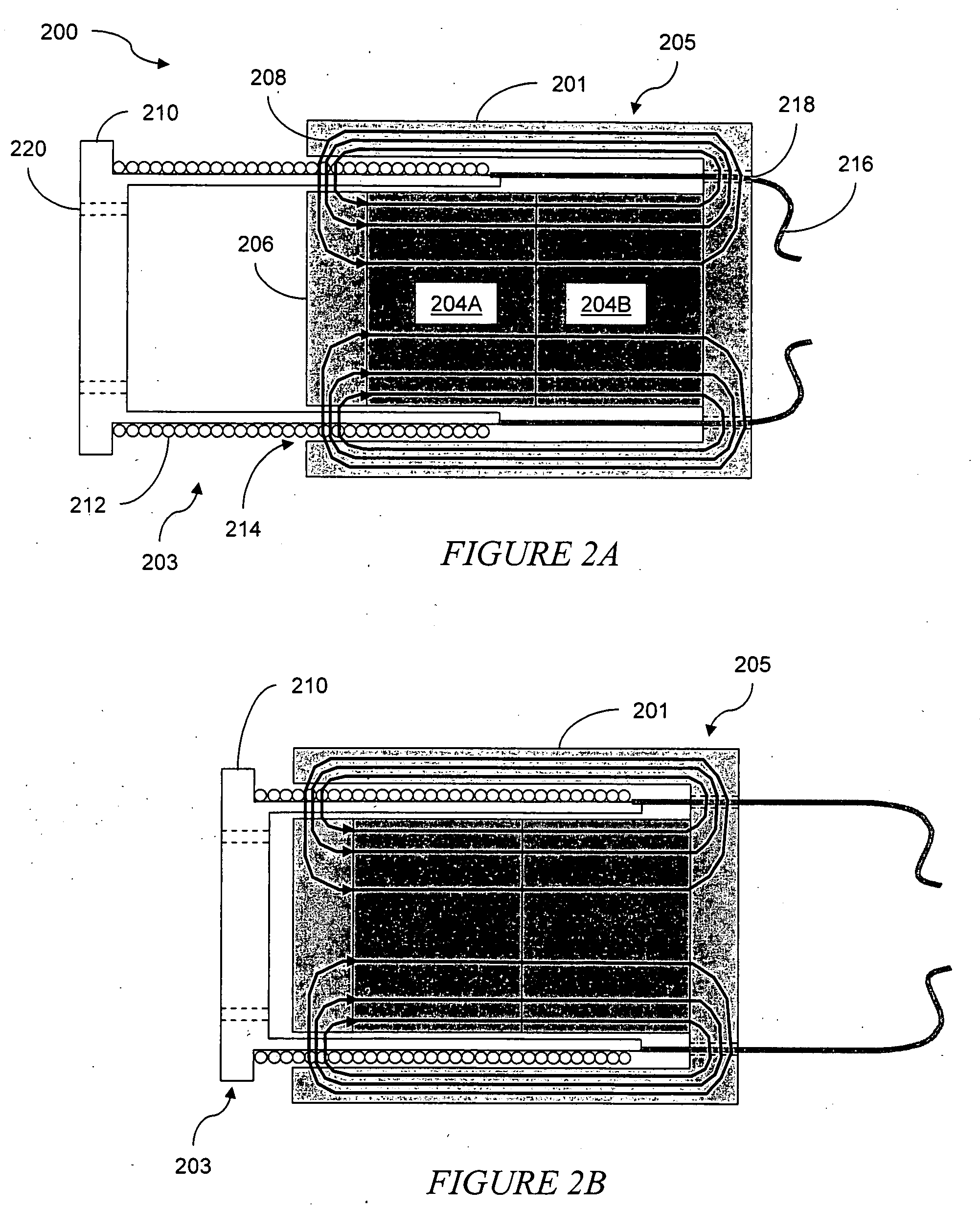
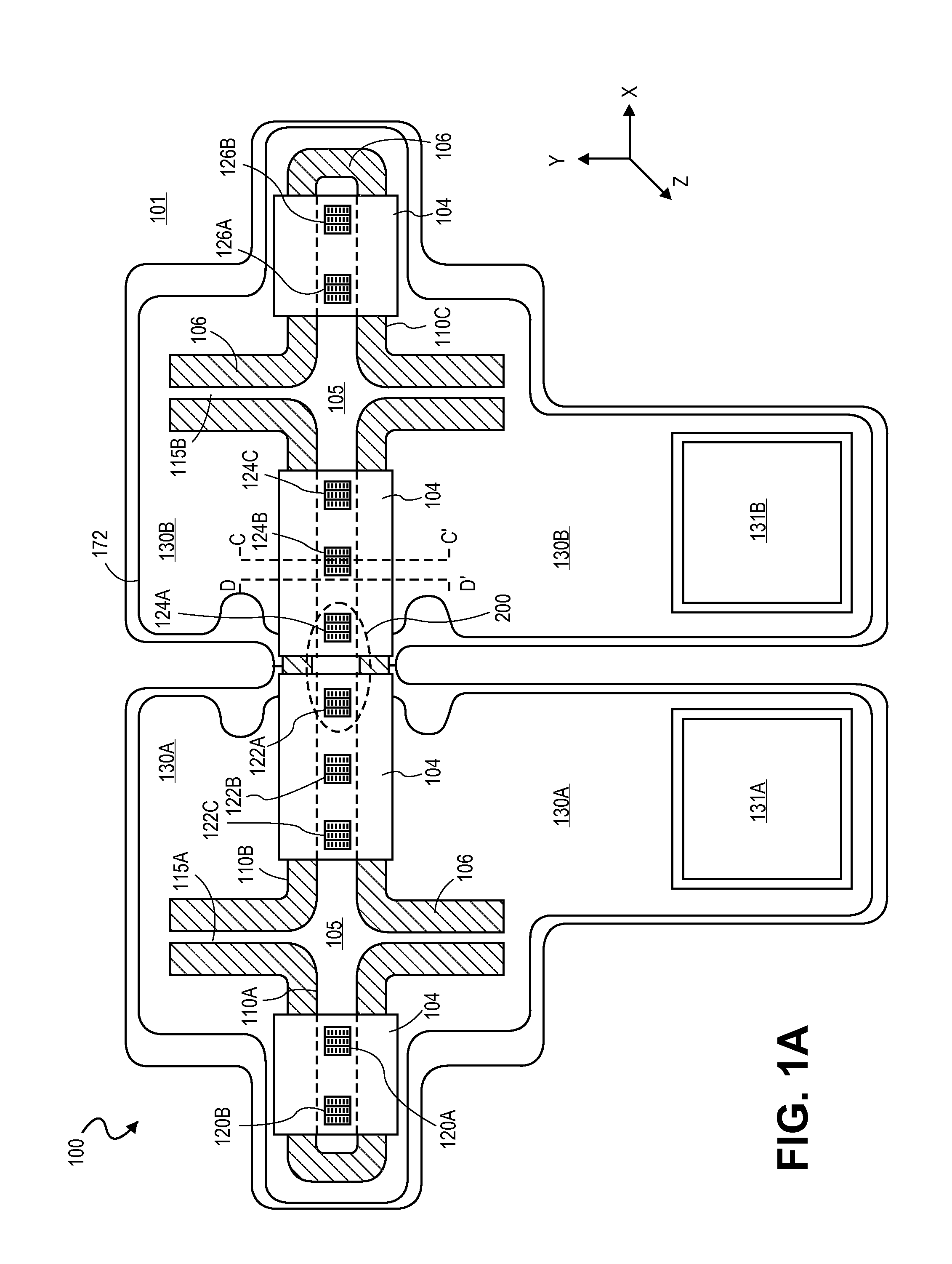
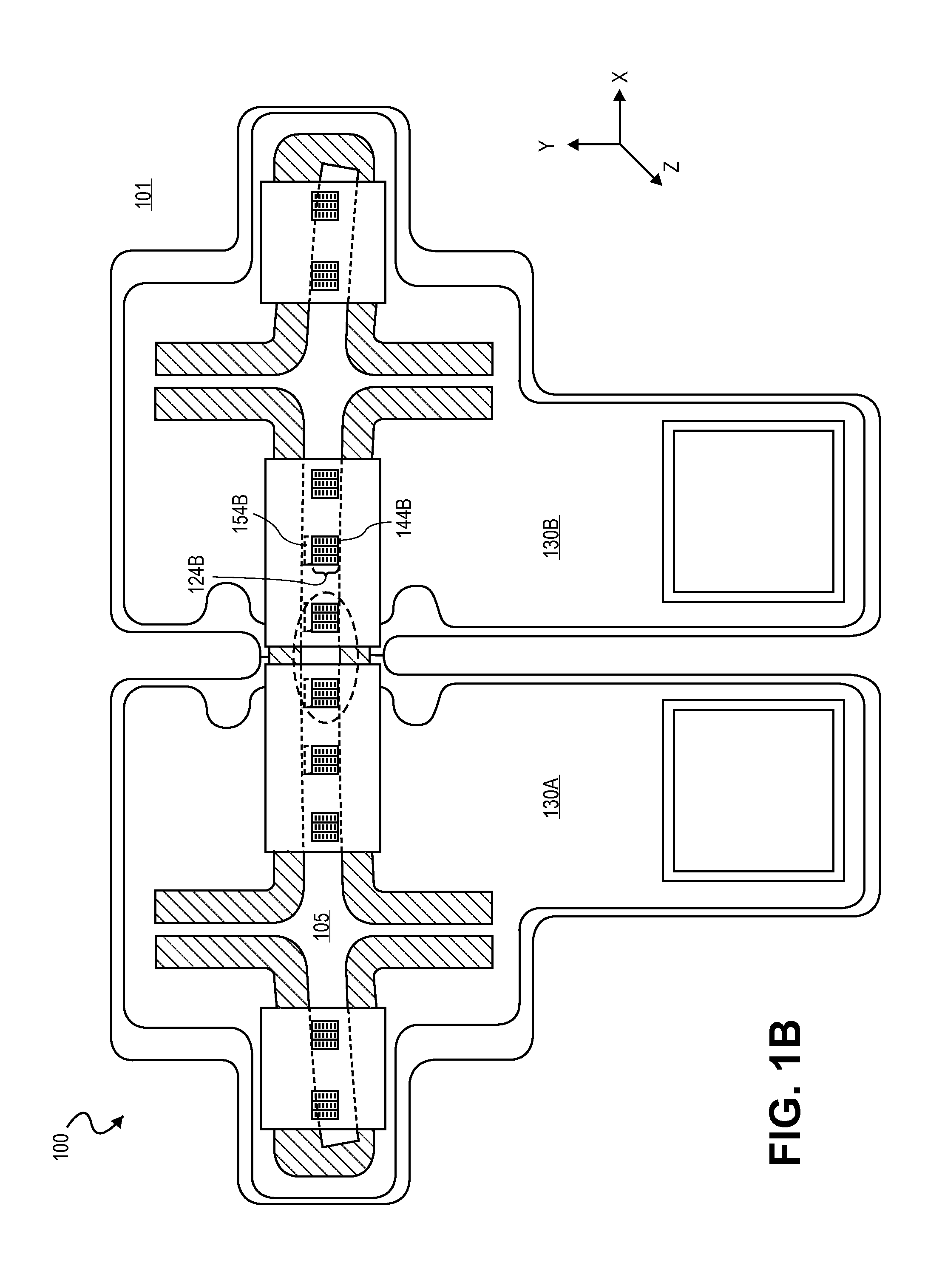
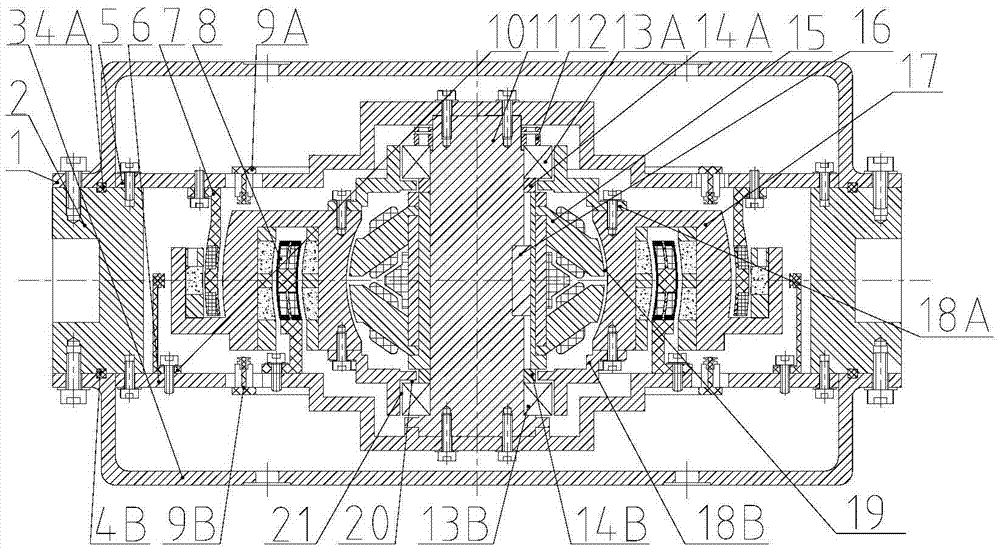
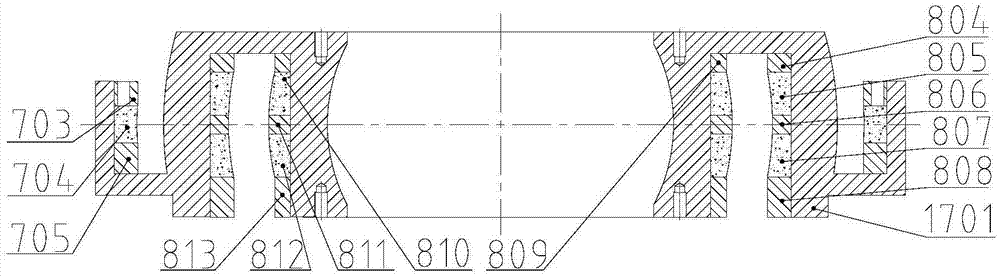
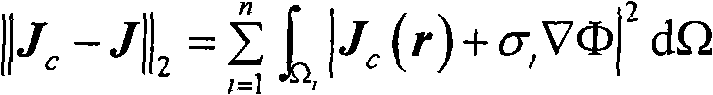Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
840 results about "Lorentz force" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
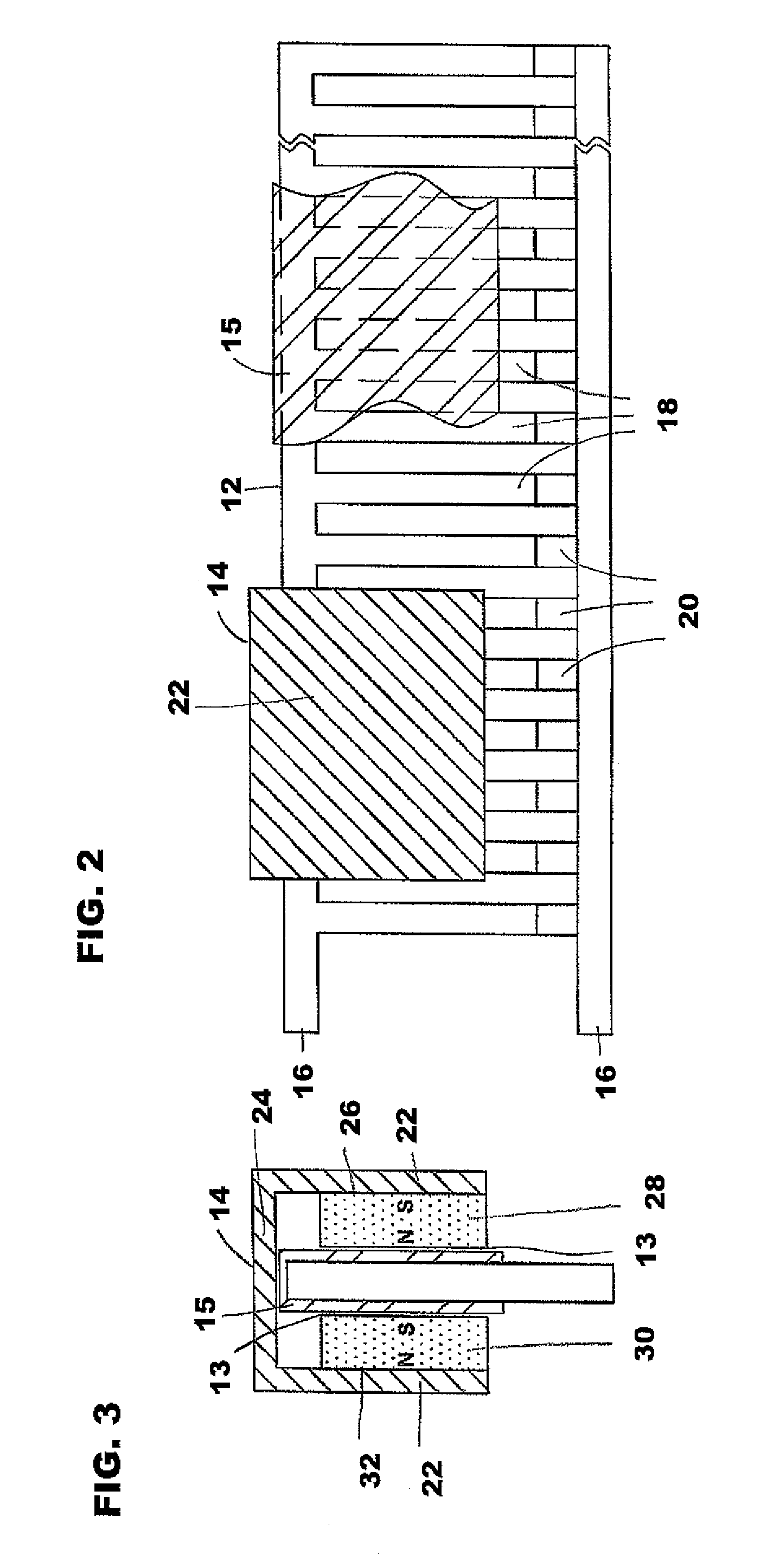
In physics (specifically in electromagnetism) the Lorentz force (or electromagnetic force) is the combination of electric and magnetic force on a point charge due to electromagnetic fields. A particle of charge q moving with a velocity v in an electric field E and a magnetic field B experiences a force of 𝐅=q𝐄+q𝐯×𝐁 (in SI units). Variations on this basic formula describe the magnetic force on a current-carrying wire (sometimes called Laplace force), the electromotive force in a wire loop moving through a magnetic field (an aspect of Faraday's law of induction), and the force on a charged particle which might be traveling near the speed of light (relativistic form of the Lorentz force).
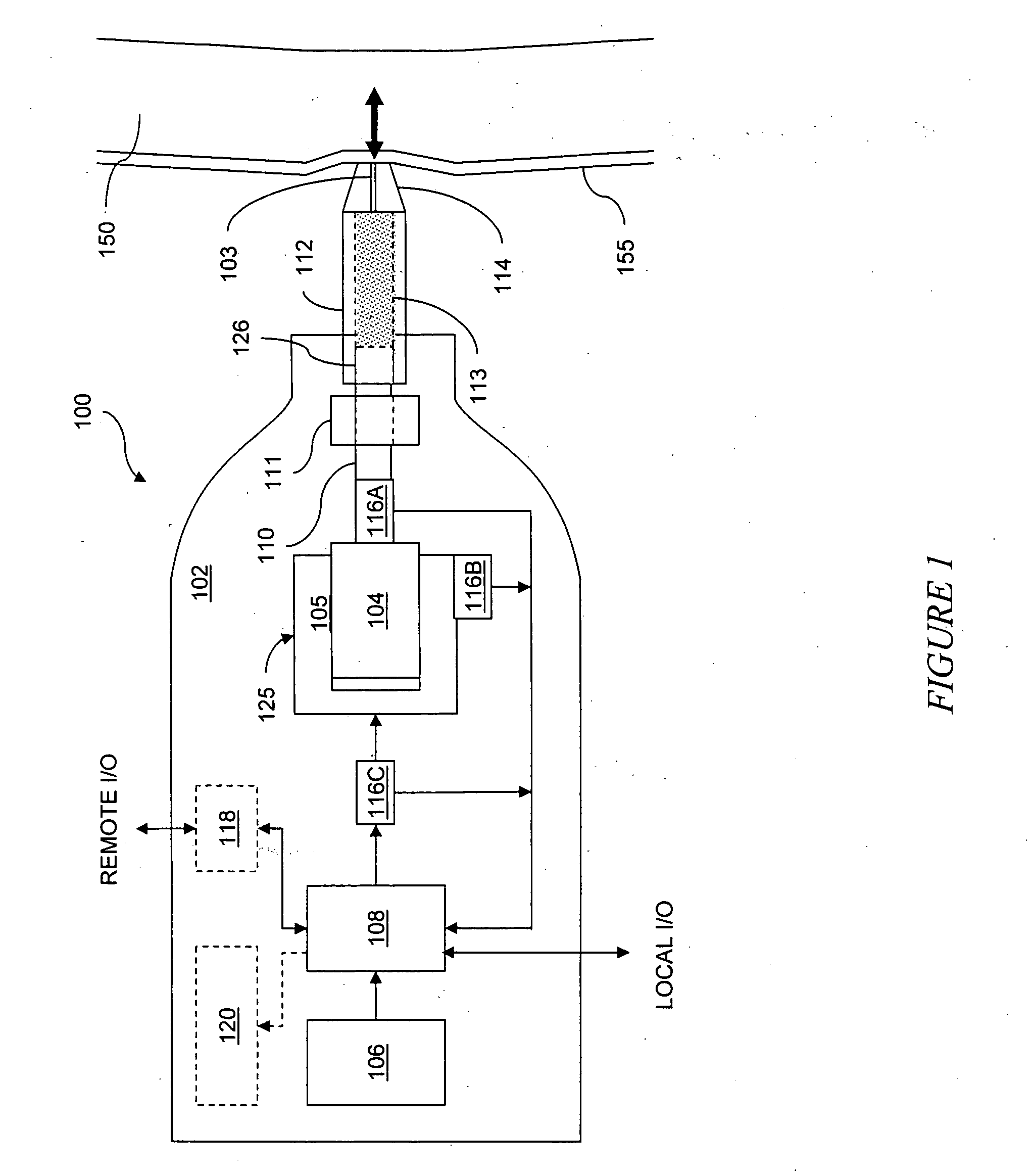
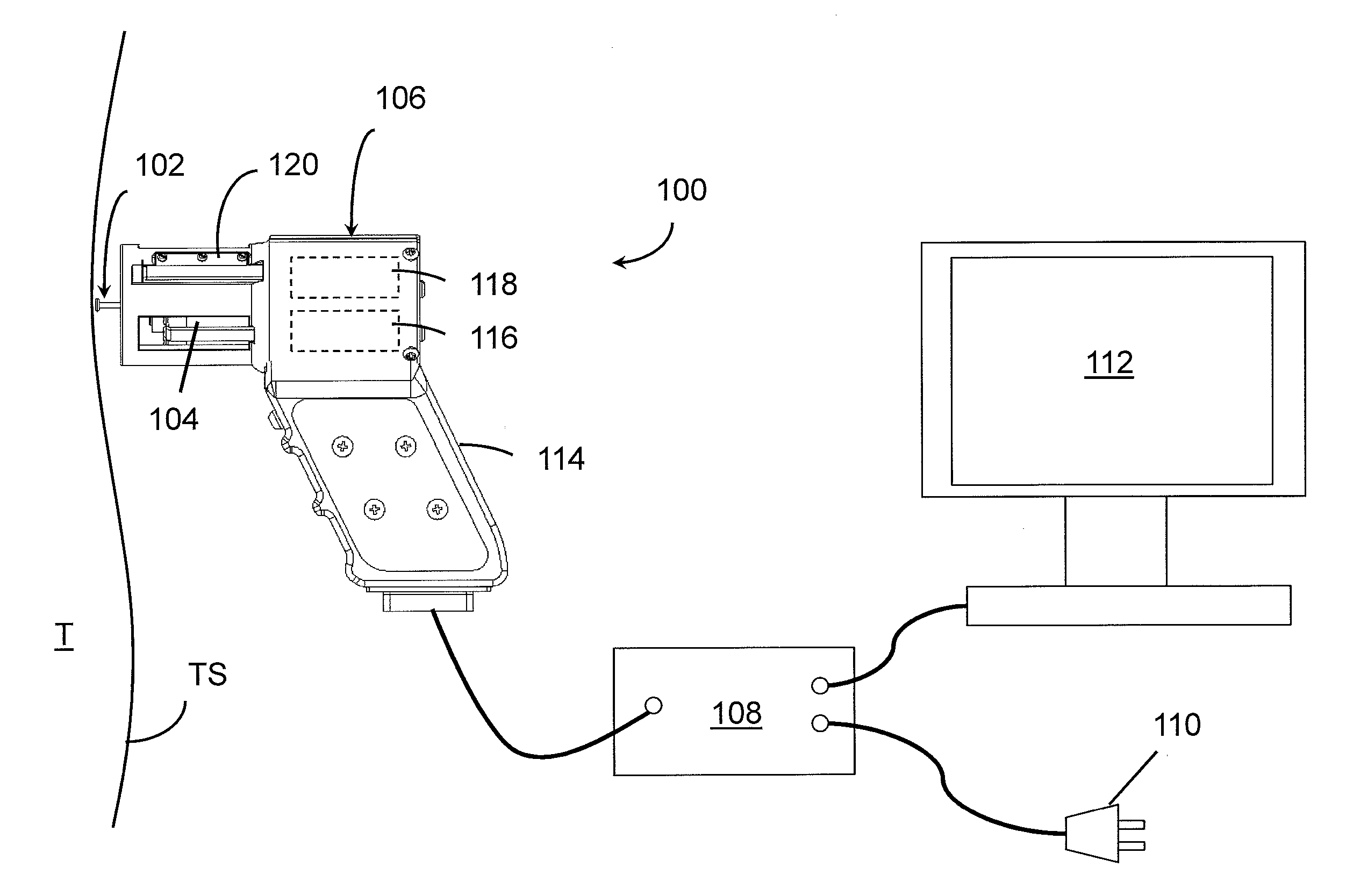
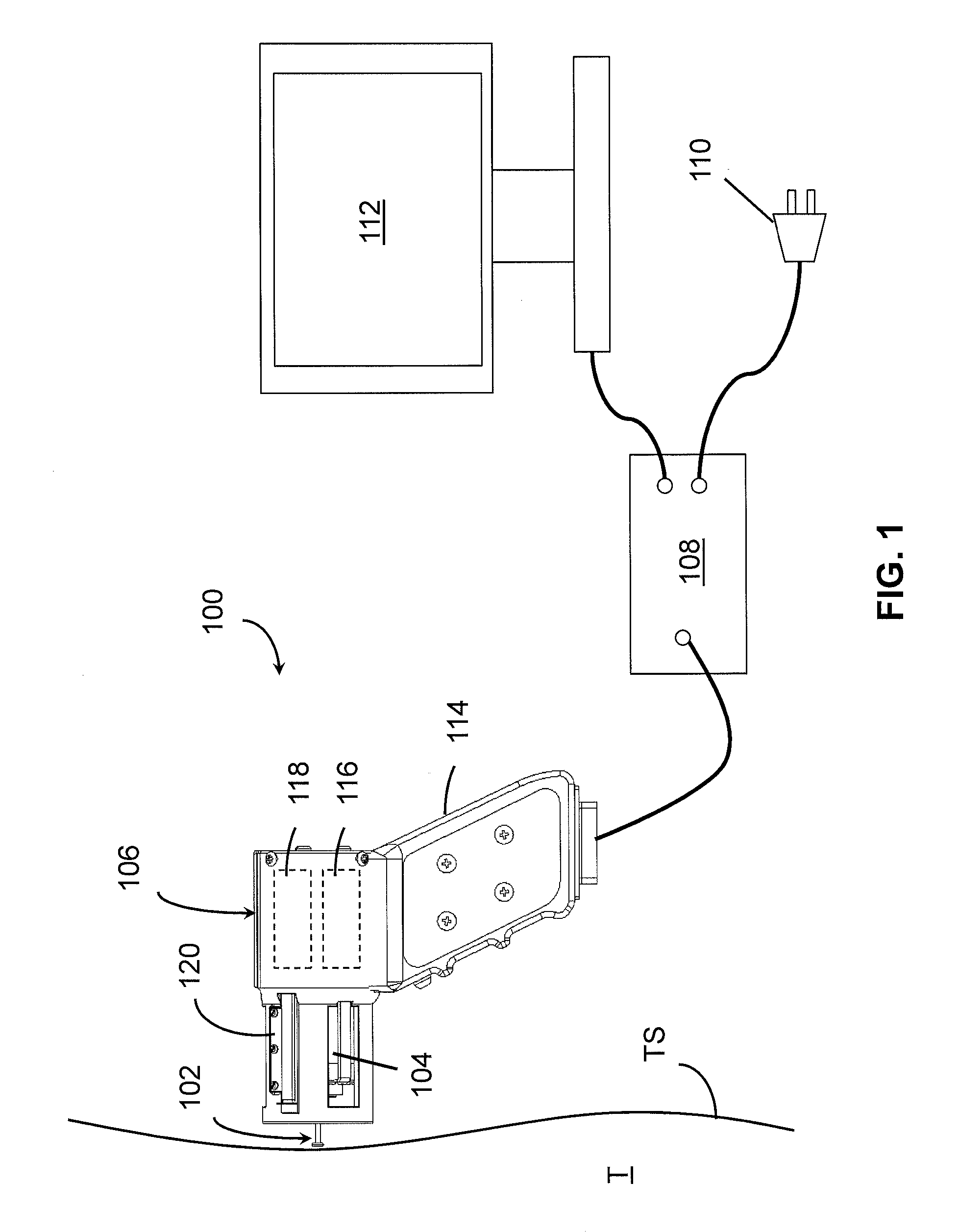
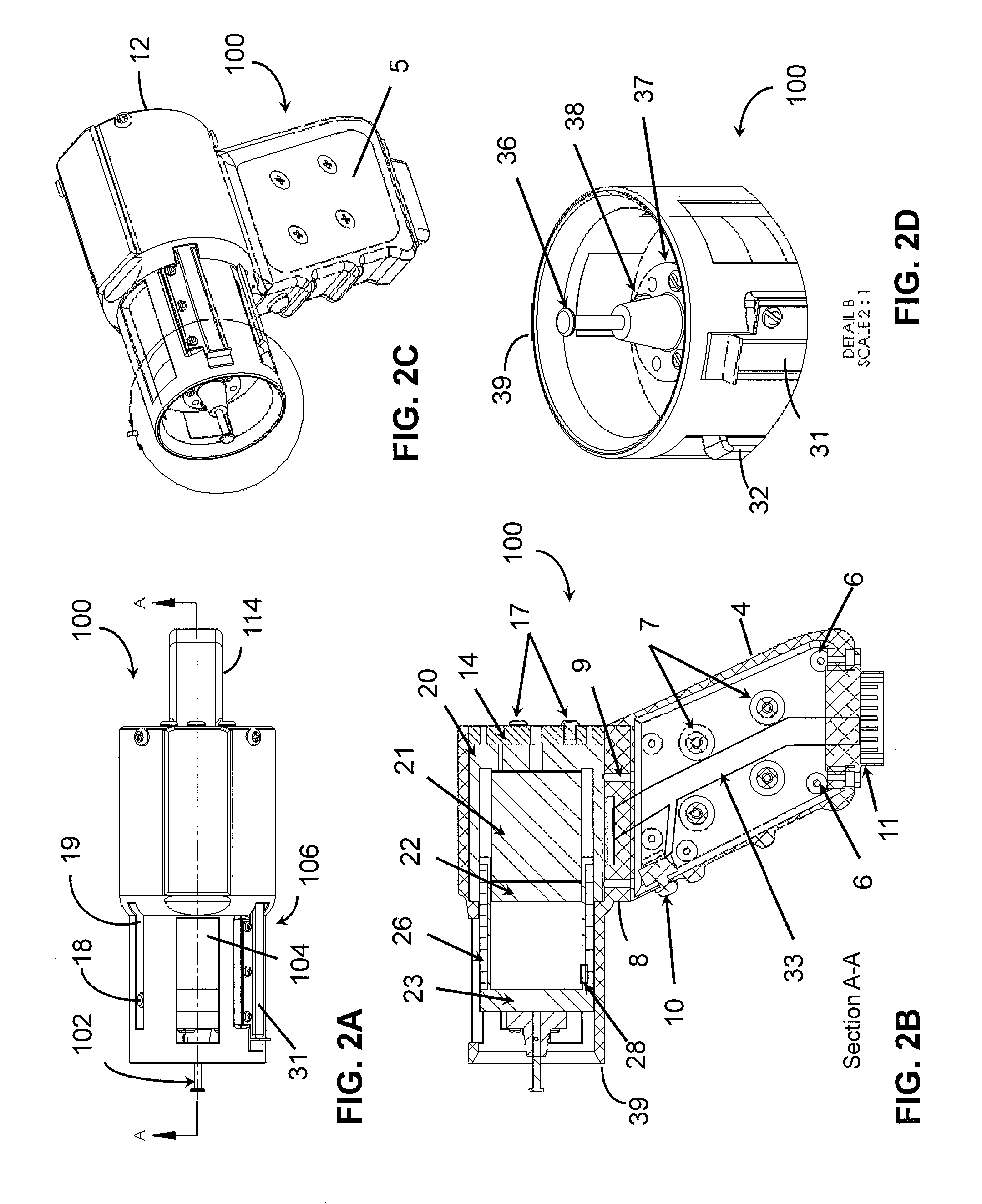
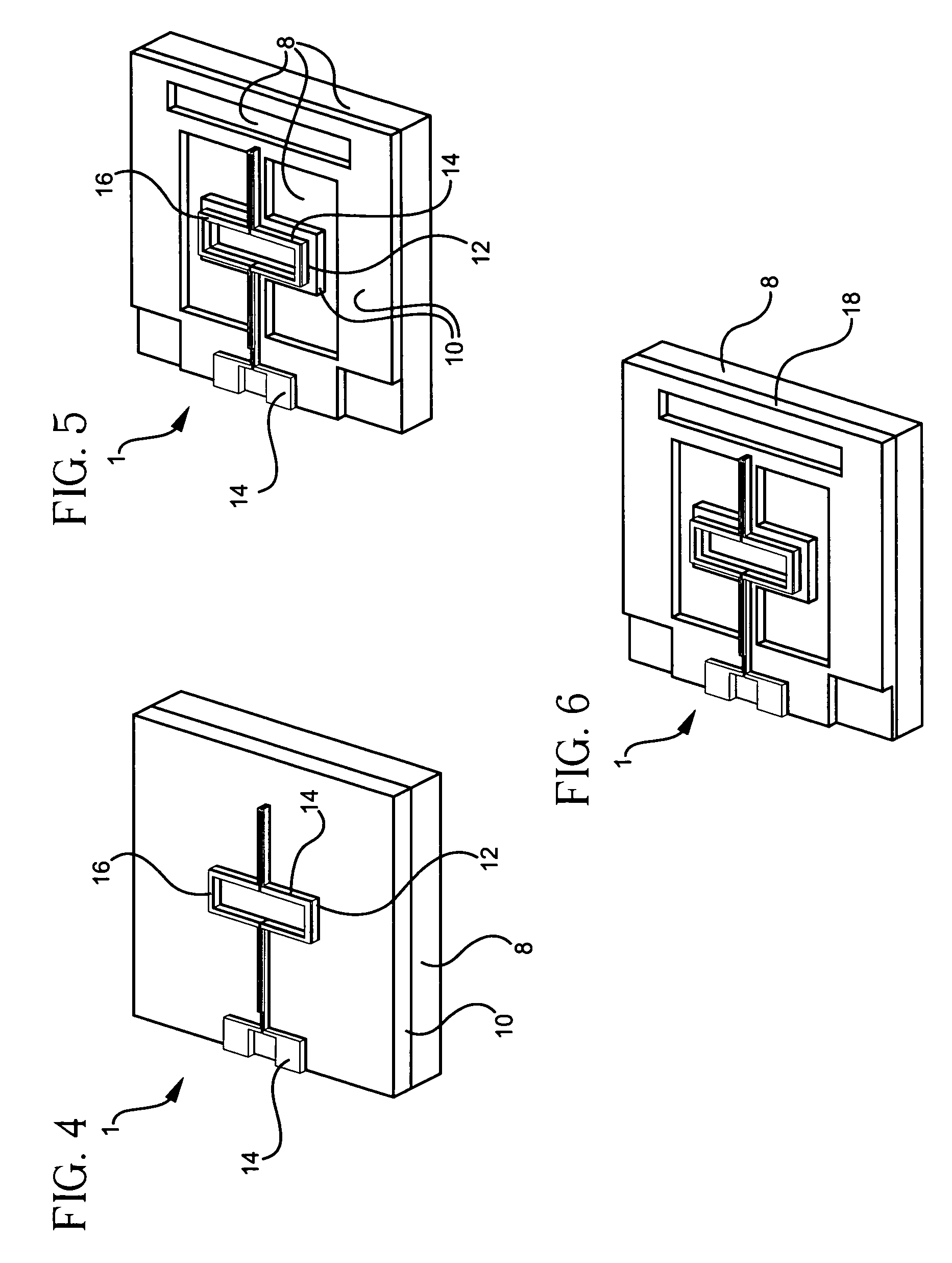
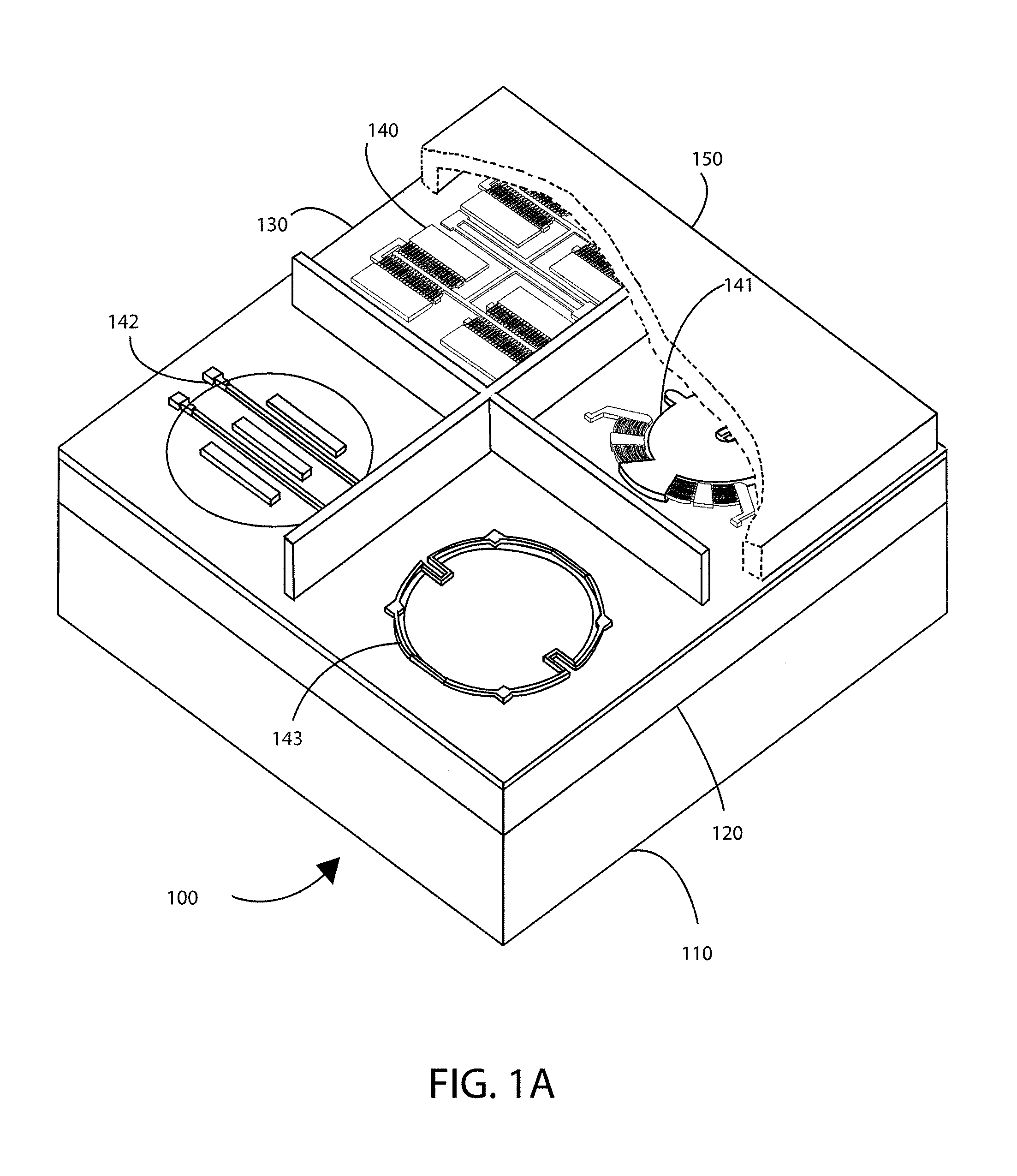
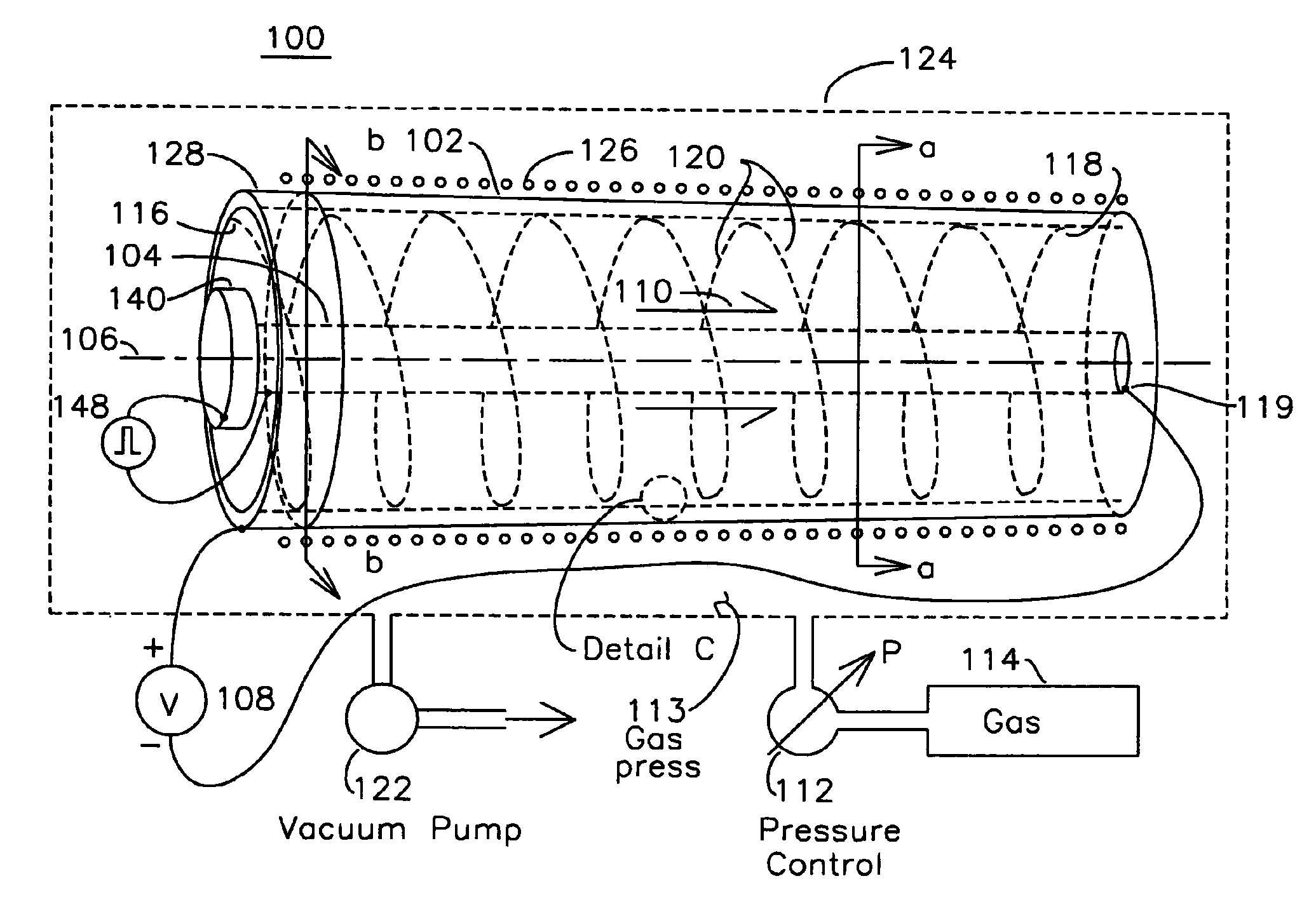
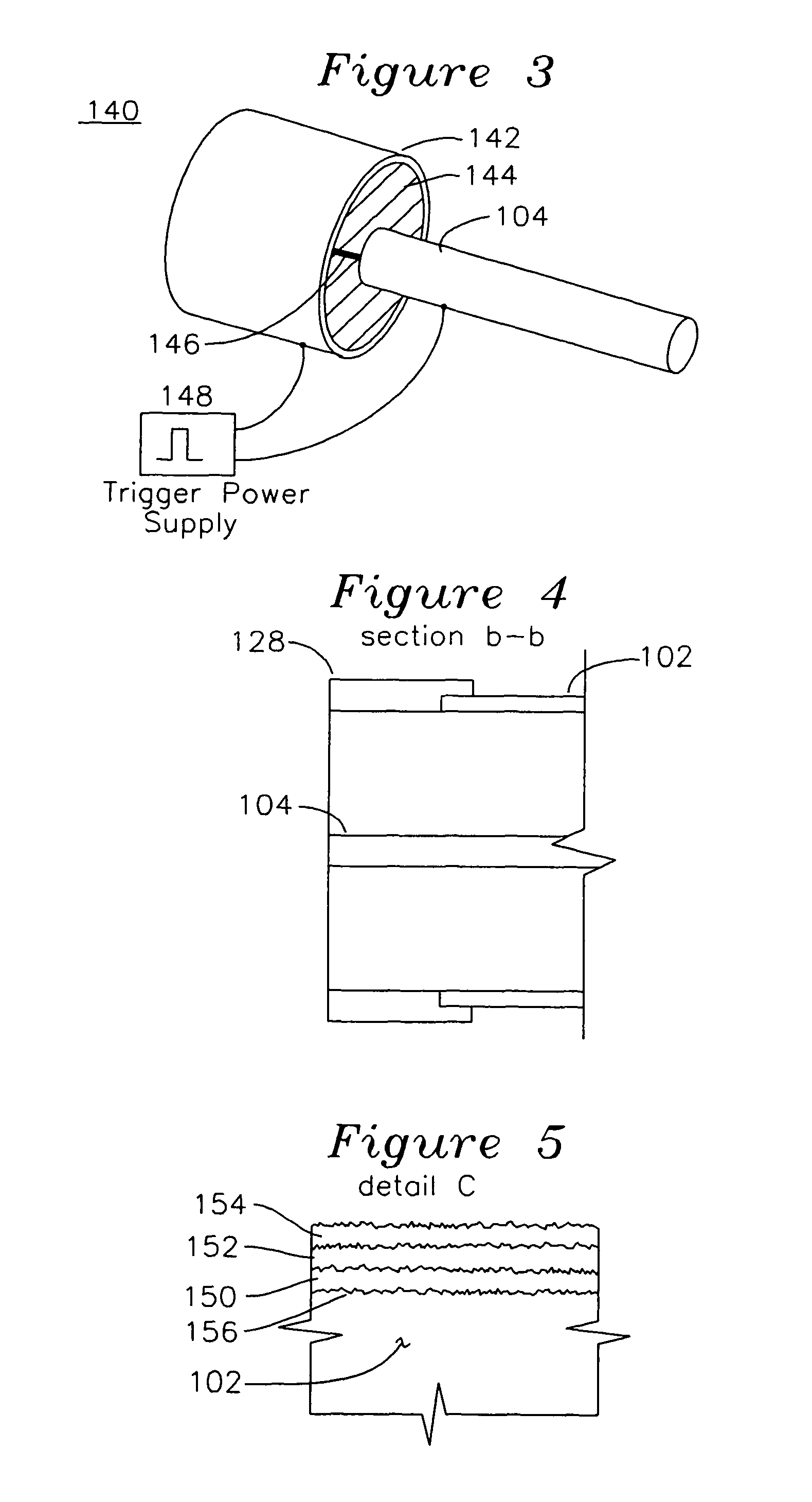
Controlled needle-free transport
InactiveUS20060258986A1Easy to controlJet injection syringesAutomatic syringesNeedle freeBiological body
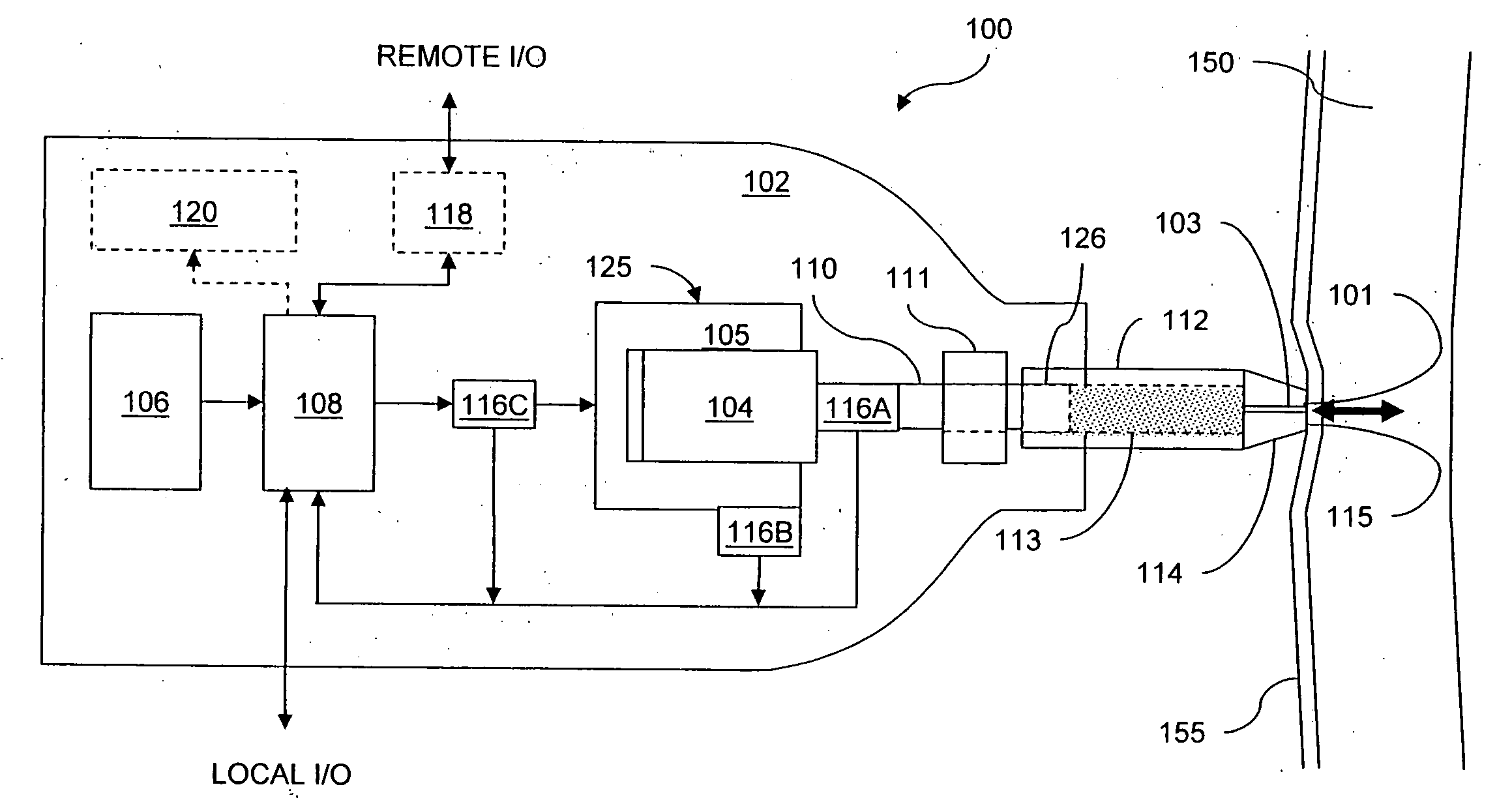
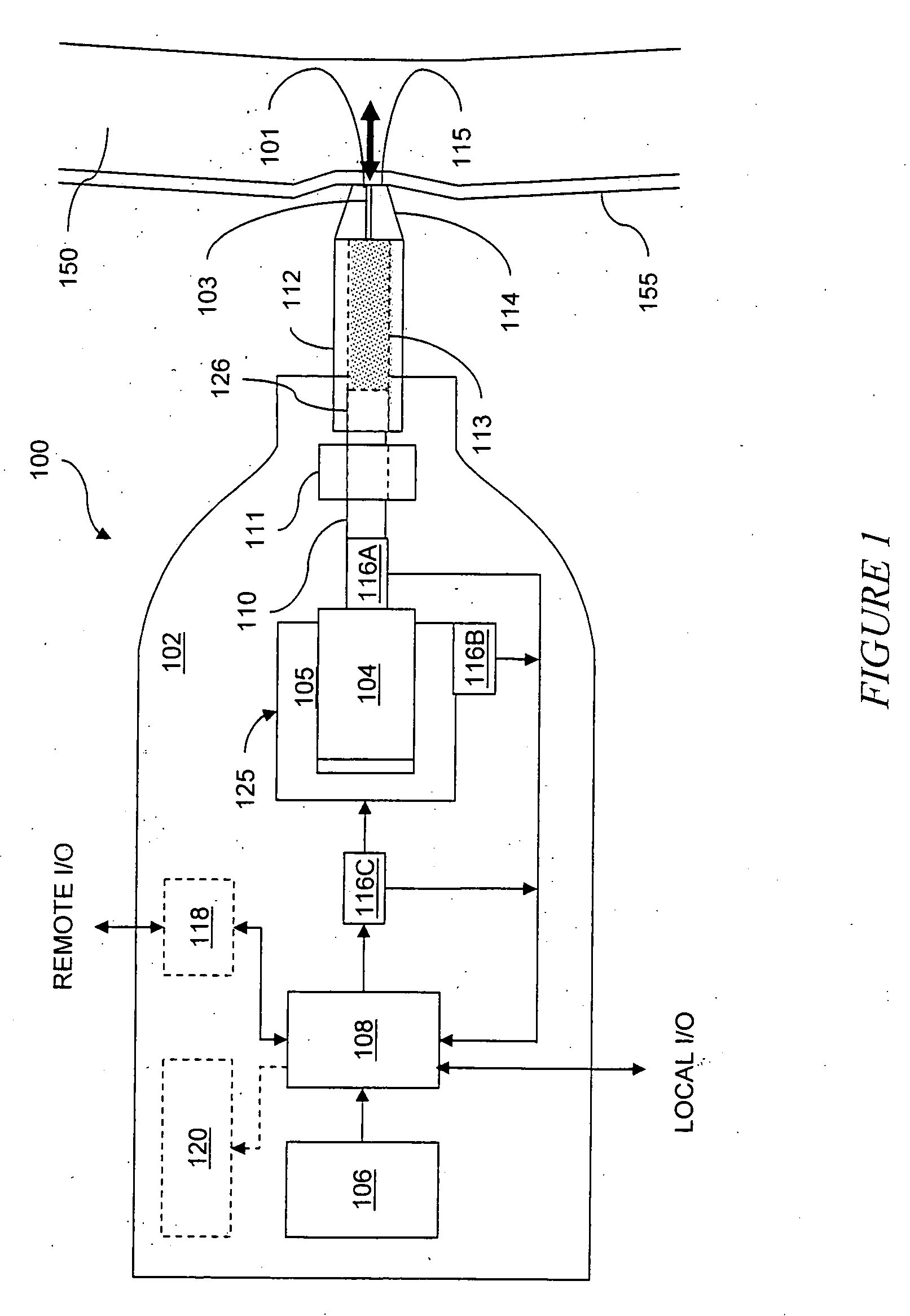
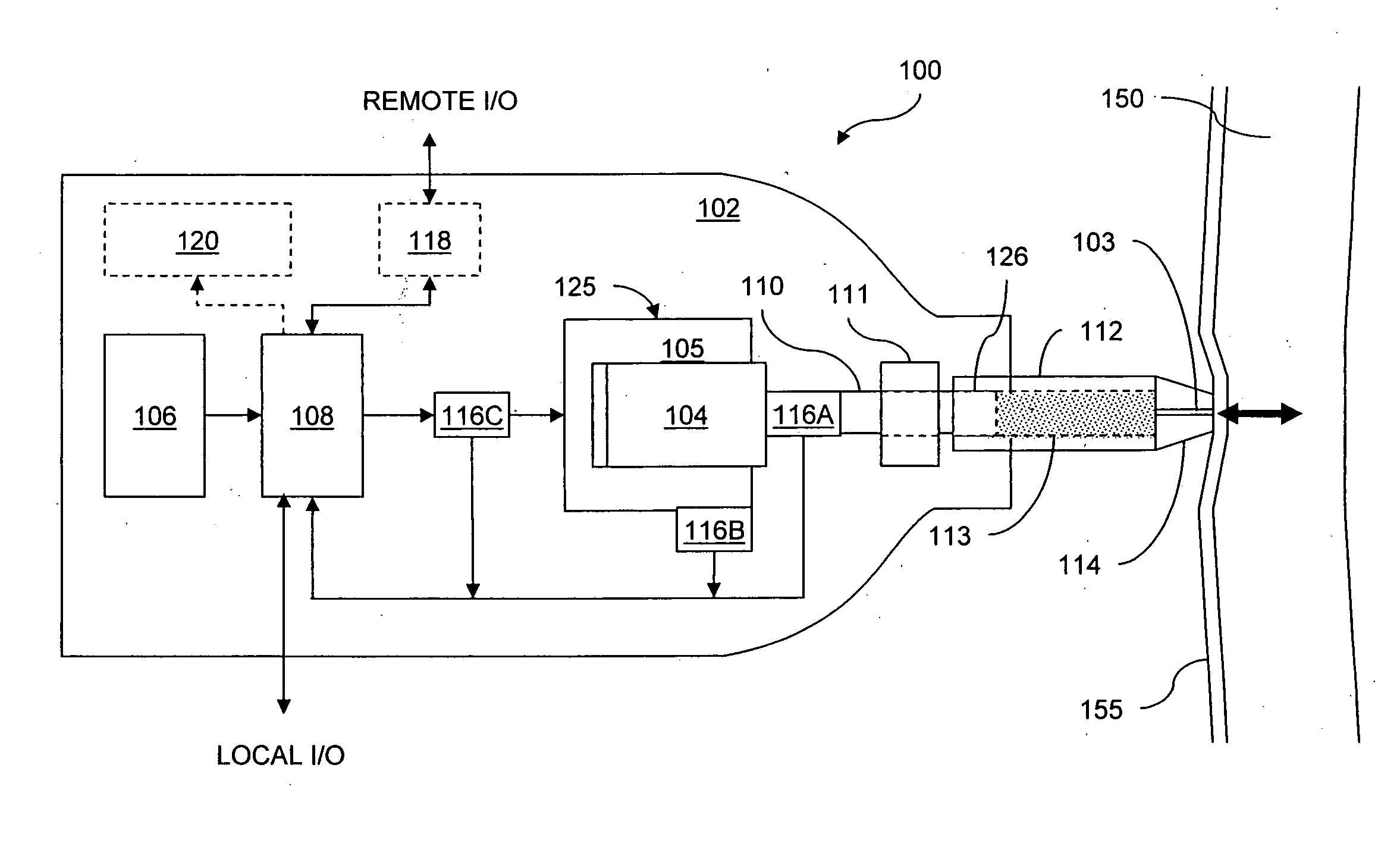
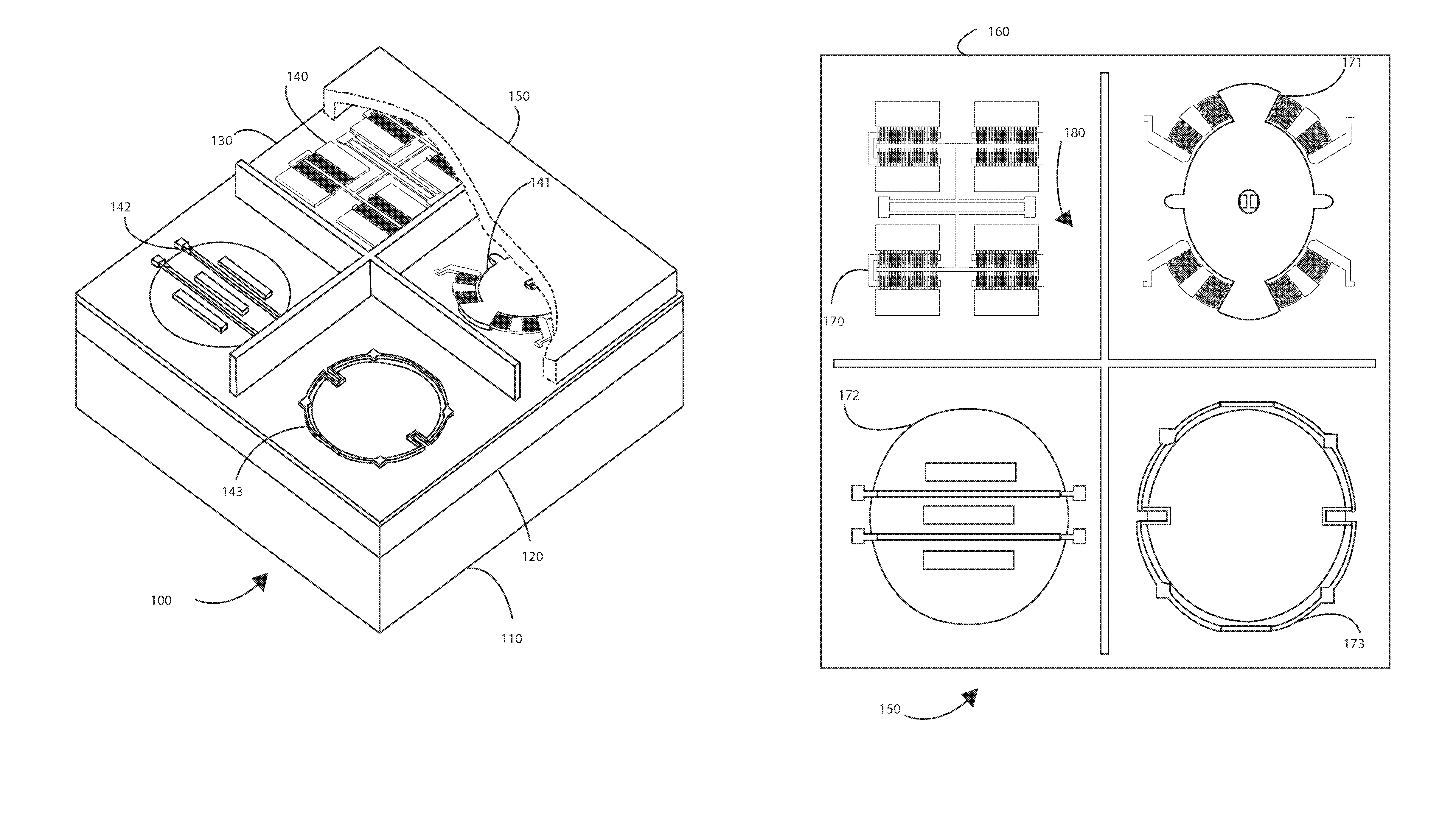
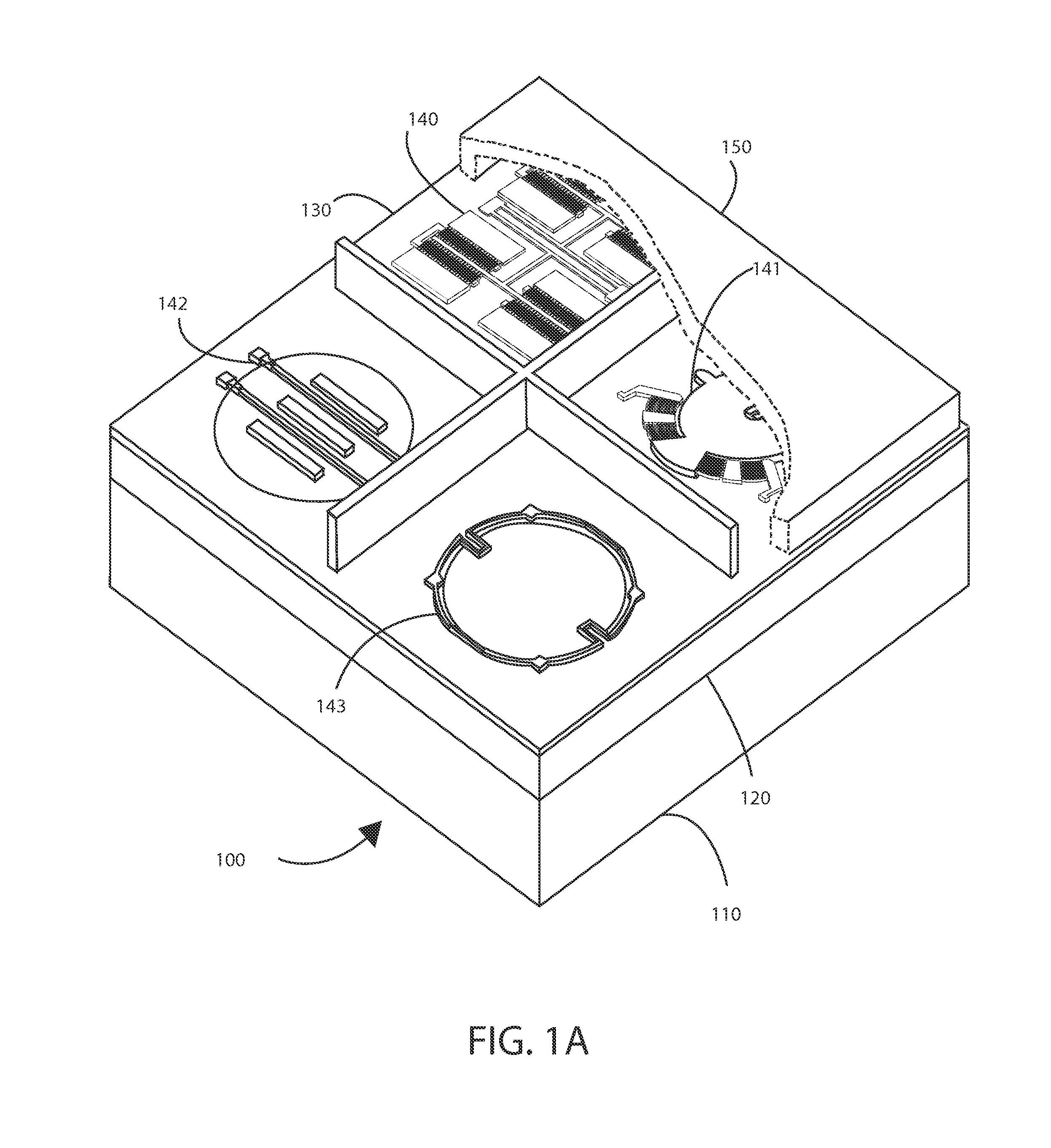
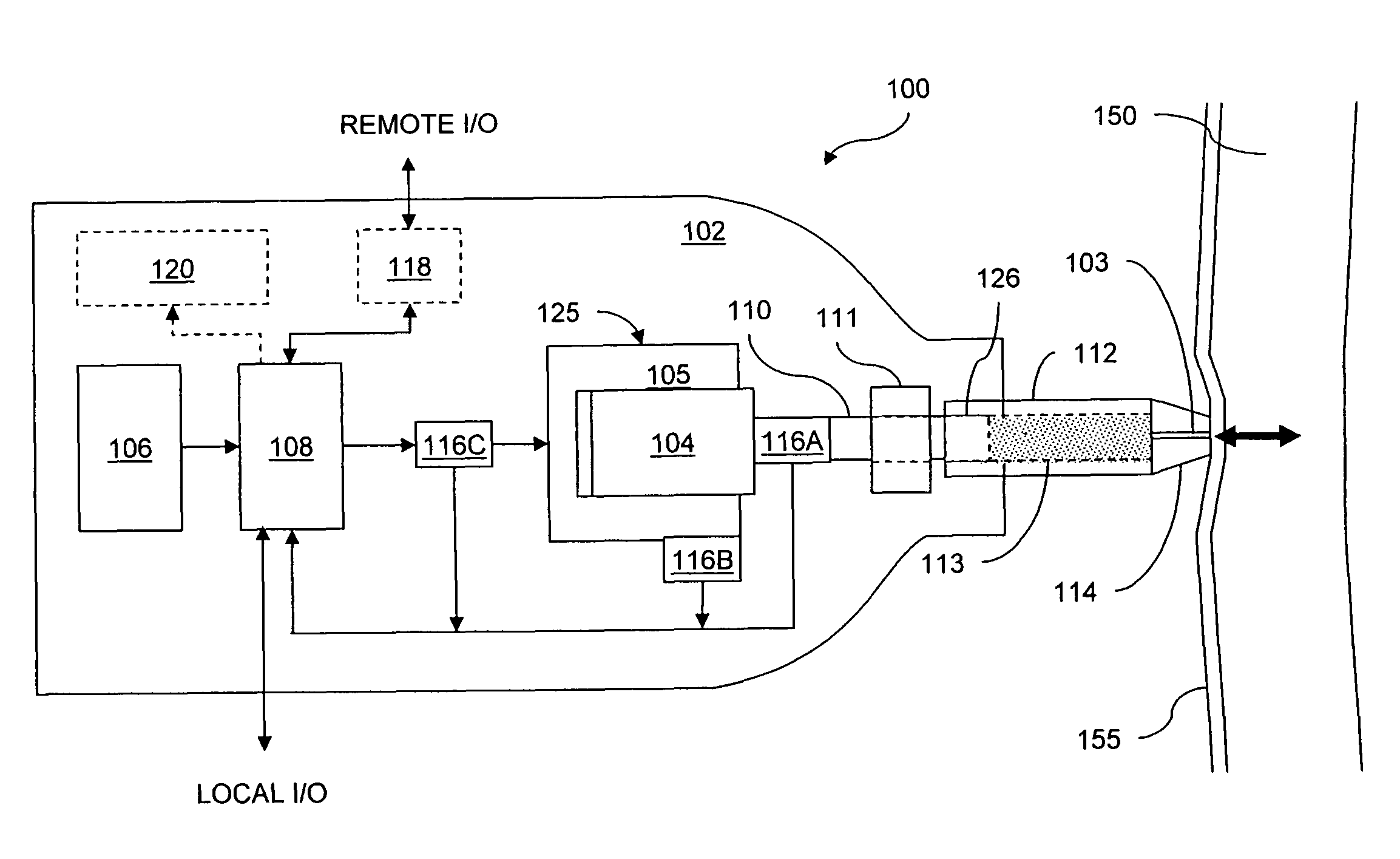
A needle-free transdermal transport device for transferring a substance across a surface of a biological body includes a reservoir for storing the substance, a nozzle in fluid communication with the reservoir and a controllable electromagnetic actuator in communication with the reservoir. The actuator, referred to as a Lorentz force actuator, includes a stationary magnet assembly and a moving coil assembly. The coil assembly moves a piston having an end portion positioned within the reservoir. The actuator receives an electrical input and generates in response a corresponding force acting on the piston and causing a needle-free transfer of the substance between the reservoir and the biological body. The magnitude, direction and duration of the force are dynamically controlled (e.g., servo-controlled) by the electrical input and can be altered during the course of an actuation cycle. Beneficially, the actuator can be moved in different directions according to the electrical input.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Controlled needle-free transport
ActiveUS20070191758A1Magnetic field is facilitatedJet injection syringesSurgeryNeedle freeElectricity
A needle-free transdermal transport device for transferring a substance across a surface of a biological body includes a reservoir for storing the substance, a nozzle in fluid communication with the reservoir and a controllable electromagnetic actuator in communication with the reservoir. The actuator, referred to as a Lorentz force actuator, includes a stationary magnet assembly and a moving coil assembly. The coil assembly moves a piston having an end portion positioned within the reservoir. The actuator receives an electrical input and generates in response a corresponding force acting on the piston and causing a needle-free transfer of the substance between the reservoir and the biological body. The magnitude, direction and duration of the force are dynamically controlled (e.g., servo-controlled) by the electrical input and can be altered during the course of an actuation cycle. Beneficially, the actuator can be moved in different directions according to the electrical input.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Nonlinear System Identification Techniques and Devices for Discovering Dynamic and Static Tissue Properties
ActiveUS20110054354A1Quickly mechanical propertyLow costDiagnostics using suctionDiagnostics using pressureAccelerometerEngineering
A device for measuring a mechanical property of a tissue includes a probe configured to perturb the tissue with movement relative to a surface of the tissue, an actuator coupled to the probe to move the probe, a detector configured to measure a response of the tissue to the perturbation, and a controller coupled to the actuator and the detector. The controller drives the actuator using a stochastic sequence and determines the mechanical property of the tissue using the measured response received from the detector. The probe can be coupled to the tissue surface. The device can include a reference surface configured to contact the tissue surface. The probe may include a set of interchangeable heads, the set including a head for lateral movement of the probe and a head for perpendicular movement of the probe. The perturbation can include extension of the tissue with the probe or sliding the probe across the tissue surface and may also include indentation of the tissue with the probe. In some embodiments, the actuator includes a Lorentz force linear actuator. The mechanical property may be determined using non-linear stochastic system identification. The mechanical property may be indicative of, for example, tissue compliance and tissue elasticity. The device can further include a handle for manual application of the probe to the surface of the tissue and may include an accelerometer detecting an orientation of the probe. The device can be used to test skin tissue of an animal, plant tissue, such as fruit and vegetables, or any other biological tissue.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
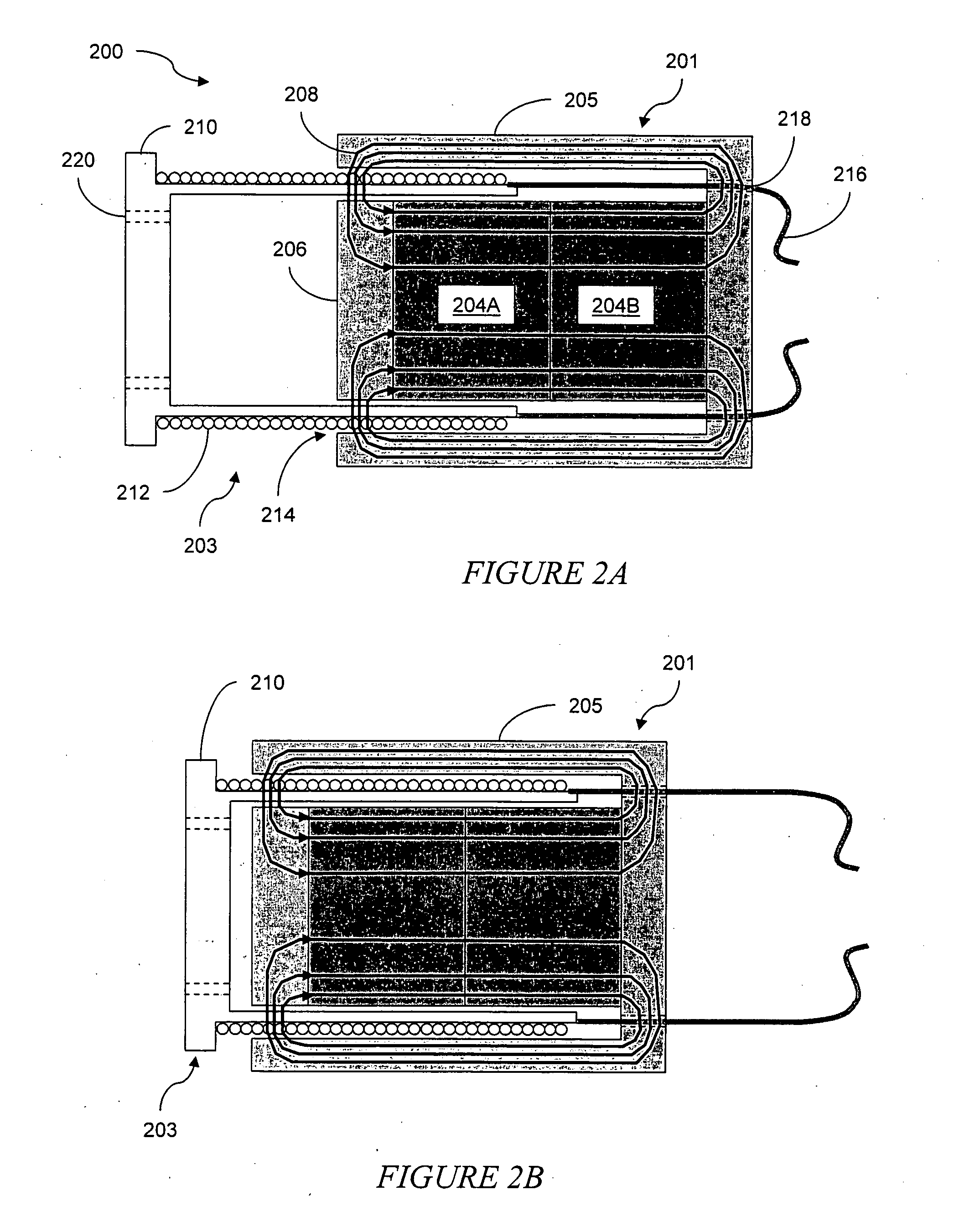
Magnetically actuated fast MEMS mirrors and microscanners
InactiveUS20050018322A1Quick scanImprove accuracyMirrorsDiffusing elementsMagnetic actuationEngineering
Magnetically and electromagnetically driven MEMS devices for reflecting light signals and for switching radio frequency (RF) signals are provided. In a preferred embodiment, a light reflecting device such as a mirror or micro-scanner comprises a plate operative to reflect light and at least two conductive flexural actuators connected to the plate and to a substrate and operative to impart a rotation or tilt motion to the plate under a force arising from the interaction of a current passing through the conductive flexural actuators and a magnetic field parallel to the substrate. An RF switch comprises a substrate and a membrane having a longitudinal dimension and a lateral dimension, the membrane positioned substantially parallel to and attached to the substrate and operative to provide at least two switching positions in response to actuation by a Lorenz force acting on it.
Owner:TERRAOP
Apparatus and method for vacuum-based nanomechanical energy force and mass sensors
InactiveUS20050161749A1Usable nonlinearityModest control forceAcceleration measurement using interia forcesImpedence networksDc currentPlasma chamber
A doubly clamped beam has an asymmetric piezoelectric layer within the beam with a gate proximate to the beam within a submicron distance with a gate and beam dipole. A suspended beam is formed using a Cl2 / He plasma etch supplied at a flow rate ratio of 1:9 respectively into a plasma chamber. A parametric amplifier comprises a NEMS signal beam driven at resonance and a pair of pump beams driven at twice resonance to generate a modulated Lorentz force on the pump beams to perturb the spring constant of the signal beam. A bridge circuit provides two out-of-phase components of an excitation signal to a first and second NEMS beam in a first and second arm. A DC current is supplied to an AC driven NEMS device to tune the resonant frequency. An analyzer comprises a plurality of piezoresistive NEMS cantilevers with different resonant frequencies and a plurality of drive / sense elements, or an interacting plurality of beams to form an optical diffraction grating, or a plurality of strain-sensing NEMS cantilevers, each responsive to a different analyte, or a plurality of piezoresistive NEMS cantilevers with different IR absorbers.
Owner:DARPA
Magnetic levitation haptic interface system
InactiveUS20110050405A1Improve spatial resolutionIncrease stiffnessControlling membersGearing controlComputer usersHuman–computer interaction
This invention discloses a haptic interface system that uses Lorentz forces to provide magnetic levitation for a handle which can be manipulated by a person, typically a computer user.
Owner:BUTTERFLY HAPTICS
PZT MEMS resonant Lorentz force magnetometer
InactiveUS7642692B1Small sizeSmall weightElectrodynamic magnetometersElectrostatic generators/motorsEngineeringConductive materials
A MEMS magnetometer comprises a deflectable resonator comprising a base layer; a Lorentz force (LF) drive conductor attached to the base layer; and a piezoelectric sensor attached to the base layer and electrically isolated from the LF drive conductor. The LF drive conductor comprises conductive material configured for receiving a current at a mechanical resonant frequency of the device capable of causing mechanical deformation of the deflectable resonator, wherein the current causes formation of Lorentz forces in a presence of a magnetic field, and wherein the deflectable resonator is mechanically deformed as a result of the formation of the Lorentz forces. The mechanical deformation of the deflectable resonator generates a detectable piezoelectric electrical signal that is proportional to the magnitude of the magnetic field.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
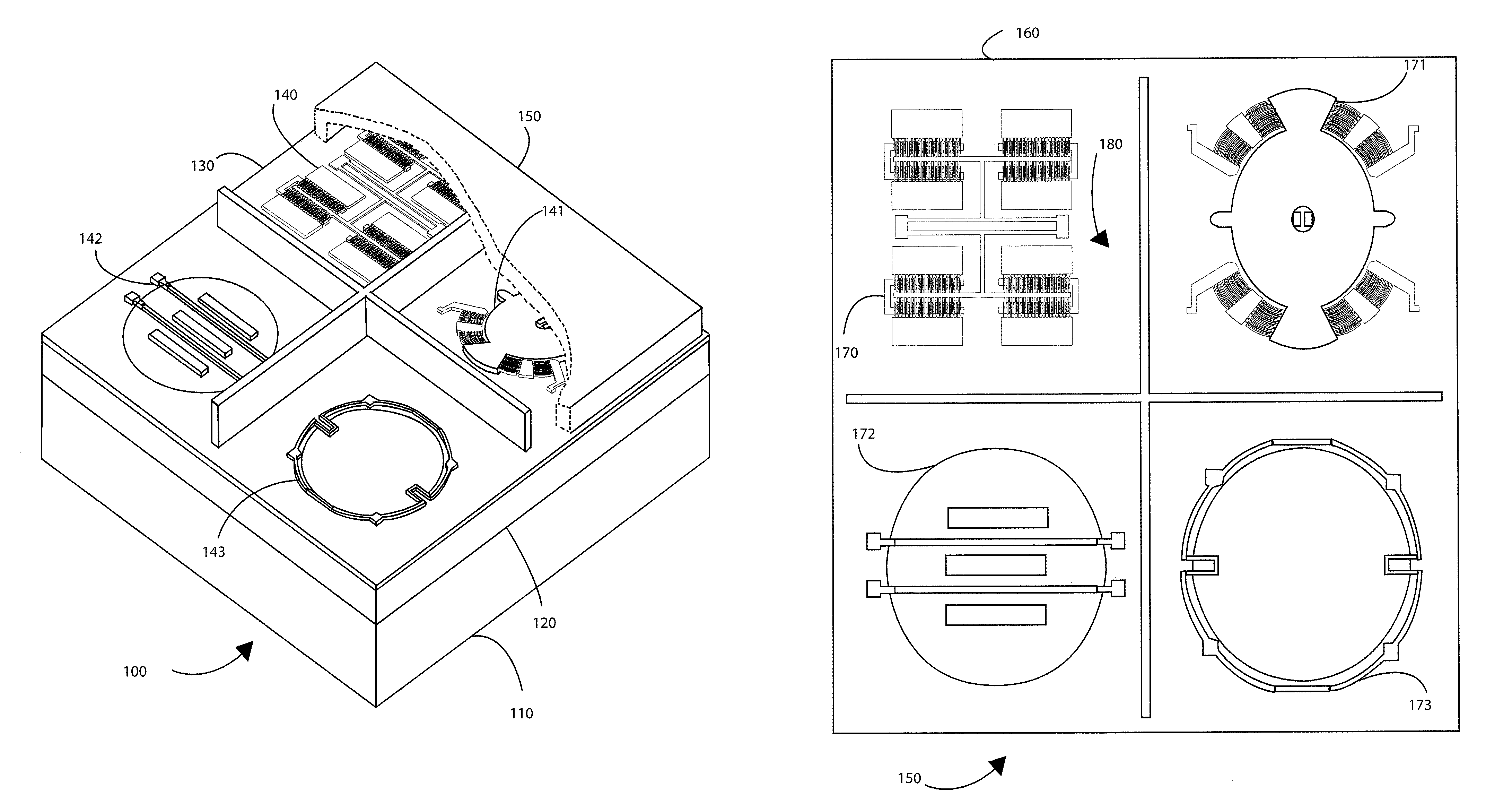
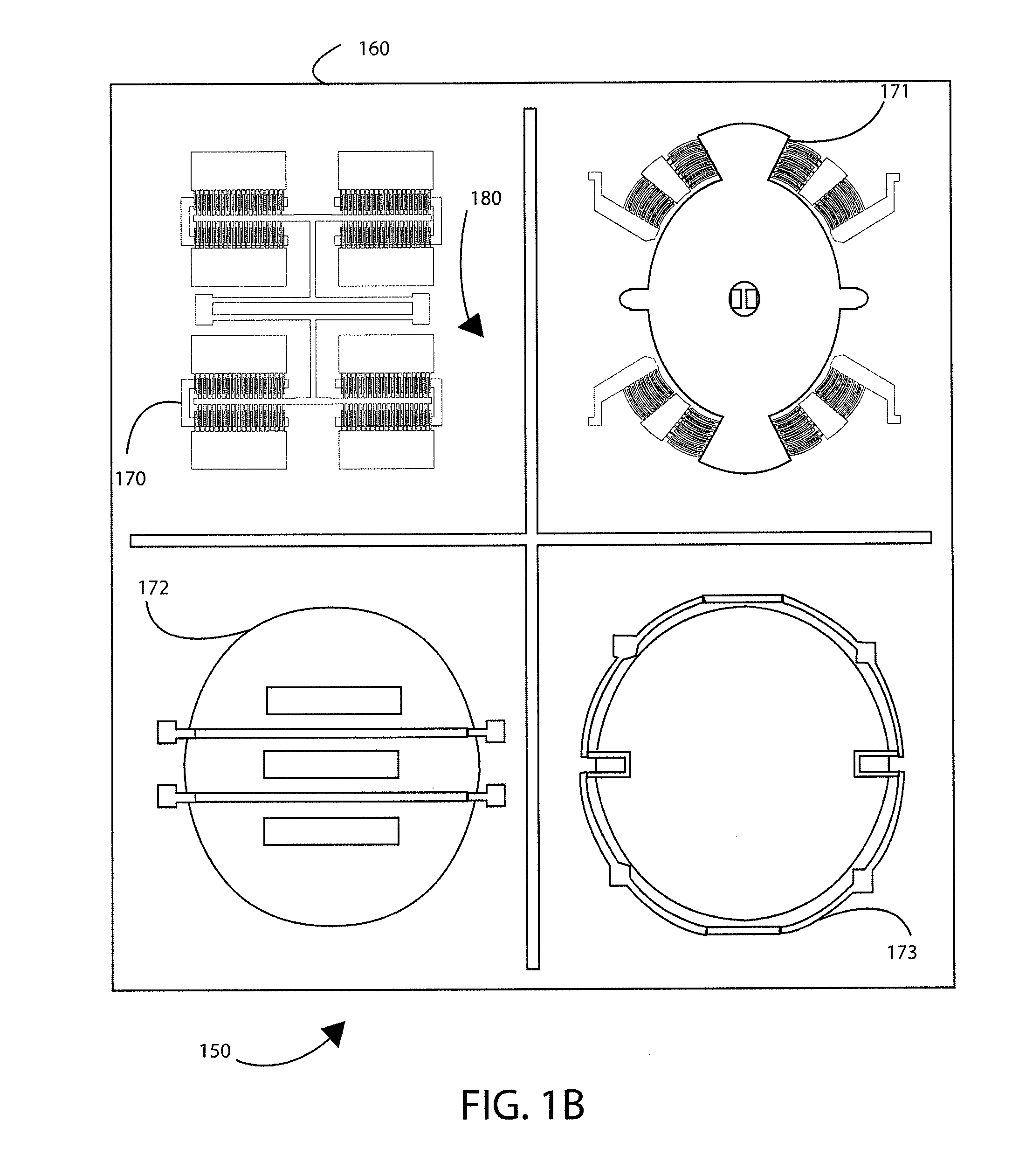
Magneto meter using lorentz force for integrated systems
ActiveUS8402666B1Easy to useHigh device yieldSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsRotary gyroscopesCMOSLorentz factor
Embodiments of the present invention can provide an integrated electronic compass and circuit system having a semiconductor substrate and one or more CMOS integrated circuits formed on one or more portions of the semiconductor substrate. The system can have an electronic compass device operably coupled to the one or more CMOS integrated circuits. The system can also have a plurality of electronic compass devices configured in a parallel arrangement in a hub and spoke configuration.
Owner:MOVELLA INC
Coaxial plasma arc vapor deposition apparatus and method
An apparatus for deposition of plasma reaction films includes a substrate for the deposition of either thin or thick films. The substrate also allows for a film deposition which adheres to the substrate, and also films which may be removed after deposition. The cathode may be fabricated from individual wires, or it may be fabricated from a single conductor. A macro-particle filter which preferentially traps larger particles may be introduced between a porous cathode and the deposition surface. The macro-particle filter may also carry electrical current as is useful for generating a magnetic field such that a Lorentz force acts preferentially on ionized particles, allowing them to pass through the filter while trapping macroparticles that are not influenced by the magnetic field.
Owner:KRISHNAN MAHADEVAN
Foundry compatible process for manufacturing a magneto meter using lorentz force for integrated systems
A method for fabricating an integrated electronic compass and circuit system. The fabrication method begins with providing a semiconductor substrate comprising a surface region. One or more CMOS integrated circuits are then formed on one or more portions of the semiconductor substrate. Once the CMOS circuits are formed, a thickness of dielectric material is formed overlying the one or more CMOS integrated circuits. A substrate is then joined overlying the thickness of the dielectric material. Once joined, the substrate is thinned to a predetermined thickness. Following the thinning process, an electric compass device is formed within one or more regions of the predetermined thickness of the substrate. Other mechanical devices or MEMS devices can also be formed within one or more regions of the thinned substrate.
Owner:MOVELLA INC
Eddy current inductive drive electromechanical linear actuator and switching arrangement
ActiveUS20060061442A1Reliable and reliableSimple designContact mechanismsElectromagnetic relaysTransfer switchEngineering
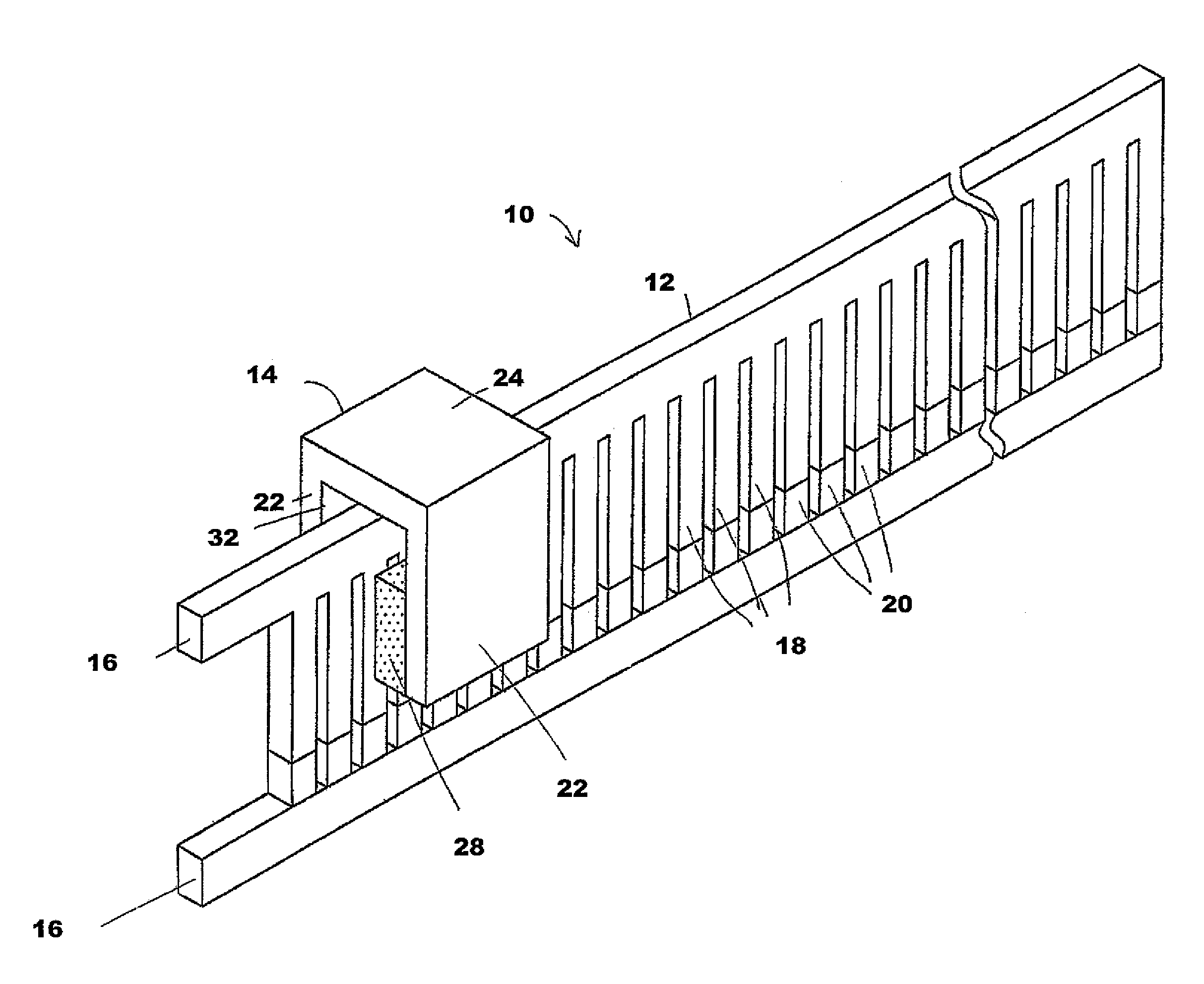
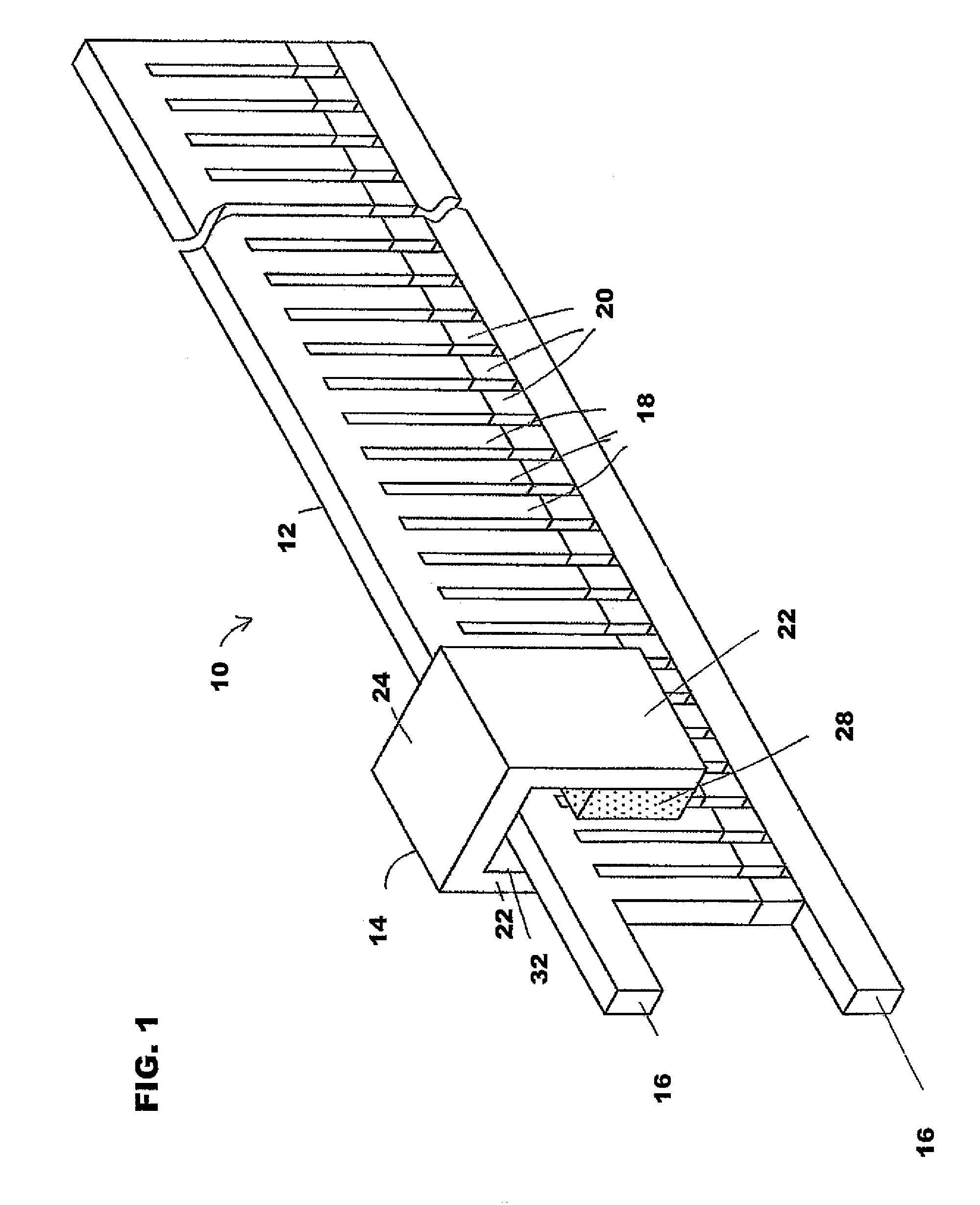
The present invention is directed to an inductively driven electromagnetic linear actuator arrangement employing eddy currents induced by a fixed drive coil to drive its armature. Eddy current focusing fields are employed to direct the eddy currents using Lorentz forces to maximize armature speed. The armature includes a shorted driven coil in a DC magnetic field. This can be supplied by a permanent magnet. When current is applied, a force is felt by the coil in a direction perpendicular to the magnetic field. Such an actuator is well suited for electrical switching applications including transfer switching applications, circuit breaker applications, and ground fault interrupter applications.
Owner:POWERPATH TECH INC
Large-torque magnetic suspension flywheel
InactiveCN102303709AAchieve outputReduce power consumptionSpacecraft guiding apparatusEarth observationMagnetic bearing
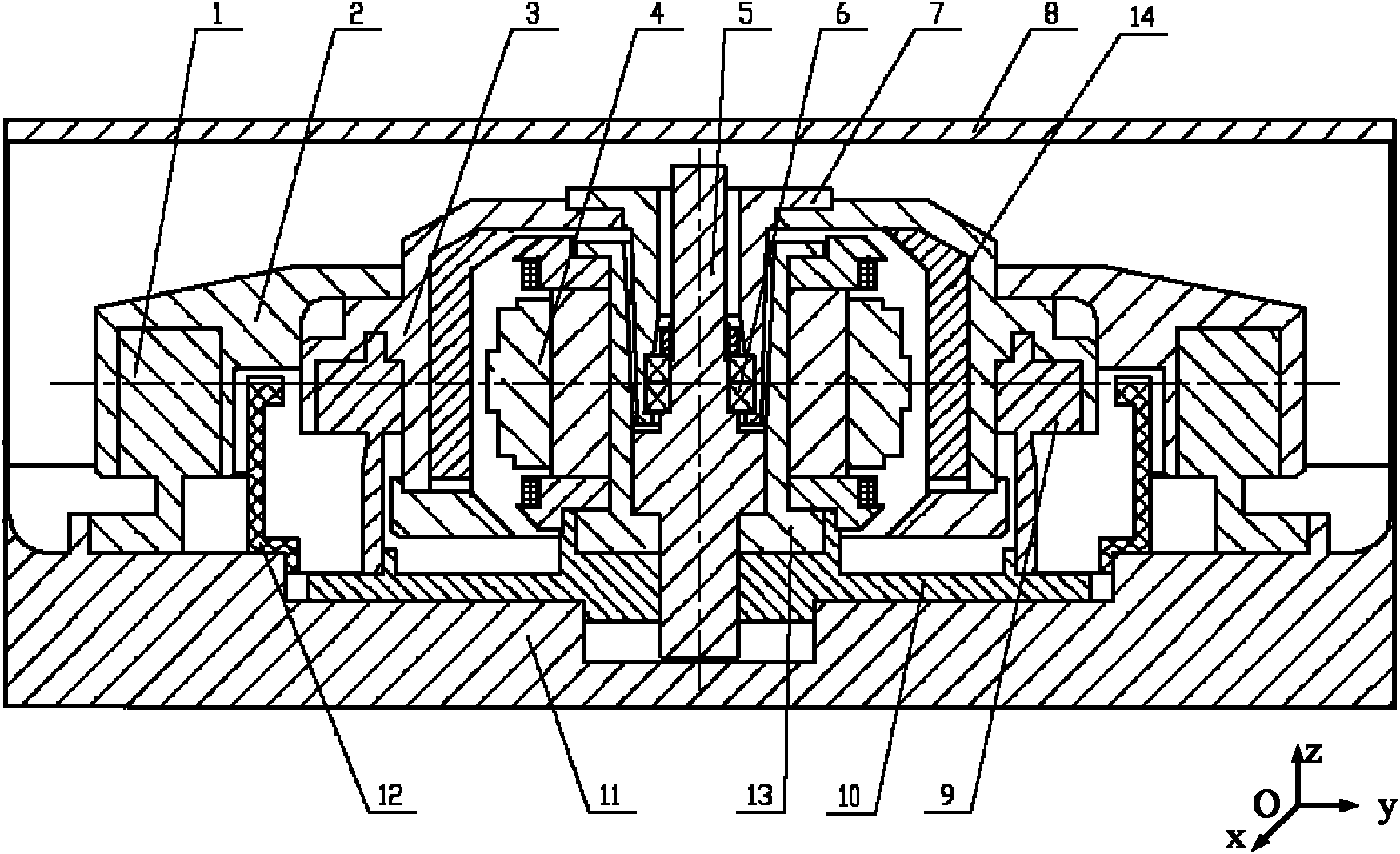
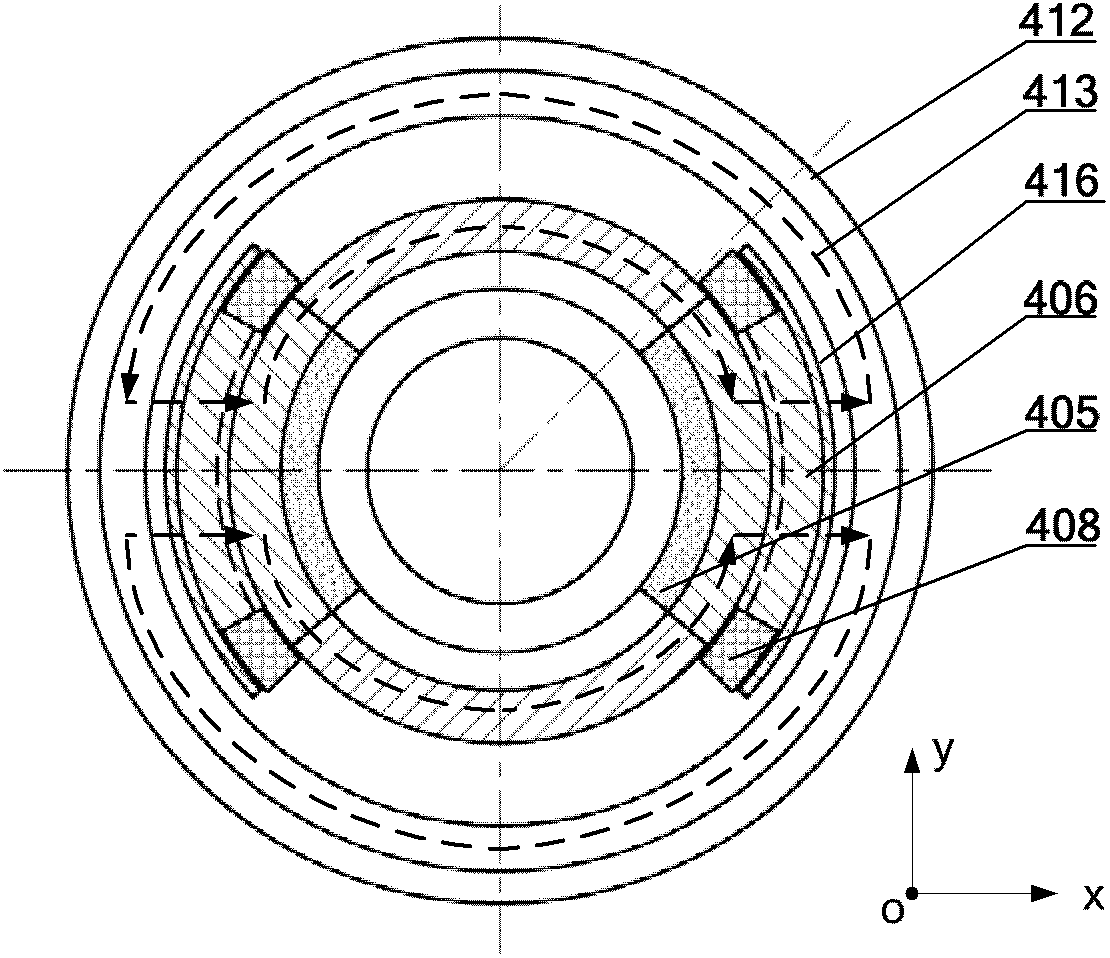
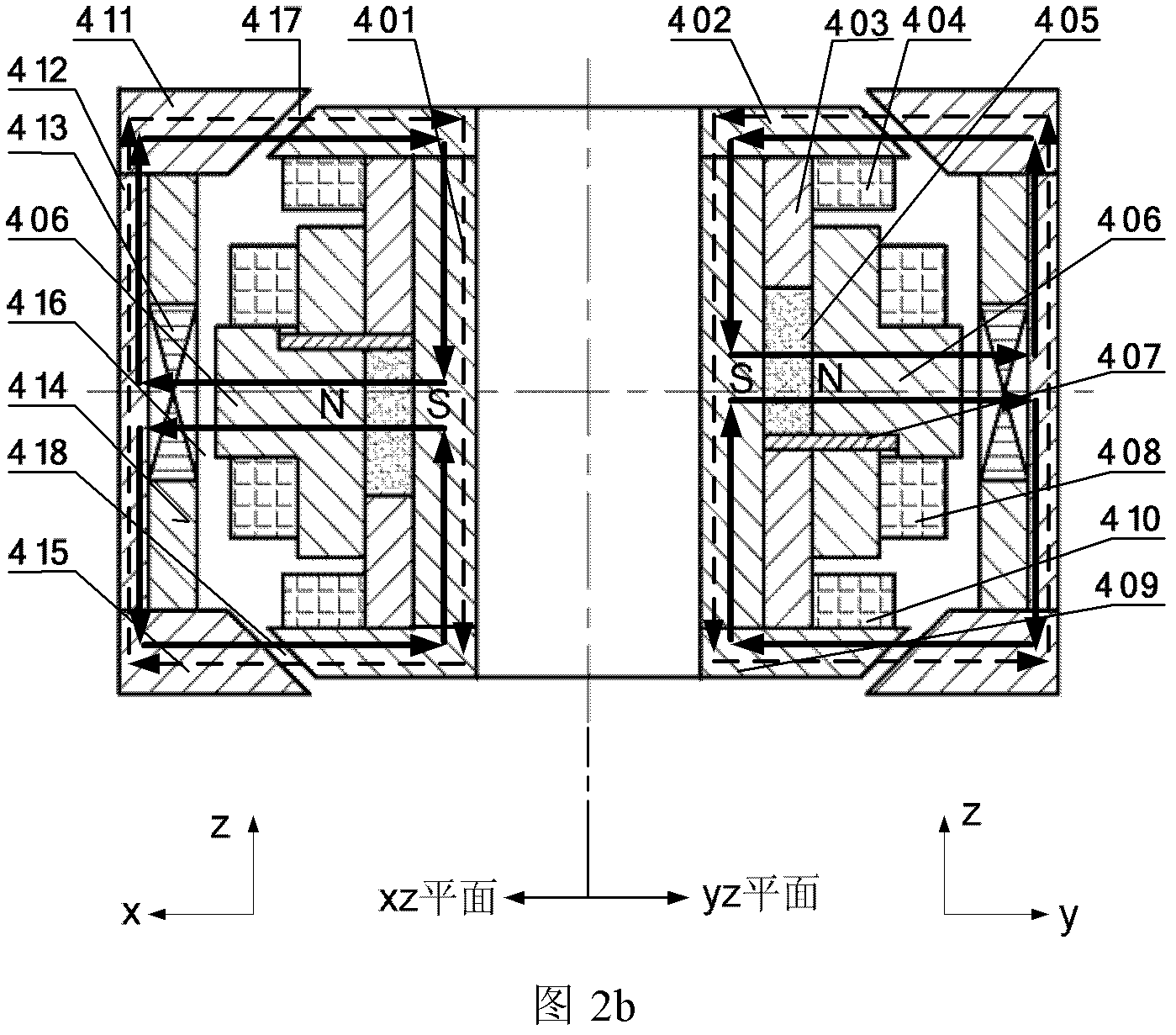
The invention discloses a large-torque magnetic suspension flywheel, which can be used as an execution mechanism for attitude stabilization and attitude maneuver of spacecrafts such as a satellite, an earth observation platform and the like. The magnetic suspension flywheel mainly consists of a base, a sealing cover, a radial decoupling conical magnetic bearing assembly, a core shaft, a rotor assembly, a Lorentz force magnetic bearing assembly, a motor assembly, a sensor assembly and the like. The core shaft is positioned in the center of the wheel body, a stator assembly is positioned at theradial outer side of the core shaft, the rotor assembly is arranged at the radial outer side of the stator assembly, the rotor assembly consists of a wheel flange and a wheel hub, and the Lorentz force magnetic bearing assembly consists of a magnetic bearing stator part and a magnetic bearing rotor part; an adapter plate is connected with the core shaft, the stator assembly and a motor stator; and the sensor assembly consists of a sensor shell and a sensor. The components of the flywheel are arranged reasonably and compactly, the flywheel can be used for attitude stabilization of the spacecraft, and attitude maneuver of the spacecraft can be realized by using large control torque provided by gyroscopic effect of the magnetic suspension flywheel.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Magneto-acoustic microscopic imaging method and imaging system
ActiveCN102788836AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringSource imagingAcoustic lens
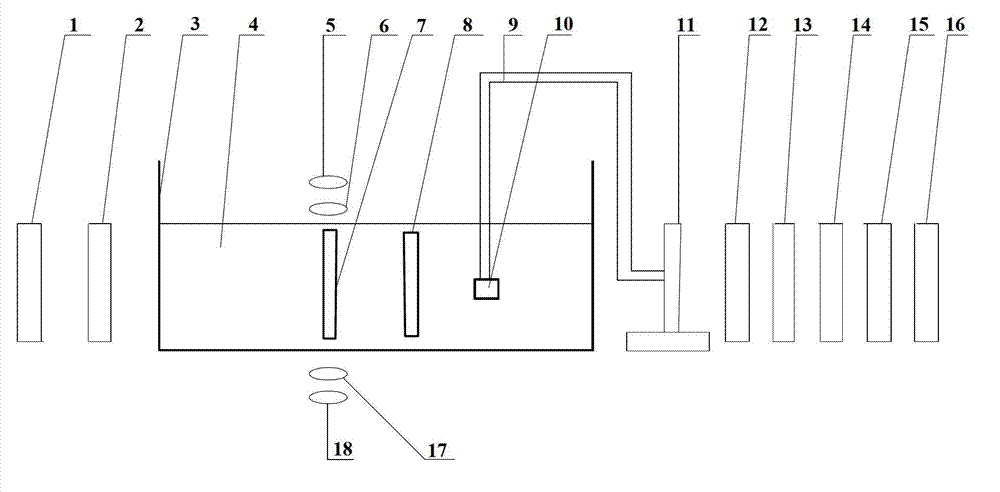
The invention discloses a magneto-acoustic microscopic imaging method, comprising the steps of applying pulse excitation on a conductive target imaging body in a static magnetic field, generating an inductive vortex in the conductive target imaging body, and generating a Lorentz force by the interaction of the inductive vortex and the static magnetic field so as to cause the vibration of mass points in the imaging body to generate ultrasonic signals; receiving image signals of the ultrasonic signals of each mass point in the conductive target imaging body by using an array ultrasonic probe on a focal plane of an acoustic lens, imaging the received image signals of each mass point in the conductive target imaging body, so that each mass point image signal is proportional to the Lorentz force divergence of a corresponding point in the conductive target imaging body, and a Lorentz force divergence image of the conductive target imaging body or a reconstructed image according to current density rotation can be obtained according to the image signals of the ultrasonic signals detected by the array ultrasonic probe. A magneto-acoustic microscopic imaging system using the imaging method disclosed by the invention comprises a synchronous trigger and control module (1), an excitation source, an imaging system and a week signal detecting system.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multiple magneto meters using Lorentz force for integrated systems
ActiveUS8407905B1Easy to useHigh device yieldSpeed/acceleration/shock instrument detailsGyroscopes/turn-sensitive devicesCMOSLorentz force
A plurality of integrated electronic compasses and circuit system. The system includes a semiconductor substrate and one or more CMOS integrated circuits formed on one or more portions of the semiconductor substrate. The system has a plurality of electronic compass devices operably coupled to the one or more CMOS integrated circuits. The plurality of electronic compass devices can be integrated with one or more sensors, MEMS, or other devices.
Owner:MOVELLA INC
Channel gun magnetic launcher
InactiveUS7614393B1Tremendously heatedTremendously destroyedAmmunition projectilesElectromagnetic launchersElectromagnetic launchPower flow
Owner:LU WEIMIN
Electric-magnetic compound field synergy laser-cladding method and device
ActiveCN104195541ARealize the enhancement of constituency customizationOvercome the defect of being unable to control the convective tendency of the molten poolMetallic material coating processesTransmission channelErbium lasers
The invention discloses an electric-magnetic compound field synergy laser-cladding method and device. In the laser-cladding process, an applied electric field and an applied magnetic field are simultaneously coupled in a workpiece, so that conductive fluid of a molten pool is capable of generating controllable lorentz force by means of the synergic effect of the electric-magnetic compound field, the heat and mass transfer behavior in the laser cladding process can be regulated and controlled, and tendency control of the molten convection can be realized to achieve the aims of regulating and controlling solidification structures, optimizing mechanical performances of the workpiece, regulating distribution of solute element or external hardness phase, improving the surface appearance of a cladding layer and the like. The electric-magnetic compound field synergy laser-cladding device comprises a laser, a laser transmission channel, a powder feeding head, a permanent magnetic or excitation device, a workpiece clamp, a lead wire, a low-voltage high-current power supply and the like. The device realizes synergic control of the electric-magnetic compound field on the laser induced molten pool, and has the characteristics of strong regulation and control capability, flexible regulation and control type, wide application range and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
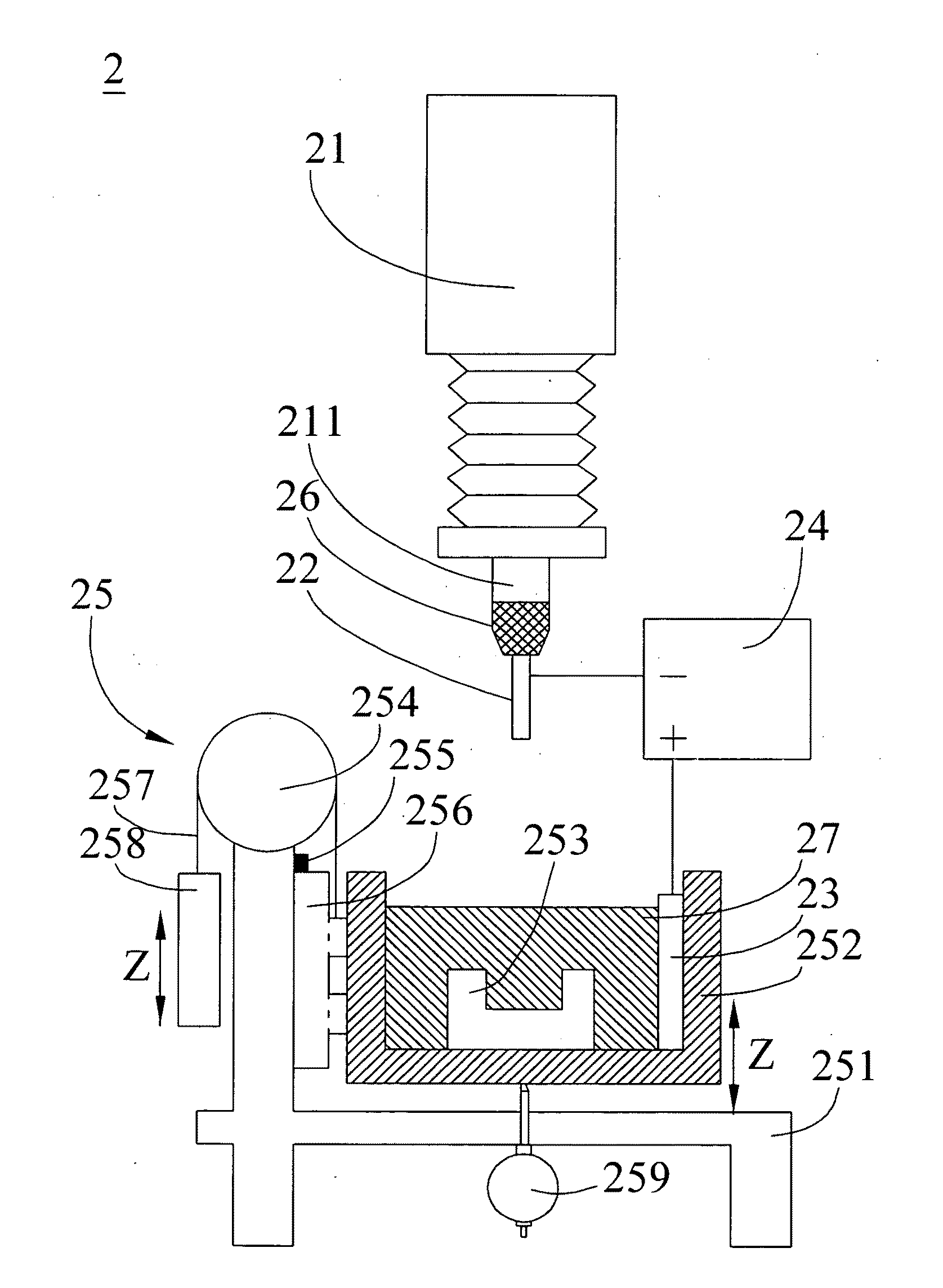
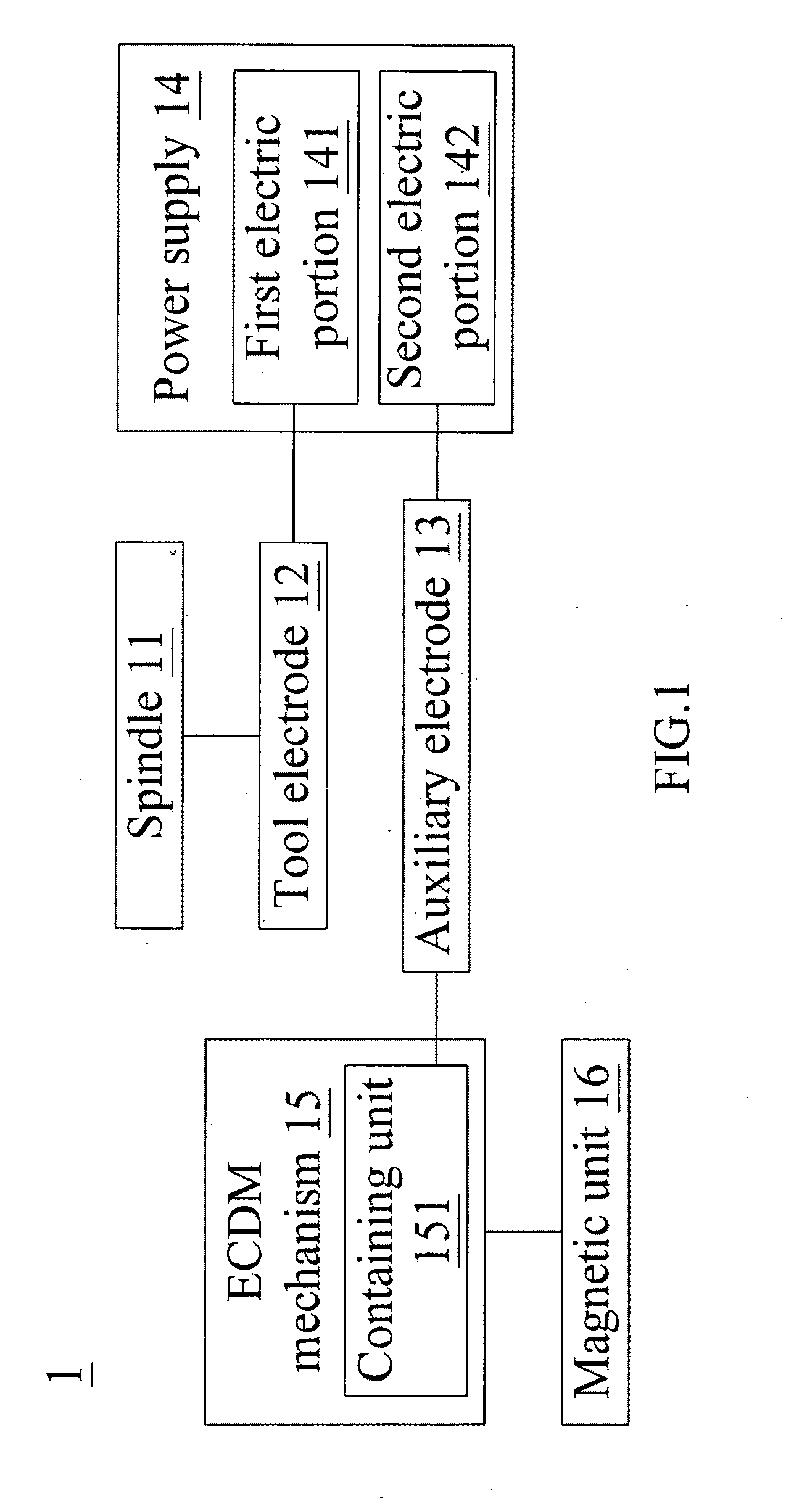
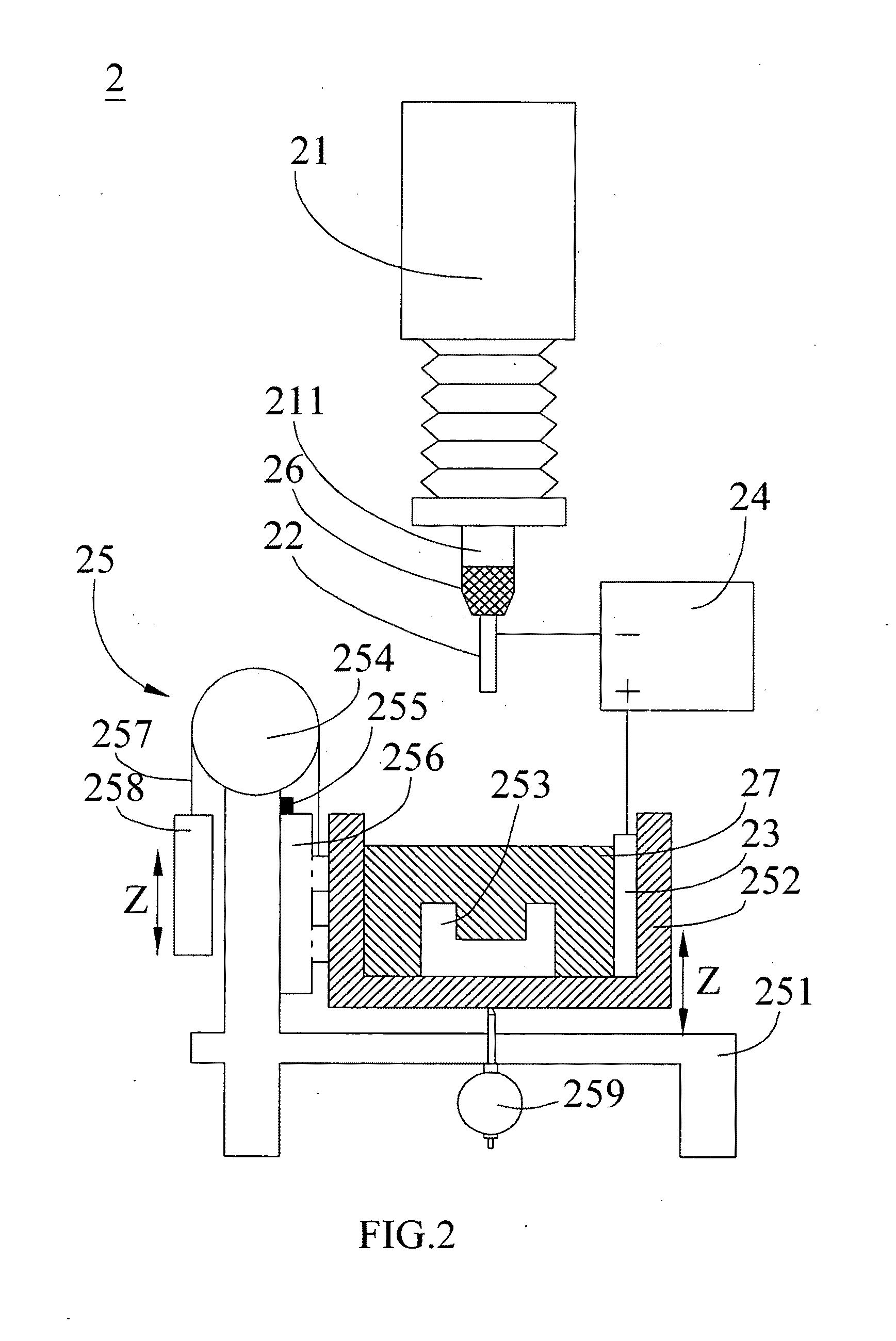
Apparatus and method for magnetic field assisted electrochemical discharge machining
ActiveUS20100243430A1Reduce thicknessIncrease loopCellsVacuum evaporation coatingElectrolysisMachined surface
In an apparatus and method for magnetic field assisted electrochemical discharge machining (ECDM), the magneto hydrodynamic (MHD) effect is utilized to improve the thickness of bubble film and the electrolyte circulation so as to enhance the machining accuracy and efficiency. Since charged ions in a magnetic field are induced by Lorenz force to move, and the electrolysis bubbles generated in the ECDM process are suffused with electrification ions on their surfaces, the electrolysis bubbles can be forced to move in the direction of the magnetic field without the need of mechanical disturbance. The present invention can be widely applied in the micro-machining of non-conductive brittle materials of different dimensions and shapes, comprising the forming of microchannels and microholes on a biochip, and in the micro-opto-electro-mechanical system (MOEMS) and various kinds of micro-machining fields. The machined surface is smooth and does not require a second time machining.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
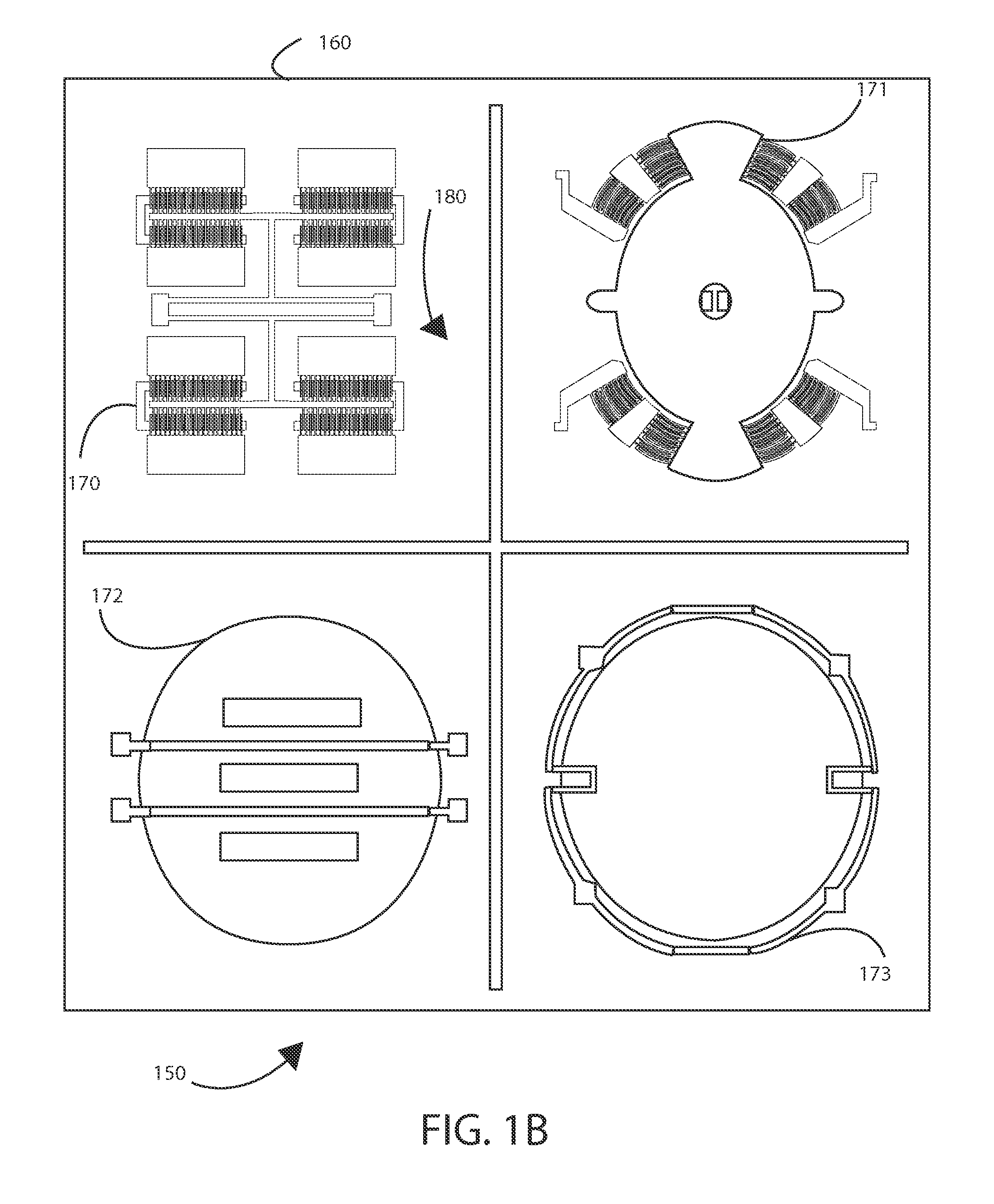
MEMS-based magnetic sensor with a lorentz force actuator used as force feedback
A magnetic sensor utilizes a MEMS device that has at least one vibrating member and at least one conductive path integral with the vibrating member so that a current flows along the vibrating member and in the presence of a magnetic field interaction of the magnetic field and the point charges in the current on the conductive path due to the Lorentz force causes a change in vibration of the vibrating member. That change can be used to provide a measure of the magnetic field.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
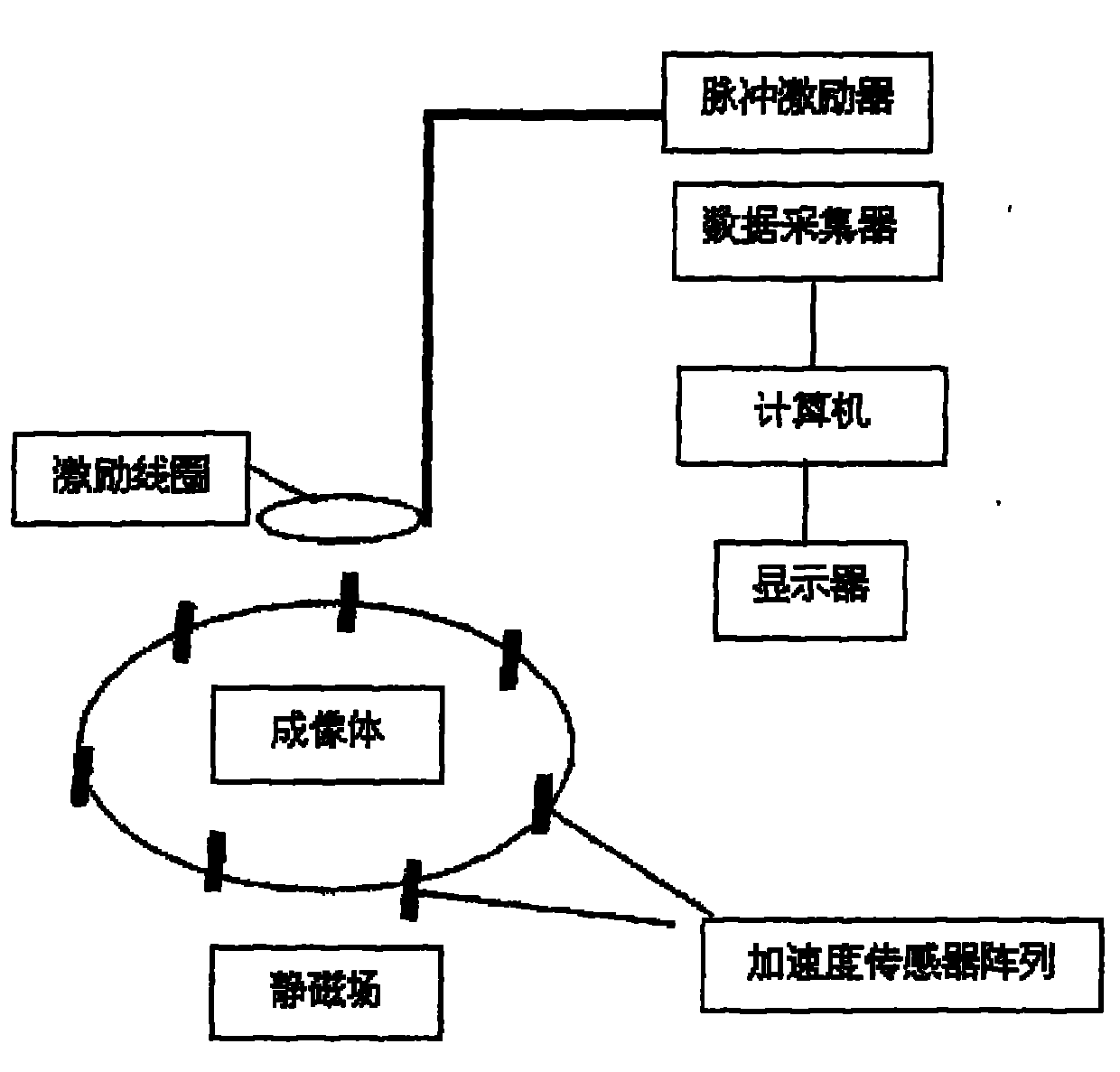
Magnetic-acoustic electrical impedance imaging method and device
The invention provides a magnetic-acoustic electrical impedance imaging method. The method is characterized by measuring a Lorentz force vibration displacement waveform signal generated under the action of a static magnetic field due to an inductive loop excited by a pulse magnetic field by using an acceleration sensor and acquiring an electric conductivity image of an imaging body through image reconstruction according to nonlinear relation between the displacement waveform signal and the electric conductivity. The device which adopts the method comprises a pulse exciter, exciting coils, a magnetostatic body, an acceleration sensor array, a data acquisition unit and a computer, wherein the exciting coils and the magnetostatic body are arranged on two sides of the imaging body; the acceleration sensor array are distributed surrounding the imaging body; the pulse exciter is connected with the exciting coils through cables; and the acceleration sensor array, the data acquisition unit and the computer are connected in turn.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
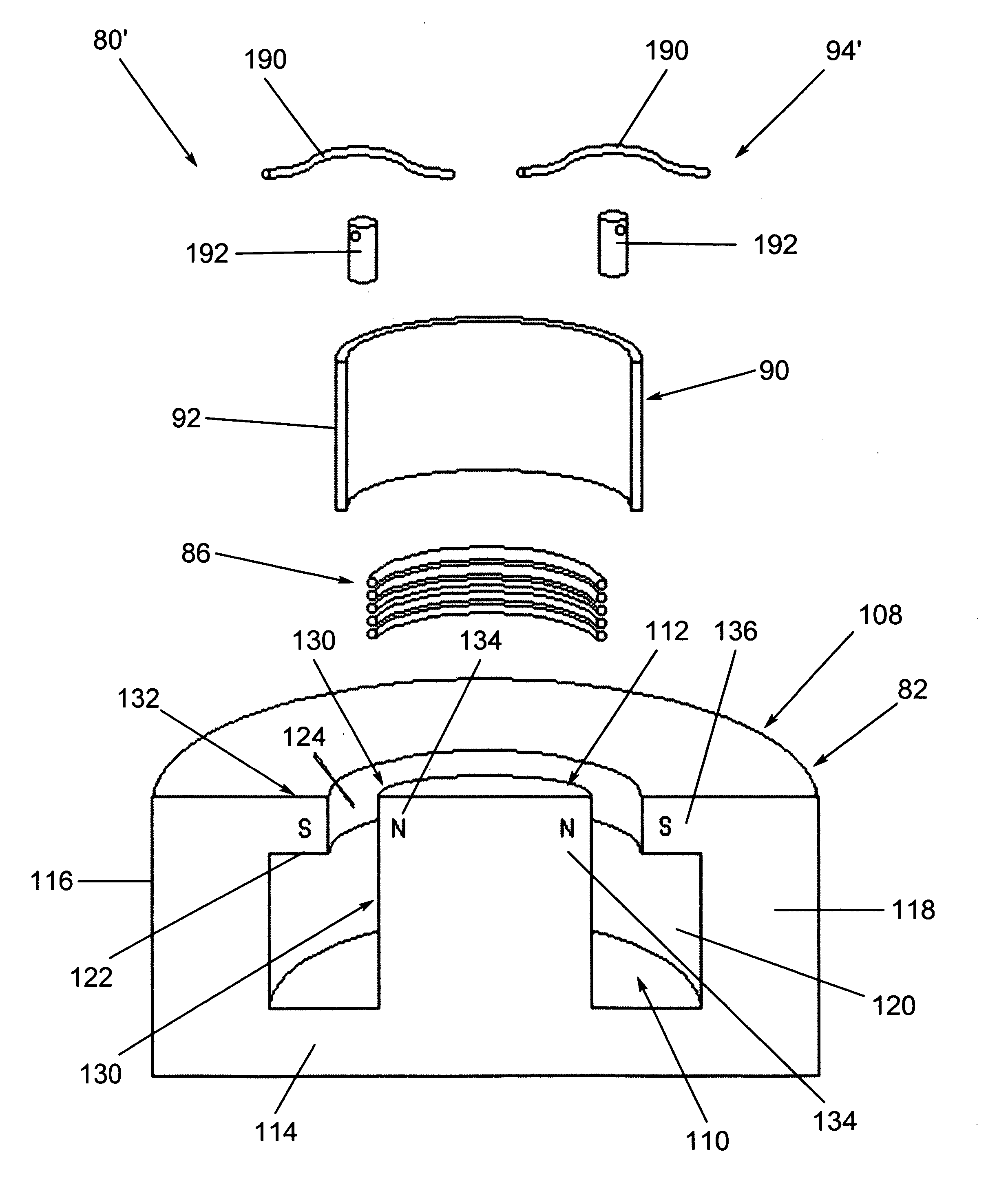
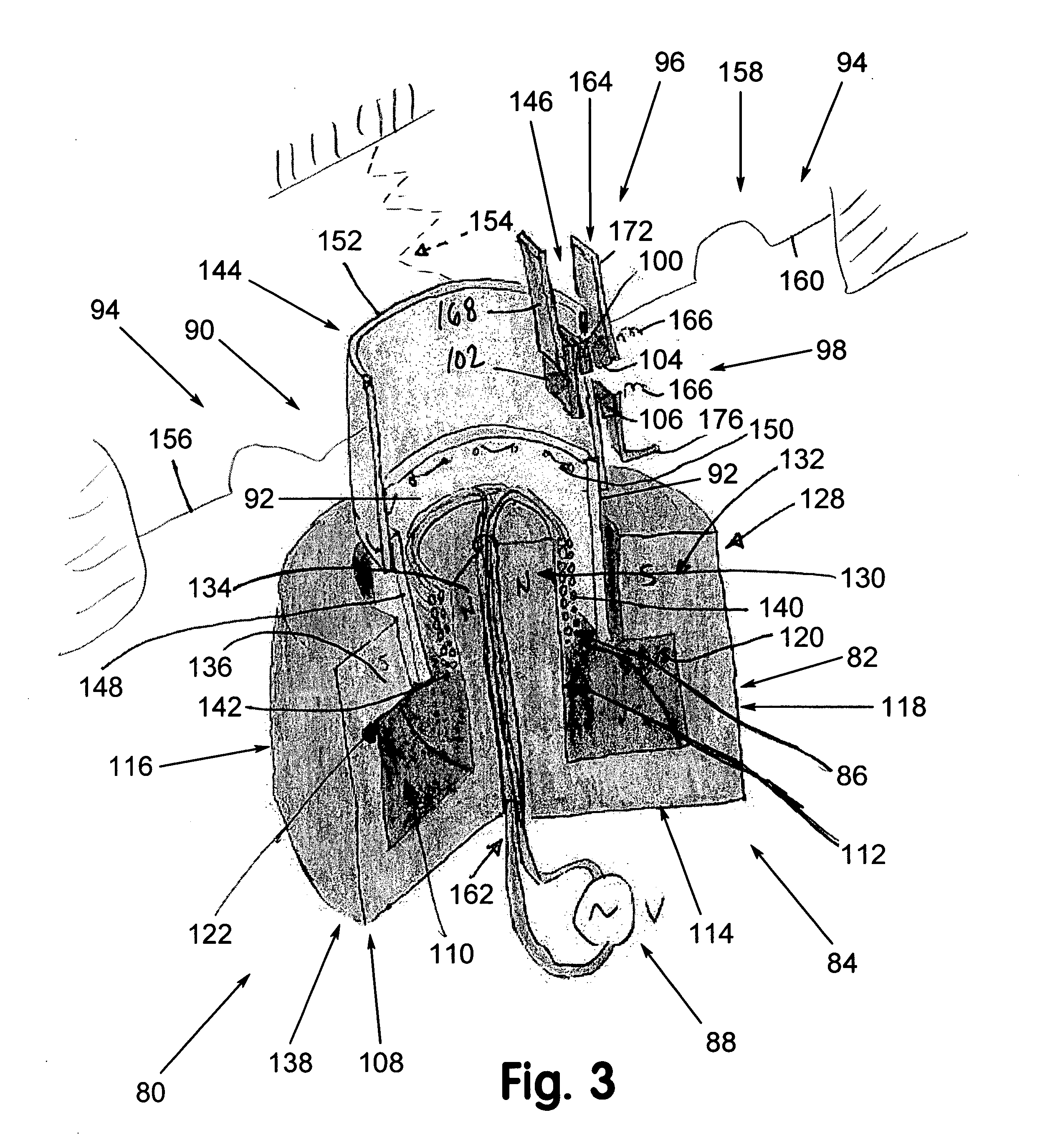
Controlled needle-free transport
A needle-free transdermal transport device for transferring a substance across a surface of a biological body includes a reservoir for storing the substance, a nozzle in fluid communication with the reservoir and a controllable electromagnetic actuator in communication with the reservoir. The actuator, referred to as a Lorentz force actuator, includes a stationary magnet assembly and a moving coil assembly. The coil assembly moves a piston having an end portion positioned within the reservoir. The actuator receives an electrical input and generates in response a corresponding force acting on the piston and causing a needle-free transfer of the substance between the reservoir and the biological body. The magnitude, direction and duration of the force are dynamically controlled (e.g., servo-controlled) by the electrical input and can be altered during the course of an actuation cycle. Beneficially, the actuator can be moved in different directions according to the electrical input.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
System and method of magnetosonic impedance imaging based on lorentz force mechanic effect
ActiveCN102860825AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringSonificationImpedance imaging
A system and a method of magnetosonic impedance imaging based on a lorentz force mechanic effect comprise an ultrasonic driving excitation source, an ultrasonic probe array, a control system, a magnet system, a direct current power supply and a signal detecting processing system. The ultrasonic probe array is in an emitting or measuring mode through the control system. The direct current power supply is in a connected or disconnected state through the control system so as to achieve two modes of exerting a magnetic field or withdrawing a magnetic field. Mass point vibration speed ratio under a magnetic field condition or a non-magnetic field condition is measured, and a conductivity image is rebuilt according to a square root of the vibration speed ratio. The imaging method does not require electric field measurement, only sound wave signals are required to be measured, a corresponding relation between measured signals and conductivity is simple and clear, and fast image rebuilding is facilitated.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Internal rotor magnetic suspension spherical surface gyro flywheel
ActiveCN105302149AImprove levitation accuracyQuality improvementSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsAttitude controlAxial displacementMagnetic bearing
The invention discloses an internal rotor magnetic suspension spherical surface gyro flywheel. The flywheel comprises a stationary part and a rotating part. The stationary part comprises an upper gyro chamber, a middle gyro chamber, a lower gyro chamber, a sealing ring, an axial spherical surface magnetic bearing stator, a protective bearing, a motor assembly stator, an axial displacement sensor assembly, a radial displacement sensor assembly, a radial spherical surface magnetic bearing stator and a Lorentz force magnetic bearing stator. The rotating part comprises a gyro outer rotating disk assembly, a gyro inner rotating shaft, sphere center adjusting backing rings and gyro rotor lock nuts. A spherical surface magnetic bearing is adopted to serve as supporting member, five-degree-of-freedom active suspension of the magnetic suspension gyro flywheel can be achieved, the interference of three times of translation control of a rotor in two times of radial twist control is eliminated, and then the moment precision of the high gyro moment instantly output by the gyro flywheel is increased.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF PETROCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY +1
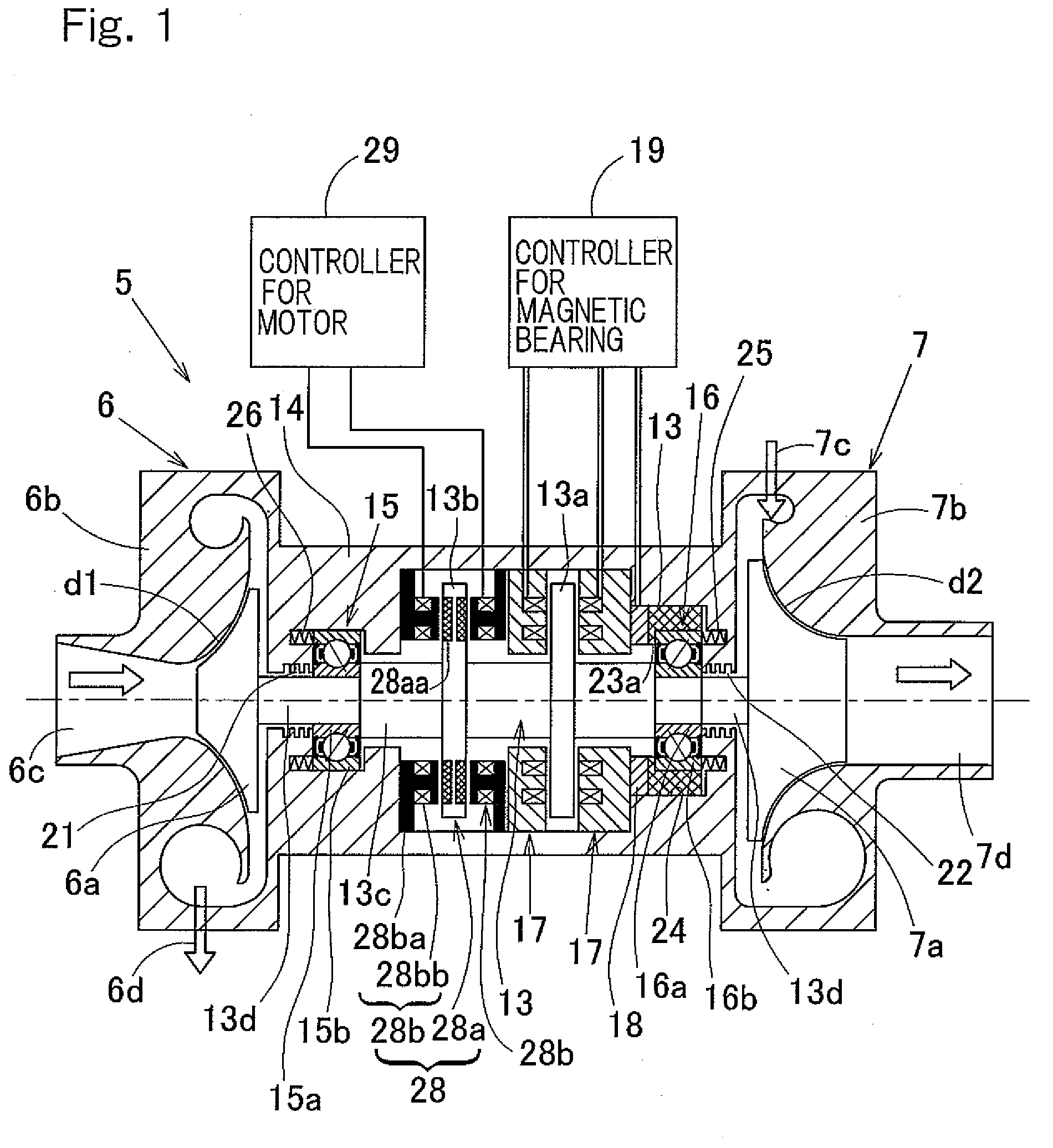
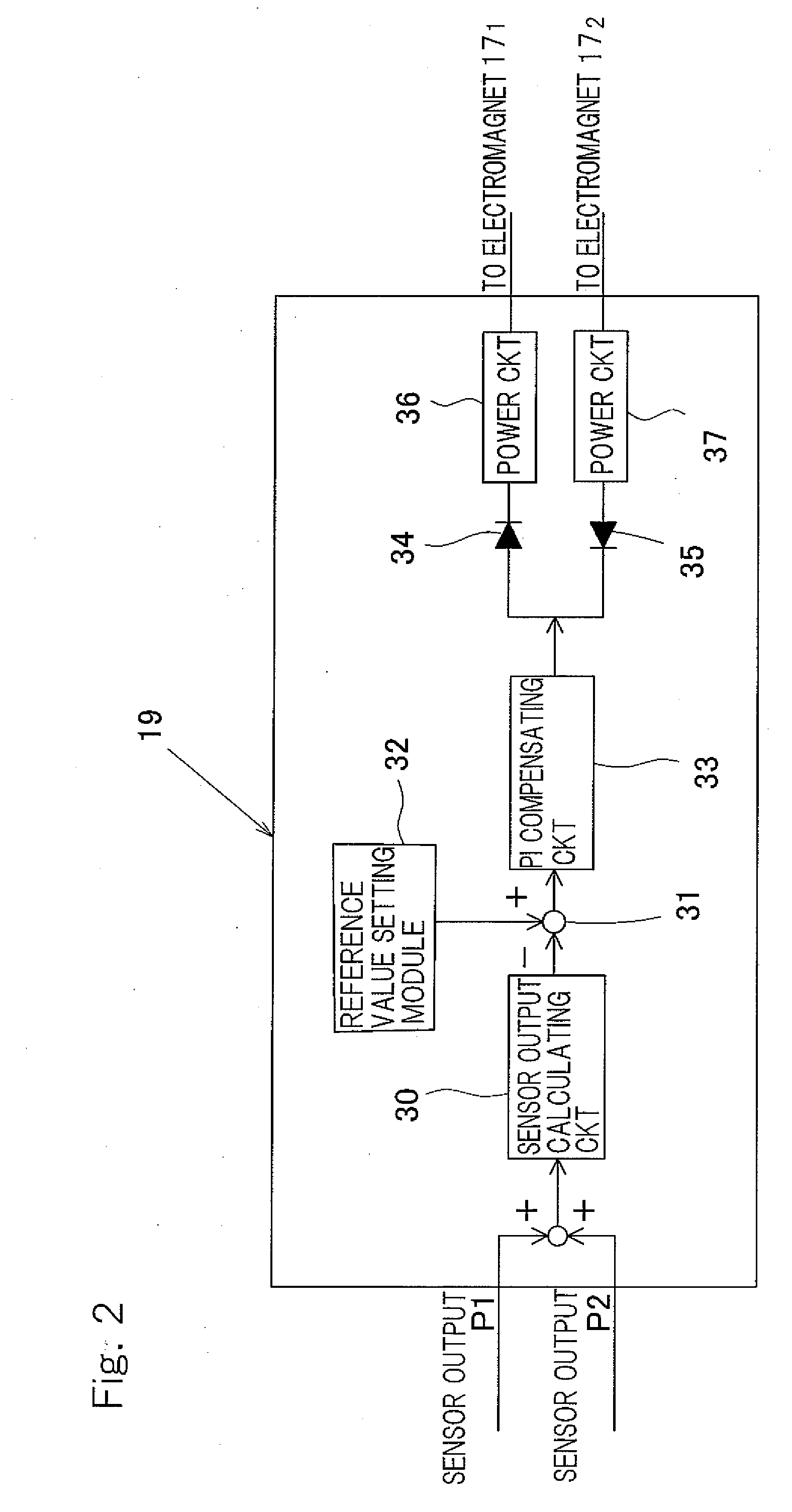
Motor built-in magnetic bearing device
InactiveUS20090127956A1Improve long-term durabilityReliabilityPump componentsFlexible member pumpsSupporting systemMagnetic bearing
The device includes a rolling bearing unit supporting a radial load and a magnetic bearing unit supporting an axial load and / or a bearing preload; an electromagnet fitted to a spindle housing so as to confront, on a non-contact basis, a flange shaped thrust plate mounted on a main shaft; a motor rotor of a motor for driving the shaft, and a motor stator opposed to the rotor, the shaft being driven by magnetic or Lorentz forces developed between the rotor and the stator; and a sensor detecting an axial force acting on the bearing unit, and a controller controlling the electromagnet. In this device, the stiffness of a composite spring formed by the bearing unit and a support system for the bearing unit is chosen to be higher than the negative stiffness of a composite spring of a motor part comprised of the electromagnet and the motor.
Owner:NTN CORP
Device for separating, lifting and moving aluminium sheets or other non-ferromagnetic material
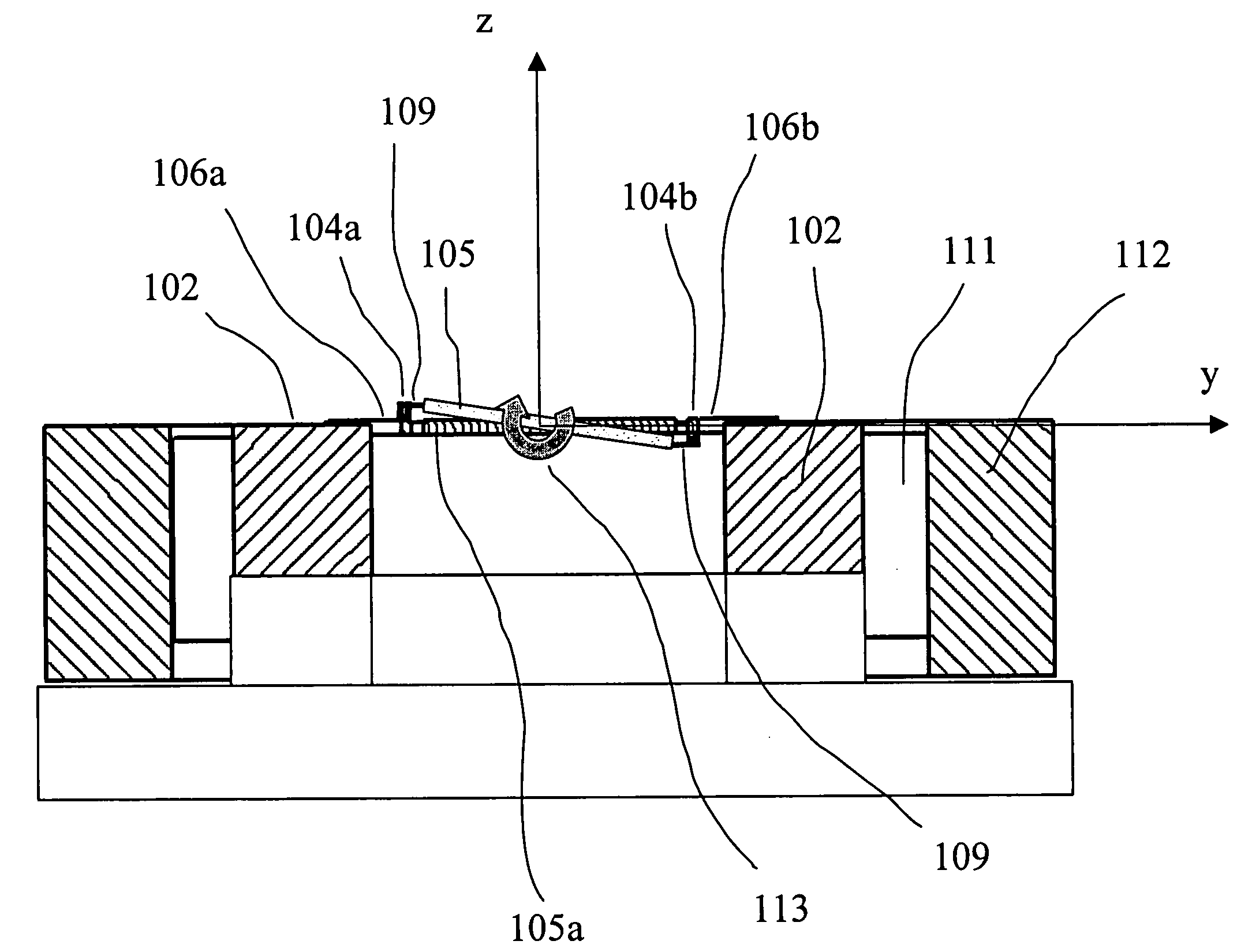
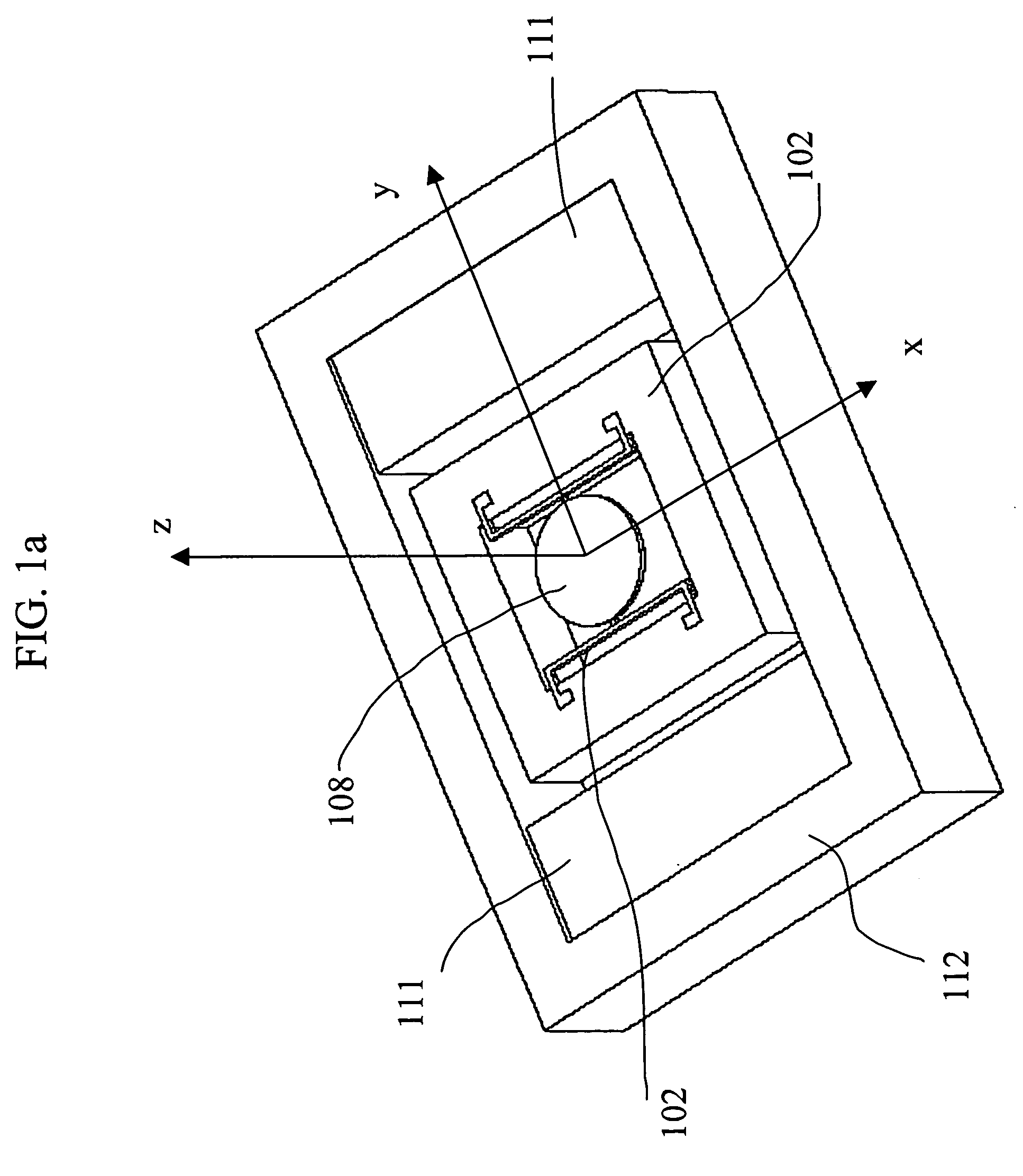
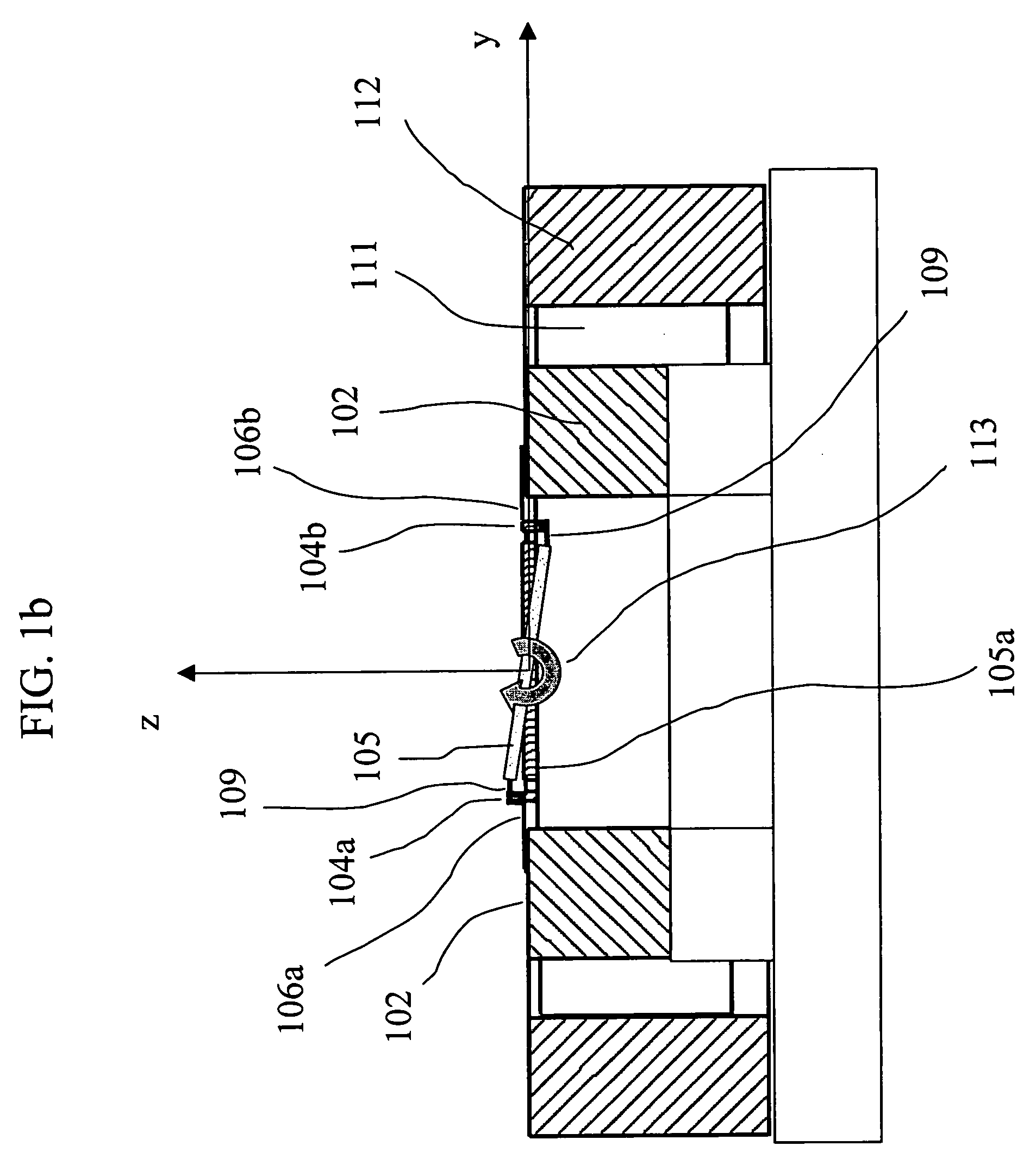
InactiveUS6746063B1Small separationLow performance of installationMetal-working feeding devicesGripping headsEngineeringLorentz force
Device for separating, lifting and transporting sheets of aluminium or other non-ferromagnetic material consisting of a spider attraction assembly provided with a series of blocks of magnets and with contact electrodes, which by way of the effects produced by Lorentz forces, together with the action of a series of vacuum pads, is provided with the capacity to attract sheets of aluminium.
Owner:ASM SA
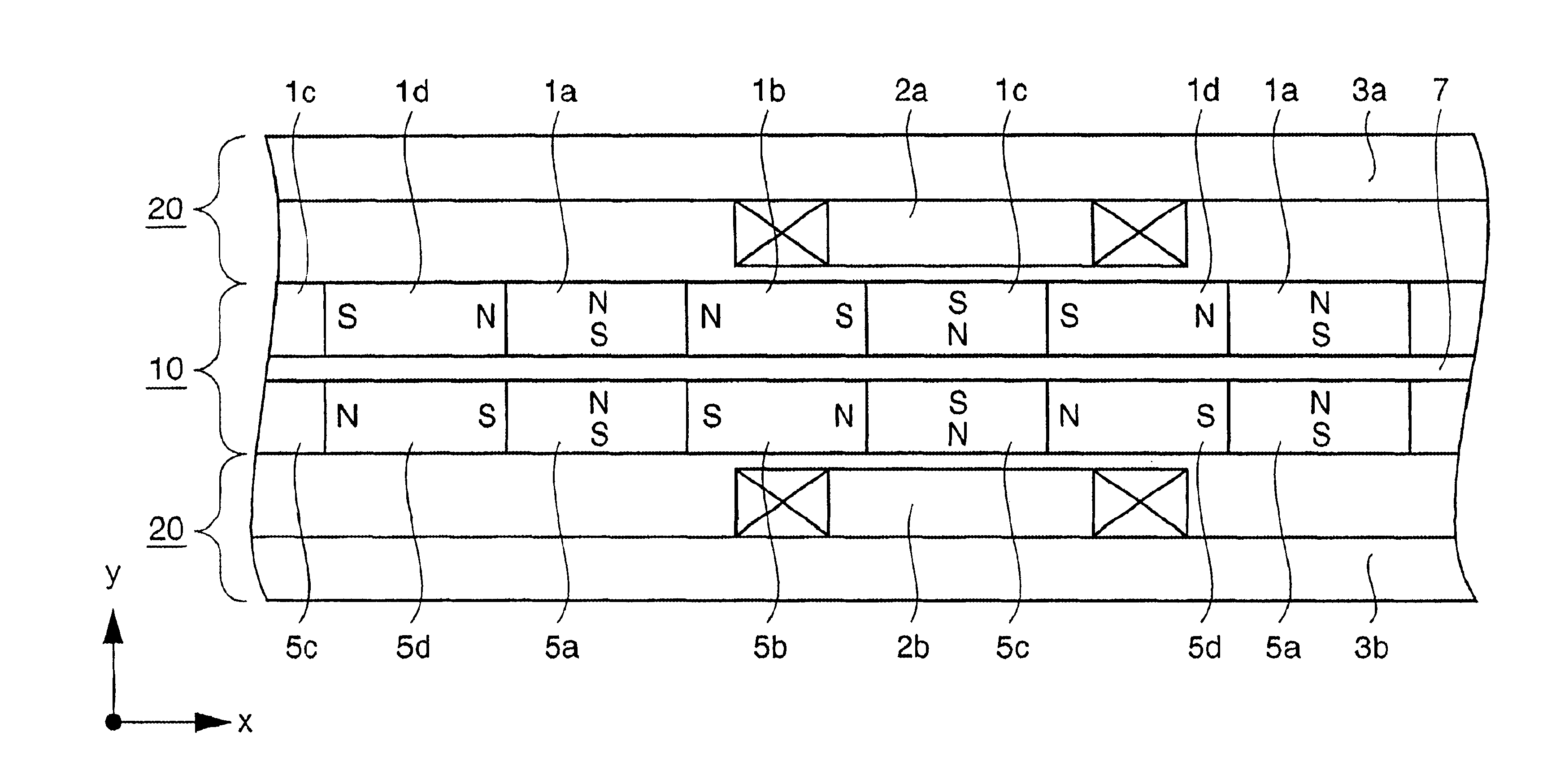
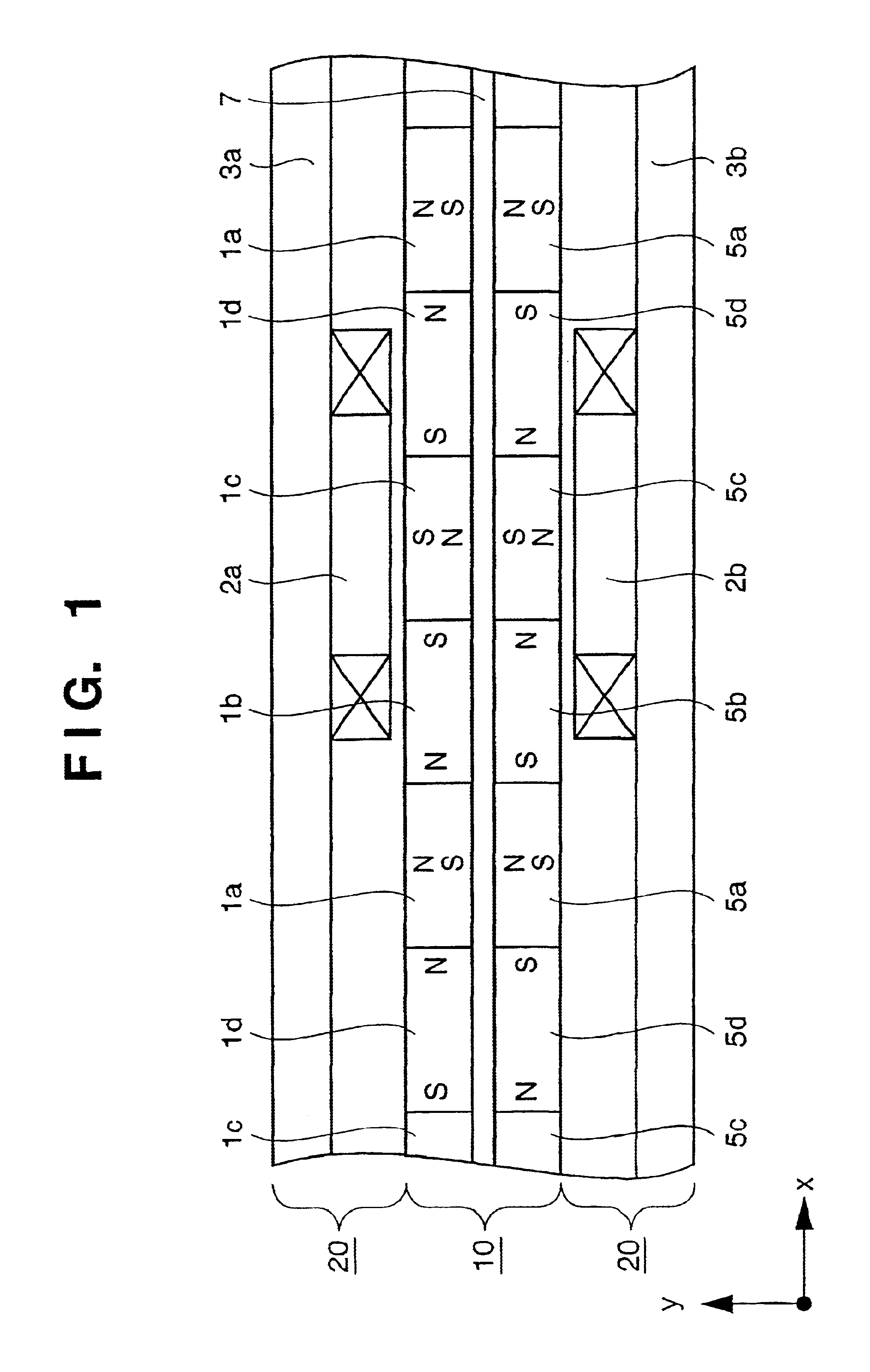
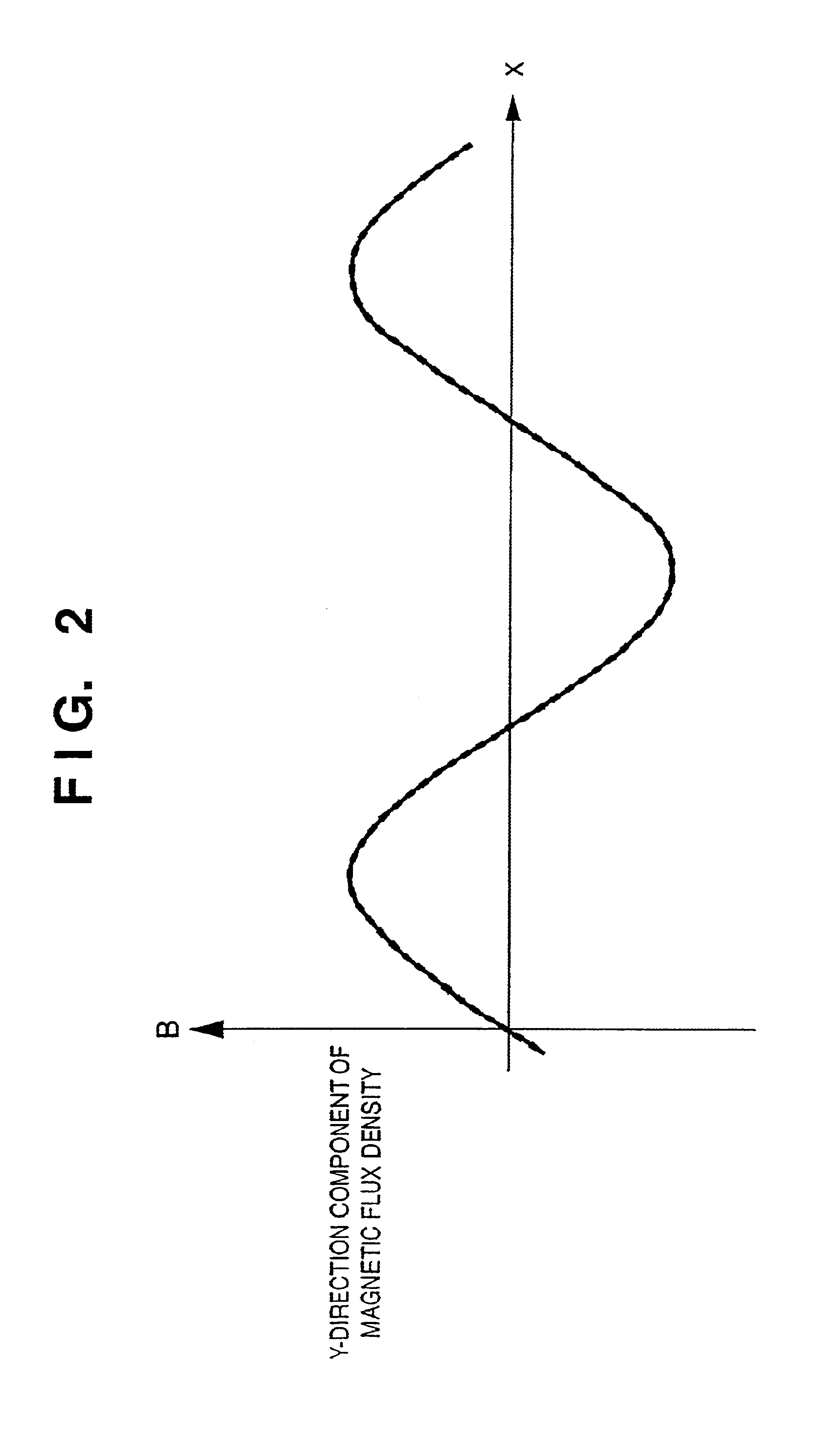
Linear motor and stage apparatus, exposure apparatus, and device manufacturing method using the same
InactiveUS6870284B2Improve driving effectLittle changeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInstrumental componentsEngineeringLinear motor
A linear motor includes a magnet array having a plurality of first magnets arrayed such that polarization directions thereof are periodically opposite, and a plurality of second magnets arrayed such that polarization directions thereof are periodically opposite and intersect those of the first magnets. The linear motor further includes an electromagnetic coil disposed to oppose the magnet array to generate a Lorentz force in cooperation with the magnet array and a yoke integrated with the coil at a first side opposite to a second side of the coil disposed opposite to the magnet array.
Owner:CANON KK
Magnetic levitation haptic interface system
This invention discloses a haptic interface system that uses Lorentz forces to provide magnetic levitation for a handle which can be manipulated by a person, typically a computer user.
Owner:BUTTERFLY HAPTICS
Tunable graphene magnetic field sensor
InactiveUS20110037464A1Improve shielding effectSensitivityMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsElectrical resistance and conductanceCharge carrier
A magnetic field sensor employing a graphene sense layer, wherein the Lorentz force acting on charge carriers traveling through the sense layer causes a change in path of charge carriers traveling through the graphene layer. This change in path can be detected indicating the presence of a magnetic field. The sensor includes one or more gate electrodes that are separated from the graphene layer by a non-magnetic, electrically insulating material. The application of a gate voltage to the gate electrode alters the electrical resistance of the graphene layer and can be used to control the sensitivity and speed of the sensor.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Optically transduced MEMS magnetometer
ActiveUS8674689B1Quality improvementImprove rigidityMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesGratingAlternating current
MEMS magnetometers with optically transduced resonator displacement are described herein. Improved sensitivity, crosstalk reduction, and extended dynamic range may be achieved with devices including a deflectable resonator suspended from the support, a first grating extending from the support and disposed over the resonator, a pair of drive electrodes to drive an alternating current through the resonator, and a second grating in the resonator overlapping the first grating to form a multi-layer grating having apertures that vary dimensionally in response to deflection occurring as the resonator mechanically resonates in a plane parallel to the first grating in the presence of a magnetic field as a function of the Lorentz force resulting from the alternating current. A plurality of such multi-layer gratings may be disposed across a length of the resonator to provide greater dynamic range and / or accommodate fabrication tolerances.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Outer rotor magnetic levitation conical spherical gyro flywheel
ActiveCN105438500AImprove levitation accuracyEliminate couplingCosmonautic vehiclesMagnetic holding devicesAxial displacementMagnetic bearing
The invention discloses an outer rotor magnetic levitation conical spherical gyro flywheel. The outer rotor magnetic levitation conical spherical gyro flywheel mainly comprises a static part and a rotor part, wherein the static part comprises an upper sealing cover, a middle gyro case, a lower sealing cover, a sealing ring, an upper gyro case, a lower gyro case, a motor component stator, an Lorentz force magnetic bearing stator, an axial displacement sensor component, a radial displacement sensor component, a mandrel, a protective bearing and a radial conical spherical magnetic bearing stator component. The rotor part comprises a gyro outer turntable component and a protective bearing cover. The outer rotor magnetic levitation conical spherical gyro flywheel disclosed by the invention adopts a spherical shell-shaped magnetic air gap structure and has the advantages of large inertia, easy control, large deflection angle, high torque accuracy and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF PETROCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY +1
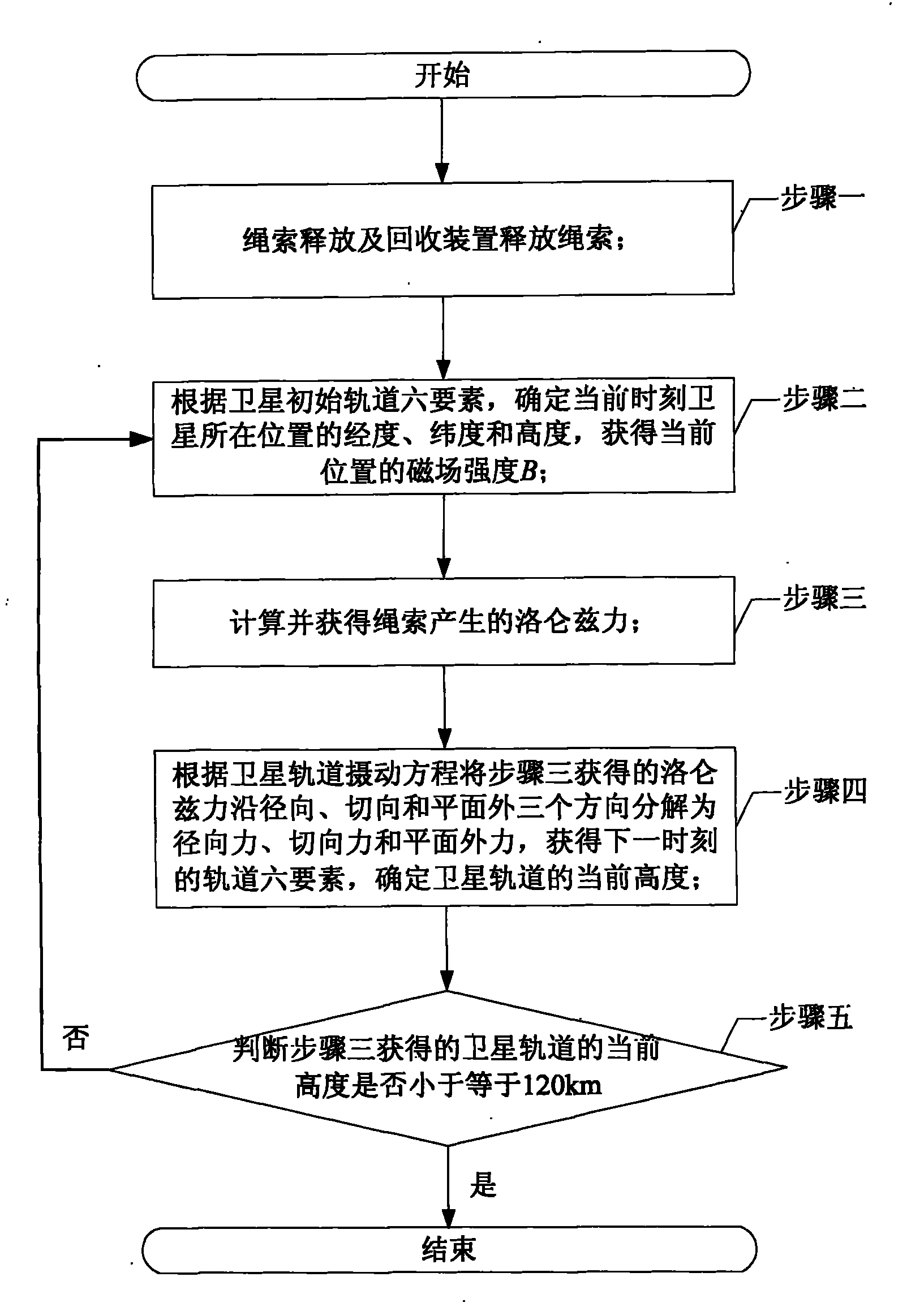
Electro-dynamic tether based satellite deorbit device and method thereof
InactiveCN101767657AGood derailment effectHigh off-track efficiencyArtificial satellitesControl signalLongitude
The invention provides an electro-dynamic tether based satellite deorbit device and a method thereof, relating to the satellite deorbit device and the method thereof. The device and the method solve the problems of high deorbit cost of a propellant deorbit method and low deorbit efficiency of an atmospheric drag deorbit method. In the system, a control signal output end of a control module is connected with a control signal input end of a tether releasing and reclaiming device; the tail end of an insulating tether section of the tether is fixed on the tether releasing and reclaiming device; and the tail end of a conductive tether section of the tether is connected with an electron collection transmitter. The method comprises the following steps: determining longitude, latitude and height of the position of a satellite at current time according to six factors of the initial orbit of the satellite to acquire the magnetic field strength of the current position; calculating the Lorentz force generated by the tether; resolving the Lorentz force along the radial direction, the tangential direction and the outerplanar direction to acquire the orbit six factors at next time, and determining a new height of the satellite orbit; and circulating the steps until the height of the satellite is less than or equal to 120km to complete the satellite deorbit process. The device and the method are applicable to the satellite deorbit process.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com