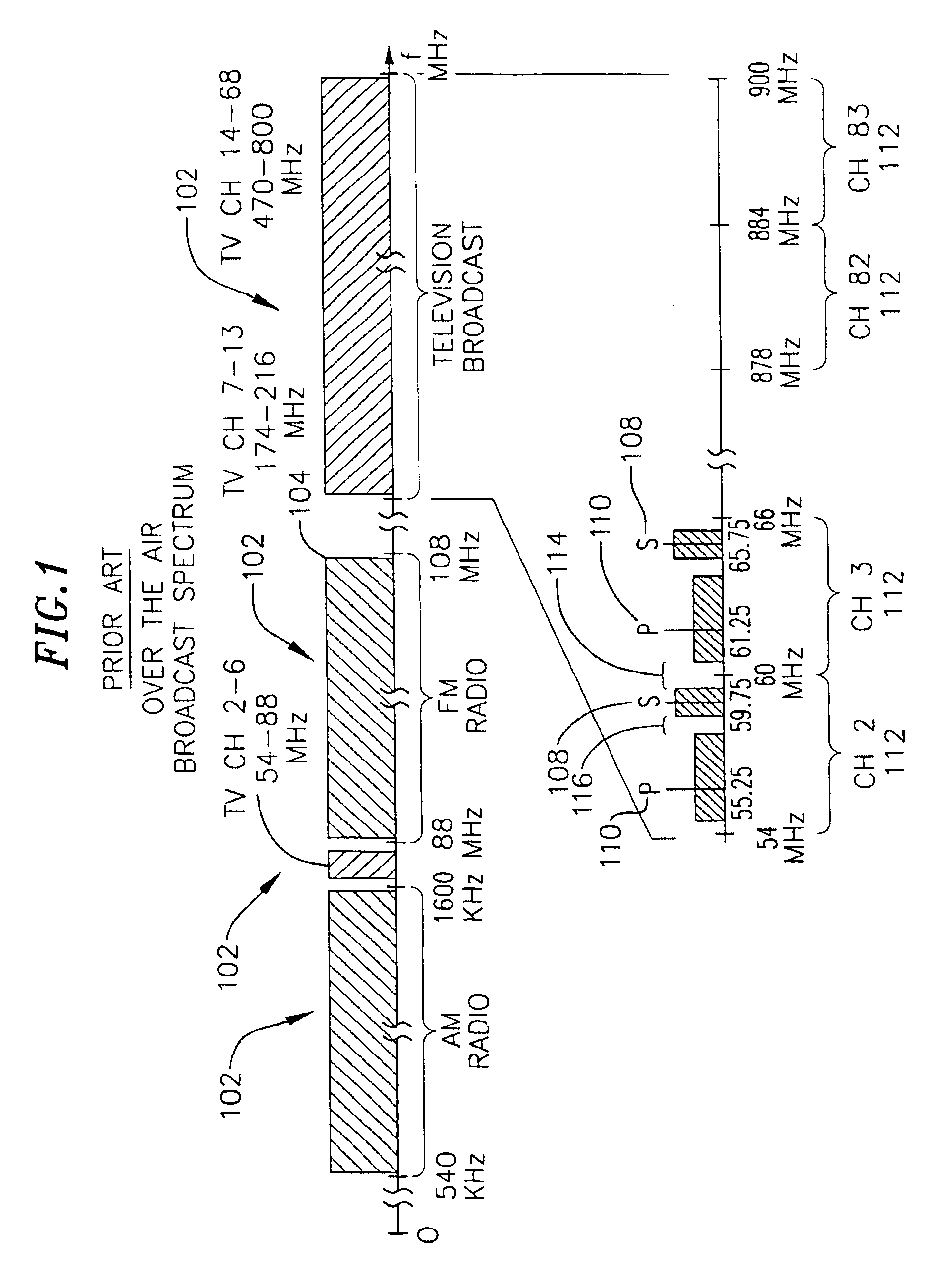
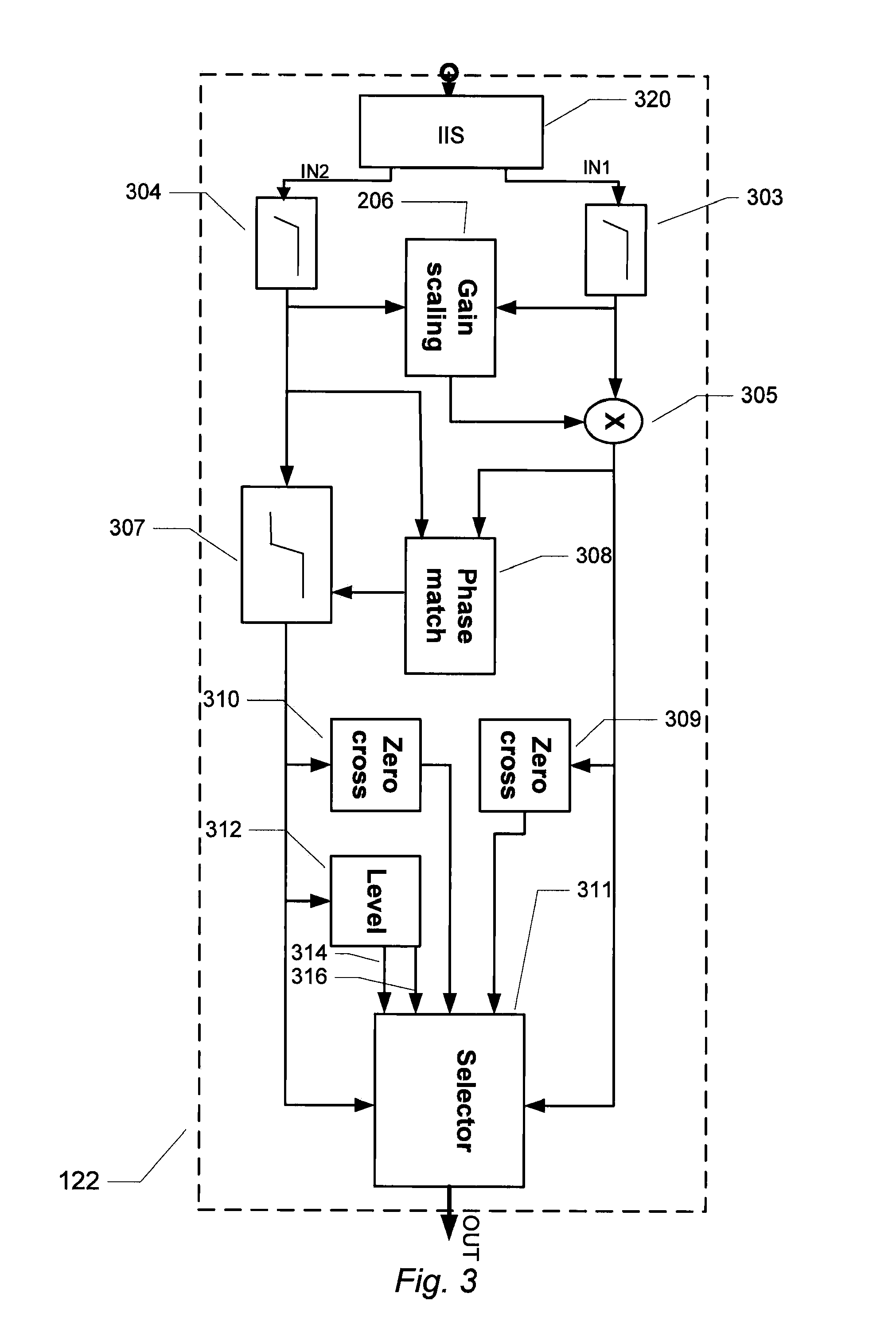
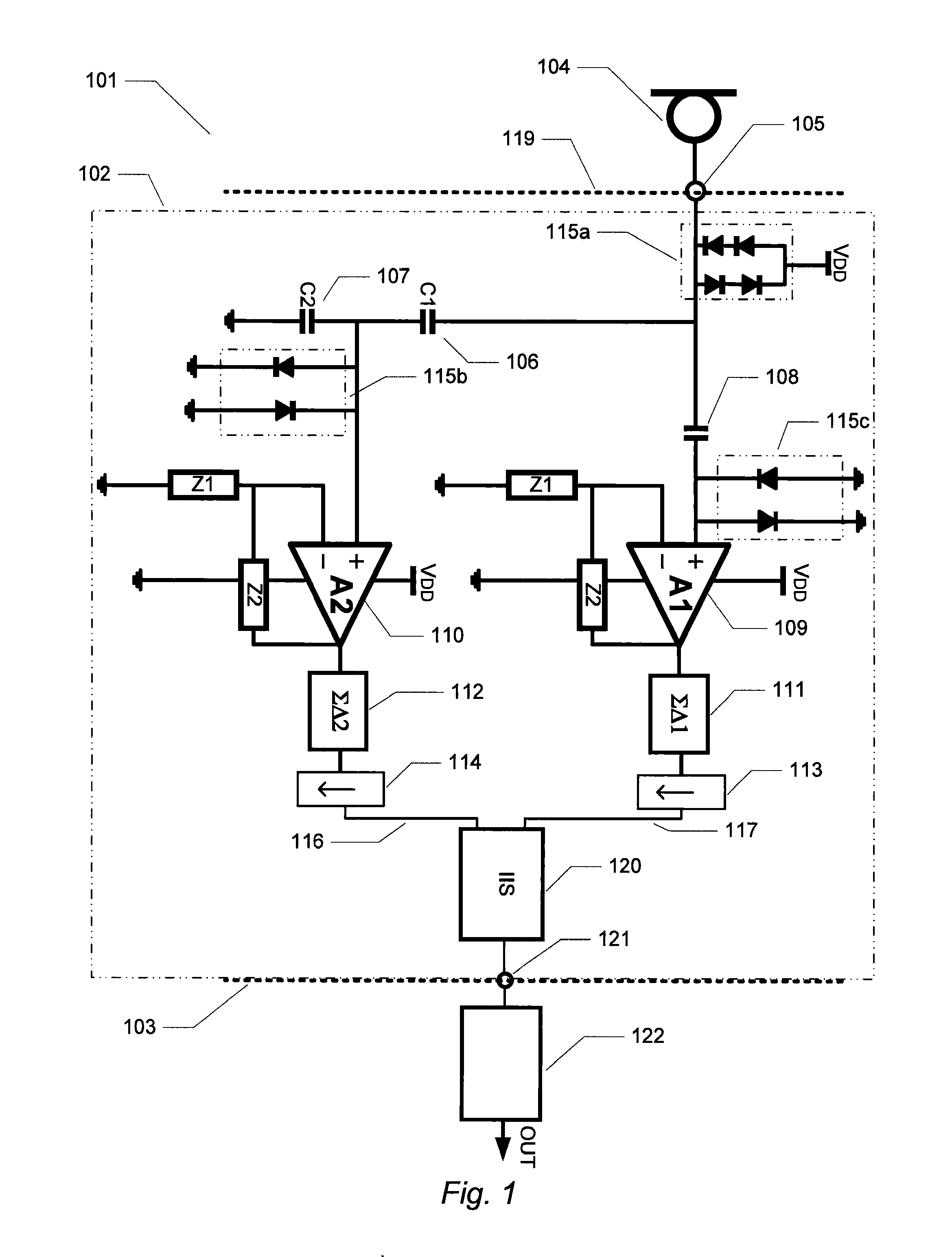
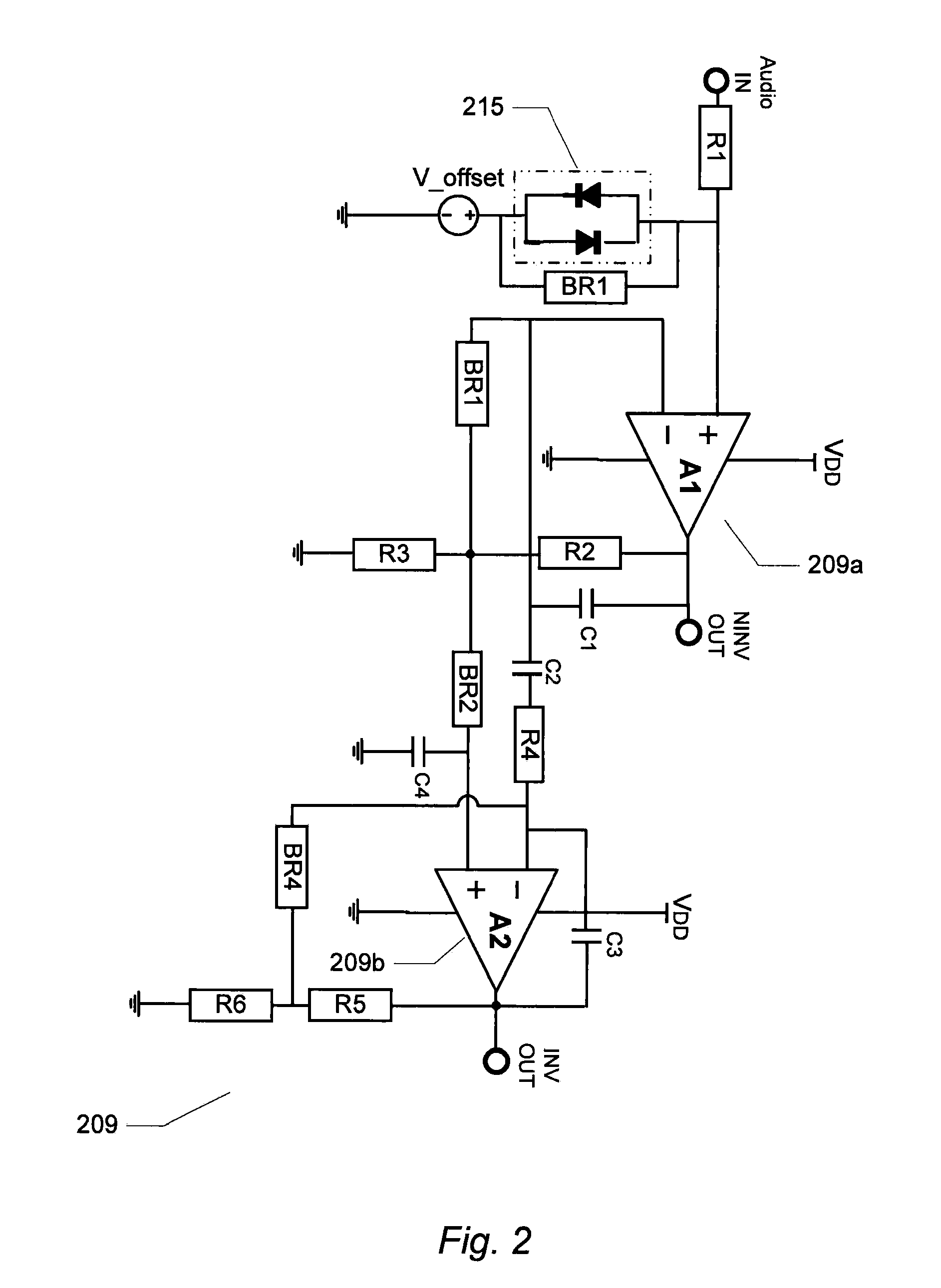
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1449results about "Amplification control details" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Modular transmission system and method
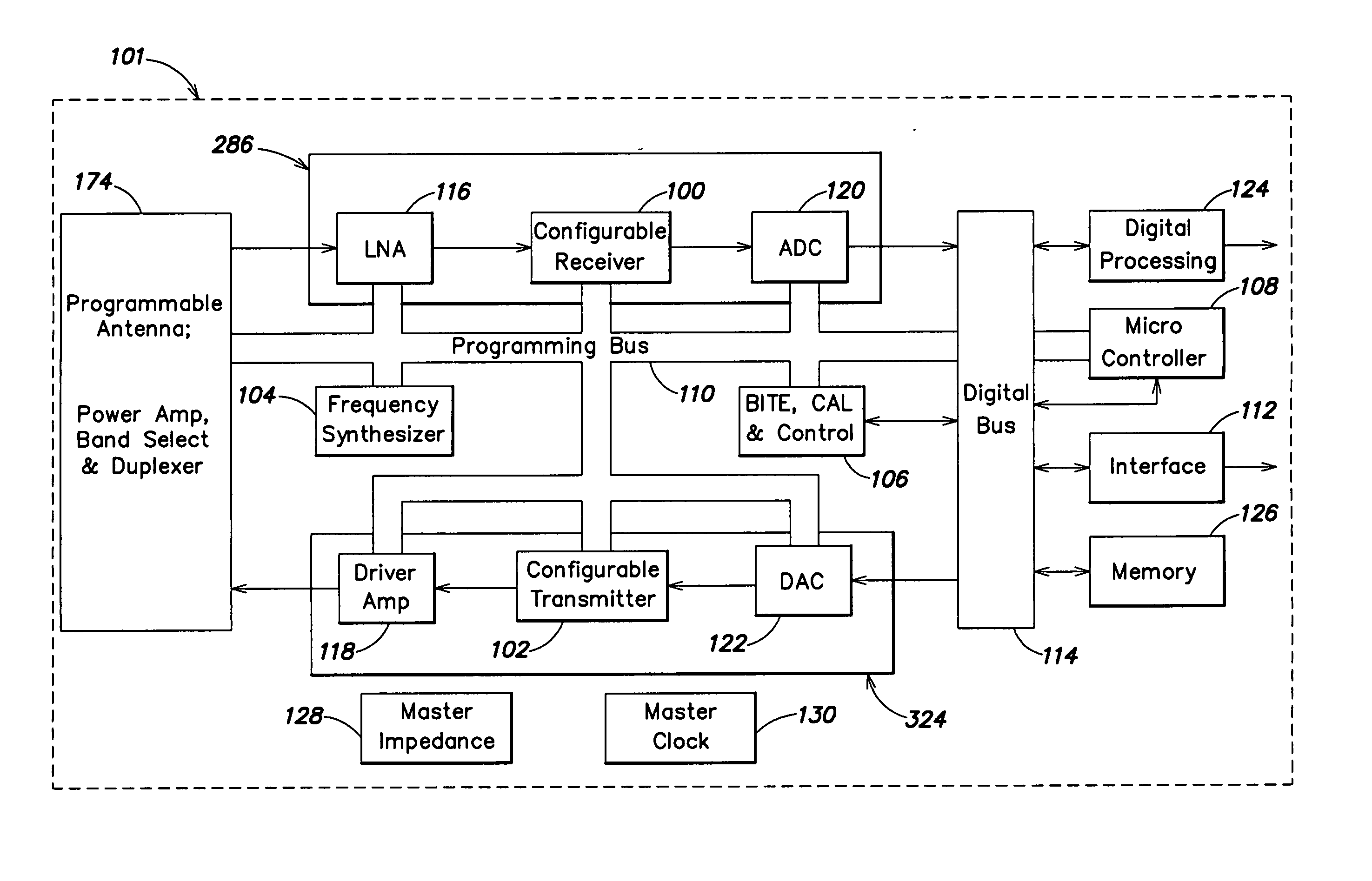
A modular broadband transmission system and method include an input signal connector that receives an input signal which is then divided into N parts and amplified with an amplifier have N power amplifier modules. Outputs of the N power amplifier modules are passed through transmission lines and to a radial combiner that combines the outputs. The radial combiner, transmission lines and power amplifier modules are configured such that if one of the power amplifier modules fails, the other power amplifier modules may still operate acceptable well, with minimal impact on total output power. An output of the amplifier is provided to a coupler that measures a power level of the output signal and feeds the measured power level back to a controller where the controller adjust an overall output power based on the number of the power amplifier modules that are functioning properly. Each of the power amplifier modules have a processor such that respective of the power amplifier modules may be taken off-line, and replaced while the other power amplifier modules continue to operate in a transmit mode of operation. The modular broadband transmission system and method may conveniently be used as either a broadband booster for amplifying a plurality of input signals, or a head and transmitter configured to amplify one or more different input signals.
Owner:THALES BROADCAST & MULTIMEDIA
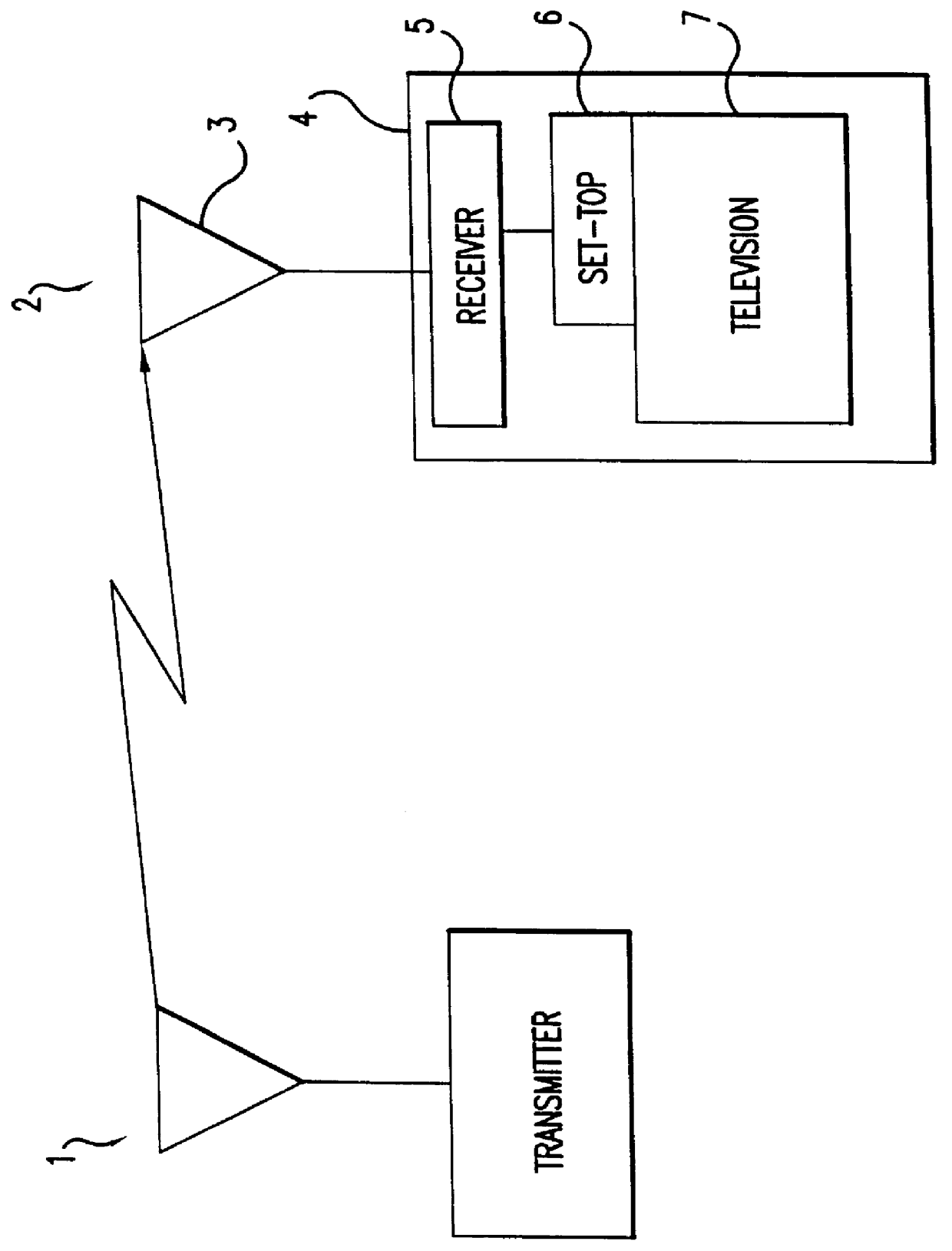
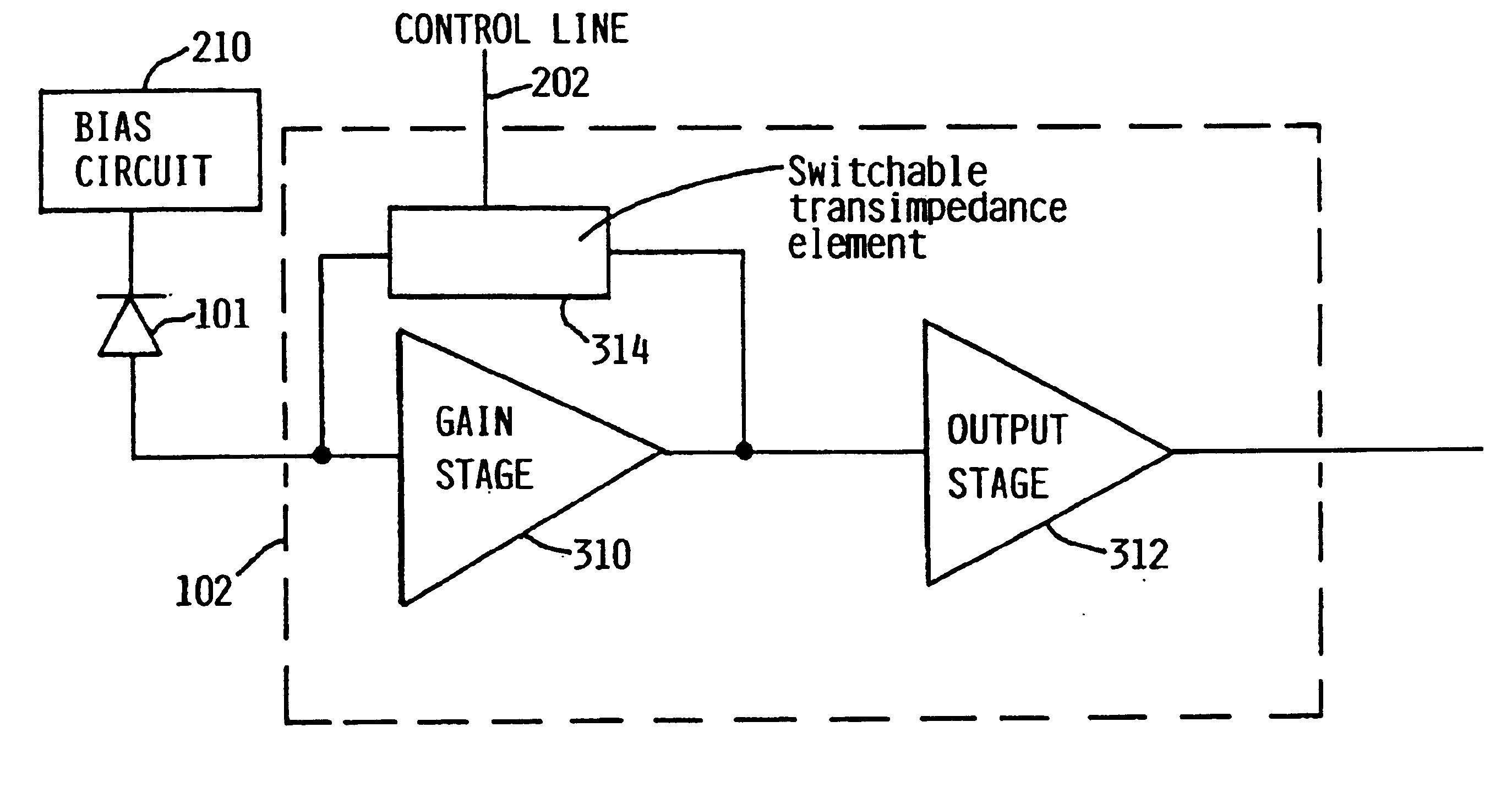
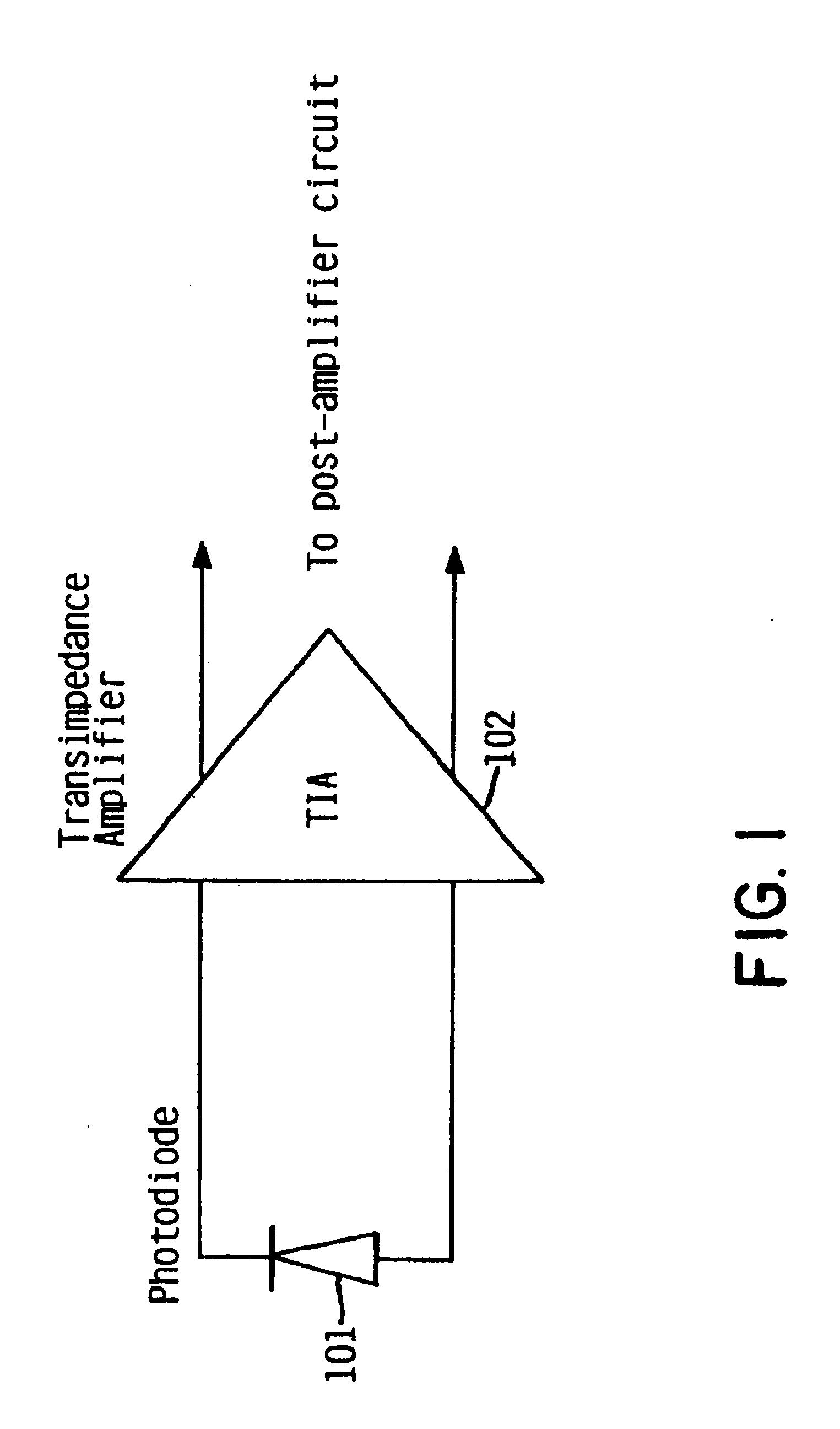
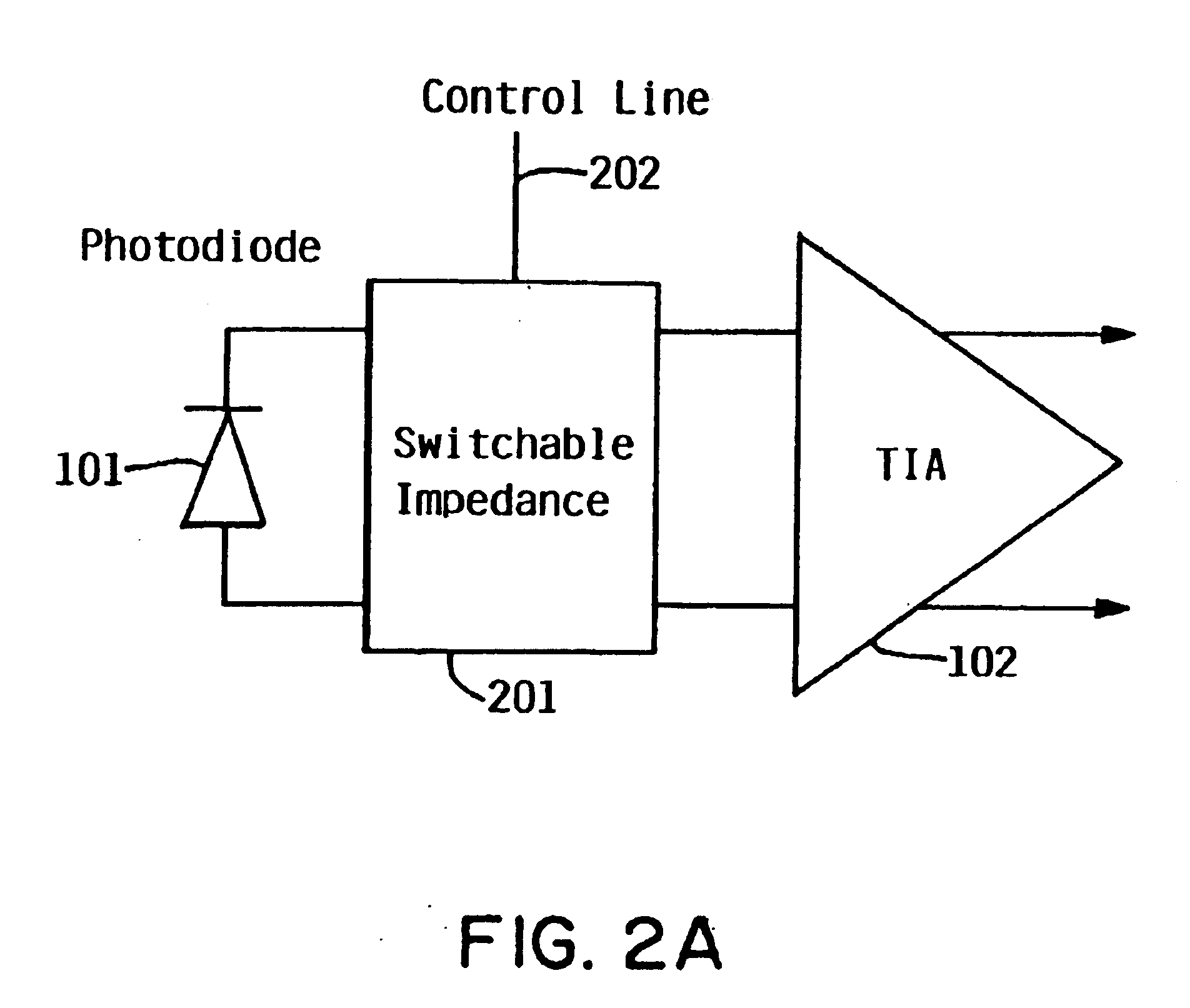
Switchable-bandwidth optical receiver
InactiveUS6862322B1Improve performanceModulated-carrier systemsGain controlAudio power amplifierEngineering
A switchable bandwidth optical receiver is implemented in a front-end of the receiver in at least one of three ways. A switchable impedance may be provided at the input to a preamplifier of the front end, the preamplifier of the front-end may have a switchable impedance therein, and / or a switchable filter may be provided at an output of the preamplifier.
Owner:IBM CORP
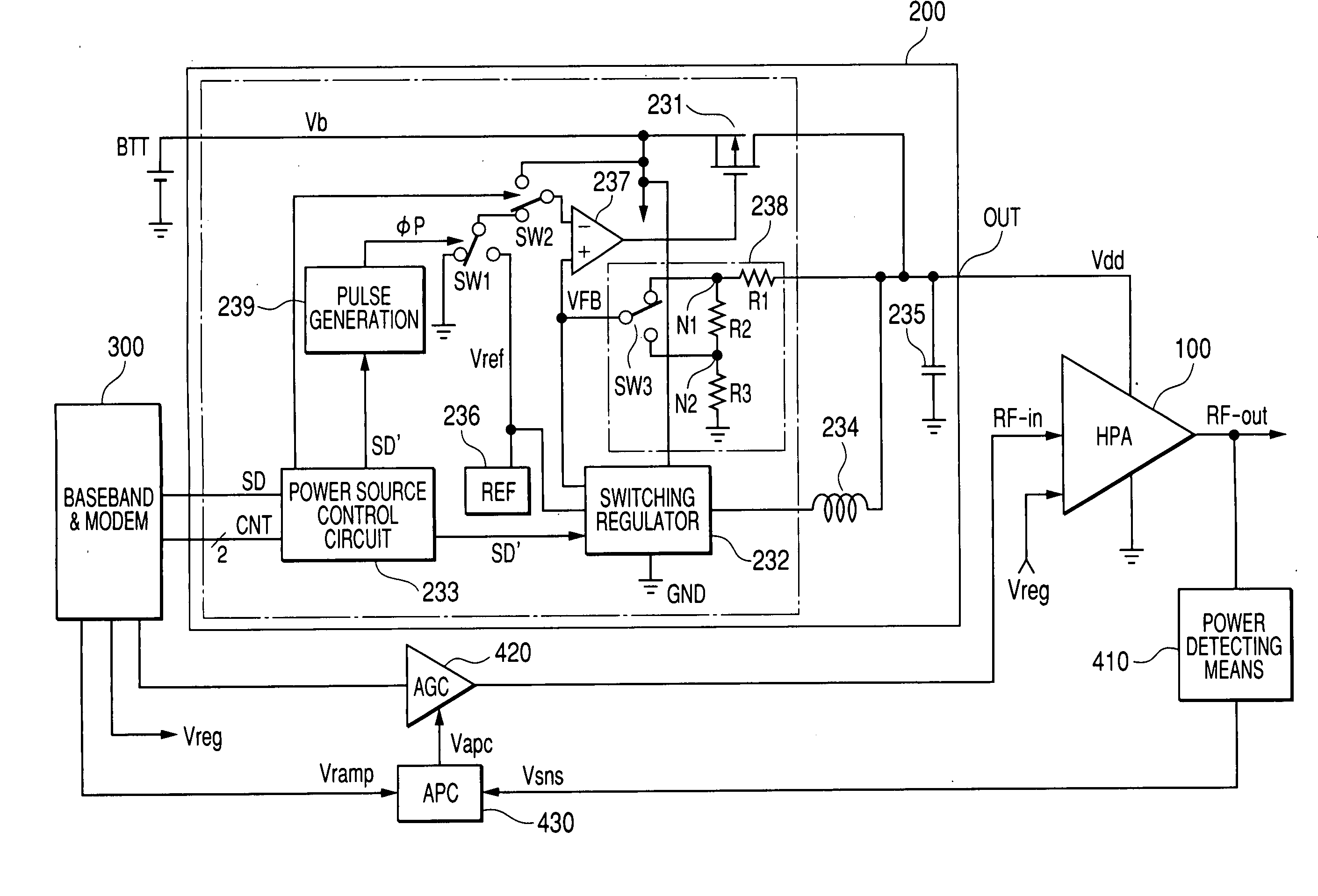
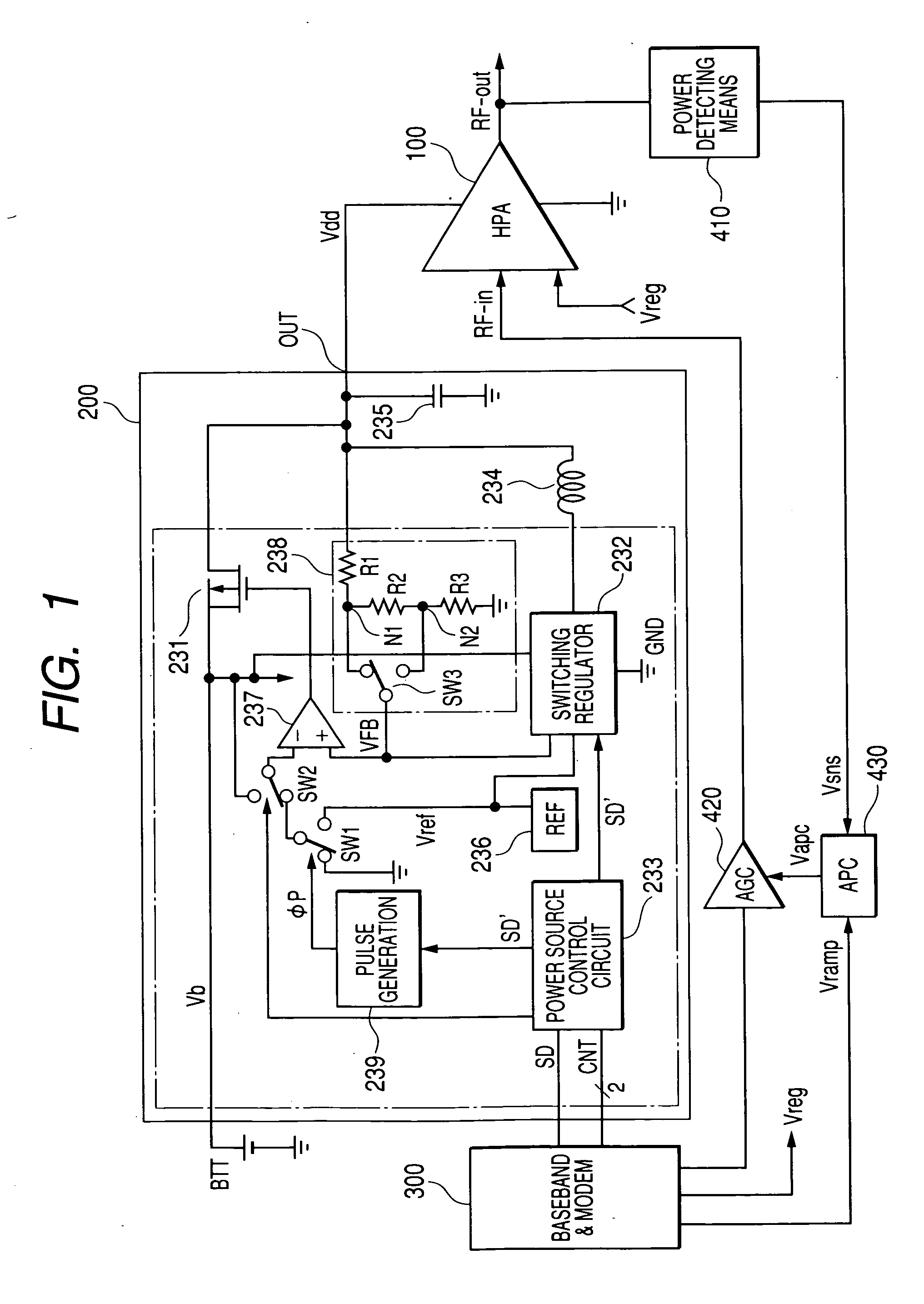
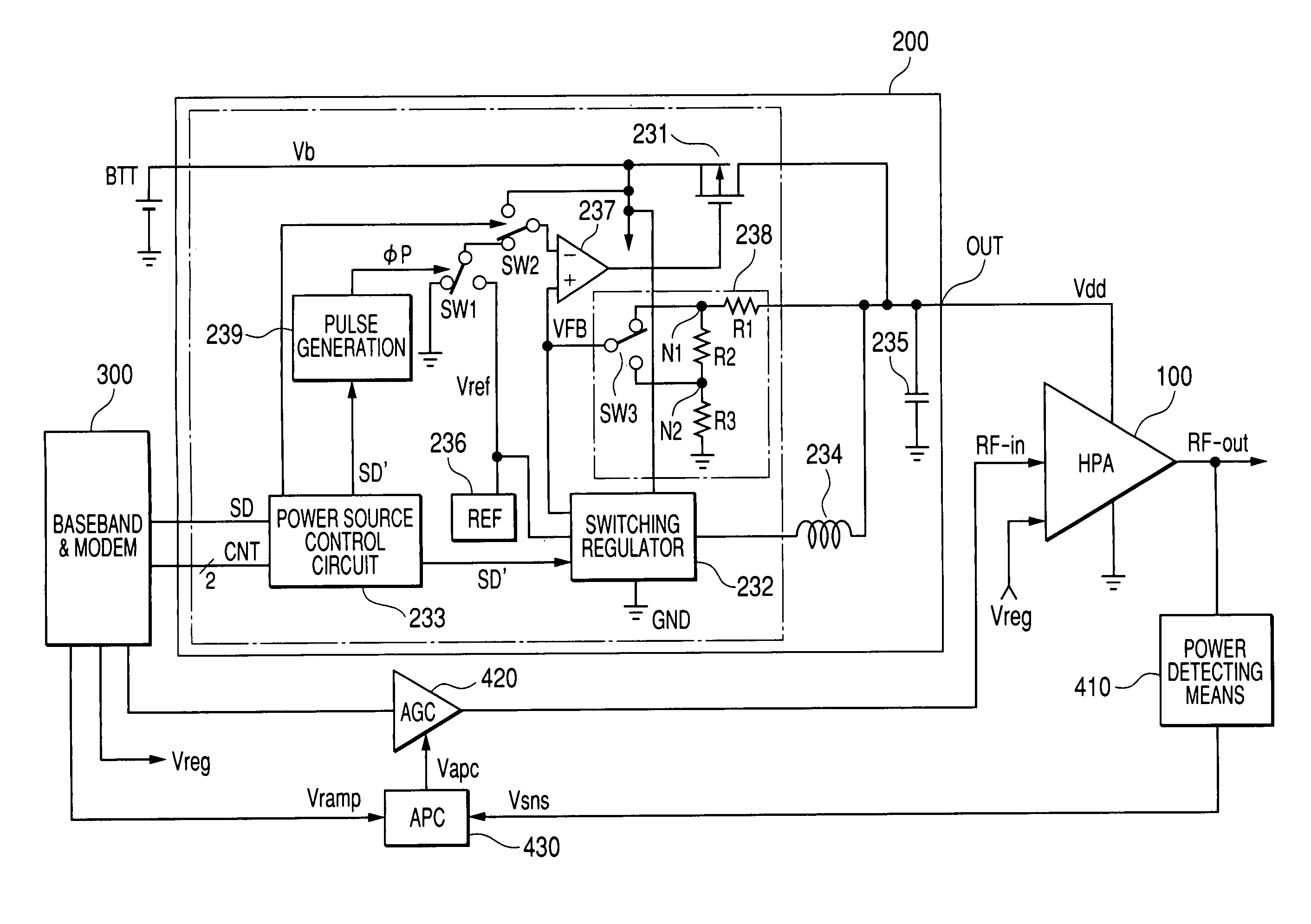
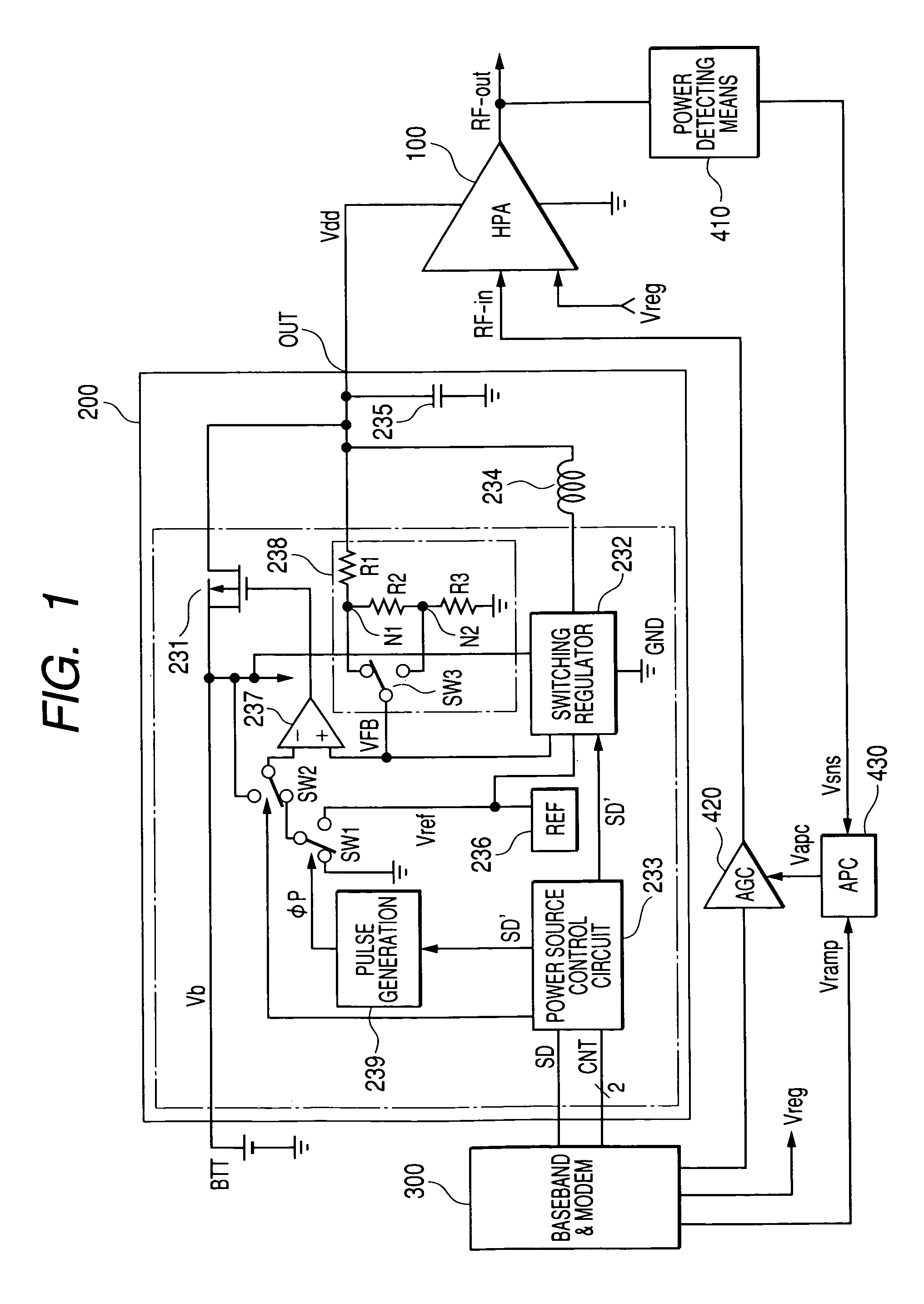
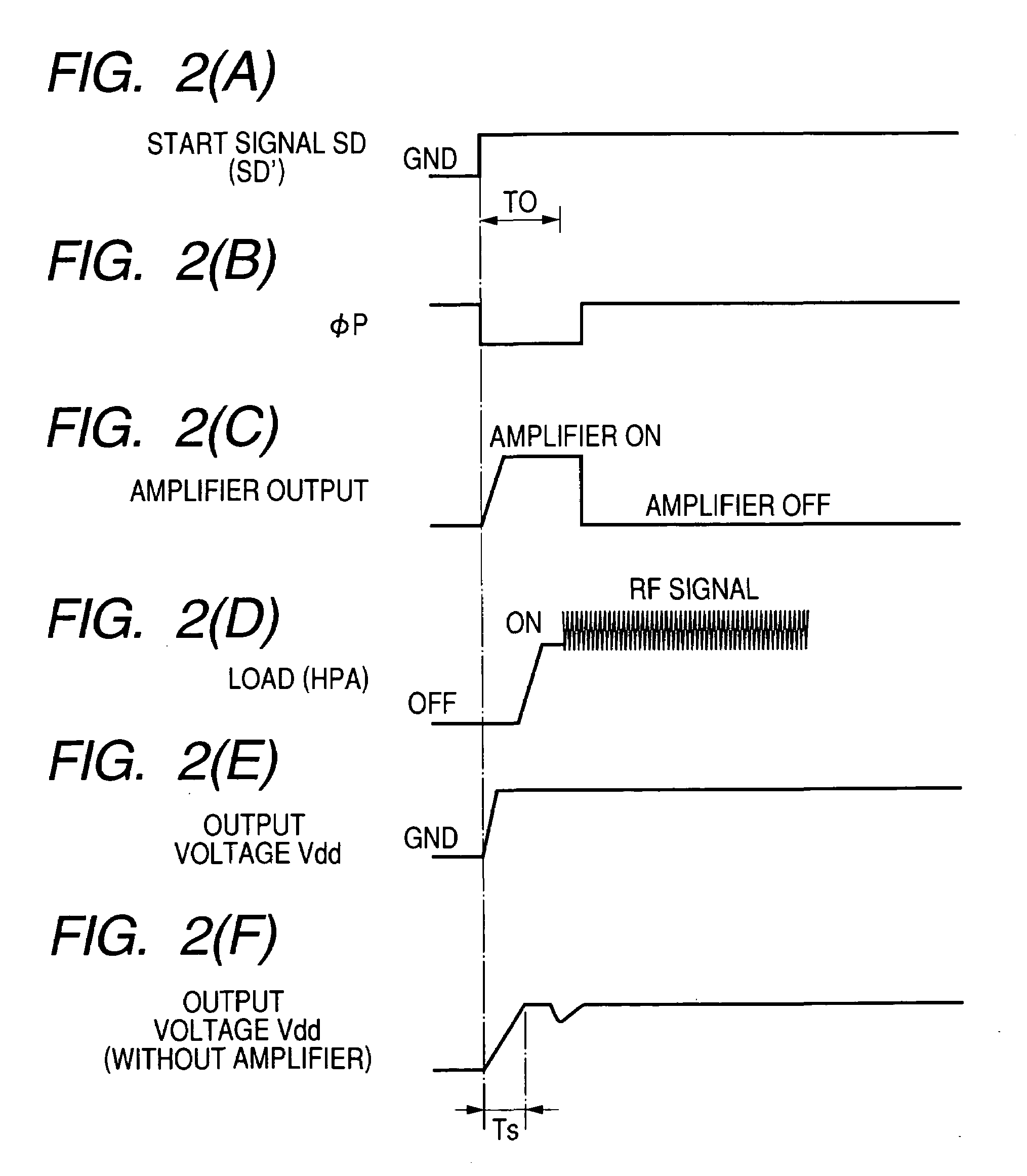
Power source circuit for high frequency power amplifying circuit and semiconductor integrated circuit for power source and electronics component for power source
InactiveUS20050122171A1Function increaseSmall sizeAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencySupply voltage varying controlHigh frequency powerGSM
The invention realizes a power source circuit for a high frequency power amplifying circuit, which achieves excellent responsiveness of output voltage, can be used for a portable telephone of the GSM or WCDMA and a portable telephone capable of performing communications in two or more communication systems such as the GSM and CDMA and, moreover, has high power efficiency. A power source circuit for a high frequency power amplifying circuit is constructed by using both a first direct current power source circuit such as a series regulator whose power efficiency is not high but which becomes the high level quickly, and a second direct current power source circuit such as a switching regulator, which does not become the high level quickly but whose power efficiency is high. When the power source voltage has to become the high level at high speed, both of the series regulator and the switching regulator are simultaneously operated. When the output power source voltage reaches a predetermined level, the operation of the series regulator is stopped.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Computer program product configured to control modular transmission system components
A computer program product is configured to control a modular transmission system having a control processor and at least N power amplifier modules, each having a controller submodule, wherein the system receives an input signal which may be a single carrier or multiple carriers. The signal is passed to a one-by-N divider which divides the signal N ways. Each of the N divided signals are independently amplified by the power amplifier (PA) modules "slices" (i.e., PA modules) that includes an RF amplifier module, a microcontroller module, and a power supply module, all of which are tightly coupled via a plurality of signal, power, control, and status connections. Each the PA slices amplifies its respective input signal and outputs a respective radio frequency output signal at a predetermined power level as controlled by the microcontrol module, the driver, and the system controller, or a network manager via a system input / output interface. The output coupler provides power coupling and status monitoring via feedback lines to support control at a module-level, a system-level, and a network-level.
Owner:THALES BROADCAST & MULTIMEDIA
Dynamic stability, gain, efficiency and impedance control in a linear/non-linear CMOS power amplifier
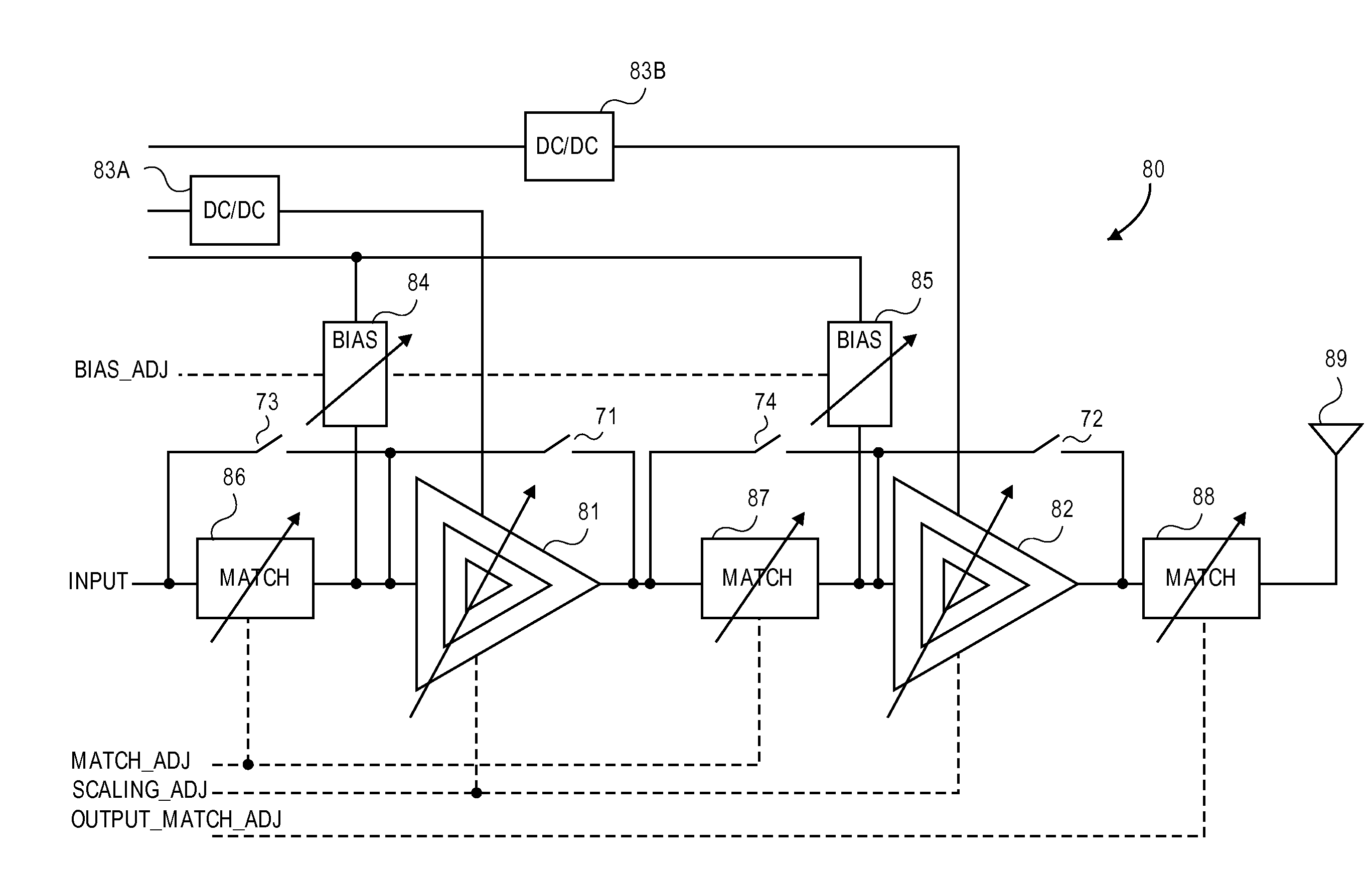
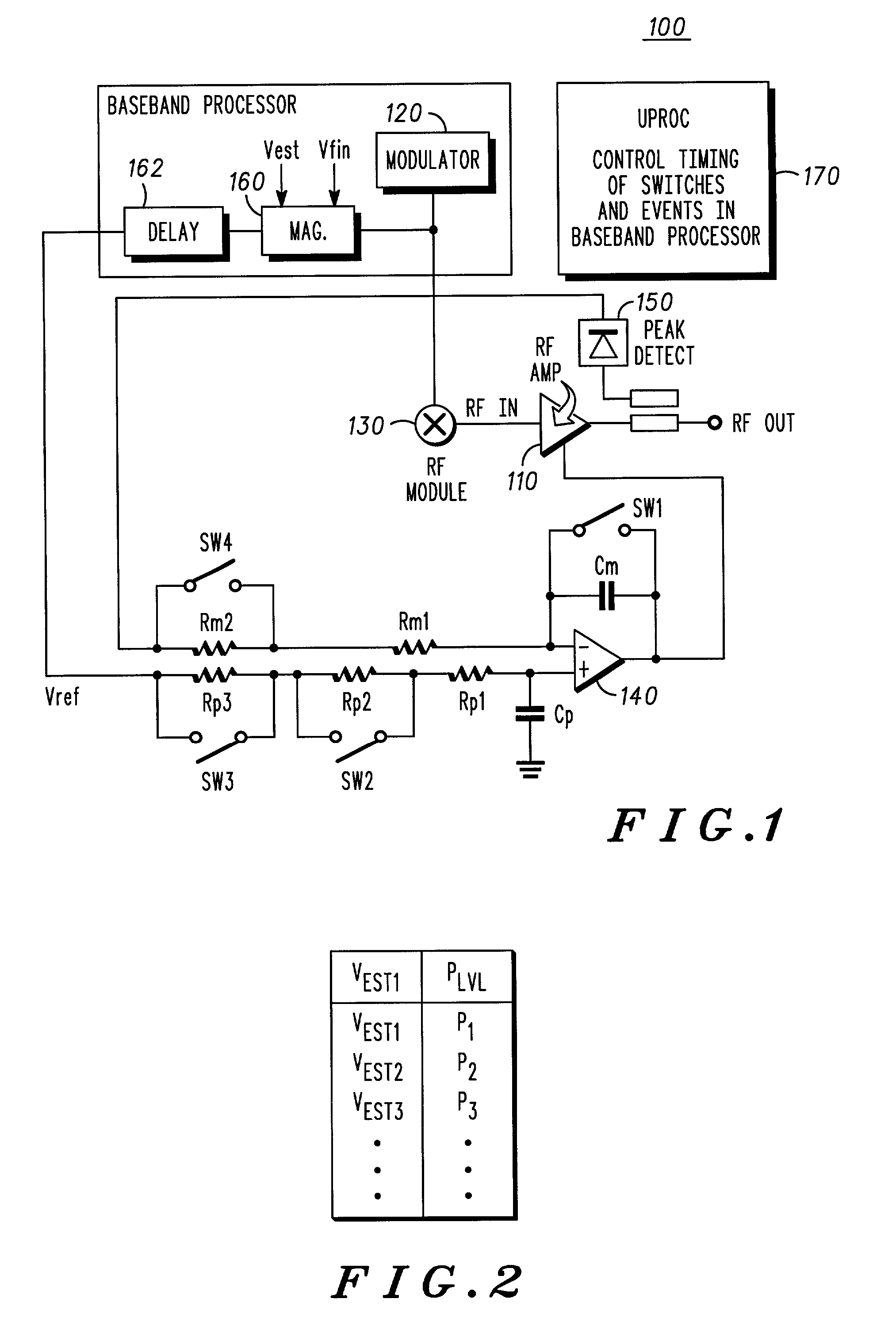
A power amplifier (PA) provides dynamic stability and gain control for linear and non-linear operation. The PA operates with a baseband processor and a transmitter, in which the PA receives a signal from the transmitter for power amplification prior to transmission of the signal. The PA is configured to select between the linear mode of operation and the non-linear mode of operation, in which device scaling within the PA is achieved by changing a device sizing of at least one stage of the PA. Further to changing the device size, the PA changes biasing resistance and impedance of a matching network in response to the changing of the device size to control power output and stability for the PA.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
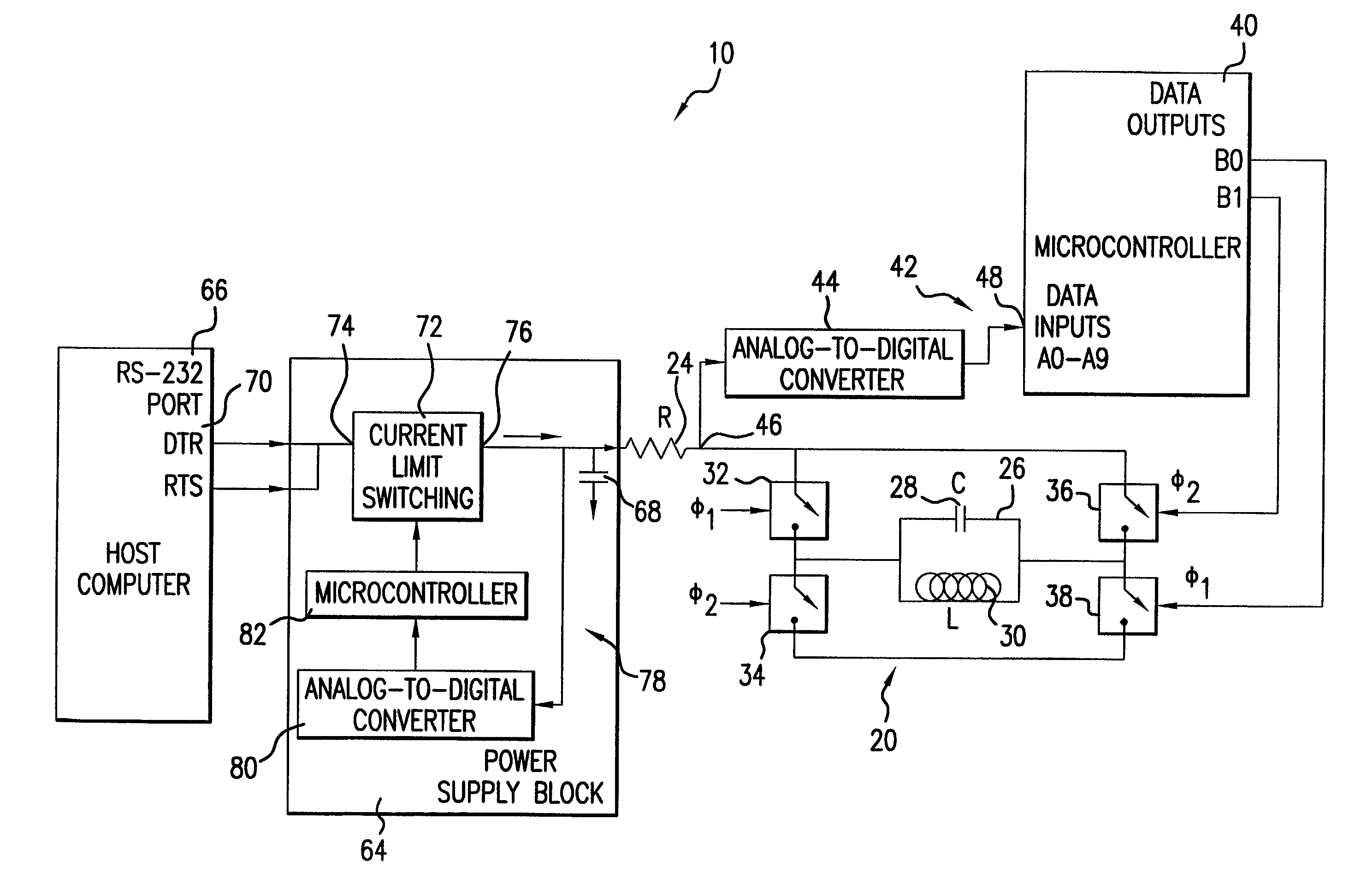
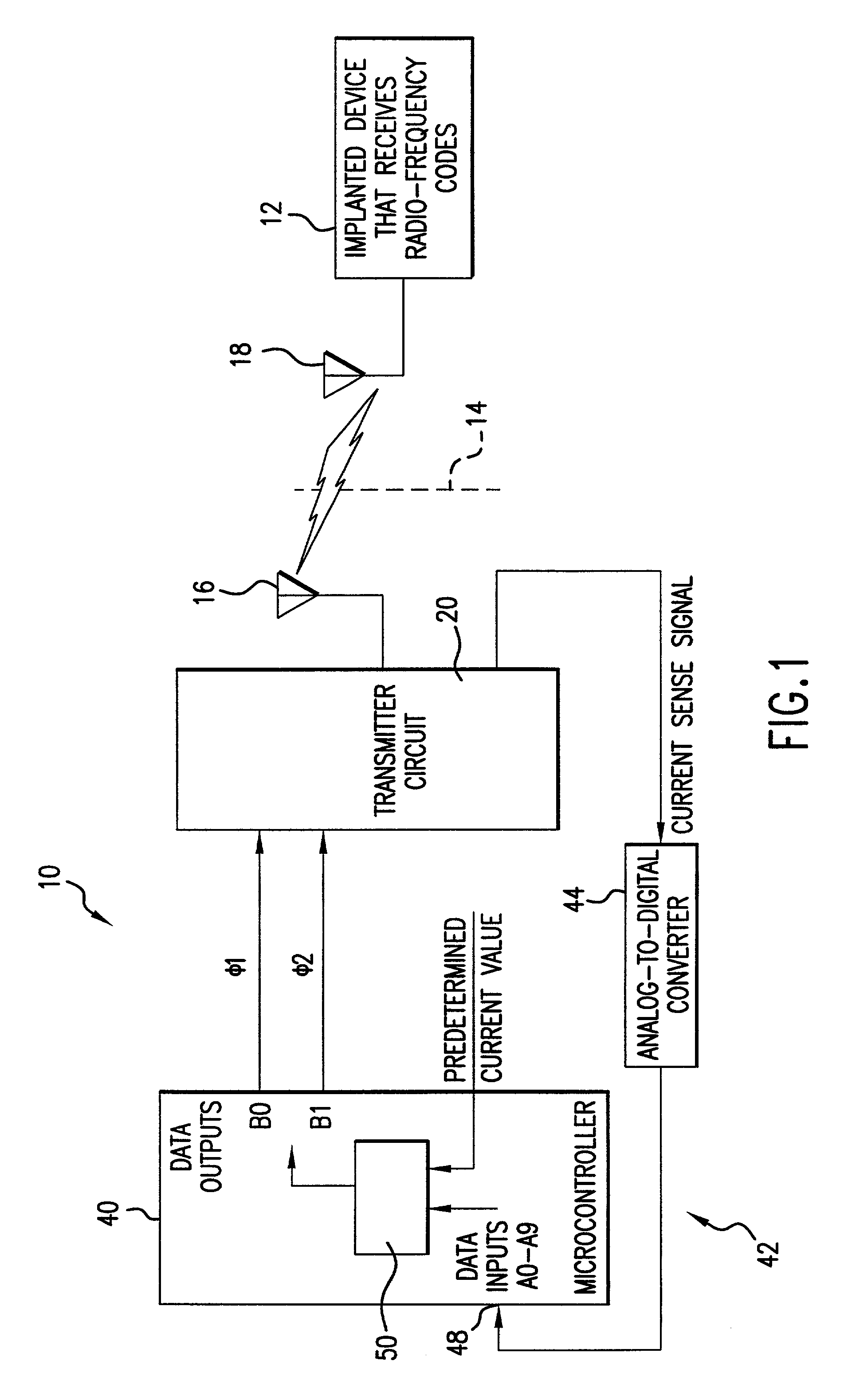
Transmitter system for wireless communication with implanted devices
ActiveUS7151914B2Low power operationCurrent consumptionResonant long antennasElectrotherapyMaximum levelFeedback circuits
A transmitter system for wireless communication with implanted medical devices includes a transmitter circuit having a resonant network the resonant frequency of which is adjusted by a feedback circuit in order to minimize the current drain from the power source and maximizing the power source life. The transmitter system may be powered by a power supply block which uses commonly available RS-232 signals of a host computer as a raw power source, combined with a high value storage capacitor to provide power for the wireless medical data programmer. A feedback circuit monitors the charging current as well as voltage impressed across the storage capacitor in order to maintain the charging current at maximum level during the charging time and in order to stop the charging once the full charge of the storage capacitor has been reached.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
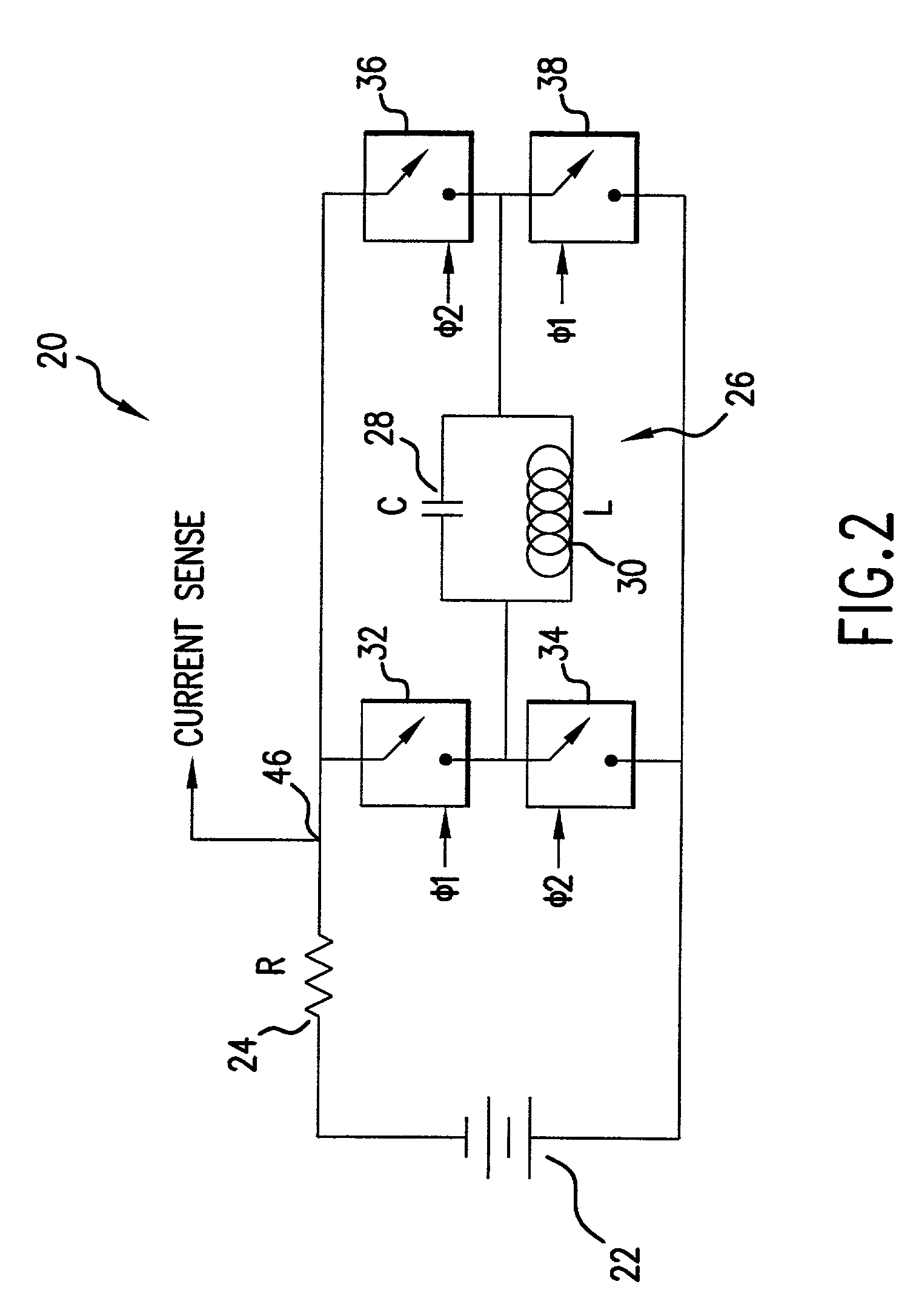
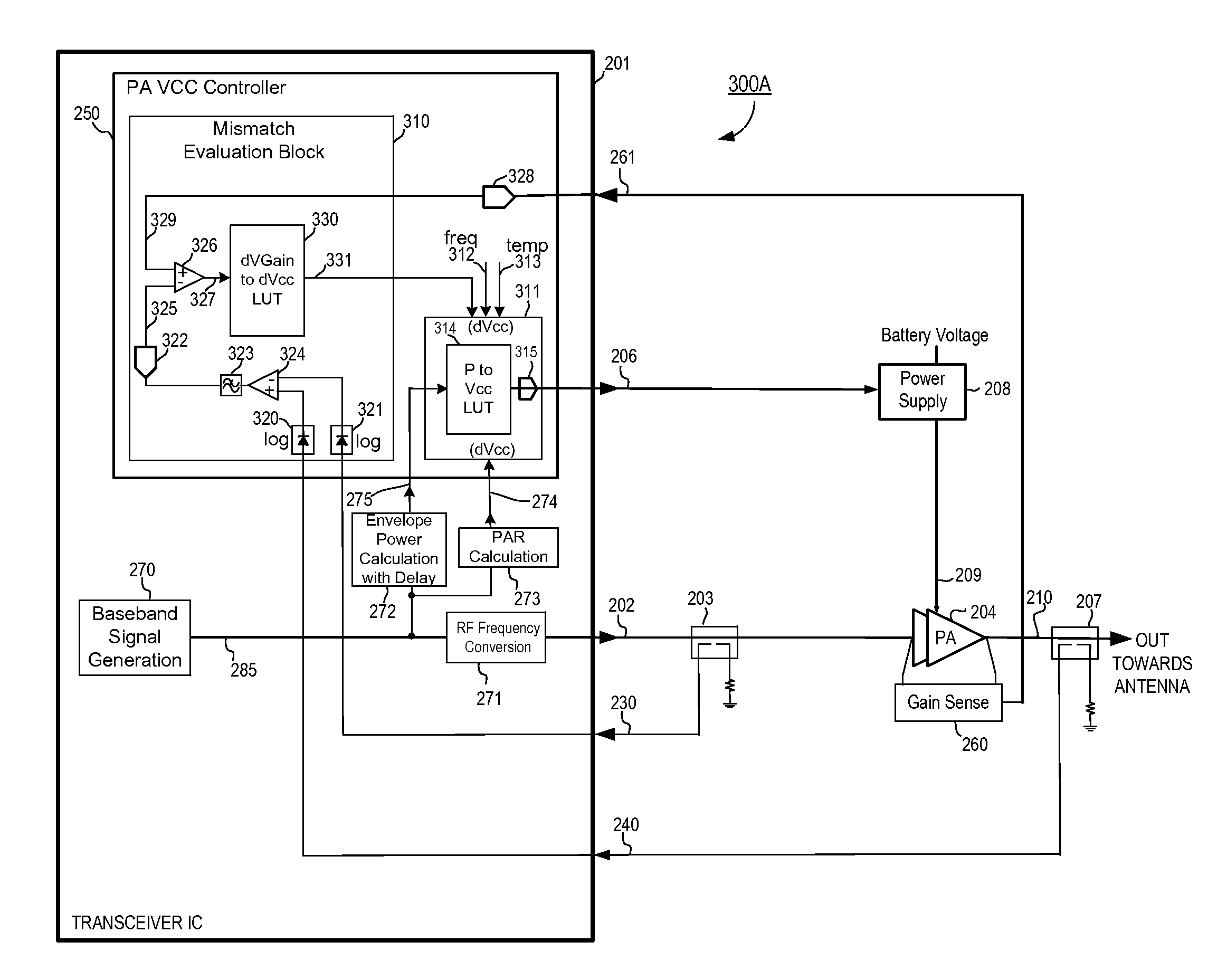
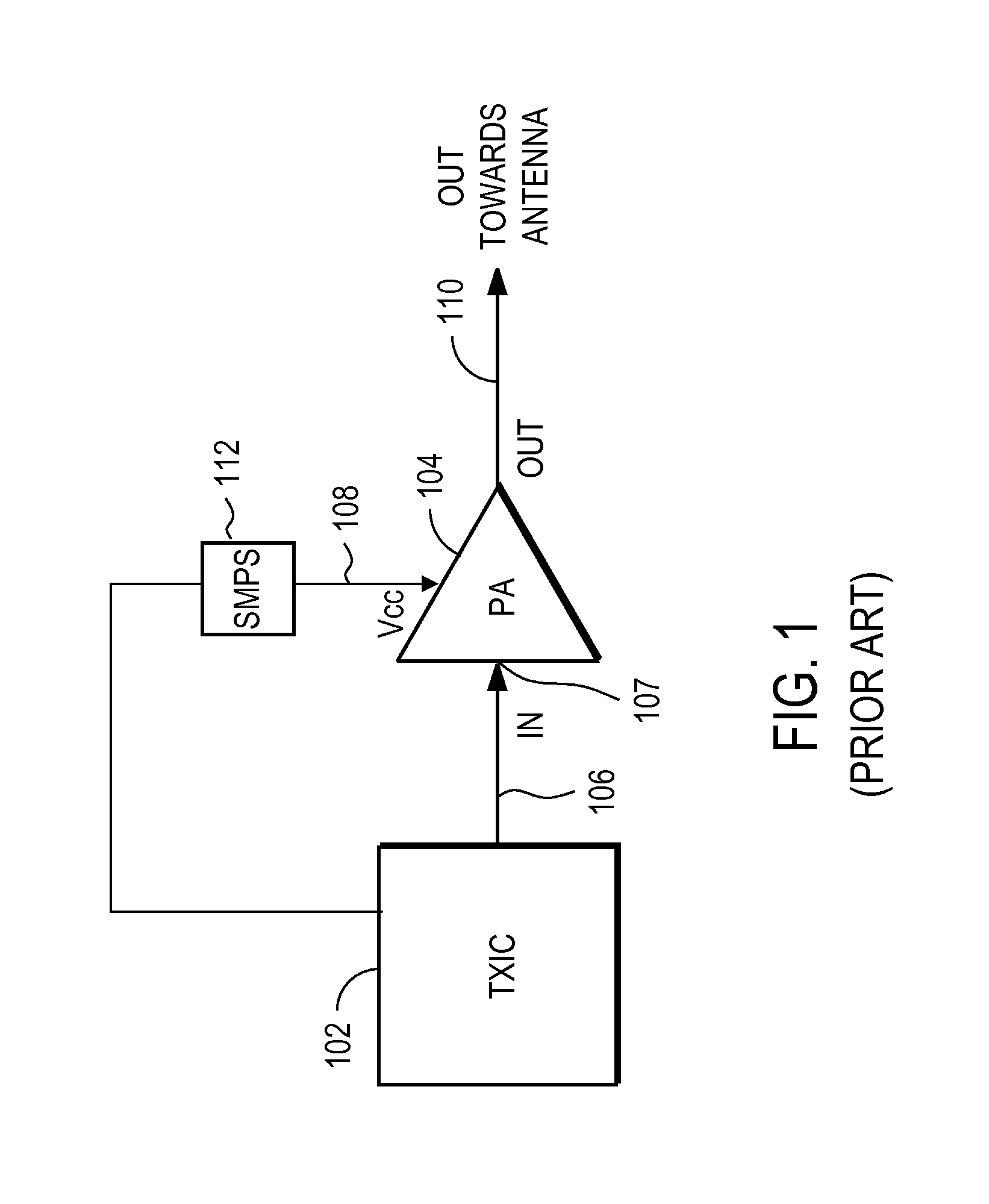
RF power amplifier circuit with mismatch tolerance
ActiveUS20110298539A1Efficiency of PA is improvedImprove efficiencyHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlAudio power amplifierControl signal
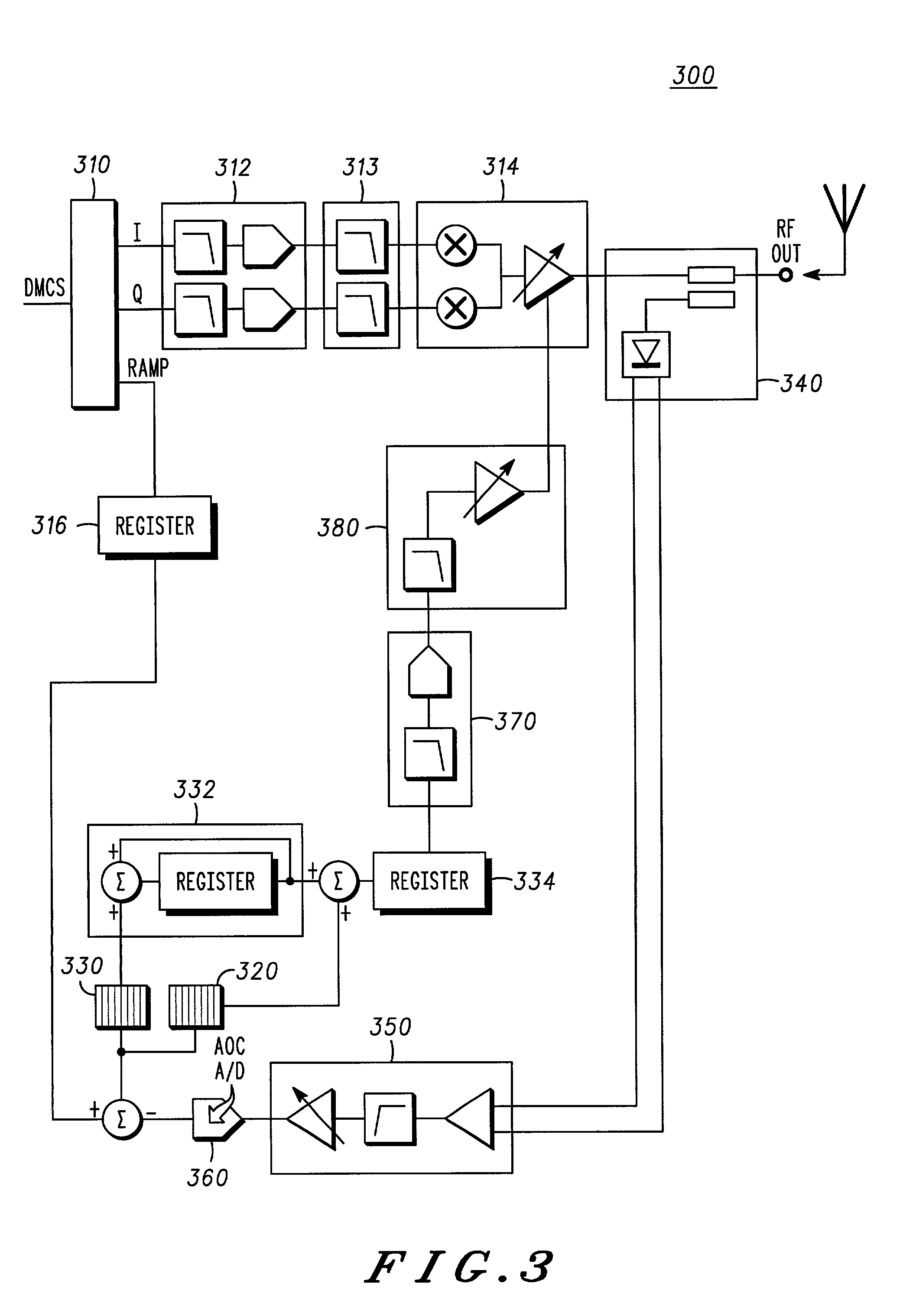
A radio frequency (RF) power amplifier system adjusts the supply voltage provided to a power amplifier (PA) adaptively, responsive to the measured or estimated power of the RF output signal of the PA. The RF PA system includes a power amplifier (PA) which receives and amplifies an RF input signal to generate an RF output signal at a level suitable for transmission to an antenna. A PA supply voltage controller generates a supply voltage control signal, which is used to control the supply voltage to the final stage of the PA. The supply voltage control signal is generated responsive to the measured or estimated power of the PA RF output signal, and also may be responsive to a parameter indicative of impedance mismatch experienced at the PA output. By controlling this supply voltage to the RF PA, the efficiency of the PA is improved.
Owner:QUANTANCE
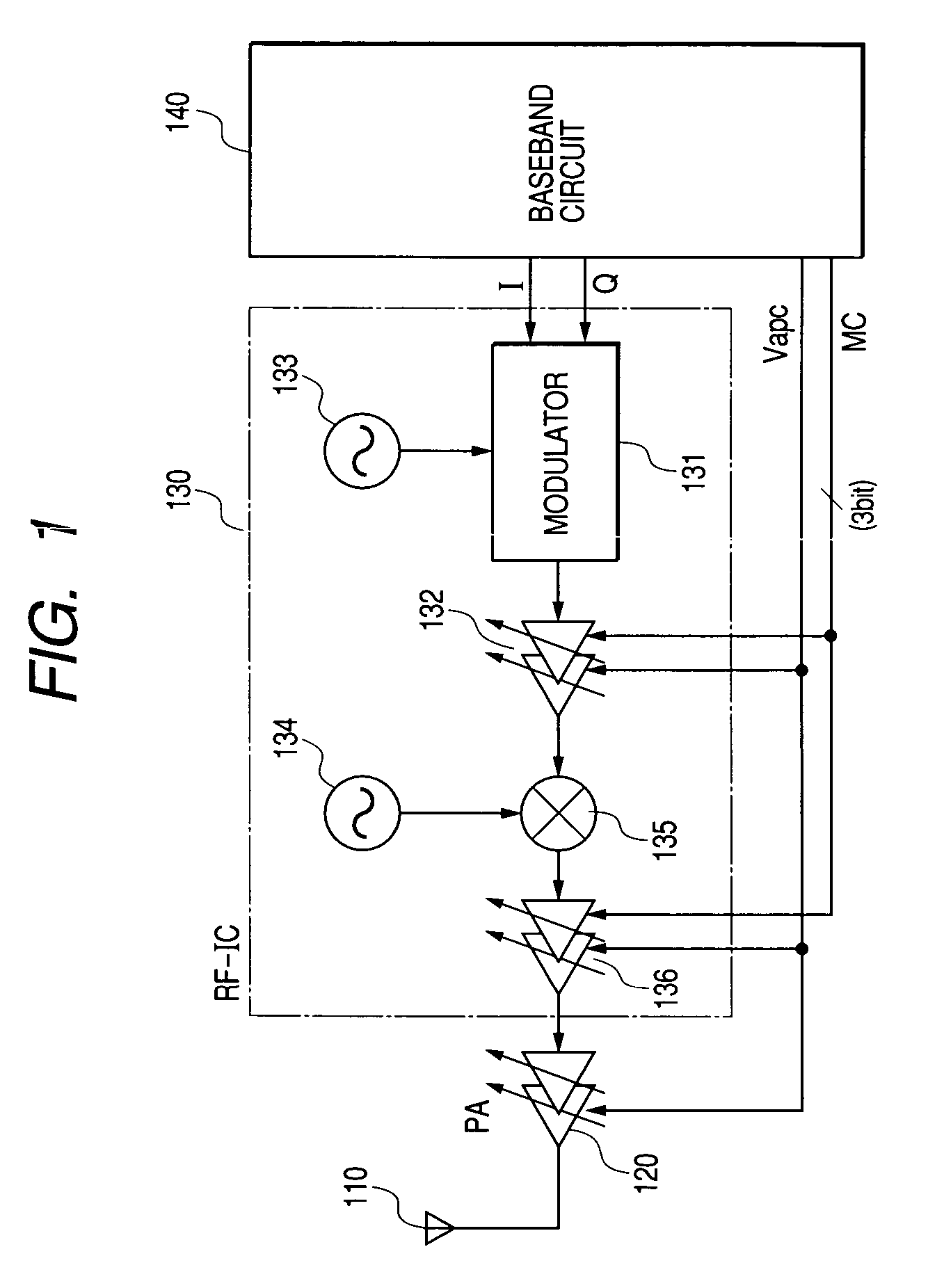
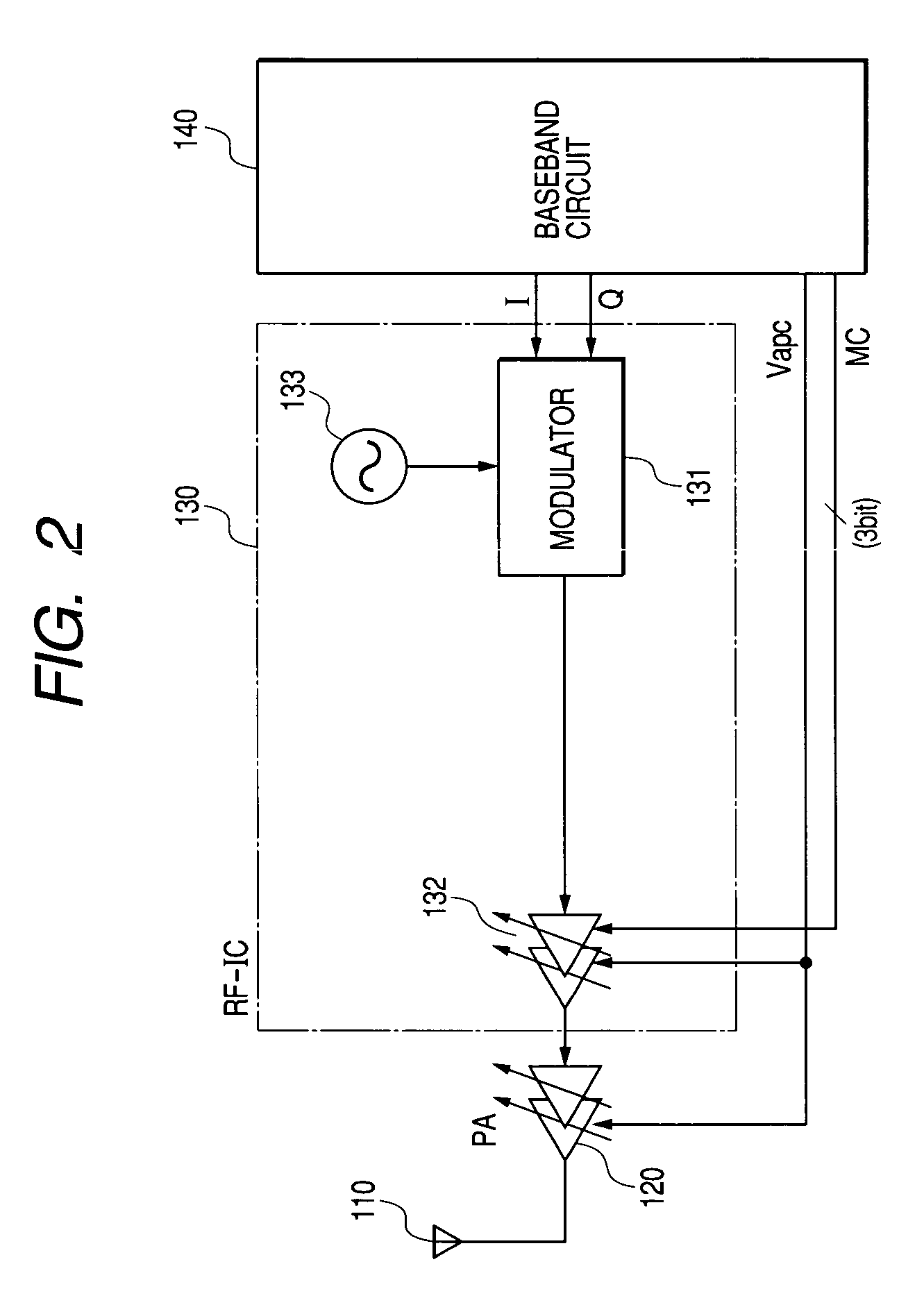
High frequency power amplifier
InactiveUS6700440B2Low efficiencyImprove efficiencyGain controlAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDc dc converterHigh frequency power
A high-frequency power amplifier system including a plurality of individual amplifiers connected in parallel, the amplifiers including switching-driven FET's. A fixed drain voltage is applied to one amplifier and a variable drain voltage is applied to another amplifier through a section including a DC-DC converter that converts the voltage according to a control value of a control signal. The turning on and off of the operation of the power amplifier is controlled by a control signal. Also, the circuit constants of a matching circuit are variable. In a high output power region, the power amplifier is turned on and, in a low output power region, turned off. Thereby, the decrease of efficiency of the power amplifier, owing to the DC-DC converter, may be suppressed to a minimum. The matching of the amplifier is adjusted when the power amplifier is switched on or off so as to improve efficiency. Consequently, it becomes possible to continuously control the output of the amplifier.
Owner:SONY CORP
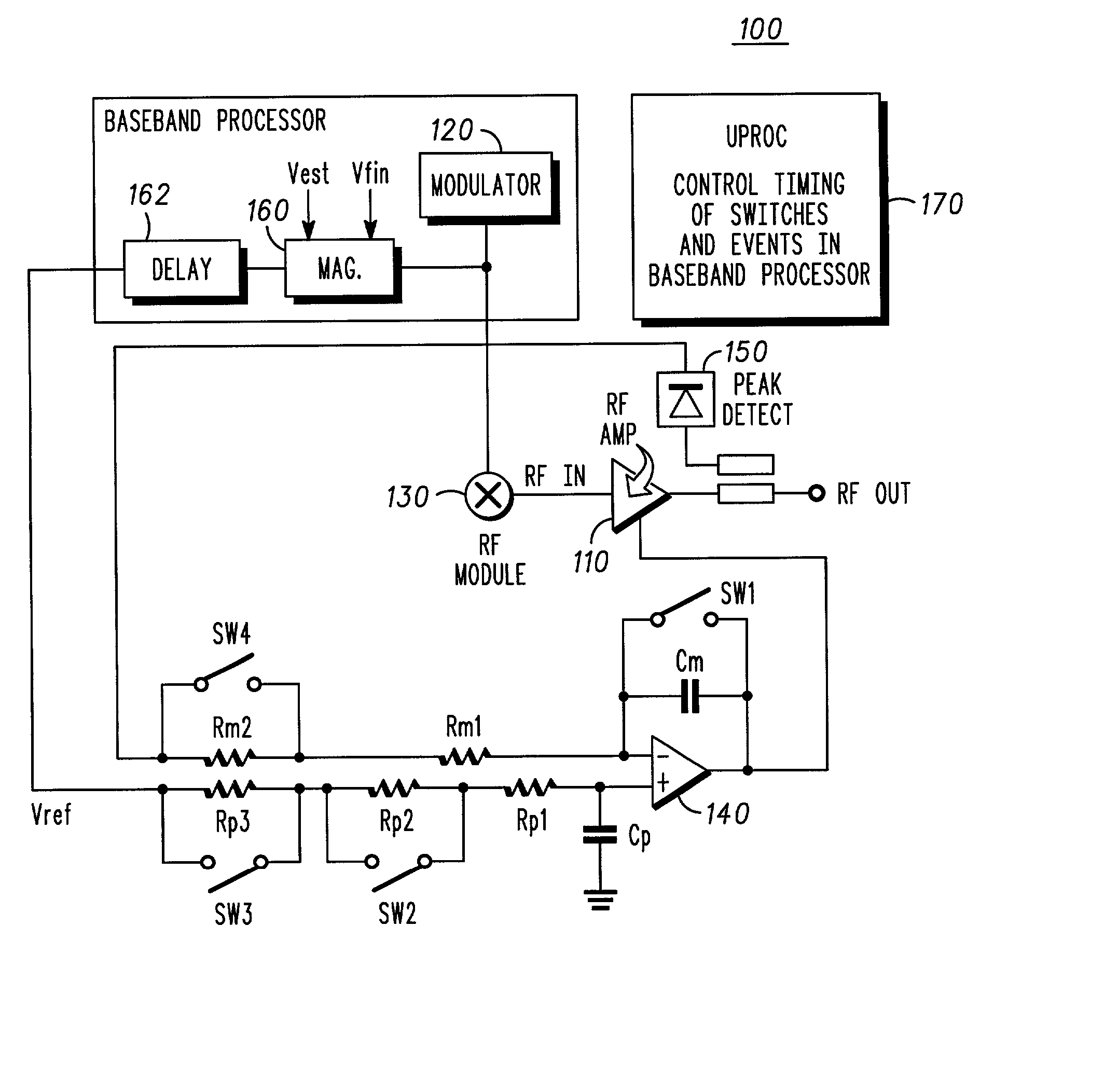
Multiple bandwidth amplifier control systems for mobile stations and methods therefor
InactiveUS20020168025A1Resonant long antennasNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierControl signal
RF amplifier control circuits for transmitters in mobile communication devices, combinations thereof and methods therefor. The control circuits include generally proportional and integral control circuits having an output coupled to a control input of an amplifier. An initial control signal is applied to the amplifier before a vector modulator output coupled an input thereof is at full output power. The vector modulator output is ramped to full output after applying the initial control signal. Thereafter, the initial control signal applied to the amplifier during ramping is corrected by integrating an output of the amplifier relative to a second reference signal with an integral control circuit coupled to the control input of the amplifier, the second reference signal is proportional to the ramping vector modulator output.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
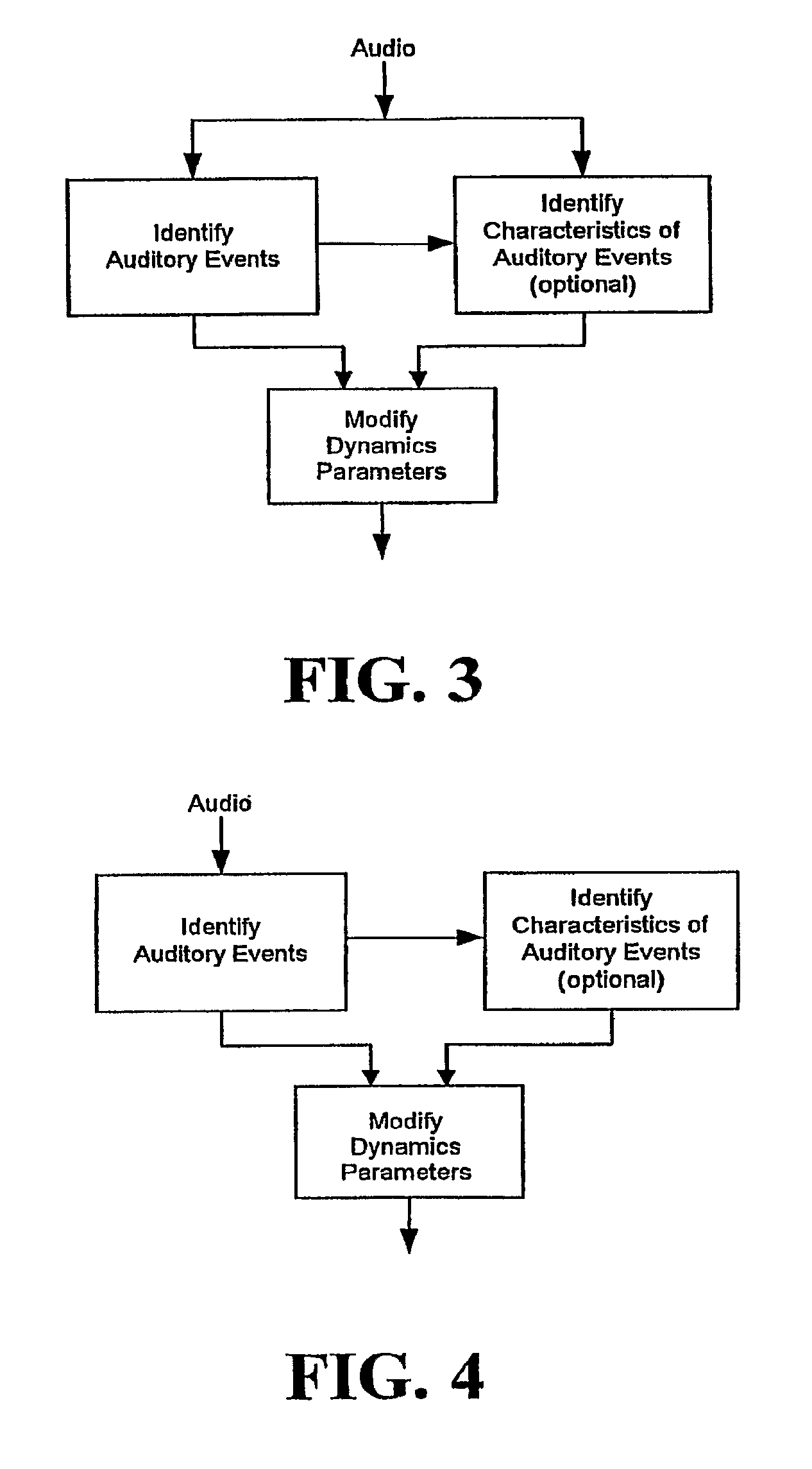
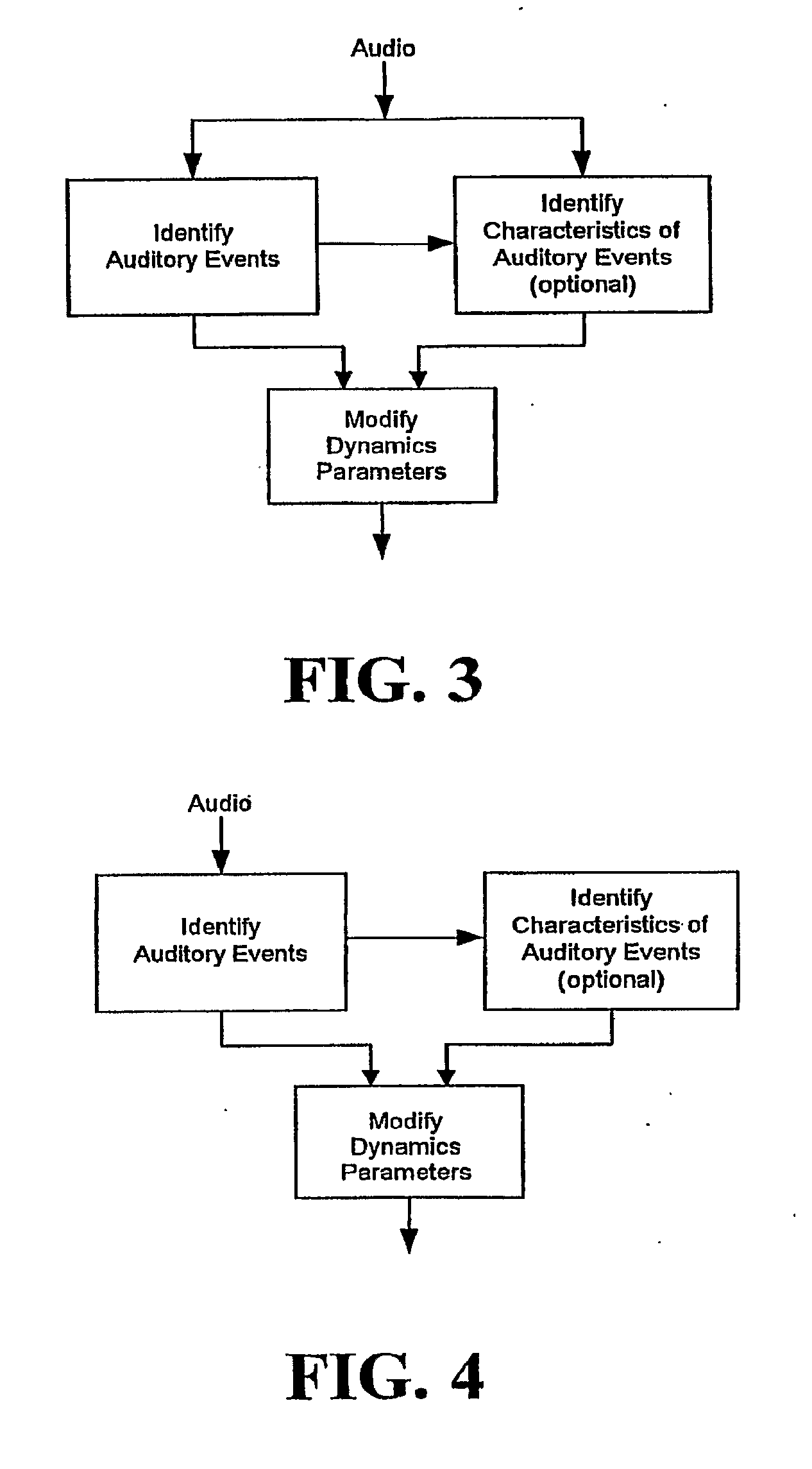
Audio gain control using specific-loudness-based auditory event detection
ActiveUS8144881B2Change damageSlow down the rate of change of gainSignal processingGain controlLoudnessComputer science
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Method and apparatus for controlling an audio signal level
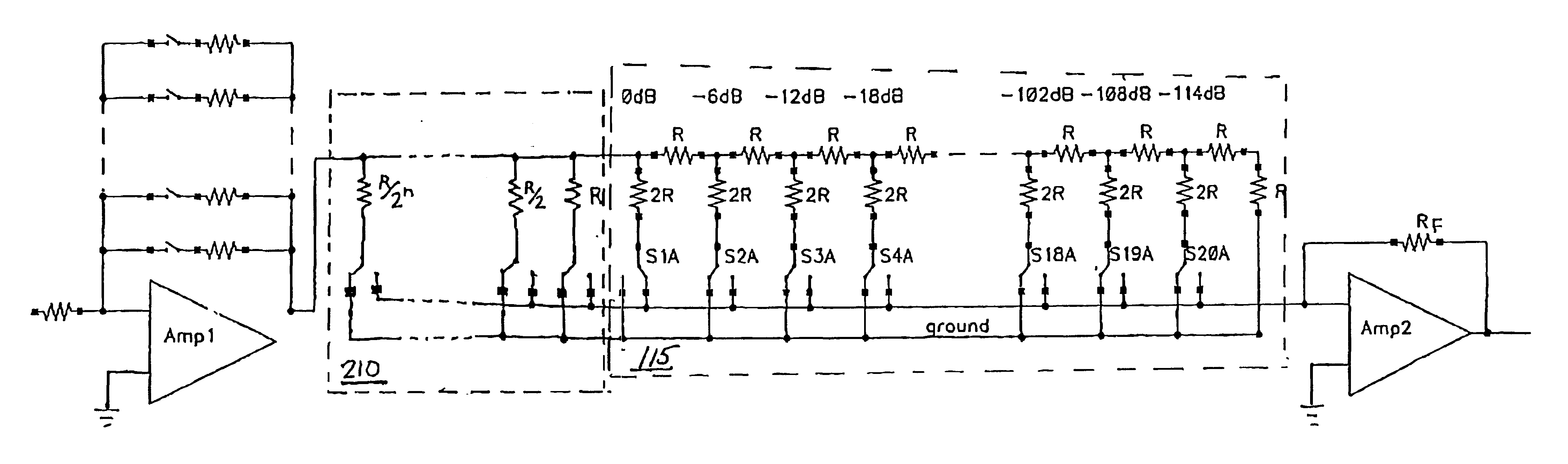
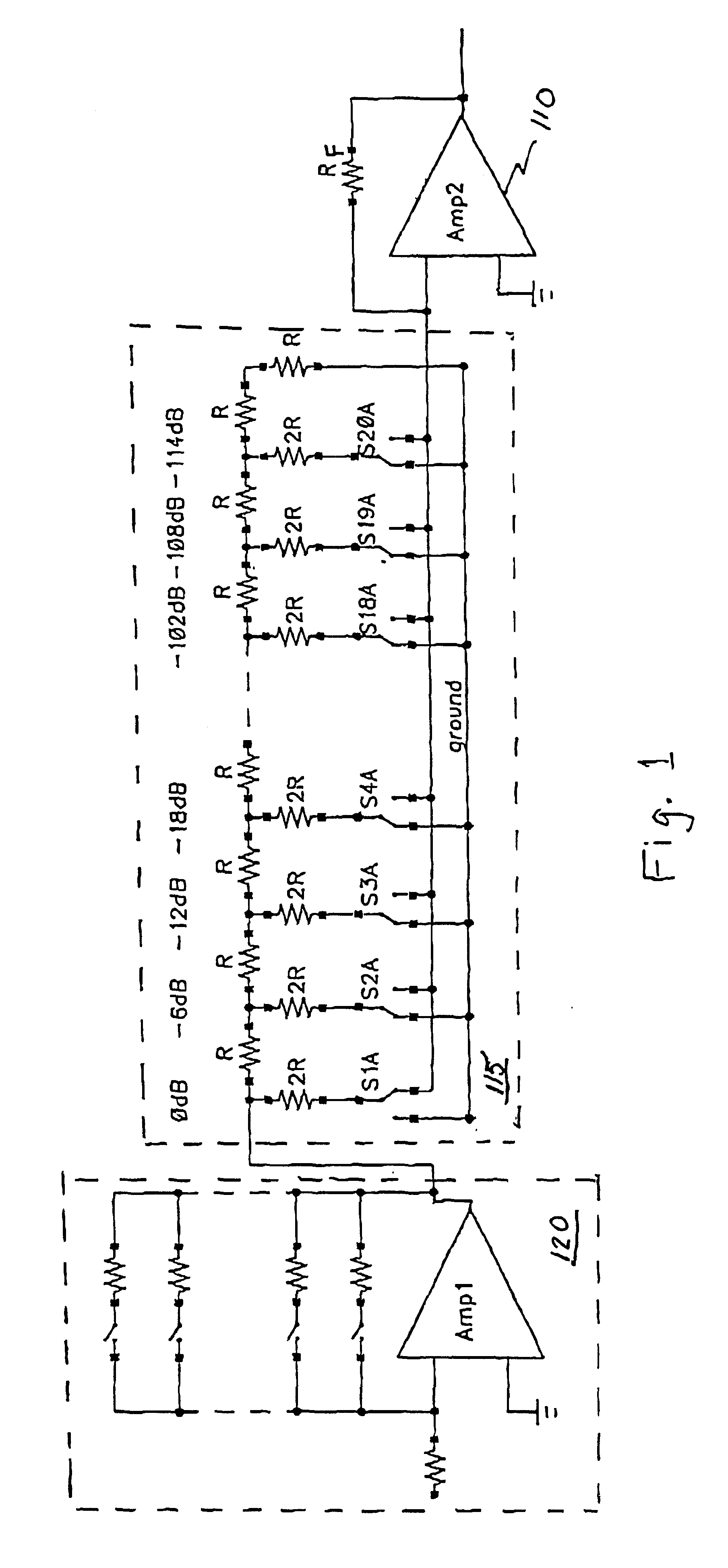
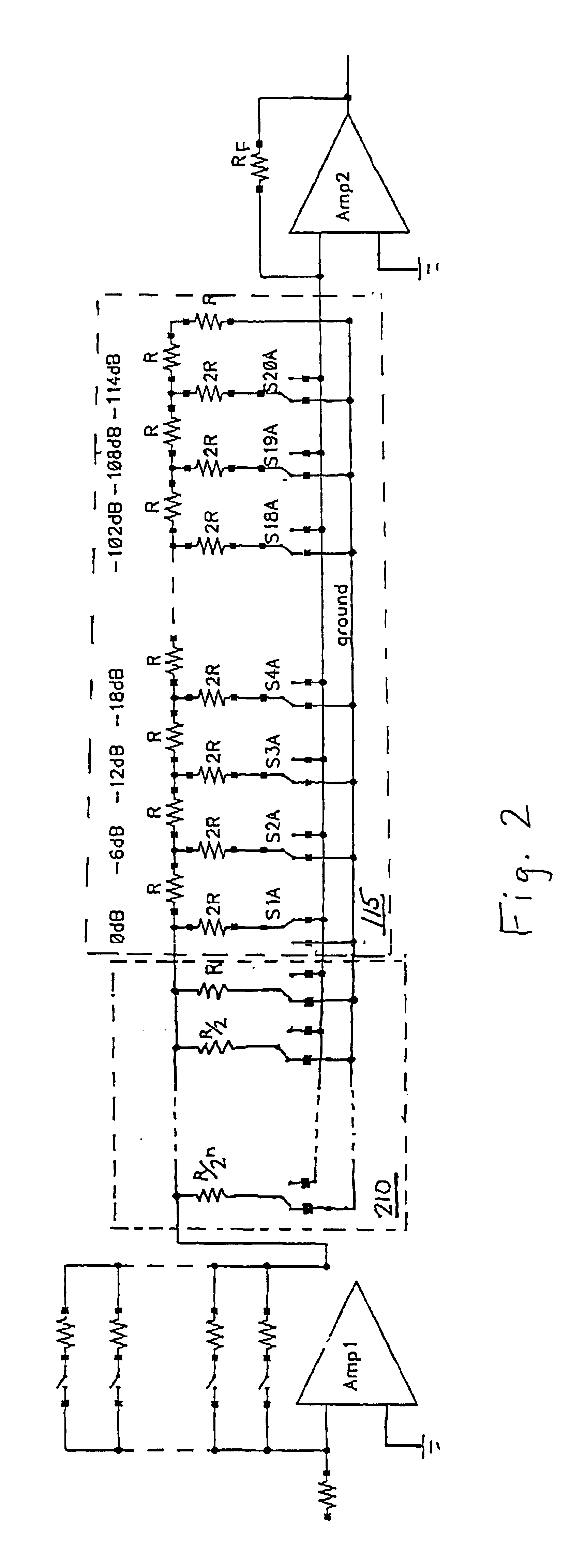
InactiveUS6693491B1Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsAudio power amplifierControl circuit
A control circuit for controlling a level of an audio signal and transmitting the signal to an amplifier is described. The control circuit is based on an R-2R resistor network having a first plurality of resistor nodes and a parallel resistor network having a second plurality of resistor nodes. Each of the resistors in the parallel network has a value equal to one-half of the value of the preceding resistor. A plurality of switches alternately connects each of the plurality of resistor nodes to one of a plurality of low impedance nodes and a low impedance input node associated with the amplifier. Switch control circuitry selectively controls the plurality of switches to transmit the audio signal to the low impedance input node.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
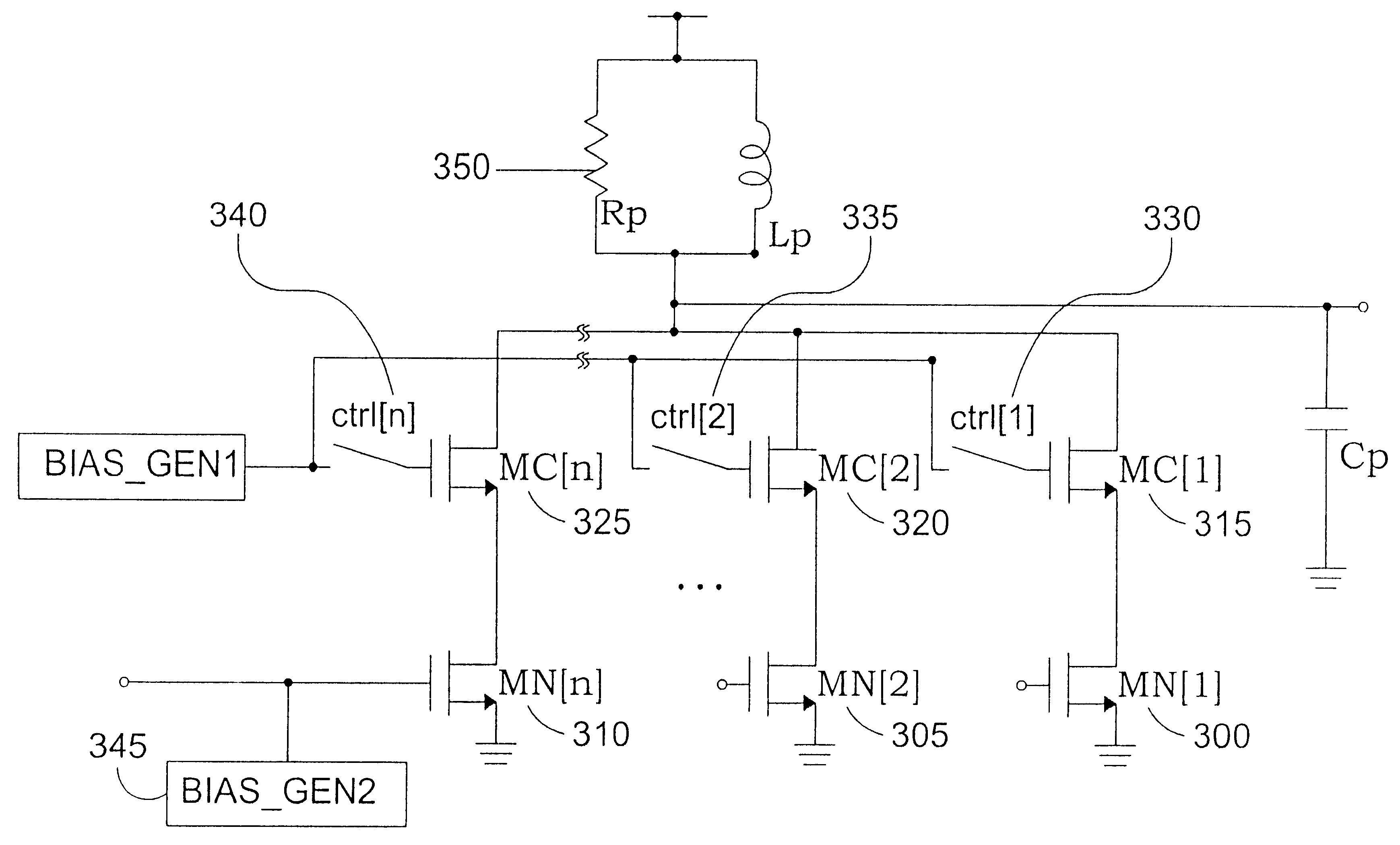
Multi-track integrated spiral inductor
InactiveUS6885275B1Resonant circuit detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSpiral inductorEngineering
An integrated circuit inductor includes a spiral pattern disposed upon a substrate. The track of the spiral is divided into multiple tracks to form a multi-track inductor. The individual tracks are disposed side by side and in different layers. Tracks that are aligned vertically are coupled by feed throughs, or vias. Multiple vias are used along the length of each of the multiple tracks. Tracks disposed in the same layer are joined together at their beginning, and at their termination. A patterned shield is fabricated from conductive fingers of n+ salicided material that is separated by non conducting polysilicon that fills the gaps between the fingers. The conductive fingers are coupled together in groups, which are in turn tied to a single point ground. In tying the groups together, a gap in the conducting path is provided to prevent ground loop currents. The shield is disposed between the multi-track inductor and the substrate.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Audio signal controller
ActiveUS20110029109A1Lower Level RequirementsLow costSignal processingLow frequency amplifiersDigital audio signalsAudio frequency
The present invention relates to an audio signal controller adapted to receiving first and second digital audio signals and estimating a signal feature of the first or second digital audio signal. The estimated signal feature is compared with a predetermined feature criterion and the audio signal controller switches from conveying the first digital audio signal to conveying the second digital audio signal to a controller output, or vice versa, at a zero-crossing of the first digital audio signal or the second digital audio signal based on the comparison between the estimated signal feature and the predetermined feature criterion.
Owner:INVENSENSE
Programmable gain current amplifier
ActiveUS20060103463A1Increase currentSimple structureGain controlGated amplifiersAmplifierCurrent mirror
A programmable gain current amplifier is provided, including a transistor pair, a plurality of differential pairs, and a control device. The transistor pair receives an input current. Each differential pairs connecting with each other in parallel is connected to the transistor pair to form a differential current mirror for amplifying the input current. The control device adjusts the output polarity of the current mirror, thereby obtaining a predetermined gain between the output of the current mirror and the input current. Therefore, amplification of the input current at a programmable gain is realized.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Variable gain amplifier
InactiveUS6163215AComputations using contact-making devicesGain controlAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
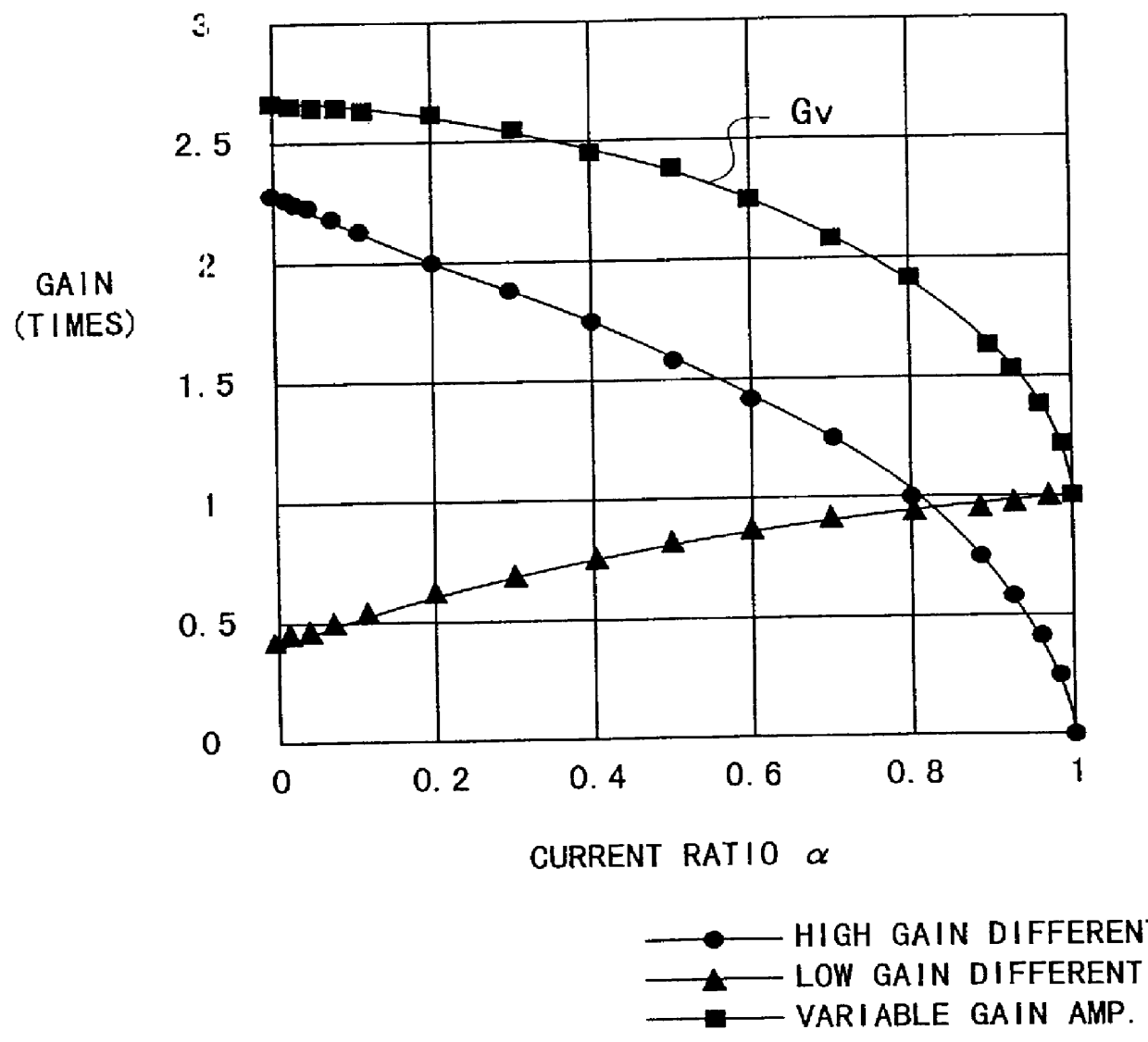
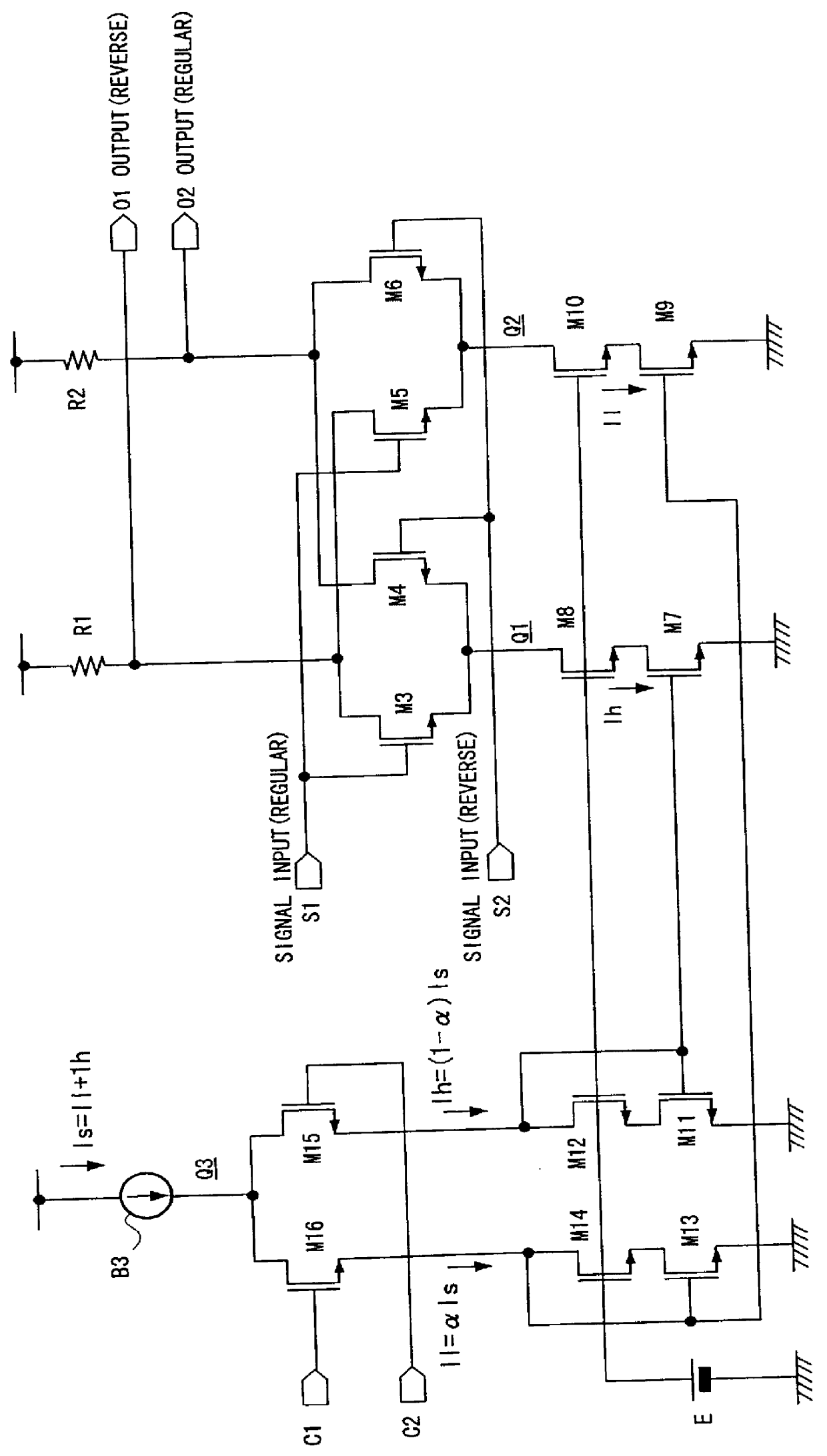
In a variable gain amplifier controlling a gain by using differential amplifiers with a gain control signal, a gain switchover differential amplifier or a bias circuit which composes a current mirror with the gain switchover differential amplifier is connected between a high and a low gain differential amplifier for the same bias current which are mutually connected to share load resistances for the same output polarity and a bias current source common to both of the differential amplifiers, to perform switchover operations of the high and the low differential amplifier by a gain control signal, and a current source which flows a fixed offset current through at least the low one of the high and the low differential amplifier is provided.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Audio Gain Control Using Specific-Loudness-Based Auditory Event Detection
ActiveUS20090220109A1Reduction of audible artifactChange damageSignal processingGain controlLoudnessComputer science
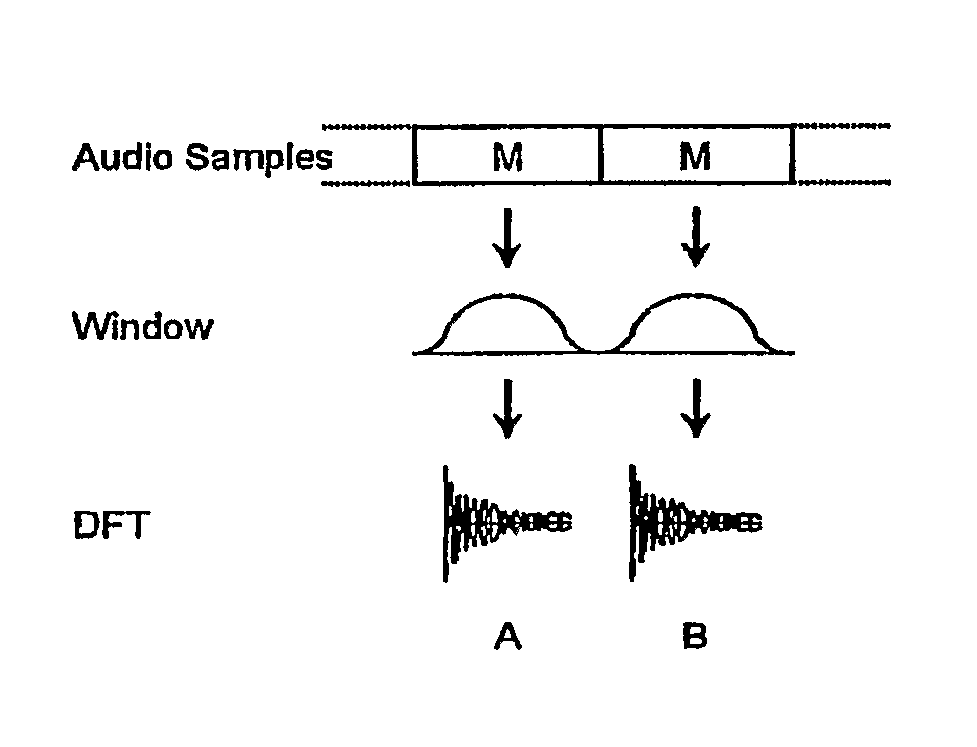
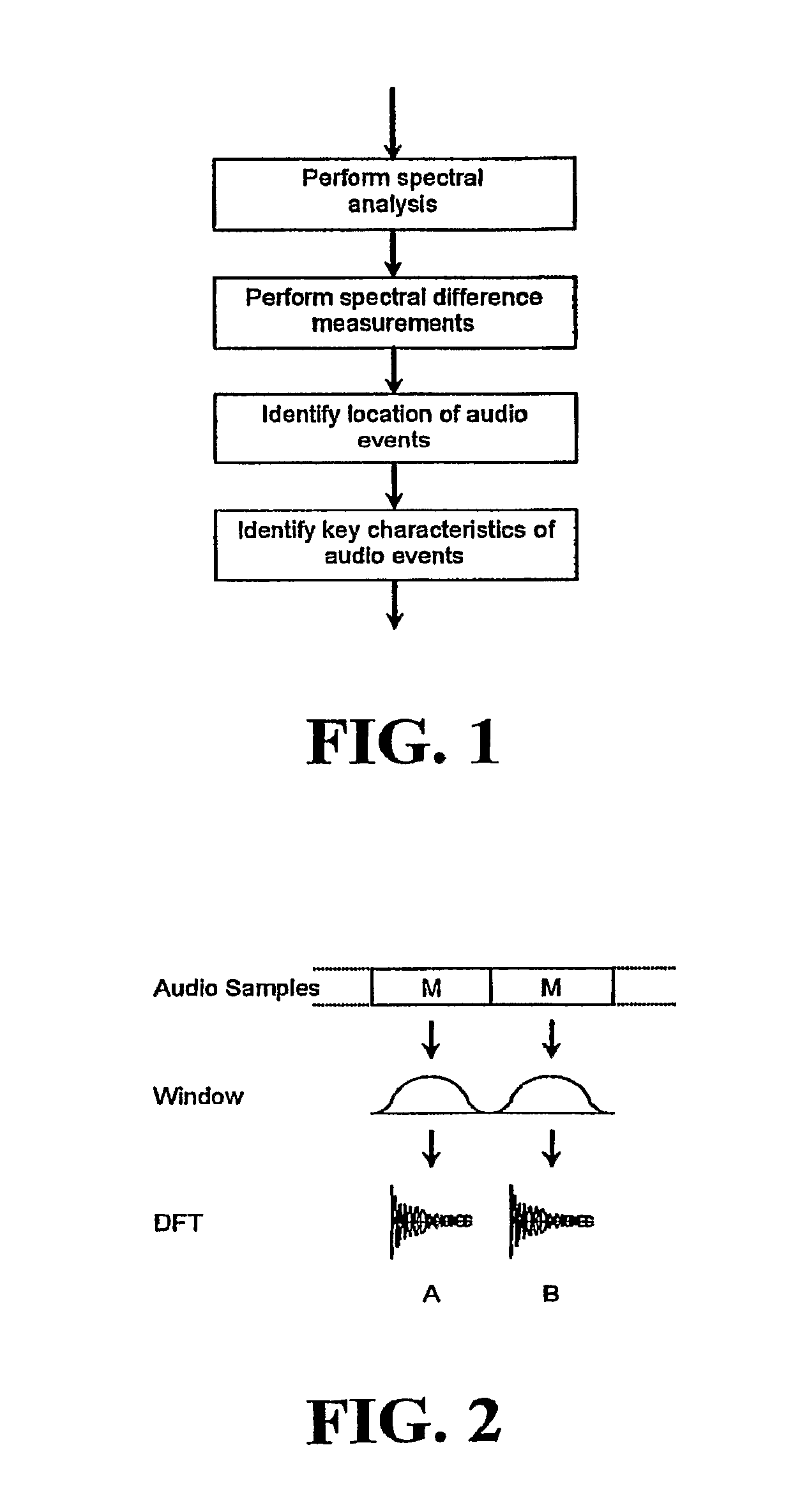
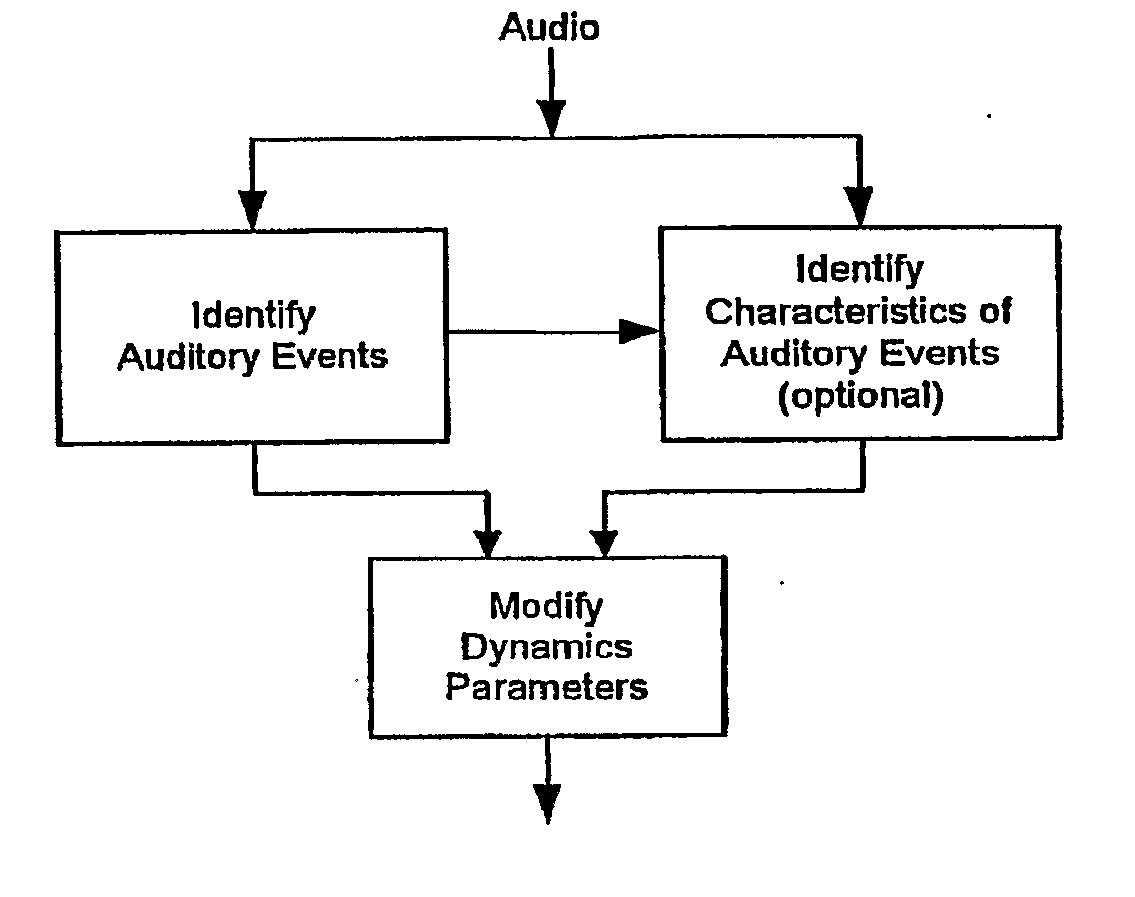
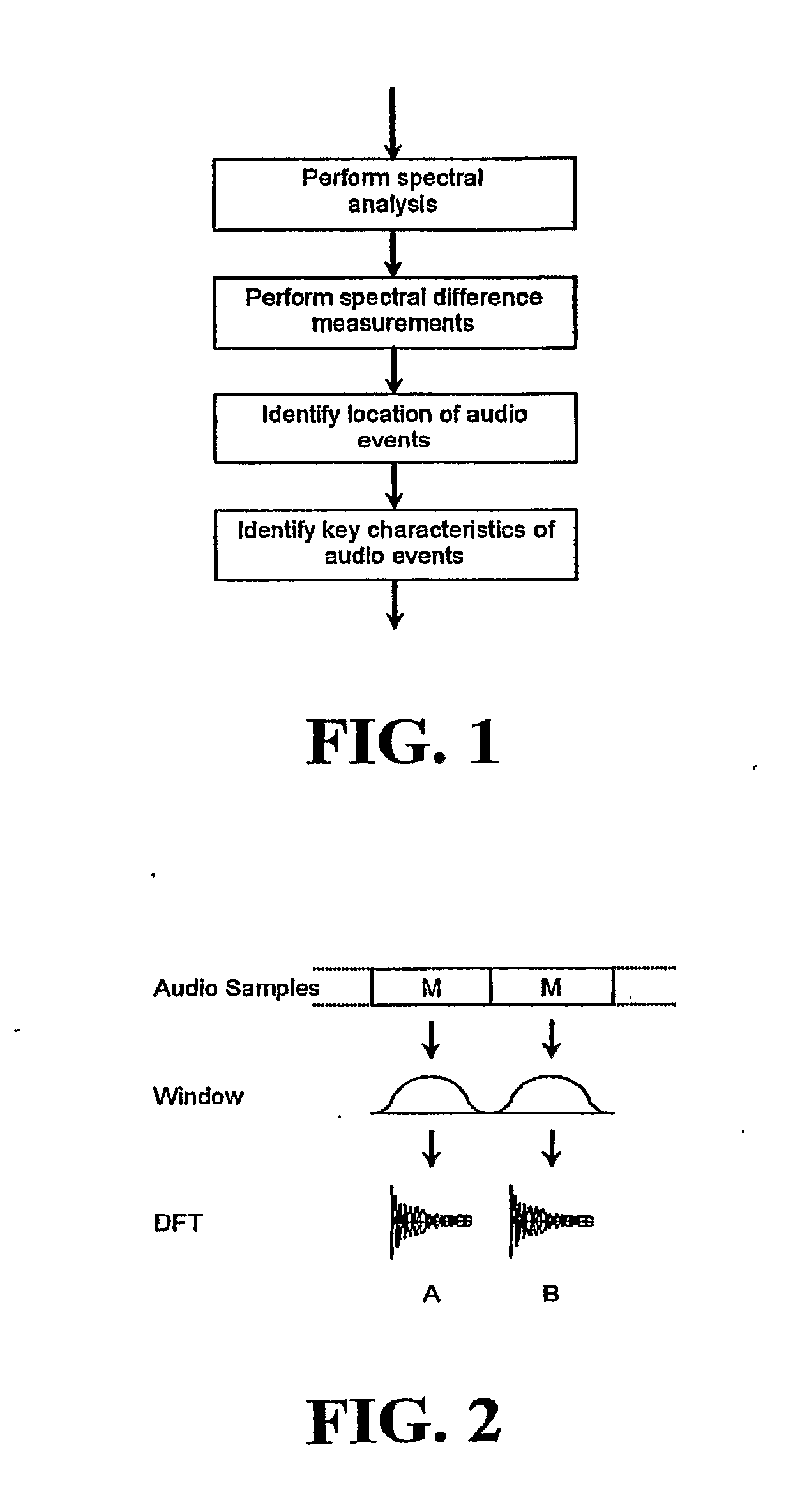
In one disclosed aspect, dynamic gain modifications are applied to an audio signal at least partly in response to auditory events and / or the degree of change in signal characteristics associated with said auditory event boundaries. In another aspect, an audio signal is divided into auditory events by comparing the difference in specific loudness between successive time blocks of the audio signal.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
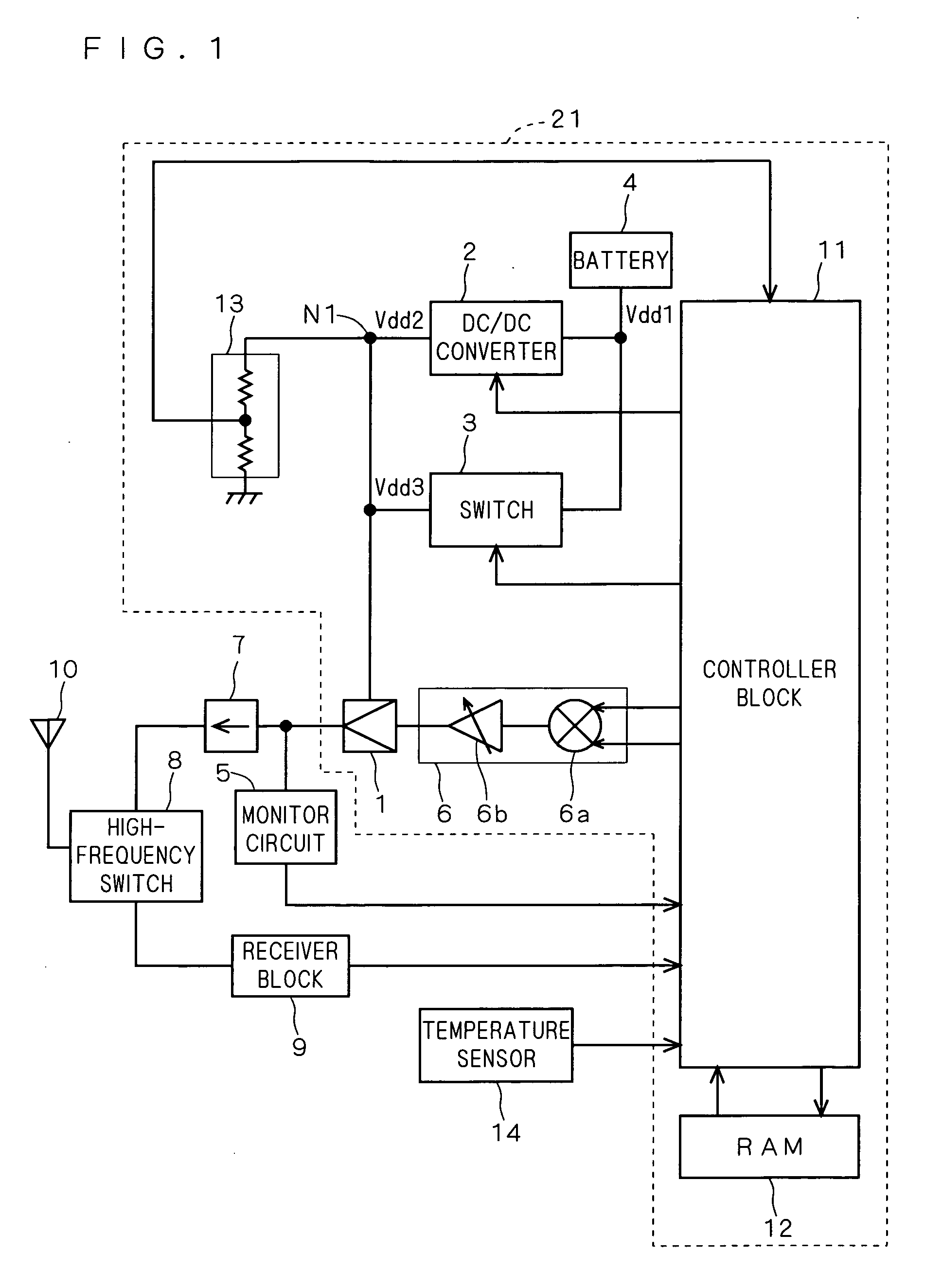
Power amplifier unit, communication terminal and control method of power amplifier unit
InactiveUS20070146076A1Easy to usePower amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierEngineering
The present invention relates to a power amplifier device having a power amplifier, and an object of the invention is to enable efficient use of the power amplifier without causing any problems in the operation of the power amplifier. In order to achieve the object, a controller block 11 judges on the basis of an estimative output power value whether a power amplifier is in a first period in which it performs low power output operation or in a second period in which it performs high power output operation, where, in the first period, the controller block 11 activates a DC / DC converter 2 to supply a power-supply voltage Vdd2 as the operating power-supply voltage to the HPA 1, and in the second period, the controller block 11 controls the DC / DC converter 2 between active and inactive states and a switch 3 between on and off states on the basis of a detected power-supply voltage value VM obtained from an operating power-supply voltage detecting circuit 13, so as to supply one of the power-supply voltage Vdd2 and a power-supply voltage Vdd3 as the operating power-supply voltage.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP +1
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and wireless communication system
InactiveUS7116949B2Total current dropImprove dynamic rangeResonant long antennasGain controlCurrent consumptionEngineering
The dynamic range is changed by switching a current applied to an amplifying circuit to obtain the minimum ICP required to keep linearity with the number of multiplexes even when the number of multiplexes of data is changed by switching the operation current of the amplifying circuits of the transmission system and also supplying the information about number of multiplexes of data to be transmitted to the amplifying circuits of the transmission system from the baseband circuit. Thereby, the signal can be transmitted without distortion even when the number of multiplexes increases and the current of the amplifying circuit may be reduced when the number of multiplexes is small in order to reduce the current consumption in the communication semiconductor integrated circuit device which can form a wireless communication system of the code division multiplex system such as W-CDMA system.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Programmable radio transceiver
ActiveUS20050212604A1Error signalAngle modulation by variable impedenceHigh frequency amplifiersCapacitanceTransceiver
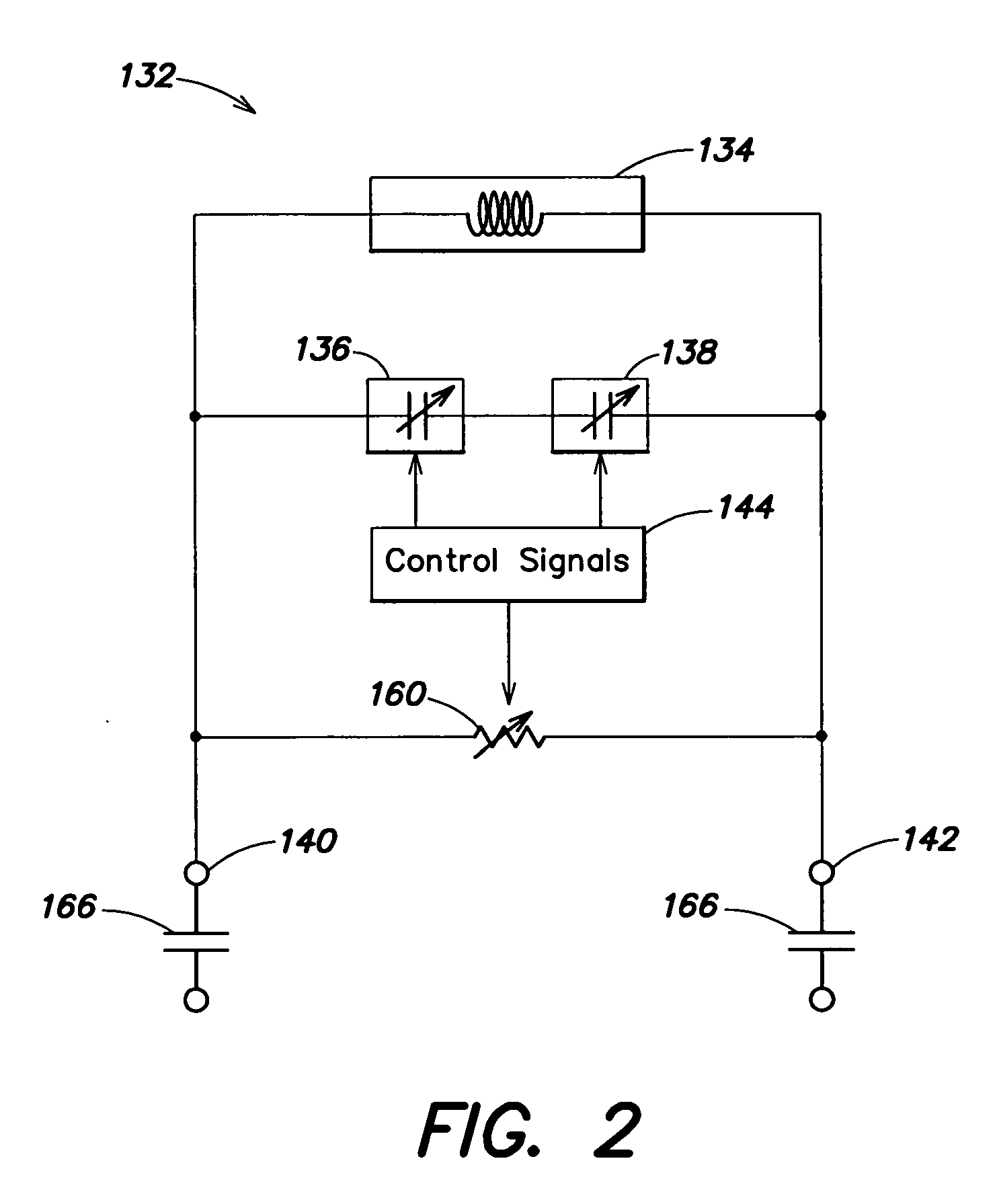
A fully integrated, programmable mixed-signal radio transceiver comprising a radio frequency integrated circuit (RFIC) which is frequency and protocol agnostic with digital inputs and outputs, the radio transceiver being programmable and configurable for multiple radio frequency bands and standards and being capable of connecting to many networks and service providers. The RFIC includes a tunable resonant circuit that includes a transmission line having an inductance, a plurality of switchable capacitors configured to be switched into and out of the tunable resonant circuit in response to a first control signal, and at least one variable capacitor that can be varied in response to a second control signal, wherein a center resonant frequency of the resonant circuit is electronically tunable responsive to the first and second control signals that control a first capacitance value of the plurality of switchable capacitors and a second capacitance value of the at least one variable capacitor.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
Method and system for controlling amplifiers
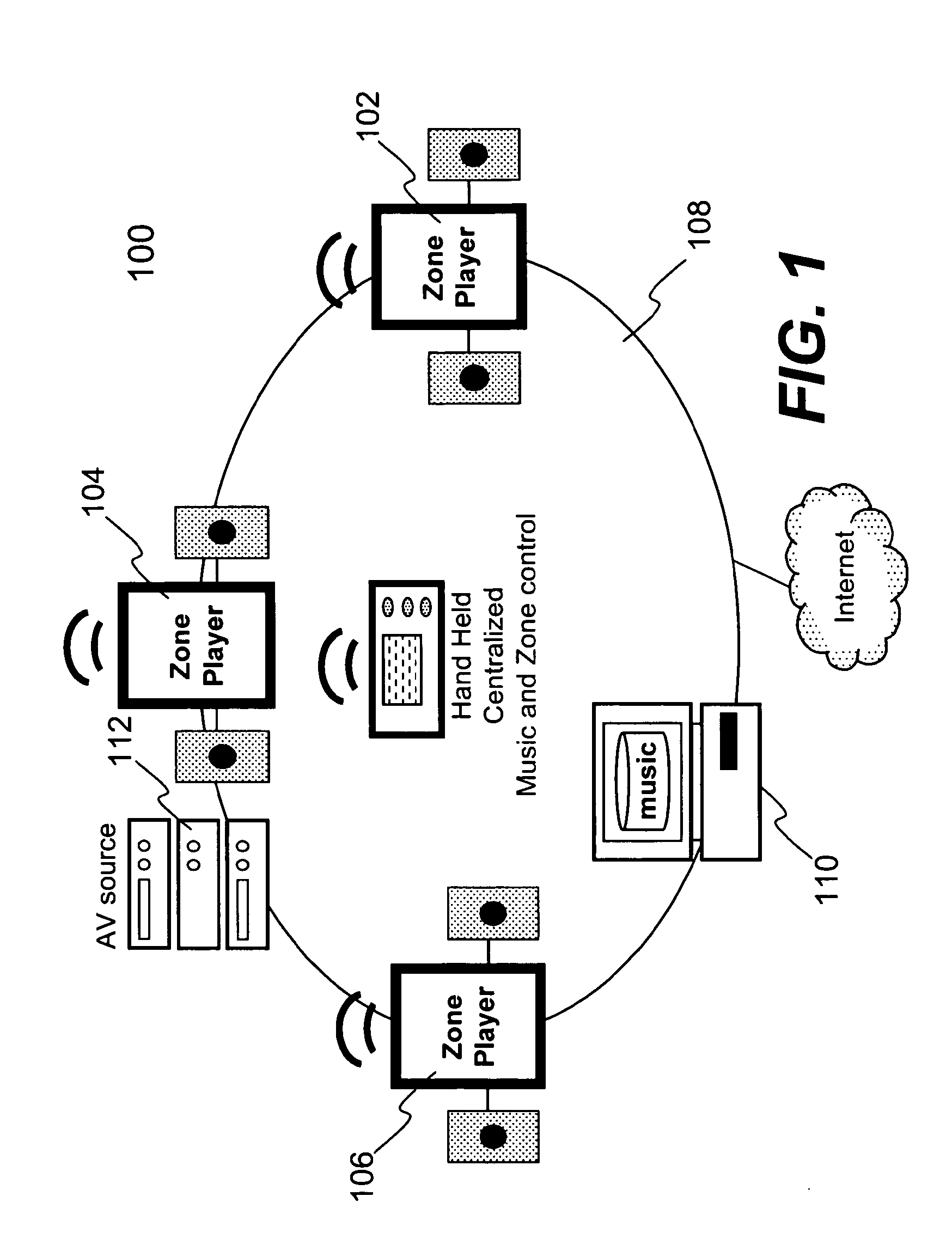
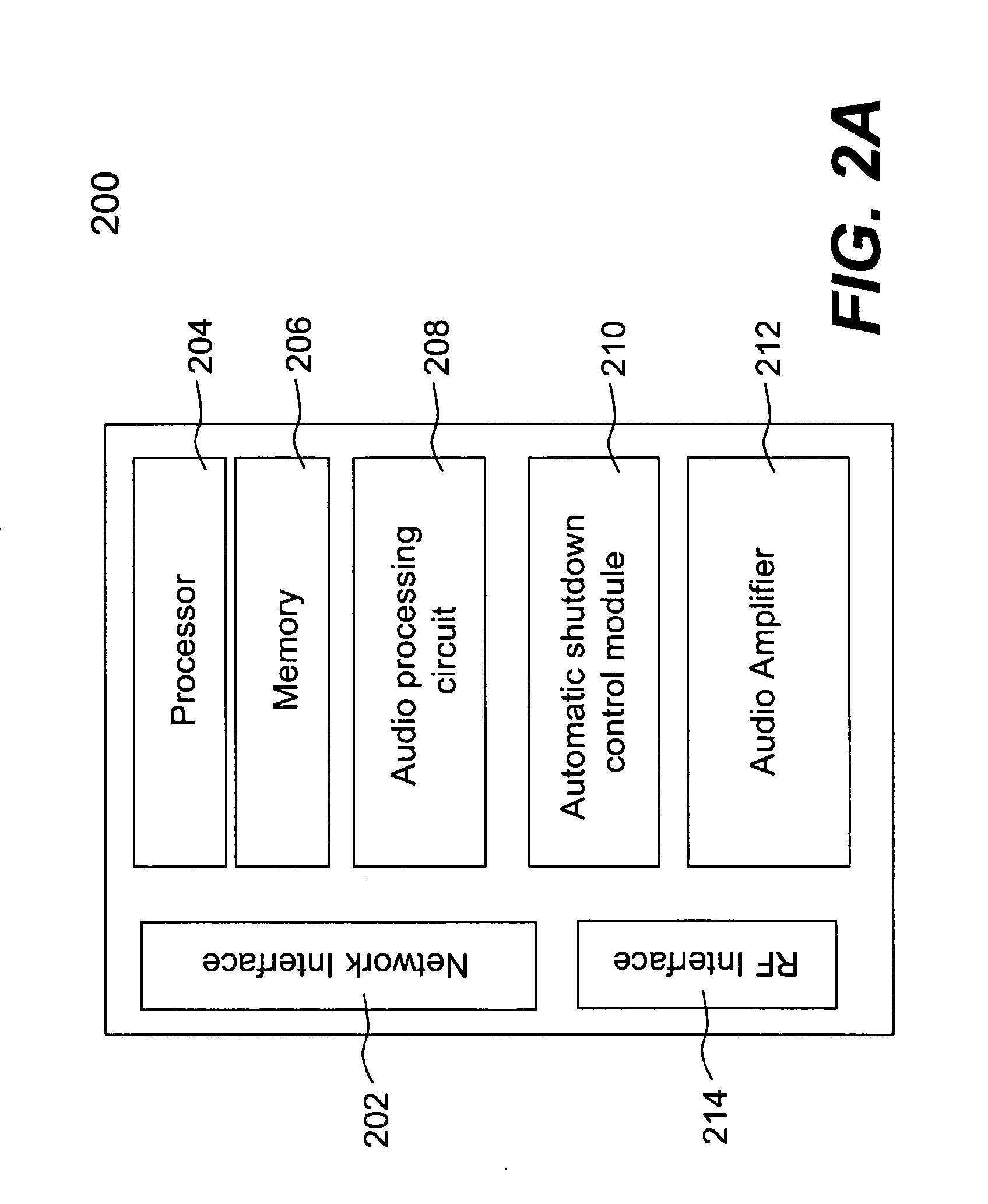
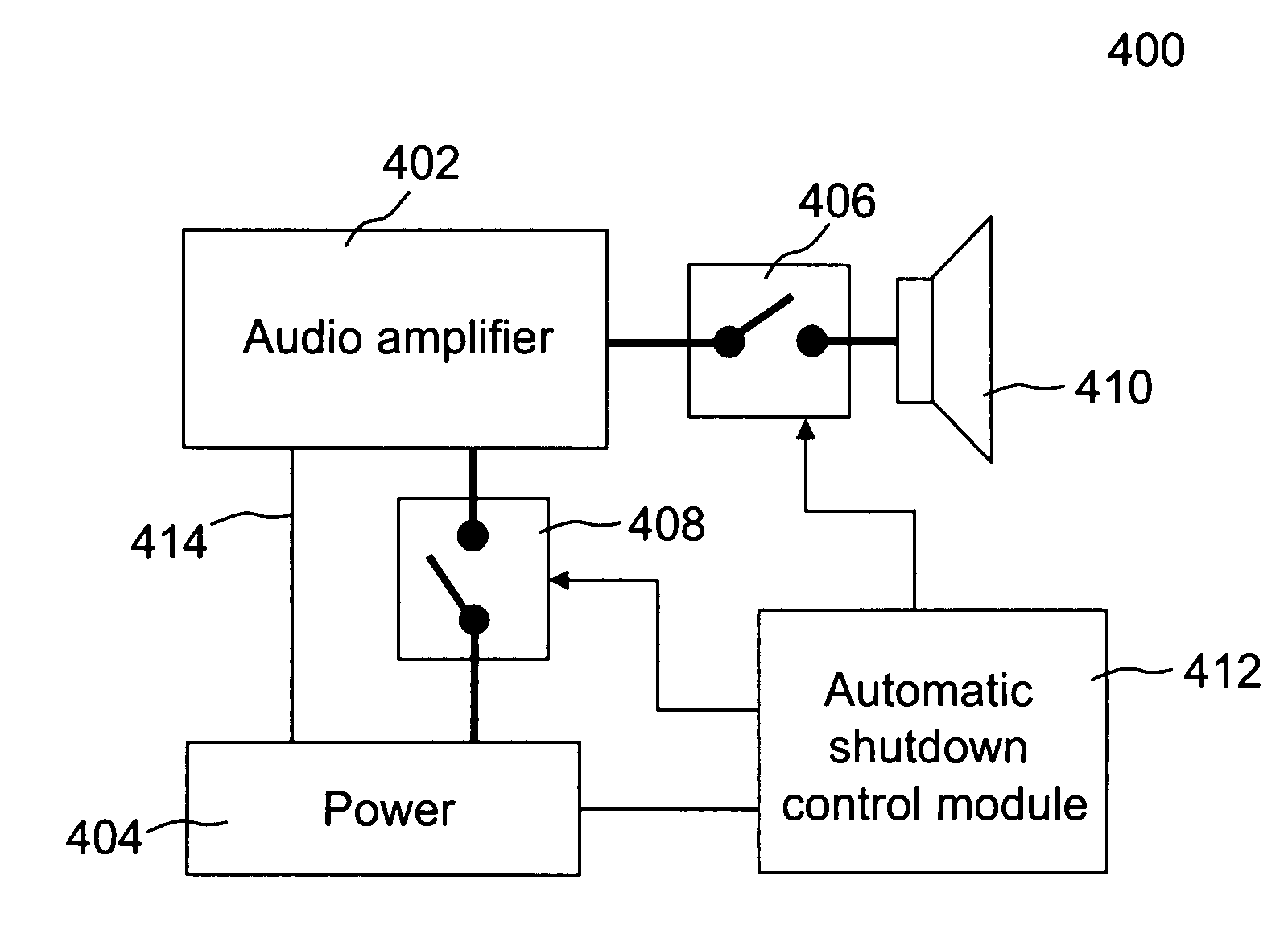
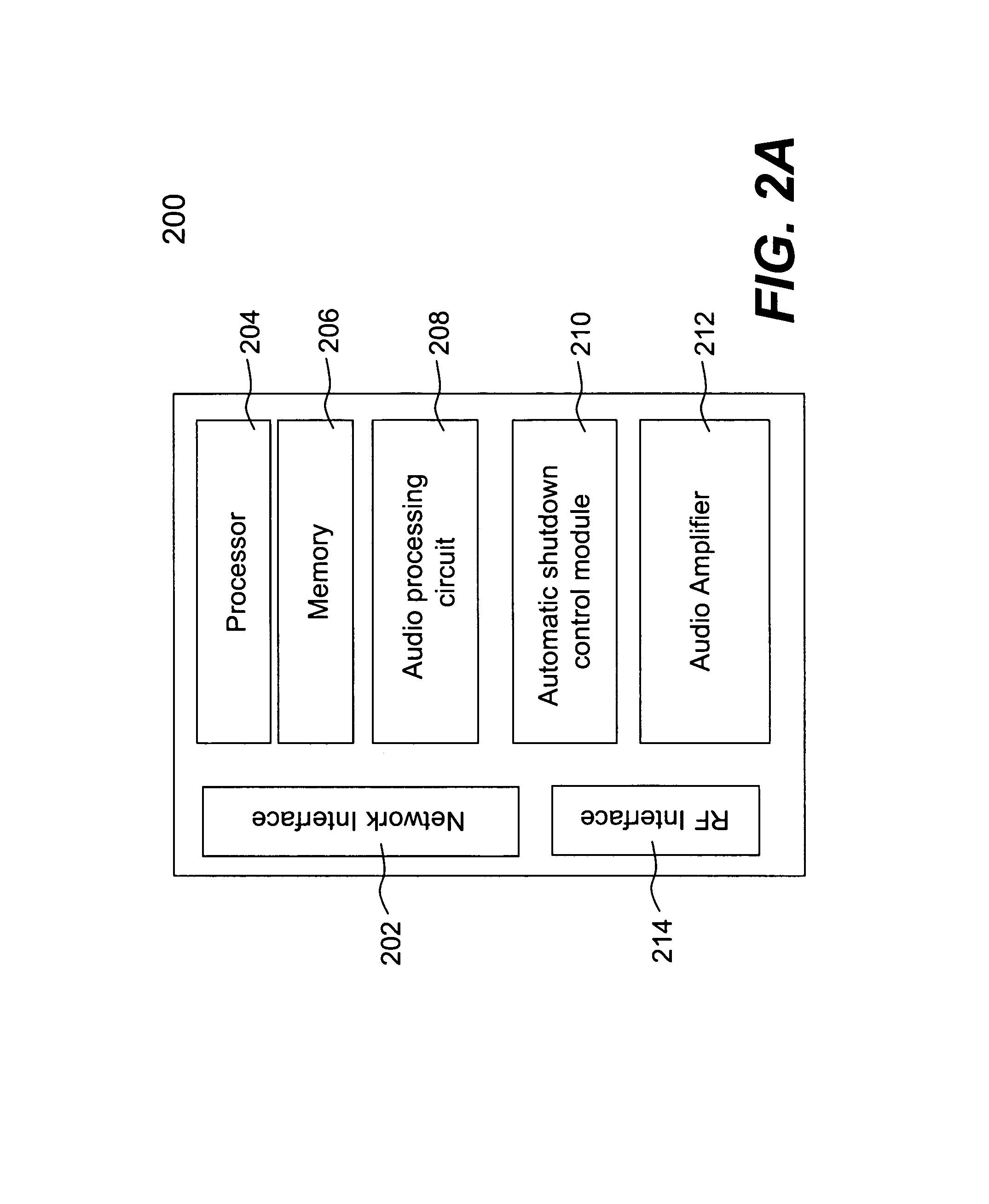
ActiveUS20110299696A1Digital data processing detailsPublic address systemsTelecommunicationsAudio power amplifier
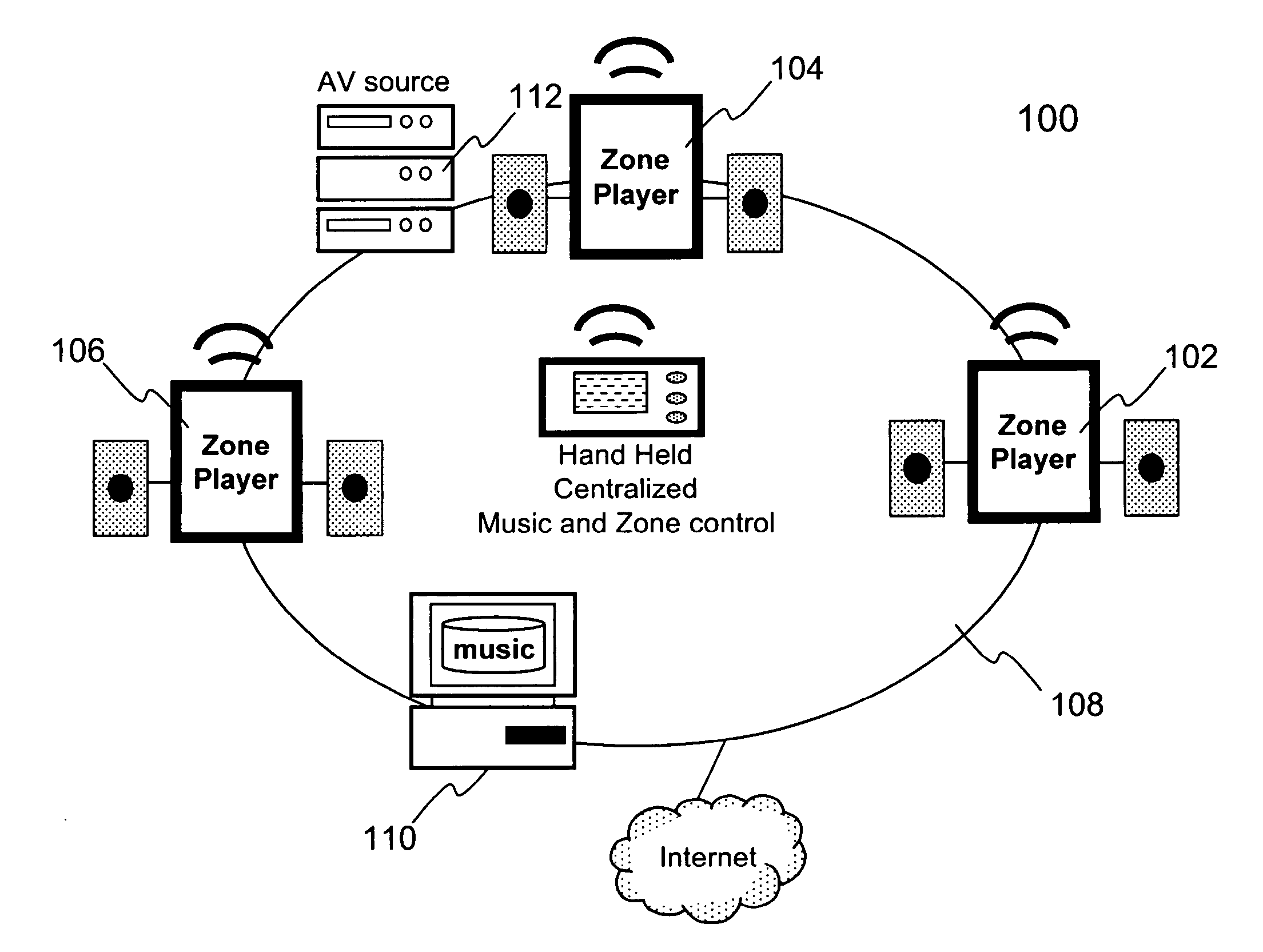
Techniques for controlling one or more audio amplifiers in or associated with a device coupled on a local area network are disclosed. The device receives at least one selected source from other devices also coupled on the network According to one aspect of the techniques, an automatic shutdown control module is provided in the device to power down the audio amplifiers when there is no audio data flow coming to the device or power up the audio amplifiers when there is audio data flow coming to the device. In one embodiment, the procedure to power down or power up the amplifiers is in accordance with a hysteresis, wherein the hysteresis, being lagging of an effect behind its cause, protects the amplifiers and makes the powering-down or powering-up procedure unnoticeable to a user.
Owner:SONOS
Variable-gain amplifier having error amplifier with constant loop gain
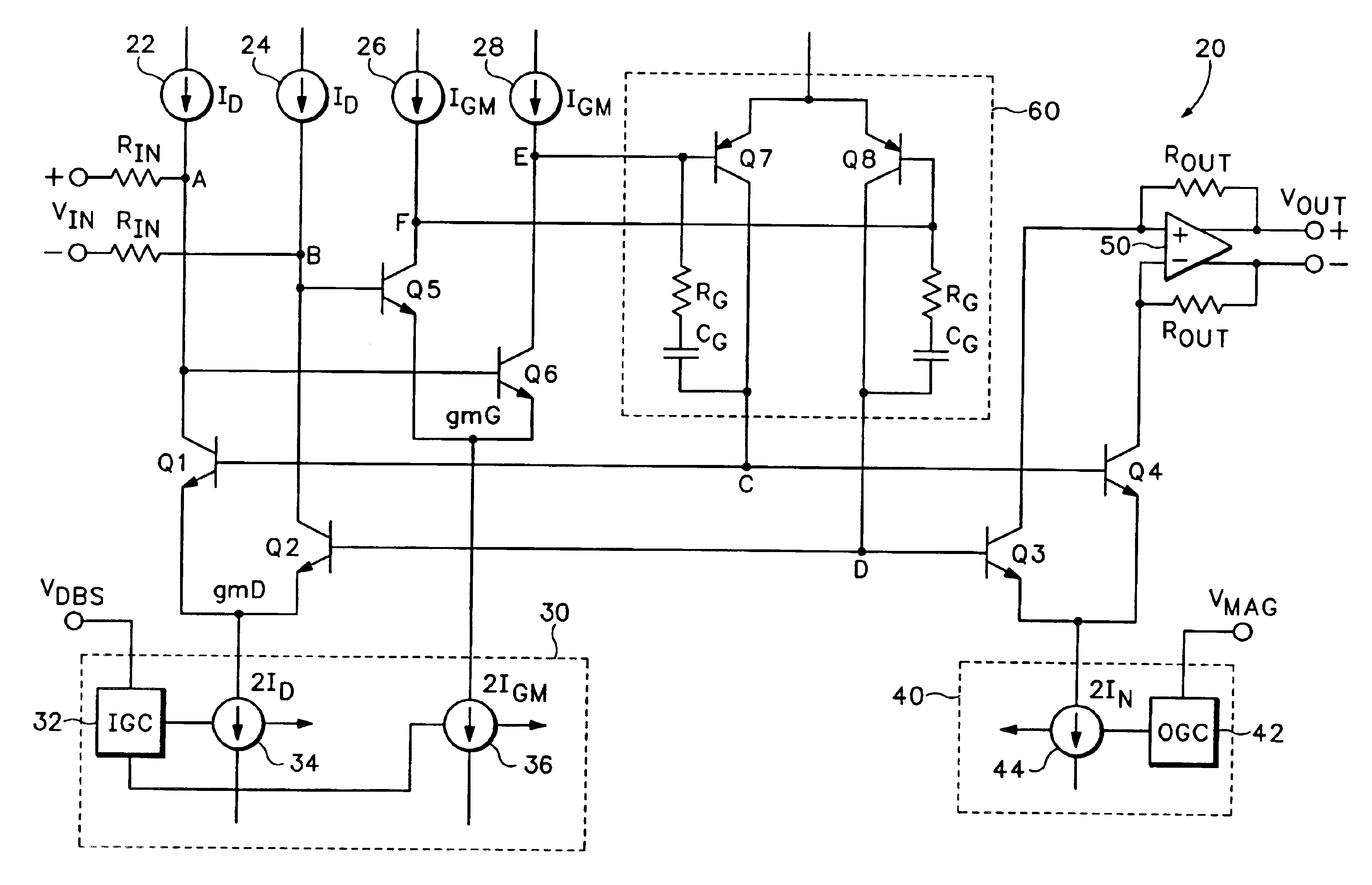
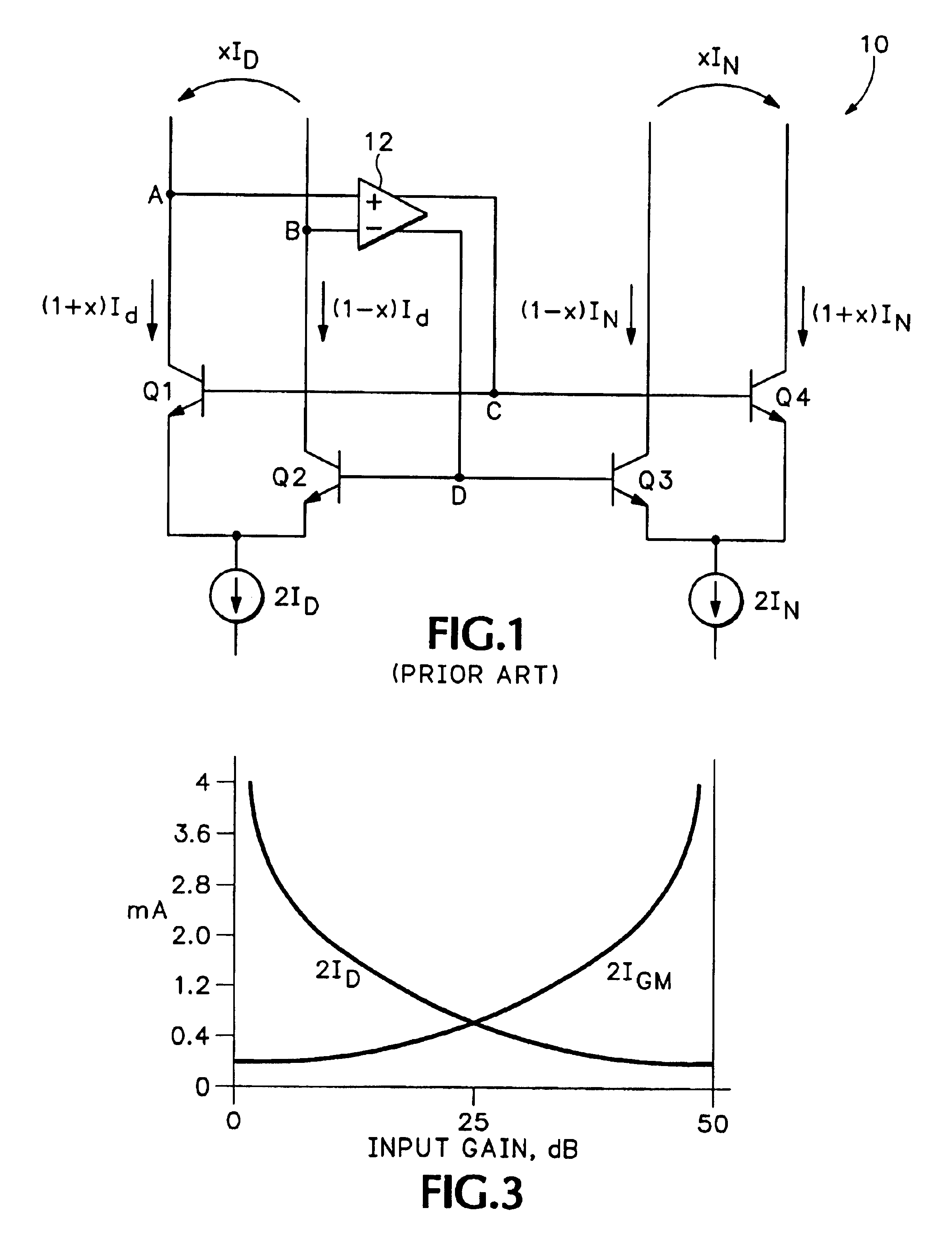
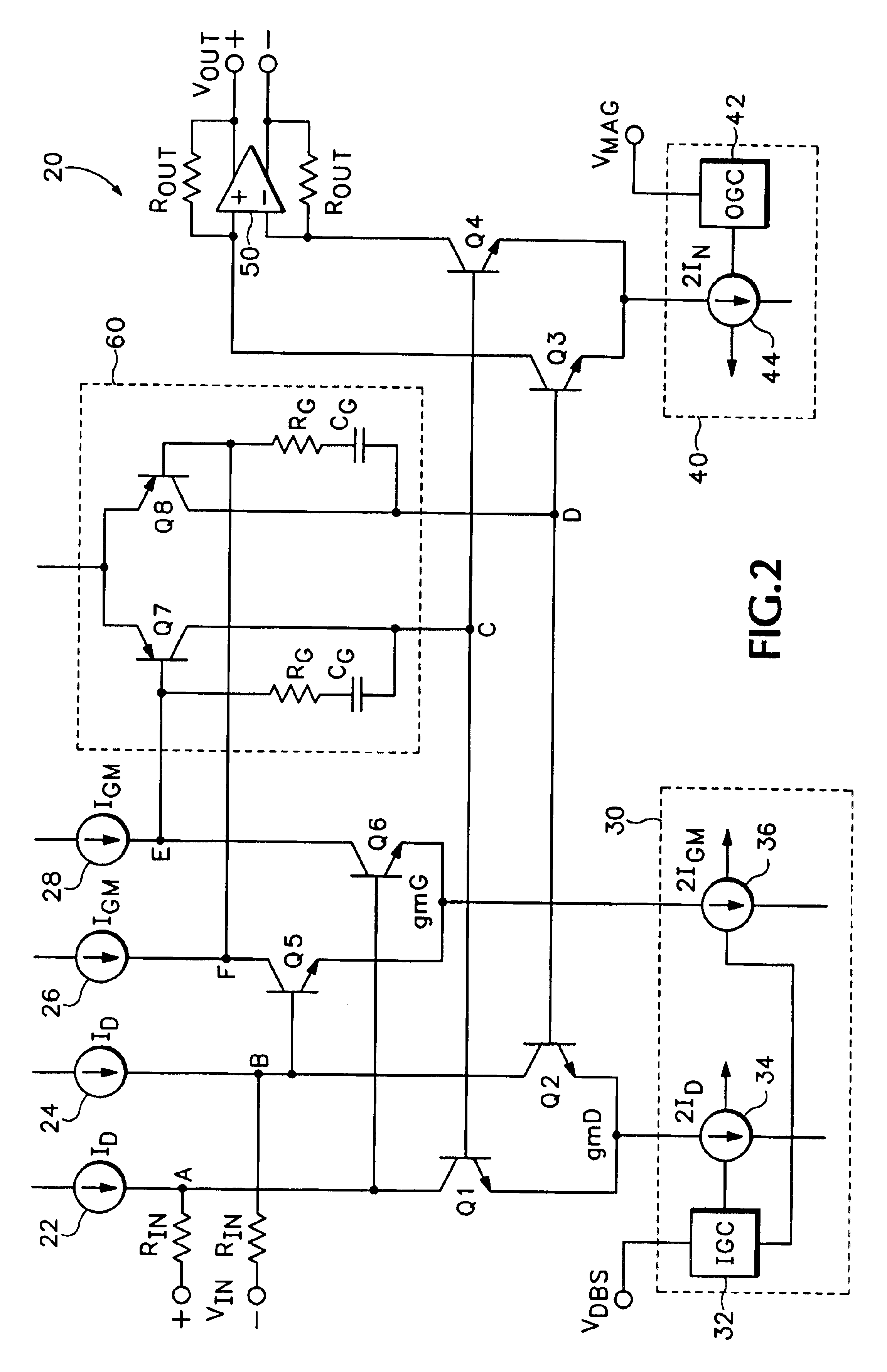
ActiveUS6894564B1Increase capacityImprove performanceDifferential amplifiersAmplification control detailsAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
A translinear amplifier is disclosed. A loop amplifier drives the bases of the input and output transistor pairs from the differential collector voltage of the input pair. The loop amplifier contains a third differential pair (a gain pair). The tail current of the gain pair is inversely related to the tail current of the input pair, such that loop amplifier gain remains stable when the transconductance of the input pair changes (due, e.g., to input gain changes). In one embodiment, a linear-in-dB interface is provided that adjusts input pair tail current exponentially (and gain pair tail current exponentially and inversely) to linear voltage changes at a gain input.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Bypass arrangement for low-noise amplifier
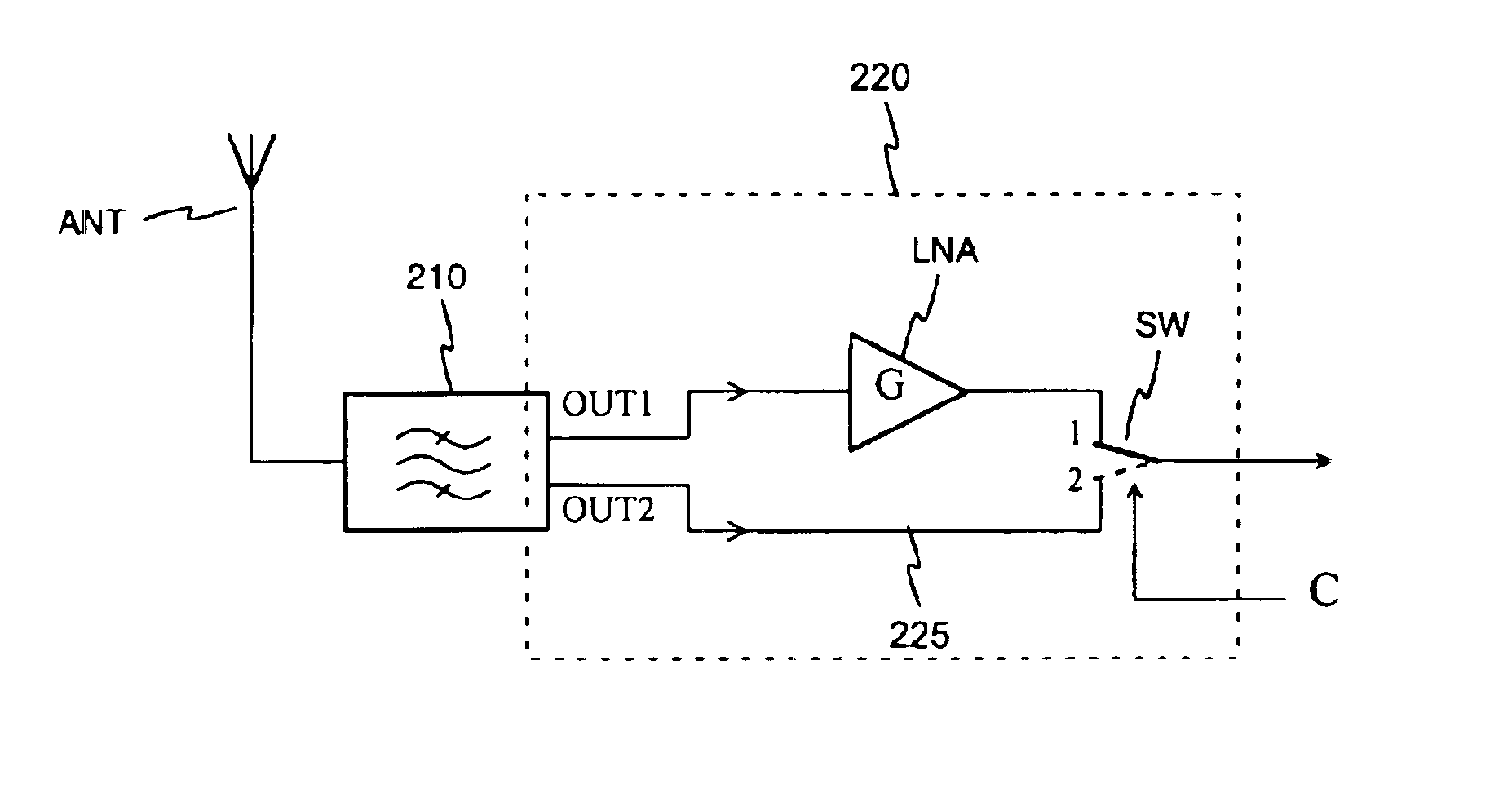
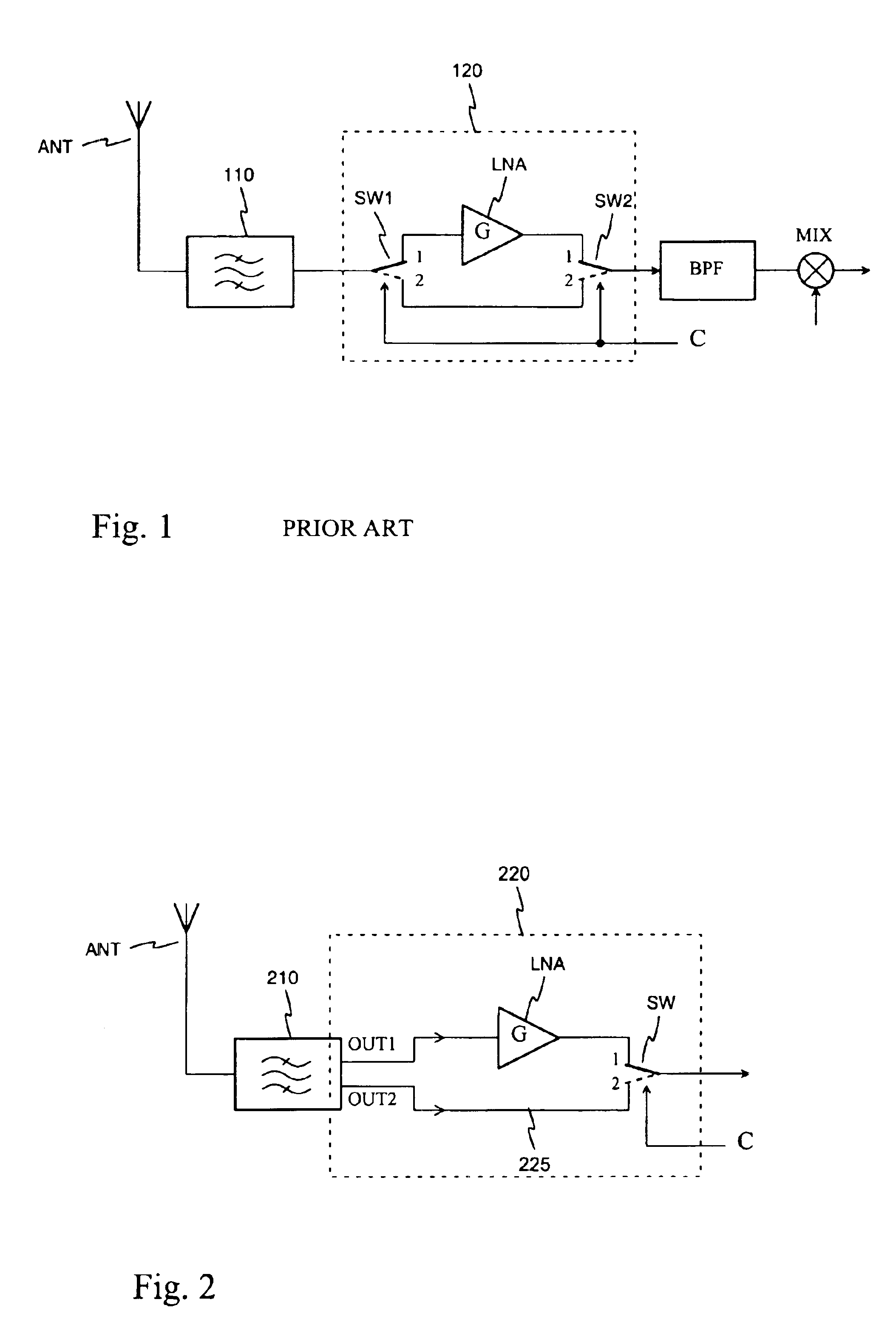
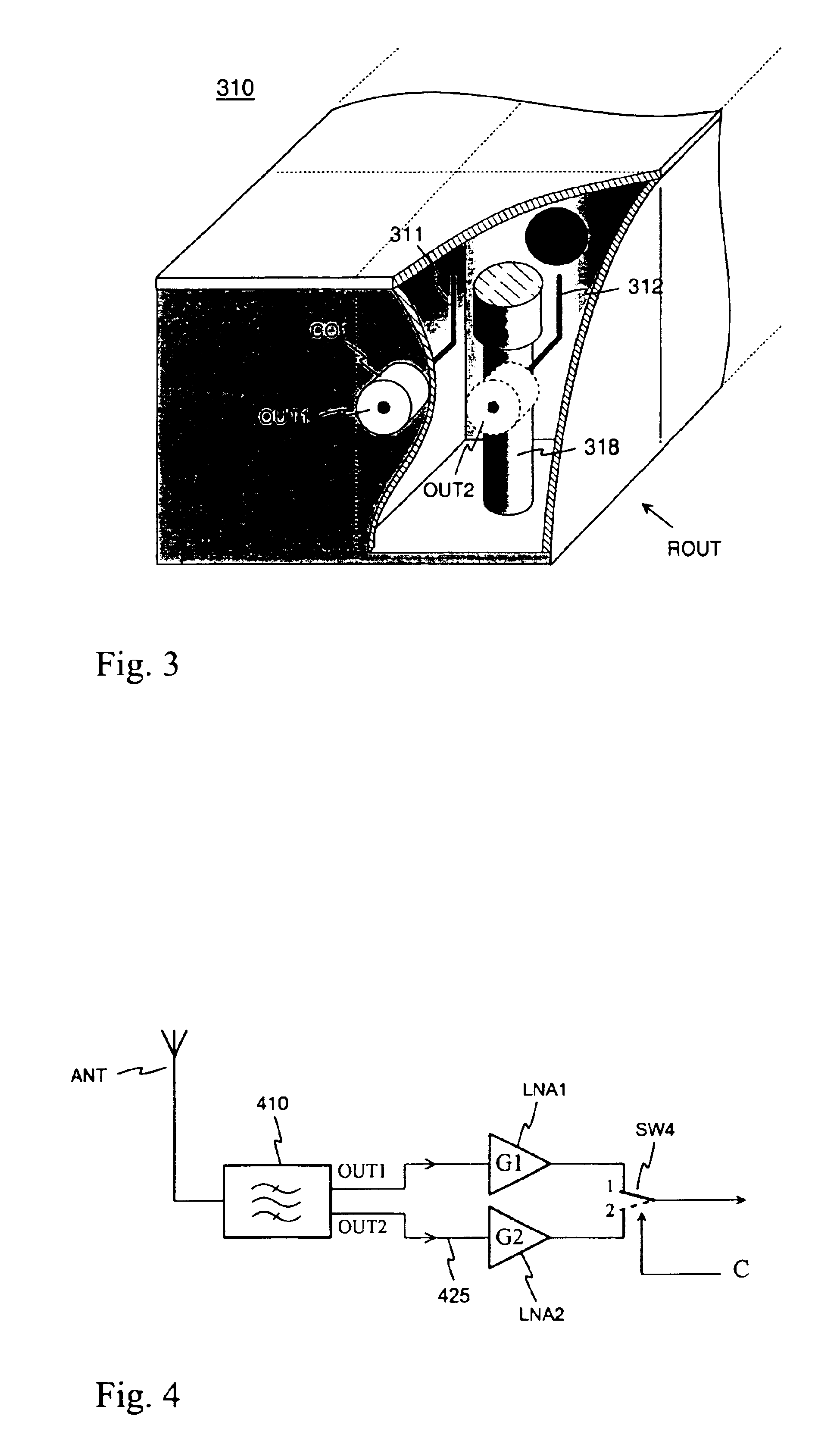
ActiveUS6927646B2Simple structureImprove noise figureGated amplifiersRadio transmissionEngineeringNoise figure
An arrangement for bypassing a low-noise amplifier (LNA), intended especially to be used in base stations of mobile networks. For the bypass, a receiver antenna filter (210) has a second output (OUT2) parallel with a first output (OUT1) connected to the LNA. The antenna filter is of the resonator type, and there is a conductive element for each of its outputs in the resonator cavity. Selection between the LNA out-put signal and signal coming direct from the antenna filter is made by a changeover switch (SW). The noise figure of the receiver front stage (220) will improve as the series switch on the signal path, which most degrades the noise figure, is removed between the filter and LNA, and isolation on the LNA bypass path increases.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Power source circuit for high frequency power amplifying circuit and semiconductor integrated circuit for power source and electronics component for power source
InactiveUS7183856B2Reduce voltageImprove power efficiencyAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencySupply voltage varying controlHigh frequency powerGSM
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Variable gain low-noise amplifier for a wireless terminal
InactiveUS6657498B2Reduces and avoids clippingNot to wasteGain controlGated amplifiersTuned amplifierEngineering
A variable gain, low noise amplifier is described, which is suitable as the input amplifier for a wireless terminal, or as the pre-amplifier stage of a wireless terminal transmitter. The amplifier may achieve variable gain by deploying a network of transistors in a parallel array, each independently selectable by a PMOS switch, and providing the variable resistance for the resonant circuit. Power dissipation can also be mitigated by using a network of driving transistors, each independently selectable by a PMOS switch. The resonant frequency of the amplifier may be made tunable by providing a selection of optional pull-up capacitors.
Owner:GCT SEMICONDUCTOR INC
High frequency amplifier circuit permitting variable gain control
InactiveUS20050118971A1Reduce noise figureAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower managementCapacitanceUltrasound attenuation
The present invention is an amplifier circuit that permits variable gain control, comprising an input terminal to which a high frequency input signal is supplied; an amplifier transistor to the gate of which the high frequency input signal supplied to the input terminal is supplied and which generates an amplified signal at the drain side; and a variable attenuator provided in a signal transmission line between the input terminal and the gate of the amplifier transistor, in which a plurality of attenuation units in which an attenuation capacitor and a switch transistor are serially connected are provided in parallel between the signal transmission line and a power supply, and the attenuation ratio of which is variably controlled by controlling the conduction of the switch transistor.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Amplifier gain control circuit for the wireless transceiver
ActiveUS7701290B2Operating areaAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsWireless transceiverTransceiver
An amplifier gain control circuit for the wireless transceiver comprises at least one amplifier, an analog to digital converter (ADC), a digital to analog converter (DAC) and a bias circuit, wherein the ADC is used for receiving an analog gain control voltage to generate a digital control signal that can be used for controlling the gain of the amplifier, the DAC is used for receiving the digital signal to generate an analog signal, and the bias circuit is used for receiving the analog signal and the analog gain control voltage to further fine-tune the gain of the amplifier by the analog process for correcting the least bit error during the digital process, therefore, the amplifier during the gain adjustment will be prevented to operate in the nonlinear area.
Owner:AIROHA TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Integrated VCO having an improved tuning range over process and temperature variations
InactiveUS7019598B2Angle modulation by variable impedenceResonant circuit detailsState variableControl circuit
An integrated VCO having an improved tuning range over process and temperature variations. There is therefore provided in a present embodiment of the invention an integrated VCO. The VCO comprises, a substrate, a VCO tuning control circuit responsive to a VCO state variable that is disposed upon the substrate, and a VCO disposed upon the substrate, having a tuning control voltage input falling within a VCO tuning range for adjusting a VCO frequency output, and having its tuning range adjusted by the tuning control circuit in response to the VCO state variable.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for controlling amplifiers
Techniques for controlling one or more audio amplifiers in or associated with a device coupled on a local area network are disclosed. The device receives at least one selected source from other devices also coupled on the network According to one aspect of the techniques, an automatic shutdown control module is provided in the device to power down the audio amplifiers when there is no audio data flow coming to the device or power up the audio amplifiers when there is audio data flow coming to the device. In one embodiment, the procedure to power down or power up the amplifiers is in accordance with a hysteresis, wherein the hysteresis, being lagging of an effect behind its cause, protects the amplifiers and makes the powering-down or powering-up procedure unnoticeable to a user.
Owner:SONOS
Variable-gain amplifier
ActiveUS7649418B2Reduce voltageImprove featuresGain controlAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Voltage detection device
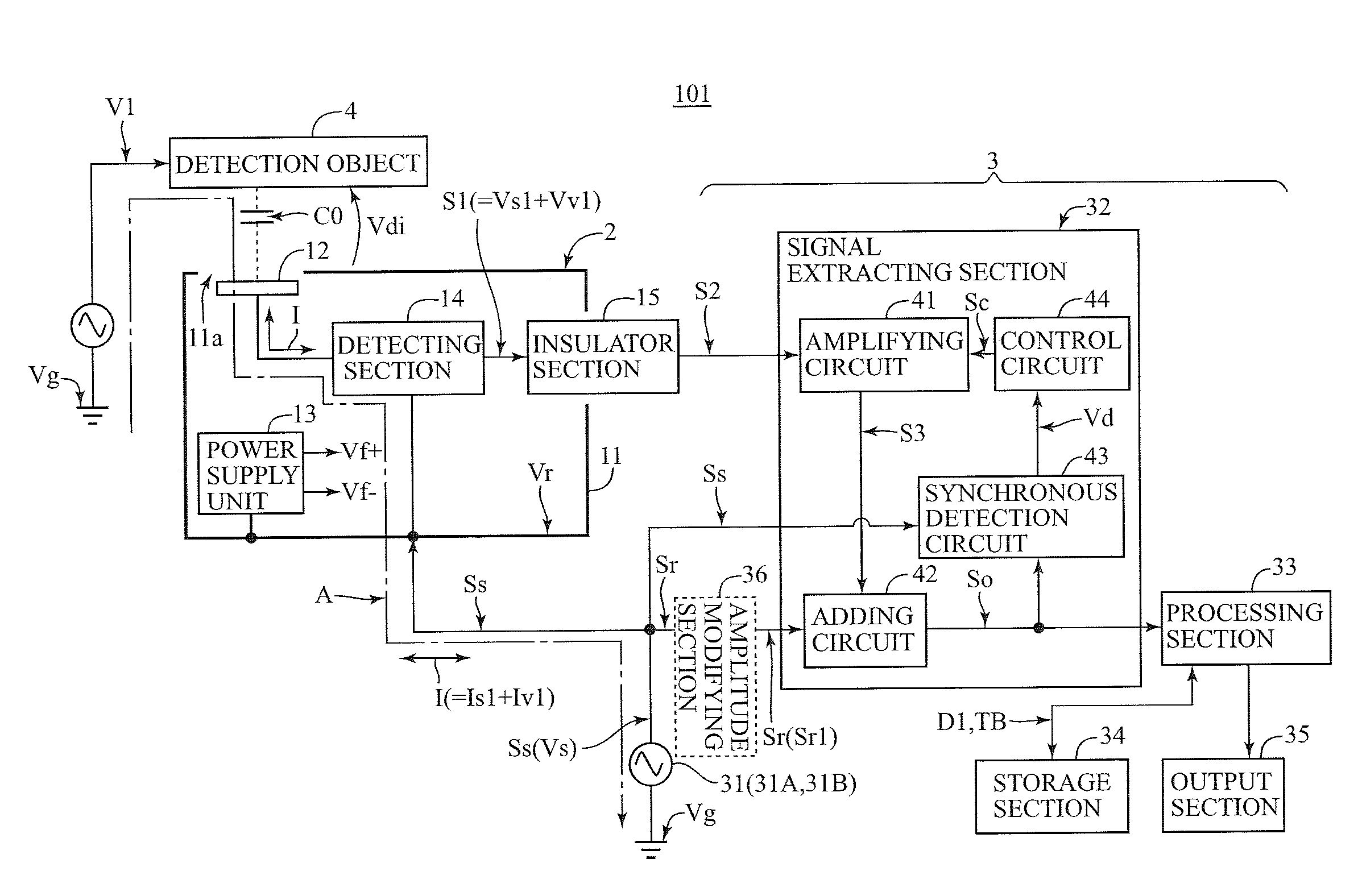
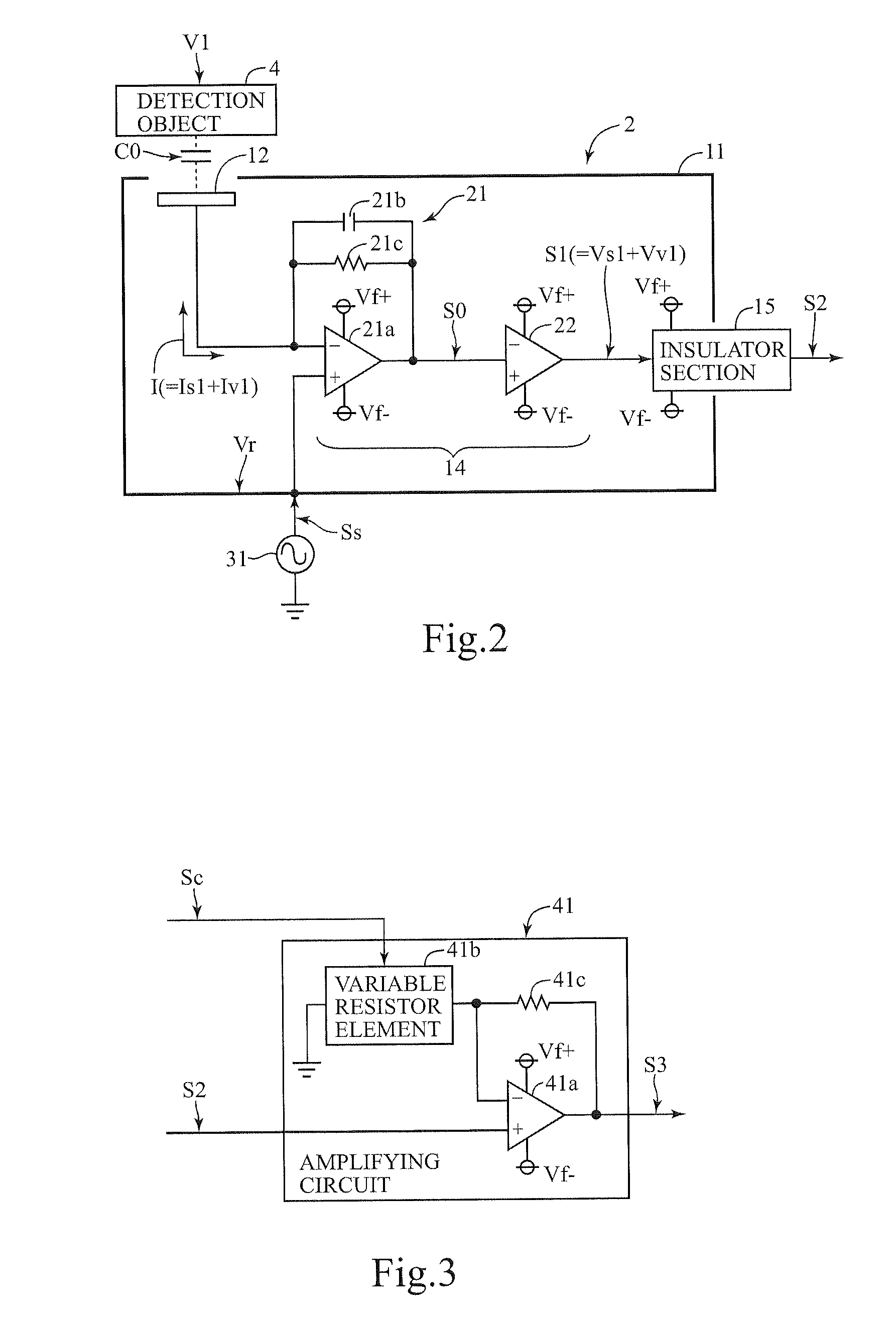
InactiveUS20100283539A1Accurate detectionMany timesGain controlVoltage dividersCapacitanceCapacitive coupling
A voltage detection device detects an objective AC voltage arising on a detection object. The voltage detection device includes; a detecting electrode placed so as to be capacitively coupled with the detection object; a reference signal output section for outputting a reference signal; a detecting section outputting a detection signal changing its amplitude in accordance with both current values of a detection object current flowing according to the objective AC voltage and a reference current flowing according to the reference signal; and a signal extracting section for extracting a signal component of the objective AC voltage from an amplified detection signal and outputting the signal component as an output signal, the amplified detection signal being obtained through controlling a gain for amplifying the detection signal so as to make a signal component of the reference signal included in the detection signal have a predetermined value.
Owner:HIOKI DENKI KK
Popular searches
Transmission control/equalising Amplifiers wit coupling networks Amplifier protection circuit arrangements Waveguide type devices Low noise amplifier Networks with variable switch closing time Time-division multiplex Amplifiers controlled by light Electromagnetic receivers Electric/magnetic detection
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com