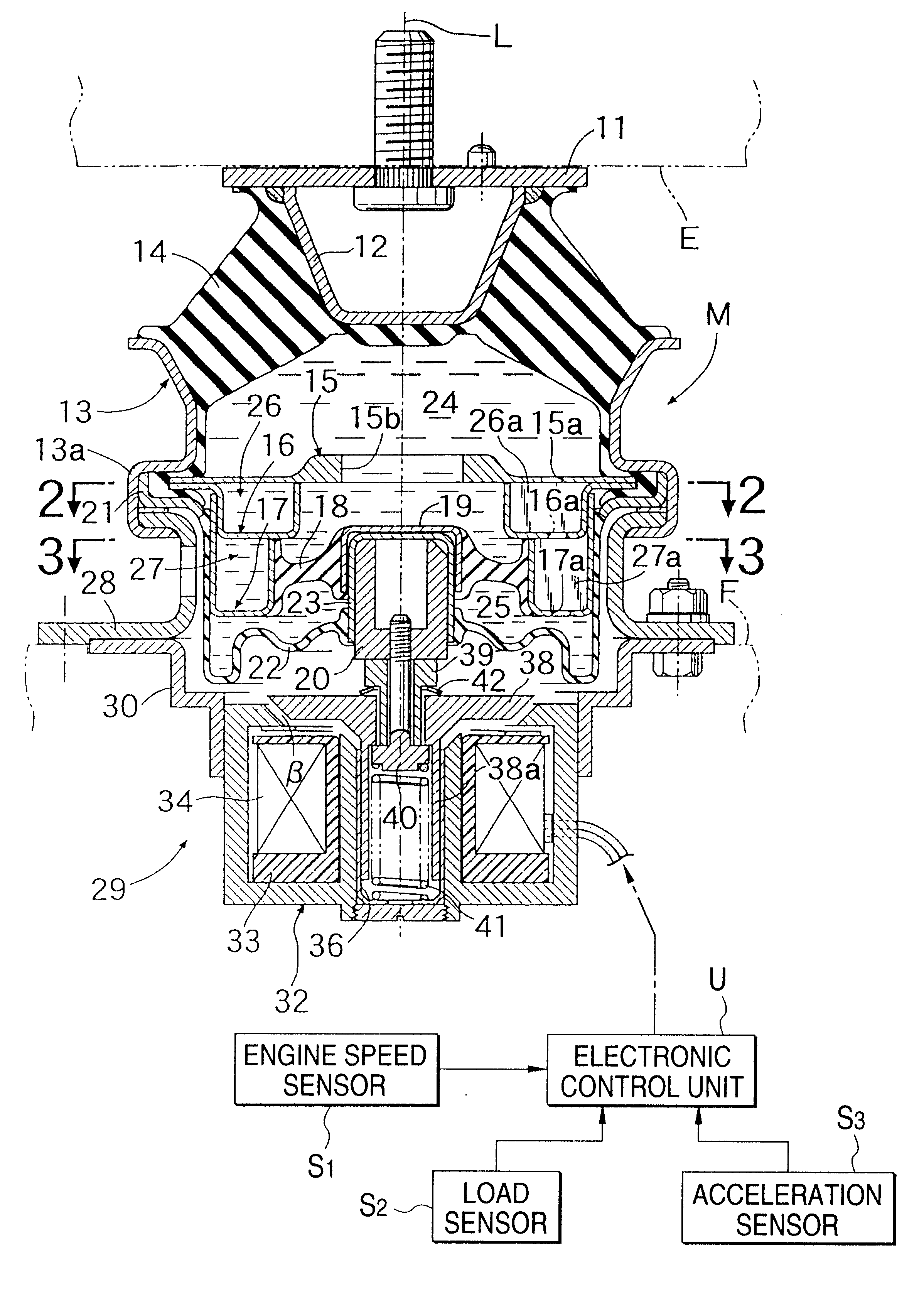
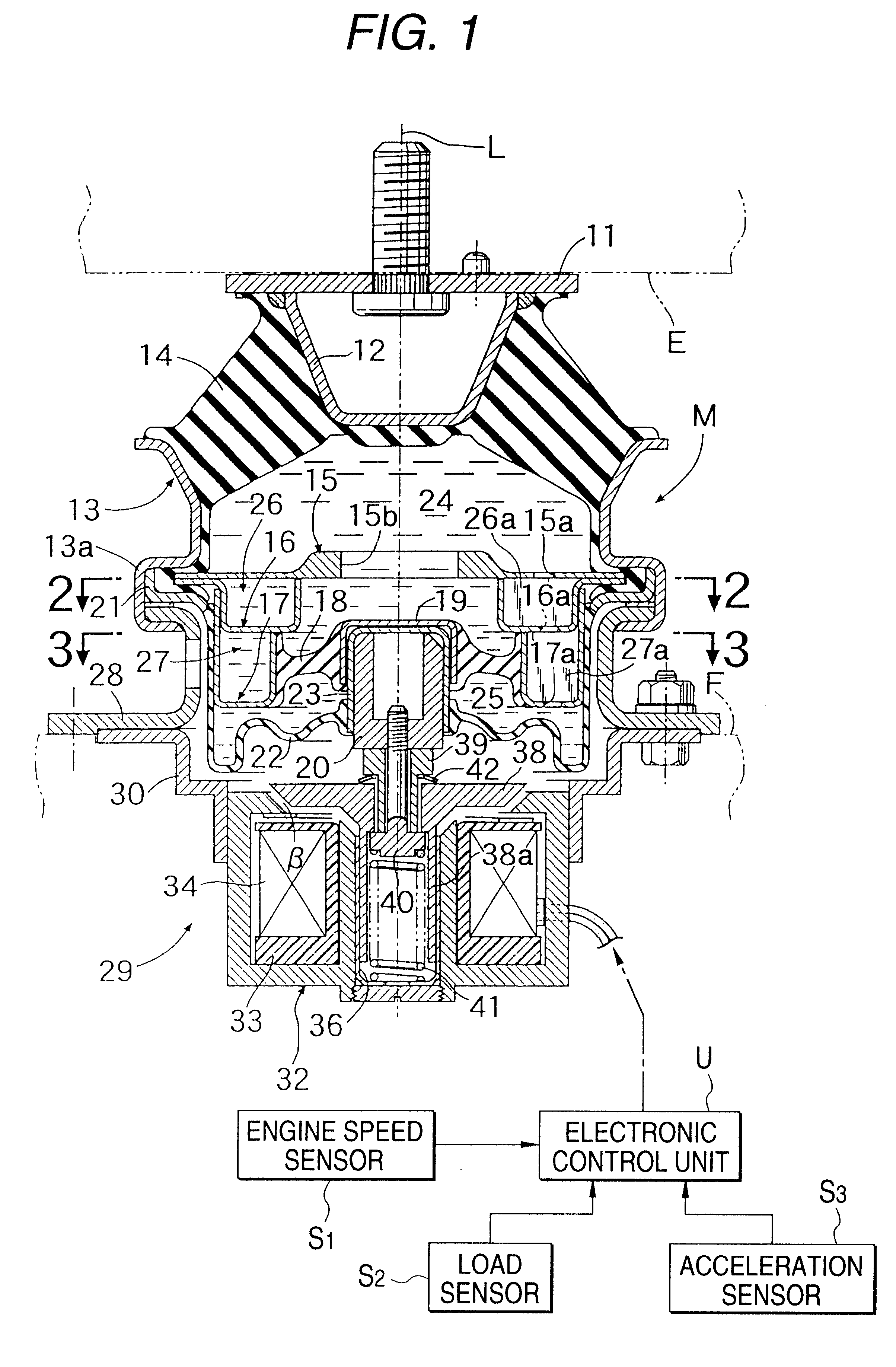
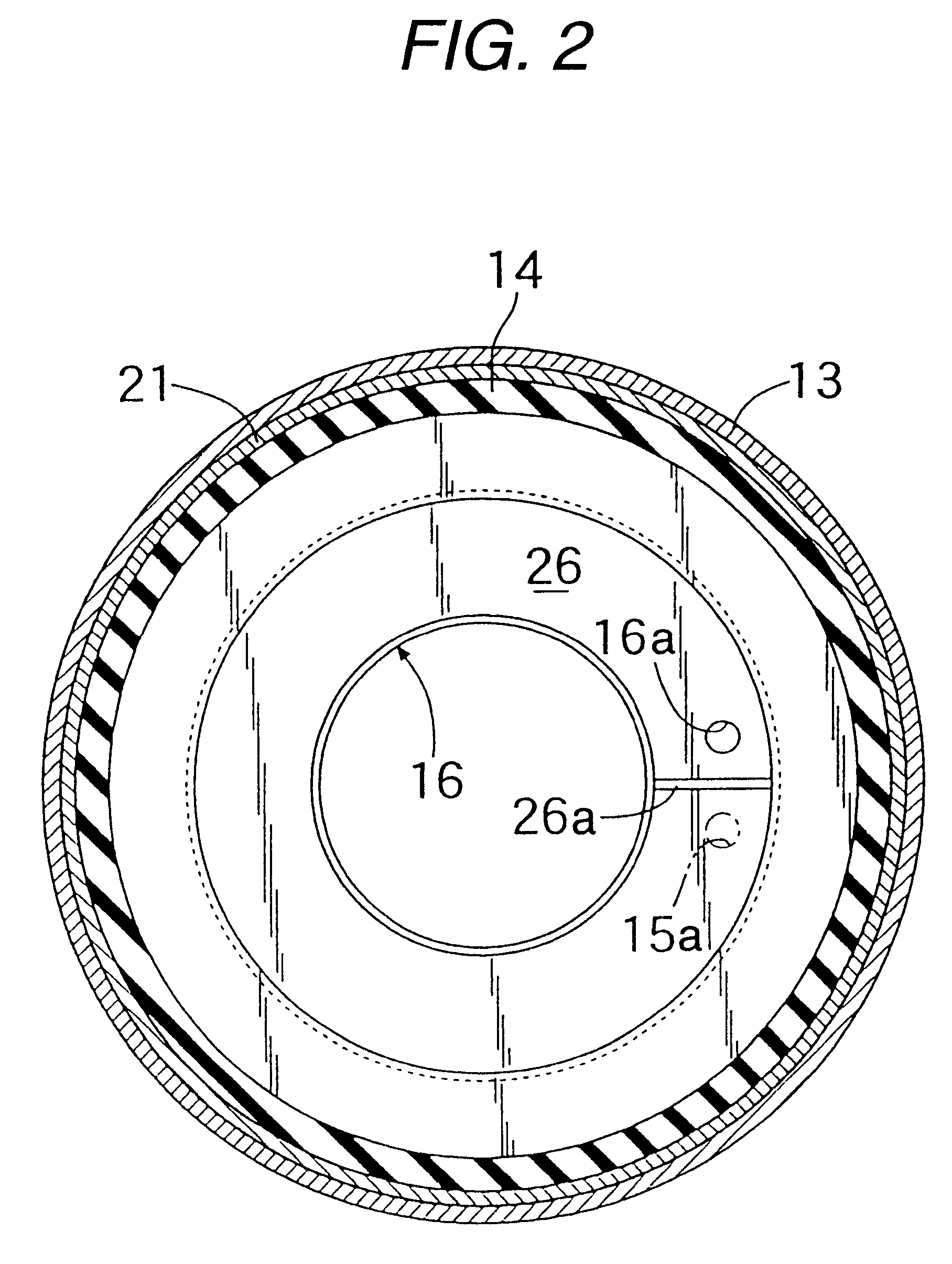
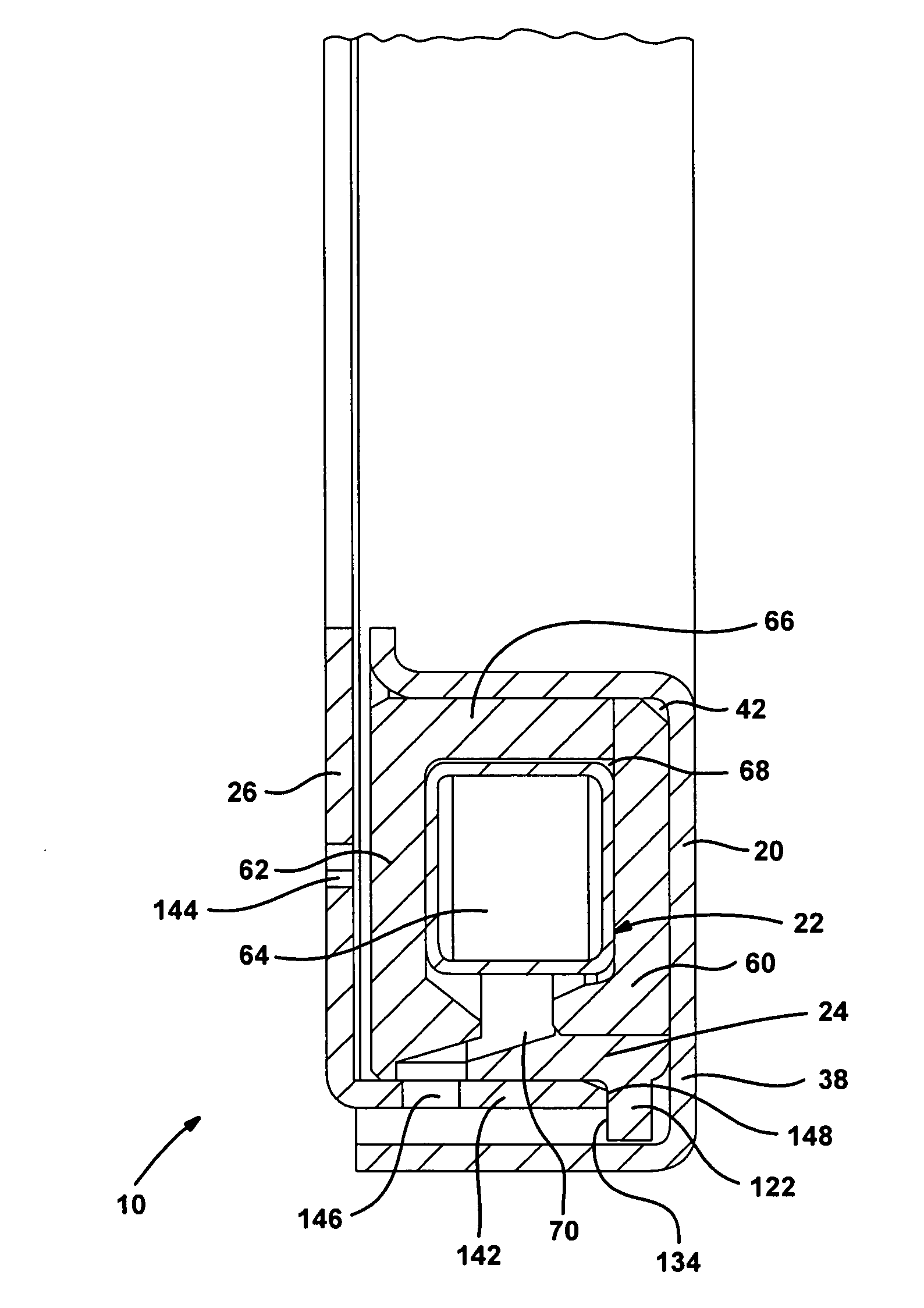
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1573 results about "Electromagnetic actuator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
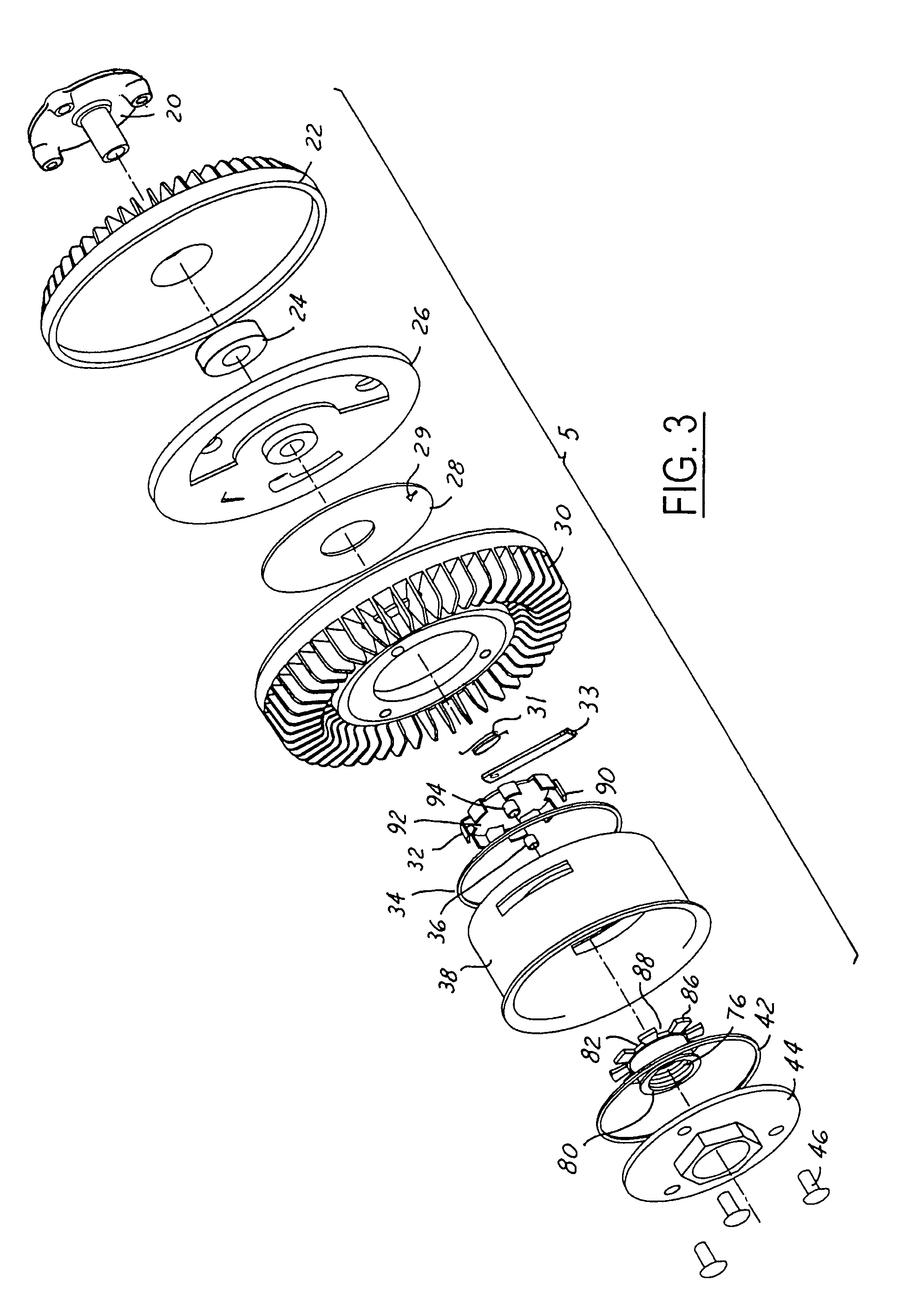
System and method for advancing, orienting, and immobilizing on internal body tissue a catheter or other therapeutic device
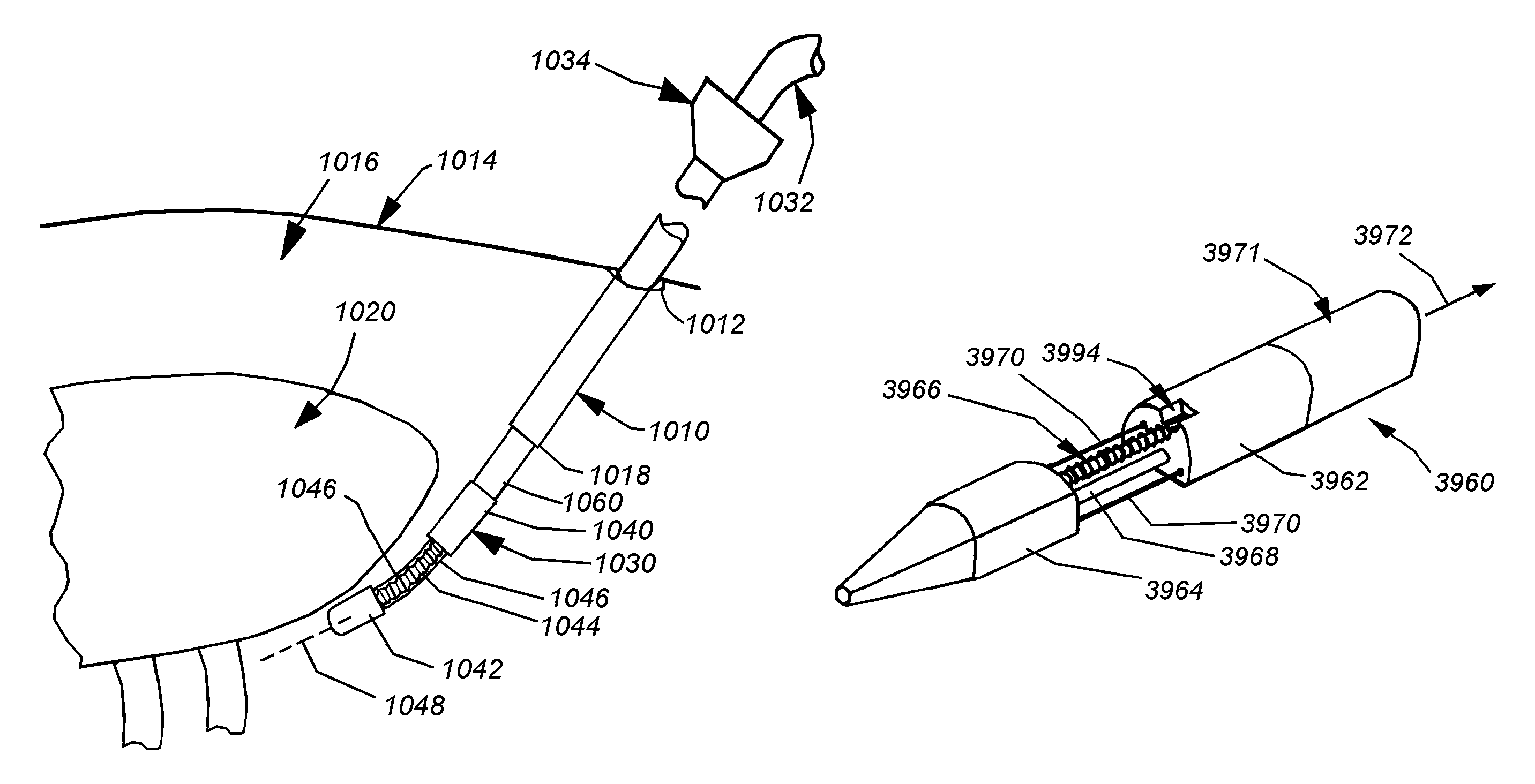
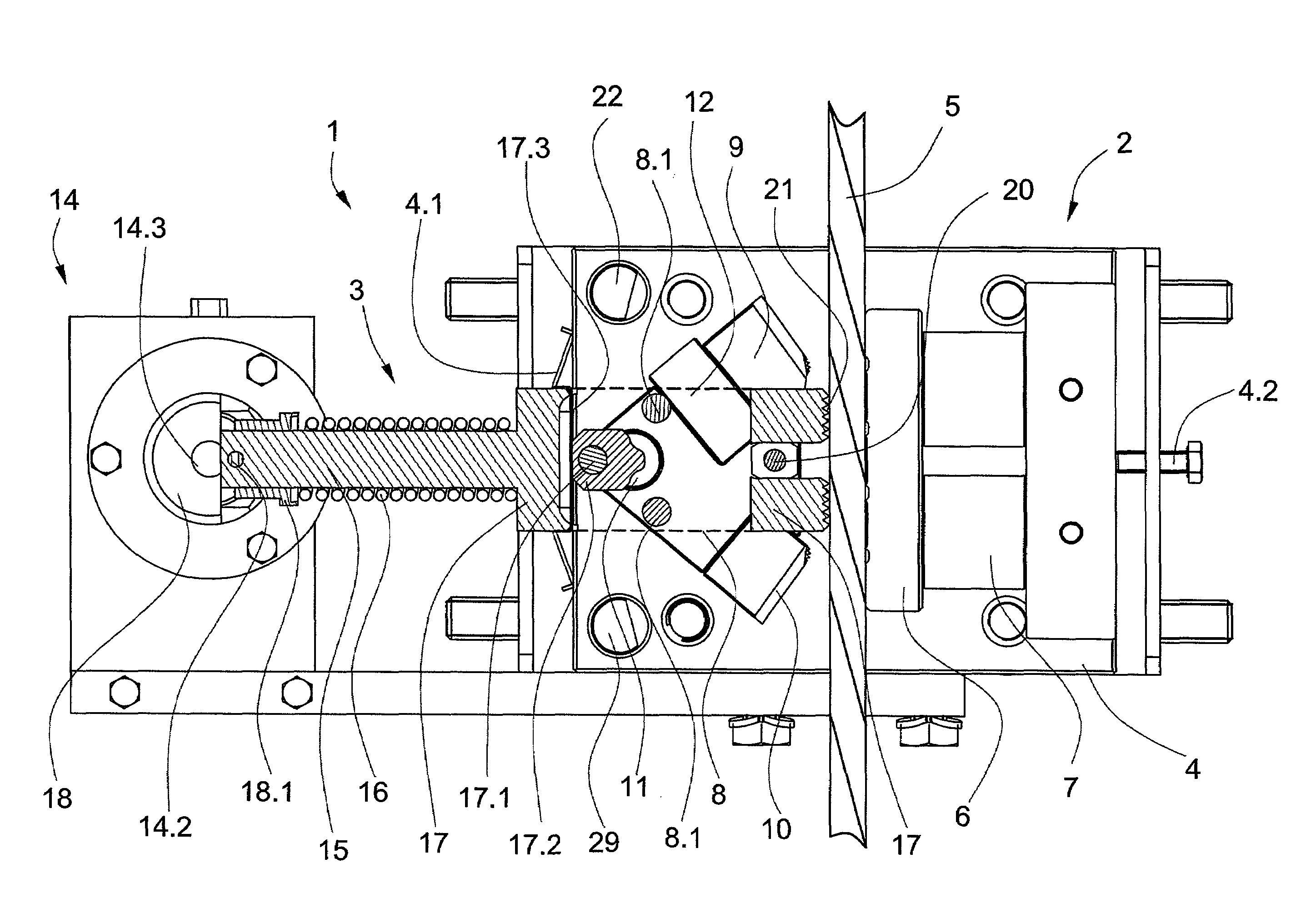
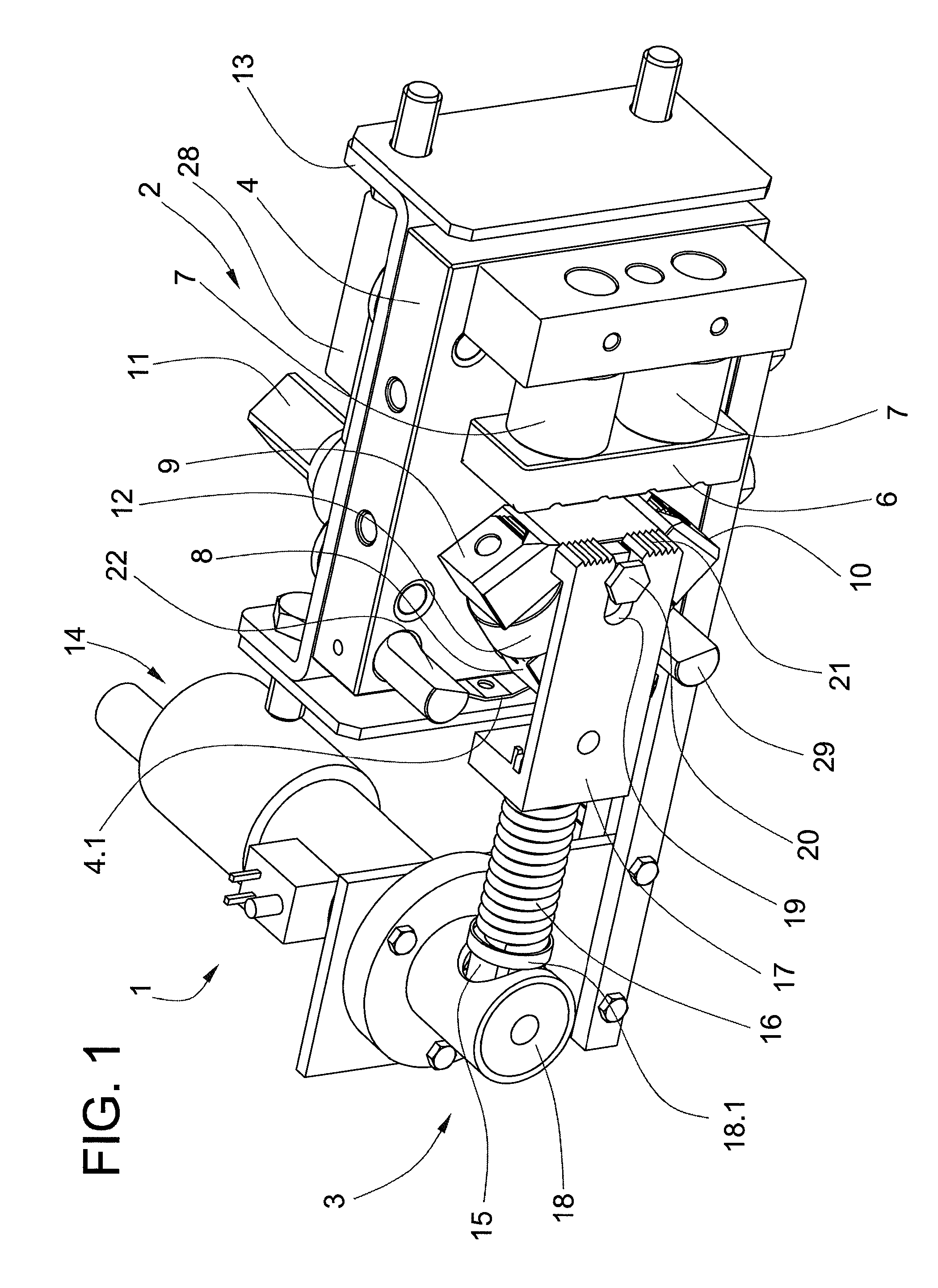
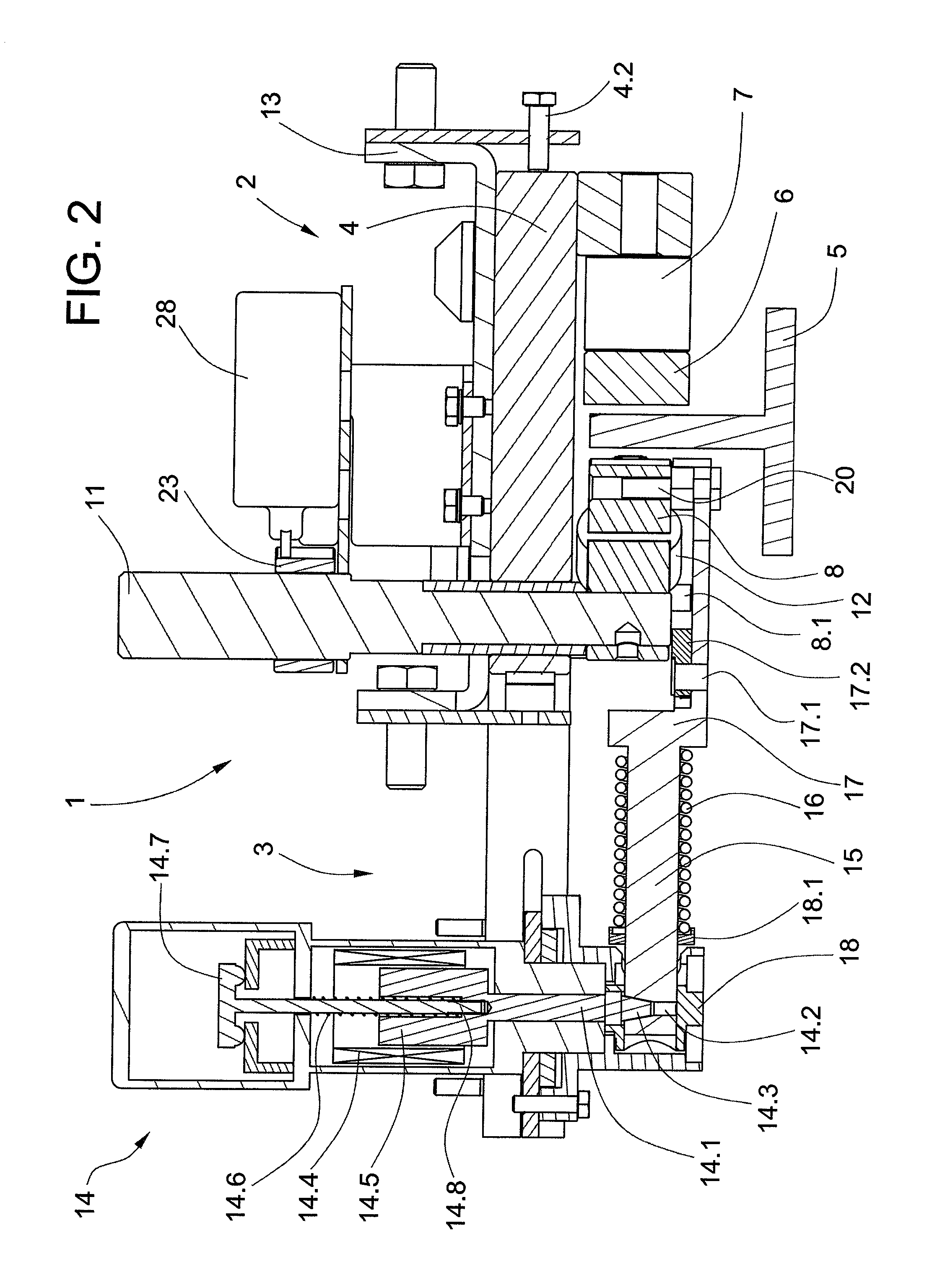
This invention provides a system and method that allows a therapeutic device, such as an atrial fibrillation microwave ablation catheter or ablation tip to be guided to a remote location within a body cavity and then accurately immobilized on the tissue, including that of a moving organ, such as the heart. In various embodiments, the system and method also enables accurate movement and steering along the tissue, while in engagement therewith. Such movement and engagement entails the use of vacuum or microneedle structures on at least two interconnected and articulated immobilizers that selectively engage to and release from the tissue to allow a crawling or traversing walking across the organ as the therapeutic catheter / tool tip applies treatment (AGE devices). In further embodiments that lack a movement capability (AID devices), the immobilizers allow a predetermined position for the introduced device to be maintained against the tissue while a treatment is applied to the location adjacent thereto. In the exemplary AID devices, variety of steering mechanisms and mechanisms for exposing and anchoring a catheter against the underlying tissue can be employed. In the exemplary AGE devices, a variety of articulation and steering mechanisms, including those based upon pneumatic / hydraulic bellows, lead screws and electromagnetic actuators can be employed.
Owner:ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY FRONTIERS SPA
Controlled needle-free transport
InactiveUS20060258986A1Easy to controlJet injection syringesAutomatic syringesNeedle freeBiological body
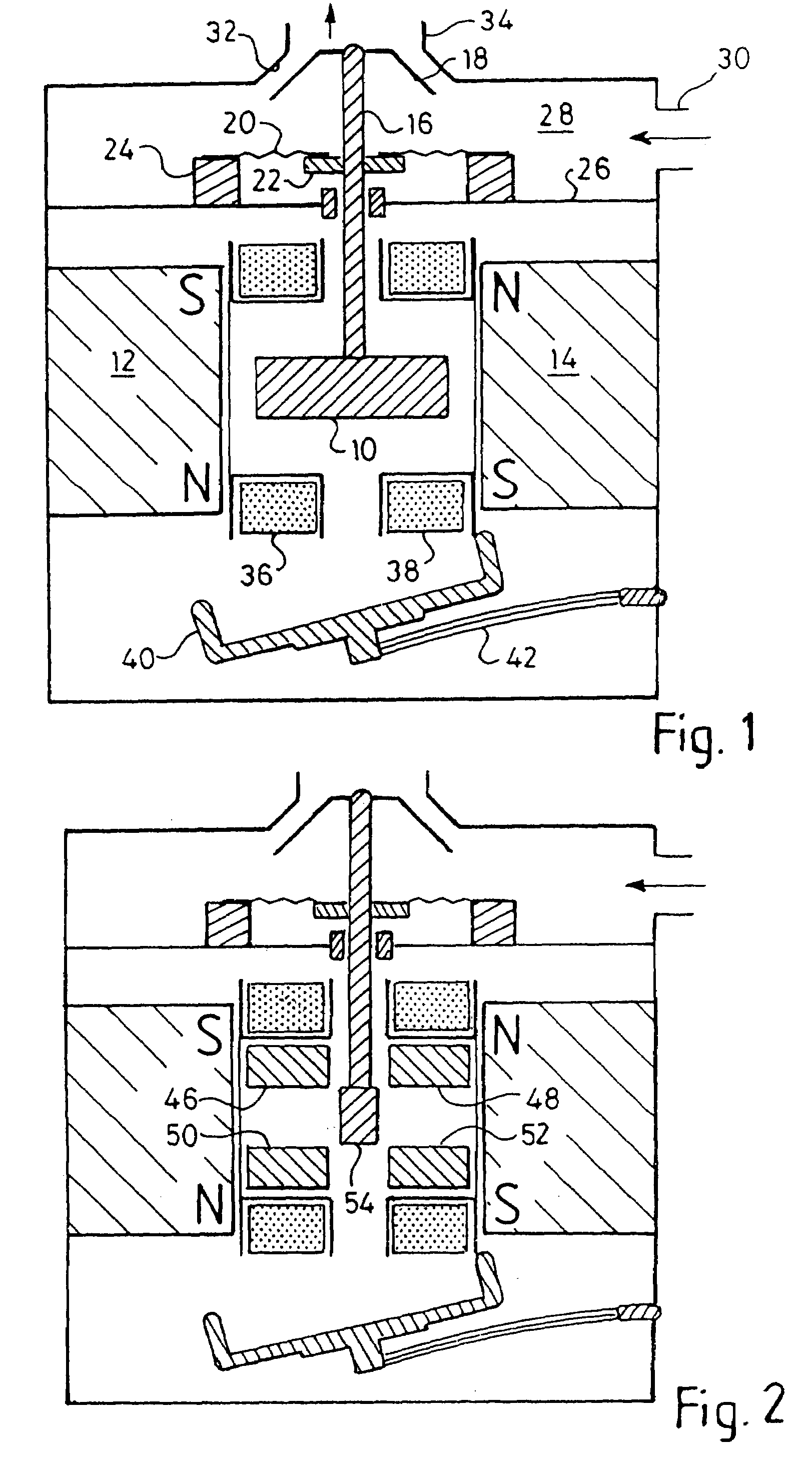
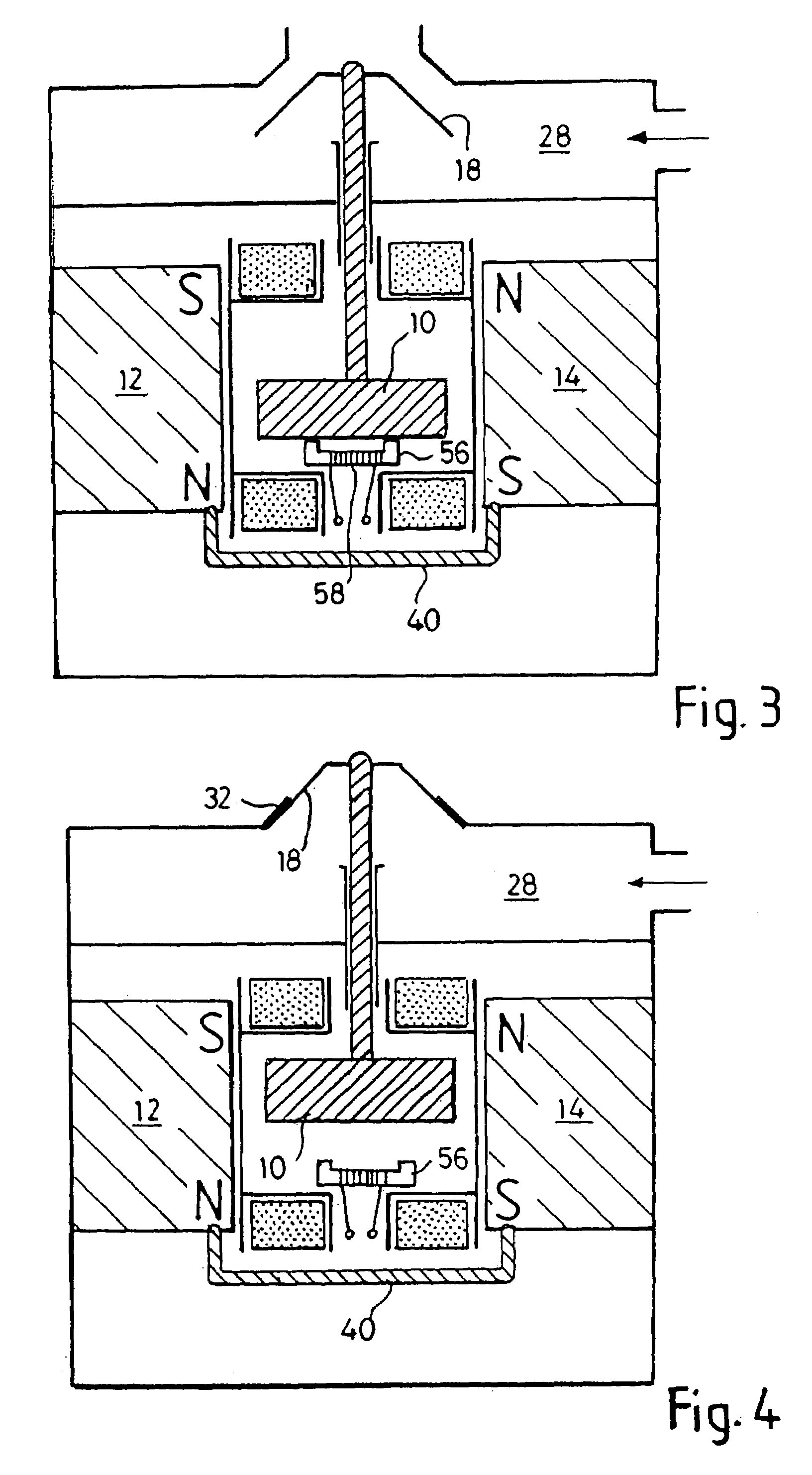
A needle-free transdermal transport device for transferring a substance across a surface of a biological body includes a reservoir for storing the substance, a nozzle in fluid communication with the reservoir and a controllable electromagnetic actuator in communication with the reservoir. The actuator, referred to as a Lorentz force actuator, includes a stationary magnet assembly and a moving coil assembly. The coil assembly moves a piston having an end portion positioned within the reservoir. The actuator receives an electrical input and generates in response a corresponding force acting on the piston and causing a needle-free transfer of the substance between the reservoir and the biological body. The magnitude, direction and duration of the force are dynamically controlled (e.g., servo-controlled) by the electrical input and can be altered during the course of an actuation cycle. Beneficially, the actuator can be moved in different directions according to the electrical input.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Single substrate electromagnetic actuator
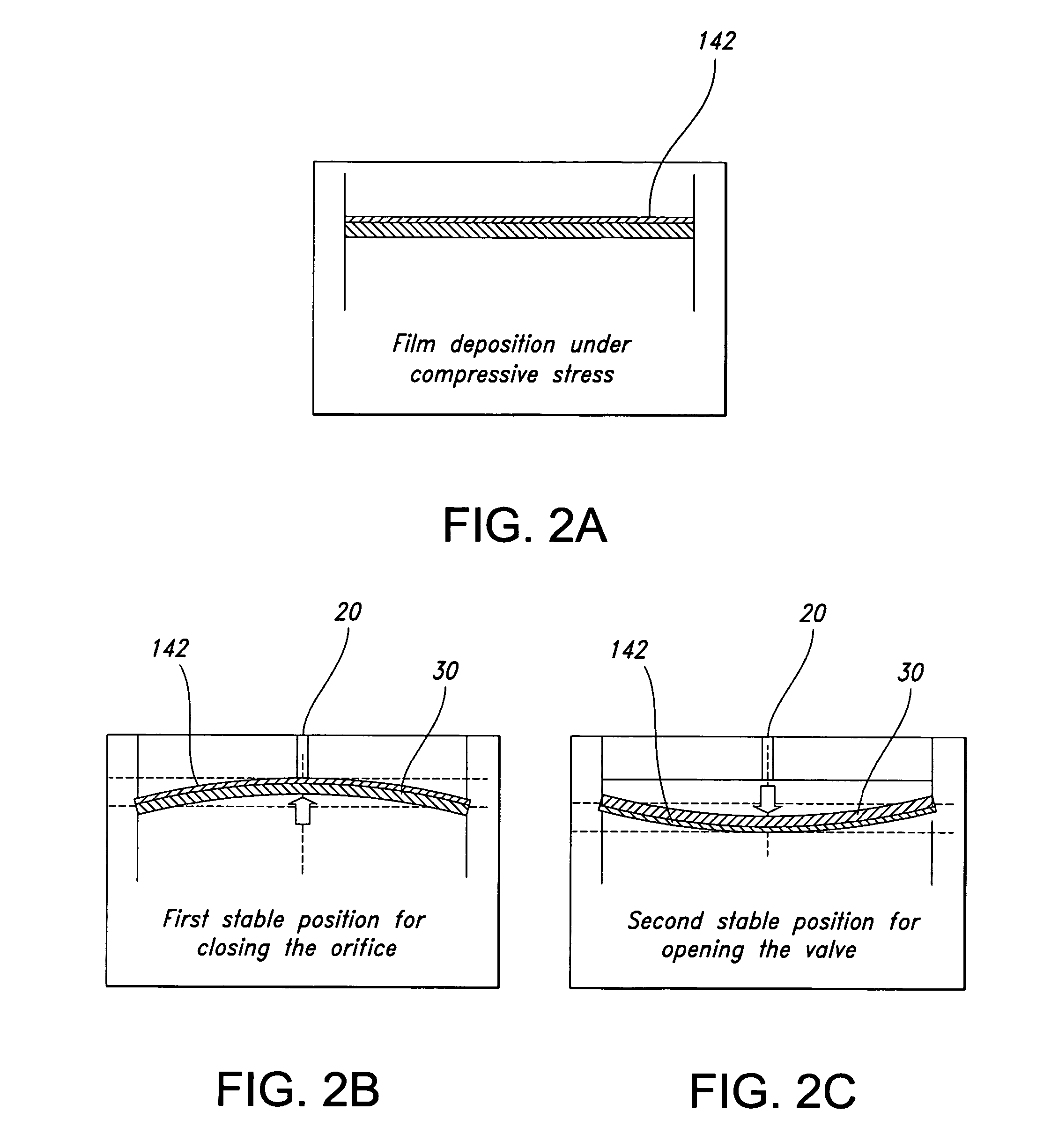
InactiveUS20050116798A1Improve dynamic operation of valveLower average currentValve arrangementsAdditive manufacturing apparatusManufacturing technologyEngineering
A microvalve which utilizes a low temperature (<300° C.) fabrication process on a single substrate. The valve uses buckling and an electromagnetic actuator to provide a relatively large closing force and lower power consumption. A buckling technique of the membrane is used to provide two stable positions for the membrane, and to reduce the power consumption and the overall size of the microvalve. The use of a permanent magnet is an alternative to the buckled membrane, or it can be used in combination with the buckled membrane, or two sets of micro-coils can be used in order to open and close the valve, providing the capability for the valve to operate under normally opened or normally closed conditions. Magnetic analysis using ANSYS 5.7 shows that the addition of Orthonol between the coils increases the electromagnetic force by more than 1.5 times. At a flow rate of 1 mL / m, the pressure drop is <100 Pa. The maximum pressure tested was 57 kPa and the time to open or close the valve in air is under 100 ms. This results in an estimated power consumption of 0.1 mW.
Owner:AIR FORCE THE US SEC THE +1
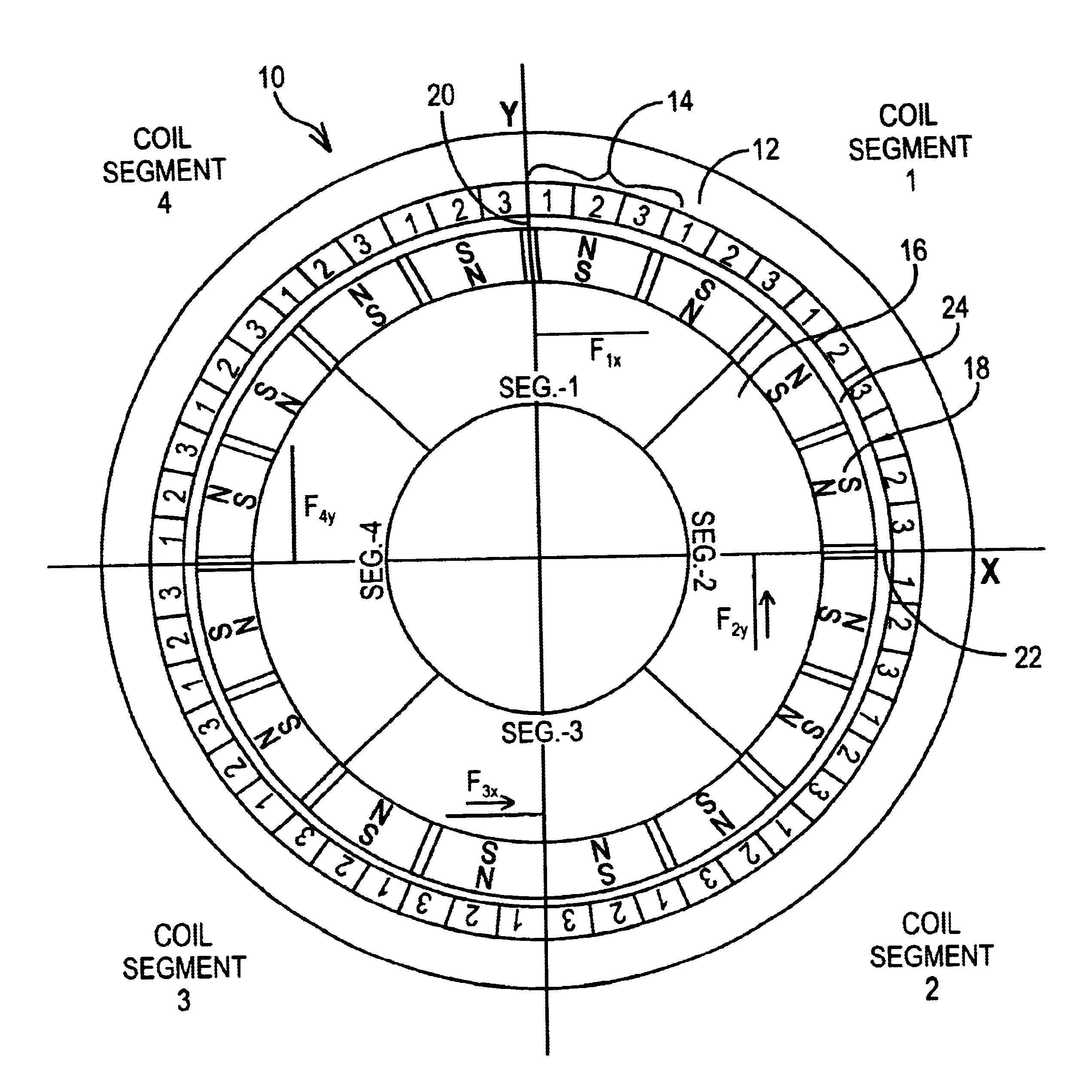
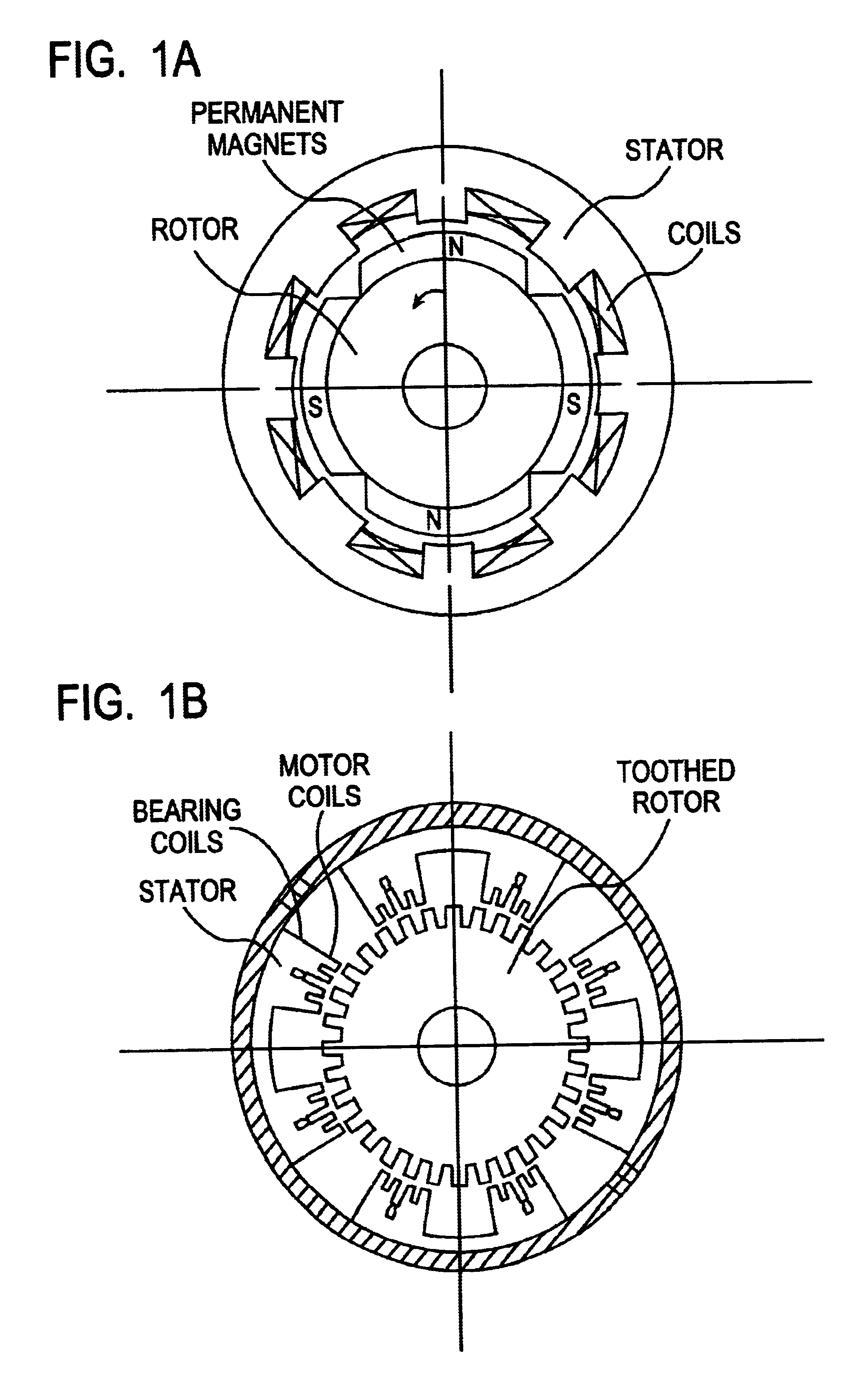
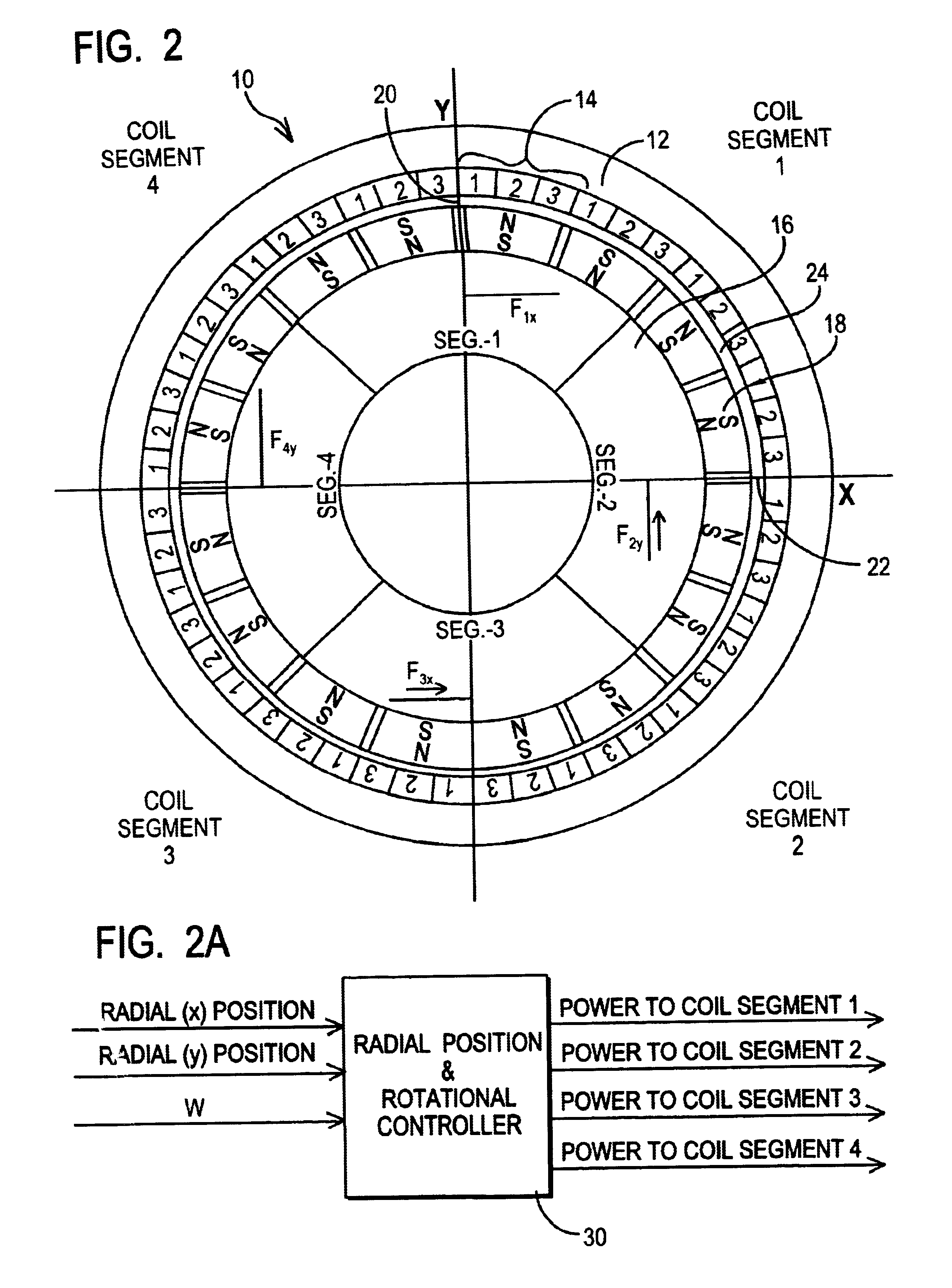
Integrated magnetic bearing
The present invention provides a rotational magnetic gimbal with an integral magnetic bearing. Brushless DC motor technology provides electromagnetic suspension, using a single electromagnetic actuator to perform both the radial bearing and rotary torque (motoring) functions. An integrated motor and magnetic bearing consistent with the invention comprises a rotor comprising a plurality of permanent magnets and a stator comprising a plurality of independently controlled coil segments magnetically coupled to the permanent magnets. Embodiments may further comprise first and second radial position sensors, the first radial position sensor disposed in or adjacent to a clearance gap between the rotor and the stator for sensing the position of the rotor with respect to the stator along a first axis, and a second radial position sensor disposed in or adjacent to the clearance gap between the rotor and the stator for sensing the position of the rotor with respect to the stator along a second axis. In method form, a method for providing integral electromagnetic motor and bearing functions comprises sensing a first radial position of a rotor, the rotor comprising a plurality of permanent magnets, with respect to a stator along a first axis, the stator comprising a plurality of independently controlled coil segments magnetically coupled to the permanent magnets; and sensing a second radial position of the rotor with respect to the stator along a second axis; and delivering current to at least one coil segment, the amount of current based on at least one sensed position.
Owner:AIREX CORP
Controlled needle-free transport
ActiveUS20070191758A1Magnetic field is facilitatedJet injection syringesSurgeryNeedle freeElectricity
A needle-free transdermal transport device for transferring a substance across a surface of a biological body includes a reservoir for storing the substance, a nozzle in fluid communication with the reservoir and a controllable electromagnetic actuator in communication with the reservoir. The actuator, referred to as a Lorentz force actuator, includes a stationary magnet assembly and a moving coil assembly. The coil assembly moves a piston having an end portion positioned within the reservoir. The actuator receives an electrical input and generates in response a corresponding force acting on the piston and causing a needle-free transfer of the substance between the reservoir and the biological body. The magnitude, direction and duration of the force are dynamically controlled (e.g., servo-controlled) by the electrical input and can be altered during the course of an actuation cycle. Beneficially, the actuator can be moved in different directions according to the electrical input.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
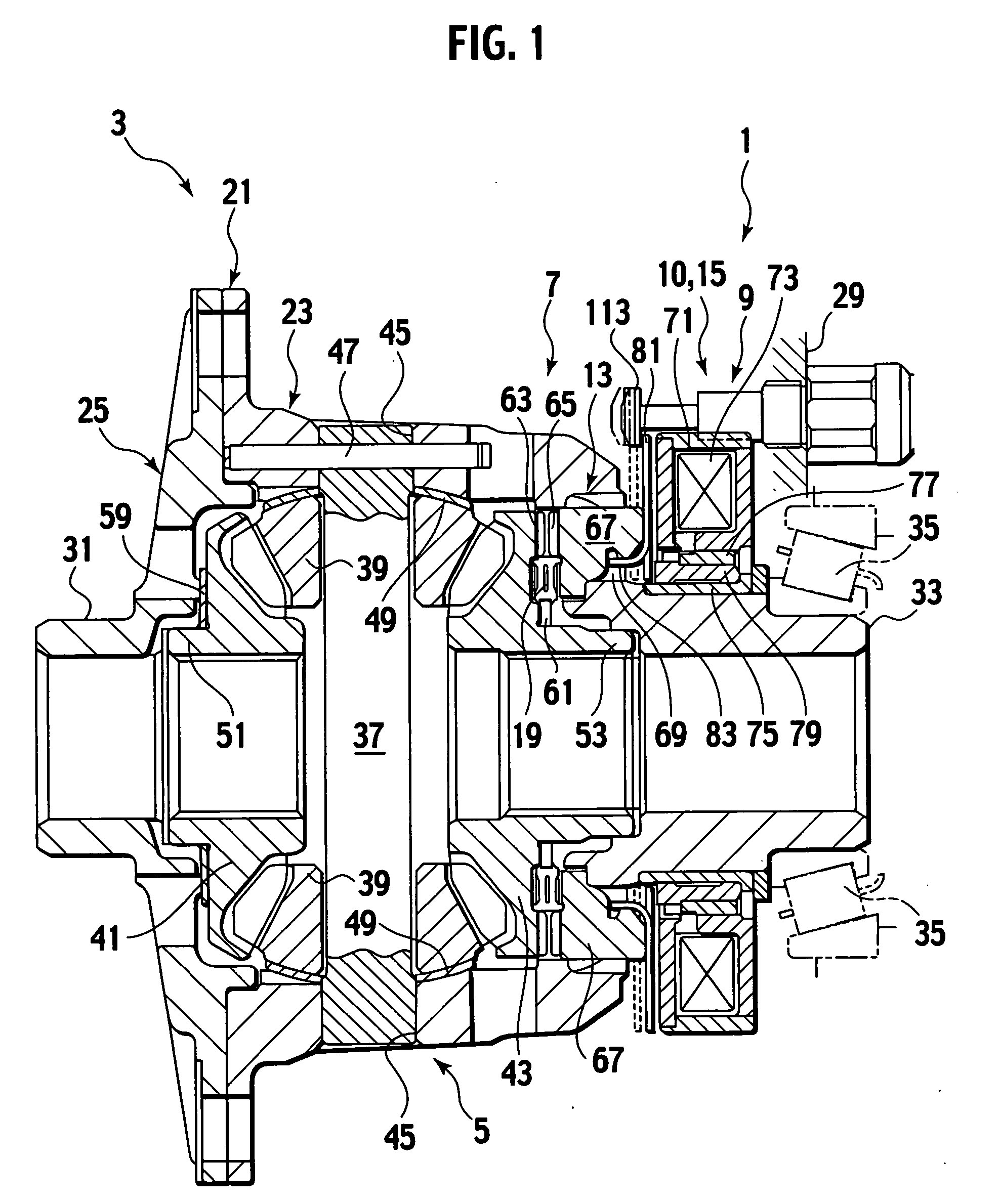
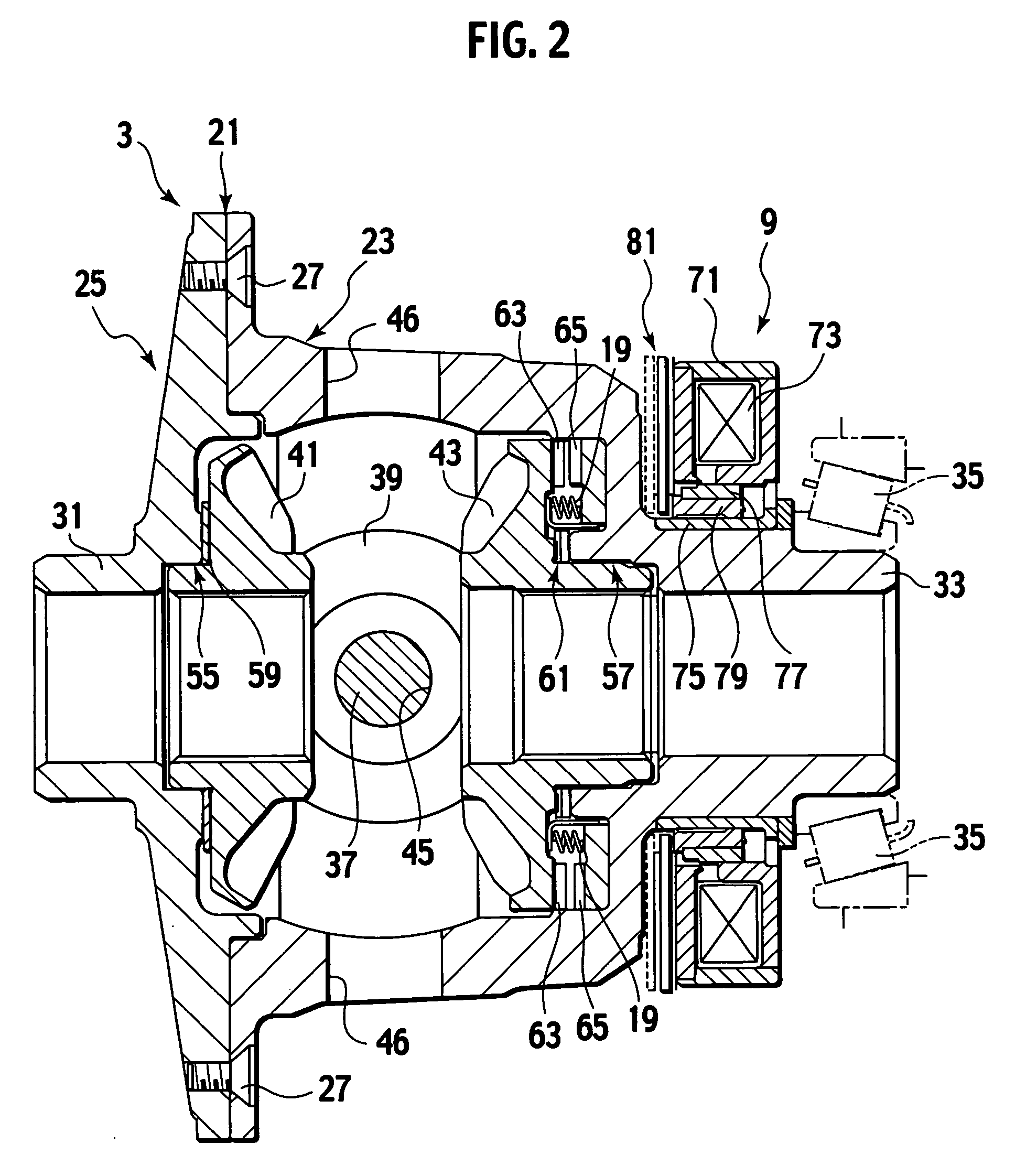
Electromagnetic actuator, and electromagnetic clutch and differential using the same
ActiveUS20050279607A1Inhibit heat generationSuppress power consumptionMechanical actuated clutchesFluid actuated clutchesElectromagnetic clutchEngineering
The electromagnetic actuator includes an electromagnetic coil configured to provide actuation force in accordance with a solenoid current to be supplied, to a clutch and configured to actuate the clutch to control relative rotation between first and second members. The electromagnetic actuator includes a detector configured to detect the clutch actuated to produce a detection signal. The electromagnetic actuator includes a controller configured to respond to the detection signal from the detector to control the solenoid current.
Owner:TOCHIGI FUJI IND CO LTD
Electromagnetic switching device
InactiveUS20060050466A1Avoid vibrationImprove abilitiesElectric switchesElectromagnetic relay detailsMiniaturizationEngineering
In the electromagnetic switching device, it is possible to miniaturize and have low costs, have quiet operation noise, and also quickly extinguish the arc. The electromagnetic switching device has an electromagnetic actuator with a movable iron core, a pair of fixed terminals that respectively have a fixed contact point, a movable contact that has movable contact points on the right and left ends, a shaft, and an enclosing component that holds the movable contact points and the fixed contact points. The pair of movable contact points respectively contact with and detach from the pair of fixed contact points, and the pair of fixed contact points respectively conduct each other and are insulated again through the shaft by moving the movable iron core along the axis using the electric magnetic actuator. A quasi-hermetically sealed space, which is the extinguishing space, is formed by the enclosing component and a first yoke. A potting compound is charged, into the space between a body and the quasi hermitically sealed space.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
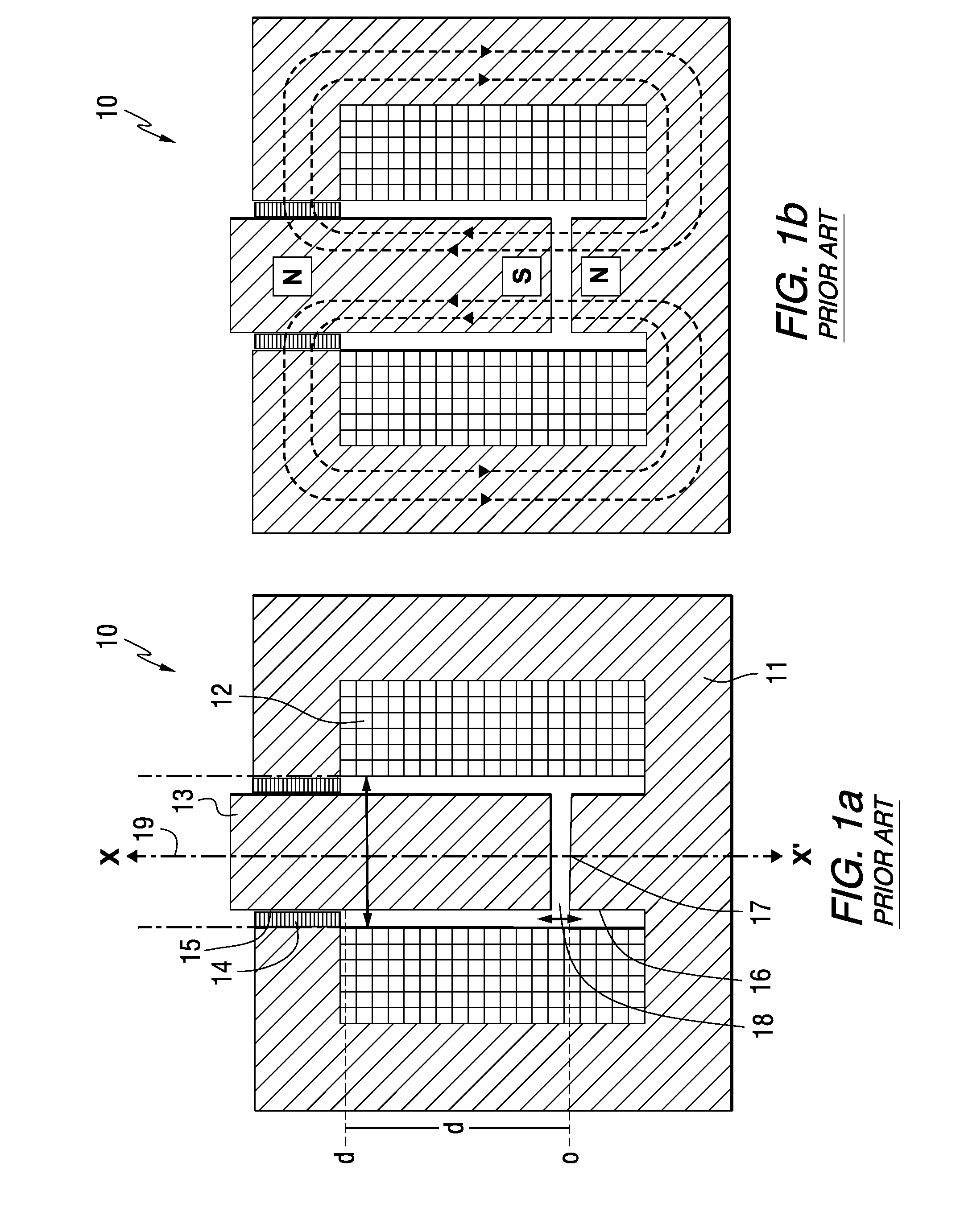
Electromagnetic actuator and integrated actuator and fluid flow control valve
InactiveUS20040025949A1Rapid responseLow driving energyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPipeline systemsMagnetic polesEngineering
A magnetic device is formed from a permanent magnet generating magnetic flux, an armature which can occupy two positions between four poles and an electromagnet winding to which current can be supplied to produce a magnetic flux in one direction or the other, the flux from the winding causing the armature to move into one position and continue to remain in that position after the current flow ceases. The device can be incorporated into a fluid valve to act as a drive for opening and closing the valve. It may also serve as the drive for opening and closing electrical contacts. Monostable operation can be achieved by locating a magnetic flux shunt at one end of the armature travel. A holding solenoid may be incorporated. A pivoting armature in a fluid tight chamber comprises a fluid flow controlling device. It can adopt either of two home positions in contact with two magnetic poles and is retained by magnetic flux from a permanent magnet. Fluid can flow into and out of the chamber via a first passage. A second passage extends through one of the poles to an opening in the pole face which is covered by the armature when the latter occupies one home position but is uncovered when the armature occupies its other home position. A third fluid passage extends through and leads to a second opening in another pole, which is covered when the armature occupies its said other home position. Passages in the poles house energy storing springs each of which is compressed as the armature approaches the pole. A push rod can extend through a passage in one of the poles for conveying armature movement externally of the device.
Owner:CAMCOM
Active vibration isolating support device
InactiveUS6422546B1Improve reliability and durabilityAvoid vibrationMachine framesNon-rotating vibration suppressionCoil springElectromagnetic actuator
An active vibration isolating support device for preventing the direct transmission of vibrations from an engine to a vehicle body frame includes an electromagnetic actuator for driving a movable member in a reciprocating fashion to change the capacity of a first liquid chamber. A shaft portion of an armature driven by a coil is supported by a bearing so that it moves along an axis, whereby the size of an air gap can be maintained as small as possible, thereby making it possible to miniaturize the coil. In addition, a connecting rod for connecting the movable member with the armature is supported so as to sway relative to a coil spring and a saucer spring, whereby the vibration of the movable member is prevented from being transmitted to the shaft portion of the armature.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
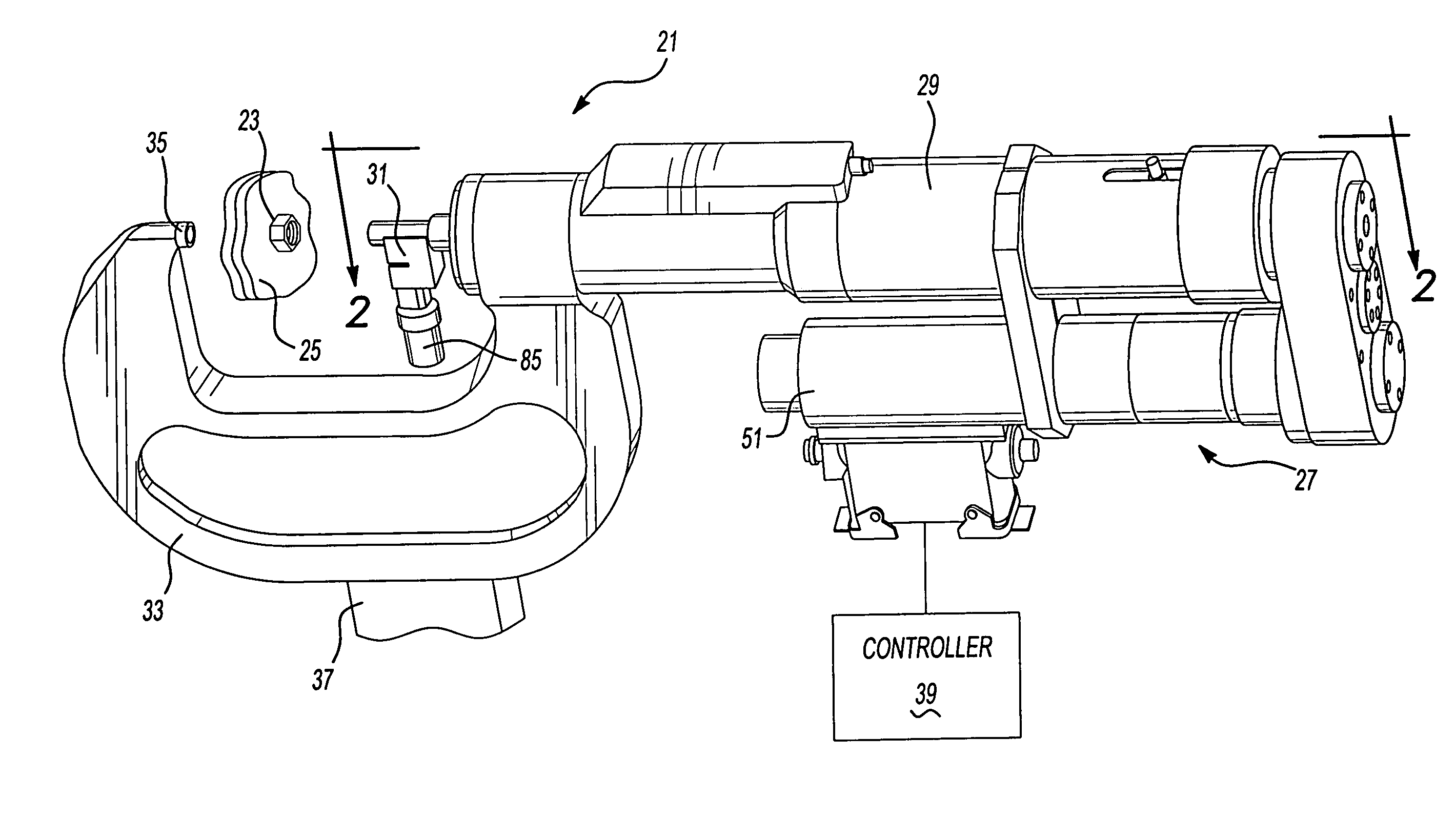
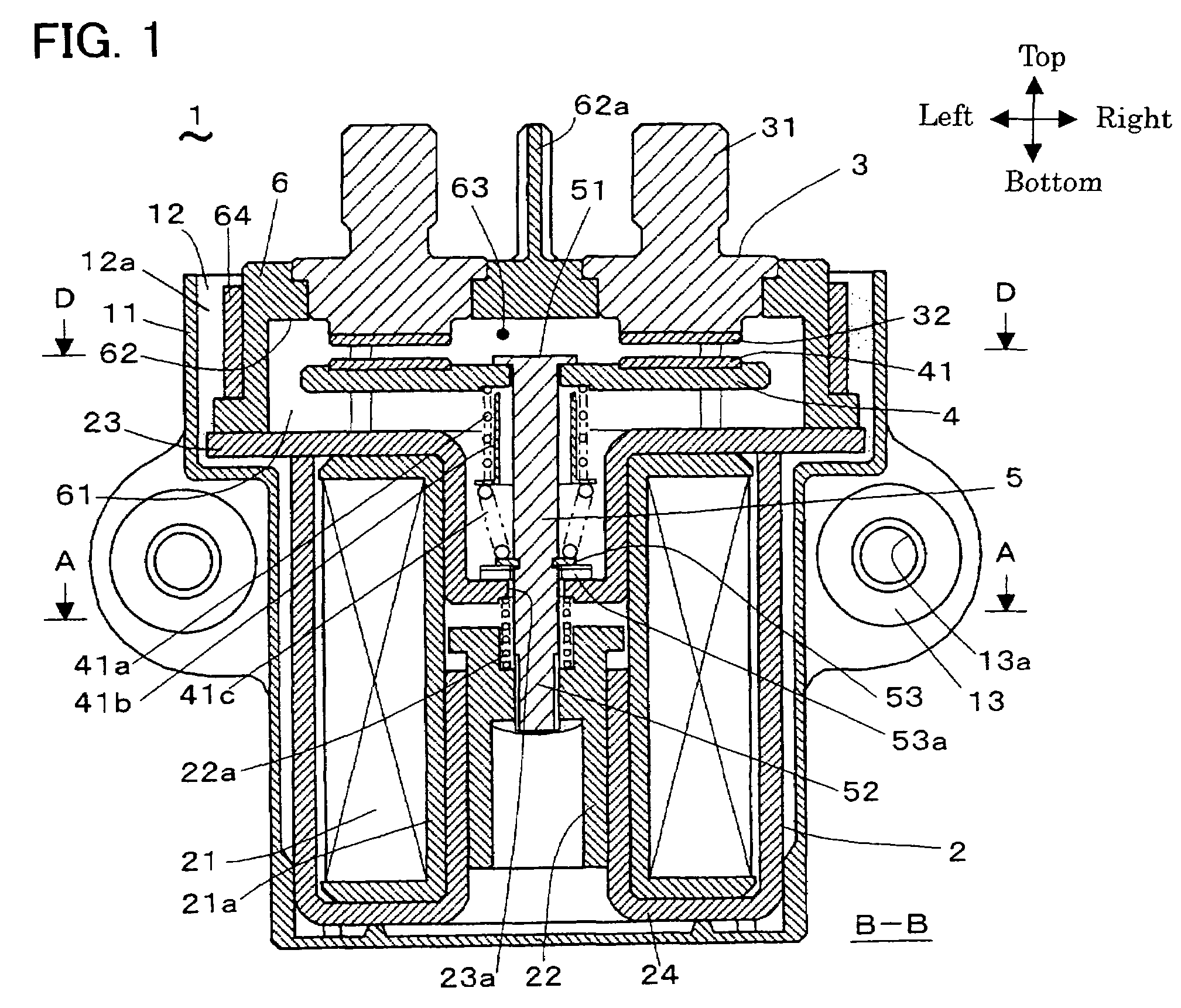
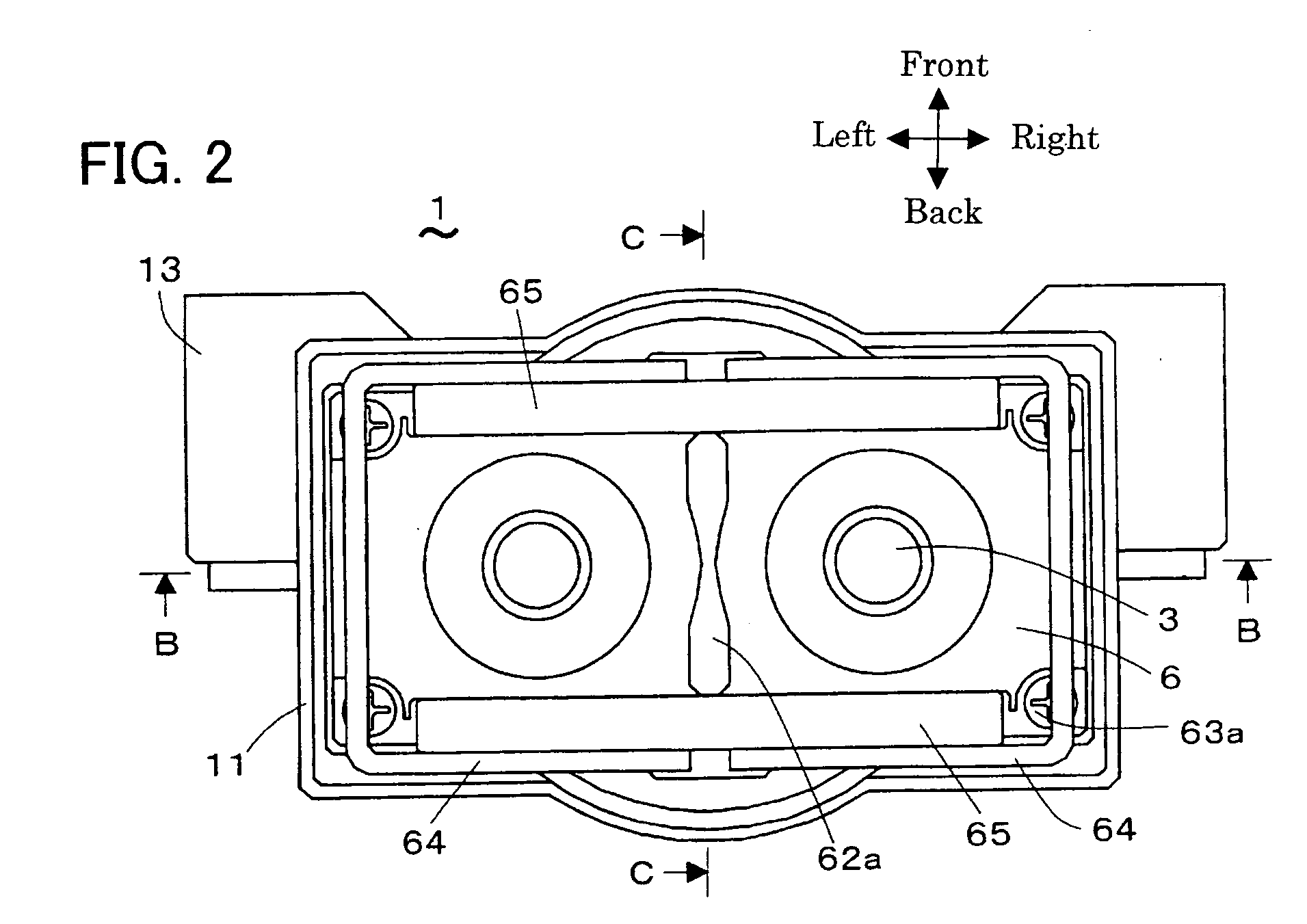
Electronically actuated apparatus using solenoid actuator with integrated sensor
An electromagnetic actuator assembly that includes an annular frame, a coil assembly, an annular armature, a plunger and a sensor. The coil assembly is coupled to the frame and includes an annular core and an annular coil. The annular armature is received in the frame and abutted against the plunger. A sensor target can be coupled to the armature or the plunger and includes a radially outwardly extending sensor target. The sensor is coupled to the frame and configured to sense a position of the sensor target. A method for operating an electromagnetic actuator is also provided.
Owner:AMERICAN AXLE & MFG
Hand-heldt type projector
InactiveUS20050099607A1Easy maintenanceShake suppressionTelevision system detailsPrintersHand shakesMicrocomputer
Modulated light (image light) which has been modulated by passing through a liquid crystal display panel passes through an apical angle variable prism (so-called, a vari-angle prism) and then is enlarged and projected by a projection lens. The apical angle variable prism is configured to change the prism apical angle with, for example, an electromagnetic actuator. The microcomputer calculates a projection optical axis correction value based on hand shake detection signals from a sensor and controls the aforementioned actuator based on the correction value. With this control, shakes of projected images due to hand shakes are prevented.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method and apparatus for the actuation of the cantilever of a probe-based instrument
InactiveUS20040020279A1NanotechAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResonanceCarrier signal
An electromagnetic drive causes a cantilever of a probe-based instrument to deform flexurally by transmitting a high frequency AC signal through an electromagnetic actuator located in the vicinity of the cantilever. The AC signal preferably is an RF carrier signal having a frequency that is substantially higher than the resonant frequency of the cantilever. The carrier signal may, if desired, be modulated with a lower frequency modulation signal to induce the cantilever to oscillate, preferably at resonance. Alternatively, the carrier signal may be transmitted to the electromagnetic actuator without being modulated in order to deflect the cantilever quasi-statically. Cantilever response can then be monitored either directly in response to the imposition of the electromagnetically induced deformation of the cantilever in response to probe / sample interaction to obtain measurements regarding characteristics of the sample, the environment, and / or the cantilever.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
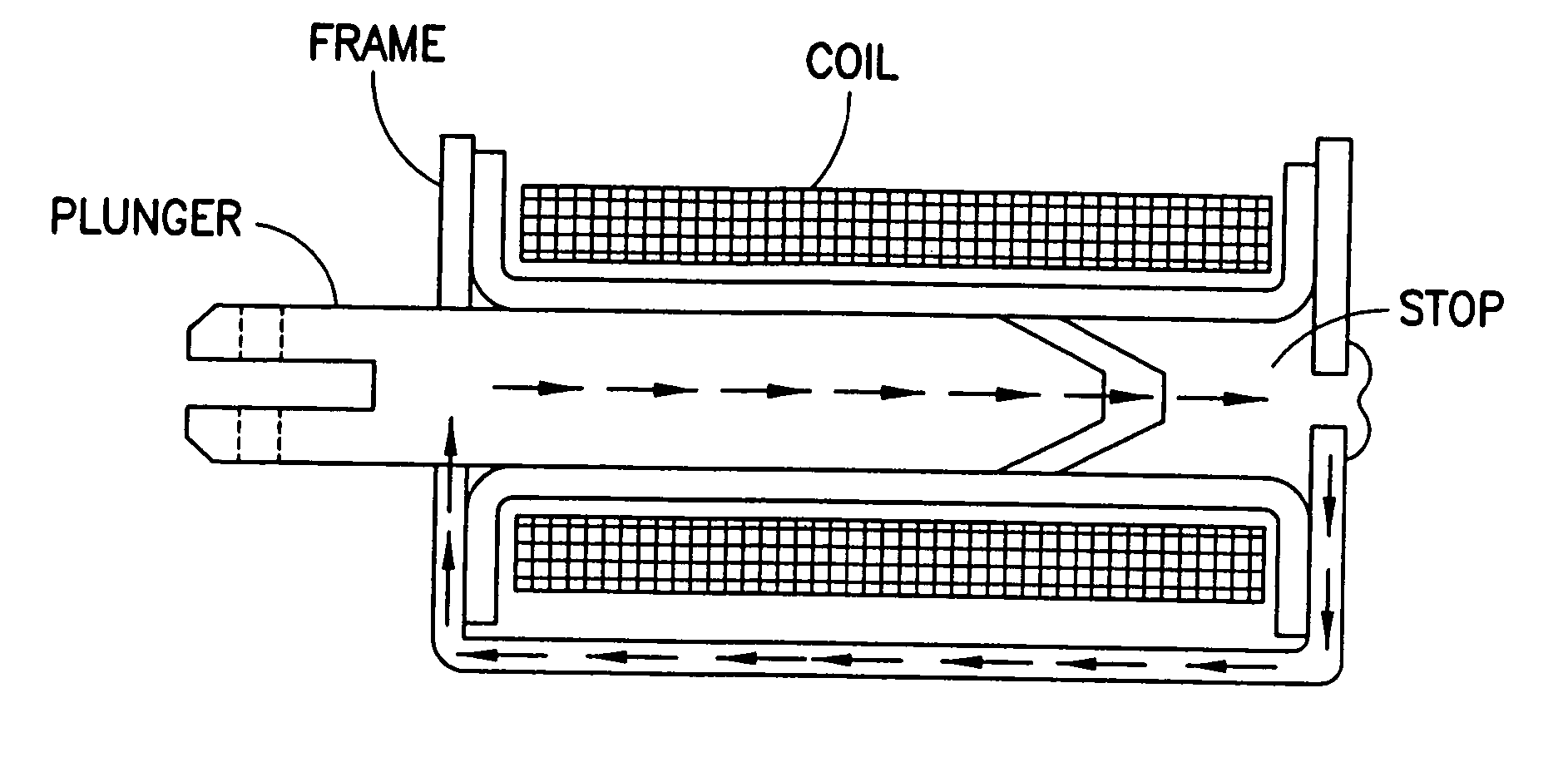
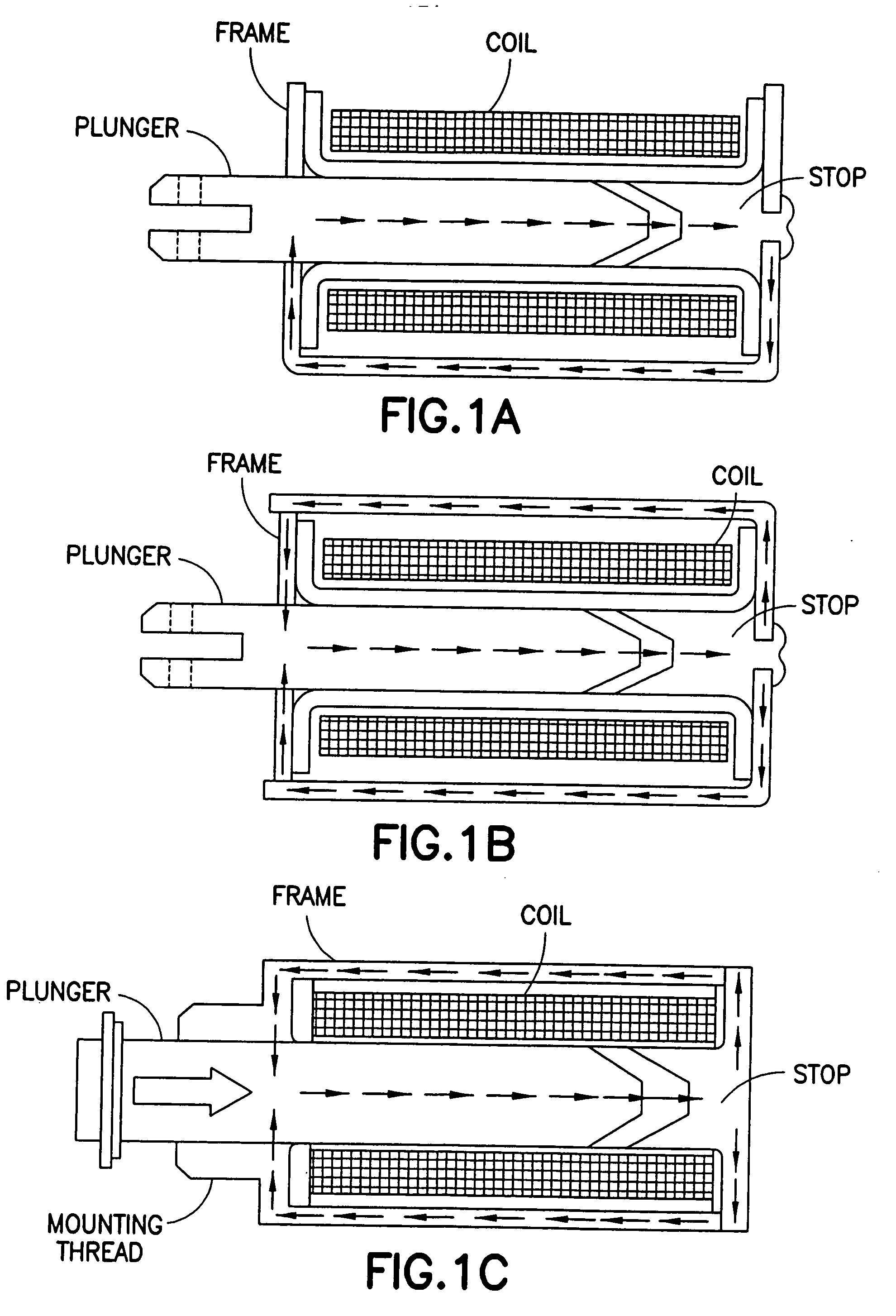
Electromagnetic opposing field actuators
ActiveUS20140354381A1Even by forceReduce in quantityPermanent magnetsElectric switchesMagnetic actuationEngineering
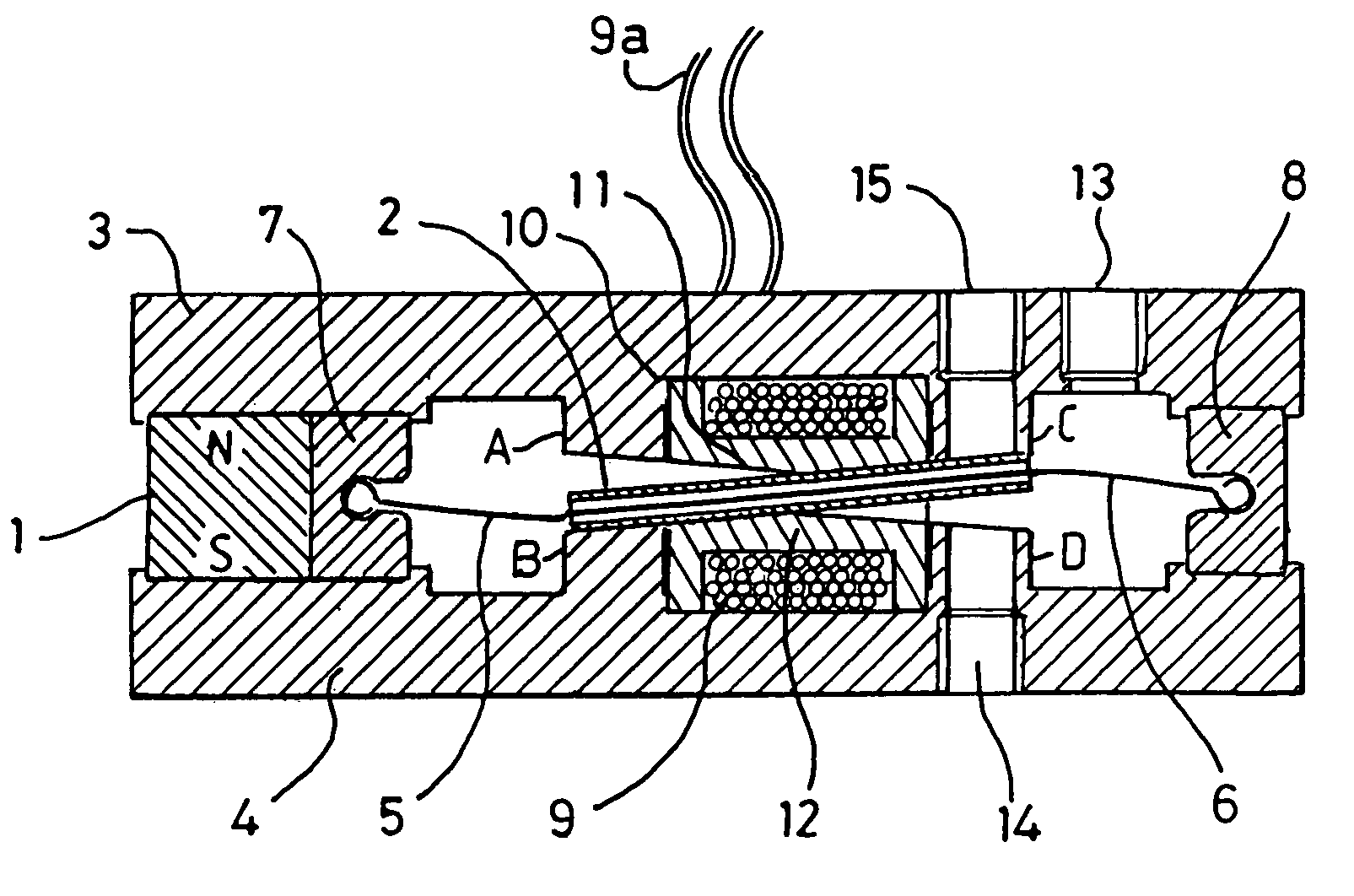
Electromagnetic actuators capable of generating a symmetrical bidirectional force are disclosed. The electromagnetic actuators include a housing made of a ferromagnetic material and a shaft made of a magnetically inert material movable along an axis within the housing. In one type of actuator, captive permanent magnets are arranged on opposite interior end walls of the housing and an electromagnetic coil is mounted on a central portion of the shaft. The electromagnetic coil is capable of generating a force when energized that causes linear displacement of the shaft in either direction along its axis depending on the direction of current through the electromagnetic coil. In another type of actuator, captive electromagnetic coils are arranged on opposing inner end walls of the housing, and a permanent magnet is mounted on a central portion of the shaft. The electromagnetic coils are capable of generating a force when energized that causes linear displacement of the shaft in either direction along its axis depending on a direction of current through the electromagnetic coils.
Owner:ACTIVE SIGNAL TECH
Self-piercing fastening system
ActiveUS7032296B2Obstruct passageIncrease flexibilityRivetsAssembly machinesEngineeringMaterial Perforation
Owner:NEWFREY
Diaphragm pump with a crinkle diaphragm of improved efficiency
ActiveUS20110176946A1Short strokeReduce vibrationFlexible member pumpsPositive-displacement liquid enginesDiaphragm pumpEngineering
A pump having an undulating diaphragm mounted for undulating between two end plates under drive from at least one electromagnetic actuator in order to transfer a fluid between an inlet of the pump and an outlet of the pump. The pump includes adapter means connecting the diaphragm support to a movable portion of the actuator in order to shorten the stroke of the movable mass of the actuator such that its stroke is shorter than the stroke of the diaphragm support.
Owner:AMS R&D
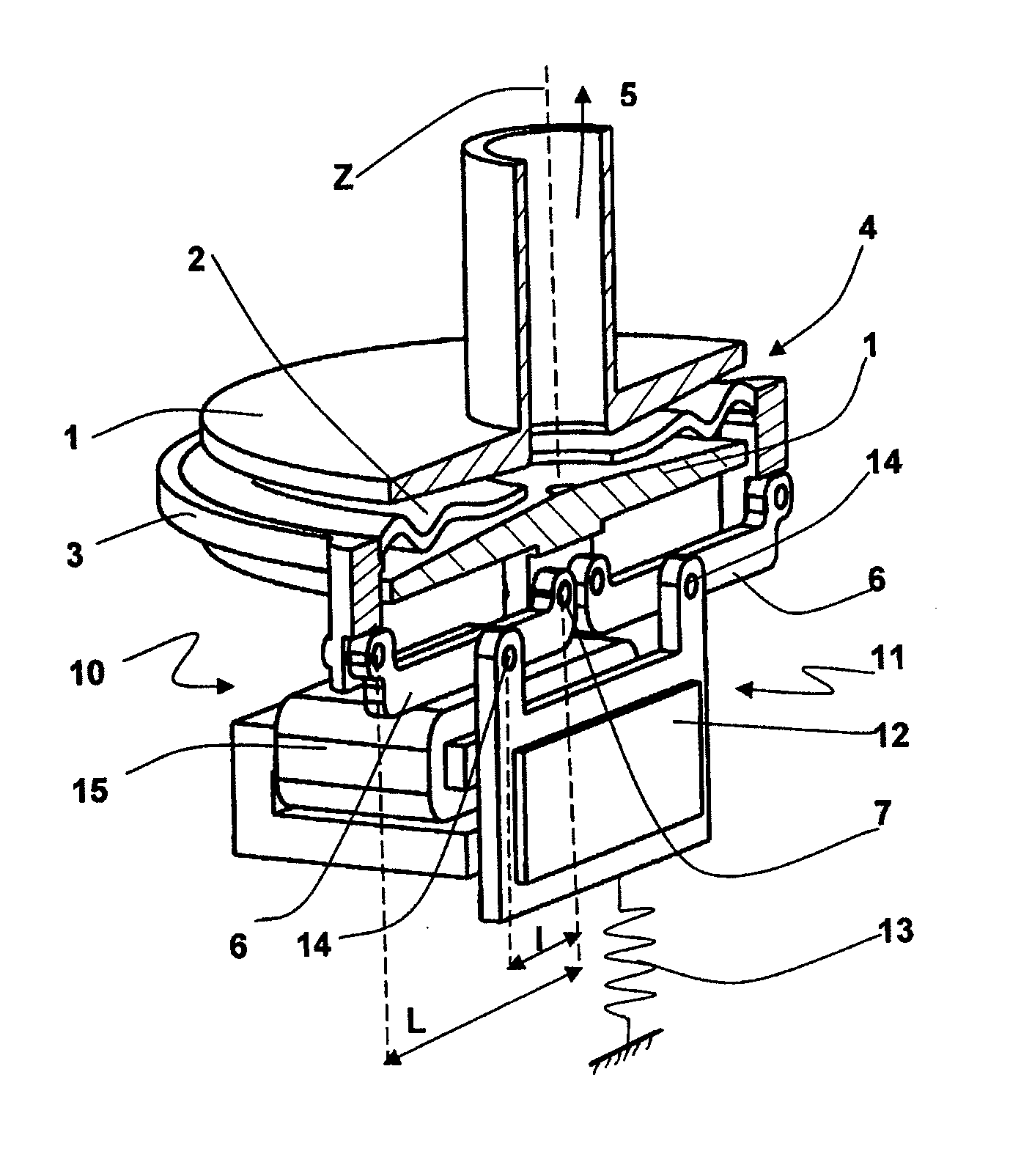
Progressive safety device
A progressive safety device for an elevator includes a brake unit and an actuating unit. The brake unit has a first brake shoe with first spring assemblies and a triangular rotatable support with second and third brake shoes. The actuating unit has an electromagnetic actuator with a locking bolt, a guide bolt with a coaxial compression spring and an actuating arm. On actuation, the compression spring moves the actuating arm against a guide rail whereby grooves on the actuating arm create a frictional engagement with the guide rail turning the actuating arm about a swivel bearing and through a follower turning the support. With the turning motion and the engagement of one of the second and third brake shoes with the guide rail, the first brake shoe is guided against the guide rail and generates the necessary braking force on the guide rail.
Owner:INVENTIO AG
Suspension Apparatus for Vehicle
InactiveUS20080164111A1Simple structureReduce transmissionSpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionControl theoryPiston rod
It is an object of the invention to improve utility in a suspension apparatus for a vehicle having an electromagnetic actuator and a hydraulic damper. In the suspension apparatus, a hydraulic damper is disposed between an electromagnetic actuator and a wheel-holding portion, and a cover tube is provided for accommodating a seal provided between a piston rod and a housing of the hydraulic damper. In the suspension apparatus according to the present invention wherein the hydraulic damper is disposed between the wheel-holding portion and the electromagnetic actuator, it is possible to effectively mitigate not only transmission of vibrations to the vehicle body from the wheel via the electromagnetic actuator but also transmission of vibrations to the electromagnetic actuator. Further, owing to the presence of the cover tube, entry of dust and the like into the hydraulic damper through the seal can be effectively prevented.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Electromagnetic switching device
InactiveUS7157996B2Improve abilitiesFast blockingElectric switchesElectromagnetic relay detailsMiniaturizationElectromagnetic actuator
In the electromagnetic switching device, it is possible to miniaturize and have low costs, have quiet operation noise, and also quickly extinguish the arc. The electromagnetic switching device has an electromagnetic actuator with a movable iron core, a pair of fixed terminals that respectively have a fixed contact point, a movable contact that has movable contact points on the right and left ends, a shaft, and an enclosing component that holds the movable contact points and the fixed contact points. The pair of movable contact points respectively contact with and detach from the pair of fixed contact points, and the pair of fixed contact points respectively conduct each other and are insulated again through the shaft by moving the movable iron core along the axis using the electric magnetic actuator. A quasi-hermetically sealed space, which is the extinguishing space, is formed by the enclosing component and a first yoke. A potting compound is charged, into the space between a body and the quasi hermitically sealed space.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Systems and methods for operating an electromagnetic actuator
InactiveUS20050279867A1Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesElectromagnetic actuatorElectrical and Electronics engineering
One embodiment of the present invention relates to a method for constructing a circuit for controlling an electromagnetic actuator. Another embodiment of the present invention relates to a method for designing a circuit for controlling an electromagnetic actuator.
Owner:COMBUSTION DYNAMICS
Fault detector and method of detecting faults
ActiveUS20090132180A1Minimize data handlingMinimize manipulation requirementElectrical controlNuclear monitoringControl theoryElectrical current
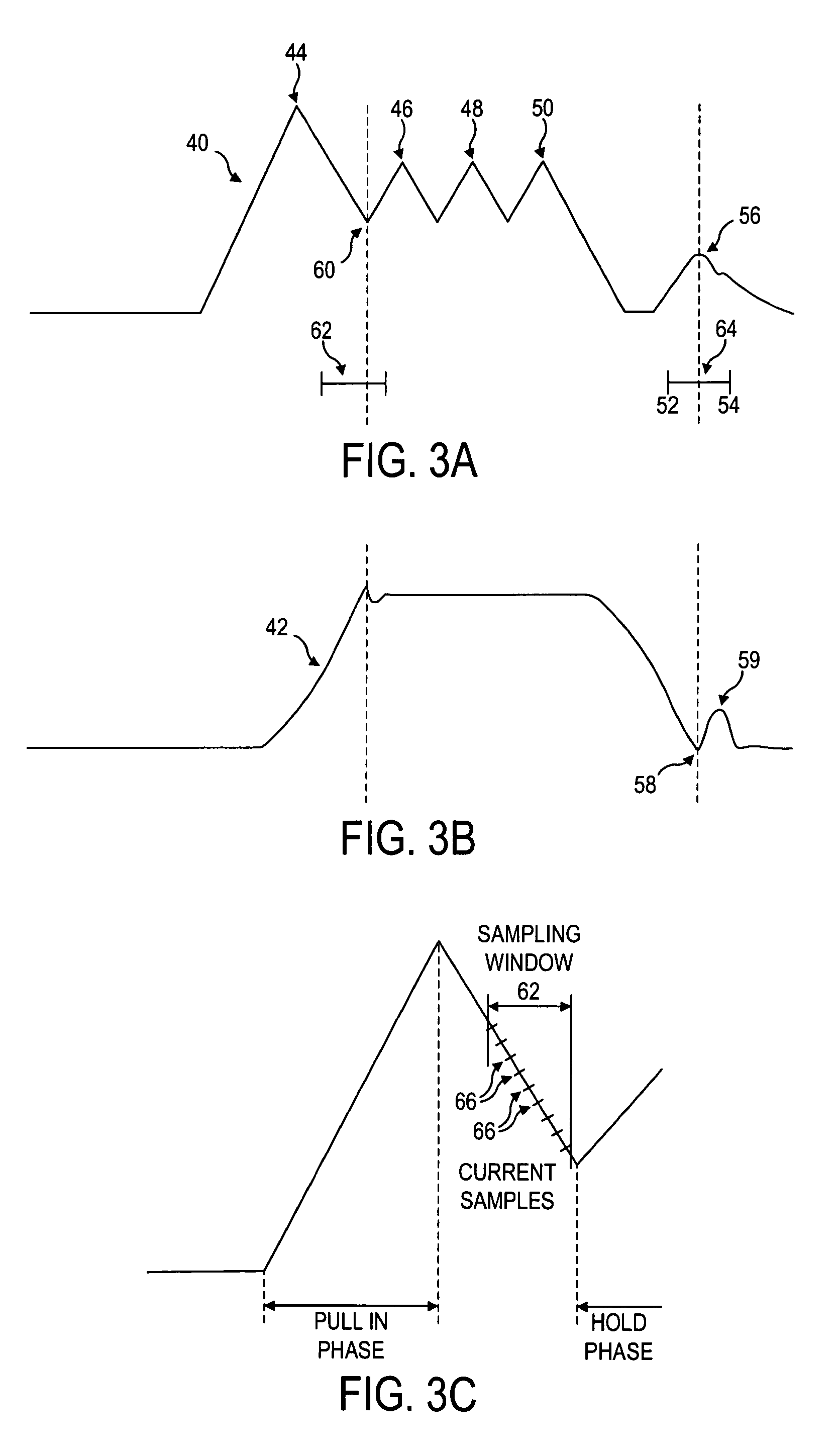
A fault detector for detecting valve movement of a valve in a fuel injector of an engine system, the valve comprising an electromagnetic actuator arranged to move the valve between first and second valve positions during a valve cycle, the engine system comprising a sensor for sensing a current through the actuator. The detector comprises a controller arranged to control the sensor; inputs for receiving from the sensor data related to the current through the actuator; a processor arranged to analyze the received data for current discontinuities; and outputs for outputting a valve movement signal in dependence upon the current discontinuities determined by the processor. The controller is arranged to enable the sensing means during a finite sampling window and to: (i) move the sampling window from a first window position for a first injection event to a progressively later window position for one or more subsequent injection events; (ii) to determine a new sampling window position on the basis of a valve movement signal output for at least two of the preceding window positions; and (iii) to feedback the new sampling window position for a subsequent injection event.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Progressive safety device
A progressive safety device for an elevator includes a brake unit and an actuating unit. The brake unit has a first brake shoe with first spring assemblies and a triangular rotatable support with second and third brake shoes. The actuating unit has an electromagnetic actuator with a locking bolt, a guide bolt with a coaxial compression spring and an actuating arm. On actuation, the compression spring moves the actuating arm against a guide rail whereby grooves on the actuating arm create a frictional engagement with the guide rail turning the actuating arm about a swivel bearing and through a follower turning the support. With the turning motion and the engagement of one of the second and third brake shoes with the guide rail, the first brake shoe is guided against the guide rail and generates the necessary braking force on the guide rail.
Owner:INVENTIO AG
Enhanced permanent magnet electromagnetic actuator for an electronic valve actuation system of an engine
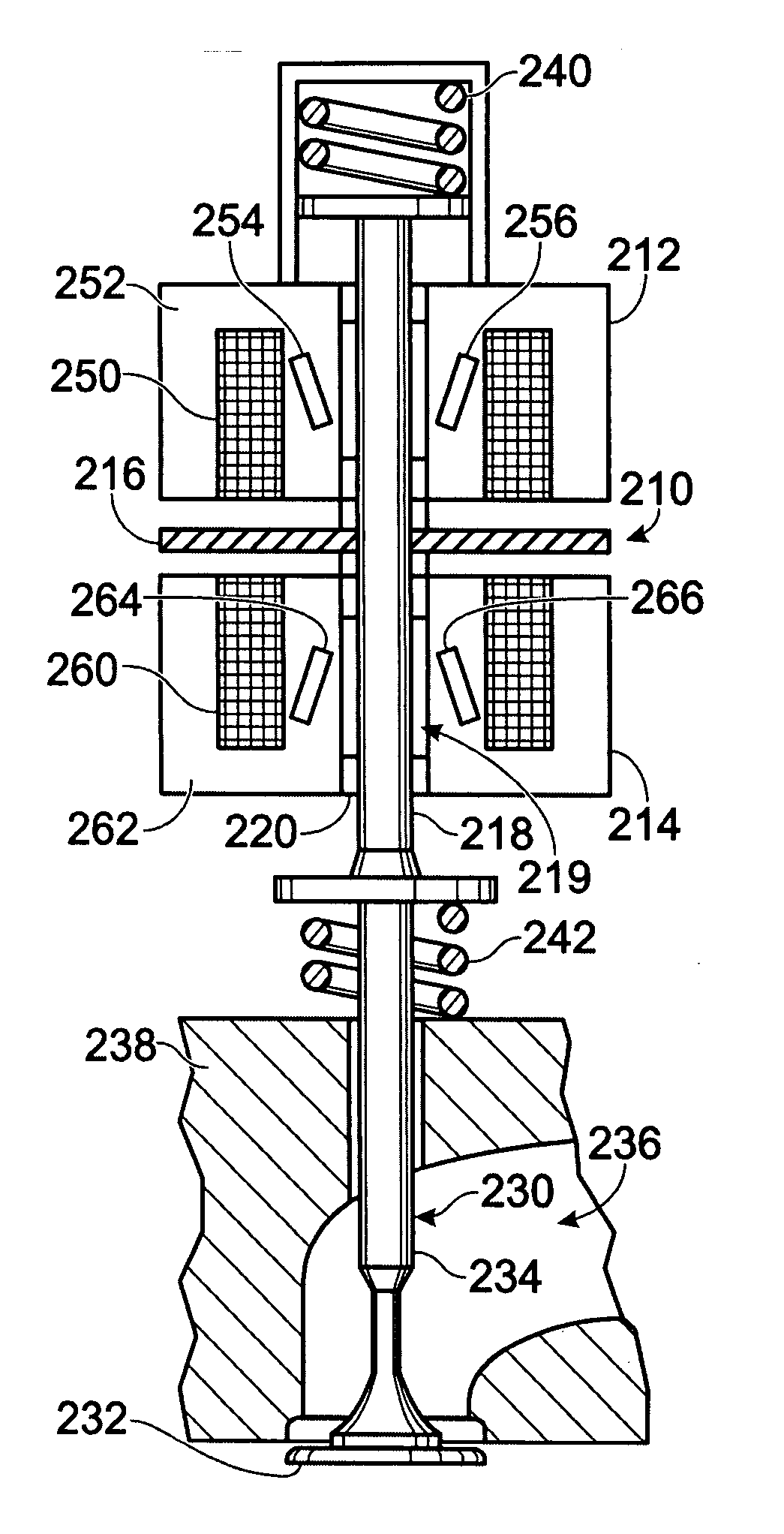
InactiveUS20050211200A1Increase the areaIncrease flux densityWindings insulation shape/form/constructionMachines/enginesValve actuatorForce generation
A valve actuator for an internal combustion engine is described having a core having a wound coil located therein, said core further having at least one permanent magnet located at least partially inside or outside said coil and positioned at an angle relative to a direction of movement of an armature. Further, various recesses, indentations, chamfers, bevels, and / or depressions may be included to affect flux leakage, and / or force generation.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Optical sensors and algorithms for controlling automatic bathroom flushers and faucets
InactiveUS20060006354A1Diaphragm valvesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesOptical radiationElectronic systems
The present invention is directed to novel optical sensors and novel methods for sensing optical radiation that can be used to control the operation of automatic faucets and flushers. The novel sensors and flow controllers require only small amounts of electrical power for sensing users of bathroom facilities, enabling battery operation for many years. An electronic system for controlling fluid flow may include an electromagnetic actuator, a controller and an optical sensor. Preferred embodiments include a control circuit constructed to sample periodically the detector based on the amount of light detected; a control circuit constructed to adjust a sample period based on the detected amount of light after determining whether a facility is in use; a detector optically coupled to the input port using an optical fiber; the input port may be located in an aerator of the electronic faucet; the system includes batteries for powering the electronic faucet. These embodiments may also include a variety of other features. A passive optical sensor includes a light detector sensitive to ambient (room) light for controlling the operation of automatic faucets or automatic bathroom flushers. An active optical sensor includes a light emitter and a light detector. The detected signals may be processed using novel algorithms
Owner:GULER FATIH +5
Electromagnetic actuator, and electromagnetic clutch and differential using the same
ActiveUS7325664B2Preventing the system from being enlargedHeat suppressionMechanical actuated clutchesMagnetically actuated clutchesElectromagnetic clutchEngineering
The electromagnetic actuator includes an electromagnetic coil configured to provide actuation force in accordance with a solenoid current to be supplied, to a clutch and configured to actuate the clutch to control relative rotation between first and second members. The electromagnetic actuator includes a detector configured to detect the clutch actuated to produce a detection signal. The electromagnetic actuator includes a controller configured to respond to the detection signal from the detector to control the solenoid current.
Owner:TOCHIGI FUJI IND CO LTD
Emergency stop system of elevator
An emergency stop system of an elevator, wherein a governor rope moving in synchronism with the lifting of a car is wrapped around a governor sheave. An emergency stop device connected to the governor rope and braking the car by the displacement of the car relative to the governor rope is mounted on the car. A control device outputs operation signals when detecting the abnormality of the speed of the car. A rope catch device is installed near the governor sheave. The rope catch device comprises an electromagnetic actuator operated by the operation signals inputted therein and a restraining part restraining the governor rope by the operation of the electromagnetic actuator.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Needle-free injector device with autoloading capability
ActiveUS8172790B2Little controlProcess controlJet injection syringesMedical devicesNeedle freeNeedle Free Injection
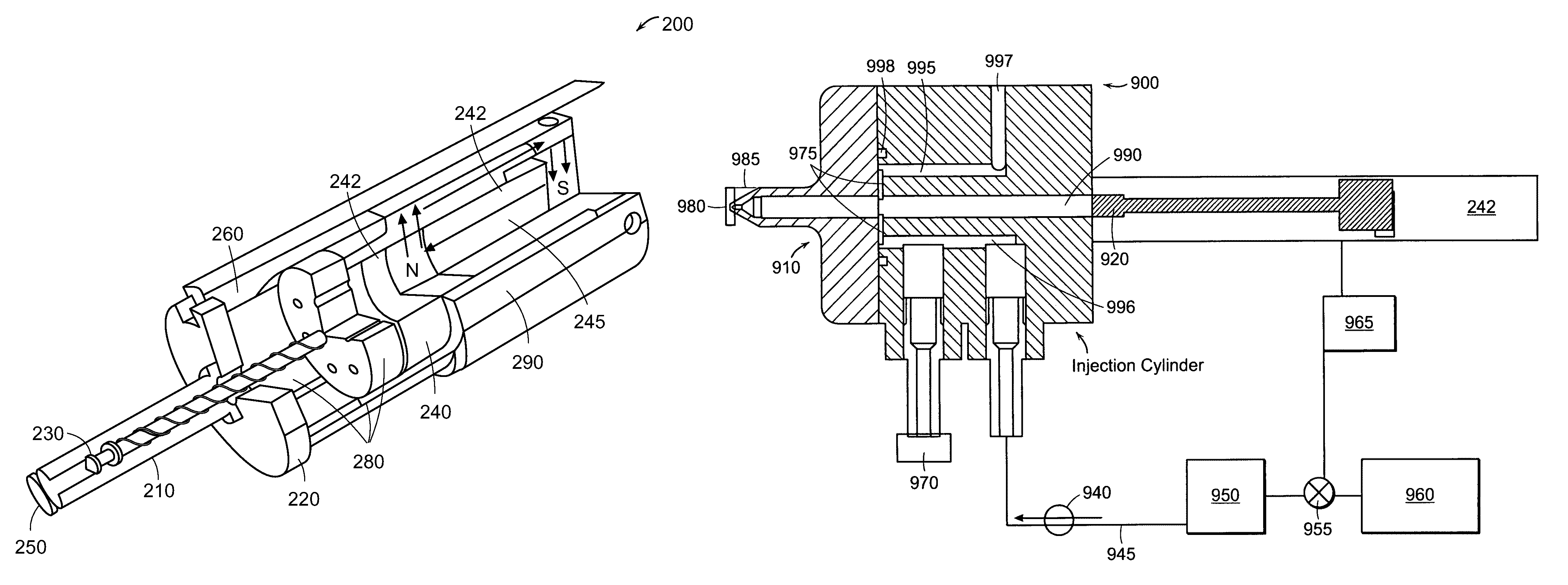
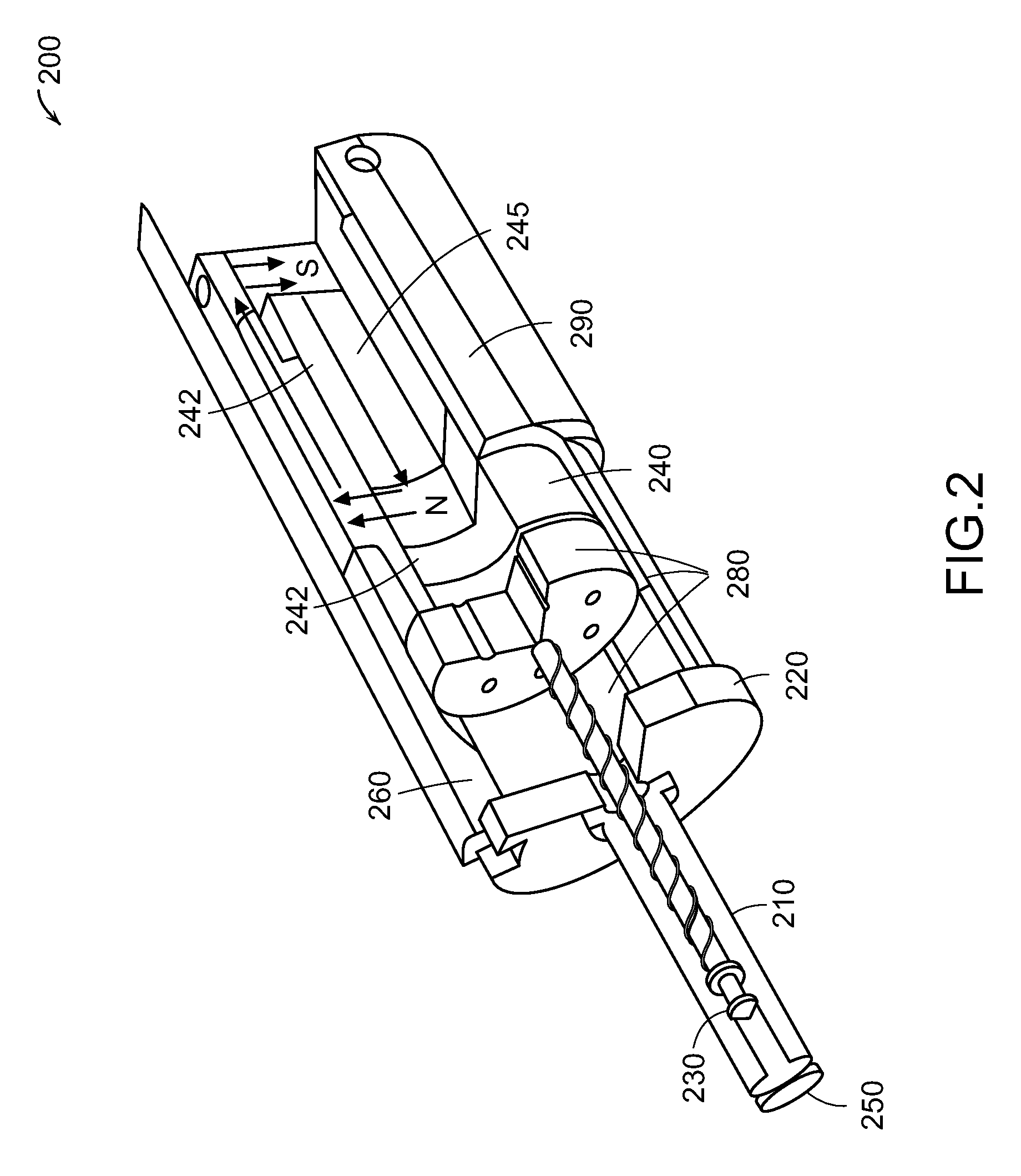
A needle-free transdermal transport device includes a chamber (900) for holding the substance to be injected, a nozzle (910) in fluid communication with the chamber, and a drug reservoir (950) for storing the substance to be transferred to the chamber. The needle-free transdermal transport device also includes a controllable magnet and coil electromagnetic actuator (242) in communication with the chamber. The actuator receives an electrical input and generates in response a force. The force then causes a needle-free transfer of the substance from the chamber to the biological body. The force is variable responsive to variations in the received input during actuation. The actuator draws the substance from the drug reservoir or alternatively, the substance can be pressurized from the drug reservoir into the chamber by a pressure source.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Jumping robot
InactiveUS20130282174A1Small sizeLong jumping distanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlSimulationArtificial intelligence
A jumping robot is provided. In another aspect, a jumping robot weighs less than 50 grams, jumps at least 20 cm high and has a maximum linear dimension of 10 cm. A further aspect provides a robot that employs an electromagnetic actuator that actuates at least two of: jumping, steering, self-righting, and / or mid-air orientation control.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Electronically controlled fluid coupling device
InactiveUS7083032B2Fast response timeOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFluid couplingsFluid couplingControl theory
An electronically-controlled fluid coupling device having a front mounted fan and electrical actuation without a tethered harness. The fluid coupling device combines an inverted viscous clutch, drive pulley and a split electromagnetic actuator package. In this arrangement, the electrical portion of the split electromagnetic actuator is not physically attached to the fan drive, but is instead mounted to a stationary member. The remaining actuator components are integral to the fan drive and are composed of only mechanical parts. The inverted clutch arrangement having remote electronic control allows three output modes: engaged, partially engaged, or disengaged.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Electromagnetic actuator and integrated actuator and fluid flow control valve
InactiveUS7021603B2Rapid responseLower average energyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPipeline systemsMagnetic polesEngineering
A magnetic device is formed from a permanent magnet generating magnetic flux, an armature which can occupy two positions between four poles and an electromagnet winding to which current can be supplied to produce a magnetic flux in one direction or the other, the flux from the winding causing the armature to move into one position and continue to remain in that position after the current flow ceases. The device can be incorporated into a fluid valve to act as a drive for opening and closing the valve. It may also serve as the drive for opening and closing electrical contacts. Monostable operation can be achieved by locating a magnetic flux shunt at one end of the armature travel. A holding solenoid may be incorporated. A pivoting armature in a fluid tight chamber comprises a fluid flow controlling device. It can adopt either of two home positions in contact with two magnetic poles and is retained by magnetic flux from a permanent magnet. Fluid can flow into and out of the chamber via a first passage. A second passage extends through one of the poles to an opening in the pole face which is covered by the armature when the latter occupies one home position but is uncovered when the armature occupies its other home position. A third fluid passage extends through and leads to a second opening in another pole, which is covered when the armature occupies its said other home position. Passages in the poles house energy storing springs each of which is compressed as the armature approaches the pole. A push rod can extend through a passage in one of the poles for conveying armature movement externally of the device.
Owner:CAMCOM
Active hydraulic anti-vibration support and an active anti-vibration system incorporating said support
InactiveUS6364294B1Overcome disadvantagesNon-rotating vibration suppressionMechanical vibrations separationElastomerControl theory
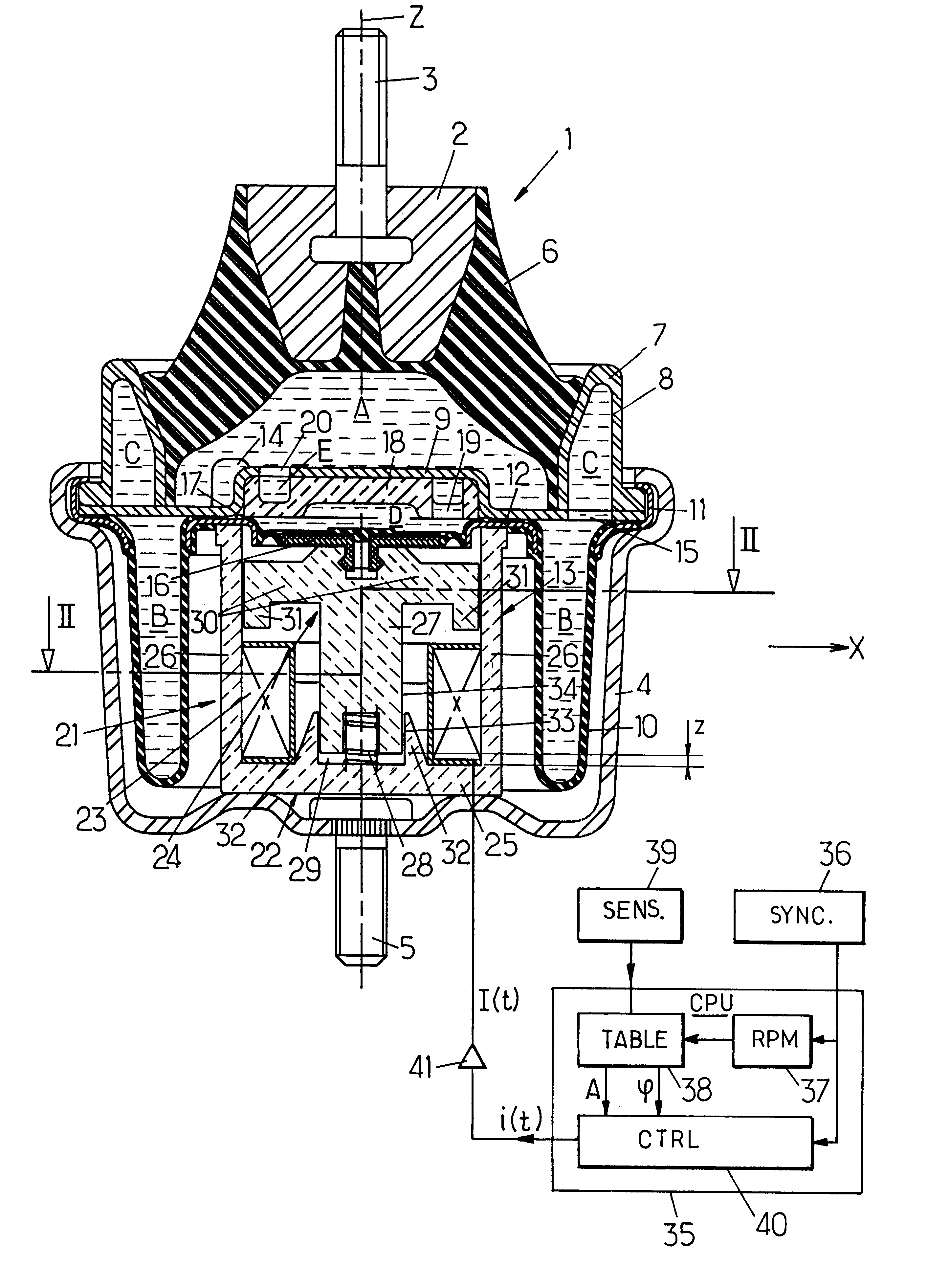
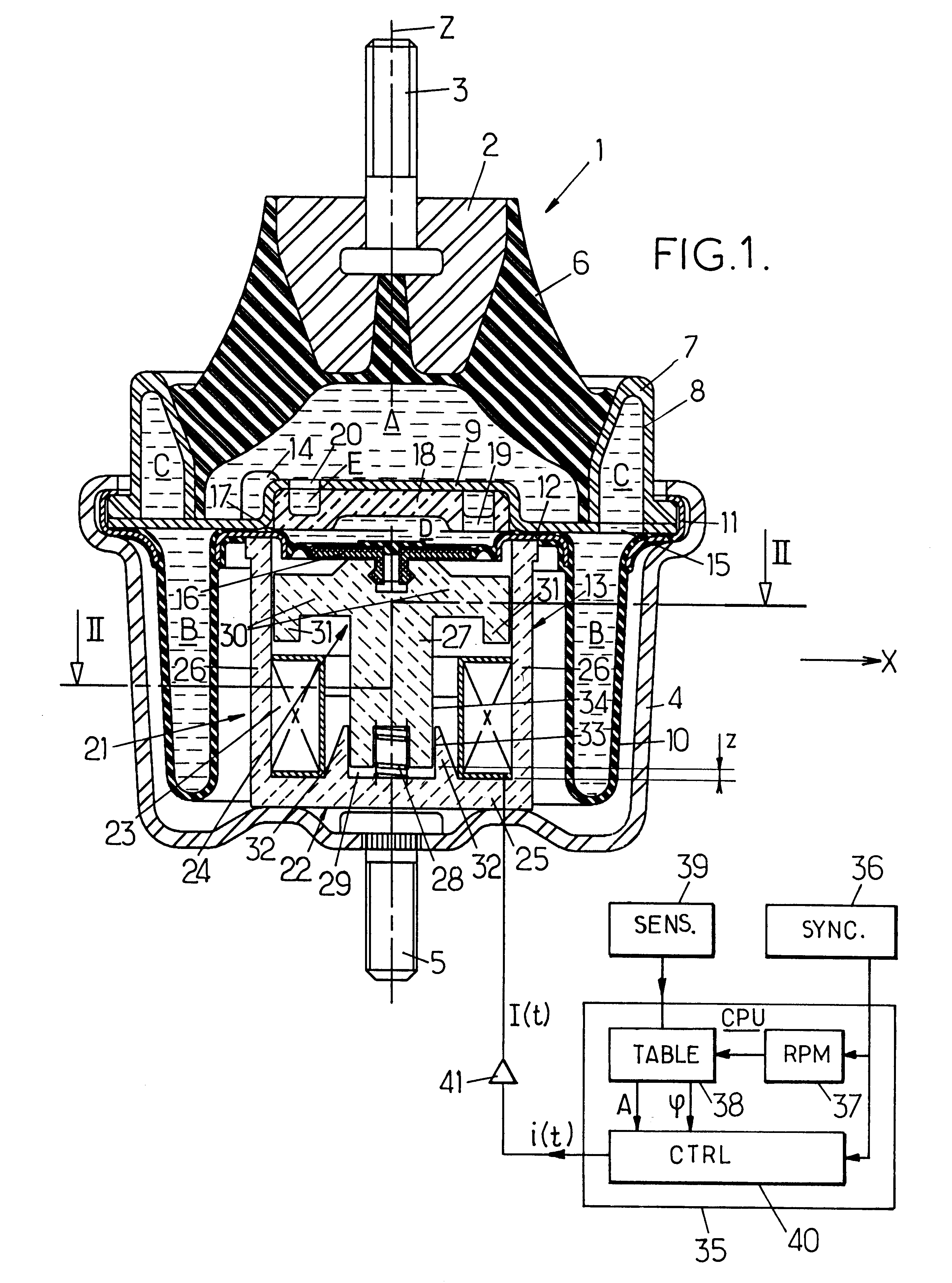
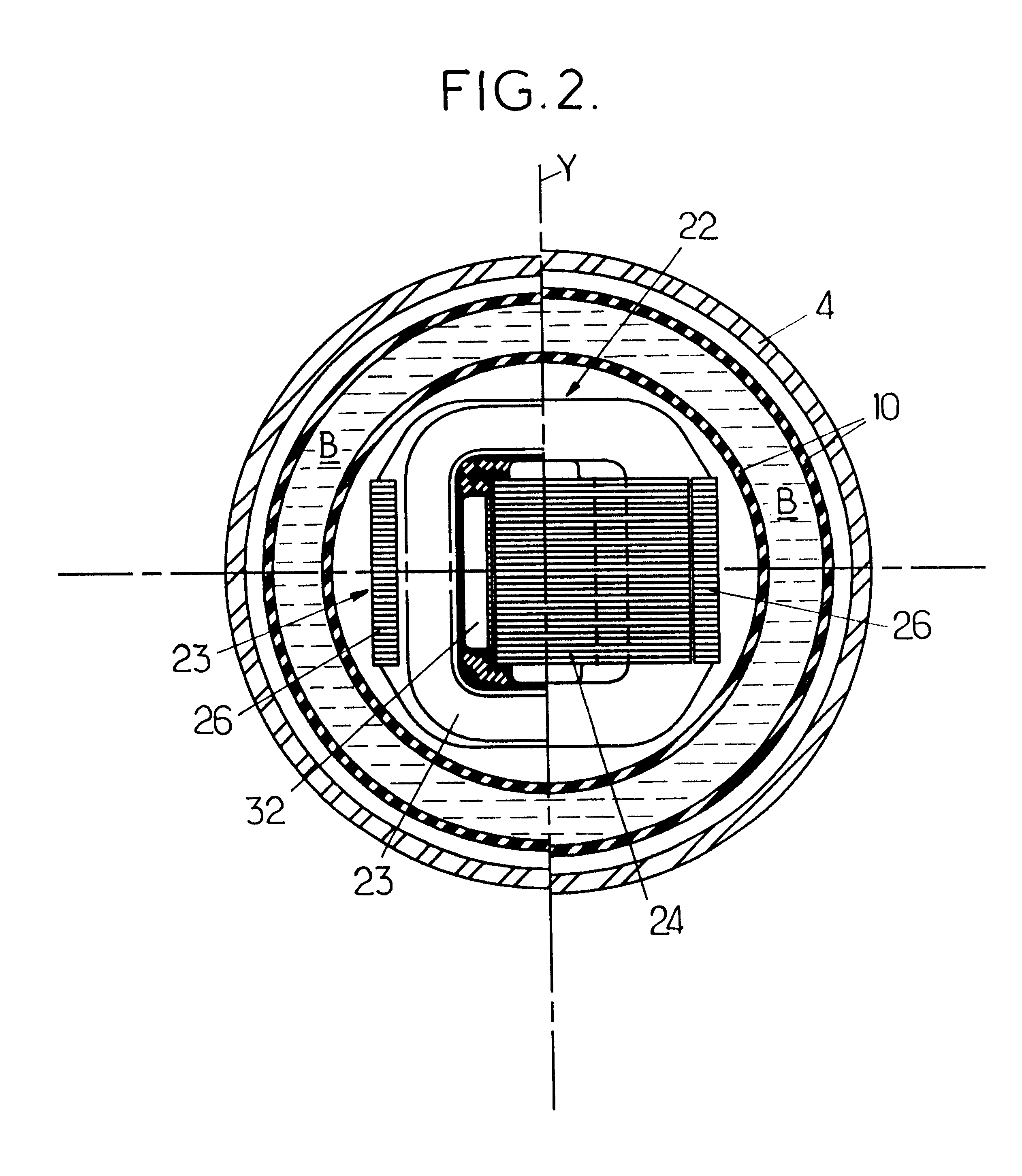
An anti-vibration support comprising two rigid frames joined to one another by an elastomer body which is applied against a rigid partition to define a hydraulic working chamber linked to a compensating chamber by a throttled passage. The liquid contained in the working chamber is in contact with a piston controlled by an electromagnetic actuator with a proportional electromagnet.
Owner:HUTCHINSON SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com