Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
757 results about "Glitch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A glitch is a short-lived fault in a system, such as a transient fault that corrects itself, making it difficult to troubleshoot. The term is particularly common in the computing and electronics industries, in circuit bending, as well as among players of video games. More generally, all types of systems including human organizations and nature experience glitches.
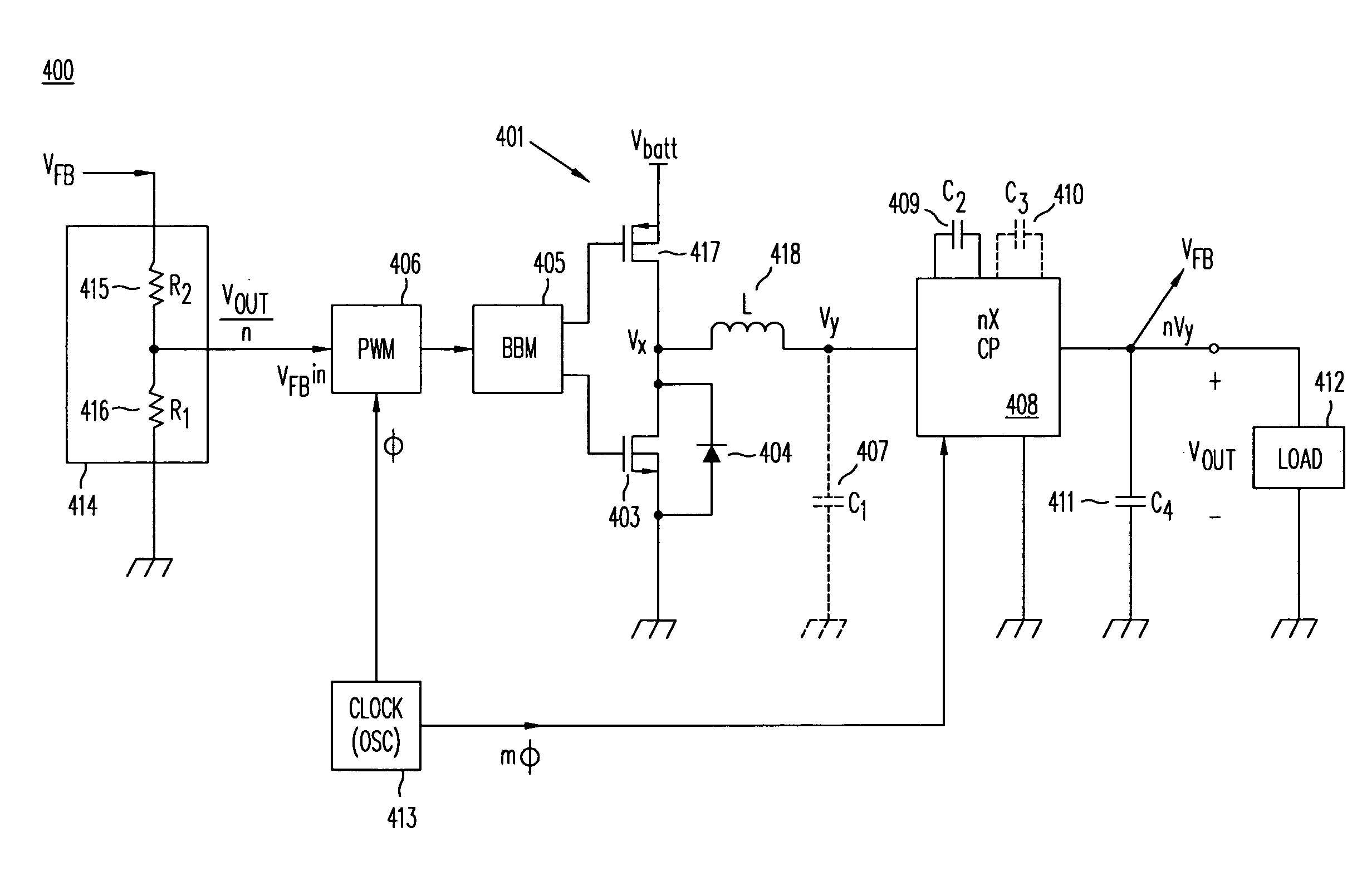
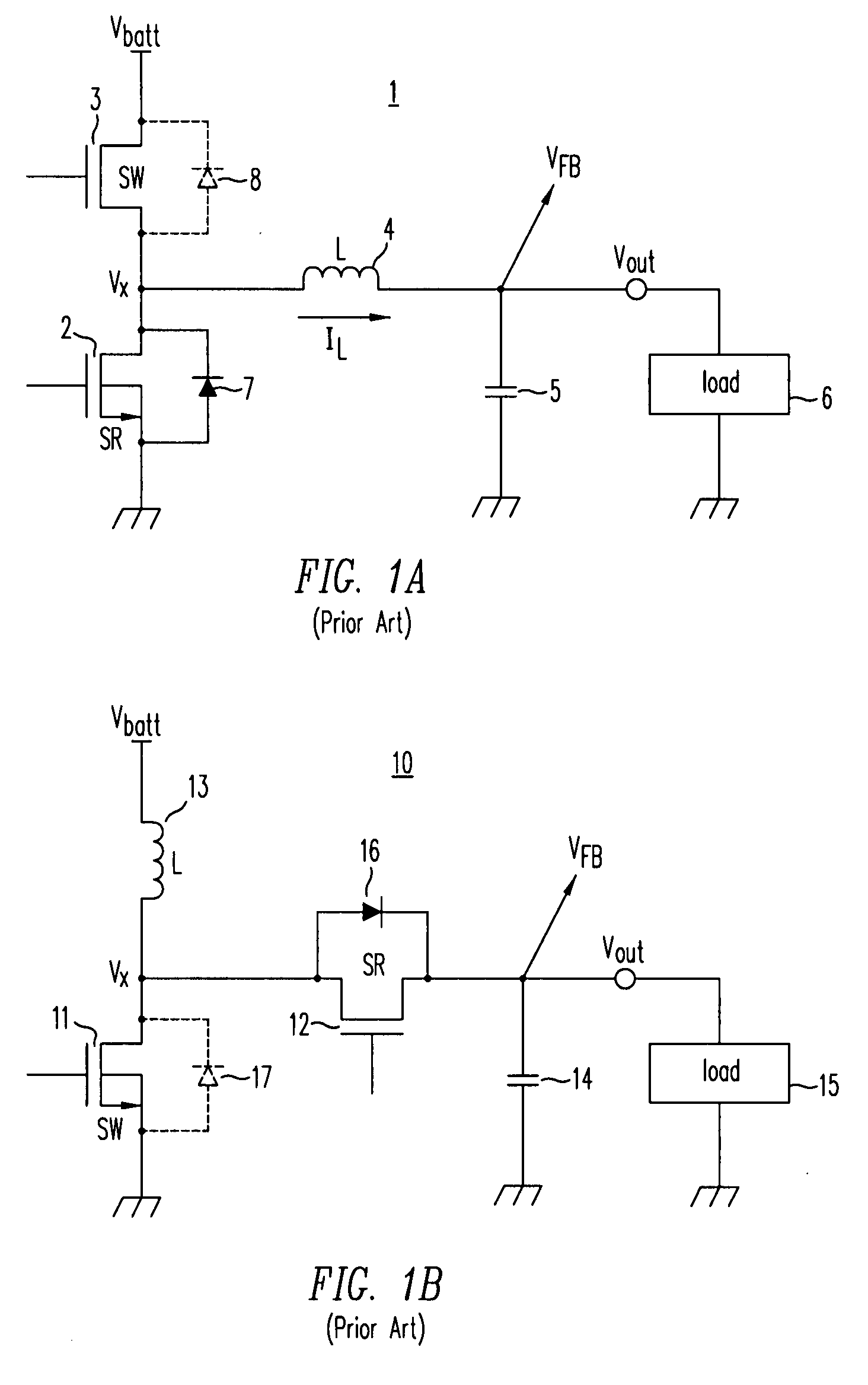
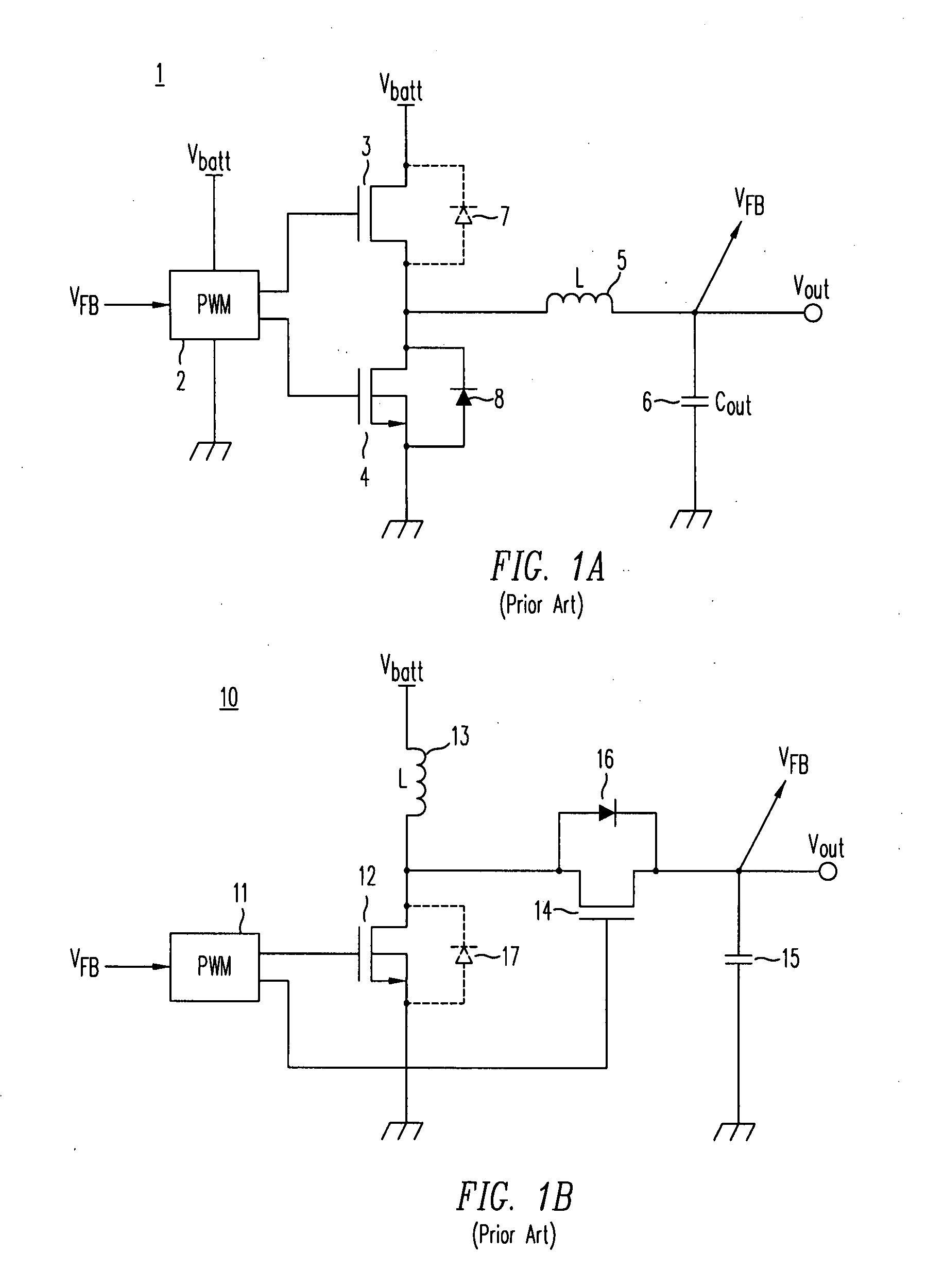
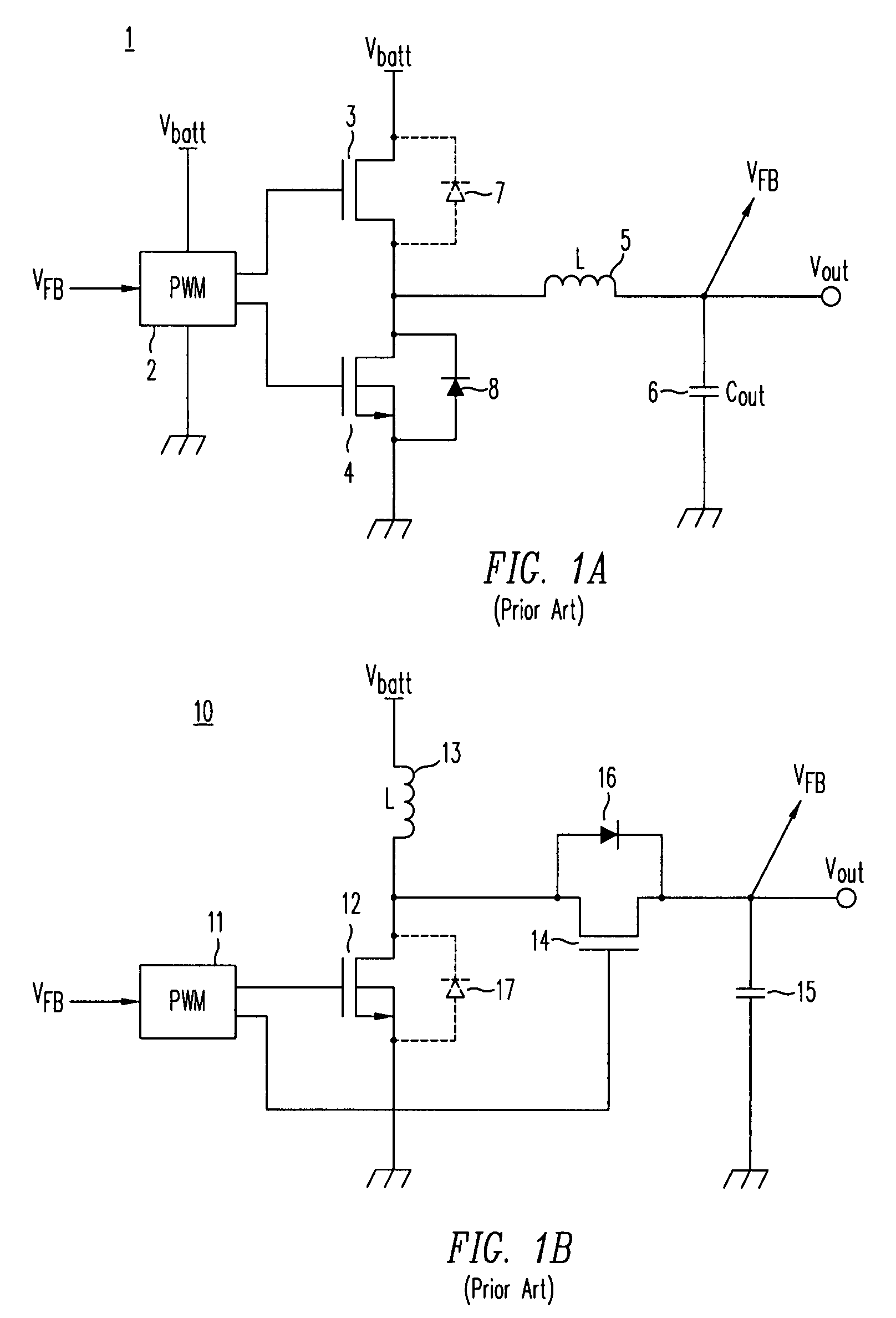
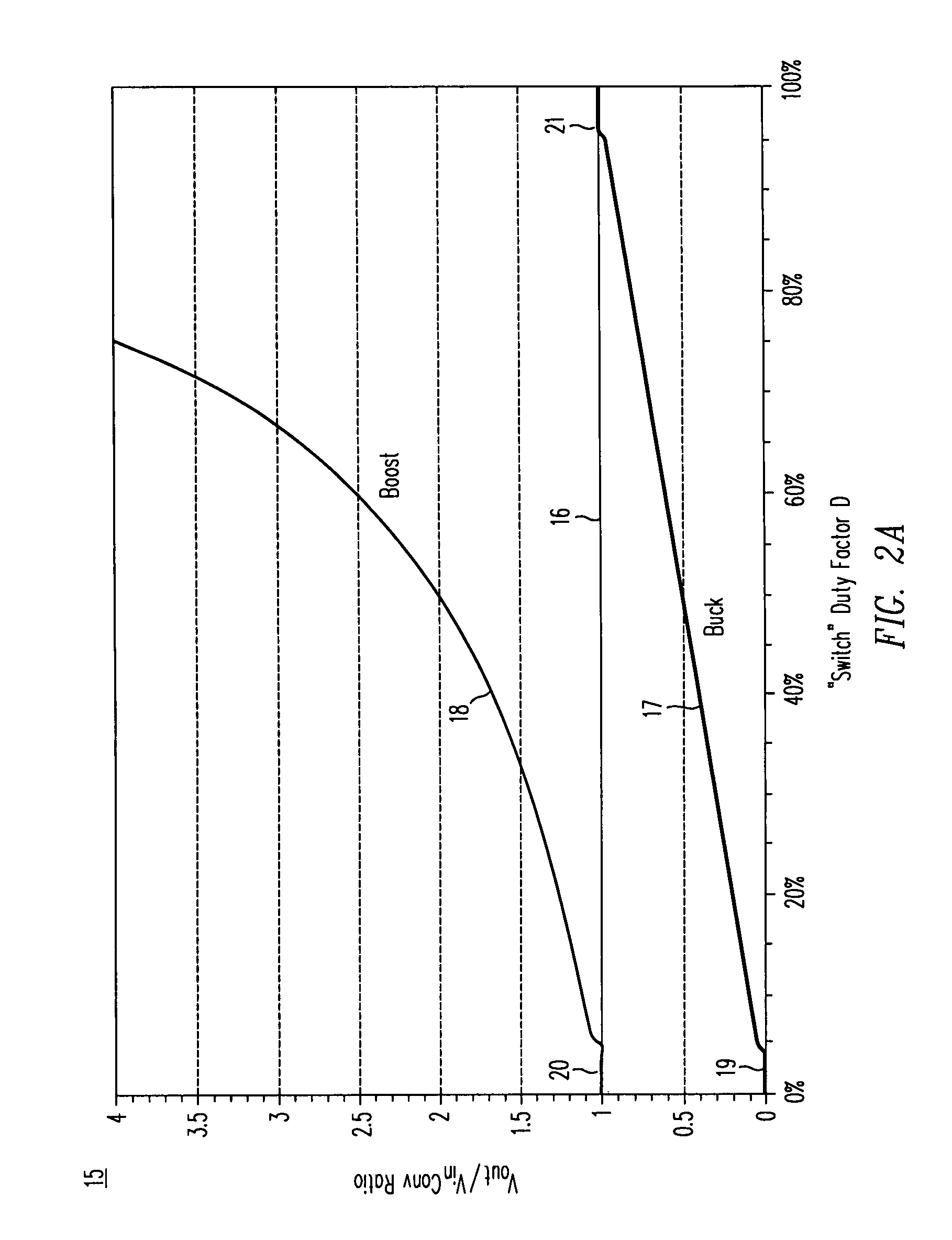
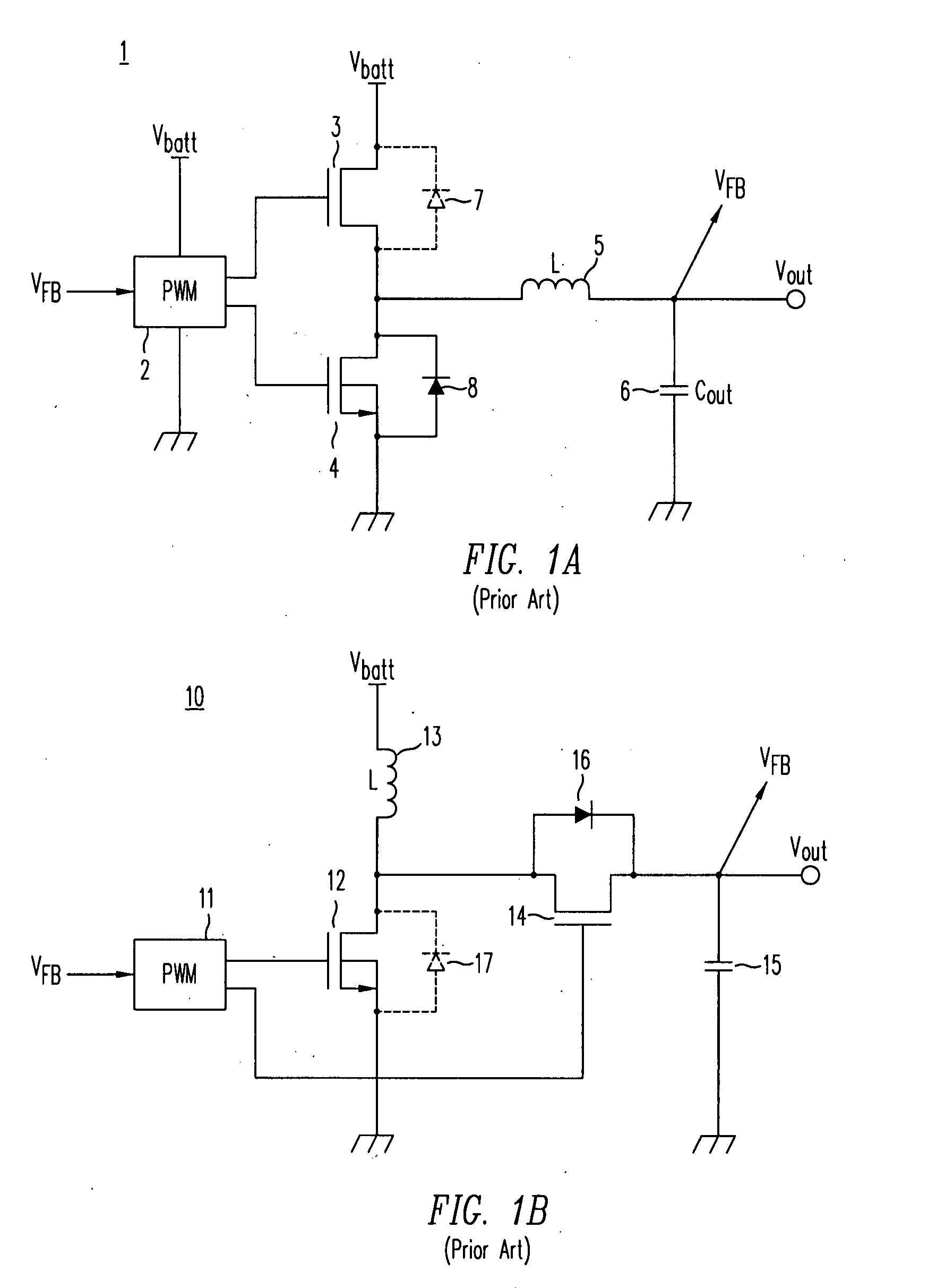
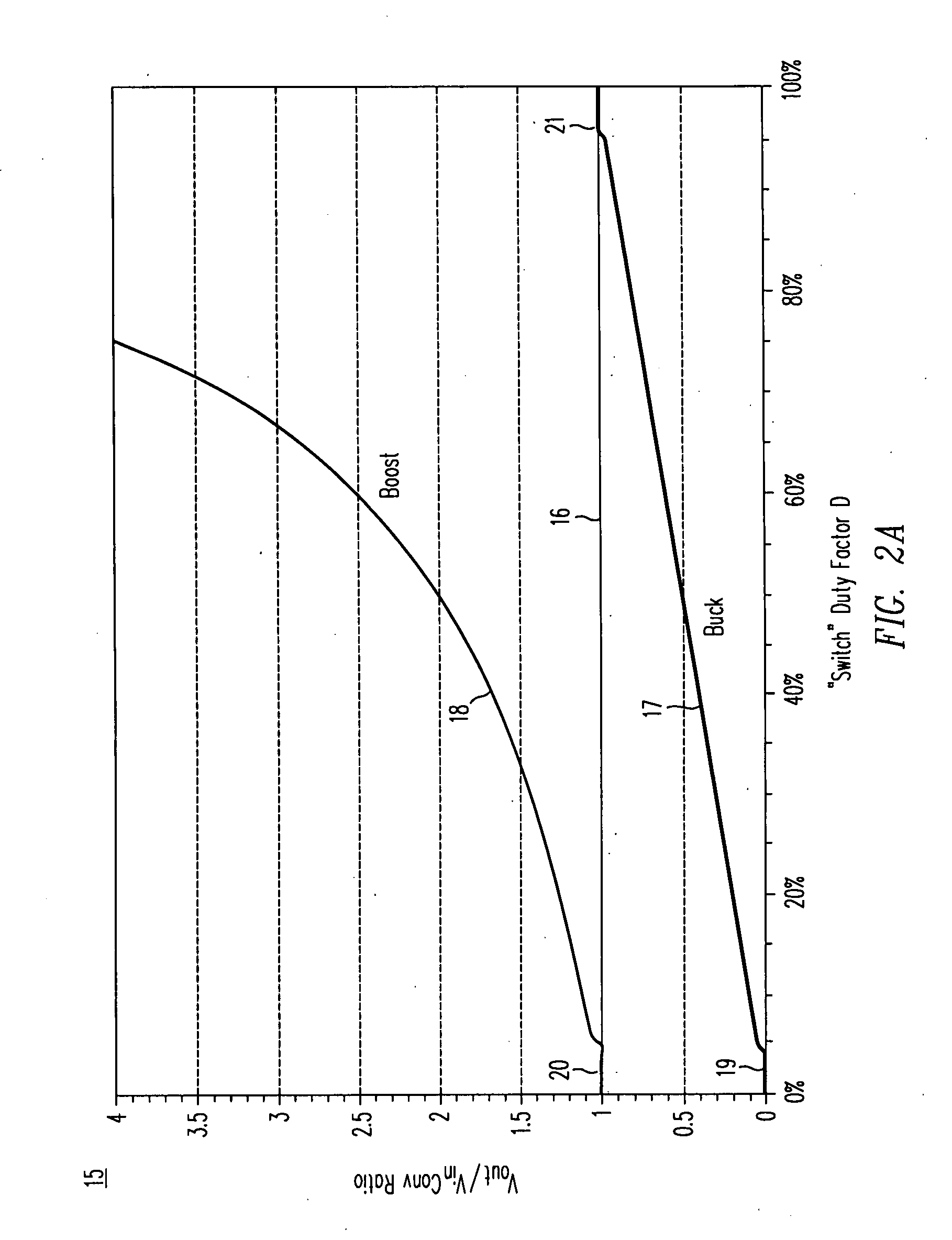
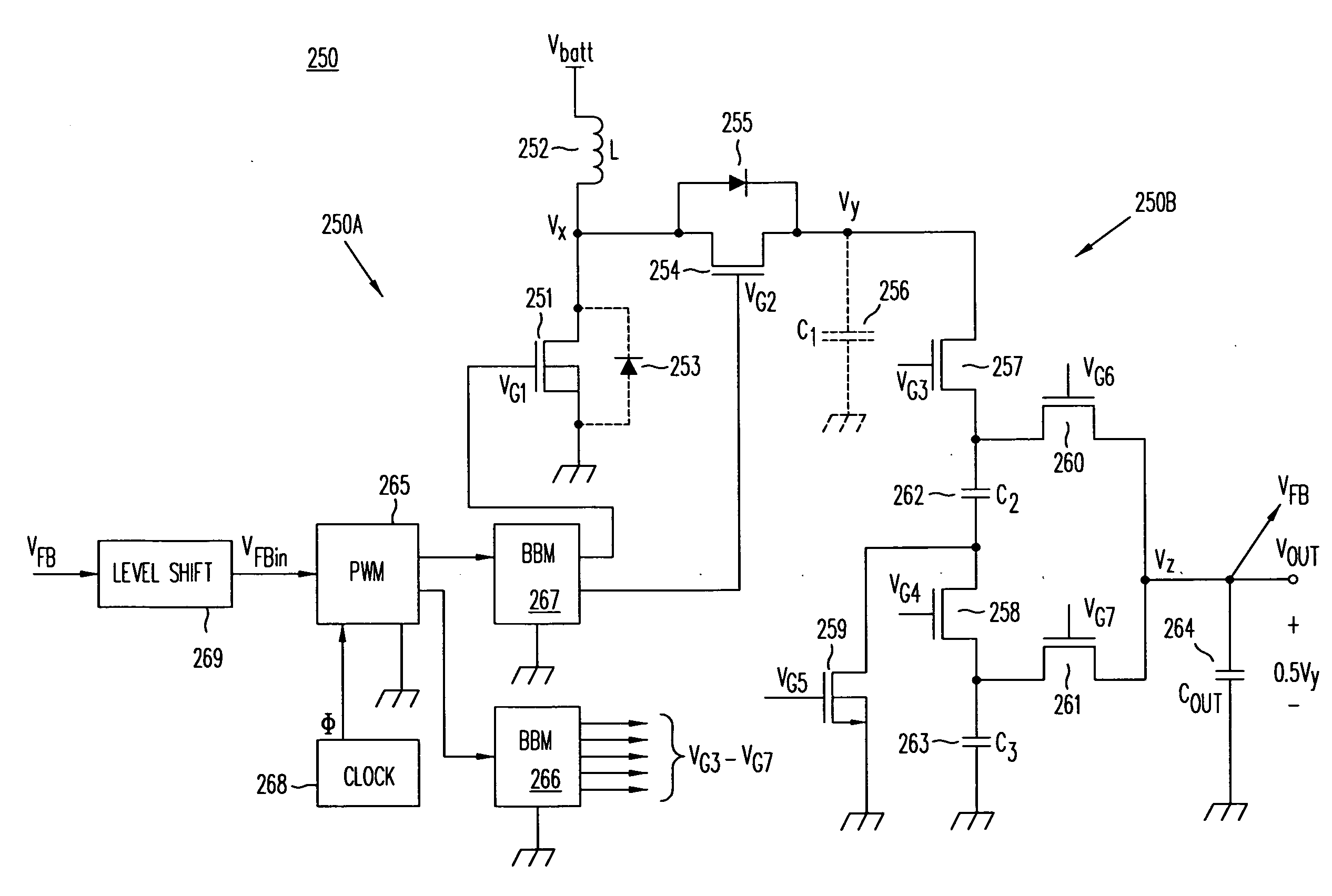
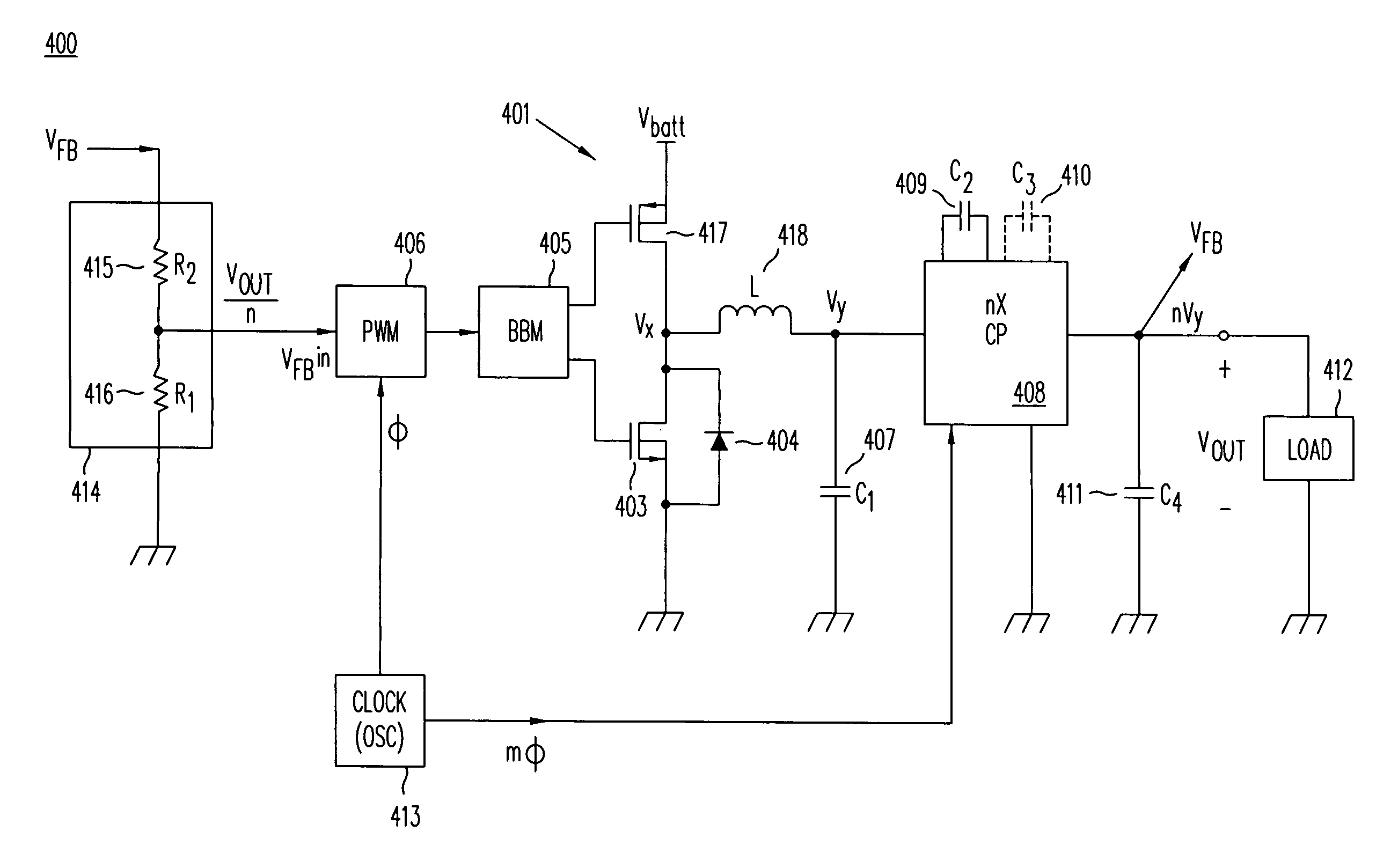
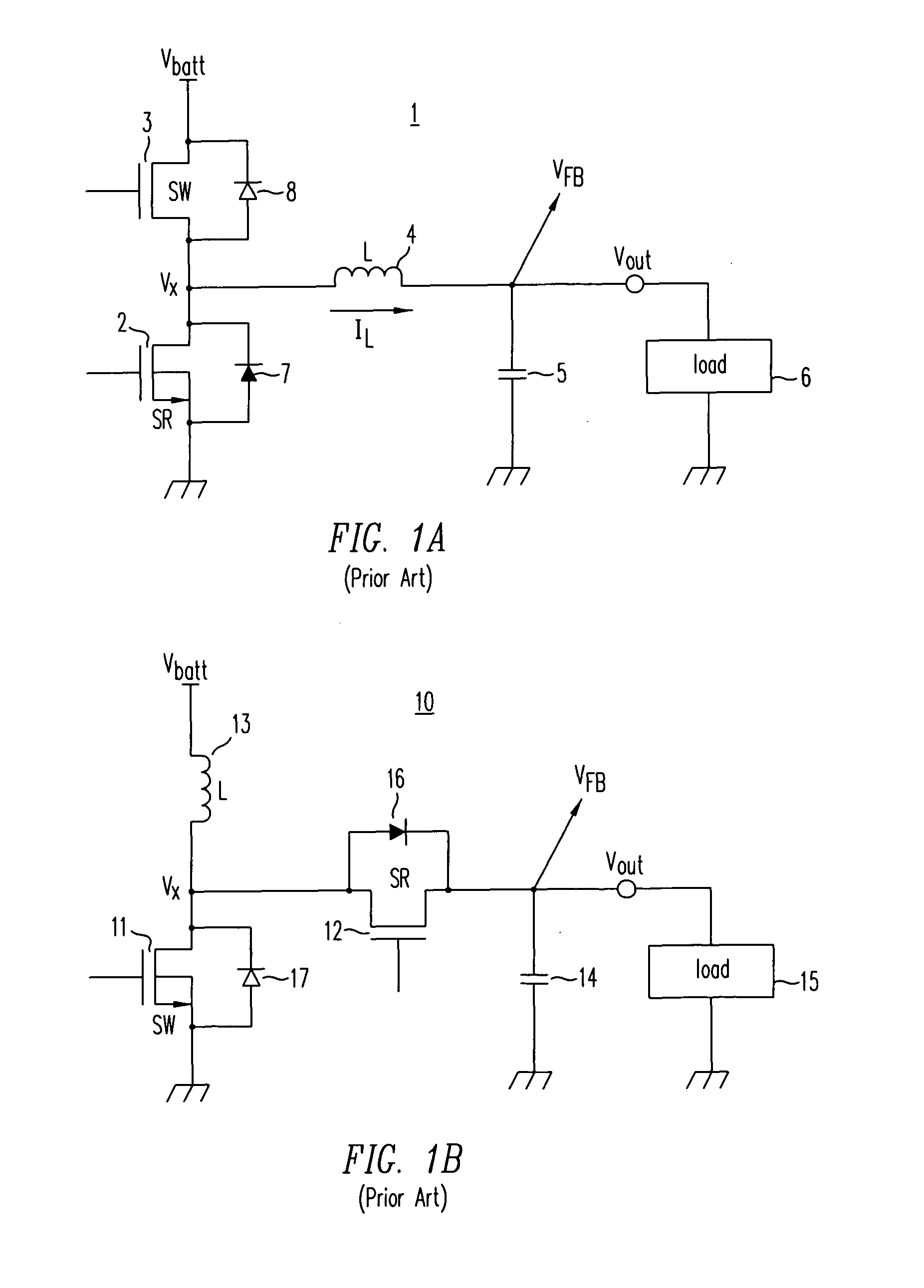
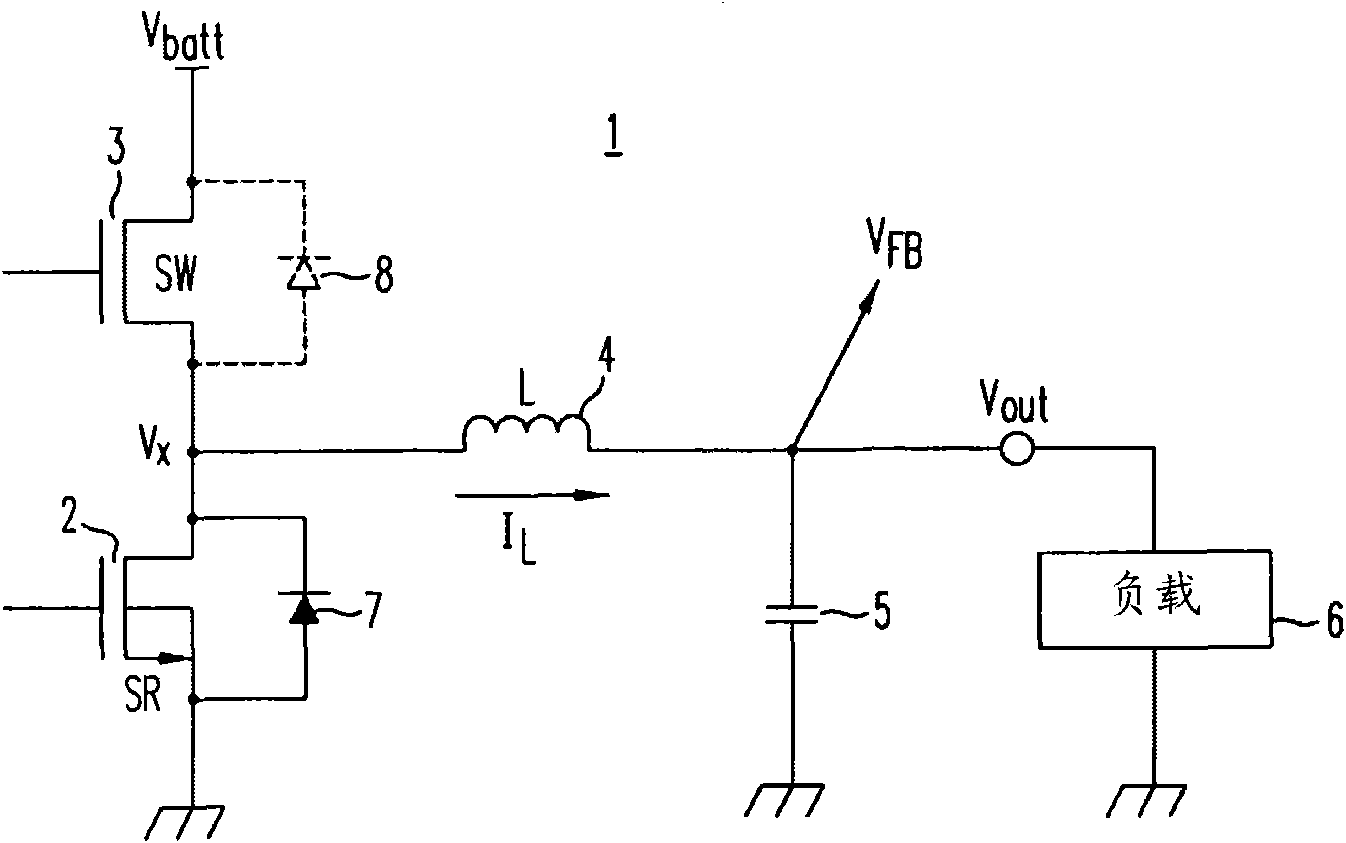
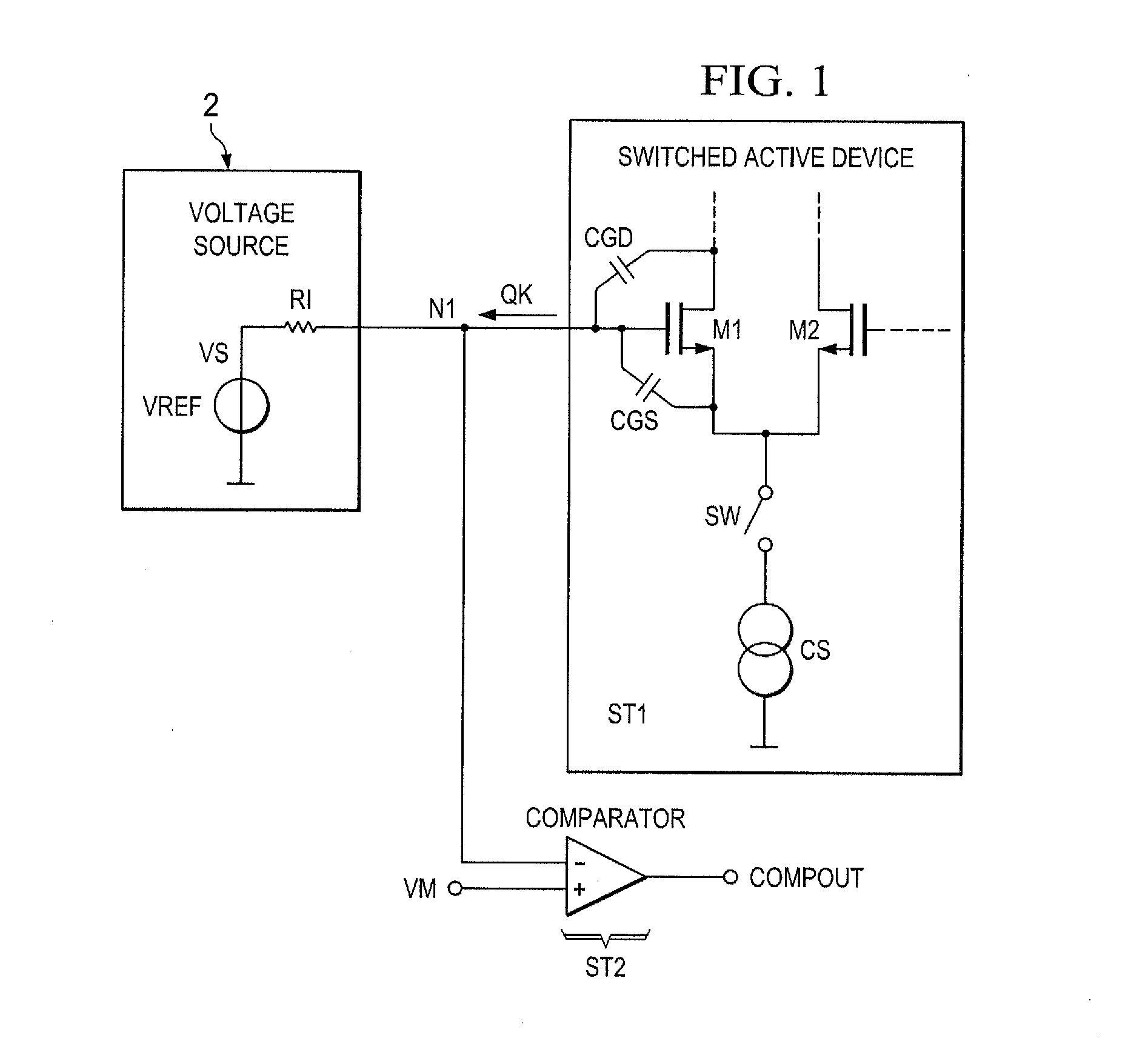
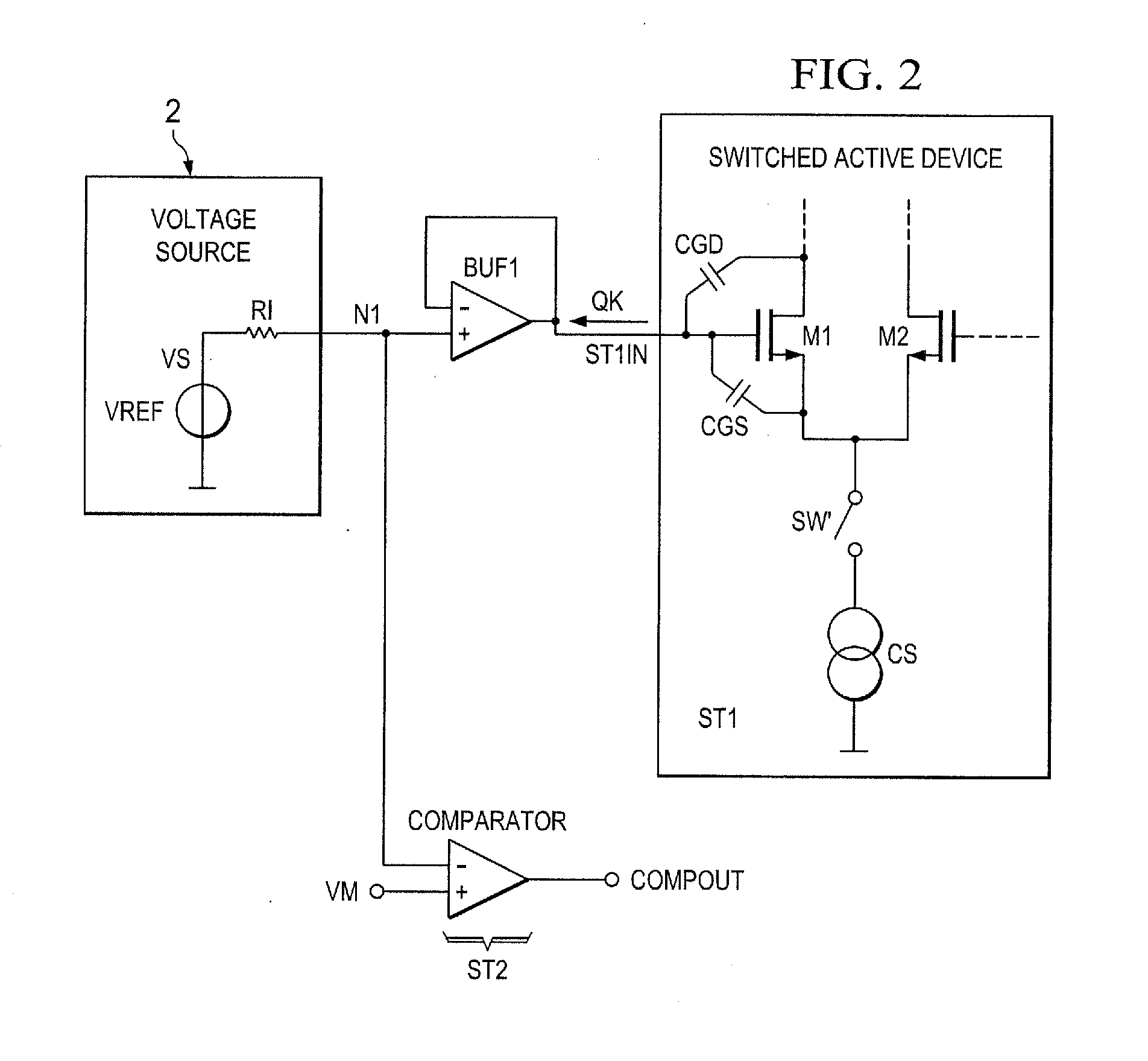
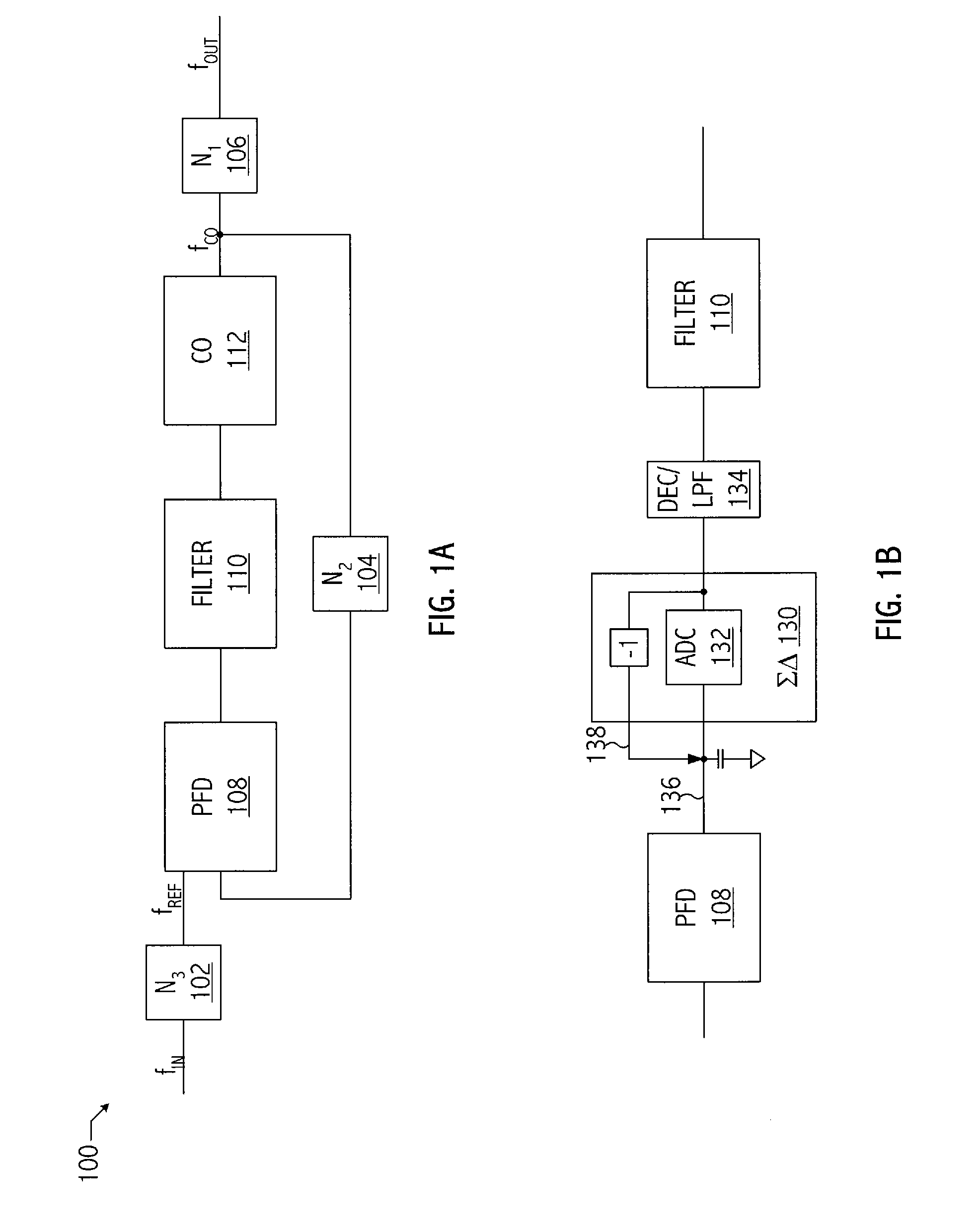
High-efficiency DC/DC voltage converter including down inductive switching pre-regulator and capacitive switching post-converter
ActiveUS20080158915A1Poor regulationAvoid problemsEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceBuck converter
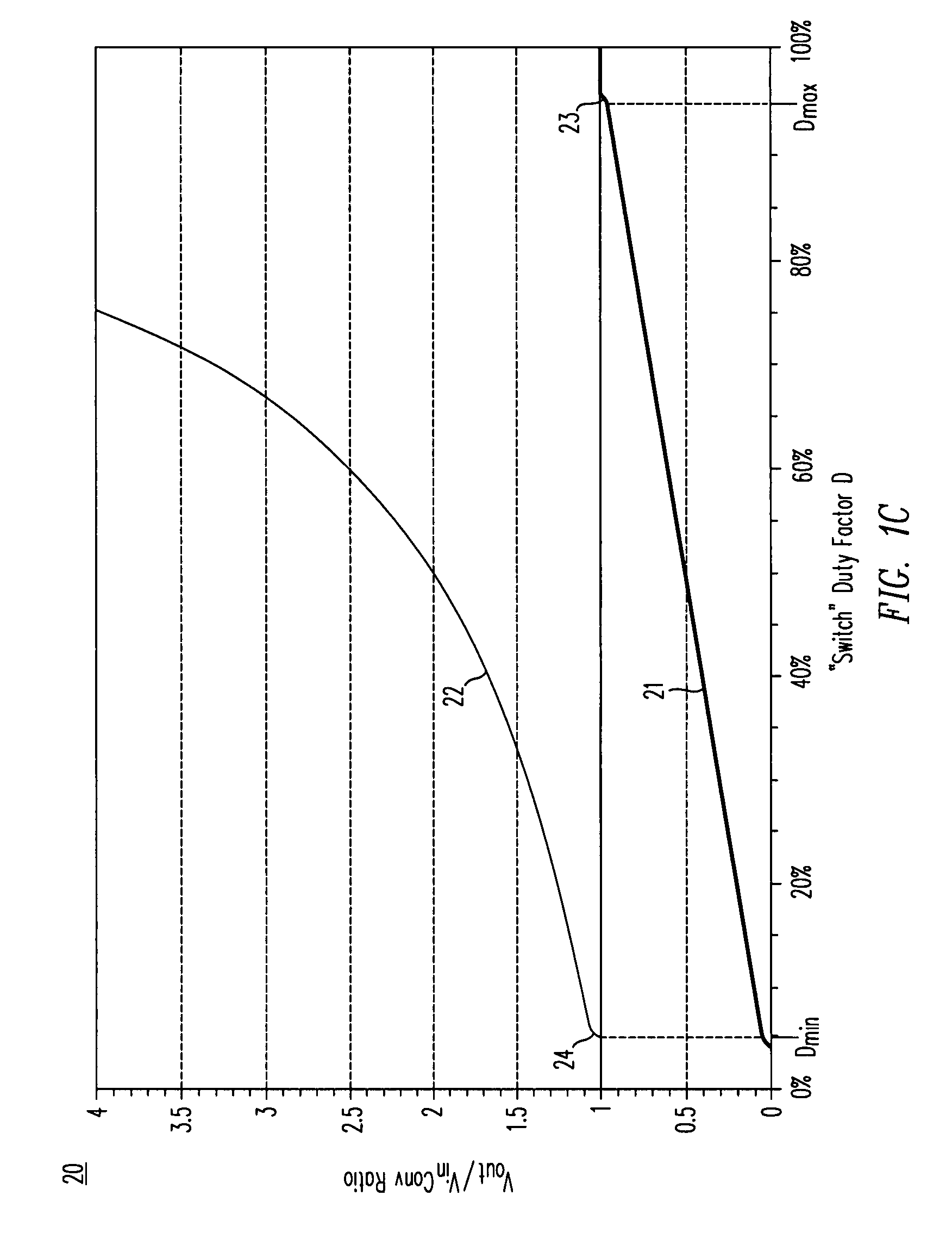
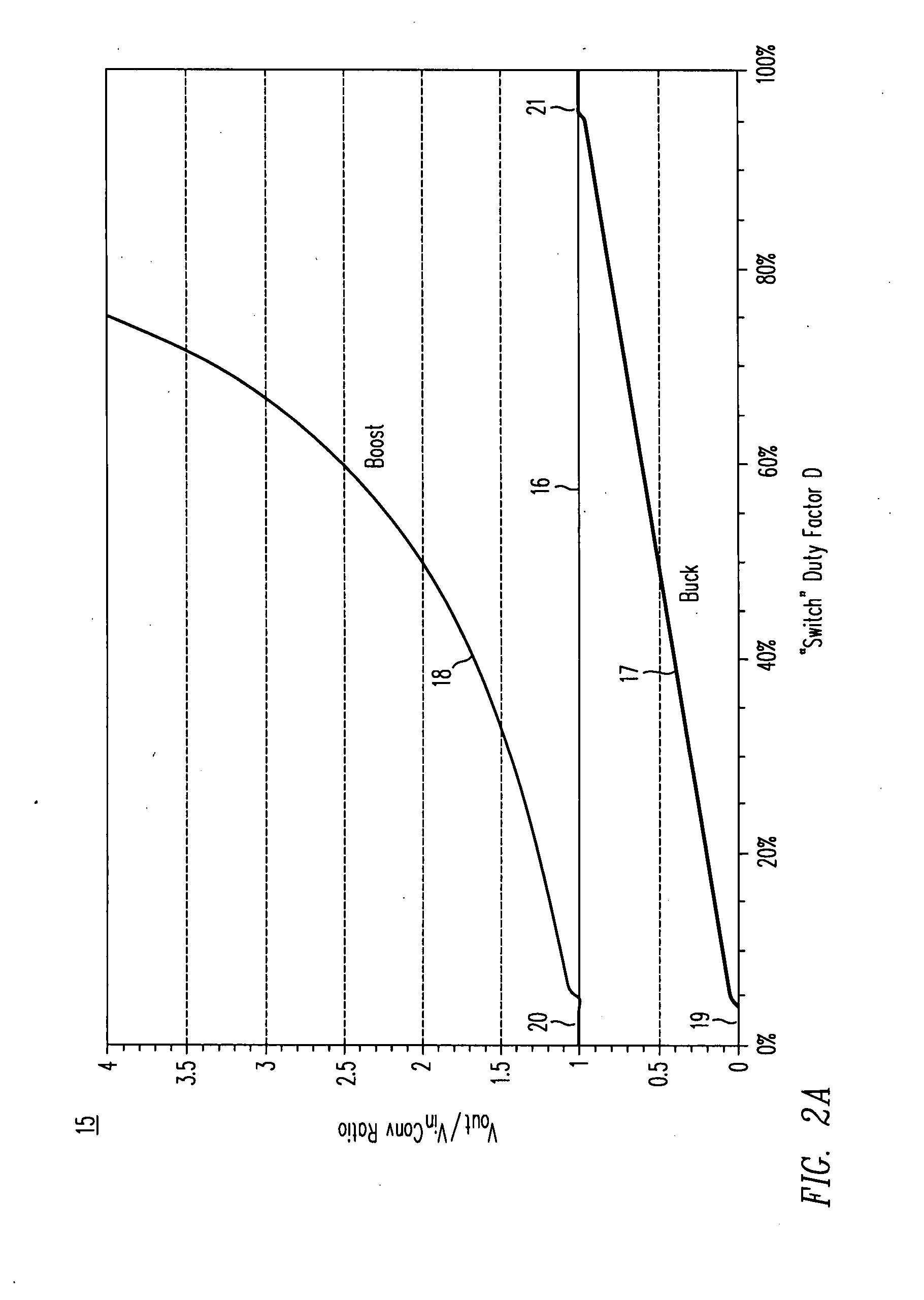
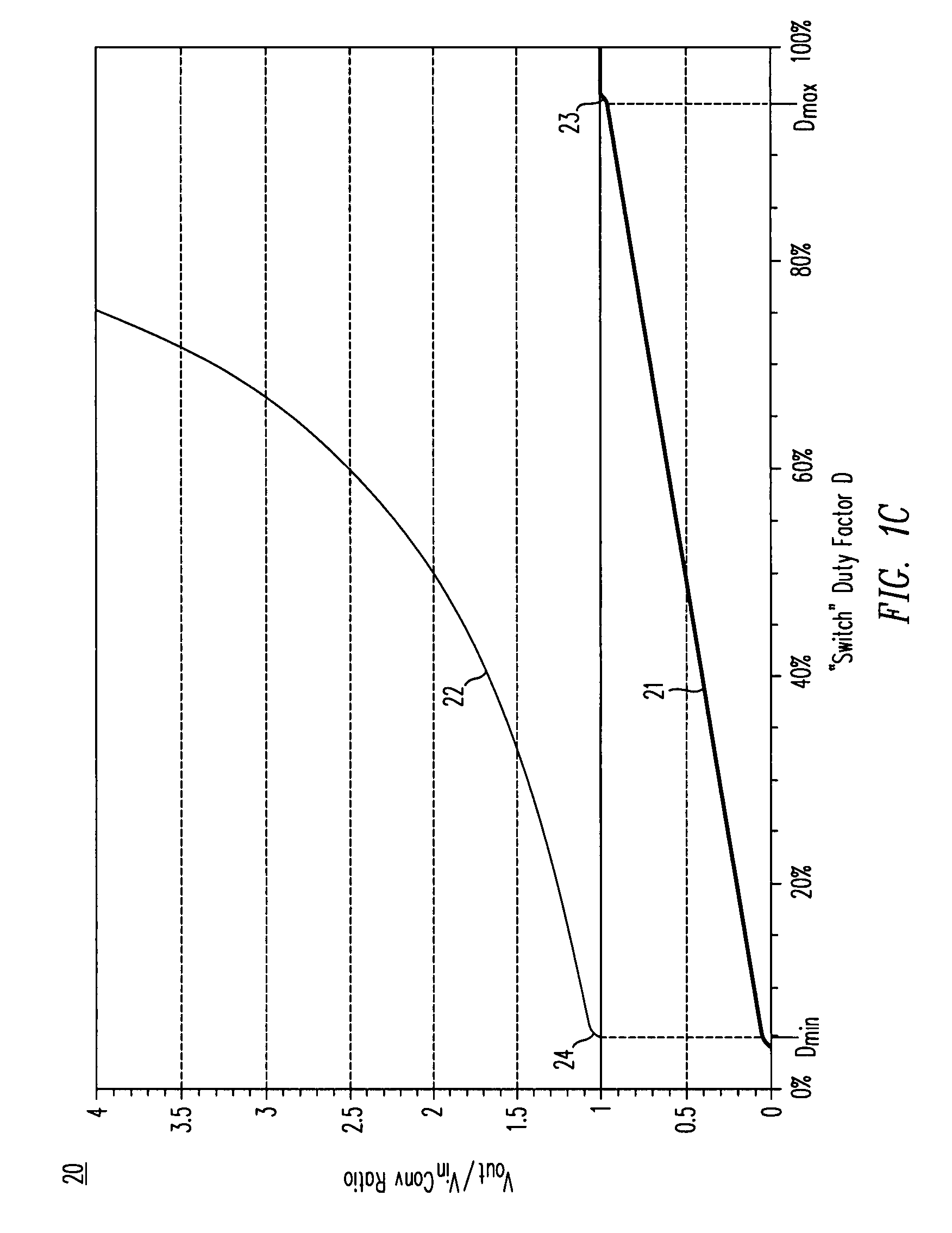
A DC / DC converter includes a pre-regulator stage, which may include a Buck converter, and a post-converter stage, which may include a charge pump. The duty factor of the pre-regulator stage is controlled by a feedback path that extends from the output terminal of the pre-regulator stage or the post-converter stage. The pre-regulator steps the input DC voltage down by a variable amount depending on the duty factor, and the post-converter steps the voltage at the output of the pre-regulator up or down by an positive or negative integral or fractional value. The converter overcomes the problems of noise glitches, poor regulation, and instability, even near unity input-to-output voltage conversion ratios.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
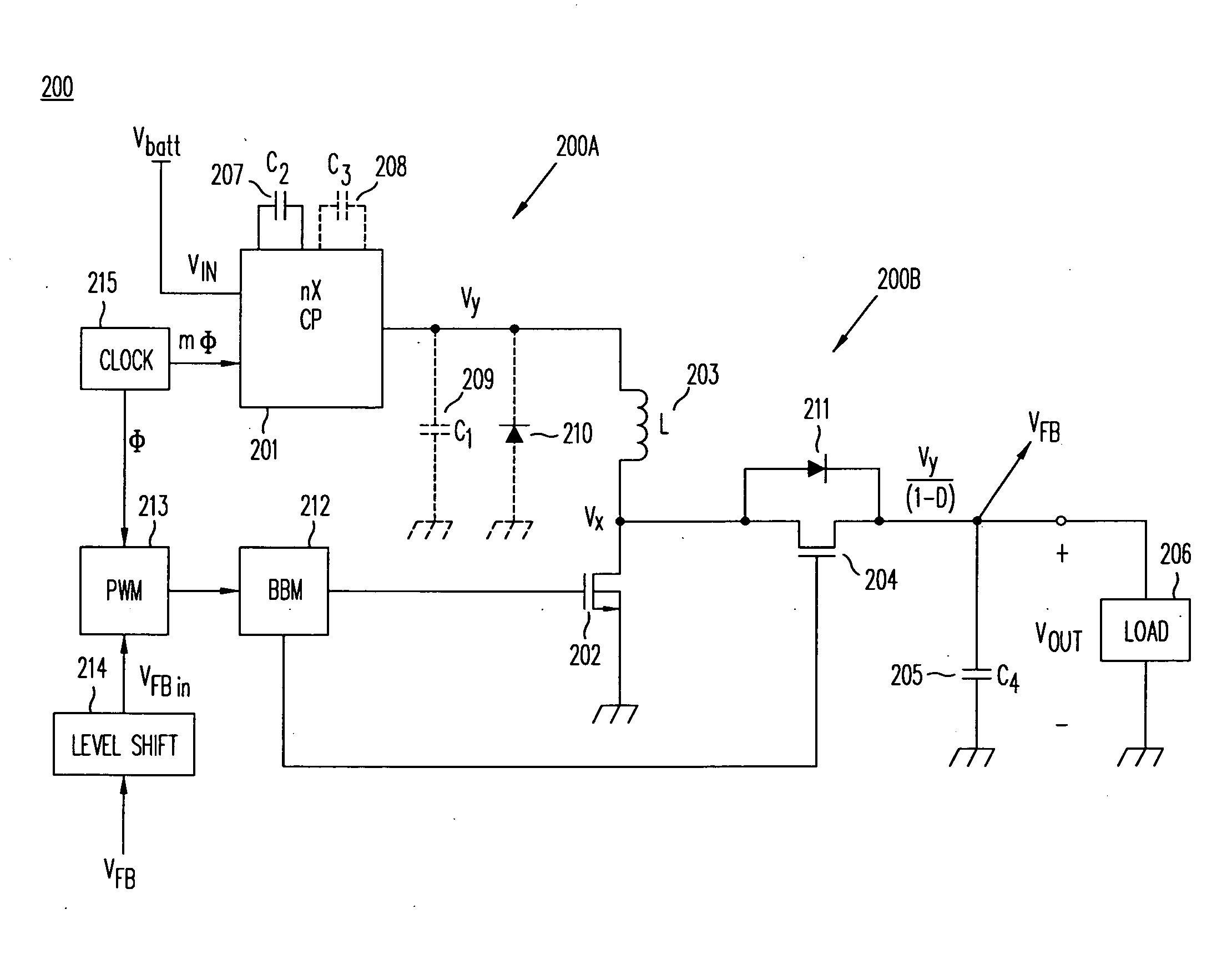
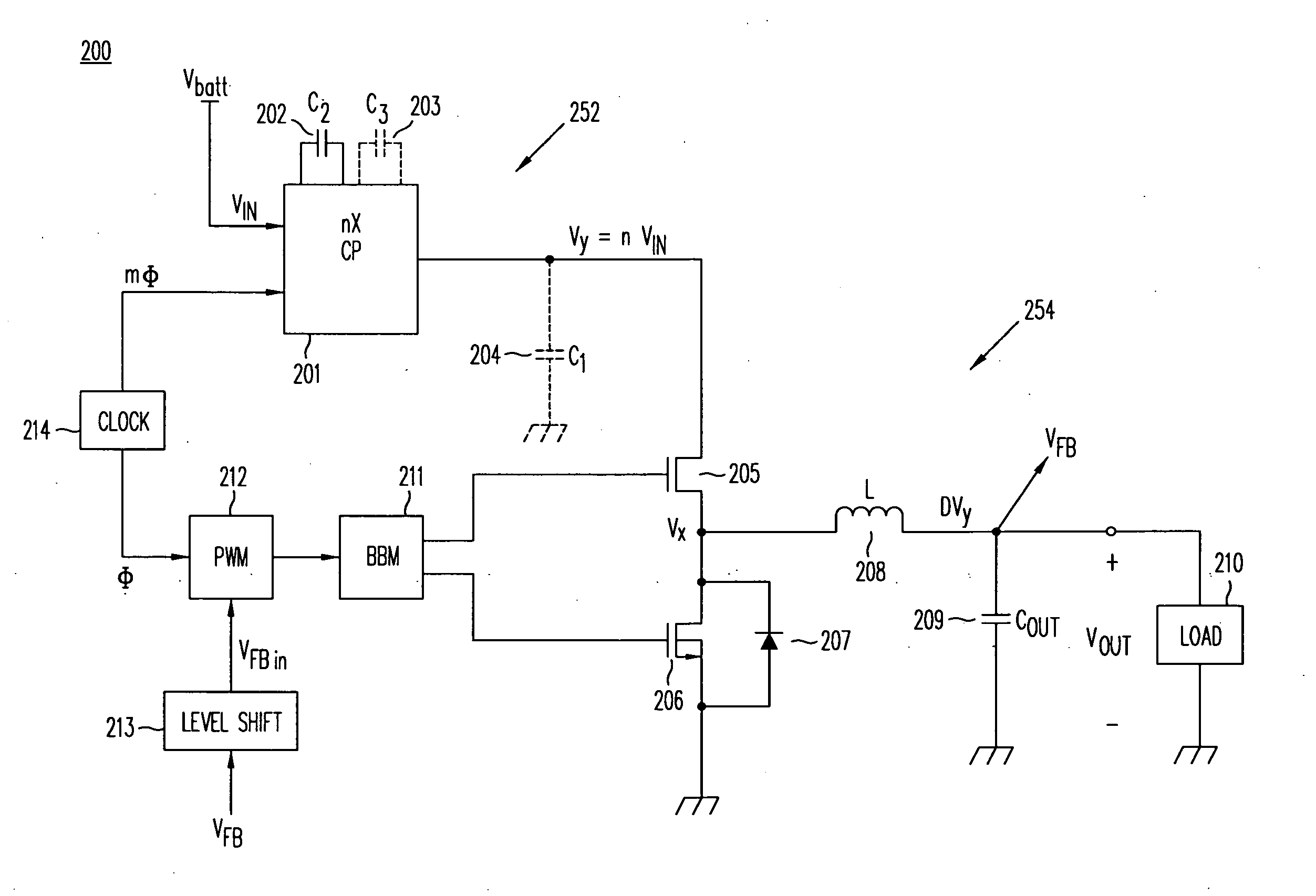
High-efficiency DC/DC voltage converter including capacitive switching pre-converter and up inductive switching post-regulator
ActiveUS20080157732A1Avoid problemsEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionInstabilityGlitch
A DC / DC converter includes a pre-converter stage, which may include a charge pump, and a post-regulator stage, which may include a boost converter. The duty factor of the post-regulator stage is controlled by a feedback path that extends from the output terminal of the DC / DC converter to an input terminal in the post-regulator stage. The pre-converter steps the input DC voltage up or down by a positive or negative integral or fractional value, and the post-regulator steps the voltage up by a variable amount depending on the duty factor at which the post-regulator is driven. The converter overcomes the problems of noise glitches, poor regulation, and instability, even near unity input-to-output voltage conversion ratios.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
High-efficiency DC/DC voltage converter including capacitive switching pre-converter and down inductive switching post-regulator
ActiveUS7777459B2Efficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionInstabilityInductance
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
High-efficiency DC/DC voltage converter including capacitive switching pre-converter and down inductive switching post-regulator
A DC / DC converter includes a pre-converter stage, which may include a charge pump, and a post-regulator stage, which may include a Buck converter. The duty factor of the post-regulator stage is controlled by a feedback path that extends from the output terminal of the DC / DC converter to an input terminal in the post-regulator stage. The pre-converter steps the input DC voltage up or down by a positive or negative integral or fractional value, and the post-regulator steps the voltage down by a variable amount depending on the duty factor at which the post-regulator is driven. The converter overcomes the problems of noise glitches, poor regulation, and instability, even near unity input-to-output voltage conversion ratios.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
System, method and computer program product for handling small aggressors in signal integrity analysis
ActiveUS7562323B1Computation using non-denominational number representationComputer aided designCapacitanceSignal integrity analysis
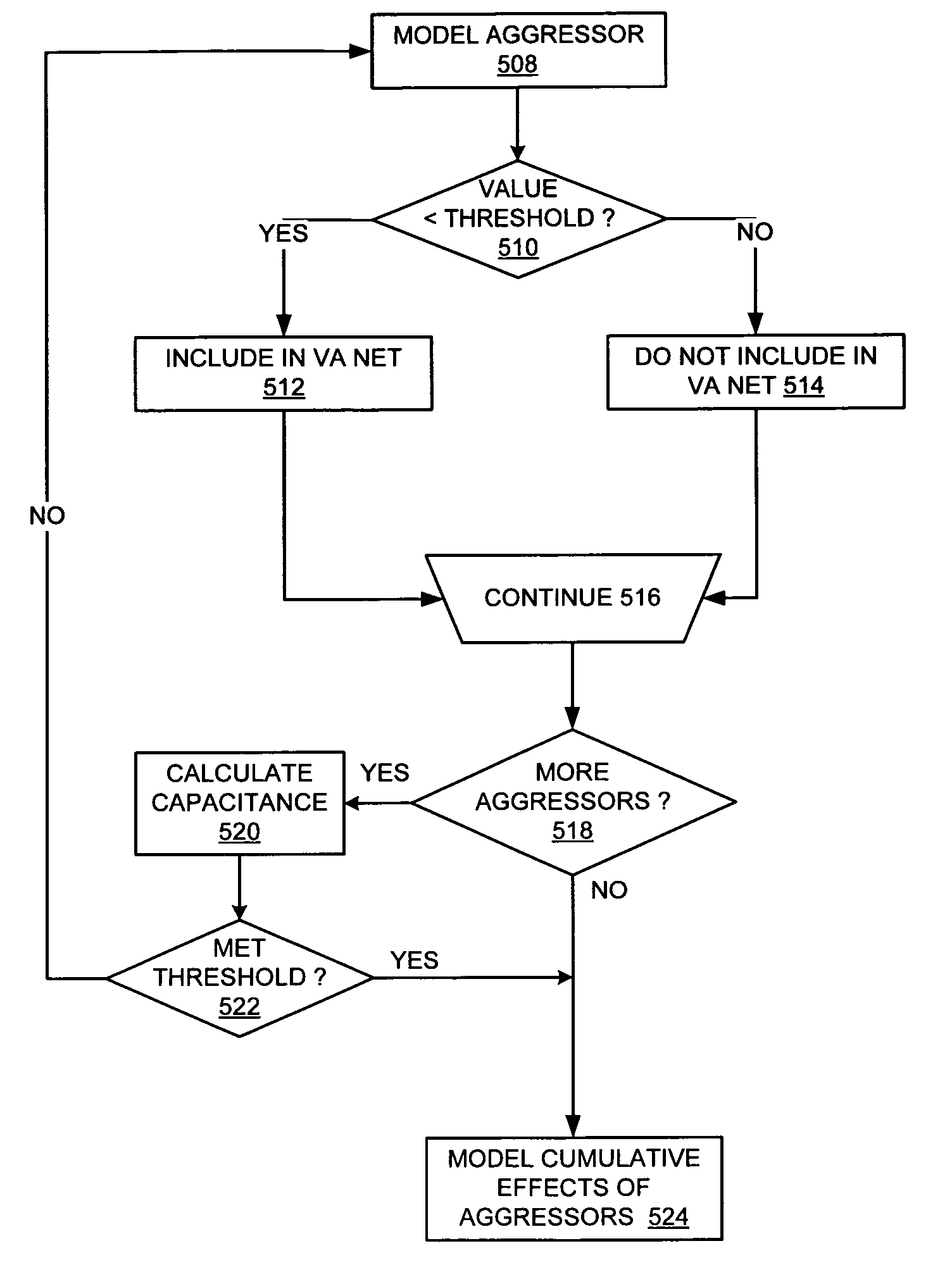
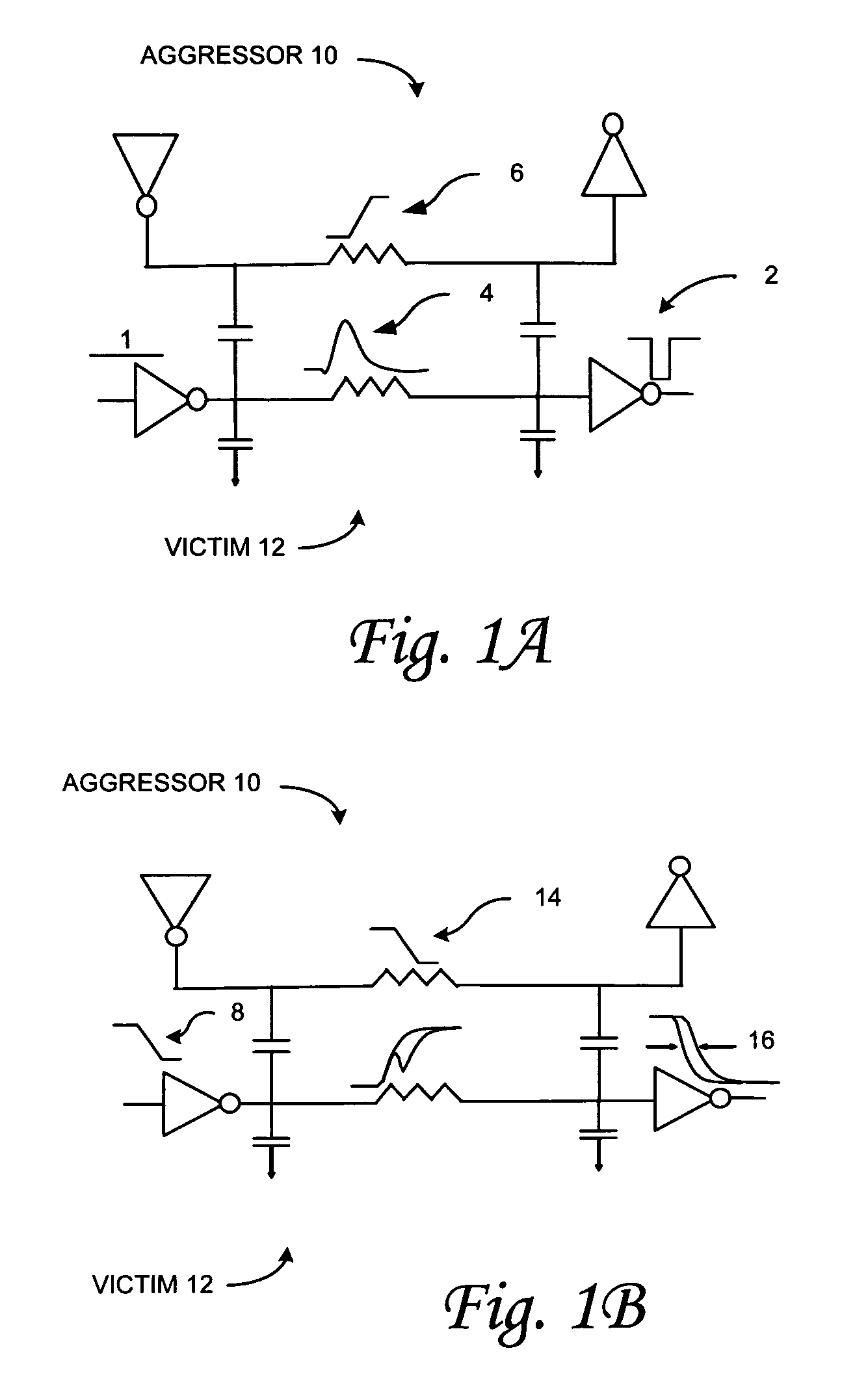
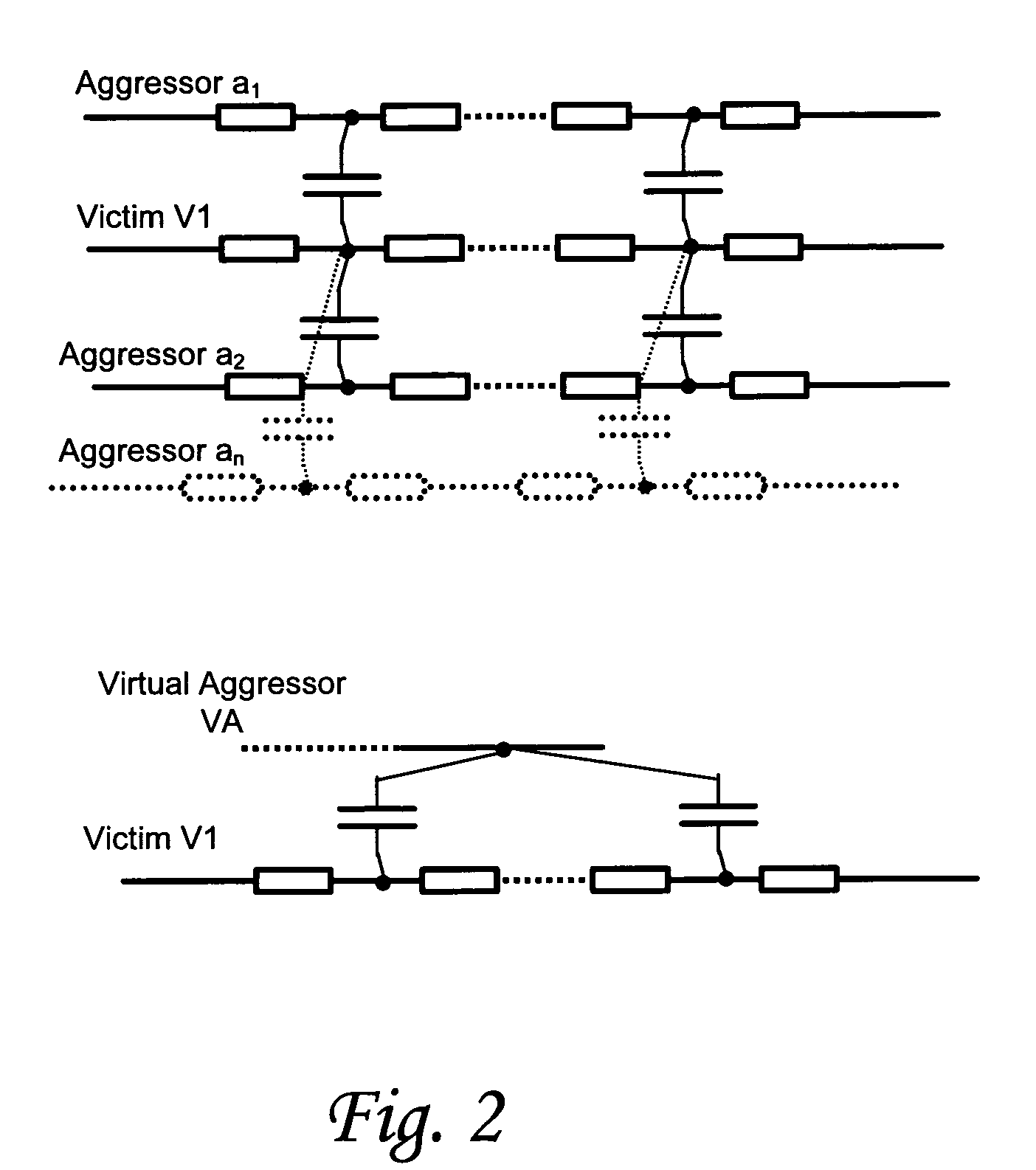
A method, system and computer program product for determining aggressor-induced crosstalk in a victim net of a stage of an integrated circuit design is provided. The methodology can include combining a plurality of aggressor nets to construct a virtual aggressor net, determining a current waveform induced on the victim net by the plurality of small aggressor nets, and modeling a current waveform induced by the virtual aggressor on the victim net based on the contribution of the current waveforms determined for the plurality of small aggressor nets. In a further embodiment, the methodology can also comprise evaluating an effect of an aggressor net on a victim net; and including that aggressor net in the virtual aggressor net if its effect is below a predetermined threshold. The effect evaluated by the methodology can, for example, be the height of a glitch induced on the victim net by a transition in the aggressor net. Additionally, the aggressor net can be included in the virtual aggressor net if the height of the glitch it induces on the victim net is less than a predetermined factor of the supply voltage. Switching probability can be used to compute a 3-sigma capacitance value, and this value can be used to limit the number of small aggressors included in the virtual aggressor net. The combined currents of the aggressor in the virtual aggressor net can be modeled using a piece-wise linear analysis.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
High-efficiency DC/DC voltage converter including up inductive switching pre-regulator and capacitive switching post-converter
ActiveUS20080157733A1Poor regulationIncrease heightEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceTransverter
A DC / DC converter includes a pre-regulator stage, which may include a boost converter, and a post-converter stage, which may include a charge pump. The duty factor of the pre-regulator stage is controlled by a feedback path that extends from the output terminal of the pre-regulator stage or the post-converter stage. The pre-regulator steps the input DC voltage up by a variable amount depending on the duty factor, and the post-converter steps the voltage at the output of the pre-regulator up or down by an positive or negative integral or fractional value. The converter overcomes the problems of noise glitches, poor regulation, and instability, even near unity input-to-output voltage conversion ratios.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
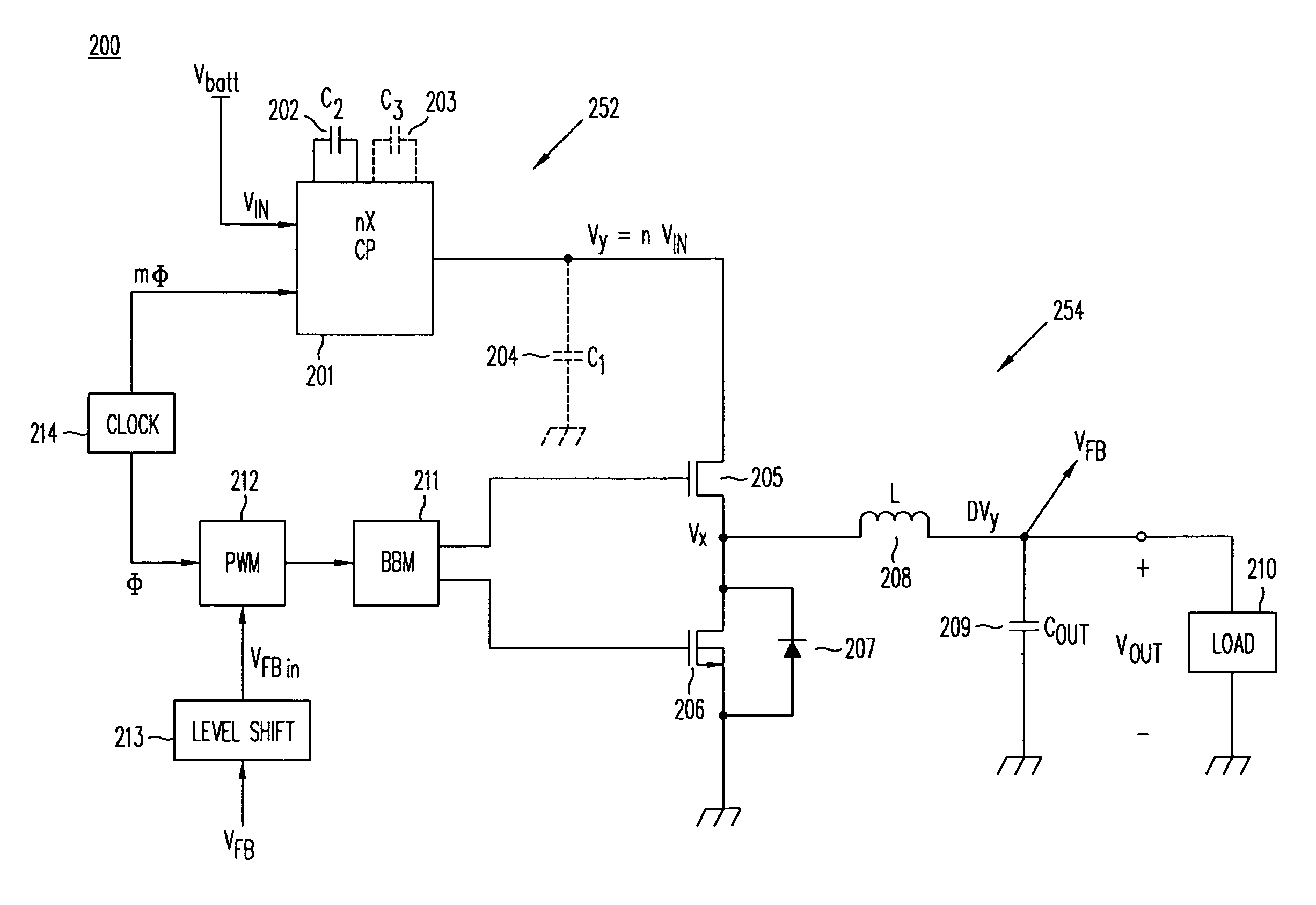
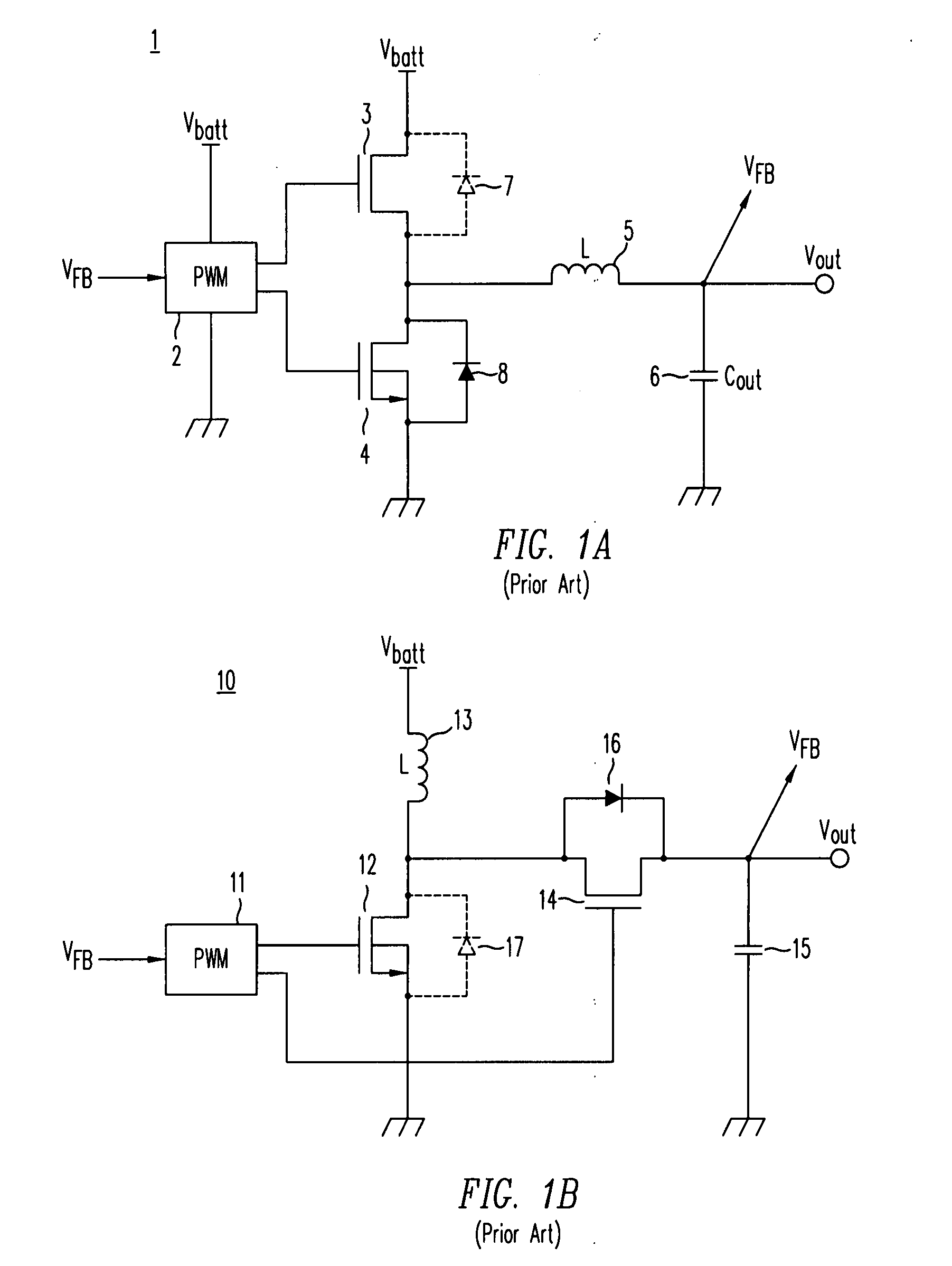
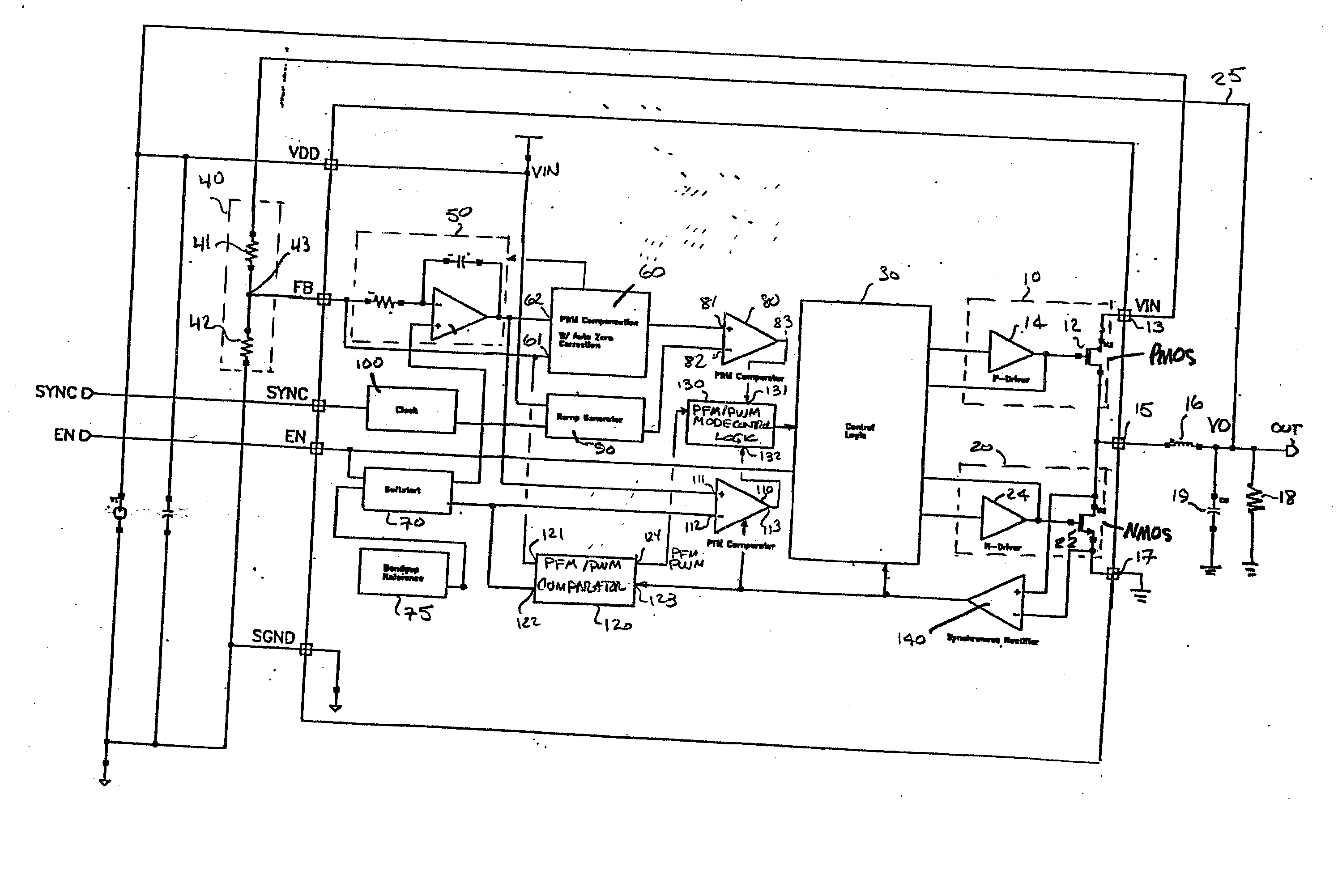
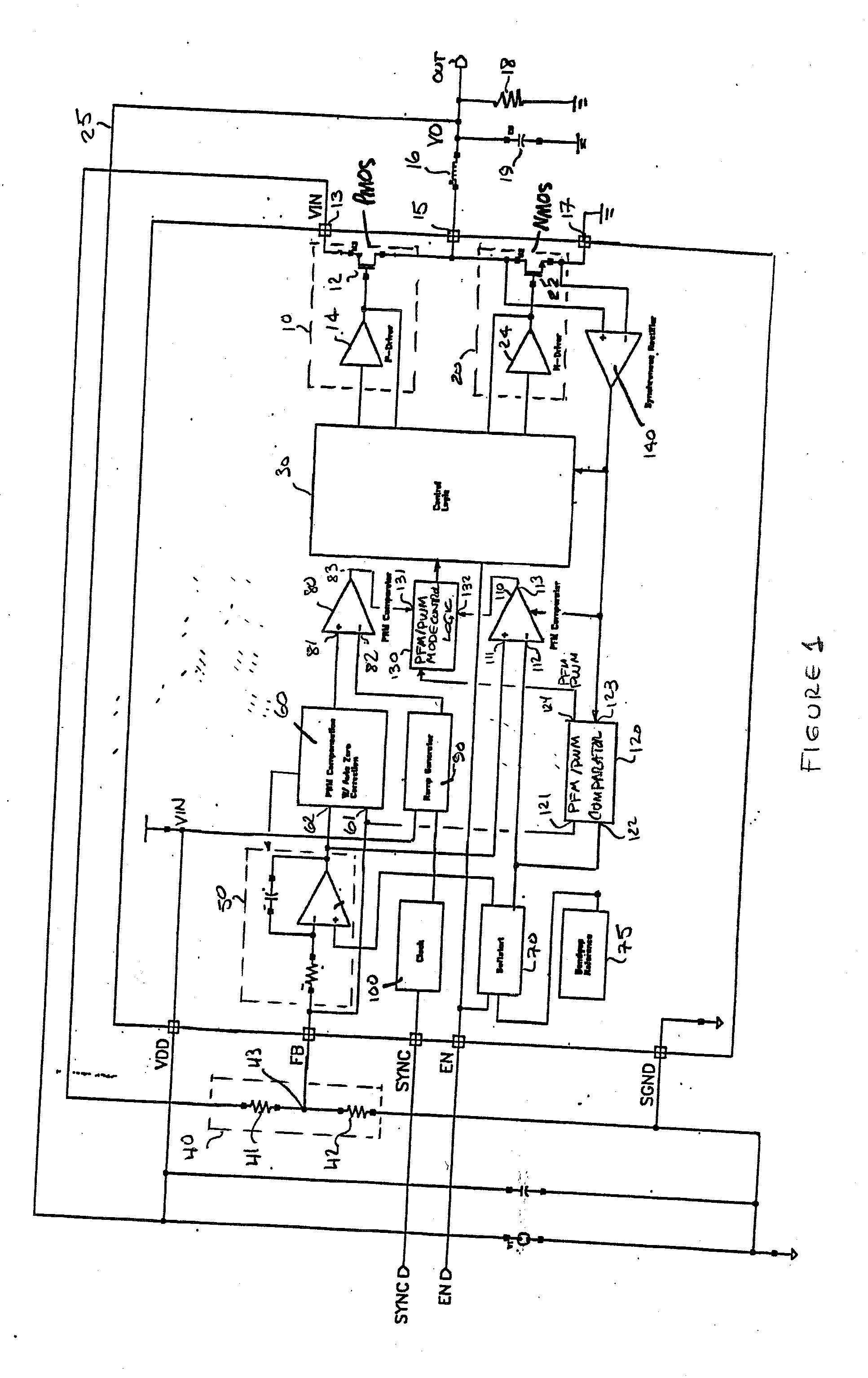
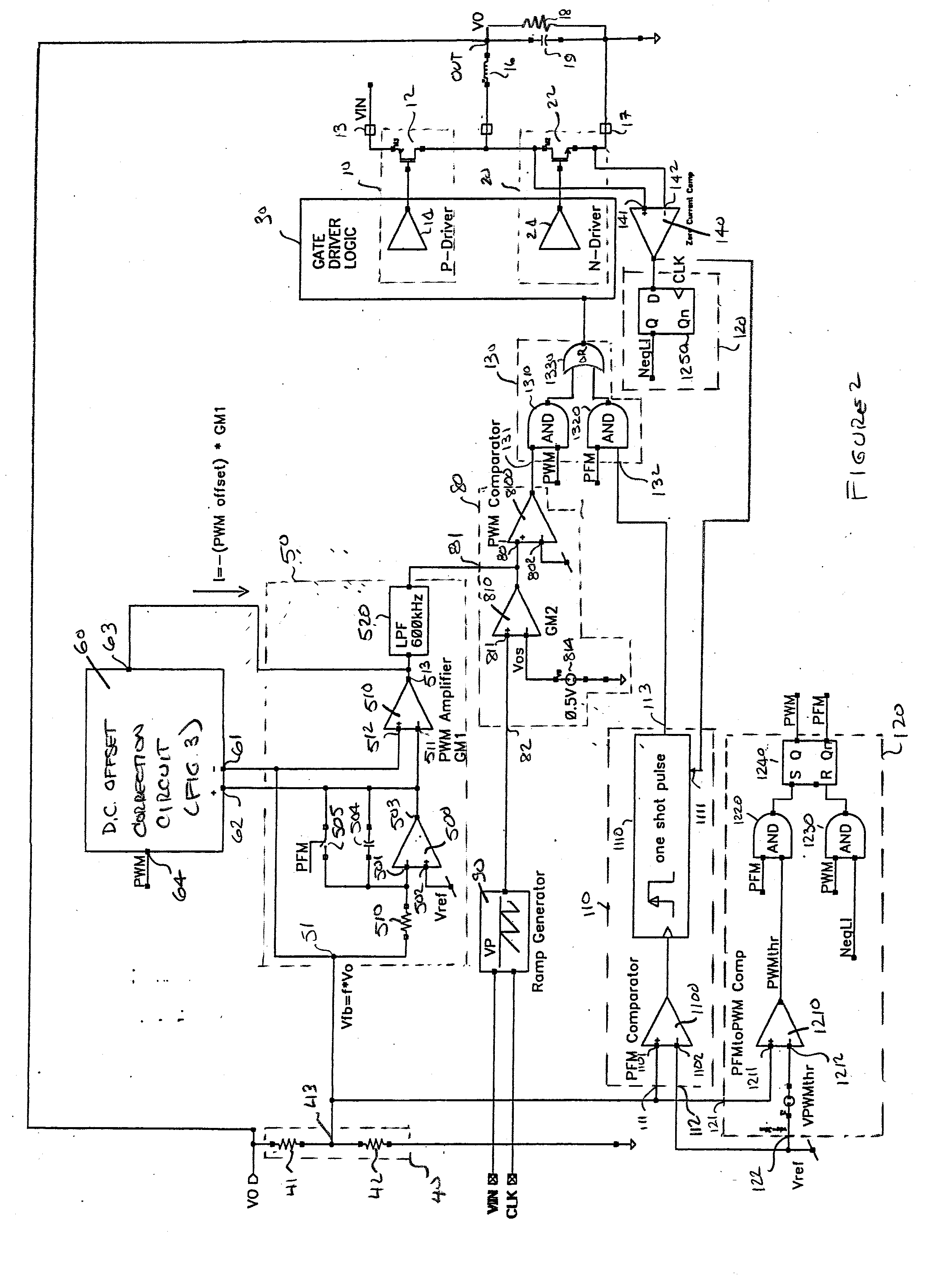
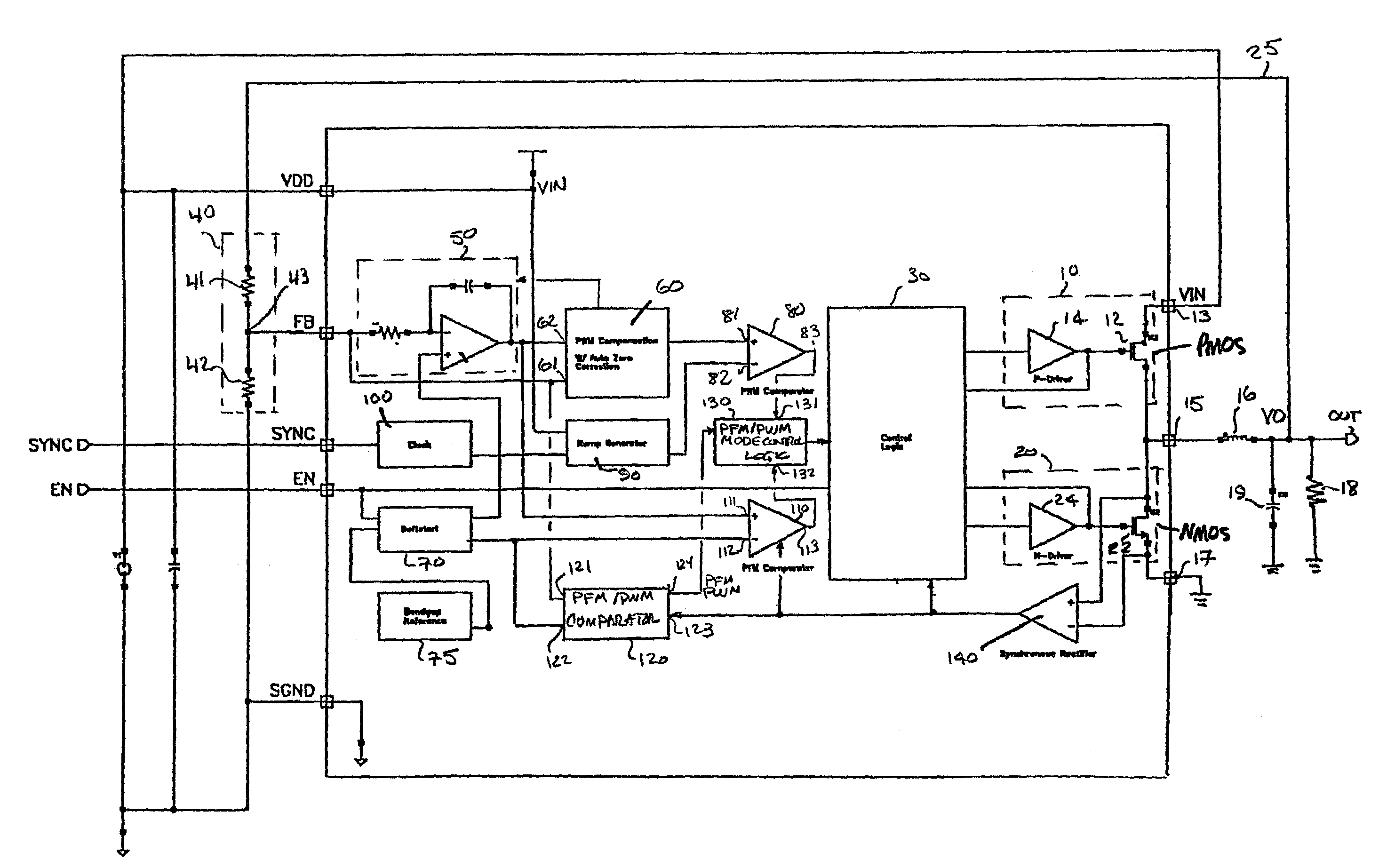
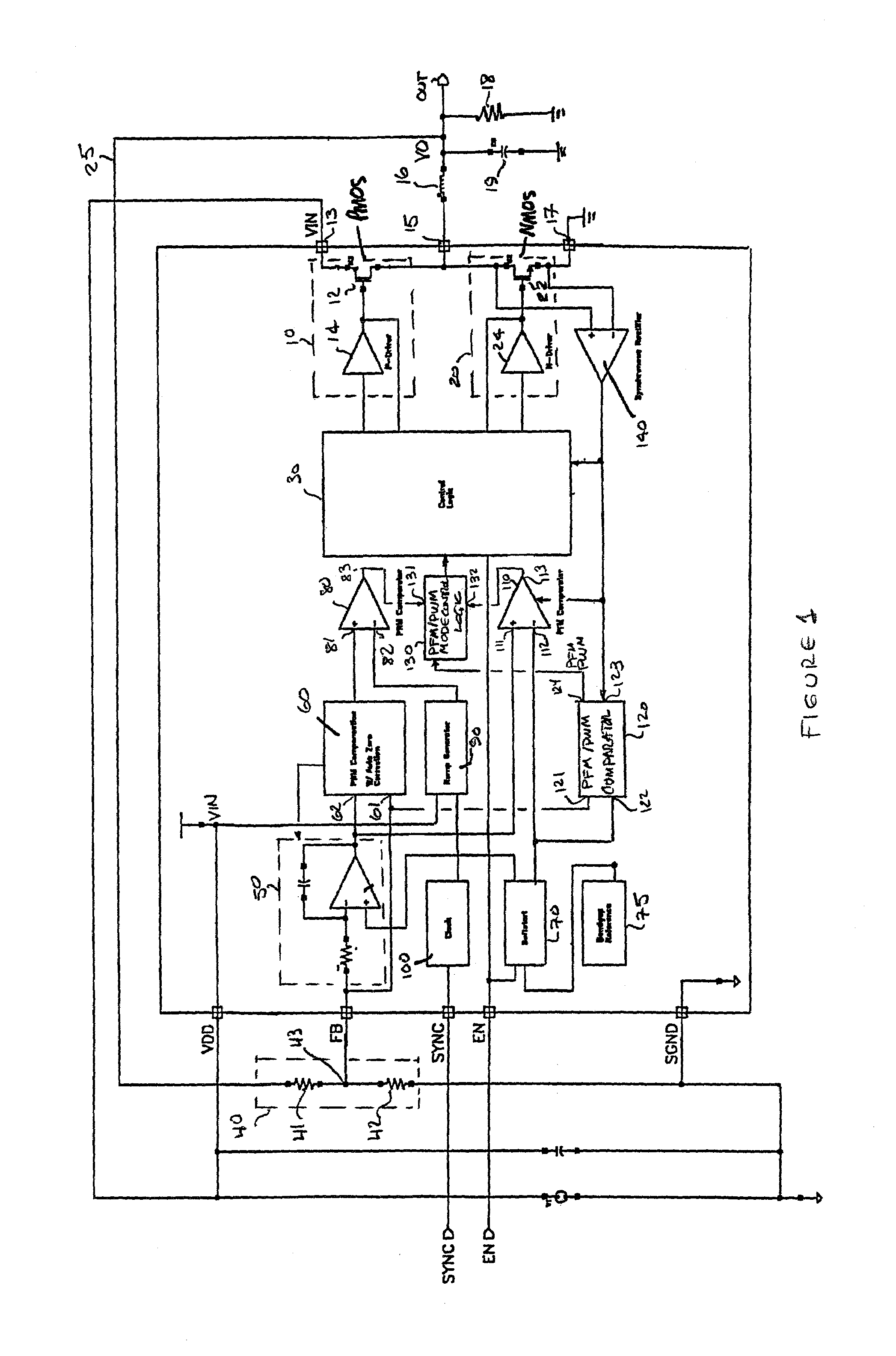
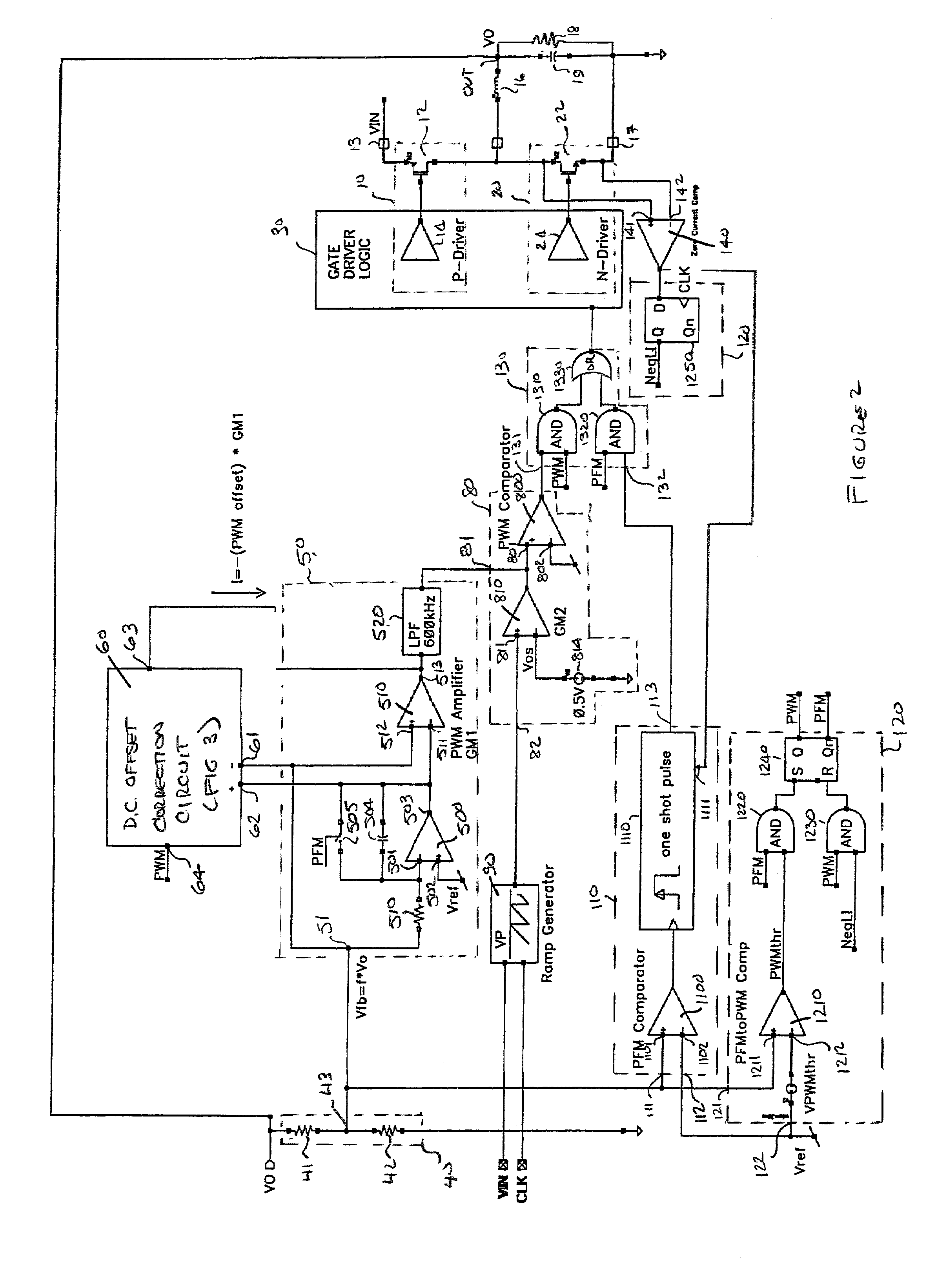
PFM-PWM DC-DC Converter Providing DC Offset Correction To PWM Error Amplifier And Equalizing Regulated Voltage Conditions When Transitioning Between PFM And PWM Modes
ActiveUS20060273772A1Accurate supervisionPrecise regulationEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDc dc converterVoltage regulation
To prevent a voltage glitch in the regulated DC output voltage of a PWM / PFM DC-DC converter when switching between PFM and PMW modes, the error amplifier of the converter's PWM regulation path is provided with a DC voltage offset correction mechanism. This mechanism “zeros-out” DC voltage offsets that may be present in the voltage regulation path, thereby enabling the error amplifier to accurately regulate the converter's output voltage. When the converter transitions between PFM and PWM modes, the DC offset correction mechanism establishes initial conditions of the error amplifier that effectively ensure that the converter's regulated output voltage at the beginning of a new “switched-to” PWM mode cycle is DC offset-free.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
High-efficiency DC/DC voltage converter including down inductive switching pre-regulator and capacitive switching post-converter
ActiveUS7782027B2Poor regulationIncrease heightEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionCapacitanceBuck converter
A DC / DC converter includes a pre-regulator stage, which may include a Buck converter, and a post-converter stage, which may include a charge pump. The duty factor of the pre-regulator stage is controlled by a feedback path that extends from the output terminal of the pre-regulator stage or the post-converter stage. The pre-regulator steps the input DC voltage down by a variable amount depending on the duty factor, and the post-converter steps the voltage at the output of the pre-regulator up or down by an positive or negative integral or fractional value. The converter overcomes the problems of noise glitches, poor regulation, and instability, even near unity input-to-output voltage conversion ratios.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
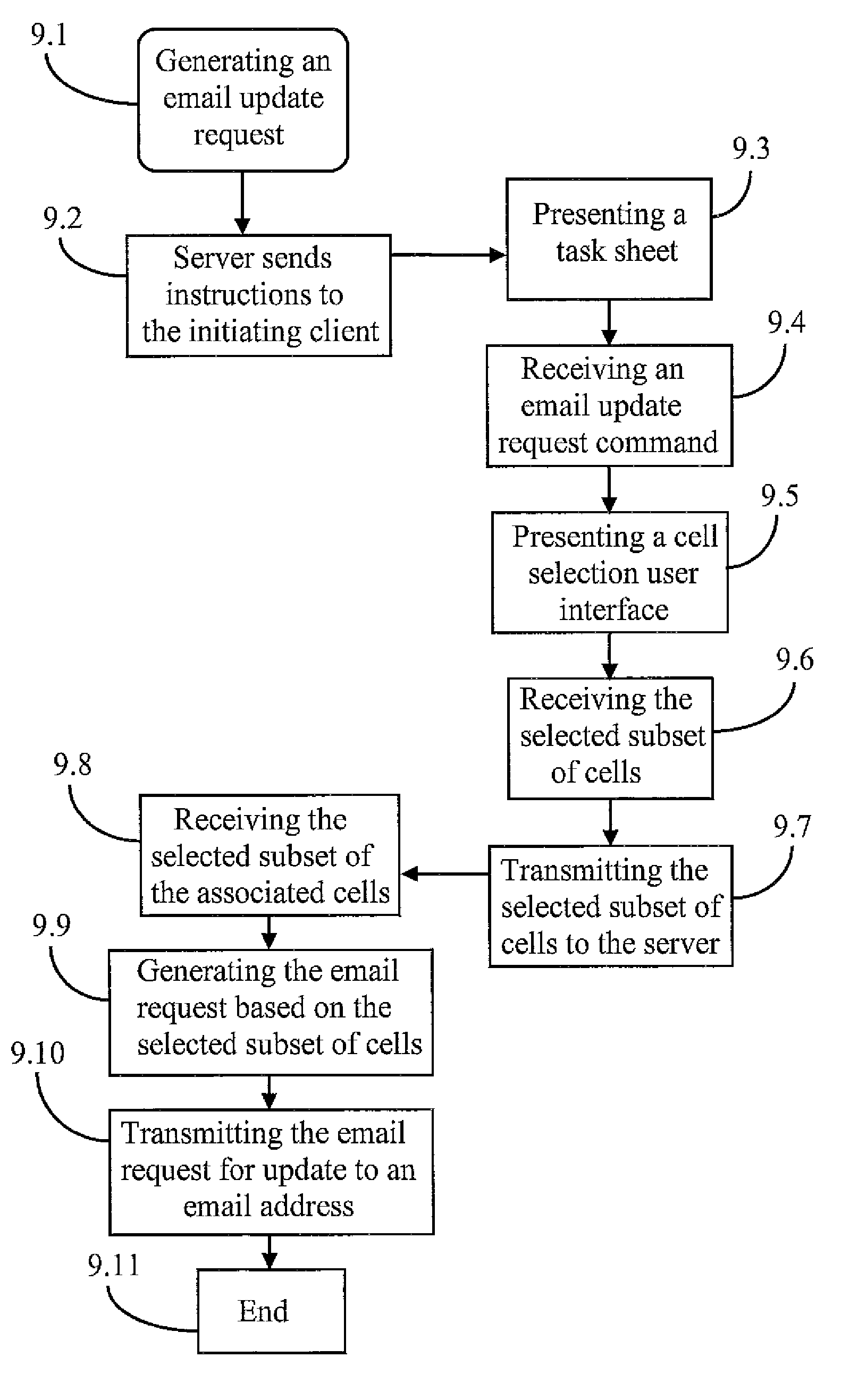
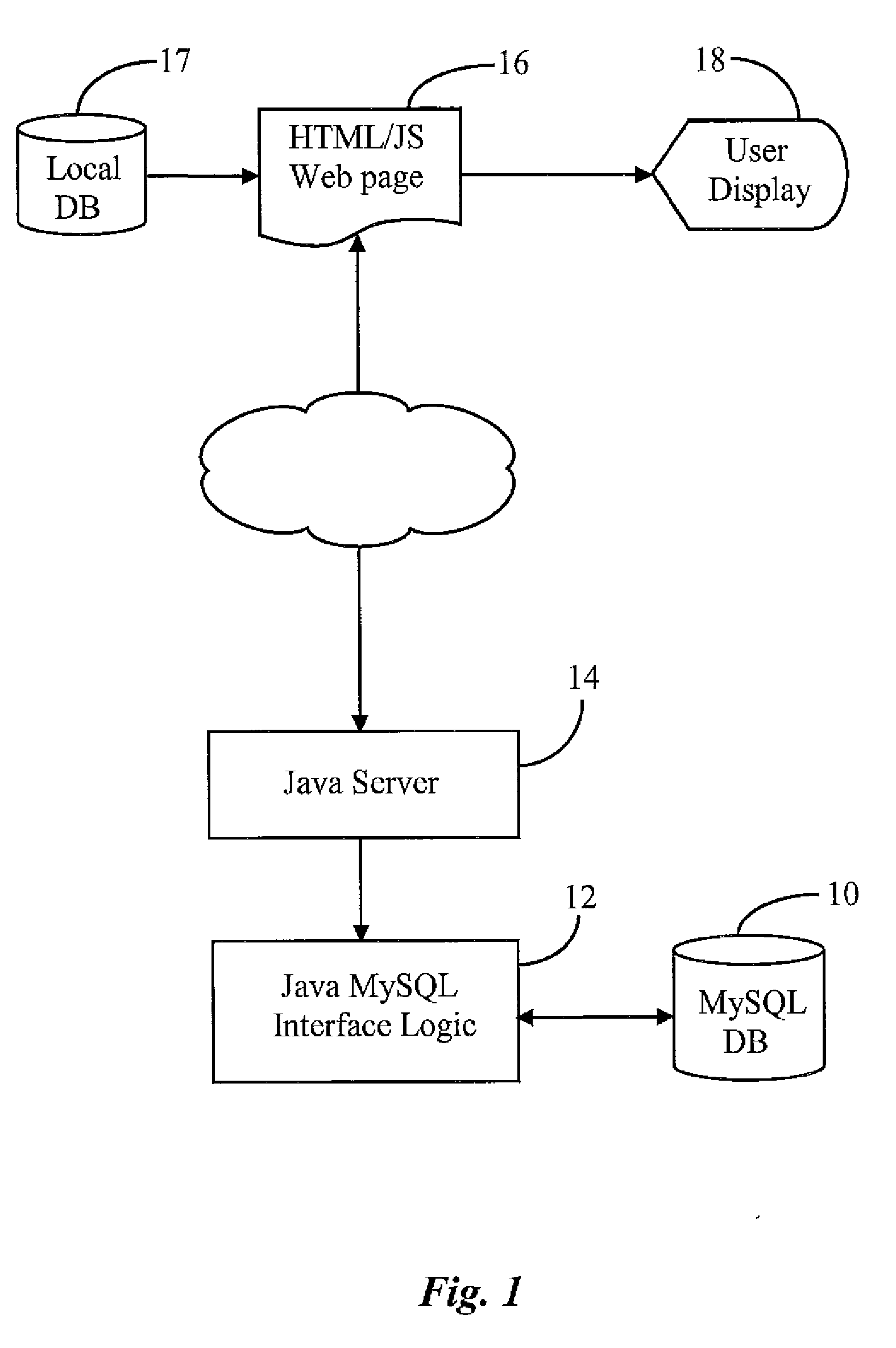
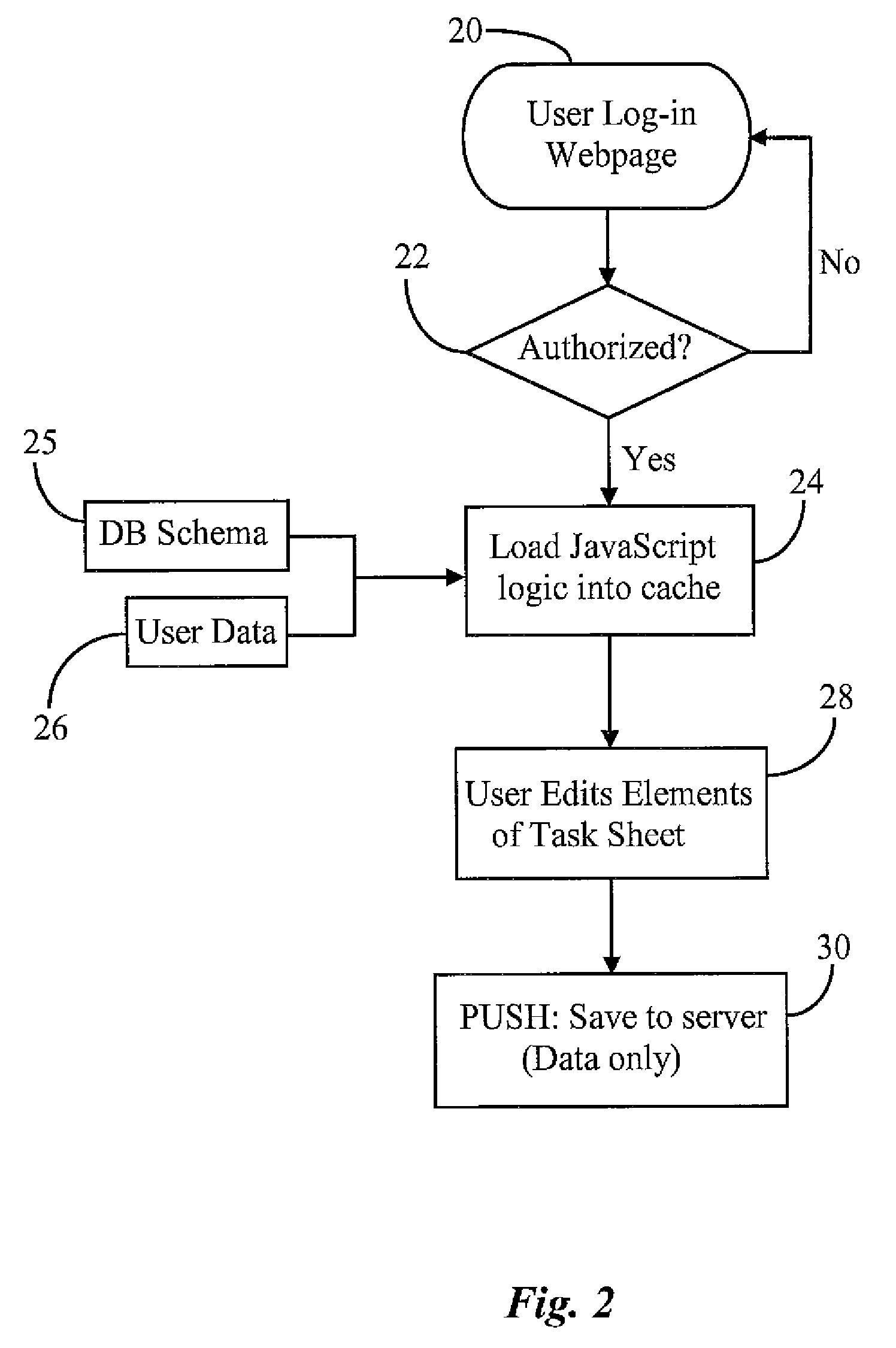
WEB-Based Task Management System and Method
InactiveUS20080244582A1Interprogram communicationData switching networksIn-memory databaseWeb browser
A task management system and method integrates rich functionality into a web-browser based application. An efficient request for an update enables a user to quickly generate a completely customizable email message to intended recipient(s). By introducing a client side, in-memory database, the client component becomes less susceptible to network connectivity glitches and enables user interfaces to be redrawn without server interaction. Additionally, the task management system and method provides flexibility by enabling tasks to be grouped and organized. Specifically, a task may be associated with multiple task sheets and a task sheet may include multiple tasks in a many-to-many manner. Also, templates may be created that enable a user to start with a base template and to add (or remove) one or more columns. Further, the task management systems allows for multiple users to access and manipulate task data concurrently. In addition, the task management system provides a means for viewing the change history of task data within a task sheet by highlighting task data within a task sheet that has been changed by another user of the task management system.
Owner:SMARTSHEET INC
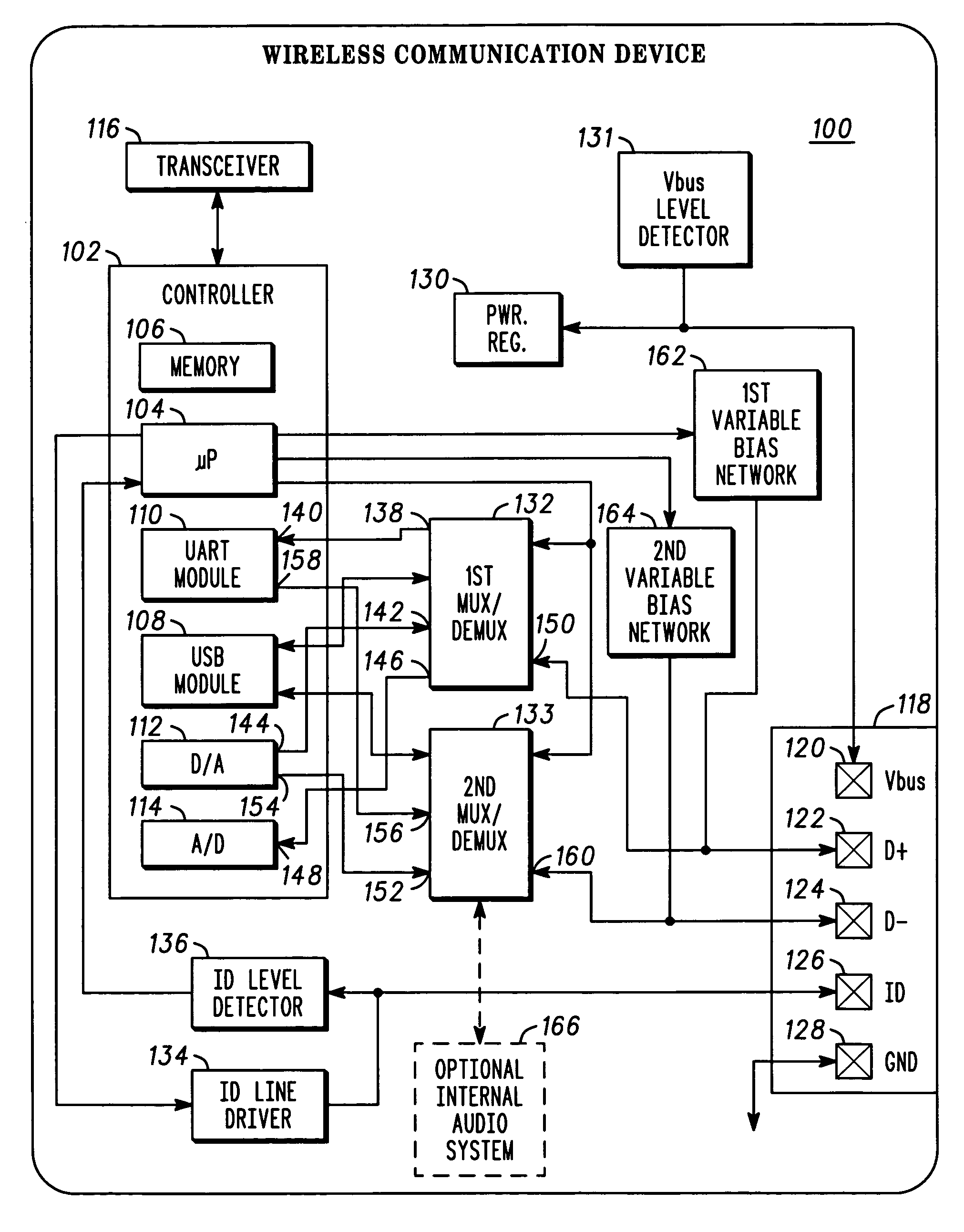
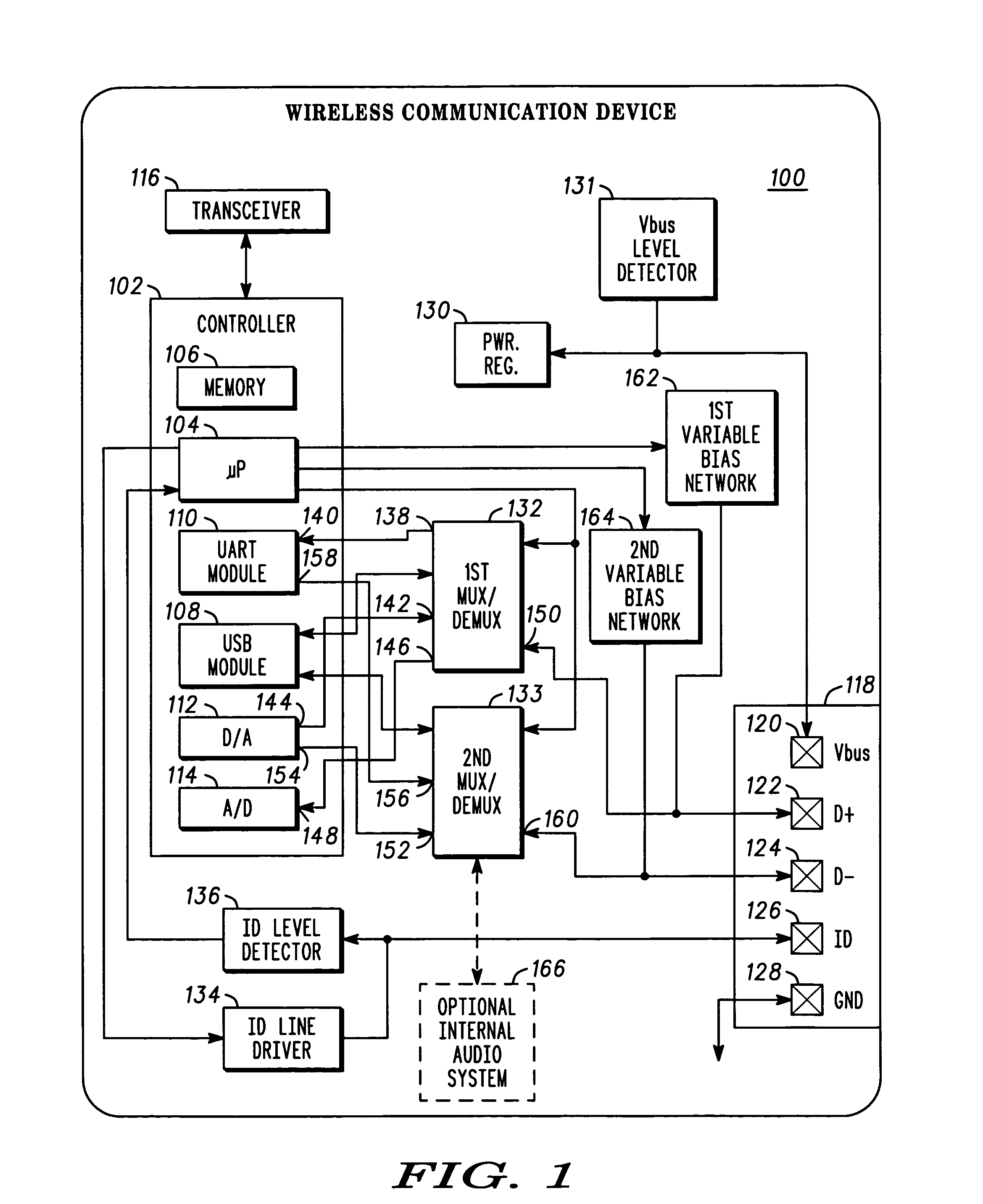
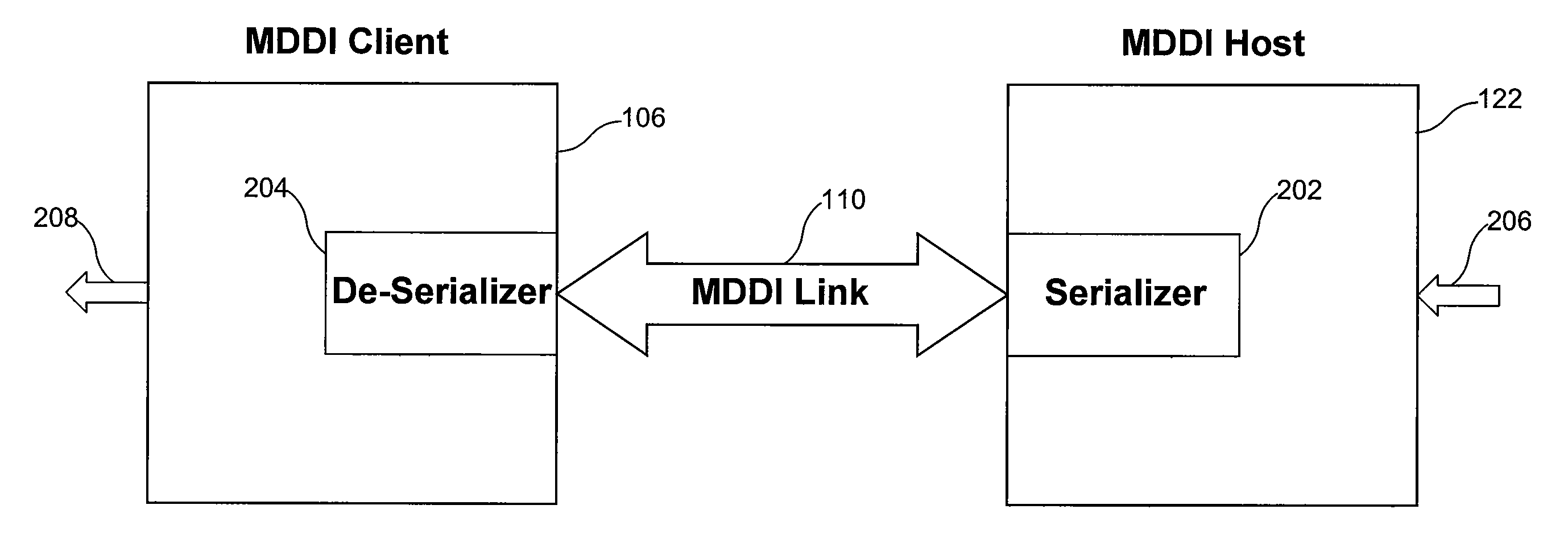
Electronic apparatus and system with multi-purpose interface
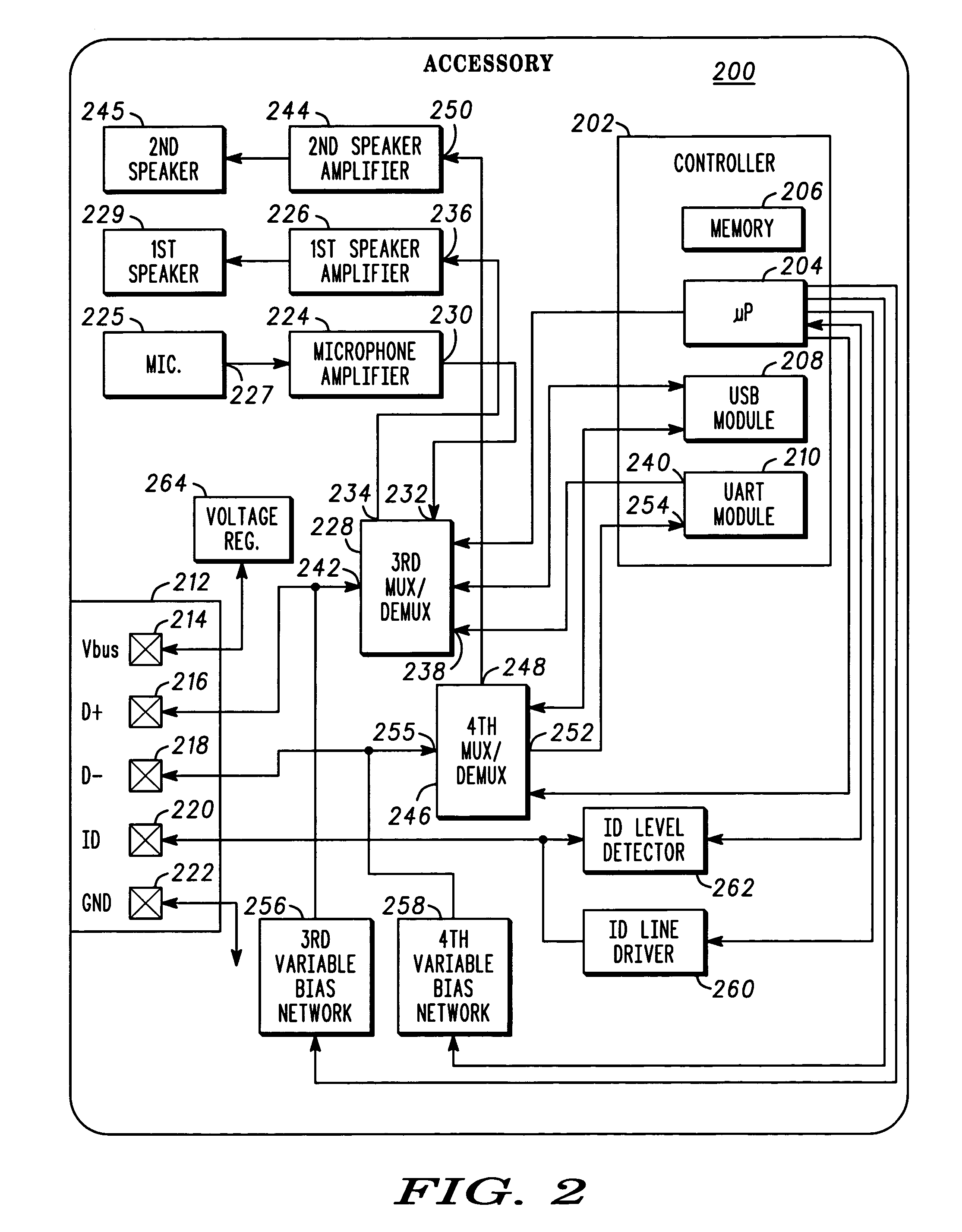
A highly versatile interface that is capable of digital and audio signal coupling is provided. The interface comprises contacts (122, 124, 216, 218) that are used to couple both audio and digital signals, and separate contacts (126, 220) that are used initiate and negotiate signaling mode transitions. Transitions can be effected without creating glitches, e.g., audible noise, in audio signals that are being coupled through the interface.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Voltage detector
InactiveUS7030668B1Pulse automatic controlInstant pulse delivery arrangementsDetector circuitsLow voltage
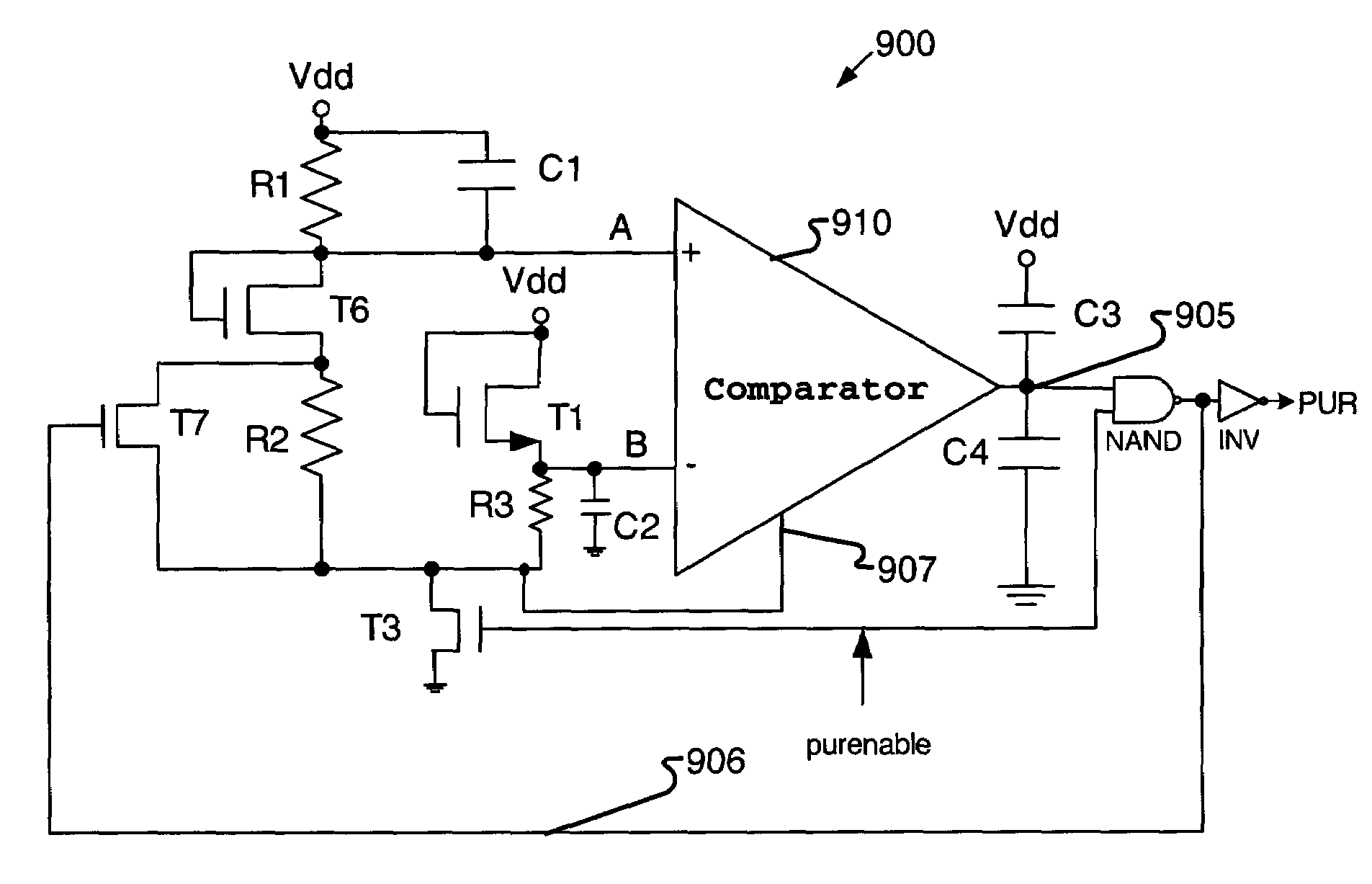
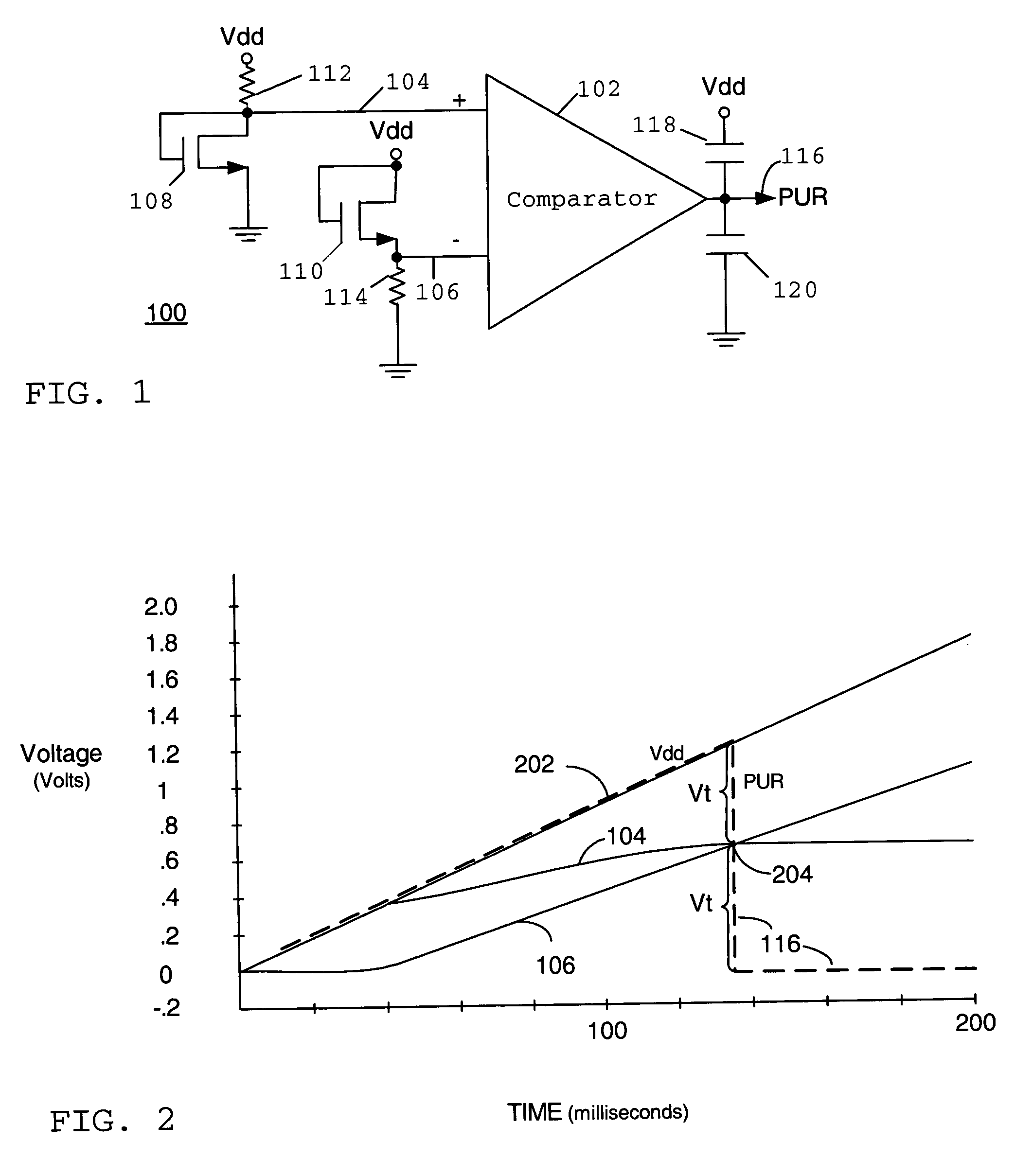
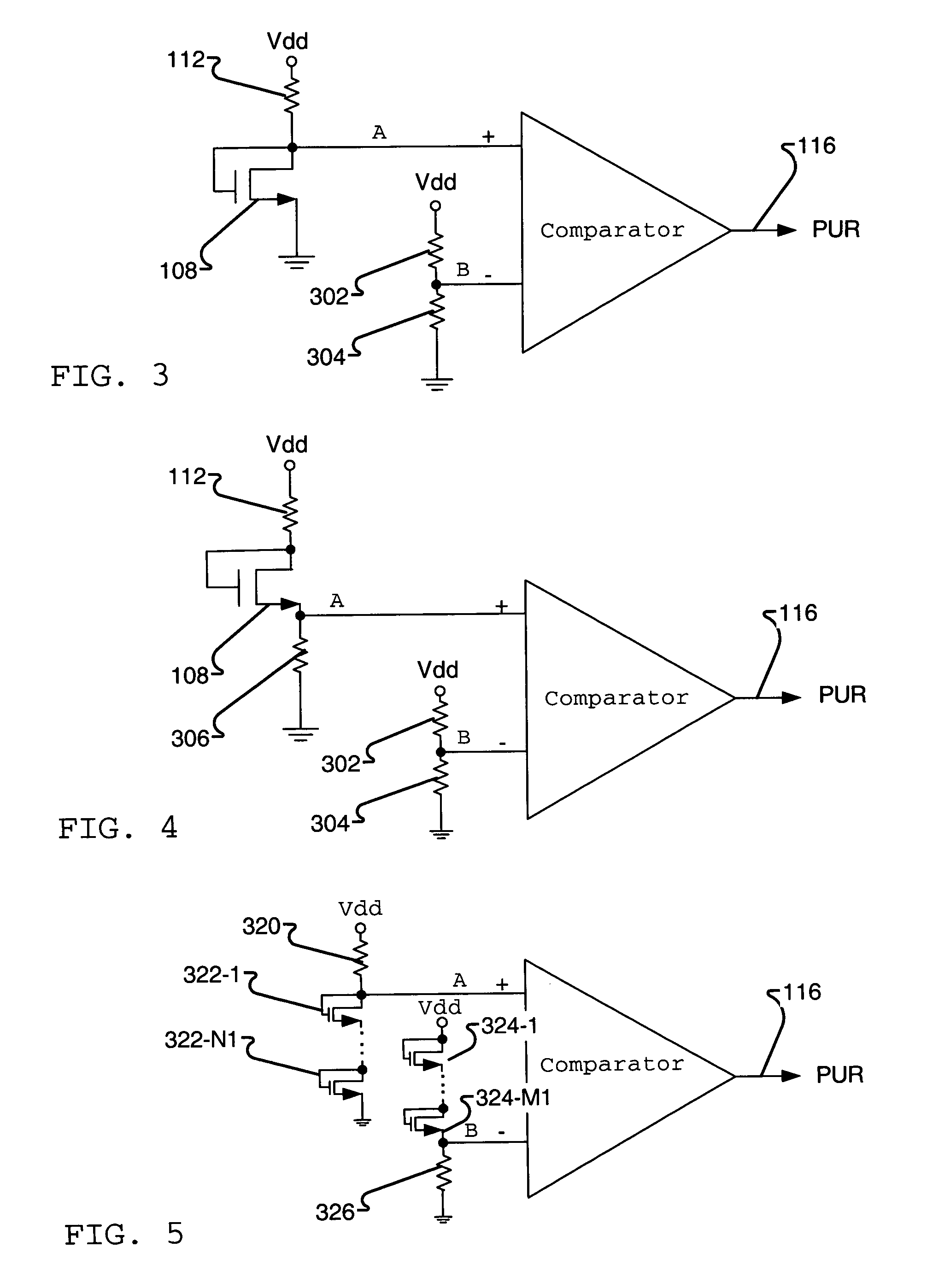
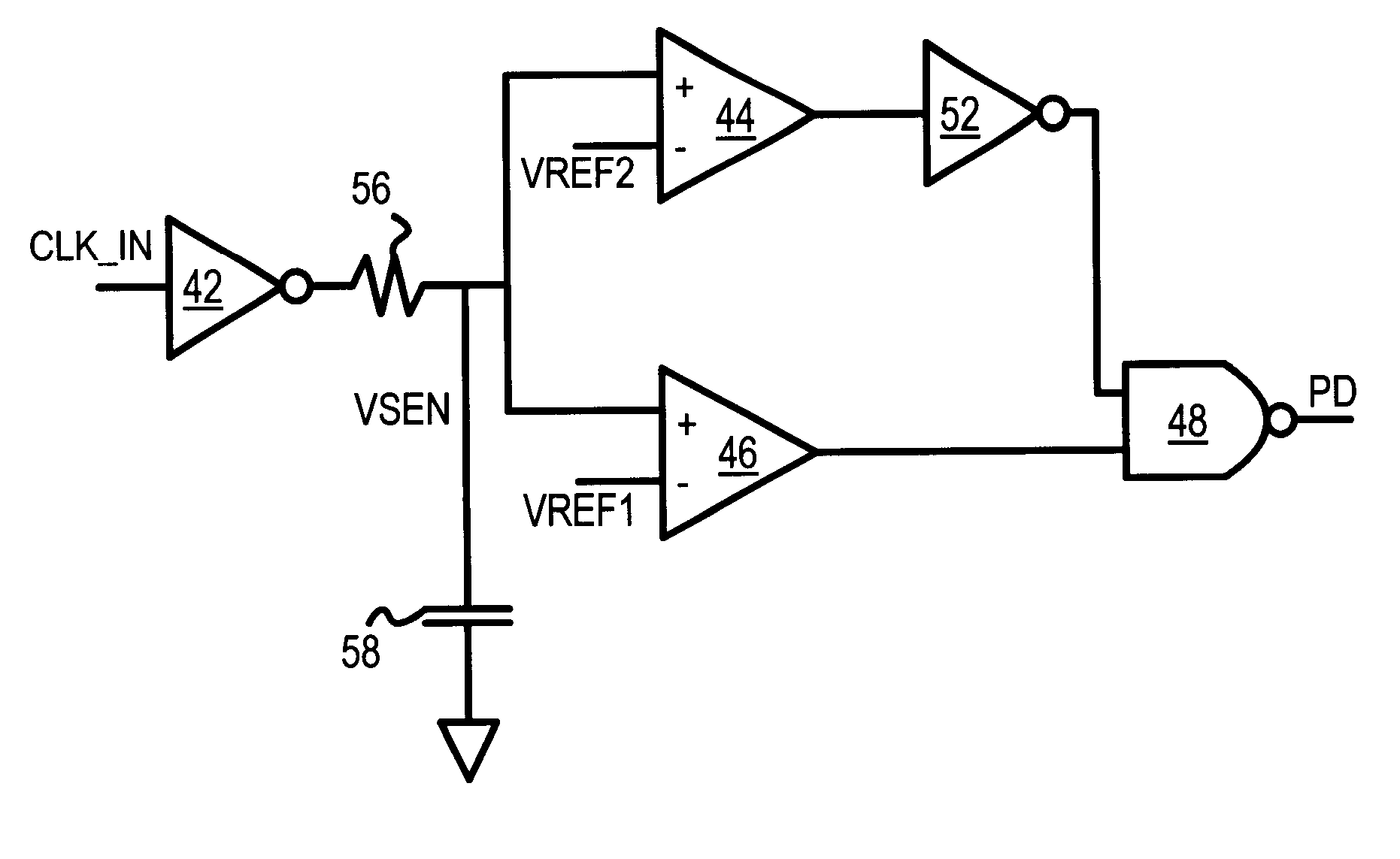
A voltage detector circuit such as a power up and / or brownout detector circuit (100) includes a comparator (102) having at least one of its inputs (104) coupled to a diode-connected transistor (108). The other input can include another diode-connected transistor (110) or a resistor divider (302). Optional compensation capacitors (118 and 120) can be added to the comparator output (116) to provide glitch compensation. Since comparator (102) only needs to output a high or low voltage level, the components that are used to build circuit (100) do not have to have very tight tolerances. Circuit (100) also can operate at very low voltages and consume low amounts of power.
Owner:XILINX INC
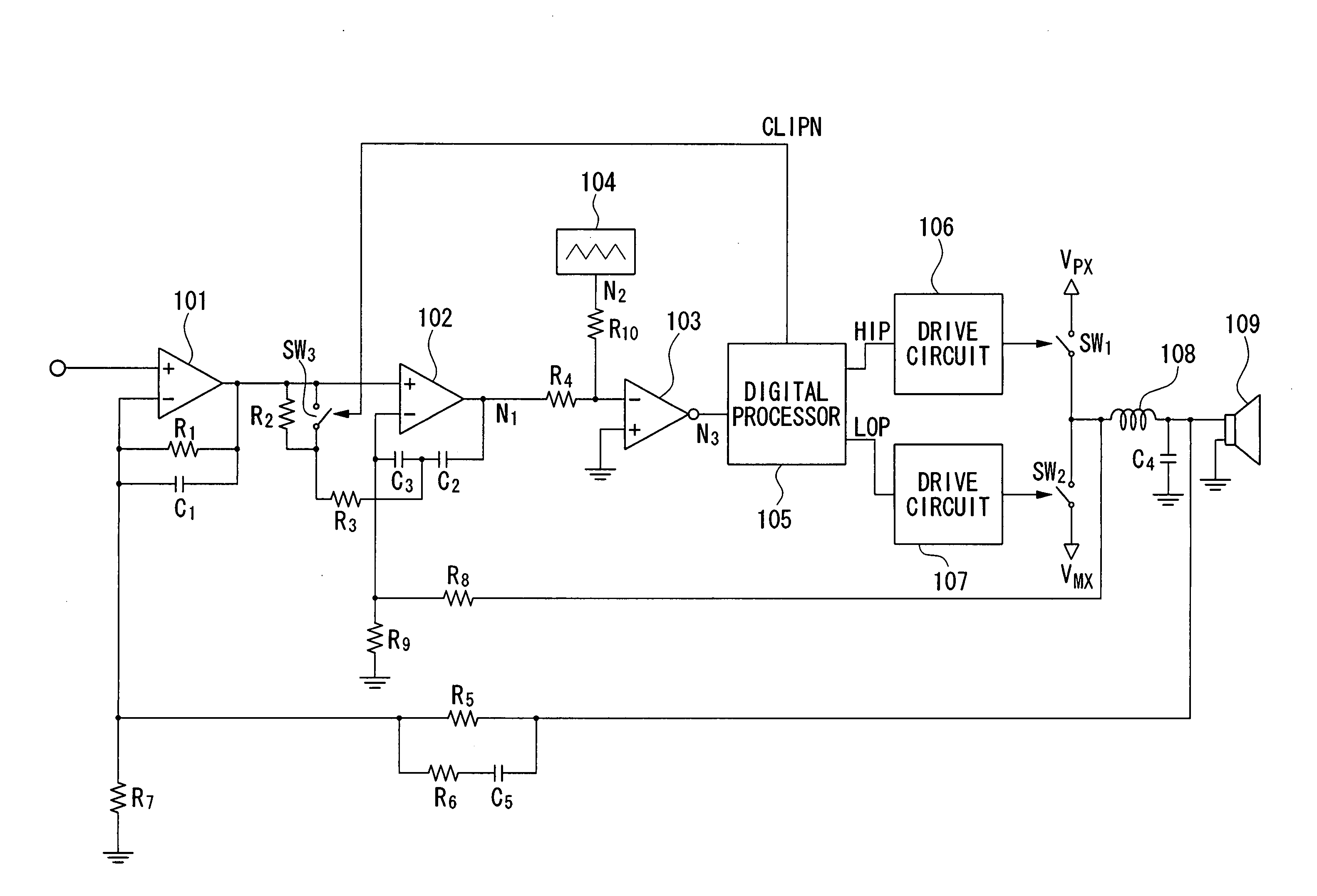
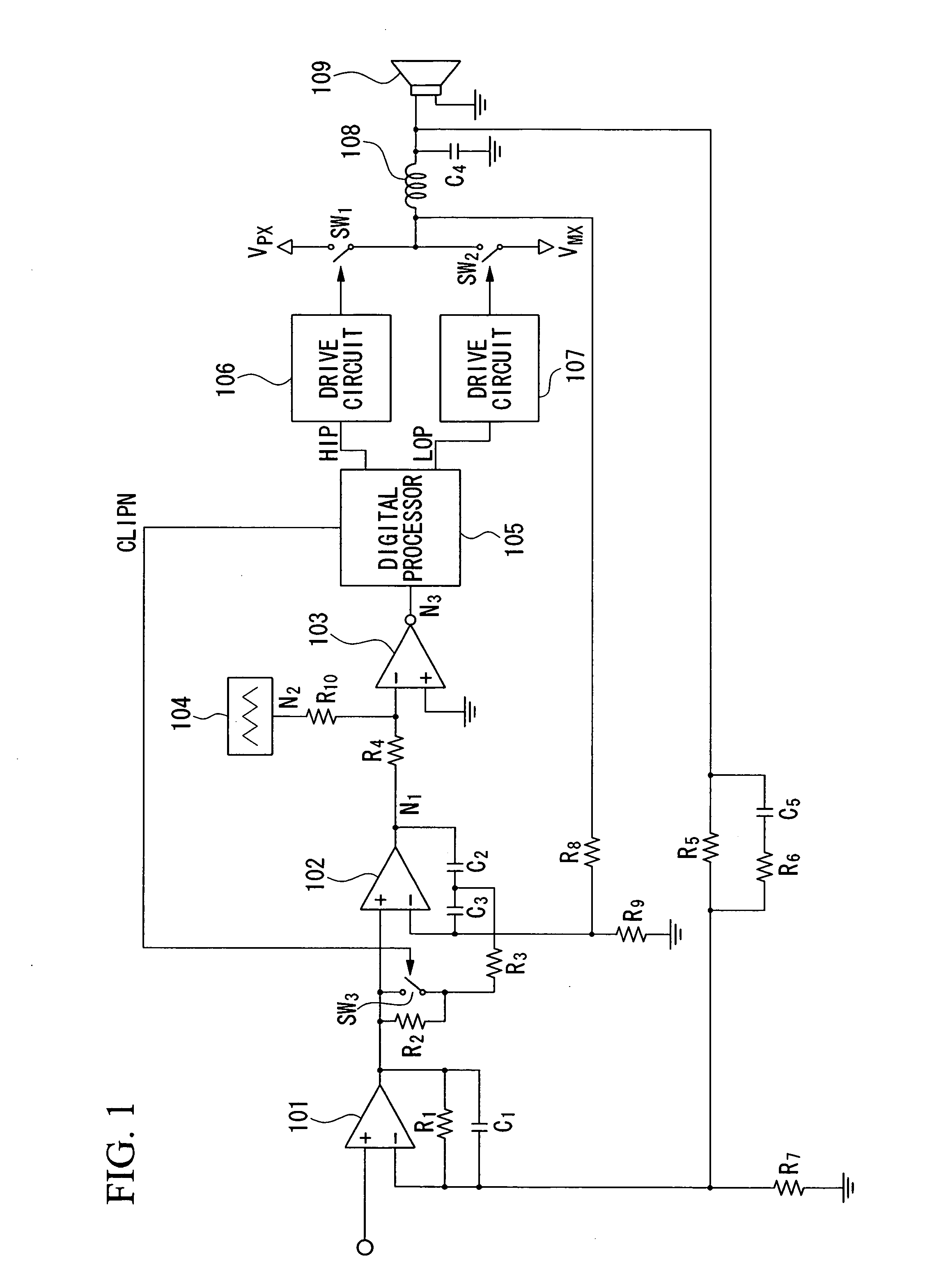
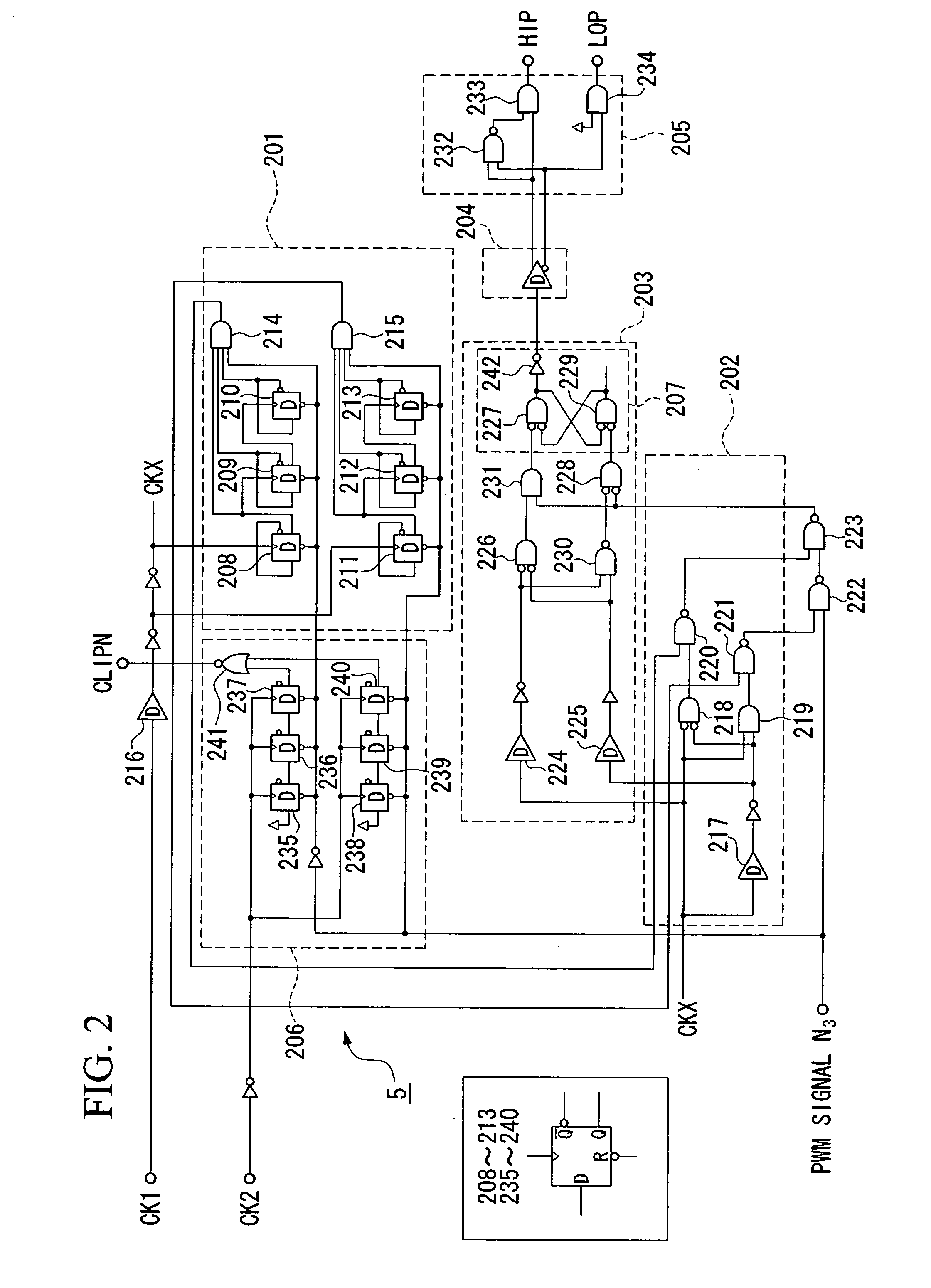
Pulse-width modulation amplifier and suppression of clipping therefor
ActiveUS20060008095A1Avoid excessive currentPower use efficiency decreaseAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlLeading edgeAudio power amplifier
A pulse-width modulation (PWM) amplifier is adapted to a class-D amplifier in which an analog input signal is subjected to integration, pulse-width modulation, and switched amplification, wherein a glitch elimination circuit eliminates noise from a pulse-width modulated signal, from which a high pulse signal and a low pulse signal are isolated such that each pulse is delayed by a dead time at the leading-edge timing thereof. When both of them are simultaneously set to a high level, one of them is reduced in level. In response to the occurrence of clipping, an integration constant applied to an operational amplifier is automatically changed from a primary integration constant to a secondary integration constant. When the clipped state is sustained for a prescribed time, an inversion pulse is compulsorily introduced into the pulse-width modulated signal.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
High-efficiency dc/dc voltage converter including down inductive switching pre-regulator and capacitive switching post-converter
ActiveCN101647181AAvoiding Minimum Pulse Width IssuesDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationInstabilityCapacitive switch
A DC / DC converter includes a pre-converter stage, which may include a charge pump, and a post-regulator stage, which may include a boost converter. The duty factor of the post-regulator stage is controlled by a feedback path that extends from the output terminal of the DC / DC converter to an input terminal in the post-regulator stage. The pre-converter steps the input DC voltage up or down by a positive or negative integral or fractional value, and the post-regulator steps the voltage up by a variable amount depending on the duty factor at which the post-regulator is driven. The converter overcomes the problems of noise glitches, poor regulation, and instability, even near unity input-to-output voltage conversion ratios.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
Low output skew double data rate serial encoder
ActiveUS20080036631A1Reduce complexitySmall sizeParallel/series conversionDouble data rateMultiplexer
A Double Data Rate (DDR) serial encoder is provided. In one aspect, the DDR serial encoder includes a non-glitchless multiplexer and digital logic for ensuring a glitch-free encoder output. By using a non-glitchless multiplexer, the size and complexity of the encoder is significantly reduced. In another aspect, the DDR serial encoder has a single layer of logic between the final register stage and the encoder output and a reduced number of paths from the final register stage to the encoder output, thereby resulting in reduced output skew and increased link rate.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
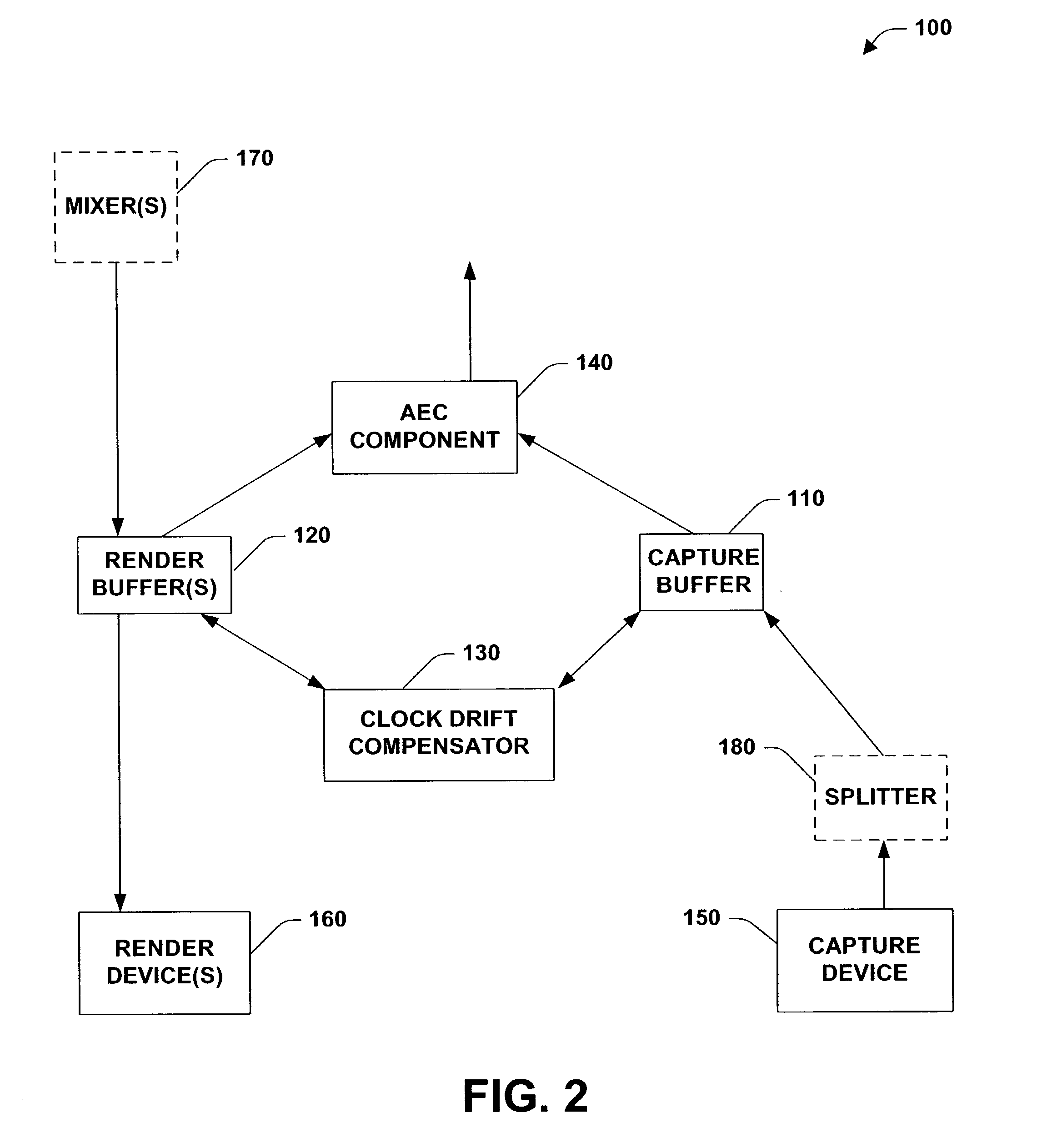
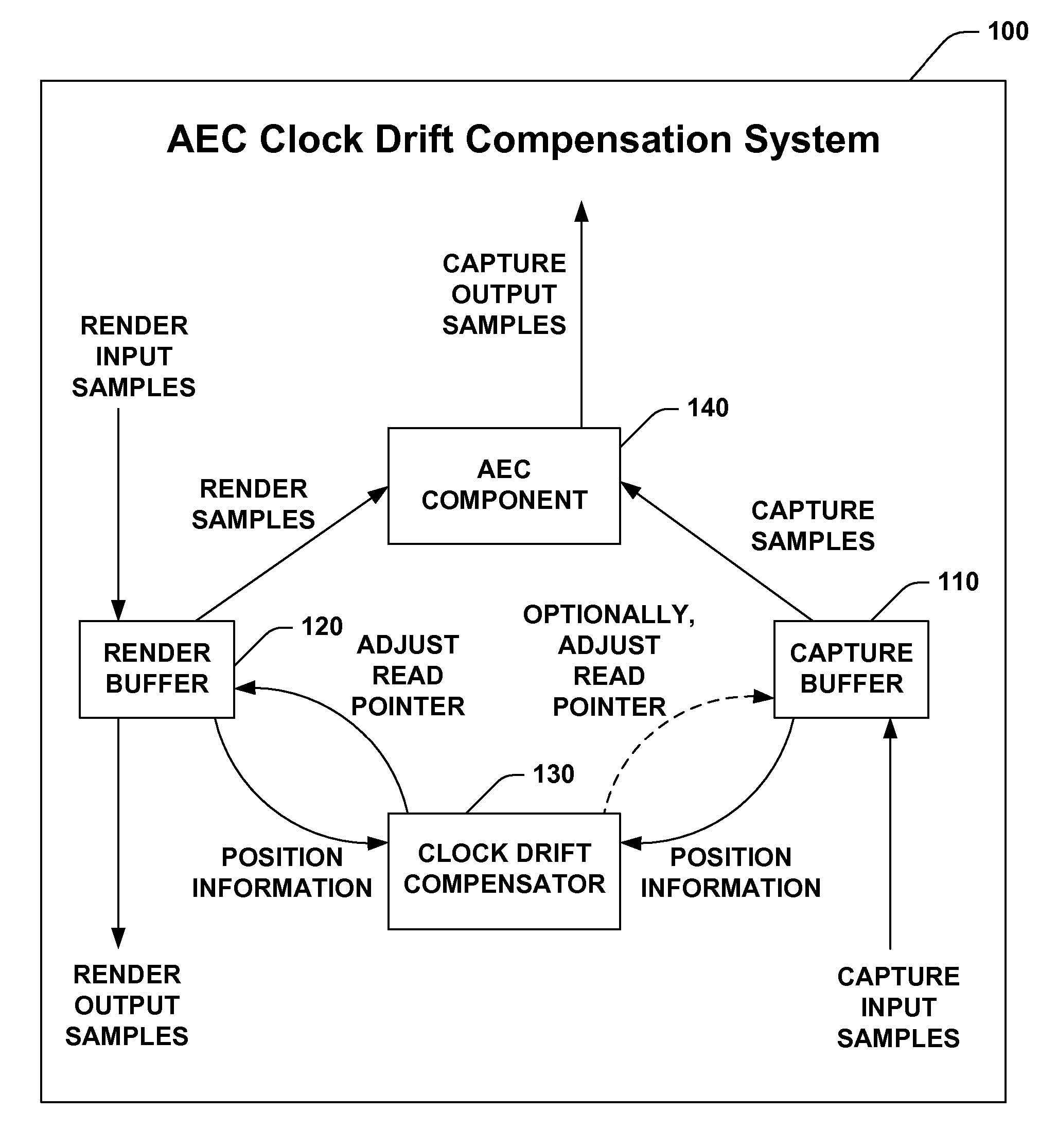
Adaptive estimation and compensation of clock drift in acoustic echo cancellers
A system and method for adaptive estimation and compensation of clock drift in echo cancellers is provided. The invention includes an acoustic echo cancellation system with a built in adaptive clock drift compensation system. The acoustic echo cancellation system has an AEC component that performs acoustic echo cancellation on data from a capture buffer, by also using information derived from a render buffer. The clock drift compensation system has access to this capture buffer and render buffer. The clock drift compensation system includes a clock drift compensator that calculates, based on the current location of the capture data being processed by the AEC component as well as additional information, the ideal location in the render buffer from which the AEC component should process data. The clock drift compensator further adjusts the current location in the render buffer from which the AEC component processes data based, at least in part, upon this ideal location. The clock drift compensator can further detect and correct for glitches in the hardware positions received from the render and capture devices.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Adaptive estimation and compensation of clock drift in acoustic echo cancellers
A system and method for adaptive estimation and compensation of clock drift in echo cancellers is provided. The invention includes an acoustic echo cancellation system with a built in adaptive clock drift compensation system. The acoustic echo cancellation system has an AEC component that performs acoustic echo cancellation on data from a capture buffer, by also using information derived from a render buffer. The clock drift compensation system has access to this capture buffer and render buffer. The clock drift compensation system includes a clock drift compensator that calculates, based on the current location of the capture data being processed by the AEC component as well as additional information, the ideal location in the render buffer from which the AEC component should process data. The clock drift compensator further adjusts the current location in the render buffer from which the AEC component processes data based, at least in part, upon this ideal location. The clock drift compensator can further detect and correct for glitches in the hardware positions received from the render and capture devices.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
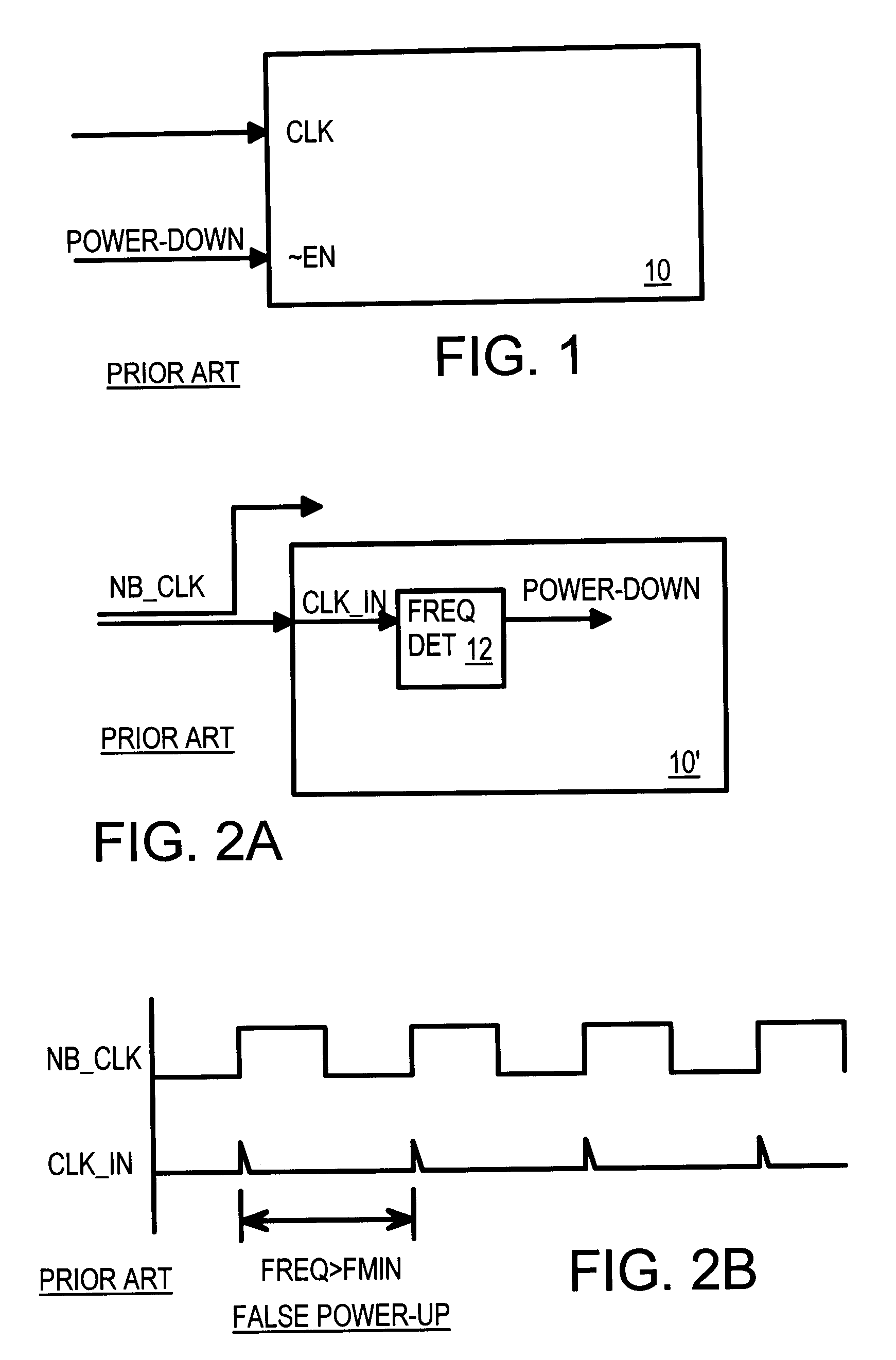
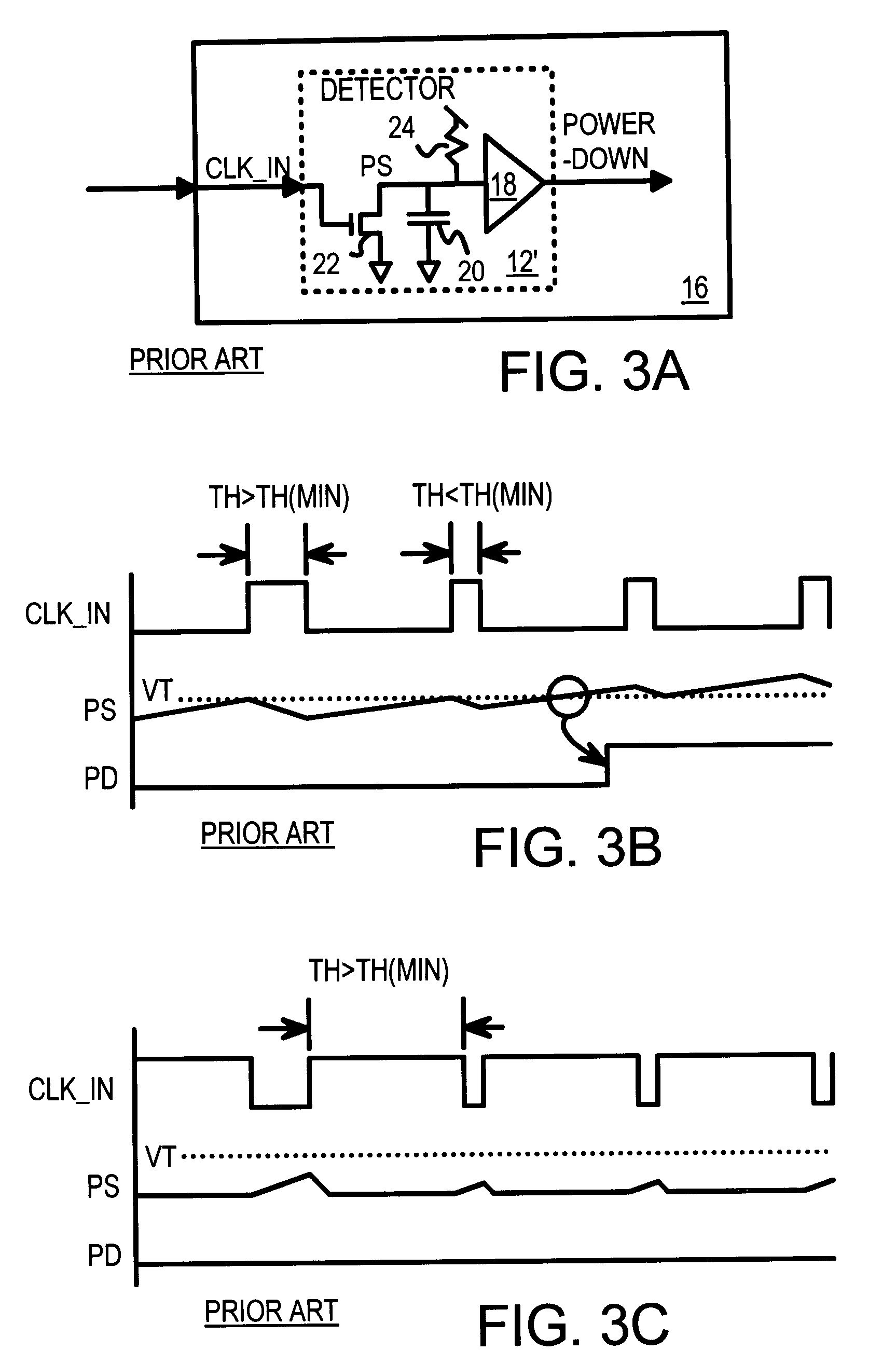
Power down circuit detecting duty cycle of input signal
InactiveUS6552578B1Energy efficient ICTMultiple input and output pulse circuitsLower limitElectricity
When the clock is stopped during a power-down mode, a clock duty-cycle detector asserts a power-down signal. The clock input is filtered to produce an average clock voltage over several clock periods. The average clock voltage is compared to an upper reference voltage to determine when the clock's duty cycle (high pulse-width percent) is above an upper limit. The average clock voltage is also compared to a lower reference voltage to determine when the clock's duty cycle is below a lower limit. When the clock's duty cycle is above the upper limit or below the lower limit the power-down signal is activated by logic. The logic disables the power-down signal when the clock's duty cycle is between the upper and lower limits. High-frequency clock glitches do not falsely trigger a power-up, since glitches are usually narrow and not sufficiently wide to reach the lower limit.
Owner:DIODES INC
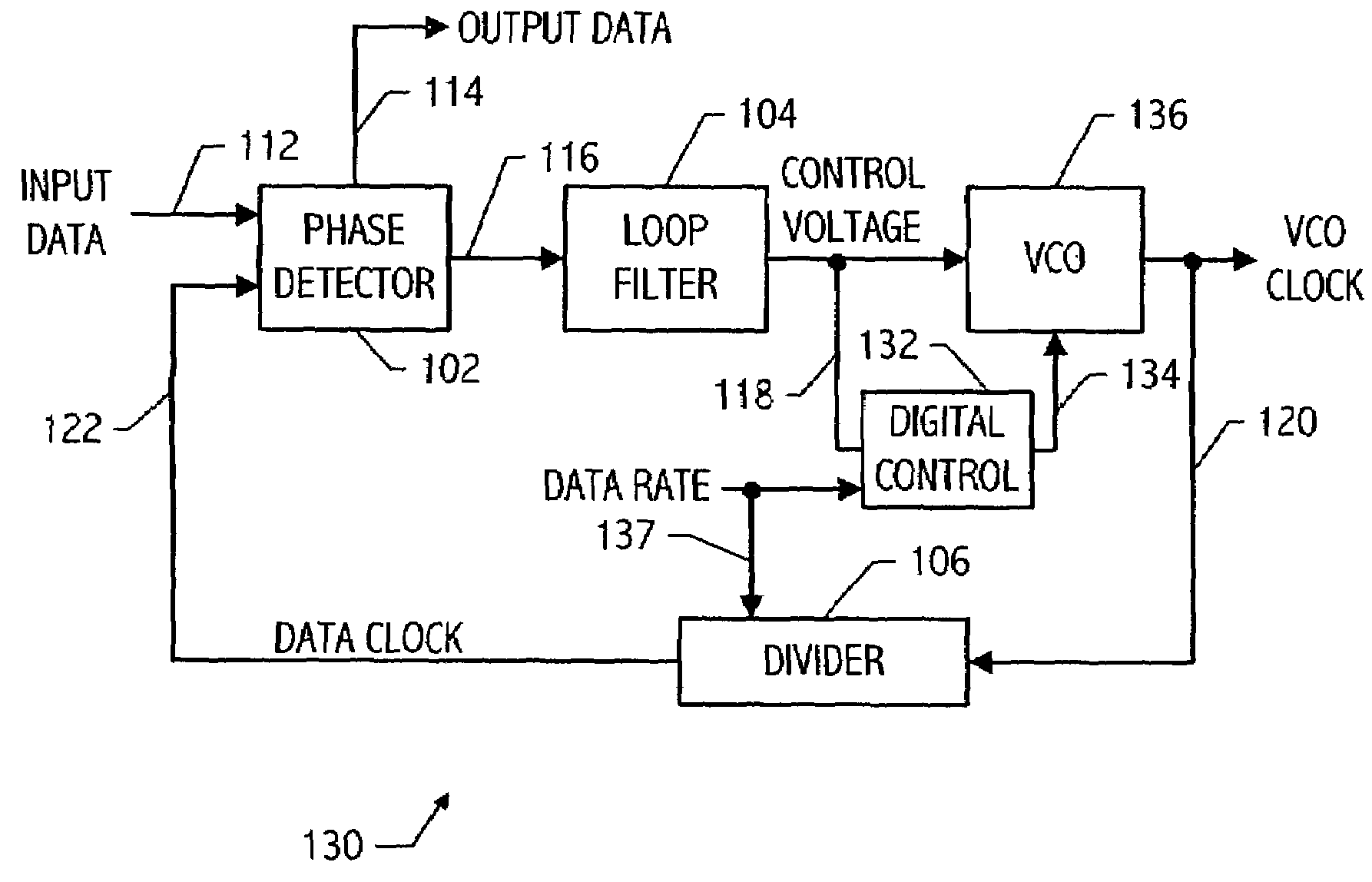
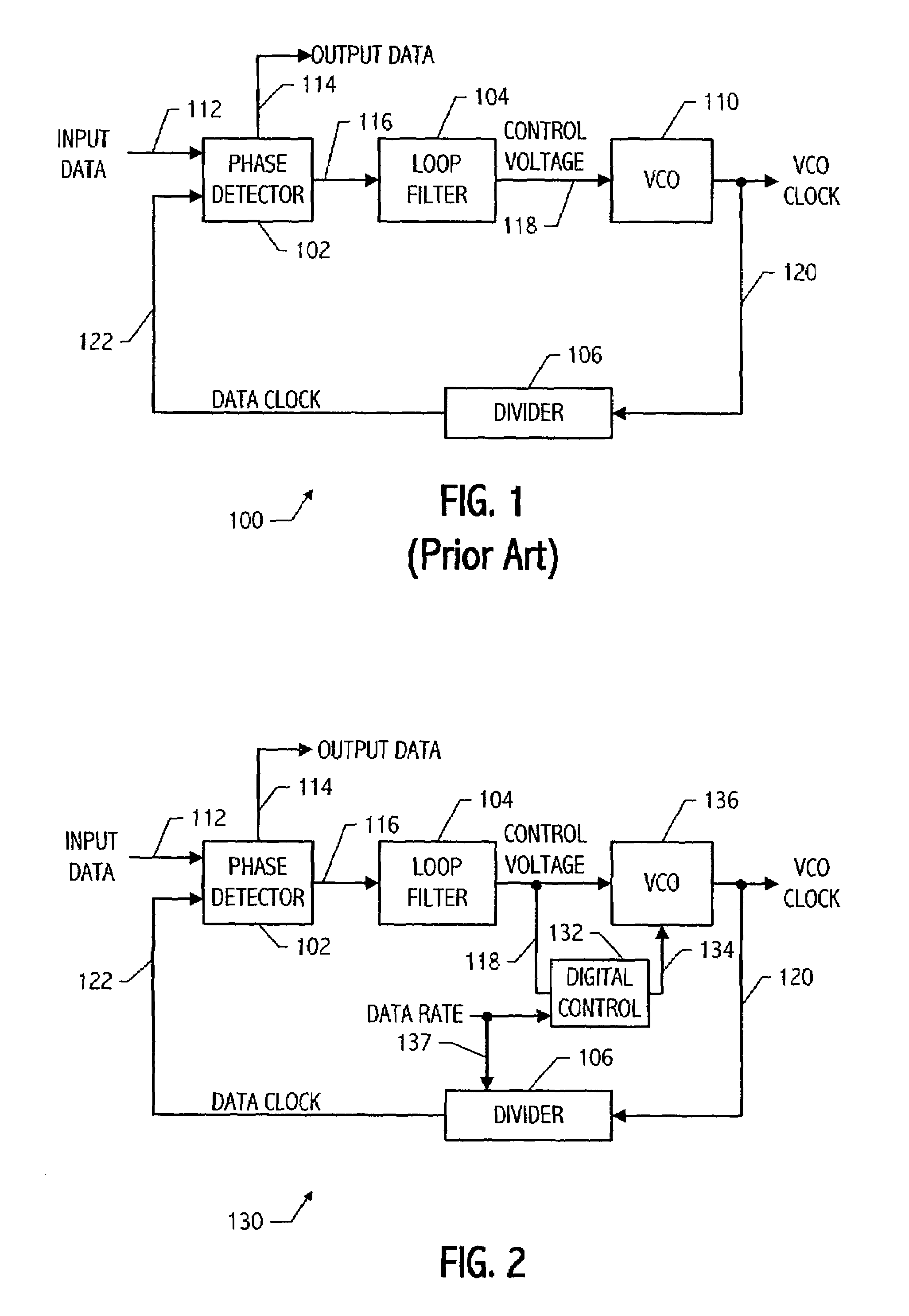
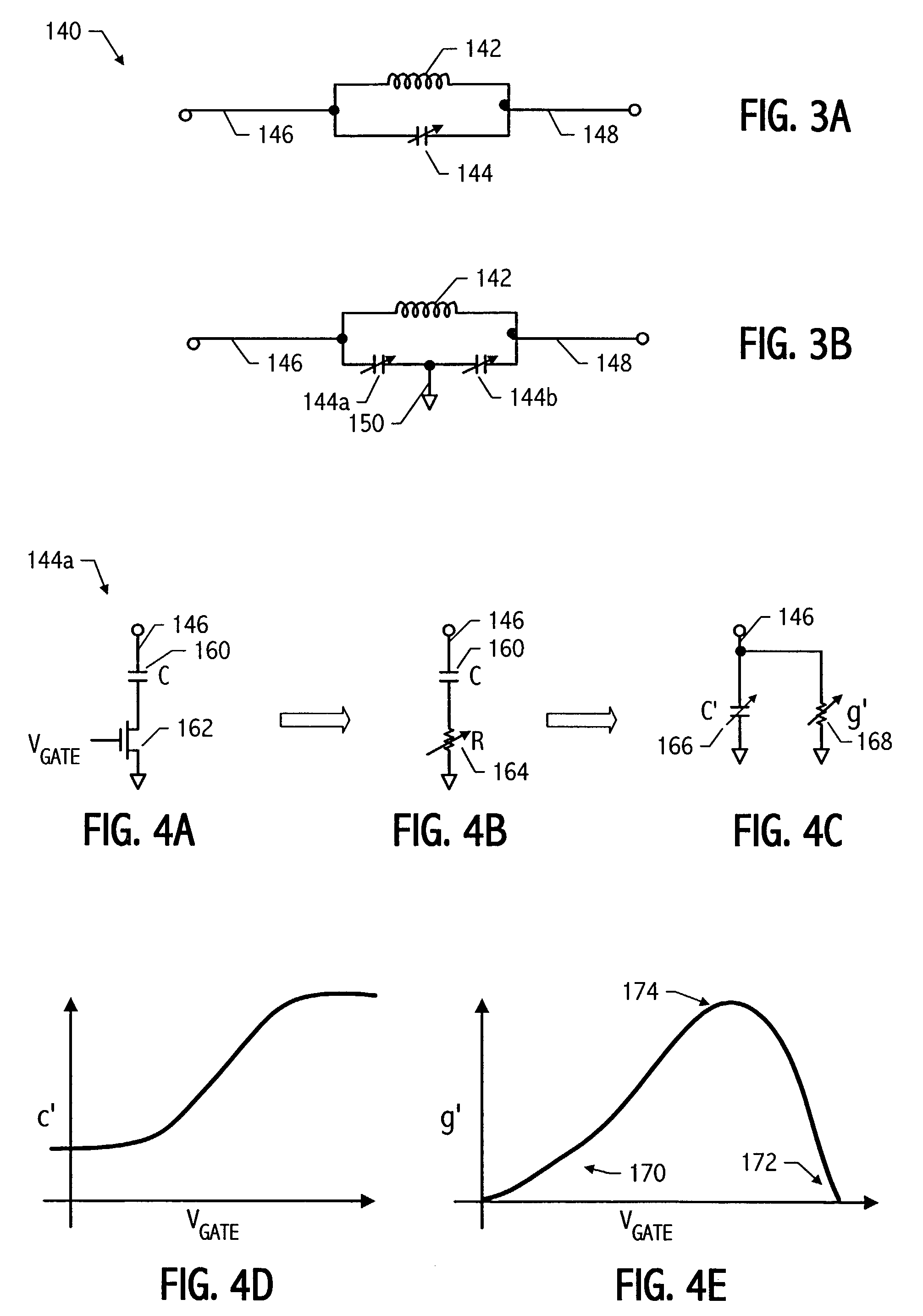
Feedback system incorporating slow digital switching for glitch-free state changes
A feedback system such as a phase locked loop (PLL) includes a second feedback loop which responds when a VCO control voltage is near either end of its range, by slowly adjusting additional tuning elements which control the VCO frequency. The second feedback loop is arranged to cause a slow enough change in the VCO frequency that the first traditional feedback loop adjusts the control voltage quickly enough in a direction toward its mid-range value to keep the VCO frequency substantially unchanged. The second feedback loop advantageously incorporates one or more digital control signals which preferably change no more than one bit at a time and with a controlled slow ramp rate. As a result, the PLL maintains phase accuracy so that the operation of the PLL, including subtle specifications such as input data jitter tolerance or output jitter generation when used for clock and data recovery applications, is not negatively impacted. An impedance tuning feedback system provides a resistance between two nodes which is proportional to a reference resistance, and preferably incorporates slow digital switching to result in near perturbation-free state changes over the tuning range of the resistance.
Owner:RPX CORP
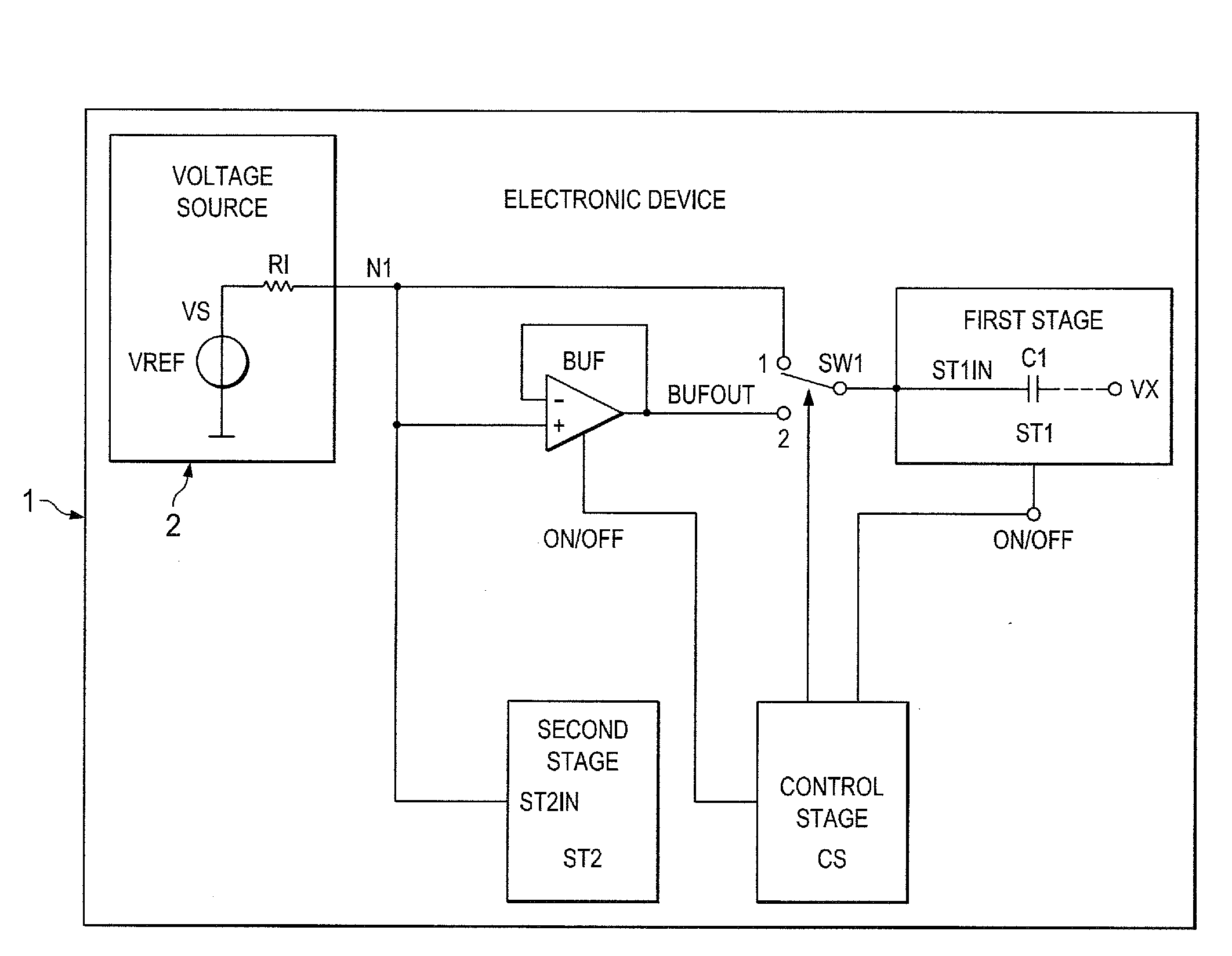
Electronic device and method for kickback noise reduction of switched capacitive loads and method of operating the electronic device
ActiveUS20120092055A1Improve offsetSmall input capacitanceAnalogue/digital conversionPulse automatic controlCapacitanceCharge injection
An electronic device which includes a first stage having an input capacitance, a switch, a buffer and a second stage having an input sensitive to charge injection and / or voltage glitches. An input of the buffer and the input of the second stage are coupled together at a first node which is configured to be coupled to a voltage source for supplying a reference voltage to the input of the first stage having the input capacitance. In a first configuration of the switch, the switch is arranged to either connect the input of the first stage to the first node and to disconnect the input of the first stage from an output of the buffer. In a second configuration of the switch, to connect the input of the first stage to the output of the buffer and to disconnect the input of the first stage from the first node.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
PFM-PWM DC-DC converter providing DC offset correction to PWM error amplifier and equalizing regulated voltage conditions when transitioning between PFM and PWM modes
ActiveUS7382114B2Accurate supervisionEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDc dc converterTransverter
To prevent a voltage glitch in the regulated DC output voltage of a PWM / PFM DC-DC converter when switching between PFM and PMW modes, the error amplifier of the converter's PWM regulation path is provided with a DC voltage offset correction mechanism. This mechanism “zeros-out” DC voltage offsets that may be present in the voltage regulation path, thereby enabling the error amplifier to accurately regulate the converter's output voltage. When the converter transitions between PFM and PWM modes, the DC offset correction mechanism establishes initial conditions of the error amplifier that effectively ensure that the converter's regulated output voltage at the beginning of a new “switched-to” PWM mode cycle is DC offset-free.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
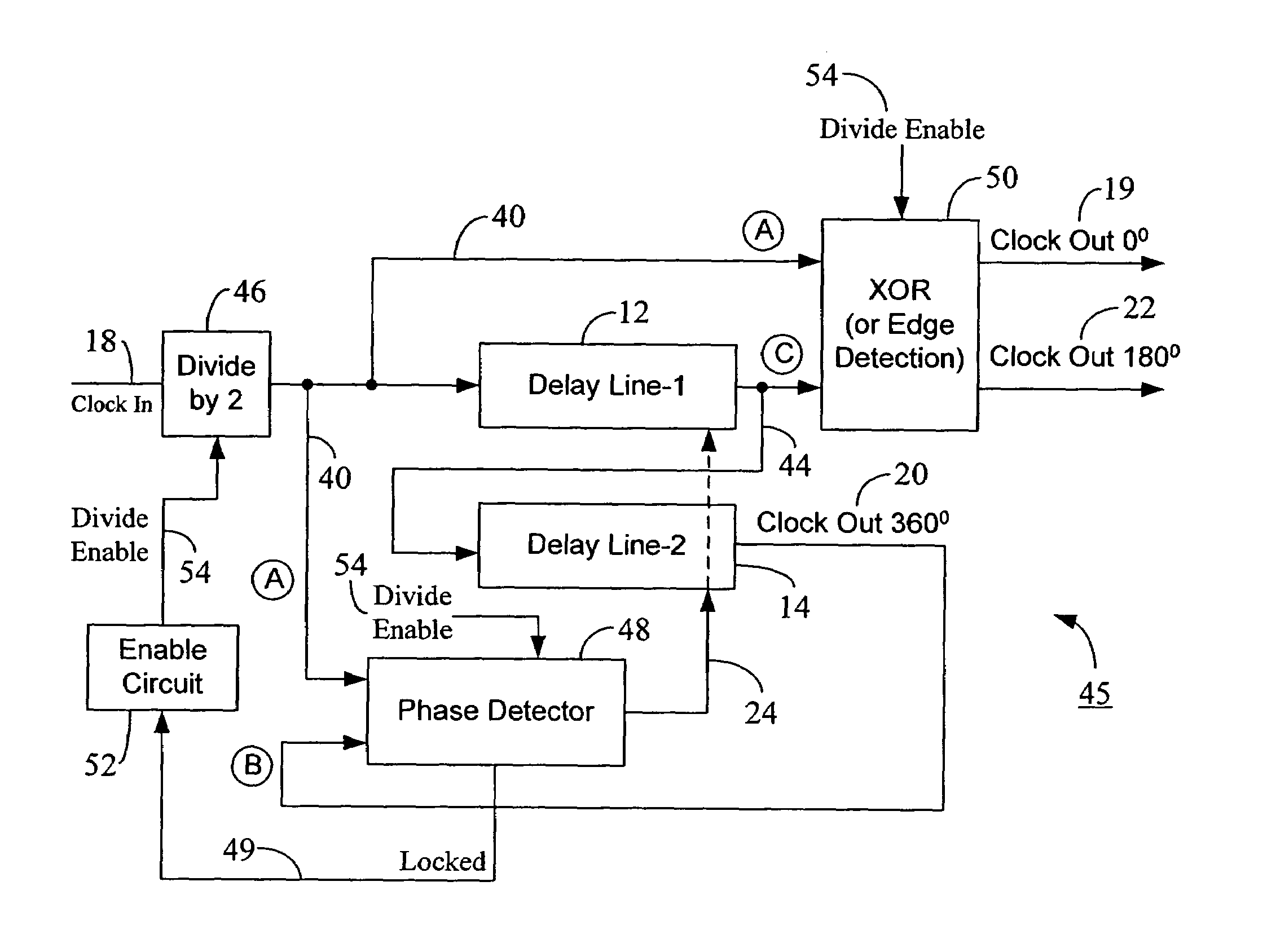
Initialization scheme for a reduced-frequency, fifty percent duty cycle corrector
ActiveUS7259604B2Avoid instabilityReduced-frequency operationPulse automatic controlDigital storageMemory chipInstability
A reduced-frequency, 50% duty cycle corrector (DCC) circuit may be used in an electronic device (e.g., a memory chip) to generate output clocks with 50% duty cycle irrespective of the duty cycle of the clock input to the DCC circuit. A DCC initialization scheme selectively activates the frequency division and edge detection operations in the DCC based on the lock status of the DCC during initialization. Upon initialization, the frequency division and edge detection operations are turned off or disabled. After the DCC is properly locked, these operations are enabled to obtain the 50% duty cycle output clock. This approach initializes the reduced-frequency DCC without output glitches, which can affect locking of a DLL with which the DCC may be used. The prevention of instability in locking of the DCC and DLL upon system initialization results in swift establishment of DCC and DLL locks without significant power consumption or loss of clock cycles. Once the DCC is locked during its initialization, the reduced-frequency operation of DCC further saves current consumption. Because of the rules governing abstracts, this abstract should not be used to construe the claims.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
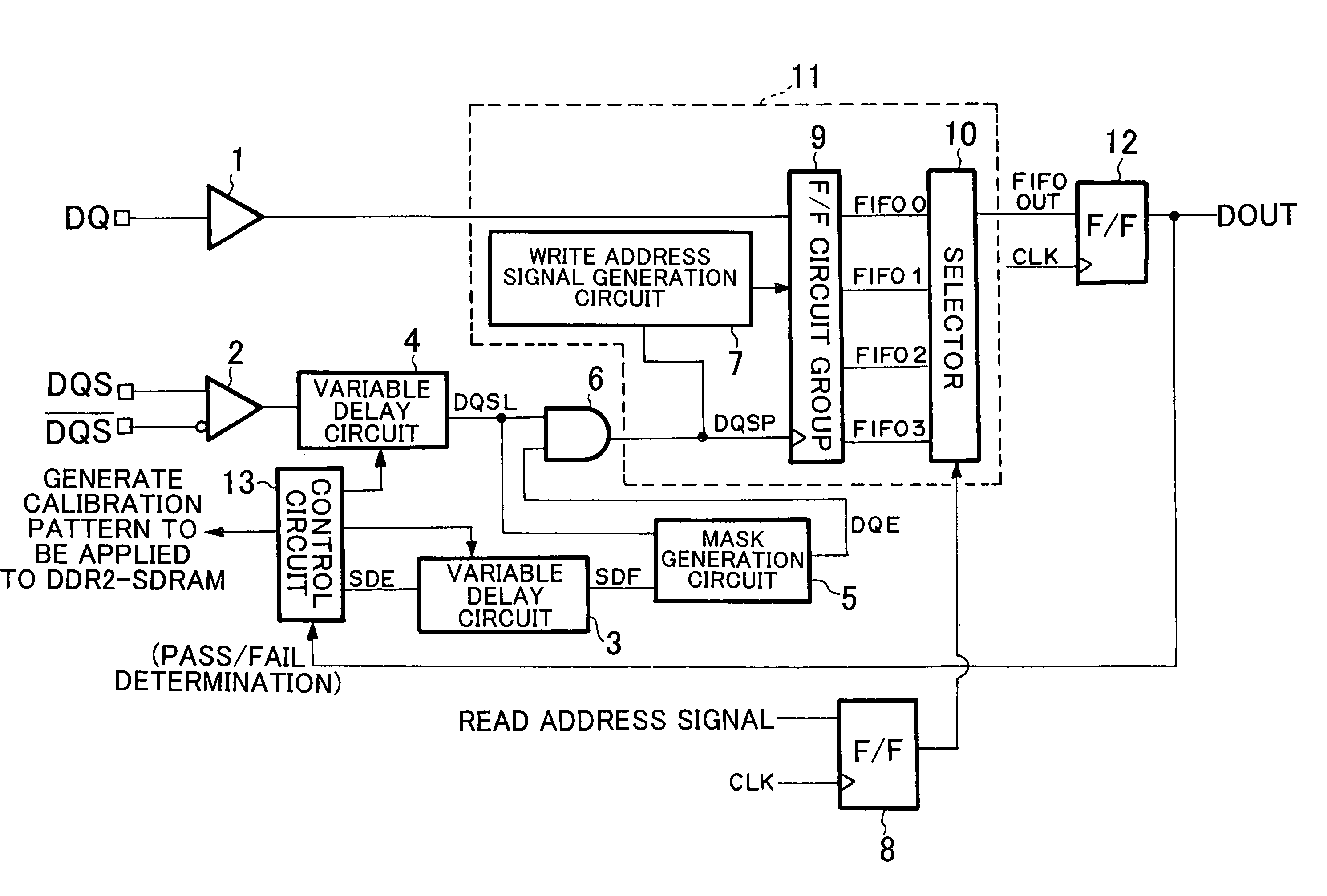
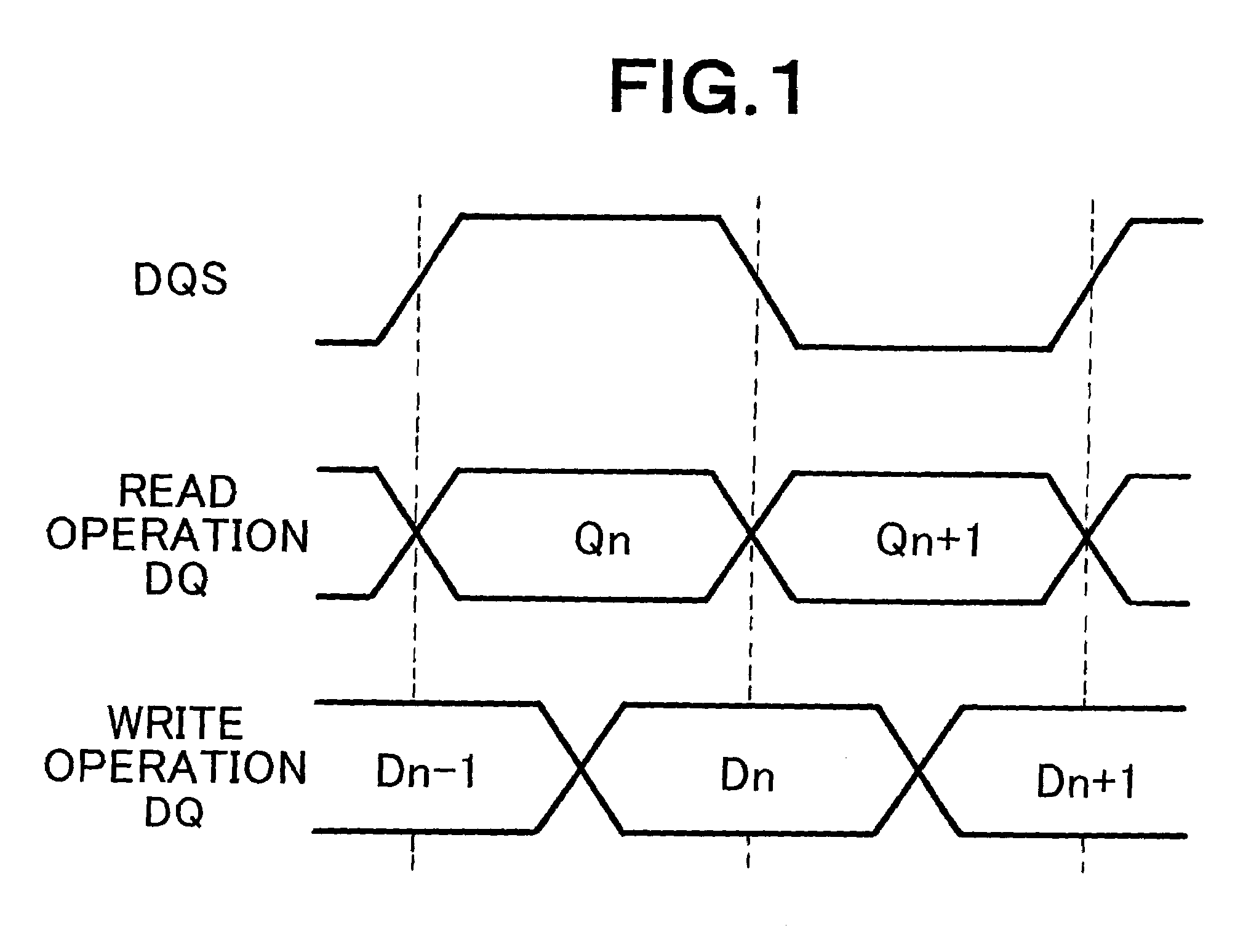
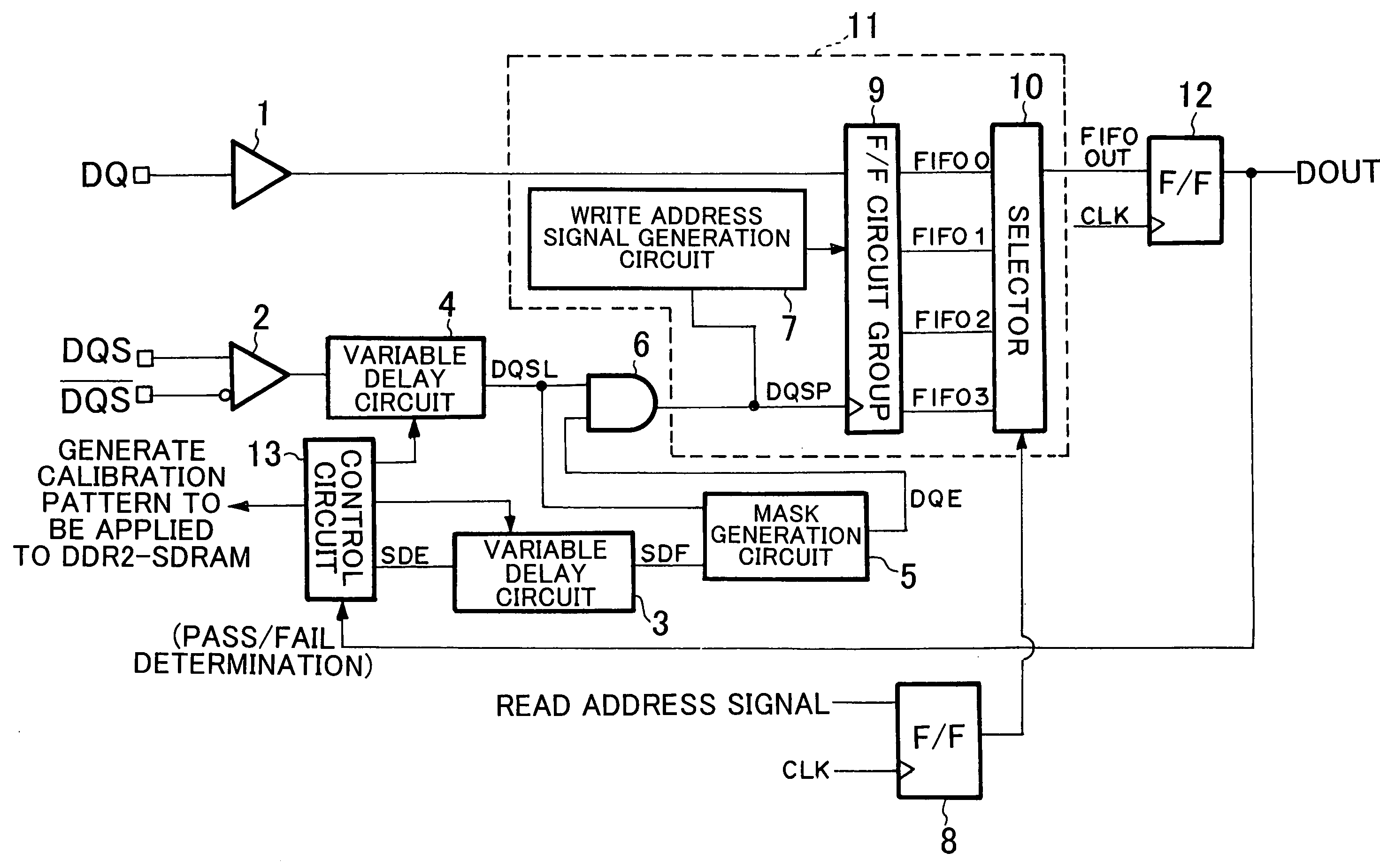
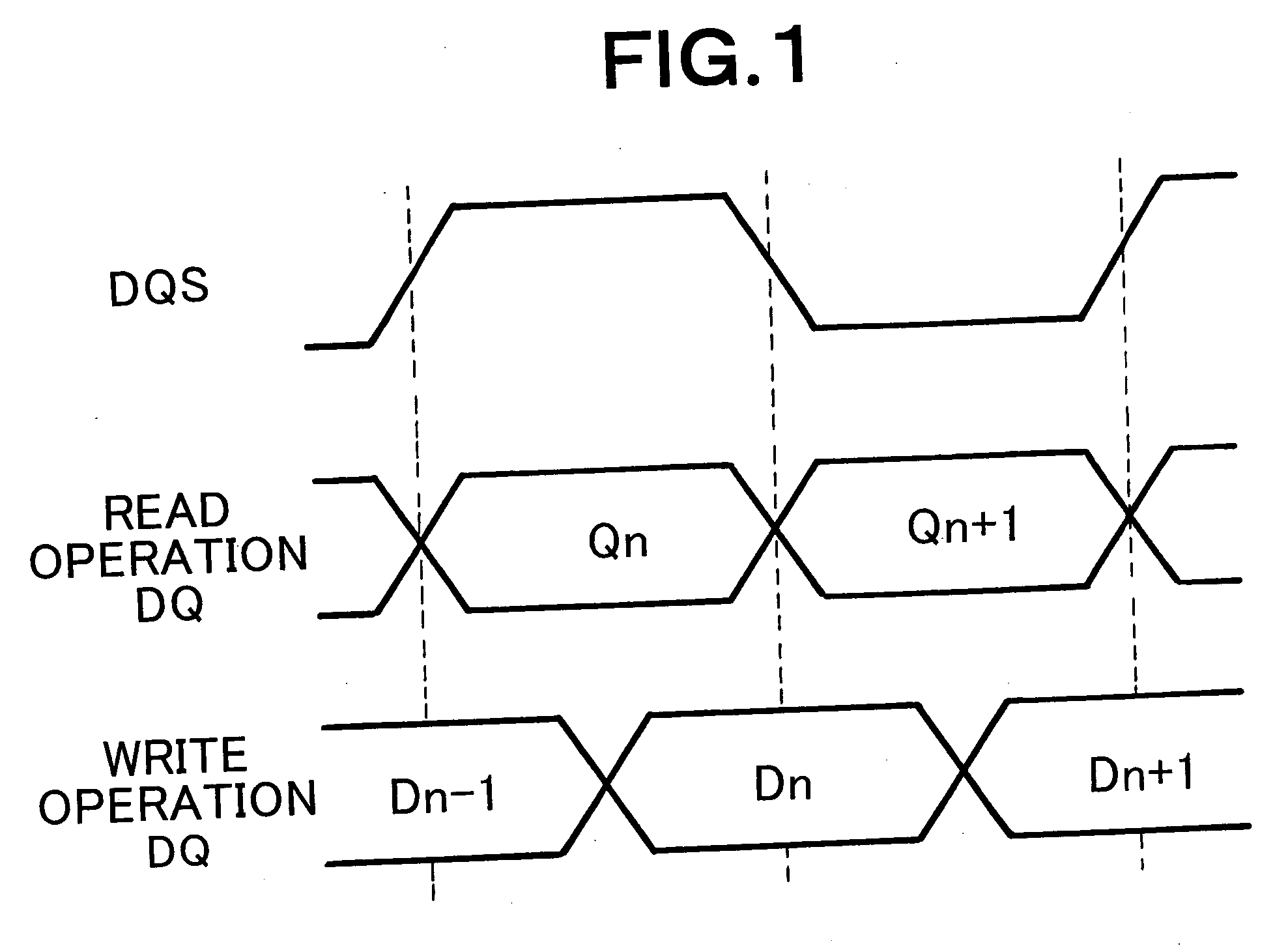
Memory interface control circuit and memory interface control method
ActiveUS7038953B2Improve noise immunityDwelling equipmentDigital storageControl signalMemory interface
According to one embodiment, one variable delay circuit adjusts a data strobe signal to be delayed, a control circuit generates an auxiliary signal, another variable delay circuit adjusts the auxiliary signal to be delayed, a mask generation circuit generates a mask signal based on the delayed data strobe signal and the delayed auxiliary signal, and an AND circuit applies the mask signal to the delayed data strobe signal, thereby generating a data strobe signal without a glitch. A write address signal generation circuit generates a control signal for controlling a flip-flop group based on the data strobe signal without the glitch, and the flip-flop group stores read data according to the control signal. A selector selects data from among pieces of data stored in the flip-flop group according to the read address signal.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method and apparatus for quick clock swapping using much slower asynchronous clock for power savings
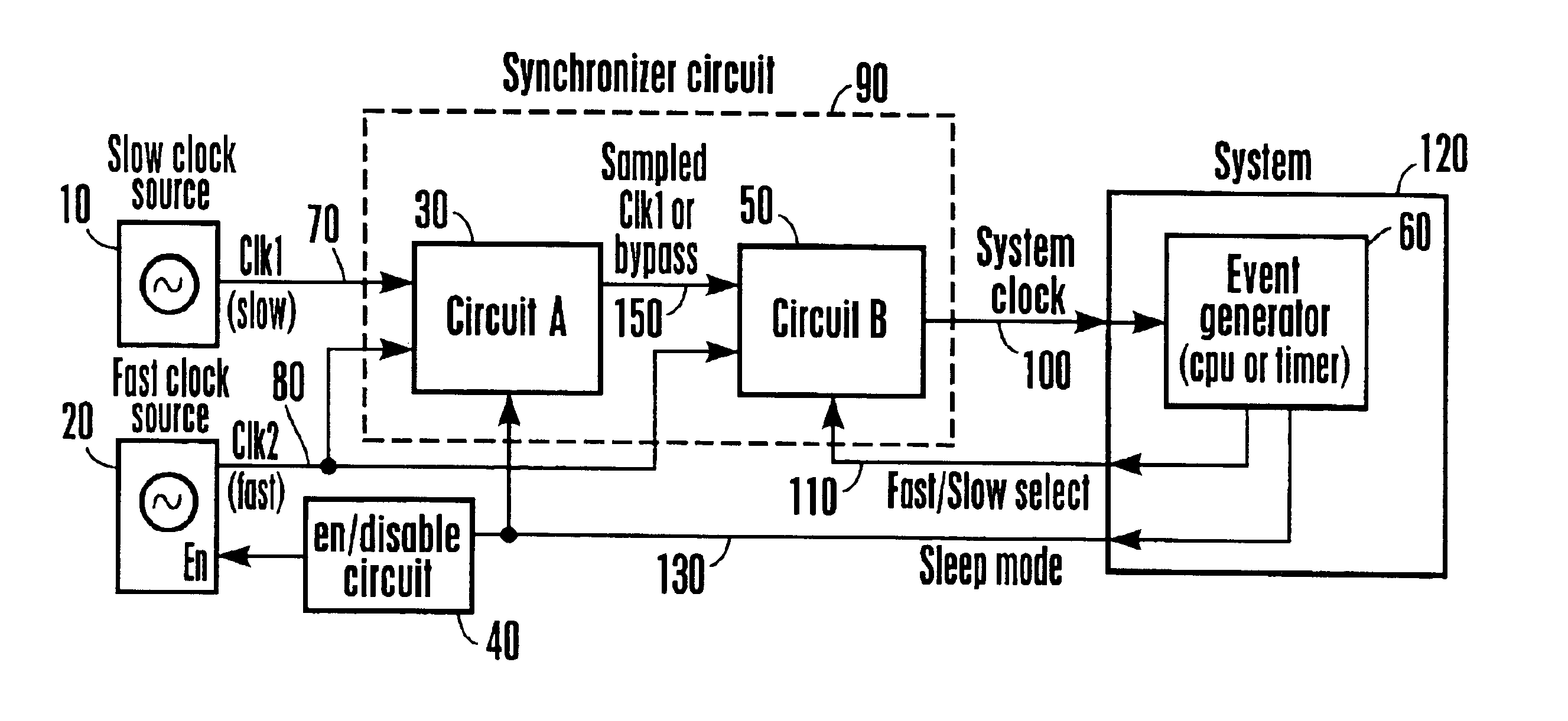
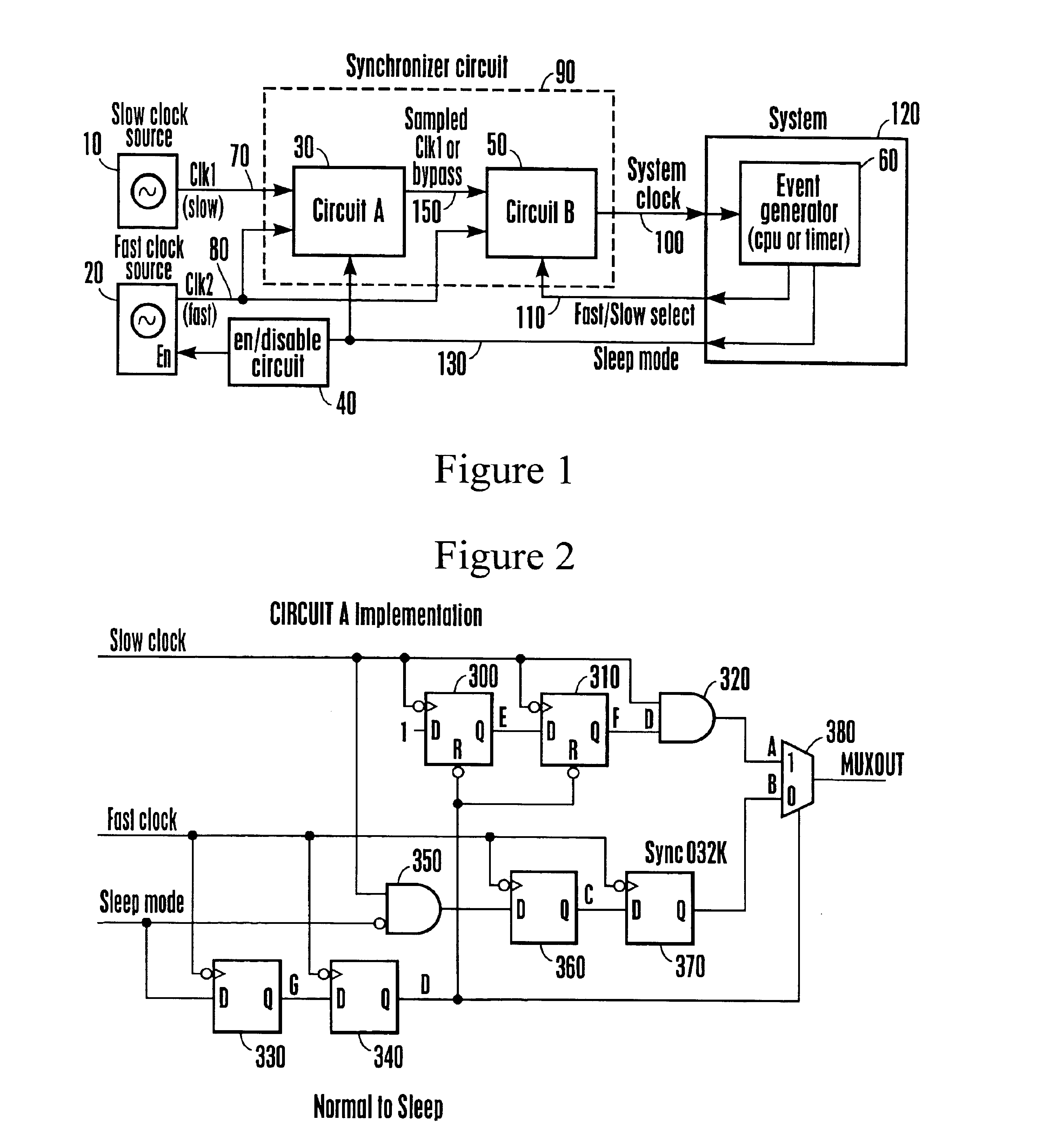
A power reduction device which includes a first clocking device for generating a first clocking signal, a second clocking device for generating a second clocking signal, a synchronizer device for receiving the first and second clocking signals and being responsive to a first select signal and to a second control signal wherein upon receipt of either of the select or control signals, the synchronizing device generating a synchronized signal without a glitch therefrom wherein the synchronized signal corresponding to either the first or second clocking signals.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
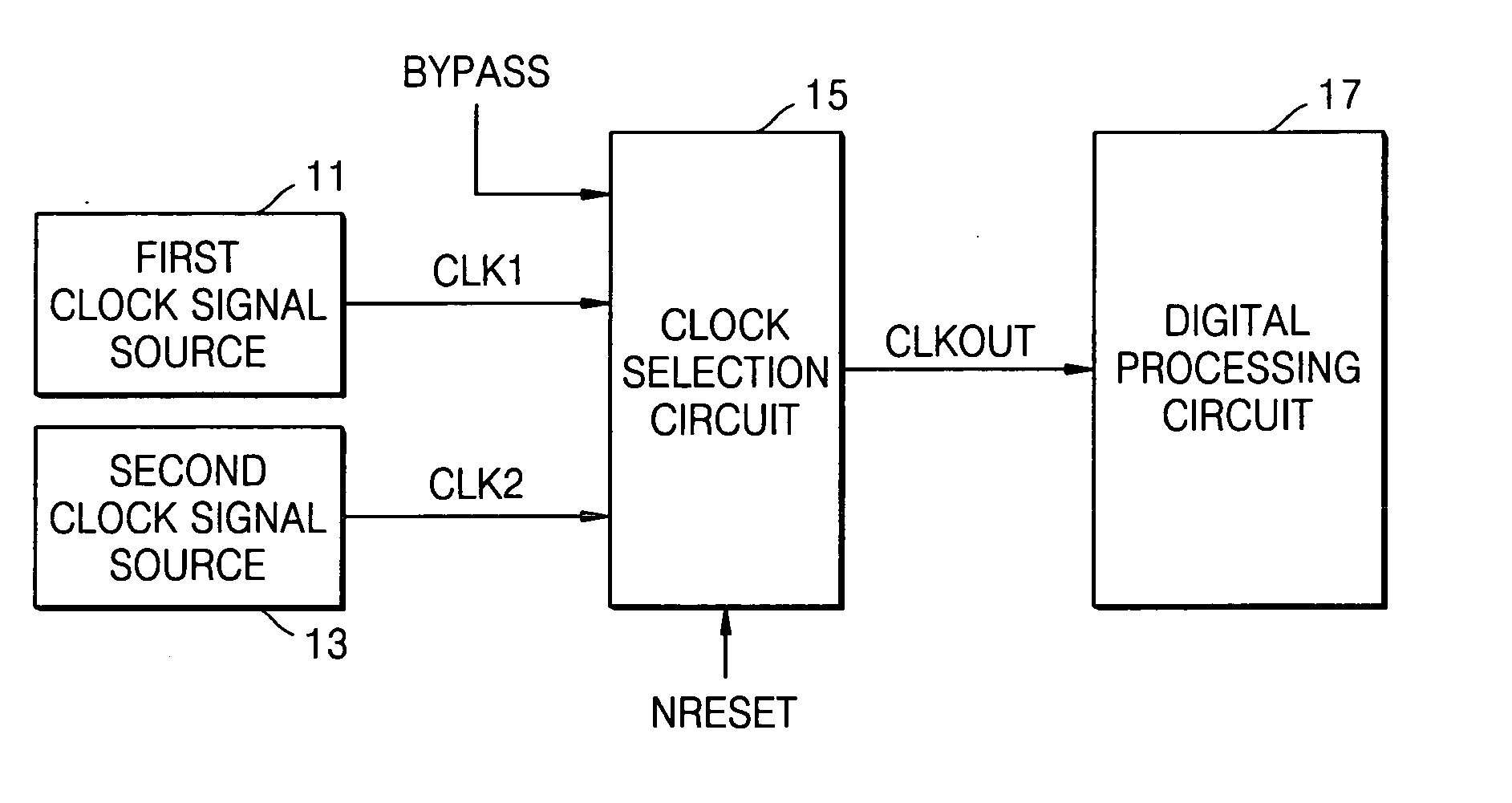
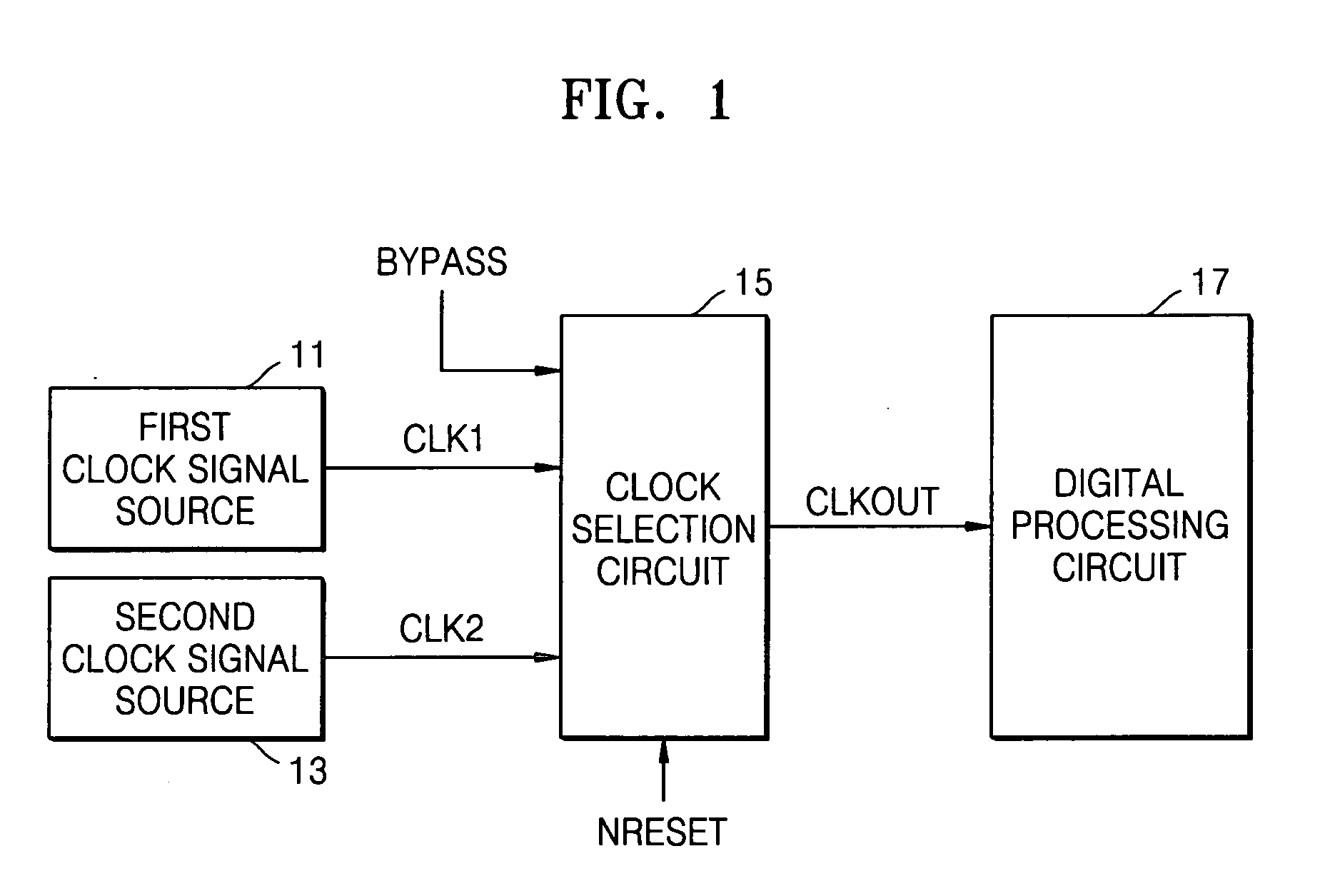
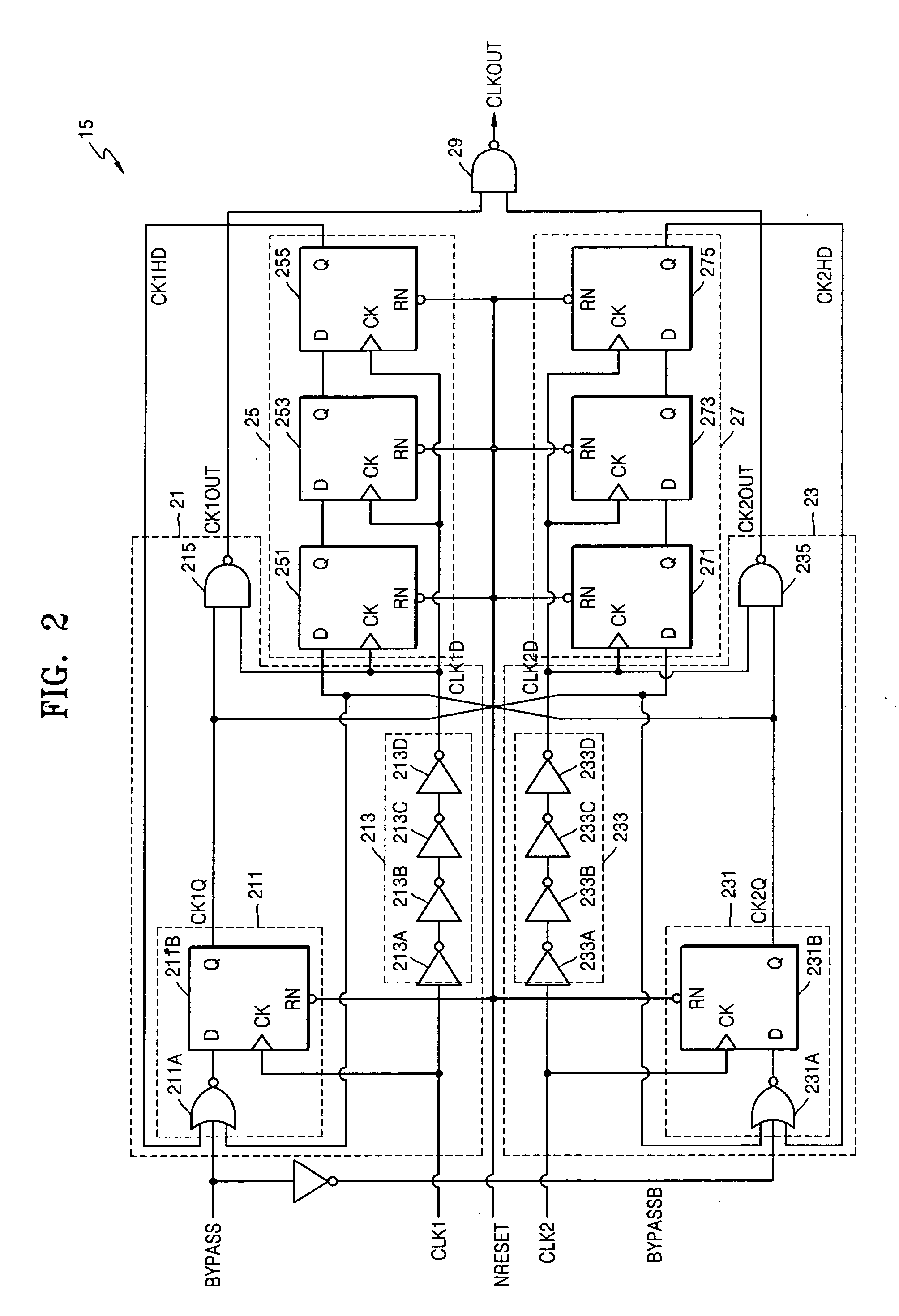
Clock selection circuit and digital processing system for reducing glitches
InactiveUS20050225361A1Reduce the possibilityReduce power levelElectronic switchingPower supply for data processingGlitchEngineering
A clock selection circuit and method may operate to generate a clock signal for a digital processing system. In the clock selection circuit, first and second clock control signals may be generated based on a received control signal and / or the inverse of a received clock signal. A first clock signal may be selected when the first clock control signal is activated, and may be output as the selected clock signal. A second clock signal may be selected when the second clock control signal is activated, and may be output as the selected clock signal. The selection operation of the clock selection circuit may reduce the likelihood that a glitch occurs and / or may reduce the amount of power consumed when compared to a conventional clock selection circuit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
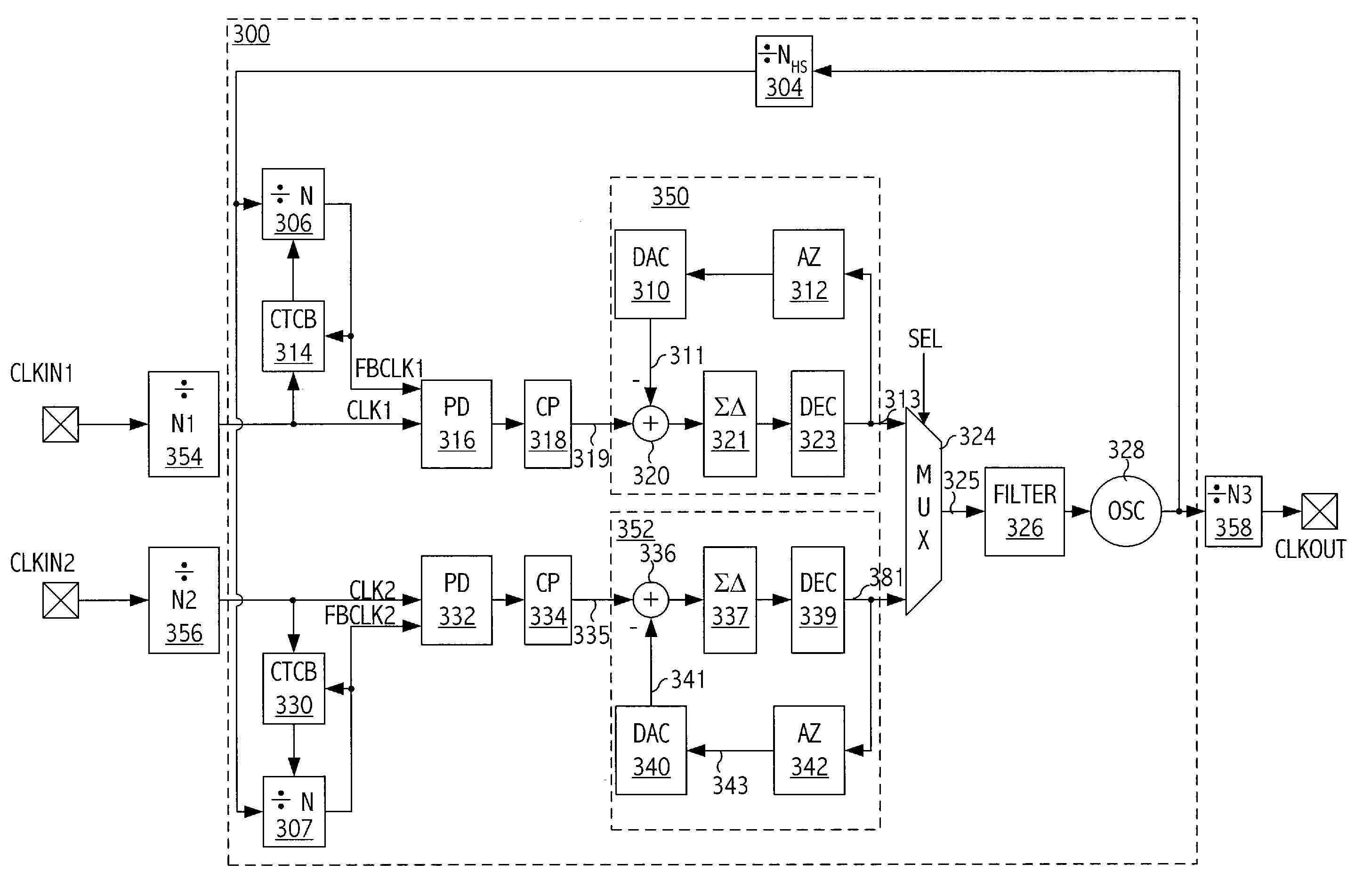
Technique for switching between input clocks in a phase-locked loop
ActiveUS7405628B2Reduces and eliminates phase glitchEasy to implementPulse automatic controlPhase differenceHarmonic
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Memory interface control circuit and memory interface control method
ActiveUS20050213396A1High glitch noise resistancePlacement is limitedDwelling equipmentDigital storageControl signalMemory interface
According to one embodiment, one variable delay circuit adjusts a data strobe signal to be delayed, a control circuit generates an auxiliary signal, another variable delay circuit adjusts the auxiliary signal to be delayed, a mask generation circuit generates a mask signal based on the delayed data strobe signal and the delayed auxiliary signal, and an AND circuit applies the mask signal to the delayed data strobe signal, thereby generating a data strobe signal without a glitch. A write address signal generation circuit generates a control signal for controlling a flip-flop group based on the data strobe signal without the glitch, and the flip-flop group stores read data according to the control signal. A selector selects data from among pieces of data stored in the flip-flop group according to the read address signal.
Owner:NEC CORP
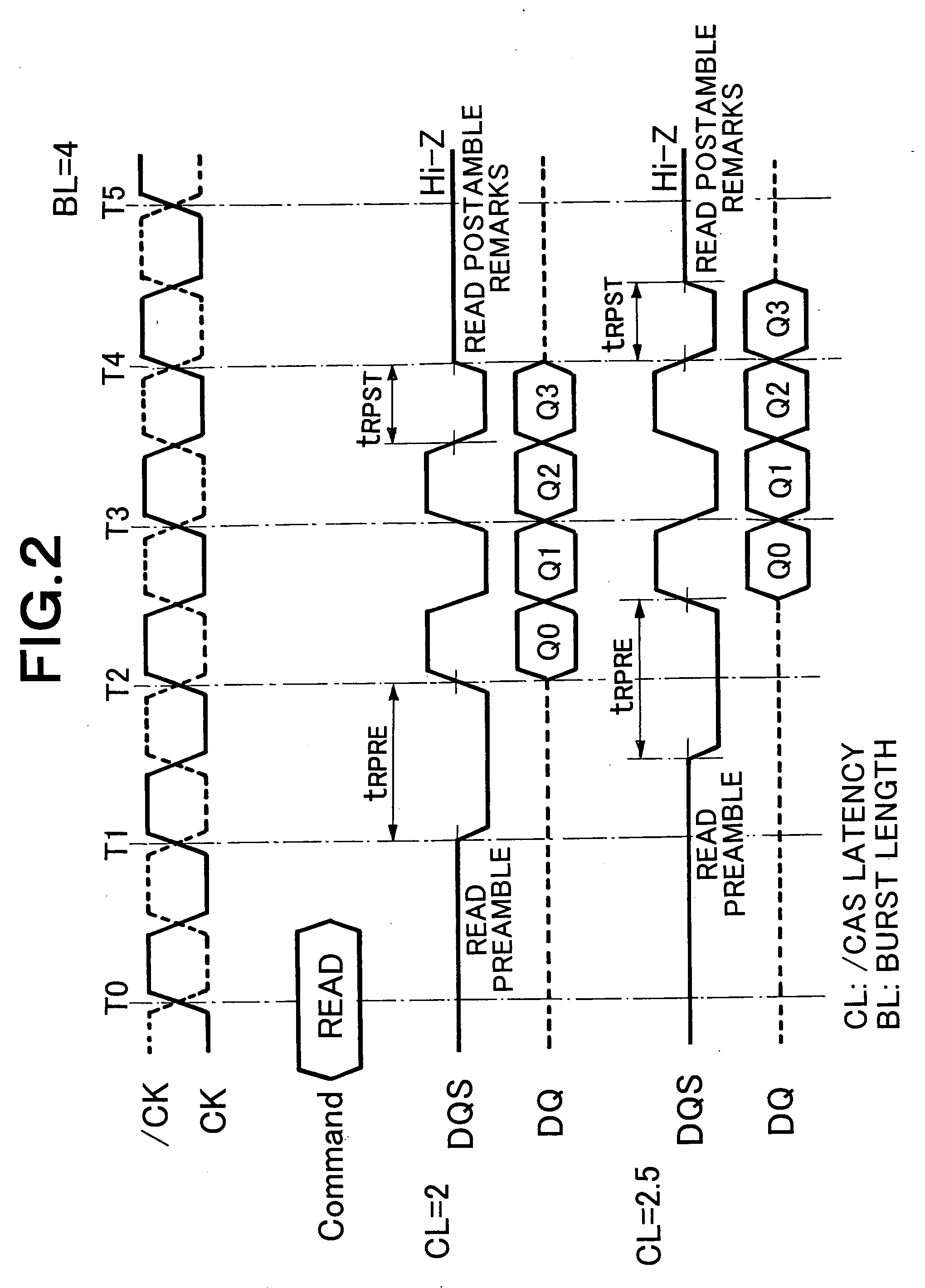
Audio splice process for digital Ad insertion
InactiveUS20050022253A1Avoid underflowPrevent overflowPulse modulation television signal transmissionColor signal processing circuitsComputer hardwareVariable bit rate vbr
A system and method for audio splicing (insertion) of an Ad audio stream in the compressed domain, where variable early delivery of the Ad audio stream and variable bit rate are allowed, without creating audio distortion, glitches, or other digital artefacts or errors, in the resultant audio stream is disclosed. The present system and method provides for a splice delay buffer which delays the first five Ad audio frames until transmission of the last frame of the primary audio stream, but before the splice time. Subsequent Ad audio frames are delayed by a fixed amount, where the fixed amount is greater than the frame delay of the primary audio stream, to allow for ease of splice back to the primary audio stream.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Non-abrupt switching of sleep transistor of power gate structure
InactiveUS6876252B2Reduce ground bounceWeakening rangeElectronic switchingStatic storageMinimum timeGround bounce
A semiconductor integrated circuit including a non-abrupt switching mechanism for a sleep transistor of a power gate structure to reduce ground bounce is provided. The semiconductor integrated circuit comprises a supply voltage line; a ground voltage line; a virtual ground voltage line; a logic circuit coupled to the supply voltage line and the virtual ground voltage line; at least one sleep transistor for controlling current flow to the logic circuit, the sleep transistor being coupled to the virtual ground voltage line and the ground voltage line; and a non-abrupt switching circuit for sequentially controlling the sleep transistor. The switching mechanism reduces the magnitude of voltage glitches on the power and ground rails as well as the minimum time required to stabilize power and ground.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Microprocessor with power saving clock
ActiveUS20050184773A1Reduce clock frequencyEnergy efficient ICTPulse automatic controlDigital dataElectric force
A data processing chip with a flexible timing system and method for supplying clocks to a digital data processing system useful for power conservation. A phase locked loop generates a master clock from which a core clock and a system clock are derived. The frequency of each of the core and system clocks is independently controllable relative to the master clock and can be changed on the fly with glitch free and jitter free operation. The data processing chip is well suited for use in hand held electronic devices where power management is a concern. Power can be saved by lowering the frequency of the core clock, even for short intervals of time.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Interface circuit
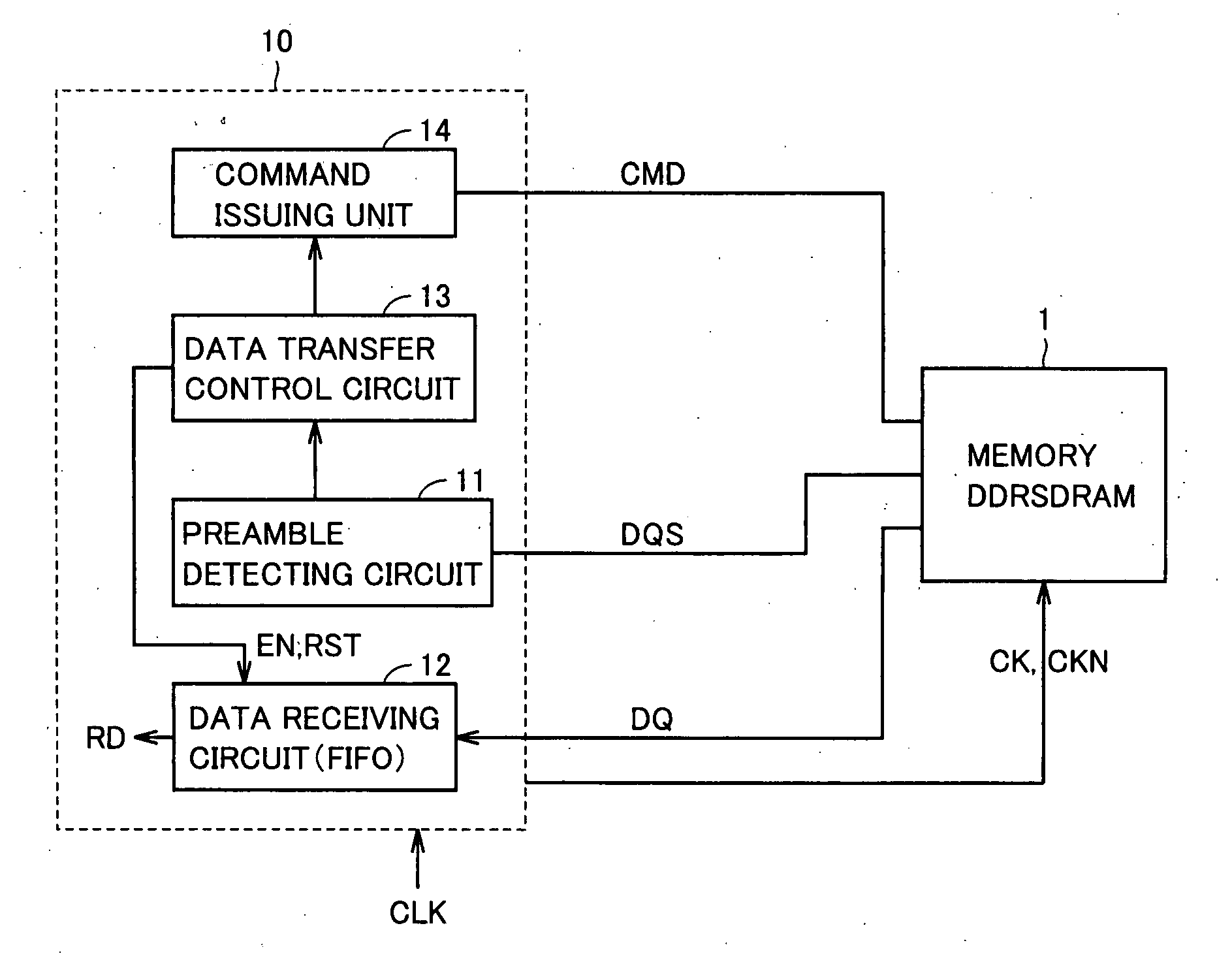
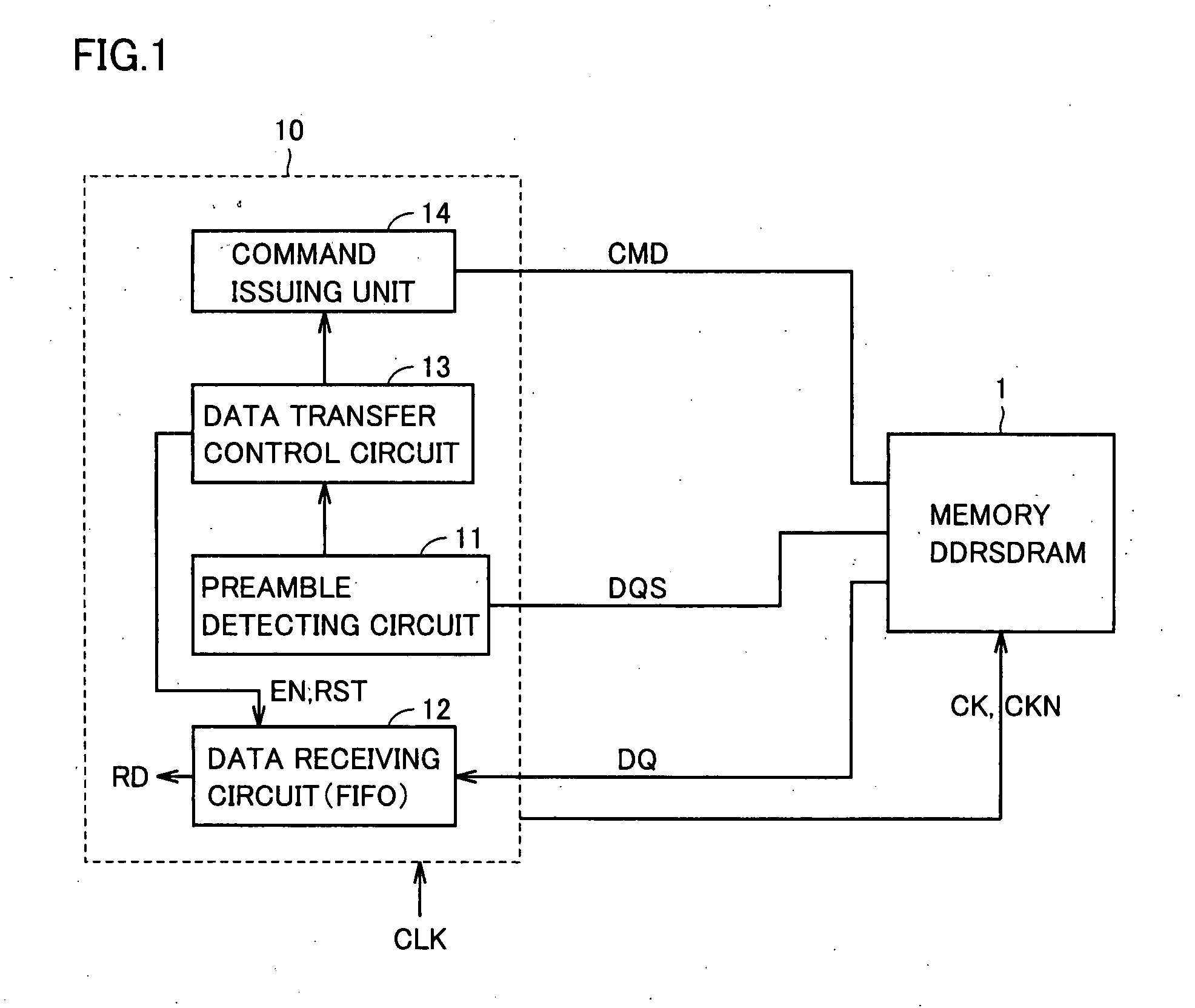
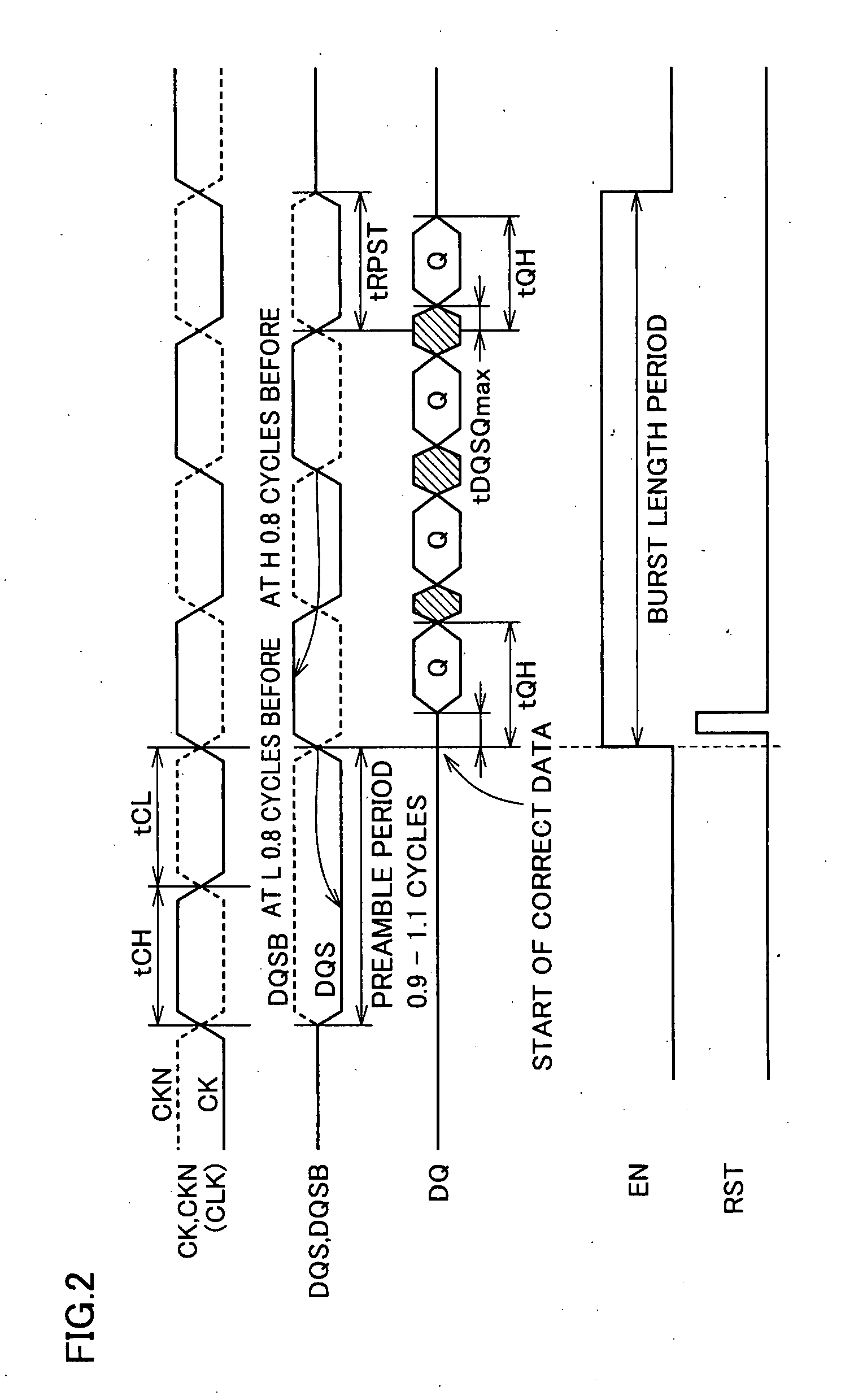
InactiveUS20080031079A1Simple circuit configurationReliably takenDigital storageData sourceData transmission
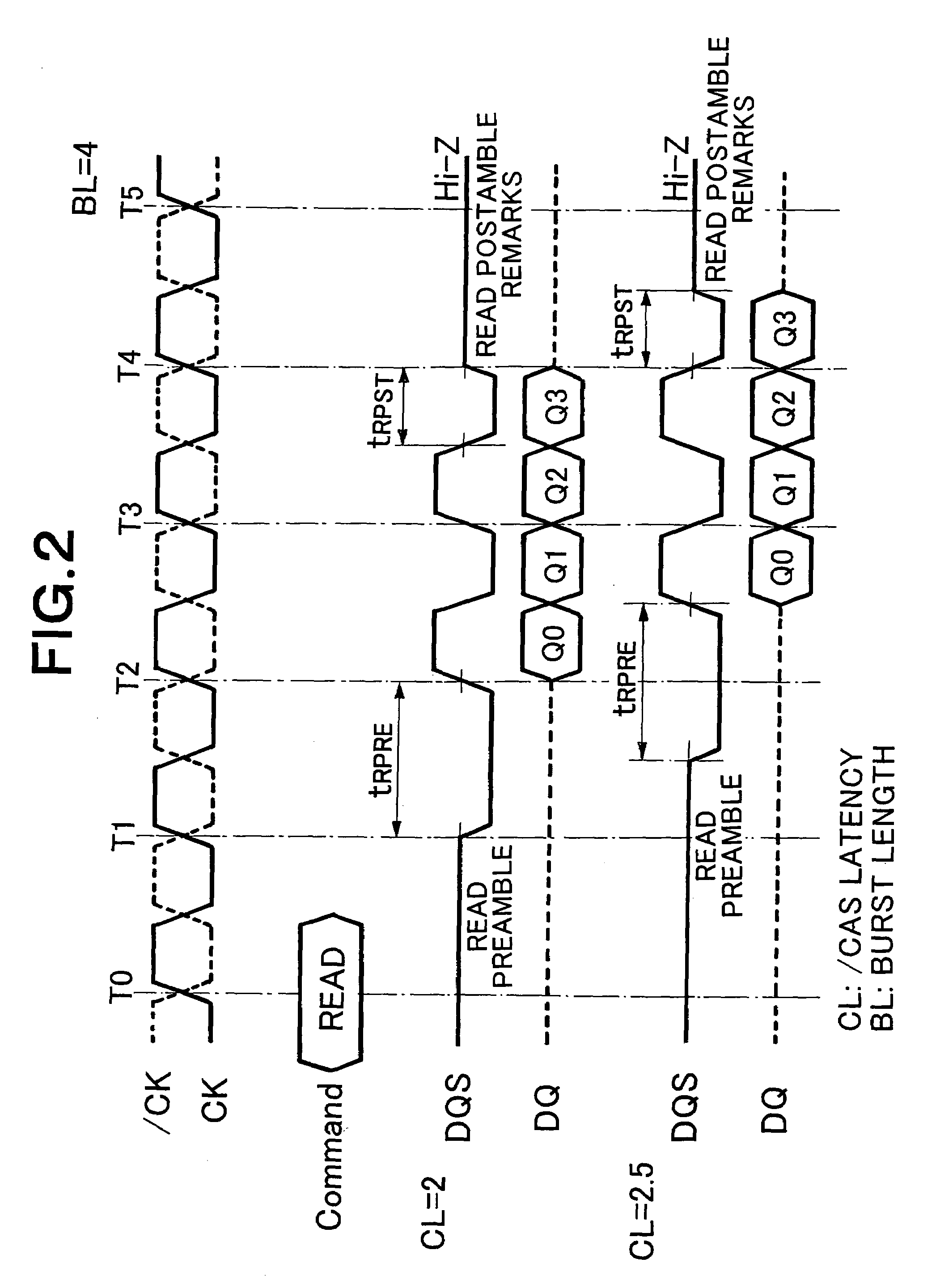
A variable delay line receives and delays a data strobe signal transferred from a data source side in synchronization with a transfer data by a predetermined period, and produces a delayed data strobe signal and the non-delayed data strobe signal to a detector. The detector determines that a preamble period ends and effective data is transferred, when the delayed data strobe signal is at the L level at the time of rising of the non-delayed data strobe signal from the L level to the H level. According to a result of detection, an interface circuit unit takes in the transfer data and initializes a take-in address. The data strobe signal changes to a high-impedance state when a postamble ends. An influence of a glitch noise is avoided upon this change of the data strobe signal, and the data transfer can be executed fast and accurately.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com