Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2610 results about "Noise level" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
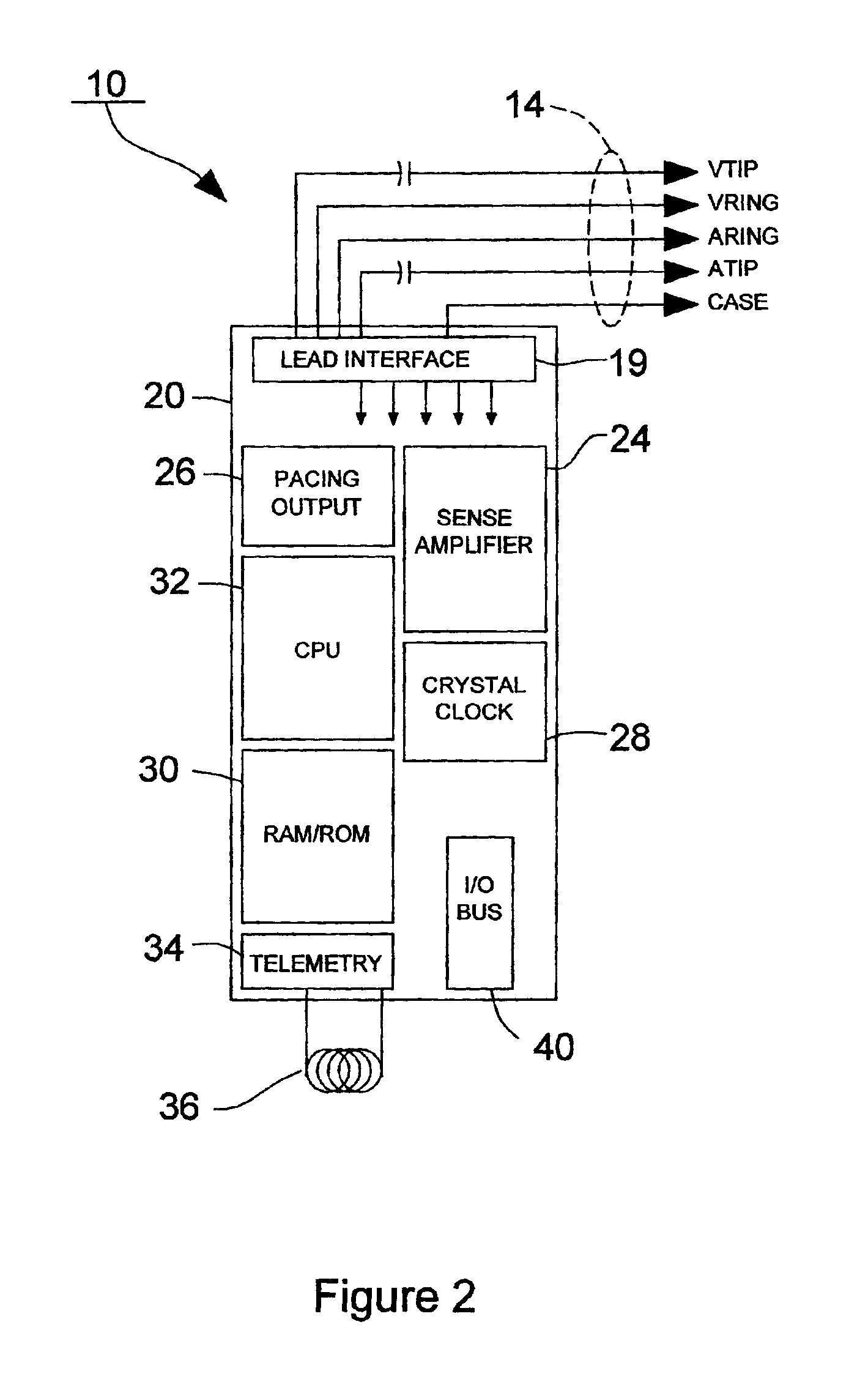
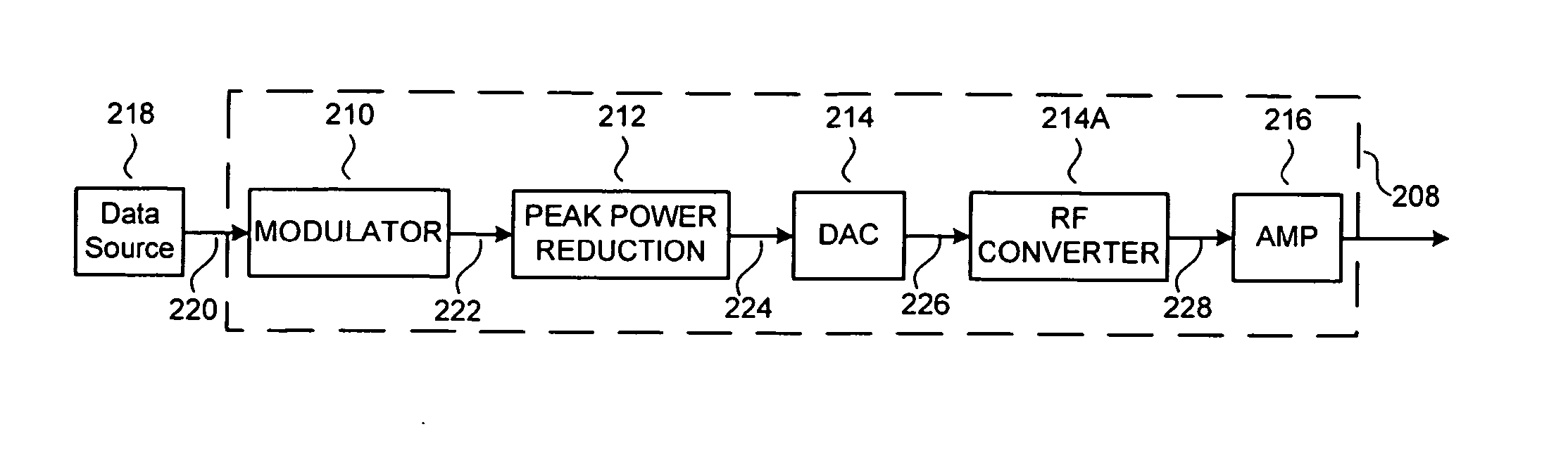
Implanted medical device telemetry using integrated thin film bulk acoustic resonator filtering
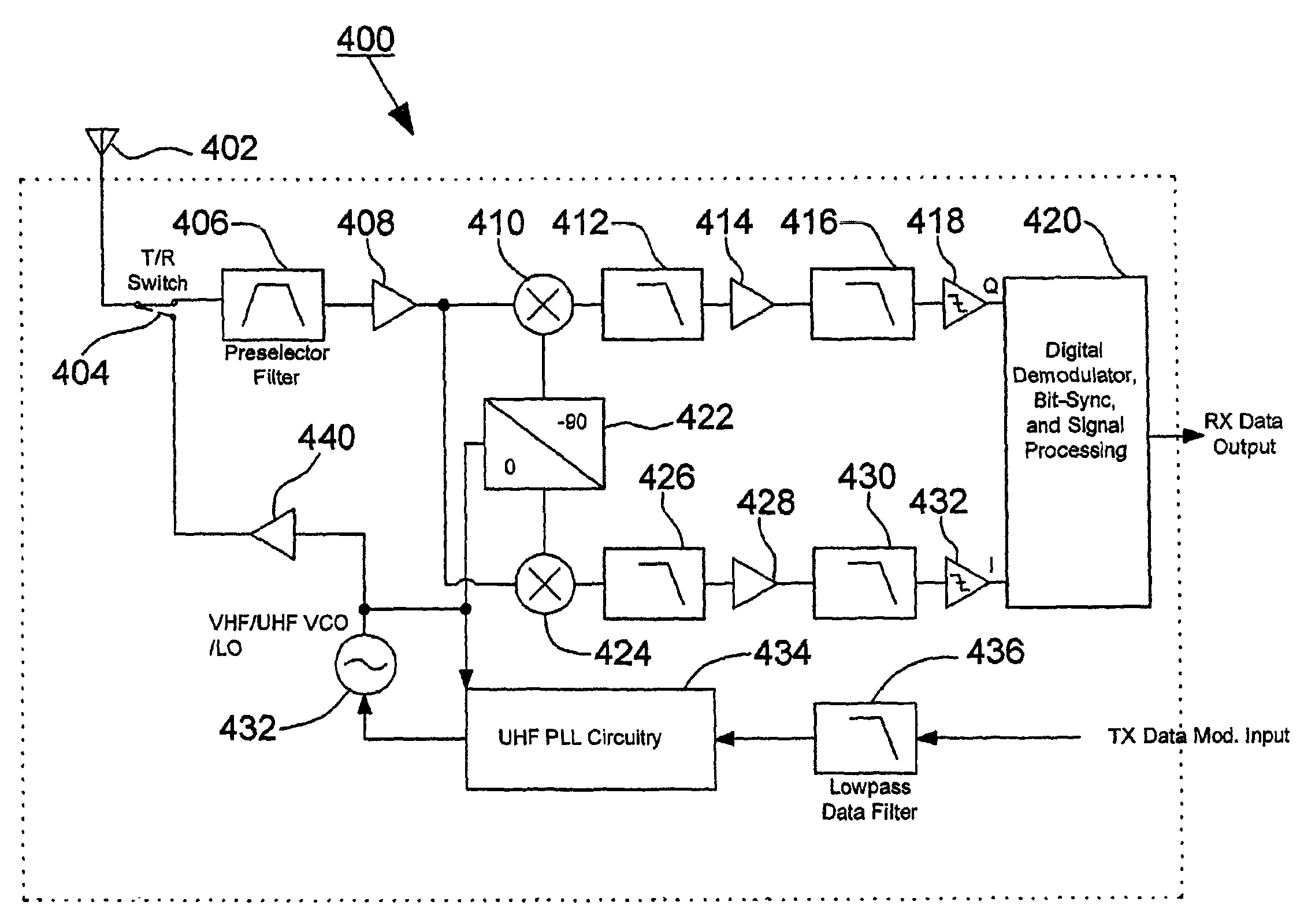
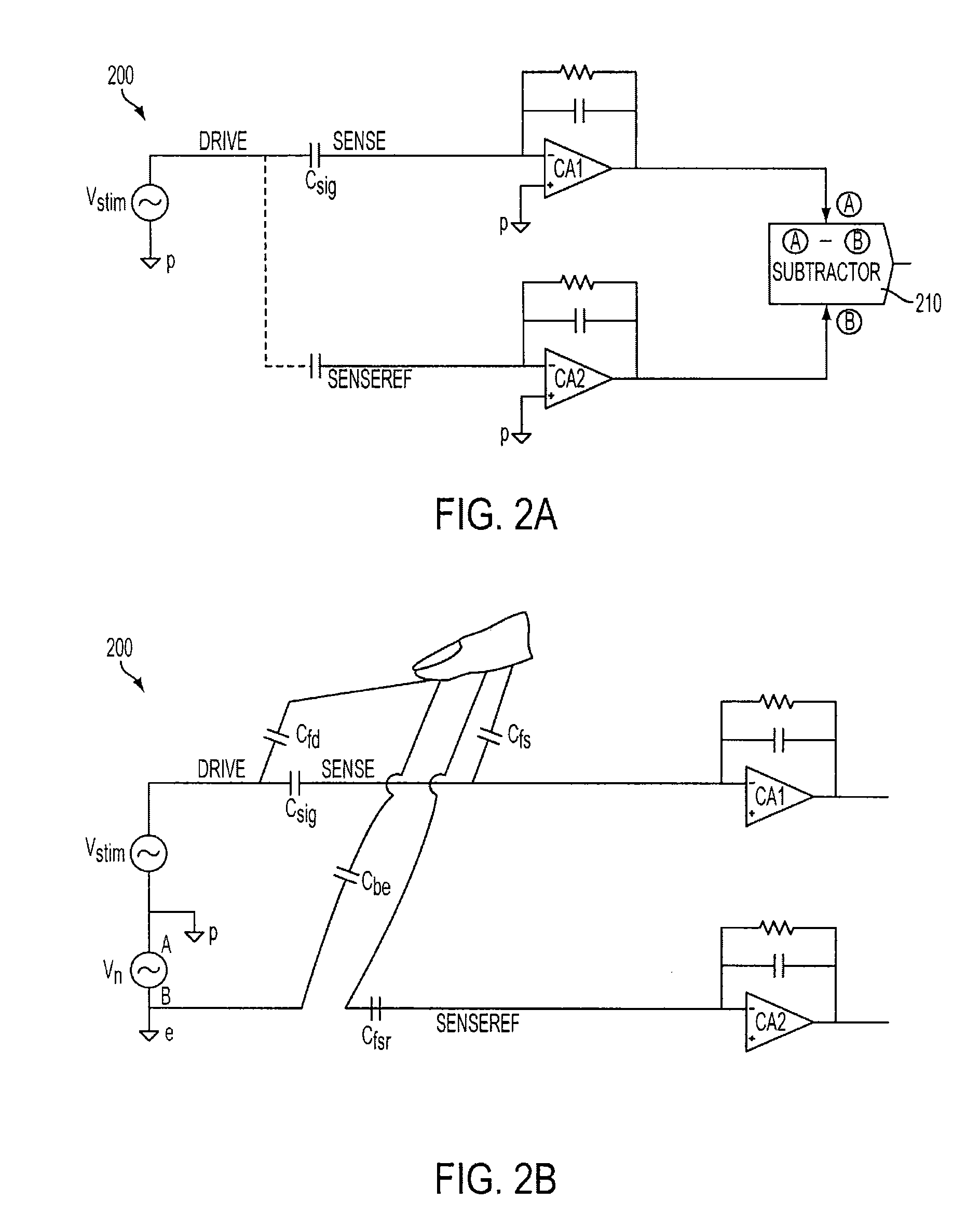
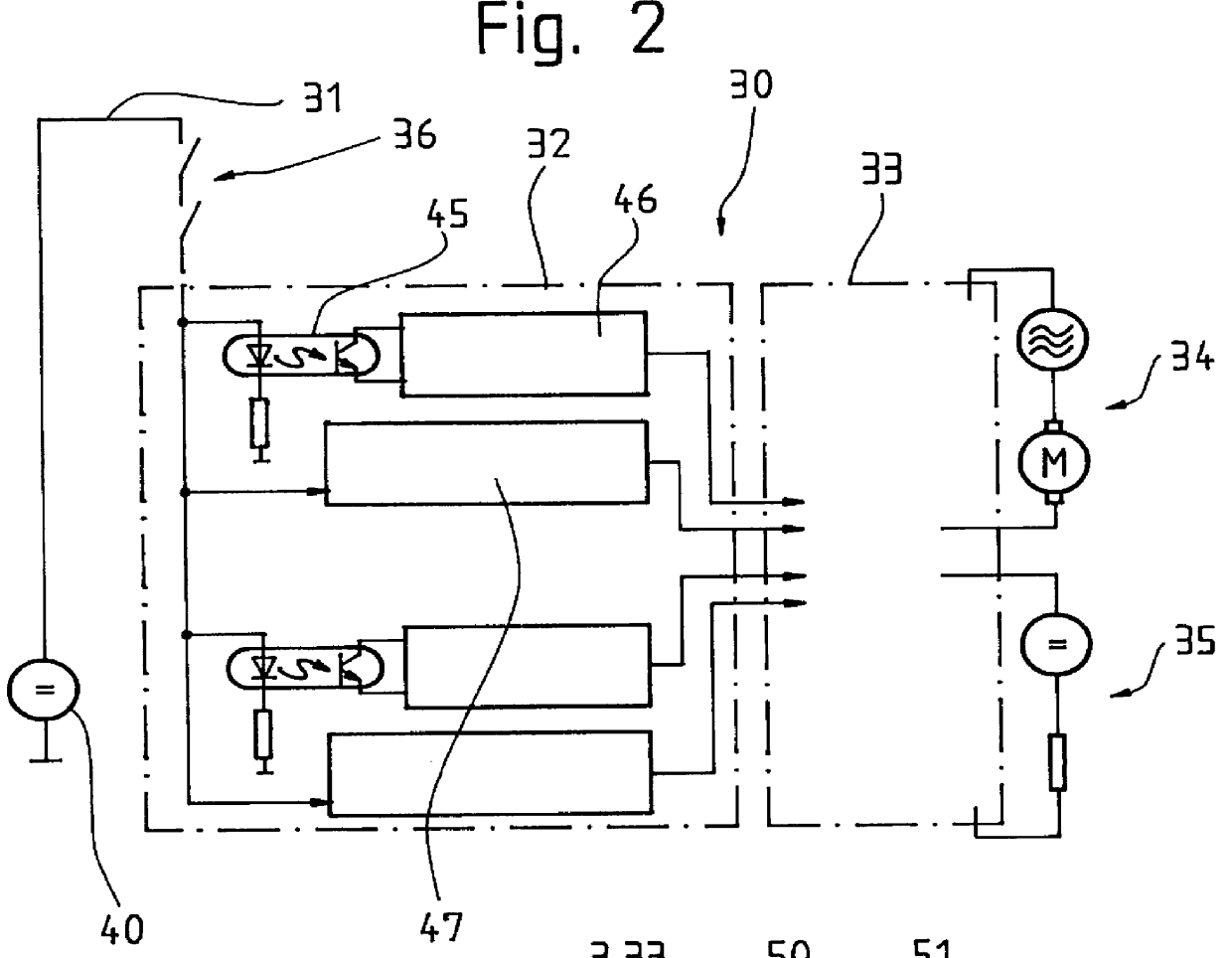
A telemetry receiver for an implantable medical device (IMD) such as a cardiac pacemaker has an RF antenna coupled to a telemetry circuit that includes an out-of-band rejection filter comprising a thin film bulk acoustic resonator filter. The telemetry circuit includes an amplifier coupled to the thin film bulk acoustic resonator filter and a demodulator coupled to the amplifier. The filter, amplifier and demodulator are all fabricated on a common integrated circuit die. A multichannel telemetry receiver for an IMD has a plurality of thin film bulk acoustic resonator bandpass filters defining individual channels. Identification of a preferred data transmission channel for communication of programming data to the IMD is determined by obtaining samples of the signals being passed by each of a plurality of thin film bulk acoustic resonator bandpass filters that define individual channels and evaluating the samples to determine the noise level for each channel.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
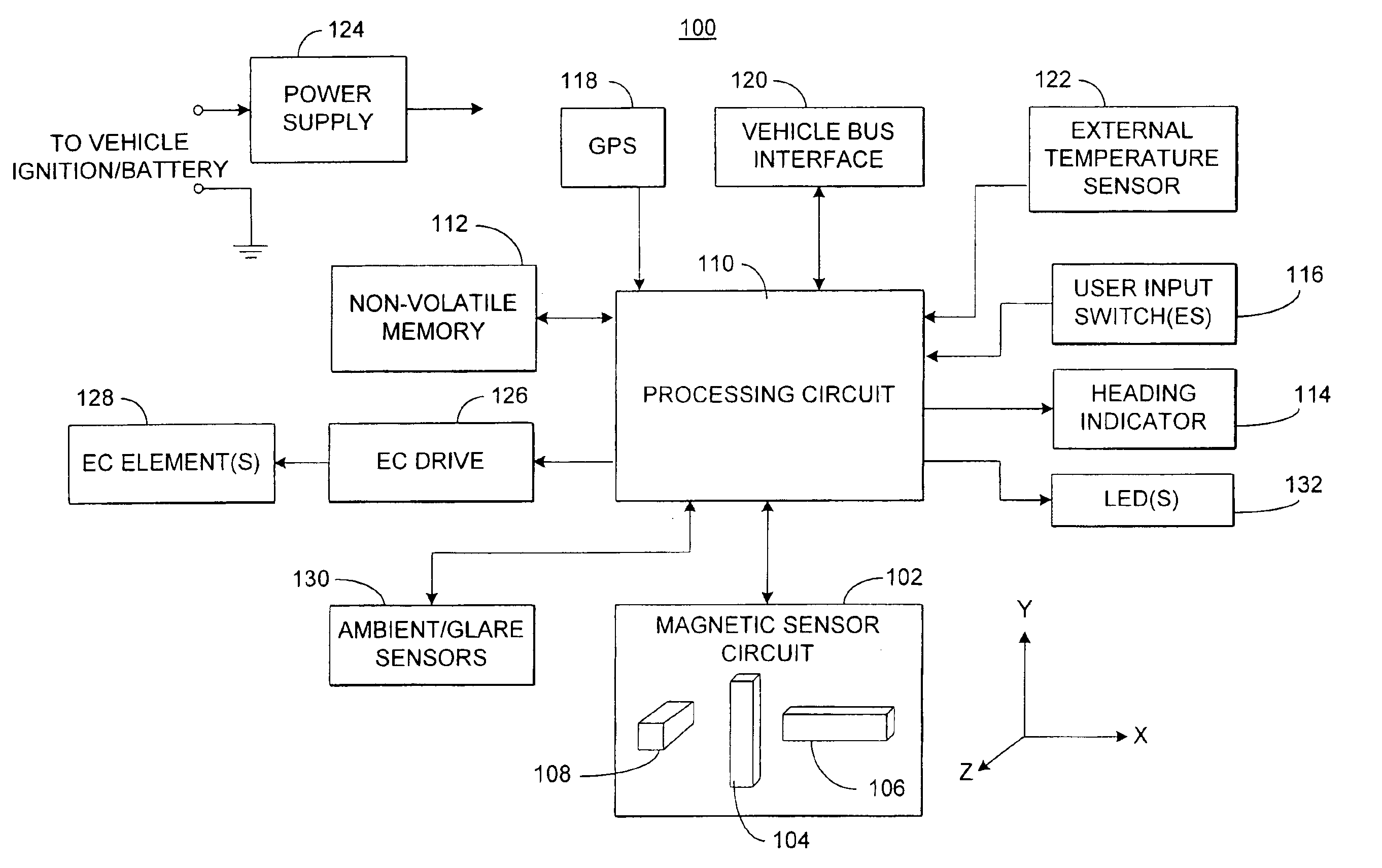
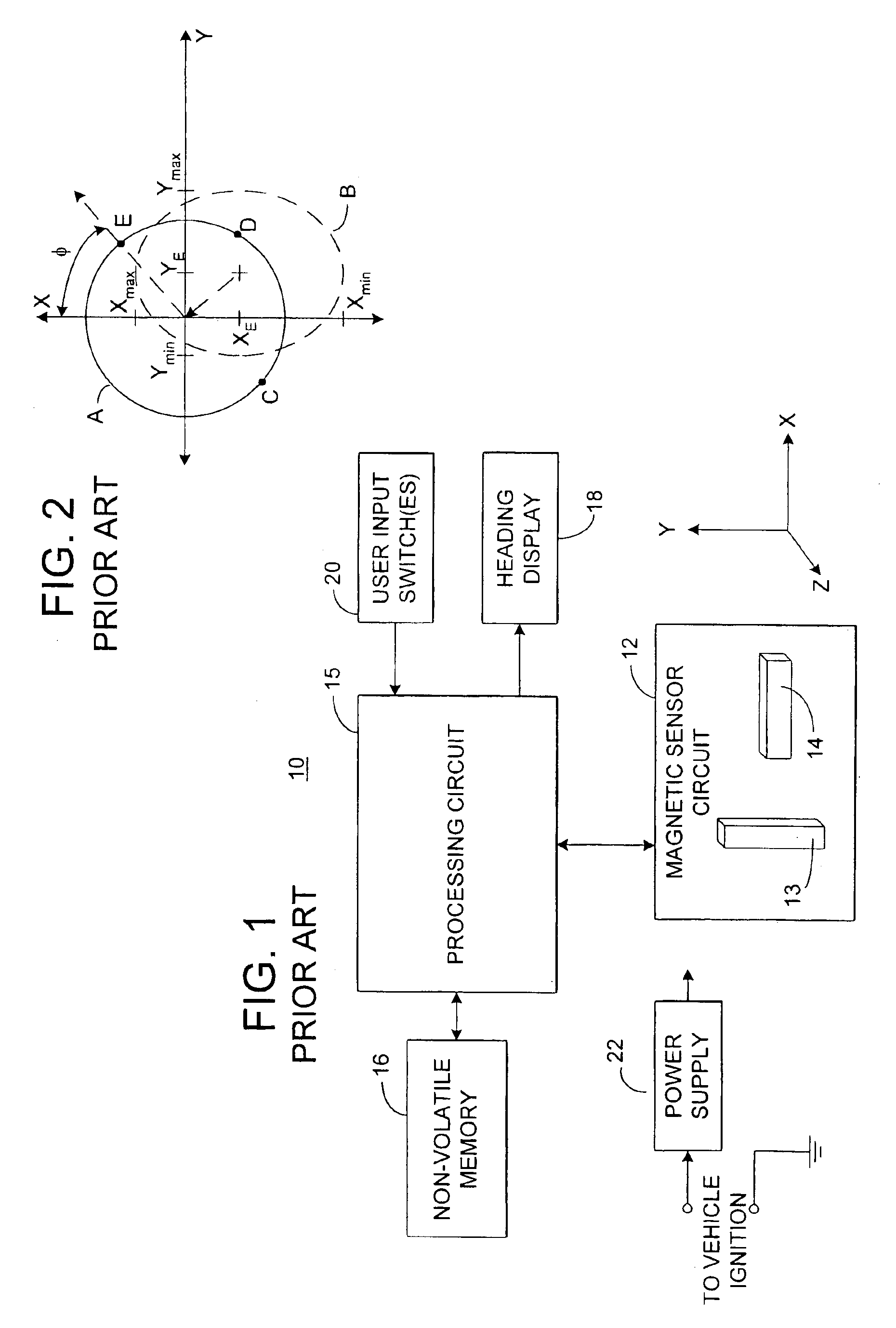
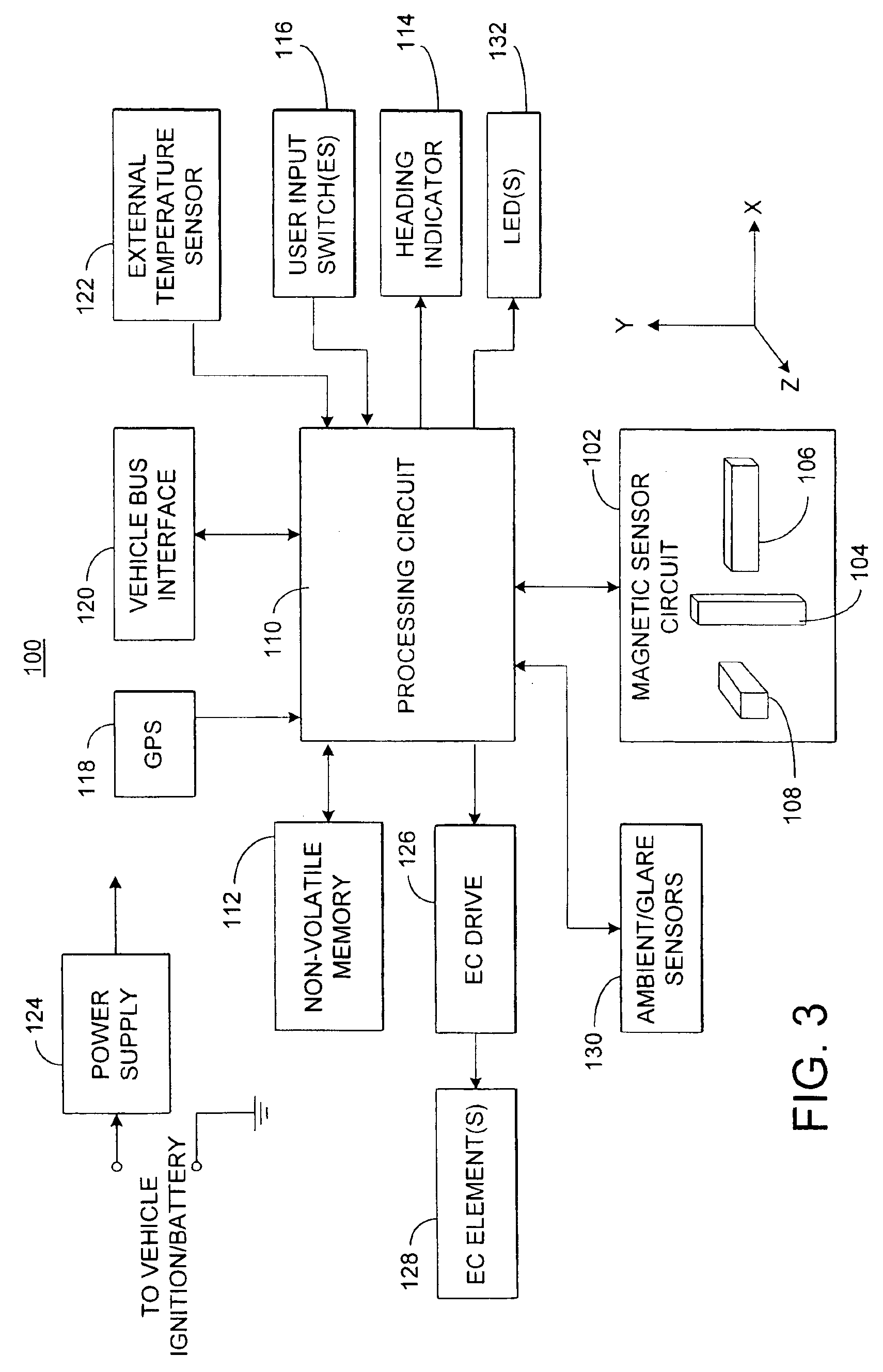
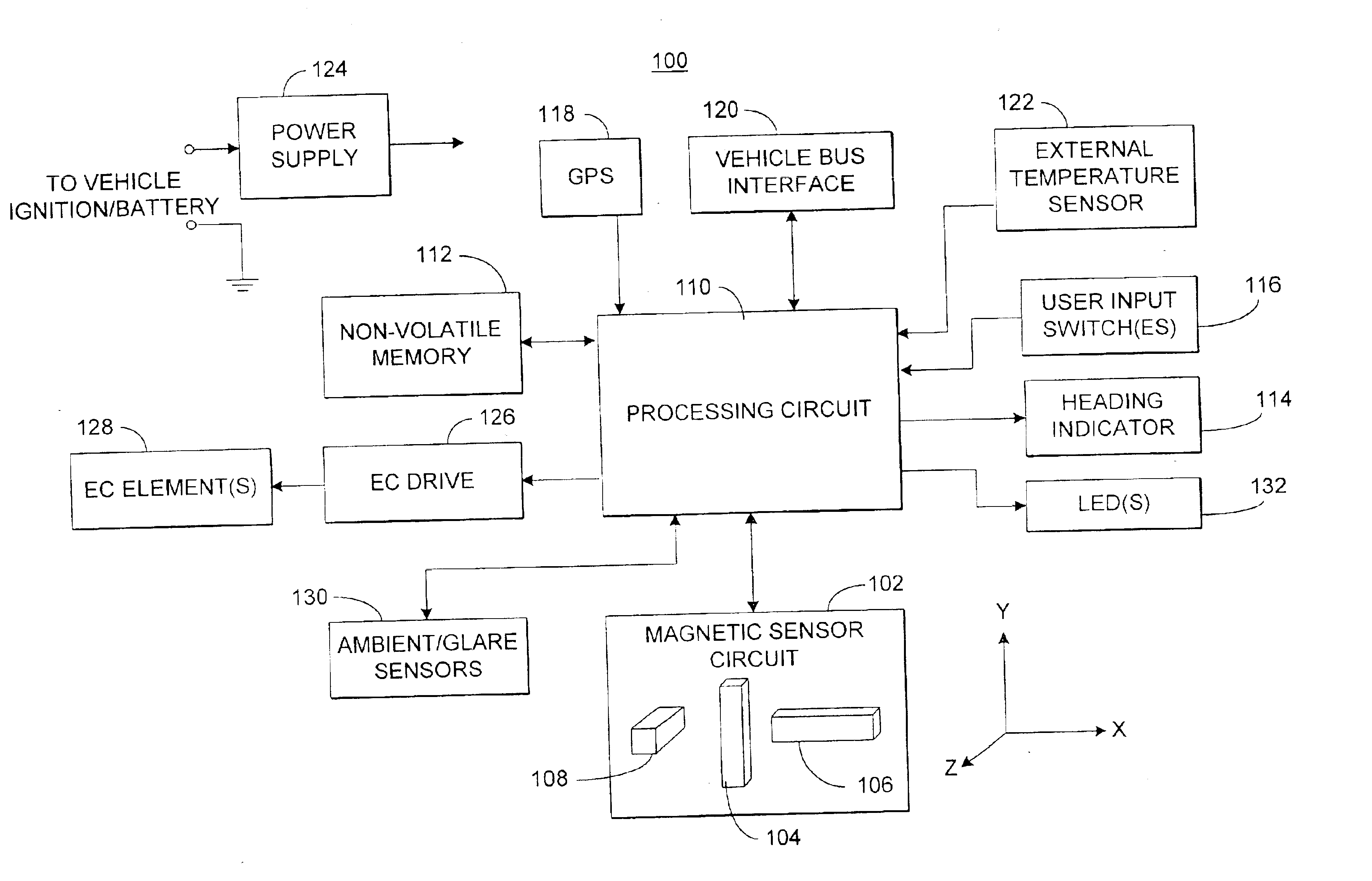
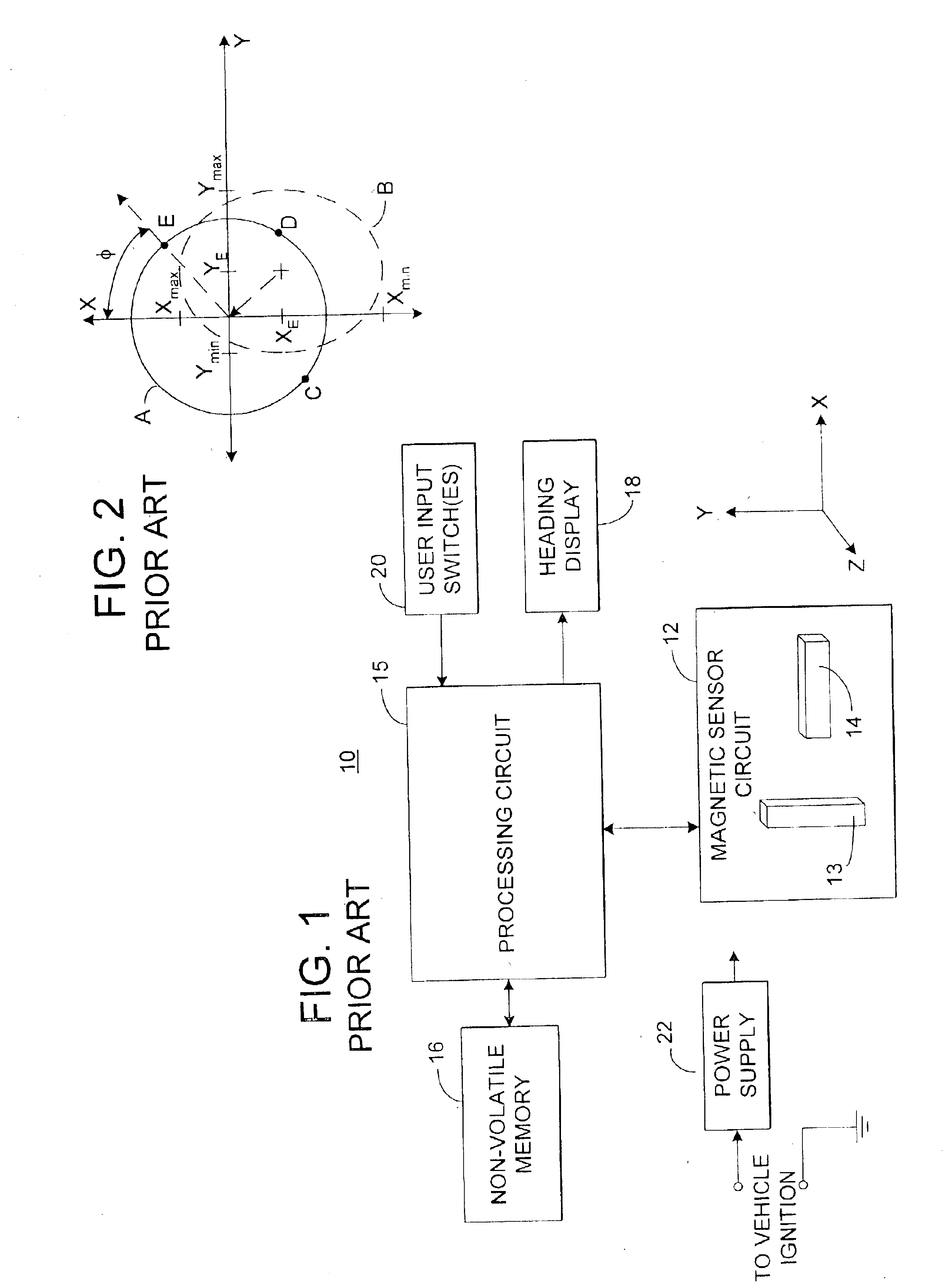
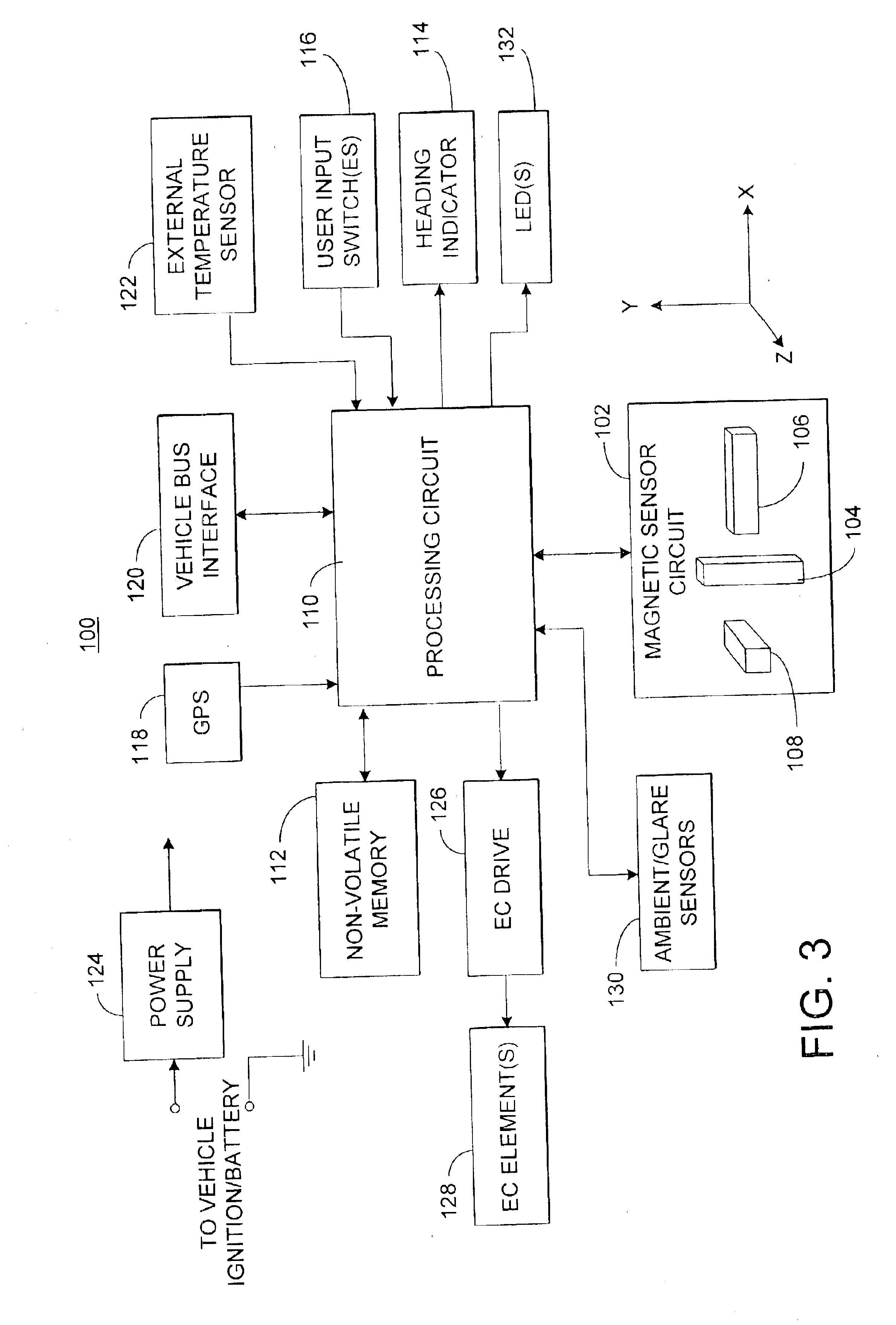
Electronic compass system
An electronic compass system includes a magnetic sensor circuit having at least two sensing elements for sensing perpendicular components of the Earth's magnetic field vector. A processing circuit is coupled to the sensor circuit to filter, process, and compute a heading. The processing circuit further selects an approximating geometric pattern, such as a sphere, ellipsoid, ellipse, or circle, determines an error metric of the data points relative to the approximating pattern, adjusts the pattern to minimize the error, thereby obtaining a best fit pattern. The best fit pattern is then used to calculate the heading for each successive sensor reading provided that the noise level is not noisy and until a new best fit pattern is identified. The electronic compass system is particularly well suited for implementation in a vehicle rearview mirror assembly.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Electronic compass system
An electronic compass system includes a magnetic sensor circuit having at least two sensing elements for sensing perpendicular components of the Earth's magnetic field vector. A processing circuit is coupled to the sensor circuit to filter, process, and compute a heading. The processing circuit further selects an approximating geometric pattern, such as a sphere, ellipsoid, ellipse, or circle, determines an error metric of the data points relative to the approximating pattern, adjusts the pattern to minimize the error, thereby obtaining a best fit pattern. The best fit pattern is then used to calculate the heading for each successive sensor reading provided that the noise level is not noisy and until a new best fit pattern is identified. The electronic compass system is particularly well suited for implementation in a vehicle rearview mirror assembly.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
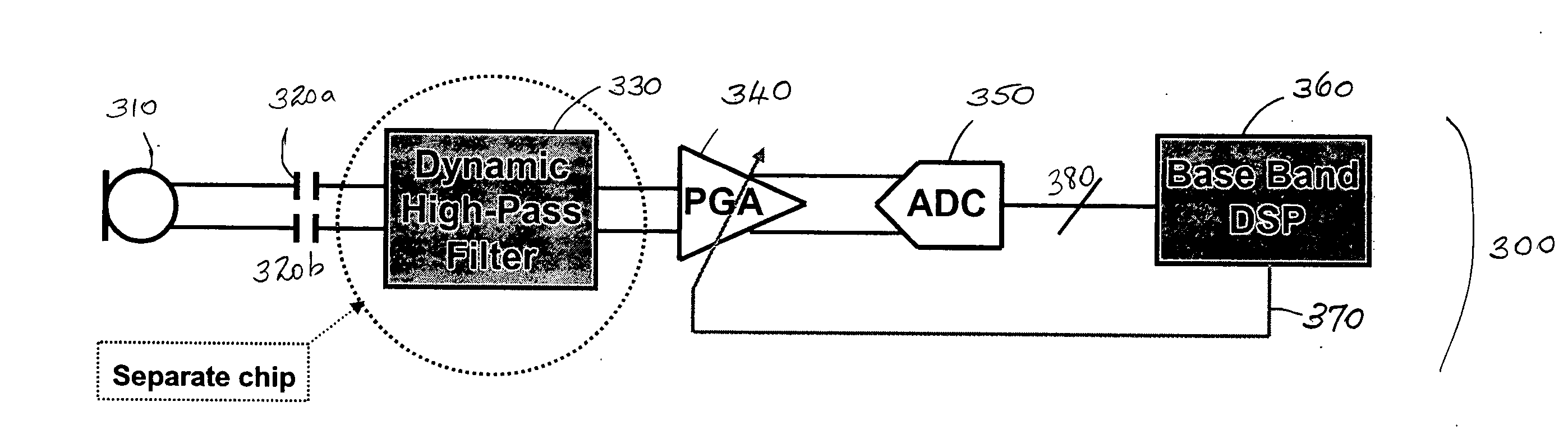
Low frequency noise reduction circuit architecture for communications applications
ActiveUS20080069373A1Economical yet effective high-pass filterAchieve adaptiveFrequency response correctionTransmission noise suppressionCapacitanceLow noise
A noise reduction circuit for reducing the effects of low frequency noise such as wind noise in communications applications is described. In one embodiment, the noise reduction circuit features a high pass filter formed by exploiting the existing off-chip AC coupling capacitances in making the connection to the source of audio signals. The filter may be adaptive to environmental low frequency noise level through programming the shunt resistances. A low-noise wide dynamic range programmable gain amplifier is also described. Adaptive equalization of the audio signal is also described through the utilization of programmable front-end resistors and a back-end audio equalizer.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
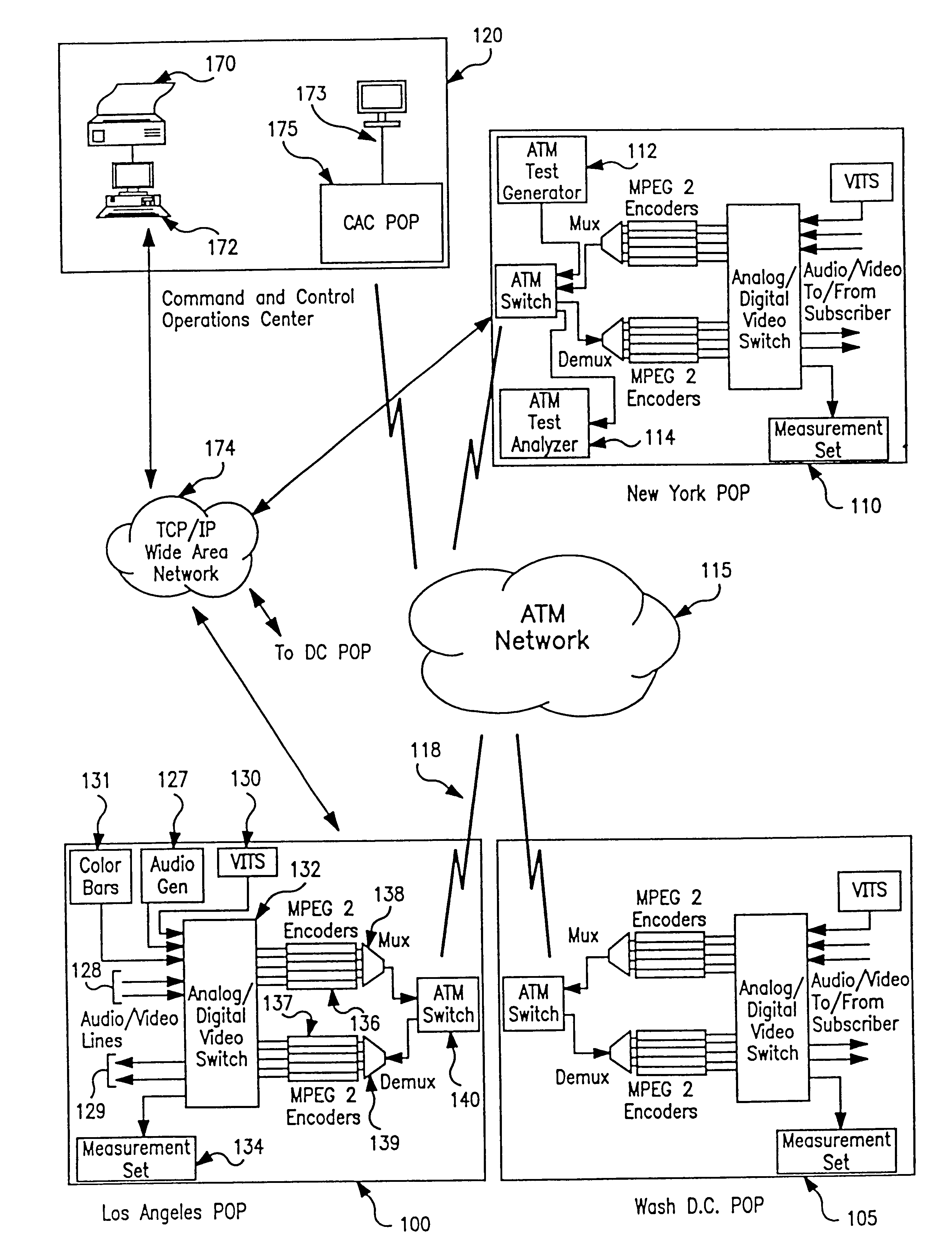
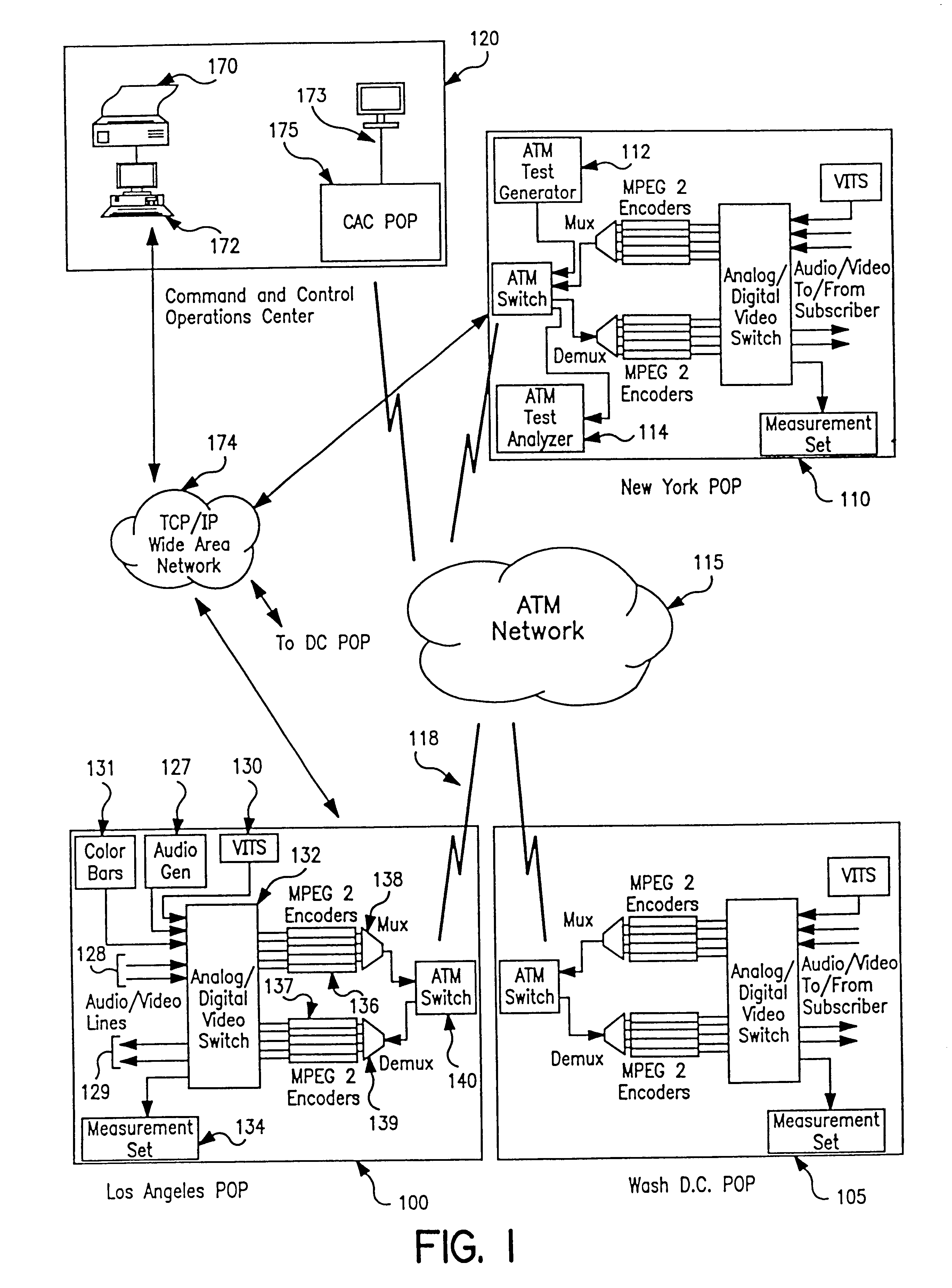
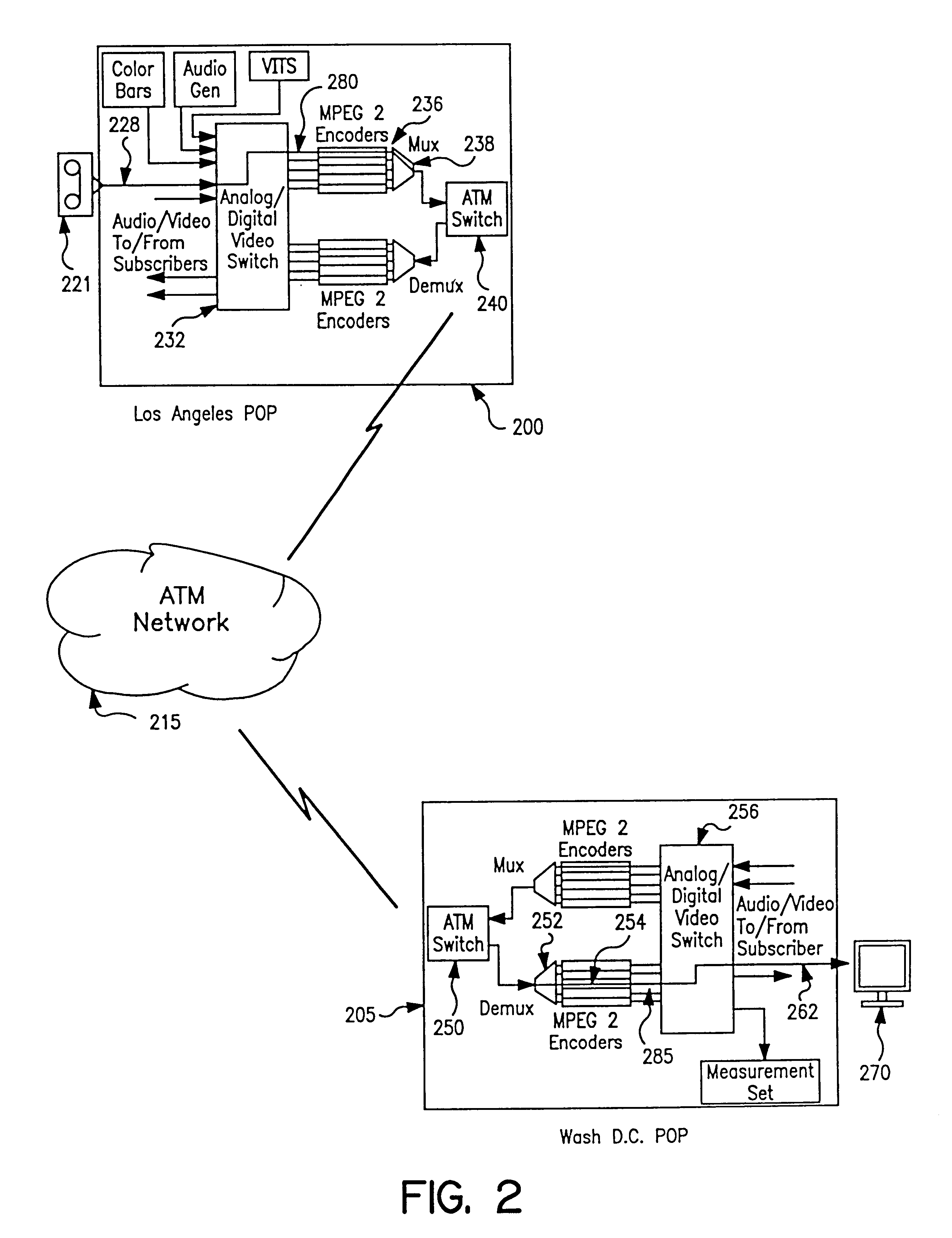
Apparatus and method of in-service audio/video synchronization testing
InactiveUS6414960B1Easy to testTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationVideo-signal generatorNoise level
An apparatus and method provide non-intrusive in-service testing of audio / video synchronization testing without using traditional audio marker tones. The network includes an A / V synchronous test signal generator which injects video and audio markers into the video and audio non-intrusively and routes the two signals into a switch where they are switched into a channel for encoding and transmission via the ATM network. At the distant end the signal is decoded and routed by a switch into the A / V test generator and measurement set where the markers are detected and the A / V skew calculated, after which the audio and video are routed to the subscriber. The A / V test set signal generator includes a Video Blanking Interval (VBI) test signal generator and a white noise generator, the former injecting a marker into the video signal and the later injecting an audio marker into the audio signal. The video marker is injected into the VBI and broadband, background audio noise to measure the delay between the audio and video components of a broadcast. The marking of the audio is accomplished by gradually injecting white noise into the audio channel until the noise level is 6 dB above the noise floor of the audio receiver. As a precursor A / V sync signal, a small spectrum of the white noise is notched or removed. This signature precludes inadvertent recognition of program audio noise as the audio marker.
Owner:IBM CORP
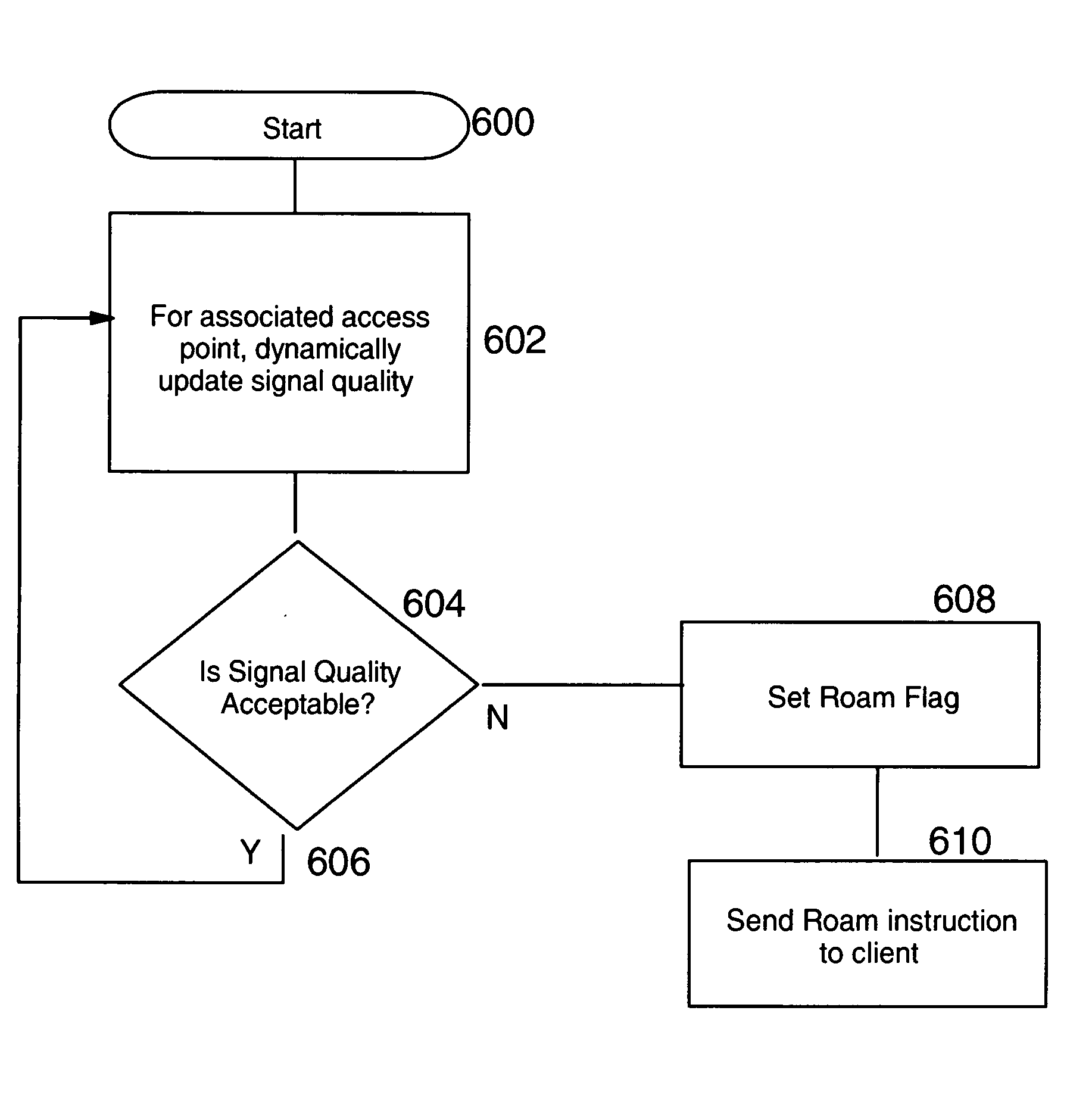
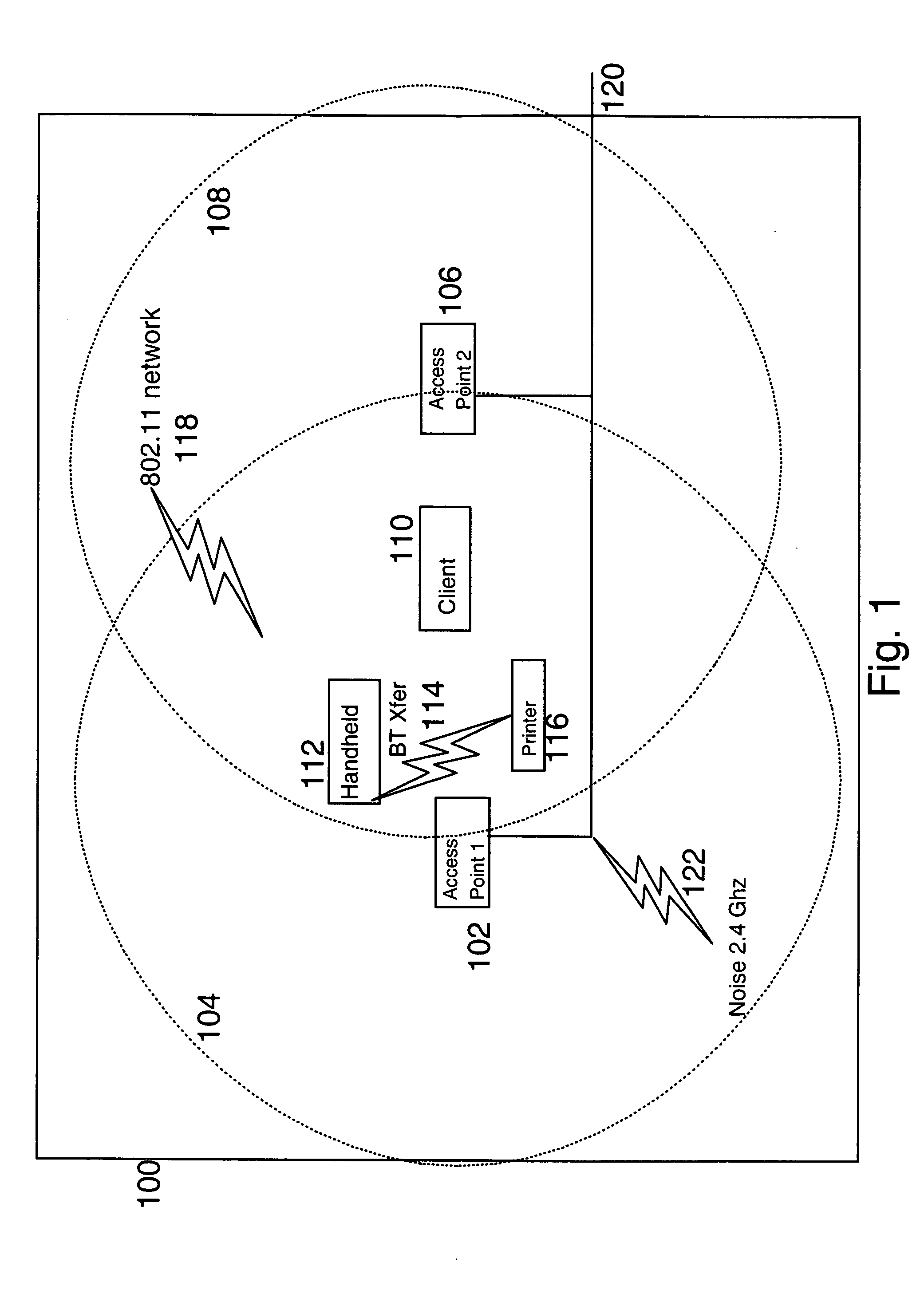
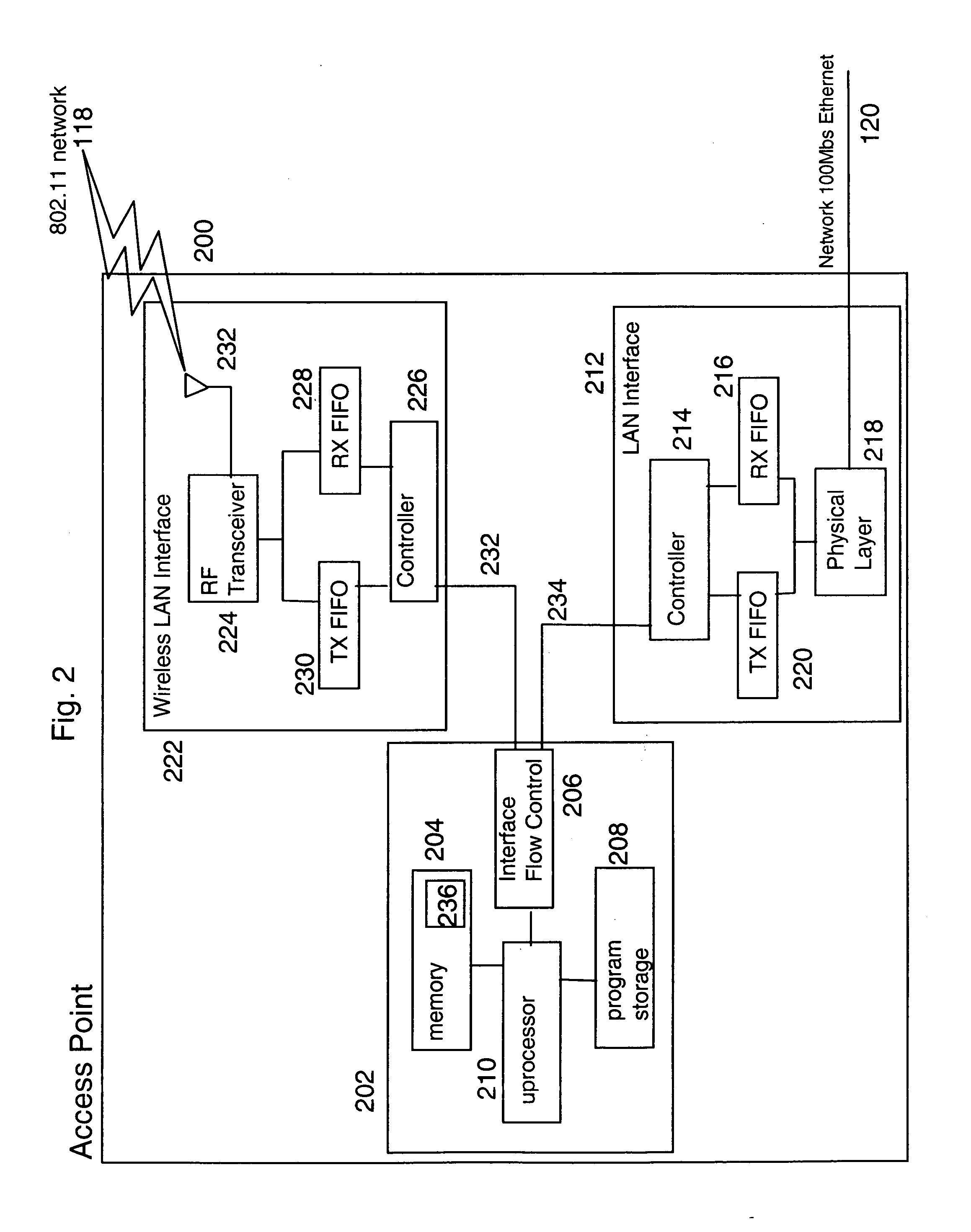
Forced roaming to avoid interference
ActiveUS20060025127A1Minimize impactInterference minimizationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesTelecommunicationsNoise level
In a wireless network in which a client has access to multiple Access Points the client usually attaches to one of the Access Points (AP) and stays attached even though signal transmission is impaired, whereas transmission would not be impaired if the client attaches to another one of the multiple APs. Apparatus and method are described to detect interference noise level and force the client to roam and attach to another AP if interference noise level impairs signal transmission.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
Enhancing audio using a mobile device
ActiveUS20160035337A1Gain controlVolume compression/expansion in untuned/low-frequency amplifiersNoise levelSound quality
Embodiments disclosed herein enable detection and improvement of the quality of the audio signal using a mobile device by determining the loss in the audio signal and enhancing audio by streaming the remainder portion of audio. Embodiments disclosed herein enable an improvement in the sound quality rendered by rendering devices by emitting an test audio signal from the source device, measuring the test audio signal using microphones, detecting variation in the frequency response, loudness and timing characteristics using impulse responses and correcting for them. Embodiments disclosed herein also compensate for the noise in the acoustic space by determining the reverberation and ambient noise levels and their frequency characteristics and changing the digital filters and volumes of the source signal to compensate for the varying noise levels.
Owner:CAAVO INC
Radio frequency characterization of cable plant and corresponding calibration of communication equipment communicating via the cable plant
Owner:ADVENT NETWORKS +1
Display device
ActiveUS20100033443A1High detection sensitivityImprove reliabilityDigital data processing detailsCross-talk/noise/interference reductionCapacitanceNoise level
A display device having a highly reliable electrostatic capacitive type touch panel which allows finger touch inputting and possesses excellent detection sensitivity is provided. With respect to X electrodes and Y electrodes which are formed on an electrostatic capacitive type touch panel, either one of the X electrodes and the Y electrodes is divided corresponding to a ratio between the number of X electrodes and the number of Y electrodes, and a floating electrode is formed in gaps formed along with the reduction of area of the electrode thus adjusting the area of the electrode. Due to the contraction of the area of the individual electrode, a noise level can be lowered more compared to lowering of a signal level and hence, an S / N ratio can be increased thus enhancing the detection sensitivity. Further, a line is branched on a flexible printed circuit board, intersecting lines are formed on a back surface of the flexible printed circuit board, and the intersecting lines are arranged to orthogonally intersect with lines formed on a front surface of the flexible printed circuit board thus lowering line capacitance.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY INC +1
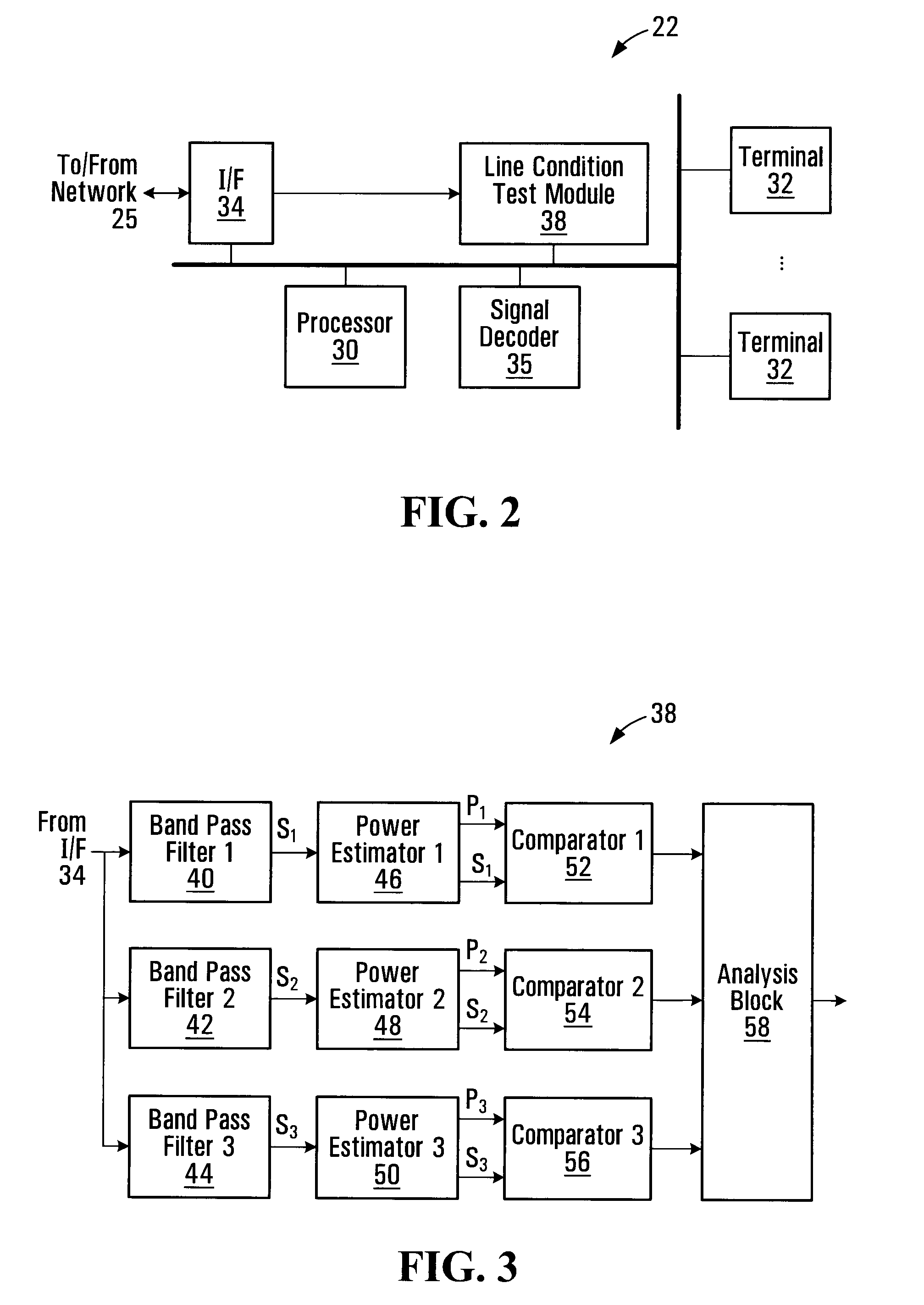
Alarm monitoring telecommunications line condition detection and automatic calibration
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TYCO IP HLDG LLP
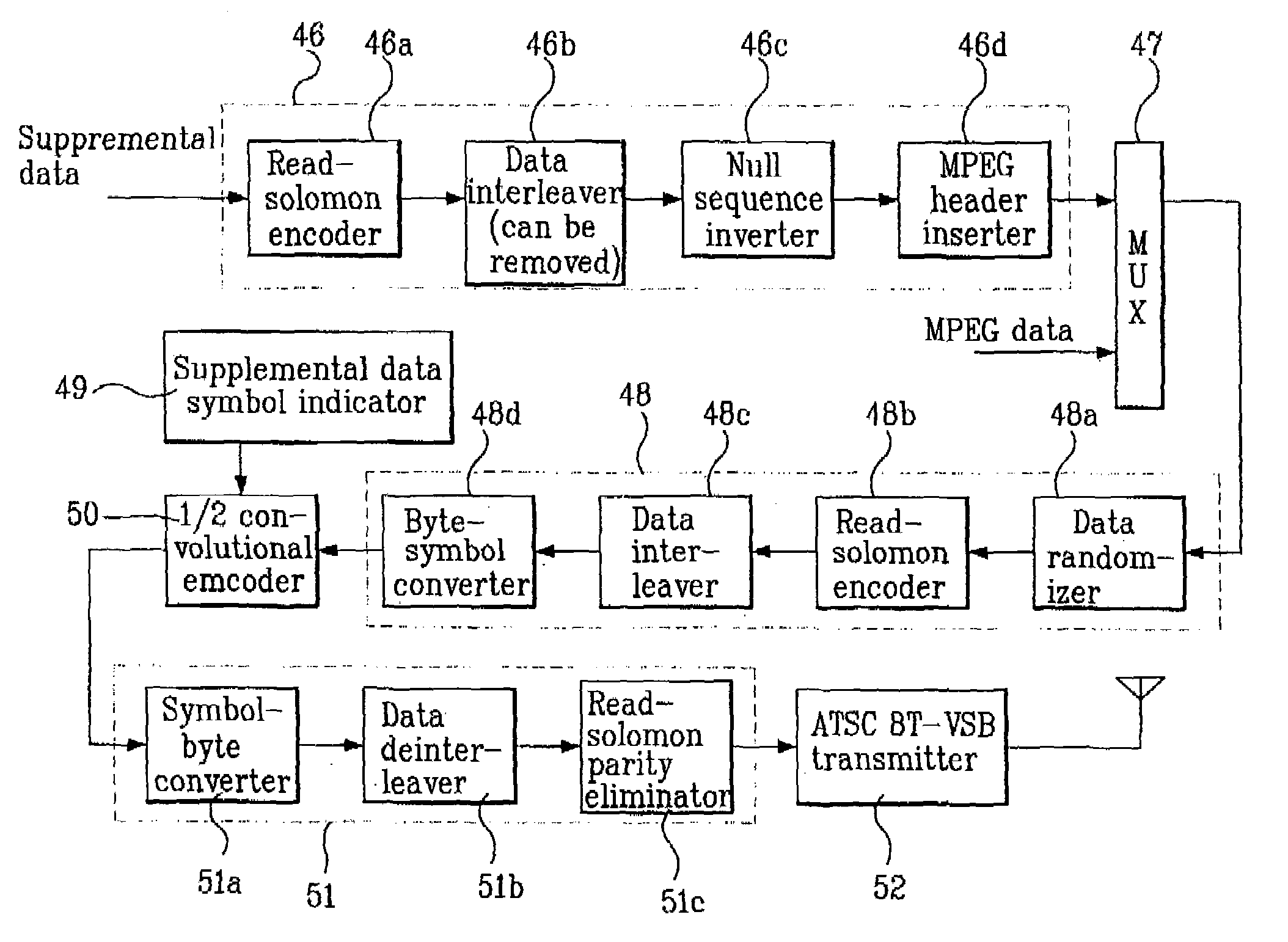
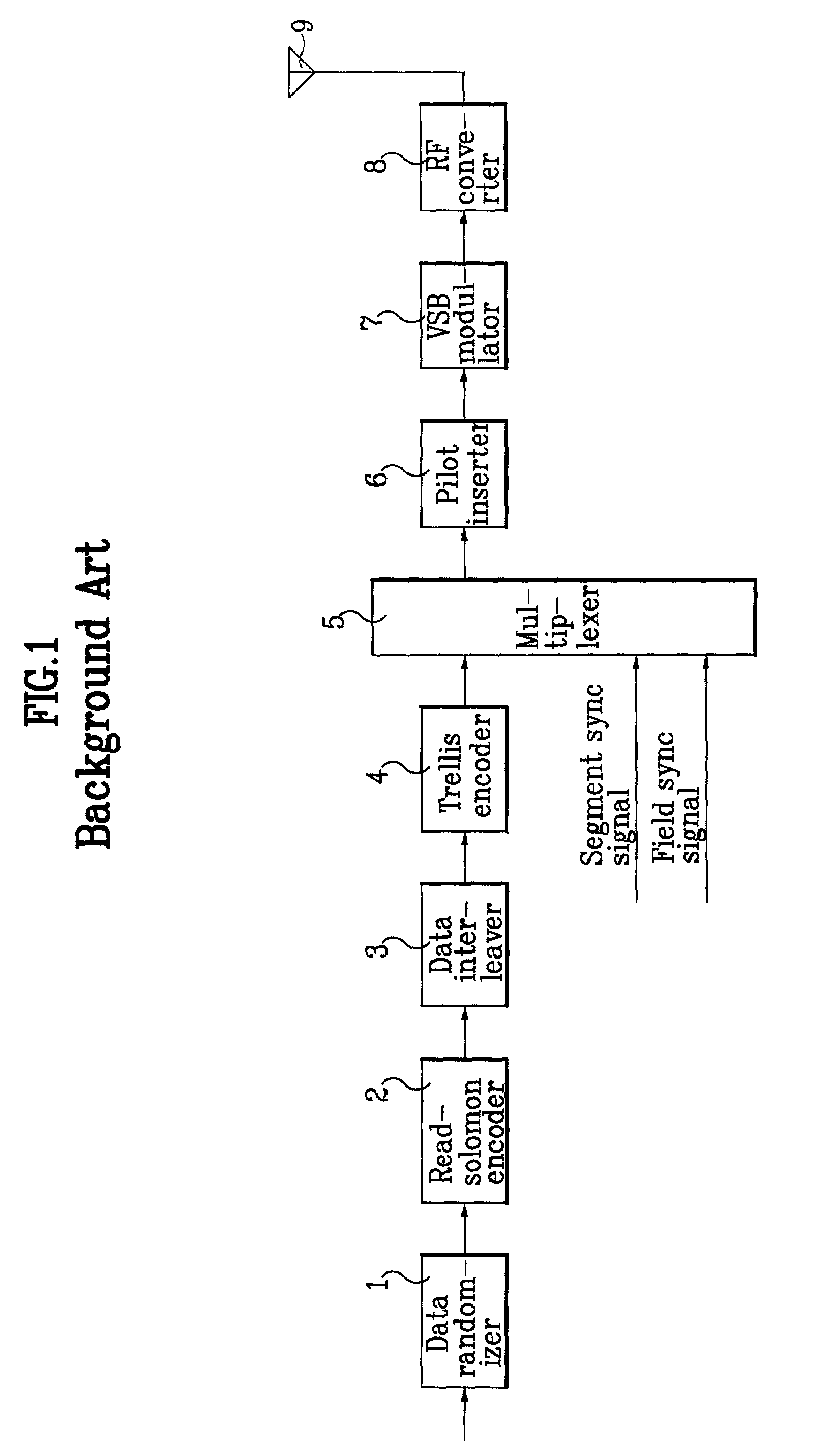
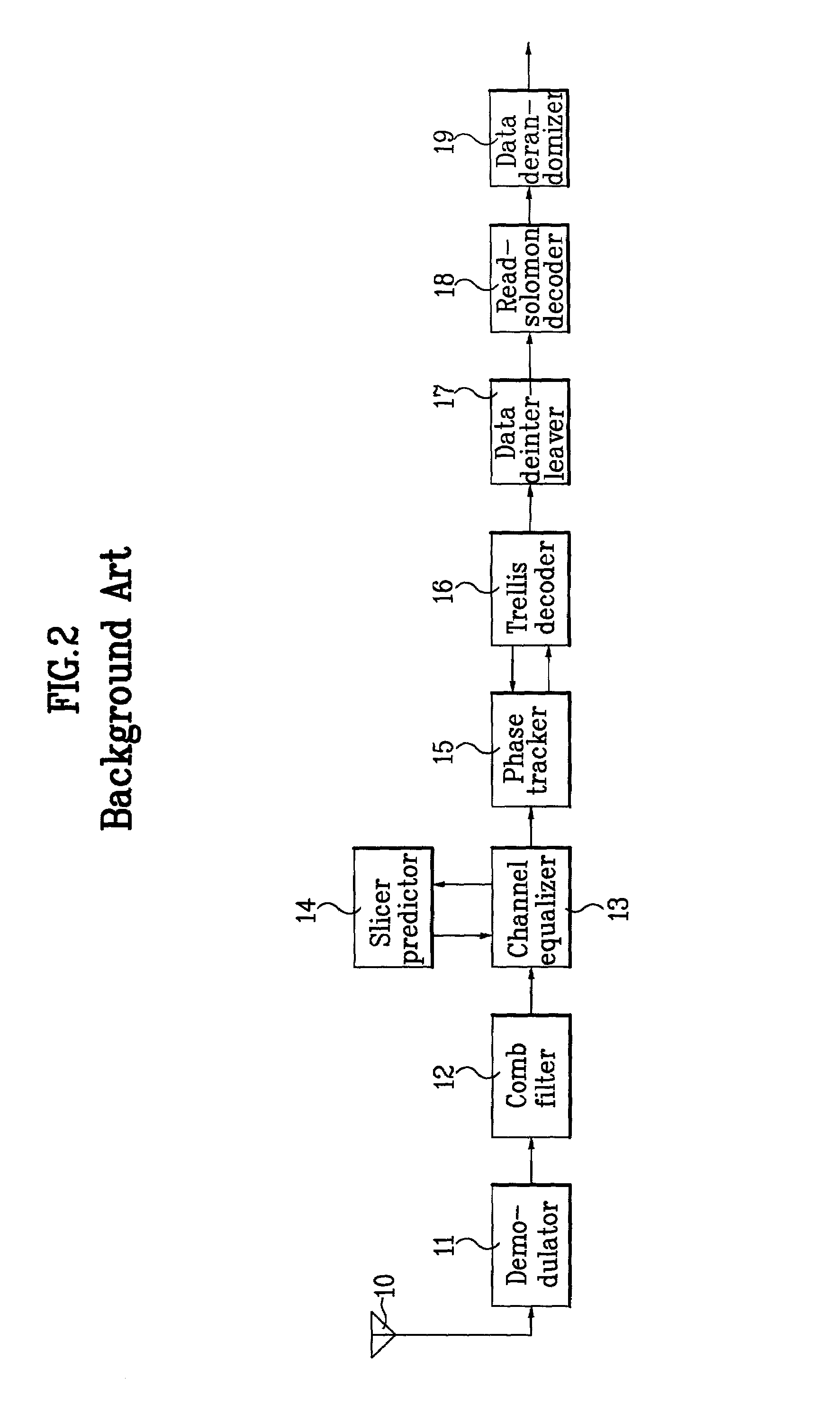
Digital VSB transmission system
InactiveUS6980603B2Noise robustData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionNoise levelComputer science
A digital VSB transmission system in disclosed. The system is compatible with the existing ATSC 8T-VSB receiver and able to transmit additional supplemental data as well as MPEG image / sound data. It initially encodes the information bit of the supplemental data with a ½ encoding rate in order to produce a parity bit and sends the parity bit together with the information bit. Therefore, both of the MPEG image / sound data and the supplemental data can be transmitted properly even through a channel having a high ghost and / or noise level. Particularly, it can significantly improve performances of the slicer predictor and trellis decoder of the VSB receiver.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
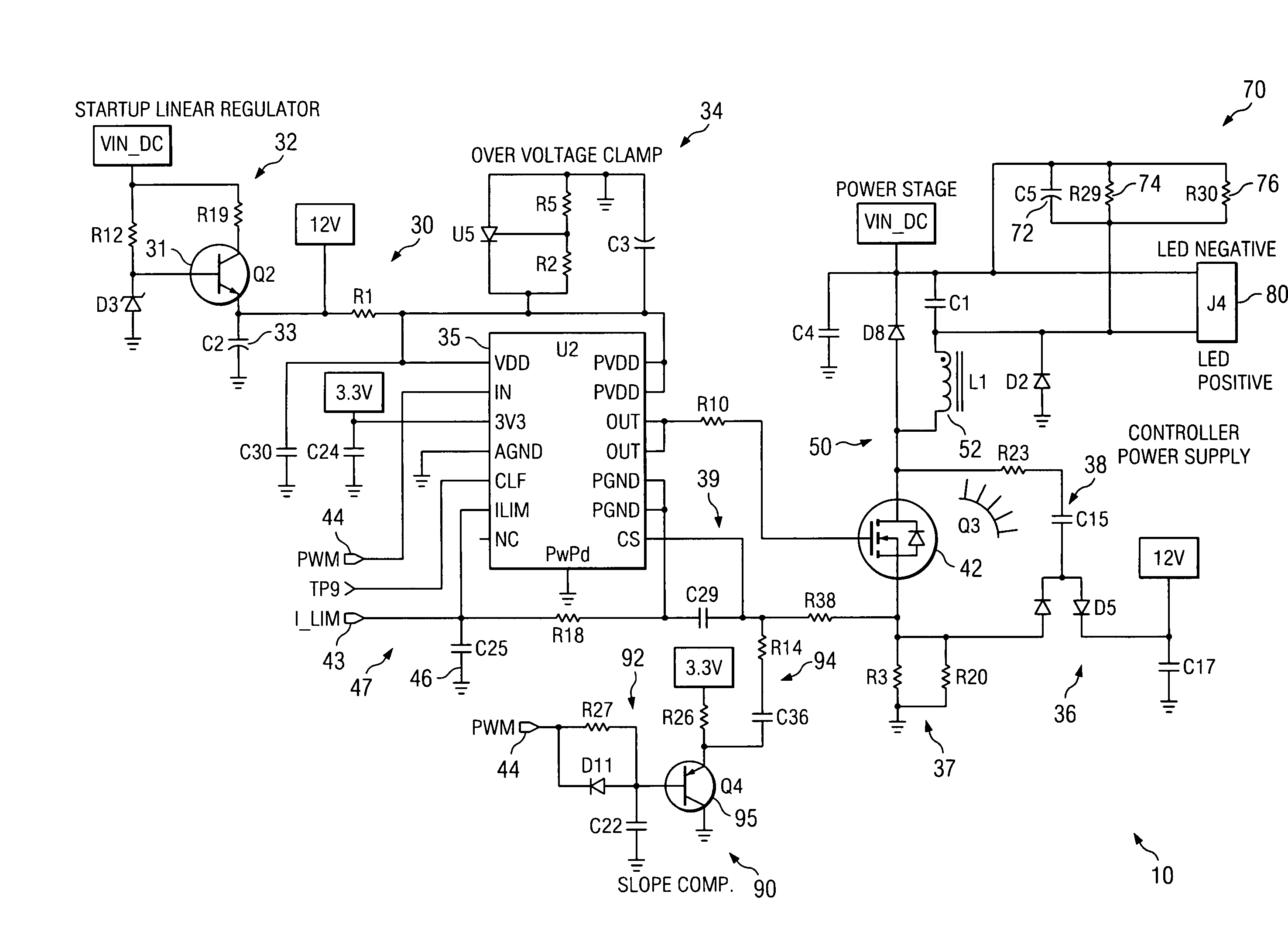
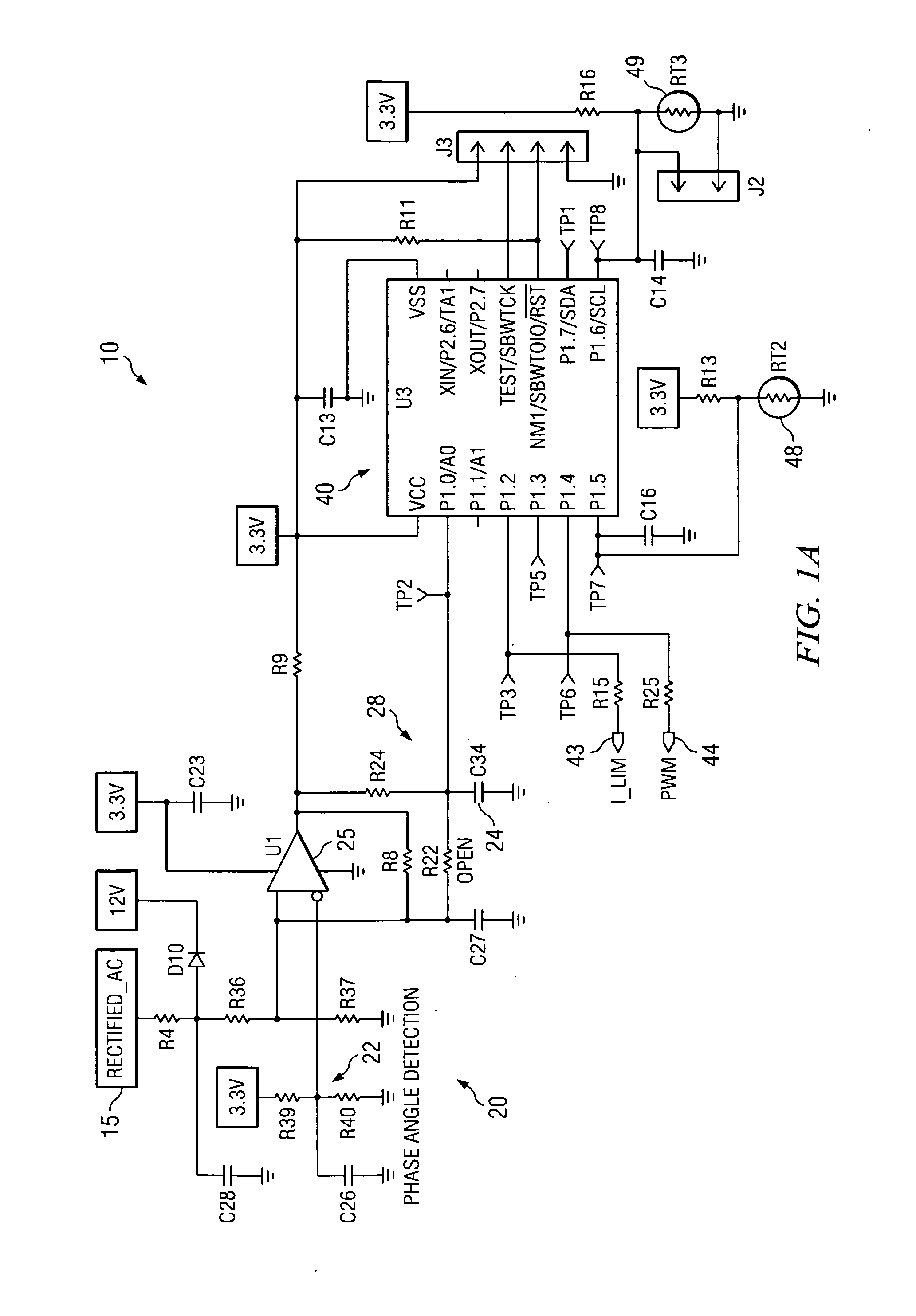
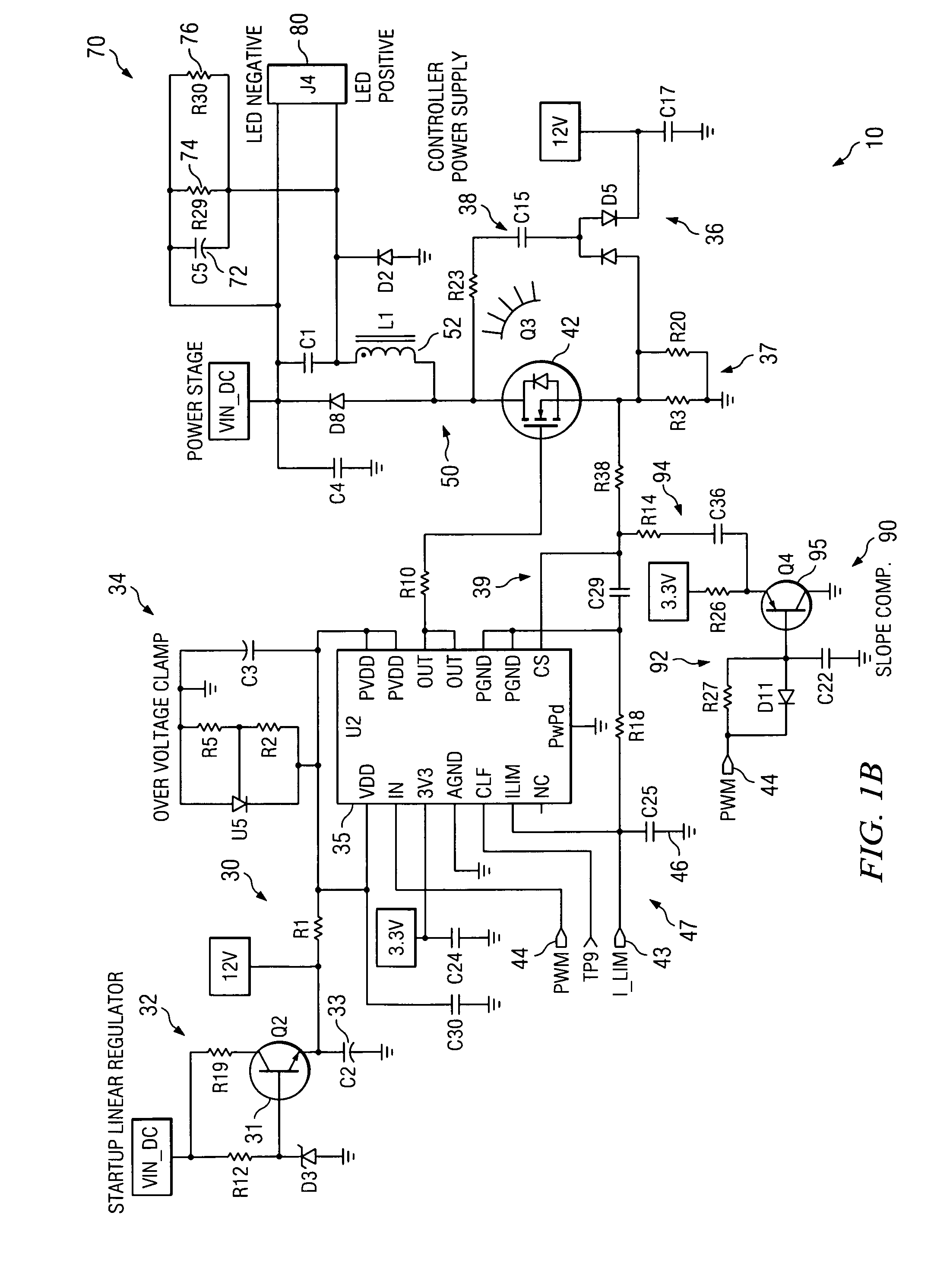
AC-powered, microprocessor-based, dimming LED power supply
ActiveUS20090167203A1Level of audible noise may increaseTotal current dropDc network circuit arrangementsElectroluminescent light sourcesNoise levelAverage current
A dimmable, light-emitting diode (LED) power supply adapted to provide a direct current (DC), constant current (“constant current source”) from a conventional, phase-controlled 120 VAC, 60 Hz power source is disclosed. The constant current source of the present invention utilizes two processes to control dimming. In a first process, the phase angle of the input voltage is used to control the duty cycle of a line frequency pulse width modulation (PWM). In a second process, a proportional-current limit adjustment is used to control the average current to the LED during the ON time of the line frequency by PWM. As a result, at relatively low phase angles, peak currents can be lowered, reducing flicker and improving the audible noise levels generated by the circuit.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Fully Homomorphic Encryption
InactiveUS20130170640A1Reduce noise levelGrowth inhibitionPublic key for secure communicationSecret communicationRoundingNoise level
In one exemplary embodiment of the invention, a method and computer program include: receiving first and second ciphertexts having first and second data encrypted per an encryption scheme, the encryption scheme has public / secret keys and encryption, decryption, operation and refresh functions, the encryption function encrypts data, the decryption decrypts ciphertext, the operation receives ciphertexts and performs operation(s) on them, the refresh operates to prevent growth of the magnitude of noise for a ciphertext while reducing the modulus of the ciphertext without using the secret key, utilizing a modulus switching technique that involves transforming a first ciphertext c modulo q into a second ciphertext c′ modulo p while preserving correctness, the technique includes scaling by p / q and rounding, p<q; using the operation function(s), performing operation(s) on them to obtain a third ciphertext; and reducing a noise level of the third ciphertext using the refresh function.
Owner:IBM CORP
Differential sensing for a touch panel
ActiveUS20100079401A1Reduce adverse effectsHinder recognitionInput/output processes for data processingNoise levelEngineering
A touch panel can configured to reduce adverse effects associated with noise that can be injected into the panel when touched by performing a sensing operation at each sensor in both a panel-stimulated and non panel-stimulated state. The touch panel can detect a touch event by sensing touch in a non-stimulated state to quantify a noise level injected into the touch panel by the touch, and subtracting that noise level from a detection signal sensed in the stimulated state. In one embodiment, a sensing operation can be performed for a particular sensor at two successive time periods—one for each state—within a single scan cycle. In another embodiment, a sensing electrode configuration can be provided that enables a sensing operation to be performed for a particular sensor in both a panel-stimulated and non panel-stimulated state concurrently.
Owner:APPLE INC
Dynamic range compressor-limiter and low-level expander with look-ahead for maximizing and stabilizing voice level in telecommunication applications
InactiveUS6535846B1Avoid excessive amplificationMaximizing and stabilizing voice levelInterconnection arrangementsSpeech analysisTelecommunication applicationSpeech recognition
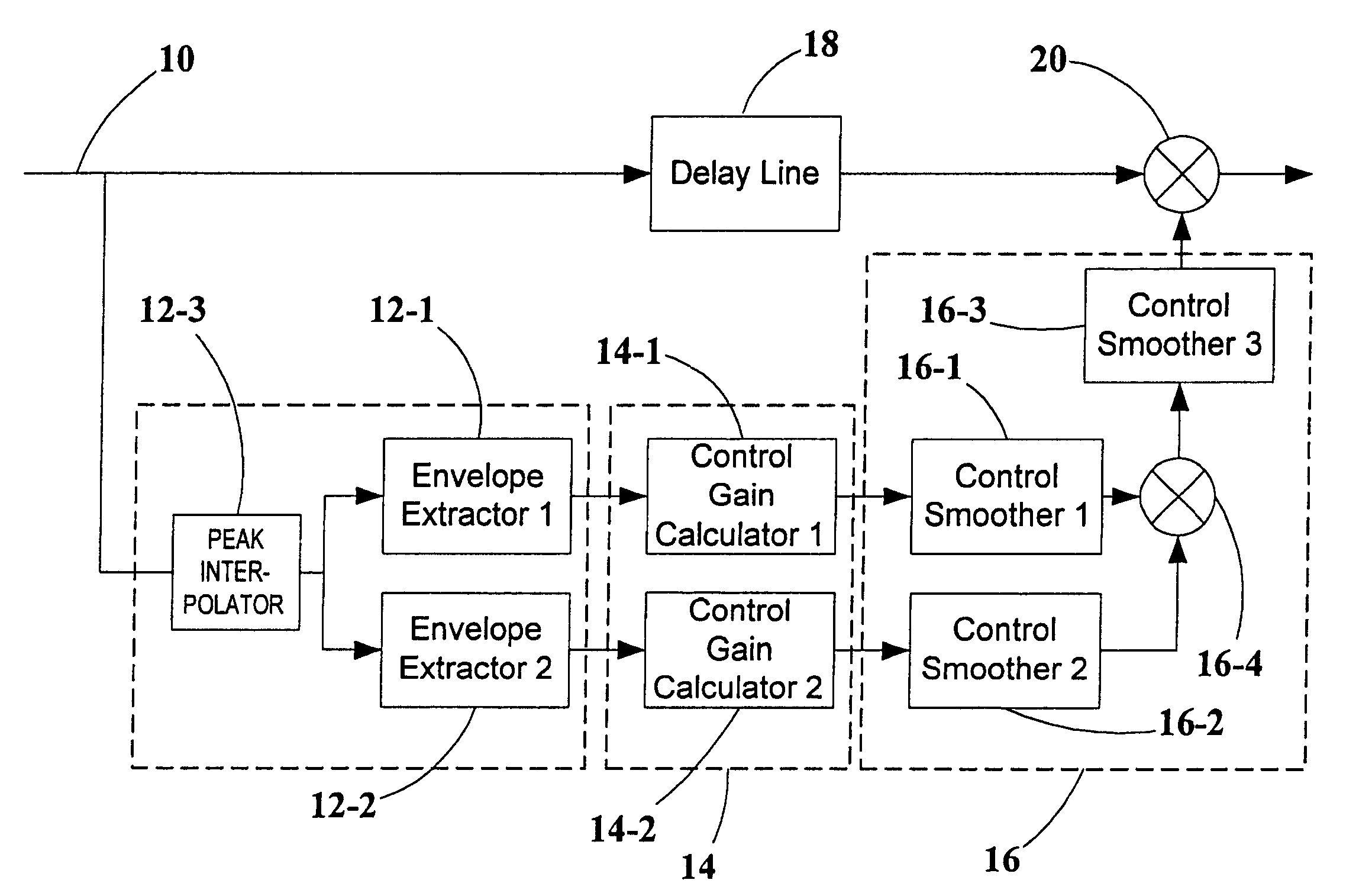
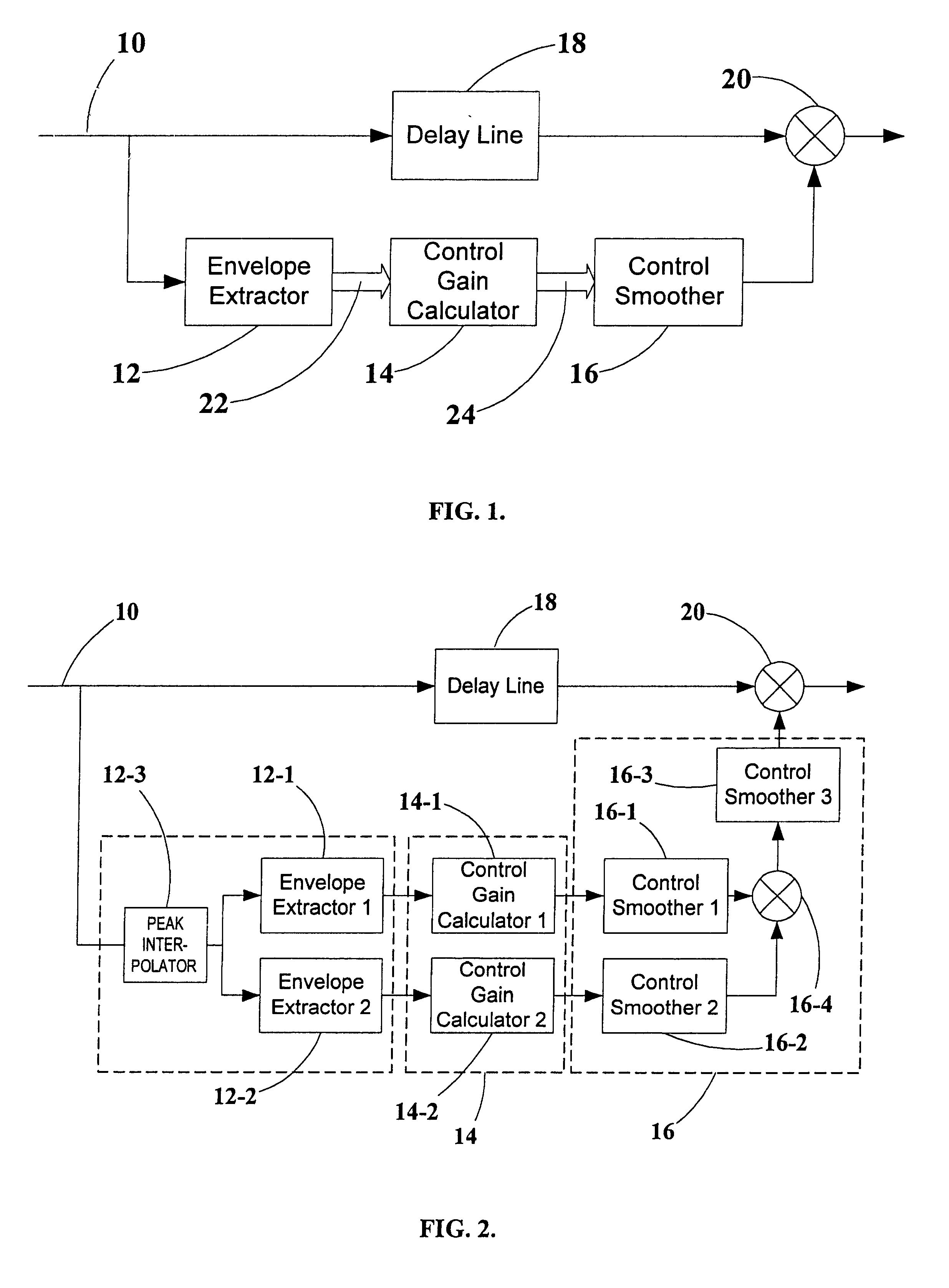
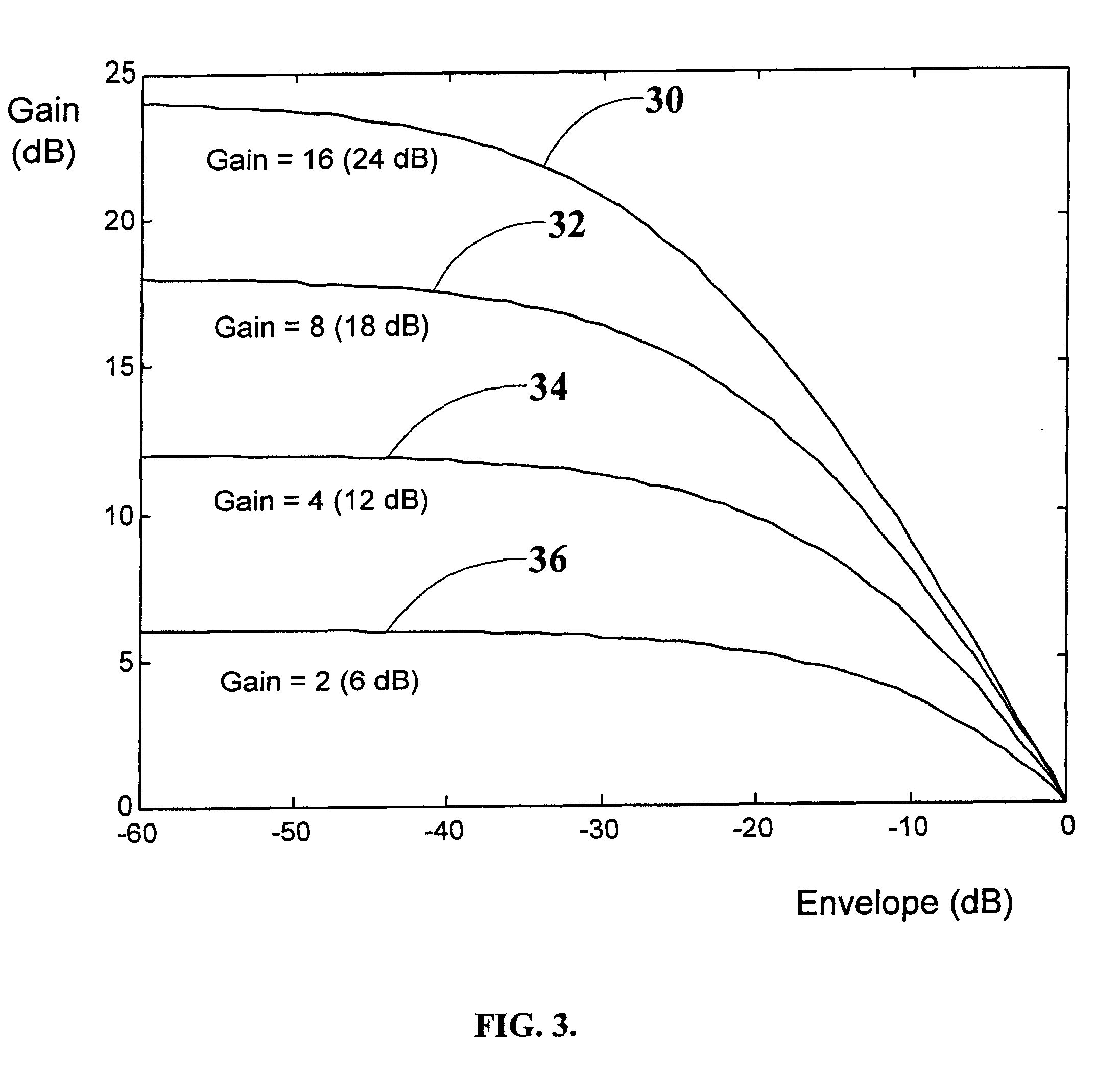
A voice signal processing system with multiple parallel control paths, each of which address different problems, such as the high peak-to-RMS signal ratios characteristic of speech, wide variations in RMS speech levels, and high background noise levels. Different families of input-output control curves are used simultaneously to achieve efficient peak limiting and dynamic range compression as well as low-level dynamic expansion to prevent excessive amplification of background noise. In addition, a delay in the audio path relative to the control path makes it possible to employ an effective look-ahead in the control path, with FIR filtering smoothing-matched to the look-ahead. Digital domain peak interpolators are used for estimating the peaks of the input signal in the continuous time domain.
Owner:K S WAVES
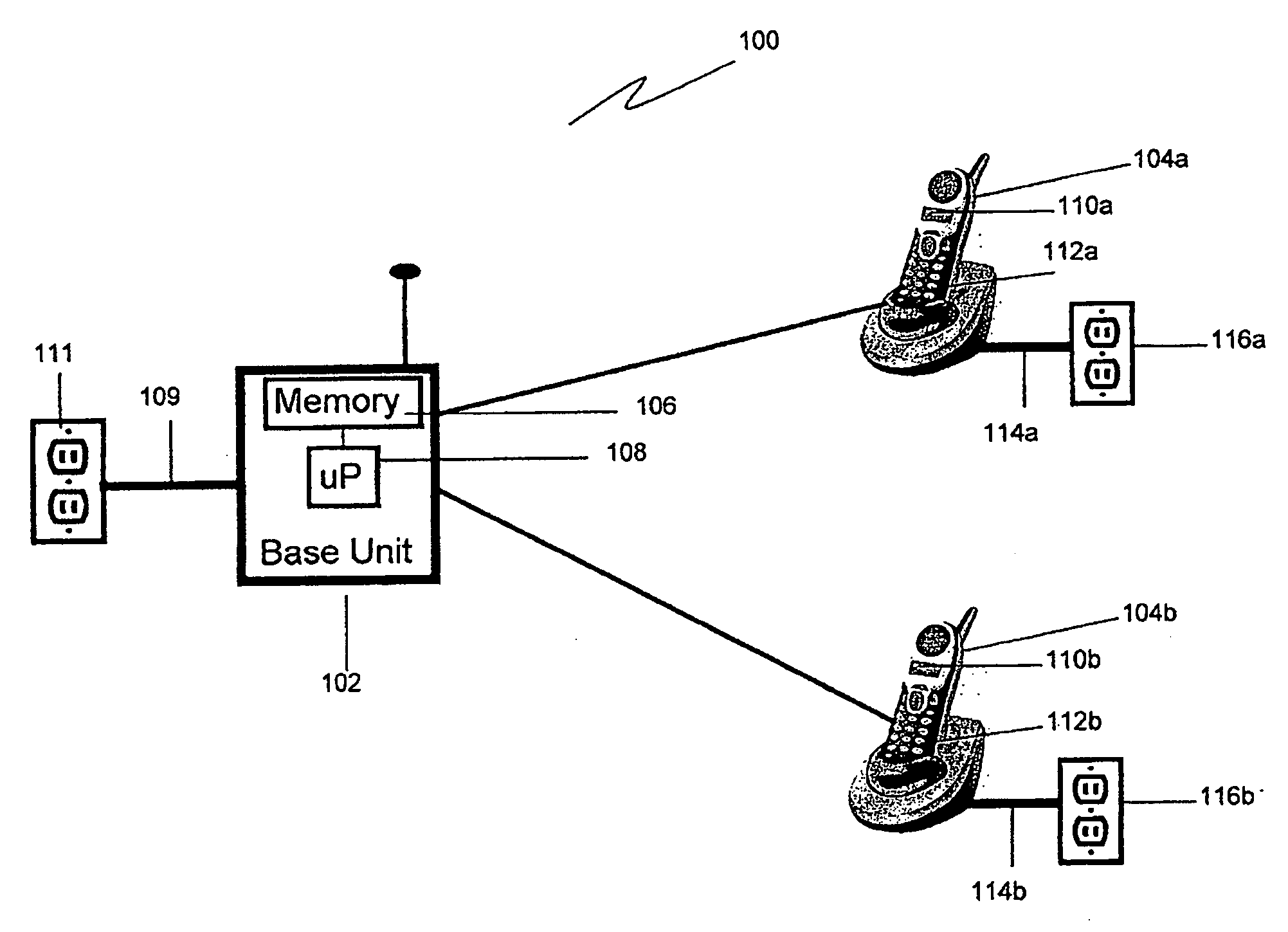
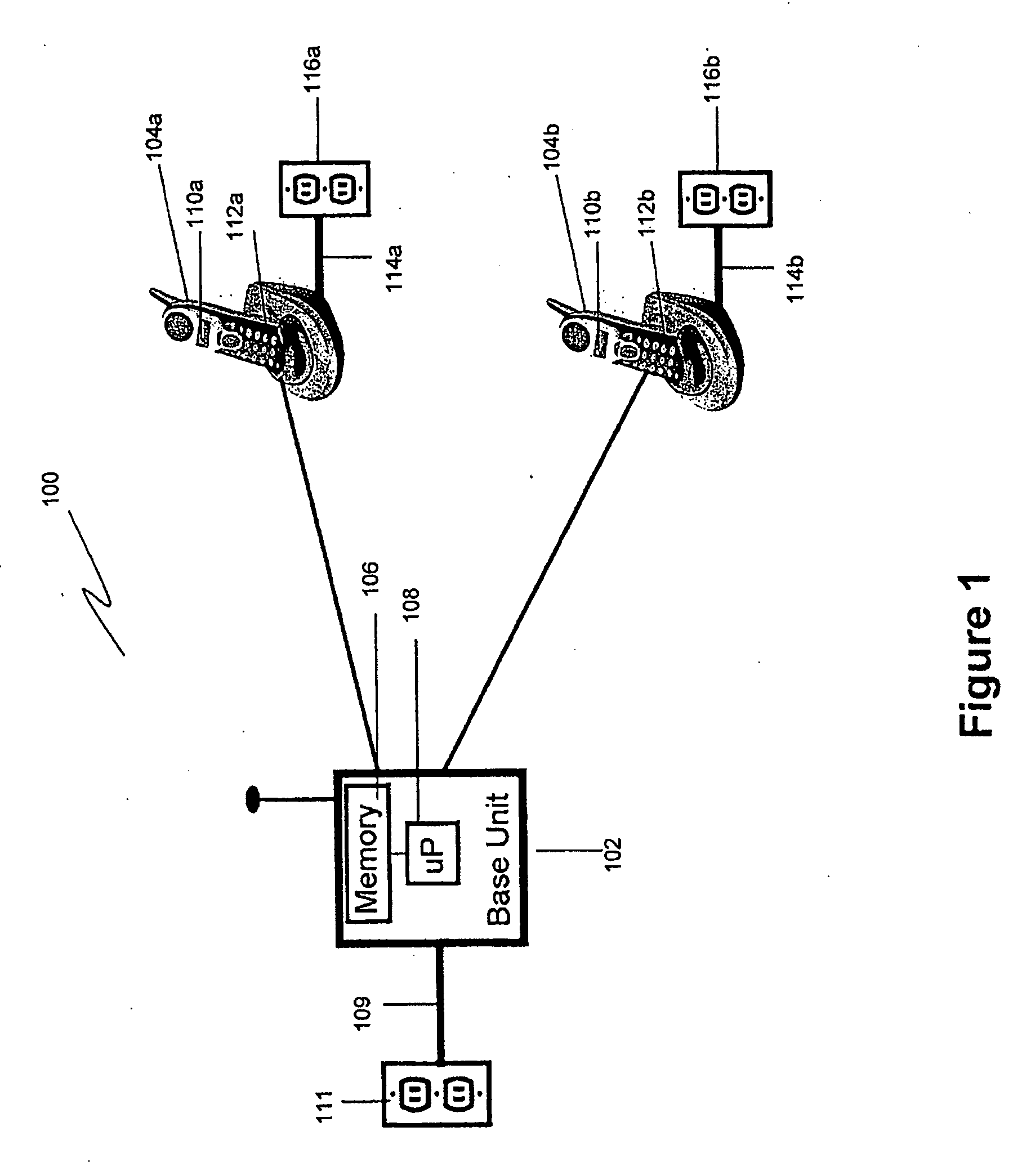
Cordless phone system with integrated alarm & remote monitoring capability
InactiveUS20070161372A1Affordable home securityProvide securityDevices with sensorRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsHandsetNoise level
A cordless telephone system provides home security. Each handset associated with the cordless telephone system detects a noise level. If the detected noise level exceeds a threshold level, the handset detecting the noise level exceeding the threshold level initiates a telephone call through the base unit to an alert telephone number. When the telephone call to the alert telephone number is established, a message is played to provide notification of a possible home security breach, such as an intruder.
Owner:VTECH TELECOMM
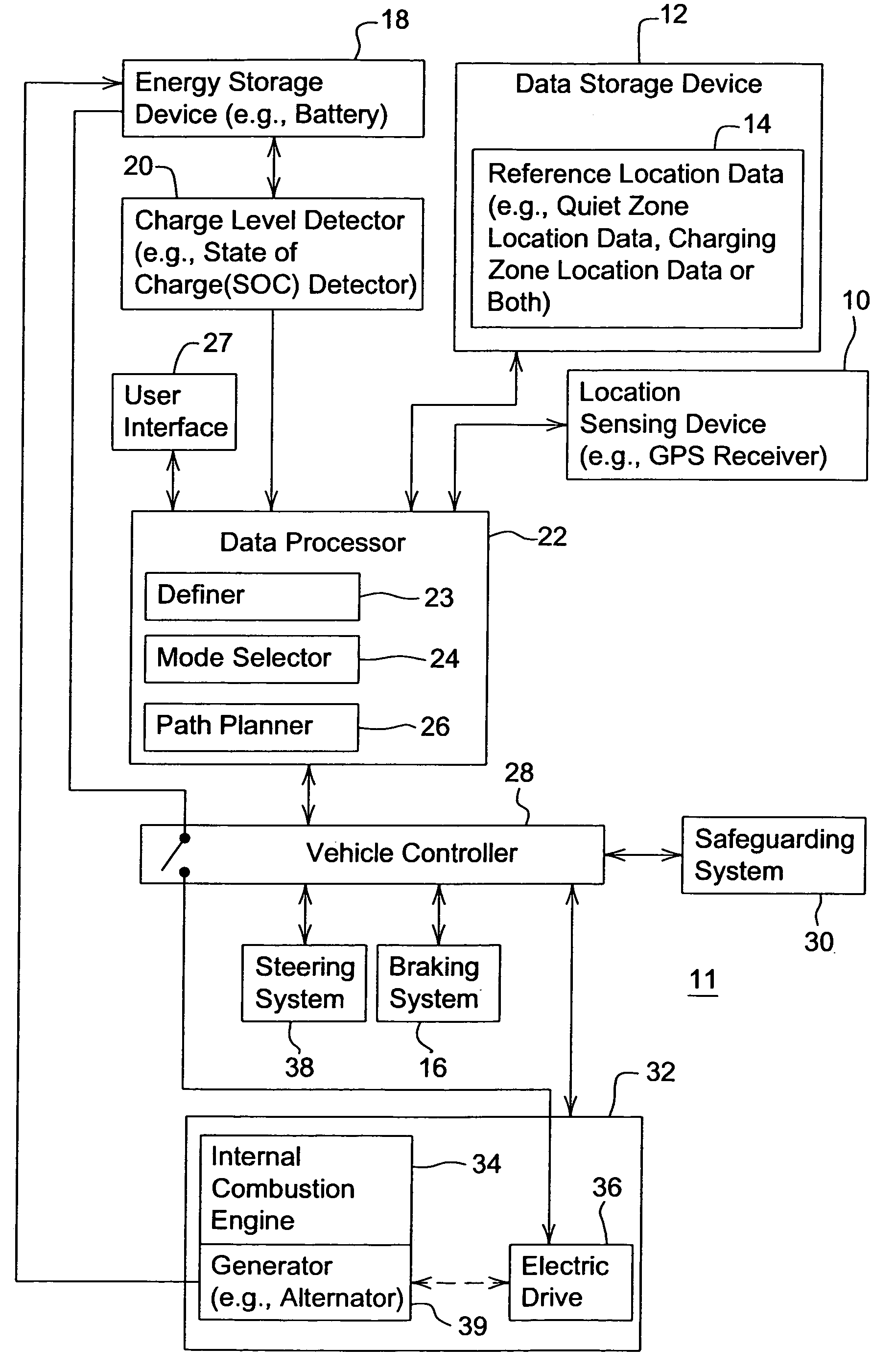
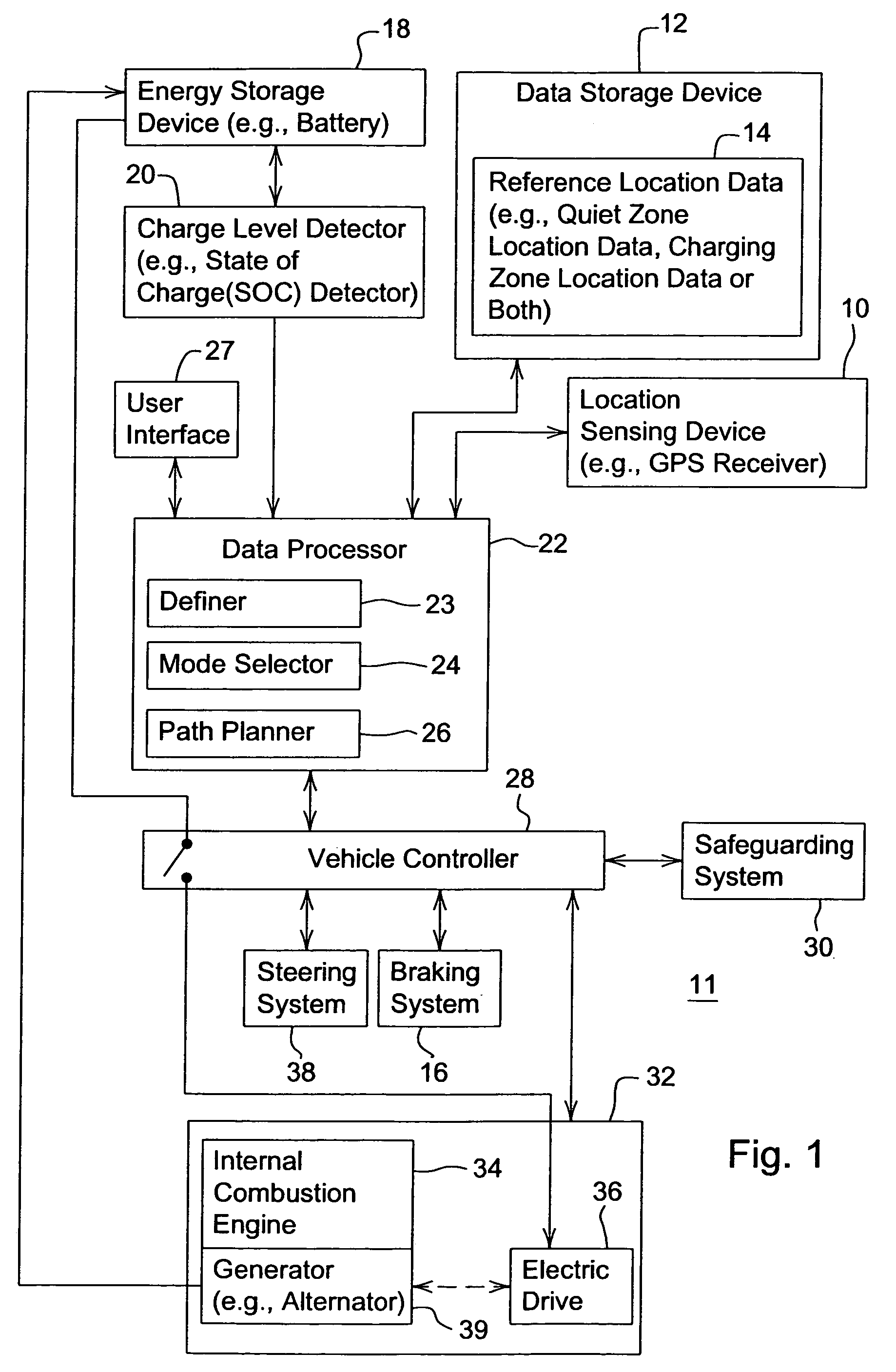
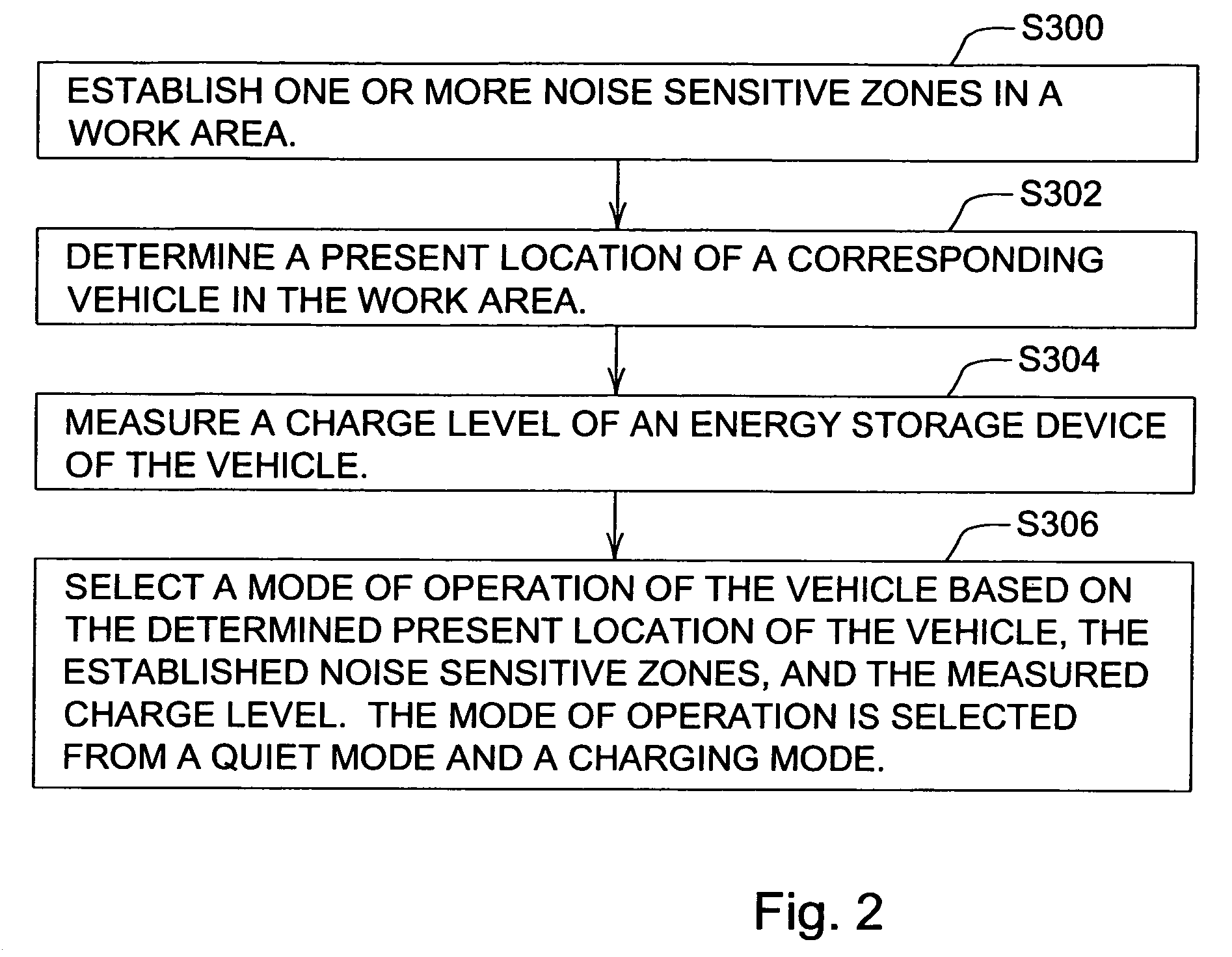
Vehicular navigation with location-based noise reduction
A method or system for managing the noise level of a vehicle establishes one or more noise sensitive zones in a work area. A present location is determined for a corresponding vehicle in the work area. A charge level is measured. The charge level pertains charge level of an energy storage device of the vehicle. A mode of operation of the vehicle is selected based on the determined present location of the vehicle, the established noise sensitive zones, and the measured charge level. The mode of operation is selected from a quiet mode and a charging mode, or the equivalent of either.
Owner:DEERE & CO
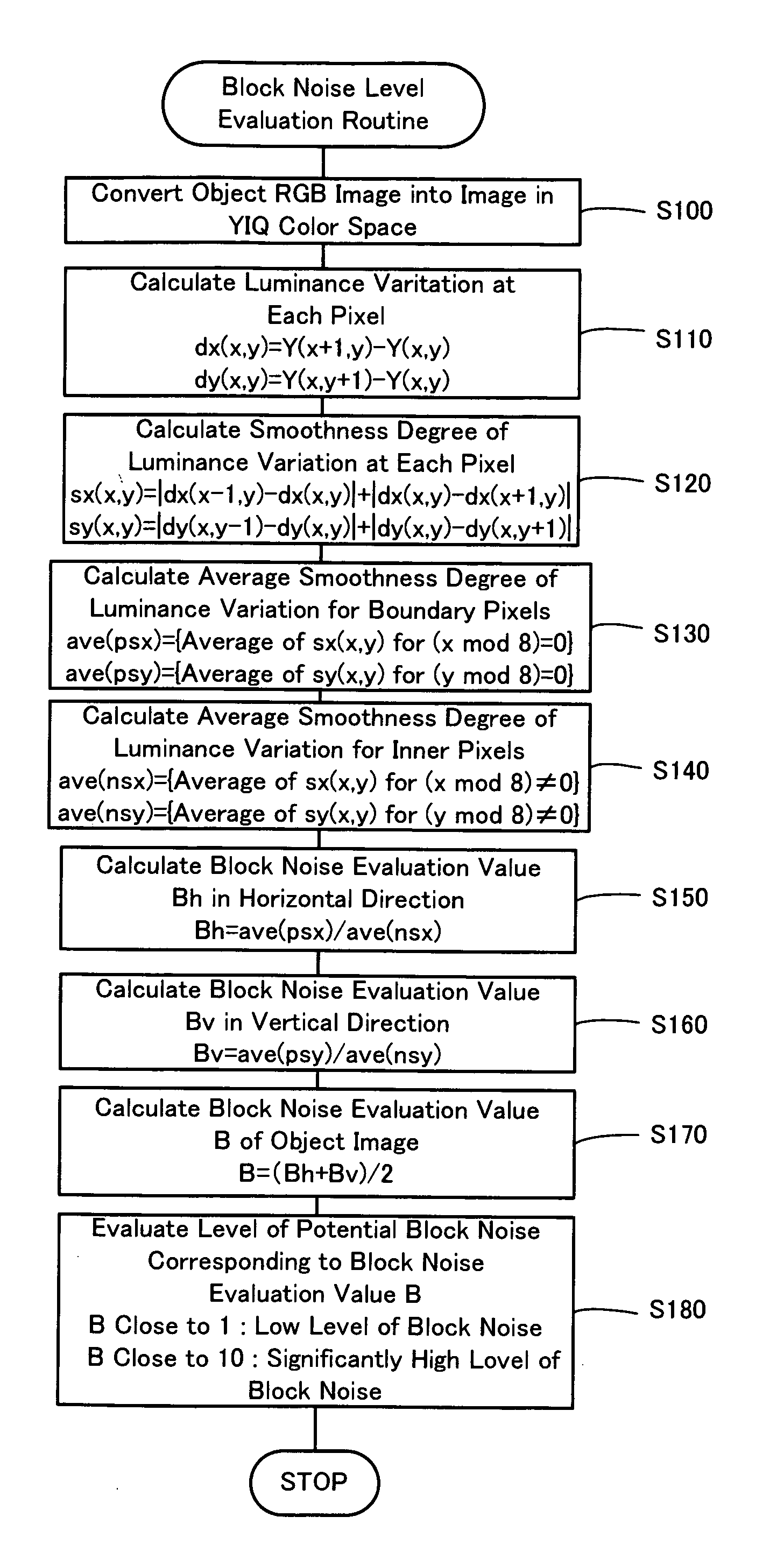
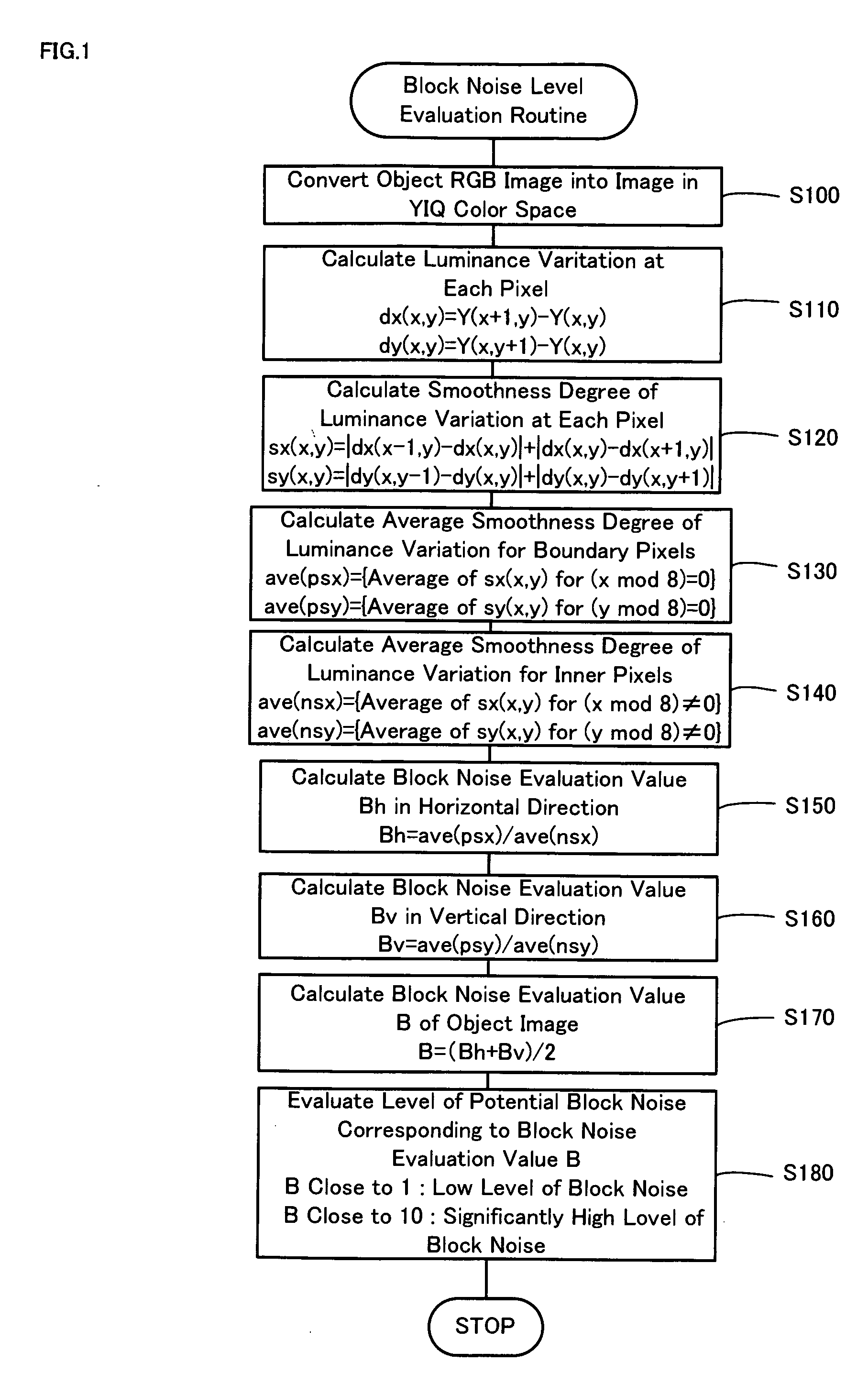
Block noise level evaluation method for compressed images and control method of imaging device utilizing the evaluation method
InactiveUS20060034531A1Reducing influence level of noiseReduce in quantityImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionNoise level
The technique of the invention converts an object RGB image into an image in a YIQ color space, calculates a luminance variation at each target pixel from Y channel values of the target pixel and an adjacent pixel adjoining to the target pixel, and computes a smoothness degree of luminance variation at the target pixel as summation of absolute values of differences between luminance variations at the target pixel and adjacent pixels. A block noise evaluation value B is obtained as a ratio of an average smoothness degree ave(psx), ave(psy) of luminance variation for boundary pixels located on each block boundary to an average smoothness degree ave(nsx), ave(nsy) of luminance variation for inner pixels not located on the block boundary. The block noise evaluation value B closer to 1 gives an evaluation result of a lower level of block noise, whereas the block noise evaluation value B closer to 10 gives an evaluation result of a higher level of block noise.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method and apparatus for adaptively controlling signals
ActiveUS20070254592A1Enhance peak reductionReduce peakModulated-carrier systemsGain controlSignal qualityFrequency spectrum
A signal processing system according to various aspects of the present invention includes an excursion signal generator, a scaling system and a filter system. The excursion signal generator identifies a peak portion of a signal that exceeds a threshold and generates a corresponding excursion signal. The scaling system applies a real scale factor to contiguous sets of excursion samples in order to optimize peak-reduction performance. The filter system filters the excursion signal to remove unwanted frequency components from the excursion signal. The filtered excursion signal may then be subtracted from a delayed version of the original signal to reduce the peak. The signal processing system may also control power consumption by adjusting the threshold. The signal processing system may additionally adjust the scale of the excursion signal and / or individual channel signals, such as to meet constraints on channel noise and output spectrum, or to optimize peak reduction. The magnitude threshold, excursion signal and / or individual channel signals may also be adaptively adjusted based on, for example, a channel signal quality such as a noise level specification.
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
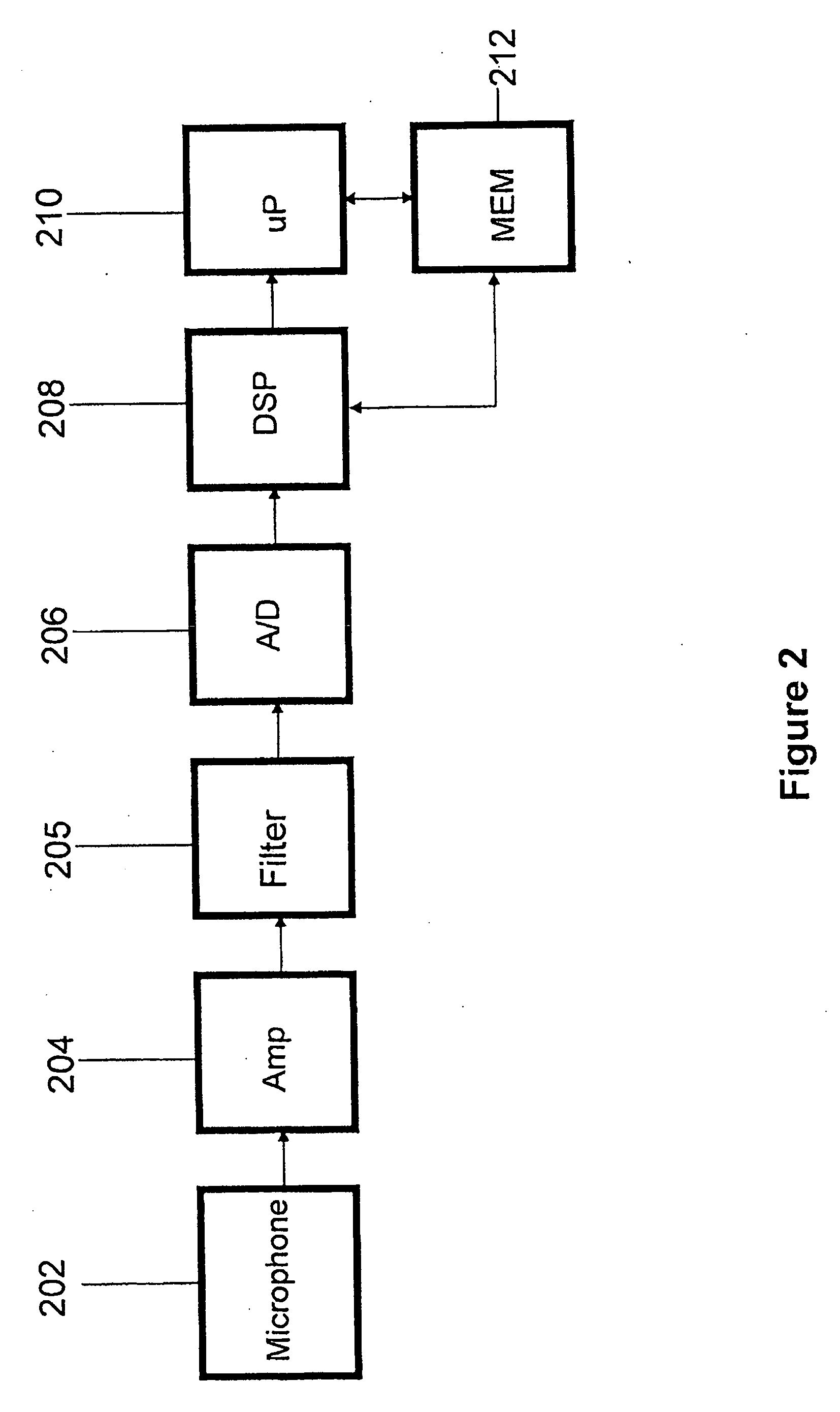
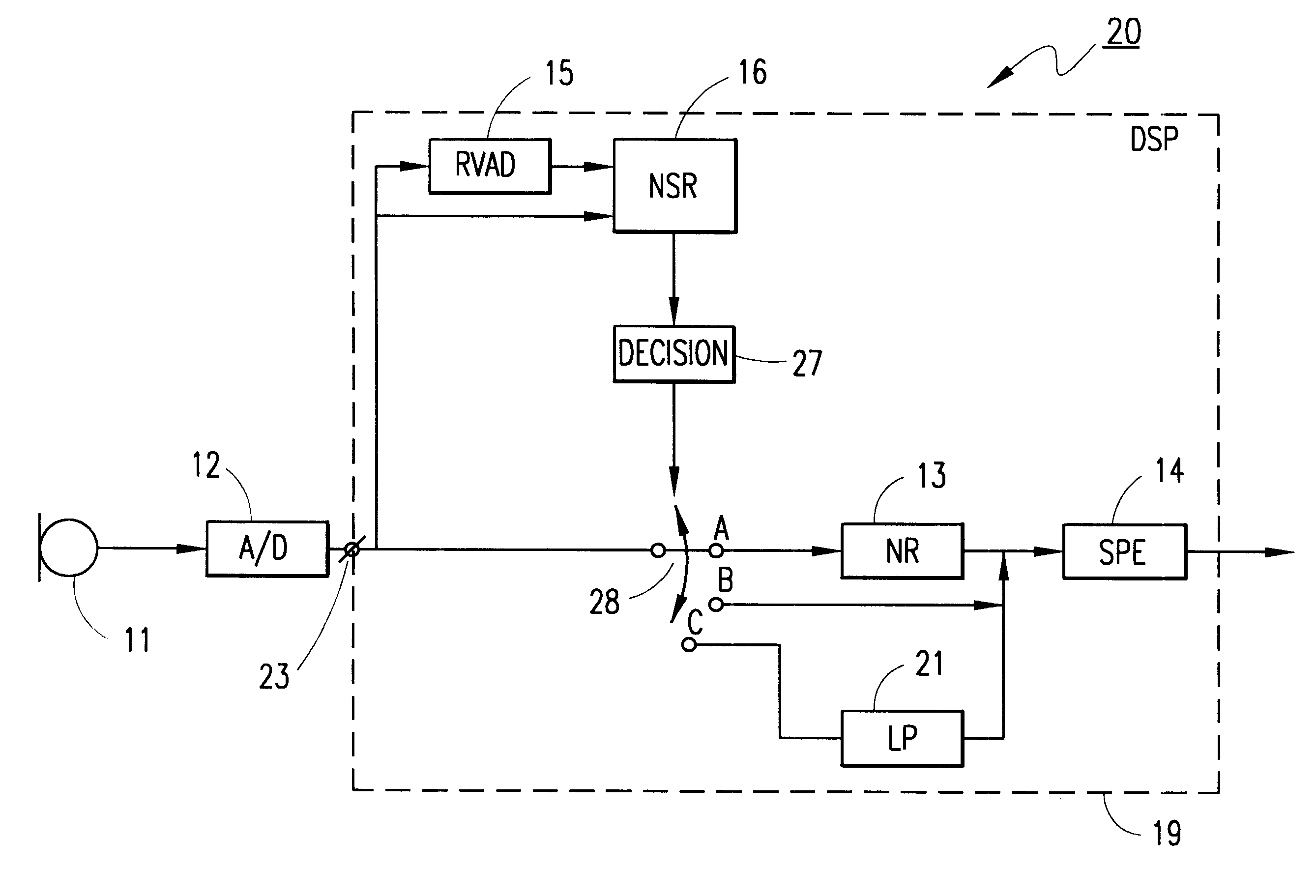
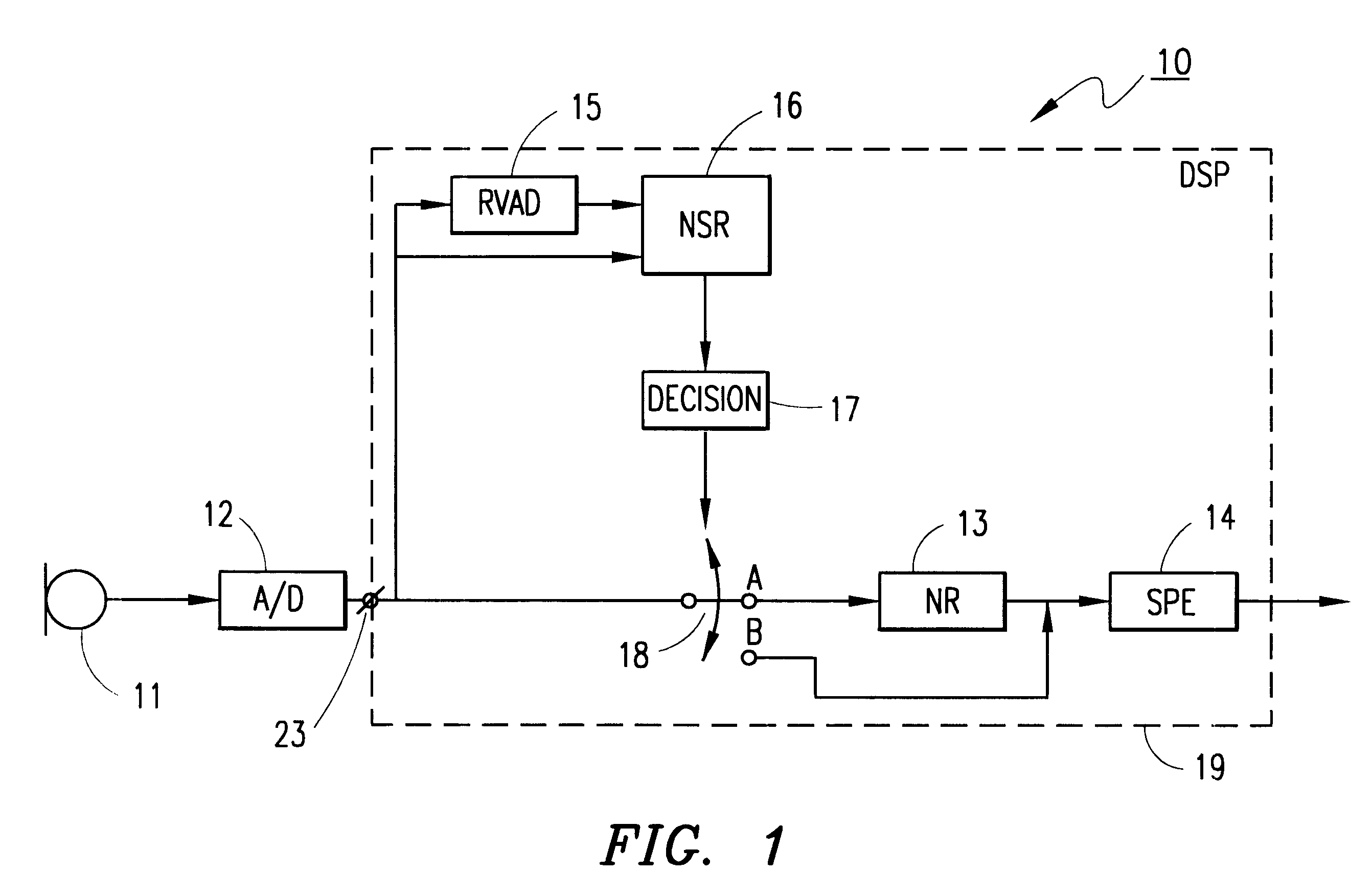
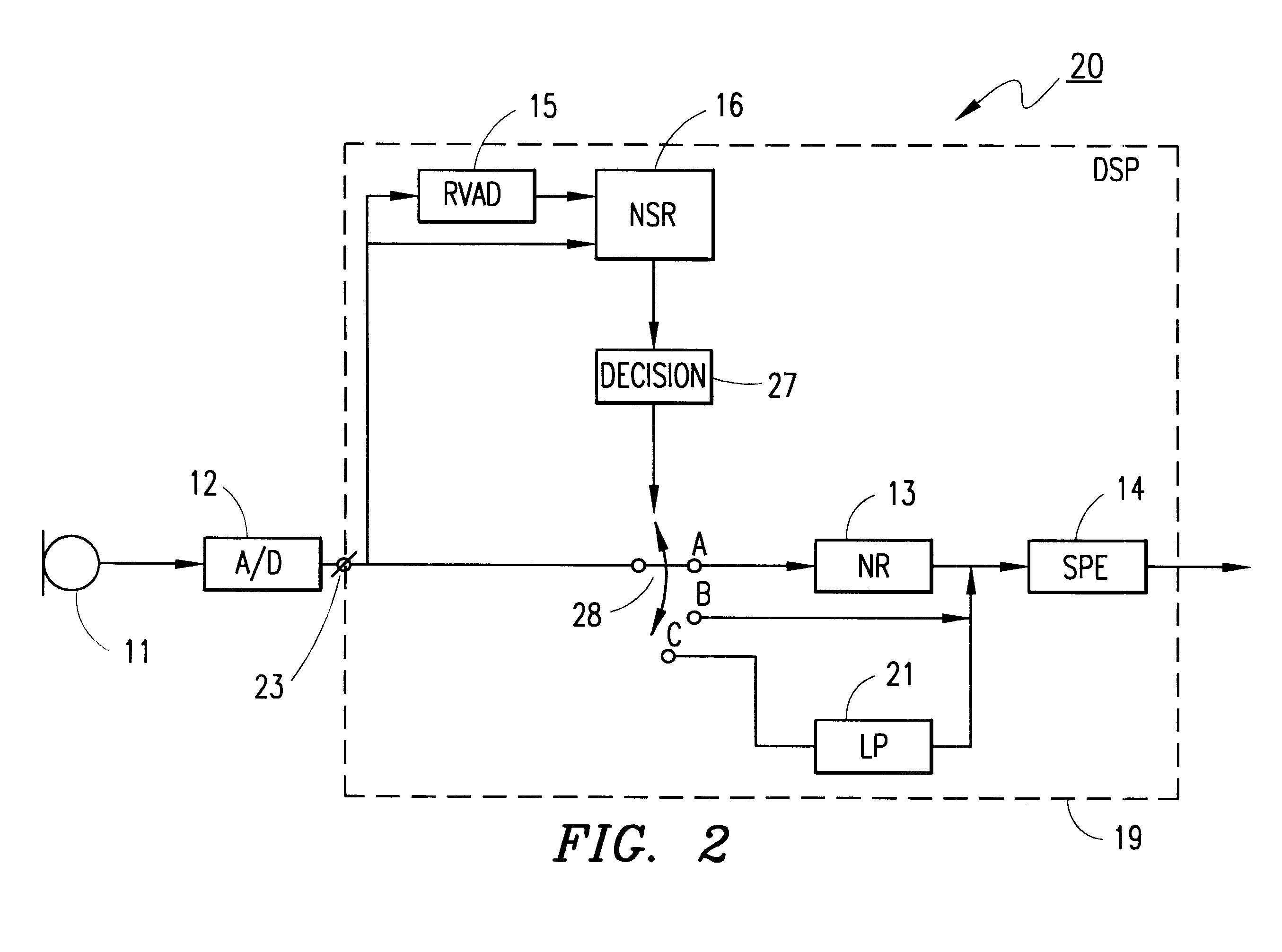
Noise reduction method and apparatus
Apparatuses for noise reduction and noise processing methods for reducing noise in audio signals are presented. The noise level of an input signal at an input terminal is measured and the noise-to-signal ratio is established. A reduced voice activity detector is used to determine whether the input signal comprises speech or not. If the measured noise level exceeds a threshold level a switch connects the input signal to means for noise reduction. However, if the measured noise level does not exceed the threshold level, i.e. when noise reduction is not needed, the switch disconnects the means for noise reduction and the input signal is passed unchanged. Power is saved by powering off the means for noise reduction when it is not needed.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Patient interface with venting
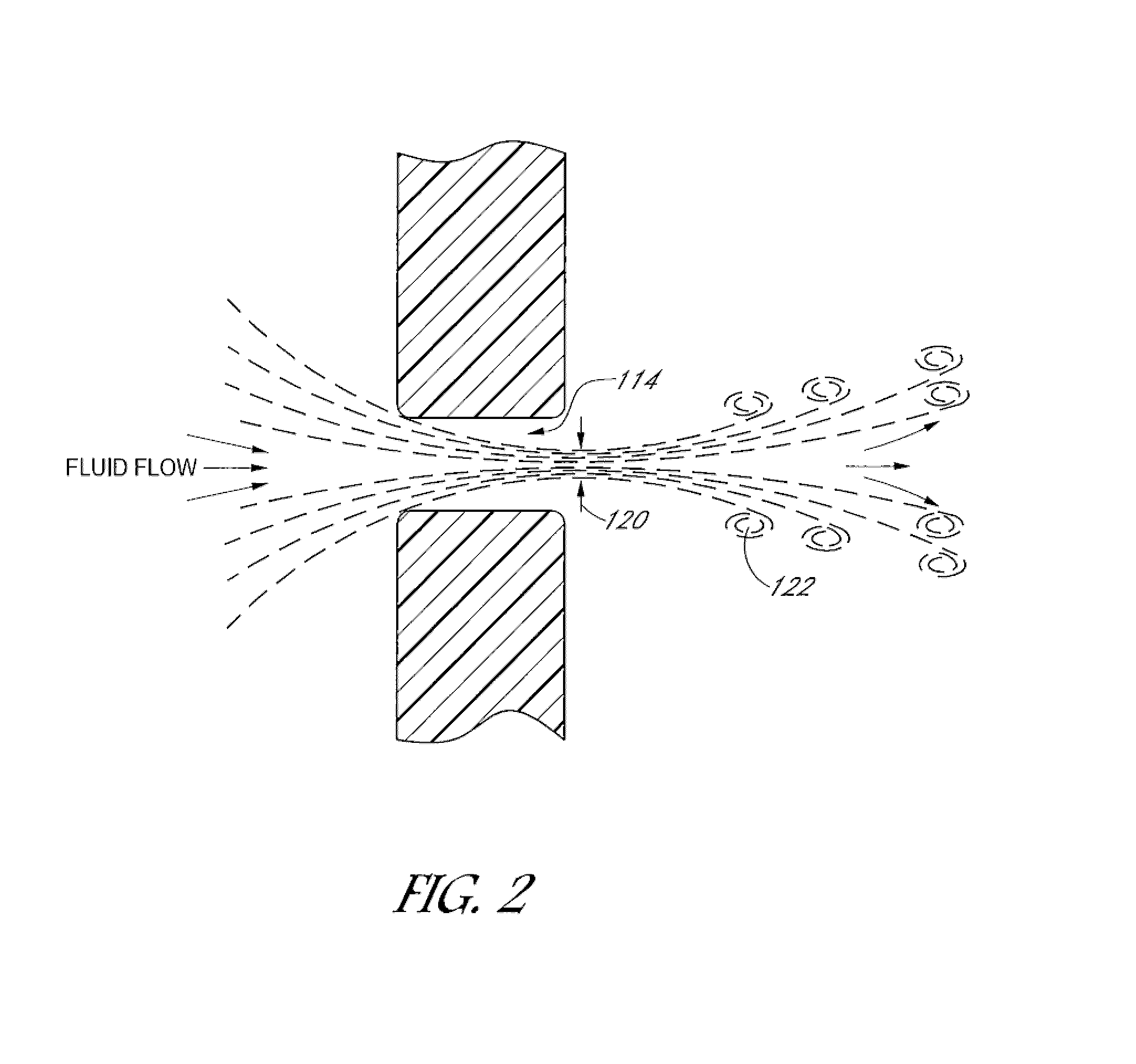
Interfaces for positive pressure therapy having various vent designs are disclosed herein. The interfaces include a bias flow vent with design geometries that help reduce and / or minimize draft and noise levels of the fluids exiting the vents. Some of the vent designs include particular vent hole geometries, plenum spaces, diffusers and fibrous media.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL HEALTHCARE LTD
Power Management For Wireless Earpieces Utilizing Sensor Measurements
ActiveUS20170188132A1Hearing device energy consumption reductionDigital data processing detailsNoise levelHeadphones
A system, method and wireless earpieces for managing power utilized by a pair of wireless earpieces. Ambient light conditions and noise levels in an environment of the pair of wireless earpieces are determined. The low power settings are activated for the pair of wireless earpieces in response to determining the ambient light conditions are below a light threshold or the noise levels are below a noise threshold; signal activity is below an activity threshold.
Owner:BRAGI
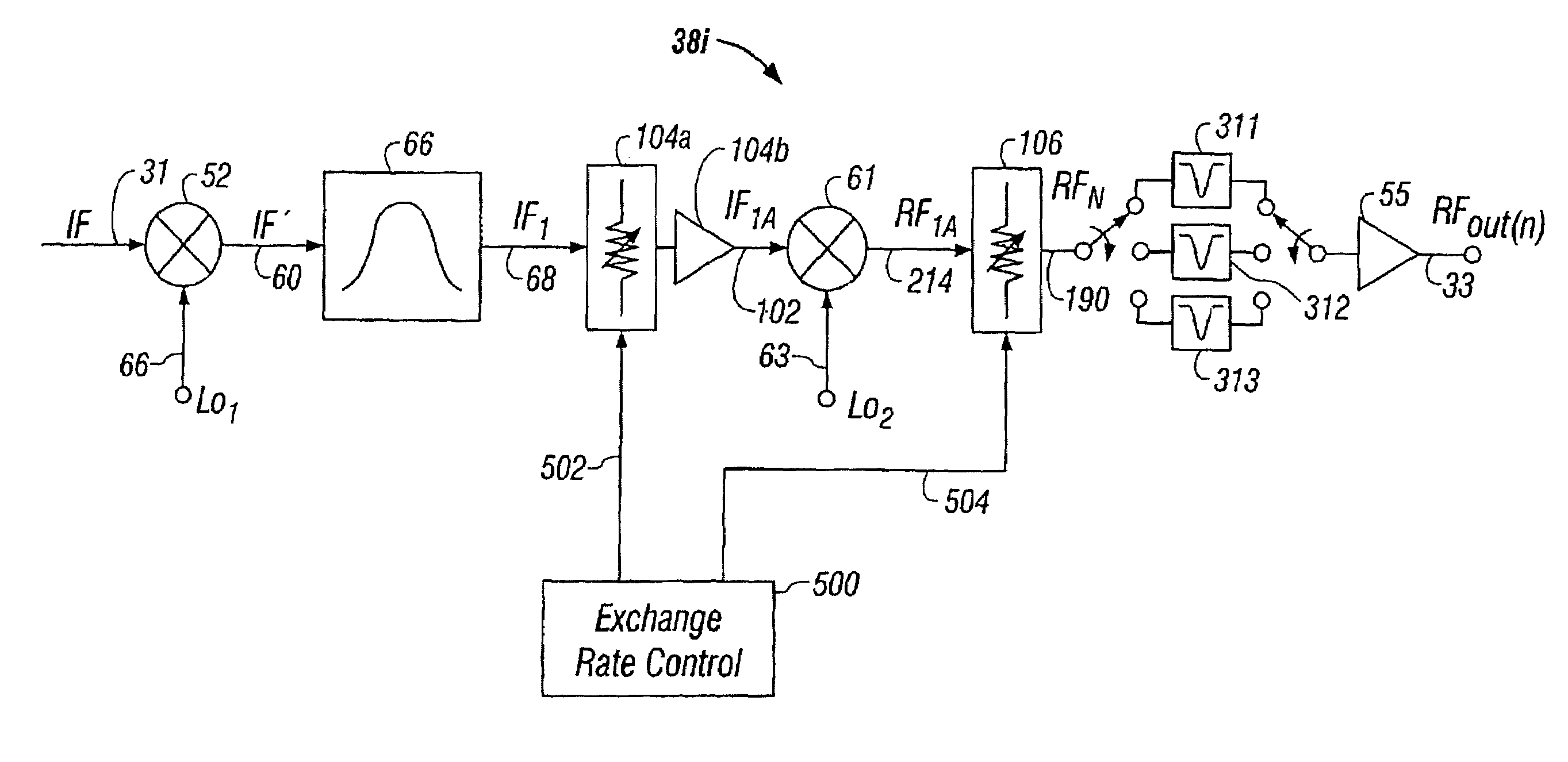
Agile frequency converter for multichannel systems using IF-RF level exhange and tunable filters
InactiveUS7003275B1Increasing unloaded QReduced insertion lossResonant long antennasFrequency-division multiplex detailsMicrocontrollerFrequency changer
Agile frequency converter and method, IF-RF level exchange process, and notch filtering techniques. System noise and spurious levels generated by channel frequency conversion is reduced in applications requiring broadband combining of frequency converters to form multichannel composite signal. Converter employs two-stage frequency conversion process, with gain exchange system using variable pre-mixer gain and variable post-mixer attenuation to maintain constant RF output signal power level. For those few conversion frequencies where distortion component(s) cannot be filtered without degrading desired signal, IF-RF level exchange is optimized for meeting the carrier-to-distortion (C / D) ratio specifications at slight expense of noise level for that channel only, while still meeting aggregate combined carrier-to-noise (C / N) specification requirements. Optimal apportionment of level exchange for each channel depends on specific frequency rejection capability of spurious components and is matched to filtering capability and stored within non-volatile memory of a microcontroller used in the frequency converter.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
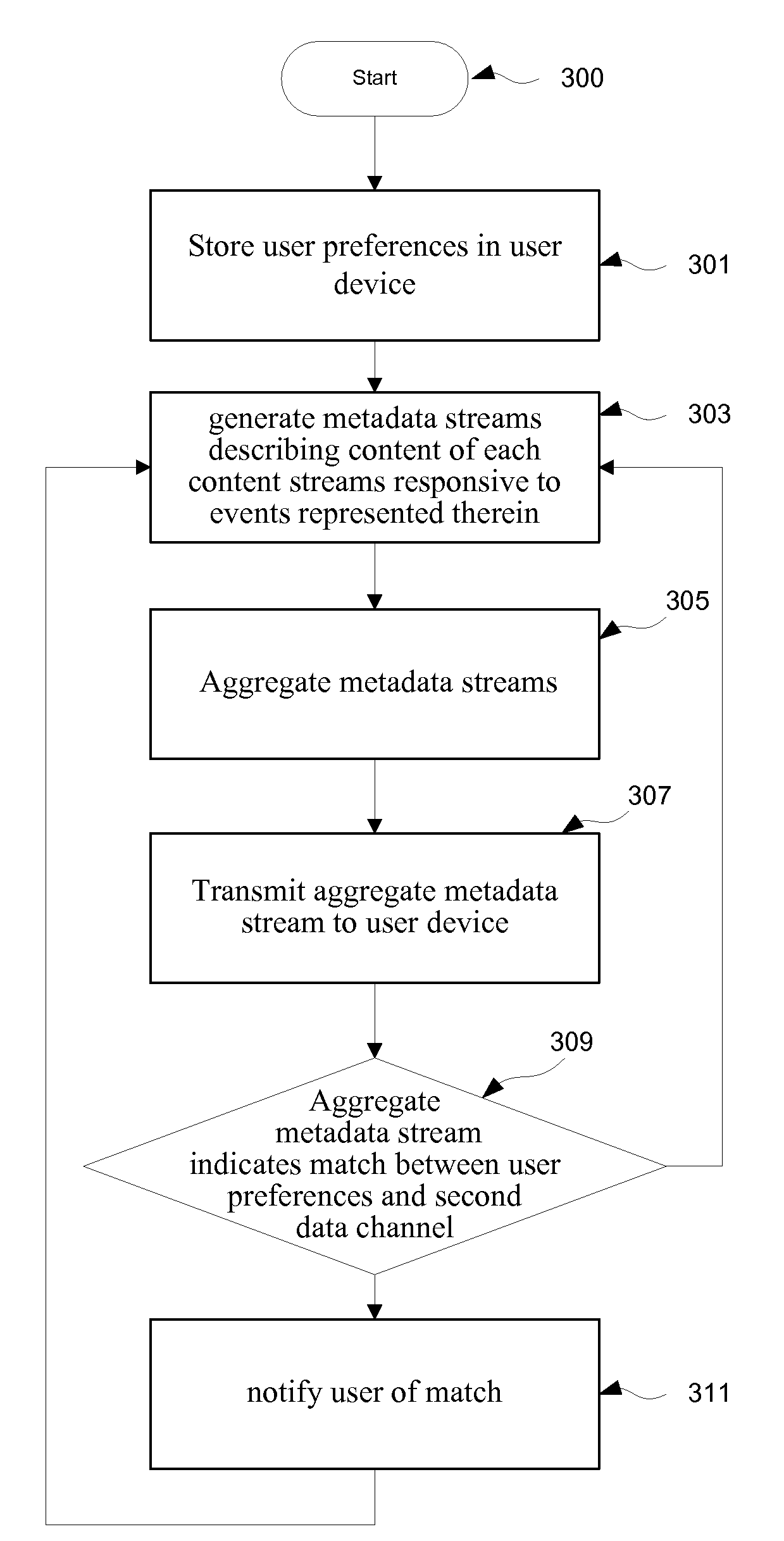
Method and system for preferred content identification
A content stream user defines preferences, which are compared to aggregated metadata describing in real time a plurality of content streams to which the user has access. The metadata for each content stream may be generated by automated analysis of onscreen indicators, noise levels in standard video or audio sequences, or speech recognition or image recognition data applied to identify particular keywords, individuals, etc. Where a match between content and user preferences is identified, the user is notified, and may be given the option of switching to the matching content stream. A number of approaches are used to ensure that the user is able to access the whole of the content of interest, and does not miss the starting porting. Certain parts of the content streams may be cached for video on demand viewing, or the content streams may be buffered allowing access to various portions of the stream, or a delay in content transmission may be introduced relative to the metadata transmission so as to allow time for a content stream change.
Owner:IBM CORP
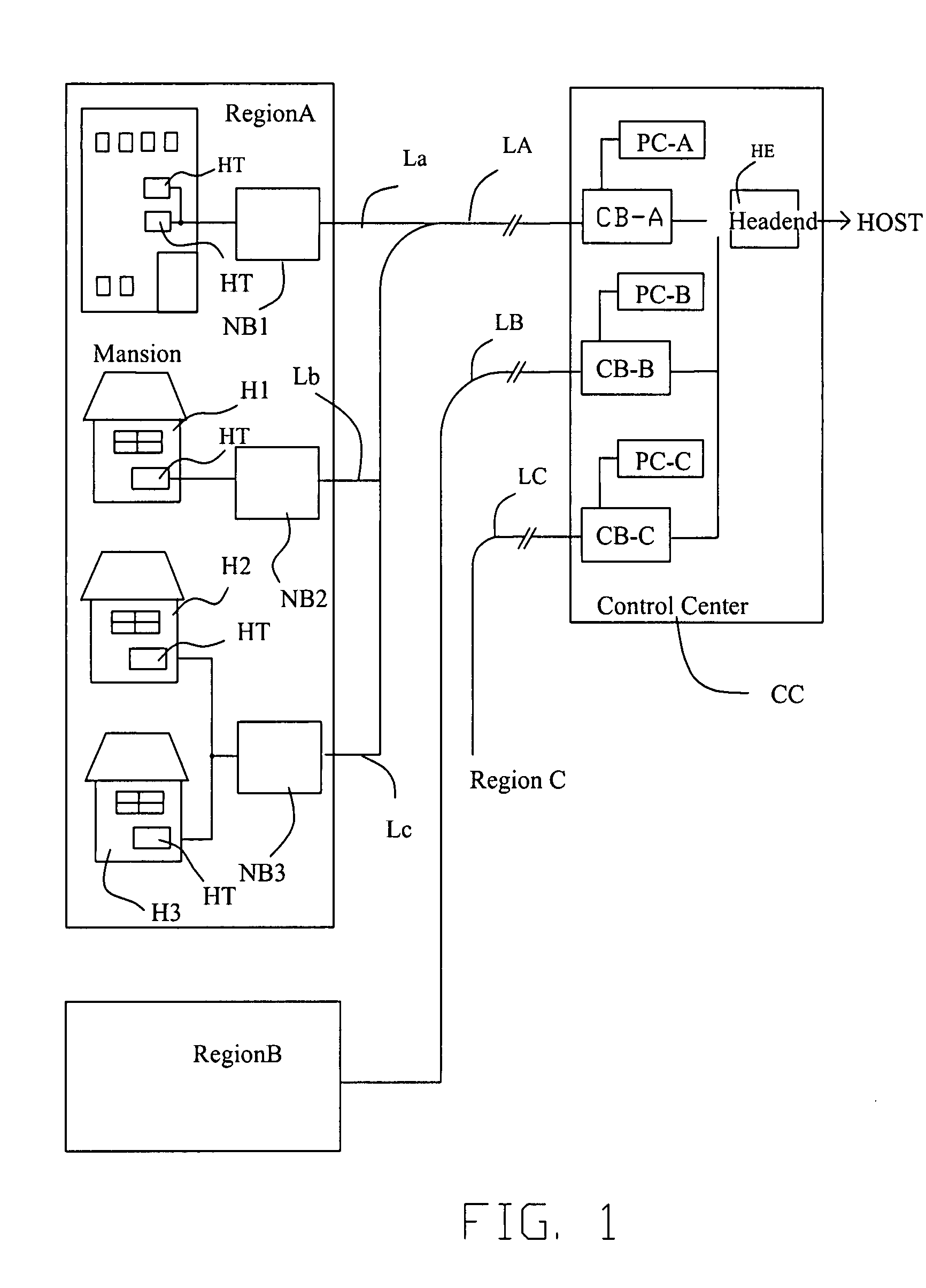
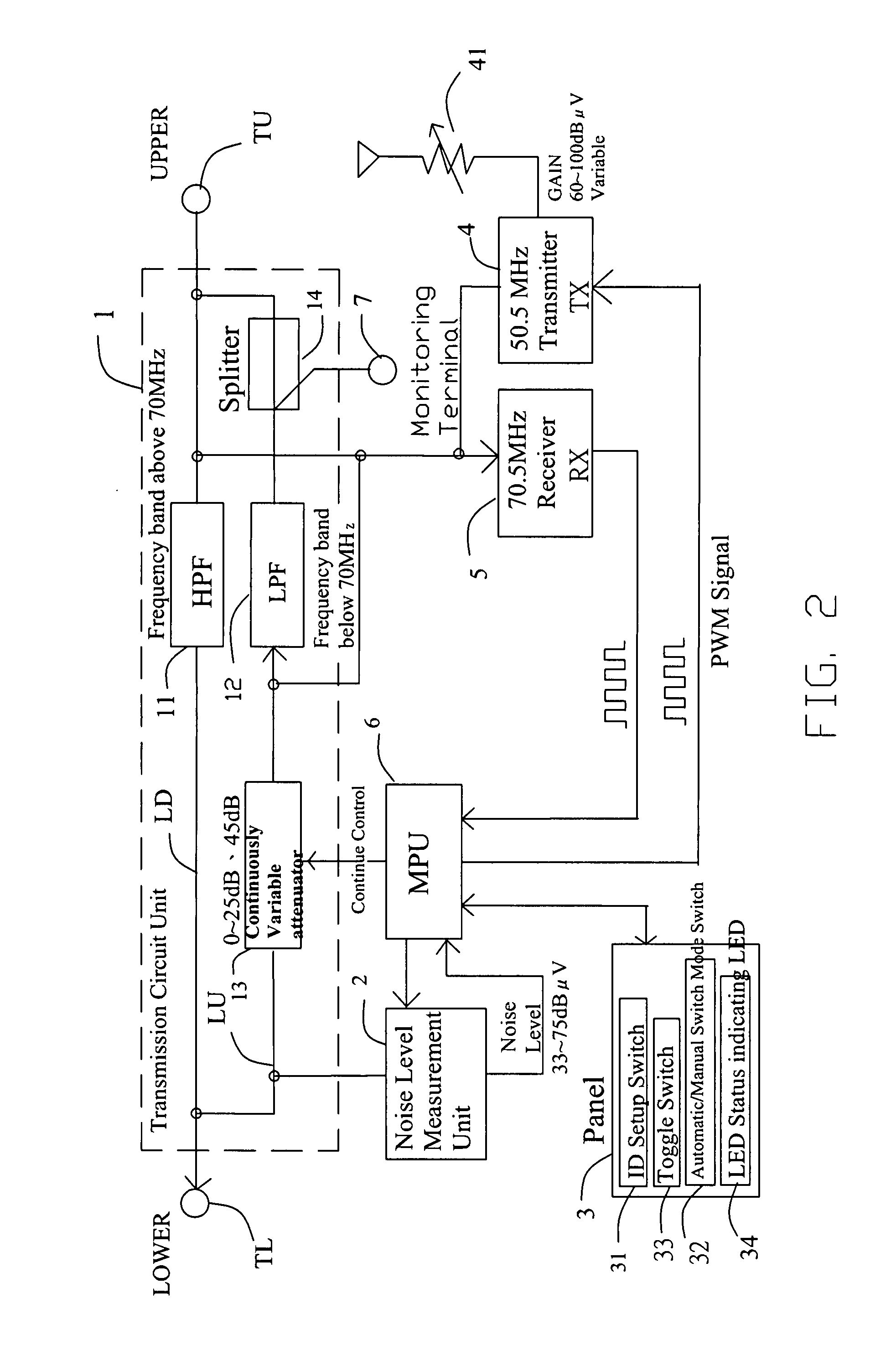
CATV system and automatic noise controller
InactiveUS20070288981A1Reduce noiseLower Level RequirementsBroadcast-related systemsTwo-way working systemsUltrasound attenuationNoise level
The present invention relates to a CATV circuit with an automatic noise controller and a CATV system using the CATV circuit. The CATV circuit is used for automatically reducing upstream noises occurred in a CATV circuit for bidirectional communications between a control center and a home terminal. A variable attenuation method is applied to the CATV circuit, and a noise level measurement method is applied to measure the upstream noise level and control the attenuation rate according to the measured noise level.
Owner:HWA LIN ELECTRONICS SHENZHEN +1
GNSS navigation solution integrity in non-controlled environments
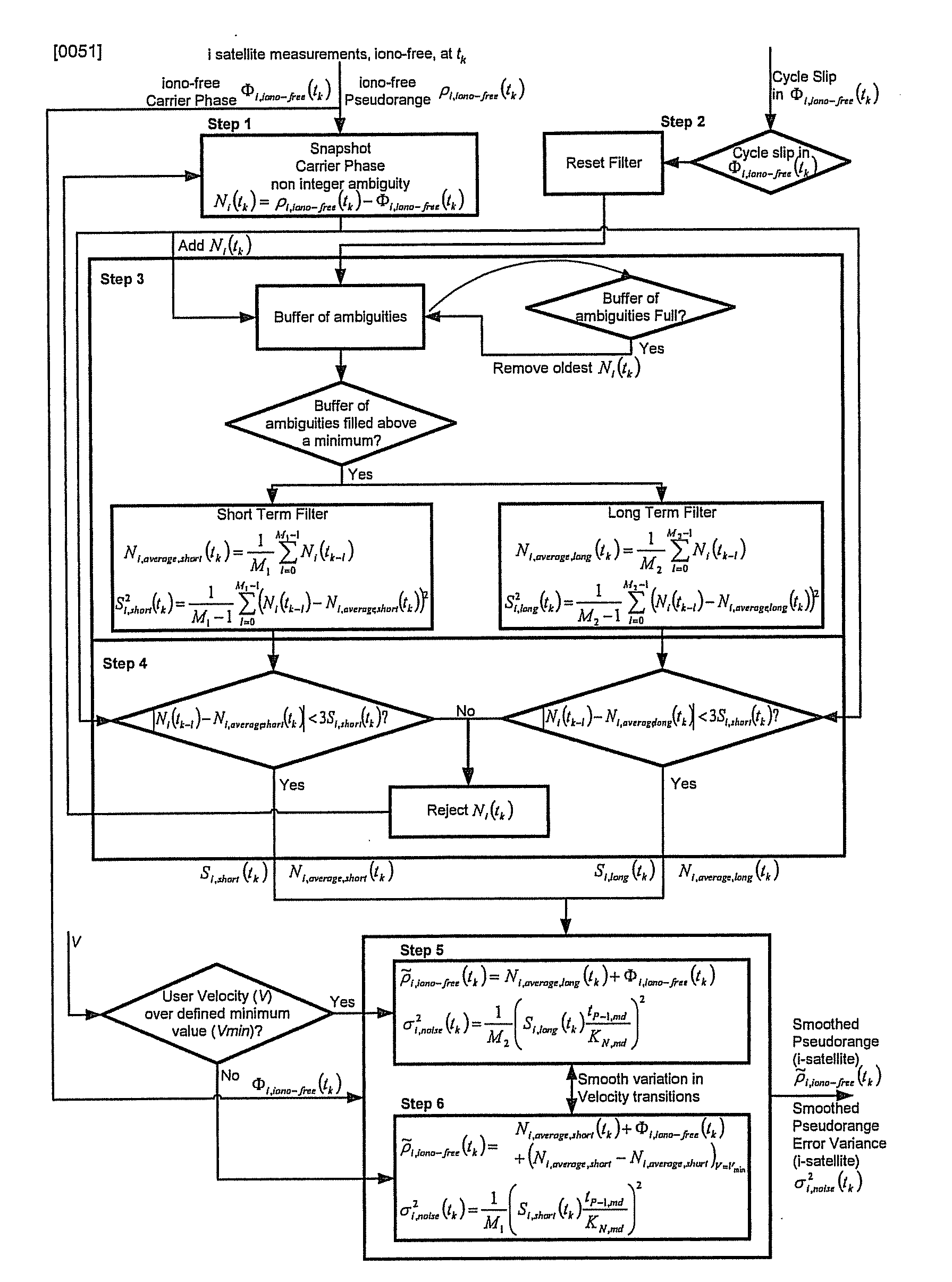
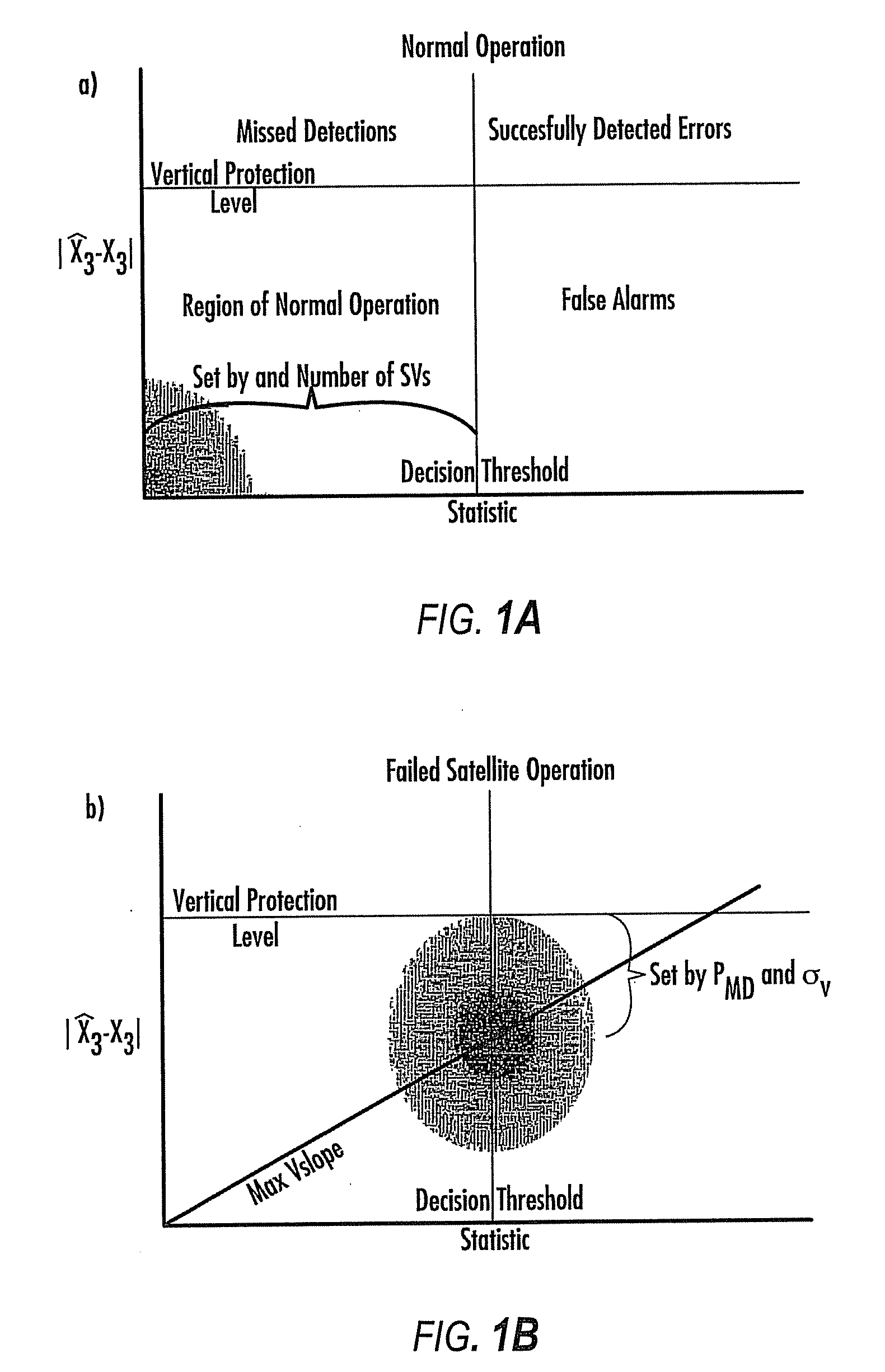
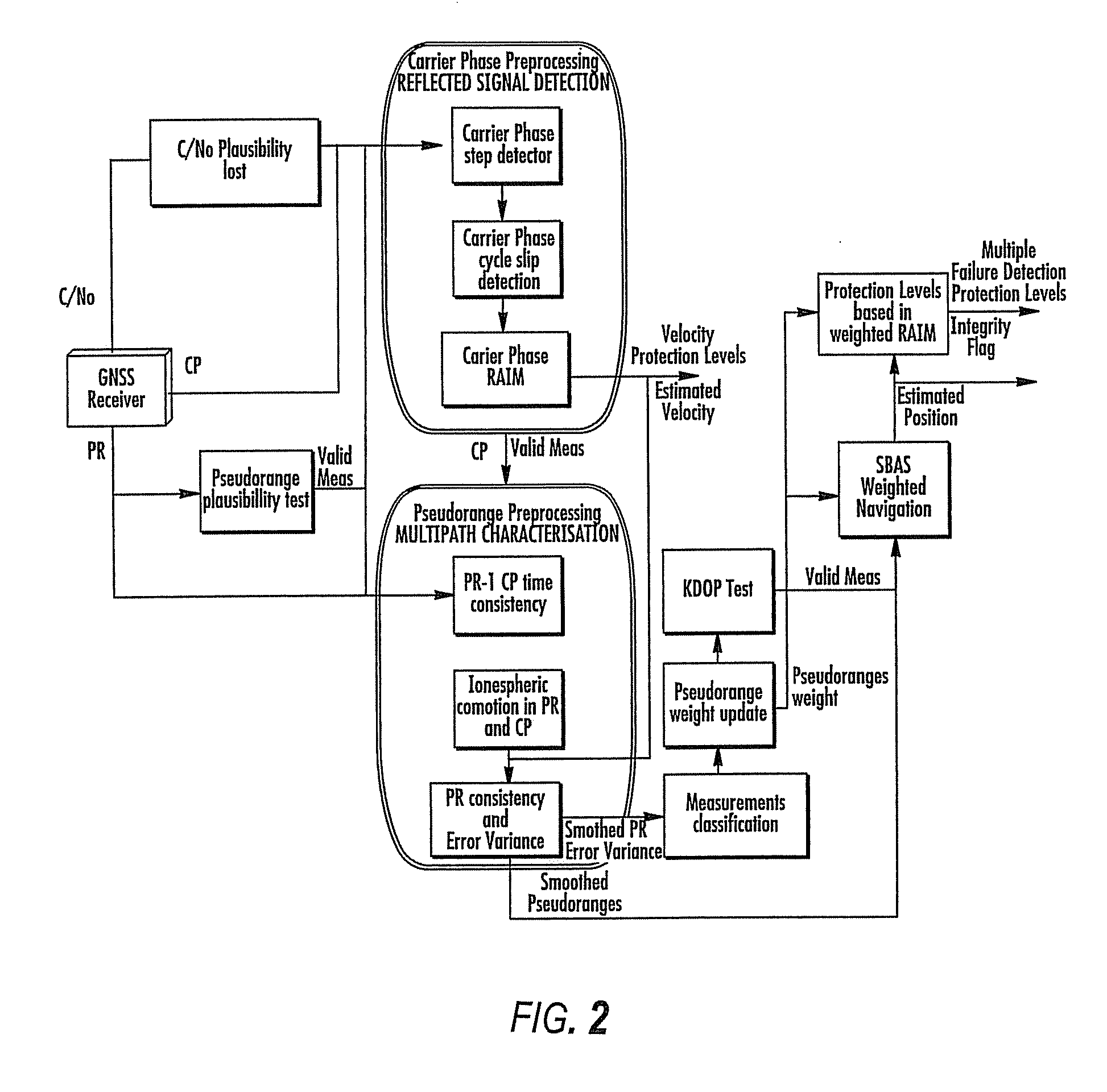
ActiveUS20100033370A1Efficient methodImprove navigation accuracyPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsNoise levelMarine navigation
Disclosed is a method for providing a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) navigation position solution with guaranteed integrity in non-controlled environments, the method including processing a (GNSS) signal including multiple satellites generating at least one signal to obtain carrier phase and pseudorange measurements; pre-processing the measurements to detect and characterize local errors in the measurements, wherein the local errors cannot be ascertained a priori, the characterization including providing error bounds estimated by measuring the carrier phase and pseudoranges measurements, thereby providing a set of measurements rejections when the characterization is not possible; and using the estimated error bounds, together with error bounds provided by the GNSS signal concerning satellite and ionospheric errors, to build in each measurement an estimated noise level in the measurements as input to a weighted Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring (RAIM) algorithm in order to compute position coordinates and associated protection levels in the non-controlled environments.
Owner:GMV AEROSPACE & DEFENCE
Pattern recognition adaptive controller
InactiveUS6937909B2Sampled-variable control systemsIgnition automatic controlNoise levelTime control
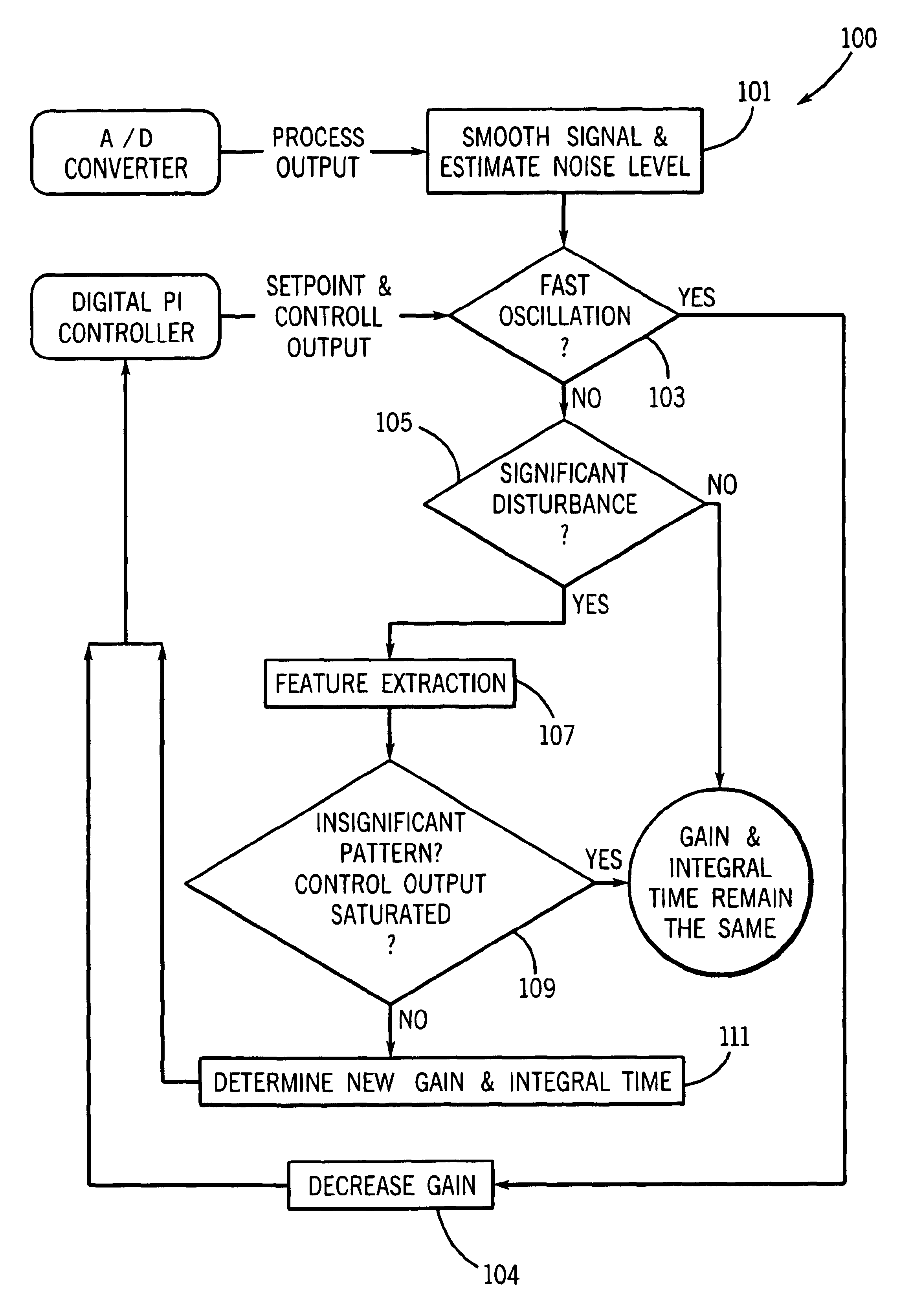
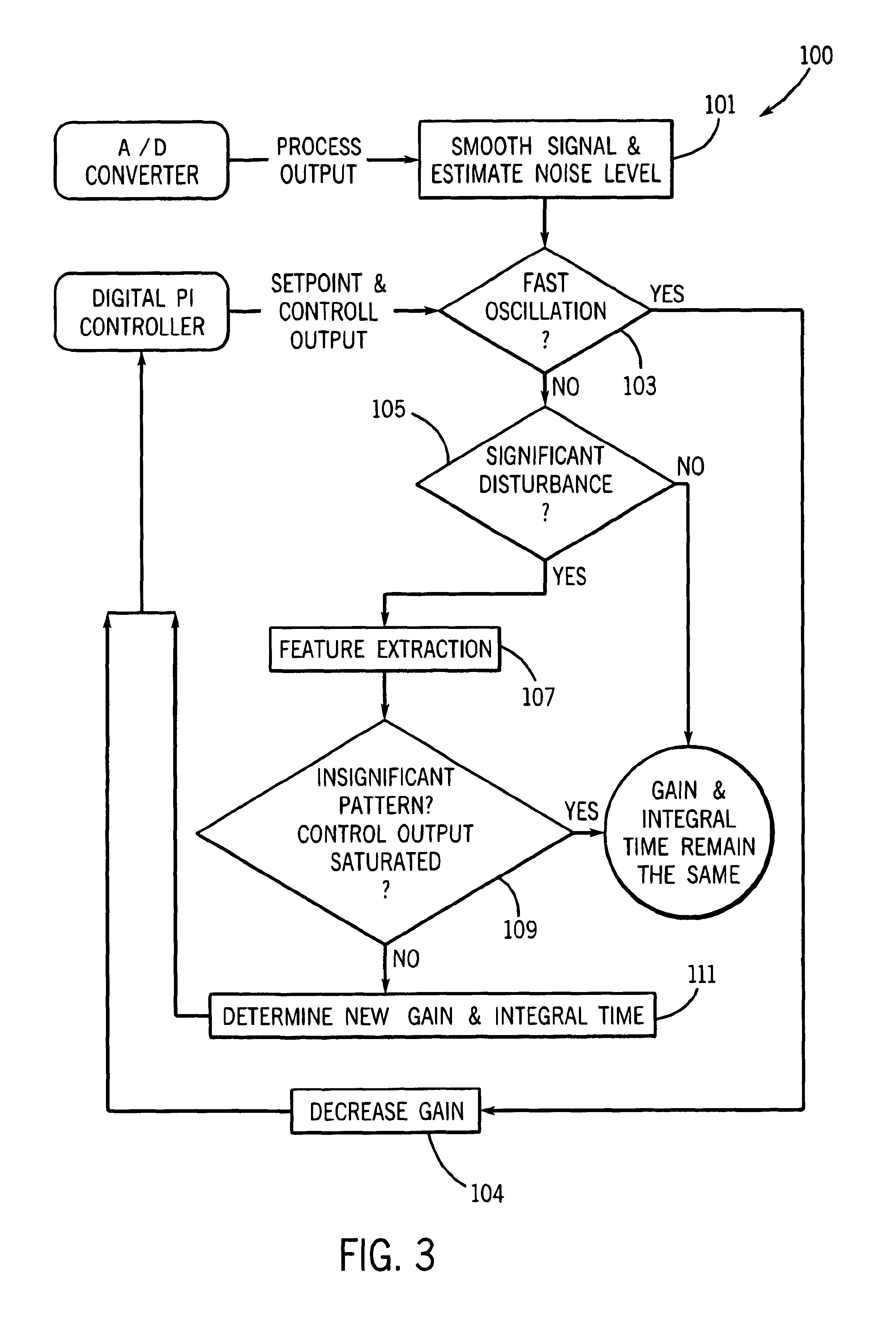
A pattern recognition adaptive controller configured to dynamically adjust proportional gain and integral time control parameters based upon patterns that characterize the closed-loop response. The pattern recognition adaptive controller receives a sampled signal representative of the controlled variable, and determines a smoothed signal based on the sampled signal. The controller determines an estimated noise level of the sampled signal and determines if the control output and process output are oscillating quickly based on predefined criteria. The controller adjusts the gain used by the controller if the control output and process output are oscillating quickly. If the control output and process are not oscillating quickly, the controller determines whether there has been a significant load disturbance, whether there is an insignificant pattern, and / or whether the control output is saturated. Based on the results of these determinations, the controller either leaves the gain and integral time unchanged or determines new gain and integral time. The adjusted control parameters are then used to control the actuator, thereby causing the controller to affect the process.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TECH CO
Elevator safety circuit monitor and control for drive and brake
InactiveUS6056088AAvoiding electrically conductive separating locationReduce noise levelSafety arrangmentsAlarmsManufacturing cost reductionNoise level
Monitoring equipment for an elevator drive control includes two modules, a safety circuit sensor system and a motor-switching and / or brake-switching circuit, wherein the monitoring of a safety circuit and the consequential actions resulting therefrom takes place exclusively by means of electronic components while avoiding electrically conductive separating locations. By the use of electronic components, electromechanical switching elements, which have electrically conductive separating locations, can be dispensed with. In addition, an appreciable reduction in the noise level is achieved, since switching noises no longer arise. This has an advantageous effect particularly in the case of elevator installations without a machine room. Furthermore, the manufacturing costs can be significantly reduced and a high security and reliability of the monitoring equipment can be ensured by the use of usual electronic components.
Owner:INVENTIO AG
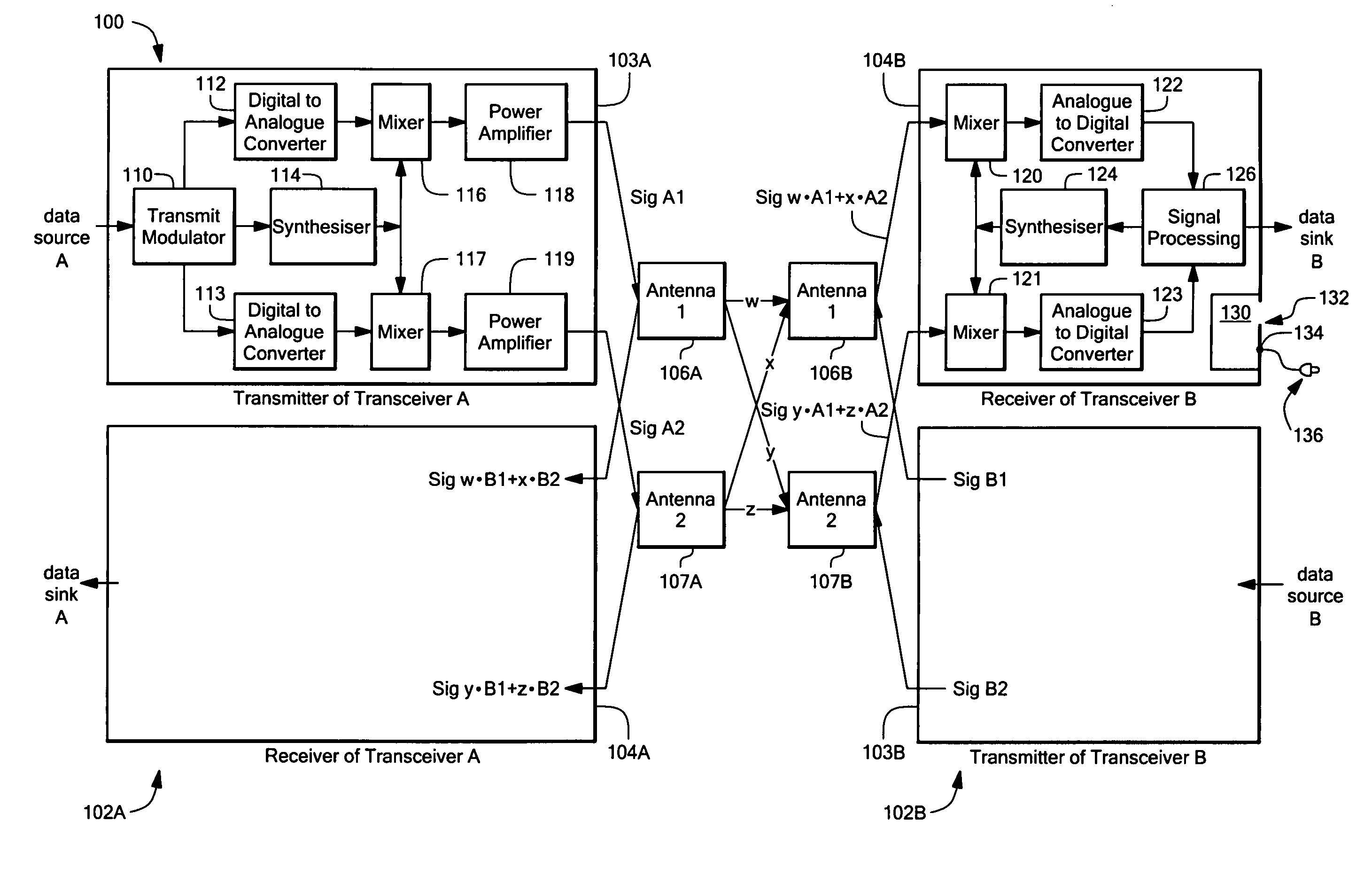
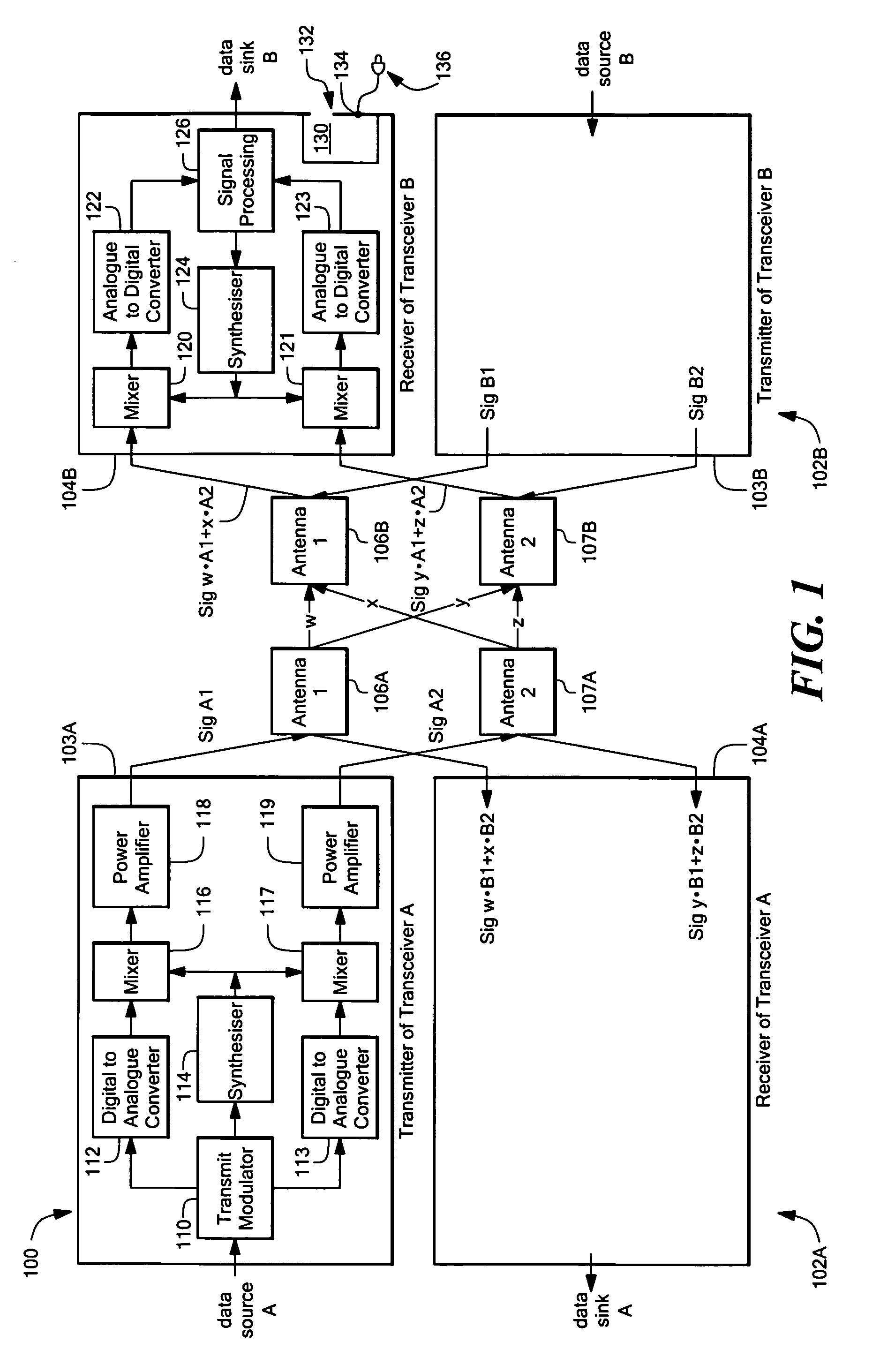
Intelligent adaptive modulation in a multiple input multiple output (MIMO) wireless communications system
ActiveUS7469013B1Reduce power levelIncreased de-correlationSpatial transmit diversityError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorOperational systemDynamic channel
A wireless broadband communications system that can maintain high data rates while taking into account channel interference resulting from operating in shared frequency bands, signal fading resulting from dynamic channel degradation, and signal distortion resulting from compliance with maximum power output regulations. In one mode of operation, the system performs adaptive modulation by transmitting a first signal over a selected channel using a first modulation mode having a level of distortion associated therewith resulting from operating the system at a predetermined maximum power output level. Next, a SINAD level is measured on the first channel. The level of distortion associated with the first modulation mode is then subtracted from the measured SINAD level to obtain a first noise level. In the event the first noise level is less than a noise level required to achieve an acceptable error rate in a next modulation mode, a second signal is transmitted over the selected channel using the next modulation mode.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
System and method for automatically measuring uplink noise level of distributed antenna system
A method of automatically measuring noise levels of a plurality of uplink paths in a Distributed Antenna System (DAS) includes: sequentially measuring a noise level of each uplink path of the plurality of uplink paths; extracting the noise level of each uplink path at a final end of the uplink path; detecting the noise level of each uplink path; and determining a status of each uplink path by comparing the detected noise level with a threshold value.
Owner:ADVANCED RF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com