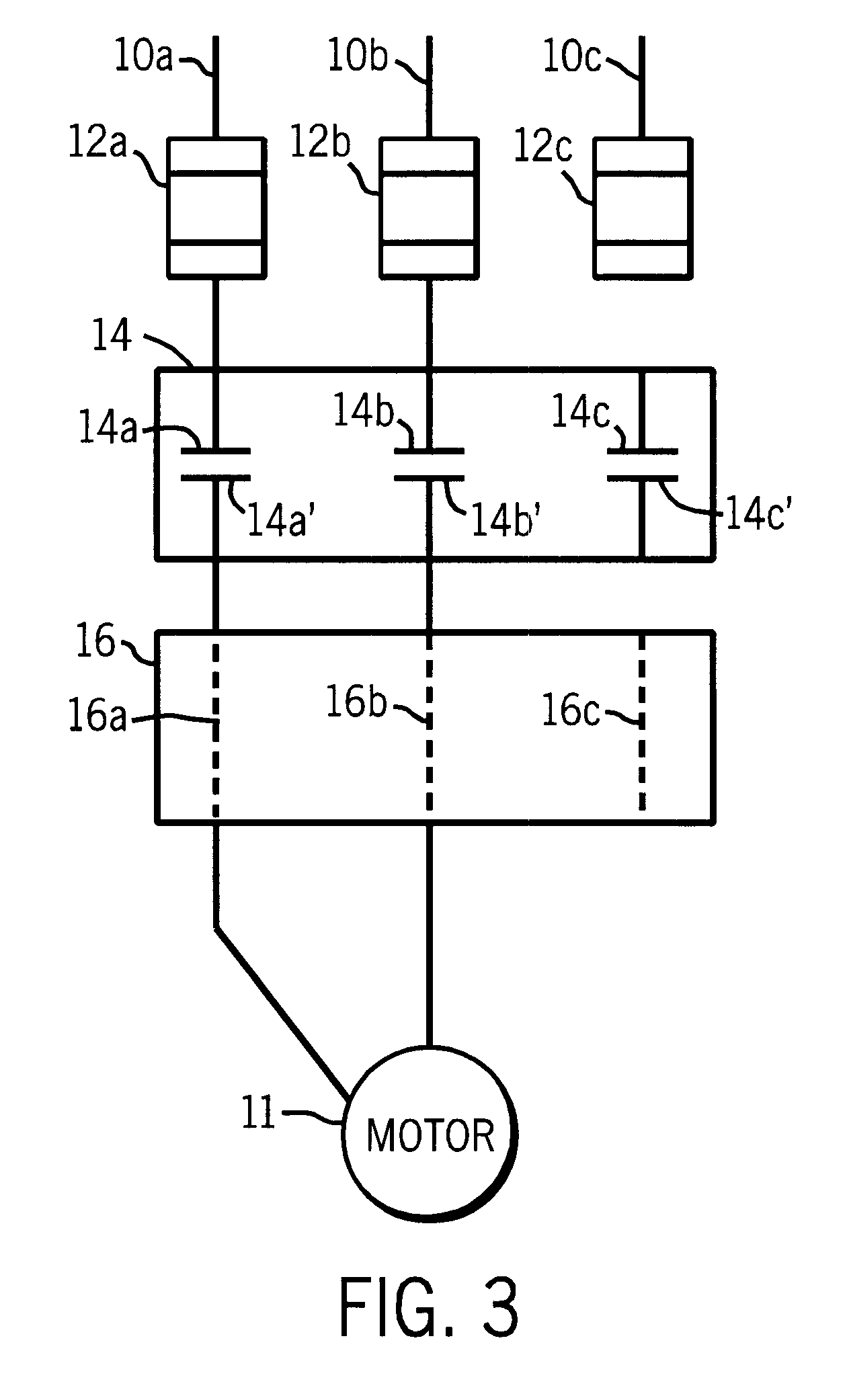
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5900 results about "Phase currents" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Line current means the current flowing through the AC supply lines.phase current means current flowing through each phases like R or Y or B phases.relation between line & phae currents are star connected system: phase current =linecurrent delta connected system: phase current ={ linecurrent/√3}.
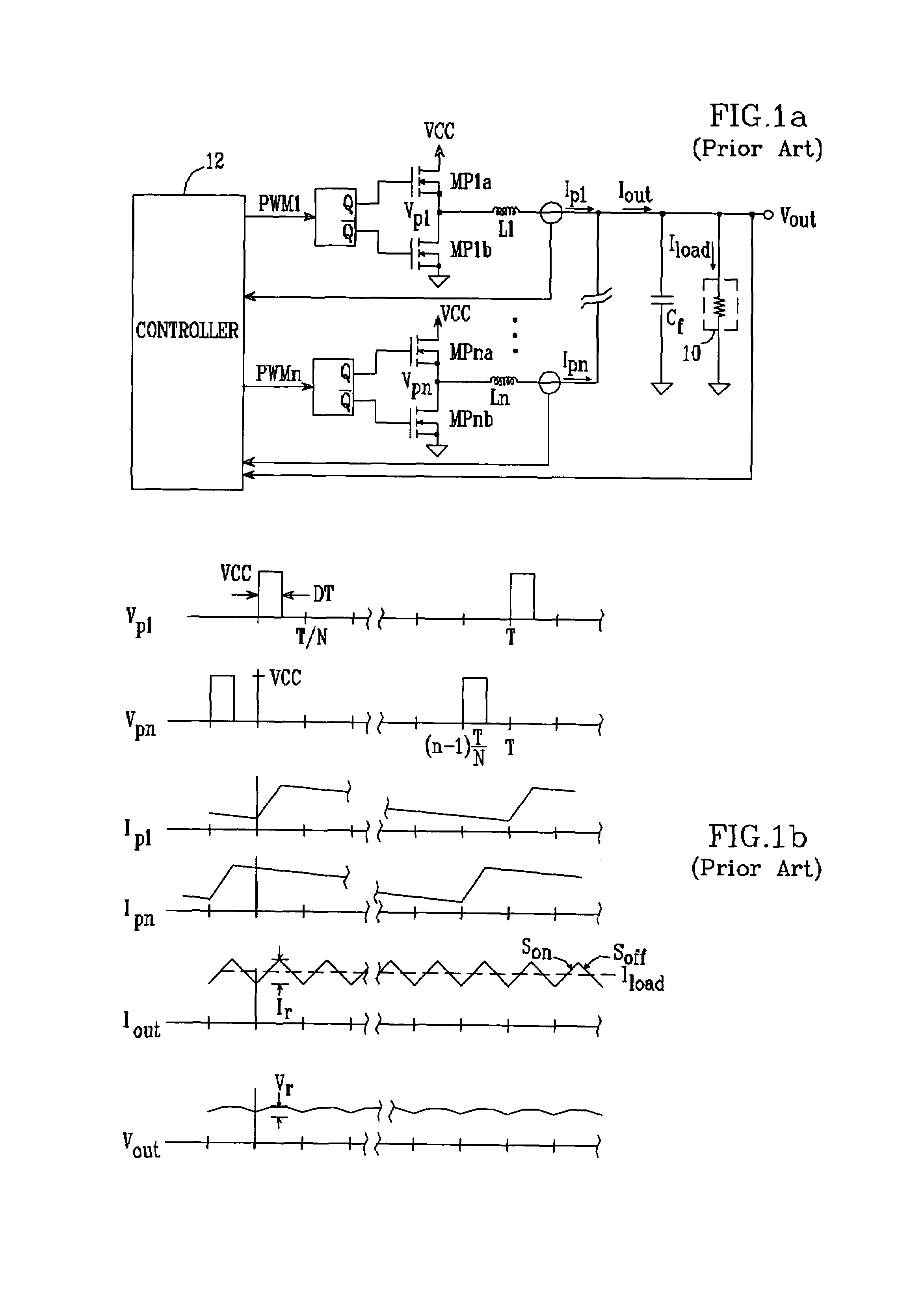
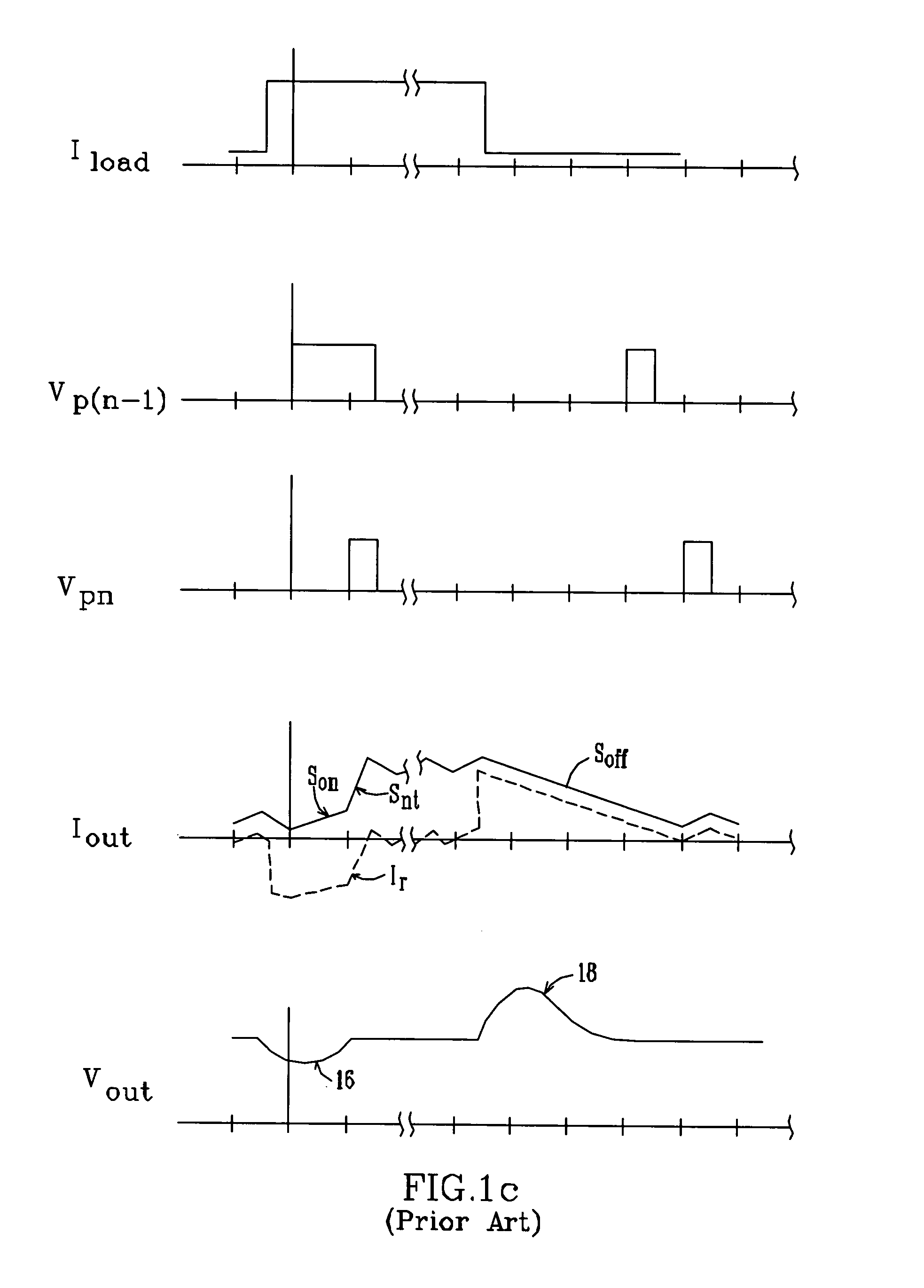
Multi-phase switching regulator
InactiveUSRE39976E1Overcome problemsEasy to controlDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationPhase currentsAudio power amplifier
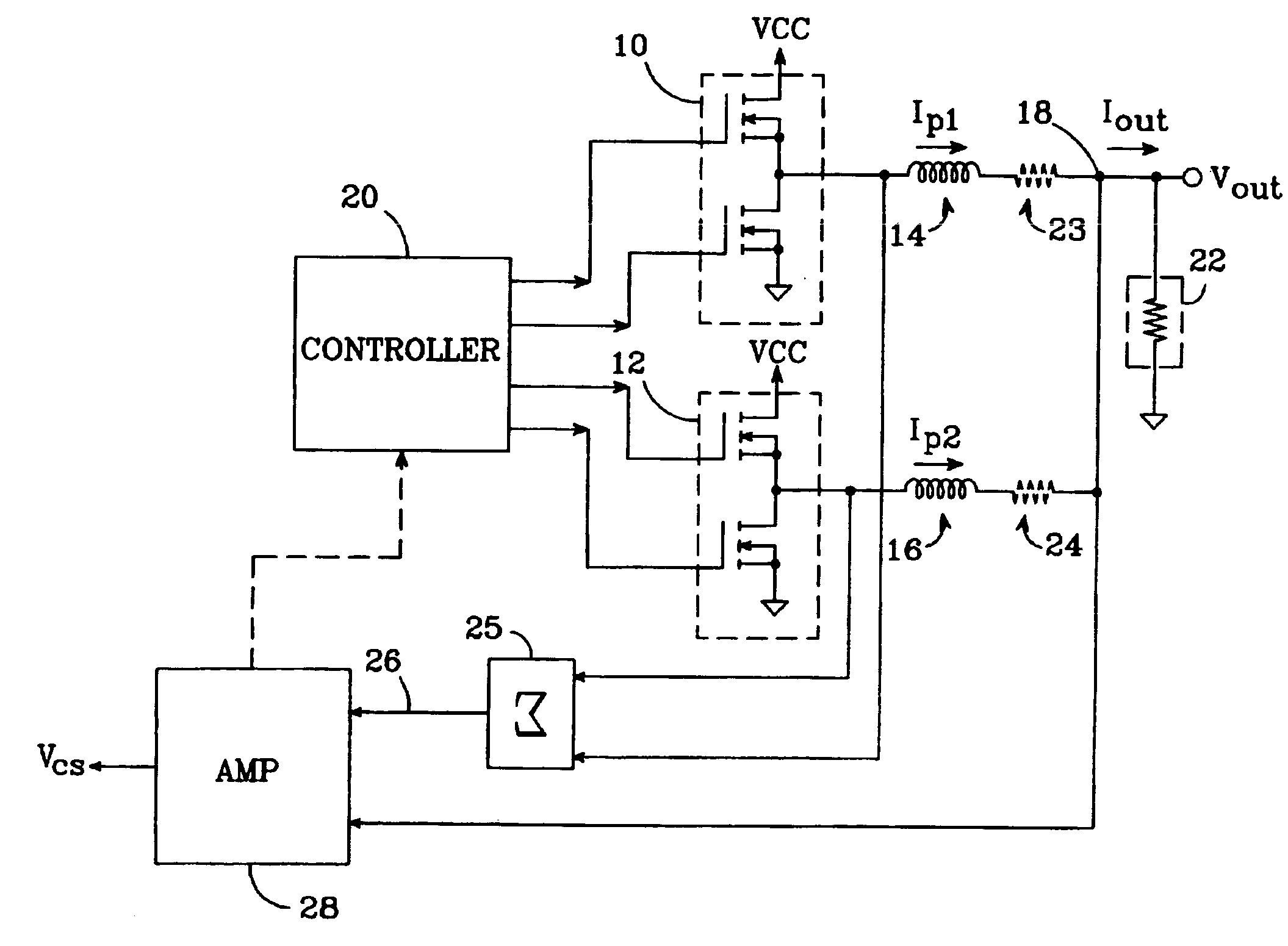
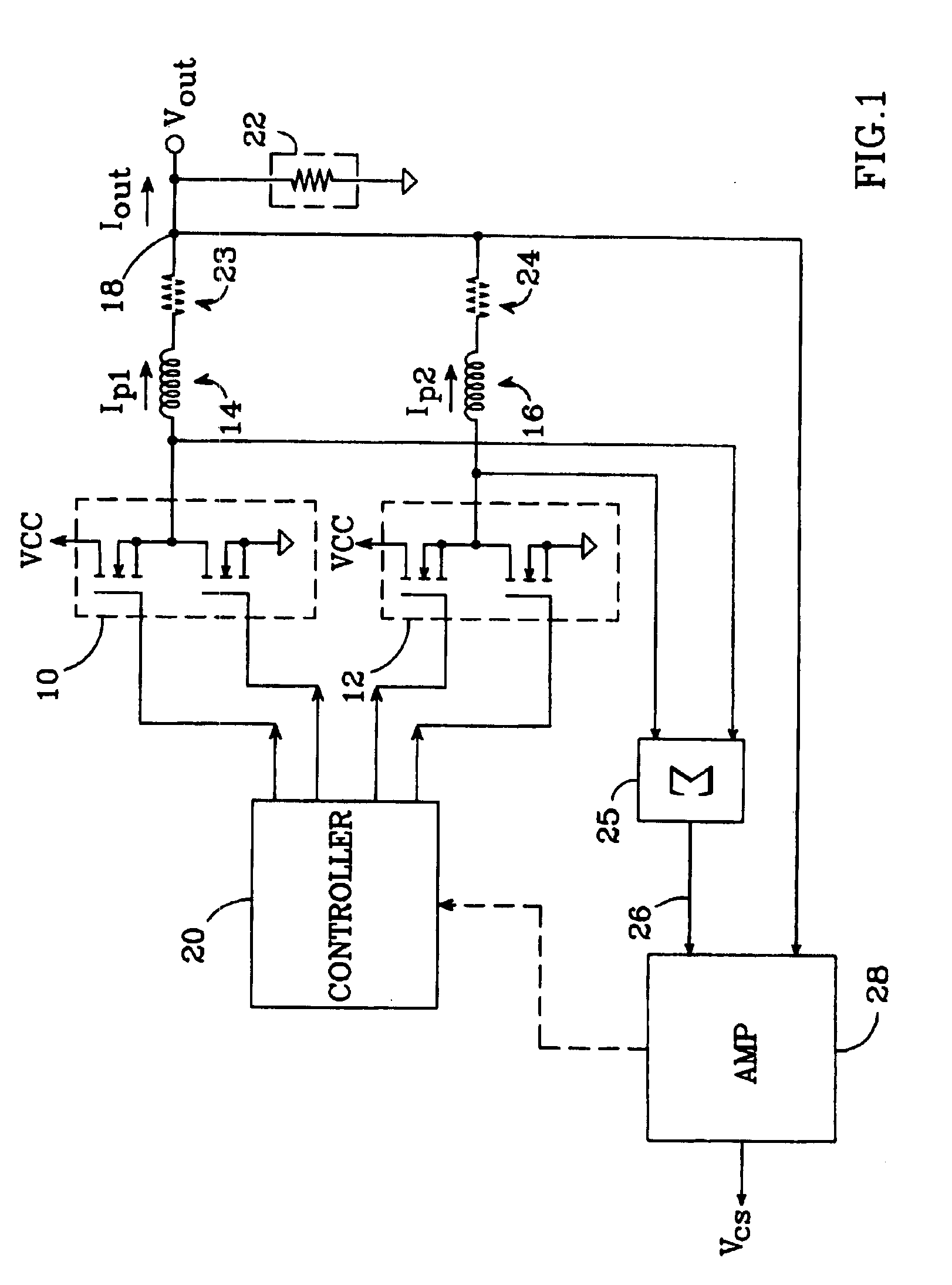
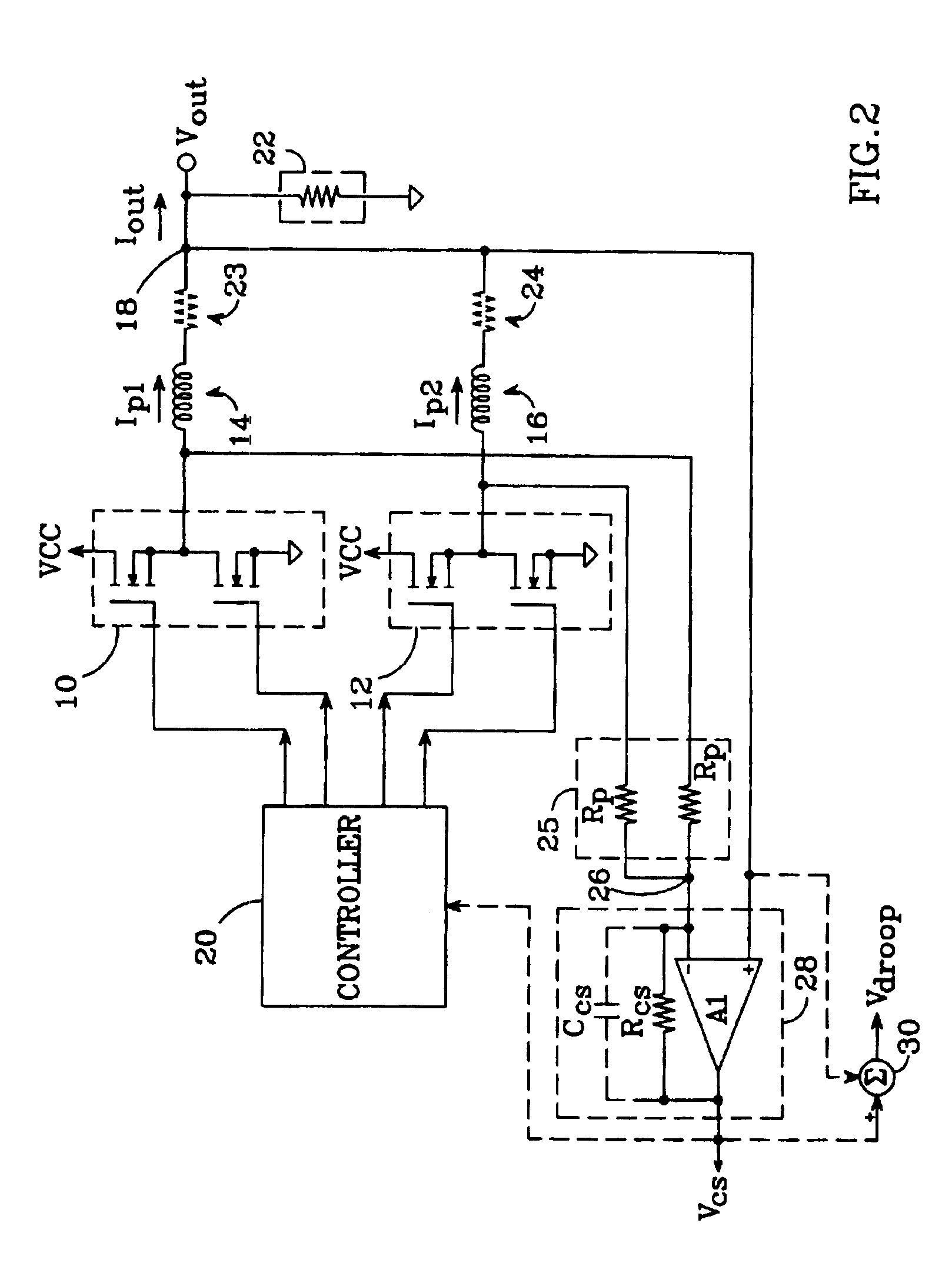
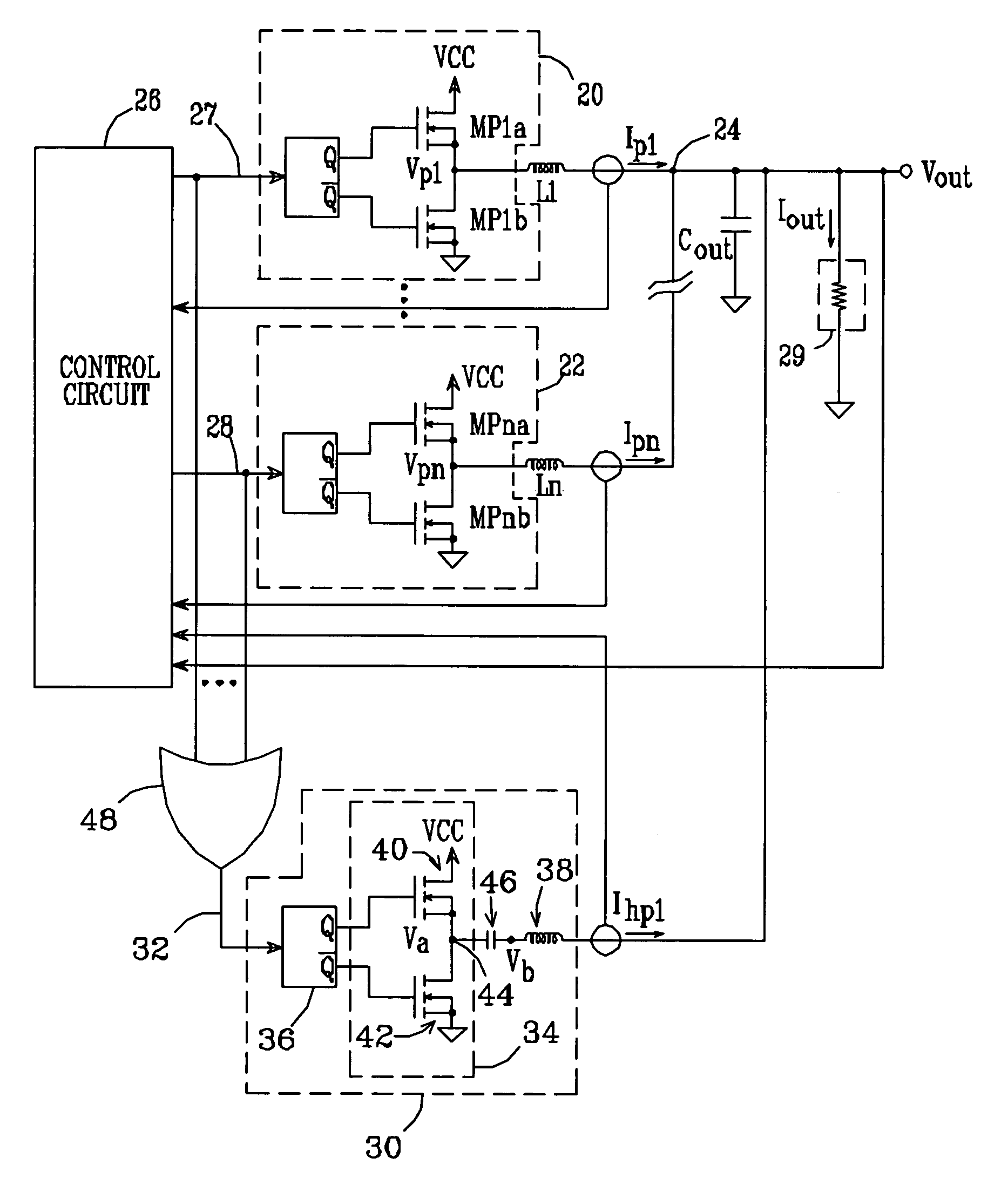
An N-phase switching voltage regulator includes N current sensing elements which carry respective phase currents. The voltages present at the switch node sides of the sensing elements are summed and presented to an amplifier which also receives the regulator's output voltage, to produce an output which is proportional to the regulator's total output current Iout. The invention also provides a means for direct insertion of total inductor output current information into a regulator's voltage-mode control loop, to provide active voltage positioning (AVP) for the output voltage. A voltage based on total inductor output current is summed with the regulator's reference voltage; this sum and Vout are applied to the voltage control error amplifier, the output of which is processed to operate the regulator's switches. This enables the regulator's output to have a desired droop impedance and to provide AVP of Vout as a function of total filtered inductor output current Iout(fltr).
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Permanent magnetically excited electrical rotary drive
InactiveUS6278251B1Improve fault toleranceGuaranteed uptimeSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlPhase currentsElectricity
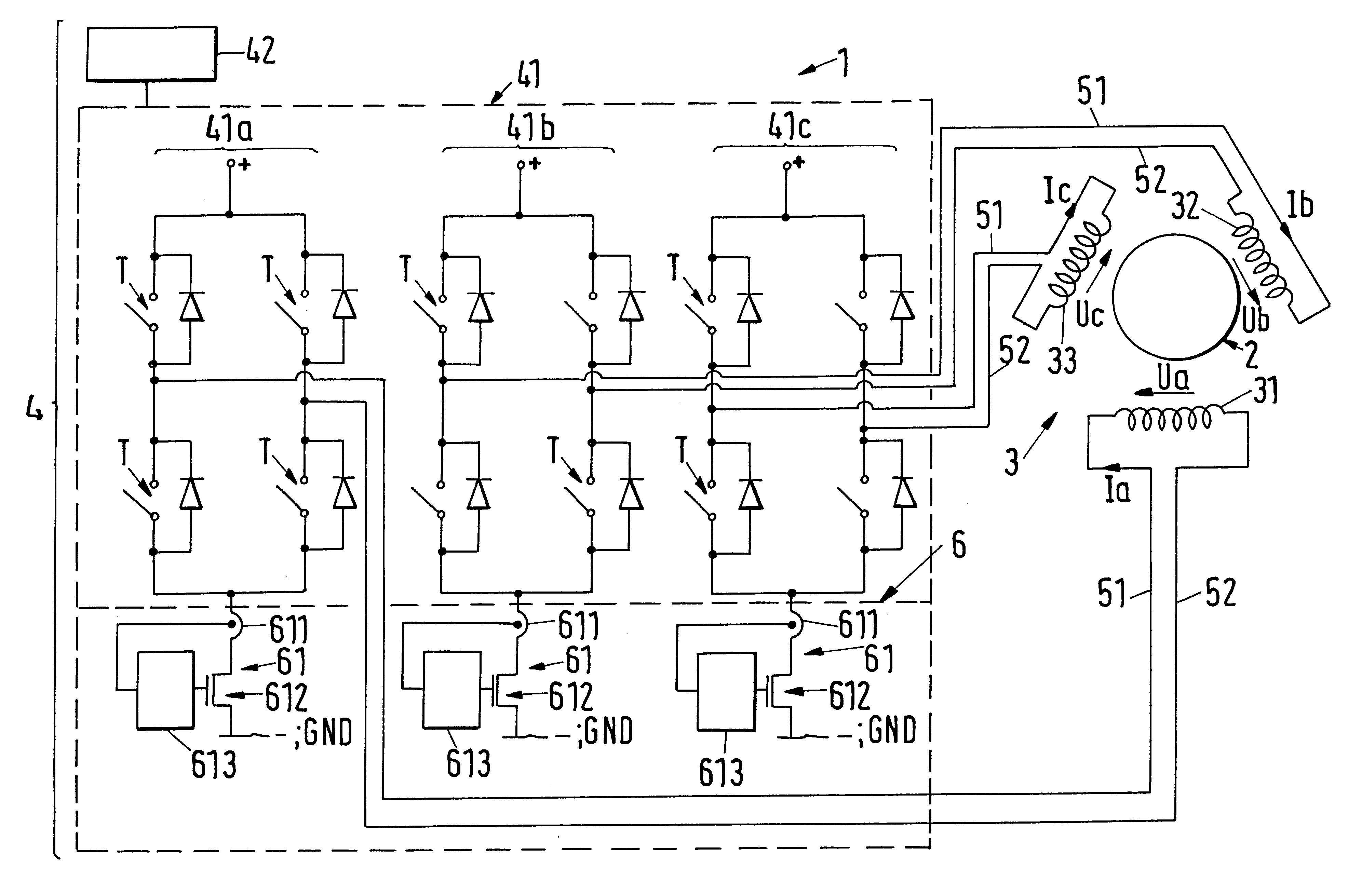
A permanent magnetically excited electrical rotary drive for a blood pump is proposed, comprising a permanent magnetic rotor and a stator, said stator comprising a drive winding having at least two loops for the production of a magnetic drive field which produces a torque on the rotor, with each loop belonging to a different electrical phase, furthermore comprising a setting device which supplies each loop in each case with a phase current or in each case with a phase voltage as a setting parameter, with the setting device comprising a separate power amplifier for each loop so that the setting parameter for each loop can be regulated independently of the setting parameter for the other loops.
Owner:THORATEC CORPORTION
Offset PWM signals for multiphase motor
A multi phase motor includes a switching array for interconnecting a power source to each phase. A current sensor senses current supplied from the power source via the switching array to the winding and a controller generates offset PWM signals for controlling the switching array to supply power to each of the phases of the winding. The offset timing allows the individual phase currents to be determined from a single current sensor.
Owner:COPELAND LP
Permanent magnet synchronous motor and controller therefor
InactiveUS20050248306A1Low costReduce impactTorque ripple controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersPhase currentsLoop control
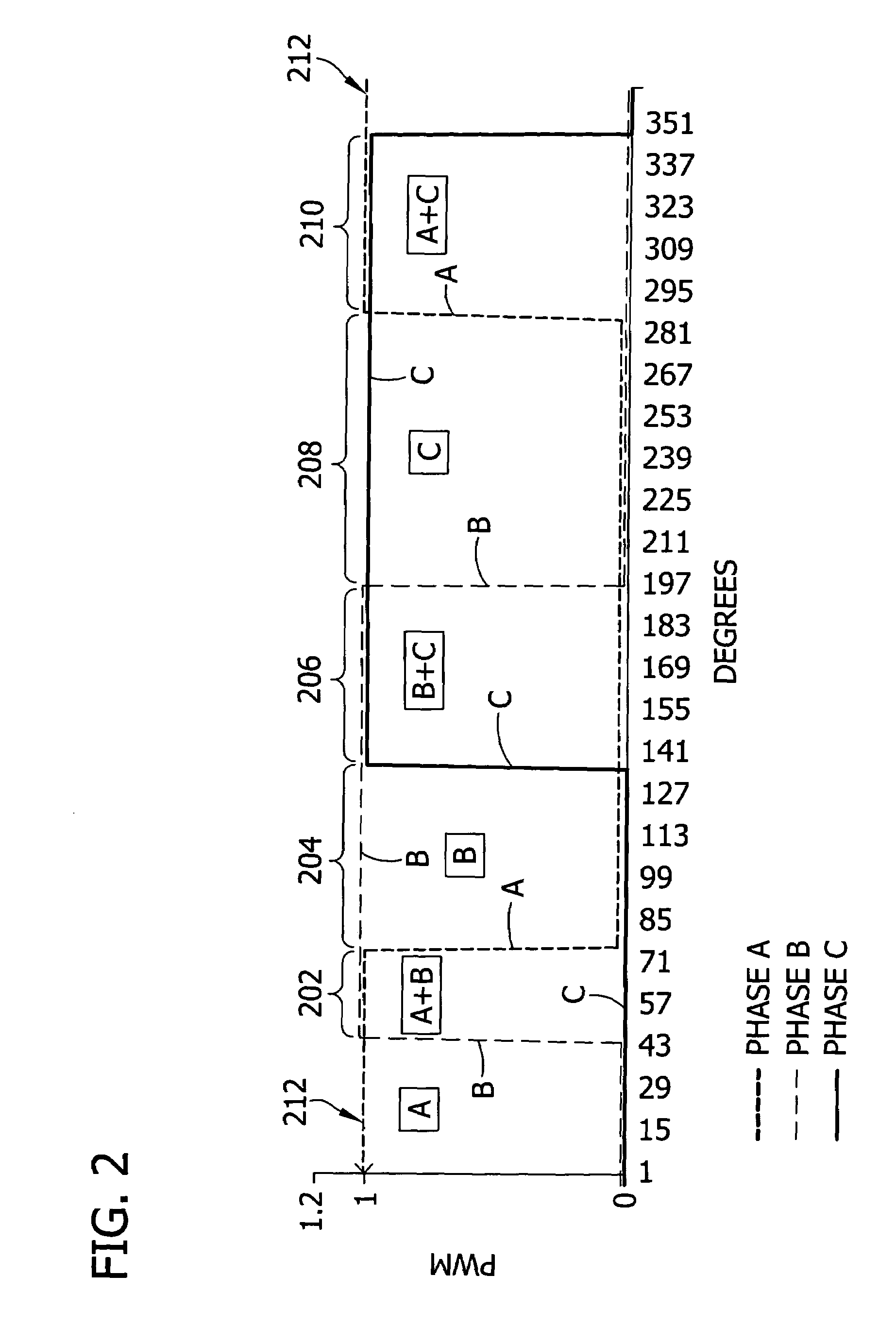
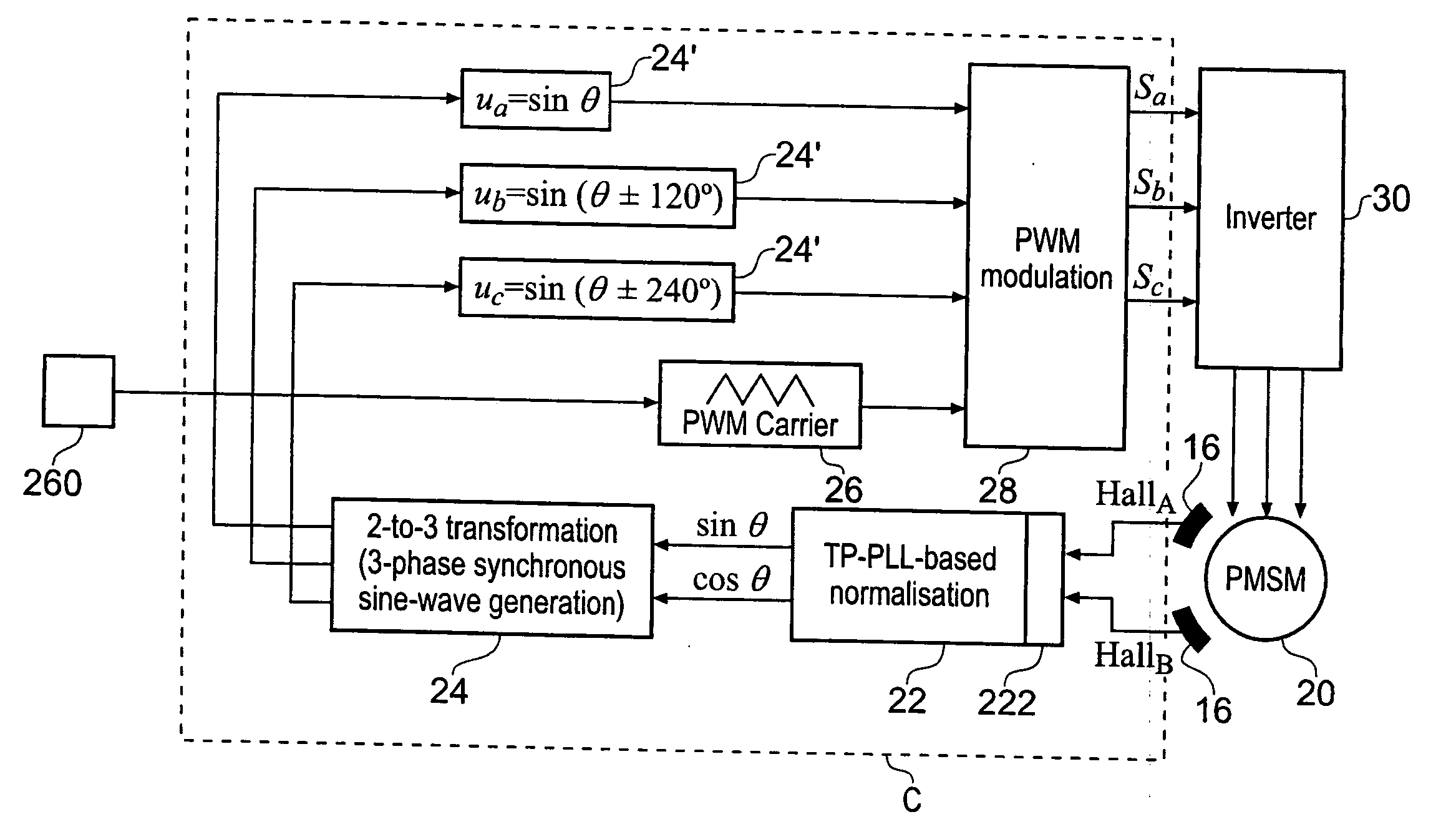
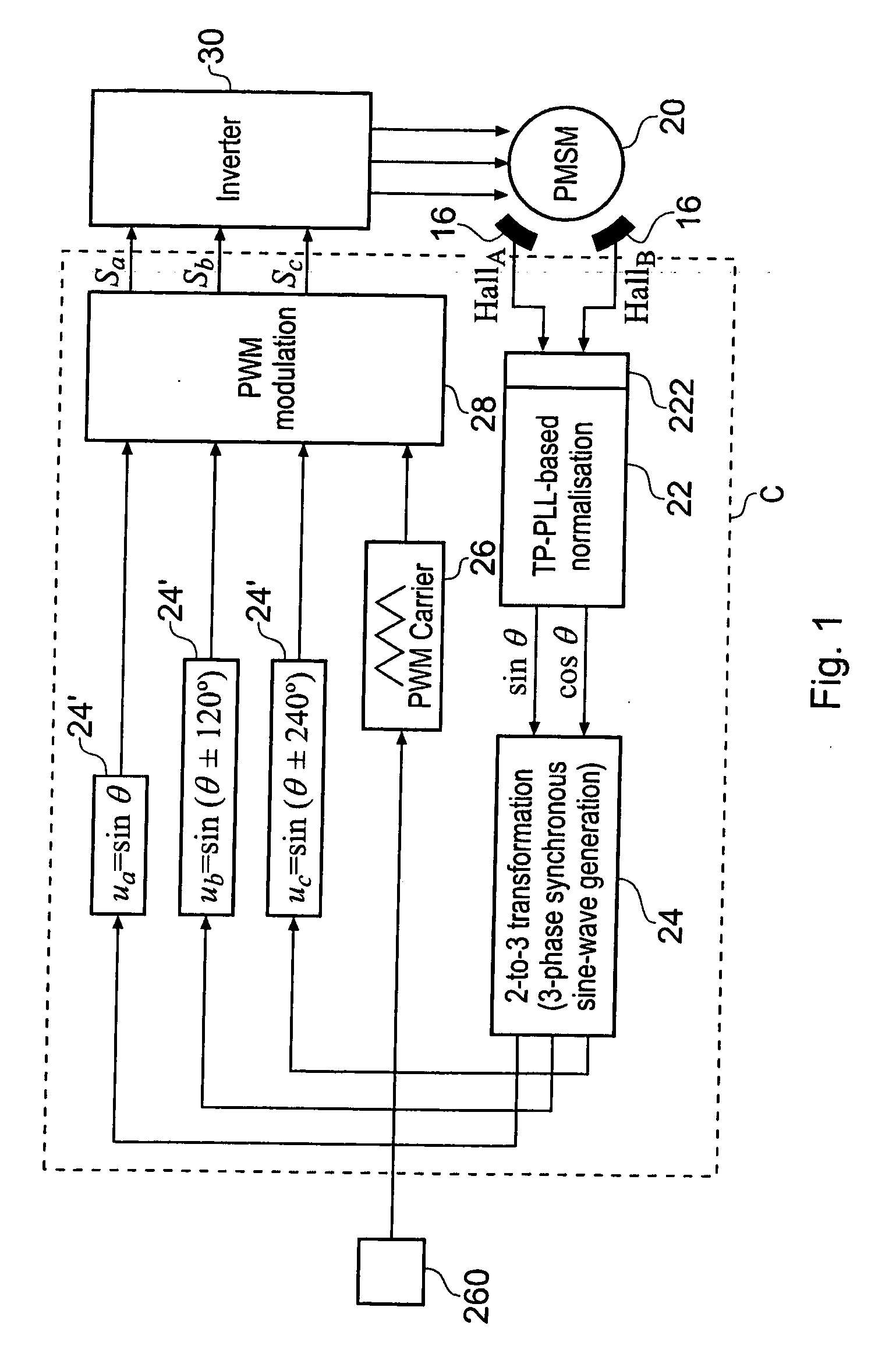
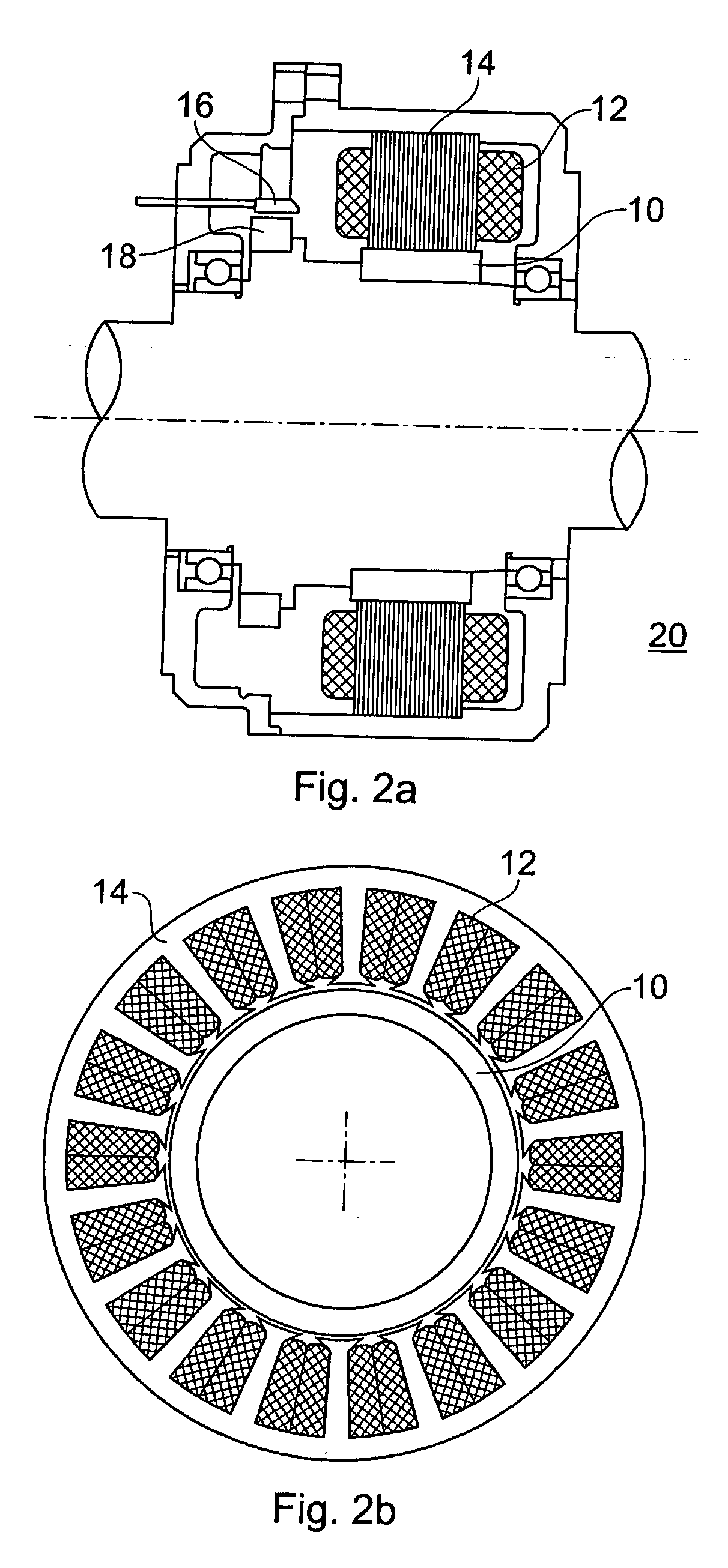
A low-cost sine-wave drive for a 3-phase permanent magnet synchronous AC machines (PMSM) in open-loop control is based on the measurements of two linear Hall sensors. The two Hall sensors are excited by a magnetic ring with the same pole number as the PMSM rotor magnet and sinusoidal flux distributions. The output signals of the Hall sensors are unified through a two-phase-type phase-lock-loop in order to reduce the impact of the sensor mounting non-uniformity during mass production. The peak torque and speed of motor is simply controlled by adjusting the amplitude of pulse-width-modulation carrier. Smooth torque control is achieved due to sinusoidal 3-phase currents. Such a simple sine-wave drive can be achieved with or without the assistance of a micro-controller unit (MCU). No current sensor is required for the motor phase current detection. This motor can be used in industrial applications where there is no strict requirement on torque response and constant speed control of PMSM machines.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
Smart electricity meter with function of monitoring and protecting power failure
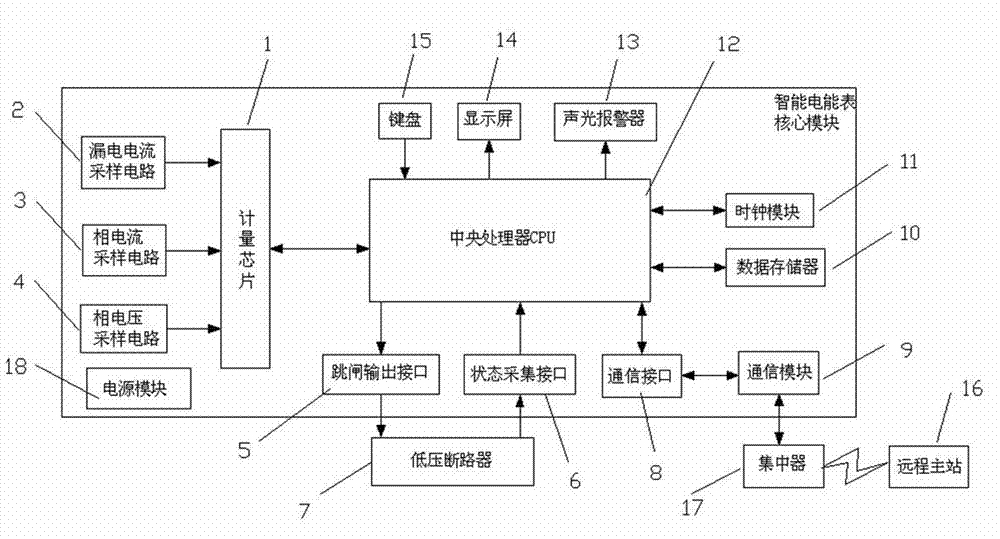
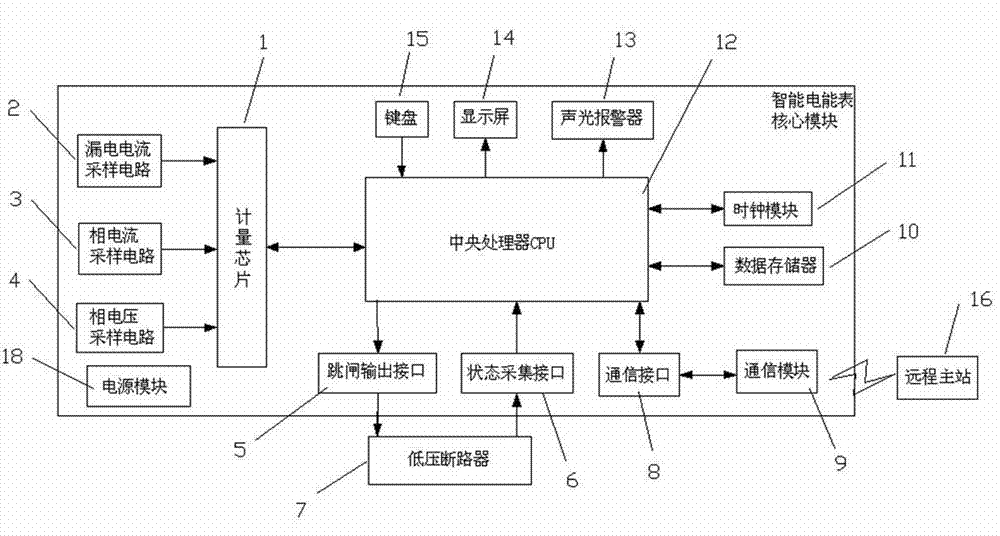
InactiveCN102830255AImprove practicalityLow failure rateTime integral measurementPhase currentsHemt circuits
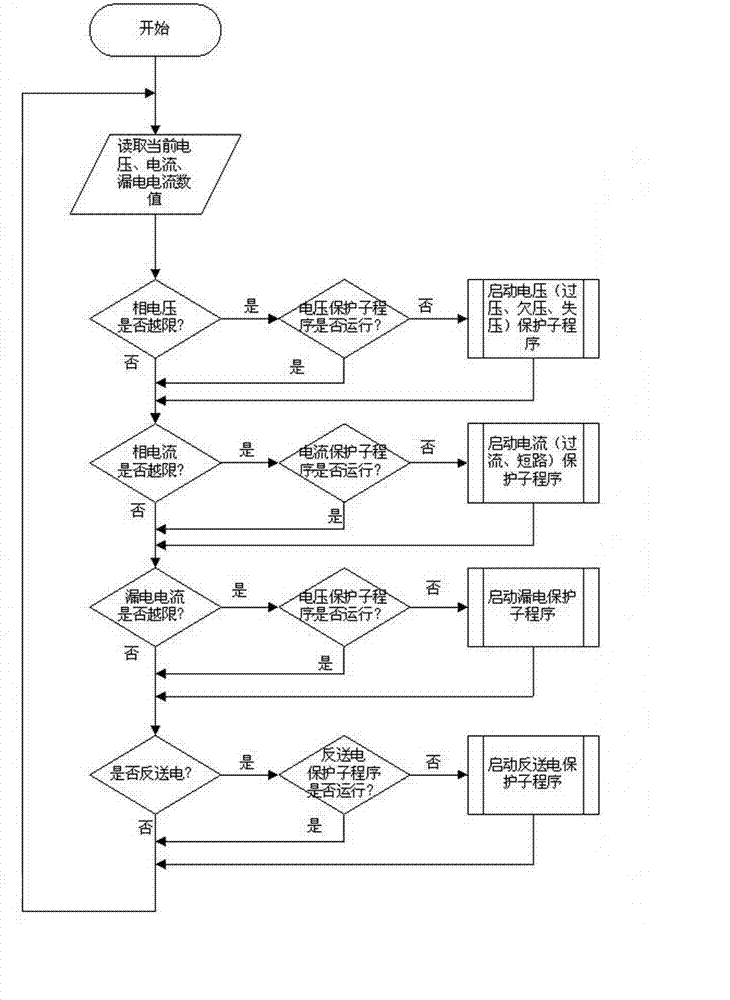
A smart electricity meter with a function of monitoring and protecting power failure comprises a metering chip, a leakage current sampling circuit, a phase current sampling circuit, a phase voltage sampling circuit, a CPU (central processing unit), a power module and a low voltage breaker. The leakage current sampling circuit is electrically connected with the metering chip which is mutually electrically connected with the CPU. The CPU is electrically connected with the low voltage breaker through a trip output port. The low voltage breaker is electrically connected with the CPU through a status acquisition interface. The invention further provides a power failure monitoring and controlling method of the smart electricity meter. The smart electricity meter has the advantages that the reliable power module for power failure protection and control is provided, various types of power failure warning and protection are provided, failure warning and failure protection for voltage, current, power and the like are achieved for power users, failure spots are prevented and isolated, economic loss and personal safety accidents due to failure of electric circuit equipment of the users are prevented and reduced, and reliability of low voltage grids is effectively improved.
Owner:王金泽
Multiple-phase DC-DC converter topology
ActiveUS6943535B1Improve responseIncrease speedDc-dc conversionAc network voltage adjustmentPhase currentsDc dc converter
A multiple-phase DC—DC converter adds at least one additional phase to an N-phase DC—DC converter to improve the converter's response to changes in load. In one embodiment, an additional phase operates at a switching frequency greater than that of the N phases, to generate a current which is added to the N phase currents to improve the converter's response to changes in load. In another embodiment, an additional phase is configured to improve the converter's response to a load release. Here, the additional phase is kept off during load increase and steady-state conditions. However, when a load release occurs, the additional phase is turned on and acts to extract current from the converter's output terminal while the N phase currents slowly fall, to reduce the magnitude of output voltage overshoot that occurs on load release.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
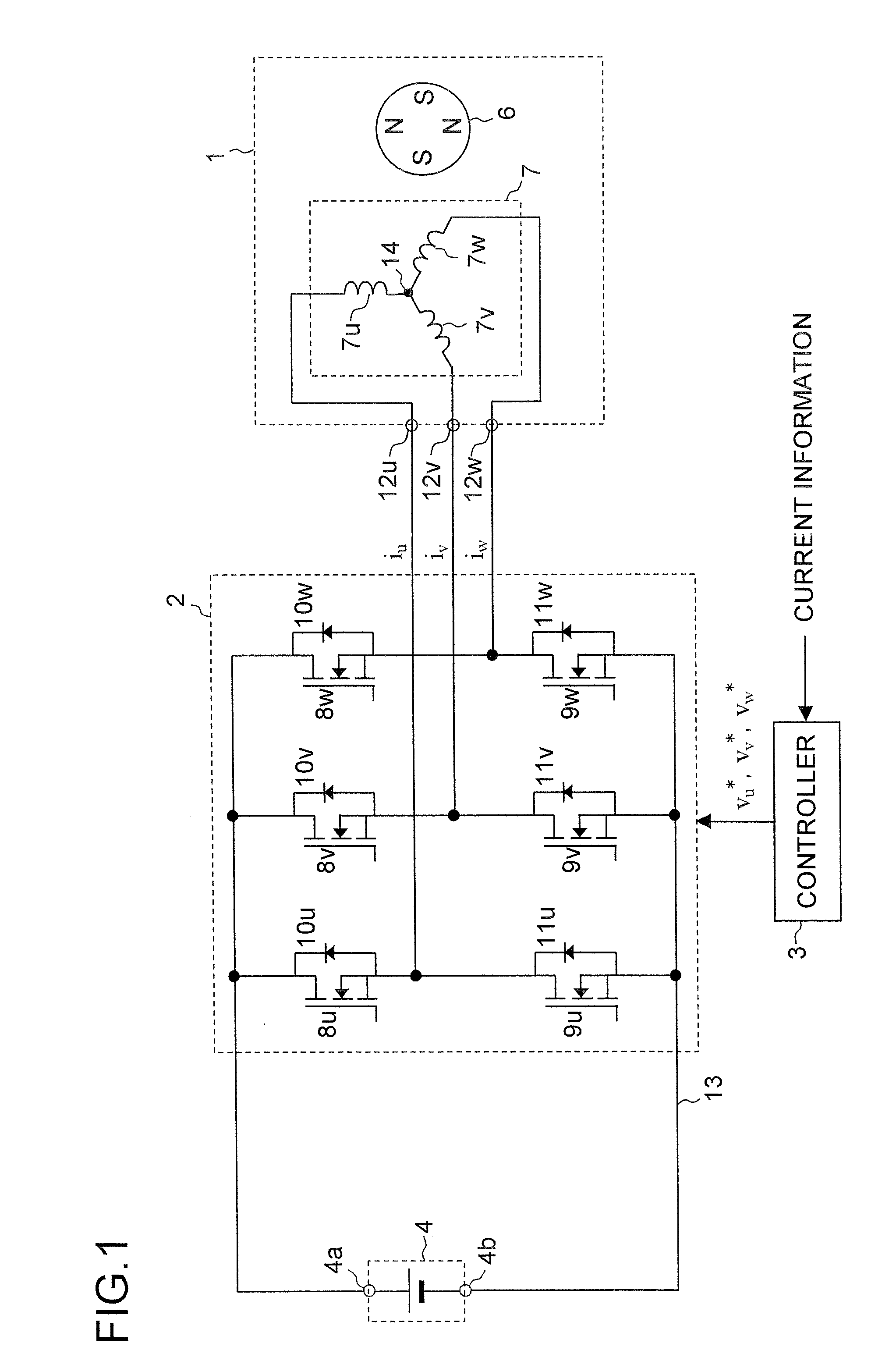
Motor control device
A motor control device includes a current detecting portion that detects phase current of one phase among three phase currents supplied from an inverter to a motor, and a current estimator that estimates phase current of phases other than the detected phase current by using a specified current value indicating current to be supplied to the motor, and derives control current corresponding to the specified current value from the estimated phase current and the phase current of one phase. The motor control device controls the motor via the inverter so that the control current follows the specified current value.
Owner:III HLDG 12 LLC
Constant detecting apparatus for brushless DC motor, control apparatus for brushless DC motor, and program for detecting constant of brushless DC motor
InactiveUS20020113615A1Easy to calculateImprove errorAnalogue computers for vehiclesSynchronous motors startersPhase currentsConductor Coil
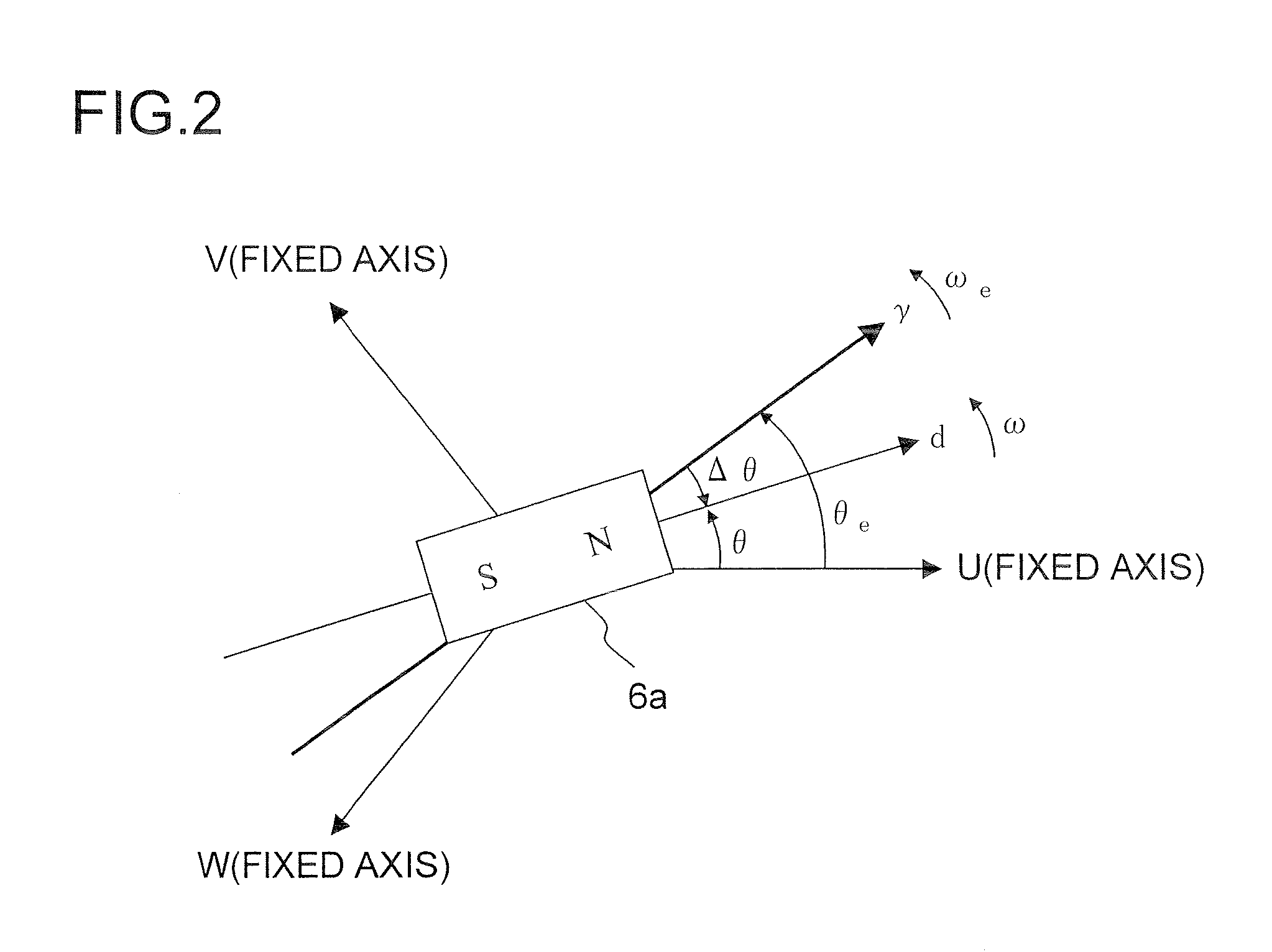
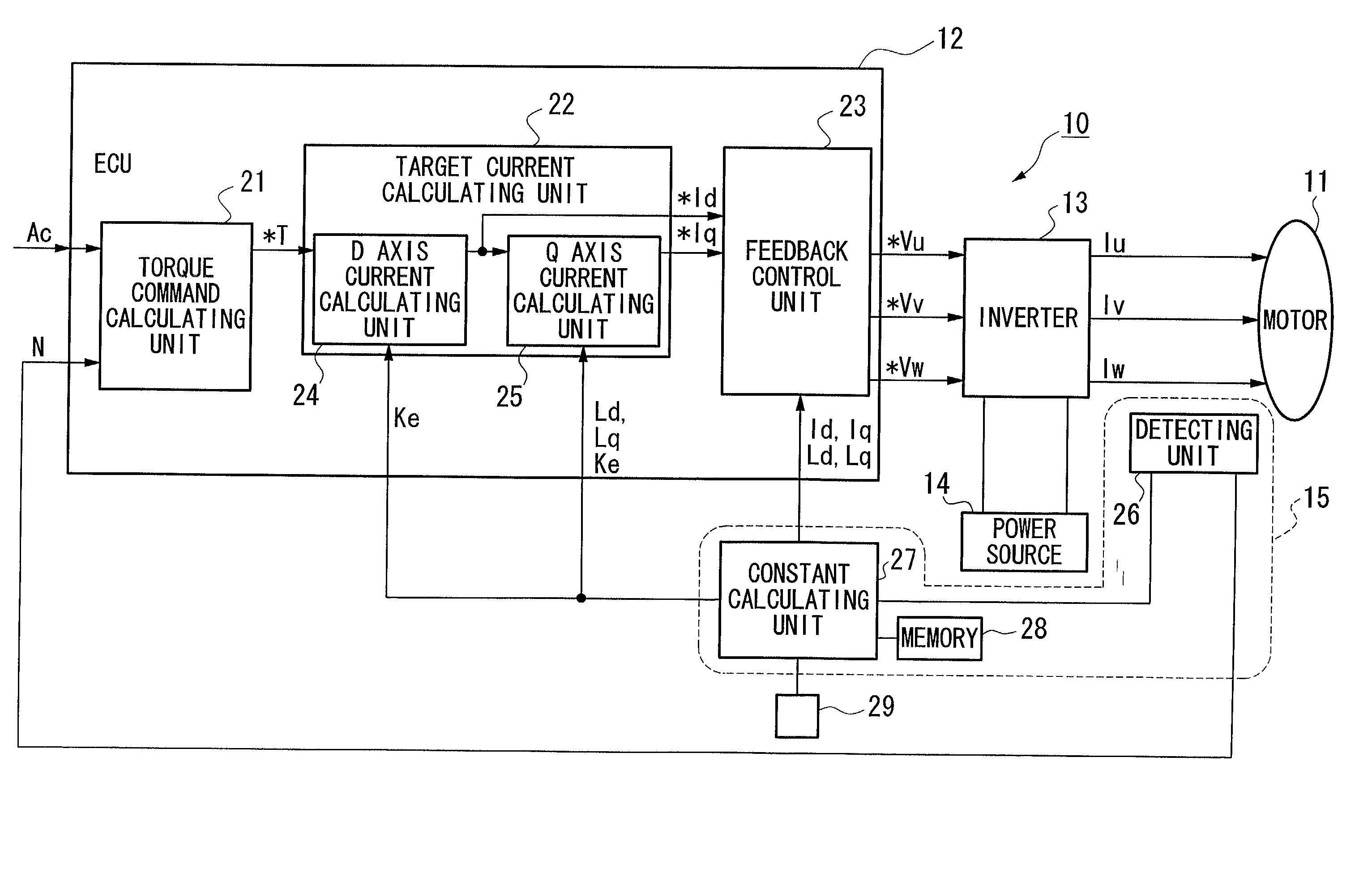
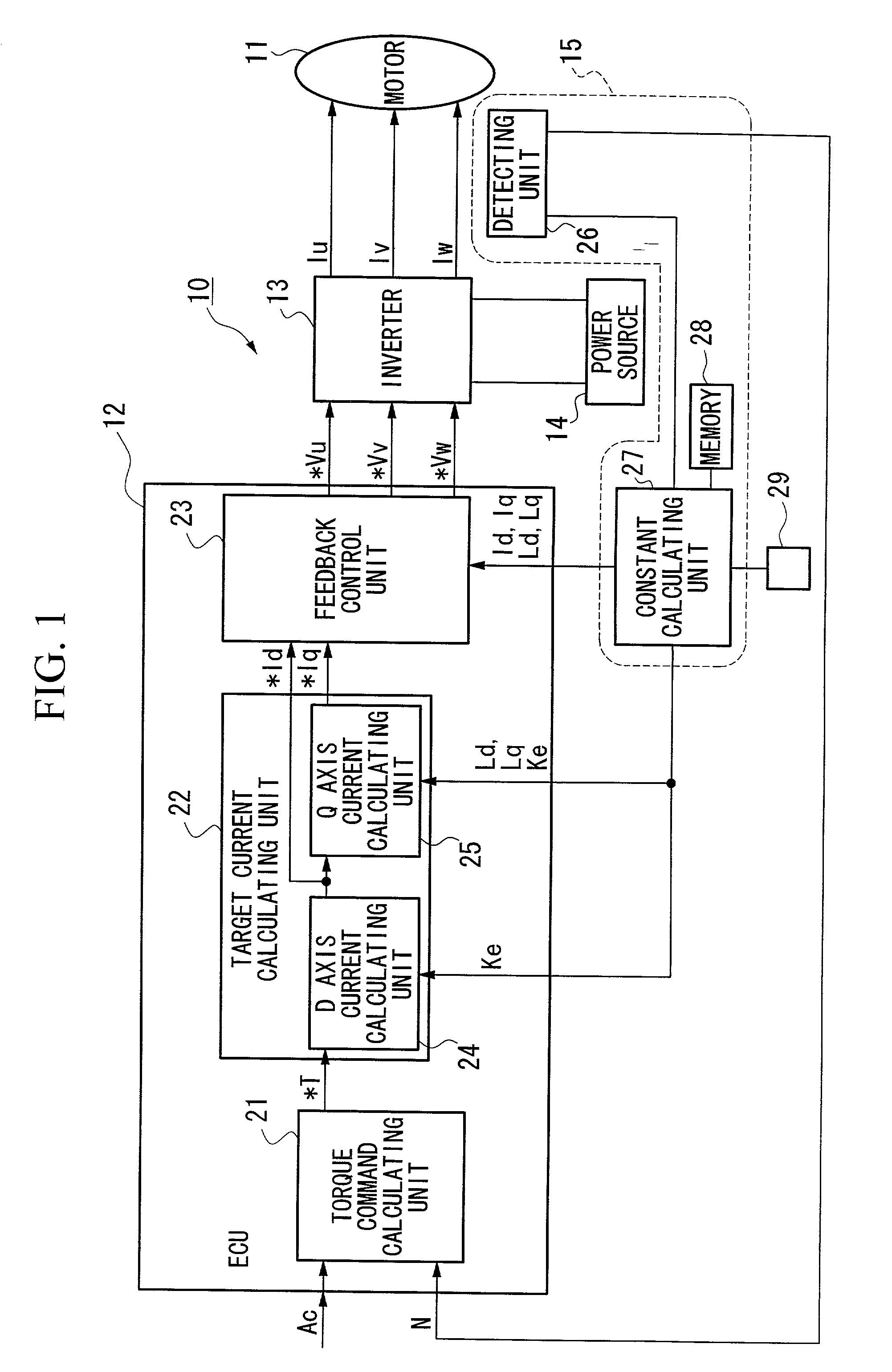
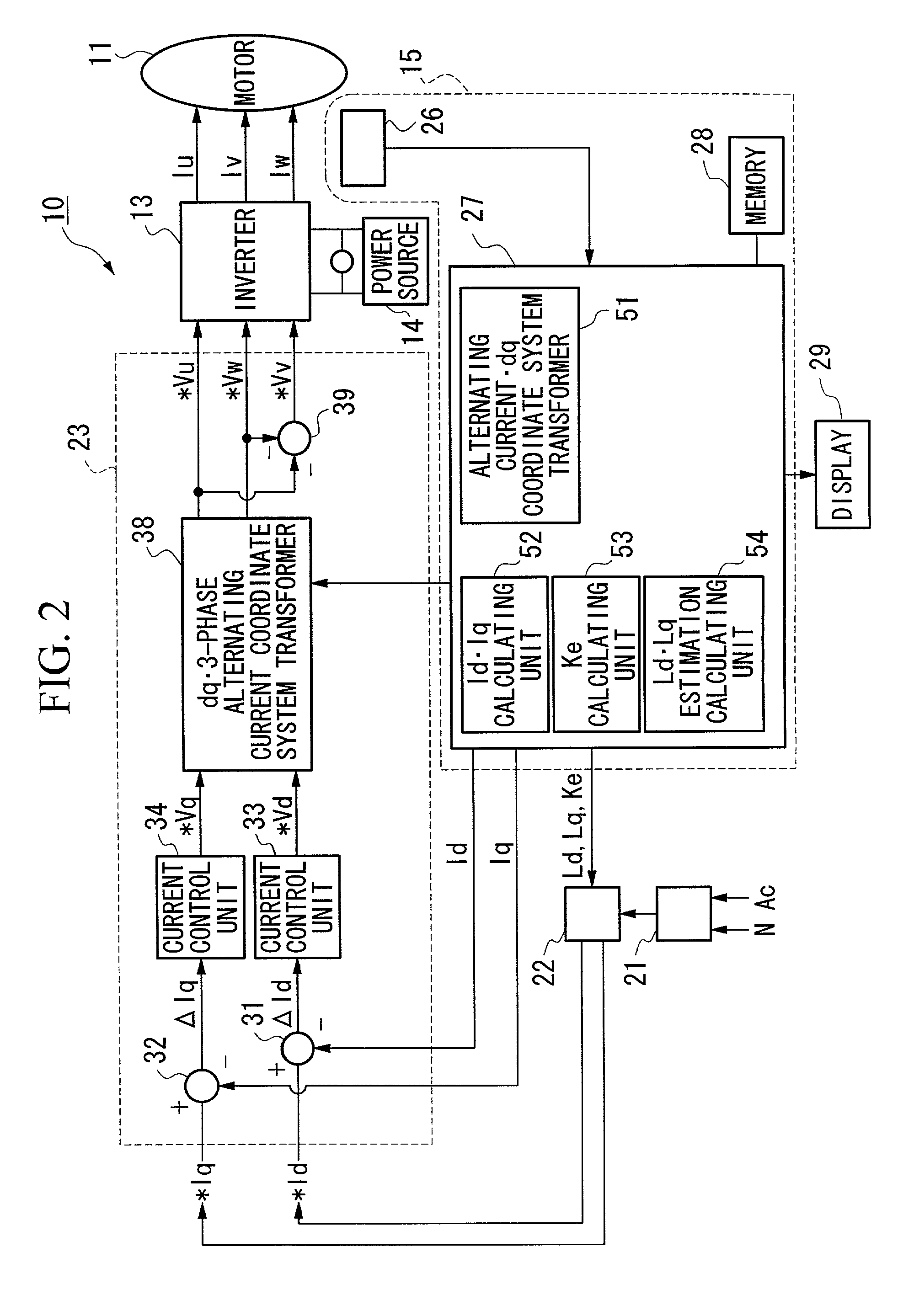
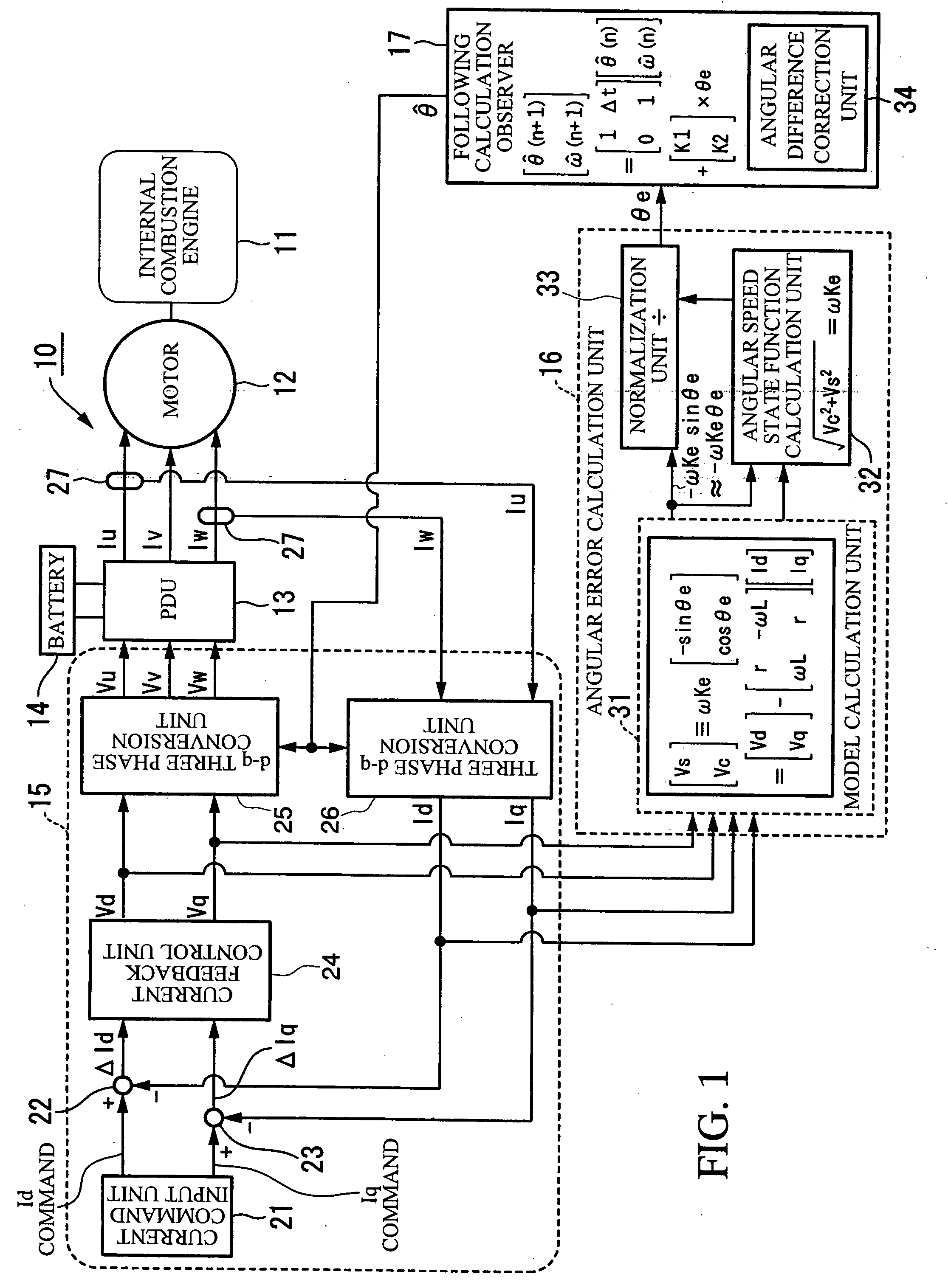
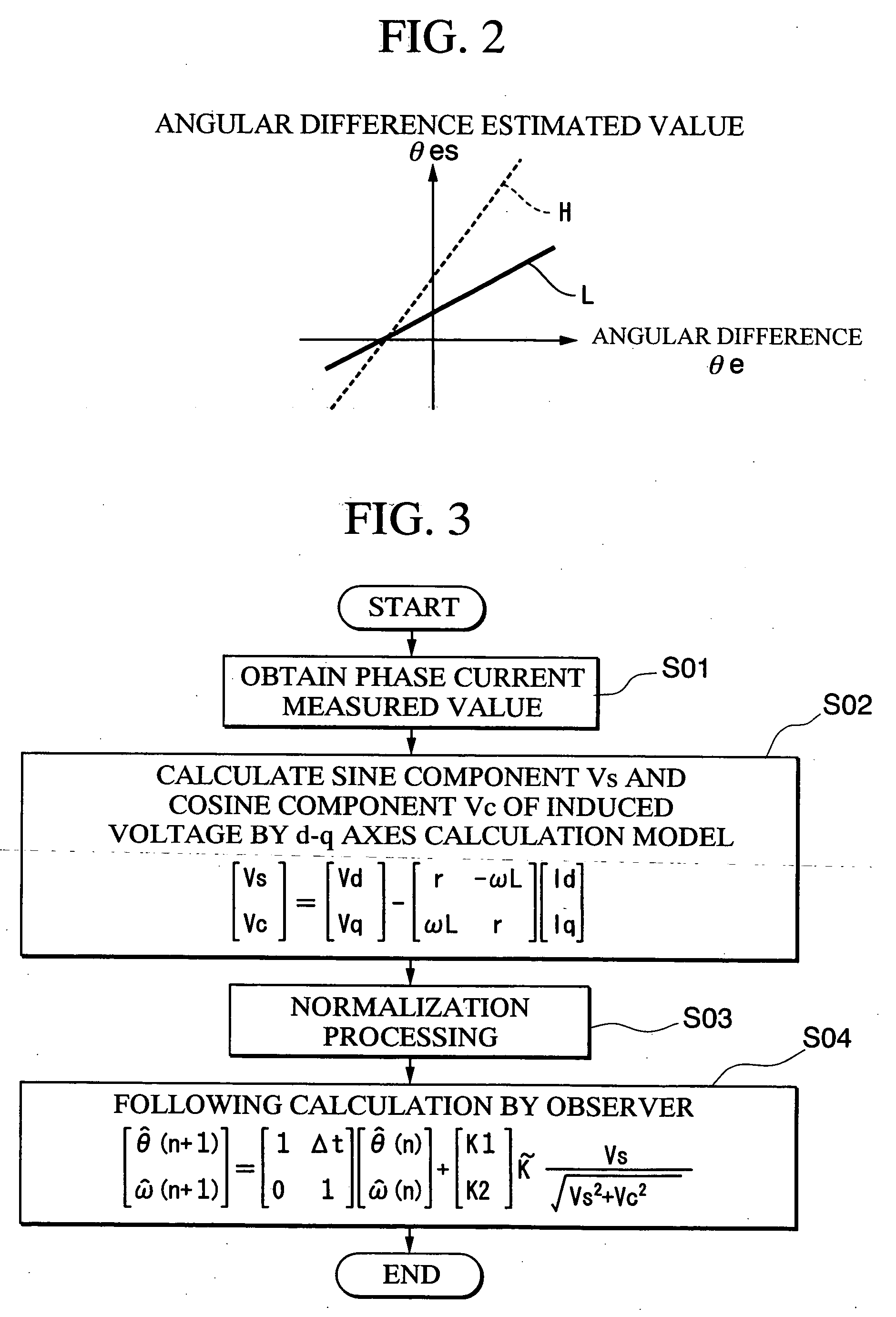
A constant detecting apparatus 15 comprising a detecting unit 26 and a calculating unit 27. The detecting unit 26 is structured comprising a rotation sensor 41, a torque sensor 42, a position sensor 43, a rotor temperature sensor 44, a winding temperature sensor 45, a phase voltage detector 46, and phase current detectors 47 and 47. The calculating unit 27 calculates the induced voltage constant Ke that changes depending on the motor temperature Tmag while the motor 11 is being driven based on each of the detected signals from the detecting unit 26, and at the same time, the d axis current Id and the q axis current Iq are calculated after elimination of the iron loss, and the d axis inductance Ld and the q axis inductance Lq in the actual operating state of the motor 11 are calculated.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
System and method for clamp current regulation in field-weakening operation of permanent magnet (PM) machines
ActiveUS20050046370A1Maximize processing efficiencyMaximum possible torqueAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlPhase currentsIntegrator
A device to regulate current produced by a permanent magnet machine responsive to a plurality of phase current signals. The motor produces torque for application on a shaft. A processing and drive circuit responsive to a direct current command signal and a quadrature current command signal produces phase current signals for input to the motor. A command circuit responsive to the phase current signals, an angular position of said shaft, and a voltage input command signal to produce a direct current error signal and a quadrature current error signal. A control circuit responsive to the direct and quadrature current error signals produces the direct voltage signal command and the quadrature voltage signal command. The control circuit has a direct and quadrature proportional gain, integrator and clamp circuits. An algorithm produces limited or clamped voltage modulation index signals to obtain maximum efficiency and maximum torque per ampere in the speed range. The algorithm ensures that the current regulator does not run out of voltage by limiting the voltage vector to the achievable voltage vector range that provides maximum torque per ampere and maximum efficiency.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Permanent magnetism synchronous electric machine - compressor system high speed operation control method
InactiveCN101252336AImprove voltage utilizationAC motor controlVector control systemsPhase currentsSynchronous motor
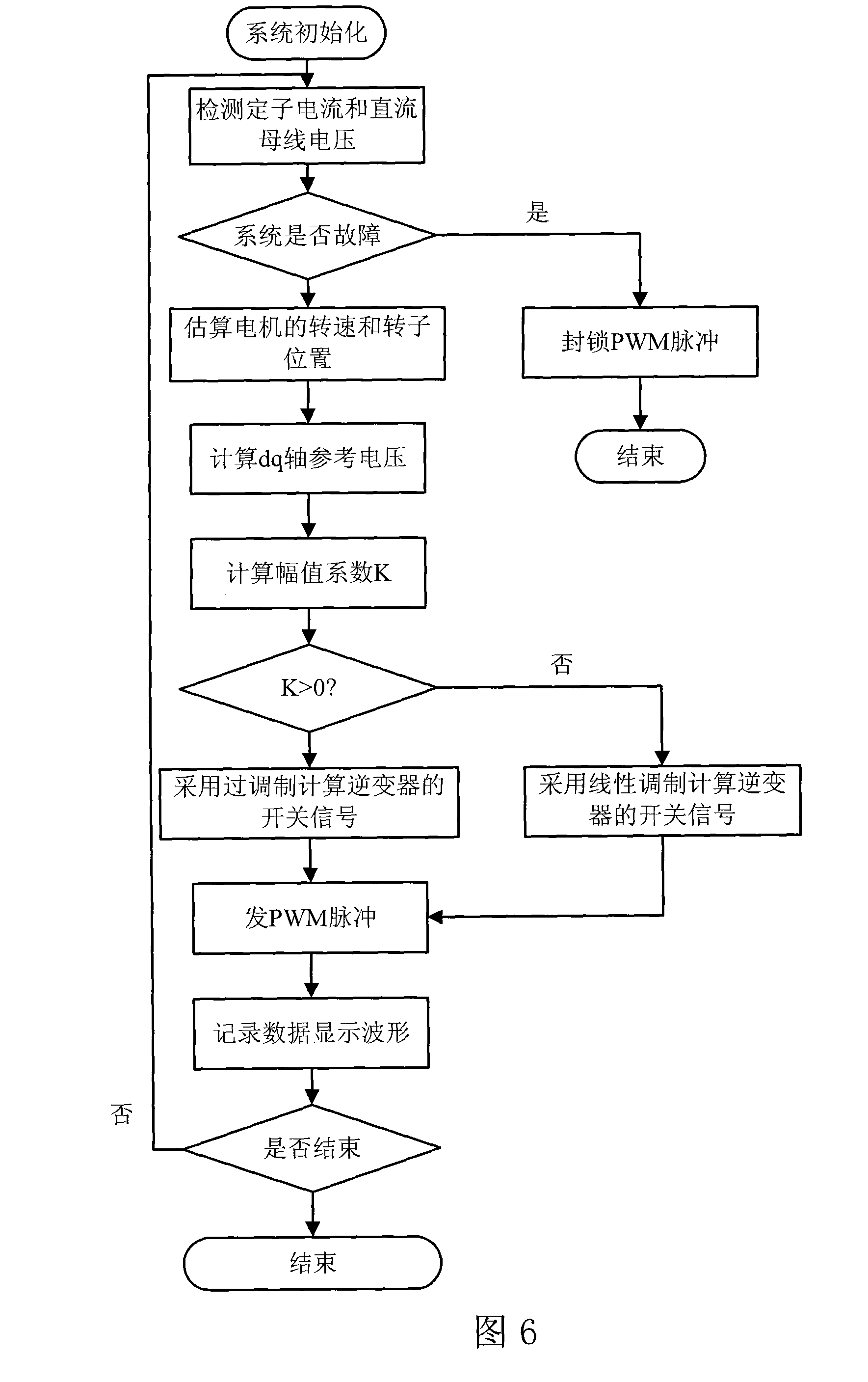
Disclosed is a high-speed control method for a permanent magnet synchronous motor-compressor system, including the following steps: initial design is carried out; a motor is detected through DSP, including detecting the two-phase current of the stator of the motor, the voltage Udc of a DC generatrix; the voltage of a d-p shaft is calculated; faults of overcurrent, overpressure and undervoltage are detected; if any fault exists, the PWM pulse signals are blocked and then the control program is paused; if no fault exists, the following steps will be carried out; the rotating speed of the motor and the position of the rotor are identified in the process of speed-position estimation; the current and the voltage of the reference d-q shaft of the motor are calculated; switching signals of an inverter are acquired through haplotype over-modulation; the data are recorded and waveforms are displayed; judgment of whether to pause the control program is carried out; if not, the second step is carried out again; if yes, the control program will be paused. The control method applies haplotype over-modulation method into the permanent magnet synchronous motor-compressor system, realizing sensorless over-modulation to the synchronous motor-compressor vector control system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Sensorless motor driving device and its driving method
ActiveUS6979970B2Prompt and reliable startImprove accuracySynchronous motors startersDC motor speed/torque controlPhase currentsMotor drive
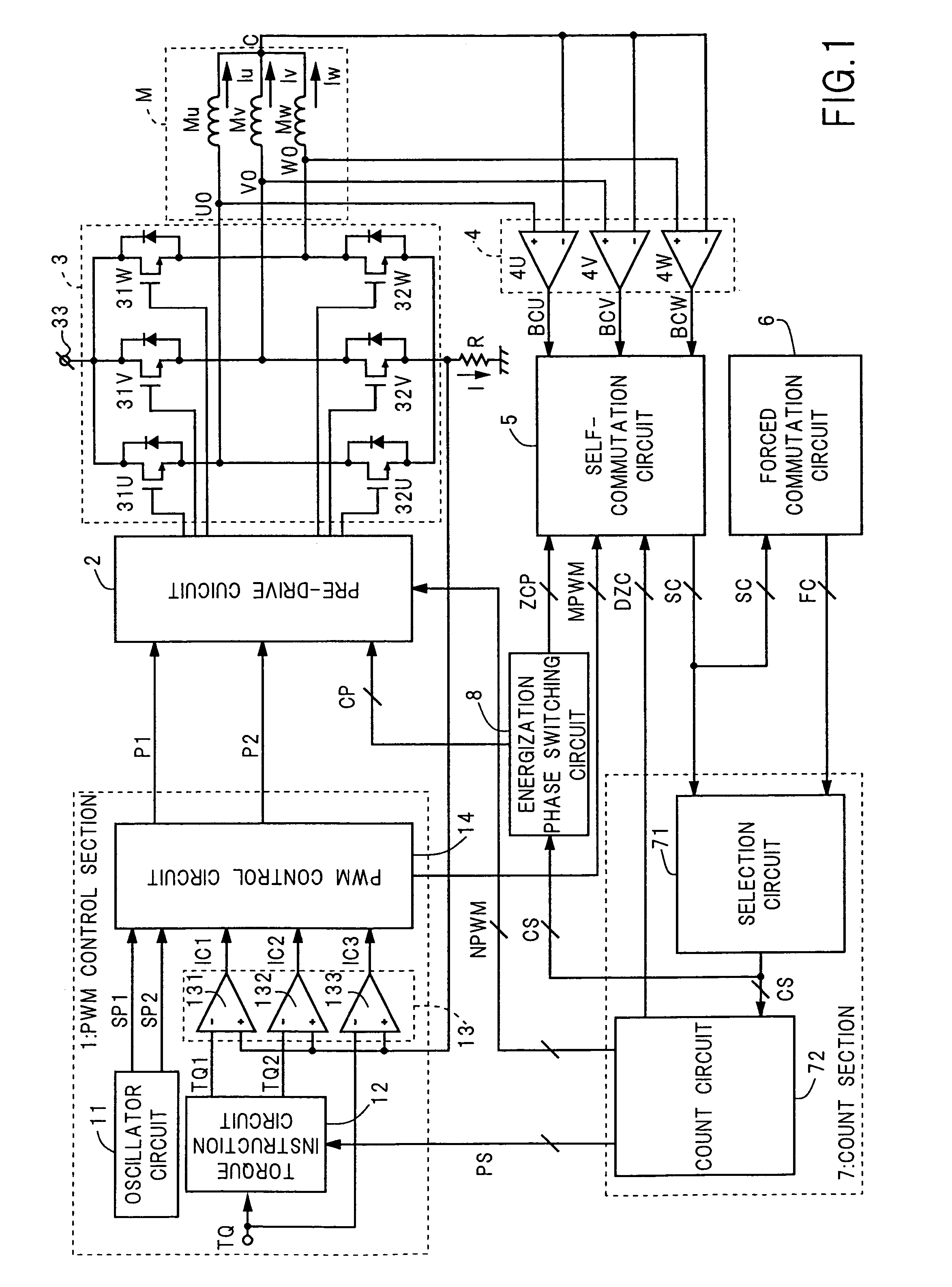
A PWM control section (1) gently changes phase currents (Iu, Iv, and Iw) under a current driving control over a pre-drive circuit (2) and an output circuit (3). The pre-drive circuit (2) suspends energizing of the specific motor coil (Mu, Mv, and Mw) according to a PWM disable signal (NPWM) at PWM disable periods. A self-commutation circuit (5) performs zero crossing detection according to a BEMF detection signal (DZC) during BEMF detection periods. A count section (7) selects either a self-commutation signal (SC) or a forced commutation signal (FC) as a commutation signal (CS), whichever enters earlier, and, based on its intervals, generates the PWM disable signal (NPWM) and the BEMF detection signal (DZC). The BEMF detection period starts after the start of the PWM disable period, and finishes together with the PWM disable period at the switching of the energization phases.
Owner:COLLABO INNOVATIONS INC
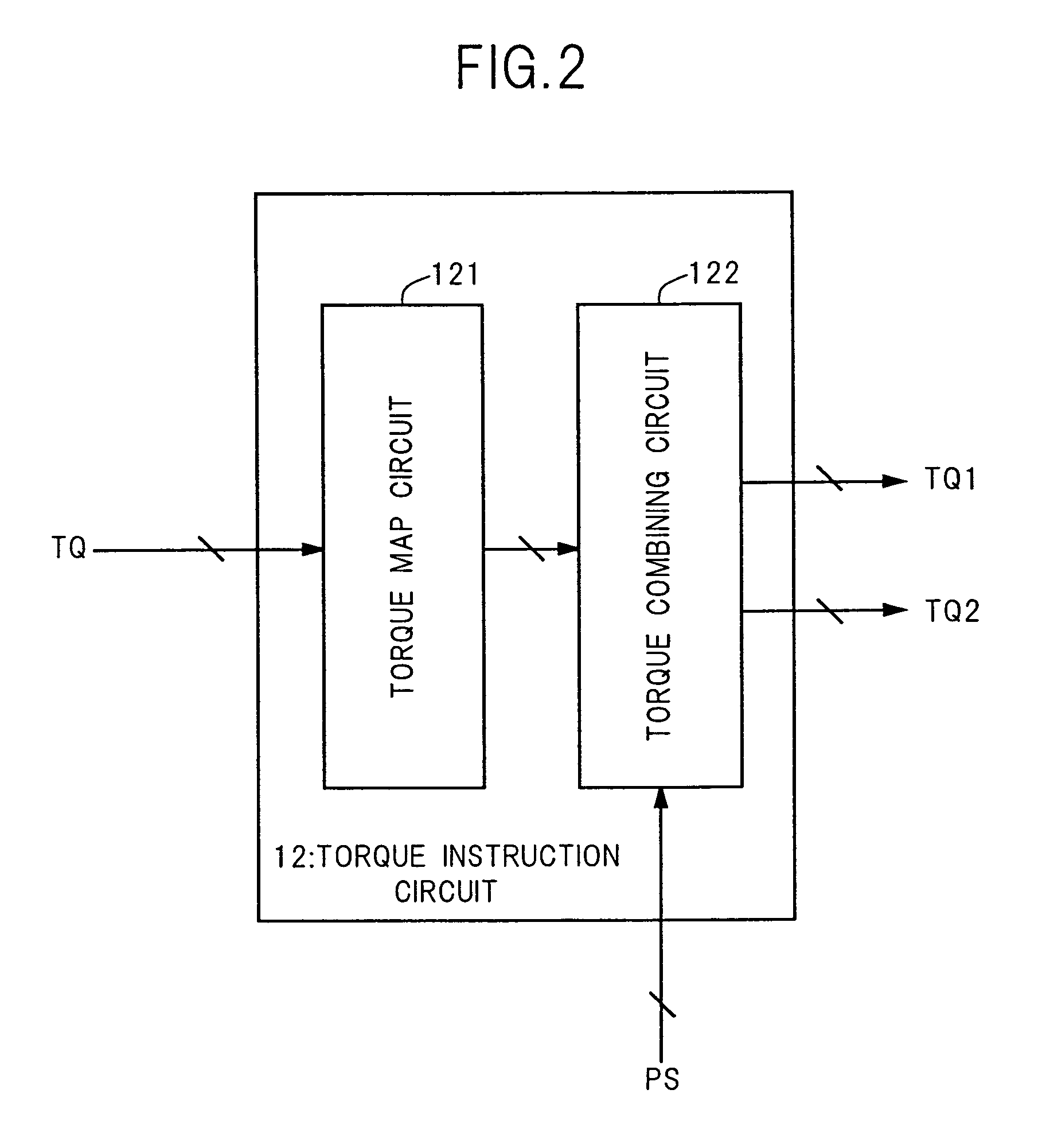
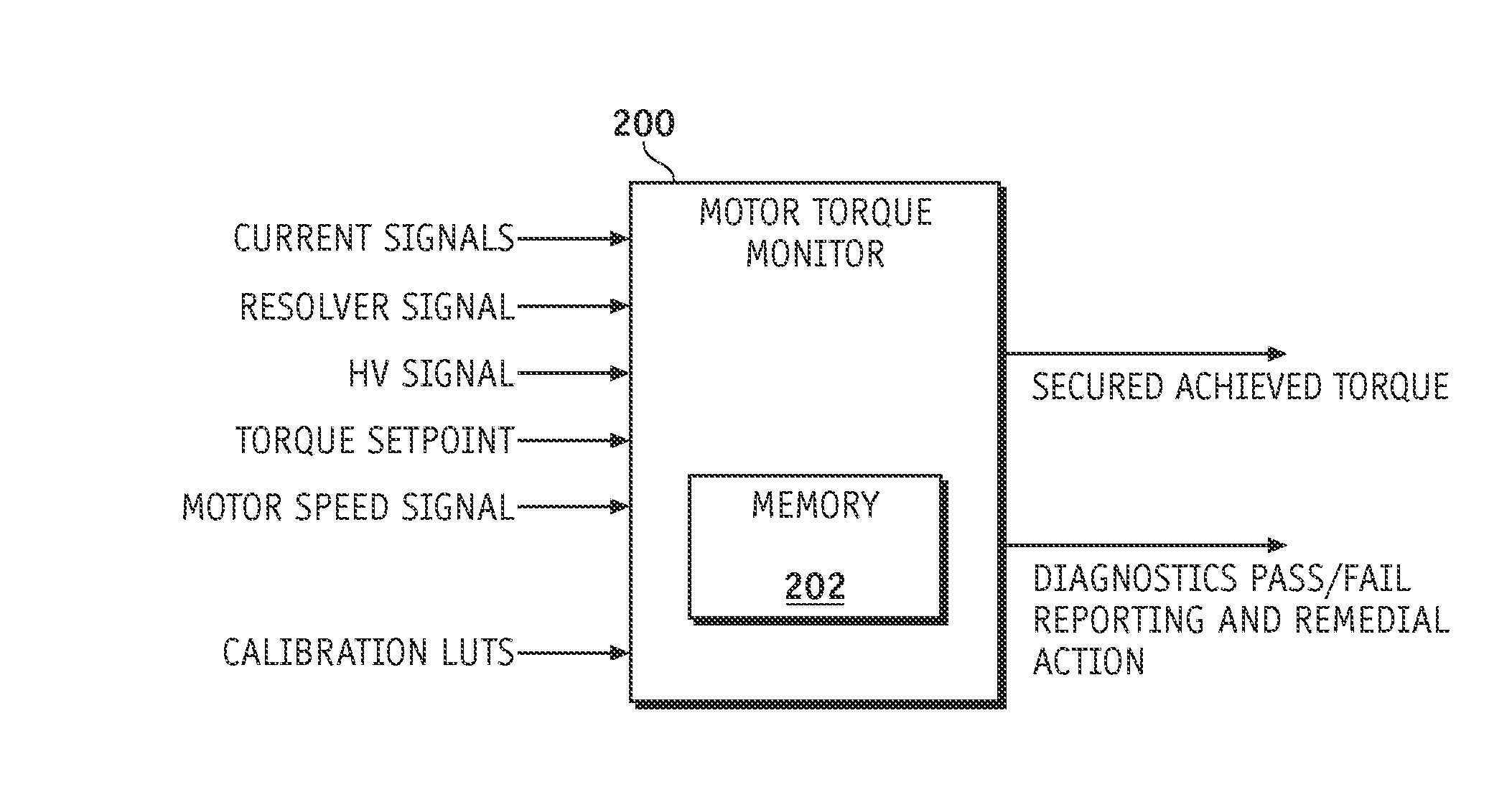
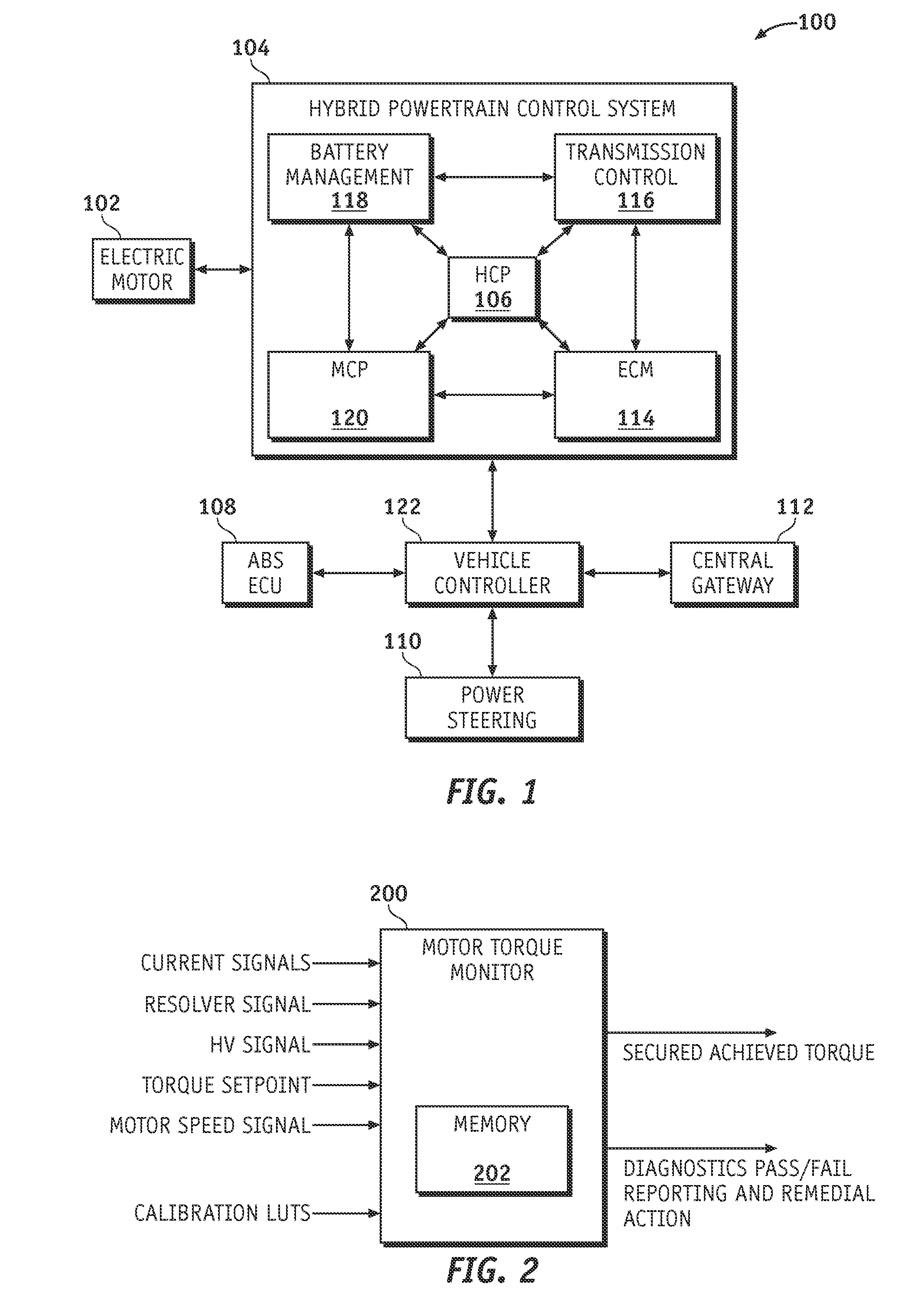
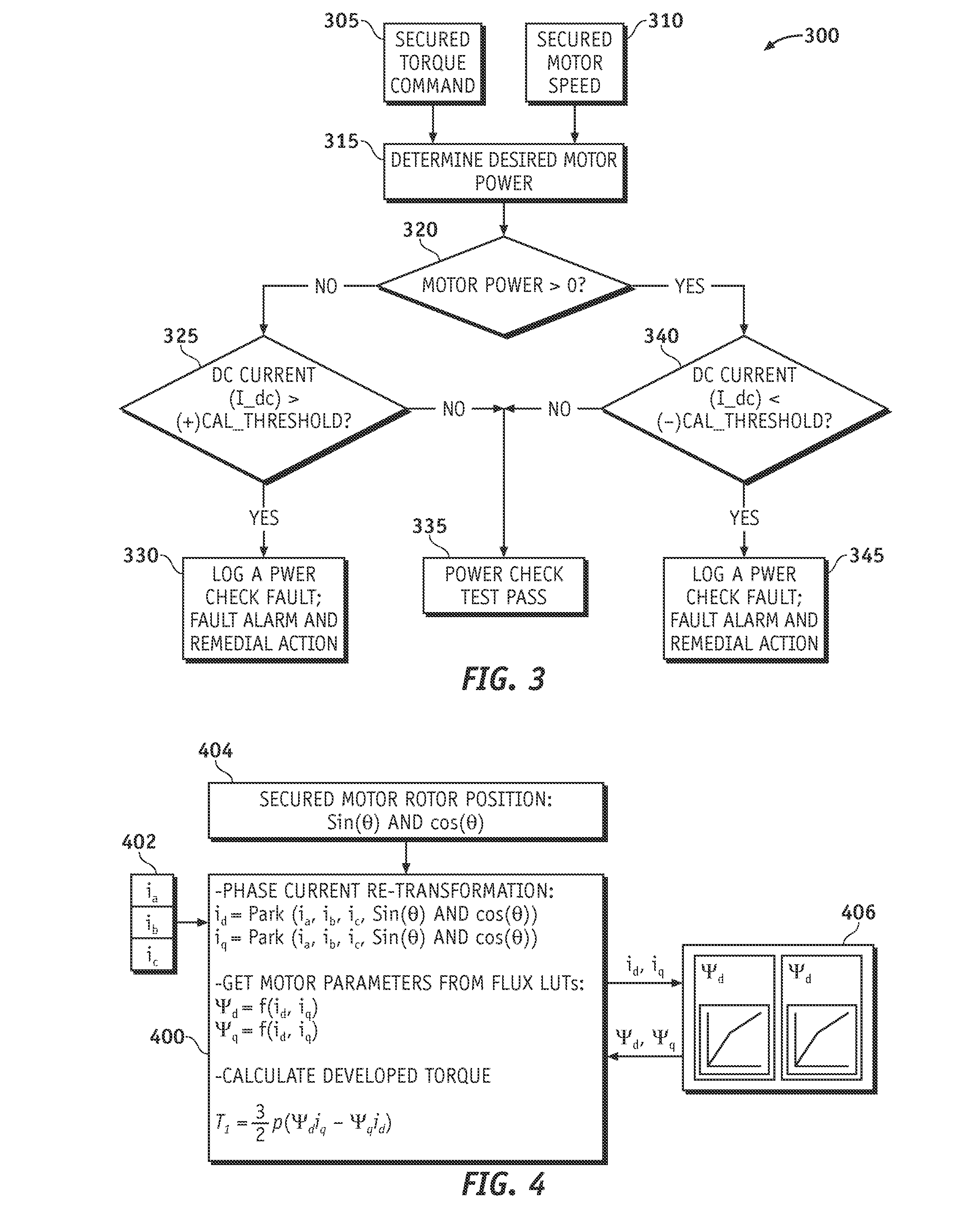
Method and apparatus for electric motor torque monitoring
Methods and apparatus are provided for monitoring an achieved motor torque produced by an electric motor. The method includes determining the achieved motor torque based on a rotor position of the electric motor and a phase current of the electric motor when the motor speed is not greater than a first pre-determined threshold, determining the achieved motor torque based on a loss-compensated power supplied to the electric motor when the motor speed is greater than the first pre-determined threshold, comparing the achieved motor torque with the torque command, and indicating a fault when the achieved motor torque is not within a pre-determined margin of the torque command.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Distributing capacitance current and transition resistance influence resisting line one-end fault ranging method
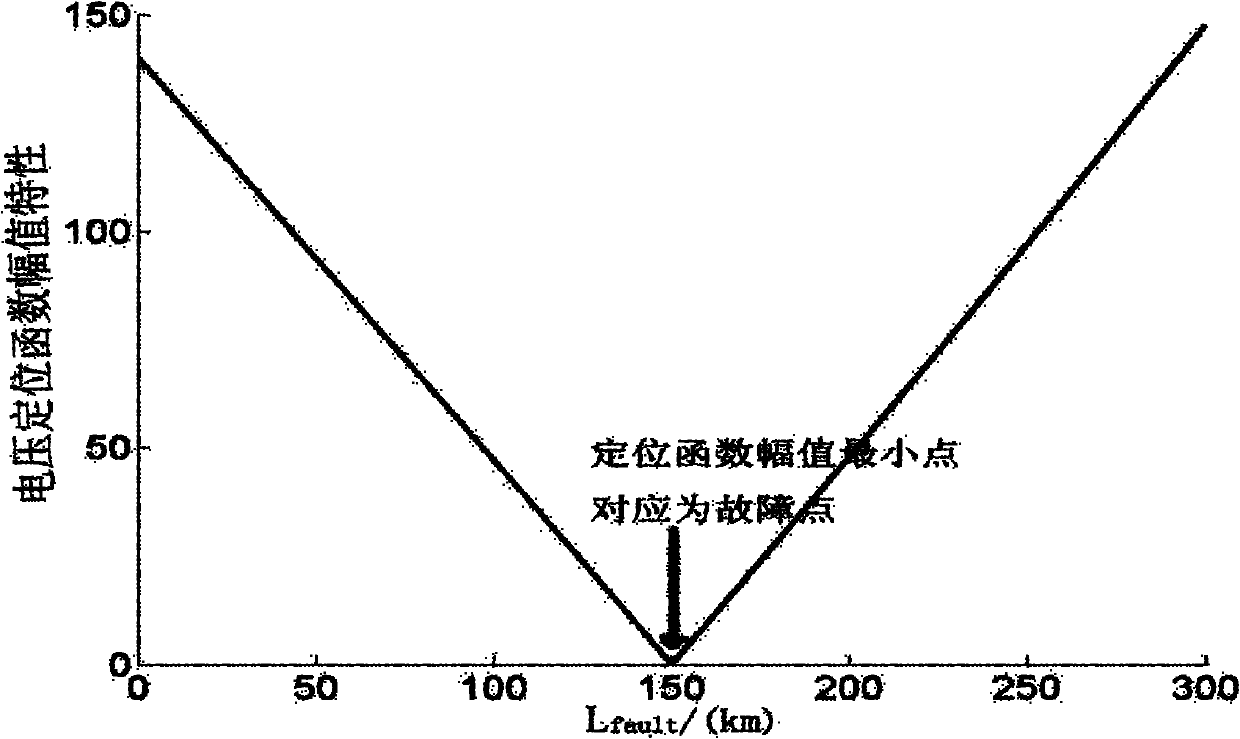
ActiveCN101067641ADescribe physical propertiesThere is no non-convergence problemFault locationCapacitancePhase currents
The invention belongs to the electrical power system domain, specially relates to the line single end fault distance measuring method of the anti- distributed capacity electric current and the transition resistance influence. Including: surveys the transformer substation protection installment place fault phase voltage, the phase current, the zero sequence voltage, the zero sequence electric current and the negative sequence electric current as the input value; using the fault voltage cross zero time to measure the resistance characteristic which is not influence by transition resistance, from the protected line begin end start, computing the measure voltage real part computed value of the fault point voltage cross zero point time, compared with the measured value of the measure voltage real part, computing the error; and taking the delta-S as the step size, in turn computing the setting range which is protected by the send tripping signal, if cannot obtain the protect tripping signal, searching the total track length which is protected, taking the minimum point as the fault point. The invention method is not influenced by the distributed capacity electric current and transition resistance, does not have the false root problem of solving equation method and non convergence question of the iterative method, and has the very high practical value.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Control apparatus for brushless DC motor
ActiveUS20050029972A1Improve estimation accuracySynchronous motors startersVector control systemsPhase currentsConductor Coil
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
System and method for shaped phased current delivery
A method of treating an ailment suffered by a patient using one or more electrodes adjacent spinal column tissue of the patient, comprises delivering electrical modulation energy from the one or more electrodes to the spinal column tissue in accordance with a continuous bi-phasic waveform having a positive phase and a negative phase, thereby modulating the spinal column tissue to treat the ailment. An implantable electrical modulation system, comprises one or more electrical terminals configured for being coupled to one or more modulation leads, output modulation circuitry capable of outputting electrical modulation energy to the electrical terminal(s) in accordance with a continuous bi-phasic waveform, and control circuitry configured for modifying a shape of the continuous bi-phasic waveform, thereby changing the characteristics of the electrical modulation energy outputted to the electrode(s).
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
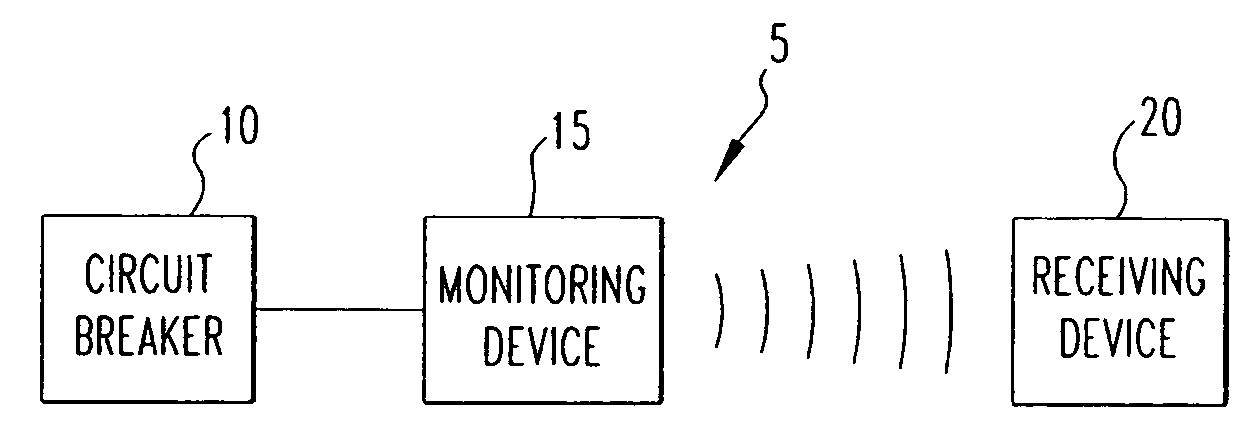
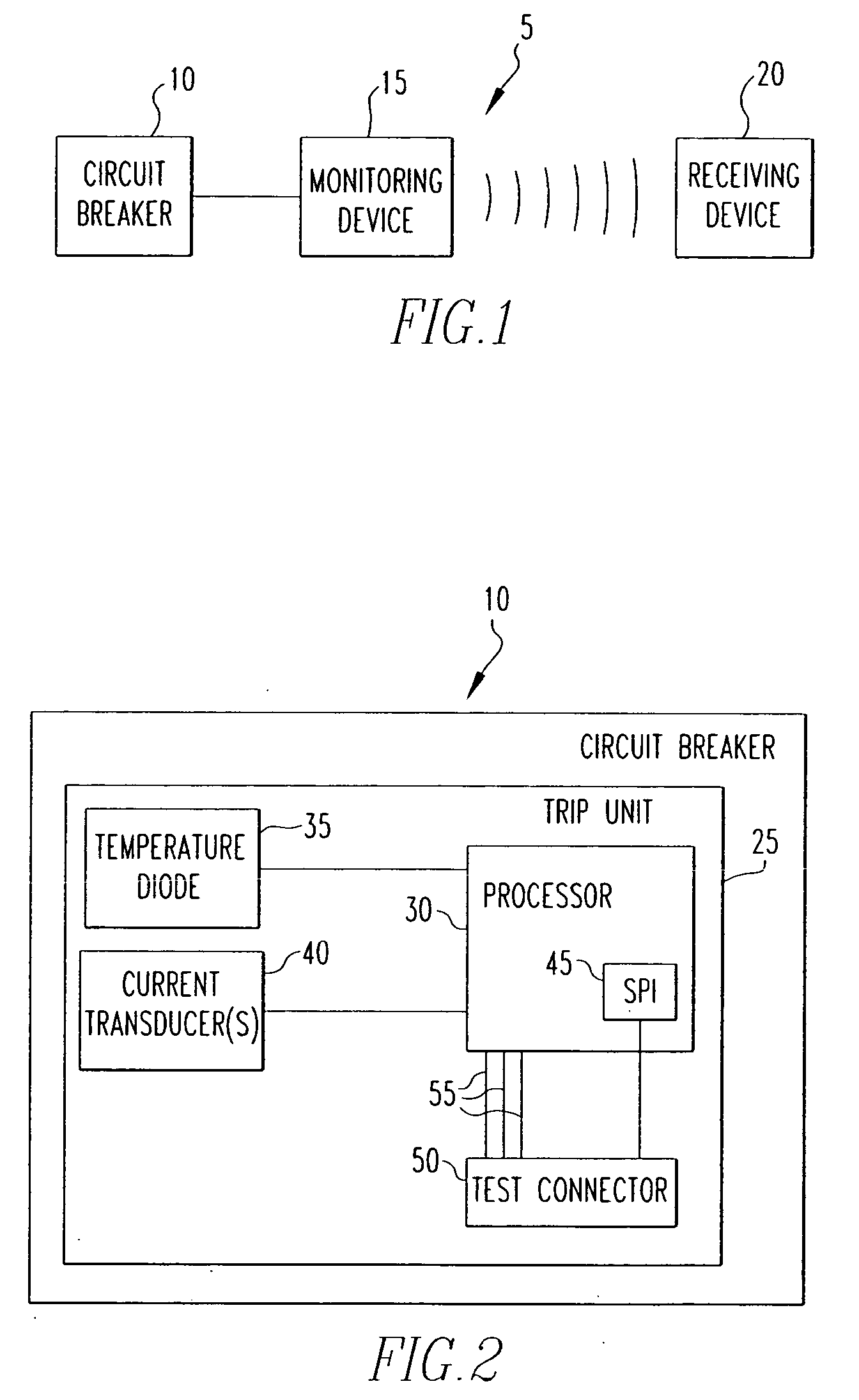
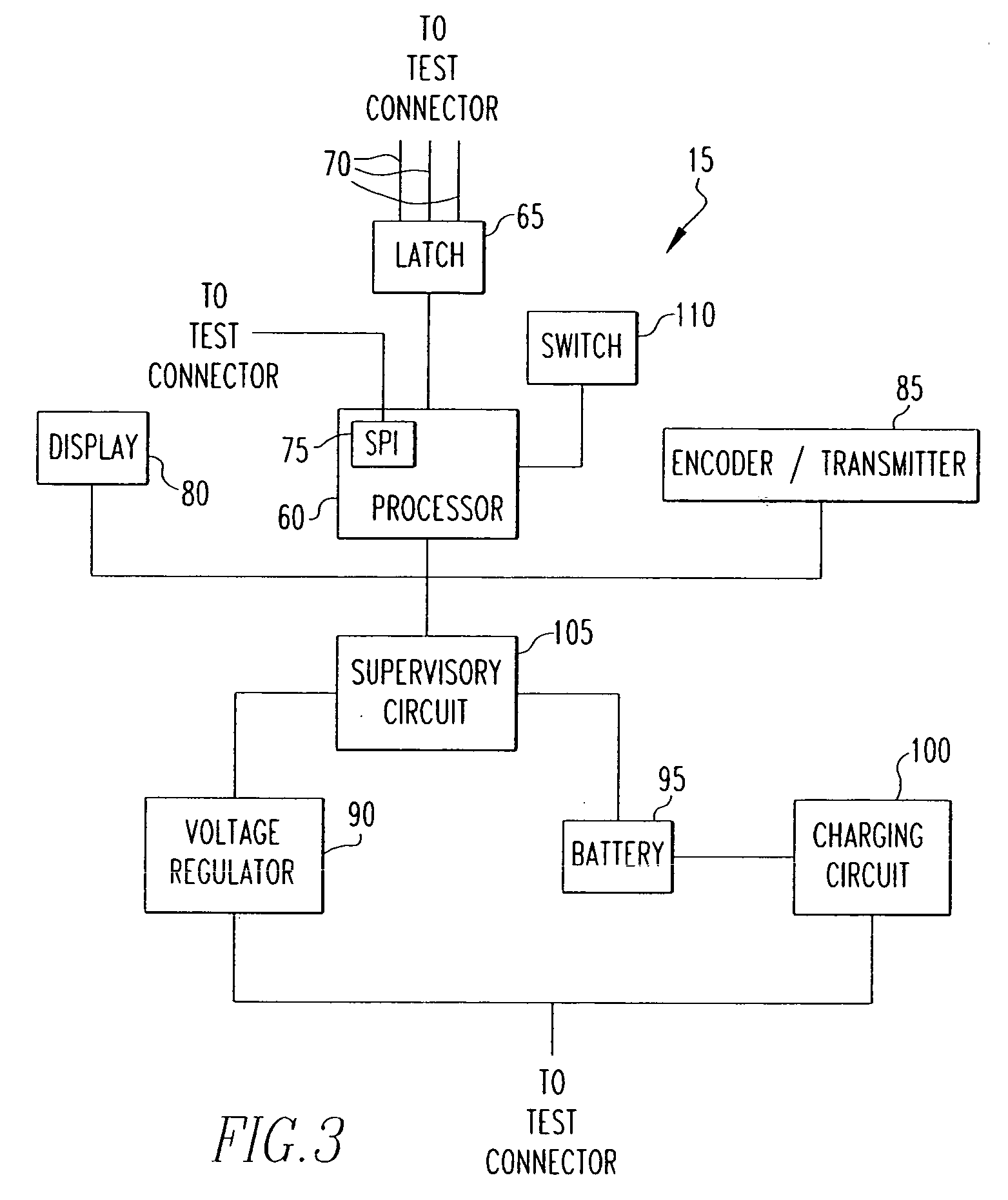
System for wireless monitoring of circuit breakers
ActiveUS20060176630A1Emergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionEmergency protection for supplying operative powerPhase currentsWireless transmission
A system for monitoring a circuit breaker that includes a monitoring device in electronic communication with the circuit breaker and a receiving device located separately from the monitoring device. The monitoring device receives data from the circuit breaker and wirelessly transmits at least a portion of the data such as one or more phase currents measured from a network which the circuit breaker protects, an ambient temperature within the circuit breaker, and / or data relating to a trip condition of the circuit breaker. The receiving device receives the transmitted data and displays all or a portion thereof. The monitoring device also includes a display that displays all or a portion of the data.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
Line single-phase earth fault single-terminal location method based on positioning function amplitude characteristics
ActiveCN102200563AAvoid influenceThere is no false root problemFault locationPhase currentsCapacitance
The invention discloses a line single-phase earth fault single-terminal location method based on positioning function amplitude characteristics. The method comprises the following steps of: measuring fault phase voltage, fault phase current, fault phase negative-sequence current and zero-sequence current at a protection installation position of a transformer substation as input variables; with the origin of a protected line as a start point, calculating the positioning function amplitude of each point on a fault phase line one by one in a way that step length increases gradually till a trip signal setting range is reached; if protection trip signals cannot be obtained, searching all over the protected line, taking the point with the smallest positioning function amplitude as a fault pointand setting the distance between the point and the line protection installation position. The method is not influenced by distributed capacitance, or load current or transition resistance, does not have the problems of false root existing in the method of solving equation or non-convergence existing in the iteration method and achieves very high practical value.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Distribution network line fault section positioning method based on full-waveform information
ActiveCN104155582AHigh sensitivityImprove reliabilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault location by conductor typesPhase currentsCorrelation function
The invention discloses a distribution network line fault section positioning method based on full-waveform information. For the grounding fault, line selection is carried out through extreme value points of a cross-correlation function of the bus zero-sequence voltage and all outgoing line zero-sequence currents, and positioning is carried out according to the adjacent detection point zero-sequence current waveform standard drift rate of the whole action process of a fault occurrence and compensation device; for the interphase fault, line selection is carried out according to the overcurrent information obtained before action of a relay protection device, and positioning is carried out according to the adjacent detection point fault phase current waveform standard drift rate. The waveform data of the whole action process of a fault and arc extinction device are utilized, the current ubiquitous problems that when a small current grounding system encounters the single-phase grounding phase, the fault current is weak, the reliability is poor, and the sensitivity is low can be well solved, and meanwhile the system cannot get interference.
Owner:SHANGHAI MAINE ENERGY TECH CO LTD
System for Accurately Detecting Electricity Theft
There is disclosed a method of monitoring an electrical network of the type having a feeder line connected to a plurality of distribution transformers, each distribution transformer being in turn coupled to a load which may be provided with a customer meter. The method includes the steps of recording an accumulated in-phase current at each of the distribution transformers over a time period and recording for the same time period an accumulated in-phase current at the feeder line. The sum of the accumulated in-phase currents recorded at the distribution transformers are then compared to the accumulated in-phase current recorded at the feeder line. The method may also include the steps of recording accumulated in-phase currents at the customer meters and comparing their sum with the accumulated in-phase current measured at the distribution transformers coupled to the customer meters. The method may further include a method of automatically detecting the configuration of the network to determine on which phase the customer meters are connected to, and to which distribution transformer said customer meters are connected to, and further, where on the network, relative to a plurality of feeder meters, each of the distribution transformers are connected.
Owner:GRID2020
Phase current measurements in a three phase inverter using a single common dc-link current sensor
ActiveUS20090284194A1Sufficient durationImprove performanceSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlPhase currentsCurrent sensor
A method for measuring current in each phase of a three-phase inverter driven motor is based on the three-phase inverter being controlled in a PWM mode by three PWM signals including the use of a common DC-link current sensing resistor. The current on the sensing resistor is intermittently sampled. The method includes determining a modulation index for the voltage demand set by a motor controller. Based on specific mutual duty cycle conditions of the three PWM phase driving signals, sampling windows of sufficient duration are created for allowing distinct sampling of two of the phase currents.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
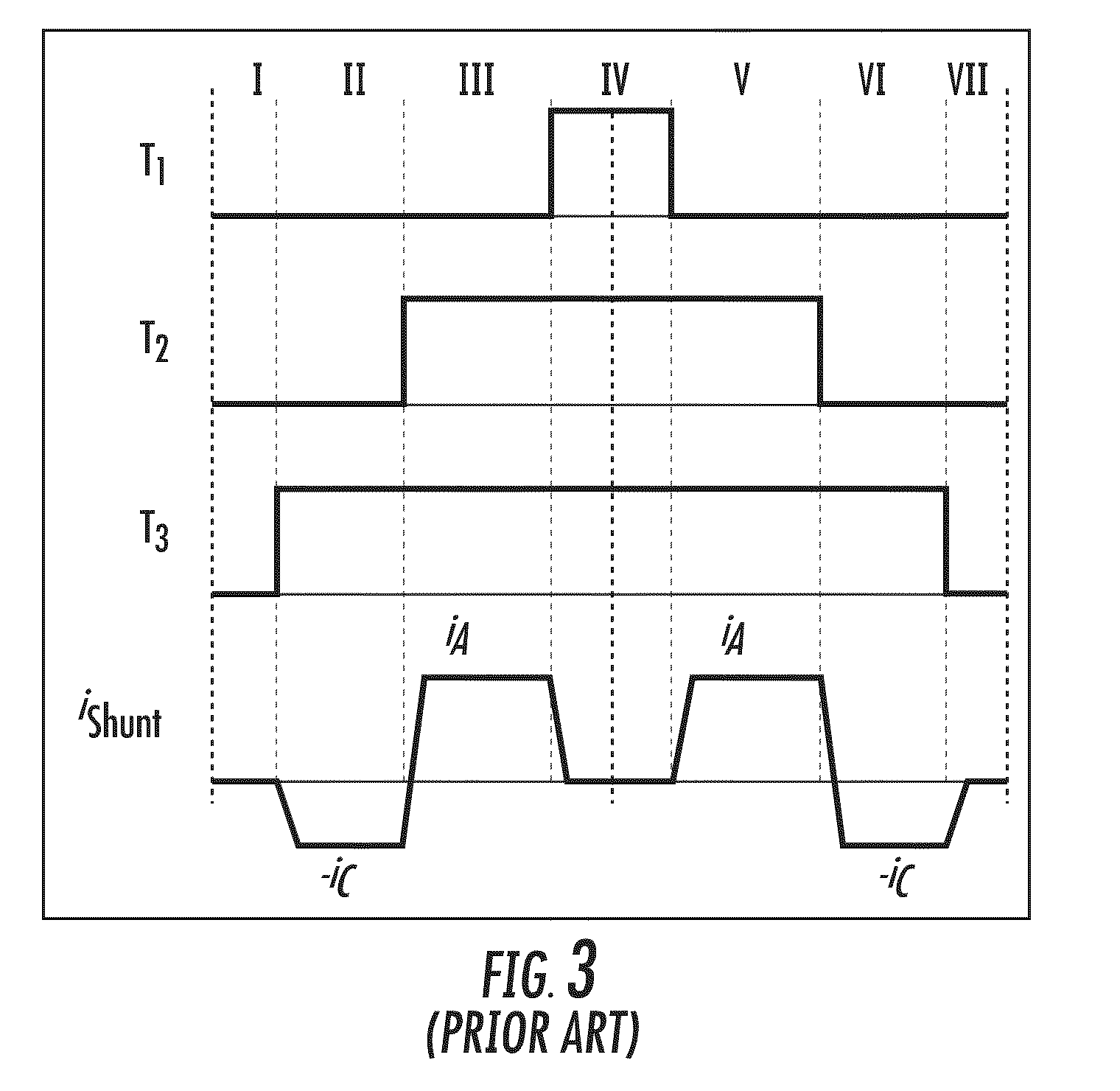
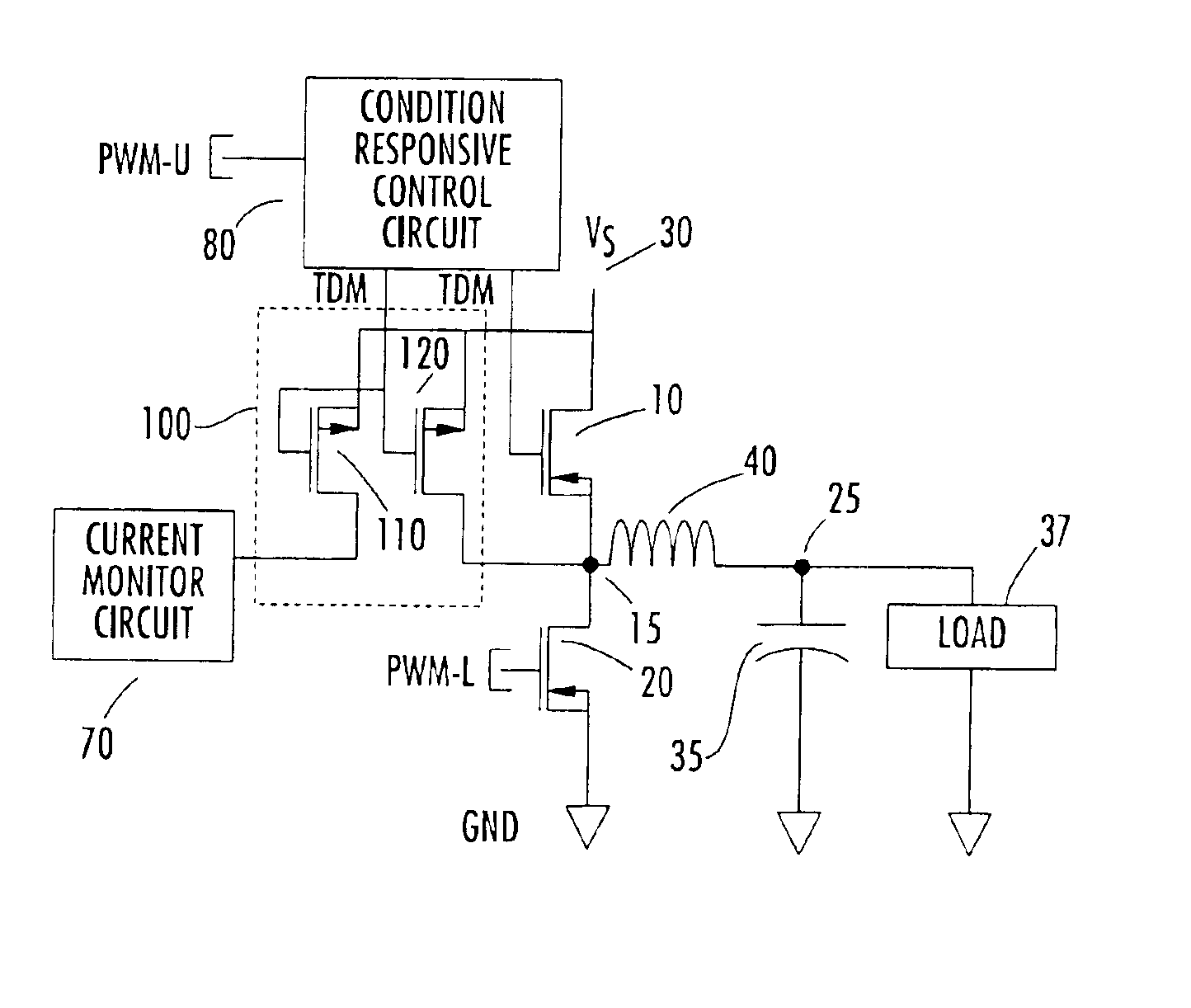
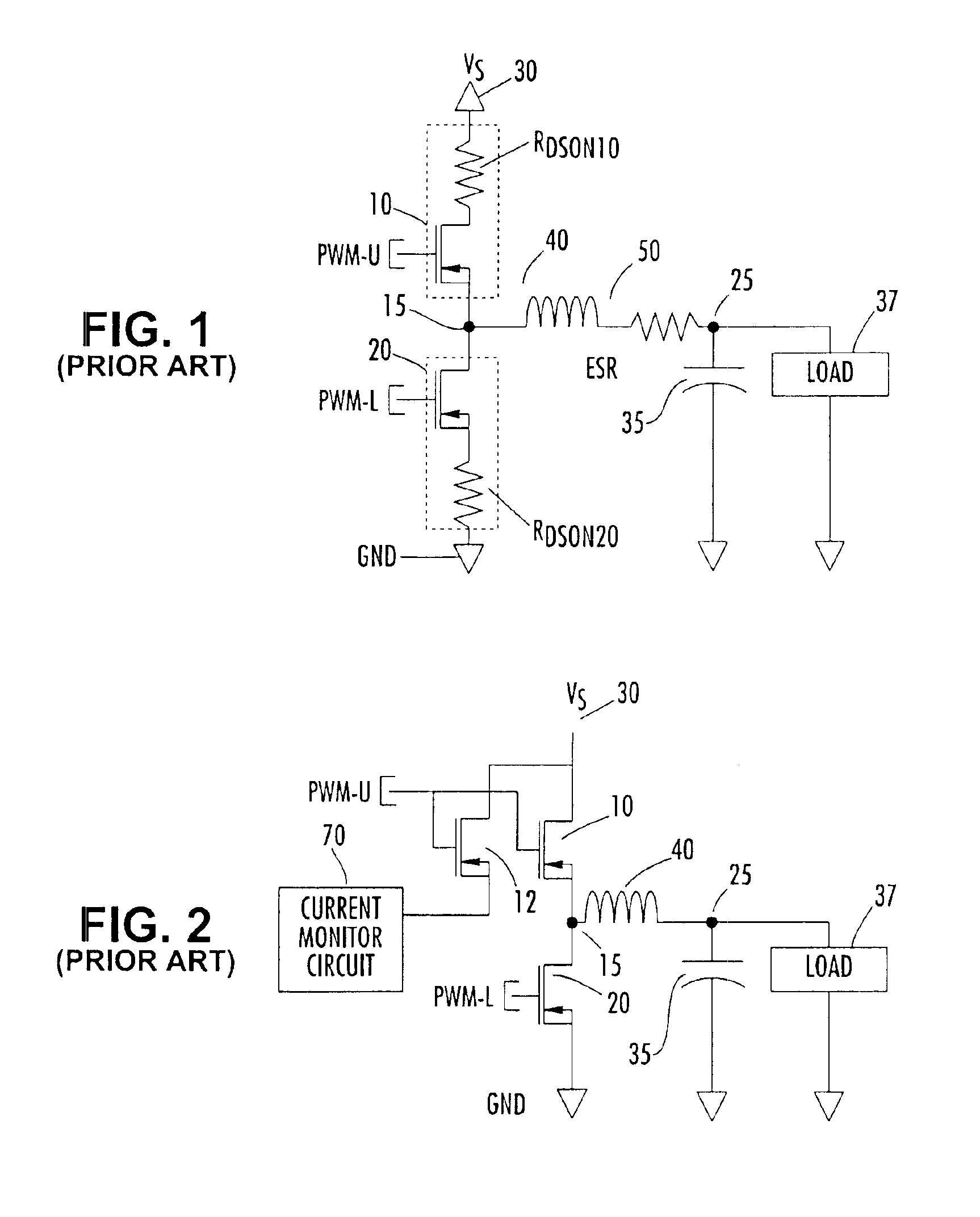
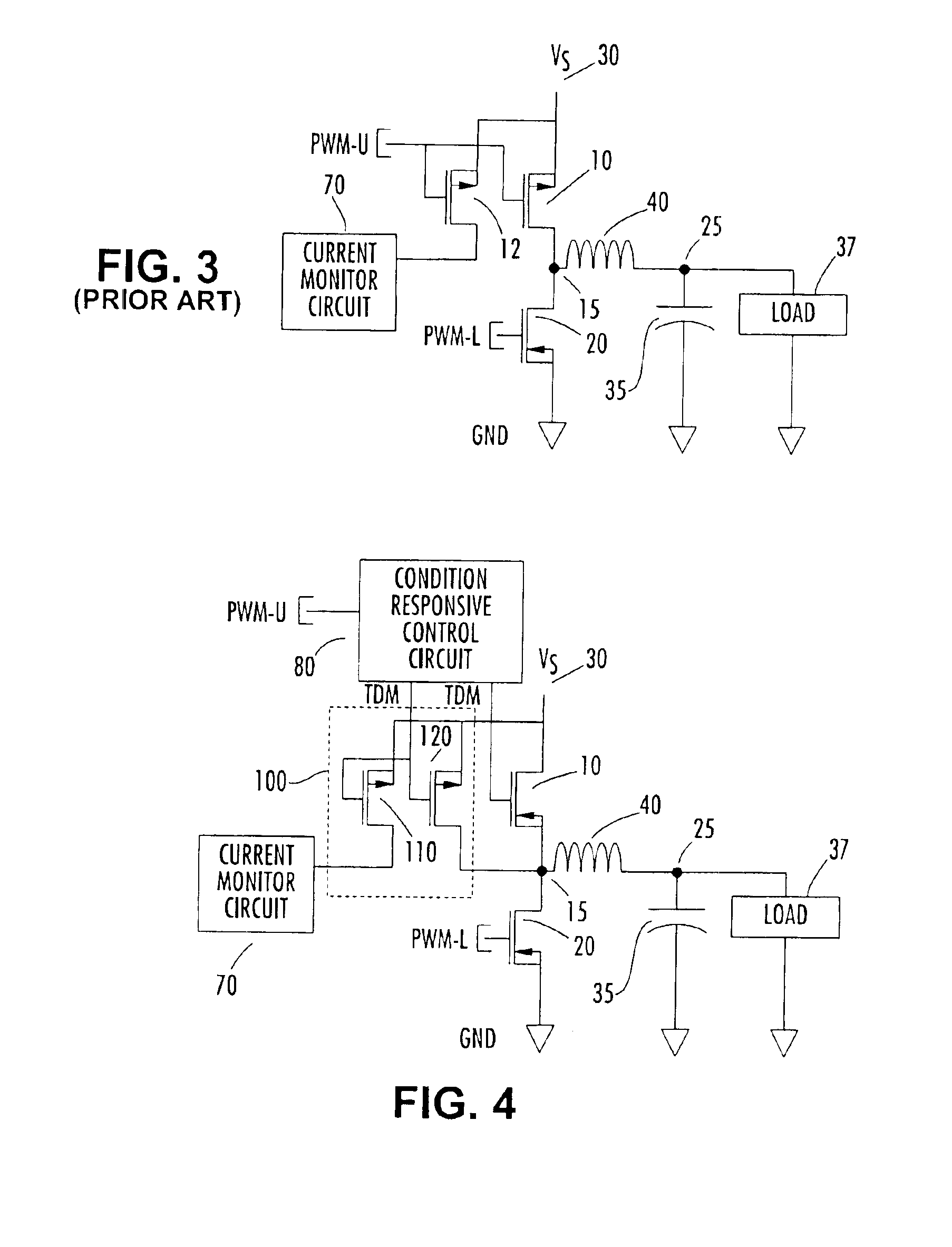
Time division multiplexed, piloted current monitoring in a switched mode DC-DC voltage converter and phase current measurement calibration for a multiphase converter
InactiveUS6906536B2Easy to operateAccurate measurementEfficient power electronics conversionResistance/reactance/impedencePhase currentsDc dc converter
An arrangement for measuring current through a phase section of a buck mode DC-DC converter includes an auxiliary integrated circuit containing an auxiliary power MOSFET and a pilot MOSFET coupled in parallel with a current path through a high side MOSFET of a half-bridge of the converter. The pilot MOSFET has a current path coupled to a current measurement terminal. The MOSFETs of the auxiliary circuit are time division multiplexed with the high side MOSFET, whereby a determination of current through the auxiliary high side MOSFET is based upon current through the pilot device and the geometric ratio of the size of the pilot device to that of the high side auxiliary MOSFET. The high side MOSFET is activated for a large number of switching cycles relative to the pilot circuitry, but the pilot circuitry is activated sufficiently often to derive a relatively accurate measure of current flow.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Multiphase grid synchronized regulated current source inverter systems
ActiveUS20090302686A1Reduce Harmonic DistortionIncrease the number ofDc network circuit arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationPhase currentsPower grid
Power from the dc outputs of wind-generated power collection nodes is converted to ac power of suitable quality for injection into an electric power grid. Conversion is accomplished by current regulation of the dc outputs of the wind-generated power collection nodes to the input of each one of multiple inverters in a system, with each inverter outputting multiple phase currents that are out of phase with the multiple phase currents outputted from all other inverters in the system. The multiple phase currents from all of the inverters in a system are connected to the secondary windings of a phase transformation network that produces a three phase current output having a step-shaped waveform for injection into the electric power grid. Alternatively the dc input to each one of the multiple inverters may be a combination of the dc outputs of wind-generated power collection nodes and the dc outputs of solar photovoltaic power collection nodes.
Owner:ALENCON ACQUISITION
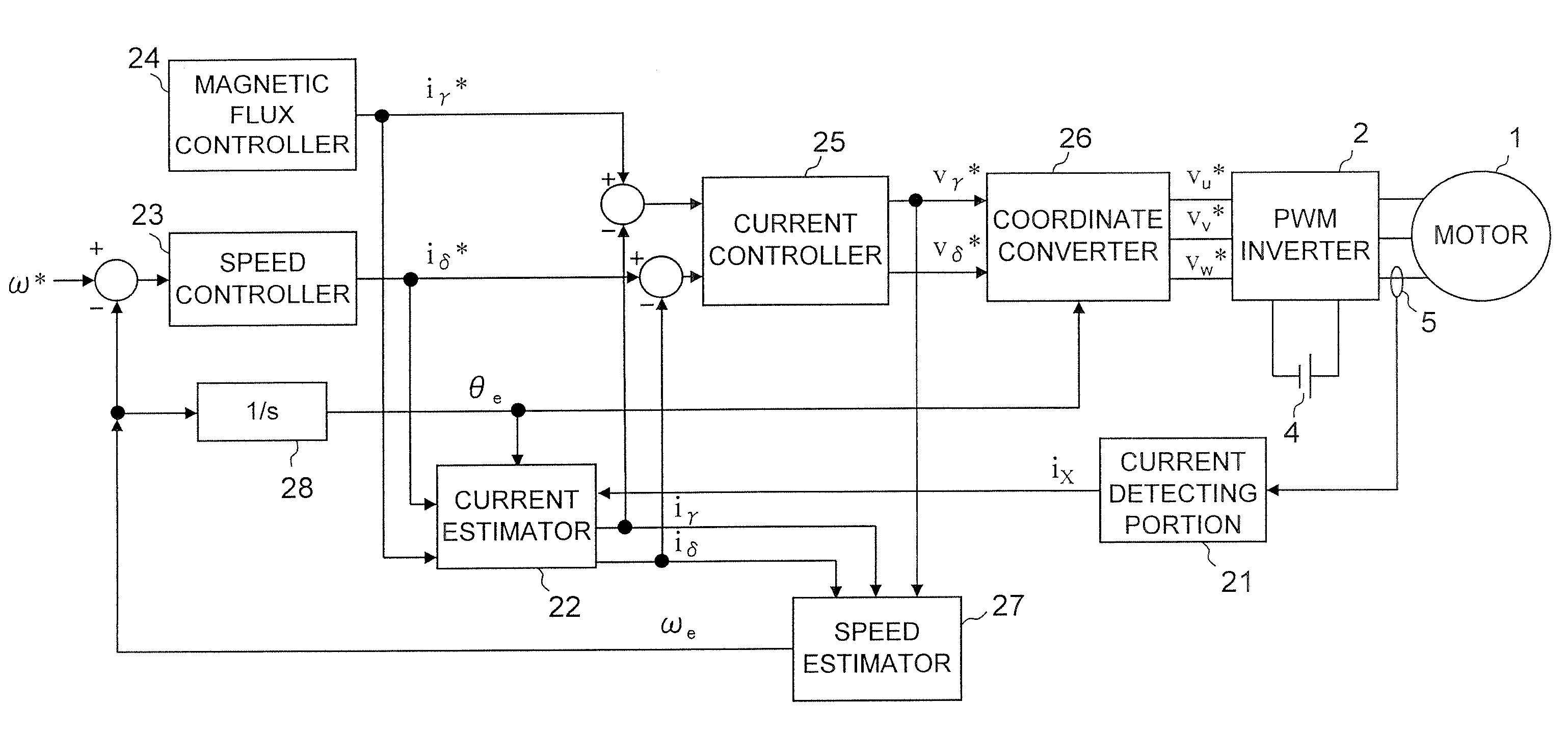
Motor control device
ActiveUS7482777B2Small sizeSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsPhase currentsPhase conversion
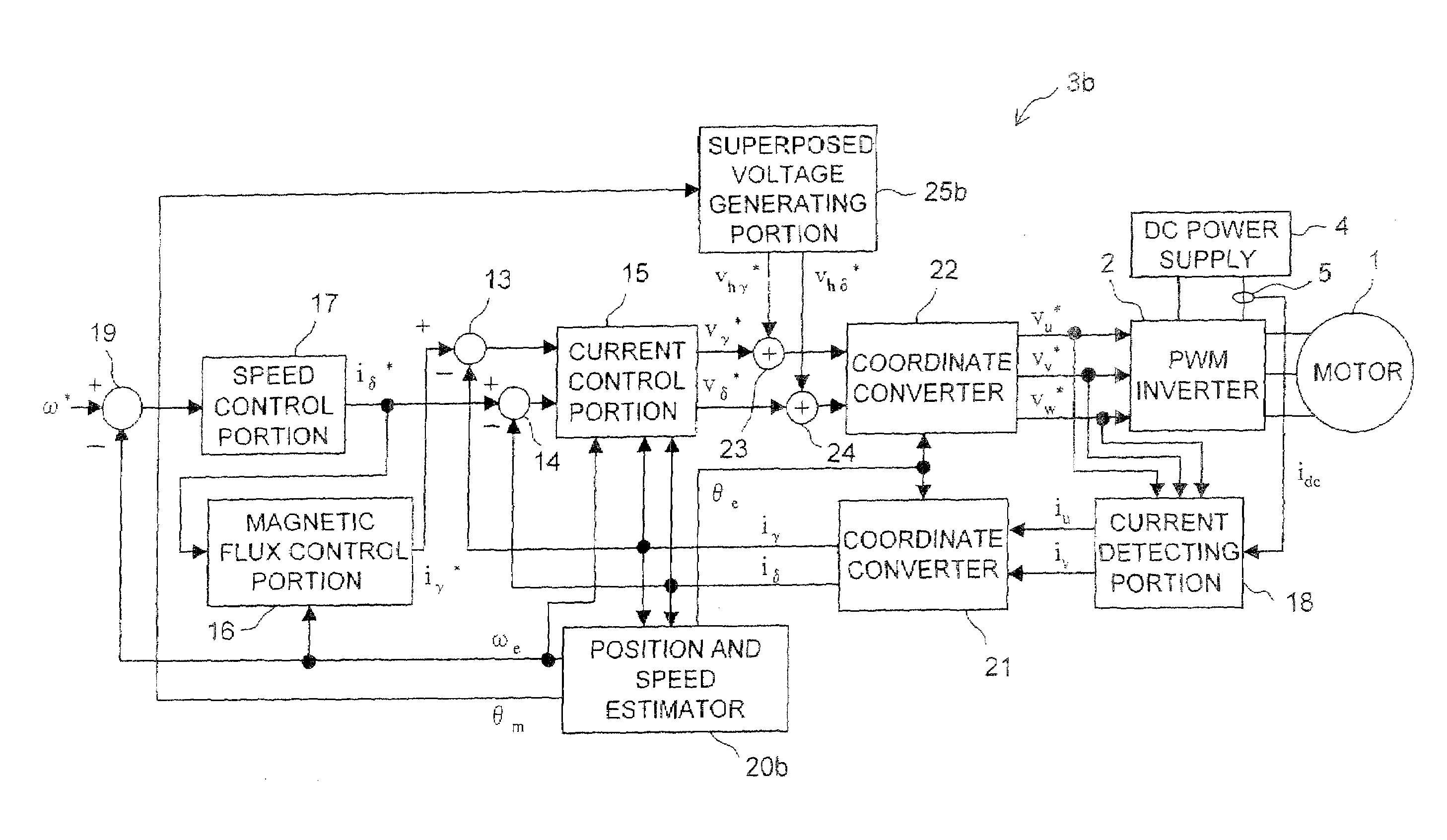
The motor control device includes a current detecting portion for detecting a phase current that flows in an armature winding of a stator of a three-phase motor based on current that flows between an inverter for driving the motor and a DC power supply. The motor control device performs a position sensorless vector control for the motor based on a control current that is obtained by a three-phase to two-phase conversion of the phase current based on an estimated rotor position of the motor. The motor control device farther includes a superposing portion for superposing a superposed voltage having a predetermined frequency on a drive voltage for driving the motor and an estimating portion for deriving the estimated rotor position based on the superposed current that is extracted from the control current and flows in the motor in accordance with the superposed voltage. A voltage vector locus of the superposed voltage from the superposing portion presents an ellipse.
Owner:III HLDG 7
Dead-time compensation algorithm for 3-phase inverter using svpwm
InactiveUS20130088905A1Minimizing distortion of output voltageReduce voltageDc-ac conversion without reversalPhase currentsSwitching signal
Disclosed is a dead-time compensation method of a 3-phase inverter using an SVPWM scheme. The dead-time compensation method includes generating a switching signal having dead-time with respect to the power semiconductor switches of the upper and lower arms in order to obtain a predetermined output through the SVPWM scheme, detecting medium phase current from each phase current output through the switching signal, determining polarity of the medium phase current, and generating a switching signal by calculating switching time in order to compensate for time to apply effective voltage according to the polarity of the medium phase current. Through the dead-time compensation method, the distortion of the output voltage and the reduction of voltage having a fundamental wave in the output voltage, which are caused by the dead-time, are minimized through the switching of compensating for the time to apply effective voltage based on the polarity of the load current.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND +1
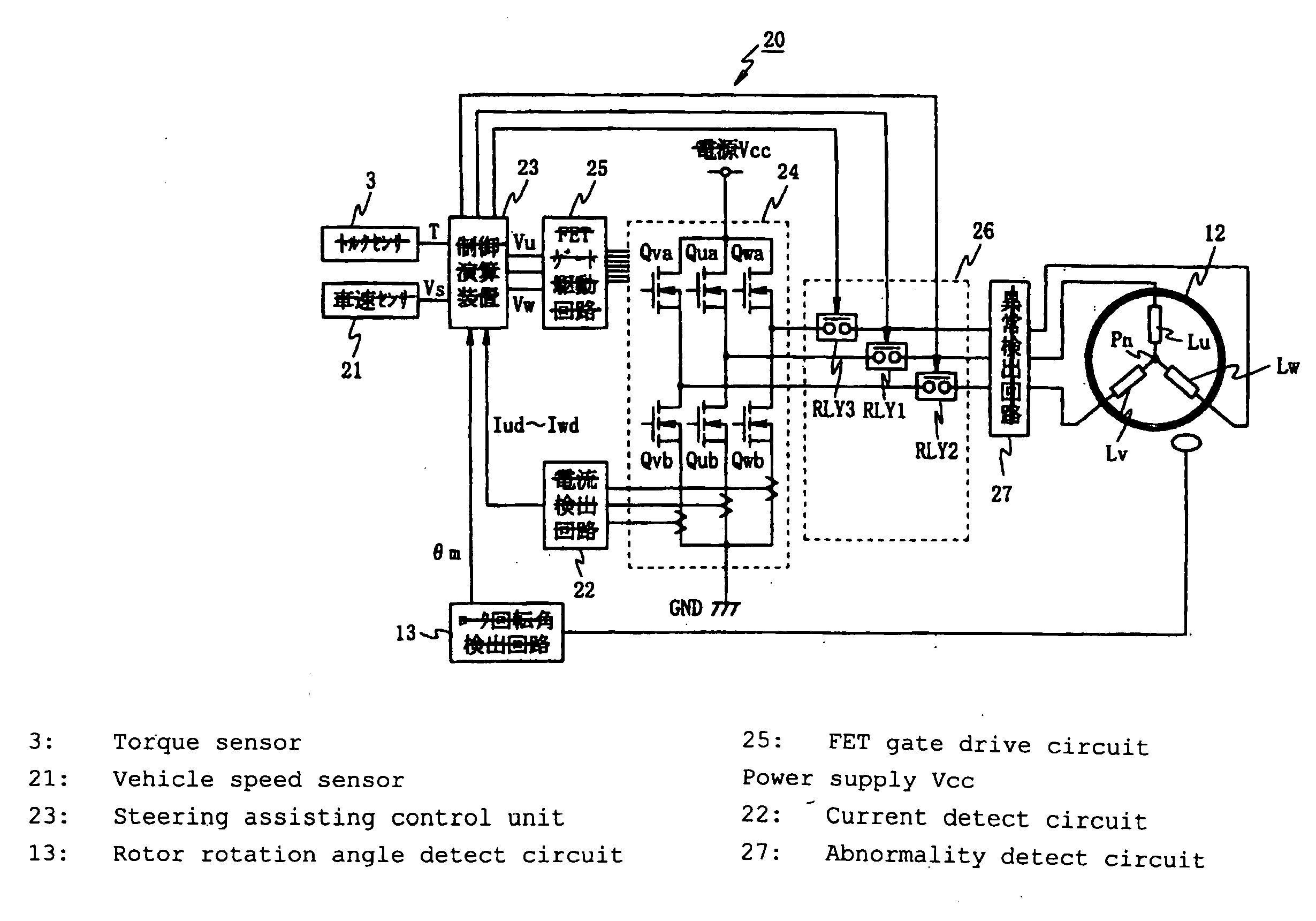
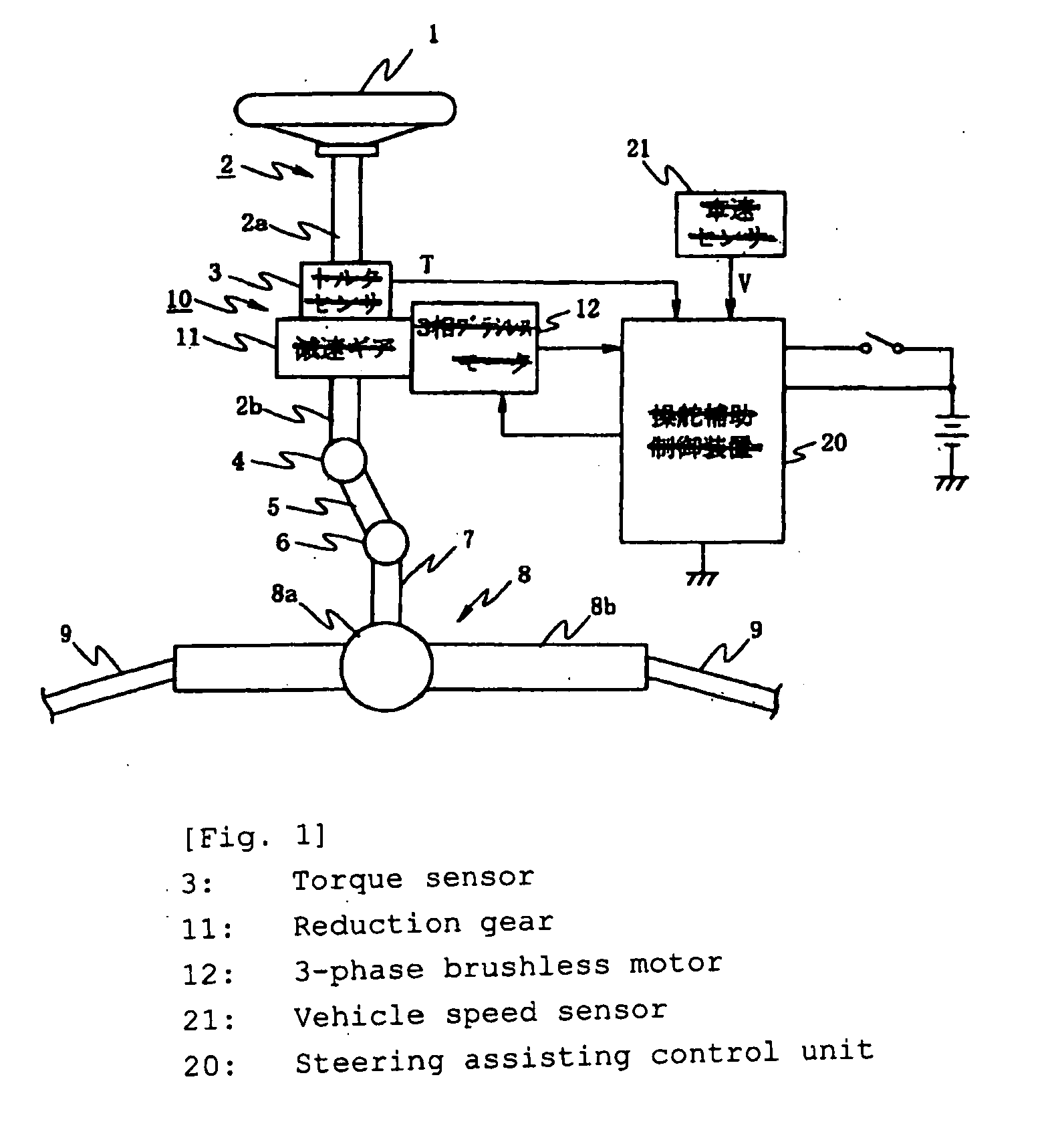
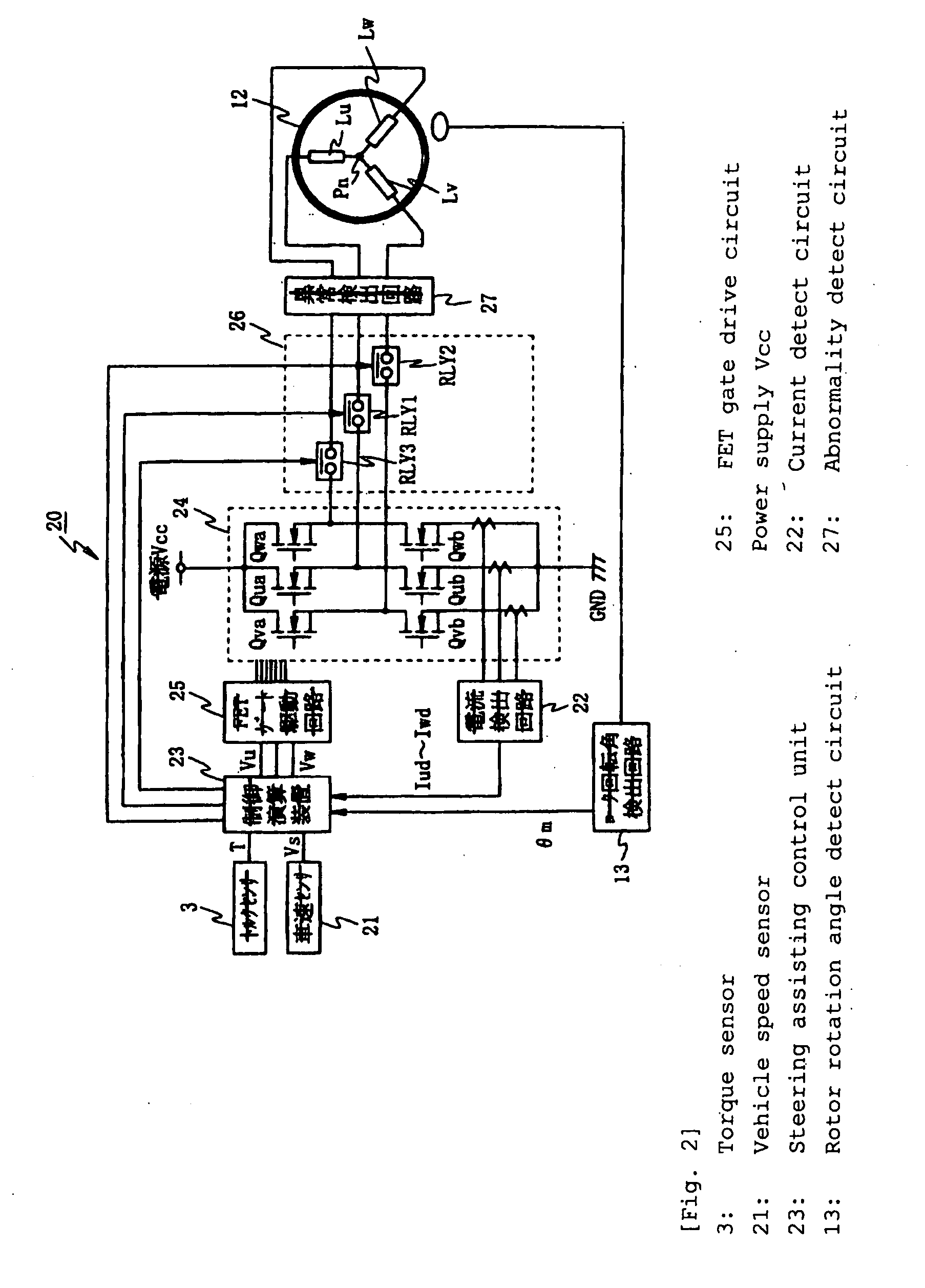
Electric power steering apparatus
InactiveUS20100017063A1Reduce loadCommutation monitoringDigital data processing detailsPhase currentsElectric power steering
An electric power steering apparatus in which the intensity and directions of drive currents flowing in remaining phases continues motor rotation driving. An abnormality detect unit (27) detects a conduction abnormality in drive systems for the respective phase coils of the 3-phase brushless motor (12). A steering assisting current command value calculating unit (31) calculates a steering assisting current command value. A normal time motor command value calculating unit (33) calculates three phase current command values according to the steering assisting current command value. An abnormal time motor command value calculating unit (34) calculates two phase current command values for using the two remaining phase coils. A command value select portion (35) selects the phase current command values calculated by the normal or abnormal time motor command value calculating unit. A motor control unit (36) drives the electric motor (12) according to the selected phase current command value.
Owner:NSK LTD
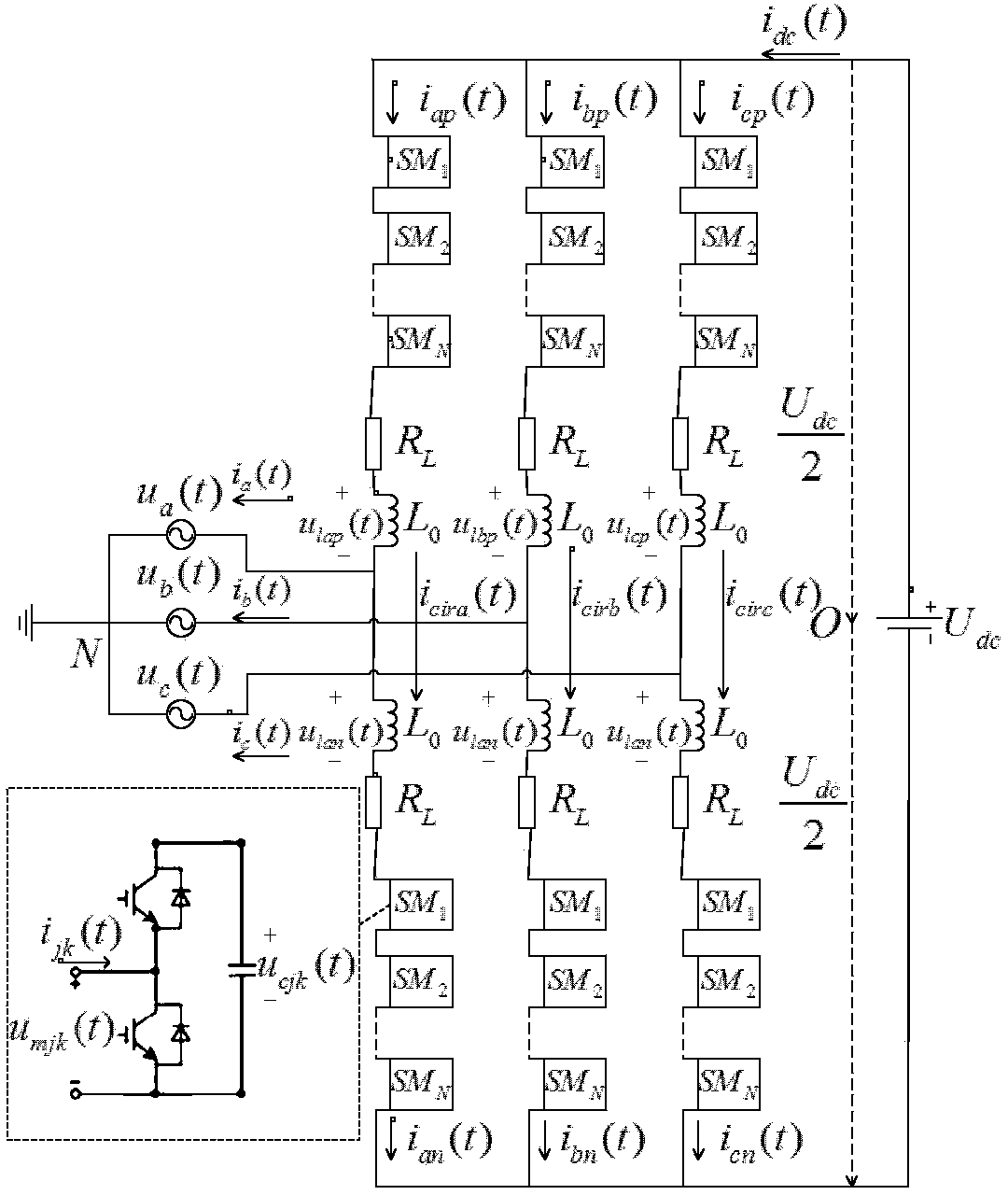
Modular multi-level converter capacitor voltage fluctuation inhibition method under low-frequency working condition
ActiveCN103701350AGuaranteed symmetrySymmetry helpsDc-ac conversion without reversalPhase currentsCapacitor voltage
The invention relates to a modular multi-level converter capacitor voltage fluctuation inhibition method under a low-frequency working condition, and belongs to the technical field of power electronics and motor drive. The method comprises the following steps: the alternating-current side three-phase phase current which meets the low-frequency working need is obtained by performing closed-loop control on the modular multi-level converter alternating-current side three-phase phase current; loop current only contains a direct-current component and a high-frequency alternating-current component by closed-loop control of the three-phase loop current, and a bridge arm voltage contains a high-frequency zero sequence component by overlapping high-frequency voltage at the midpoint electric potential at the direct-current side; the amplitude values, the frequencies and the phases of the loop current high-frequency alternating-current component and the bridge arm voltage high-frequency zero sequence component are obtained by operation, so that the phase voltage and the phase current of the alternating-current side do not contain high-frequency harmonic waves, moreover, the cycles of charging and discharging submodules are shortened, and the effect of inhibiting the capacitor voltage vibration of the submodules is realized; the electrical quantity of each bridge arm is kept to be balanced by the balancing control on the bridge arm energy so as to guarantee that the modular multi-level converter runs symmetrically and stably.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Configurable single/multi-phase overload relay
InactiveUS6459557B1Parameter calibration/settingMechanical power/torque controlPhase currentsElectrical conductor
A configurable overload relay selectively operable in a single-phase mode of operation and a multi-phase mode of operation is configured to sense current flow through power conductors. The relay is further configured to determine a parameter related to the current flow, such as average current, vector sum of phase currents, and current imbalance, based on selection of either the single-phase or multi-phase mode of operation. Regardless of the selected mode of operation, the relay can provide protection for multiple types of power conductor fault conditions, including ground faults, overloads, and phase loss. The relay further can be configured to provide a reporting signal indicative of the value of the determined current-related parameter and / or the occurrence of the fault condition.
Owner:ROCKWELL TECH
Method for controlling a steer-by-wire system
InactiveUS20030114969A1Improve the protective effectEasy to carrySteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsPhase currentsMicrocomputer
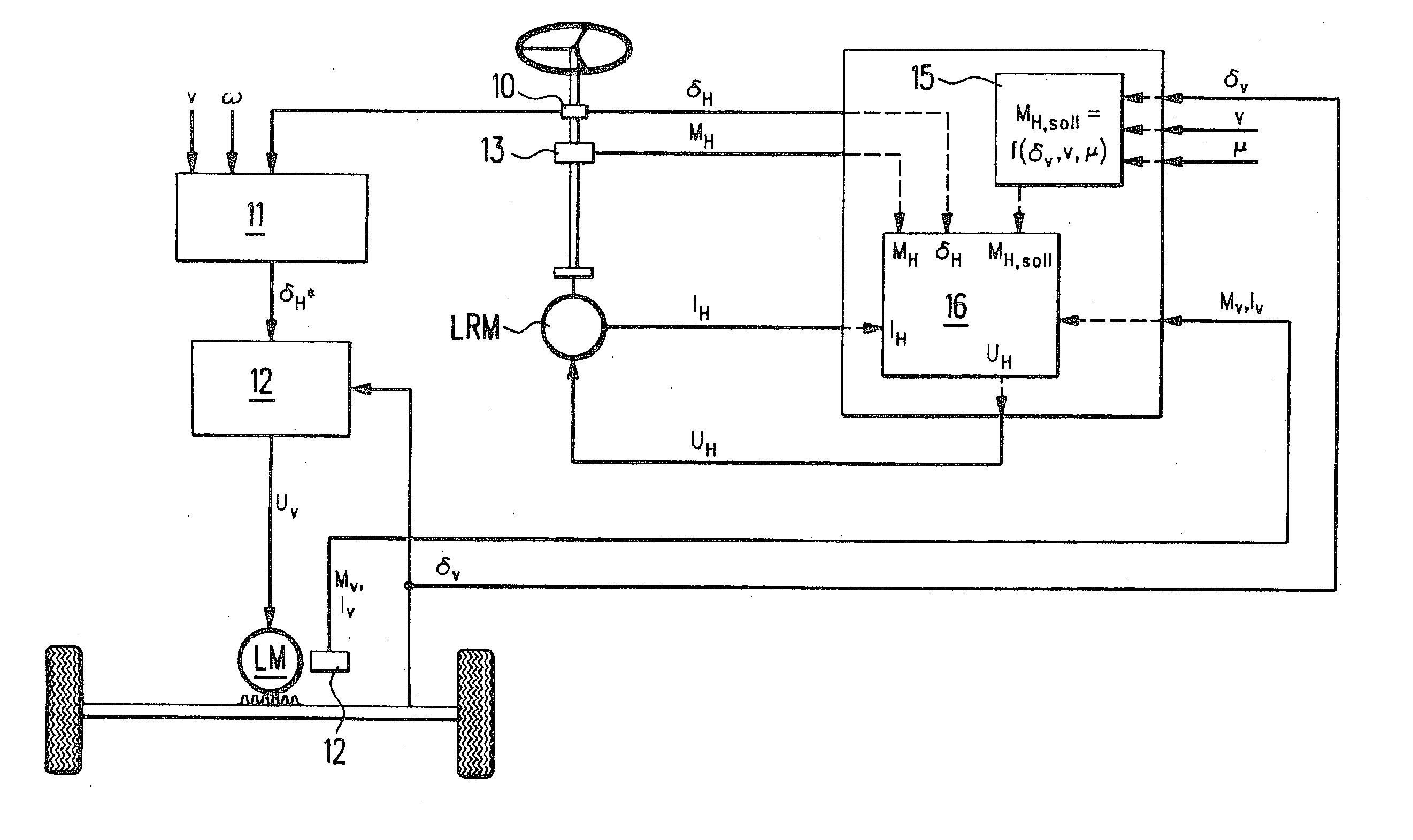
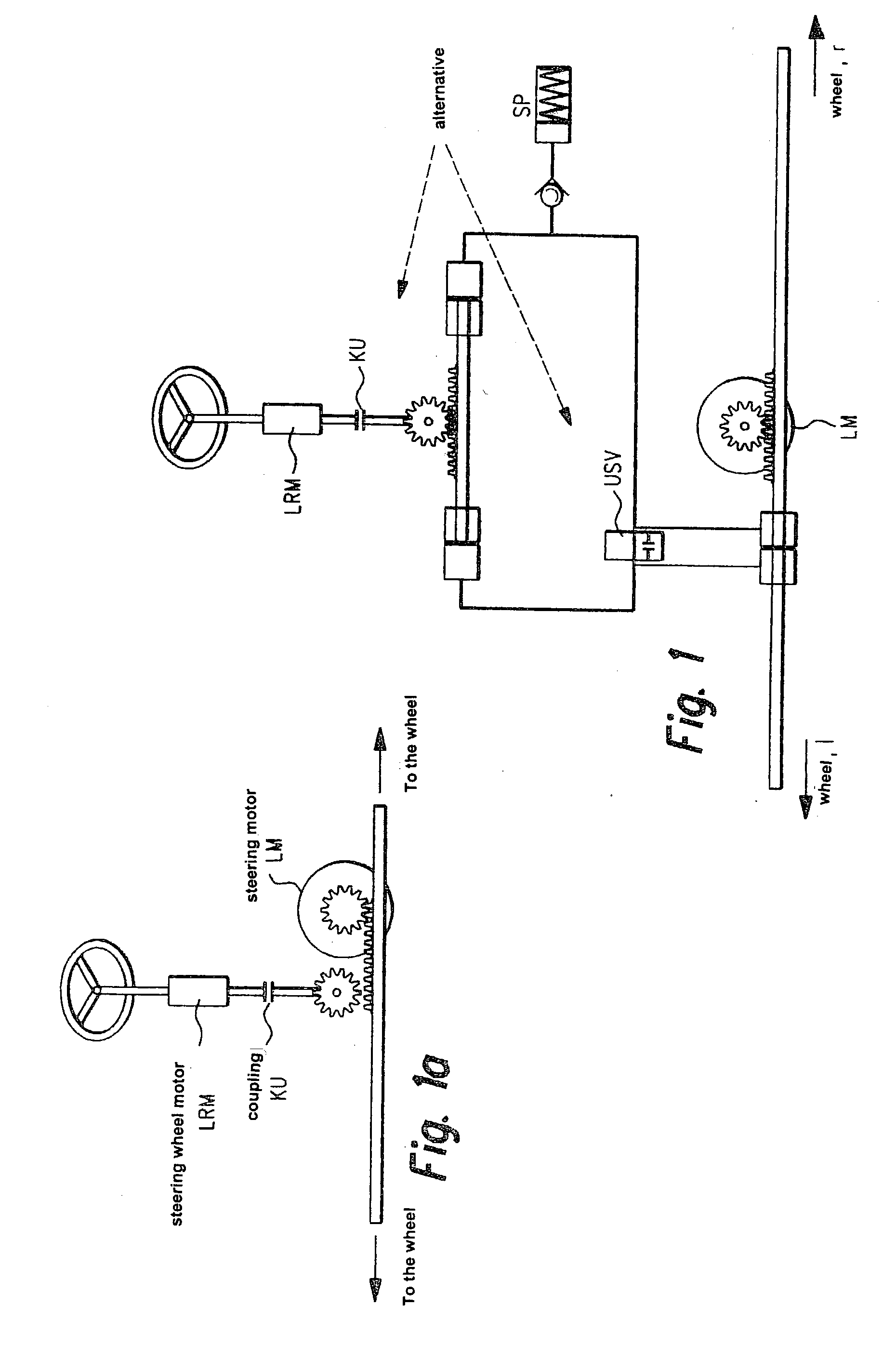
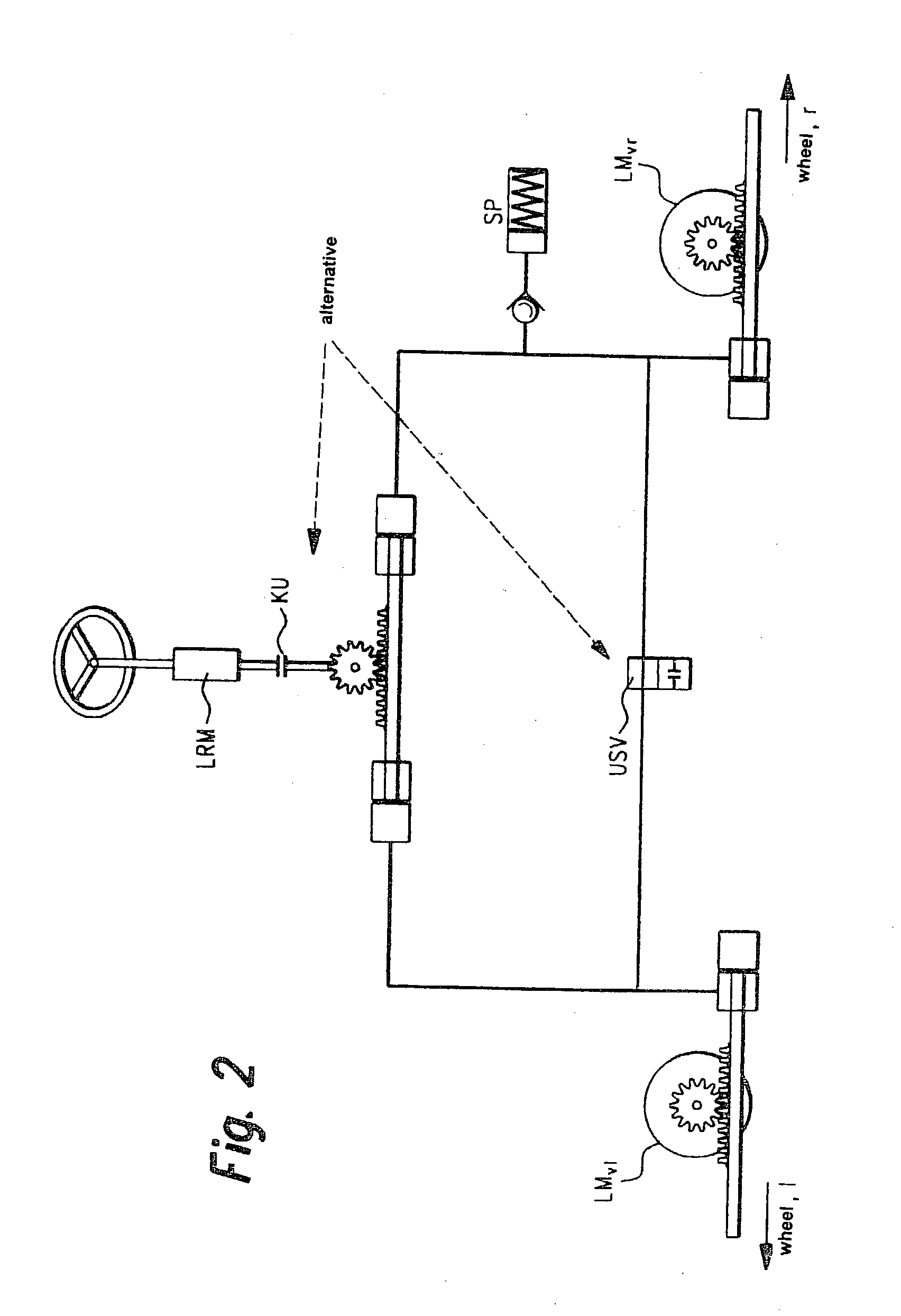
A device for controlling a steer-by-wire steering system in a vehicle is described. The redundantly generated sensor signals (deltav1, deltav2, deltaH1, deltaH2) for regulating a steering motor (LM) and for a feedback actuator (LRM) that transfers the restoring torques from the road to the driver via the steering wheel are received by a control device having the form of a microcomputer (RM) and plausibility checks of the sensor signals are performed therein and in an operatively associated monitoring module (ÜM). Microcomputer module (RM) and monitoring module (ÜM) monitor each other reciprocally. An auxiliary level for the steer-by-wire steering system is also monitored by the control device (RM) which, in the case of error, switches to this auxiliary level or a mechanical auxiliary level. In order to further increase the degree of safety, the steering wheel motor (LRM) is triggered via control signals (UH) for its phase currents and by a steering wheel motor enable signal (gRH), and similarly the steering motor (LM) is triggered via control signals (Uv) for its phase currents and via a steering motor enable signal (gRV). (FIG. 5)
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH +1
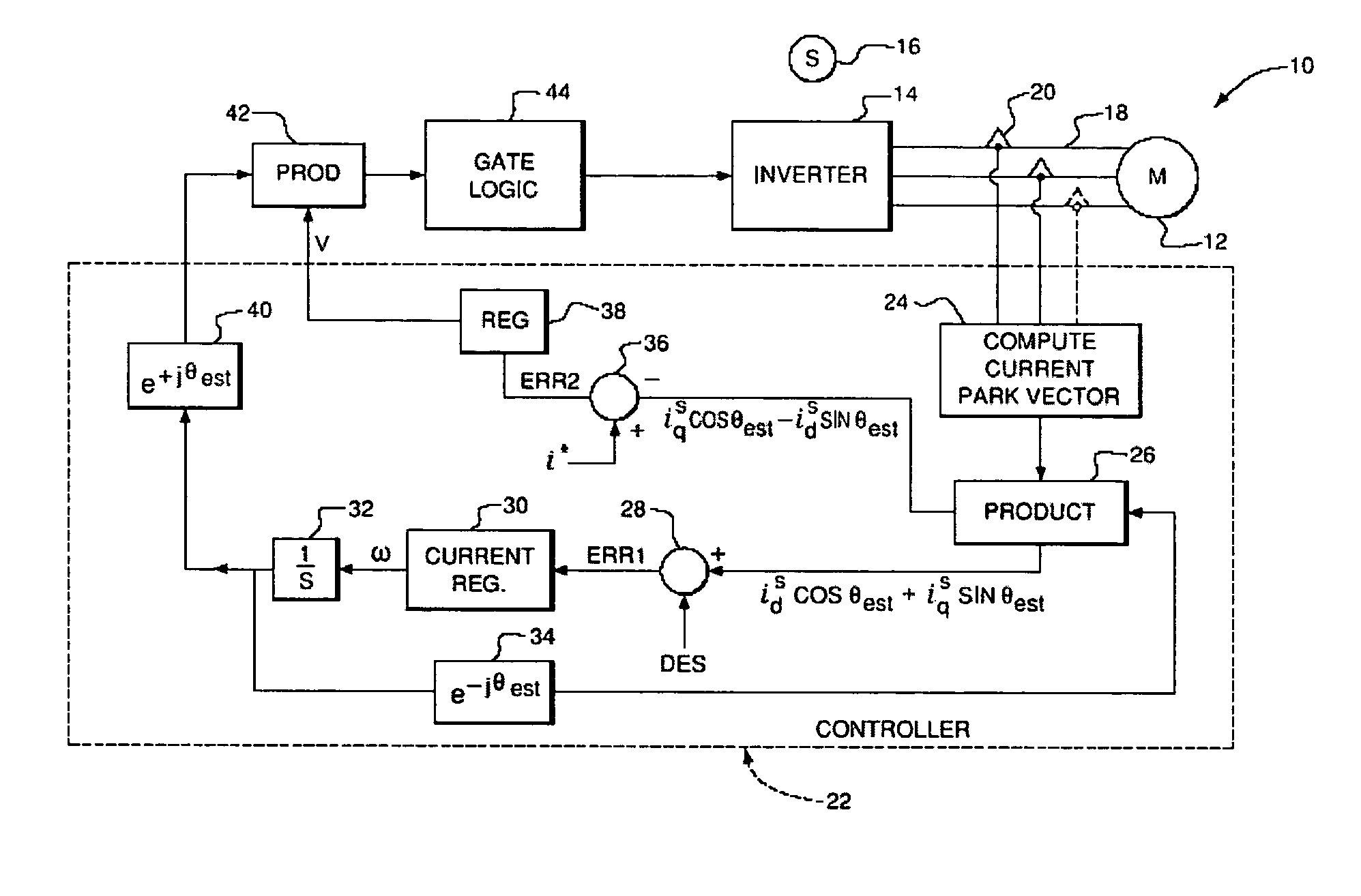
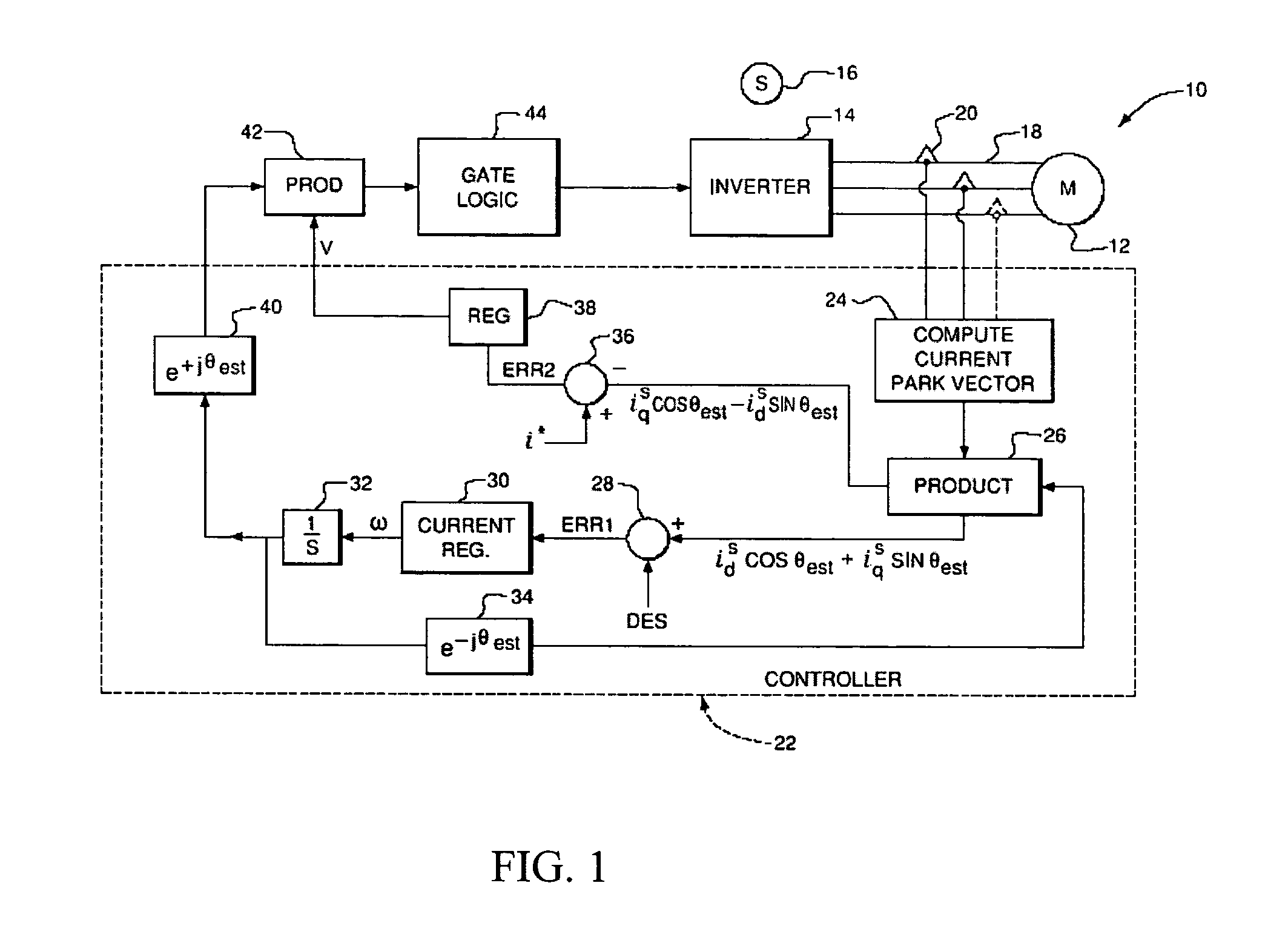
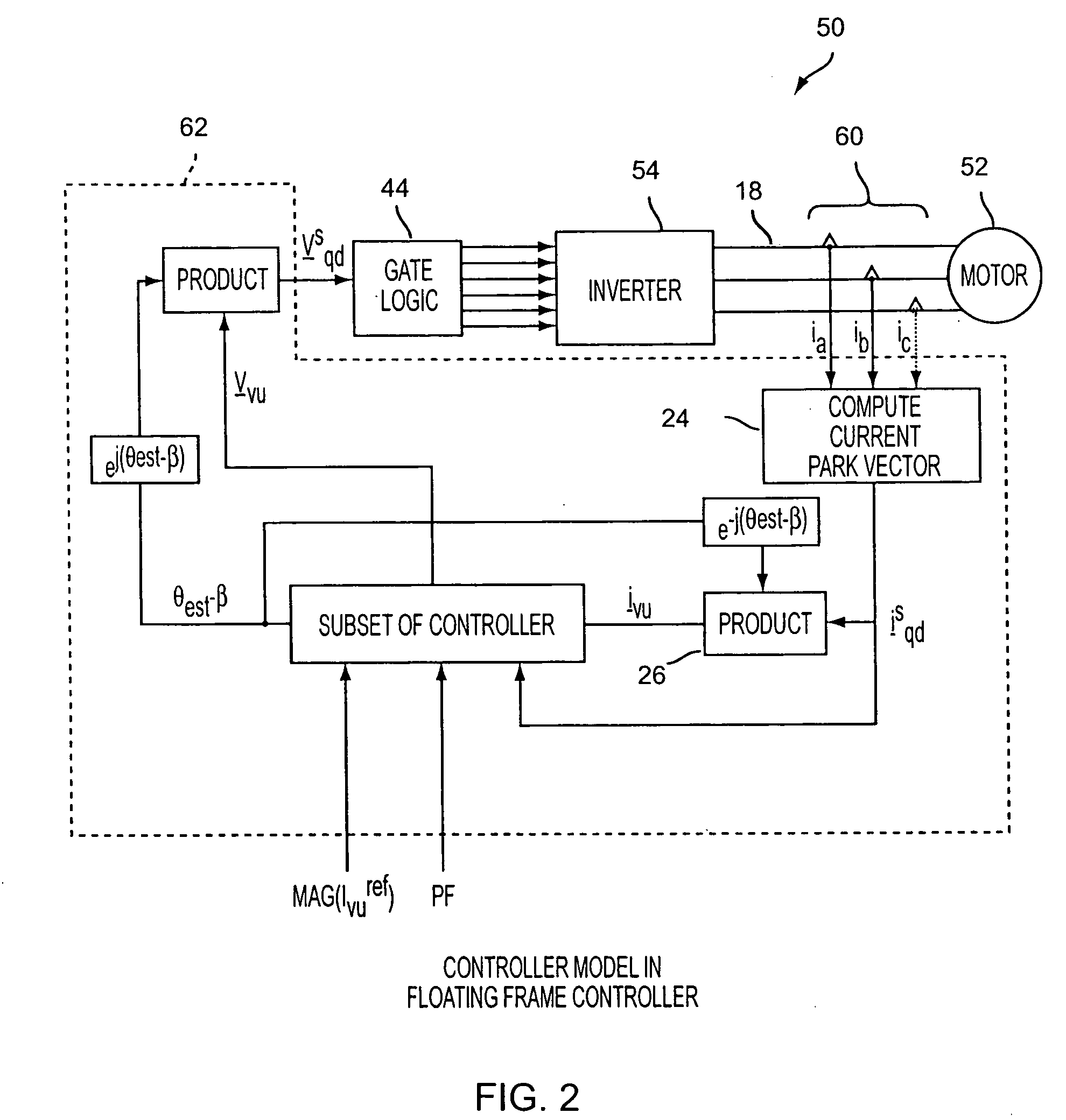
Power factor control for floating frame controller for sensorless control of synchronous machines
ActiveUS20070040524A1Electronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersPhase currentsControl system
A system and method of controlling the power factor for providing either unity, leading or lagging results for the sensorless control of synchronous machines. The system and method provides an estimated angle of the phase current Park vector and uses a floating synchronous reference frame that is shifted from the estimated angle of the phase current Park vector by an angle β to allow the active control and change of the power factor during operation for applications such as producing reluctance torque of a salient pole synchronous machine during Main Engine Start (MES), and field weakening for Environmental Control Systems (ECS) and MES applications.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
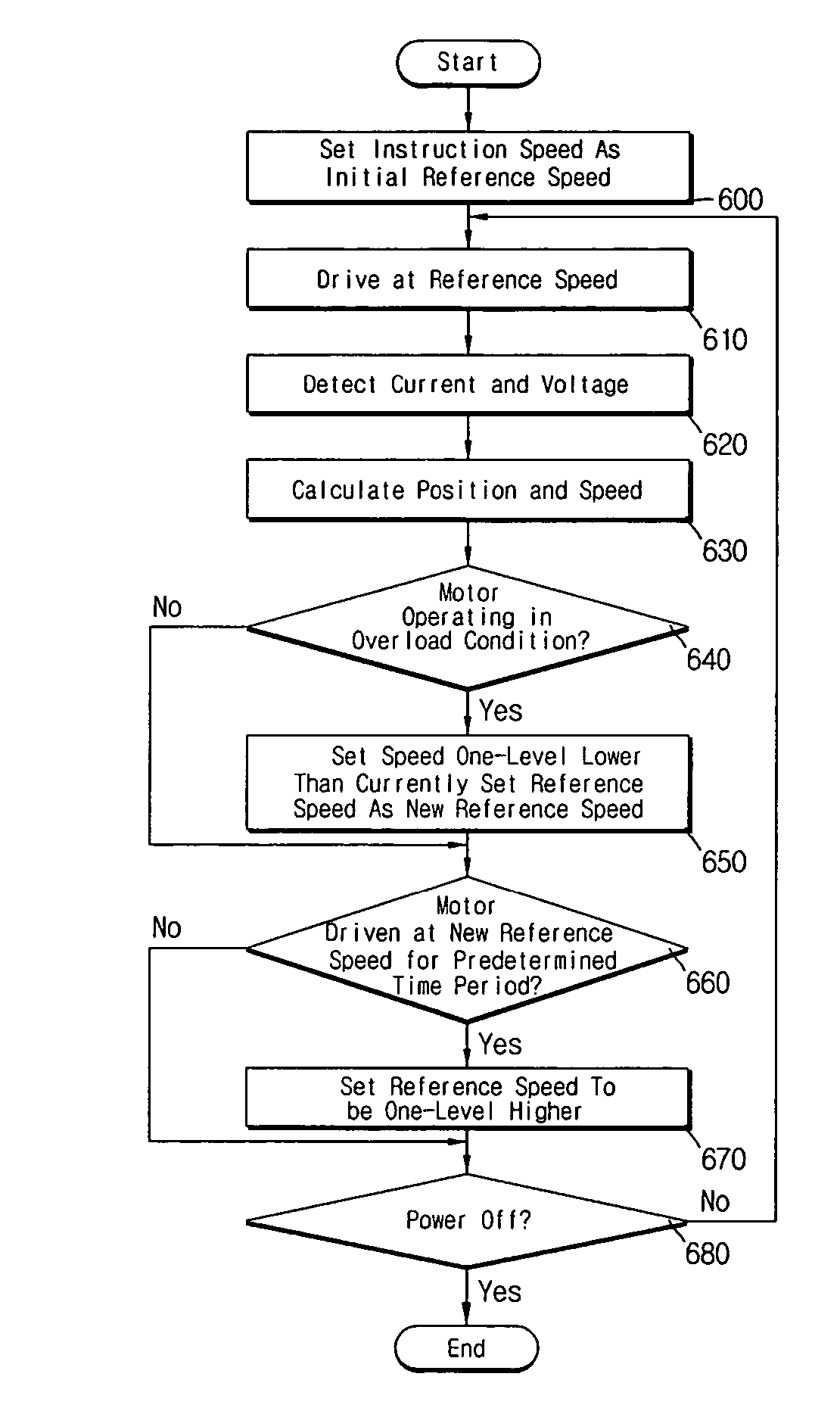
Method of controlling motor drive speed
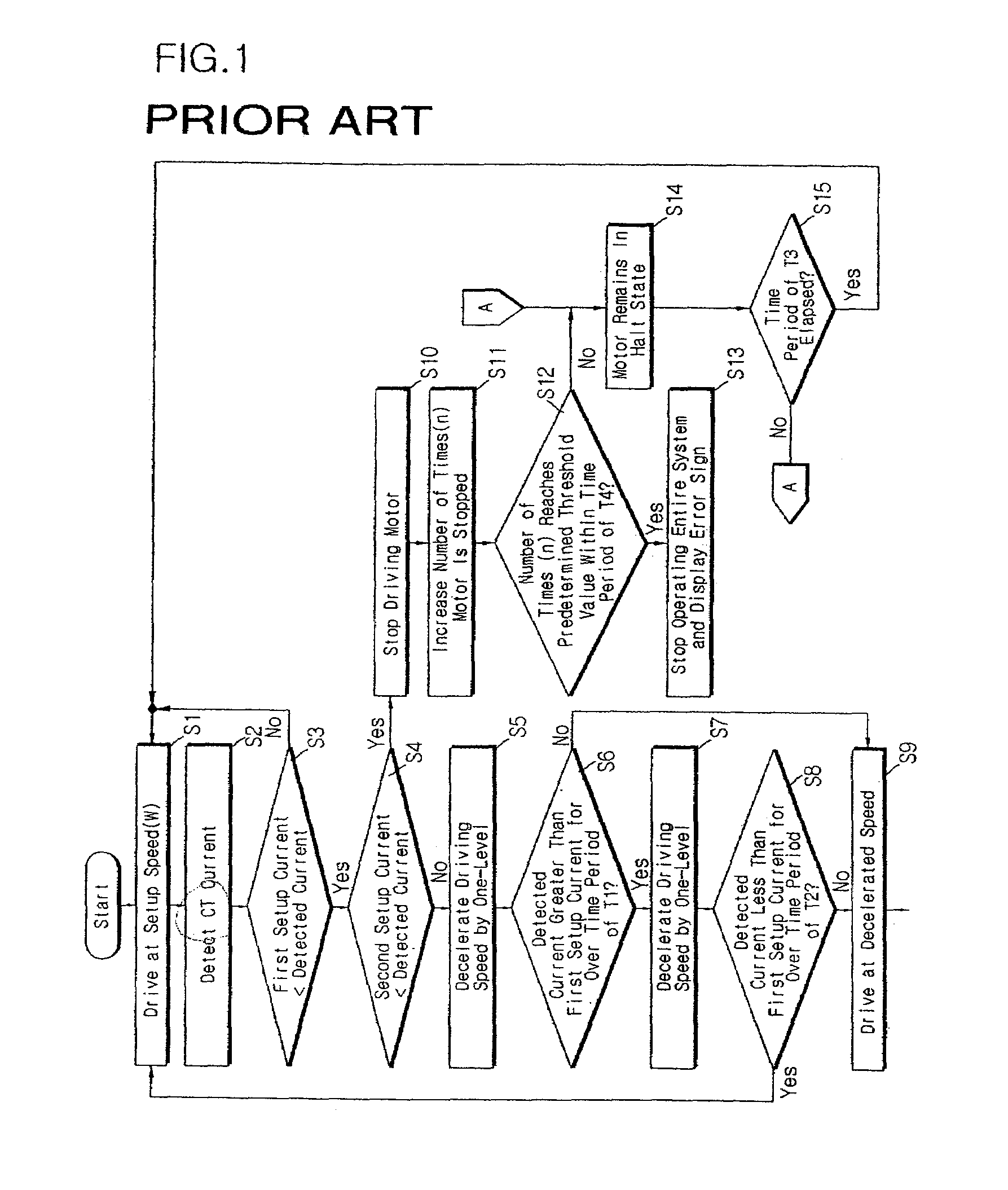
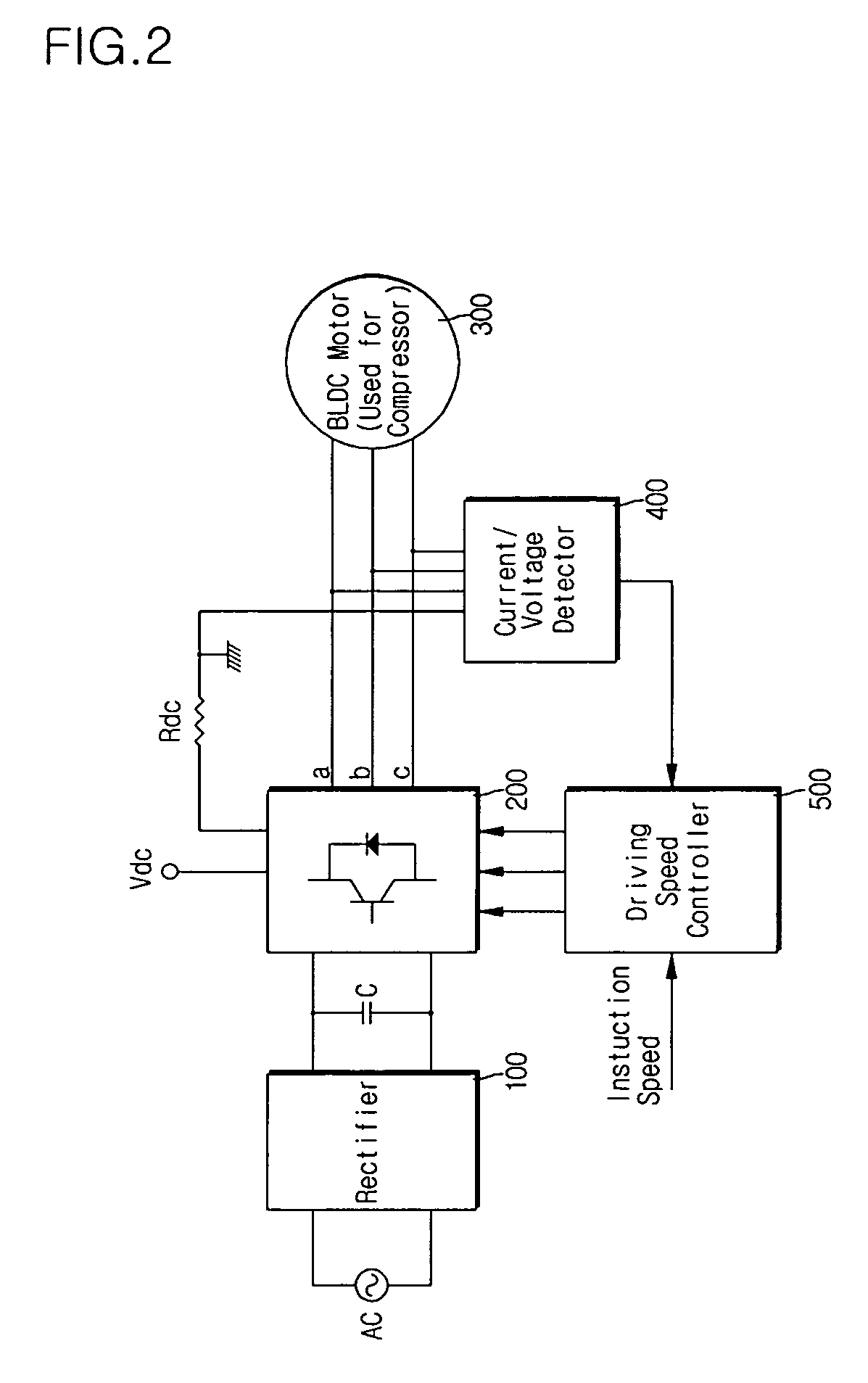
ActiveUS7259533B2Avoid it happening againDC motor speed/torque controlPump componentsPhase currentsMotor drive
Disclosed is a method of controlling drive speed of a motor operating in overload conditions. The method includes the steps of: driving the motor at a predetermined reference speed; detecting phase voltage and phase current applied to the motor; determining whether or not the motor is operating in overload conditions based on the detected phase voltage and phase current; and controlling the motor according to whether or not the motor is operating in overload conditions. Accordingly, the present invention can prevent occurrence of over-current due to the instantaneous acceleration of the motor to a predetermined initial speed.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com