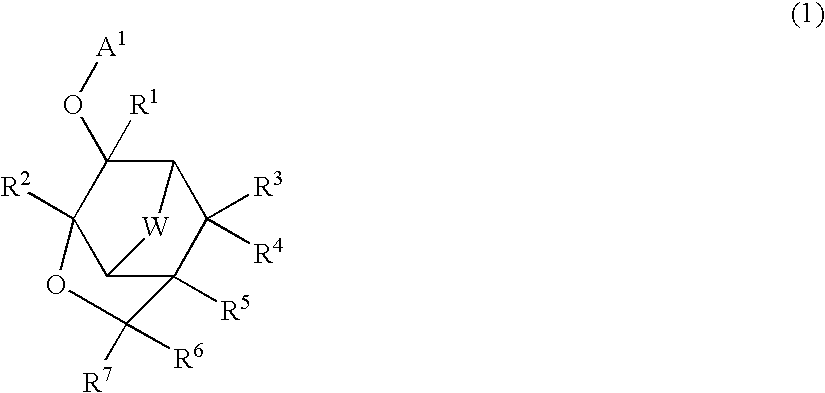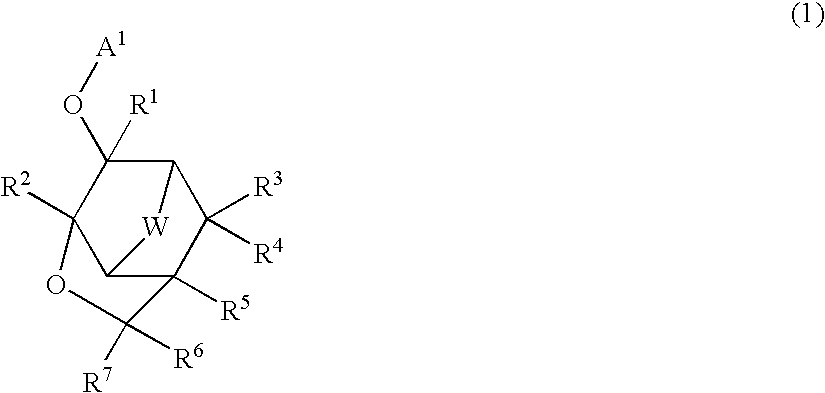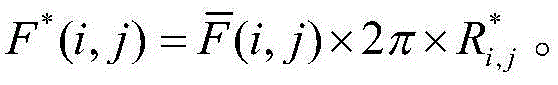Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
131results about How to "Sensitivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
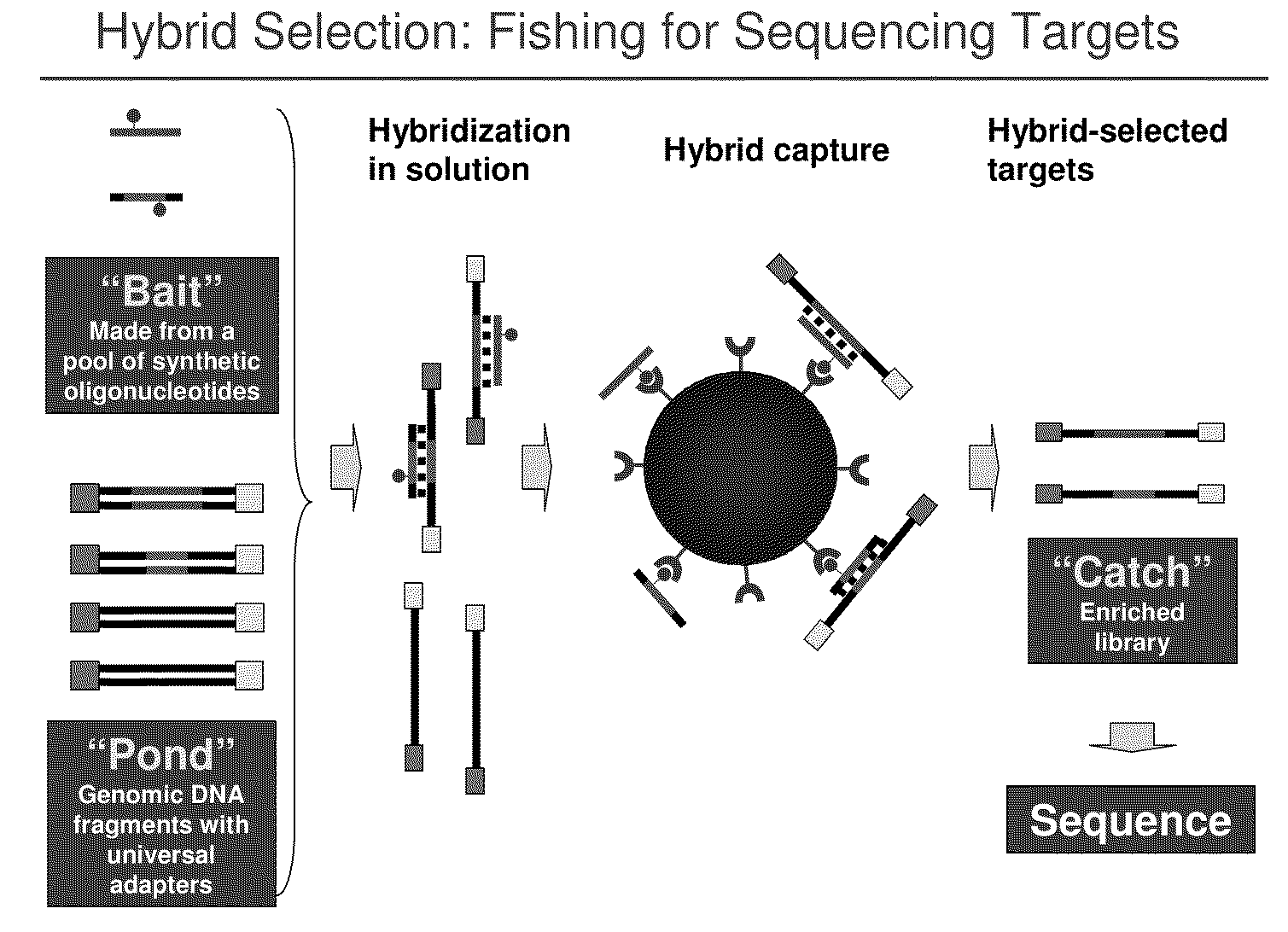
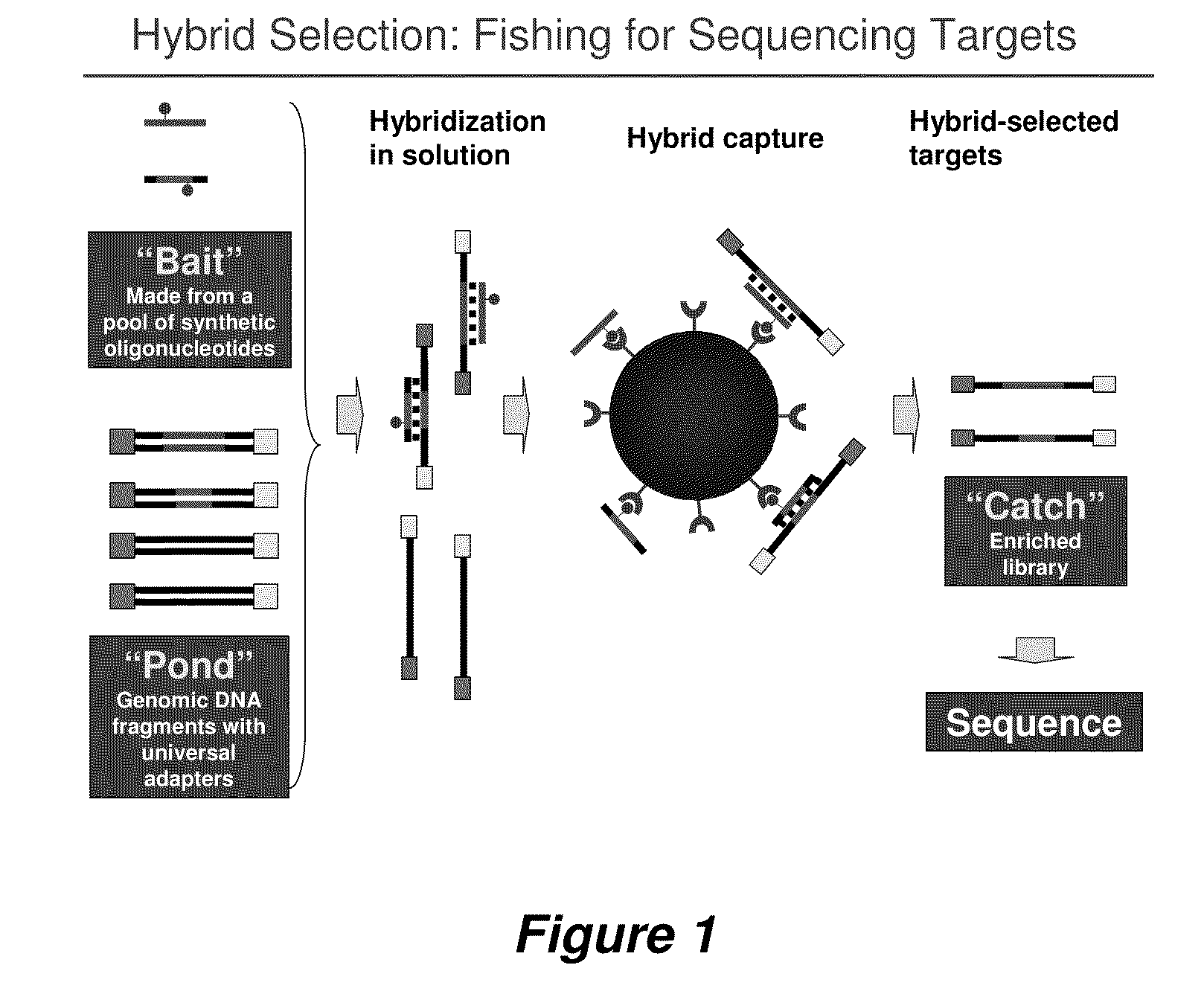
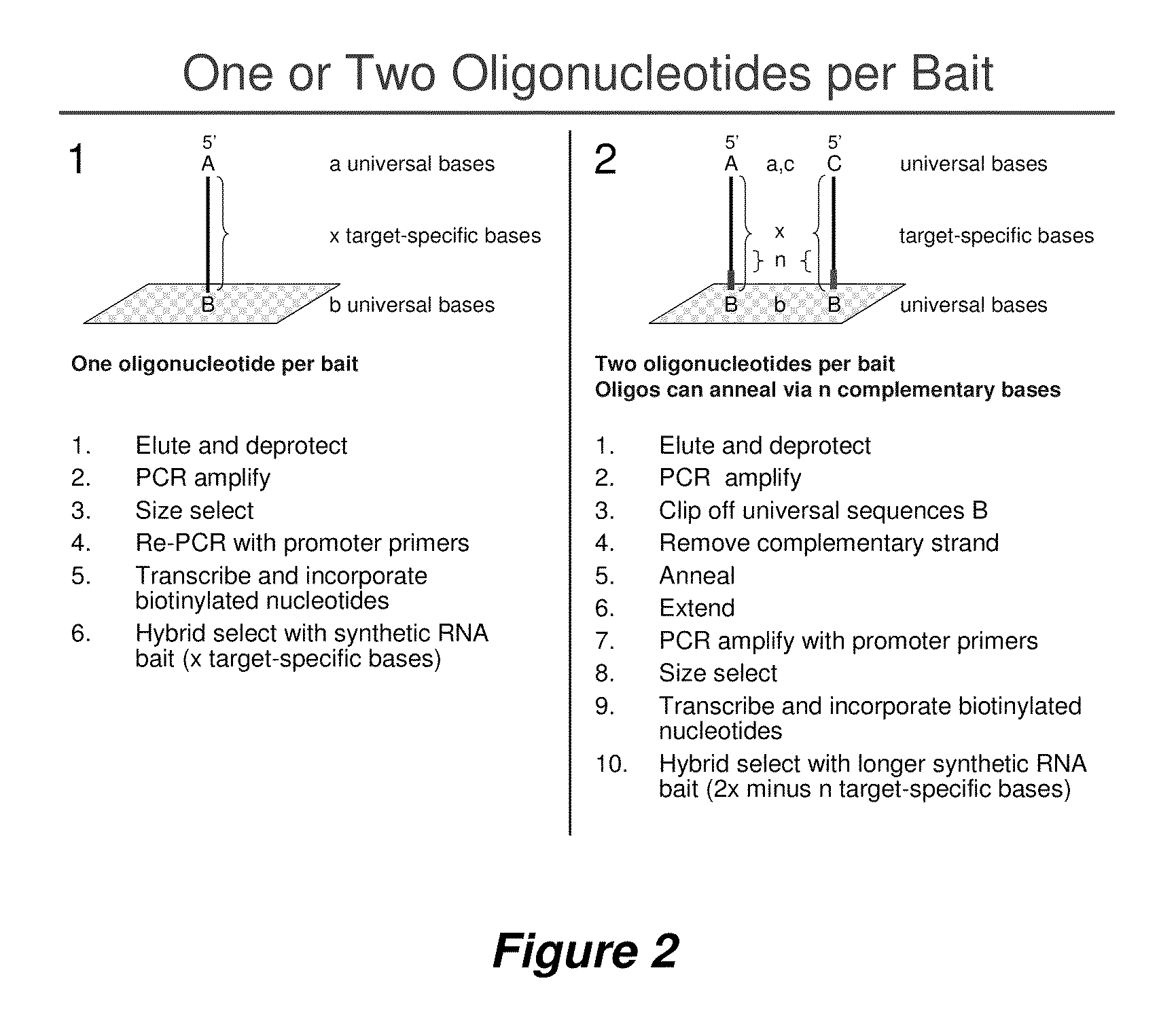
Selection of nucleic acids by solution hybridization to oligonucleotide baits
InactiveUS20100029498A1Minimize the differenceGood reproducibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningSolution hybridizationOligonucleotide
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +2
miRNA IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF OVARIAN CANCER
ActiveUS20120309645A1Improve accuracySensitivityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyHealthy control
The present invention provides novel methods for diagnosing a state of health based on the determination of specific miRNAs that have altered expression levels in different conditions, e.g. disease states compared to healthy controls.
Owner:HUMMINGBIRD DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
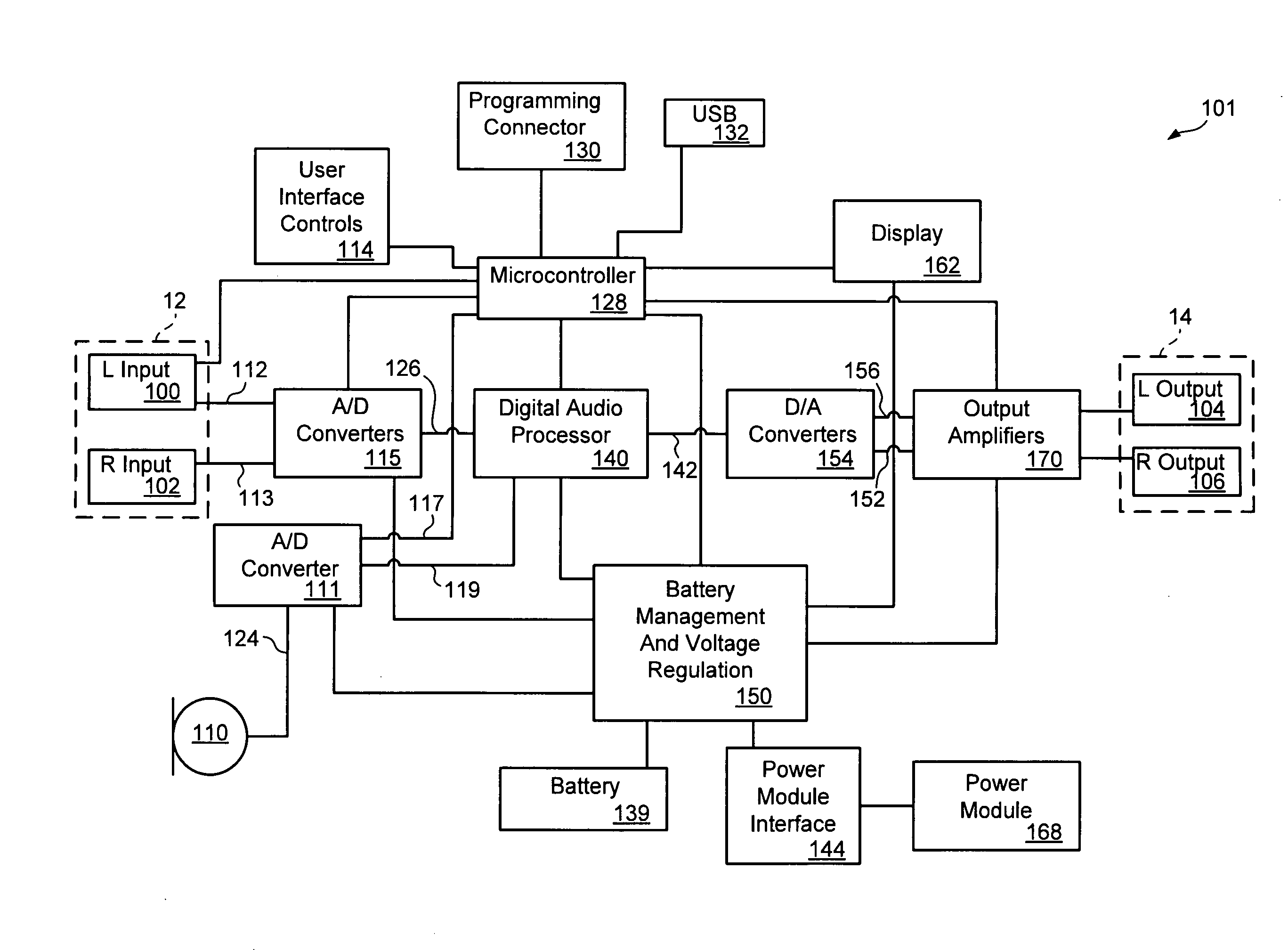
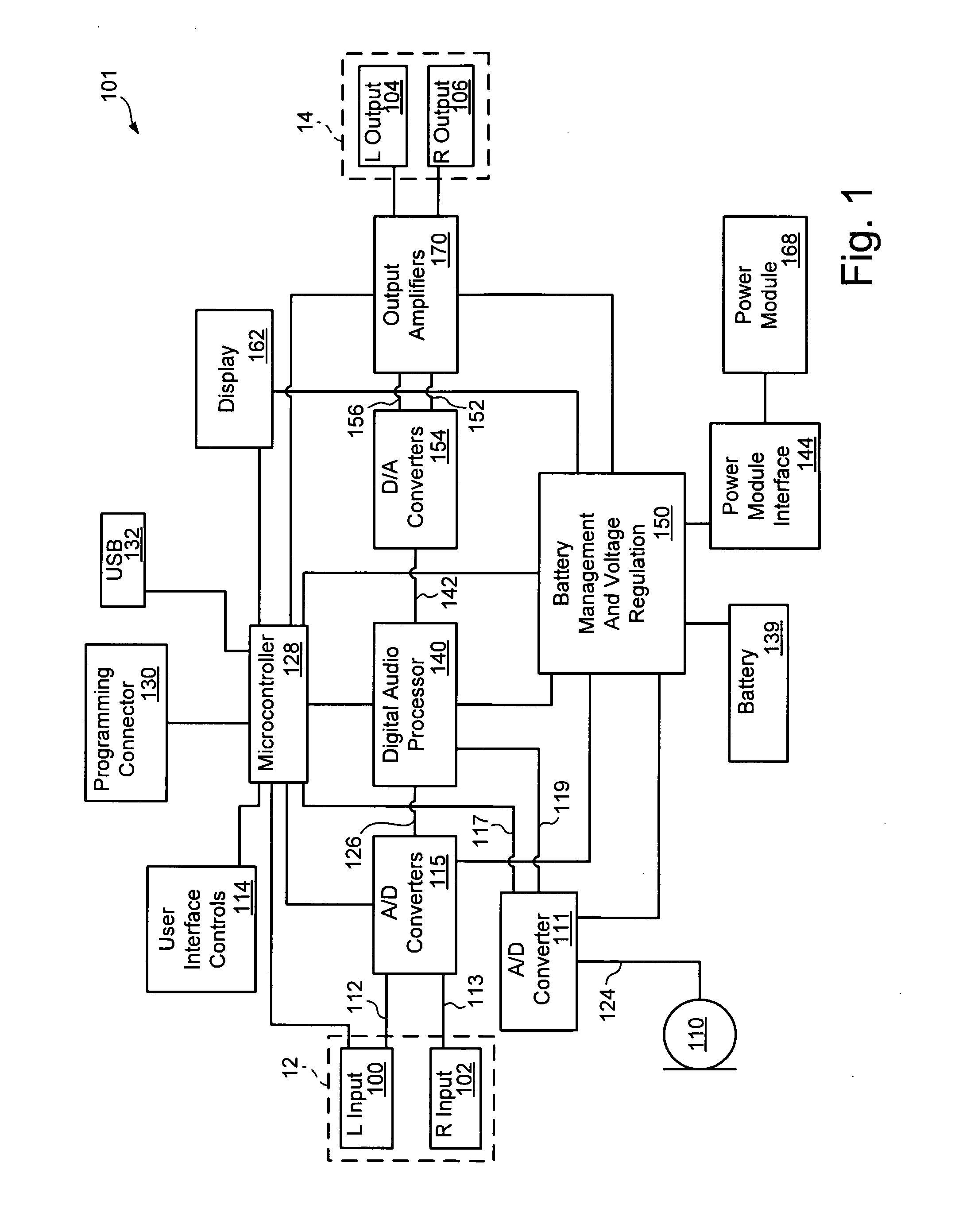
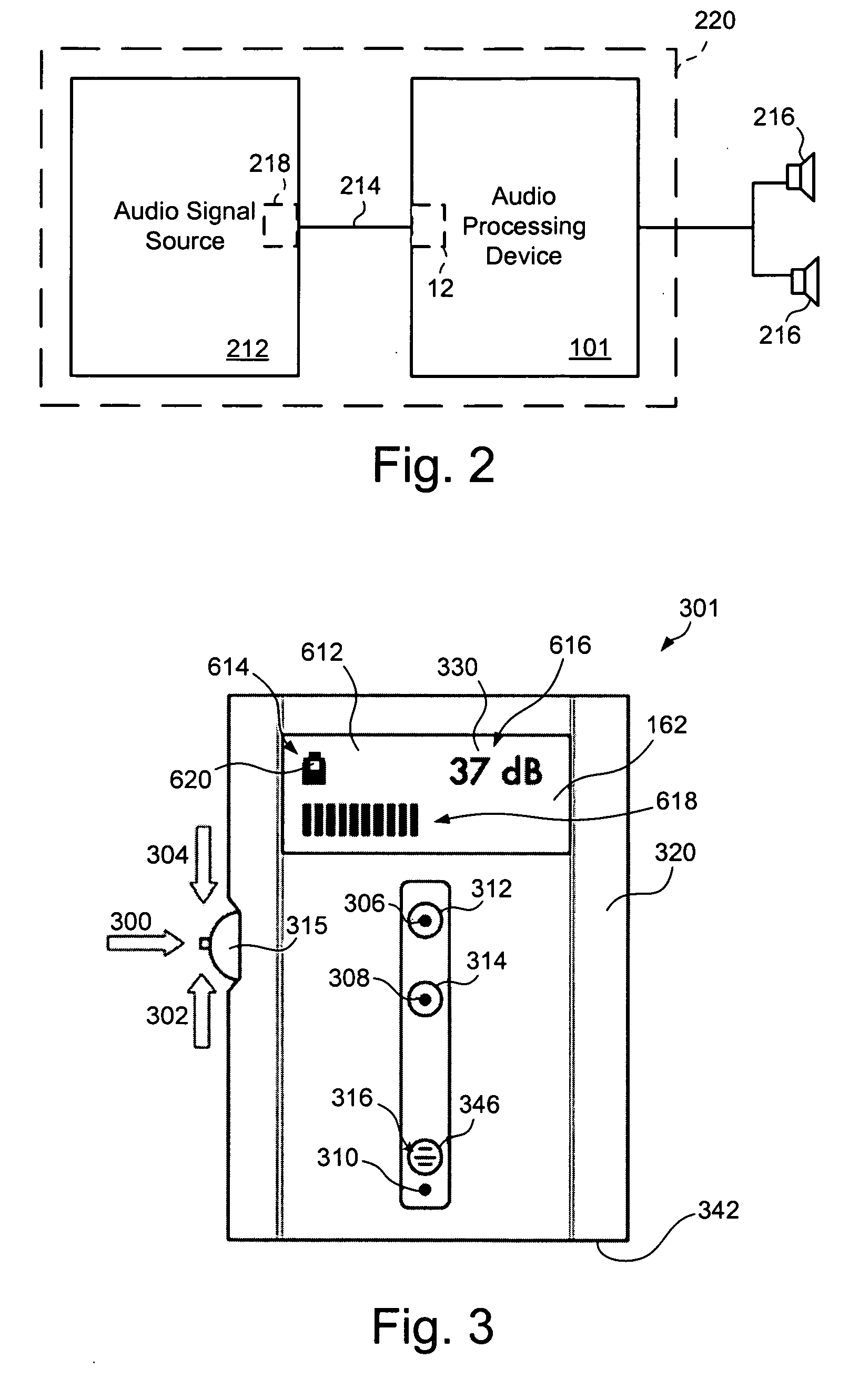
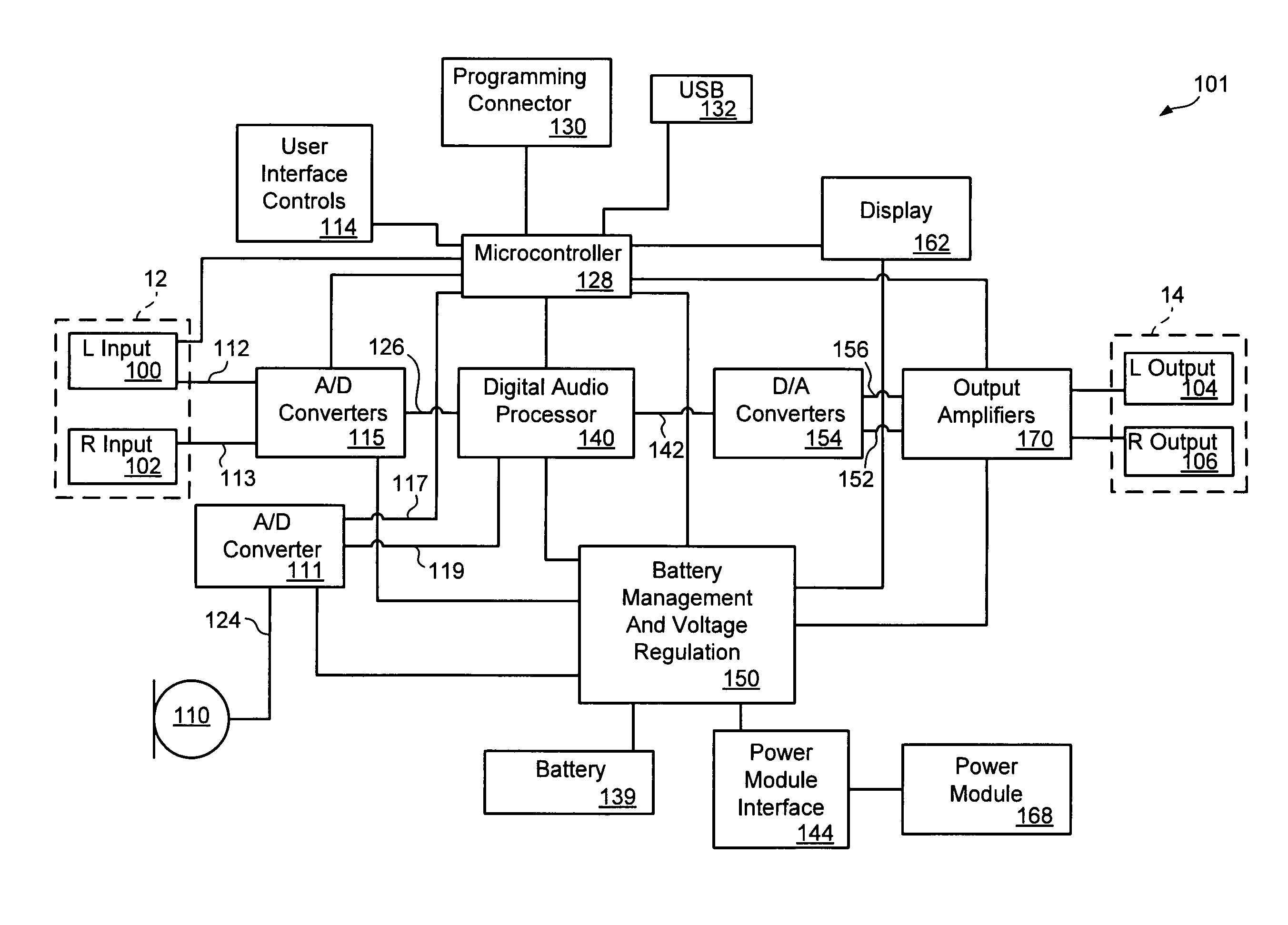
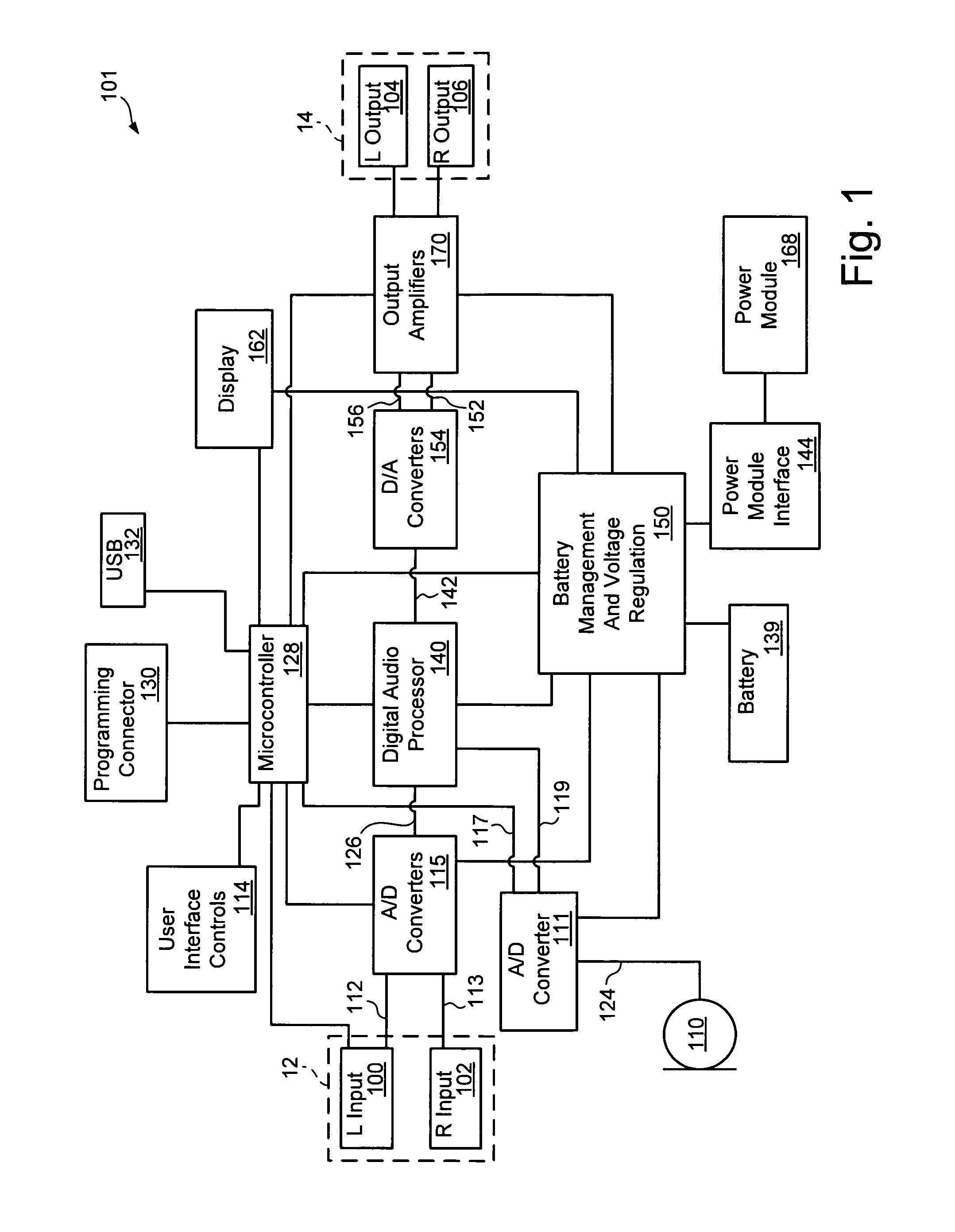
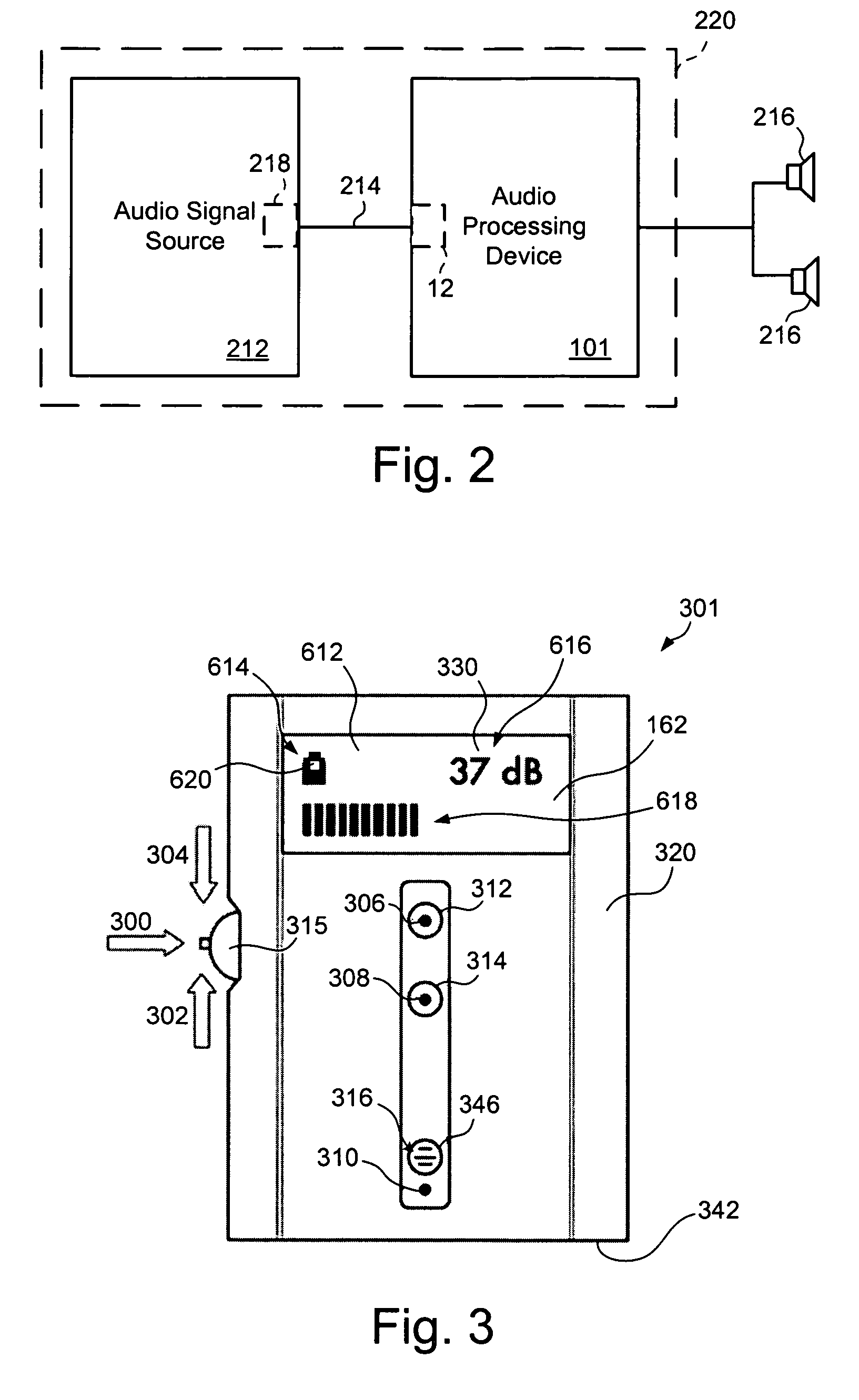
Digital audio processor device and method
ActiveUS20080181424A1Accurate assessmentSensitivitySignal processingStereophonic circuit arrangementsAudio frequencySound pressure
An audio processor device and method is disclosed which measures and provides information relating to the audio level being applied to the ear of a user. The processor device uses a preset or calibrated sensitivity of the applied earphones in combination with an analysis of the audio stream to provide sound-pressure-level or time-weighted exposure information to the user or limit the output when preset levels have been achieved. Also disclosed is the use of microphones, internal or external, to combine an additional audio stream, typically the ambient environment, into the main audio channel.
Owner:TENSION LABS
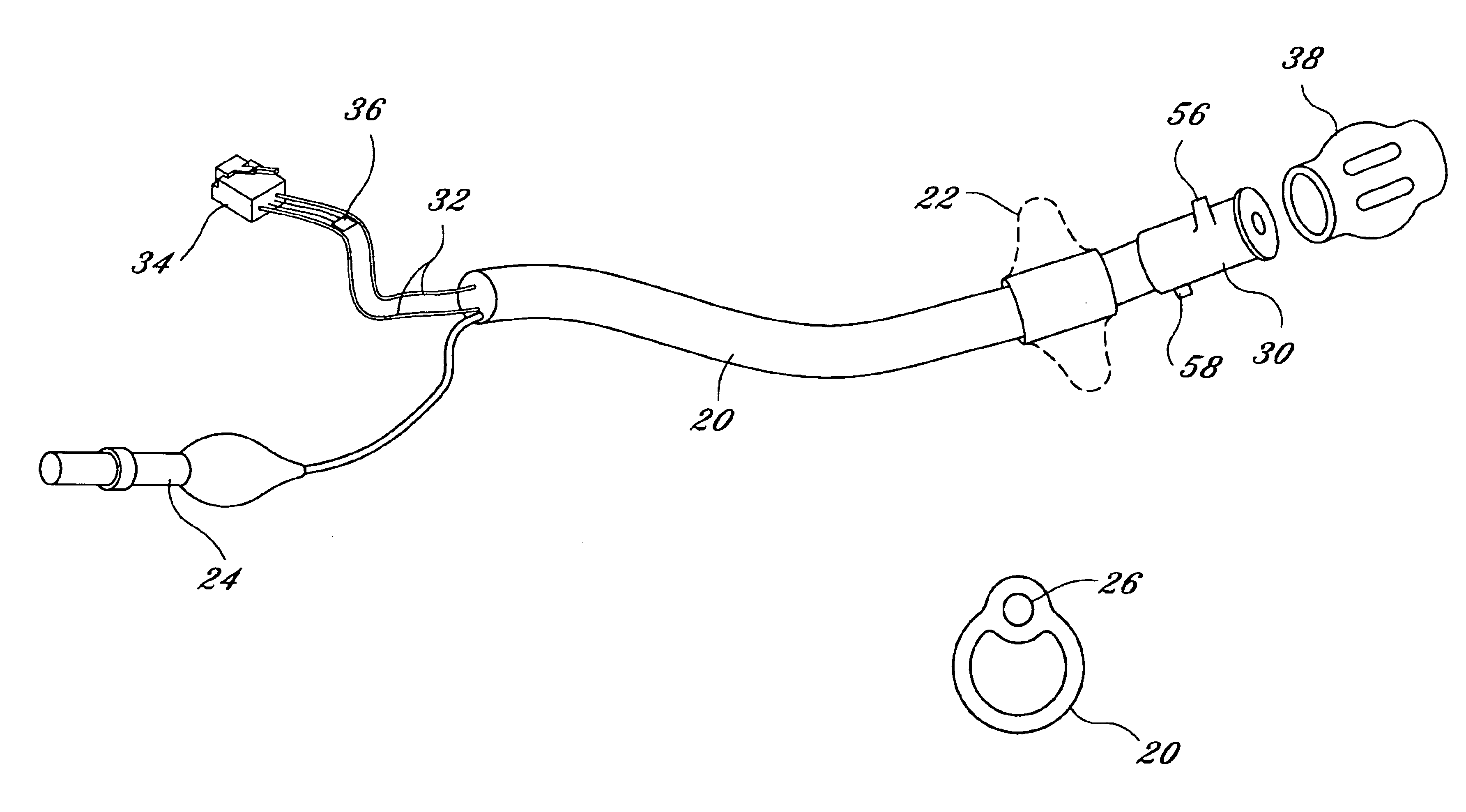
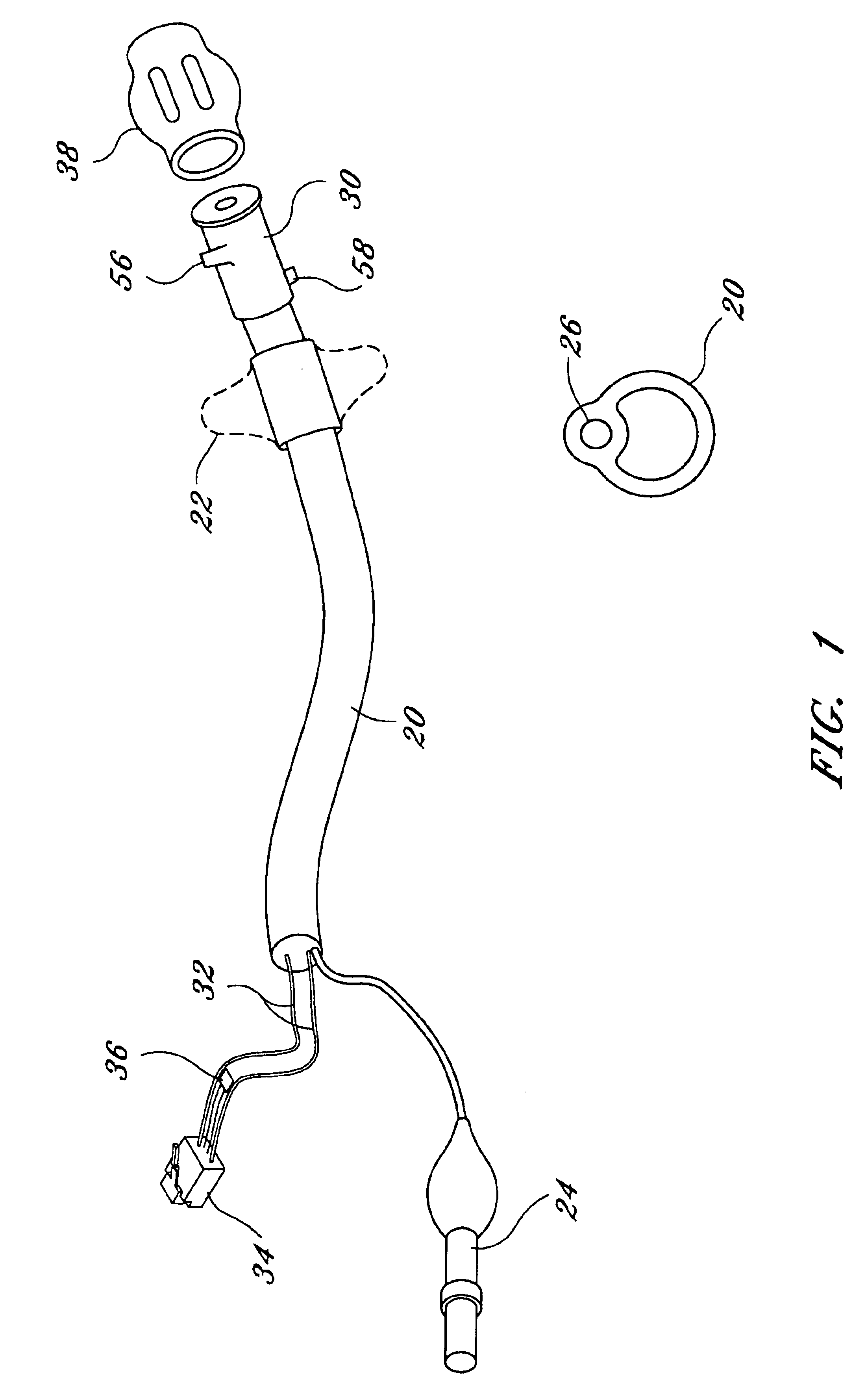
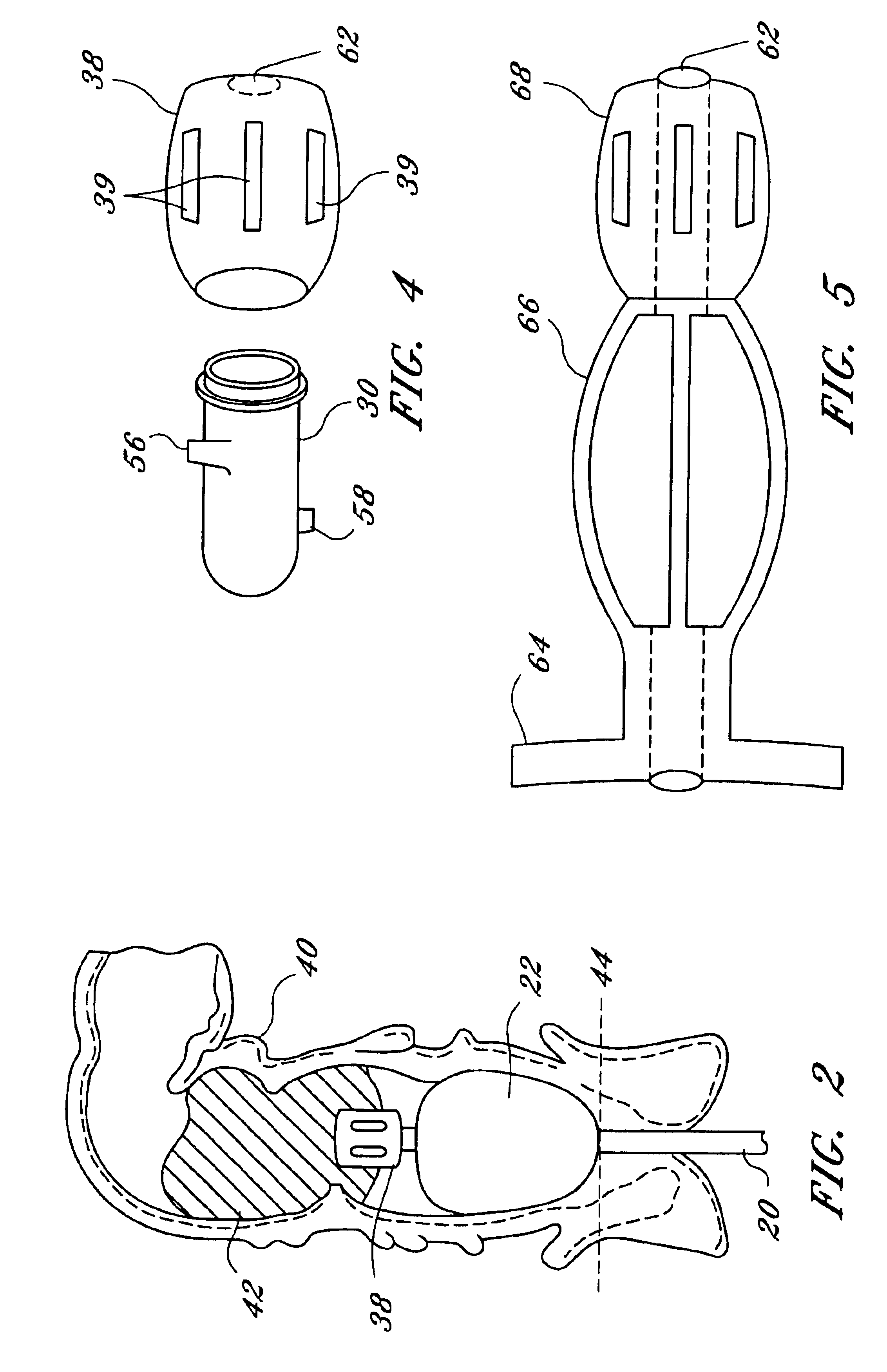
Fecal incontinence management device
InactiveUS6843766B1Reduce generationMinimum level of attentionAnti-incontinence devicesFecal incontinenceRectal continence
An apparatus, and corresponding method, for management of fecal incontinence comprising a catheter having at least two electrodes and an inflatable balloon, a non-conductive sleeve surrounding the electrodes, and an alarm box, wherein the catheter is insertable into a rectal vault and is inflatable to serve as a block to passage of stool and wherein moisture sensed by the electrodes triggers the alarm box and thereby notifies a user that fecal material has entered the rectal vault.
Owner:DIGNITY INC OKLAHOMA
Nanowire-based sensor configurations
ActiveUS20090124025A1Increase hydrodynamic dragIncrease rangeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityNanowire
This invention provides nanowire based molecular sensors and methods for detecting analytes in a microfluidic system. Methods for sensing analytes include detecting changed electrical parameters associated with contact of a nanowire with the analyte in a microfluidic system. Sensors of the invention include nanowires mounted in microchambers of a microfluidic system in electrical contact with the detector, whereby electrical parameter changes induced in the nanowire by the analyte can be monitored by the detector.
Owner:NANOSYS INC
Optical inspection apparatus for defect detection
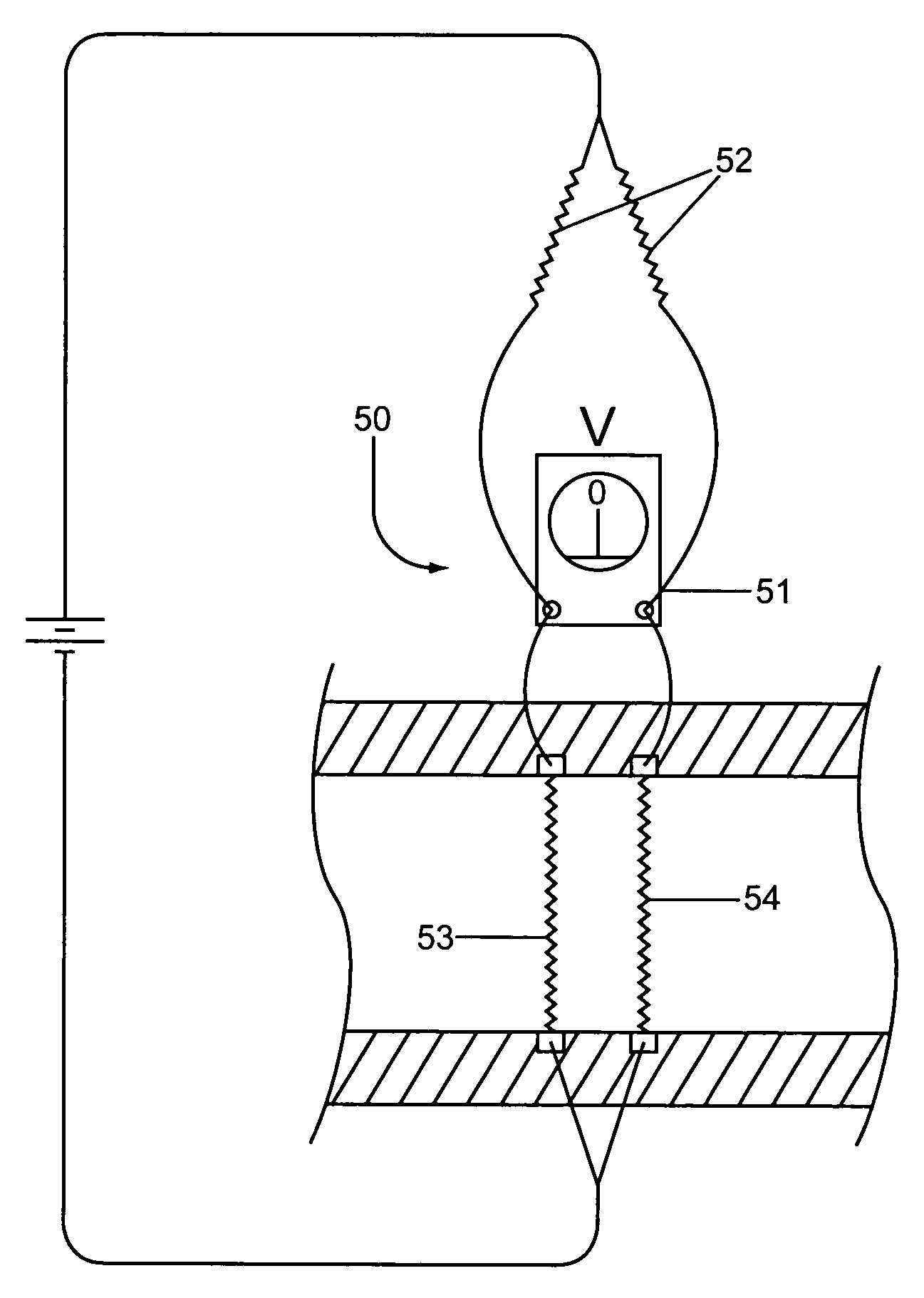
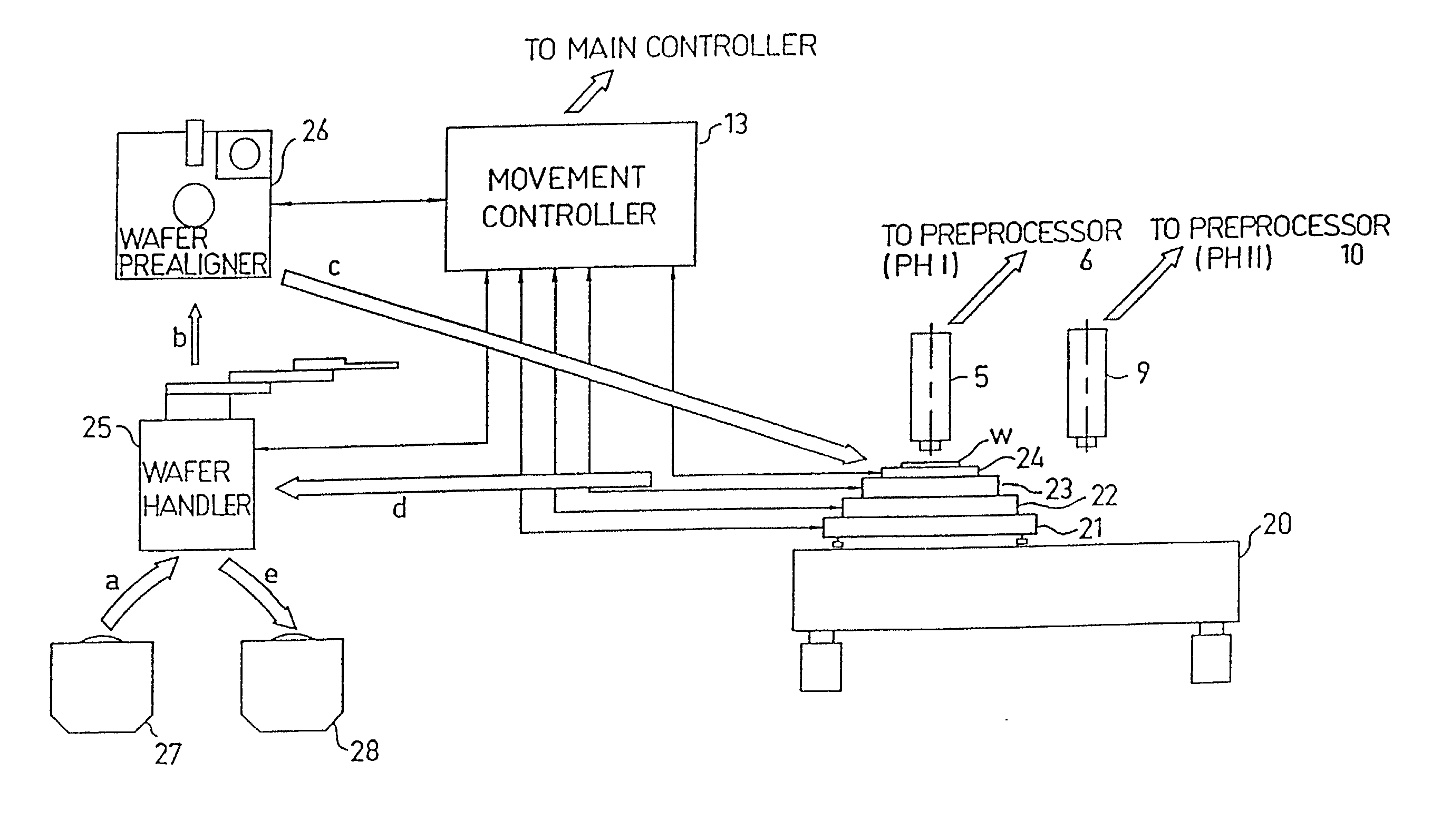
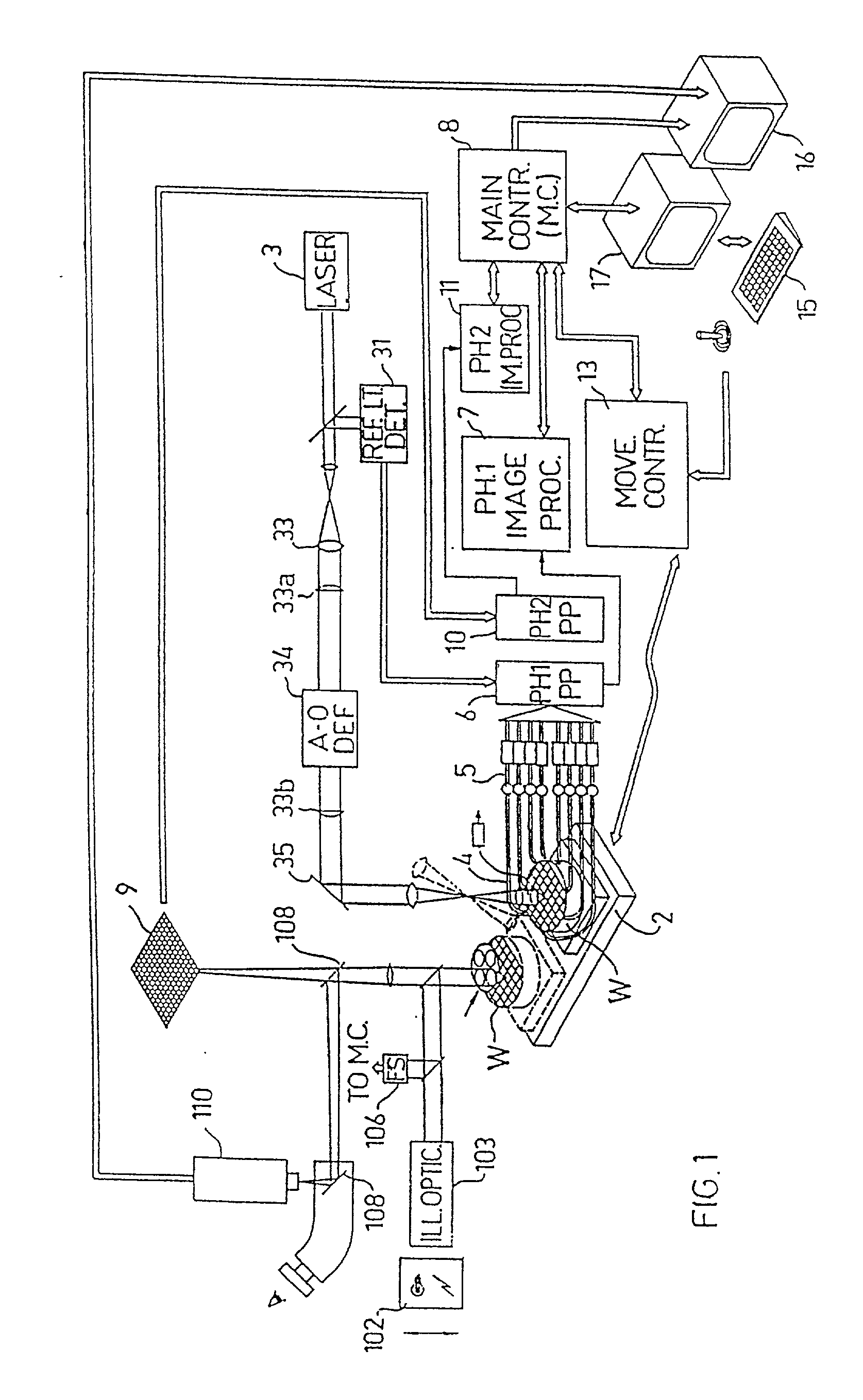
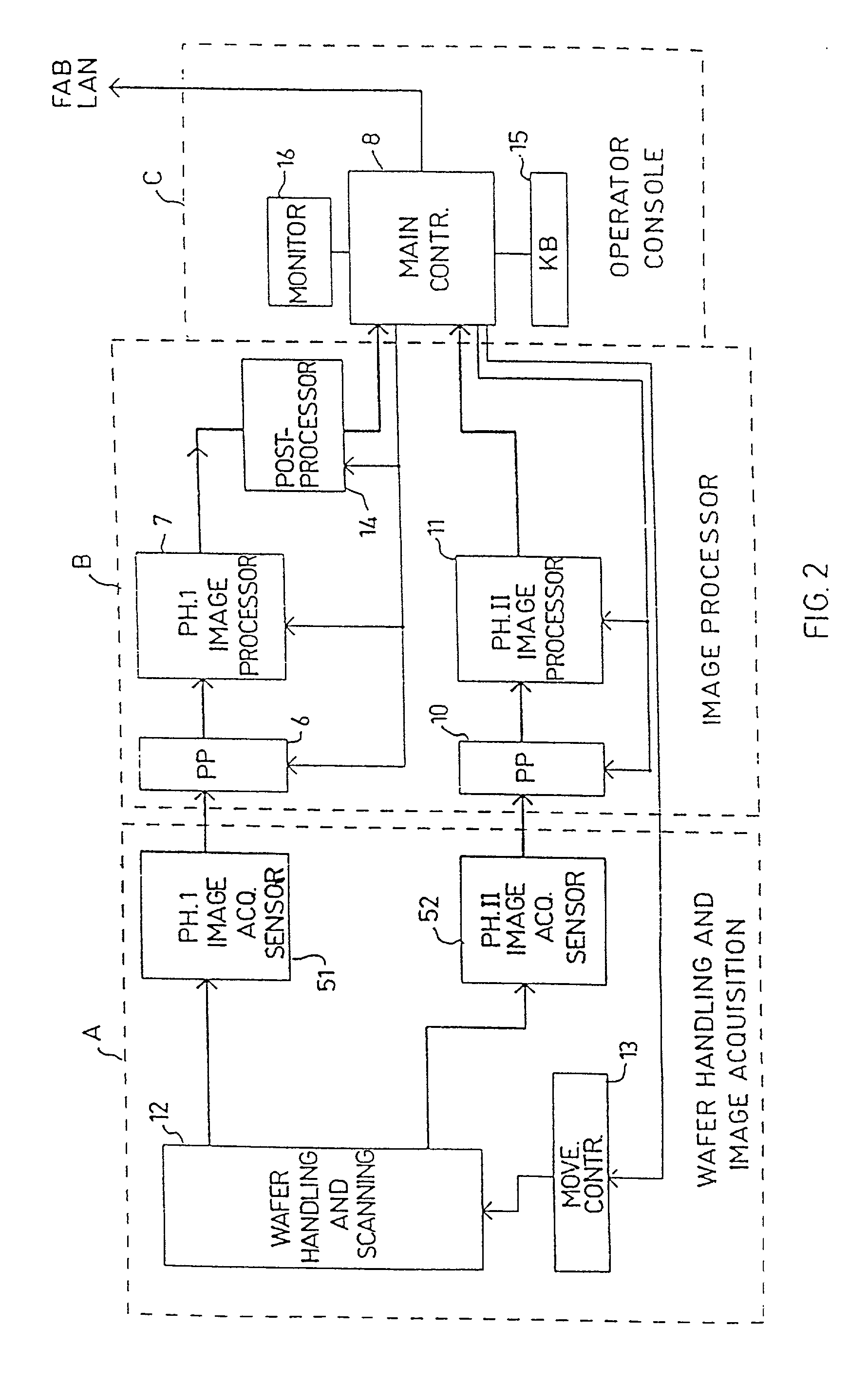
InactiveUS20020039436A1Increase speedLow rateCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsImage resolutionHigh spatial resolution
A method and apparatus for inspecting the surface of articles, such as chips and wafers, for defects, includes a first phase of optically examining the complete surface of the article inspected at a relatively high speed and with a relatively low spatial resolution, and a second phase of optically examining with a relatively high spatial resolution only the suspected locations for the presence or absence of a defect therein.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Methods and nucleic acids for the analyses of cellular proliferative disorders
ActiveUS20060286576A1High sensitivityStrong specificitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseGenome
The invention provides methods, nucleic acids and kits for detecting, or for detecting and distinguishing between or among liver cell proliferative disorders or for detecting, or for detecting and distinguishing between or among colorectal cell proliferative disorders. The invention discloses genomic sequences the methylation patterns of which have utility for the improved detection of and differentiation between said class of disorders, thereby enabling the improved diagnosis and treatment of patients.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
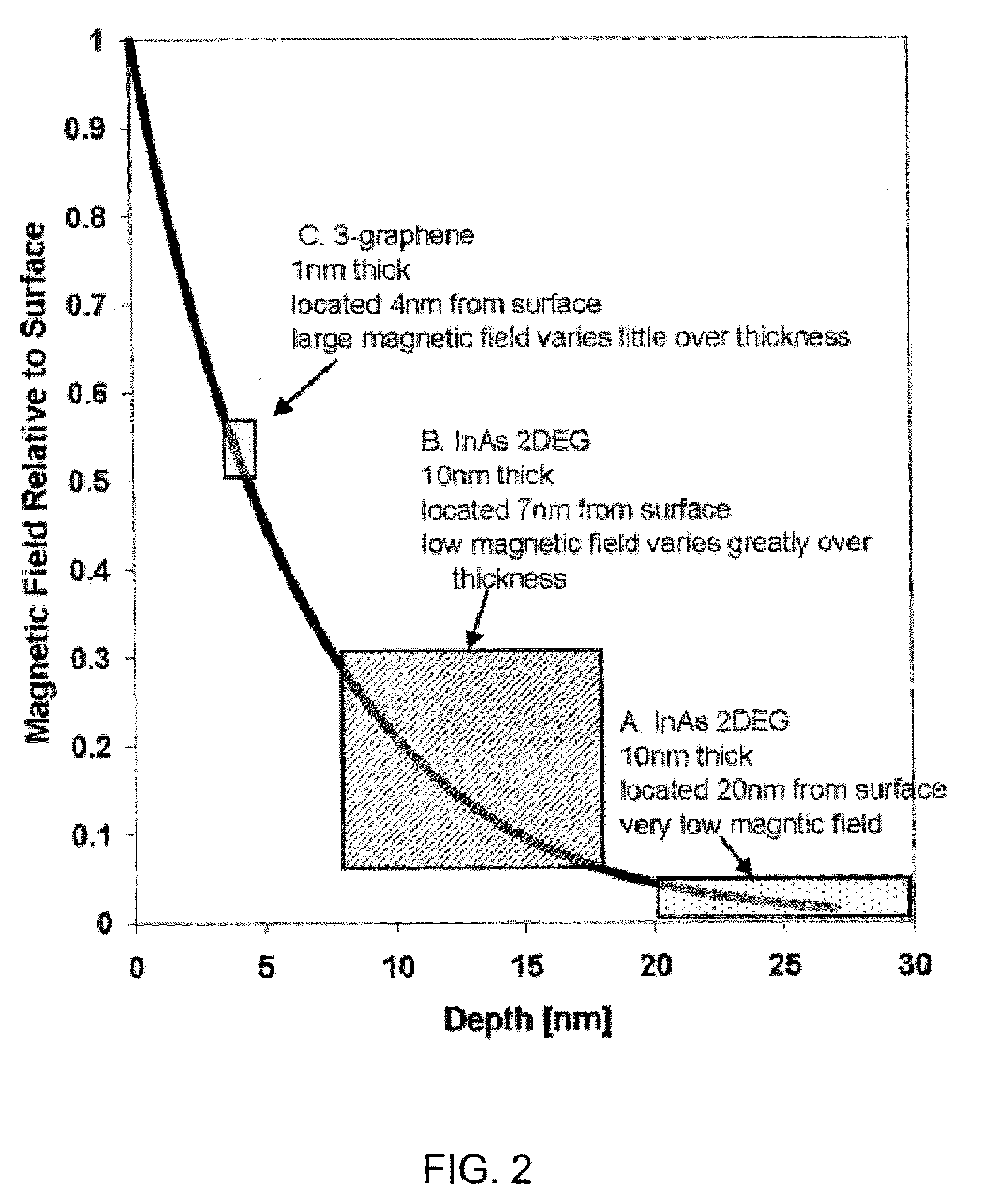
Tunable graphene magnetic field sensor
InactiveUS20110037464A1Improve shielding effectSensitivityMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsElectrical resistance and conductanceCharge carrier
A magnetic field sensor employing a graphene sense layer, wherein the Lorentz force acting on charge carriers traveling through the sense layer causes a change in path of charge carriers traveling through the graphene layer. This change in path can be detected indicating the presence of a magnetic field. The sensor includes one or more gate electrodes that are separated from the graphene layer by a non-magnetic, electrically insulating material. The application of a gate voltage to the gate electrode alters the electrical resistance of the graphene layer and can be used to control the sensitivity and speed of the sensor.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
MEMS microphone
InactiveUS20100142325A1SensitivityReduce sensitivityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesMems microphoneMechanical engineering
A MEMS microphone comprising:a) a case with an open front side;b) a MEMS membrane mounted on one face of a base, the base being mounted inside the case on a substantially closed side; andc) a mesh covering the front side, substantially transparent acoustically to at least some of a range of operating frequencies at which the microphone is sensitive.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Dielectric materials and methods for integrated circuit applications
InactiveUS20050032357A1Reduce in quantitySensitivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringConductive materials
An integrated circuit device is provided having a substrate and areas of electrically insulating and electrically conductive material, where the electrically insulating material is a hybrid organic-inorganic material that requires no or minimal CMP and which can withstand subsequent processing steps at temperatures of 450° C. or more.
Owner:SILECS OY
Fecal incontinence management device
InactiveUS20050038380A1Reduce generationSeepage around the balloon is reducedAnti-incontinence devicesMedical devicesFecal incontinenceRectal continence
An apparatus, and corresponding method, for management of fecal incontinence comprising a catheter having at least two electrodes and an inflatable balloon, a non-conductive sleeve surrounding the electrodes, and an alarm box, wherein the catheter is insertable into a rectal vault and is inflatable to serve as a block to passage of stool and wherein moisture sensed by the electrodes triggers the alarm box and thereby notifies a user that fecal material has entered the rectal vault.
Owner:X L SYNERGY
Inertial sensor and manufacturing method of the same
InactiveUS20080196502A1Increase rangeWide dynamic rangeLine/current collector detailsAcceleration measurement using interia forcesClassical mechanicsAcceleration Unit
A weight of an inertial sensor if formed from a plurality of divided weights, and the divided weights are connected to each other by elastically deformable beams. A movable range and a mass of each of the divided weights and a rigidity of each of the beams are adjusted and a plurality of deformation modes having different sensitivity ranges with respect to the acceleration are used in combination. By this means, it is possible to improve a detecting sensitivity of an acceleration and widen an acceleration response range.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
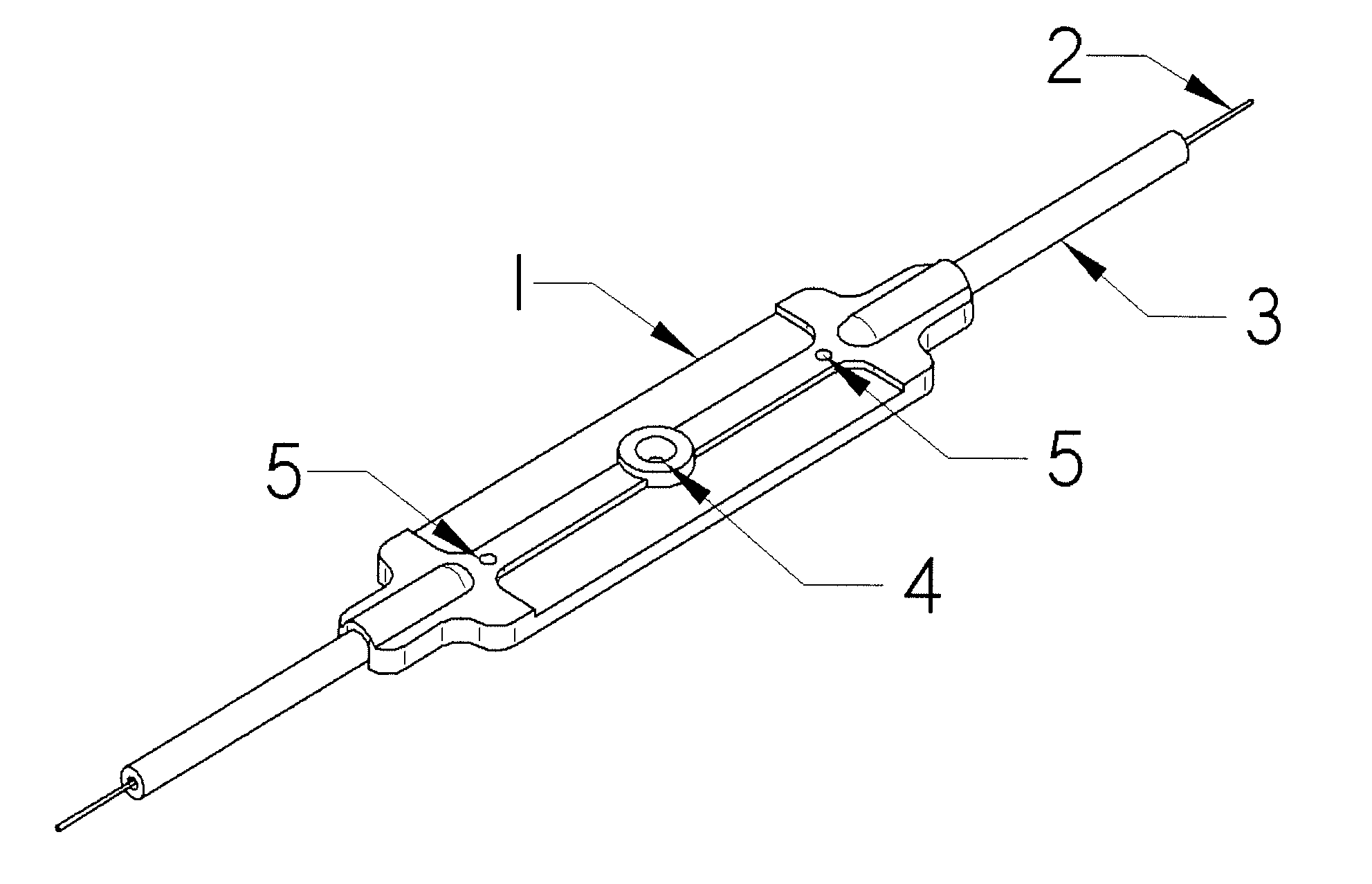
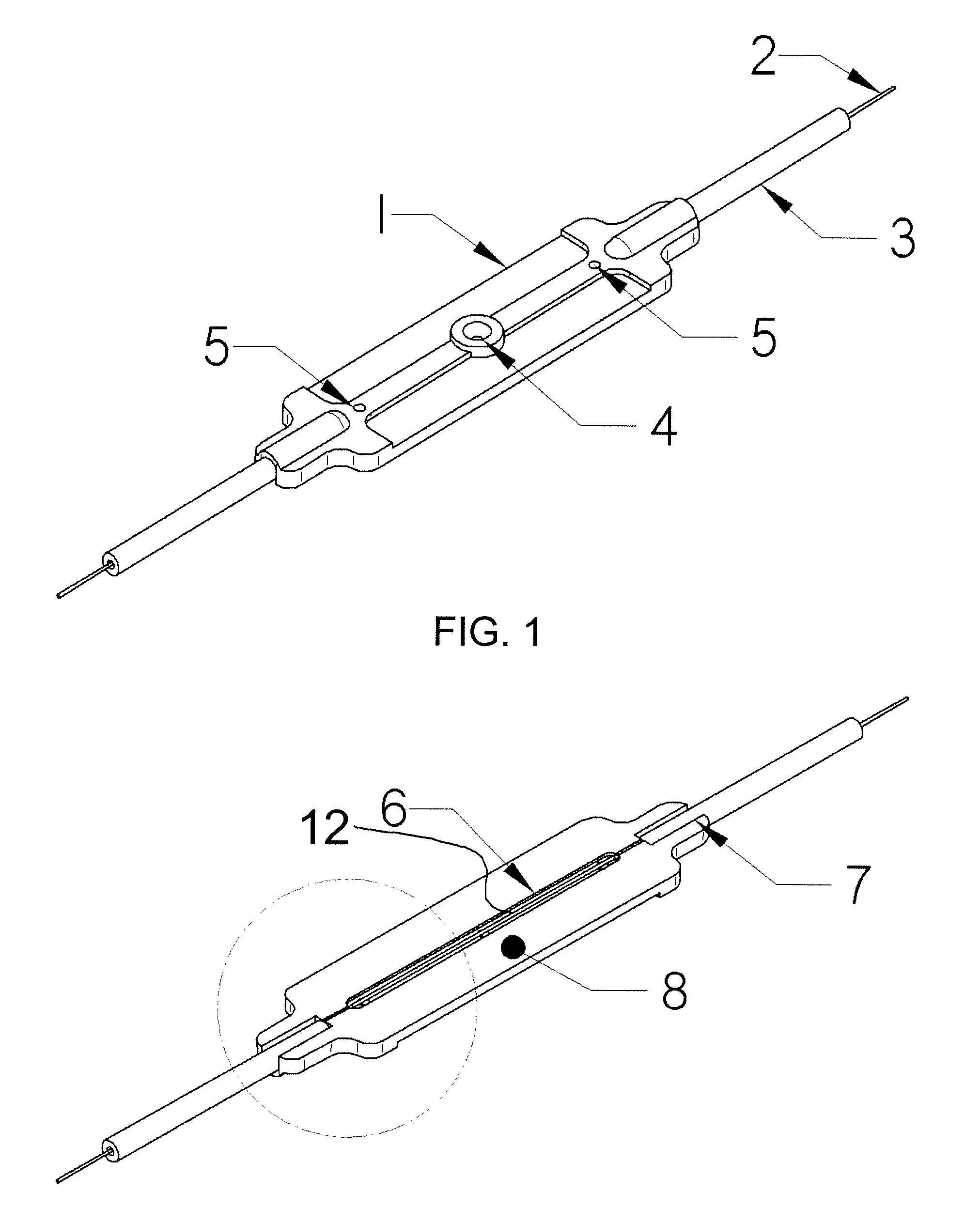
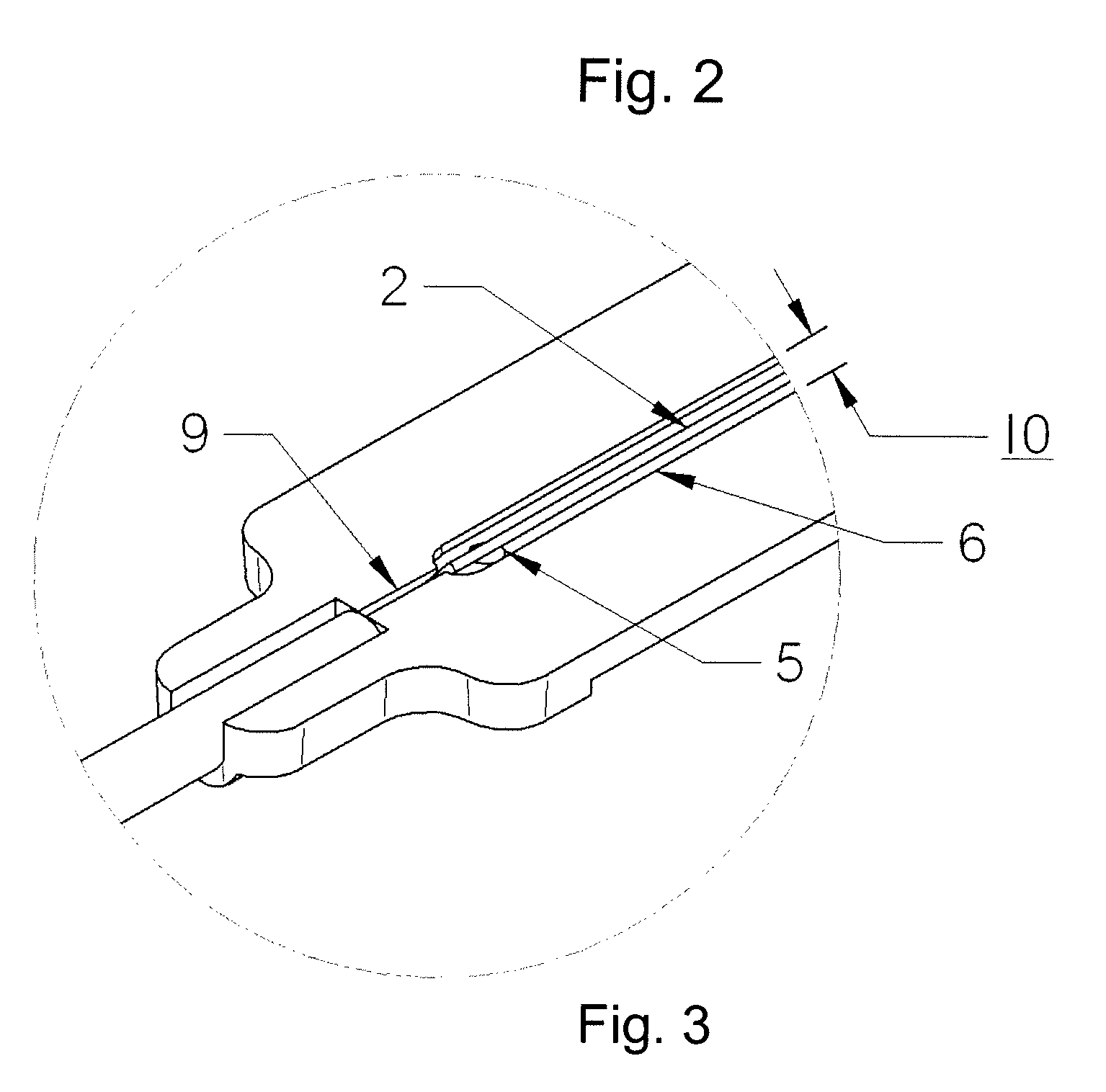
Fiber optic strain gage and carrier
ActiveUS7856888B2Quickly and easily attachedLittle resistanceForce measurement by measuring optical property variationUsing optical meansFiberGrating
The current invention relates to optical gages designed to measure strain on the surface of a test specimen. The gages of this invention is designed to be installed and used in a manner similar to conventional electronic foil strain gages, but to have the advantages of an all-optical gage. The gage of this invention is constructed to allow surface strain on the test specimen to be transferred to a length of optical fiber containing a fiber Bragg grating (FBG). As strain is applied to the fiber, the optical spectrum center wavelength reflected by the Bragg grating shifts in wavelength. This shift in wavelength can be converted directly to units of strain. The current invention provides a gage carrier design for use with fiber optic strain sensors comprising one or more FBGs which provide the benefits of a carrier for ease of handling and mounting without degrading gage performance. The gage carrier provides features that allow the FBG to be precisely positioned and securely bonded to the test specimen in a controlled manner. The carrier additionally provides fiber protection to the installed FBG.
Owner:LUNA INNOVATIONS
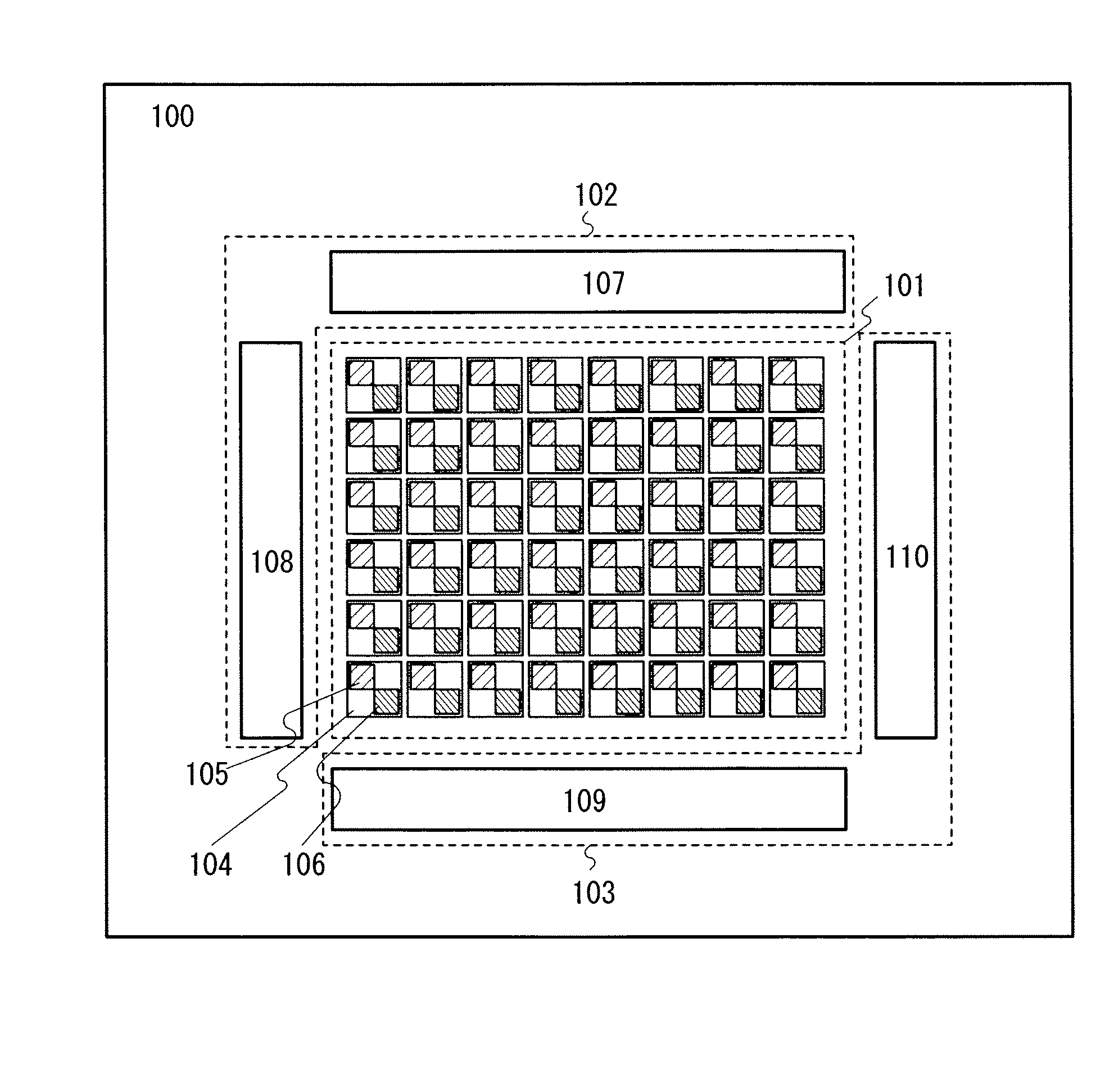
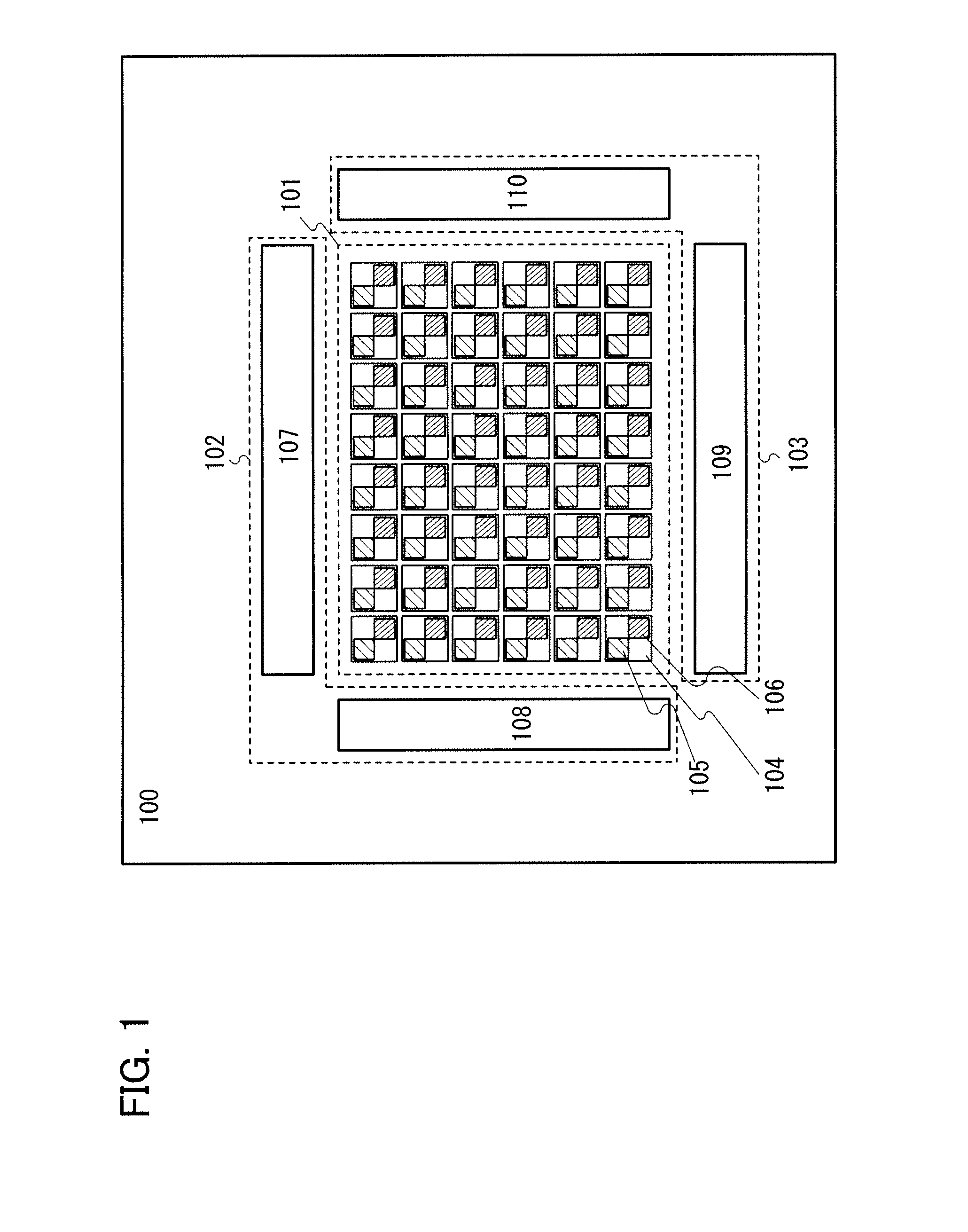
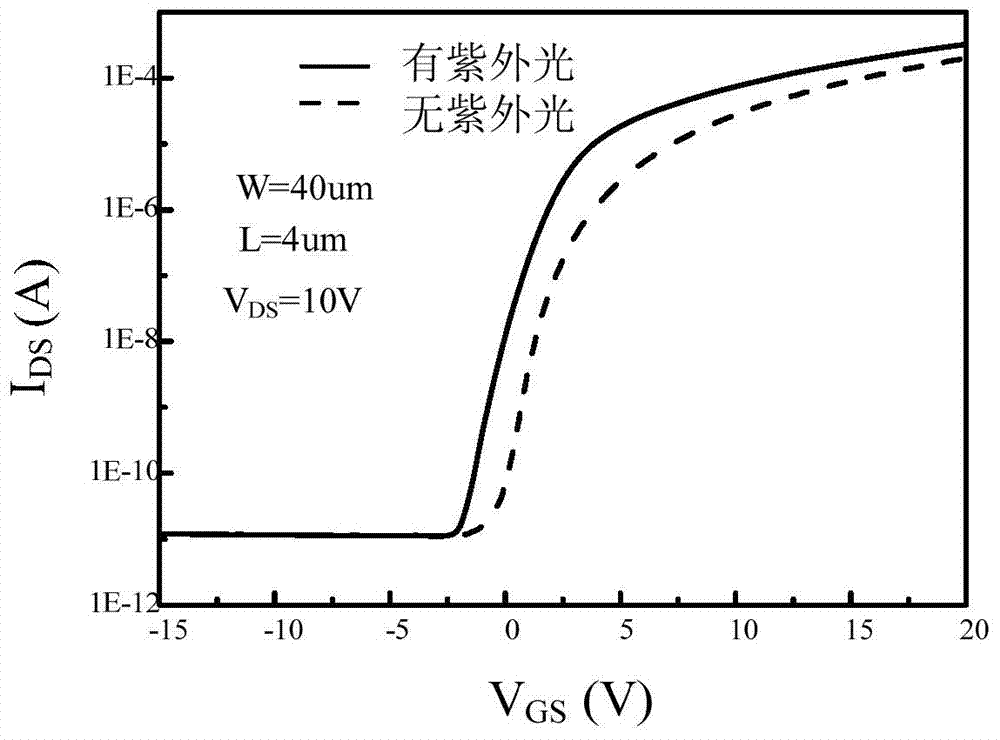
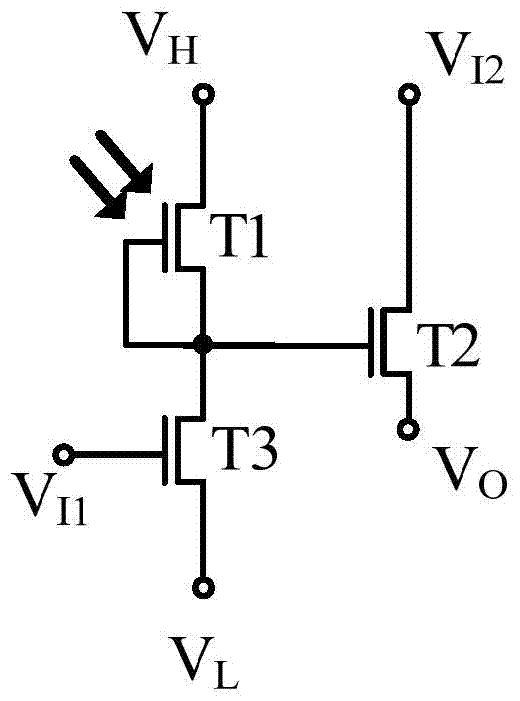
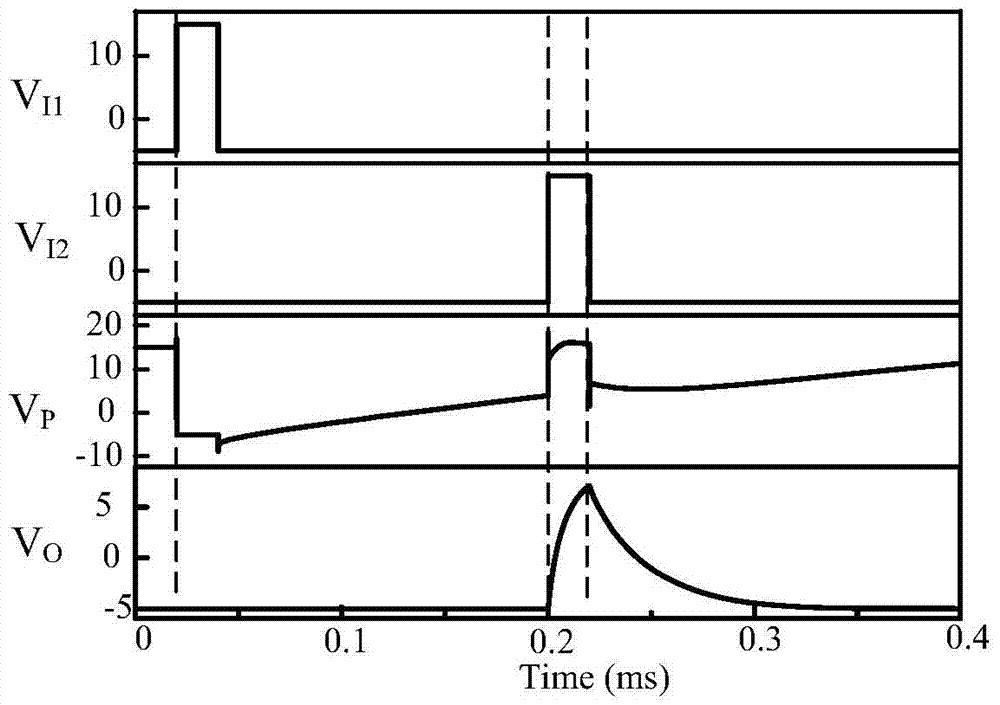
Semiconductor device and display device
InactiveUS20110122108A1SensitivityHigh-resolution imageTransistorTelevision system detailsPower semiconductor deviceDisplay device
It is an object to perform imaging a high-resolution image in a display device including a photosensor regardless of the intensity of incident light on the photosensor. A display device including a display panel which is provided a photosensor and having a function of imaging by a change of the sensitivity of the photosensor in accordance with the incident light is provided. The sensitivity of the photosensor is improved when the intensity of the incident light is low, so that the imaging accuracy is improved; therefore, misperception of contact is prevented and an obtained image can be clear.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Fiber optic strain gage and carrier
ActiveUS20090126501A1Quickly and easily attachedLittle resistanceForce measurement by measuring optical property variationUsing optical meansFiberGrating
The current invention relates to optical gages designed to measure strain on the surface of a test specimen. The gages of this invention is designed to be installed and used in a manner similar to conventional electronic foil strain gages, but to have the advantages of an all-optical gage. The gage of this invention is constructed to allow surface strain on the test specimen to be transferred to a length of optical fiber containing a fiber Bragg grating (FBG). As strain is applied to the fiber, the optical spectrum center wavelength reflected by the Bragg grating shifts in wavelength. This shift in wavelength can be converted directly to units of strain. The current invention provides a gage carrier design for use with fiber optic strain sensors comprising one or more FBGs which provide the benefits of a carrier for ease of handling and mounting without degrading gage performance. The gage carrier provides features that allow the FBG to be precisely positioned and securely bonded to the test specimen in a controlled manner. The carrier additionally provides fiber protection to the installed FBG.
Owner:LUNA INNOVATIONS
Novel compound, polymer, resist composition, and patterning process
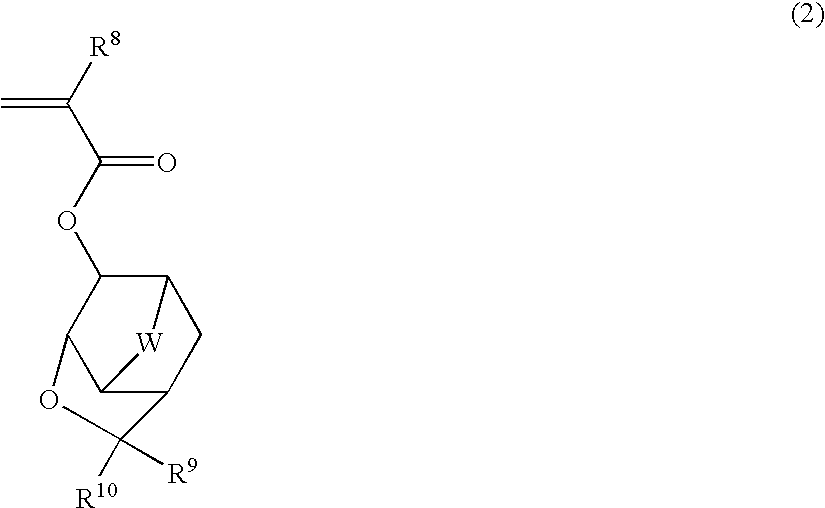
ActiveUS20050014092A1Improve powerIncrease resistanceOrganic chemistryPhotoprinting processesResistPhotoresist
There is disclosed a polymer containing at least a repeating unit represented by the following general formula (1), and the resist composition containing the polymer as a base resin, especially a chemically amplified resist composition. There can be provided a resist composition which has etching resistance in a practical use level, and is excellent in an adhesion property with a substrate and an affinity with a developer, and has a sensitivity and resolving power which is far excellent compared with a conventional one, wherein swelling is small at the time of development, especially for photolithography which uses a high-energy beam as a light source, and especially be provided a chemically amplified resist composition.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Vibration-resistant rotation rate sensor
ActiveUS20150128700A1Improve vibration resistanceGuaranteed uptimeAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSeismic massClassical mechanics
A rotation rate sensor includes a substrate having a main extension plane and multiple seismic masses, in which for each seismic mass the following applies: the seismic mass is drivable at a drive oscillation, which occurs along a drive direction situated parallel to the main extension plane, the seismic mass is deflectable along two different deflection directions, each direction being perpendicular to the drive direction, the rotation rate sensor being configured to generate detection signals as a function of detected deflections of the seismic masses, one detection signal of the detection signals being associated with each deflection direction of the seismic masses, the rotation rate sensor being configured so that a linear, rotational and centrifugal acceleration of the rotation rate sensor are compensated with respect to at least one rotation axis of the rotation rate sensor through compensation in each case of two corresponding detection signals of the detection signals.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Inertial sensor and manufacturing method of the same
InactiveUS7658109B2Achieve the wholeSensitivityLine/current collector detailsAcceleration measurement using interia forcesClassical mechanicsHigh acceleration
A weight of an inertial sensor if formed from a plurality of divided weights, and the divided weights are connected to each other by elastically deformable beams. A movable range and a mass of each of the divided weights and a rigidity of each of the beams are adjusted and a plurality of deformation modes having different sensitivity ranges with respect to the acceleration are used in combination. By this means, it is possible to improve a detecting sensitivity of an acceleration and widen an acceleration response range.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
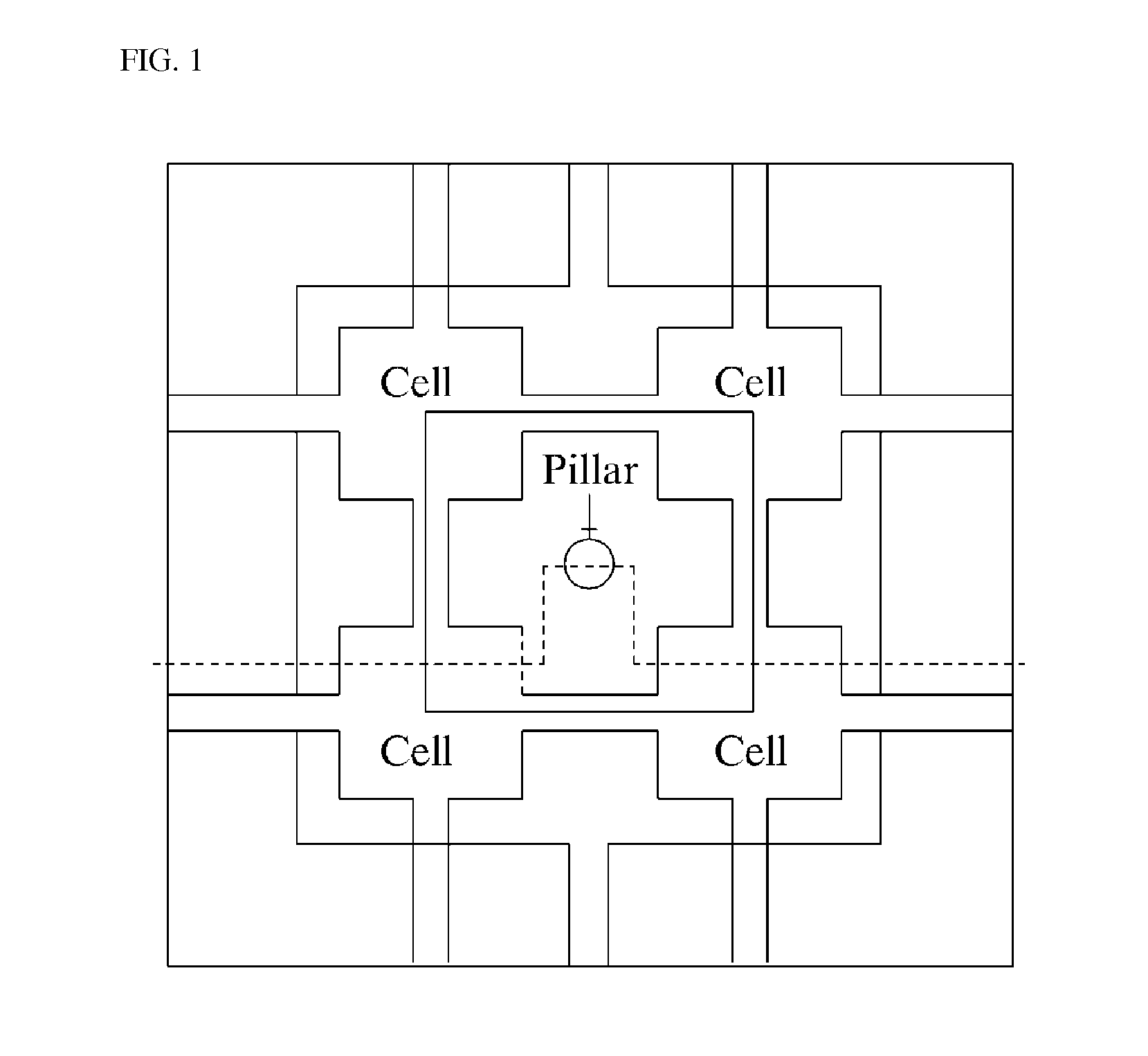
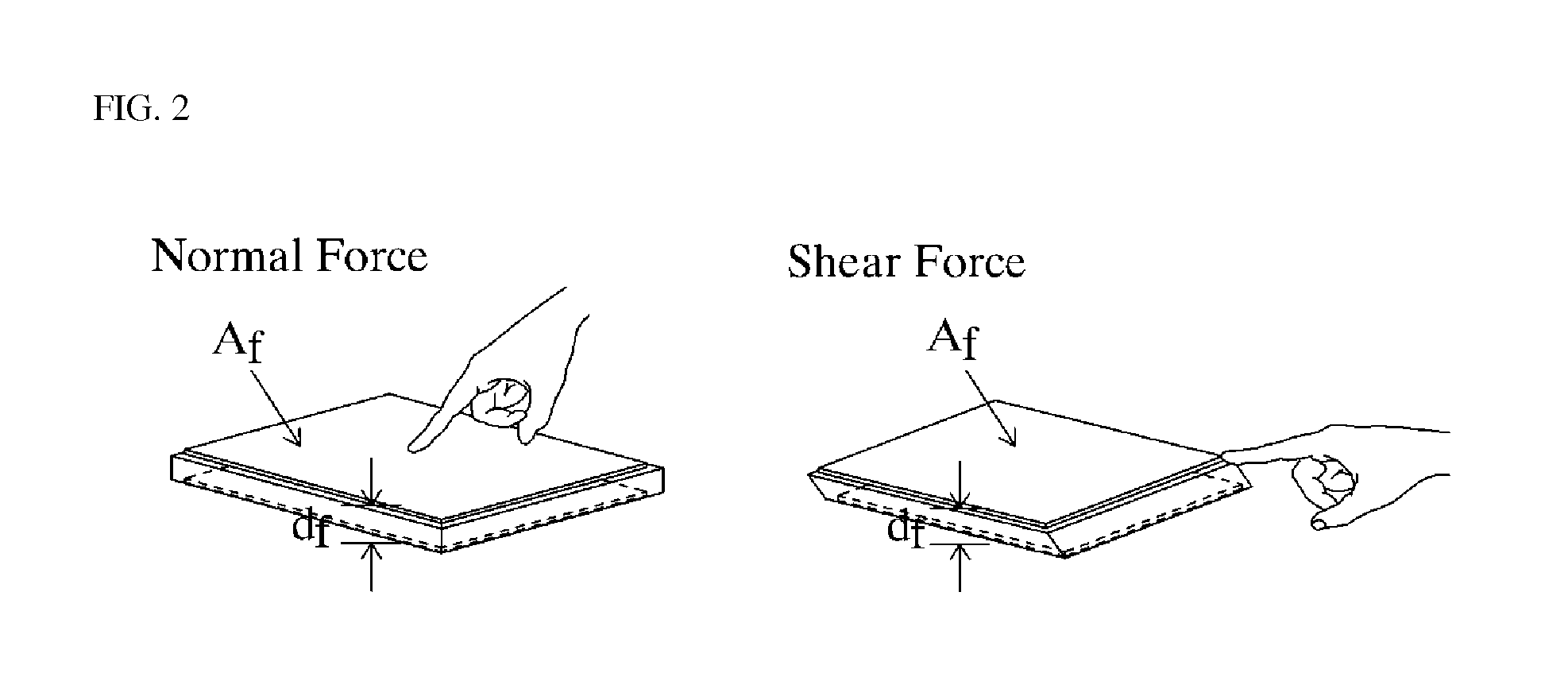
Capacitor sensor capable of controlling sensitivity
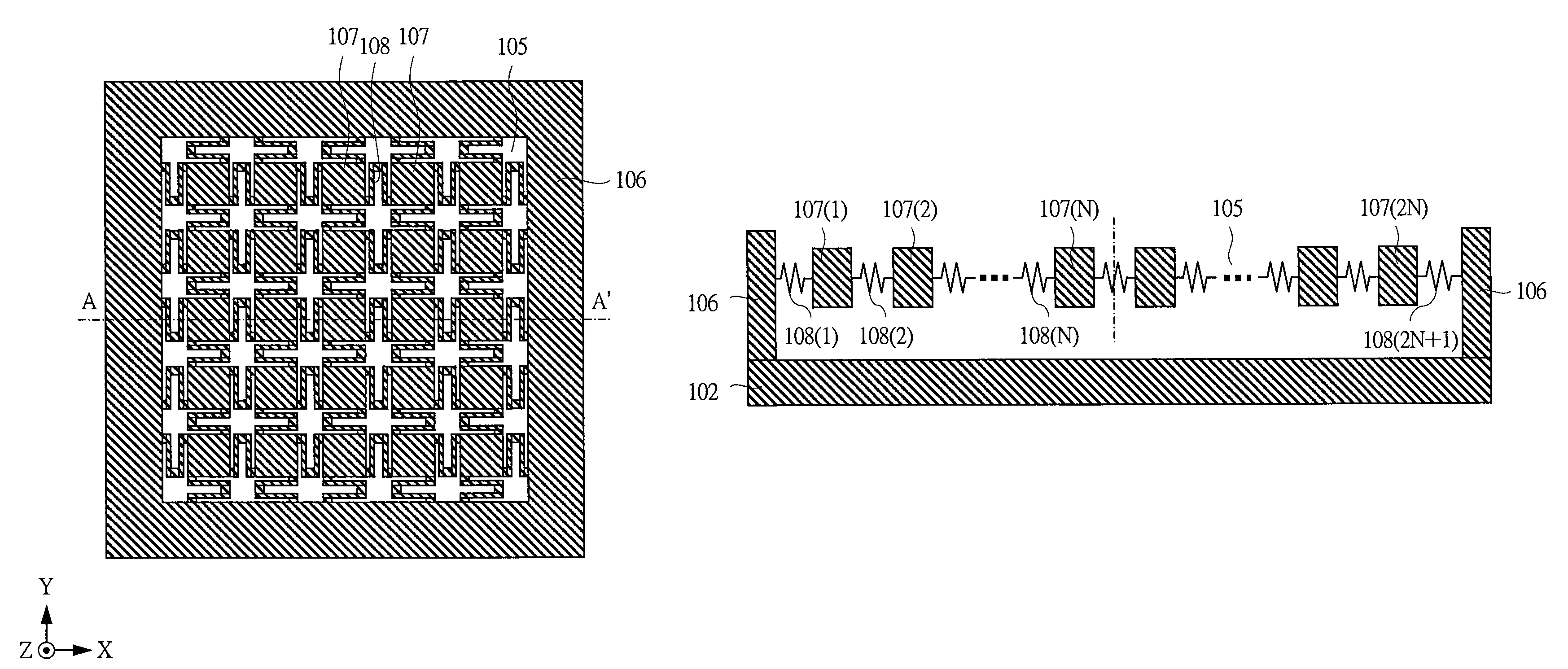
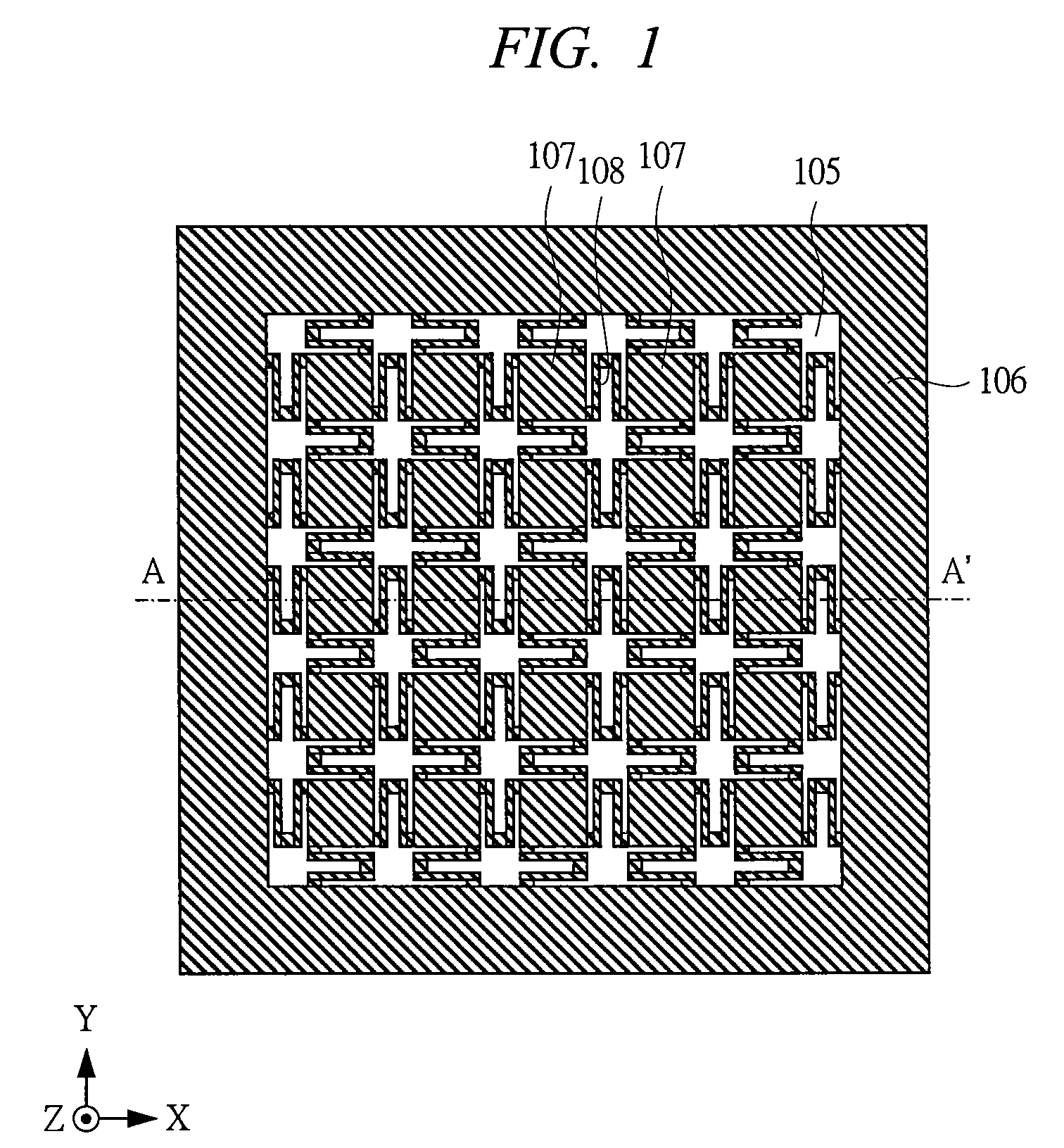
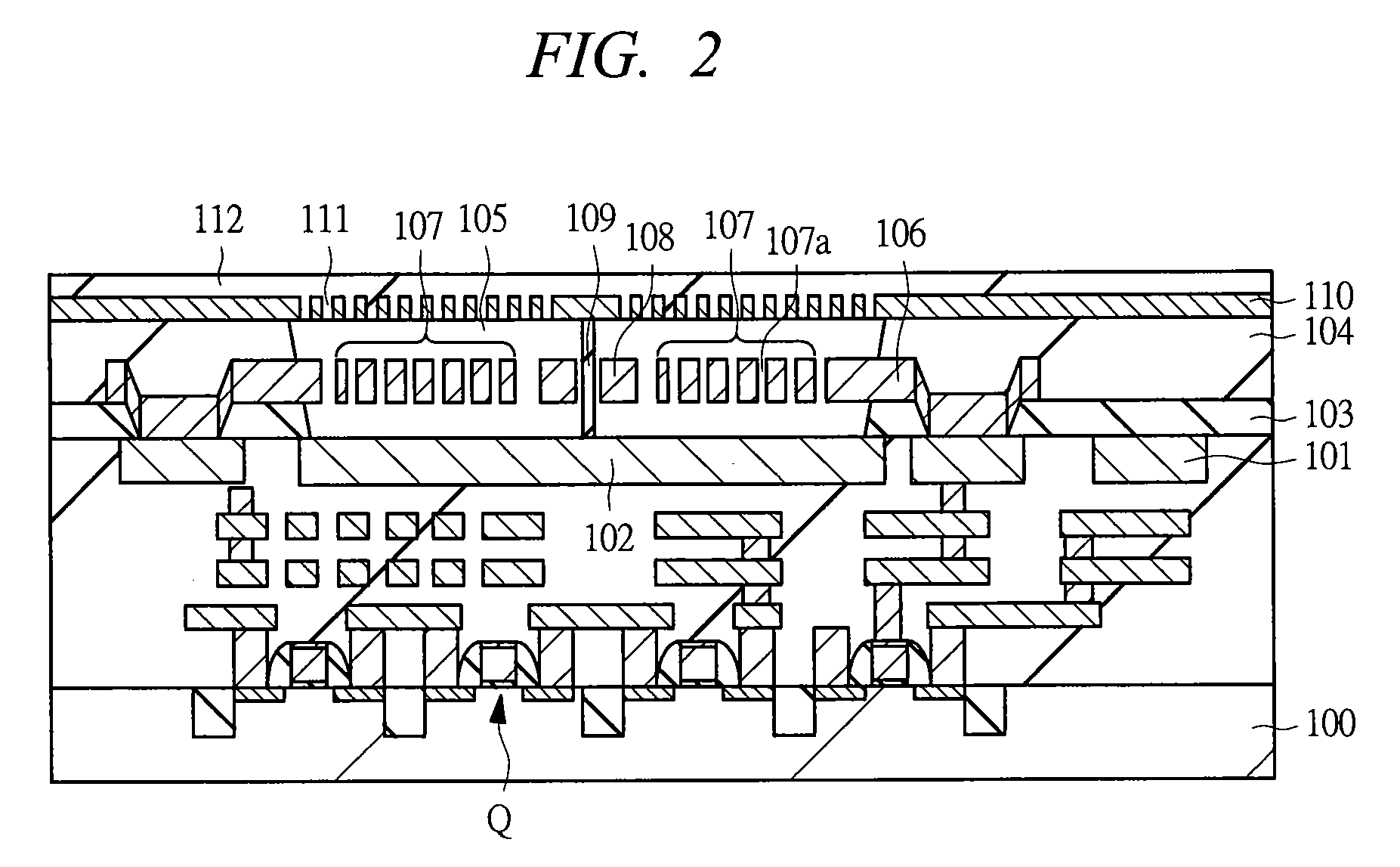
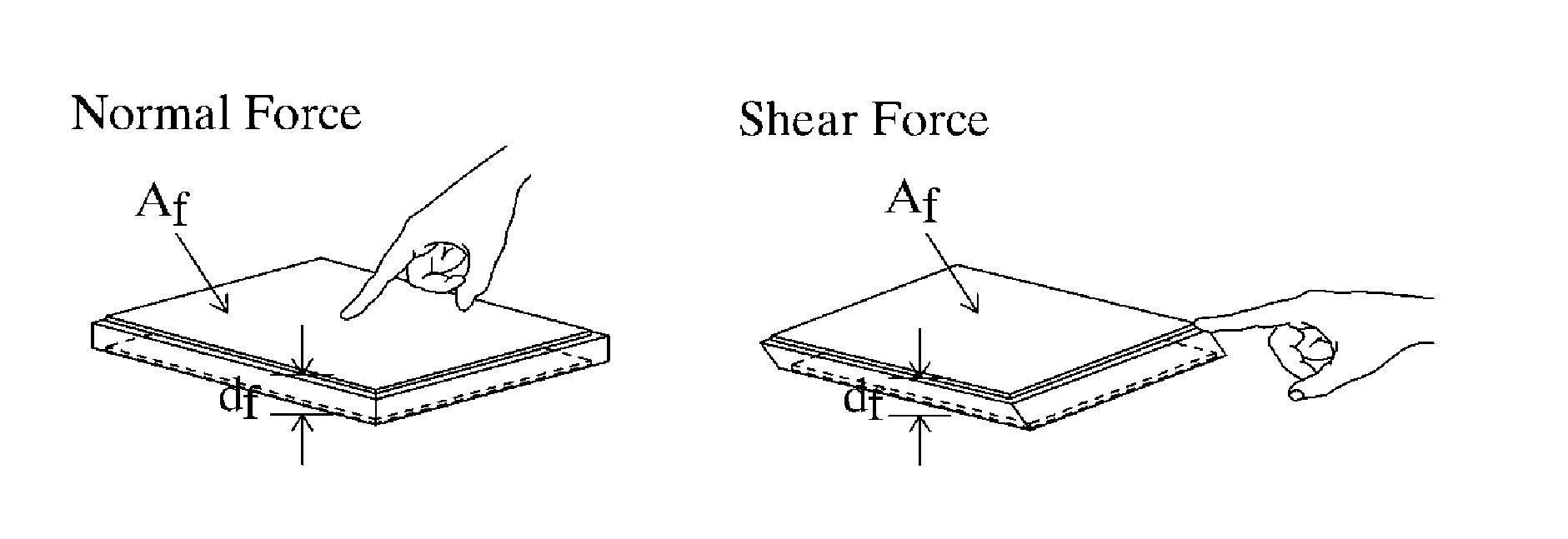
ActiveUS20130093437A1SensitivityReduce sensitivityCapacitance measurementsForce measurementEngineeringCapacitor
There is provided a capacitor sensor capable of controlling sensitivity, wherein the capacitor sensor measures the magnitude and direction of a shear force applied to the sensor, as well as the magnitude of a normal force applied on the surface of the sensor, and consists of a single cell including a pattern electrode capable of varying its shape to control the sensitivity of the sensor.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
Digital audio processor device and method
ActiveUS8218784B2SensitivityAccurate assessmentSignal processingStereophonic circuit arrangementsAudio frequencySound pressure
An audio processor device and method is disclosed which measures and provides information relating to the audio level being applied to the ear of a user. The processor device uses a preset or calibrated sensitivity of the applied earphones in combination with an analysis of the audio stream to provide sound-pressure-level or time-weighted exposure information to the user or limit the output when preset levels have been achieved. Also disclosed is the use of microphones, internal or external, to combine an additional audio stream, typically the ambient environment, into the main audio channel.
Owner:TENSION LABS
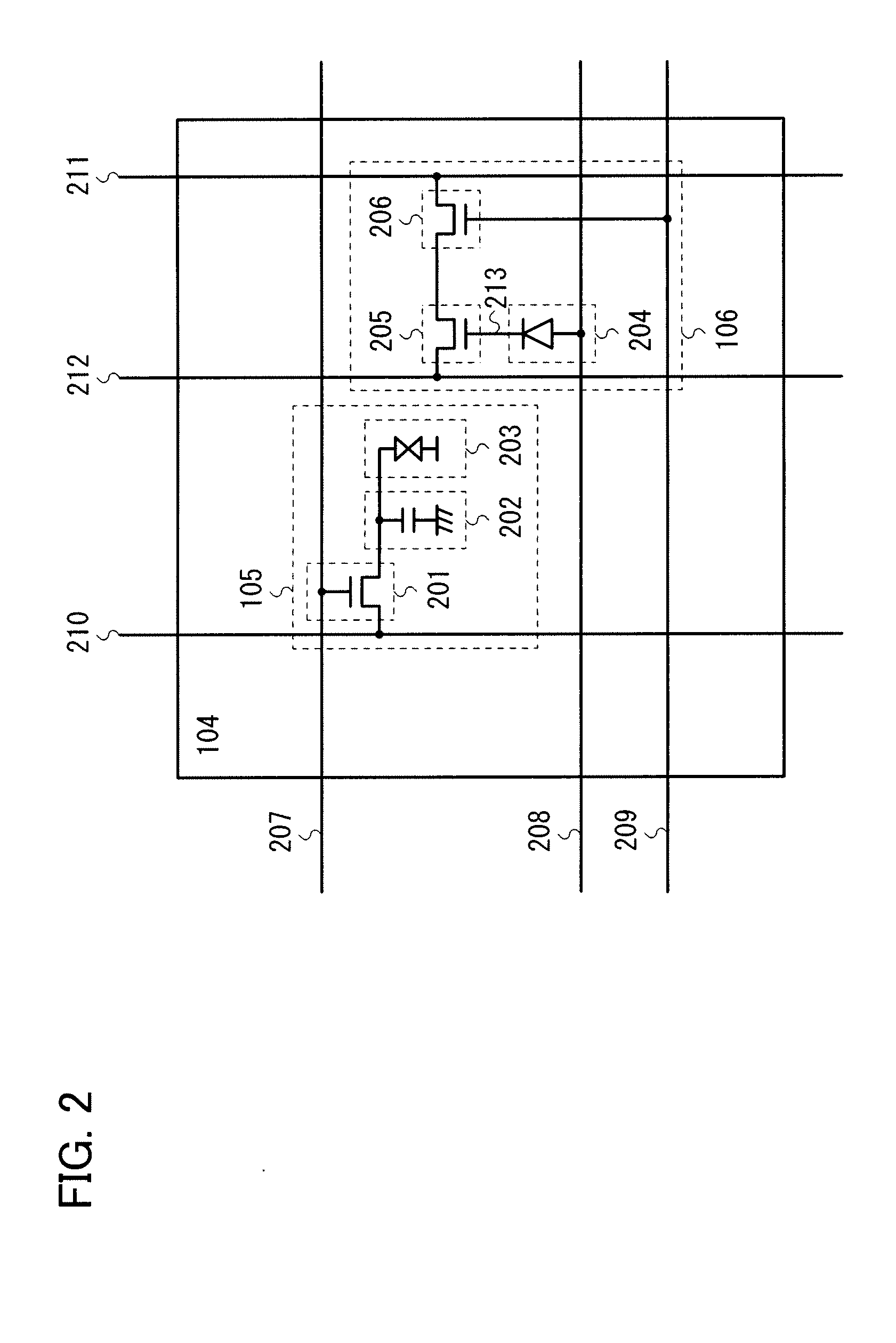
Touch circuit, touch circuit unit, touch display panel and touch display device
ActiveCN103761002ASimple structureSensitiveInput/output processes for data processingPower flowPanel design
The invention discloses a touch circuit unit suitable for an in-cell type touch technology. The touch circuit unit comprises an induction transistor, a reset transistor and a reading transistor. First the reset transistor responds to a first pulse signal to reset the touch circuit unit, the induction transistor senses touch movement of outside invisible light, and finally induction information is output through the reading transistor. The touch circuit unit can generate a wide-amplitude current or voltage signals to a peripheral circuit according to the invisible light low in strength and is high in noise resistance. A touch circuit distributed in a pixel circuit matrix, a touch display panel designed on the basis of the touch circuit and a touch display device are further disclosed simultaneously.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
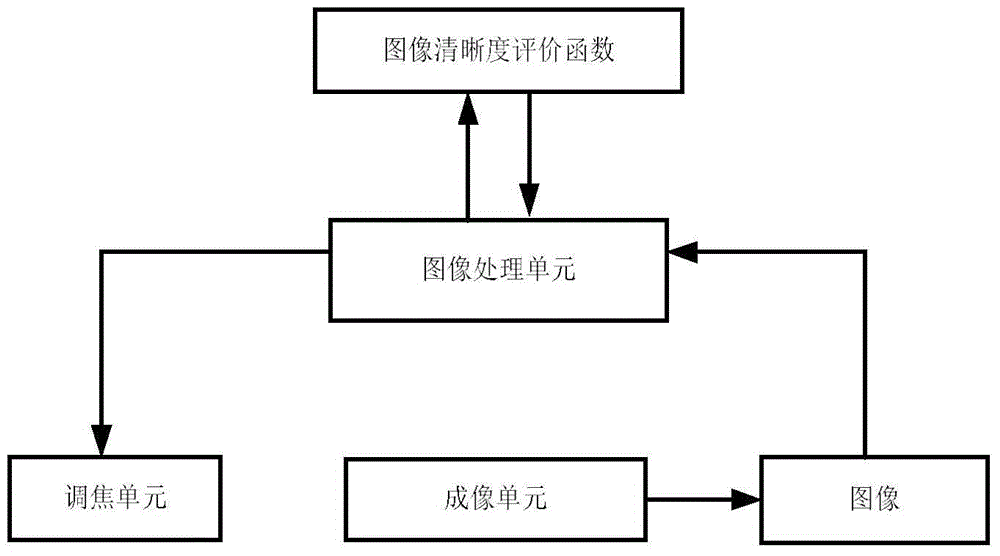
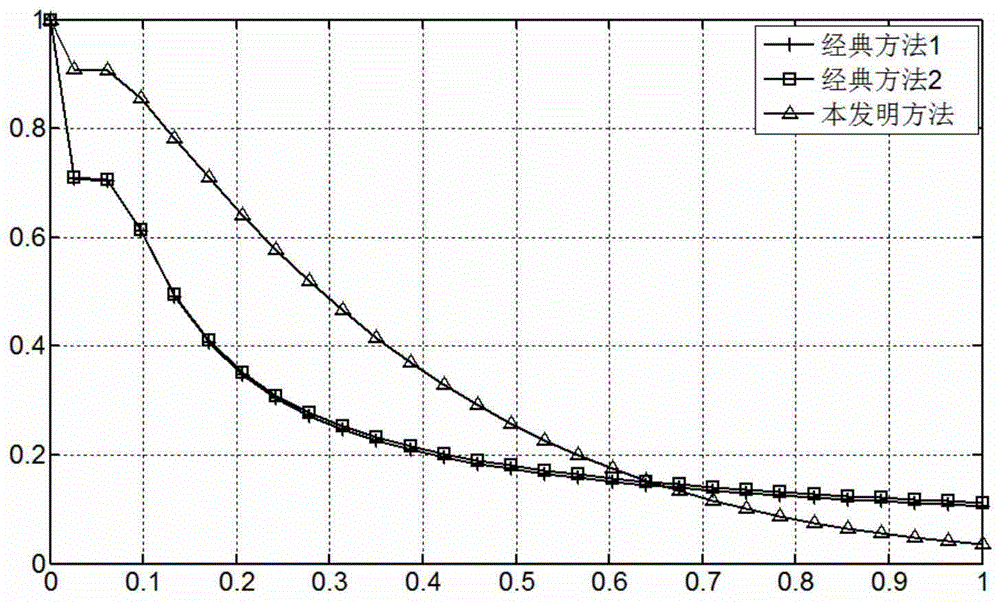
Automatic focusing method
InactiveCN104917970ASensitivityImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDistinctness of imageHigh frequency
The invention discloses an automatic focusing method, comprising the steps as follows: collecting an image; an image processing unit using a definition evaluation function value to evaluate defocusing amount, and controlling a focusing unit to focus according to the defocusing amount, wherein the image definition evaluation function value is a specific value of a high-frequency component amplitude and a low frequency component amplitude, and the frequency of a low frequency component is less than that of a high-frequency component, and the proportion that the low frequency component occupies the number of all frequency components obtained by calculating is 3 to 6 percents. The method of the invention improves sensitivity and accuracy of the image definition evaluation function value at a server defocusing place so as to be beneficial to realize fast and accurate automatic focusing.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Force measuring device, in particular for seat weight determination in a motor vehicle
InactiveUS6986293B2Improve accuracyAccurate detectionVehicle seatsWeighing apparatus using elastically-deformable membersMobile vehicleMeasurement device
A force measuring device for seat weight determination in a motor vehicle includes a taking up element which has at least two bearing points. The device further includes a mechanism forming a first recess in the taking up element in a region between at least two bearing points and a rod-shaped element which extends in the longitudinal axis of the taking up element and is not loaded by bending forces. The rod-shaped element has a free end which deviates from the longitudinal axis of the taking up element when a force to be measured acts on the taking up element, and a measuring unit with a magnet and a magnetic field-sensitive sensor The magnet and the magnetic field-sensitive sensor are arranged immovably relative to one another so that the distance from the magnet to a ferromagnetic material changes under loading with the force.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Oxygen-enriched nano bio-enzyme electrode as well as sensor device, preparation method and application of oxygen-enriched nano bio-enzyme electrode
ActiveCN108872344ADetection limit widthSensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEnzyme electrodeOxygen storage
The invention provides an oxygen-enriched nano bio-enzyme electrode as well as a sensor device and a preparation method and application of oxygen-enriched nano bio-enzyme electrode. According to the oxygen-enriched nano bio-enzyme electrode, an electrode substrate is modified with a hollow structure nano material with the oxygen enrichment function, catalyst particles of hydrogen peroxide and an oxidase corresponding to a substance to be detected. The oxygen-enriched nano bio-enzyme electrode and the device have the advantages that the detection linear range is wide, the sensitivity is high, the anti-interference performance is good, and in addition, batch production can be carried out; and the advantages are mainly derived from the hollow structure material with the oxygen storage function.
Owner:SCITECH CENTRY SUZHOU BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for detecting atmosphere granule trace polychlorinated biphenyls by ion trap tandem mass spectrometry
InactiveCN101105477AThe detection method is simpleQuick checkComponent separationWithdrawing sample devicesParticulatesIon trap mass spectrometry
The invention provides a method of detecting the trace polychlorinated biphenyls in atmospheric particulates by ion trap tandem mass spectrometry; the steps of the method comprises sample collection, sample leach, sample concentration and purification and the detection of pilot sample by chromatography-ion trap mass spectrometry; by optimizing the conditional parameters of gas phase chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry, the invention has better selectivity and better sensitivity in the detection of titled compound compared with the conventional detection method; the invention solves the mutual interference between PCBs and multi-chlorine organic compounds in the traditional analysis and detection method by SRM technique of gas phase chromatography / ion trap tandem mass spectrometry (GC / ITMS), and greatly simplifies the fussy steps of purification and separation in sample pretreatment; SRM technique has the advantages of sensitivity, selectivity, low detecting expense and reliable and accurate determination of the nature; therefore, the invention has remarkable advantage compared with the traditional detecting instrument such as GC / ECD,GC / LRMS,GC / HRMS.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Swimming pool touchpad
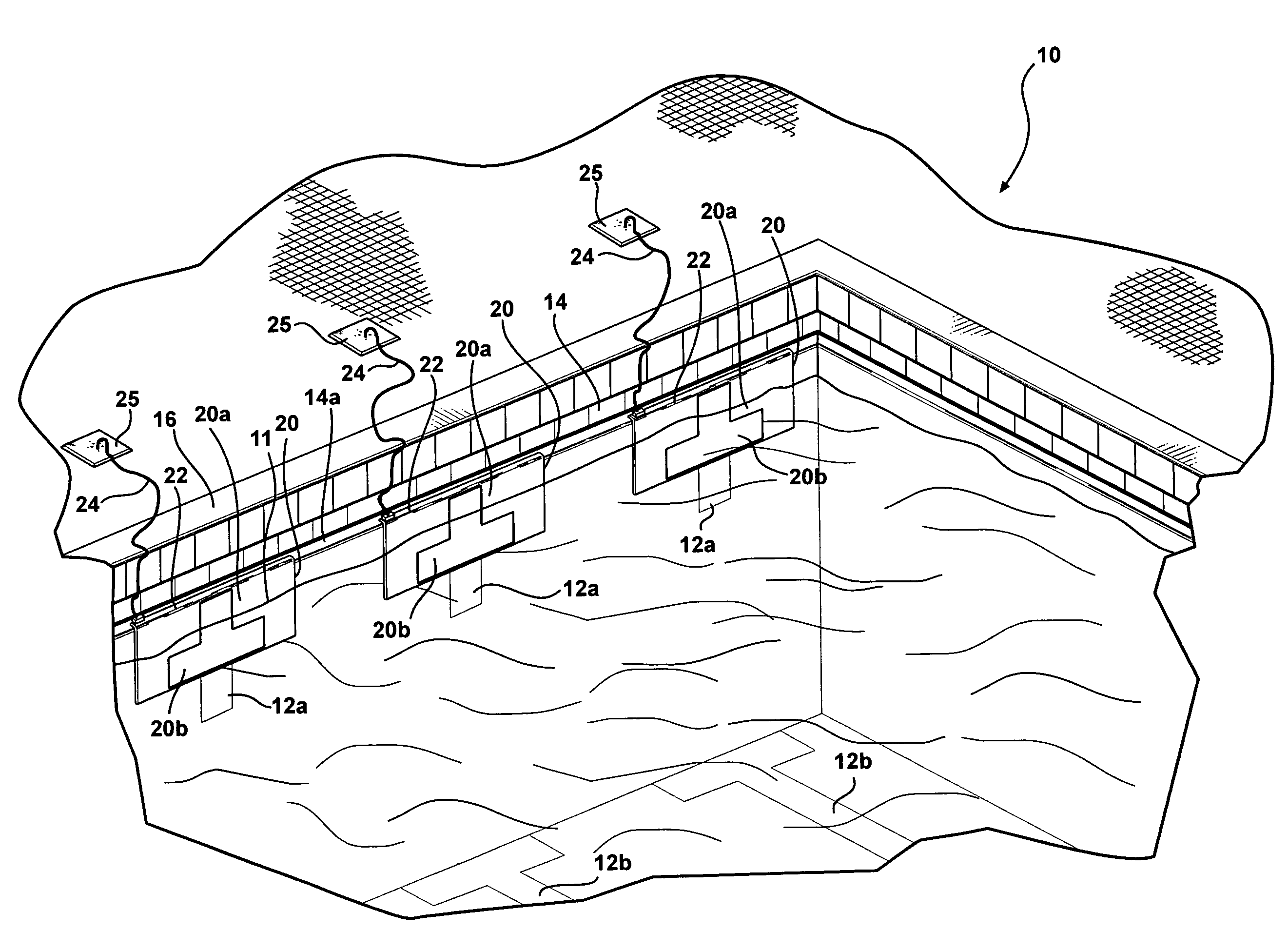
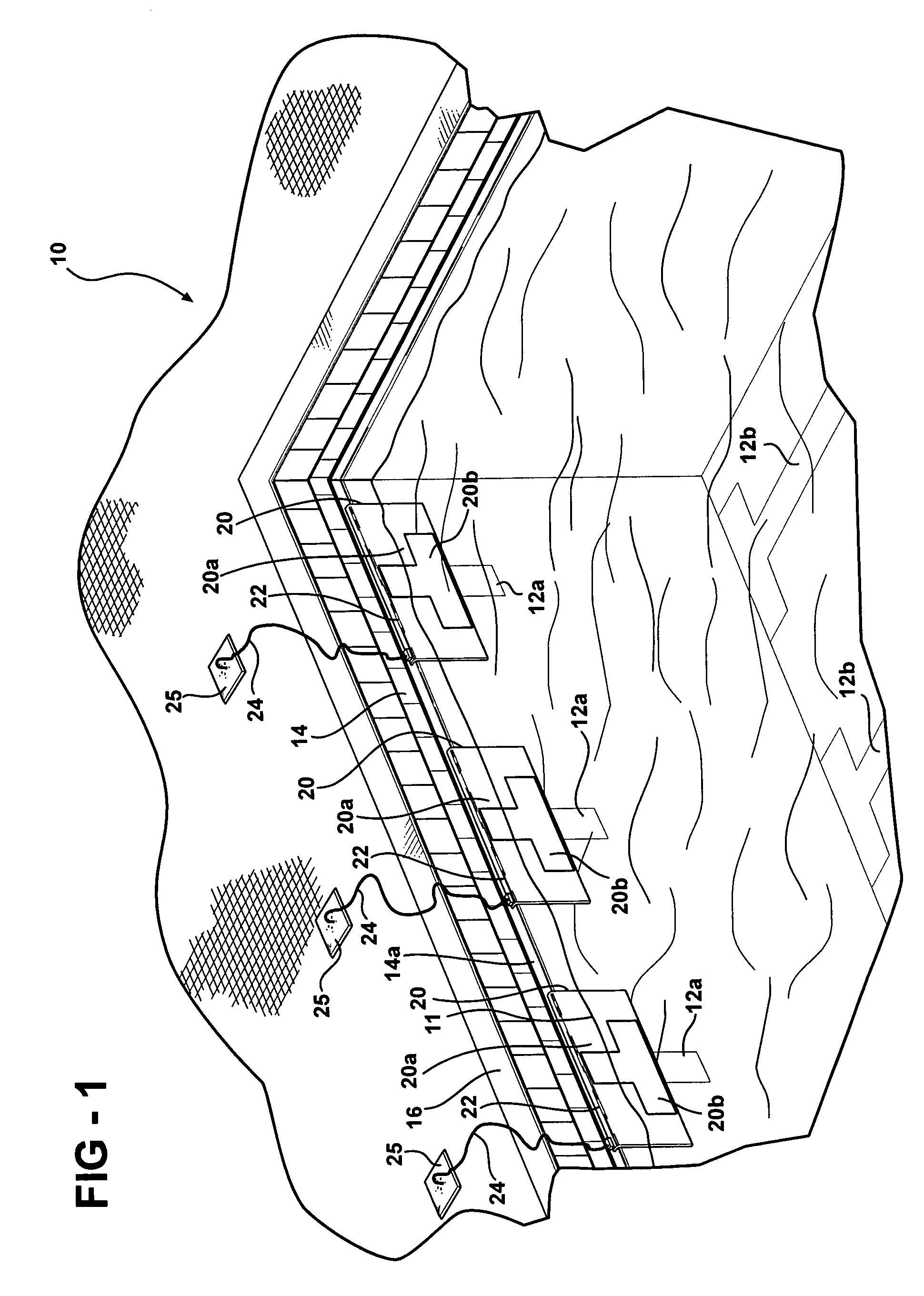
ActiveUS7358456B1Simpler and more dependableEasy to closeContact mechanismsContact surface shape/structureTouchpadEngineering
A sealed two-plate swimming pool touchpad construction that is unaffected by pressure, in which a resilient, compressible, non-conductive spacer material such as rubber tubing is seated in an array of spaced recesses or grooves on the inside face of the rear plate to insulatively space a conductive, flexible front plate from the rear plate. The front plate is joined and sealed in watertight fashion to the rear plate around the array of grooves and spacer material. Conductive portions of the inside face of the front plate are flexed into switch-closing / signaling contact with conductive portions of the inside face of the rear plate between the spacer material when a swimmer makes contact with the front plate.
Owner:INDAL SERVICE TECH
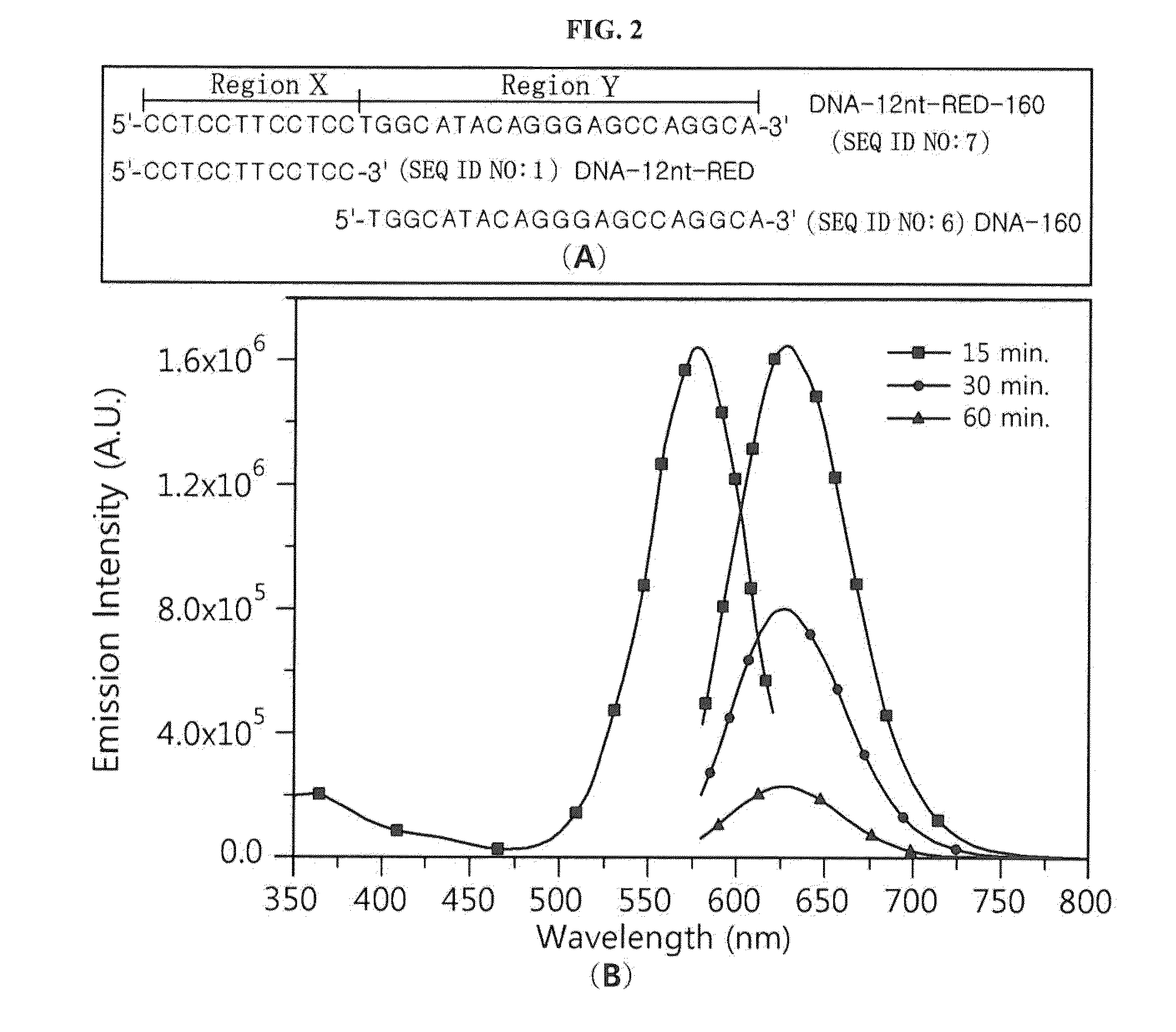
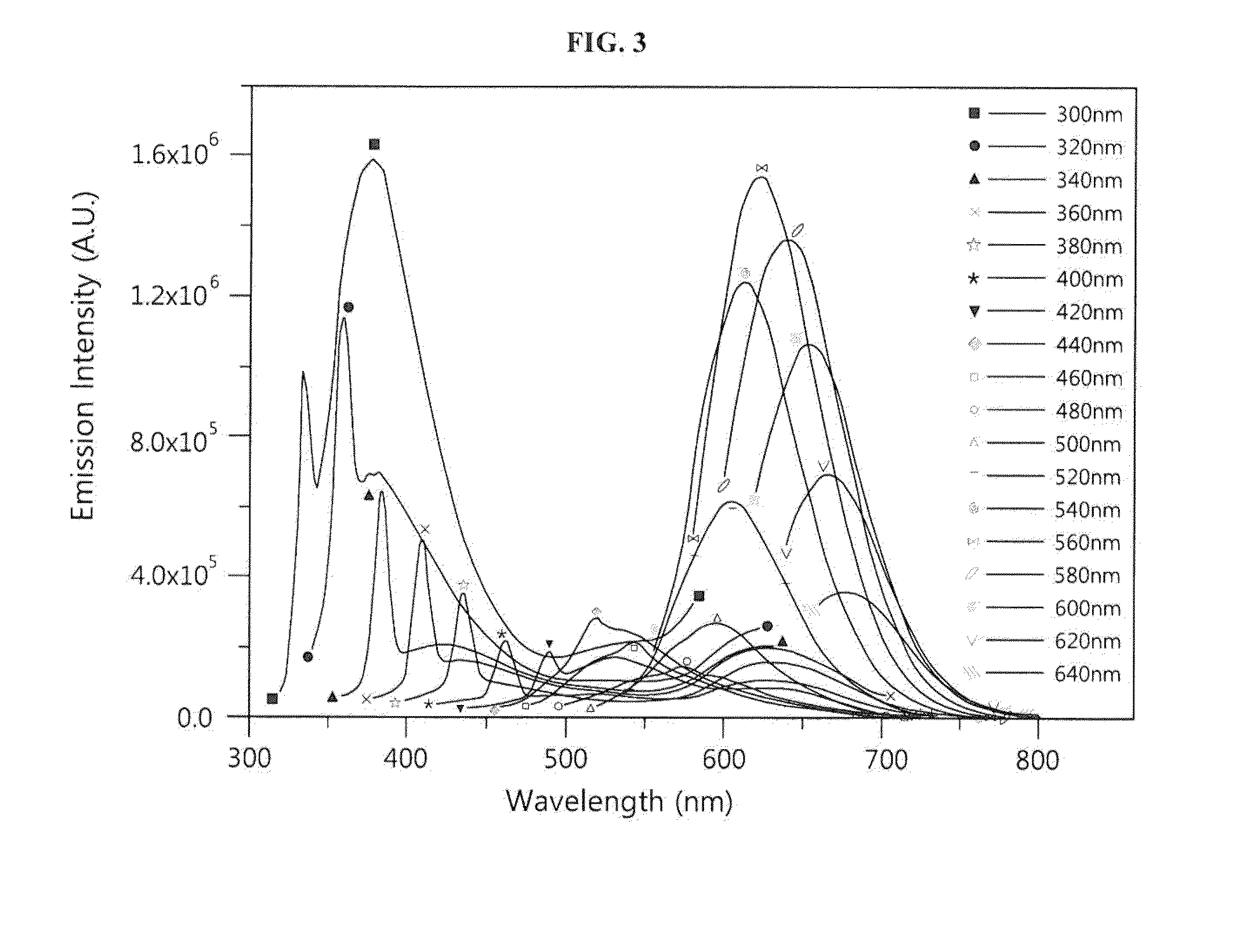
Silver nanocluster probe and target polynucleotide detection method using same, and silver nanocluster probe design method
ActiveUS20150225781A1Rapidly and conveniently detectingRapid and convenient mannerSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotide sequencingPolynucleotide
The present invention provides a silver nanocluster probe which comprises a silver nanoparticle binding region and a specific nucleotide sequence region that specifically binds to a target polynucleotide, wherein the silver nanocluster probe is configured such that it will emit detectable light when silver nanoparticles bind to the silver nanoparticle binding region to form a silver nanocluster, but light emission from the silver nanocluster probe will decrease or decay when the target polynucleotide binds to the specific nucleotide sequence region. According to the present invention, either the presence of a target polynucleotide in a sample or a mutation in the target polynucleotide can be detected in a rapid and convenient manner by determining whether light emission decreases or decays when the target polynucleotide binds to the specific nucleotide sequence region of the silver nanocluster probe that emits detectable light.
Owner:SEOULIN BIO SCI
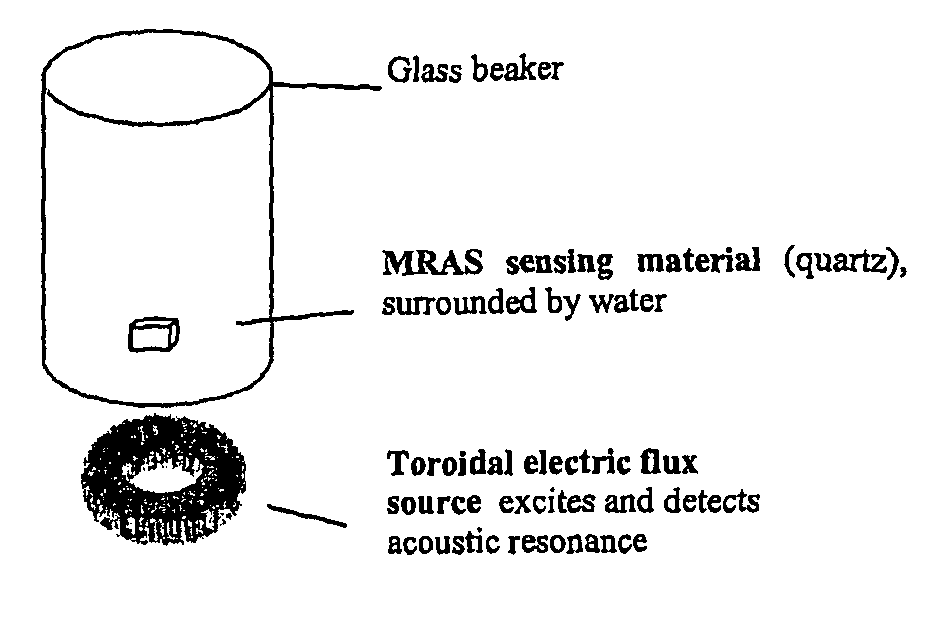
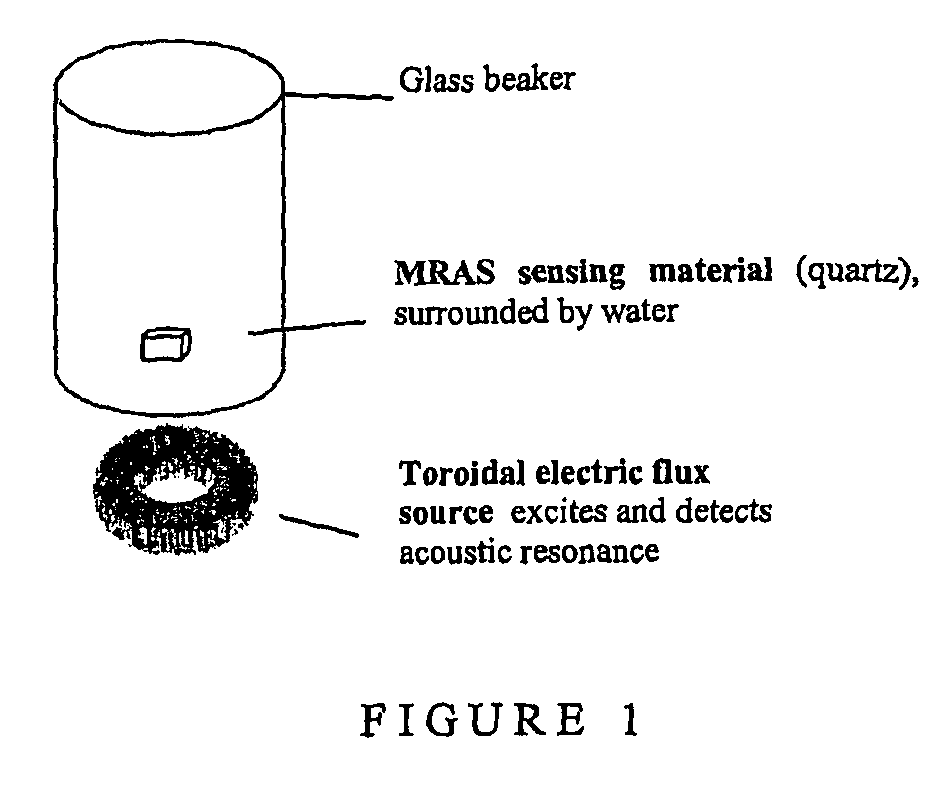
Electromagnetic piezoelectric acoustic sensor
InactiveUS20100164488A1SensitivityHigh sensitivityAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMagnetic property measurementsElectromagnetic fieldResonator
Provided is a remote sensing apparatus comprising: (a) an electromagnetic field detector and (b) an acoustic resonator comprising an electromagnetic field generator and a sensing material in wireless communication with the generator; wherein the sensing material is in wireless communication with the detector, and an acoustic property of the sensing material is responsive to a change in state of an environment to which the sensing material is exposed, and wherein the sensing material is in the form of one or more particles and / or fragments.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
Bone densitometer and a method thereof
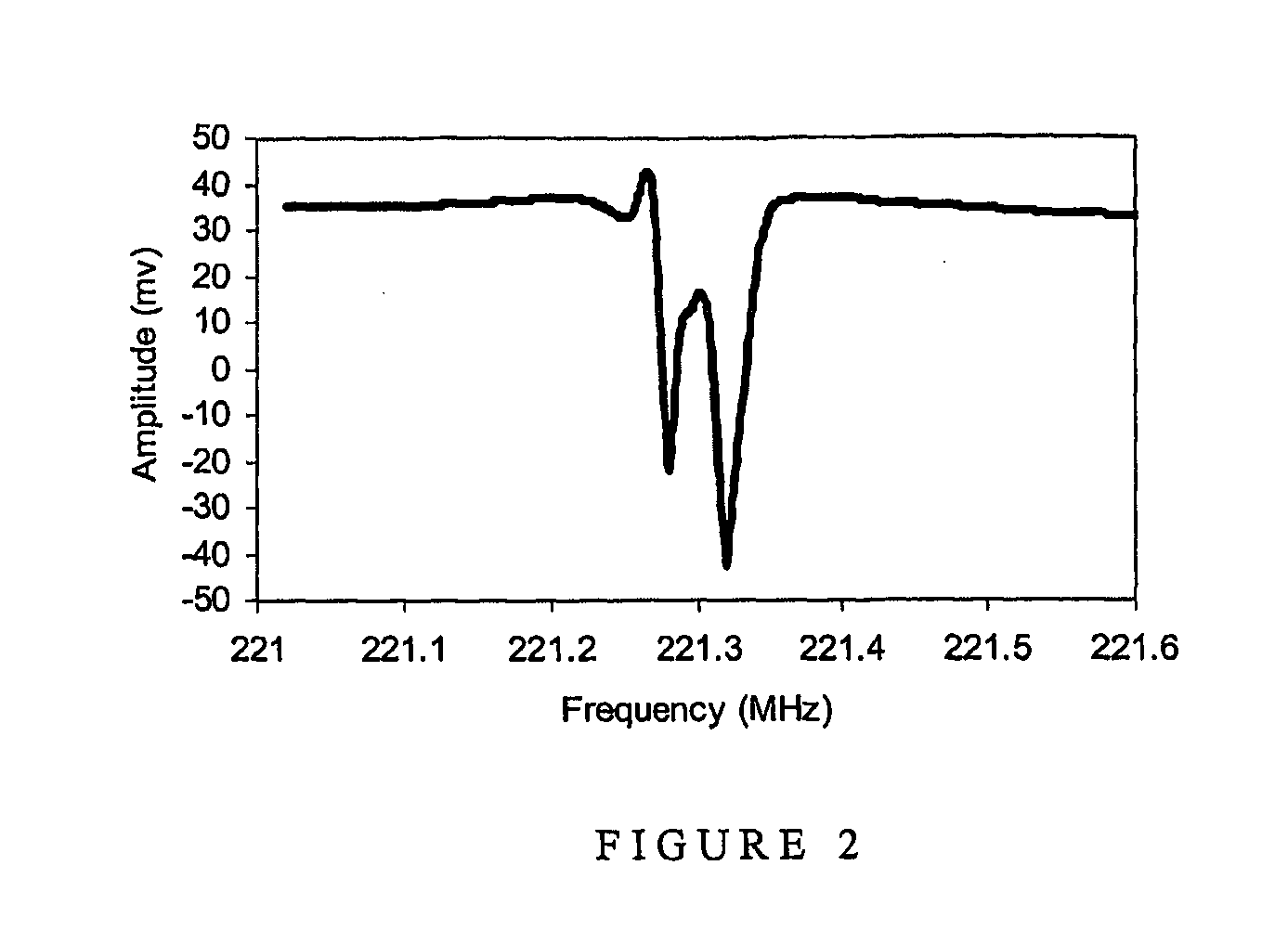
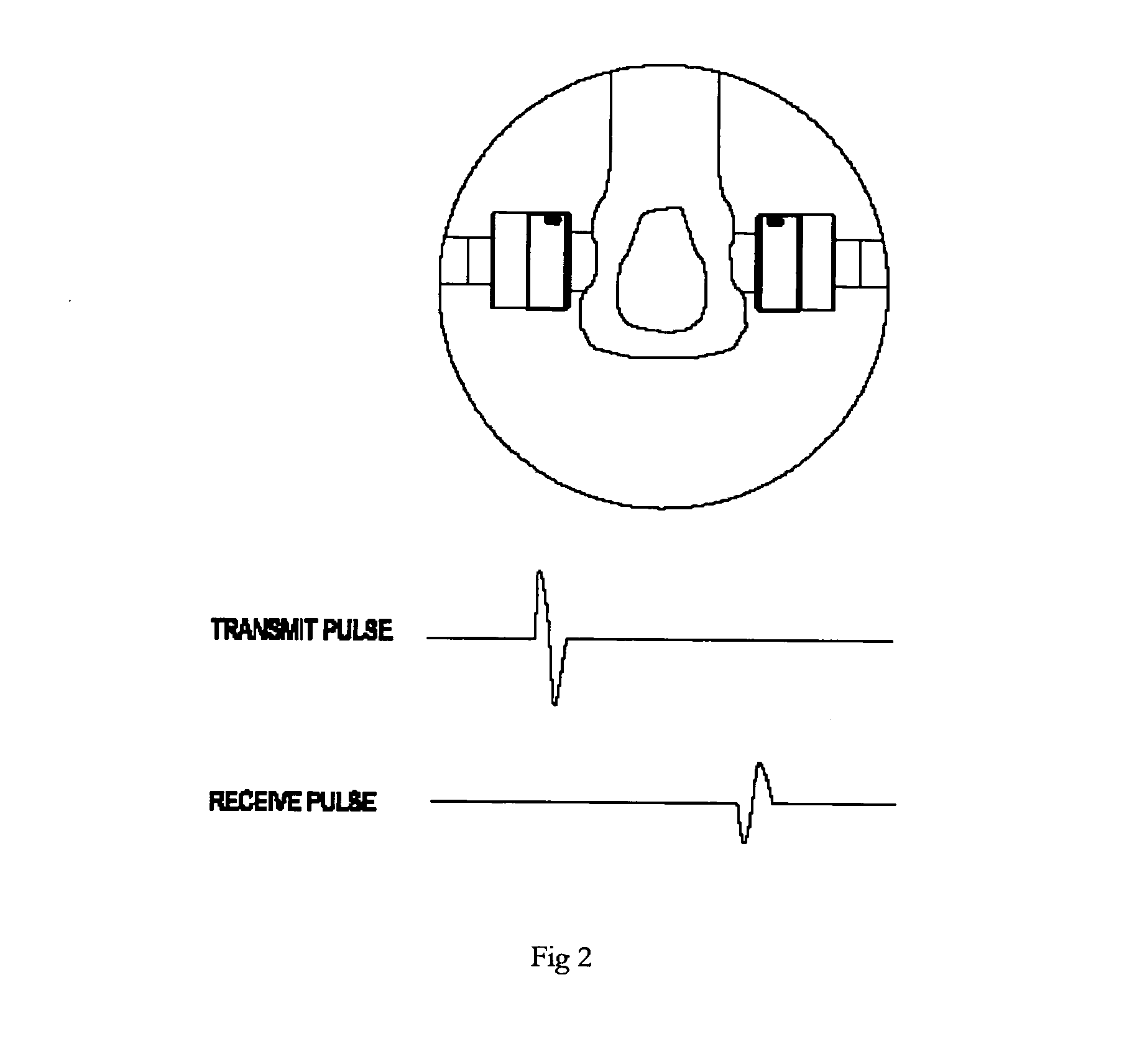
InactiveUS20070078341A1AccuracySensitivityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringVolumetric Mass DensityMineral density
The present invention provides a system for improving the accuracy of the measurement of the osteoporosis condition of the human body parts especially bones using more than three parameters, viz., the broadband ultrasonic attenuation (BUA) quantity, the velocity of ultrasound (SOS) in the bone, the broadband ultrasonic back scattering (BUB) intensity, and the Width of received maximum (WORM) values are calculated from received ultrasound signals. The accuracy of each measured diagnostic parameter is improved by measuring the tissue thickness and the squish amount in the coupling pad instead of assuming constant thickness for the tissue. The several operating modes of the device are controlled and the frequency and the timing of the emitted ultrasounds signals are adjusted by using a field programmable gate array. The error generated in the measurement of the bone mineral density due to the variation in the anatomy and the size of the foot, is removed by using a removable footpad. The present invention provides a mechanism to replace the gel pads easily. The generation of cross infection is prevented by using the disposable and replaceable coupling pads.
Owner:LARSEN & TOUBRO
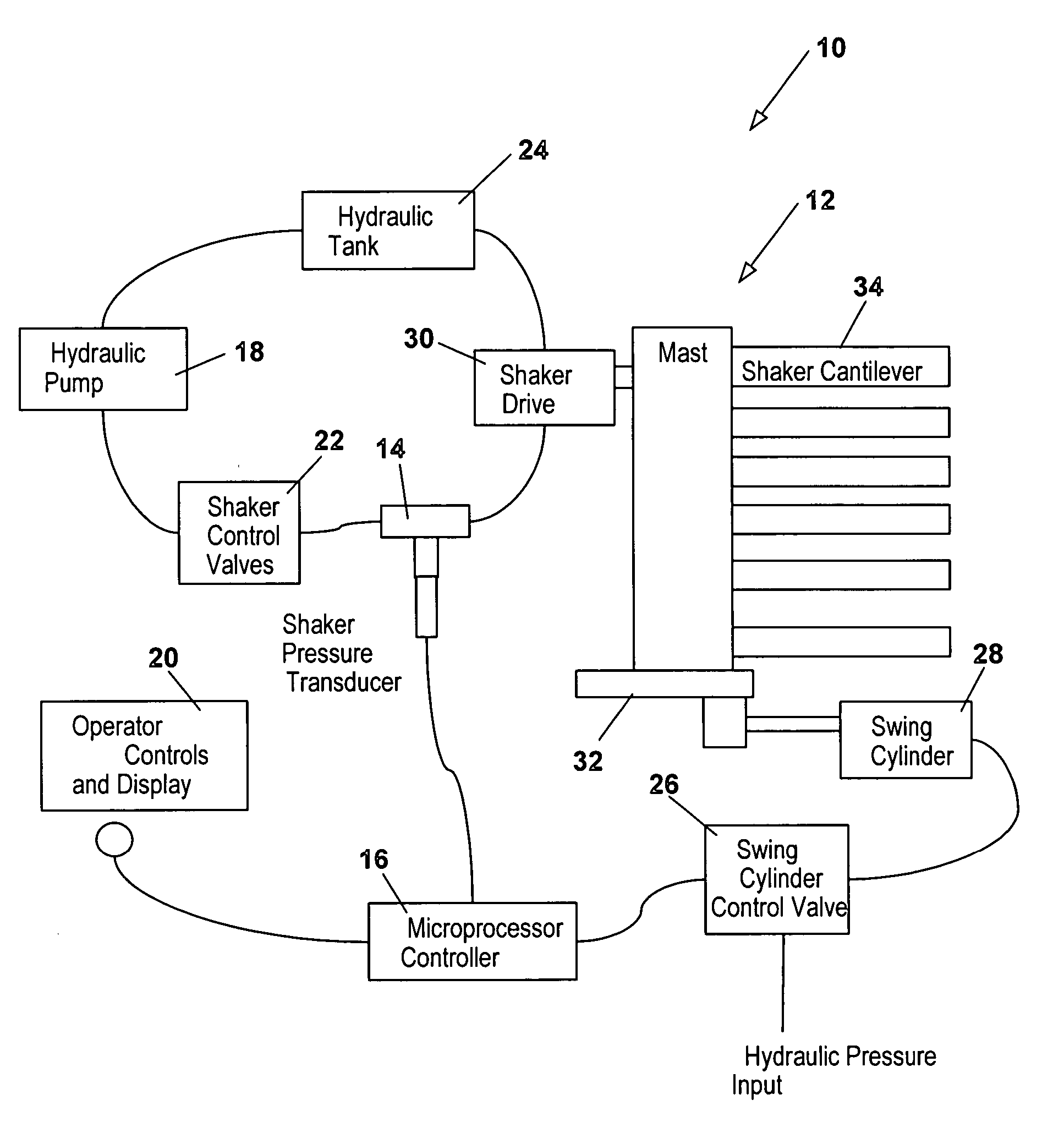
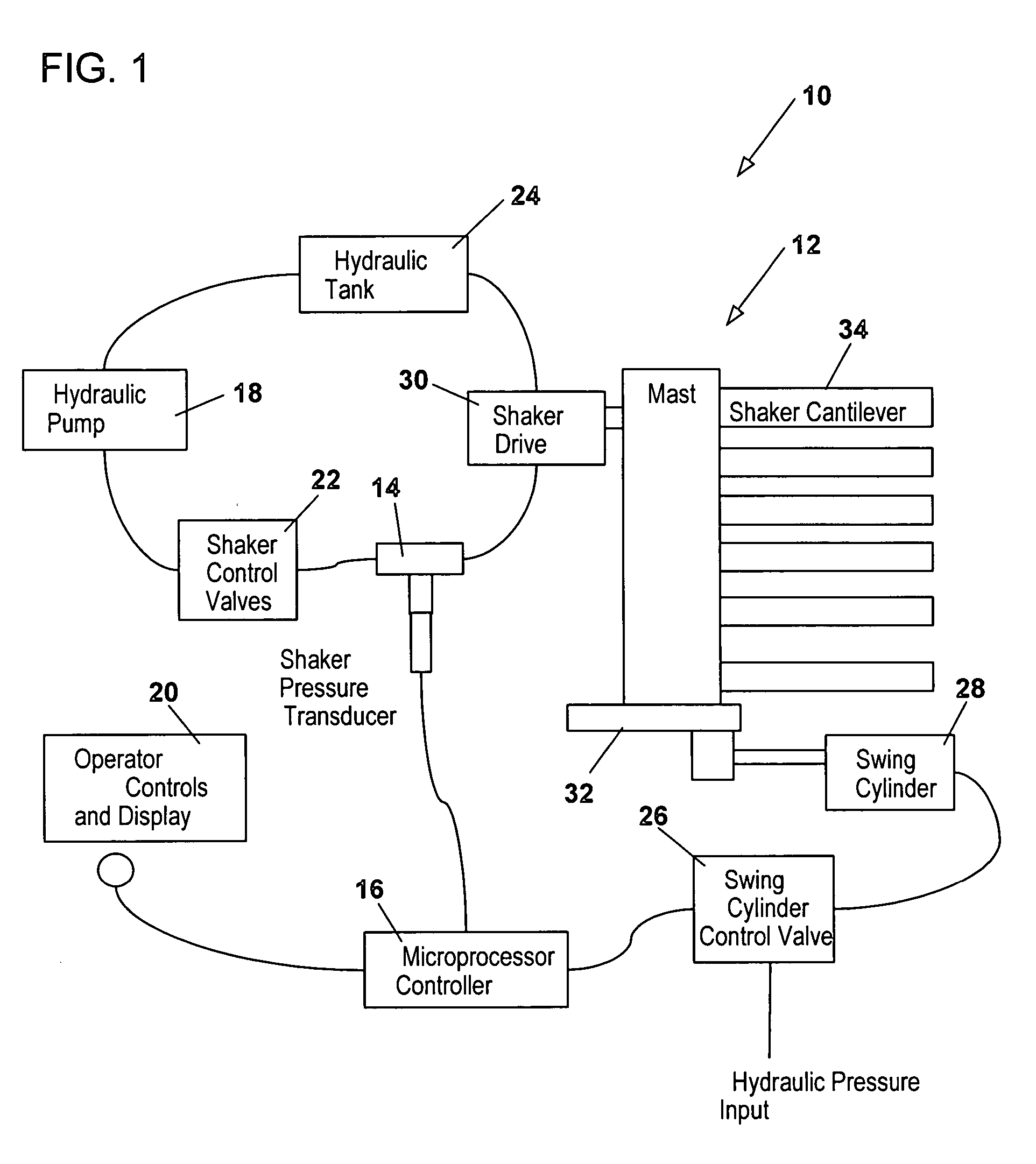
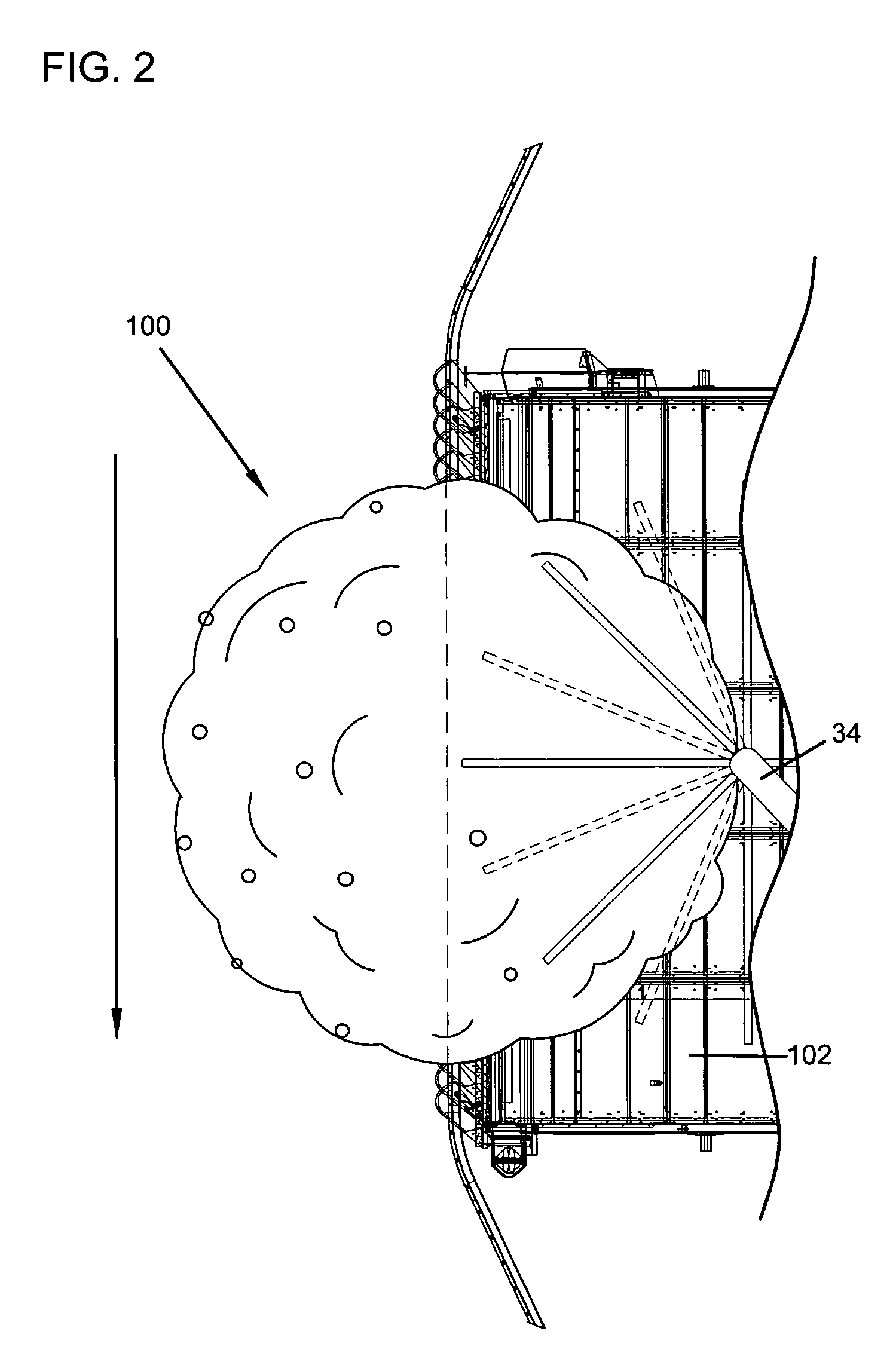
Tree follower
The present invention is directed to a tree follower device. The tree follower device includes an engagement assembly that penetrates into and shakes the branches of fruit trees to dislodge the fruit. A pressure transducer in communication with a controller measures the pressure resistance from engagement with the branches and moves the tree follower device further into and out of the branches depending upon the resistance. The present invention allows for programming various upper and lower limits and for operating in different modes for different types of trees. The present invention also provides for varying the sensitivity and the speed at which the engagement devices moves into or out of the tree.
Owner:OXBO INT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com