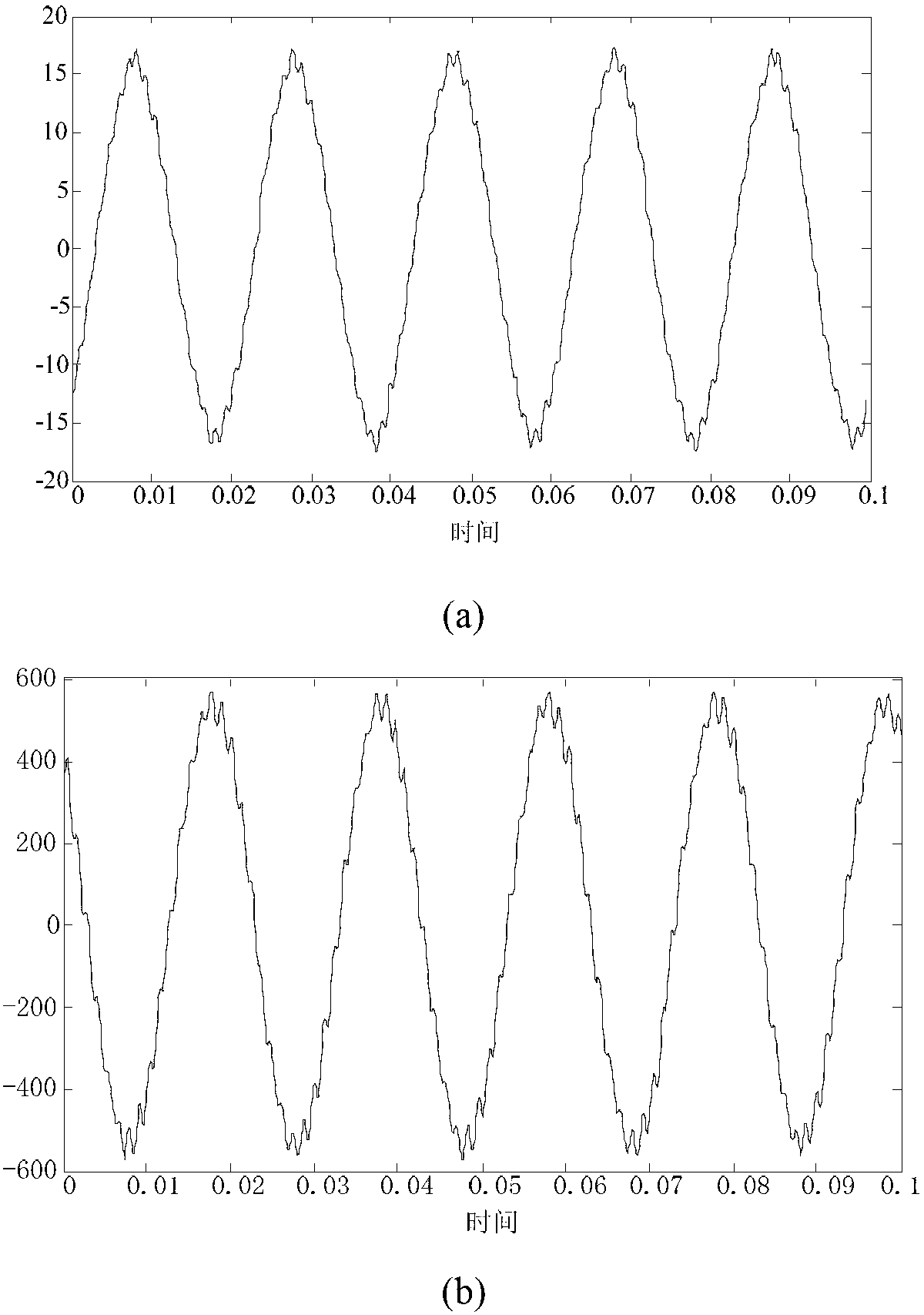
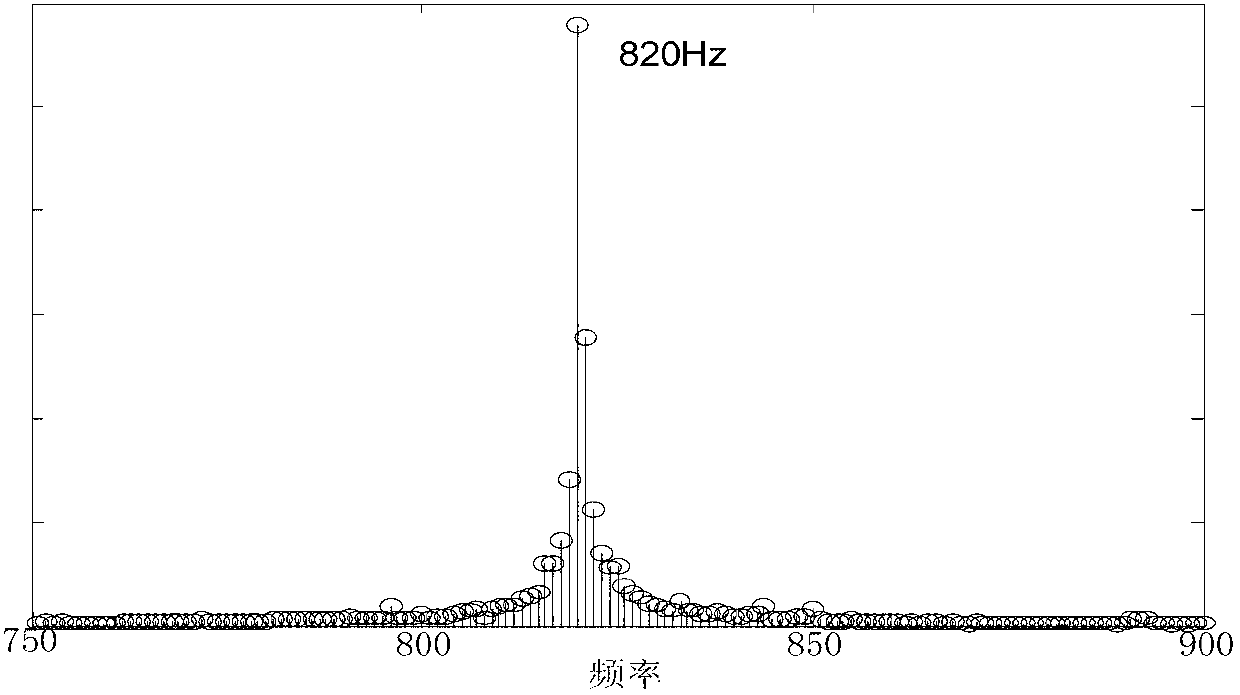
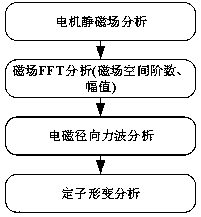
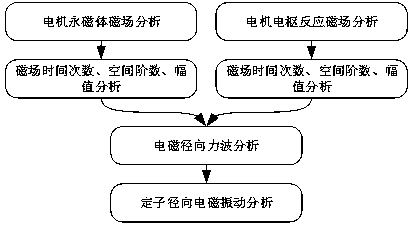
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
377 results about "Magnetomotive force" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
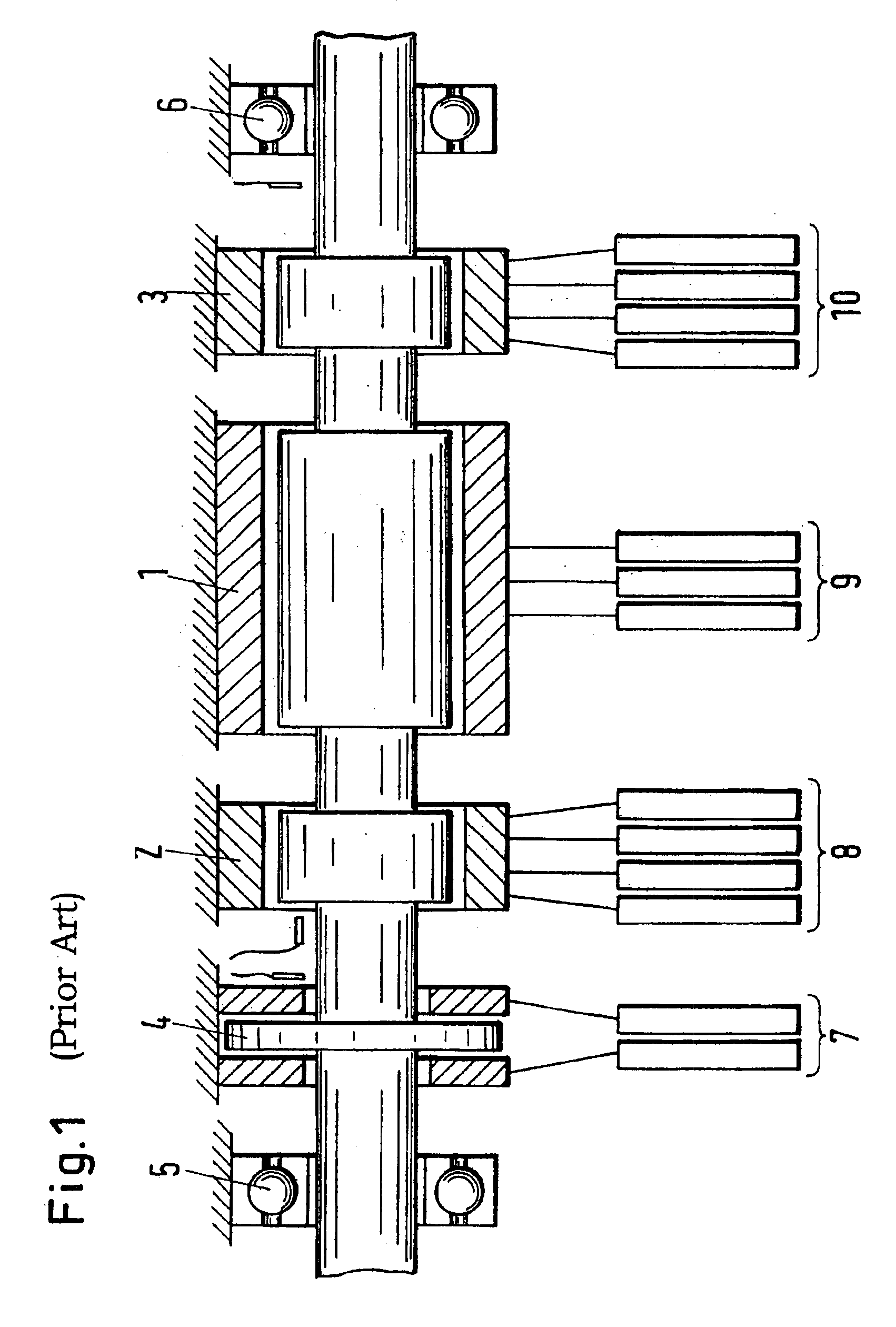
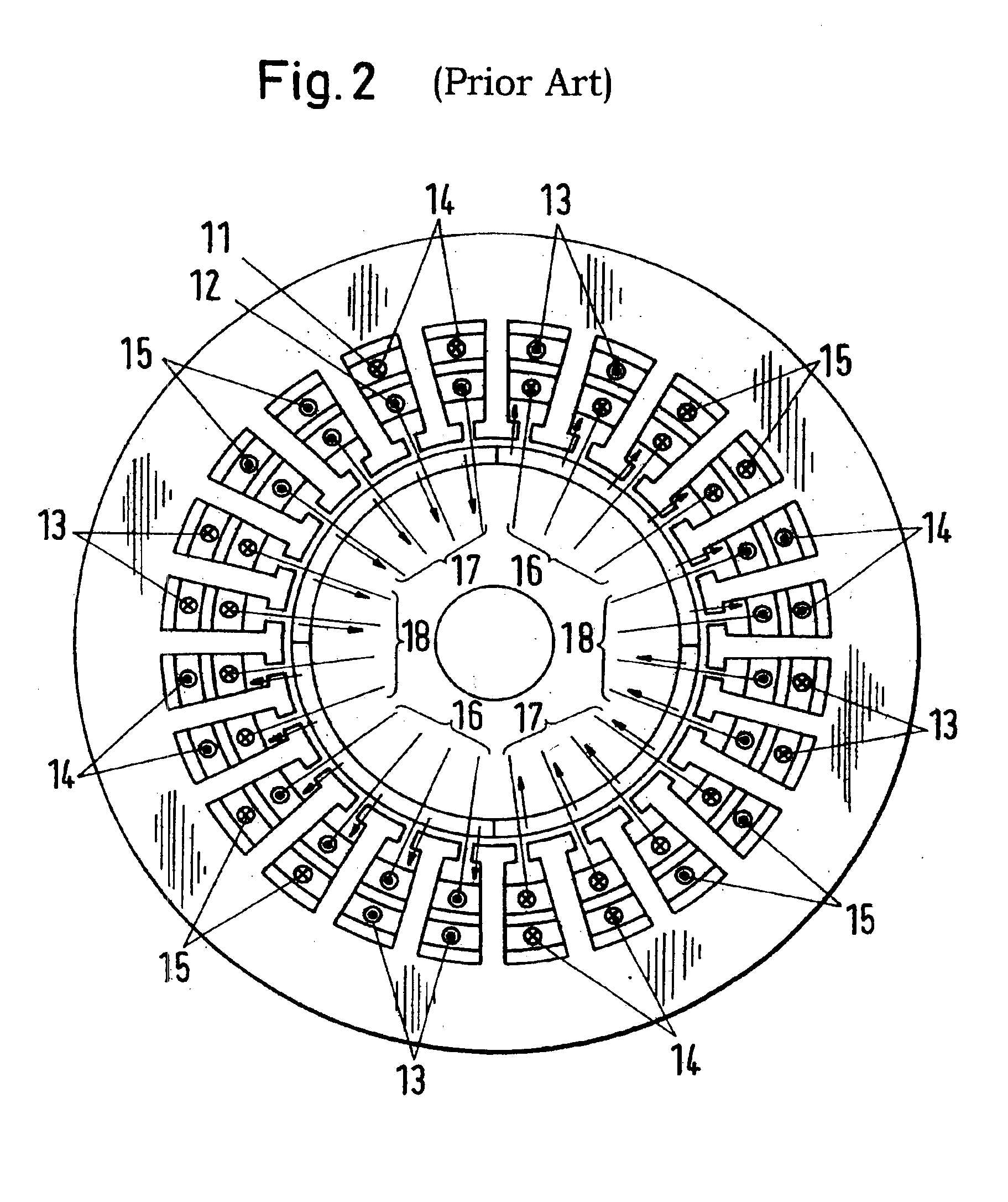
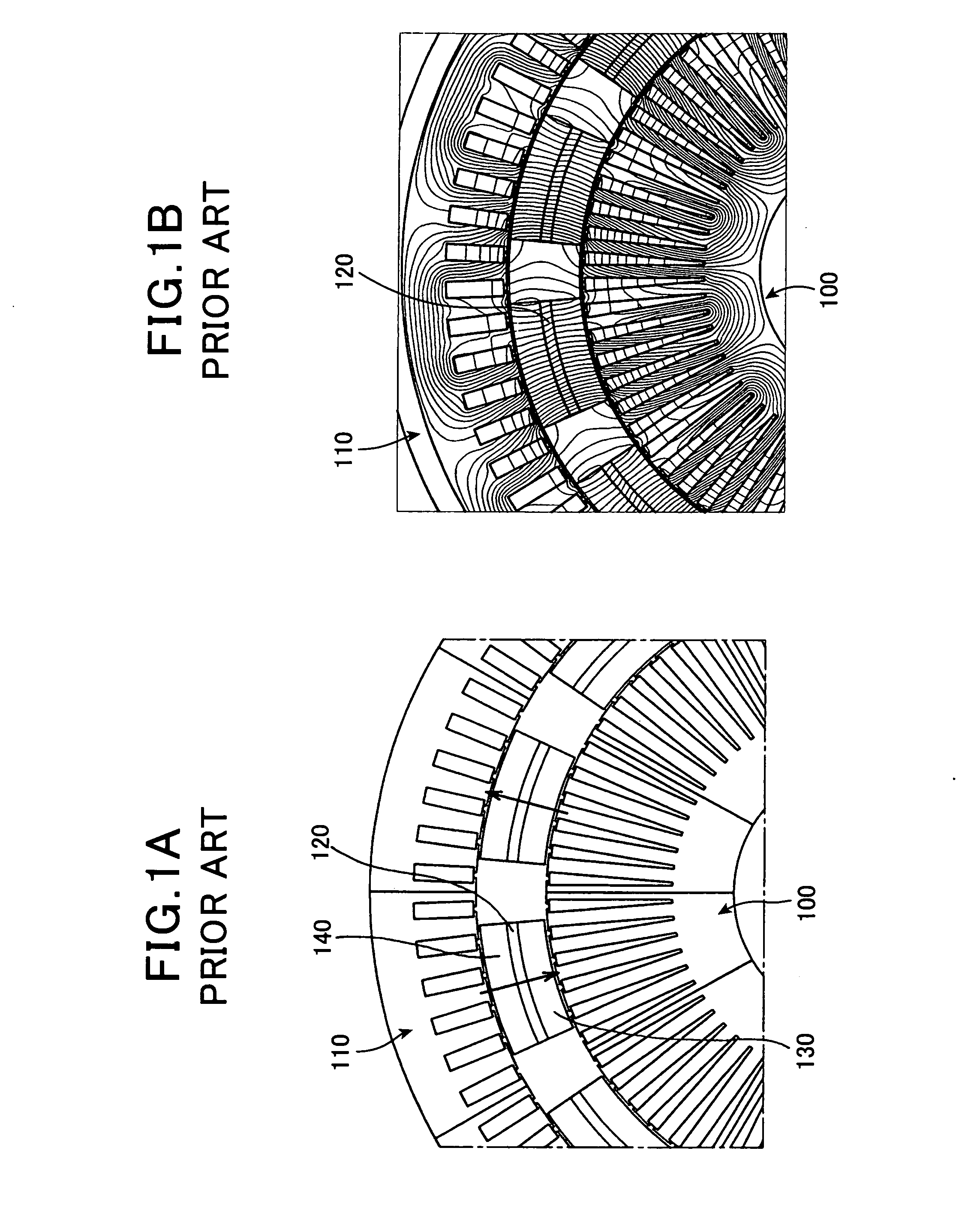
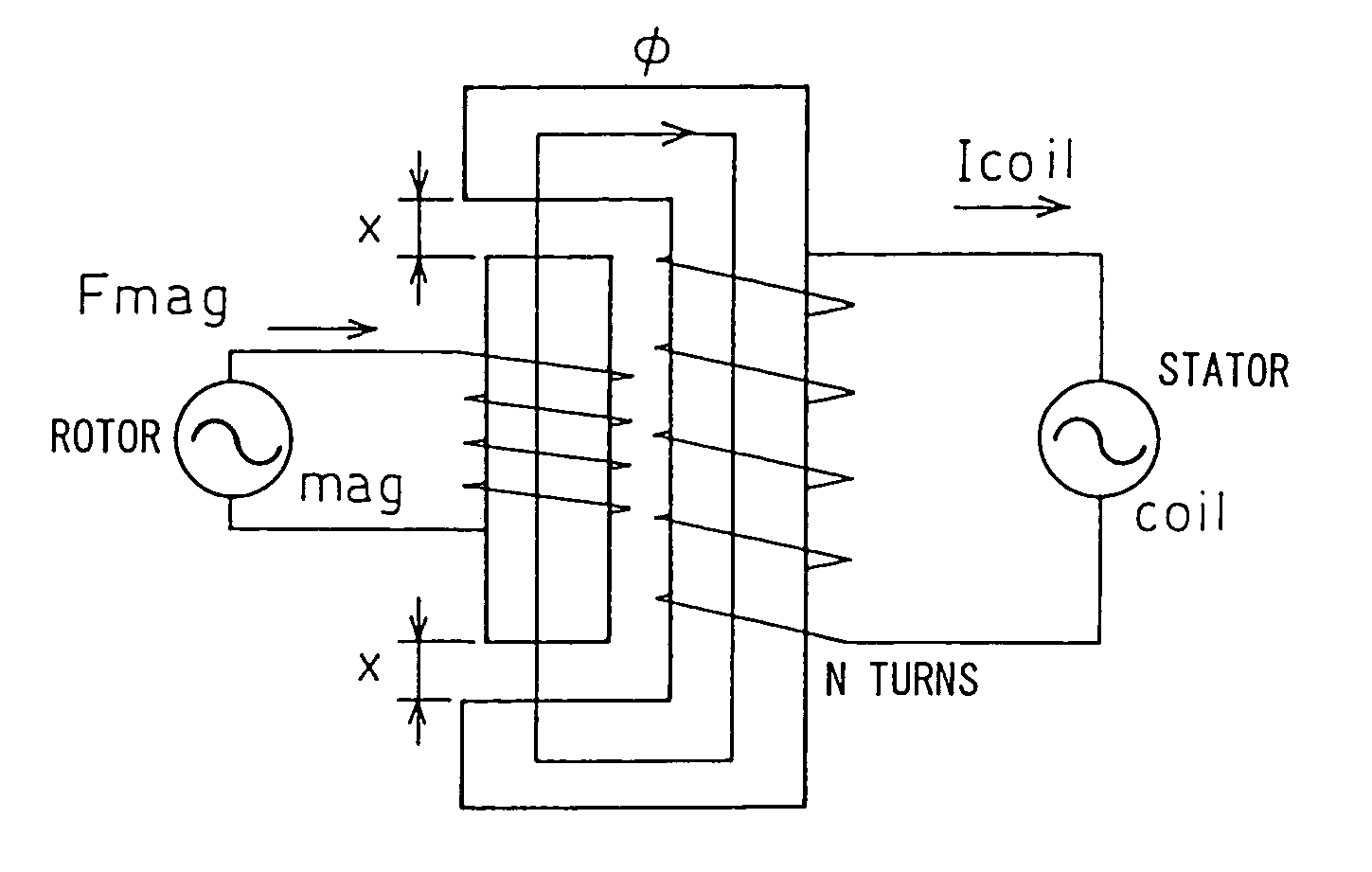
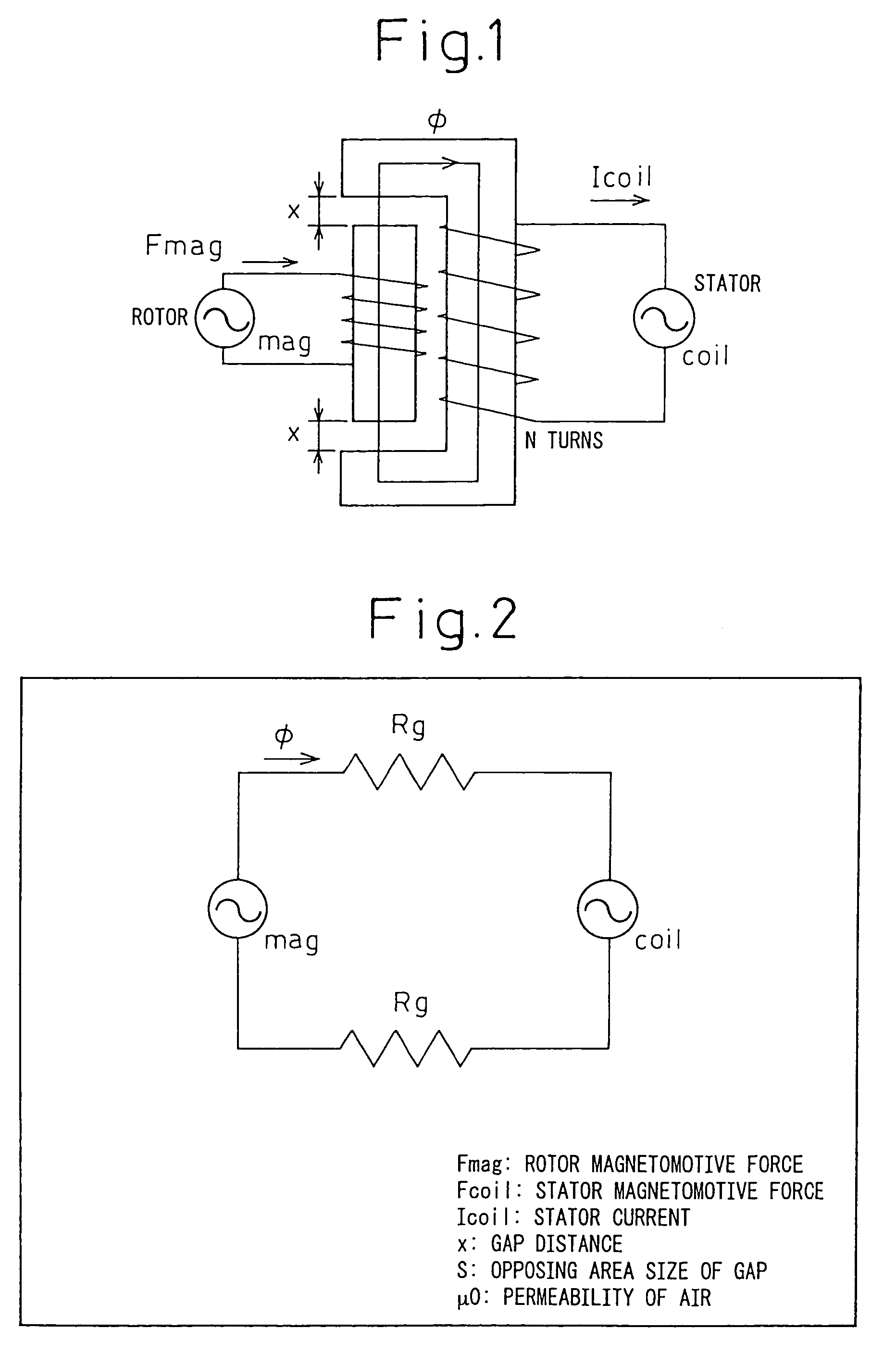
In physics, the magnetomotive force (mmf) is a quantity appearing in the equation for the magnetic flux in a magnetic circuit, often called Ohm's law for magnetic circuits. It is the property of certain substances or phenomena that give rise to magnetic fields: F=ΦR, where Φ is the magnetic flux and R is the reluctance of the circuit. It can be seen that the magnetomotive force plays a role in this equation analogous to the voltage V in Ohm's law: V = IR, since it is the cause of magnetic flux in a magnetic circuit: ℱ = NI where N is the number of turns in the coil and I is the electric current through the circuit.
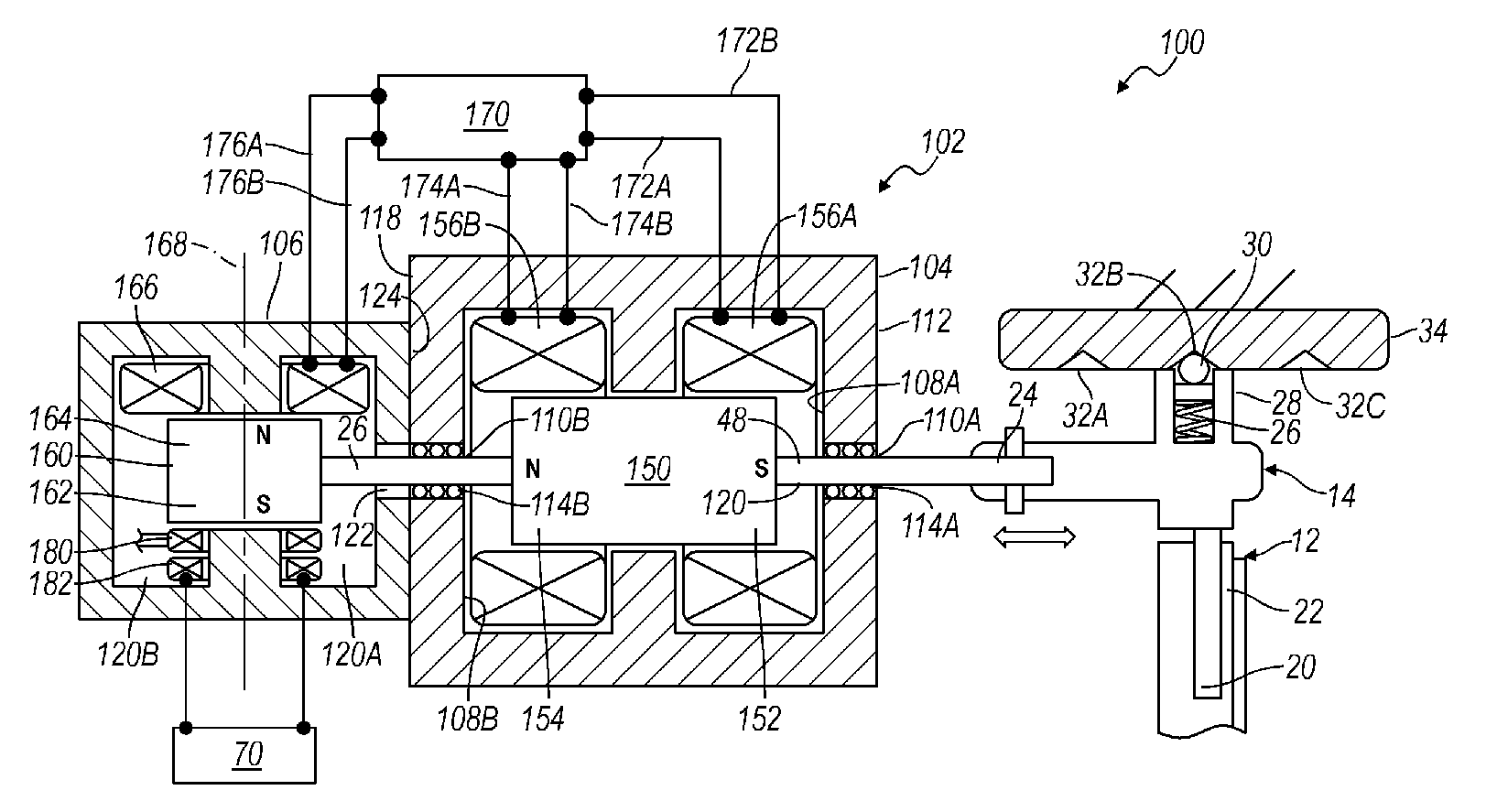
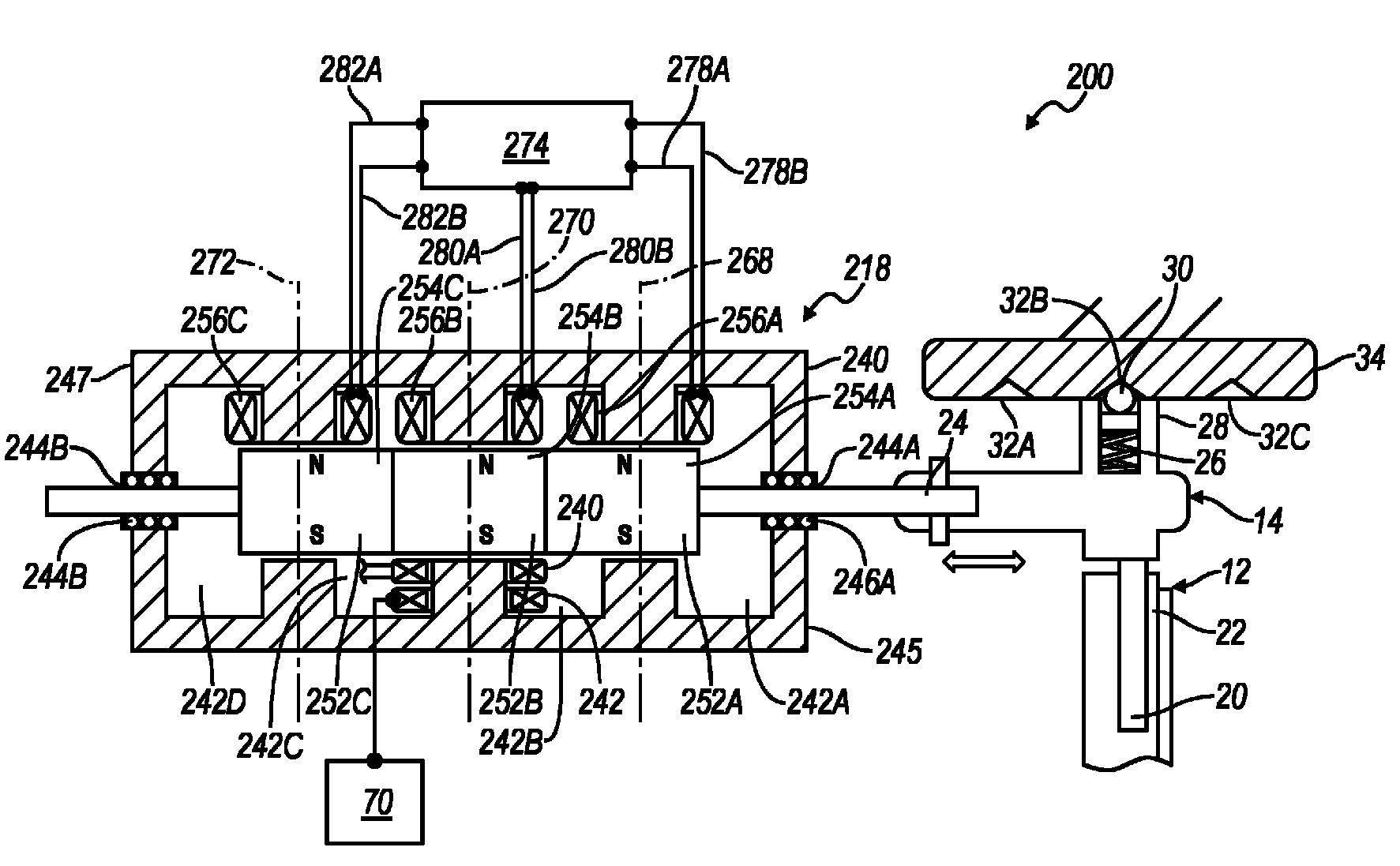
Magnetic drive devices, and related systems and methods
A magnetic drive device may comprise a stator comprising a plurality of windings for generating a first number of magnetic pole pairs and a rotor comprising a plurality of permanent magnets for generating a second number of magnetic pole pairs that differs from the first number of magnetic pole pairs. The magnetic drive device may further comprise a plurality of free-spinning interpole elements disposed within an air gap between the stator and the rotor. The interpole elements may produce a magnetomotive force and harmonically couple the magnetic pole pairs of the stator with the magnet pole pairs of the rotor.
Owner:NAT OILWELL VARCO LP
Stator field providing torque and levitation
InactiveUS6879074B2Easy constructionSimple electrical controlShaftsMechanical energy handlingMagnetomotive forceLevitation
The invention relates to an economical, non-wearing, electrical permanent magnet drive for actively controlling the rotor position in three degree of freedom. The stator windings produce superimposed fields with different pole numbers in the pole pitches by unsymmetrical magnetomotive force distributions.
Owner:LEVITRONIX TECH +1
Electric machine
InactiveUS20070194650A1Reducing eddy current lossLower average currentSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuitMagnetomotive forceHarmonic
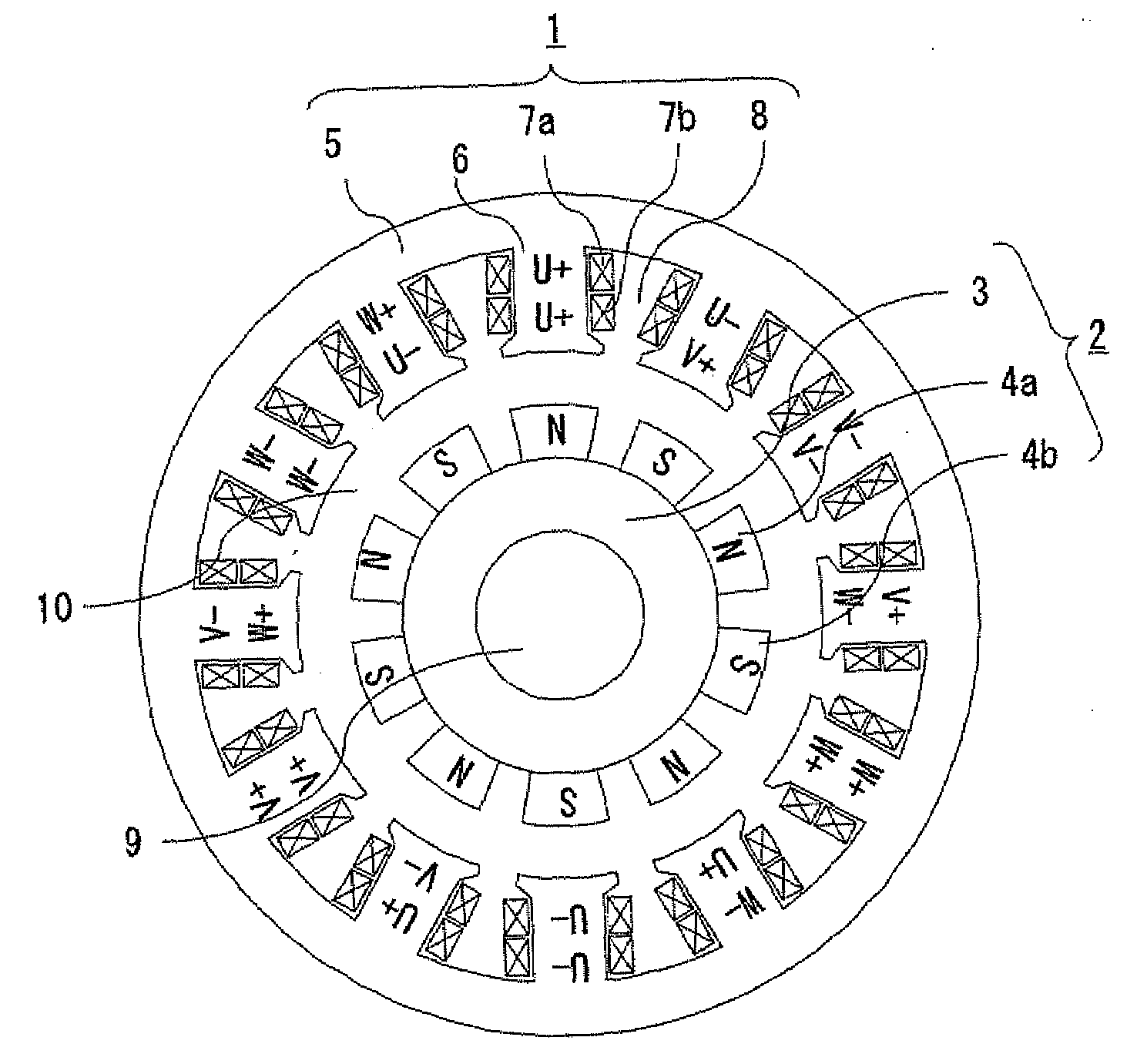
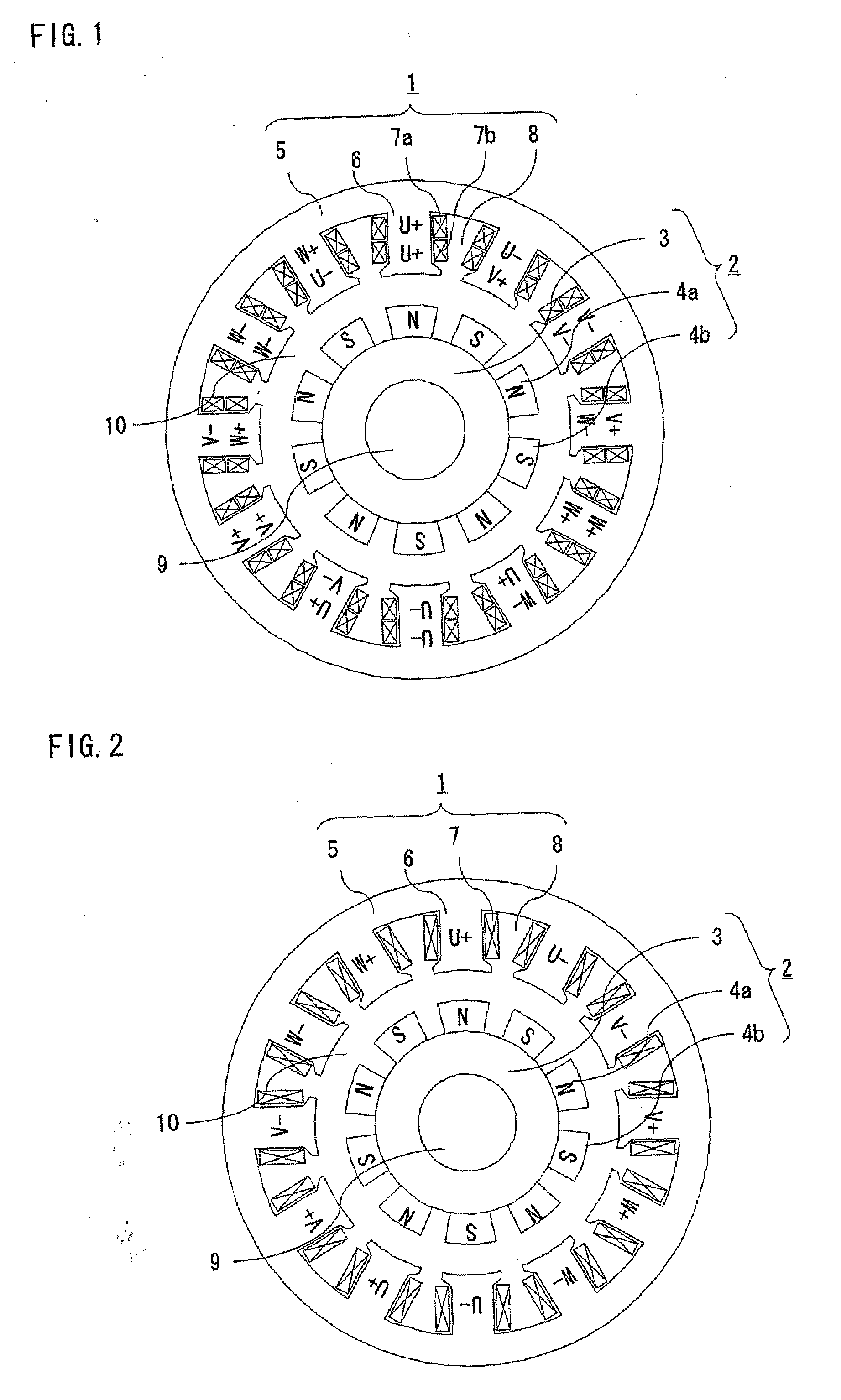
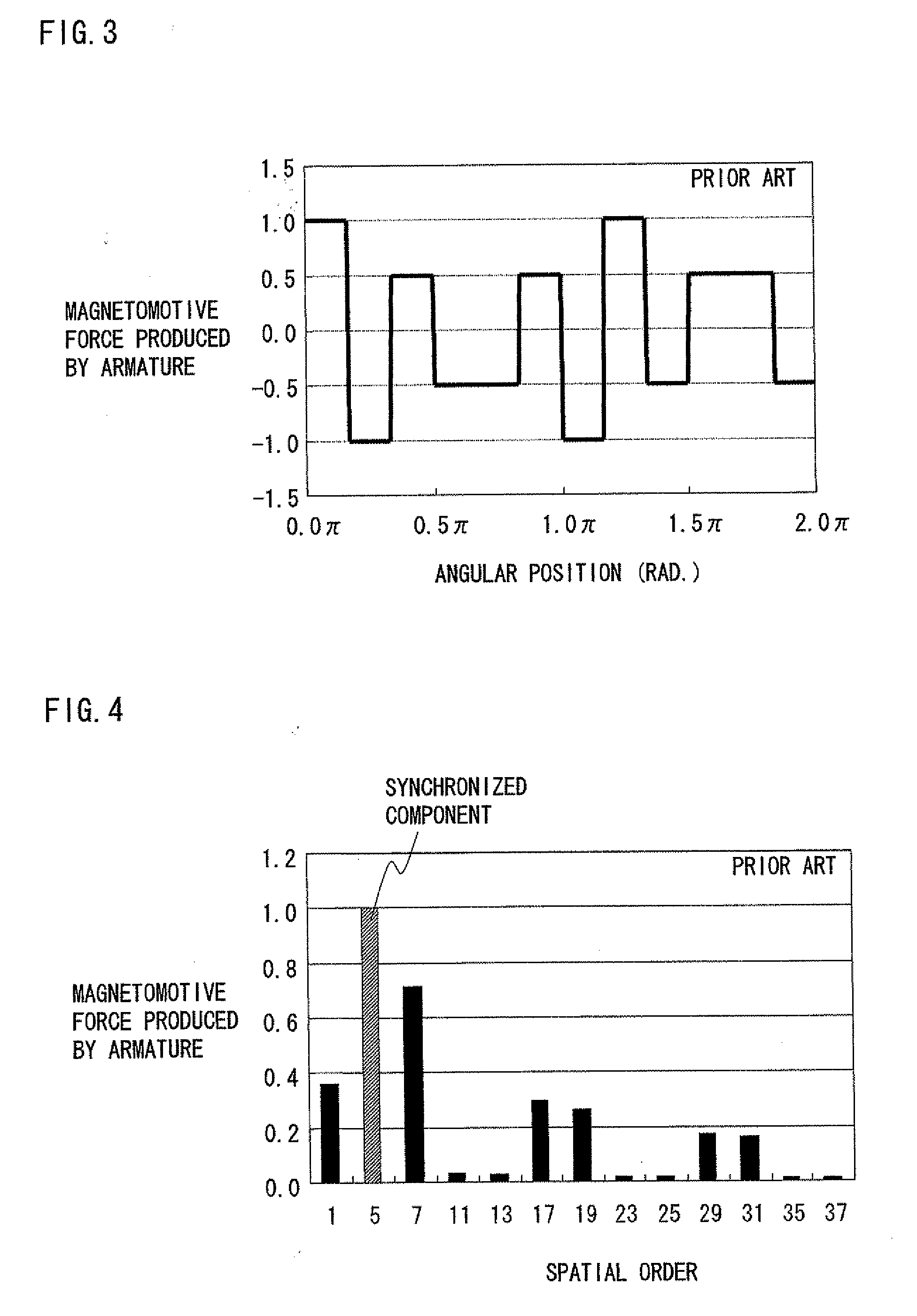
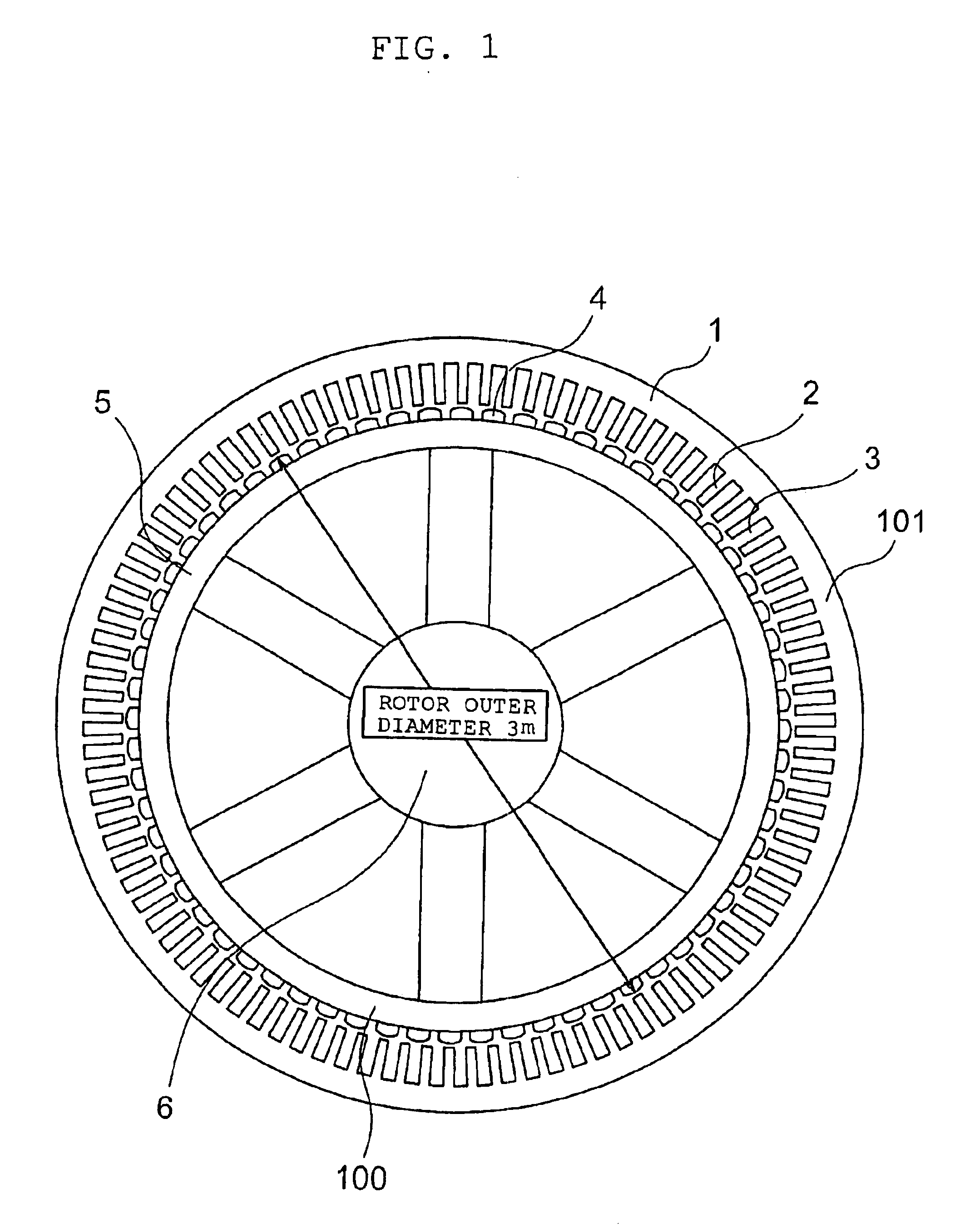
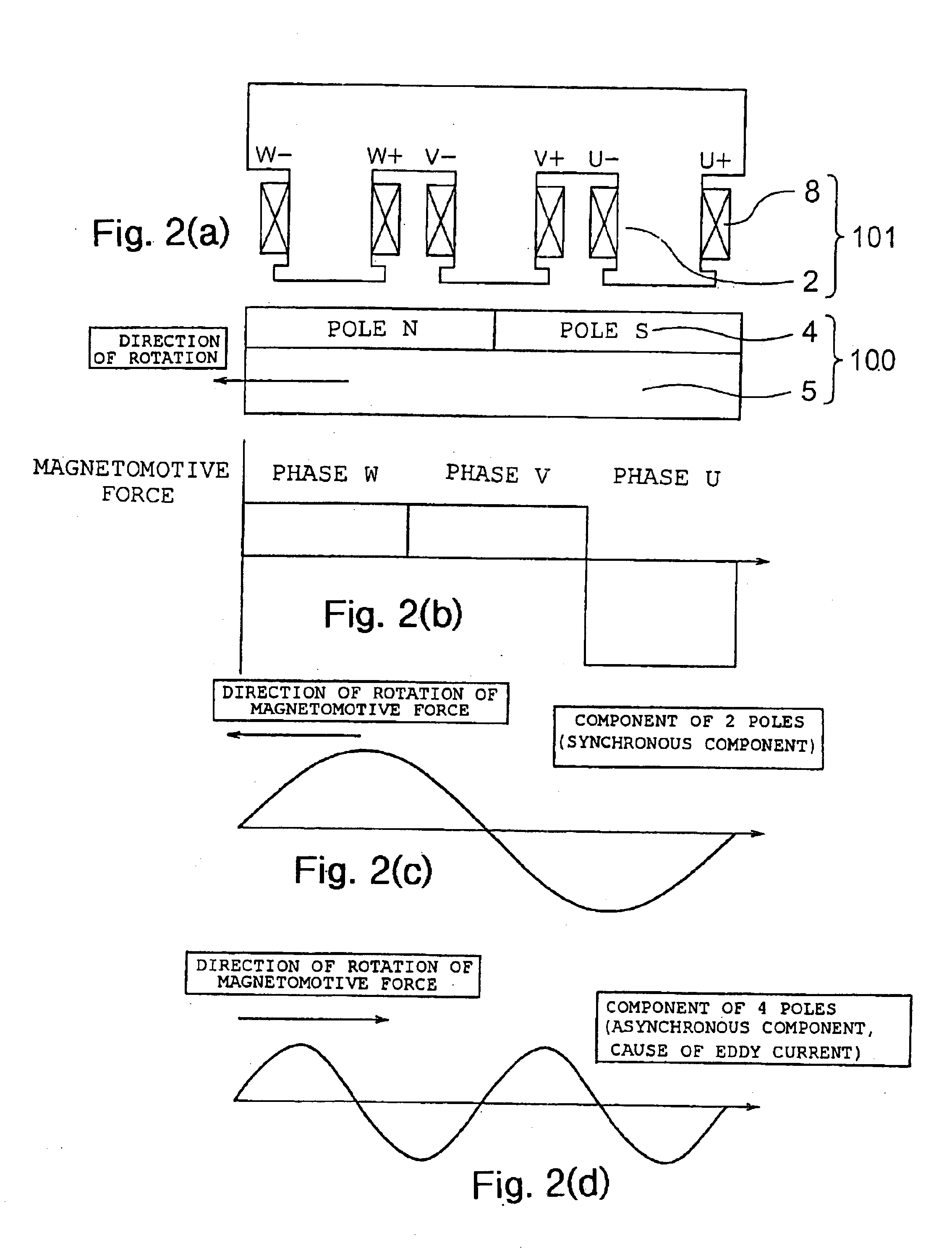
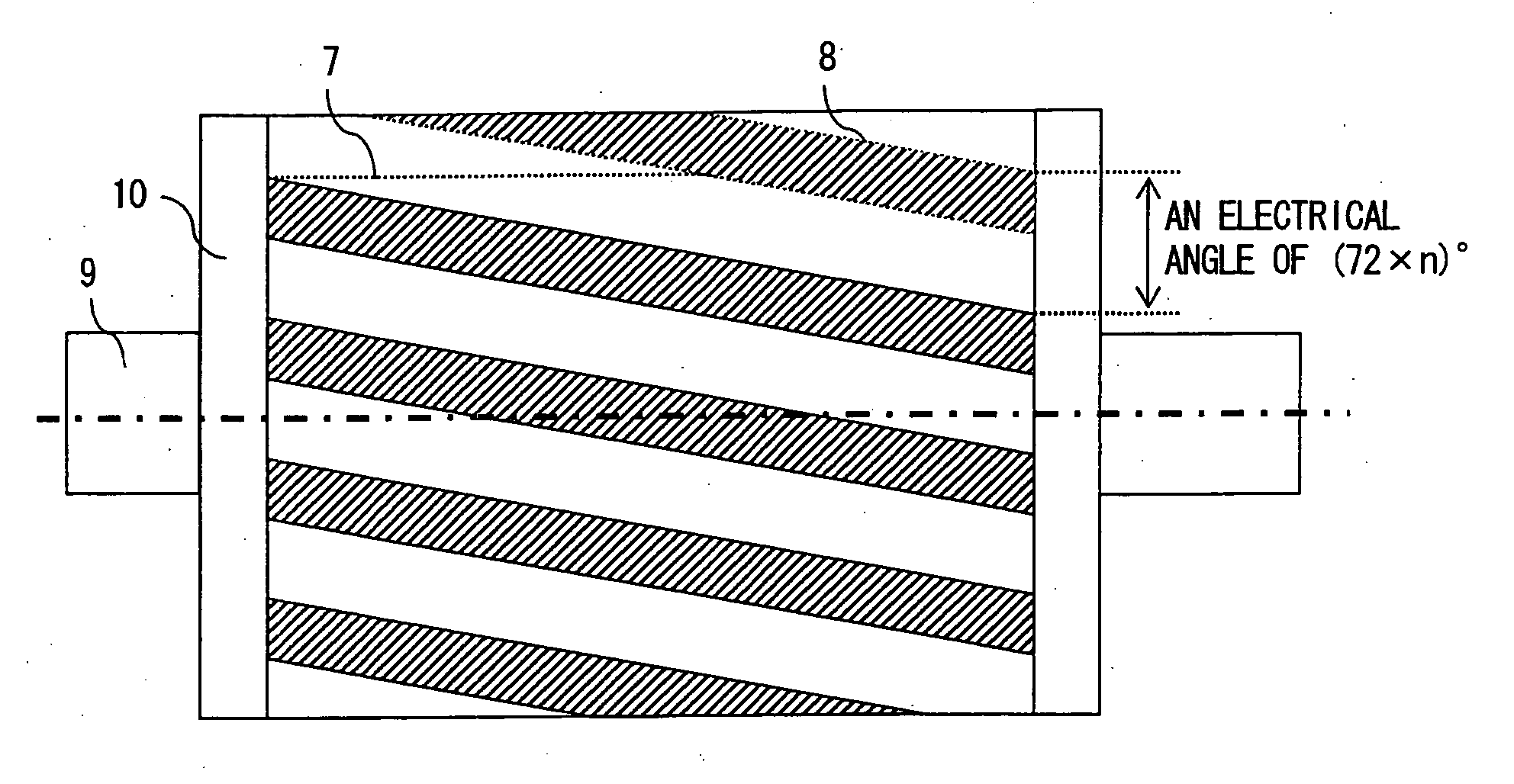
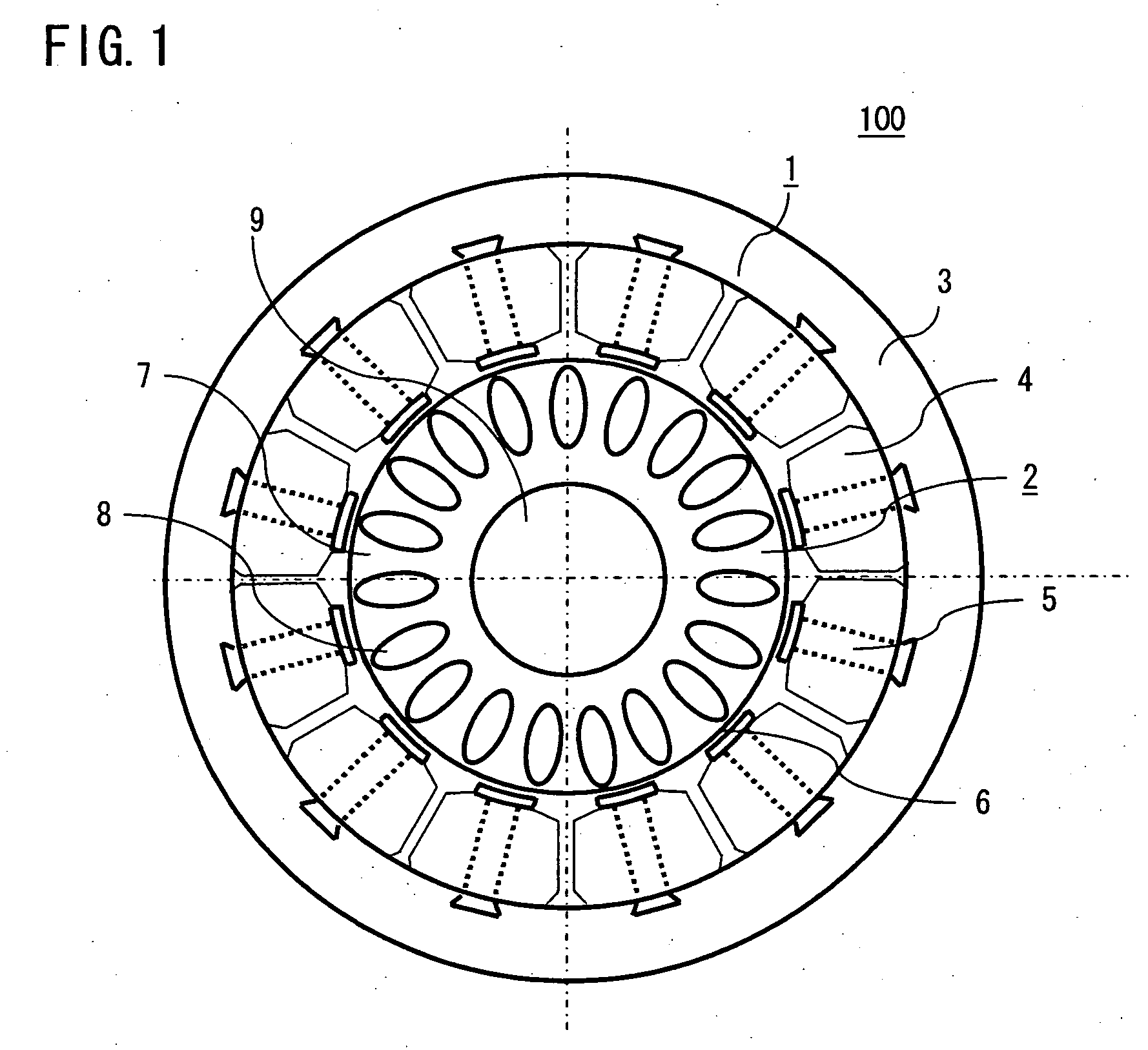
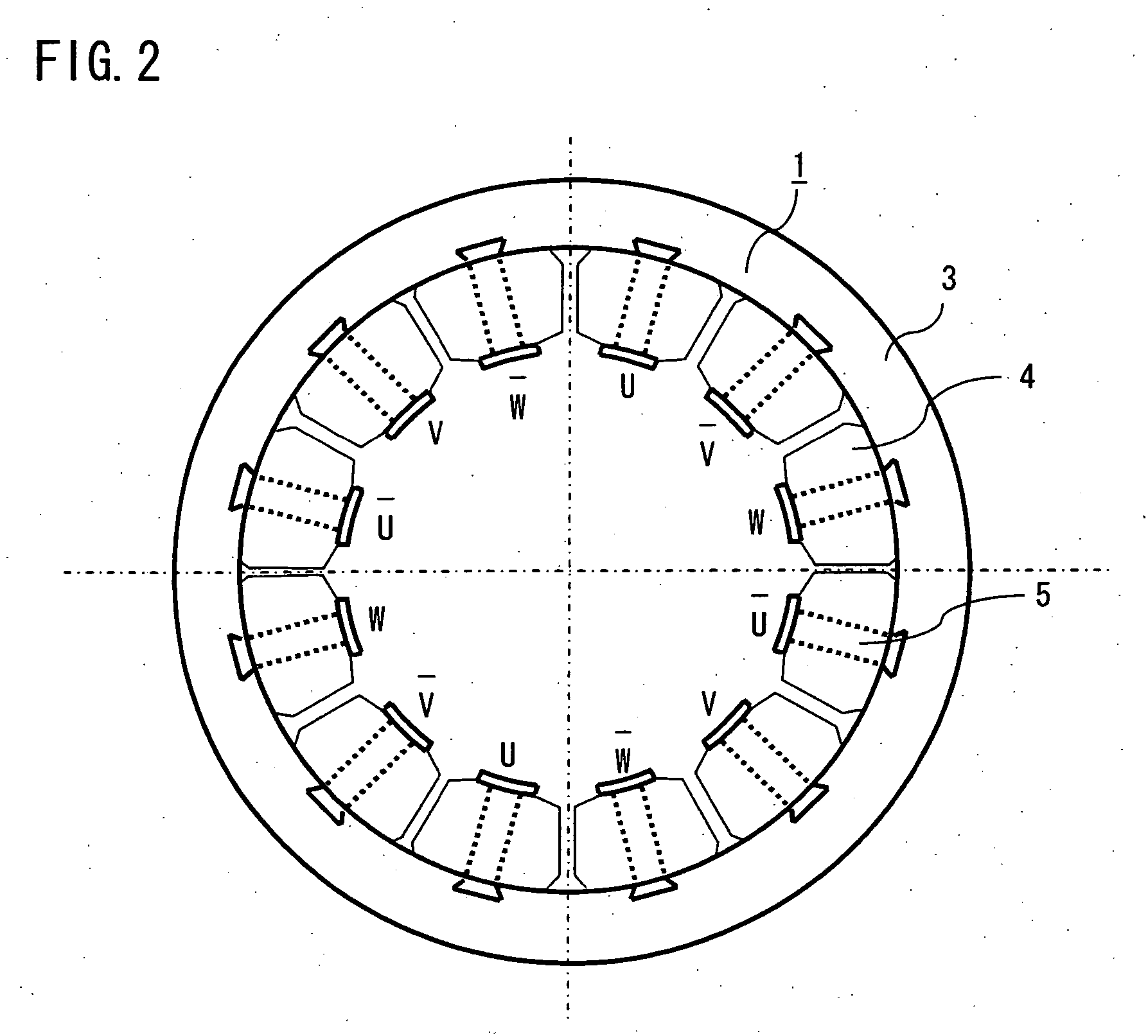
In a rotating electric machine including a field pole unit having ten magnetic poles (P=10) and an armature having twelve teeth (Q=12), armature coils are wound around the successive teeth with phase relationships and winding polarities arranged in the order of U+ / U+, U− / V+, V− / V−, W− / V+, W+ / W+, W− / U+, U− / U−, U+ / V−, V+ / V+, W+ / V−, W− / W− and W+ / U−, where “U,”“V” and “W” represent three phases of the individual armature coils while “+” and “−” denote winding polarities. Among all harmonic components of magnetomotive forces produced by the armature coils, harmonic components of orders lower than a synchronized component can be reduced in this rotating electric machine. This structure decreases eddy currents flowing in the field pole unit, resulting lower eddy current loss in the field pole unit of the rotating electric machine.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Double-stator motor
InactiveUS20110285238A1Low costImprove efficiencySynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetomotive forceMagnetic poles
In a double-stator motor has a rotary shaft, an annular rotor is coupled with a rotary shaft. First and second three-phase stators are arranged inside and outside to the rotor in the radial direction and formed to generate first and second rotating magnetic fields in response to three-phase currents, respectively. The rotor has an even number of segment poles made of soft magnetic material and arranged mutually separately at positions of the rotor. The positions are equally distanced apart from the rotary shaft in the radial direction and in the circumferential direction. Each of the first and second three-phase stators has magnetic poles which are the same in the number of poles as the segment poles and the magnetic poles are positioned such that magnetomotive forces from the magnetic poles are faced to each other between the magnetic poles of the first and second three-phase stators.
Owner:DENSO CORP
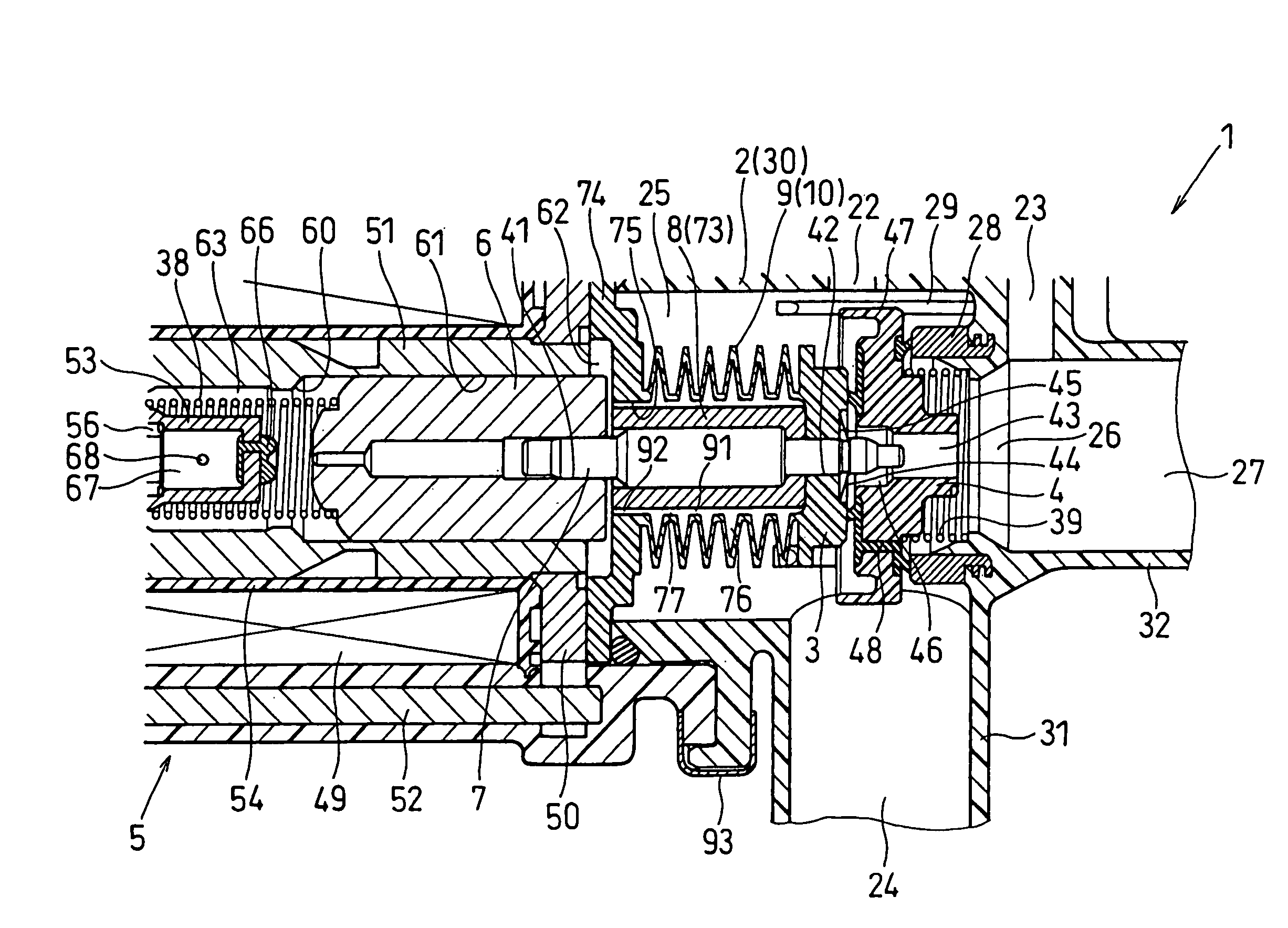
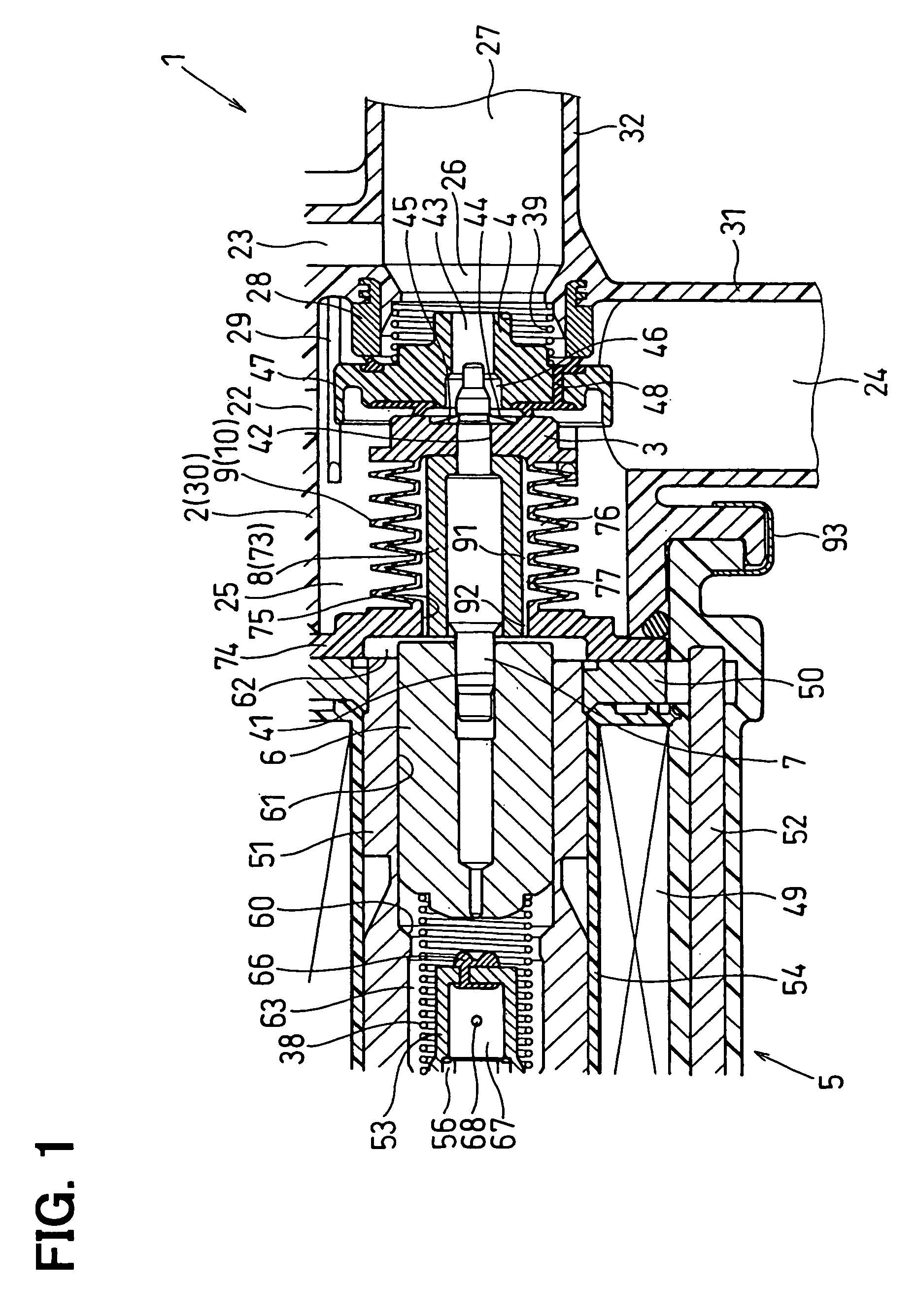
Electromagnetic valve
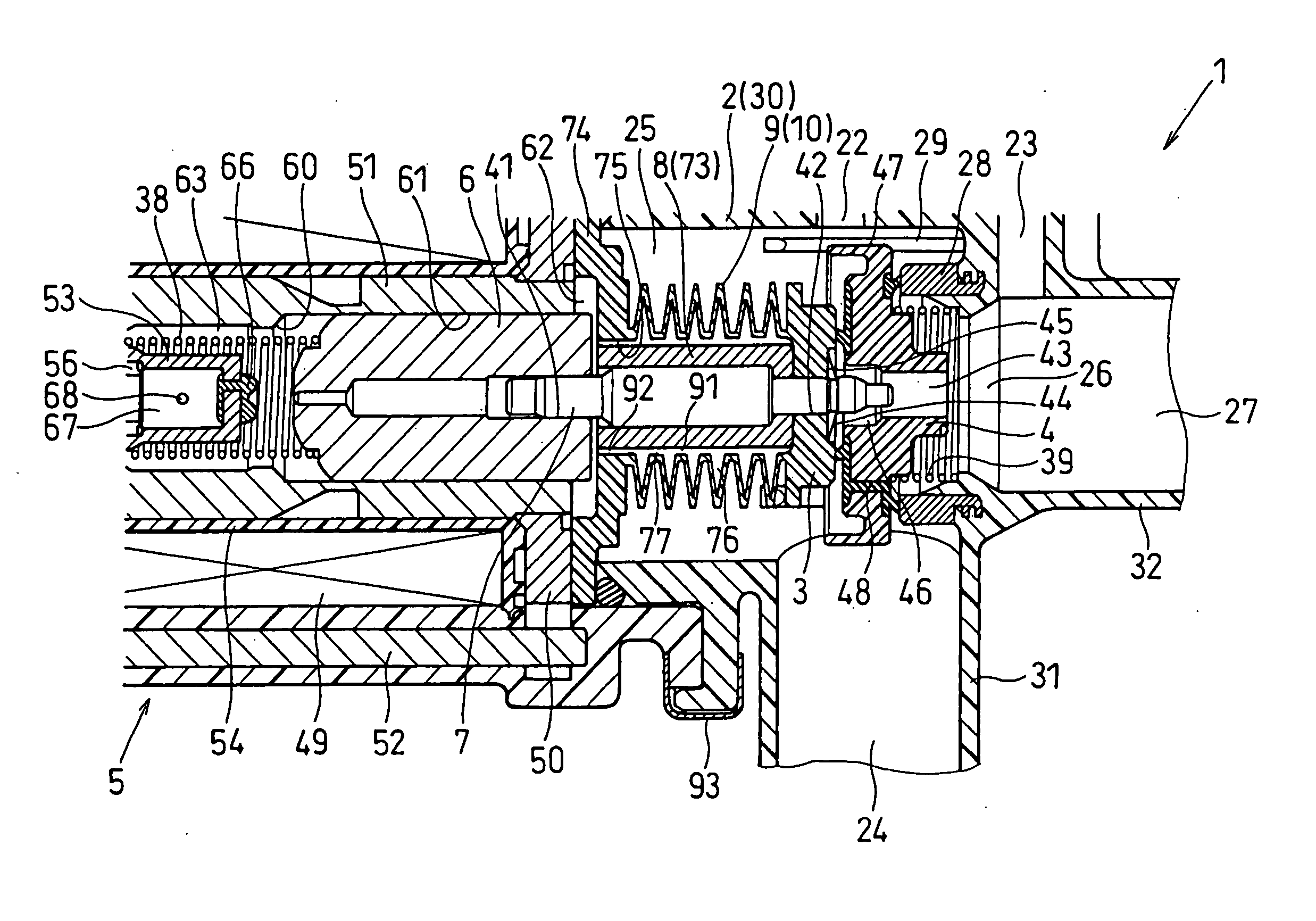
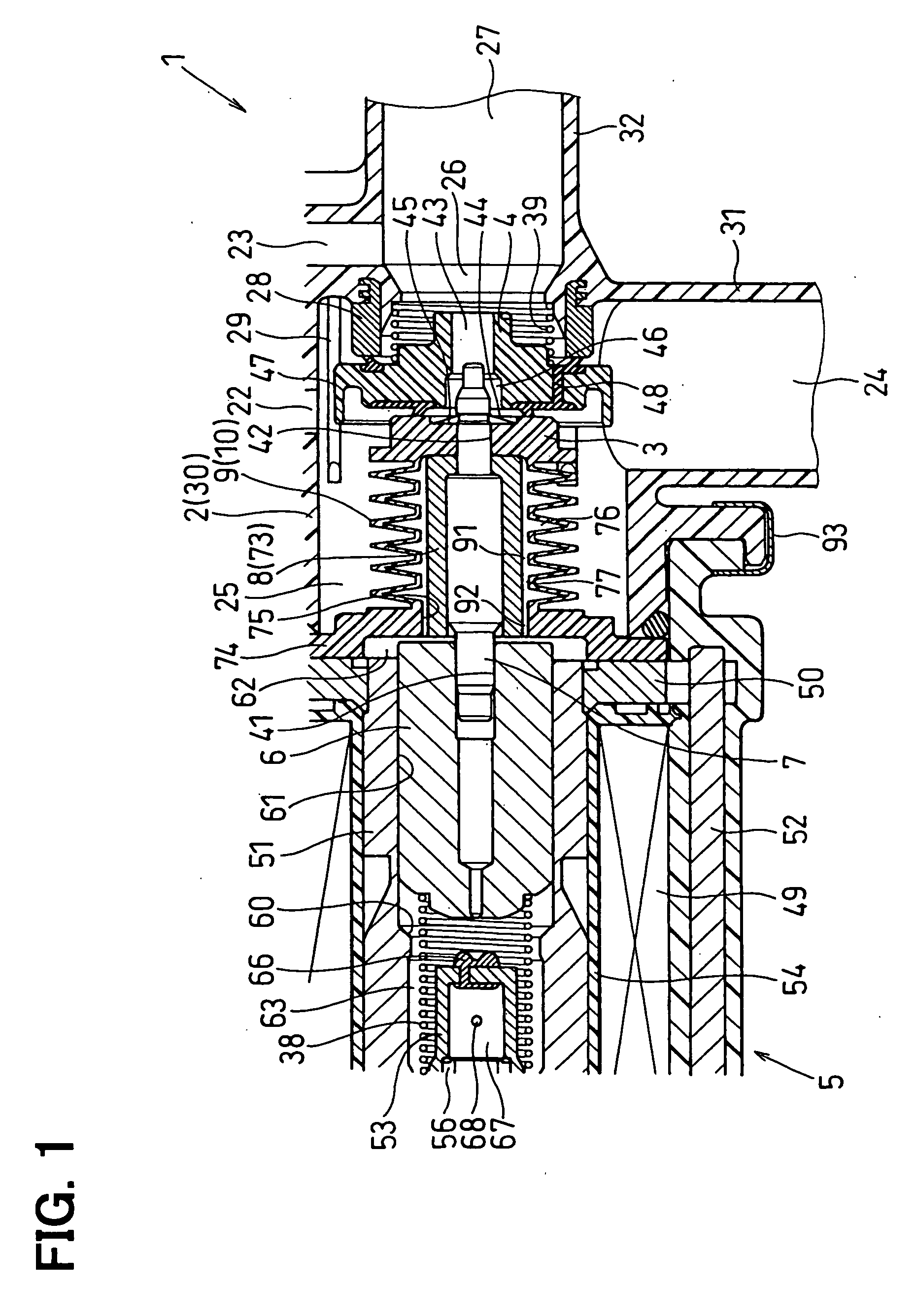
InactiveUS20060207663A1Reduce running noiseLow reliabilitySpindle sealingsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesInterior spaceMagnetomotive force
In an electromagnetic valve, a valve member is slidably installed in a housing to open and close a valve hole. A moving core is slidably installed in the housing, and a coil generates a magnetomotive force to attract the moving core to one side when it is energized. The valve shaft links a motion of the moving core with a motion of the valve member. A bellows surrounds the valve shaft to form a cylindrical inner space between the valve shaft and itself. The bellows is subjected to both positive and negative pressures to extend and shrink in accordance with the motions of the valve member and the moving core. An inner volume of the inner space increasing and decreasing in accordance with extending and shrinking operations of the cylindrical bellows portion. The opening of the bellows and the valve shaft form a narrow opening passage.
Owner:DENSO CORP
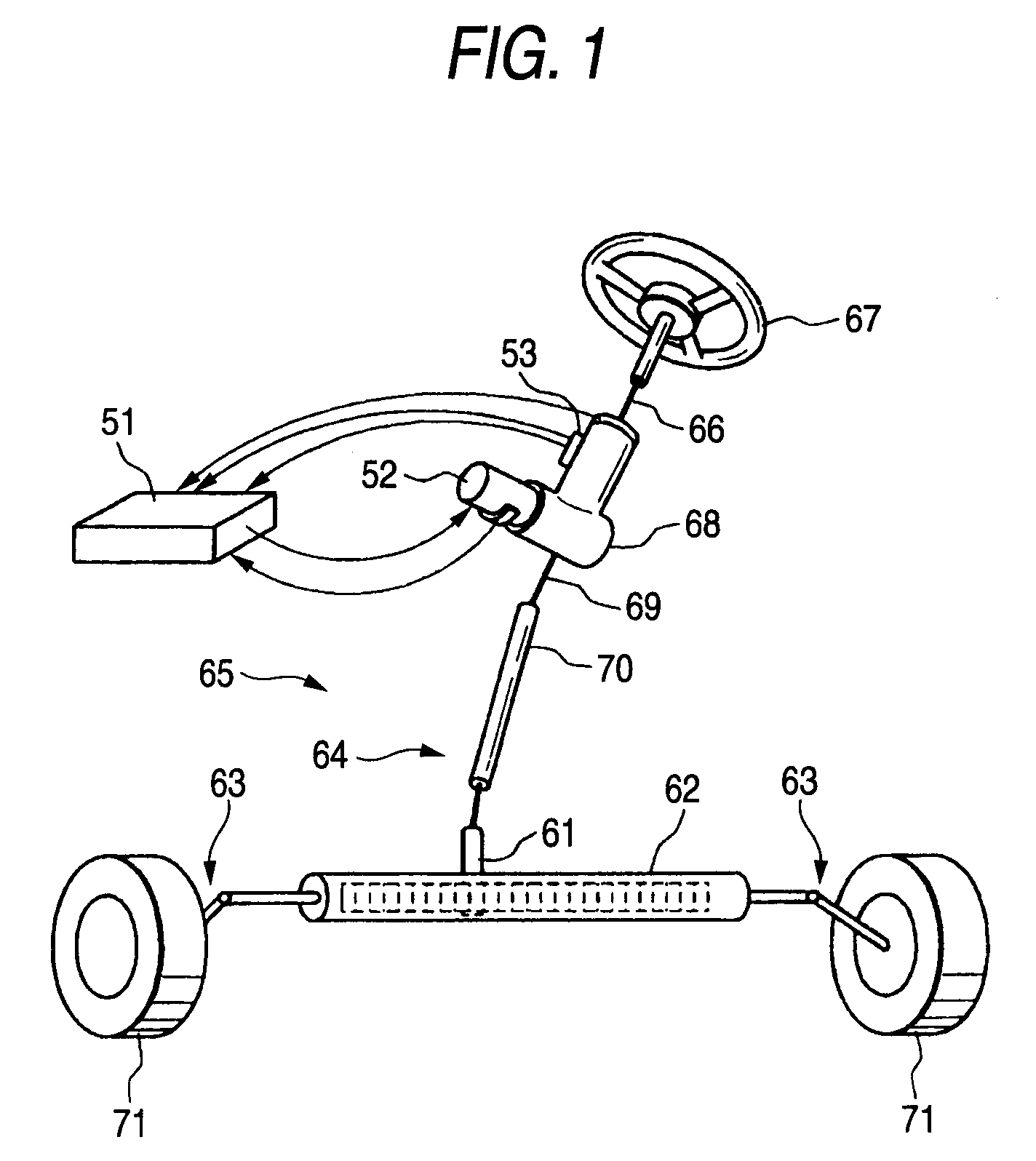
Brushless motor and electric power steering system
InactiveUS20070273241A1Not easily affectedMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsElectric power steeringBrushless motors
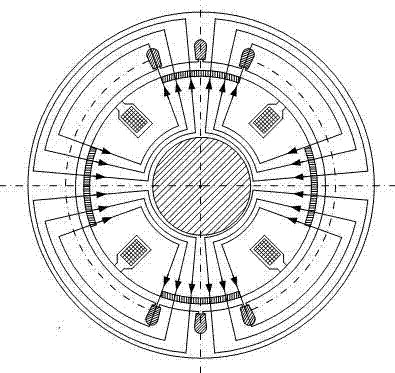
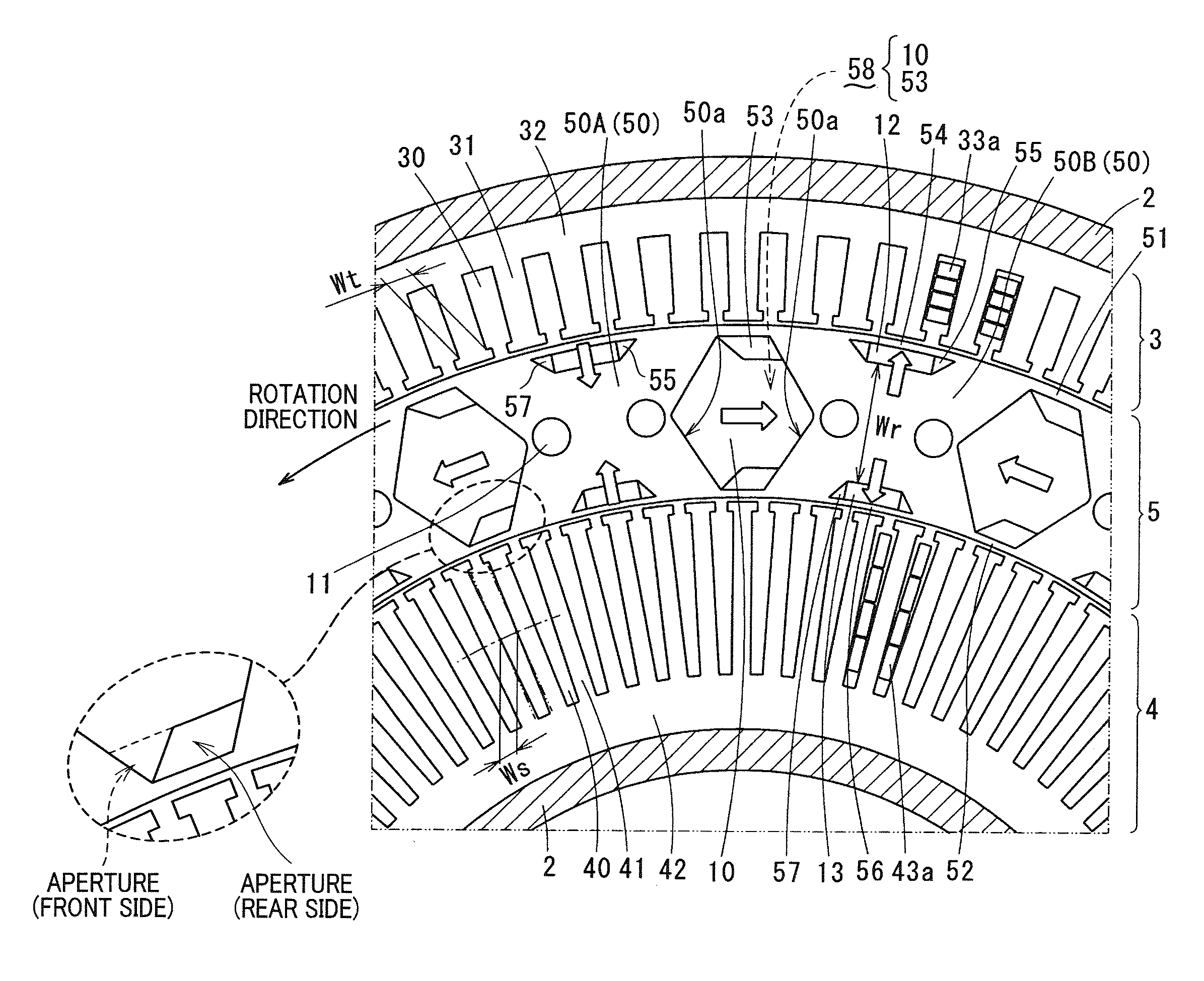
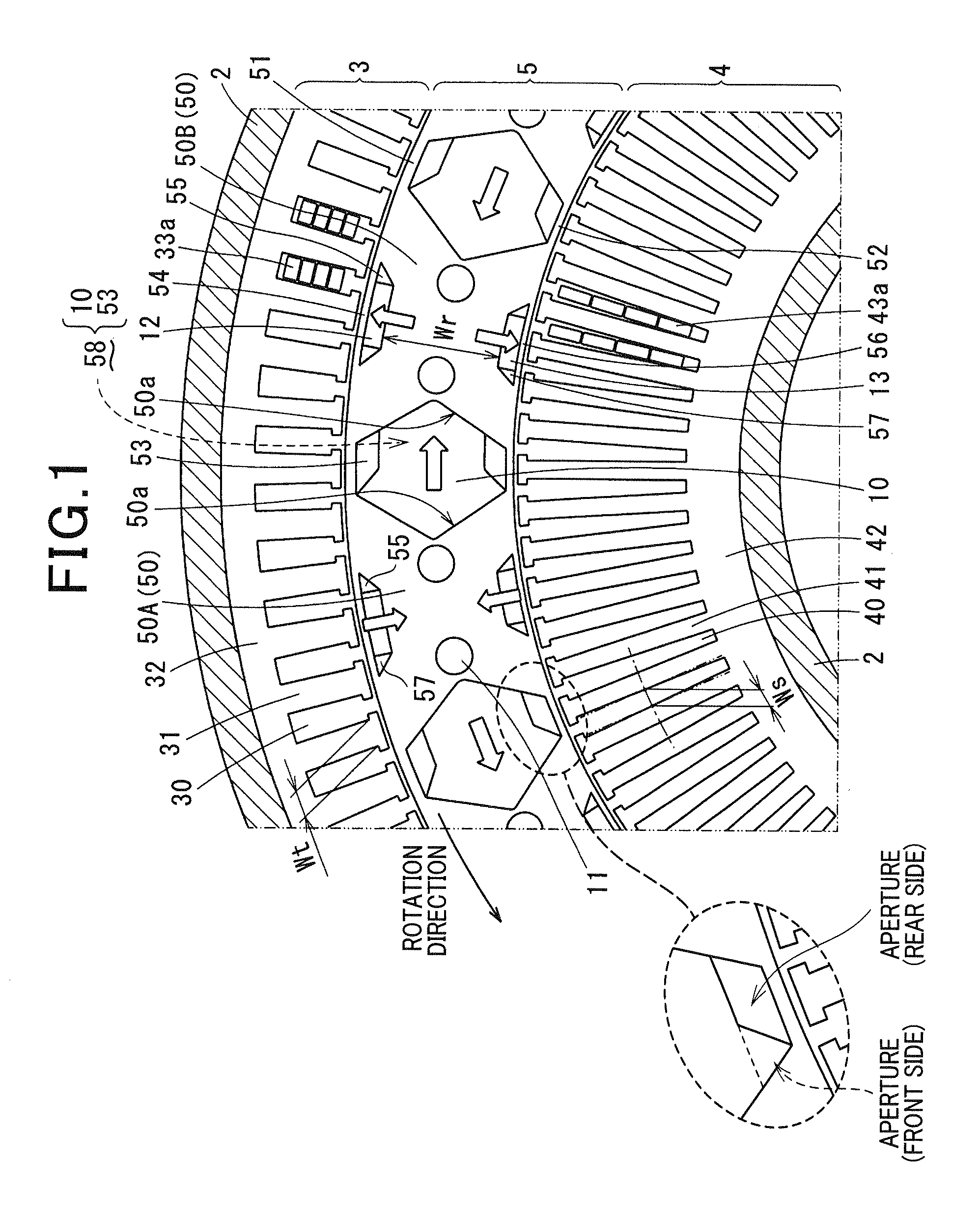
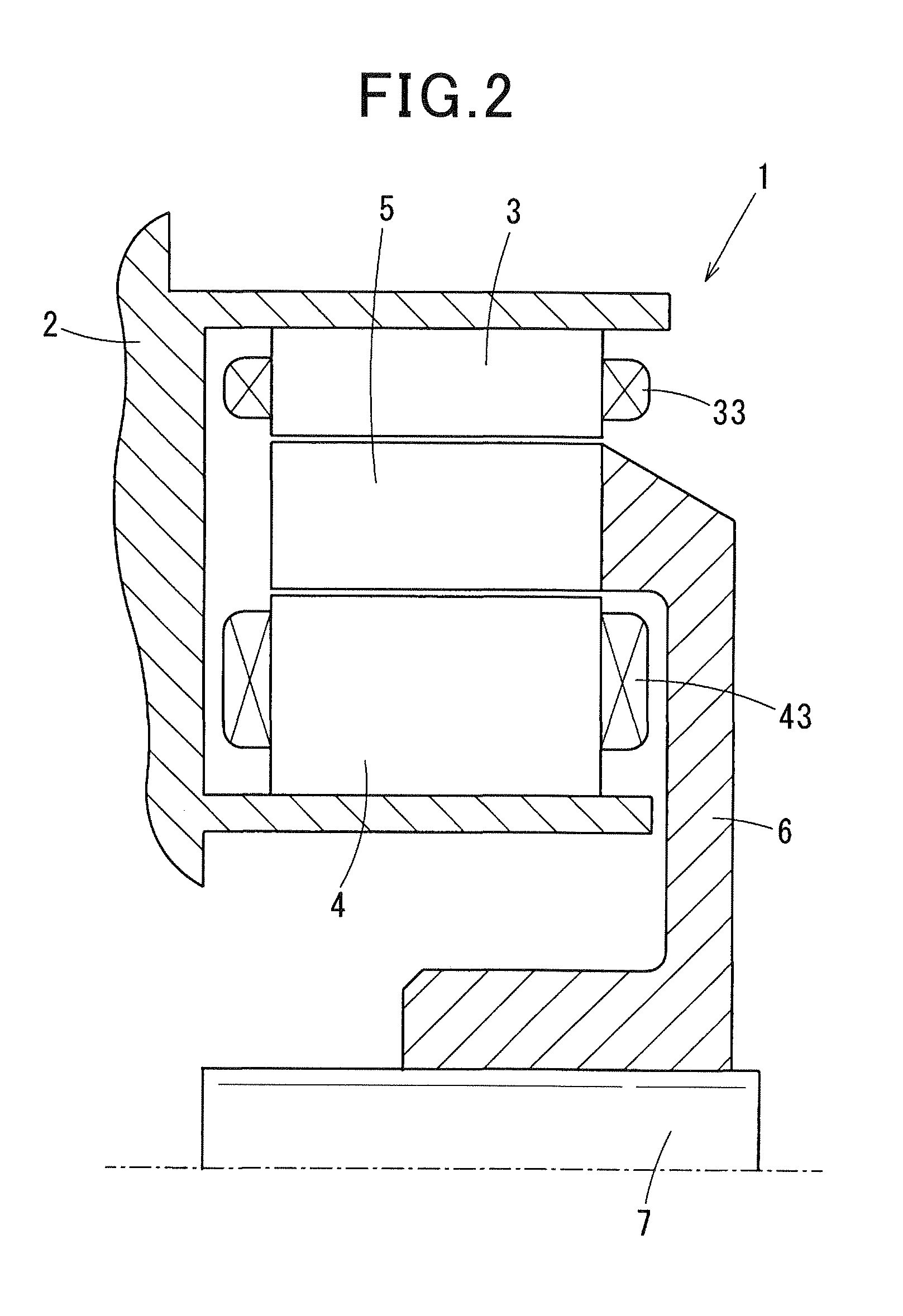
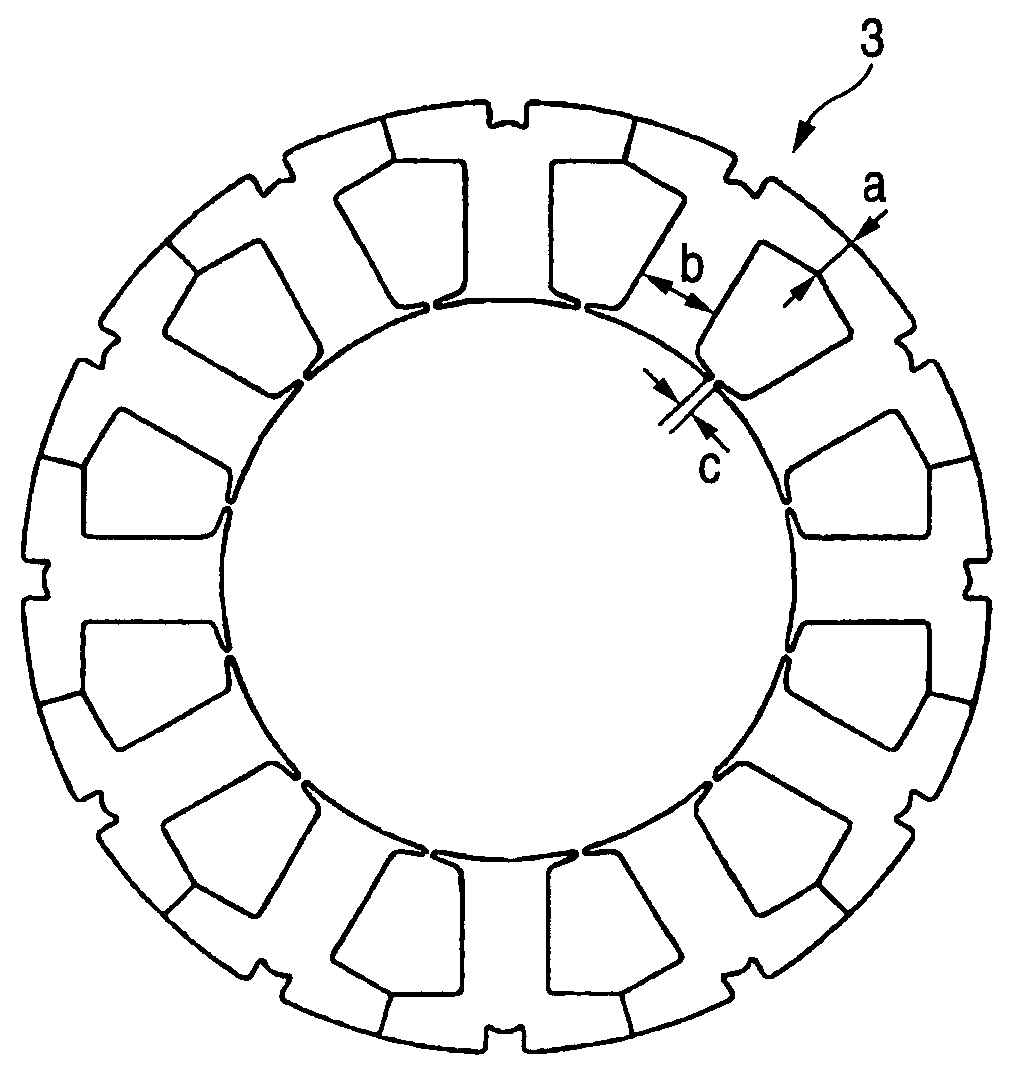
A brushless motor including a rotor which has ten permanent magnets each containing rare earth neodymium and provided around a rotor yoke and an outside diameter of 45 mm to 55 mm, and a stator which has a stator core having twelve slots and an outside diameter of 75 mm to 85 mm and whose magnetomotive force at maximum current is 700 AT or more. The stator core is configured such that a teeth width b is 0.14 times or more of the outside diameter of the rotor.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Magnetic write head employing multiple magnetomotive force (MMF) sources
InactiveUS20080112080A1Vary amountMaximize write fieldConstruction of head windingsRecord information storageMagnetomotive forceMagnetic media
A write head for perpendicular magnetic recording having a write pole and first and second return poles. The write head can include a first magnetomotive force source for delivering a magnetomotive force to the first return pole and the write pole and a second magnetomotive force source for delivering magnetomotive force to the second return pole and the write pole. The first and second magnetomotive force sources can be operated independently of one another so that different relative amounts of magnetomotive force can be applied to the first and second return poles. A trailing magnetic shield can be connected with one of the return poles, such as the second return poles, and the variation in magnetomotive force can be used to increase the amount of flux flowing through the trailing shield when increased field gradient is desired (such as when writing a transition), and to decrease the amount of flux through the trailing shield when decreased field gradient and increased write field are desired (such as when writing a long magnetic section on a magnetic medium).
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Magnetic noise reduction method for AC rotary electric machine, and motor control apparatus and AC rotary electric machine apparatus using the same
InactiveUS7151354B2Reduce magnetic noiseSimple and reliable processSingle-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlMagnetomotive forceHarmonic
The invention provides techniques for reducing or altering the magnetic noise of an AC rotary electric machine. A magnetic noise reducing harmonic current of order n, whose frequency is n times the frequency of the fundamental frequency component of a polyphase AC current fed to an armature of a polyphase AC rotary electric machine, is superimposed on the polyphase AC current, thereby reducing or altering a harmonic component having a frequency (n−1) times the frequency of the fundamental frequency component and occurring due to a radial magnetic excitation force acting radially on an iron core of the AC rotary electric machine. Magnetic noise is caused by a vibration whose energy is the sum of the circumferential and radial vibrations of the iron core occurring due to the magnetomotive force of the rotor, and altering the radial vibration is particularly effective in altering the magnetic noise; as the harmonic component of the radially acting magnetic excitation force, occurring due to harmonic components having frequencies 3, 5, 7, and 13 times the fundamental frequency, has a frequency 6 or 12 times the fundamental frequency, the magnetomotive force of the rotor can be effectively reduced or altered when a current having a frequency 7 or 13 times the fundamental frequency is superimposed on the stator current.
Owner:DENSO CORP
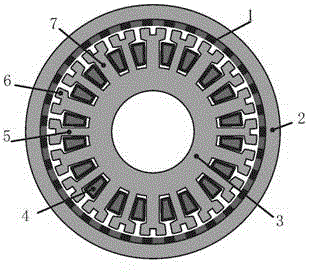
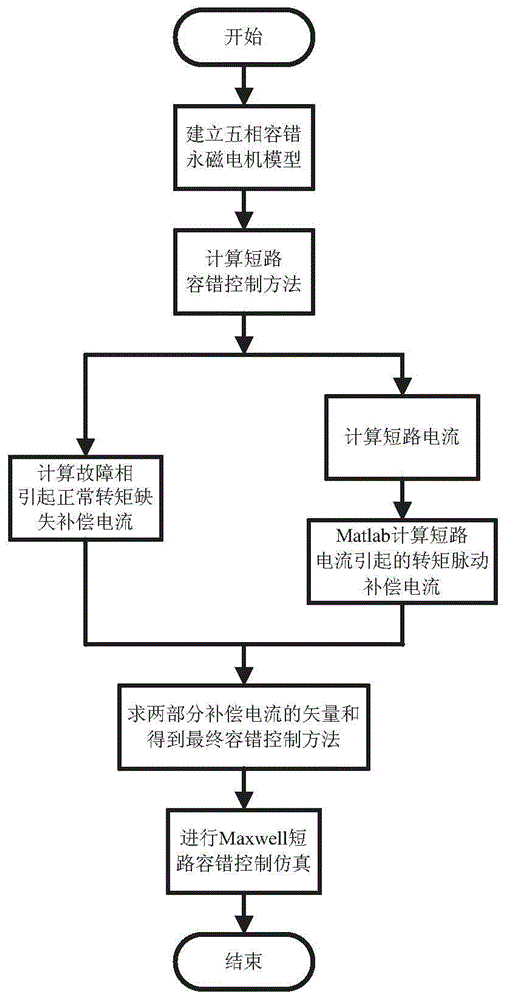
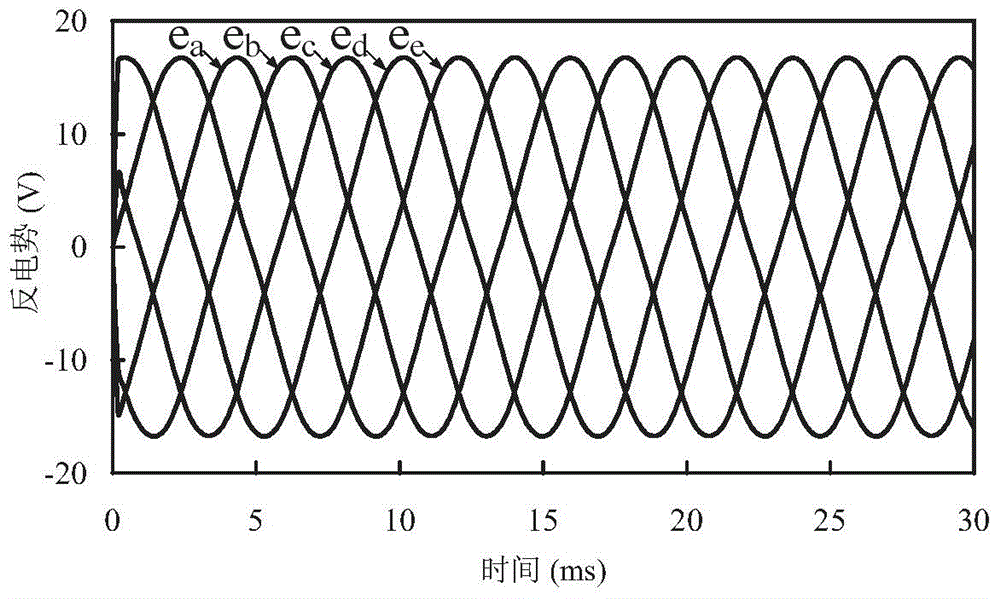
Short circuit fault tolerant control method for five-phase fault tolerant permanent magnet motor
ActiveCN104682807AReduce torque rippleRealize short-circuit fault operationElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPhase currentsMagnetomotive force
The invention discloses a short circuit fault tolerant control method for a five-phase fault tolerant permanent magnet motor. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a five-phase fault tolerant permanent magnet motor model; compensating a short circuit fault phase normal torque loss by using non-fault phase current by directly adopting a compensation strategy of an open fault; compensating the fluctuated magnetic motive force caused by the short circuit fault phase current by using non-fault phase current, so that the synthetic magnetic motive force is zero; eliminating torque ripple caused by the short circuit current; synthesizing the vectors of the compensating current of the steps 2 to 3 to obtain the short circuit fault tolerant current; performing control and simulation on Maxwell short circuit fault tolerant. According to the short circuit fault tolerant control method for the five-phase fault tolerant permanent magnet motor, one-phase short circuit fault tolerant control is performed on the motor according to the specific situation of the no-load counter electromotive force of the motor, so that the fault is equivalent to the output torque in a normal operating state; the torque ripple is reduced; the operation of the five-phase fault tolerant permanent magnet motor with a short circuit fault is realized.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Permanent magnet dynamo electric machine, and permanent magnet synchronous generator for wind power generation
A dynamo electric machine includes a rotor having magnetic poles with permanent magnets and a stator having armature windings concentratedly wound around teeth. When the number of pole pairs of the magnetic poles of the rotor is P, diameter of the rotor is D (meters), and a spatial harmonic order of a predetermined harmonic component of an armature magnetomotive force of the rotor is N ((N=P to the 1.5th power)×(N to the minus 4-th power)×(the square of P)×D<0.6 (in meters).
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Single-phase induction motor and method for reducing noise in the same
ActiveUS7245105B2Reduce noiseReduce vibrationSingle-phase induction motor startersSynchronous motors startersLow noiseMagnetomotive force
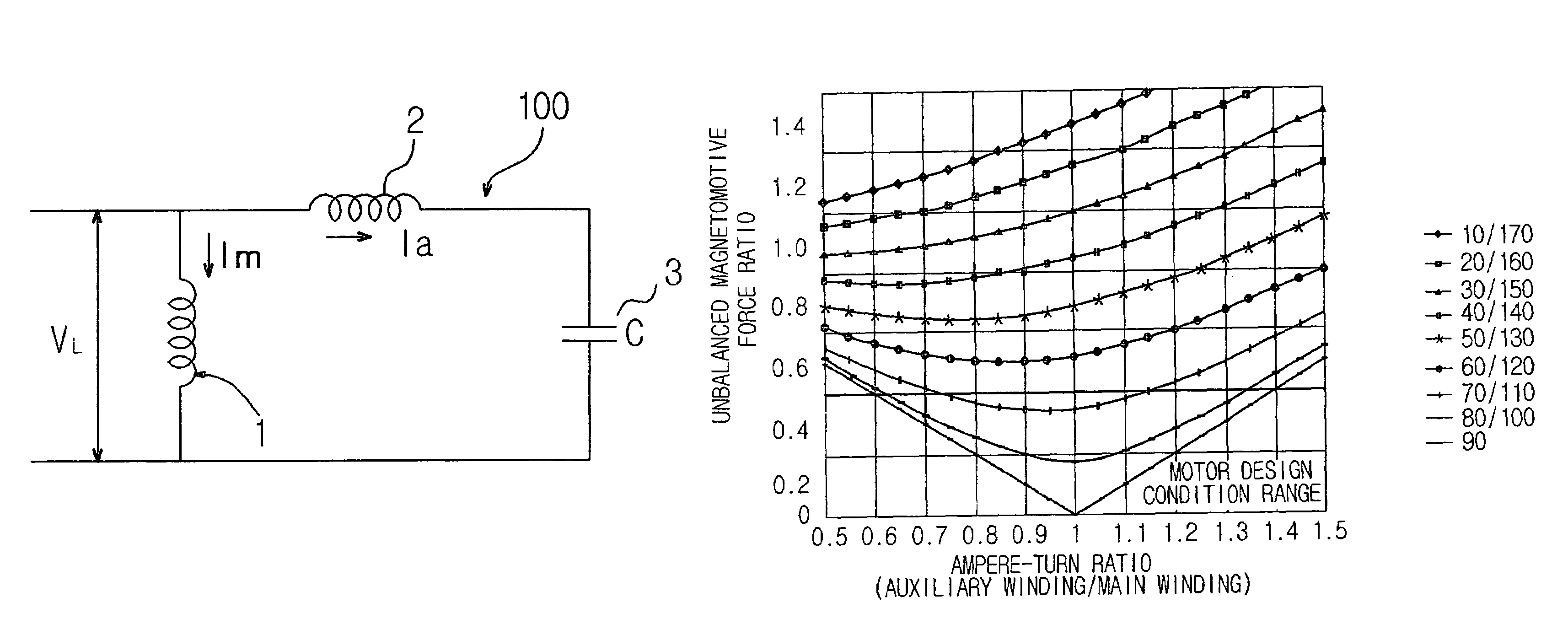
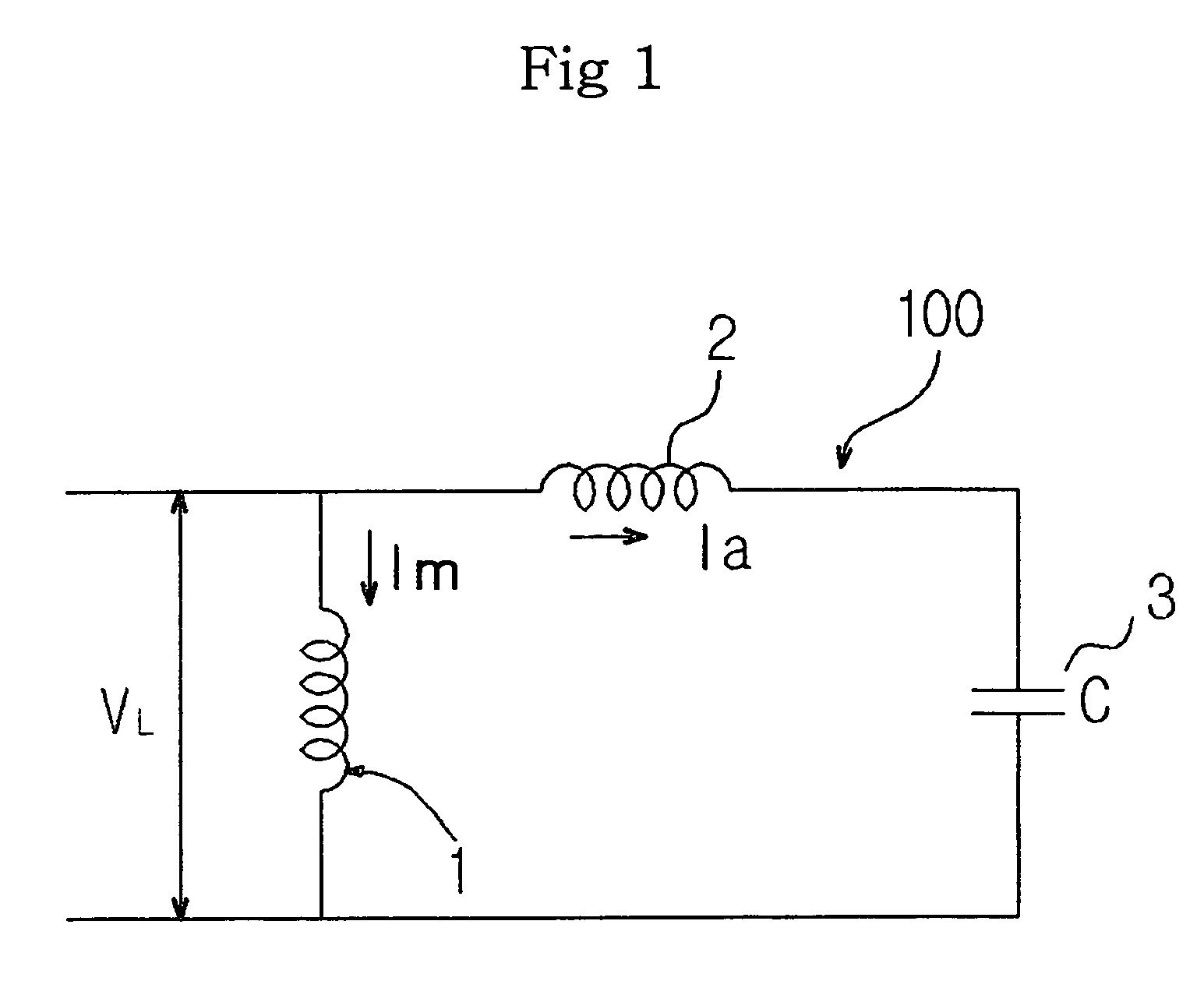
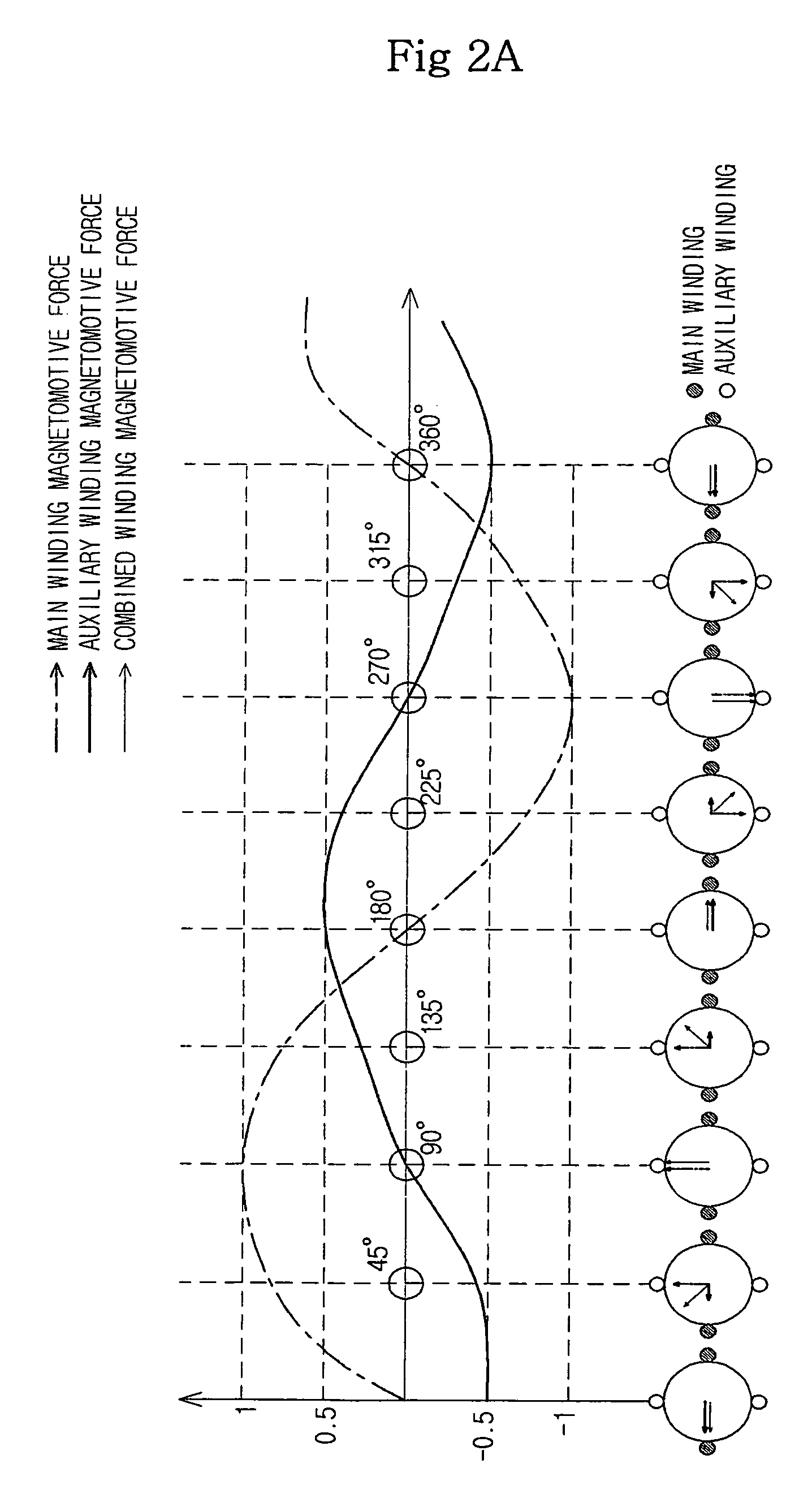
A single-phase induction motor and a method for reducing noise in the same, which can eliminate unbalance between magnetomotive forces of main and auxiliary windings in a stator of the motor, thereby implementing a low noise, low vibration motor, and can also achieve balance between the magnetomotive forces of the stator windings in the entire running range of the motor, and can further achieve balance between the magnetomotive forces of the stator windings on the basis of temperature increase of the motor as it runs. The amplitude of a main-winding current flowing through the main winding in the stator is controlled to be equal to the amplitude of an auxiliary-winding current flowing through the auxiliary winding in the stator, and the phase difference between the main-winding and auxiliary-winding currents is controlled to be maintained at a predetermined value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electromagnetic valve
InactiveUS7591281B2Low reliabilityReduce running noiseSpindle sealingsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesInterior spaceMagnetomotive force
In an electromagnetic valve, a valve member is slidably installed in a housing to open and close a valve hole. A moving core is slidably installed in the housing, and a coil generates a magnetomotive force to attract the moving core to one side when it is energized. The valve shaft links a motion of the moving core with a motion of the valve member. A bellows surrounds the valve shaft to form a cylindrical inner space between the valve shaft and itself. The bellows is subjected to both positive and negative pressures to extend and shrink in accordance with the motions of the valve member and the moving core. An inner volume of the inner space increasing and decreasing in accordance with extending and shrinking operations of the cylindrical bellows portion. The opening of the bellows and the valve shaft form a narrow opening passage.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Automotive tandem alternator having reduced axial length and capable of effectively suppressing magnetic leakage
InactiveUS7602095B2Shorten the lengthSuppressing Flux LeakageSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetomotive forceAlternator
According to the invention, a tandem alternator includes a rotary shaft, a first and a second field arranged in tandem on the rotary shaft, and a first and a second armature arranged in tandem in the axial direction of the rotary shaft. The first armature is provided on an outer periphery of the first field to constitute a first power generation unit. The second armature is provided on an outer periphery of the second field to constitute a second power generation unit. The first and second fields are arranged to abut each other in the axial direction of the rotary shaft, so as to minimize the axial length of the alternator. The first and second fields are configured to respectively create a first and a second magnetomotive force whose directions are opposite to each other, so as to minimize magnetic leakage between the first and second power generation units.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Electron equipment
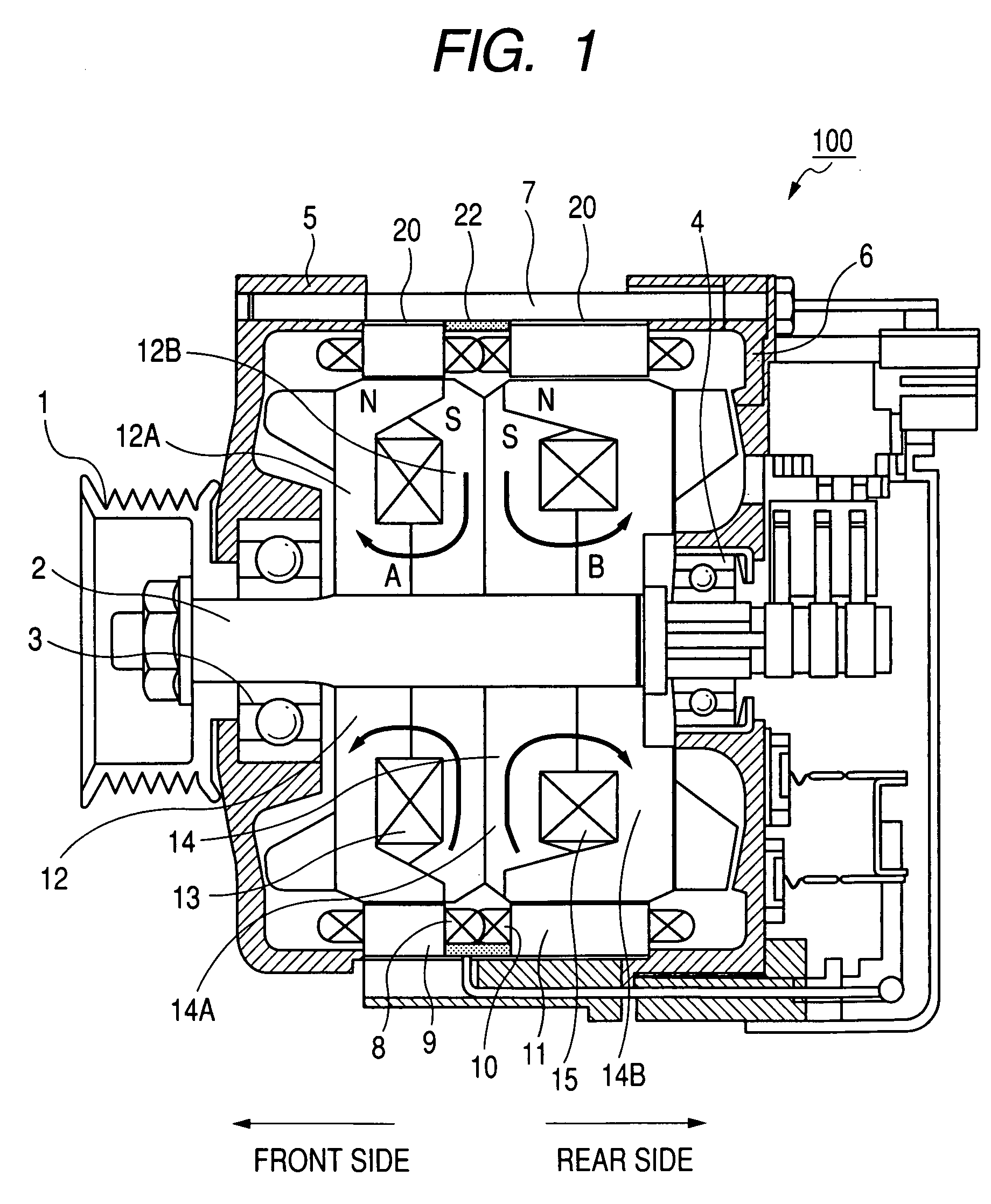
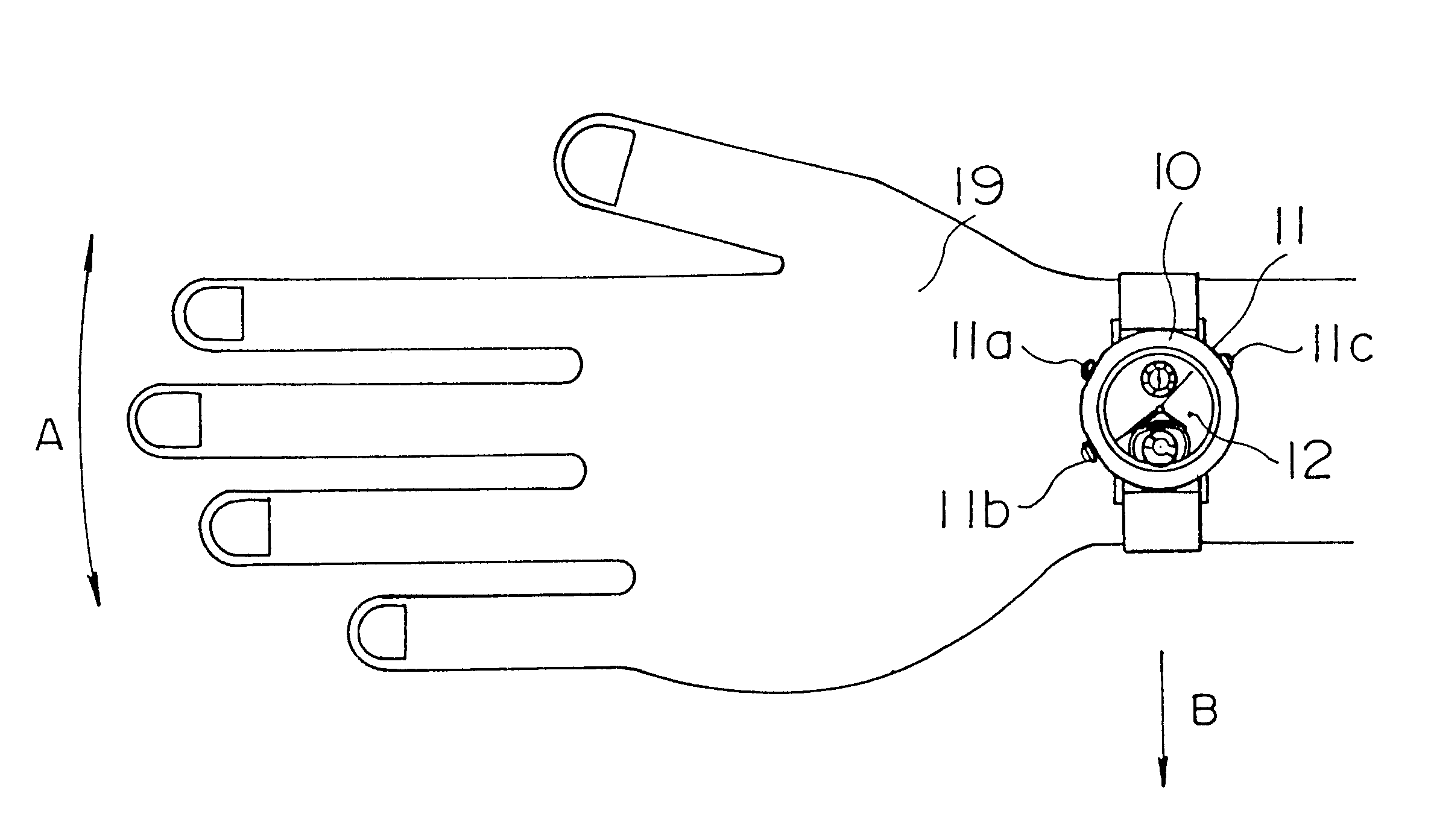
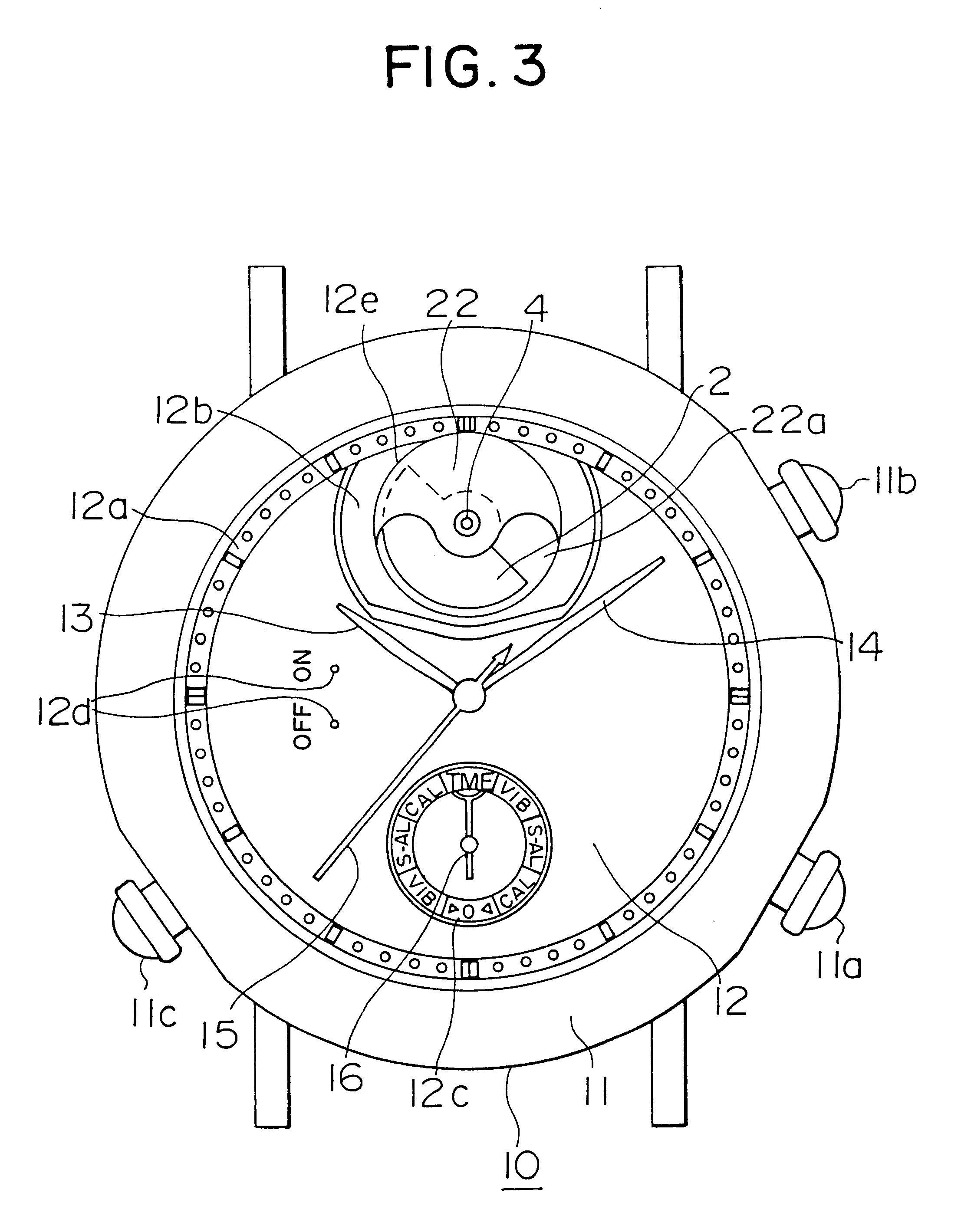
InactiveUS6349075B1Increased durabilityEasy to assembleVisual indicationAcoustic time signalsMagnetic polesElectric equipment
A small electronic equipment with a vibration alarm has, as a drive source, a flat stator type bipolar stepping motor, which has a rotor having high durability, can be assembled easily, requires low power consumption, is started constantly stably, and can be rotated at a high speed. In this electronic equipment with the vibration alarm, a rotor (1) is rotated by a rotary drive system including a drive pulse generating means (112, 113, 114), a drive circuit (110), a flat stator (6), a counter electromotive voltage detection coil (306), and a magnetic pole position detection means (107, 115, 116), so that an eccentric weight (2) fixed to the rotor is rotated, thereby generating vibration. The drive pulse generating means outputs a pulse signal for driving the stepping motor on the basis of an alarm signal output at alarm time. The drive circuit supplies a drive current to a drive coil (305) on the basis of the pulse signal from the drive pulse generating means. The flat stator transmits the magnetomotive force generated in the drive coil to the rotor (1). The counter electromotive voltage detection coil detects a counter electromotive voltage generated by rotation of the rotor. The magnetic pole position detection means detects the magnetic pole position of the rotor (1), which is rotating, with respect to the flat stator (6) on the basis of the counter electromotive voltage generated in the counter electromotive voltage detection coil, and outputs, to the drive pulse generating means, a detection signal for controlling the output timing of the pulse signal supplied from the drive pulse generating means (114).
Owner:CITIZEN WATCH CO LTD
Structure for modular motor stator and end part overlapping fractional slot windings of modular motor stator
ActiveCN105680585ASmall torqueReduce torque rippleMagnetic circuit stationary partsWindings conductor shape/form/constructionMagnetomotive forceHarmonic
The invention provides a structure for a modular motor stator and end part overlapping fractional slot windings of the modular motor stator. The number of stator slots and the number of winding pole pairs are set to be 2Z and p respectively, wherein the stator slots are evenly distributed on the circumference; the stator comprises two sets of three-phase symmetric AC windings; the windings are evolved from traditional single-layer concentrated fractional slot windings; the arrangement of each set of windings is the same as that of the traditional single-layer concentrated fractional slot windings with Z slots and p pole pairs; the staggered angle of two sets of windings is one half of a coil span mechanically; overlapping regions at the end parts of the windings are distributed on the circumference of the stator at intervals; and modularization can be achieved by cutting the stator in the non-overlapping regions at the end parts of the windings. The structure can greatly reduce the non-working tooth harmonic content in magnetomotive force of the traditional concentrated fractional slot windings, so that the motor loss can be reduced; torque pulsation is stabilized; the noise is reduced; meanwhile, the structure has the advantage that the motor stator with the concentrated fractional slot windings can be modularized; manufacturing, transportation and assembly of a large motor are facilitated; the interphase mutual inductance is small; and improvement of the fault-tolerant capability of the motor is facilitated.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Electromagnetic synchronizer actuating system
An assembly for actuating a synchronizer includes a shift fork, a shift rail, and a permanent magnet connected to the shift rail. A first control coil is disposed in proximity to the permanent magnet. The first control coil is operable to produce a magnetomotive force on the permanent magnet in a first direction when a current is applied to the first control coil. A second control coil is disposed in proximity to the permanent magnet. The second control coil is operable to produce a magnetomotive force on the permanent magnet in a second direction when a current is applied to the second control coil. The permanent magnet is moved to a first position when the current is applied to the first control coil and the permanent magnet is moved to a second position when the current is applied to the second control coil. Movement of the magnet in turn moves the synchronizer between engaged positions.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
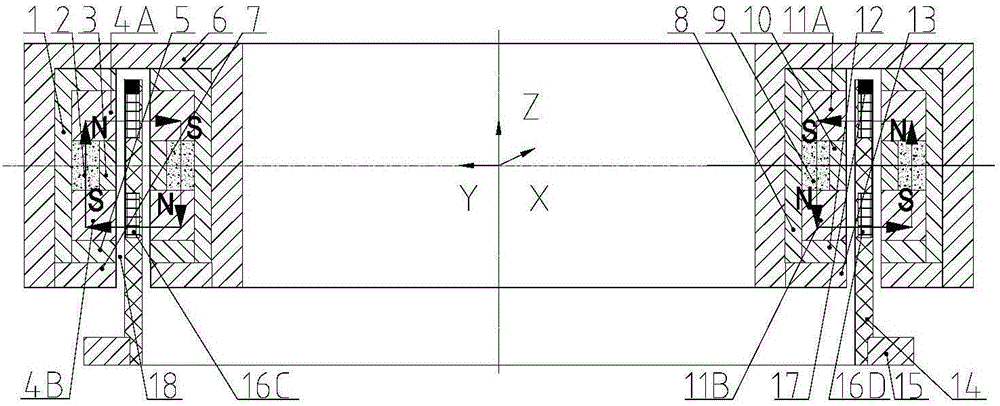
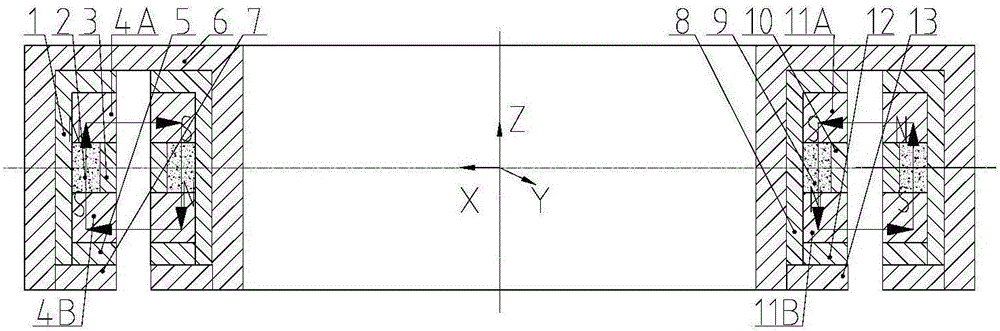
Asymmetric permanent-magnet bias axial magnetic bearing
The invention relates to an asymmetric permanent-magnet bias axial magnetic bearing. The asymmetric permanent-magnet bias axial magnetic bearing is composed of a stator iron core, a rotor iron core with a thrust disc, permanent magnets and an exciting coil. The double-E-shaped stator iron core forms four stator magnetic poles in Z positive and negative directions of the magnetic bearing, and two stator magnetic poles are disposed in each of the Z positive and negative directions. The two stator magnetic poles in each of the Z positive and negative directions are two annular permanent magnets different in magnetomotive force and can produce different static carrying forces in the two axial directions while providing bias magnetic flux density. According to the asymmetric permanent-magnet bias axial magnetic bearing, the asymmetric annular permanent magnets different in magnetomotive force are used in the Z positive and negative directions for producing different static carrying forces in the two axial directions while providing bias magnetic fields, so that static bias current is greatly reduced; the exciting coil is disposed in radial space of the double-E-shaped stator iron core, and accordingly axial space is saved, and unnecessary radial force is prevented from being produced; the asymmetric permanent-magnet bias axial magnetic bearing has the advantages of being reliable in performance, convenient to control and low in loss.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Low-vibration noise performance fractional slot concentrated winding permanent magnet motor and design method
ActiveCN107579606AReduce harmonic amplitudeReduce MMF tooth harmonicsMagnetic circuit stationary partsWindings conductor shape/form/constructionControl theoryConductor Coil
The invention discloses a low-vibration noise performance fractional slot concentrated winding permanent magnet motor and a design method, and belongs to the field of rotating motors. On the basis ofa motor matched with an existing notched pole, and some stator additional teeth are correspondingly added (the specific number of the teeth is determined according to the matched notched pole of the motor). For a three-phase 18 / 16 motor, six additional teeth are added, the position of each stator notch is calculated, and the winding structure adopts a concentrated winding structure corresponding to the three-phase 18 / 16 motor. The rotor structure adopts the common surface-mounted structure, and radial magnetizing is adopted; the motor has the advantages that the stator structure is changed, the content of tooth harmonic waves in the winding magnetomotive force in an air gap is lowered, therefore, the motor vibration and noise are lowered, and meanwhile the rotating torque of the motor is ensured. In addition, due to changes of the stator structure, the content of subharmonic waves of the magnetomotive force in the air gap is lowered, and then eddy-current losses generated in the permanent magnet are lowered. Accordingly, the motor has the great significance in motor body designing.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
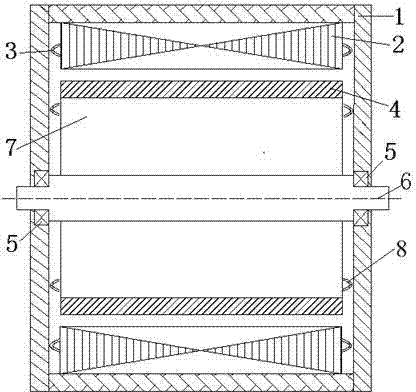
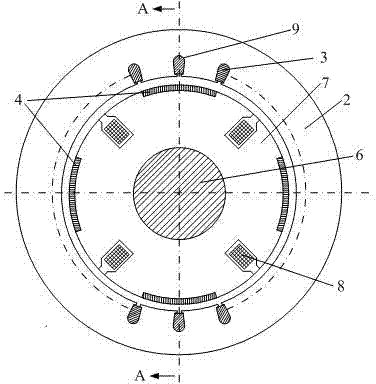
Lorentz force type magnetic bearing capable of realizing double permanent magnet deflection
ActiveCN106090010AReduce lapsReduced dimensional accuracyMagnetic bearingsMagnetic bearingMagnetic poles
The invention discloses a Lorentz force type magnetic bearing capable of realizing double permanent magnet deflection. The bearing comprises a rotor system and a stator system, wherein the rotor system mainly comprises an outer mounting sleeve, outer magnetic steel, an outer magnetism isolating ring, an outer upper magnetism conducting ring, an outer lower magnetism conducting ring, an outer lower magnetism conducting ring lock nut, a turntable, an outer assembly lock nut, an inner mounting sleeve, inner magnetic steel, an inner magnetism isolating ring, an inner upper magnetism conducting ring, an inner lower magnetism conducting ring, an inner lower magnetism conducting ring lock nut and an inner assembly lock nut; the stator system mainly comprises a stator framework, an aluminum substrate, a winding and epoxy resin glue. The magnetic steel axial magnetization scheme is adopted, the number of magnetic steel turns is reduced, the gap flux density fluctuation caused by uneven magnetomotive force of the magnetic steel is reduced, the paramagnetic effect is realized by the aid of the magnetism conducting rings, the gap flux density fluctuation caused by assembly of the outer magnetic steel and the inner magnetic steel is further reduced, and high-precision deflection control torque can be realized. Besides, a magnetism conducting material is used as a magnetic pole material, precision machining of a magnetic pole surface is facilitated, and requirements for size precision and surface roughness of the magnetic steel are reduced.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF PETROCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Parallel-magnetic-circuit hybrid-excitation permanent magnet motor
InactiveCN103051133AFully utilizeAdjusting the air gap magnetic fieldSynchronous machine detailsMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetomotive forceExcitation current
The invention relates to a parallel-magnetic-circuit hybrid-excitation permanent magnet motor, which comprises a case. A stator consisting of a stator core and a stator winding, and a rotor consisting of a permanent magnet, a rotating shaft, a rotor core and an excitation winding are installed in the case. The stator winding is distributed in a slot which is circumferentially arranged in the stator core. The permanent magnet and the excitation winding are arranged on the rotor core. Magnetomotive forces established by the permanent magnet and the excitation winding are connected in parallel in the form of magnetic circuits. By adjusting the current of the excitation winding, the air-gap magnetic field of a ferromagnetic pole can be conveniently adjusted to realize the adjustment of the air-gap magnetic field of the motor. Since a permanent magnet magnetomotive force and an electrically excited magnetic magnetomotive force are connected in parallel in the form of magnetic circuits, the needed exciting current is smaller and the efficiency of the permanent magnet motor is kept to be high; since magnetic fluxes produced by two kinds of excitation magnetomotive forces flow through the same motor iron core, the material utilization rate is high and the power density of the permanent magnet motor is kept to be high; and the structure of the parallel-magnetic-circuit hybrid-excitation permanent magnet motor is similar to the structure of a common permanent magnet synchronous motor, an axial magnetic circuit and an additional air gap do not exist and the motor has the advantage of simple structure.
Owner:南京维特力源自动化控制有限公司
Synchronous motor
InactiveUS20130207498A1Increase output torqueReduce concentrationMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsSynchronous motorMagnetomotive force
A double-stator synchronous motor has a rotor, an inner stator and an outer stator. The rotor has segment-magnetic poles arranged in a ring shape. Magnetic poles formed in the inner stator and the outer stator face to each other in a same circumferential position. Each stator has q (q≧2) slots per pole and phase to disperse magnetomodive force. A radially minimum width Wr of each segment magnetic pole is within a range of 1.3q to 2.3q times of a minimum width Wt of outer teeth. A magnetic depth of a magnetic concave section formed in the segment magnetic pole is within a range of not less than an average width Ws of the inner slots. Because this suppresses demagnetization in the permanent magnets caused by stator magnetomotive force, ferrite magnets are used as buried magnets and magnetic-pole central magnets, and suppress the amount of neodymium magnet used in the rotor.
Owner:DENSO CORP
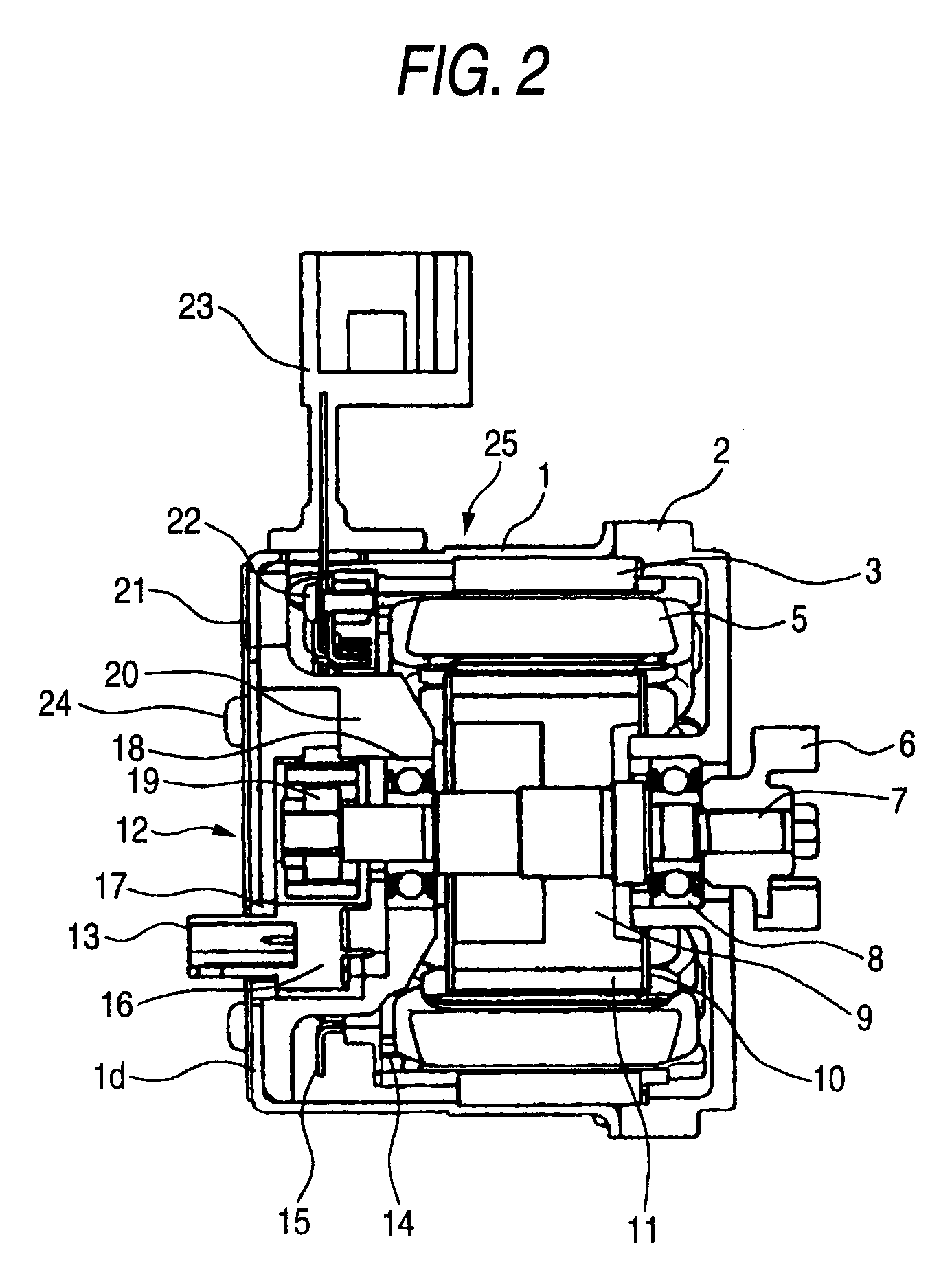
Electric rotating machine
InactiveUS20060192457A1Easy to operateImprove productivityWindingsMagnetic circuit rotating partsThumb oppositionEngineering
An electric rotating machine comprises: a stator in which a coil is wound on a plurality of teeth in concentrated winding, and the coil is connected to a three-phase power supply; and a rotor disposed in opposition to the teeth of the stator; wherein a ratio between the number of poles and the number of slots of the stator is 1:3. There is no higher harmonics of magnetomotive force in low order close to fundamental wave, thus enabling efficient operation of the electric rotating machine. Furthermore, owing to the stator of concentrated winding, it is possible to provide an electric rotating machine of high productivity with small coil end, high mass production, and high space factor.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
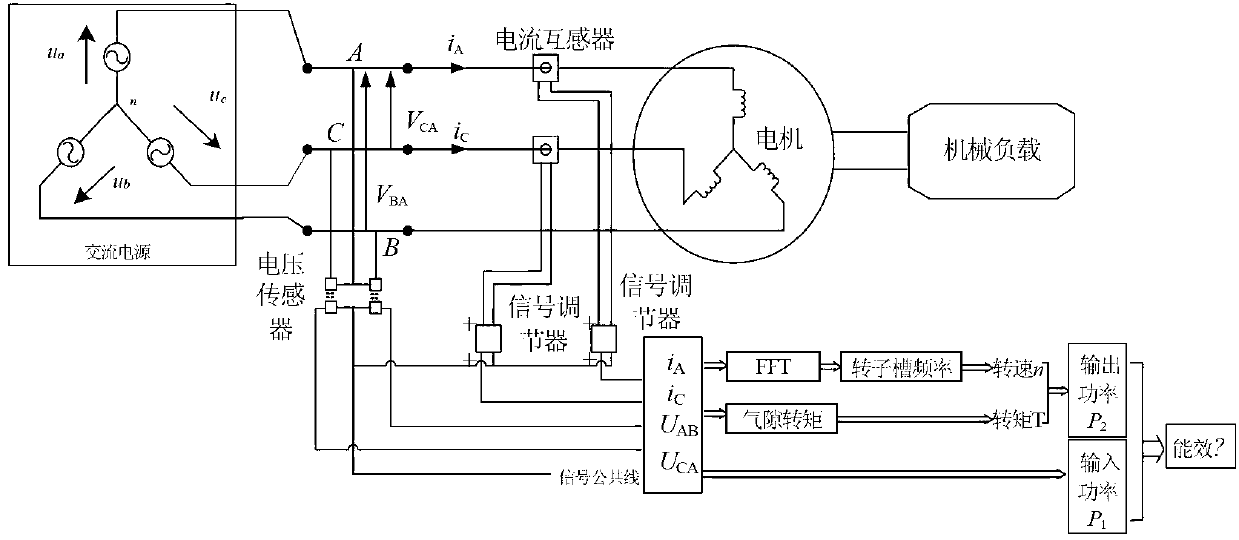
Squirrel-cage type asynchronous motor energy efficiency online monitoring method based on measurable electrical amount
ActiveCN103344368AEasy to operateSimple test methodWork measurementTorque measurementStator voltageMagnetomotive force
The invention discloses a squirrel-cage type asynchronous motor energy efficiency online monitoring method based on measurable electrical amount in the technical field of squirrel-cage type asynchronous motor energy efficiency online monitoring. Firstly, a collected rotor slot harmonic signal in stator current is analyzed and identified so that the rotation speed of a rotor can be obtained; stator voltage and stator winding current at the motor end are collected and analyzed so that output torque of a rotor shaft of a motor can be obtained, output power of the motor can be obtained through the output torque and the rotation speed, and the purpose that motor operation energy efficiency is identified can be achieved. According to the squirrel-cage type asynchronous motor energy efficiency online monitoring method based on the measurable electrical amount, the problem that the output torque and the rotation speed of the rotor shaft of the motor can not be directly measured is solved, operation is simple in field application, the operation energy efficiency of the motor can be rapidly obtained, the method is suitable for common taper slot rotor motors and motors with aliasing of motor rotor slot harmonic magnetomotive force and air gap harmonic magnetomotive force.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Field-circuit coupling analysis method for radial electromagnetic vibration of motor
ActiveCN107608934APrecise positioningRapid assessmentComplex mathematical operationsMagnetic field amplitudeElement model
The invention discloses a field-circuit coupling analysis method for radial electromagnetic vibration of a motor. The method comprises the steps of a) performing calculation by utilizing a closed slotfinite element model of the motor to obtain an air-gap magnetic field of a permanent magnet; b) according to a characteristic of synchronous rotation of harmonics in the magnetic field of the permanent magnet, performing analysis; c) according to the arrangement of a motor winding, performing harmonic analysis on armature reaction magnetomotive force; d) performing FFT analysis for a magnetic field model obtained by magnetic permeance of each harmonic, and in combination with a time harmonic number and a rotation direction in the magnetomotive force, obtaining a space number, a rotation direction, an initial phase and a magnetic field amplitude value of the magnetic field of each harmonic; e) performing vector synthesis on the magnetic fields of all the harmonics obtained by analysis in the steps a)-d); f) transmitting a radial force wave acting on the surface of a stator to a yoke part through a modulation effect of stator teeth to generate vibration; and g) performing scanning analysis on a stator mode by adopting a frequency sweeping method to obtain a resonant frequency of each low order. According to the method, the locating of a source of the radial electromagnetic vibrationof the motor is more accurate; and the vibration characteristic can be quickly assessed.
Owner:ACTION STAR TECH CO LTD
Double-stator permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN108390529AImprove efficiencyImprove reliabilityMagnetic circuit stationary partsWindings conductor shape/form/constructionMagnetomotive forceElectric machine
The invention discloses a double-stator permanent magnet synchronous motor, and relates to the field of motors. The invention aims at solving problems that a conventional double-stator permanent magnet synchronous motor usually employs a fractional-slot concentrated winding, the number of coils of the fractional-slot concentrated winding is large and the manufacturing cost is larger; and problemsthat the big eddy-current loss of a rotor permanent magnet and the rising of the temperature of the permanent magnet are liable to cause the irreversible demagnetization because the harmonic content of the magnetomotive force of the fractional-slot concentrated winding is large when the power-on frequency of a motor winding is higher and the overload multiples is large. The double-stator permanentmagnet synchronous motor provided by the invention enables the harmonic contents of a synthetic magnetomotive force and the magnetomotive force of two armatures to be small through the correspondingstaggering of double-stator windings, and is small in eddy-current loss of the rotor permanent magnet. Moreover, the end parts of the windings are not overlapped, thereby improving the motor efficiency and reliability.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Magnetic resonance imaging system
InactiveUS7057391B1Reduce feelingsReduce forceMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetomotive forceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Multi-axis Magnetic Lens for Focusing a Plurality of Charged Particle Beams
ActiveUS20130153782A1Reduce componentsEffective controlThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsElectricityMagnetomotive force
The present invention provides two ways to form a special permeability-discontinuity unit inside every sub-lens of a multi-axis magnetic lens, which either has a simpler configuration or has more flexibility in manufacturing such as material selection and mechanical structure. Accordingly several types of multi-axis magnetic lens are proposed for various applications. One type is for general application such as a multi-axis magnetic condenser lens or a multi-axis magnetic transfer lens, another type is a multi-axis magnetic non-immersion objective which can require a lower magnetomotive force, and one more type is a multi-axis magnetic immersion objective lens which can generate smaller aberrations. Due to using permeability-discontinuity units, every multi-axis magnetic lens in this invention can also be electrically excited to function as a multi-axis electromagnetic compound lens so as to further reduce aberrations thereof and / or realize electron beam retarding for low-voltage irradiation on specimen.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Synchronous generator rotor turn-to-turn short circuit monitoring method based on excitation magnetic potential calculation
InactiveCN102841291AShort circuit sensitiveShort circuit fault monitoringElectrical testingPhase currentsMagnetomotive force
The invention provides a synchronous generator rotor turn-to-turn short circuit monitoring method based on excitation magnetic potential calculation and belongs to the field of primary device relaying protection and online monitoring technology in an electric power system. The synchronous generator rotor turn-to-turn short circuit monitoring method is characterized in that first, phase voltage, phase current and stator leakage impedance of a generator are used to work out excitation magnetic potential in actual operation; second, according to exciting current on the same operating condition, excitation magnetomotive force which a normal exciting winding should generate can be calculated; and in normal operation, calculating results of two excitation magnetomotive force should be identical, but the actual excitation magnetomotive force can be smaller than the calculating result obtained according to the normal exciting winding when rotor turn-to-turn short circuit happens, and therefore a breakdown criterion is formed. An experiment that the rotor turn-to-turn short circuit happens to a typical synchronous generator in load operation condition indicates that the synchronous generator rotor turn-to-turn short circuit monitoring method can be used to achieve monitoring to rotor turn-to-turn short circuit faults and can be applied to synchronous generators which are not provided with the condition of installing branch current transformers.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
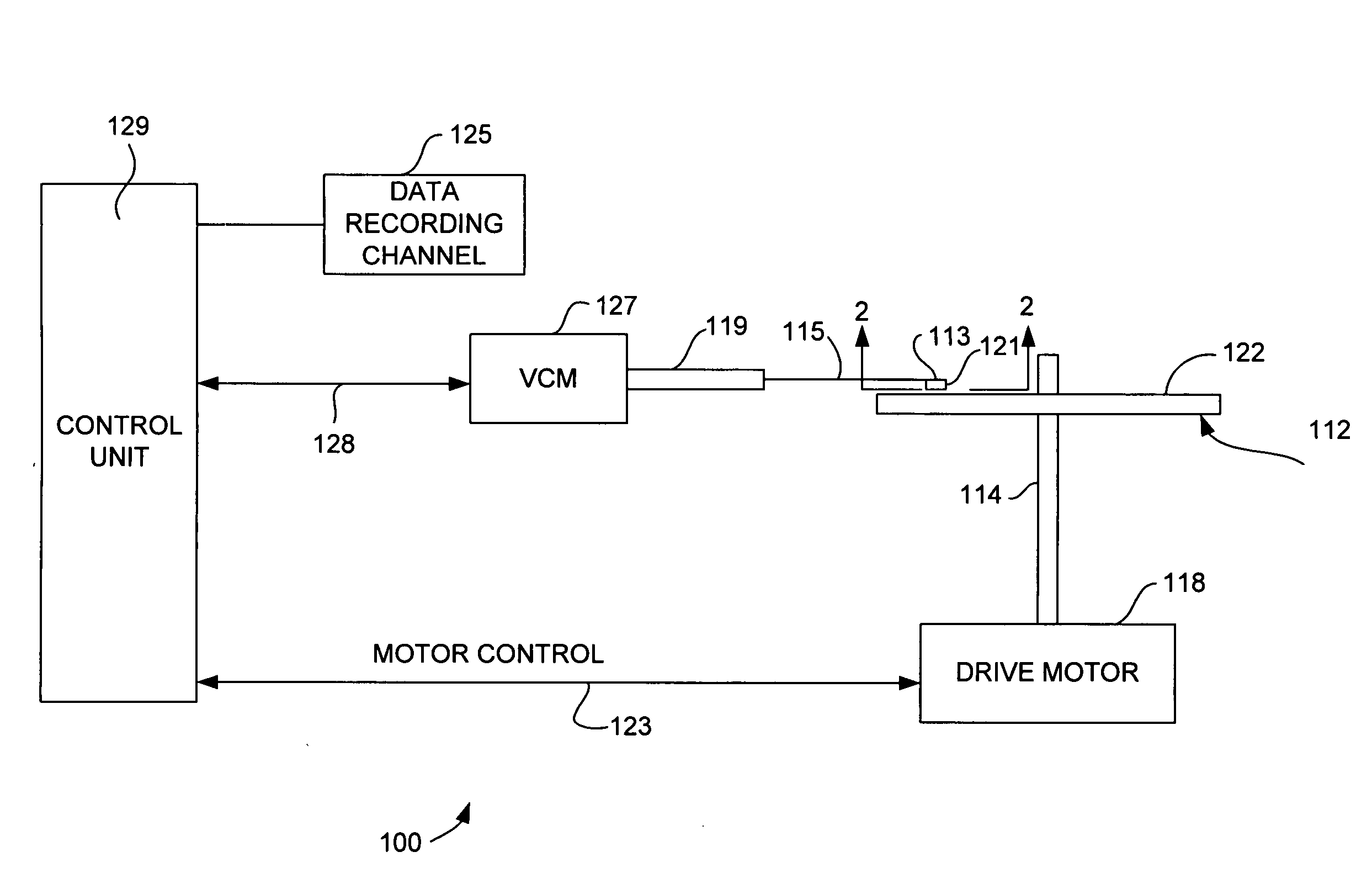
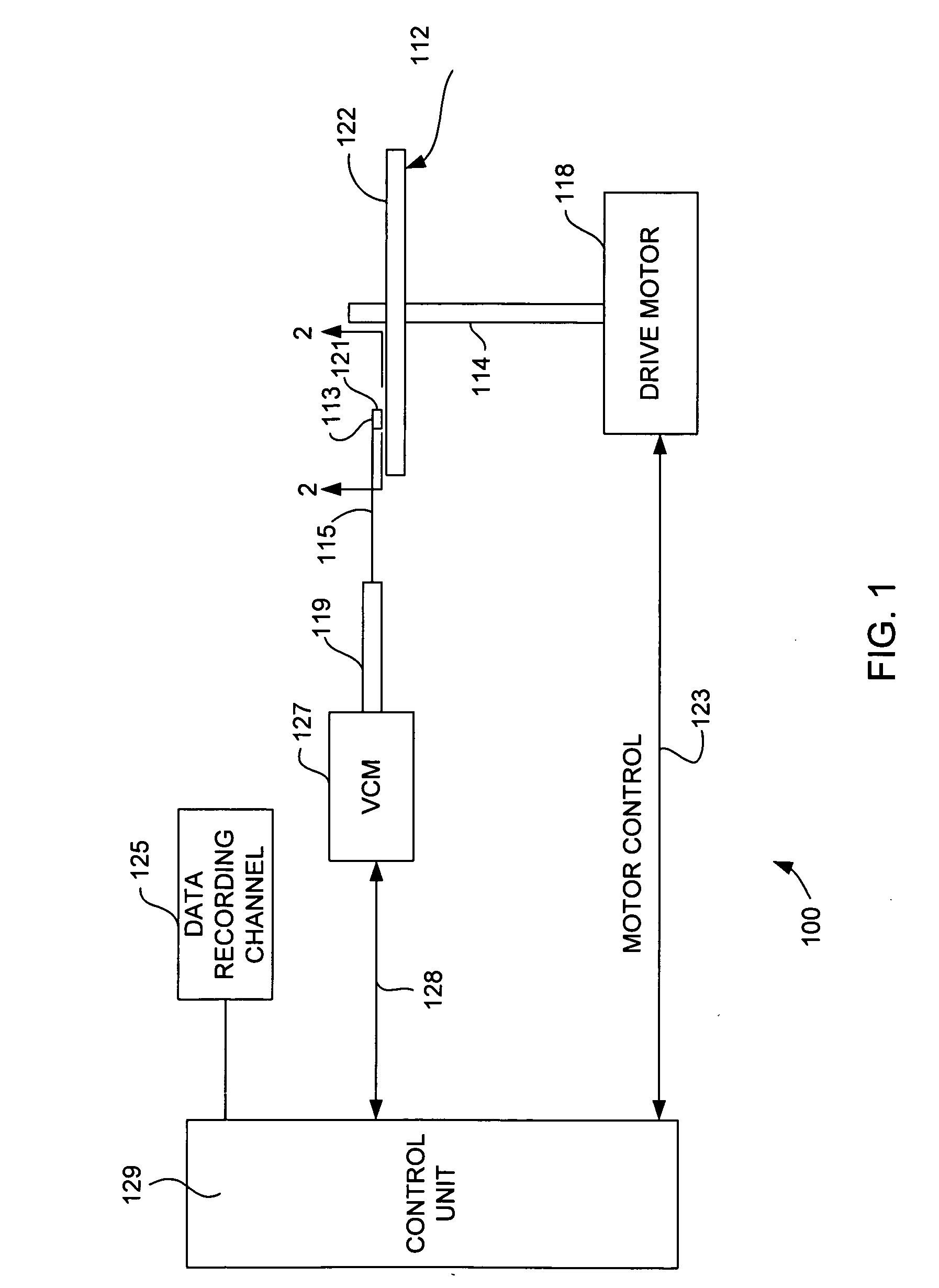
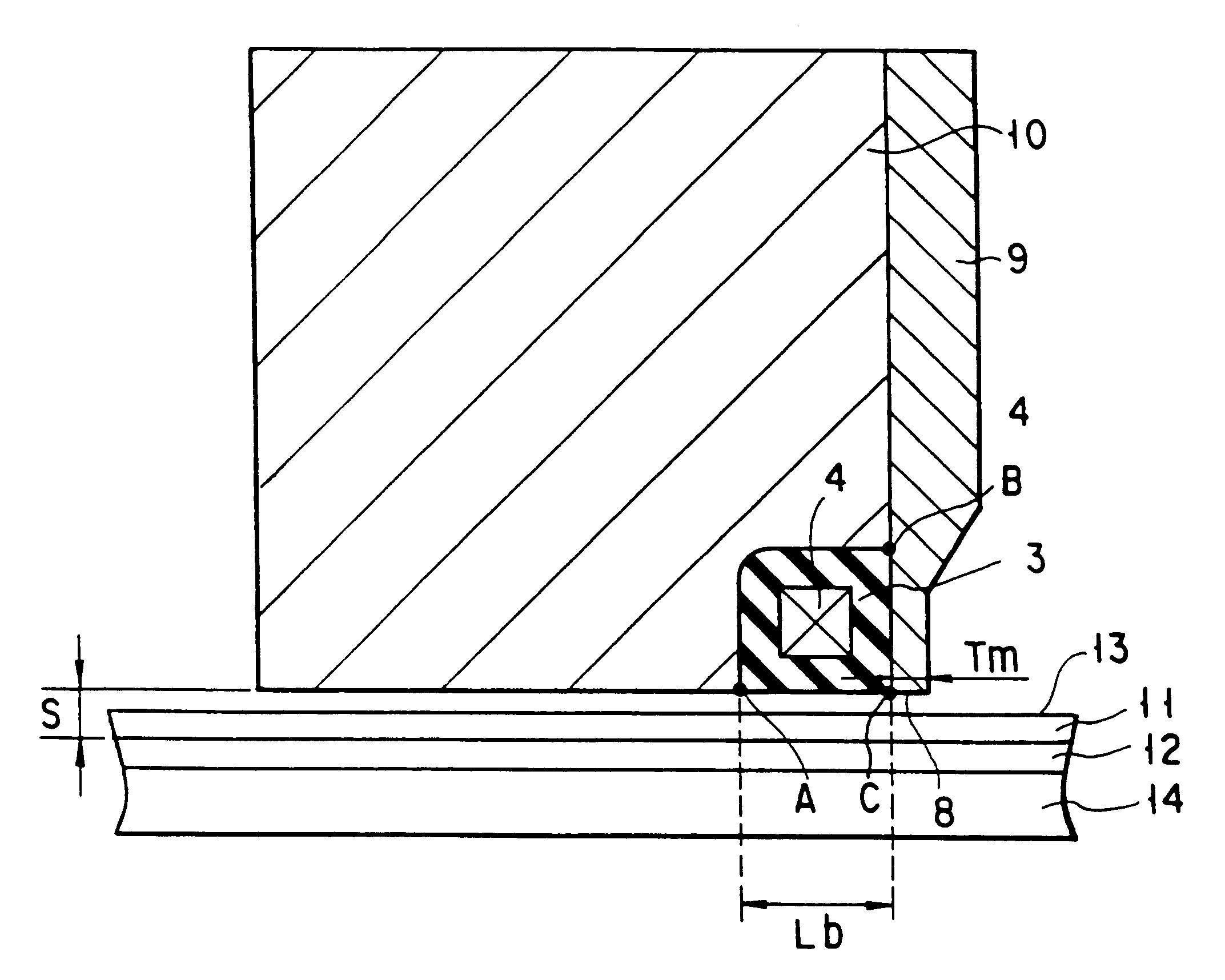
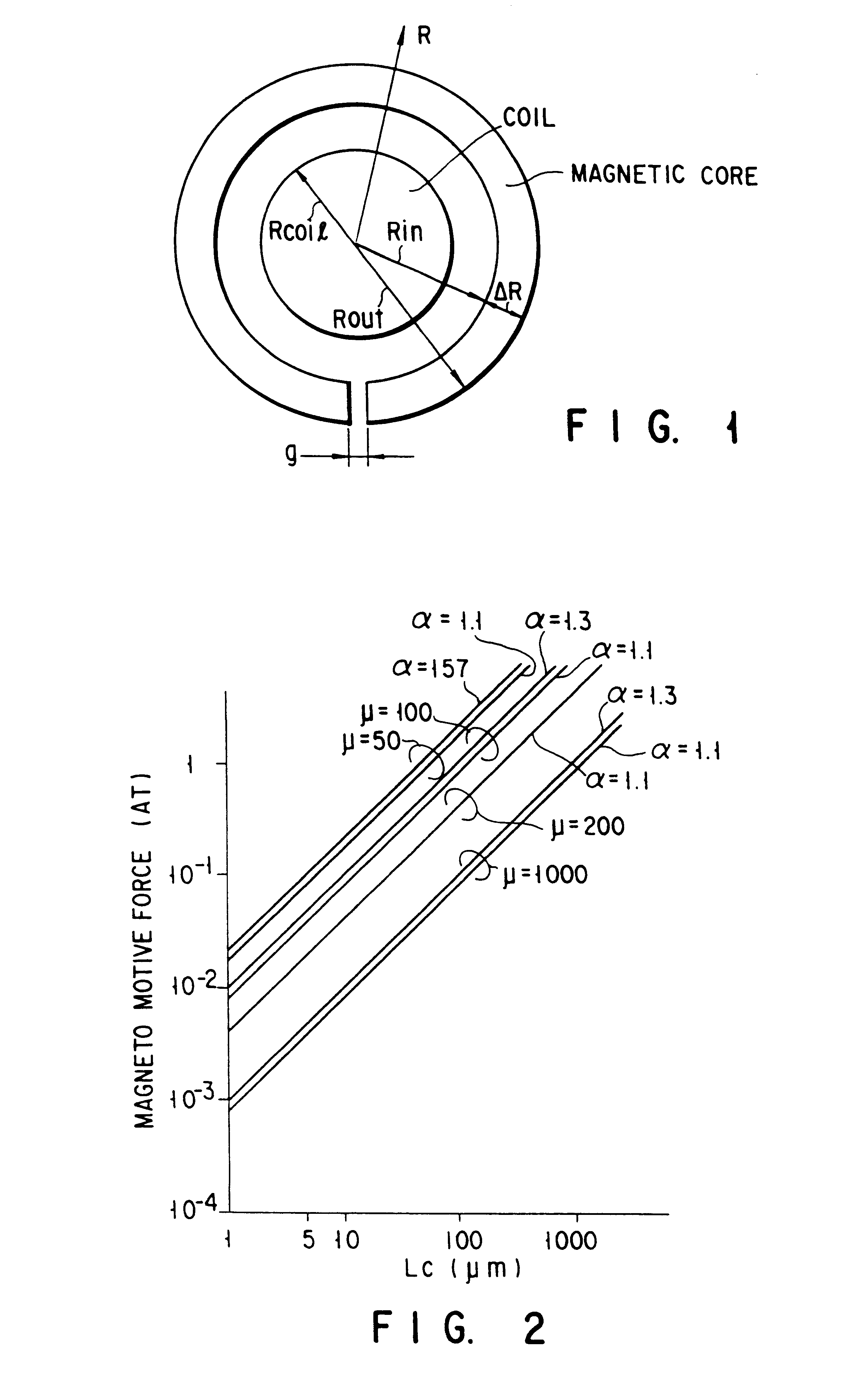
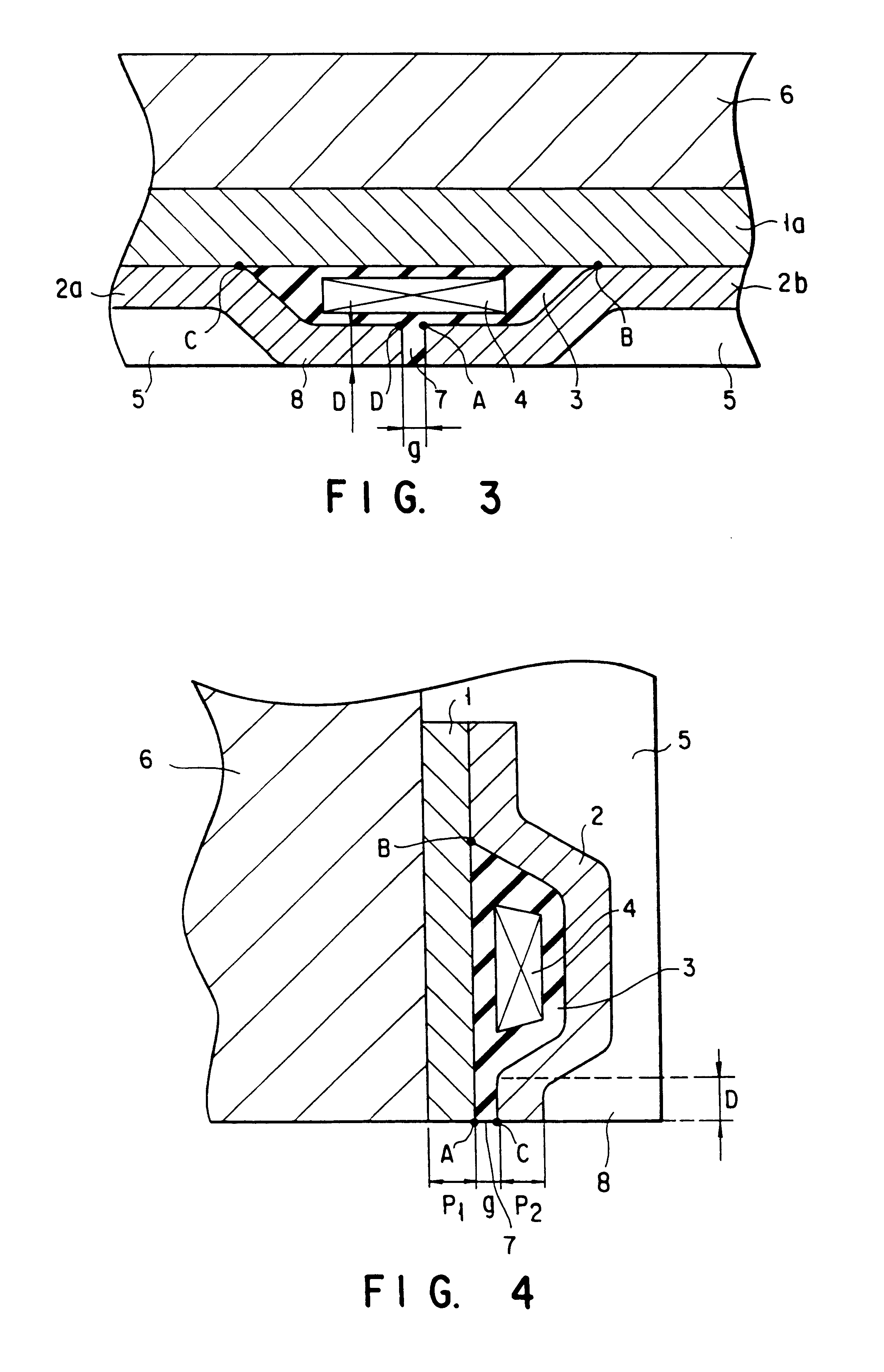
Perpendicular thin-film magnetic head
Disclosed is a thin-film magnetic head comprising a ring-shaped magnetic core and a coil surrounded by the magnetic core, given that an inner circumferential length of the magnetic core surrounding the coil is Lc, a magnetic gap length is g, a magnetic gap depth is D, an average magnetic flux density (unit: T (tesla)) is Bav and an effective magnetic permeability of the magnetic core is mu, Lc, g and D being determined in such a manner that a magnetomotive force I needed for recording, expressed by a following equation (1), becomes equal to or less than 0.1 A.T (Ampere.Turn):where Log is a natural logarithm, and variables in the equation (1) are expressed in SI units.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Brushless motor and electric power steering system
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com