Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
649results about "Electrostatic generators/motors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
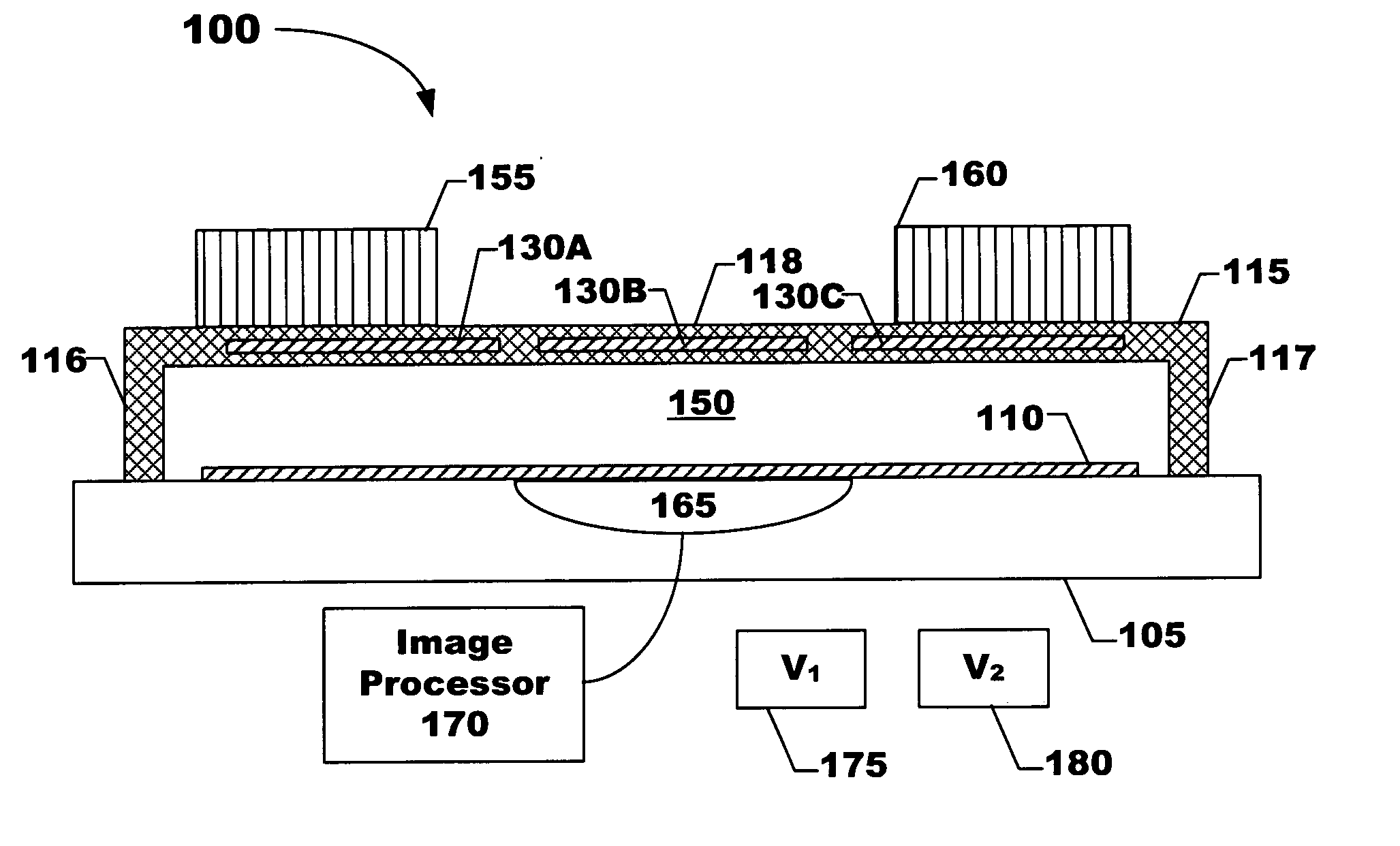
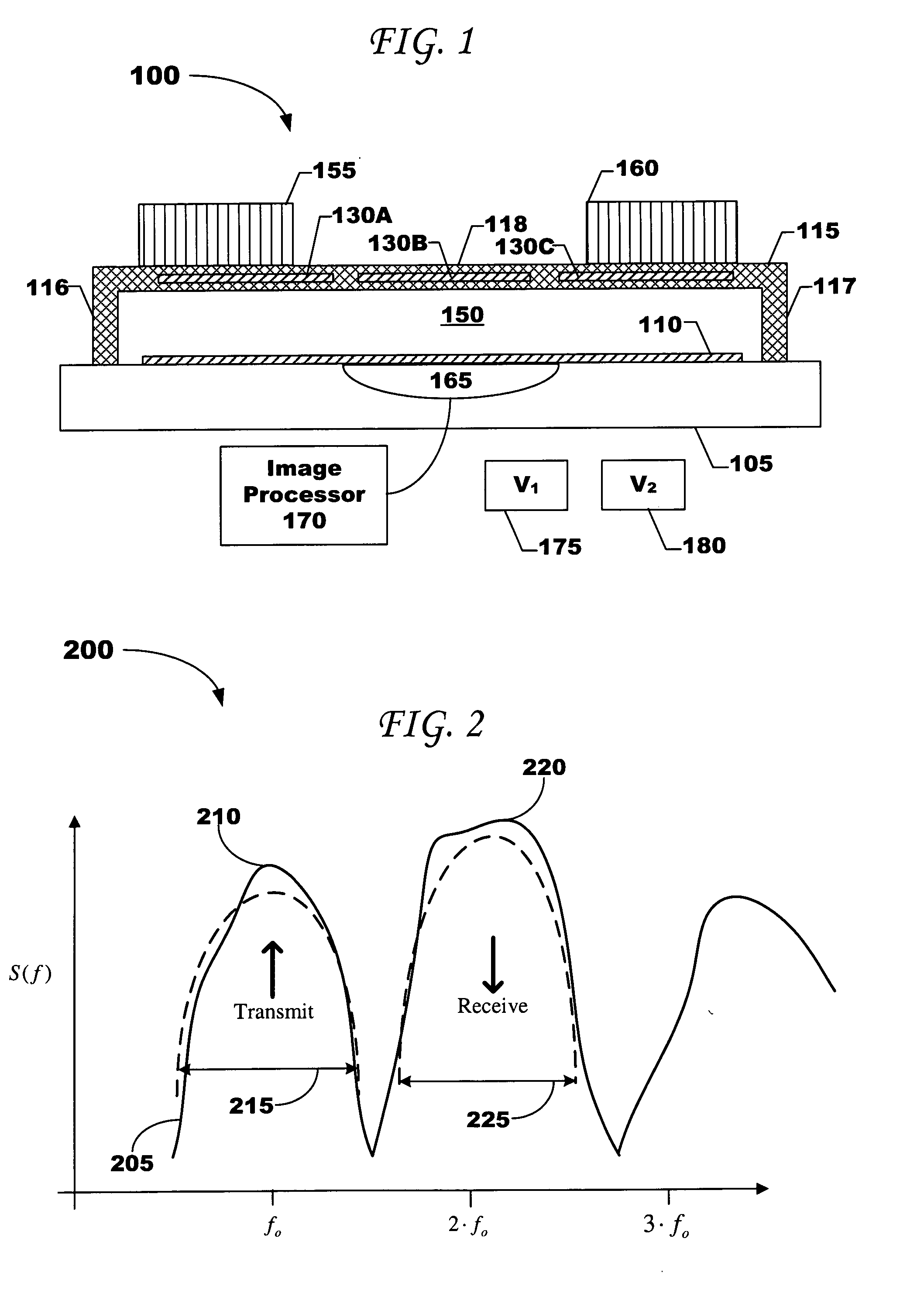
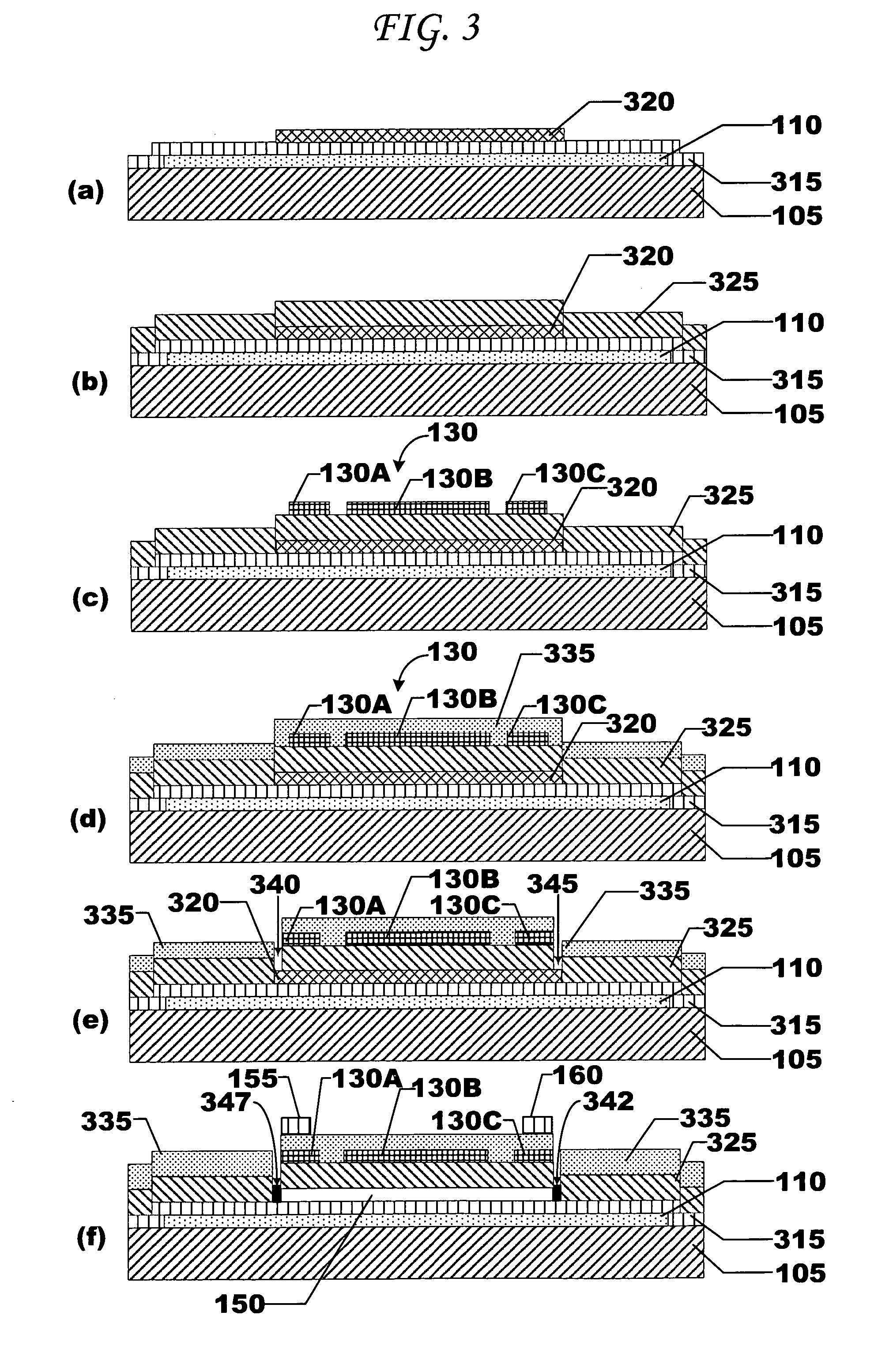
Electroactive polymer generators
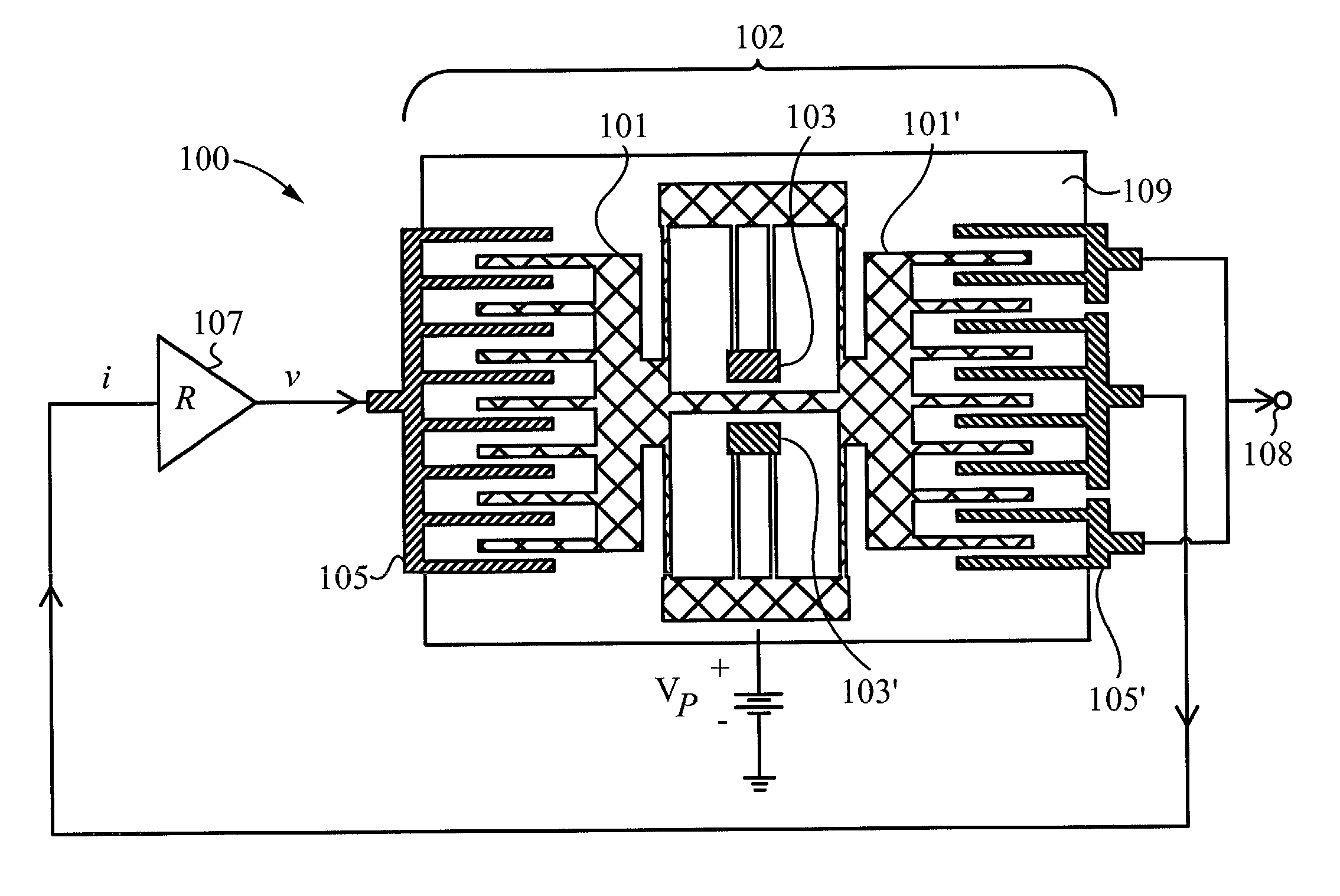
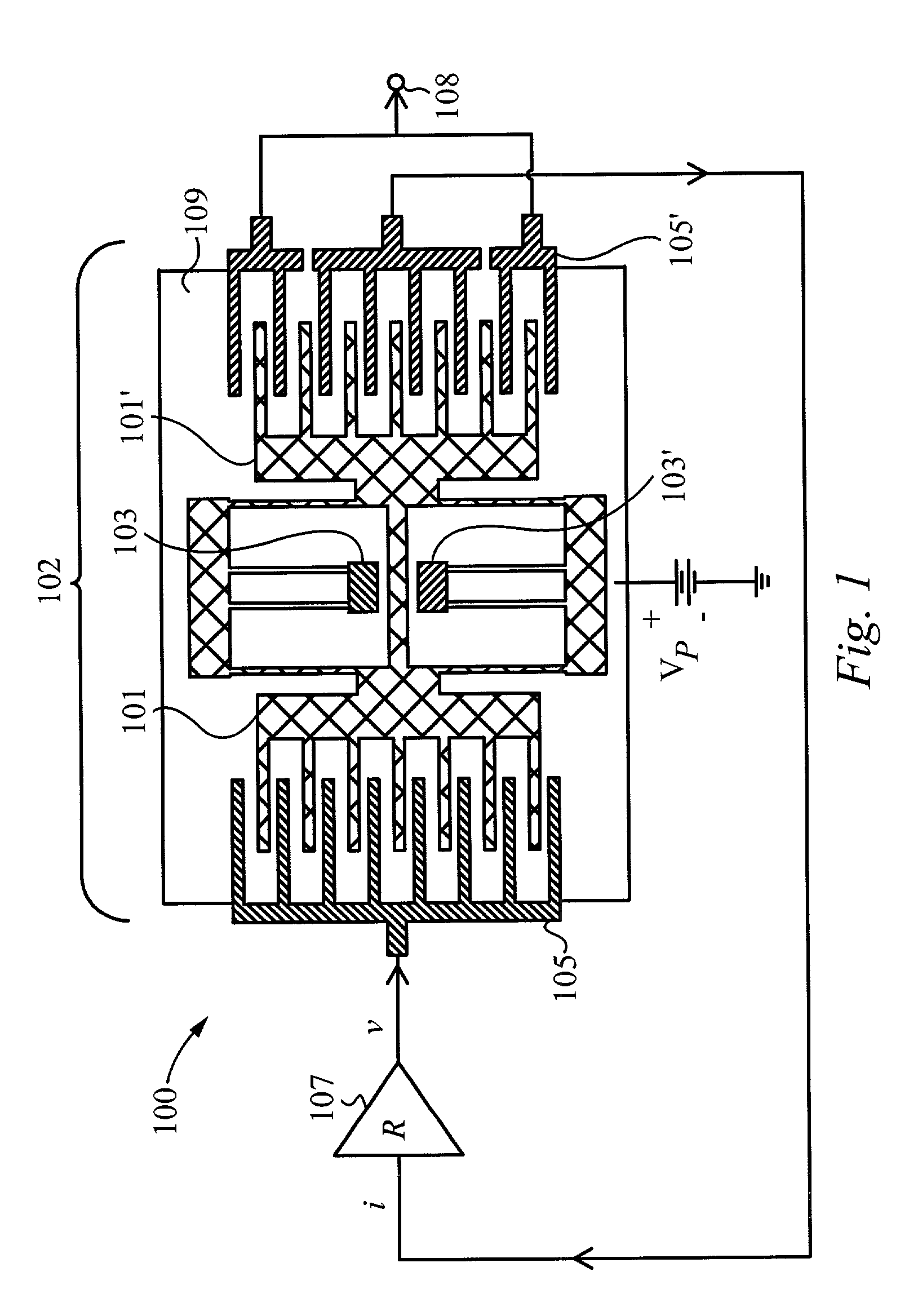
InactiveUS7034432B1Speed up the conversion processImprove responseTransducer detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPre strainActive polymer
The present invention relates to transducers, their use and fabrication. The transducers convert between mechanical and electrical energy. Some transducers of the present invention include a pre-strained polymer. The pre-strain improves the conversion between electrical and mechanical energy. The present invention also relates to devices including an electroactive polymer to convert between electrical and mechanical energy. The present invention further relates to compliant electrodes that conform to the shape of a polymer included in a transducer. The present invention provides methods for fabricating electromechanical devices including one or more electroactive polymers.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Multiple element electrode cMUT devices and fabrication methods
ActiveUS20050200241A1Optimizing receiptFacilitate transmissionMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCapacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducersBiomedical engineering
Multiple electrode element capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducer (“cMUT”) devices and fabrication methods are provided. A cMUT device generally comprises a top electrode disposed within a membrane, a bottom electrode disposed on a substrate, and a cavity between the membrane and the bottom electrode. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, at least one of the first electrode and the second electrode comprises a plurality of electrode elements. The electrode elements can be positioned and energized to shape the membrane and efficiently transmit and receive ultrasonic energy, such as ultrasonic waves. Other embodiments are also claimed and described.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Non-volatile MEMS micro-relays using magnetic actuators
InactiveUS6124650AElectrostatic generators/motorsElectromagnetic relay detailsRelative displacementElectrical conductor
An actuation device employing square-loop latchable magnetic material having a magnetization direction (polarization) capable of being changed in response to exposure to an external magnetic field is disclosed. The magnetic field is created by a conductor assembly with non-solenoid configuration. Once the magnetization direction of the material is so changed, the external magnetic field is no longer required to maintain the new magnetization direction. The latchable magnetic material is disposed on the mobile electrode of a switching device, and another magnetic material is disposed in spaced relation to the latchable magnetic material on a stationary electrode or surface. By applying an electrical current to a conductor assembly arranged proximate the latchable material, a magnetic field is created about the latchable magnetic material, to change the magnetization direction and thereby enable the attraction or repulsion of another magnetic material located on the stationary electrode. The resulting relative displacement of the mobile and stationary electrodes effects the selective connection or disconnection of electrical contacts carried on or associated with the respective electrodes of the actuation device without requiring additional power in order to maintain the switched state of the electrodes.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
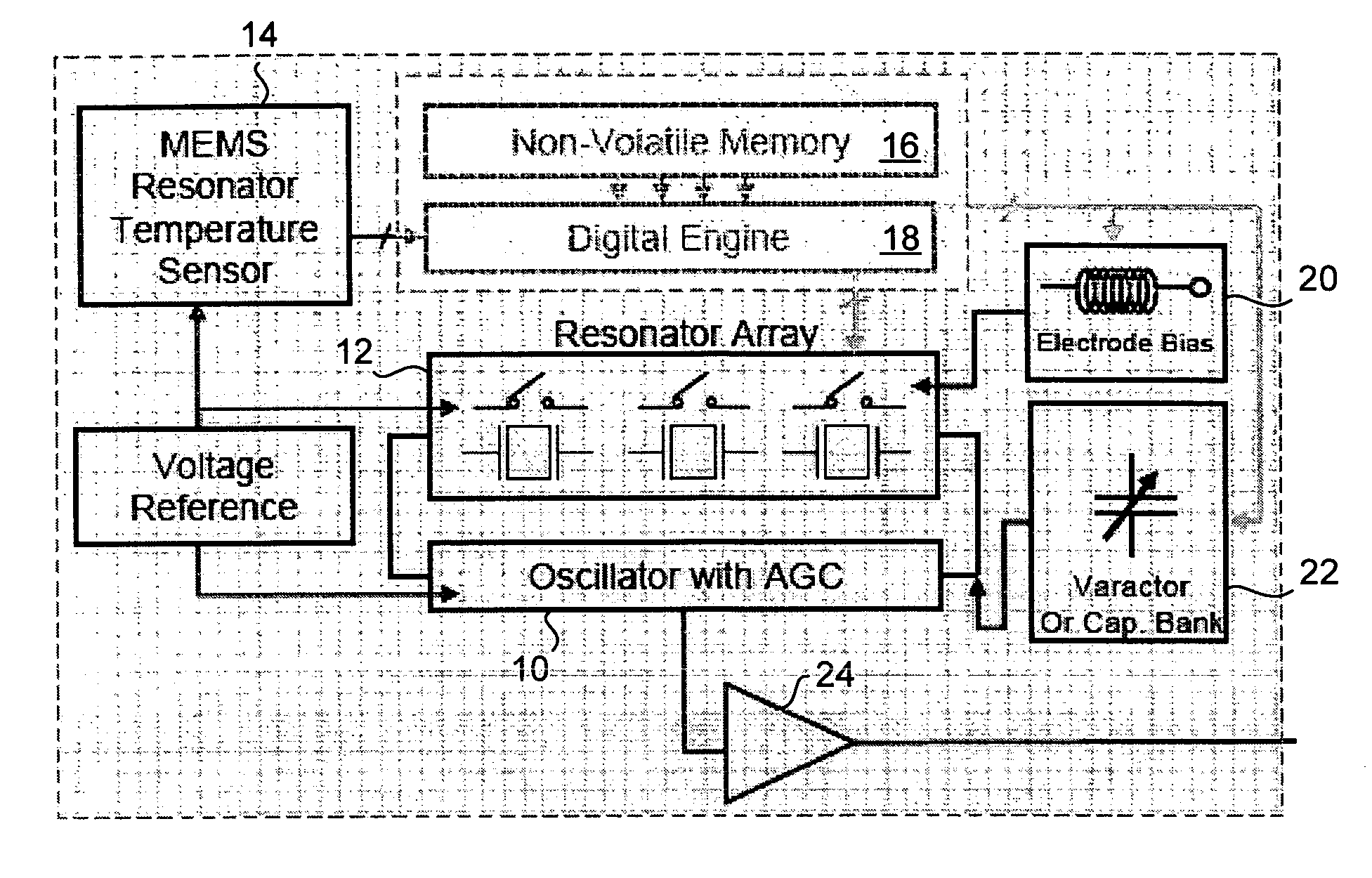
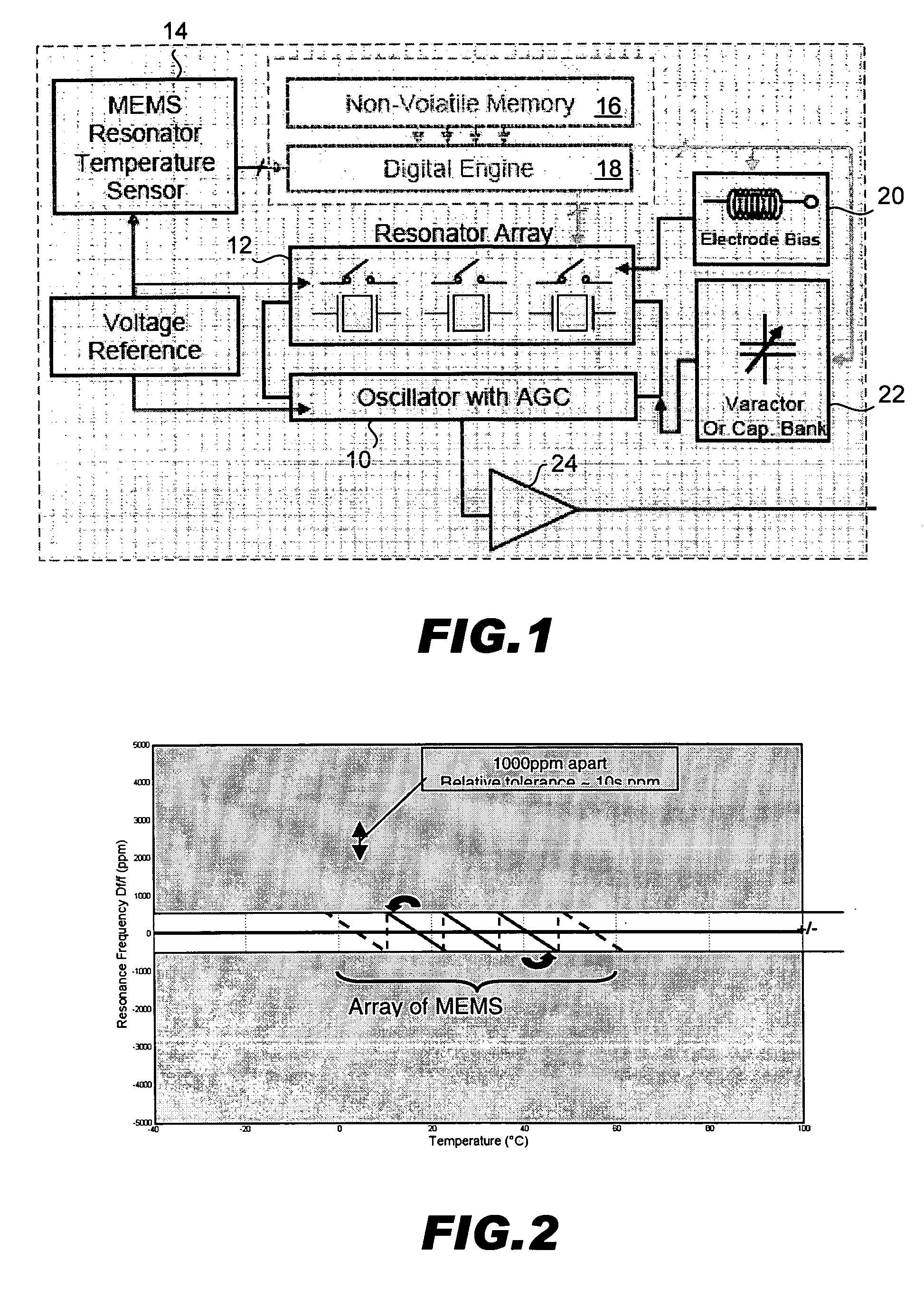
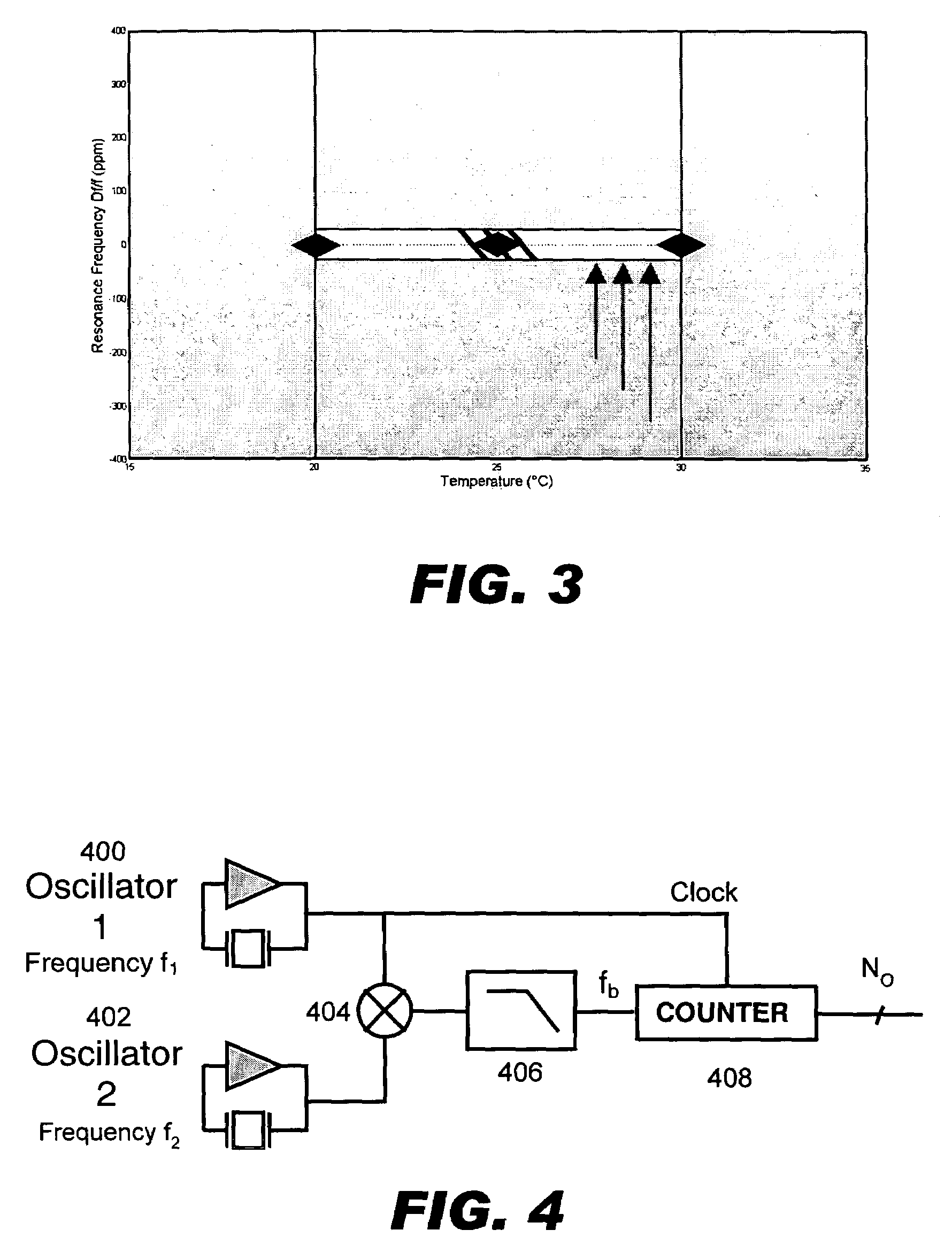
Temperature compensated oscillator including MEMS resonator for frequency control
ActiveUS7211926B2Small deviceLow costPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTemperatue controlQuartz resonatorSignal function
Disclosed is an oscillator that relies on redundancy of similar resonators integrated on chip in order to fulfill the requirement of one single quartz resonator. The immediate benefit of that approach compared to quartz technology is the monolithic integration of the reference signal function, implying smaller devices as well as cost and power savings.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Microelectronic mechanical system and methods
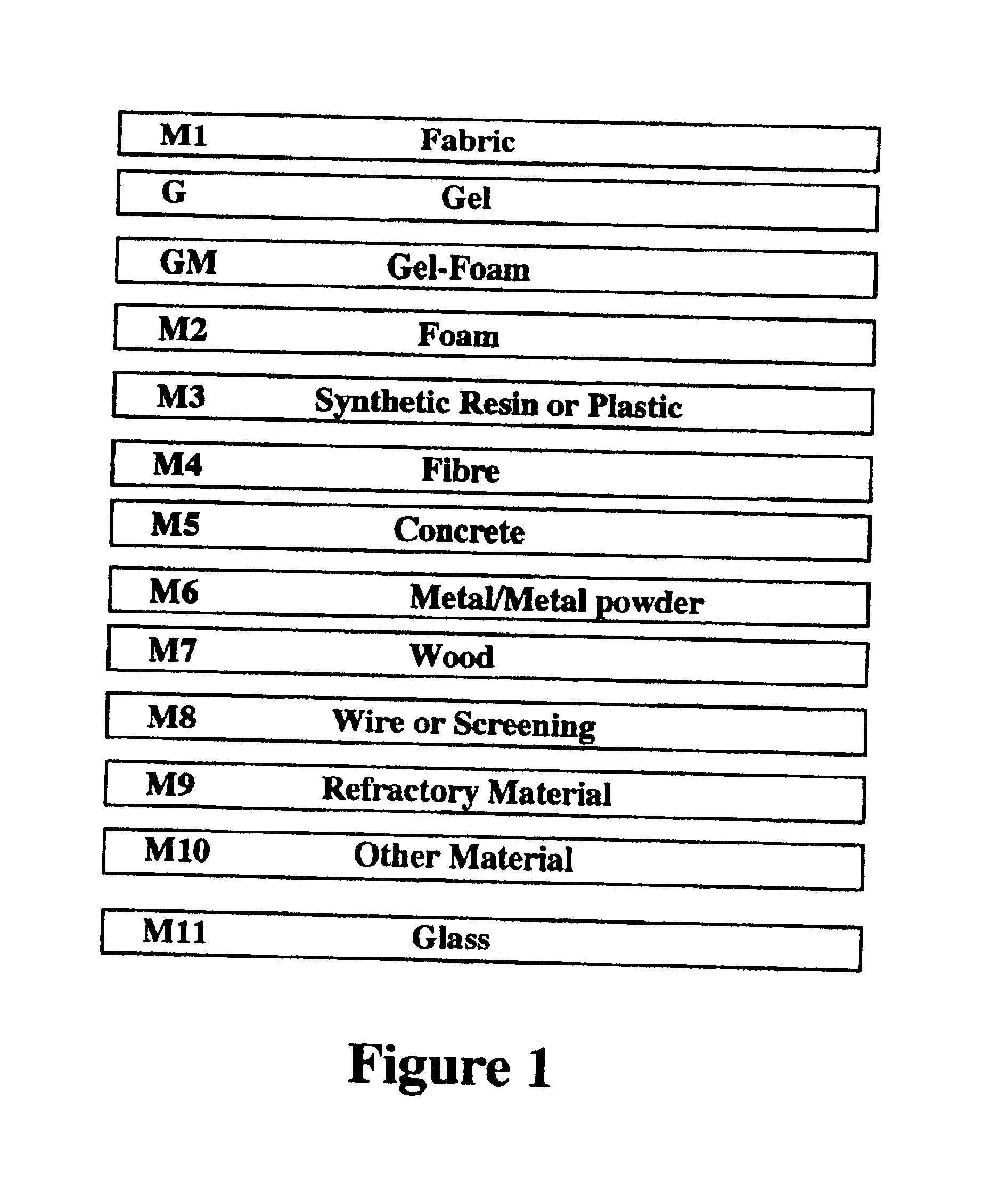
InactiveUS20040053434A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNoble gasSilicon oxide
The current invention provides for encapsulated release structures, intermediates thereof and methods for their fabrication. The multi-layer structure has a capping layer, that preferably comprises silicon oxide and / or silicon nitride, and which is formed over an etch resistant substrate. A patterned device layer, preferably comprising silicon nitride, is embedded in a sacrificial material, preferably comprising polysilicon, and is disposed between the etch resistant substrate and the capping layer. Access trenches or holes are formed in to capping layer and the sacrificial material are selectively etched through the access trenches, such that portions of the device layer are release from sacrificial material. The etchant preferably comprises a noble gas fluoride NGF2x (wherein Ng=Xe, Kr or Ar: and where x=1, 2 or 3). After etching that sacrificial material, the access trenches are sealed to encapsulate released portions the device layer between the etch resistant substrate and the capping layer. The current invention is particularly useful for fabricating MEMS devices, multiple cavity devices and devices with multiple release features.
Owner:SILICON LIGHT MACHINES CORP
Electroactive polymer animated devices
InactiveUS7211937B2Simple and light weight and customizable and efficient replacementDollsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesAnimationTransducer
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Micromechanical electrostatic resonator
InactiveUS7215061B2CapacitanceLarge capacitancePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesDecorative surface effectsCapacitanceAlternating current
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
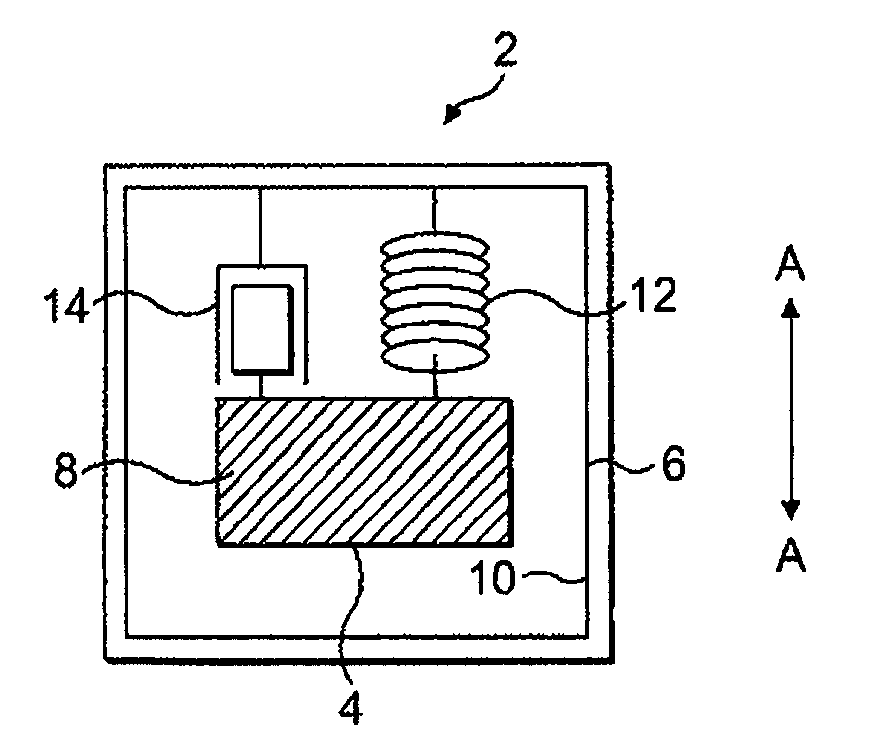
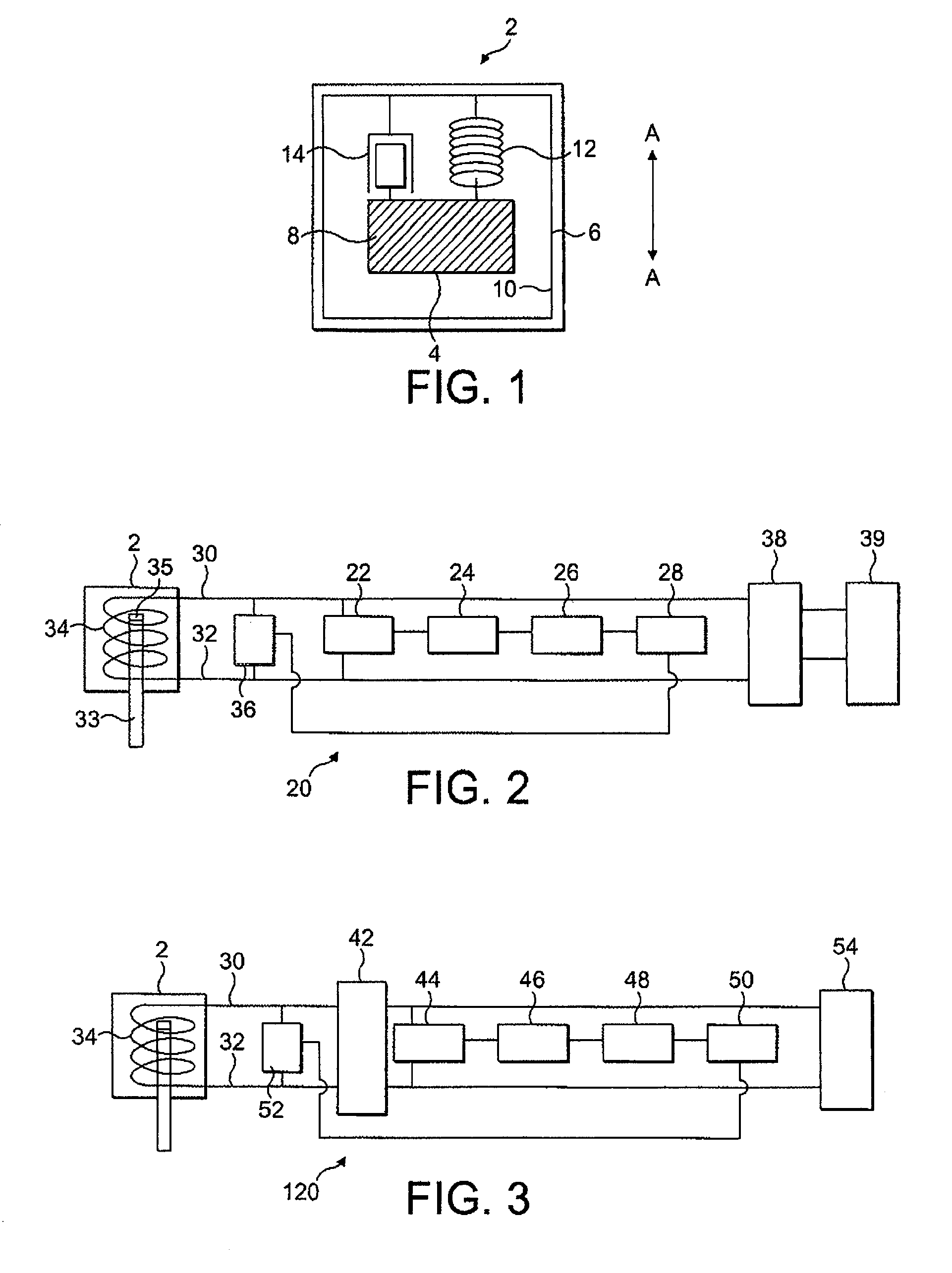
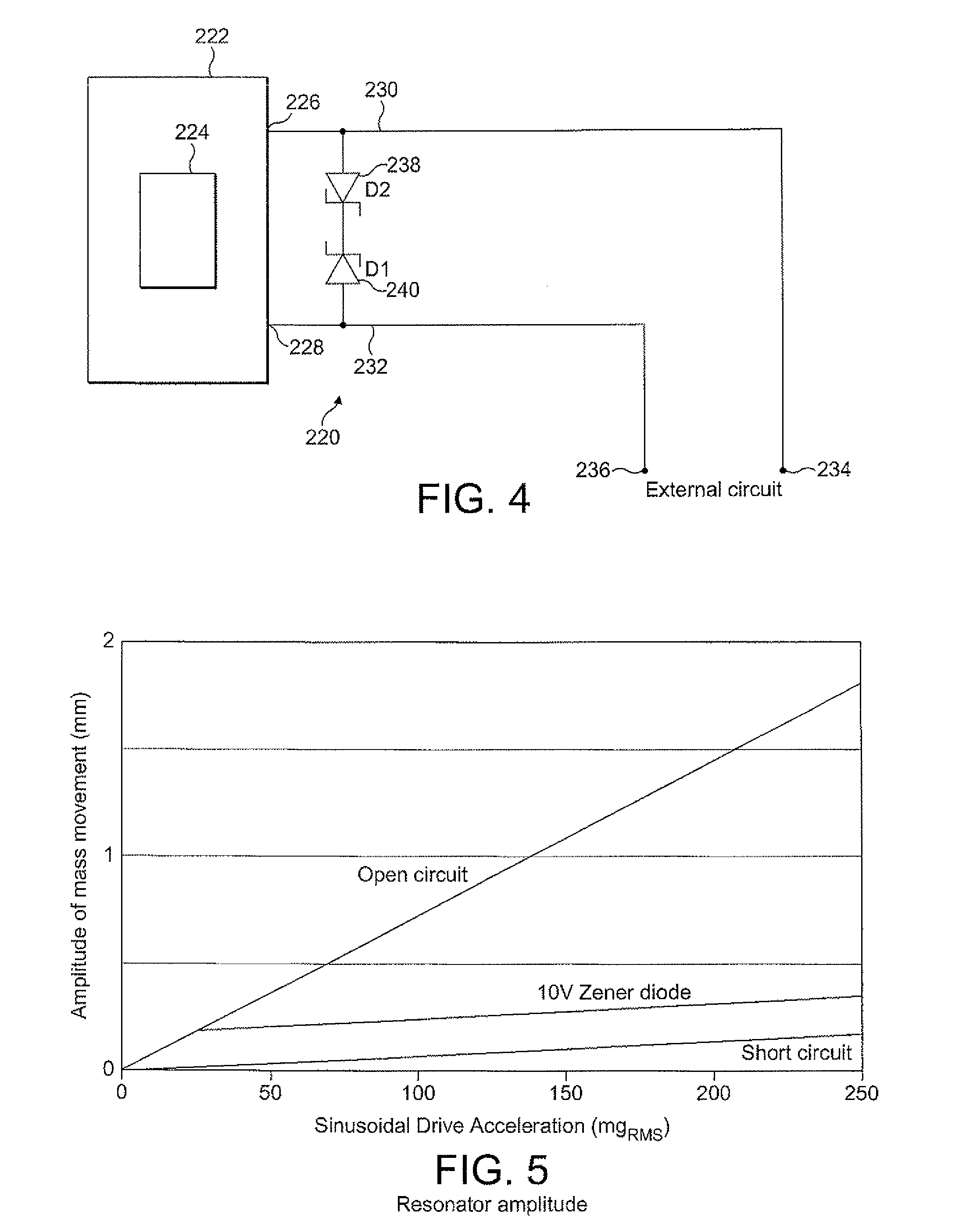
Electromechanical generator for, and method of, converting mechanical vibrational energy into electrical energy
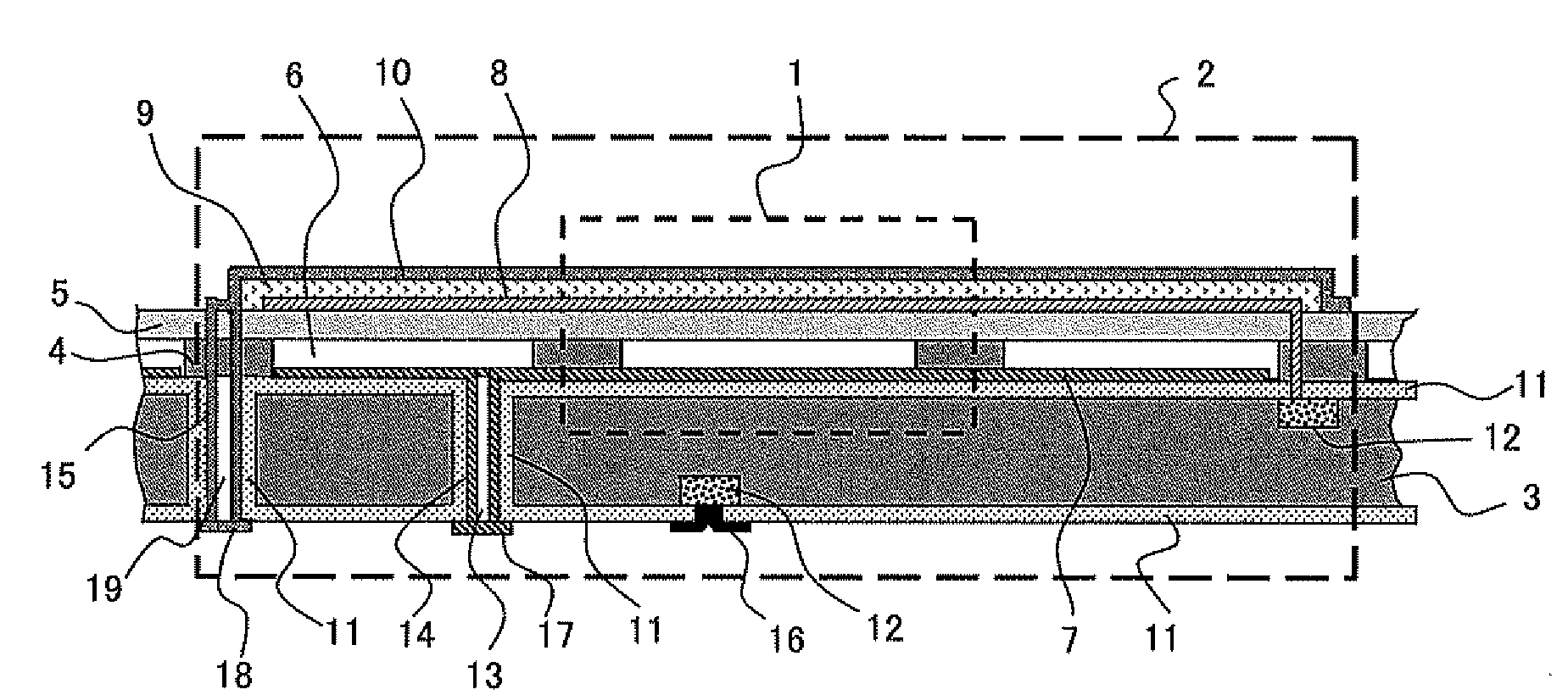
ActiveUS7345372B2Reduce the possibility of damageEasy to operateGeneration protection through controlMachines/enginesEngineeringFrequency oscillation
An electromechanical generator comprising an electromechanical device for converting mechanical vibrational energy into electrical energy, the electromechanical device having a vibratable mass adapted to resonate with an oscillation amplitude at a frequency and a regulator for regulating the oscillation amplitude to a value not greater than a maximum threshold.
Owner:PERPETUUM +1
Method of manufacturing a device with a cavity
ActiveUS20090267166A1More BEOL-processing compatibleReduce the temperatureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPorous layerDevice material
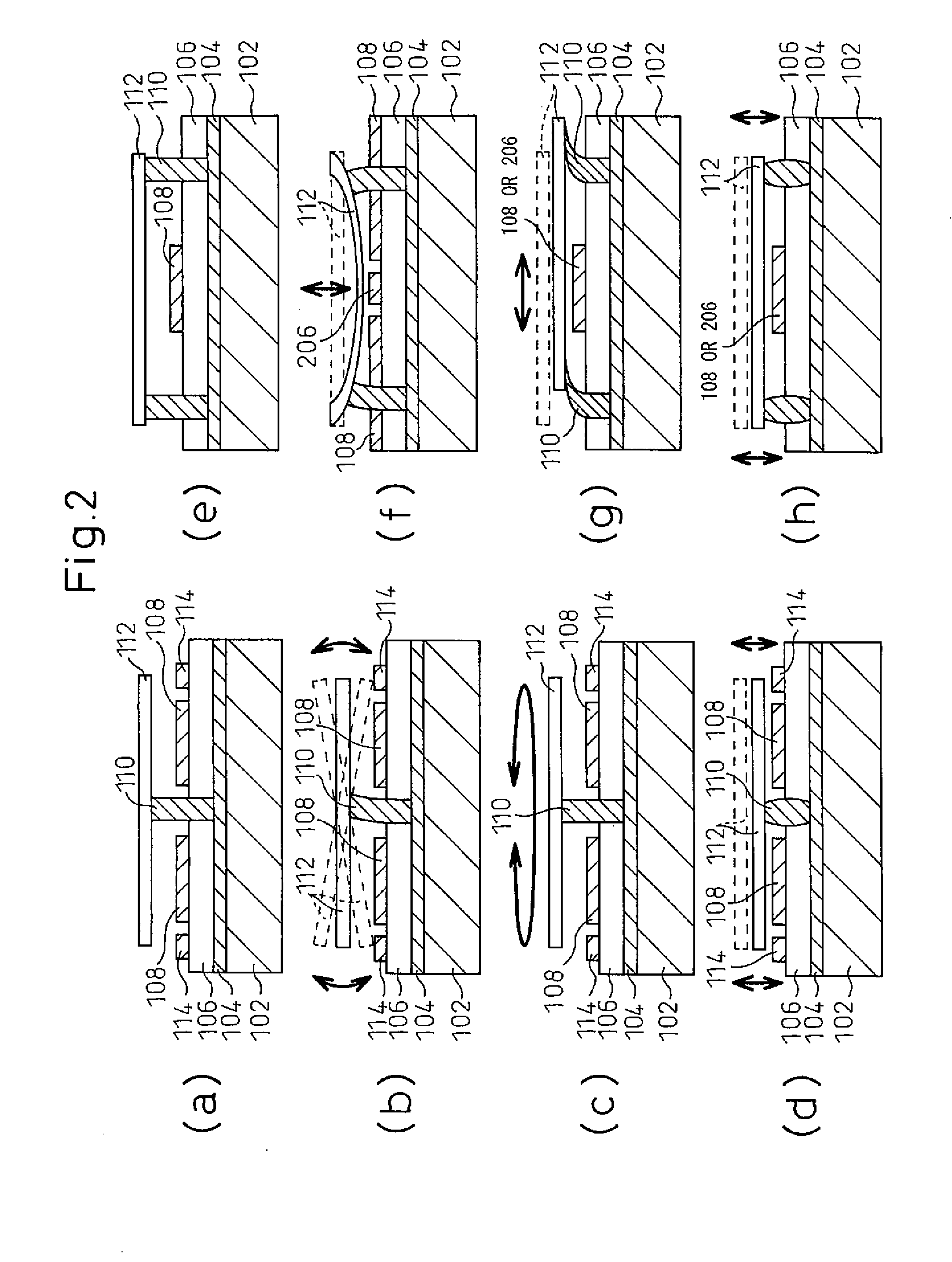
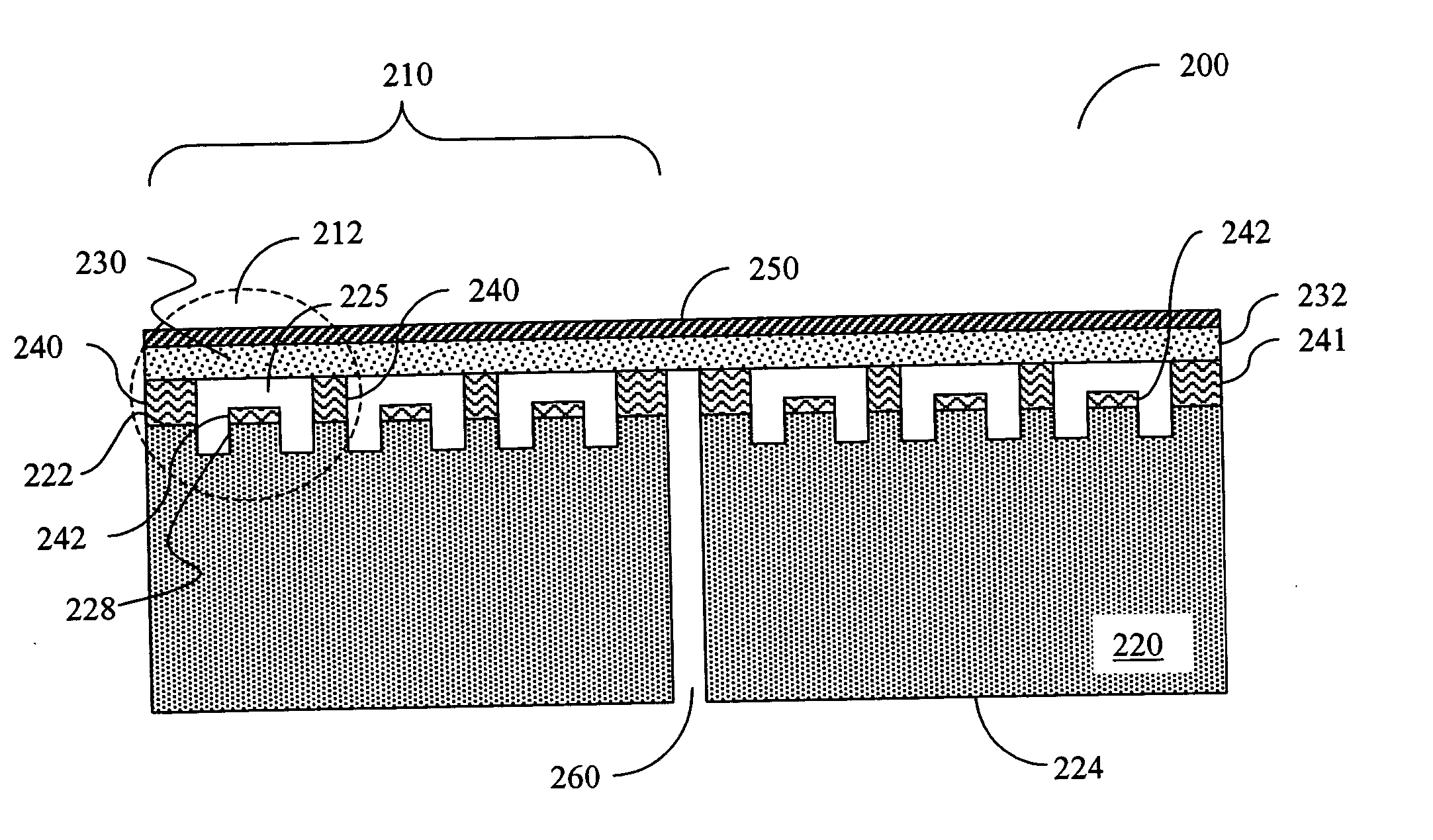
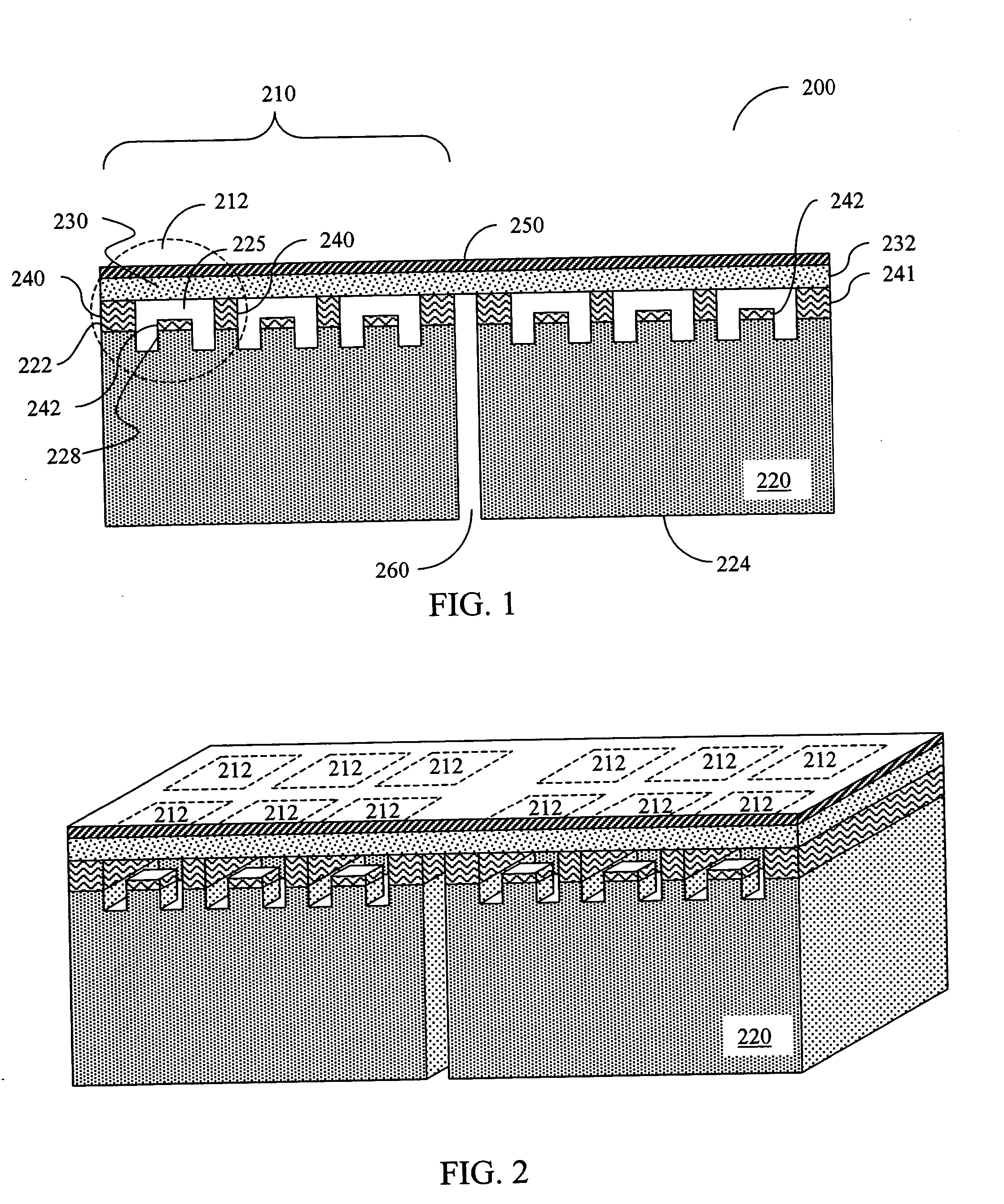
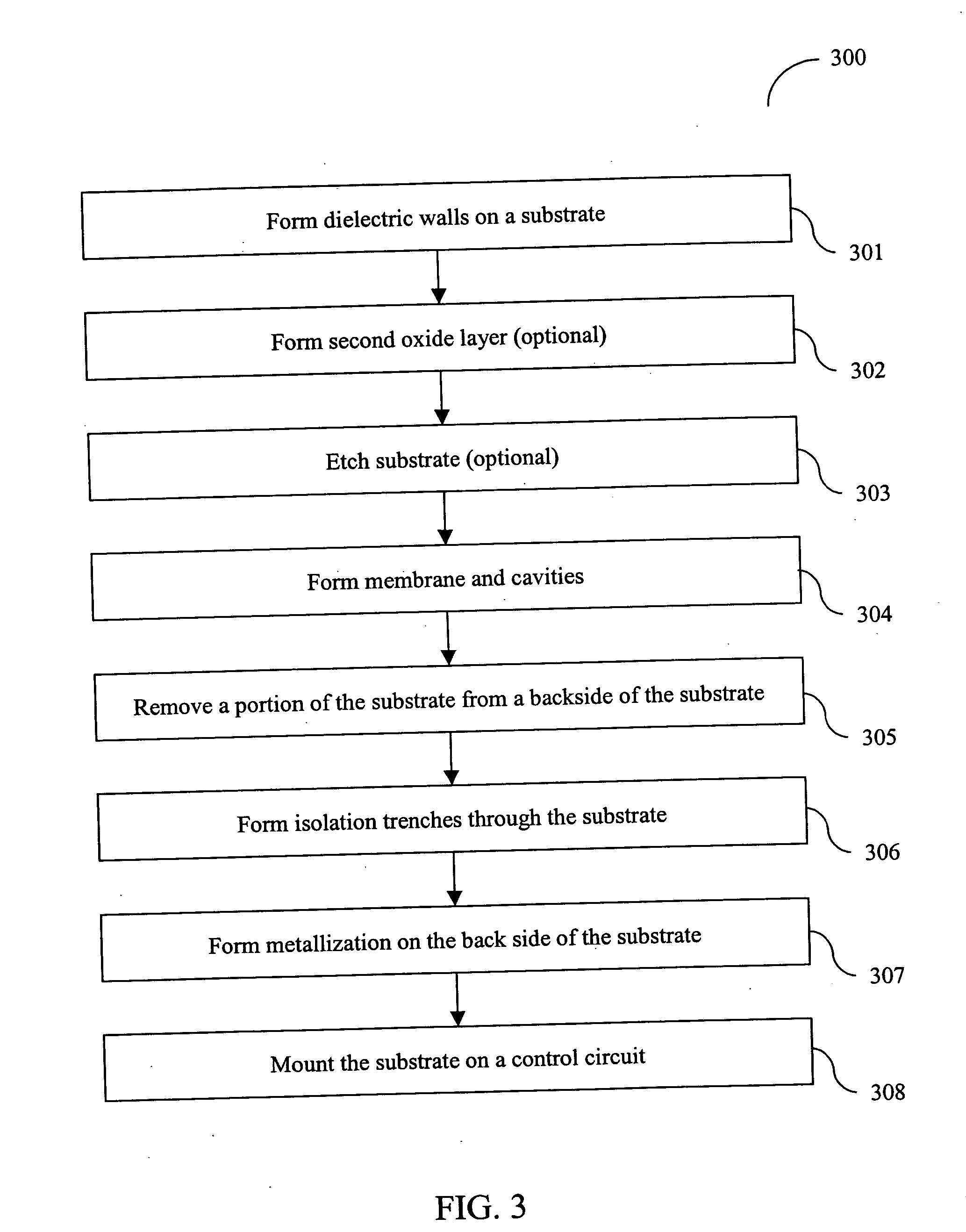
The invention relates to a micro-device with a cavity (50), the micro-device comprising a substrate (10, 110), the method comprising steps of: A) providing the substrate (10, 110), having a surface and comprising a sacrificial oxide region (20, 107, 115) at the surface ( ); B) covering the sacrificial oxide region (20, 107, 115) with a porous layer (40, 114, 124) being permeable to a vapor HF etchant (100), and C) selectively etching the sacrificial oxide region (20, 107, 115) through the porous layer (40, 114, 124) using the vapor HF etchant (100) to obtain the cavity (50). This method may be used in the manufacture of various micro-devices with a cavity (50), i.e. MEMS devices, and in particular in the encapsulation part thereof, and semiconductor devices, and in particular the BEOL-part thereof.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Movable device
InactiveUS20090021884A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesAcceleration measurementCarbon nanotubeMobile device
A movable device simultaneously enabling reduction of size down to the submicron level, higher speed operation, a streamlined production process, low costs, and greater reliability. A movable device provided with bottom electrodes and a basic conductive layer fixed to a substrate, an elastic shaft of a carbon nanotube with a bottom end fixed on the basic conductive layer and standing up, and a top structure including a top electrode spaced away from the bottom electrode and fixed to a top end of the elastic shaft, wherein when applying voltage between a bottom electrode and the top electrode, the top electrode displaces relatively to the bottom electrodes within an allowable range of elastic deformation of the elastic shaft.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducer array with through-substrate electrical connection and method of fabricating same
InactiveUS20060075818A1Improve utilization efficiencyImprove device performanceMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementCapacitanceCapacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers
The embodiments of the present invention provide a CMUT array and method of fabricating the same. The CMUT array has CMUT elements individually or respectively addressable from a backside of a substrate on which the CMUT array is fabricated. In one embodiment, a CMUT array is formed on a front side of a very high conductivity silicon substrate. Through wafer trenches are etched into the substrate from the backside of the substrate to electrically isolate individual CMUT elements formed on the front side of the substrate. Electrodes are formed on the backside of the substrate to individually address the CMUT elements through the substrate.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Asymetric membrane cMUT devices and fabrication methods
ActiveUS20050203397A1Reduce parasitic capacitanceImprove electrical performanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryCapacitanceCapacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers
Asymmetric membrane capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducer (“cMUT”) devices and fabrication methods are provided. In a preferred embodiment, a cMUT device according to the present invention generally comprises a membrane having asymmetric properties. The membrane can have a varied width across its length so that its ends have different widths. The asymmetric membrane can have varied flex characteristics due to its varied width dimensions. In another preferred embodiment, a cMUT device according to the present invention generally comprises an electrode element having asymmetric properties. The electrode element can have a varied width across its length so that its ends have different widths. The asymmetric electrode element can have different reception and transmission characteristics due to its varied width dimensions. In another preferred embodiment, a mass load positioned along the membrane can alter the mass distribution of the membrane. Other embodiments are also claimed and described.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Magnetically actuated micro-electro-mechanical apparatus and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20020050744A1Increase torqueReduce the numberForming microstructural systemsElectrostatic generators/motorsEngineeringMagnet
An array of magnetically actuated MEMS mirror devices is provided having stationary magnets configured to provide strong magnetic fields in the plane of the mirrors without any magnets or magnet-system components in the plane of the mirrors. Also, a magnetically actuated mirror device is provided that includes an improved actuation coil configuration that provides greater torque during mirror actuation. In addition, a mechanism is provided to detect the angular deflection of a moveable mirror. Also, an improved process is provided for manufacturing MEMS mirror devices.
Owner:CORNING INC
Micromechanical resonator device and micromechanical device utilizing same
InactiveUS6856217B1Improving QHigh Power Handling CapabilityPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksWireless transceiverTransceiver
A micromechanical resonator device and a micromechanical device utilizing same are disclosed based upon a radially or laterally vibrating disk structure and capable of vibrating at frequencies well past the GHz range. The center of the disk is a nodal point, so when the disk resonator is supported at its center, anchor dissipation to the substrate is minimized, allowing this design to retain high-Q at high frequency. In addition, this design retains high stiffness at high frequencies and so maximizes dynamic range. Furthermore, the sidewall surface area of this disk resonator is often larger than that attainable in previous flexural-mode resonator designs, allowing this disk design to achieve a smaller series motional resistance than its counterparts when using capacitive (or electrostatic) transduction at a given frequency. Capacitive detection is not required in this design, and piezoelectric, magnetostrictive, etc. detection are also possible. The frequency and dynamic range attainable by this resonator makes it applicable to high-Q RF filtering and oscillator applications in a wide variety of communication systems. Its size also makes it particularly suited for portable, wireless applications, where, if used in large numbers, such a resonator can greatly lower the power consumption, increase robustness, and extend the range of application of high performance wireless transceivers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Electroactive polymer devices for controlling fluid flow
InactiveUS7320457B2Improve mechanical responseImprove responsePiezoelectric/electrostrictive gramophone pickupsTransducer detailsMomentumTransducer
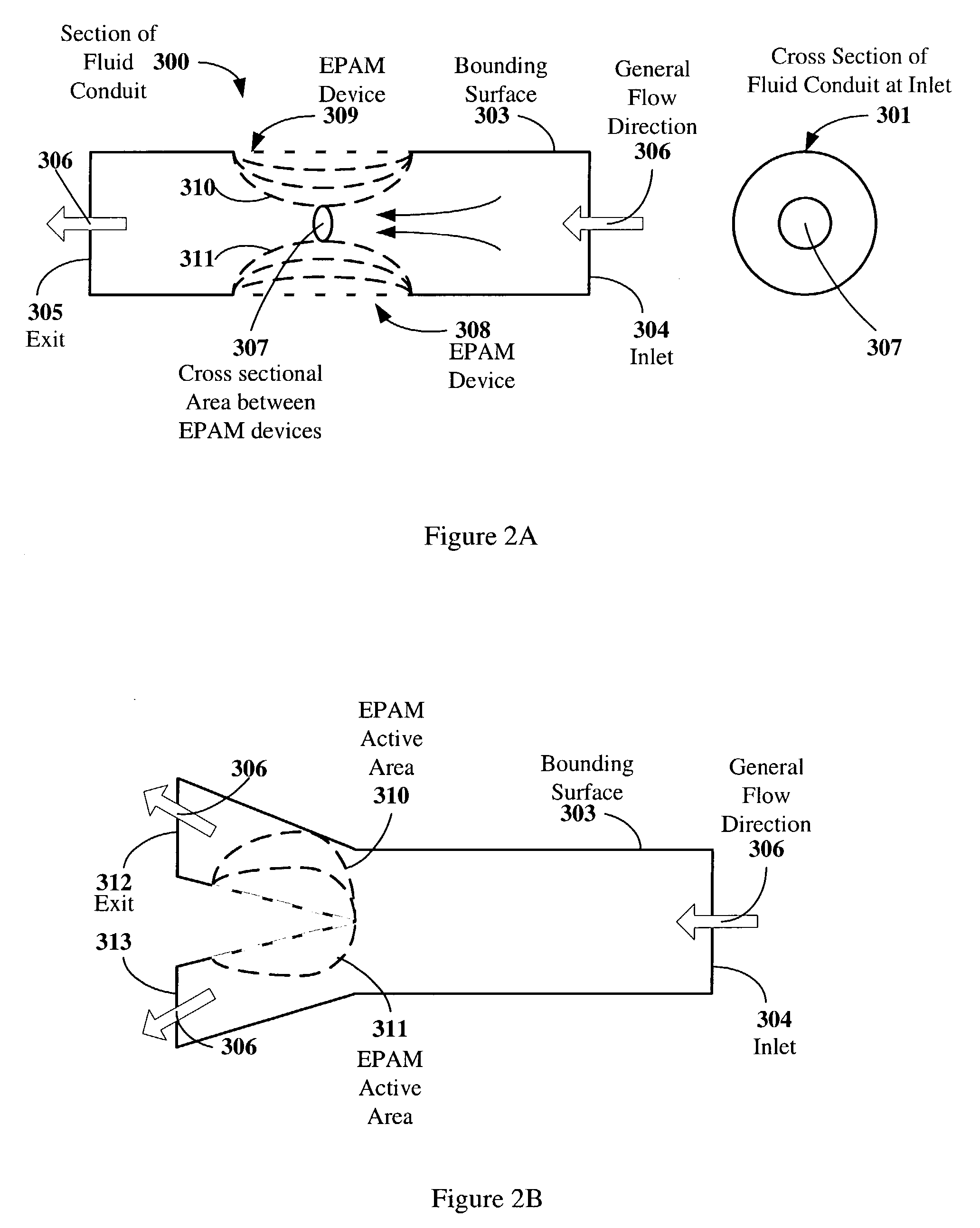
The invention describes devices for controlling fluid flow, such as valves. The devices may include one or more electroactive polymer transducers with an electroactive polymer that deflects in response to an application of an electric field. The electroactive polymer may be in contact with a fluid where the deflection of the electroactive polymer may be used to change a characteristic of the fluid. Some of the characteristic of the fluid that may be changed include but are not limited to 1) a flow rate, 2) a flow direction, 3) a flow vorticity, 4) a flow momentum, 5) a flow mixing rate, 6) a flow turbulence rate, 7) a flow energy, 8) a flow thermodynamic property. The electroactive polymer may be a portion of a surface of a structure that is immersed in an external fluid flow, such as the surface of an airplane wing or the electroactive polymer may be a portion of a surface of a structure used in an internal flow, such as a bounding surface of a fluid conduit.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Piezoelectric-driven MEMS device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050242687A1Fabricated reliably and consistentlyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesThin membraneEngineering
A piezoelectric-driven MEMS device can be fabricated reliably and consistently. The piezoelectric-driven MEMS device includes: a movable flat beam having a piezoelectric film disposed above a substrate with a recessed portion such that the piezoelectric film is bridged over the recessed portion, piezoelectric drive mechanisms disposed at both ends of the piezoelectric film and configured to drive the piezoelectric film, and a first electrode disposed at the center of the substrate-side of the piezoelectric film, and a second electrode disposed on a flat part of the recessed portion of the substrate and facing the first electrode of the movable flat beam.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Harmonic cMUT devices and fabrication methods
InactiveUS7612483B2Reduce parasitic capacitanceImprove electrical performancePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMechanical vibrations separationCapacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducersHarmonic
Harmonic capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducer (“cMUT”) devices and fabrication methods are provided. In a preferred embodiment, a harmonic cMUT device generally comprises a membrane having a non-uniform mass distribution. A mass load positioned along the membrane can be utilized to alter the mass distribution of the membrane. The mass load can be a part of the membrane and formed of the same material or a different material as the membrane. The mass load can be positioned to correspond with a vibration mode of the membrane, and also to adjust or shift a vibration mode of the membrane. The mass load can also be positioned at predetermined locations along the membrane to control the harmonic vibrations of the membrane. A cMUT can also comprise a cavity defined by the membrane, a first electrode proximate the membrane, and a second electrode proximate a substrate. Other embodiments are also claimed and described.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Electromechanical generator for, and method of, converting mechanical vibrational energy into electrical energy
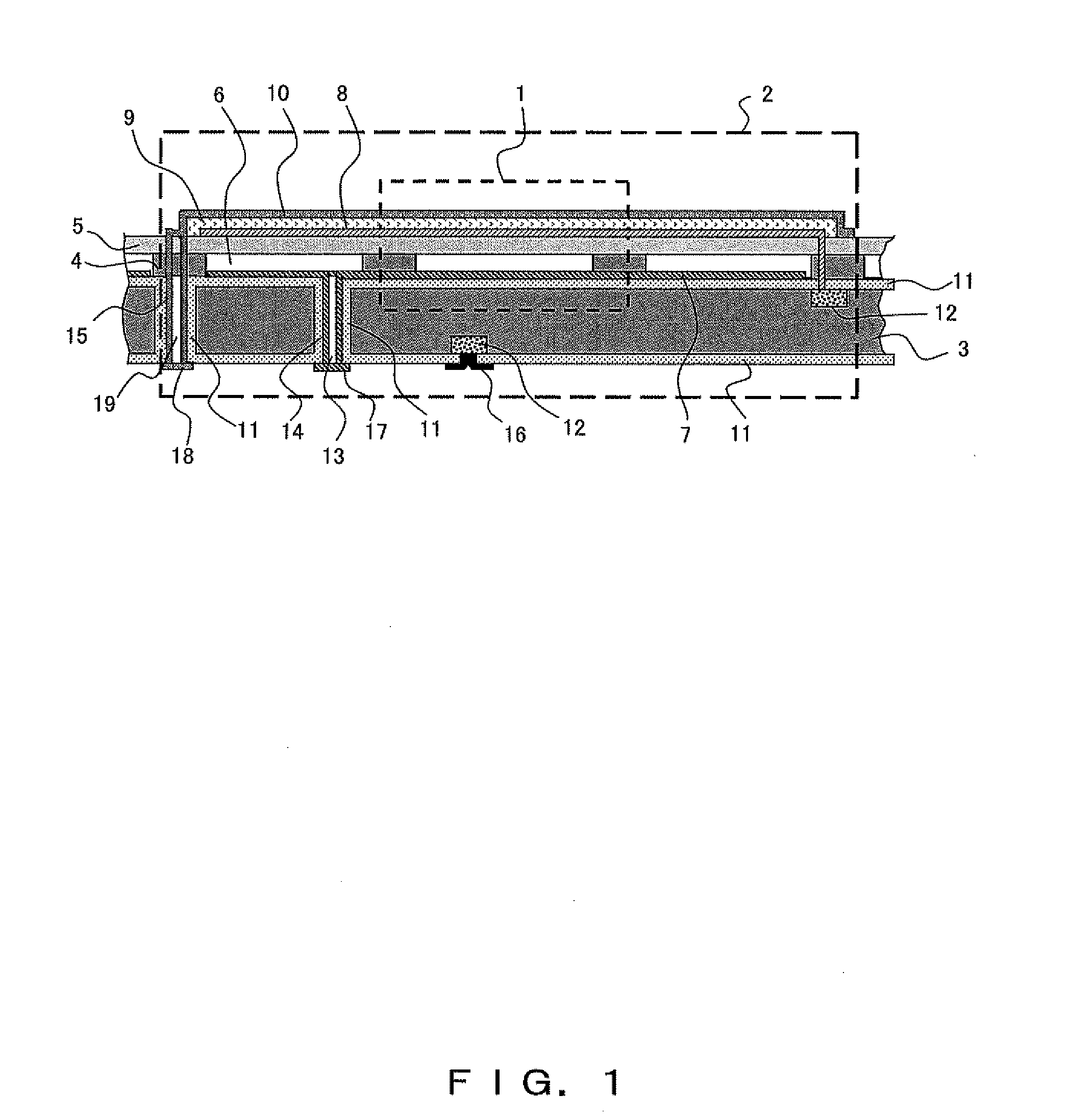
ActiveUS20070210580A1Reduce the possibility of damageExtended service lifeGeneration protection through controlMachines/enginesEngineeringFrequency oscillation
An electromechanical generator comprising an electromechanical device for converting mechanical vibrational energy into electrical energy, the electromechanical device having a vibratable mass adapted to resonate with an oscillation amplitude at a frequency and a regulator for regulating the oscillation amplitude to a value not greater than a maximum threshold.
Owner:PERPETUUM +1
Asymmetric membrane cMUT devices and fabrication methods
ActiveUS7646133B2Reduce parasitic capacitanceImprove electrical performanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCapacitanceCapacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers
Asymmetric membrane capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducer (“cMUT”) devices and fabrication methods are provided. In a preferred embodiment, a cMUT device according to the present invention generally comprises a membrane having asymmetric properties. The membrane can have a varied width across its length so that its ends have different widths. The asymmetric membrane can have varied flex characteristics due to its varied width dimensions. In another preferred embodiment, a cMUT device according to the present invention generally comprises an electrode element having asymmetric properties. The electrode element can have a varied width across its length so that its ends have different widths. The asymmetric electrode element can have different reception and transmission characteristics due to its varied width dimensions. In another preferred embodiment, a mass load positioned along the membrane can alter the mass distribution of the membrane. Other embodiments are also claimed and described.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
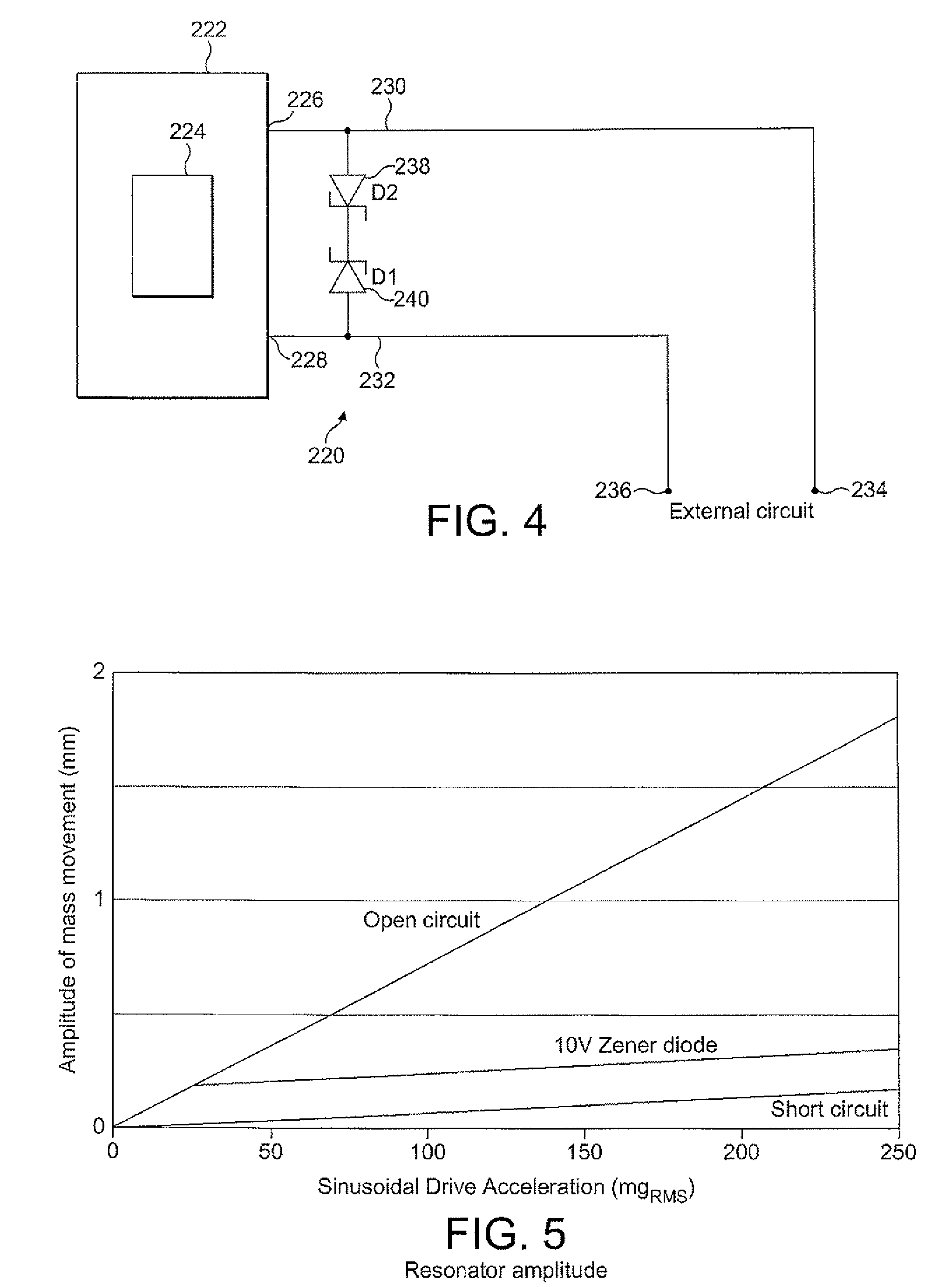
Accelerometer and methods thereof
InactiveUS6854330B2More sensitiveInvention is highAcceleration measurement using interia forcesElectrostatic generators/motorsElectrical and Electronics engineeringAccelerometer
An accelerometer includes a housing with a chamber, a member with a stored static charge, and a pair of electrodes connected to the housing. The member is connected to the housing and extends at least partially across the chamber. The pair of electrodes are each spaced from and on substantially opposing sides of the member from each other and are at least partially in alignment with each other. The member is movable with respect to the pair of electrodes or one of the pair of electrodes is movable with respect to the member.
Owner:NTH TECH
High strain tear resistant gels and gel composites for use as artificial muscle actuators
InactiveUS6909220B2Improve propertiesImprove tear resistanceCellsSludge treatmentPolymer sciencePlasticizer
Novel gels and articles are formed from one or more copolymers having at least one poly(ethylene) components and high levels of one or more plasticizers, said gels having an amount of crystallinity, glassy components, and selected plasticizers sufficient to achieve improvements in one or more physical properties including improved crack propagation resistance, improved tear resistance, improved resistance to fatigue, resistance to catastrophic failure, and exhibiting high strain under elongations not obtainable in amorphous gels which high strain making the gel suitable for use as film layers for artificial muscles.
Owner:APPLIED ELASTOMERICS
Ultrasound transducer manufactured by using micromachining process, its device, endoscopic ultrasound diagnosis system thereof, and method for controlling the same
ActiveUS20090001853A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesUltrasonic sensorControl signal
An ultrasound transducer manufactured by using a micromachining process comprises: a first electrode into which a control signal for transmitting ultrasound is input; a substrate on which the first electrode is formed; a second electrode that is a ground electrode facing the first electrode with a prescribed space between the first and second electrodes; a membrane on which the second electrode is formed and which vibrates and generates the ultrasound when a voltage is applied between the first and second electrodes; a piezoelectric film contacting the membrane; and a third electrode electrically continuous to the piezoelectric film.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Method of manufacturing ultrasound transducer device having acoustic backing
InactiveUS20050046311A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrical testingSonificationAcoustic energy
An ultrasonic transducer device comprising: an ultrasonic transducer array micromachined on a substrate; flexible electrical connections connected to the transducer array; and a body of acoustically attenuative material that supports the substrate and the flexible electrical connections. The acoustic backing material may contain additional features, such as tabs or notches, for use in positioning the transducer on fixtures during manufacturing or positioning the transducer within a housing during final assembly. Tabs or other features that are used only during manufacturing may be subsequently removed from the device. The MUT device itself may also be thinned so as to provide flexibility as desired. The backing material is preferably matched in acoustic impedance to the silicon wafer so as to prevent reflection at the interface of any acoustic energy propagating rearward, i.e., in the direction away from the device front surface. The backing material may also possess a high thermal conductivity to assist in removal of heat from the device.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Harmonic cMUT devices and fabrication methods
InactiveUS20050200242A1Reduce parasitic capacitanceImprove electrical performancePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMechanical vibrations separationCapacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducersHarmonic
Harmonic capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducer (“cMUT”) devices and fabrication methods are provided. In a preferred embodiment, a harmonic cMUT device generally comprises a membrane having a non-uniform mass distribution. A mass load positioned along the membrane can be utilized to alter the mass distribution of the membrane. The mass load can be a part of the membrane and formed of the same material or a different material as the membrane. The mass load can be positioned to correspond with a vibration mode of the membrane, and also to adjust or shift a vibration mode of the membrane. The mass load can also be positioned at predetermined locations along the membrane to control the harmonic vibrations of the membrane. A cMUT can also comprise a cavity defined by the membrane, a first electrode proximate the membrane, and a second electrode proximate a substrate. Other embodiments are also claimed and described.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
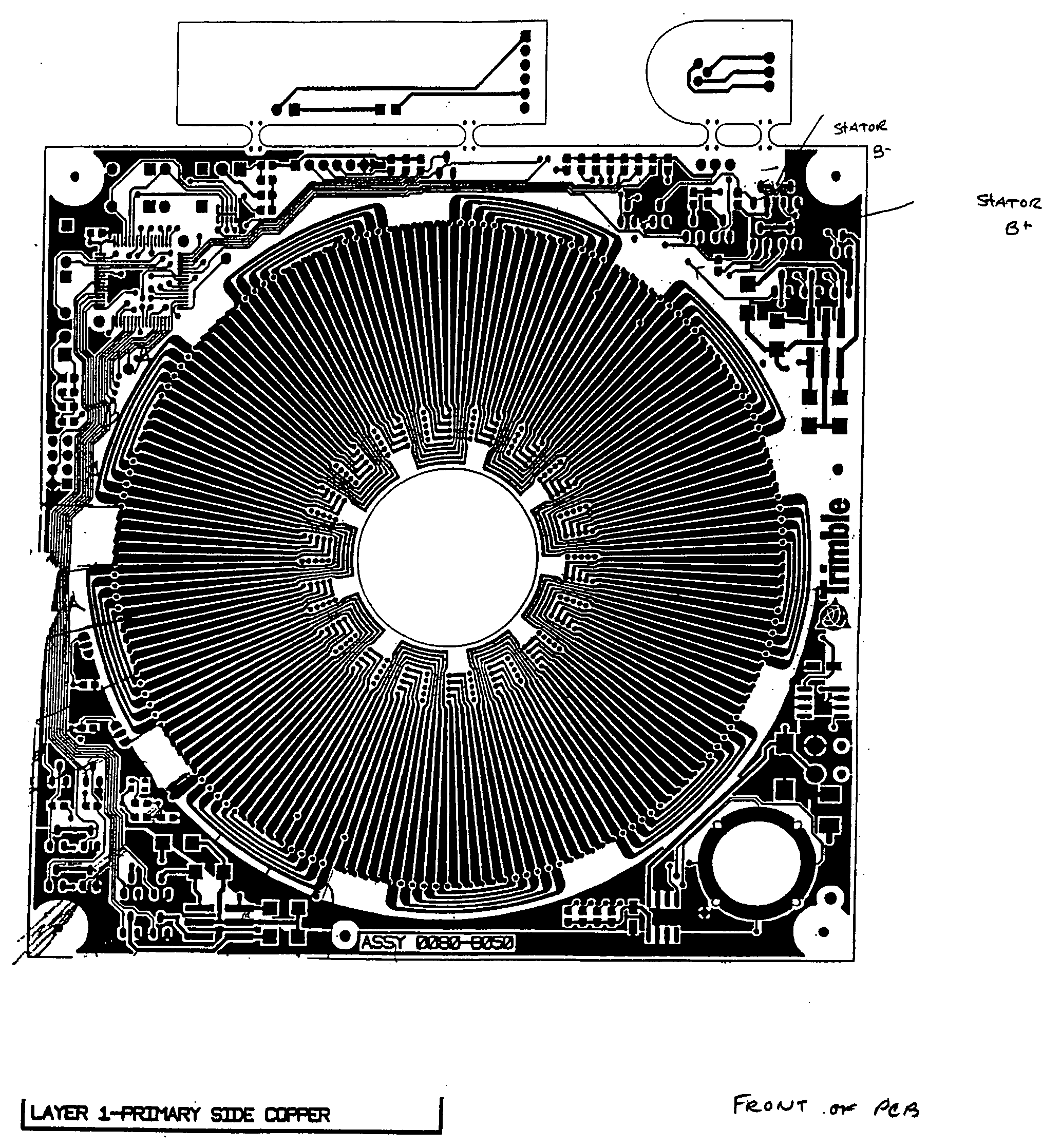
Printed circuit board motor
InactiveUS20060055265A1Easy to controlCurrent consumptionAssociation with control/drive circuitsMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectrical conductorAverage current
A printed circuit board motor is disclosed. The motor comprises a rotor plate embedded with magnets, an axle, and a printed circuit board stator. The printed circuit board comprises two conductors printed on the same surface or on opposite surfaces of the printed circuit board The two conductors produce alternating “square wave” patterns. The printed circuit board circuitry causes the direction of the current flow to reverse at intervals. The rotor rotates in response to the current flow in the stator. The rotation rate can be accurately controlled. The torque and average current consumption can be controlled by “chopping” the current with high frequency modulation whose duty cycle is proportional to the torque and average current consumption which will prolong the battery life of the motor.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducer array with through-substrate electrical connection and method of fabricating same
InactiveUS7545075B2Improve utilization efficiencyImprove performanceMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementCapacitanceCapacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers
The embodiments of the present invention provide a CMUT array and method of fabricating the same. The CMUT array has CMUT elements individually or respectively addressable from a backside of a substrate on which the CMUT array is fabricated. In one embodiment, a CMUT array is formed on a front side of a very high conductivity silicon substrate. Through wafer trenches are etched into the substrate from the backside of the substrate to electrically isolate individual CMUT elements formed on the front side of the substrate. Electrodes are formed on the backside of the substrate to individually address the CMUT elements through the substrate.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Tunneling-effect energy converters
InactiveUS6946596B2Preventive effectThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesThermal energyElectricity
Tunneling-effect converters of thermal energy to electricity with an emitter and a collector separated from each other by a distance that is comparable to atomic dimensions and where tunneling effect plays an important role in the charge movement from the emitter to the collector across the gap separating such emitter and collector. At least one of the emitter and collector structures includes a flexible structure. Tunneling-effect converters include devices that convert thermal energy to electrical energy and devices that provide refrigeration when electric power is supplied to such devices.
Owner:MICROPOWER GLOBAL
Electroactive polymer generators
InactiveUS20060238066A1Speed up the conversion processImprove responseTransducer detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPre strainActive polymer
The present invention relates to transducers, their use and fabrication. The transducers convert between mechanical and electrical energy. Some transducers of the present invention include a pre-strained polymer. The pre-strain improves the conversion between electrical and mechanical energy. The present invention also relates to devices including an electroactive polymer to convert between electrical and mechanical energy. The present invention further relates to compliant electrodes that conform to the shape of a polymer included in a transducer. The present invention provides methods for fabricating electromechanical devices including one or more electroactive polymers.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
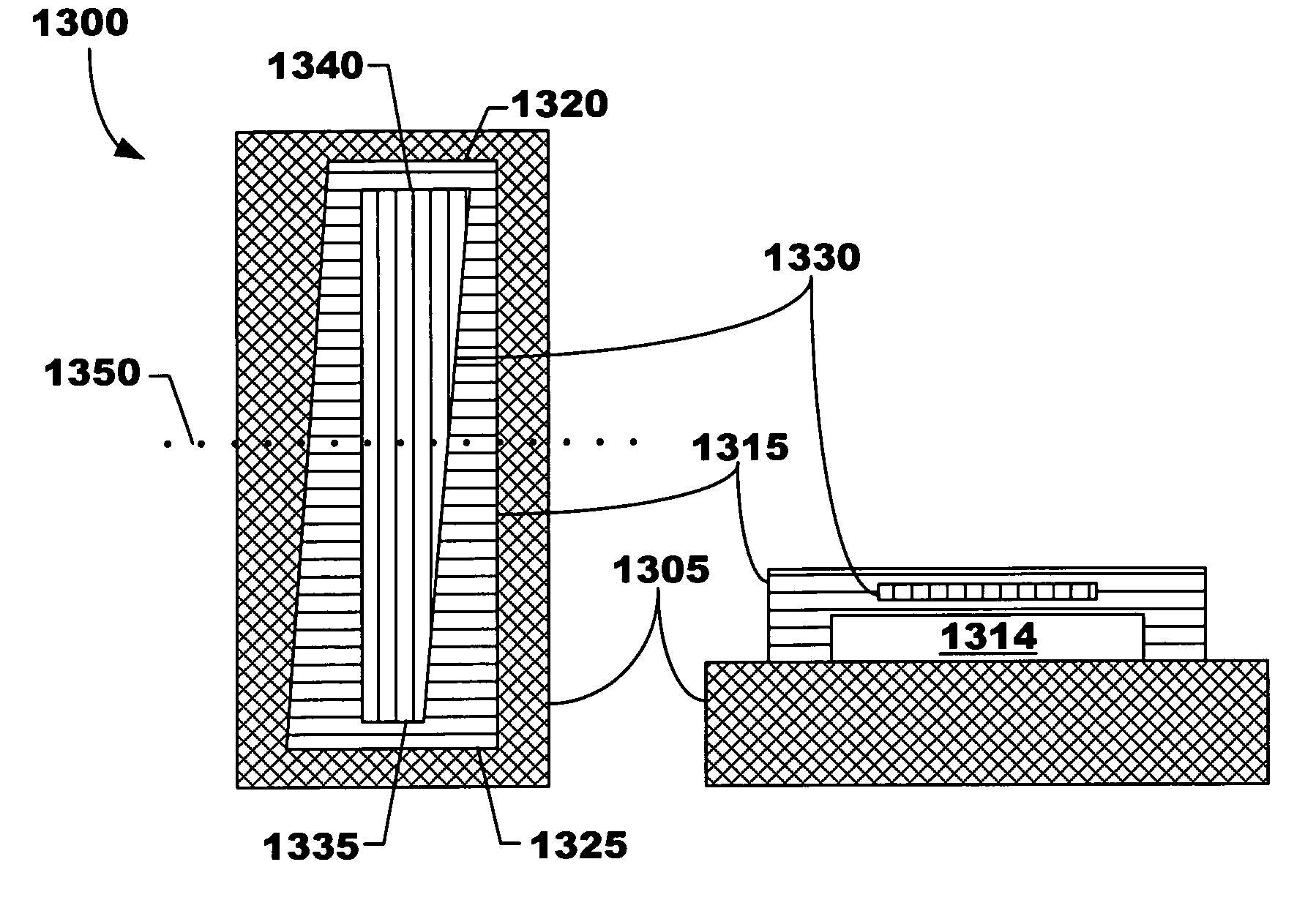
Three-dimensional structures having feature sizes smaller than a minimum feature size and methods for fabricating
ActiveUS20050126916A1Small feature sizeImprove efficiencyAdditive manufacturing apparatusDuplicating/marking methodsFeature DimensionComputer science
Owner:MICROFAB
Electrostatic membranes for sensors, ultrasonic transducers incorporating such membranes, and manufacturing methods therefor
ActiveUS20080184549A1Maximize energy conversionEfficiently and effectively implementPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUltrasonic sensorTransducer
Owner:VERMON
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com