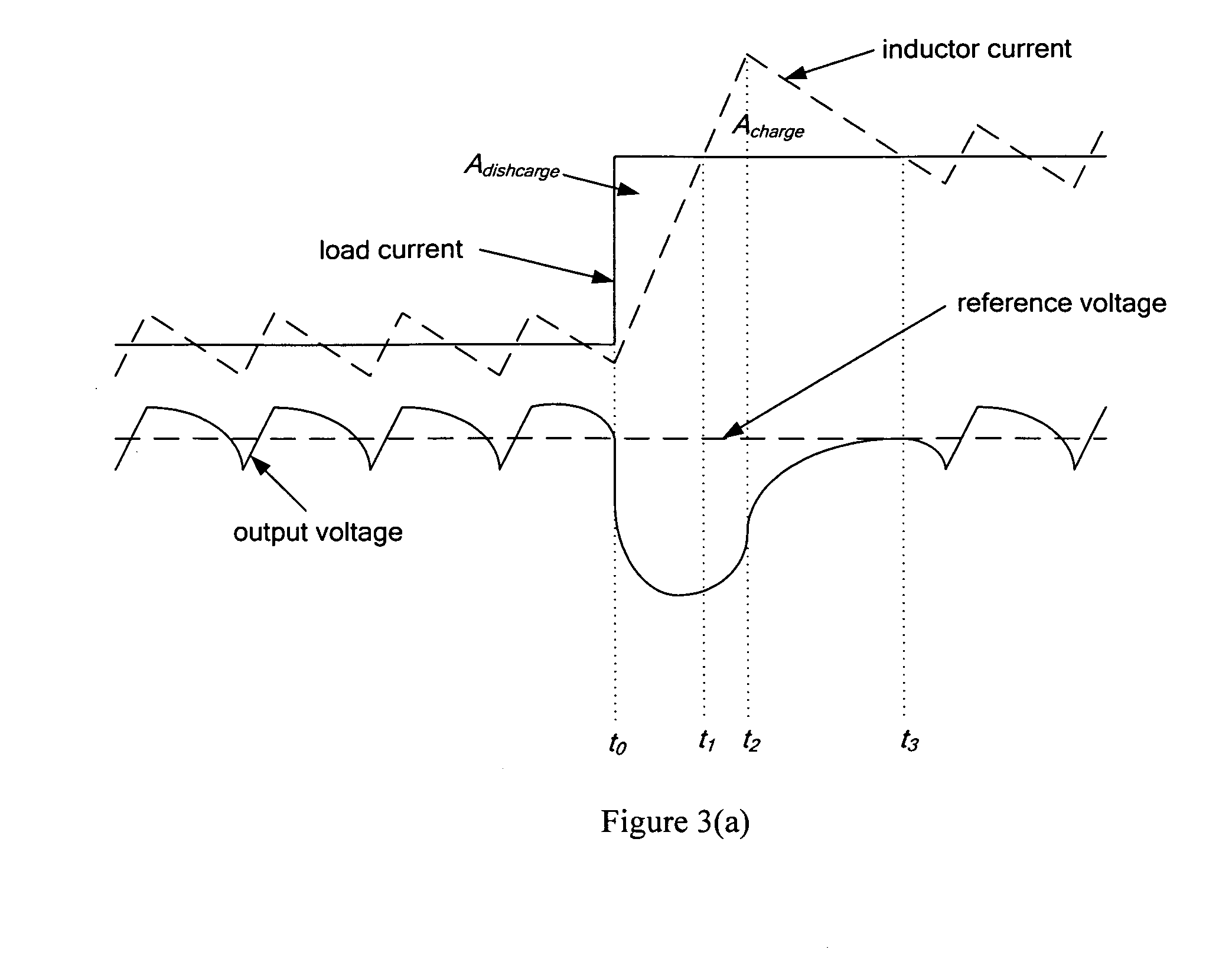
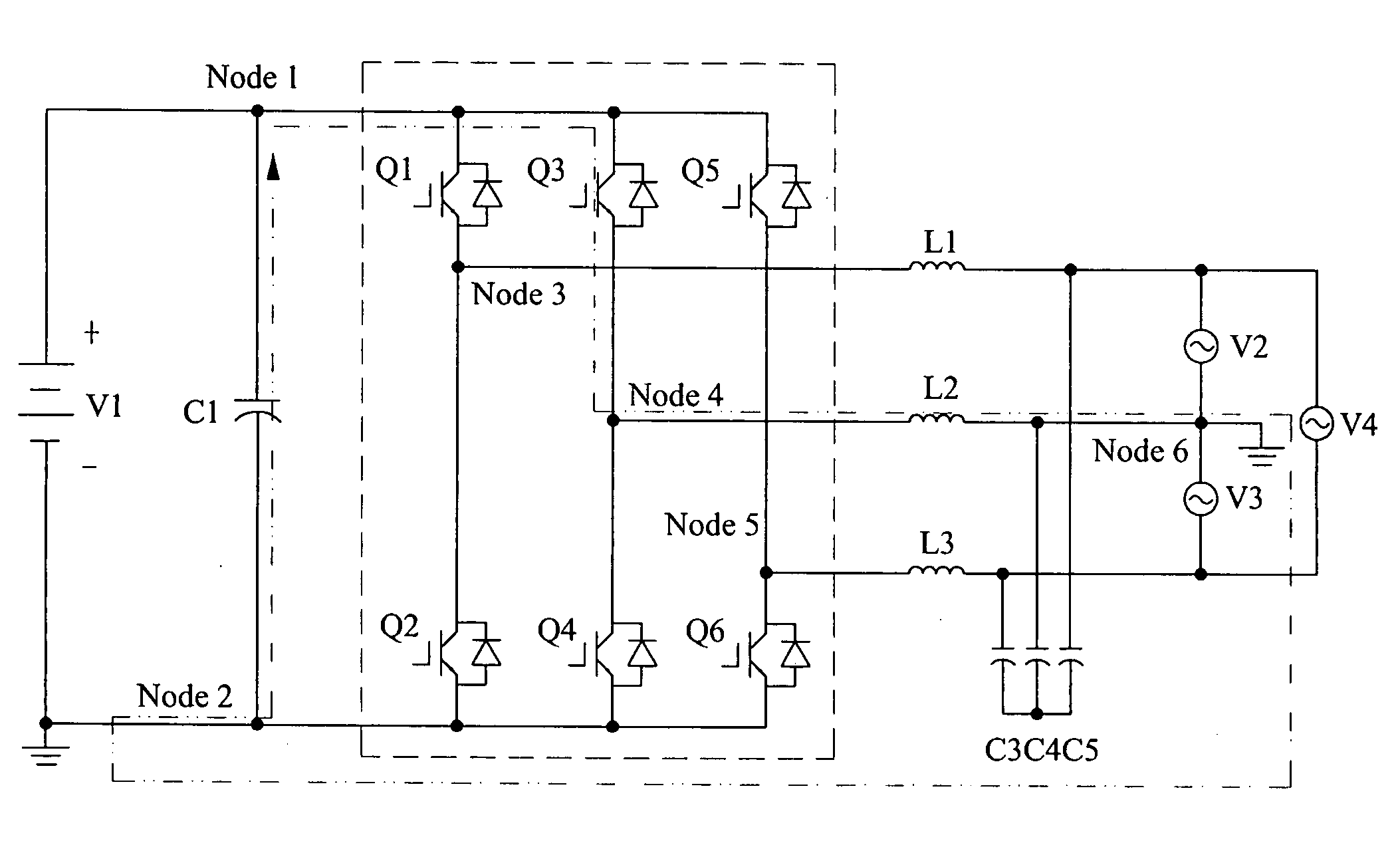
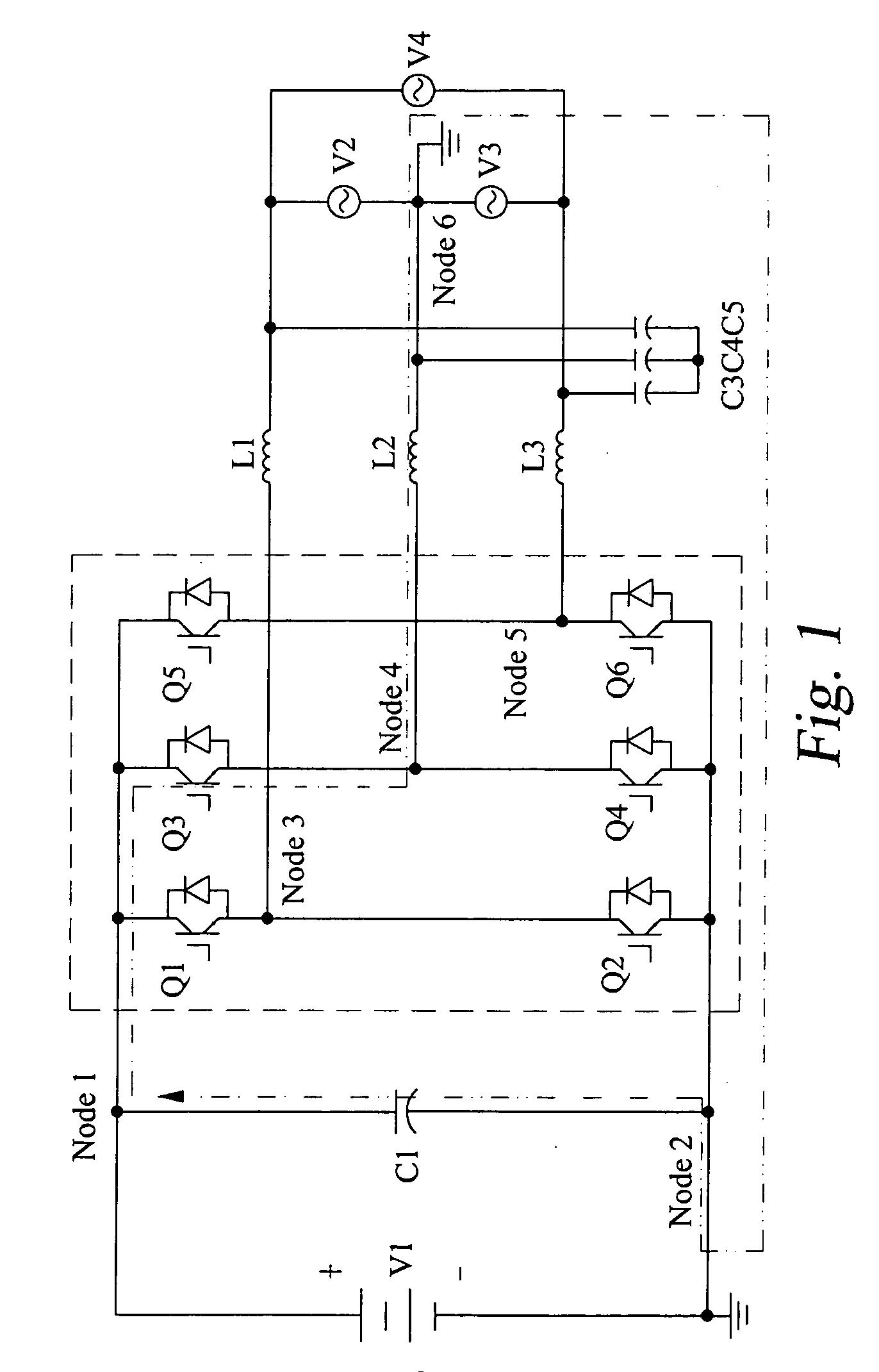
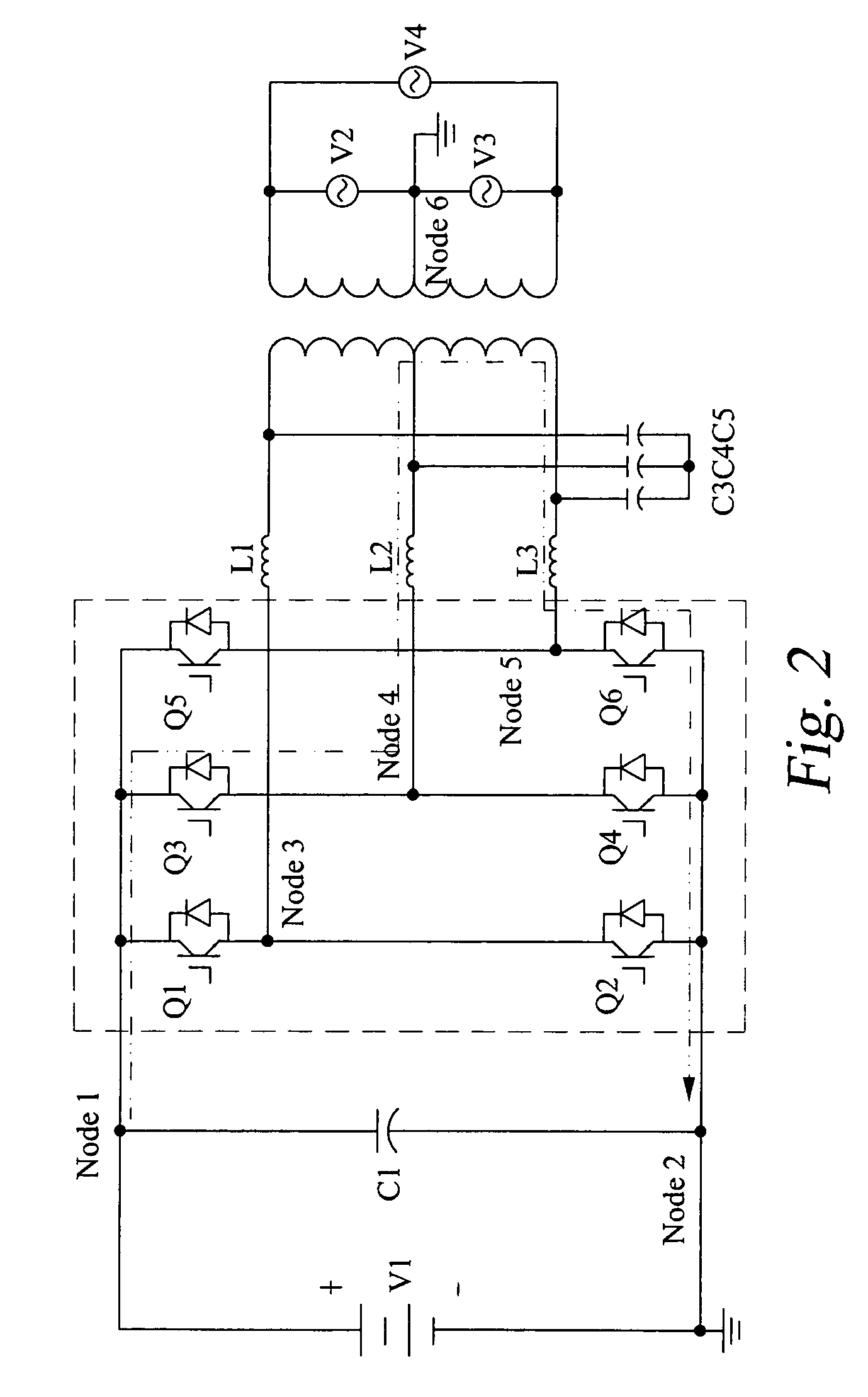
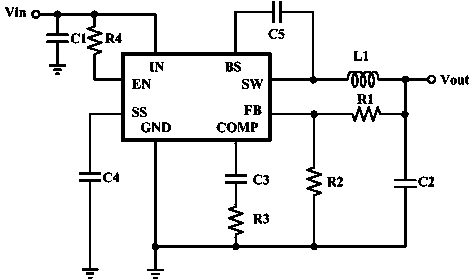
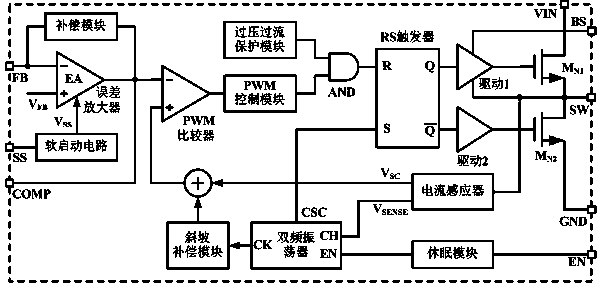
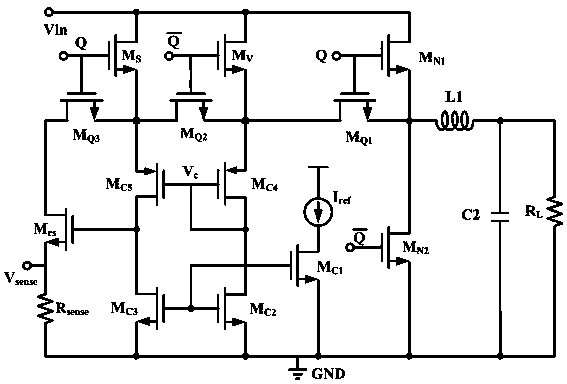
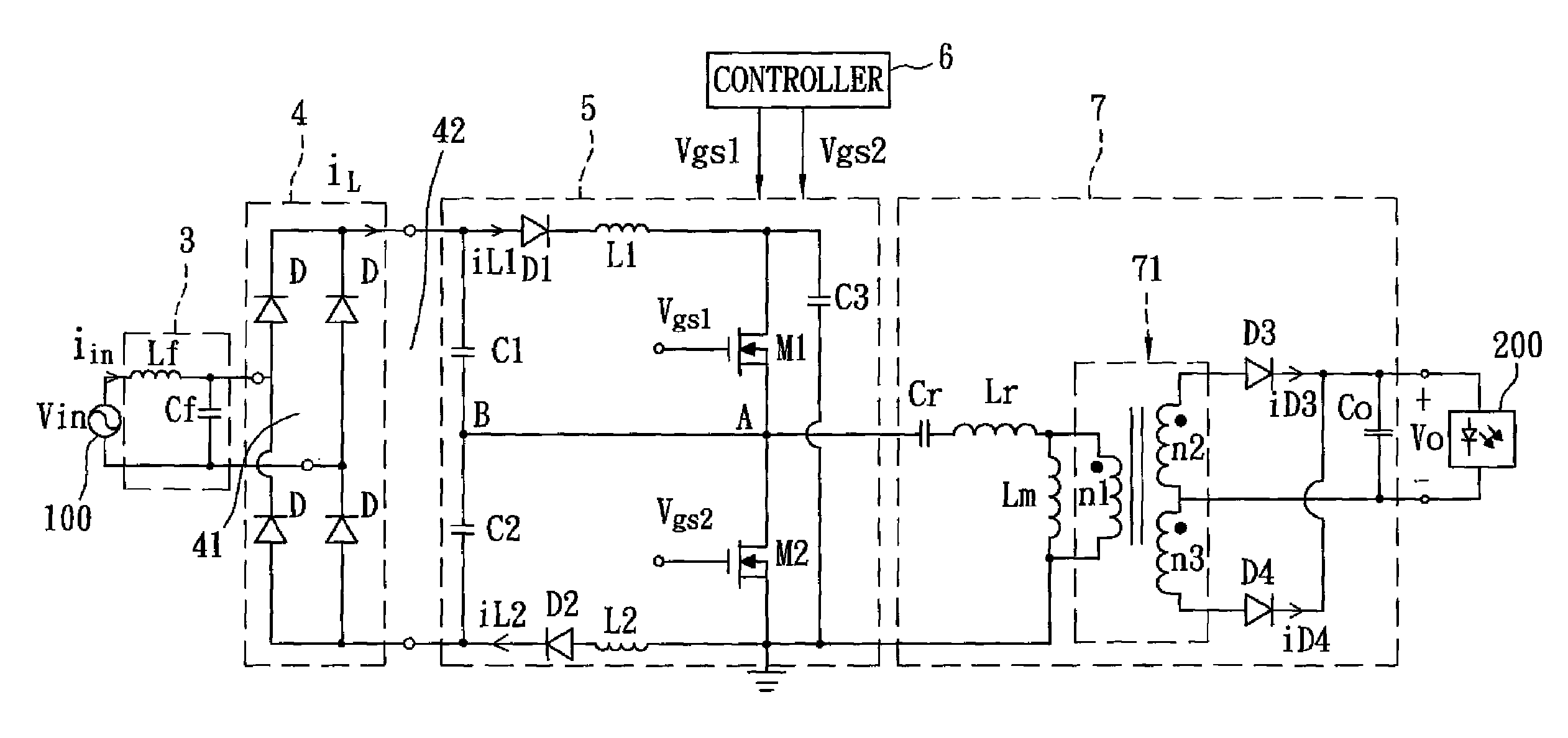
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
405 results about "Step down converter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
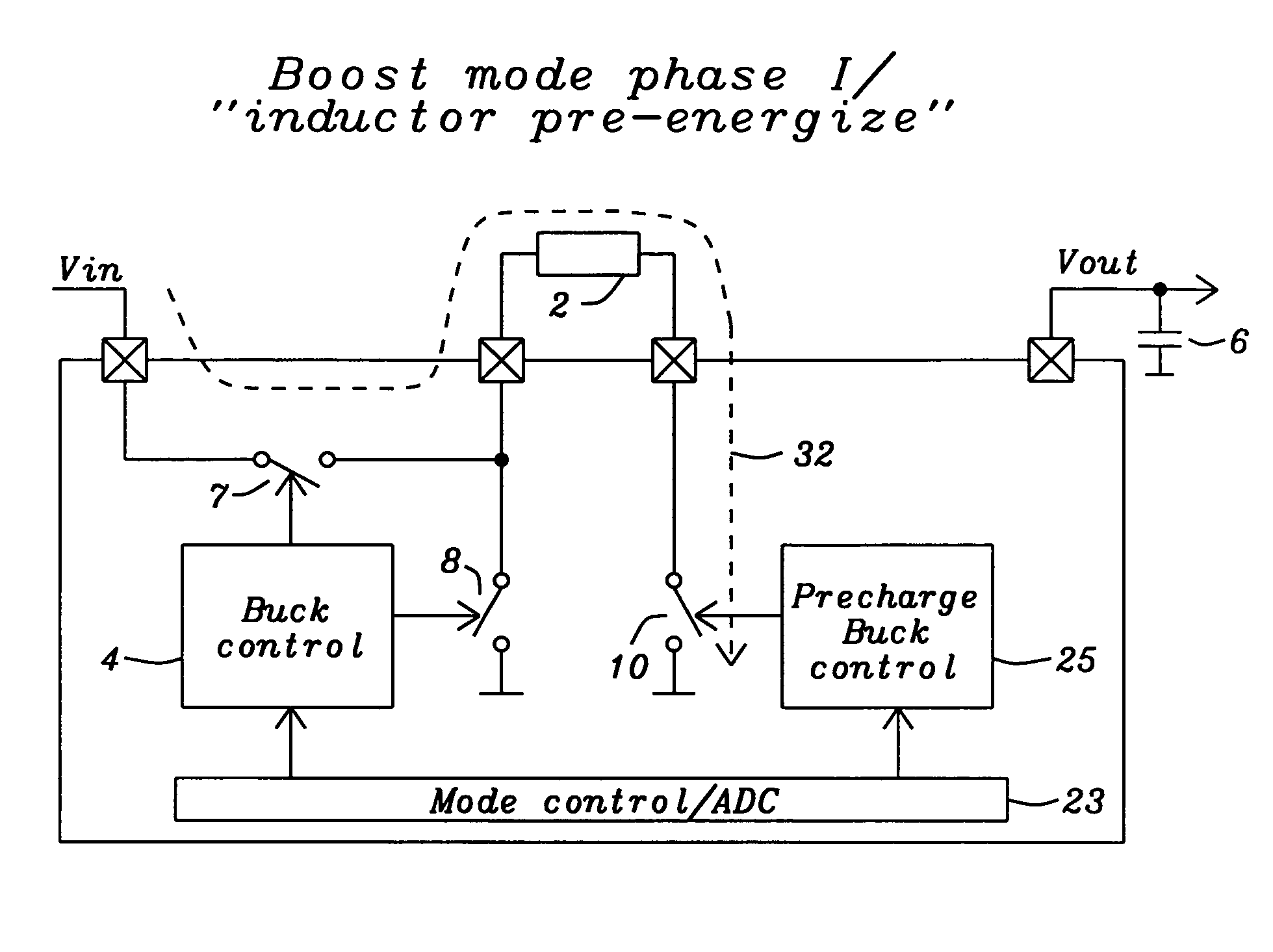
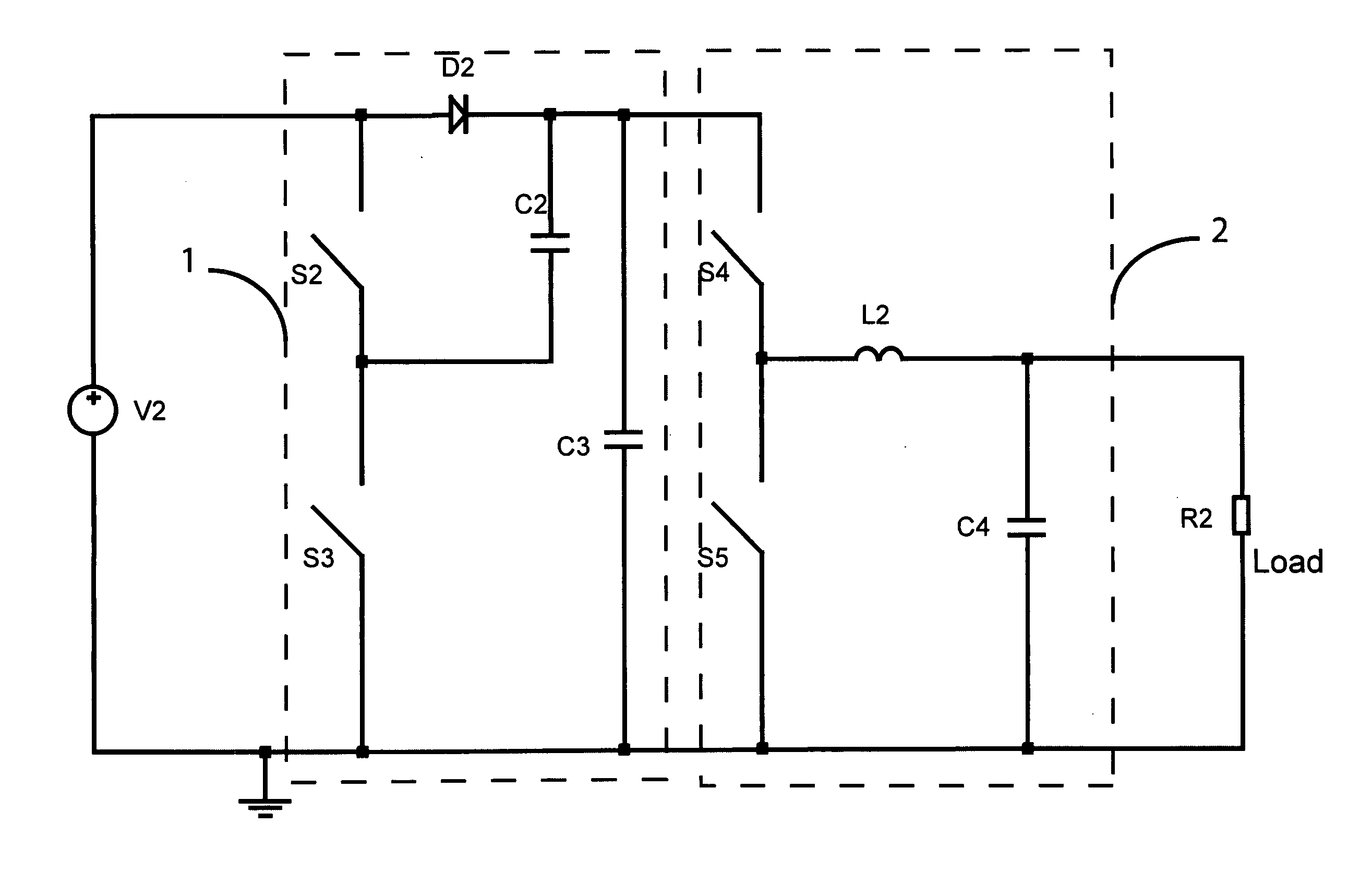
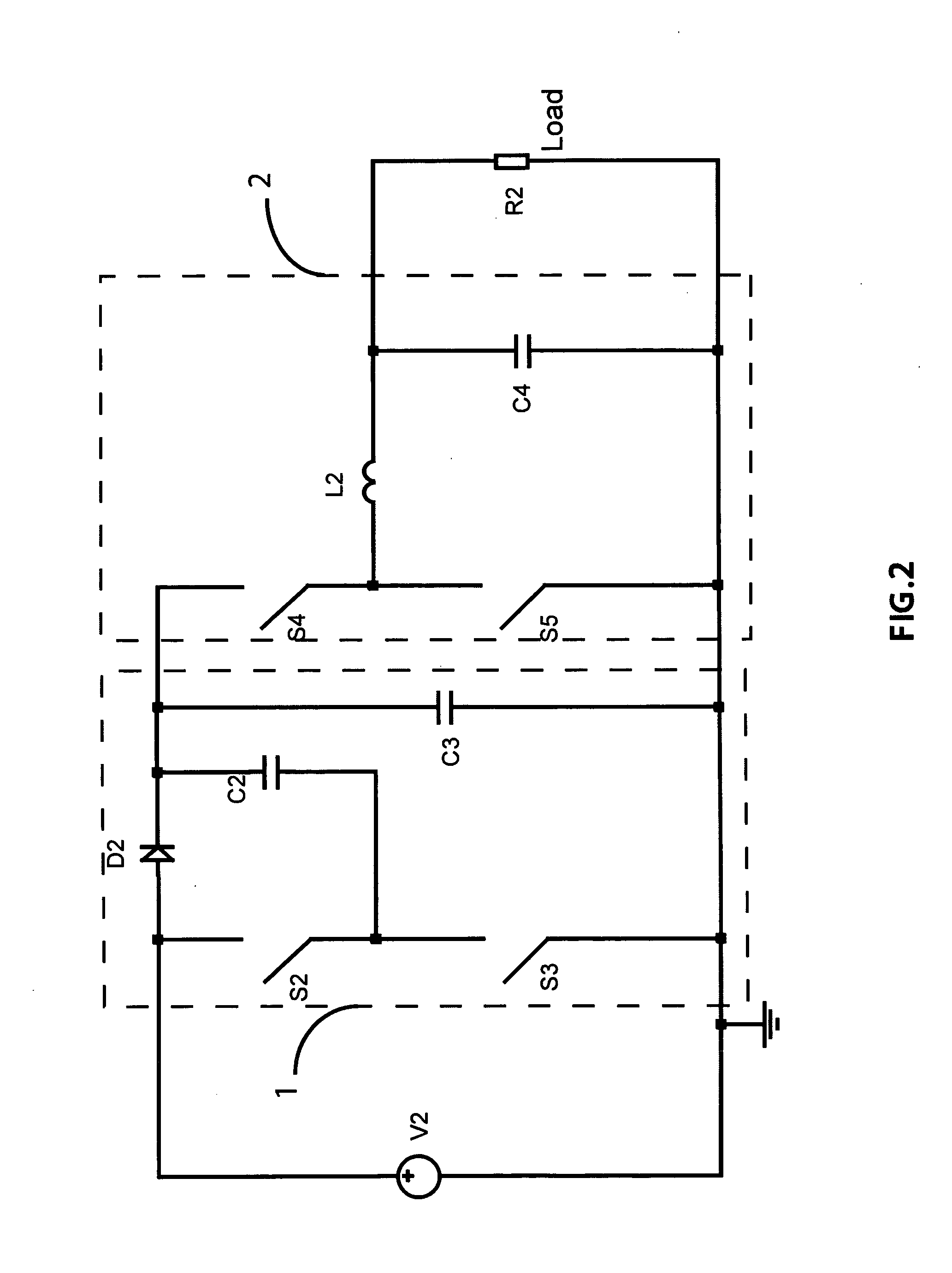
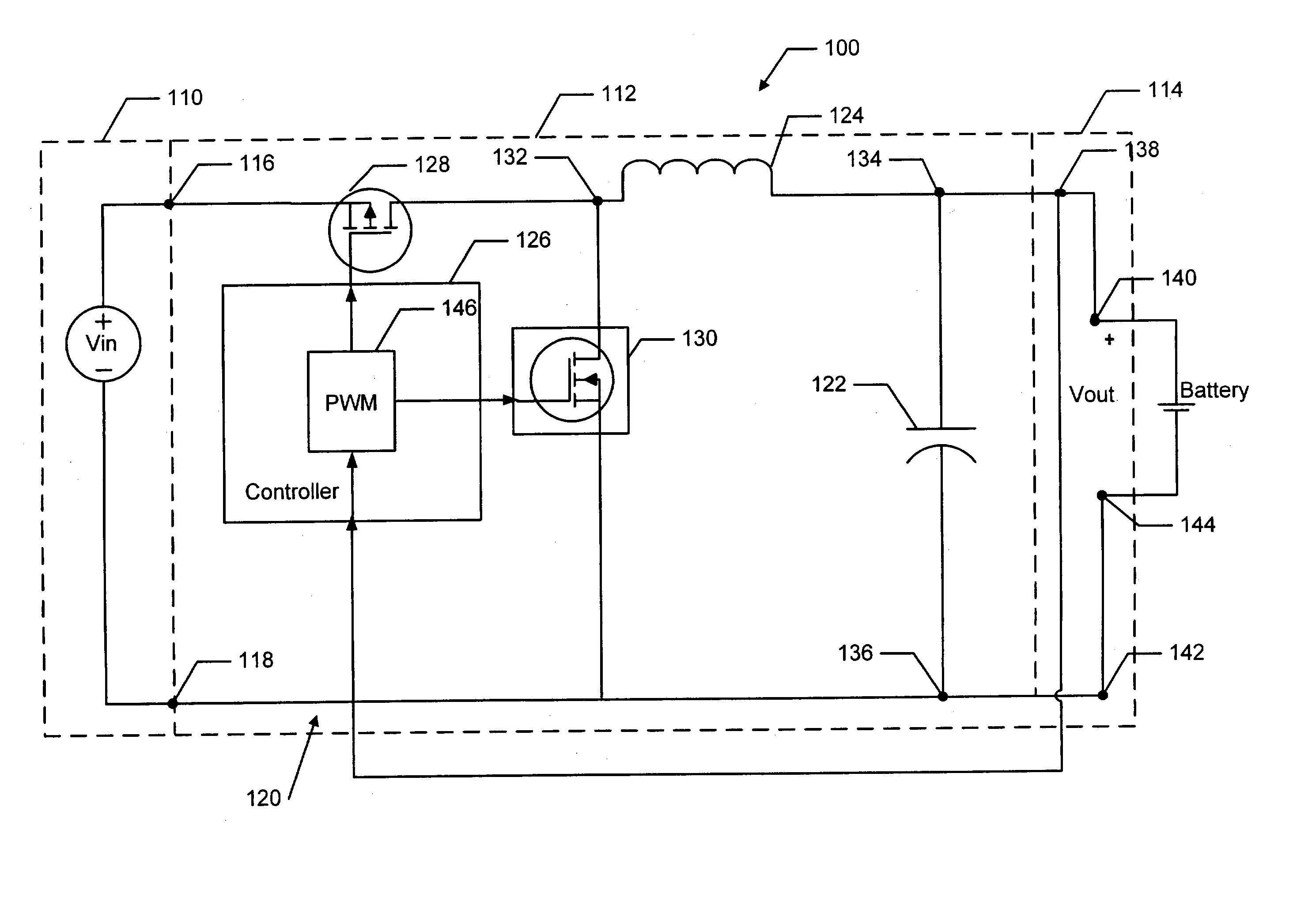
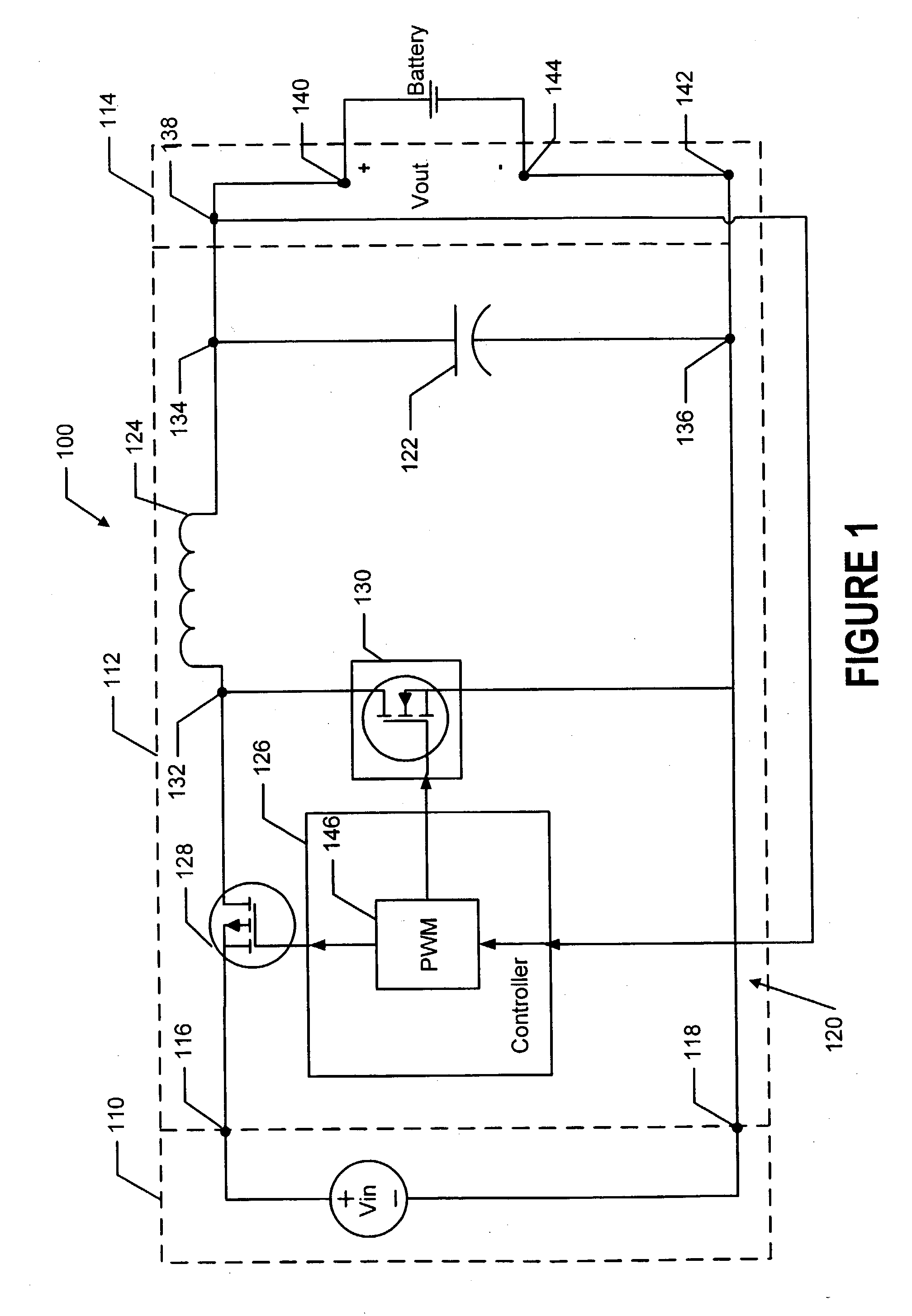
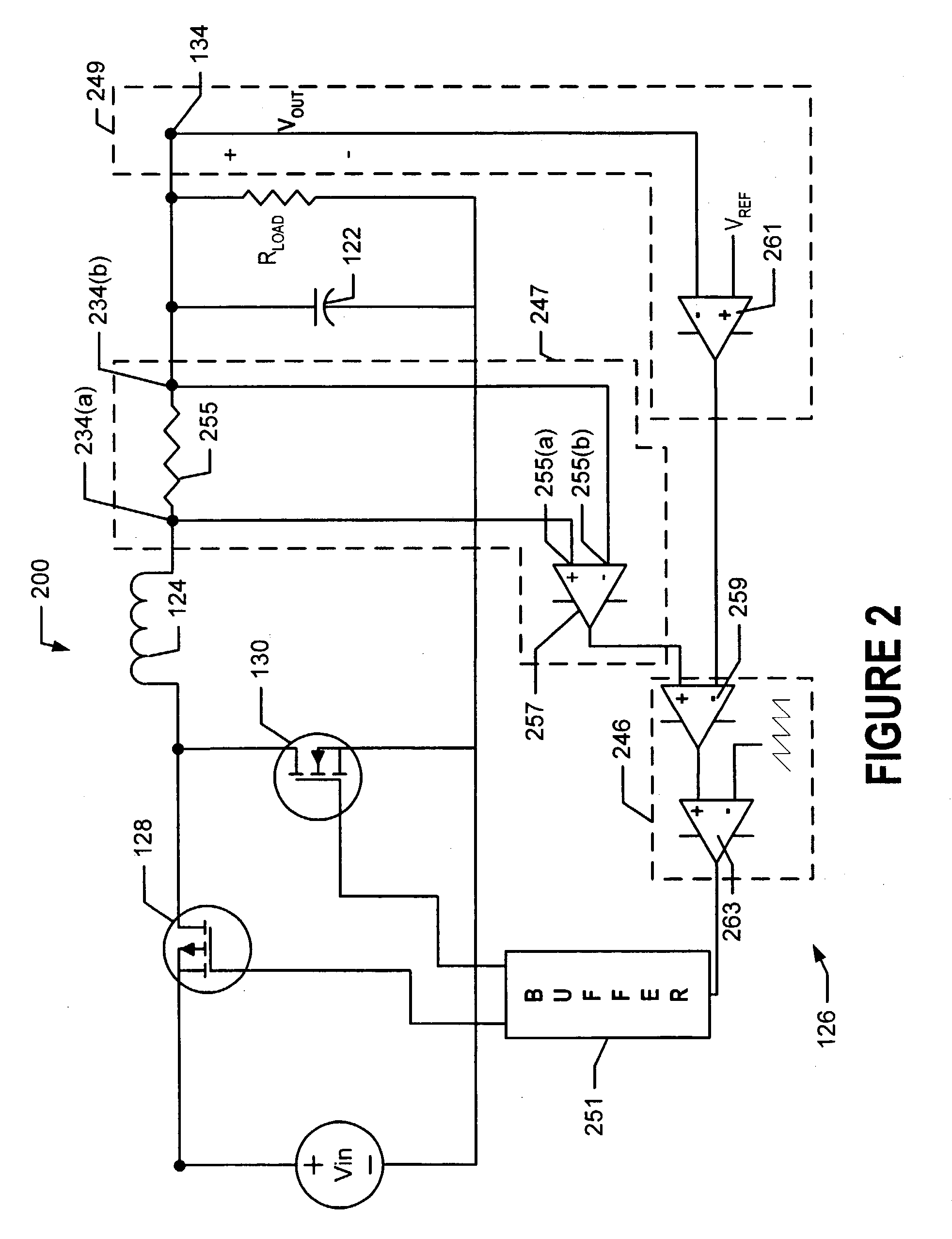
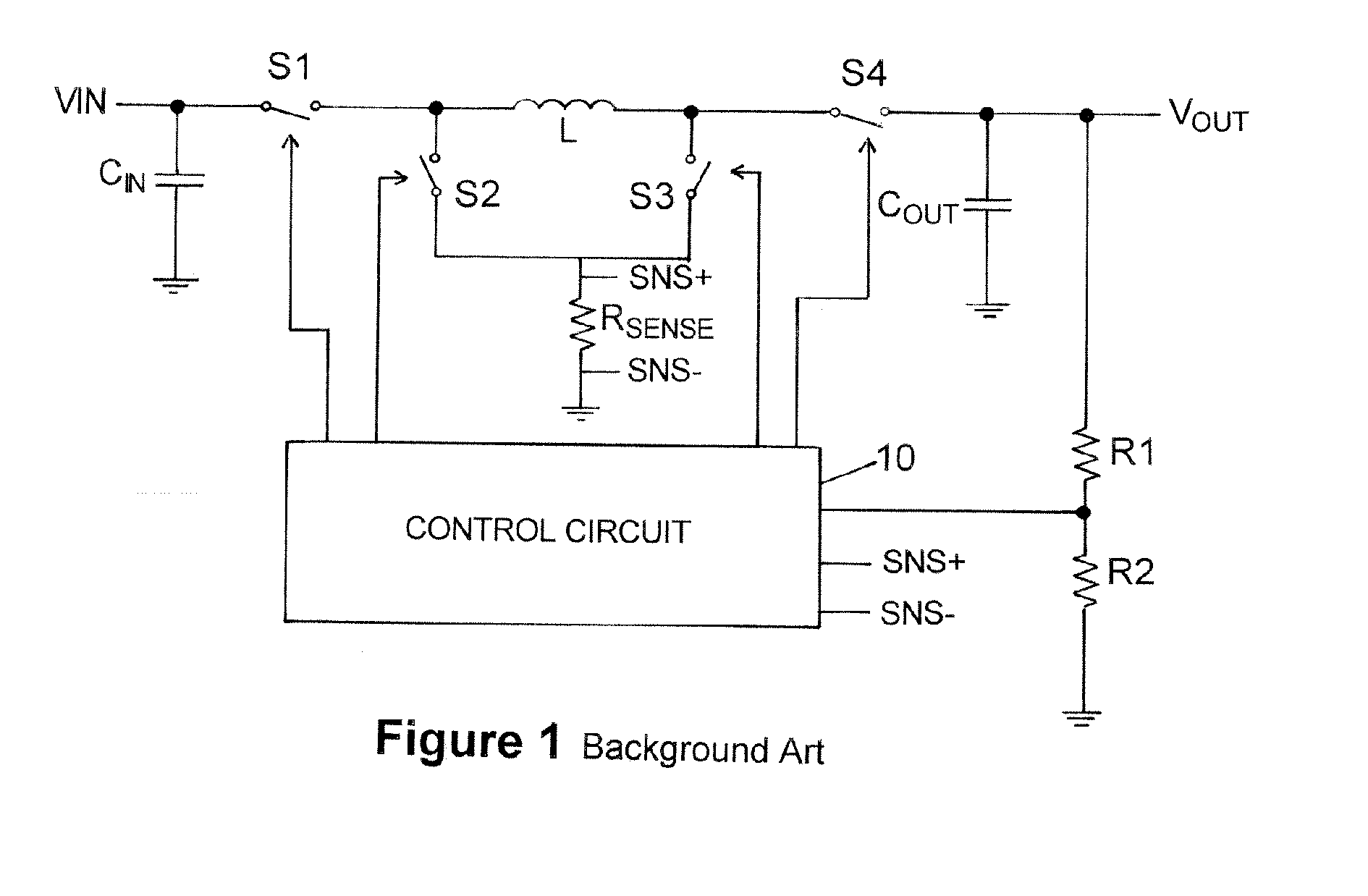
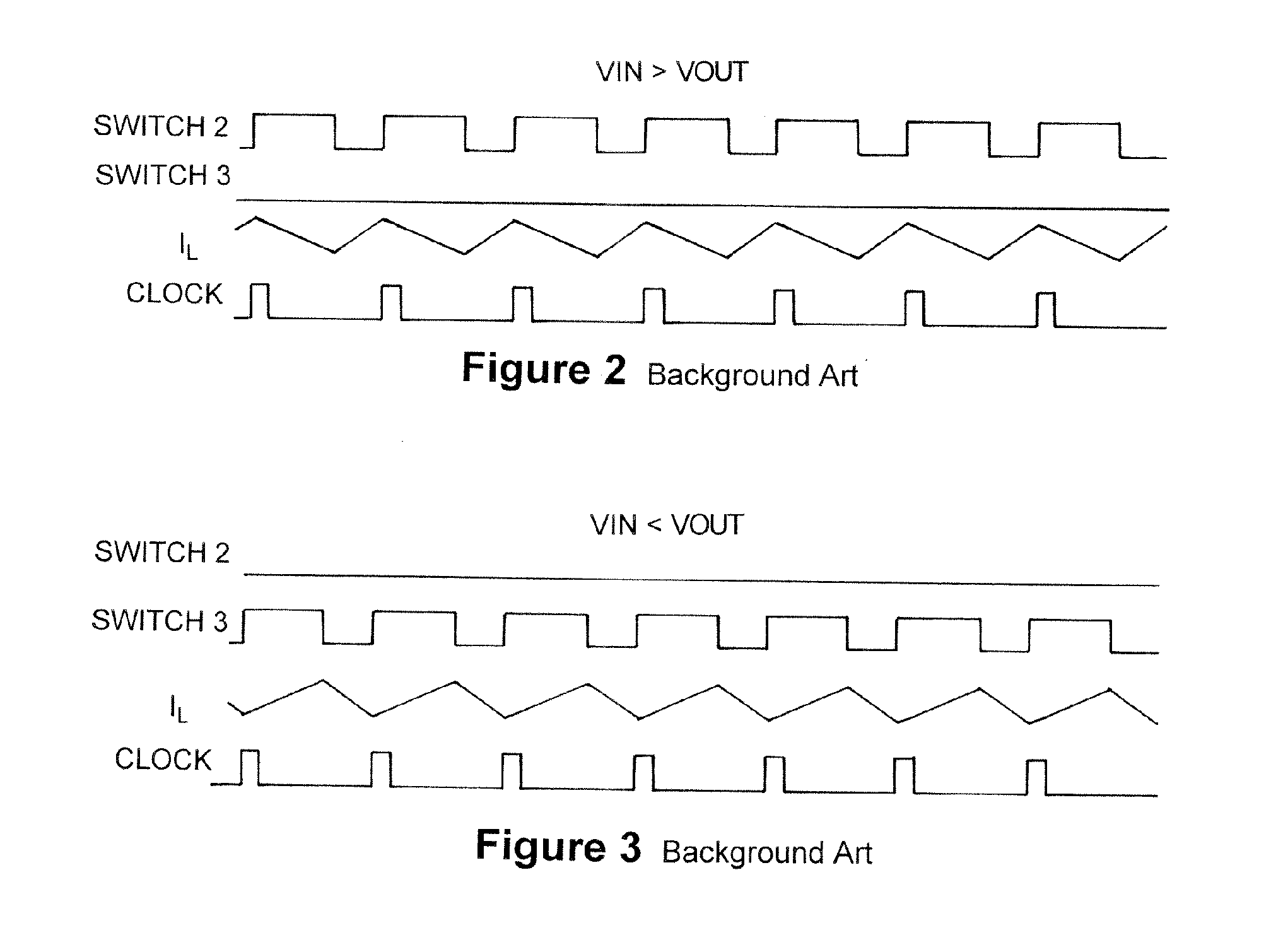
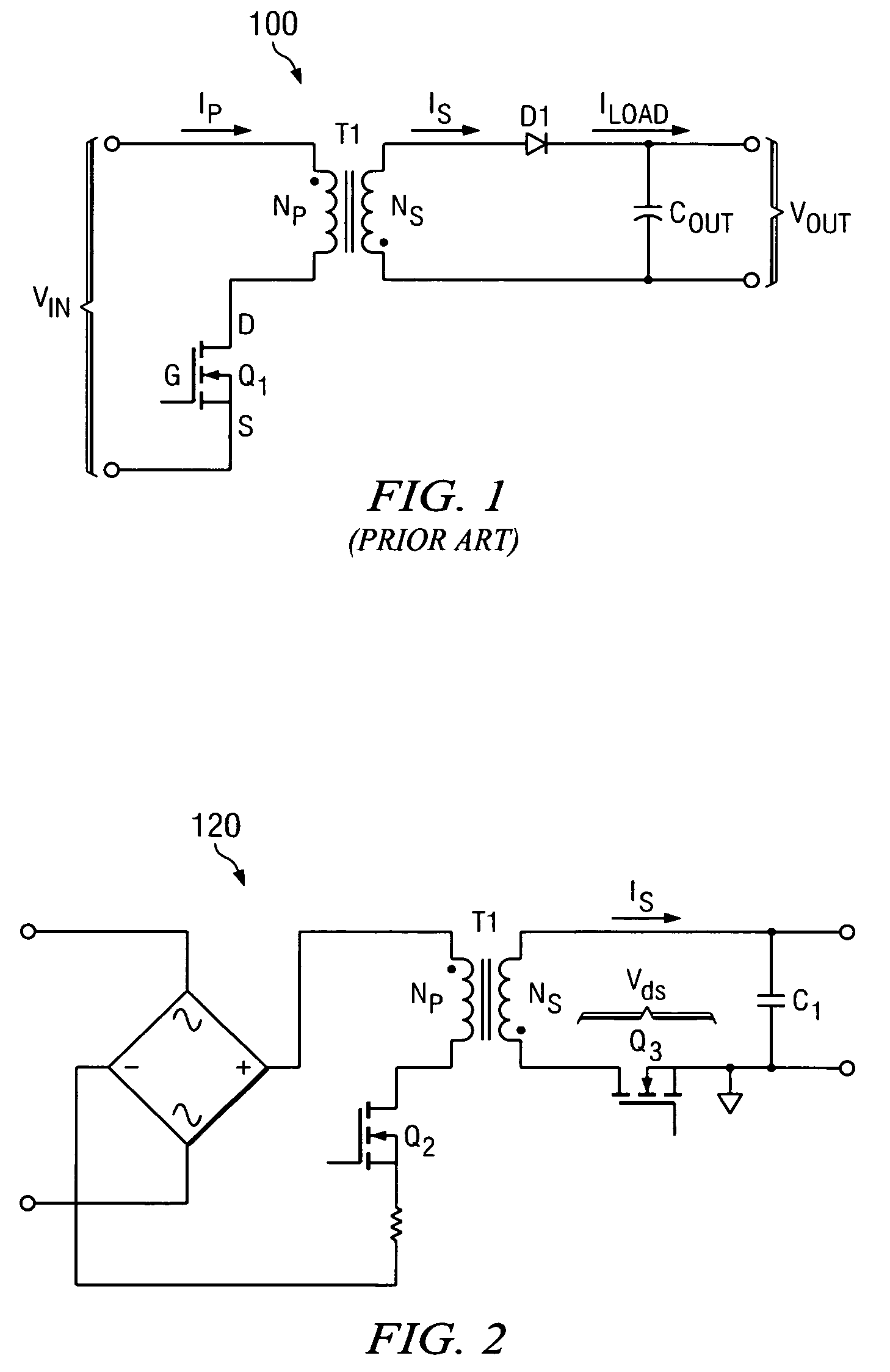
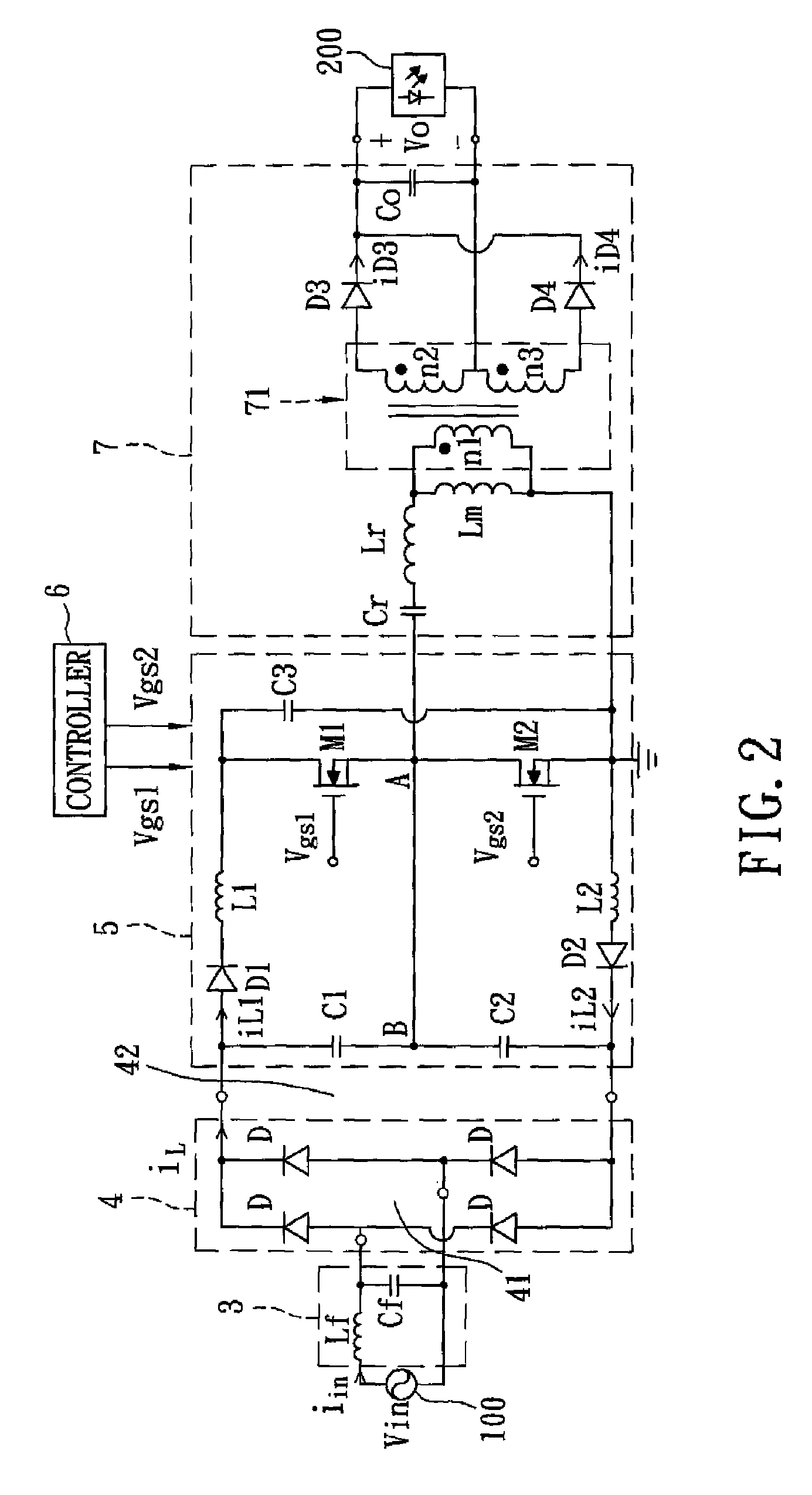
Buck converter with inductor pre-energizing
ActiveUS7804282B2Simple control circuitDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationBuck converterĆuk converter
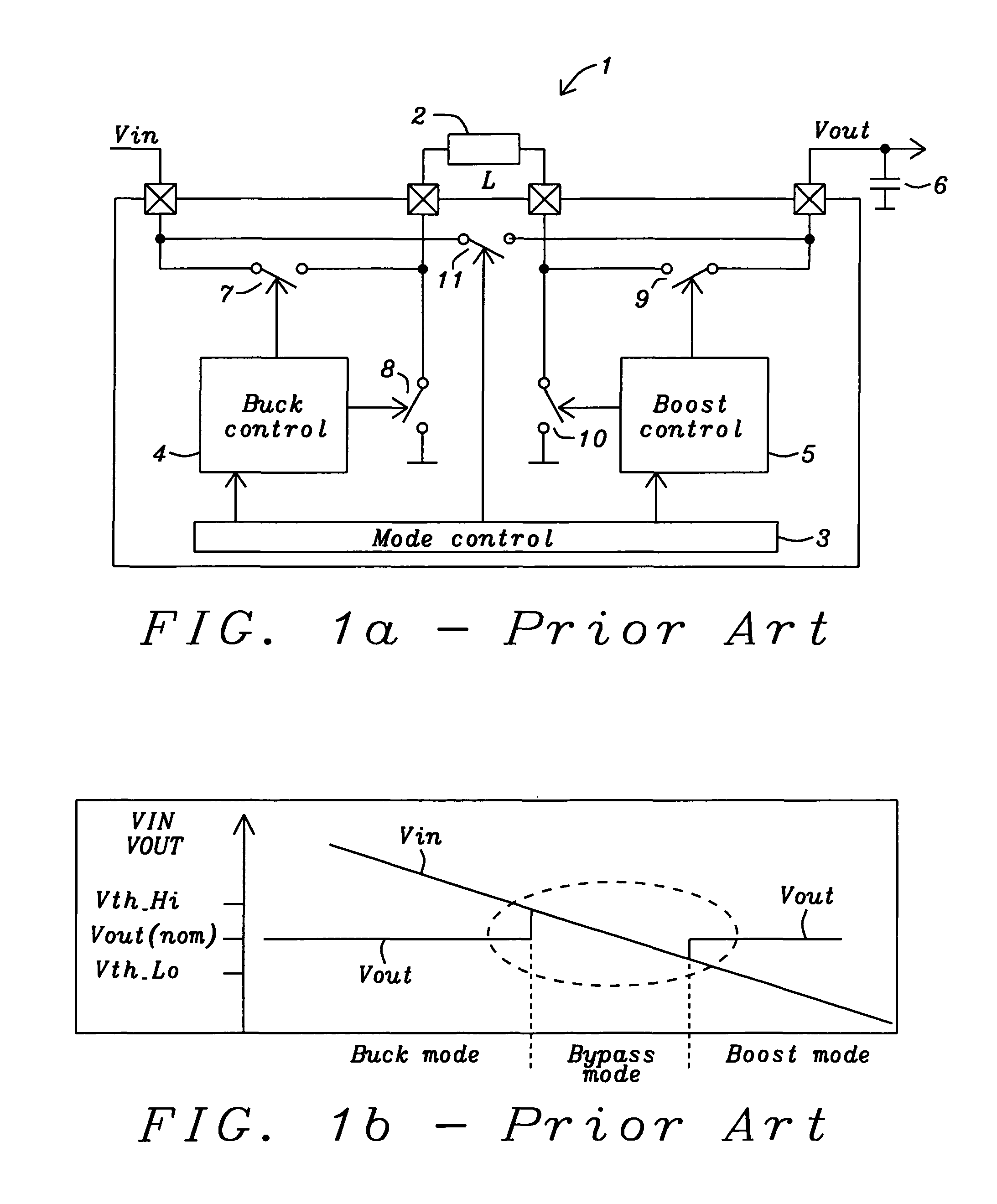
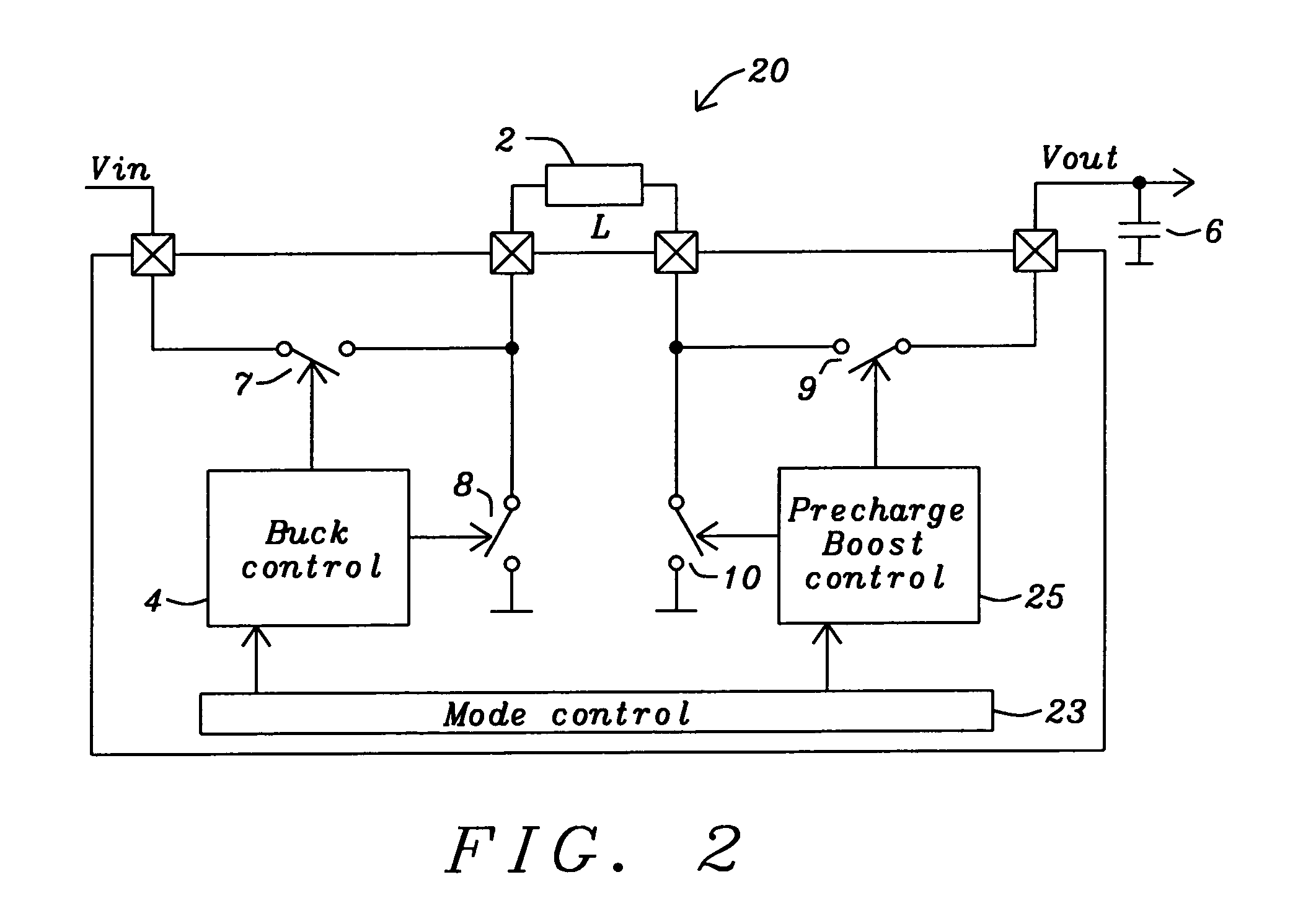
Circuits and methods to achieve a buck-boost converter, capable to achieve a constant output voltage by pre-charging of an inductor if the input voltage is close to the output voltage has been achieved. The prior art problem of output voltage variations occurring while the input voltage is close to the output voltage is avoided. In case the input voltage is lower than a defined threshold voltage or the duty cycle exceeds a defined maximum allowable level, the inductor of the converter is pre-charged followed by boosting of the energy of the inductor to the output of the converter. In both modes the control loops of the buck converter can be used for buck duty cycle control. The duration of the pre-charge depends upon the level of the input voltage, the lower the input level is the longer is the pre-charge performed.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
High-efficiency DC/DC voltage converter including capacitive switching pre-converter and down inductive switching post-regulator
ActiveUS7777459B2Efficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionInstabilityInductance
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
High-efficiency DC/DC voltage converter including capacitive switching pre-converter and down inductive switching post-regulator
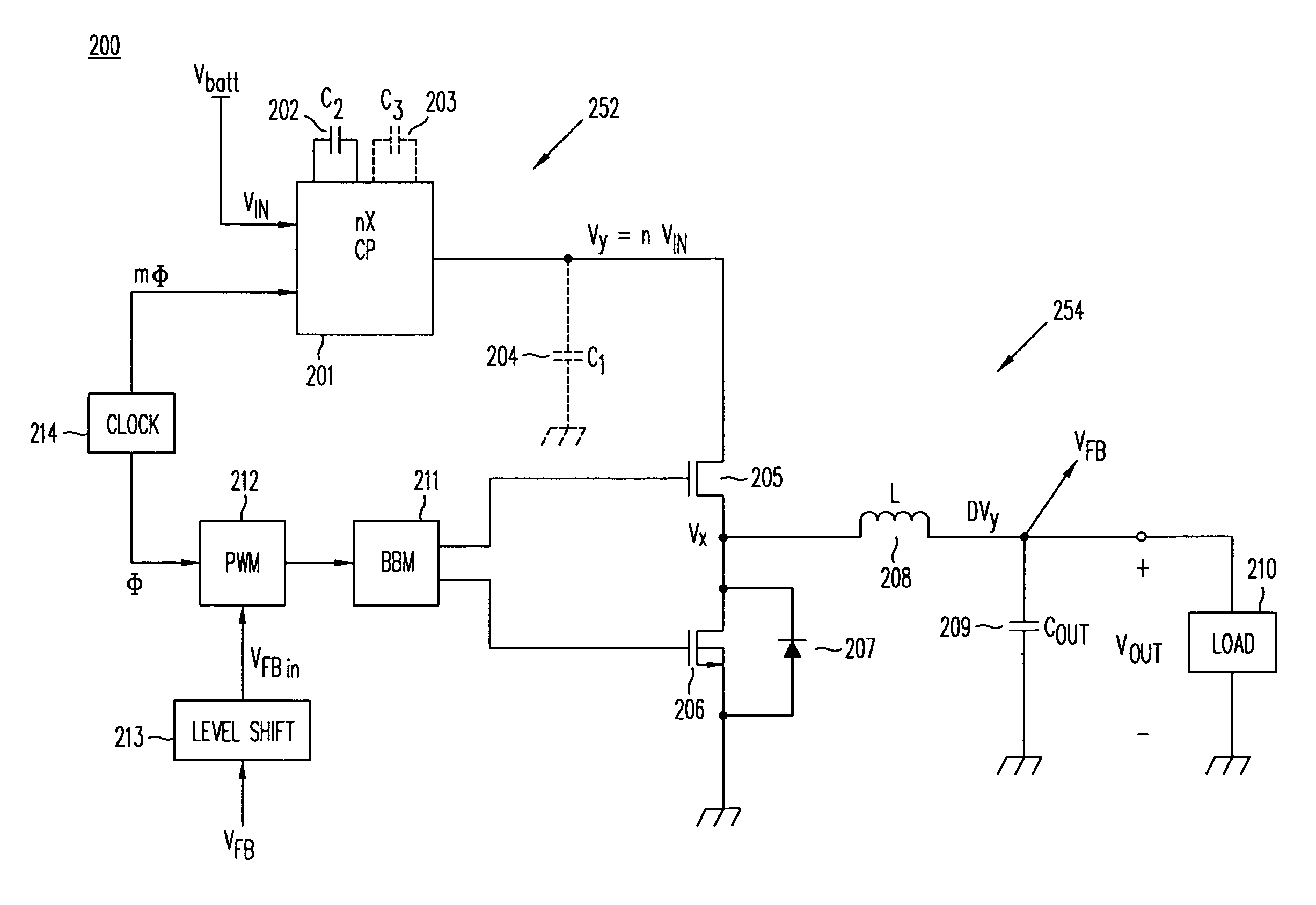
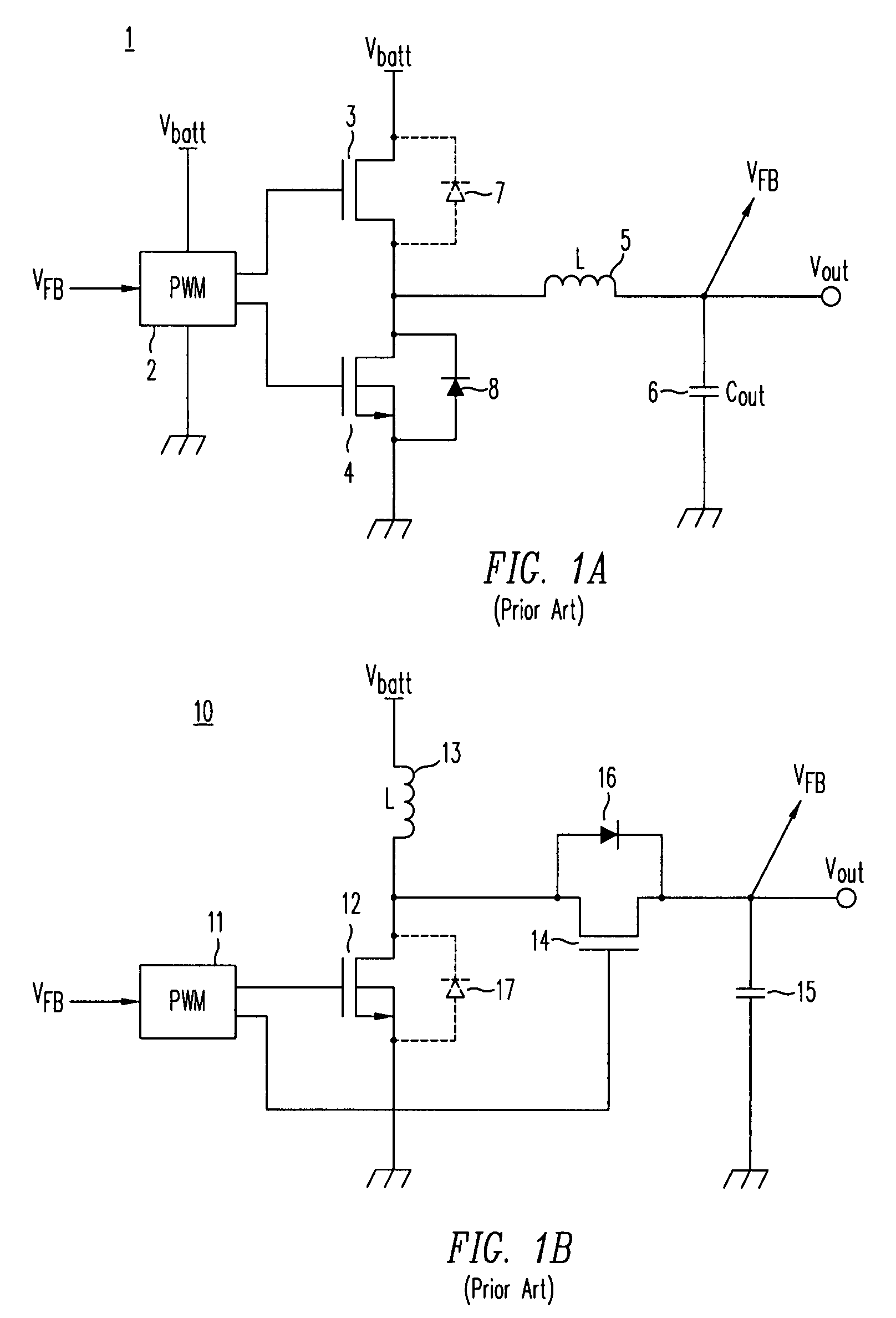
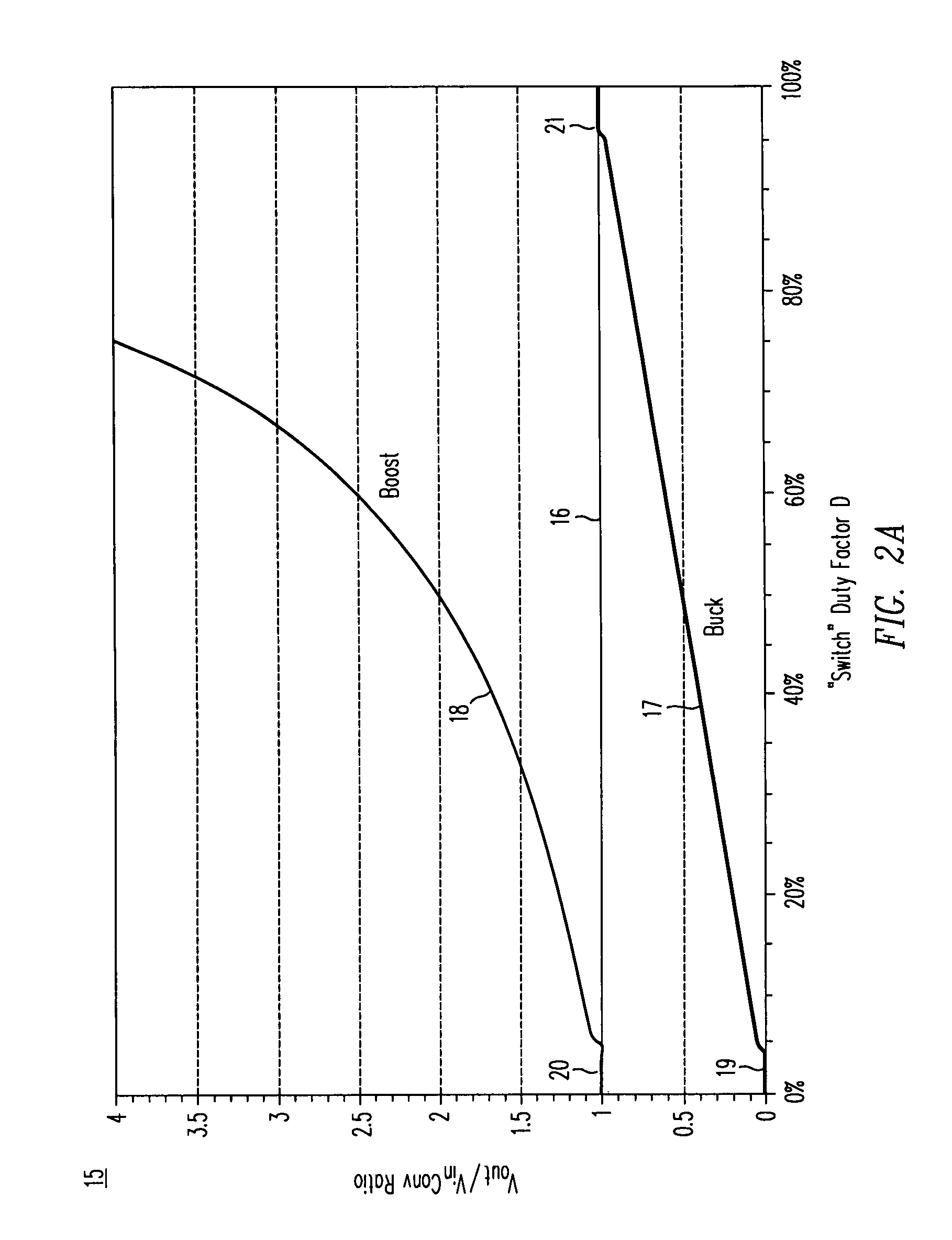
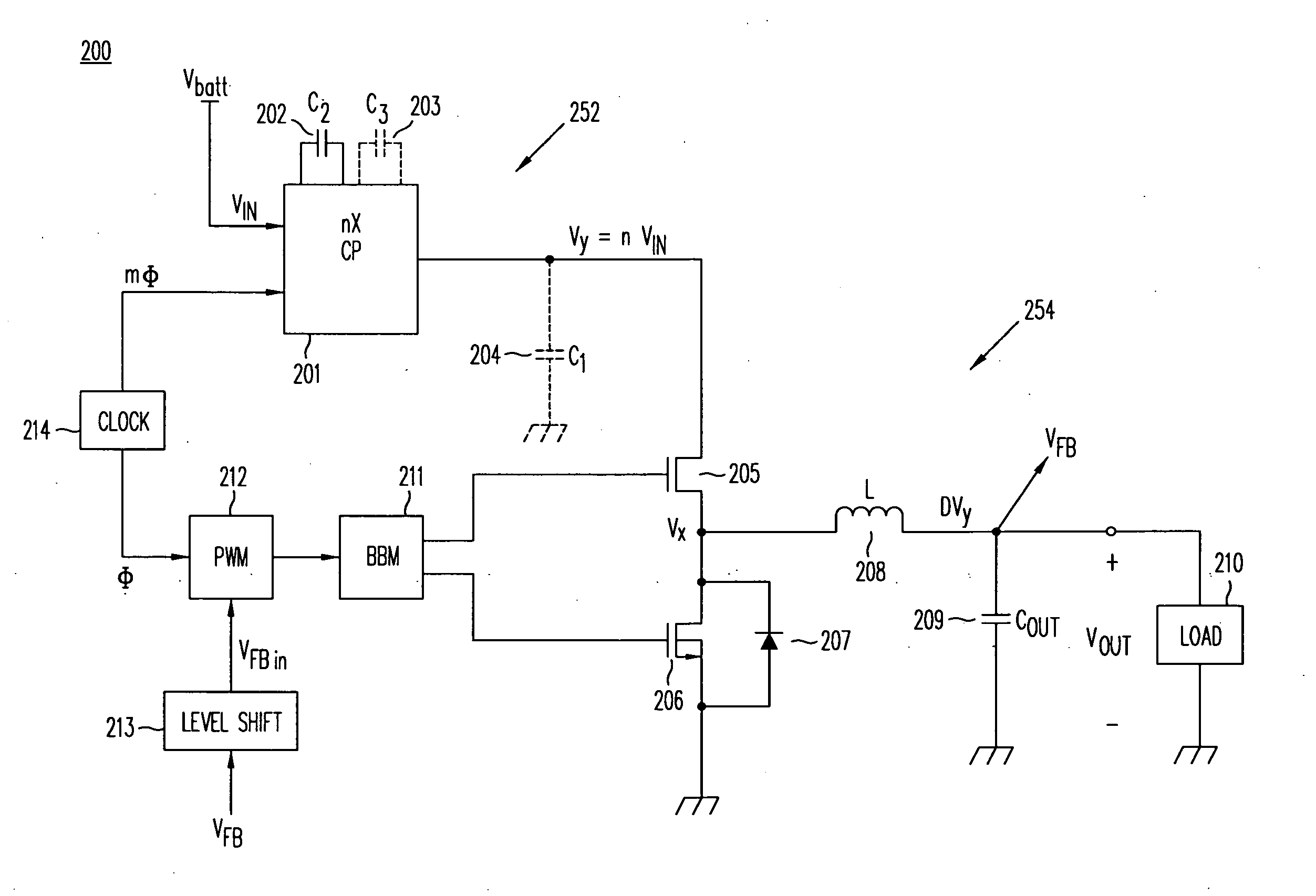
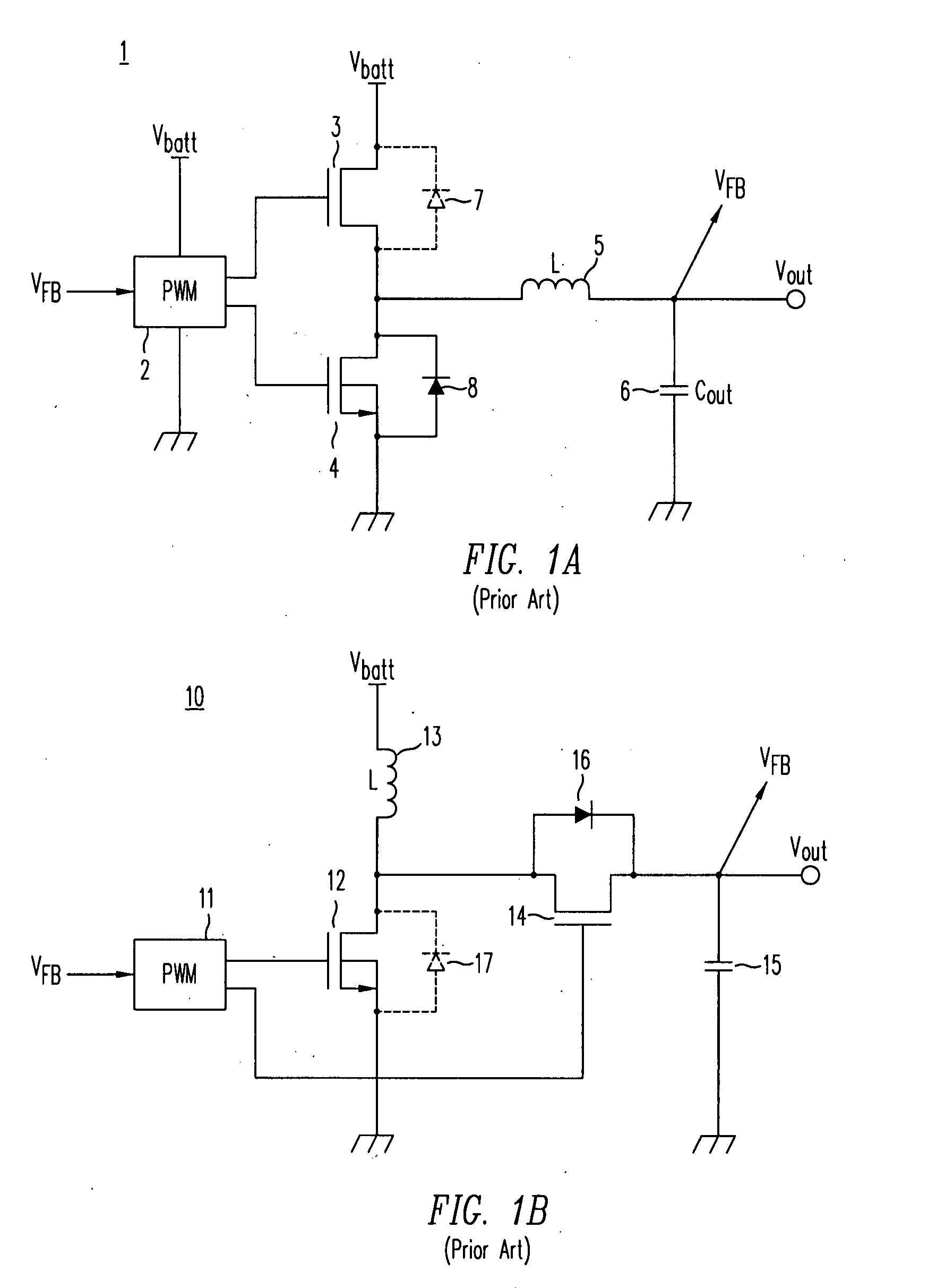
A DC / DC converter includes a pre-converter stage, which may include a charge pump, and a post-regulator stage, which may include a Buck converter. The duty factor of the post-regulator stage is controlled by a feedback path that extends from the output terminal of the DC / DC converter to an input terminal in the post-regulator stage. The pre-converter steps the input DC voltage up or down by a positive or negative integral or fractional value, and the post-regulator steps the voltage down by a variable amount depending on the duty factor at which the post-regulator is driven. The converter overcomes the problems of noise glitches, poor regulation, and instability, even near unity input-to-output voltage conversion ratios.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
Three-stage electronic ballast for metal halide lamps
InactiveUS6856102B1Reduce power lossImprove efficiencyElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementFull bridgeThree stage
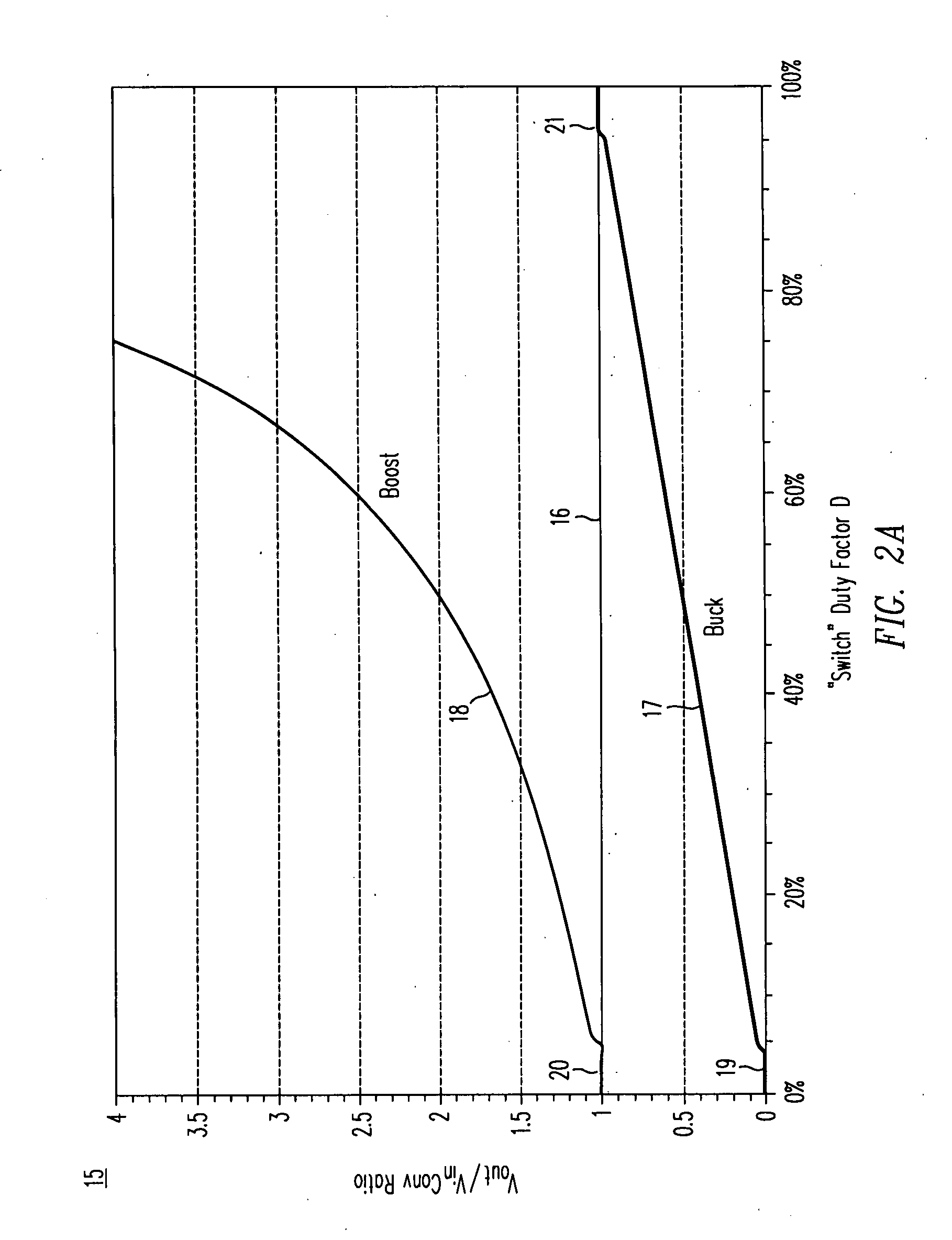
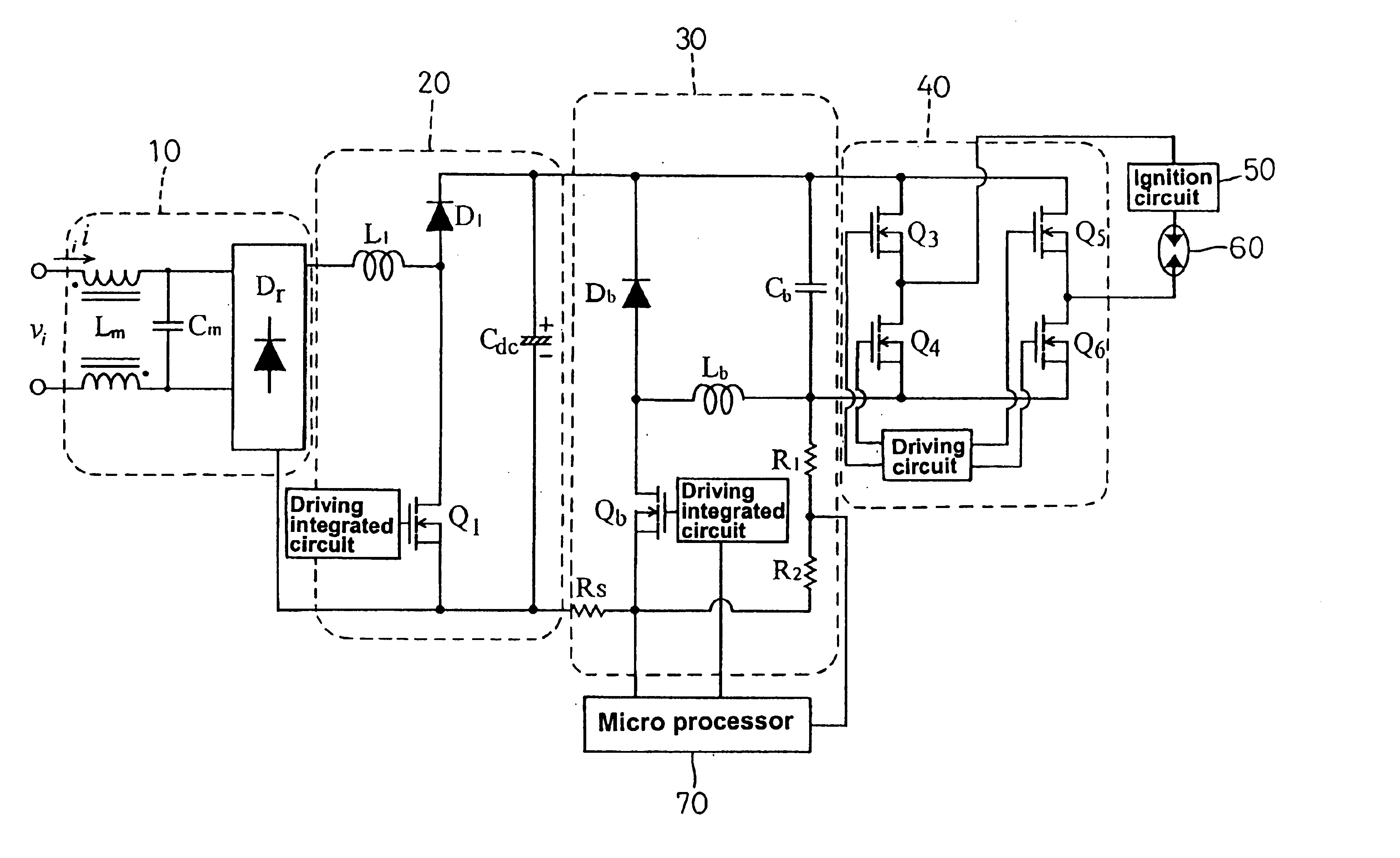
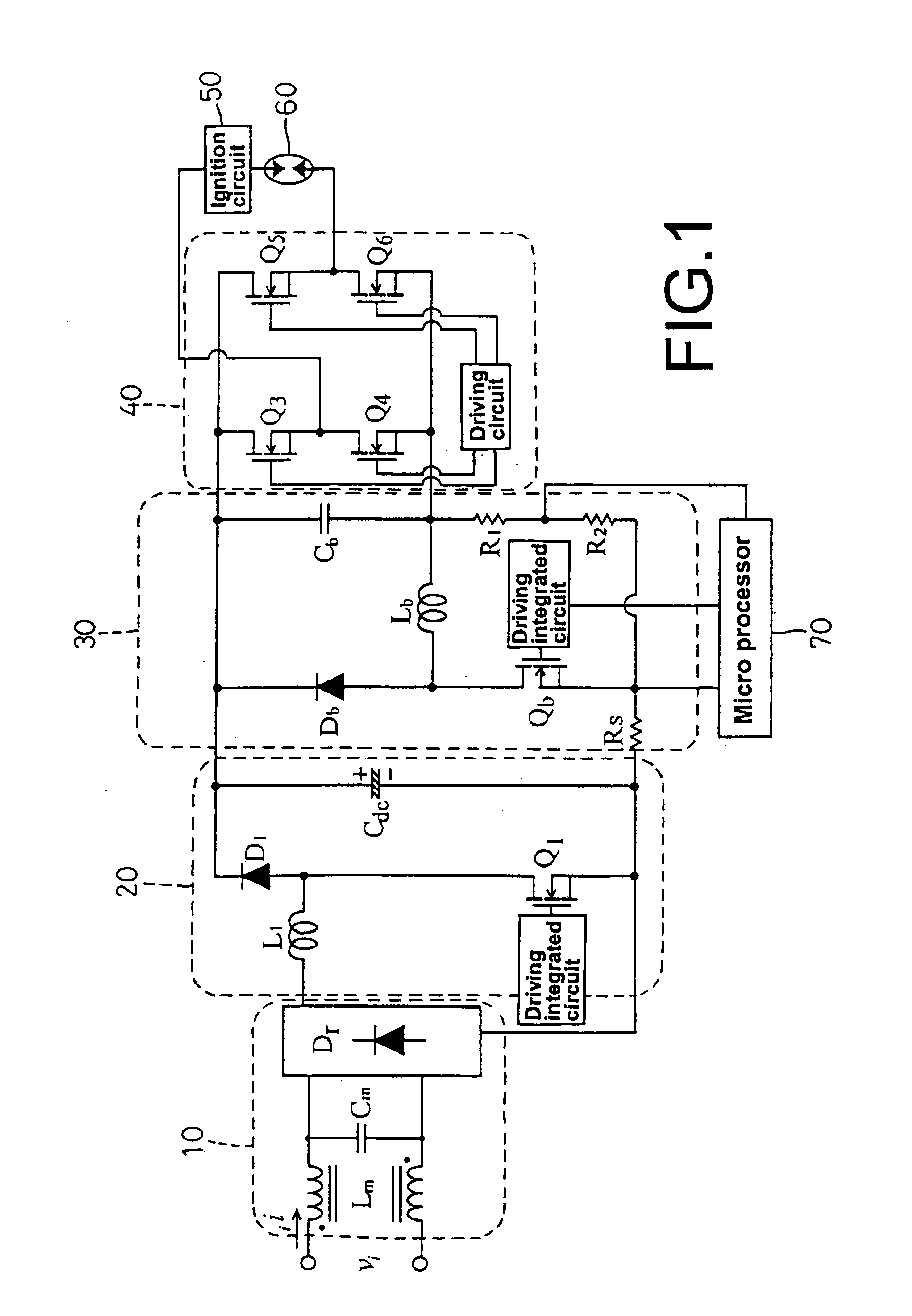
A three-stage electronic ballast for metal halide lamps mainly comprises a step-up converter, a step-down converter and a full-bridge DC-AC converter, wherein the step-down converter operates an inductor in a continuous boundary current mode to achieve reducing power loss and enhancing efficiency. Equipped with a micro processor, the electronic ballast further possesses the function of power regulation. The electronic ballast can be added with various protective functions without complex control circuits and sensing elements, thereby becoming a high-quality and low-cost electronic ballast for metal halide lamps.
Owner:LIGTEK ELECTRONICS
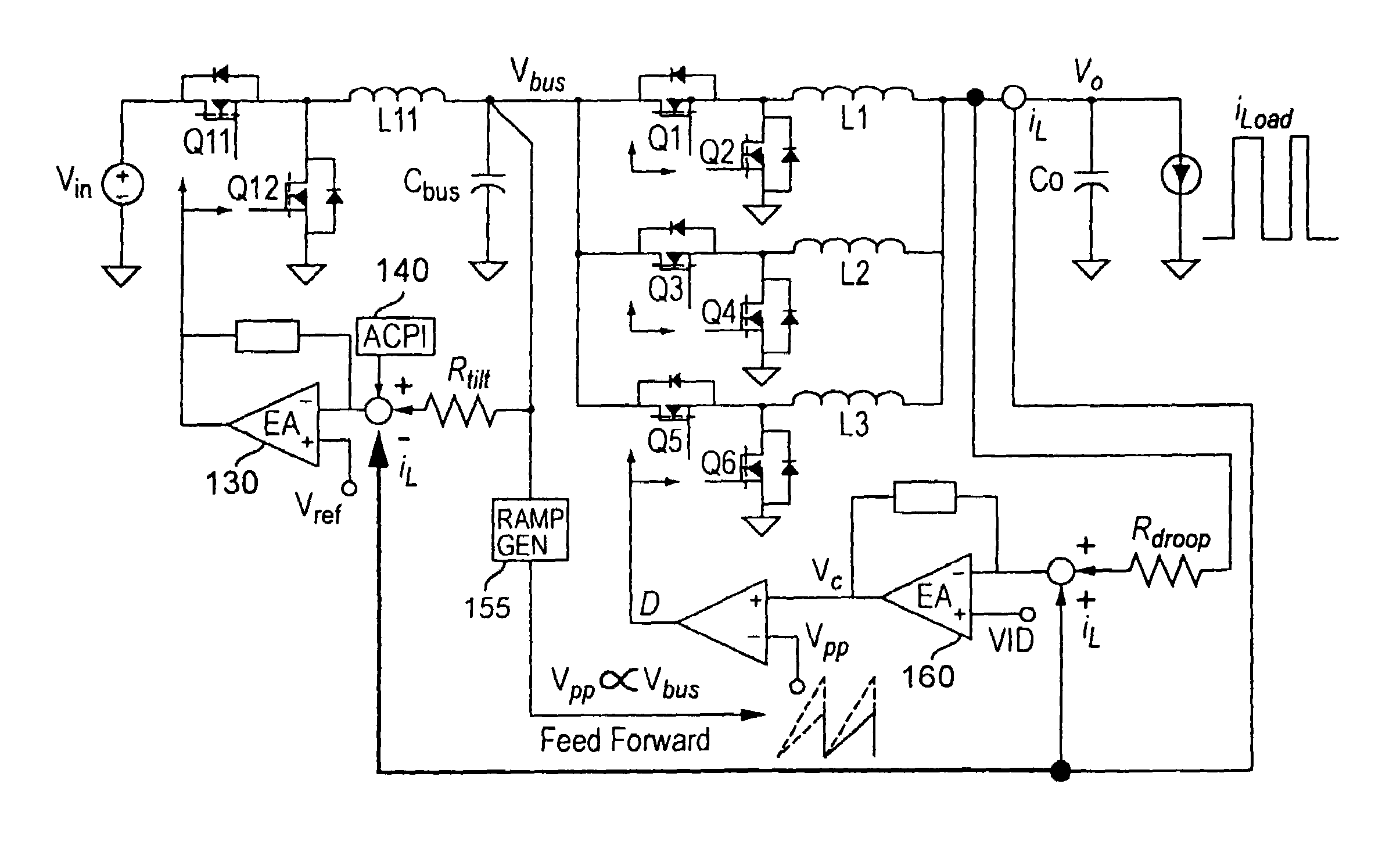
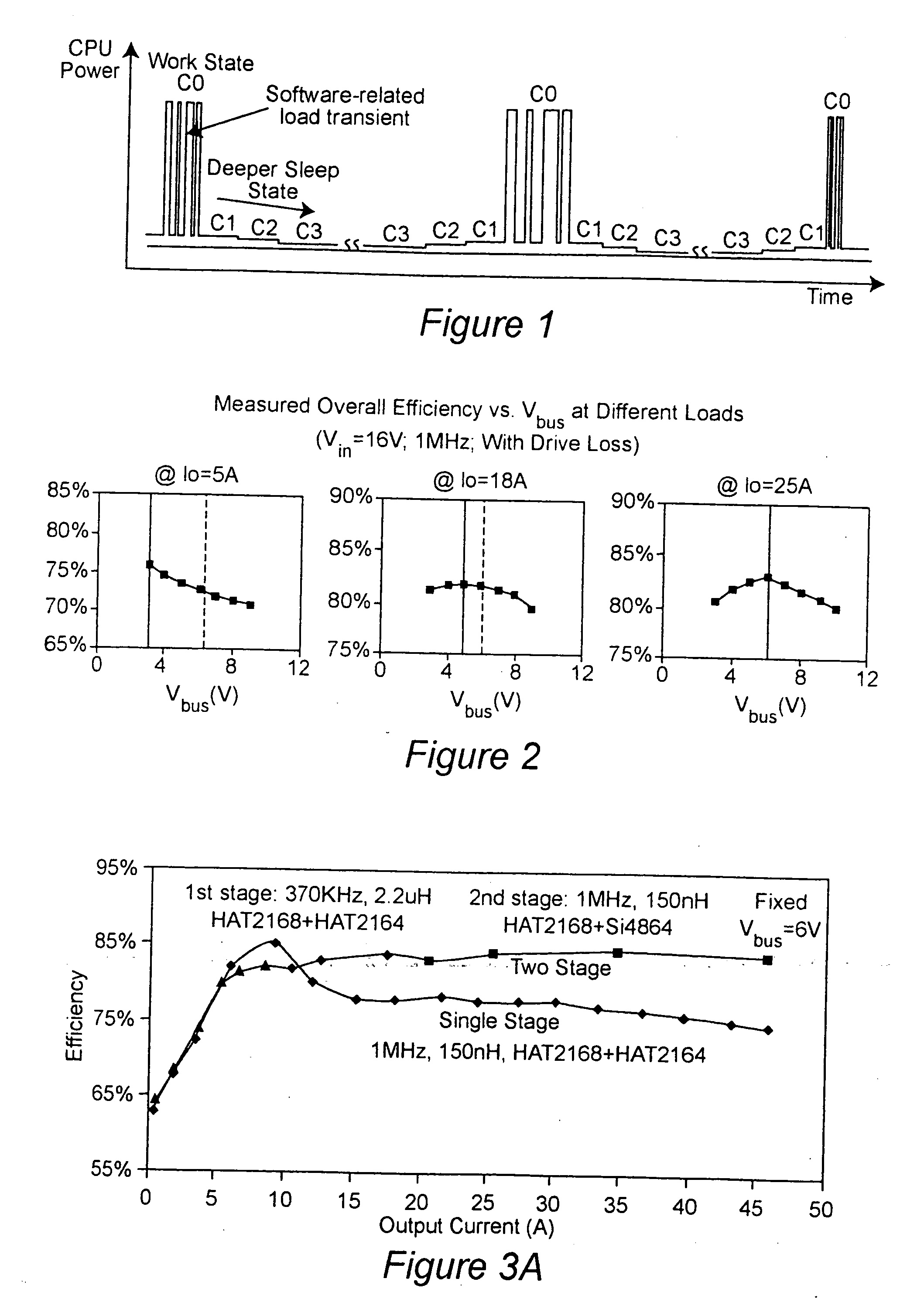
Two-stage voltage regulators with adjustable intermediate bus voltage, adjustable switching frequency, and adjustable number of active phases
InactiveUS7071660B2Improve efficiencyWide variationEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionBuck converterSwitching frequency
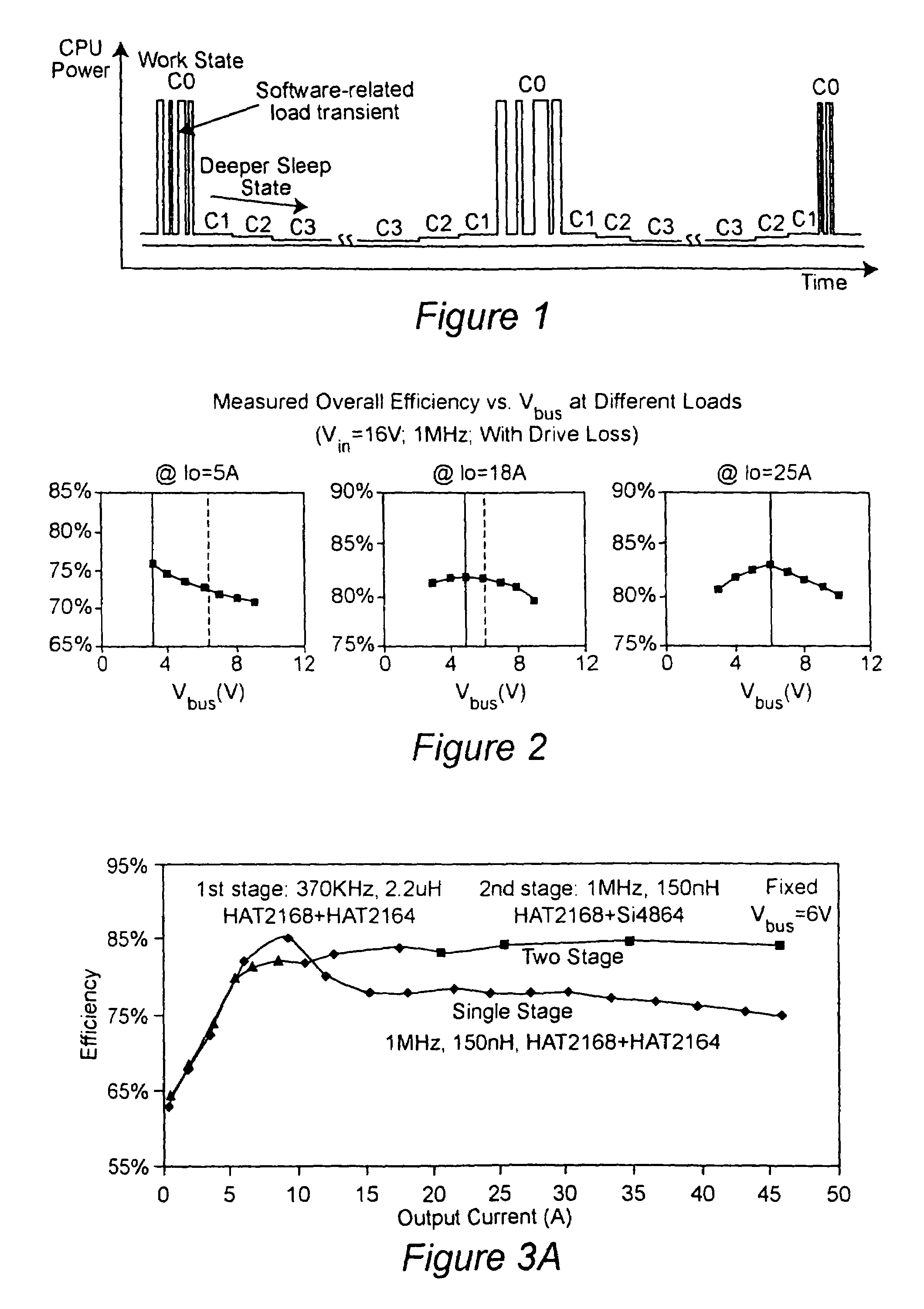
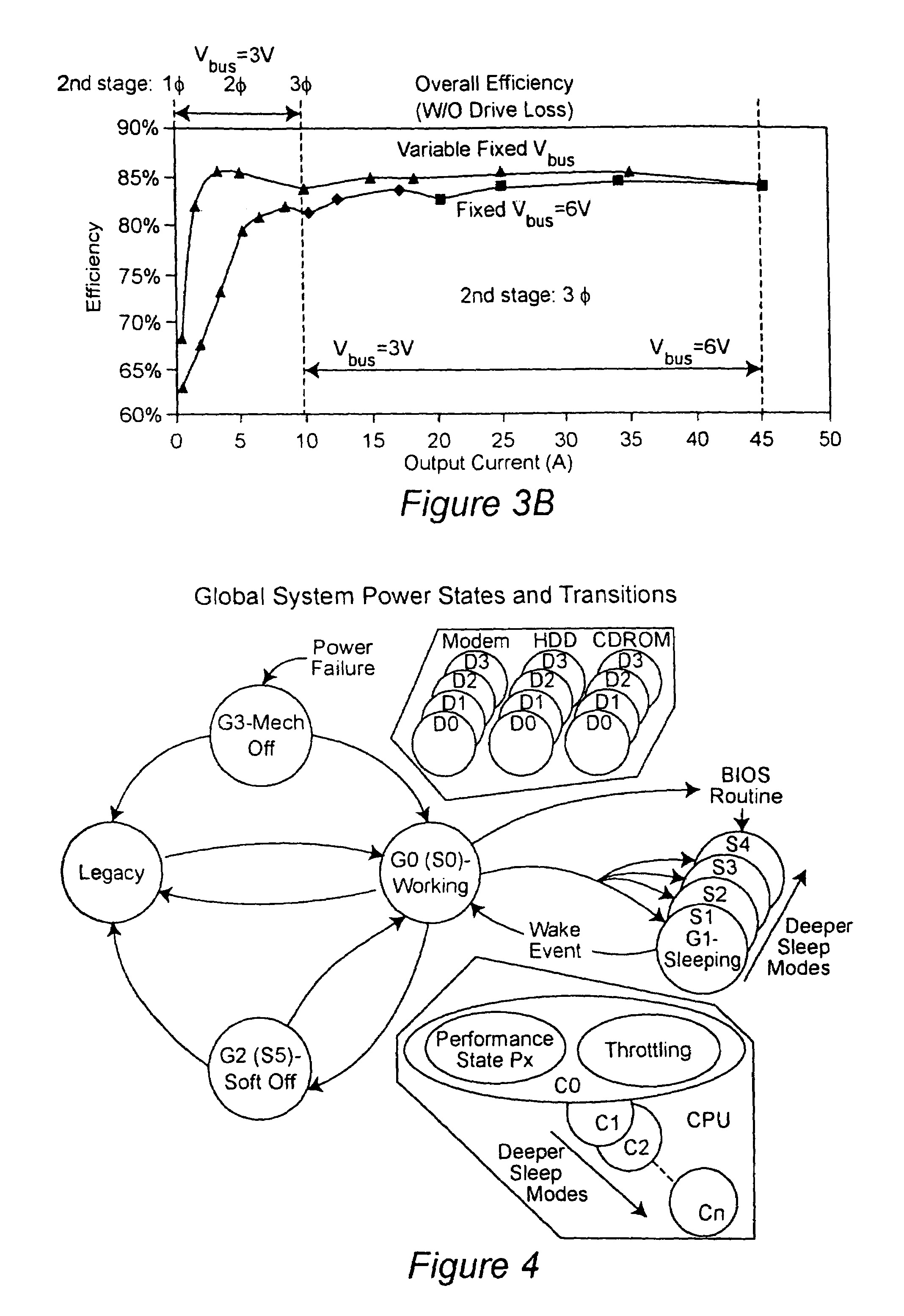
A two-stage power converter that dynamically adjusts to output current requirements includes a first stage regulator that provides power to a second stage regulator. The first stage can be a buck converter, and the second stage can be a multiple-phase buck converter. The output voltage of the first stage (intermediate bus voltage Vbus) is varied according to the load current to optimize conversion efficiency. To provide maximum efficiency, the Vbus voltage is increased as load current increases. The Vbus voltage provided by the first stage can be varied by duty cycle or operating frequency control. In another embodiment, the switching frequency of the second stage is varied as output current changes so that output current ripple is held constant. In an embodiment employing a multiple-phase buck converter in the second stage, the number of operating phases are varied as output current changes.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
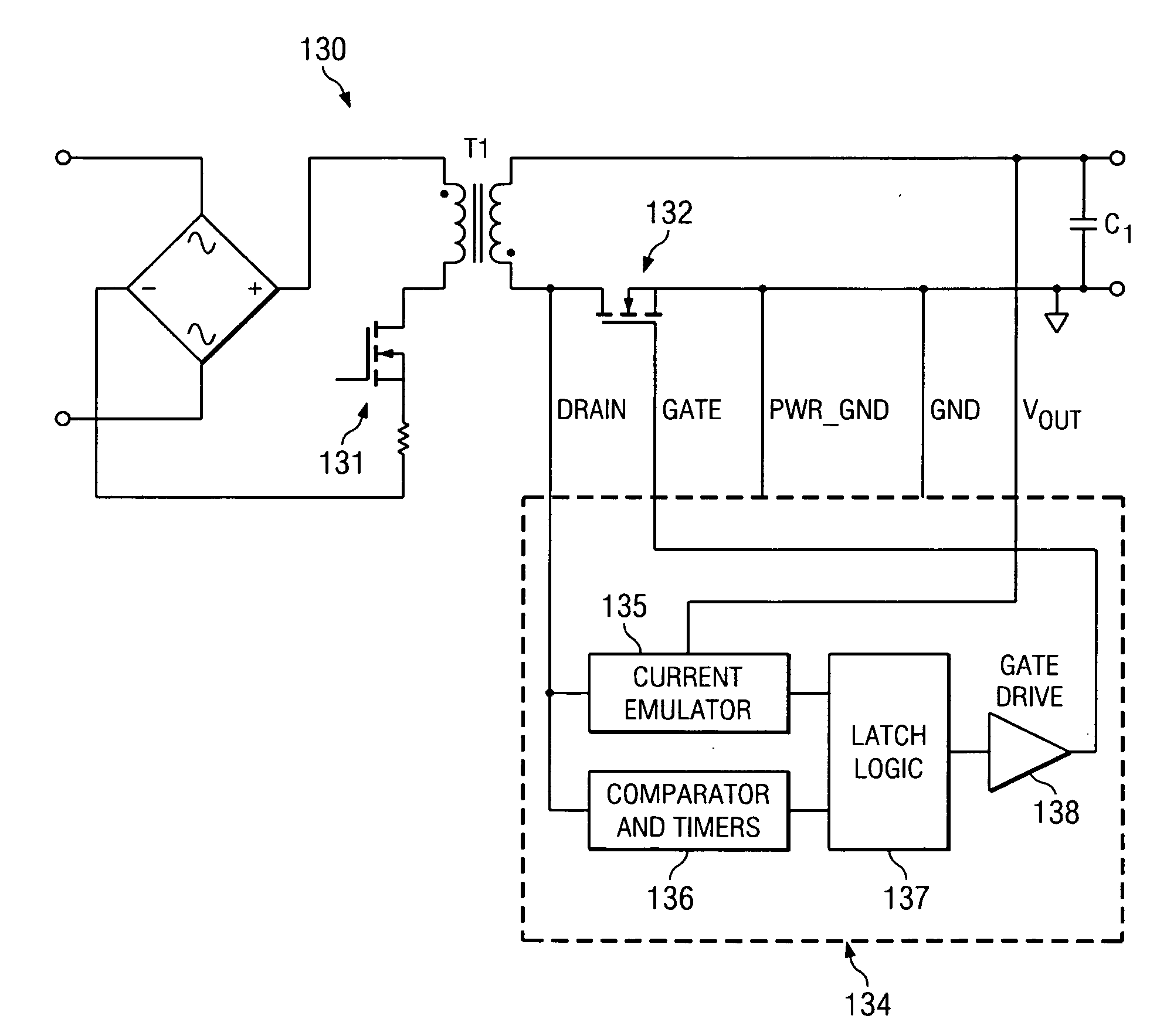
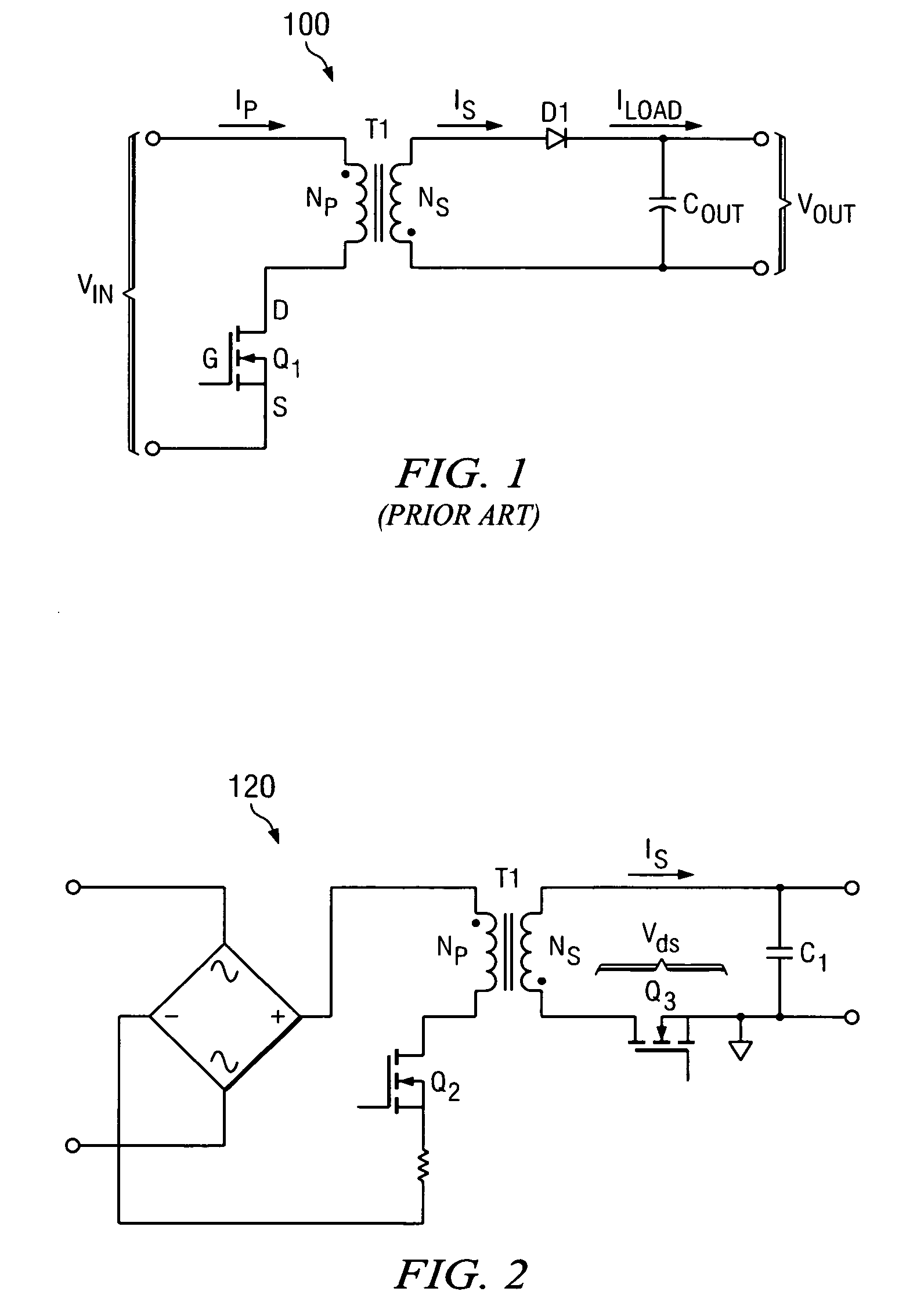
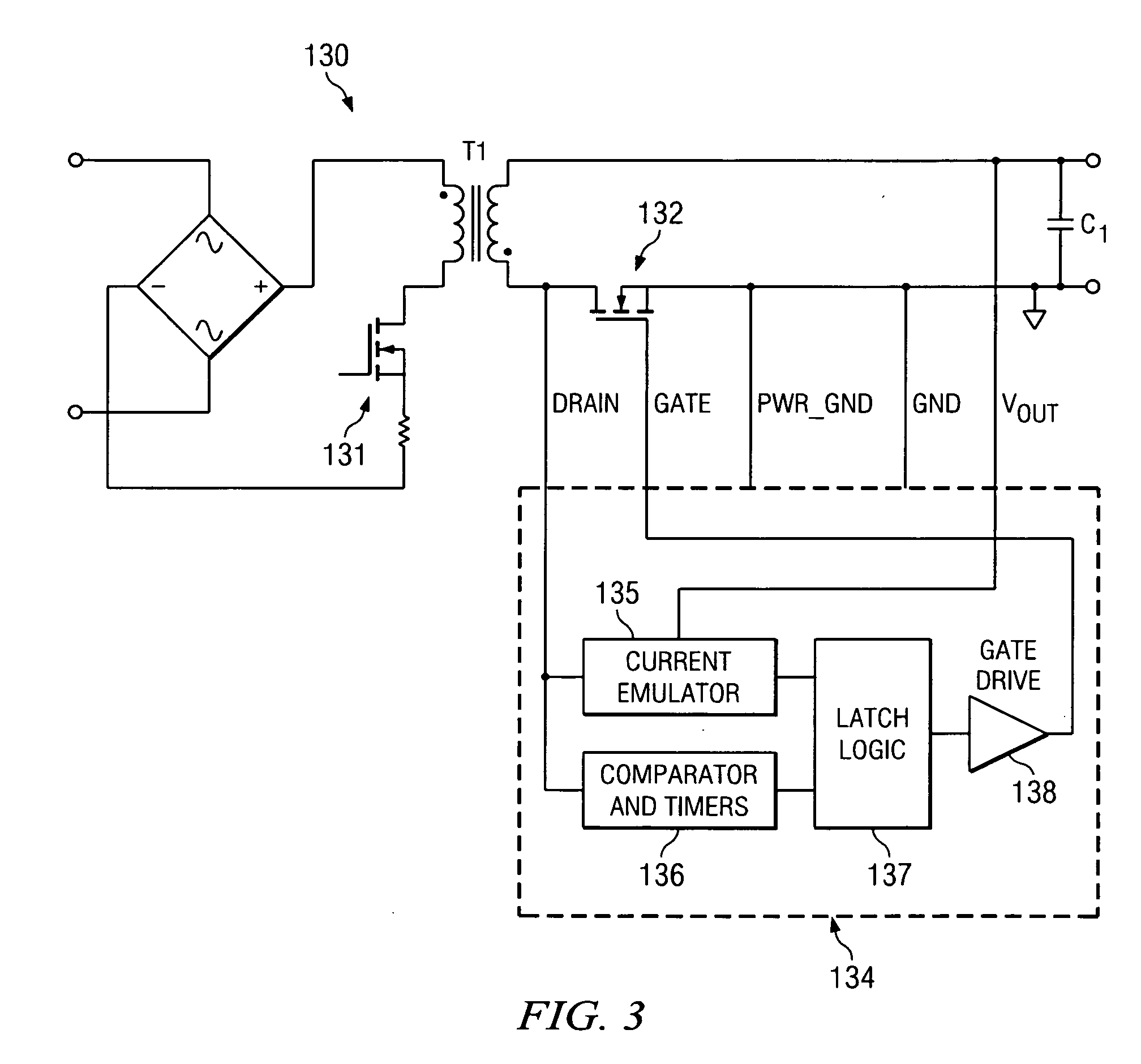
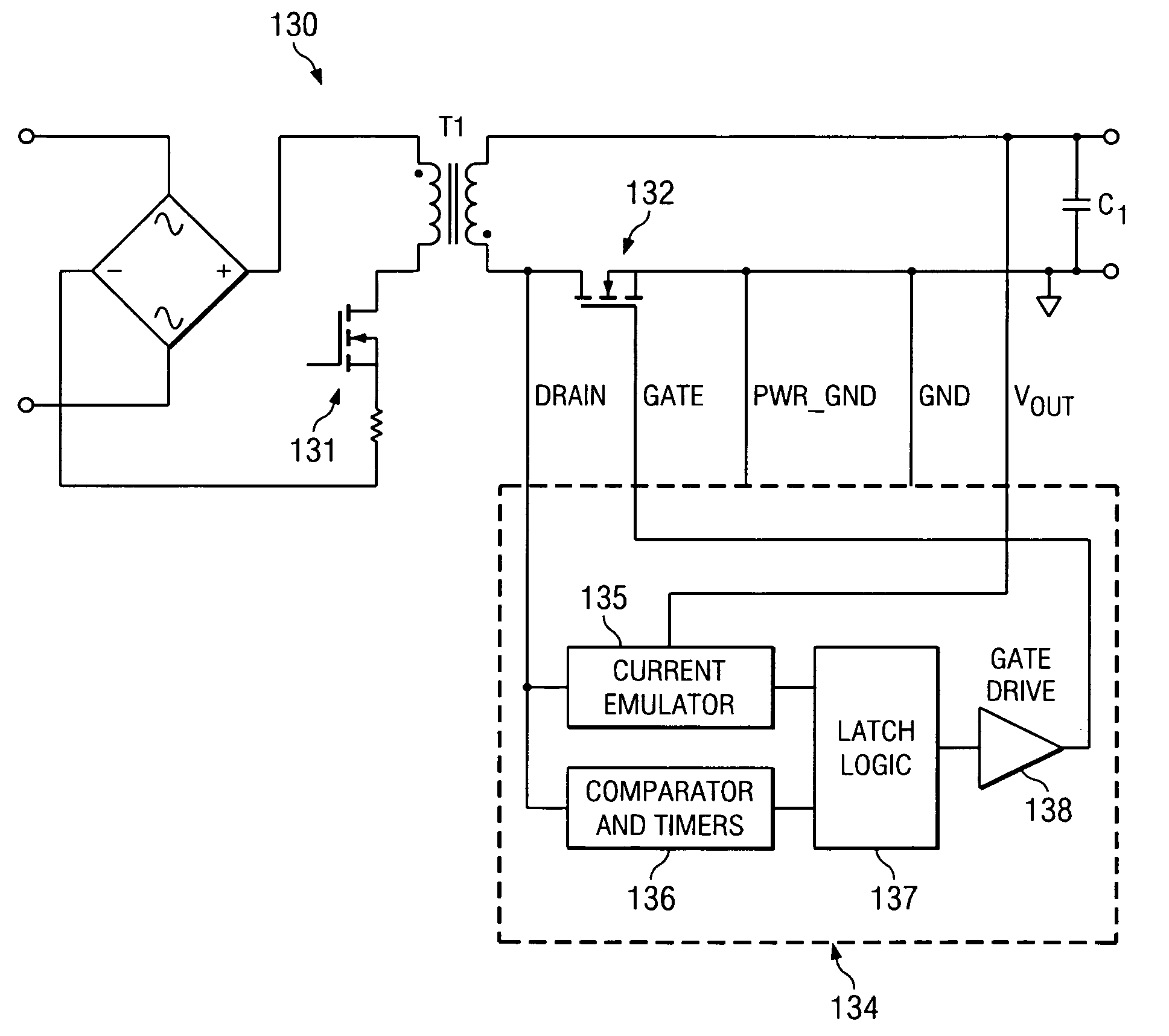
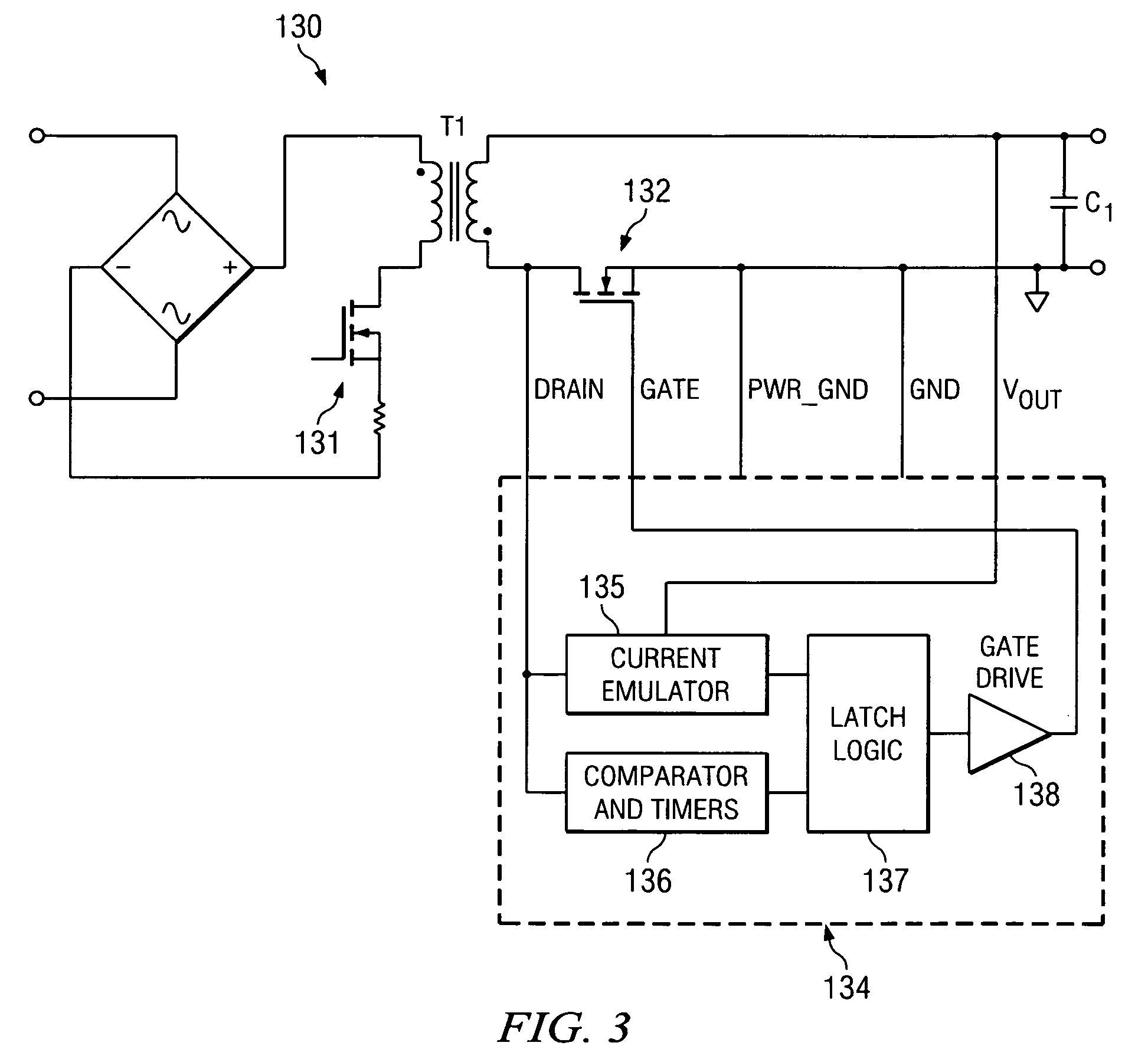
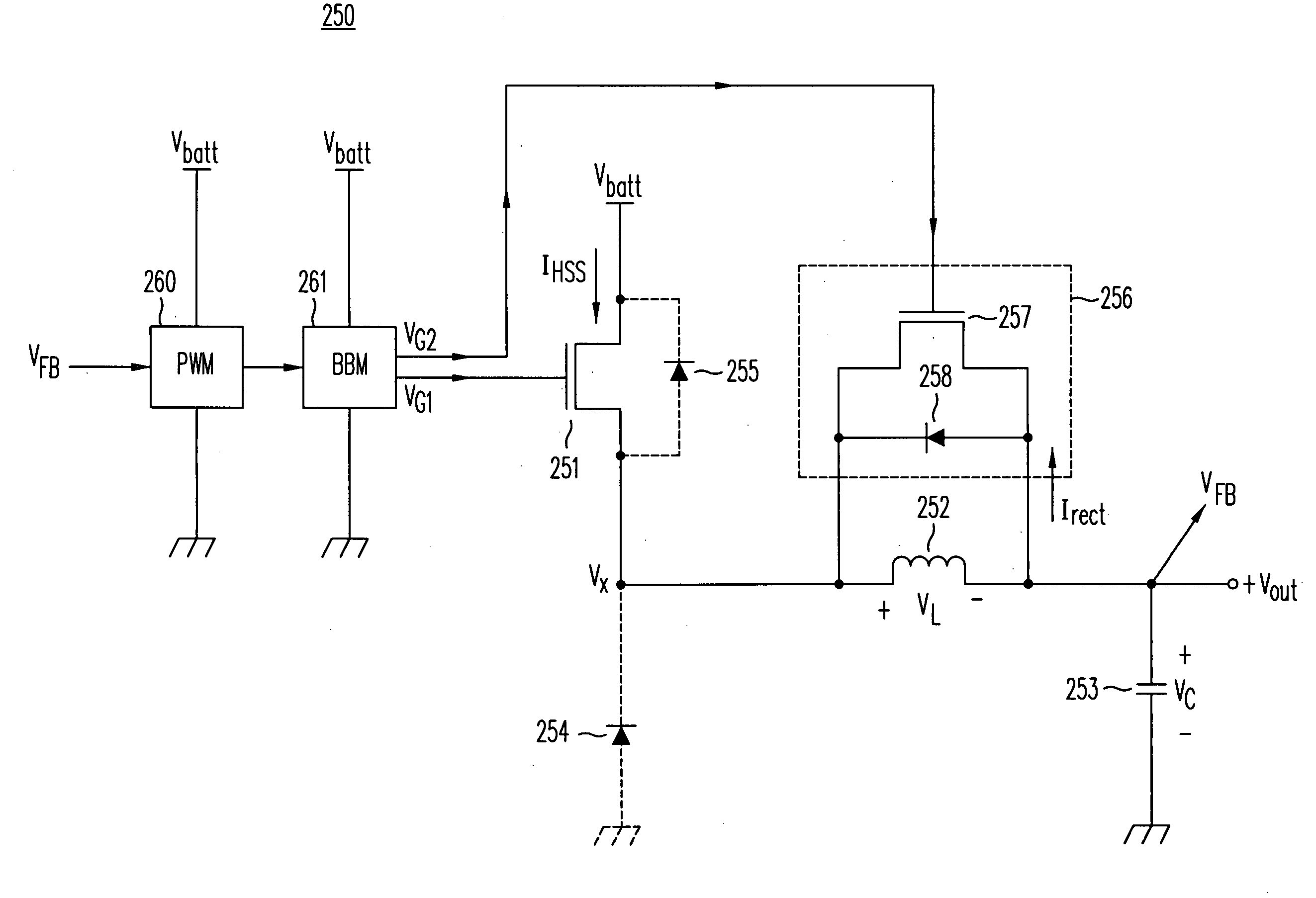
System and method for synchronous rectifier drive that enables converters to operate in transition and discontinuous mode
ActiveUS20100027298A1Inhibition transitionWithout significant lossEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionTransverterSecondary side
A synchronous rectifier is switched in accordance with a primary switch transition and a reference signal representing current in a current storage device to which the synchronous rectifier is coupled. A current emulator provides a signal representing current in the current storage device as a volt-second product so that current stored in the current storage device while the primary switch is on is discharged by the synchronous rectifier. The use of a current emulator provides an inexpensive solution for controlling synchronous rectifier transitions without resorting to more expensive current sensing solutions that are commercially impracticable. Blanking intervals are provided for avoiding false transitions of the synchronous rectifier when the primary switch turns on and after the synchronous rectifier turns off. The disclosed system and method can be applied to flyback converters for a synchronous rectifier on the secondary side of a transformer, or the inductor of buck converters.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
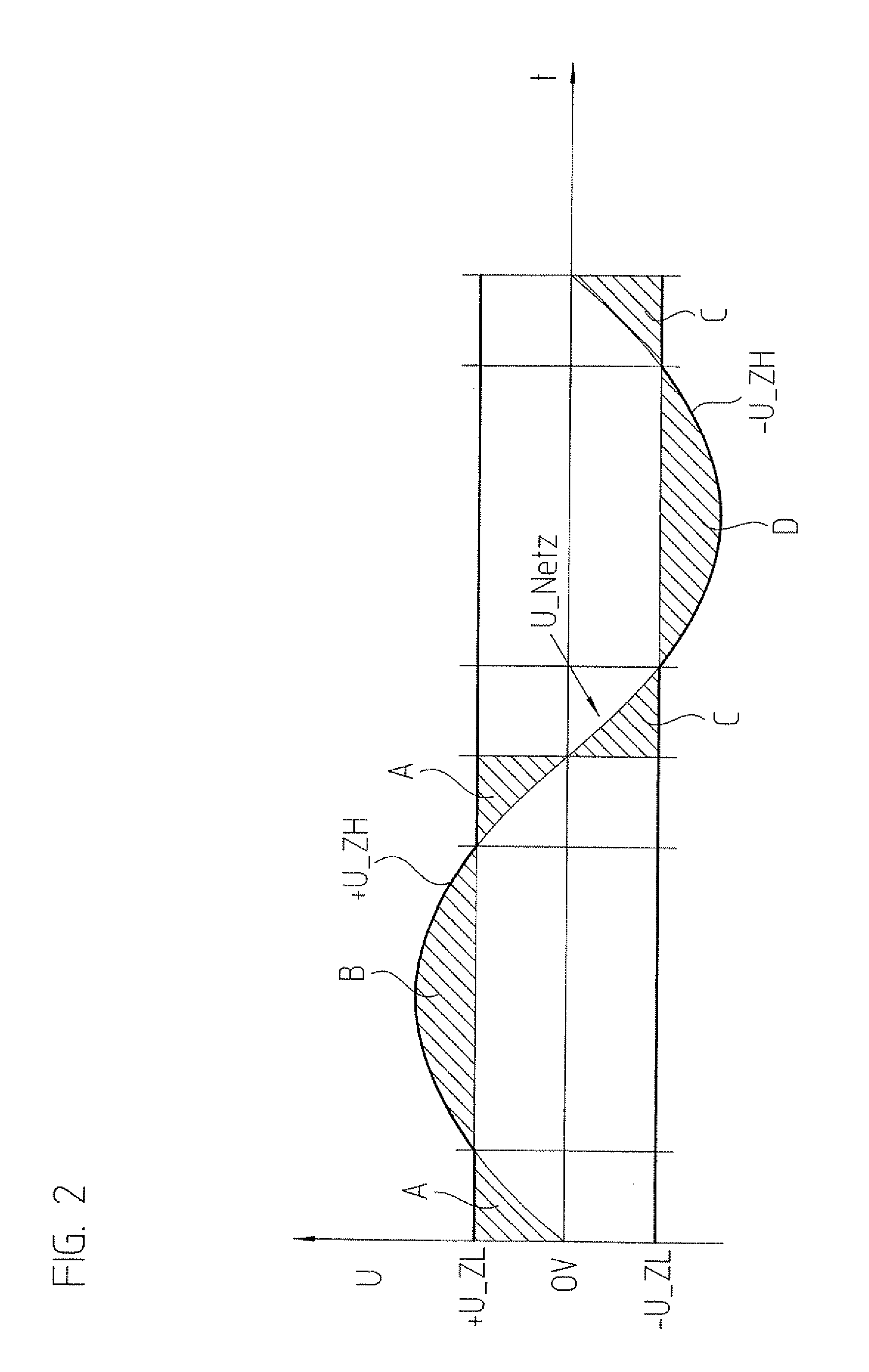
Method for operating an inverter, and inverter
InactiveUS20110080147A1Improve efficiencySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationVoltage generatorLow voltage
In an inverter and a method for operating an inverter, the inverter includes a step-up converter circuit, a dynamic intermediate circuit, and a step-down converter circuit for converting a direct voltage of a direct voltage generator or string into an alternating voltage for supplying a network. The step-up converter circuit increases the direct voltage if the latter is lower than a peak-to-peak maximum of the network voltage, and the step-down converter circuit lowers a dynamic intermediate circuit voltage, as needed, to a lower voltage currently required in the network. The step-up converter circuit dynamically increases the direct voltage to the value currently required in the network and in the process temporarily supplies an approximately sinusoidal voltage curve for the intermediate circuit voltage.
Owner:DR JOHANNES HEIDENHAIN GMBH
Hysteretic CL power converter
ActiveUS20120170334A1Reduce the valueSmall sizeEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionĆuk converterSwitching frequency
A novel switching hysteretic power converter is presented. The power converter combines the function of a capacitive charge pump with the function of an inductive step down converter to obtain a switching boost converter with a much simpler control method with respect to conventional inductive boost power converters. The hysteretic control provides stable operation in all conditions with excellent load transient response. Furthermore the hysteretic control allows high frequency switching reducing the size and cost of the passive components. The Discontinuous Conduction Mode of operation provides very high efficiency even at light loads. The presented power converter can be operated as a boost converter or as a buck converter simply by changing the switching phase of one switch. In both types of operation the efficiency of the hysteretic power converter can be quite high even at high switching frequencies.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Power factor corrected single-phase AC-DC power converter using natural modulation
InactiveUS7564706B1Reduce lossesMost efficientAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionLevel shiftingElectric power system
A power factor corrected (pfc) ac-dc converter has a modified boost input and a modified buck output. Unlike the prior art boost input, the boost switch returns to the output, not to ground. Unlike the prior art buck output stage, a third switch connects to the input. This allows much of the input current to pass through the converter to the output. There is no input current measurement, but nearly ideal power factor correction is achieved through “natural modulation.” A preferred pfc ac-dc converter uses a variable dc-dc transformer on its output, as a post regulator, to provide dielectric isolation and to provide voltage level shifting. The output of the pfc ac-dc converter has the control characteristics of a buck converter, so it is a natural mate for the variable dc-dc transformer. An ac-dc buck converter is most efficient at its maximum duty cycle. It cannot regulate for a lower input voltage, but it can reduce its duty-cycle to control for higher input voltages. A variable dc-dc transformer is most efficient at its maximum ratio. It cannot regulate for a higher input voltage, but it can reduce its effective turns ratio to control for a lower input voltage. With a small overlap in their control ranges, both parts of the power system can operate at maximum efficiency. The variable dc-dc transformer controls the output voltage for nominal and low input voltage. The ac-dc buck converter limits over-voltage transients.
Owner:HERBERT EDWARD
Two-stage voltage regulators with adjustable intermediate bus voltage, adjustable switching frequency, and adjustable number of active phases
InactiveUS20050184713A1Improve efficiencyWide variationEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionBuck converterEngineering
A two-stage power converter that dynamically adjusts to output current requirements includes a first stage regulator that provides power to a second stage regulator. The first stage can be a buck converter, and the second stage can be a multiple-phase buck converter. The output voltage of the first stage (intermediate bus voltage Vbus) is varied according to the load current to optimize conversion efficiency. To provide maximum efficiency, the Vbus voltage is increased as load current increases. The Vbus voltage provided by the first stage can be varied by duty cycle or operating frequency control. In another embodiment, the switching frequency of the second stage is varied as output current changes so that output current ripple is held constant. In an embodiment employing a multiple-phase buck converter in the second stage, the number of operating phases are varied as output current changes.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
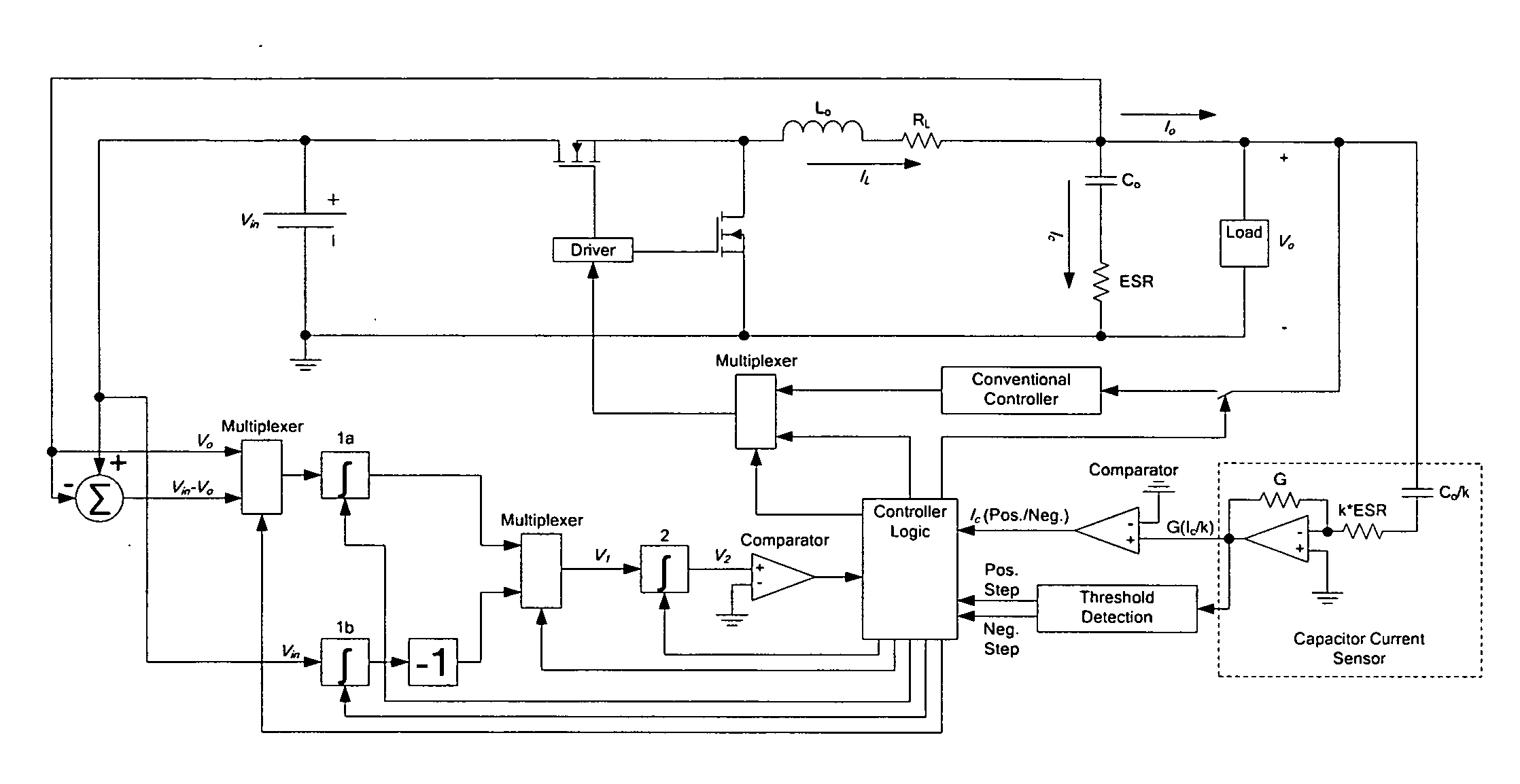
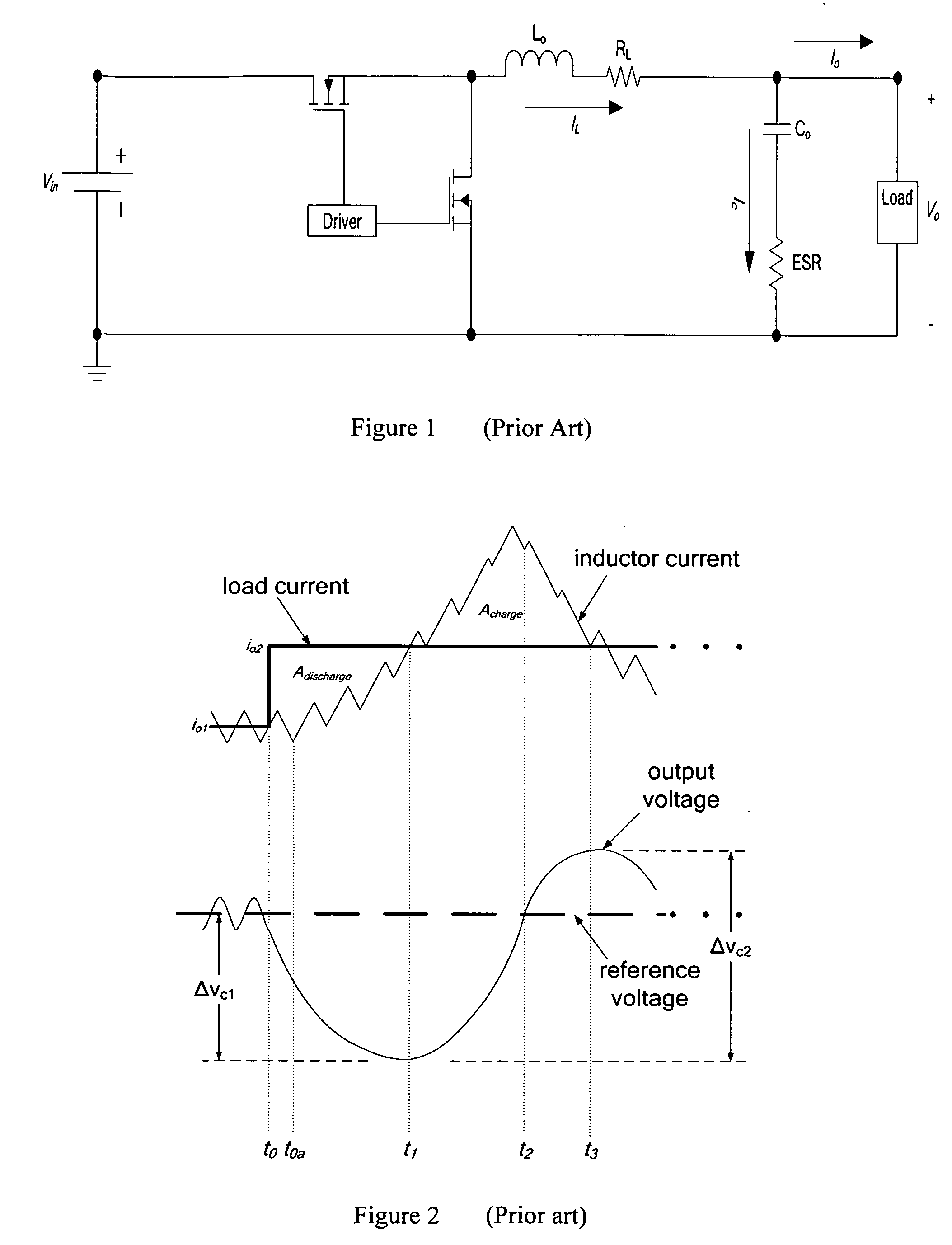
DC-DC converter with improved dynamic response
ActiveUS20080258701A1Improve dynamic performanceLow implementation costMultiple-port networksDc network circuit arrangementsFull bridgePush pull
The invention relates to a control method and a controller for a DC-DC converter, such as a synchronous Buck converter, which exploits the principle of capacitor charge balance to allow the converter to recover from a positive and / or negative load current step in the shortest achievable time, with the lowest possible voltage undershoot / overshoot. The control method may be implemented by either an analog or a digital circuit. The controller may be integrated with existing controller schemes (such as voltage-mode controllers) to provide superior dynamic performance during large-signal transient conditions while providing stable operation during steady state conditions. The invention also relates to a method and a modification of a DC-DC converter topology that comprises connecting a controlled current source between an input terminal and an output terminal of the DC-DC converter; detecting a load current step to a new load current; modifying a duty cycle of the DC-DC converter; and modifying current through a parallel output capacitor of the DC-DC converter by controlling current of the current source. The methods and circuits provided herein are applicable to Buck converters and Buck-derived converters such as forward, push-pull, half-bridge, and full-bridge converters.
Owner:GANPOWER SEMICON FOSHAN LTD
Transformerless power conversion circuit for grid-connected power generation systems
ActiveUS20070047277A1Improvement device sizeIncrease manufacturing costConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionConvertersAlternating current
A transformerless power conversion circuit is interconnected with an electric grid and converts an input DC power provided by a power generator into an AC power and feeding the AC power into the grid. The power conversion circuit includes a buck-boost converter converting the input DC power into two sets of DC power levels; and at least one half-bridge inverter converting the two sets of DC power levels into the AC power for feeding into the grid. The isolating transformer can be eliminated and the common ground problem for DC side and AC side is also solved. The power conversion circuit has significant improvement for device size, manufacture cost and conversion efficiency.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Low Ripple Step-Up/Step-Down Converter
ActiveUS20140070787A1Low rippleHigh bandwidthApparatus without intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationAbsolute differenceOperation mode
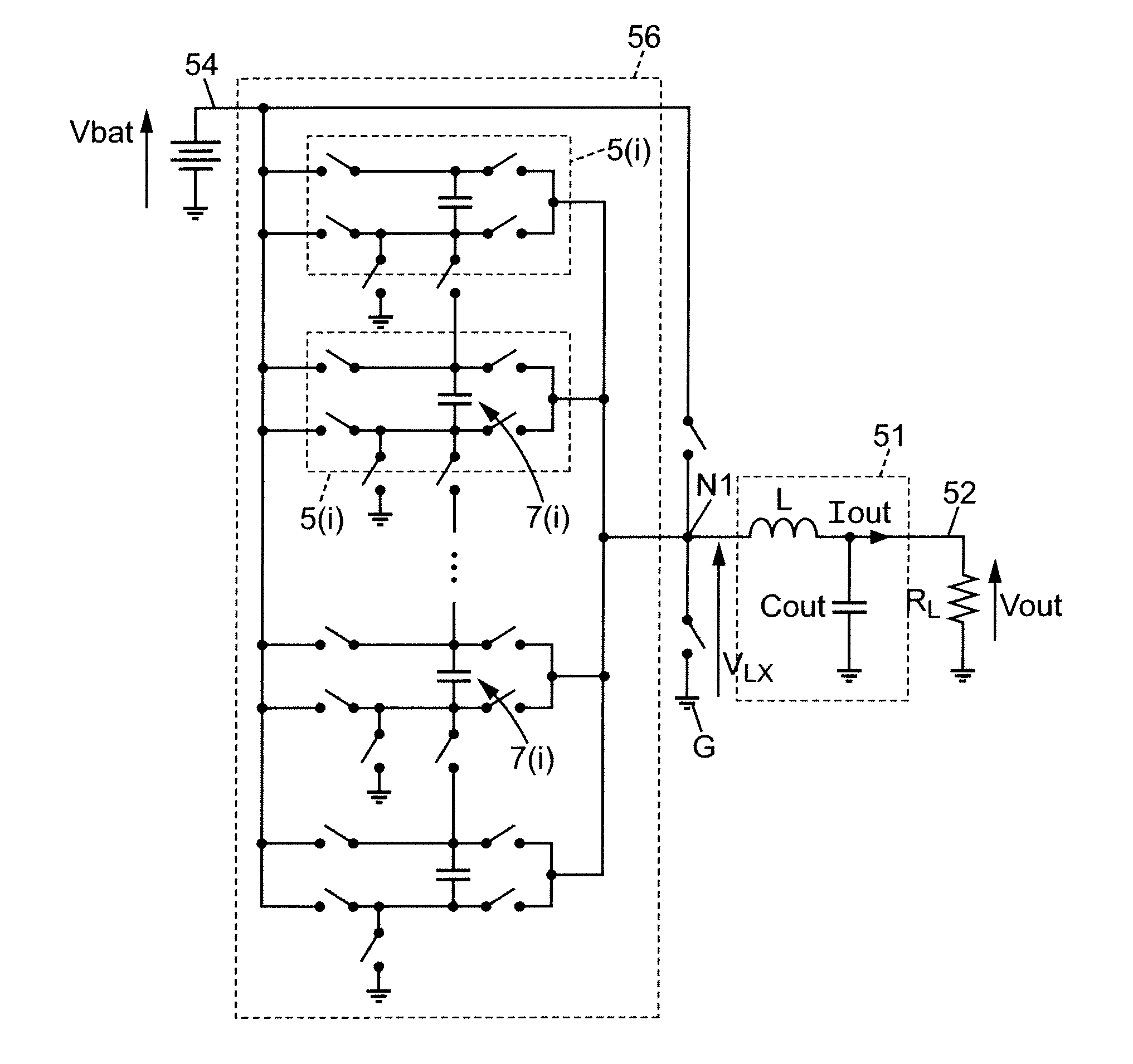
There is described a device for converting an input signal having a given input voltage (Vbat) value (Vbat) into an output signal having an output voltage (Vout) (Vout) different from the input voltage (Vbat). The device comprises a main module (56), arranged between an input terminal (54) and a first circuit node (N1), The device is adapted to output at the first circuit node (N1) a pulse-width-modulated (PWM) signal switching between a first voltage value and a second voltage value, defining a switching range (SR(i)), by switching successively between a first mode of operation and a second mode of operation. The switching range (SR(i)) of the pulse width modulation (PWM) has an amplitude, calculated as the absolute difference between the first and the second voltage value, inferior or equal to Vout half the input voltage (Vbat).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
High efficiency, multi-source photovoltaic inverter
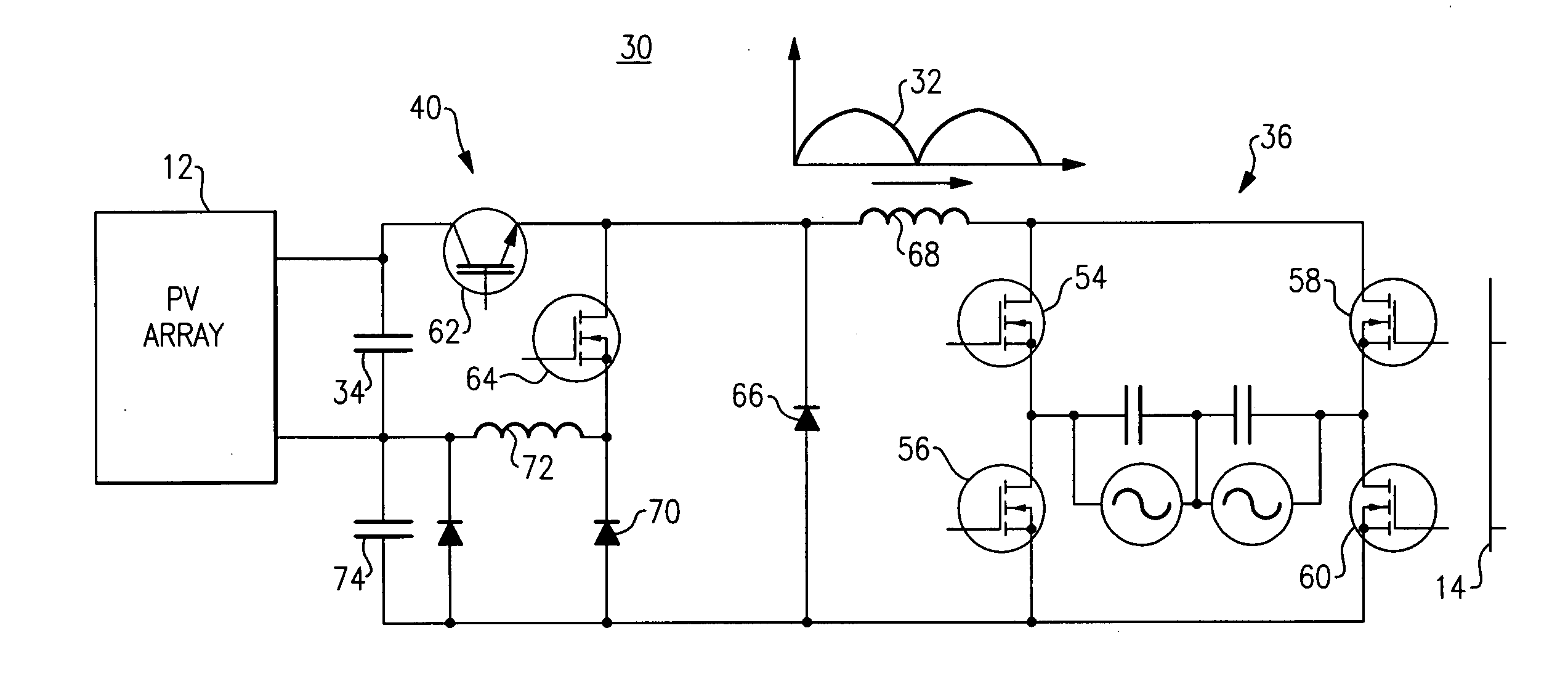
ActiveUS20090296434A1Improve the level ofImpacts system efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionFull waveEngineering
A photovoltaic (PV) inverter system operates continuously in a buck converter mode to generate a sum of full wave rectified sine wave currents at a current node common to a plurality of buck converters in response to a plurality of full wave rectified sine wave currents generated via the plurality of buck converters. The PV inverter system increases the level of the voltage sourcing each buck converter when a corresponding DC power source voltage is lower than the instantaneous voltage of a utility grid connected to the PV inverter system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
High efficiency coupled inductor soft switching power converters
InactiveUS6272023B1Reduce switching lossesLow component part countEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcEngineeringVoltage source
The power converter of this invention accomplishes zero voltage switching at both turn on and turn off transitions of all primary switches. A pair of coupled inductors serve as both energy storage devices and isolation mechanisms. The placement of a small inductor in series with the coupled inductors enables the invariance of primary current direction throughout the switching transition which provides for zero voltage switching for all switches for all transitions. The power converter behaves as a pair of interleaved coupled inductor buck converters with oppositely directed magnetizing currents. During a first half cycle, while one inductor is coupled to the output, the other uncoupled inductor behaves as a current source, setting the primary winding currents for both inductors equal to the magnetizing current of the uncoupled inductor. The inductor which is coupled to the output appears as an output filter capacitor or voltage source to the uncoupled inductor during the first half cycle. During the alternate half cycle the roles of the two inductors are reversed.
Owner:TECHN WITTS
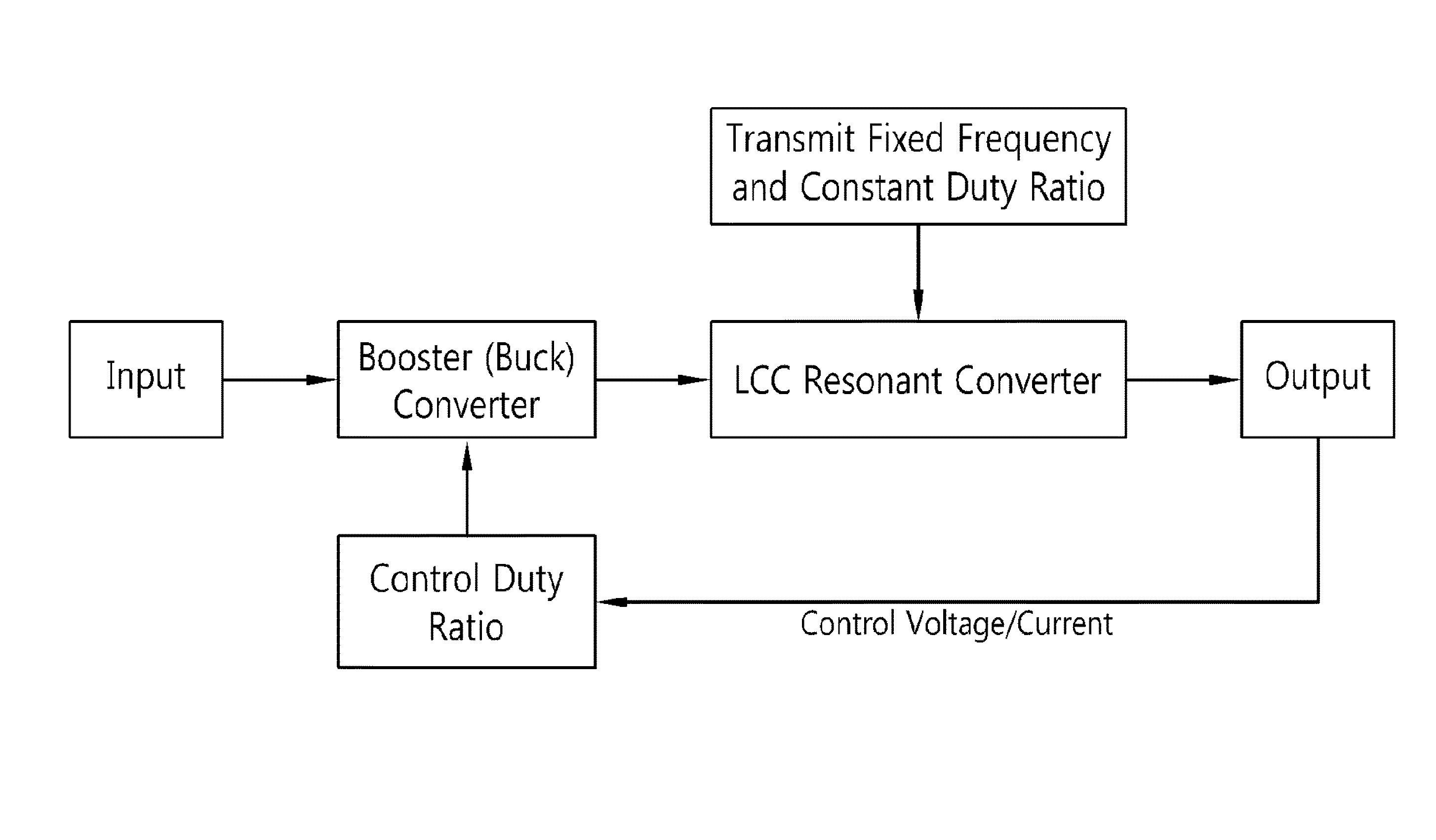
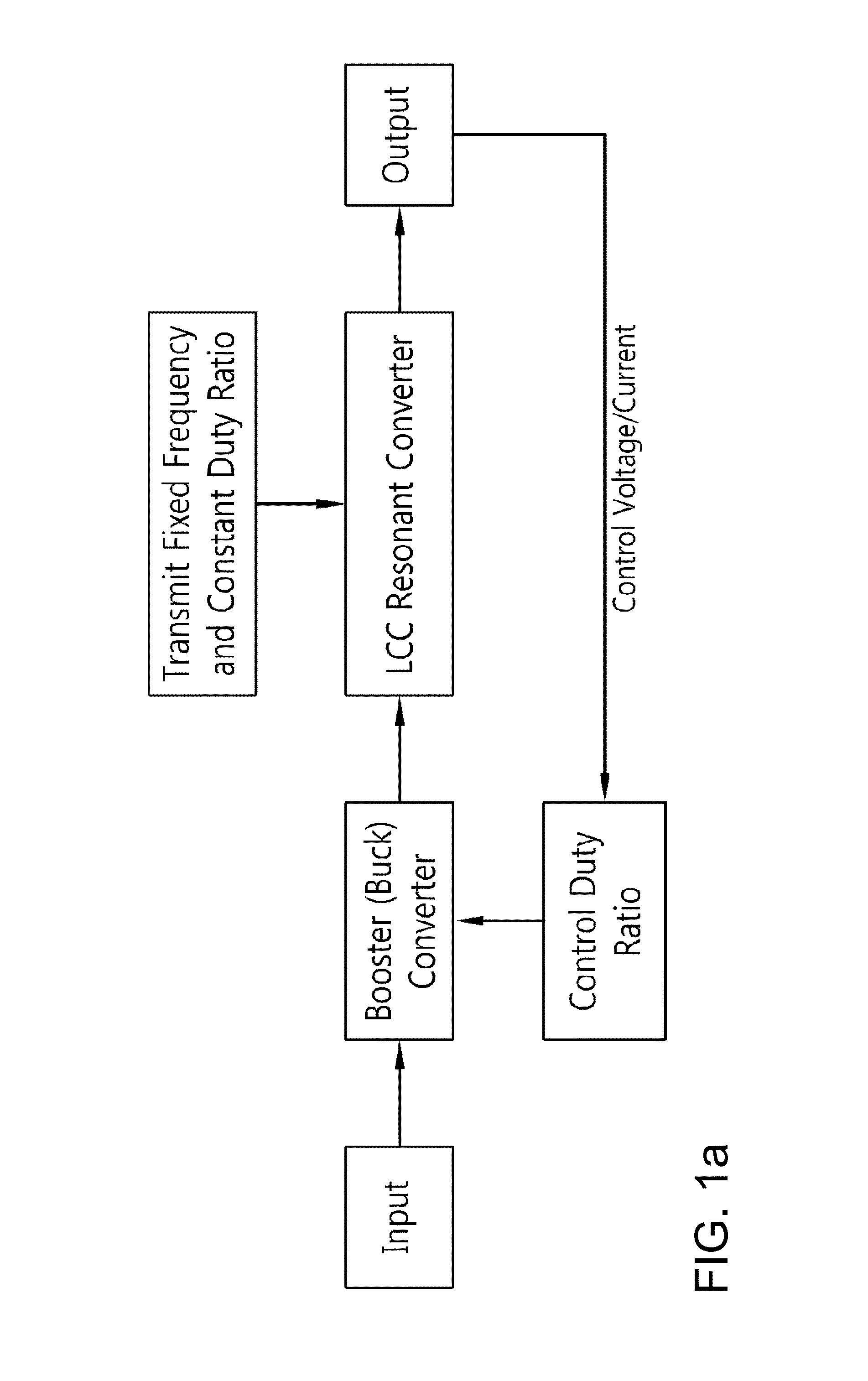
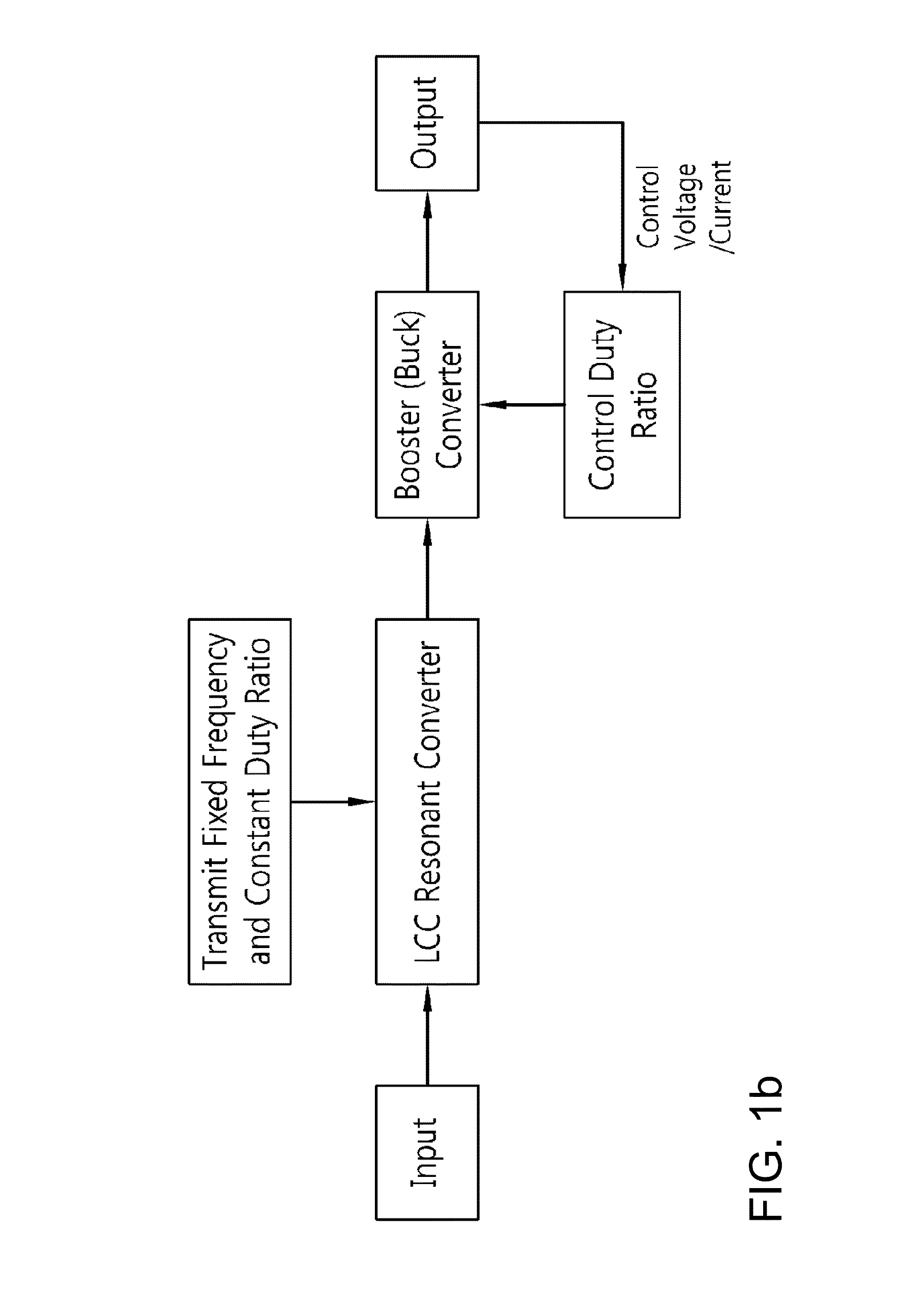
Two-stage insulated bidirectional DC/DC power converter using a constant duty ratio LLC resonant converter
ActiveUS8467199B2Stable energy transferComplexity in output controlEfficient power electronics conversionEnergy industryTransverterBuck converter
A two-stage insulated bidirectional DC / DC power converter is disclosed. A two-stage insulated bidirectional DC / DC power converter according to an embodiment of the invention has the characteristic of including: an LLC resonant converter operating at a constant duty ratio; a bidirectional converter joined to a front part of the LLC resonant converter and configured to perform a booster converter function of outputting the input voltage at a consistent input voltage for the LLC resonant converter, and a buck converter function of reducing the voltage by way of the LLC resonant converter and then outputting a consistent voltage; and a bidirectional converter control unit configured to control changes in an input voltage of the bidirectional converter and regulate an output voltage of the LLC resonant converter to thereby maintain a consistent input voltage of the LLC resonant converter, such that the LLC resonant converter operates at a constant duty ratio.
Owner:MYONGJI UNIV IND & ACAD COOPERATION FOUND +1
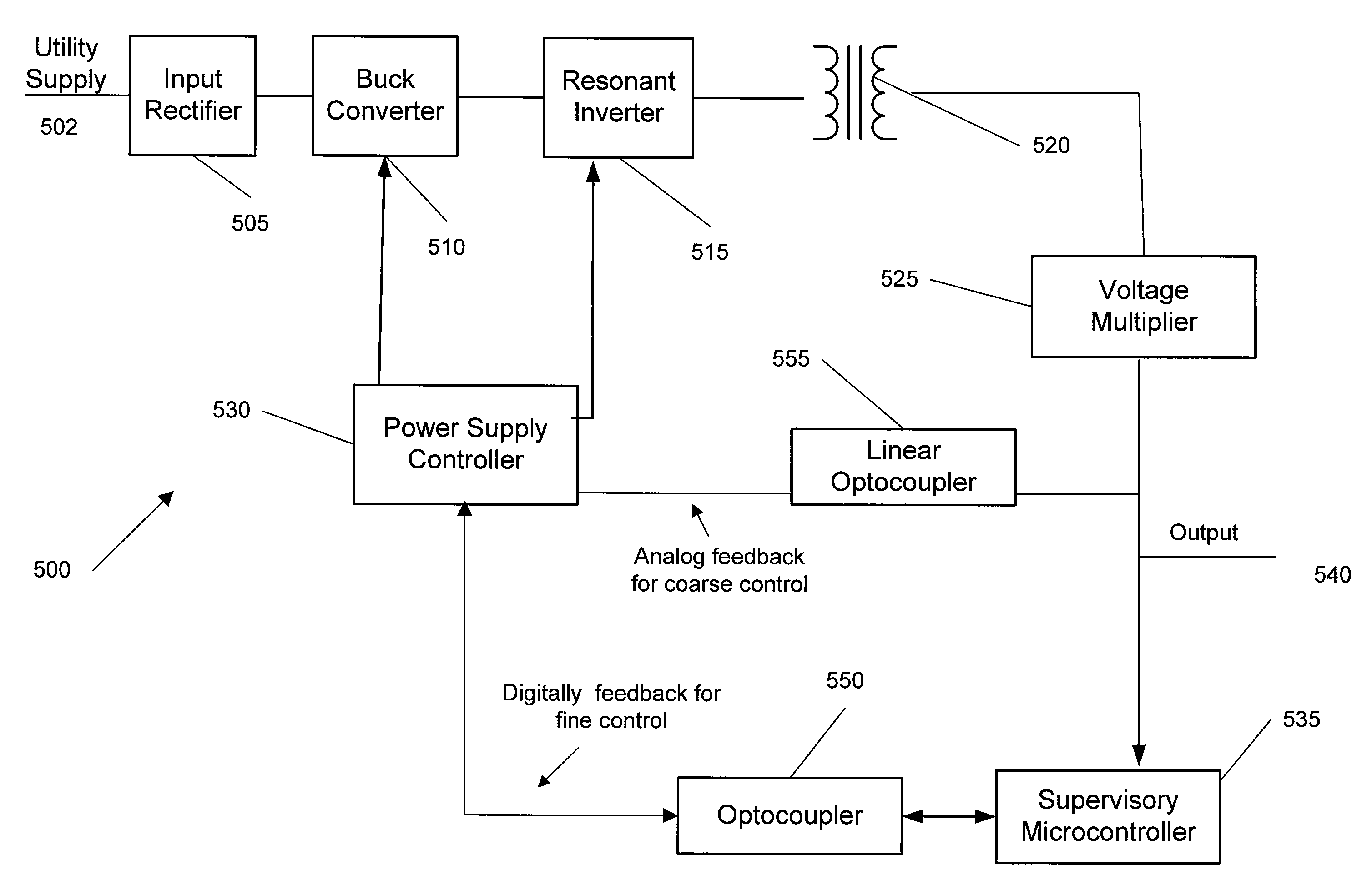
Power supply with a digital feedback loop
ActiveUS7324354B2High operating requirementsLow costEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcResonant inverterDigital feedback
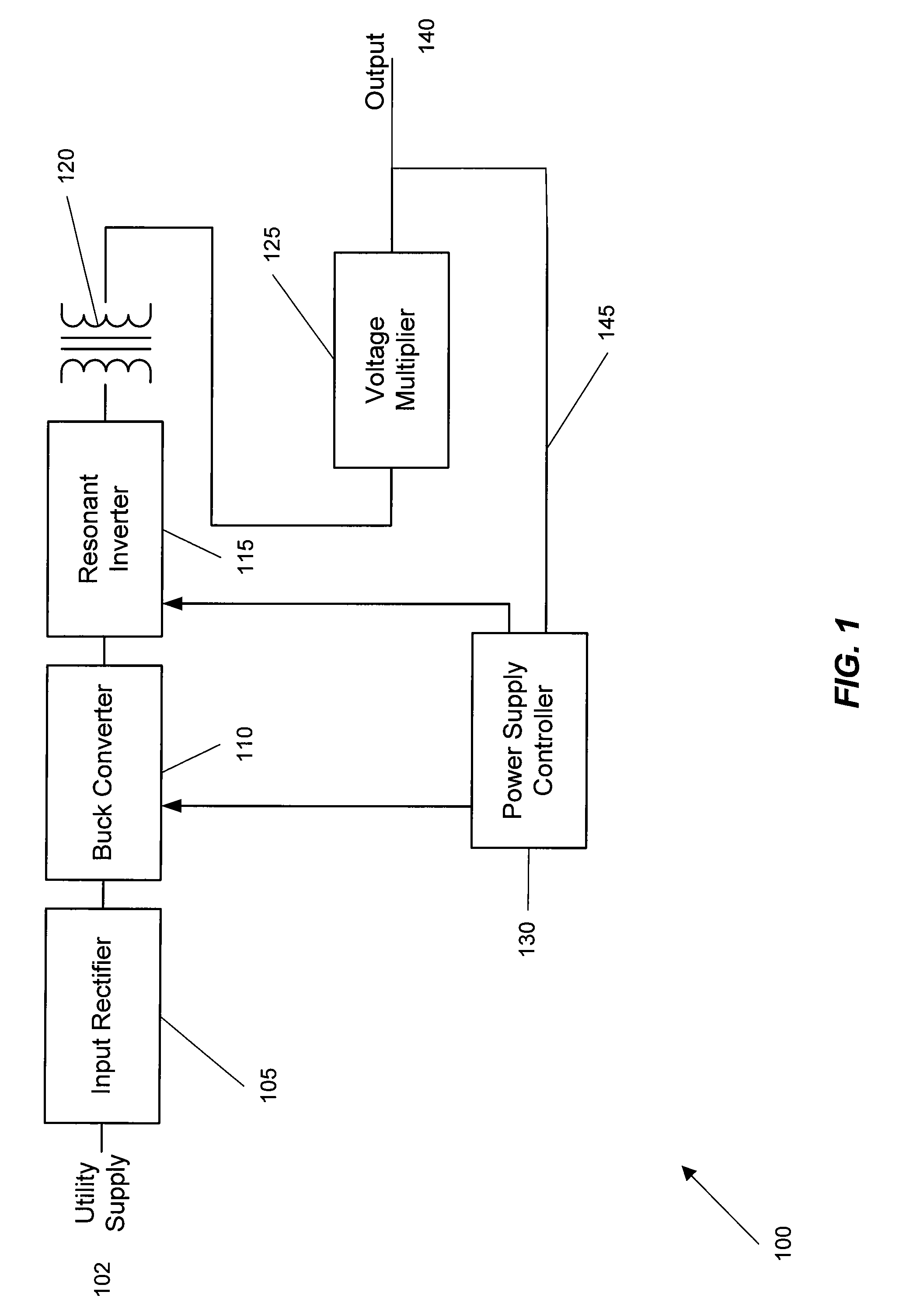
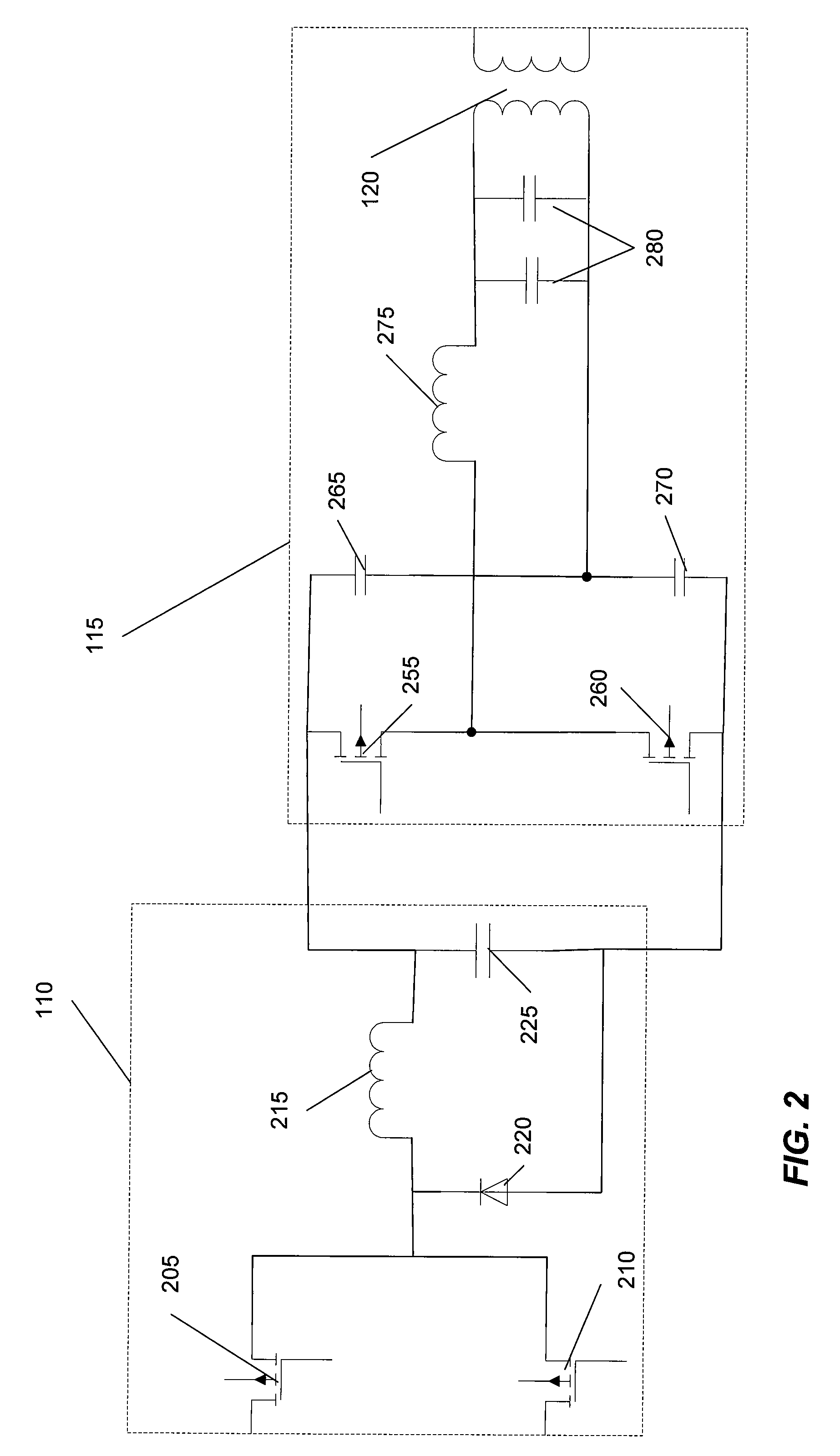
A wide range power supply capable of delivering 20V to 5000V is provided. The power supply of the present invention uses switch mode technology to achieve high overall operating efficiency and is capable of operating from no load to full load without loss of regulation. The power supply in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention operates directly from the utility supply (e.g., 110V / 220V and 50 Hz / 60 Hz). In one embodiment, the power supply's power conversion stage includes the following stages: an input rectifier; a buck converter; a quasi-resonant inverter; and a voltage multiplier. The above indicated stages are connected in series to achieve the large output voltage range. High precision is obtained from a use of a digital feedback loop, possibly in connection with an analog feedback loop.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Monolithic battery charging device
InactiveUS6791298B2Batteries circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionEngineeringBattery charger
A monolithically formed battery charger may be fabricated as an integral part of a multifunctional integrated circuit or as independent monolithically formed integrated circuit. The monolithically formed battery charger includes at least one step-down converter having a given duty ratio coupled to a battery-terminal interface that provides a stepped-down output voltage and current that may be used to charge a rechargeable battery.The step-down converter includes one or more cascaded monolithically-formed synchronous-buck regulators operating at a frequency of at least one megahertz. Each regulator may include a capacitor, inductor, controller, switch, and rectifier. When cascaded, the high-side output node of a preceding synchronous-buck regulator is connected to the switch in a successive synchronous-buck regulator.
Owner:SHAKTI SYST
Server and uninterruptable power supply housed in that server
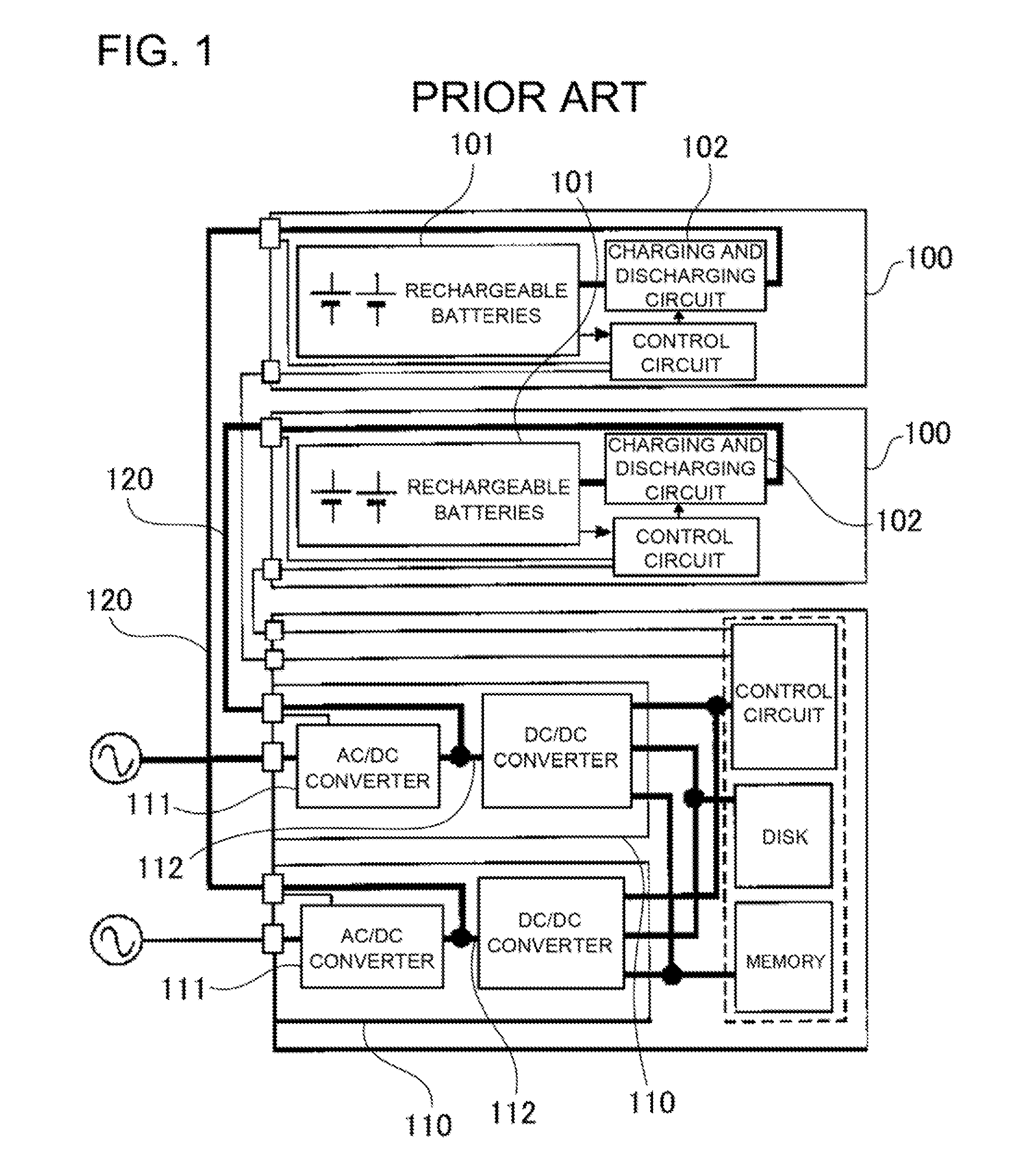
InactiveUS20110133560A1Stable strengthGuaranteed uptimeBatteries circuit arrangementsPower supply for data processingControl circuitUninterruptible power supply
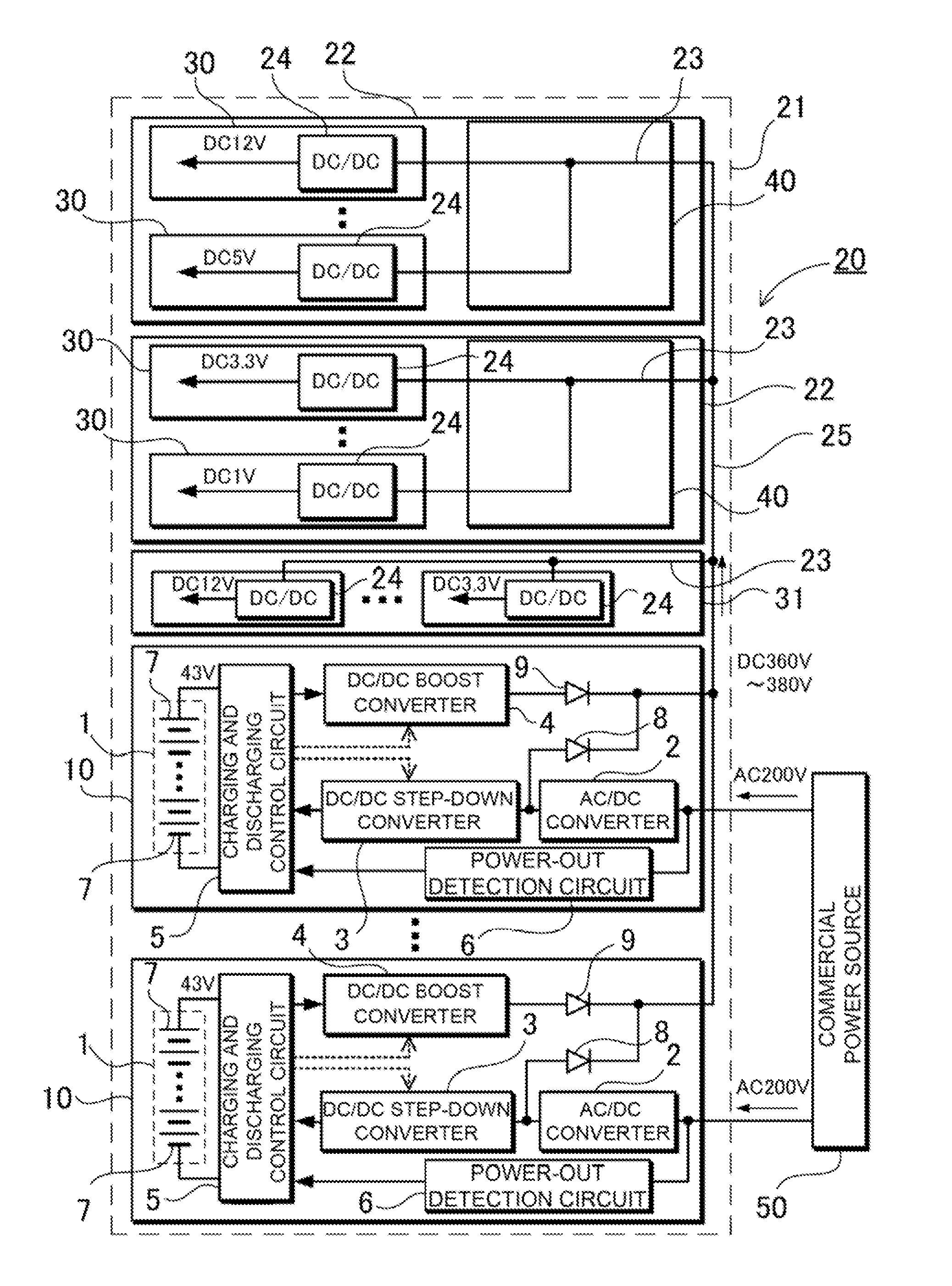
The main server block 20 houses uninterruptible power supplies 10 that supply 150V-400V DC operating power to the main server block 20 input power supply lines 23 both with and without power outage. An uninterruptible power supply 10 has rechargeable batteries 1 having a voltage specification of 60V or less, an AC / DC converter 2 that converts power input from an external commercial power source 50 to DC and supplies it to the input power supply lines 23, a DC / DC step-down converter 3 that steps-down the AC / DC converter 2 output voltage to the rechargeable battery 1 charging voltage, a DC / DC boost converter 4 that steps-up the rechargeable battery 1 voltage and supplies it to the input power supply lines 23 during power outage, and a charging and discharging control circuit 5 that detects commercial power source 50 outage and switches the DC / DC boost converter 4 to the operating state.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Maximum power tracing method for solar power system and solar power device
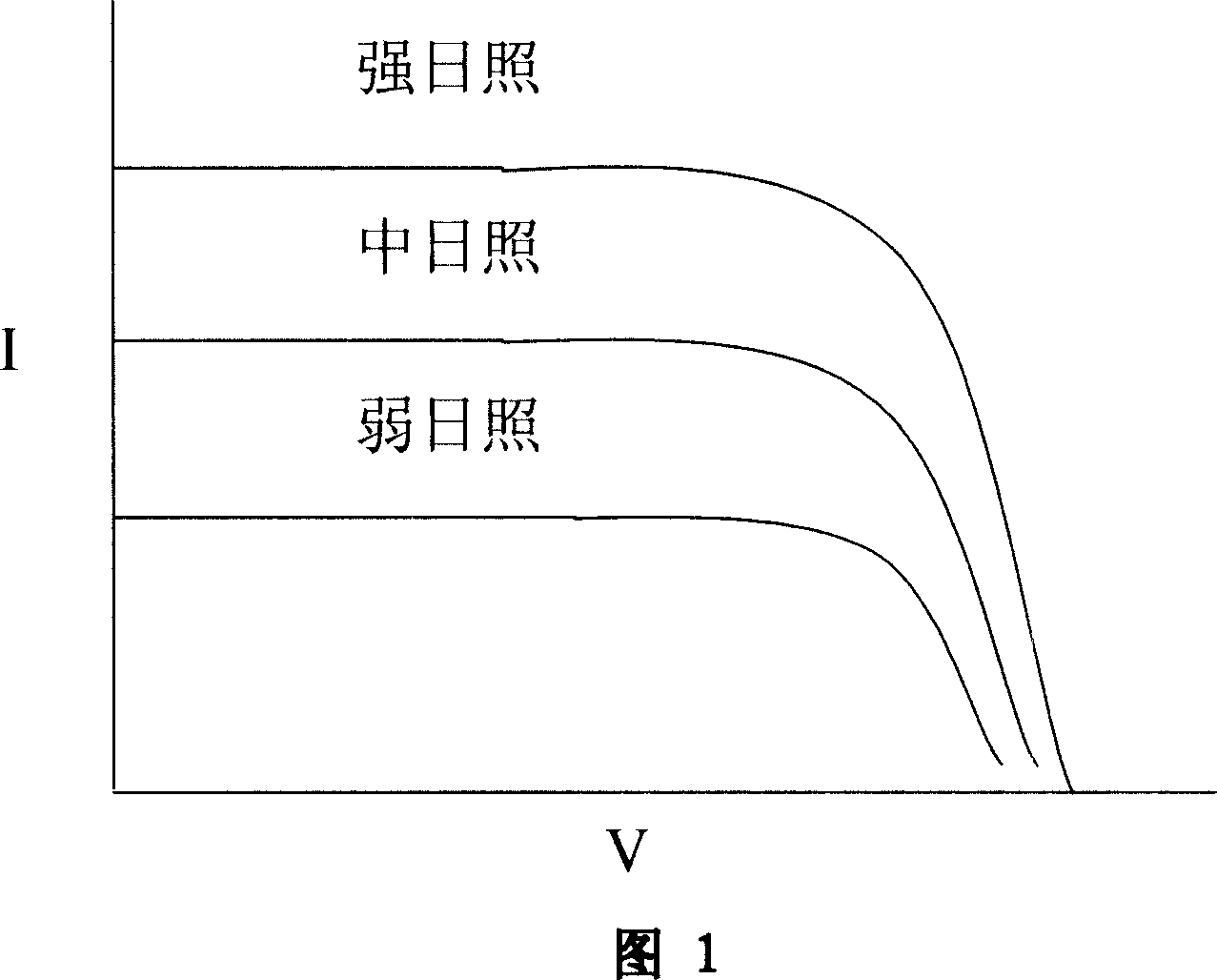
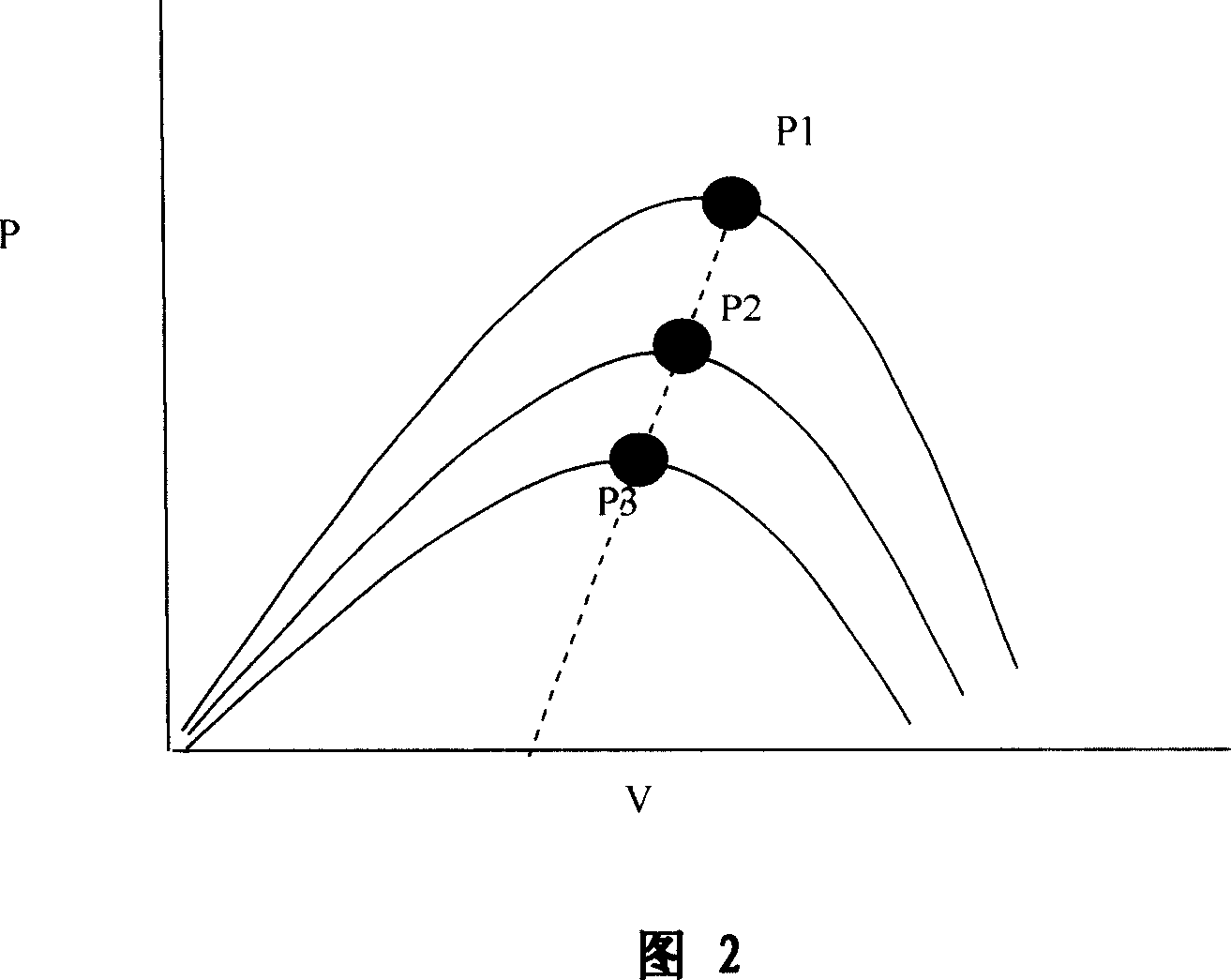
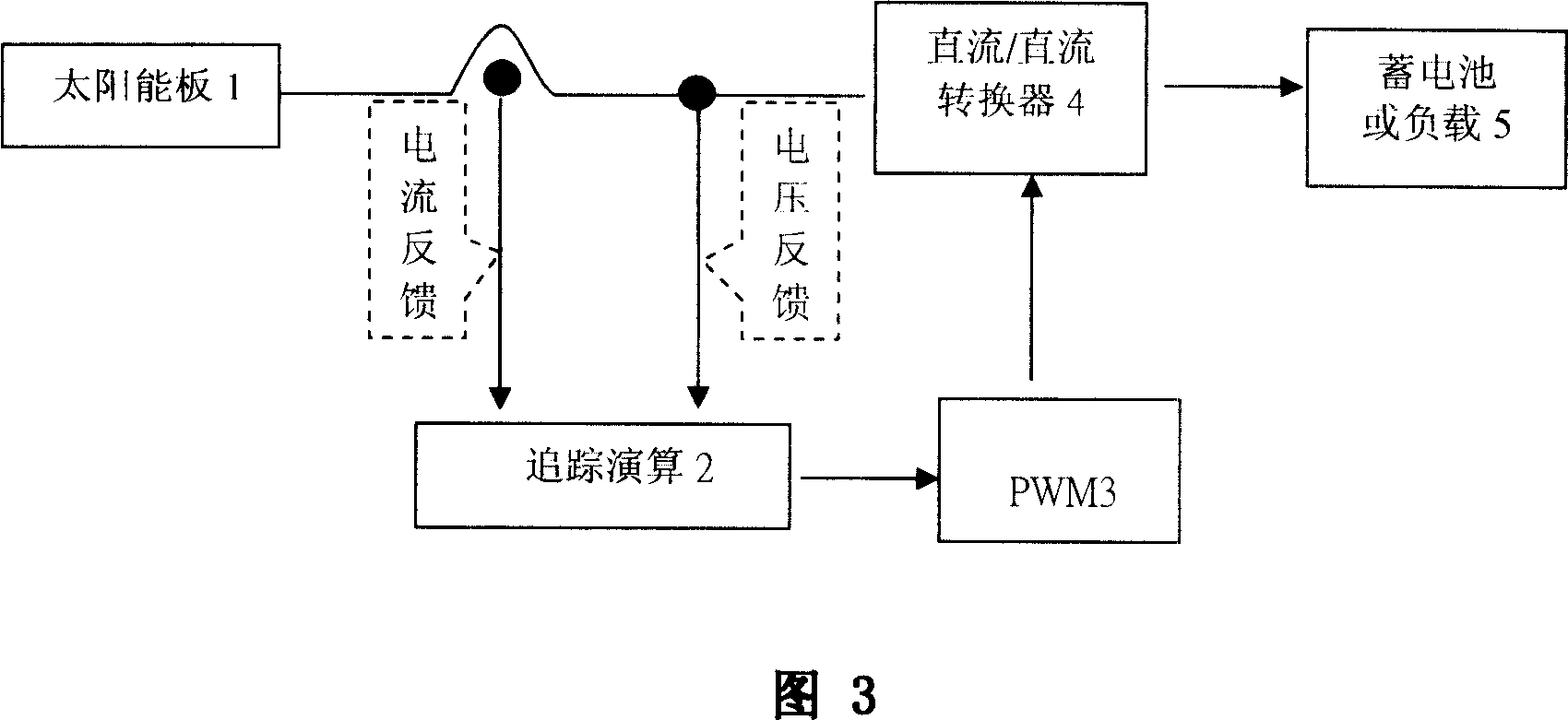
InactiveCN1949624AHigh energyThe method of maximum power tracking is simpleElectrical storage systemBatteries circuit arrangementsTraffic signalDynamic balance
The invention discloses a maximum power tracking method for a solar energy power supply system and the solar energy power supply unit thereof, relating to solar power generation technical field. And the method tracks the maximum power of the solar energy system by dynamic balancing. According to the method, it adds in intelligent charging-discharing mechanism to form an intelligent coordination solar energy device, comprising at least a solar panel, super capacitor, DC / DC buck-boost converter, pulse width modulation driver, storage battery, logic controller and load; and the method is characterized in that an instant power type super capacitor is connected between the solar panel and the DC / DC buck-boost converter to act as an energy dynamic balancer; it converts the electric energy produced by the solar panel into capacitor type electric energy to make the maximum power calculation, able to largely simplify calculation program, improving tracking calculation real-timeness and reliability and raising solar energy system efficiency. And the invention can be widely applied to solar LED lamps, and solar energy lamps, especially solar energy street lamps, solar traffic signal lamps, solar energy engineering lamps, etc.
Owner:孙民兴
Monolithic battery charging device
InactiveUS20030090237A1Batteries circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionBattery chargeTransverter
A monolithically formed battery charger may be fabricated as an integral part of a multifunctional integrated circuit or as independent monolithically formed integrated circuit. The monolithically formed battery charger includes at least one step-down converter having a given duty ratio coupled to a battery-terminal interface that provides a stepped-down output voltage and current that may be used to charge a rechargeable battery The step-down converter includes one or more cascaded monolithically-formed synchronous-buck regulators operating at a frequency of at least one megahertz. Each regulator may include a capacitor, inductor, controller, switch, and rectifier. When cascaded, the high-side output node of a preceding synchronous-buck regulator is connected to the switch in a successive synchronous-buck regulator.
Owner:SHAKTI SYST
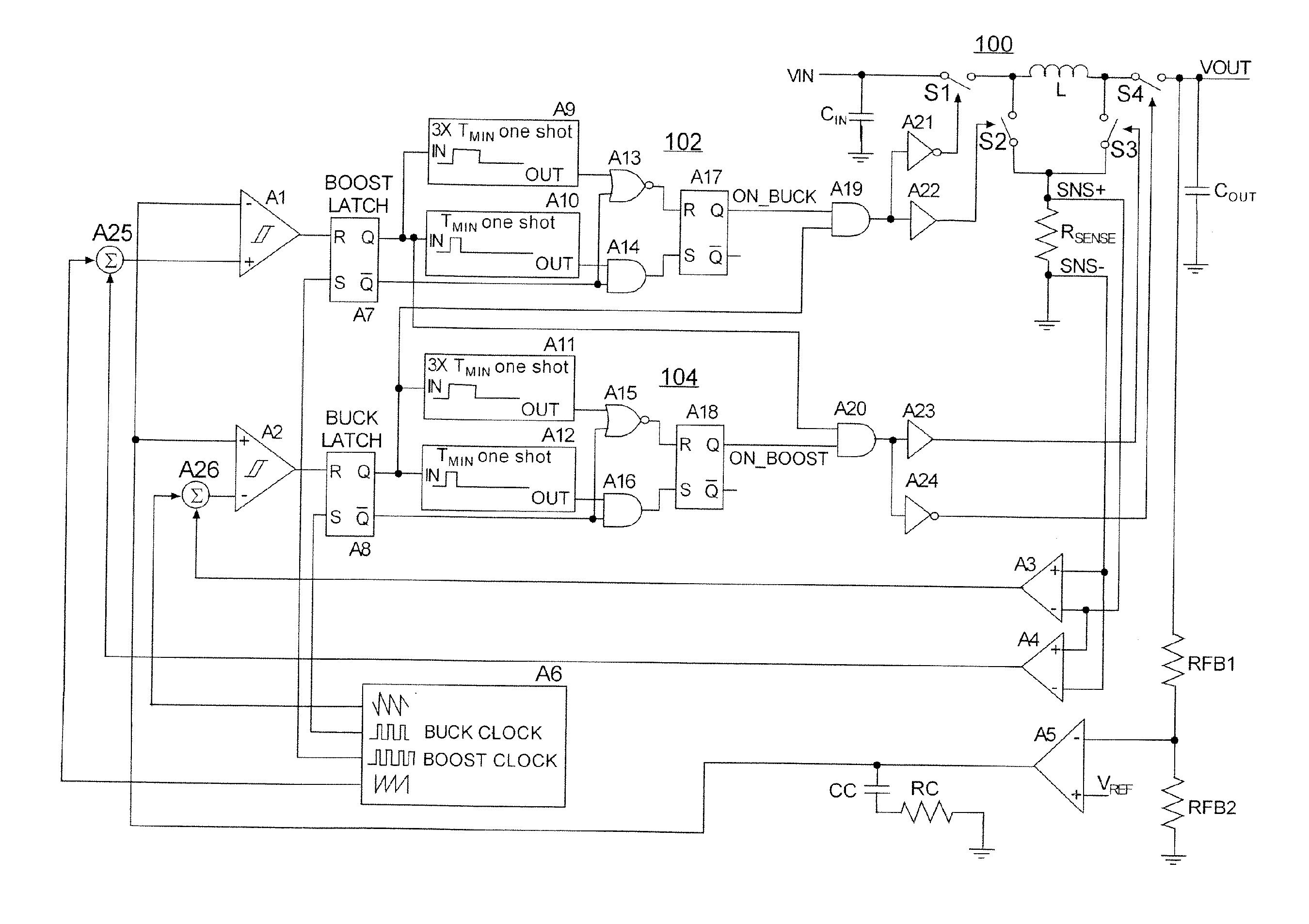
Switching scheme for step up-step down converters using fixed frequency current-mode control
ActiveUS20110279098A1Inhibition transitionDc-dc conversionAc network voltage adjustmentCurrent mode controlMode control
Novel circuitry and methodology for controlling a step up-step down switching regulator that produces a regulated output signal at an output node in response to an input signal at an input node, and has an inductive device, a plurality of switching circuits for providing connection of the inductive device to the input and output nodes and a ground node, and a switch control circuit for driving the switching devices so as to enable the power supply system to operate in a boost mode to increase the input signal, in a buck mode to decrease the input signal, and in a buck-boost mode when a difference between the input signal and the output signal is within a predetermined range. Buck-boost latch circuitry is provided for latching a transition between the buck mode and the buck-boost mode, or between the boost mode and the buck-boost mode based on a predetermined condition.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
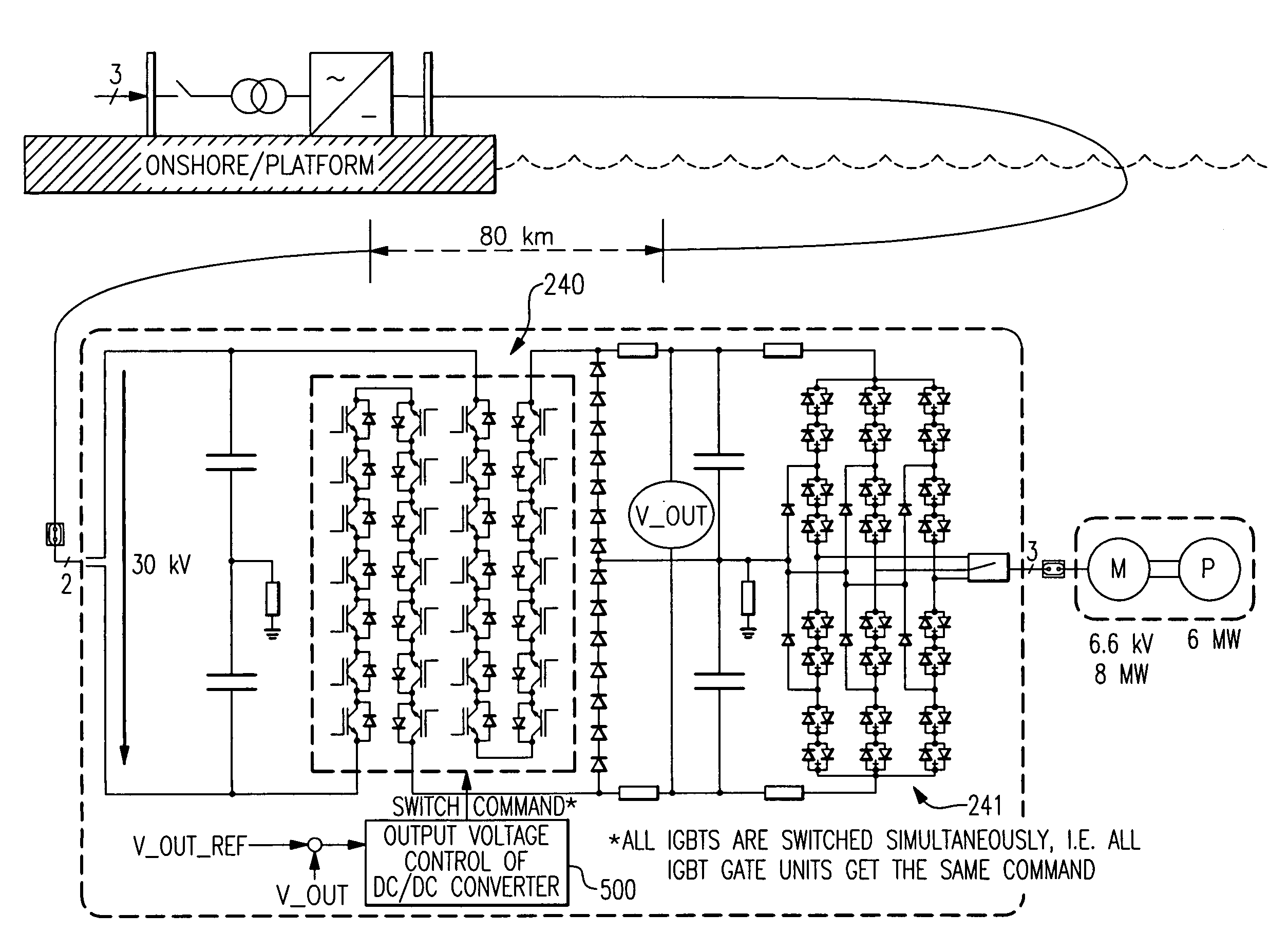
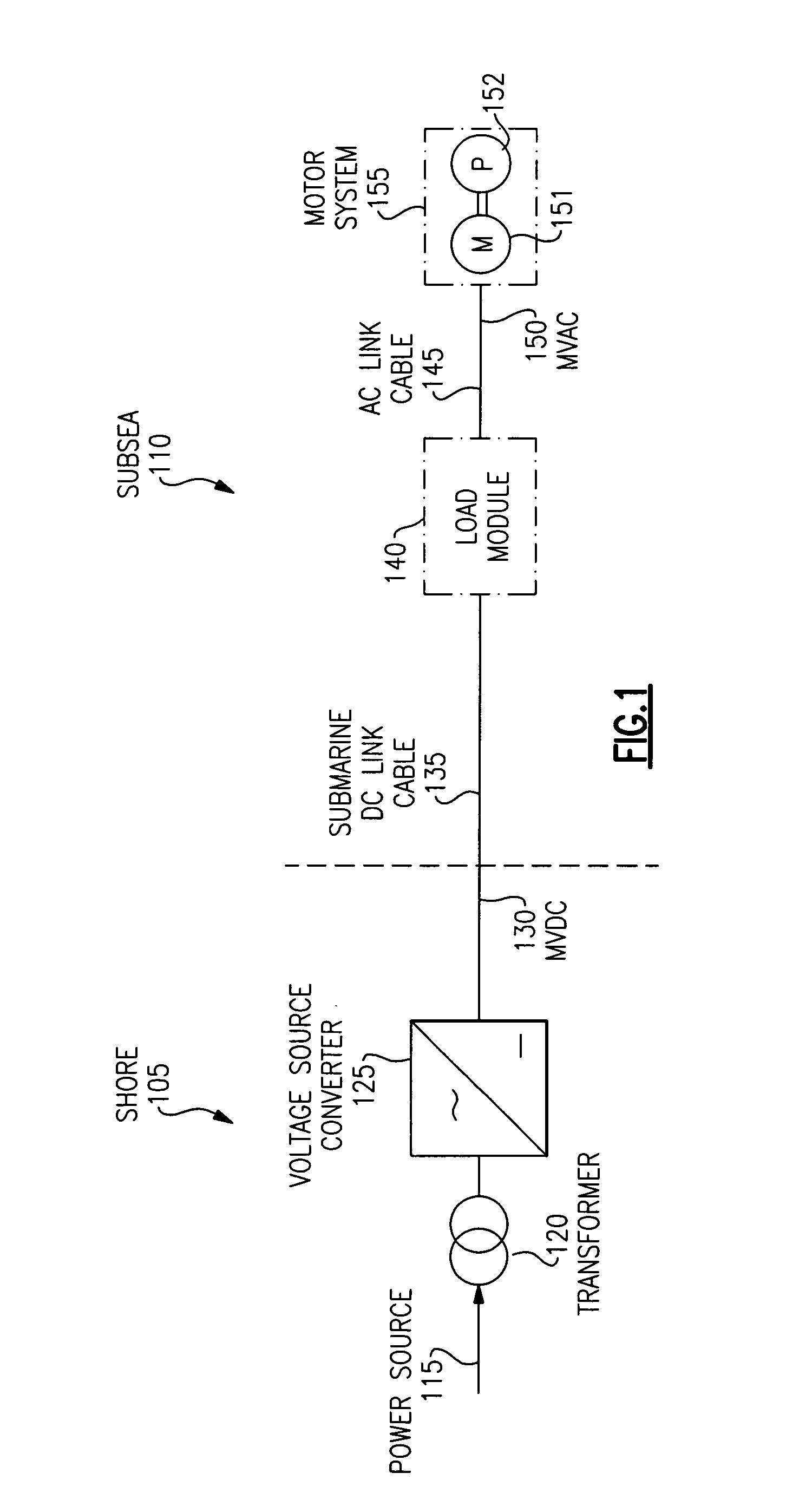
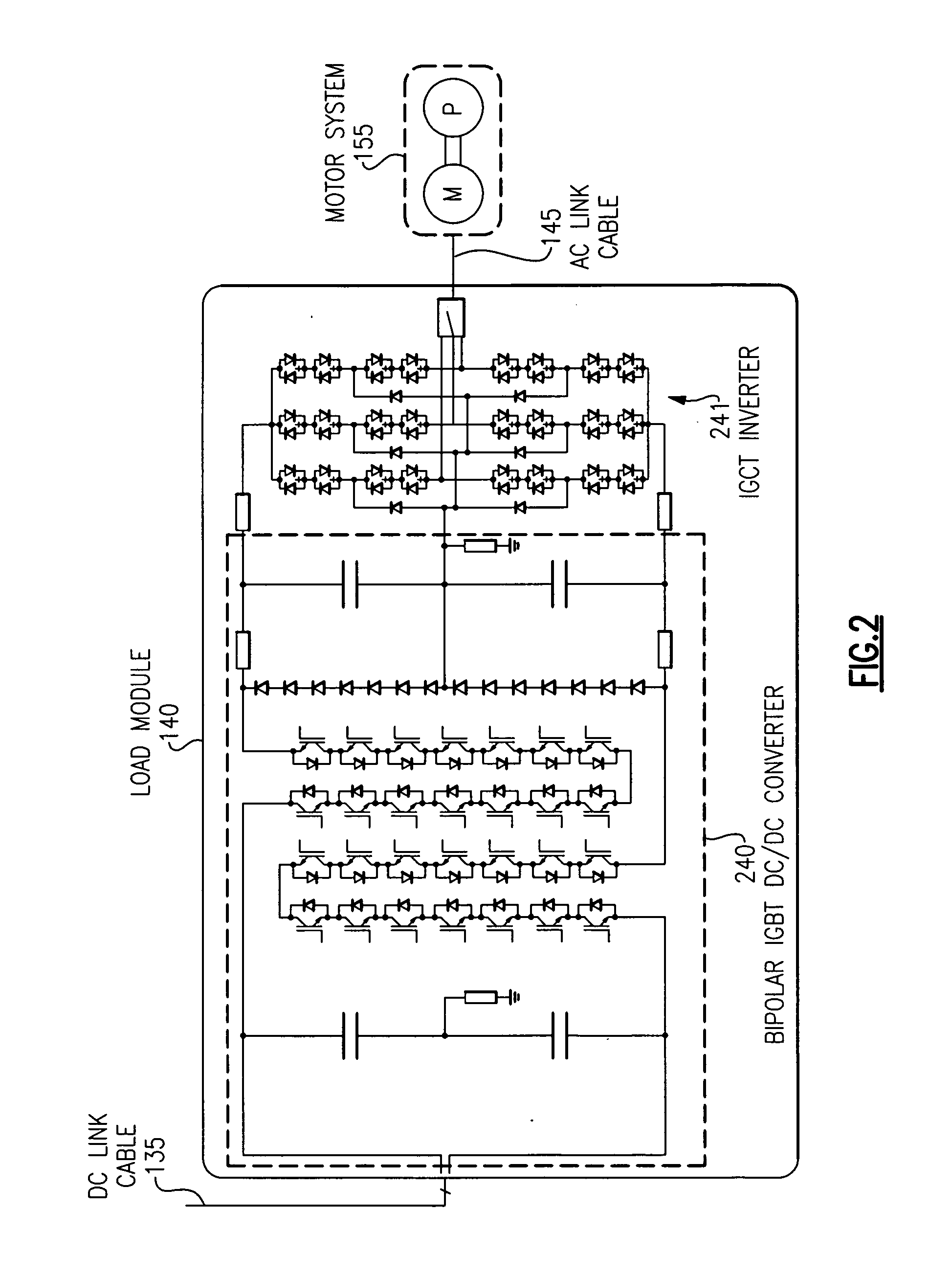
MVDC power transmission system for sub-sea loads
ActiveUS20090146603A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlElectric power transmissionShore
A system for the transmission of a direct current (DC) at a medium voltage level includes a system DC link configured to carry power from a source to a load module. The load module includes a DC-to-DC voltage step-down converter, a DC-to-AC inverter coupled downstream to the DC-to-DC voltage step-down converter, and a system AC link for carrying power from the load module to a motor system on a load side of the system AC link. The system is effective for delivering power over distances that are greater than 30 kilometers, and for delivery of power from an on-shore to offshore and sub-sea load.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for synchronous rectifier drive that enables converters to operate in transition and discontinuous mode
ActiveUS7869231B2Without significant lossHigh currentEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionTransverterSecondary side
A synchronous rectifier is switched in accordance with a primary switch transition and a reference signal representing current in a current storage device to which the synchronous rectifier is coupled. A current emulator provides a signal representing current in the current storage device as a volt-second product so that current stored in the current storage device while the primary switch is on is discharged by the synchronous rectifier. The use of a current emulator provides an inexpensive solution for controlling synchronous rectifier transitions without resorting to more expensive current sensing solutions that are commercially impracticable. Blanking intervals are provided for avoiding false transitions of the synchronous rectifier when the primary switch turns on and after the synchronous rectifier turns off. The disclosed system and method can be applied to flyback converters for a synchronous rectifier on the secondary side of a transformer, or the inductor of buck converters.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
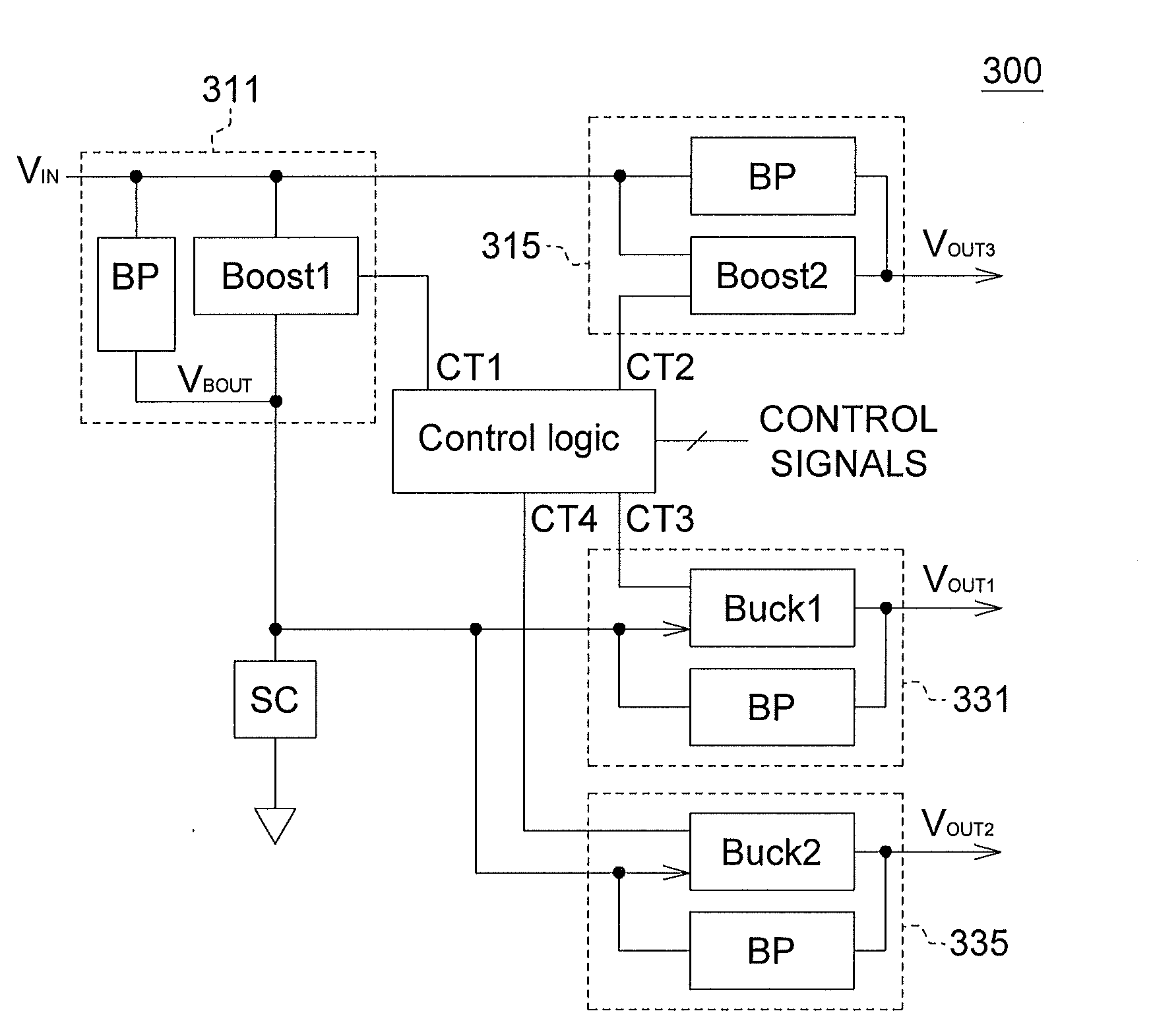
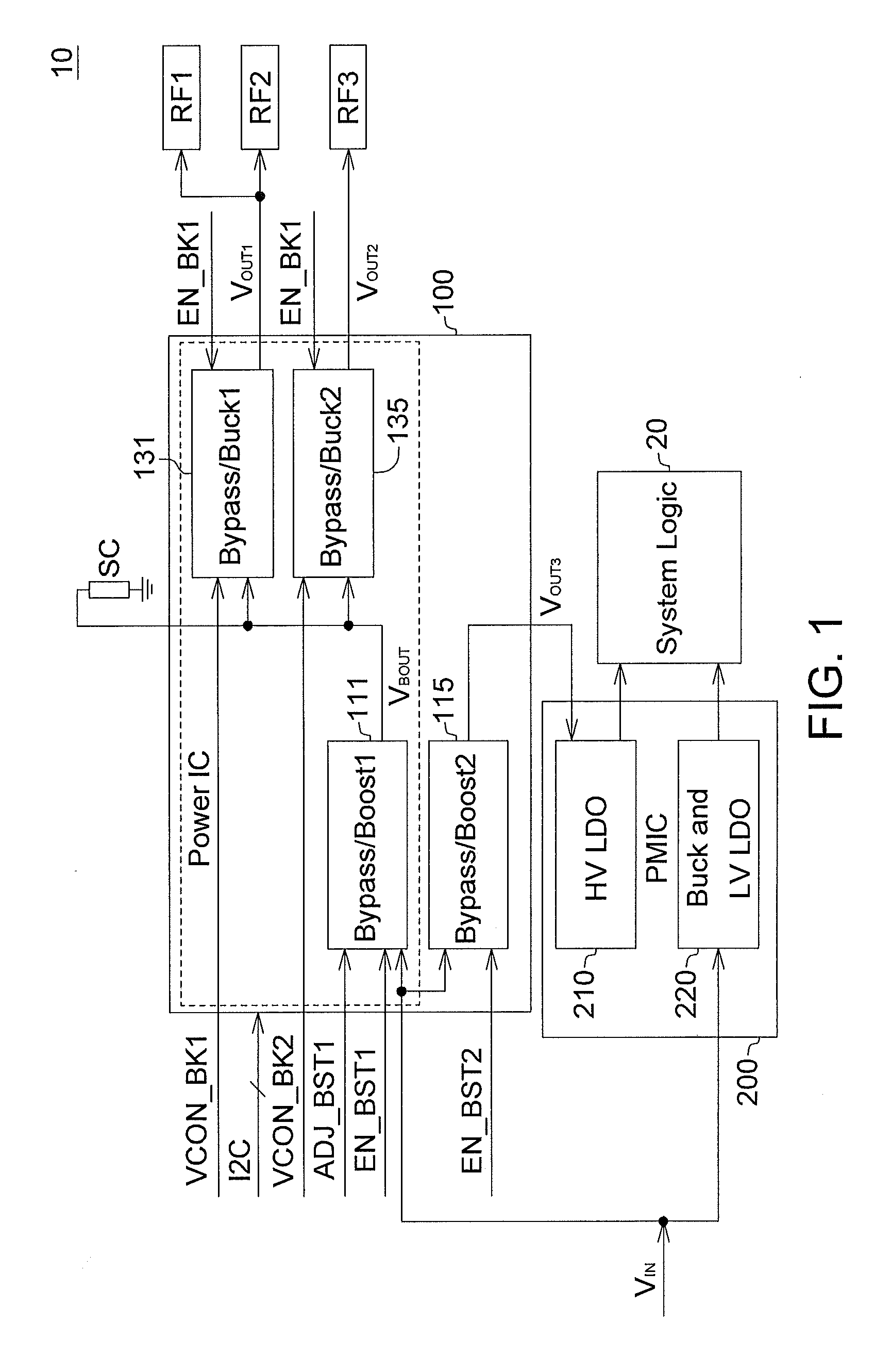
System power integrated circuit and architecture, management circuit, power supply arrangement, and portable apparatus
ActiveUS20130009470A1Dc network circuit arrangementsAc network voltage adjustmentComputer moduleEngineering
According to one embodiment, a management circuit for a portable device includes an input terminal, a first step-up converter, a first step-down converter, and a second step-down converter. The input terminal is coupled to receive a supply voltage from a power supply. The first step-up converter, coupled to the input terminal, selectively converts the supply voltage to a boosted voltage. The first step-down converter, coupled to the first step-up converter, selectively provides a first output power voltage to a first radio frequency (RF) module. The second step-down converter, coupled to the first step-up converter, selectively provides a second output power voltage to a second radio frequency (RF) module. The first step-up converter performs the conversion of the supply voltage when the supply voltage is under a threshold voltage.
Owner:HTC CORP
Photovoltaic module-mounted ac inverter
ActiveUS20130070494A1Control power consumptionMaximize available powerConversion constructional detailsElectric power transfer ac networkEngineeringIntegrated circuit
Owner:ENPHASE ENERGY
Bootstrap circuit and step-down converter using same
InactiveUS20090108908A1Avoid performanceFully chargedEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionĆuk converterEngineering
The invention provides a bootstrap circuit which enables adequate charging of a capacitor used in the bootstrap circuit even during light load or no load conditions, and which does not impede the performance of a step-down converter proper, as well as a step-down converter using the bootstrap circuit. A capacitor charge / discharge path formation mechanism is provided in the bootstrap circuit that enables a terminal of a capacitor used in the bootstrap circuit to be separated and made independent from a step-down converter circuit.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Synchronous rectification step-down converter chip with high-precision current detection function
ActiveCN104319996ASimple structureAccurate and timely detectionEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDouble frequencyLED lamp
The invention belongs to the field of power management and relates to a DC-DC step-down converter, in particular to a synchronous rectification step-down converter chip with a high-precision current detection function. The chip is based on a current PWM-mode DC-DC step-down converter. In the chip, the synchronous rectification switch PWM-mode current control technology is adopted, so the efficiency of the converter is greatly improved, and the output current can reach 2 A. By the adoption of a novel current detection sensing module with extremely high precision, the magnitude of a current can be detected more accurately in time, and the chip can be subjected to reliable overcurrent protection. Besides, according to the design of the chip, a double-frequency oscillator is adopted, so the frequency of a switching tube can be selected automatically according to the load capacity, the efficiency of the chip can be improved, and the working time of the chip can be prolonged. Lastly, the chip integrates a soft start circuit, so a surge current and an overshoot voltage which are generated during start can be suppressed, and an LED lamp and a driving chip can be protected against damage.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
AC-to-DC power converting device
InactiveUS8854839B2Eliminate high frequency noiseEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEngineeringInductance
An AC-to-DC power converting device includes: a filter for filtering an external AC input voltage; a rectifier for rectifying the AC input voltage filtered by the filter to output a rectified voltage; a power factor corrector for receiving the rectified voltage from the rectifier to generate a boosted voltage; and a step-down converter for receiving the boosted voltage from the power factor corrector to output a DC output voltage. The power factor corrector includes first and second capacitors connected in series across an output side of the rectifier, a series connection of a first diode, a first inductor, a third capacitor, a second inductor and a second diode coupled to the output side of the rectifier, and first and second switches connected in series across the third capacitor. A common node between the first and second capacitors is coupled to a common node between the first and second switches.
Owner:I-SHOU UNIVERSITY
Step-down switching regulator with freewheeling diode
ActiveUS20080291711A1High and voltage overshootEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionMOSFETVoltage overshoot
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com