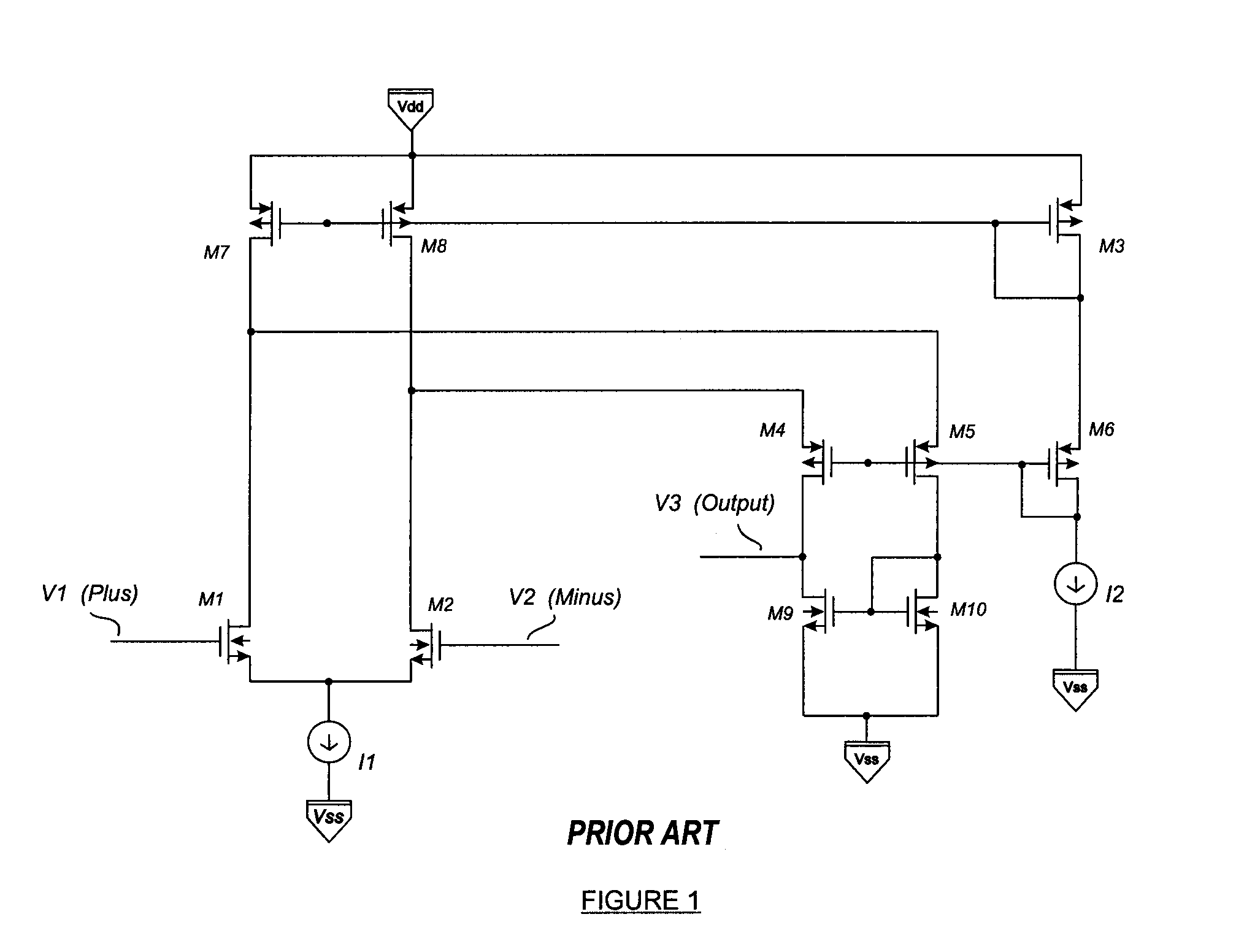
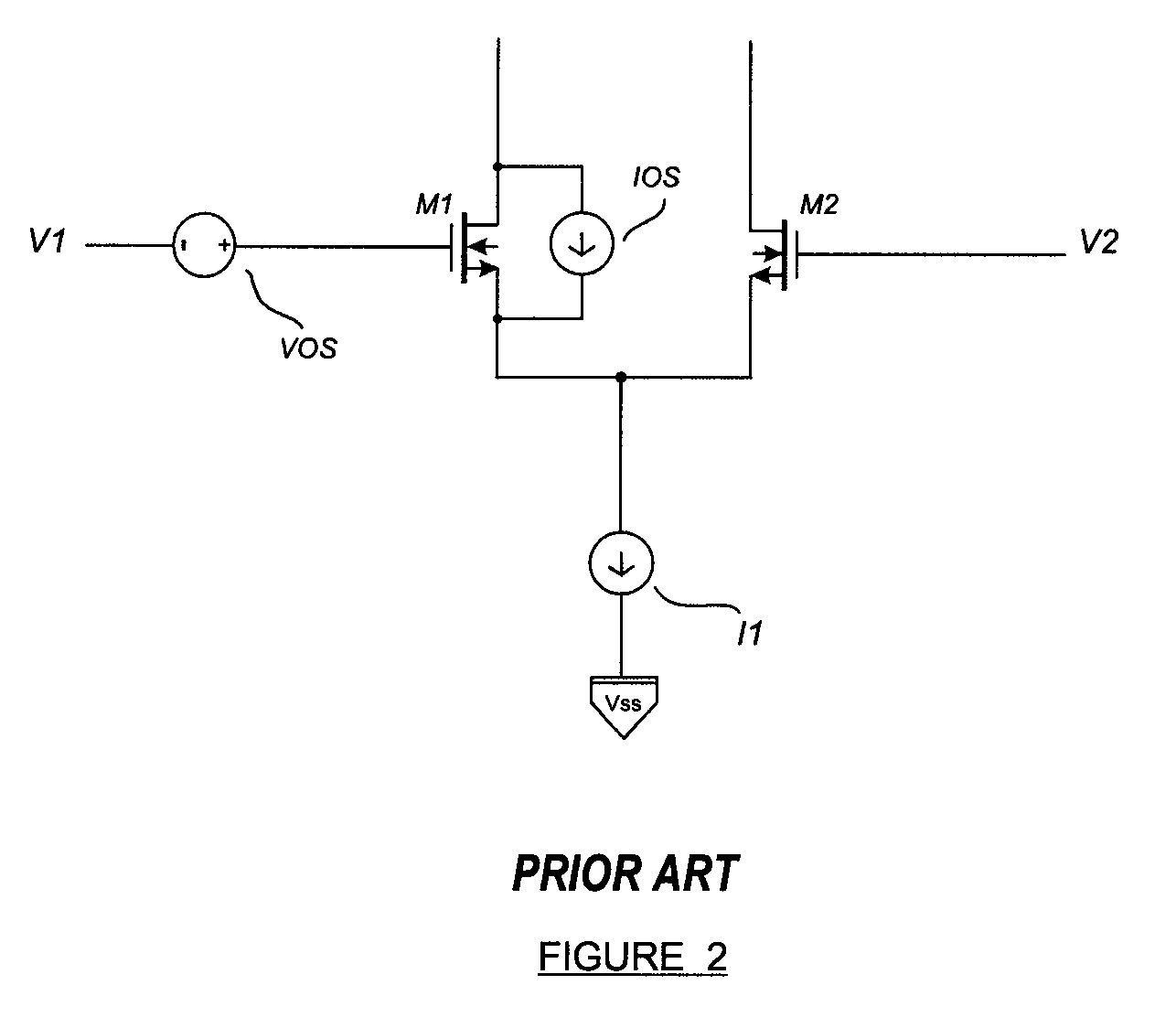
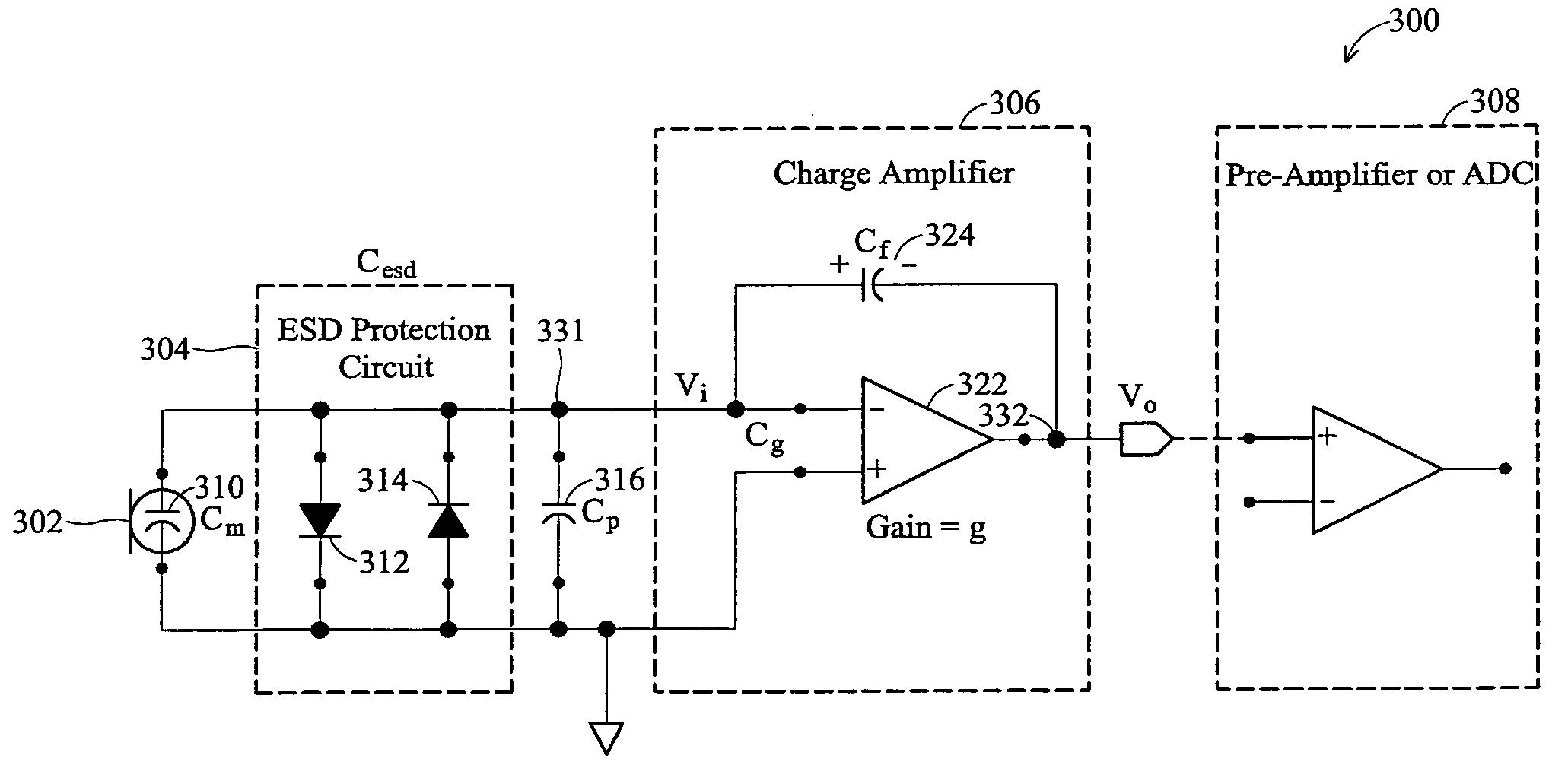
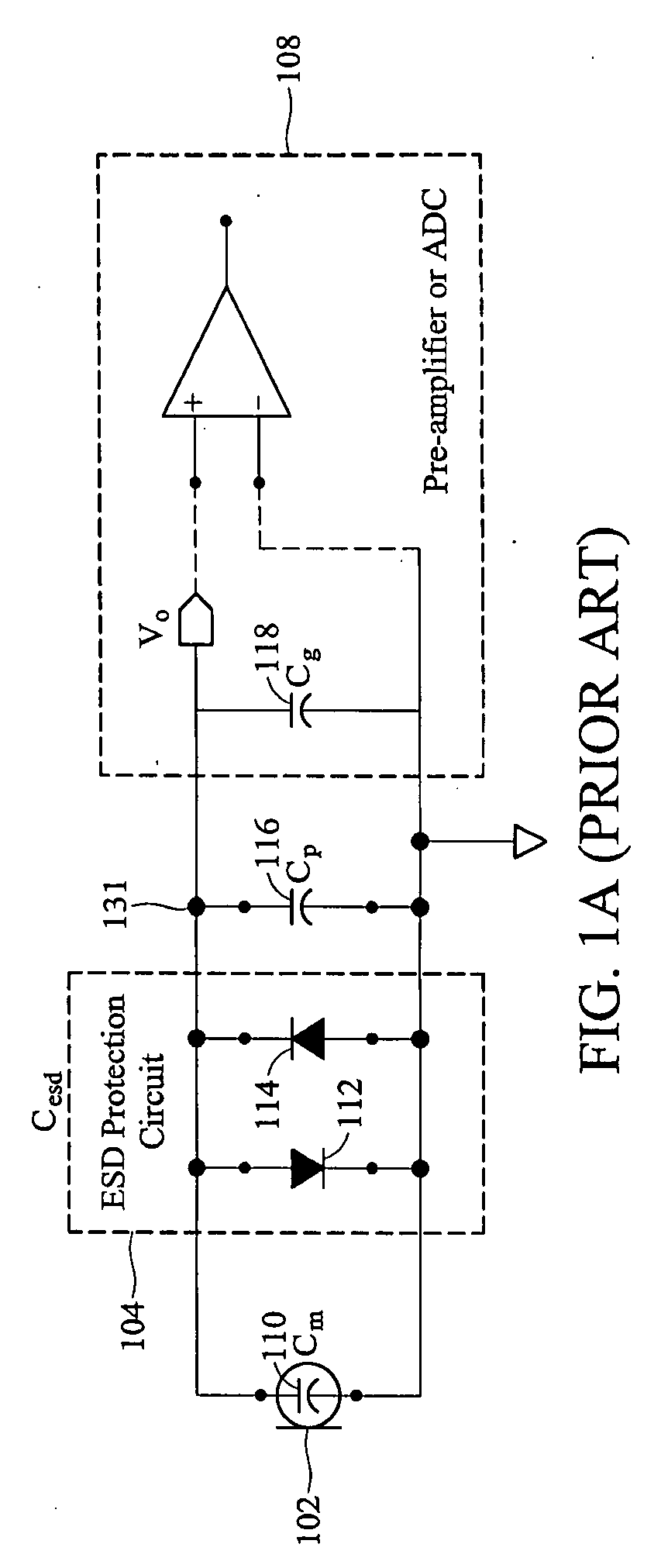
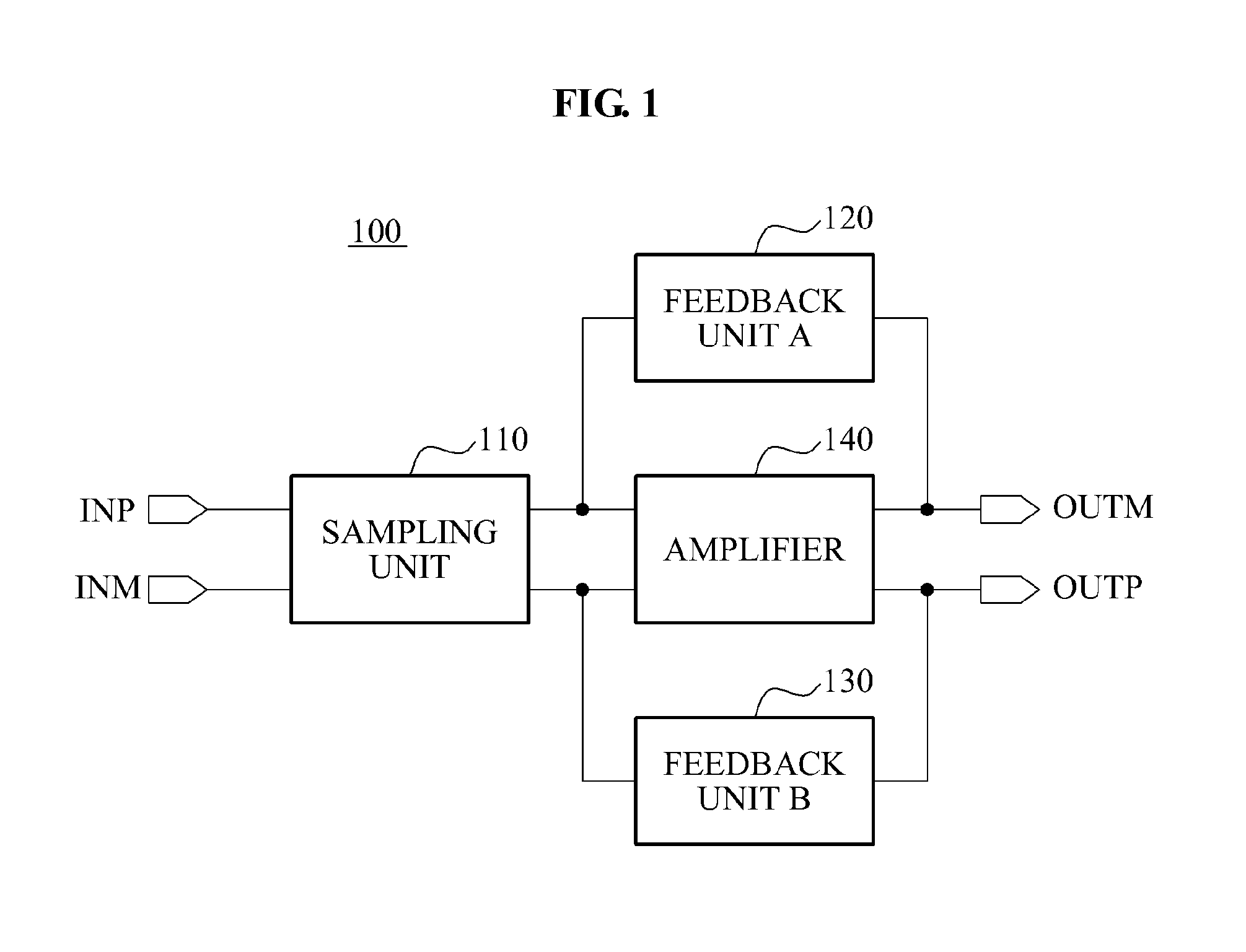
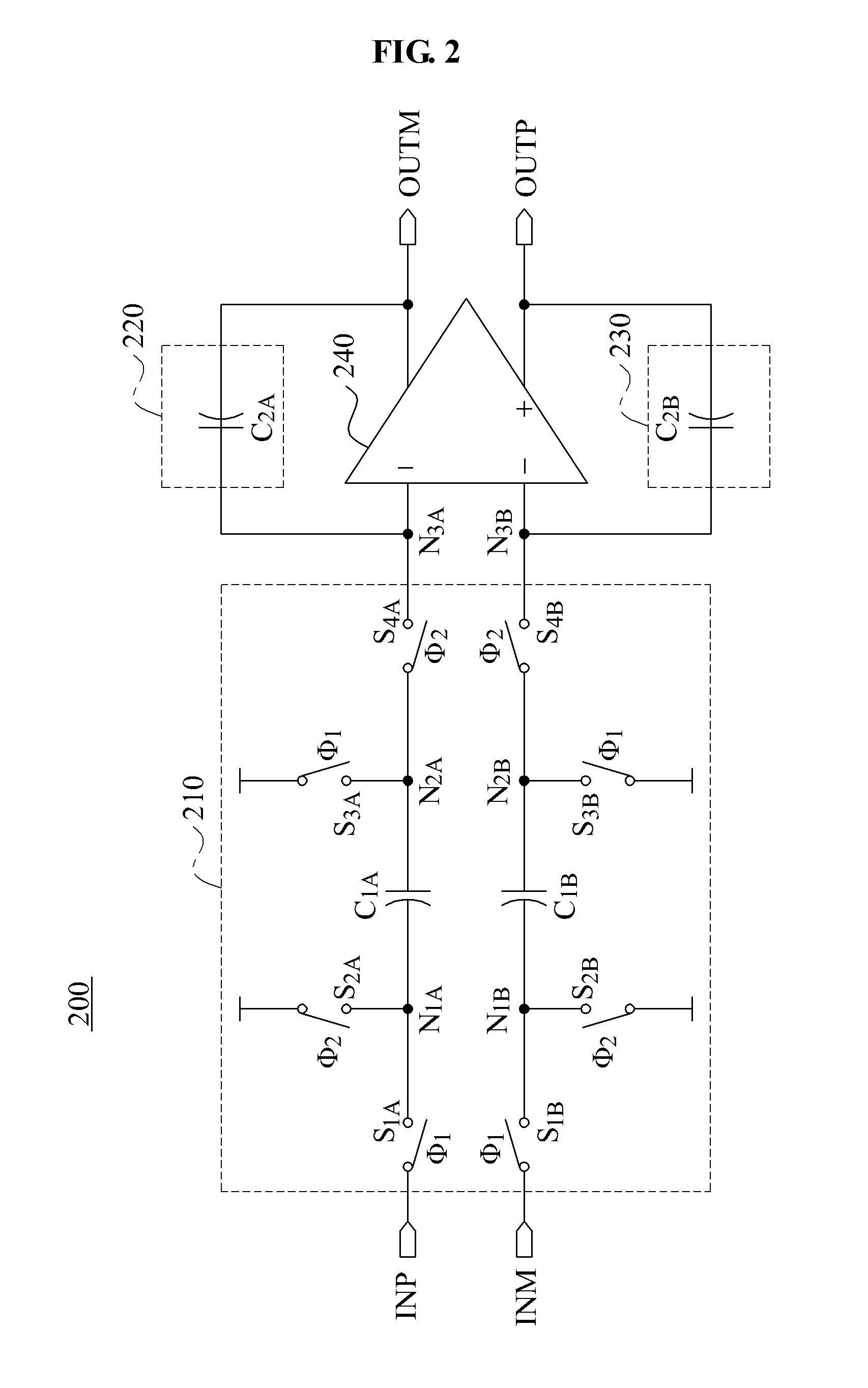
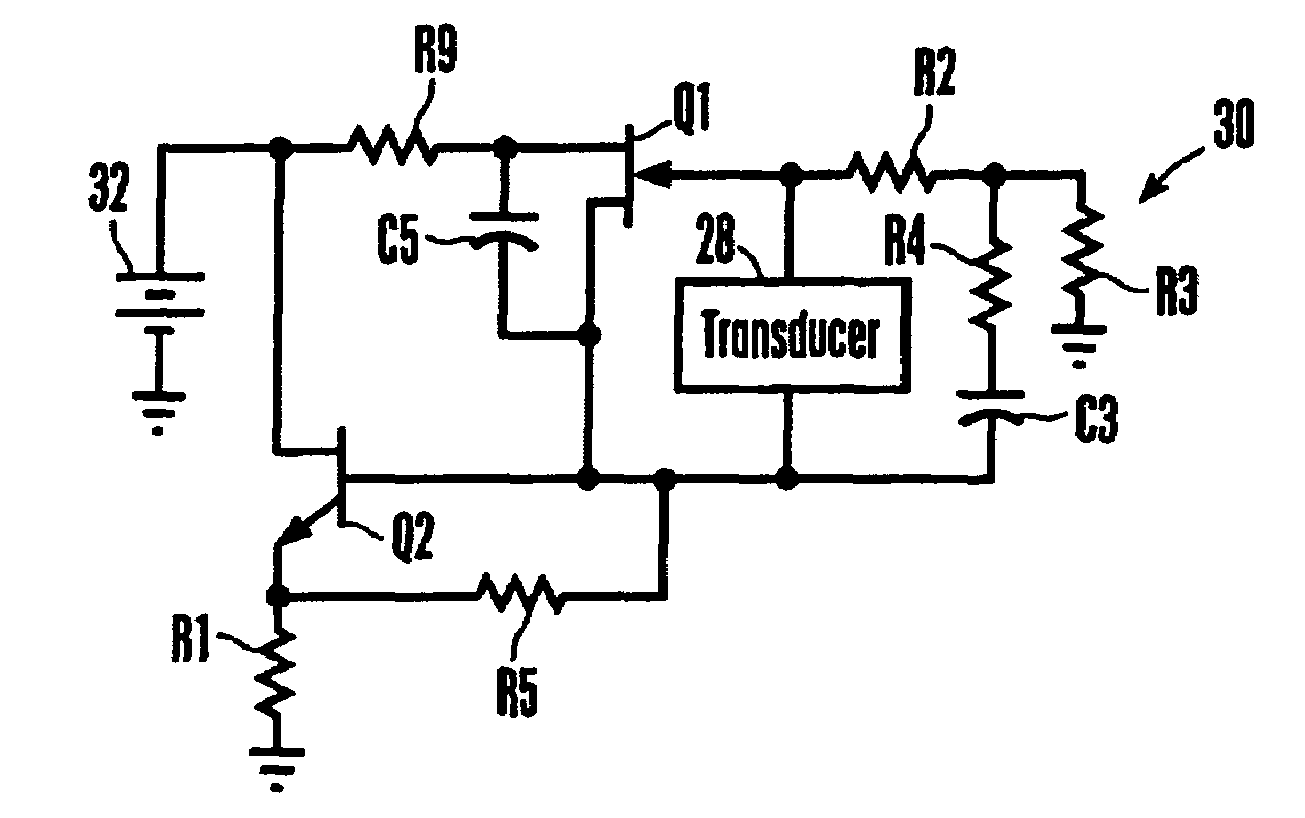
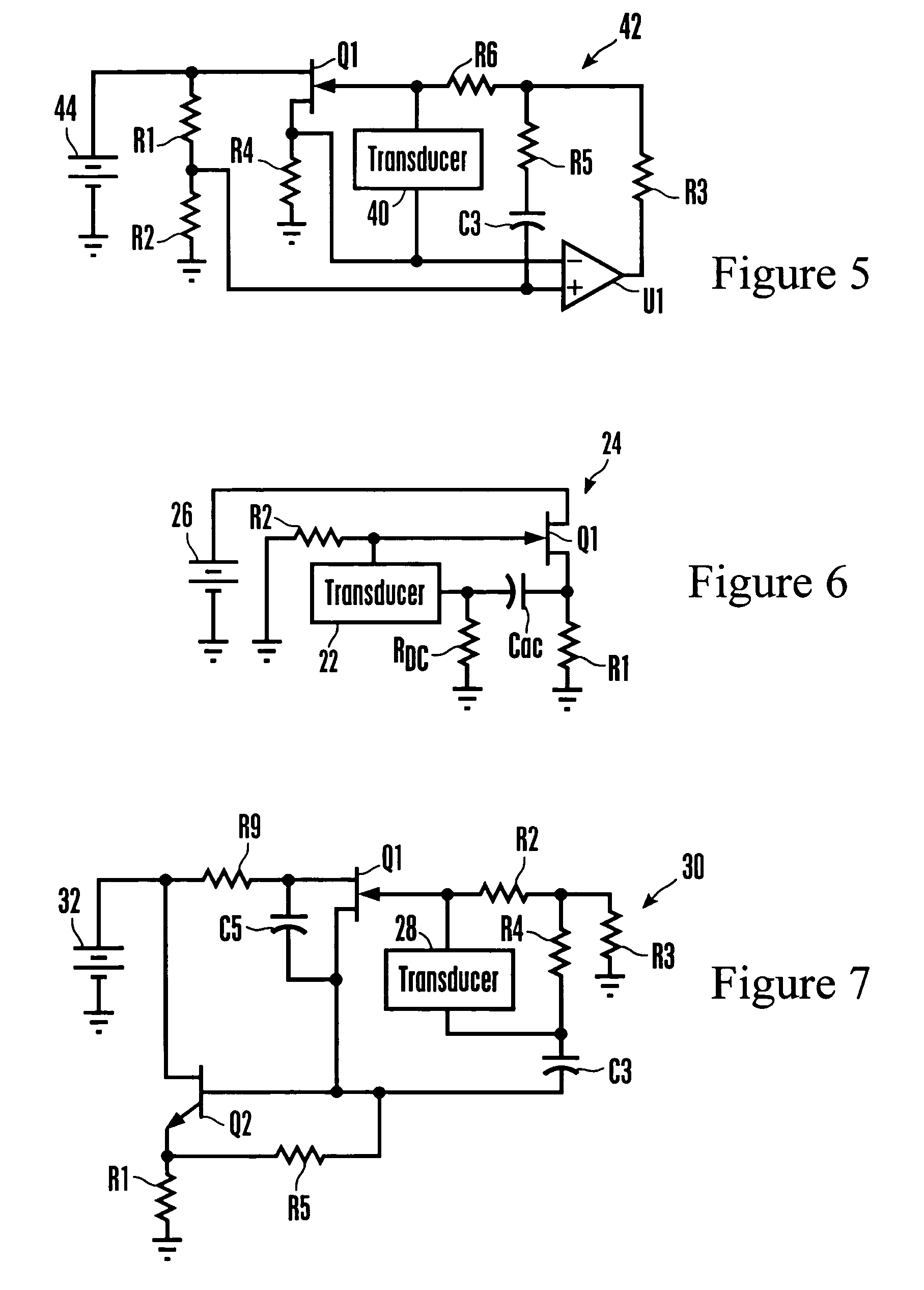
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
233results about "Charge amplifiers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High Sensitivity RFID TAG Integrated Circuits
InactiveUS20070046369A1Reduce the required powerMore sensitiveCharge amplifiersRecord carriers used with machinesElectricityTag antenna
A method and apparatus for an ultra-high sensitivity, low cost, passive (no battery) low-power energy harvesting data transmitting circuit energy, such as a RFID (Radio Frequency IDentification) tag integrated circuit “chip.” By using combinations of special purpose design enhancements, the low-power energy harvesting passive data transmitting circuit, such as the RFID tag chip, operates in the sub-microwatt power range. The chip power should be derived from a low-microwatt per square centimeter RF field radiated to the RFID tag antenna from the tag reader (interrogator) or derived from a suitable low signal source, such as a sonic transducer (e.g., a piezoelectric transducer or a low level DC source, such as a bimetallic or chemical source).
Owner:INNURVATION IP LLC
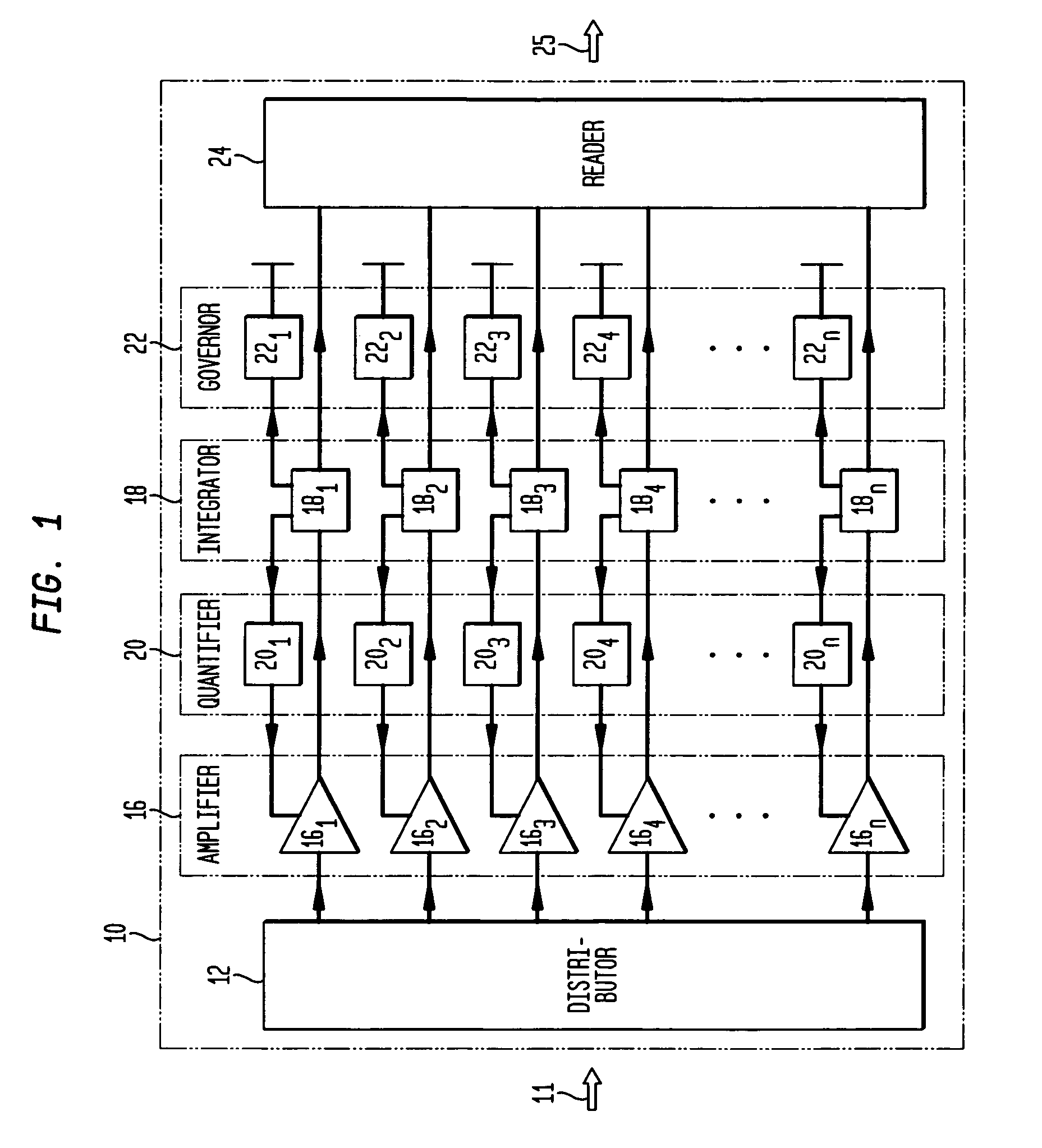
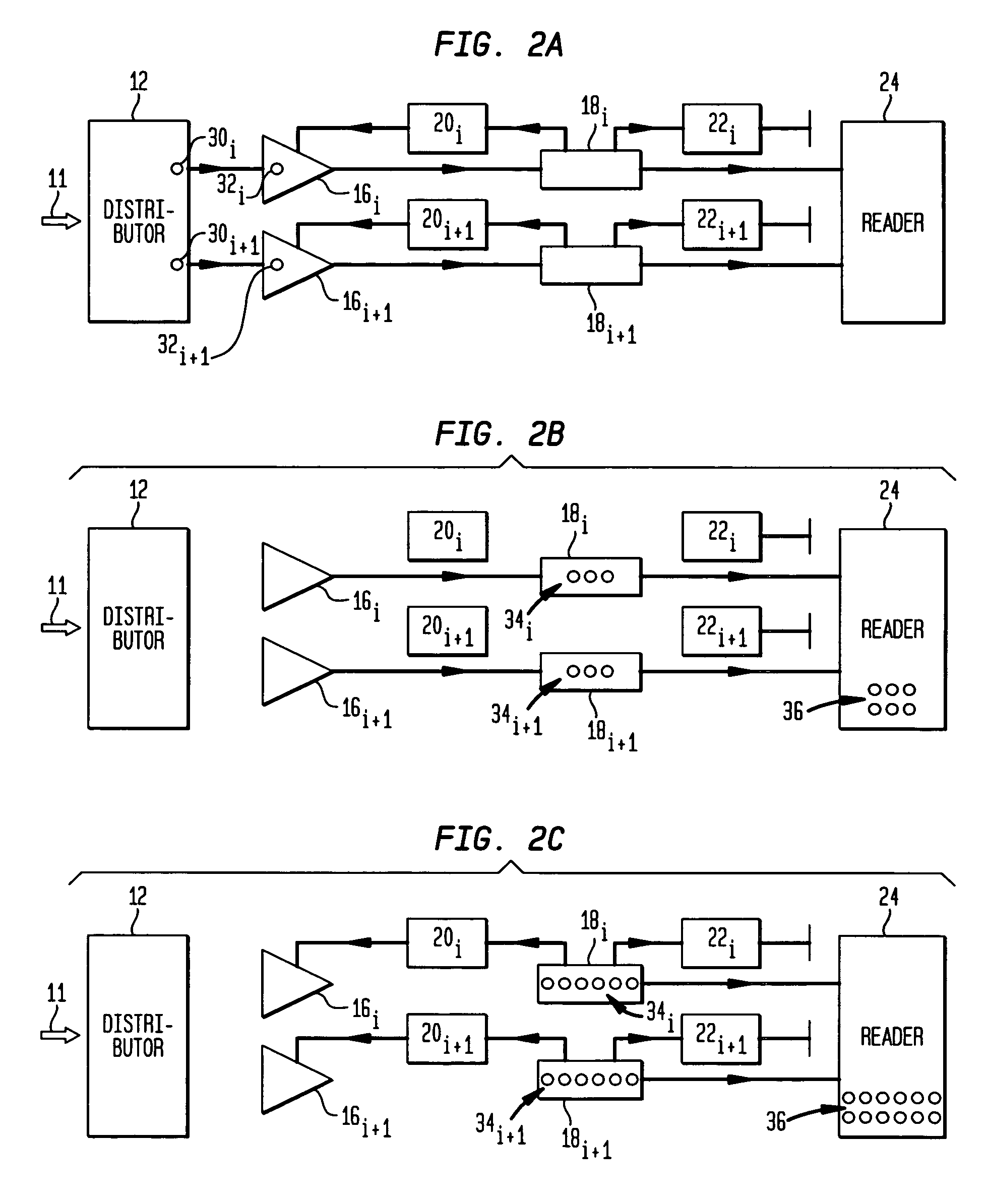
High sensitivity, high resolution detection of signals
A system and method providing for the detection of an input signal by distributing the input signal into independent signal components that are independently amplified. Detection of an input signal comprises generating from the input signal a plurality of spatially separate elementary charge components, each having a respective known number of elementary charges, the number of the plurality of spatially separate elementary charge components being a known monotonic function of the magnitude of said input signal; and independently amplifying each of the plurality of spatially divided elementary charge components to provide a respective plurality of signal charge packets, each signal charge packet having a second number of elementary charges greater than the respective known number by a respective amplification factor.
Owner:AMPLIFICATION TECH INC
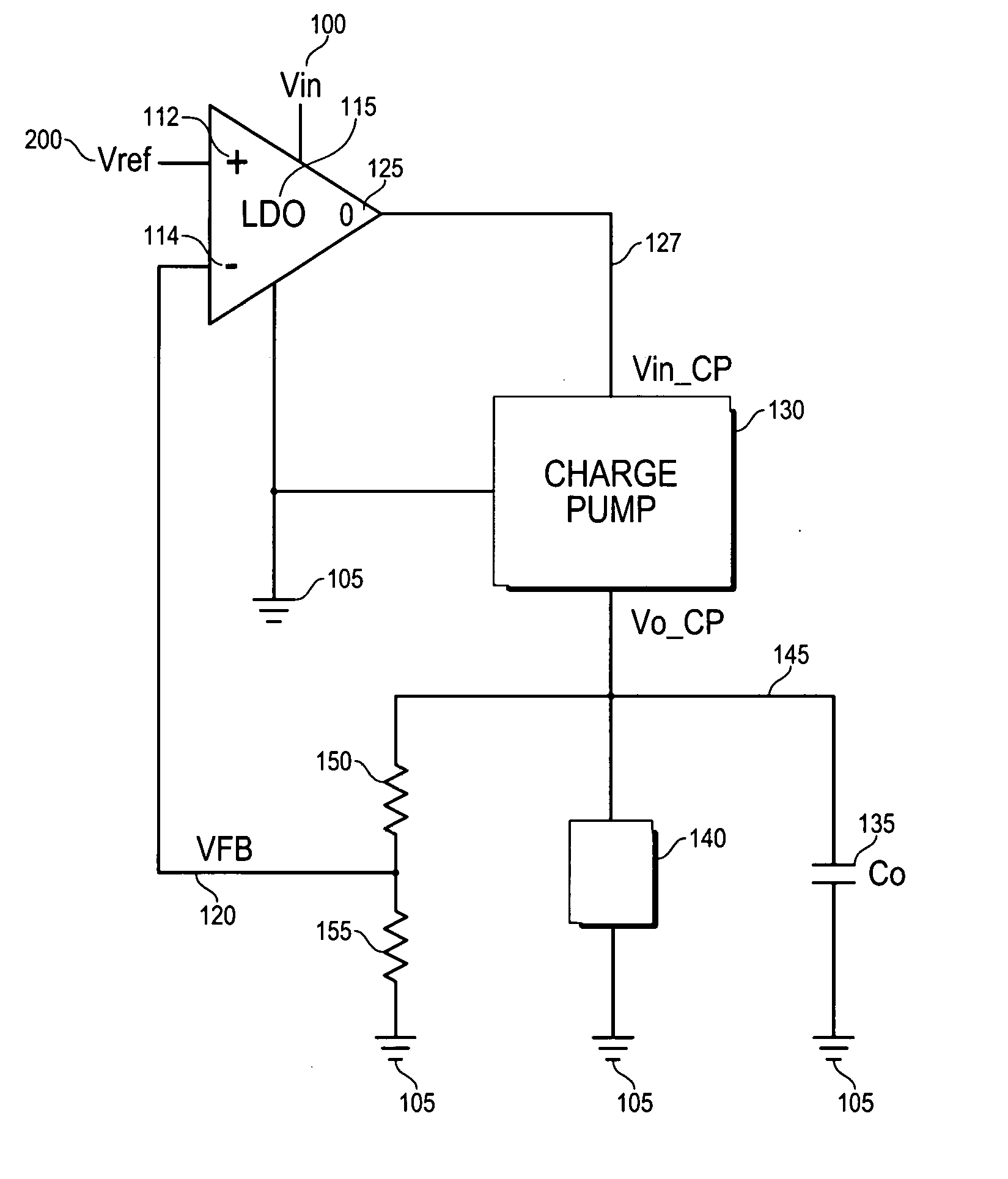
Regulating charge pump
InactiveUS20060181340A1Lower battery costsReduce headroomGalvano-magnetic amplifiersCharge amplifiersLinear regulatorEngineering
Owner:ZYWYN CORP
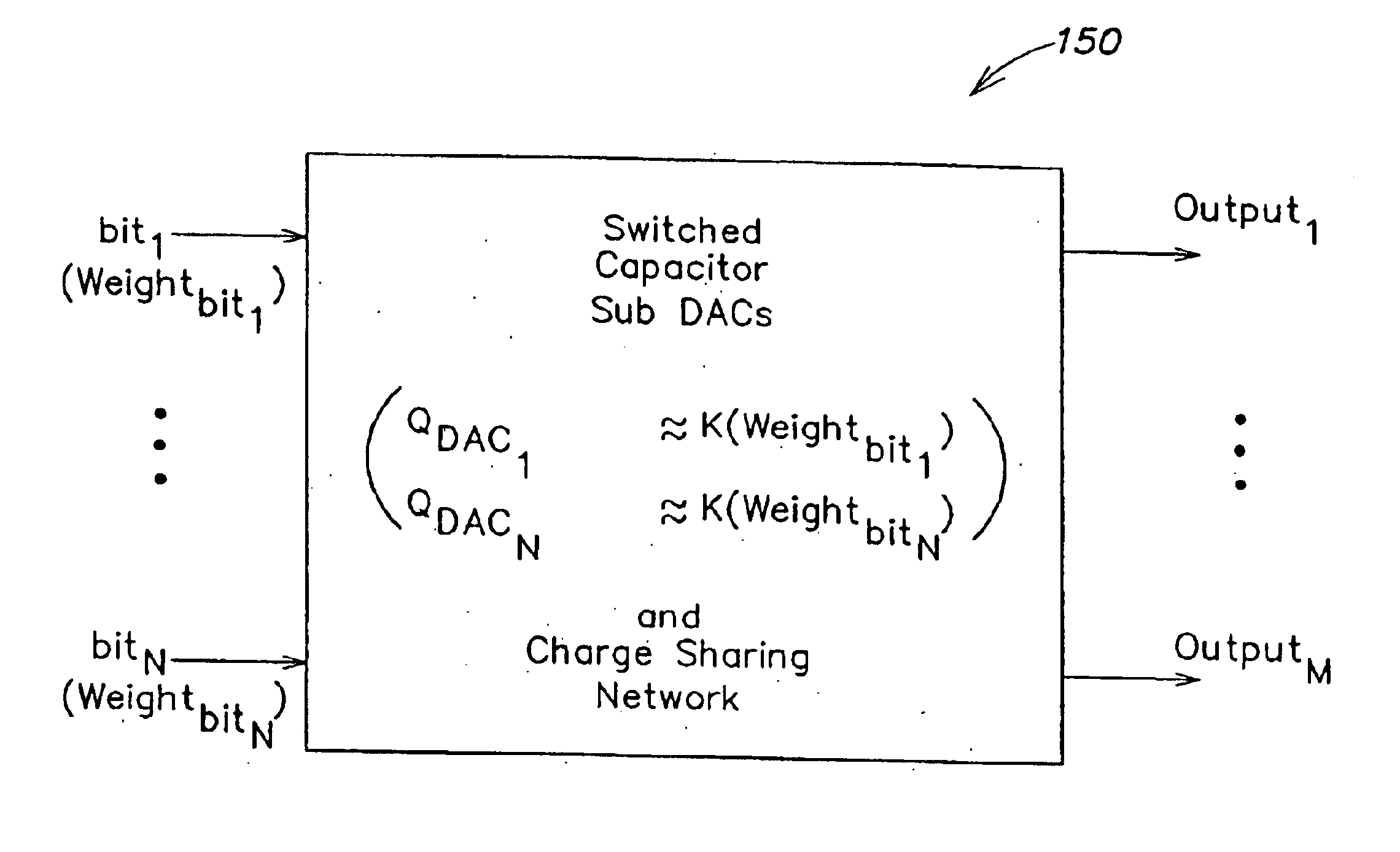
Method and apparatus for use in switched capacitor systems
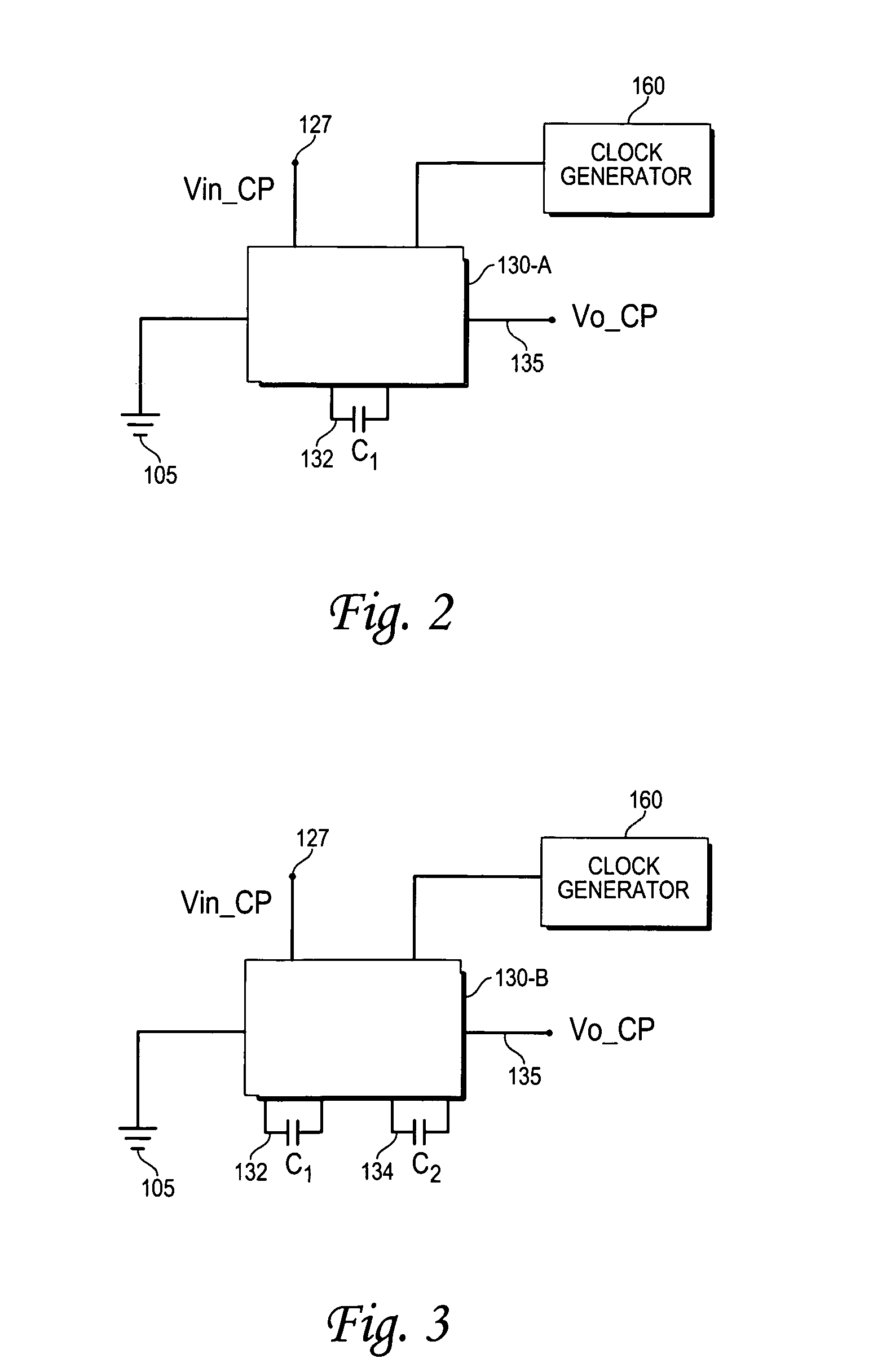
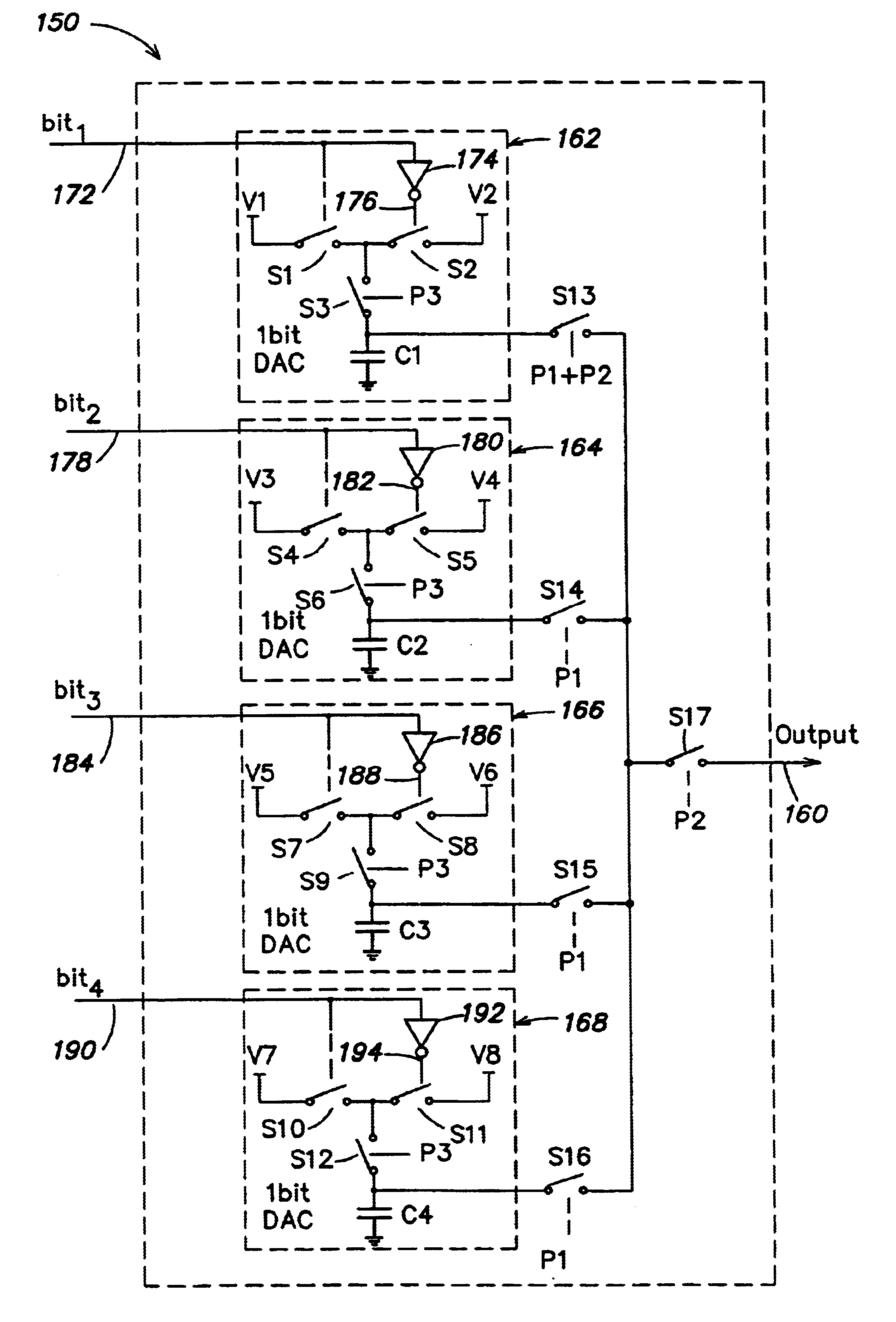
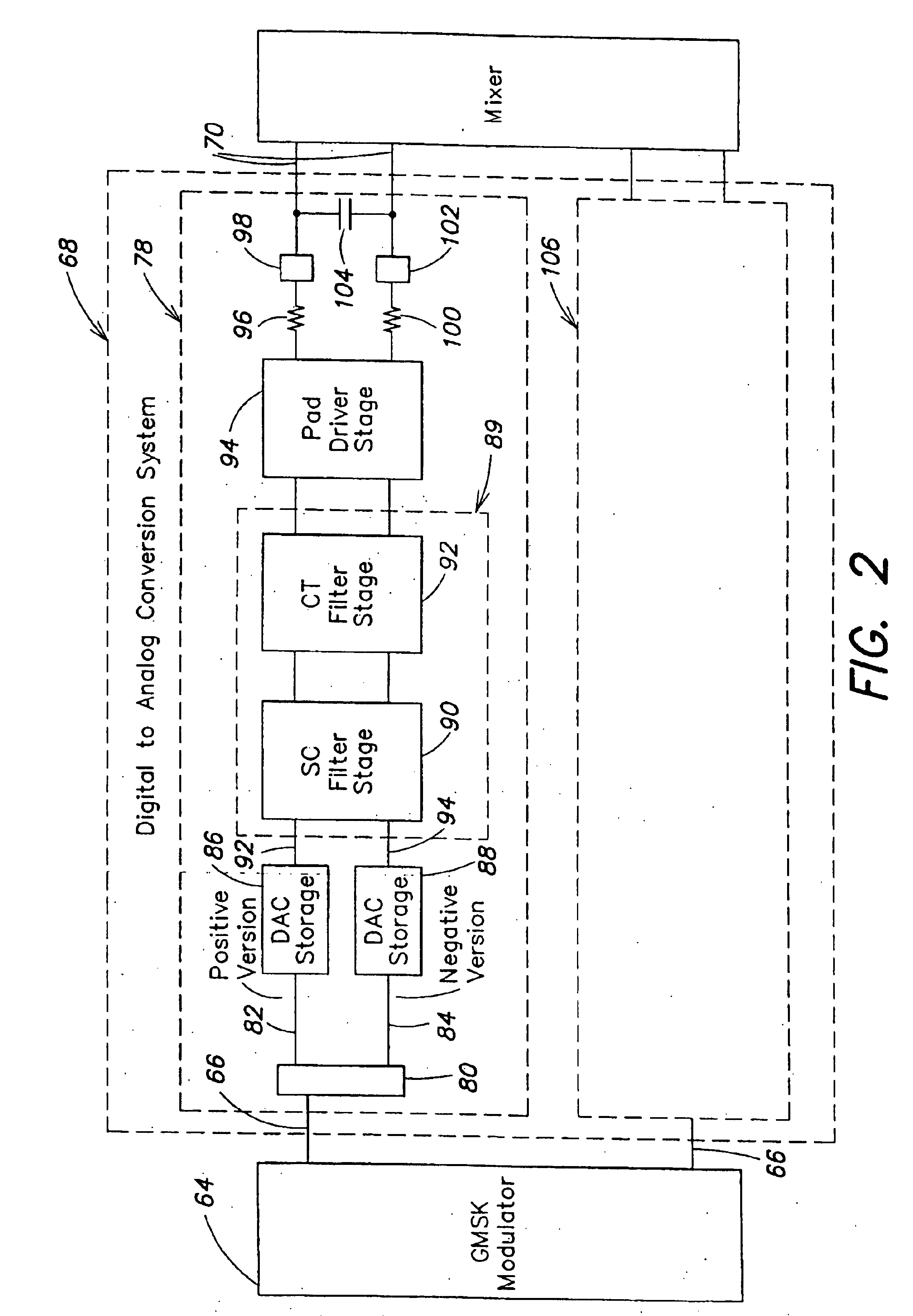
InactiveUS6917321B1Electric signal transmission systemsCharge amplifiersSignal conditioningData rate
Systems and methods receive a digital signal and generate an analog signal indicative thereof. In one embodiment, a system includes a DAC that receives a multi-bit digital signal, generates at least two analog signals each indicative of the value of the multi-bit digital signal, and filters two or more of the at least two analog signals. In another embodiment, a system includes a DAC that receives digital input signals at an input data rate and outputs analog signals indicative of the digital signals to a signal conditioning stage at an output data rate different than the input data rate.
Owner:XUESHAN TECH INC
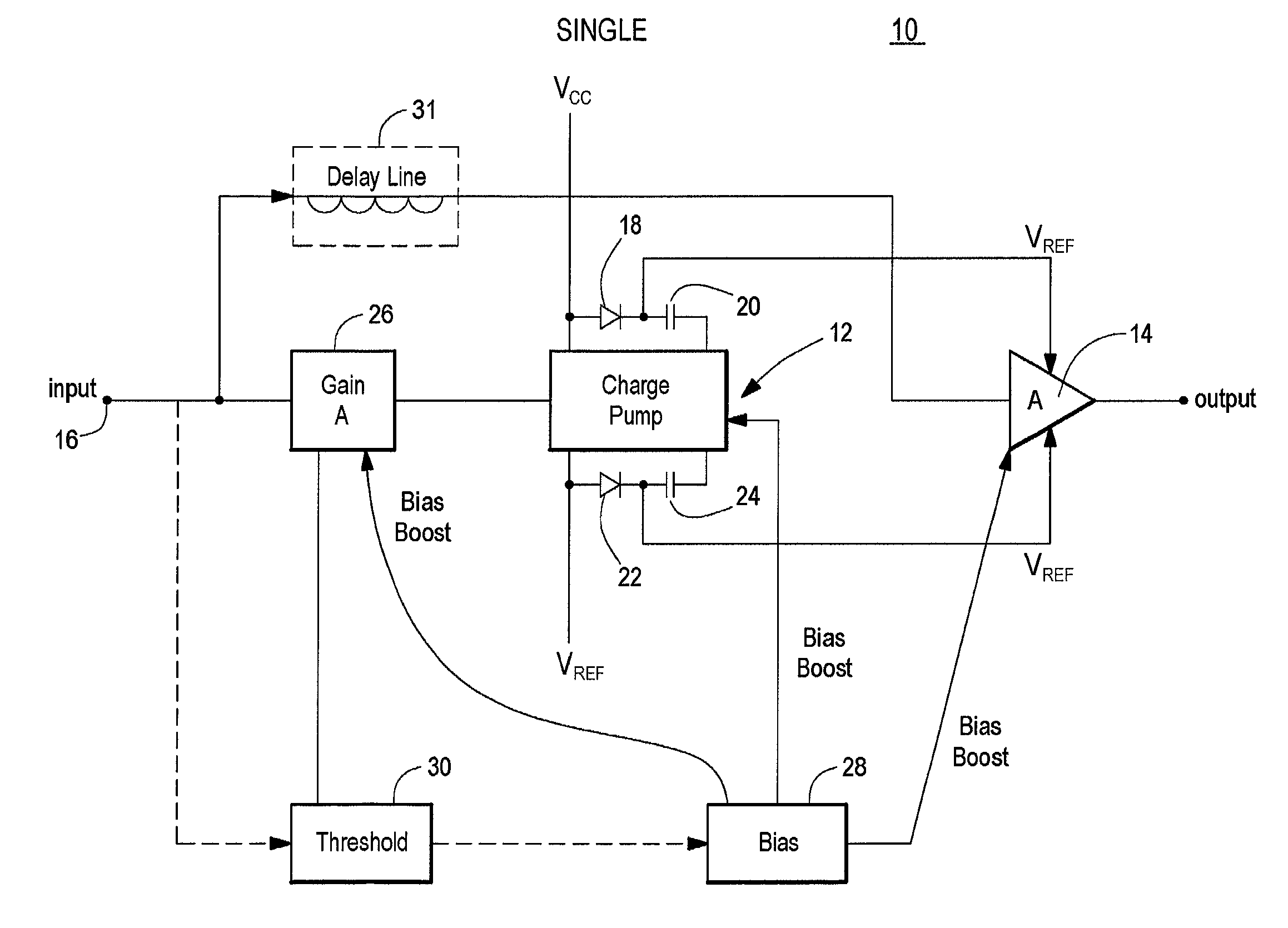
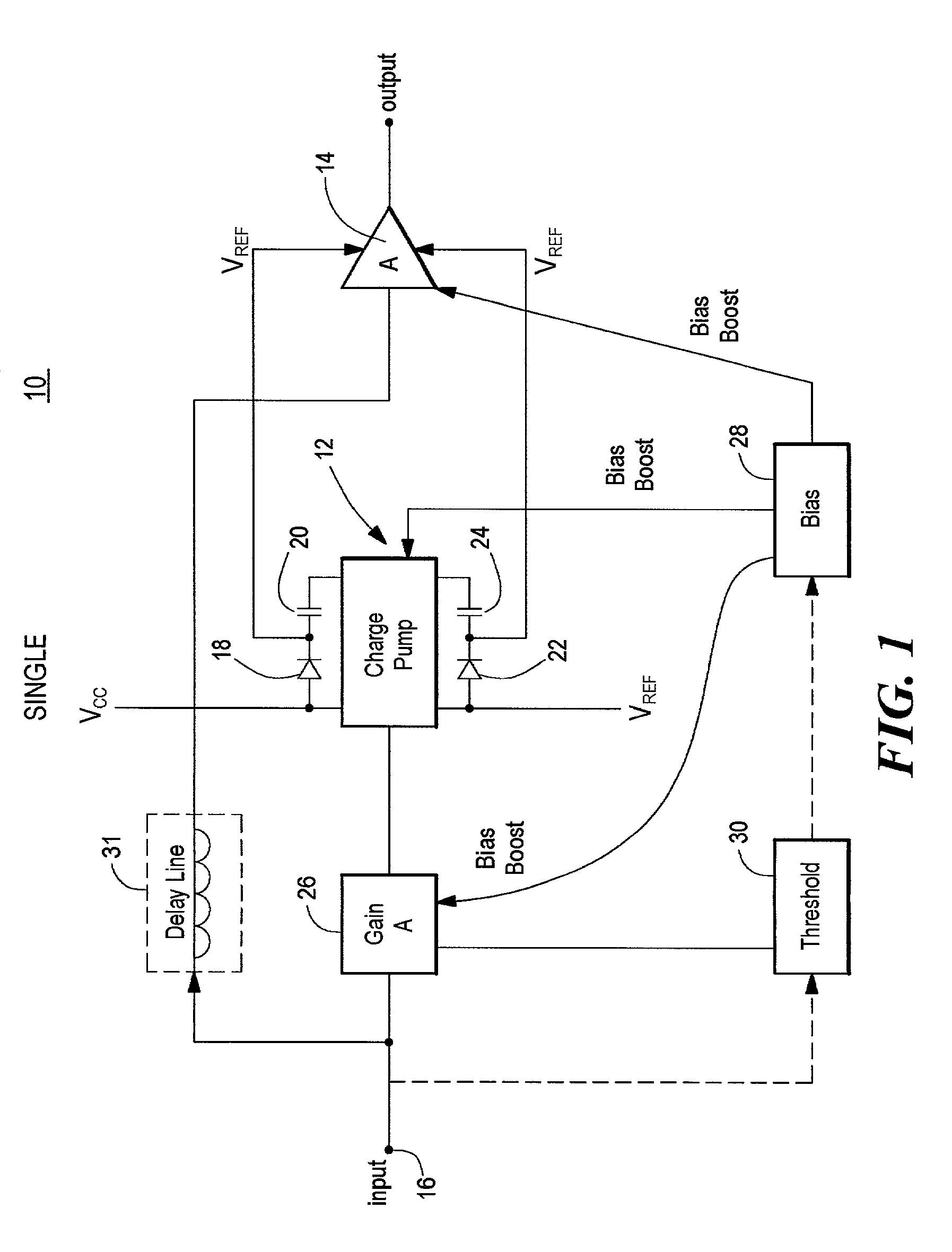
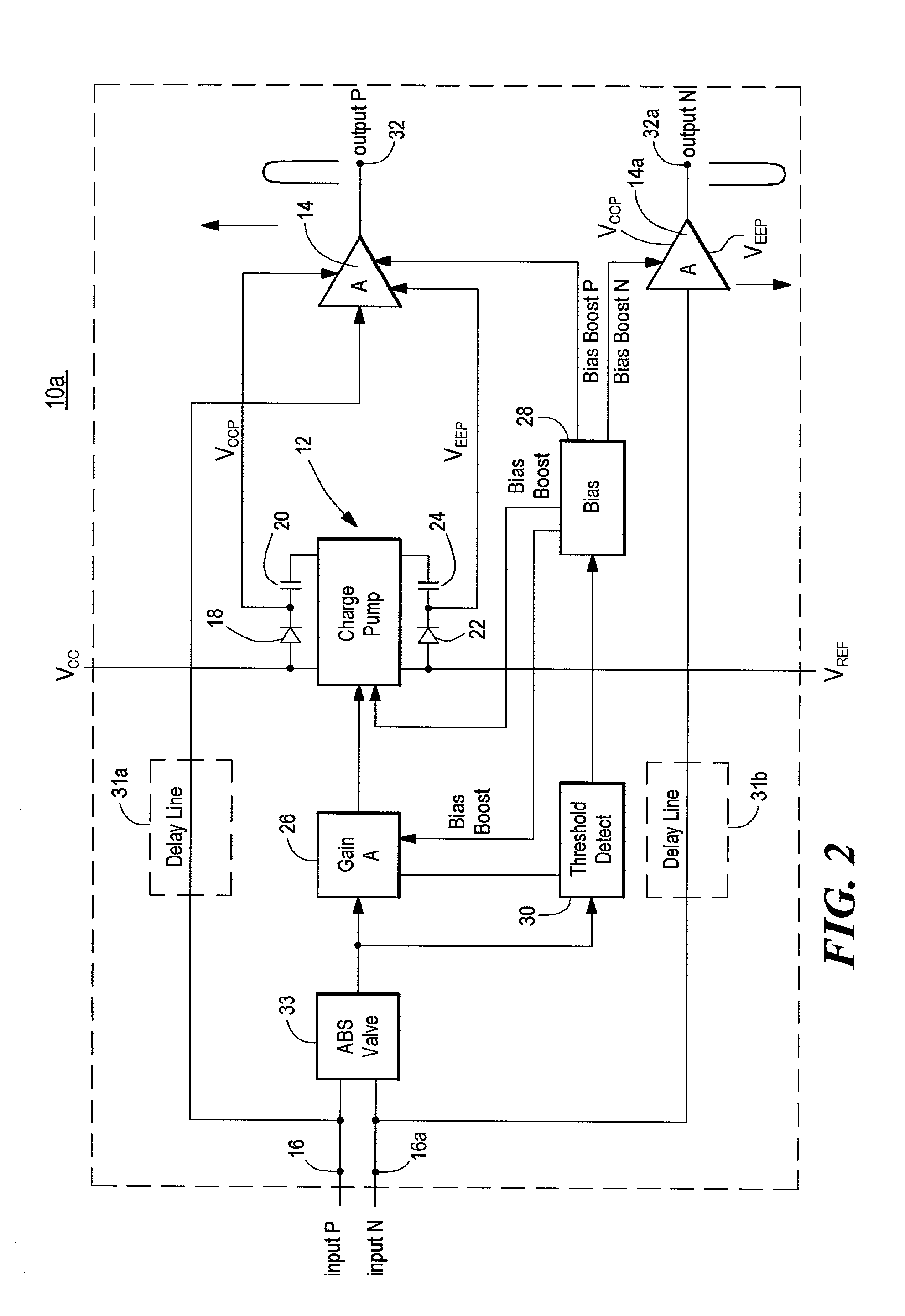
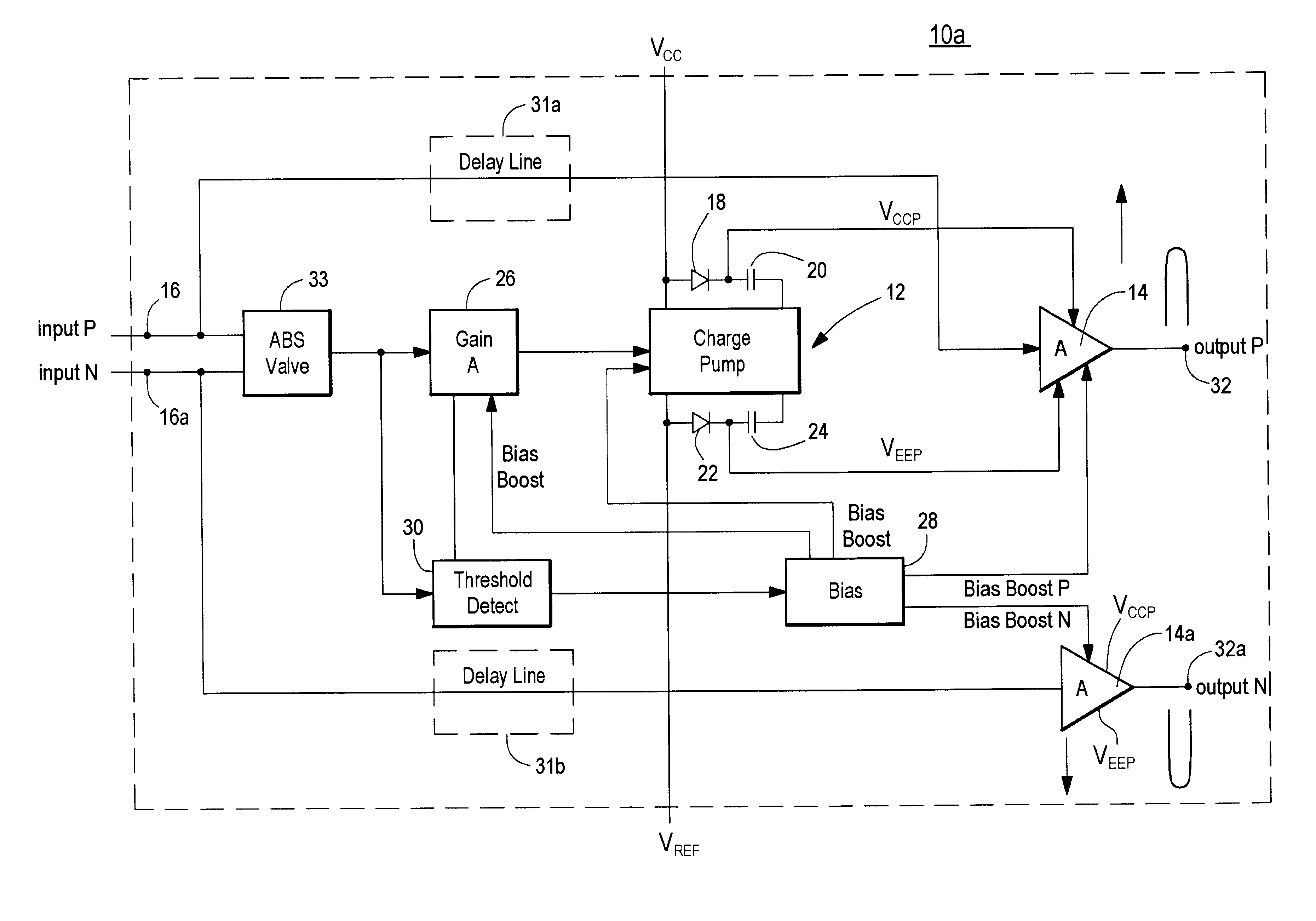
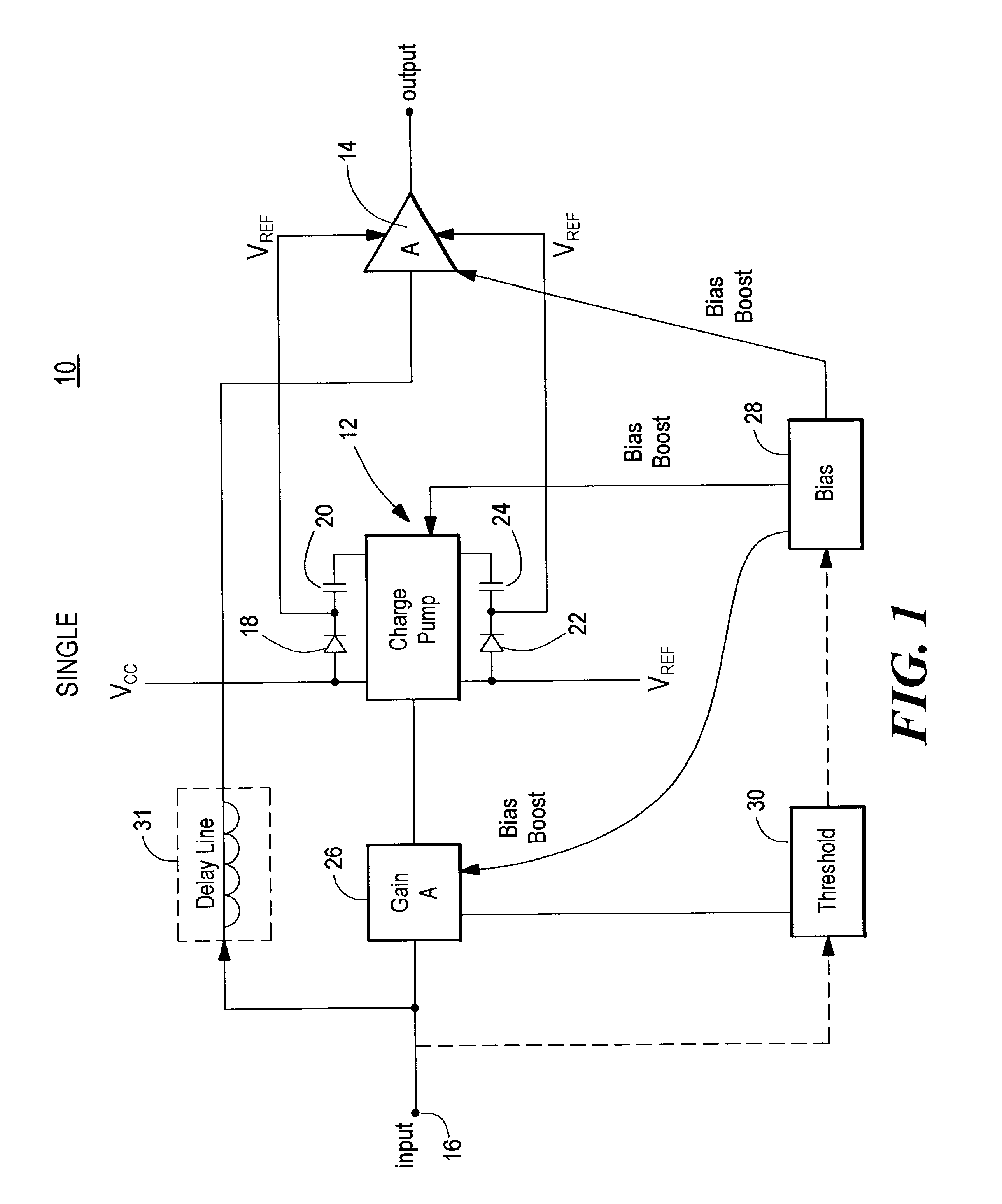
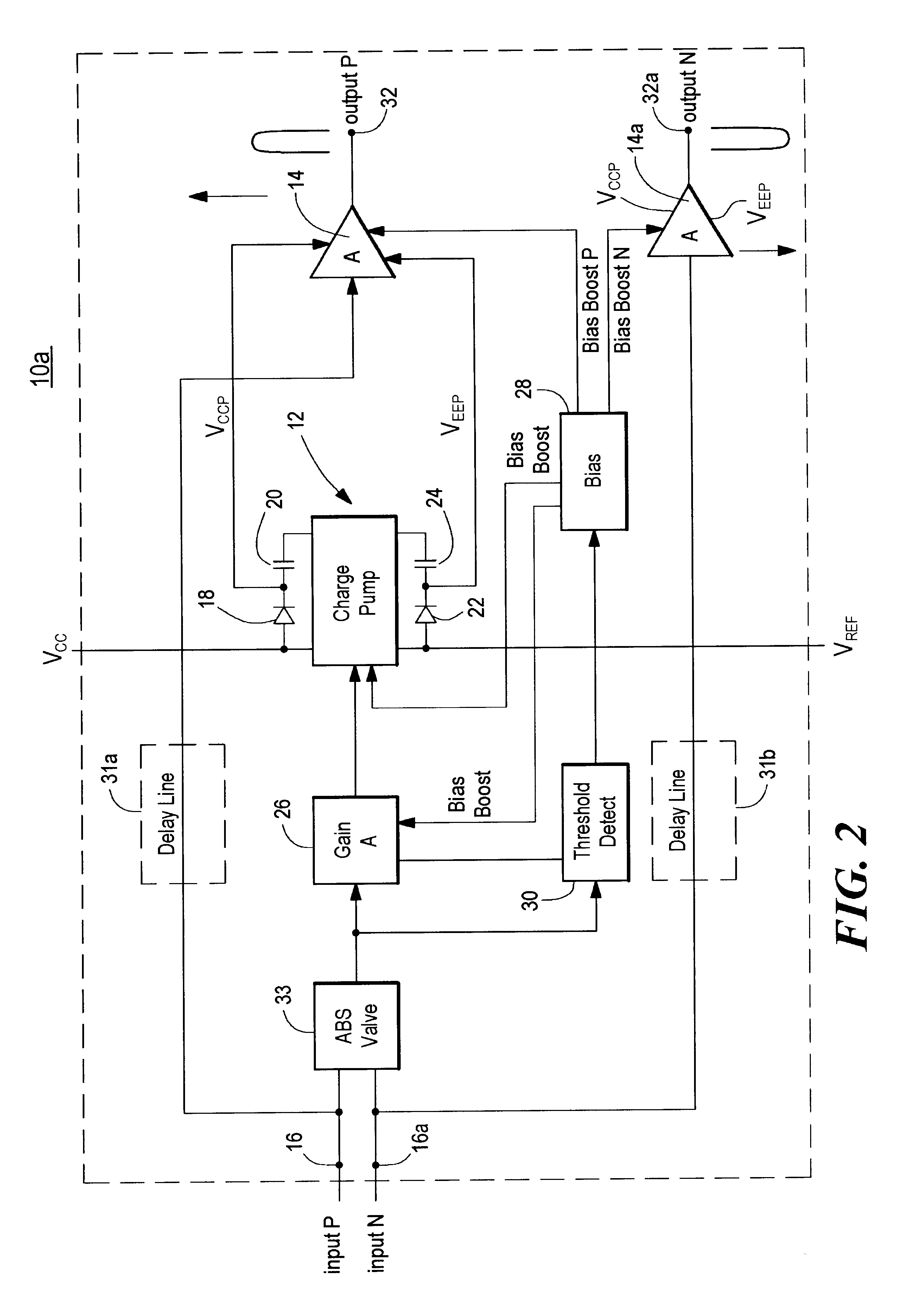
Amplifier system with on-demand power supply boost
InactiveUS20020153940A1Less powerMore efficientCharge amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDriver circuitAudio power amplifier
An amplifier system with on-demand power supply boost includes an amplifier circuit for receiving an input signal and a charge pump connected to positive and negative power supplies and having predetermined supply voltages and being responsive to the input signal for increasing beyond the predetermined supply voltages the supply voltage applied to the amplifier in response to an increase in the input signal and a tracking charge pump usable in the amplifier system which includes a charge storage device; a unidirectional isolation device interconnecting the charge storage device and one pole of a power supply; a driver circuit responsive to an input signal and interconnected between both poles of the power supply; the power supply having predetermined power supply voltages; and a bias circuit for biasing the driver circuit to charge the charge storage device in the charge mode and in the boost mode, for increasing beyond the predetermined power supply voltages, the supply voltage supplied by the storage device to an external load in response to an increase in the input signal.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Amplifier system with on-demand power supply boost
InactiveUS6636103B2Less powerMore efficientCharge amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDriver circuitAudio power amplifier
An amplifier system with on-demand power supply boost includes an amplifier circuit for receiving an input signal and a charge pump connected to positive and negative power supplies and having predetermined supply voltages and being responsive to the input signal for increasing beyond the predetermined supply voltages the supply voltage applied to the amplifier in response to an increase in the input signal and a tracking charge pump usable in the amplifier system which includes a charge storage device; a unidirectional isolation device interconnecting the charge storage device and one pole of a power supply; a driver circuit responsive to an input signal and interconnected between both poles of the power supply; the power supply having predetermined power supply voltages; and a bias circuit for biasing the driver circuit to charge the charge storage device in the charge mode and in the boost mode, for increasing beyond the predetermined power supply voltages, the supply voltage supplied by the storage device to an external load in response to an increase in the input signal.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Integrated implementation of a collector boost scheme and method therefor
A collector boost circuit is disclosed for providing a first voltage in a first mode of operation to a power amplifier, and a second voltage in a second mode of operation to the power amplifier. The collector boost circuit uses a switch and an indicator signal for triggering the switch between the first and the second mode of operation. The second voltage is a boosted voltage greater than the first voltage and is provided during peak excursions through a boost capacitor.
Owner:SIGE SEMICON
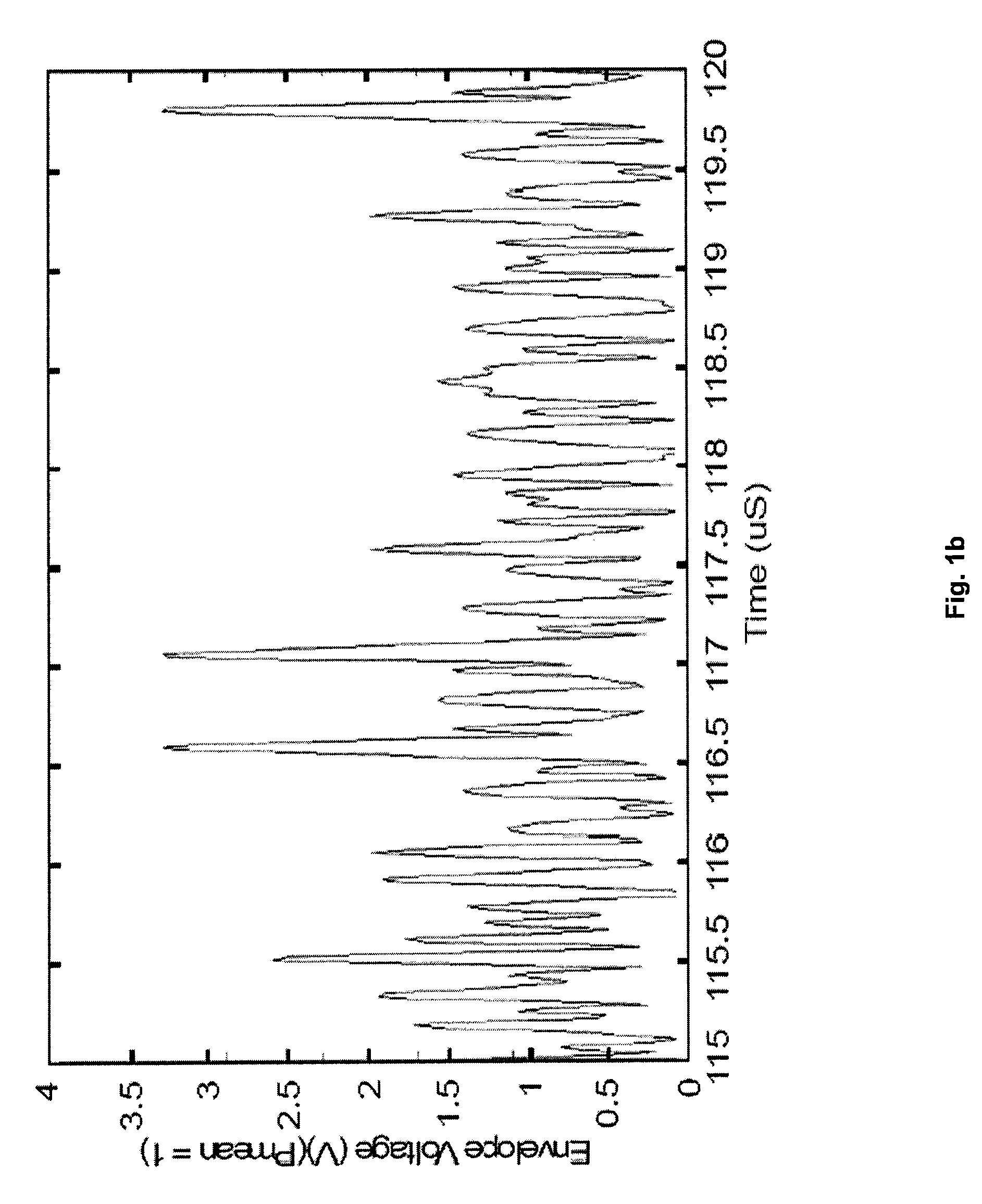
Microelectromechanical gyroscope with position control driving and method for controlling a microelectromechanical gyroscope
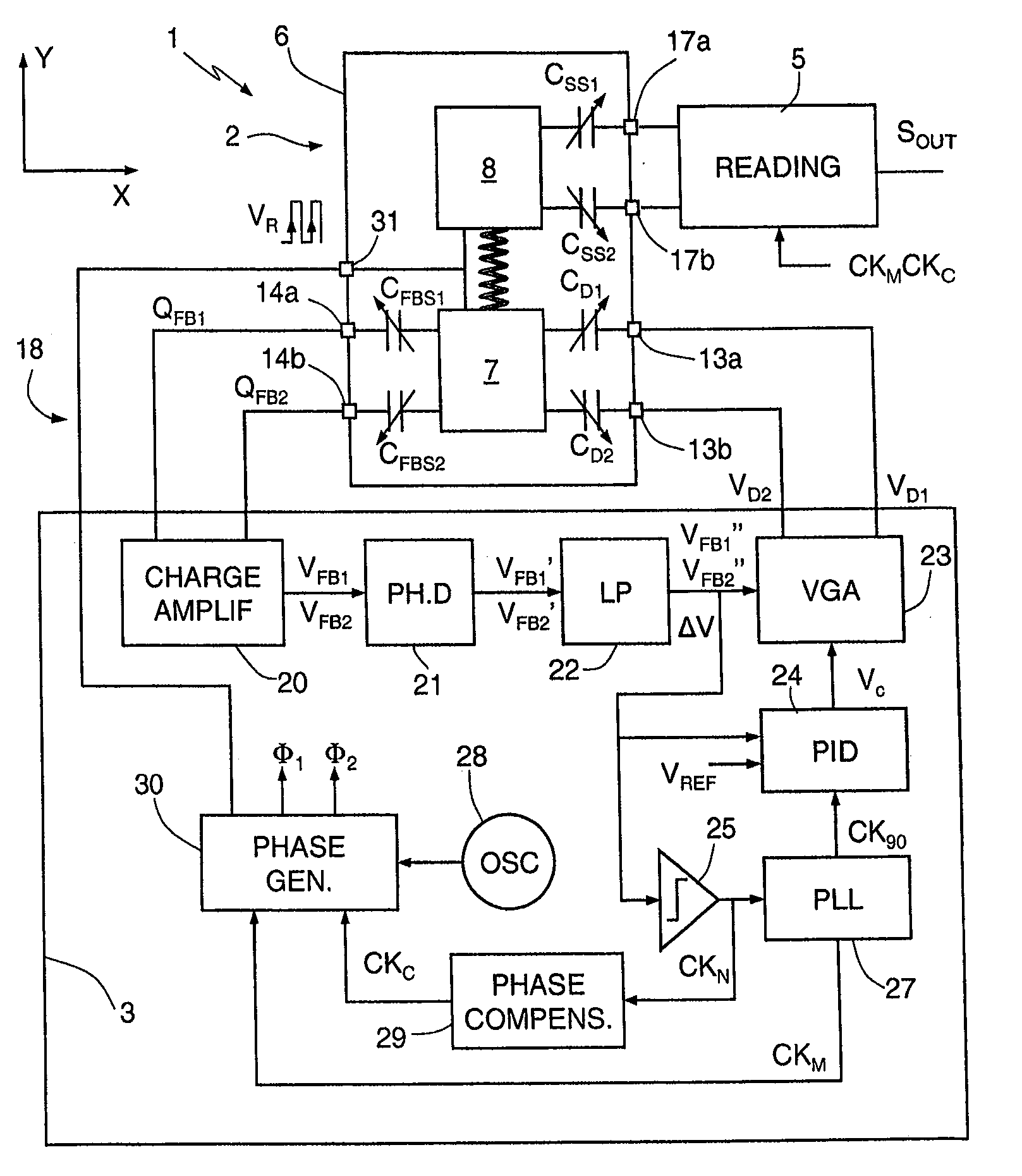
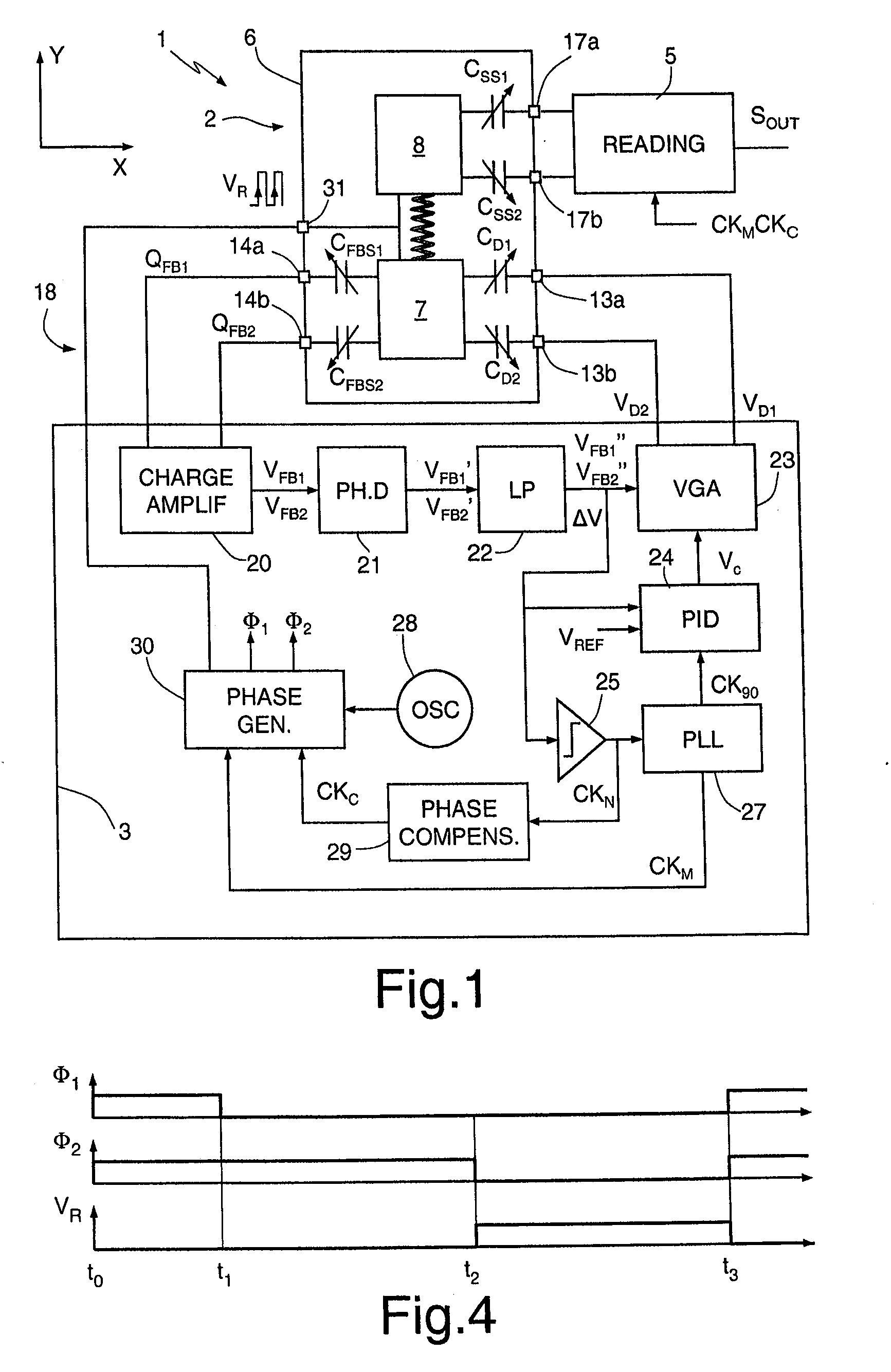
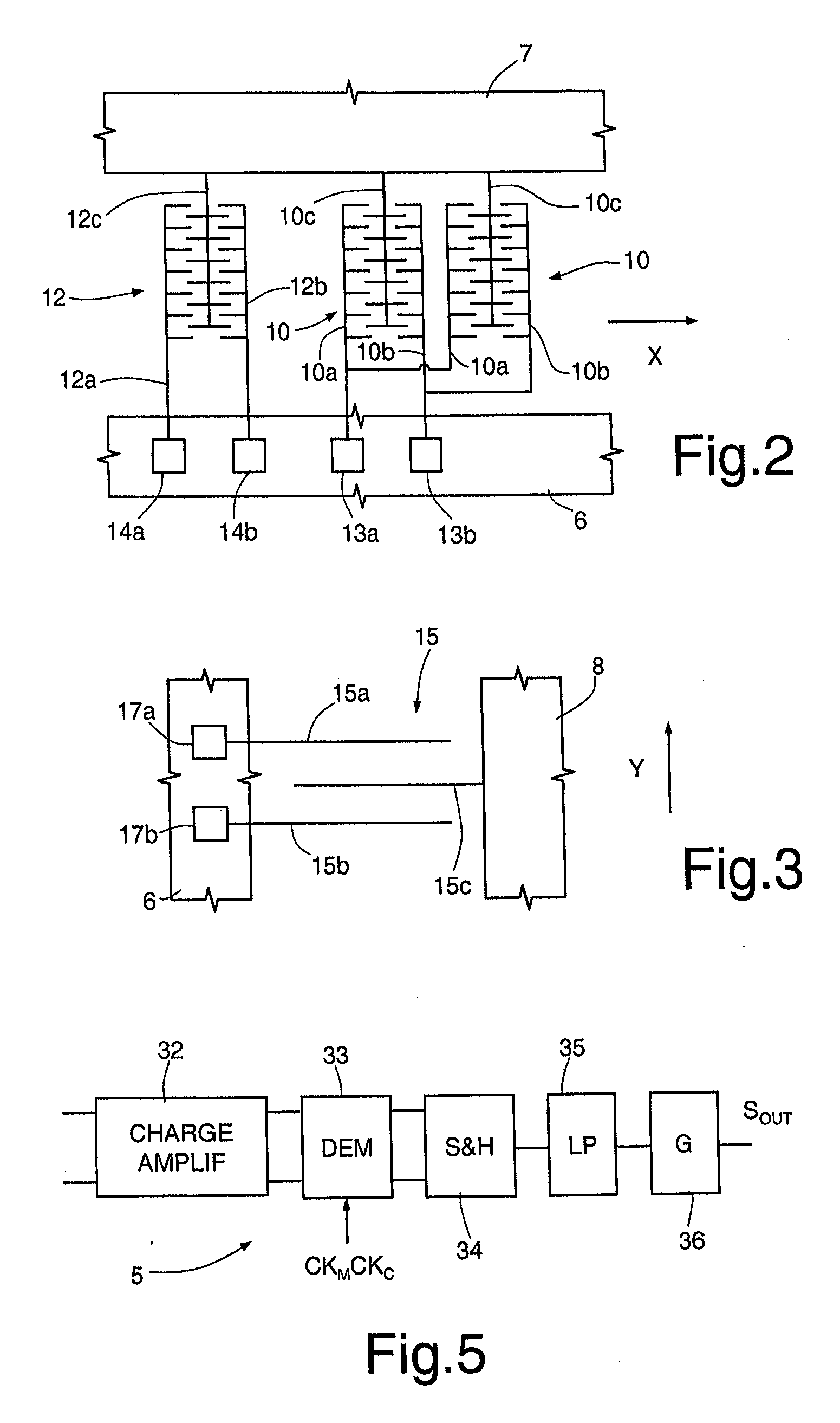
ActiveUS8375789B2Accurate and reliable processAcceleration measurement using interia forcesCharge amplifiersGyroscopeEngineering
A MEMS gyroscope includes: a microstructure having a fixed structure, a driving mass, movable with respect to the fixed structure according to a driving axis, and a sensing mass, mechanically coupled to the driving mass so as to be drawn in motion according to the driving axis and movable with respect to the driving mass according to a sensing axis, in response to rotations of the microstructure; and a driving device, for keeping the driving mass in oscillation with a driving frequency. The driving device includes a discrete-time sensing interface, for detecting a position of the driving mass with respect to the driving axis and a control stage for controlling the driving frequency on the basis of the position of the driving mass.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Microelectromechanical gyroscope with position control driving and method for controlling a microelectromechanical gyroscope
ActiveUS20100307243A1Accurate and reliable processAcceleration measurement using interia forcesCharge amplifiersGyroscopeMicroelectromechanical systems
A MEMS gyroscope includes: a microstructure having a fixed structure, a driving mass, movable with respect to the fixed structure according to a driving axis, and a sensing mass, mechanically coupled to the driving mass so as to be drawn in motion according to the driving axis and movable with respect to the driving mass according to a sensing axis, in response to rotations of the microstructure; and a driving device, for keeping the driving mass in oscillation with a driving frequency. The driving device includes a discrete-time sensing interface, for detecting a position of the driving mass with respect to the driving axis and a control stage for controlling the driving frequency on the basis of the position of the driving mass.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
System and Method for Capacitive Signal Source Amplifier
ActiveUS20130015919A1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsCharge amplifiersCapacitanceCapacitive coupling
According to an embodiment, a system for amplifying a signal provided by a capacitive signal source includes a first stage and a second stage. The first stage has a voltage follower device including an input terminal configured to be coupled to a first terminal of the capacitive signal source, and a first capacitor having a first end coupled to an output terminal of the capacitive signal source. The second stage includes a differential amplifier capacitively coupled to the output terminal of the voltage follower device.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
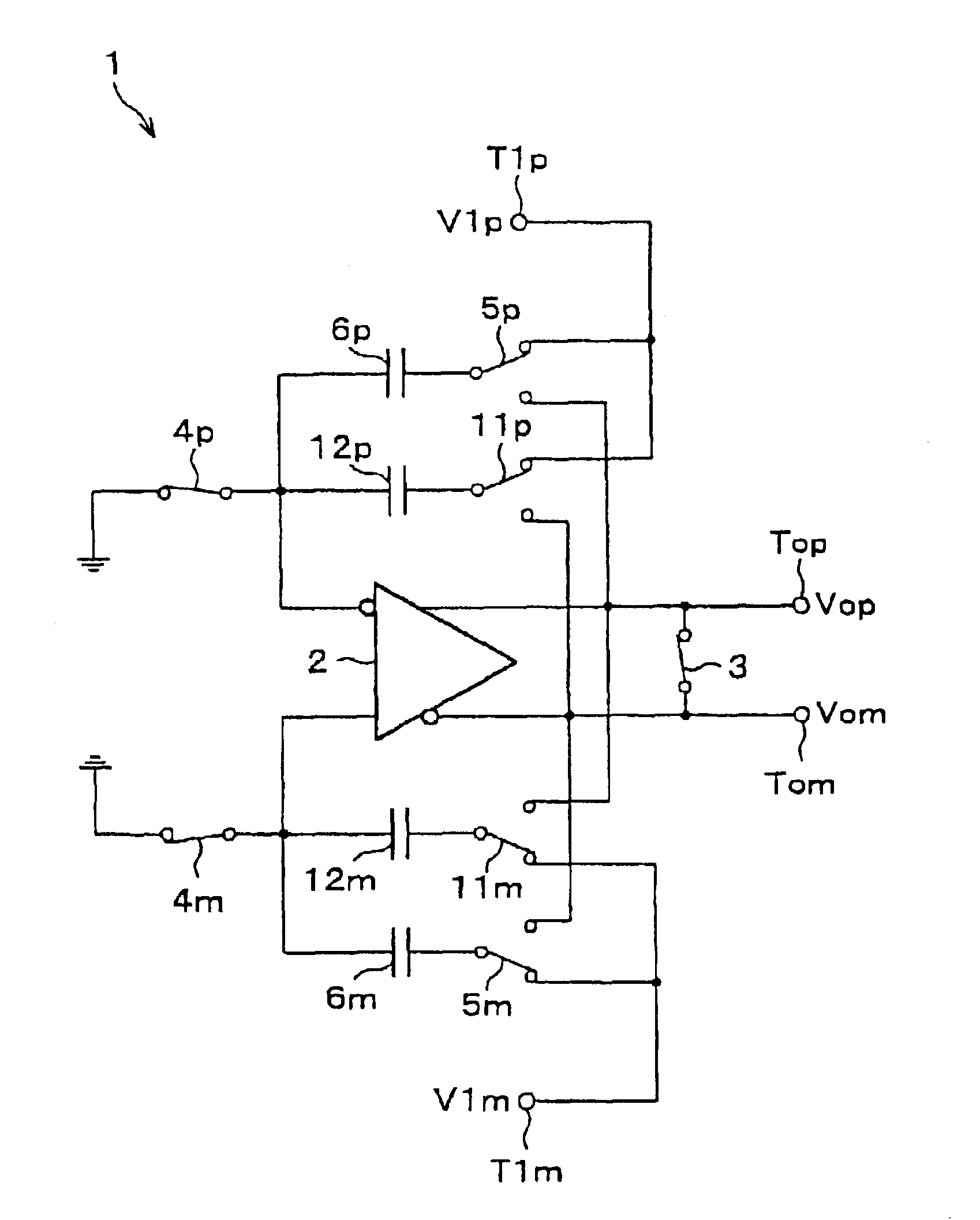
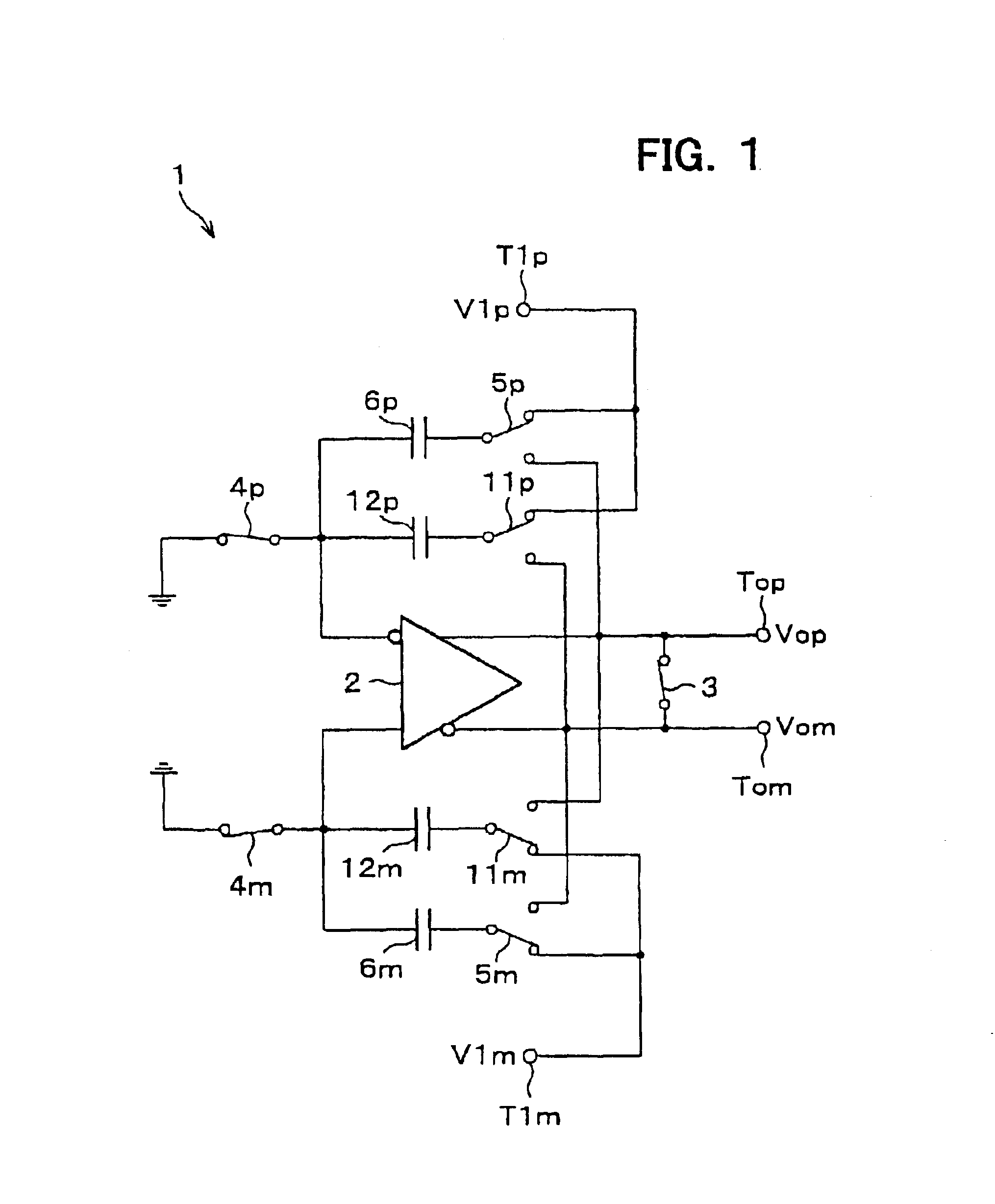
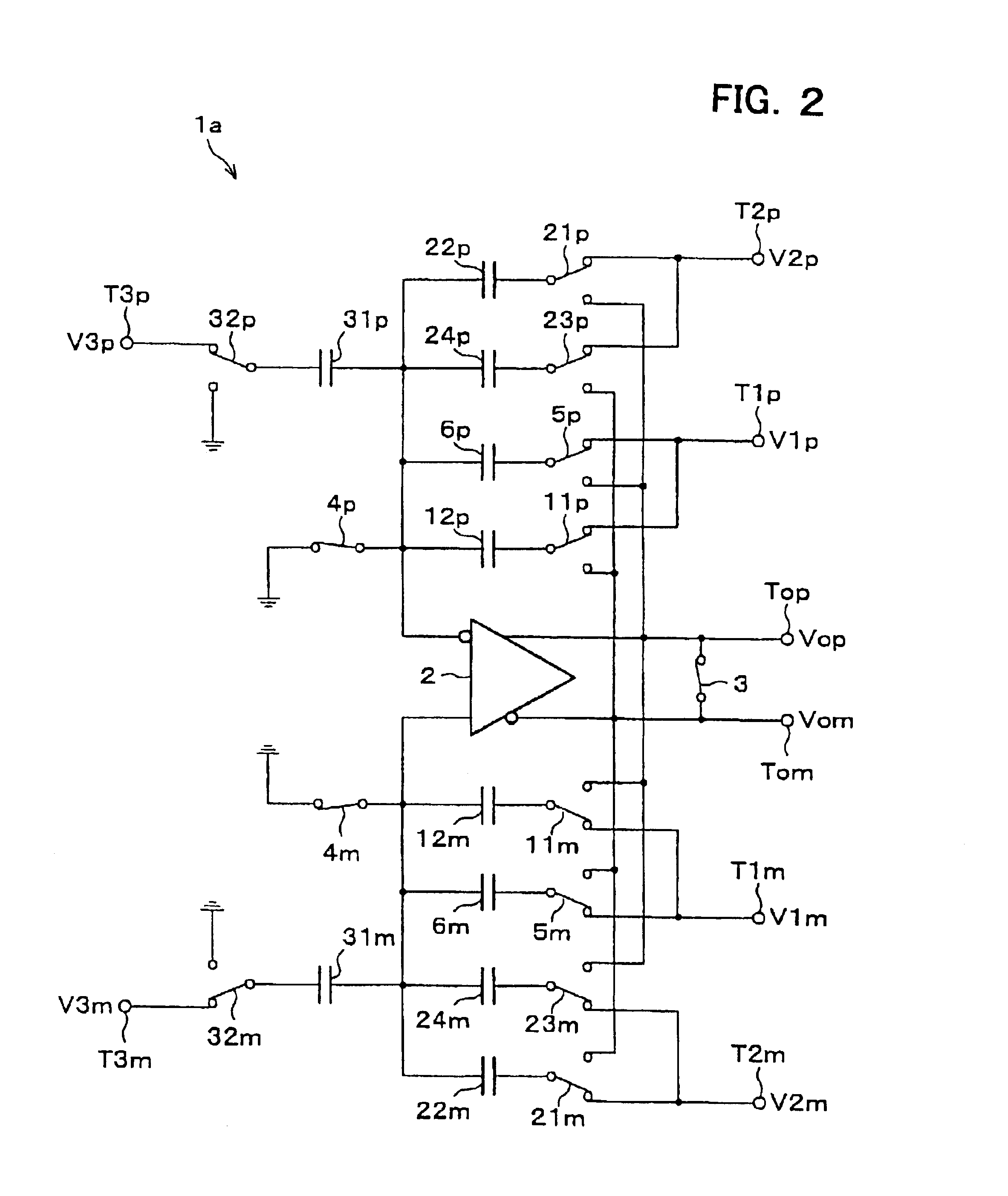
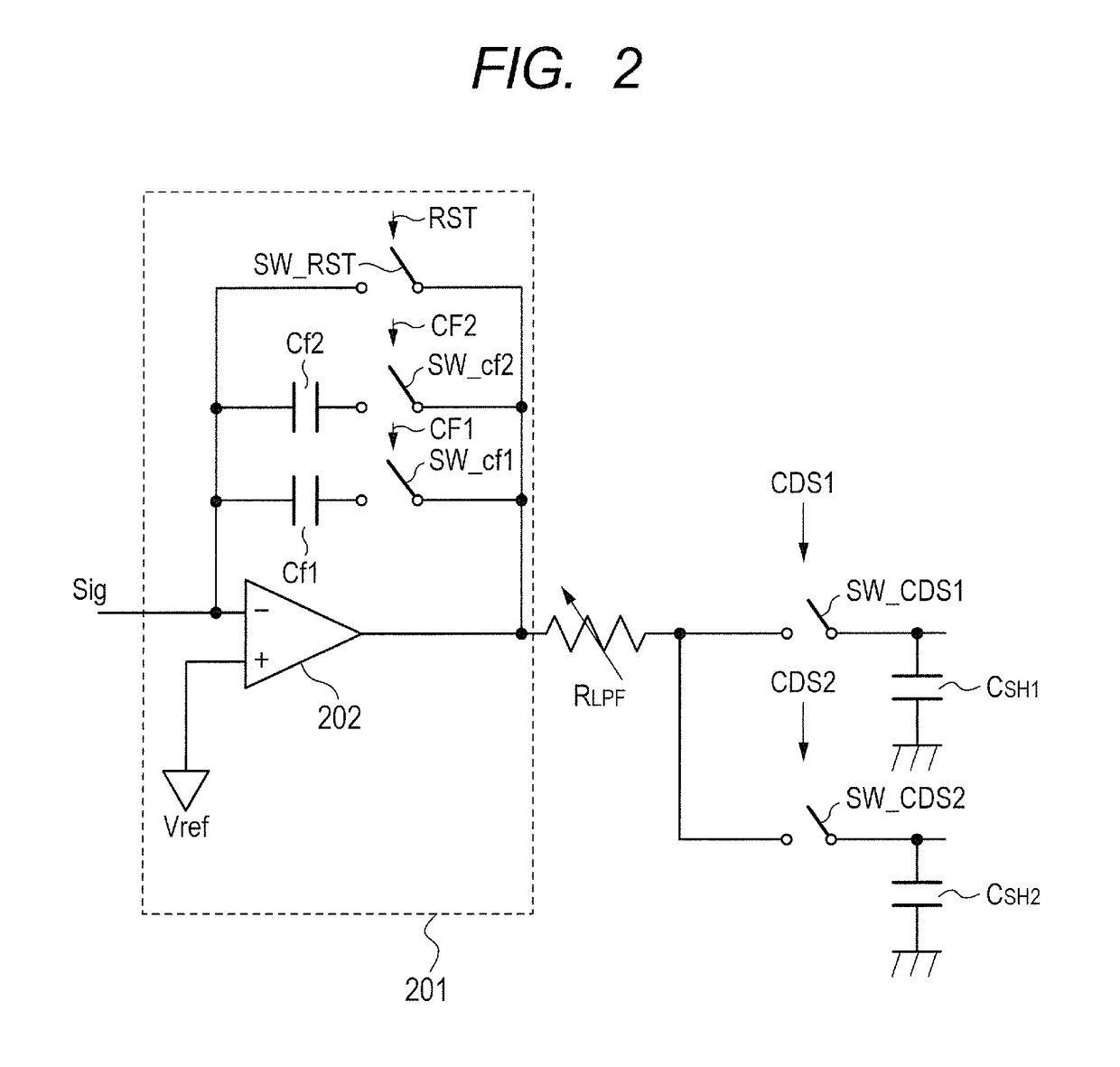
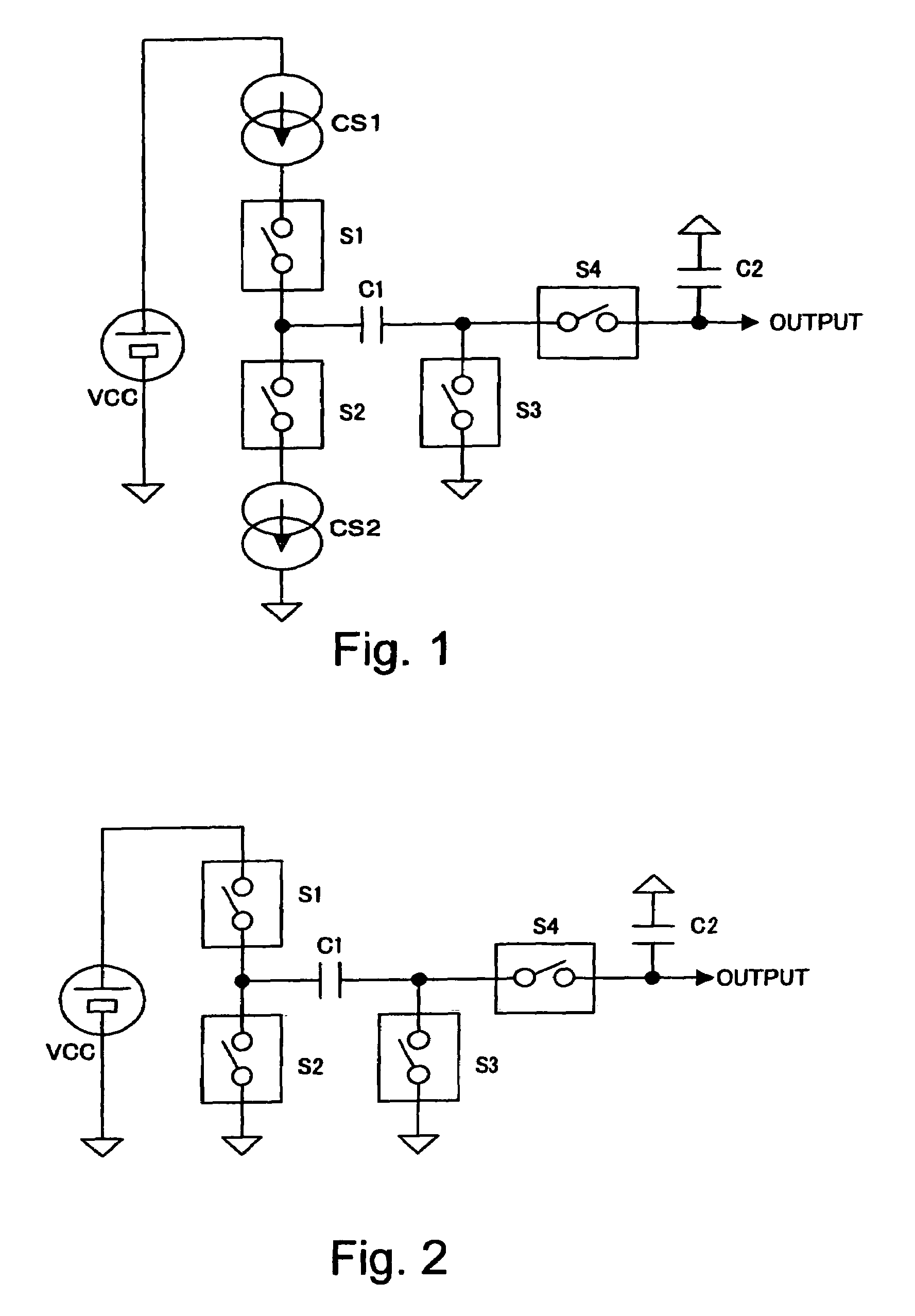
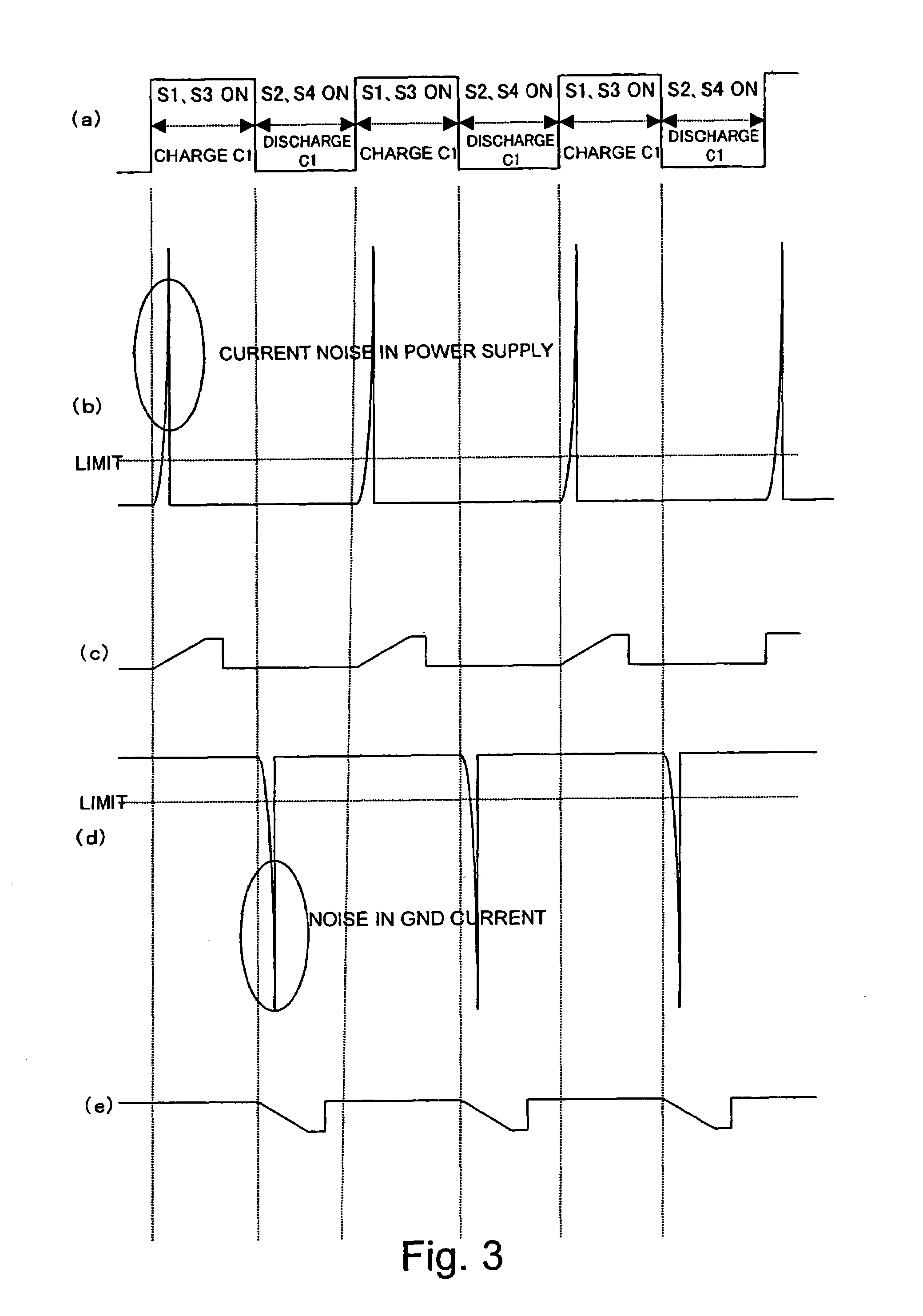
Switched-capacitor amplifier and analog interface circuit for charge coupled element adopting the same
InactiveUS6853241B2Reduction in capacitor ratioRaise the ratioCharge amplifiersTime-varying networkCapacitanceNegative feedback
In the hold phase, two negative feedback circuits constituted by the negative feedback capacitors 6p and 6m and two positive feedback circuits constituted by positive feedback capacitors are provided between an input terminal and an output terminal of an operational amplifier. Here, in a sampling phase before a hold phase, charges according an input signal V1p is stored in each of the capacitors, and charges according to an input signal V1p are stored in each of the capacitors. As a result, a gain of the switched capacitor amplifier circuit is derived from (Ca+C) / (Ca−Cx) wherein Ca indicates an electrostatic capacitance of the negative feedback capacitors, and Cx indicates an electrostatic capacitance of the positive feedback capacitors, and thus the gain can be increased without significantly increasing an electrostatic capacitance ratio.
Owner:SHARP KK
Sample hold circuit, and pipeline ad converter using the circuit
InactiveCN101040441AOperating current variableLower operating average currentElectric signal transmission systemsCharge amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
A switched capacitor sample hold circuit using a source-earthed input operation amplifier. This operation circuit is provided with a feed forward circuit or a feedback circuit, which is connected with a feedback capacitor of the operation amplifier through a switch. An input common voltage or the middle point voltage of an output is detected to precharge the feedback capacitor beforehand with the difference from a reference voltage thereby to suppress fluctuations in an output operation point at the time of amplifying the operation amplifier.
Owner:SONY CORP
Improved low power consumption two-wire system vortex shedding flowmeter
InactiveCN101451864AImprove the extraction effectHigh precisionCharge amplifiersPulse shapingFrequency spectrumLow-pass filter
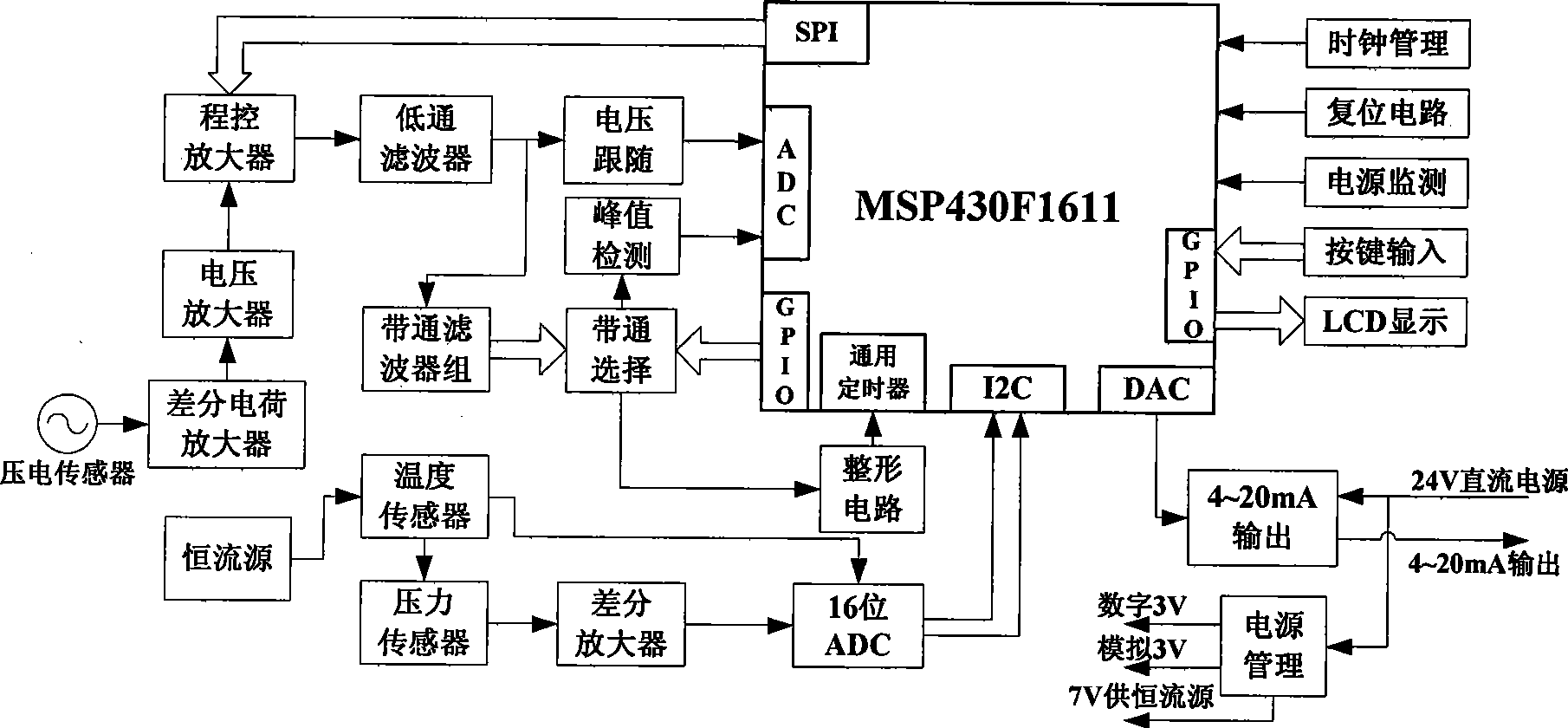
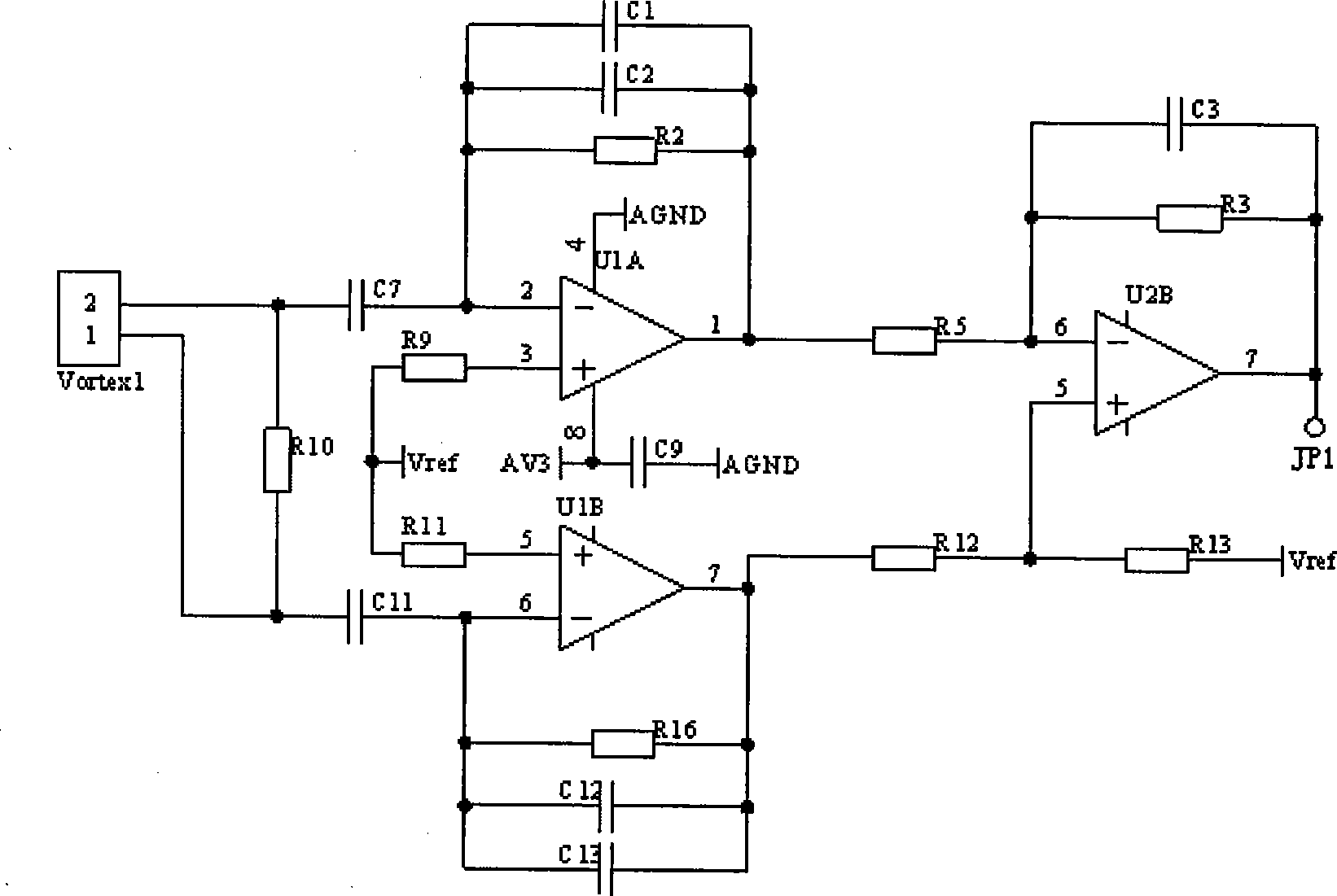
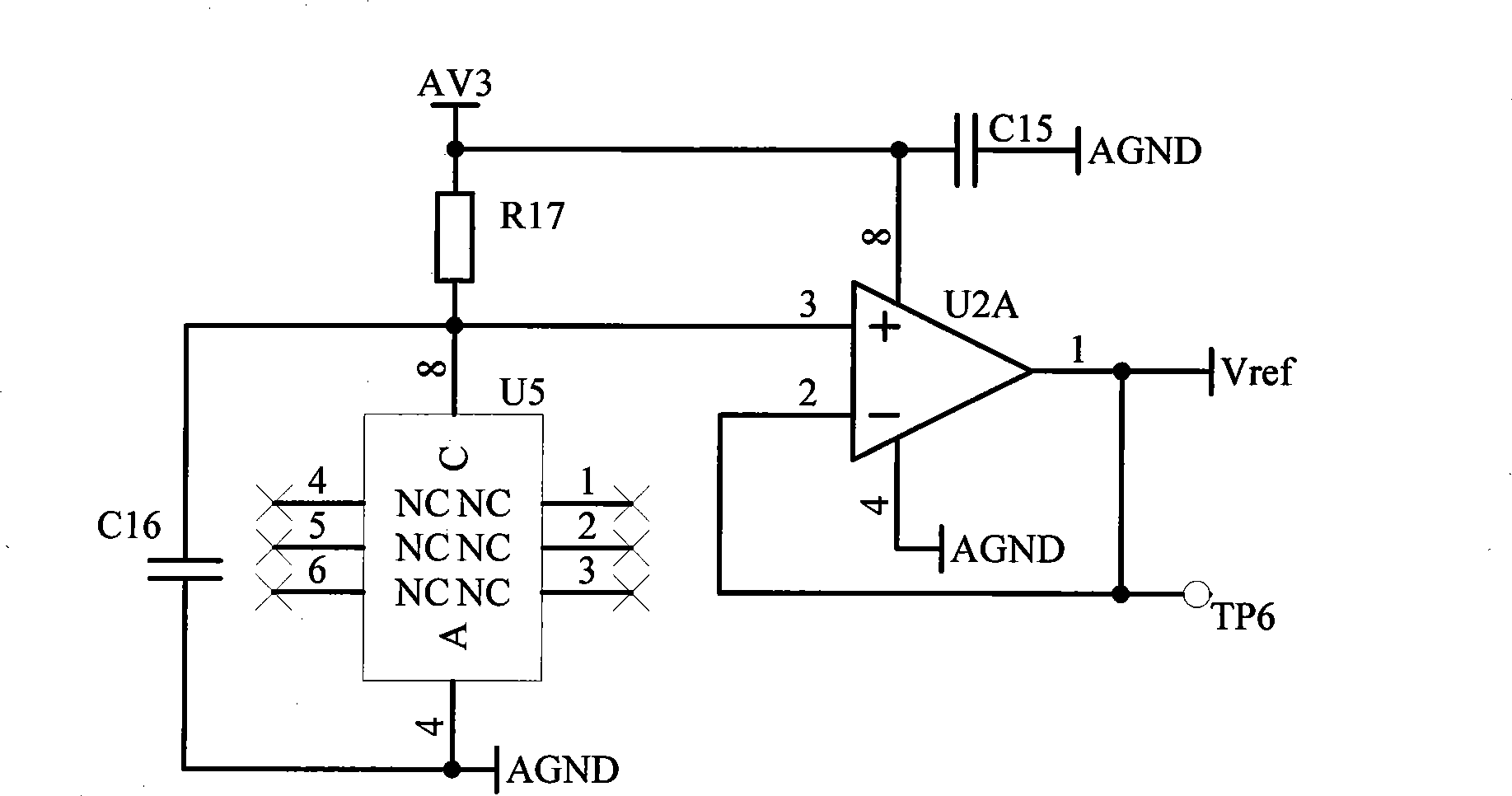
The invention relates to the field of flow detection, as an advanced low power consumption two-wire system vortex-shedding meter, comprising a piezo-electric transducer, a differential charge amplifier, a voltage amplifier, a programmable amplifier, a low pass filter, a voltage follower, a band-pass filter set, a band-pass select switch circuit, a peak detection circuit, a wave shaping circuit, asinglechip, a human-computer interface circuit, a 4-20mA output and power management circuit, a constant flow source, a temperature sensor, a pressure sensor, a differential amplifier and a 16-bit analog-to-digital converter. Mini FFT spectral decomposition is used to be combined with the analog band-pass filter set to process signals of a vortex sensor and a multicycle frequency measurement method of precision is used, thereby having temperature and pressure compensating circuit and function, outputting 4-20mA direct current and having two-wire system work. The advanced low power consumptiontwo-wire system vortex-shedding meter has greatly improved measure ratio, measurement precision and capacity of resisting disturbance.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
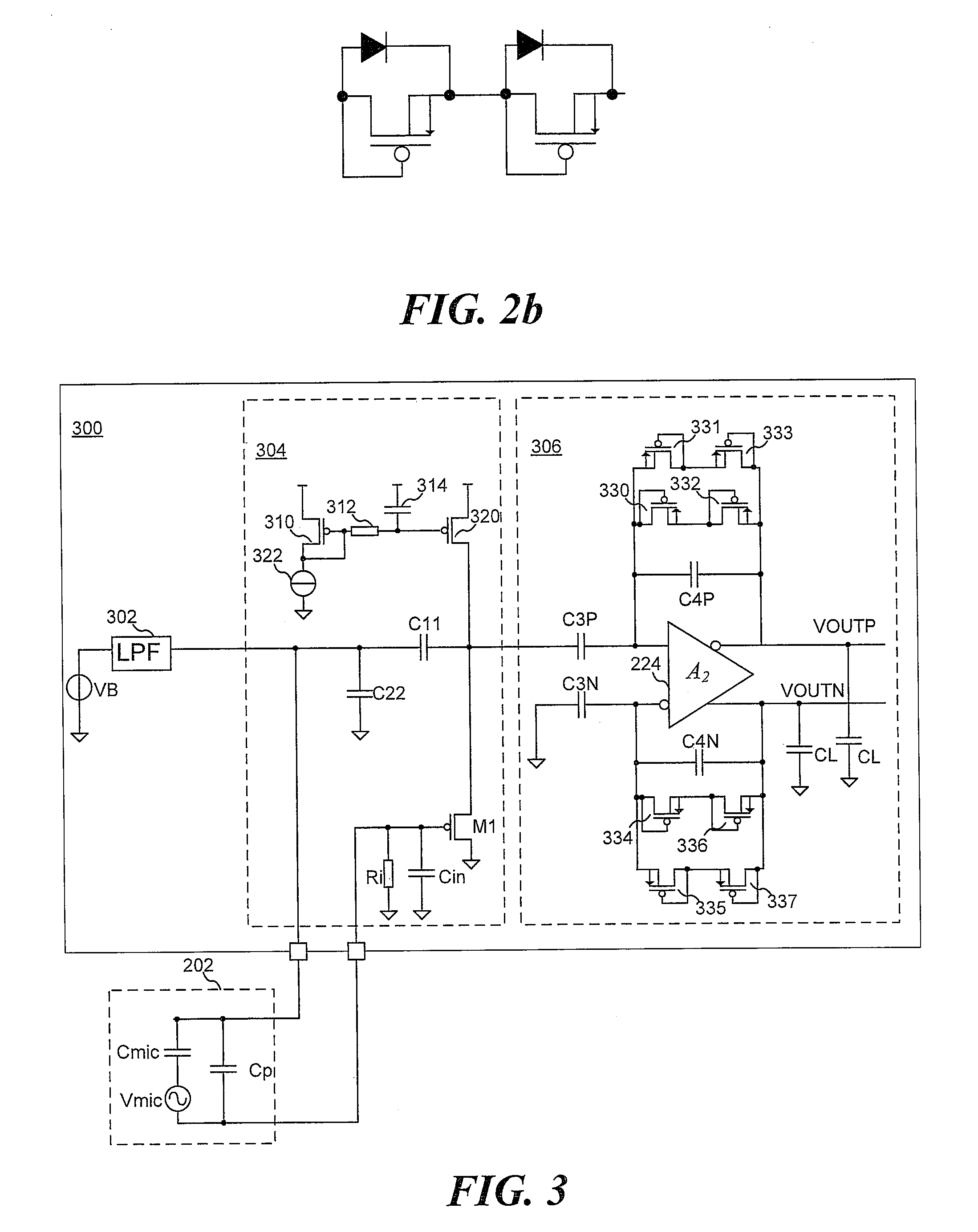
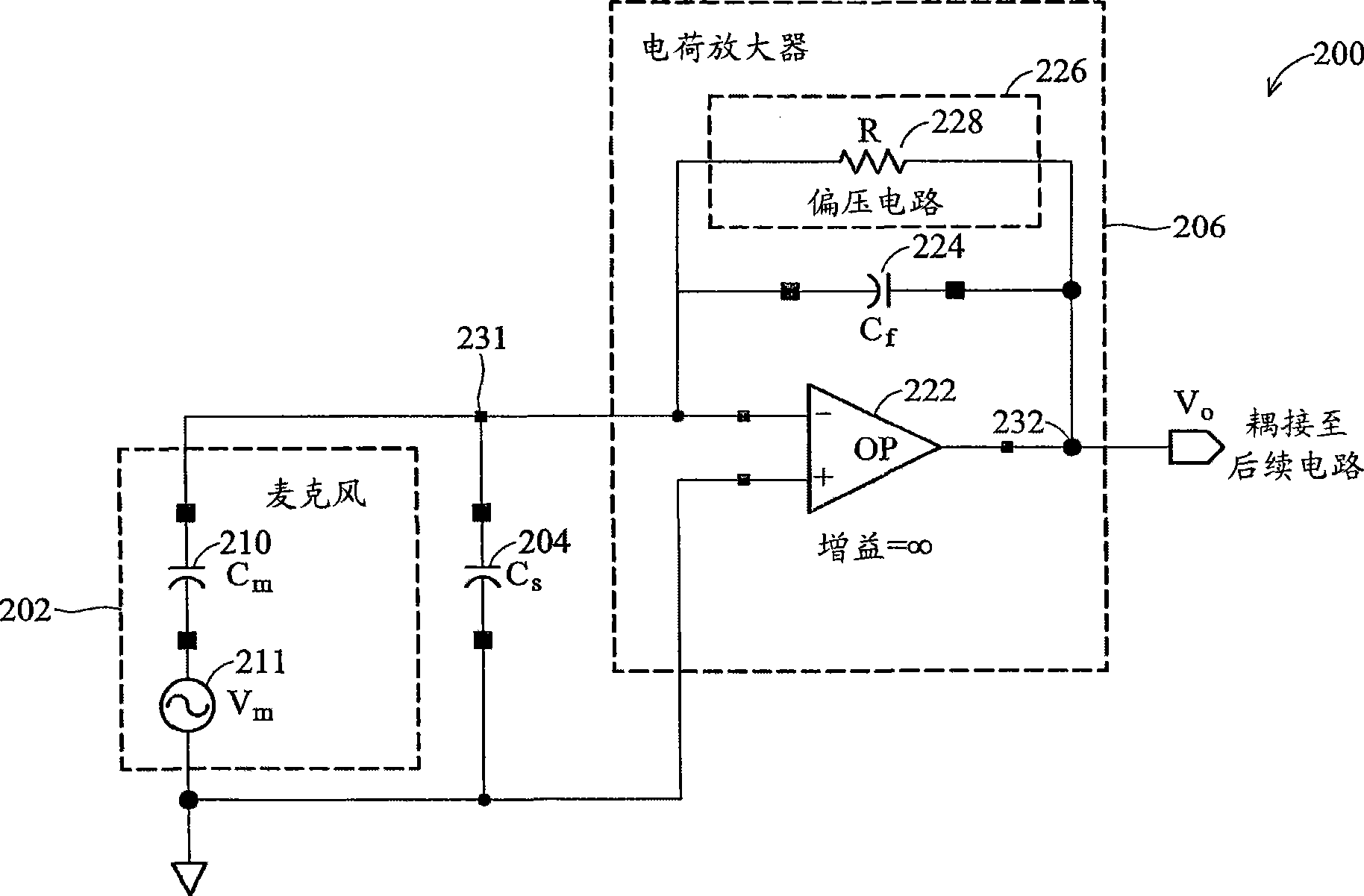
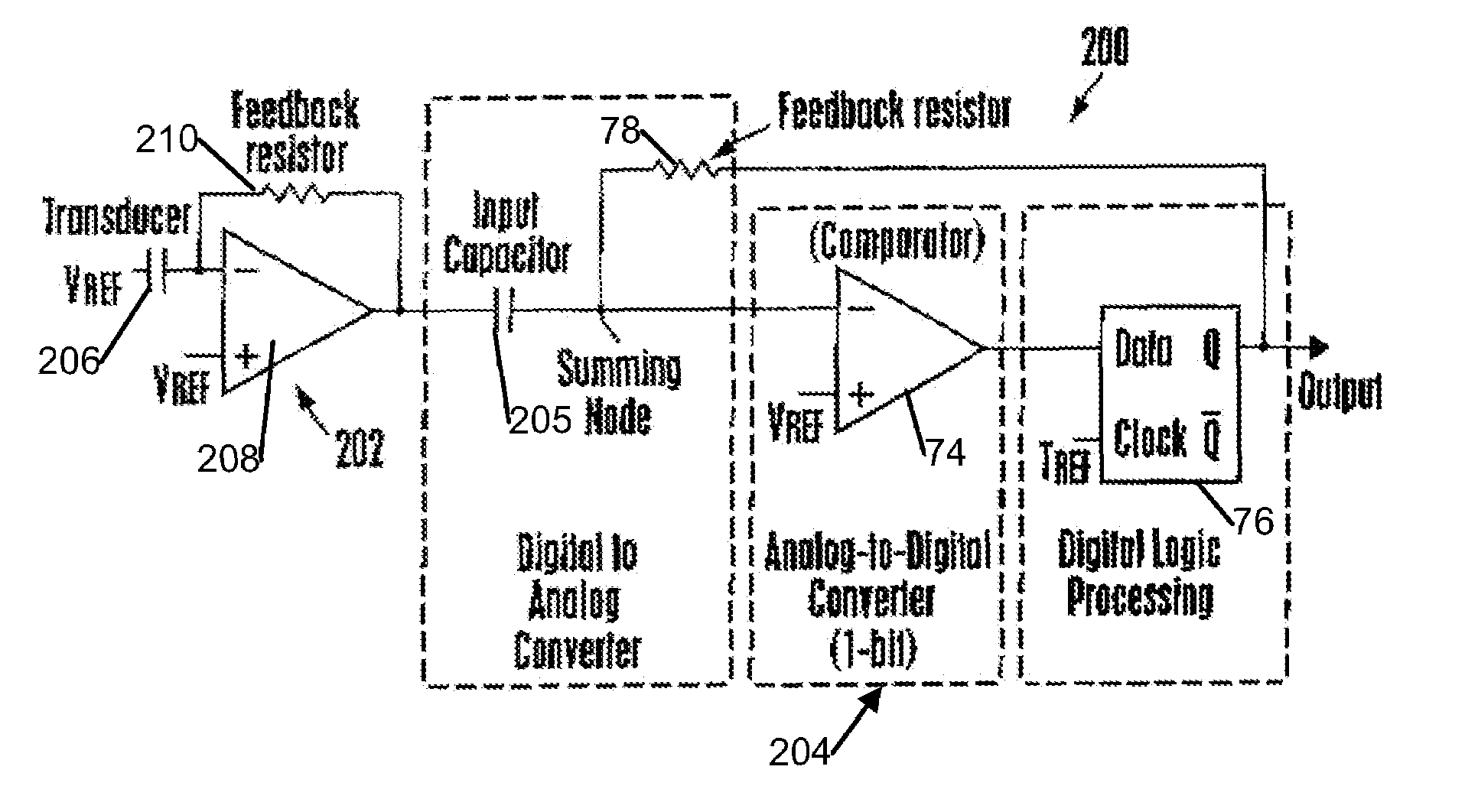
Piezoelectric Transducer Signal Processing Circuit
ActiveUS20070109064A1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityDetector circuits
A piezoelectric detector circuit has at least one input line, a piezoelectric transducer in the input line, an amplifier receiving signals on the input line and generating an output, and one or two feedback elements through which the output is sent back to the input line. The circuit may be a discrete time sampled operational amplifier (DTOA) based transconductance or “voltage output mode” circuit. In one embodiment, protection elements are associated with amplifier input lines to establish a reference voltage.
Owner:SUREN SYST
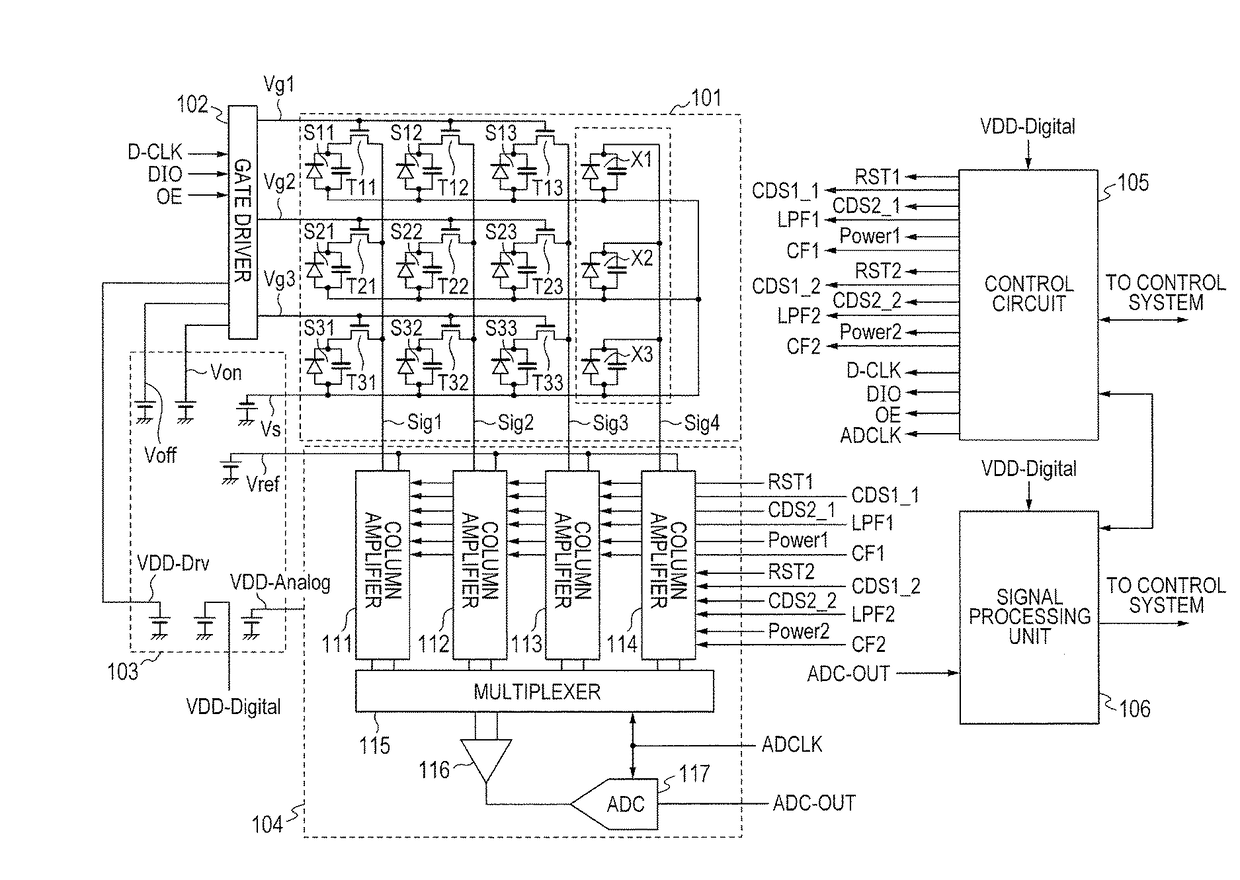
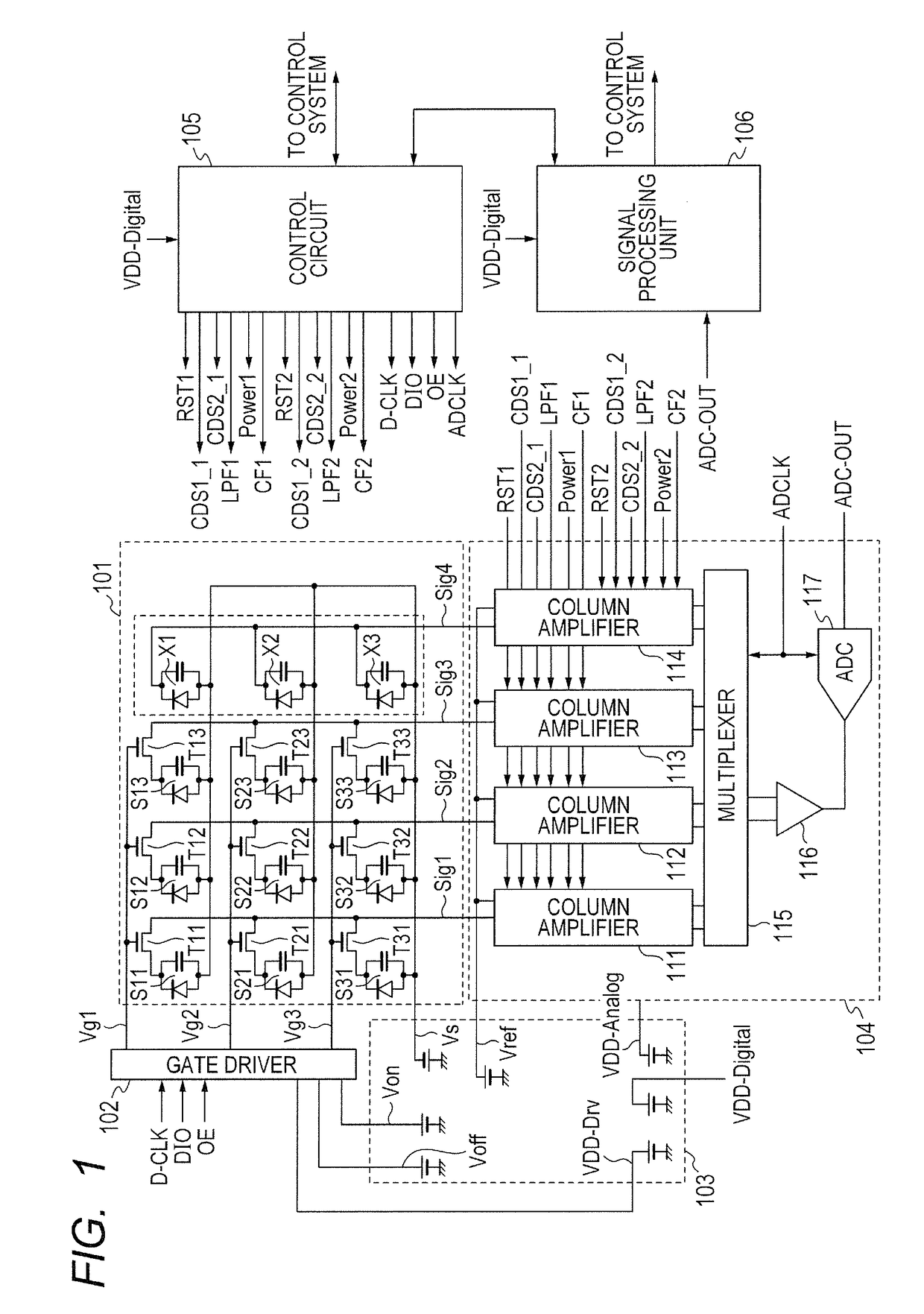
Radiation imaging apparatus and radiation imaging system
ActiveUS9655586B2Short timeReduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsCharge amplifiersAudio power amplifierRadiation imaging
Provided is a radiation imaging apparatus, including: a first conversion element arranged to convert a radiation ray into electric charge in order to obtain a radiographic image; a first amplifier arranged to output a voltage corresponding to the electric charge of the first conversion element; a second conversion element arranged to convert the radiation ray into electric charge in order to detect radiation irradiation; a second amplifier arranged to output a voltage corresponding to the electric charge of the second conversion element; and a control circuit configured to control the first amplifier and the second amplifier, in which the control circuit is capable of controlling the second amplifier independently of control that is exerted over the first amplifier.
Owner:CANON KK
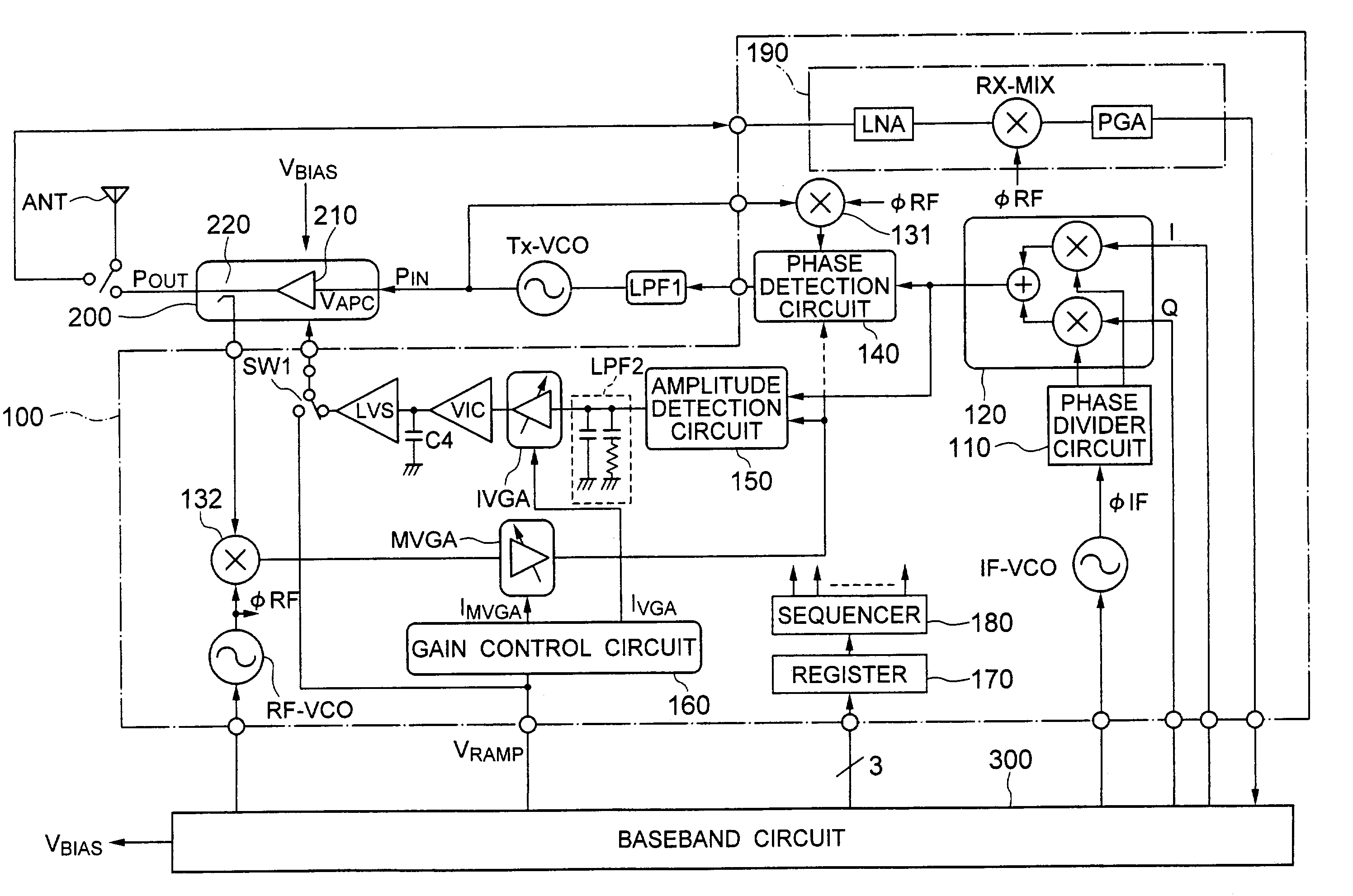
Apparatus for radio telecommunication system and method of building up output power
InactiveUS7209717B2Preventing long delay in stabilizingReduced stabilityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierCarrier signal
A polar loop based radio telecommunication apparatus which has a phase control loop for controlling the phase of a carrier outputted from an oscillator for transmitter, and an amplitude control loop for controlling the amplitude of a transmission output signal outputted from a power amplifier circuit, wherein precharge means is provided on a forward path from a current source, through the power amplifier circuit, to a detection circuit, forming the amplitude control loop, for rapidly increasing a control voltage for the power amplifier circuit to a power threshold upon starting transmission.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC +2
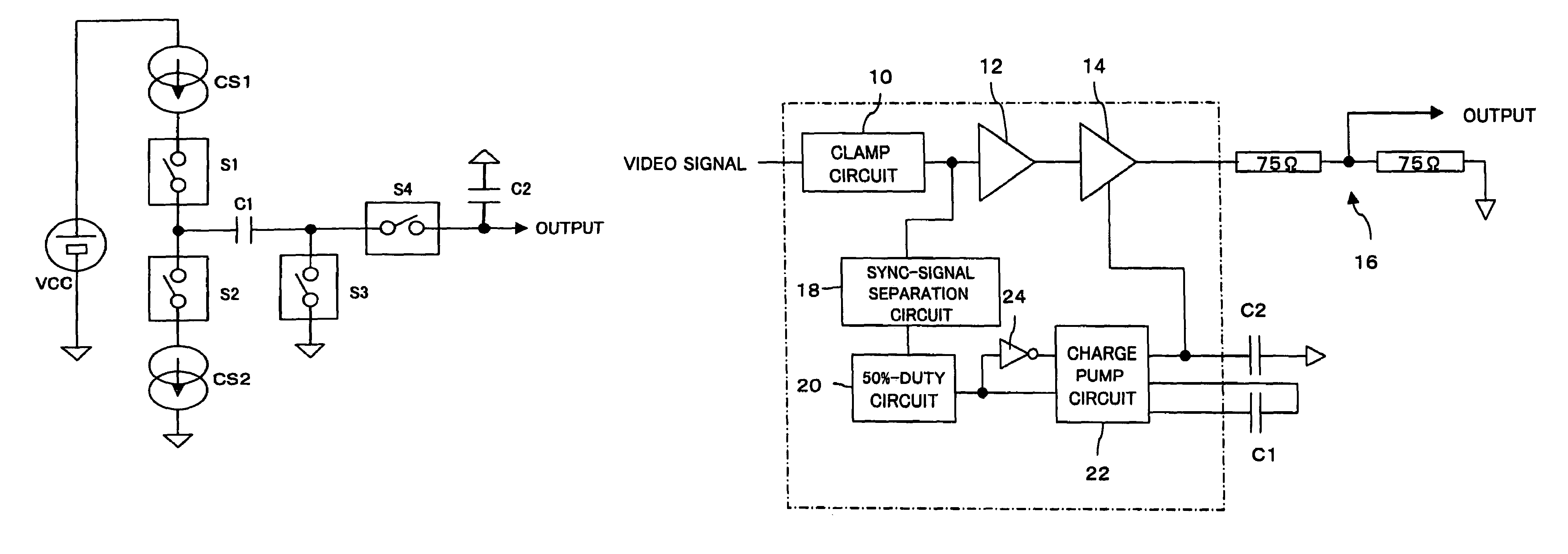
Analog buffer, display device having the same, and method of driving the same
ActiveUS20050258997A1Small sizeElectric signal transmission systemsCharge amplifiersDisplay deviceComparator
An analog buffer, display device having the same and a method of drving the same are provided. The analog buffer applies an analog voltage to a load. The analog buffer includes a comparator and a transistor. The comparator is configured to compare an input voltage provided from an external device with the analog voltage applied to the load. The transistor is turned on to electrically charge the load when the analog voltage is lower than the input voltage or turned on to electrically discharge the load when the analog voltage is higher than the input voltage, and turned off when the analog voltage becomes substantially the same as the input voltage.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
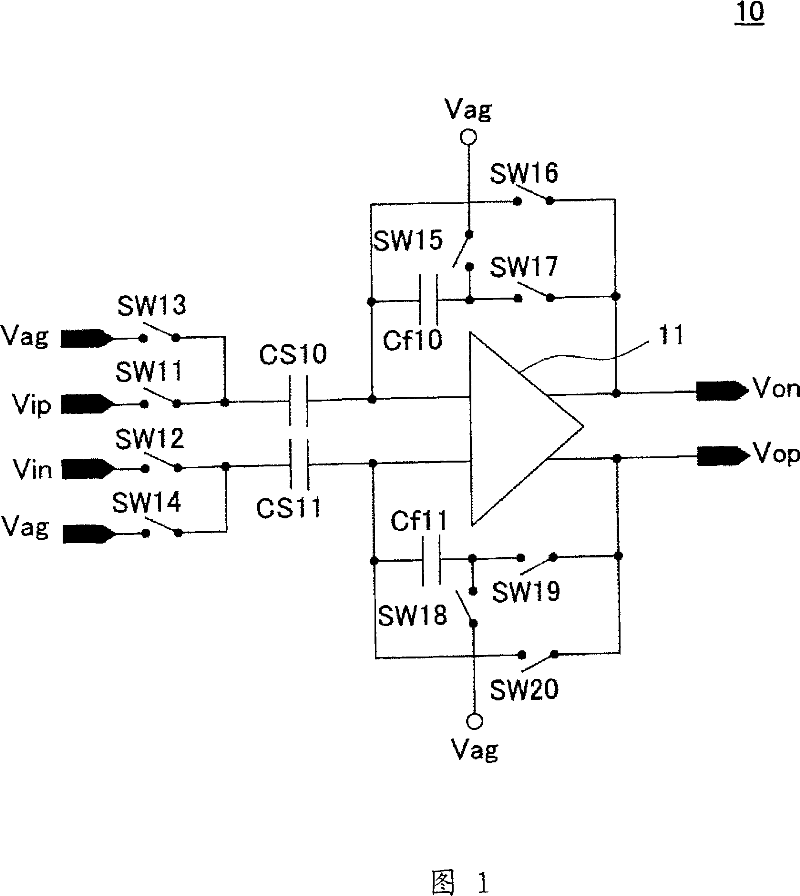
Zero-power sampling sar adc circuit and method
ActiveCN103688468APrevent leakageCharge amplifiersAnalogue-digital convertersAudio power amplifierIntegrator
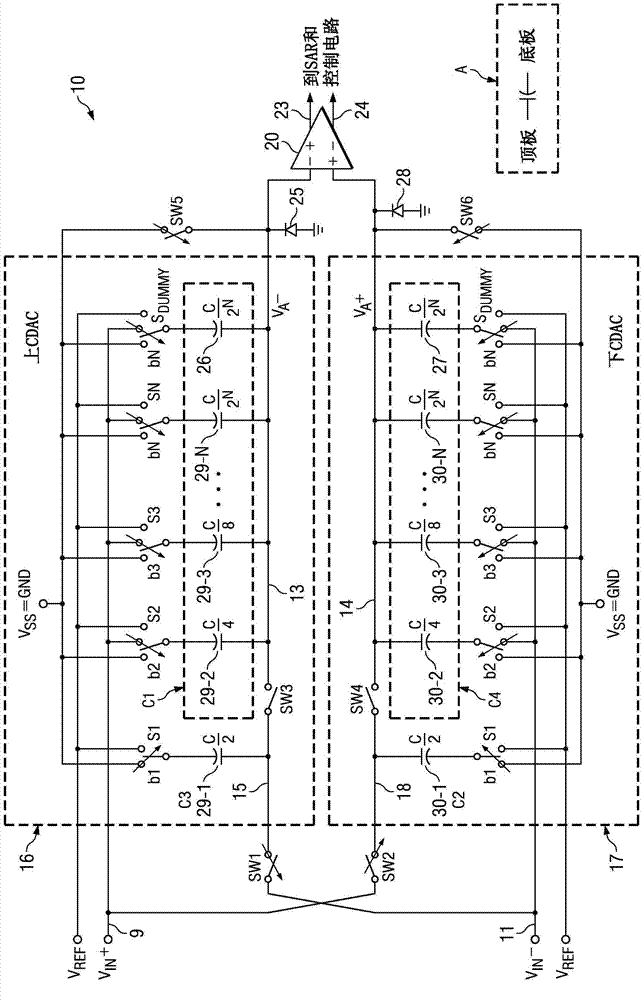
A switched-capacitor circuit (10, 32 or 32A) samples a first signal (VIN+) onto a first capacitor (C1 or CIN1) by switching a top plate thereof via a summing conductor (13) to a first reference voltage (VSS) and switching a bottom plate thereof to the first signal. A second signal (VIN-) is sampled onto a second capacitor (C3 or CIN3) by switching a top plate thereof to the second signal and switching a bottom plate thereof to the first reference voltage. After the sampling, the top plate of the second capacitor is coupled to the top plate of the first capacitor. The bottom plate of the second capacitor is coupled to the first reference voltage.; The bottom plate of the first capacitor is coupled to a second reference voltage (VDD or VREF), to thereby cancel at least a portion of a common mode input voltage component from the first conductor (13), hold the sampled differential charge on the summing conductor and establish a predetermined common mode voltage thereon, and prevent the summing conductor from having a voltage which allows the leakage of charge therefrom. The switched-capacitor circuit may be a SAR, an integrator, or an amplifier.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
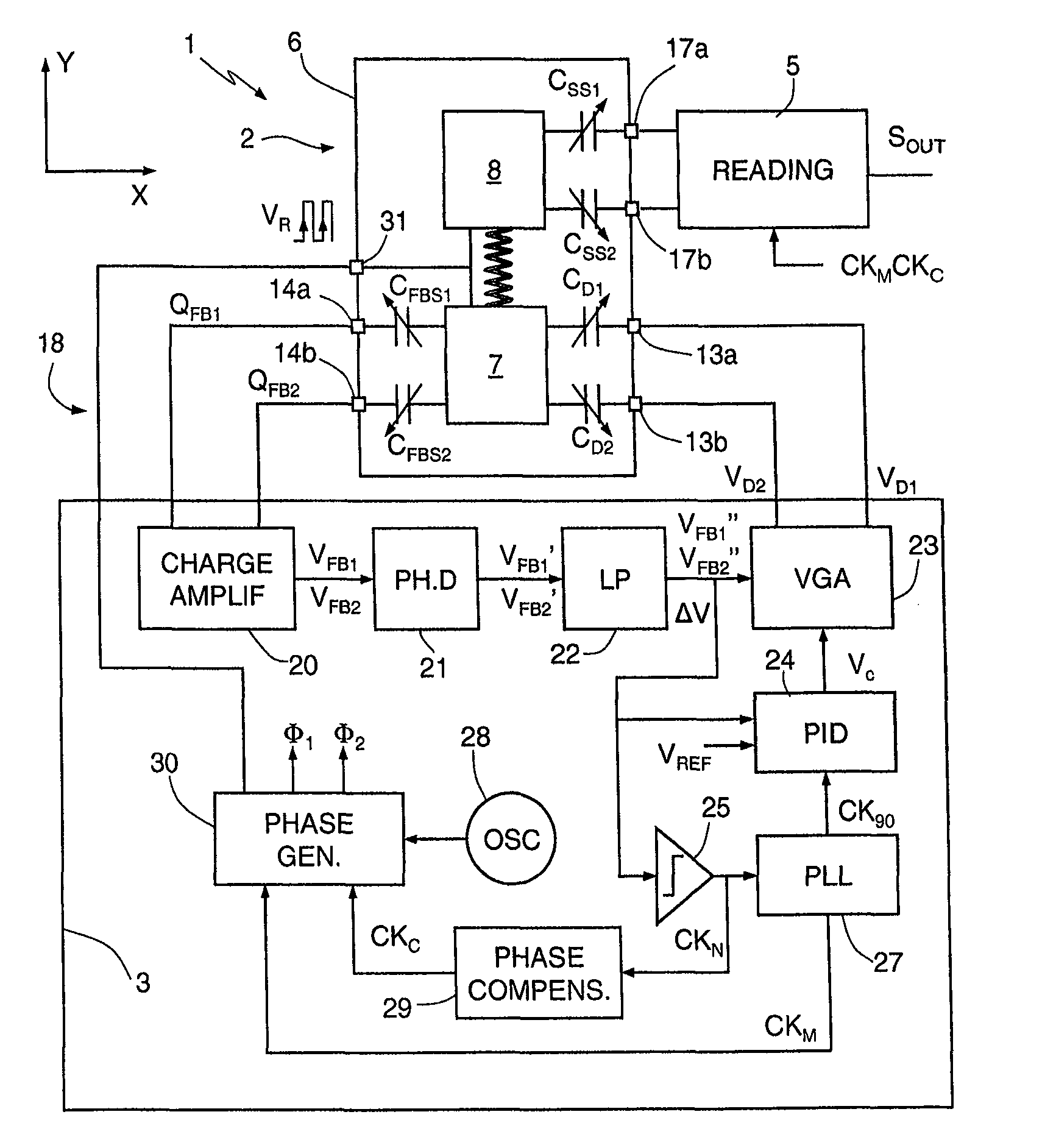
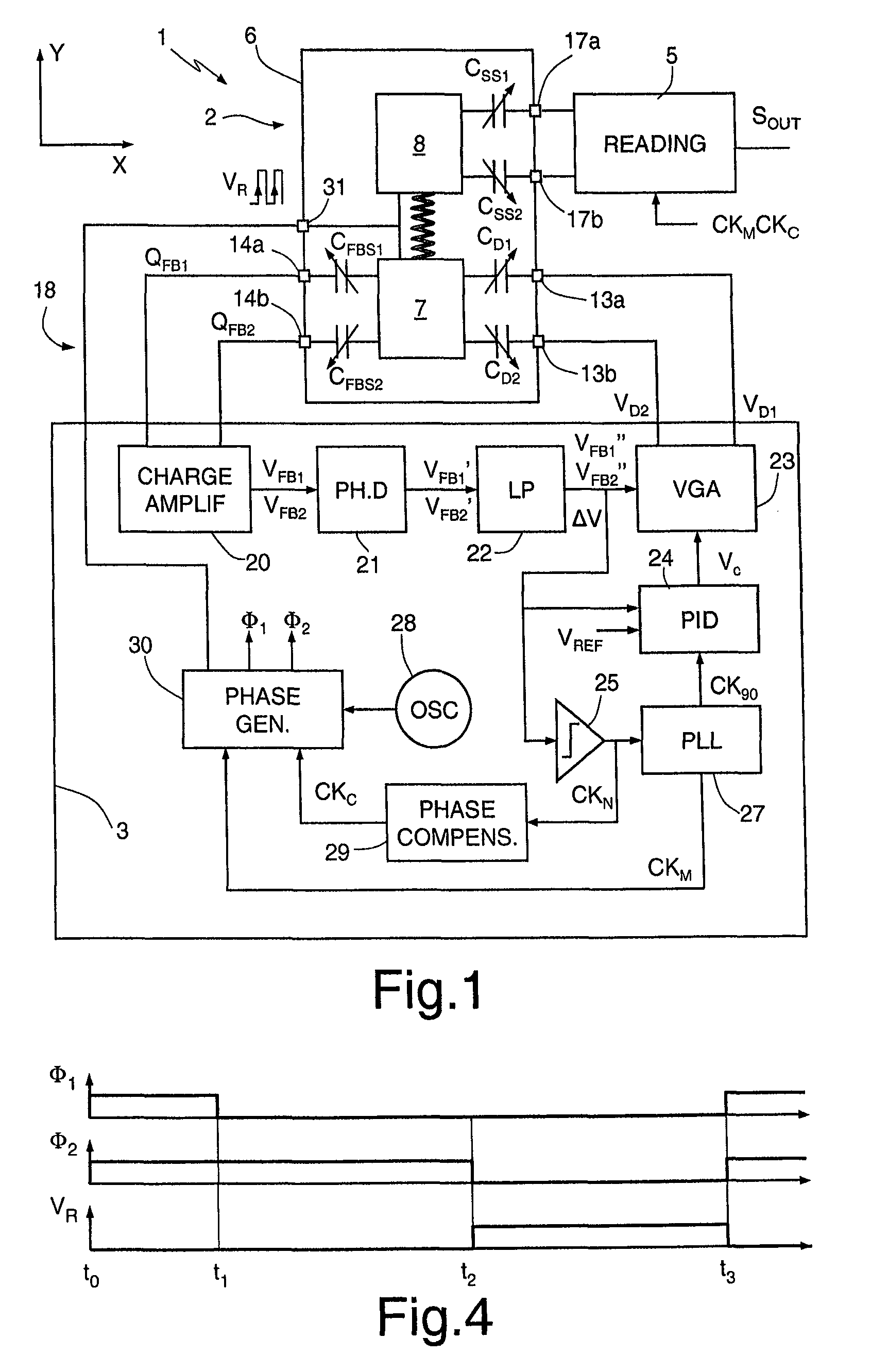
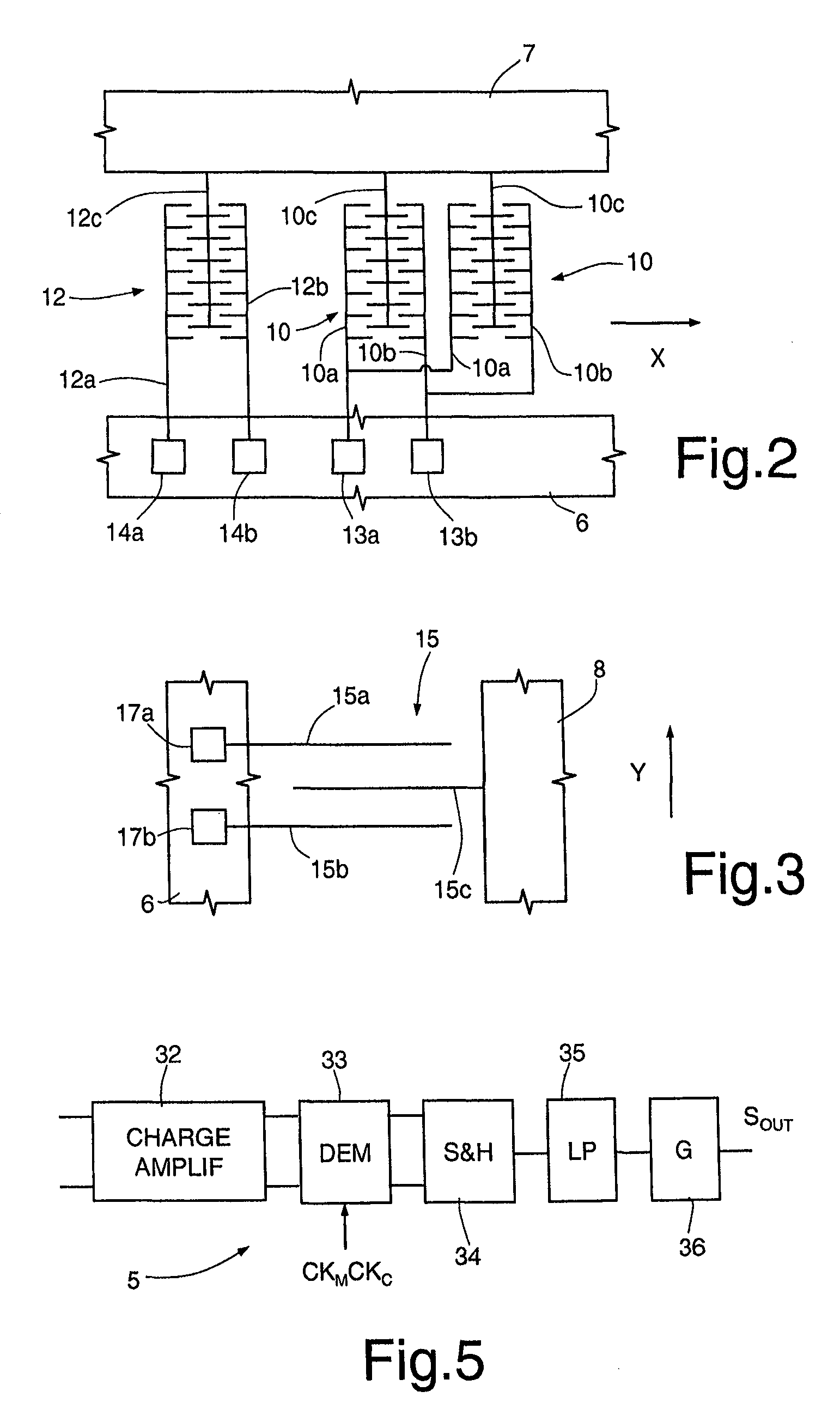
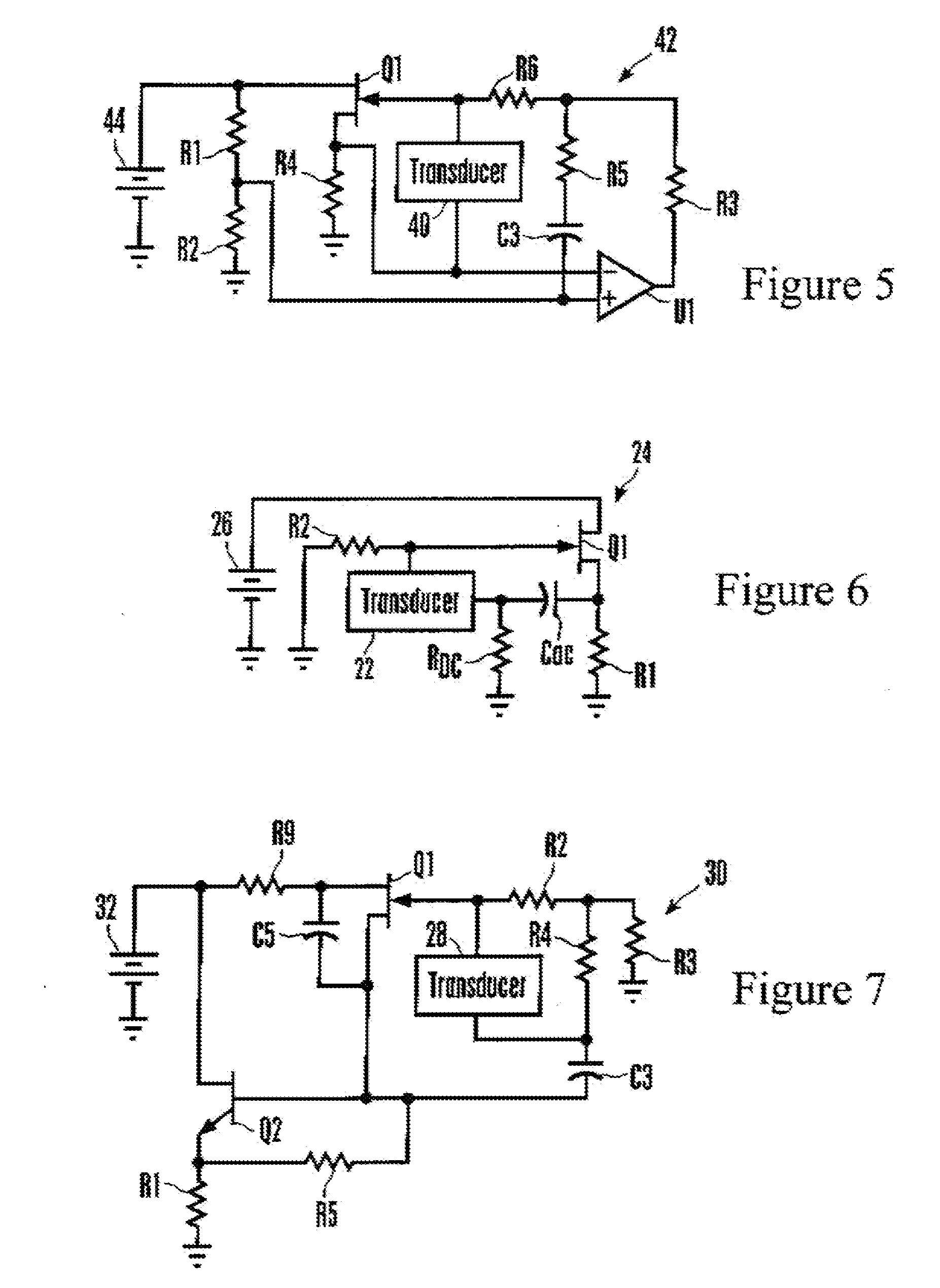
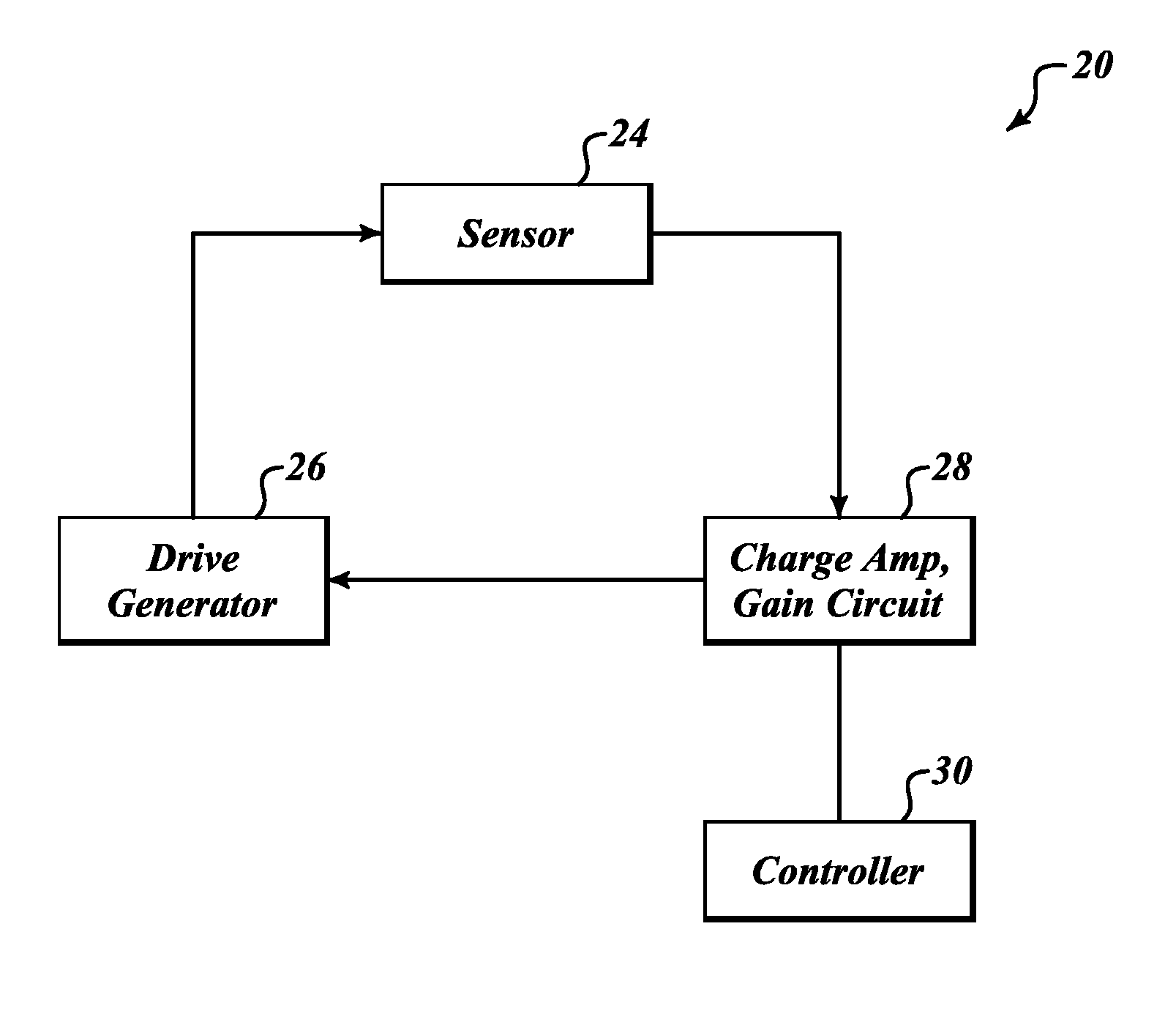
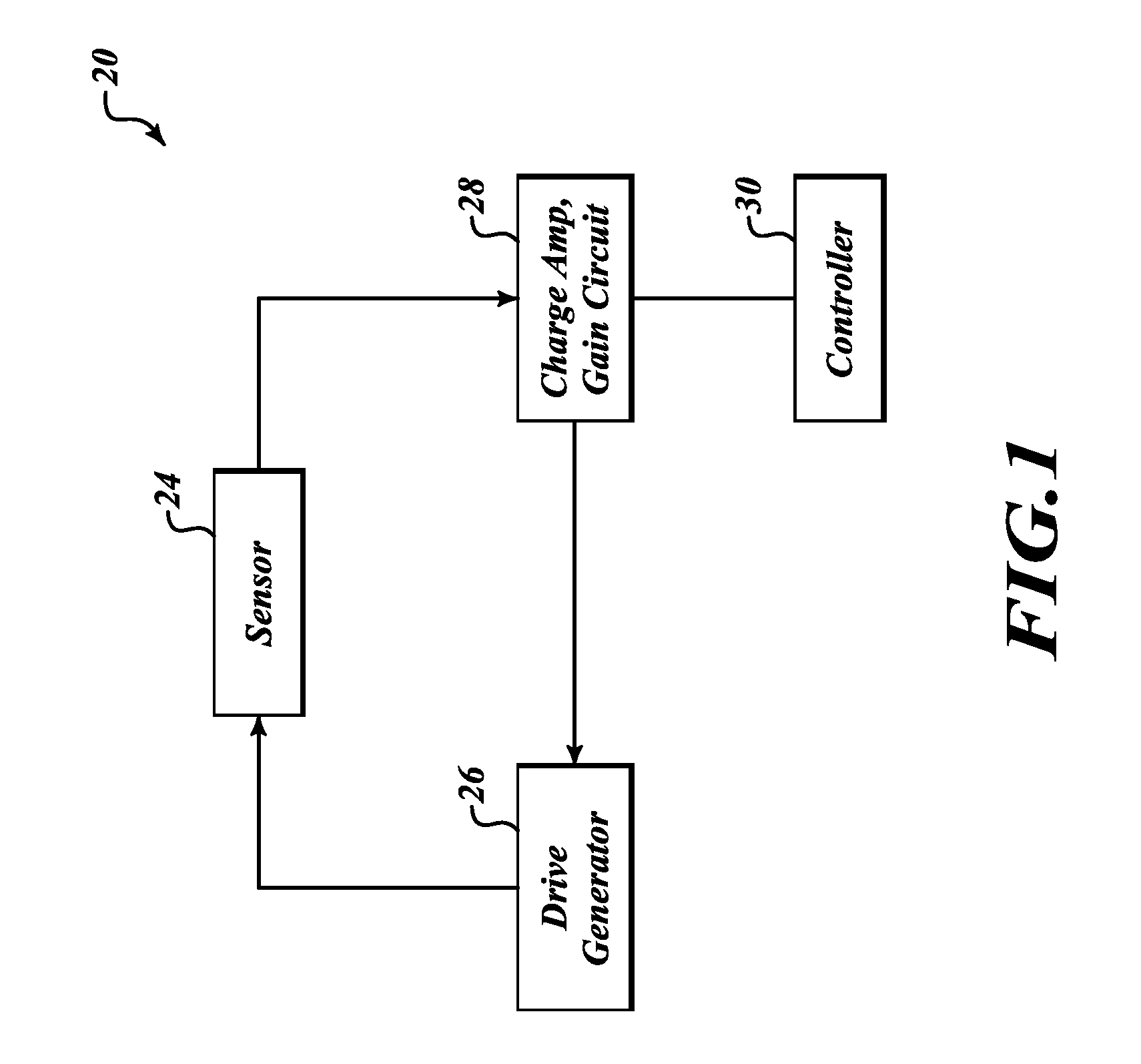
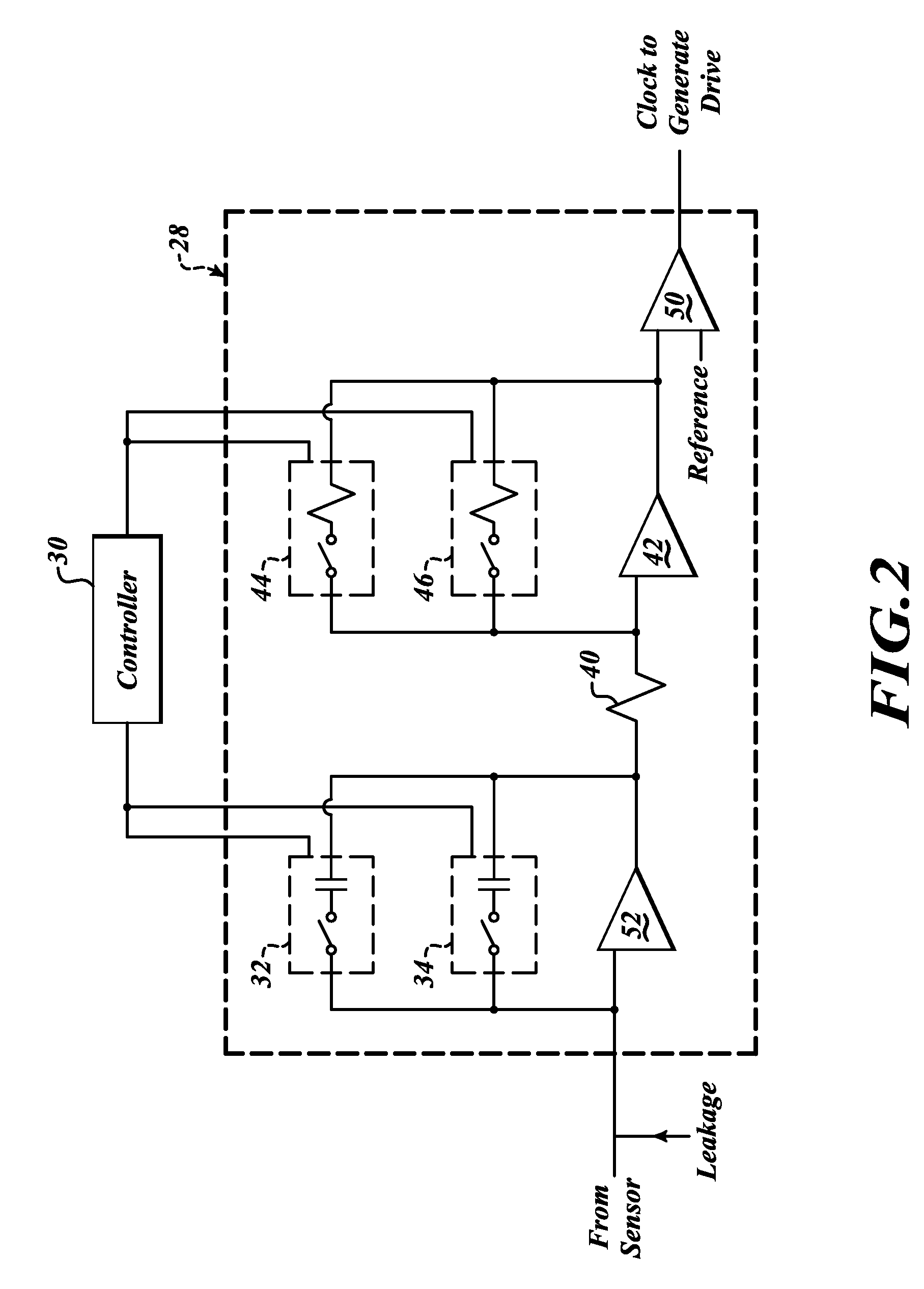
Systems and methods to overcome DC offsets in amplifiers used to start resonant micro-electro mechanical systems
ActiveUS7859352B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksAudio power amplifierEngineering
Systems and methods for insuring successful initiation of a resonating micro-electro mechanical systems (MEMS). An example system includes a resonating sensor, a drive device, a charge amplifier, and a voltage gain circuit. At start up, the charge amplifier and voltage gain circuit receives signals from the resonating sensor, compensates this signal for DC offsets, and generates a clock signal for the drive, thus placing the resonating sensor in a steady state operating mode. The circuit includes a plurality of gain switches that are toggled to produce a glitch in the signal associated with the received signal. The glitch overcomes the DC offset. A comparator generates the clock signal for the drive device if a signal associated with the received signal exceeds a reference signal.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
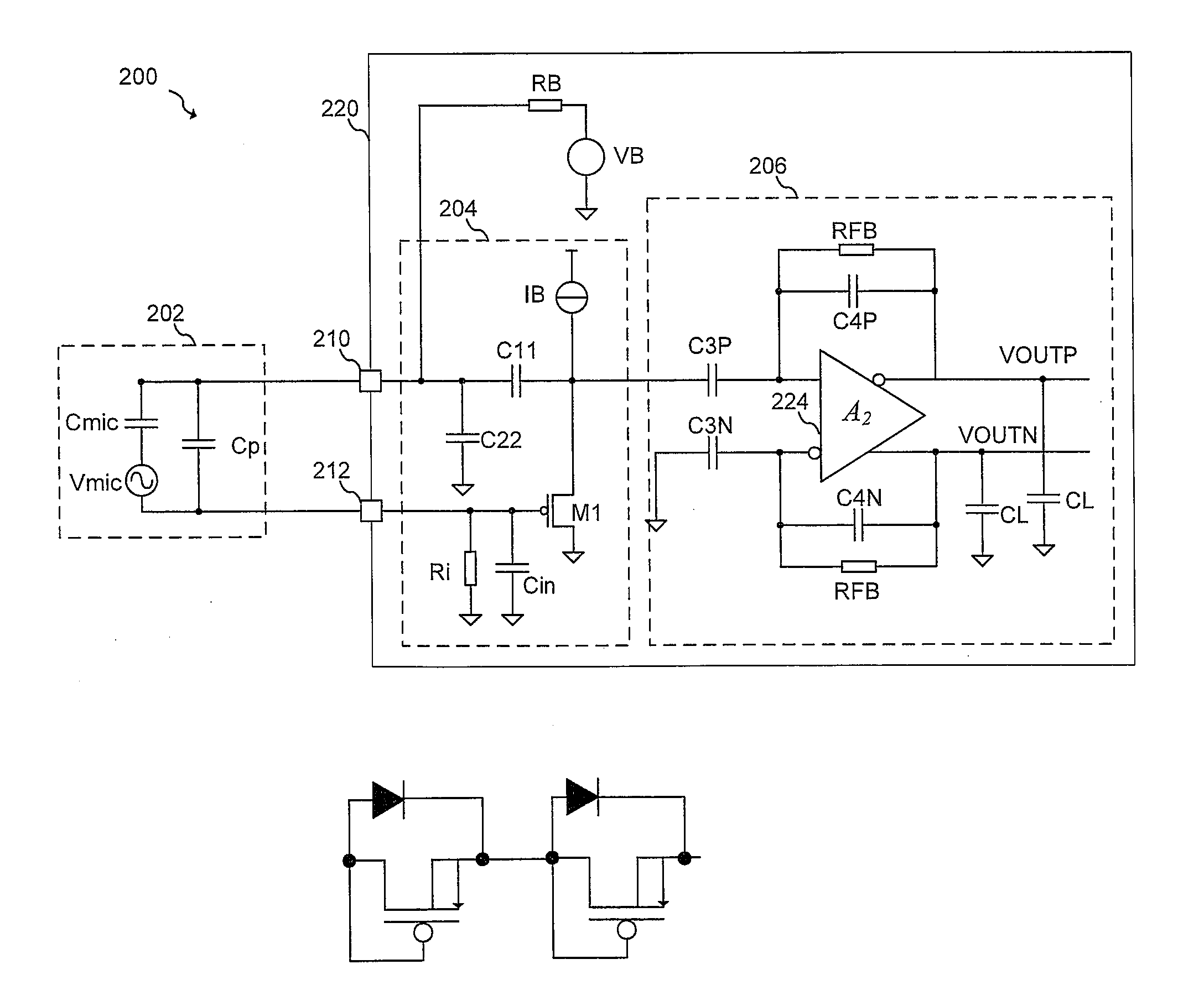
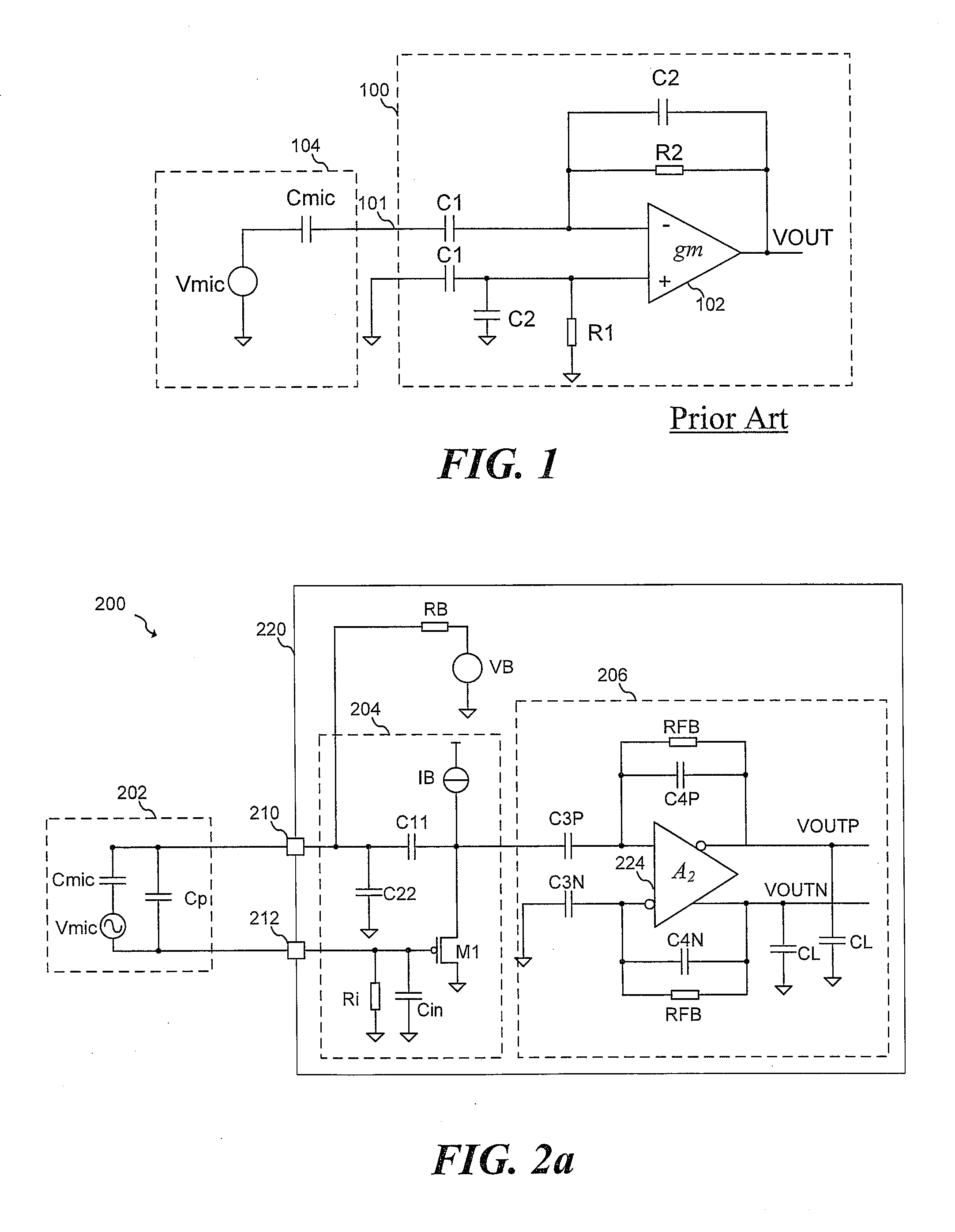
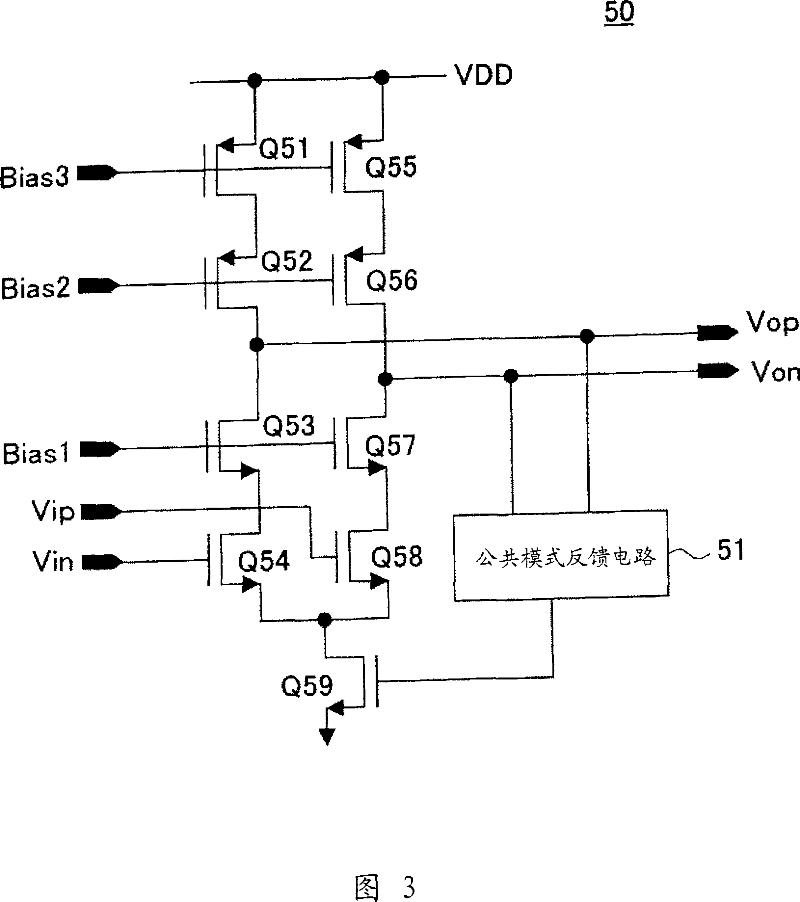
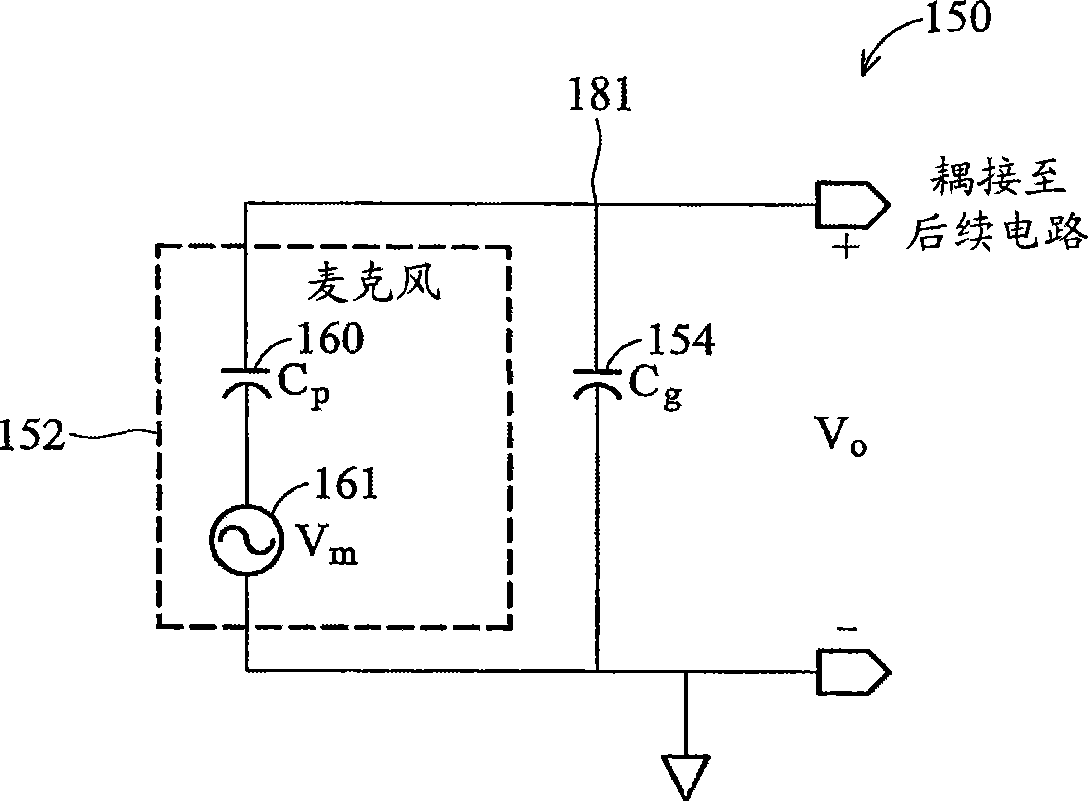
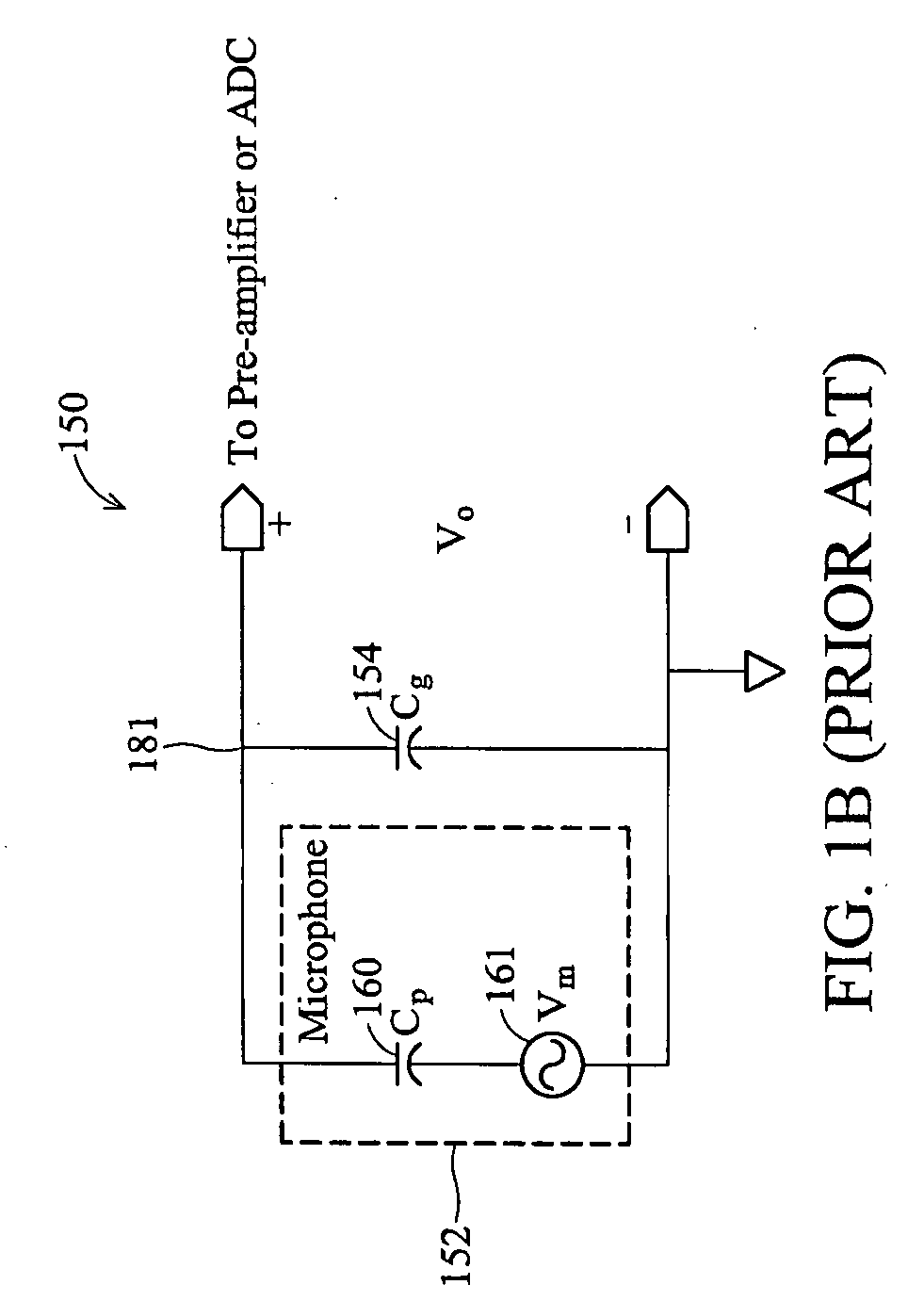
Microphone circuit
The invention provides a microphone circuit. In one embodiment, the microphone circuit comprises a microphone, a self-biased amplifier with a finite gain, and a feedback capacitor. The microphone coupled between a ground and a first node generates a first voltage at the first node according to sound pressure. The self-biased amplifier has a positive input terminal coupled to the ground and a negative input terminal coupled to the first node and amplifies the first voltage according to the finite gain to generate a second voltage at a second node. The feedback capacitor coupled between the first node and the second node feeds back the second voltage to the first node. The second voltage is then output to a following module subsequent to the microphone circuit.
Owner:FORTEMEDIA
Method and apparatus for use in switched capacitor systems
InactiveUS6873278B1Electric signal transmission systemsCharge amplifiersSignal conditioningData rate
Systems and methods receive a digital signal and generate an analog signal indicative thereof. In one embodiment, a system includes a DAC that receives a multi-bit digital signal, generates at least two analog signals each indicative of the value of the multi-bit digital signal, and filters two or more of the at least two analog signals. In another embodiment, a system includes a DAC that receives digital input signals at an input data rate and outputs analog signals Indicative of the digital signals to a signal conditioning stage at an output data rate different the input data mute.
Owner:XUESHAN TECH INC
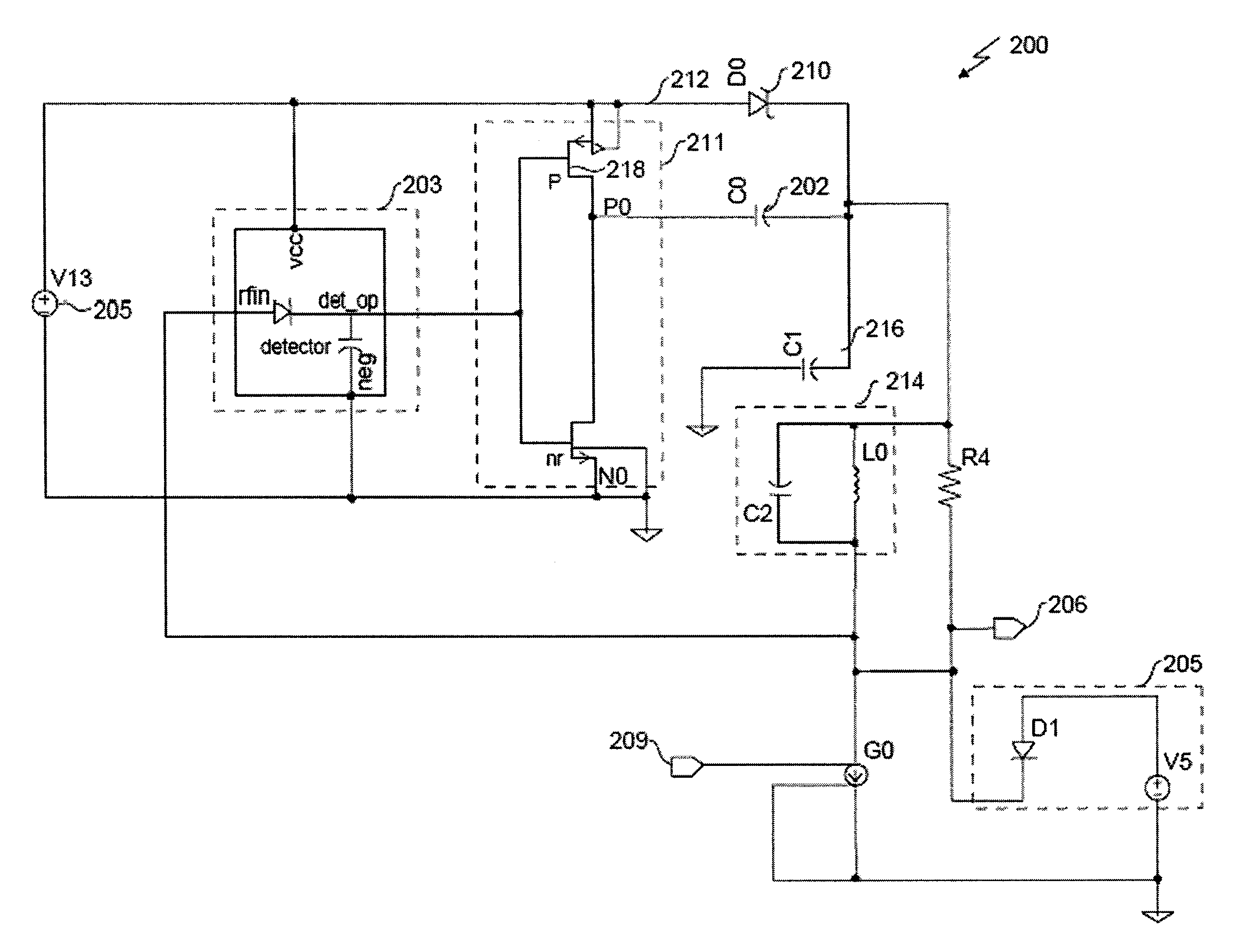
Charge pump circuit and amplifier
A charge pump circuit which uses a constant current from a constant current source for charging or discharging a capacitor and which obtains an output voltage by shifting a power supply voltage using a charged voltage of the charged capacitor. With this structure, a large current can be limited and generation of noise can be prevented.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
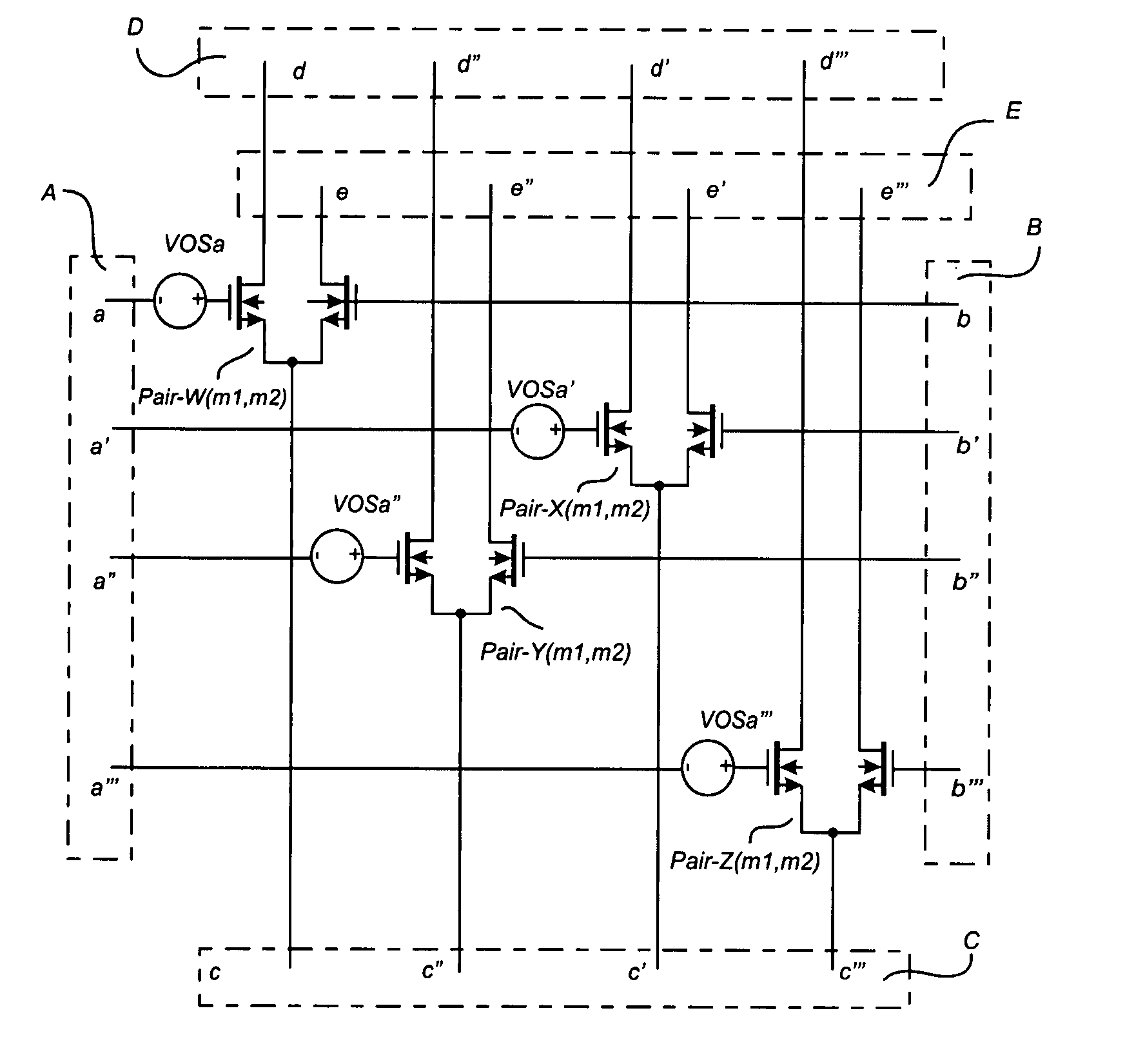
Method and apparatus for calibrating analog circuits using statistical techniques
ActiveUS20060125563A1Regard to overcoming effectsCharge amplifiersAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationEngineeringAnalog chip
The performance of precision analog integrated electronic circuits is directly related to the degree of matching between electrical circuit elements. Any residual mismatch of circuit elements after manufacturing must be calibrated out using numerous techniques such as adjusting potentiometers, trimming capacitors, modifying binary-weighted resistor strings, etc. Prior art matching techniques entail the use of large area circuit elements or a large number of elements arranged in a prescribed manner on the surface of a silicon die to minimize the residual calibration. The present invention utilizes a multiplicity of circuit elements that are interconnected in distinct groups to achieve a higher degree of element matching and the ensuing benefits thereof. The elements are interconnected to yield a prescribed minimum mismatch error.
Owner:ELDER J SCOTT
High sensitivity, high resolution detection of signals
A system and method providing for the detection of an input signal by distributing the input signal into independent signal components that are independently amplified. Detection of an input signal comprises generating from the input signal a plurality of spatially separate elementary charge components, each having a respective known number of elementary charges, the number of the plurality of spatially separate elementary charge components being a known monotonic function of the magnitude of said input signal; and independently amplifying each of the plurality of spatially divided elementary charge components to provide a respective plurality of signal charge packets, each signal charge packet having a second number of elementary charges greater than the respective known number by a respective amplification factor.
Owner:AMPLIFICATION TECH INC
Fully integrated long time constant integrator circuit
InactiveUS6476660B1Extension of timeConstant gainComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationCapacitanceIntegrator
The present invention provides a long time constant integrator circuit as part of an integrated circuit. The integrator circuit is fully integrated on chip with no external capacitive or resistive components for enhancing the circuit's time constant. It achieves a -3 dB cut-off frequency of 1.6 Hz. The circuit is realisable on a very small area of silicon being formed by a bipolar process using npn transistors, resistive and capacitive elements. The integrator circuit comprises a transconductance stage as an input to an operational amplifier. The circuit design is fully differential and employs realisable resistors and capacitors.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Method for forming elements with reduced variation
ActiveUS7358809B2Reduce stepsCharge amplifiersAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationEngineeringSilicon
The performance of precision analog integrated electronic circuits is directly related to the degree of matching between electrical circuit elements. Any residual mismatch of circuit elements after manufacturing must be calibrated out using numerous techniques such as adjusting potentiometers, trimming capacitors, modifying binary-weighted resistor strings, etc. Prior art matching techniques entail the use of large area circuit elements or a large number of elements arranged in a prescribed manner on the surface of a silicon die to minimize the residual calibration. The present invention utilizes a multiplicity of circuit elements that are interconnected in distinct groups to achieve a higher degree of element matching and the ensuing benefits thereof. The elements are interconnected to yield a prescribed minimum mismatch error.
Owner:ELDER J SCOTT
Microphone circuit and charge amplifier thereof
The invention provides a microphone circuit. In one embodiment, the microphone circuit comprises a microphone, a self-biased amplifier with a finite gain, and a feedback capacitor. The microphone coupled between a ground and a first node generates a first voltage at the first node according to sound pressure. The self-biased amplifier has a positive input terminal coupled to the ground and a negative input terminal coupled to the first node and amplifies the first voltage according to the finite gain to generate a second voltage at a second node. The feedback capacitor coupled between the first node and the second node feeds back the second voltage to the first node. The second voltage is then output to a following module subsequent to the microphone circuit.
Owner:FORTEMEDIA
Piezoelectric transducer signal processing circuit
ActiveUS7622845B2Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsCharge amplifiersDetector circuitsAudio power amplifier
A piezoelectric detector circuit has at least one input line, a piezoelectric transducer in the input line, an amplifier receiving signals on the input line and generating an output, and one or two feedback elements through which the output is sent back to the input line. The circuit may be a discrete time sampled operational amplifier (DTOA) based transconductance or “voltage output mode” circuit. In one embodiment, protection elements are associated with amplifier input lines to establish a reference voltage.
Owner:SUREN SYST
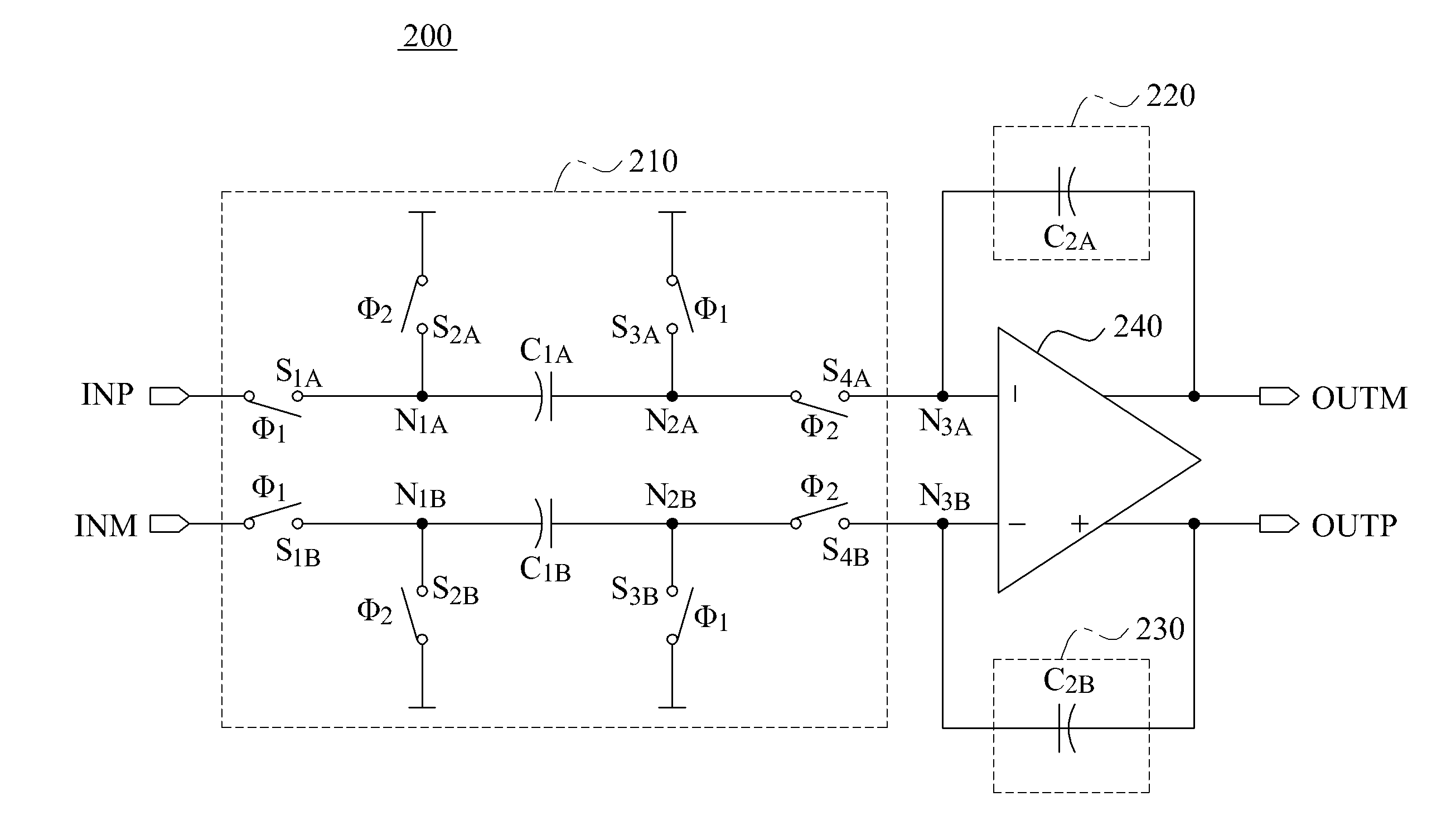
Switched capacitor circuit
ActiveUS20120229204A1Reduce areaReduce power consumptionCharge amplifiersSwitched capacitor networksCapacitanceEngineering
According to the present invention, a switched capacitor circuit comprises: an inverting amplifier for removing the offset by using a chopper stabilization circuit; a sampling unit which is connected between an input terminal and the inverting amplifier; and a feedback unit which is connected to the inverting amplifier in parallel.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
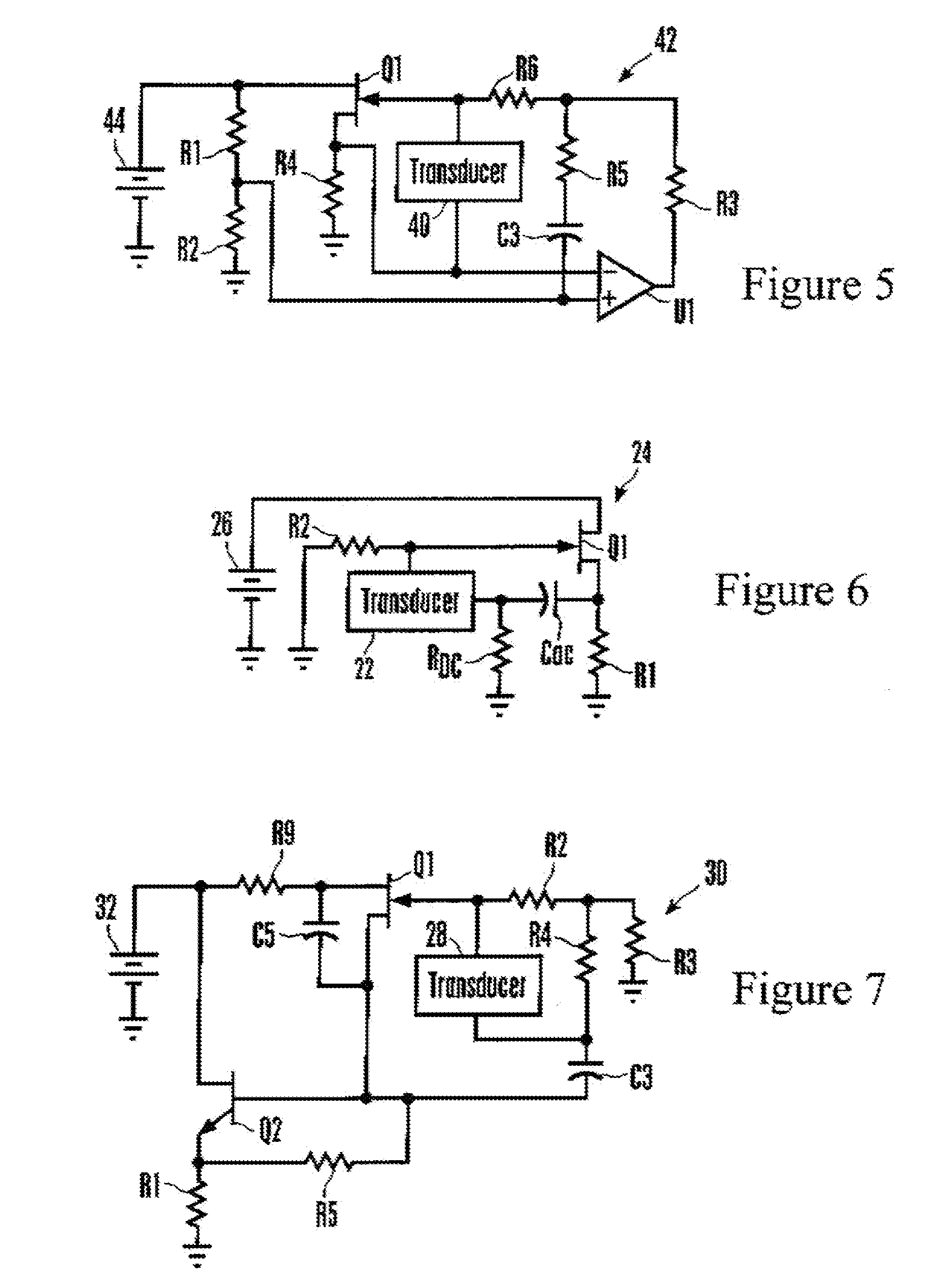
Transconductance circuit for piezoelectric transducer
ActiveUS7352107B2Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMotion detectorAudio power amplifier
A transconductance monitoring and amplifying circuit for a piezoelectric transducer that may be used in, e.g., a motion detector system includes a FET, with the transducer (and, hence, the signal voltage reference) floating between the gate and source of the FET, as opposed to being connected to the common ground of the circuit. This permits the development of a larger detector signal and concomitantly the use of a relatively inexpensive FET instead of a relatively more expensive high impedance operational amplifier as must be used in conventional transconductance circuits. The FET and transducer can be held in a single four-pin package. A discrete time sampled operational amplifier may also be used.
Owner:SUREN SYST
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com