Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1539 results about "Variable-gain amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A variable-gain or voltage-controlled amplifier is an electronic amplifier that varies its gain depending on a control voltage (often abbreviated CV). VCAs have many applications, including audio level compression, synthesizers and amplitude modulation.
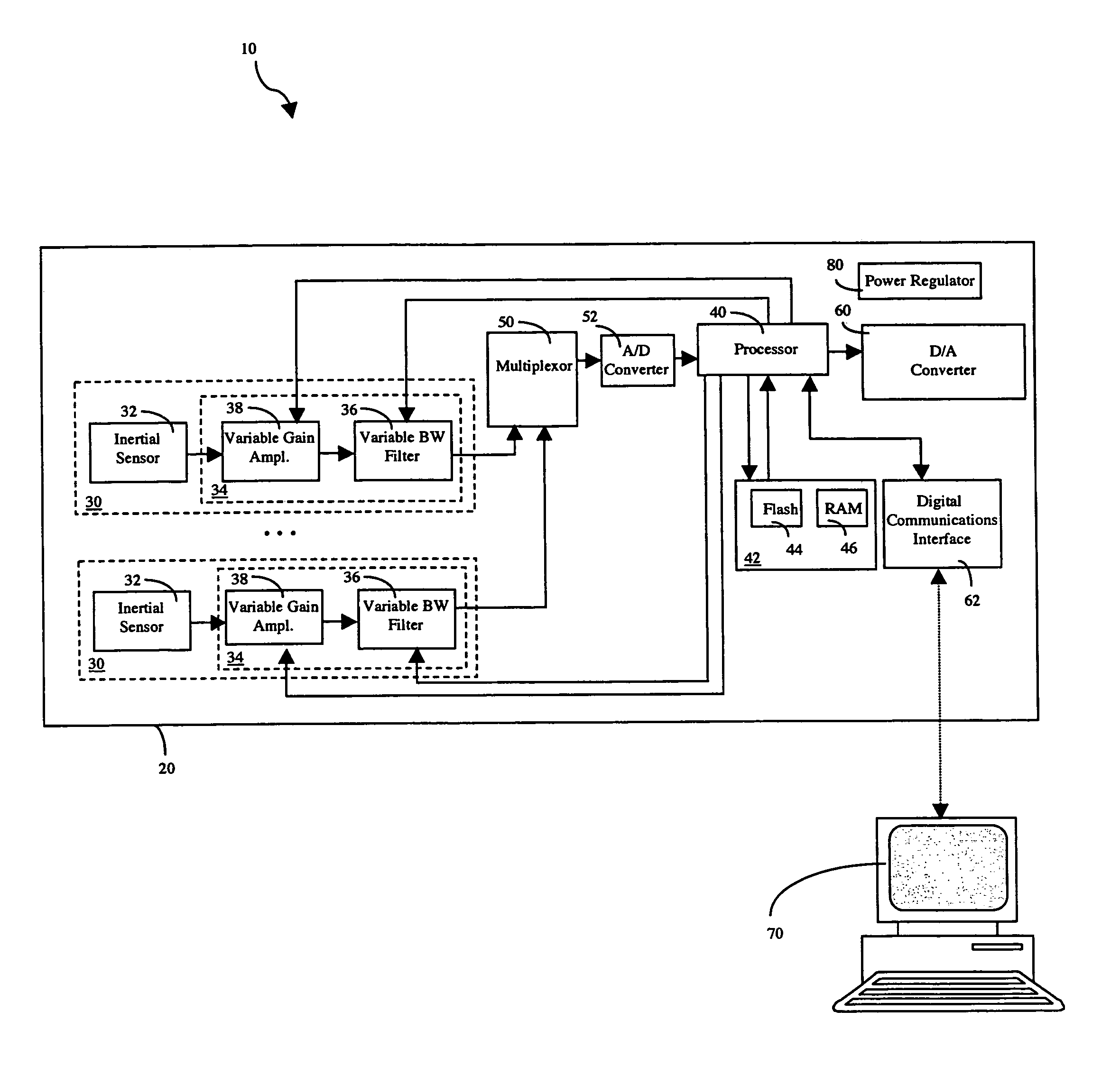
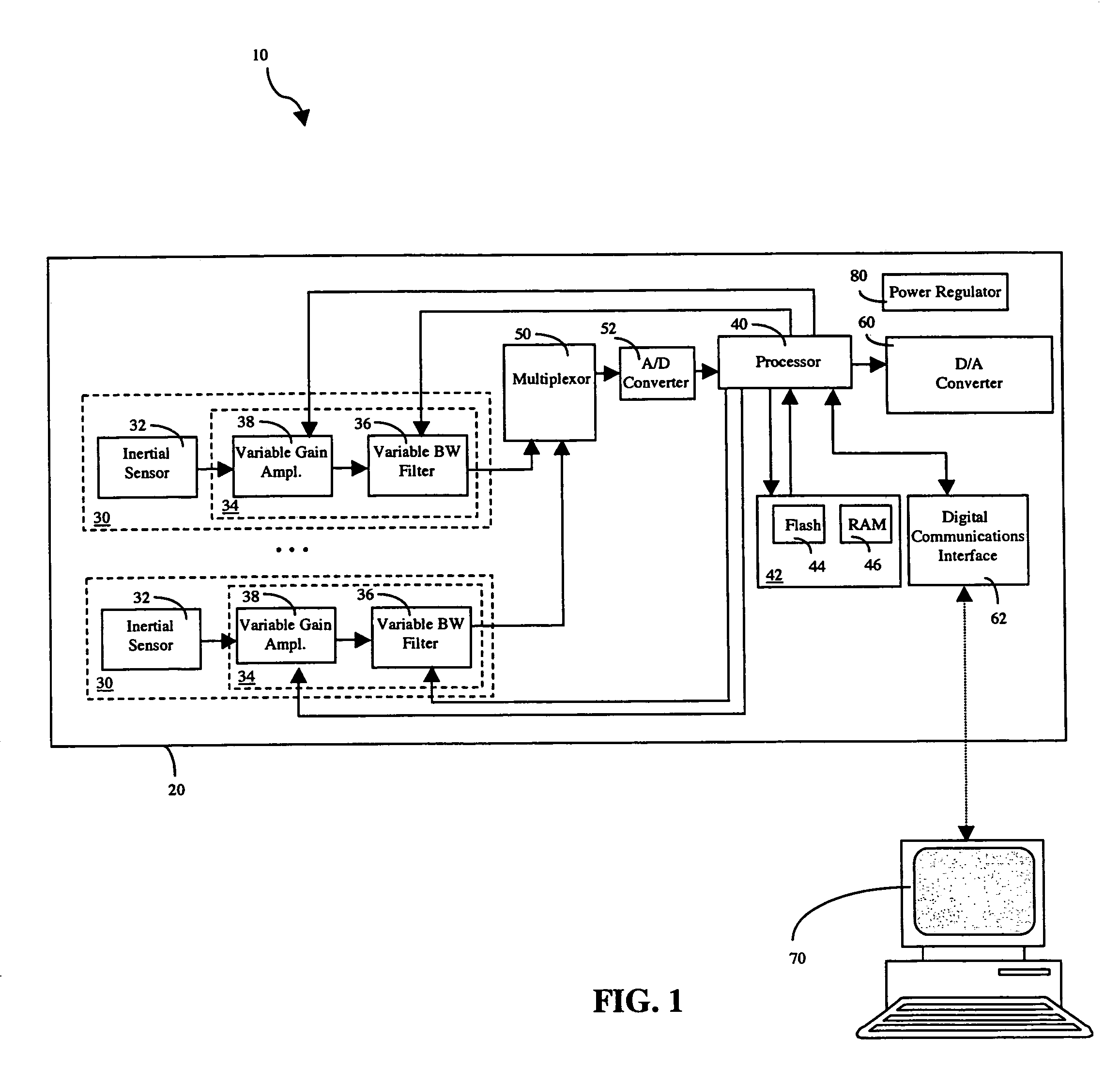
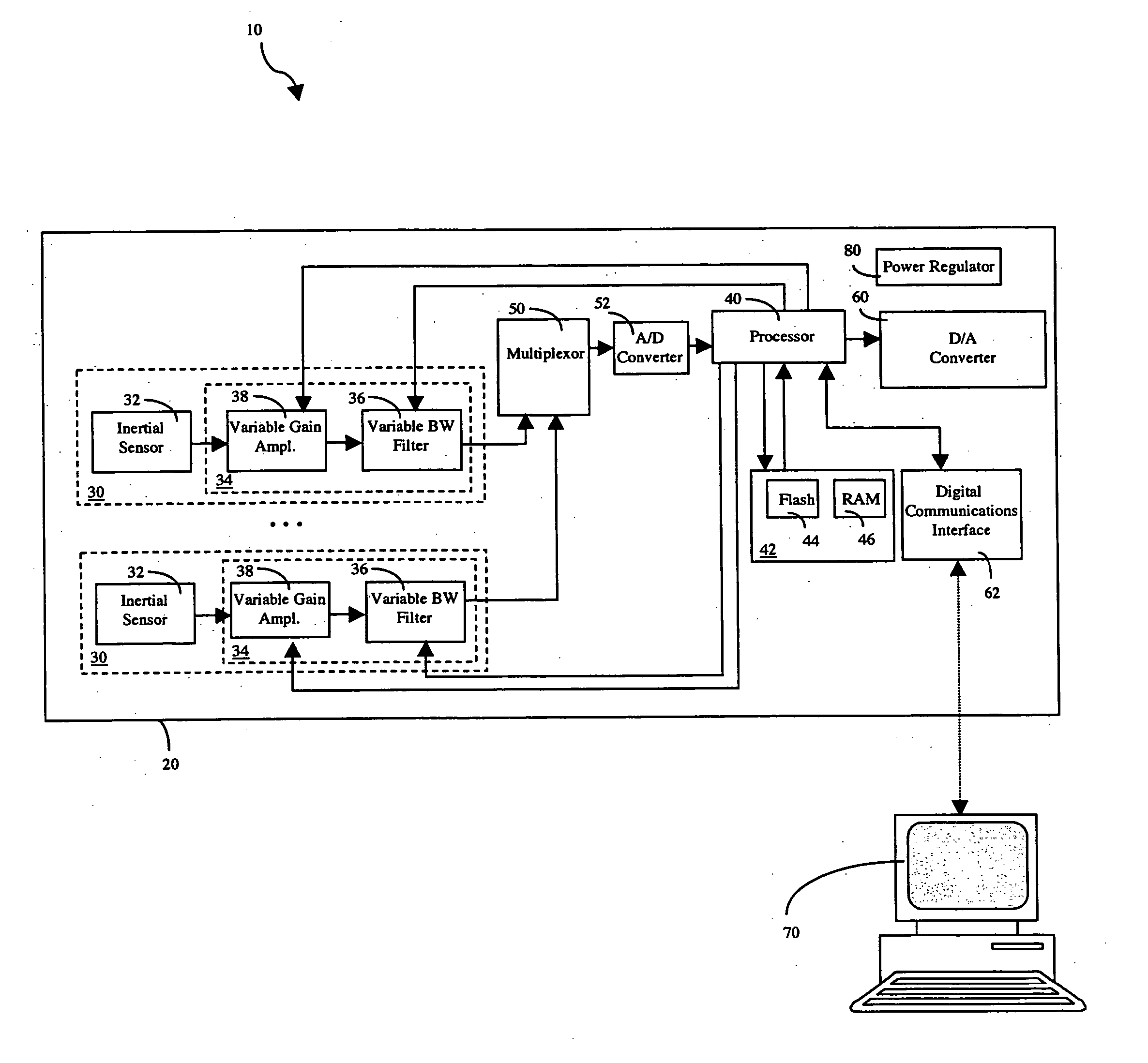
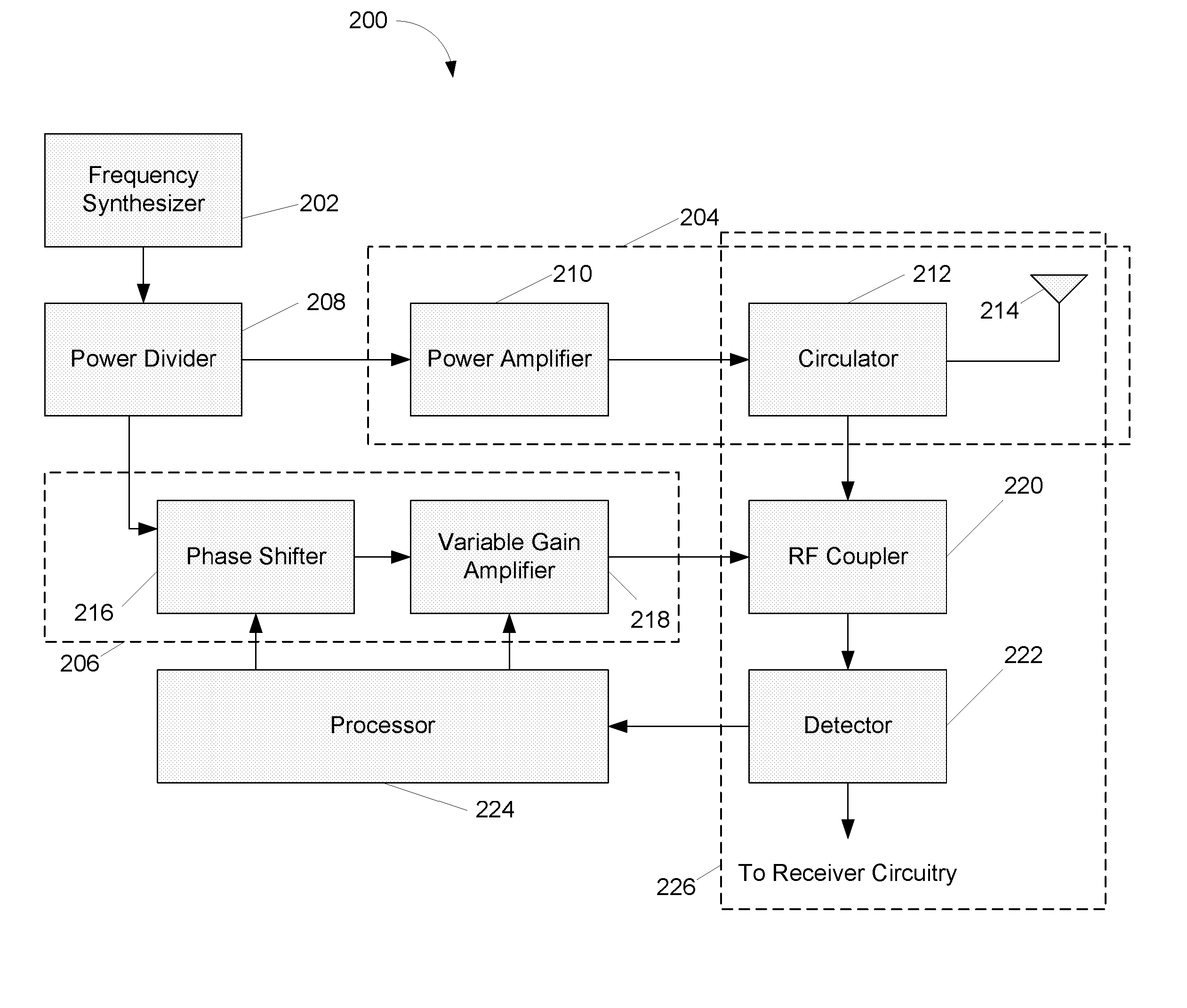
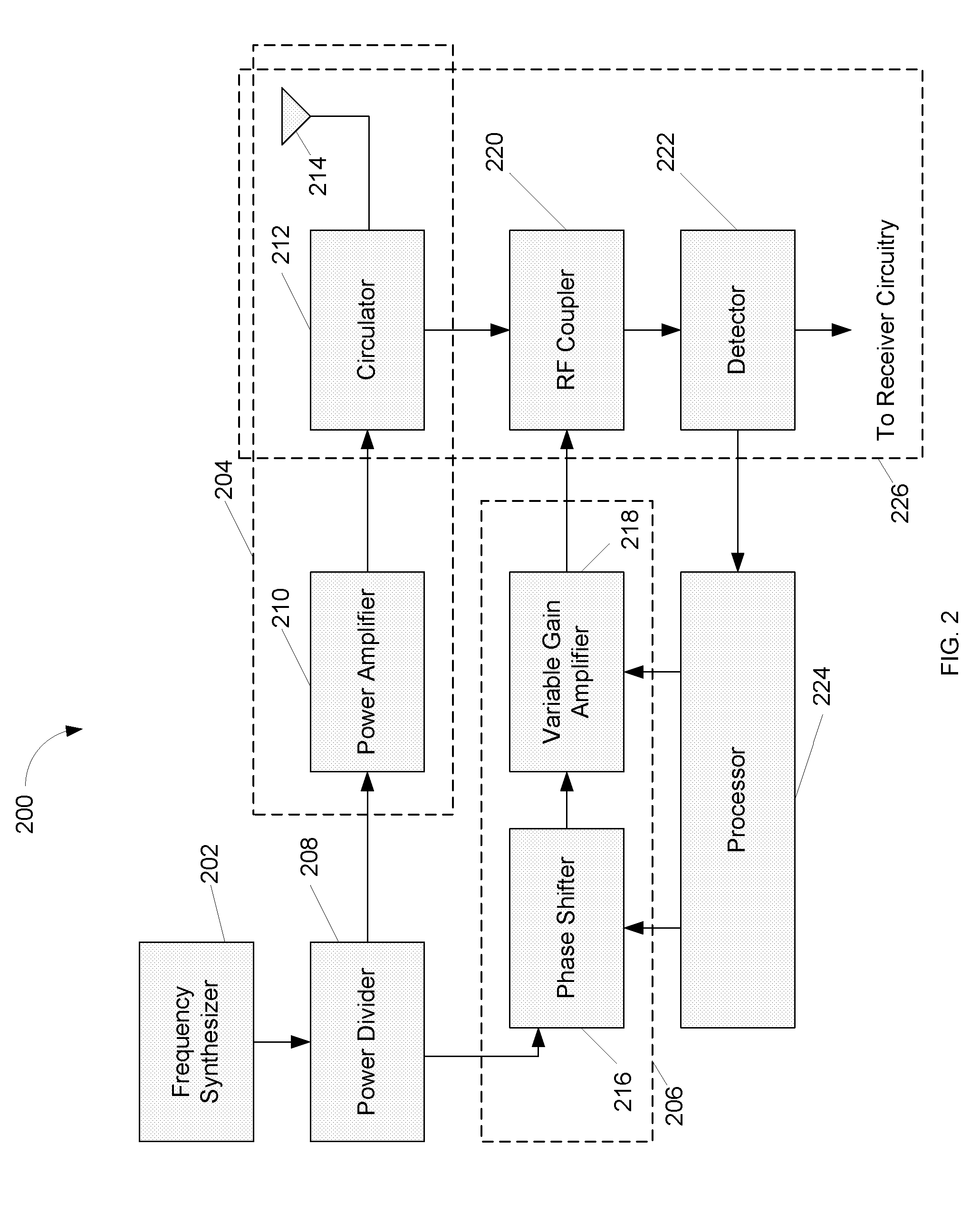
Configurable vibration sensor
InactiveUS7093492B2Vibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingVibration measurementVariable-gain amplifier
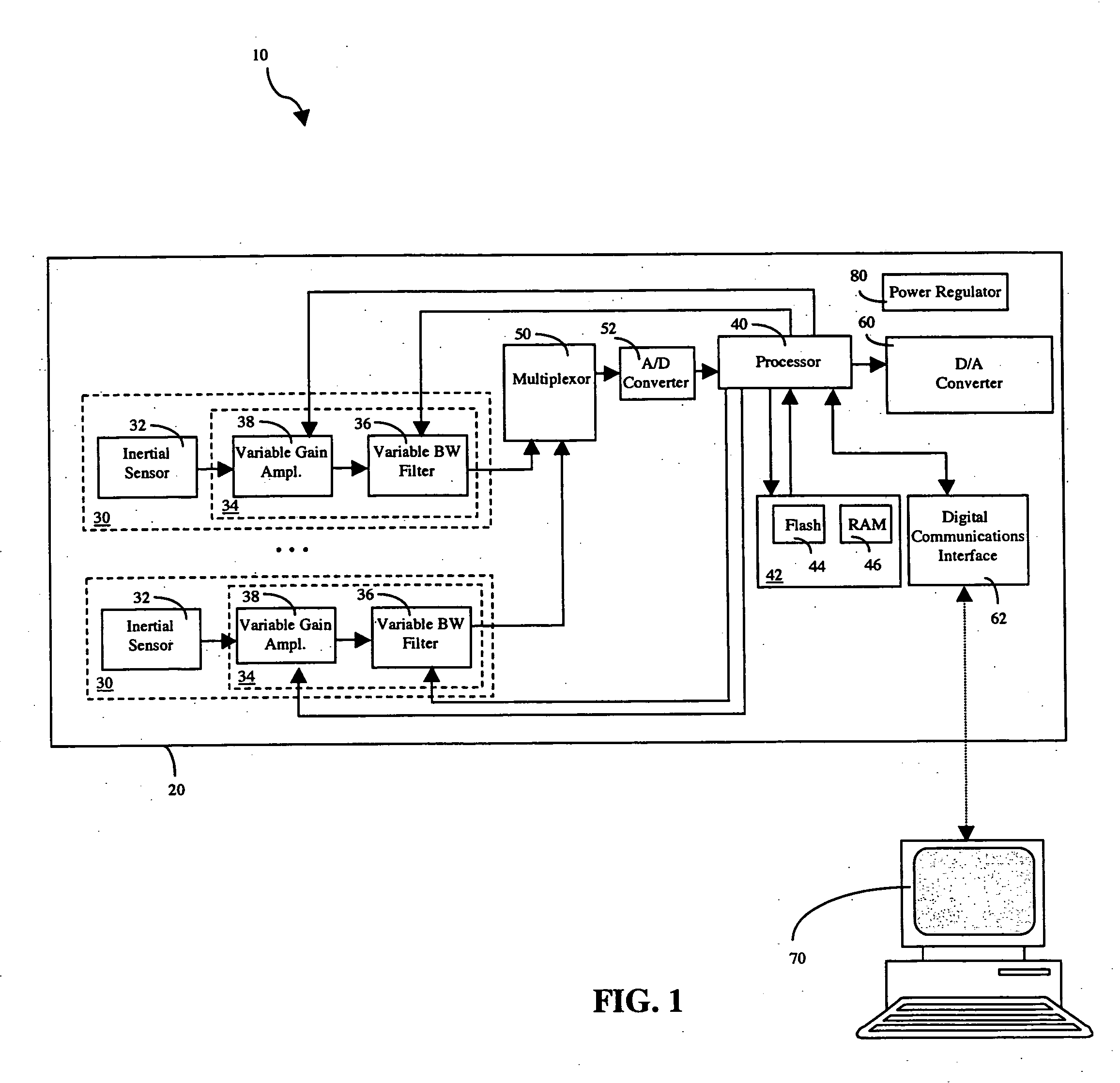
A configurable vibration sensor having a sensor circuit, an analog-to-digital converter and a processor is provided. The sensor circuit employs a vibration sensing element and a variable bandwidth filter controllable by the processor. In addition to the variable bandwidth filter, other configurable elements may also be employed in the sensor circuit, including a variable gain amplifier. These configurable elements allow the configurable vibration sensor to be configured for different vibration measurement applications when measuring vibrations from vibrating structures such as machinery and the like.
Owner:MECHWORKS SYST
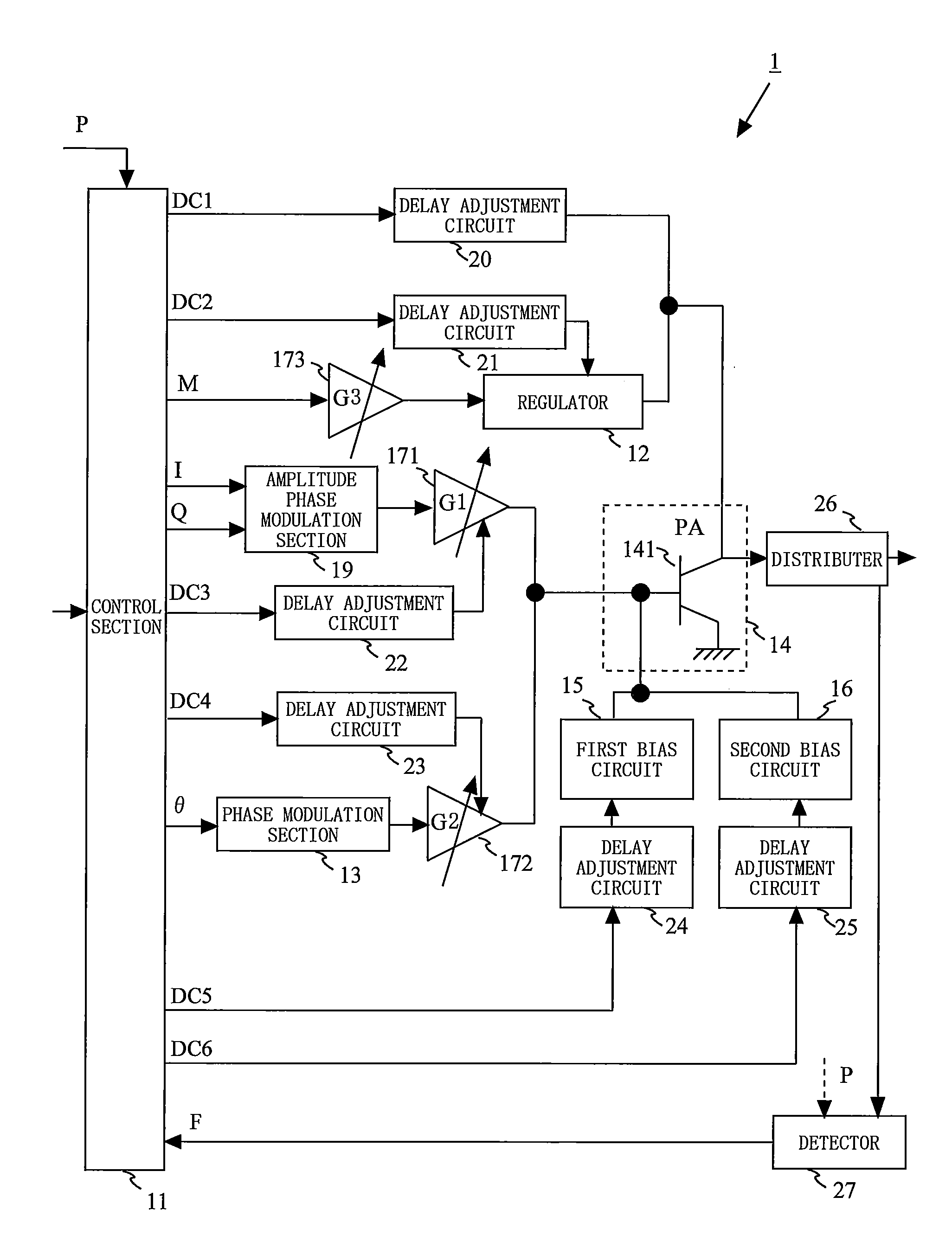
Transmission circuit and communication device
InactiveUS20120099675A1Smooth switchingPrevent stateHigh frequency amplifiersModulation with suppressed carrierAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
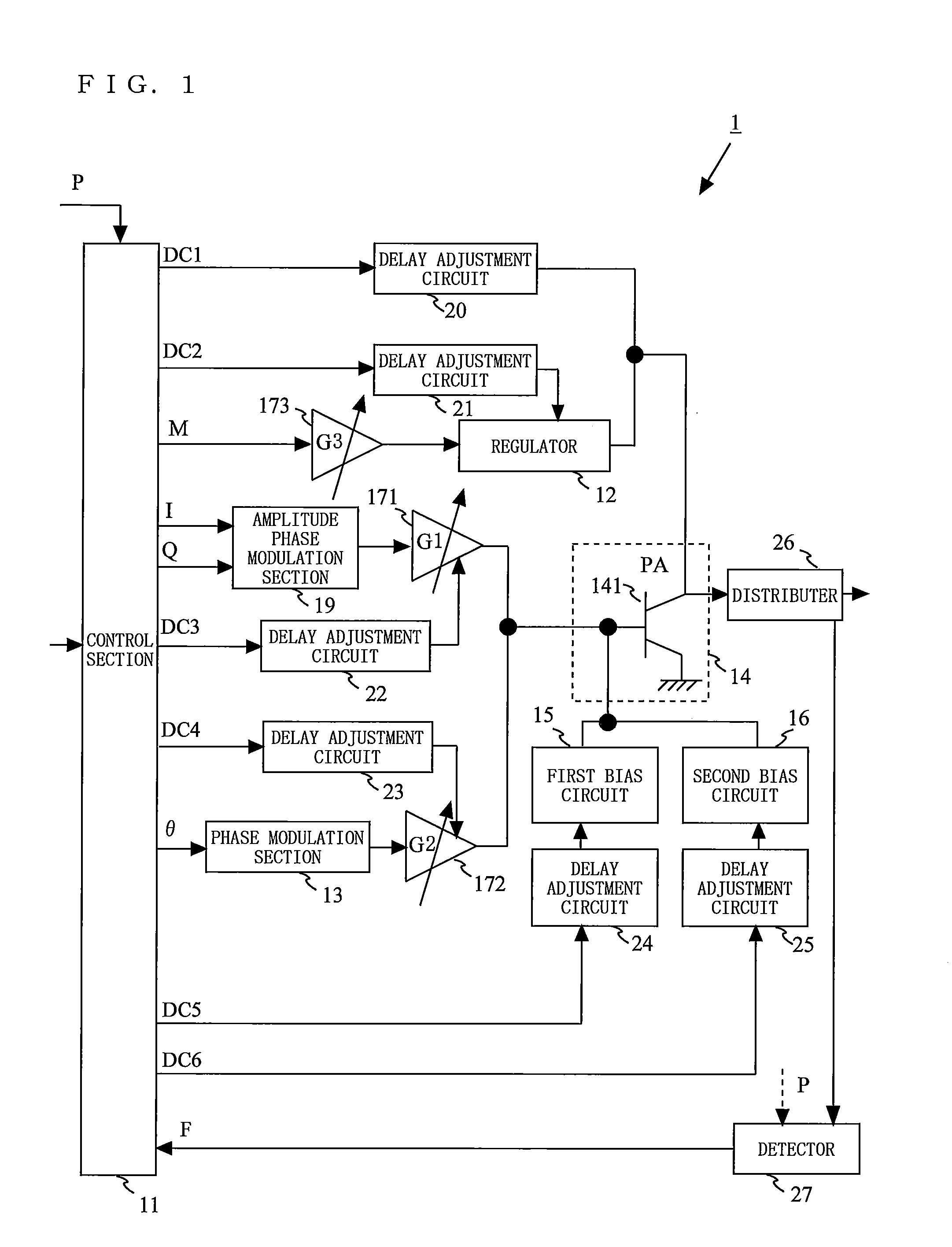
Provided is a transmission circuit which allows smooth switching of the operation mode when switching the operation mode of the transmission circuit. A power amplifier 14 includes: a first input terminal to which a direct-current voltage or a voltage in accordance with an amplitude signal M is supplied; a second input terminal to which an output signal from a first variable gain amplifier 171 or an output signal from a second variable gain amplifier 172 is inputted; and a third input terminal to which an output signal from a first bias circuit 15 or an output signal from a second bias circuit 16 is inputted. A control section 11 switches the operation mode of the transmission circuit so that at least one of the first input terminal, the second input terminal, and the third input terminal of the power amplifier is prevented from being in a no input state.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
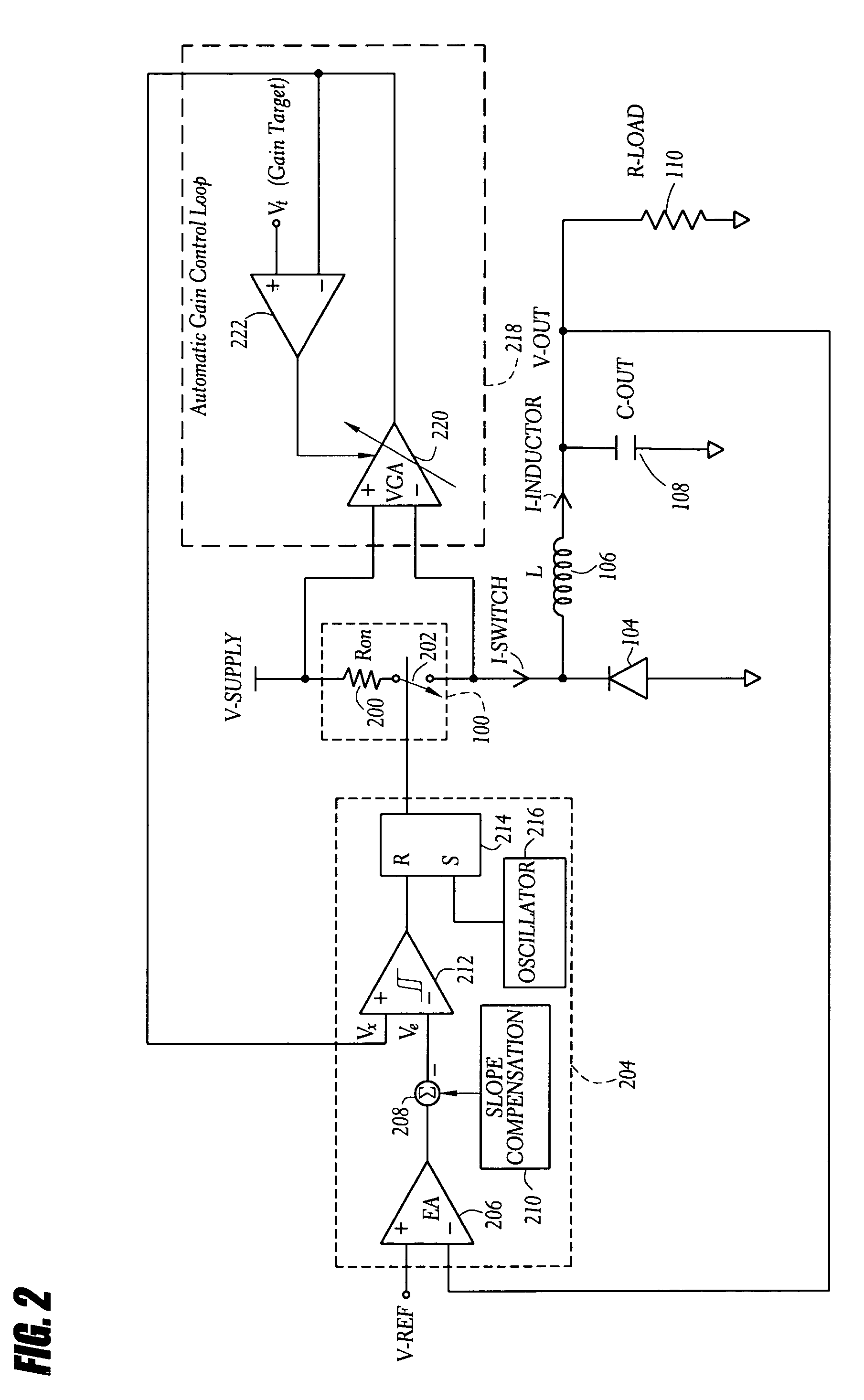
Automatic gain control technique for current monitoring in current-mode switching regulators
InactiveUS7919952B1Reduce component count and circuit board sizeFacilitates efficient and reliable monitoringDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationEngineeringCurrent mode
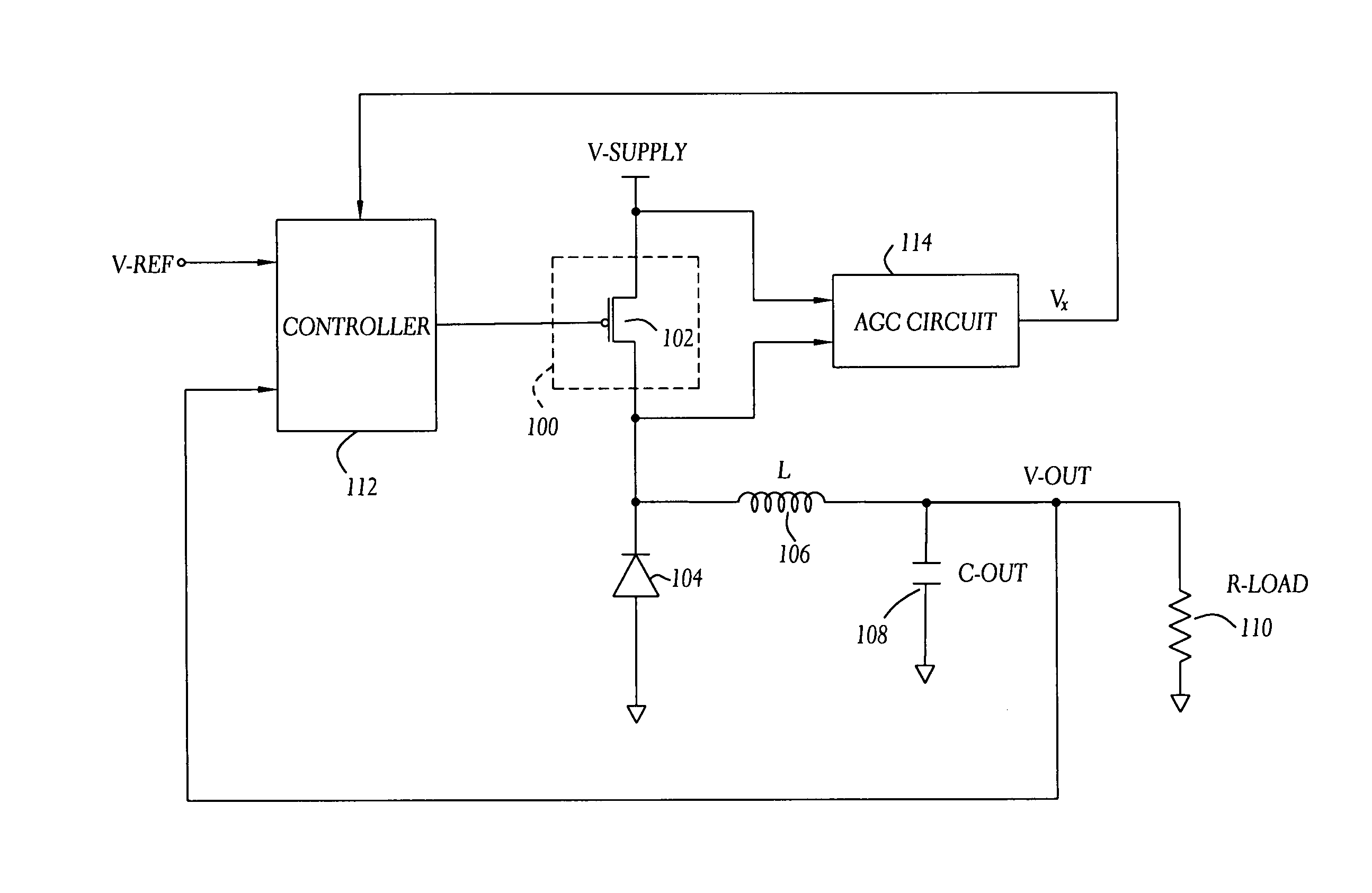
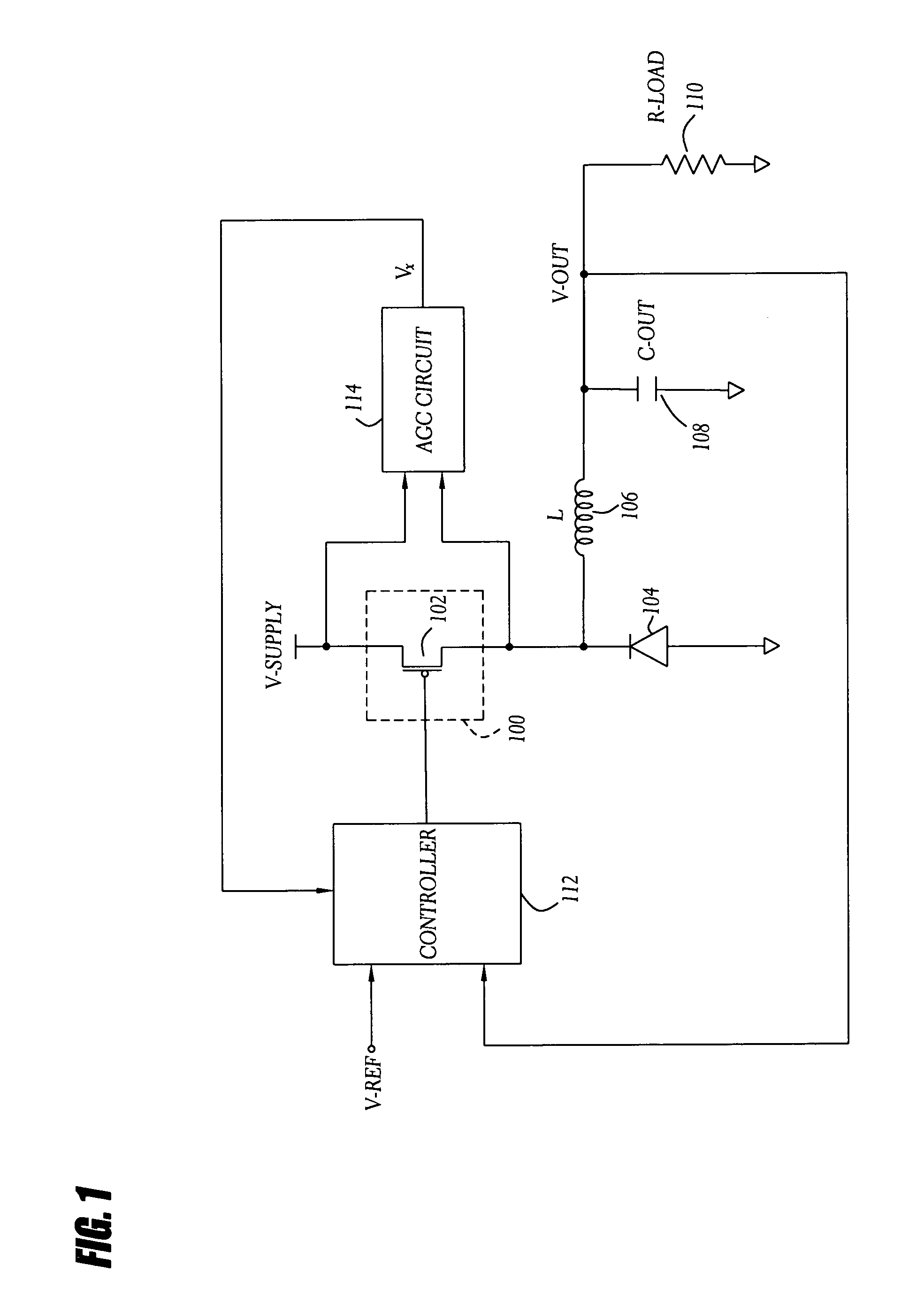
A current-mode switching regulator uses adaptive current sensing to reliably monitor an inductor current in a cost-efficient and power-efficient manner. A semiconductor switch periodically turns on to conduct the inductor current. A voltage drop across the semiconductor switch is monitored when the semiconductor switch is on. A variable gain amplifier with an automatic gain control loop generates a feedback signal from the voltage drop of the semiconductor switch when conducting to provide an indication of the inductor current to a controller. The automatic gain control loop compensates for any variations in the on-resistance of the semiconductor switch.
Owner:MICROSEMI
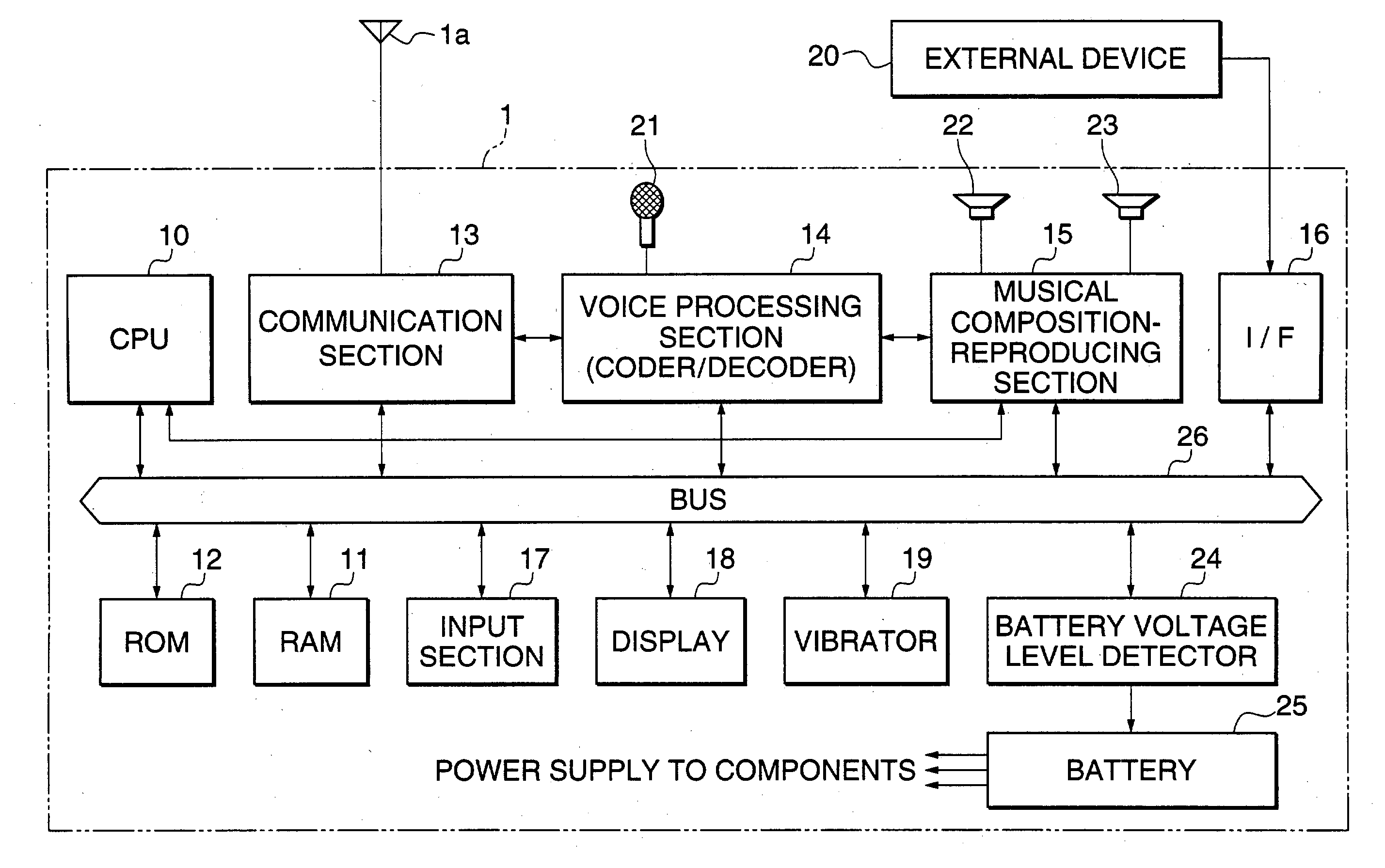
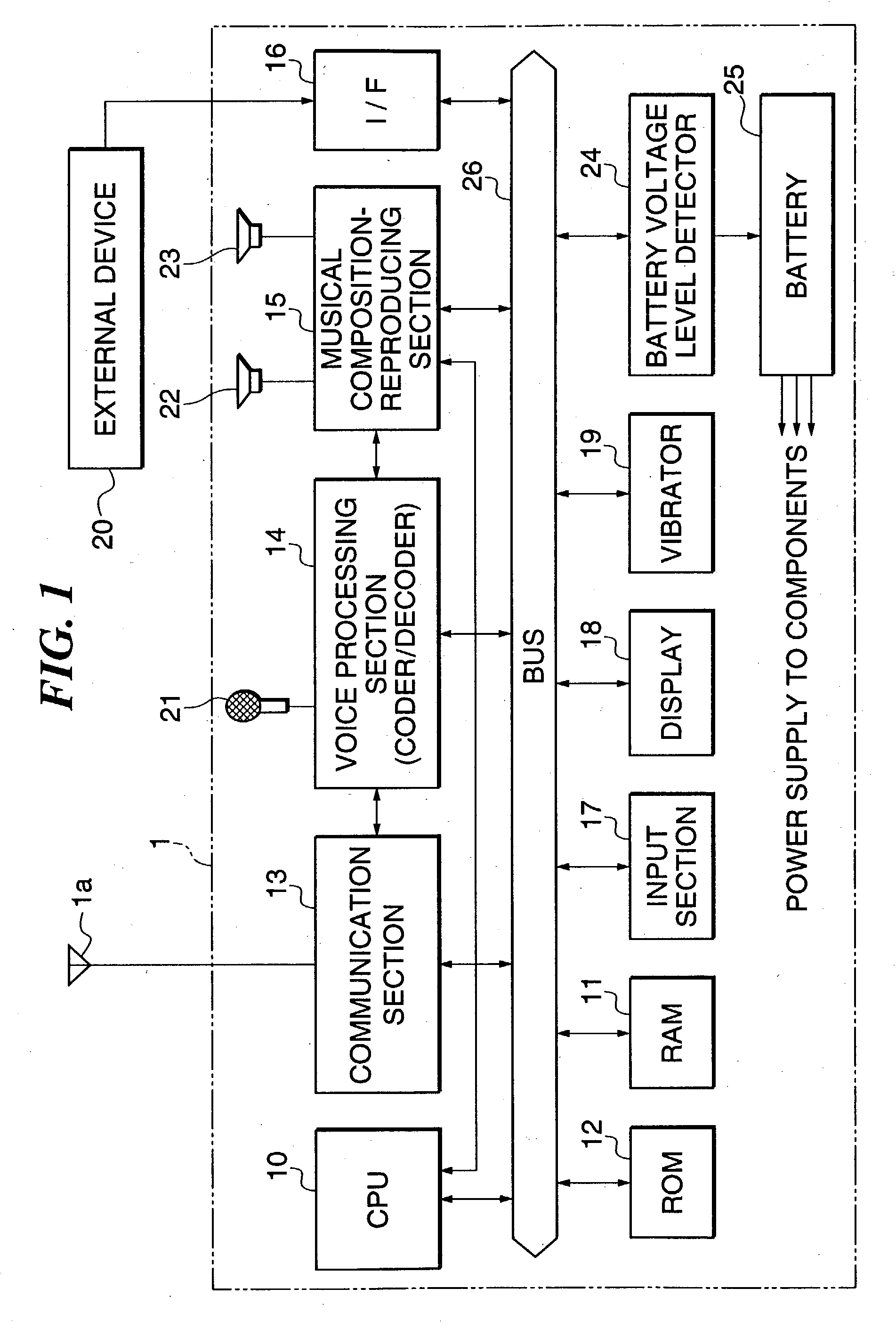
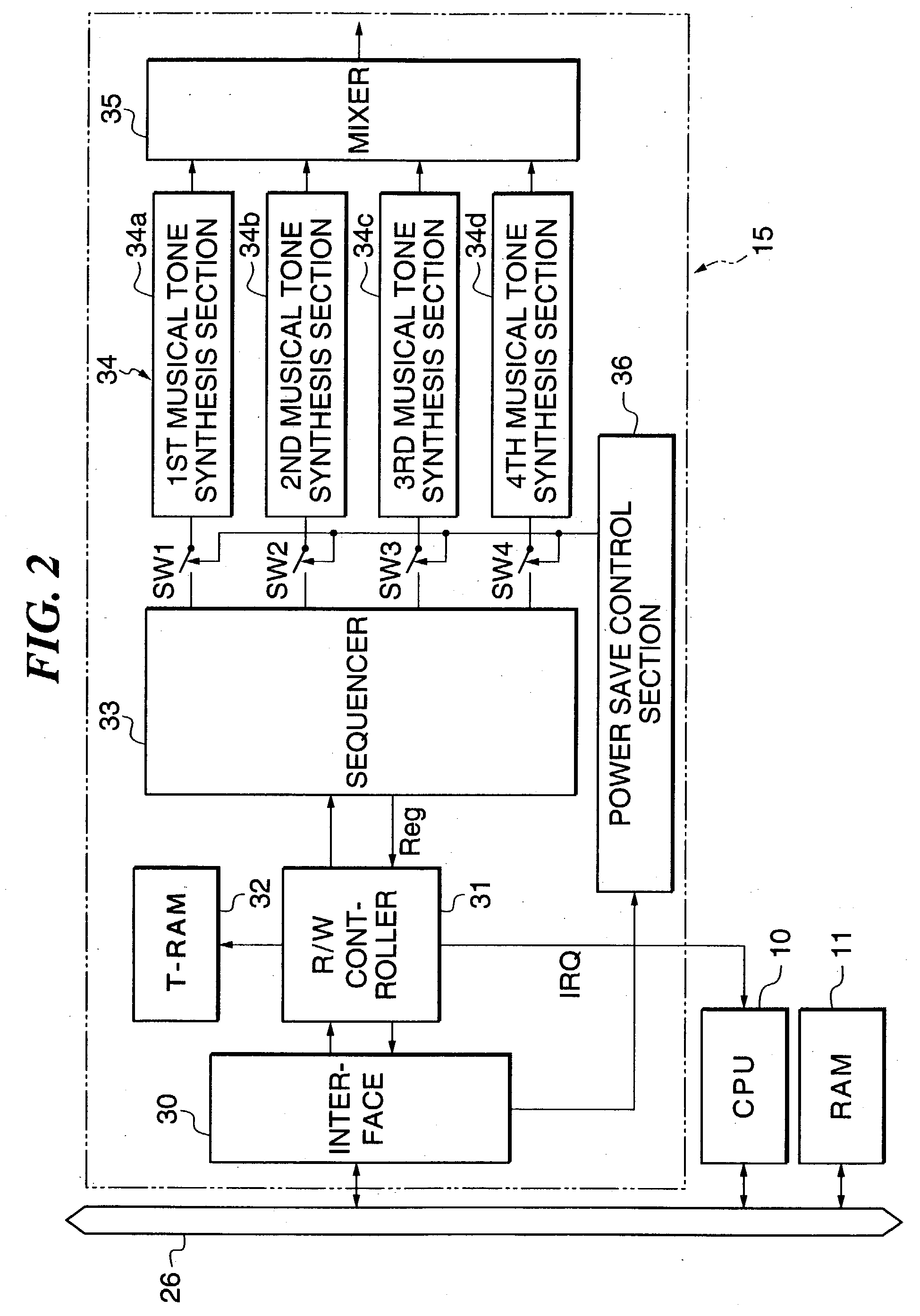
Portable appliance, power saving method and sound volume compensating method, and storage medium
InactiveUS20030160702A1Reduce partReduce battery consumptionPower managementElectrophonic musical instrumentsVariable-gain amplifierElectrical battery
There are provided a mobile device that is equipped with a musical composition-reproducing section and capable of curtailing the battery drain as much as possible, and a mobile device that prevents the quality of reproduced musical tones from being degraded even if the voltage level of the battery lowers. A battery voltage detector monitors an voltage level of a battery. The musical composition-reproducing section is controlled such that the number of parts of the musical composition reproduced by the musical composition-reproducing section is reduced when the monitored voltage level of the battery becomes lower than a reference value. In other forms of the invention, when the monitored voltage level of the battery becomes lower than a reference value, a first predetermined number of parts of the musical composition data are assigned to intrinsic ones of a larger second predetermined number of parts that correspond to the first predetermined number of parts of said musical composition, as well as to other ones of the second predetermined number of parts than the intrinsic ones, for reproduction of the musical composition, or the gain of a variable-gain amplifier is increased to compensate for the lowering of the volume of the reproduced parts.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
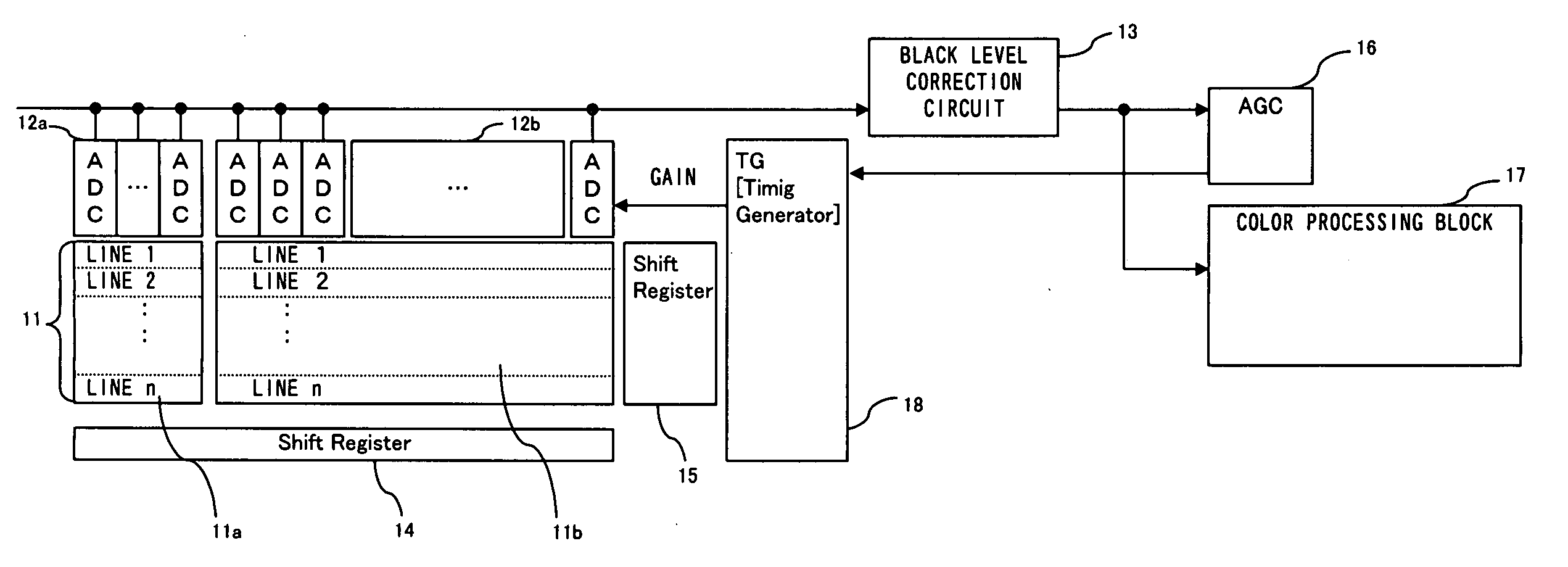
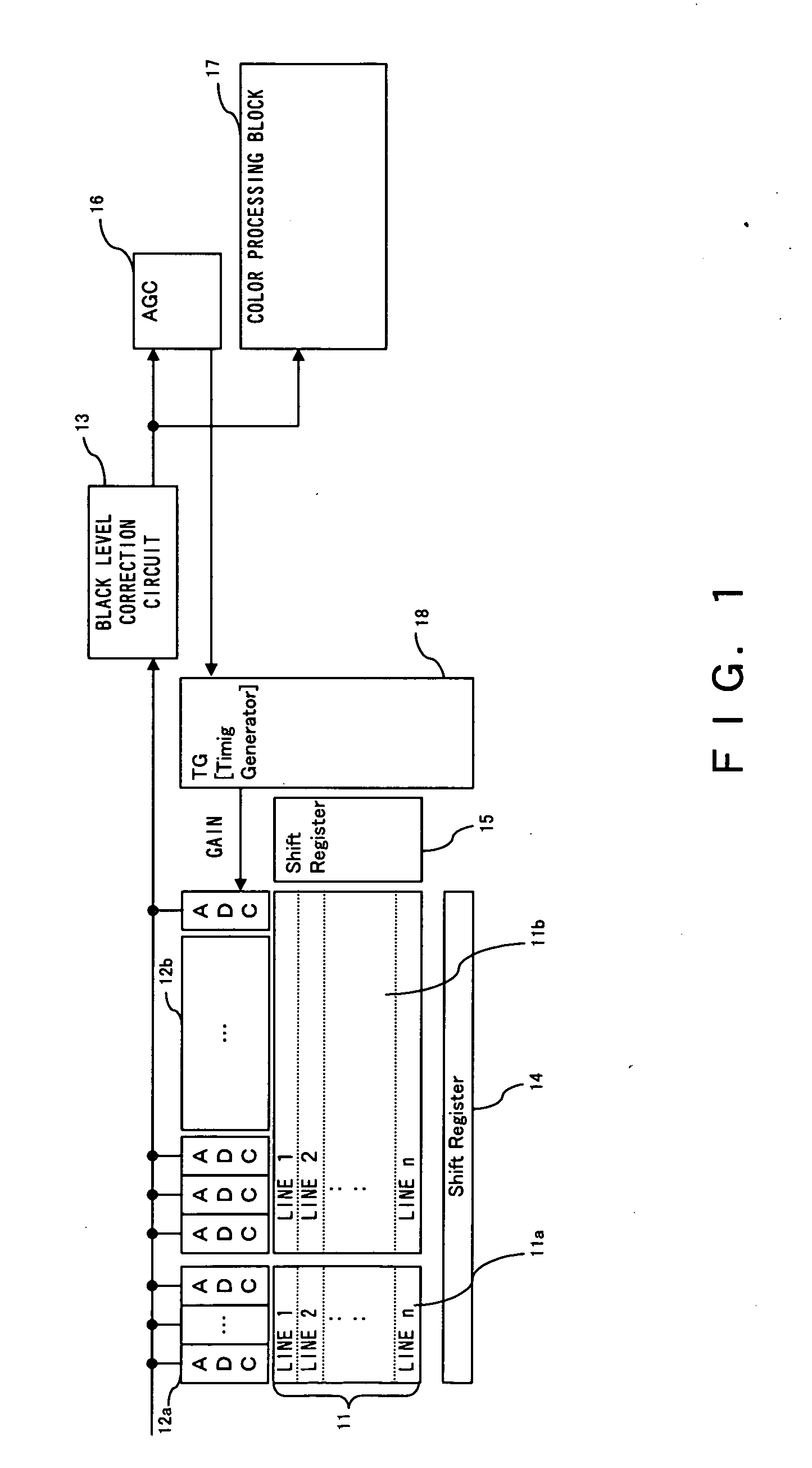
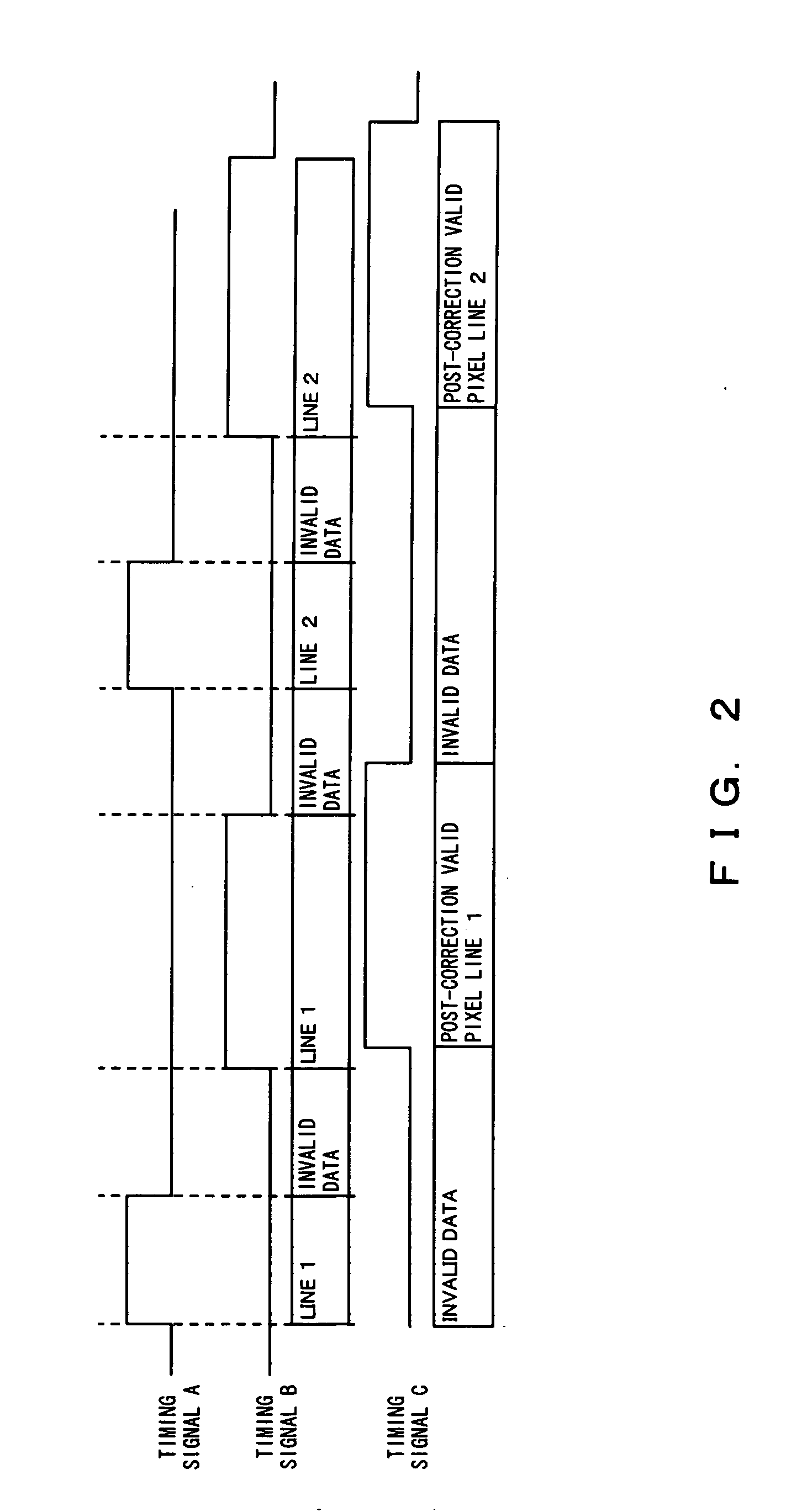
Semiconductor integrated apparatus and black level correction method for image sensor
InactiveUS20070075772A1Suppress brightness changesShort timeTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
The challenge of the present invention is to suppress a variation in brightness of an image and make a reference value of a black level converge at an appropriate value in a short time. Acondition judgment circuit judges whether or not a frame of an amount of change in gains of a variable gain amplifier being equal to or greater than a threshold continues for a predefined frames or more. If a frame of an amount of change in the gains being equal to or greater than the threshold continues for the predefined frames, a black level value of the current frame is set for new black level reference. If not continues for the predetermined number, the previous black level reference value is retained in lieu of correcting the black level.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Configurable vibration sensor
InactiveUS20050204820A1Vibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingVibration measurementAudio power amplifier
A configurable vibration sensor comprising a sensor circuit, an analog-to-digital converter and a processor, where each sensor circuit comprises a vibration sensing element and a variable bandwidth filter controllable by the processor. In addition to the variable bandwidth filter, other configurable elements may also be employed in the sensor circuit, including a variable gain amplifier. These configurable elements allow the configurable vibration sensor to be configured for different vibration measurement applications when measuring vibrations from vibrating structures such as machinery and the like.
Owner:MECHWORKS SYST
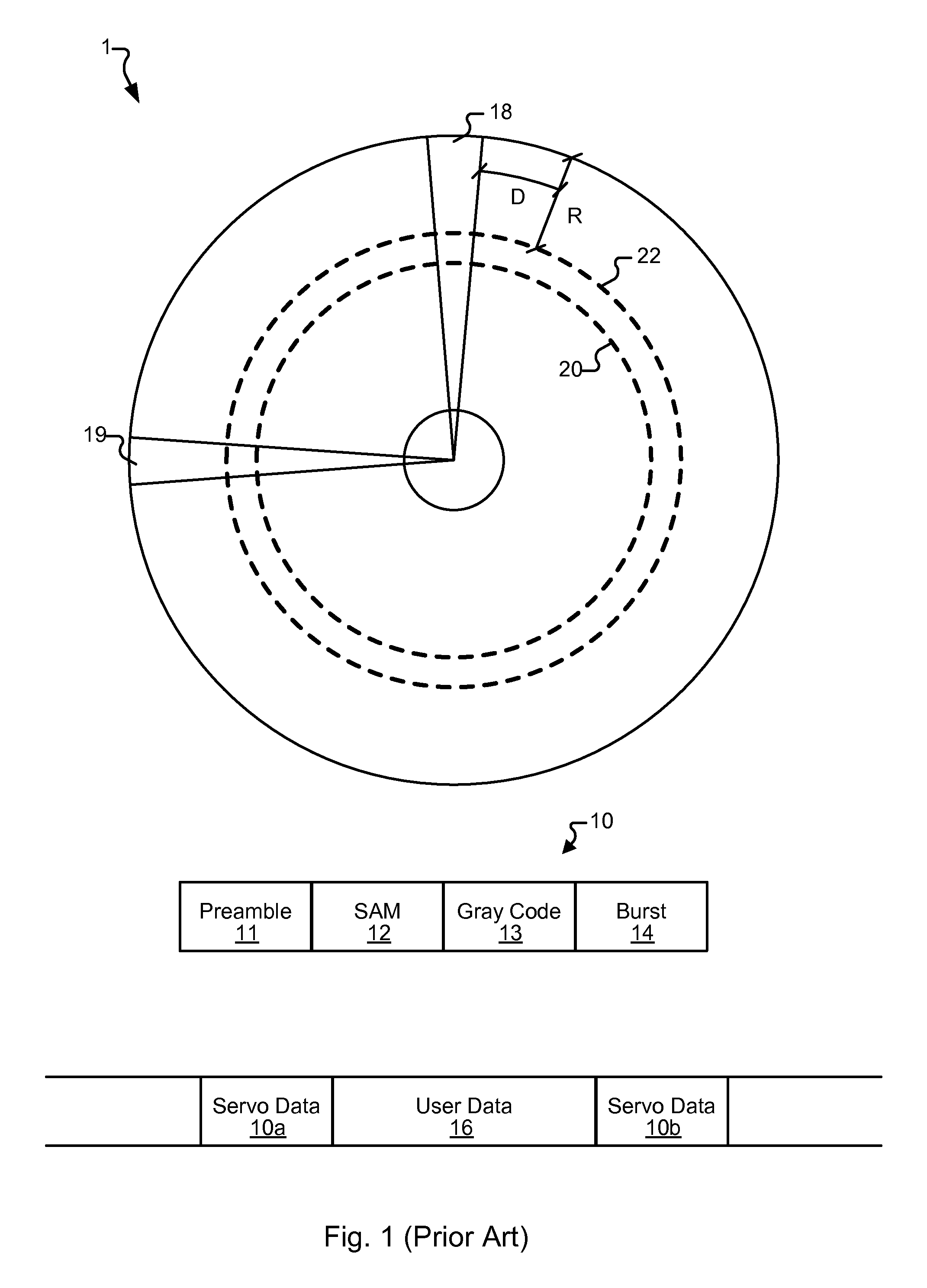
Calculation of head media separation (HMS) from servo preamble in a hard disk drive
InactiveUS8654466B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageHard disc driveAudio power amplifier
A method of calculating a Head Media Separation (HMS) from a preamble of embedded servo sectors in a disk drive may include steps of reading the preamble, the read preamble being amplified by a variable gain amplifier (VGA) set at a predetermined gain; transforming samples of the read preamble into a first and a second frequency using a discrete time-to-frequency domain transform such as a Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT); calculating the ratio of the magnitude of the discrete time-to-frequency domain transform of the first frequency to the magnitude of the discrete time-to-frequency domain transform of the second frequency; determining the HMS from the calculated ratio, and enabling the predetermined gain to be updated in synchronism with the transforming step.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
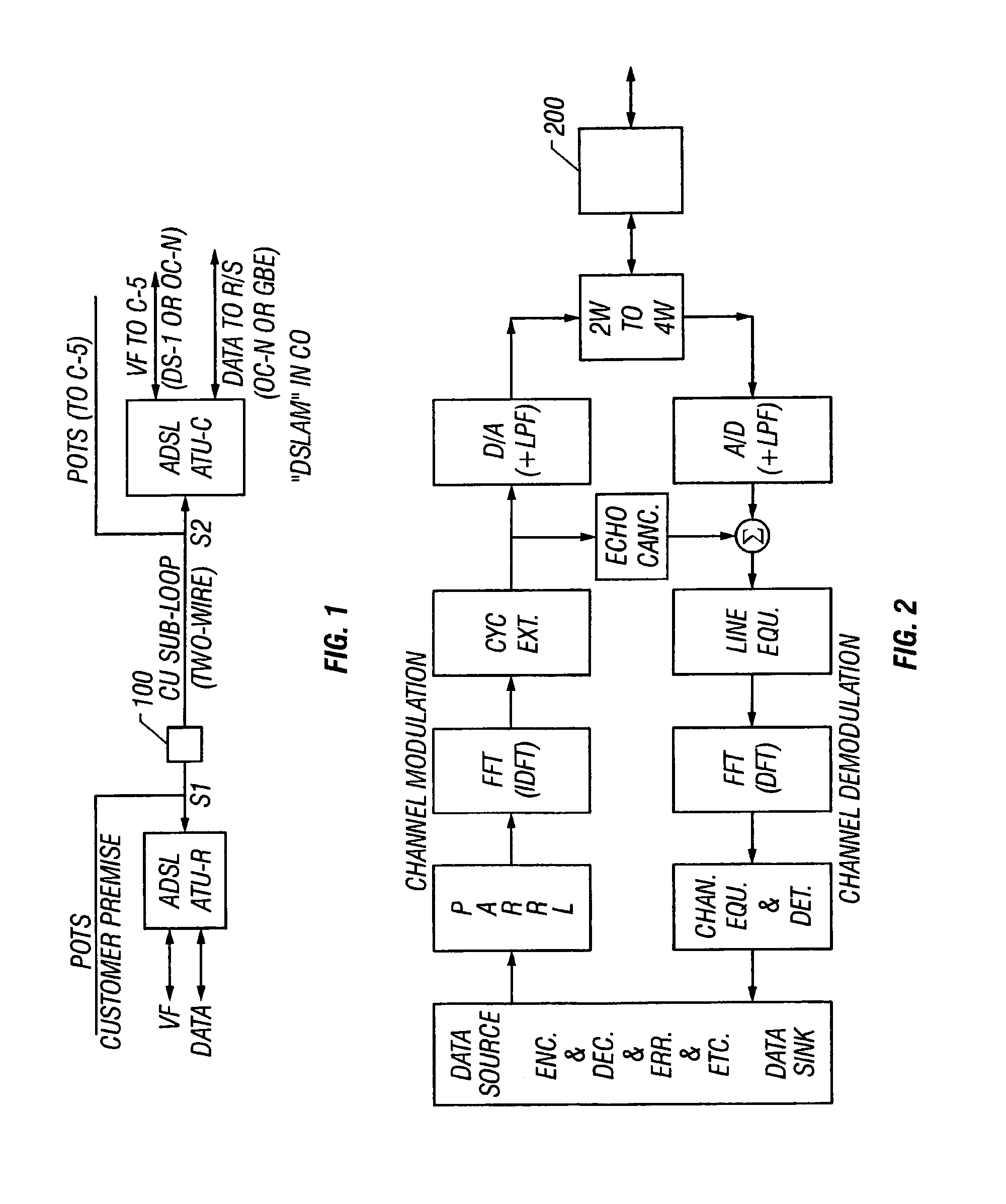
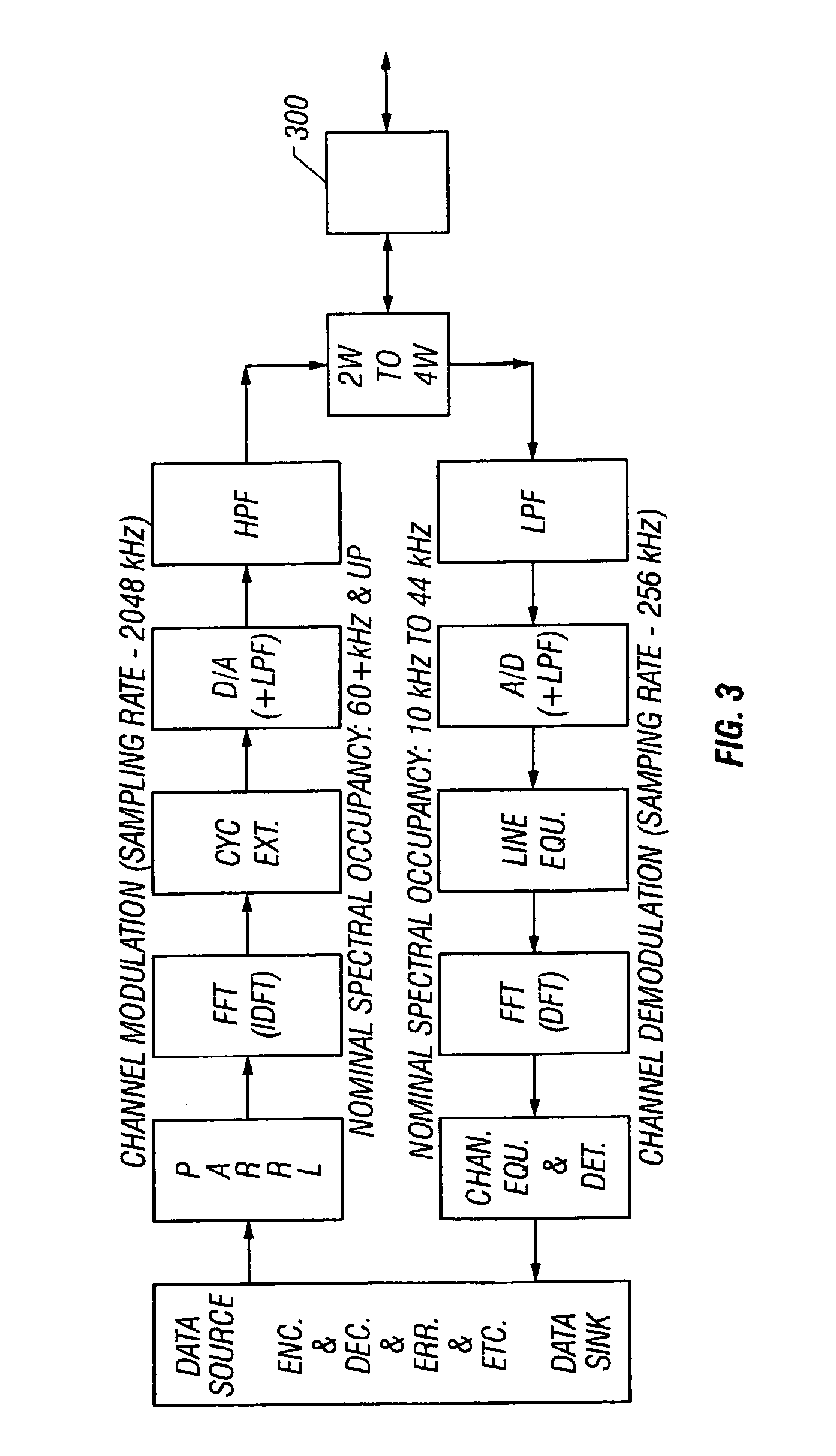
Long subscriber loops using automatic gain control mid-span extender unit
InactiveUS7142619B2Transmission control/equlisationRepeater/relay circuitsVariable-gain amplifierAudio power amplifier
Systems and methods are described for long subscriber loops using automatic gain control. A method includes extending a digital subscriber loop including: producing an output signal in a first direction from a variable gain amplifier at a mid-span extender unit responsive to an input signal in the first direction from the digital subscriber loop; monitoring a signal strength of said output signal in the first direction at the mid-span extender unit; generating a gain control signal responsive to the signal strength at the mid-span extender unit; controlling a gain of the variable gain amplifier at the mid-span extender unit responsive to the gain control signal; and controlling a second gain of a second variable gain amplifier at said mid-span extender unit responsive to said gain control signal to produce an output signal in a second direction from said second variable gain amplifier at said mid-span extender unit responsive to a second input signal in said second direction from said digital subscriber loop.
Owner:SYMMETRICOM
Wireless local area network repeater with in-band control channel
InactiveUS20060063484A1Cost of device is highReduce disadvantagesInformation formatNetwork topologiesVariable-gain amplifierEngineering
A frequency translating repeater (200) for use in a WLAN environment includes an in-band management link. A signal received on an antenna (300) is split to provide signal detection in a detection and control unit (385) wherein detection is performed by detectors (370, 371) filters (375, 376), converters (380, 381) and a processor (385). Delay is added using delay lines (360, 361). The in-band signal envelope may be modulated with variable gain amplifier (330) and demodulated with detectors (370, 371) to establish the management link with higher protocol layer capability. Alternatively, a modern function at least partially compliant to 802.11 modulation may be used in parallel with the frequency translating repeater.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
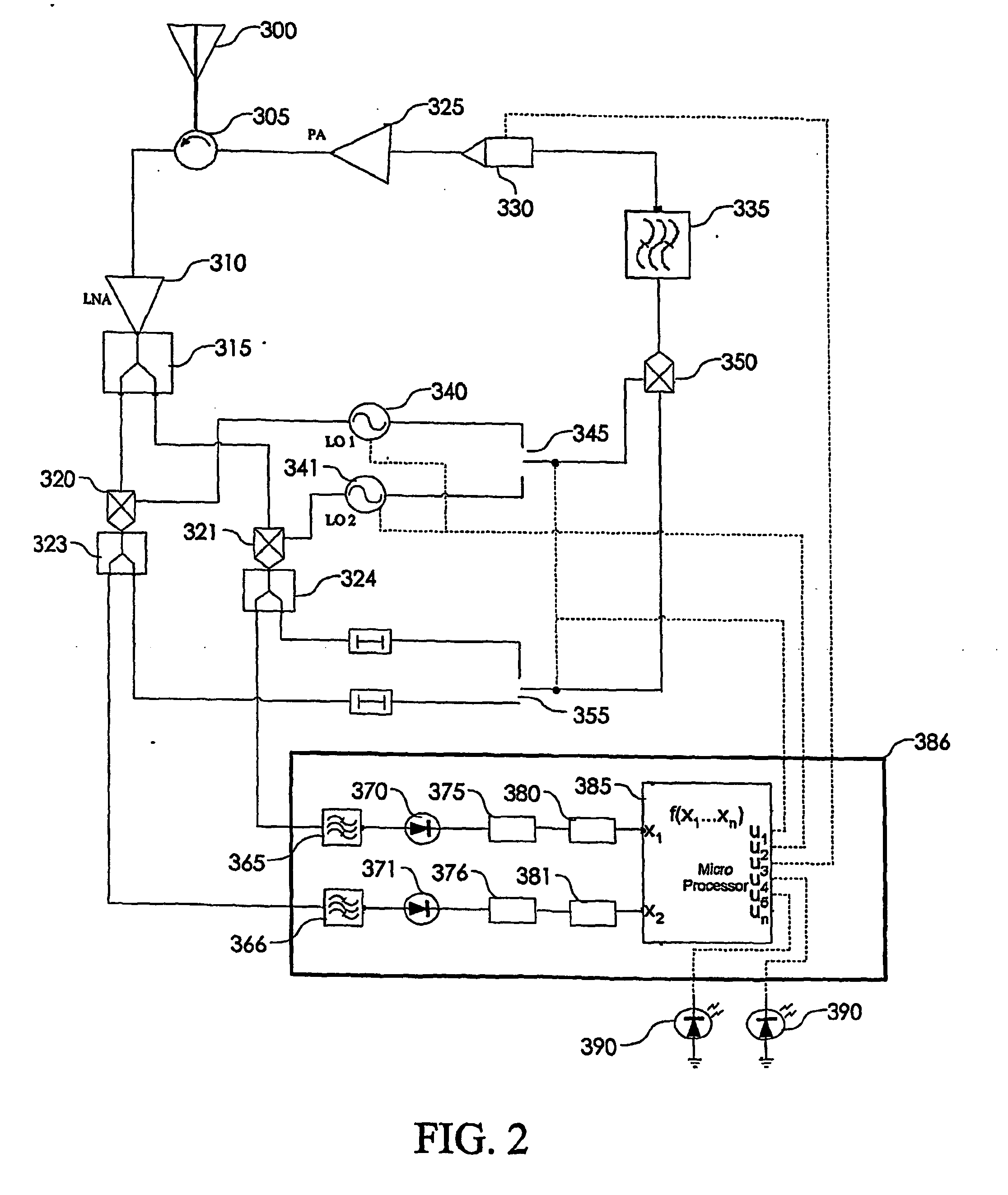
Transmitter with transmitter chain phase adjustment on the basis of pre-stored phase information
ActiveUS20030095608A1High frequency signalSecret communicationPhase-modulated carrier systemsFrequency changerQuadrature modulator
A transmitter chain has a quadrature modulator, a variable gain amplifier, an up-converter, and a variable gain power amplifier. An overall phase of the transmitter chain is adjusted on the basis of pre-stored phase information reflecting phase changes due to simultaneous gain changes of gains of at least the variable gain amplifier and the variable gain power amplifier.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
System and method for controlling gain and timing phase in a presence of a first least mean square filter using a second adaptive filter
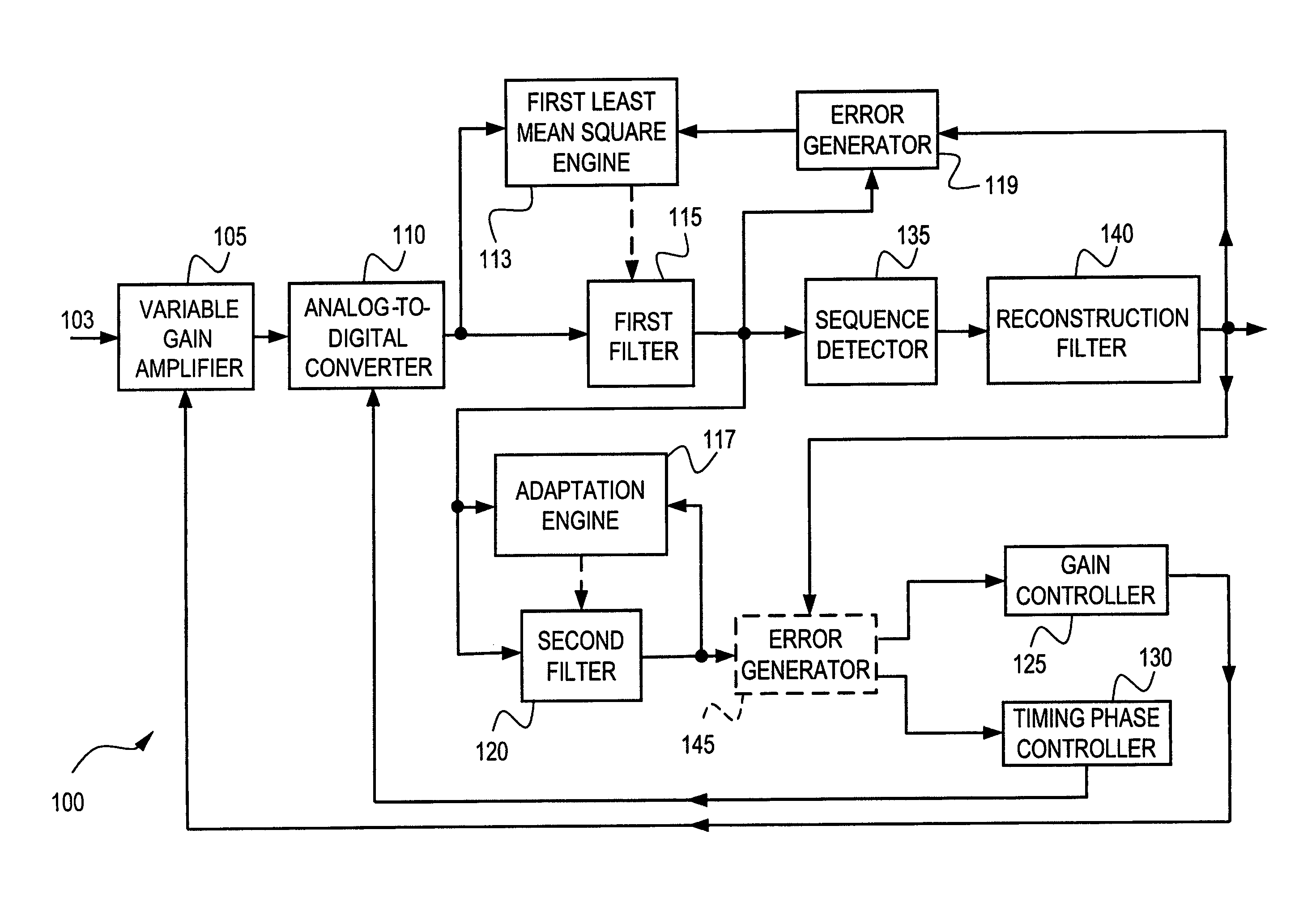
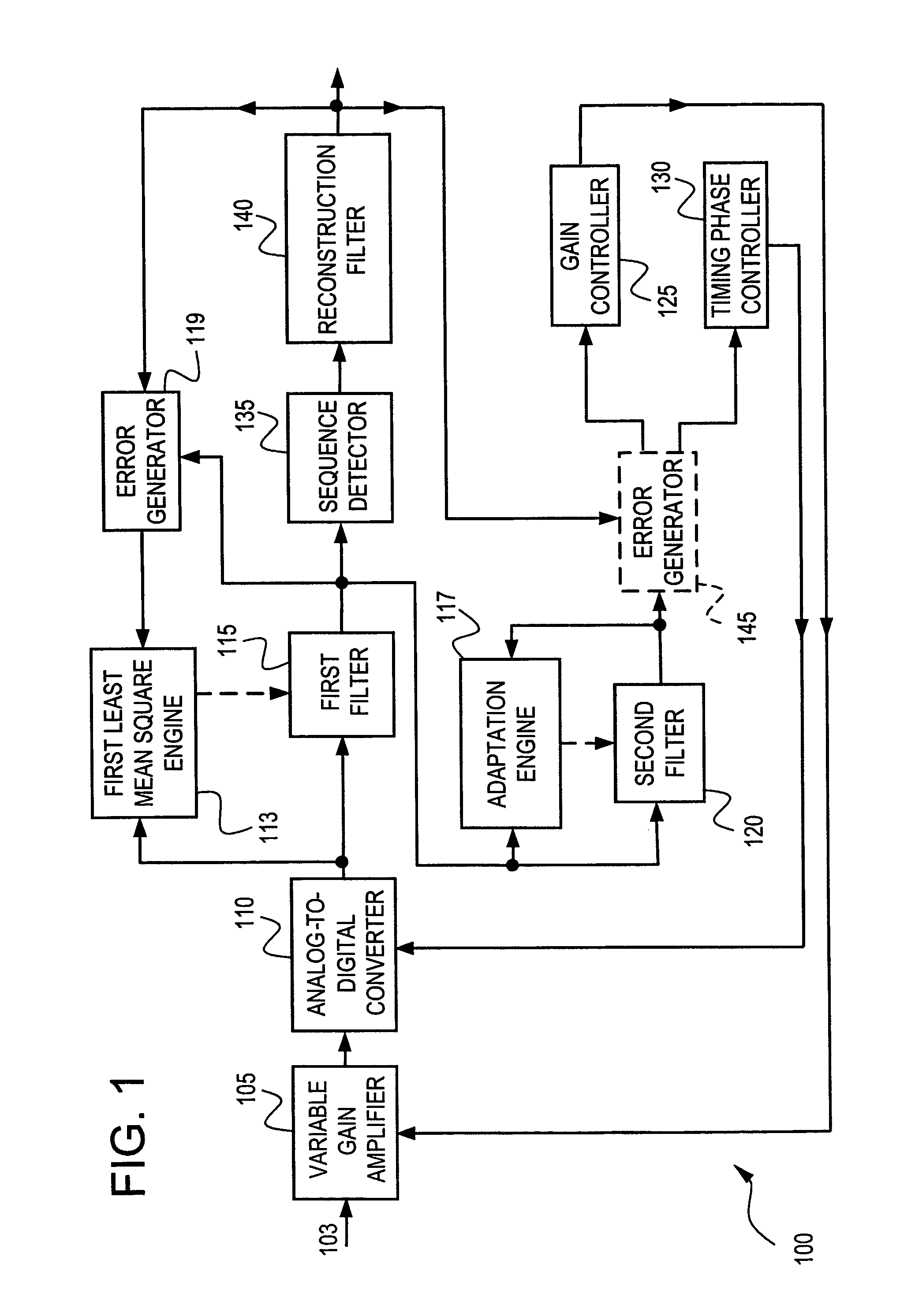
ActiveUS7505537B1Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsLeast mean squares filterVariable-gain amplifier
A system for controlling gain and timing phase includes a variable gain amplifier (VGA) responsive to an input signal, and an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) responsive to a VGA output. A first filter, with tap weight coefficients updated by a first least mean square (LMS) engine, is responsive to an ADC output. At least one tap weight coefficient of the first filter is constrained. A second filter, with tap weight coefficients updated by an adaptation engine, is responsive to a first filter output. The complexity of the second filter is less than or equal to the complexity of the first filter. The system includes: a timing phase controller, in communication with the ADC and responsive to a second filter output, for controlling ADC timing phase; and / or a gain controller, in communication with the VGA and responsive to the second filter output, for controlling VGA gain.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
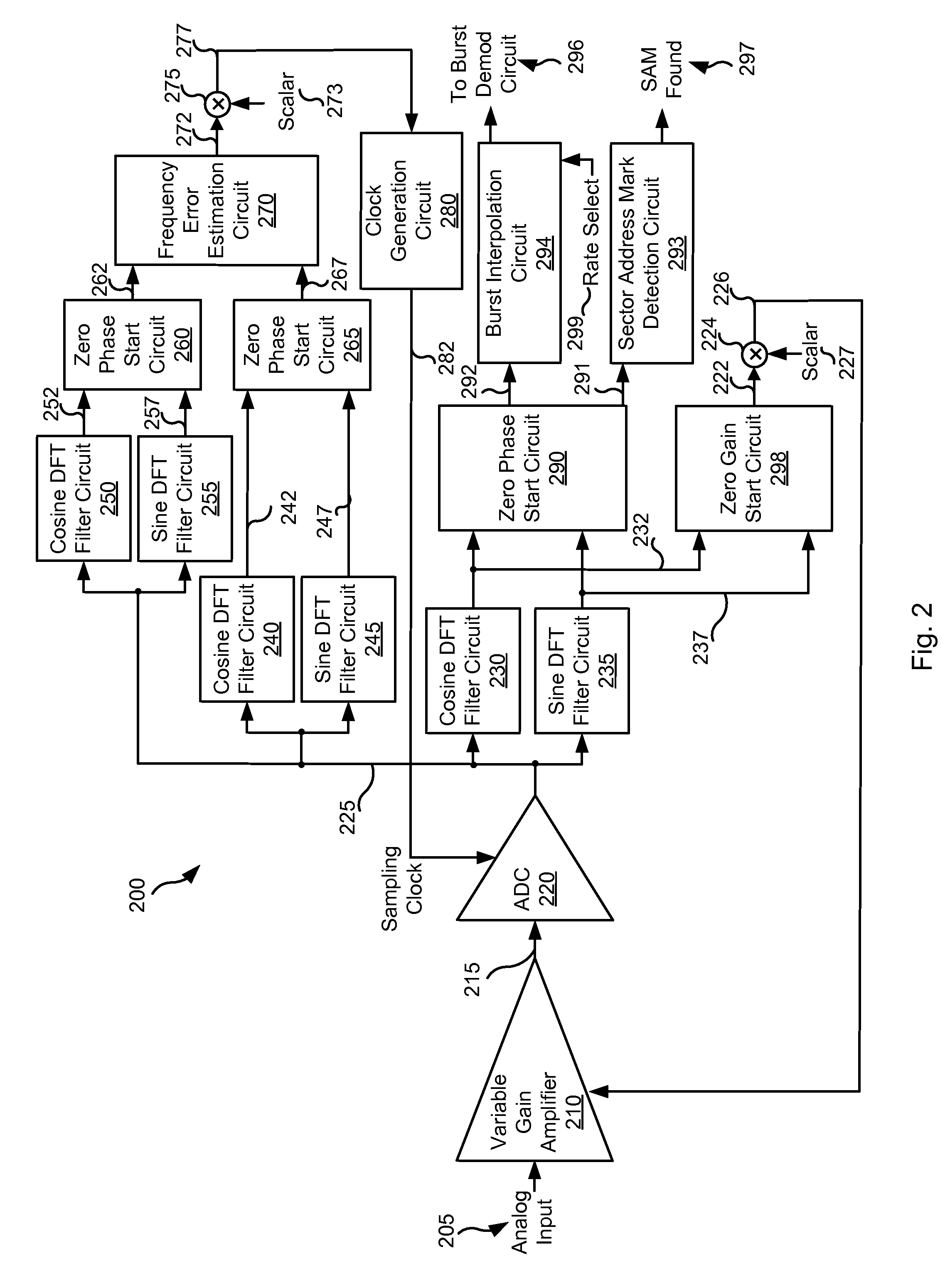
Systems and Methods for Reduced Format Data Processing
InactiveUS20120182643A1Record information storageAlignment for track following on disksAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
Various embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for data processing. For example, some embodiments of the present invention provide data processing circuits that include a variable gain amplifier circuit, an analog to digital conversion circuit, a cosine component calculation circuit, a sine calculation circuit, and a zero gain start calculation circuit. The variable gain amplifier circuit is operable to apply a gain to a data input corresponding to a gain feedback value and providing an amplified output. The analog to digital conversion circuit is operable to convert the amplified output to a corresponding series of digital samples. The cosine component calculation circuit is operable to calculate a cosine component from the series of digital samples, and the sine component calculation circuit operable to calculate a sine component from the series of digital samples. The zero gain start calculation circuit is operable to calculate a raw gain error value based on the cosine component and the sine component, where the gain feedback value is derived from the raw gain error value.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
Staggered AGC with digitally controlled VGA
ActiveUS20050058228A1Reduce gain requirementsSimple designDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionLine balance variation compensationVariable-gain amplifierA d converter
The invention relates to the field of wireless communications, more particularly to a method of and device for automatic gain control (AGC) incorporating digitally controlled variable gain amplifiers (VGAs). The invention provides an AGC circuit comprising an I / Q baseband strip comprising multiple AGC stages wherein each of the AGC stages comprises: respective I and Q VGAs; a detector for detecting respective I and Q output signals received from the respective I and Q VGAs; an analogue to digital converter (ADC) for converting the detected I and Q output signals; and a digital engine for adjusting the respective I and Q VGAs for differences between the detected I and Q output signals and a reference signal. The use of staggered AGCs incorporating respective I and Q VGAs means that the total dynamic range is split between n-stages, thereby allowing for reduced gain requirements in the VGAs. Additionally, the use of digital control for setting the VGA gains means that analogue variations and I / Q gain imbalances are reduced. Additionally, the use of multiple update rates or magnitudes in the VGA control improves the dynamic settling time.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
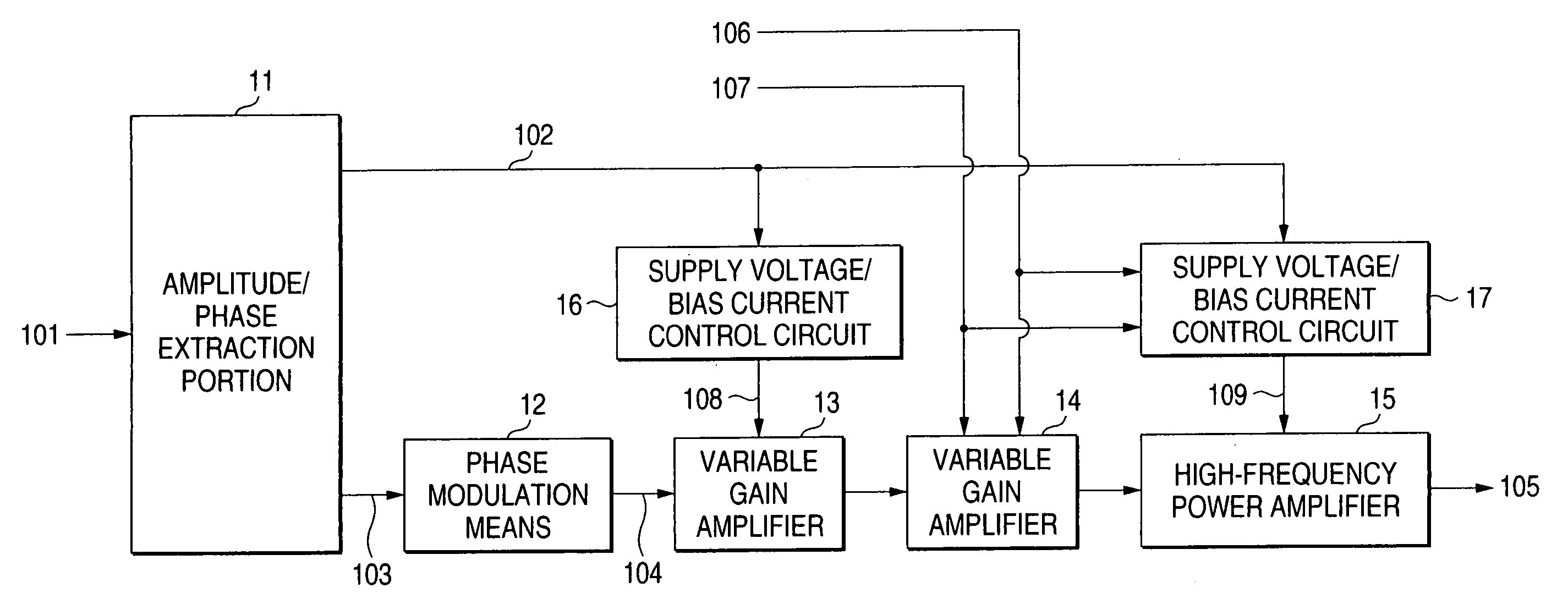
Transmission device, transmission output control method, and radio communication device
InactiveUS20060046666A1Improve efficiencyImprove linearityResonant long antennasHigh frequency amplifiersHigh frequency powerAudio power amplifier
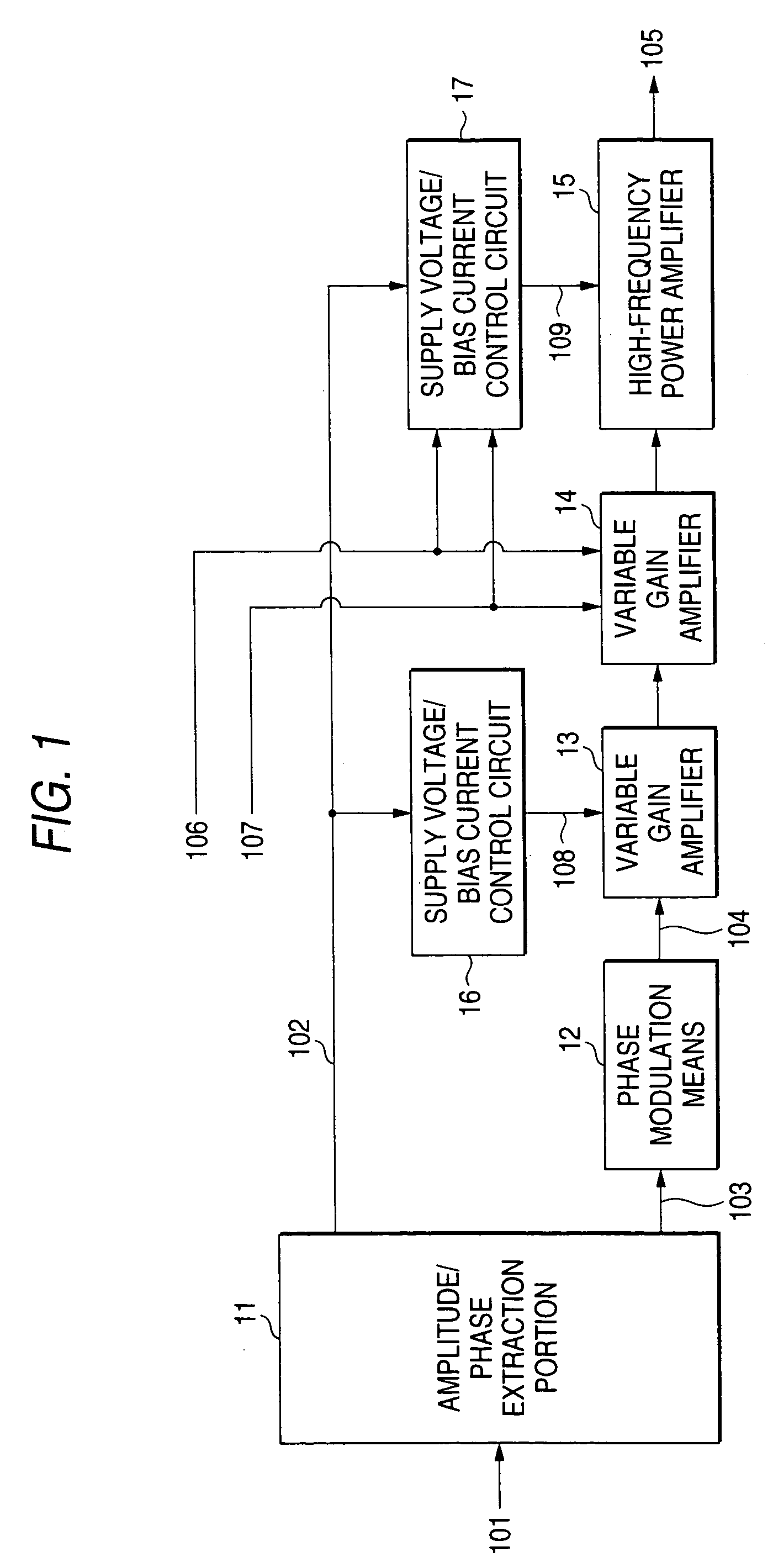
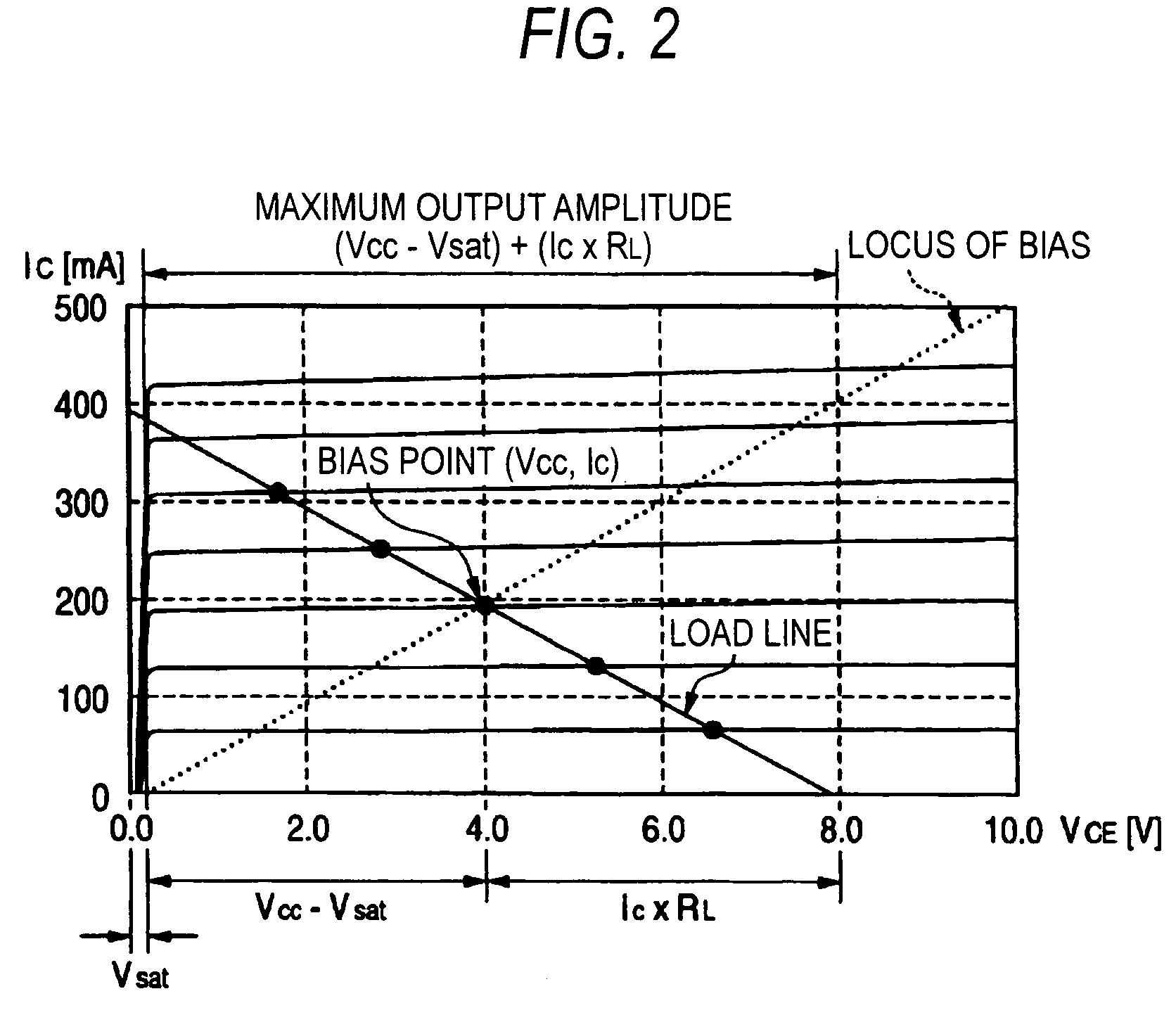
An object of the invention is to provide a transmitter high in efficiency, good in linearity and capable of covering an output level in a wide range. Either linear operating mode or saturation operating mode is set as the operating mode of a high-frequency power amplifier (15) on the basis of an operating mode set signal (107). The gain of a variable gain amplifier (14) provided in front of the high-frequency power amplifier (15) and values of output voltage (109) and bias current supplied from a supply voltage / bias current control circuit (17) to the high-frequency power amplifier (15) are switched. The gain of the variable gain amplifier (14) in the saturation operating mode is formed so as to be higher by a predetermined value than that in the linear operating mode. Accordingly, the high-frequency power amplifier 15 operates in the designated operating mode, so that the output transmission power range can be widened.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Variable gain amplifier
InactiveUS6163215AComputations using contact-making devicesGain controlAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
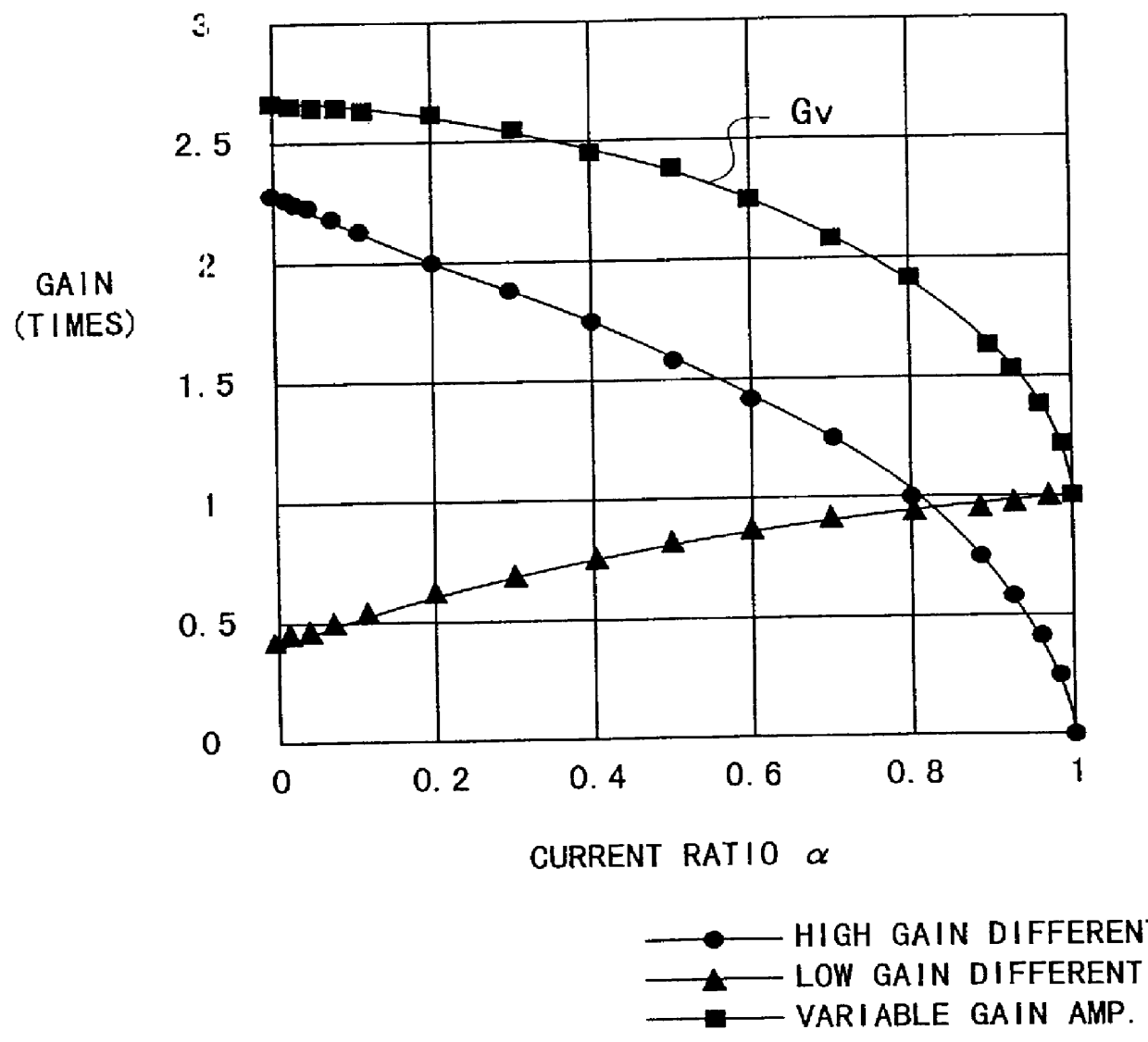
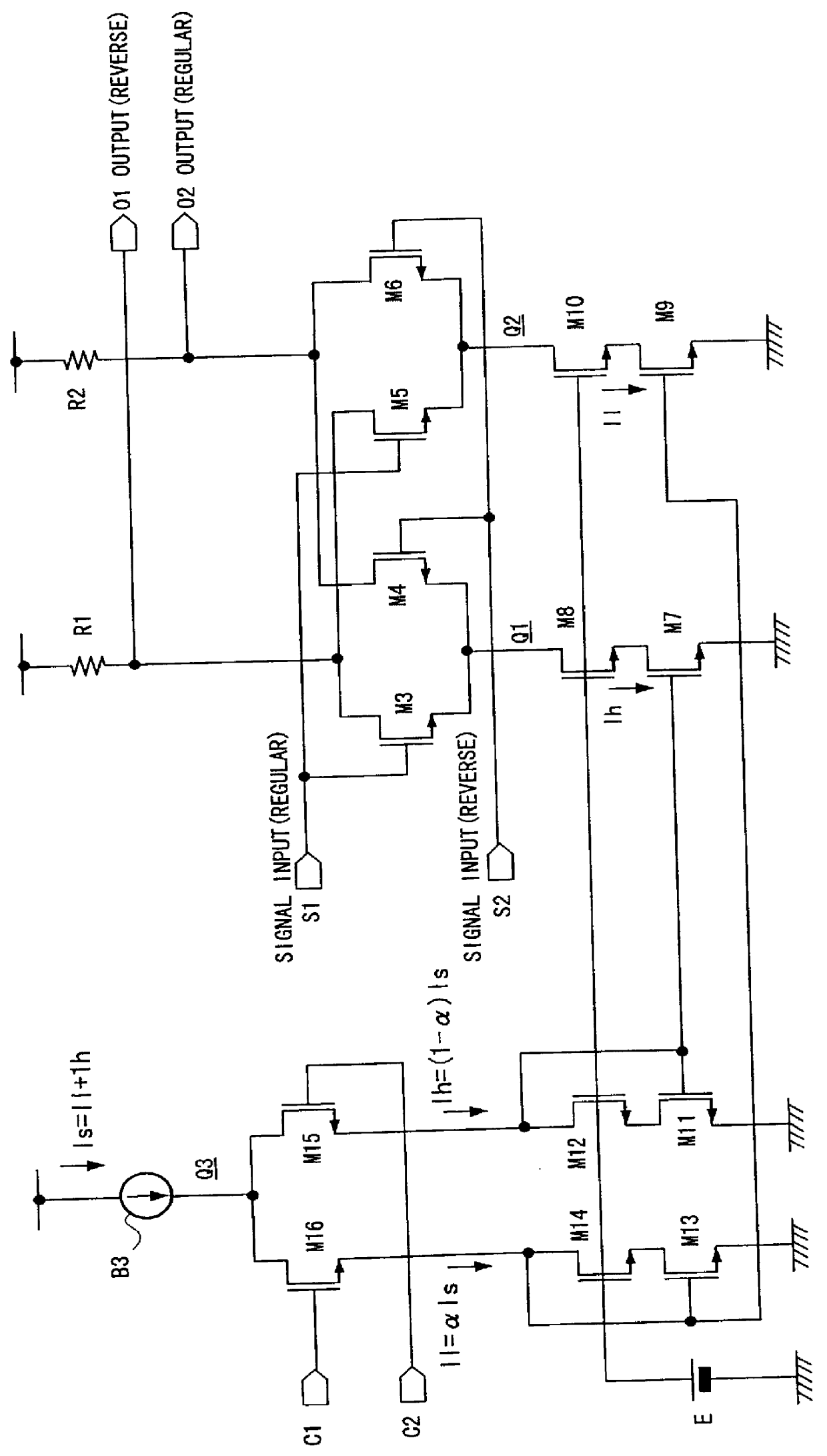
In a variable gain amplifier controlling a gain by using differential amplifiers with a gain control signal, a gain switchover differential amplifier or a bias circuit which composes a current mirror with the gain switchover differential amplifier is connected between a high and a low gain differential amplifier for the same bias current which are mutually connected to share load resistances for the same output polarity and a bias current source common to both of the differential amplifiers, to perform switchover operations of the high and the low differential amplifier by a gain control signal, and a current source which flows a fixed offset current through at least the low one of the high and the low differential amplifier is provided.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Systems and methods for an RF nulling scheme in RFID
ActiveUS20070060075A1Minimises levelReduce sensitivityResonant long antennasAntenna arraysSignal responseAudio power amplifier
Systems and methods for an RF nulling scheme are provided. An RF nulling scheme can minimize the level of unwanted RF signal reflections entering the receiver without attenuating the desired signal response from an RFID tag. In one aspect of the RF nulling scheme a synthesizer signal can be split between a main path and a nulling path. In the nulling path the signal from the splitter can be routed through an electronically variable phase shifter and variable gain amplifier to create a nulling signal. The nulling signal can cancel the unwanted reflected signal. The phase or amplitude of the nulling signal can then be adjusted to improve cancellation as necessary.
Owner:SMARTRAC TECH FLETCHER INC
Amplifier compression controller circuit
ActiveUS20070184796A1Narrow bandwidthSacrificing efficiencyResonant long antennasAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
A power amplifier controller circuit controls a power amplifier based upon an amplitude correction signal indicating the amplitude difference between the amplitude of the input signal and an attenuated amplitude of the output signal. The power amplifier controller circuit comprises an amplitude control loop and a phase control loop. The amplitude control loop adjusts the supply voltage to the power amplifier based upon the amplitude correction signal. The amplitude loop may include a variable gain amplifier adjusting the amplitude of the input signal. The amplitude loop can include a compression control block which may be configured either to adjust the gain in the variable gain amplifier or the voltage from the power supply based upon the operating level of the other, in addition to being based upon the amplitude correction signal, thus providing a way of maintaining the depth beyond the PA's compression point and allowing a control of the efficiency of the RF power amplifier.
Owner:QUANTANCE
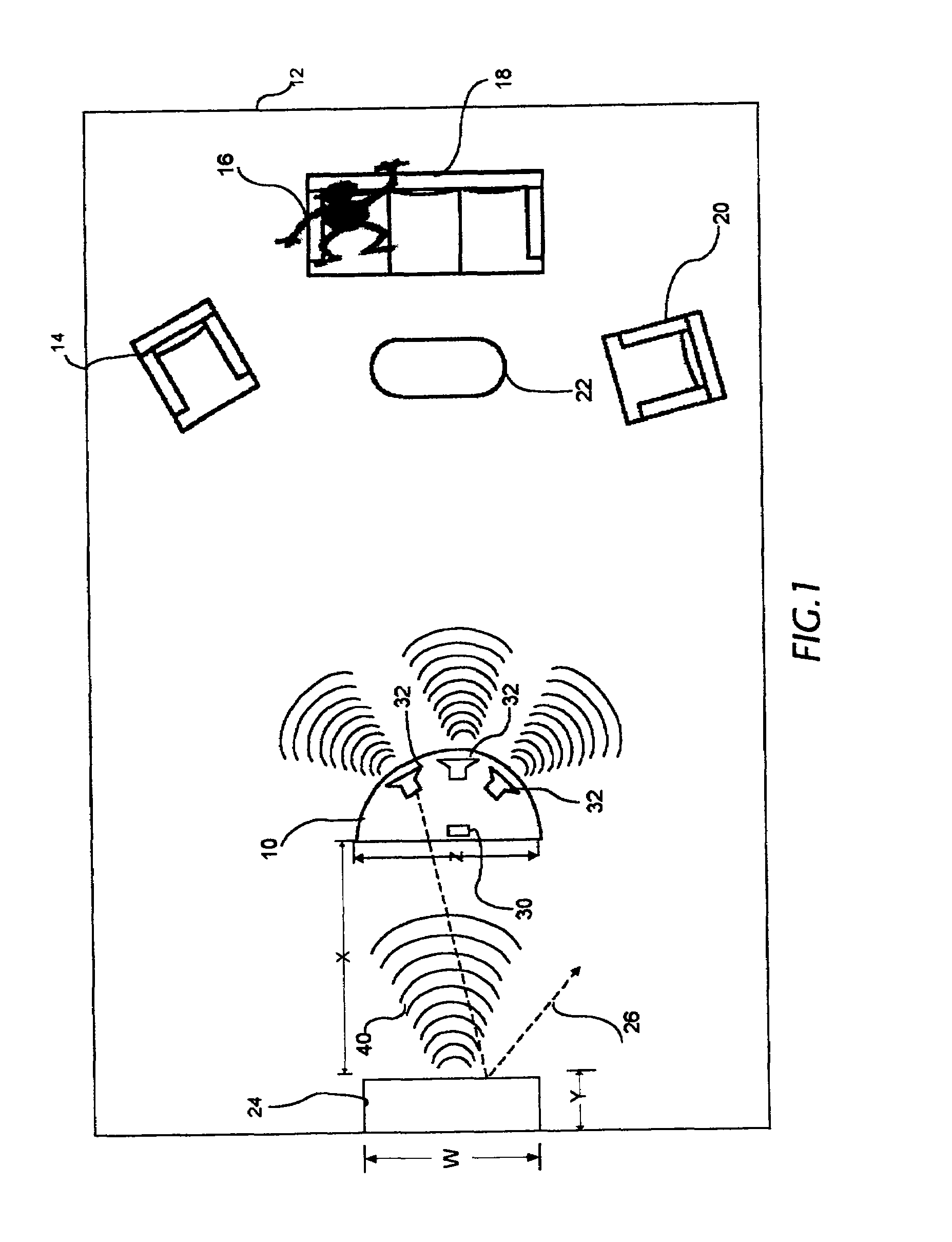
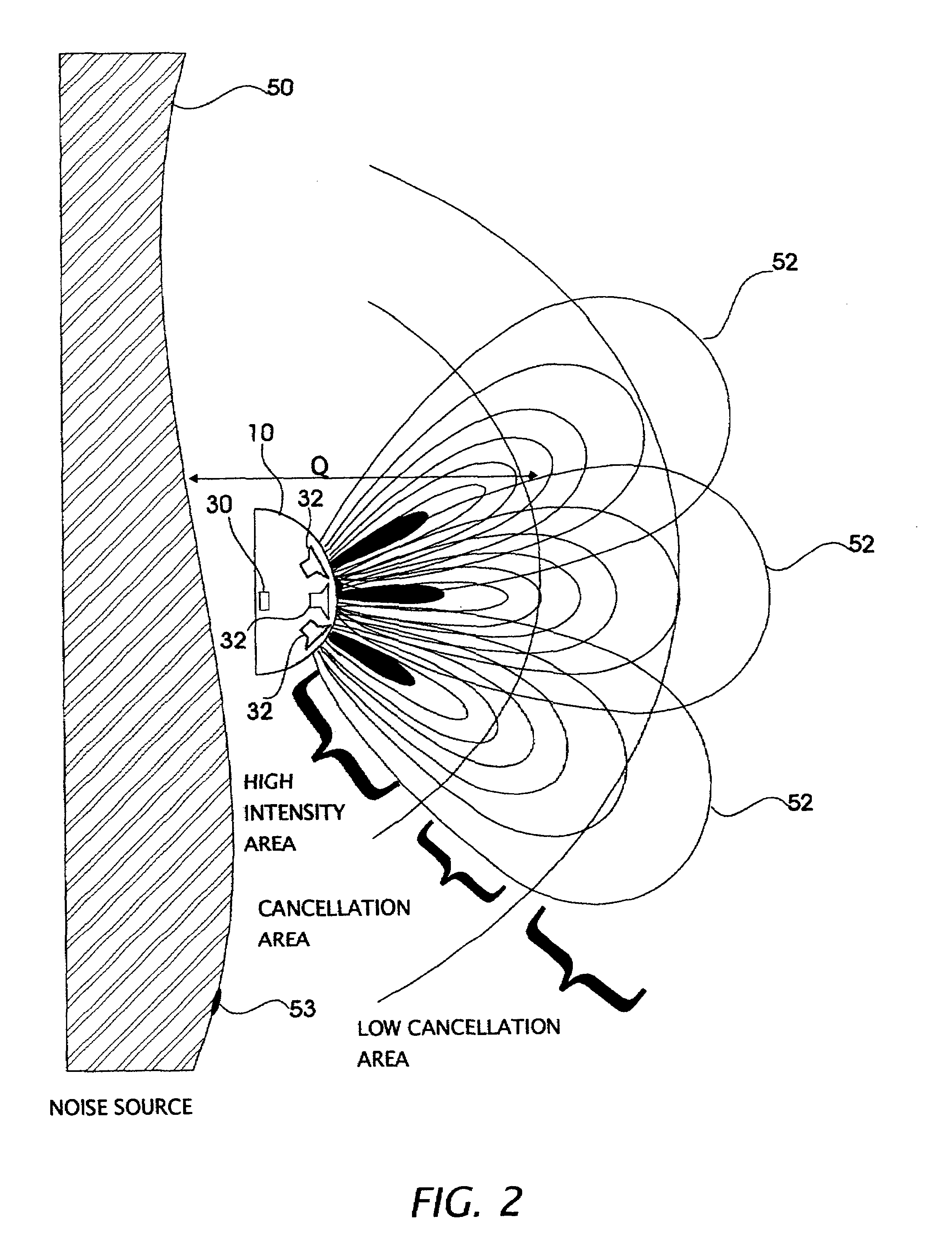
Active acoustic noise reduction system
InactiveUS7317801B1Remove feedbackReduce impactTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsEar treatmentAudio power amplifierAcoustic noise reduction
An active acoustic noise reduction system which comprises a single input transducer and an output actuator that are physically located next to each other in the same location. In one embodiment, the input transducer and the output actuator are a hybrid represented by a single element. The active noise reduction system is located as close as possible to the noise source and functions to generate an antinoise cancellation sound wave with minimum delay and opposite phase with respect to the noise source. The noise reduction system also comprises a non linearity correction circuit, a delayed cancellation circuit and variable gain amplifier. The system provides user control of the quiet zones generated by the system by varying the gain of the variable gain amplifier. The system provides a user with the ability In one embodiment, an echo canceler is utilized to remove echoes fed back from the output actuator. In another embodiment, an input decoder is used instead of an echo canceler to remove feedback picked up from the output actuator.
Owner:SILENTIUM LTD
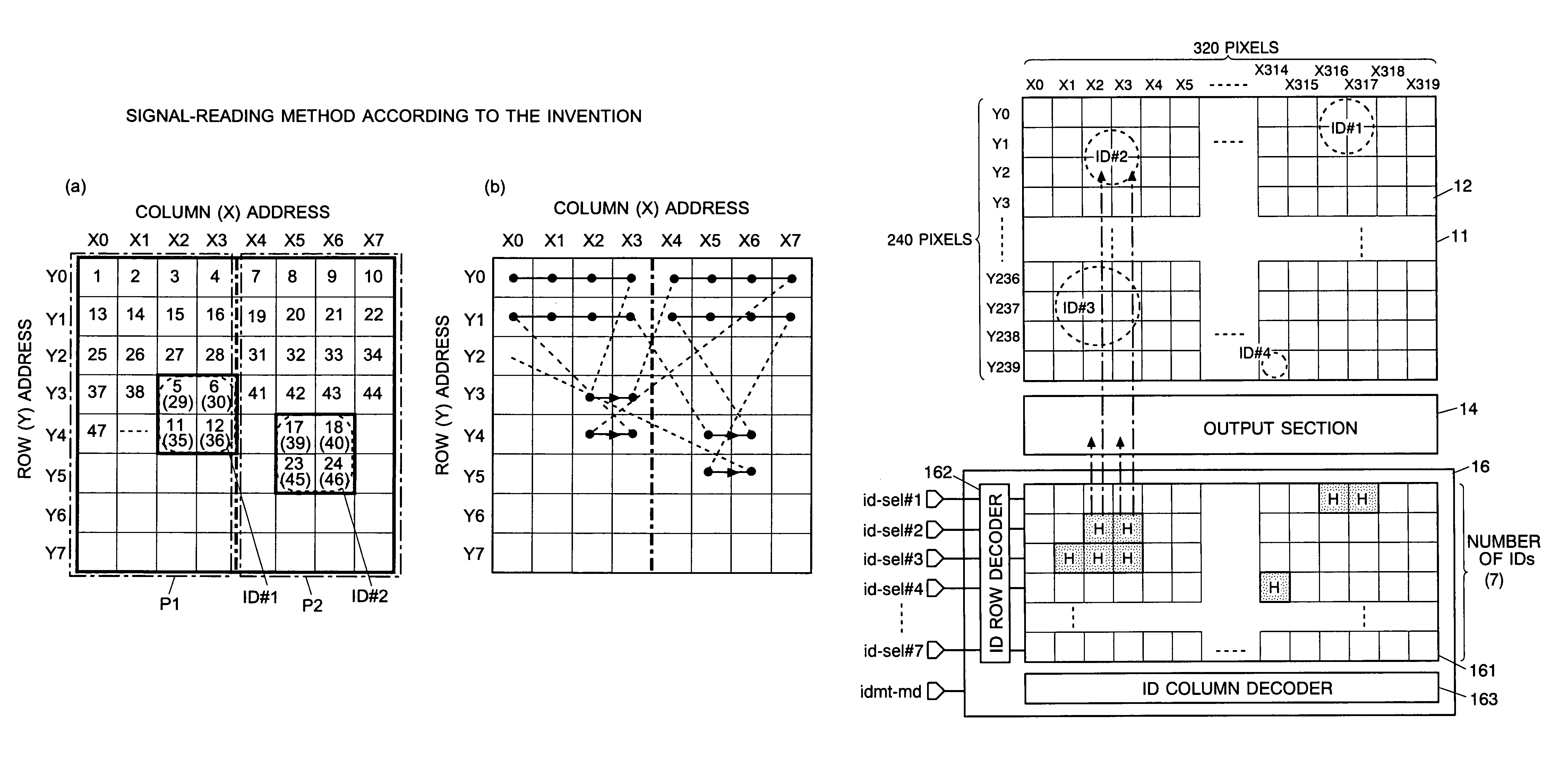
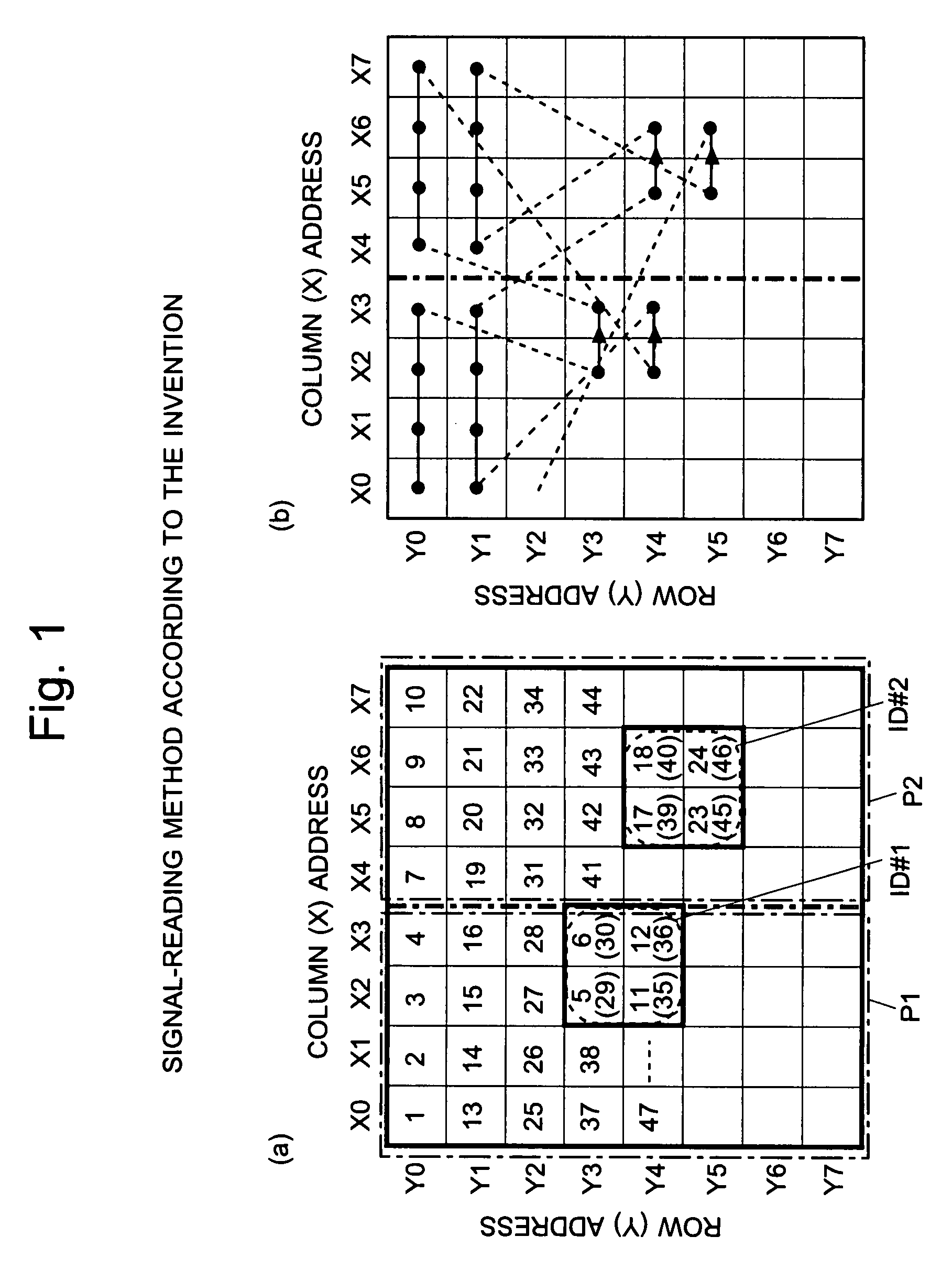
Imaging device and method for reading signals from such device
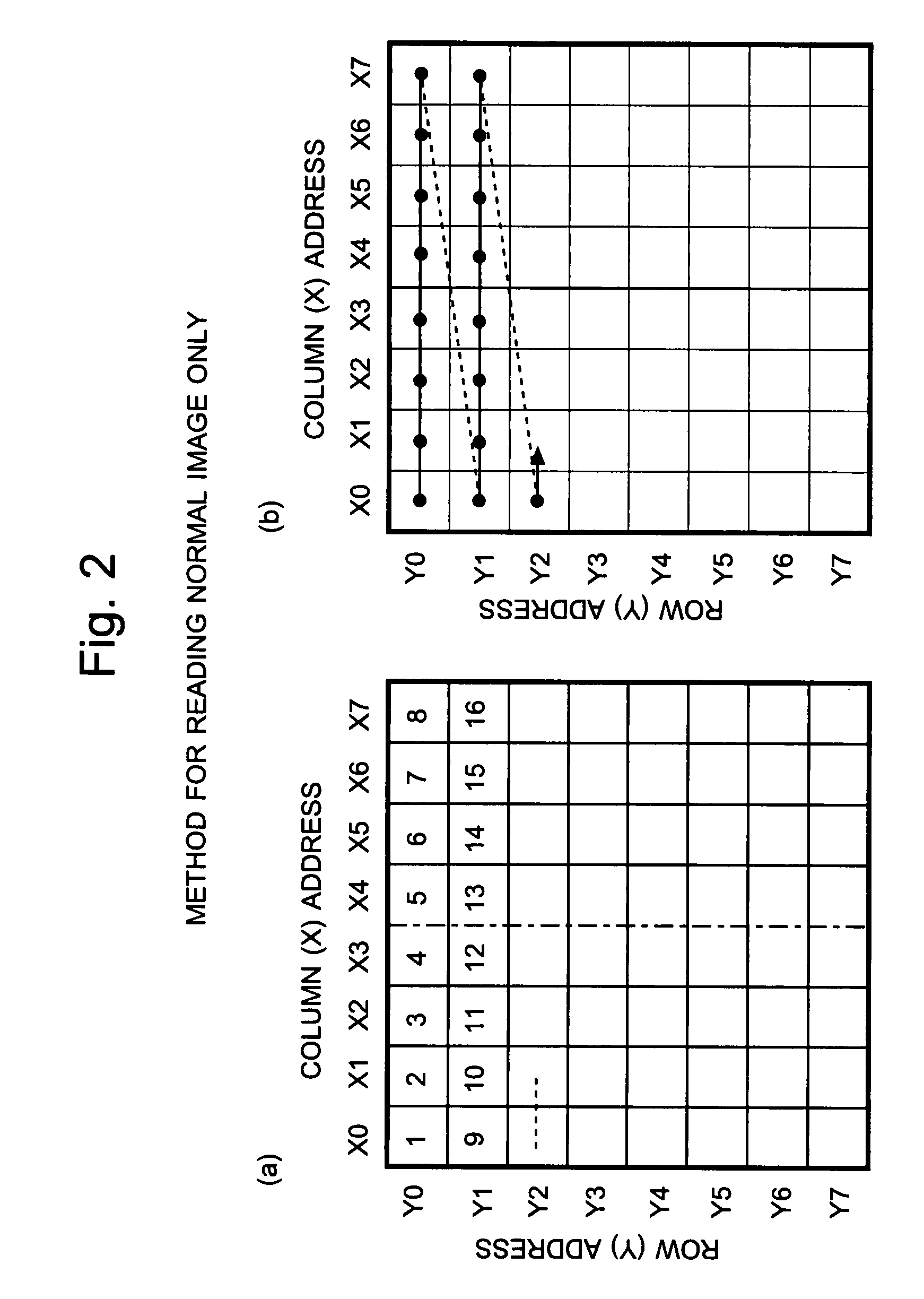
InactiveUS7728893B2Reduce the numberImprove reading speedTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
Each pixel cell (12) of an image sensor (10) is made of a 4-Tr structure, in which only one Tr for resetting a column (X) is so added to an ordinary 3-Tr APS as to reset only an arbitrary pixel selectively, thereby to confine the pixel size. When a pixel signal is to be read, the period, for which the pixel signals composing an ordinary image of one frame are read, is finely divided so that the pixel signals of the pixels receiving an ID light for the period are read out bit by bit and repeatedly. At this time, for only the column being read, an electric current is fed to a read amplifier in the pixel cell (12) or a variable gain amplifier in an output unit (14), thereby to suppress the power consumption. As a result, a lower power consumption and a higher pixel formation can be attained in an image pickup device for picking up an image and for acquiring the ID information of a light beacon existing in the image pickup range.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
Calibrated quadrature very low intermediate frequency receiver
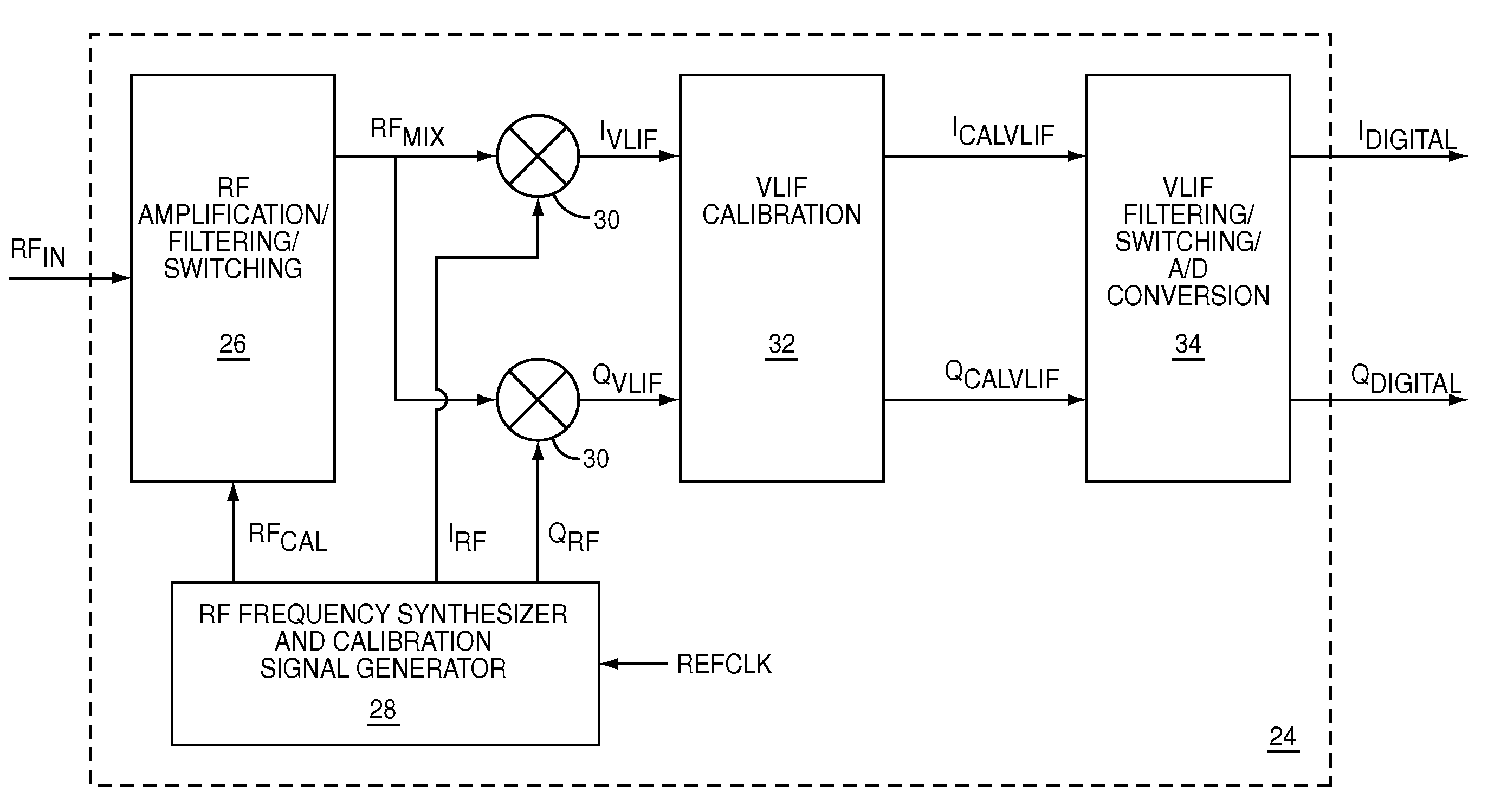
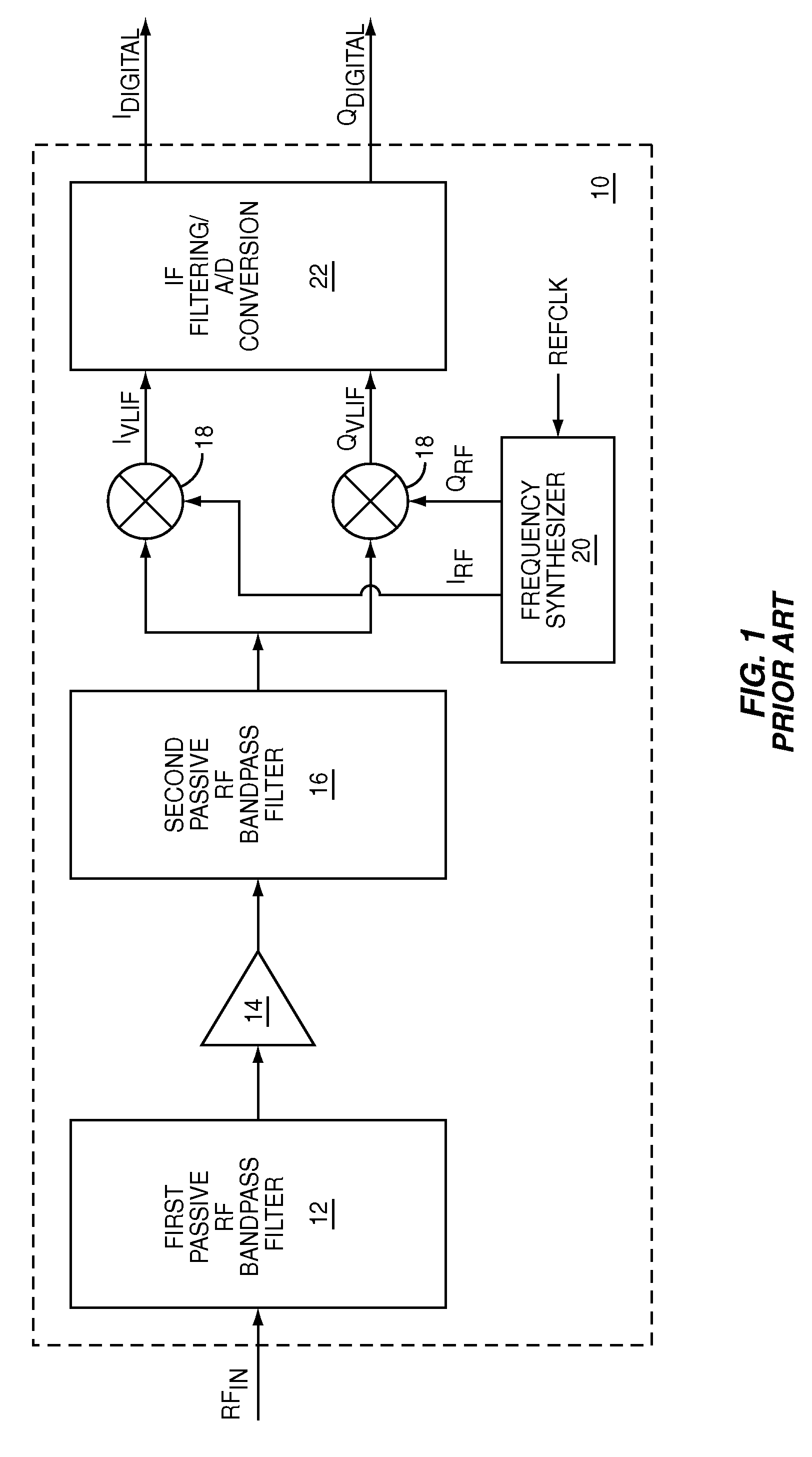
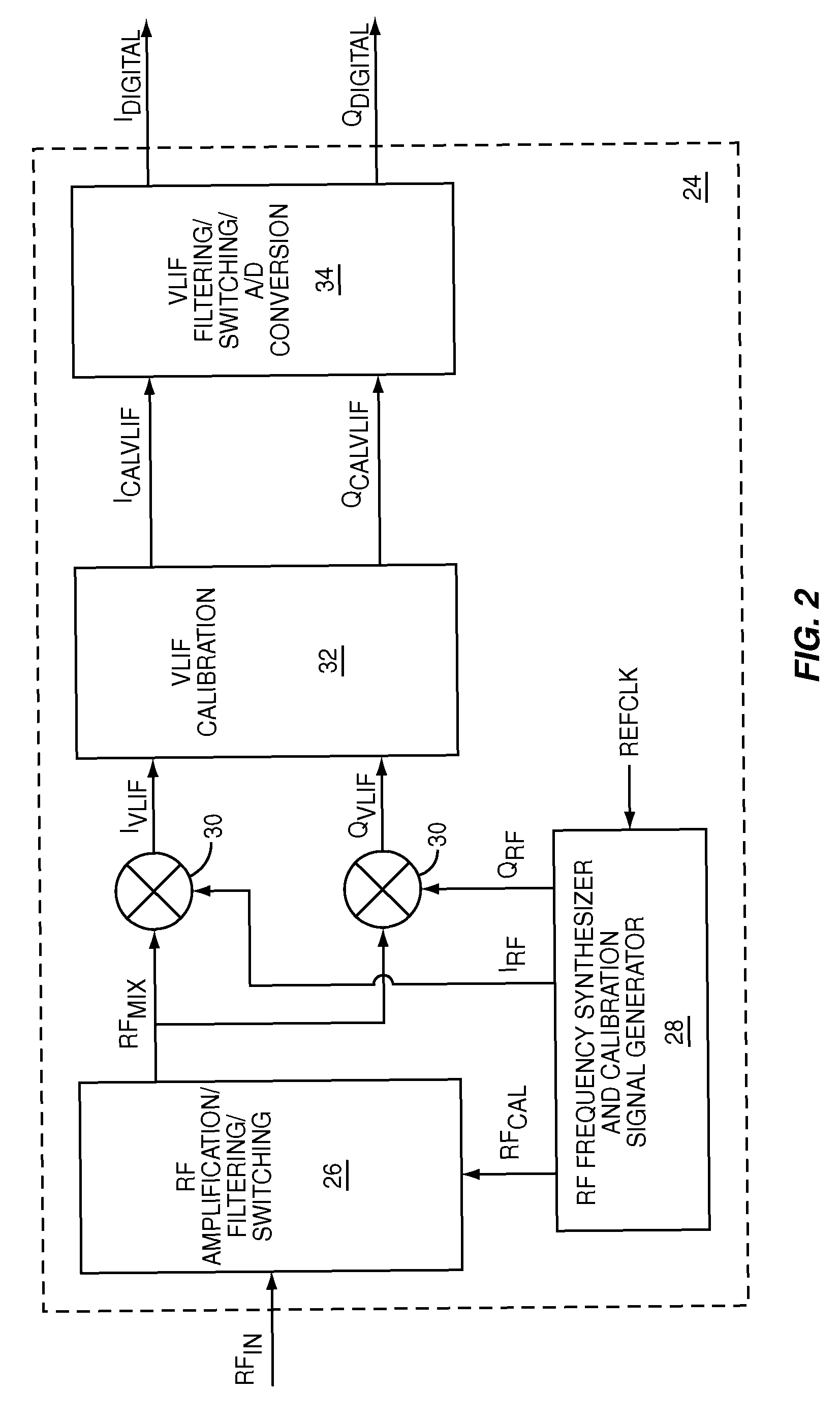
ActiveUS7773965B1Optimize VLIF image rejectionSimplifies calibration measurementTransmission monitoringAmplitude demodulationVariable-gain amplifierLocal oscillator signal
The present invention is a quadrature VLIF receiver, including calibration circuitry, and methods to closely match signal processing of an in-phase signal path and a quadrature-phase signal path to optimize VLIF image rejection. The calibration circuitry includes a variable gain variable-phase calibration signal generator, a variable gain amplifier for each signal path, phase adjustment circuitry for each signal path, and switching circuitry to support calibration steps. The calibration signal generator supplies a calibration signal at the same frequency as mixer local oscillator signals; therefore, during calibration, all signals downstream of the VLIF mixer are at DC, which simplifies calibration measurements, thereby minimizing calibration times.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Variable-gain amplifier having error amplifier with constant loop gain
ActiveUS6894564B1Increase capacityImprove performanceDifferential amplifiersAmplification control detailsAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
A translinear amplifier is disclosed. A loop amplifier drives the bases of the input and output transistor pairs from the differential collector voltage of the input pair. The loop amplifier contains a third differential pair (a gain pair). The tail current of the gain pair is inversely related to the tail current of the input pair, such that loop amplifier gain remains stable when the transconductance of the input pair changes (due, e.g., to input gain changes). In one embodiment, a linear-in-dB interface is provided that adjusts input pair tail current exponentially (and gain pair tail current exponentially and inversely) to linear voltage changes at a gain input.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
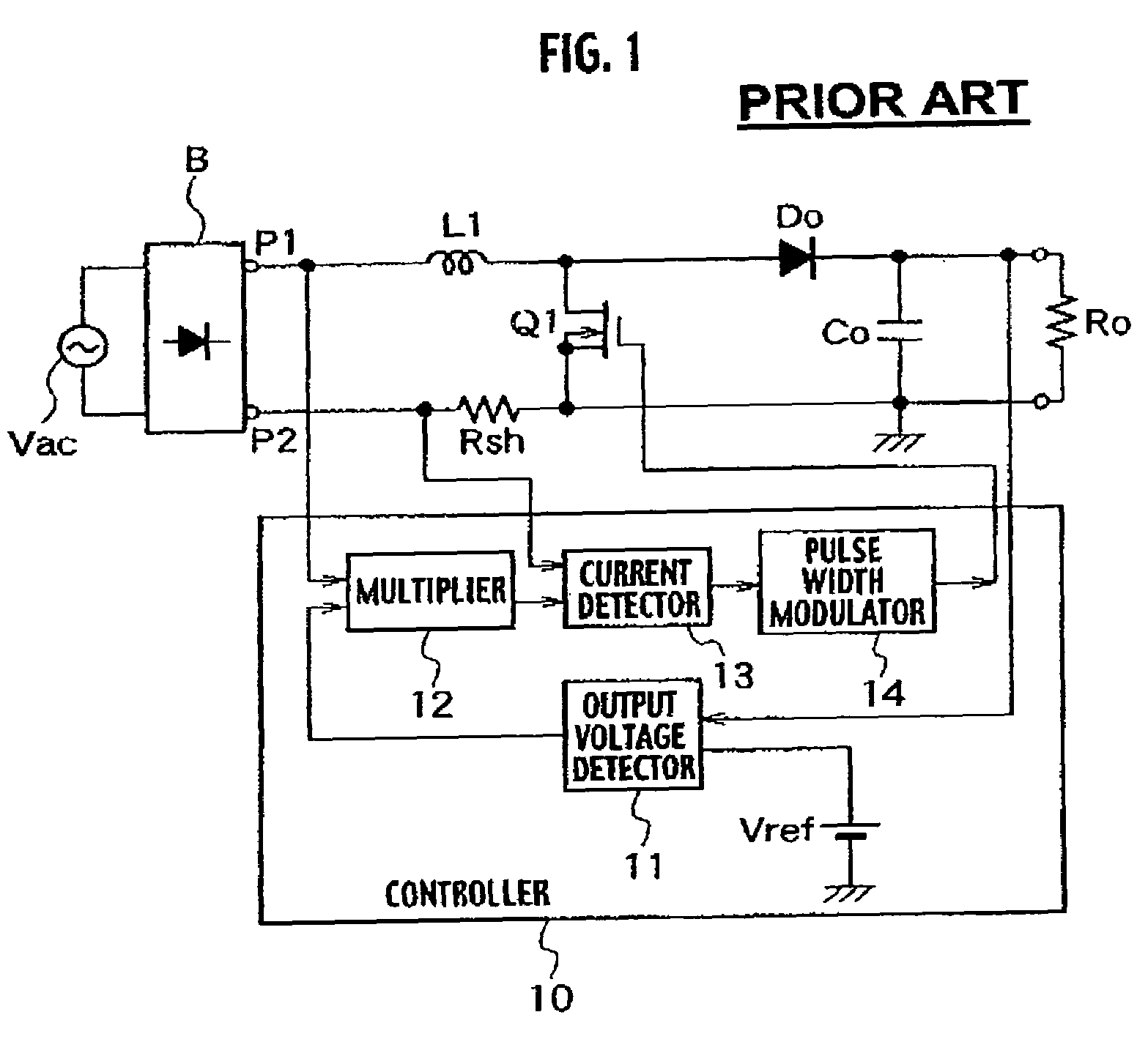
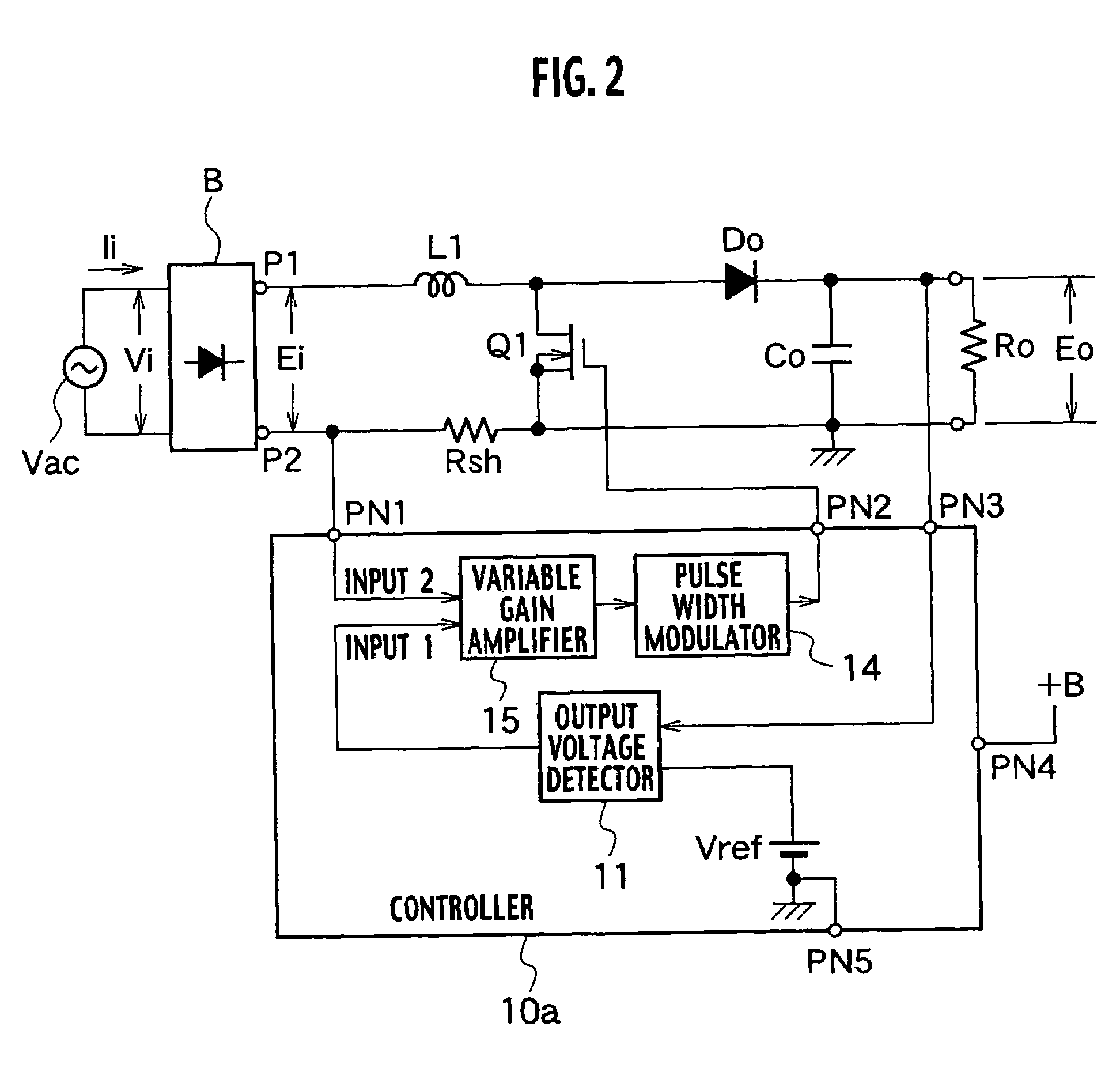
Power factor improving circuit
ActiveUS7202640B2Easy to adjustSimple structureAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
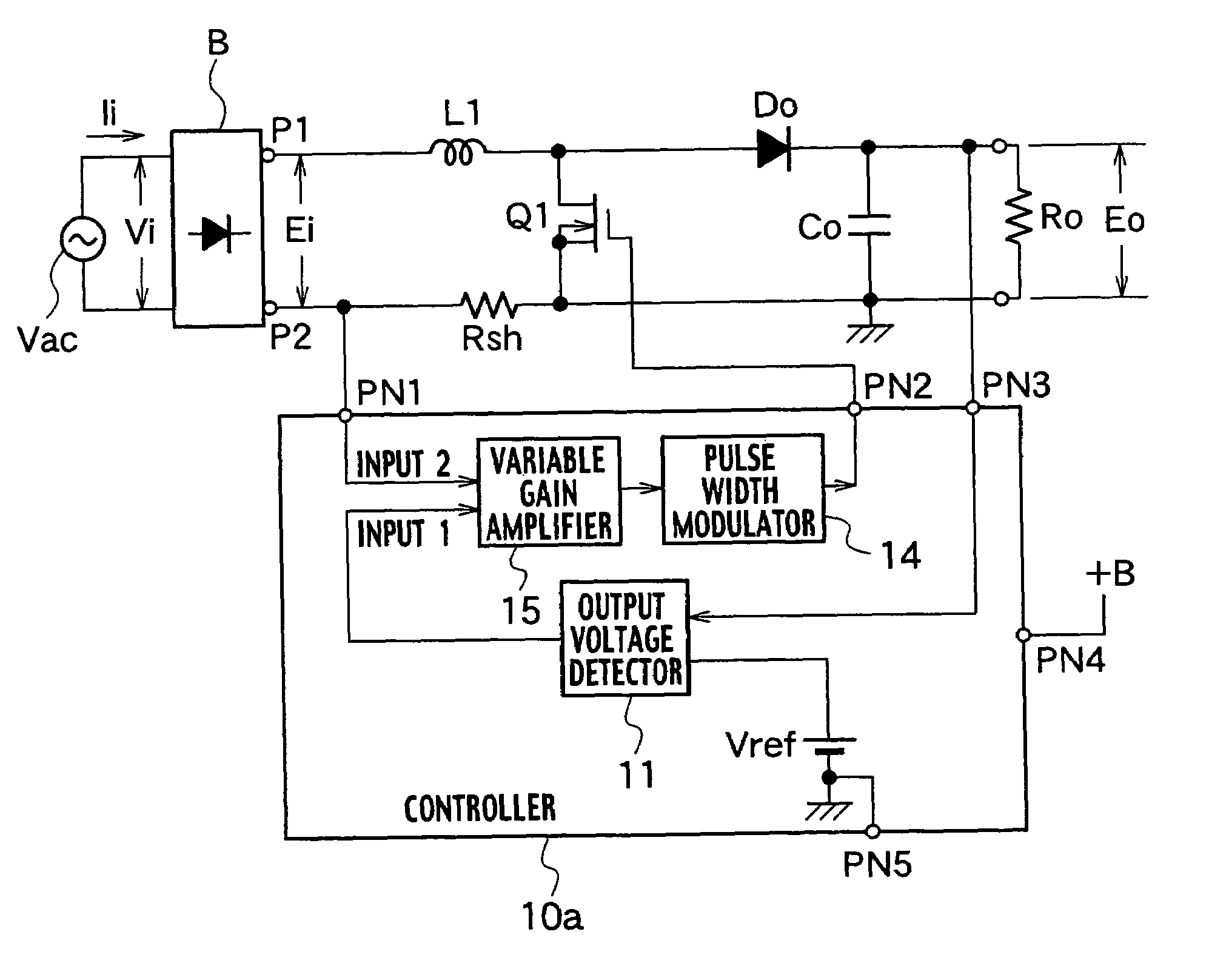
The power factor improving circuit has a current detecting resistor Rsh for detecting current conducting through a set up reactor L1 or current conducting through a switch Q1, an output voltage detector 11 which amplifies a difference between output voltage Eo and reference voltage Vref to generate error voltage, a variable gain amplifier 15 which amplifies voltage which is proportional to current detected by the current detecting resistor Rsh by varying gain in accordance with a value of the error voltage of the output voltage detector 11, and a pulse width modulator 14 which generates a pulse signal whose pulse width is controlled in accordance with a value of output of the variable gain amplifier 15 and which applies the pulse signal to the switch Q1 to control the output voltage Eo to predetermined voltage.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
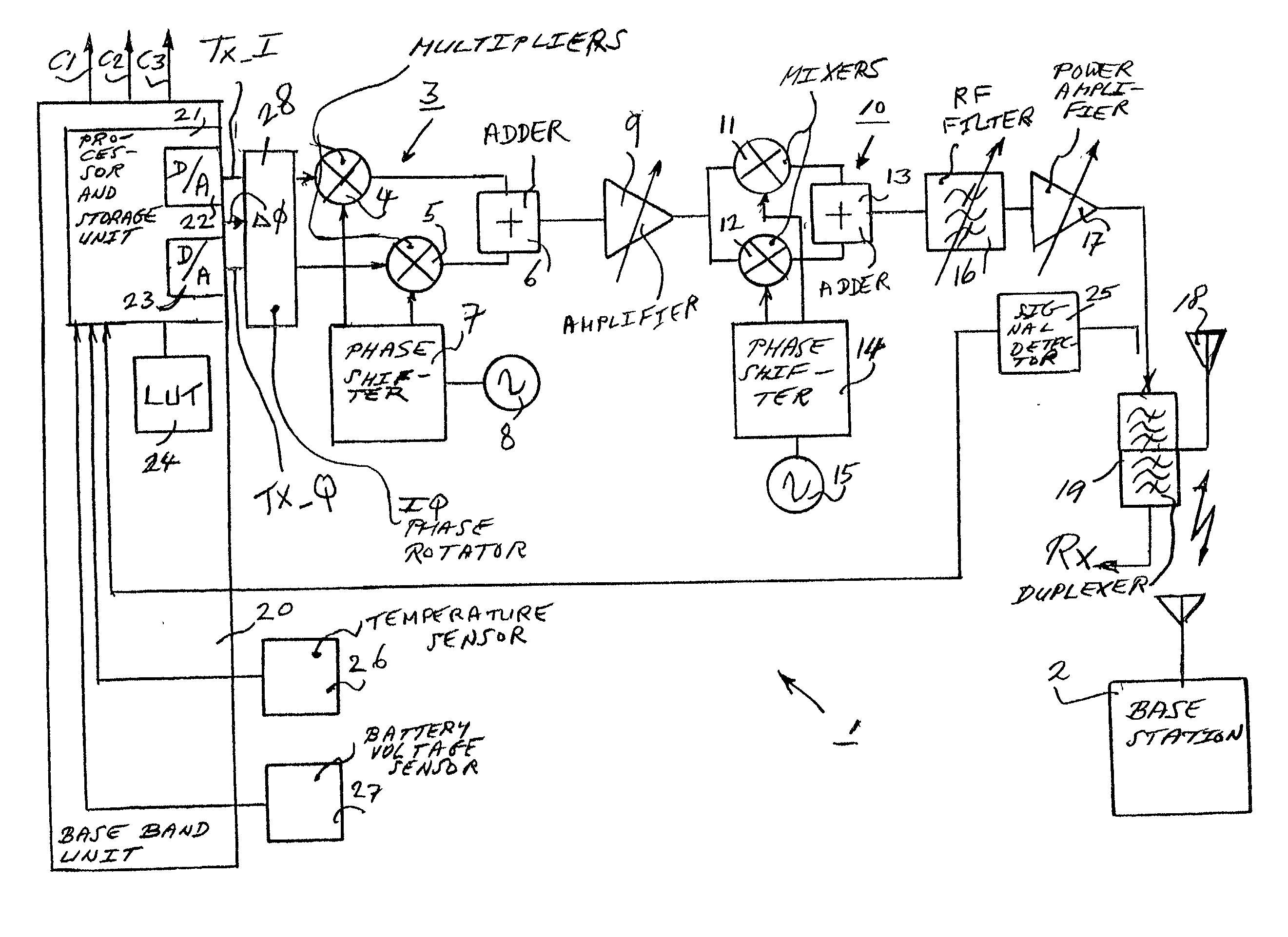
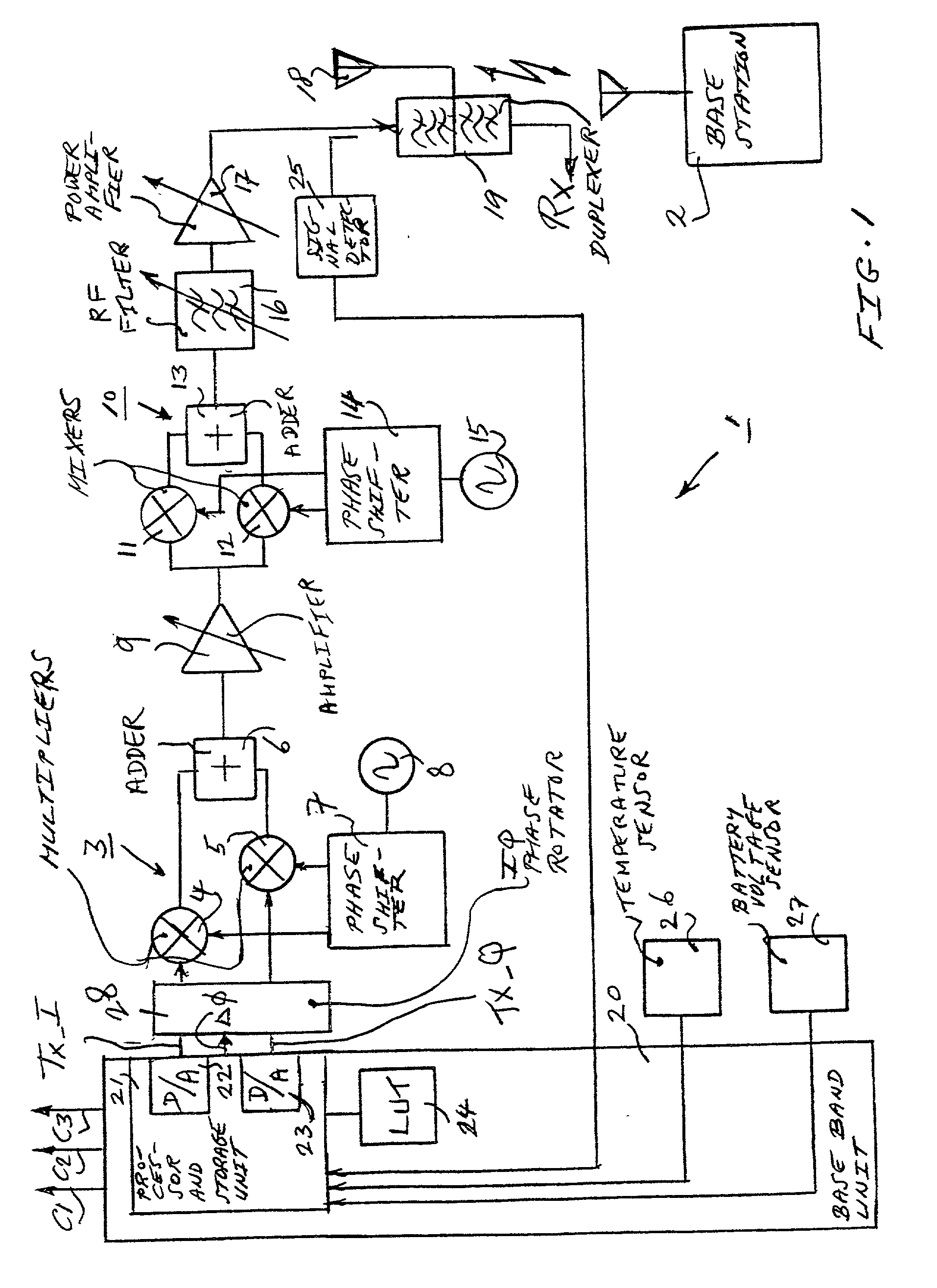
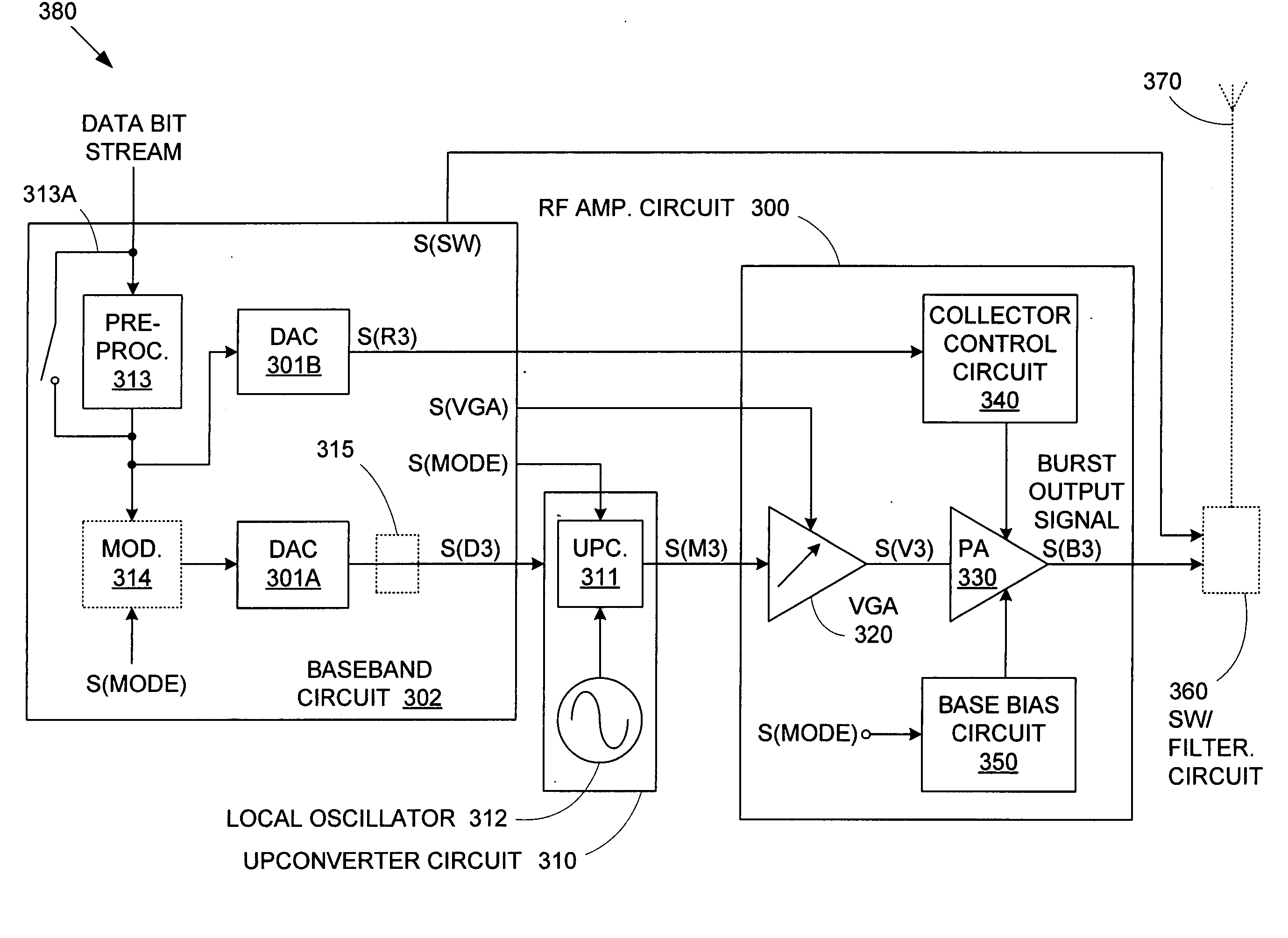
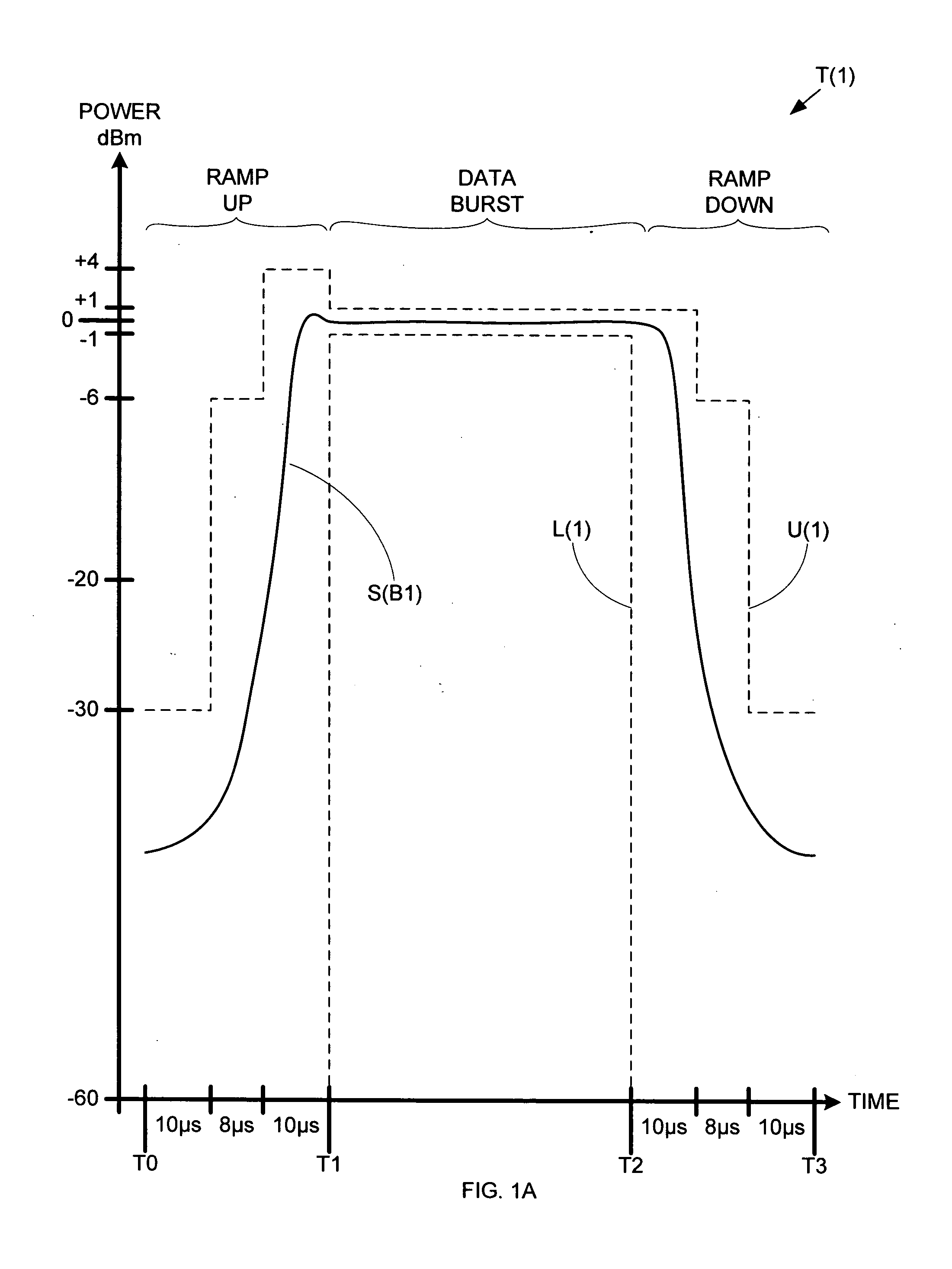
Method and architecture for dual-mode linear and saturated power amplifier operation
InactiveUS20050135502A1Eliminate needPower managementTransmission control/equalisingAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
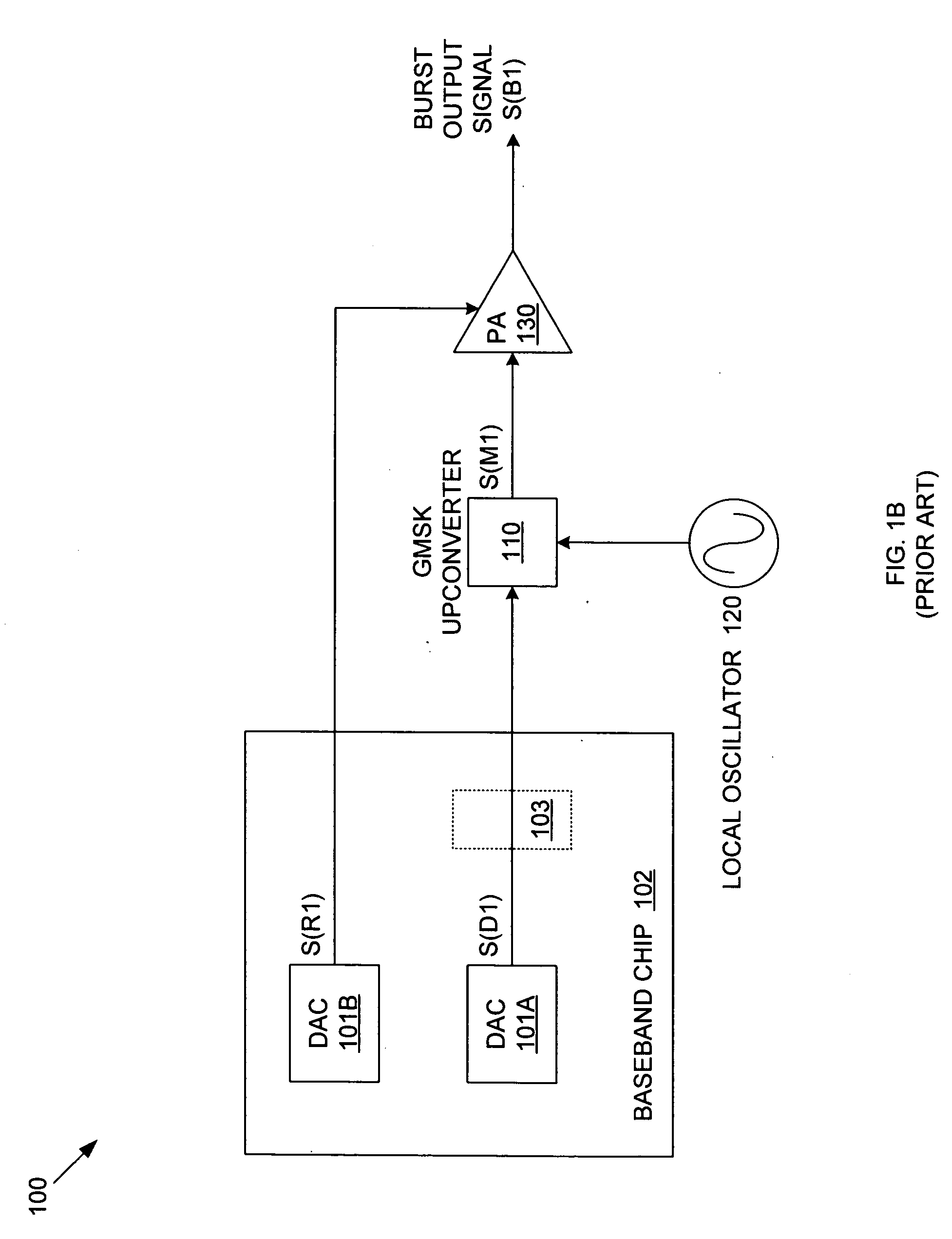
An RF transmitter provides both GSM and EDGE capability by implementing collector voltage control over the power transistor(s) in a power amplifier. During EDGE mode, linear base-biasing a power amplifier (PA) allows collector control to provide either saturated mode PA operation (during ramp up / ramp down) or linear mode PA operation (during data burst). Collector control can therefore be used to provide the accurate ramp up and ramp down profiles required for both GSM and EDGE burst output signals, and can also be used to set the level of the constant envelope data burst of a GSM burst output signal, while linear mode PA operation can provide the non-constant envelope EDGE data burst. A variable gain amplifier is used to adjust the input signal to the power amplifier such that the desired transmission level is achieved.
Owner:QORVO US INC
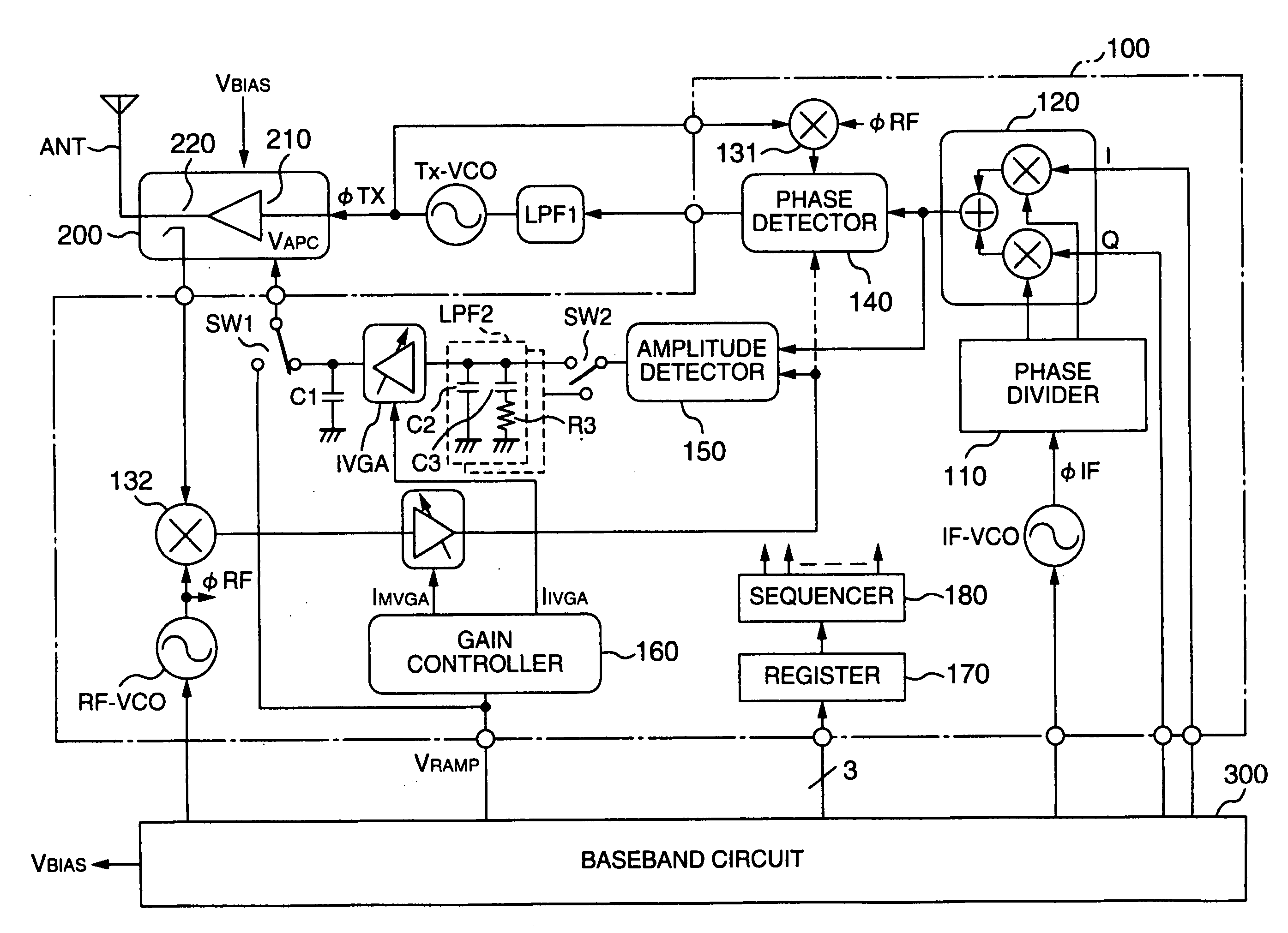
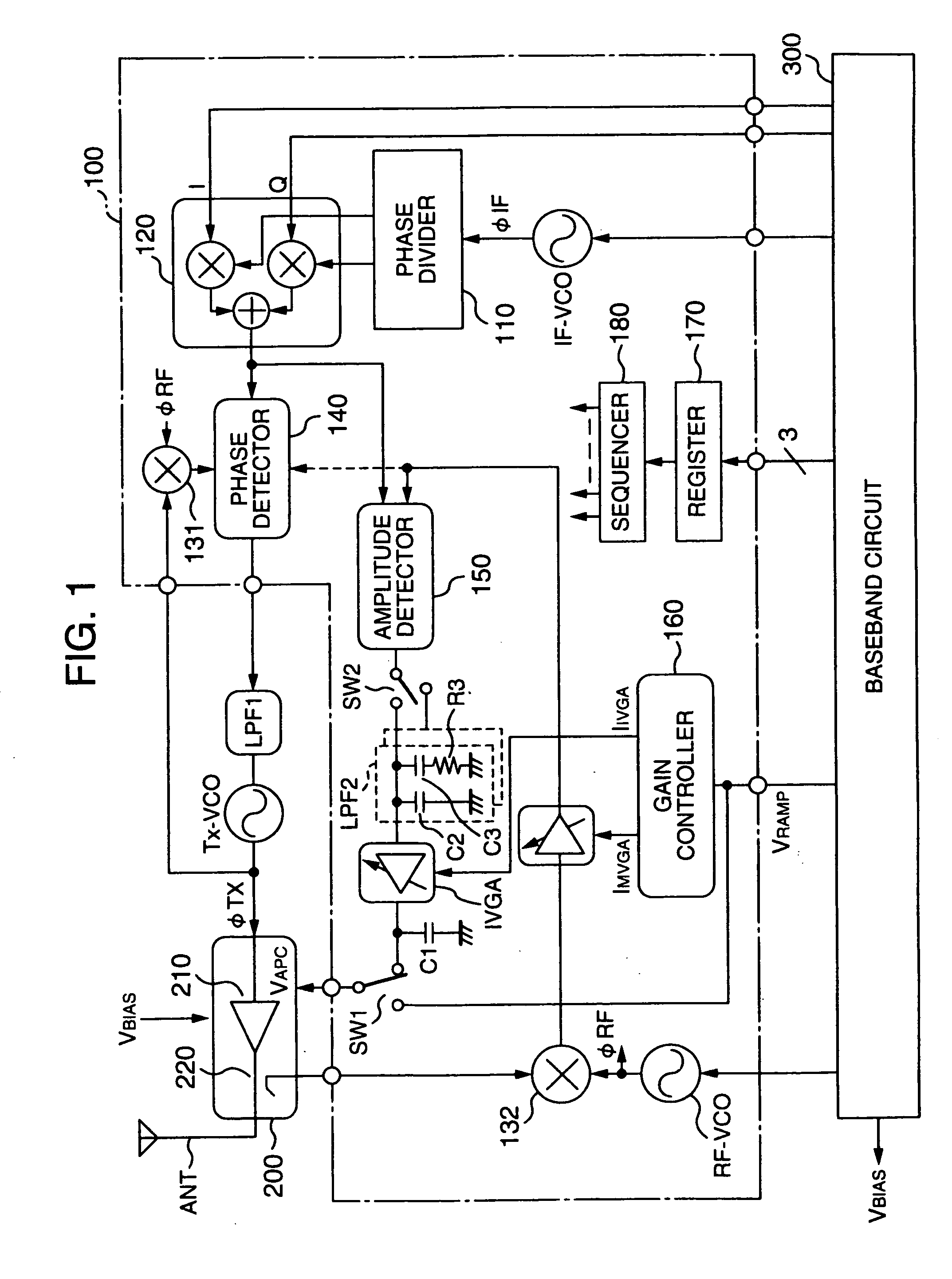
Communication semiconductor integrated circuit, a wireless communication apparatus, and a loop gain calibration method
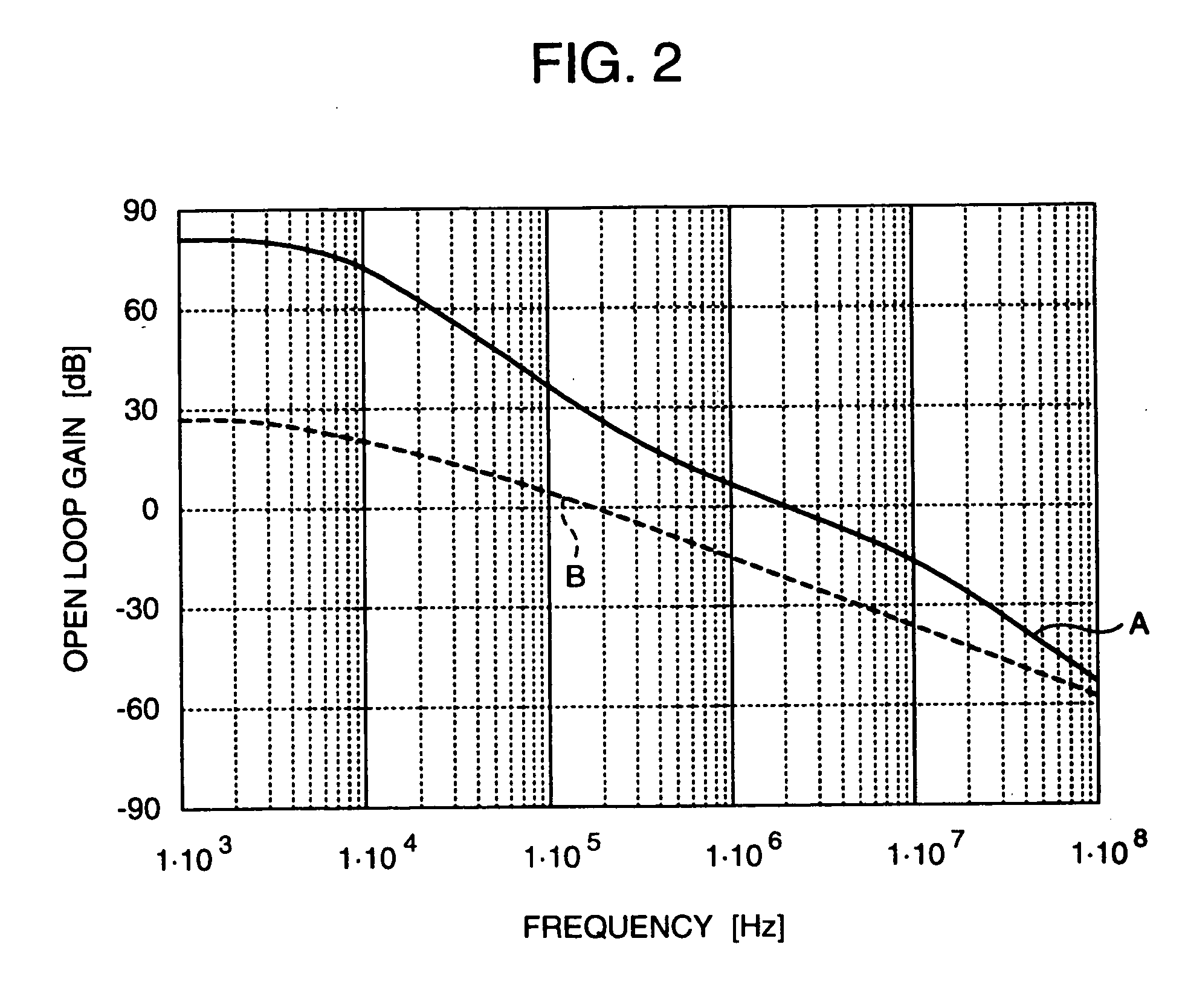
InactiveUS20060189285A1Reduced stabilityReduce a phase marginResonant long antennasGain controlControl signalAmplitude control
A polar-loop wireless communication apparatus includes, on a forward path between an amplitude detector and a power amplifier which constitute an amplitude control loop, a variable gain amplifier and a switch to change characteristics of a loop filter to output a frequency bandwidth of the amplitude control loop to an order less than an order for normal operation. The system is operated with the characteristics set to the lower order to measure outputs from the power amplifier to calibrate the output power of the power transmitter, and the register is operated with the characteristics set to the higher order to measure the open loop gain of the amplitude control. According to results of the calculation, data to correct gain characteristics of the variable gain amplifier with respect to an output control signal is stored in a nonvolatile memory of a baseband circuit.
Owner:TAKANO RYOICHI +4
High frequency signal receiver and semiconductor integrated circuit
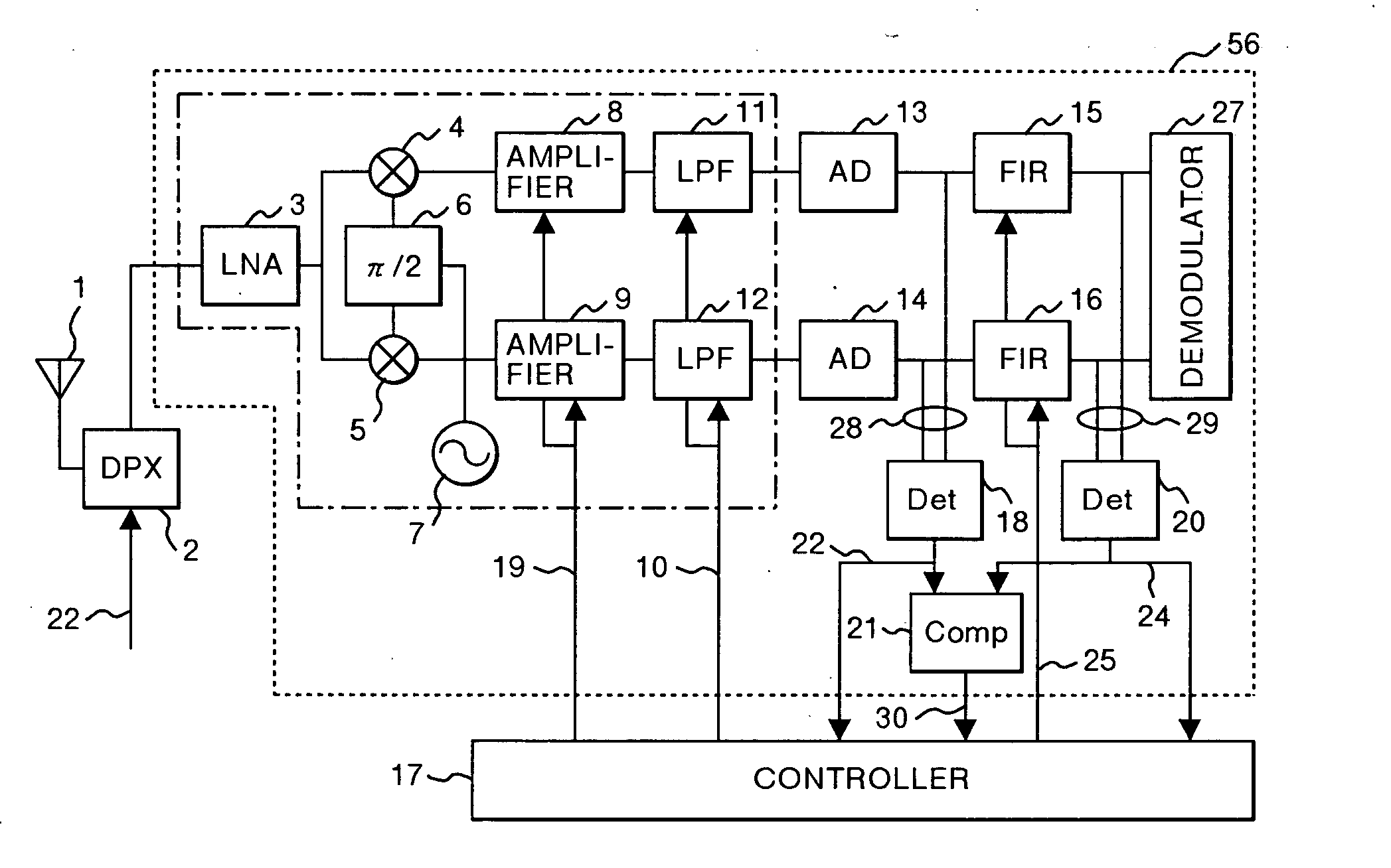
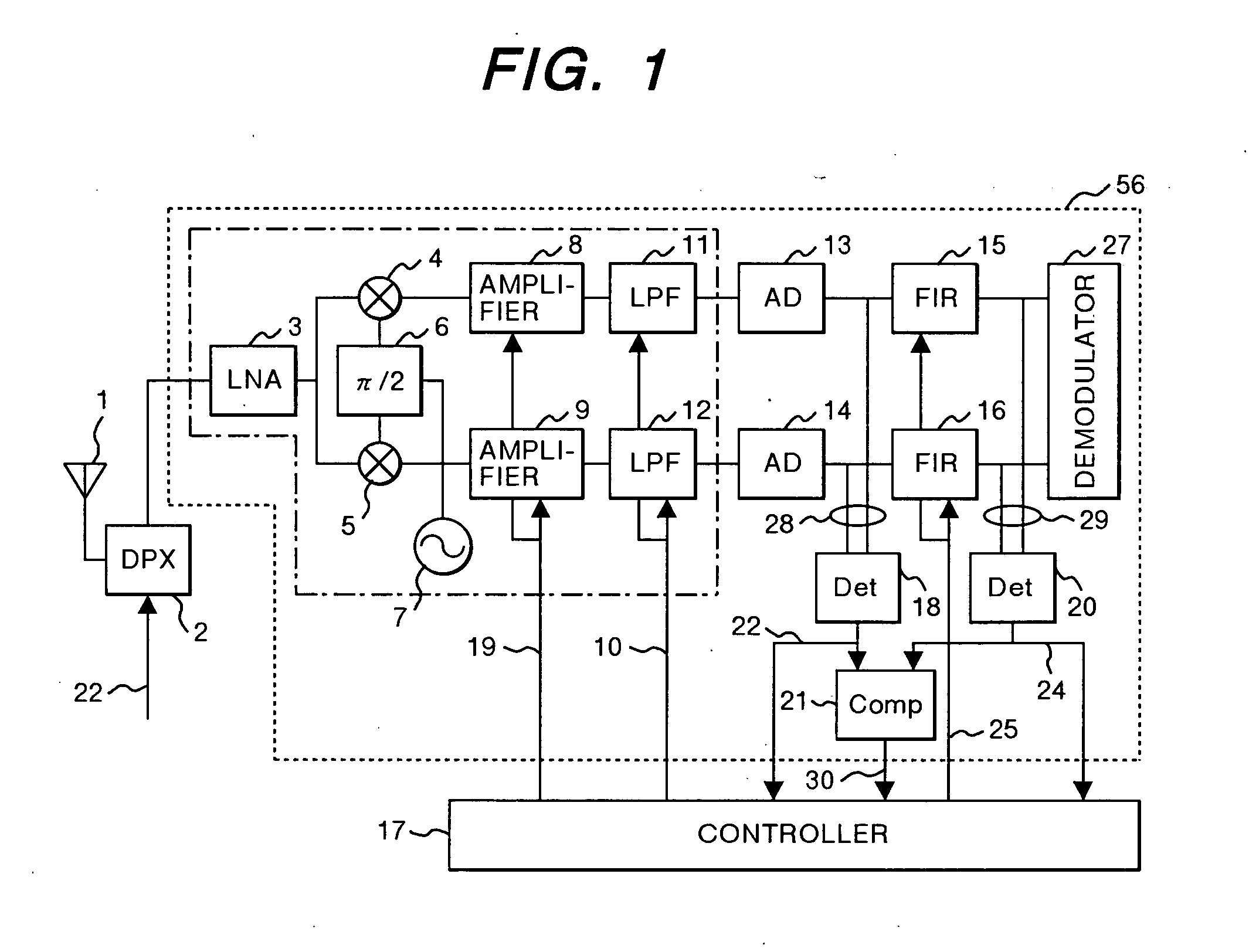
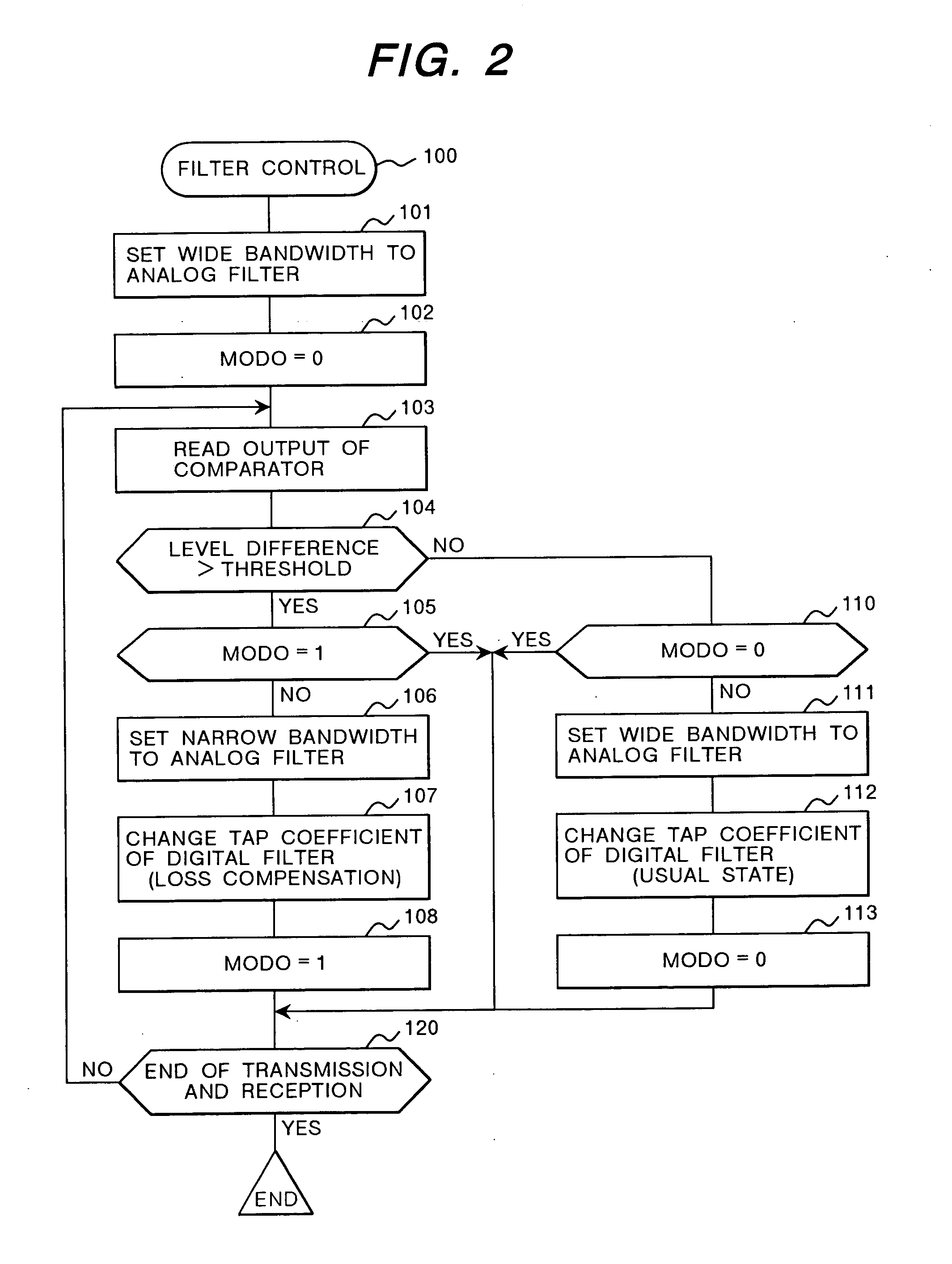
InactiveUS20050147192A1Wide dynamic rangeDeterioration of characteristicGain controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsVariable-gain amplifierInterference wave
A high frequency signal receiver comprising a variable gain amplifier, a first filter for restricting a bandwidth of an analog baseband signal, an AD converter connected to the first filter, a second filter for restricting the bandwidth of an output of the AD converter, an interference wave detection circuit for detecting the level of an interference wave in the received signal, and a controller for controlling the first filter to have a wide bandwidth when the level of the interference wave is lower than a threshold level, and switching the first filter to have a narrow bandwidth while changing the characteristics of the second filter so as to compensate deterioration of the pass-band of the first filter when the level of the interference wave is equal to or greater than the threshold level.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Downstream transmitter and cable modem receiver for 1024 QAM
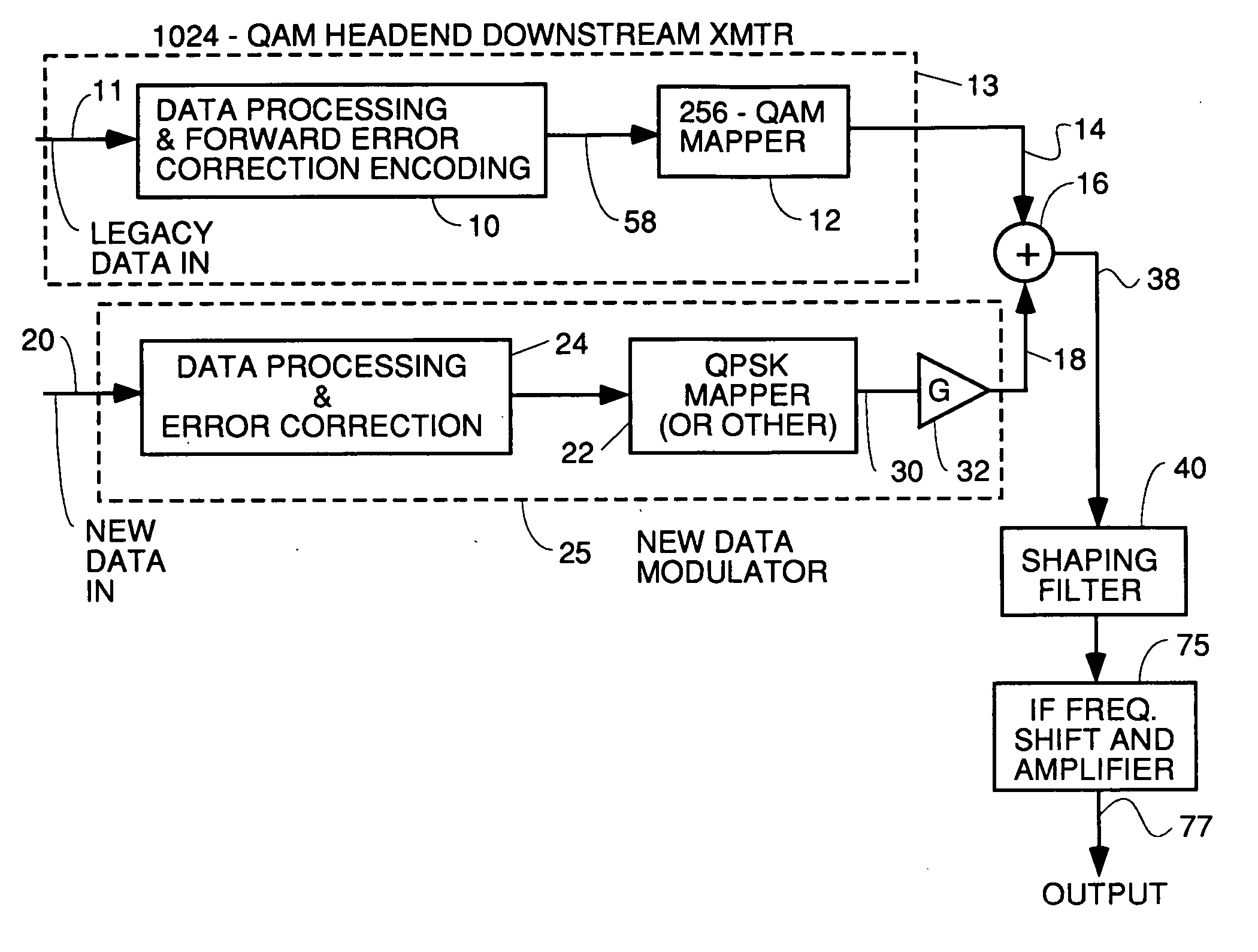
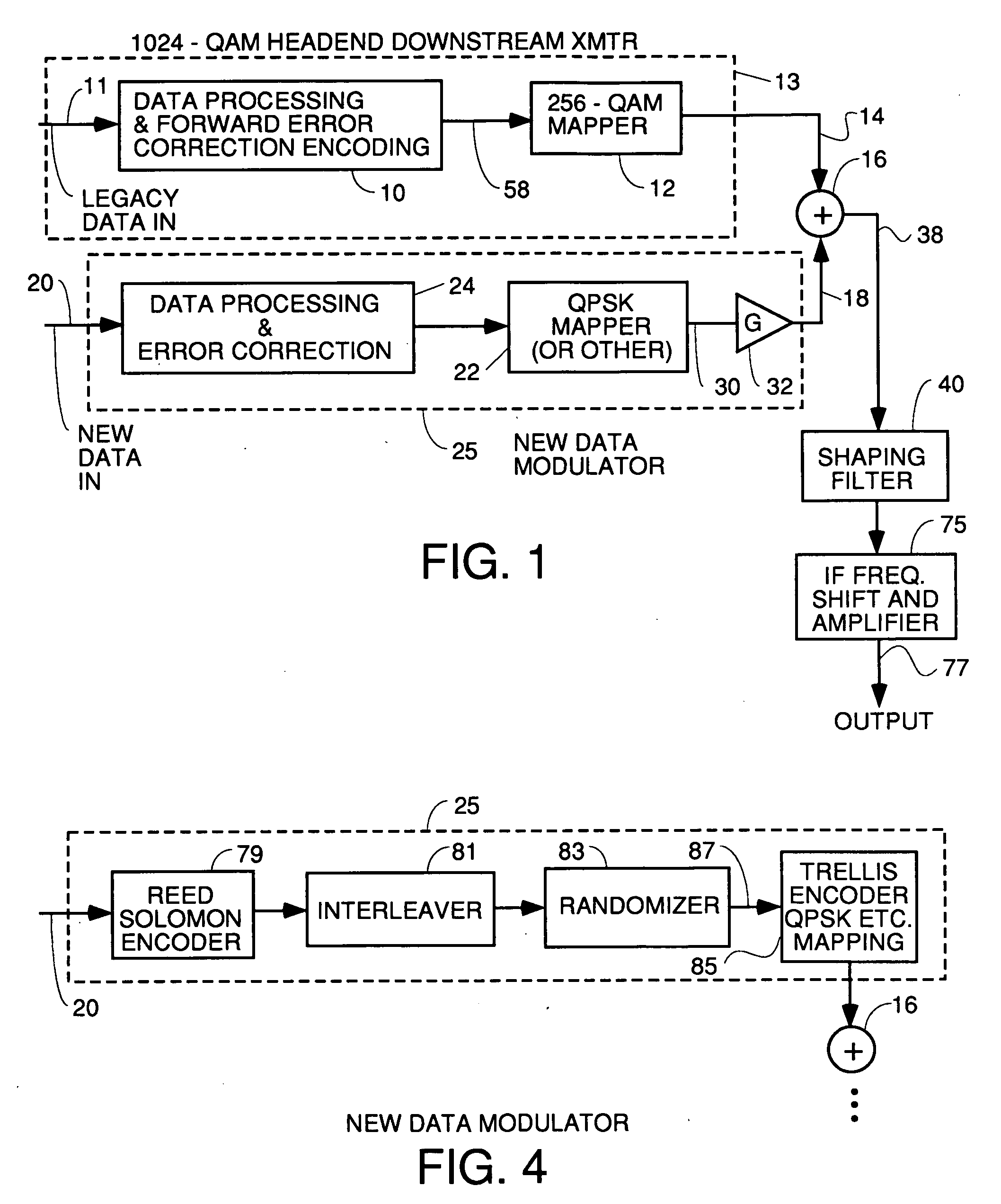
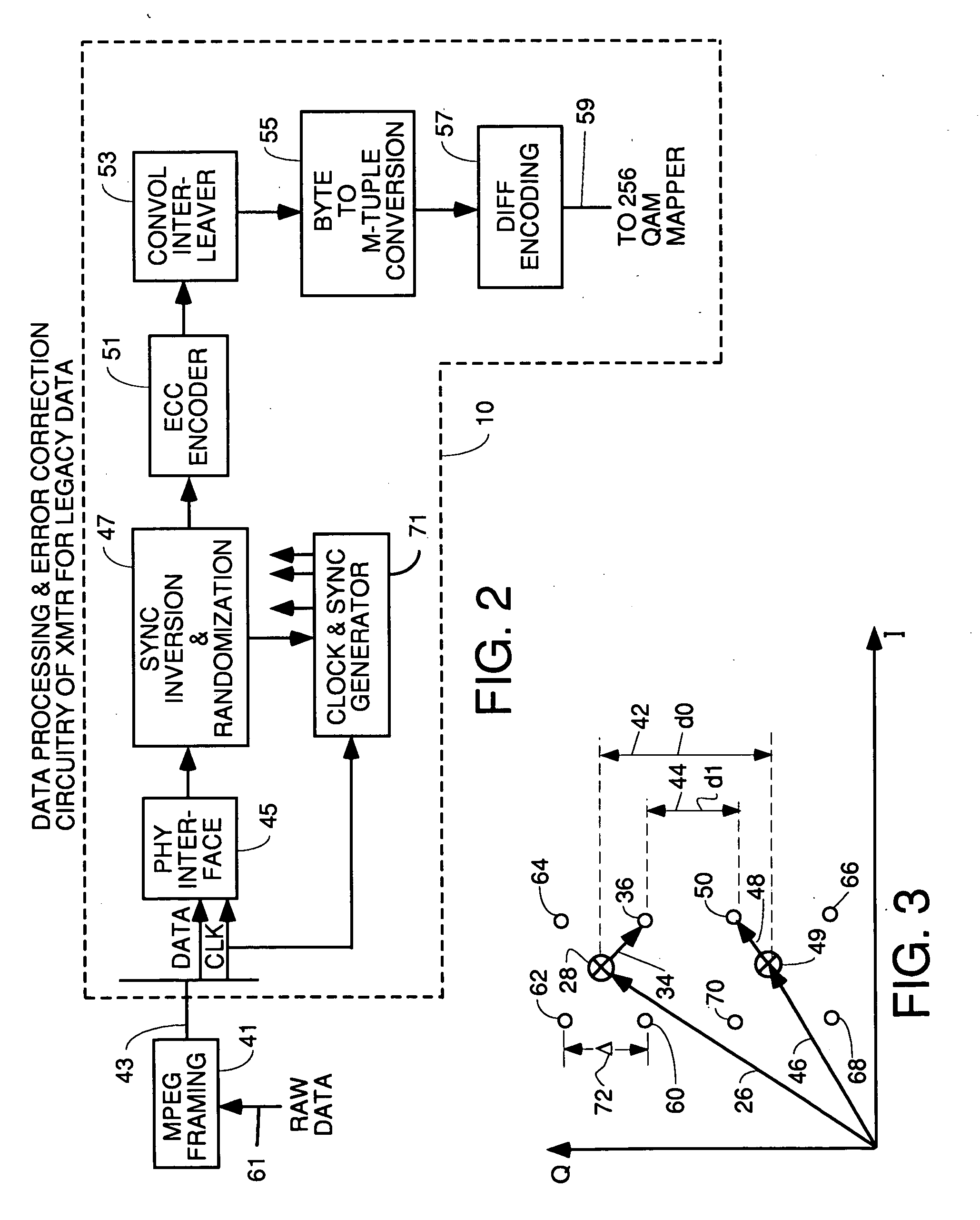
InactiveUS20060085727A1Shortening HFC lengthMinimize reflectionSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationData representation error detection/correctionModem deviceAudio power amplifier
A headend transmitter that transmits 1024 QAM including a 256 QAM modulator which has been modified to have more aggressive forward error correction processing. The 256 QAM modulator outputs 256 QAM points to a summer. Another data modulator receives additional data to be transmitted in a separate, substantially less complex constellation. This modulator processes the additional data to do forward error correction thereon and then maps the encoded data into a less complex constellation such as QPSK, 16 QAM etc. The additional data constellation points are then amplified in a variable gain amplifier and fed to a summer where each additional data point is added by vector summation to one 256 QAM point. The output 1024 QAM point is filtered and shifted to the desired transmission frequency. Legacy cable modem receivers can still receive the 256 QAM point since the addition of the new data just appears to be noise which they can overcome using the parity bits encoded in the transmitted symbols. 1024 QAM cable modem receivers receive both the 256 QAM points and the new data points and output both.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
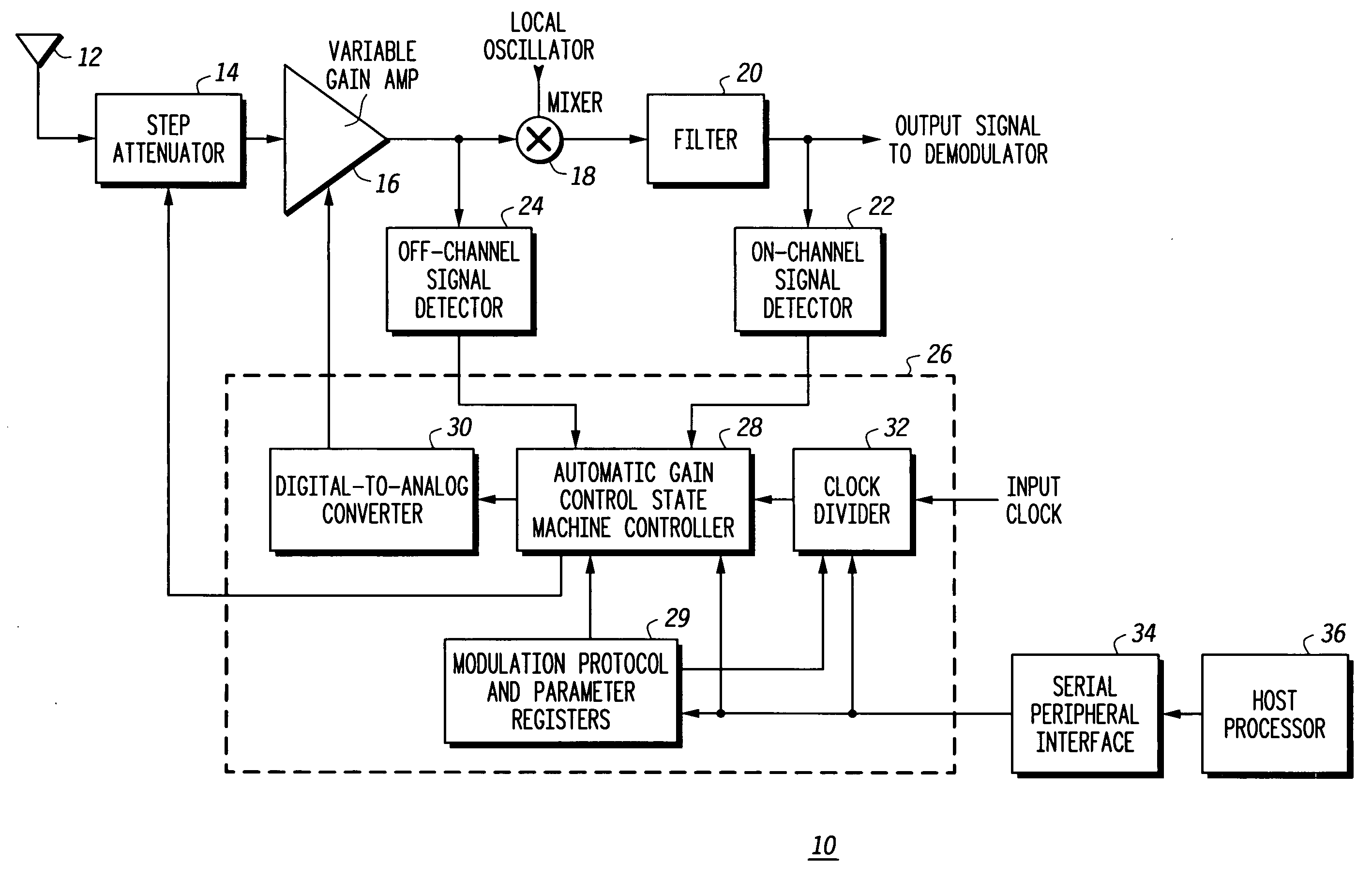
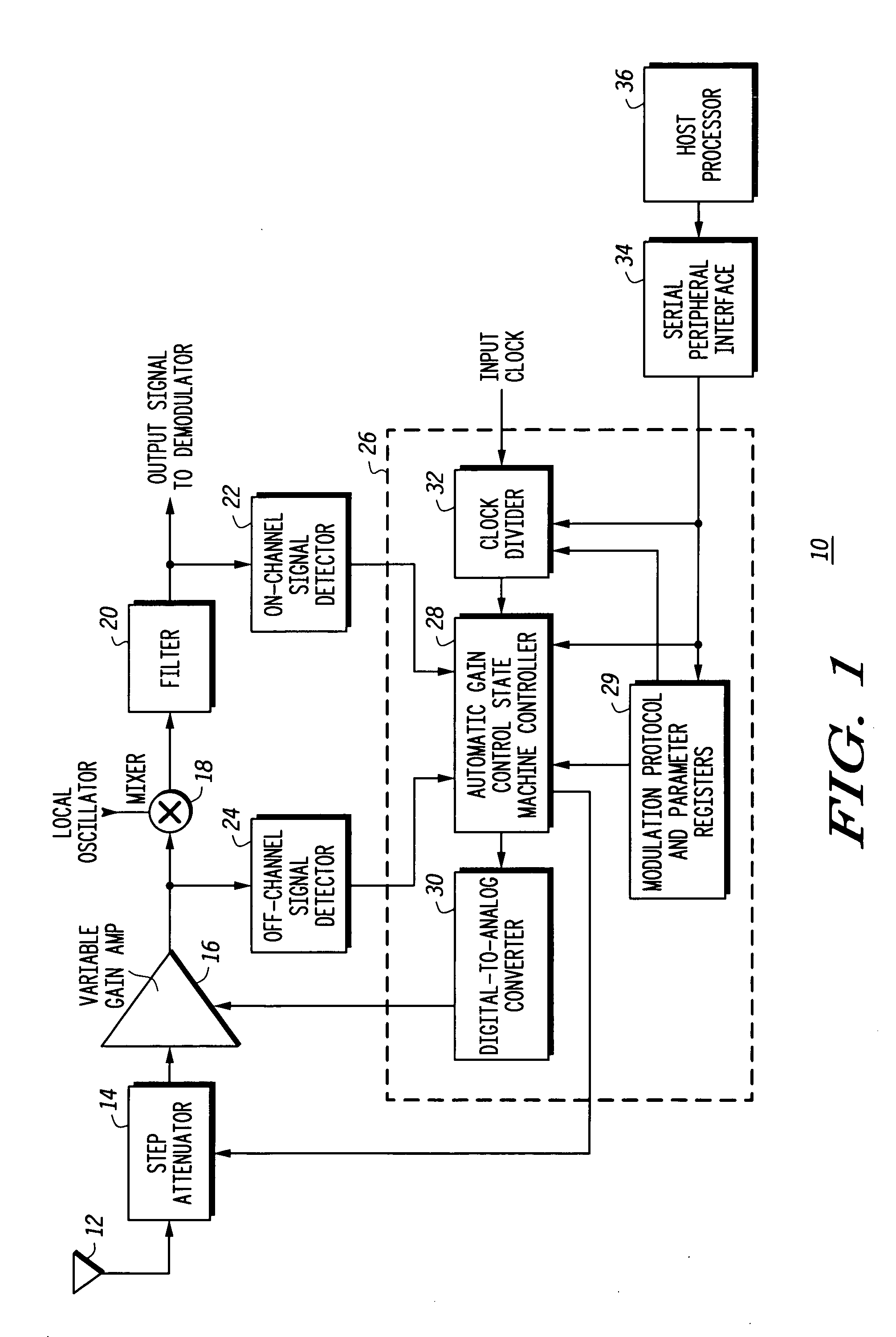
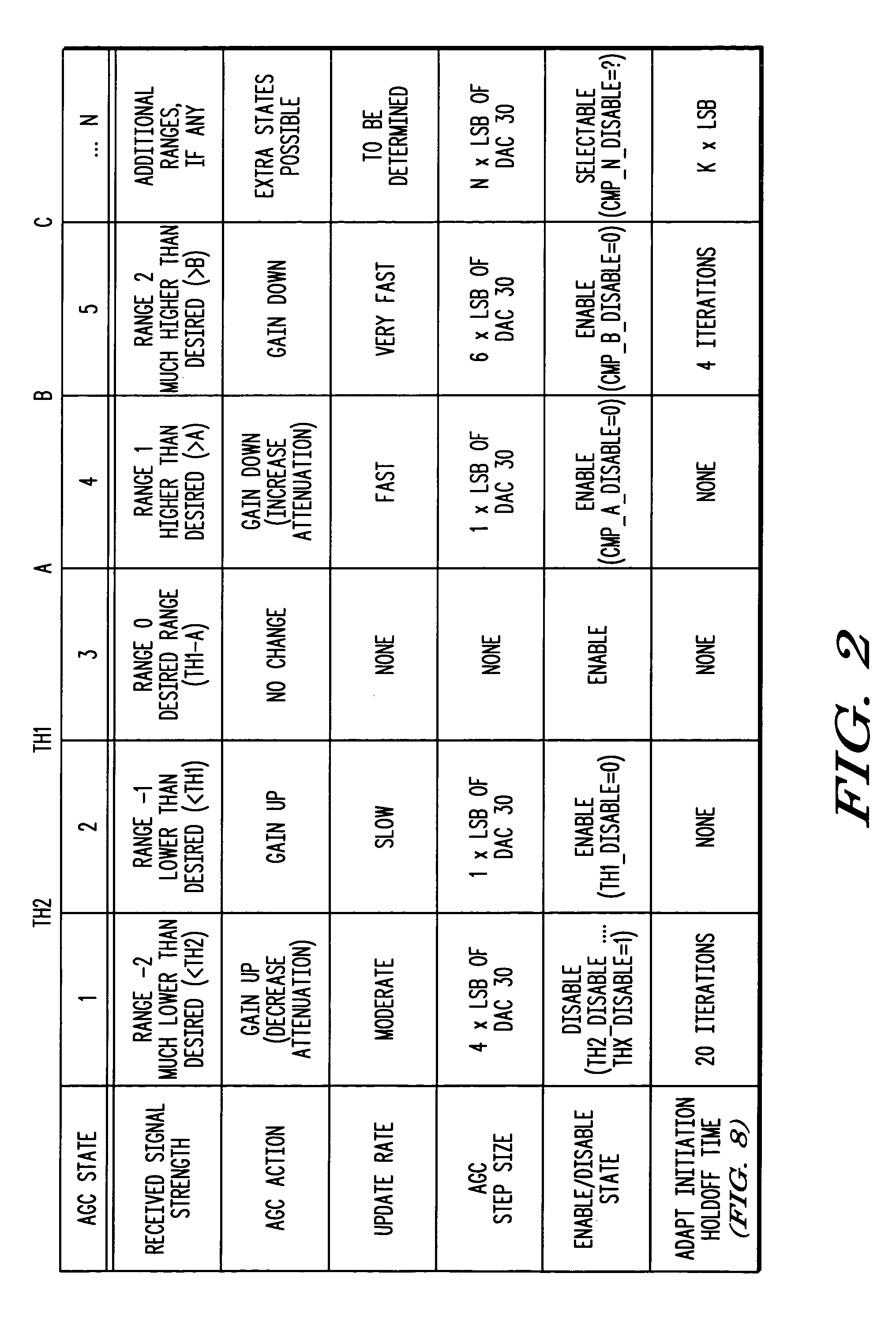
Receiver with automatic gain control that operates with multiple protocols and method thereof
ActiveUS20050047533A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAnalog signal digital controlAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
An automatic gain control (AGC) method and circuit (10) within a receiver uses a digital state machine (26) to implement the AGC function. independent from interaction with a host processor (36) and for multiple modulation protocols without duplicating circuitry. Modulation protocol and parameters for any of various gain responses are stored in a register (29). Multiple states, each corresponding to a predetermined range of RF input signal strength, are stored in the register. Each state contains parameters that determine a gain control signal for controlling a variable gain amplifier (16). The states are independent and may be selectively disabled to create asymmetric responses. Within any state, an adaptable number of iterations may be set to implement a different update rate or step size after a predetermined number of closed loop gain change iterations has not resulted in a transition to a state that represents a desired output gain.
Owner:APPLE INC
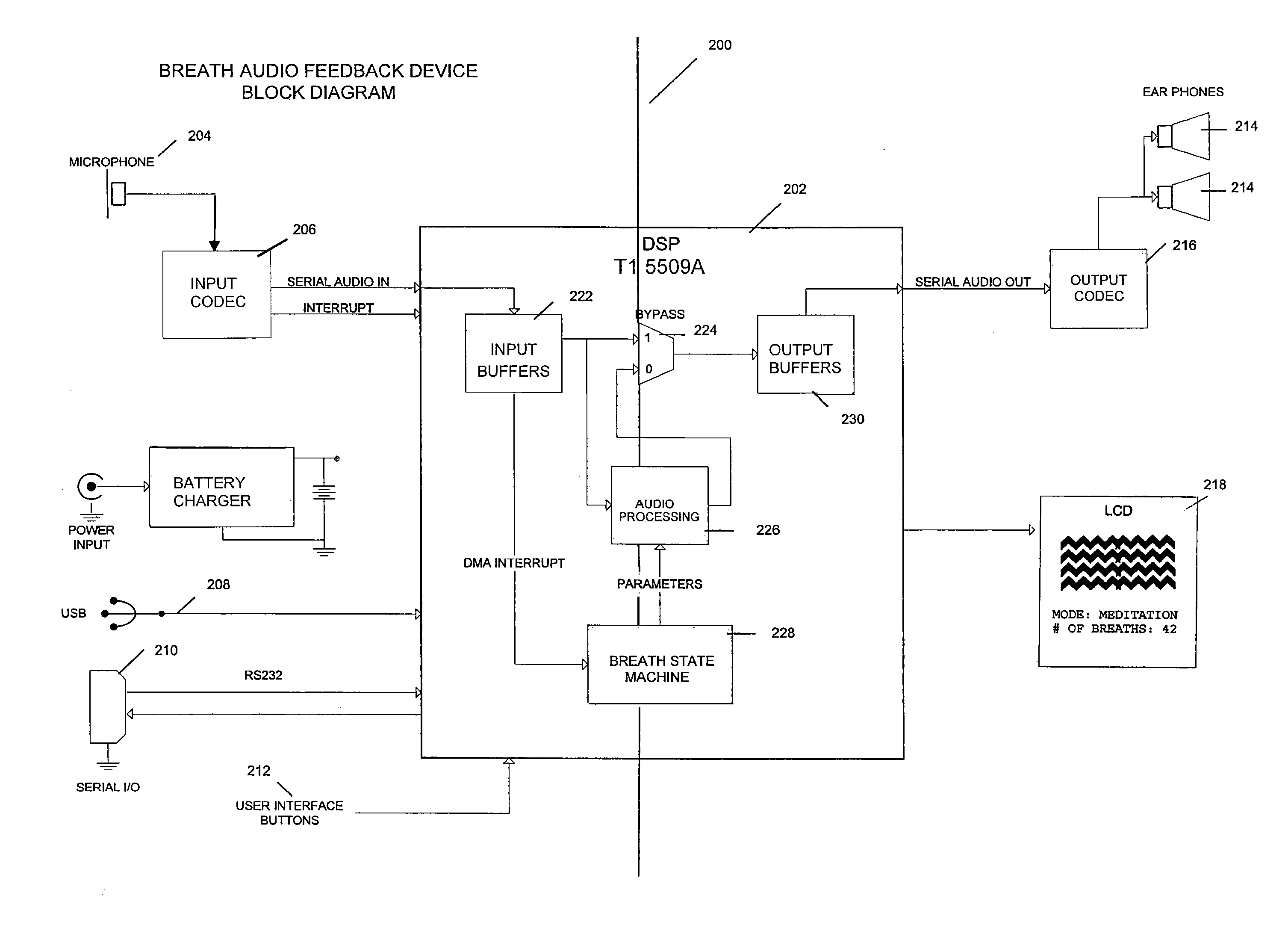
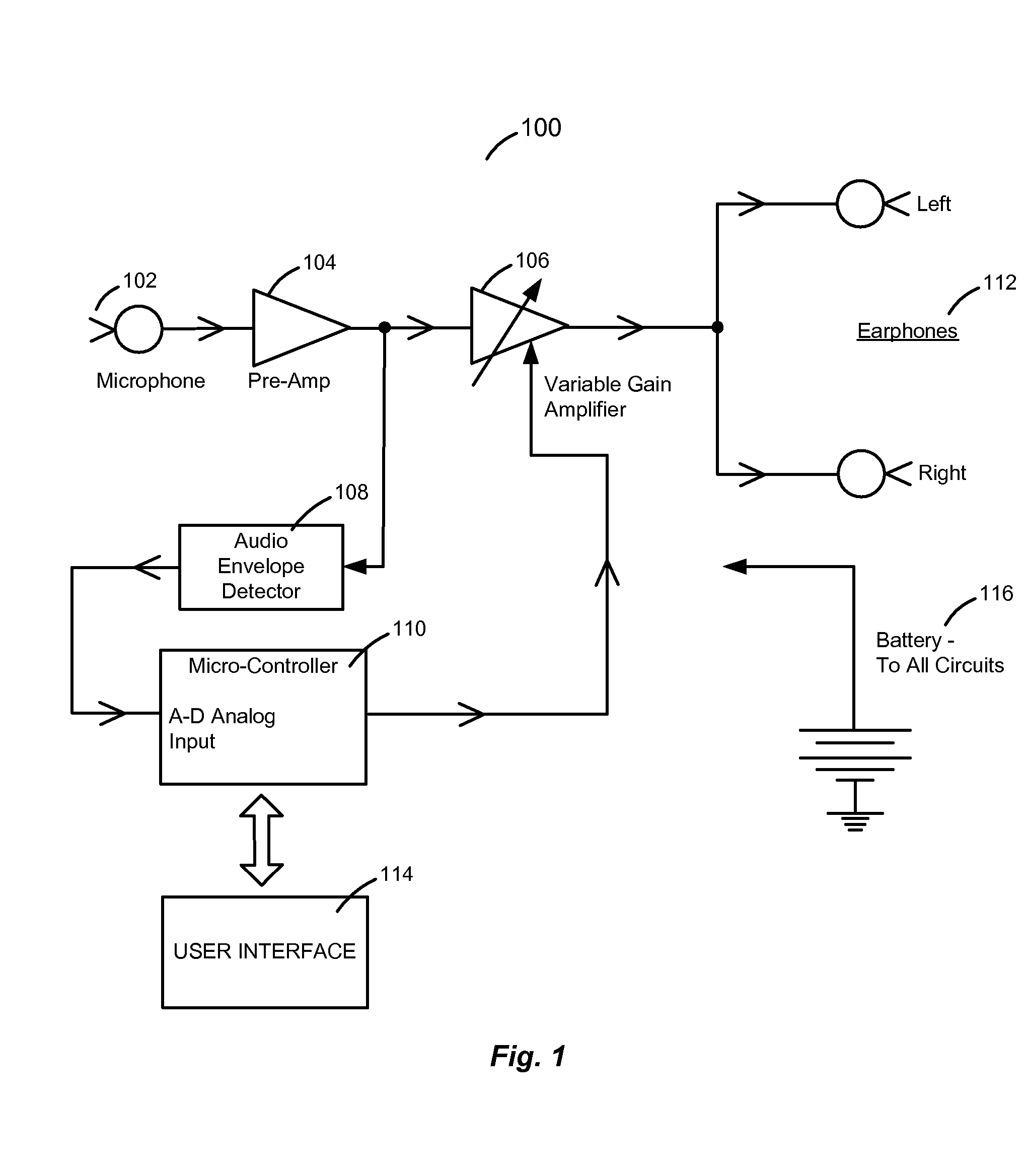
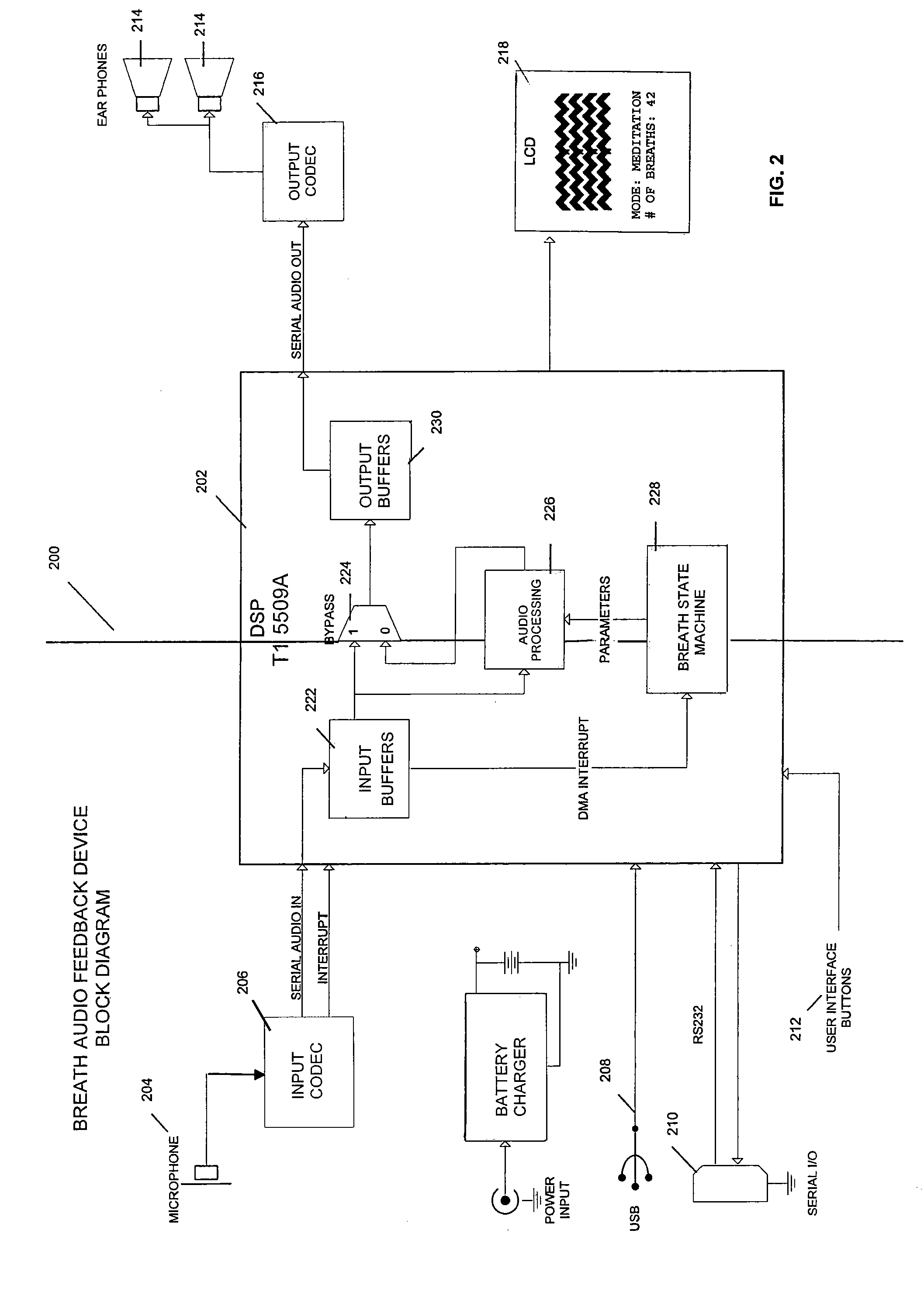
Breathing biofeedback device
ActiveUS20070173730A1Prevent sound leakagePhysical therapyAuscultation instrumentsAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
A breathing biofeedback device, having a microphone configured to acquire sounds of a user's breathing; a controller communicatively connected with the microphone, the controller processing the signals acquired by the microphone to produce an output signal, the controller processing the signal whereby the microphone signal is first pre-amplified to a voltage level that can be processed by an audio envelope detector circuit, the envelope detector signal is then fed into the analog-to-digital converter input of the controller allowing it to constantly sample the input volume level, the controller then controlling the output volume level fed to the headphones utilizing a digitally controlled variable-gain amplifier, wherein the output signal is not modified in any manner from the original input, except in volume; and a pair of earphones connected with the controller and configured to convey the output signal to the user.
Owner:AIREHEALTH INC
Automatic gain control device for electronic endoscope
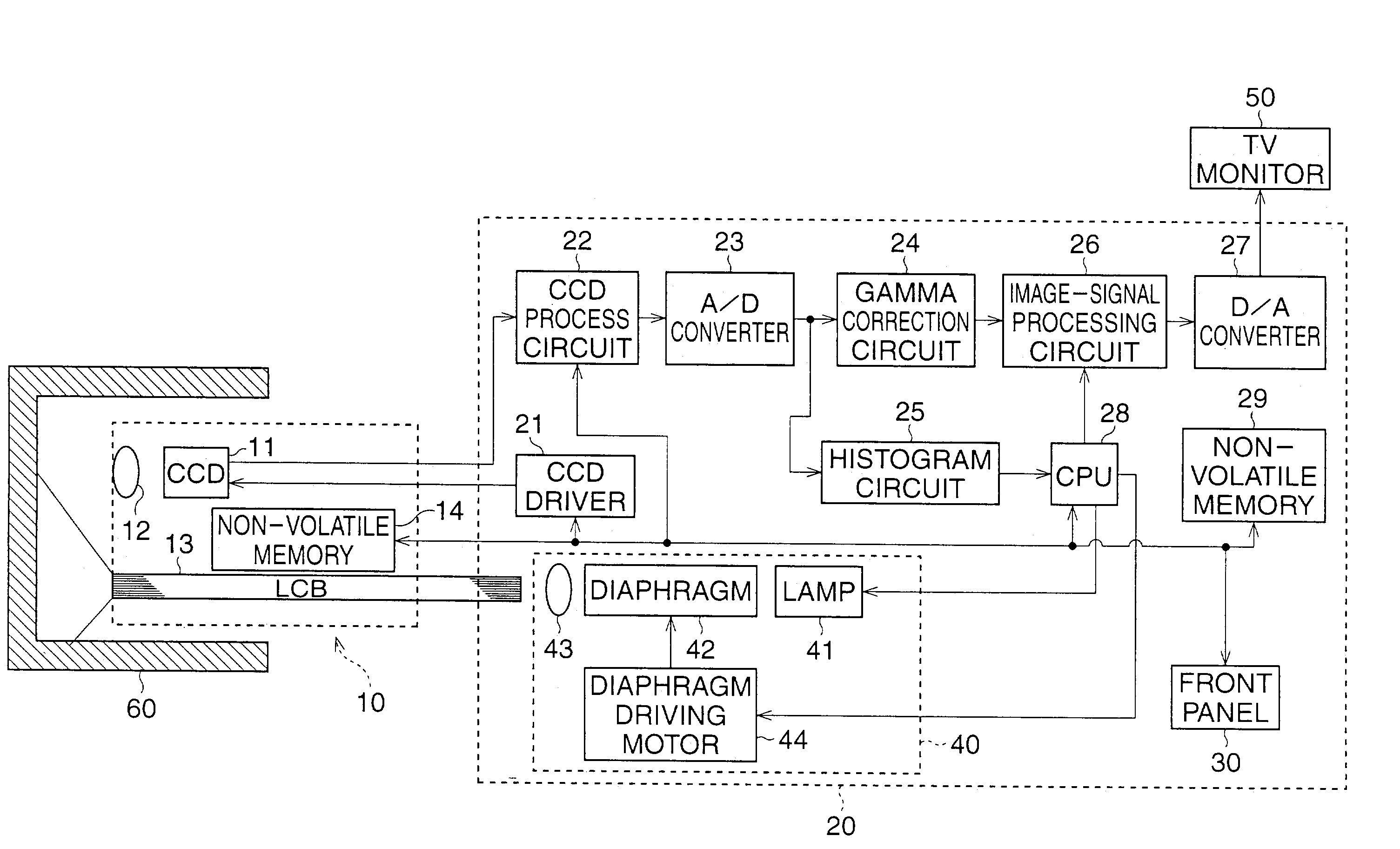
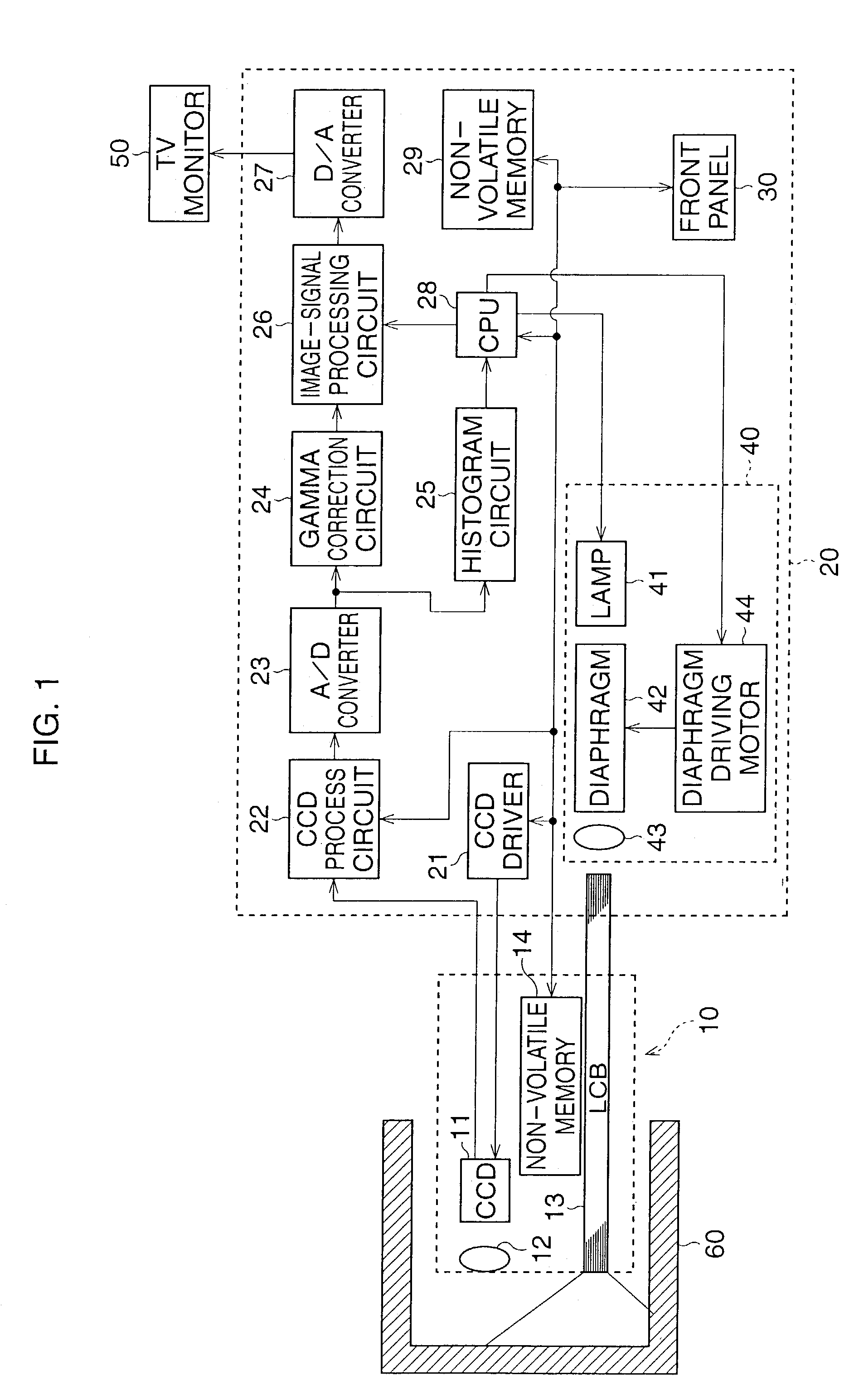
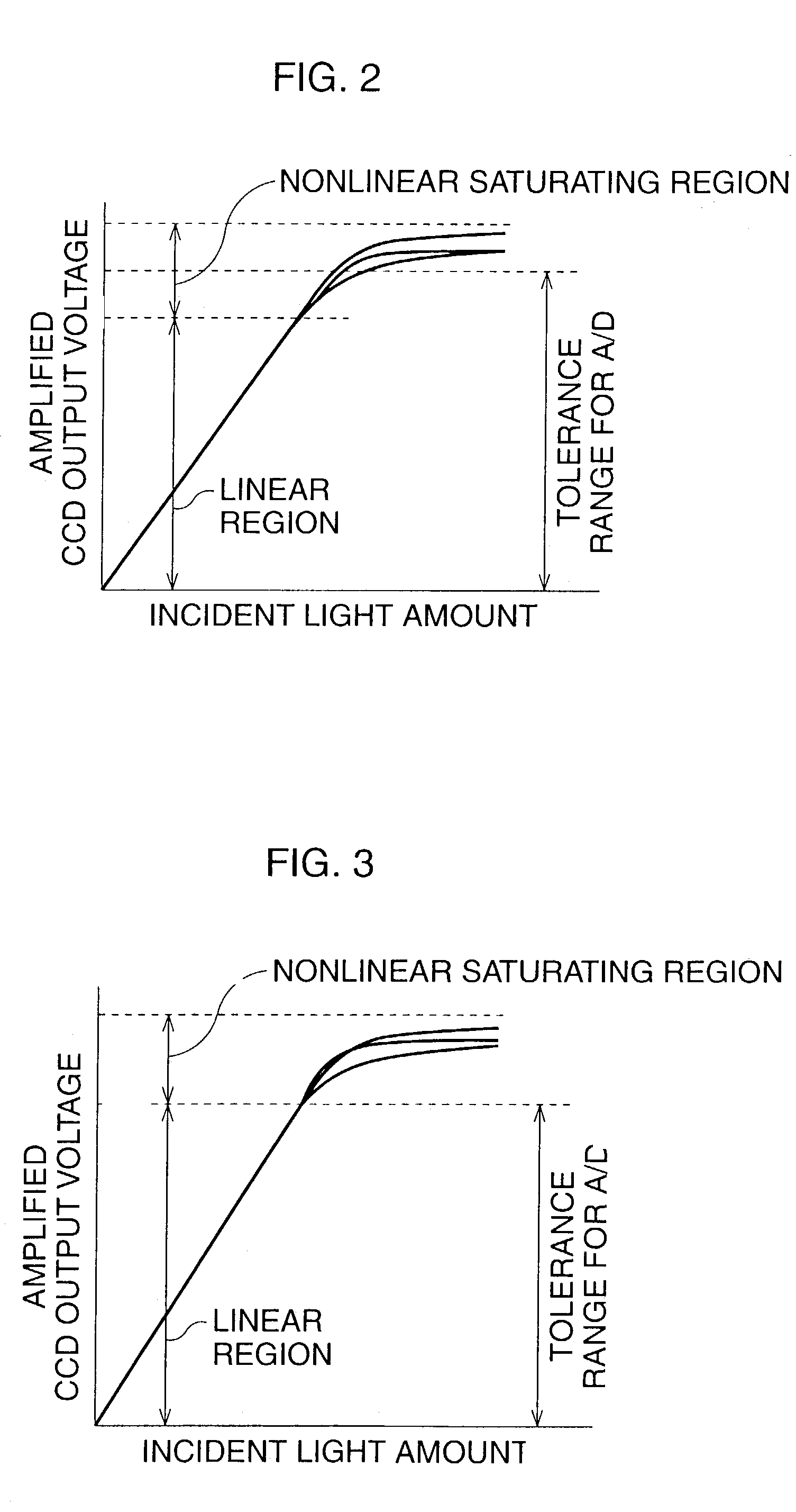
InactiveUS7248296B2Accurate gainTelevision system detailsEndoscopesVariable-gain amplifierLinear region
An automatic gain control device for an electronic endoscope is provided and comprises a controllable gain amplifier, an A / D converter, a histogram circuit, and a CPU. The controllable gain amplifier amplifies image signals from an imaging device. Amplified image signals from the controllable gain amplifier are input to the A / D converter. A histogram of the amplified image signals from the controllable gain amplifier is produced by the histogram circuit when an image taken in a white-balance test accessory is taken. By using the CPU, the gain of the controllable gain amplifier is adjusted in accordance with the determination of whether a saturated pixel exists for signals in the tolerance range of the A / D converter, so that a linear region of the image signals from the controllable gain amplifier substantially coincides with the tolerance range.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Communication apparatus
InactiveUS20050058300A1Improve performanceSubstation speech amplifiersPublic address systemsUltrasound attenuationAudio power amplifier
A communication apparatus used for two-way speech wherein the acoustic couplings between a speaker and microphones can be made equal by a simple method, wherein radially arranged microphones are located at equal distances from a speaker, a test signal generation unit outputs a pink noise signal to the speaker, the signal is input to a microphone detecting the sound of the speaker through variable gain amplifiers, attenuated in variable attenuation units, the peak value of absolute values of differences between the signals of an opposing pair of microphones is detected at level detection units, and a level judgment and gain control unit adjusts the gains of the variable gain amplifiers or attenuation amounts of the variable attenuation units so that the value becomes within a sensitivity difference adjustment error.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com