Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1435results about "Amplifier protection circuit arrangements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
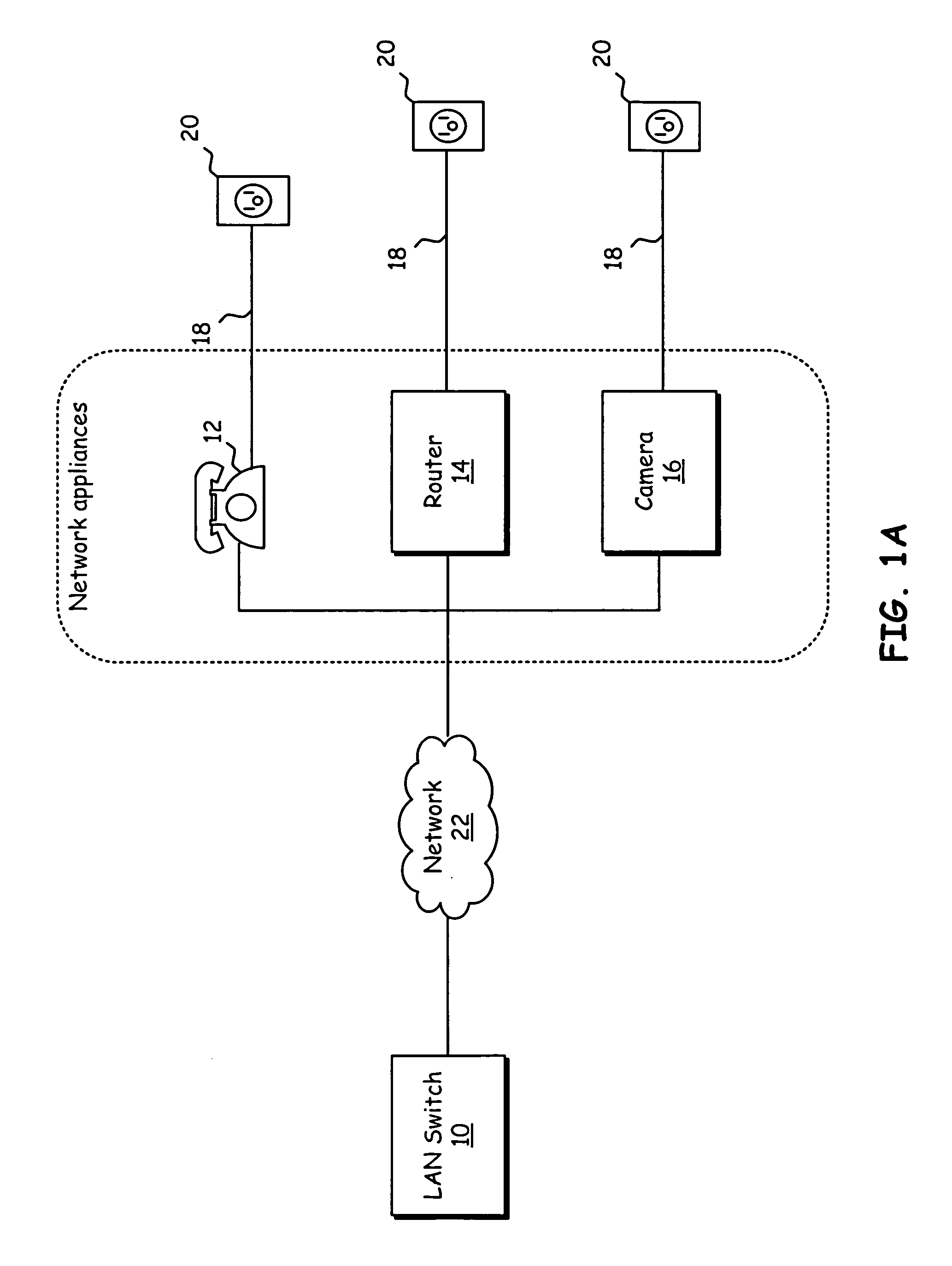
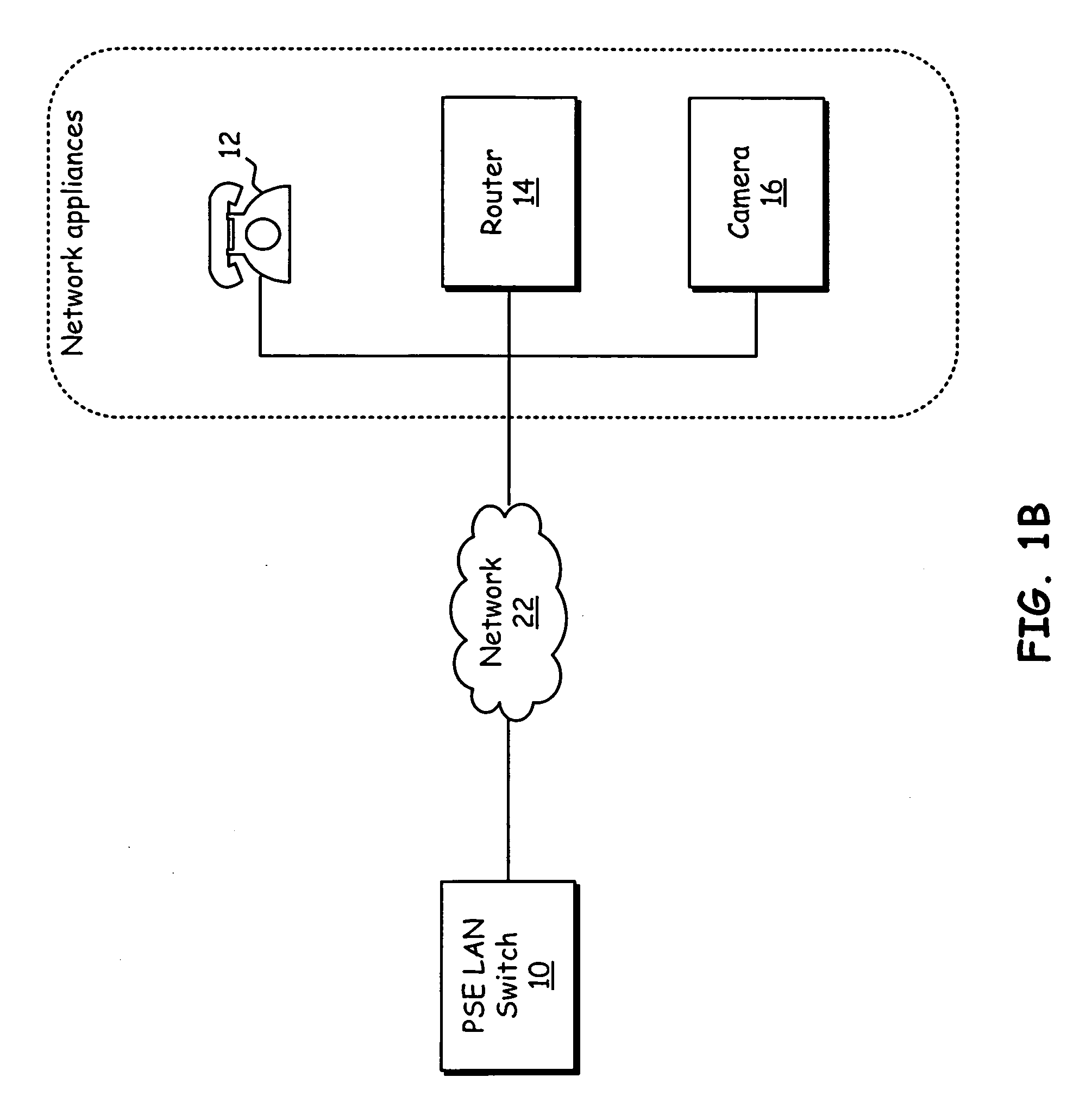
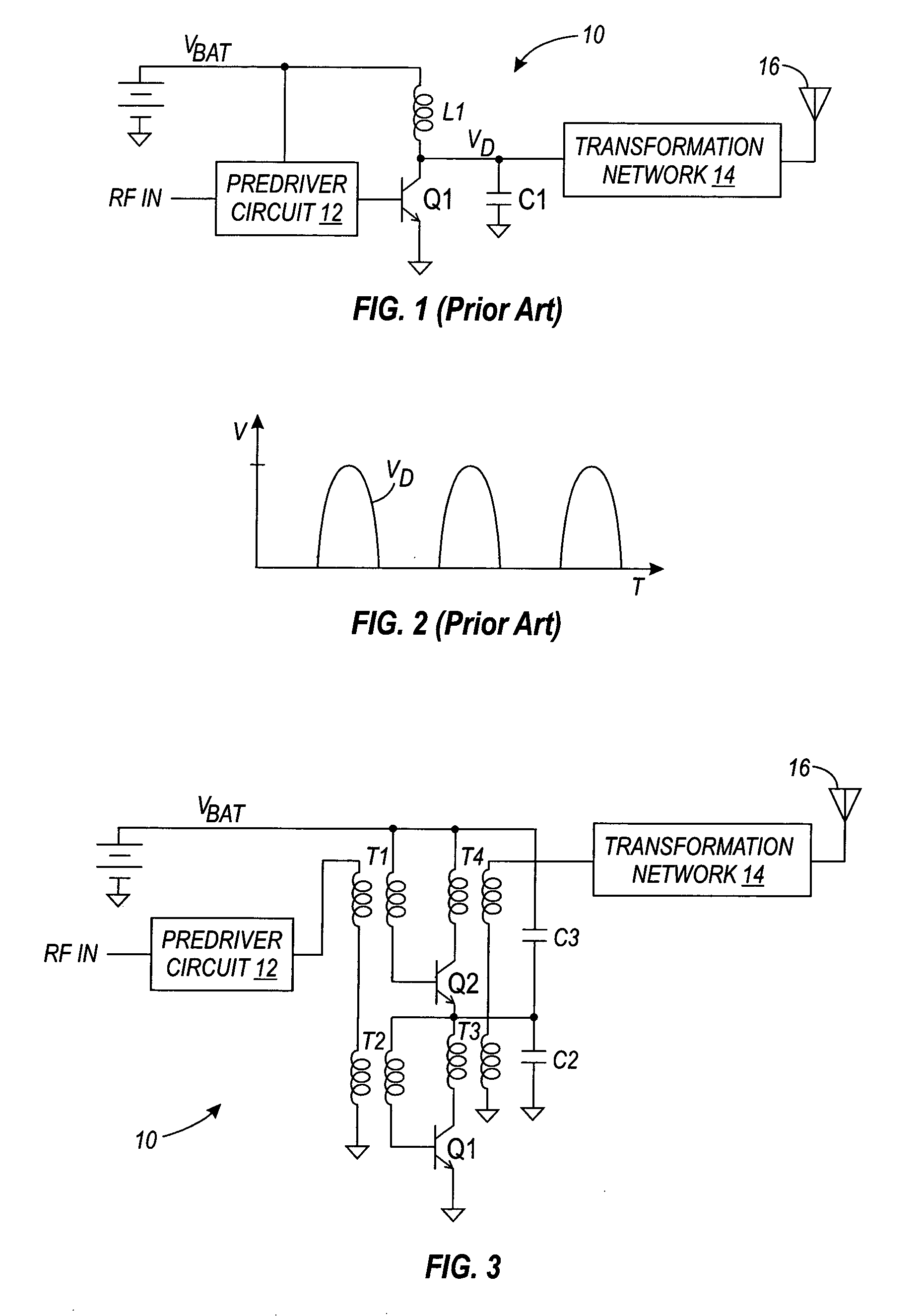
Modular transmission system and method
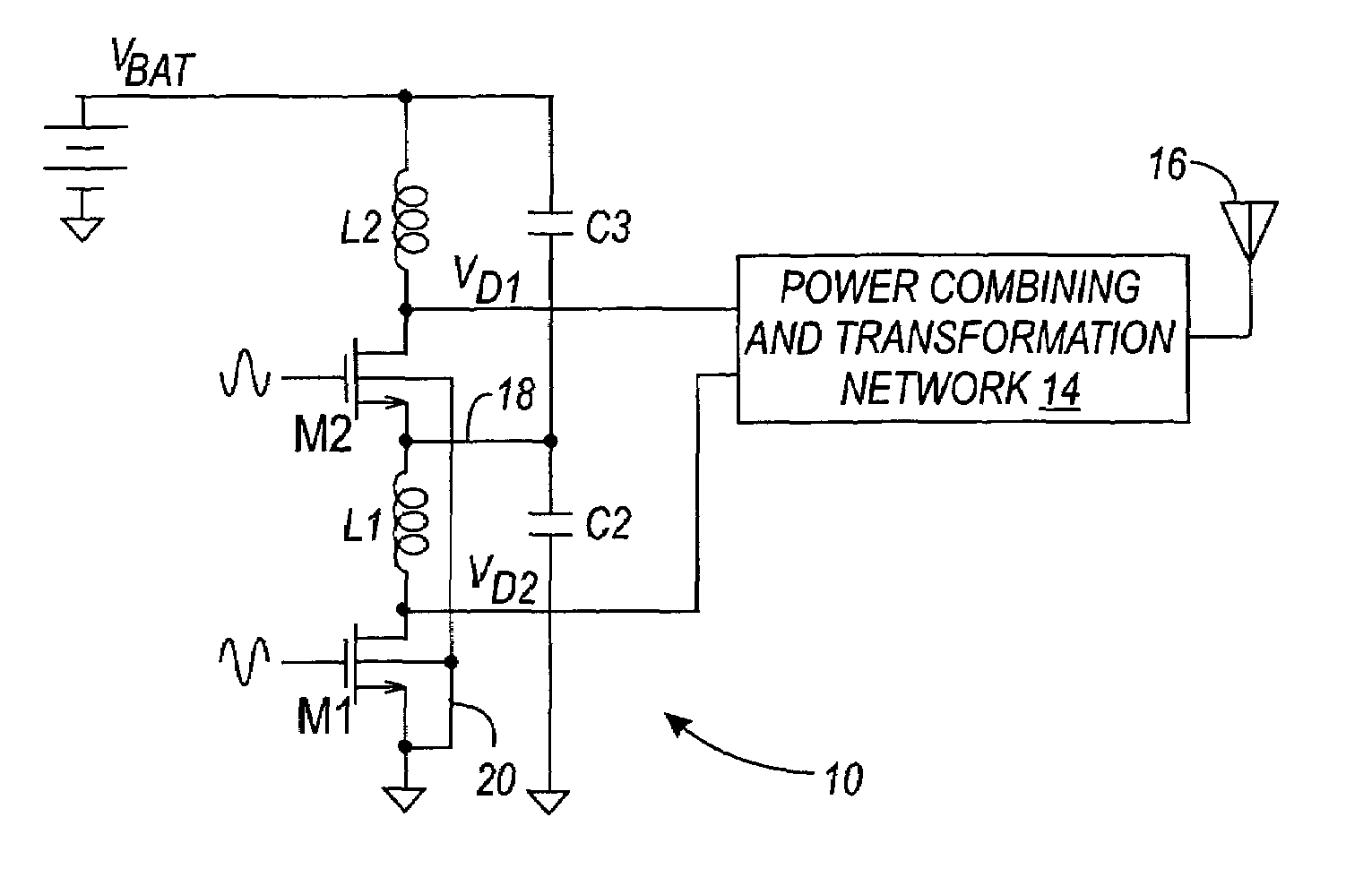
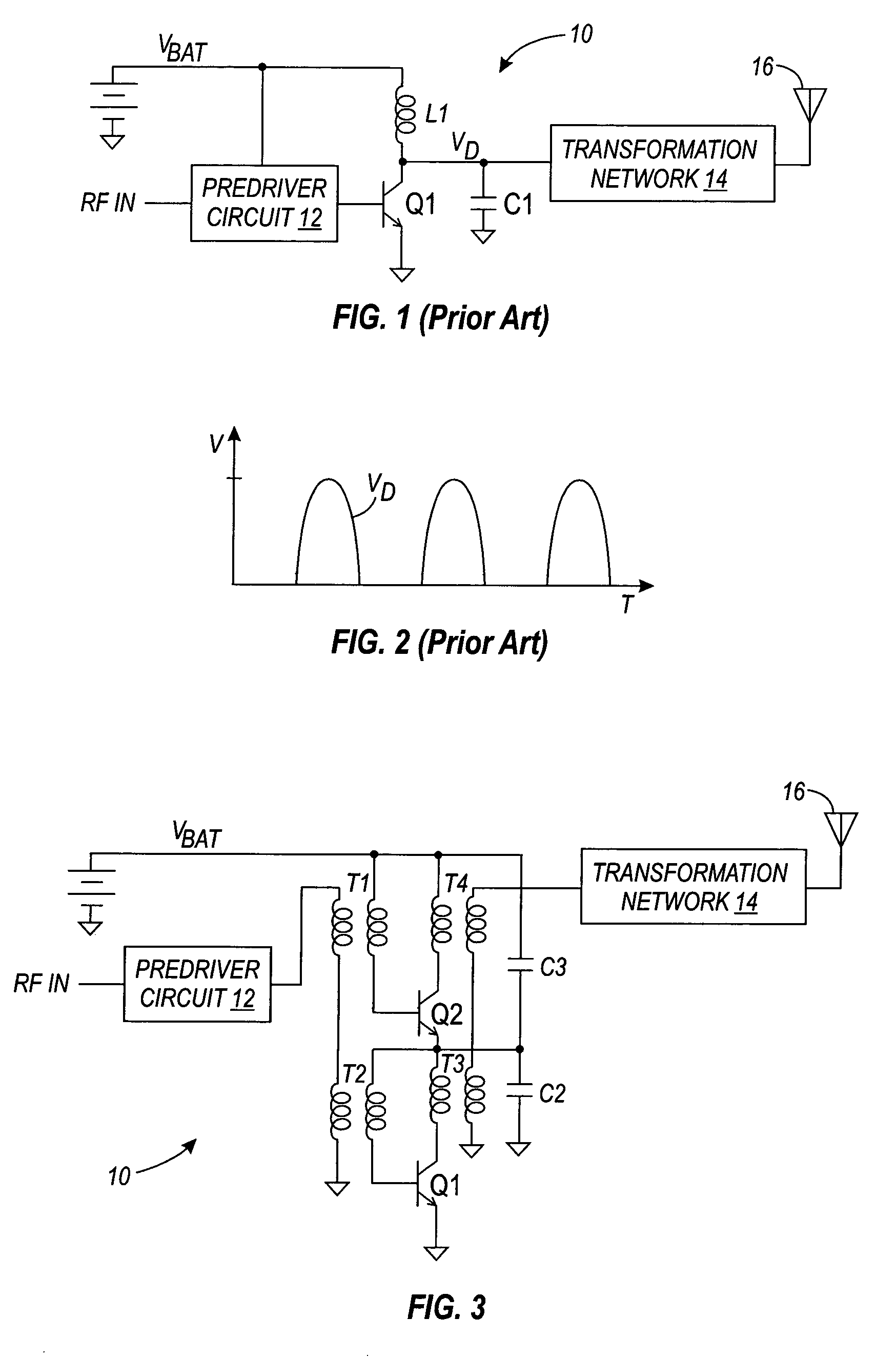
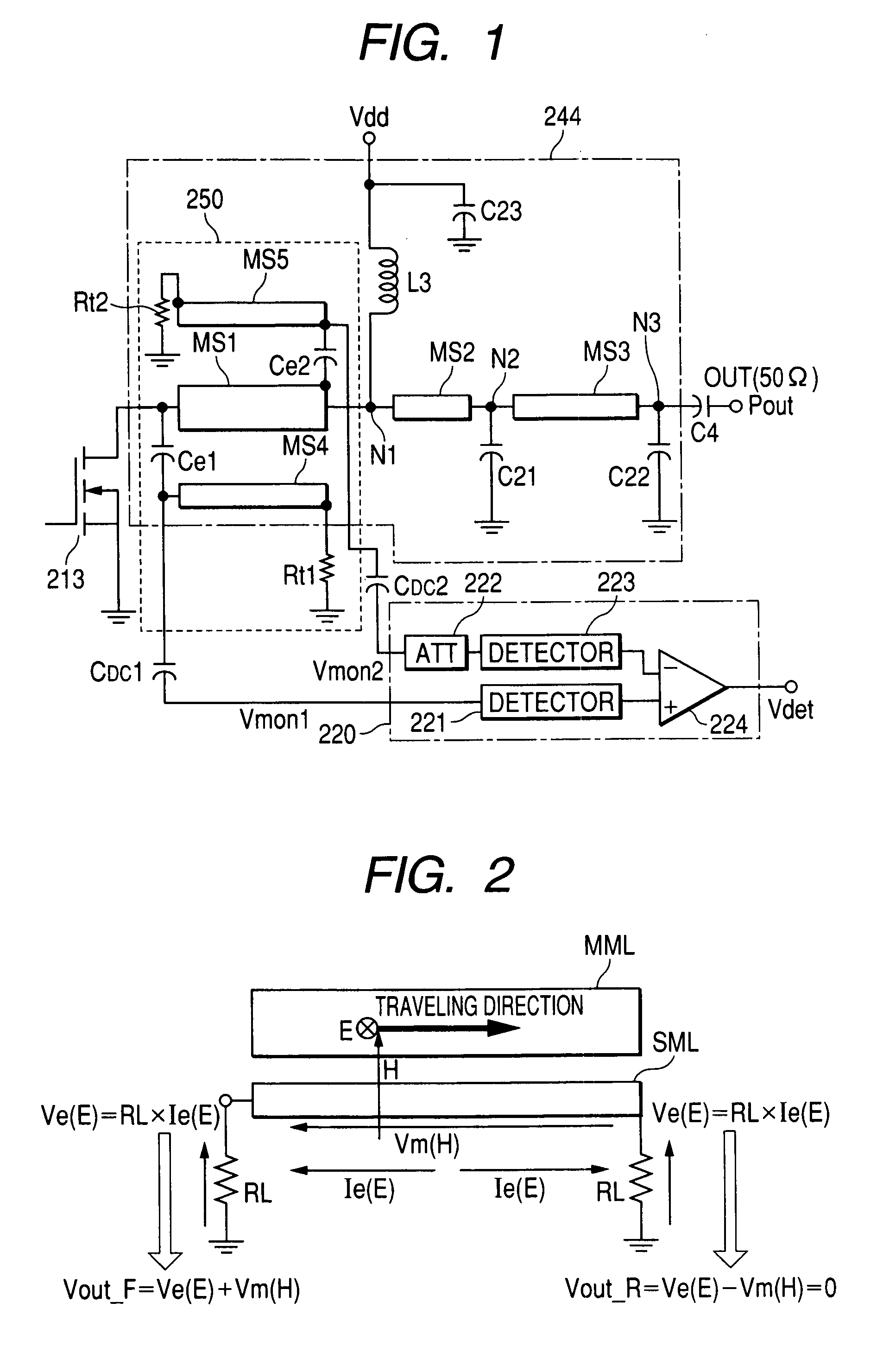
A modular broadband transmission system and method include an input signal connector that receives an input signal which is then divided into N parts and amplified with an amplifier have N power amplifier modules. Outputs of the N power amplifier modules are passed through transmission lines and to a radial combiner that combines the outputs. The radial combiner, transmission lines and power amplifier modules are configured such that if one of the power amplifier modules fails, the other power amplifier modules may still operate acceptable well, with minimal impact on total output power. An output of the amplifier is provided to a coupler that measures a power level of the output signal and feeds the measured power level back to a controller where the controller adjust an overall output power based on the number of the power amplifier modules that are functioning properly. Each of the power amplifier modules have a processor such that respective of the power amplifier modules may be taken off-line, and replaced while the other power amplifier modules continue to operate in a transmit mode of operation. The modular broadband transmission system and method may conveniently be used as either a broadband booster for amplifying a plurality of input signals, or a head and transmitter configured to amplify one or more different input signals.
Owner:THALES BROADCAST & MULTIMEDIA
Semiconductor device, module, and electronic device including a conversion circuit having a second switch rendered conductive together with a first switch
InactiveUS7608810B2High voltageGuaranteed uptimeTransistorTelevision system detailsEngineeringSemiconductor
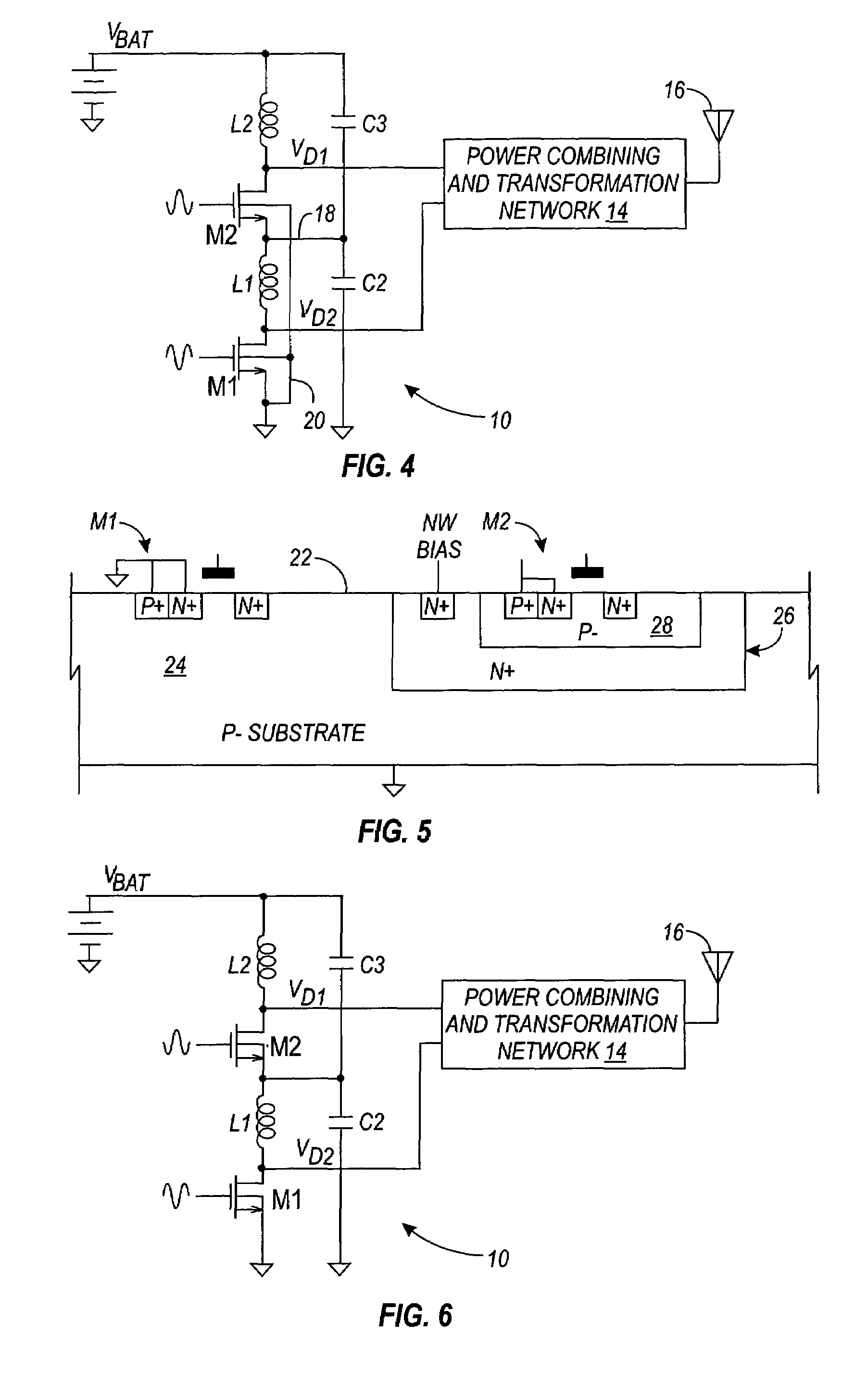
The breakdown voltage between the potential of a terminal and the ground potential (or power supply potential) is improved by increasing the gate width of an MOS transistor included in a switch. Accordingly, another switch and the like are protected even when surge is applied to the terminal. By increasing the gate width of the MOS transistor included in the switch, the size of the other switch does not have to be increased. Therefore, variation in the potential at a node occurring when the other switch attains a non-conductive state from a conductive state can be suppressed. Therefore, a semiconductor device having the electrostatic breakdown voltage improved without influence on processing carried out based on an input potential from an external source, a module including a plurality of such semiconductor devices, and an electronic device including such a module can be provided.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
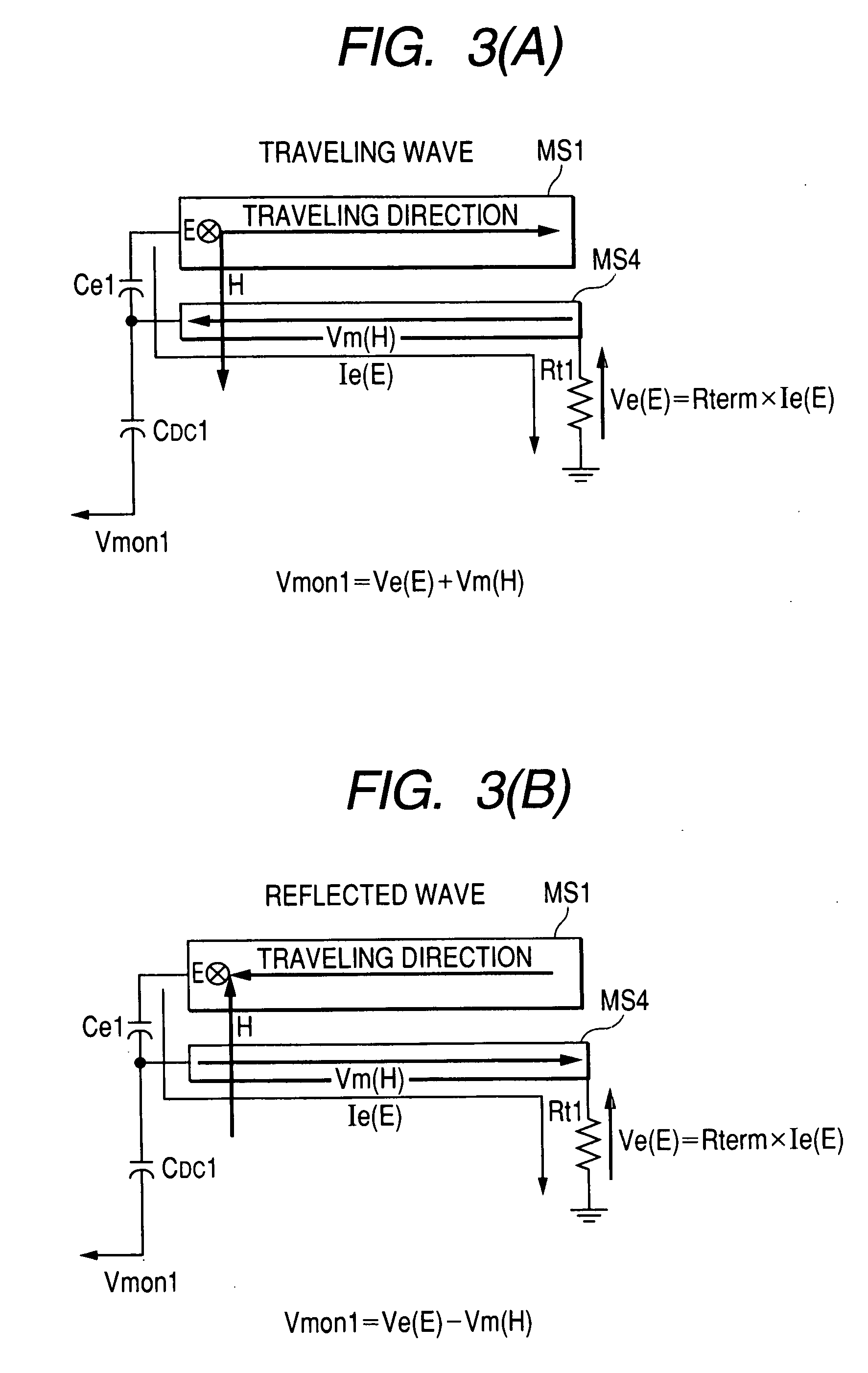
Method and arrangement for detecting load mismatch, and a radio device utilizing the same
ActiveUS6965837B2Reduce lossesAccurate and reliable detectionResonant long antennasResistance/reactance/impedenceRadio equipmentEngineering
A method and an arrangement for detecting impedance mismatch between an output of a radio frequency amplifier (200, 901, 911, 921, 1101) which has an amplifying component (201, 301, Q46, 701, 801) and an input of a load (203, 302) coupled to the output of the radio frequency amplifier having: first monitoring means (401) to monitor a measurable electric effect (311) at a side of the amplifying component (201, 301, Q46, 701, 801) other than the load (203, 302) and to produce a first measurement signal (411). Second monitoring means (402) monitor a measurable electric effect (312) between the amplifying component (201, 301, Q46, 701, 801) and the load (203, 302) and produce a second measurement signal (412). Decision-making means (204, 902, 912, 923, 1102) receive said first (411) and second (412) measurement signals and decide, whether said first and second measurement signals together indicate impedance mismatch.
Owner:III HLDG 3
Method for dynamic insertion loss control for 10/100/1000 mhz ethernet signaling
ActiveUS20060238250A1Suppression of insertion lossReduced insertion lossResistance/reactance/impedenceDigital data processing detailsNetworking protocolNetwork connection
The present invention provides for dynamic insertion loss control for a 10 / 100 / 1000 megahertz Ethernet power on differential cable pairs. A power feed circuit supplies power to a network attached device (PD). An insertion loss control circuit limits power loss in a coupled power feed circuit. The insertion loss control circuit determines an insertion loss limit and senses an average power of the power signals to produce a common mode feedback signal to the power feed circuit. The insertion loss limit is determined for the received signals based on a differential RMS of the received Ethernet power signals as seen by a differential transistor pair. Alternatively, the insertion loss limit may be determined logically by the higher layers of the network protocol based on the AC differential portion of the network power signal. When the insertion loss limit is determined based on the differential RMS, the insertion loss control circuit is operable to automatically reduce the insertion loss based upon transmission losses experienced over the network connection between the power sending equipment and network-attached device.
Owner:KINETIC TECH INT HLDG LP
Computer program product configured to control modular transmission system components
A computer program product is configured to control a modular transmission system having a control processor and at least N power amplifier modules, each having a controller submodule, wherein the system receives an input signal which may be a single carrier or multiple carriers. The signal is passed to a one-by-N divider which divides the signal N ways. Each of the N divided signals are independently amplified by the power amplifier (PA) modules "slices" (i.e., PA modules) that includes an RF amplifier module, a microcontroller module, and a power supply module, all of which are tightly coupled via a plurality of signal, power, control, and status connections. Each the PA slices amplifies its respective input signal and outputs a respective radio frequency output signal at a predetermined power level as controlled by the microcontrol module, the driver, and the system controller, or a network manager via a system input / output interface. The output coupler provides power coupling and status monitoring via feedback lines to support control at a module-level, a system-level, and a network-level.
Owner:THALES BROADCAST & MULTIMEDIA
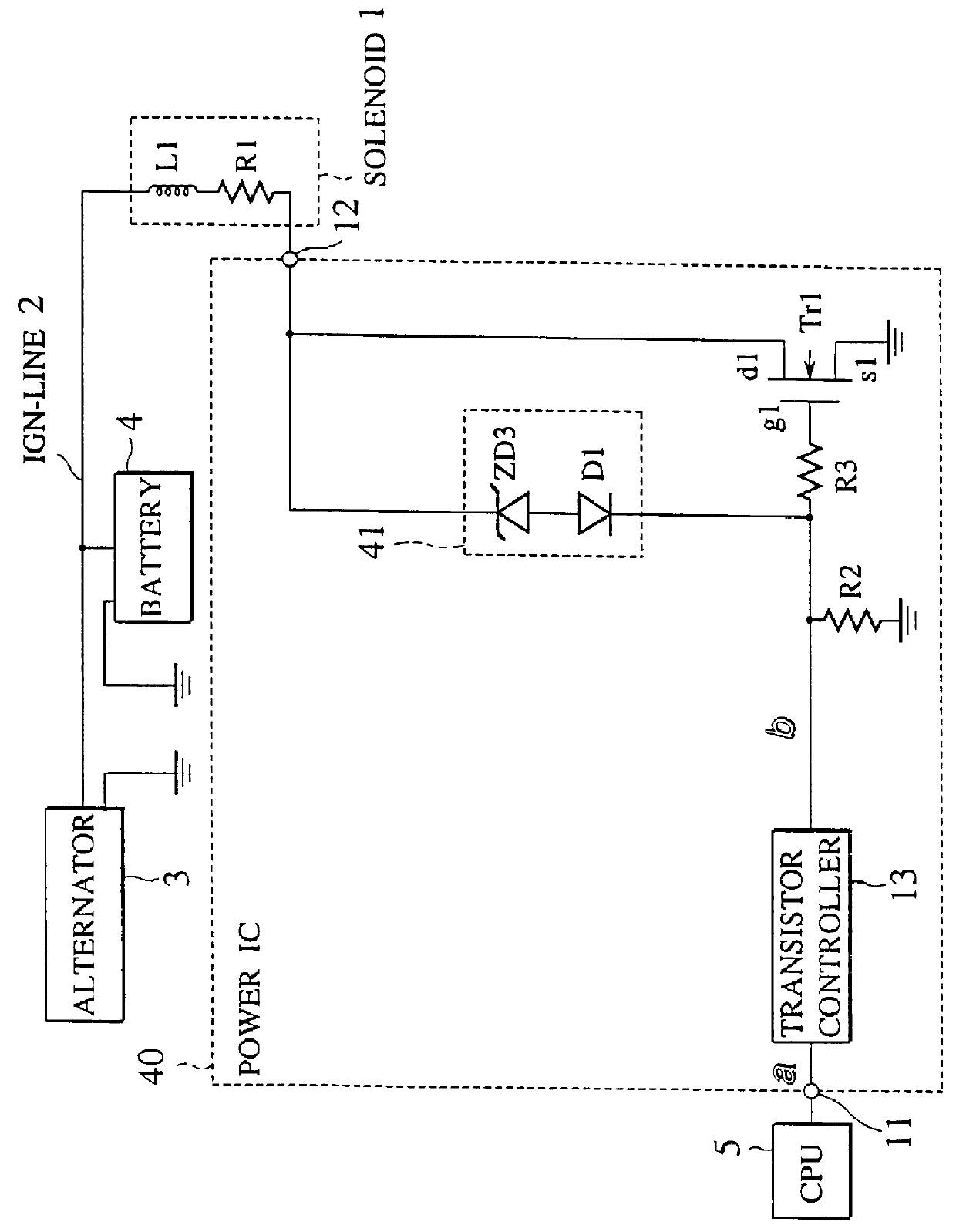
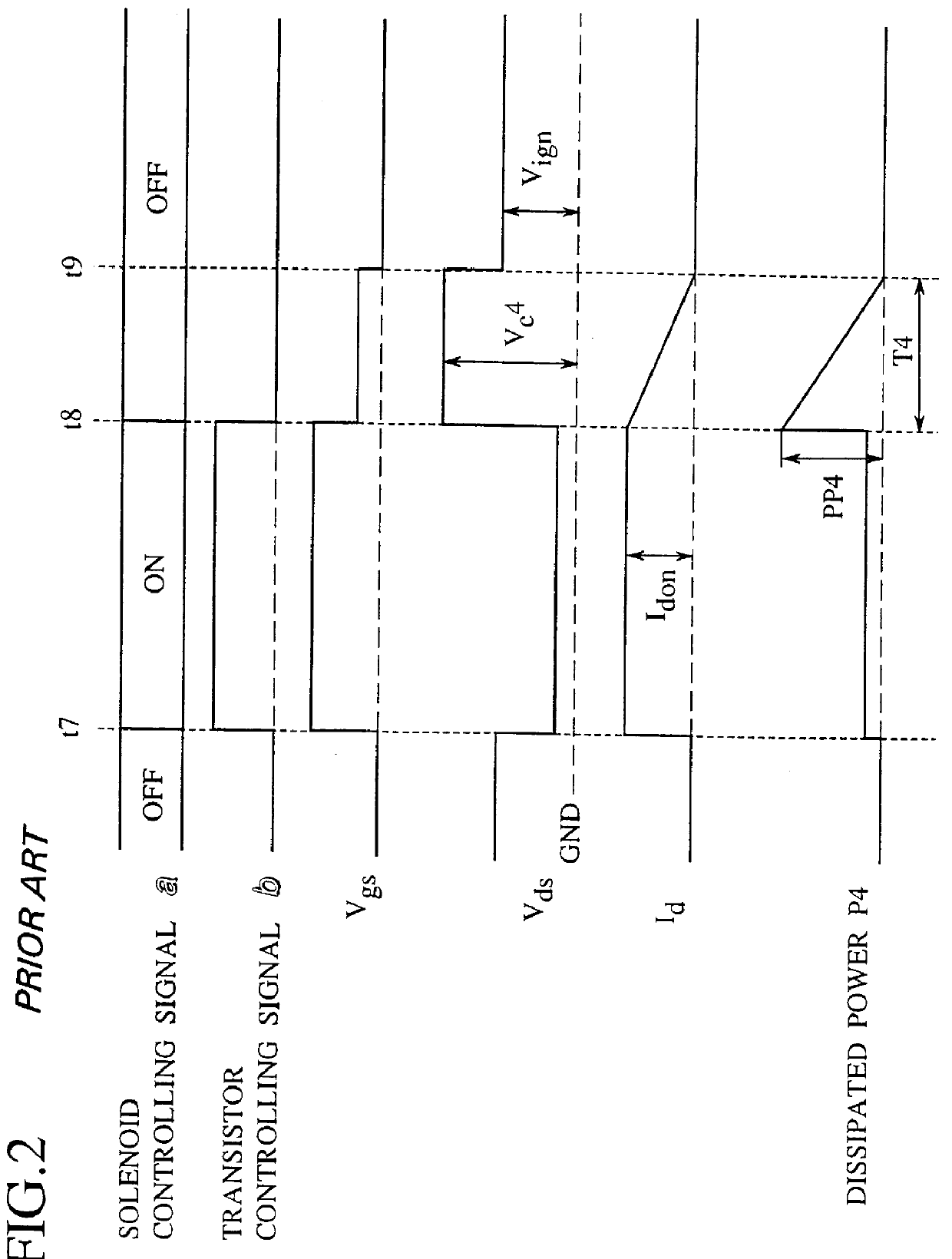
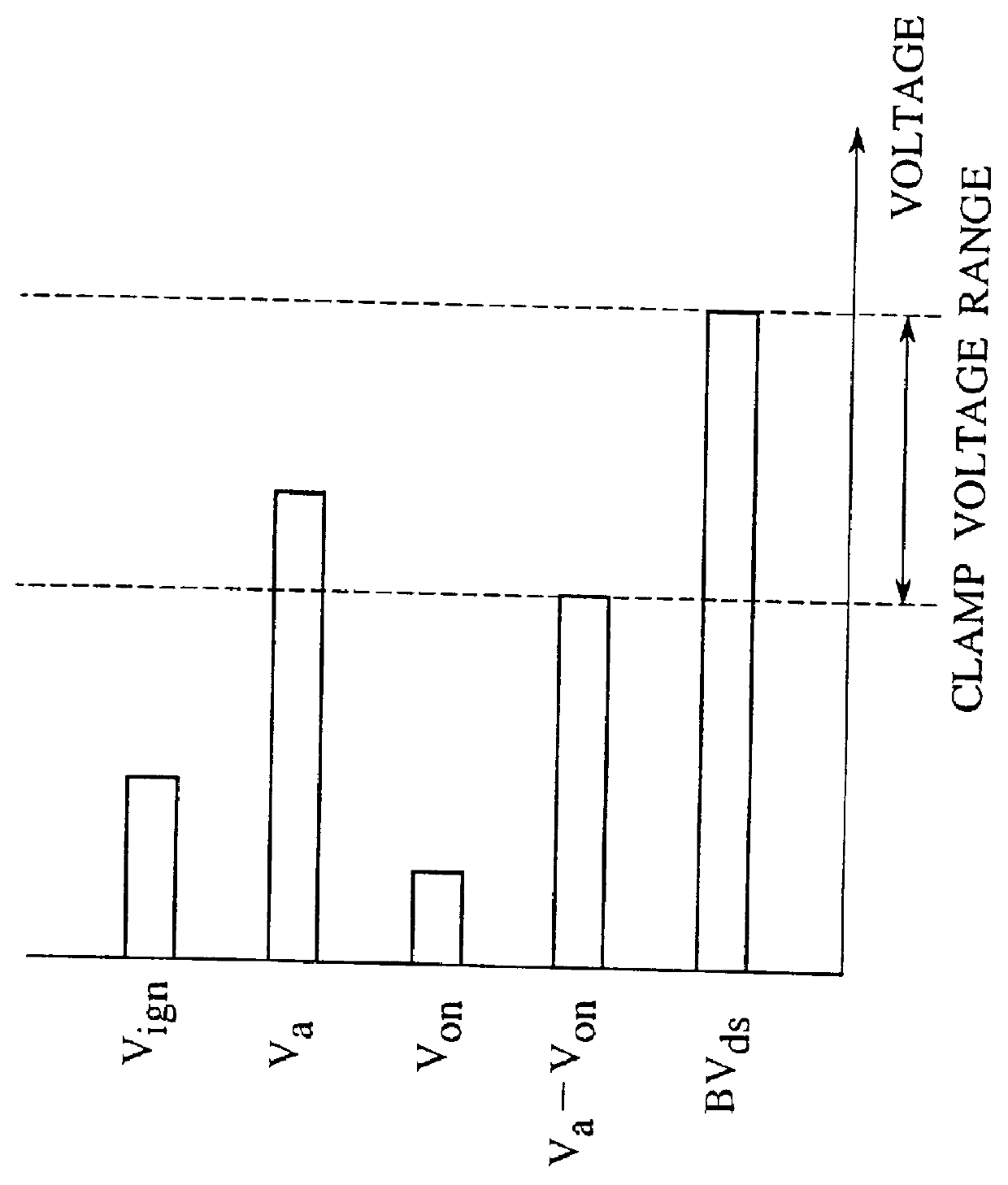
Integrated circuit having surge protection circuit
A trailing edge of a control signal of a transistor controller for controlling an output transistor is detected by an edge detector of a clamp controlling circuit. A surge voltage from a back electromotive voltage induced in an inductance L1 is absorbed from the output transistor, only for a given period immediately after the solenoid is turned off, by turning a switching transistor into an on-state by a timer to force a clamping circuit into conduction. At a normal operation, since the clamping circuit is cut off from an output terminal, the clamping voltage can be set in a manner to reduce to a normal voltage in an IGN-line. Therefore, a peak power value of a power loss caused by the surge voltage at the output transistor can be reduced, whereby generation of heat at the output transistor can be reduced. Therefore, the chip size of the power IC can be reduced.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
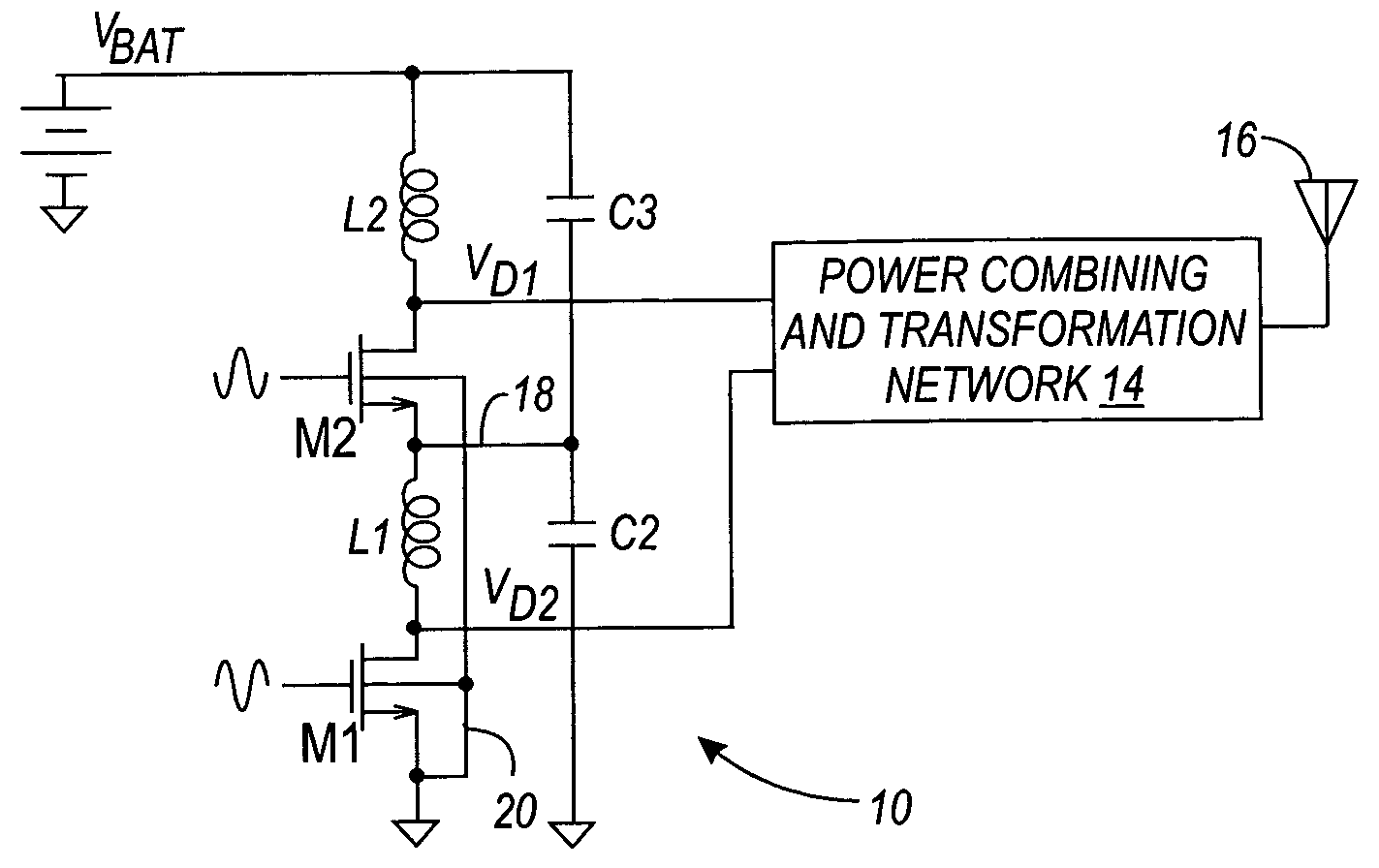
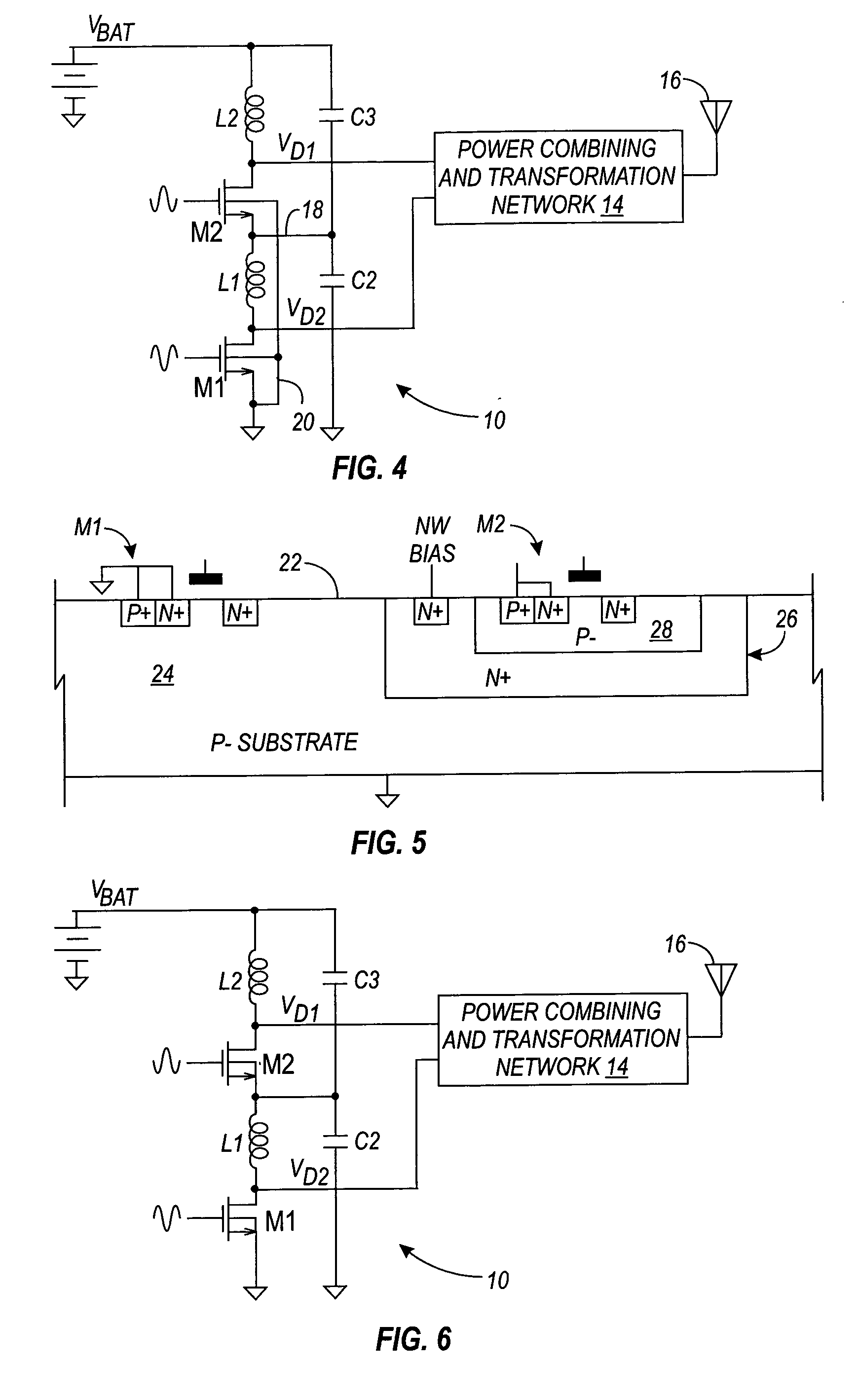
Stacked RF power amplifier
A method and apparatus provides techniques for electrically isolating switching devices in a stacked RF power amplifier, which prevents the switching devices from being subjected to high breakdown voltages. The isolation provided allows the power amplifier to be implemented on an integrated circuit.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Transmission device with digital predistortion, and method for regulating predistortion in a transmission device
InactiveUS20050111574A1Improve efficiencyReduce power consumptionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionTransmission control/equalisingAudio power amplifierControl signal
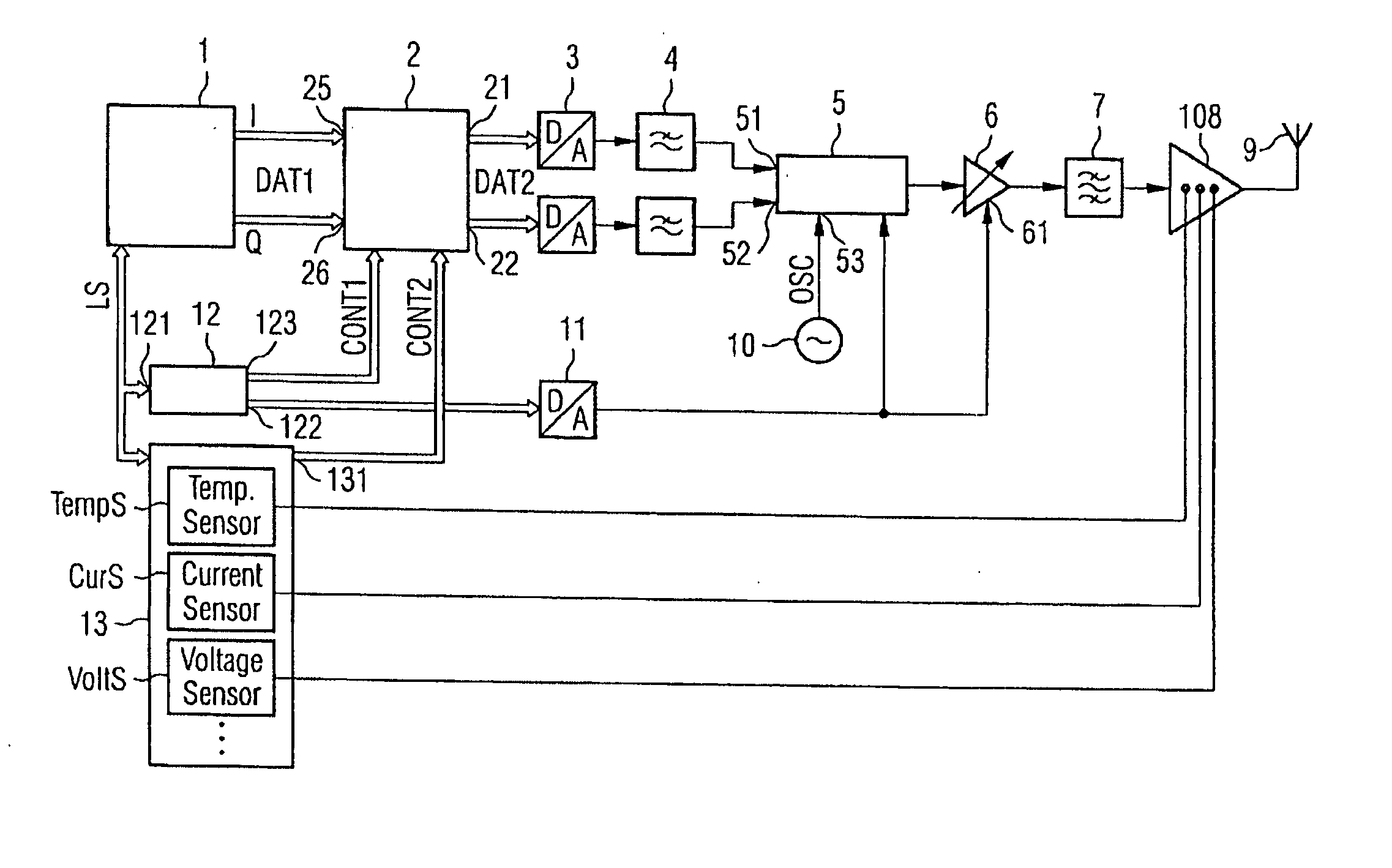
One or more aspects of the present invention relate to a transmission device having a digital predistortion unit which has a control input to which a control signal (CONT1) is applied. The control signal is output by a power control unit which evaluates a power control signal (LS). The predistortion unit distorts a baseband signal which is to be transmitted whenever the linearity of a power amplifier can no longer be observed at the currently required power without predistortion. To this end, the baseband signal is multiplied in complex fashion by a predistortion coefficient which is dependent on the level of the baseband signal.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Circuit for power amplification
ActiveUS20060066396A1Reduce decreaseReduce variationHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlAudio power amplifierReference current
A radio frequency (RF) power amplifier, including an external control loop and a protection circuit, which functions to maintain a constant output power during variations in impedance on the RF load. In the external control loop a collector current from an output transistor is detected and then regulated with respect to a reference current. The regulated signal is utilised to generate a bias control signal which is input to the base electrode of both a driver transistor and the output transistor. The protection circuit detects a voltage envelope at the collector electrode of the output transistor and utilises this signal to form a bias reduction signal which is input to the base electrode of the driver transistor.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Detection of DC output levels from a class D amplifier
ActiveUS7078964B2Simple analog portionLow cutoff frequencyDuration/width modulated pulse demodulationPulse duration/width modulationUnsafe conditionAudio power amplifier
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
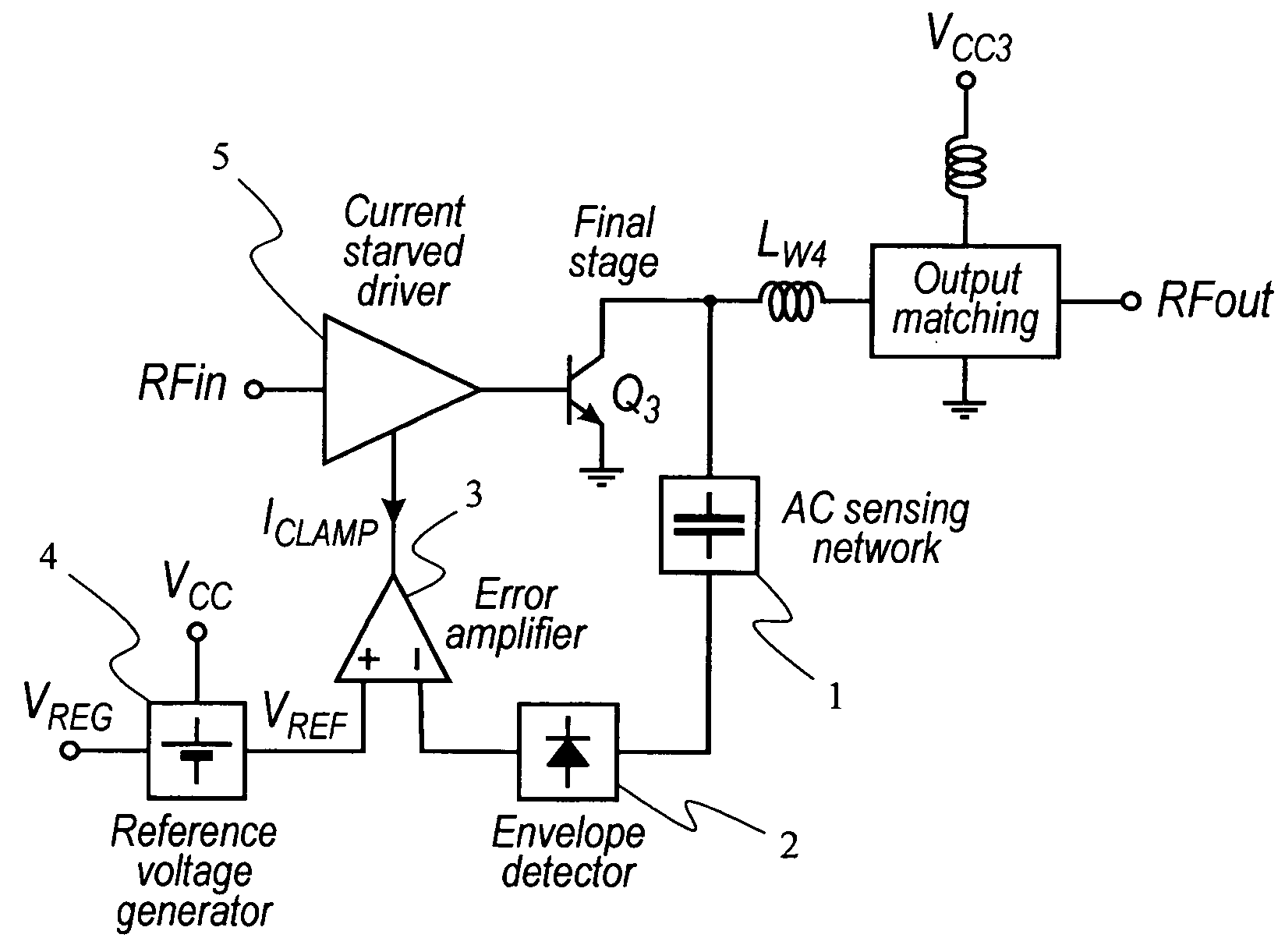
Protection of output stage transistor of an RF power amplifier
ActiveUS7358807B2Guaranteed reliable outputImprove protection reliabilityHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlOvervoltagePeak value
A protection method may prevent a load-mismatch-induced failure in solid-state power amplifiers. In an RF power amplifier, the load voltage standing-wave ratio results in very high voltage peaks at the collector of the final stage and may eventually lead to permanent failure of the power transistor due to avalanche breakdown. The method avoids breakdown by attenuating the input power to the final stage during overvoltage conditions, thus limiting the output collector swing. This is accomplished by a feedback control system, which detects the peak voltage at the output collector node and clamps its value to a given threshold by varying the circuit gain. Indeed, the control loop is unlocked in the nominal condition and it acts when an output mismatching condition is detected. A control circuit also allows a supply-independent collector-clamping threshold to be accurately set.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
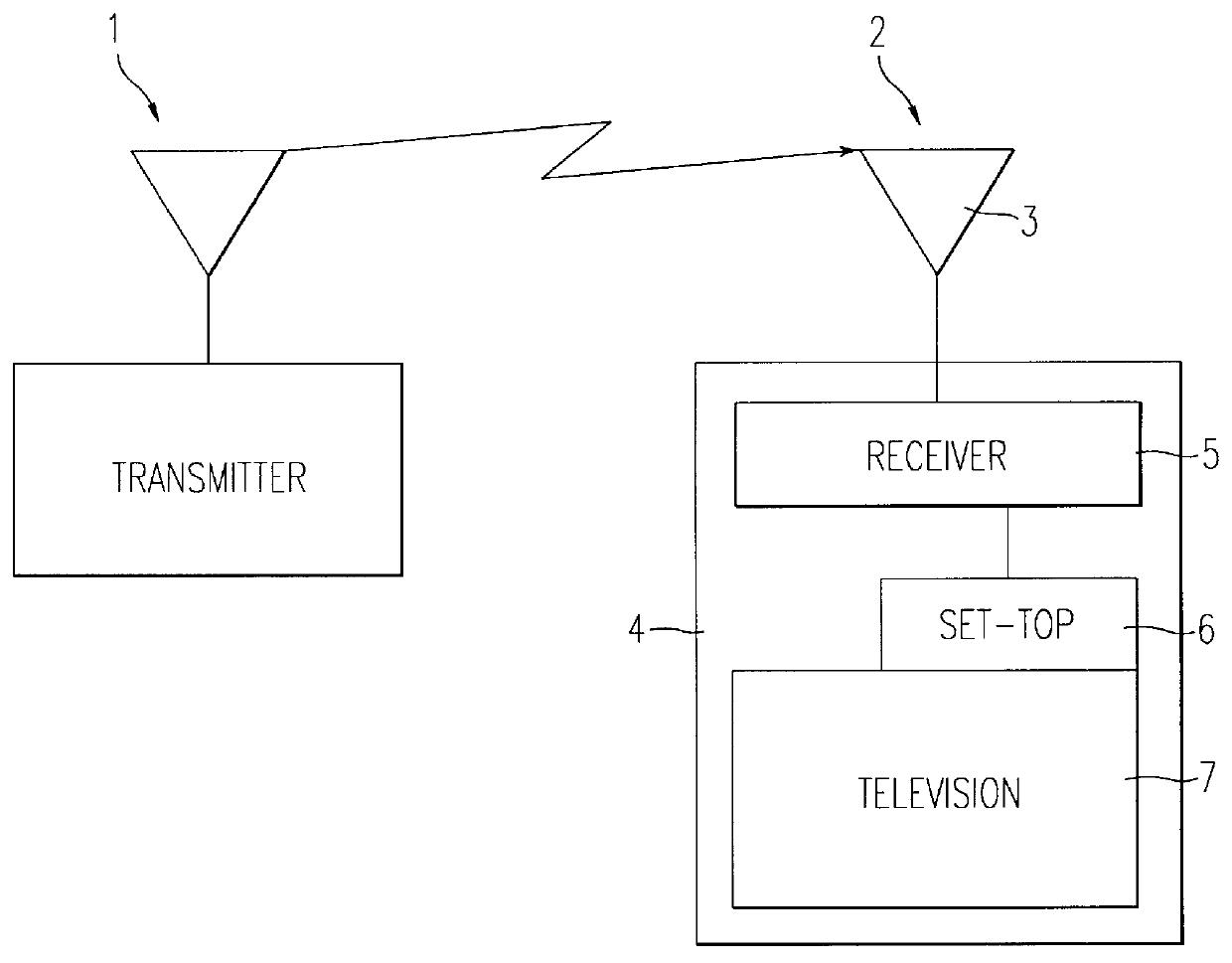
Radio frequency transmitting circuit
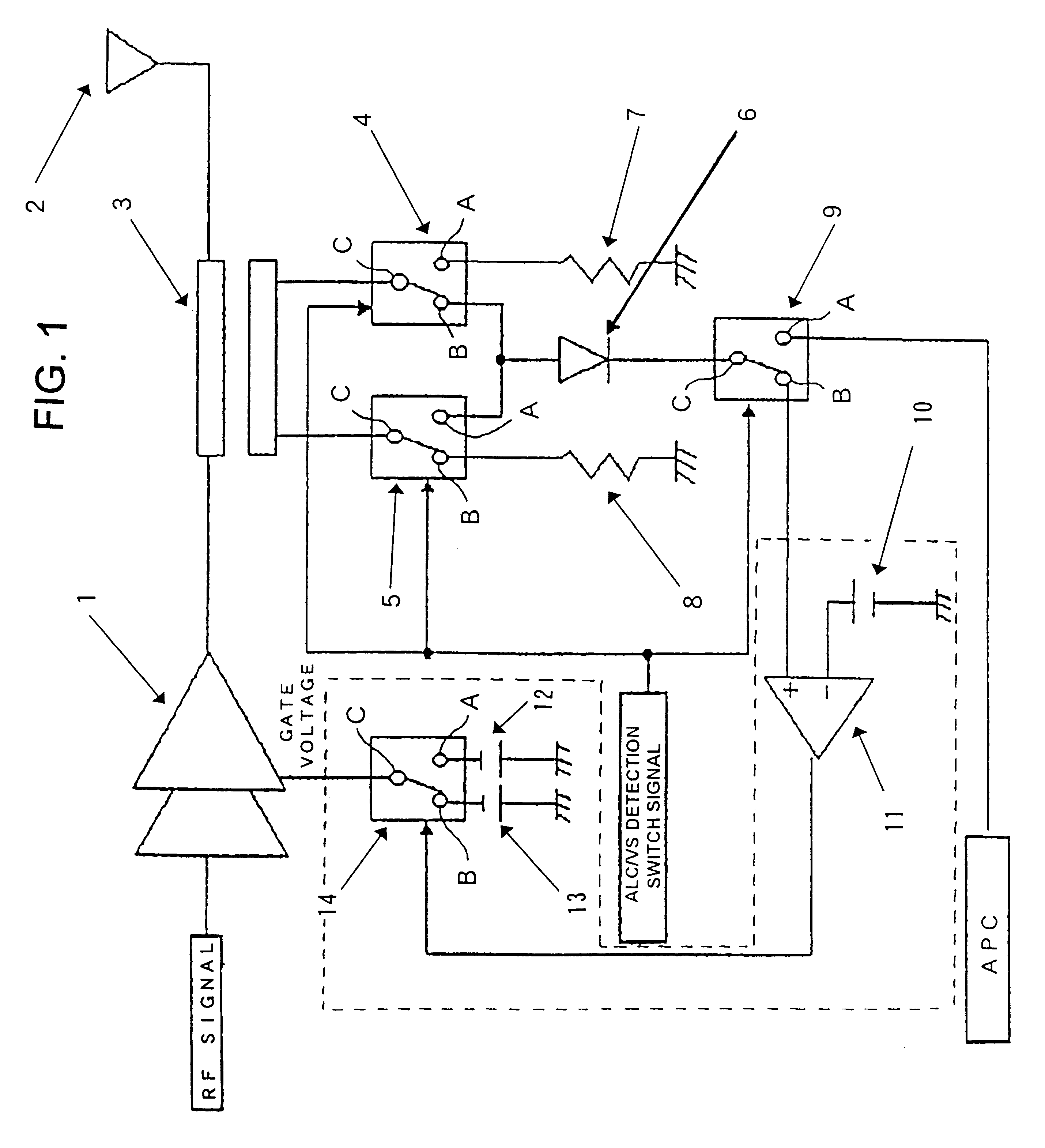
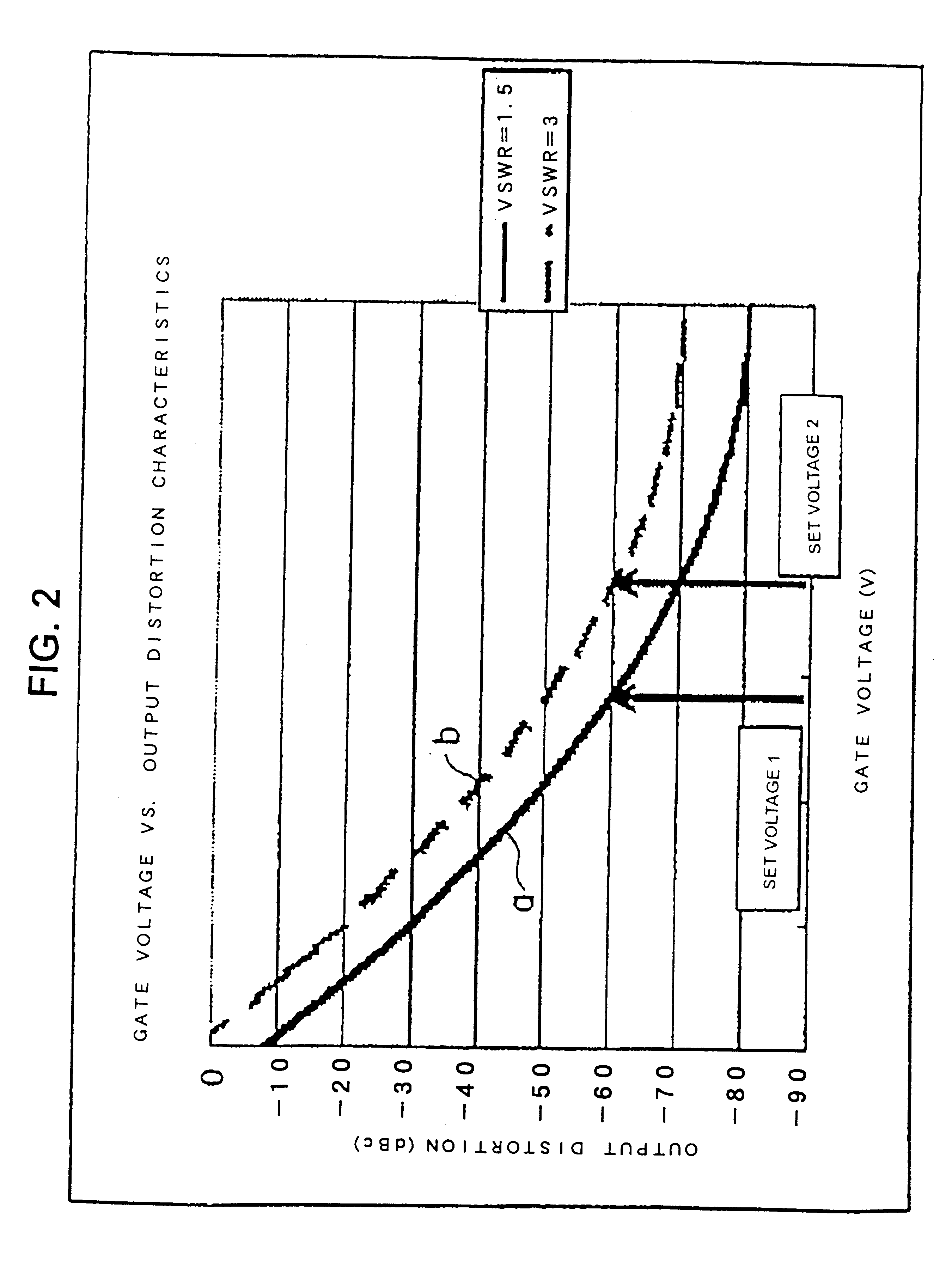
InactiveUS6329880B2Excellent electrical propertiesMiniaturize a mobile communication equipmentGain controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierReflected waves
An object of the present invention is to allow the miniaturization of a mobile communication equipment and the reduction of consumption power, and to improve the electrical characteristics of a final stage amplifier. An inputted RF signal is amplified to a specified transmission output by a final stage amplifier, the output power and a reflected wave generated by mismatching between an output impedance of the final stage amplifier and a load impedance connected to an output side of the final stage amplifier are detected by a directional coupler. Two switches are selectively switched in a time division manner, a DC voltage corresponding to the reflected wave is selected, a comparator compares a threshold voltage with the DC voltage, a switch is switched by an output of the comparator outputted in accordance with the comparison, and gate voltages are selectively applied to the final stage amplifier.
Owner:NEC CORP
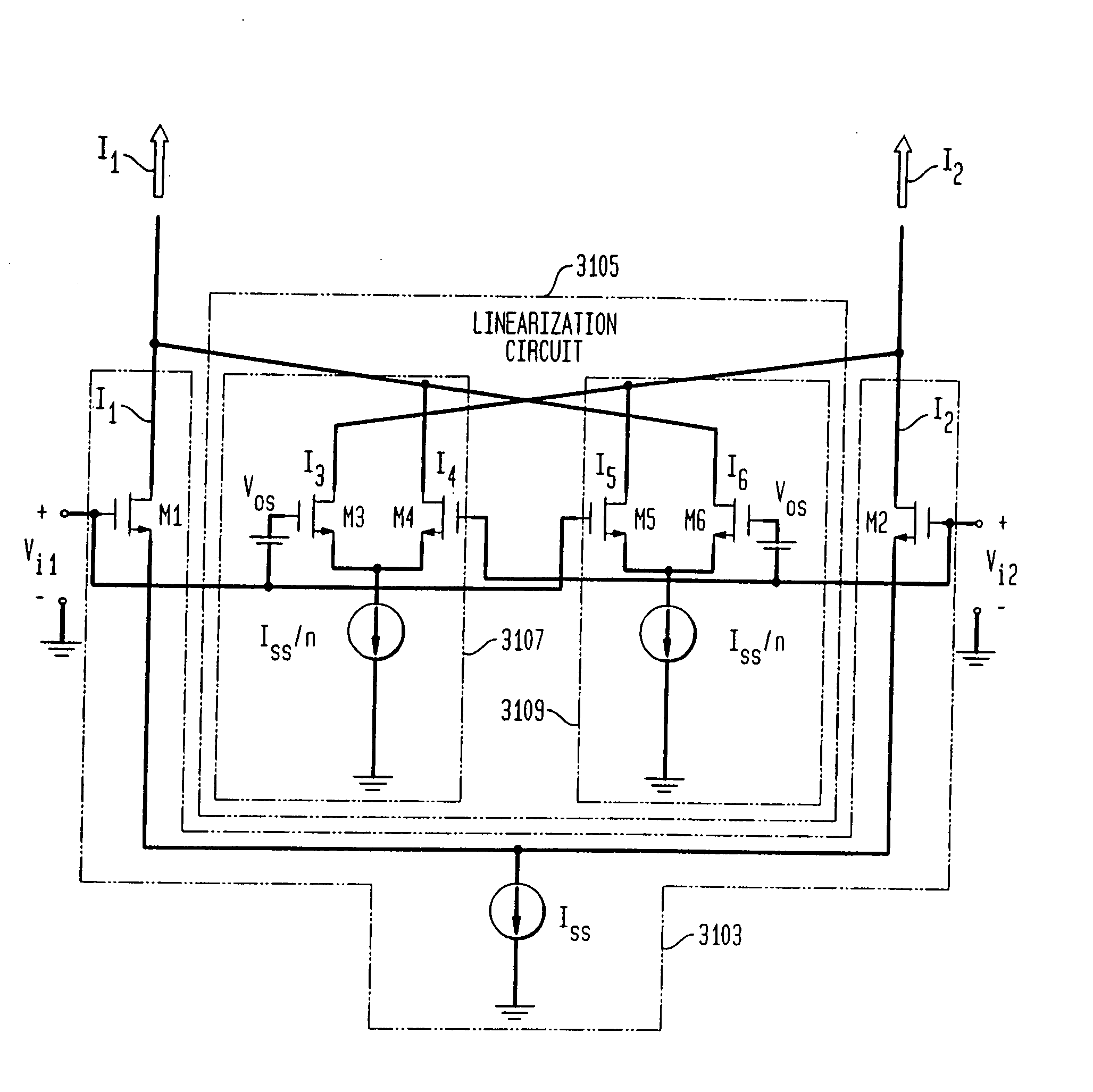
System and method for linearizing a CMOS differential pair
InactiveUS20080036536A1Multiple-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsShunt DeviceFilter tuning
An integrated receiver with channel selection and image rejection substantially implemented on a single CMOS integrated circuit. A receiver front end provides programmable attenuation and a programmable gain low noise amplifier. LC filters integrated onto the substrate in conjunction with image reject mixers provide image frequency rejection. Filter tuning and inductor Q compensation over temperature are performed on chip. Active filters utilize multi track spiral inductors with shields to increase circuit Q. The filters incorporate a gain stage that provides improved dynamic range through the use of cross coupled auxiliary differential pair CMOS amplifiers to cancel distortion in a main linearized differential pair amplifier. Frequency planning provides additional image rejection. Local oscillator signal generation methods on chip reduce distortion. A PLL generates needed out of band LO signals. Direct synthesis generates in band LO signals. PLL VCOs are centered automatically. A differential crystal oscillator provides a frequency reference. Differential signal transmission throughout the receiver is used. ESD protection is provided by a pad ring and ESD clamping structure. Shunts utilize a gate boosting at each pin to discharge ESD build up. An IF VGA utilizes distortion cancellation achieved with cross coupled differential pair amplifiers having their Vds dynamically modified in conjunction with current steering of the differential pairs sources.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
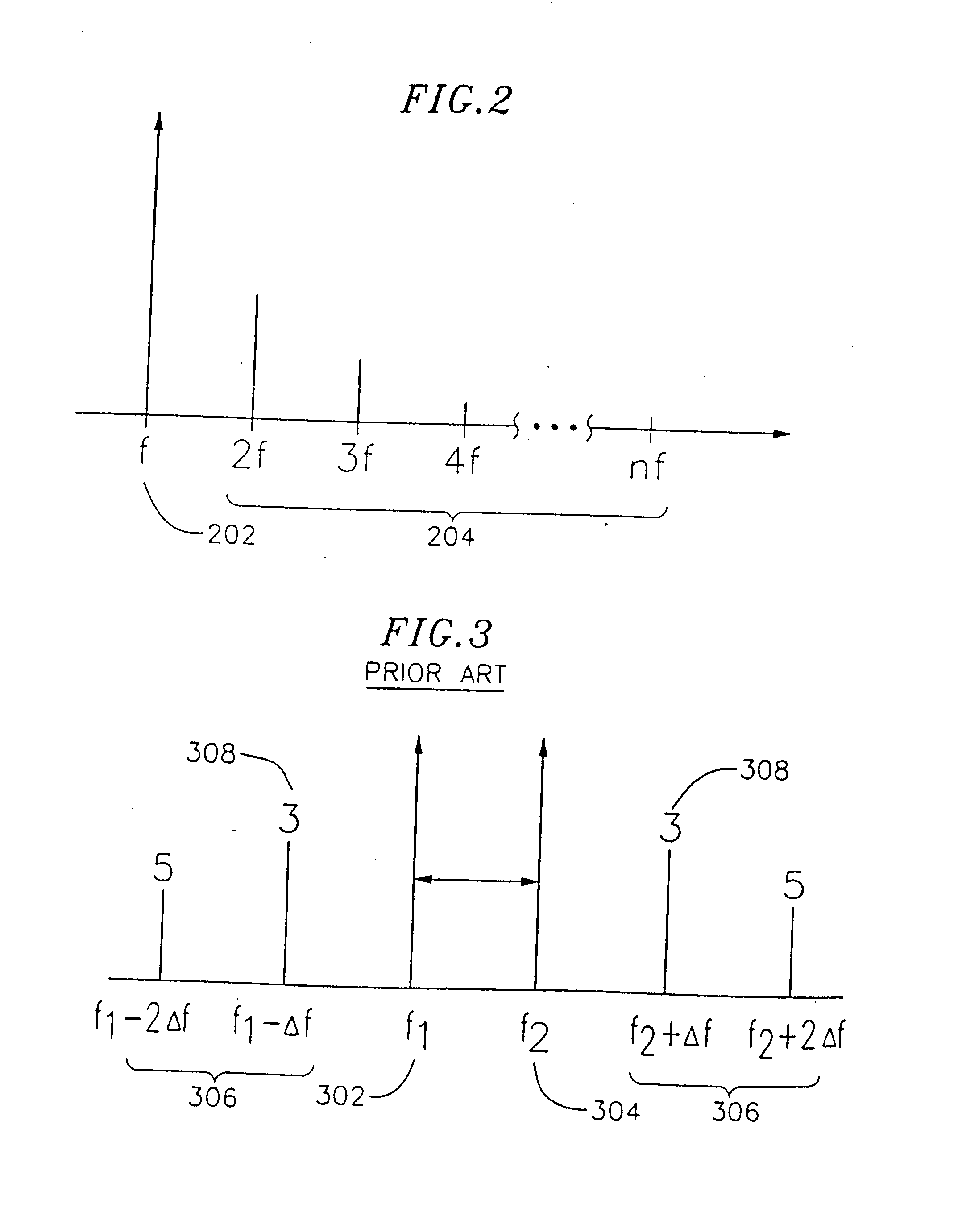
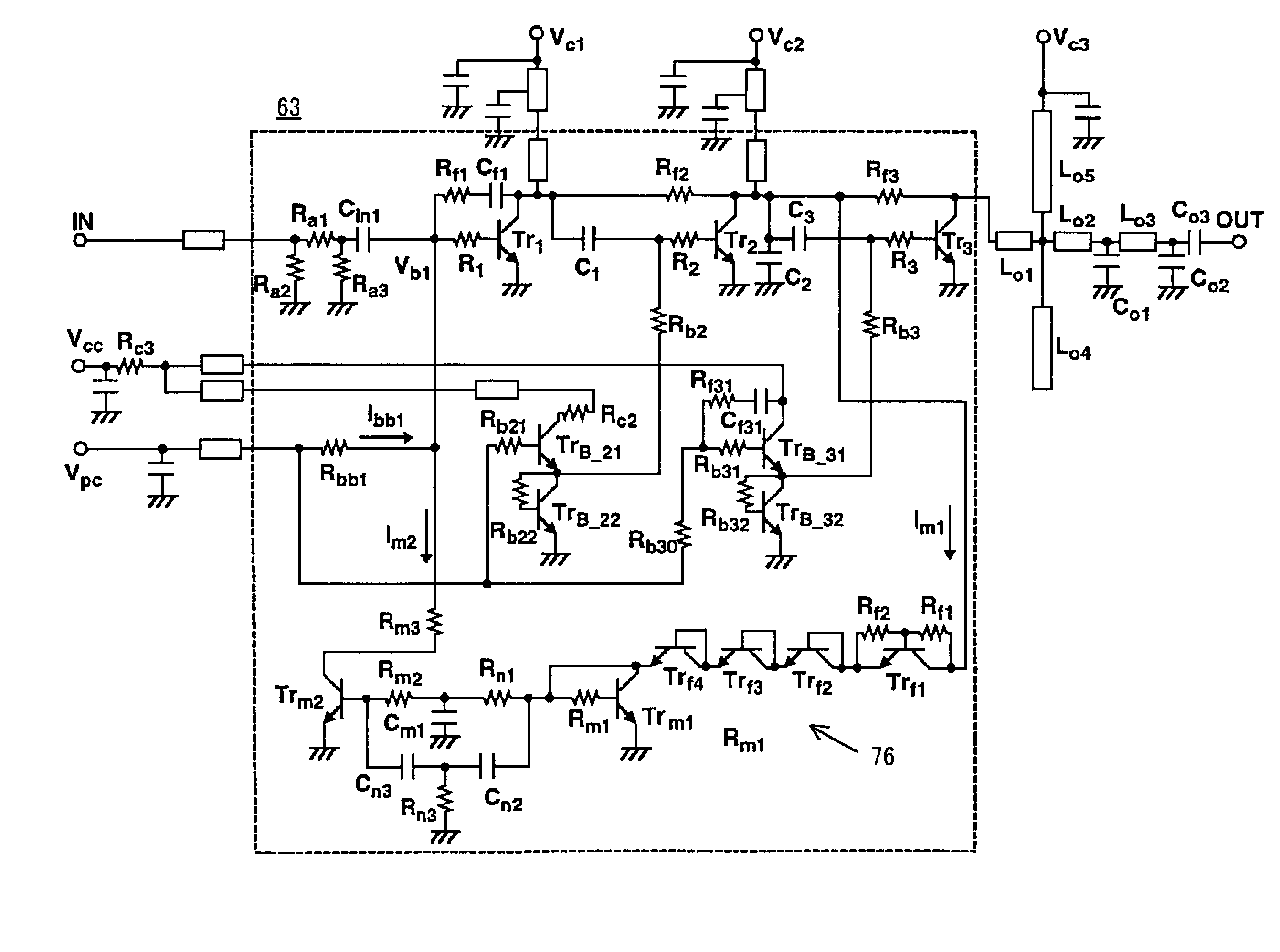
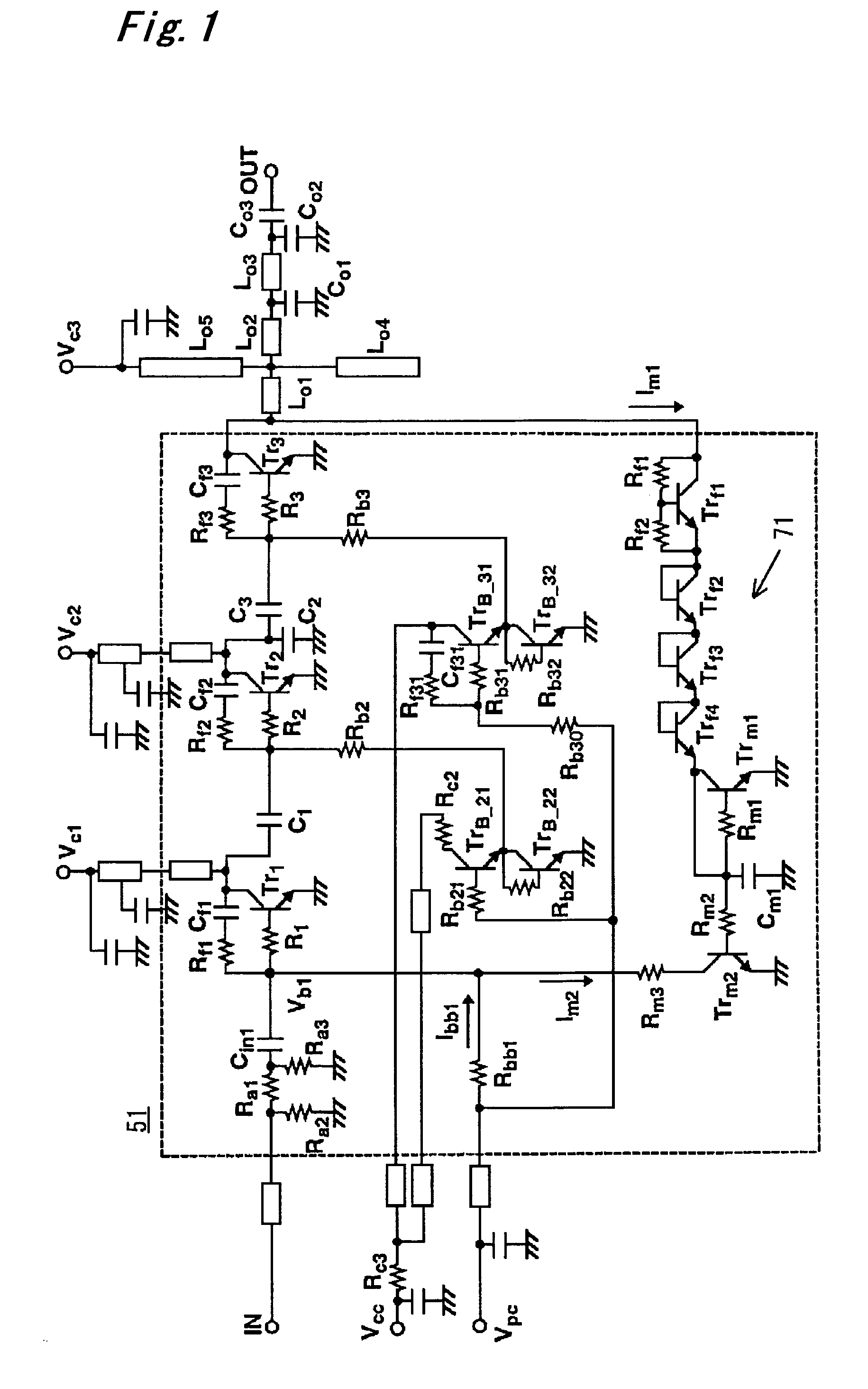
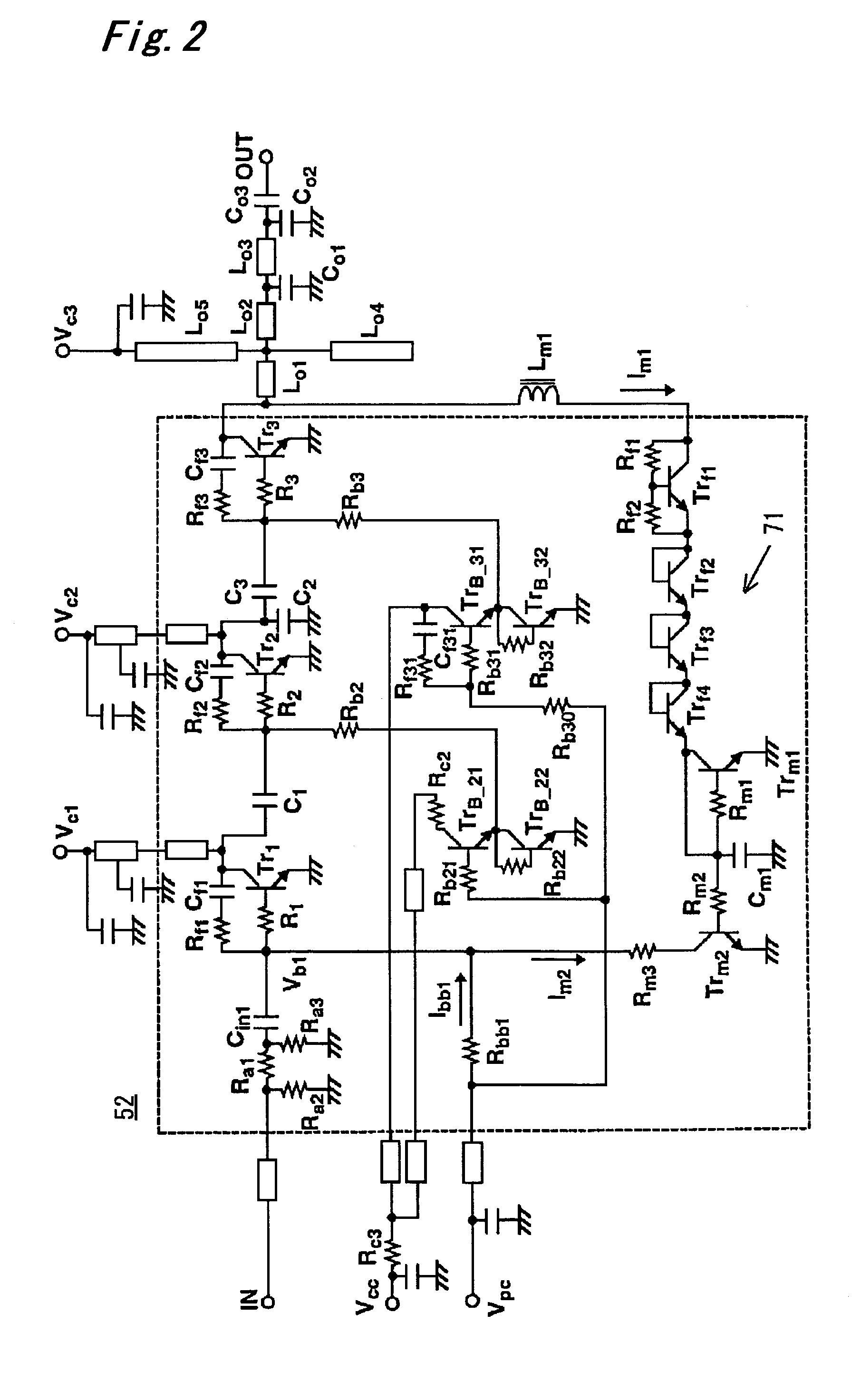
Output overvoltage protection circuit for power amplifier
ActiveUS7145397B2Reduce outputBias of the first-stage transistorPower amplifiersEmergency protective circuit arrangementsOvervoltageAudio power amplifier
Disclosed is an output overvoltage protection circuit for a power amplifier having a plurality of stages, which comprises a monitor circuit for monitoring an output overvoltage of an output transistor in the final stage of the power amplifier and allowing a current to flow therethrough in response to the monitored output overvoltage, and a current mirror circuit for supplying a current proportional to the current from the monitor circuit in such a manner that the base bias of the first-stage transistor of the power amplifier is reduced in response to the current supplied from the current mirror circuit, to reduce the output of the final-stage output transistor.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Detection of DC output levels from a class D amplifier
ActiveUS20050083116A1Simple analog portionLow cutoff frequencyDuration/width modulated pulse demodulationPulse duration/width modulationUnsafe conditionAudio power amplifier
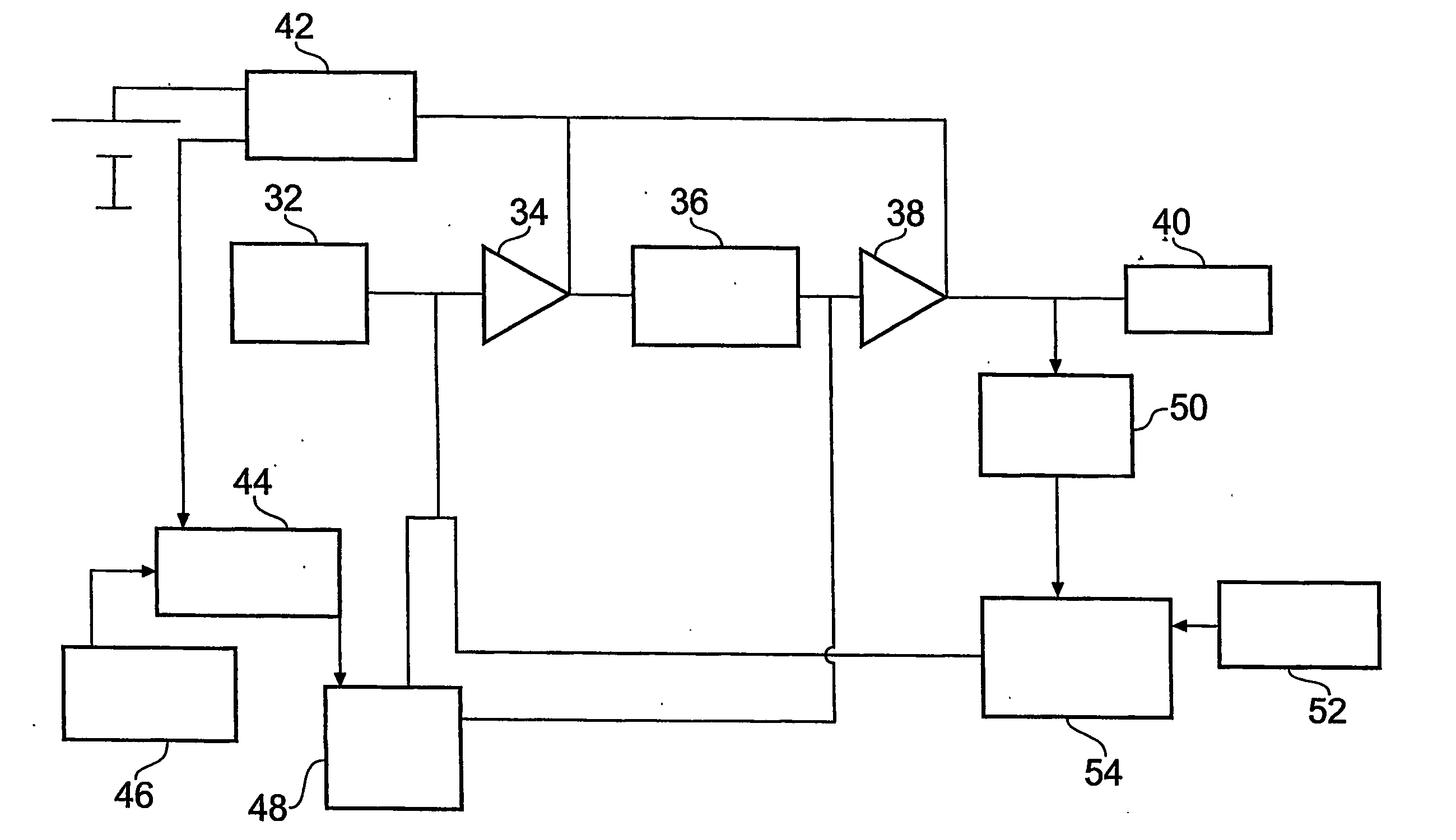
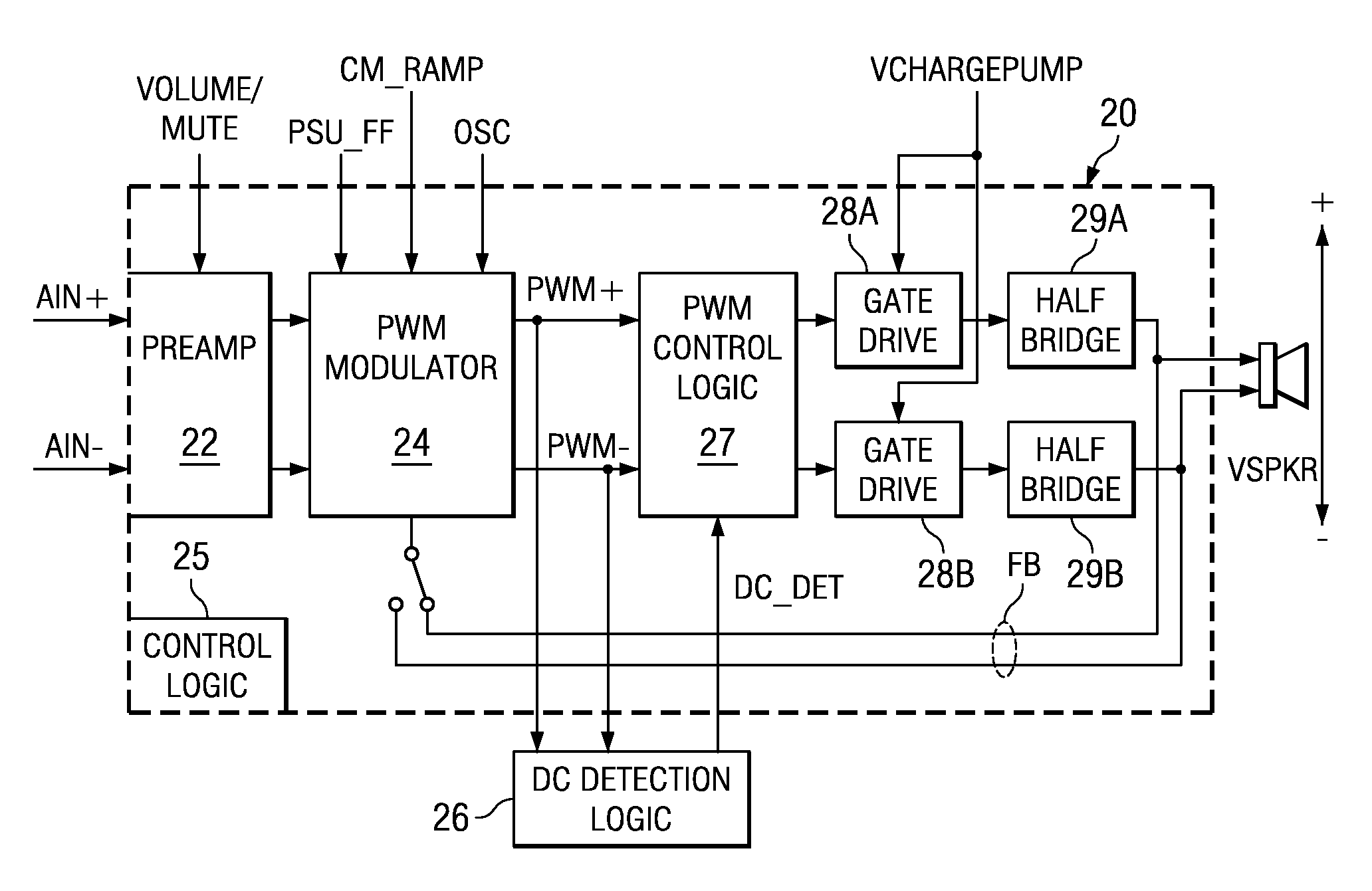
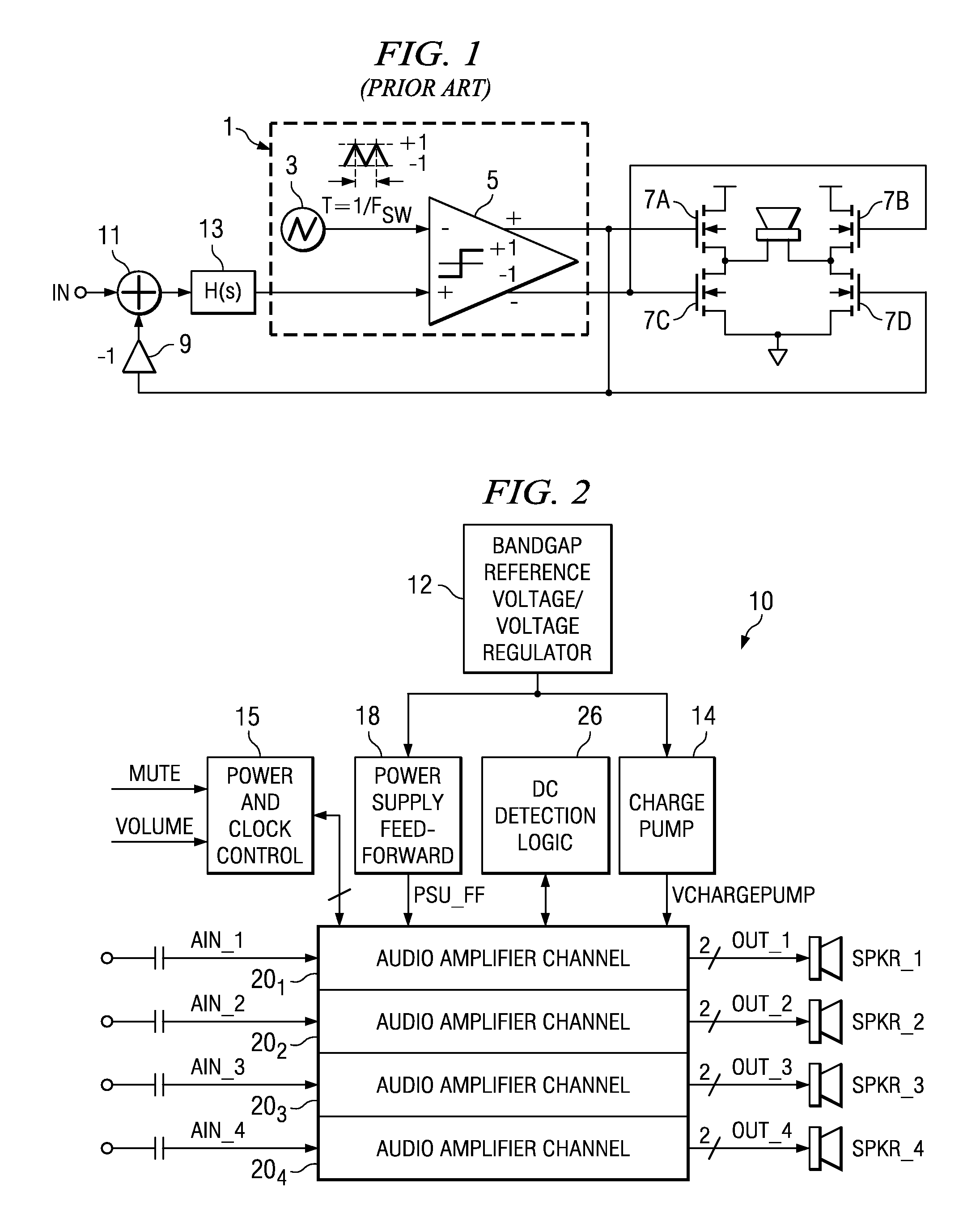
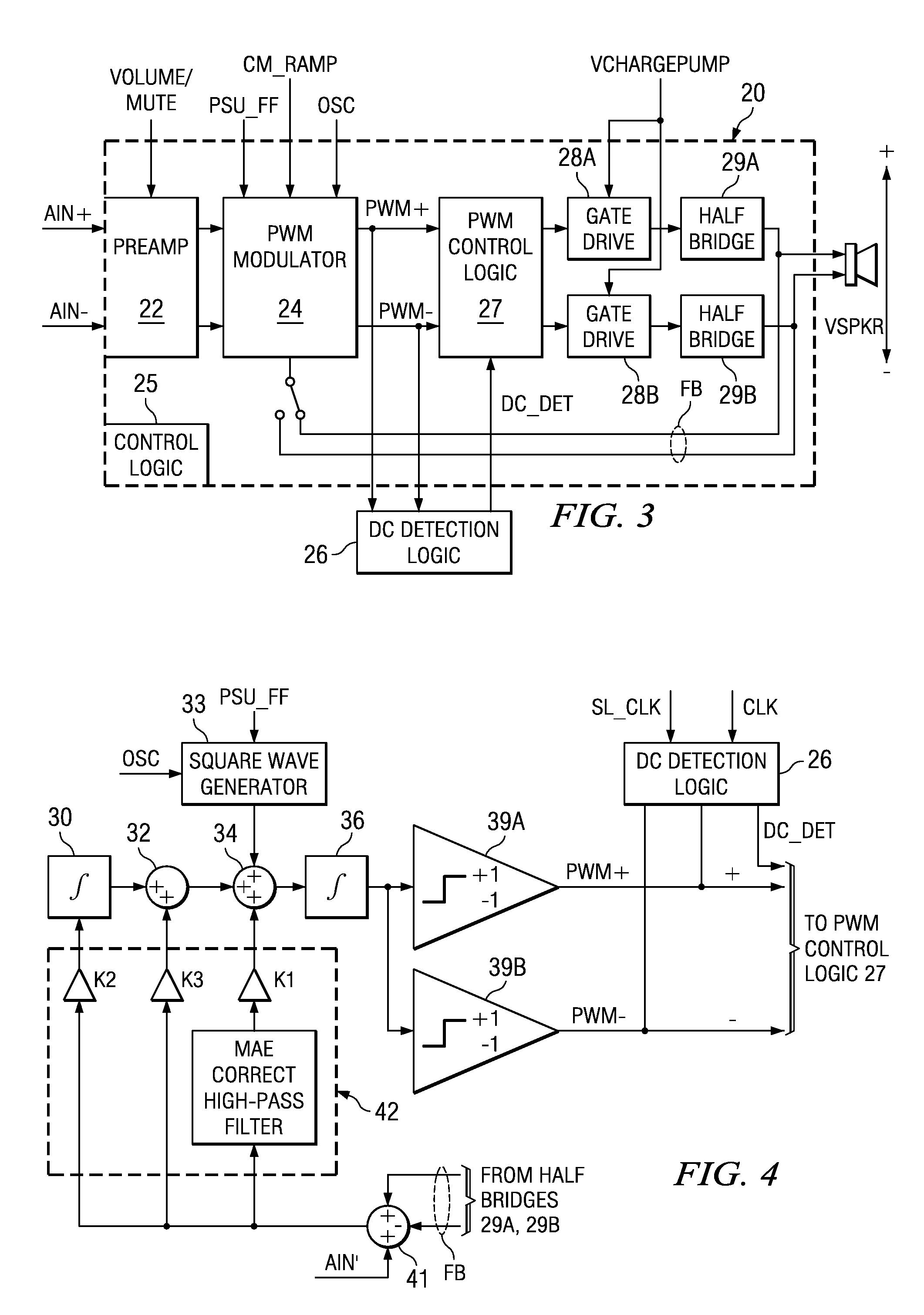
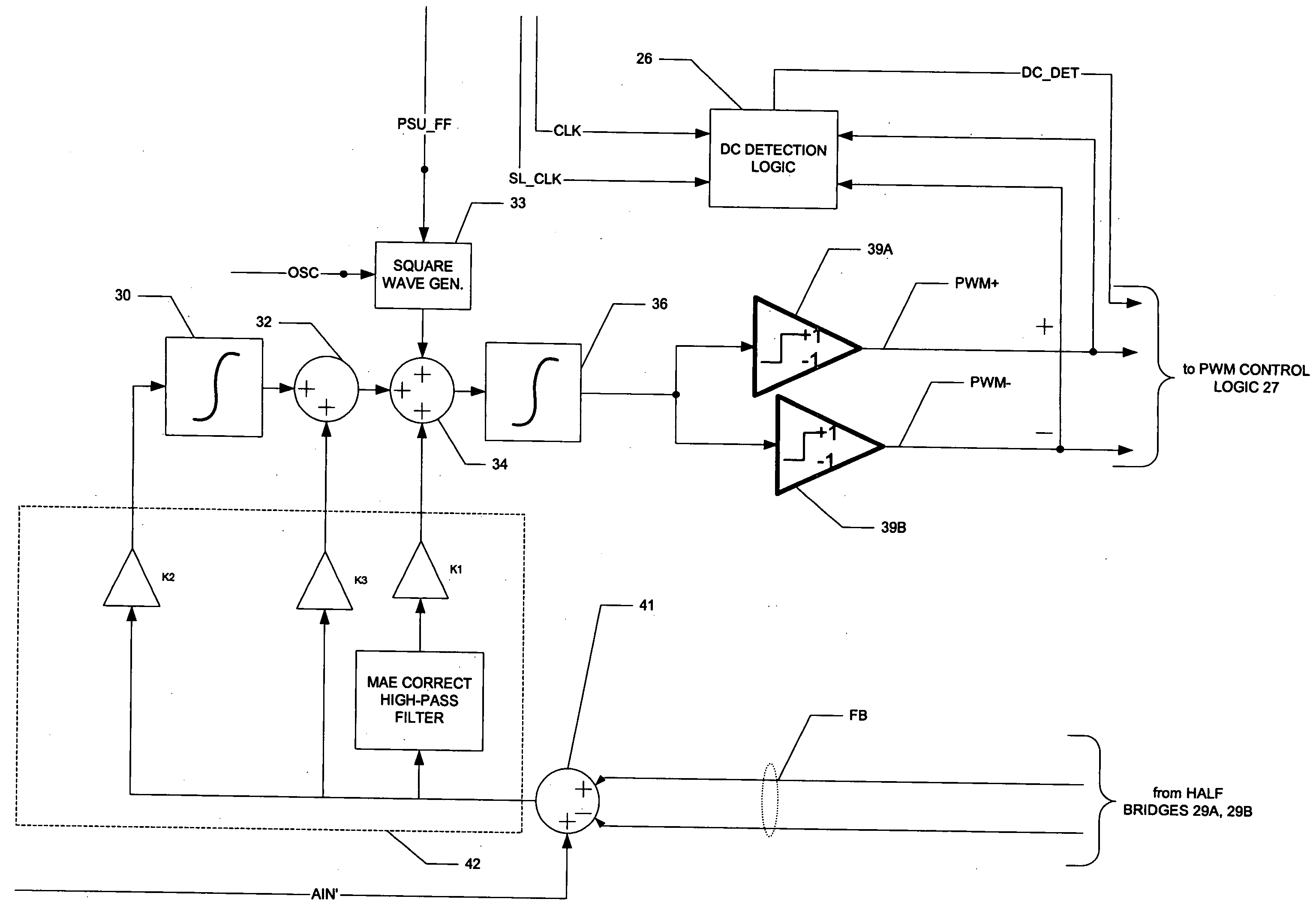
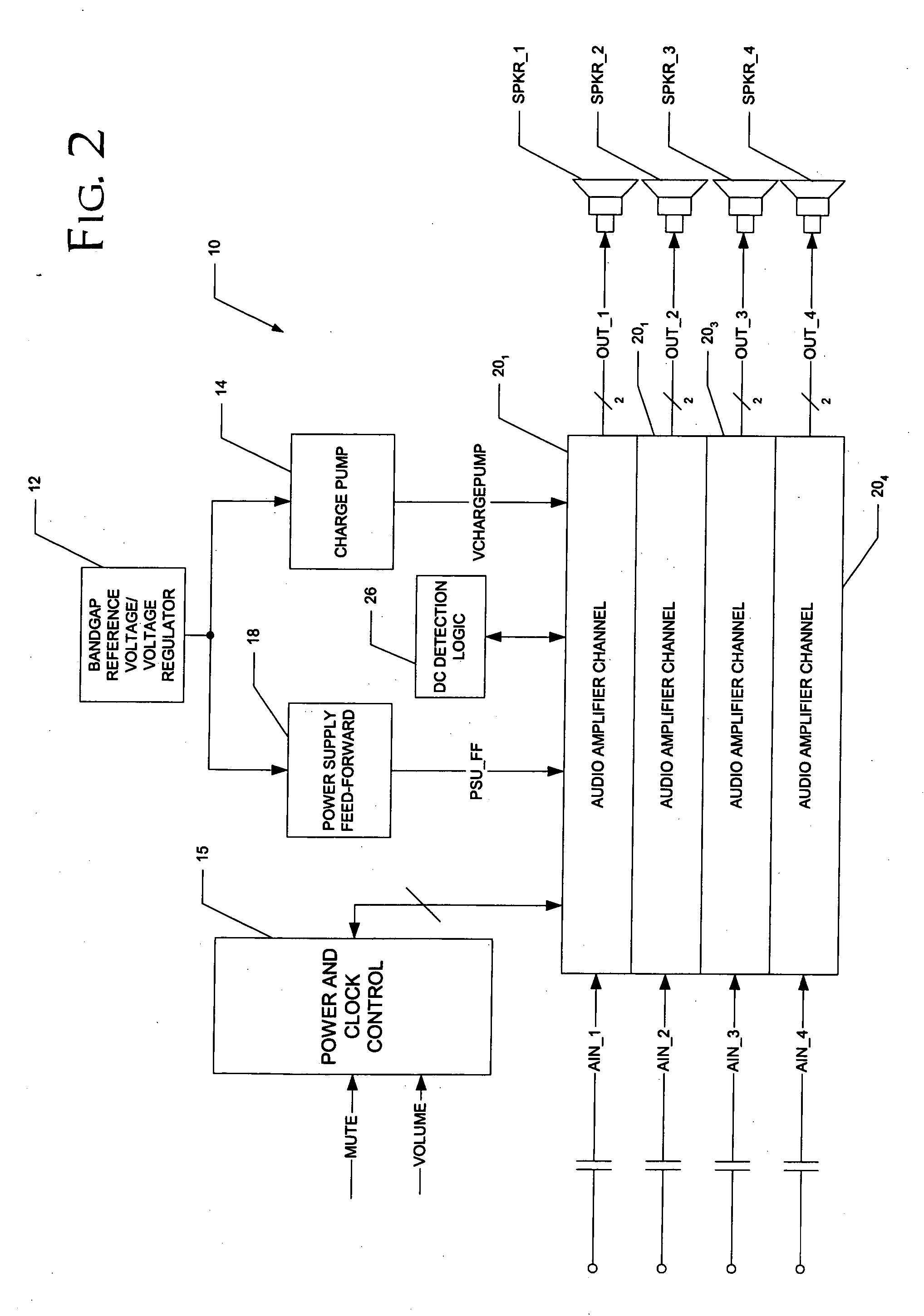
A class AD audio amplifier system (10) with DC output detection logic (26) is disclosed. The amplifier system (10) includes multiple audio channels (20), each of which includes a pulse-width-modulator (PWM) (24). The DC detection logic (26) includes a sigma-delta modulator (60) and a digital low-pass filter (62) that monitors the PWM output signals from the PWM modulators (24). The sigma-delta modulator (60) operates at a first clock frequency, while the low-pass filter (62) operates at a much lower clock frequency, so that AC audio components, PWM harmonics, and sigma-delta quantization error is suppressed from the DC detection. The modulated filtered signal is compared against a threshold level (THRSH) to determine whether the amplitude of a DC component at the PWM output is sufficiently high to constitute a fault. If so, a fault detection signal (DC_DET) is issued, and the PWM modulators (24) are disabled to prevent unsafe conditions in the system (10).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Electronic parts for high frequency power amplifier
InactiveUS20070069820A1Small sizeImprove accuracyNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsHigh frequency amplifiersCapacitanceHigh frequency power
An electronic part for a high frequency power amplifier is provided which is designed to constitute at least a part of a wireless communication system for performing feedback control by detecting an output power, and which can miniaturize a directional coupler. Also, the electronic part permits control of the output power with high accuracy without having any influence on a monitor voltage by a reflected wave propagating through a line of the directional coupler. The directional coupler includes a subline disposed in parallel to and in the vicinity of a part of a main line of an impedance matching circuit on the last output stage side of a power amplifier circuit, a capacitance element connected to between the main line and the subline, and a resistor element connected to between a constant potential point and a termination side of the subline. An output power detection circuit includes a first detection circuit for detecting an alternating current signal taken from a beginning side of the subline, a second detecting circuit for detecting an alternating current signal taken from a termination side of the subline, and a subtracting circuit for performing subtraction between an output of the first detection circuit and an output of the second detection circuit.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
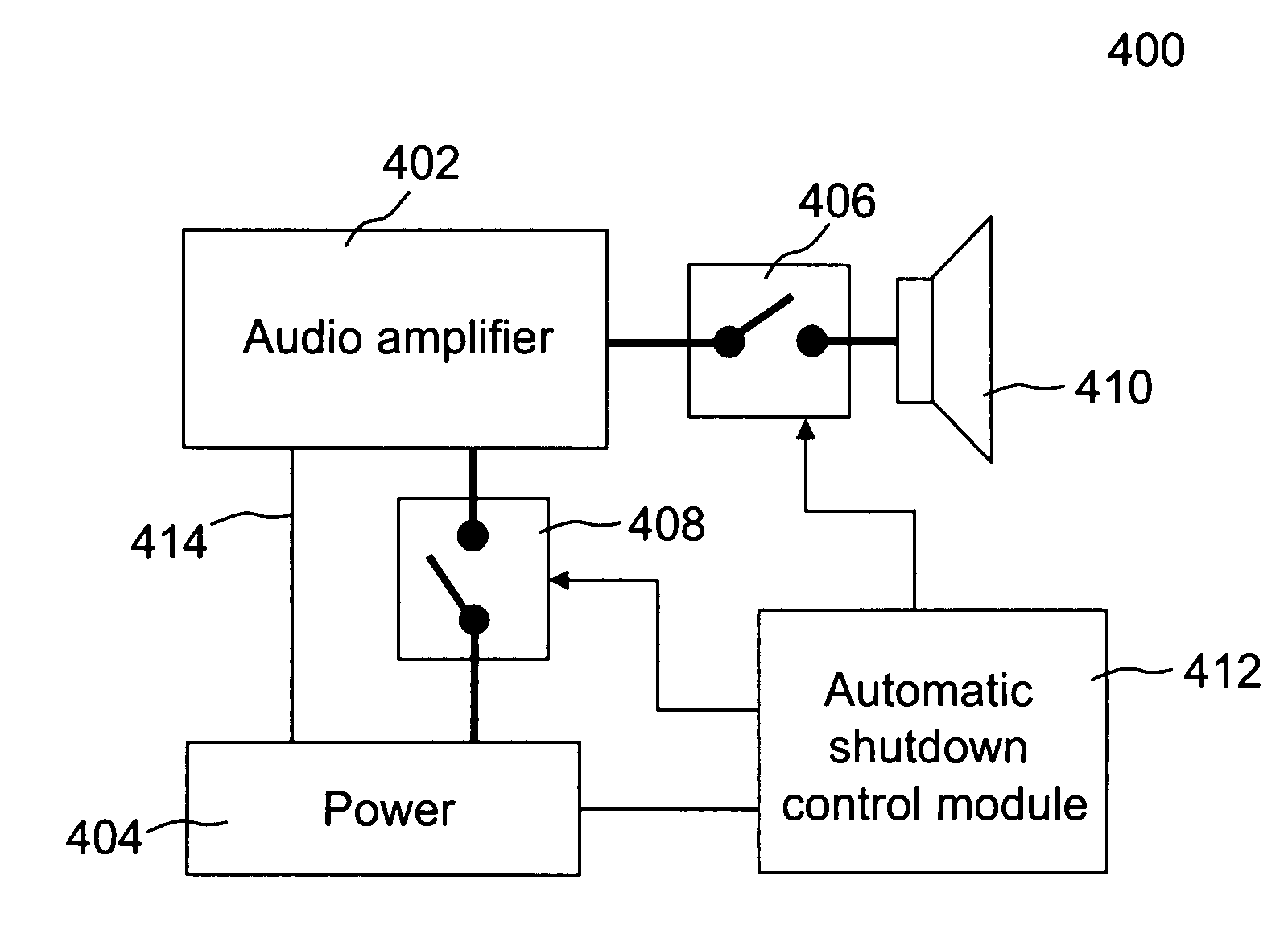
Method and system for controlling amplifiers
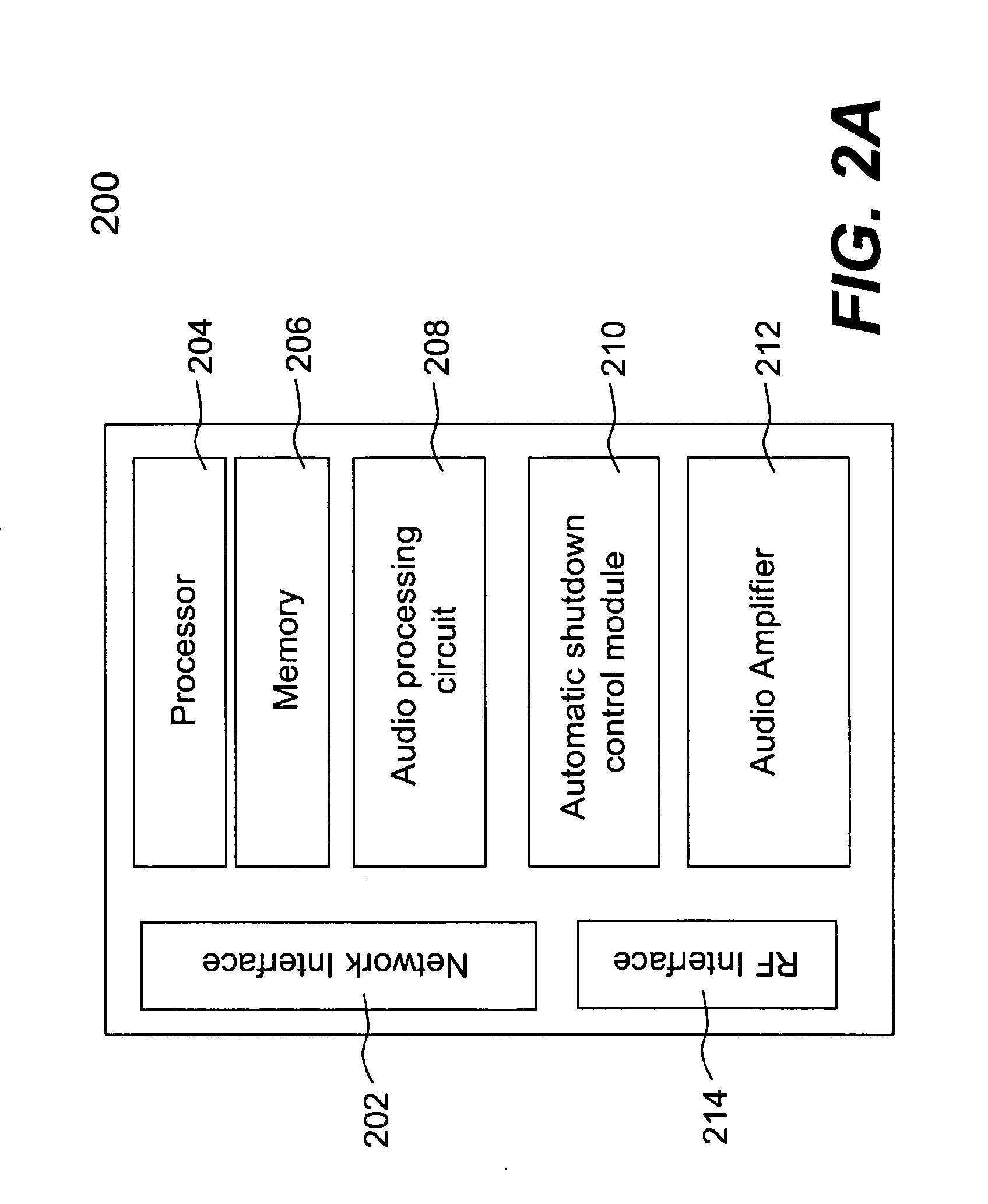
ActiveUS20110299696A1Digital data processing detailsPublic address systemsTelecommunicationsAudio power amplifier
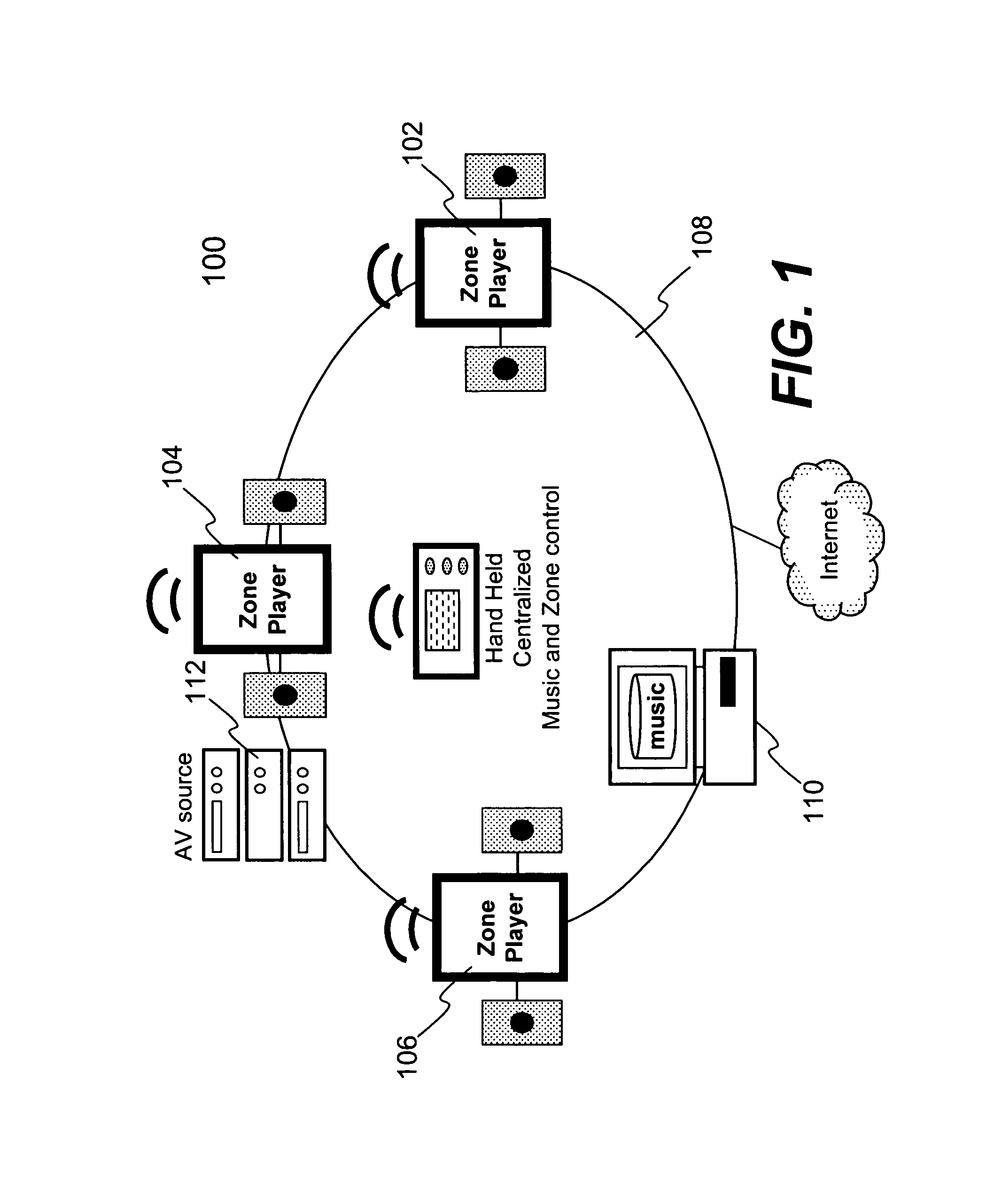
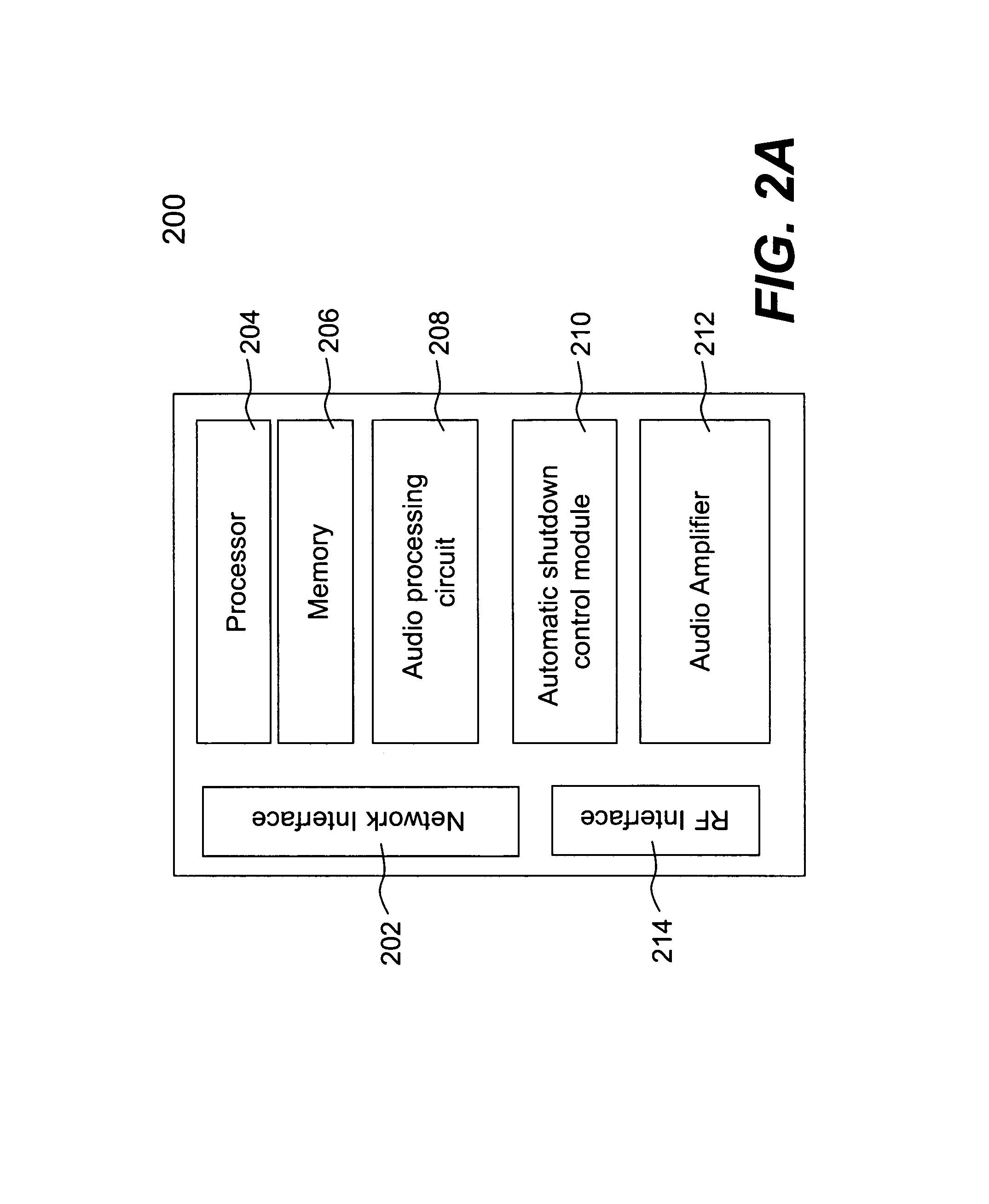
Techniques for controlling one or more audio amplifiers in or associated with a device coupled on a local area network are disclosed. The device receives at least one selected source from other devices also coupled on the network According to one aspect of the techniques, an automatic shutdown control module is provided in the device to power down the audio amplifiers when there is no audio data flow coming to the device or power up the audio amplifiers when there is audio data flow coming to the device. In one embodiment, the procedure to power down or power up the amplifiers is in accordance with a hysteresis, wherein the hysteresis, being lagging of an effect behind its cause, protects the amplifiers and makes the powering-down or powering-up procedure unnoticeable to a user.
Owner:SONOS
Monolithic class D amplifier
InactiveUS7076070B2Minimized cell areaMaximizing specific channel widthTransistorGated amplifiersDriver circuitAudio power amplifier
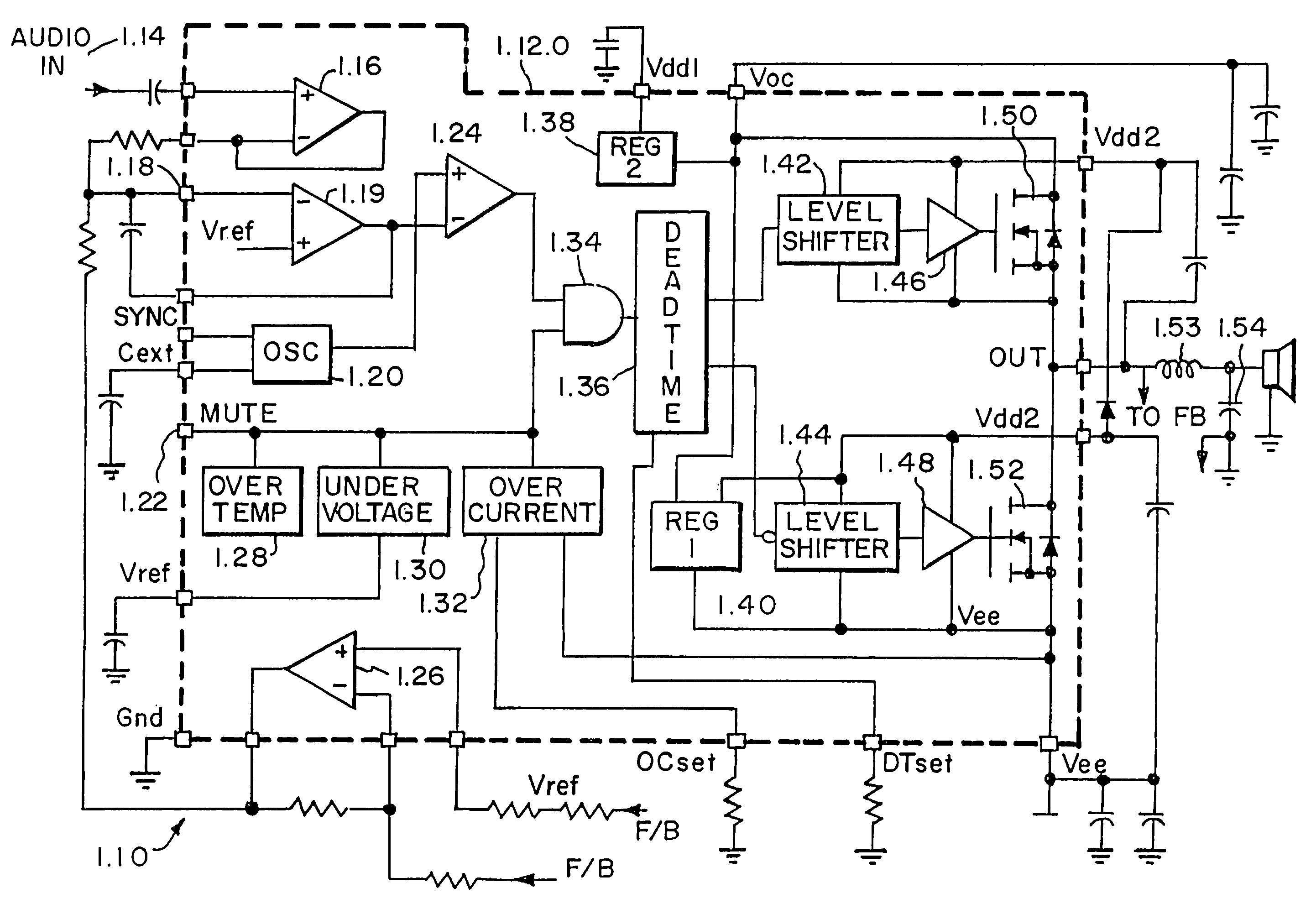
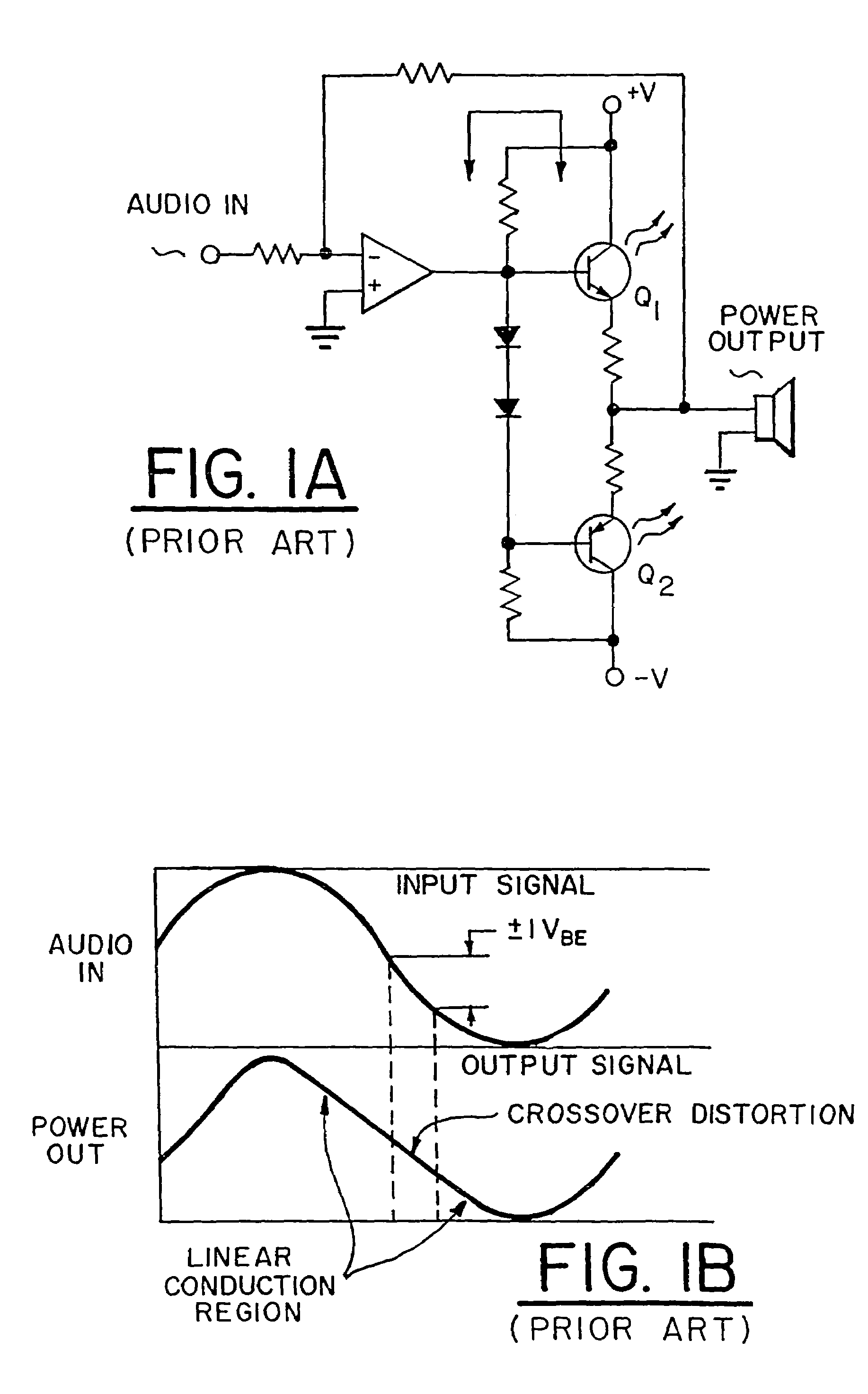
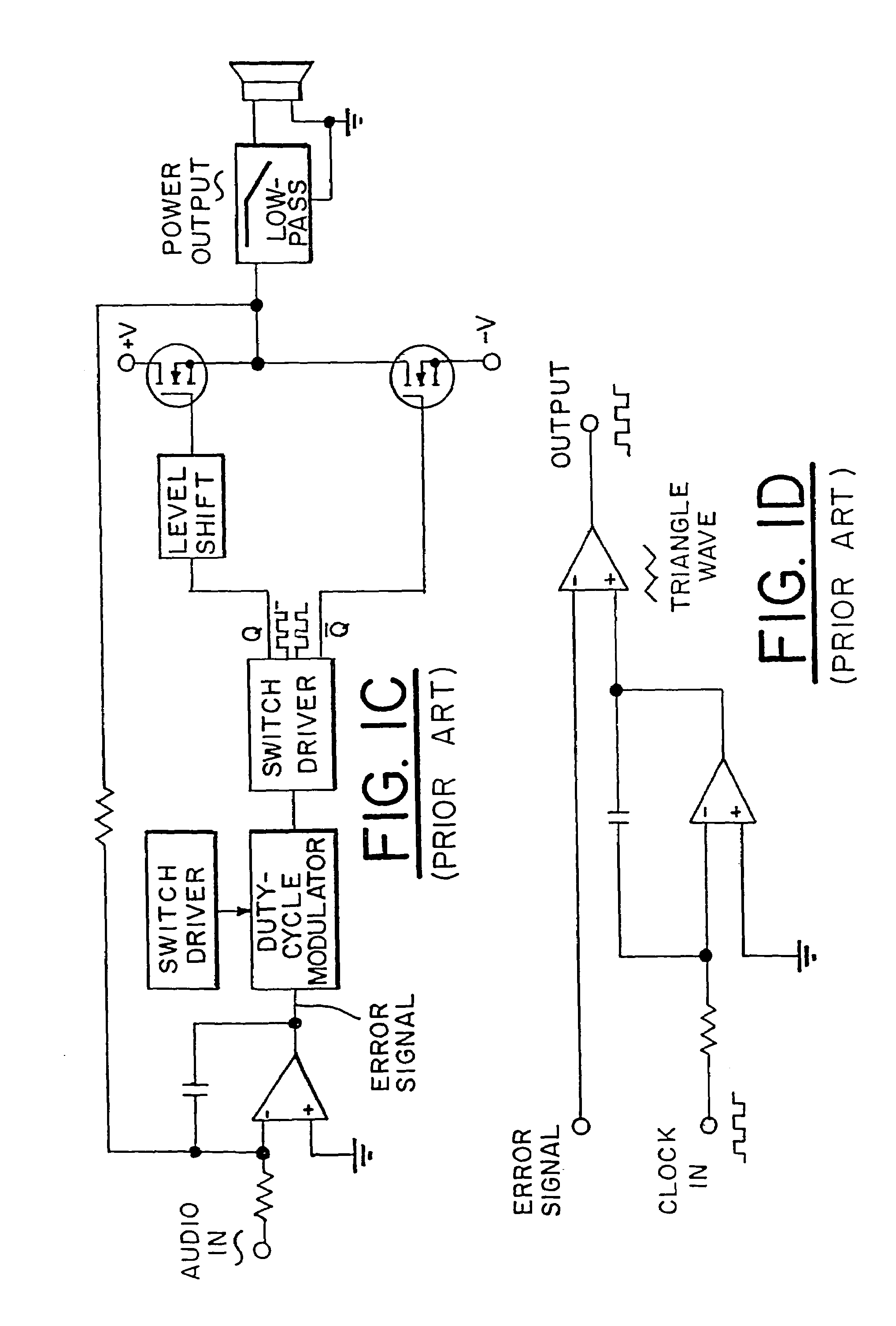
A monolithic 1.75 is mounted in a speaker cabinet 1.71 to drive the voice coil 1.74 of the speaker 1.70. The monolithic integrated circuit may be a class D amplifier 1.10, and is at least a half-bridge or full bridge power MOSFET device. Structures and process for forming the mos switching devices 2.20 of the bridge driver circuits are disclosed. Also disclosed is the N+ buried layer 4.14 of the QVDMOS transistors 4.43 of the bridge circuits.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Class E amplifier with inductive clamp
InactiveUS7180758B2High frequency amplifiersEmergency protective circuit arrangementsEngineeringSignal source
A power supply including an inverter receiving a DC input signal from a DC input source (11). The inverter is implemented as a single-ended inverter. Each inverter is driven by a signal source (13A, 13B), which outputs an AC signal. The output from each inverter is input to a first stage harmonic filter. The power supply includes an output circuit that includes a rectifier (D1) arranged about a point so that if the inverter attempts to drive the point beyond a predetermined voltage, the rectifier conducts in order to return at least one of power and current to the DC input source. The output from the first harmonic filter (L1A, C1; L1B, C1) is output to a second harmonic filter (L2, C2) and is then output from the power supply.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Audio amplification circuit
InactiveUS20130129117A1Increase investmentEfficiently maskedHearing device energy consumption reductionSemiconductor electrostatic transducersAudio power amplifierA d converter
Disclosed is an audio amplification circuit comprising: an input terminal for receipt of an audio input signal; a first preamplifier having an input operatively coupled to the input terminal and operable to provide a first amplified audio signal with a first signal amplification; a second preamplifier having an input operatively coupled to the input terminal and operable to provide a second amplified audio signal with a second signal amplification, smaller than the first signal amplification; a switch having a first input operatively coupled to the first preamplifier, a second input operatively coupled to the second preamplifier, and an output; an analogue-to-digital converter operatively coupled to the output of the switch and operable to provide a digital audio signal; a signal selection circuit operable to control the switch to selectively provide one of the first and second amplified audio signals on the output of the switch.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES GLOBAL
Stacked RF power amplifier
A method and apparatus provides techniques for electrically isolating switching devices in a stacked RF power amplifier, which prevents the switching devices from being subjected to high breakdown voltages. The isolation provided allows the power amplifier to be implemented on an integrated circuit.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
Into an internal circuit to operate in a high-frequency band, there is incorporated a protective circuit of a multistage connection which is constructed to include a plurality of diode-connected transistors having a low parasitic capacity and free from a malfunction even when an input signal higher than the power supply voltage is applied. Into an internal circuit to operate in a low-frequency band, there is incorporated a protective circuit which is constructed to include one diode-connected transistor. The protective circuits include two lines of protective circuit, in which the directions of electric currents are so reversed as to protect the internal circuits against positive / negative static electricities.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method and system for controlling amplifiers
Techniques for controlling one or more audio amplifiers in or associated with a device coupled on a local area network are disclosed. The device receives at least one selected source from other devices also coupled on the network According to one aspect of the techniques, an automatic shutdown control module is provided in the device to power down the audio amplifiers when there is no audio data flow coming to the device or power up the audio amplifiers when there is audio data flow coming to the device. In one embodiment, the procedure to power down or power up the amplifiers is in accordance with a hysteresis, wherein the hysteresis, being lagging of an effect behind its cause, protects the amplifiers and makes the powering-down or powering-up procedure unnoticeable to a user.
Owner:SONOS
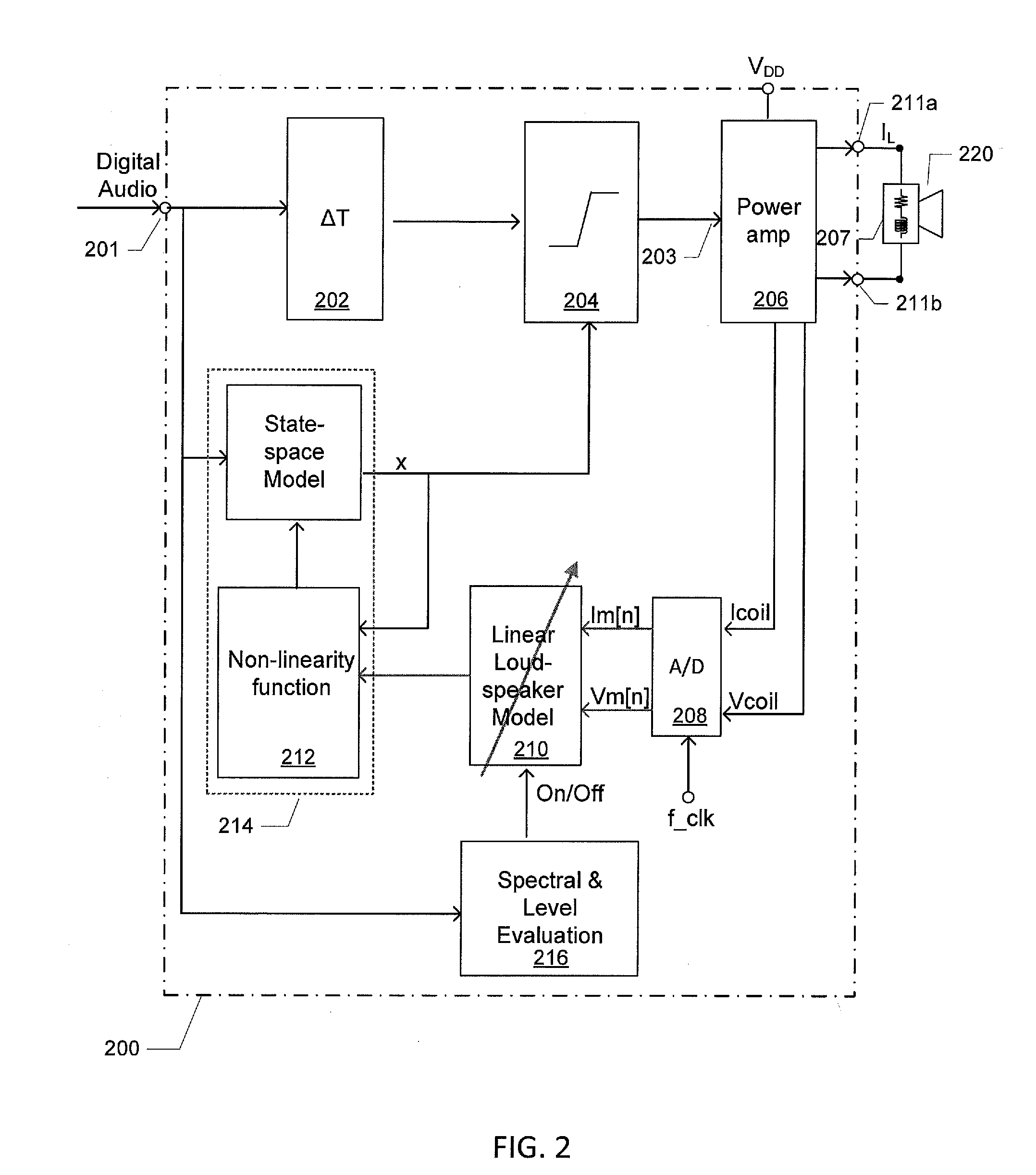
Method of estimating diaphragm excursion of a loudspeaker
ActiveUS20150124982A1Improve accuracyReduce computing loadVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesTransducer circuit dampingAudio power amplifierEngineering
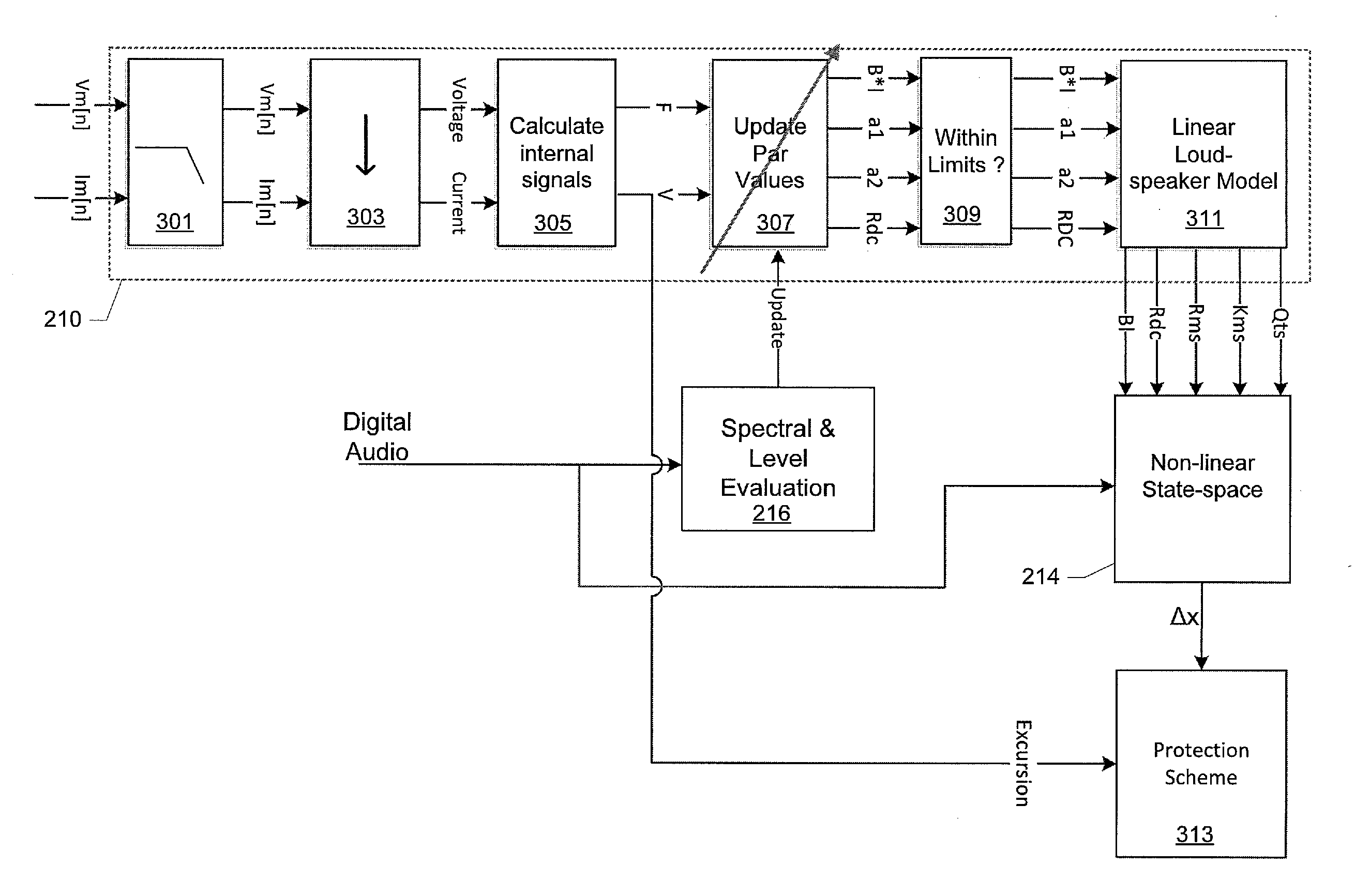
A method of estimating diaphragm excursion of an electrodynamic loudspeaker may be performed using audio signals. An audio output signal may be applied to a voice coil of the electrodynamic loudspeaker through an output amplifier to produce sound. A detected voice coil current and a determined voice coil voltage may be applied to a linear adaptive digital loudspeaker model that has a plurality of adaptive loudspeaker parameters. The parameter values of the adaptive loudspeaker parameters may be computed based on the linear adaptive digital loudspeaker model and applied to a non-linear state-space model of the electrodynamic loudspeaker. For the non-linear state-space model, a predetermined non-linear function may be applied to at least one of the plurality of received parameter values to compute at least one non-linearity compensated parameter value of the adaptive loudspeaker parameters, to determine an instantaneous excursion of the diaphragm.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
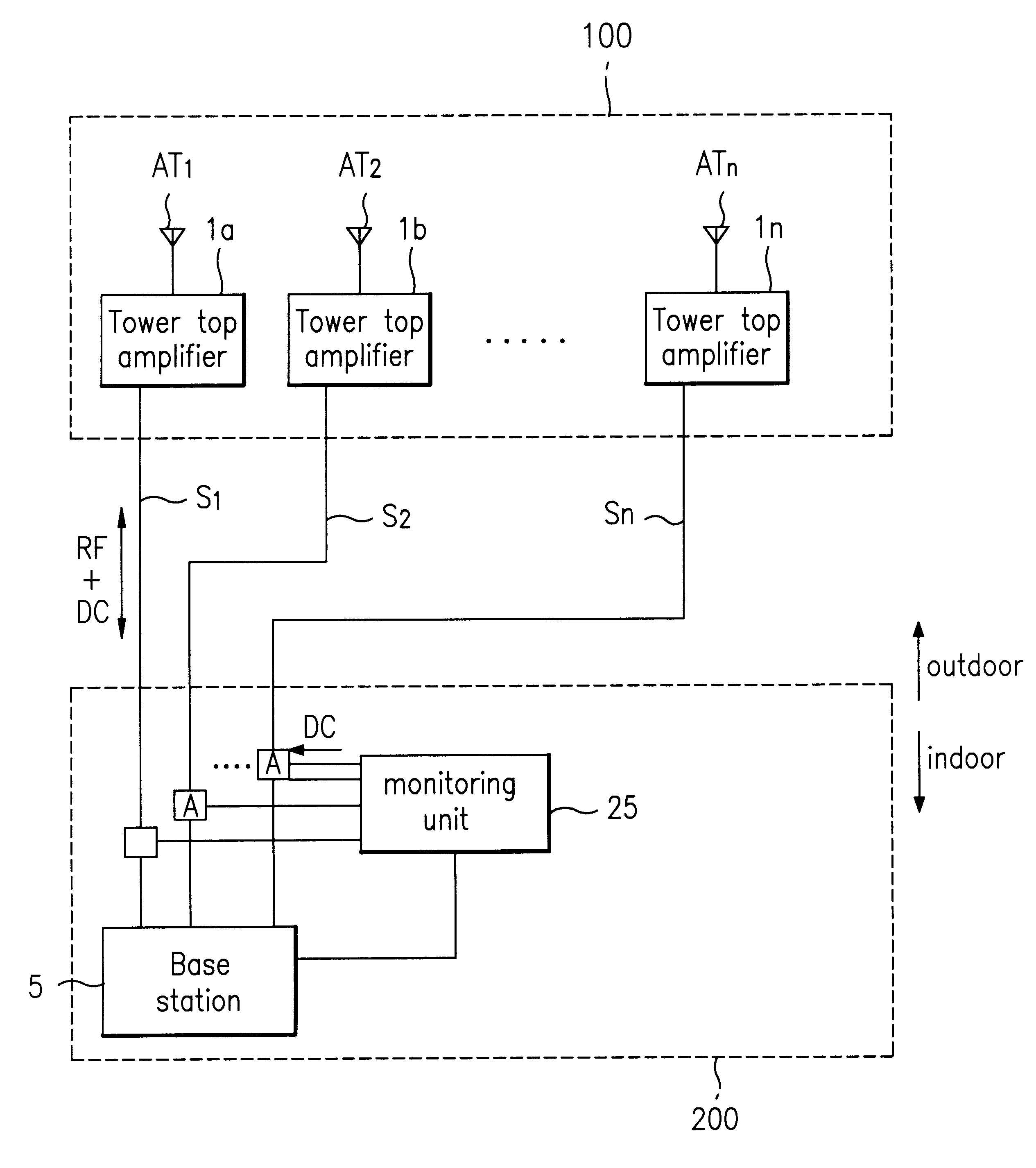
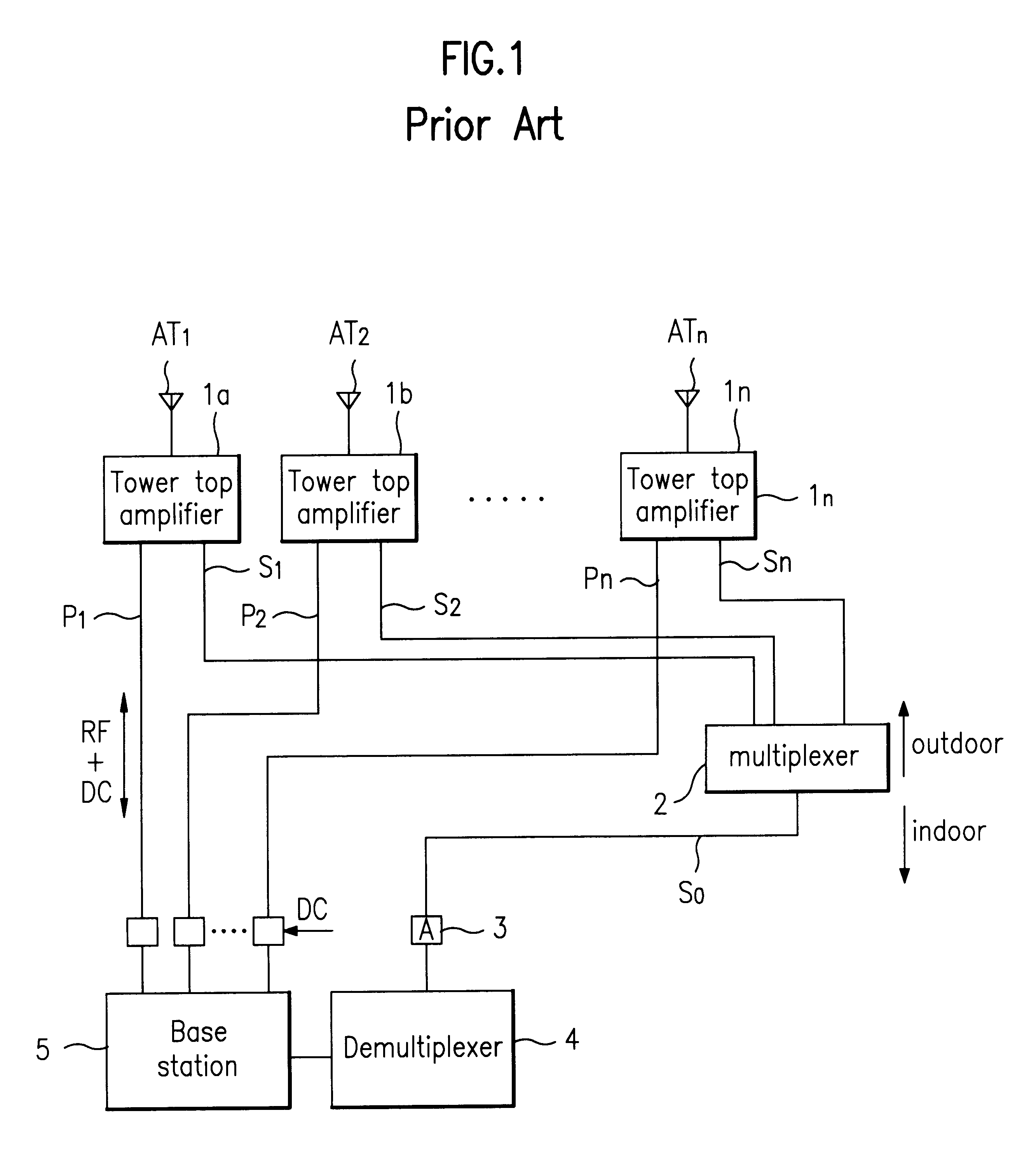
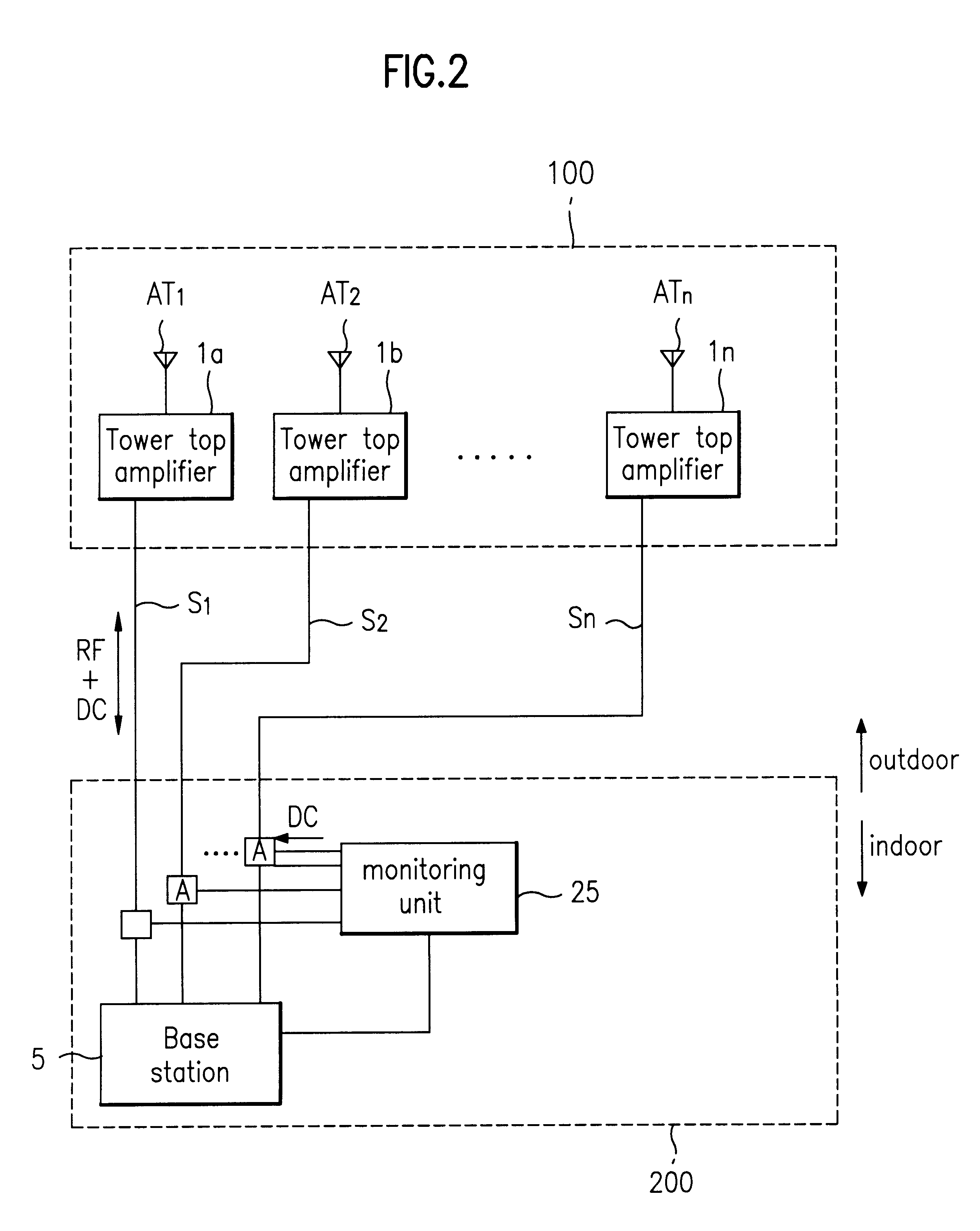
System for sensing operating state of tower top amplifier for mobile communication system and method of sensing the same
InactiveUS6169451B1Transmitters monitoringElectronic circuit testingAudio power amplifierPotential difference
A system for sensing the operating state of a tower top amplifier for mobile communication system, includes a plurality of tower top amplifiers each connected to communication antennas; and an operating state management part monitoring the operating state of each tower top amplifier. The operating state management part monitors the operating state of each tower top amplifier by the use of a single power supply line connected between itself and each tower top amplifier. In a method of sensing the operating state of a tower top amplifier for mobile communication system, the operating state of each tower top amplifier is monitored by using an amount of consumed DC power applied to the respective tower top amplifiers. This method includes the steps of measuring a potential difference of a given section of the DC power applied to each tower top amplifier; and comparing a result obtained by the measuring step and determining the normal or abnormal states of the tower top amplifiers.
Owner:LG ERICSSON
Device and method for pre-distorting a base-band digital signal
ActiveUS20080095264A1Increased base efficiencyImprove efficiencySecret communicationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksNonlinear filterAudio power amplifier
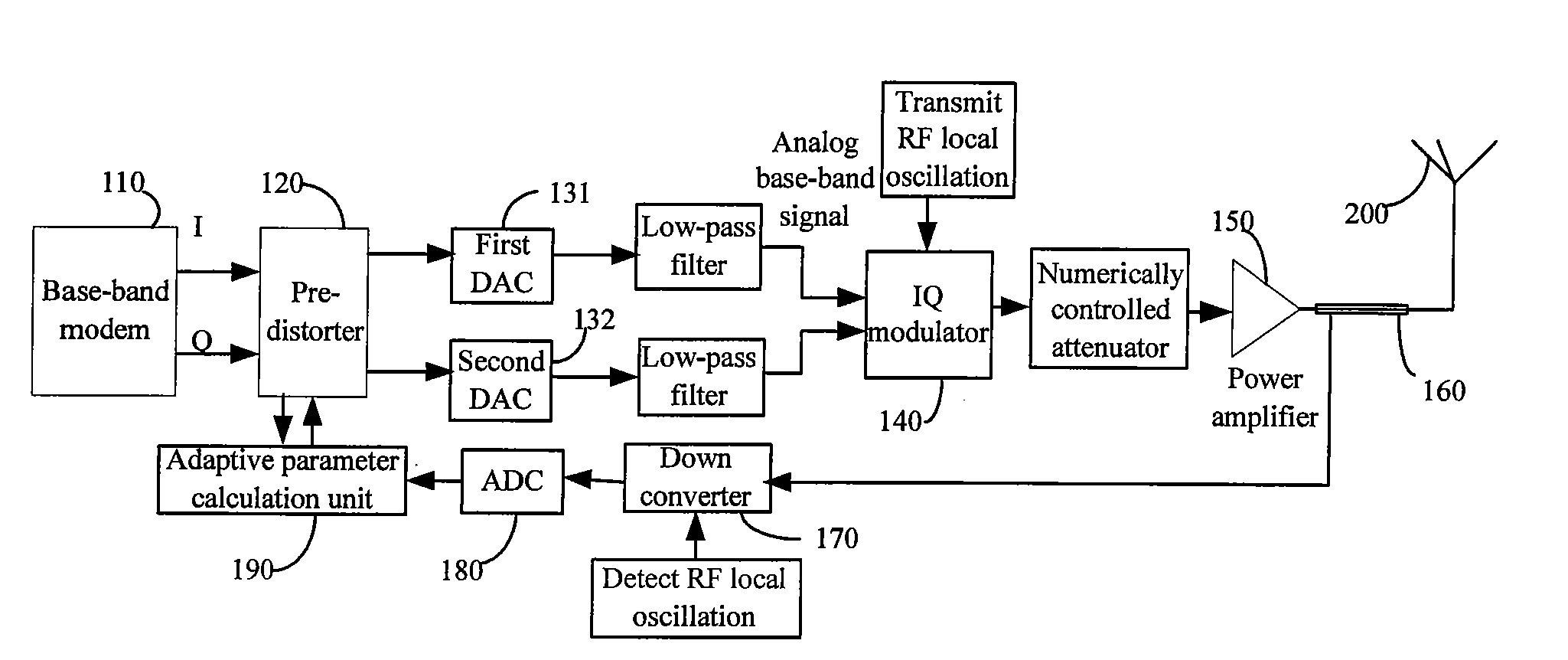
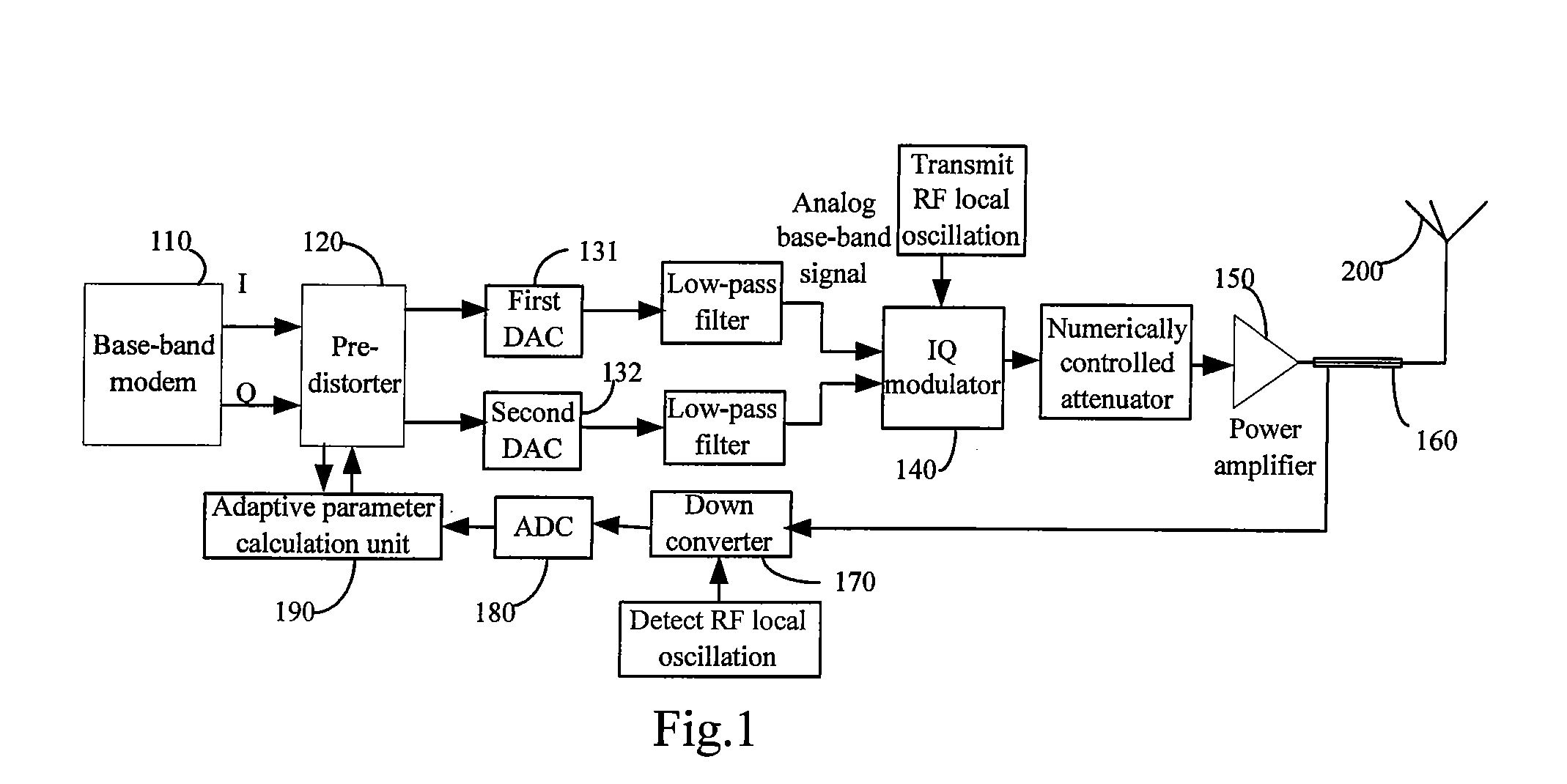
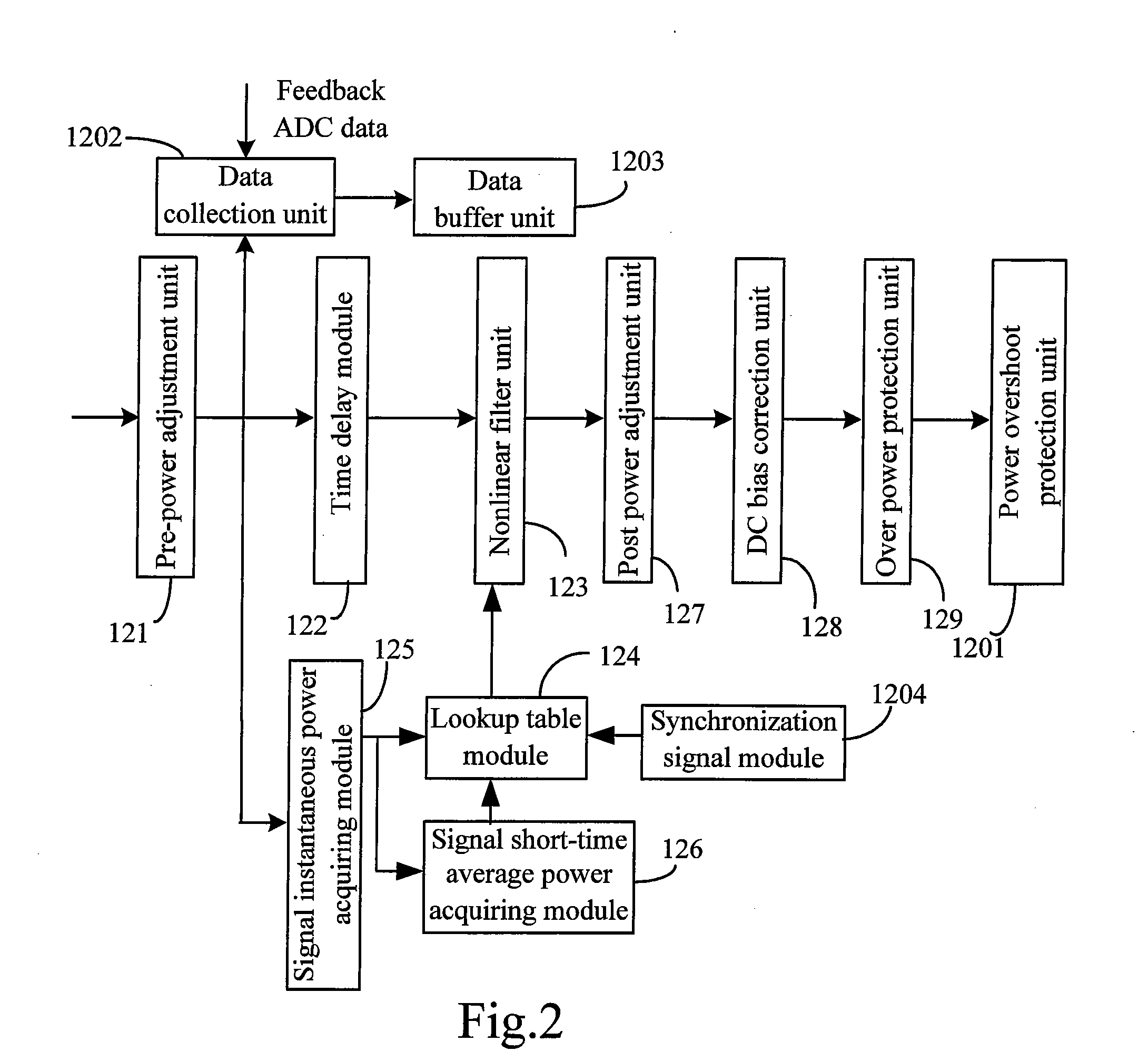
A baseband signal predistortion processing device and method. Said device includes: a predistorter, for preserving and updating nonlinear filter parameter, carrying out power statistic of input signals, selecting corresponding nonlinear filter parameter according to the power statistical result and predistortion-processing baseband digital signals by use of said corresponding nonlinear filter parameter, and outputting the predistortion processed baseband digital signals; an adaptive parameter calculating unit, for calculating nonlinear filter parameter according to received feedback signals of radio-frequency channel and sampled signals of baseband digital signals, and transmitting the calculating result to the predistorter. Said method can not only solve the nonlinear problem of power amplifier, but also can select different non-linearity inverse model according to different input signal and power amplifier characteristic, and increase whole efficiency of base station transmitter.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Class E amplifier with inductive clamp
InactiveUS20060158911A1Adjustable powerHigh frequency amplifiersEmergency protective circuit arrangementsEngineeringSignal source
A power supply including an inverter receiving a DC input signal from a DC input source (11). The inverter is implemented as a single-ended inverter. Each inverter is driven by a signal source (13A, 13B), which outputs an AC signal. The output from each inverter is input to a first stage harmonic filter. The power supply includes an output circuit that includes a rectifier (D1) arranged about a point so that if the inverter attempts to drive the point beyond a predetermined voltage, the rectifier conducts in order to return at least one of power and current to the DC input source. The output from the first harmonic filter (L1A, C1; L1B, C1) is output to a second harmonic filter (L2, C2) and is then output from the power supply.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
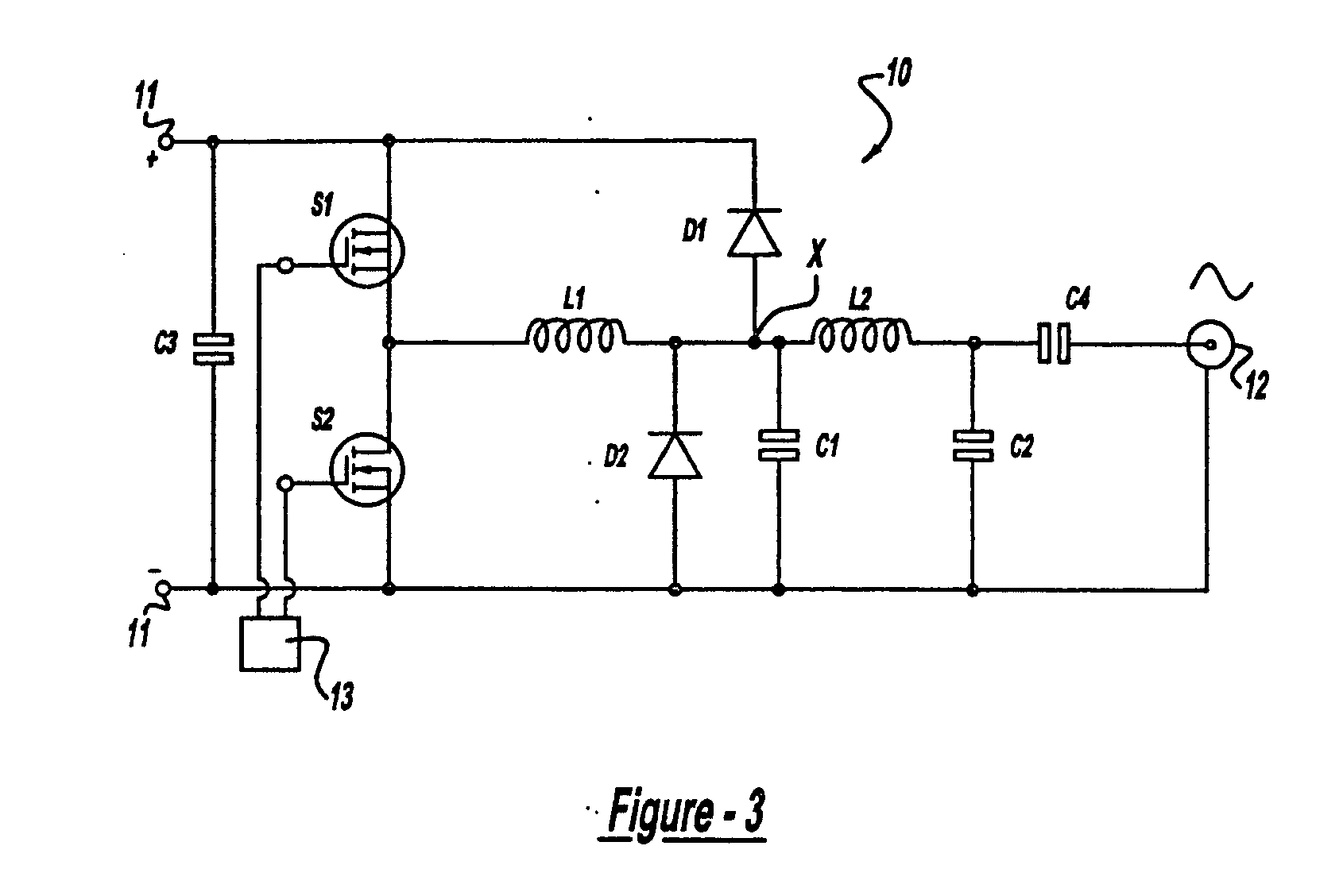
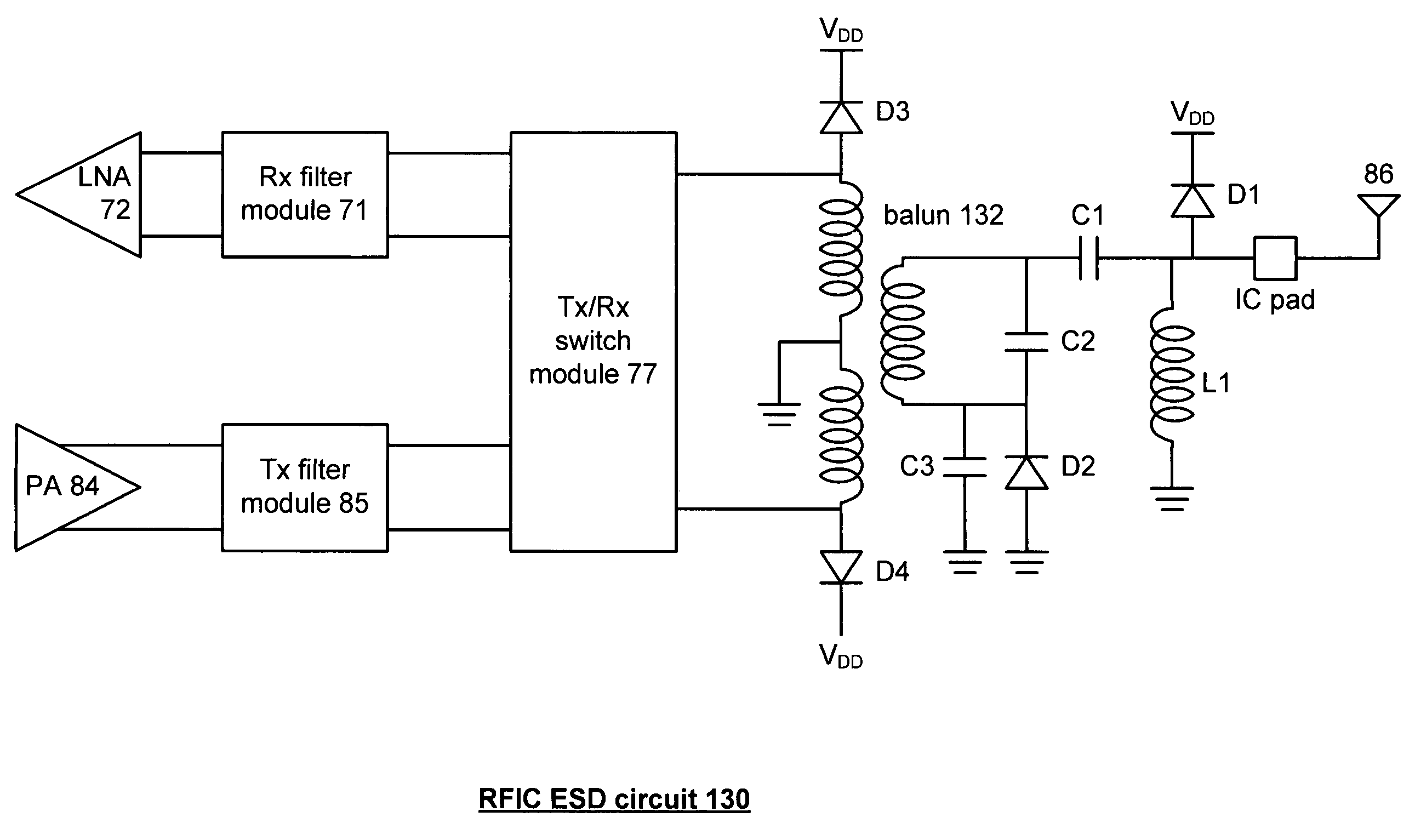
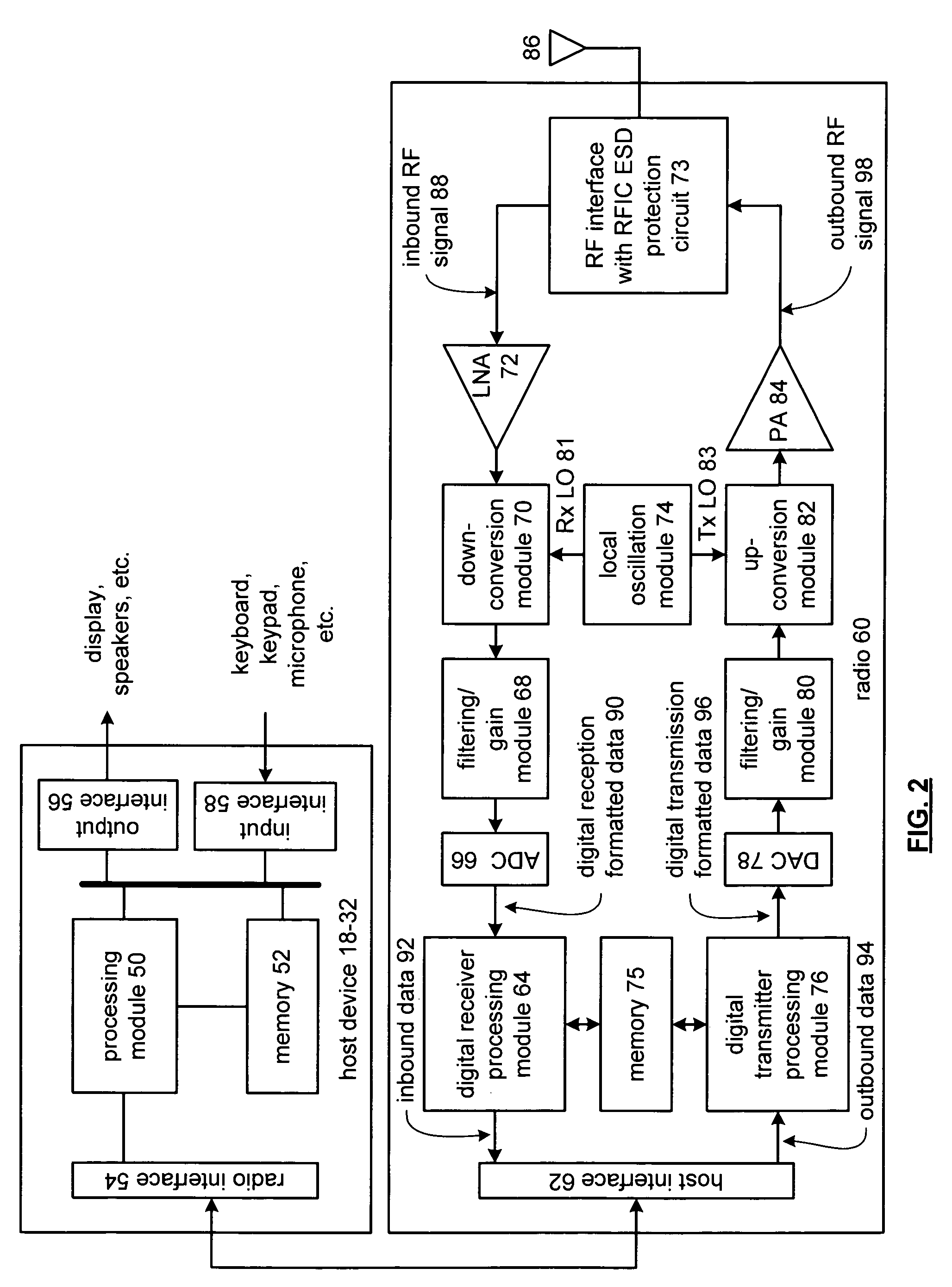
Radio frequency integrated circuit electo-static discharge circuit
The radio frequency integrated circuit (RFIC) electrostatic discharge (ESD) circuit includes an integrated circuit pin and a radio frequency (RF) ESD circuit. The integrated circuit pin provides coupling to an antenna. The RF ESD circuit is operably coupled to the integrated circuit pin, wherein the RF ESD circuit provides ESD protection at the integrated circuit pin, provides coupling of inbound RF signals from the antenna to low noise amplifier, and provides coupling of outbound RF signals from a power amplifier to the antenna.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
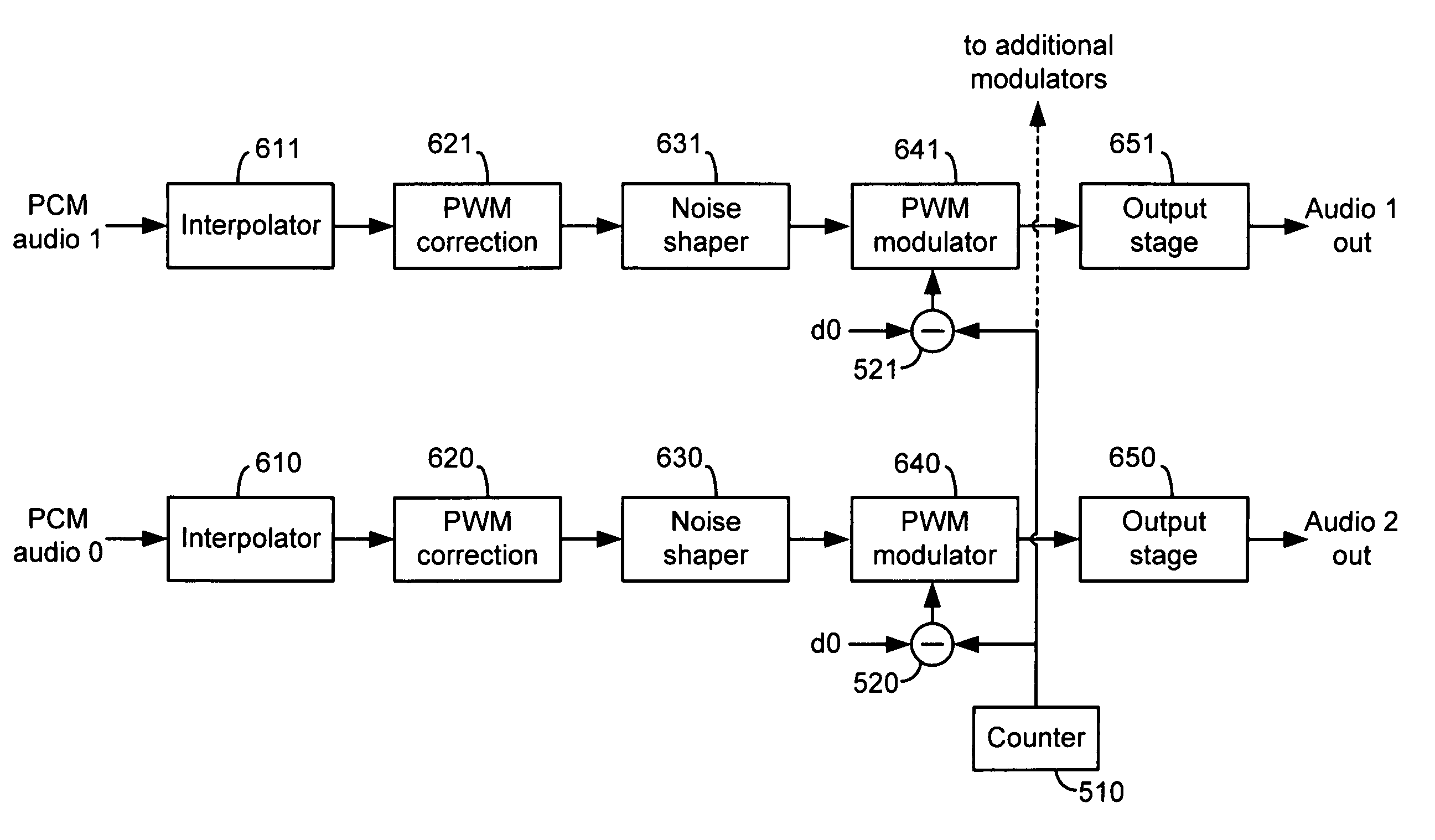
Systems and methods for providing multi channel pulse width modulated audio with staggered outputs
InactiveUS7061312B2Reduce noise levelEffectively reducing noise levelDigital technique networkAmplifier combinationsTotal delayNoise level
Systems and methods for reducing the noise level in a multi-channel digital audio system by staggering the timing of the pulse-width modulation in the different channels and thereby reducing the magnitude and increasing the frequency characteristics of the generated switching noise. One embodiment comprises a multi-channel digital PWM amplifier in which the timing signals used by each channel's modulator are staggered to evenly space the switching edges of the generated PWM signals. An additional, complementary delay is implemented in each of the channels to equalize the total delay for each channel so that the outputs of the channels are synchronized. The different channels may be implemented on different chips, in which case the chips may be synchronized prior to staggering the signals processed in each of the channels.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Digitally Controlled AC Protection and Attenuation Circuit
A protection and attenuation circuit for sensitive AC loads is described. The circuit provides AC power protection and attenuation utilizing high-efficiency switch-mode techniques to attenuate an AC power signal by incorporating a bidirectional, transistorized switch driven from a pulse width modulation signal, PWM. The circuit monitors characteristics of the AC power signal driving a known load and characteristics of the load or other elements and determines the duty cycle of the pulse width modulated signal, PWM, based upon the duration and amplitude of the over-voltage, over-current, over-limit or other event.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Popular searches
Amplifiers wit coupling networks Amplification control details Amplifier protection circuit arrangements Waveguide type devices Low noise amplifier Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influence Material analysis by optical means Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing Photoelectric discharge tubes Amplifiers controlled by light
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com