Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
11304 results about "Voltage regulator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A voltage regulator is a system designed to automatically maintain a constant voltage level. A voltage regulator may use a simple feed-forward design or may include negative feedback. It may use an electromechanical mechanism, or electronic components. Depending on the design, it may be used to regulate one or more AC or DC voltages.
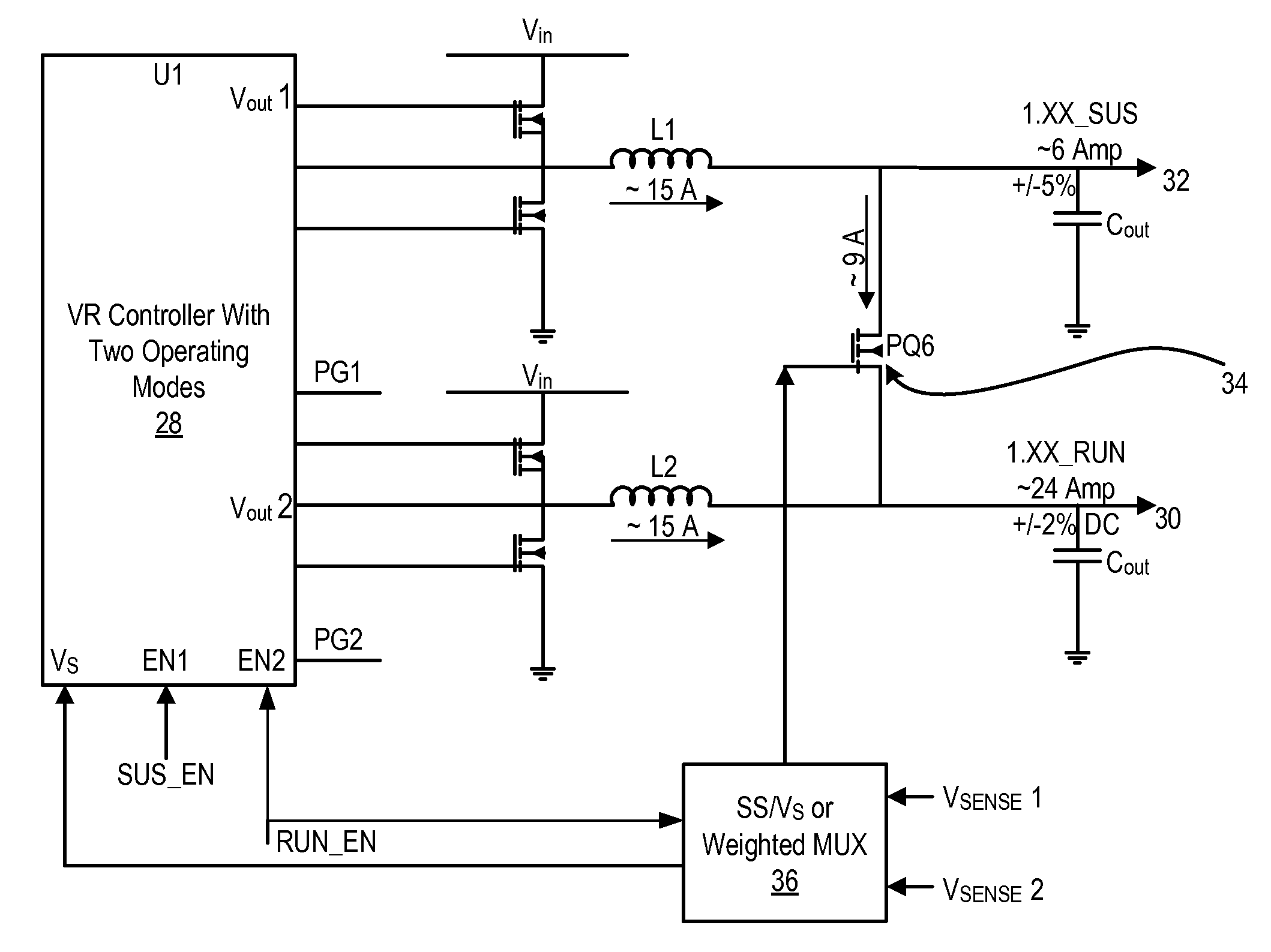
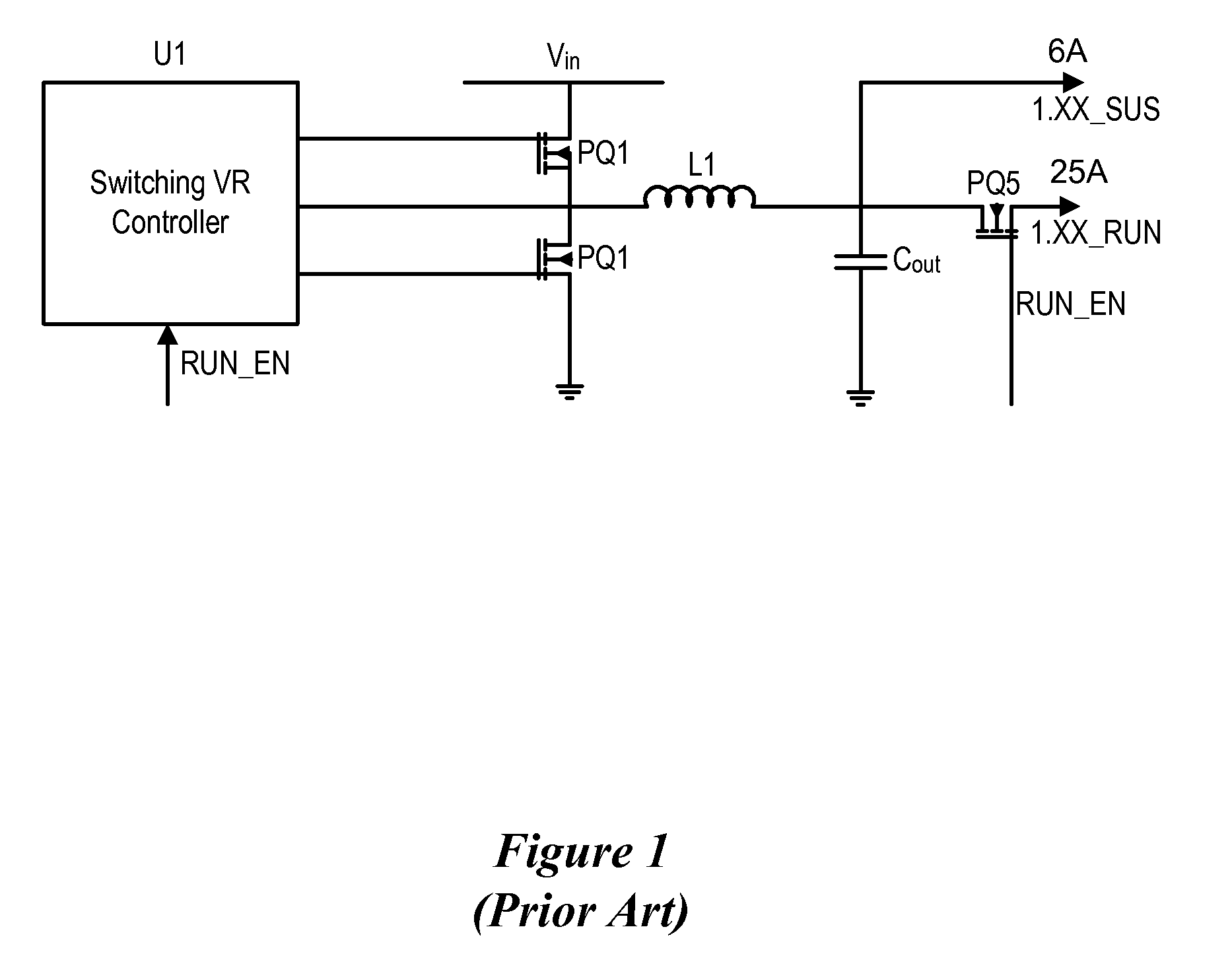
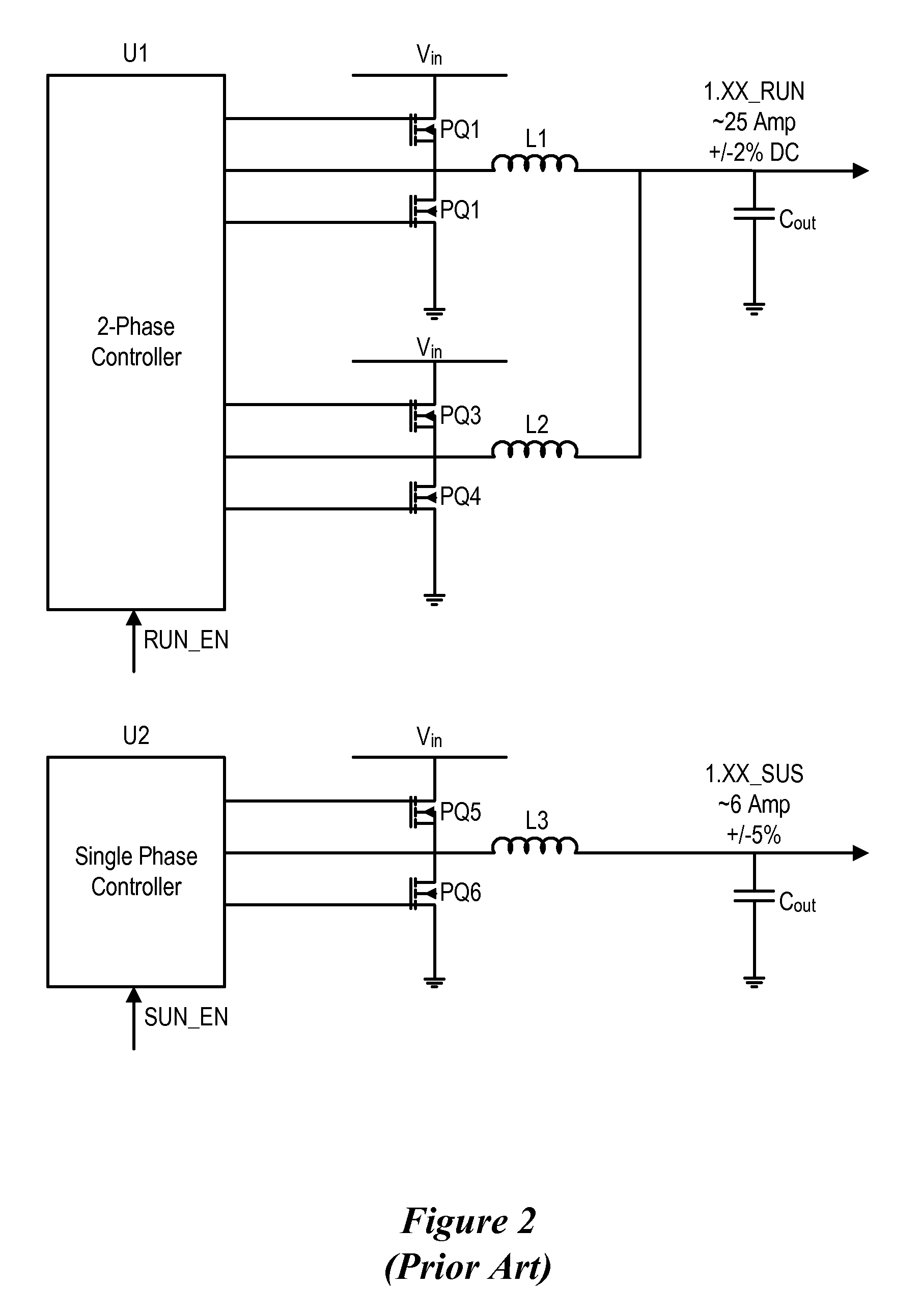
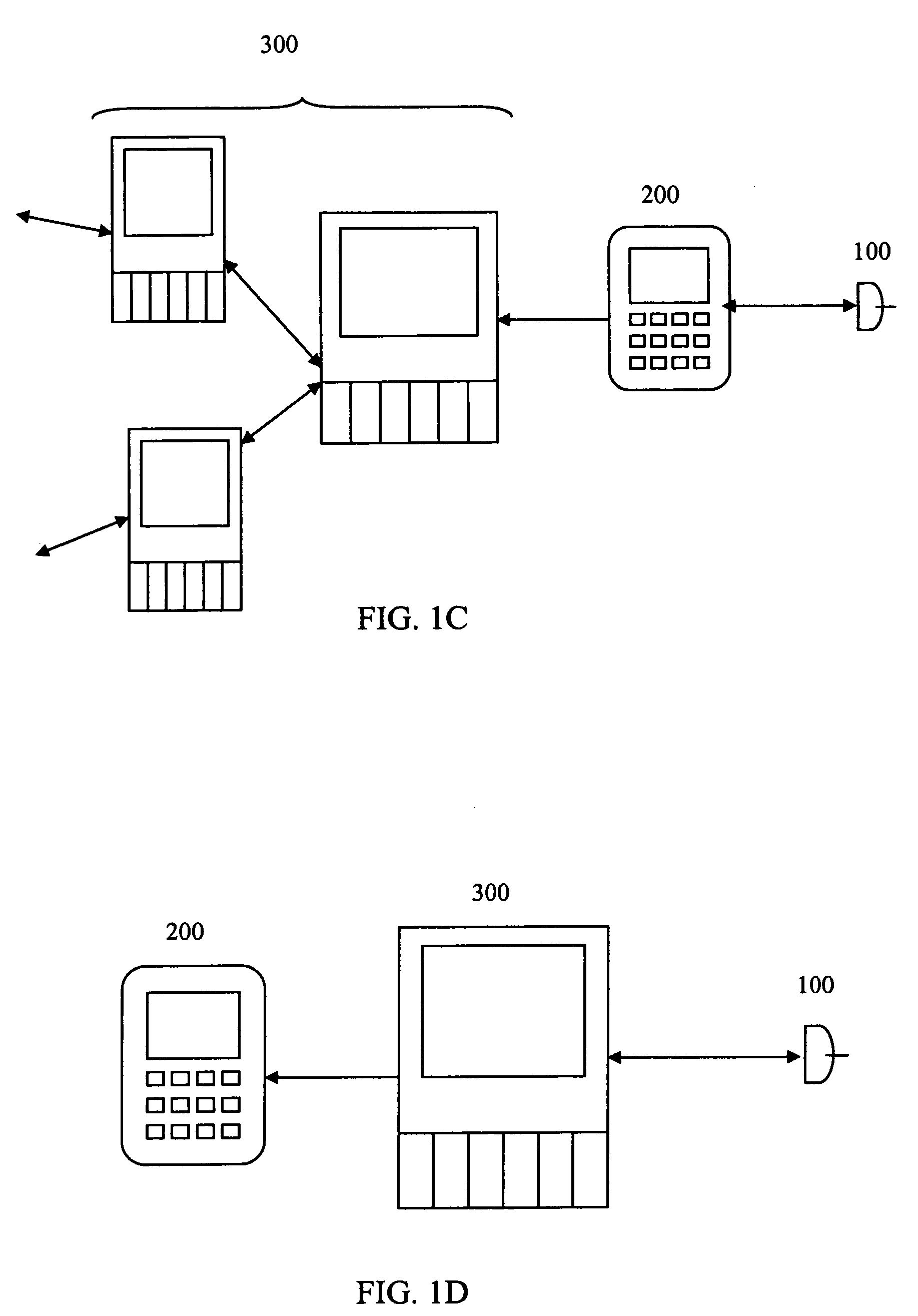
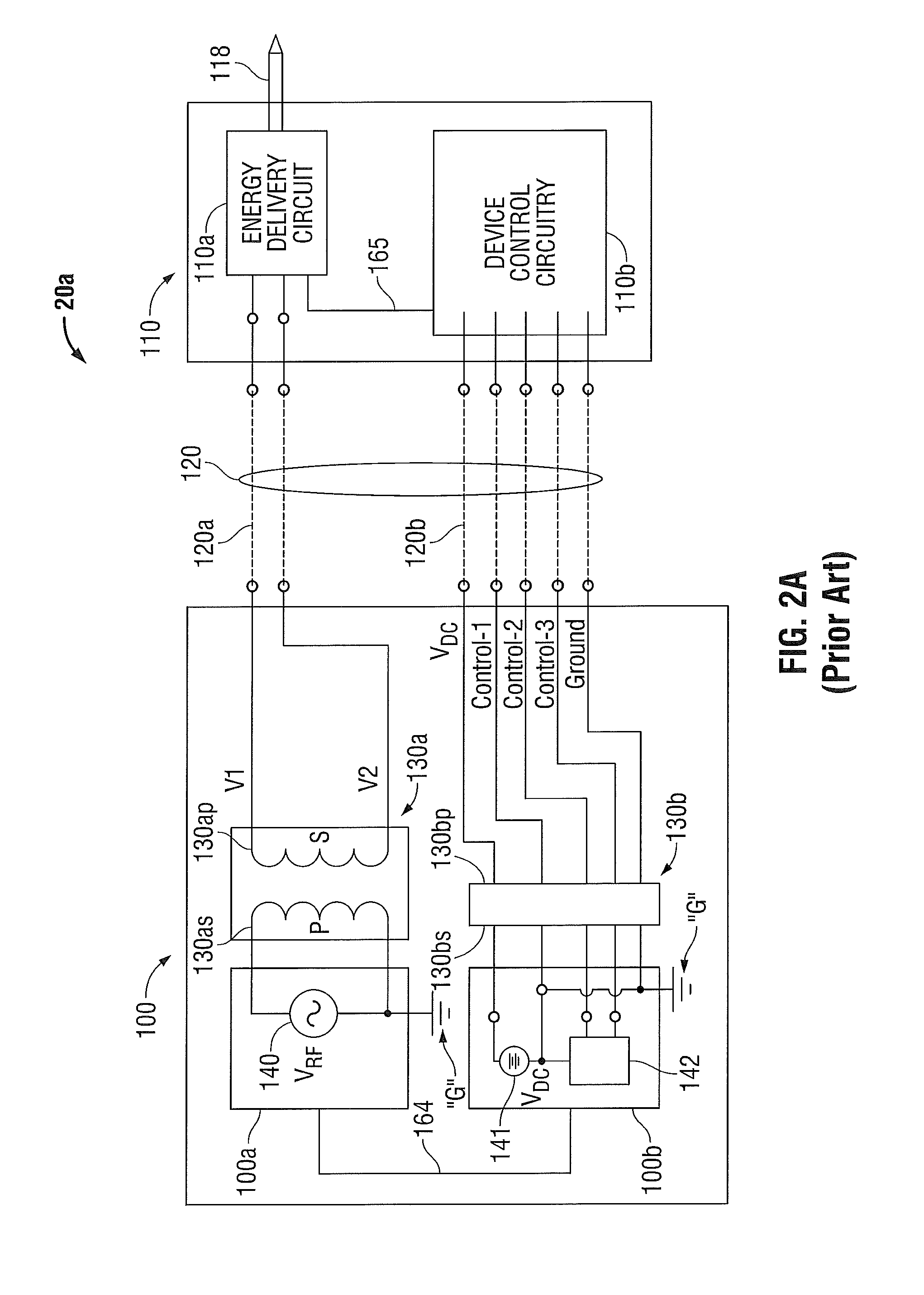
System and method for powering an information handling system in multiple power states
ActiveUS8063619B2Reduce disadvantagesReduce problemsElectric signal transmission systemsDc network circuit arrangementsMOSFETVoltage regulation
Power is supplied to an information handling system chipset with a single voltage regulator having dual phases. A first phase of the voltage regulator provides power to a low power state power rail in an independent mode to support a low power state, such as a suspend or hibernate state. A second phase of the voltage regulator provides power to a run power state power rail in combination with the first phase by activation of a switch, such as a MOSFET load switch, that connects the low power state power rail and the run power state power rail. Voltage sensed from both power rails is applied to control voltage output so that the run power state power rail is maintained within more precise constraints than the low power state power rail.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
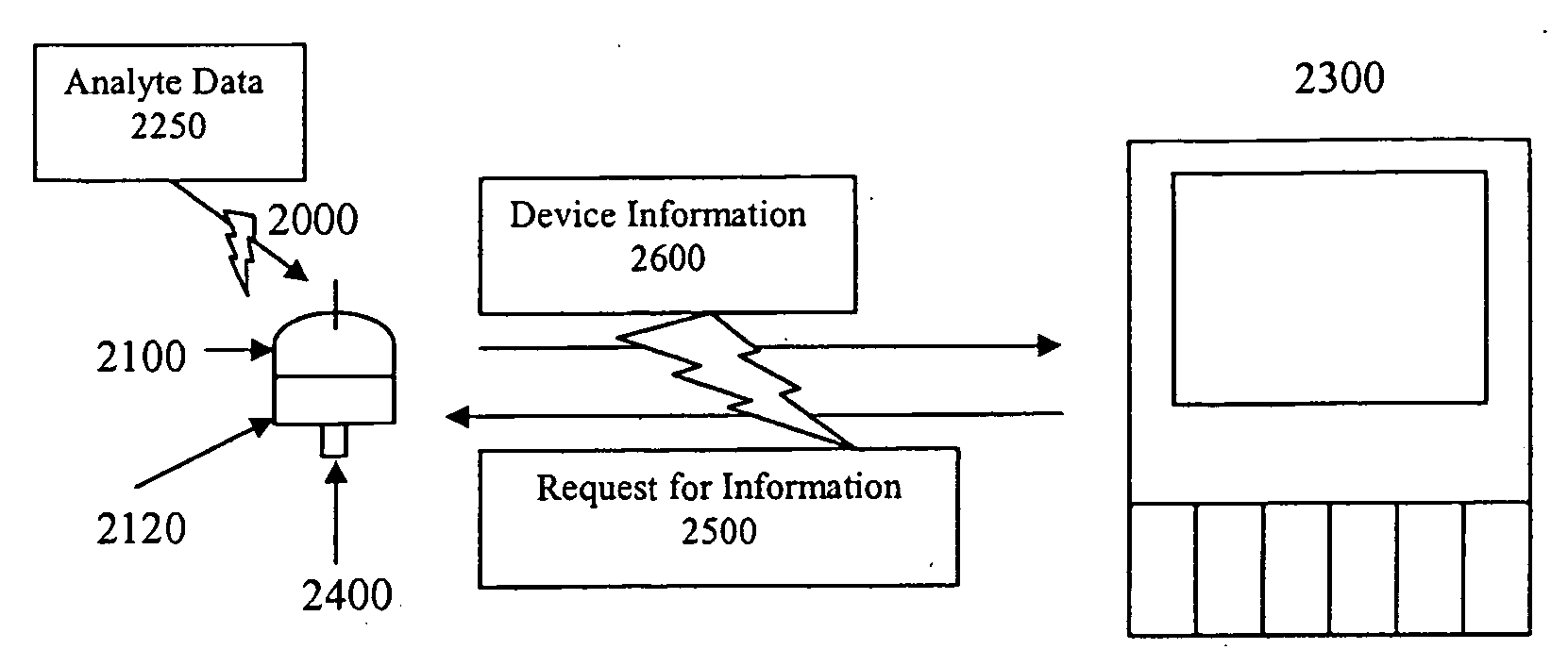
Analyte sensing apparatus for hospital use
A system is provided for monitoring blood glucose data of a patient. The system includes a sensing device and hospital monitor. The sensing device includes a sensor and sensor electronics and is adapted to transmit information to the hospital monitor while continuing to sense blood glucose data. The communication between the sensing device and the hospital monitor may be wireless. The sensor electronics may include a sensor power supply, a voltage regulator, and optionally a memory and processor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Sensing system with auxiliary display
A system is provided for sensing blood glucose data of a patient. The system includes a sensor, user interface, and an optional auxiliary device. If the connection between the sensor and user interface is by a wire, the sensor remains powered when the wire is disconnected. The communication between the sensor and the user interface may be wireless. The auxiliary device can be a patient monitor or other display or signal device, which displays information about the blood glucose data collected by the sensor. The sensor is connected to sensor electronics, which include a sensor power supply, a voltage regulator, and optionally a memory and processor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
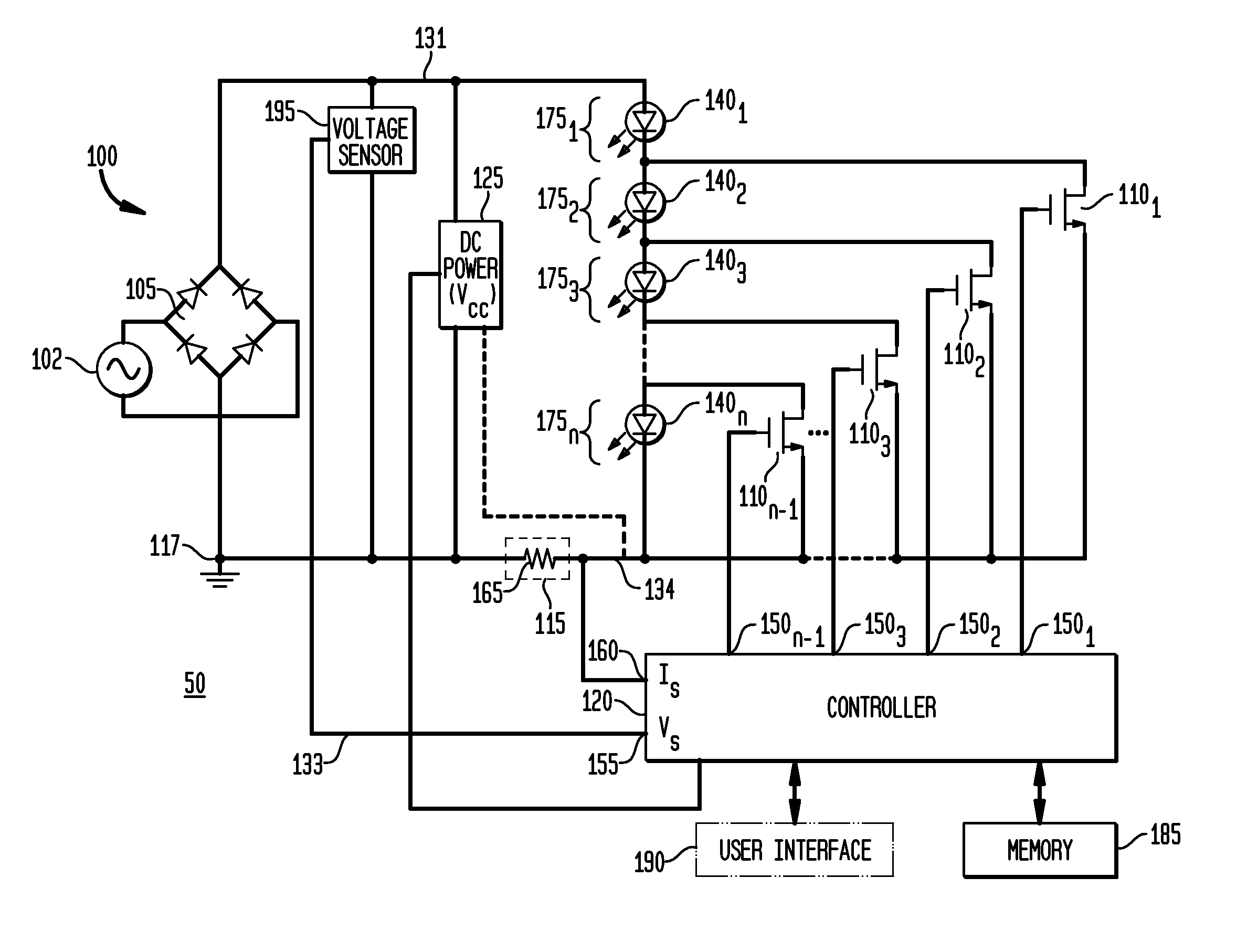
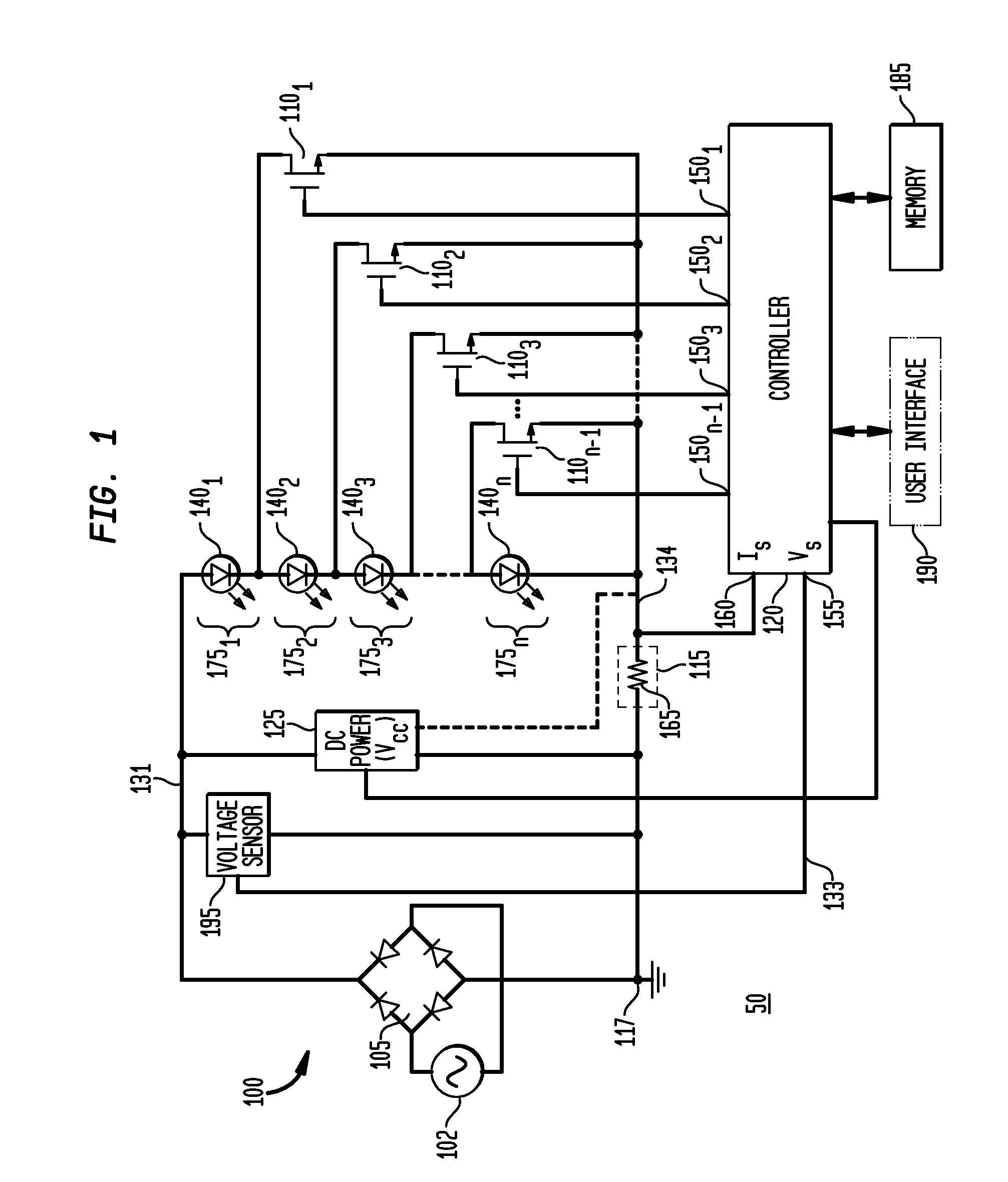
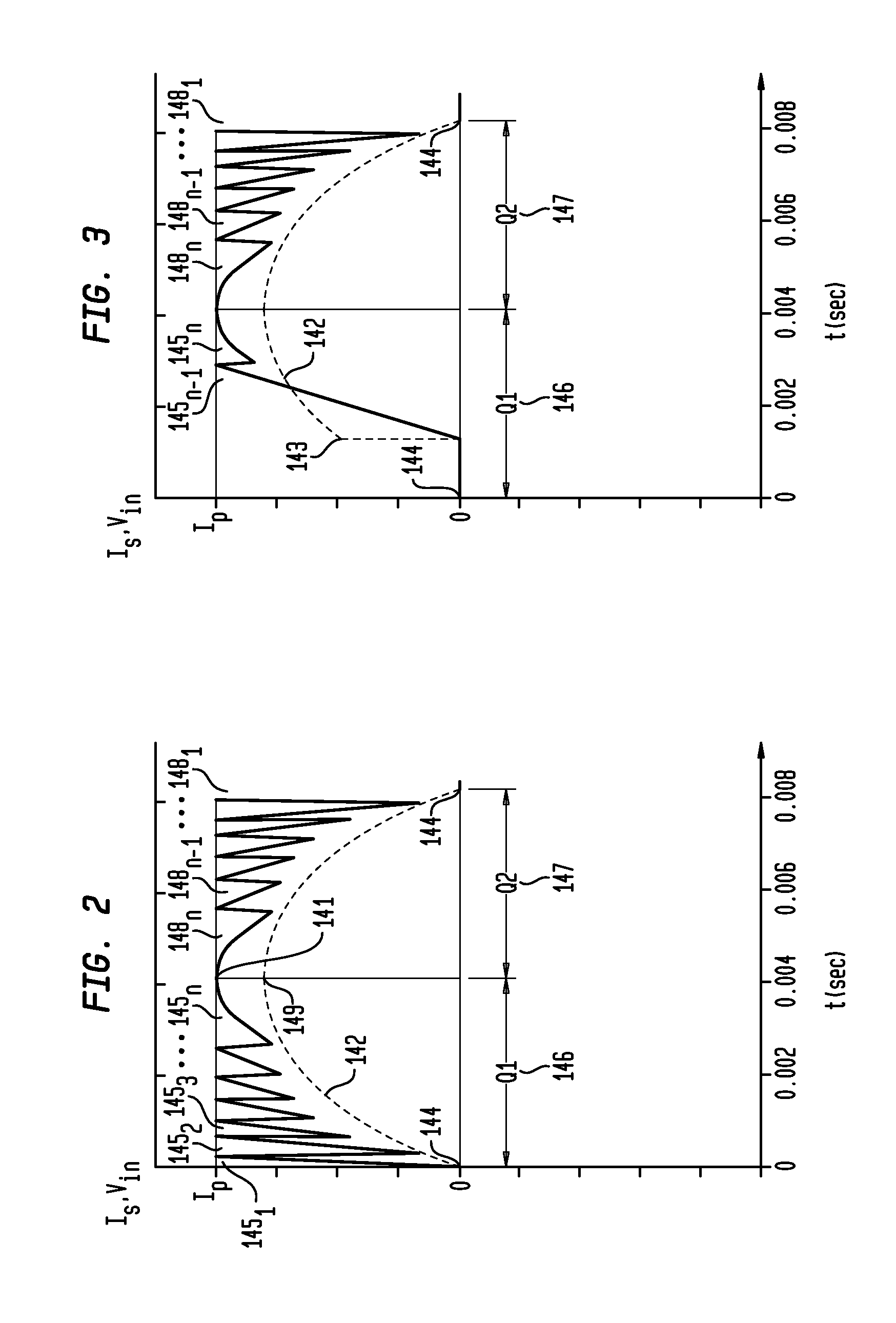
Apparatus, Method and System for Providing AC Line Power to Lighting Devices
ActiveUS20120081009A1Reduction in size and costImprove Utilization and EfficiencyElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLight equipmentVoltage regulation
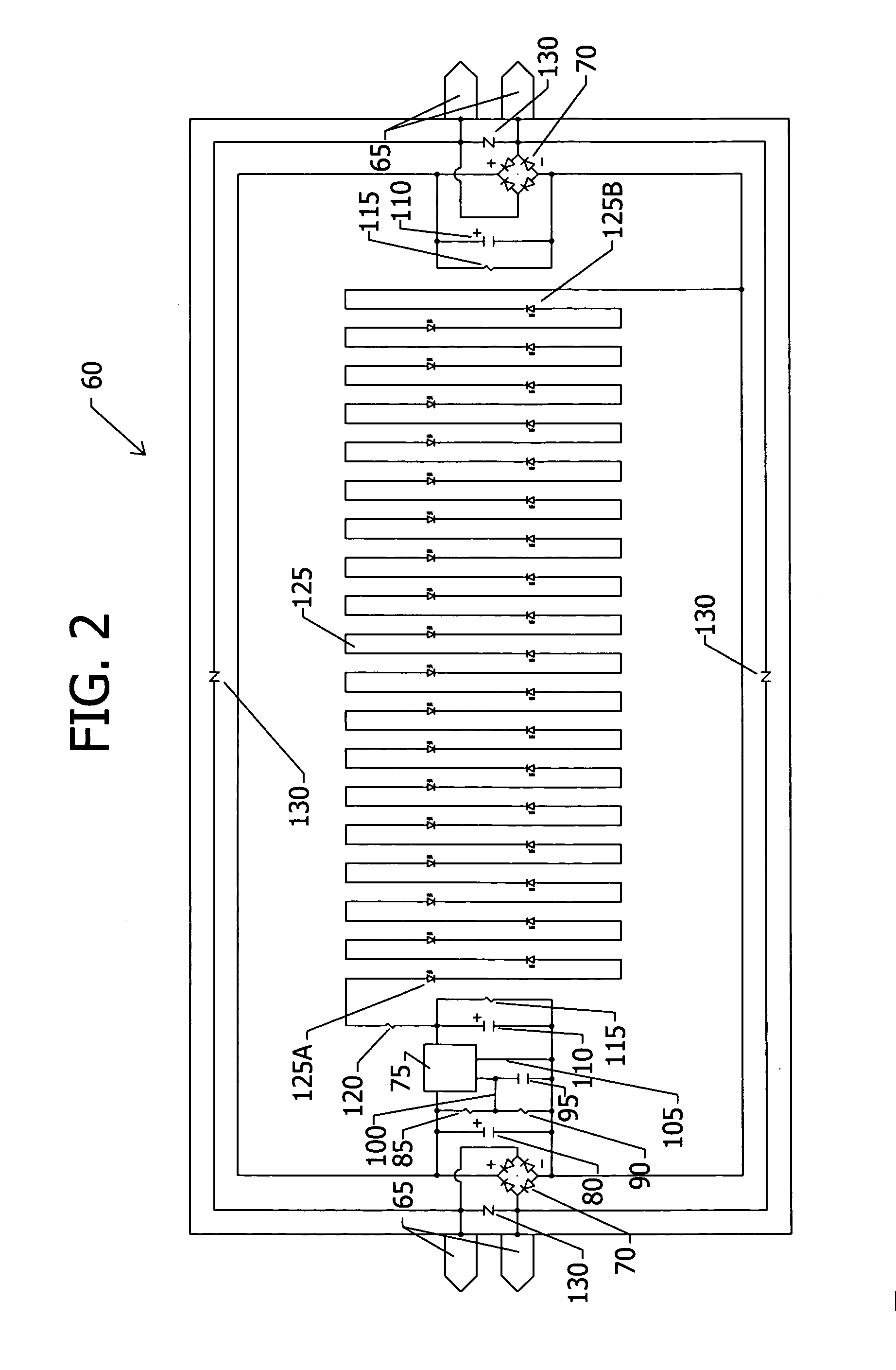
An apparatus, method and system are disclosed for providing AC line power to lighting devices such as light emitting diodes (“LEDs”). An exemplary apparatus comprises: a plurality of LEDs coupled in series to form a plurality of segments of LEDs; first and second current regulators; a current sensor; and a controller to monitor a current level through a series LED current path, and to provide for first or second segments of LEDs to be in or out of the series LED current path at different current levels. A voltage regulator is also utilized to provide a voltage during a zero-crossing interval of the AC voltage. In an exemplary embodiment, first and second segments of LEDs are both in the series LED current path regulated at a lower current level compared to when only the first segment of LEDs is in the series LED current path.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
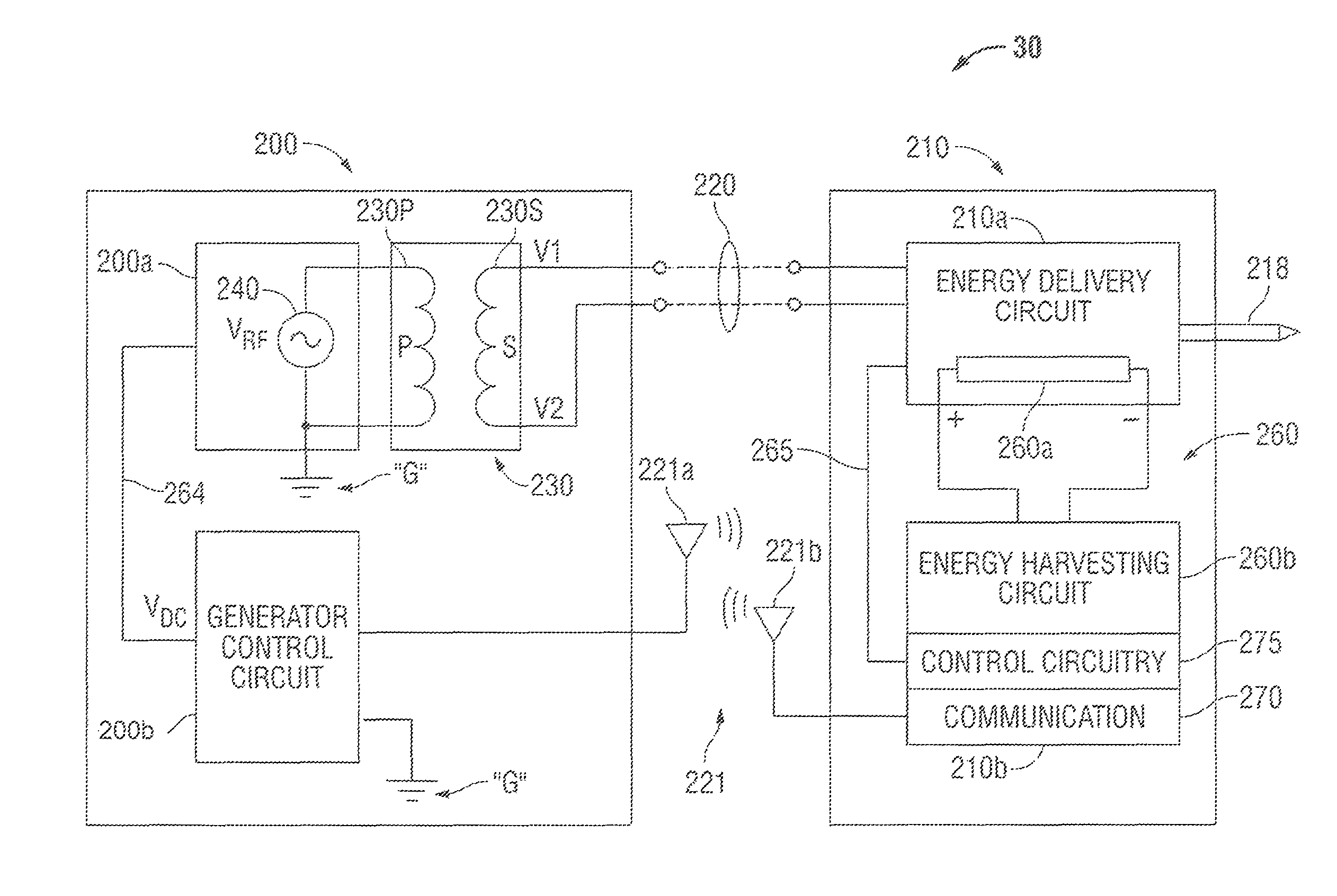
Energy-harvesting system, apparatus and methods
InactiveUS8968296B2Improve isolationImprove patient safetyBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemVoltage regulationControl circuit
An electrosurgical energy delivery apparatus includes an energy delivery circuit, a control circuit and an energy-harvesting system with a plurality of energy-harvesting circuits and a voltage regulator that provides a regulated DC voltage to the energy delivery circuit and / or the control circuit. The energy delivery circuit receives an electrosurgical energy signal having a primary frequency and selectively provides the electrosurgical energy signal to an energy delivery element. The control circuit connects to the energy delivery circuit and selectively enables the flow of electrosurgical energy to the energy delivery element. The plurality of energy-harvesting circuits each include an energy-harvesting antenna tuned to a particular frequency, a matched circuit configured to receive an RF signal from the energy-harvesting antenna, rectify the RF signal and generate a DC signal, and an energy storage device that connects to the voltage regulator to receive and store the DC signal.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Sensing system with auxiliary display
A system is provided for sensing blood glucose data of a patient. The system includes a sensor, user interface, and an optional auxiliary device. If the connection between the sensor and user interface is by a wire, the sensor remains powered when the wire is disconnected. The communication between the sensor and the user interface may be wireless. The auxiliary device can be a patient monitor or other display or signal device, which displays information about the blood glucose data collected by the sensor. The sensor is connected to sensor electronics, which include a sensor power supply, a voltage regulator, and optionally a memory and processor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Sensing system with auxiliary display
A system is provided for sensing blood glucose data of a patient. The system includes a sensor, user interface, and an optional auxiliary device. If the connection between the sensor and user interface is by a wire, the sensor remains powered when the wire is disconnected. The communication between the sensor and the user interface may be wireless. The auxiliary device can be a patient monitor or other display or signal device, which displays information about the blood glucose data collected by the sensor. The sensor is connected to sensor electronics, which include a sensor power supply, a voltage regulator, and optionally a memory and processor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
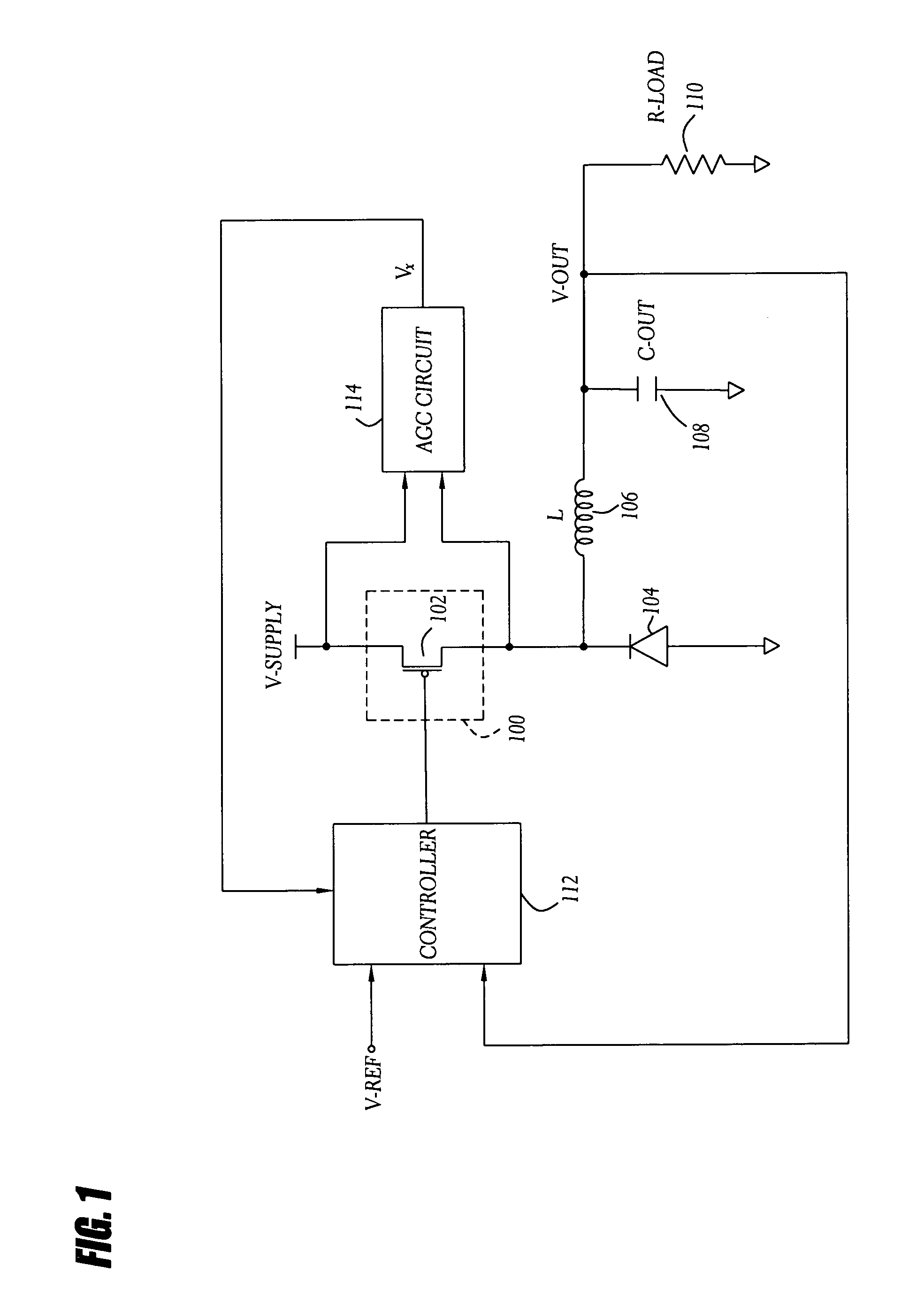
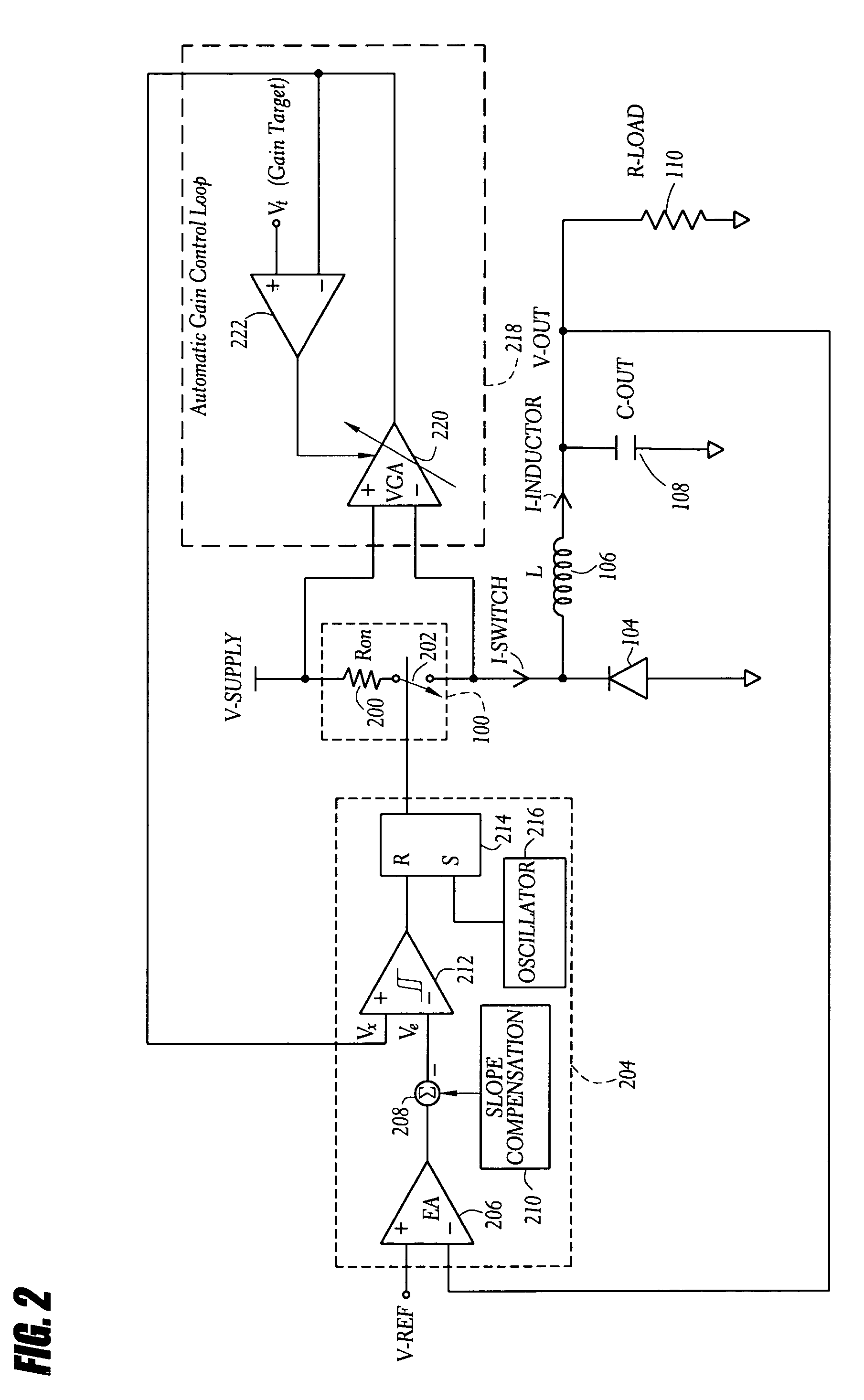
Automatic gain control technique for current monitoring in current-mode switching regulators
InactiveUS7919952B1Reduce component count and circuit board sizeFacilitates efficient and reliable monitoringDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationEngineeringCurrent mode
A current-mode switching regulator uses adaptive current sensing to reliably monitor an inductor current in a cost-efficient and power-efficient manner. A semiconductor switch periodically turns on to conduct the inductor current. A voltage drop across the semiconductor switch is monitored when the semiconductor switch is on. A variable gain amplifier with an automatic gain control loop generates a feedback signal from the voltage drop of the semiconductor switch when conducting to provide an indication of the inductor current to a controller. The automatic gain control loop compensates for any variations in the on-resistance of the semiconductor switch.
Owner:MICROSEMI
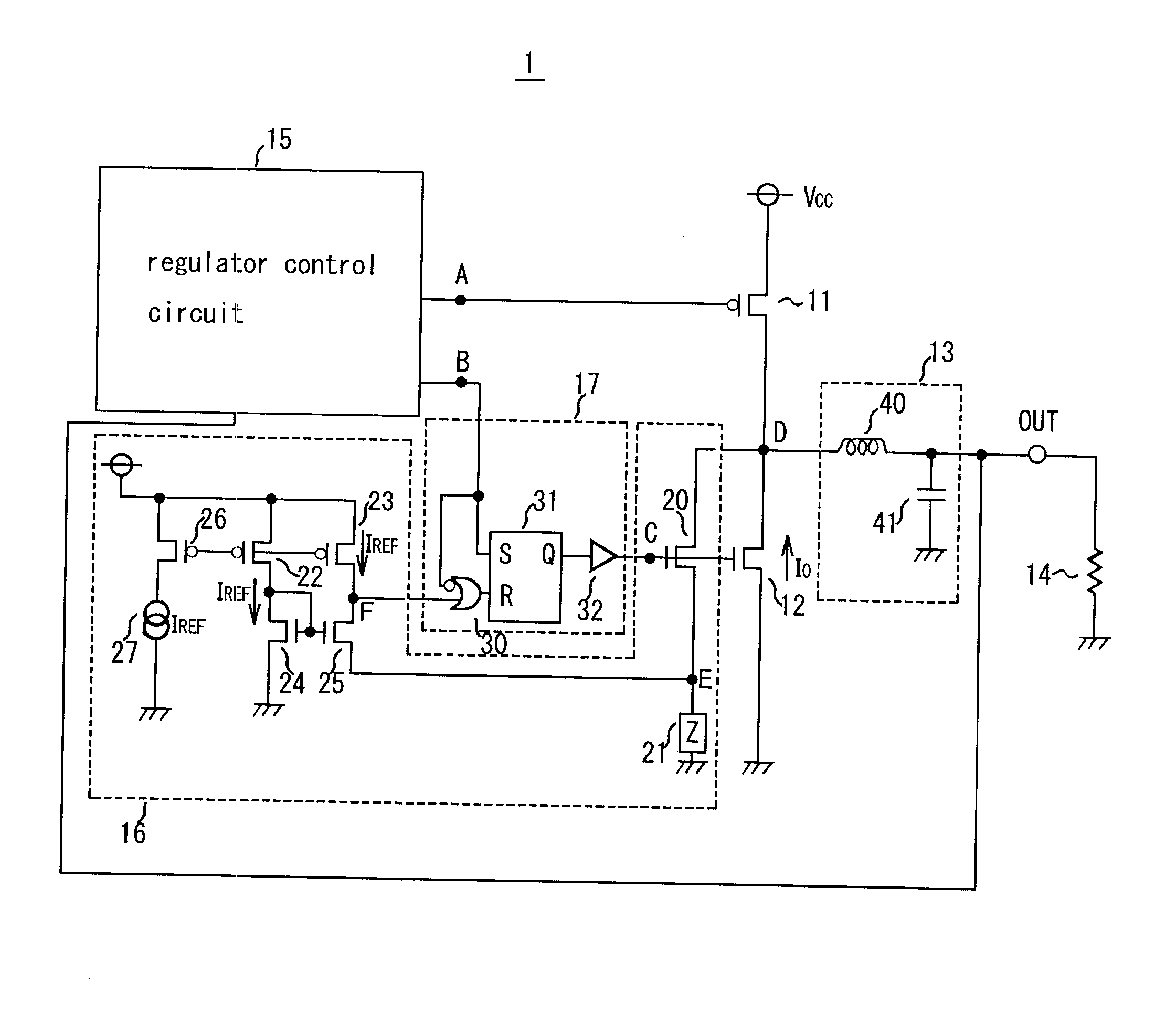
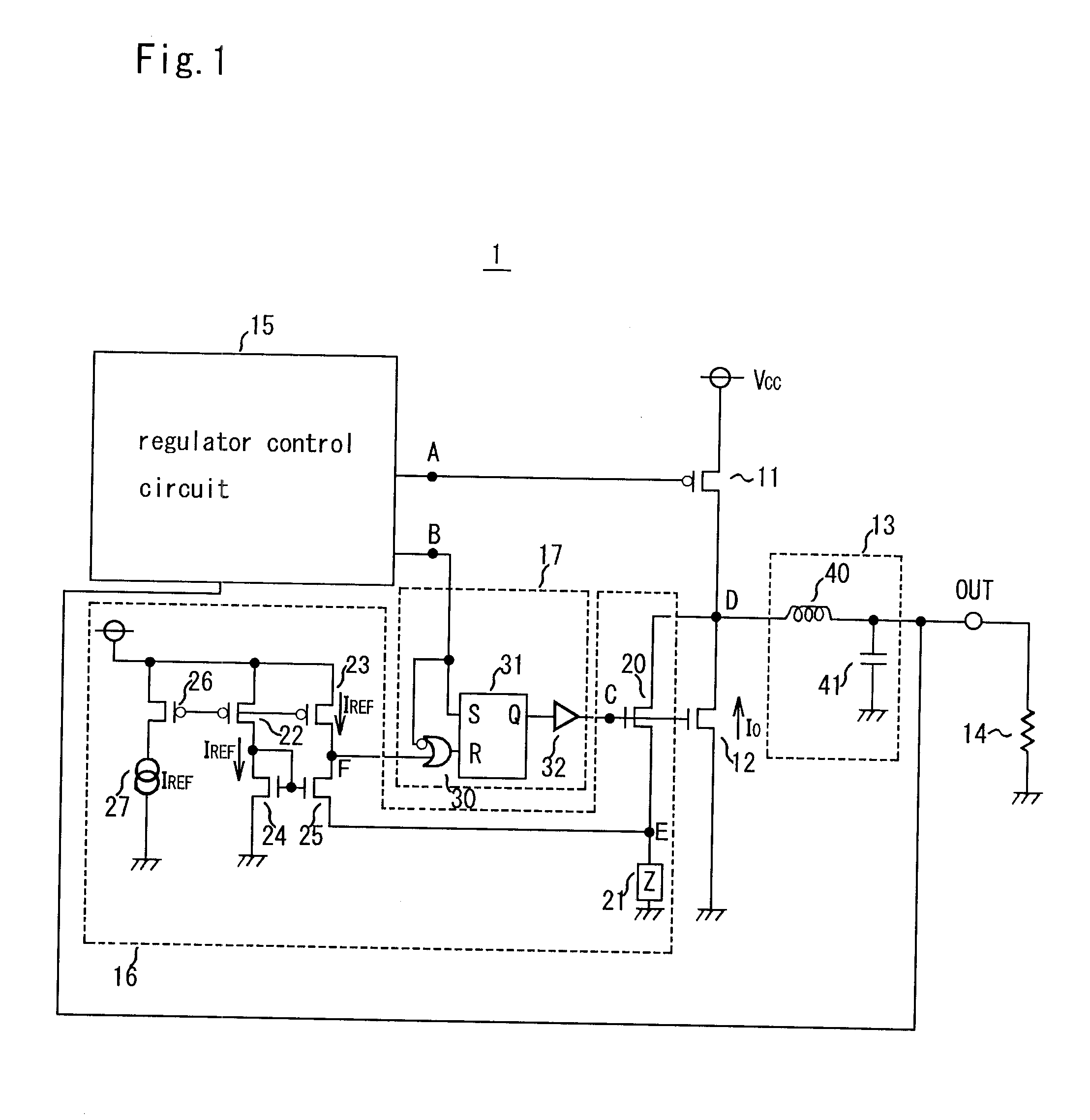
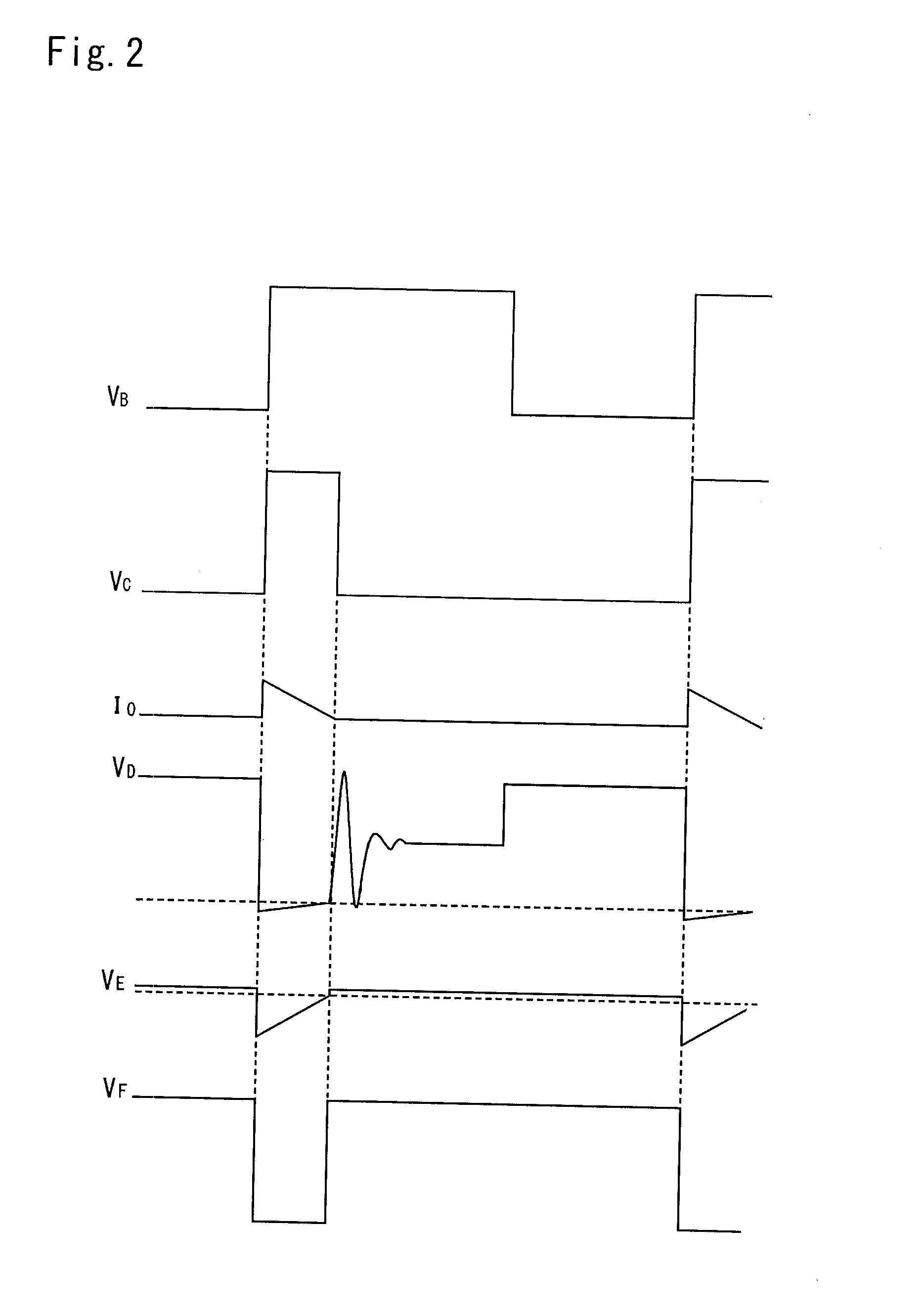
Method of regulating the supply voltage of a load and related voltage regulator
InactiveUS6894471B2Improve accuracyReduce impactApparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductanceCapacitance
The method is for regulating the supply voltage of a load via a switching voltage regulator having an inductor driven by at least a power switch for delivering current to an output capacitor having a certain parasitic series resistance, connected between the output node of the regulator and ground and to an electric load eventually connected in parallel to the output capacitor. The method includes establishing a reference voltage, generating a comparison signal as the sum of a first voltage signal proportional to the current circulating in the inductor and of a second voltage signal depending on the difference between the output voltage and the reference voltage and on the first voltage signal. The comparison signal is compared with at least a threshold for generating a logic signal that switches between an active state and an inactive state and viceversa each time that the threshold is crossed, and the turn on or the turn off of the switch is controlled as a function of the state of the logic signal.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
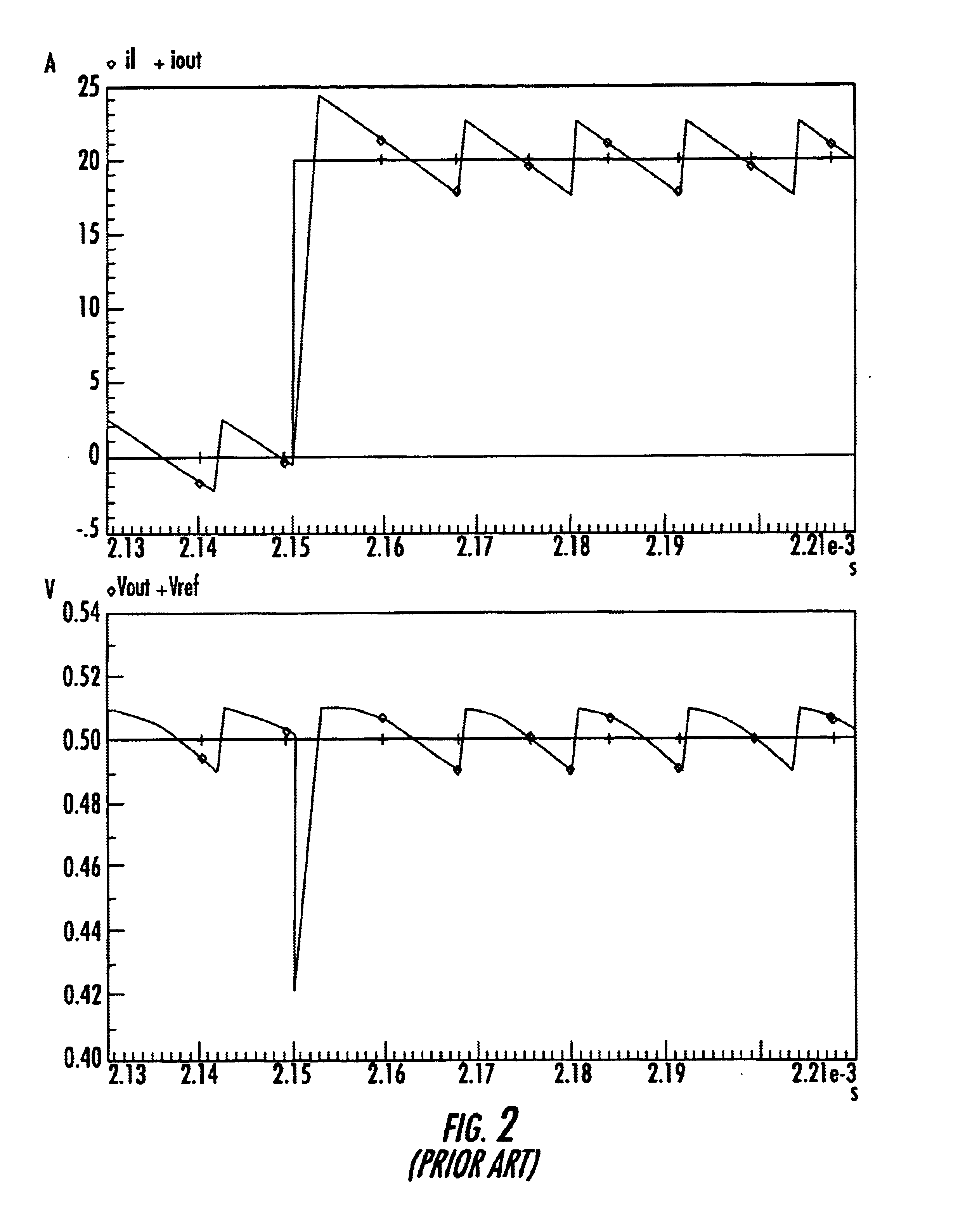
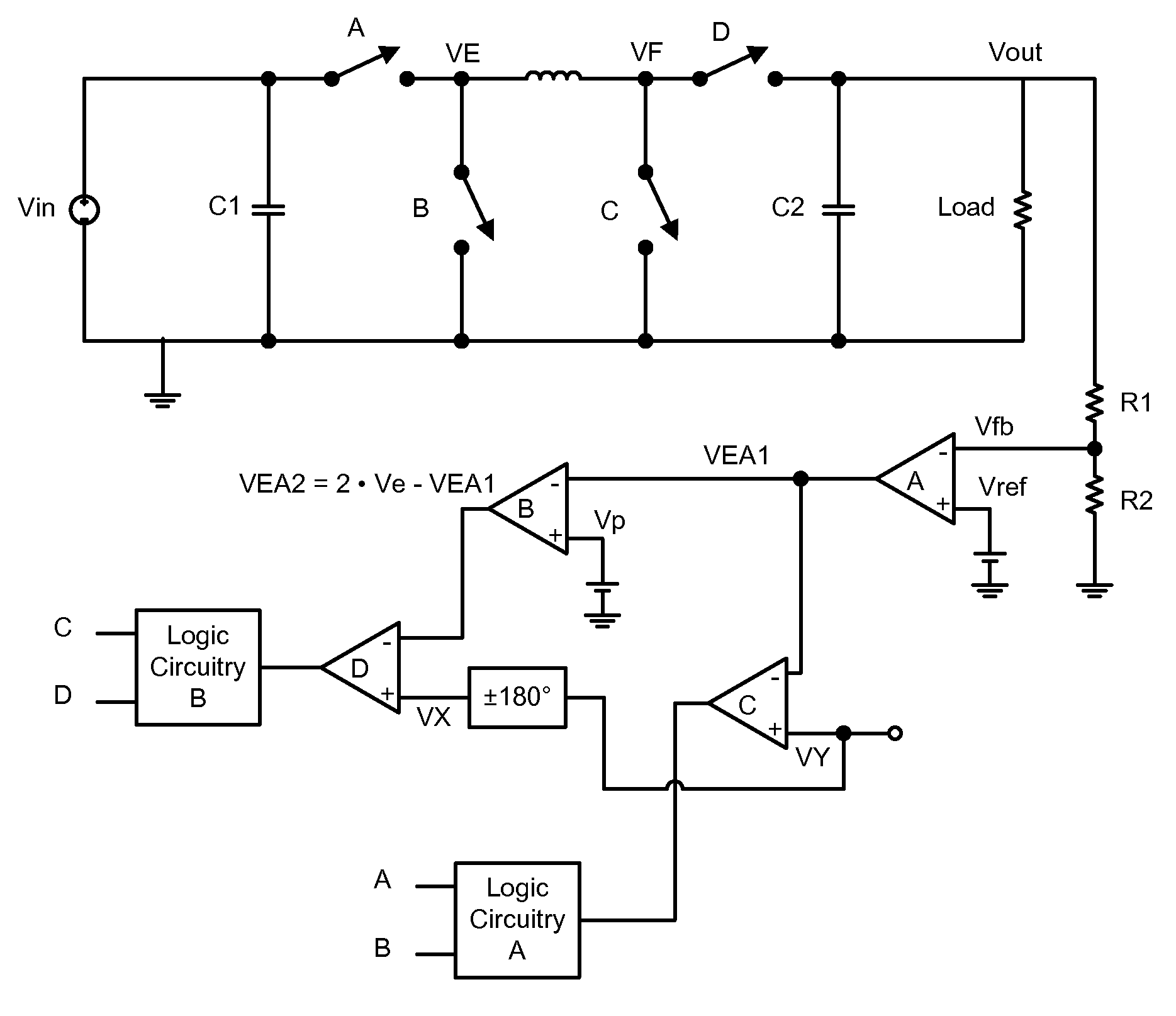
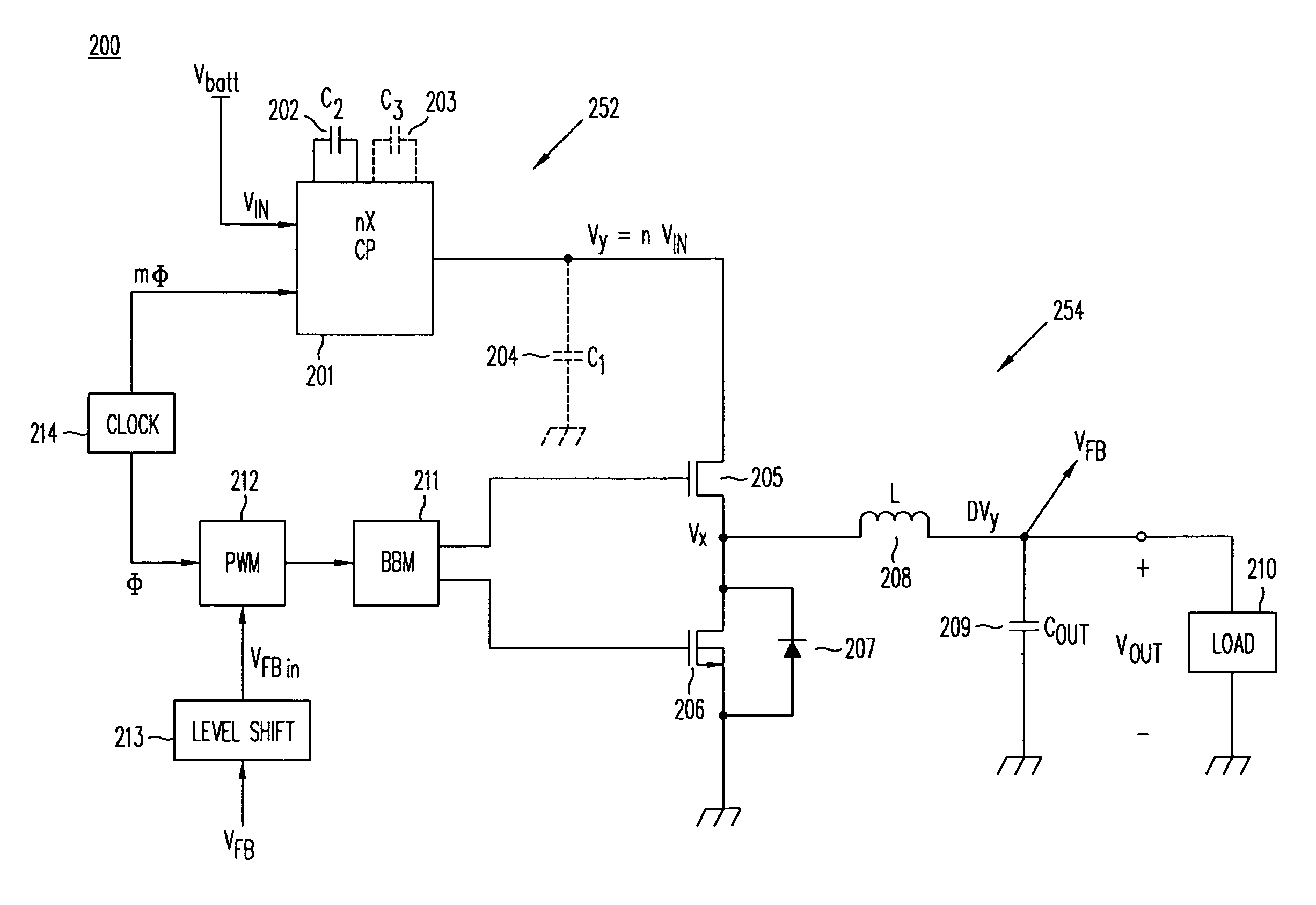
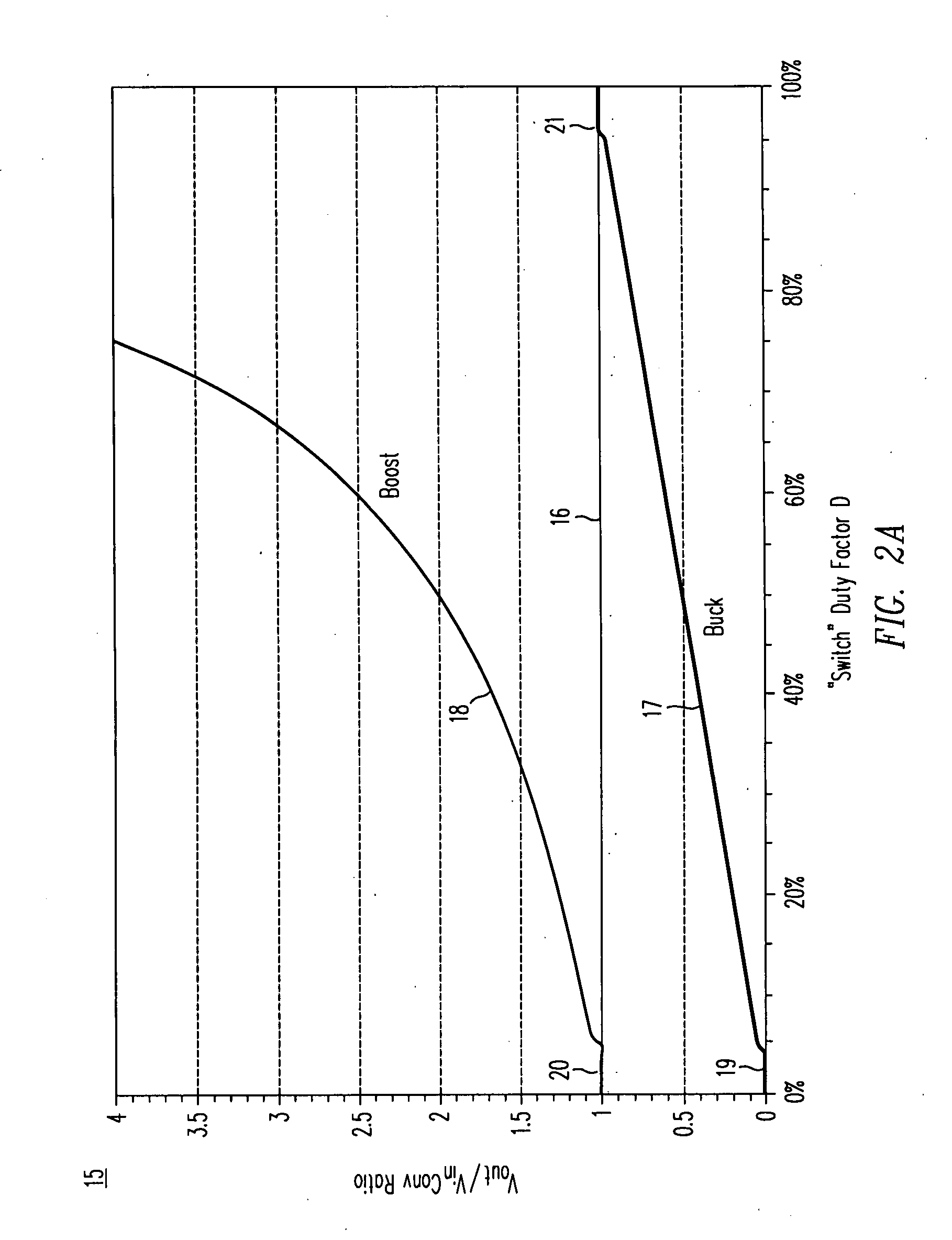
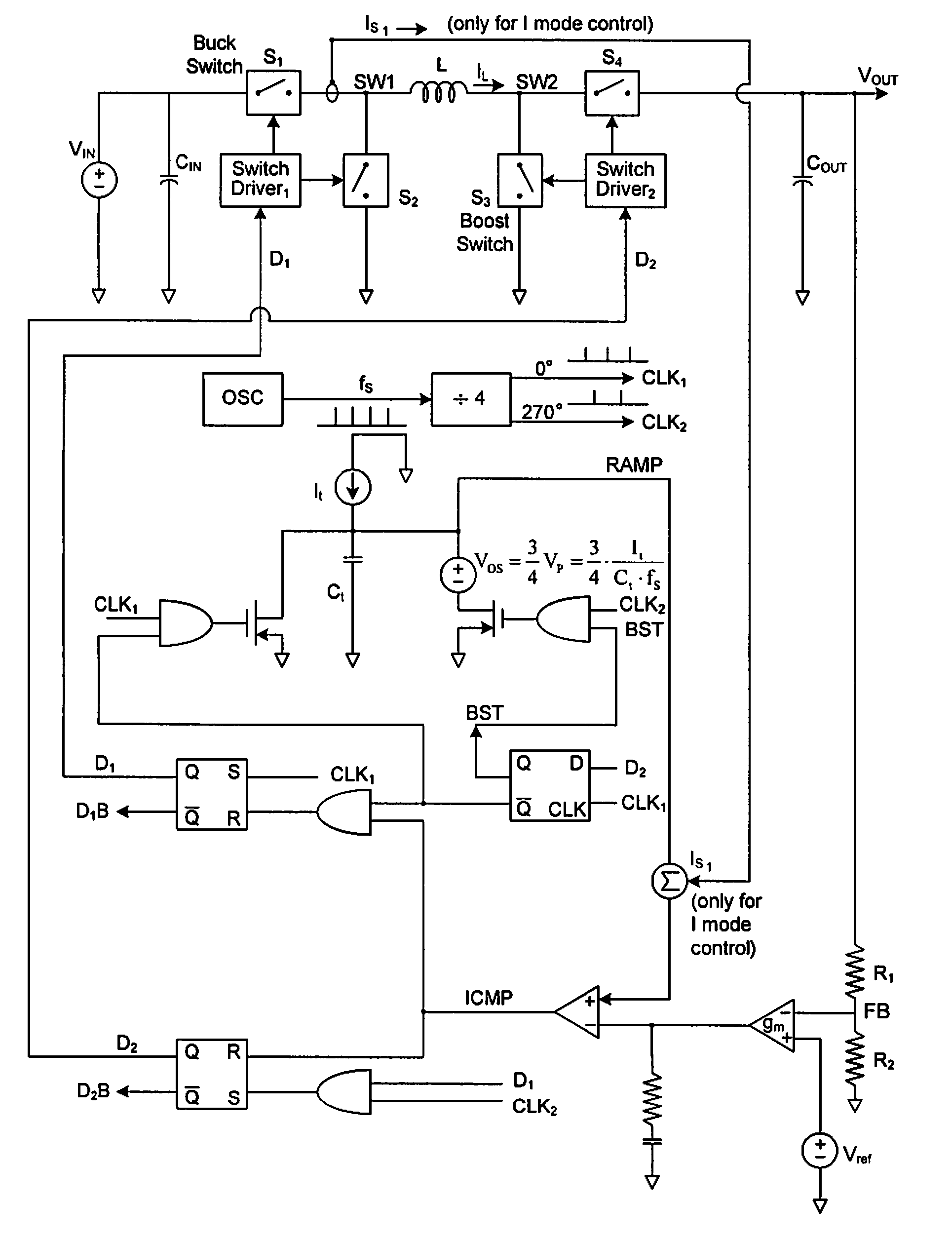
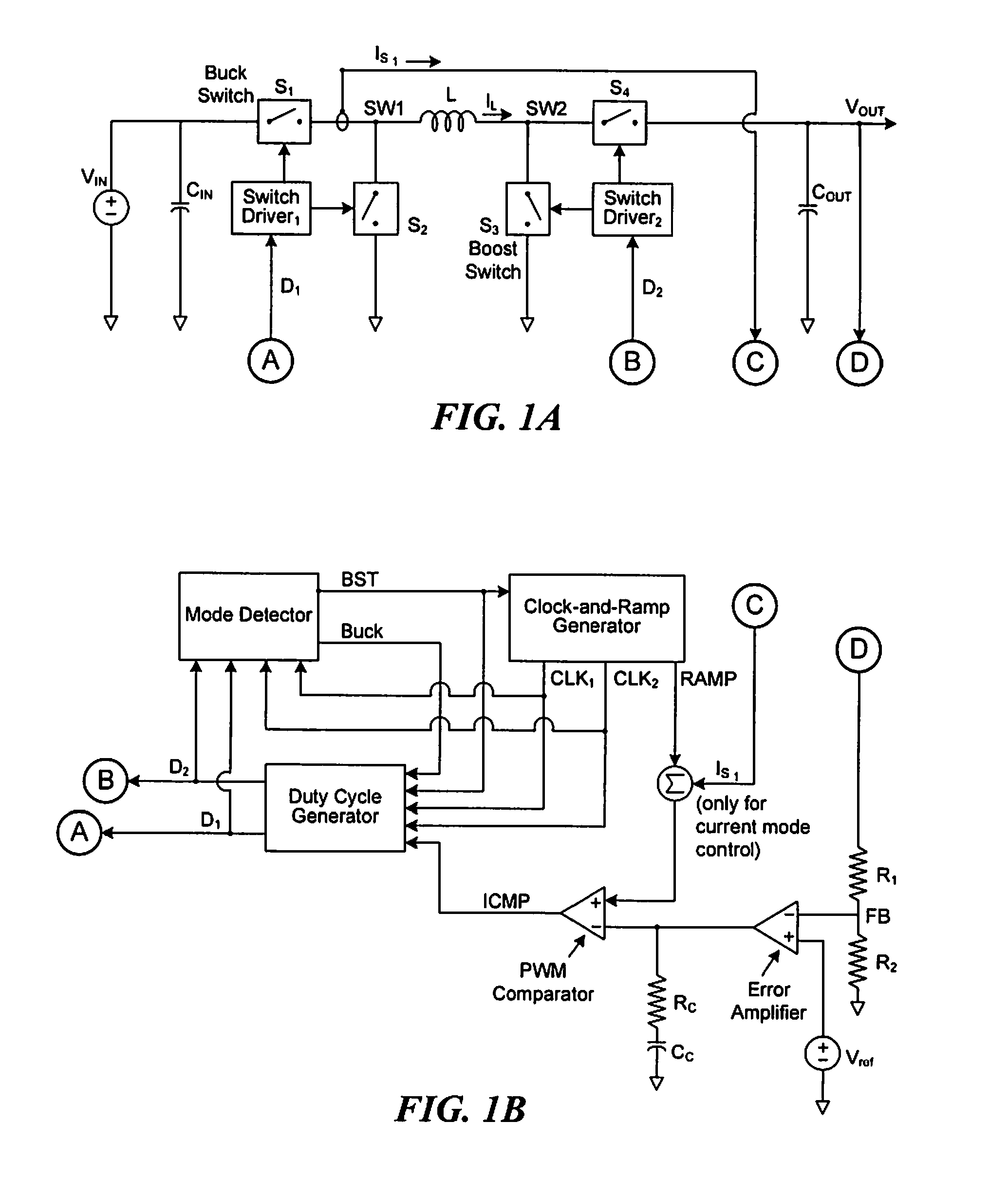
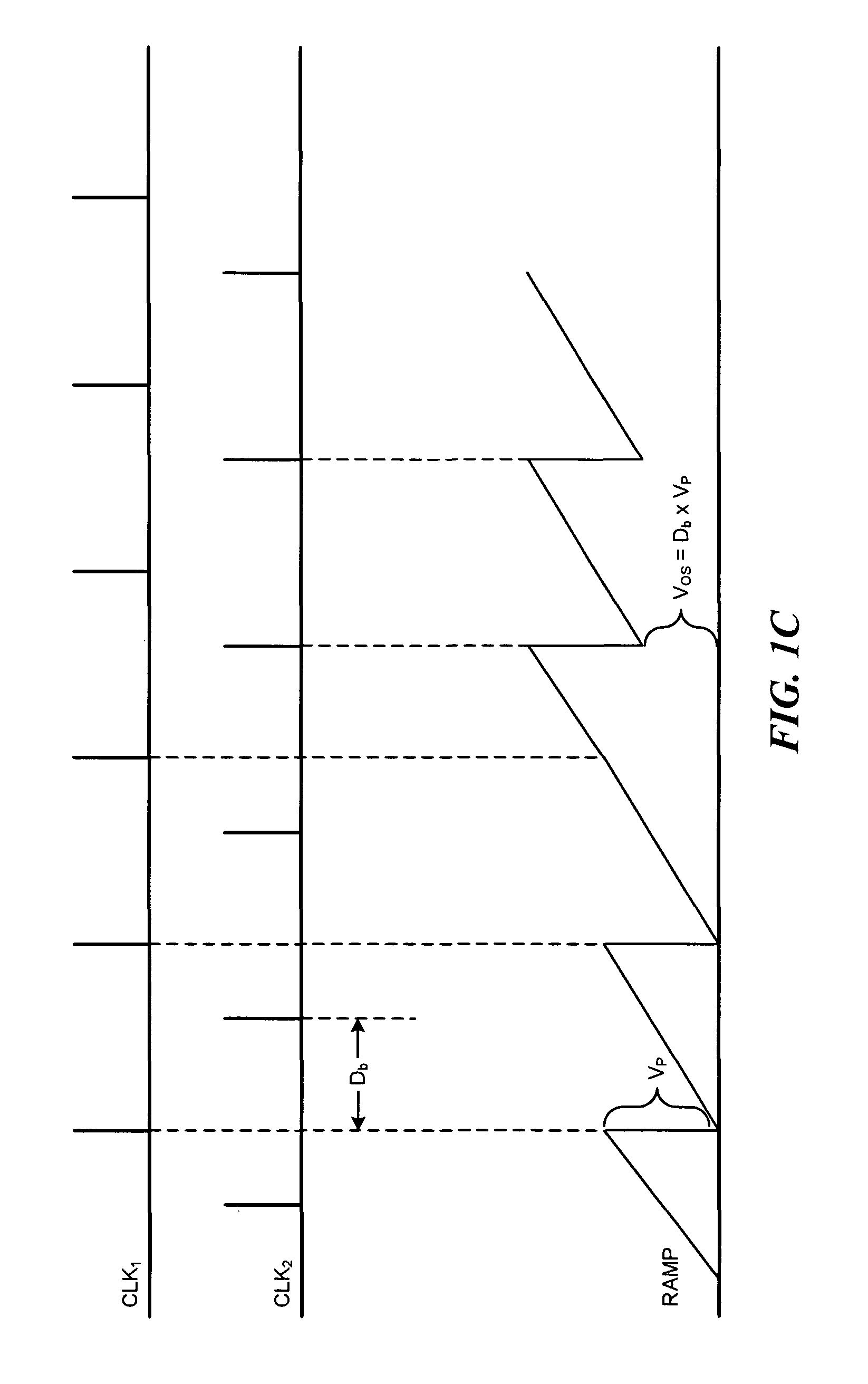
Buck-Boost Switching Voltage Regulator
InactiveUS20090102440A1Minimizing rangeDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationControl theoryVoltage regulator
A buck-boost switching regulator includes two buck switches and two boost switches. Two ramp voltages VY and VY are generated. The voltage VY is compared to a voltage VEA1 that is proportional to the output of the switching regulator. This defines the duty cycle of the two buck switches. The voltage VX is compared to a voltage VEA2 that is inversely proportional to the output of the switching regulator. This defines the duty cycle of the two boost switches. The regulator seamlessly transitions between Buck, Boost and Buck-Boost modes depending on input and output conditions.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
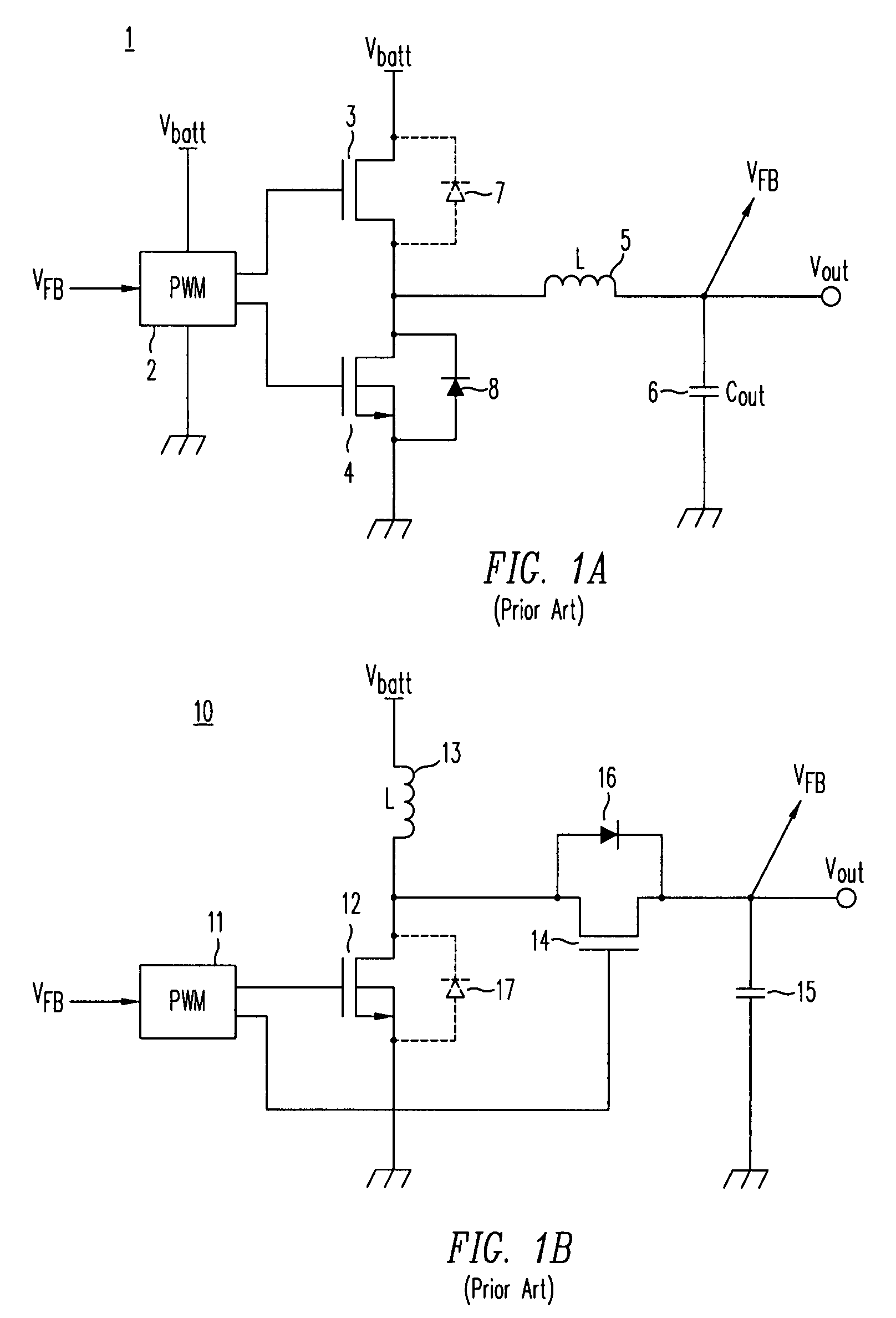
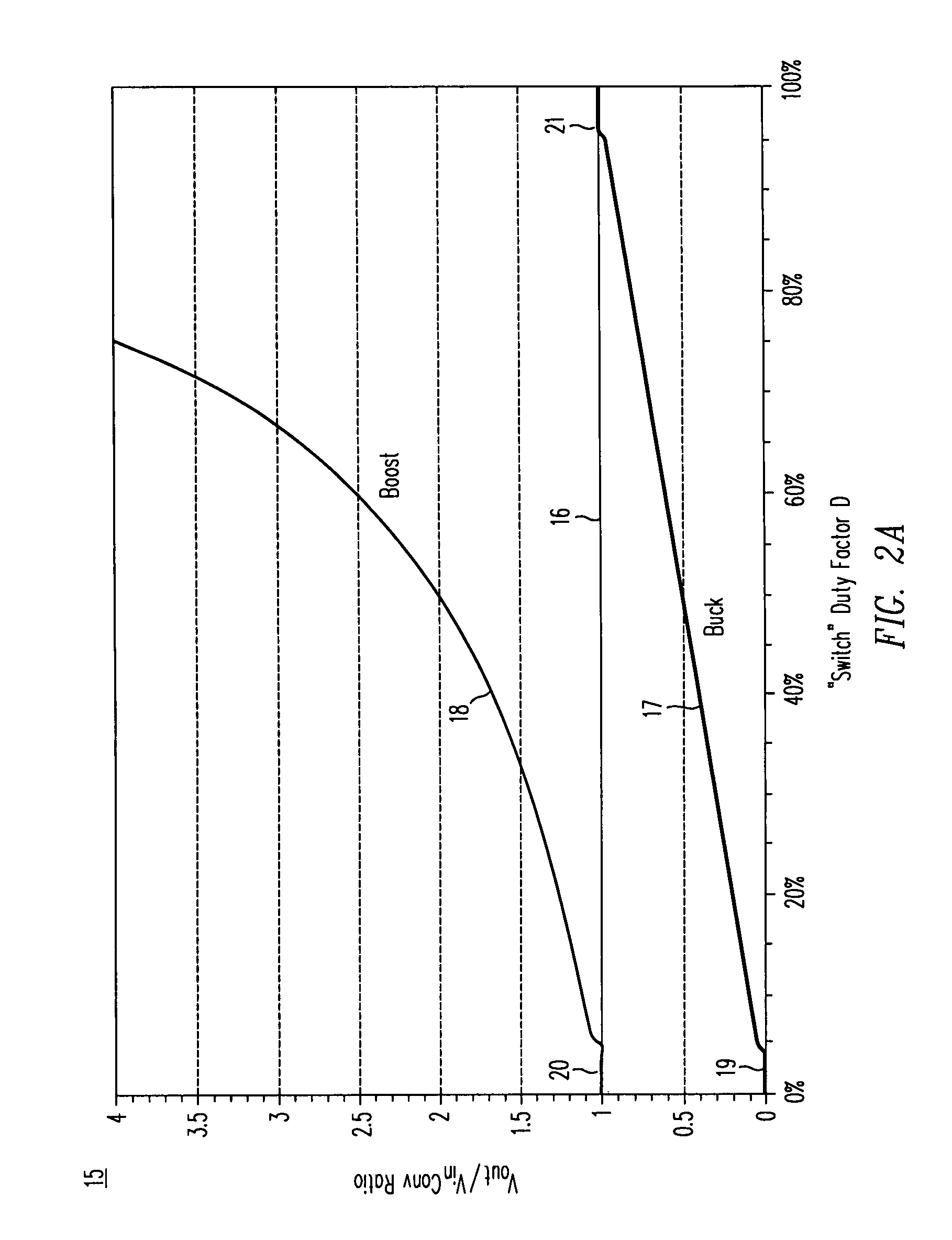
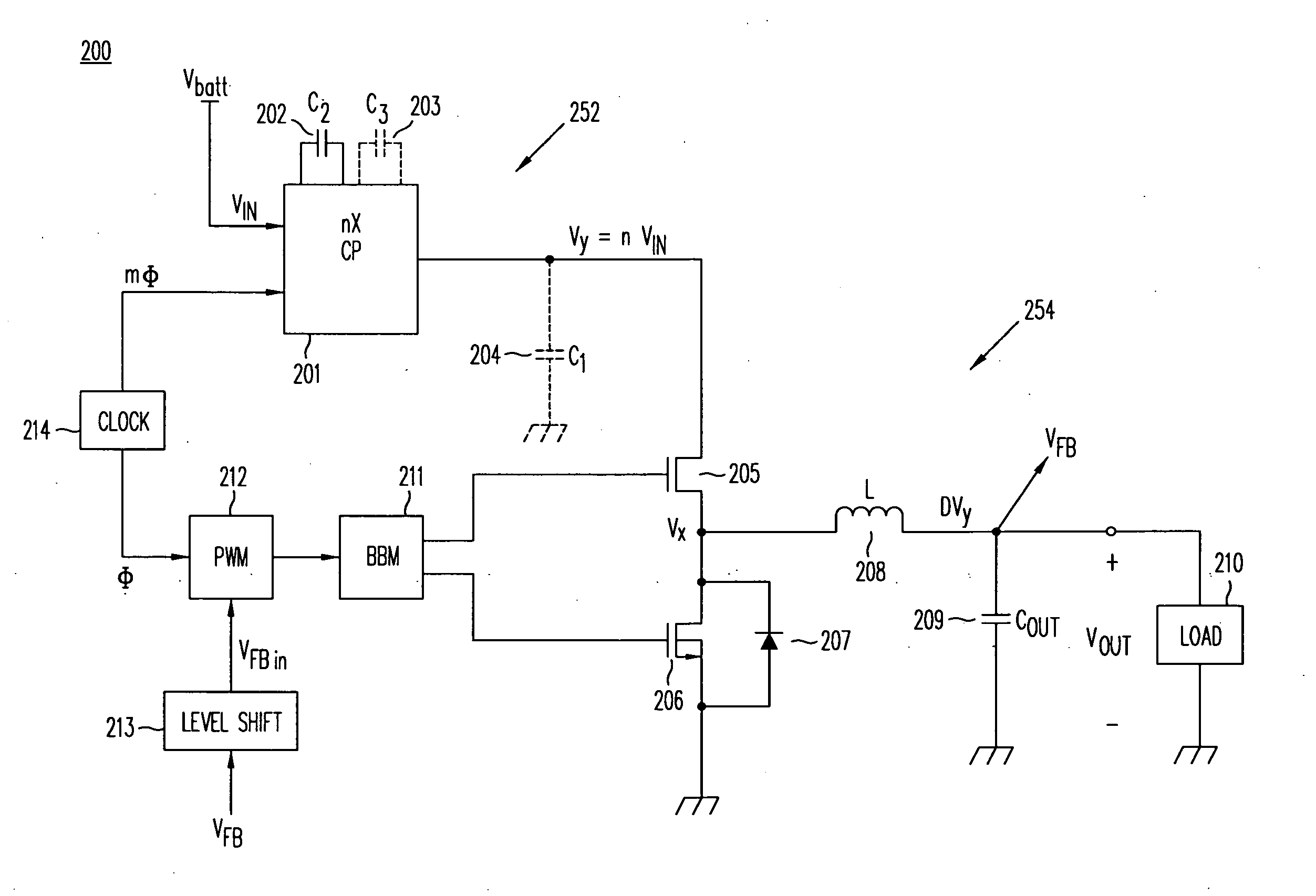
High-efficiency DC/DC voltage converter including capacitive switching pre-converter and down inductive switching post-regulator
ActiveUS7777459B2Efficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionInstabilityInductance
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
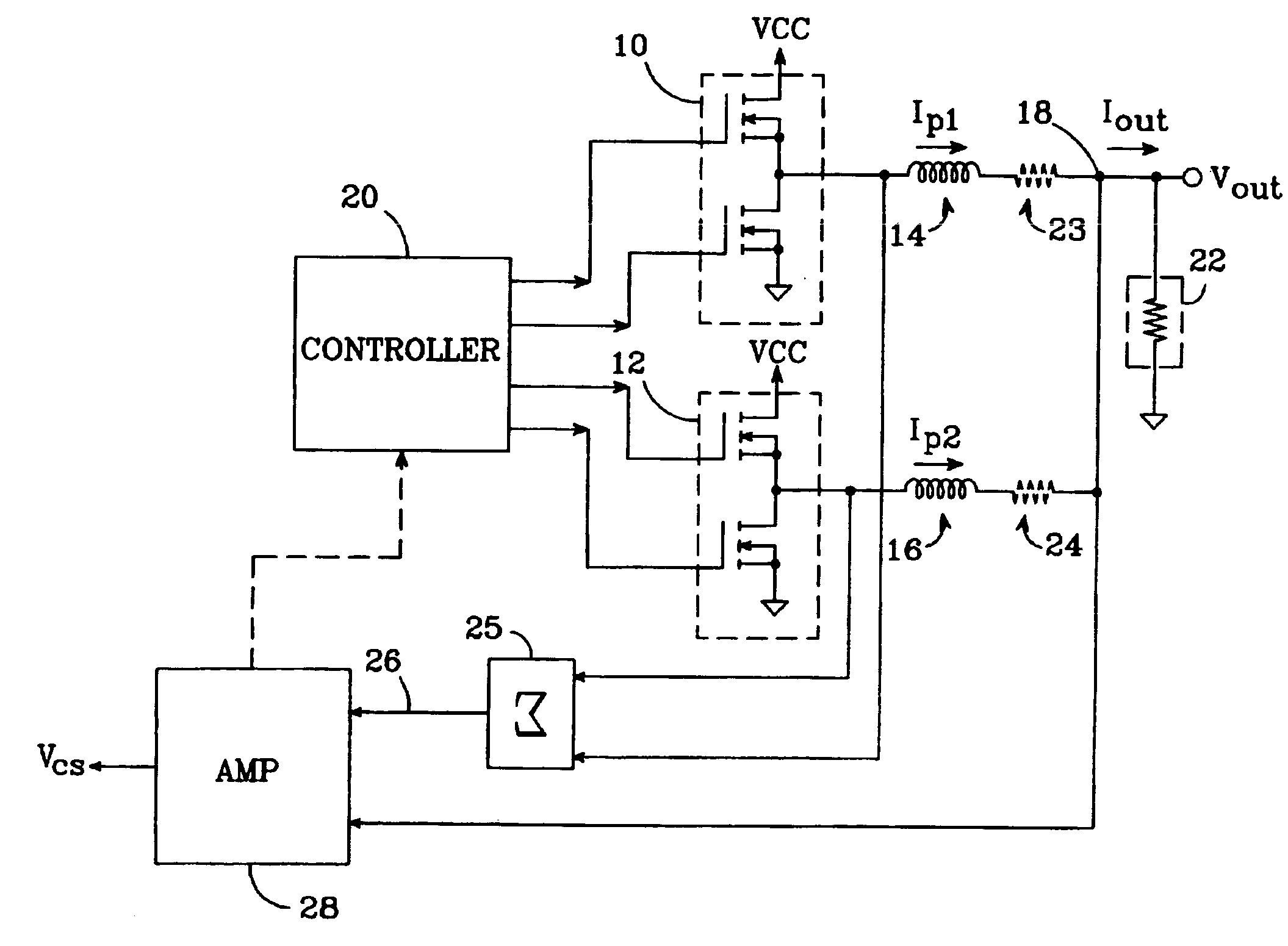
Multi-phase switching regulator
InactiveUSRE39976E1Overcome problemsEasy to controlDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationPhase currentsAudio power amplifier
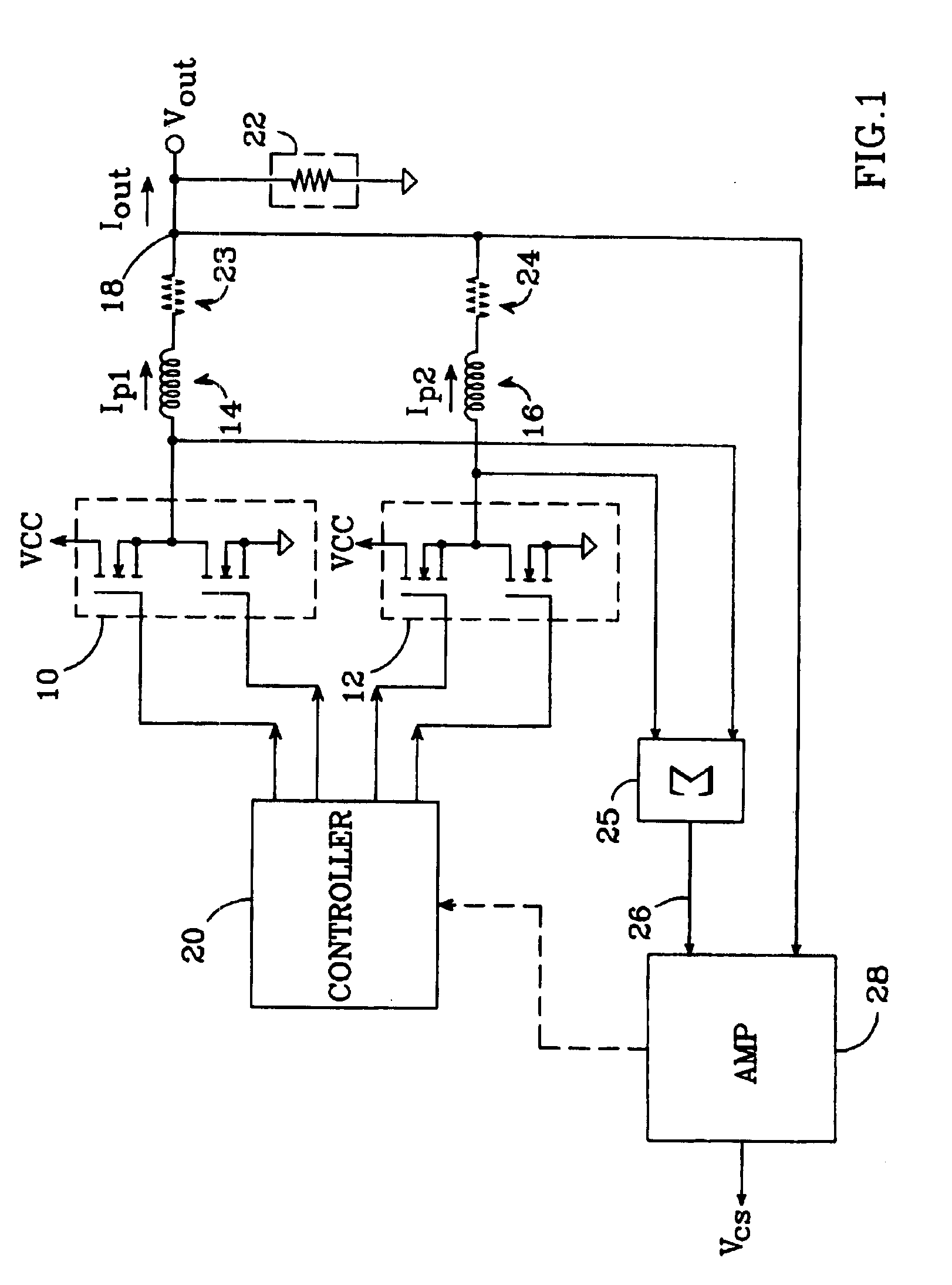
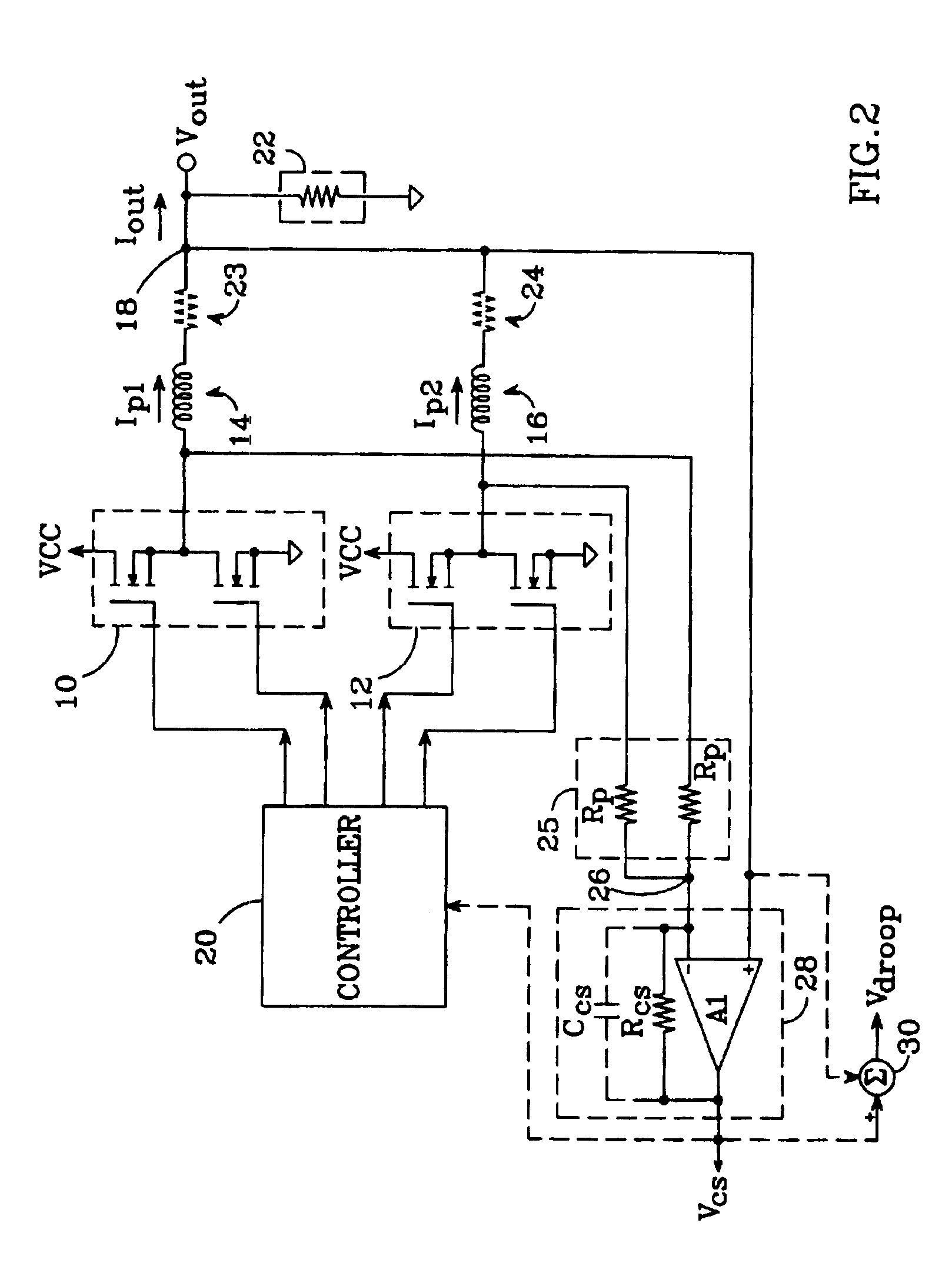
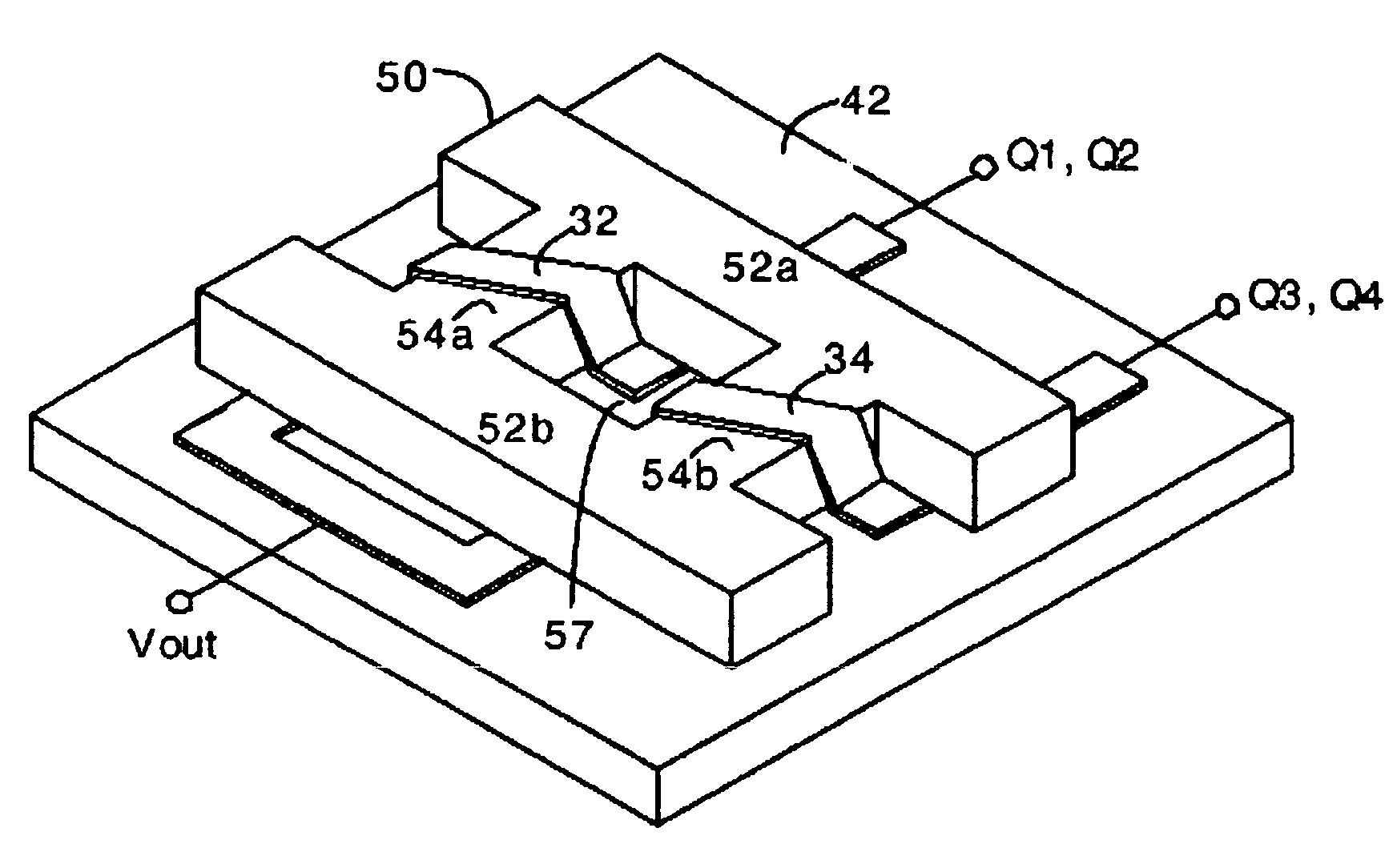
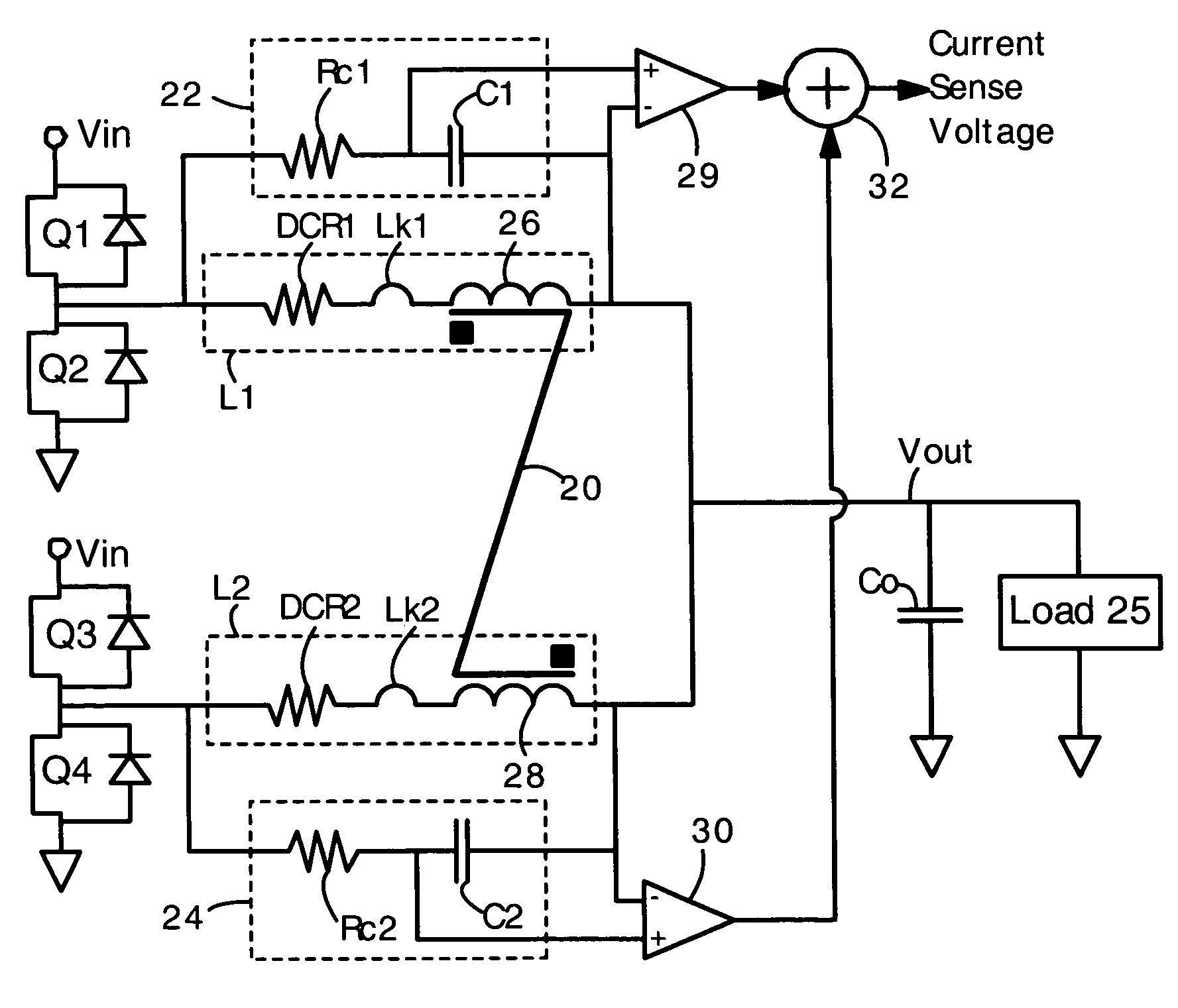
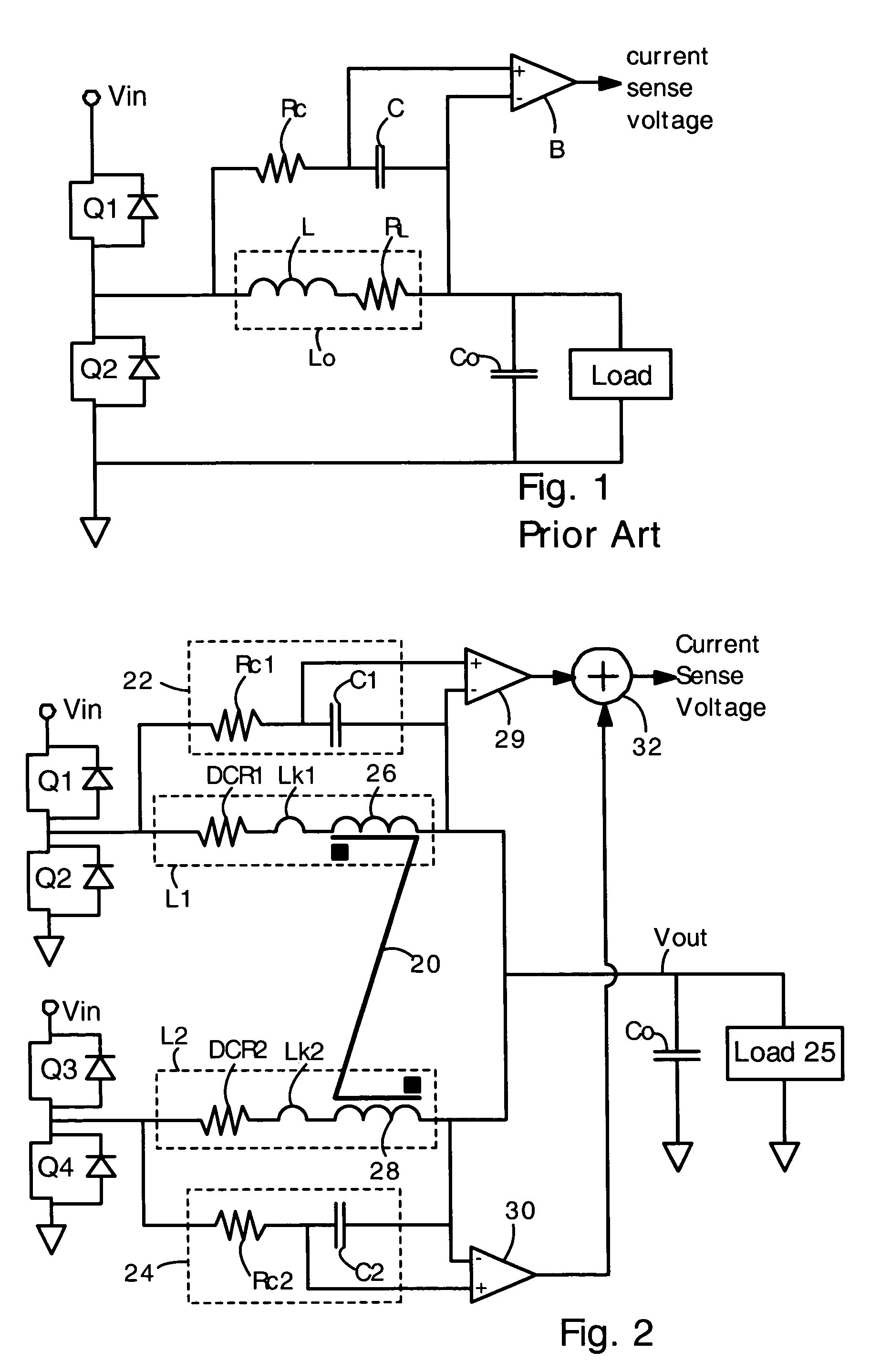
An N-phase switching voltage regulator includes N current sensing elements which carry respective phase currents. The voltages present at the switch node sides of the sensing elements are summed and presented to an amplifier which also receives the regulator's output voltage, to produce an output which is proportional to the regulator's total output current Iout. The invention also provides a means for direct insertion of total inductor output current information into a regulator's voltage-mode control loop, to provide active voltage positioning (AVP) for the output voltage. A voltage based on total inductor output current is summed with the regulator's reference voltage; this sum and Vout are applied to the voltage control error amplifier, the output of which is processed to operate the regulator's switches. This enables the regulator's output to have a desired droop impedance and to provide AVP of Vout as a function of total filtered inductor output current Iout(fltr).
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
High-efficiency DC/DC voltage converter including capacitive switching pre-converter and down inductive switching post-regulator
A DC / DC converter includes a pre-converter stage, which may include a charge pump, and a post-regulator stage, which may include a Buck converter. The duty factor of the post-regulator stage is controlled by a feedback path that extends from the output terminal of the DC / DC converter to an input terminal in the post-regulator stage. The pre-converter steps the input DC voltage up or down by a positive or negative integral or fractional value, and the post-regulator steps the voltage down by a variable amount depending on the duty factor at which the post-regulator is driven. The converter overcomes the problems of noise glitches, poor regulation, and instability, even near unity input-to-output voltage conversion ratios.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
Current direction detection circuit and switching regulator having the same
InactiveUS20080024098A1Enhanced inhibitory effectMinimise currentEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionDirection detectionConstant current source
A current direction detection circuit includes a monitoring transistor having a control terminal and an output terminal respectively connected with a control terminal and an output terminal of a ground side output transistor; an impedance element having one terminal connected with an input terminal of the monitoring transistor and the other terminal grounded; first and second constant-current sources; a diode-connected reference transistor interposed between the first constant-current source and ground potential; and a sensing transistor interposed between the second constant-current source and the impedance element and having a control terminal connected with the control terminal of the reference transistor. The current direction detection circuit is small yet capable of minimizing power loss of a switching regulator.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
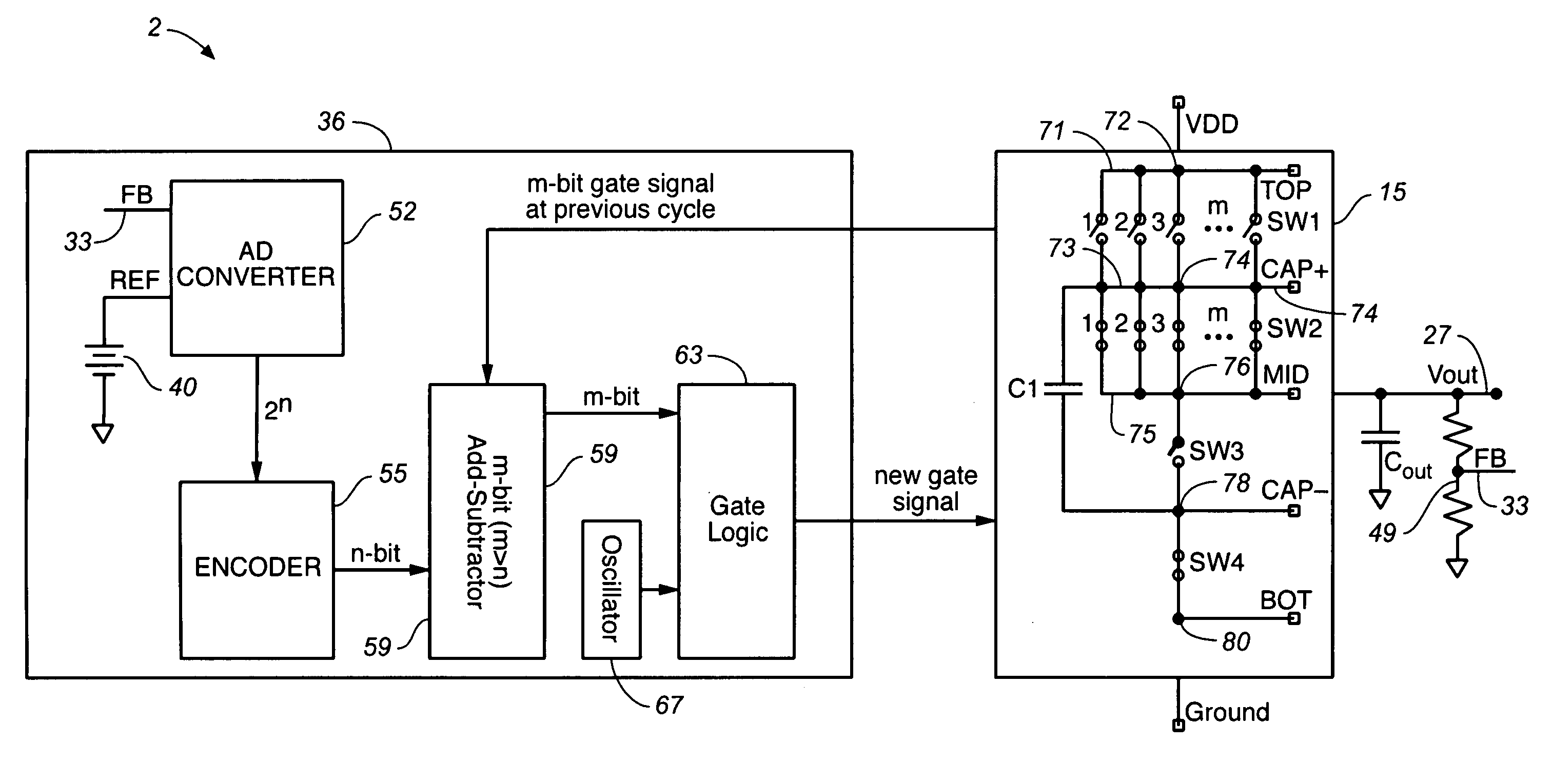
Digital loop for regulating DC/DC converter with segmented switching
InactiveUS6995995B2Save areaReduce rippleEmergency protective circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversionA d converterVoltage regulation
A power control circuit is provided containing a switch array, which includes segmented switches, a flying capacitor, an output voltage terminal, a feedback loop, and a digital voltage regulator block. The digital voltage regulator block includes an A / D converter, an encoder, an add-subtractor, and a gate logic. These power control circuits do not include pass transistors. A method is also provided, where the charge pumps of the power control circuit are operated in two-phase cycles including a charging phase and a pumping phase. The power control circuit is controlled in both of these phases, thereby reducing the ripple of the output voltage.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
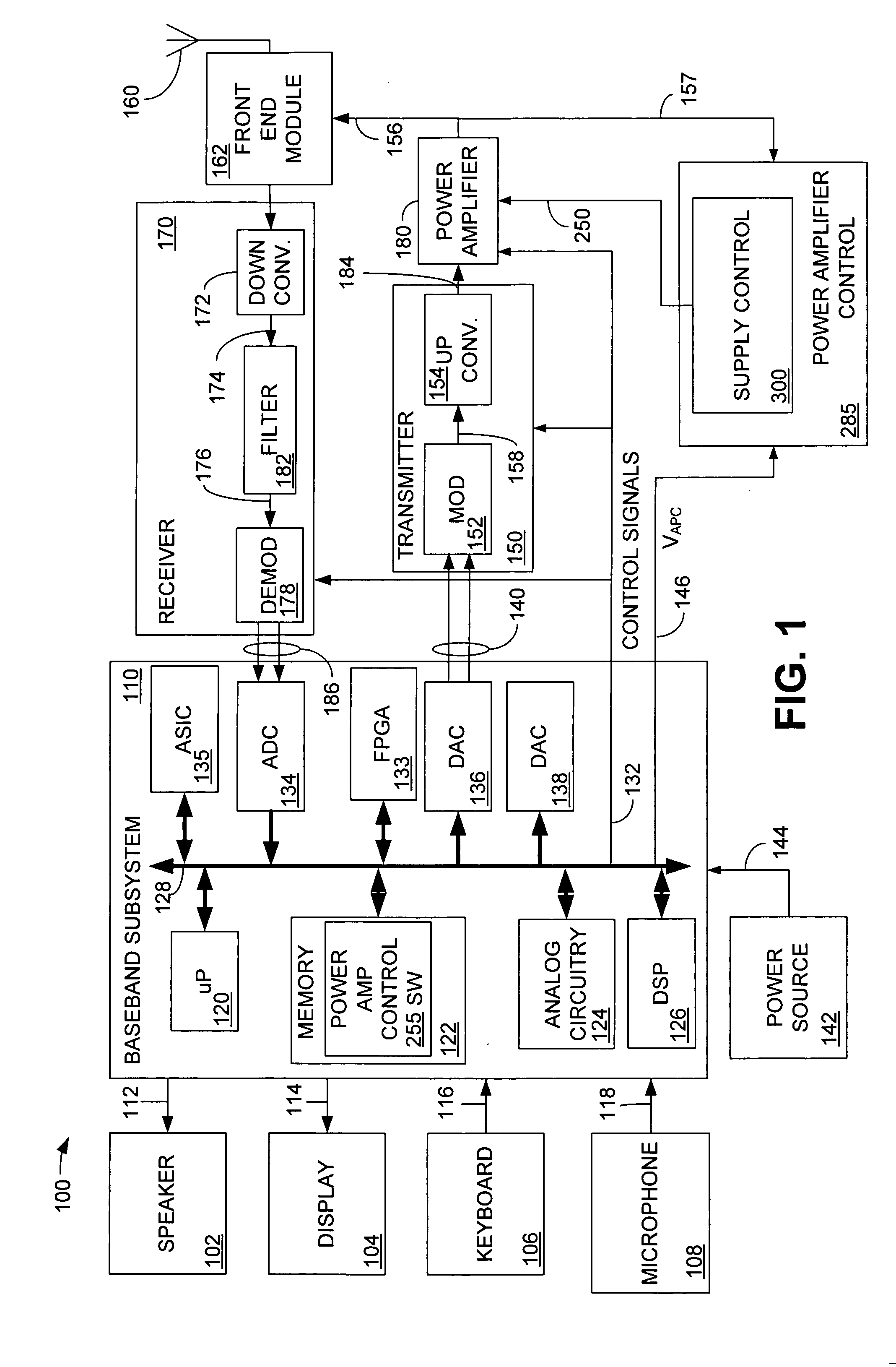
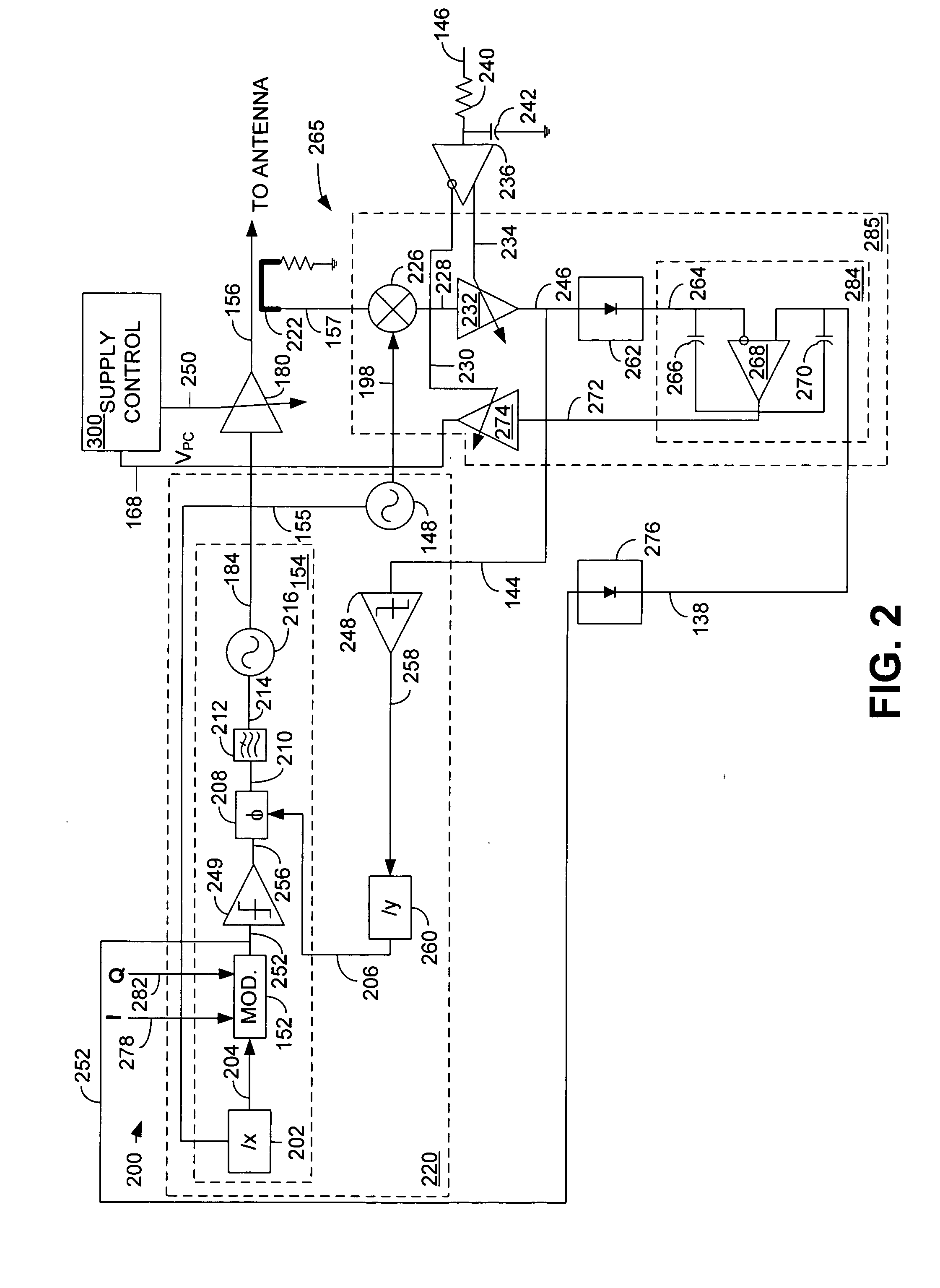
Dual voltage regulator for a supply voltage controlled power amplifier in a closed power control loop
ActiveUS20060270366A1Noise minimizationMinimize noiseResonant long antennasDc network circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierVoltage regulation
A supply voltage controlled power amplifier that comprises a power amplifier, a closed power control feedback loop configured to generate a power control signal, and a dual voltage regulator coupled to the power control feedback loop, the dual voltage regulator comprising a first regulator stage and a second regulator stage, wherein the closed power control loop minimizes noise generated by the first regulator stage.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
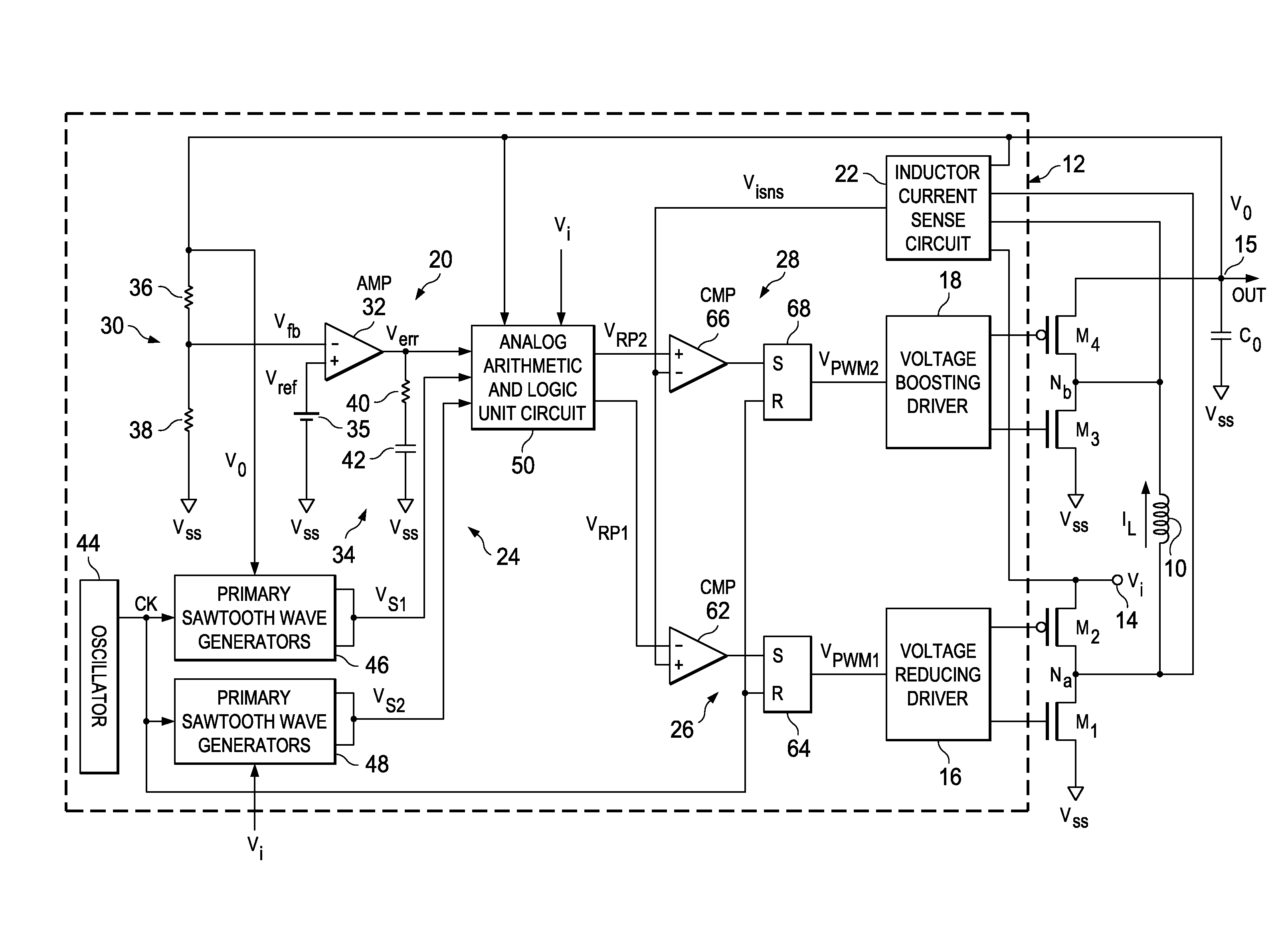
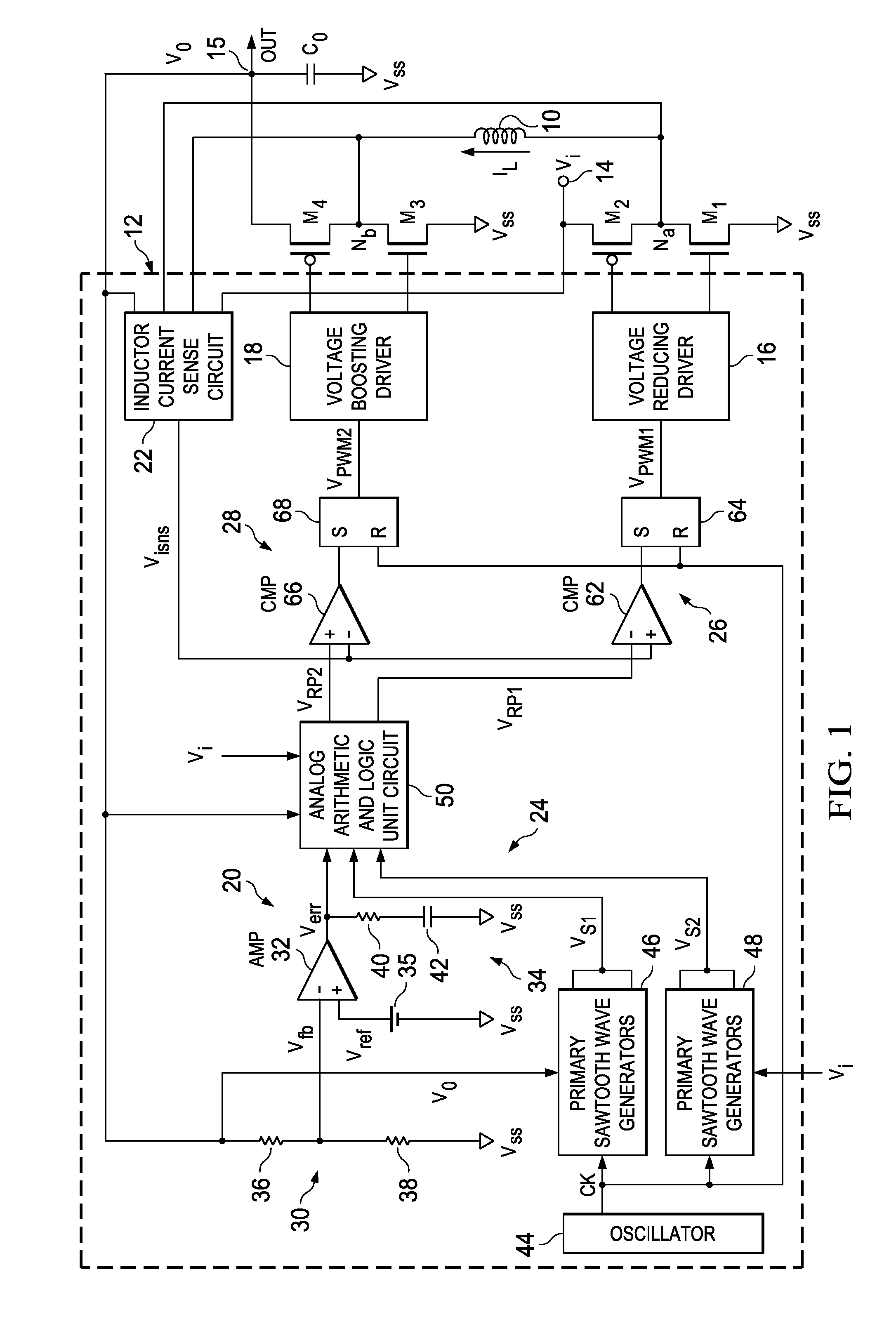
Voltage buck-boost switching regulator
ActiveUS8436592B2Stable, high-speed, high-efficiency constant-voltage output operationStop operationDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceEngineering
A stable, high-speed, high-efficiency constant voltage is provided without a complicated, large-scale, high-cost phase compensation circuit over a wide range of operating conditions. This voltage buck-boost switching regulator consists of a pair of voltage reducing transistors, a pair of voltage boosting transistors, inductance coil, output capacitor and controller. The controller has the following parts for performing PWM control of constant voltage for voltage reducing transistors and voltage boosting transistors: an output voltage feedback circuit, an inductor current sense circuit, a variable sawtooth wave signal generator, switching controllers, and a voltage boosting driver.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
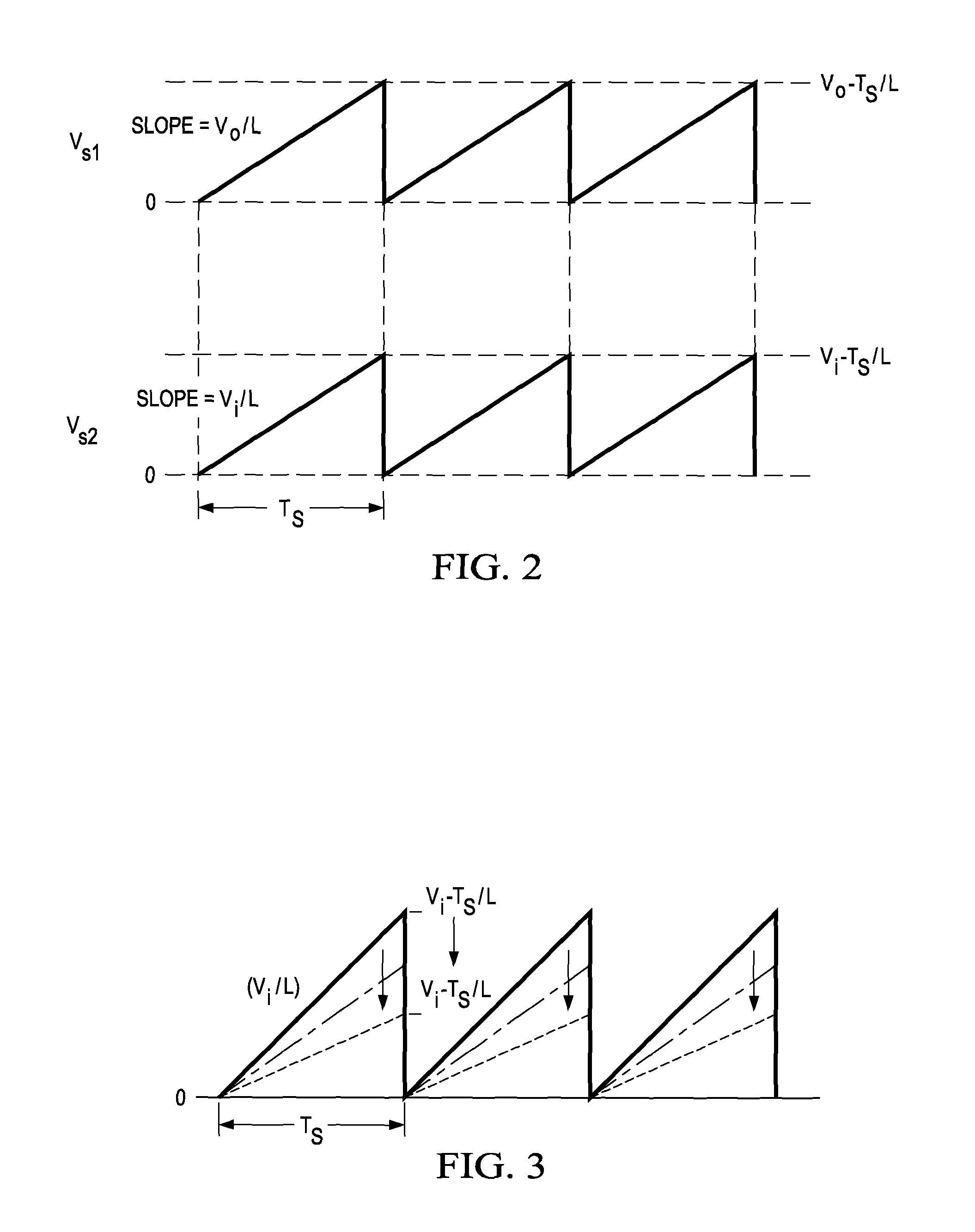
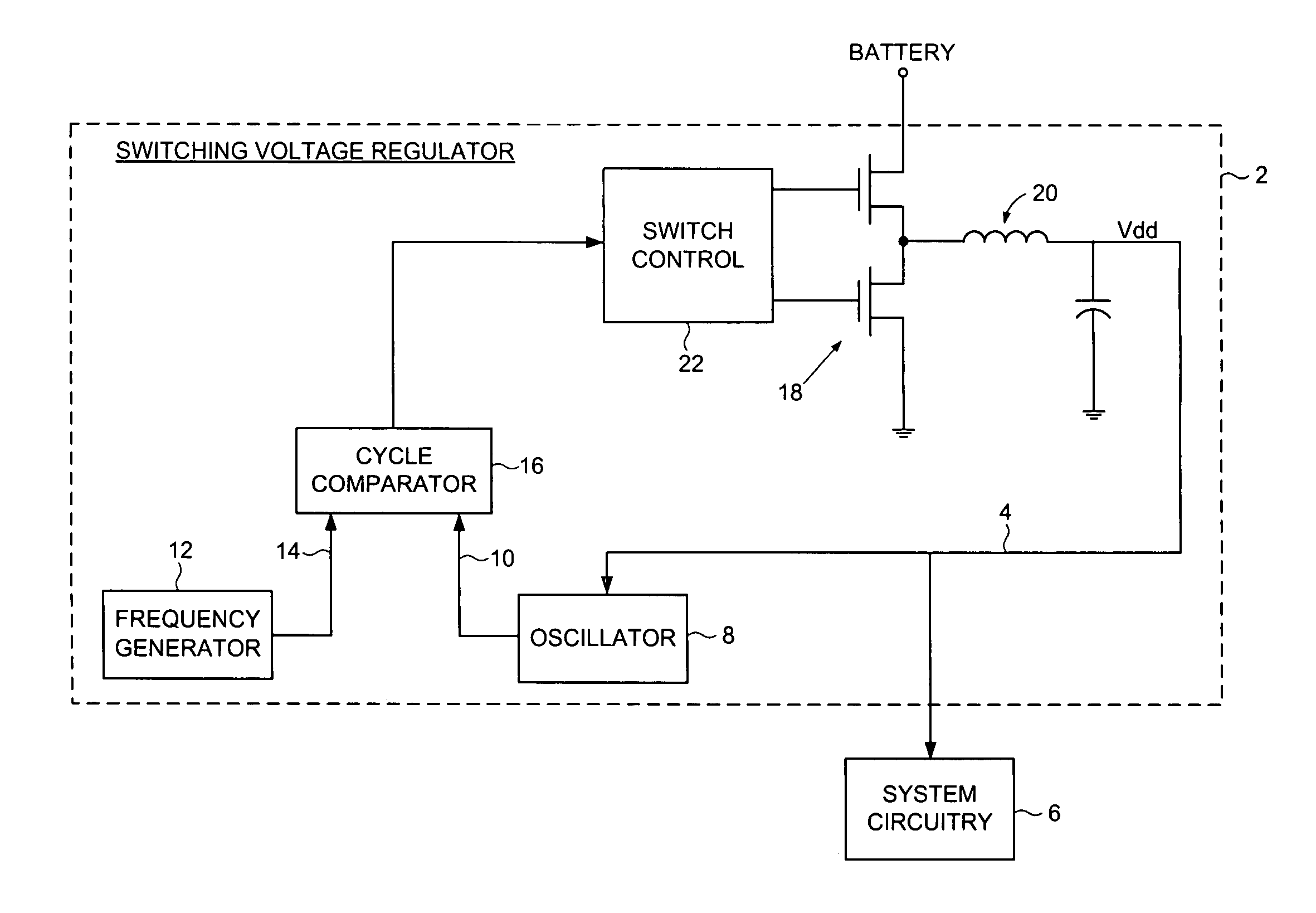
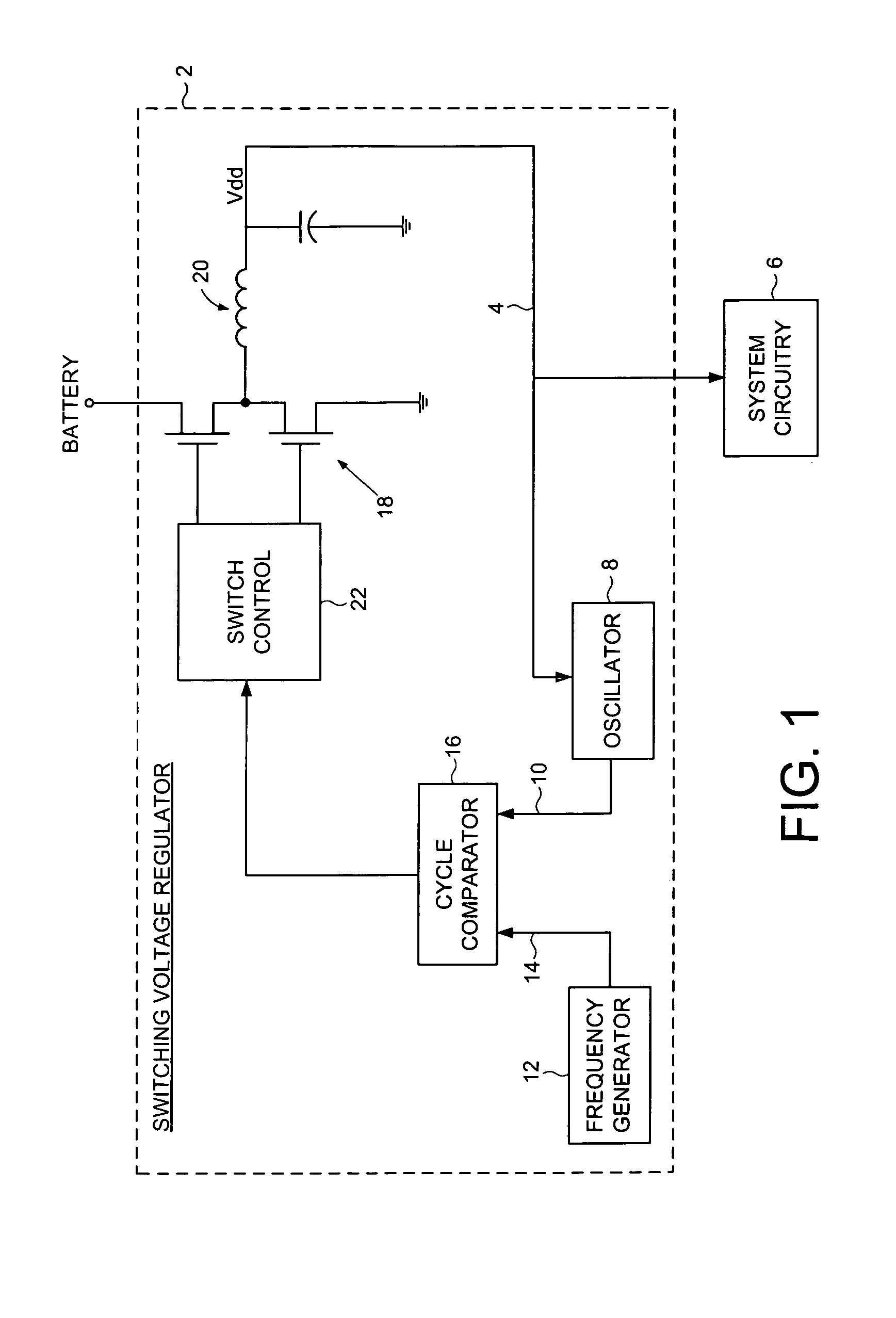
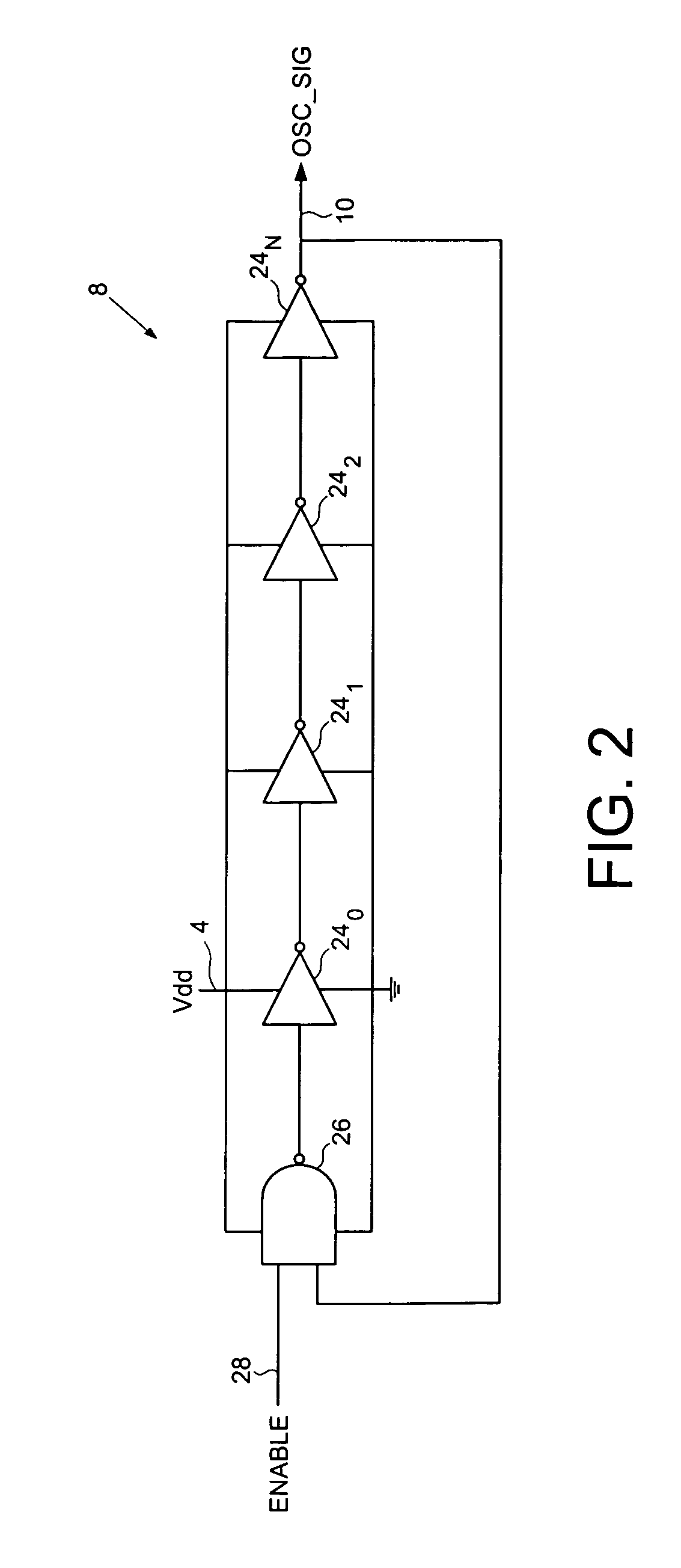
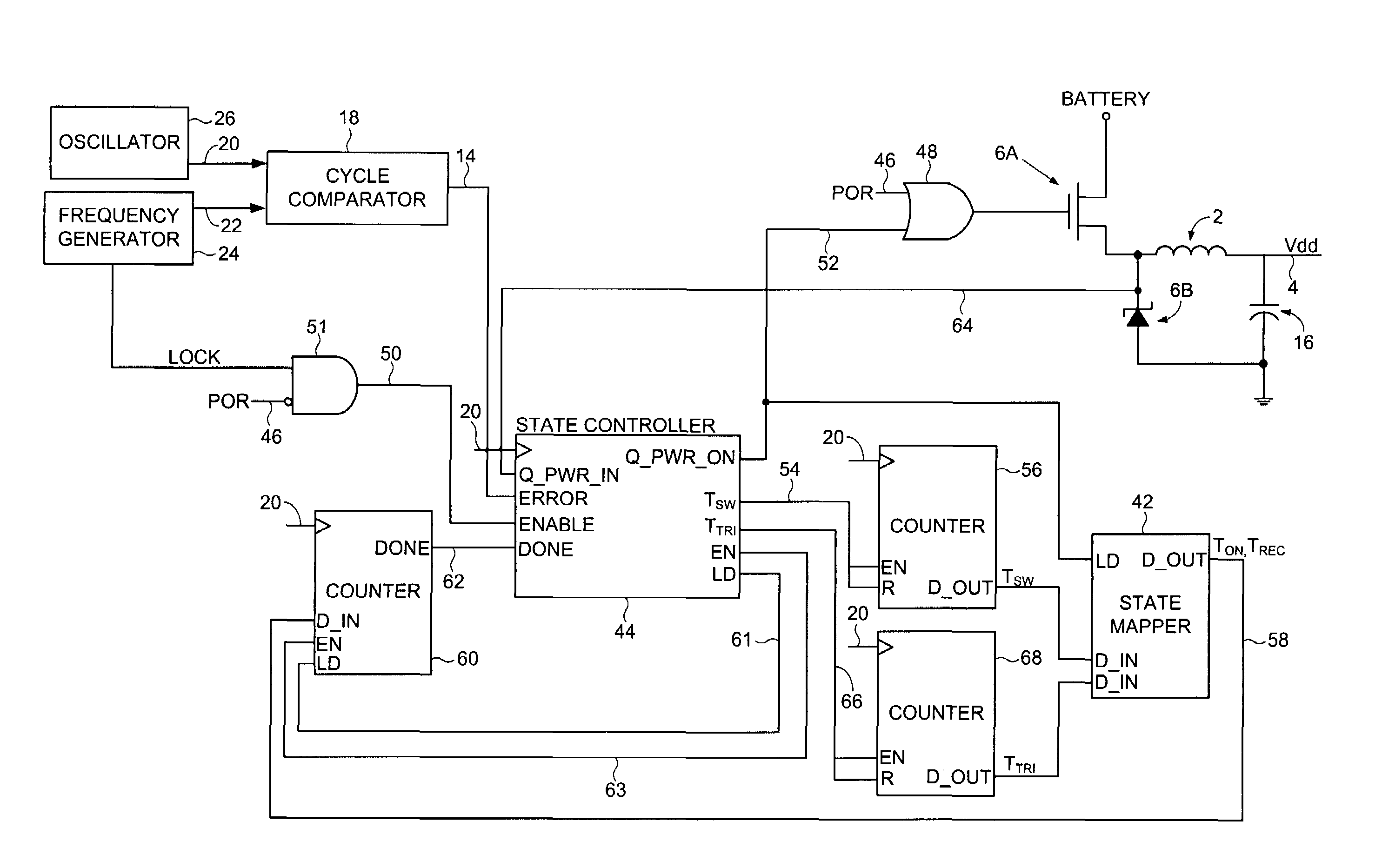
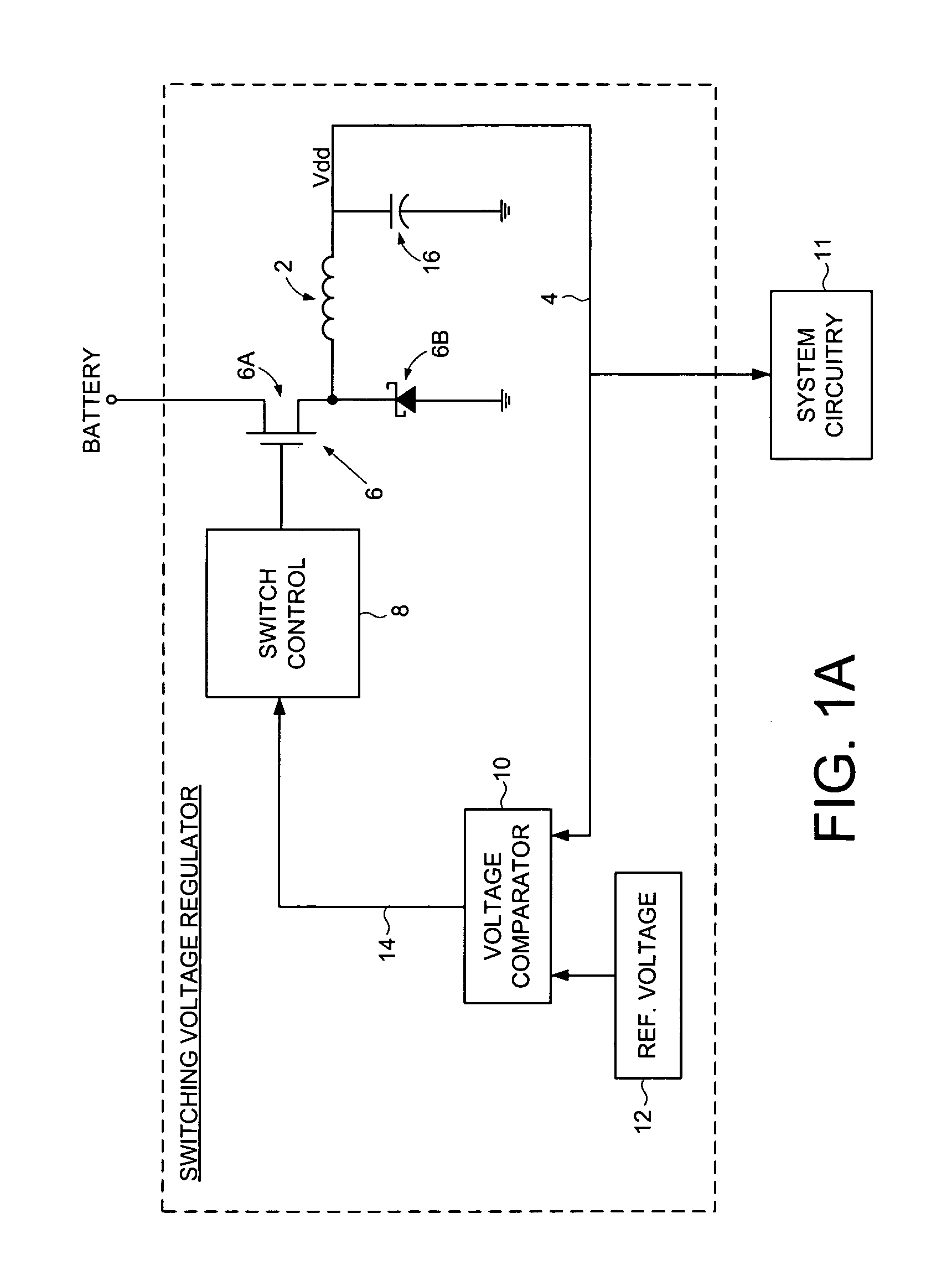
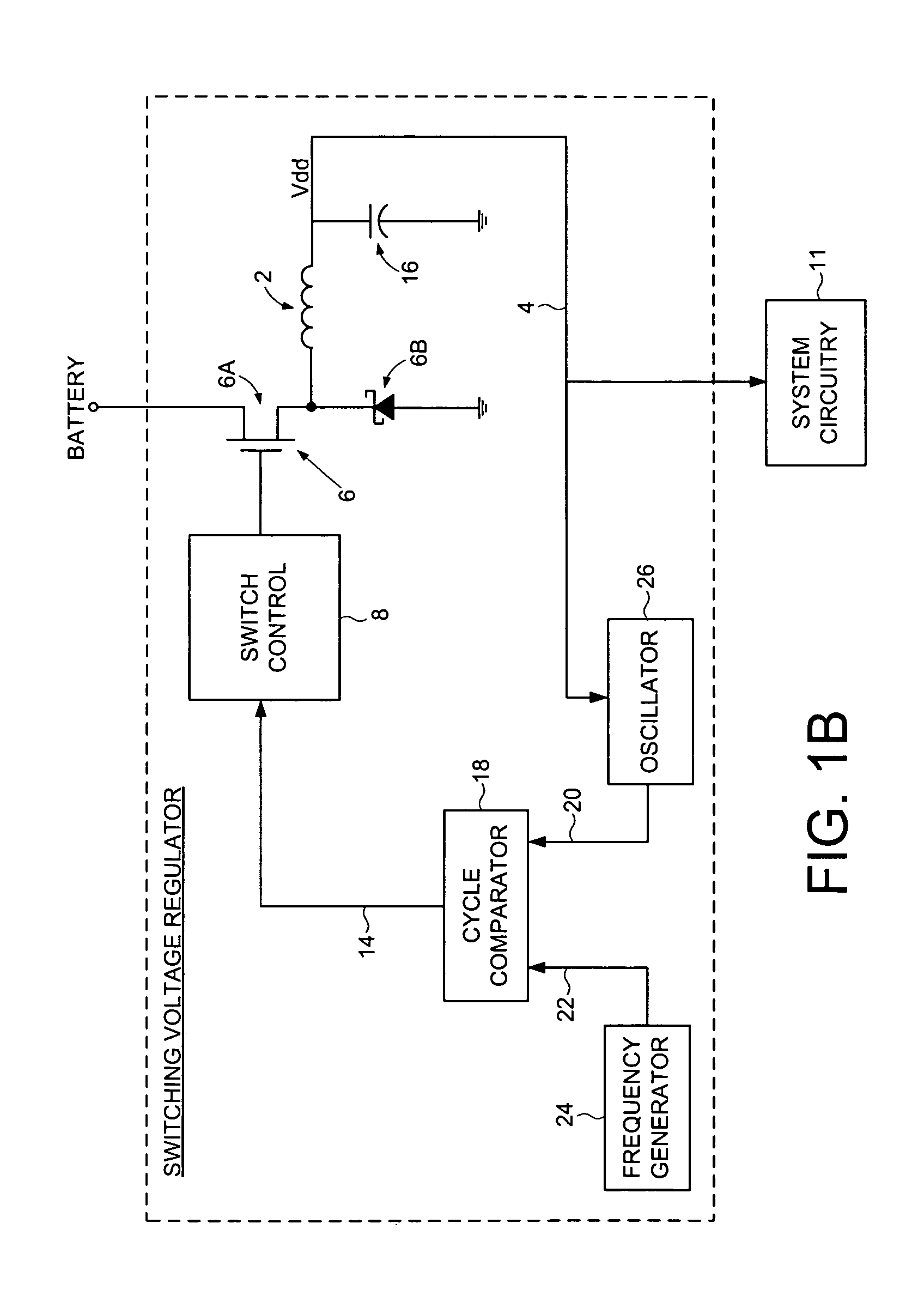
Switching voltage regulator comprising a cycle comparator for dynamic voltage scaling
A switching voltage regulator is disclosed for regulating a voltage supplied to system circuitry. The switching voltage regulator comprises an oscillator operable to generate an oscillator signal representing a gate speed of a reference circuit in the system circuitry, and a frequency generator operable to generate a reference signal representing a target gate speed of the reference circuit. A cycle comparator compares at least one cycle of the oscillator signal to at least one cycle of the reference signal, and switching circuitry charges a charging element based at least on part on the comparison.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Switching regulator with automatic multi mode conversion
ActiveUS7944191B2Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionControl theoryBoost converter
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for efficient switching regulators that adapt automatically to, and operate with, input voltages that are above, below, or equal to the output voltage. The disclosed switching regulators demonstrate advantages of both buck and boost converters at high efficiency.
Owner:MONOLITHIC POWER SYST
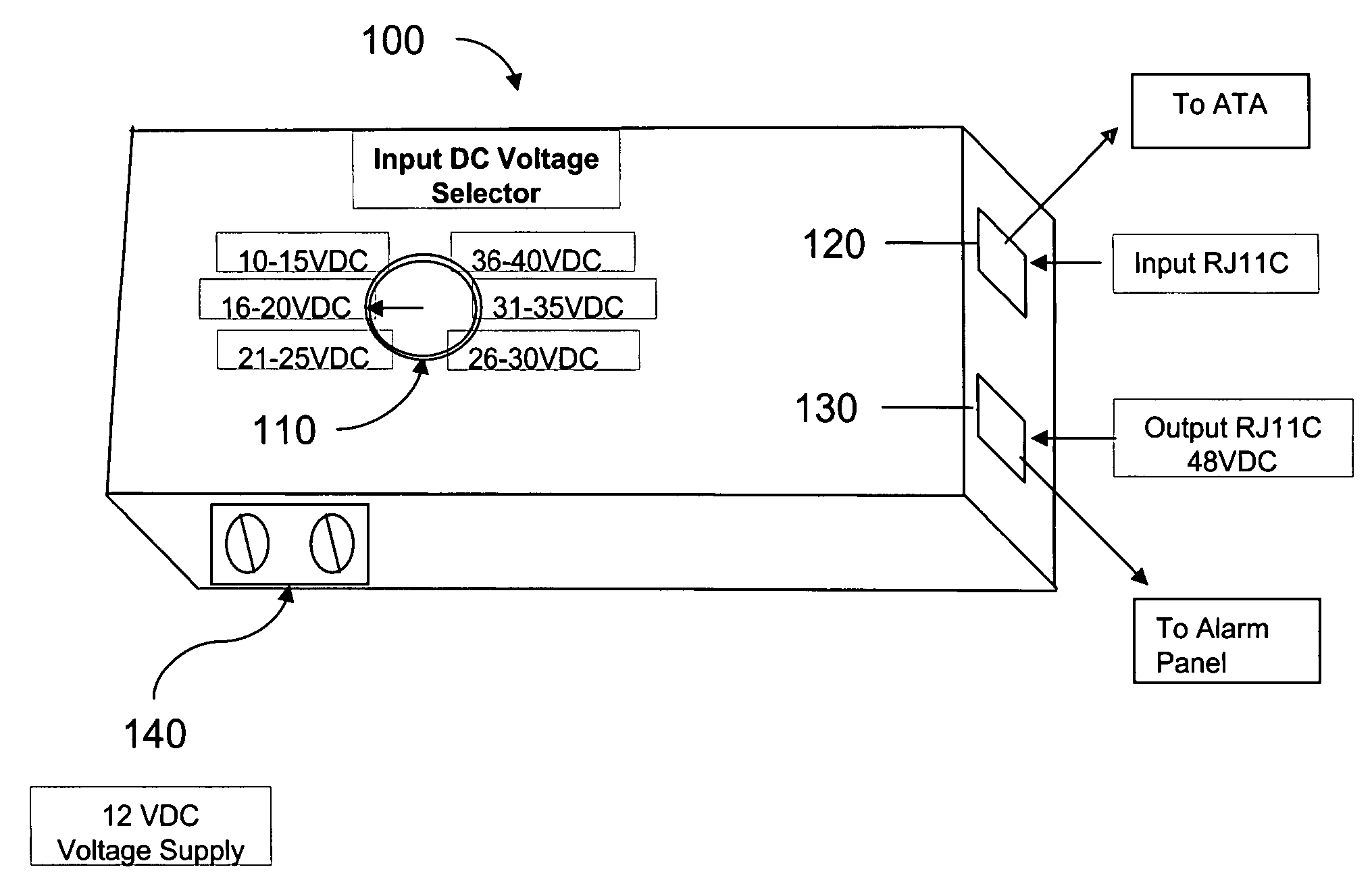
Network to alarm panel simulator for VoIp
InactiveUS20070001818A1Simple operating systemFree of corrosion and moistureTelephonic communicationOrder telegraph apparatusTelecommunications linkNetworked system
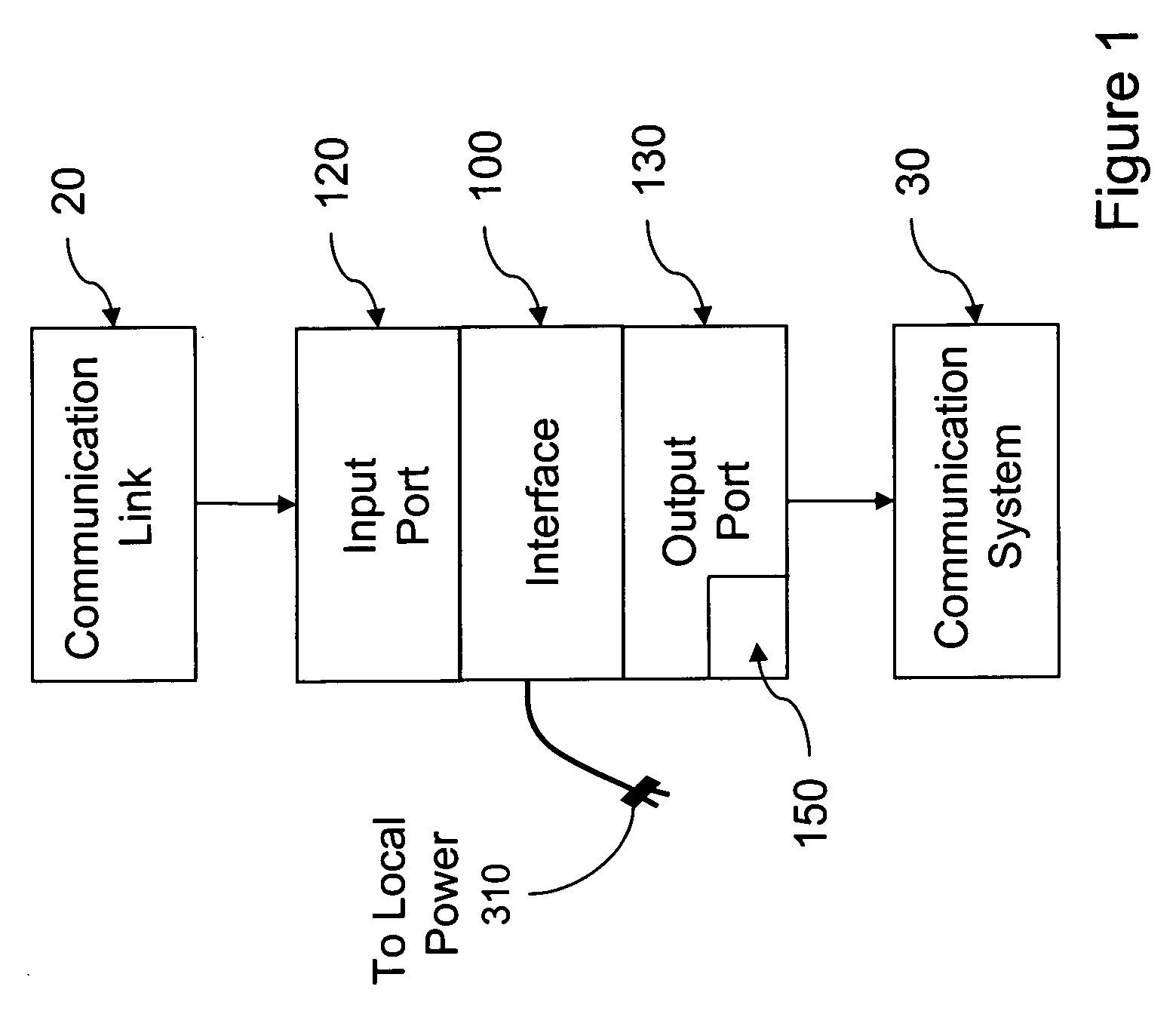
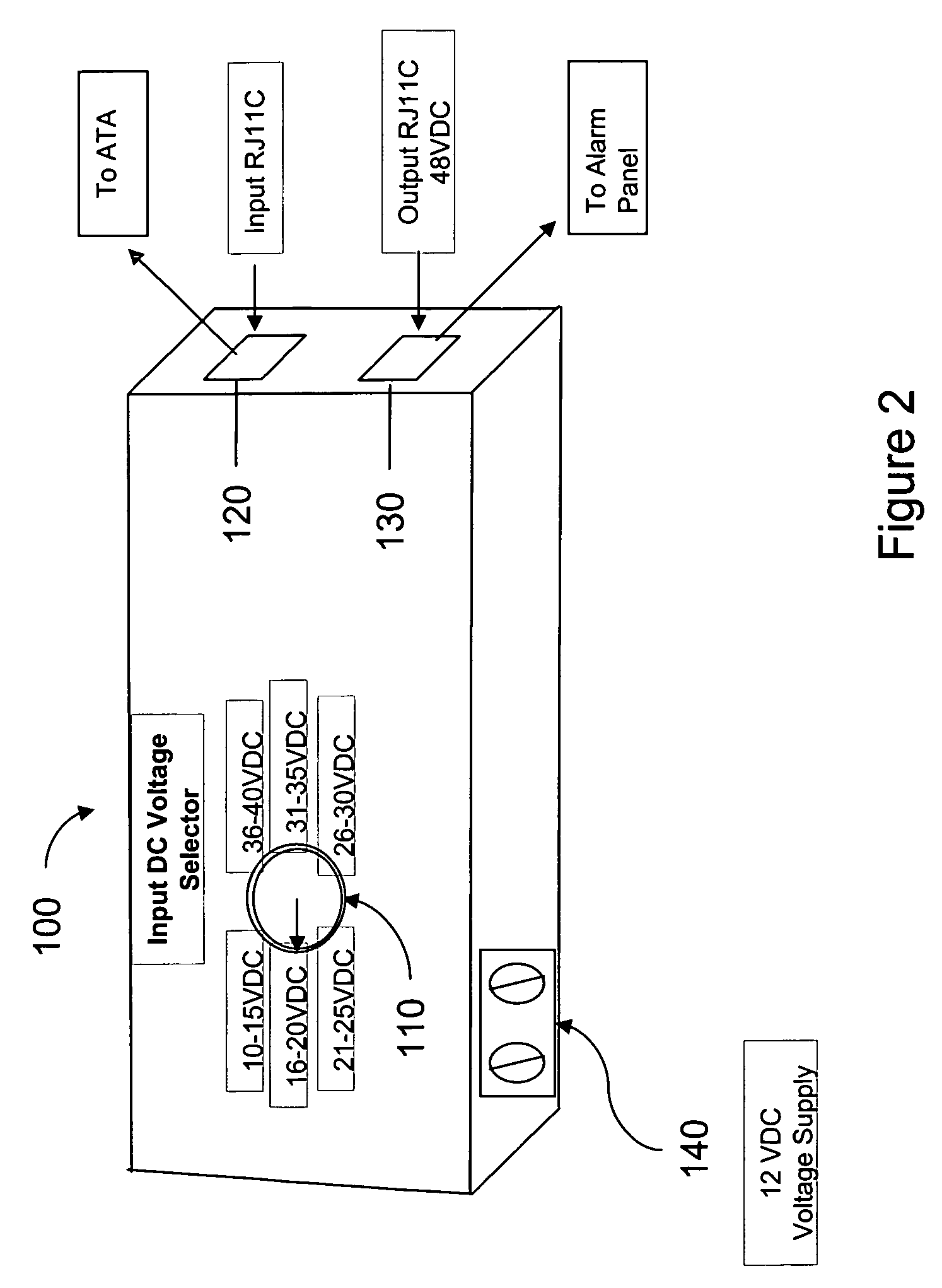
The present invention provides for a system and method for providing a signal to a communication system comprising an interface between a communication link and the communication system, like an alarm system, wherein the interface receives a signal from the communication link and provides a signal indicative of the availability of the communication link for use by the communication system. Alarm systems operations may be facilitated so that Residential Gateway components (such as voice terminal adapters) may simulate traditional telephone network systems that run on 48 VDC powered telephone lines. The system also comprises an input port associated with the interface for receiving the signal from the communication link, a transformer or a voltage regulator and an output port associated with the interface for providing the conditioned signal to the communication system. A ring voltage received from the communication link may be passed through to the alarm system.
Owner:SBC KNOWLEDGE VENTURES LP
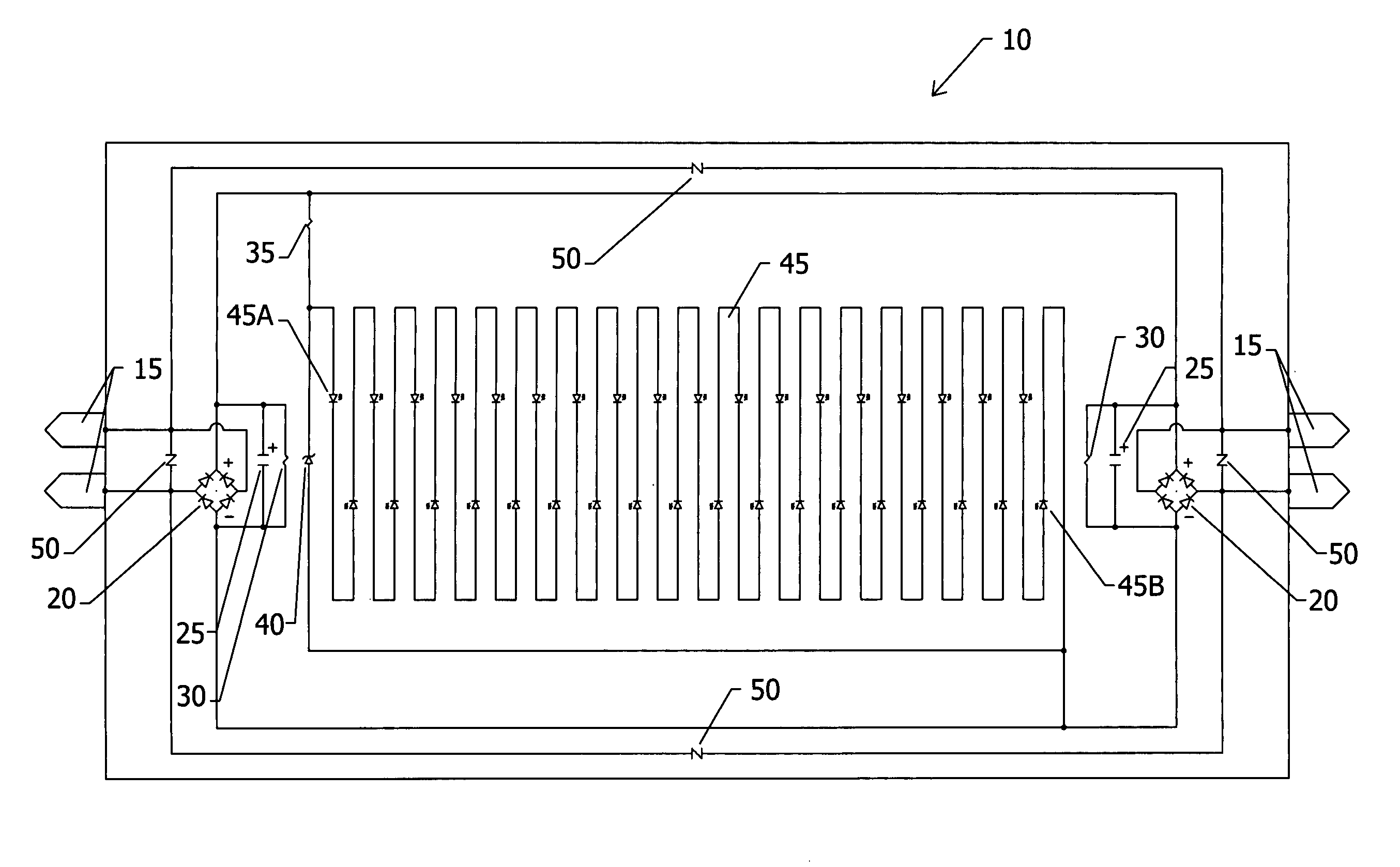
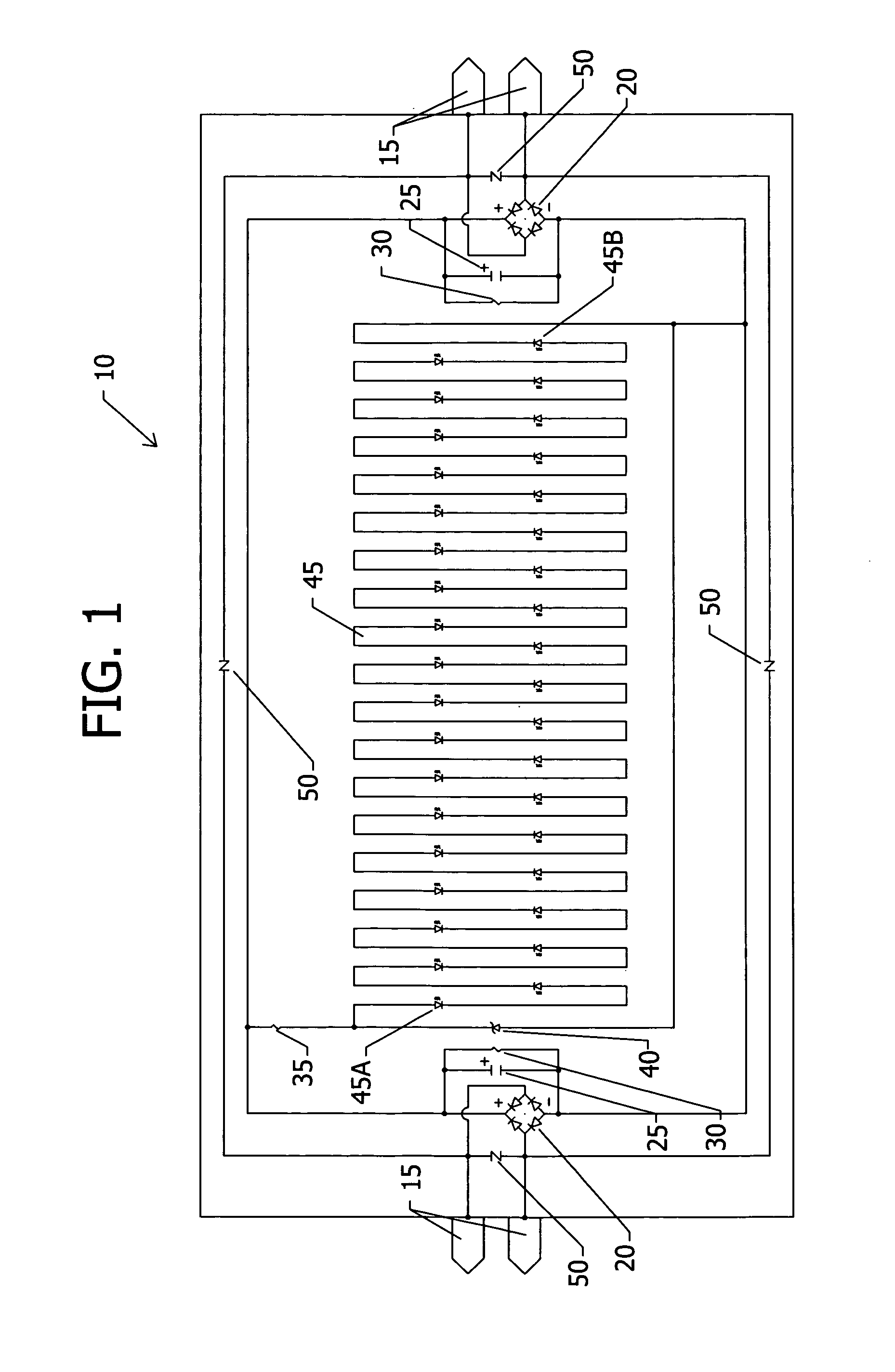
Voltage regulating devices in LED lamps with multiple power sources
ActiveUS20110057572A1Reduce materialReduce inventory costsElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesZener diodeVoltage regulation
LED driver circuits containing voltage reducing devices, voltage regulating devices, and voltage converting devices are disclosed as the main components to provide power to LEDs. The LED driver circuits are designed to work with a ballast, mains alternating current voltage, direct current voltage, and electromagnetic induction power. The voltage regulating devices can be a resistor in series with at least one zener diode or a voltage regulator both in parallel with and providing power to the LEDs. The LEDs can also be anti-parallel diode pairs consisting of one diode and one LED or two LEDs, or the LEDs can be anti-parallel diode string pairs consisting of diodes and LEDs or all LEDs. The LED driver circuits will be incorporated into LED replacement lamps, and in particular to LED lamps to replace fluorescent lamps for use with existing ballasts and other power sources where the ballast may be removed or bypassed.
Owner:DENOVO LIGHTING
Multiphase voltage regulator having coupled inductors with reduced winding resistance
InactiveUS7649434B2Transformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsDc-dc conversionBuck converterCoupling
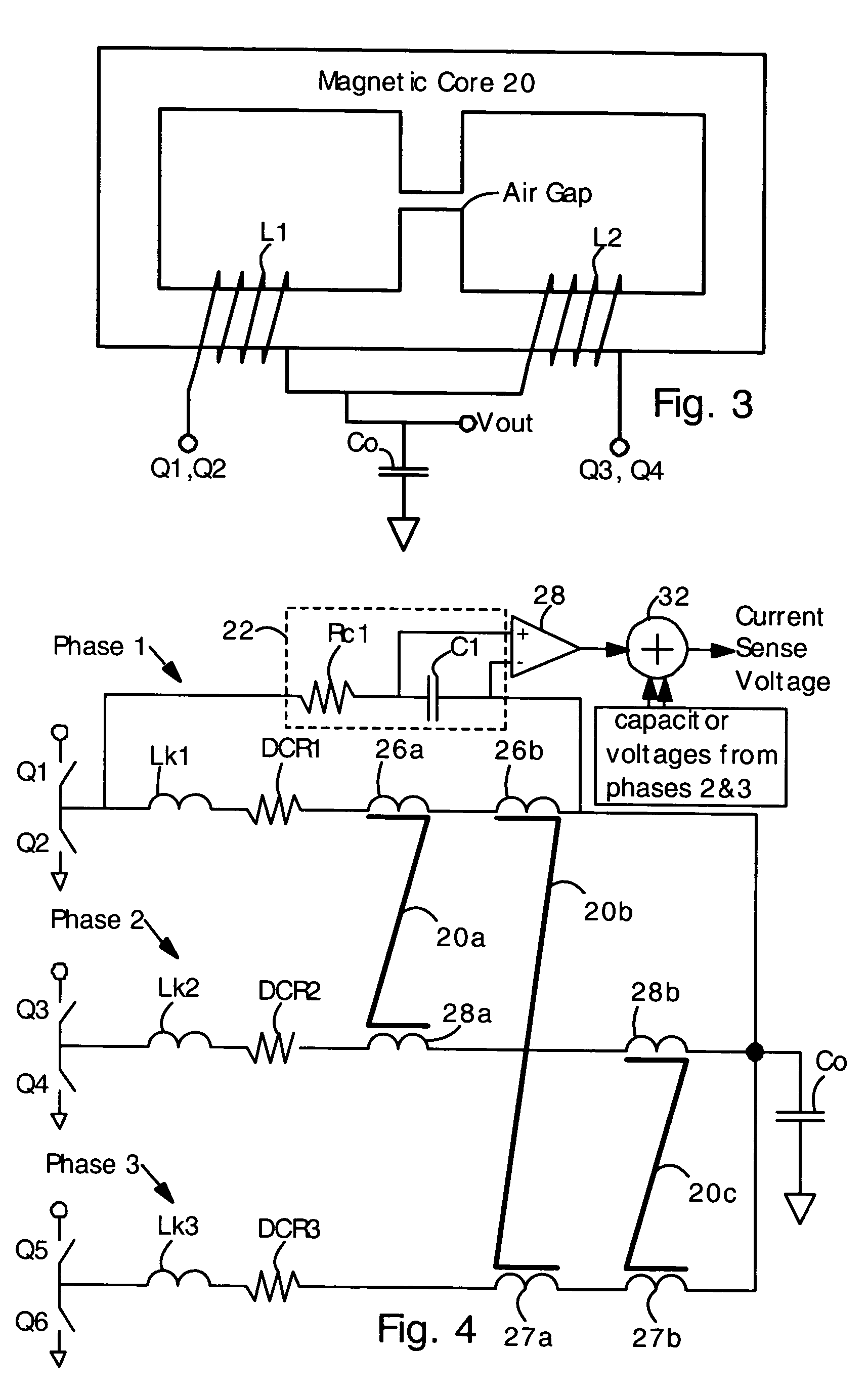
A multiple phase buck converter or boost converter, or buck-boost converter has an inductor in each phase. The inductors are inversely coupled. In a first embodiment, the converter includes a toroidal magnetic core with inductors extending under and over opposite sides of the toroidal magnetic core. The coupled inductors are thereby inversely coupled and have a relatively low ohmic resistance. In a second embodiment, the converter comprises a ladder-shaped magnetic core (i.e. having parallel sides, and connecting rungs). In this case, the inductors extend under the sides, and over the rungs. Each inductor is disposed over a separate rung. The ladder-shaped magnetic core is preferably disposed flat on a circuit board. Inverse coupling and low ohmic resistance are also provided in the second embodiment having the ladder structure.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Current sensing in multiple coupled inductors by time constant matching to leakage inductance
InactiveUS7233132B1Small and negligible leakage inductanceImprove accuracyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationRC time constantEngineering
Voltage regulators often have coupled output inductors because coupled output inductors provide improvements in cost and efficiency. Coupled inductors are often used in multi-phase voltage regulators. Feedback control of voltage regulators often requires accurate and responsive sensing of output current. Provided is a technique for accurately sensing the magnitude of output current in coupled inductors. An RC circuit (comprising a resistor and capacitor in series) is connected in parallel with the coupled inductor. The inductor has a leakage inductance Lk and a DC (ohmic) resistance of DCR. The resistor and capacitor are selected such that an RC time constant is equal to an L / R time constant of Lk / DCR. With the matching time constants, a sum of voltages on the capacitors is accurately proportional to a sum of currents flowing in the output inductors. Also provided is a technique for sensing current when an uncoupled center tap inductor is present.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP PROPERTIES
Interface bus for utility-grade network communication devices
In one embodiment, a network device having a plurality of hardware interfaces is disclosed. The network device includes a central processing unit and a main circuit board. The main circuit board has expansion slots that receivably connect corresponding secondary circuit boards to the main circuit board. The main circuit board also has sensors for detecting predetermined parameters. A voltage regulator is operative to regulate one or more particular expansion slots, in response to detection of a predetermined parameter associated with respective slots.
Owner:ITRON
Radio Frequency Generator and Method for a Cordless Medical Cauterization and Cutting Device
ActiveUS20140188101A1Precise positioningSufficient forceSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsMOSFETRadio frequency signal
A circuit for generating a radio-frequency signal for a surgical device is disclosed. The circuit has a voltage regulator that supplies direct current (DC) voltage, a first MOSFET, a second MOSFET, and a MOSFET driver. The MOSFET driver receives the DC voltage supplied from the voltage regulator and has a local oscillator. The local oscillator switches the first MOSFET and the second MOSFET on and off at a frequency generated by the local oscillator. The circuit further includes a transformer connected to the first and second MOSFETs, having a center tap and a main voltage applied at the center tap, and providing an alternating current (AC) output.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
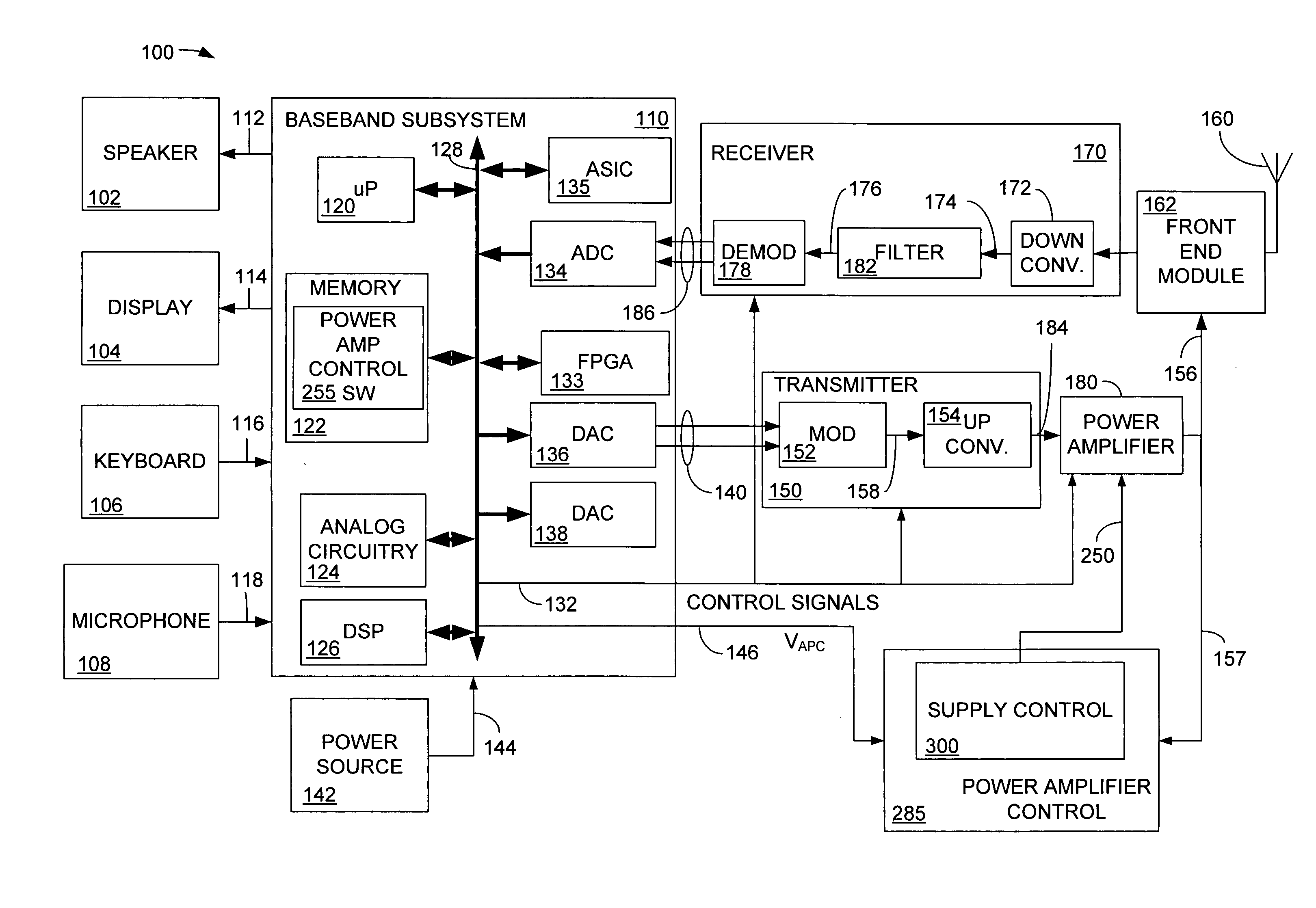
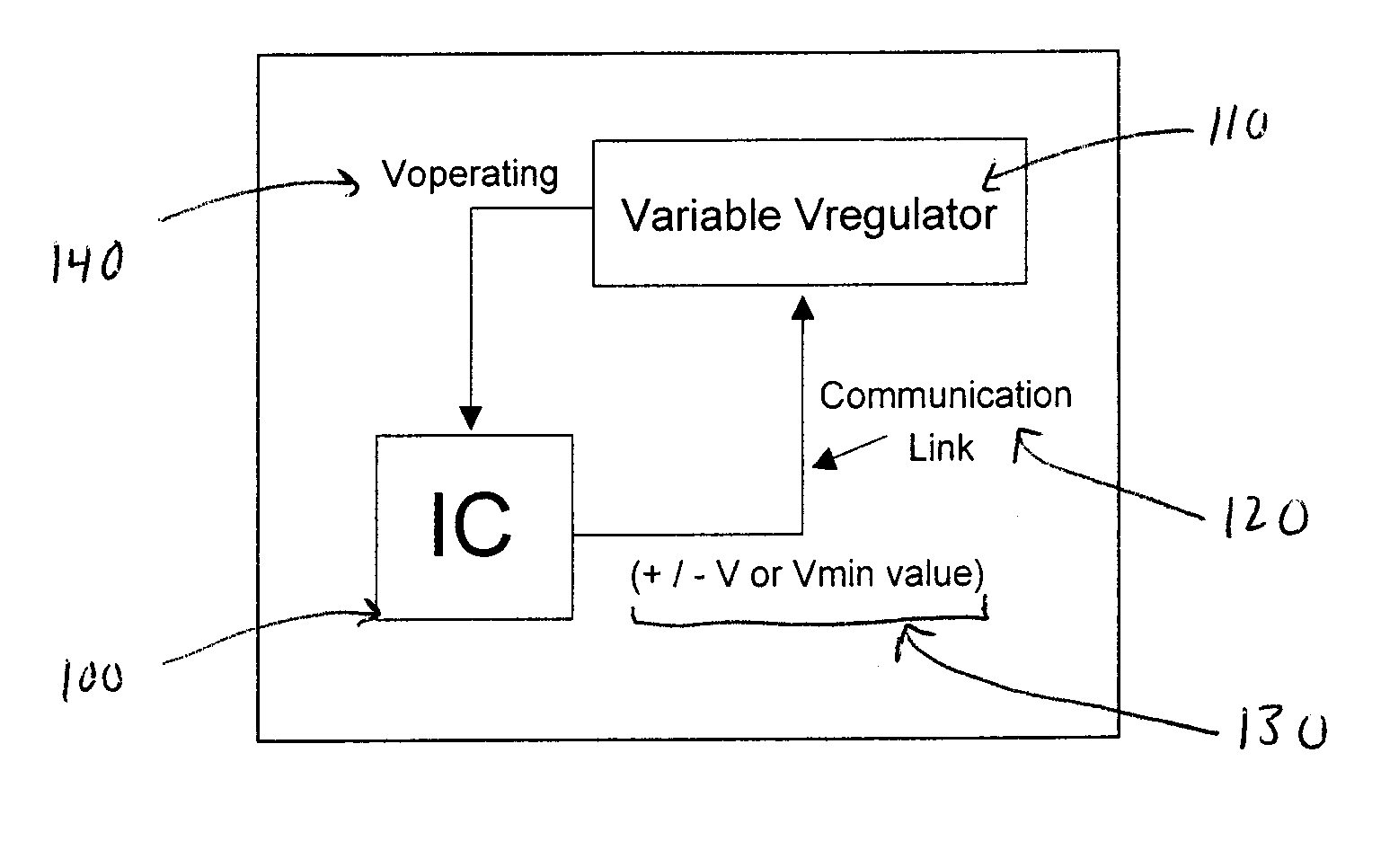
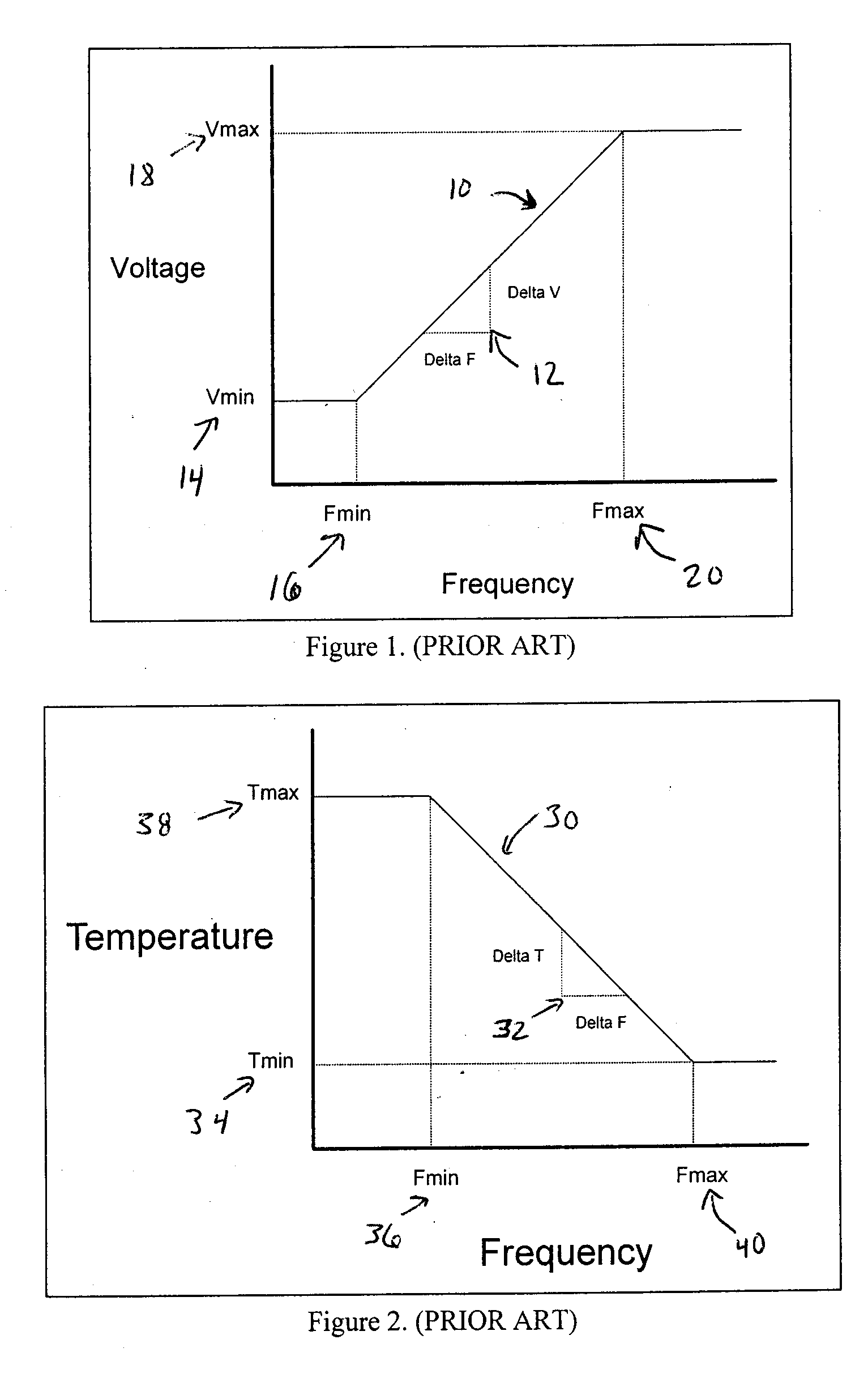
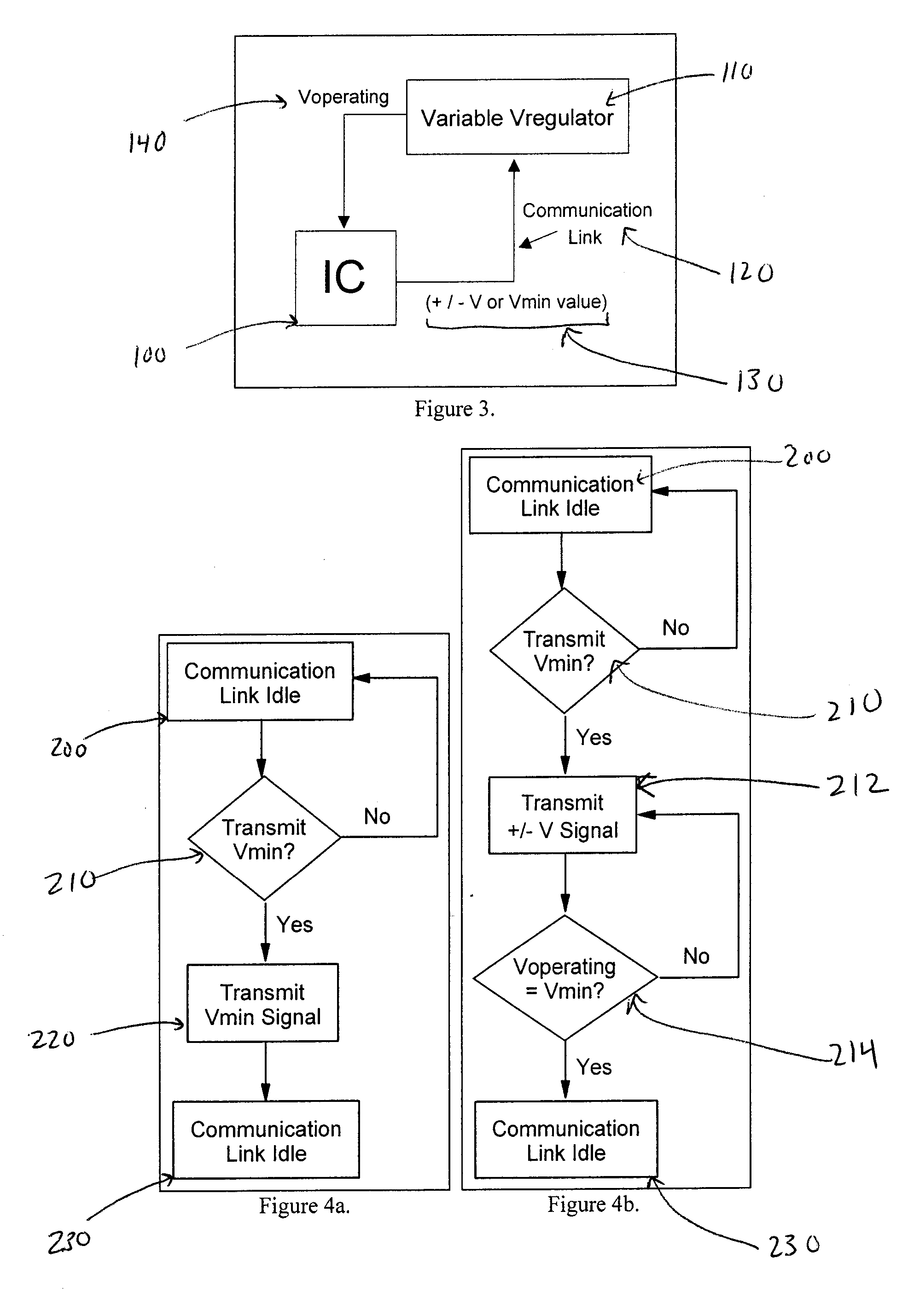
System and method of controlling power consumption in an electronic system
ActiveUS20050188230A1Readily apparentEnergy efficient ICTElectric devicesSystems designElectronic systems
A method and apparatus for adaptively adjusting the operating voltage of an integrated circuit in response to tester-to-system variations, worst-case testing techniques, process variations, temperature variations, or reliability wearout mechanisms. The minimum operating voltage of an integrated circuit is determined either during external testing of the integrated circuit or during built-in-self-testing. The minimum operating voltage is transmitted to a variable voltage regulator where it is used to set the output of the regulator. The output of the regulator supplies the integrated circuit with its operating voltage. This technique enables tailoring of the operating voltage of integrated circuits on a part-by-part basis which results in power consumption optimization by adapting operating voltage in response to tester-to-system variations, worst-case testing techniques, process variations, temperature variations or reliability wearout mechanisms. Alternatively, the invention enables adaptive adjustment of the operating frequency of an integrated circuit. The invention enables system designers to adaptively optimize either system performance or power consumption on a part-by-part basis in response to tester-to-system variations, worst-case testing techniques, process variations, temperature variations or reliability wearout mechanisms.
Owner:IBM CORP
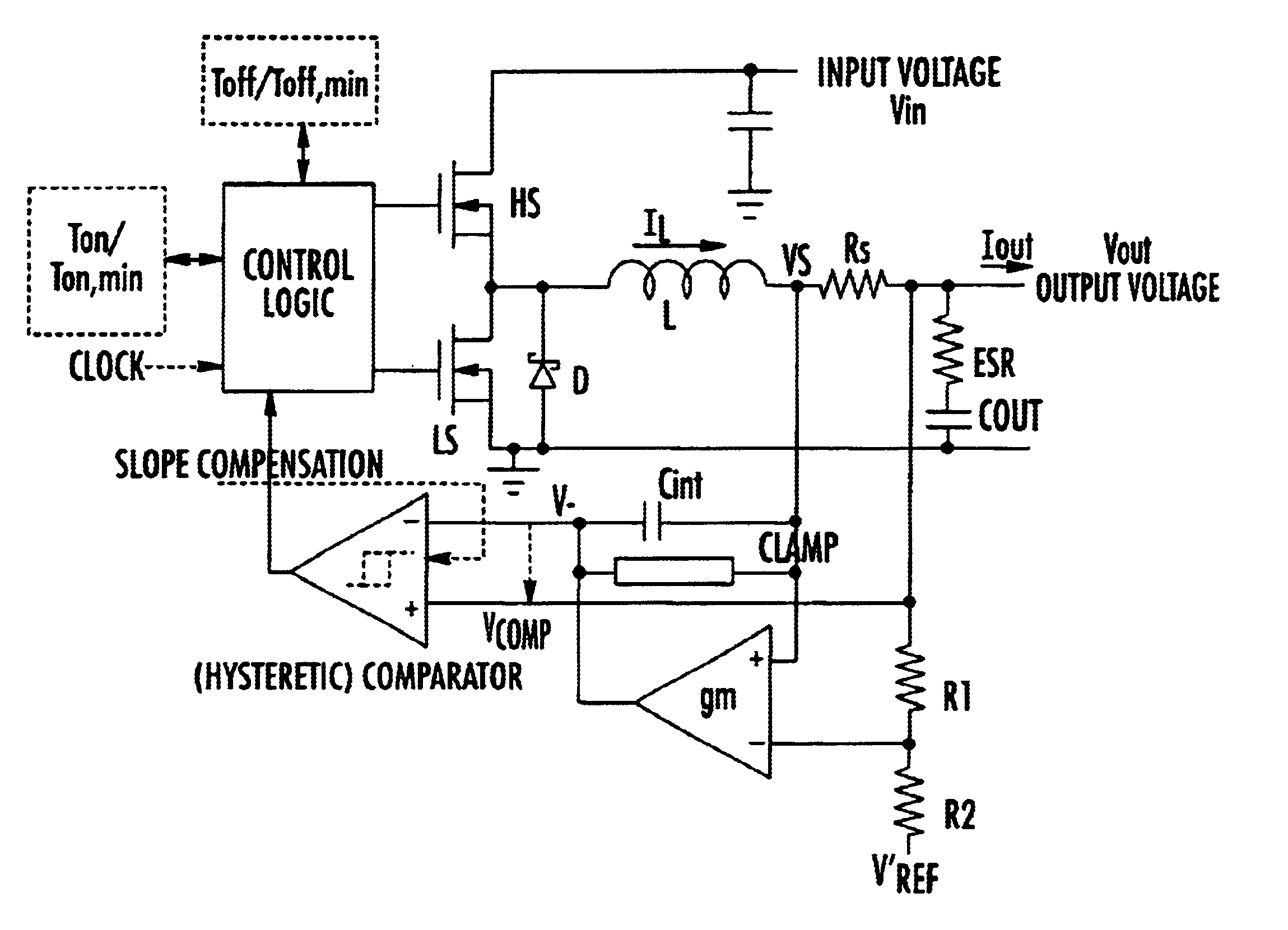
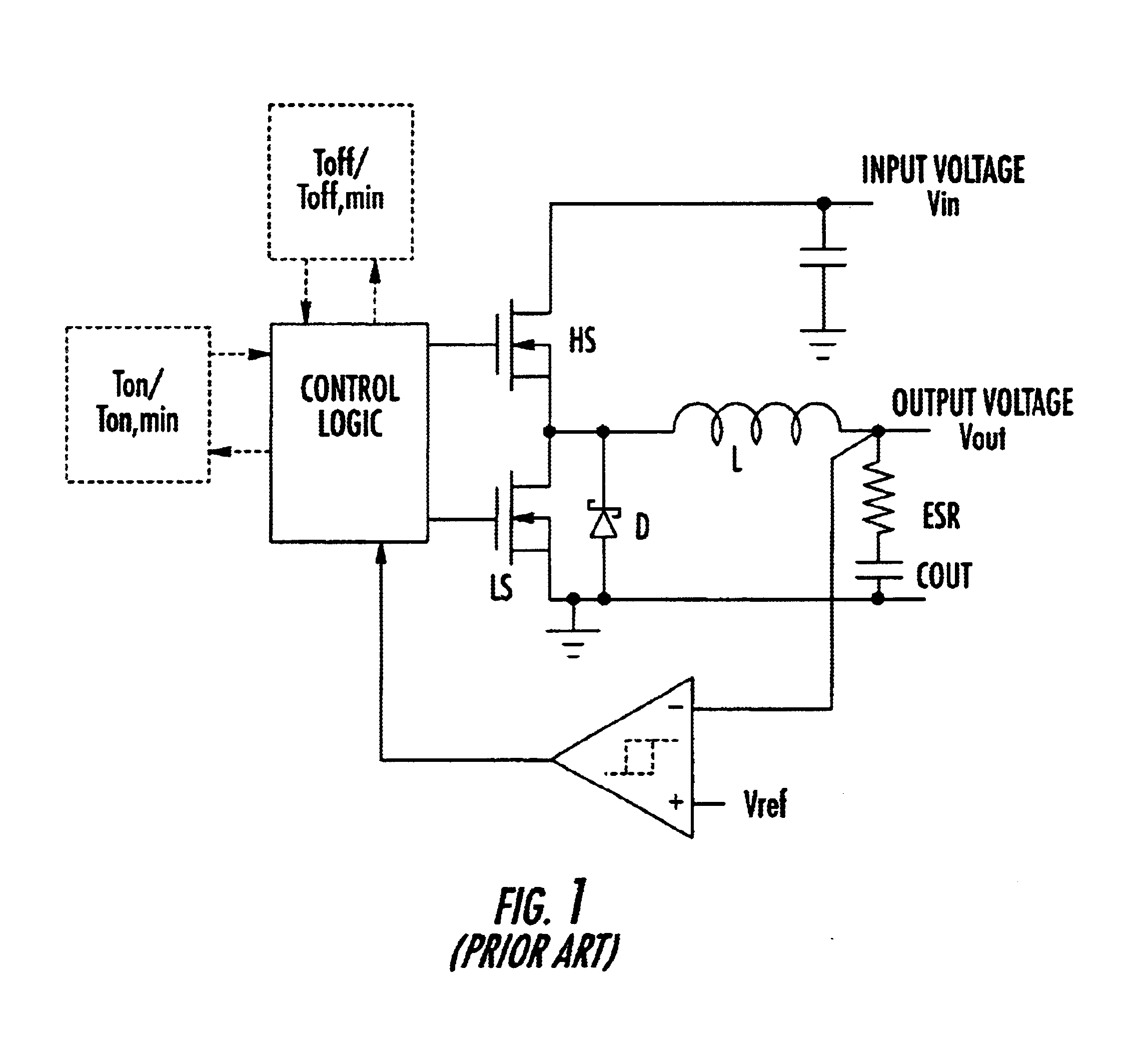
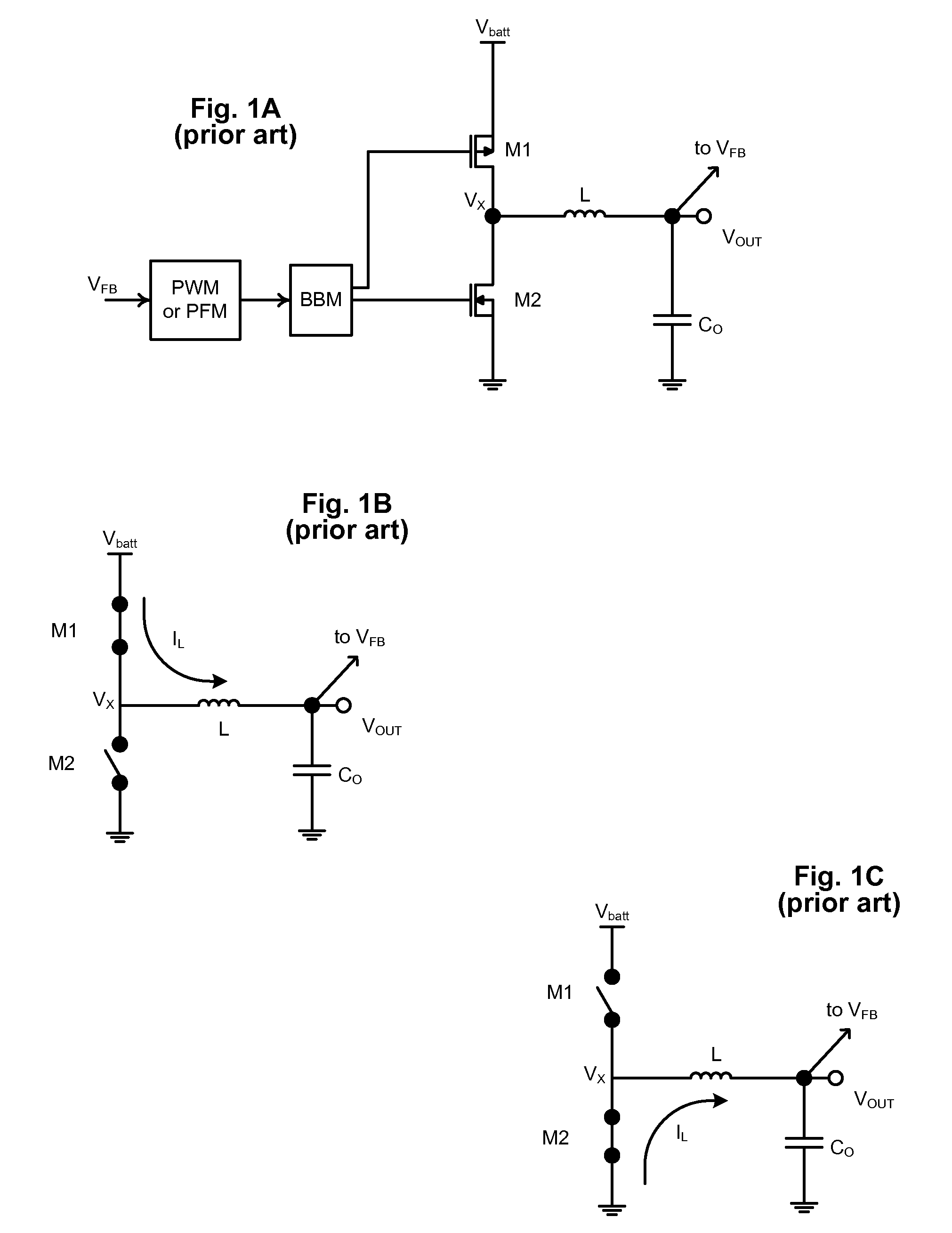
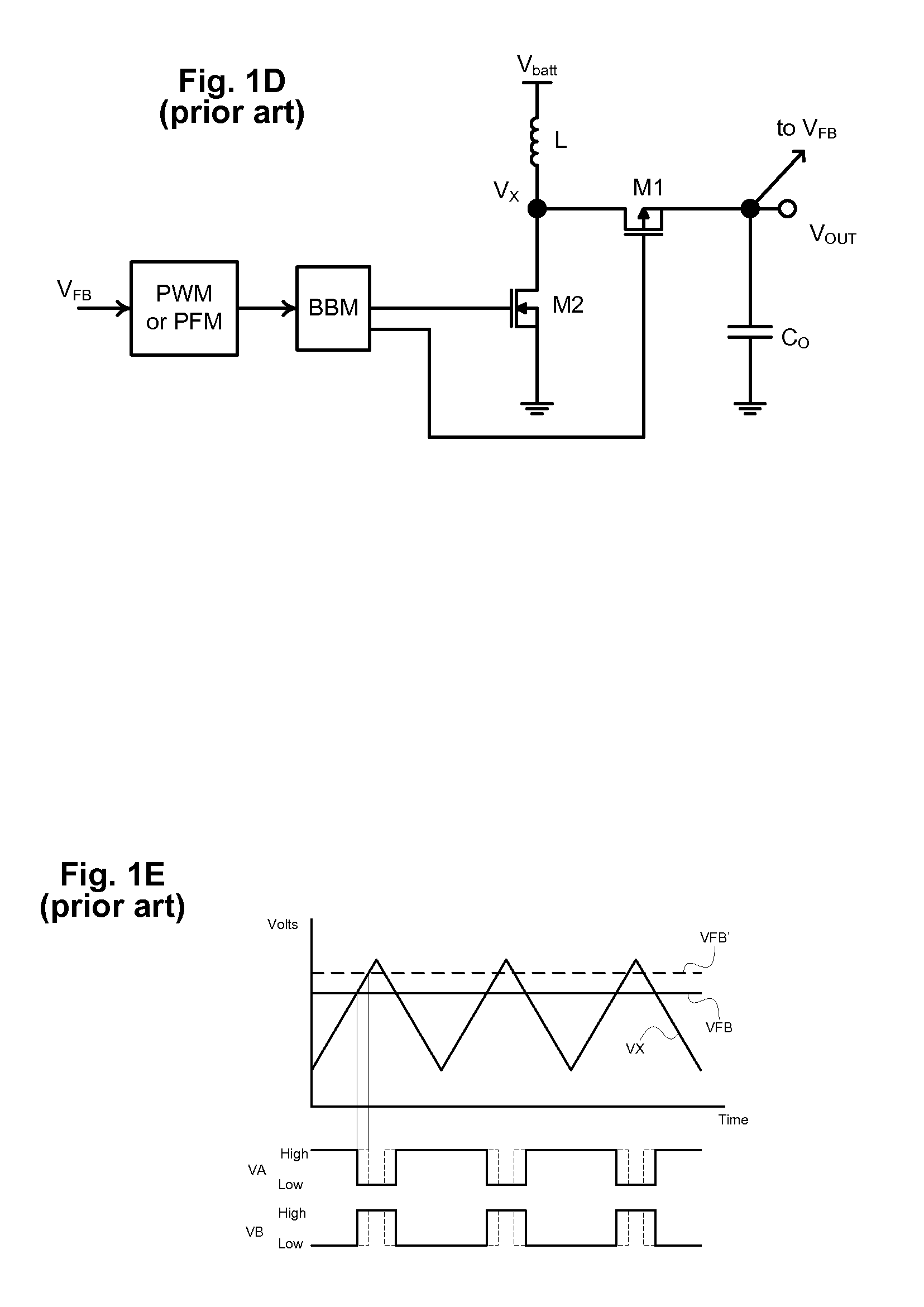
Adjusting on-time for a discontinuous switching voltage regulator
A discontinuous switching voltage regulator is disclosed including a charging element operable to generate an output voltage, switching circuitry coupled to the charging element, and switch control circuitry to configure the charging element during a cycle, including to charge the charging element for an on-time, discharge the charging element for a discharge time, and tristate the charging element for a tristate time. In operation, the on-time is initialized to a first on-time, and a first switch time is measured comprising the first on-time and a first discharge time of a first cycle. A first tristate time of the first cycle is measured, and a first ratio of the first tristate time to the first switch time is determined. The first ratio is compared to a first ratio threshold, and the on-time is adjusted to a second on-time if the first ratio exceeds the first ratio threshold.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
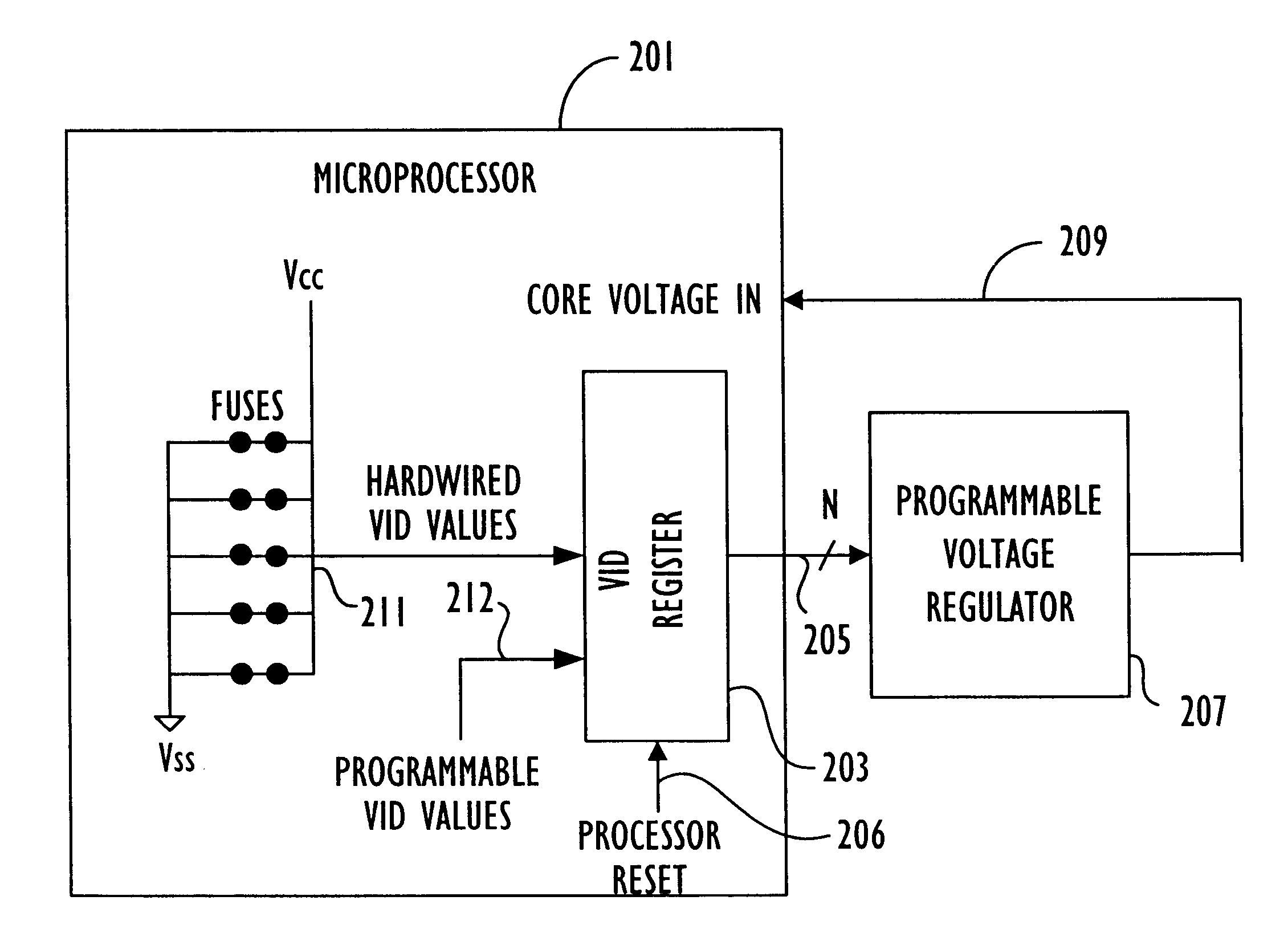
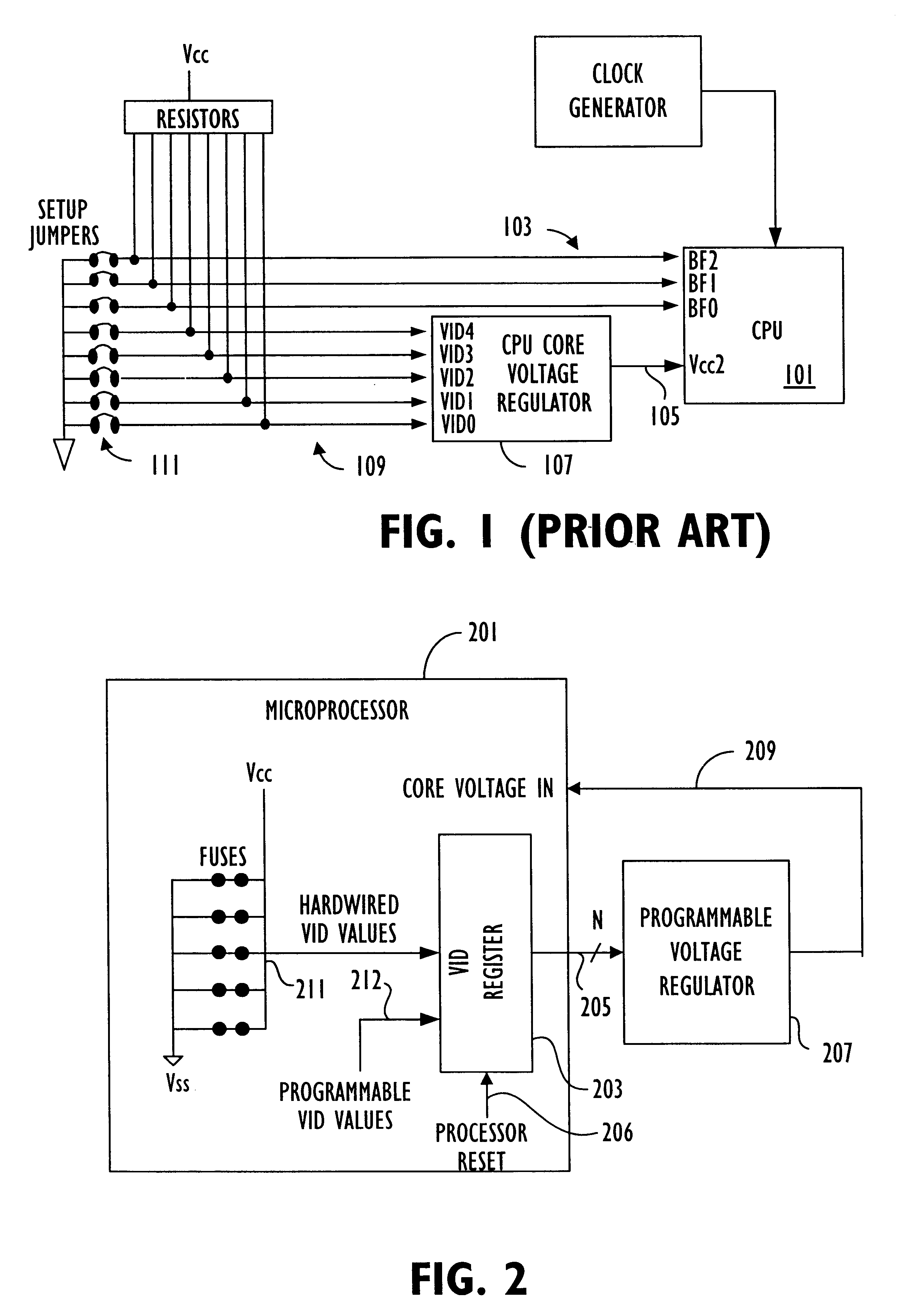
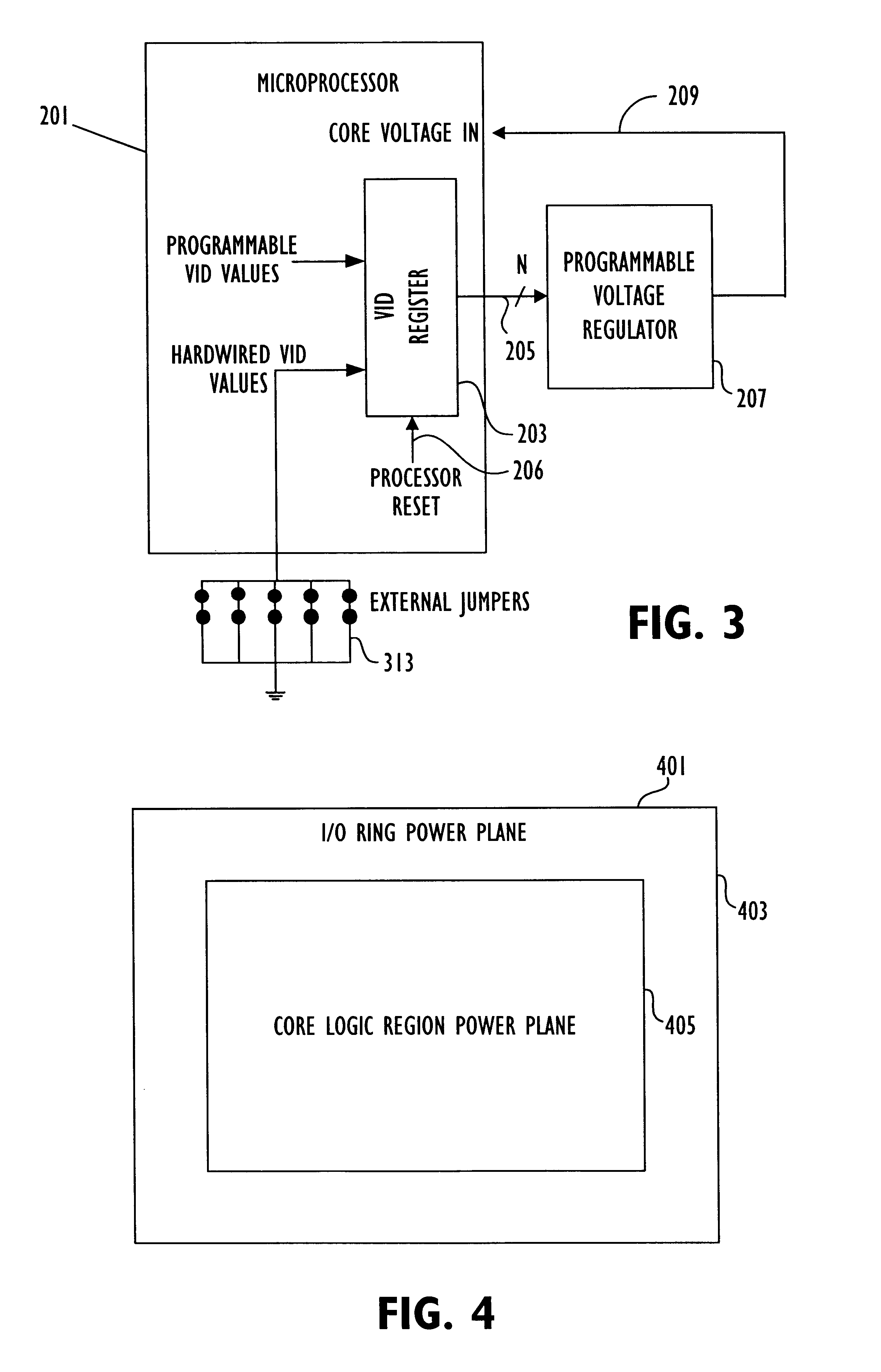
System for specifying core voltage for a microprocessor by selectively outputting one of a first, fixed and a second, variable voltage control settings from the microprocessor
InactiveUS6772356B1Energy efficient ICTSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsVoltage regulationVoltage control
A core voltage for a core logic region of an integrated circuit is specified by a programmable register on the integrated circuit. Output terminals on the integrated circuit are coupled to the programmable storage location and supply voltage control signals for a voltage regulator to specify the core voltage according to the contents of the programmable register. The output terminals may output a programmable voltage setting or a fixed voltage setting that specifies a default core voltage value, depending on reset conditions.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON TECH +1
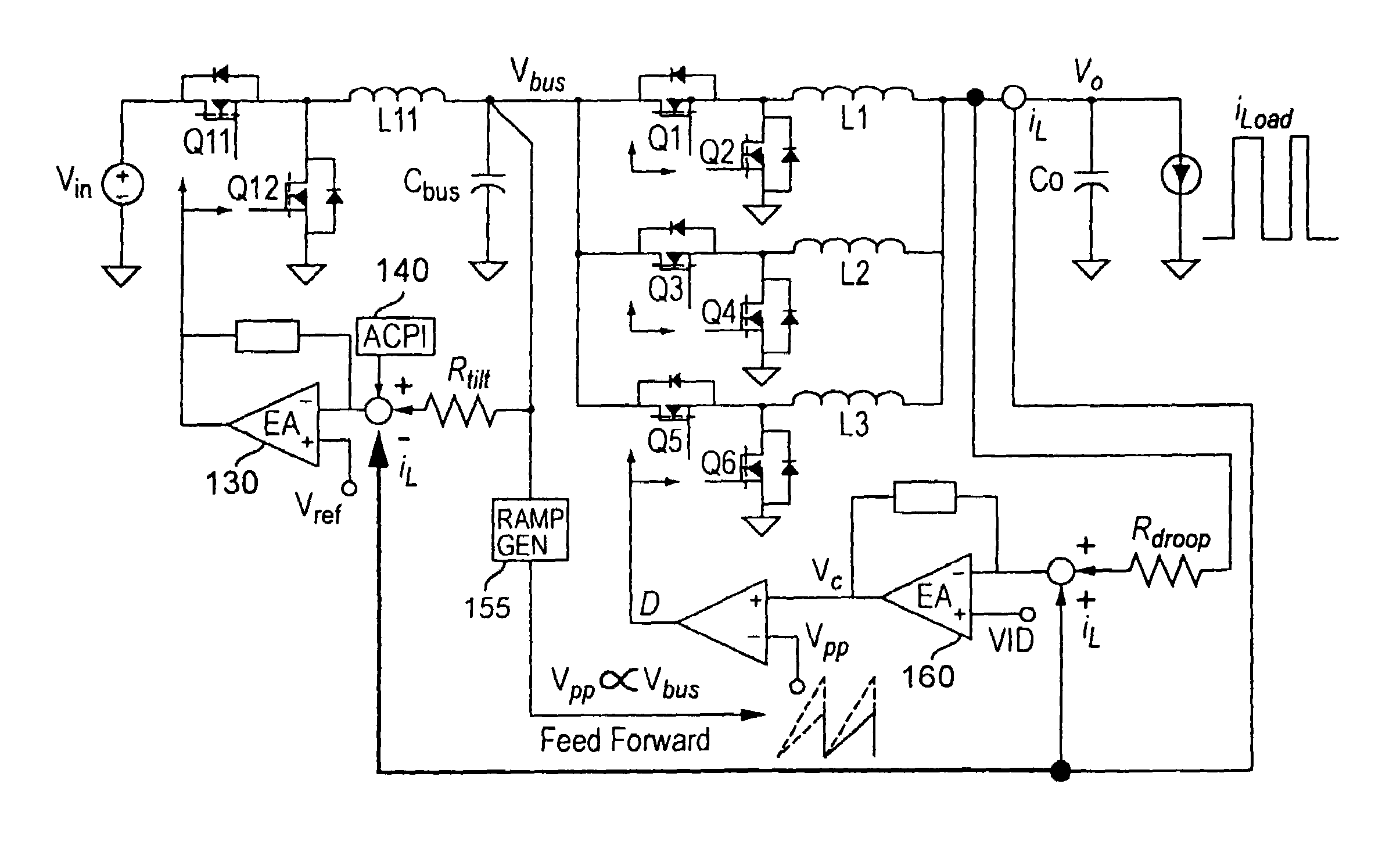
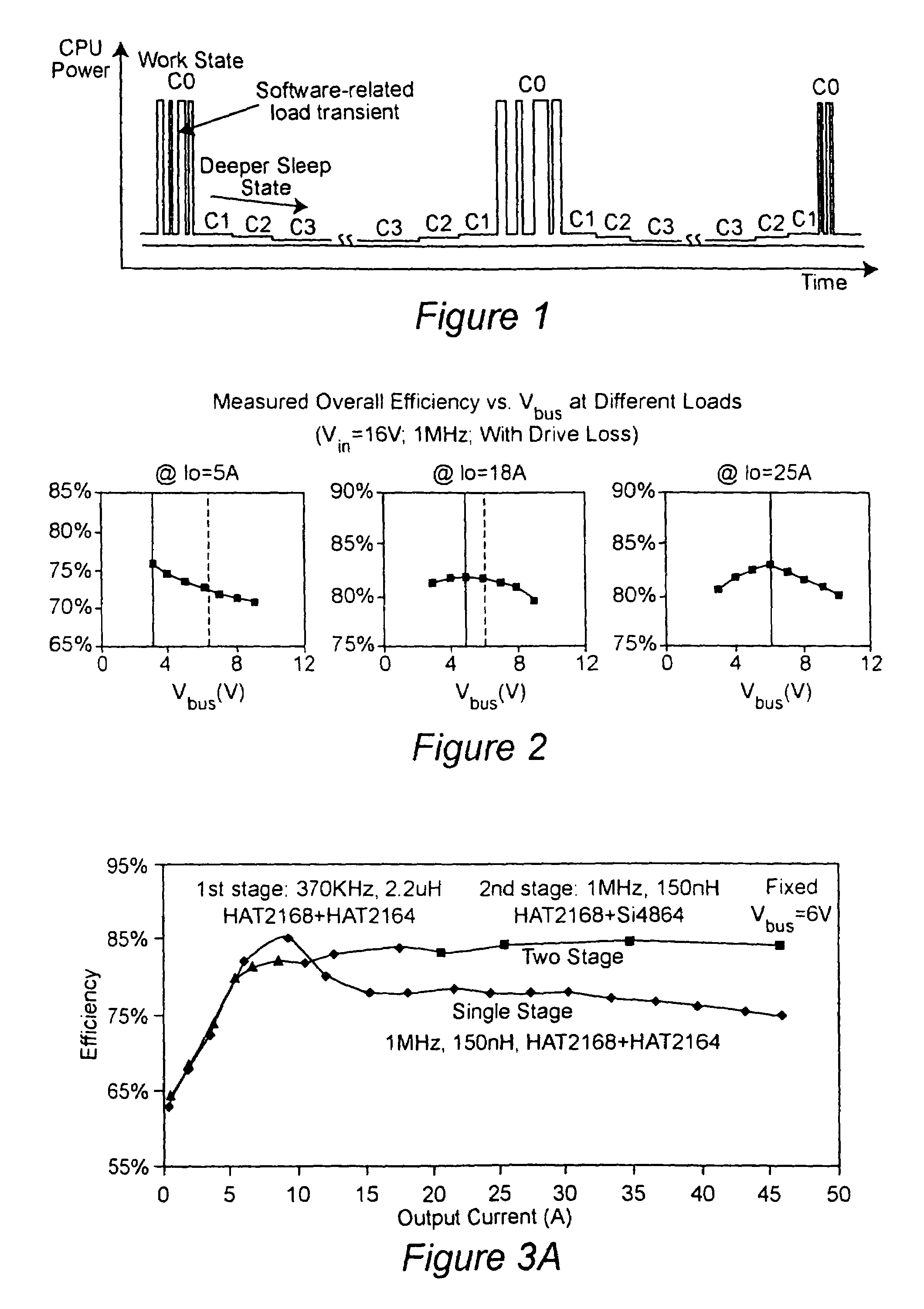
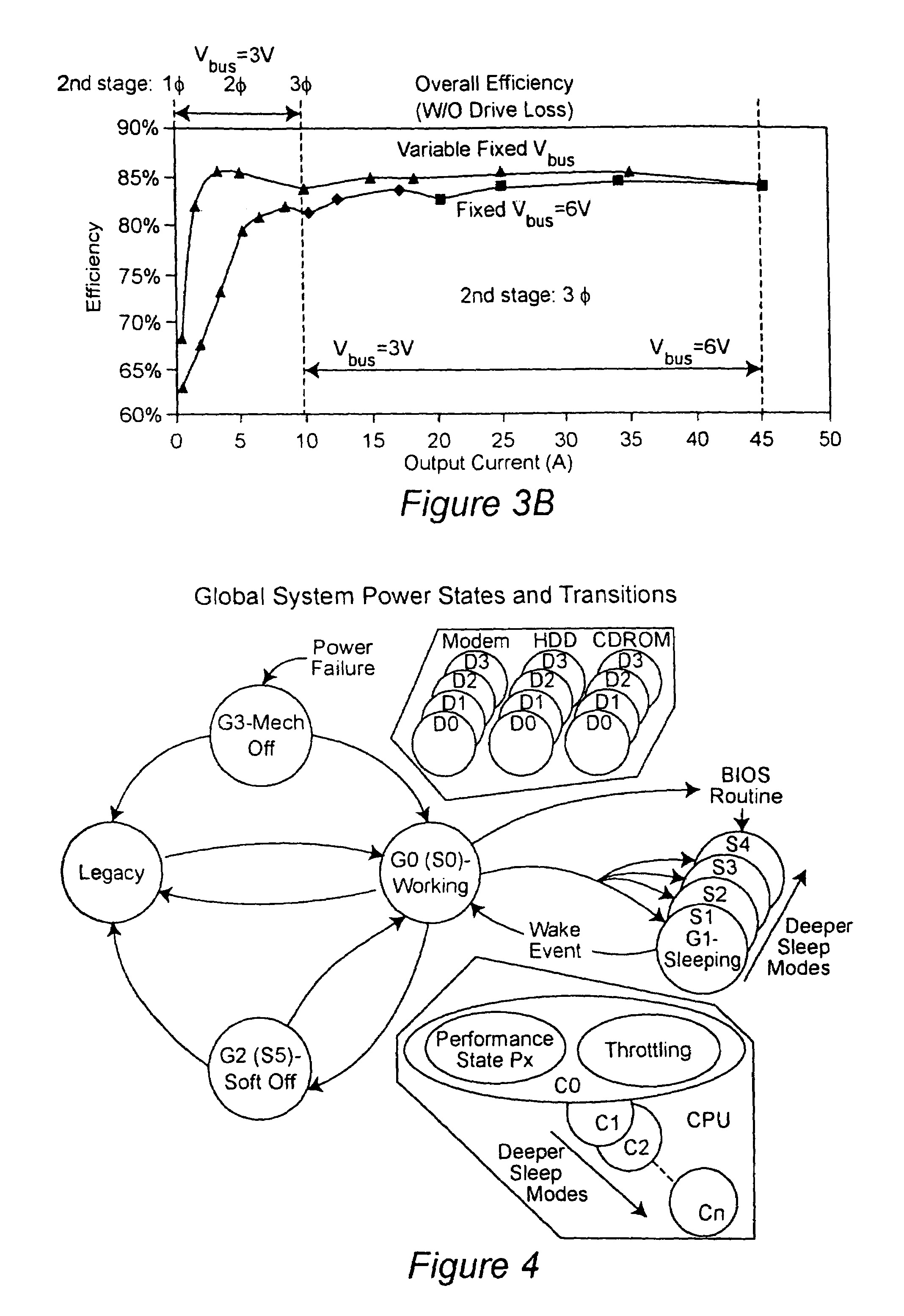
Two-stage voltage regulators with adjustable intermediate bus voltage, adjustable switching frequency, and adjustable number of active phases
InactiveUS7071660B2Improve efficiencyWide variationEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionBuck converterSwitching frequency
A two-stage power converter that dynamically adjusts to output current requirements includes a first stage regulator that provides power to a second stage regulator. The first stage can be a buck converter, and the second stage can be a multiple-phase buck converter. The output voltage of the first stage (intermediate bus voltage Vbus) is varied according to the load current to optimize conversion efficiency. To provide maximum efficiency, the Vbus voltage is increased as load current increases. The Vbus voltage provided by the first stage can be varied by duty cycle or operating frequency control. In another embodiment, the switching frequency of the second stage is varied as output current changes so that output current ripple is held constant. In an embodiment employing a multiple-phase buck converter in the second stage, the number of operating phases are varied as output current changes.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Efficiency improved voltage converter
InactiveUS20050017701A1Improve efficiencyAvoid flowElectric variable regulationVoltage converterBuck converter
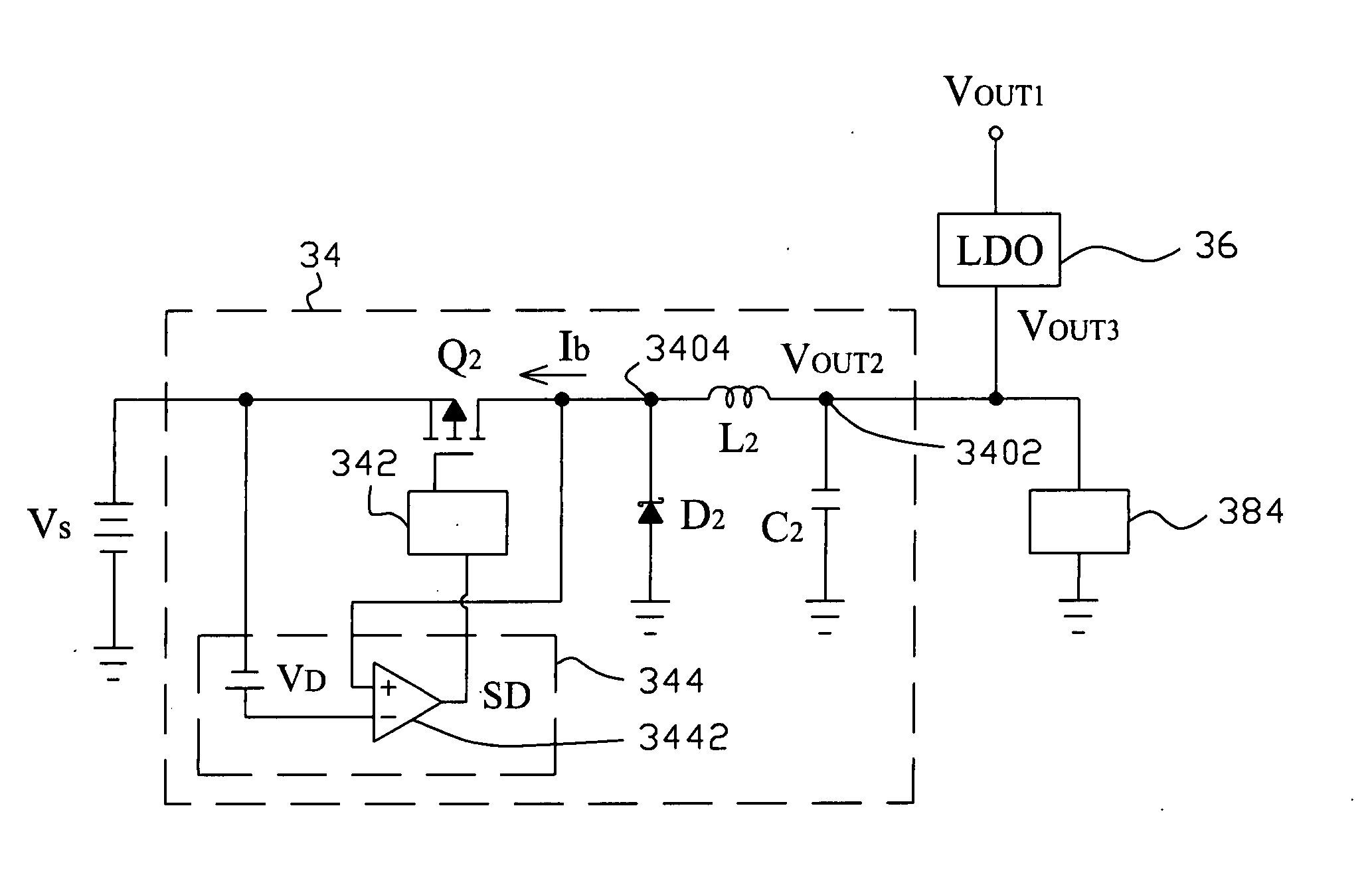
A voltage converter improves the efficiency thereof by connecting a boost converter and an LDO regulator with a buck converter in parallel. The boost converter boosts up a supply voltage to generate a first output voltage at a first output, and the buck converter bucks down the supply voltage to generate a second output voltage at a second output. When the second output voltage is lower than a threshold, the LDO regulator converts the first output voltage to a third voltage at said second output.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com