Asymmetric permanent-magnet bias axial magnetic bearing
A technology of axial magnetic bearing and permanent magnet bias, which is applied in the direction of shafts and bearings, bearings, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of increasing copper loss of windings, controlling power amplifier loss, large bias current, and increasing control current, etc., to achieve Effects of reducing winding copper loss and controlling power amplifier loss, increasing rotor mode and speed, and reducing static bias current
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
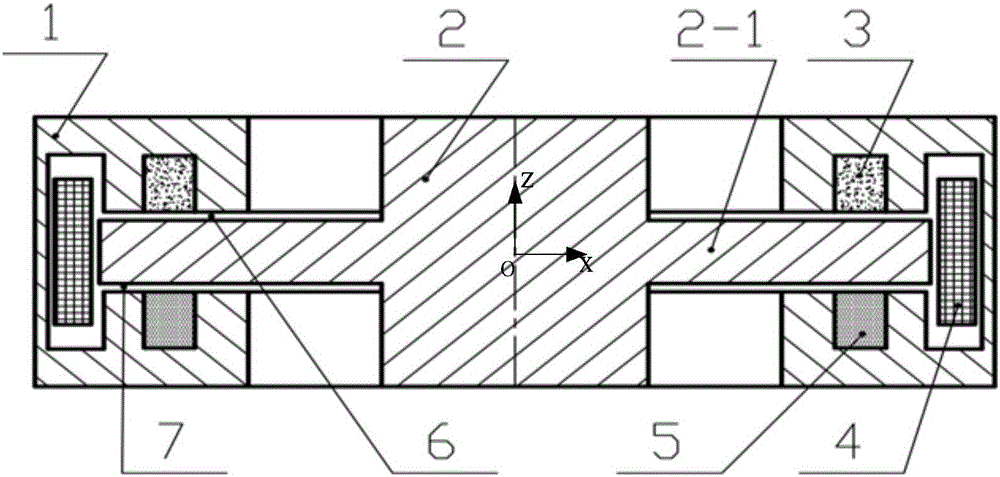
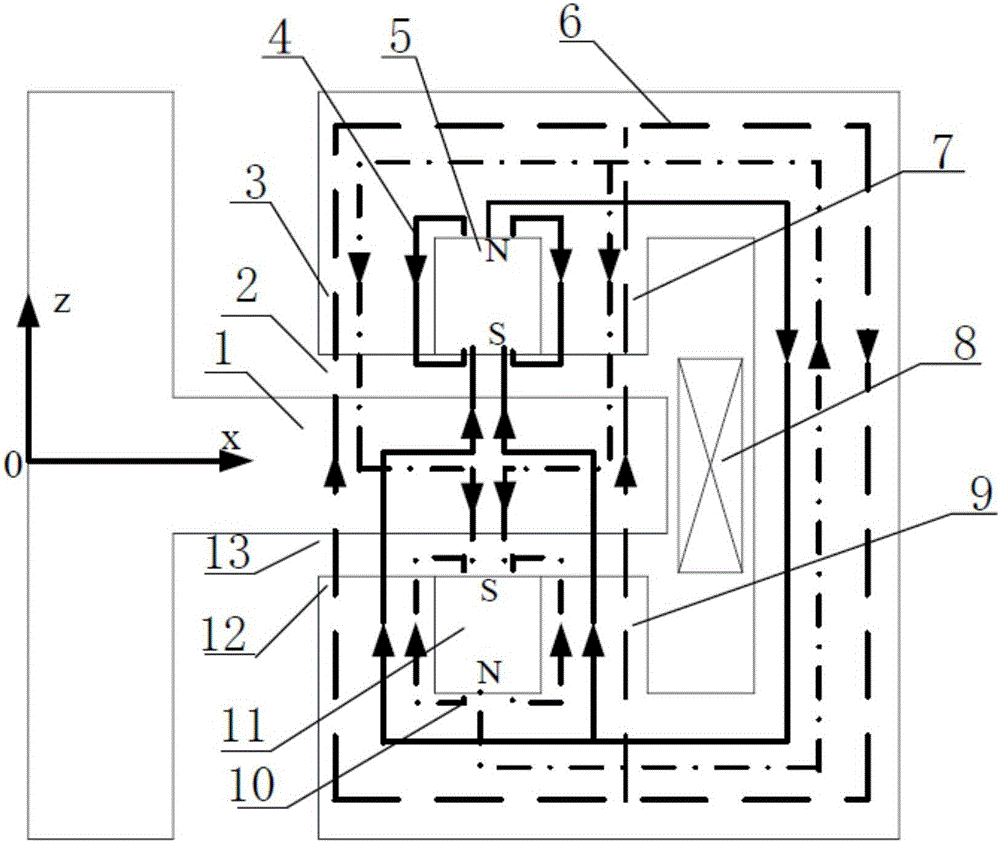
[0015] Such as figure 1 As shown, it is an asymmetric permanent magnet bias axial magnetic bearing composed of two permanent magnets with the same shape and size but different materials, which is one of the technical solutions of the present invention, which is the basic form of the present invention. It consists of stator core 1, rotor core 2 with thrust disc, first permanent magnet 3, second permanent magnet 5 and excitation coil 4. The double E-shaped stator cores form four stator poles in the positive and negative directions of the magnetic bearing Z, and two stator poles in the positive and negative directions of Z. Between the two stator poles in the Z positive direction and the Z negative direction are two annular permanent magnets with the same shape and size but different materials, which can generate different static bearing capacities in the two axial directions while providing bias magnetic density. . Two permanent magnets with different coercive forces are sele...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com