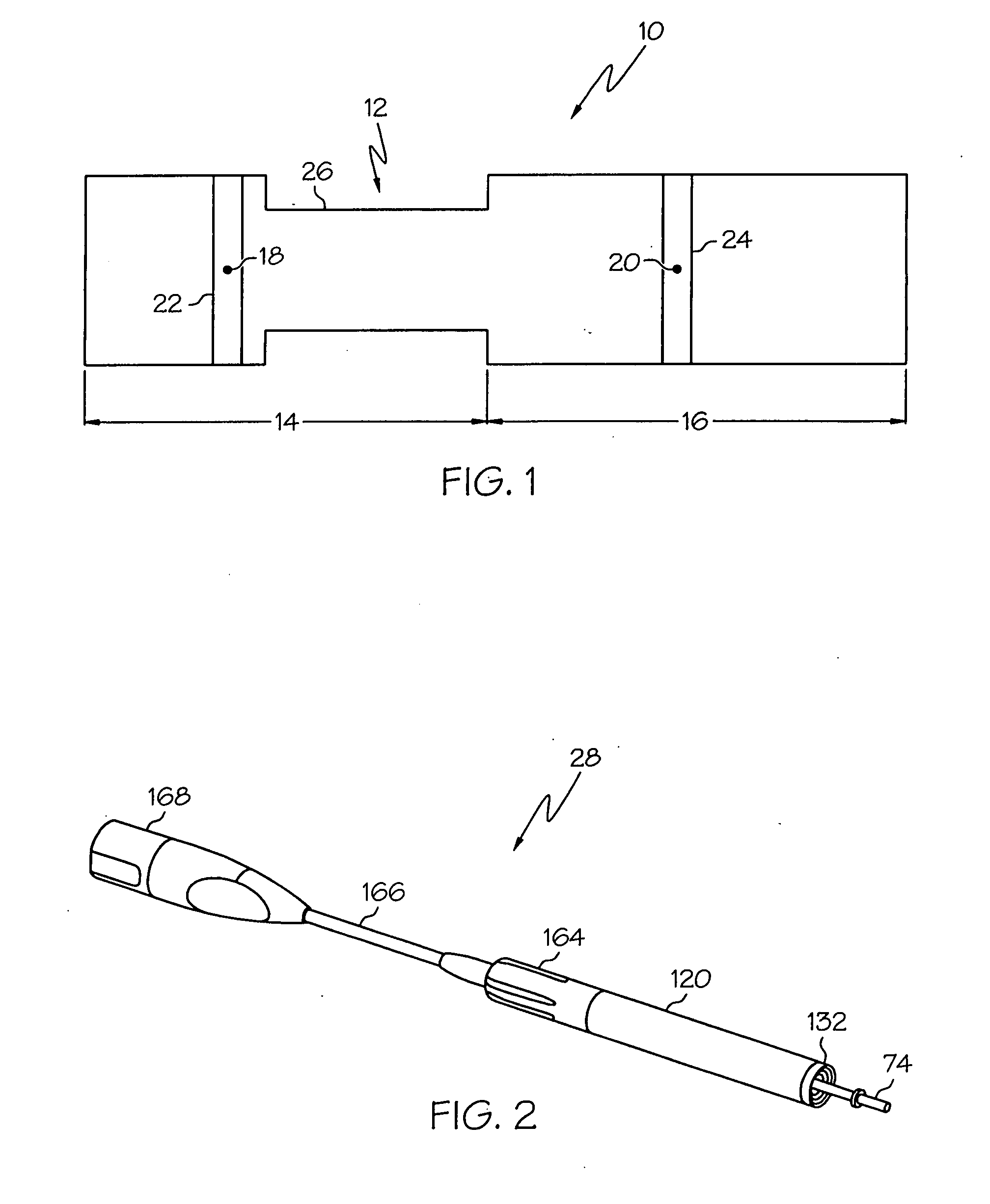
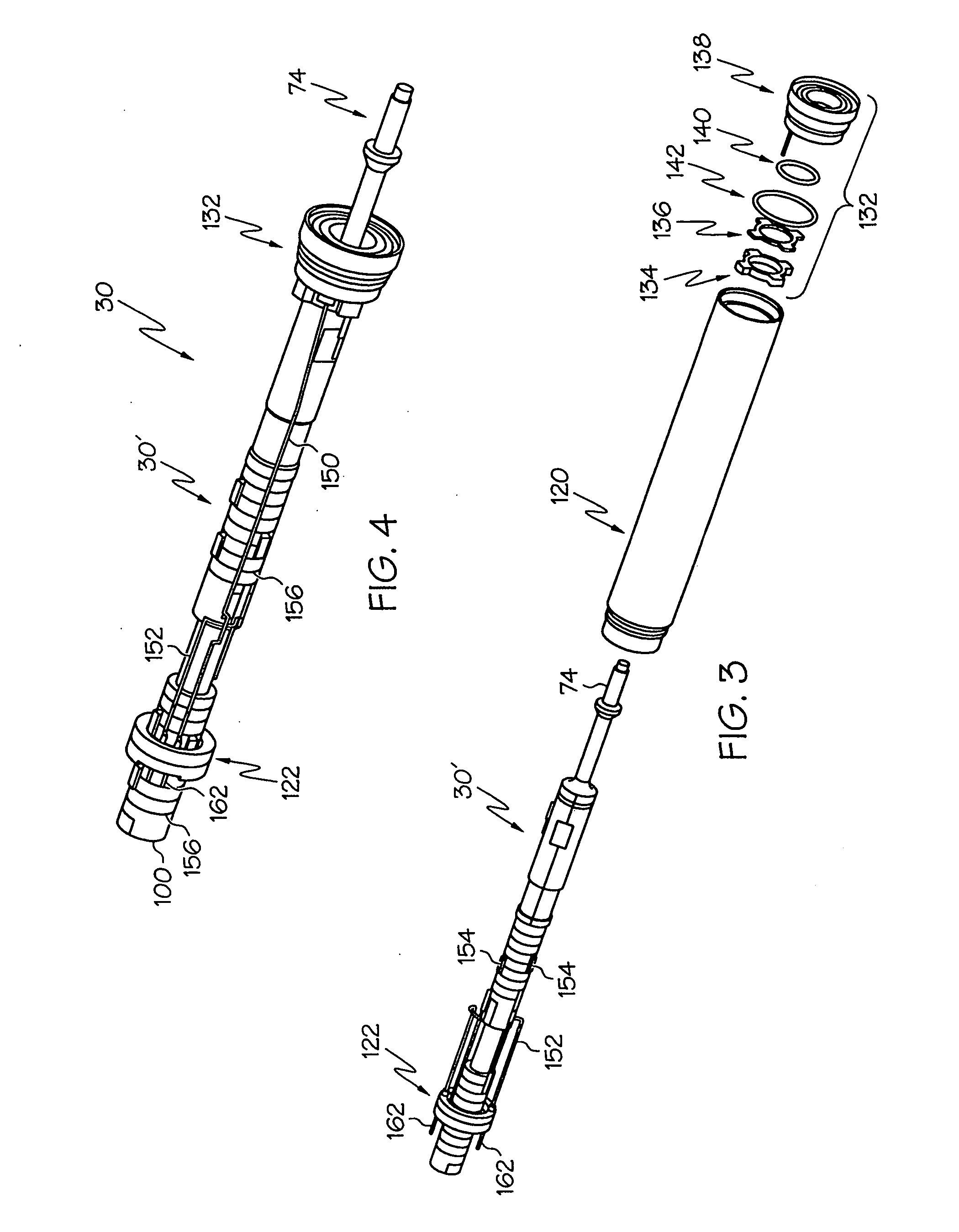
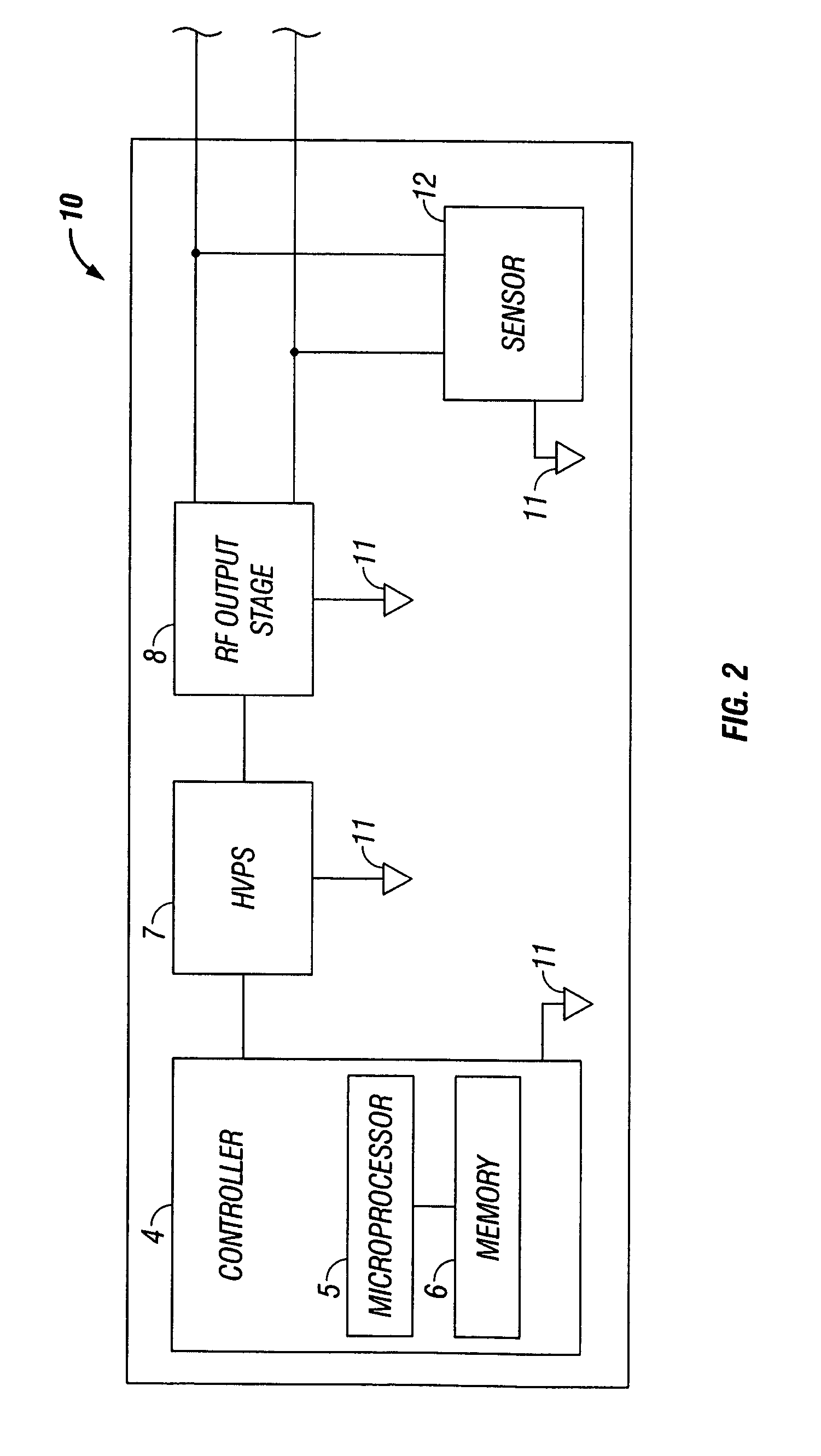
Medical ultrasound system and handpiece and methods for making and tuning
InactiveUS20070232926A1Small sizeIncrease displacementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryUltrasonographyUltrasonic sensor
Several embodiments of medical ultrasound handpieces are described each including a medical ultrasound transducer assembly. An embodiment of a medical ultrasound system is described, wherein the medical ultrasound system includes a medical ultrasound handpiece having a medical ultrasound transducer assembly and includes an ultrasonically-vibratable medical-treatment instrument which is attachable to a distal end of the transducer assembly. An embodiment of a medical ultrasound system is described, wherein the medical ultrasound system has a handpiece including a medical ultrasound transducer assembly and including a housing or housing component surrounding the transducer assembly. A method for tuning a medical ultrasound handpiece includes machining at least a distal non-threaded portion of an instrument-attachment stud of the transducer assembly to match a measured fundamental frequency to a desired fundamental frequency to within a predetermined limit. A method for making a medical ultrasound transducer assembly determines acceptable gains for gain stages of the transducer assembly.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Medical ultrasound system and handpiece and methods for making and tuning
InactiveUS20070232928A1Small sizeIncrease displacementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryUltrasonographyUltrasonic sensor
Several embodiments of medical ultrasound handpieces are described each including a medical ultrasound transducer assembly. An embodiment of a medical ultrasound system is described, wherein the medical ultrasound system includes a medical ultrasound handpiece having a medical ultrasound transducer assembly and includes an ultrasonically-vibratable medical-treatment instrument which is attachable to a distal end of the transducer assembly. An embodiment of a medical ultrasound system is described, wherein the medical ultrasound system has a handpiece including a medical ultrasound transducer assembly and including a housing or housing component surrounding the transducer assembly. A method for tuning a medical ultrasound handpiece includes machining at least a distal non-threaded portion of an instrument-attachment stud of the transducer assembly to match a measured fundamental frequency to a desired fundamental frequency to within a predetermined limit. A method for making a medical ultrasound transducer assembly determines acceptable gains for gain stages of the transducer assembly.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT +1
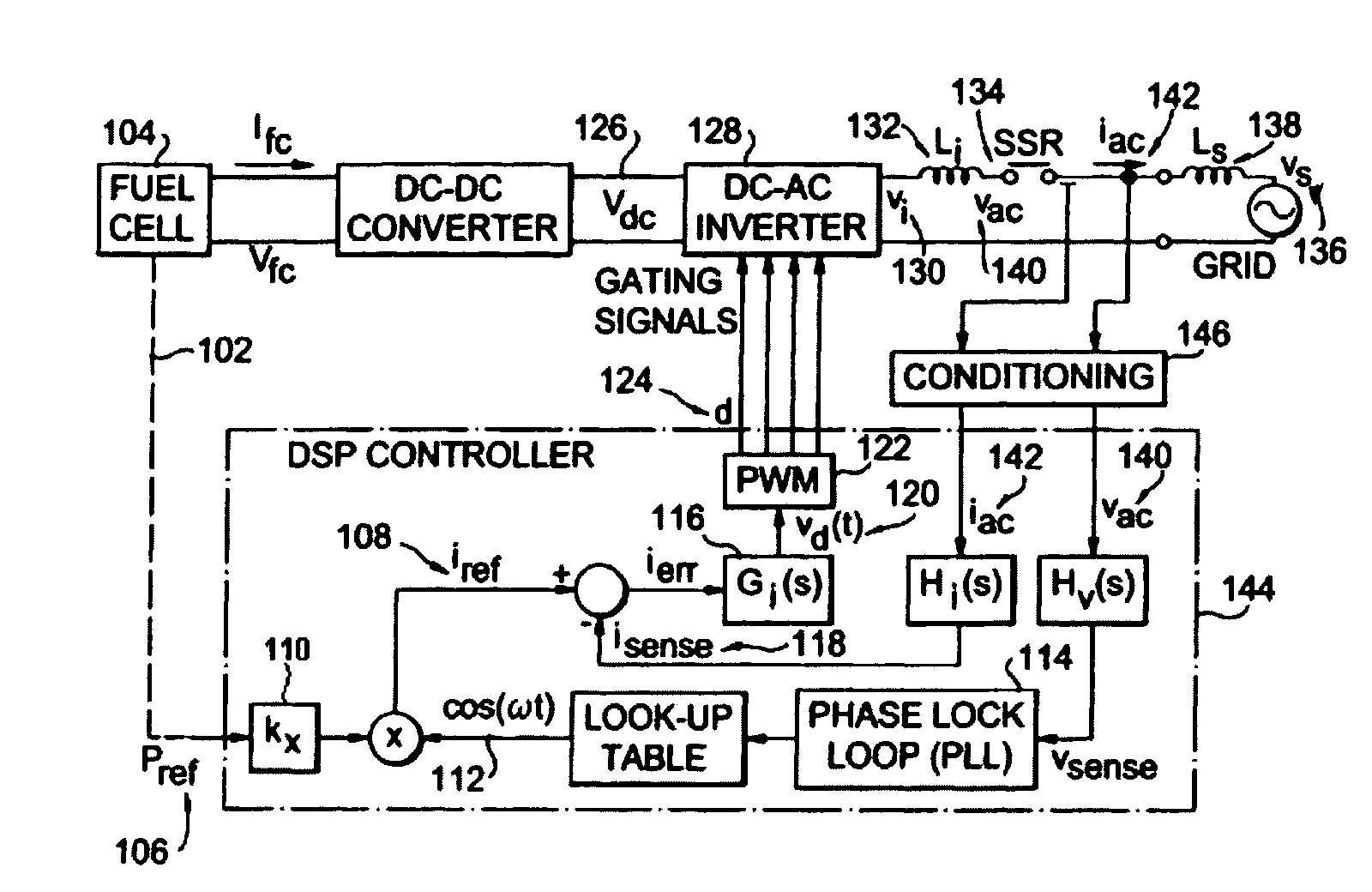
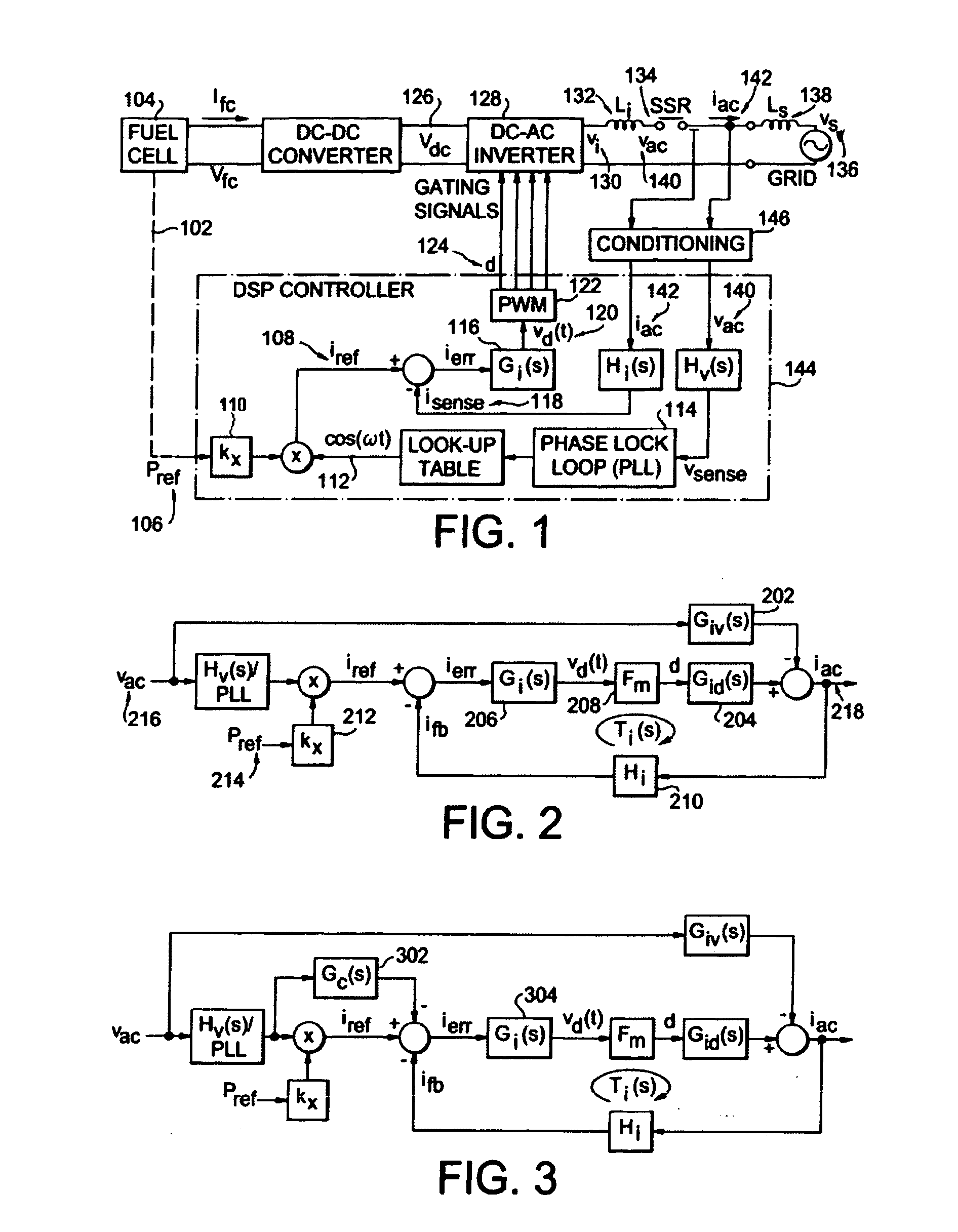
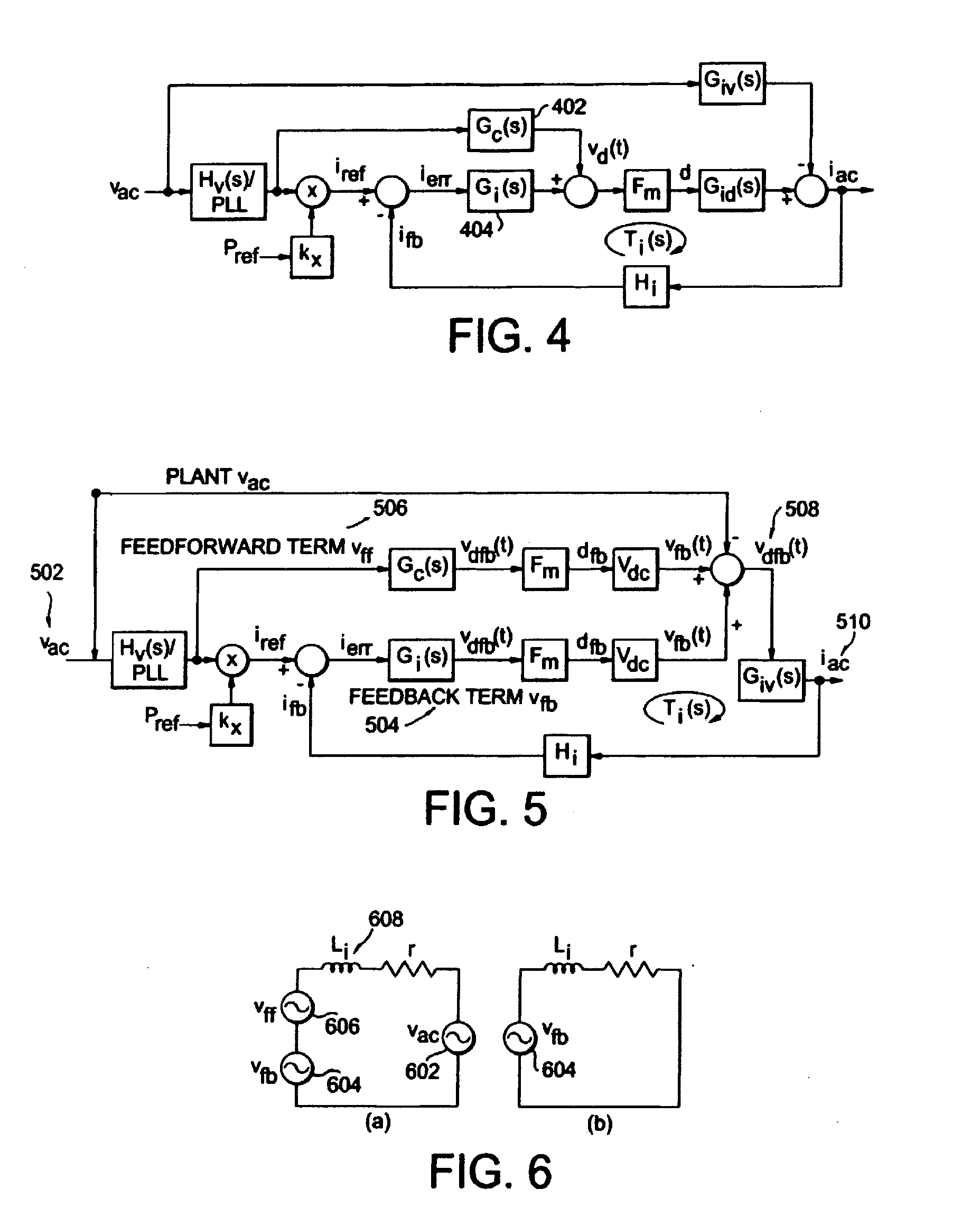
Control system and method for a universal power conditioning system
ActiveUS20080205096A1Avoid precision problemsSolve the stability is not highEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionFundamental frequencyCatastrophic failure
A new current loop control system method is proposed for a single-phase grid-tie power conditioning system that can be used under a standalone or a grid-tie mode. This type of inverter utilizes an inductor-capacitor-inductor (LCL) filter as the interface in between inverter and the utility grid. The first set of inductor-capacitor (LC) can be used in the standalone mode, and the complete LCL can be used for the grid-tie mode. A new admittance compensation technique is proposed for the controller design to avoid low stability margin while maintaining sufficient gain at the fundamental frequency. The proposed current loop controller system and admittance compensation technique have been simulated and tested. Simulation results indicate that without the admittance path compensation, the current loop controller output duty cycle is largely offset by an undesired admittance path. At the initial simulation cycle, the power flow may be erratically fed back to the inverter causing catastrophic failure. With admittance path compensation, the output power shows a steady-state offset that matches the design value. Experimental results show that the inverter is capable of both a standalone and a grid-tie connection mode using the LCL filter configuration.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
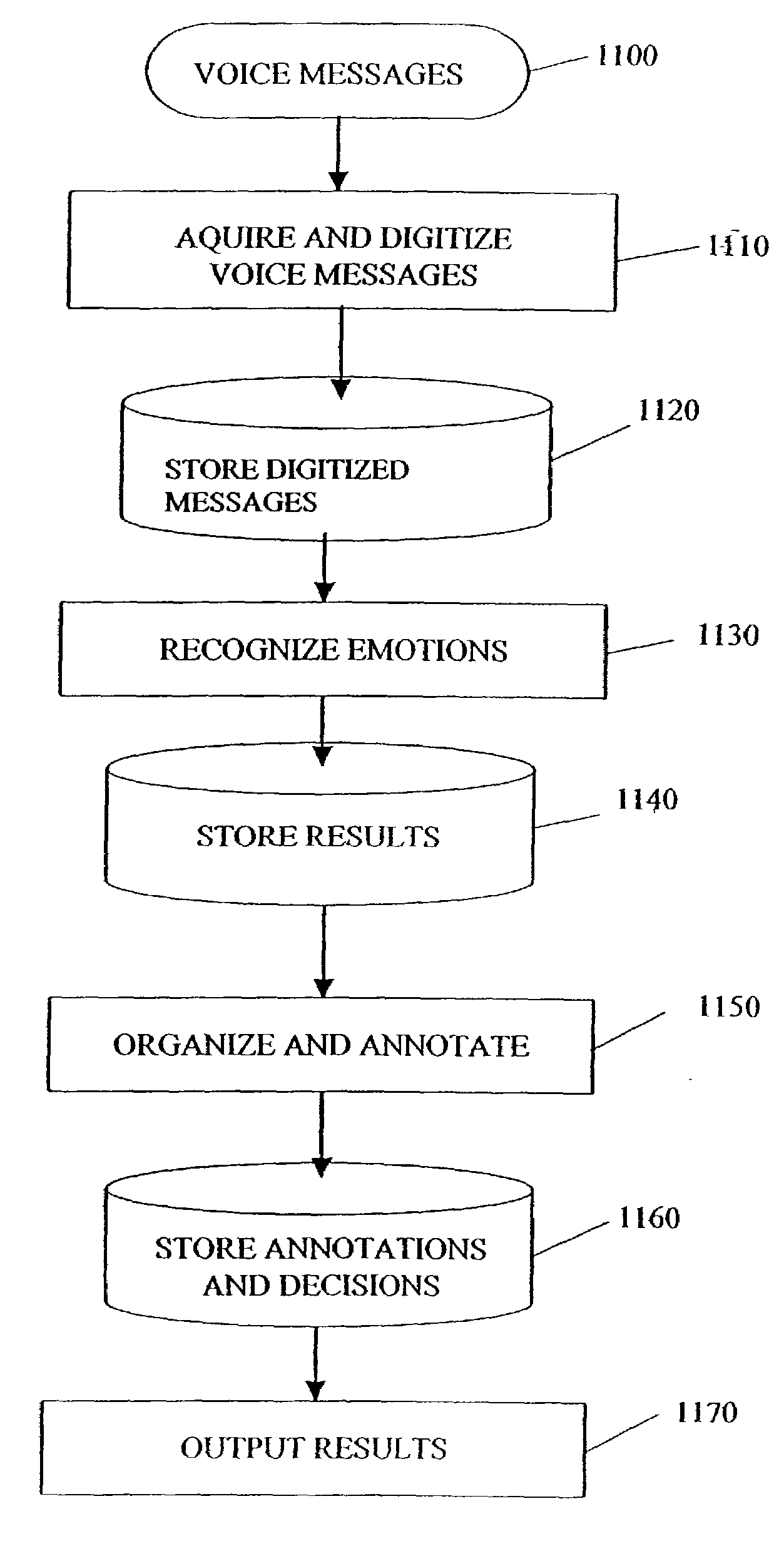
Detecting emotions using voice signal analysis
InactiveUS7222075B2Speech analysisAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingVoice analysisFundamental frequency
A system and method are provided for detecting emotional states using statistics. First, a speech signal is received. At least one acoustic parameter is extracted from the speech signal. Then statistics or features from samples of the voice are calculated from extracted speech parameters. The features serve as inputs to a classifier, which can be a computer program, a device or both. The classifier assigns at least one emotional state from a finite number of possible emotional states to the speech signal. The classifier also estimates the confidence of its decision. Features that are calculated may include a maximum value of a fundamental frequency, a standard deviation of the fundamental frequency, a range of the fundamental frequency, a mean of the fundamental frequency, and a variety of other statistics.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
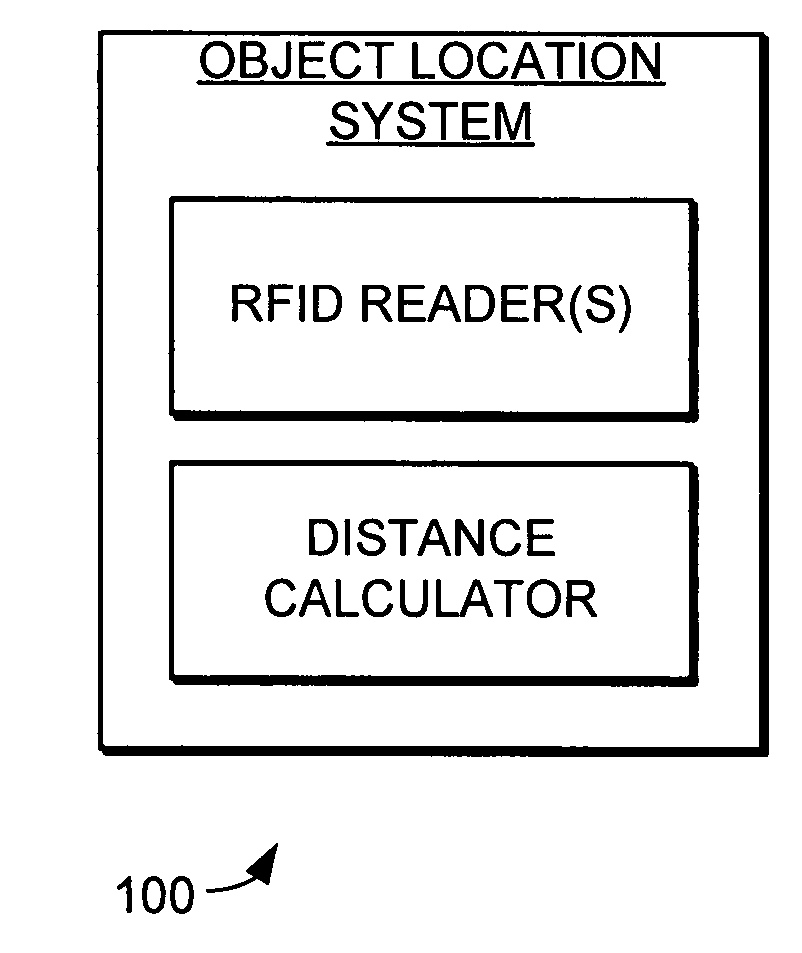
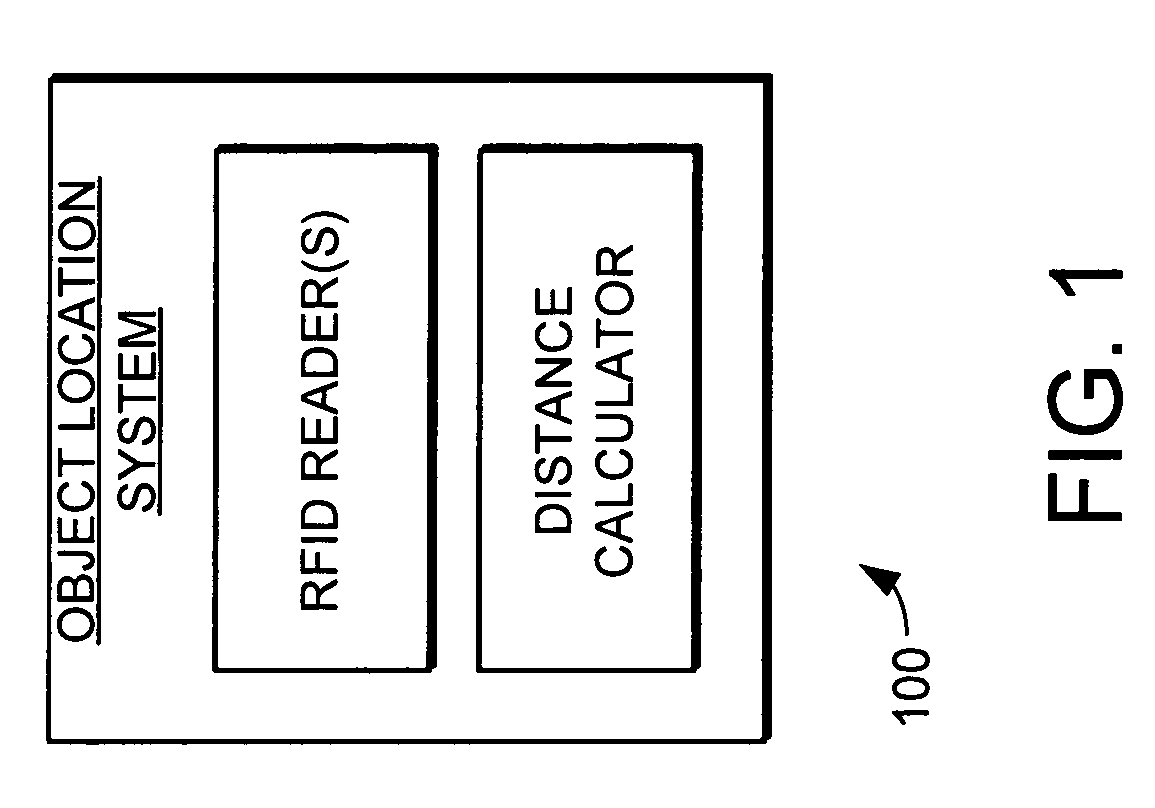
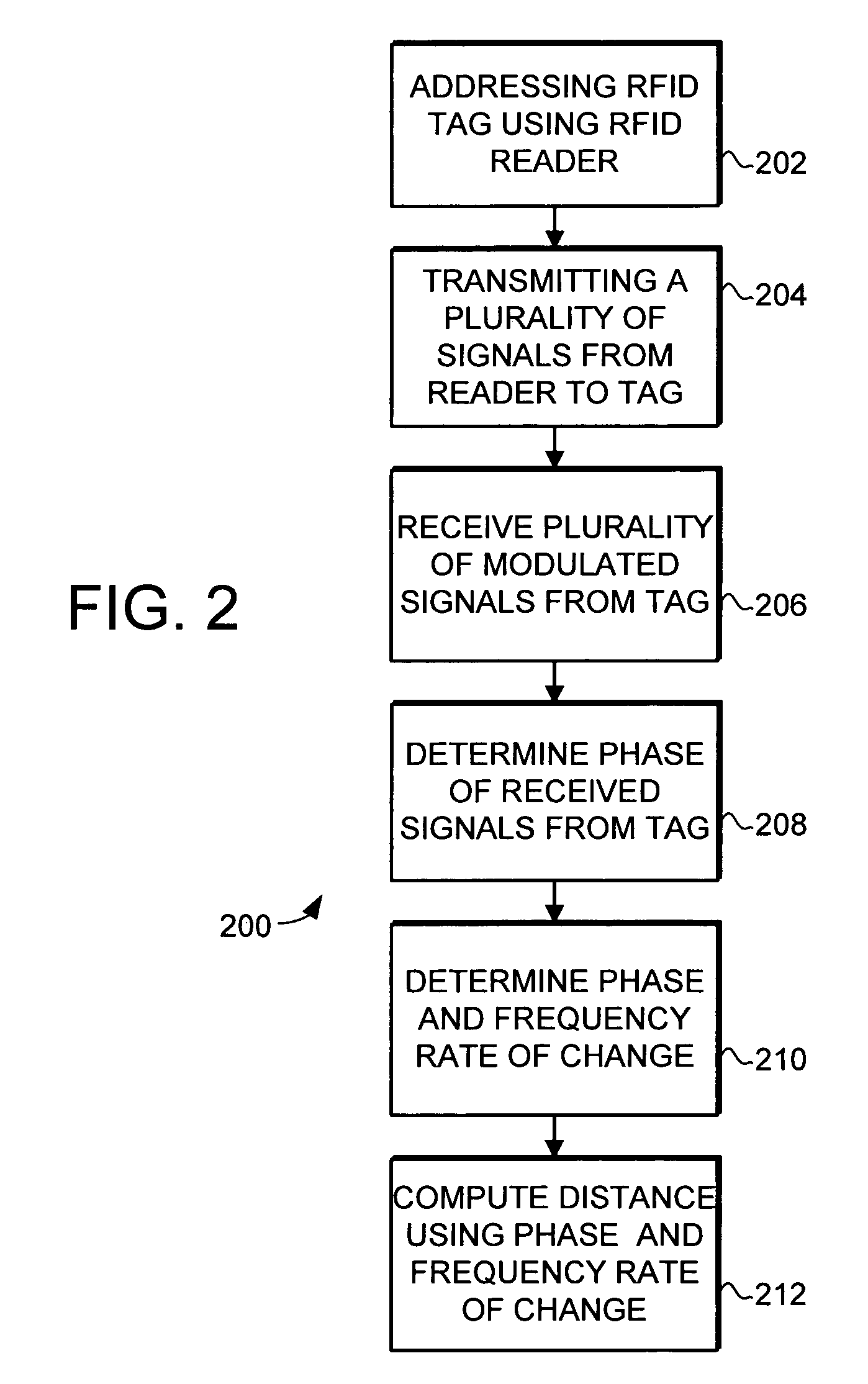
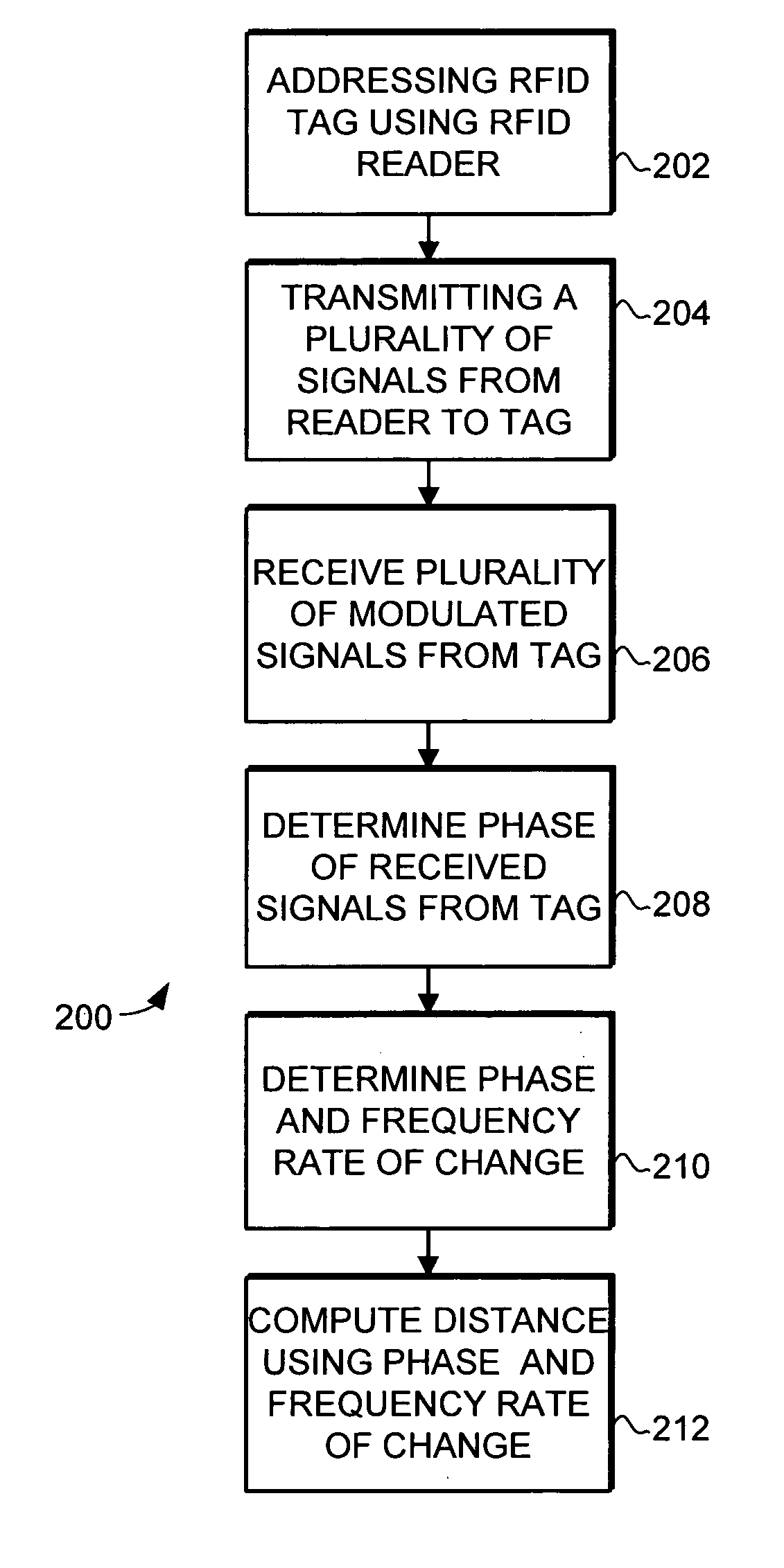
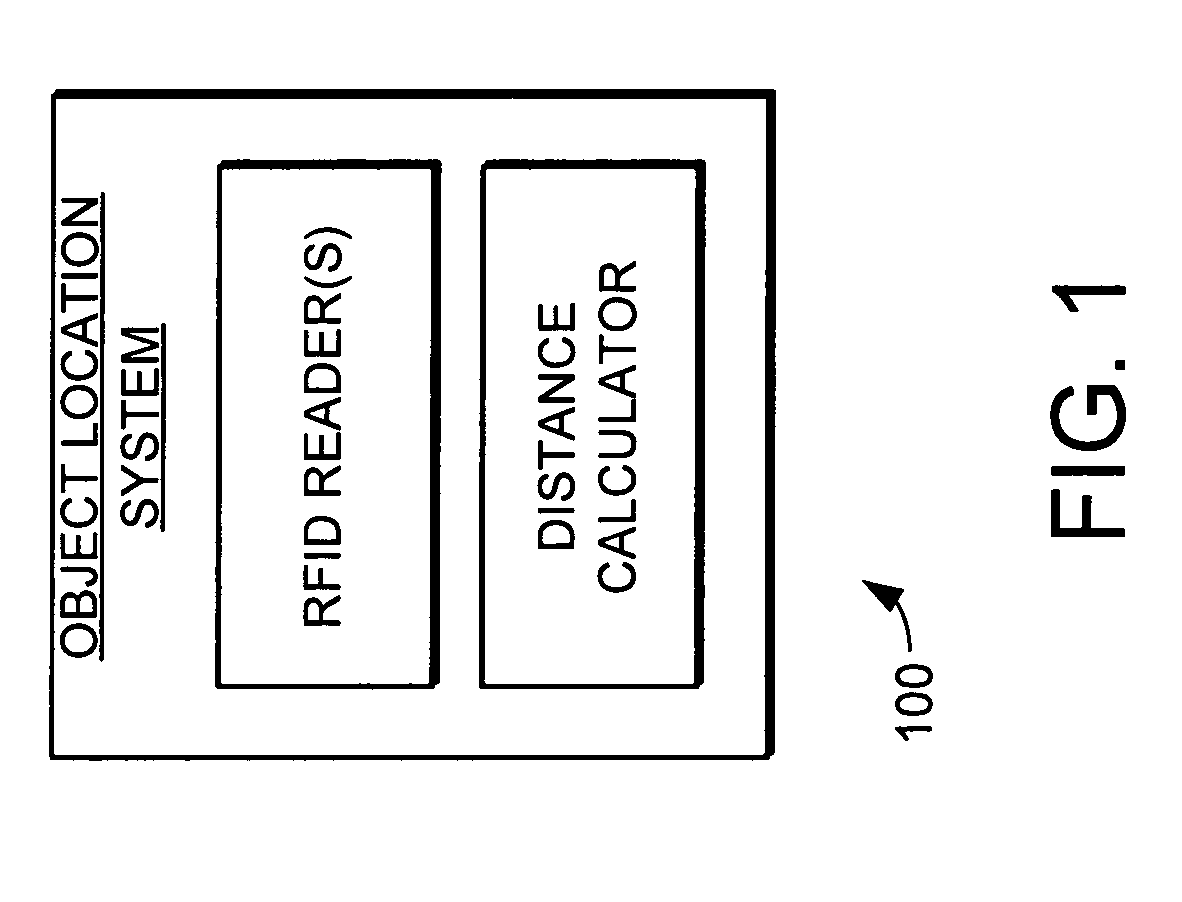
Object location system and method using RFID
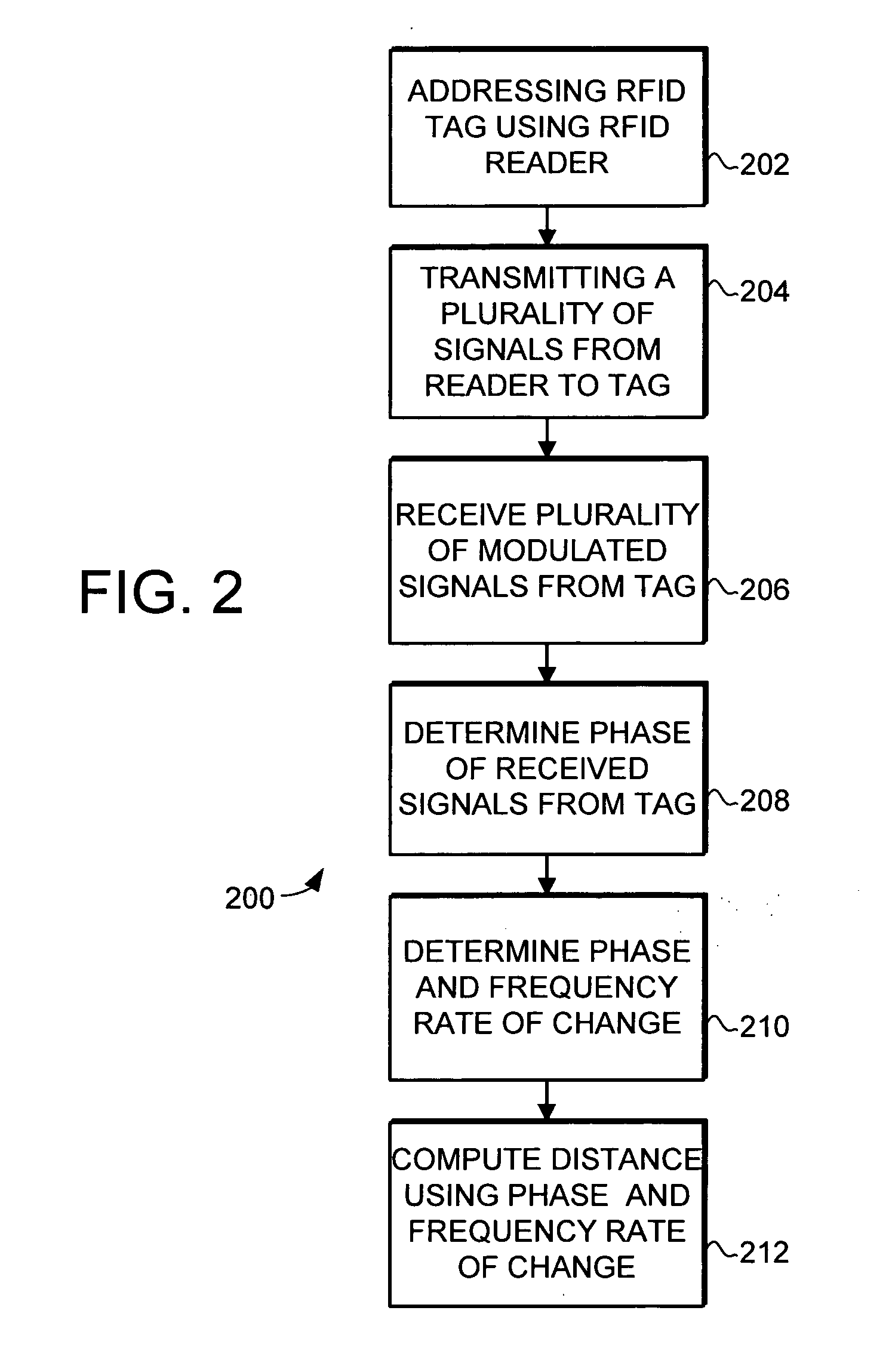
ActiveUS7119738B2Efficiently and accurately determineEfficiently determinedElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalFundamental frequencyComputer science
A system and method is provided for locating objects using RFID tags. The system and method uses an RFID reader and a distance calculator to efficiently and accurately determine the location of objects that include an RFID tag. The RFID reader transmits a plurality of signals to the RFID tag, with the plurality of signals having different fundamental frequencies. In response, the RFID tag backscatter modulates the plurality of transmitted signals to create a plurality of backscatter modulated signals. The RFID reader receives and demodulates the plurality of backscatter modulated signals. The distance calculator determines the phase of the plurality of backscatter modulated signals and determines a rate of change of the phase in the backscatter modulated signals with respect to the rate of change in the fundamental frequency of the transmitted signals and uses this information to calculate the distance to the RFID tag.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
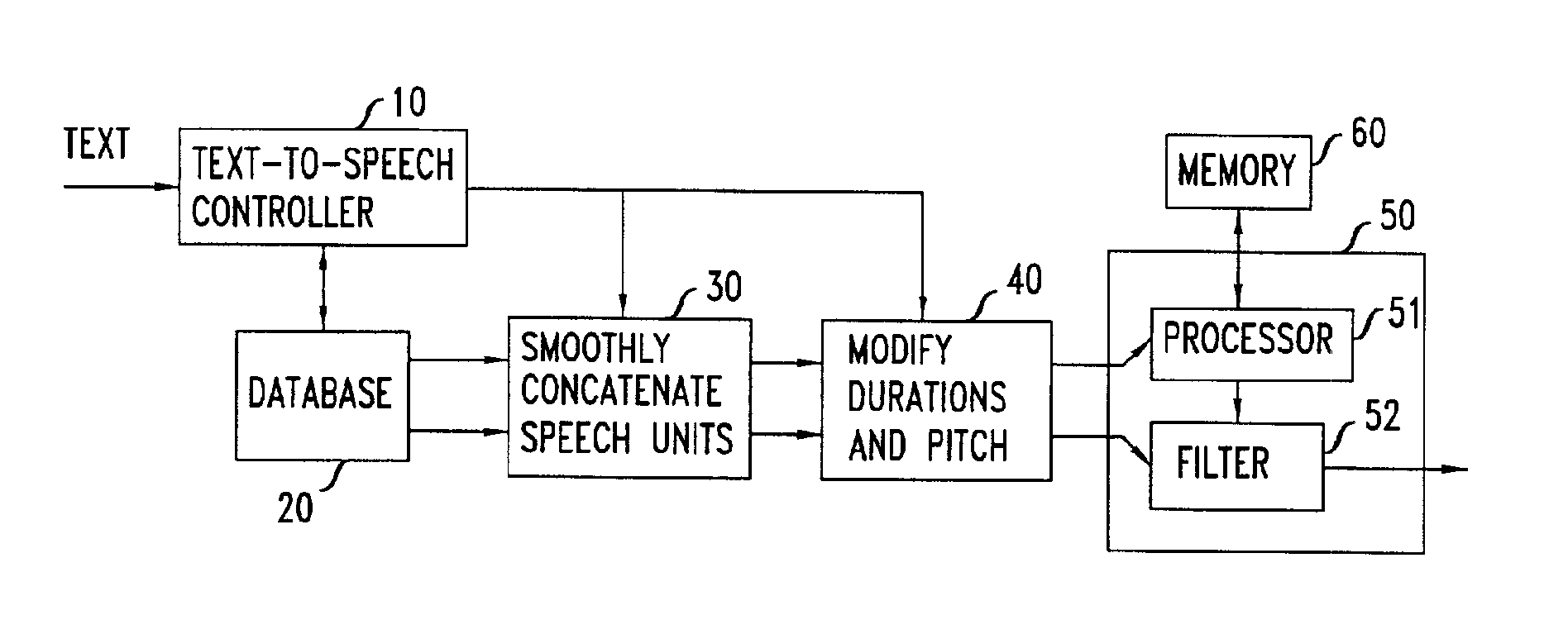
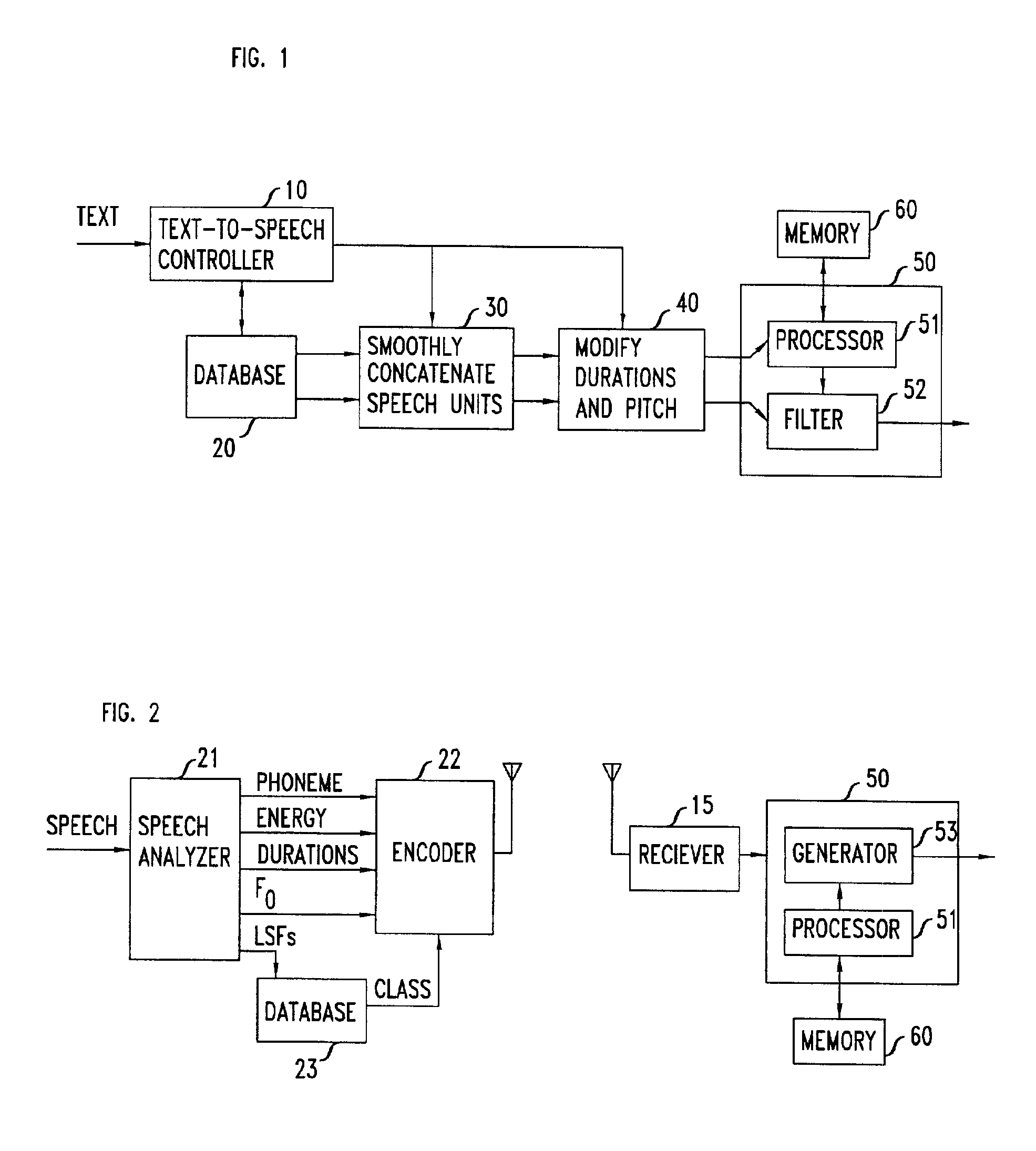
Stochastic modeling of spectral adjustment for high quality pitch modification
Natural-sounding synthesized speech is obtained from pieced elemental speech units that have their super-class identities known (e.g. phoneme type), and their line spectral frequencies (LSF) set in accordance with a correlation between the desired fundamental frequency and the LSF vectors that are known for different classes in the super-class. The correlation between a fundamental frequency in a class and the corresponding LSF is obtained by, for example, analyzing the database of recorded speech of a person and, more particularly, by analyzing frames of the speech signal.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Object location system and method using RFID
ActiveUS20050190098A1Efficiently and accurately determineAccurate locationElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalFundamental frequencyComputer science
A system and method is provided for locating objects using RFID tags. The system and method uses an RFID reader and a distance calculator to efficiently and accurately determine the location of objects that include an RFID tag. The RFID reader transmits a plurality of signals to the RFID tag, with the plurality of signals having different fundamental frequencies. In response, the RFID tag backscatter modulates the plurality of transmitted signals to create a plurality of backscatter modulated signals. The RFID reader receives and demodulates the plurality of backscatter modulated signals. The distance calculator determines the phase of the plurality of backscatter modulated signals and determines a rate of change of the phase in the backscatter modulated signals with respect to the rate of change in the fundamental frequency of the transmitted signals and uses this information to calculate the distance to the RFID tag.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
Medical ultrasound system and handpiece and methods for making and tuning
ActiveUS20070106158A1Increase displacementLarge amplitudeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesUltrasonographyUltrasonic sensor
Several embodiments of medical ultrasound handpieces are described each including a medical ultrasound transducer assembly. An embodiment of a medical ultrasound system is described, wherein the medical ultrasound system includes a medical ultrasound handpiece having a medical ultrasound transducer assembly and includes an ultrasonically-vibratable medical-treatment instrument which is attachable to a distal end of the transducer assembly. An embodiment of a medical ultrasound system is described, wherein the medical ultrasound system has a handpiece including a medical ultrasound transducer assembly and including a housing or housing component surrounding the transducer assembly. A method for tuning a medical ultrasound handpiece includes machining at least a distal non-threaded portion of an instrument-attachment stud of the transducer assembly to match a measured fundamental frequency to a desired fundamental frequency to within a predetermined limit. A method for making a medical ultrasound transducer assembly determines acceptable gains for gain stages of the transducer assembly.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
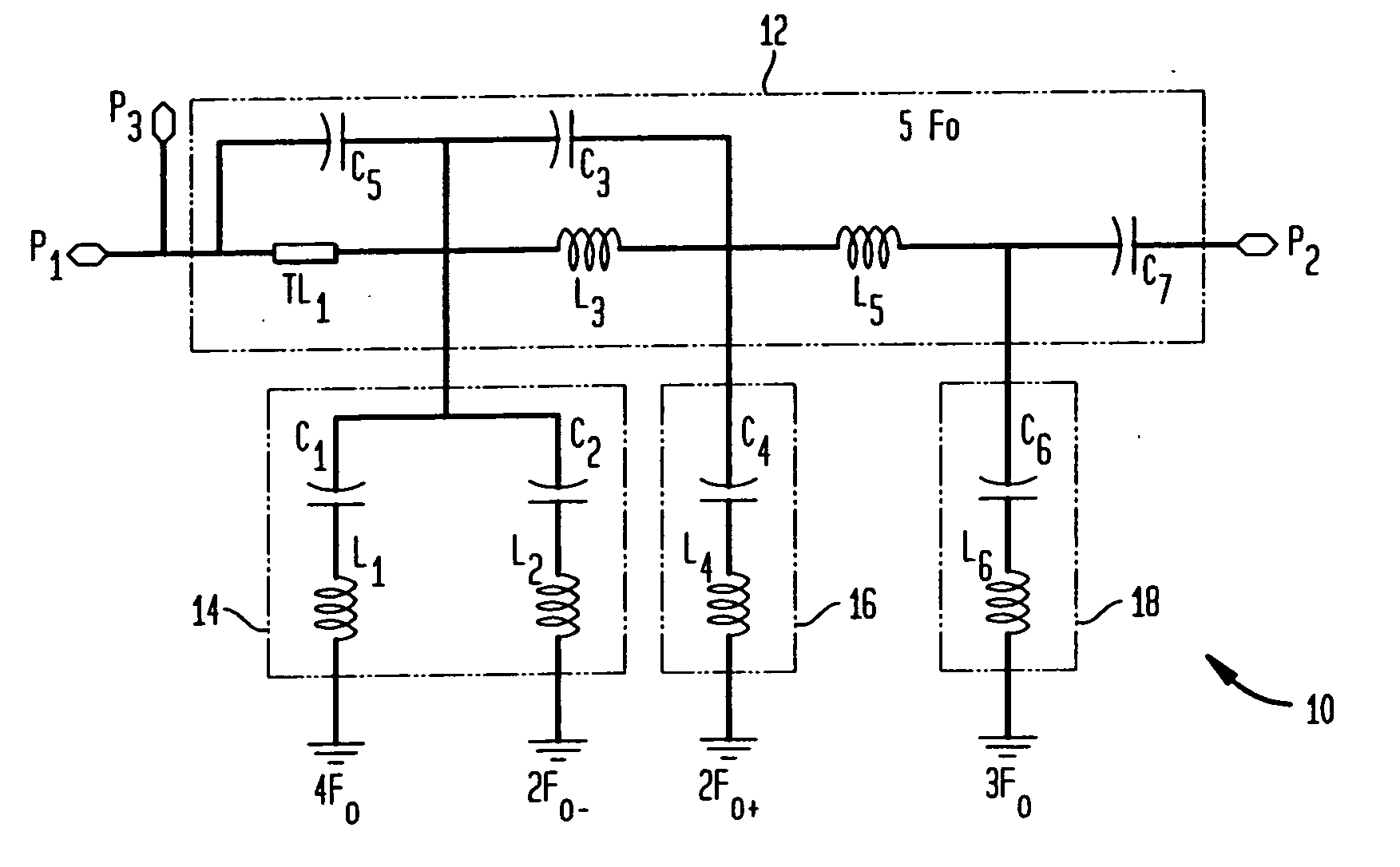
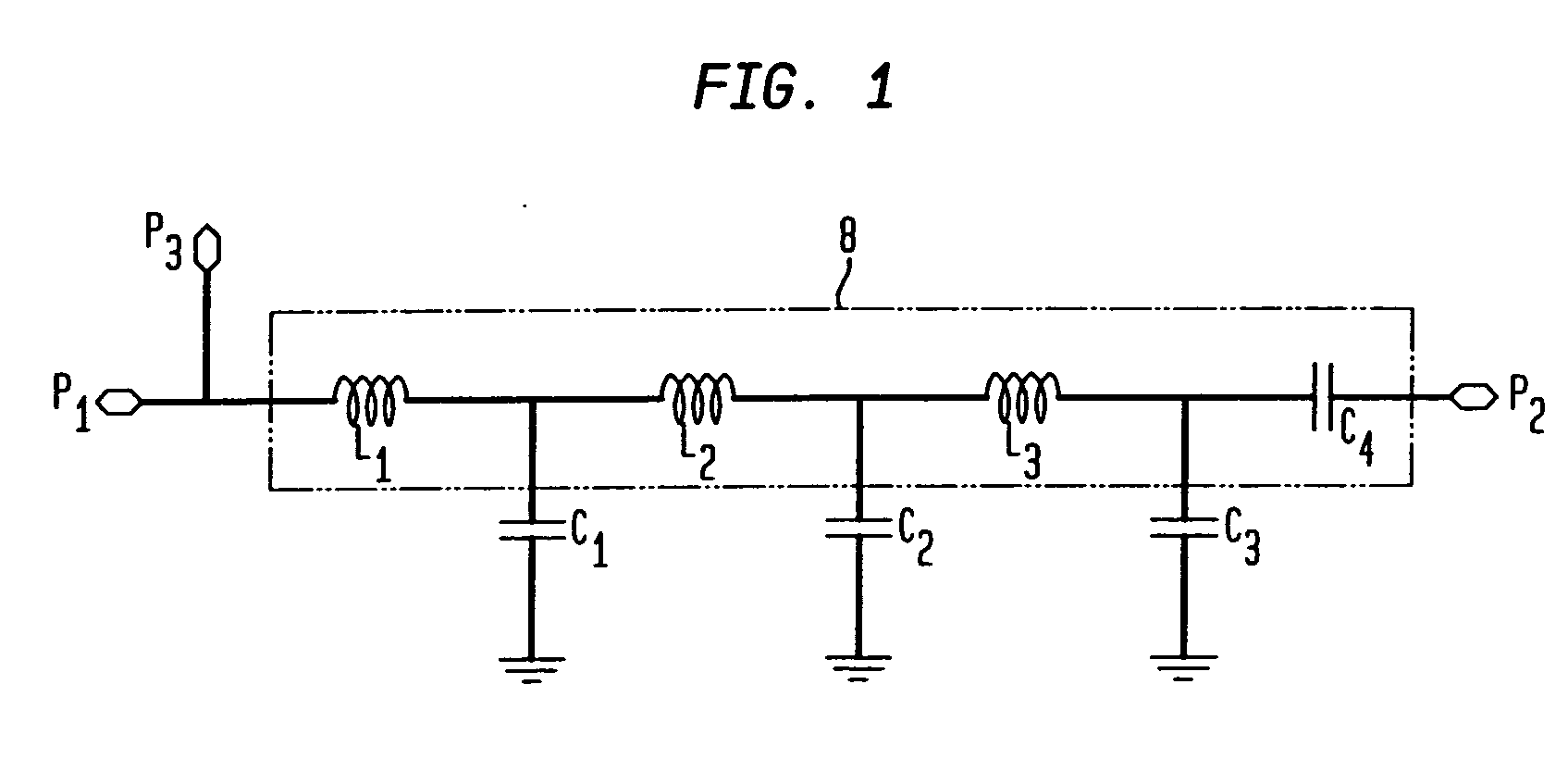
Combined matching and filter circuit
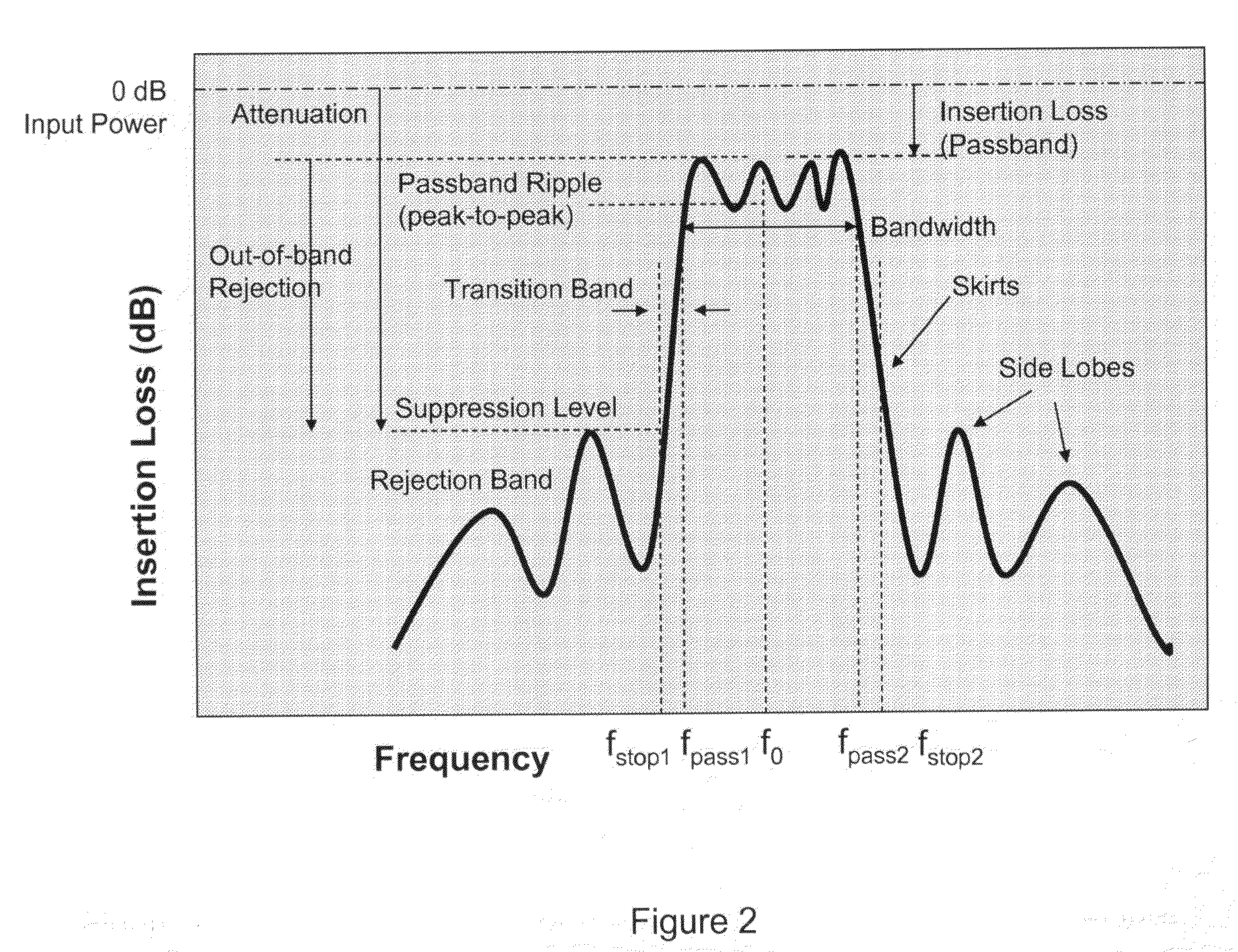
ActiveUS20050282503A1Good harmonic suppressionImprove abilitiesMultiple-port networksOne-port networksCapacitanceHarmonic
A combined matching and harmonic rejection circuit with increased harmonic rejection provided by a split resonance for one or more of the capacitive or inductive elements of the circuit. At a fundamental frequency, the circuit comprises an inductive series arm with capacitive shunt arms. The capacitance of a shunt arm may be provided by two or more parallel paths, each having a capacitor and an inductor in series so that, in addition to providing the effective capacitance necessary for impedance matching at the fundamental frequency, two separate harmonics represented by the series resonances of the parallel paths are rejected. In this manner, an extra null in the circuit's stop-band may be achieved using the same number of shunt elements necessary to achieve impedance matching at the fundamental frequency.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
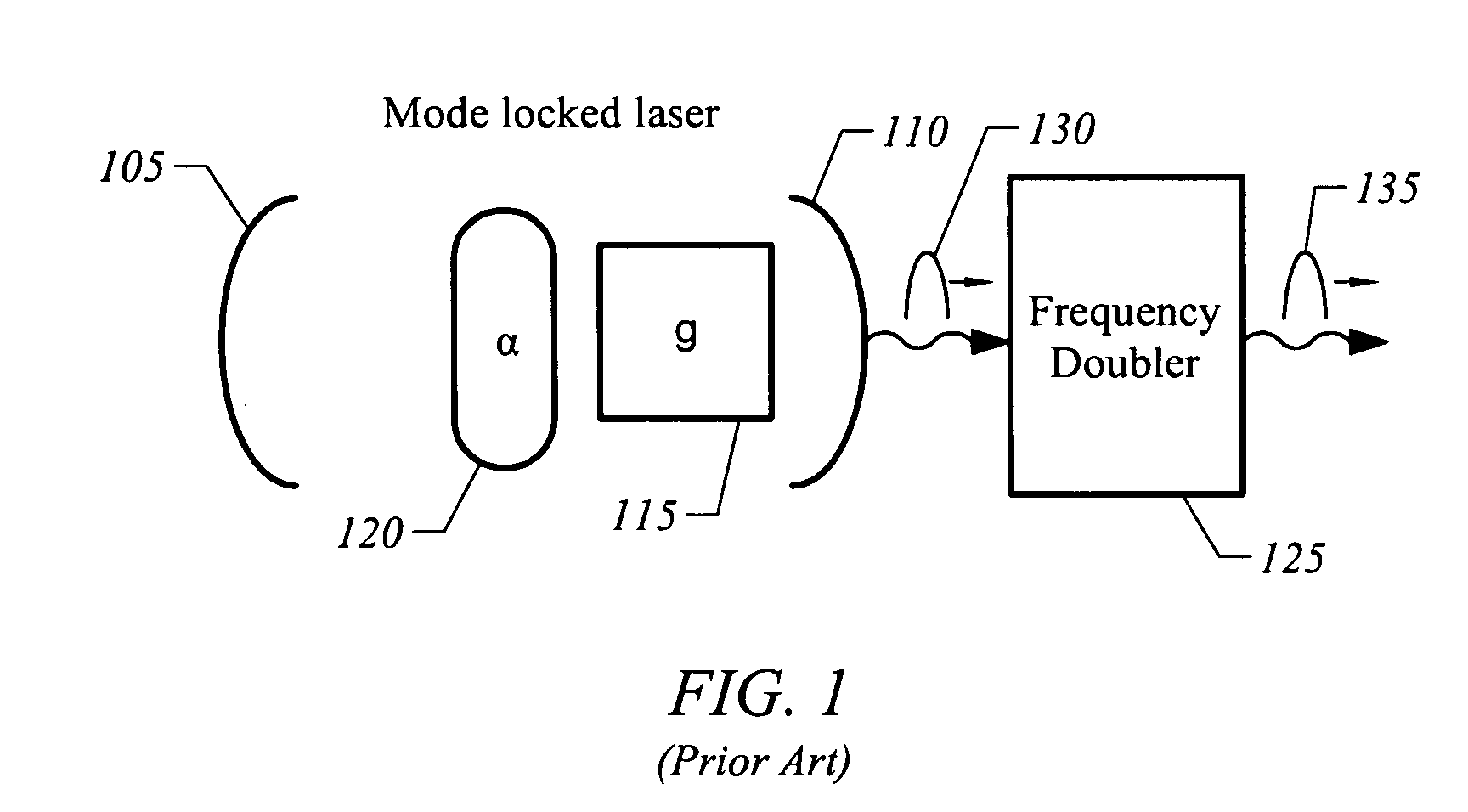
Apparatus, system, and method for wavelength conversion of mode-locked extended cavity surface emitting semiconductor lasers
InactiveUS20060023757A1Reduce polarizationReduce materialLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersFrequency conversionFundamental frequency
A mode-locked laser with intracavity frequency conversion is disclosed. In one embodiment the conversion frequency is improved by reducing the temporal, spatial, or polarization overlap between pulses at the fundamental frequency and pulses at a frequency-shifted frequency.
Owner:NECSEL INTPROP +1
Method for improved repeatable run out learning in a disk drive
InactiveUS7450336B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageControl signalFundamental frequency
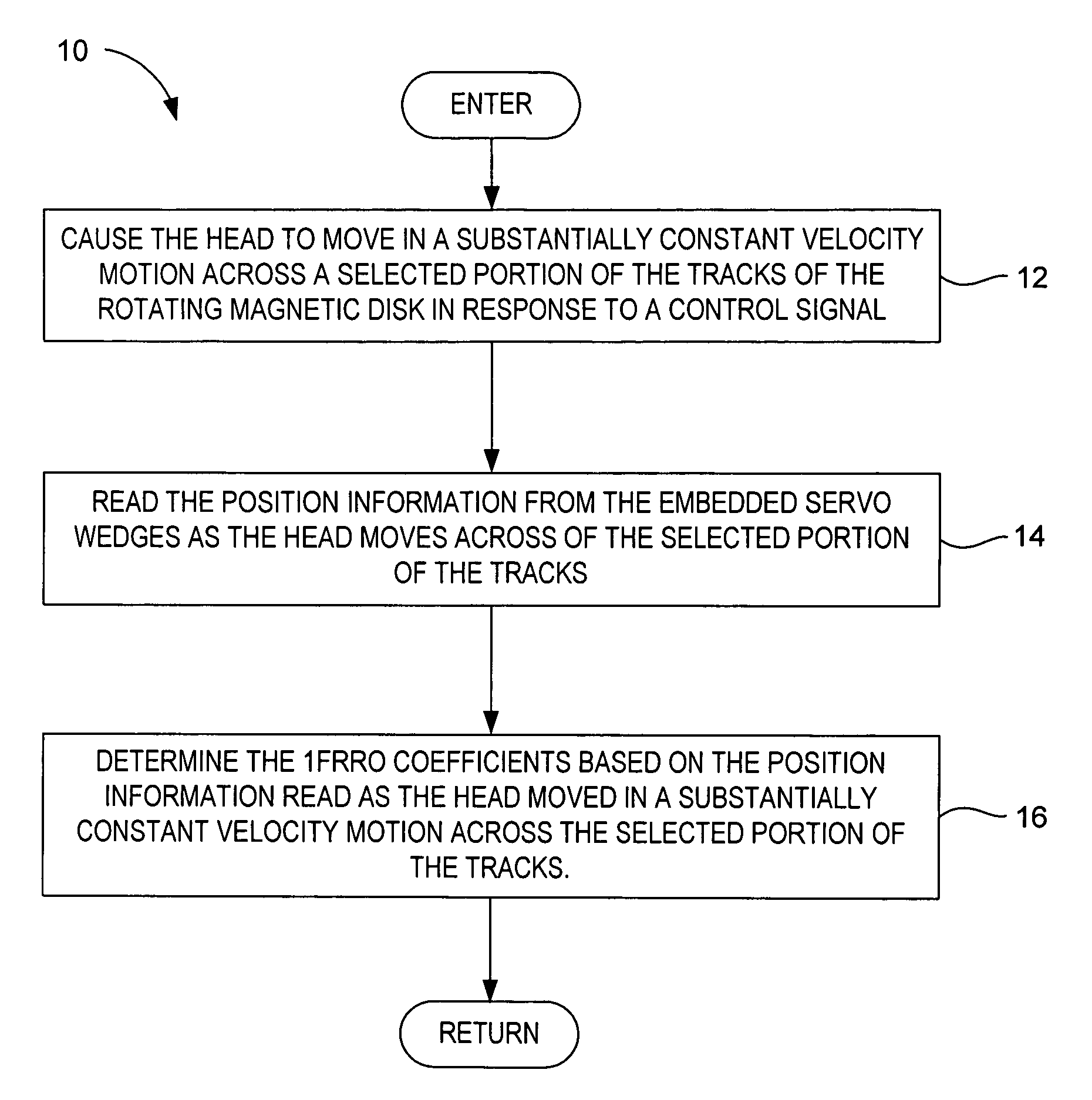
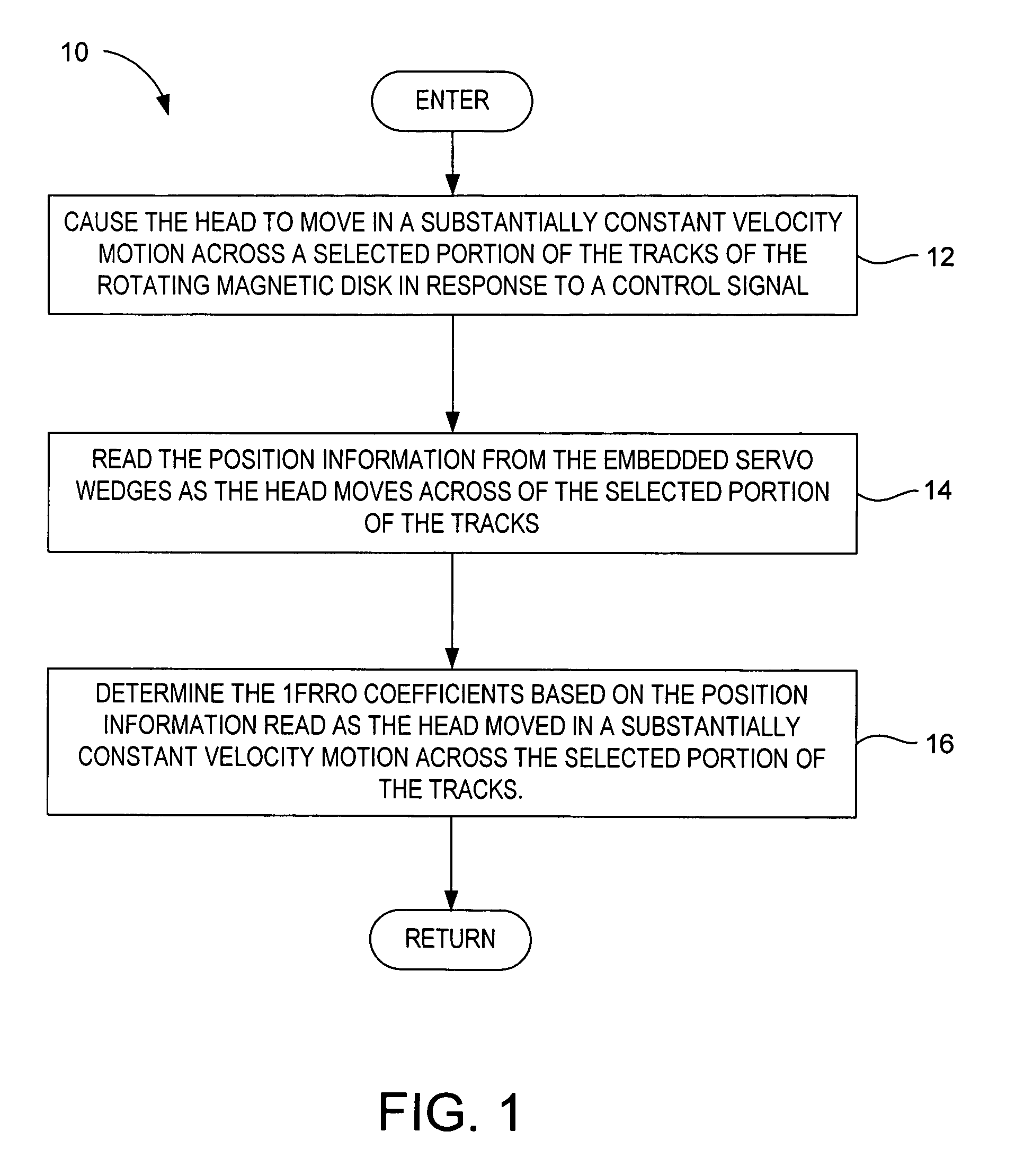
A method is disclosed for determining fundamental-frequency repeatable runout (1FRRO) coefficients in a disk drive. The disk drive includes a transducer head, a rotating magnetic disk having a plurality of concentric data tracks defined by embedded servo wedges that provide position information, and an actuator coupled to the head. In the method, the head is caused to move in a substantially constant velocity motion across a selected portion of the tracks of the rotating magnetic disk in response to a control signal. The position information is read from the embedded servo wedges as the head moves across of the selected portion of the tracks. The 1FRRO coefficients are determined based on the position information read as the head moved in a substantially constant velocity motion across the selected portion of the tracks.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
HVDC device for converting between alternating voltages and direct current voltages
InactiveUS6480403B1Ability to hold high voltageEasy to controlConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionFundamental frequencyPhase lead
A device for converting alternating voltage to direct voltage and, conversely, direct voltage into alternating voltage. A series connection between the poles of a direct voltage side has at least four units each having a semiconductor element of turn-off type and a first diode connected in anti-parallel therewith. A first midpoint of the series connection is connected to an alternating voltage phase line and forms a phase output. Second midpoints of the series connection are connected to a midpoint of the direct voltage side through such units. An apparatus is adapted to control the semiconductor elements with a pulse width modulation frequency of at least one order of magnitude higher than the fundamental frequency of the alternating voltage of the phase line and the rest of the semiconductor elements with a frequency substantially lower and within or close to the frequency range of one or a couple of times of the fundamental frequency.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
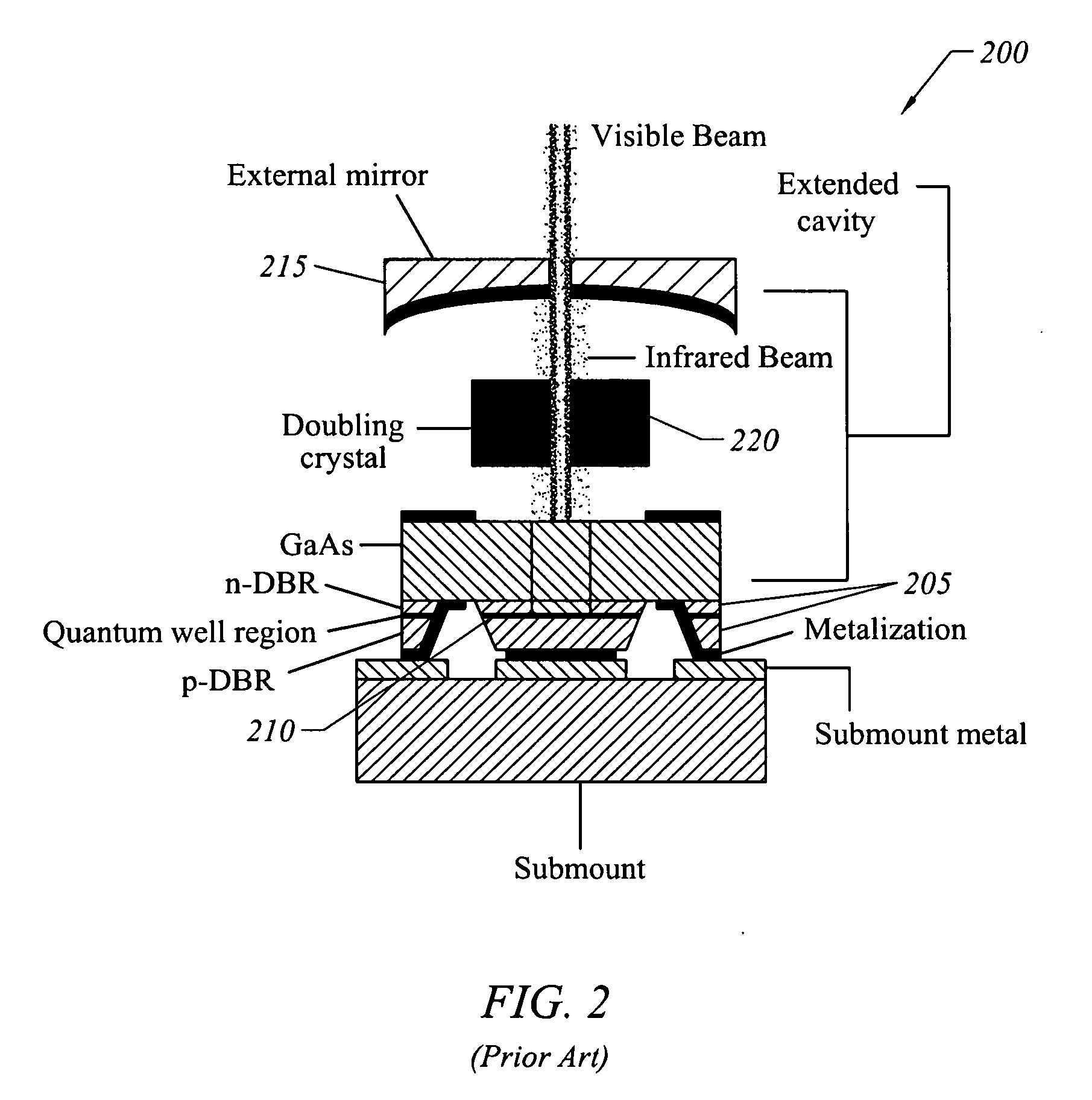
Coupled cavity high power semiconductor laser
InactiveUS20060029120A1Maximize circulating fundamental laser powerConvenient registrationOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersFundamental frequencyPartial reflection
An active gain region sandwiched between a 100% reflective bottom Bragg mirror and an intermediate partially reflecting Bragg mirror is formed on a lower surface of a supporting substrate, to thereby provide the first (“active”) resonator cavity of a high power coupled cavity surface emitting laser device. The reflectivity of the intermediate mirror is kept low enough so that laser oscillation within the active gain region will not occur. The substrate is entirely outside the active cavity but is contained within a second (“passive”) resonator cavity defined by the intermediate mirror and a partially reflecting output mirror, where it is subjected to only a fraction of the light intensity that is circulating in the gain region. In one embodiment, non-linear optical material inside each passive cavity of an array converts an IR fundamental wavelength of each laser device to a corresponding visible harmonic wavelength, and the external output cavity mirror comprises a Volume Bragg grating (VBG) or other similar optical component that is substantially reflective at the fundamental frequency and substantially transmissive at the harmonic frequency. The VBG used in an array of such devices may be either flat, which simplifies registration and alignment during manufacture, or may be configured to narrow the IR spectrum fed back into the active resonant cavity and to shape the spatial mode distribution inside the cavity, thereby reducing the size of the mode and compensating for any deformations in the semiconductor array.
Owner:ARASOR ACQUISITION +1
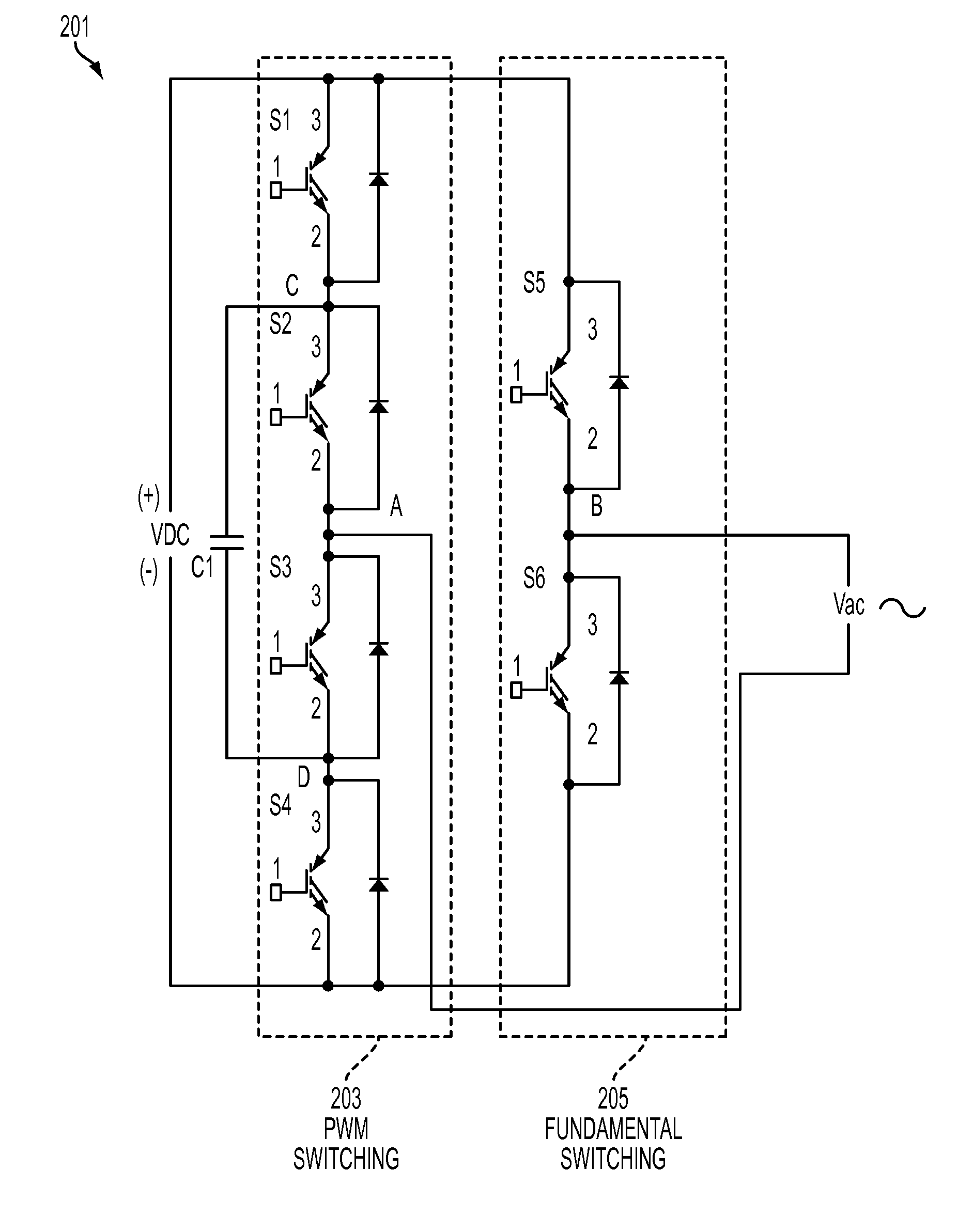
Pulse width modulated control for hybrid inverters
InactiveUS20120218795A1Reduce in quantityConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionCapacitanceEngineering
A single-phase hybrid multilevel inverter is described that combines a 3-level leg and a 2-level leg to reduce the number of overall switching devices for a 5-level inverter. The 2-level inverter leg switches at a fundamental frequency and the 3-level flying capacitor leg uses PWM modulation to switch resulting in a low THD output voltage spectrum. The control method developed for the single-phase inverter is used to build a three-phase inverter comprised of three single-phase hybrid inverters in order to achieve a line-to-neutral voltage having five levels and a line-to-line voltage having nine levels.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP
High frequency surgery apparatus and method of operating same
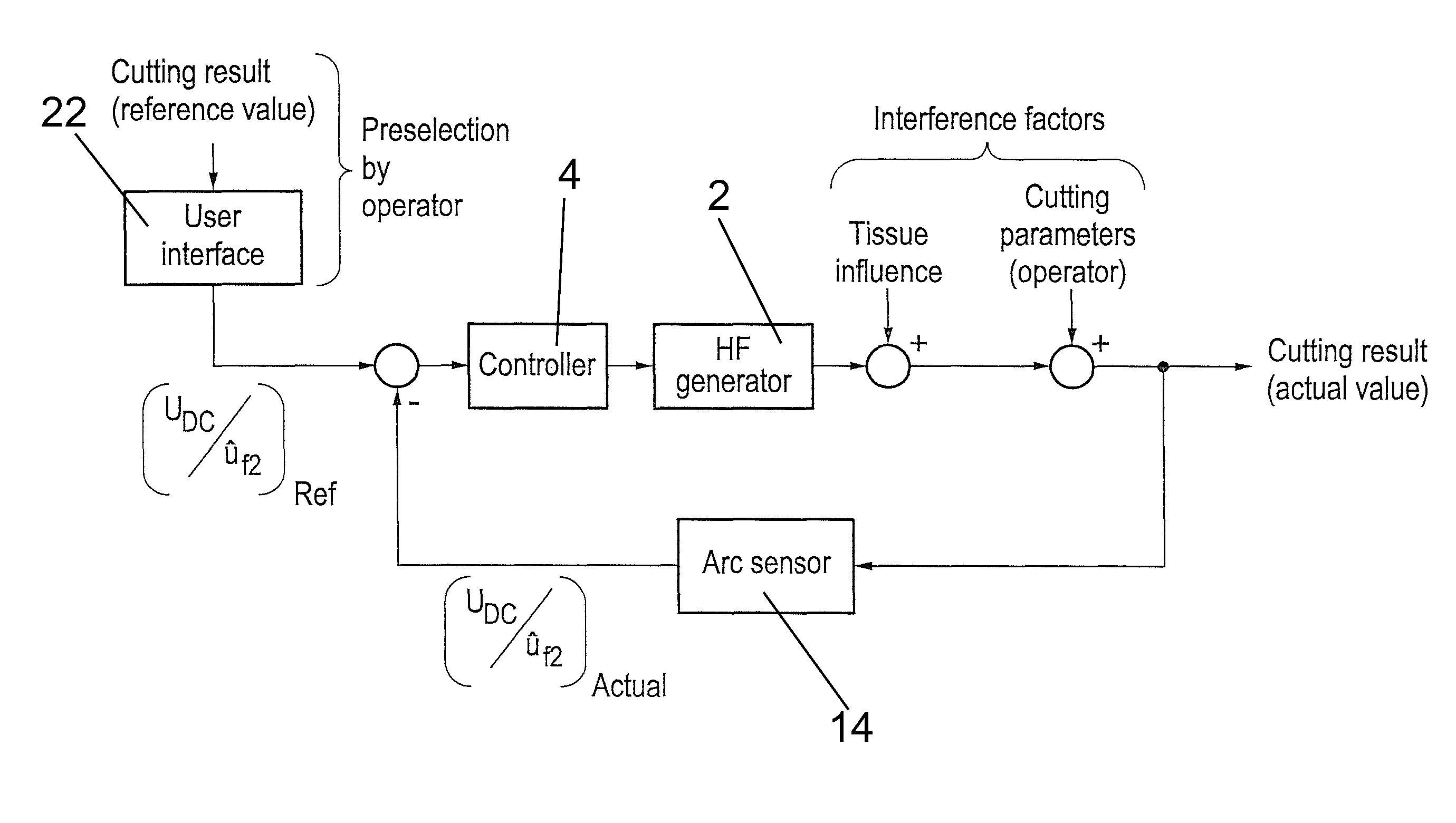
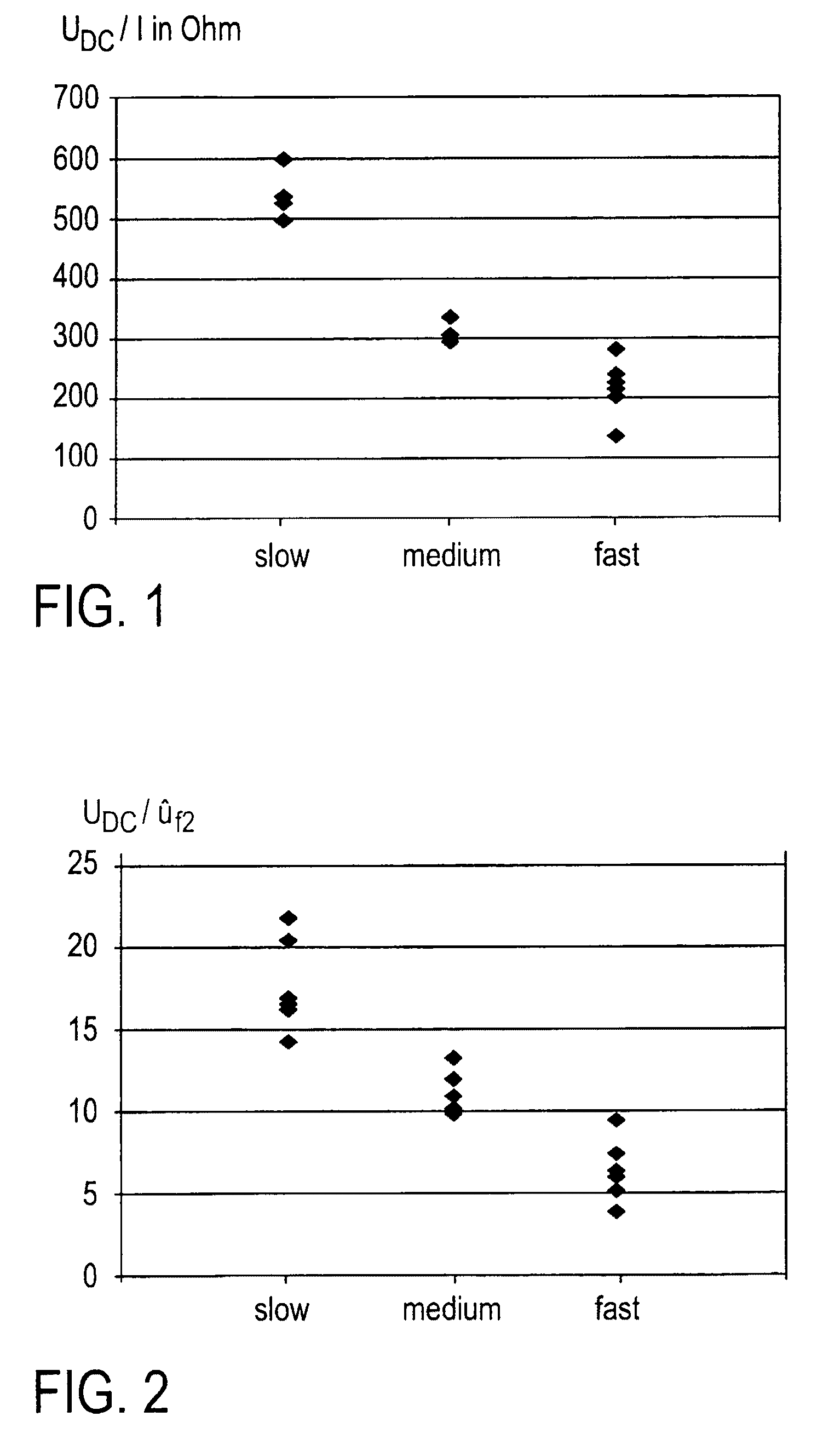
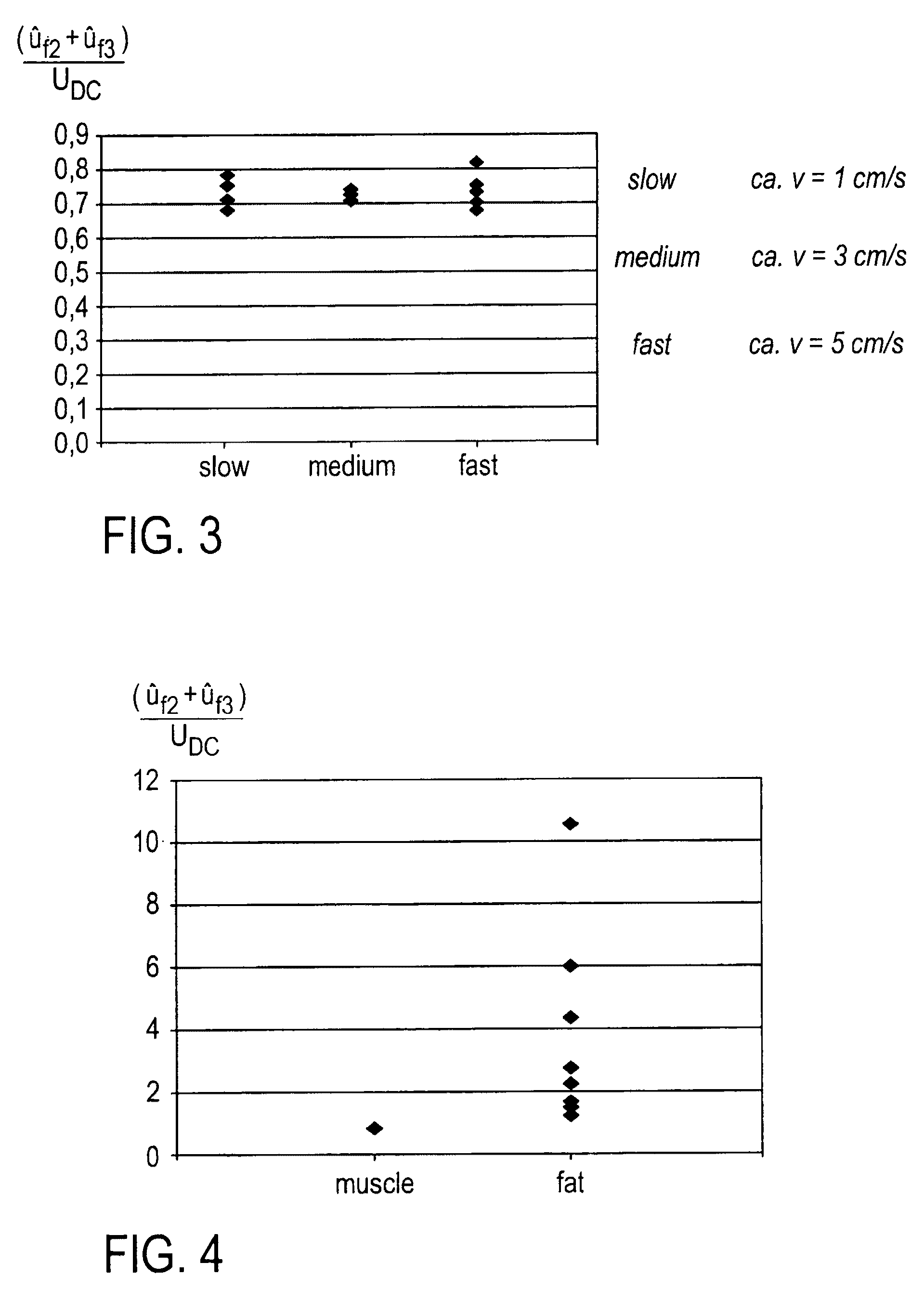
ActiveUS9186199B2Uniform cutting qualityHigh-frequency surgerySurgical instruments for heatingHarmonicFundamental frequency
The invention concerns a high frequency surgery apparatus for cutting and / or coagulating biological tissue and methods of operating same. The high frequency surgery apparatus includes at least one high frequency generator which in operation forms a high frequency circuit with the tissue to be treated, with the production of an arc, and at least one measuring and calculating device which is connected for signal transmission to the high frequency circuit and which is adapted in operation to ascertain both a DC voltage in the high frequency circuit and also the amplitudes of at least one even and at least one odd harmonic of a fundamental frequency of the high frequency generator and to form a first tissue parameter representative of the kind of tissue to be treated from the relationship of the sum of the amplitudes of the even and the odd harmonics to the DC voltage and to output a tissue signal dependent on the first tissue parameter for subsequent processing.
Owner:OLYMPUS WINTER & IBE
Inductive power coupling systems for roadways
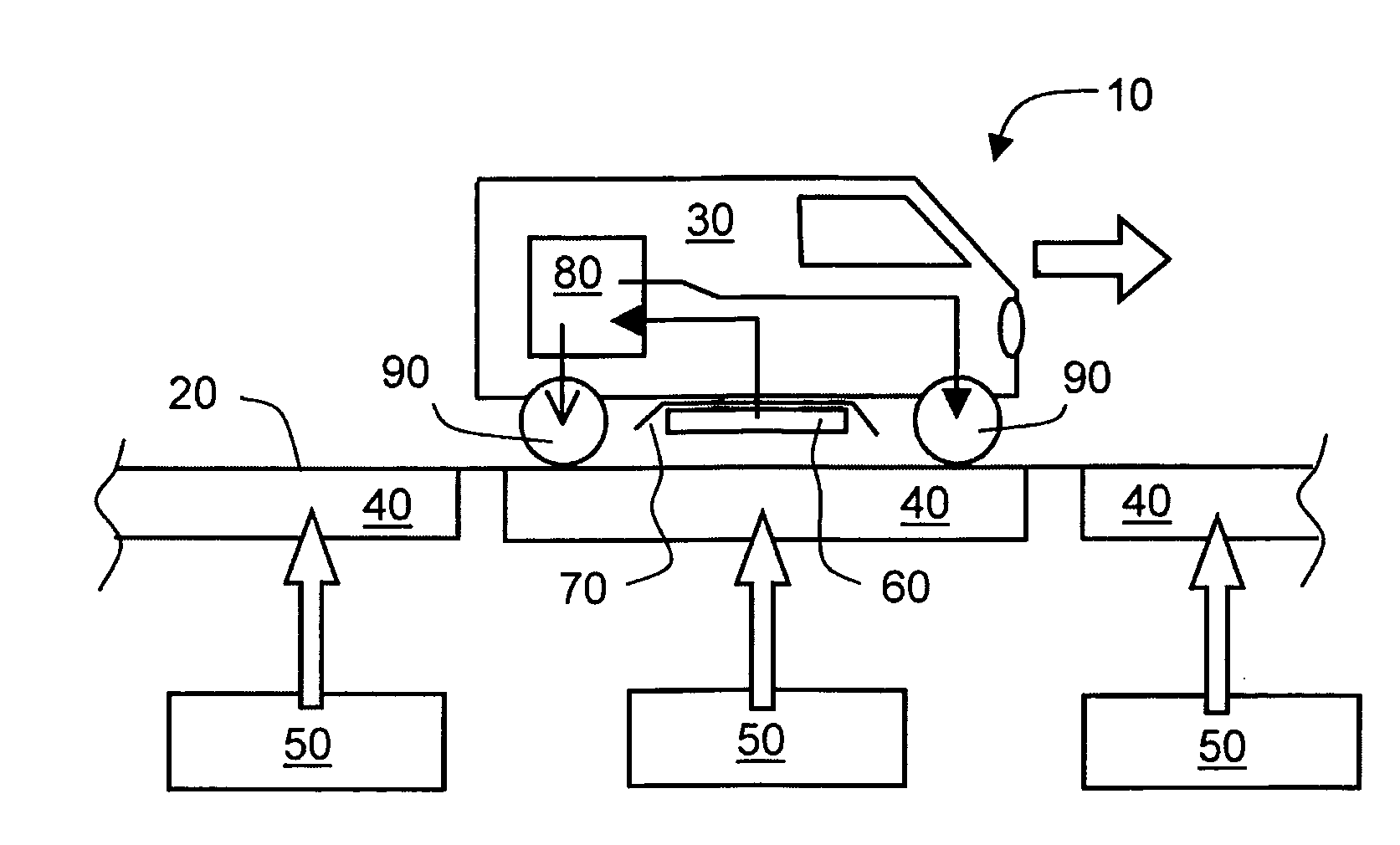
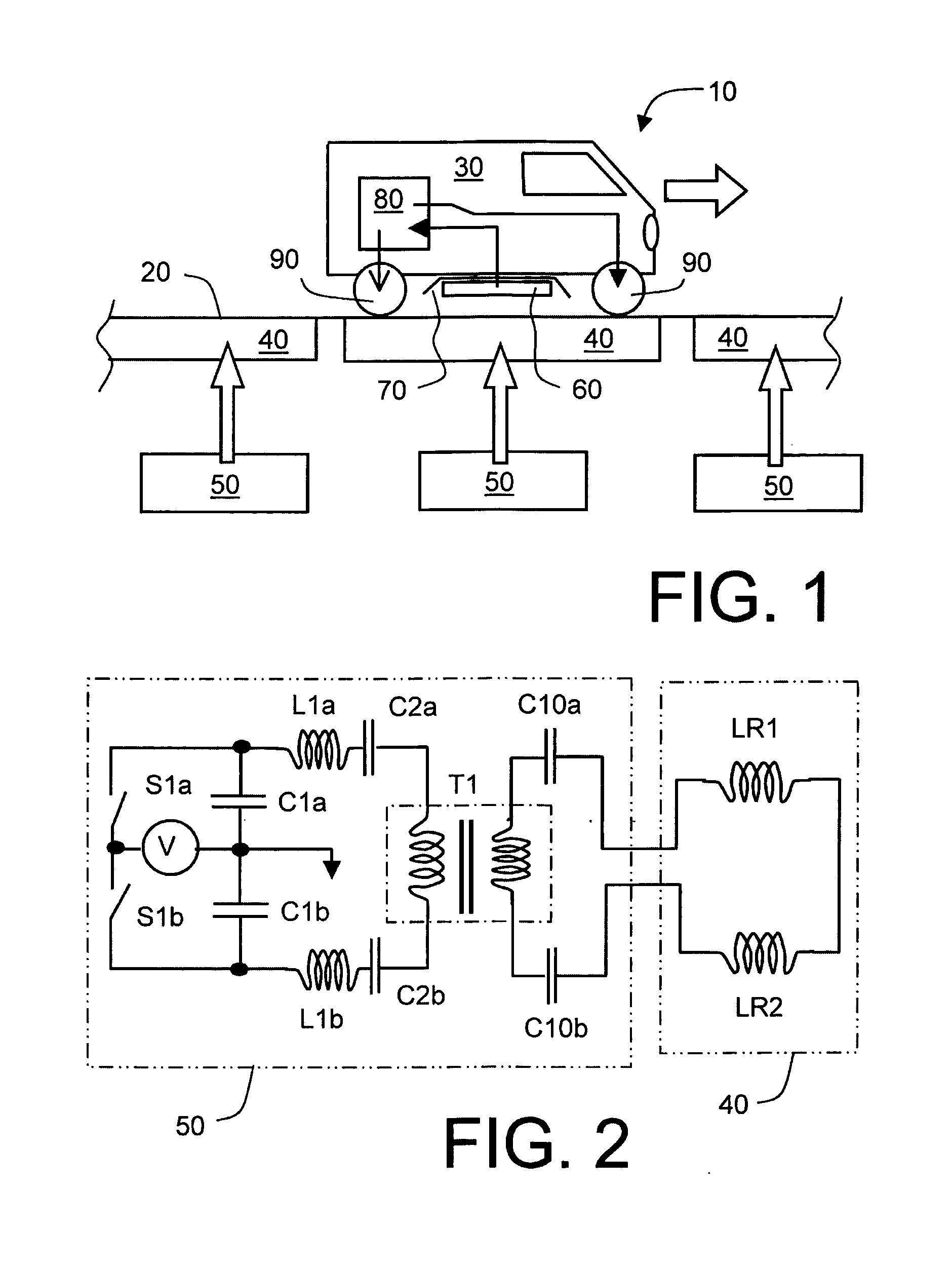
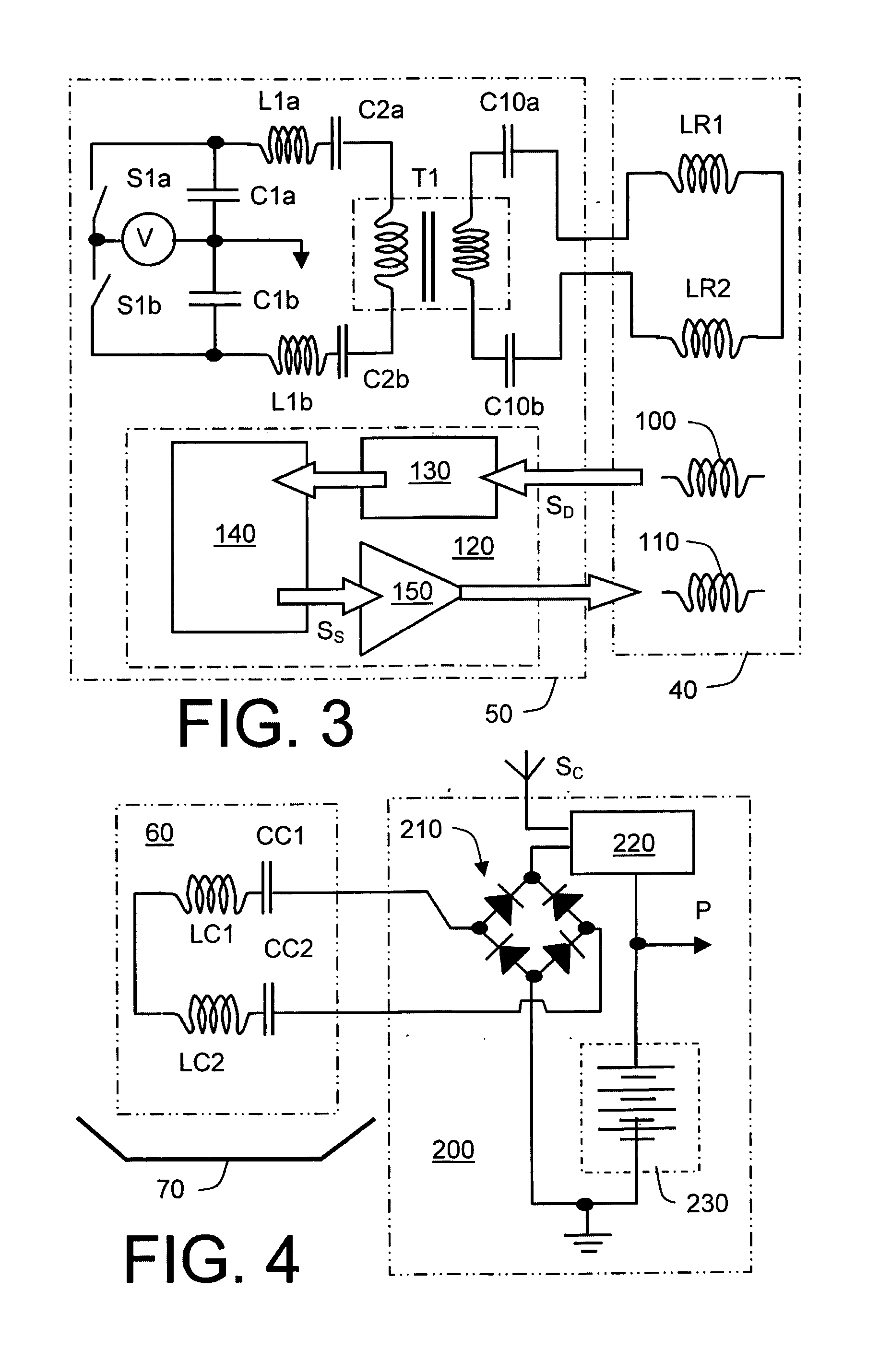
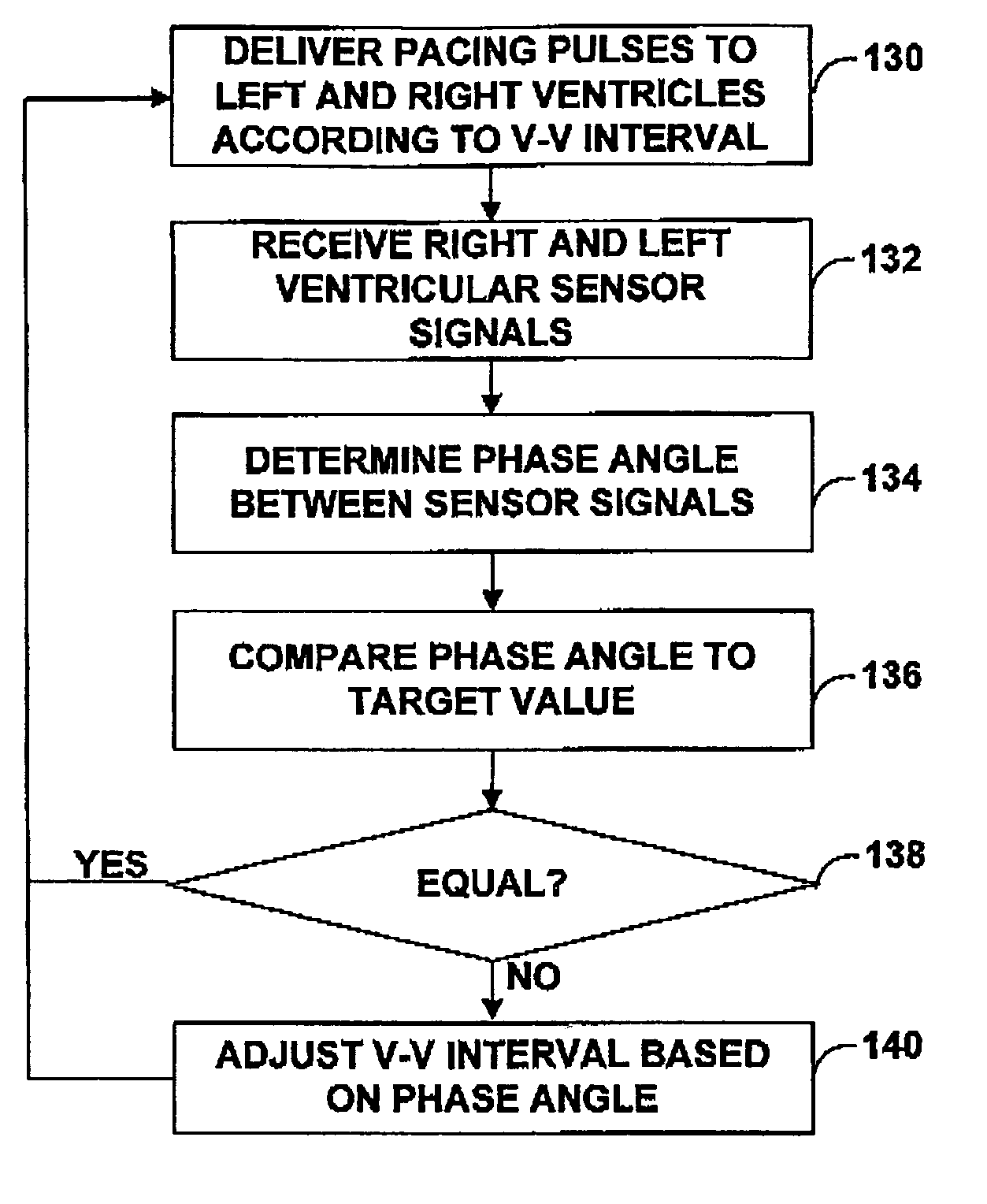
InactiveUS20150246614A1Less-expensive to implementSimpler to implementRail devicesShielding materialsFundamental frequencyEngineering
An inductive power transfer system (10) for roadways includes at least one drive unit arrangement (50) coupled to at least one drive coil arrangement (40) disposed along a roadway (20) for generating a magnetic field extending upwardly from the roadway (20), and at least one vehicle (30) including a corresponding pickup coil arrangement (60) coupled to a power conditioning circuit arrangement (80, 200) for receiving the extending magnetic field for providing power to operate the at least one vehicle (30). The at least one drive unit arrangement (50) is operable to excite, for example at resonance, the at least one drive coil arrangement (40) at a fundamental frequency (f0) of at least 30 kHz, preferably at least 50 kHz, more preferably at least 100 kHz, and most preferably at least 140 kHz. The at least one drive coil arrangement (40) is implemented to be substantially devoid of ferromagnetic components for providing a path for the extending magnetic field. Optionally, the at least one drive unit arrangement (50) is operable to employ a balanced class-E amplifier arrangement for exciting the at least one drive coil arrangement (40) at the fundamental frequency (f0). Optionally, the at least one drive unit arrangement (50) is operable to employ one or more Silicon Carbide semiconductor devices for switching the currents provided to the corresponding at least one drive coil arrangement (40). Optionally, there is further included a passive and / or active suppression arrangement (100, 110, 120, 130, 140) for suppressing harmonic magnetic field components generated by the system (10) at multiples of the fundamental frequency (f0) when in operation.
Owner:DAMES ANDREW NICHOLAS +2
Stabilizer for switch-mode powered RF plasma
InactiveUS6046546AAvoid instabilityEffect can be causedElectric discharge tubesAc-dc conversionHarmonicInstability
Circuitry and techniques designed to allow stable and continuous delivery of alternating power to a plasma with switch-mode power supply (16) include a variety of embodiments. Parallel, series, and other circuit elements connected across switching element (7) are tuned so that energy at other than the fundamental frequency is absorbed and dissipated. This energy may be only at the second harmonic or it may be across broad frequency ranges through selecting high impedance at the fundamental frequency and relatively low impedance at other frequencies. In overcoming instabilities, oscillations, and even changing class of operation of the switch-mode power supply, the stabilizing element absorbs the energy to avoid allowing it to affect switch (7) of power supply (16).
Owner:ADVANCED ENERGY IND INC
Evaluating ventricular synchrony based on phase angle between sensor signals
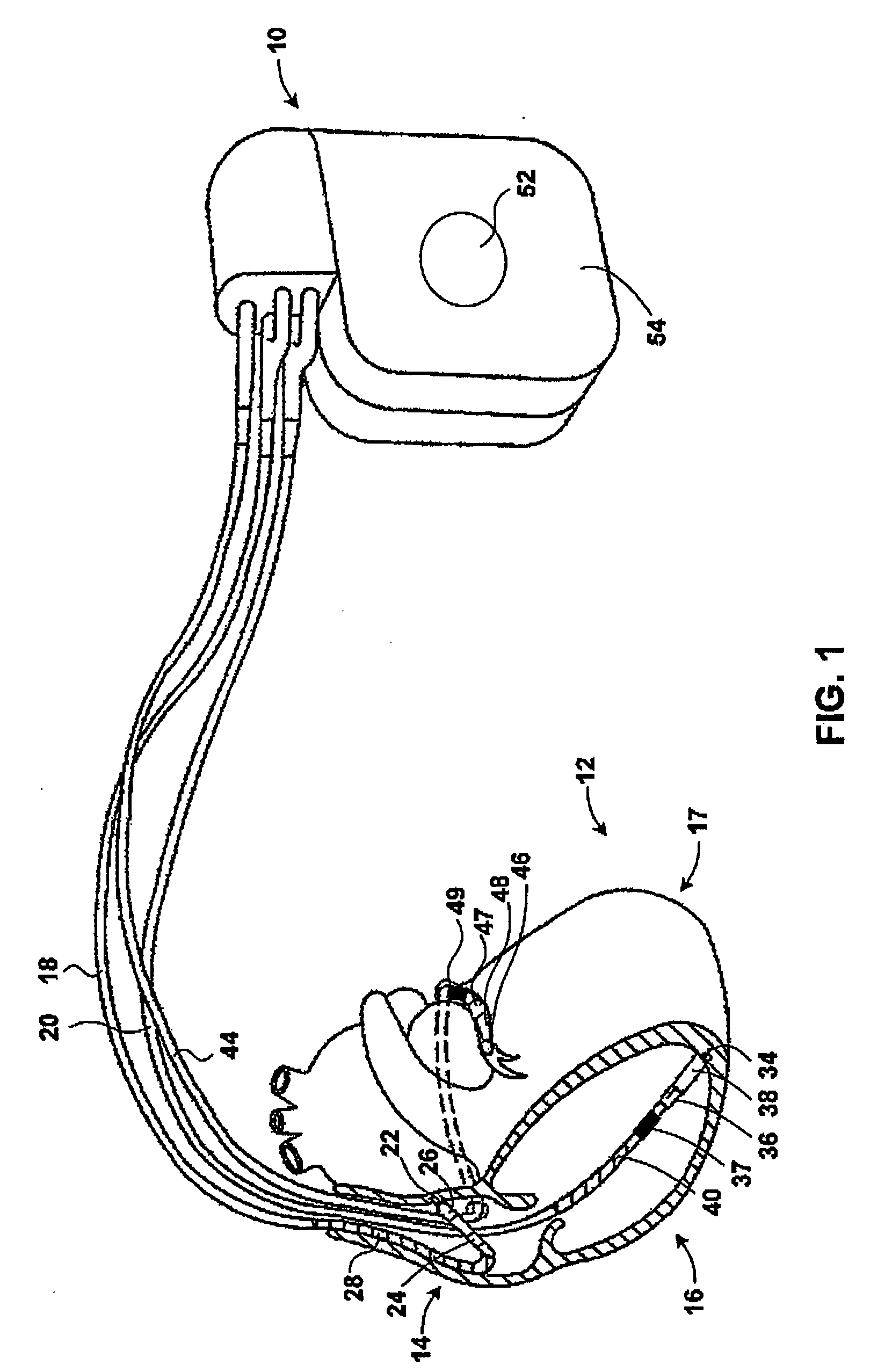
InactiveUS20050038481A1Reduce, or possibly eliminate, ventricular dysynchronyHeart stimulatorsFundamental frequencyCRTS
An implantable medical device evaluates ventricular synchrony by determining a phase angle between at least two sensor signals that reflect mechanical contraction of the ventricles. In exemplary embodiments, two intracardiac impedance signals associated with the right and left ventricles, respectively, with two points within either of the left and right ventricles, or with both the left and right ventricles relative to a reference point, are processed. In such embodiments, fundamental frequency phases of each of the impedance signals may be compared to determine the phase angle between the signals. In some embodiments, the signals are used to dynamically adjust one or more timing intervals, such as a V-V timing interval, for delivery of cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) pacing. In such embodiments, the one or more timing intervals are periodically adjusted to reduce or possibly eliminate ventricular dysynchrony as indicated by the phase angle between the sensor signals.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
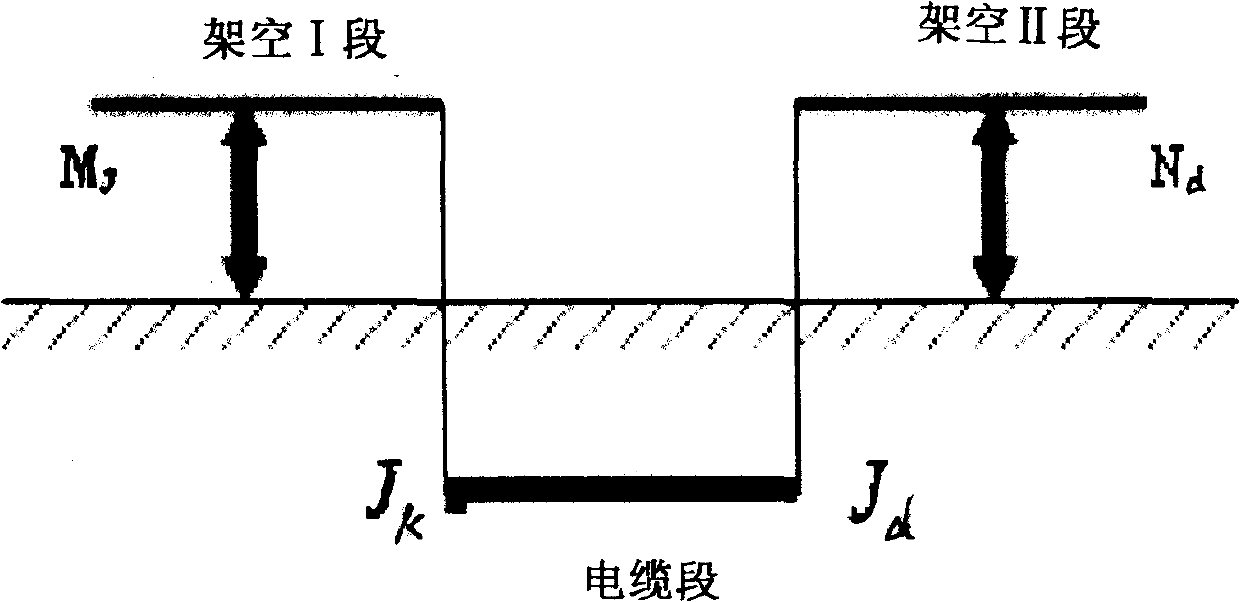
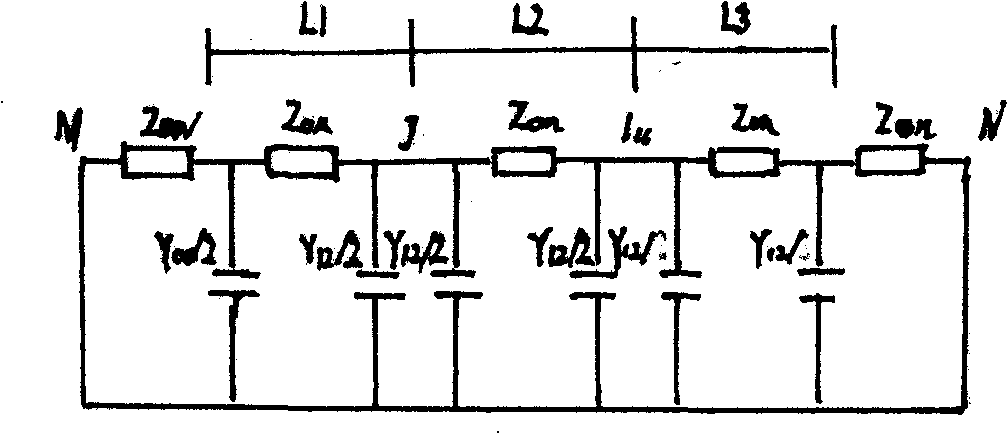
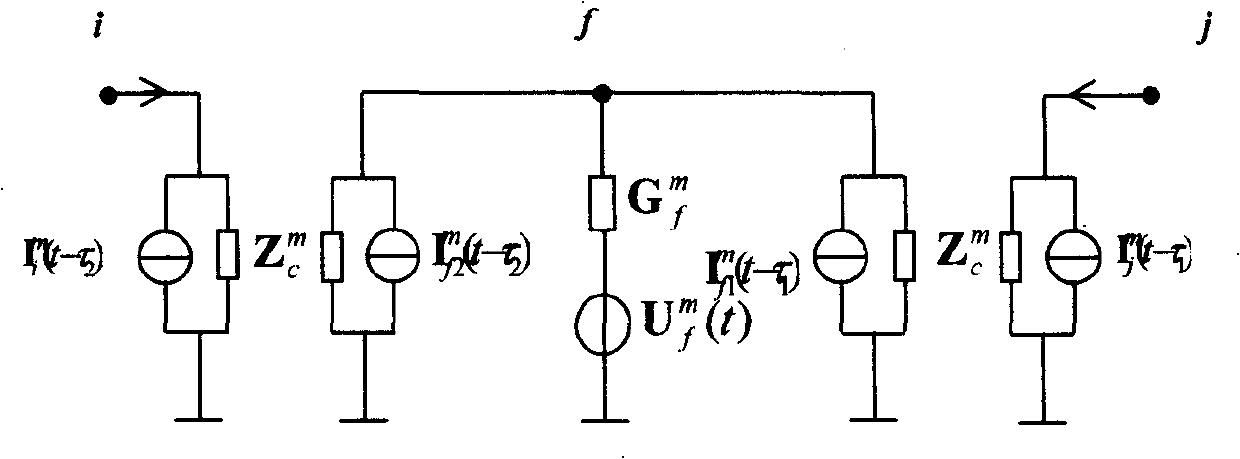
Cable-aerial mixed line fault travelling wave ranging method
InactiveCN101299538AMake up for the influence of frequency-dependent characteristicsAccurately determine the polarity of reflected wavesEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault locationElectric power systemReflected waves
The invention relates to a cable-overhead joint line failure travelling wave range count method, particularly performing the effective fusion based on the failure range count method of the fundamental frequency and the travelling wave aiming at the particularity and the complexity of the cable joint line, belonging to the technical field of the power system relay protection. The invention judges the failure generating places firstly based on the cable-overhead junction derivated through the electric quantity at the two ends of the system attached with the negative sequence net after the failure, then performs the correct range count by the range count method of the single end; on the basis of considering the line zero modulus component couple, through comparing the performance of the current travelling wave line zero modulus component, the performance of each reflected wave is judged, to find out the fault point reflected wave, and then perform the correct range count.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
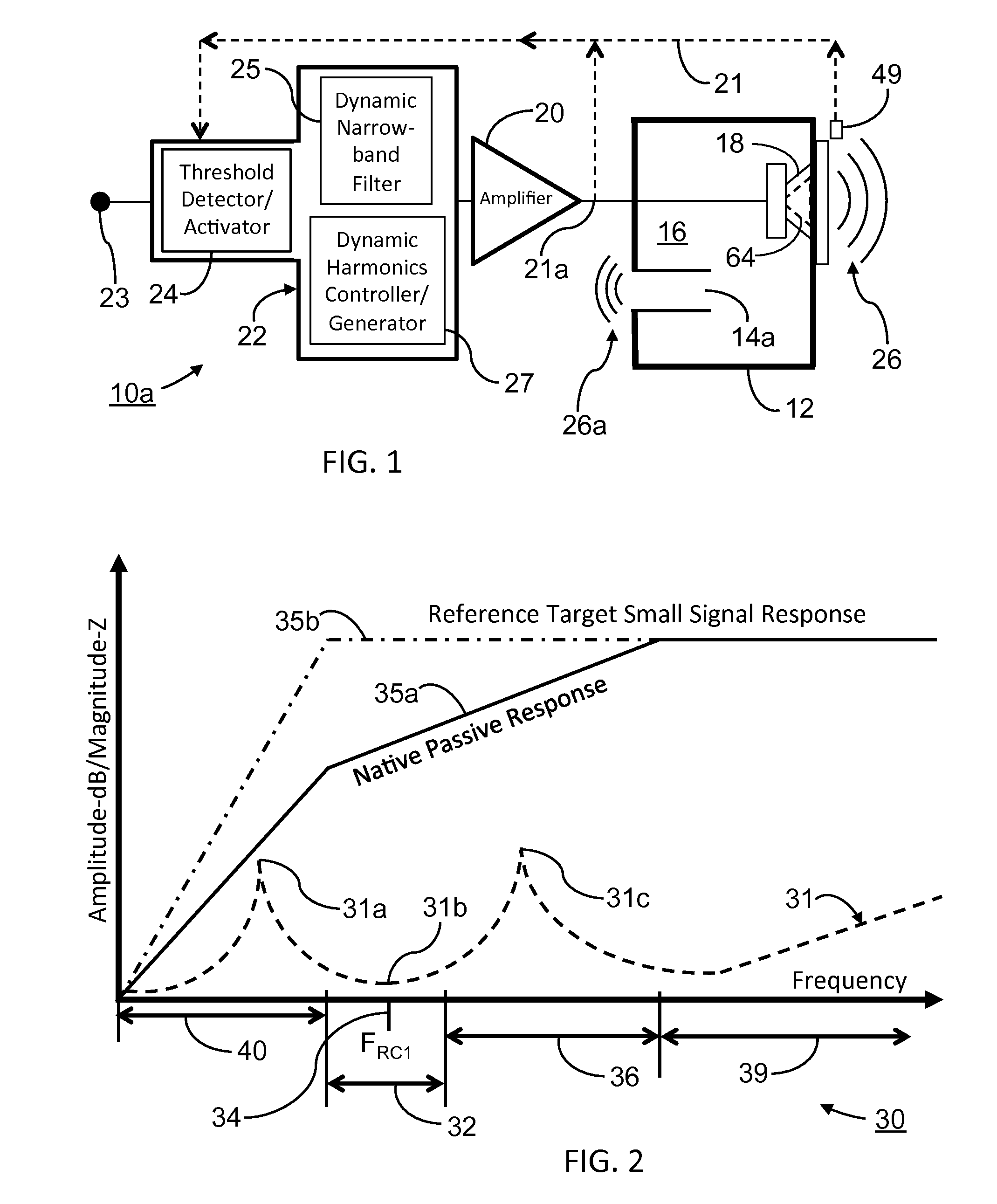
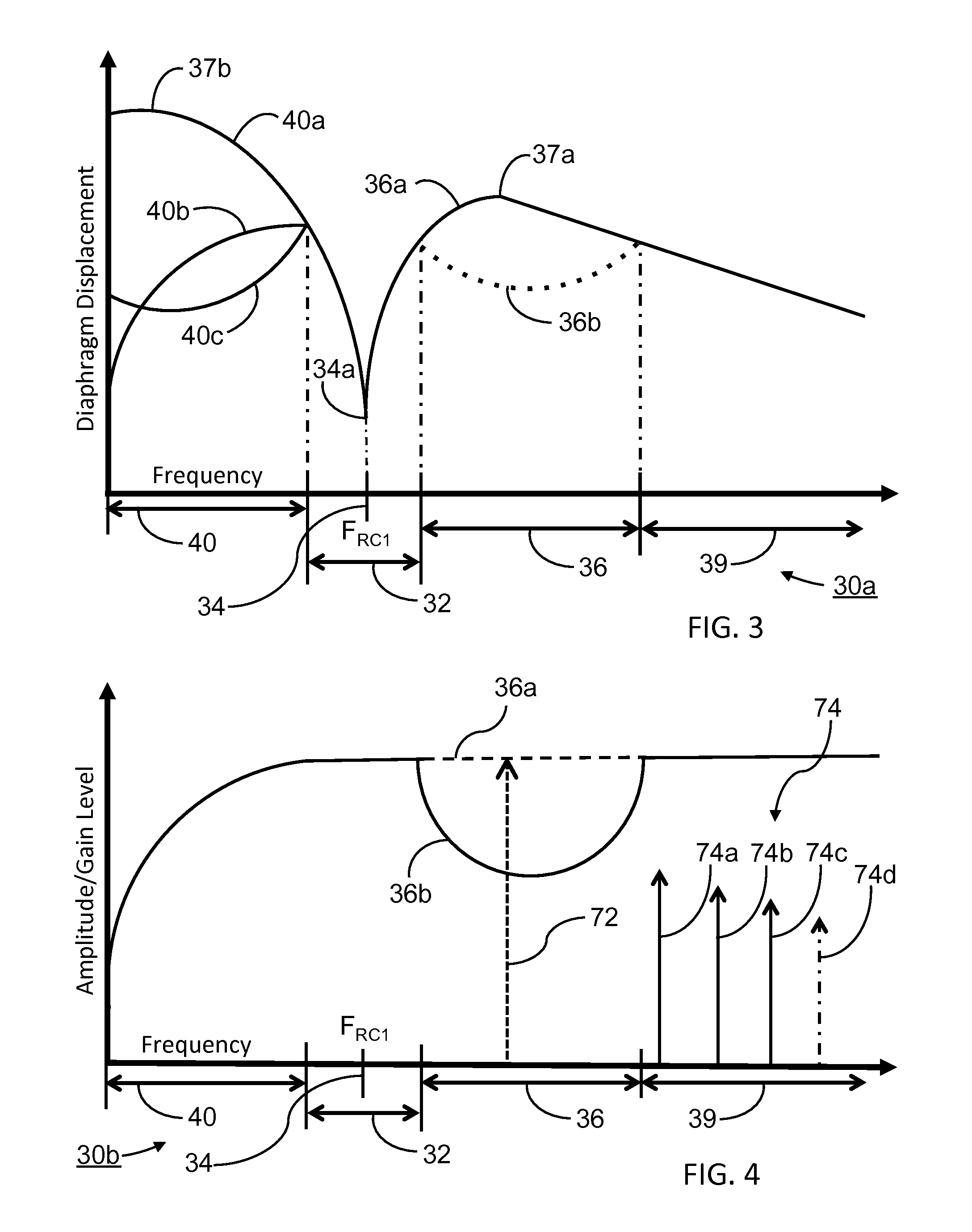
Loudspeaker Enclosure System With Signal Processor For Enhanced Perception Of Low Frequency Output
ActiveUS20140341394A1Minimize overload distortionEnhanced low frequency outputSignal processingGain controlResonant cavityHarmonic
A loudspeaker system with a transducer and an enclosure with at least one resonant chamber, including a resonant-chamber resonance frequency, at which a displacement characteristic of a vibratile diaphragm of the transducer has a minimum. The loudspeaker system further includes a multi-mode signal processor with a set of signal processes wherein in one example, a variable gain, frequency selective dynamic filter reduces the gain in a high displacement frequency range upon an output in the frequency range exceeding an overload amplitude threshold. The gain reduction is compensated for by complimentary frequency generating signal processes, including at least one of a harmonics generator and a transpositional gain controller, with the signal processor adapted to match the resonant chamber enclosure by substantially maintaining or increasing acoustic output at the resonant chamber resonance and generating harmonics associated with fundamental frequencies in the gain reduced frequency range to maintain a perception of tonal quality and physical bass impact, increasing low frequency capability while minimizing audible overload distortion.
Owner:CROFT III JAMES J
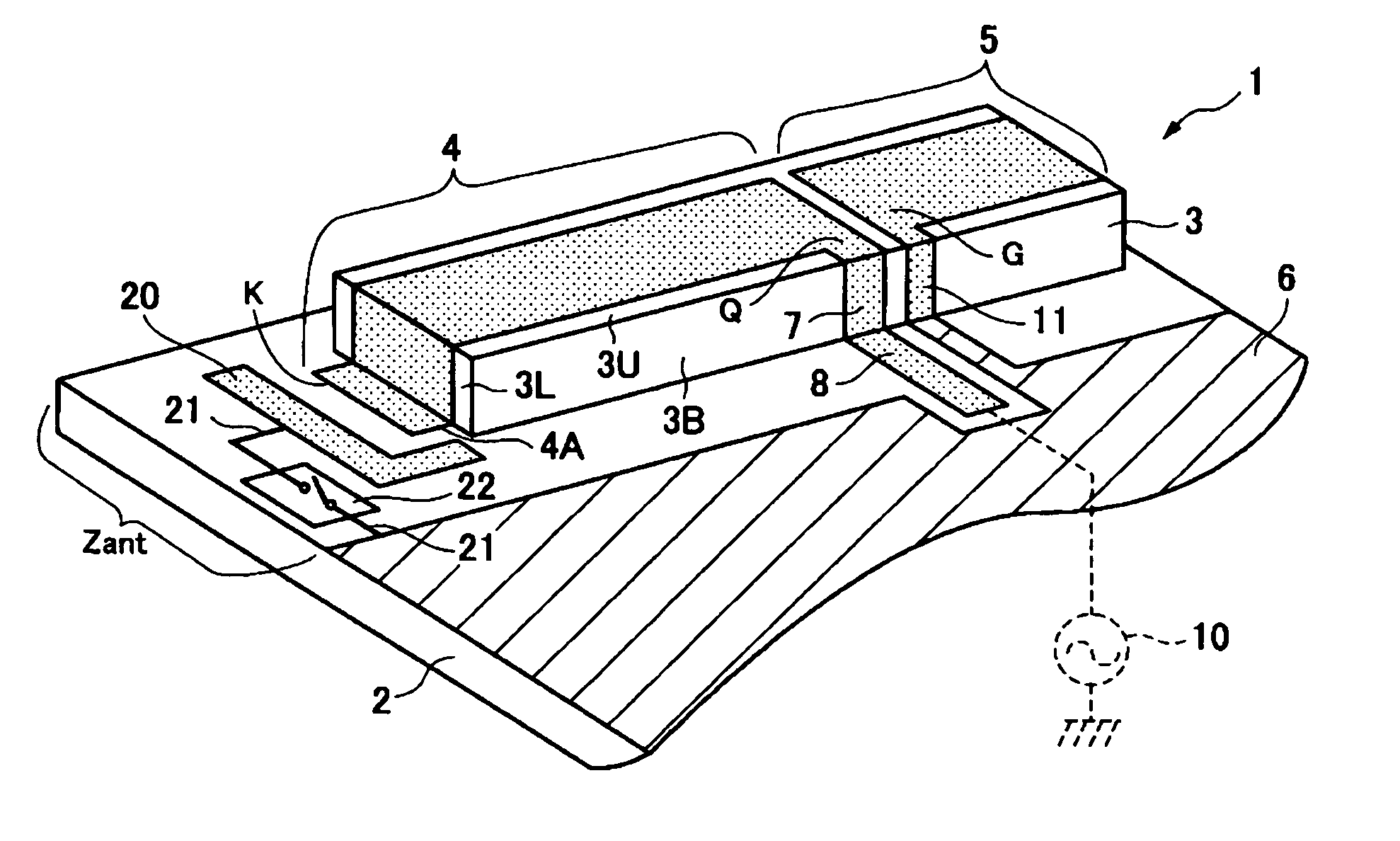
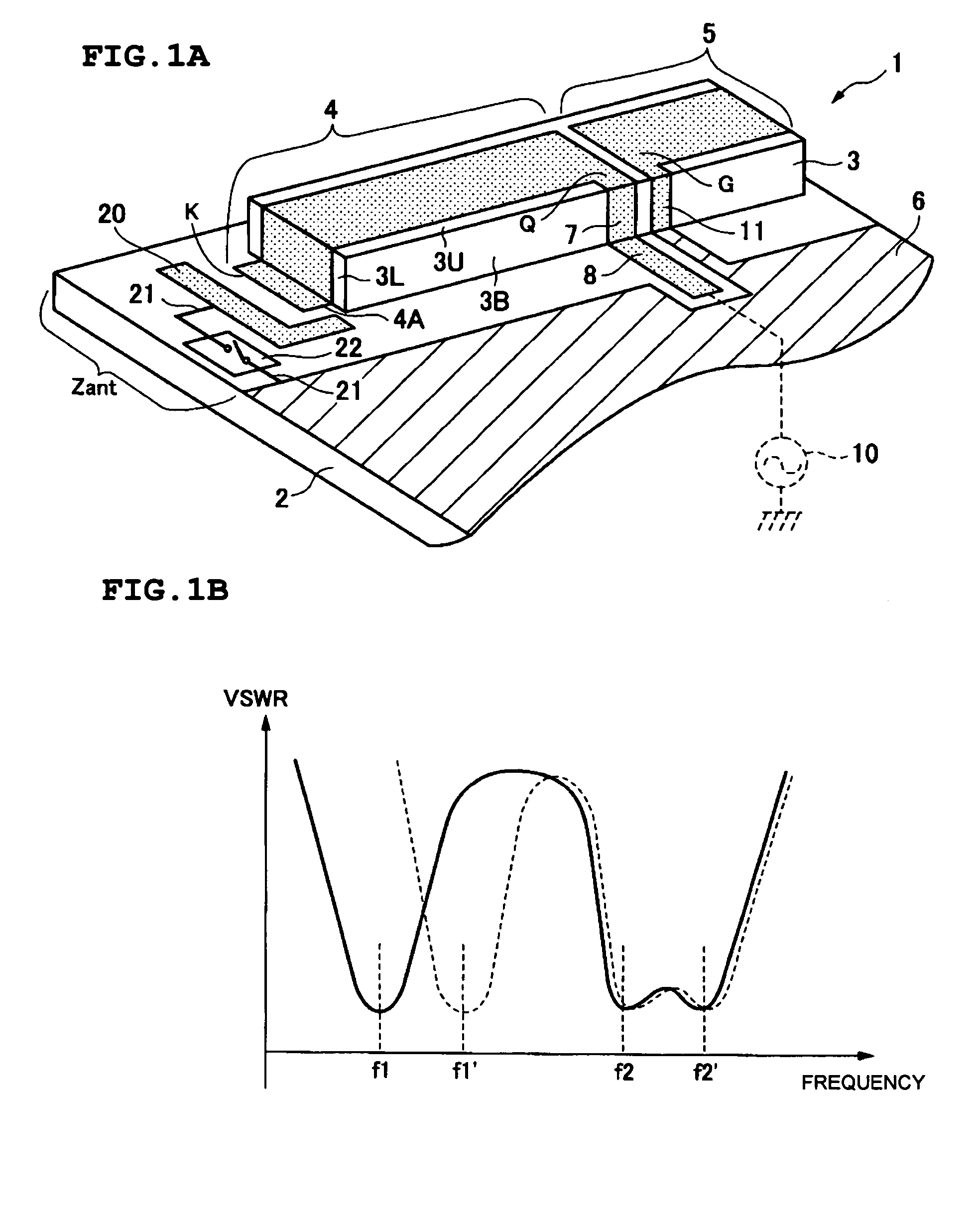
Antenna structure and communication device using the same
ActiveUS7136020B2Degree of influence is relatively smallIncrease electrical lengthSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsCapacitanceFundamental frequency
An antenna structure includes a capacitance-rendering portion located between an open end portion of a feed radiation electrode and a ground portion. A switch for changing the capacitance between the open end portion of the feed radiation electrode and the ground portion rendered by the capacitance-rendering portion is provided. When the capacitance between the open end portion of the feed radiation electrode and the ground portion is increased by the capacitance-rendering portion, a resonant frequency in the fundamental frequency band, caused by the antenna operation of the feed radiation electrode, is reduced corresponding to the increased amount of the capacitance. When the capacitance between the open end portion of the feed radiation electrode and the ground portion is decreased by the changing operation of the capacitance-rendering portion, the resonant frequency in the fundamental frequency band is increased corresponding to the decreased amount of the capacitance.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
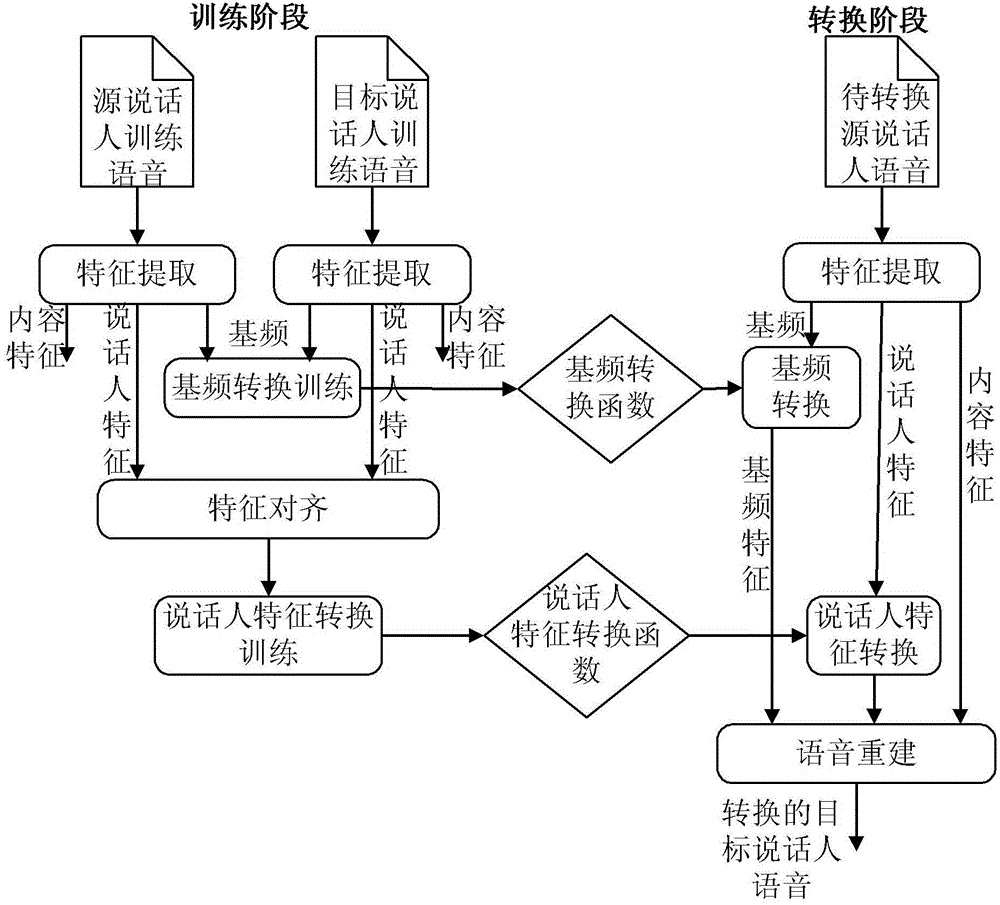
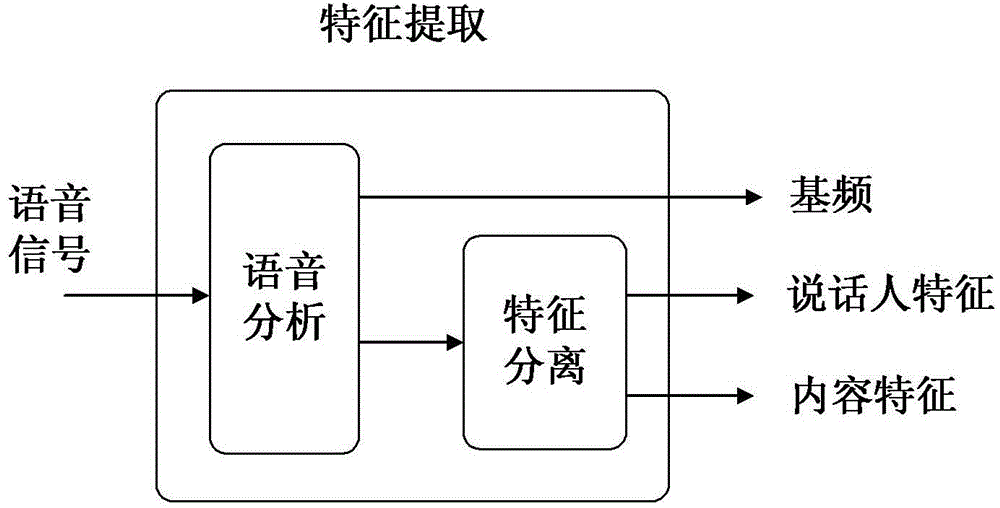
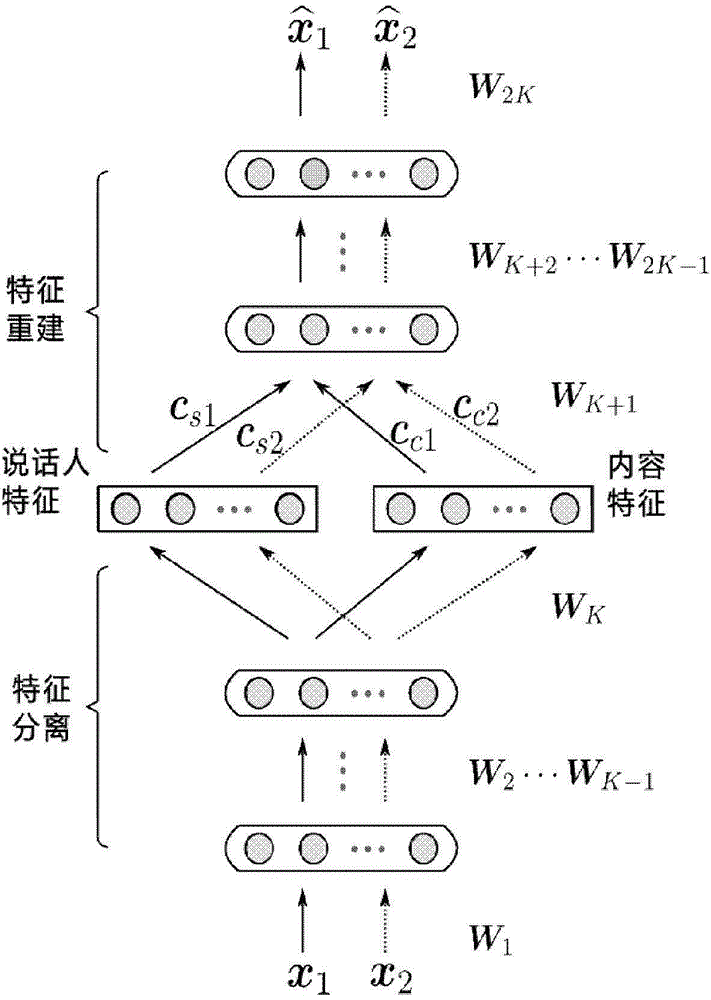
Conversion method for sound of speaker
ActiveCN102982809AAchieve separationMeet the needs of processing tasksSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumSound quality
The invention discloses a conversion method for sound of a speaker. The method comprises a training stage and a conversion stage, wherein the training stage comprises the steps of respectively extracting a fundamental frequency characteristic, a speaker characteristic and a content characteristic from training voice signals of a source speaker and a target speaker, constructing a fundamental frequency conversion function according to the fundamental frequency characteristic, and constructing a speaker conversion function according to the speaker characteristic. The conversion stage comprises the steps of extracting a fundamental frequency characteristic and a spectrum characteristic from a voice signal to be converted of the source speaker, using the fundamental frequency conversion function and the speaker conversion function obtained in the training stage to convert the fundamental frequency characteristic and the speaker characteristic extracted from the voice signal to be converted, obtaining the converted fundamental frequency characteristic and the speaker characteristic, and synthesizing voices of the target speaker according to the obtained converted fundamental frequency characteristic, the speaker characteristic and the content characteristic in the voice signal to be converted. The method is easy to realize, and the converted sound quality and similarity are higher.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
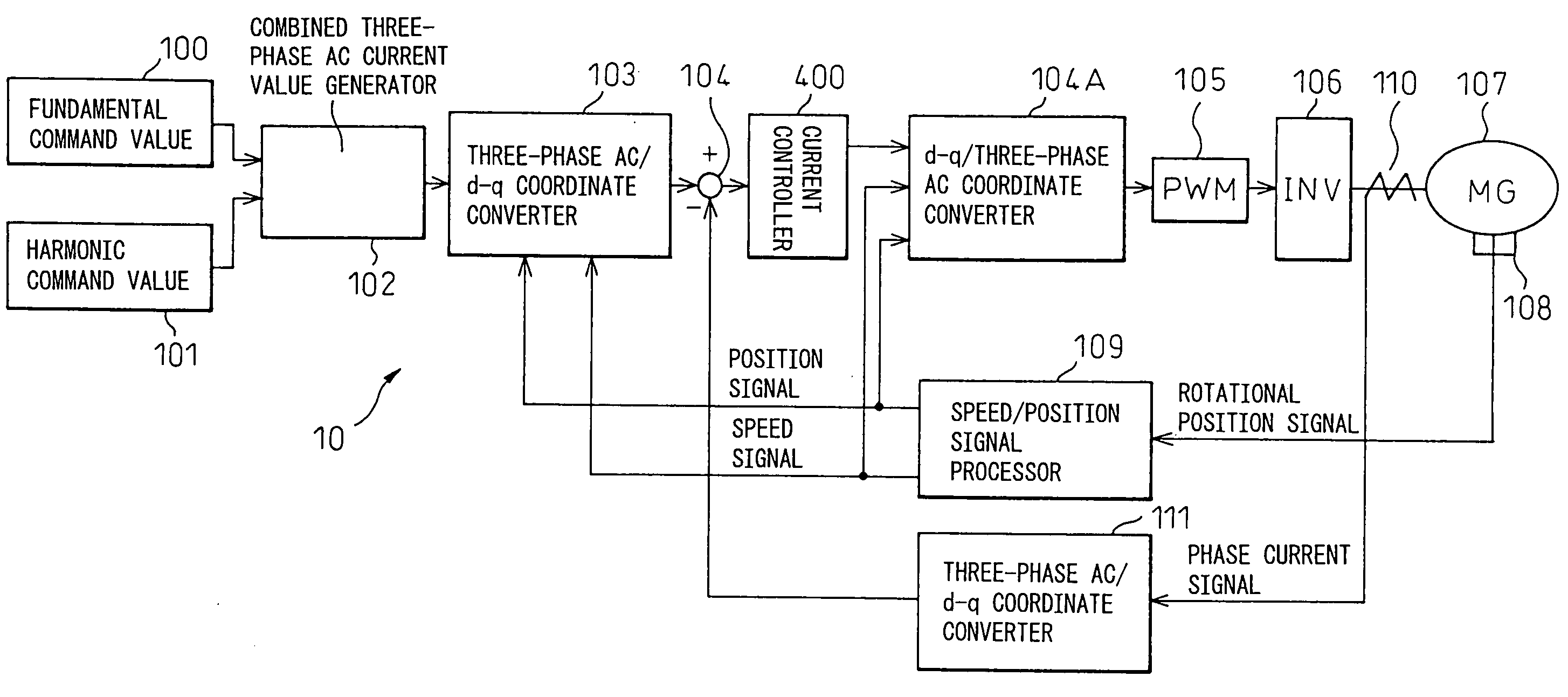
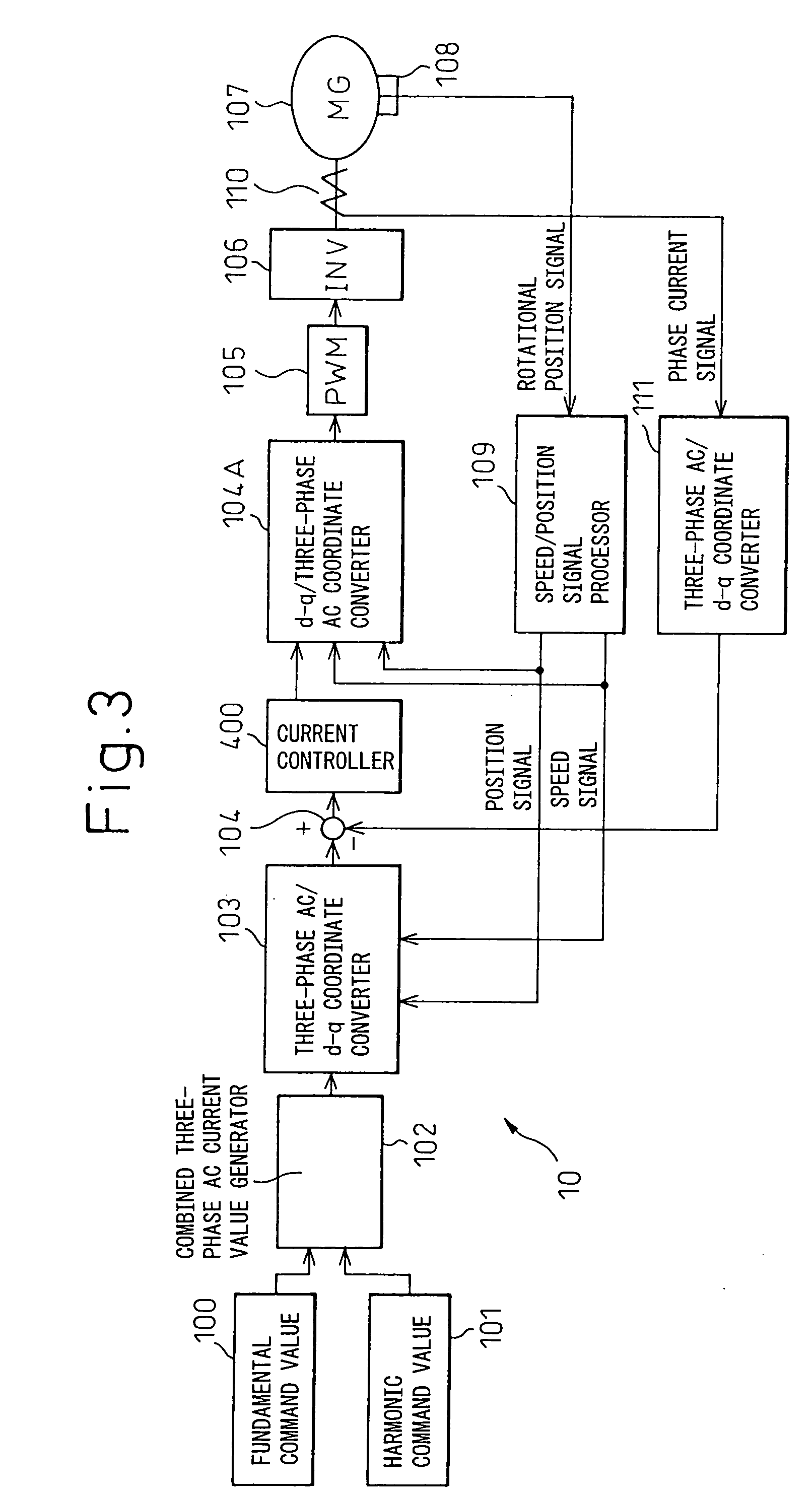
Magnetic noise reduction method for AC rotary electric machine, and motor control apparatus and AC rotary electric machine apparatus using the same
ActiveUS20050073280A1Quieter operationImprove comfortSingle-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlMagnetic noiseFundamental frequency
The invention provides techniques for reducing or altering the magnetic noise of an AC rotary electric machine. A magnetic noise reducing harmonic current of order n, whose frequency is n times the frequency of the fundamental frequency component of a polyphase AC current fed to an armature of a polyphase AC rotary electric machine, is superimposed on the polyphase AC current, thereby reducing or altering a harmonic component having a frequency (n−1) times the frequency of the fundamental frequency component and occurring due to a radial magnetic excitation force acting radially on an iron core of the AC rotary electric machine. Magnetic noise is caused by a vibration whose energy is the sum of the circumferential and radial vibrations of the iron core occurring due to the magnetomotive force of the rotor, and altering the radial vibration is particularly effective in altering the magnetic noise; as the harmonic component of the radially acting magnetic excitation force, occurring due to harmonic components having frequencies 3, 5, 7, and 13 times the fundamental frequency, has a frequency 6 or 12 times the fundamental frequency, the magnetomotive force of the rotor can be effectively reduced or altered when a current having a frequency 7 or 13 times the fundamental frequency is superimposed on the stator current.
Owner:DENSO CORP
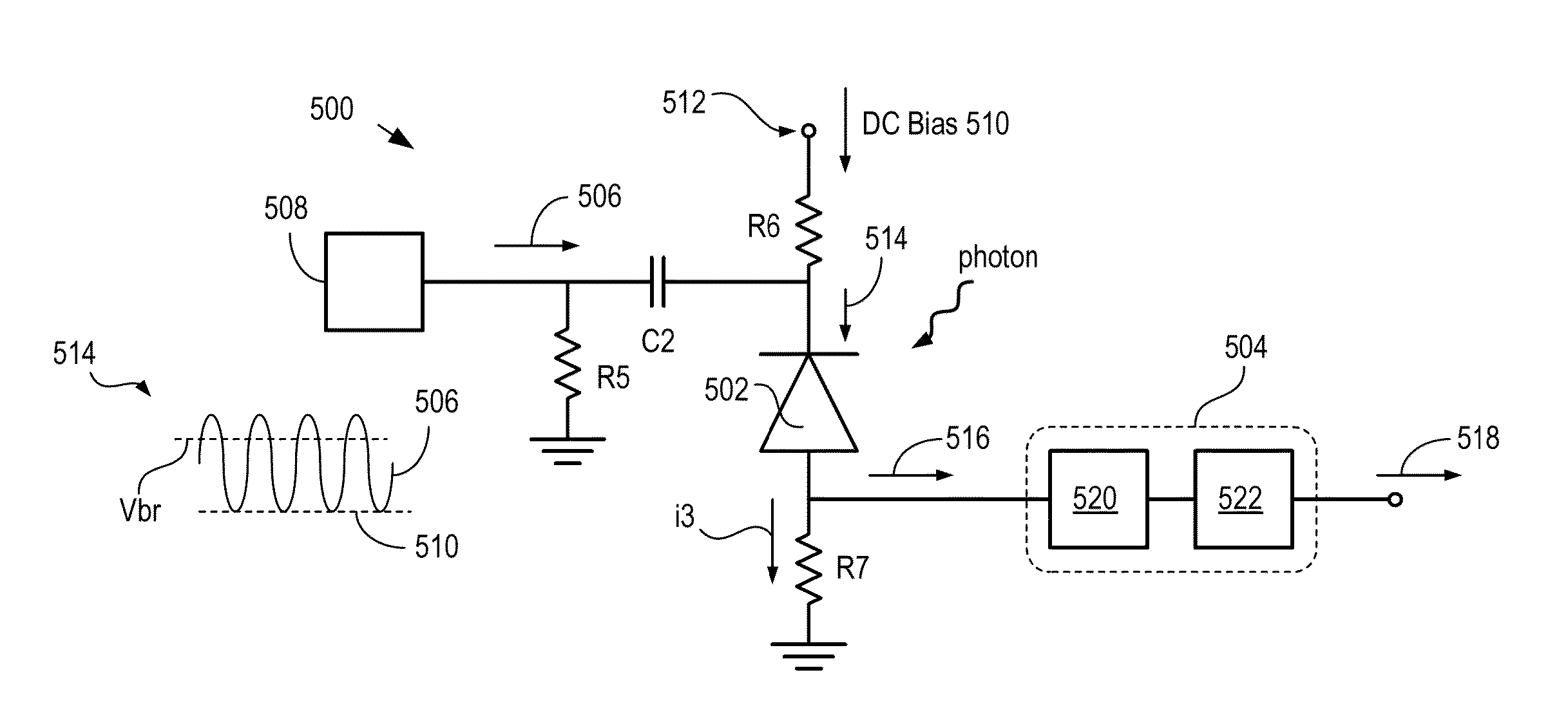
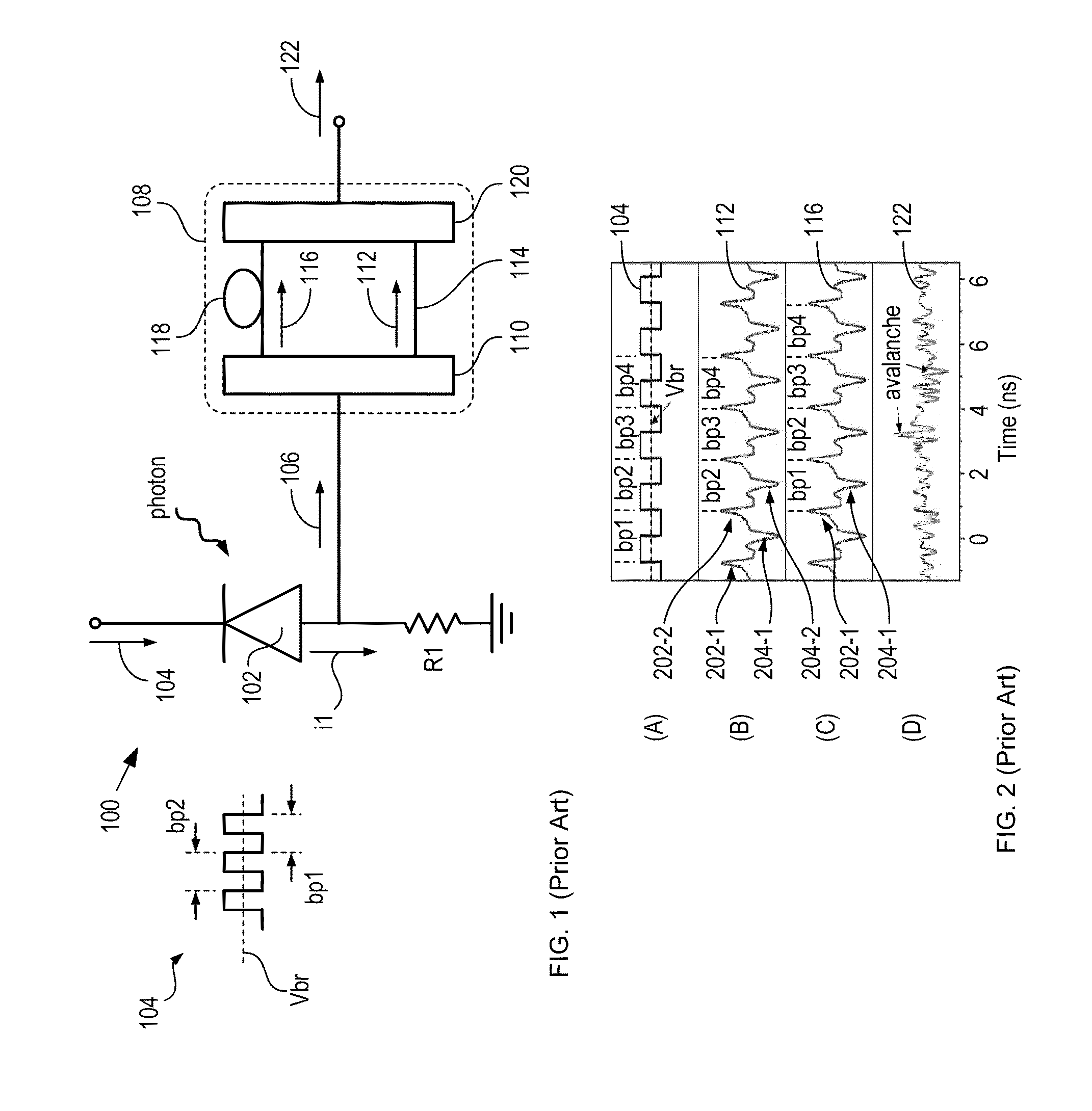
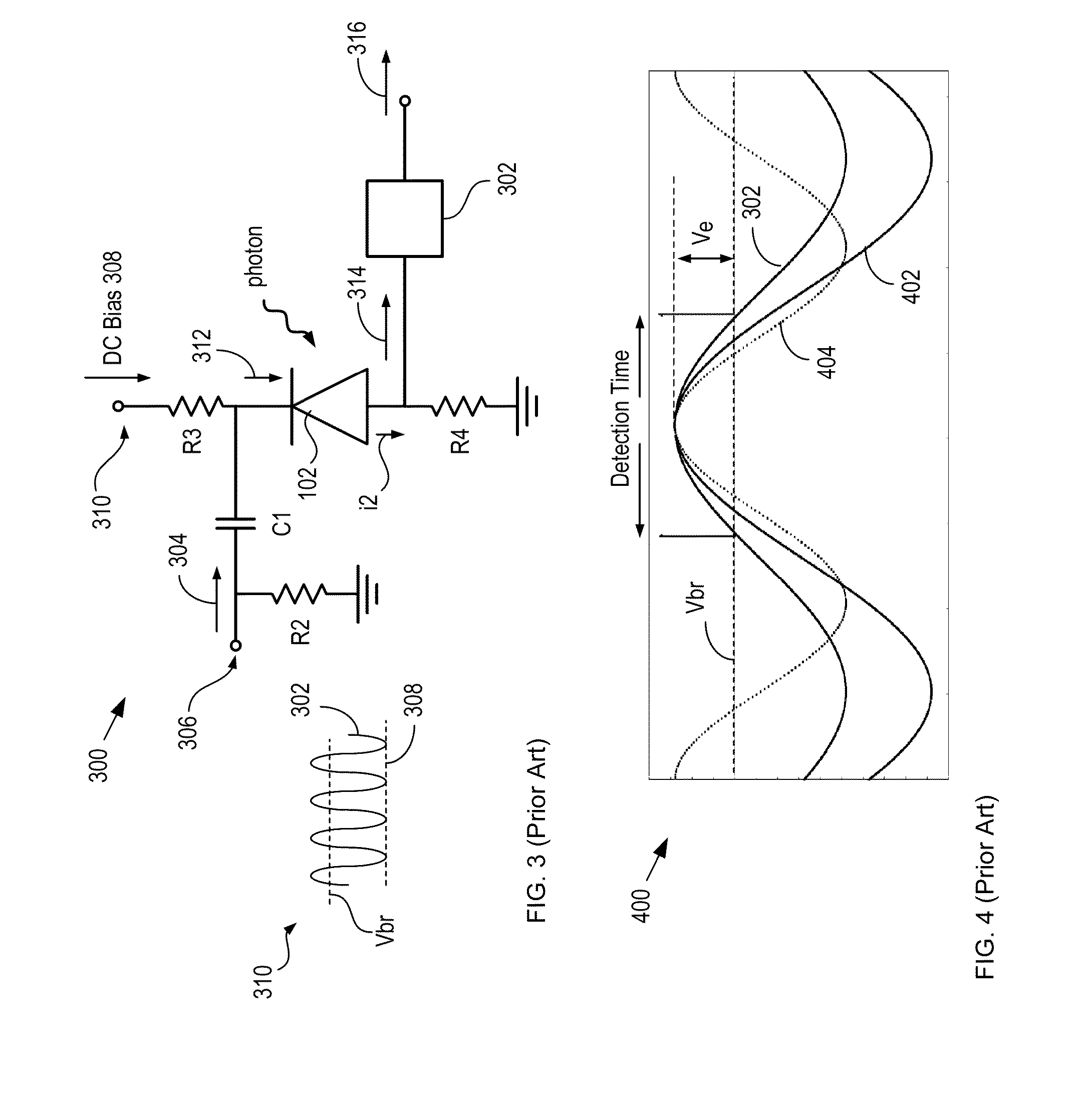
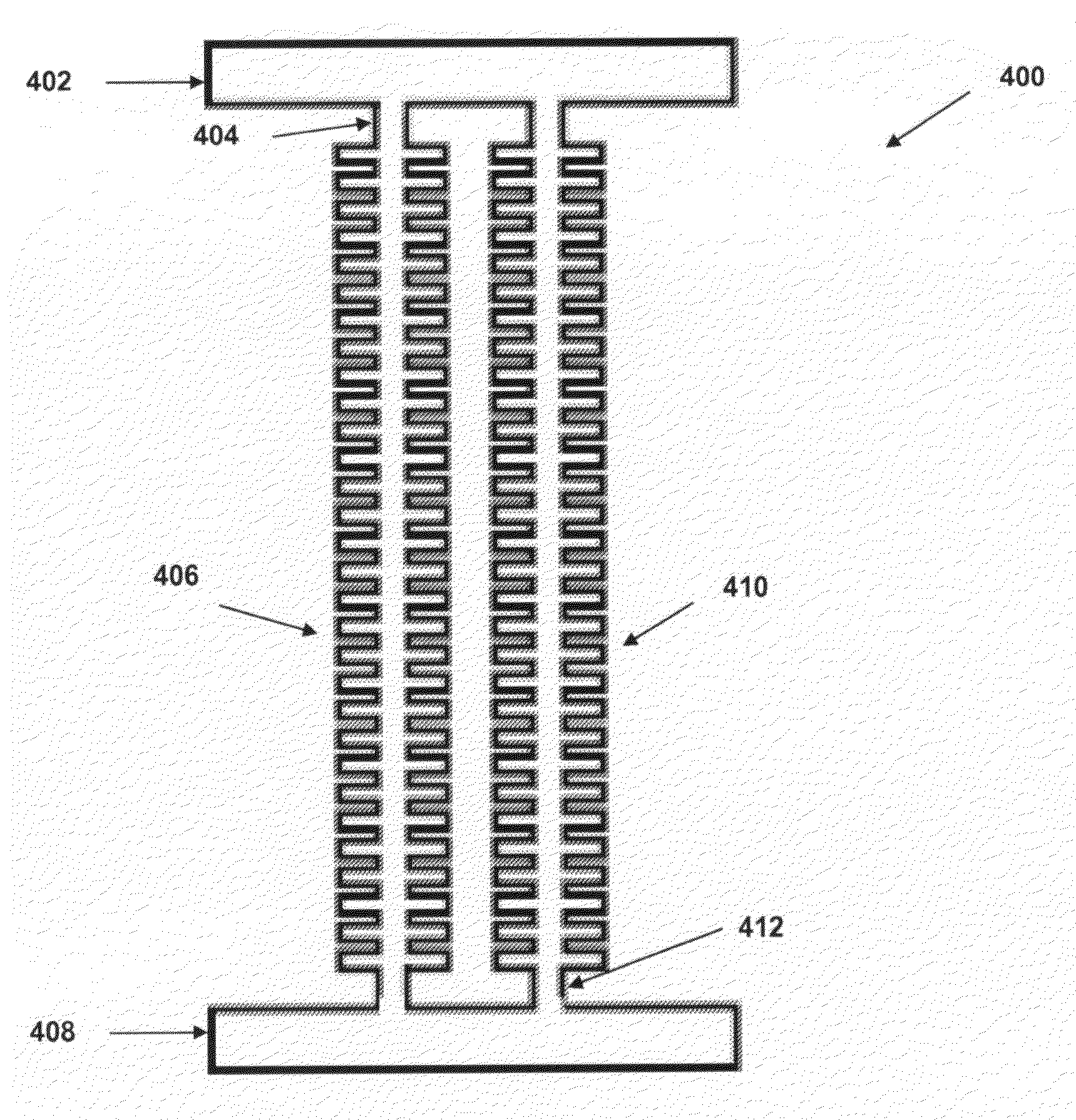
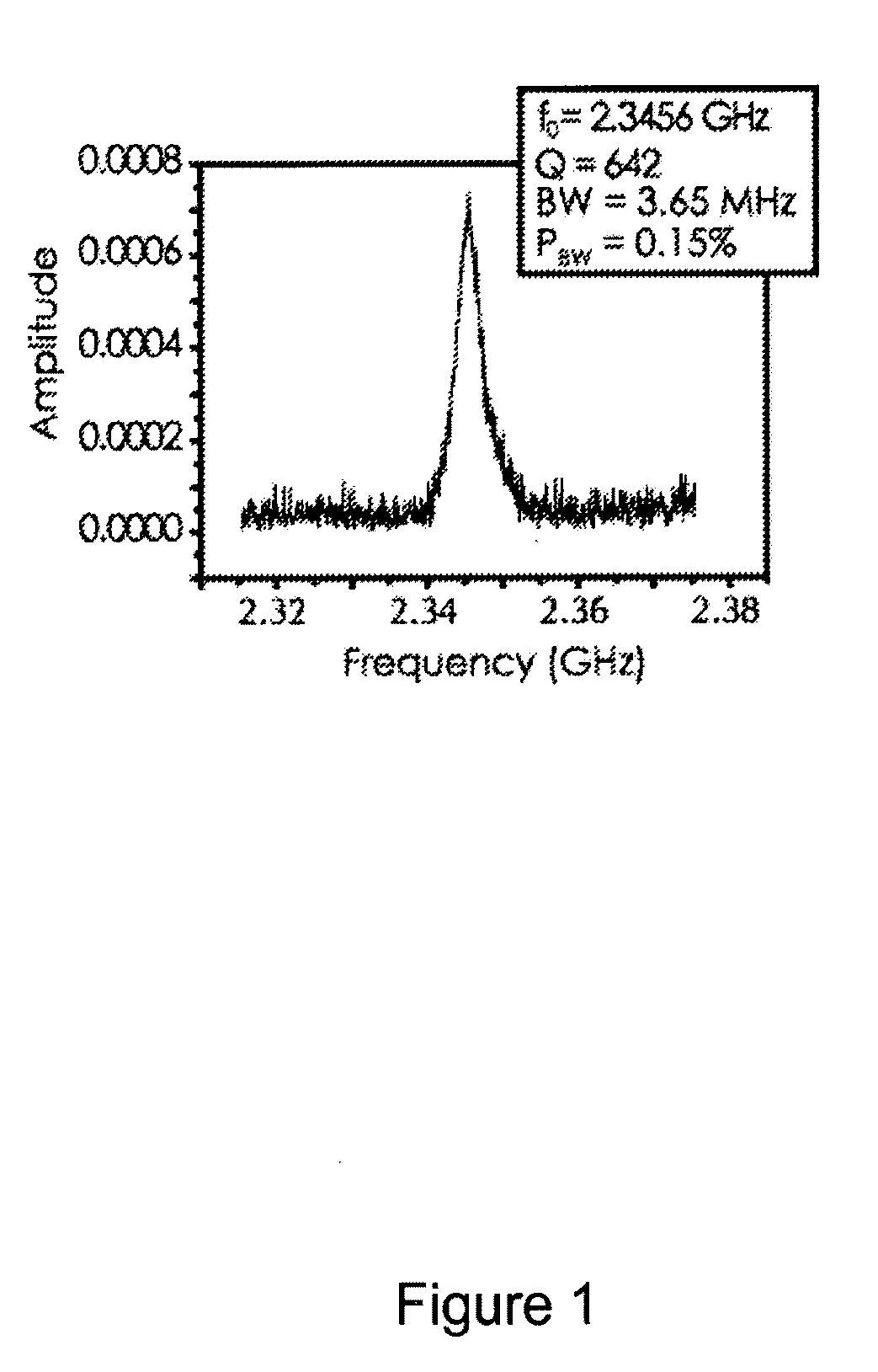
High-repetition-rate single-photon receiver and method therefor
ActiveUS8796605B2Material analysis by optical meansElectronic switchingSignal qualityLow-pass filter
A single-photon receiver and method for detecting a single-photon are presented. The receiver comprises a SPAD that receives a gating signal having a fundamental frequency in the 100 MHz to multiple GHz range. The receiver further comprises a two-stage frequency filter for filtering the output of the SPAD, wherein the filter has: (1) a notch filter response at the fundamental frequency; and (2) a low-pass filter response whose cutoff frequency is less than the first harmonic of the fundamental frequency. As a result, the frequency filter removes substantially all the frequency components in the SPAD output without significant degradation of the signal quality but with reduced complexity, cost, and footprint requirement relative to receivers in the prior art.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
Nano electromechanical integrated-circuit filter
InactiveUS20100007443A1More powerIncrease spaceImpedence networksSemiconductor devicesFundamental frequencySilicon
A nano electromechanical integrated circuit filter and method of making. The filter comprises a silicon substrate; a sacrificial layer; a device layer including at least one resonator, wherein the resonator includes sub-micron excitable elements and wherein the at least one resonator possess a fundamental mode frequency as well as a collective mode frequency and wherein the collective mode frequency of the at least one resonator is determined by the fundamental frequency of the sub-micron elements.
Owner:CLARIANT INT LTD +1
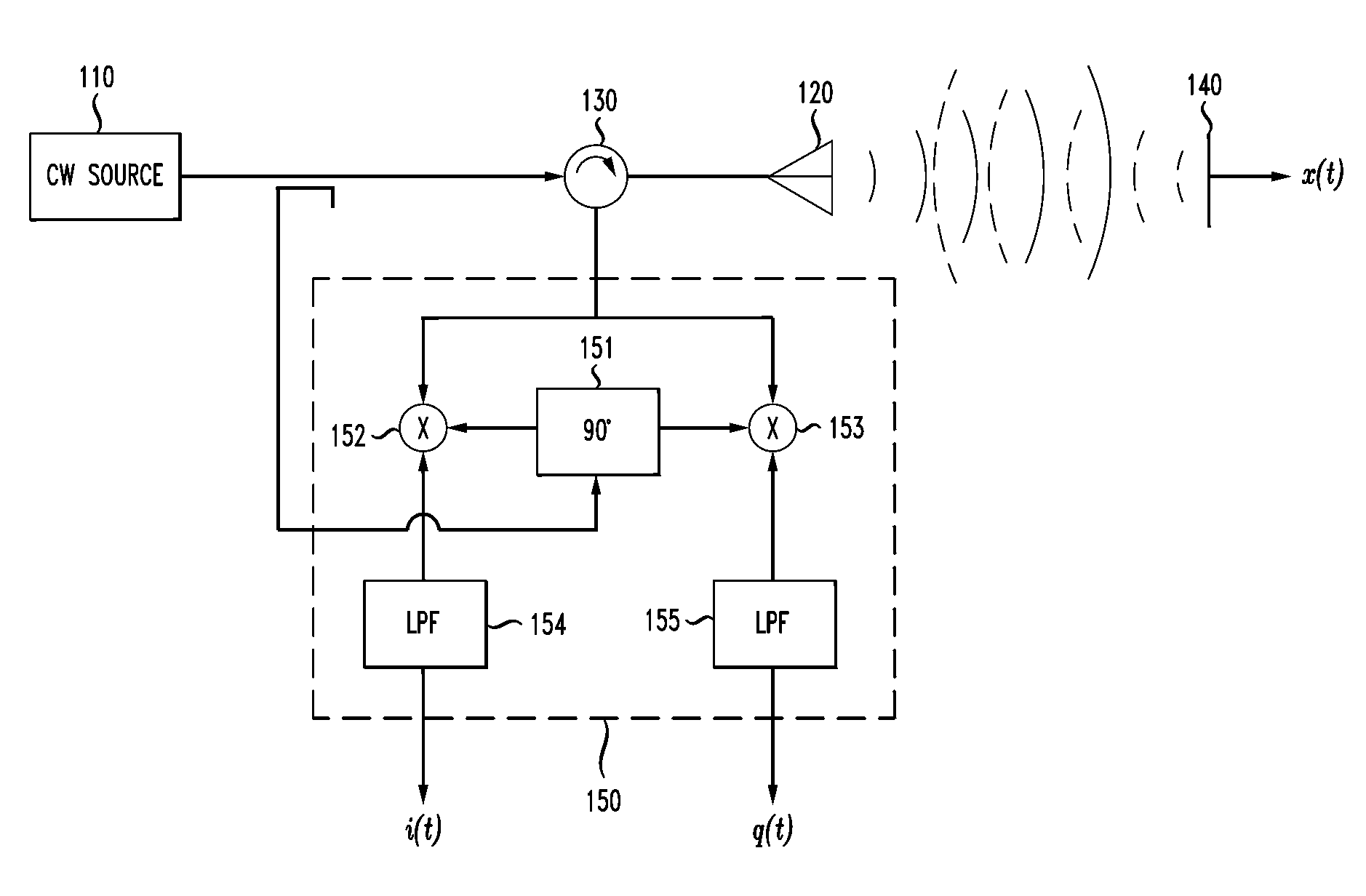
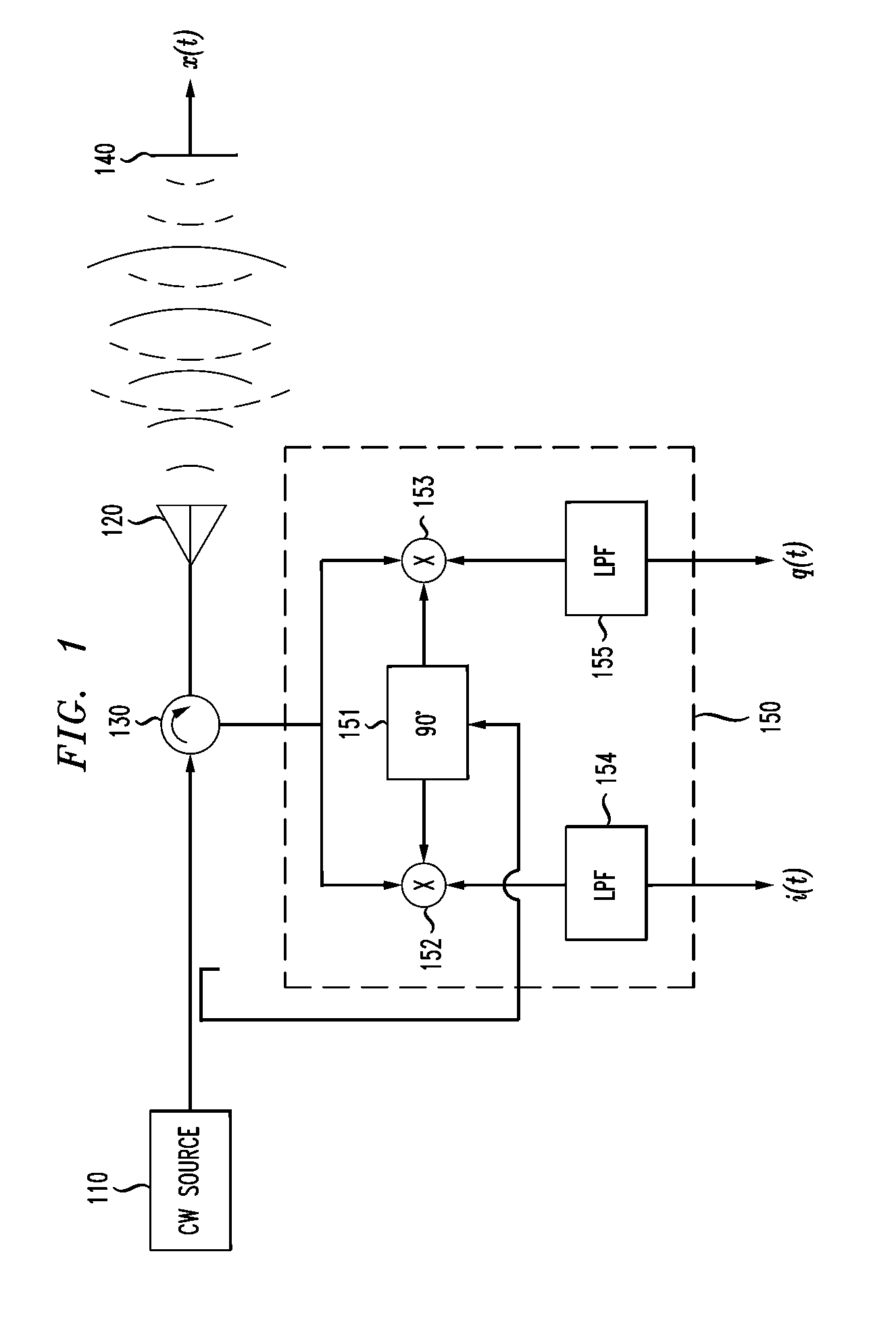
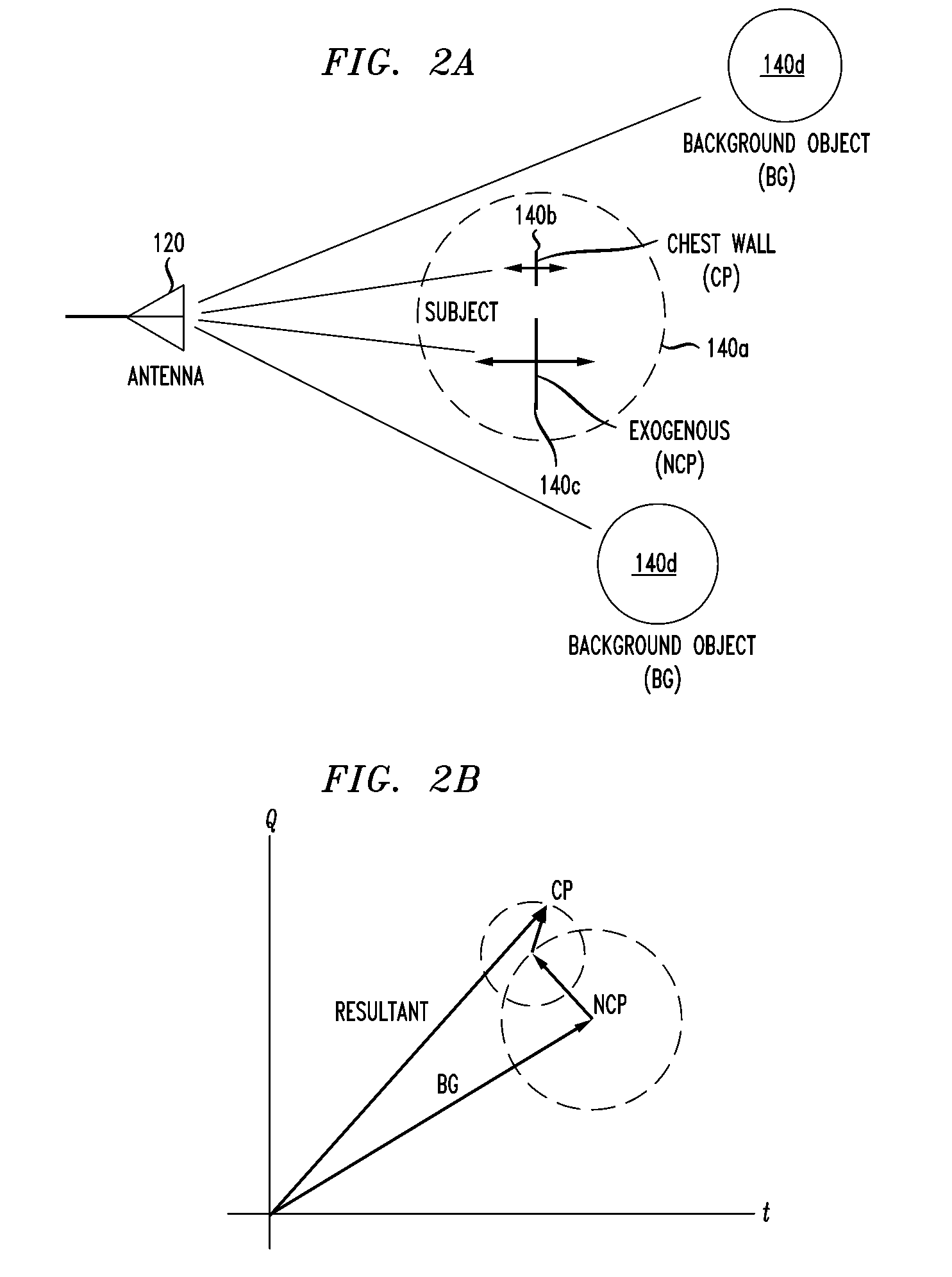
Doppler Radar Cardiopulmonary Sensor and Signal Processing System and Method for Use Therewith
A Doppler radar signal processing system and method and a Doppler radar employing the system or the method. In one embodiment, the system includes: (1) an input configured to receive at least one radar output signal representing a reflected Doppler radar signal, (2) signal processing circuitry coupled to the input and configured to produce an arc-length cardiopulmonary signal from the at least one radar output signal and employ a respiration fundamental frequency estimate to extract a heart rate signal from the arc-length cardiopulmonary signal and (3) an output coupled to the signal processing circuitry and configured to provide the heart rate signal.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Medical ultrasound system and handpiece and methods for making and tuning
ActiveUS20070232920A1Small sizeIncrease displacementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryUltrasonographyUltrasonic sensor
Several embodiments of medical ultrasound handpieces are described each including a medical ultrasound transducer assembly. An embodiment of a medical ultrasound system is described, wherein the medical ultrasound system includes a medical ultrasound handpiece having a medical ultrasound transducer assembly and includes an ultrasonically-vibratable medical-treatment instrument which is attachable to a distal end of the transducer assembly. An embodiment of a medical ultrasound system is described, wherein the medical ultrasound system has a handpiece including a medical ultrasound transducer assembly and including a housing or housing component surrounding the transducer assembly. A method for tuning a medical ultrasound handpiece includes machining at least a distal non-threaded portion of an instrument-attachment stud of the transducer assembly to match a measured fundamental frequency to a desired fundamental frequency to within a predetermined limit. A method for making a medical ultrasound transducer assembly determines acceptable gains for gain stages of the transducer assembly.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Method of detecting RF powder delivered to a load and complex impedance of the load
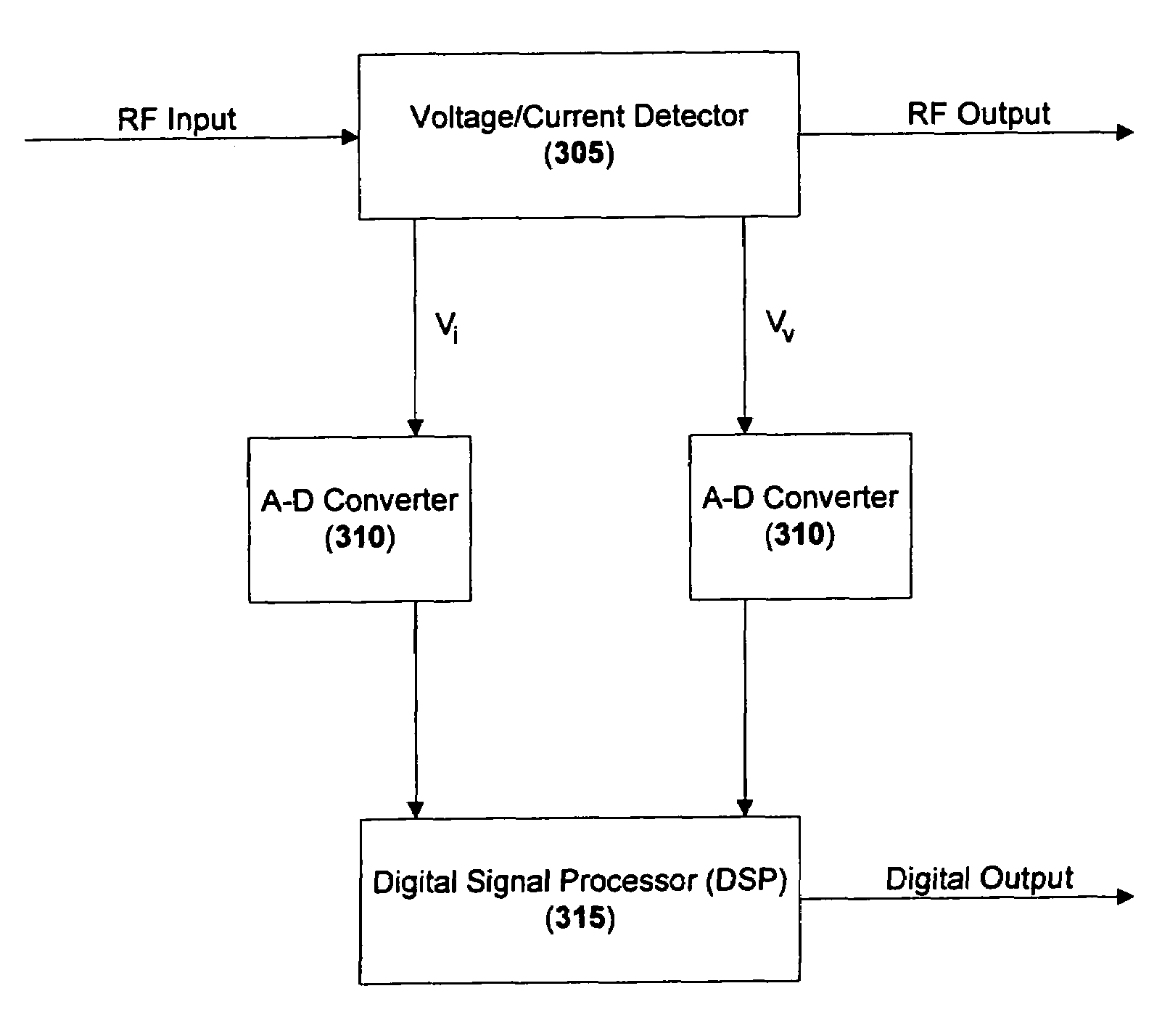
ActiveUS7298128B2Spectral/fourier analysisProduction of permanent recordsEngineeringFundamental frequency
Methods and systems of detecting one or more characteristics of a load are disclosed. One or more characteristics of a first signal may be detected at the output of a Radio Frequency (RF) power generator. The first signal may have a fundamental frequency. The one or more characteristics of the first signal may be sampled at a sampling frequency to produce a digital sampled signal. The sampling frequency may be determined based on a function of the fundamental frequency of the first signal. One or more characteristics of a load in communication with the RF power generator may then be determined from the digital sampled signal.
Owner:ASM AMERICA INC
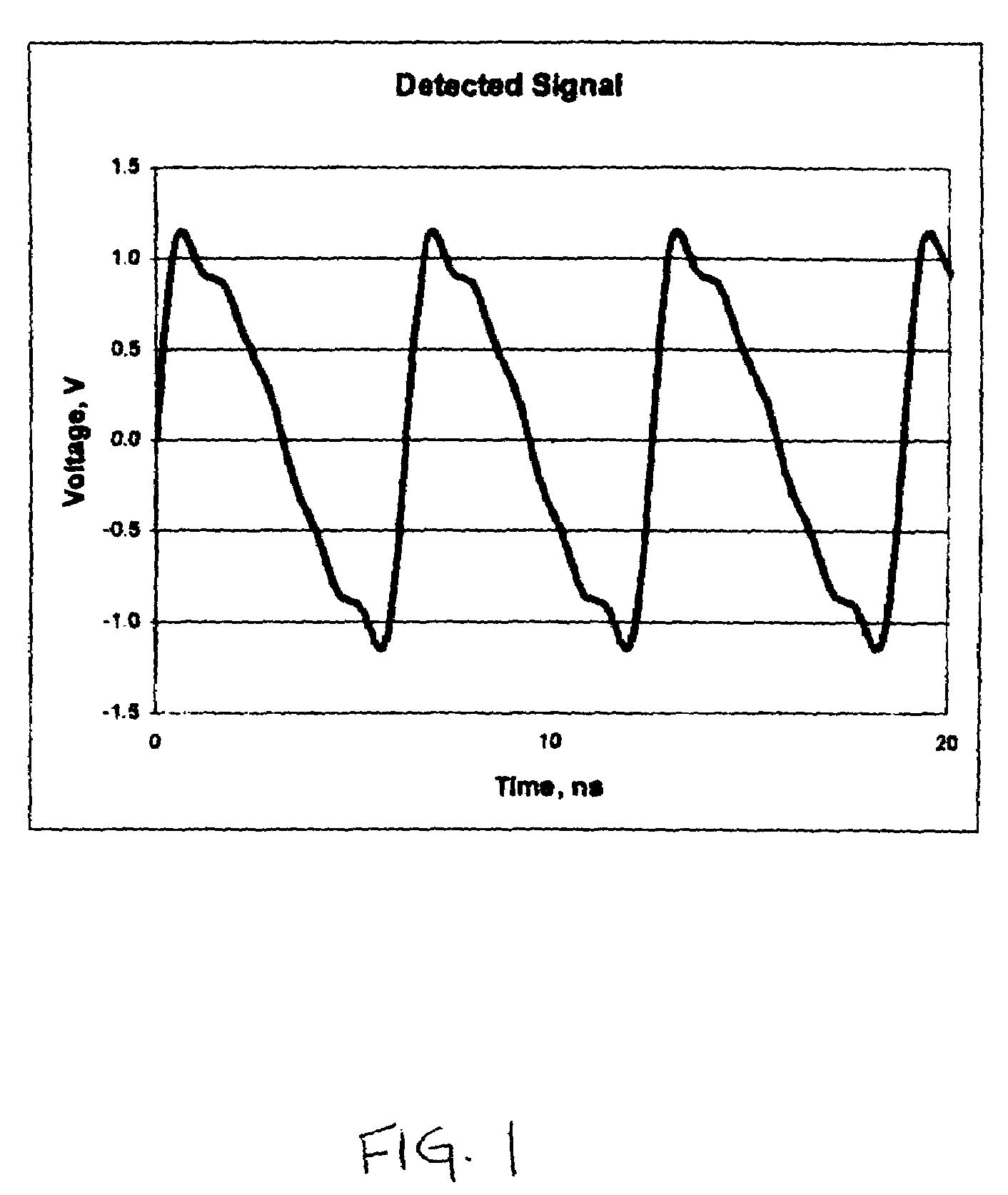
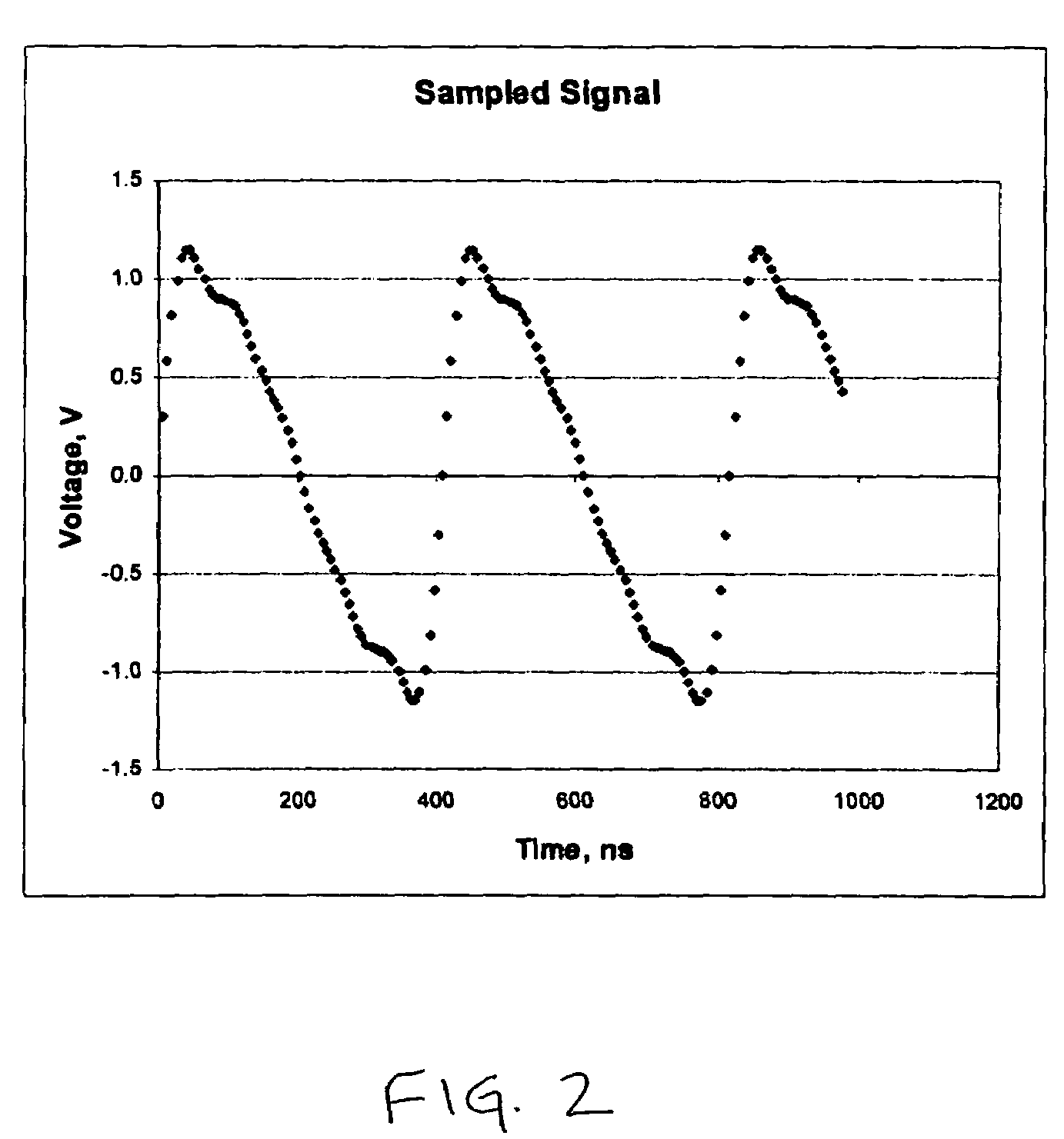
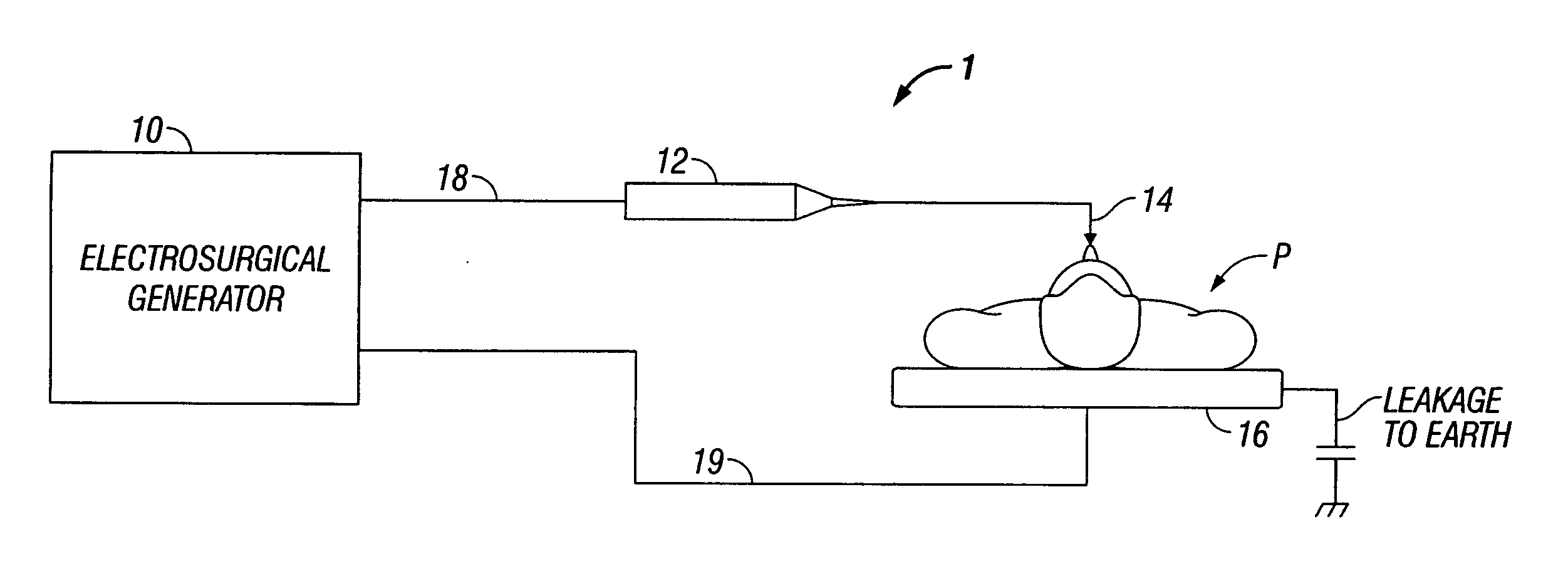
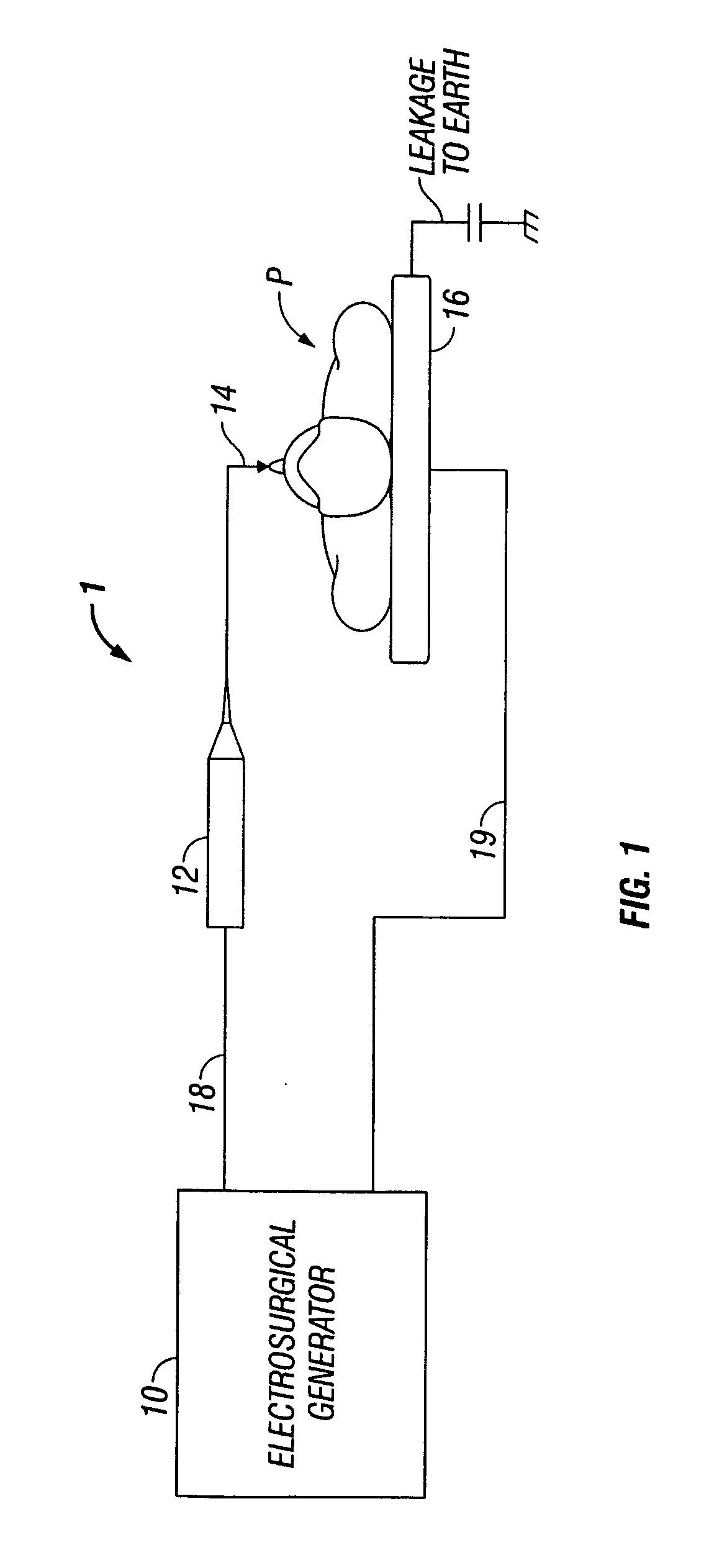
System and method for reducing leakage current in an electrosurgical generator
ActiveUS20070265612A1Minimize flowAvoid flowControlling energy of instrumentSurgical instruments for heatingCapacitanceEngineering
A system and method for reducing leakage current in an electrosurgical generator are disclosed. The system includes an electrosurgical generator configured to provide high frequency electrosurgical energy at a fundamental frequency. The generator includes one or more circuit boards having a board ground. The generator further includes a inductor-capacitor filter connected in series with the board ground and an earth ground. The inductor capacitor filter includes a capacitor connected in parallel with an inductor and is tuned to be at an operational frequency which is resonant at or near the fundamental frequency.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
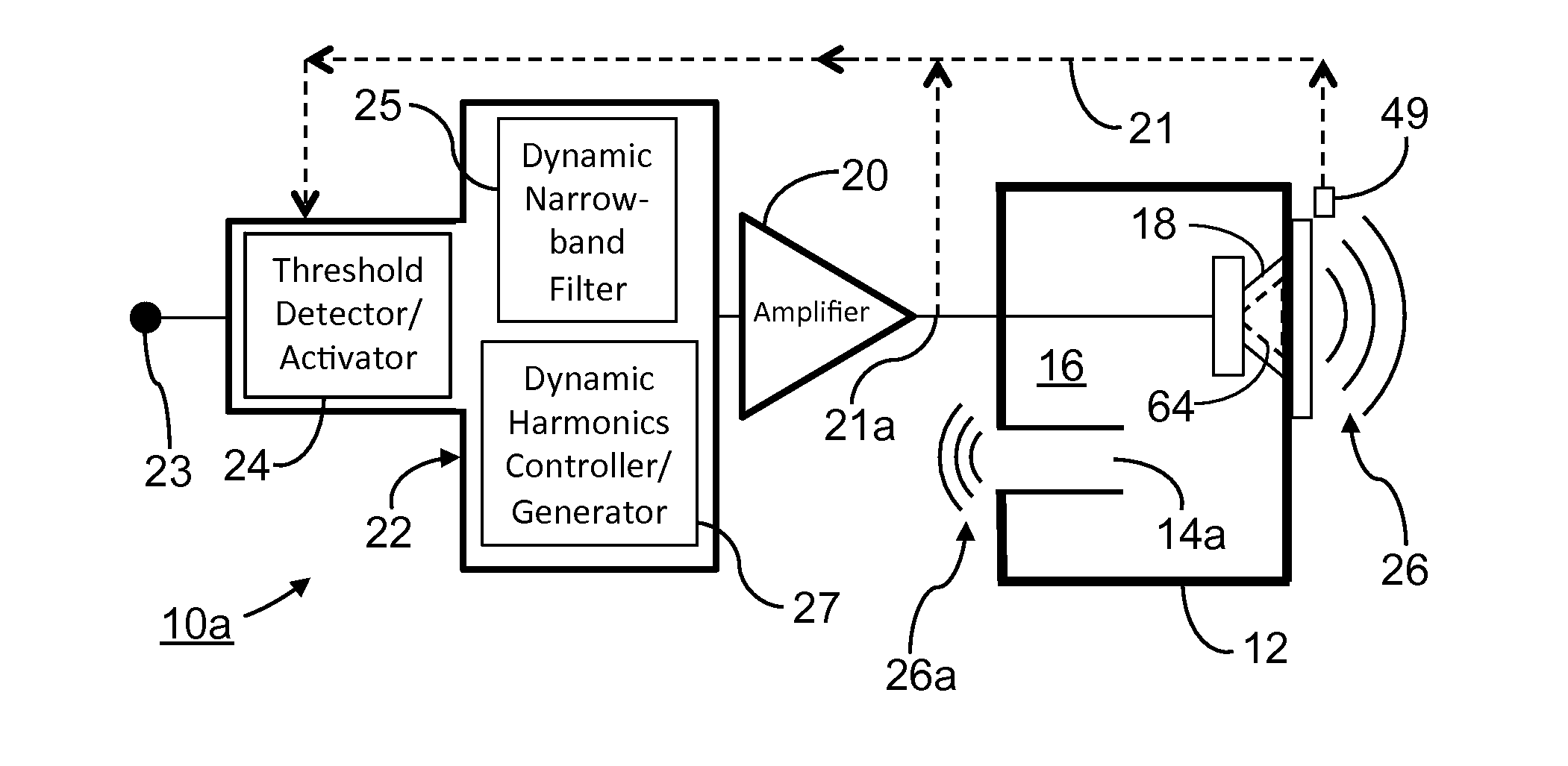
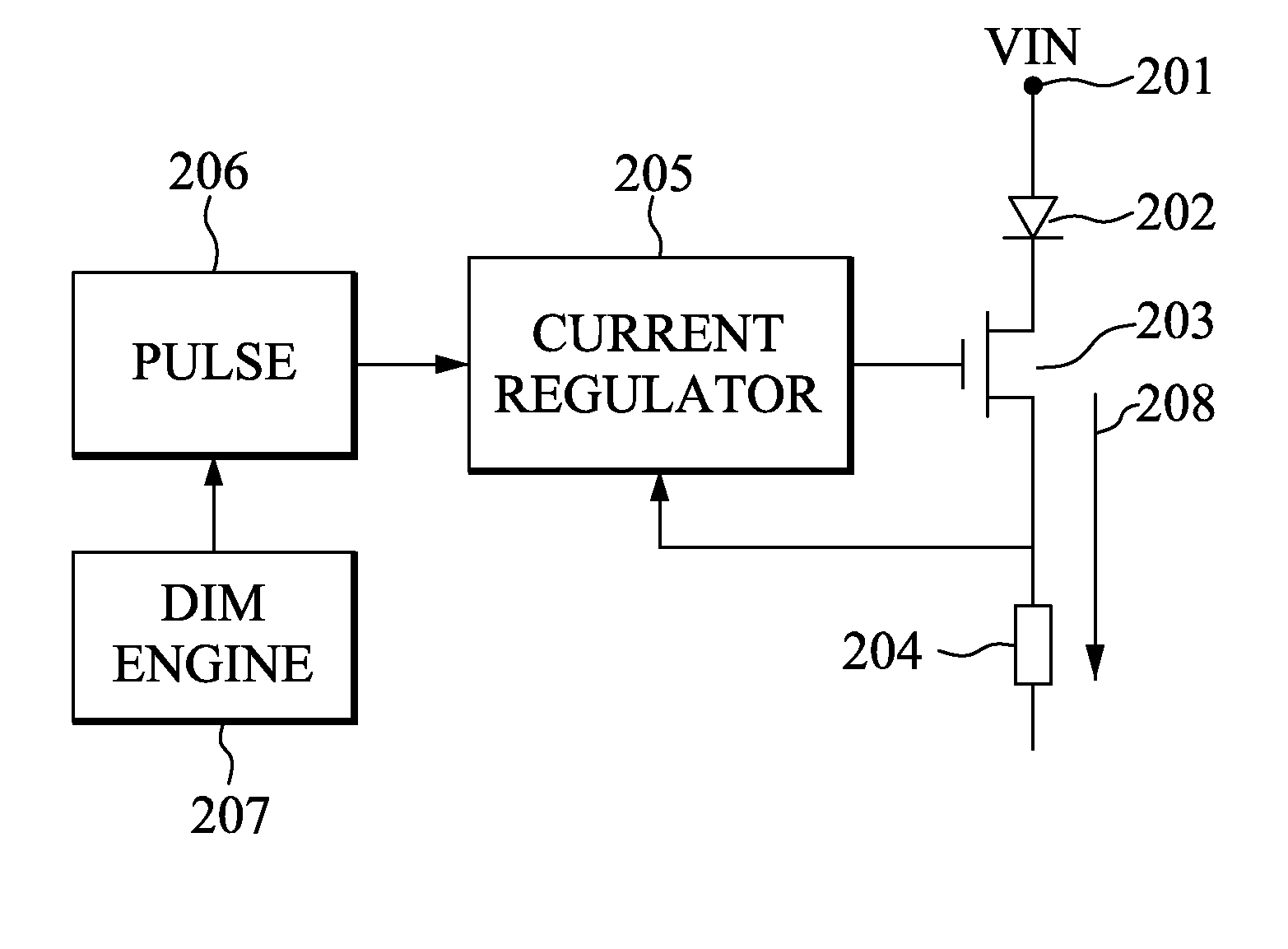
LED Dimming Techniques Using Spread Spectrum Modulation
InactiveUS20100109550A1Easy to controlElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesHarmonicFundamental frequency
Circuits and methods of LED dimming are disclosed. Frequency modulation using controlled modulation depth generates deterministic sidebands of both the fundamental frequency and its harmonics. Various filters including low-pass, band-pass, high-pass and combinations of those are used to selectively filter the deterministic frequency components generated by the frequency modulation to achieve LED dimming.
Owner:HUDA MUZAHID BIN +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com