Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
8214results about "Power amplifiers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
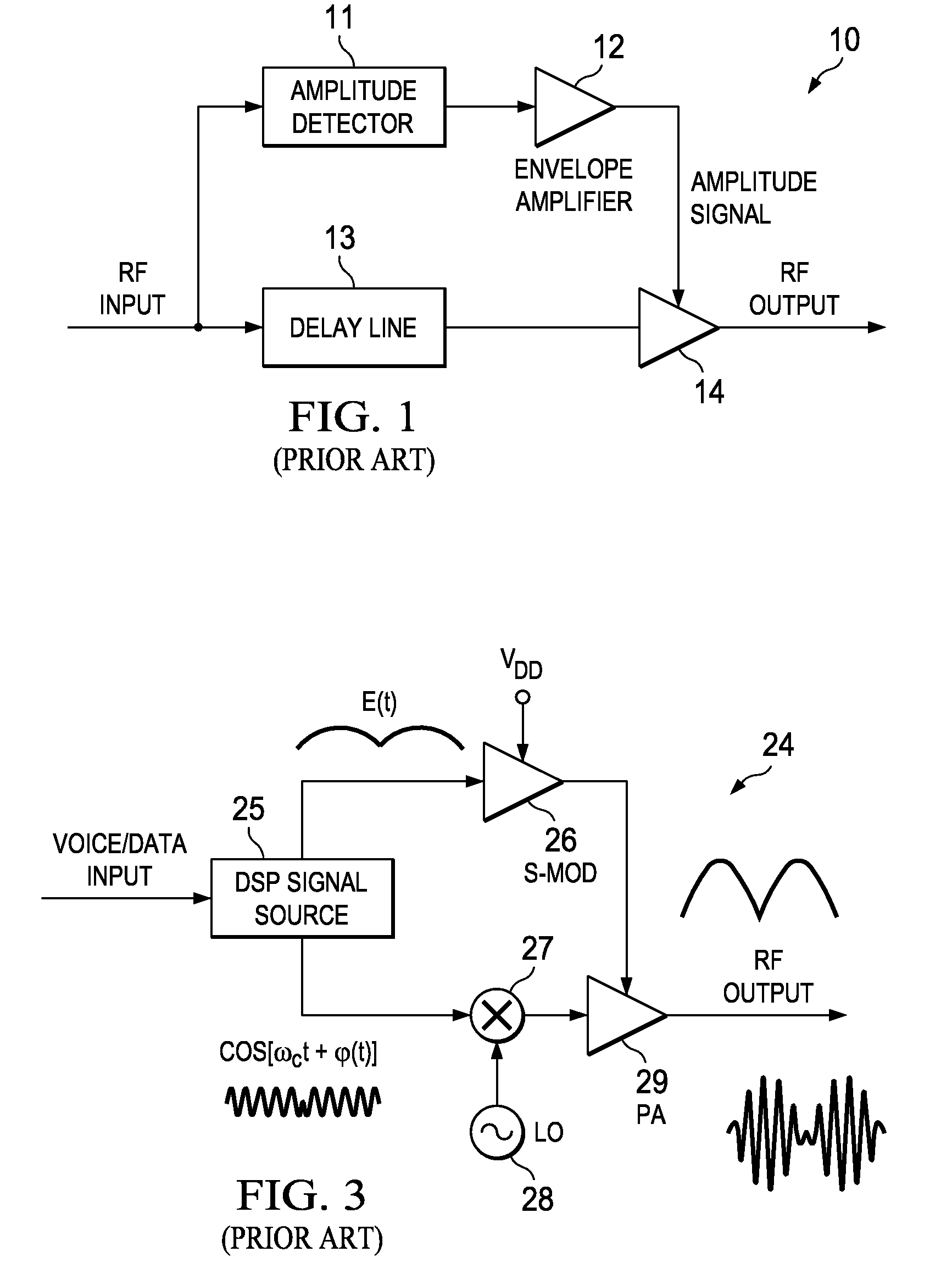
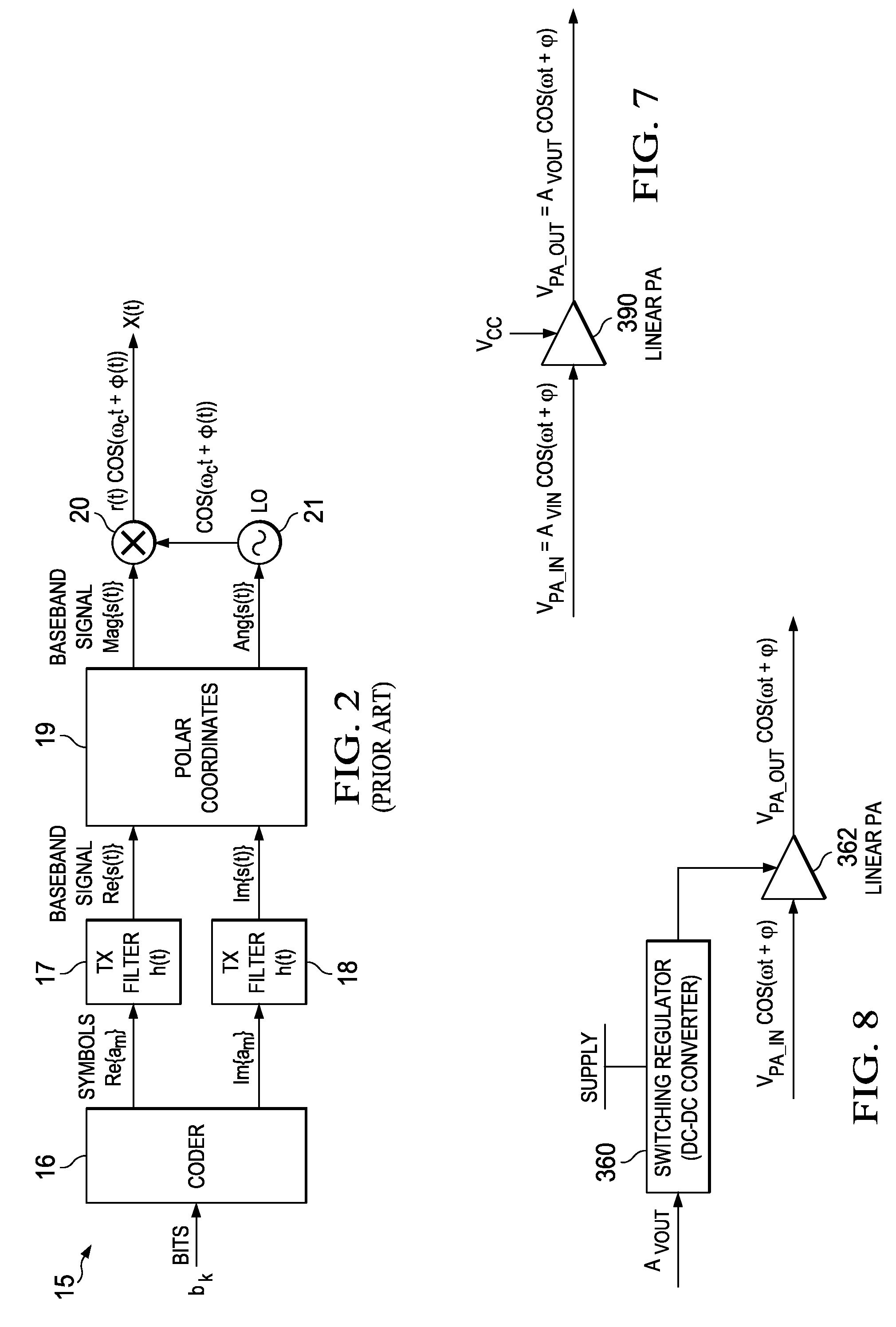
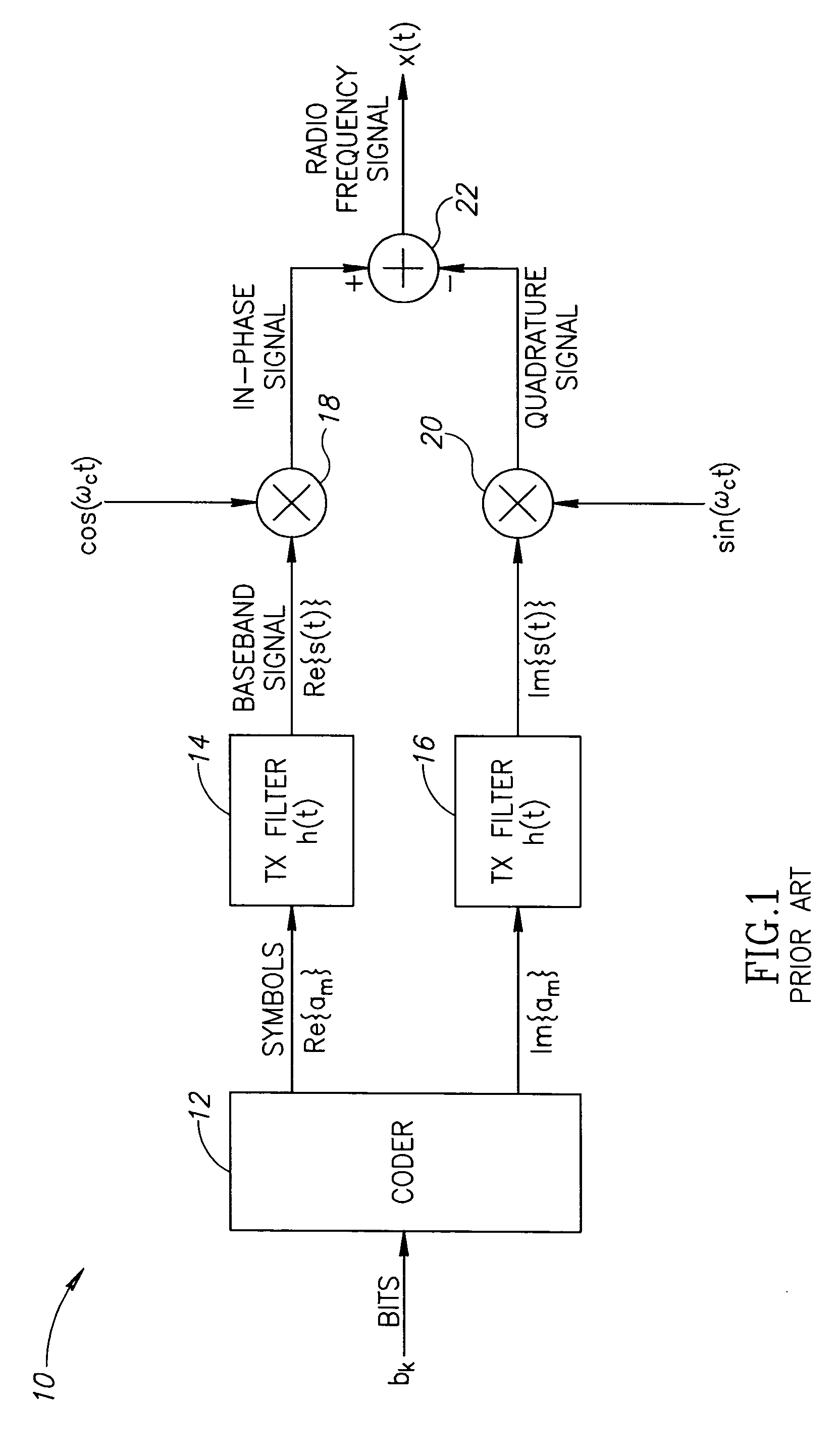
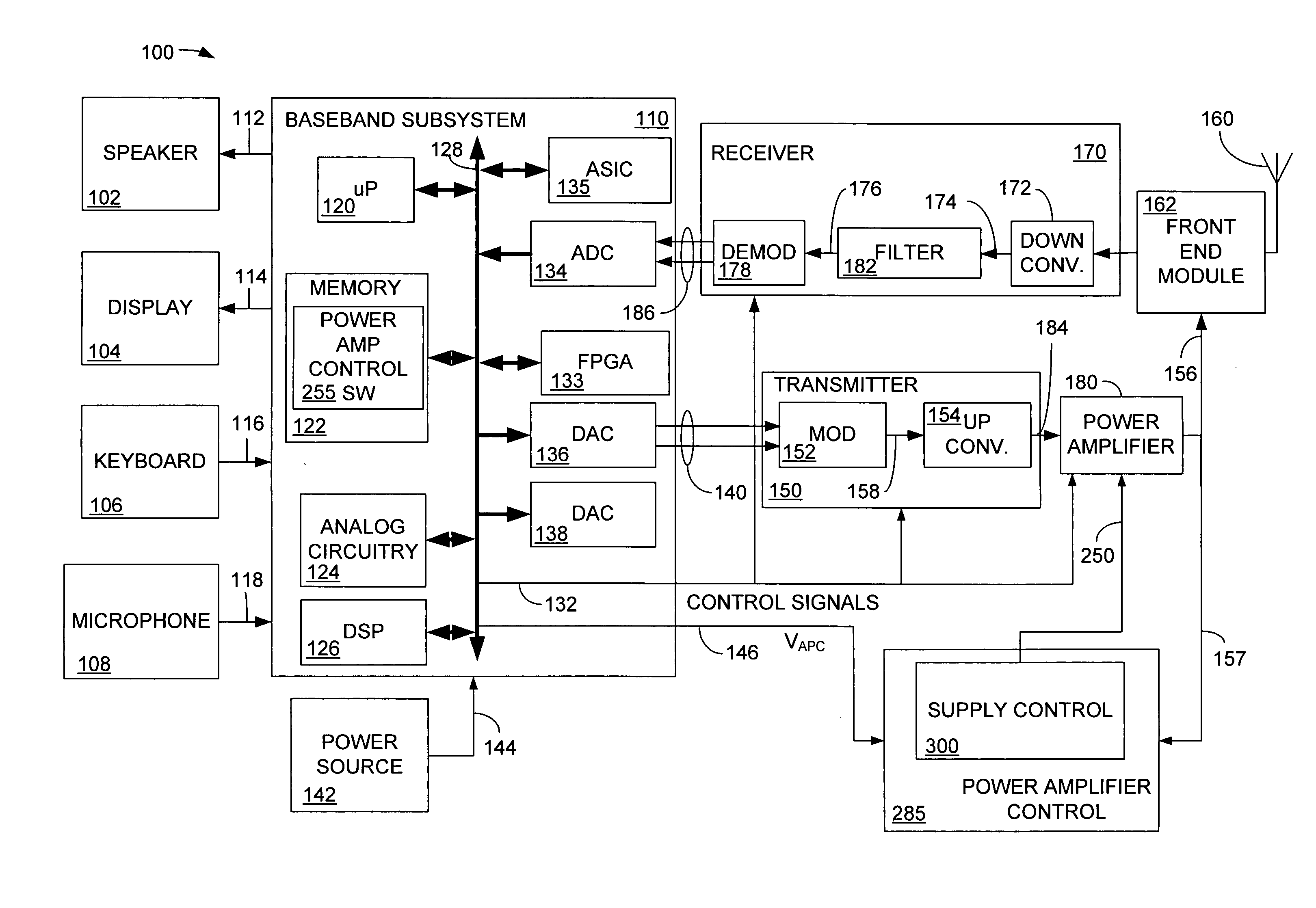
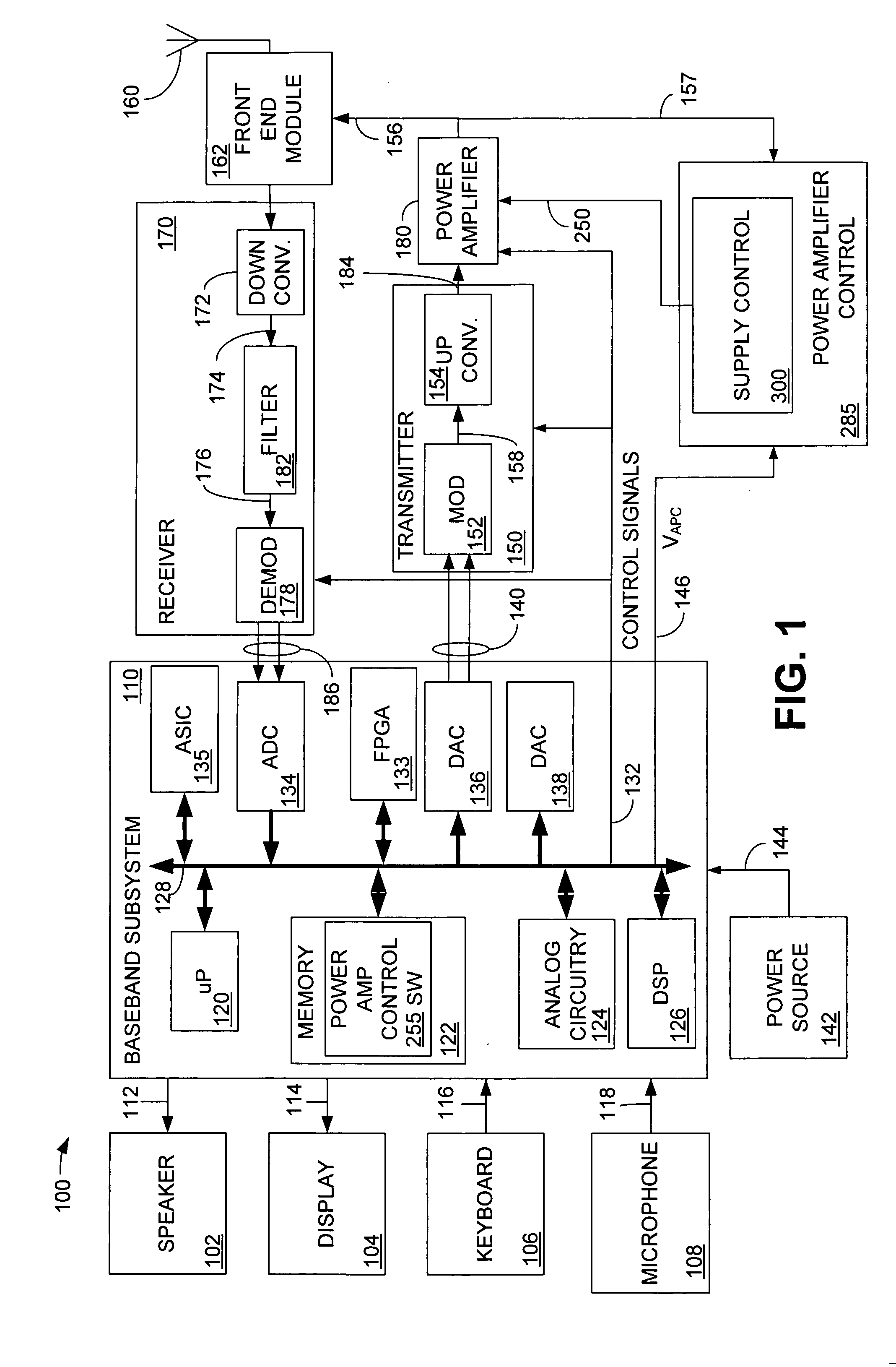
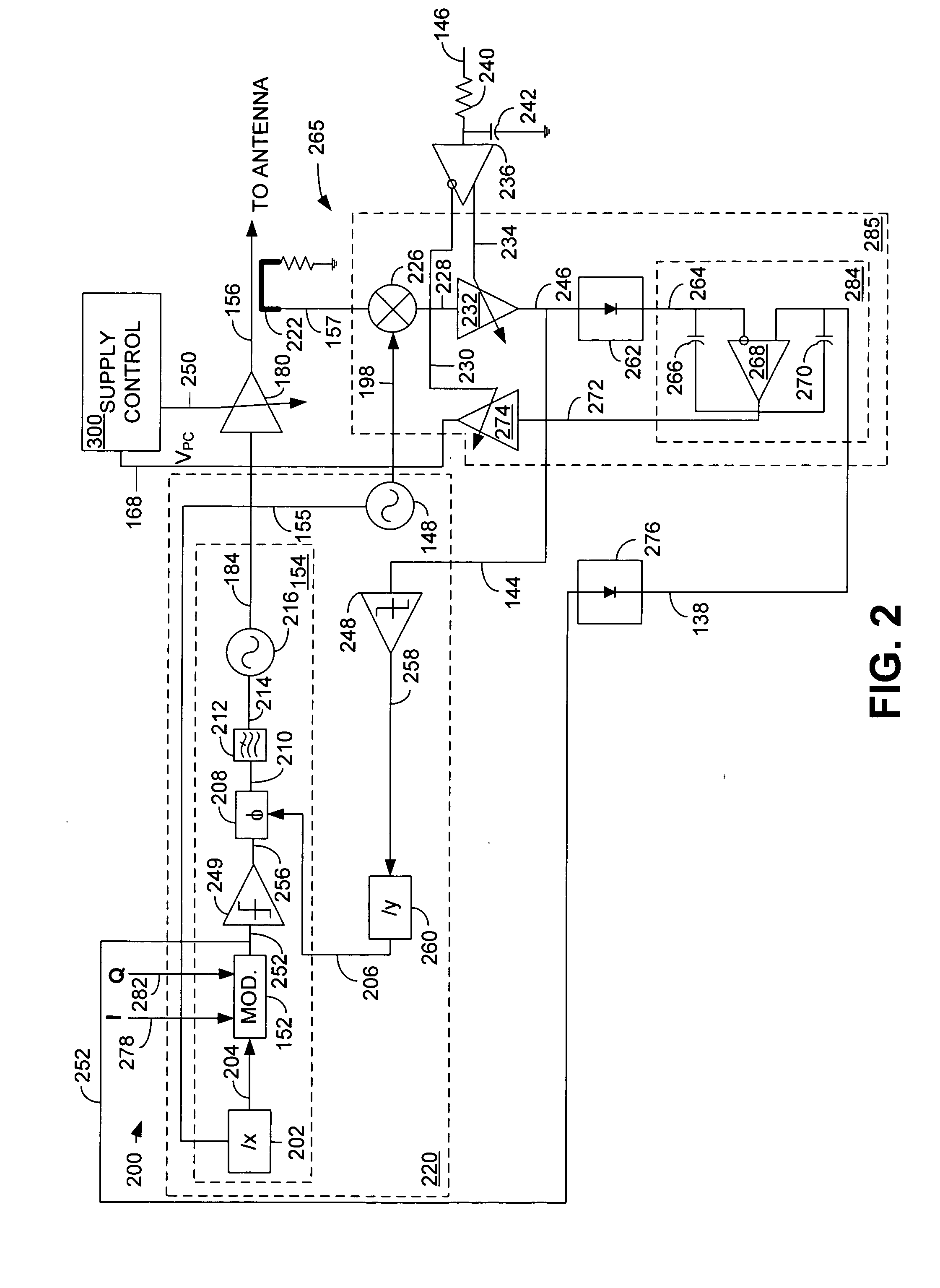
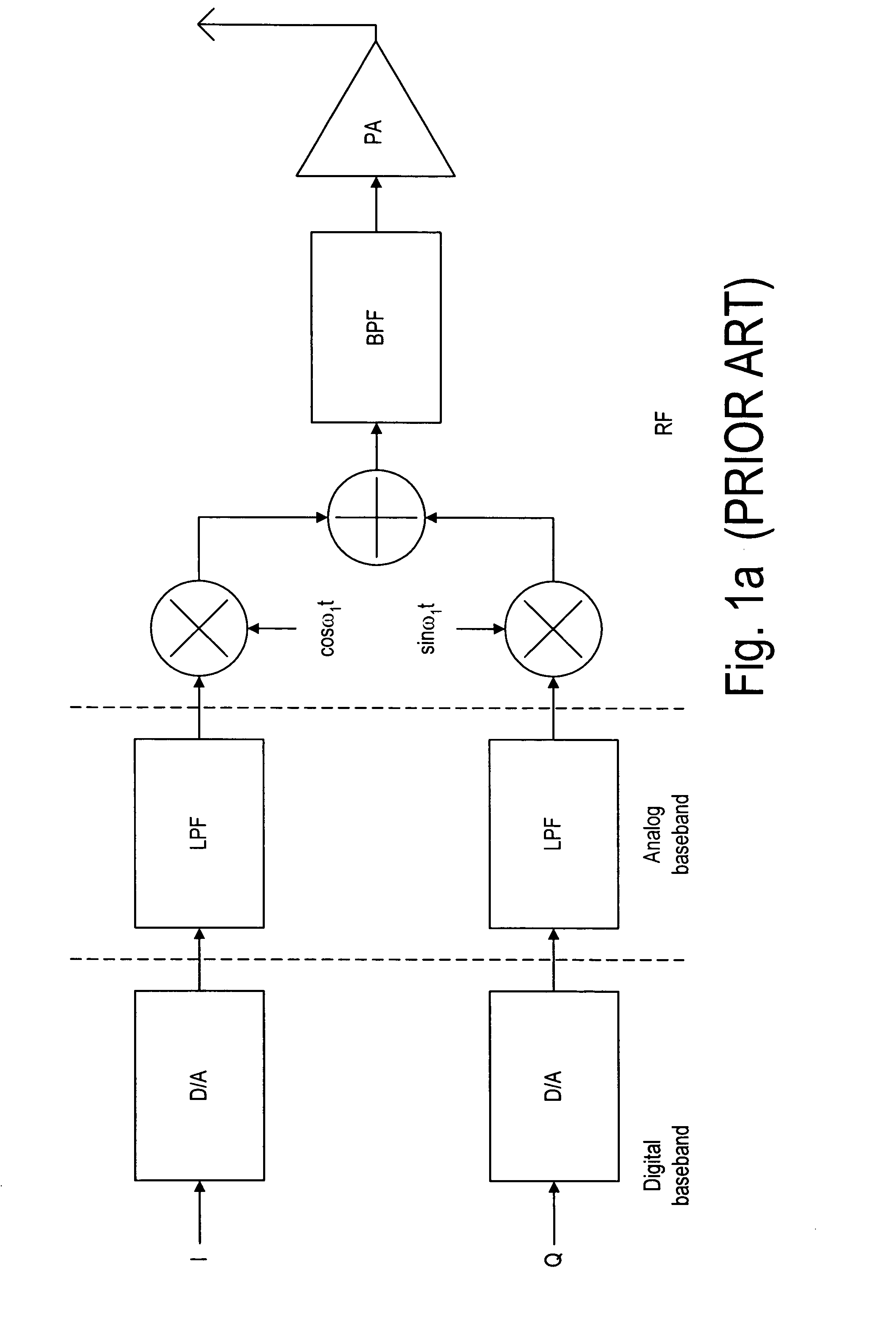
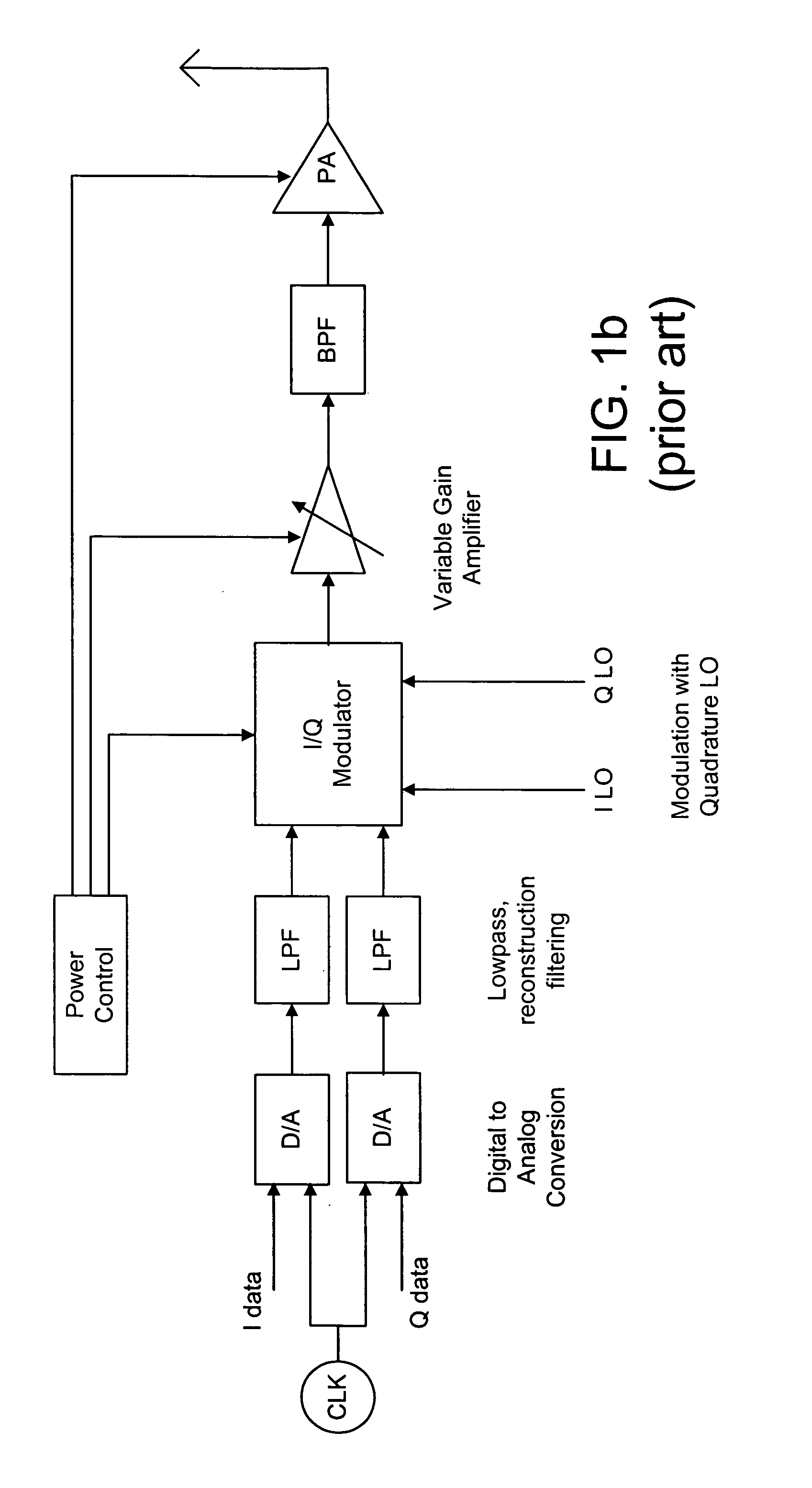
High efficiency digital transmitter incorporating switching power supply and linear power amplifier
InactiveUS20090004981A1Improve efficiencyAttenuation bandwidthResonant long antennasPower amplifiersDigital signal processingDc current
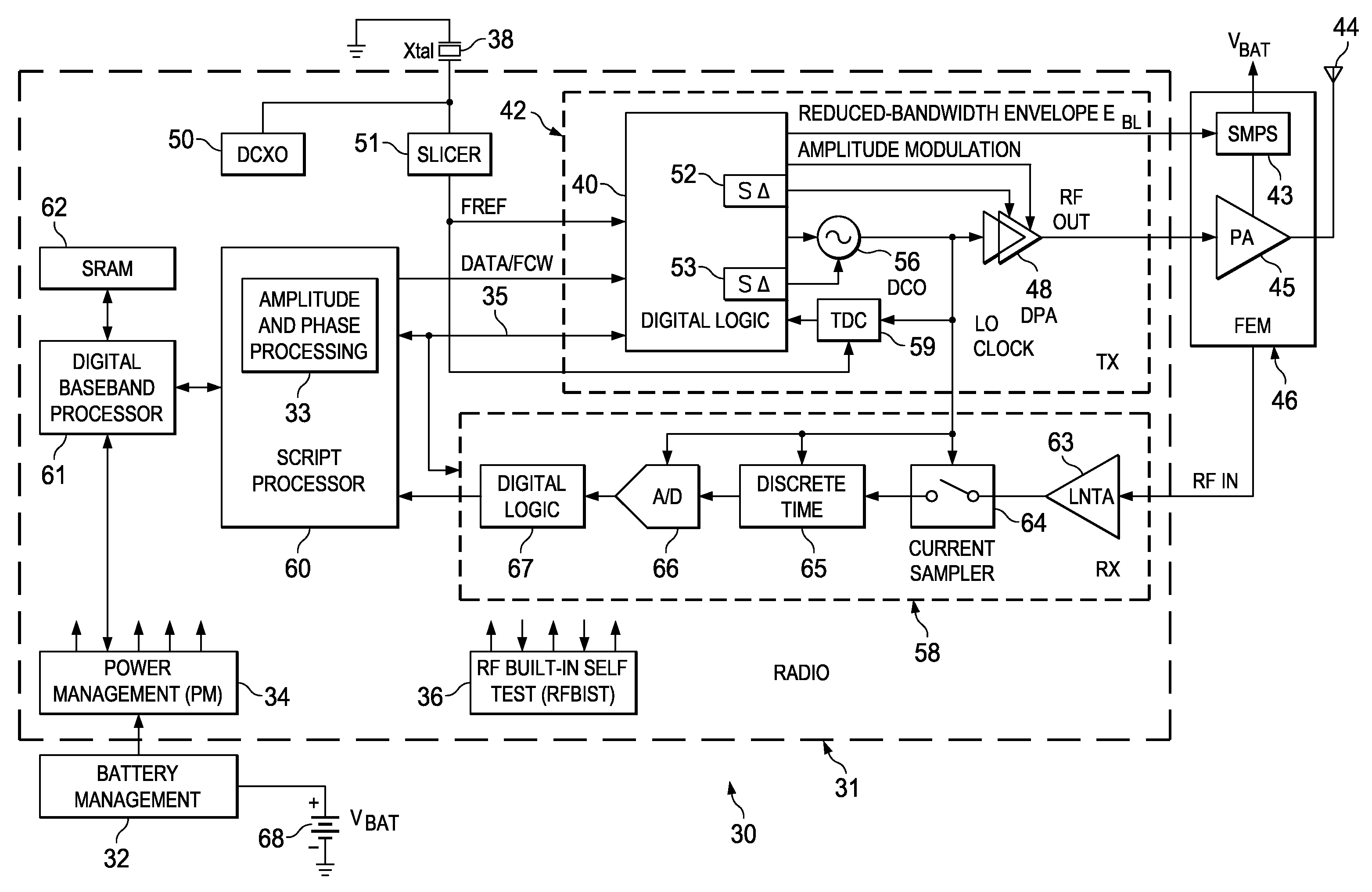
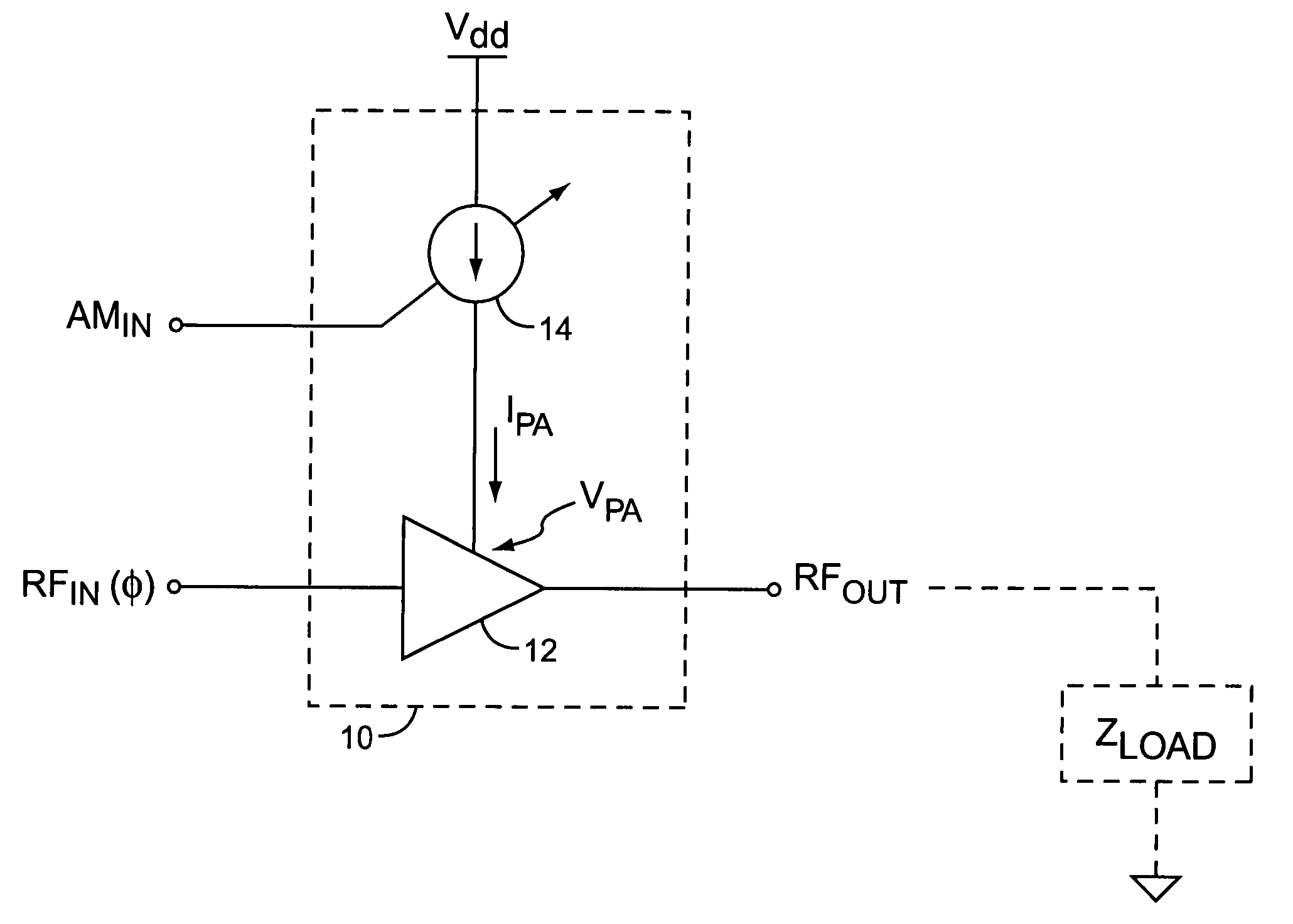
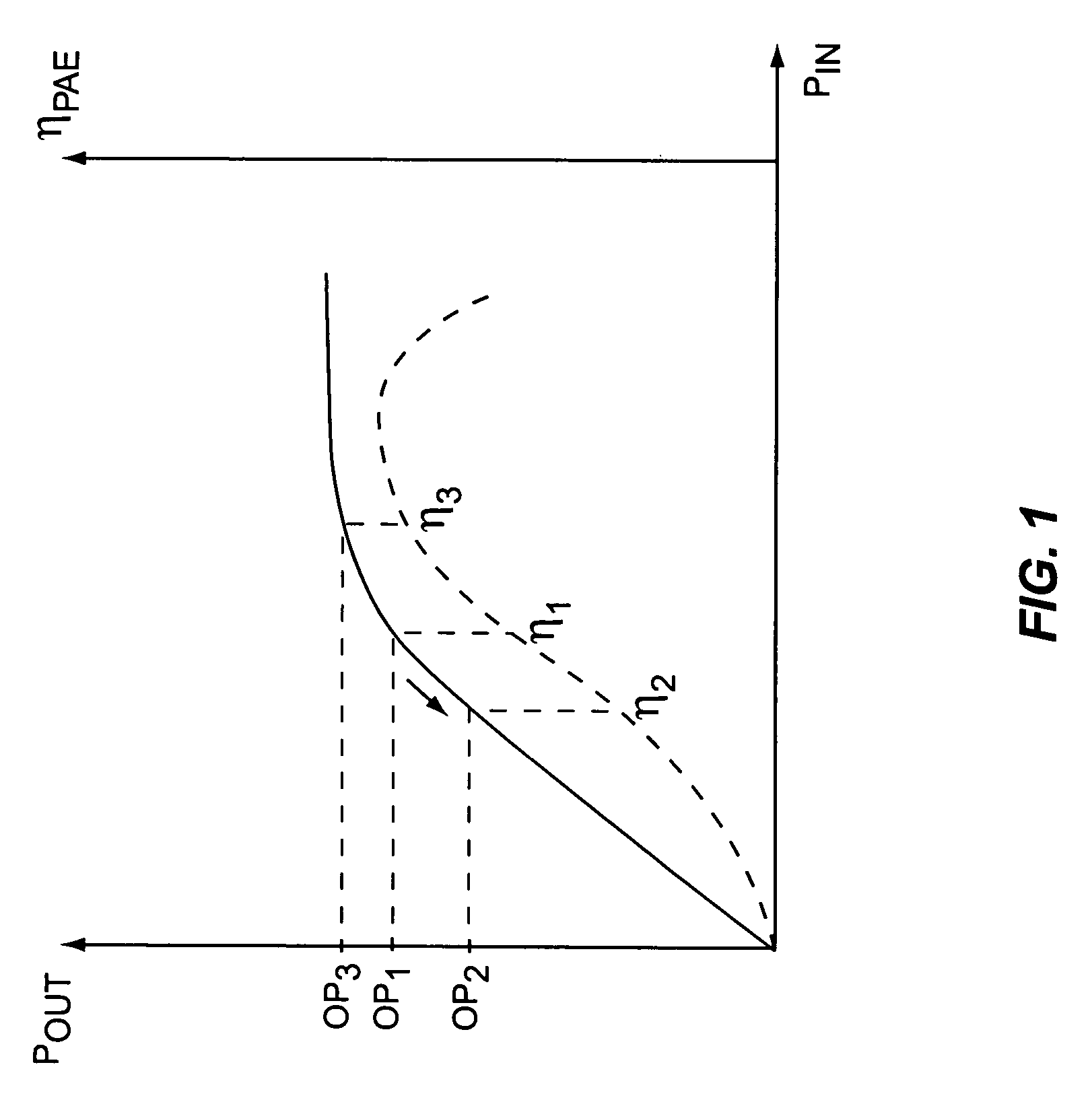
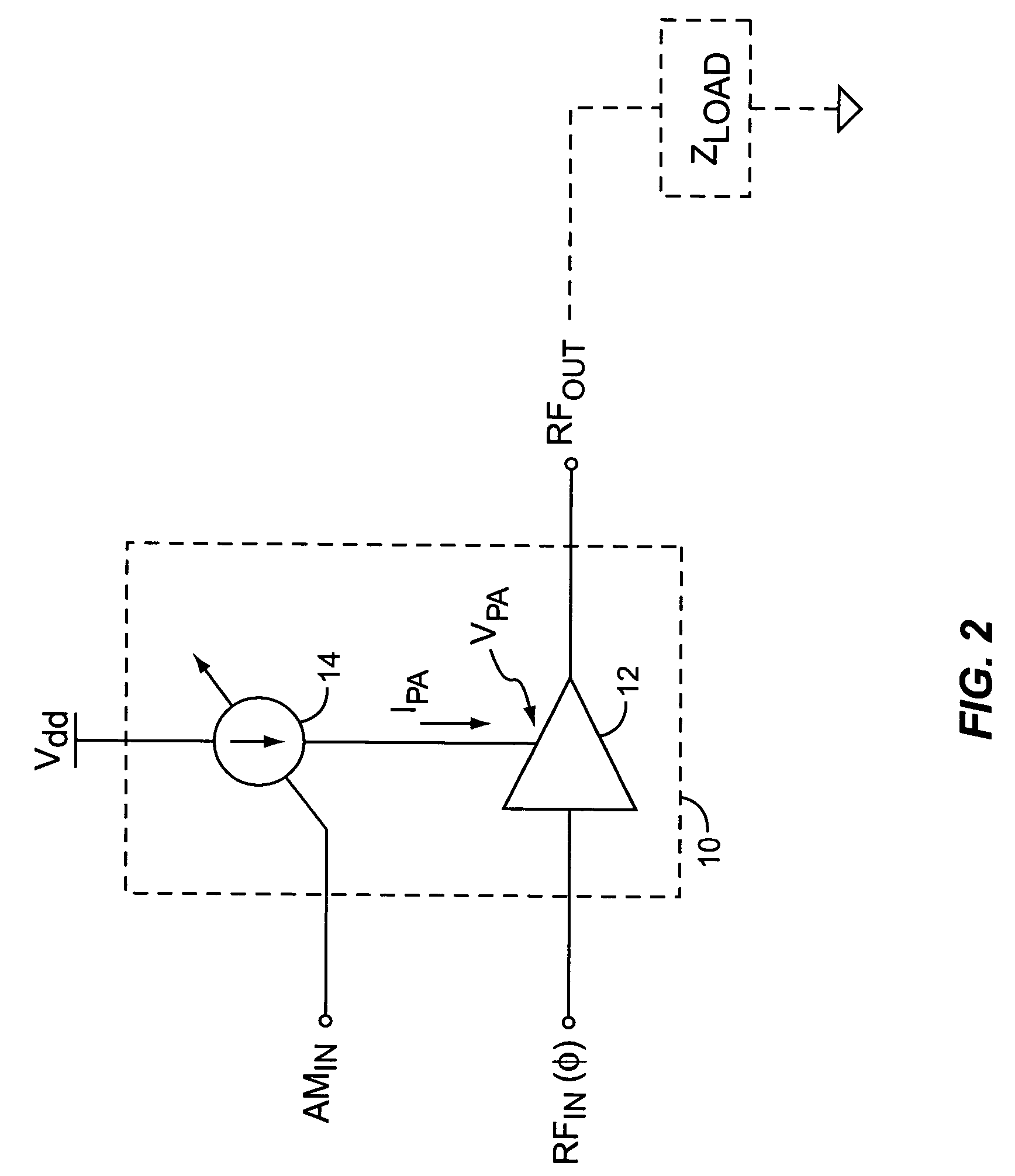
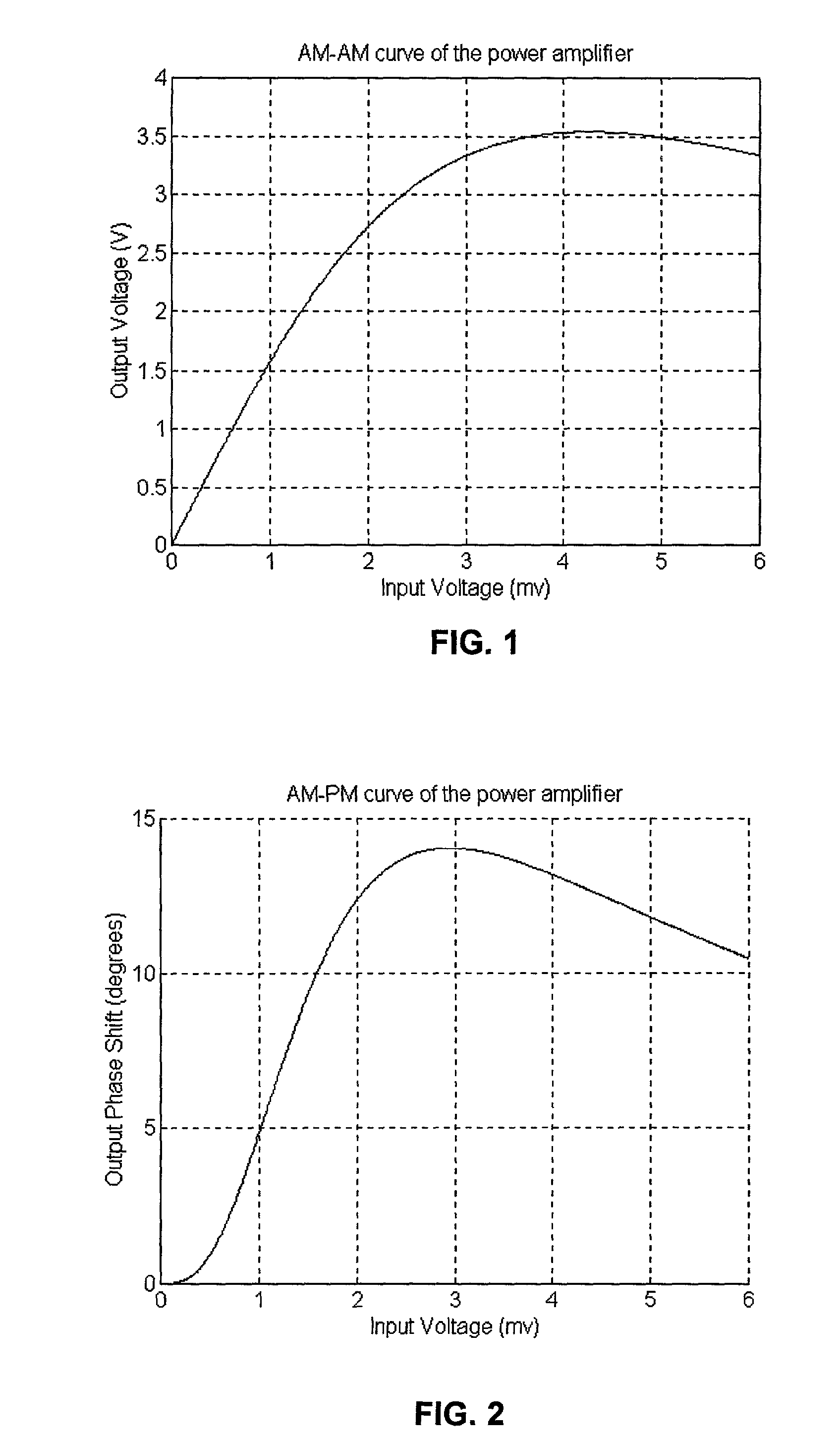
A novel apparatus and method of improving the power efficiency of a digital transmitter for non-constant-amplitude modulation schemes. The power efficiency improvement mechanism of the invention leverages the high efficiency of a switched-mode power supply (SMPS) that supplies the high DC current to the transmitter's power amplifier, while compensating for its limitations using predistortion. The predistortion may be achieved using any suitable technique such as digital signal processing, hardware techniques, etc. A switched mode power supply (i.e. switching regulator) is used to provide a slow form (i.e. reduced bandwidth) of envelope tracking (based on a narrower bandwidth distorted version of the envelope waveform) such that the switching regulator can use a lower switching rate corresponding to the lower bandwidth, thereby obtaining high efficiency in the switching regulator. The resulting AM-AM and AM-PM distortions in the power amplifier are compensated through predistortion of the digital amplitude modulating signal which dictates the envelope at the PA input. Similarly, the phase modulation is also compensated prior to the PA, such that once it undergoes the distortion in the PA, the end result is sufficiently close to the desired phase.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
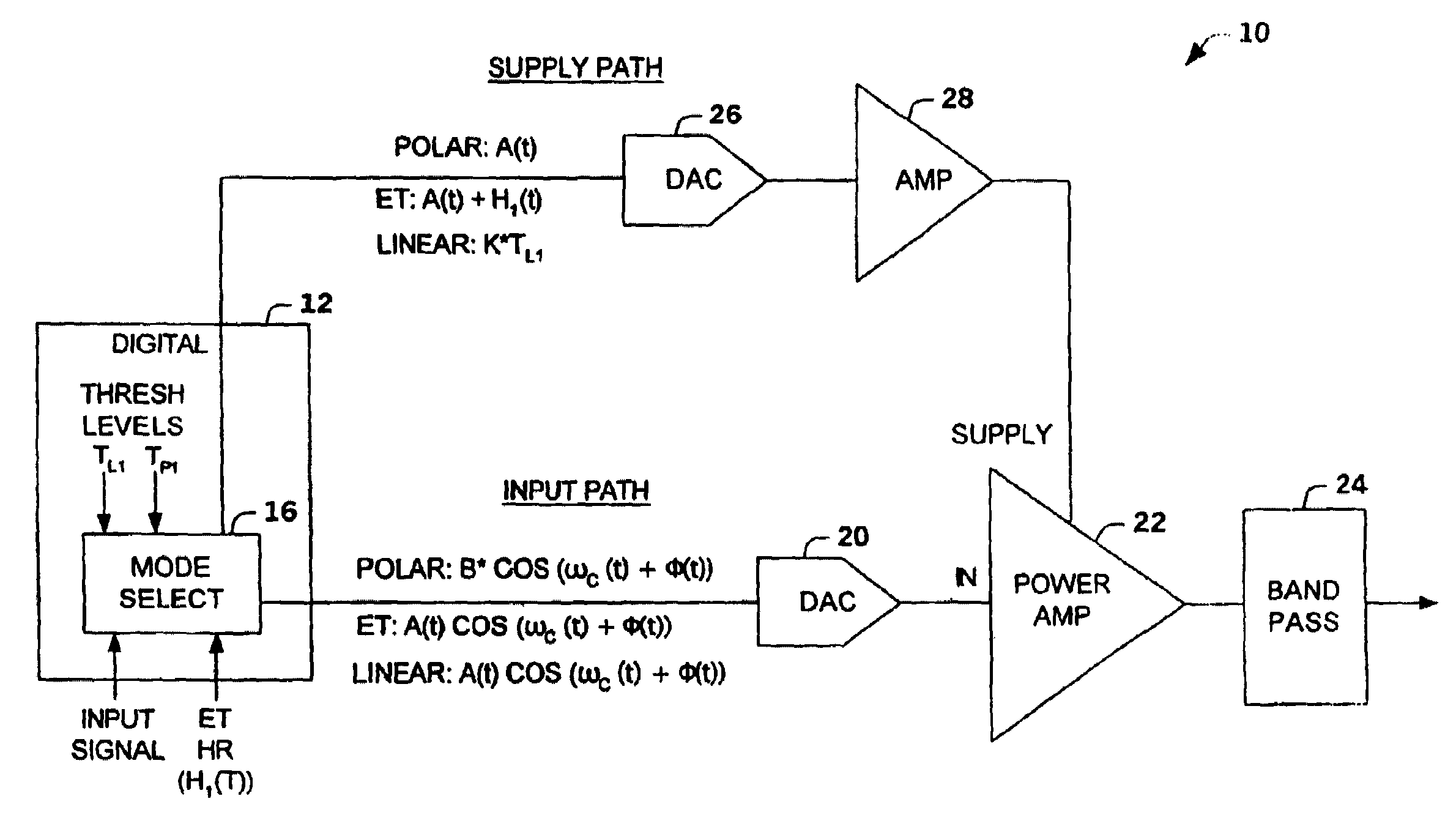
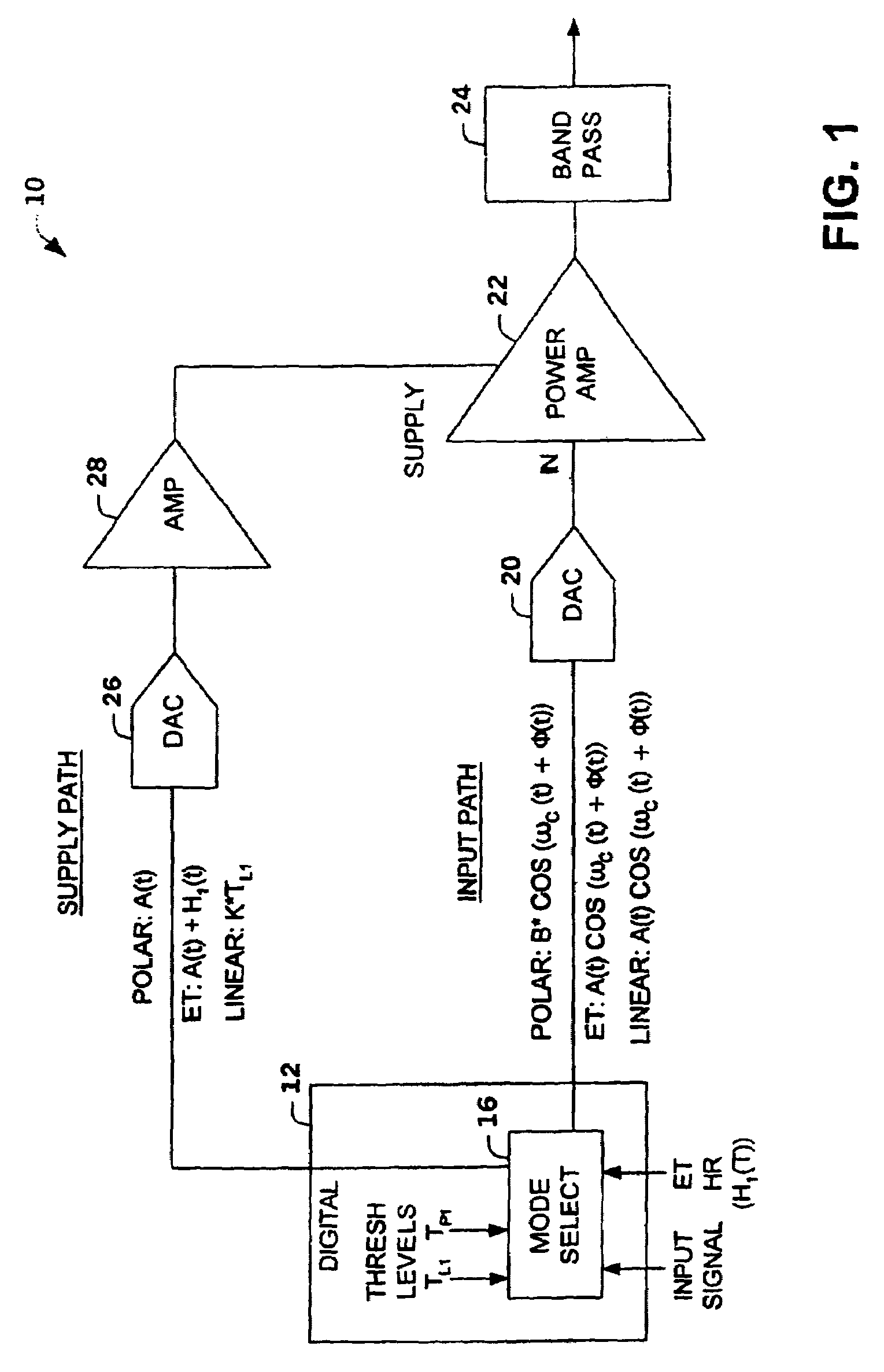
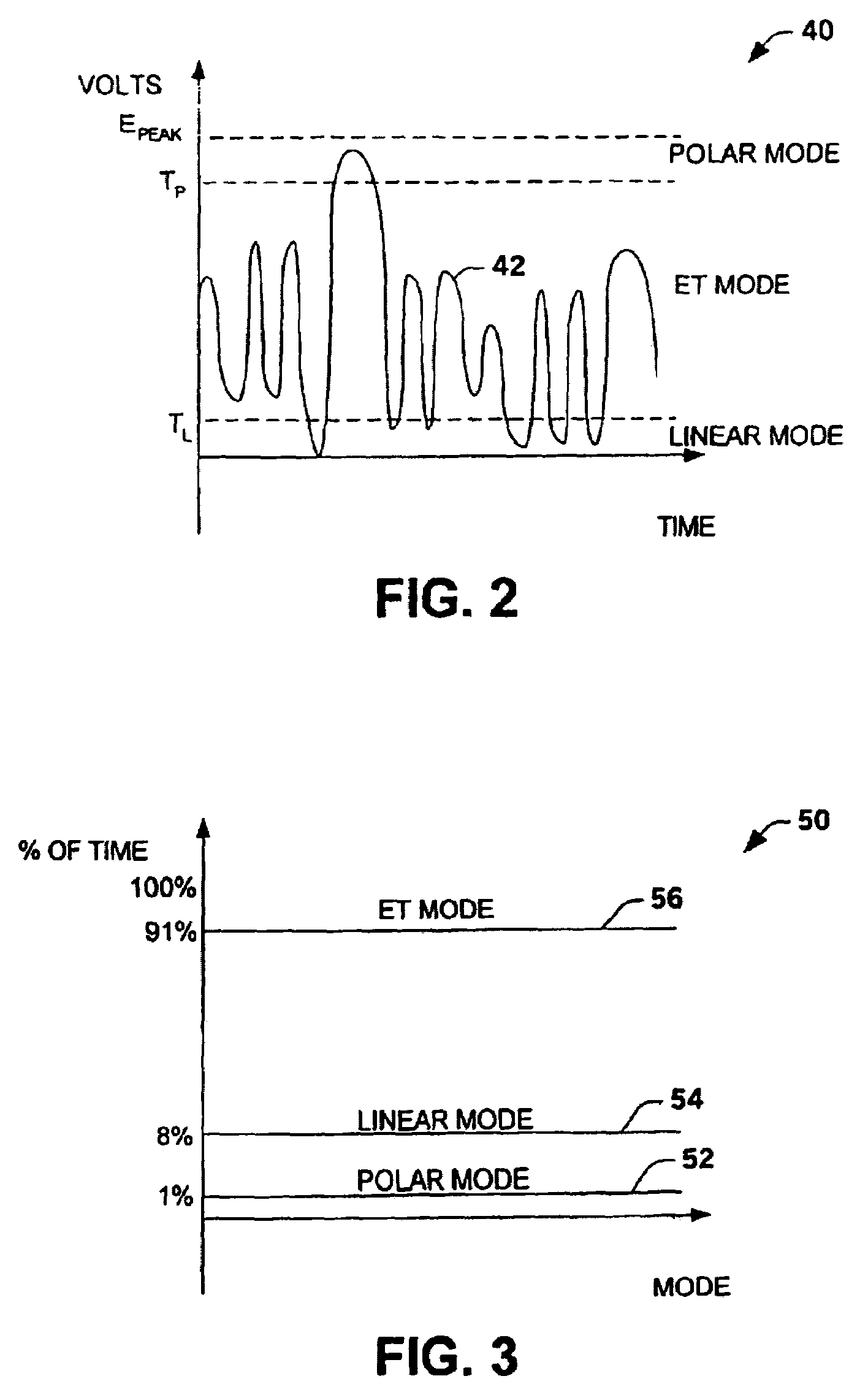
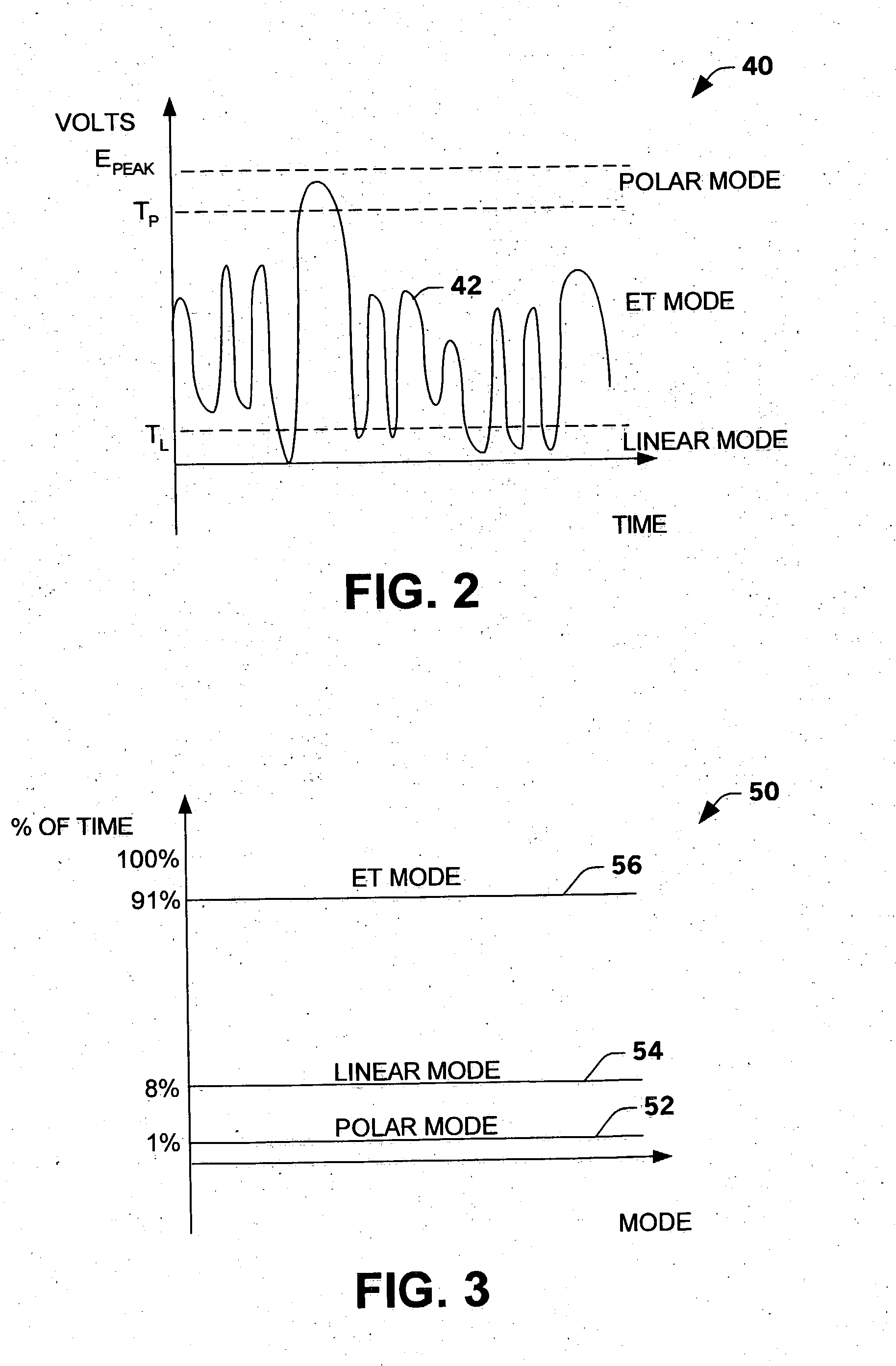
Multi-mode amplifier system
ActiveUS7043213B2Improve efficiencyOptimize emissionsAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierOperation mode
An amplifier system is provided that switches between a linear mode of operation, an envelope tracking mode of operation and a polar mode of operation. The amplifier system switches between modes of operation based upon a characteristic of an input signal relative to a first threshold level and a second threshold level. A mode selector selects the operation mode by transmitting an amplitude modulated signal plus a variable headroom voltage to a supply terminal of a power amplifier during the envelope tracking mode, an amplitude modulated signal to the supply terminal and phase modulated input signal during the polar mode and a substantially constant amplitude signal to the supply terminal during the linear mode.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
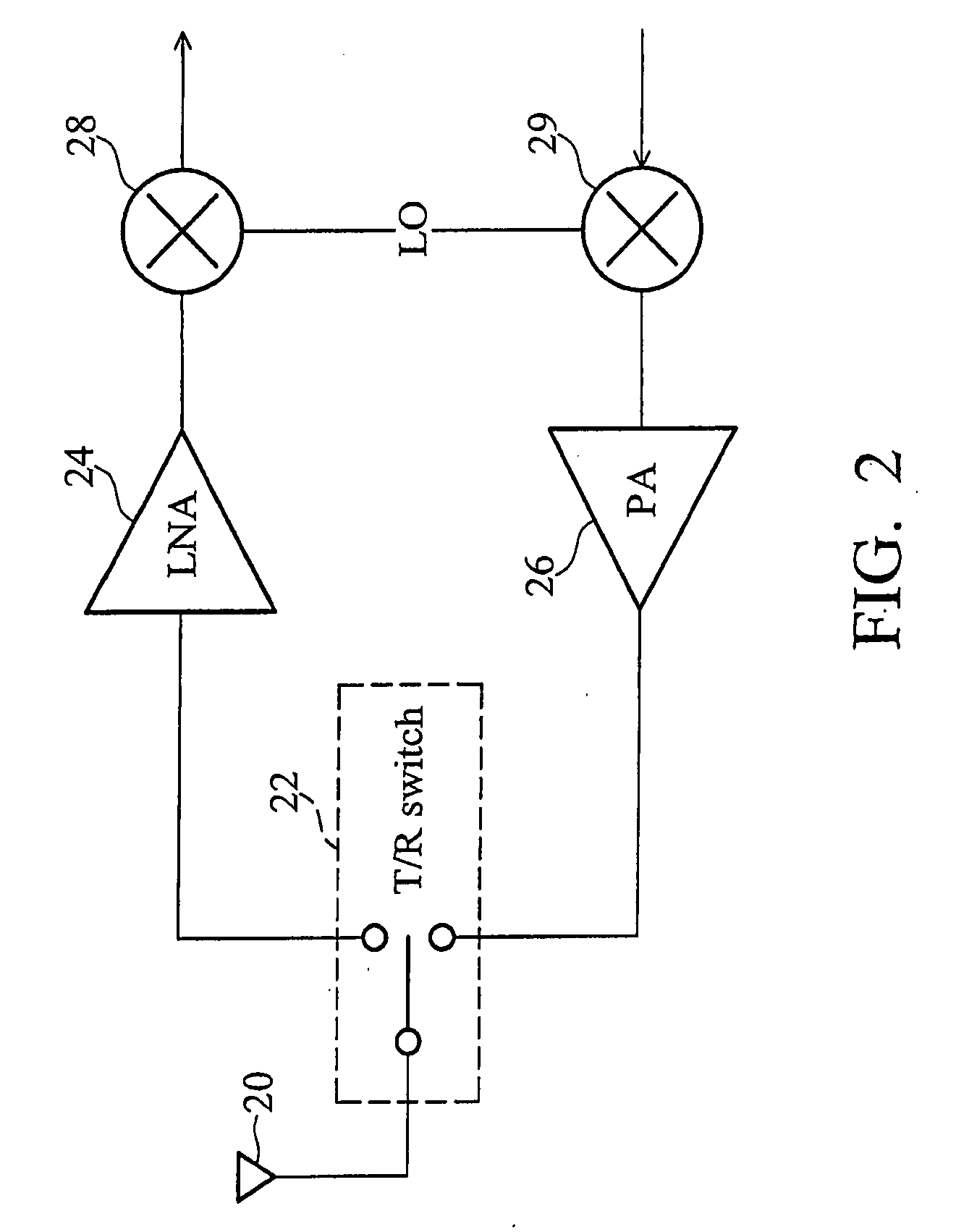
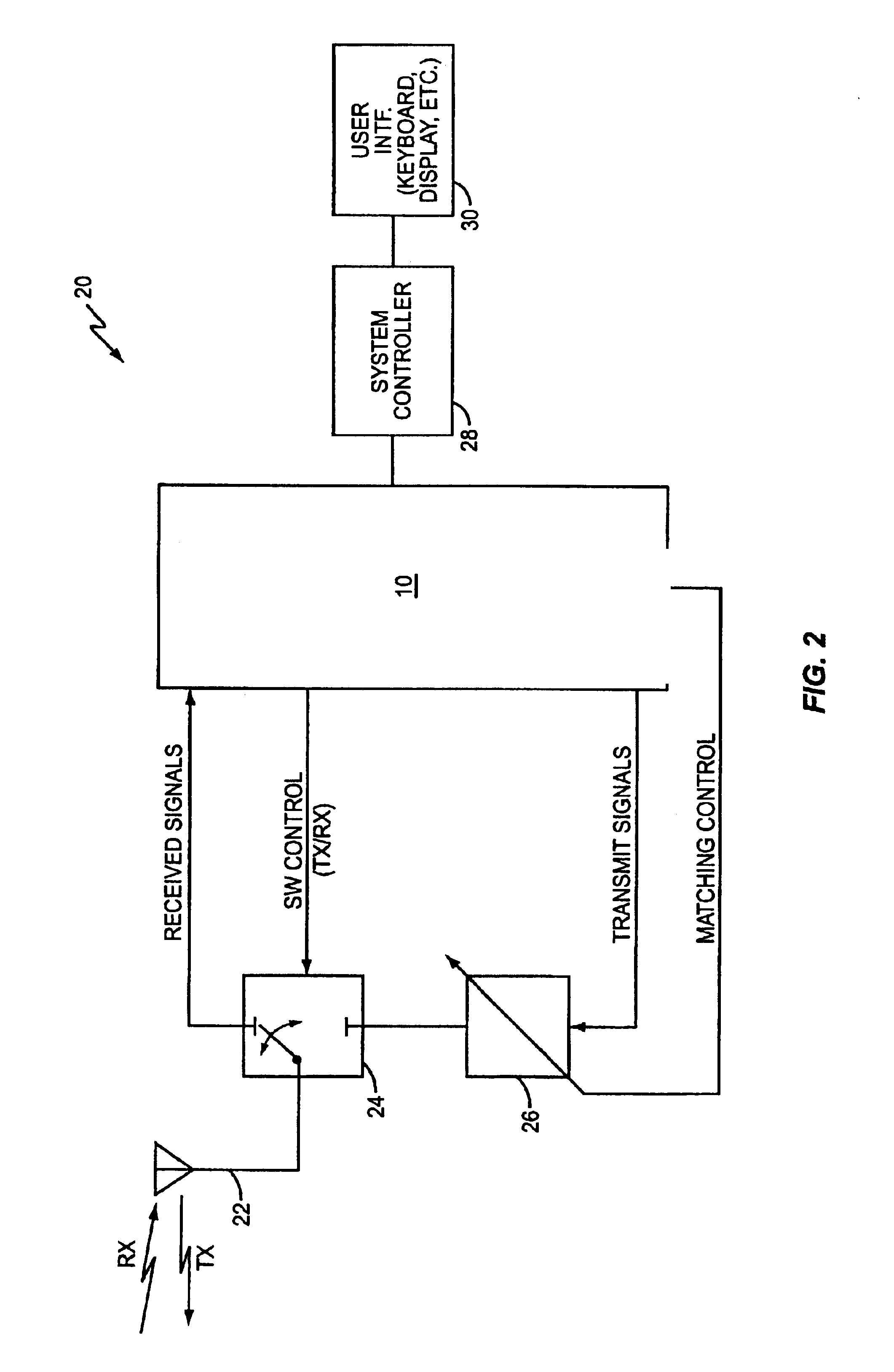
Transmit/receive switch
ActiveUS20090036065A1Reduce noiseMultiple-port networksResonant long antennasEngineeringImpedance matching
A radio frequency (RF) transmit / receive switch. The transmit / receive switch comprises an impedance matching circuit and a voltage scaling circuit. The impedance matching circuit matches an incoming RF signal to a low noise amplifier and an outgoing RF signal from a power amplifier. The voltage scaling circuit, coupled to the impedance matching circuit, the power amplifier, and the low noise amplifier, attenuates the outgoing RF signal to a scaled signal within a breakdown voltage of a transistor device in the low noise amplifier during transmission of the outgoing RF signal.
Owner:MEDIATEK USA INC
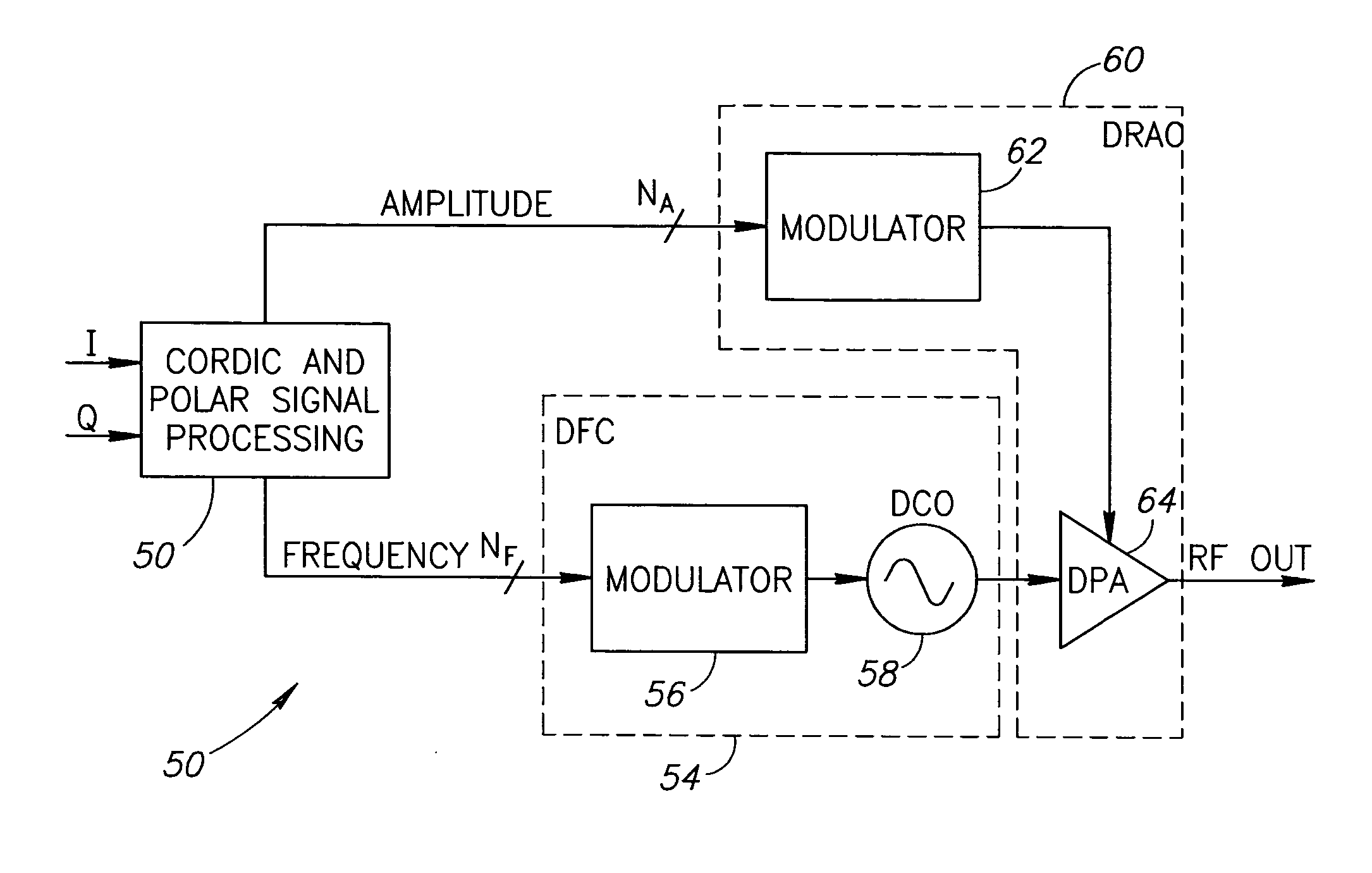
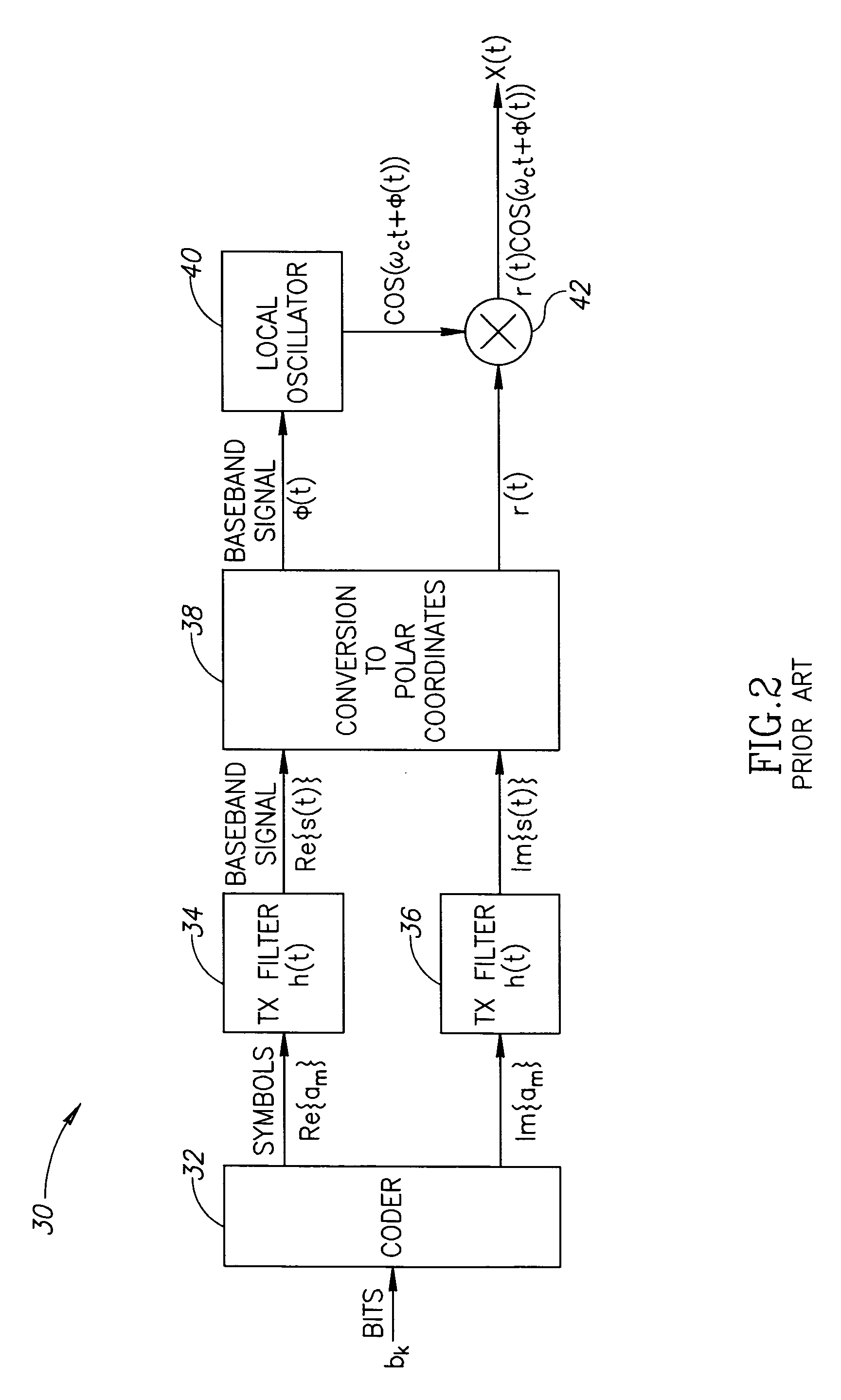
Hybrid polar/cartesian digital modulator
ActiveUS20060038710A1Reconfigurable analogue/digital convertersAnalogue conversionControl powerEngineering
A novel apparatus and method for a hybrid Cartesian / polar digital QAM modulator. The hybrid technique of the present invention utilizes a combination of an all digital phase locked loop (ADPLL) that features a wideband frequency modulation capability and a digitally controlled power amplifier (DPA) that features interpolation between 90 degree spaced quadrature phases. This structure is capable of performing either a polar operation or a Cartesian operation and can dynamically switch between them depending on the instantaneous value of a metric measured by a thresholder / router. In this manner, the disadvantages of each modulation technique are avoided while the benefits of each are exploited.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
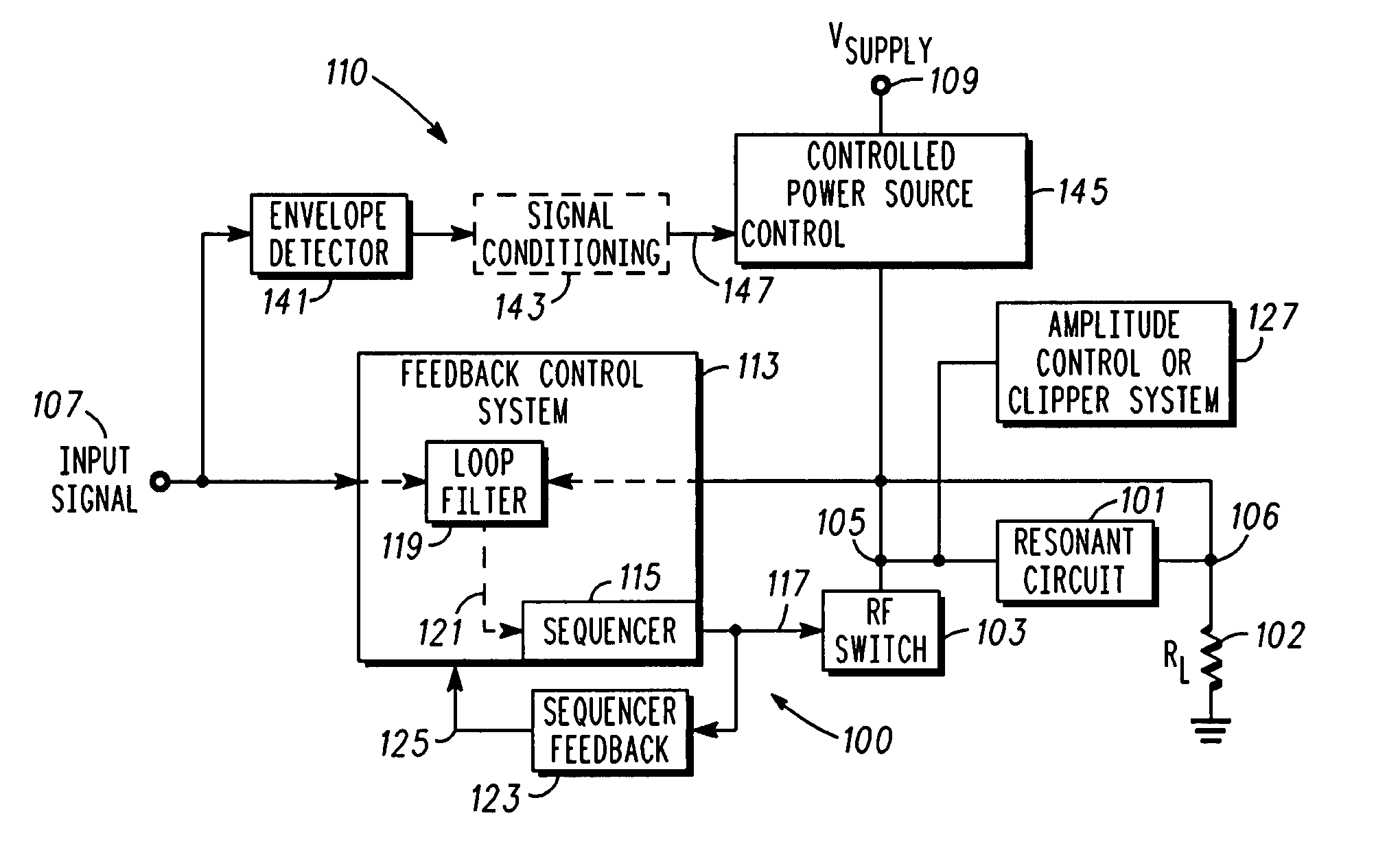
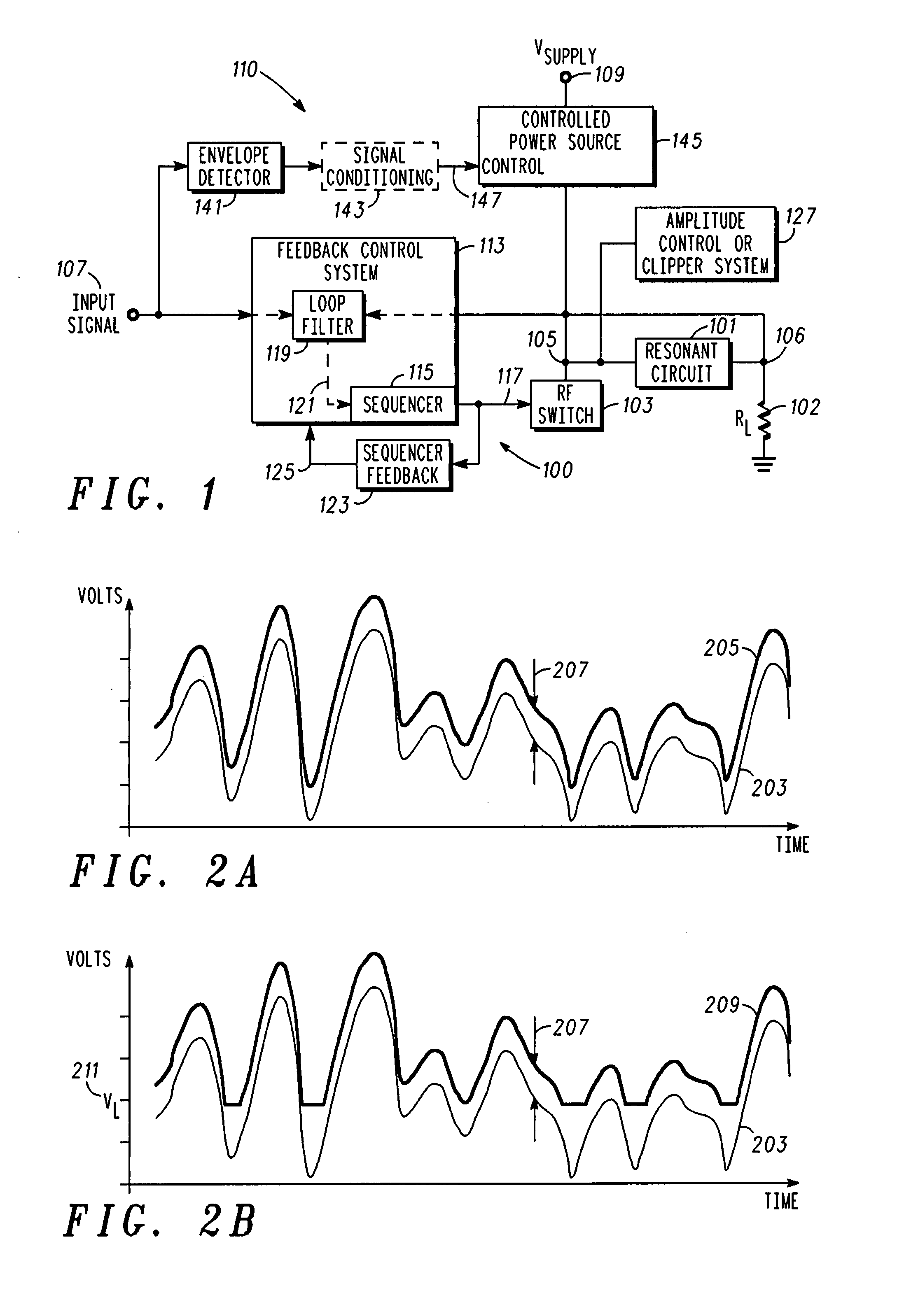
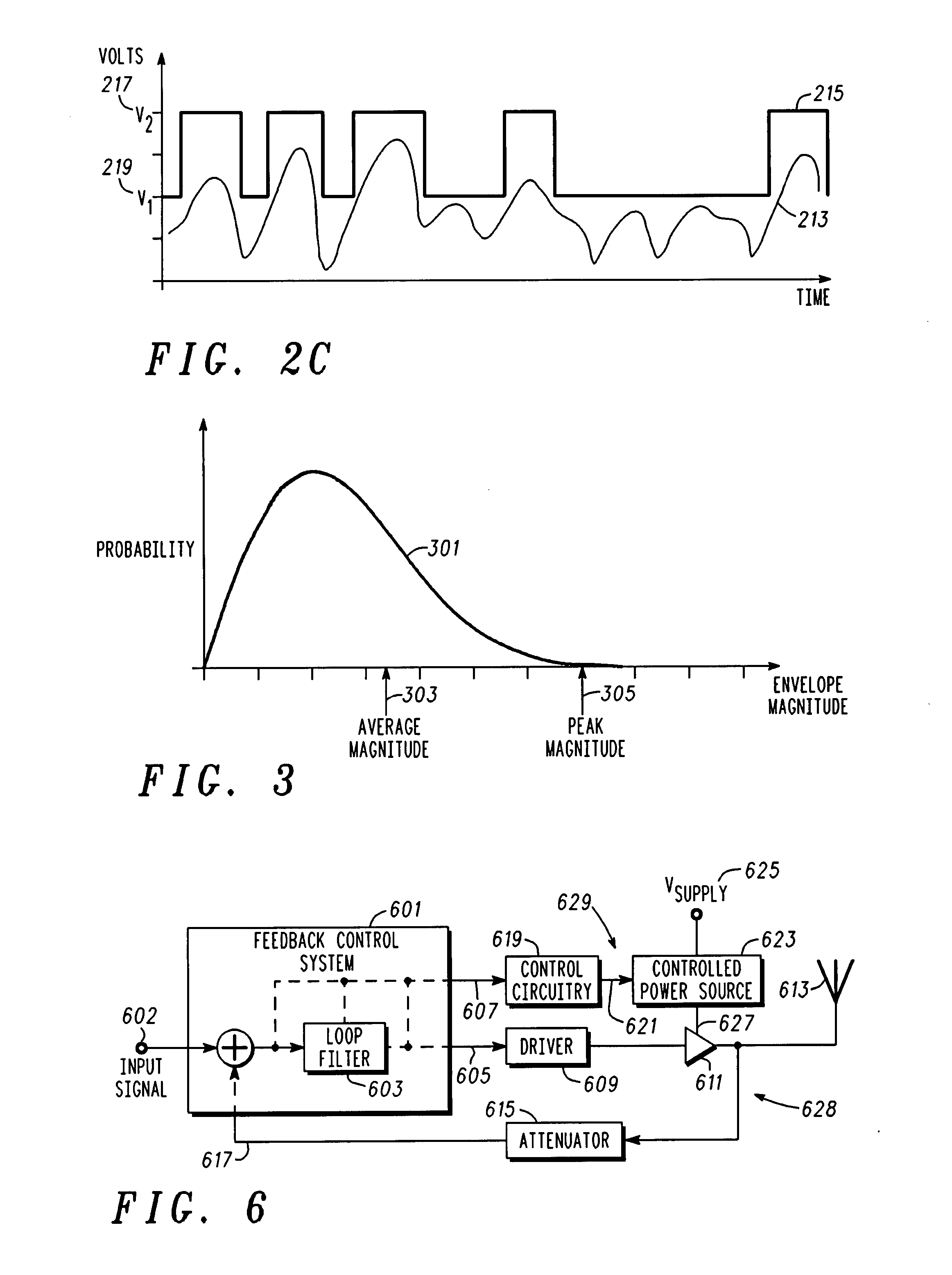
Radio frequency power amplifier and method using a controlled supply
A radio frequency power amplifier includes a feedback control system coupled to an input signal and a first feedback signal and configured to provide an output; a controlled supply configured to provide power that is controlled in accordance with a signal; and a radio frequency gain stage powered from the controlled supply, driven by the output from the feedback control system, and configured to provide an output signal at the radio frequency to a resonant load, where the first feedback signal corresponds to the output signal. Some embodiments include a sequencer in the feedback control system and others utilize an additional feedback loop to control the power provided by the controlled supply.
Owner:PWRF
Method and apparatus for a fully digital quadrature modulator
ActiveUS20060291589A1Little or no reuseMinimize impactSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationPower amplifiersTransistor arrayQuadrature modulator
A novel apparatus and method for a fully digital quadrature architecture for a complex modulator. The complex modulator can substitute for existing prior art analog quadrature modulator structures and those based on a digital polar architecture (r, θ). The modulator effectively operates as a complex digital-to-analog converter where the digital inputs are given in Cartesian form, namely I and Q representing the complex number I+jQ, while the output is a modulated RF signal having a corresponding amplitude and phase shift. The phase shift being with respect to a reference phase dictated by the local oscillator, which is also input to the converter / modulator. Several embodiments are provided including modulators incorporating dual I and Q transistor arrays, a single shared I / Q transistor array, modulators with single ended and differential outputs and modulators with single and dual polarity clock and I / Q data signals.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
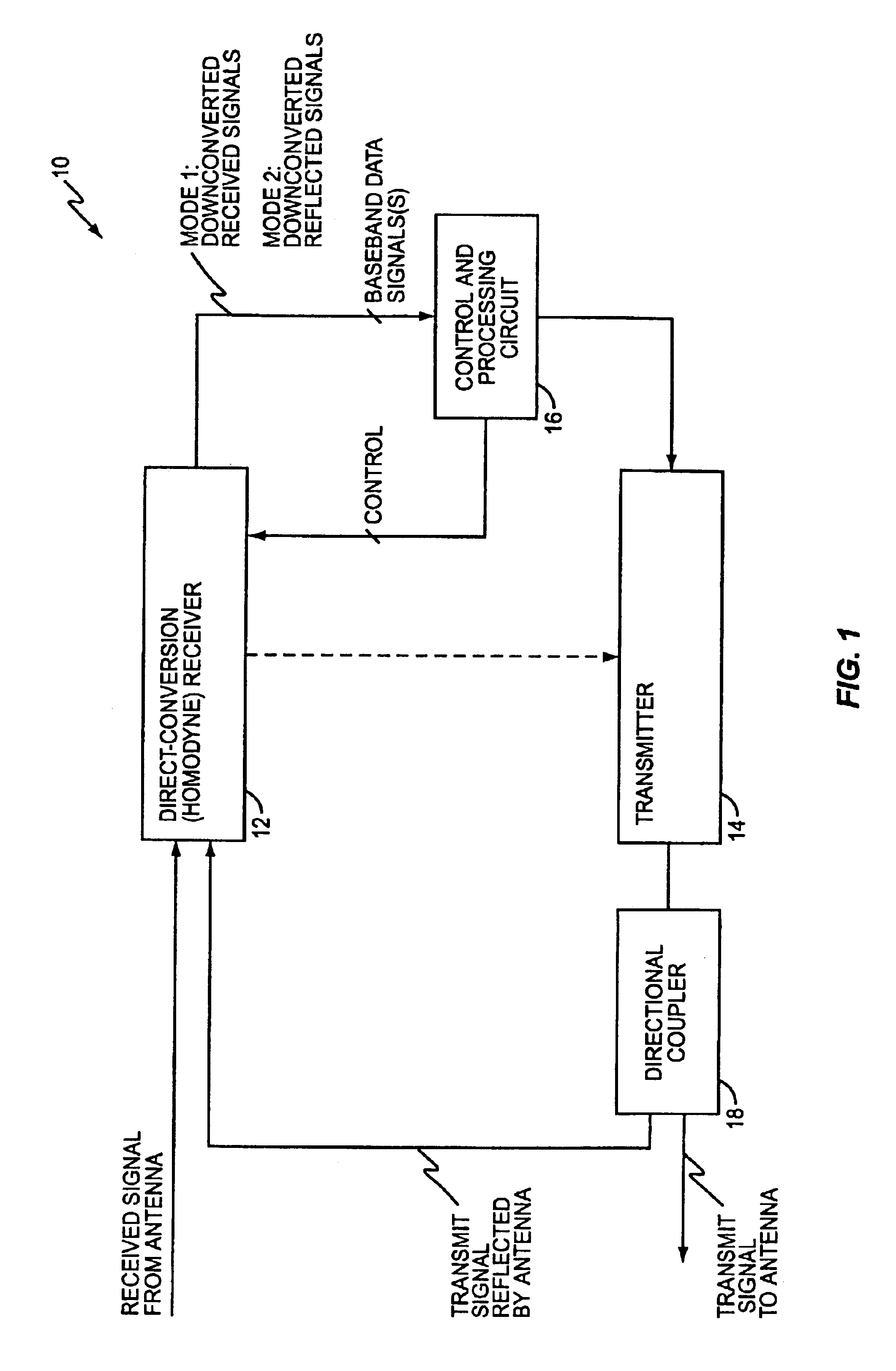
System and method for adaptive antenna impedance matching
InactiveUS6845126B2Remove transmit signal modulationSimple signal processingMultiple-port networksPower amplifiersMulti bandAntenna impedance
A transceiver includes a transmitter and a homodyne receiver, wherein the receiver is used to process both antenna-received and antenna-reflected signals. Thus, during a receive mode, for example, the receiver downconverts antenna-received signals to baseband signals, which are then processed to recover receive signal information. Then, during a transmit mode for example, antenna-reflected transmit signals are fed back to the receiver, which is retuned to the desired transmit frequency, and thus downconverts the reflected transmit signals to baseband signals. These baseband signals are then processed to obtain a characterization of impedance mismatch between the transceiver's transmitter and the associated antenna. An adjustable matching network disposed in the transmit signal path thus may be adjusted based on the characterization to reduce the mismatch. Such configurations may be used with either single-band or multi-band embodiments of the transceiver, and the transceiver may be used in both TDMA and CDMA communication systems.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
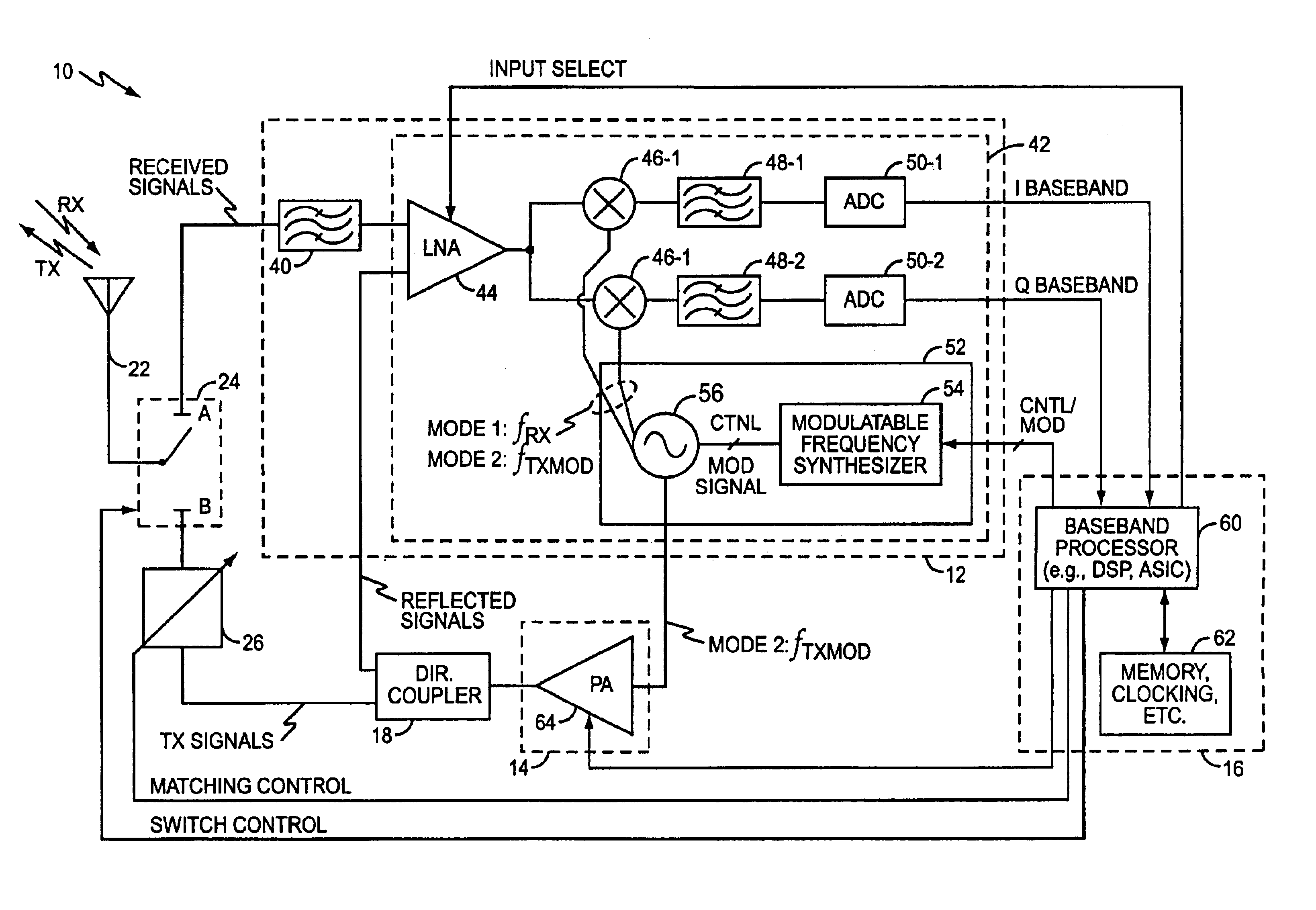
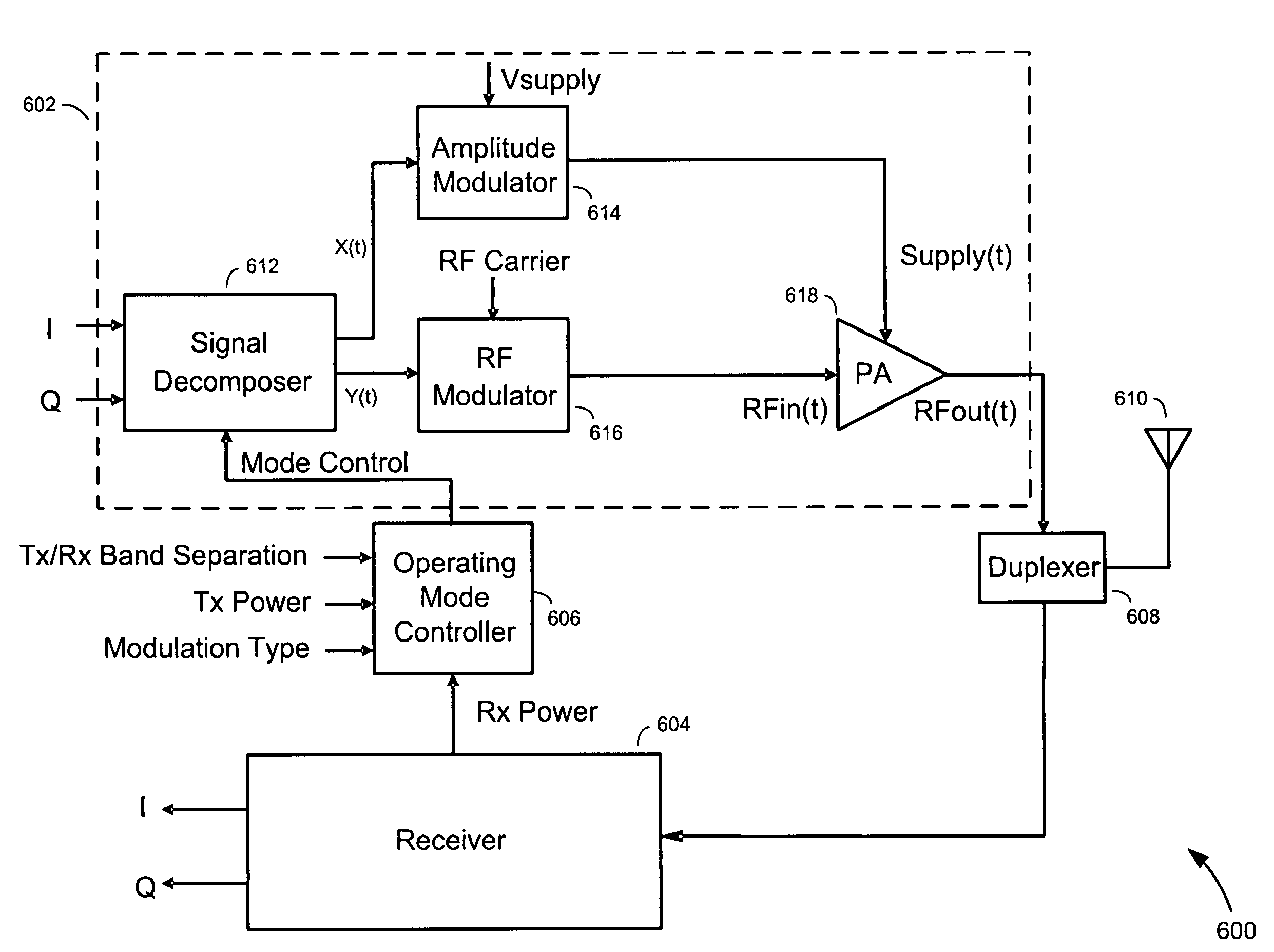
Multi-mode transmitter having adaptive operating mode control
ActiveUS8095093B2Improve power efficiencyPower efficiency and noiseResonant long antennasPower amplifiersPower efficientTransceiver
Methods and apparatus for transmitting communications signals that are both power efficient and effective at avoiding or reducing transmitter-generated receive band noise. An exemplary transceiver apparatus includes a multi-mode transmitter that is configurable to operate in a plurality of operating modes (e.g., a polar mode, a quadrature mode and a hybrid mode), a receiver, and an operating mode controller. The operating mode controller is configured to control which operating mode the transmitter is to operate, depending on one or more of a transmit (Tx) power, receive (Rx) power, the Tx power relative to the Rx power, a level of frequency separation between a Tx frequency band and a Rx frequency band (Tx / Rx band separation), and modulation type employed by the transmitter.
Owner:APPLE INC
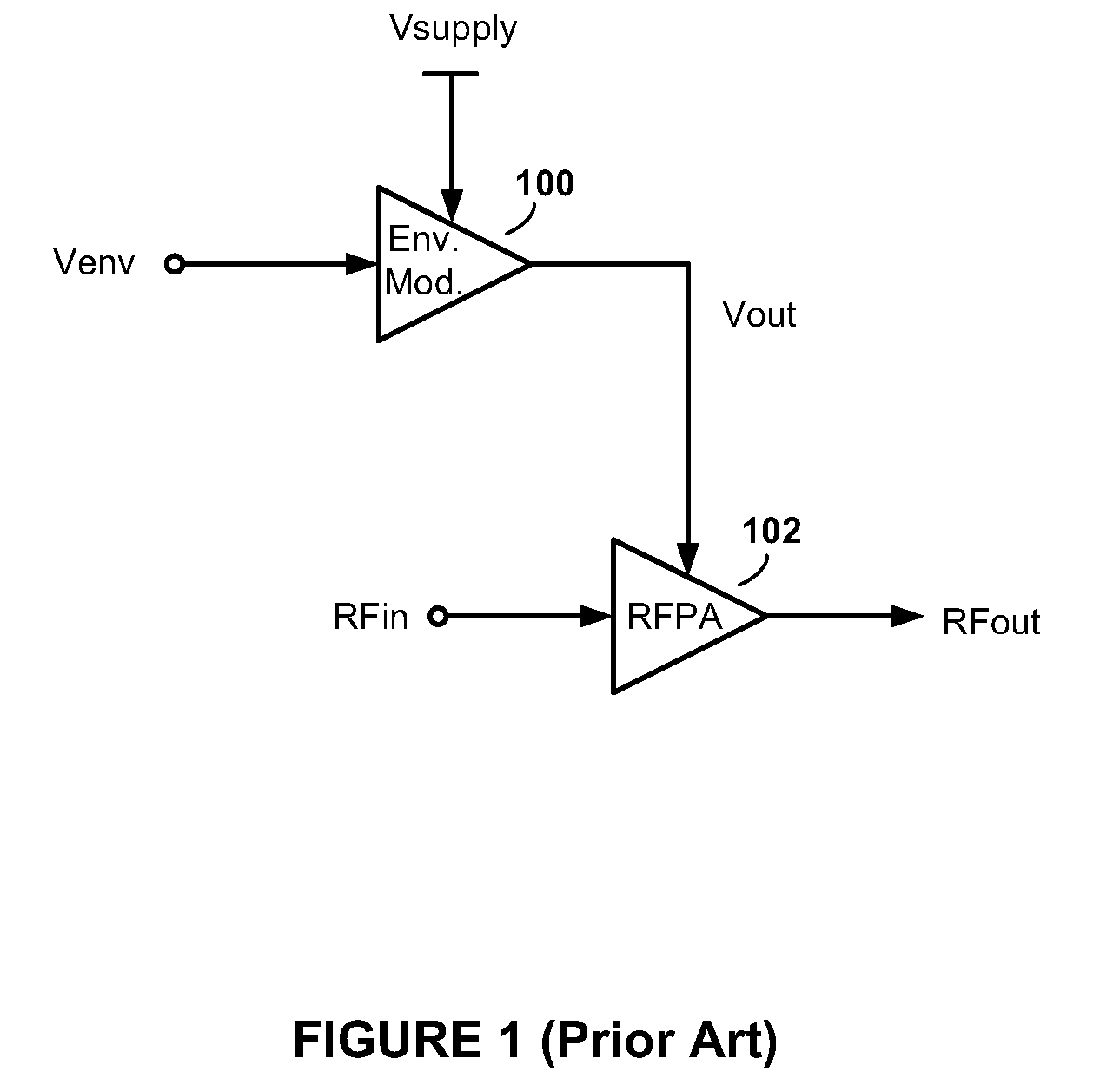
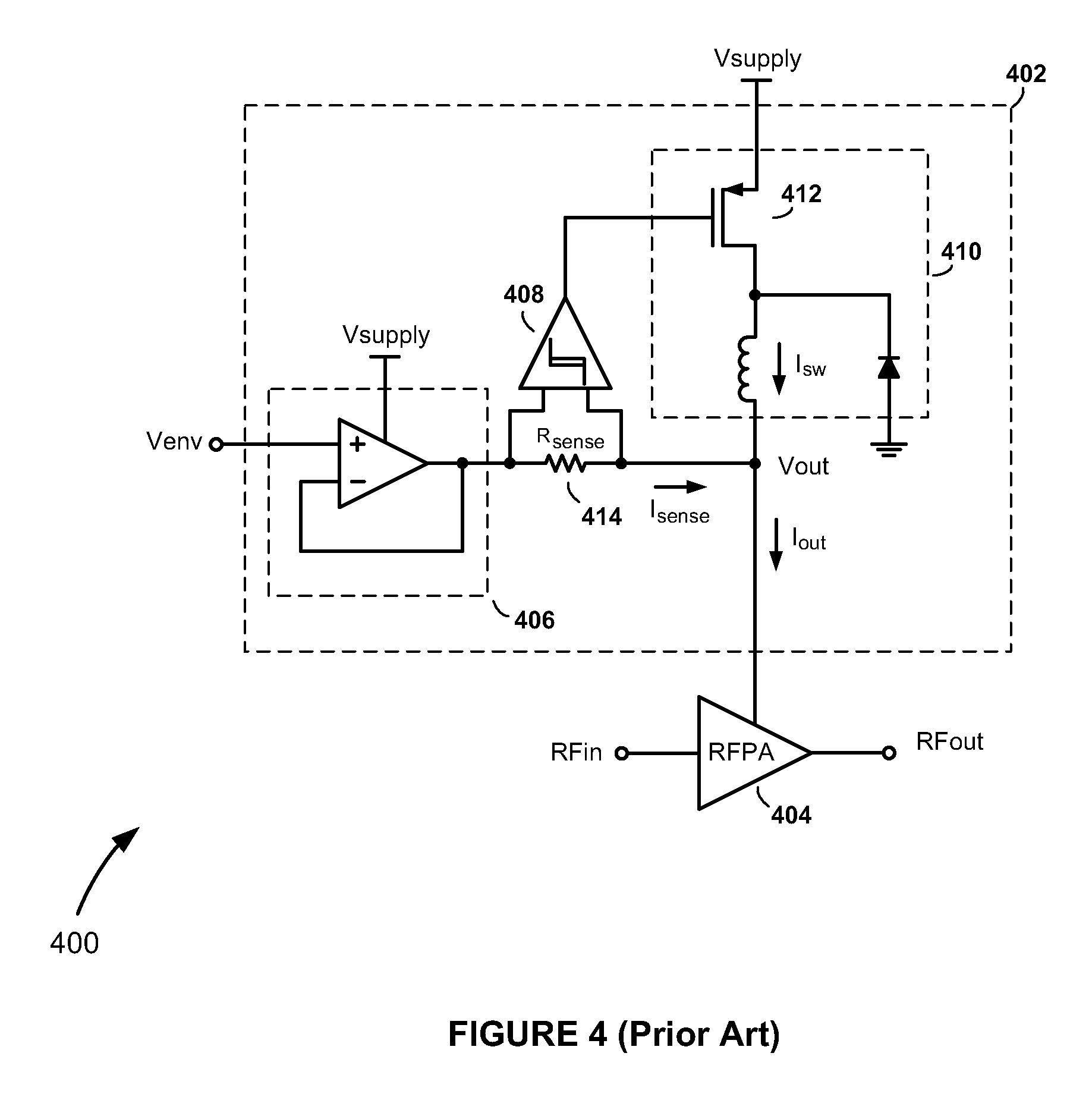
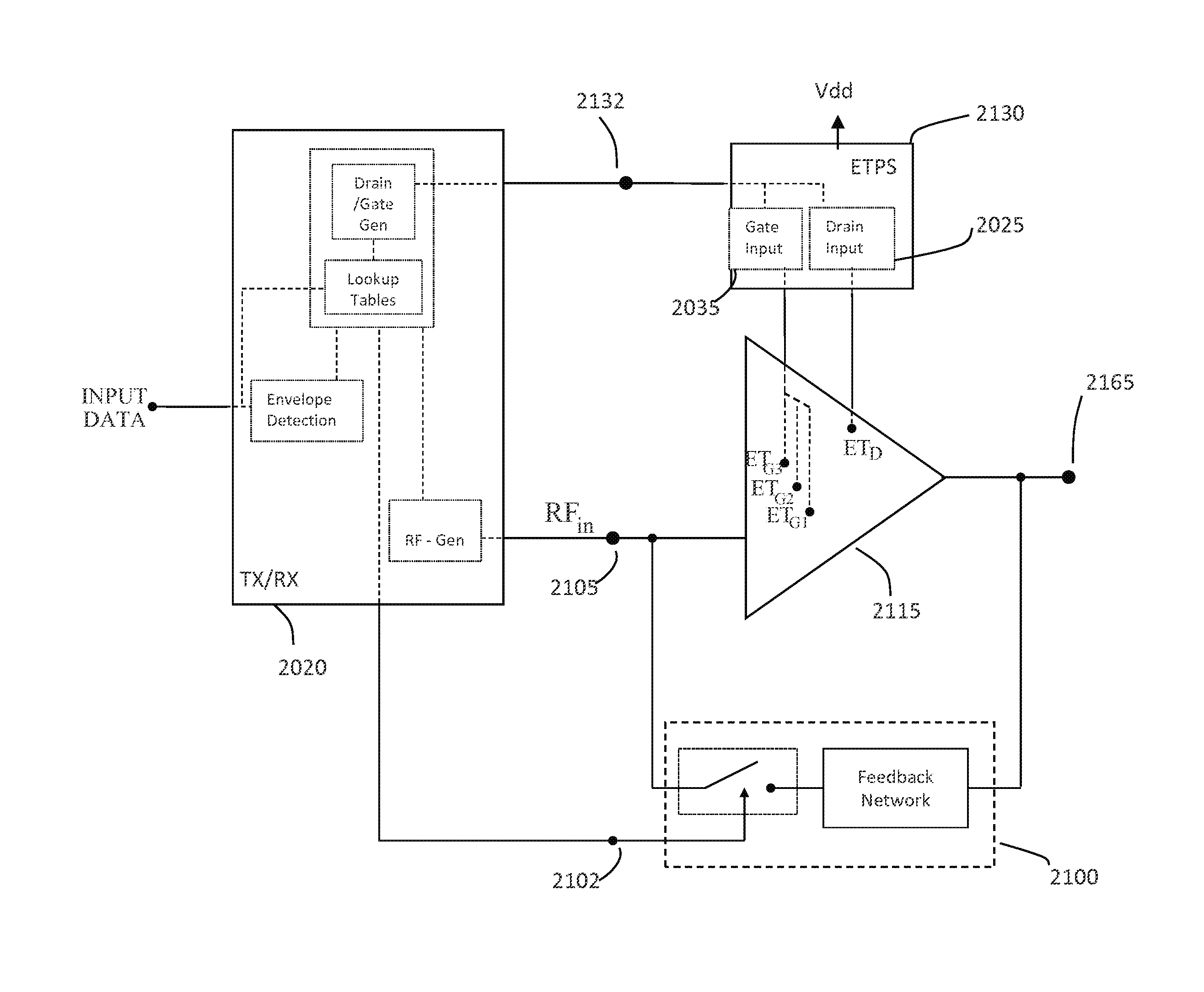
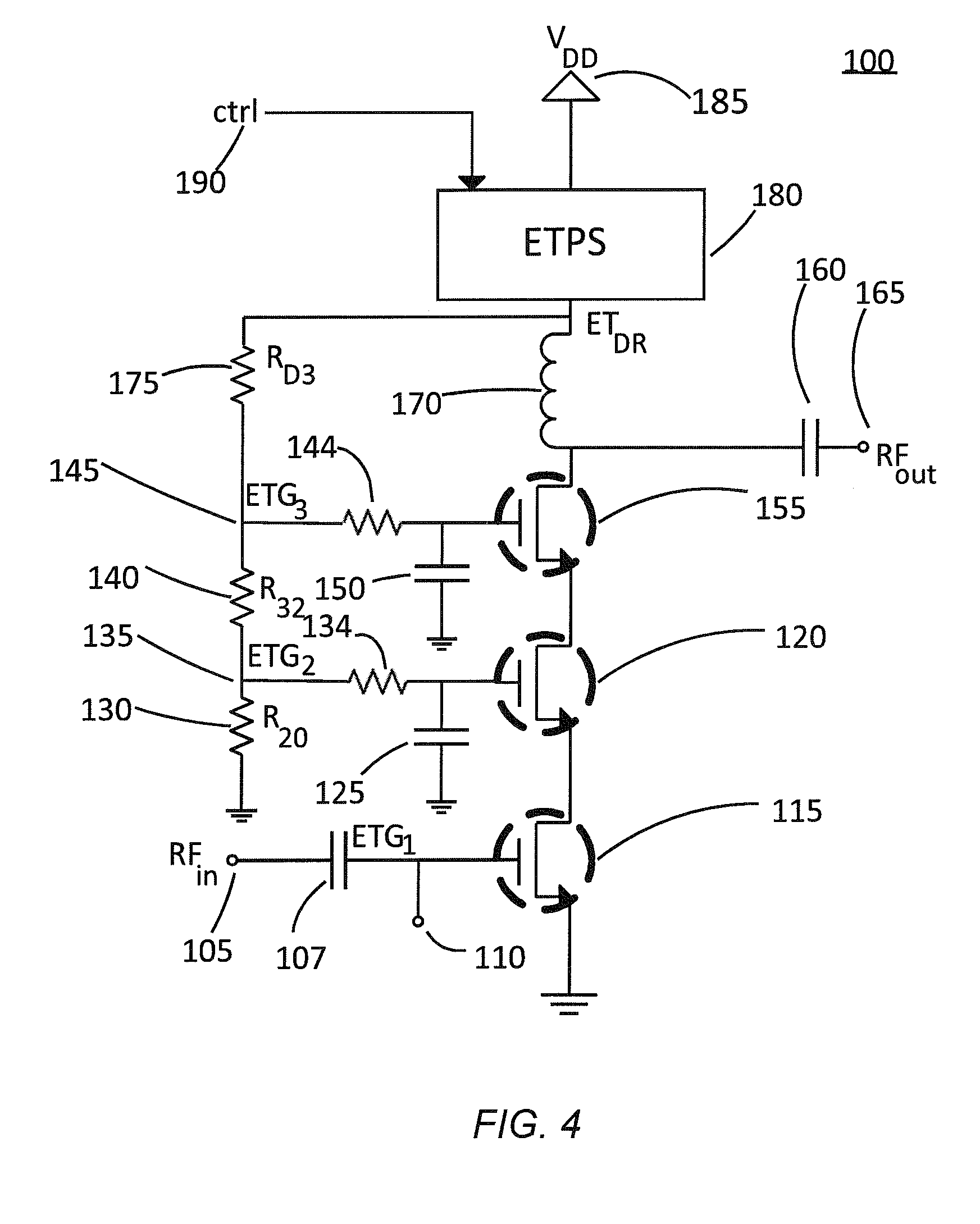
High-Efficiency Envelope Tracking Systems and Methods for Radio Frequency Power Amplifiers
ActiveUS20090289720A1Efficiency penaltyDc network circuit arrangementsPower amplifiersLinear regulatorControl power
High-efficiency envelope tracking (ET) methods and apparatus for dynamically controlling power supplied to radio frequency power amplifiers (RFPAs). An exemplary ET circuit includes a switch-mode converter coupled in parallel with a split-path linear regulator. The switch-mode converter is configured to generally track an input envelope signal Venv and supply the current needs of a load (e.g., an RFPA). The split-path linear regulator compensates for inaccurate envelope tracking by sourcing or sinking current to the load via a main current path. A current sense path connected in parallel with the main current path includes a current sense resistor used by a hysteresis comparator to control the switching of the switch-mode converter. The split-path linear regulator is configured so that current flowing in the current sense path is a lower, scaled version of the current flowing in the main current path.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Intelligent backhaul radio
ActiveUS8238318B1Lower latencyEfficient use of resourcesSpatial transmit diversitySimultaneous aerial operationsFrequency spectrumLatency (engineering)
A intelligent backhaul radio is disclosed that is compact, light and low power for street level mounting, operates at 100 Mb / s or higher at ranges of 300 m or longer in obstructed LOS conditions with low latencies of 5 ms or less, can support PTP and PMP topologies, uses radio spectrum resources efficiently and does not require precise physical antenna alignment.
Owner:COMS IP HLDG LLC
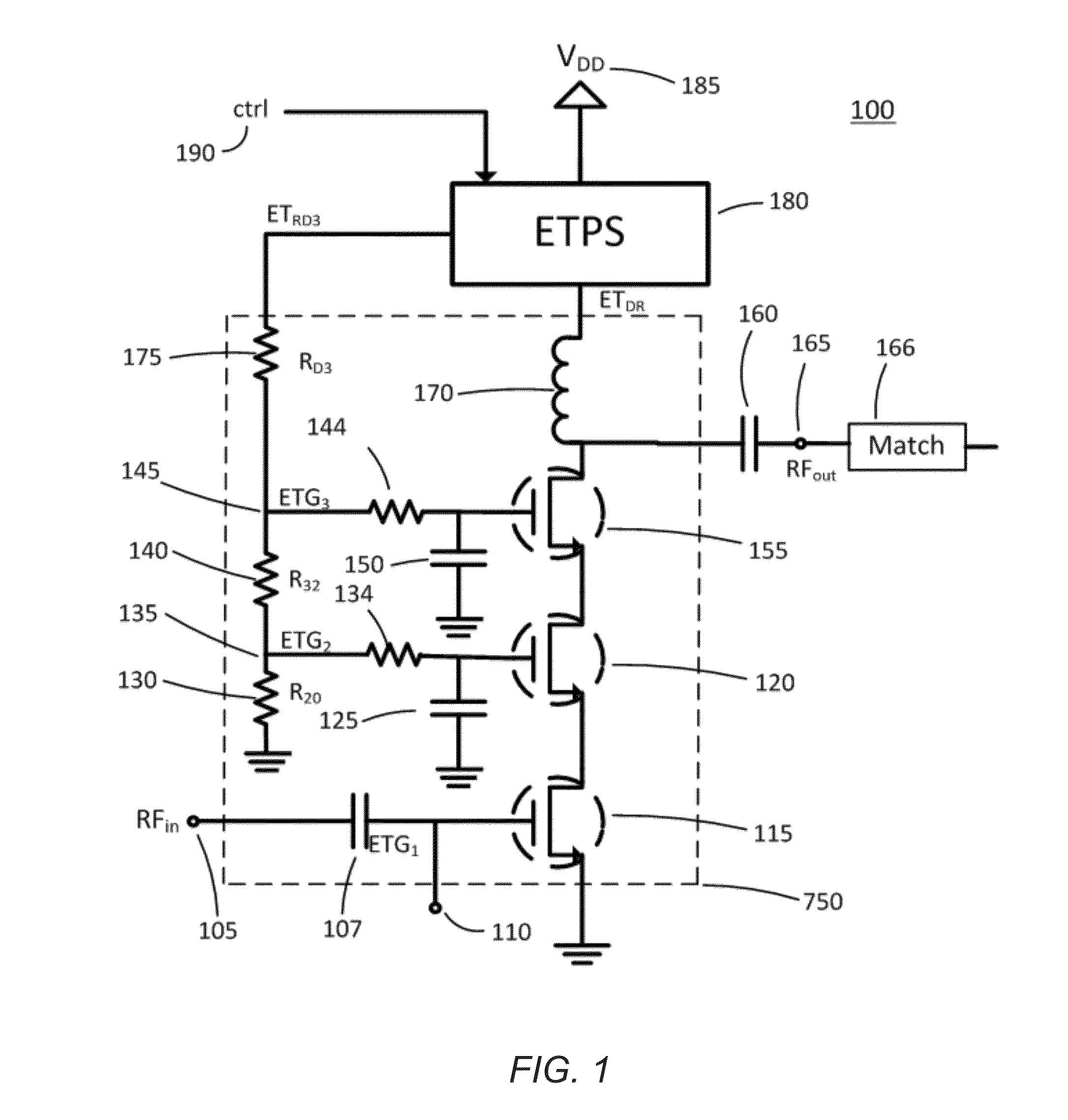
Bias Control for Stacked Transistor Configuration
Various methods and circuital arrangements for biasing one or more gates of stacked transistors of an amplifier are presented, where the amplifier can be an envelope tracking amplifier. Circuital arrangements to generate reference gate-to-source voltages for biasing of the gates of the transistors of the stack are also presented. Particular biasing for a case of an input transistor of the stack is also presented.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Multi-mode amplifier system
ActiveUS20040266366A1Improve linearizationMitigate out-of-band emissionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierOperation mode
An amplifier system is provided that switches between a linear mode of operation, an envelope tracking mode of operation and a polar mode of operation. The amplifier system switches between modes of operation based upon a characteristic of an input signal relative to a first threshold level and a second threshold level. A mode selector selects the operation mode by transmitting an amplitude modulated signal plus a variable headroom voltage to a supply terminal of a power amplifier during the envelope tracking mode, an amplitude modulated signal to the supply terminal and phase modulated input signal during the polar mode and a substantially constant amplitude signal to the supply terminal during the linear mode.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
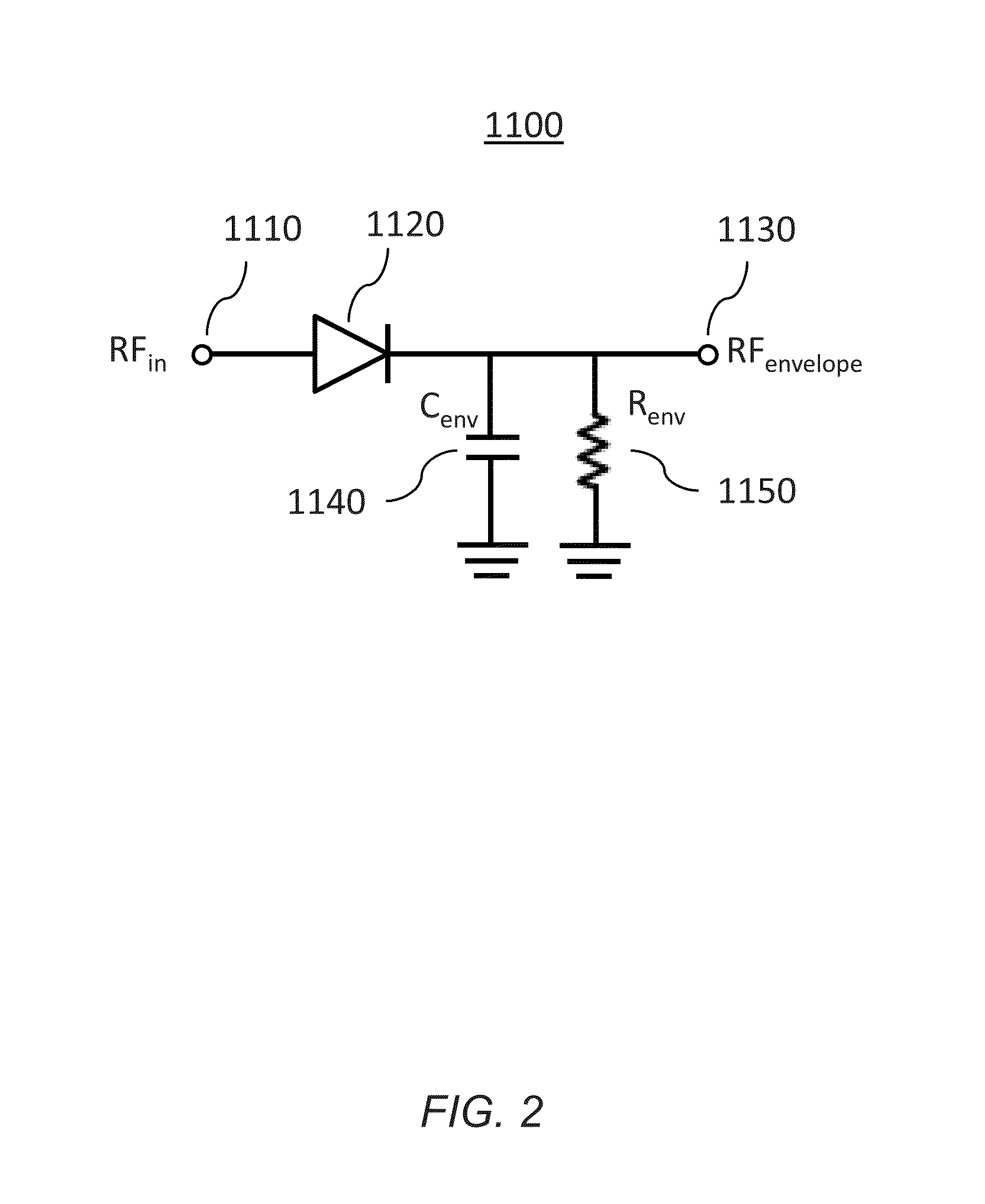
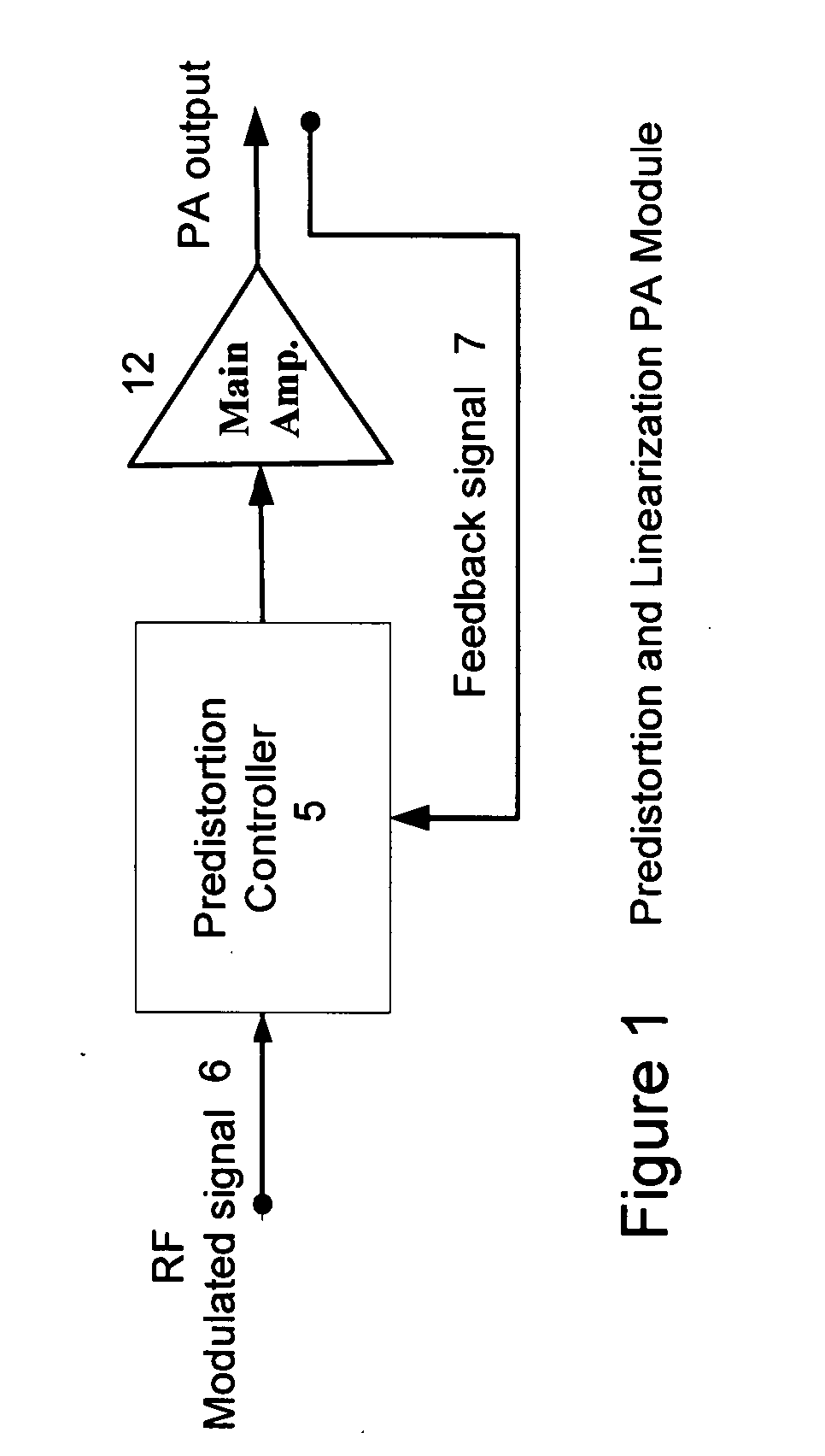
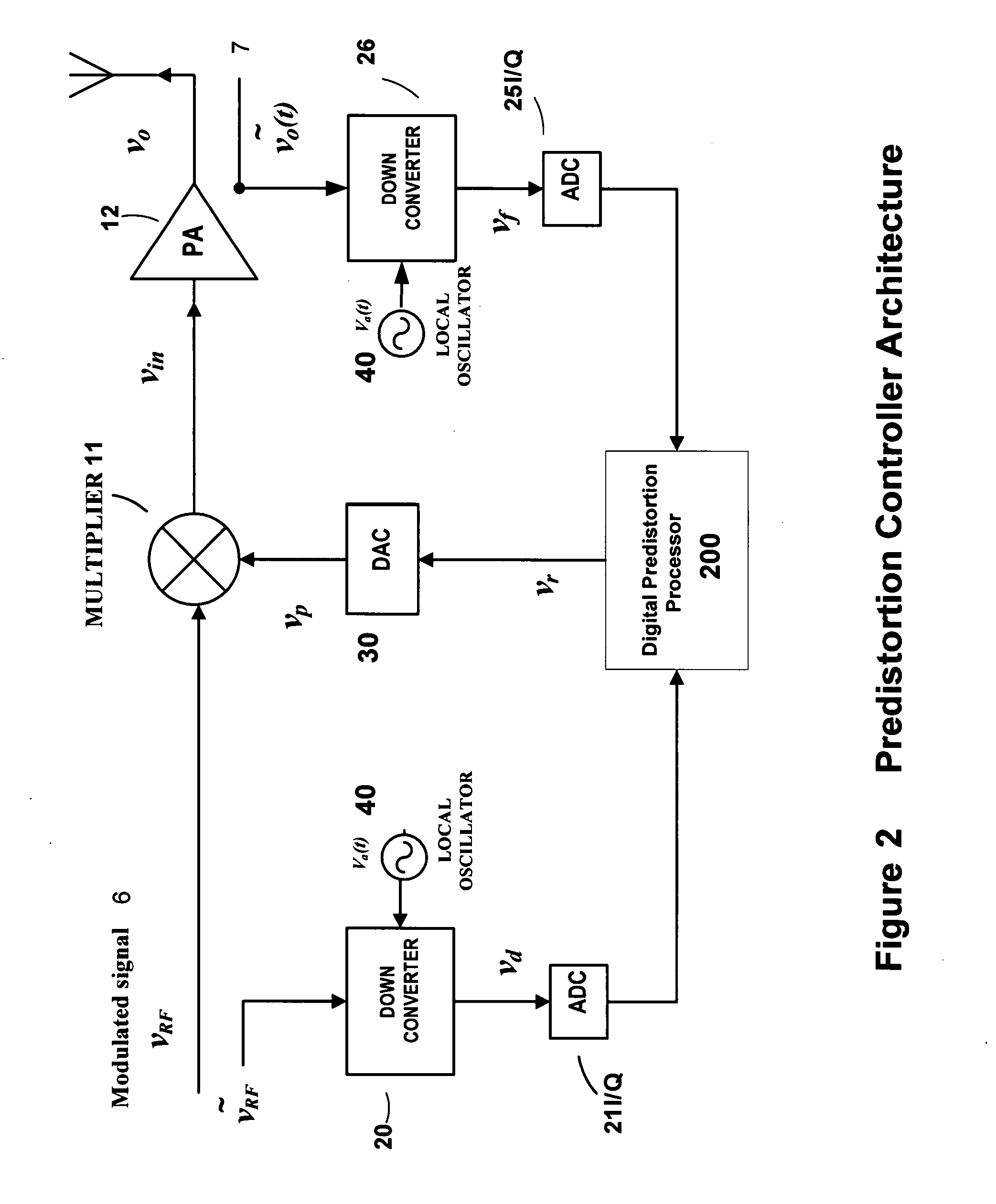
High efficiency linearization power amplifier for wireless communication
ActiveUS20070241812A1Improve efficiencyImprove linearityEnergy efficient ICTAmplifier details to increase power/efficiencyFrequency changerControl signal
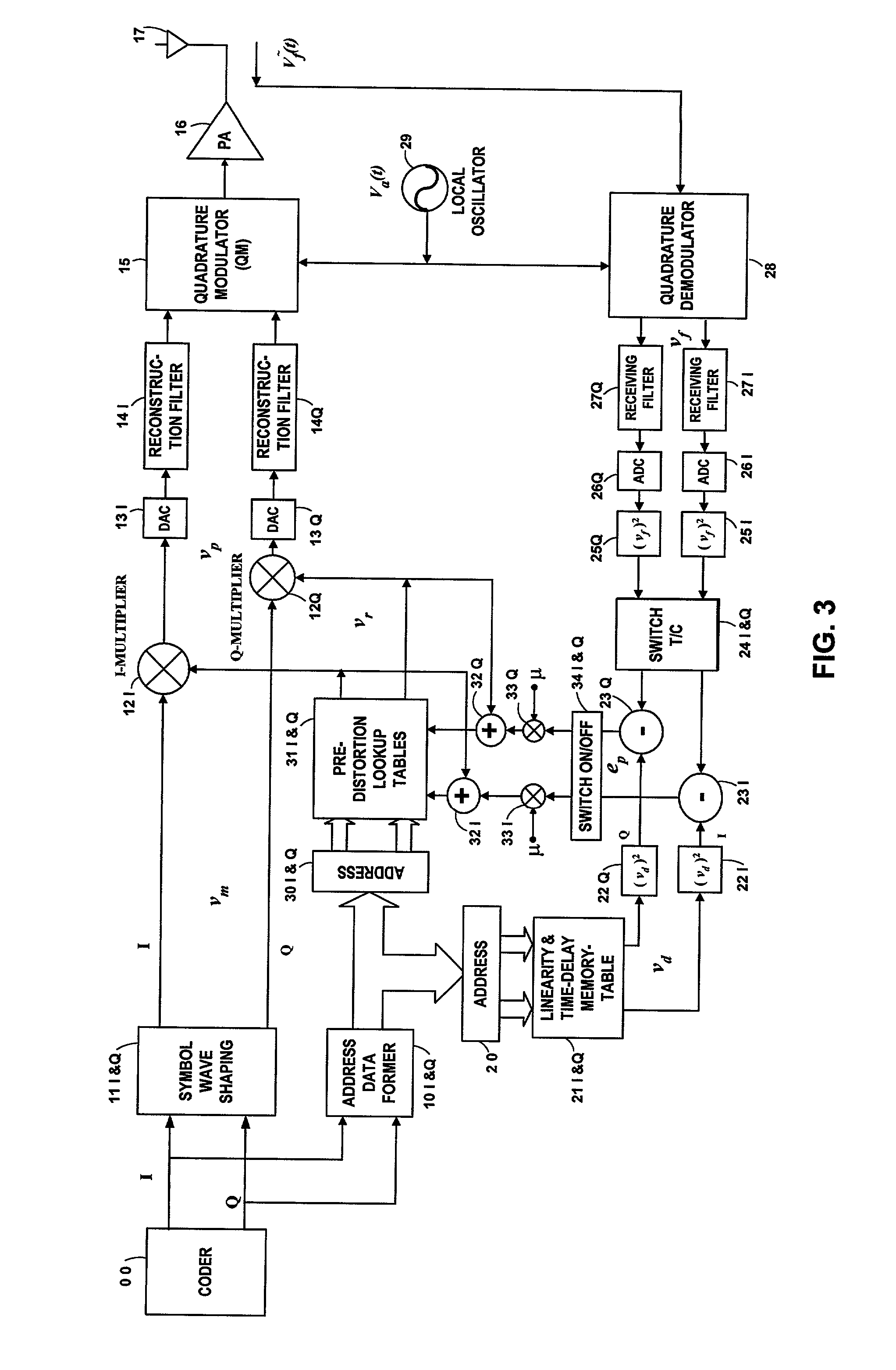
An embodiment of the invention uses a predistortion correction signal to combination the modulated RF signal by an analog multiplier for linearization of power amplifiers having nonlinear characteristics such as those used in wireless RF transmitters. A predistortion controller comprises a plurality of down converters for retrieving both the ideal non-distorted information and the feedback distorted information, together with pre-stored digitally-indexed predistortion information stored, for example, in a look-up table. The digitally-indexed information models nonlinear characteristics of the high power amplifier, and is stored prior to processing of pre-compensation in the power amplifier. When the predistortion information is combined with the modulated RF signal in the analog multiplier, the result is a substantially linear information transmission from the power amplifier. In an embodiment of the system, the modulated RF input signal and the feedback signal from PA output are down-converted, respectively, by analog devices, such as mixers, after which the analog intermediate frequency (IF) signals are digitized by analog-to-digital converters for digital predistortion correction processing, followed by predistortion processing performed by, for example, a DSP or FPGA chip to generate a digital correction control signal, which is then converted to an analog signal by a digital-to-analog converter, followed by combining the analog correction signal with the RF modulated input signal to yield the input to the power amplifier.
Owner:DALI WIRELESS
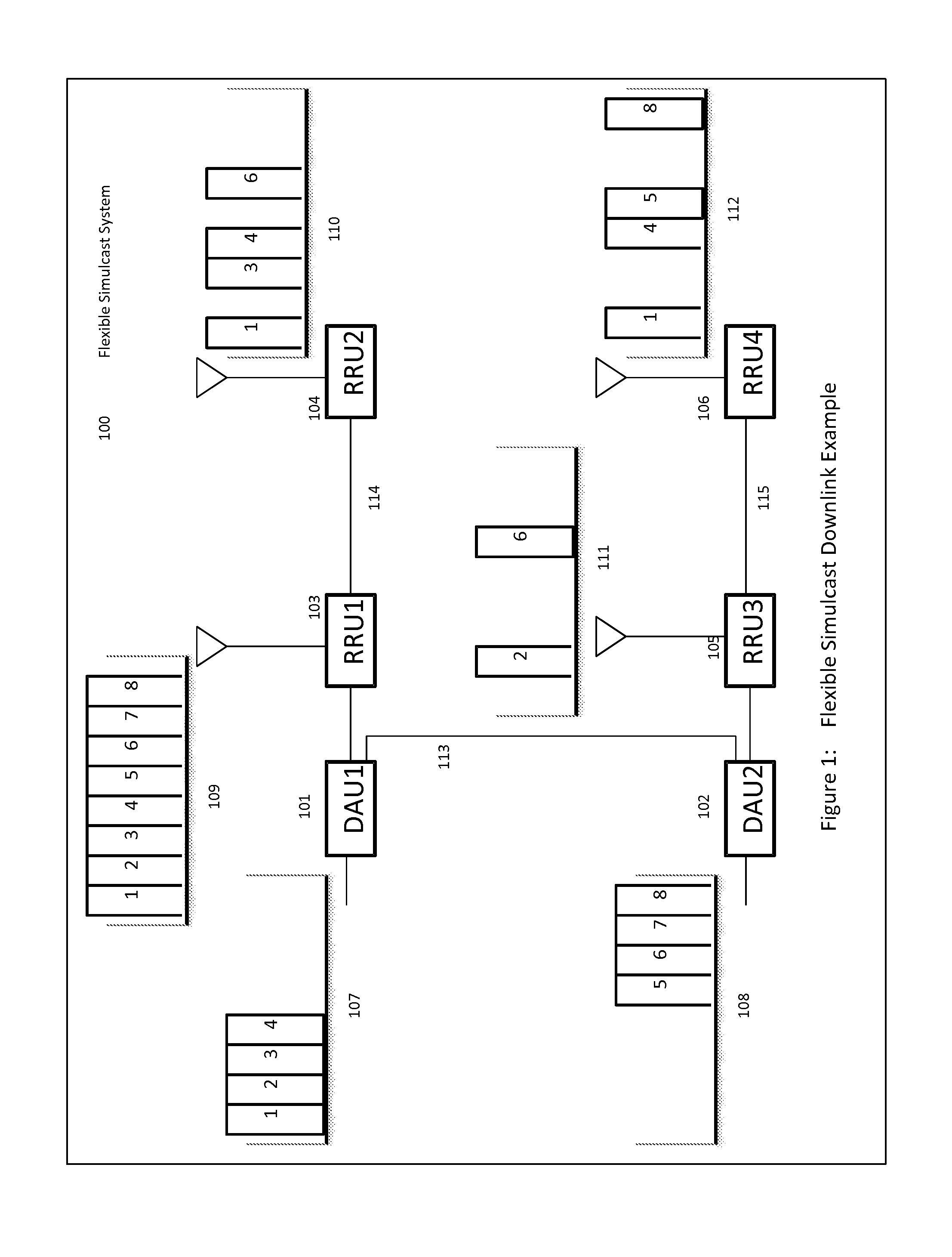
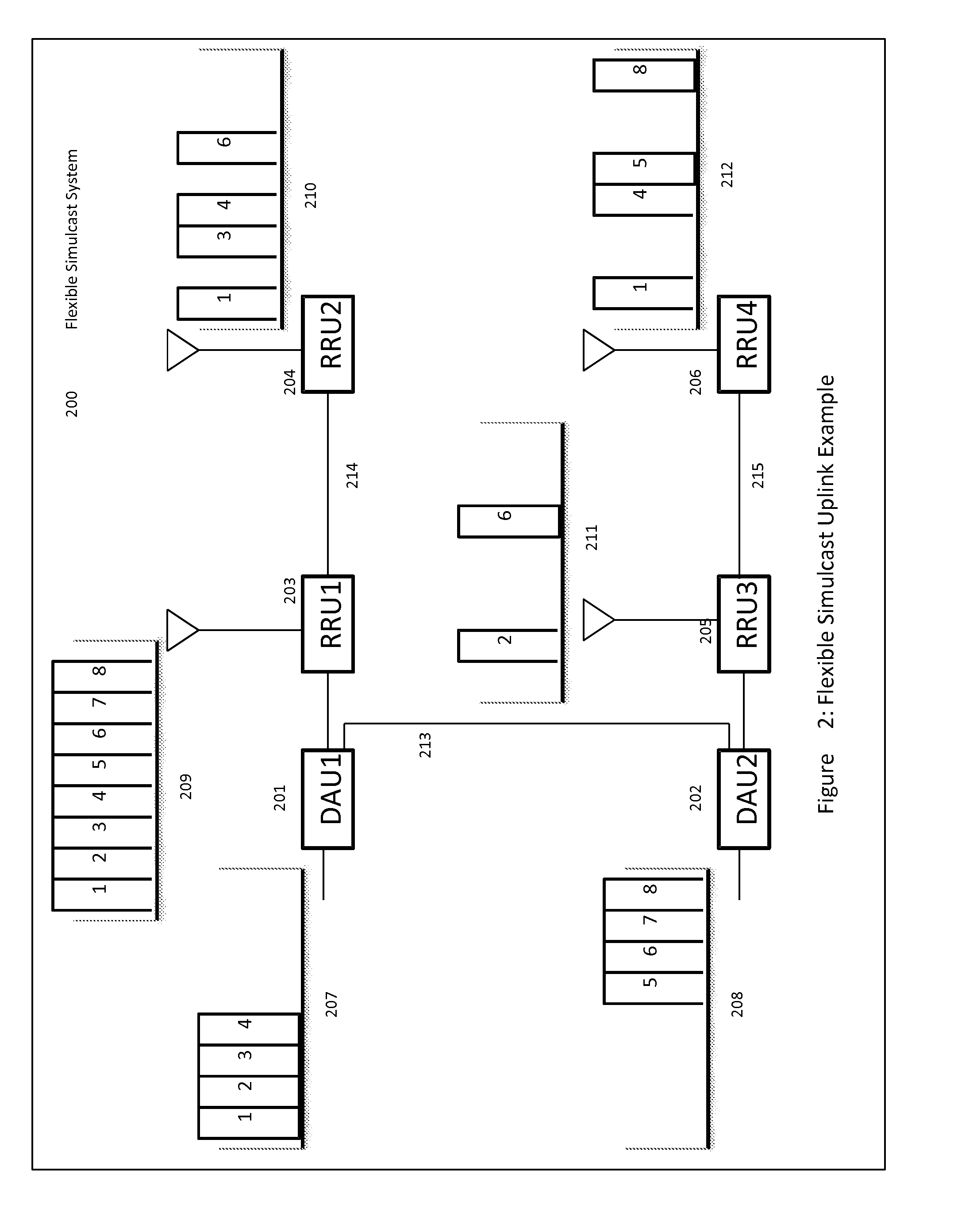
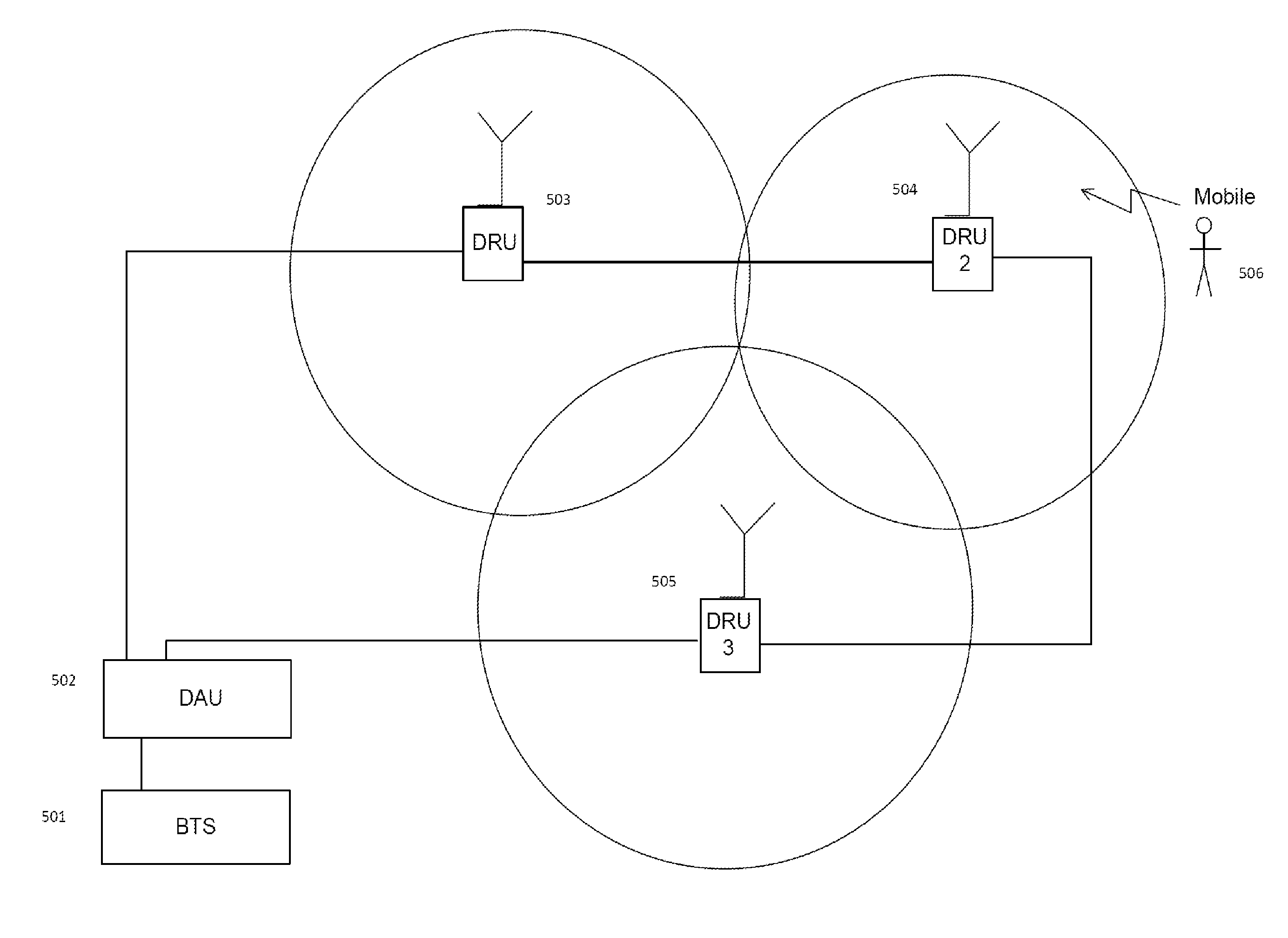
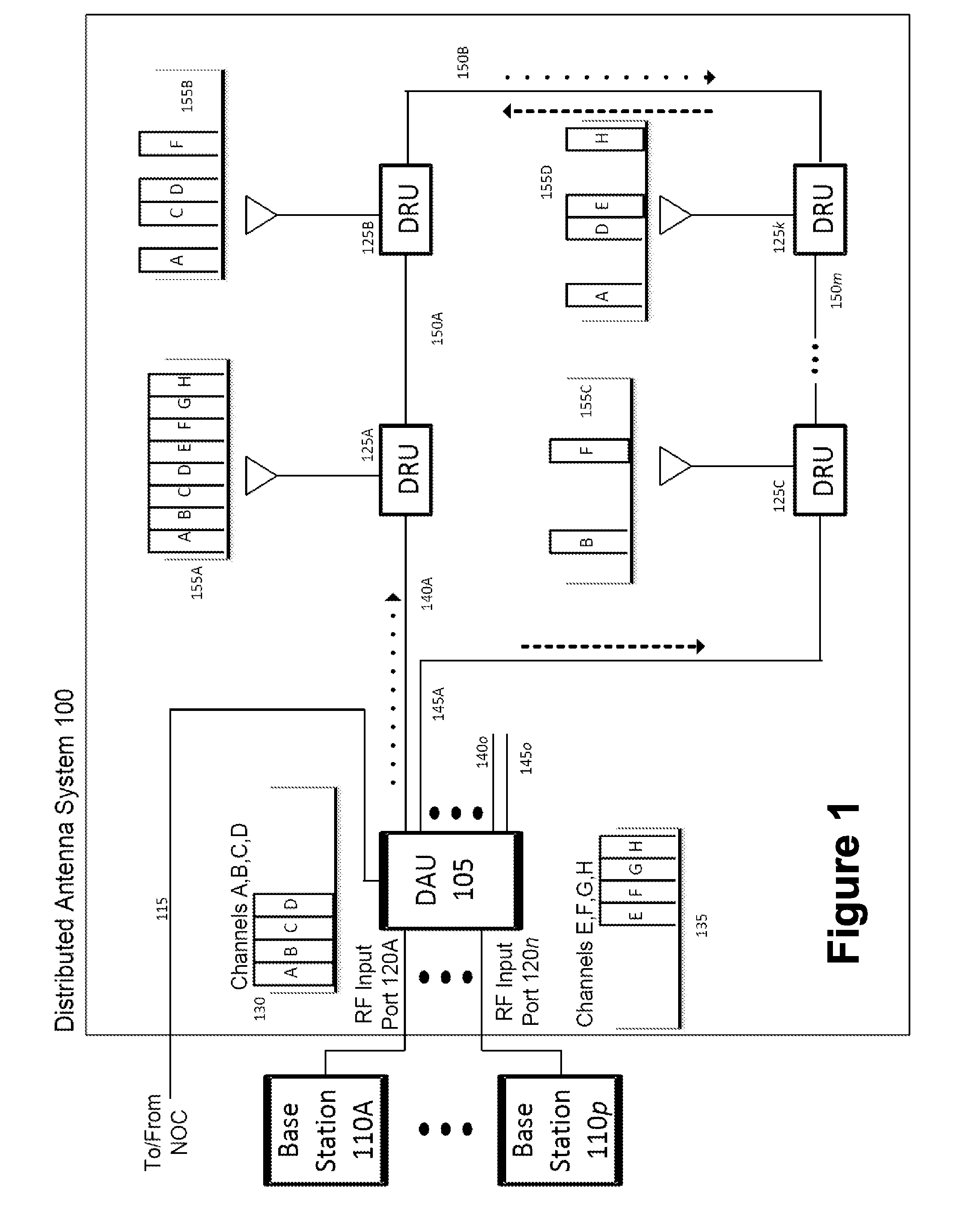
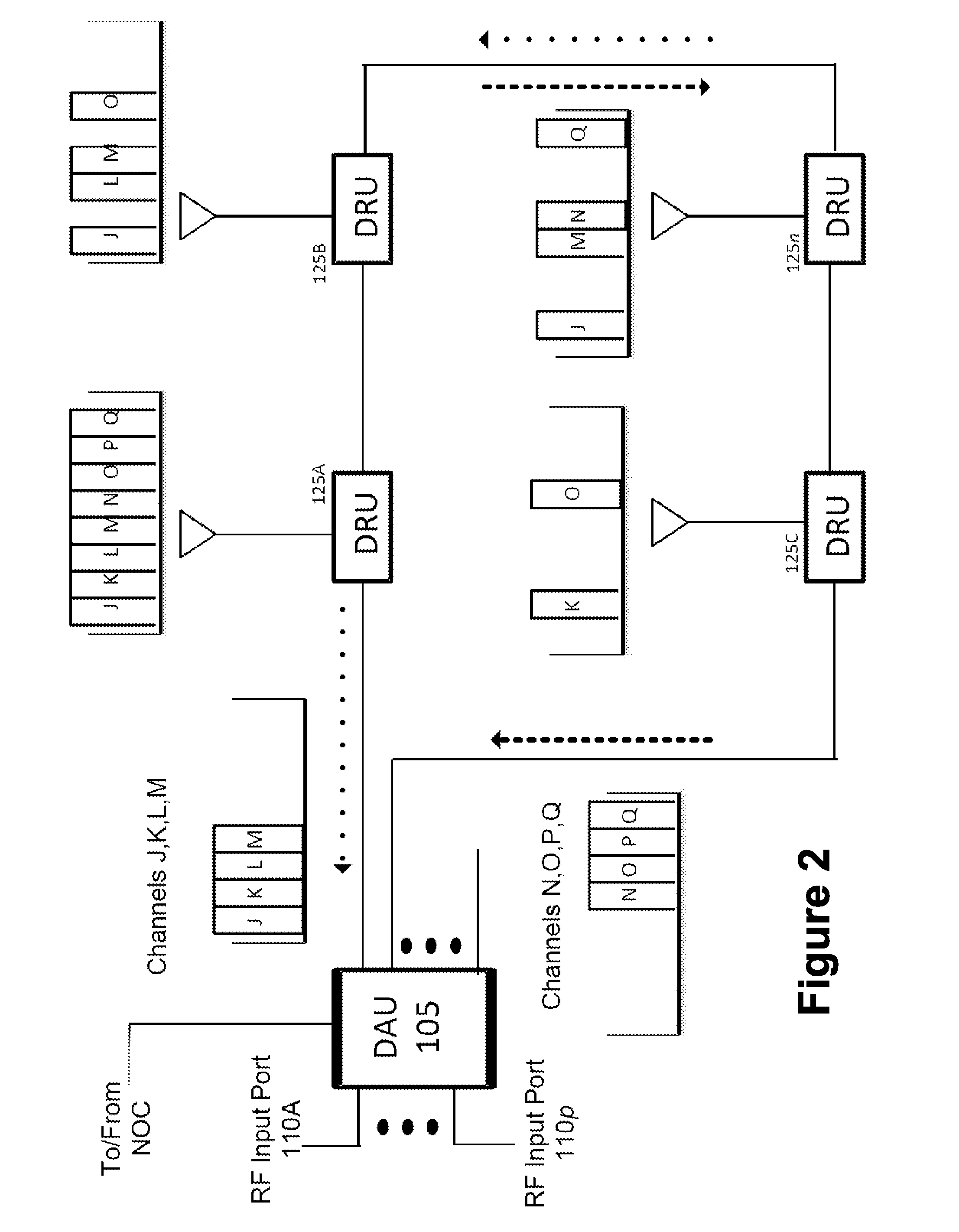
Remotely Reconfigurable Distributed Antenna System and Methods
ActiveUS20120039320A1Improve efficiencyImprove traffic capacityMultiplex system selection arrangementsPower amplifiersDistributed antenna systemCarrier signal
The present disclosure is a novel utility of a software defined radio (SDR) based Distributed Antenna System (DAS) that is field reconfigurable and support multi-modulation schemes (modulation-independent), multi-carriers, multi-frequency bands and multi-channels. The present disclosure enables a high degree of flexibility to manage, control, enhance, facilitate the usage and performance of a distributed wireless network such as flexible simulcast, automatic traffic load-balancing, network and radio resource optimization, network calibration, autonomous / assisted commissioning, carrier pooling, automatic frequency selection, frequency carrier placement, traffic monitoring, traffic tagging, pilot beacon, etc. As a result, the SDR DAS can increase the efficiency and traffic capacity of the operators' wireless network.
Owner:DALI WIRELESS
Amplifiers Operating in Envelope Tracking Mode or Non-Envelope Tracking Mode
ActiveUS20140184335A1Power amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierEngineering
Various envelope tracking amplifiers are presented that can be switched between an ET (envelope tracking) mode and a non-ET mode. Switches and / or tunable components are utilized in constructing the envelope tracking amplifiers that can be switched between the ET mode and the non-ET mode.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
High sensitivity, high resolution detection of signals
A system and method providing for the detection of an input signal by distributing the input signal into independent signal components that are independently amplified. Detection of an input signal comprises generating from the input signal a plurality of spatially separate elementary charge components, each having a respective known number of elementary charges, the number of the plurality of spatially separate elementary charge components being a known monotonic function of the magnitude of said input signal; and independently amplifying each of the plurality of spatially divided elementary charge components to provide a respective plurality of signal charge packets, each signal charge packet having a second number of elementary charges greater than the respective known number by a respective amplification factor.
Owner:AMPLIFICATION TECH INC
Daisy-Chained Ring of Remote Units For A Distributed Antenna System
ActiveUS20120039254A1High degree of flexibility to manage, controlIncrease capacitySite diversityModulated-carrier systemsDistributed antenna systemCarrier signal
Owner:DALI WIRELESS
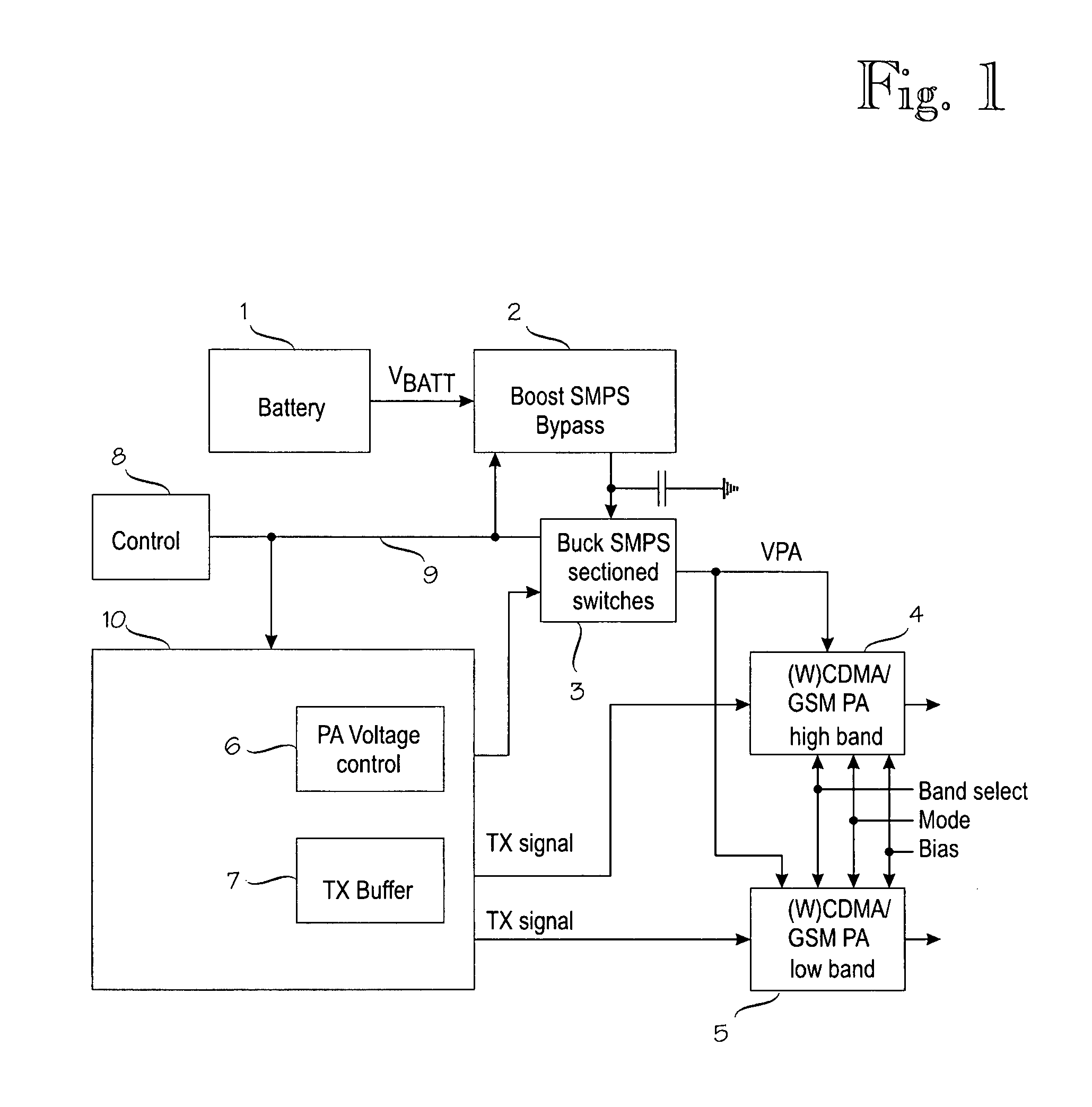
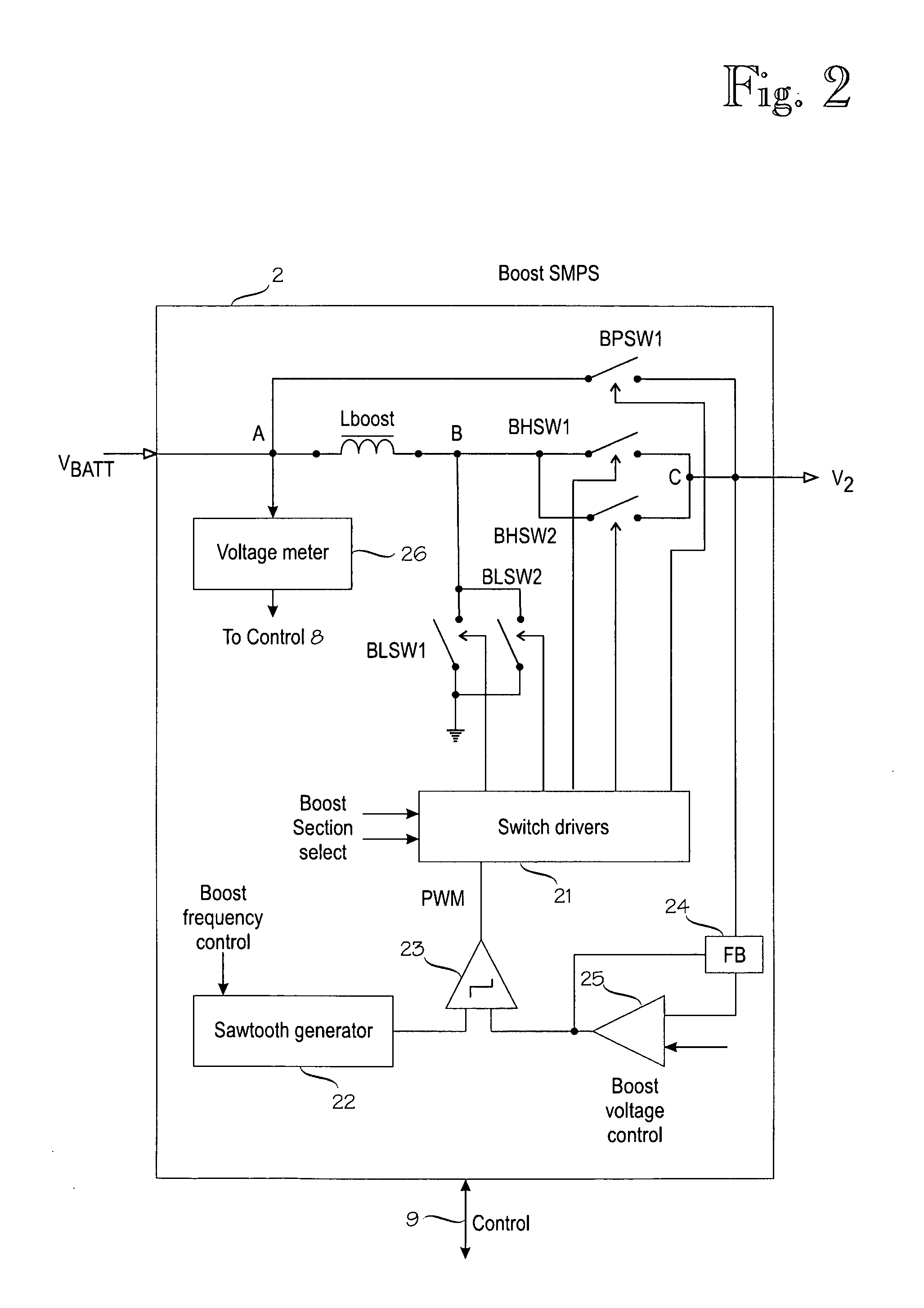
Power supplies for RF power amplifier
ActiveUS20080278136A1Increase the switching frequencyReduce switching frequencyBatteries circuit arrangementsPower amplifiersElectrical batteryEnvelope Tracking
Switched-mode power supplies (SMPSs) and their control methods for radio frequency (RF) power amplifiers in battery-powered wireless transmitter devices involve a Boost-type SMPS and a Buck-type SMPS in cascade connection which are controlled so that high efficiency is maintained for various loads and transmission power levels. The Boost SMPS and the Buck SMPS can be controlled based on the mode of operation of the transmitter, such as the actual battery voltage, the needed output power, the selected frequency band, the selected RF power amplifier (PA), the selected modulation method of the transmission signal, and / or the selected PA voltage control method, such as the envelope elimination and restoration (EER) technique, the envelope tracking (ET) technique, or the power-level tracking (PT) technique.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Dualband power amplifier control using a single power amplifier controller
InactiveUS6216012B1Avoid radiationMinimize size cost complexityPower managementTransmission control/equalisingSignal qualityAudio power amplifier
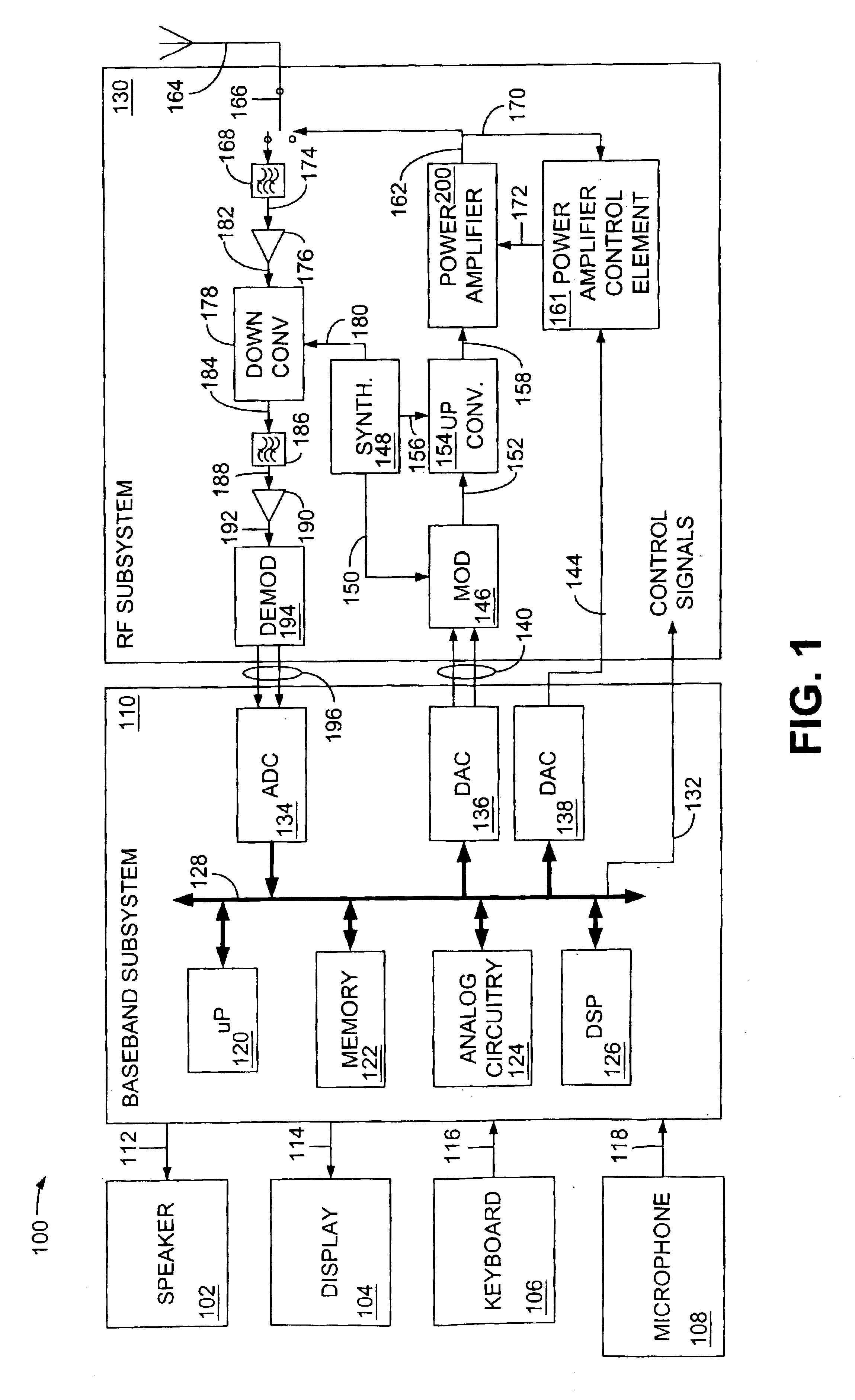
A system having dualband power amplifier control in a dualband phone is provided using a single power amplifier controller. The dualband phone includes two power amplifiers, where each power amplifier amplifies the power of a signal transmitted at a different frequency band. A power amplifier controller is provided for controlling the amount of amplification performed by both of the power amplifiers, and a power amplifier switching device is connected to the power amplifier controller for switching the connection of the power amplifier controller between the two power amplifiers. The system further includes a processing device which monitors the quality and strength of the received signal transmitted by various base stations in the transmission region of the dualband phone. The processing device instructs the power amplifier switching device to switch its connection between the two power amplifiers based upon a determination of which frequency band provides the optimal balance between signal quality and signal strength, and the dualband phone then transmits its signal within the selected optimal frequency band. The system measures the power of the signal transmitted from the power amplifier connected to the power amplifier controller and feeds the measured power value back to the power amplifier controller, so that the power amplifier controller may adjust the voltage driving the power amplifier connected thereto based upon any differences found between the desired power output of the connected power amplifier and the measured power output.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Dual voltage regulator for a supply voltage controlled power amplifier in a closed power control loop
ActiveUS20060270366A1Noise minimizationMinimize noiseResonant long antennasDc network circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierVoltage regulation
A supply voltage controlled power amplifier that comprises a power amplifier, a closed power control feedback loop configured to generate a power control signal, and a dual voltage regulator coupled to the power control feedback loop, the dual voltage regulator comprising a first regulator stage and a second regulator stage, wherein the closed power control loop minimizes noise generated by the first regulator stage.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
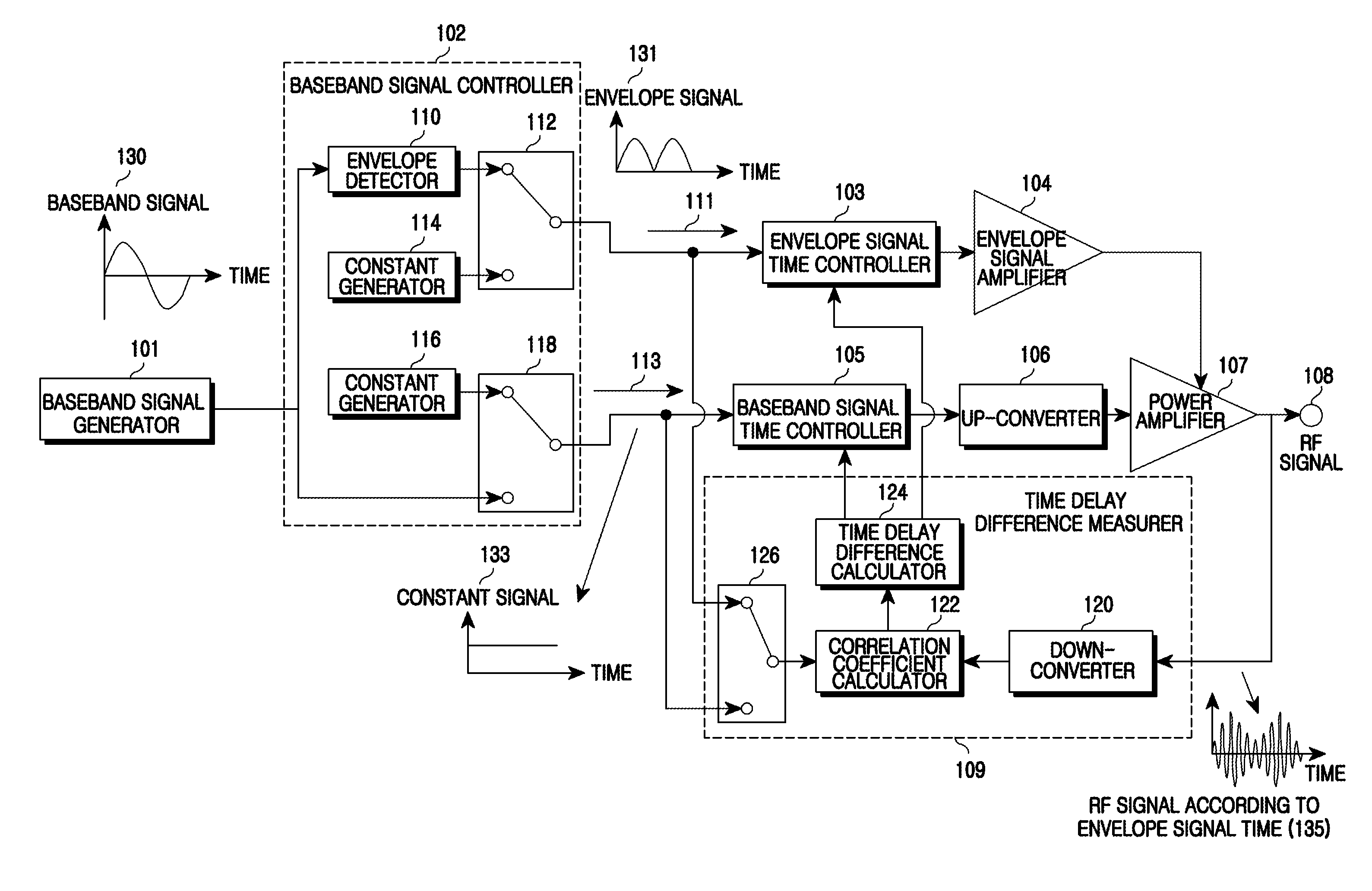
Apparatus and method for envelope tracking power amplification in wireless communication system
InactiveUS20090097591A1Modulated-carrier systemsPower amplifiersCorrelation coefficientCommunications system
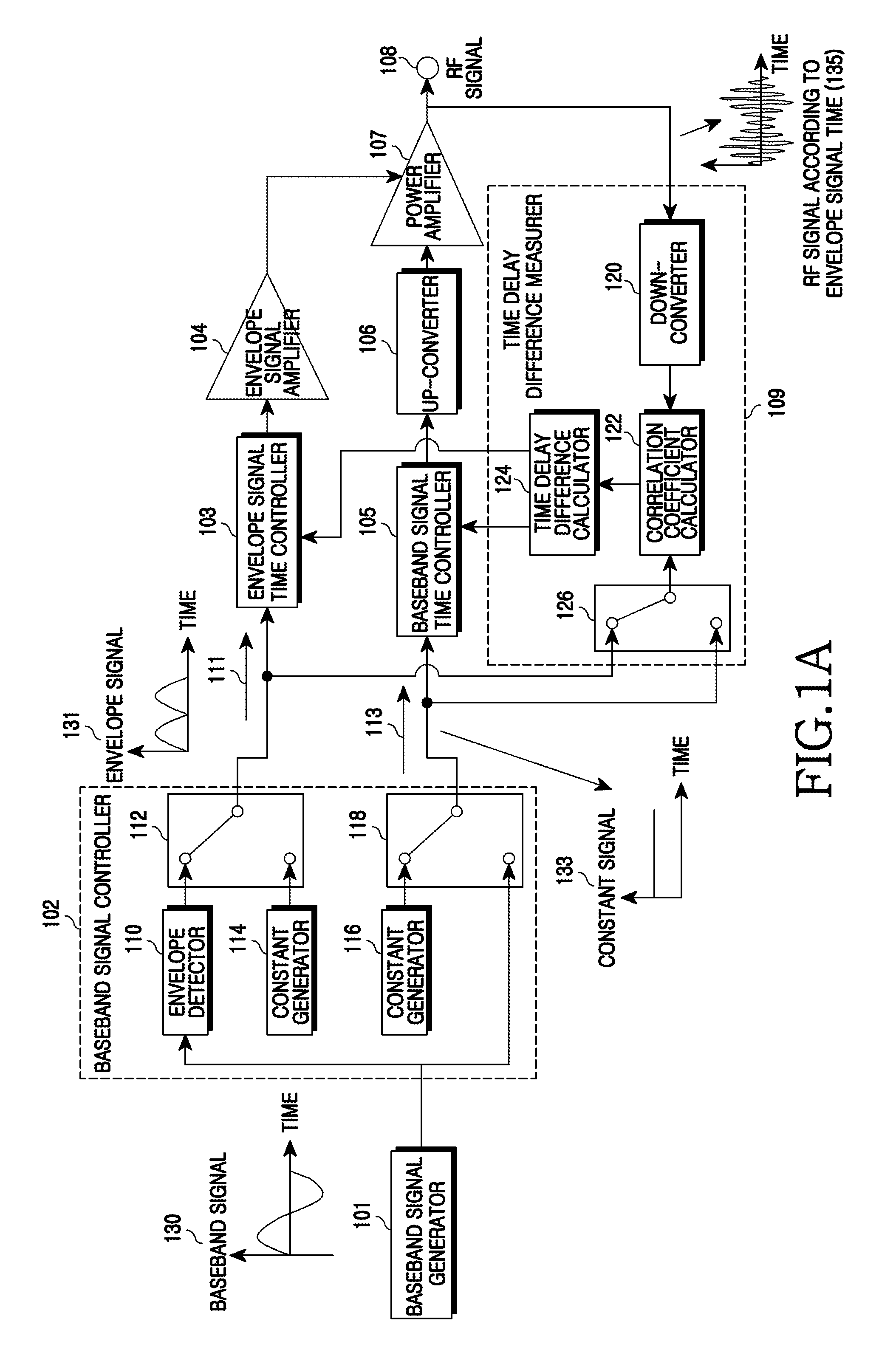
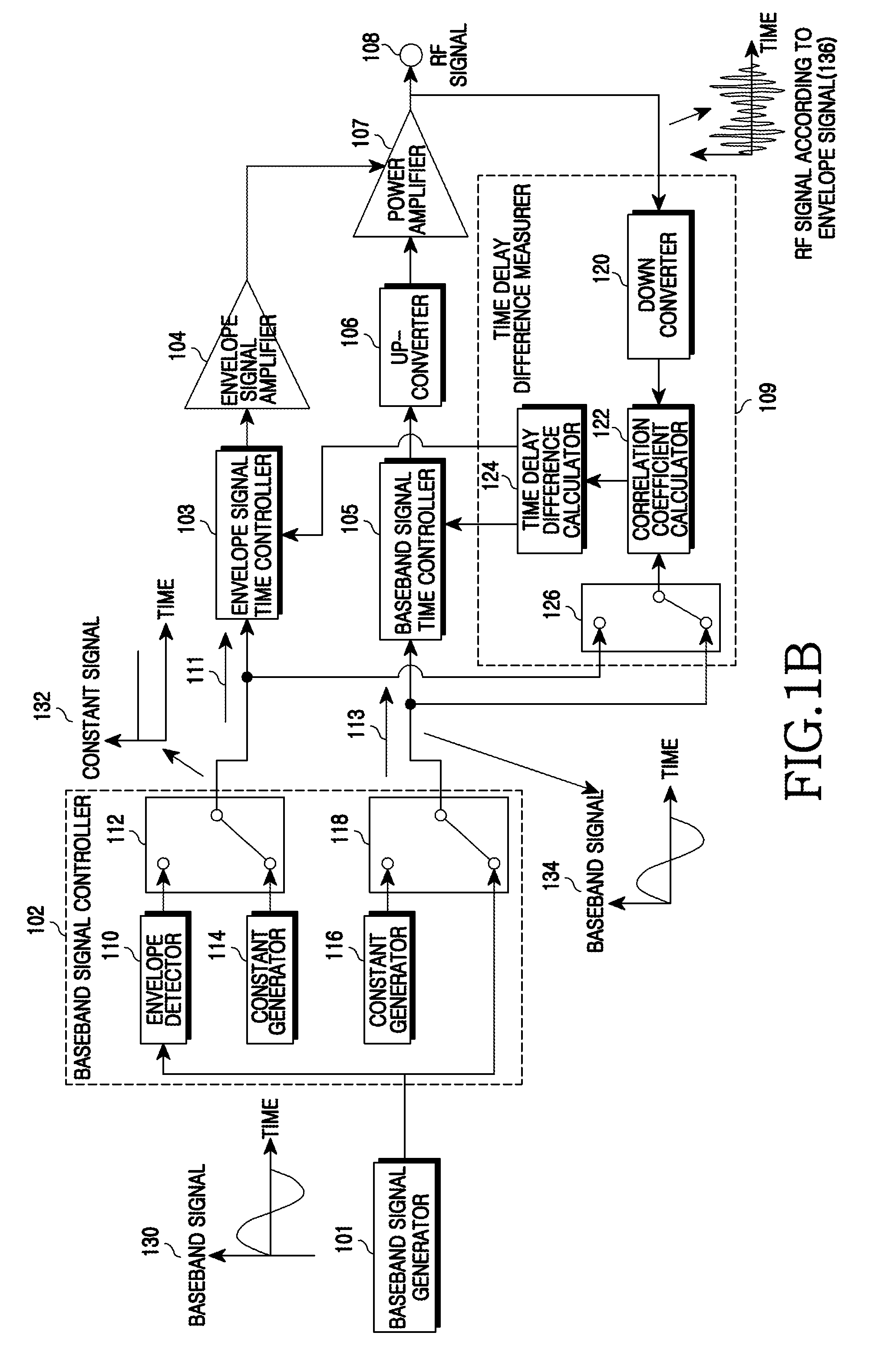
An apparatus and a method for Envelope Tracking (ET) power amplification in a wireless communication system are provided. The apparatus includes a baseband signal controller for outputting an envelope signal in an envelope signal path and outputting a constant signal in a baseband signal path when measuring a time delay of the envelope signal path, and for outputting a constant signal in the envelope signal path and outputting a baseband signal in the baseband signal path when measuring a time delay of the baseband signal path, a time delay difference measurer for measuring a time delay of each path by calculating a correlation coefficient between the envelope signal path and the baseband signal path and a signal time controller for setting a time delay in a corresponding path using the time delay difference of each path and aligning times.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
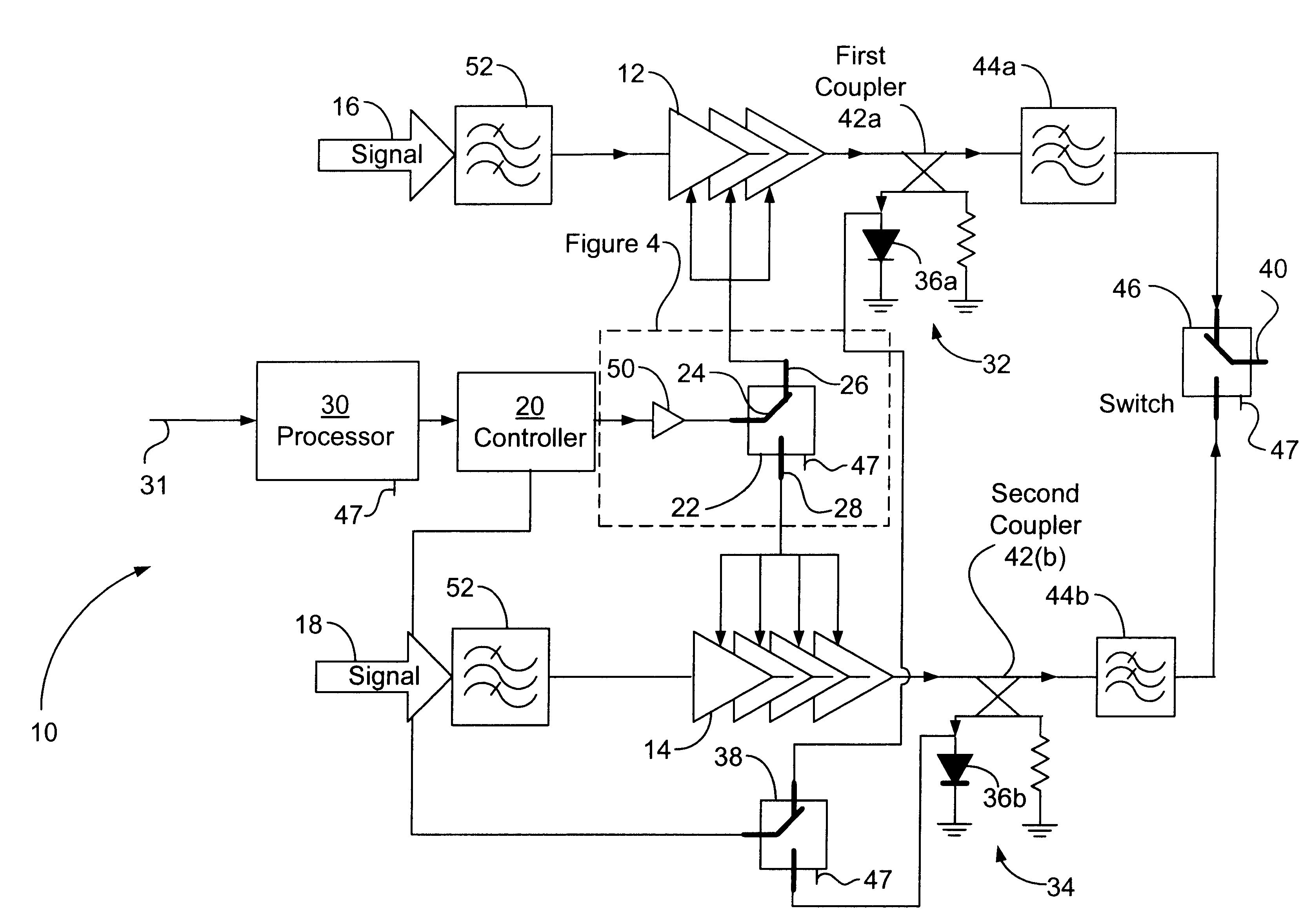
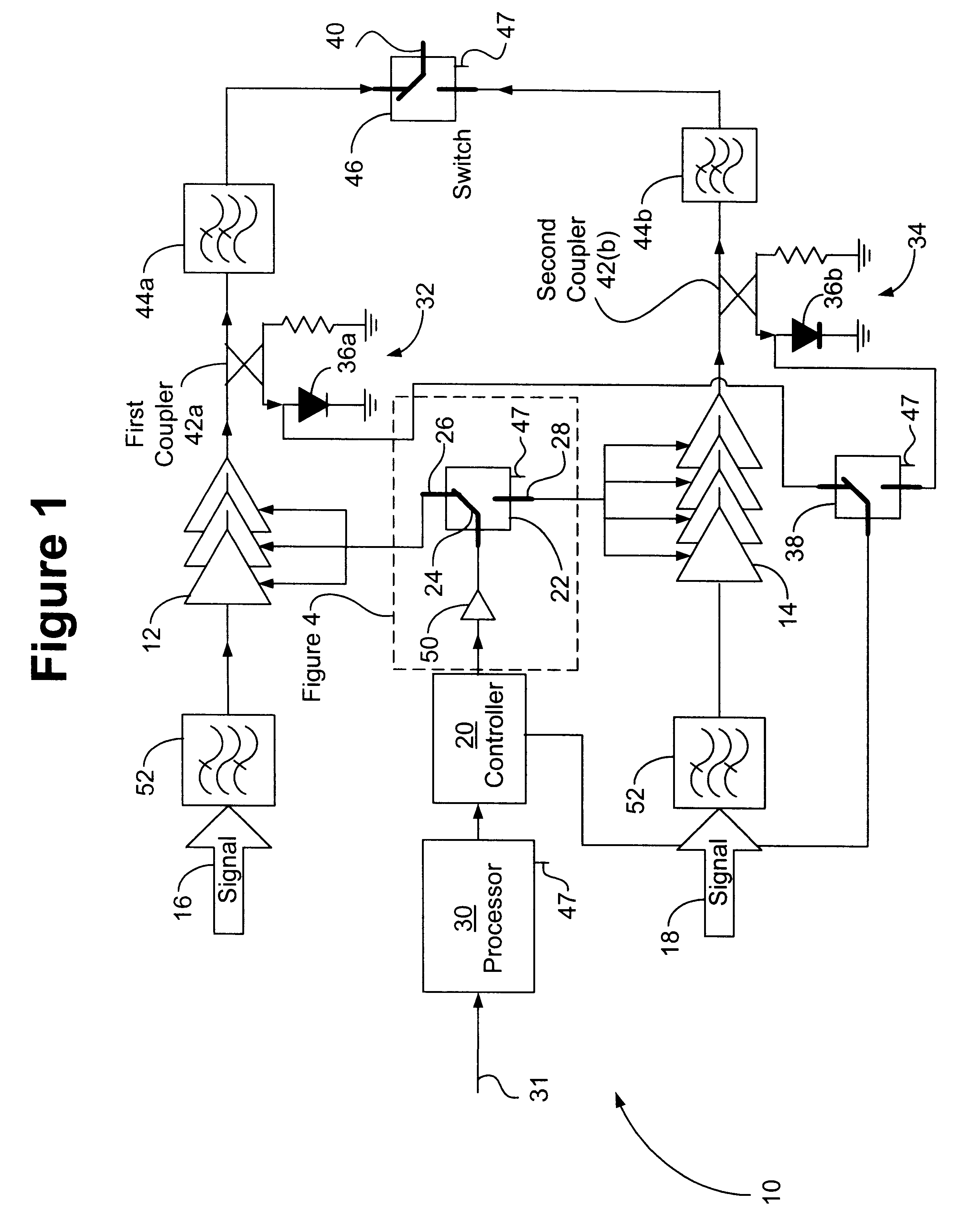
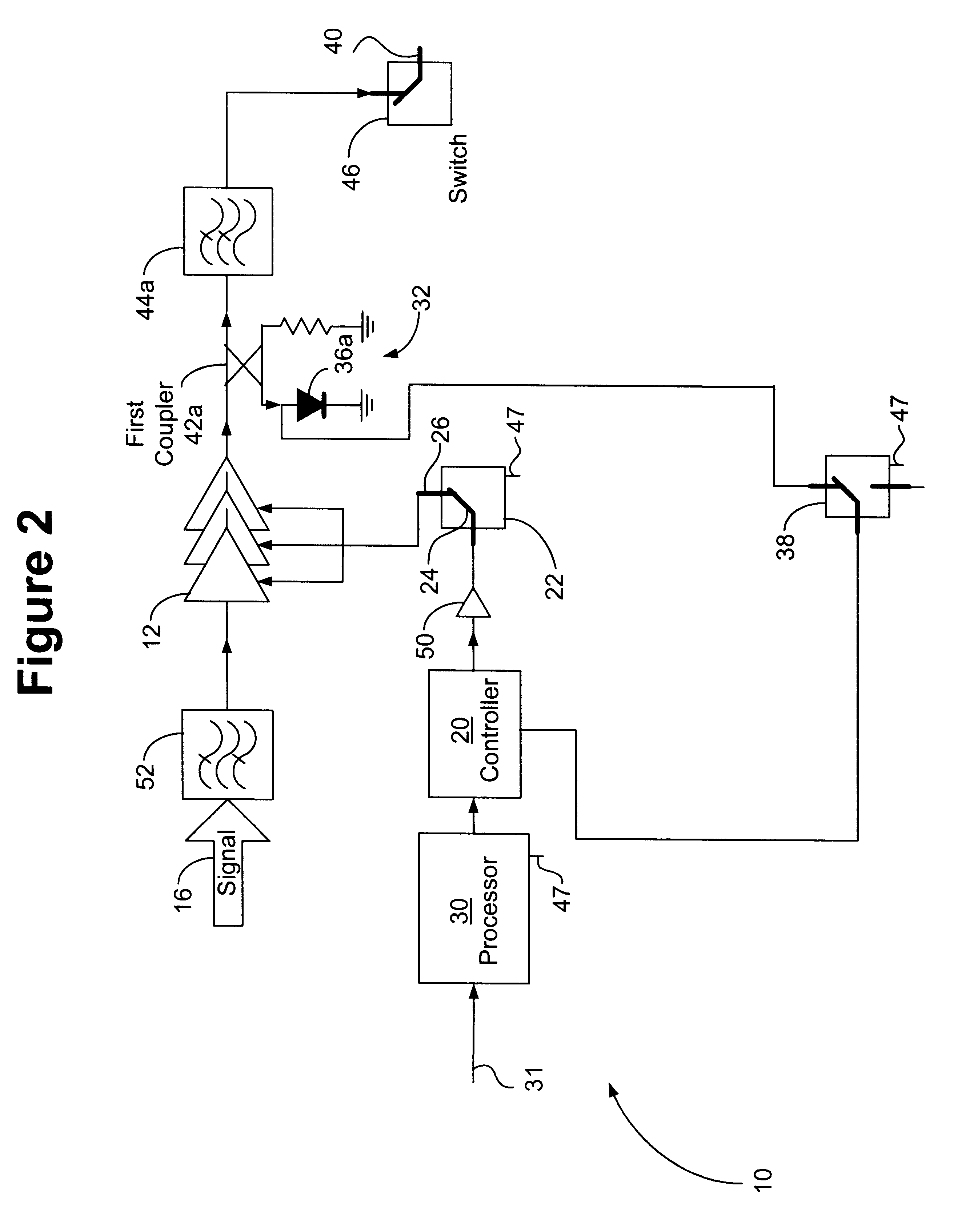
RF power transmission, modulation, and amplification embodiments
InactiveUS20070096806A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasEngineeringFrequency characteristic
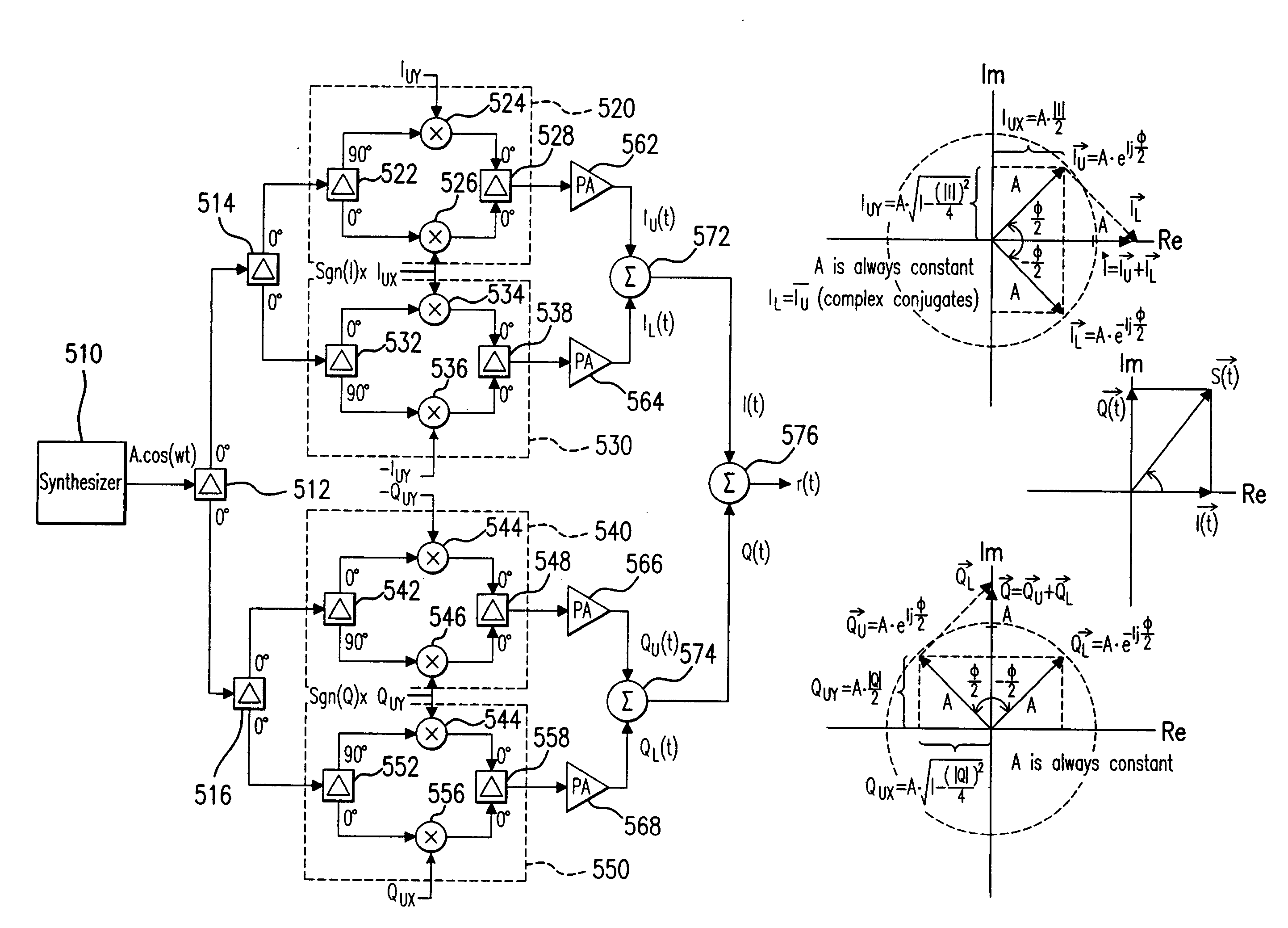
Methods and systems for vector combining power amplification are disclosed herein. In one embodiment, a plurality of signals are individually amplified, then summed to form a desired time-varying complex envelope signal. Phase and / or frequency characteristics of one or more of the signals are controlled to provide the desired phase, frequency, and / or amplitude characteristics of the desired time-varying complex envelope signal. In another embodiment, a time-varying complex envelope signal is decomposed into a plurality of constant envelope constituent signals. The constituent signals are amplified equally or substantially equally, and then summed to construct an amplified version of the original time-varying envelope signal. Embodiments also perform frequency up-conversion.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
Transmitting method and transmitter apparatus
InactiveUS20050079835A1Component distortionAccurate timingAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasEngineeringDistributor
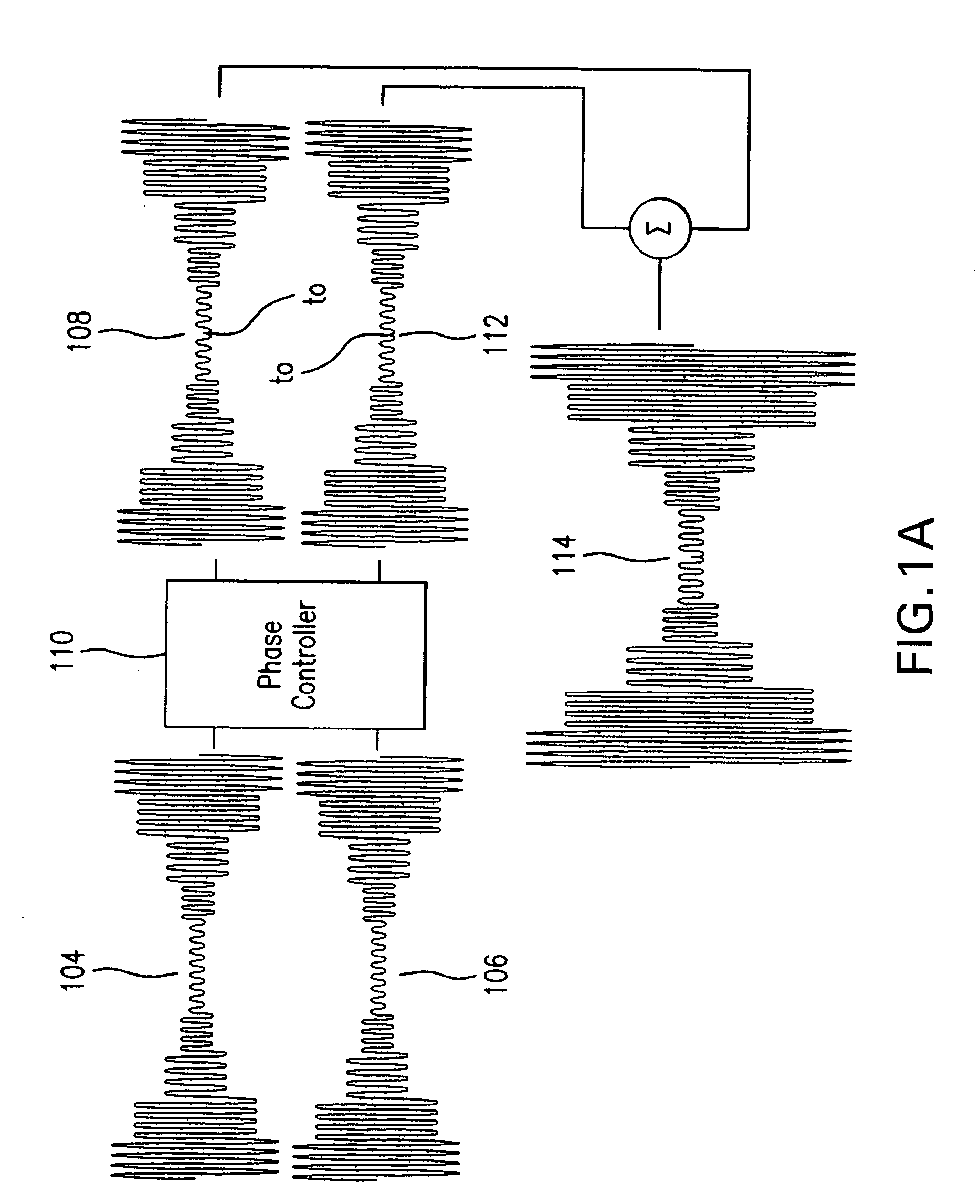
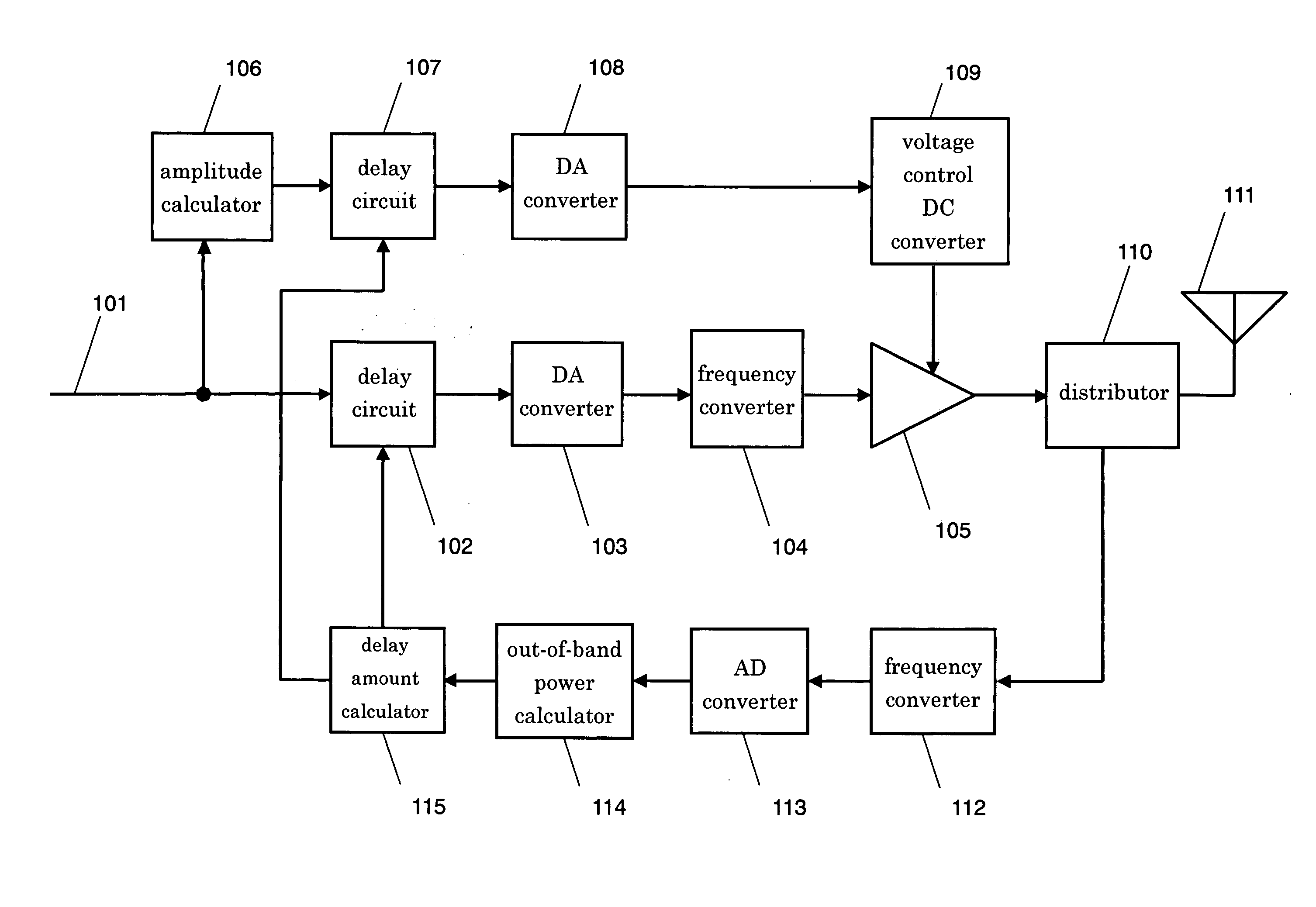
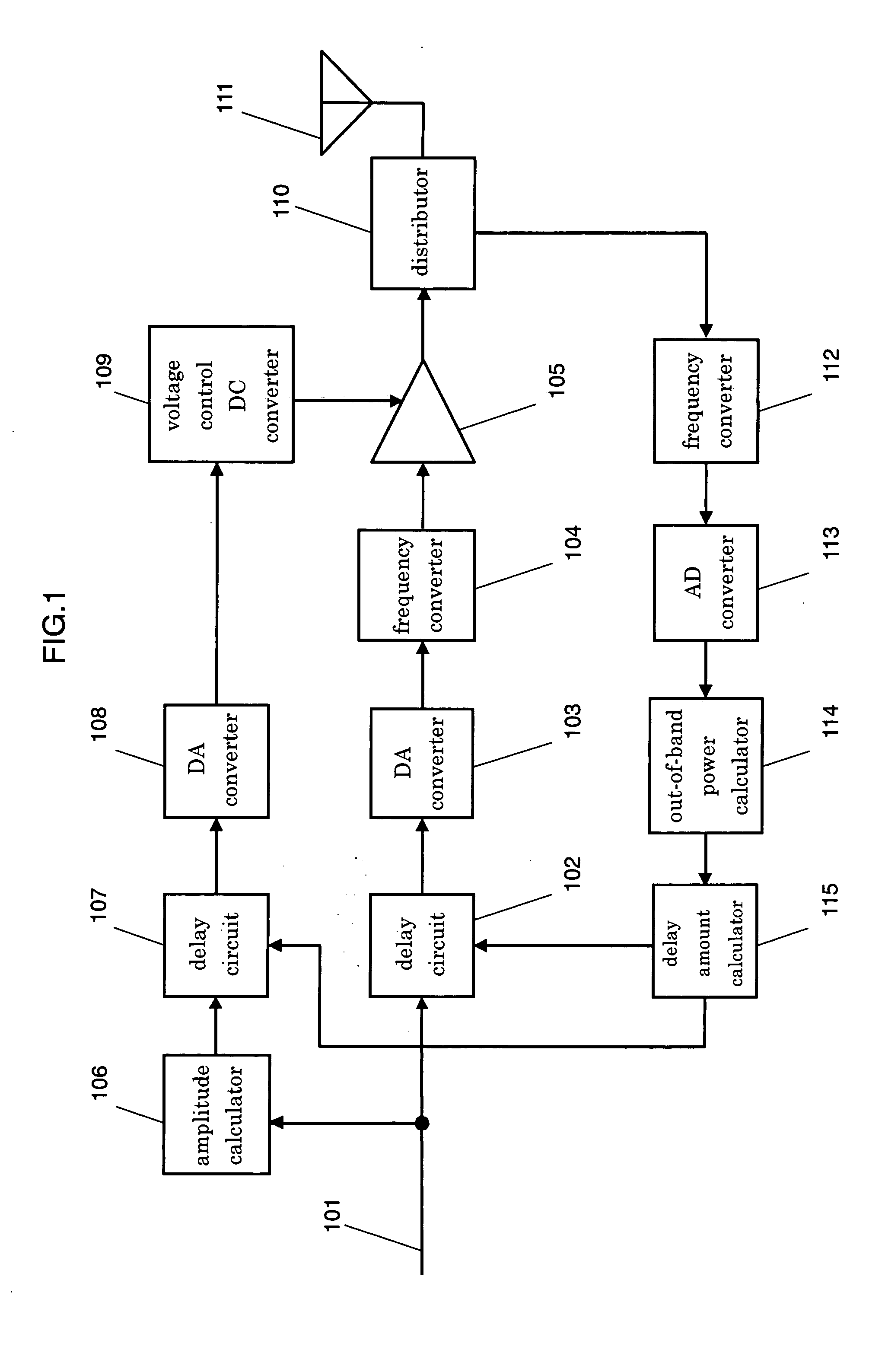
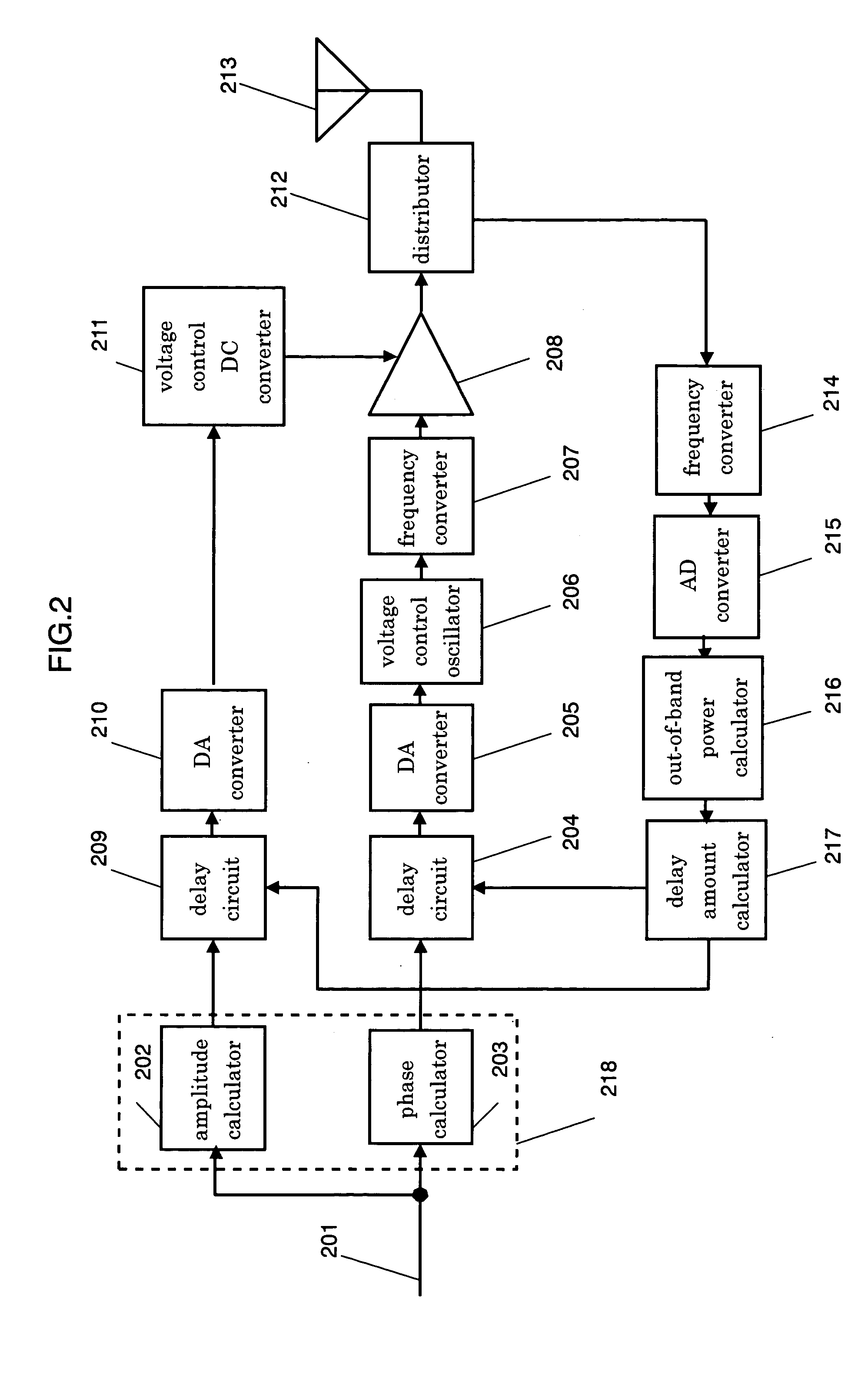
A transmitting method and a transmitter apparatus, which need no manual adjustment, are disclosed. A delay amount of a delay means is automatically adjusted such that an out-of-band distortion component of a transmission signal is minimized, and a correct timing is produced by the method and the apparatus. In this transmitter apparatus, a first delay means adjusts a control timing over a voltage that controls a power amplifying means, and a distributor distributes an output from the power amplifying means in order to feedback parts of the output. A distortion adjusting means calculates a distortion component of the transmission signal by using the signal fed back by the distributor, and adjusts automatically a delay amount of the first delay means so as to minimize the distortion component. This structure allows eliminating manual adjustment, and obtaining high power-efficiency with fewer distortions.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
System and method for current-mode amplitude modulation
InactiveUS20050032488A1Efficient and linear amplificationHighly linear envelope modulationSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAntenna impedanceAudio power amplifier
An amplifier circuit includes a power amplifier biased for saturated mode operation, and a controllable current source to provide supply current to the power amplifier. The controllable current source effects desired amplitude modulation of the output signal from the power amplifier by modulating the supply current it provides responsive to an amplitude information signal. In one or more embodiments, the current source includes a circuit that is configured to adjust one or more transmitter operating parameters responsive to detecting changes in the effective DC resistance of the power amplifier. For example, the circuit may generate a compensation signal that reduces the effective DC resistance responsive to detecting that the effective DC resistance has undesirably increased. By way of non-limiting examples, such compensation may be effected by changing a current mirror, an amplifier-to-antenna impedance matching, an amplifier bias or device size, or imposing some form of transmit signal back-off.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
Reconfigurable transmitter with direct digital to RF modulator
InactiveUS20050191976A1Analogue/digital conversionResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierData signal
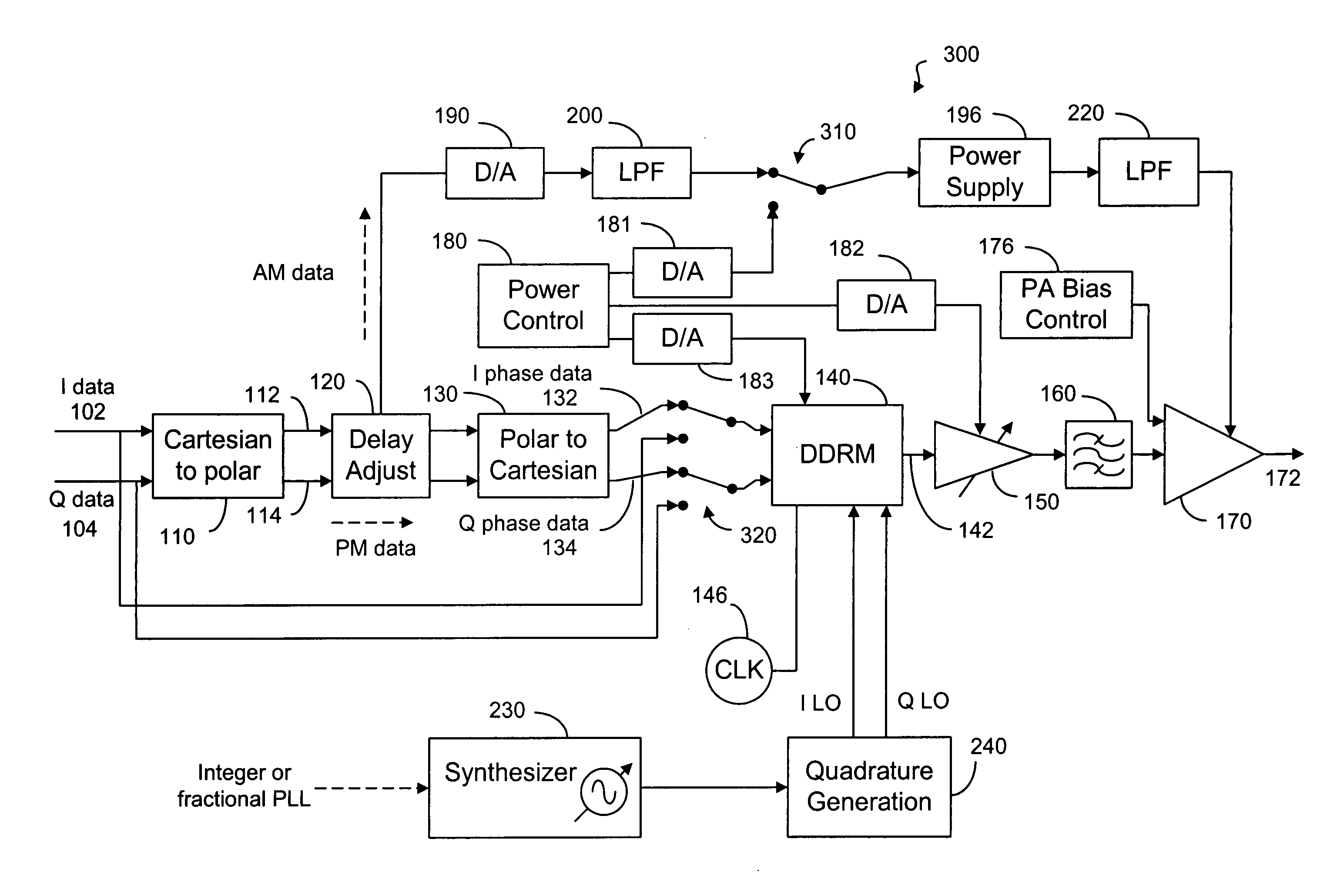
An RF transmitter uses two digital-to-RF conversion modules to convert digital baseband signals into RF signals. In Cartesian mode, baseband signals are conveyed to the conversion modules for RF conversion. In polar mode, baseband signals are converted into amplitude and phase data parts. Phase data part is converted into I and Q data parts to be converted by the conversion modules into RF signals, which are modulated in a power amplifier by amplitude data part through the power supply of the power amplifier. Each digital-to-RF module uses parallel unit cells to perform D / A conversion function and upconversion function by an IF signal. Each unit cell, adapted to receive a control voltage indicative of a data signal value, is a mixer cell type converter having a differential data switch section connected in series to a differential LO-switch pair. LO-switch is further connected in series to a current source.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
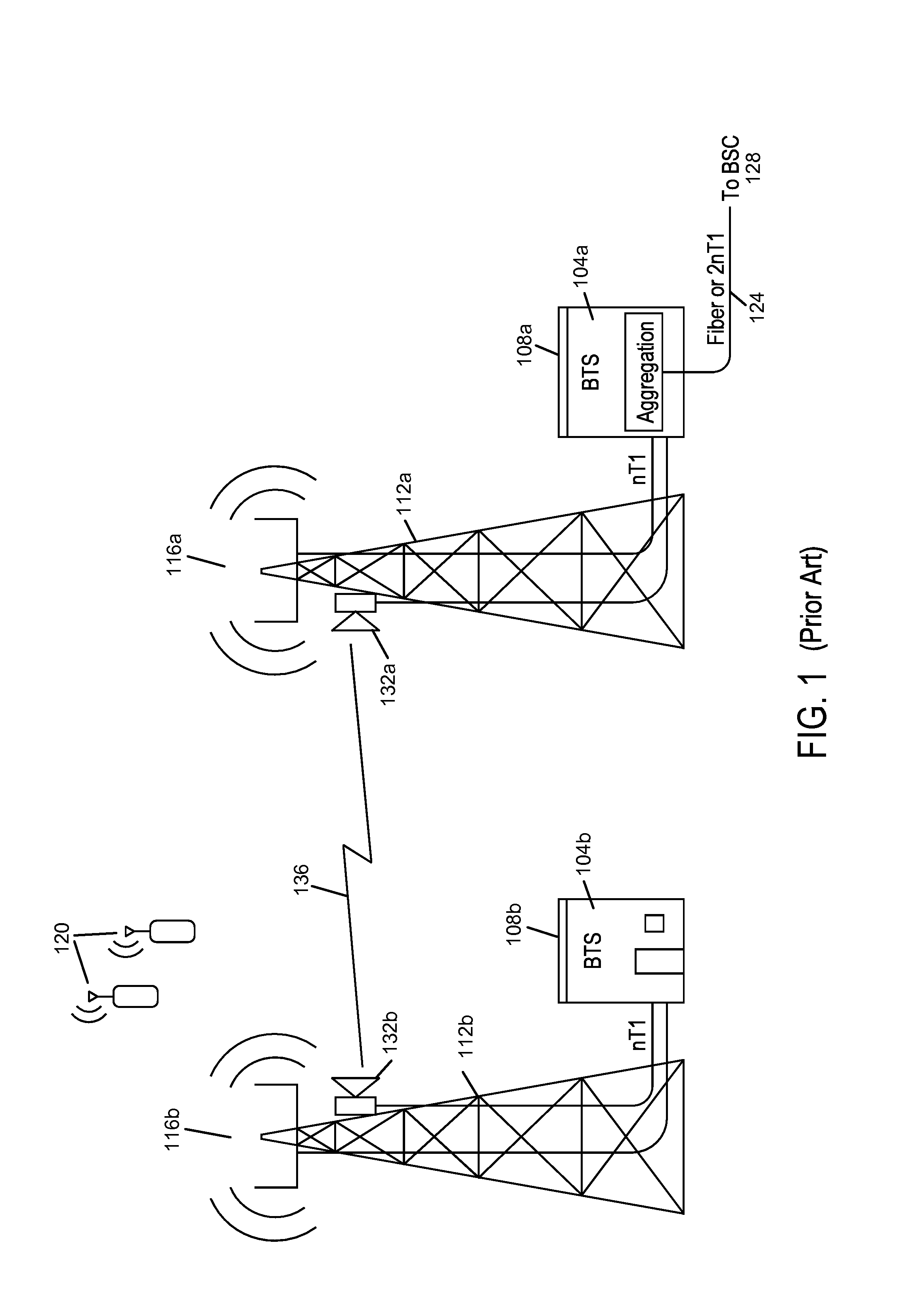
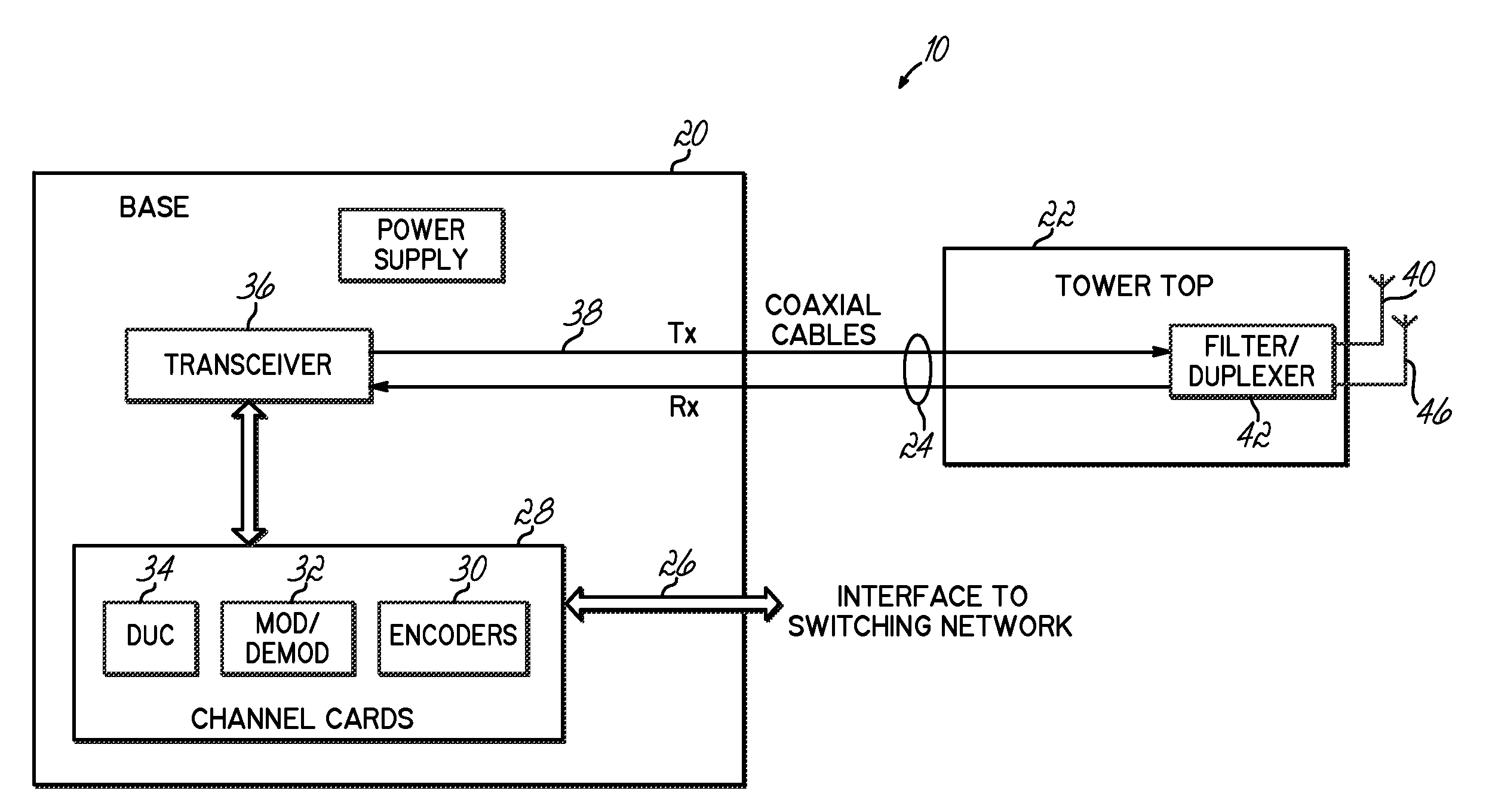
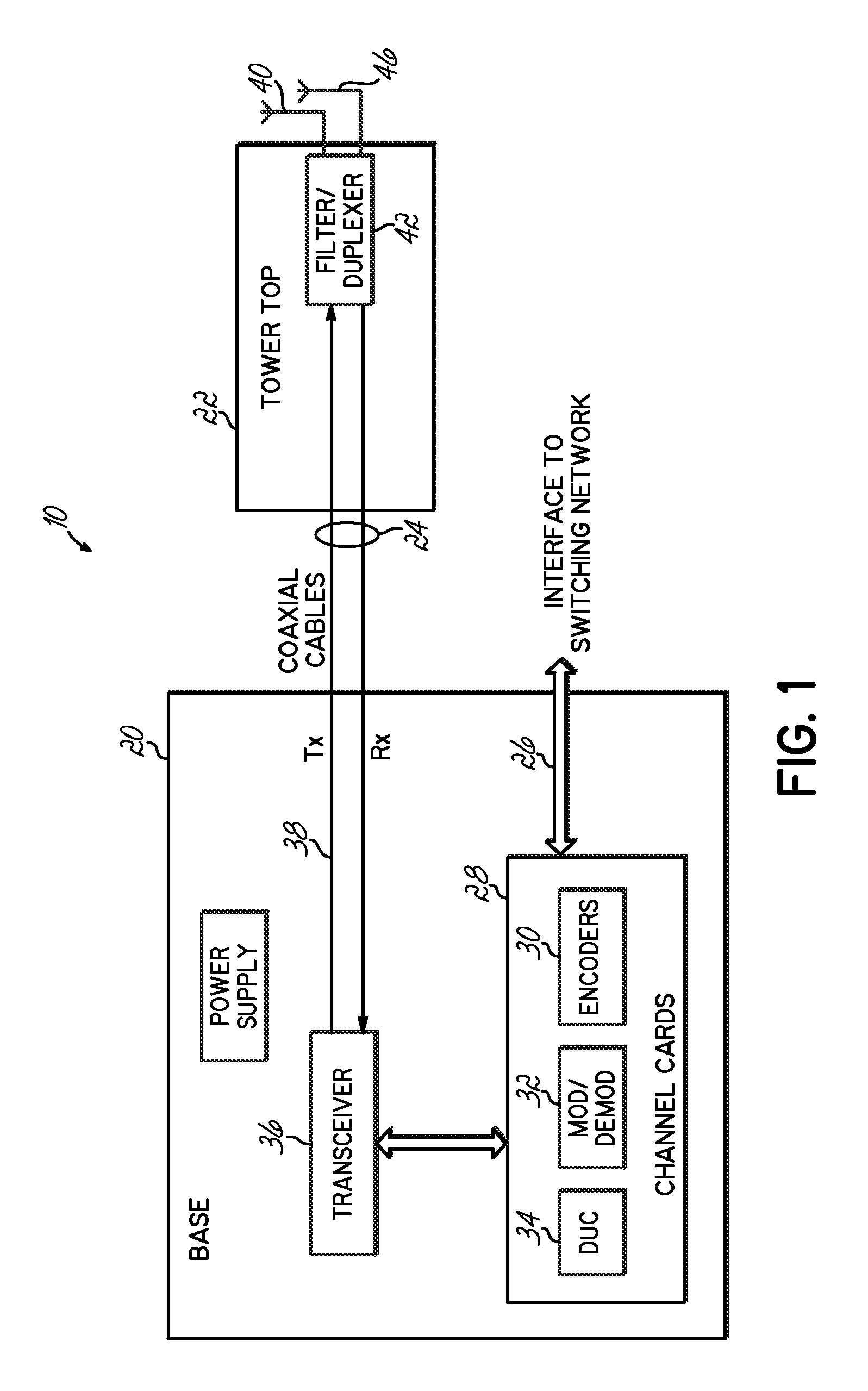
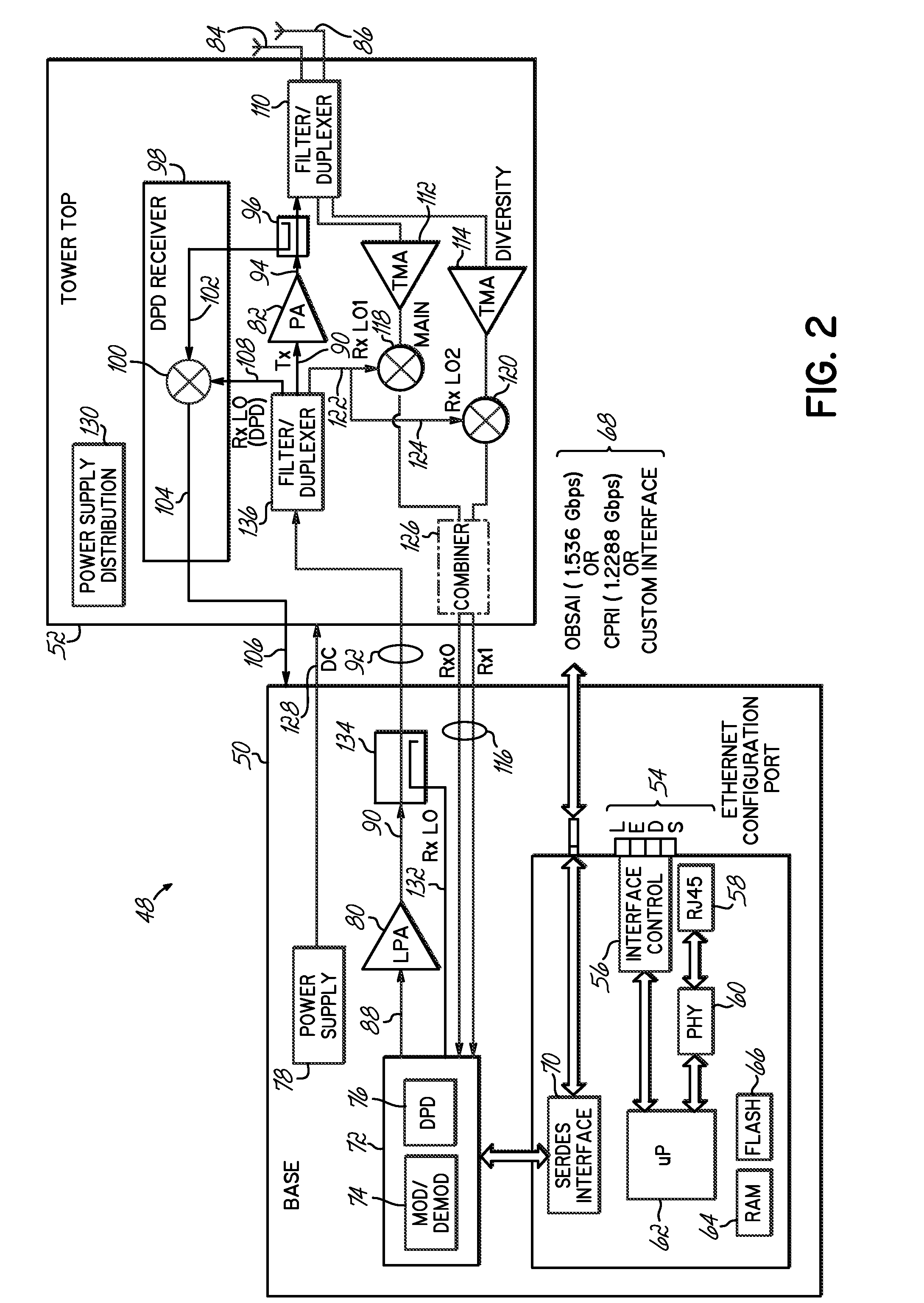
Transceiver architecture and method for wireless base-stations
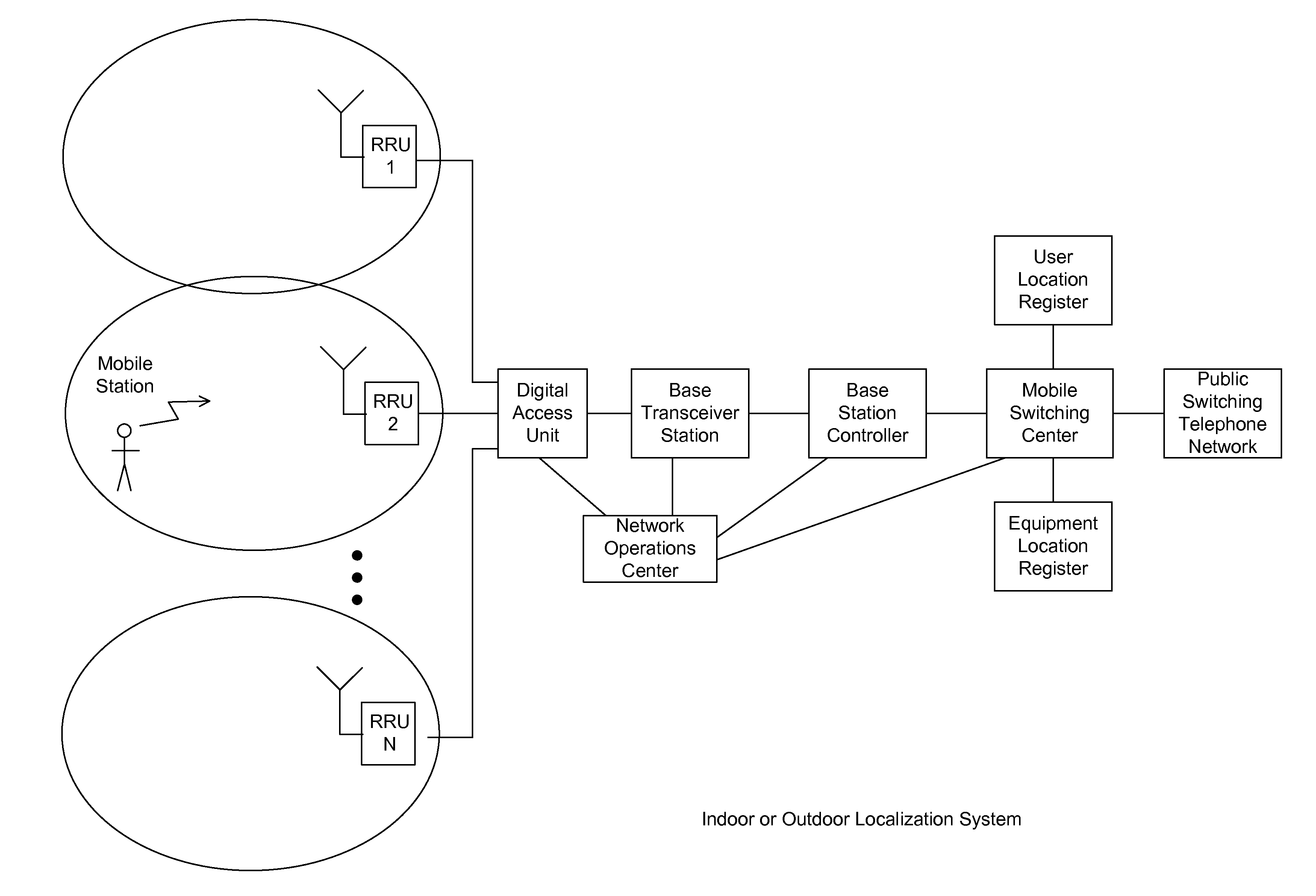
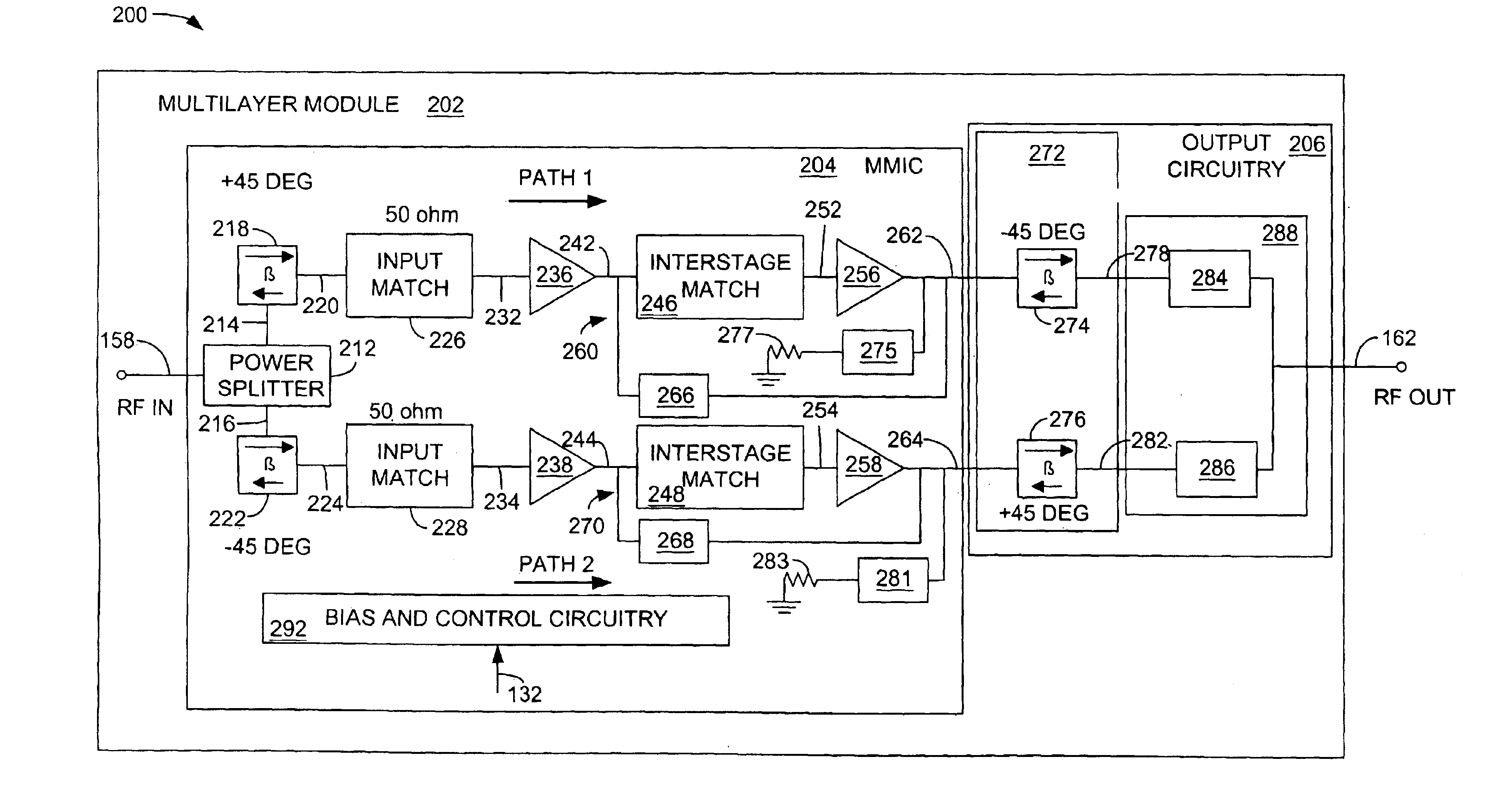
A system for wireless communications includes a tower structure supporting at least one transmit antenna at an elevated position on the tower structure and base electronics positioned proximate a base of the tower structure. The base electronics are coupled with the transmit antenna and include an initial stage amplifier for amplifying an input signal to provide a low power transmission signal that is provided to the transmit antenna at the elevated position.A final stage amplifier is positioned proximate the transmit antenna. The final stage amplifier is a high efficiency amplifier for efficiently amplifying the low power transmission signal from the base electronics to provide a high power transmission signal to be transmitted from the transmit antenna.
Owner:ANDREW LLC
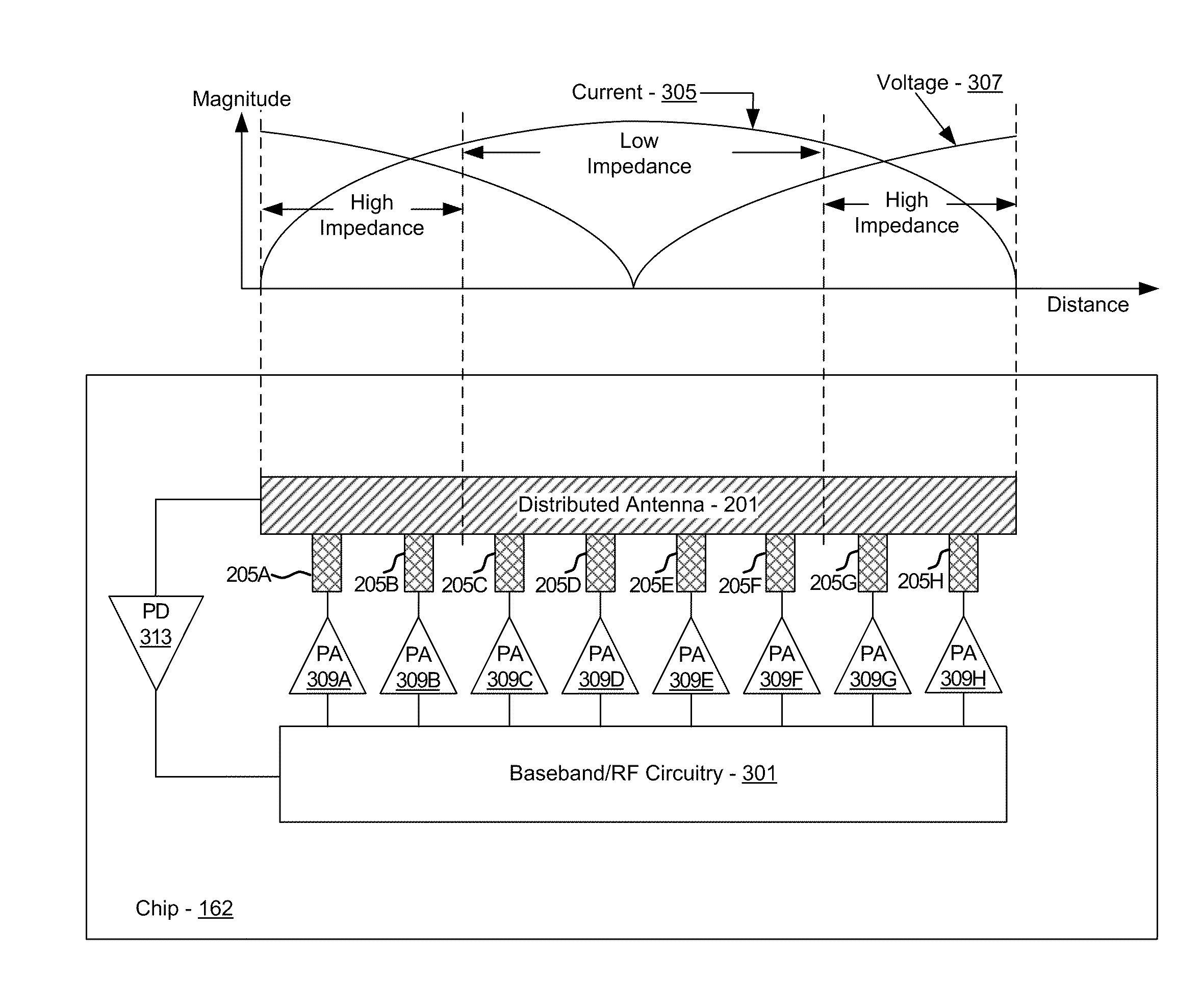
Method and system for power control with optimum power efficiency with a multi-port distributed antenna
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
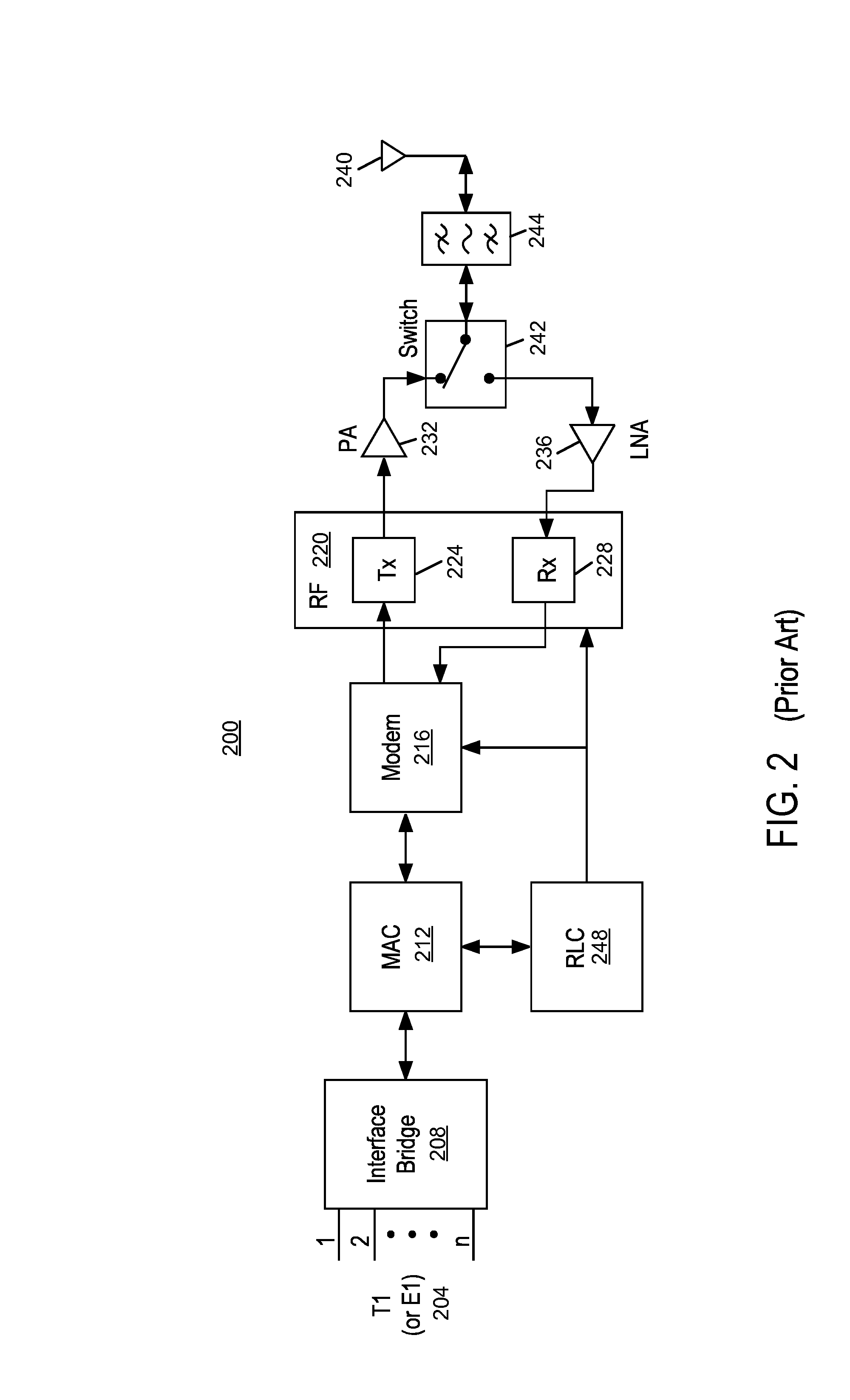
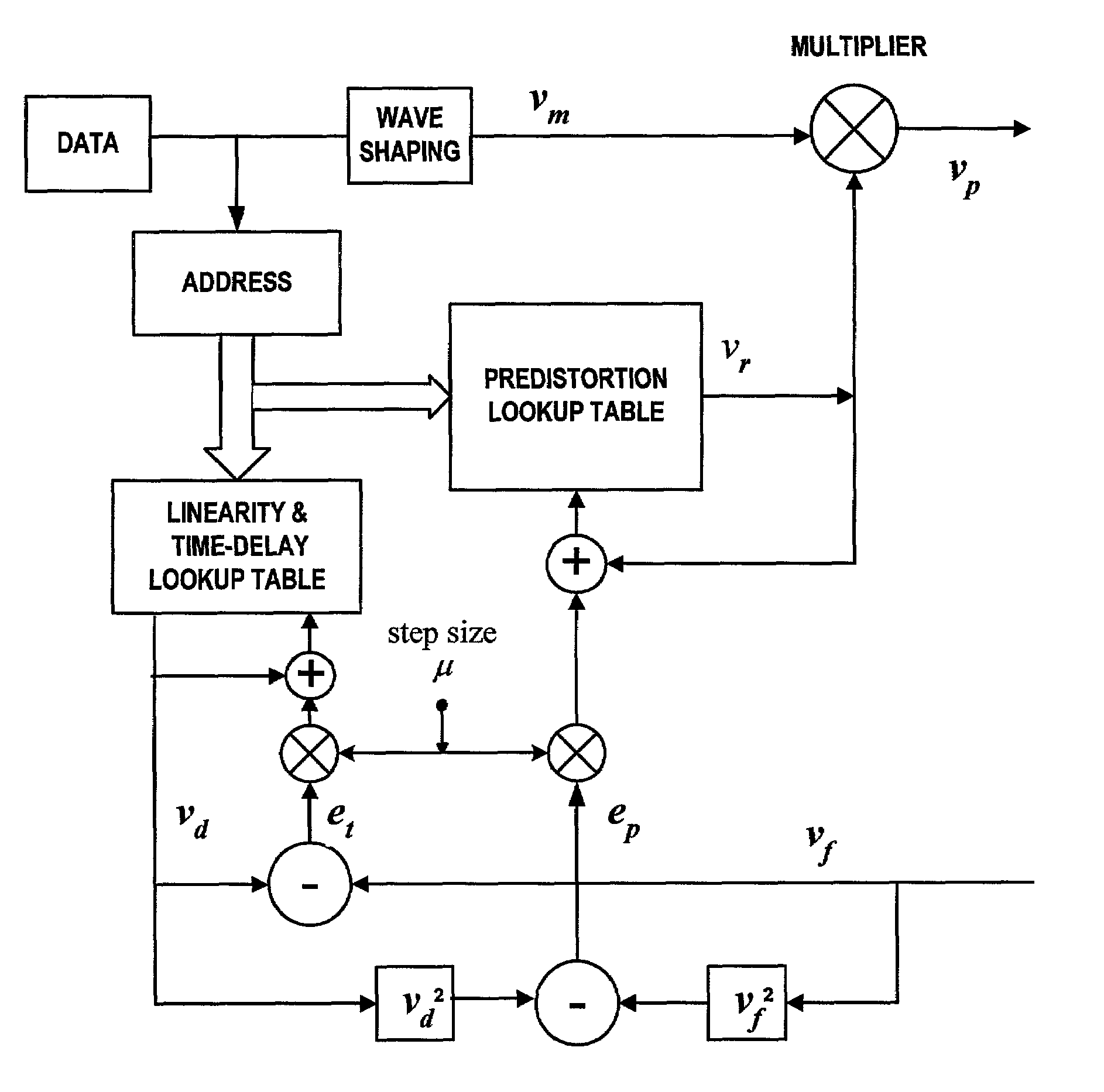
System and method for digital memorized predistortion for wireless communication
ActiveUS6985704B2Error preventionModulated-carrier systemsAudio power amplifierWireless transmission
An embodiment of the invention is a system for signal processing in preparation for wireless transmission, the wireless transmission being from a portable wireless communication device and including use of a power amplifier having nonlinear characteristics. The system includes memory for storing digitally-indexed information. The digitally-indexed information models nonlinear characteristics of the power amplifier, and the digitally-indexed information is stored prior to processing of a first signal that reflects information to be communicated. The system further includes first logic, configured to accept the first signal and to retrieve, based on the first signal, a portion of the digitally-indexed information stored in the memory, and second logic, configured to generate a second signal based on the portion of the digitally-accessed information and on the first signal. The second signal pre-compensates for the nonlinear characteristics of the power amplifier, and the second signal is for wireless transmission based on the second signal.
Owner:DALI WIRELESS
Load variation tolerant radio frequency (RF) amplifier
A power amplifier having a phase shift and impedance transformation element is disclosed. The power amplifier comprises a plurality of amplification paths, a first phase shift element at an input of each amplification path and a second phase shift element at an output of each amplification path. The amplifier also comprises an impedance transformation element associated with the second phase shift element and a power combiner configured to combine an output of each amplification path into a single output.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Transmitter predistortion circuit and method therefor
InactiveUS7469491B2Compensation DistortionMultiple-port networksPower amplifiersNonlinear distortionData stream
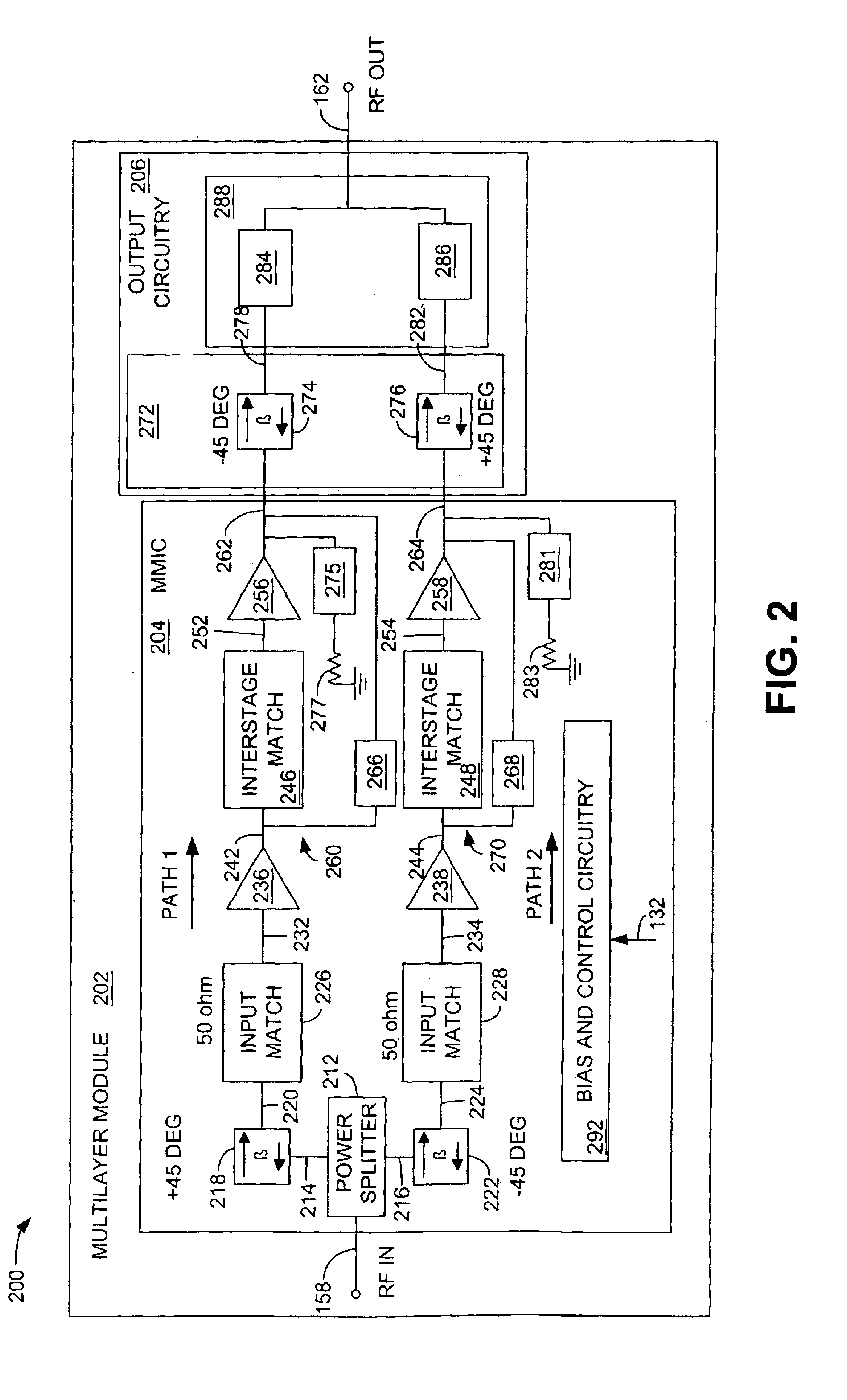
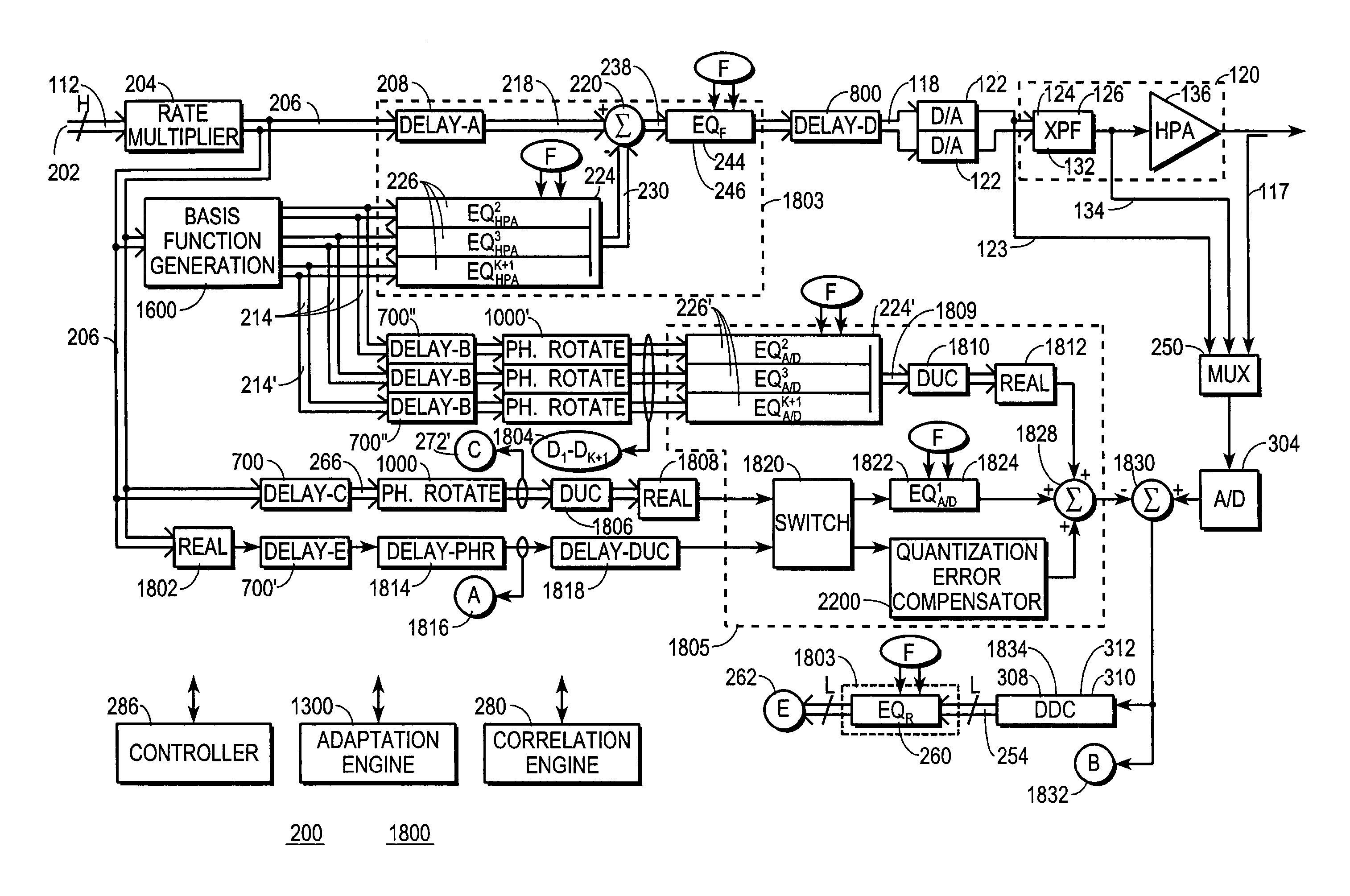
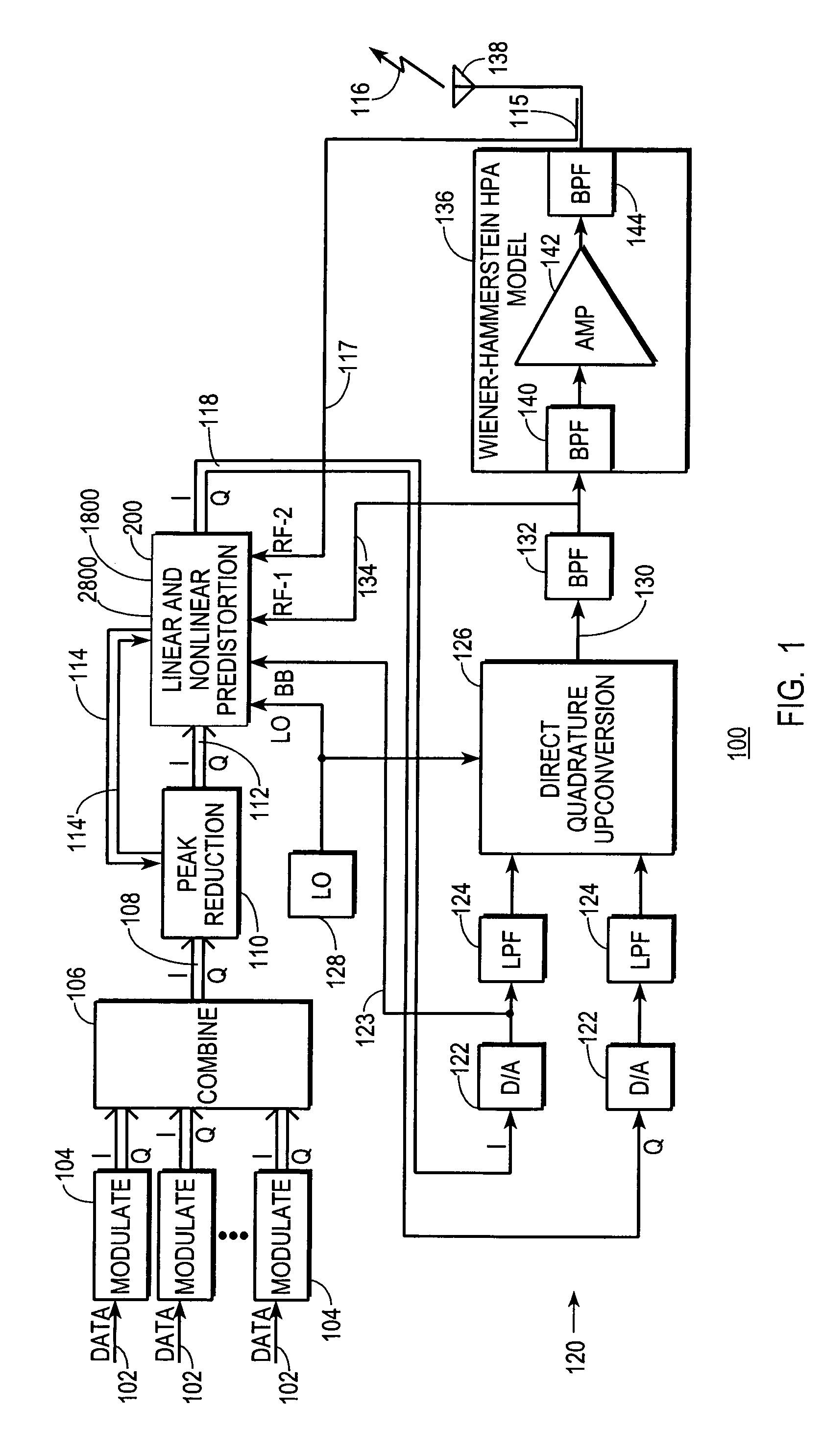
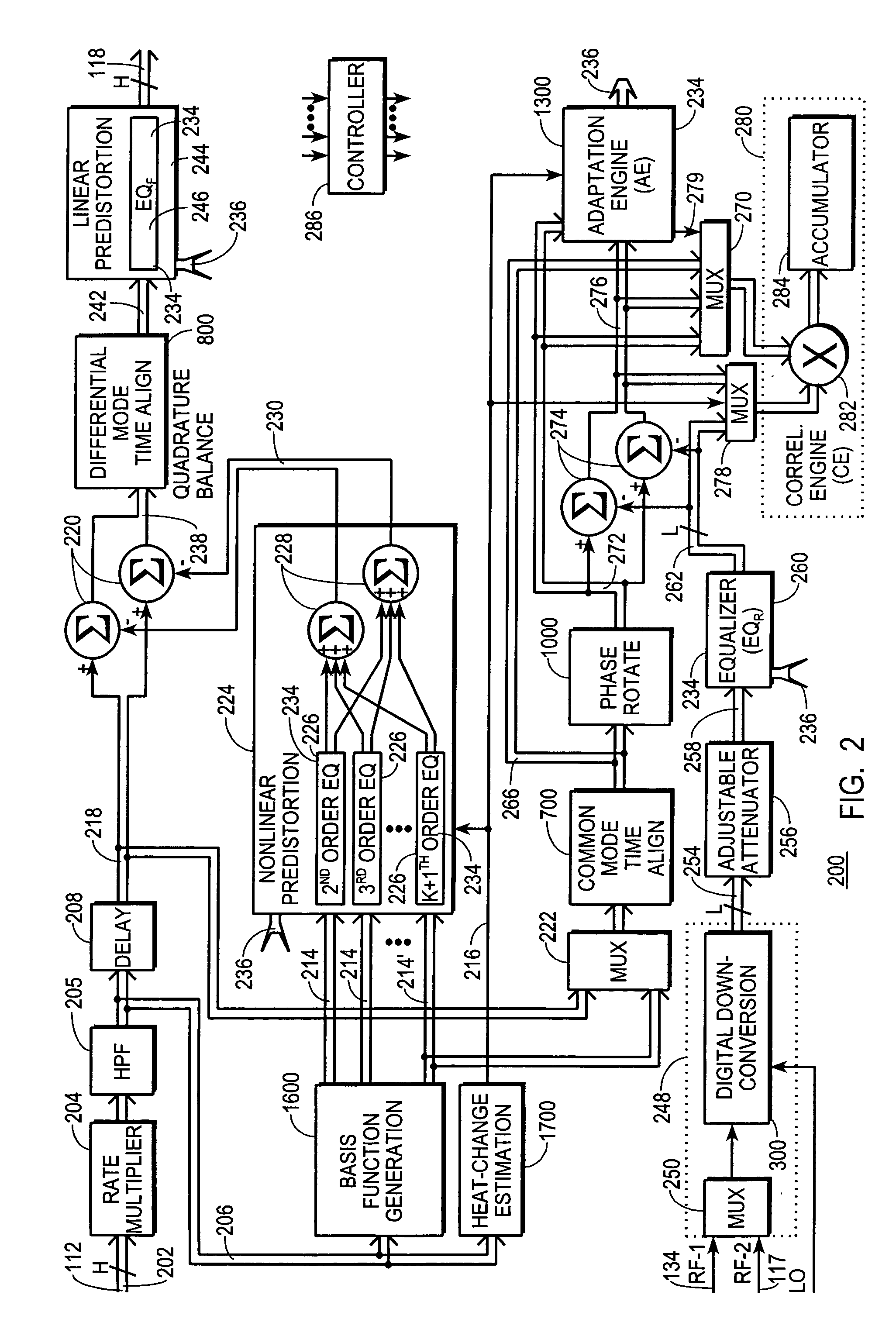
A digital communications transmitter (100) includes a digital linear-and-nonlinear predistortion section (200, 1800, 2800) to compensate for linear and nonlinear distortion introduced by transmitter-analog components (120). A direct-digital-downconversion section (300) generates a complex digital return-data stream (254) from the analog components (120) without introducing quadrature imbalance. A relatively low resolution exhibited by the return-data stream (254) is effectively increased through arithmetic processing. Distortion introduced by an analog-to-digital converter (304) may be compensated using a variety of adaptive techniques. Linear distortion is compensated using adaptive techniques with an equalizer (246) positioned in the forward-data stream (112). Nonlinear distortion is then compensated using adaptive techniques with a plurality of equalizers (226) that filter a plurality of orthogonal, higher-ordered-basis functions (214) generated from the forward-data stream (112). The filtered-basis functions are combined together and subtracted from the forward-data stream (112).
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com