Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
89 results about "Voltage down converter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
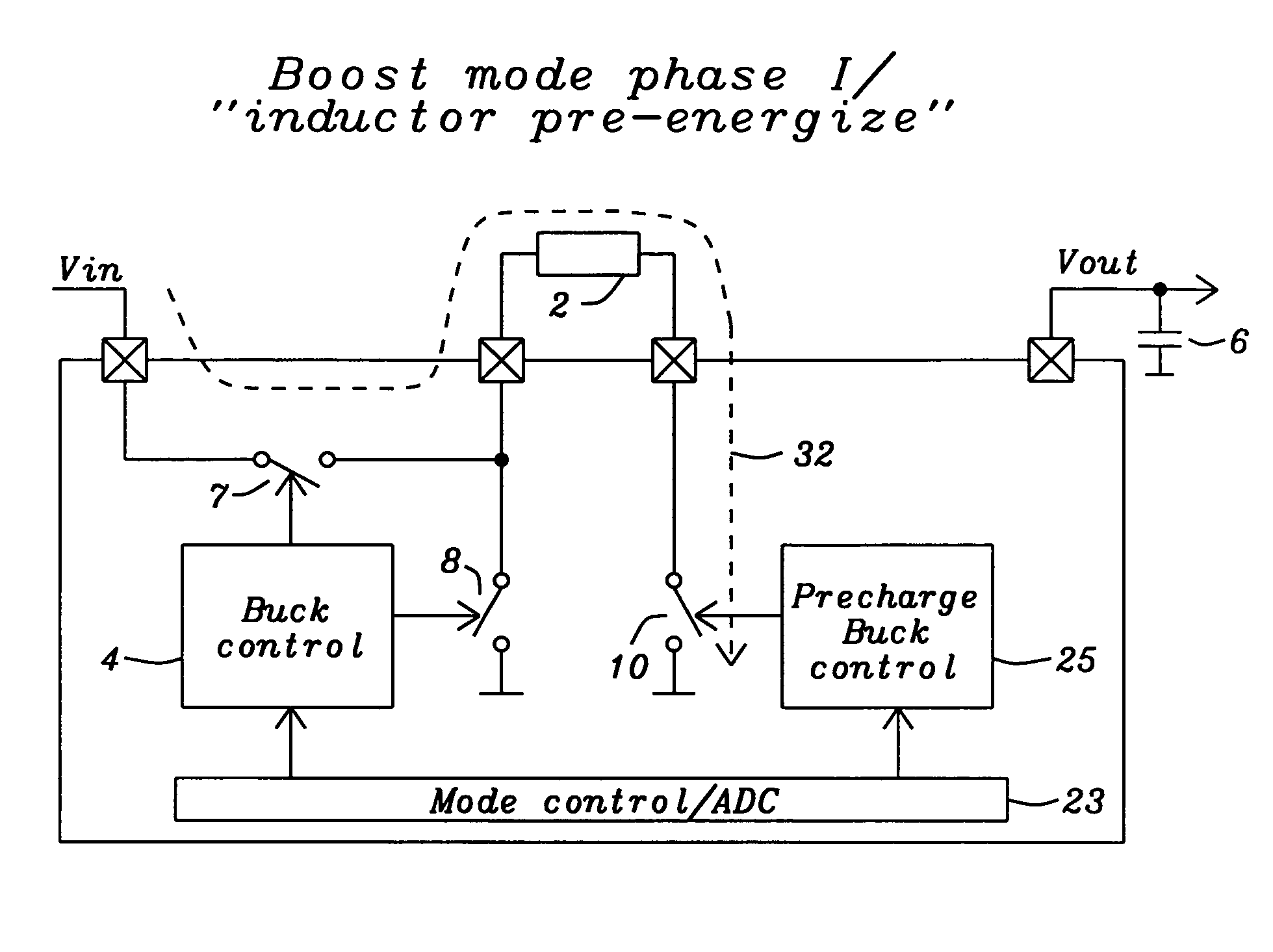
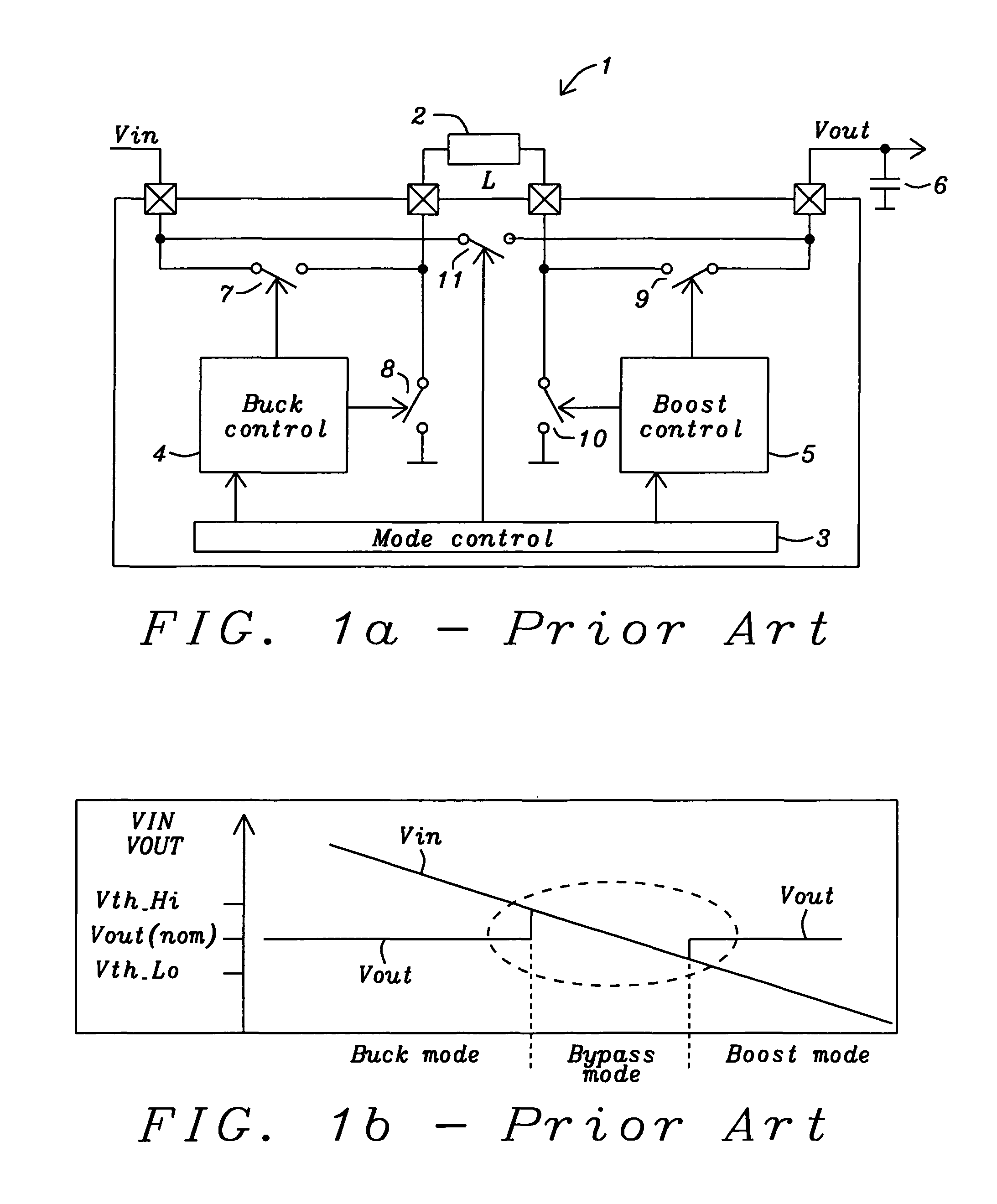
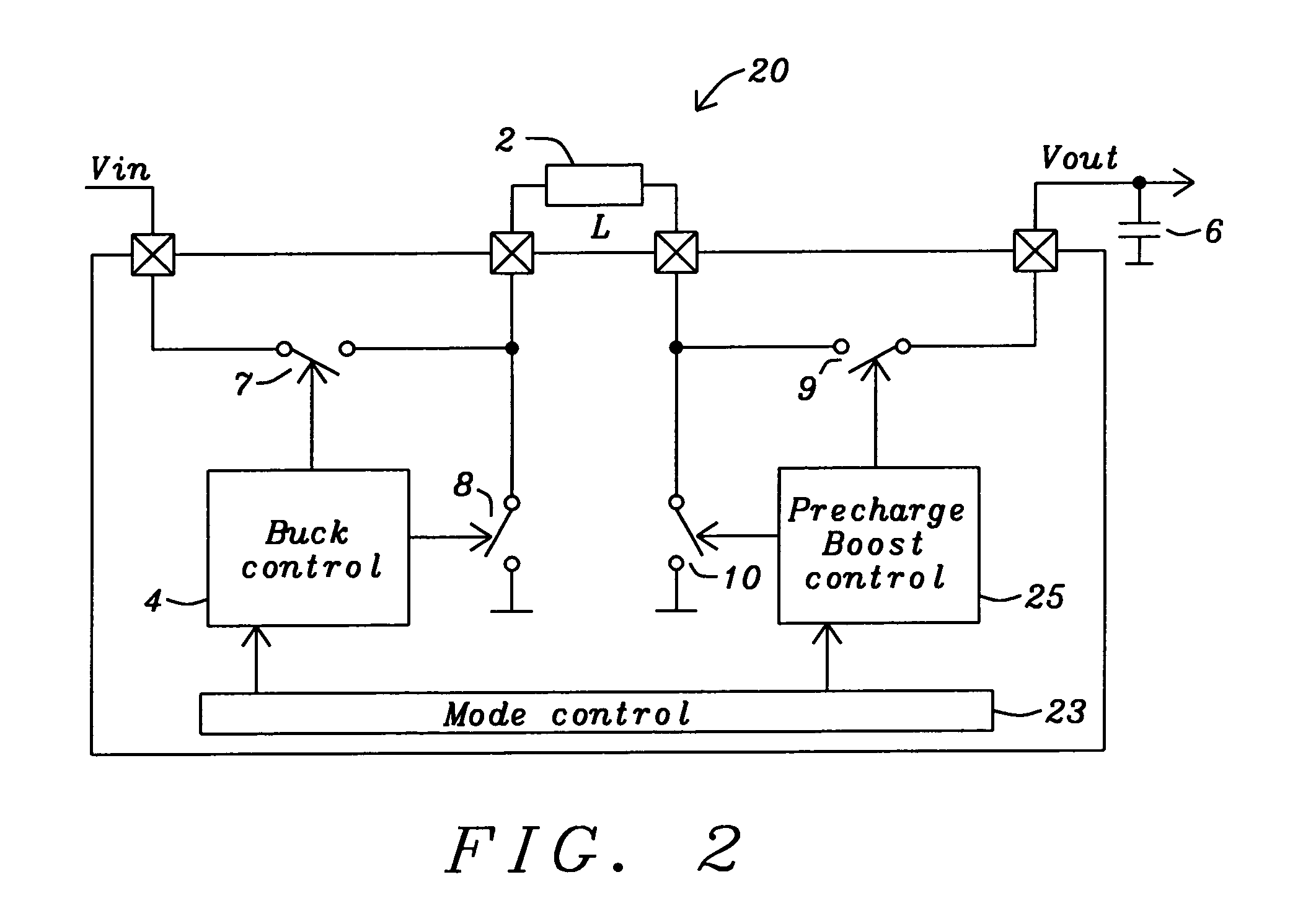
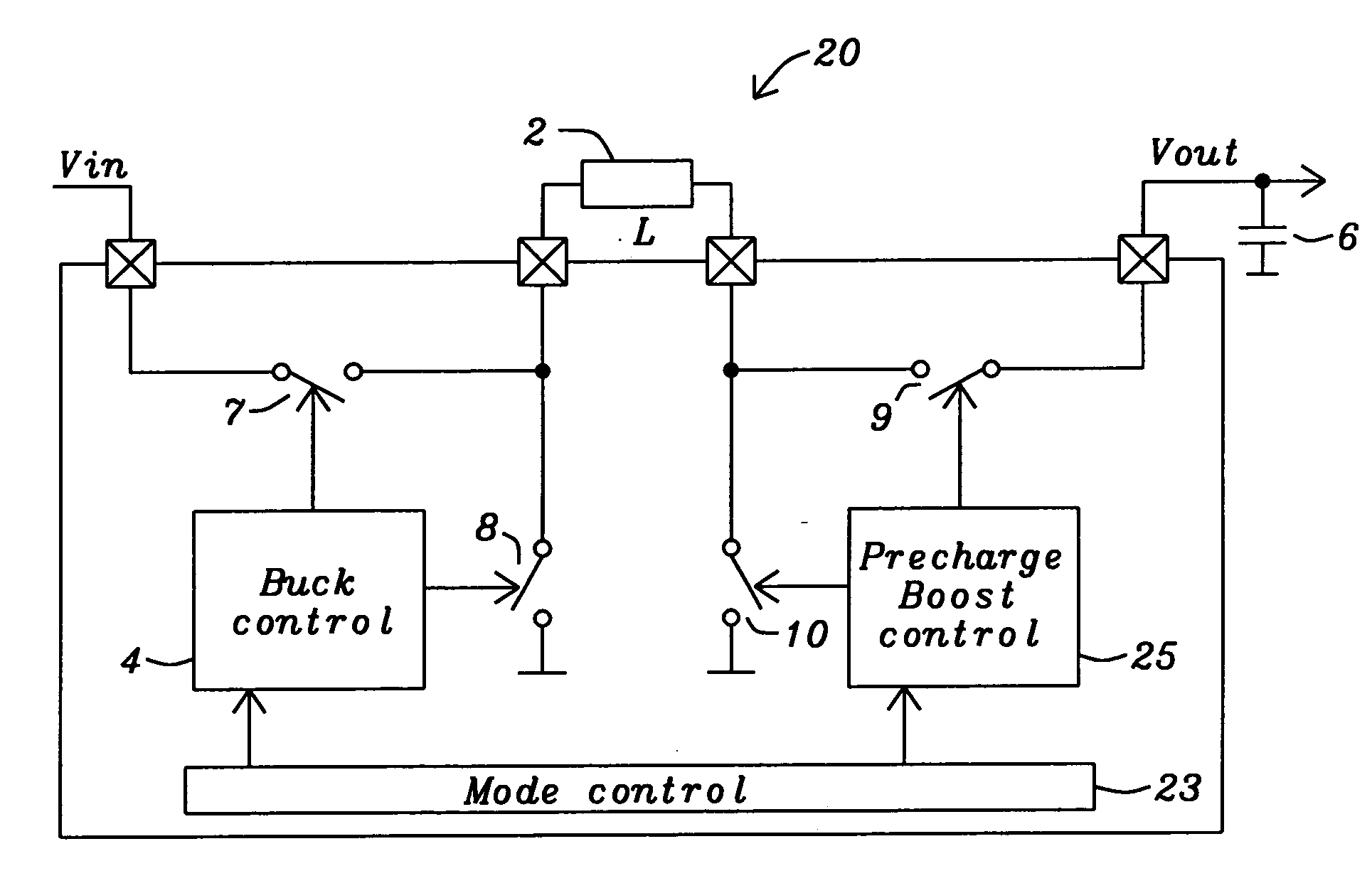
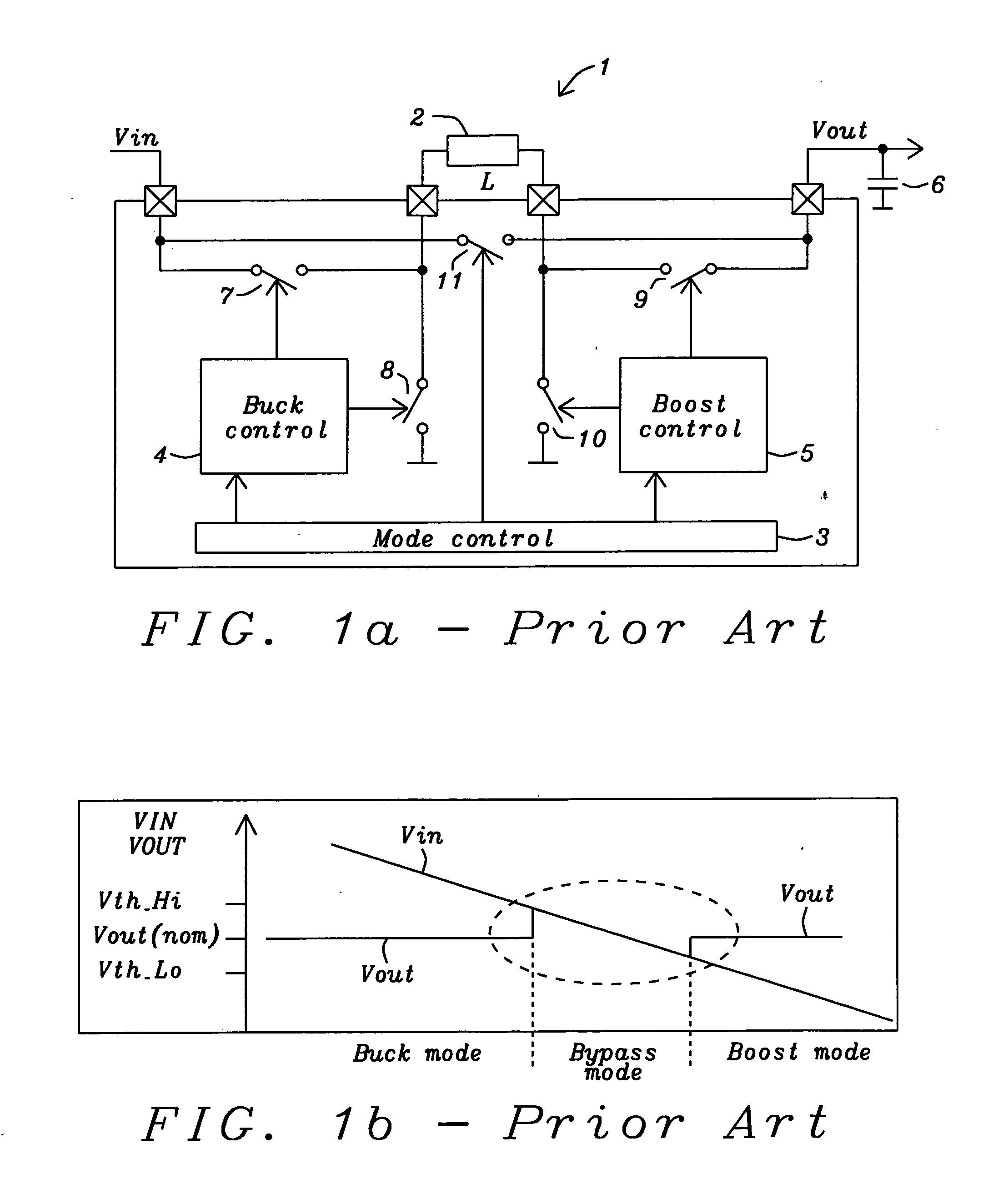
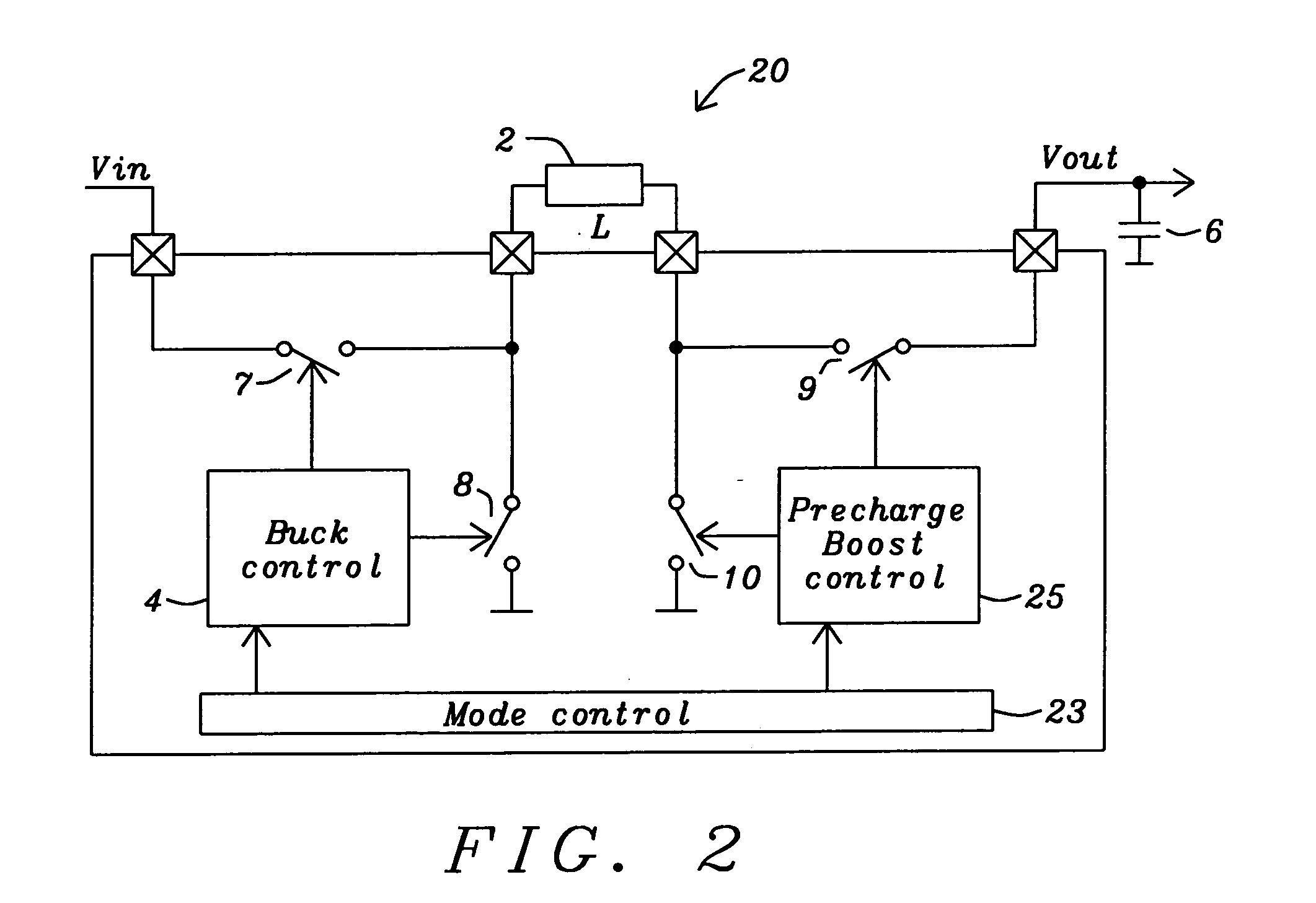
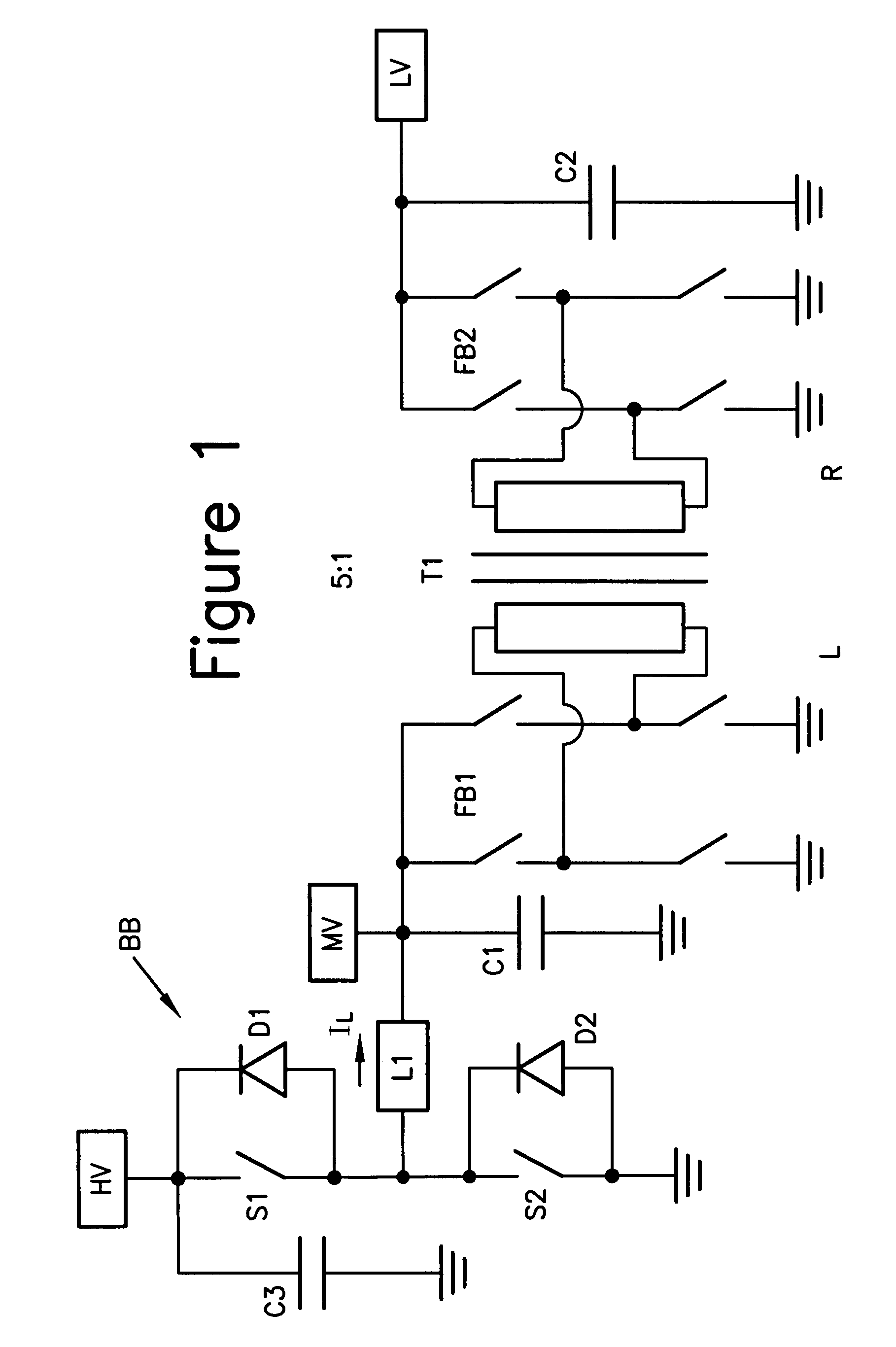
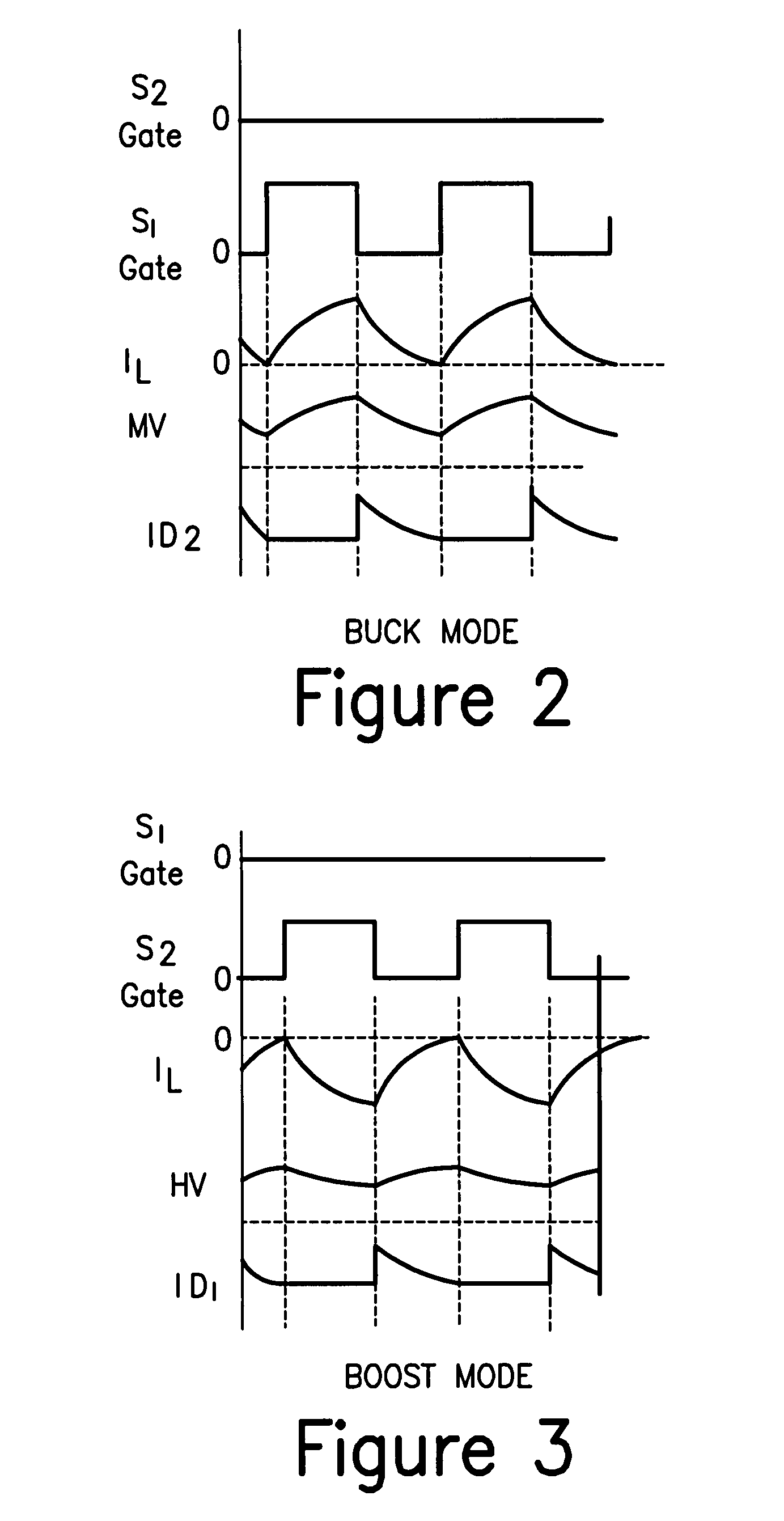
Buck converter with inductor pre-energizing
ActiveUS7804282B2Simple control circuitDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationBuck converterĆuk converter
Circuits and methods to achieve a buck-boost converter, capable to achieve a constant output voltage by pre-charging of an inductor if the input voltage is close to the output voltage has been achieved. The prior art problem of output voltage variations occurring while the input voltage is close to the output voltage is avoided. In case the input voltage is lower than a defined threshold voltage or the duty cycle exceeds a defined maximum allowable level, the inductor of the converter is pre-charged followed by boosting of the energy of the inductor to the output of the converter. In both modes the control loops of the buck converter can be used for buck duty cycle control. The duration of the pre-charge depends upon the level of the input voltage, the lower the input level is the longer is the pre-charge performed.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
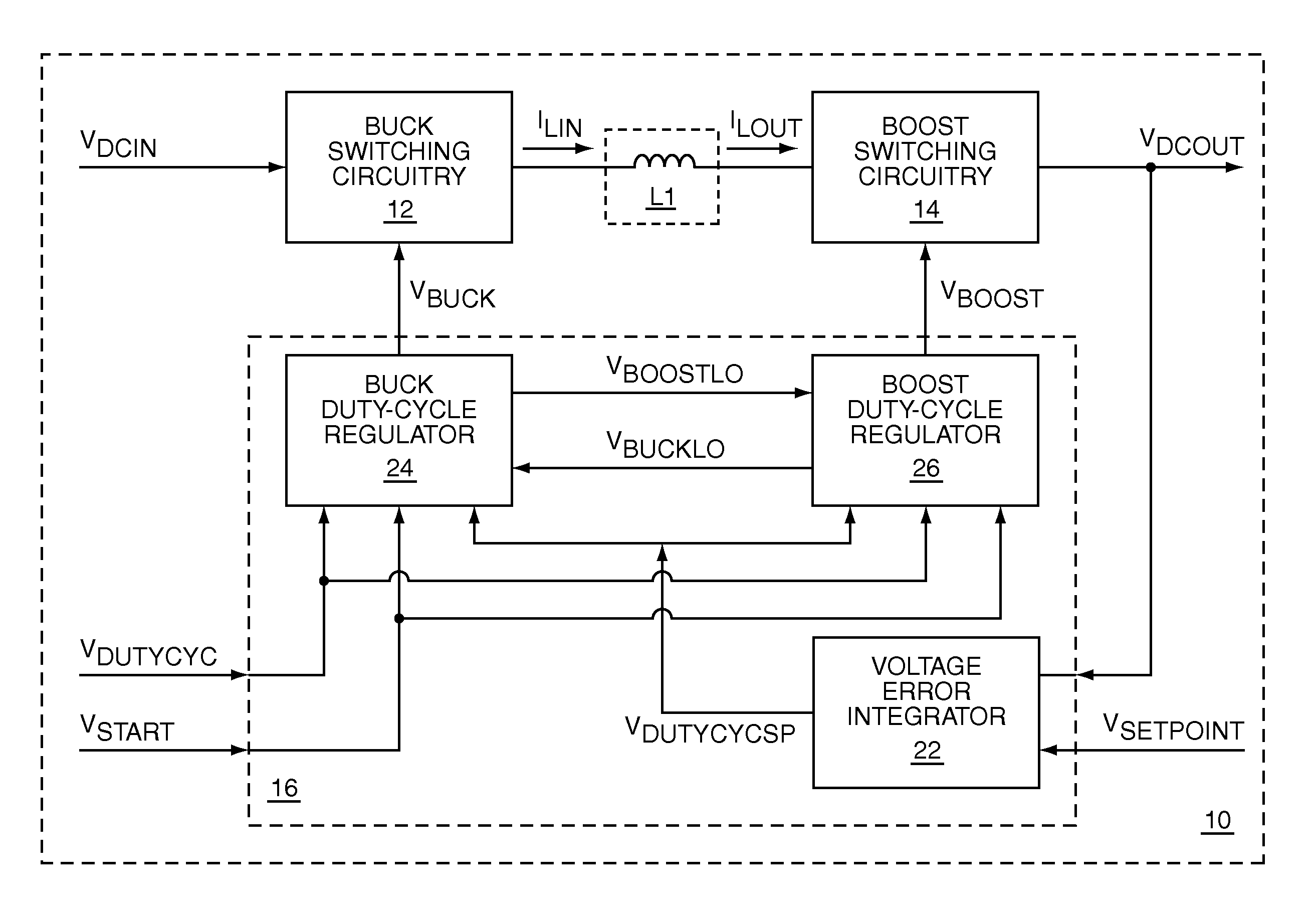
Switching power converter that supports both a boost mode of operation and a buck mode of operation using a common duty-cycle timing signal
ActiveUS7336056B1Remove overlapSmooth transitEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionIntegratorBuck converter
The present invention is a switching power converter that supports both a boost mode of operation and a buck mode of operation, uses one energy storage element, transitions smoothly between boosting and bucking, and avoids simultaneous boosting and bucking. The switching power converter uses a common duty-cycle timing signal and a common duty-cycle setpoint signal to provide a smooth transition between boosting and bucking, and to eliminate overlap between boosting and bucking. A voltage input error integrator is used to integrate out errors between an output voltage and a setpoint voltage to provide the common duty-cycle setpoint signal. Duty-cycle error integrators are used to integrate out errors between the common duty-cycle setpoint signal and the actual duty-cycle of either the buck converter or the boost converter. Non-overlapping boost operating and buck operating ranges are provided by the common duty-cycle setpoint signal.
Owner:QORVO US INC
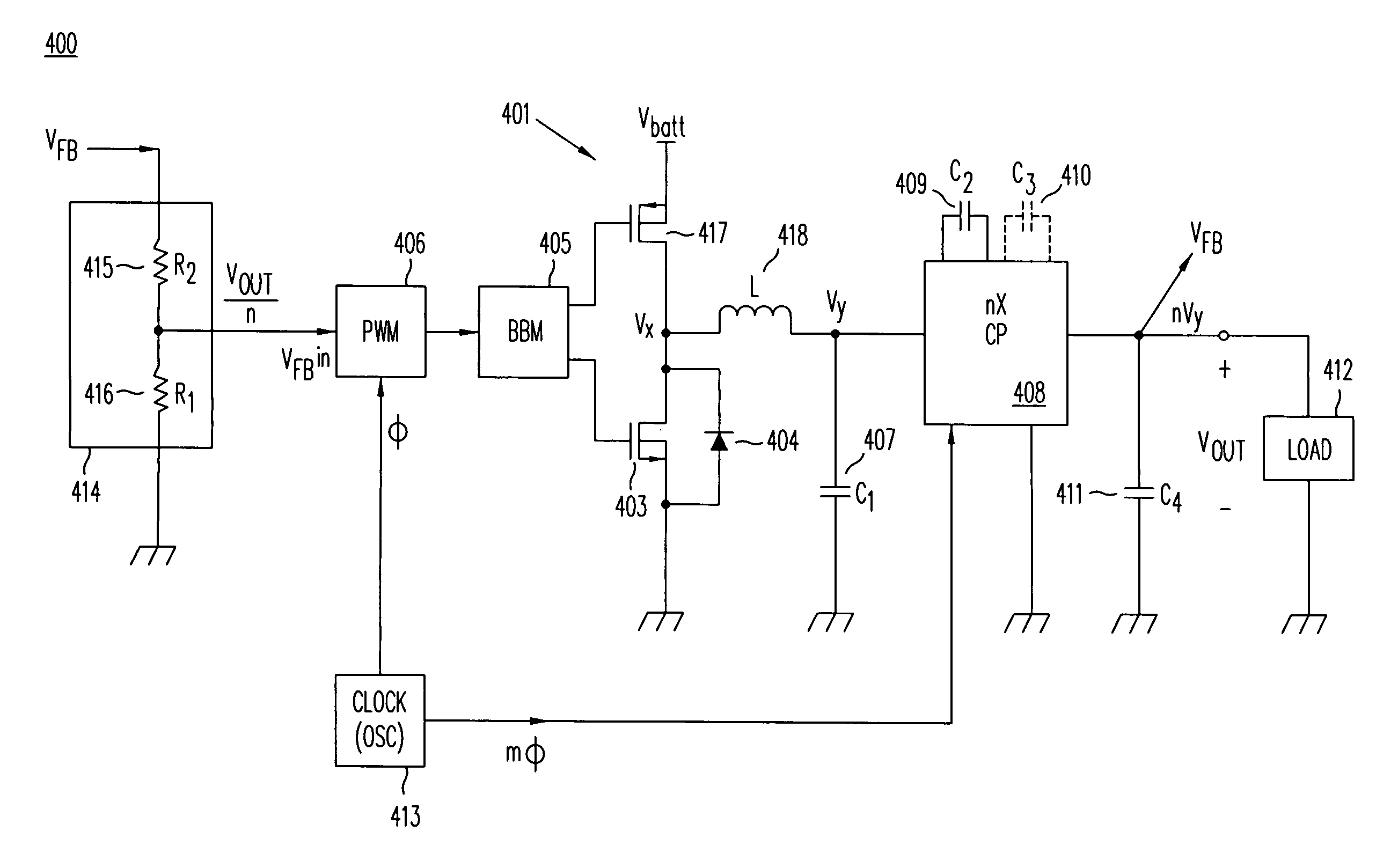
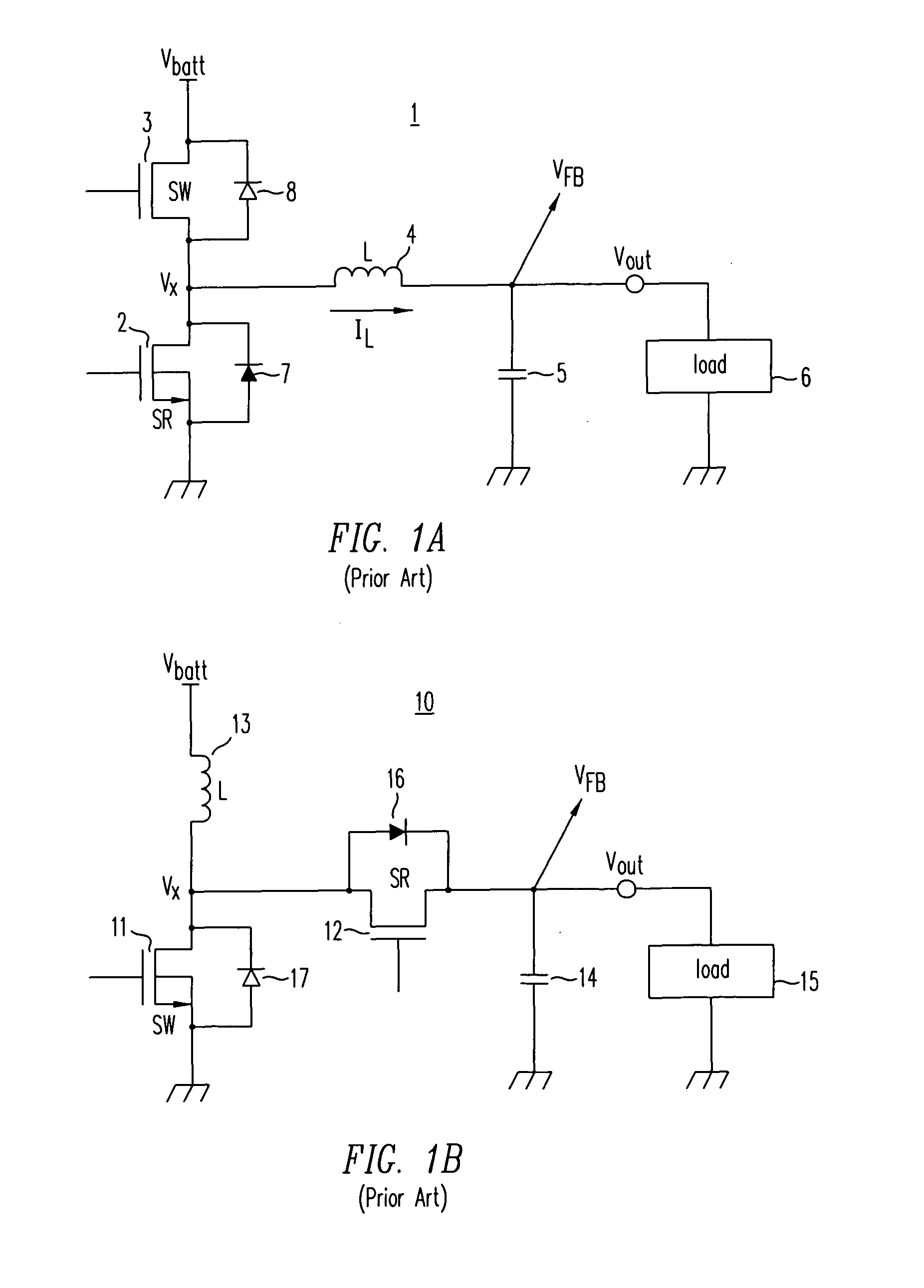
High-efficiency DC/DC voltage converter including down inductive switching pre-regulator and capacitive switching post-converter
ActiveUS7782027B2Poor regulationIncrease heightEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionCapacitanceBuck converter
A DC / DC converter includes a pre-regulator stage, which may include a Buck converter, and a post-converter stage, which may include a charge pump. The duty factor of the pre-regulator stage is controlled by a feedback path that extends from the output terminal of the pre-regulator stage or the post-converter stage. The pre-regulator steps the input DC voltage down by a variable amount depending on the duty factor, and the post-converter steps the voltage at the output of the pre-regulator up or down by an positive or negative integral or fractional value. The converter overcomes the problems of noise glitches, poor regulation, and instability, even near unity input-to-output voltage conversion ratios.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
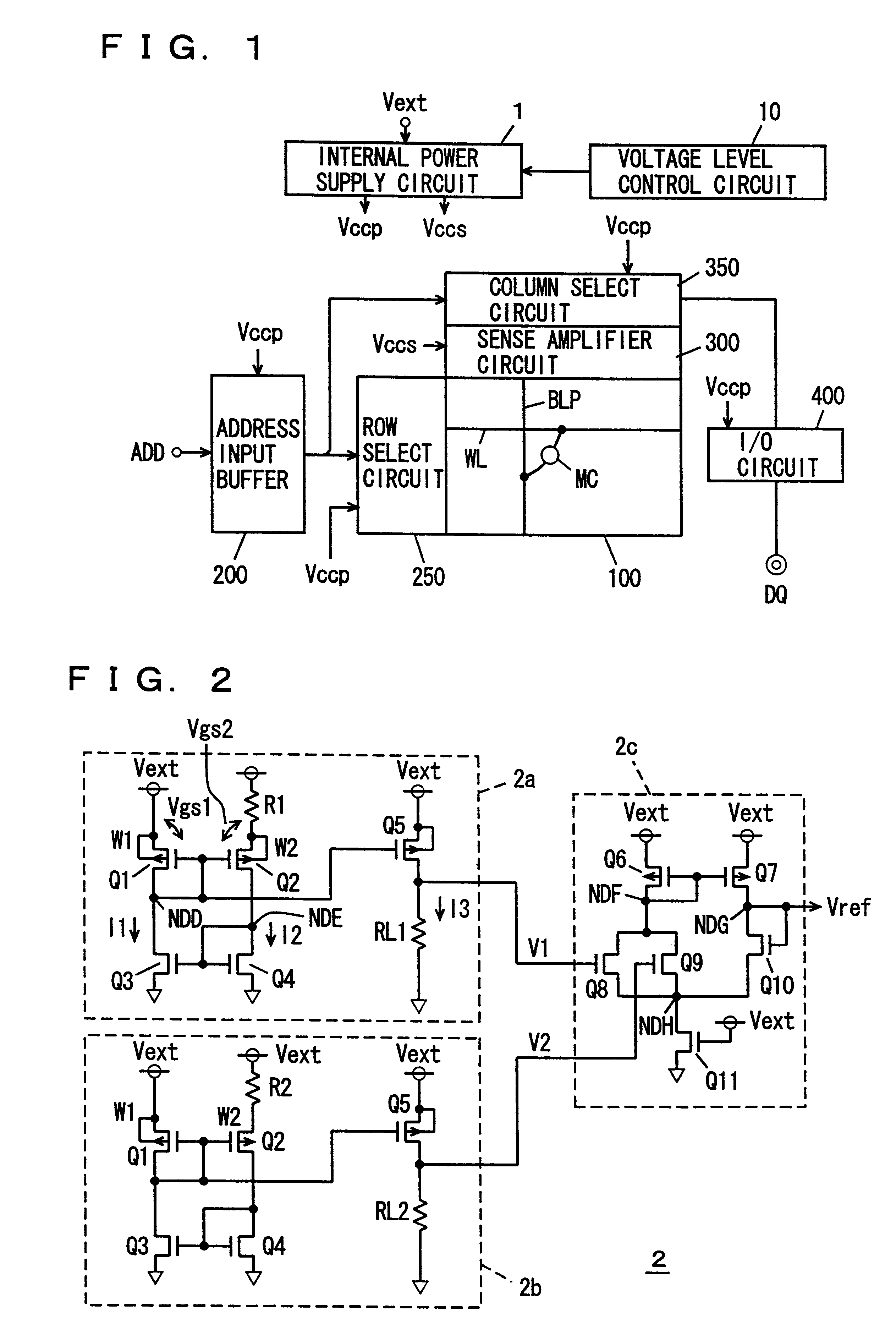
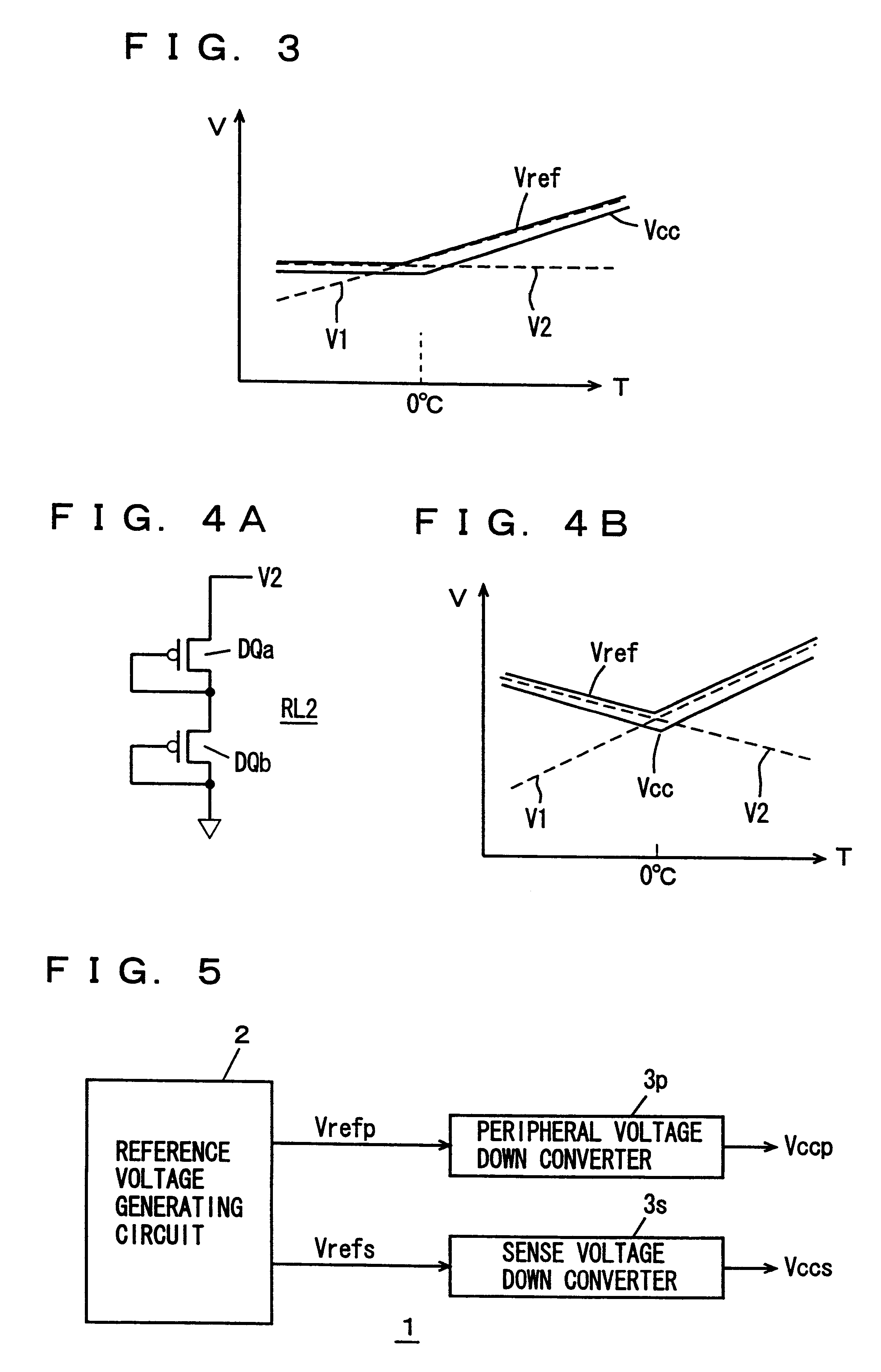
Semiconductor device having an internal voltage generating circuit
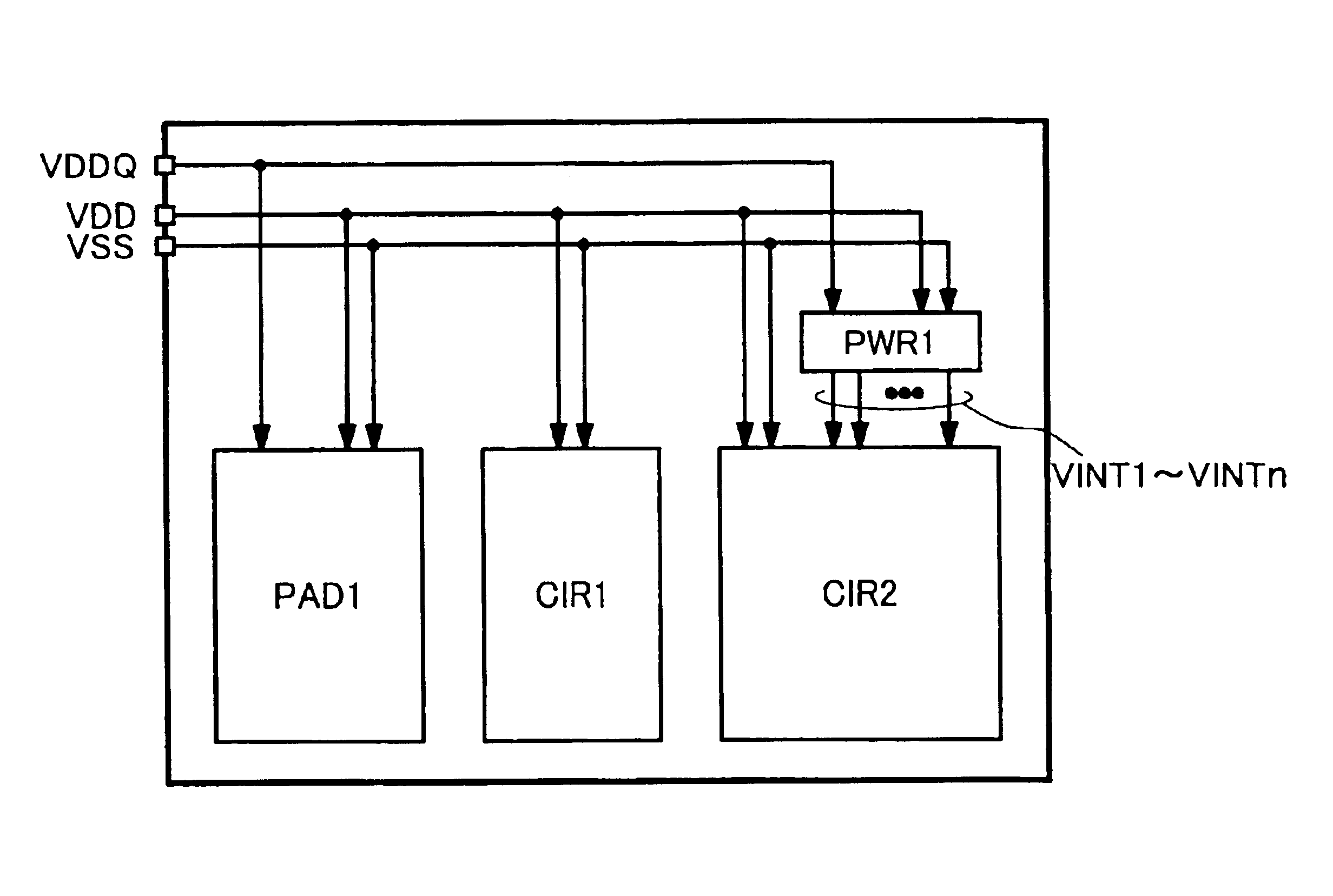
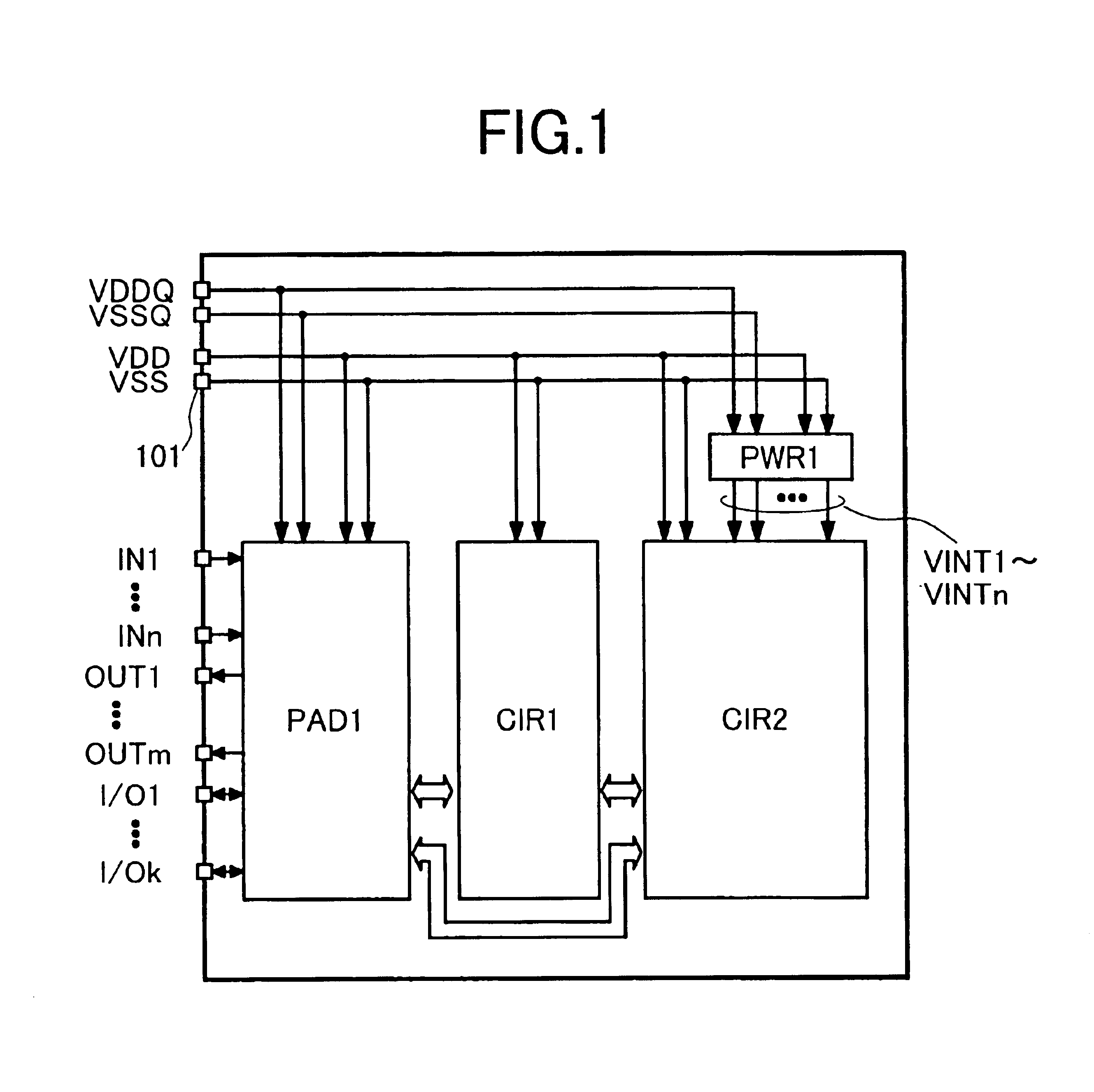
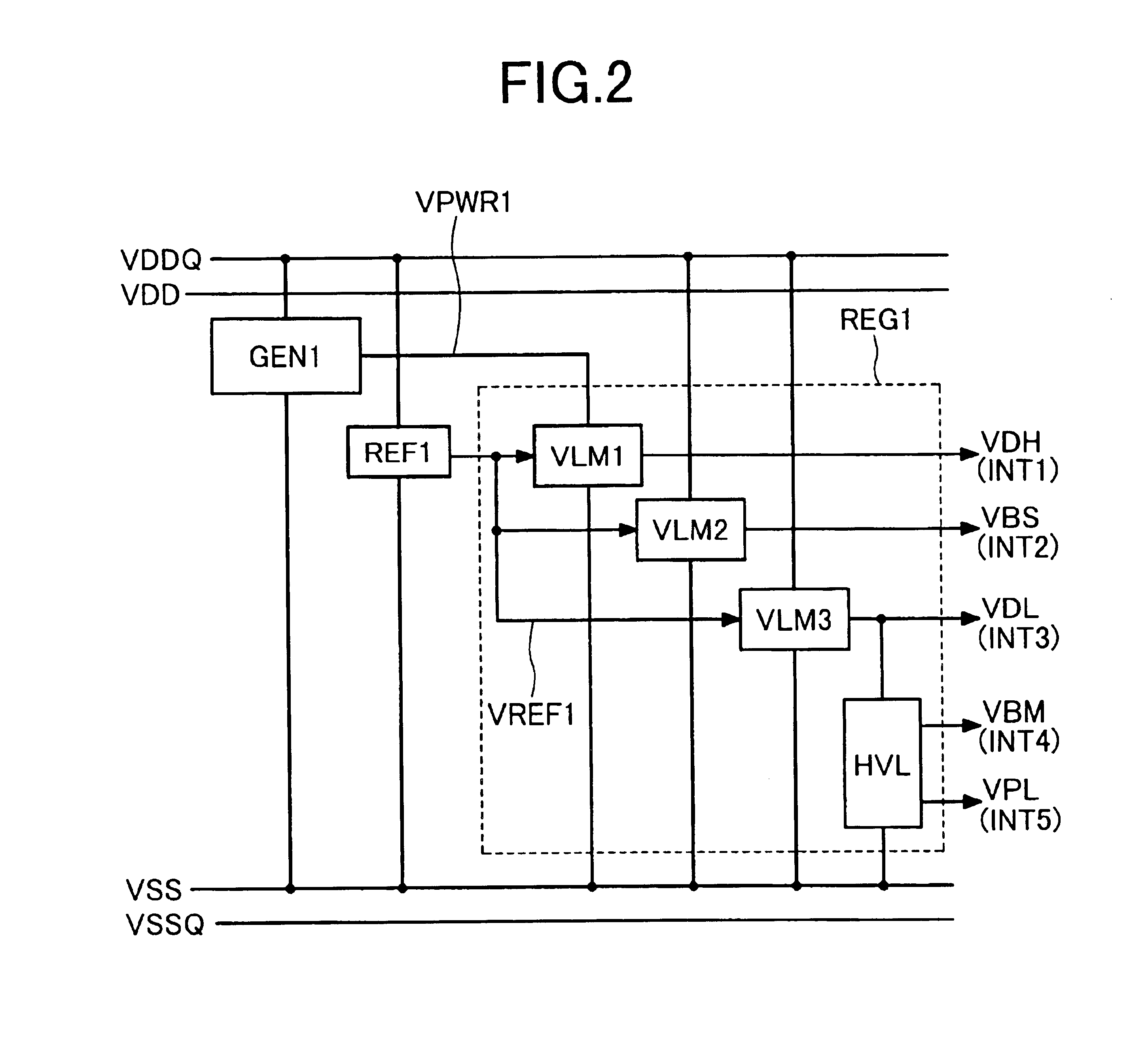
An internal power supply circuit produces an internal power supply voltage from an external power supply voltage. A voltage level control circuit controls a voltage level and a temperature characteristic of the internal power supply voltage generated by the internal power supply circuit. The internal power supply circuit produces the internal power supply voltage having a negative or zero temperature characteristic in a low temperature region and a positive temperature characteristic in a high temperature region. The voltage level control circuit includes a structure optimizing a capacitance value of a sense power supply line stabilizing capacitance for driving a sense amplifier circuit, a level converting circuit determining the lowest operable region of the external power supply voltage of the internal power supply circuit, or a structure forcedly operating the internal voltage down converter upon power-on. The internal power supply voltage at a desired level is stably produced with a small occupied area and a low current consumption.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method and converter circuitry for improved-performance AC chopper
InactiveUS20060103365A1Easy constructionImprove reliabilityAc-ac conversionElectric variable regulationEngineeringPower supply voltage
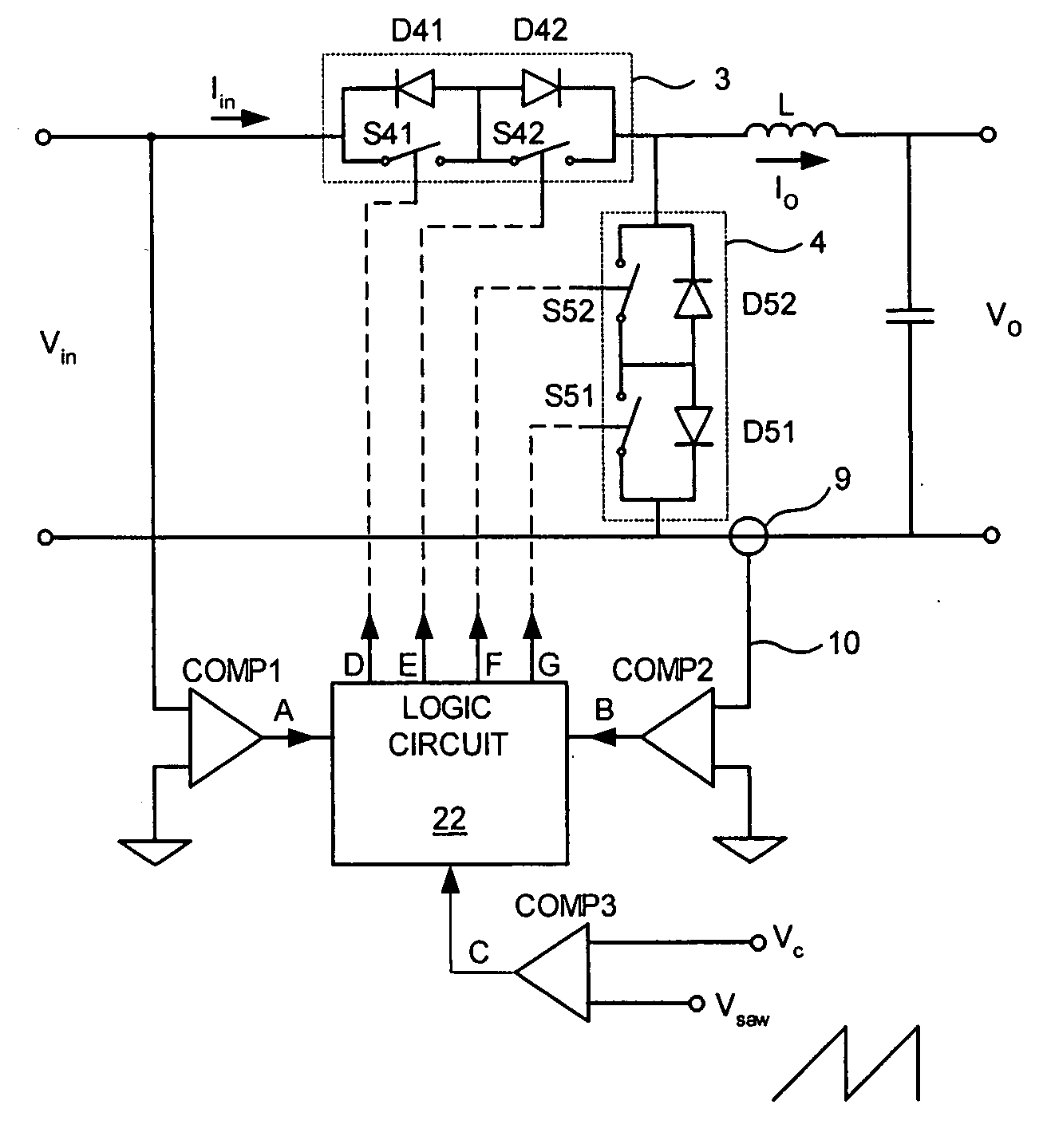
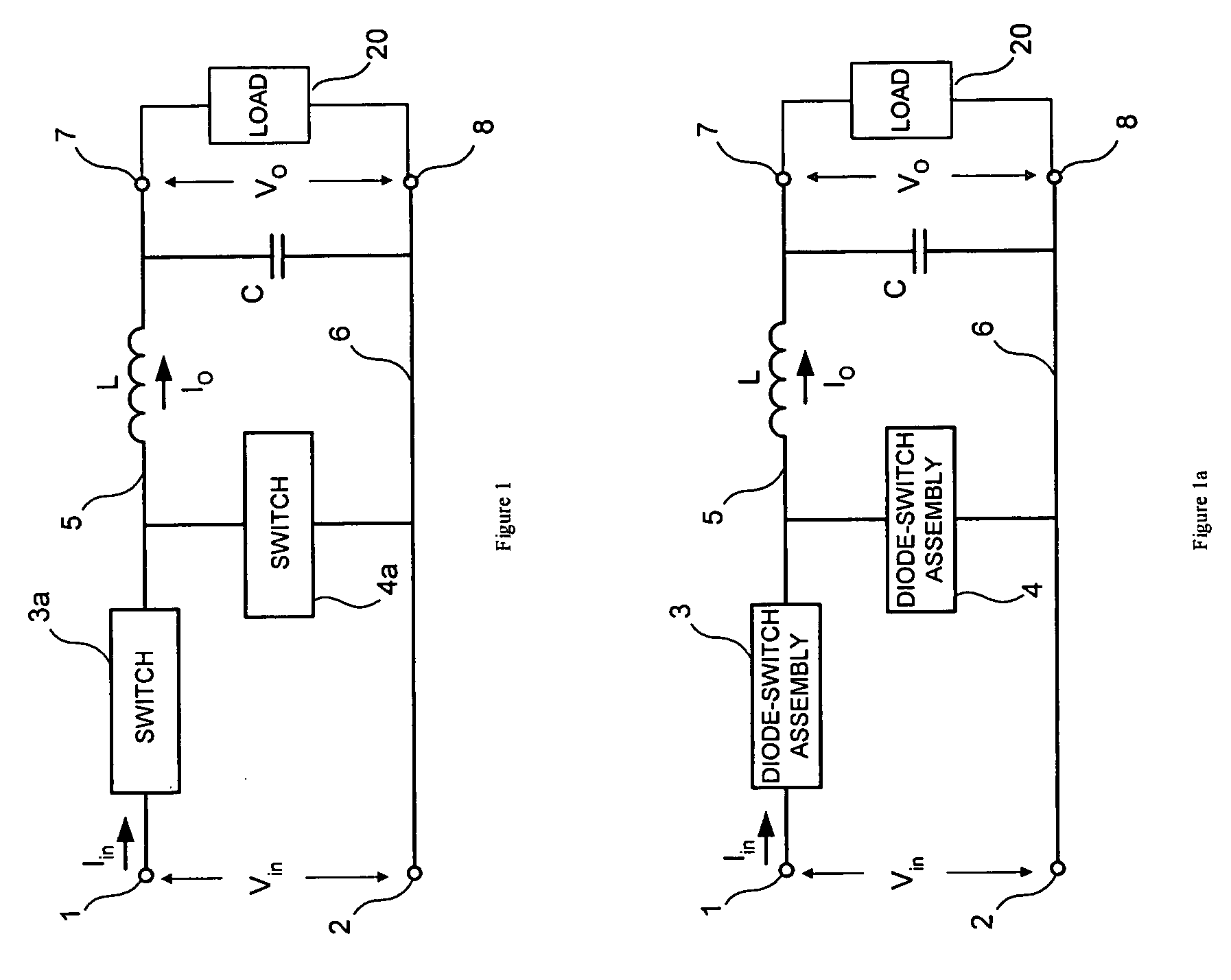
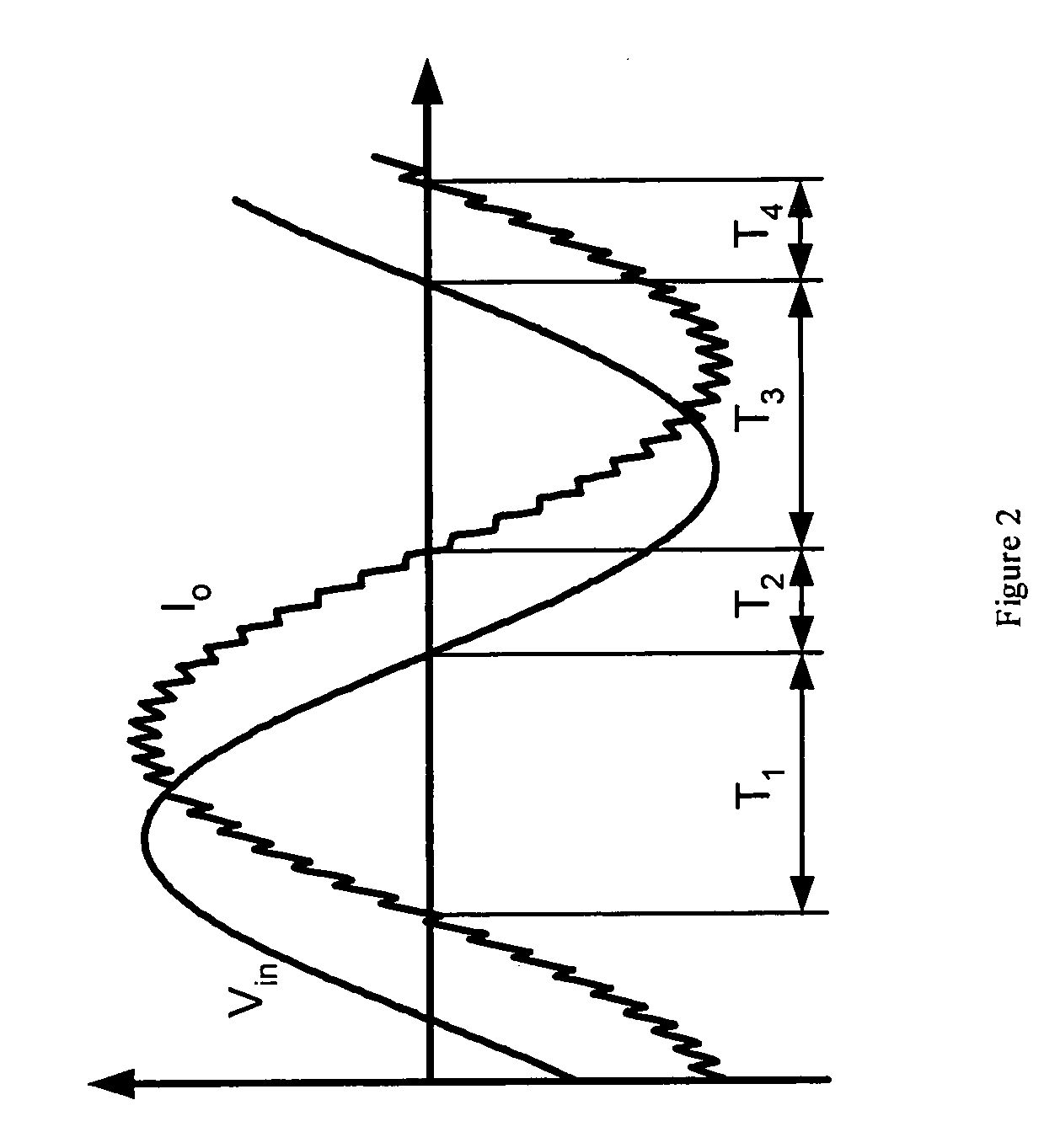
A system and method for single phase AC power conversion for delivery to a load of AC voltage less than or equal to the supply voltage. The system includes a high frequency chopper converter having a series diode-switch assembly and a shunt diode-switch assembly. During intervals when the inductor carries current in phase with the power line, the diode-switch assemblies are configured such that the system operates as a buck converter, and during intervals when the inductor carries current out of phase with the power line, and power flow is reversed, the diode-switch assemblies are configured such that the system operates as a boost converter, boosting the load voltage to the power line voltage. Optionally, feedback is used to adjust the duty cycles of the diode-switch assemblies to shape the input and / or output current and to optimize performance of the load.
Owner:COMPULITE SYST 2000
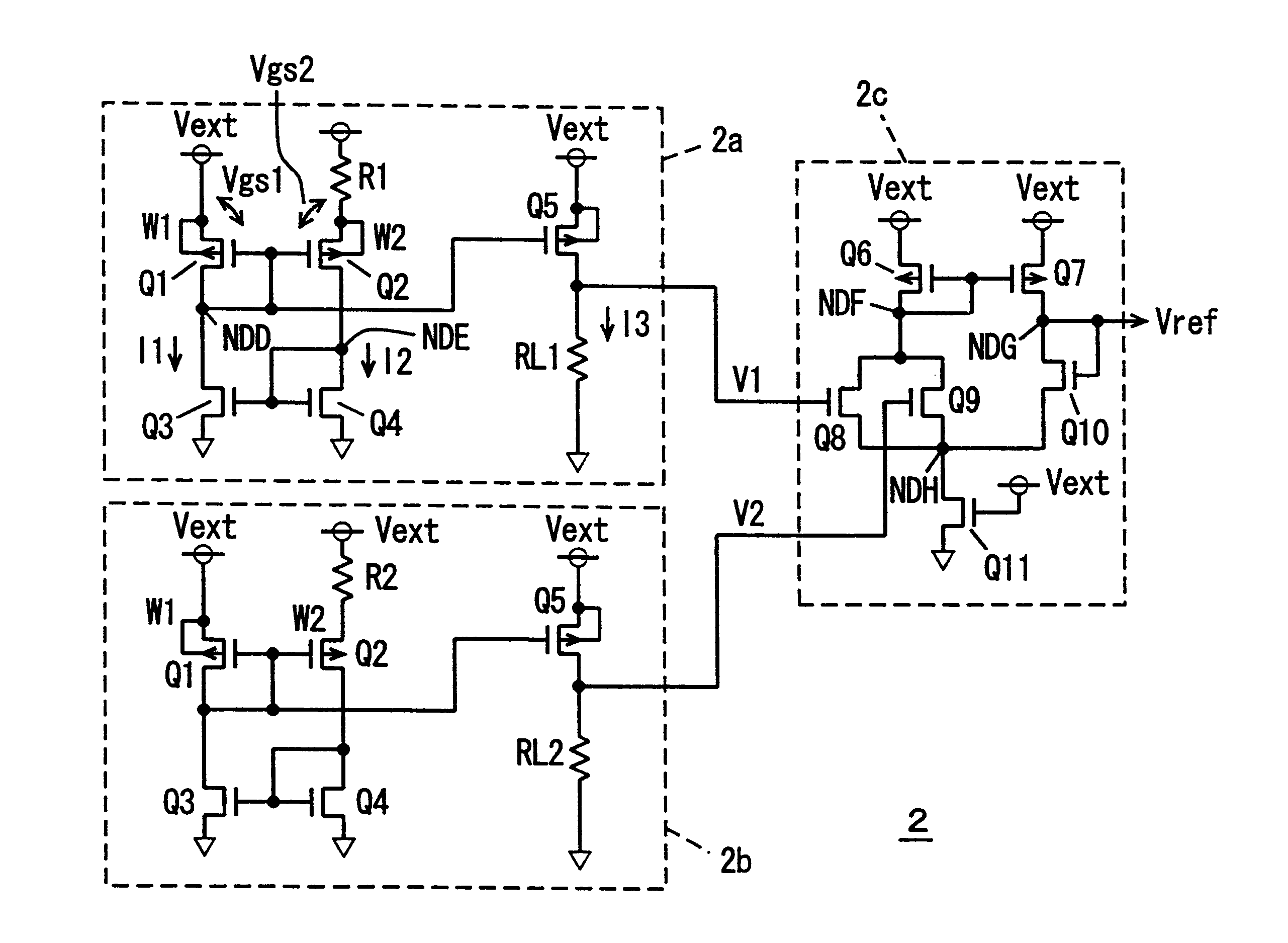
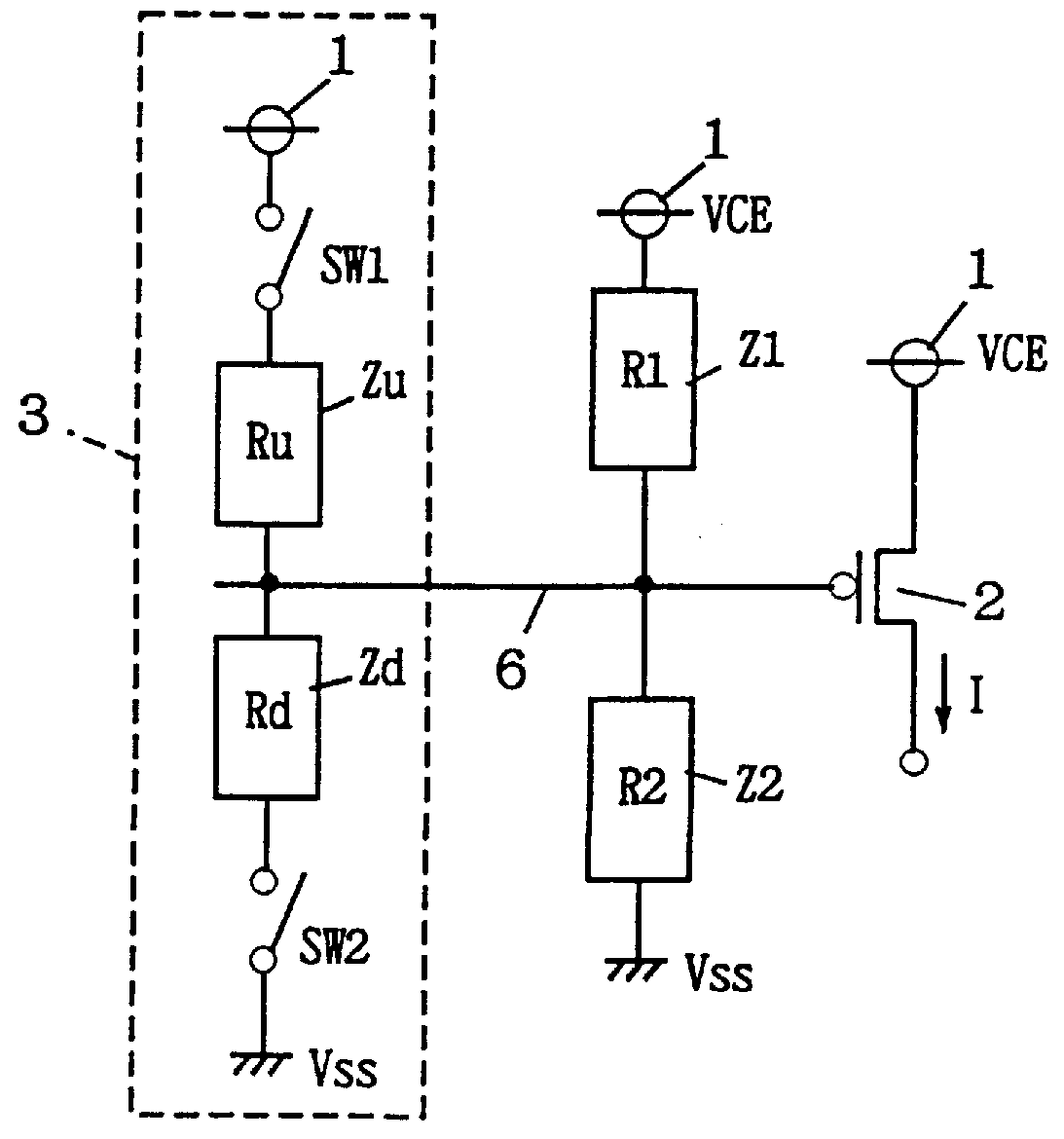
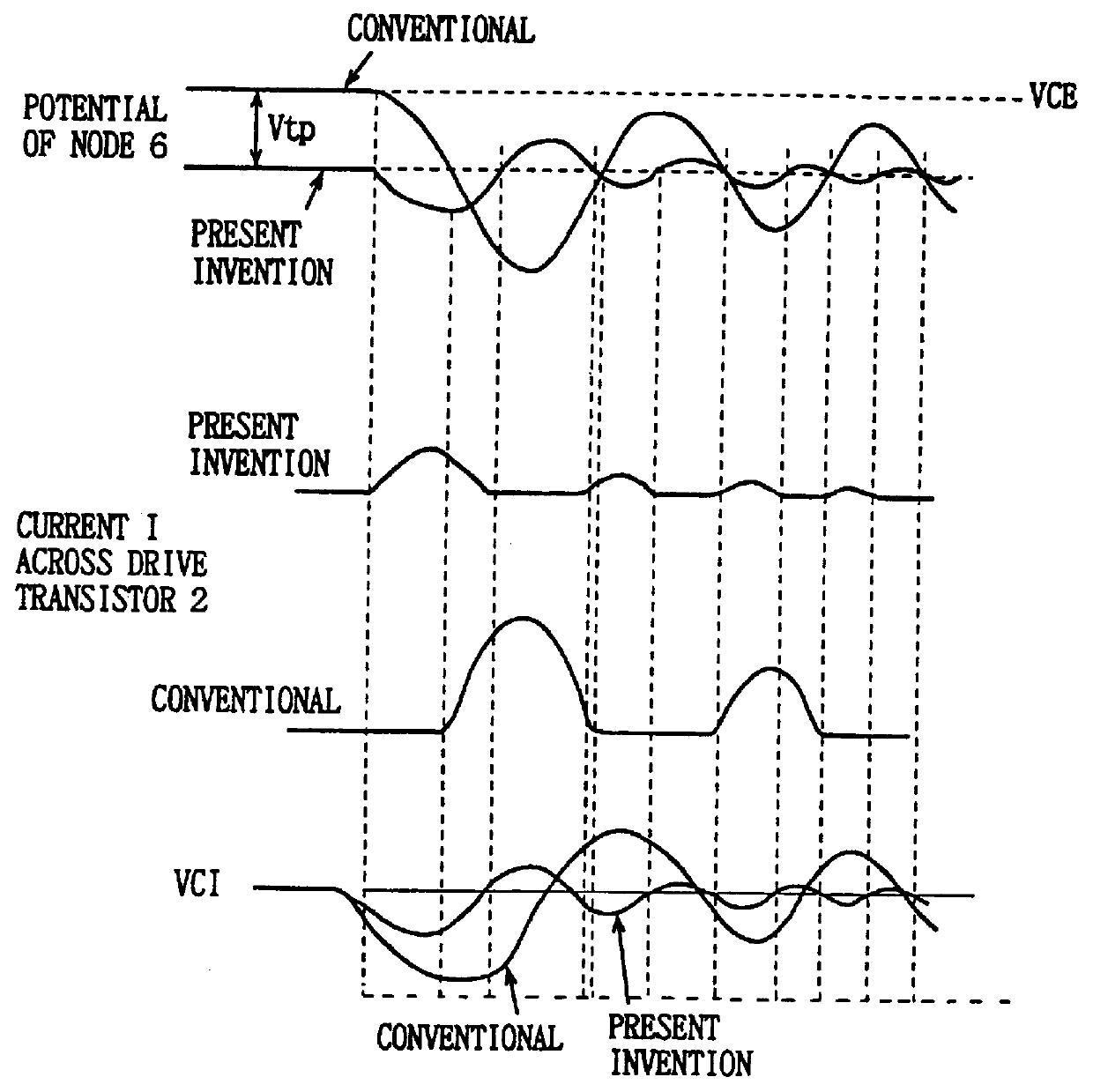
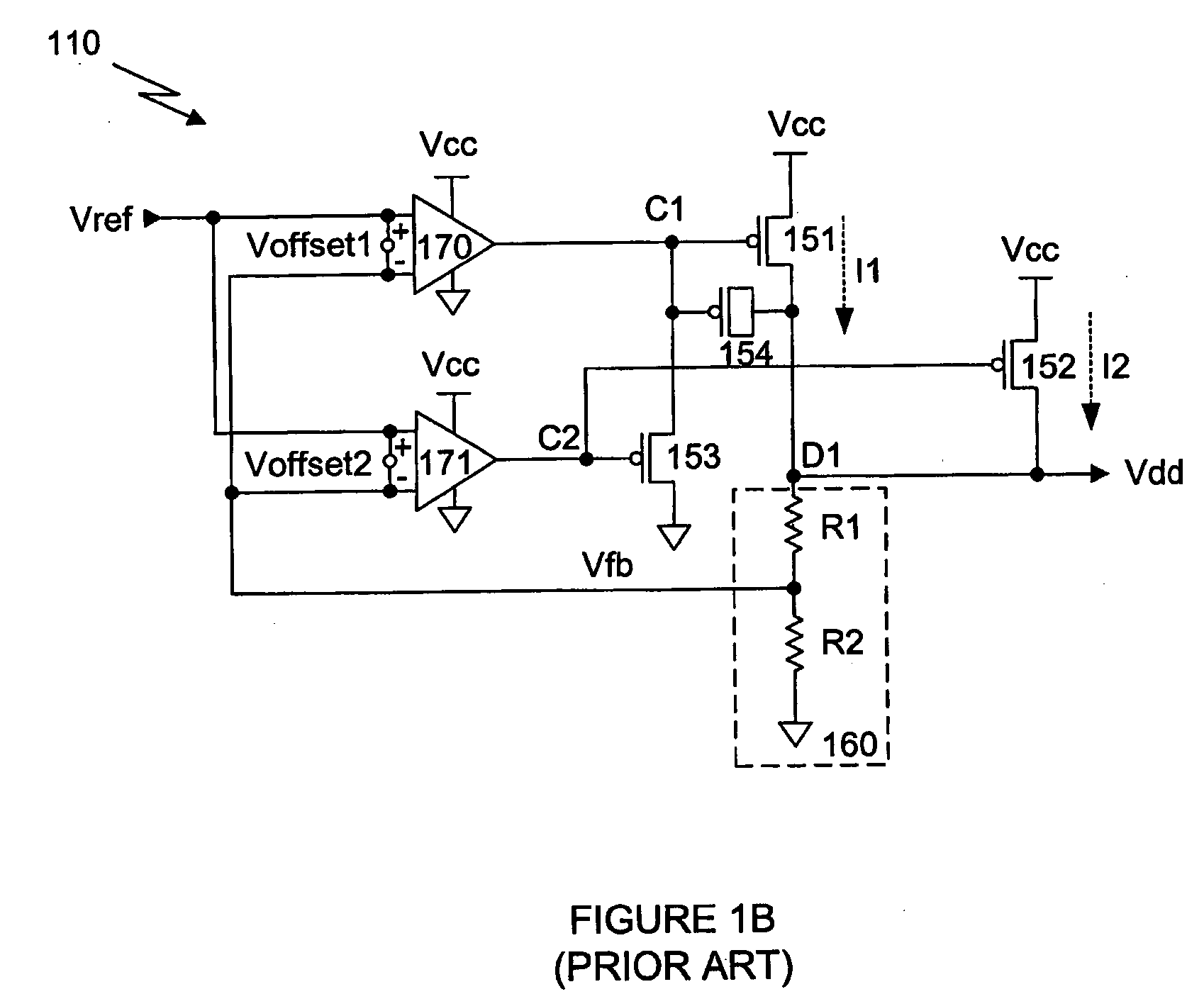
Semiconductor memory device with a voltage down converter stably generating an internal down-converted voltage
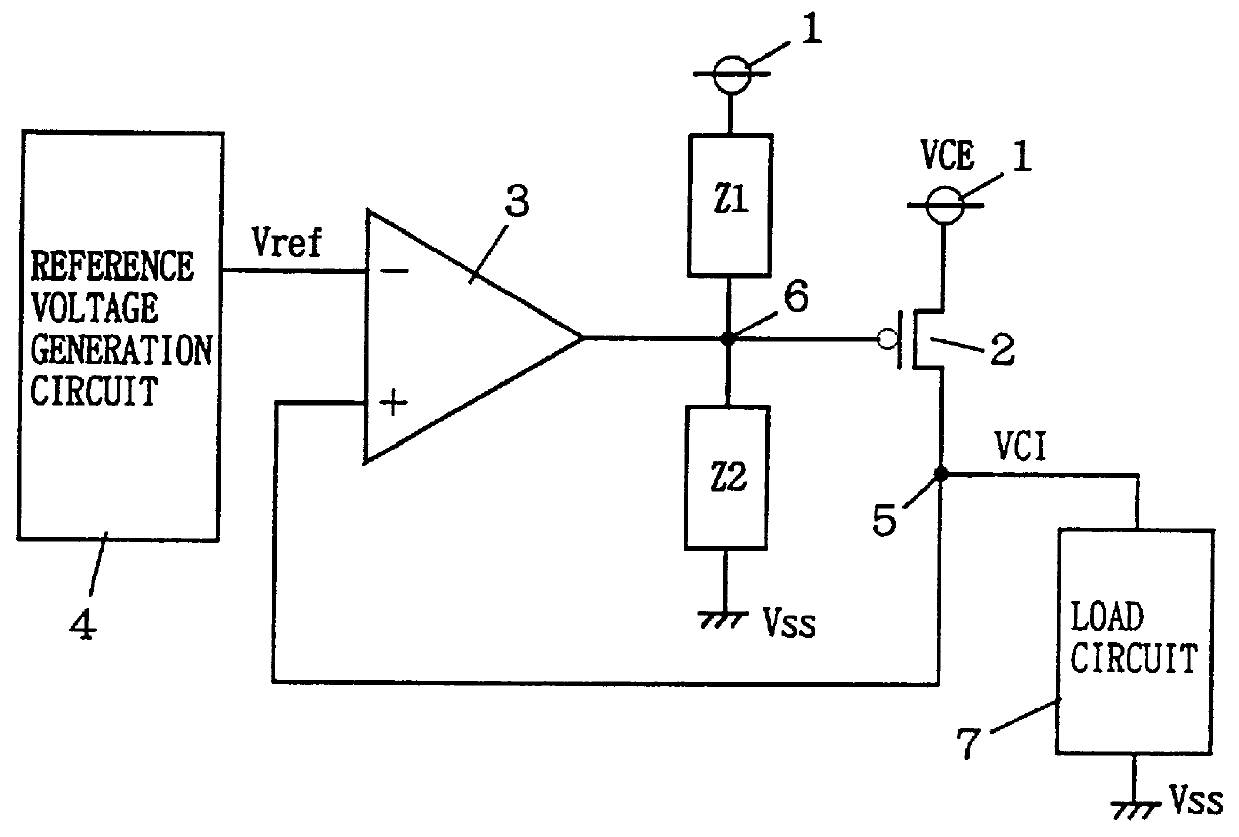
A comparison circuit compares a reference voltage Vref from a reference voltage generation circuit with an internal power supply voltage VCI on an internal power supply line to provide a signal according to the comparison result. A drive transistor supplies current to the internal power supply line from an external power supply node according to the output signal of the comparison circuit. A resistance element connected between the external power supply node and the output node of the comparison circuit and a resistance element connected between the output node of the comparison circuit and a ground node VSS suppresses the amplitude of an output signal of the comparison circuit. Thus, overdrive of the drive transistor can be suppressed, and a current corresponding to an abrupt change of the internal power supply voltage can be supplied from the external power supply node to the internal power supply line by the amplitude limitation function. Thus, an internal power supply voltage generation circuit is provided superior in high frequency response that can generate an internal power supply voltage stably.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
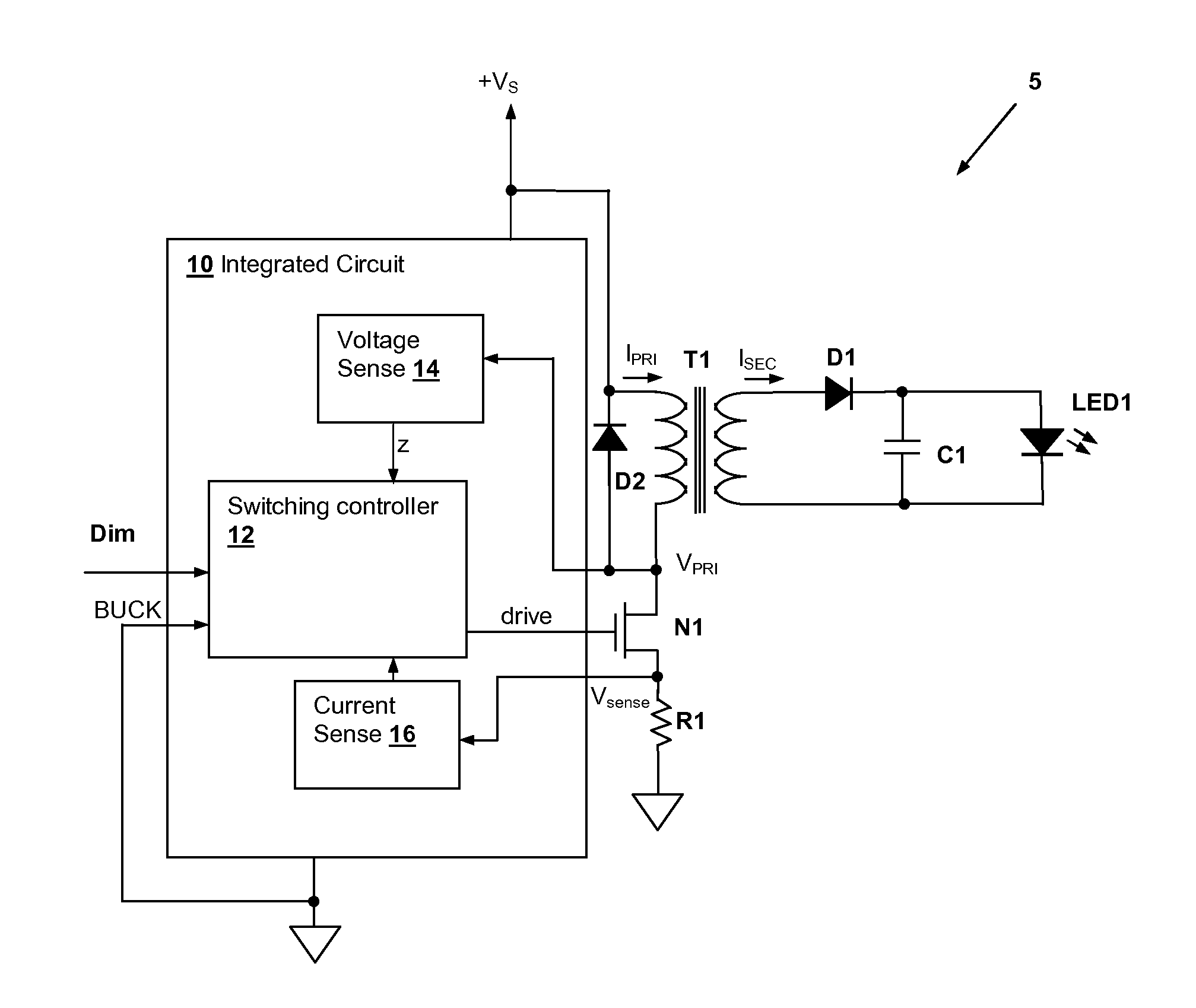
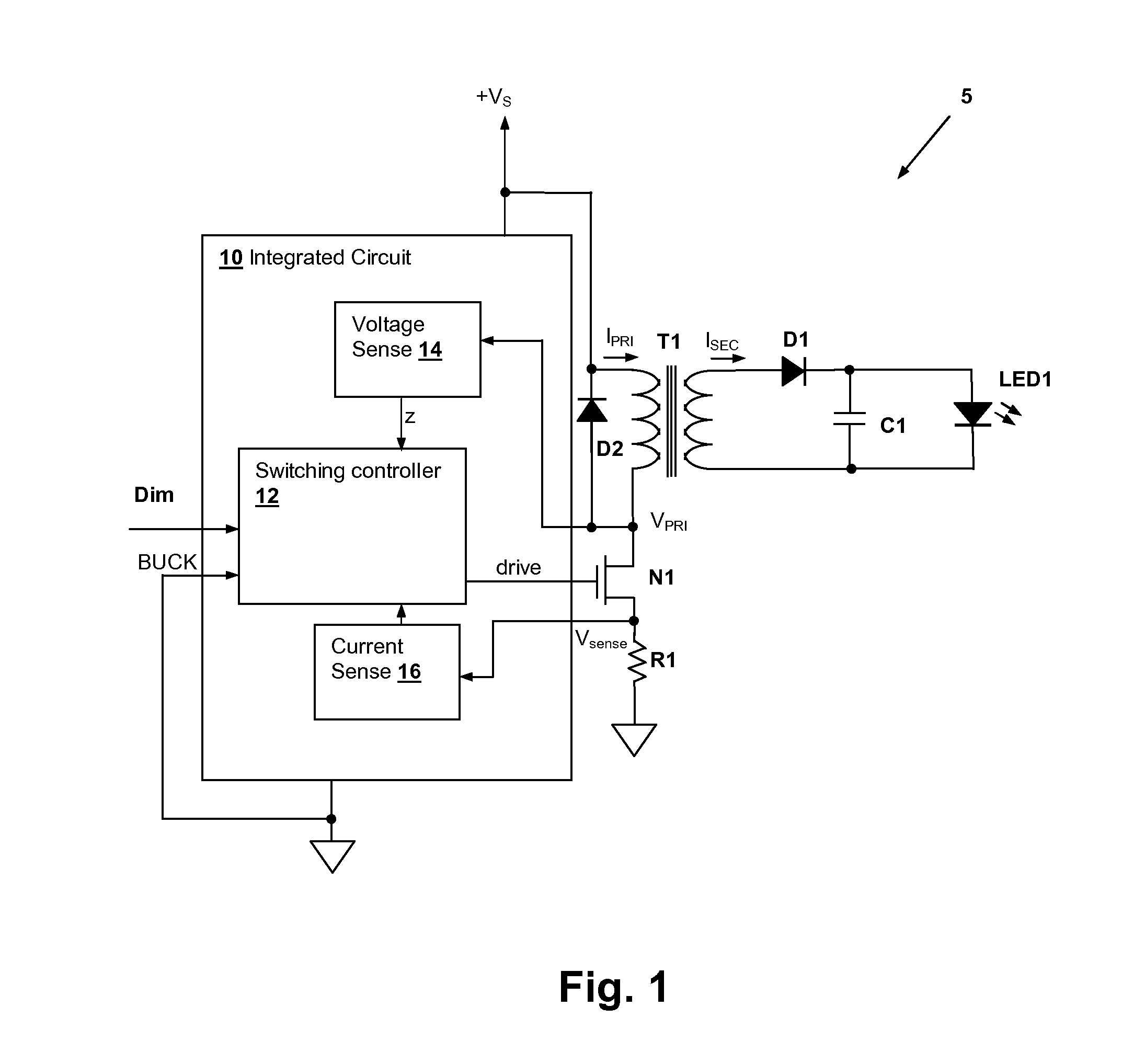
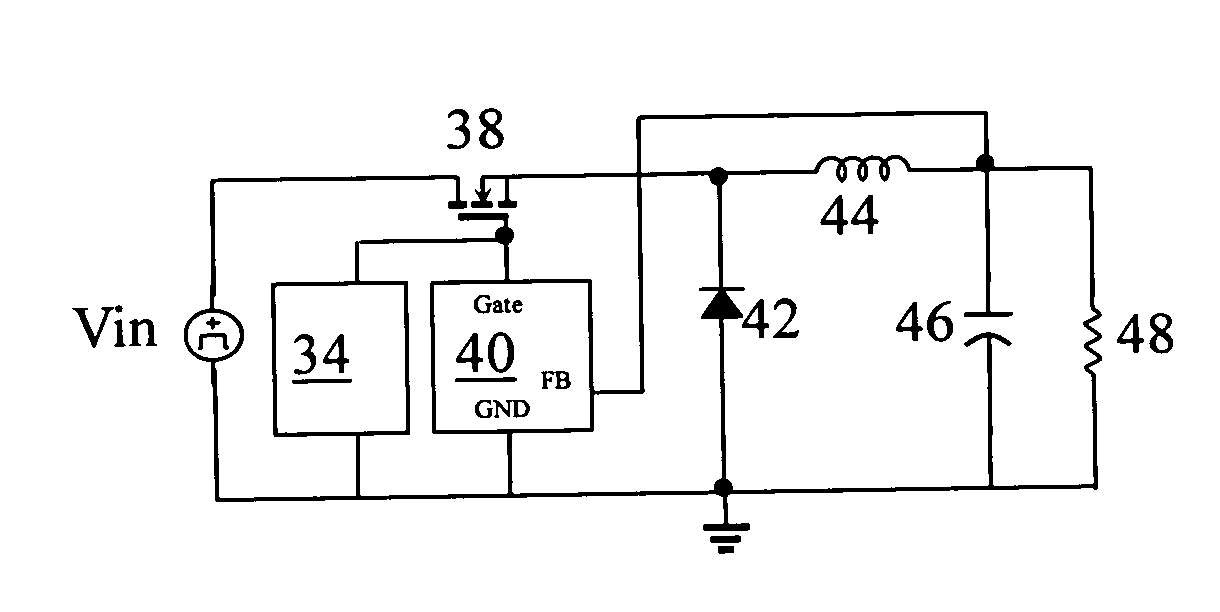
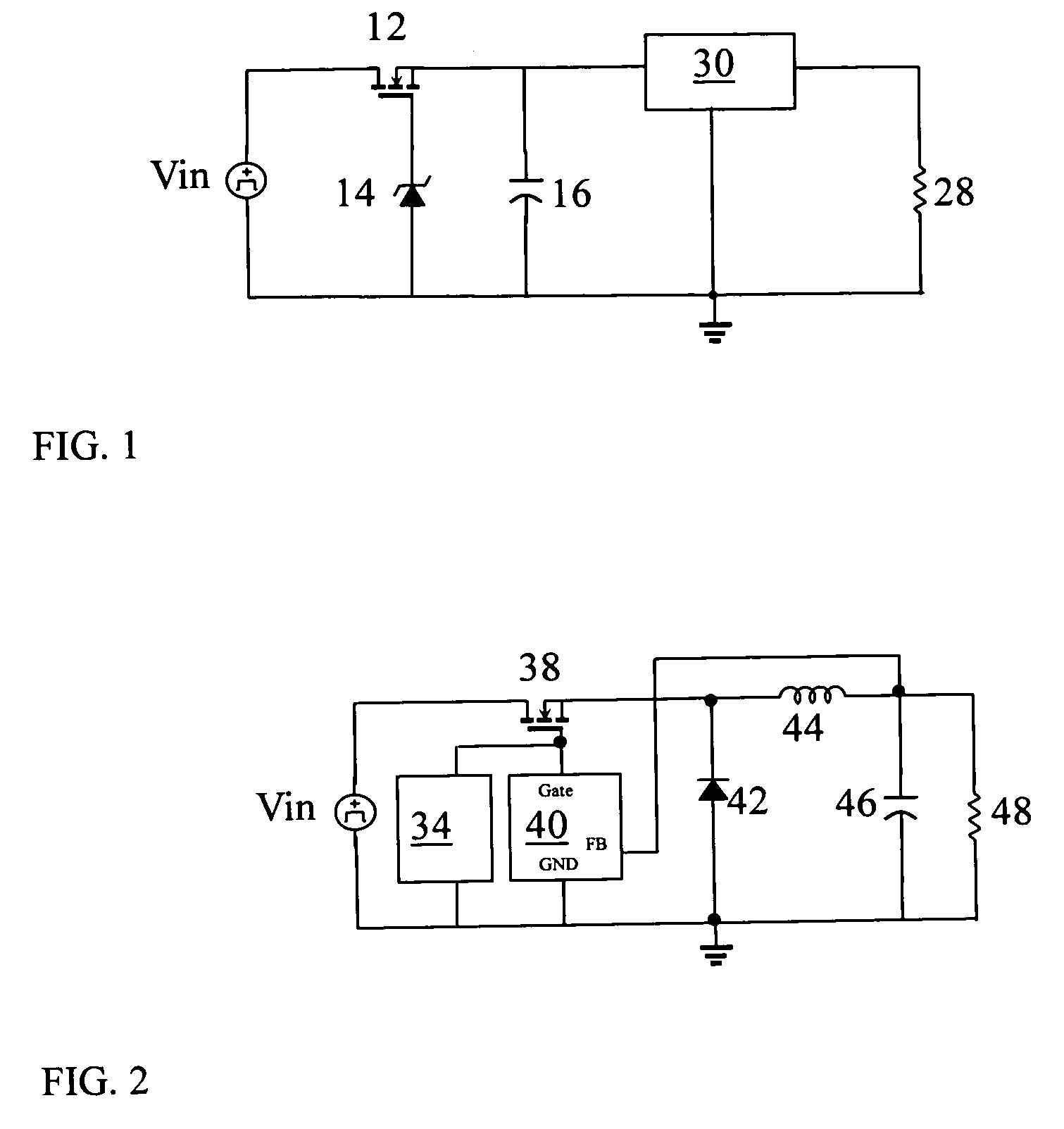
Integrated circuit switching power supply controller with selectable buck mode operation
An integrated circuit (IC) controller for a switching power supply has a selectable operating mode for supporting multiple switching power supply topologies. The IC controls current by controlling a cycle rate of the switching power supply to provide a constant or variable output current, which may be provided to lighting devices such as light-emitting diodes (LEDs). The selectable operating mode includes at least a buck converter operating mode and another operating mode, which may be a flyback converter operating mode.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Maximum Power Point Tracking Charge Controller with Coupled Inductor Multi-phase Converter
A maximum power point tracking (MPPT) charge controller for photovoltaic (PV) systems employs a maximum power point tracking algorithm for tracking the maximum power point voltage of a PV array at which the PV array produces maximum power voltage, and a buck converter for converting the maximum power voltage to the voltage required to charge one or more batteries. The buck converter includes multiple buck converter phase configurations phase shifted from one another. Each of the buck converter phase configurations has a phase inductor, and the phase inductors are combined on a single core to form a coupled inductor. One of the buck converter phase configurations is intentionally temporarily shut down when the output power is low. A first switch or a second switch of the buck converter phase configuration that is intentionally temporarily shut down is turned on to conduct electrical current when predetermined conditions are satisfied. A method of controlling battery charging in a photovoltaic system involves operating a coupled inductor multi-phase buck converter of a charge controller so that one of the buck converter phase configurations is intentionally temporarily shut down when the power output is below a predetermined value.
Owner:MORNINGSTAR CORP
Buck converter with inductor pre-energizing
ActiveUS20080136387A1Simple control circuitDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationĆuk converterPre-charge
Circuits and methods to achieve a buck-boost converter, capable to achieve a constant output voltage by pre-charging of an inductor if the input voltage is close to the output voltage has been achieved. The prior art problem of output voltage variations occurring while the input voltage is close to the output voltage is avoided. In case the input voltage is lower than a defined threshold voltage or the duty cycle exceeds a defined maximum allowable level, the inductor of the converter is pre-charged followed by boosting of the energy of the inductor to the output of the converter. In both modes the control loops of the buck converter can be used for buck duty cycle control. The duration of the pre-charge depends upon the level of the input voltage, the lower the input level is the longer is the pre-charge performed.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
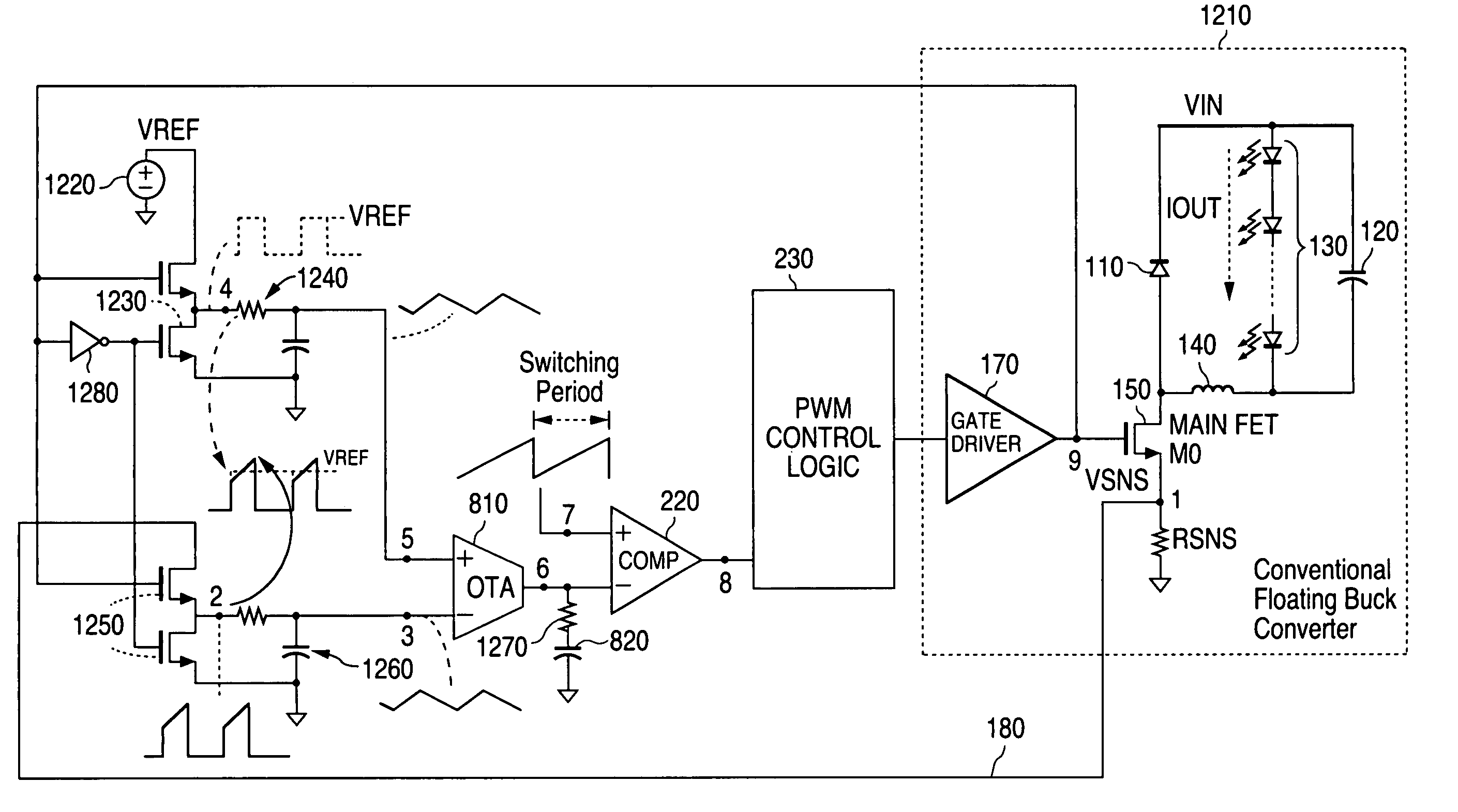
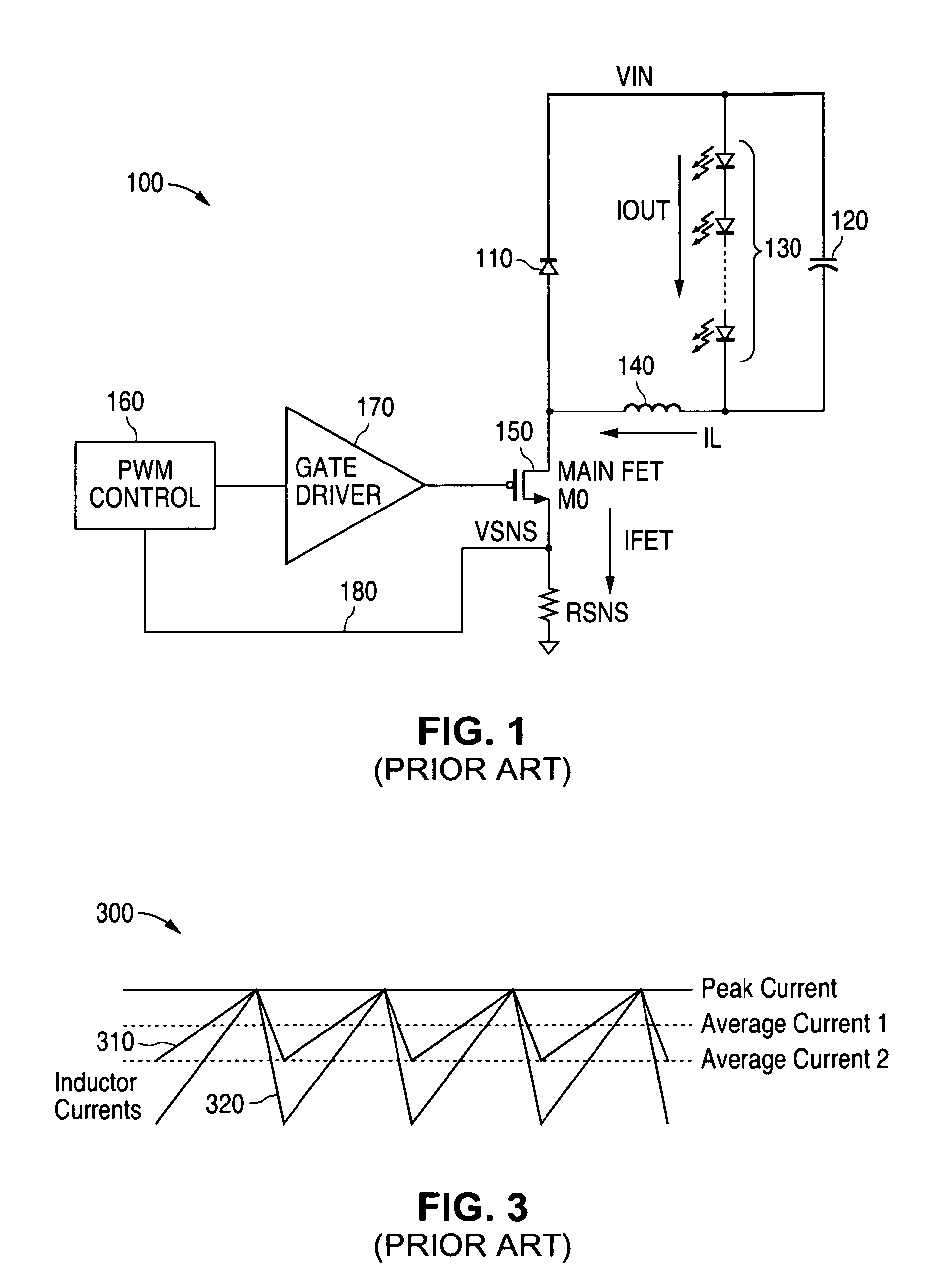
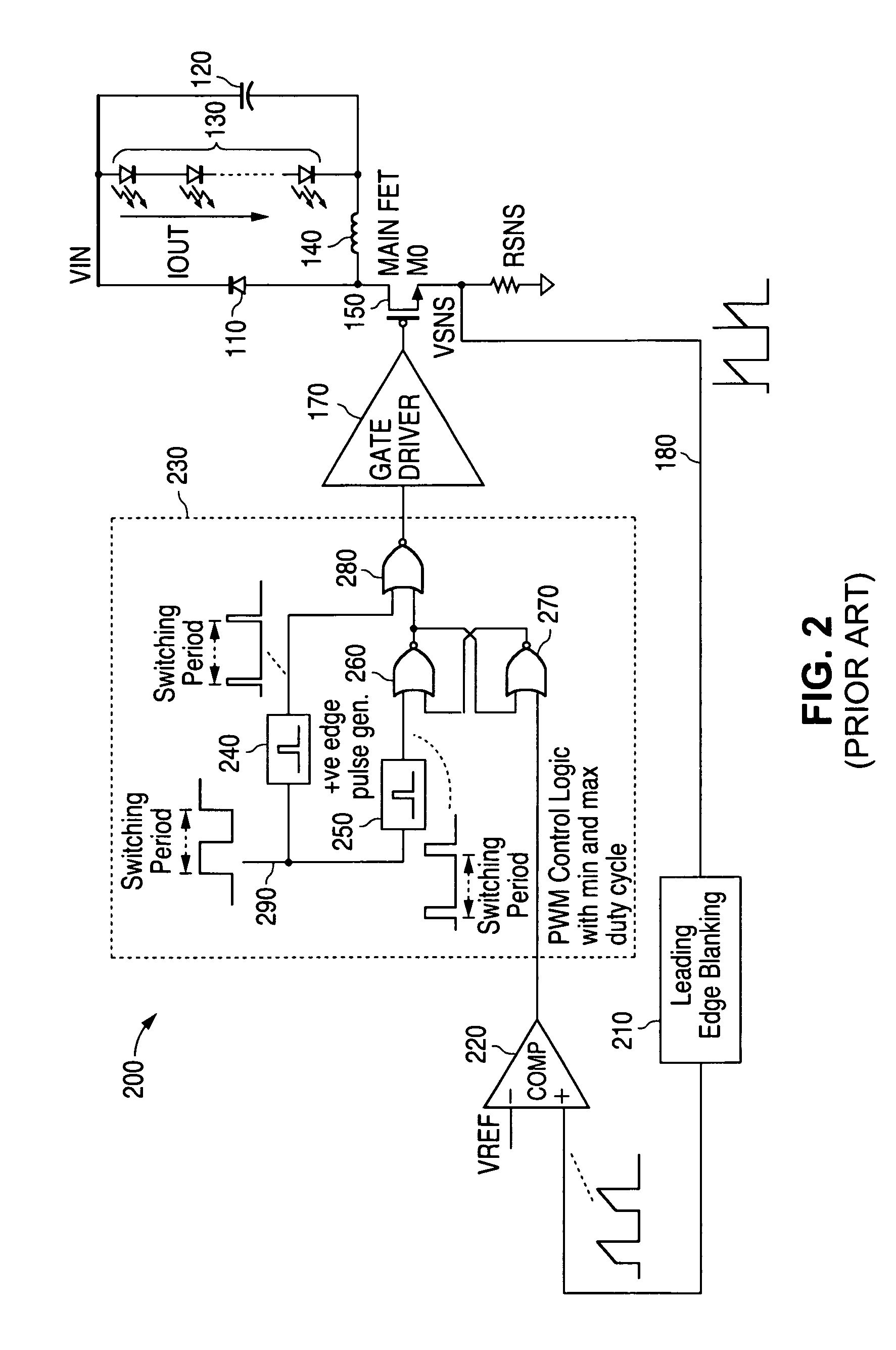
Constant current output using transconductance amplifier
An apparatus in an electronic device such as a buck converter circuit receives as a first input a voltage signal VSNS from the electronic device that represents a current through the electronic device, and receives as a second input a direct current reference voltage signal from a reference voltage source VREF. The apparatus regulates a direct current output IOUT of the electronic device with respect to the reference voltage source VREF by applying a pulse level transformation to the voltage signal VSNS using an operational transconductance amplifier.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
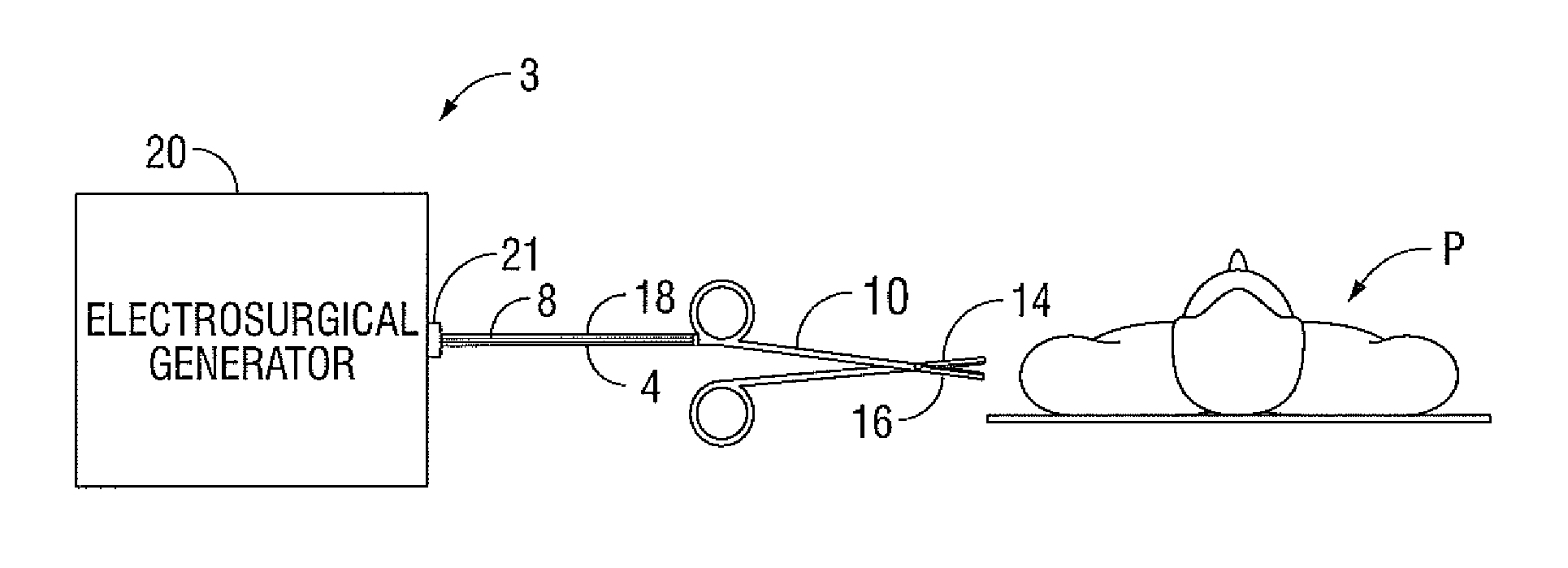
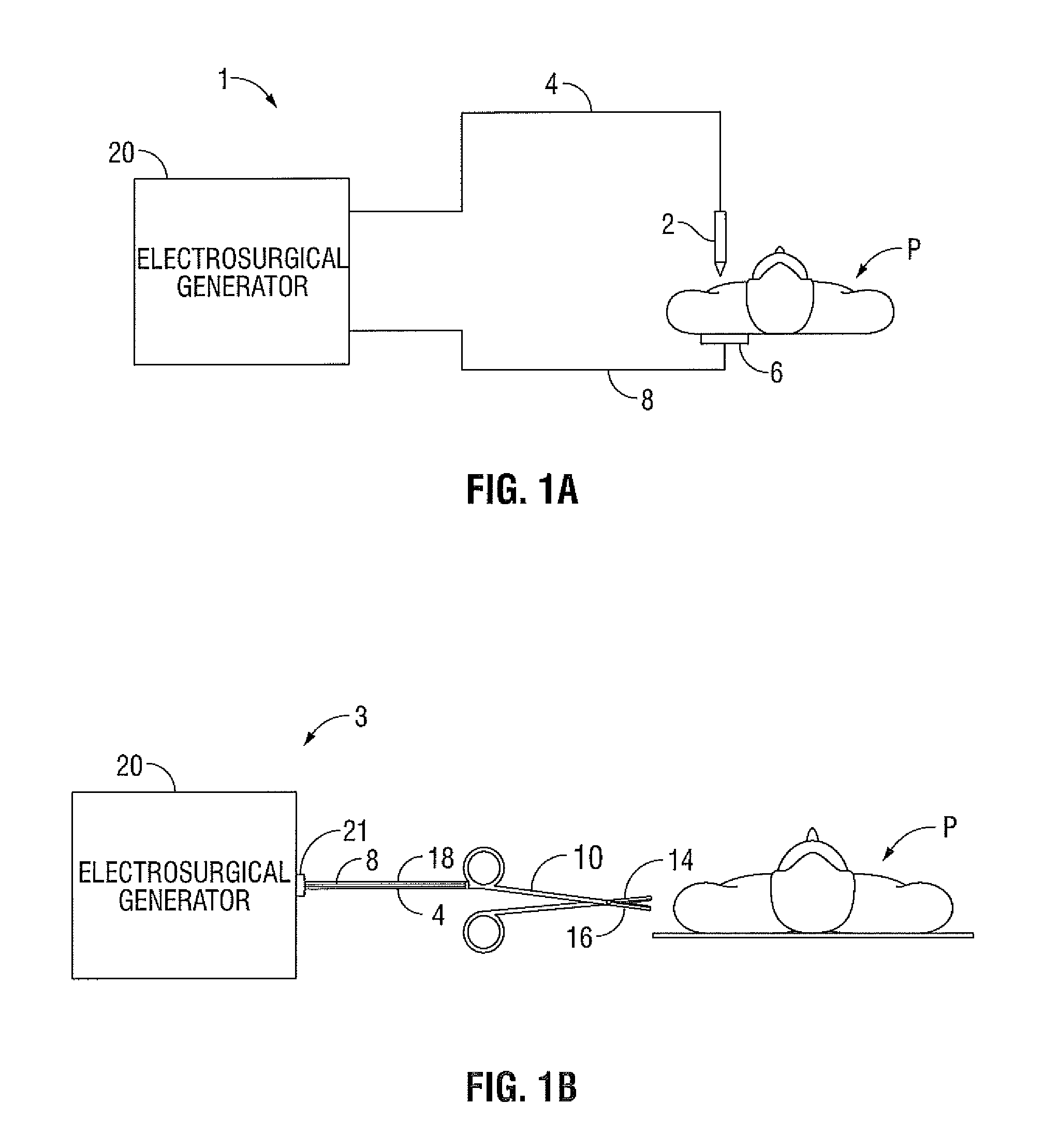
Current-Fed Push-Pull Converter with Passive Voltage Clamp
ActiveUS20110319881A1Controlling energy of instrumentSurgical instruments for heatingBuck converterInductor
An electrosurgical generator configured to output radio frequency (RF) energy having a current-source type behavior is provided. The generator has a buck converter having a voltage source, at least one switch and an inductor. The generator also has an RF stage configured to output the RF energy. A sensor circuit configured to measure at least one parameter of the RF energy and a controller configured to receive the measured parameter from the sensor circuit and control the output of the electrosurgical generator based on the measured parameter may also be provided in the electrosurgical generator.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
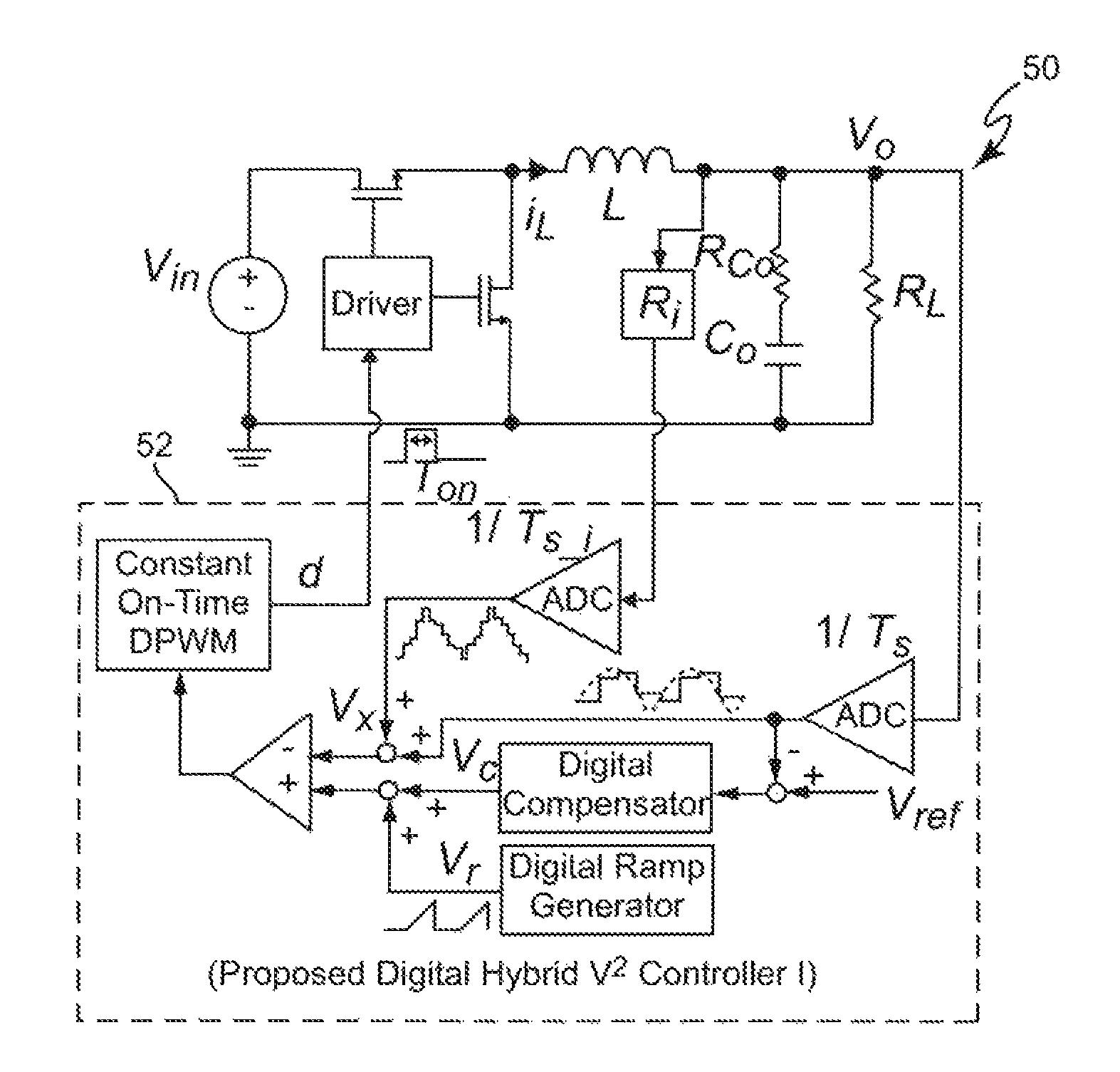
Digital hybrid V2 control for buck converters
ActiveUS8575911B2Avoid instabilityIncrease sampling rateEfficient power electronics conversionPulse generatorCapacitanceĆuk converter
Stabilization of a switching voltage regulator employing V2 control against ripple oscillation instability when the equivalent series resistance (ESR) of an output capacitor is small is provided by providing both an external ramp and an internal ramp (only the latter of which requires an approximation of inductor current) in the control feedback path, preferably including both inner and outer feedback loops. Approximation of inductor current using such an arrangement is non-critical and may be estimated based on power input voltage. Drift of a circuit providing such an inductor current estimation is preferably avoided by adjusting control duty cycle or slew rate of the positive-going ramp portion of the estimated inductor current triangular waveform.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Method for controlling a dc-to-dc converter
ActiveUS20150326120A1Minimizing voltage deviationShorten total active timeDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationFull bridgePush pull
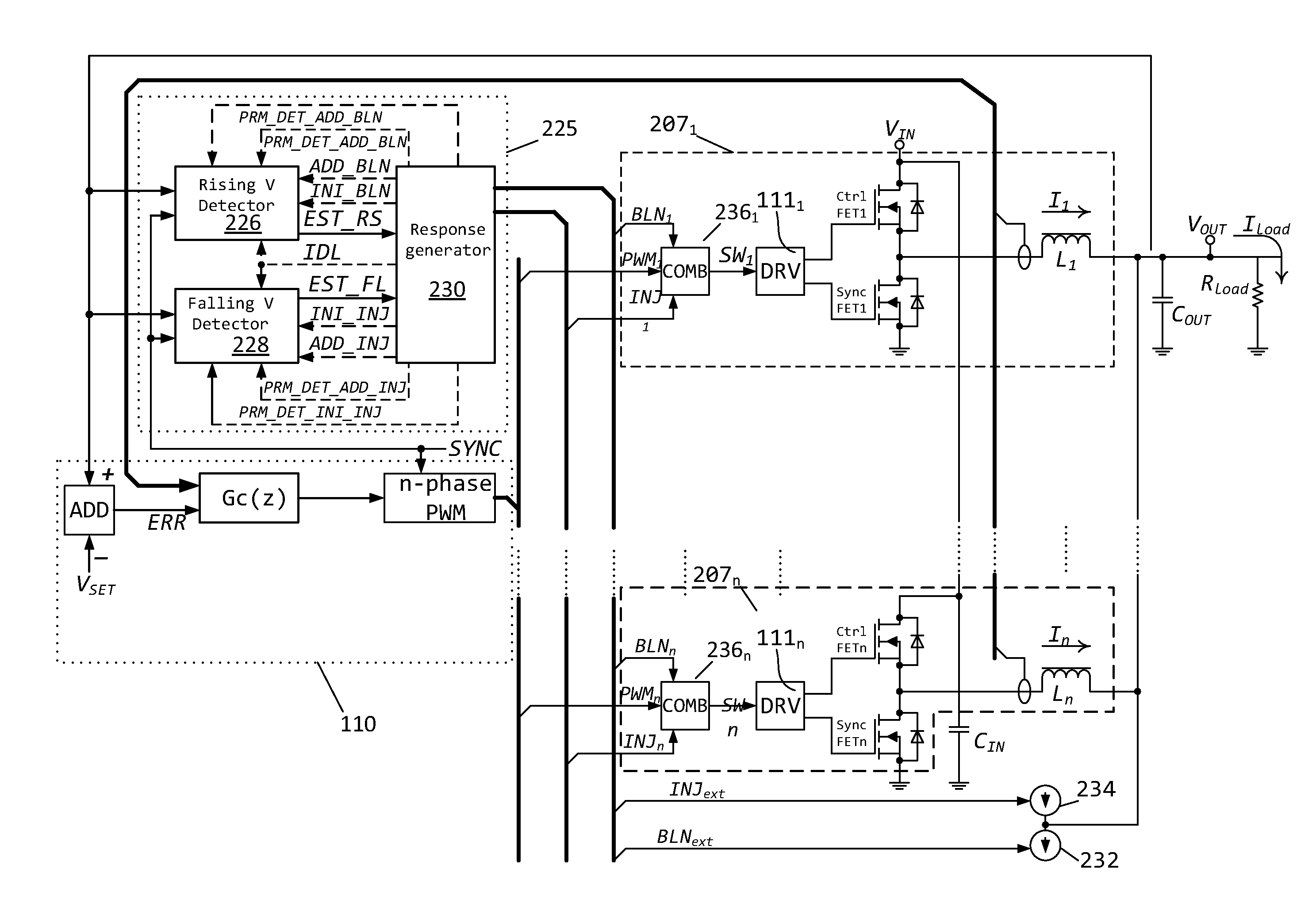
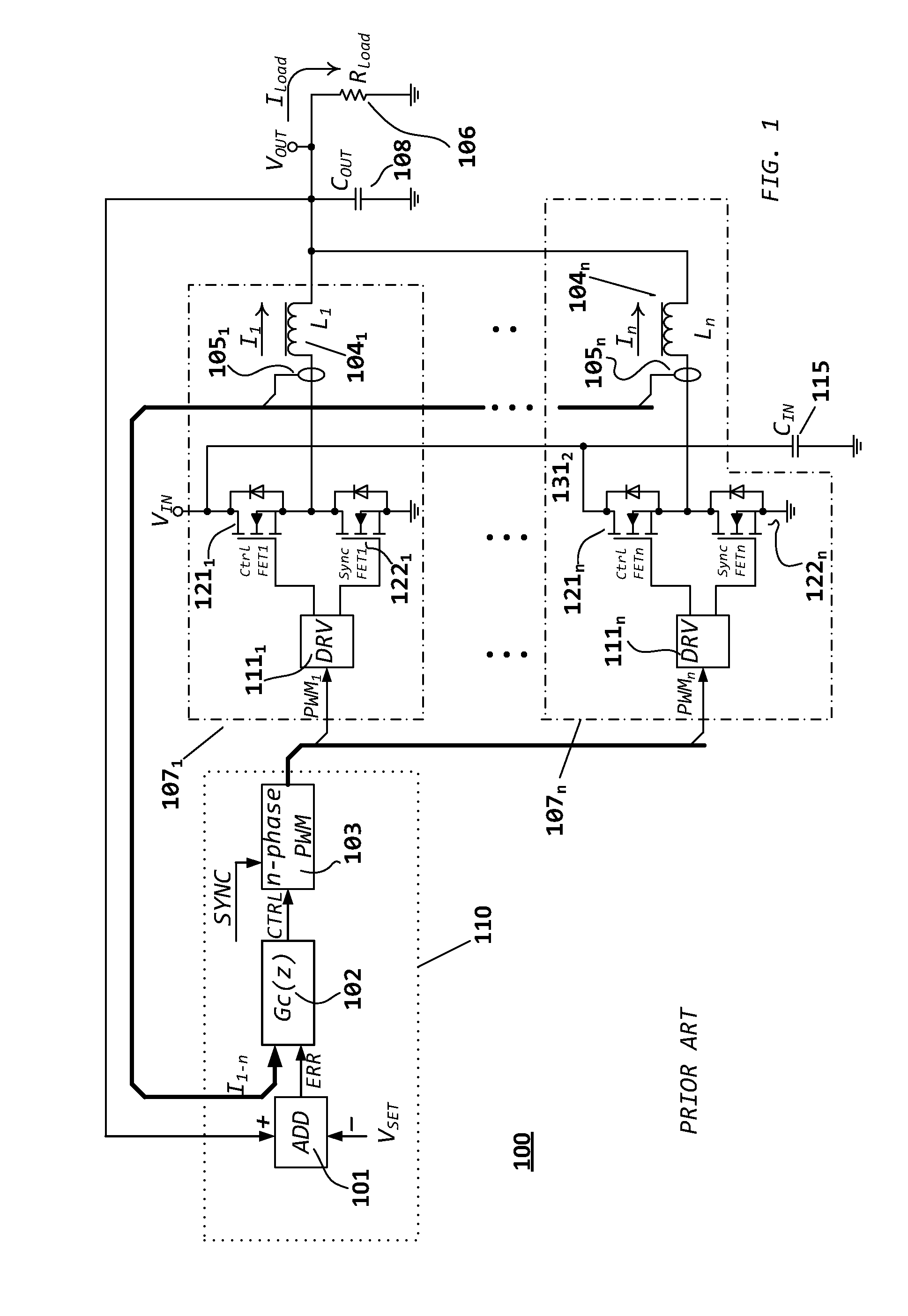
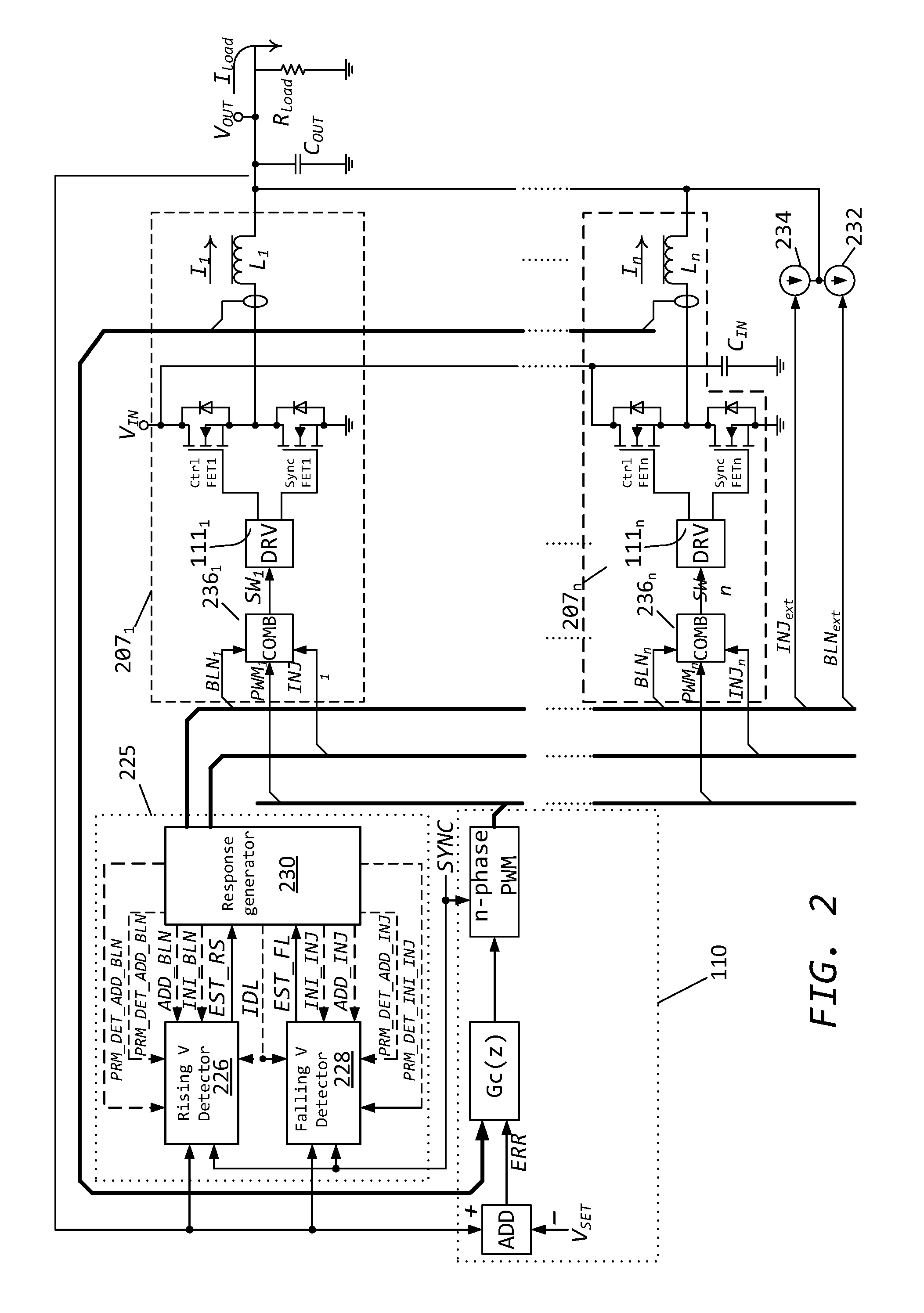
Methods and circuits for power supply arrangement and control are disclosed herein. More specifically the application relates to a control method and a controller for a DC-to-DC converter, such as a synchronous Buck converter, which implements a transient detection scheme together with response generation to allow the converter to recover from a positive and / or negative load current step in the robust way, with low undershoot / overshoot at the output voltage. The control method may be implemented by either an analog or a digital circuit. The controller may be integrated with existing controller schemes (such as voltage-mode controllers) to provide superior dynamic performance during large-signal transient conditions while providing stable operation during steady state conditions. The methods and circuits provided herein are applicable to Buck converters and Buck-derived converters such as forward, push-pull, half-bridge, and full-bridge converters.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Buck converter and method for providing a current for at least one LED
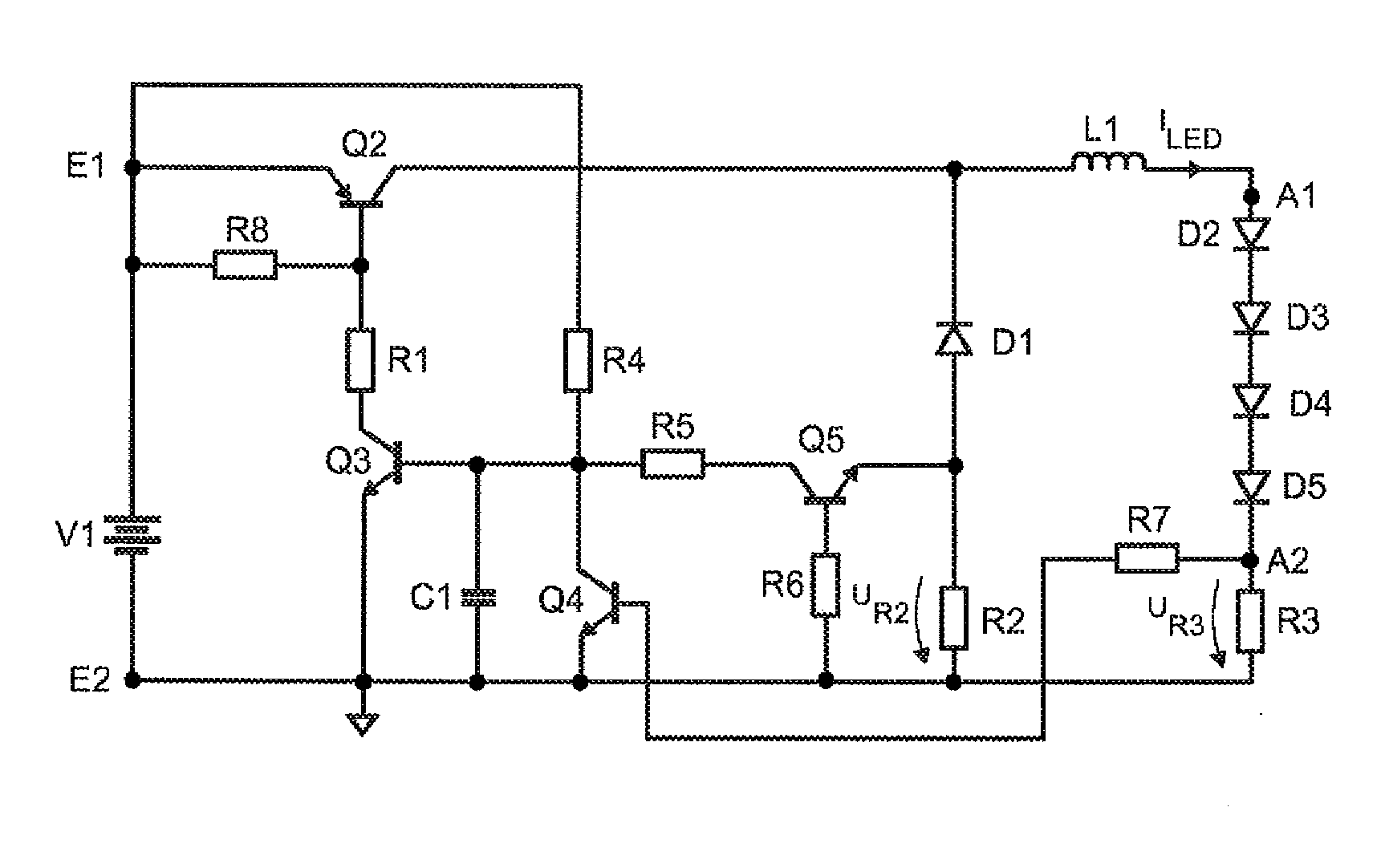
ActiveUS20110050130A1Speed up clearanceIncrease supplyElectroluminescent light sourcesDc-dc conversionTransverterBuck converter
A Buck converter may include an input for connecting a DC voltage source; an output for connecting an LED; and a diode, an inductor and a main switch; wherein the diode and the main switch are coupled in series, wherein the inductor is coupled between the connecting point for the diode and the main switch, and a first output connection, wherein the converter further includes: a first auxiliary switch supplied with a first voltage; and a second auxiliary switch supplied with a second voltage, wherein the first auxiliary switch and the second auxiliary switch are coupled to the main switch such that the first voltage stipulates the switch-off time for the main switch and the second voltage stipulates the switch-on time for the main switch.
Owner:LEDVANCE GMBH
Buck converter with demagnetization detection of the inductor
InactiveUS7495425B2Reduce switching lossesEasy to operateDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationBuck converterĆuk converter
A buck converter is equipped with a switch, a diode, an inductance, a capacitor, an input with a first connection and second connection, and an output with a first connection and second connection. The first connection of the input is connected to the first connection of the output via a series circuit comprised of the switch and the inductance; in particular, the switch is provided on the input side and the inductance is provided on the output side. In addition, the cathode of the diode is connected to the connection between the switch and the inductance while the anode of the diode is connected to the second connection of the input and to the second connection of the output. The capacitor is connected in parallel with the connections of the output. It is possible to trigger the switch by combining a first signal with a second signal and a third signal corresponding to a control variable from the output of the buck converter may be used to adjust the output signal.
Owner:PULS GMBH
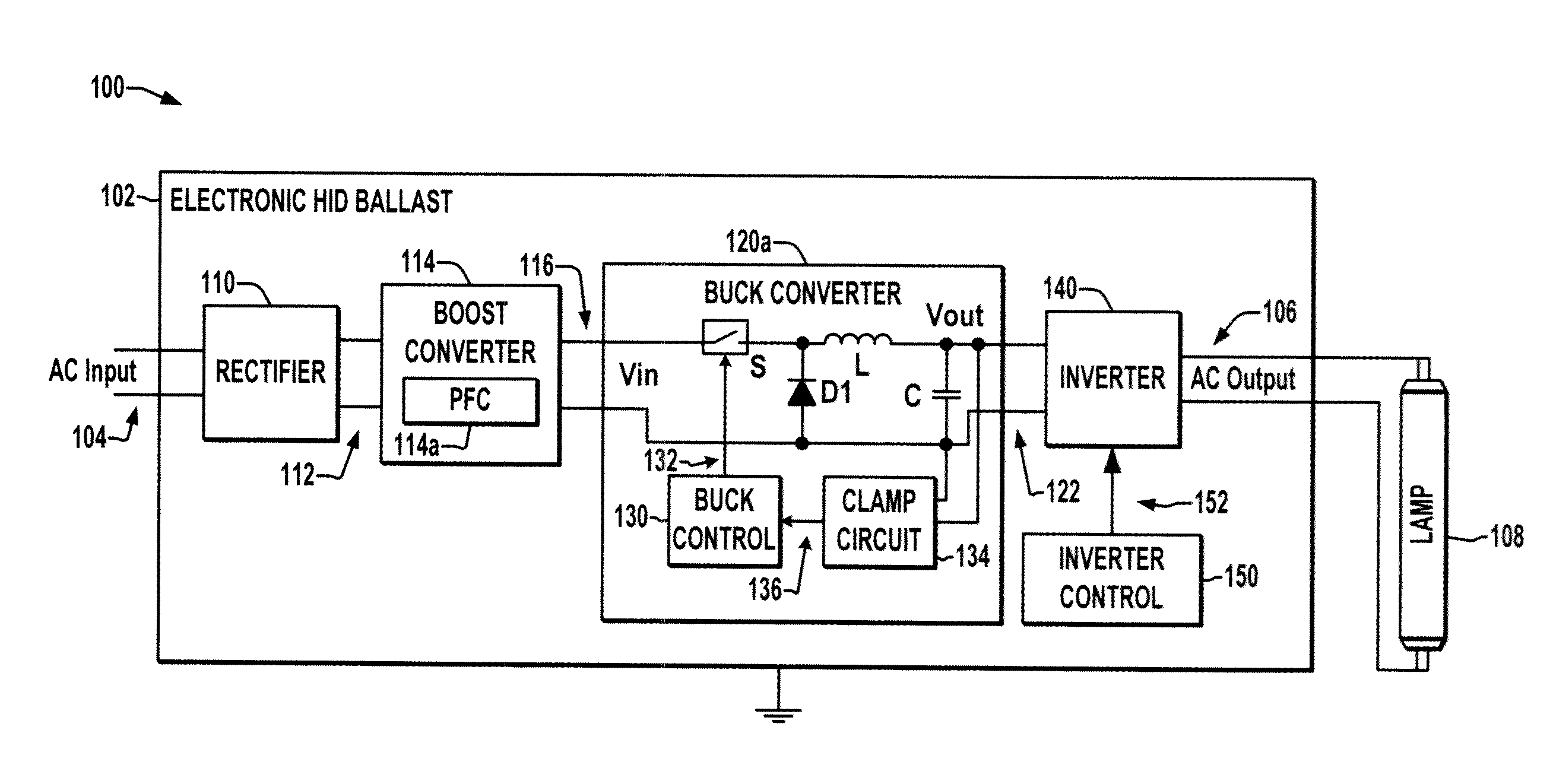
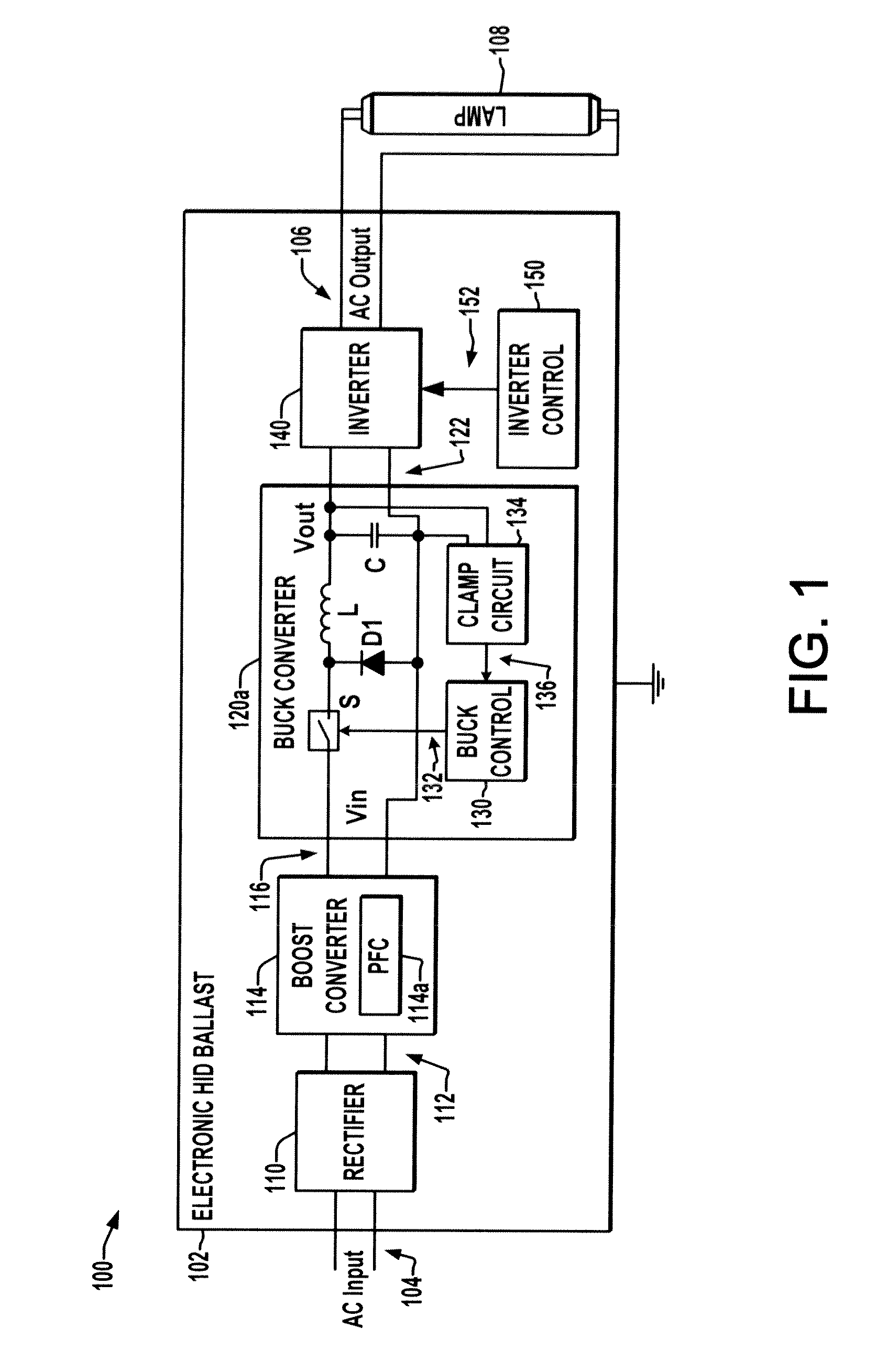
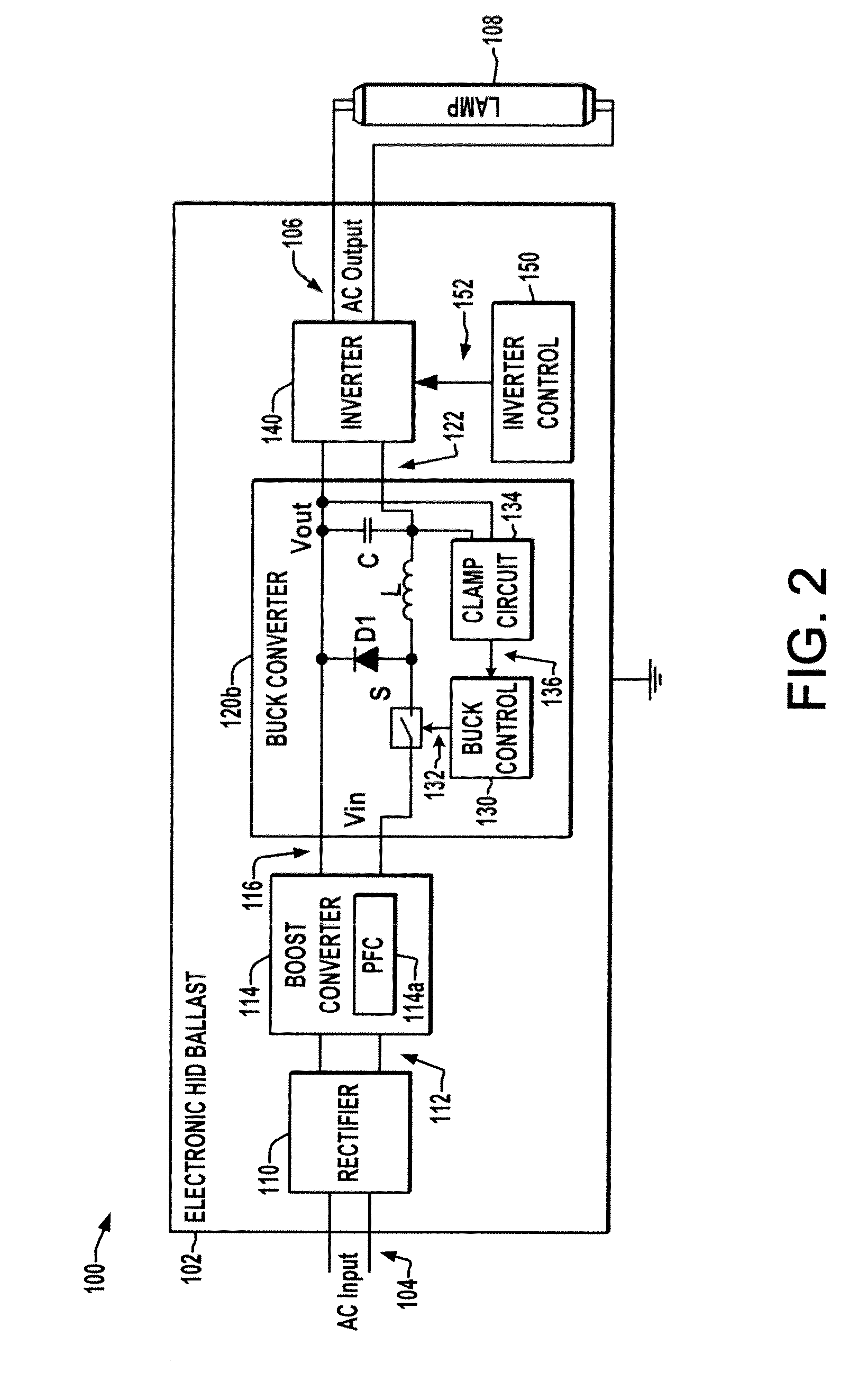
Open circuit voltage clamp for electronic hid ballast
InactiveUS20110304279A1Electrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementElectrical ballastBuck converter
An electronic high intensity discharge (HID) ballast (102) is presented which includes a dual mode buck converter (120) providing a DC output voltage (122) to drive an inverter (140), where the buck converter (120) regulates the DC output voltage (122) to a first value in normal operation and a clamp circuit (134) changes the converter mode to clamp the DC output open circuit voltage when the converter DC output exceeds a reference value (Vref).
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
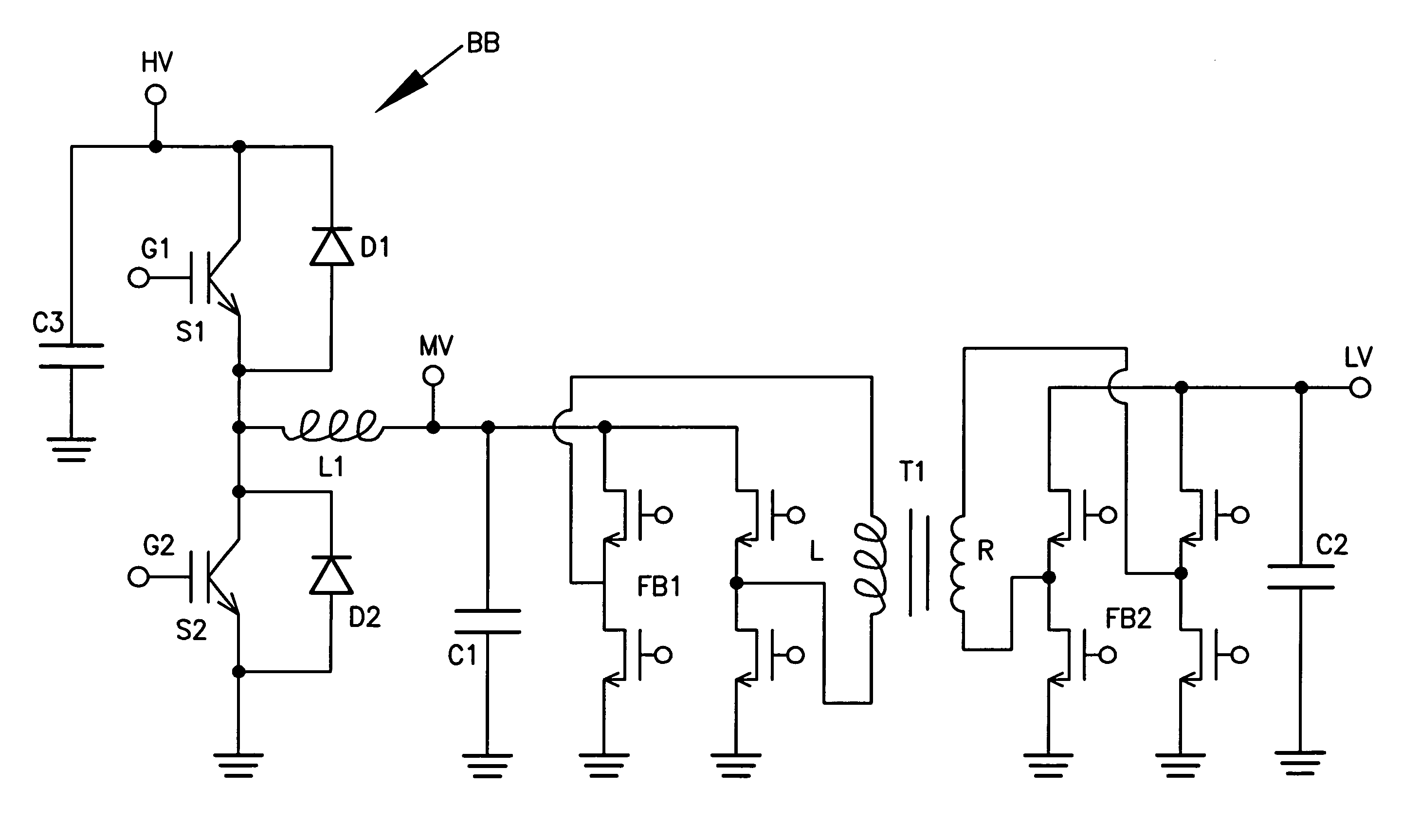
Bi-directional isolated DC/DC converter
A bi-directional converter for converting voltage bi-directionally between a high voltage bus and a low voltage bus, having a switching converter connected across the high voltage bus, the switching converter having first and second switching modules connected in series across the high voltage bus, a switched node disposed between the switching modules being coupled to an inductor, the first and second switching modules being controllable so that the switching converter can be operated as a buck converter or a boost converter depending upon the direction of conversion from the high voltage bus to the low voltage bus or vice versa; the mid-voltage bus being coupled to a first full bridge switching circuit having two pairs of series connected switches with switched nodes between each of the pairs of switches being connected across a first winding of a transformer having a preset turns ratio.
Owner:ASBU HLDG
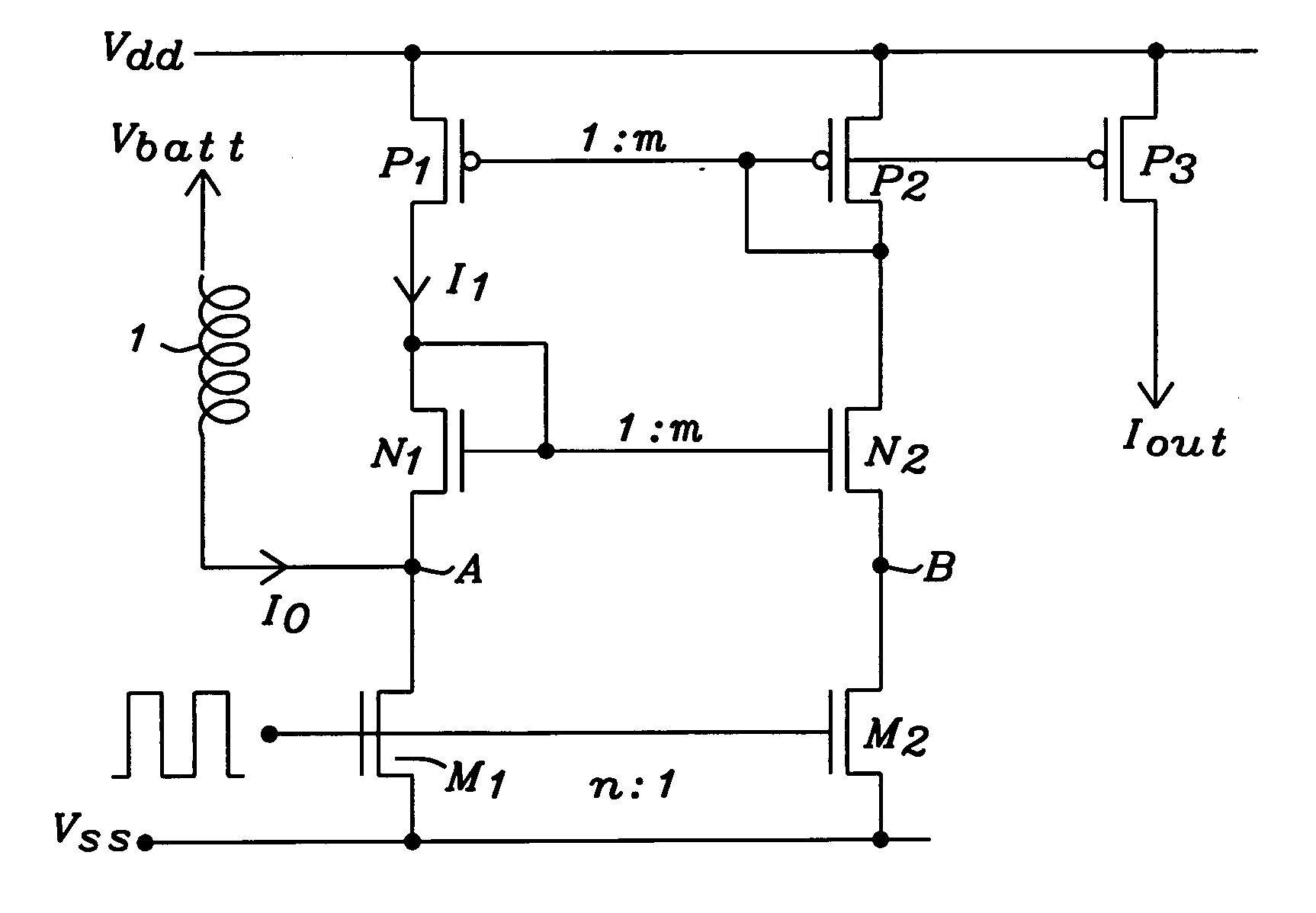
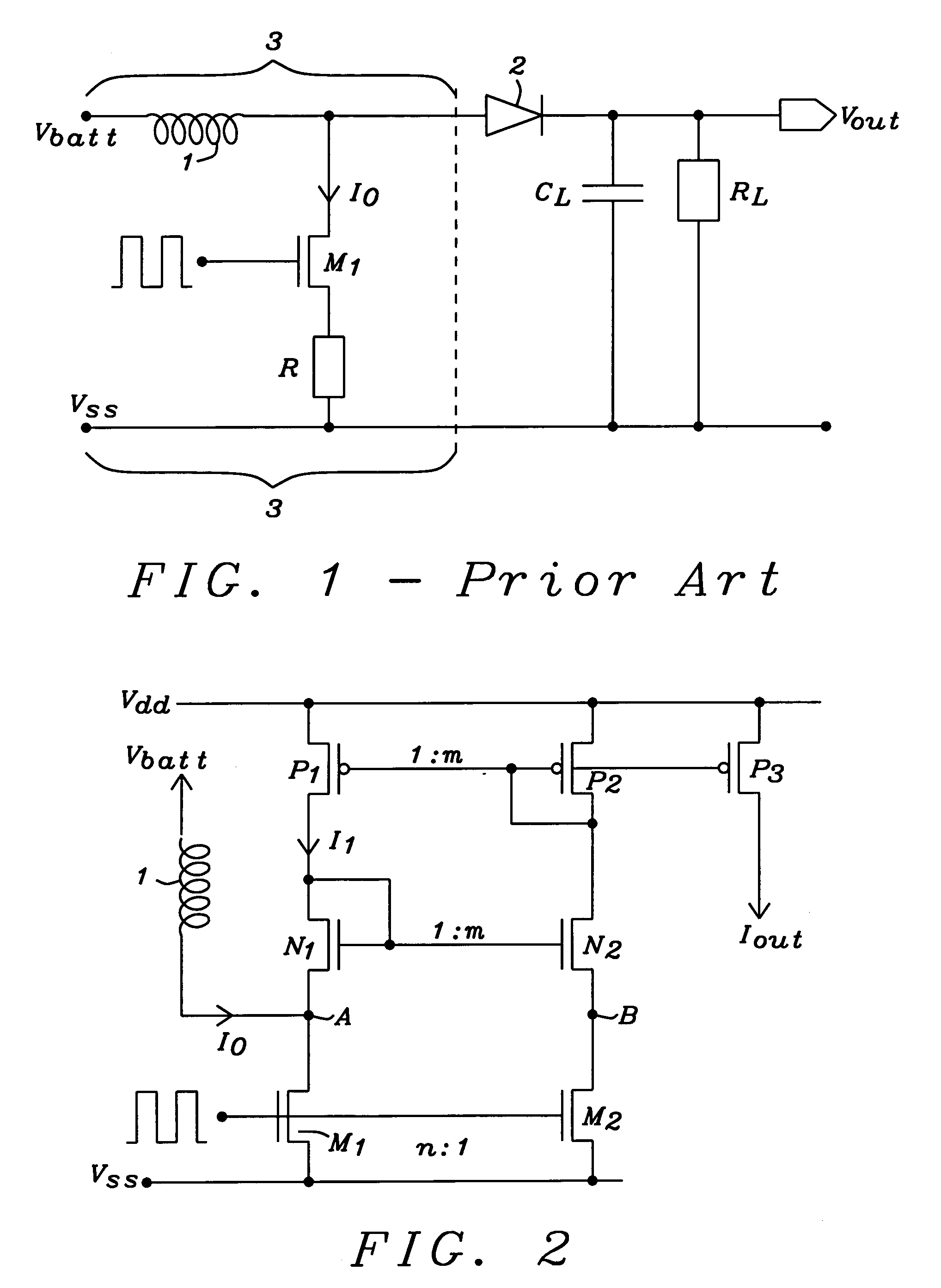
Current sensing structure for integrated power switches
ActiveUS20060158158A1Stable currentStable and fastMeasurement using dc-ac conversionMeasurement using ac-dc conversionBuck converterPower switching
Circuits and methods to sense the current through a coil of an integrated switching converter, applicable to boost and to buck converters, have been achieved. The present invention uses a “replica biasing” technique to avoid a resistor for current measurement. The current through a pass device is mirrored into a replica, having a scale of n and being much smaller in size, of said pass device. The current through the replica is mirrored to another branch of the circuit and back again to achieve a fast stabilization of the current. The current through the replica is mirrored again to an output branch of the circuit, which conducts exactly a fraction 1 / n of the current flowing through the pass device. The self-biasing current loop of the invention adapts quickly to the actual current level through the pass device of the switching converter. Accuracies better than 5% are achieved over a wide range of dynamic range.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
Bi-directional Boost-Buck Voltage Converter
InactiveUS20100045248A1Low costImprove efficiencyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationElectrical batteryHigh voltage capacitors
A bi-directional Boost-Buck voltage converter includes a controller, a high-voltage capacitor, a lower-voltage battery, a resistive load, an inductor, and three or four switches, and provides a mechanism to efficiently provide power to the resistive load from the battery. It uses two configurations of the switches to configure the battery, the inductor, and the capacitor in a boost converter configuration to charge the capacitor from the battery. It uses two different configurations of the switches to configure the capacitor, the inductor, and the resistive load in a buck converter configuration to discharge the capacitor through the inductor and the resistive load.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
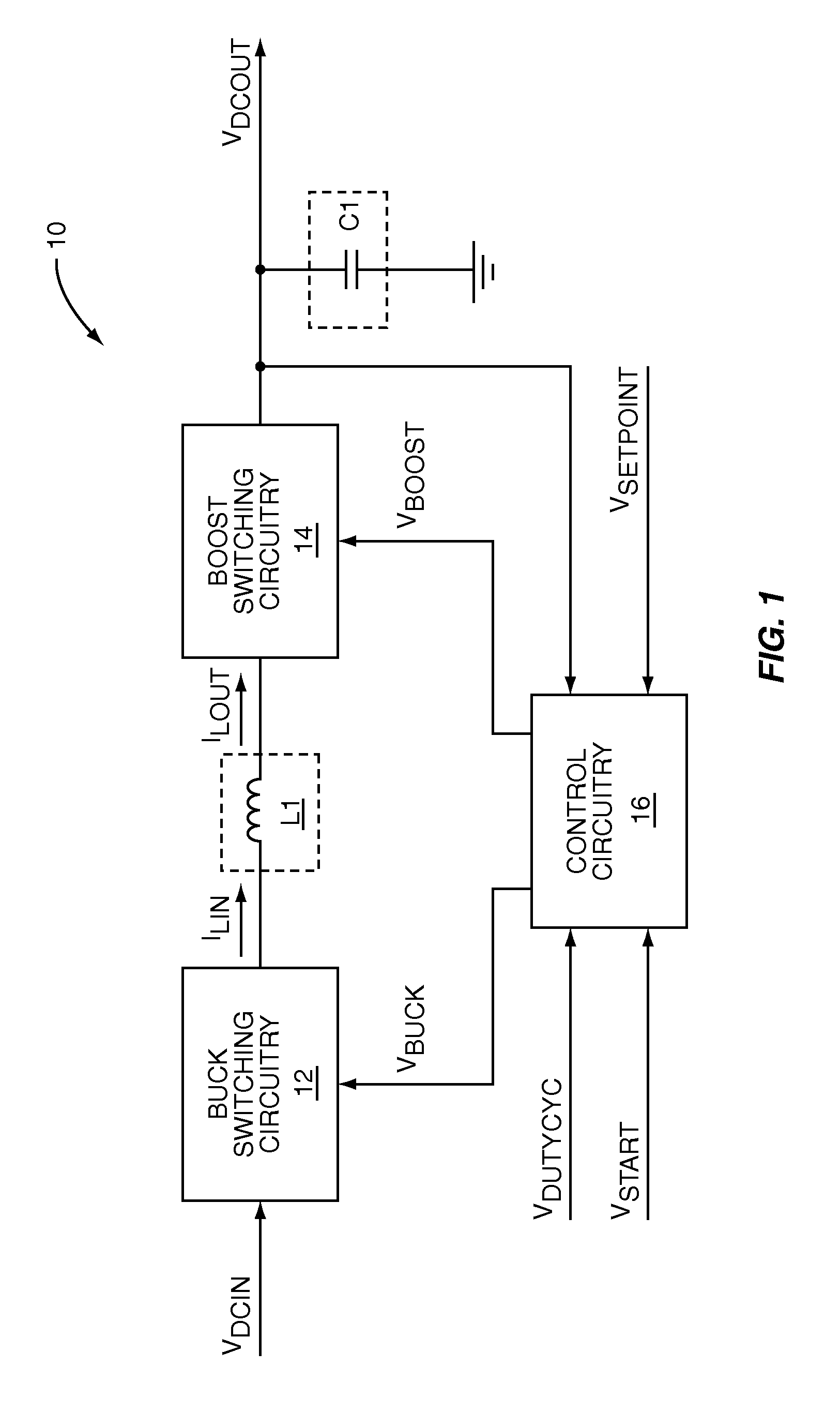
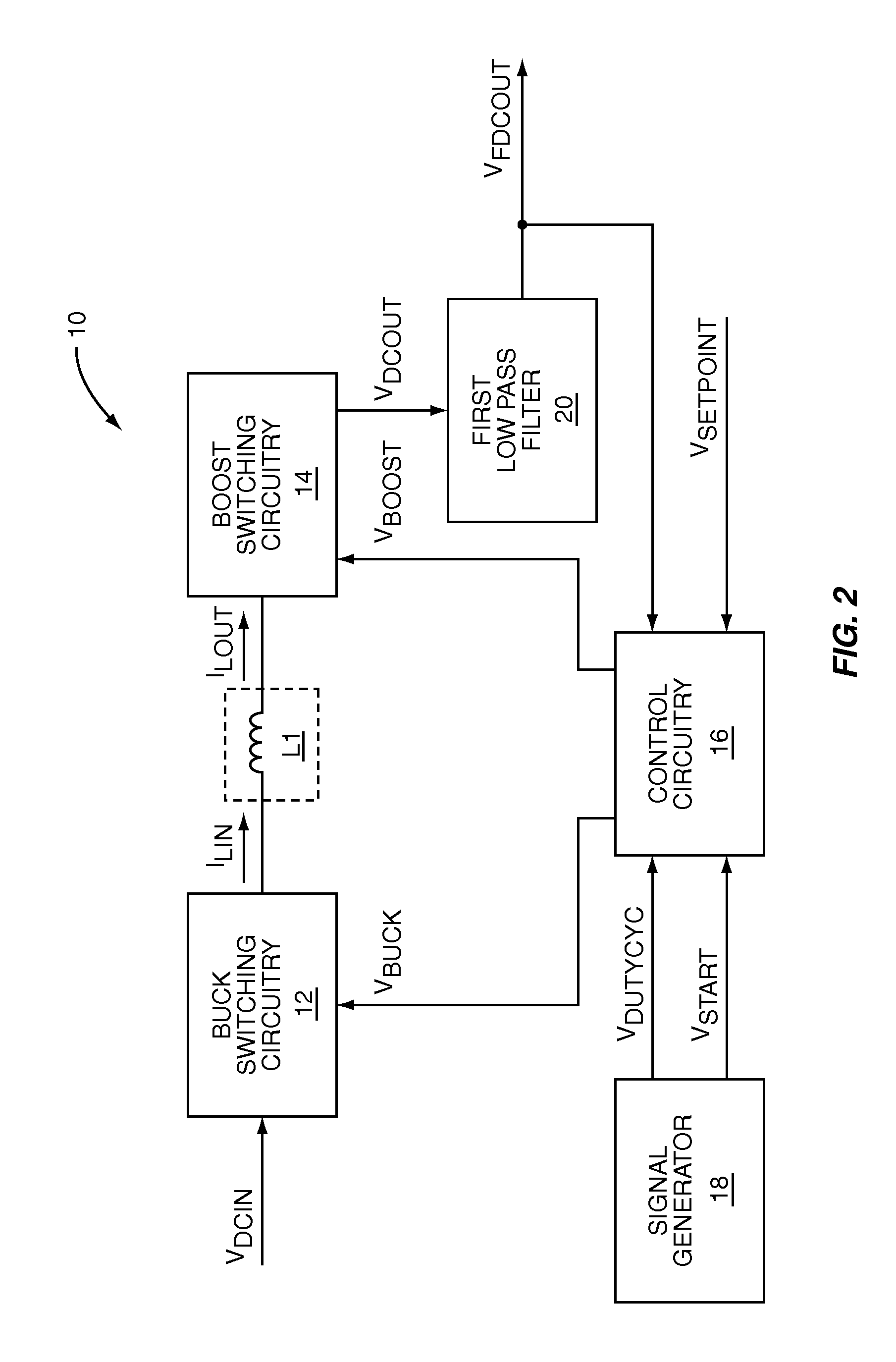
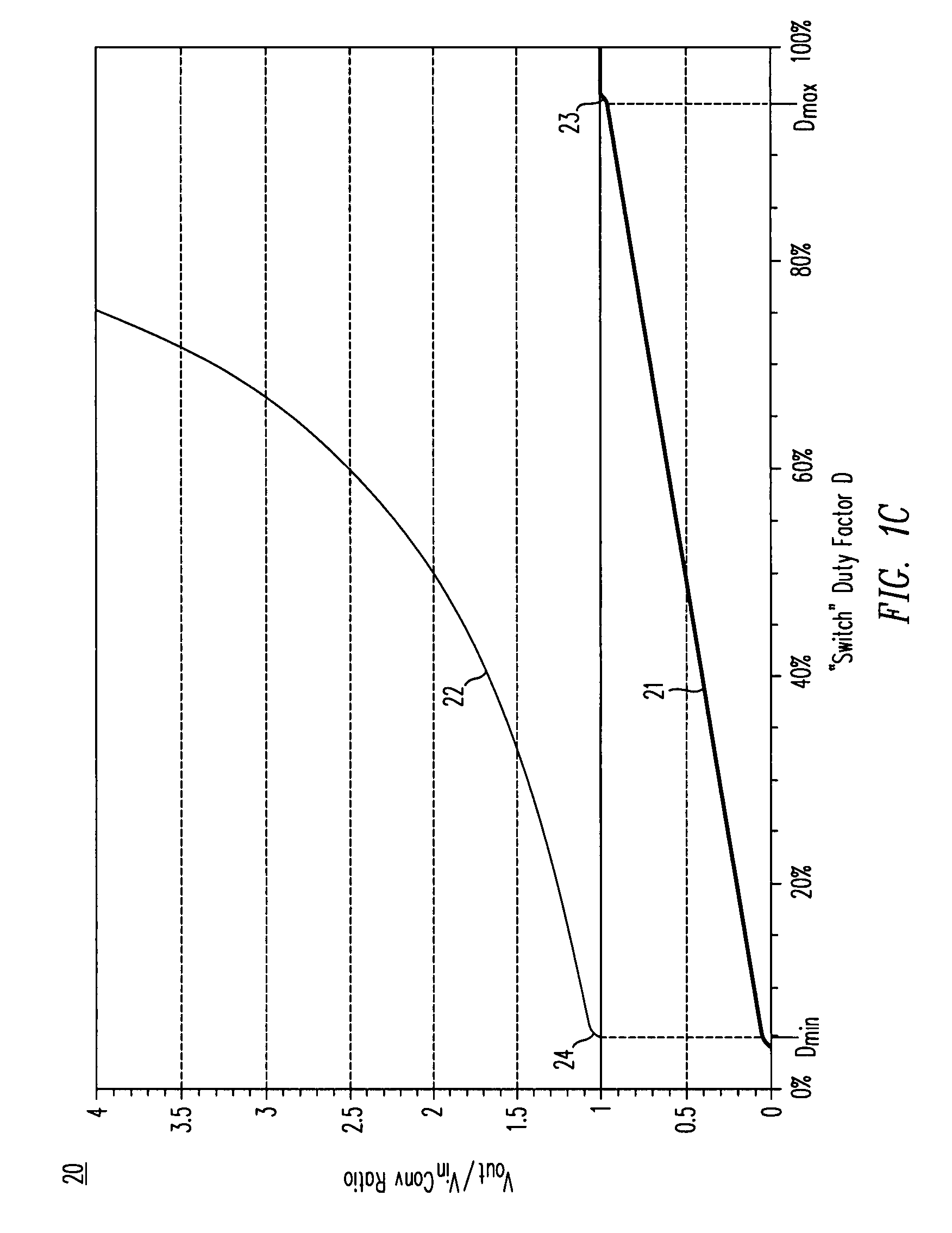
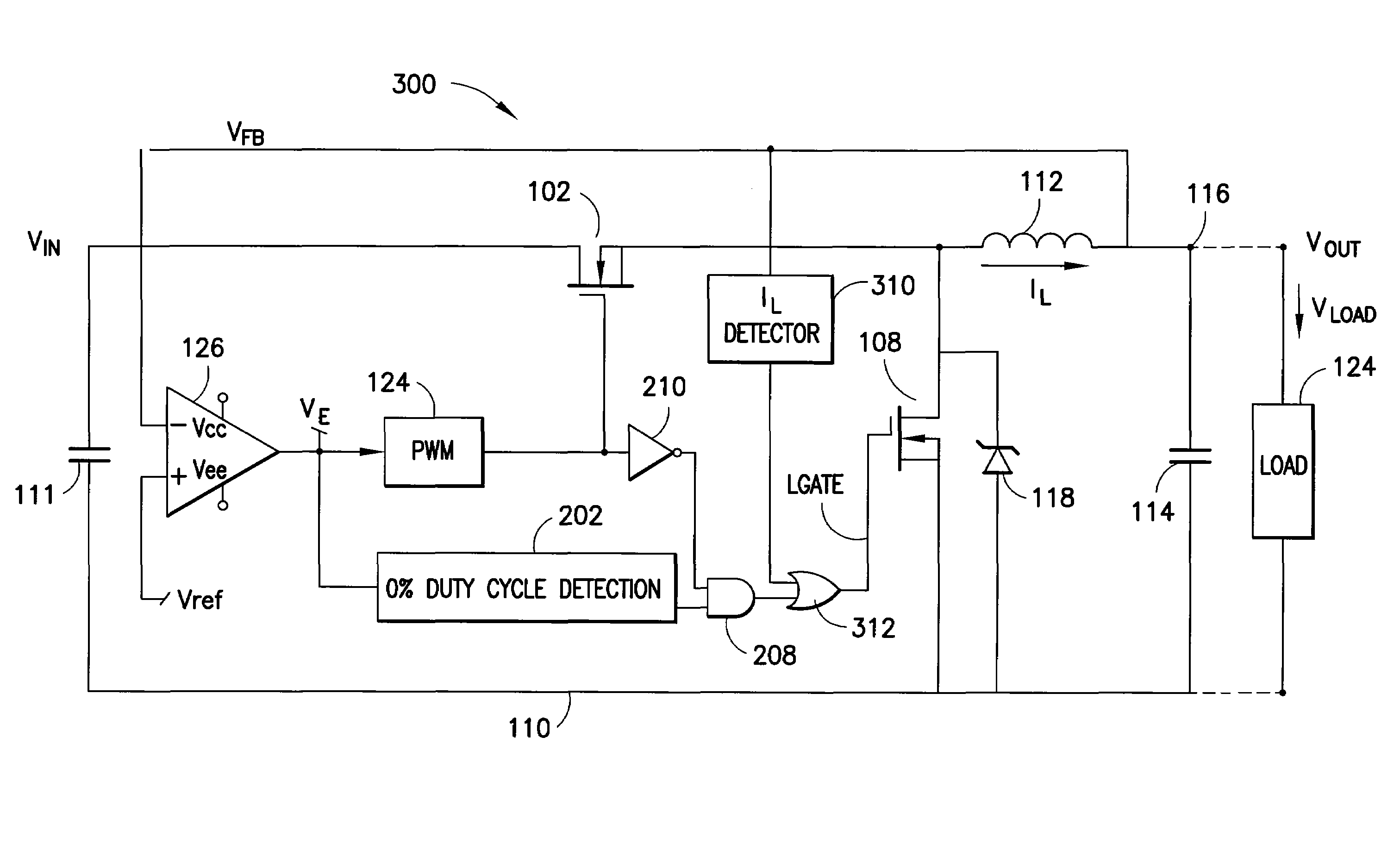
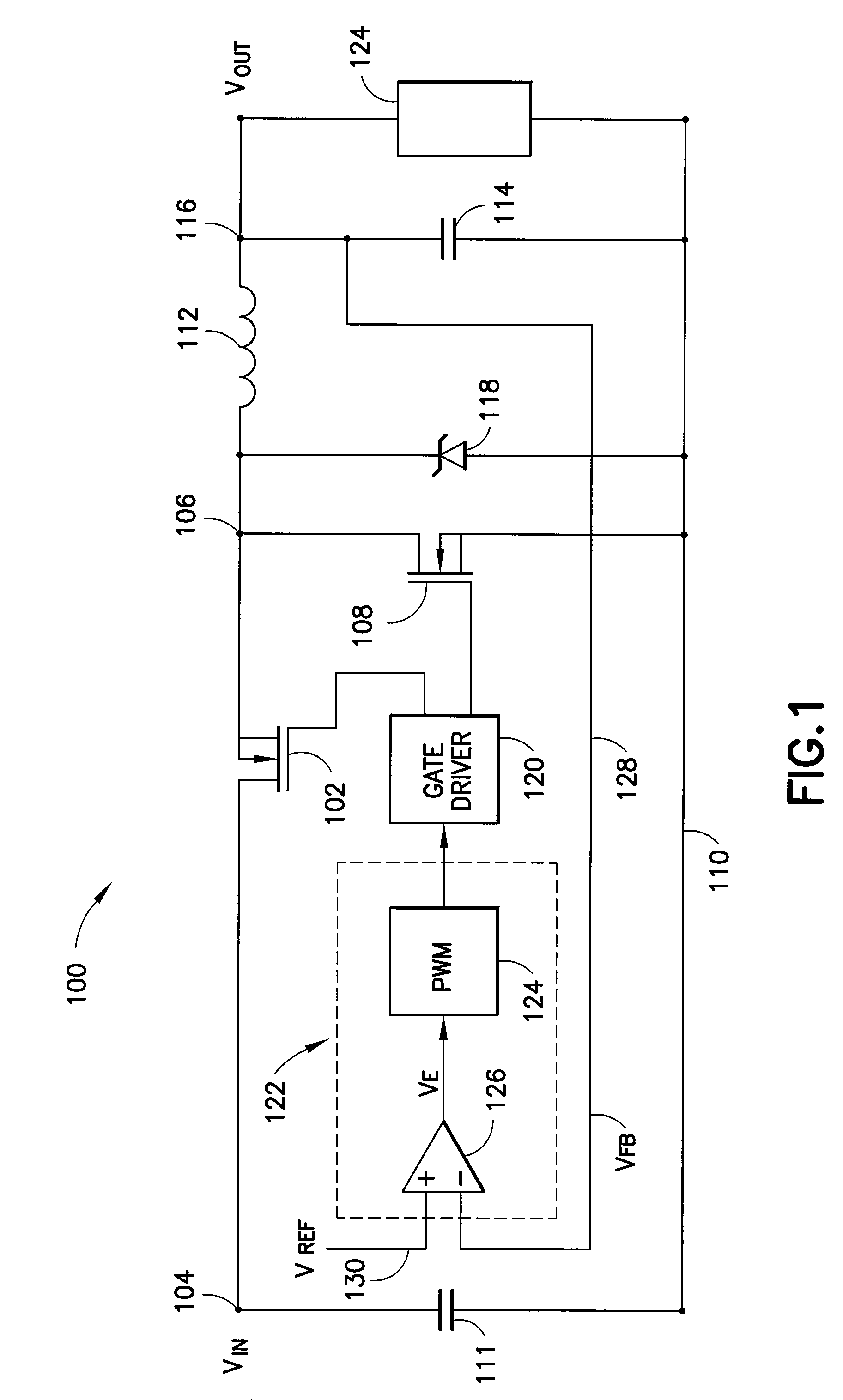
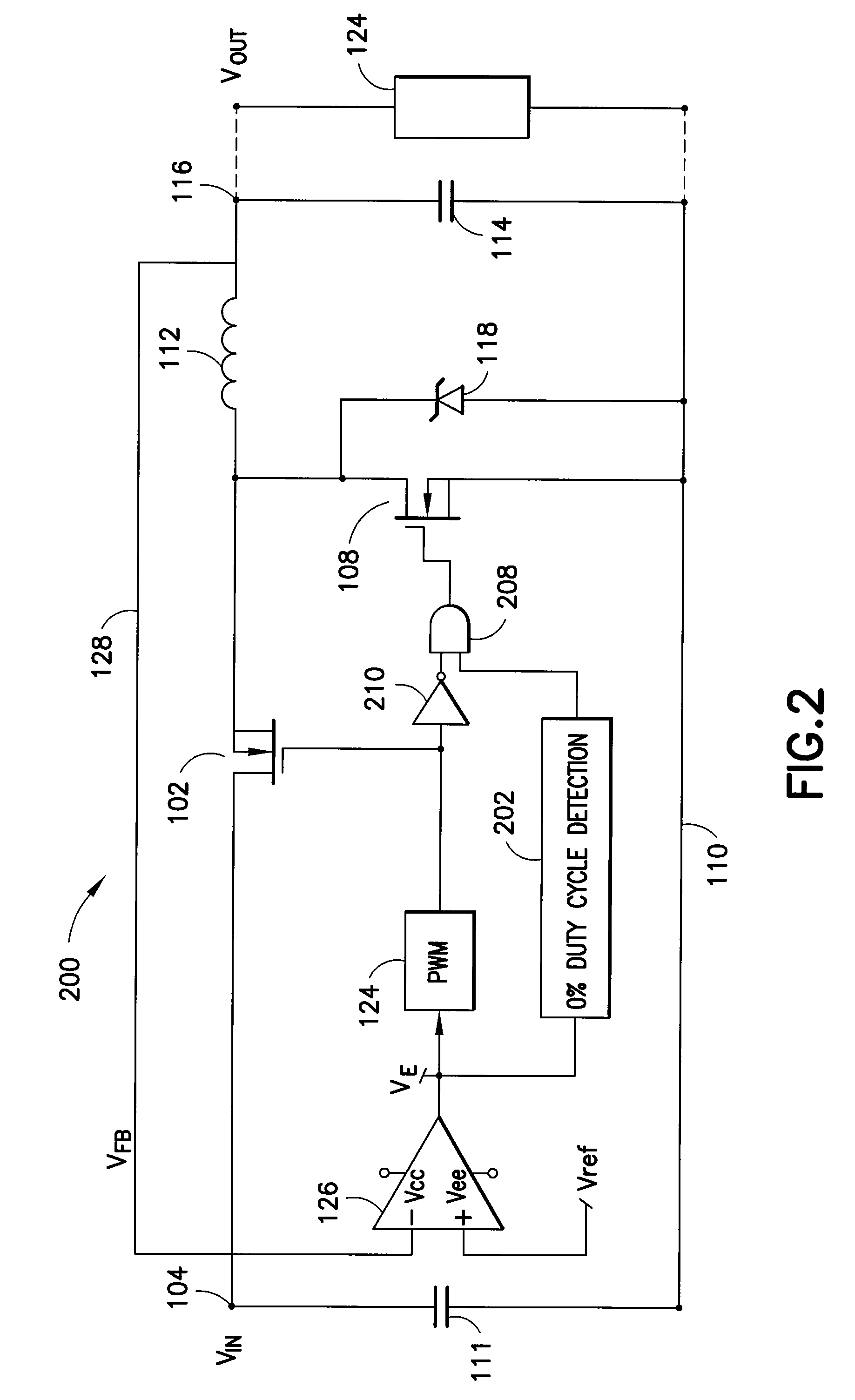
Voltage down converter
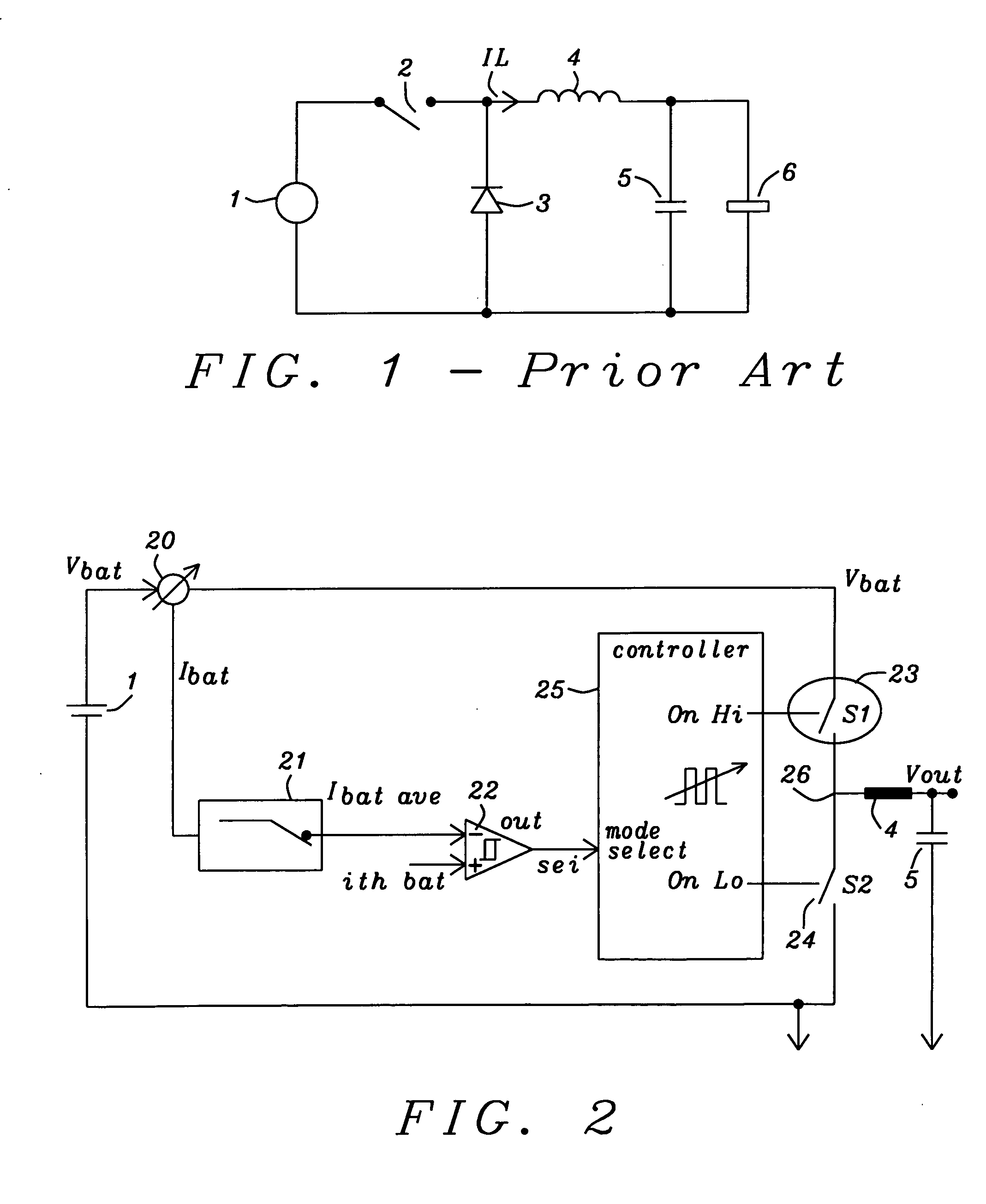
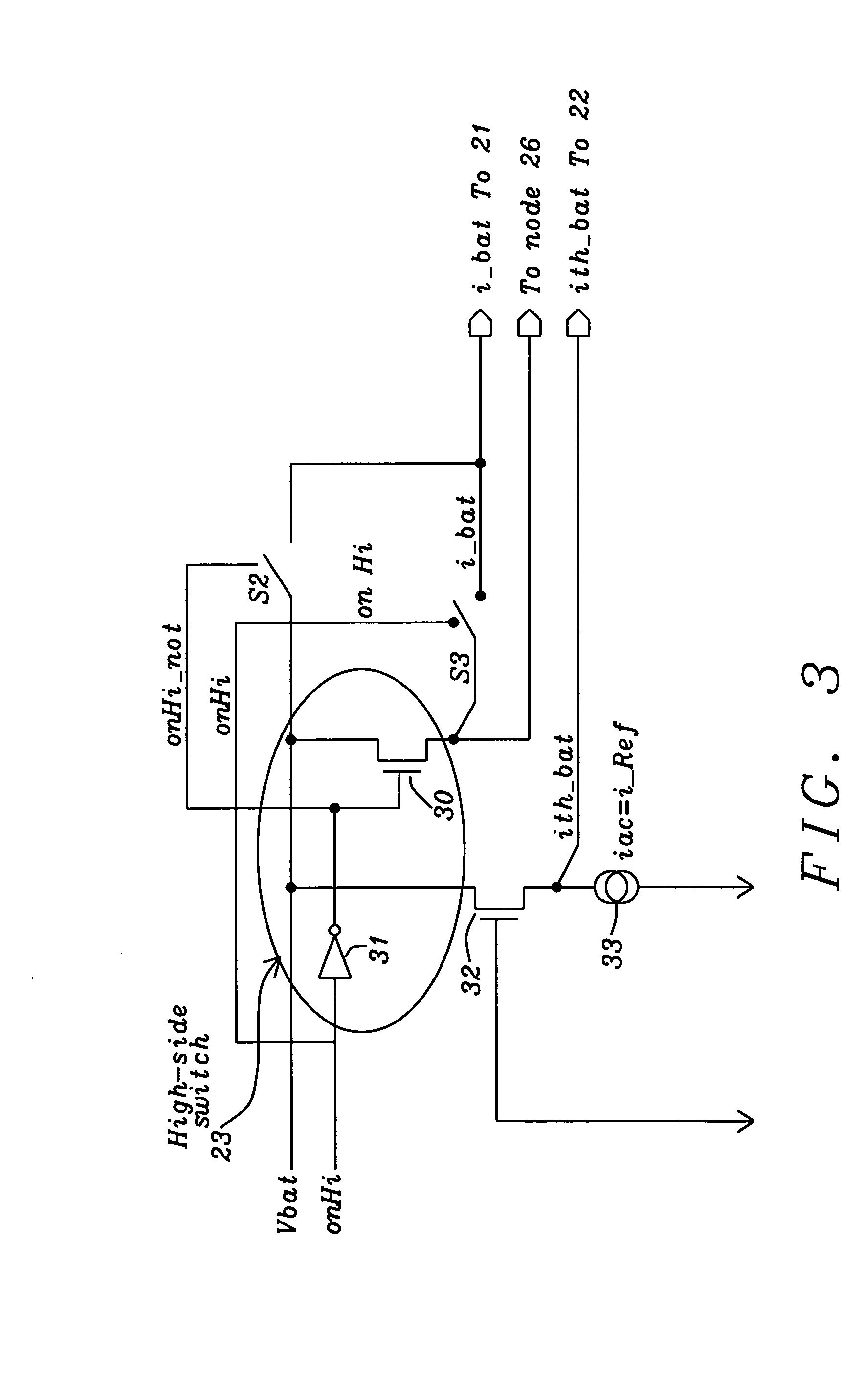
InactiveUS20060103453A1Lower average response timeStatic storageElectric variable regulationDriver circuitVoltage regulation
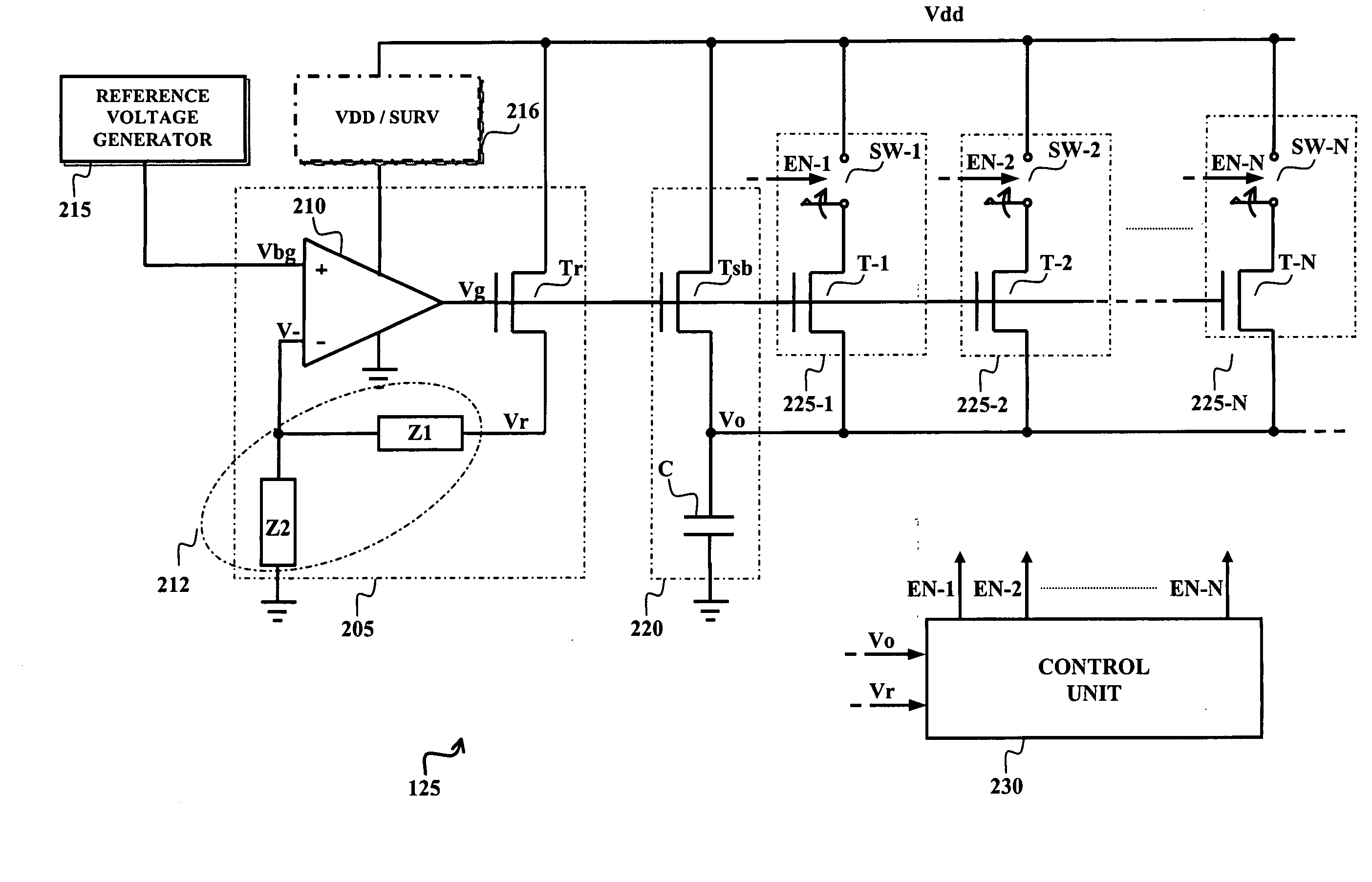
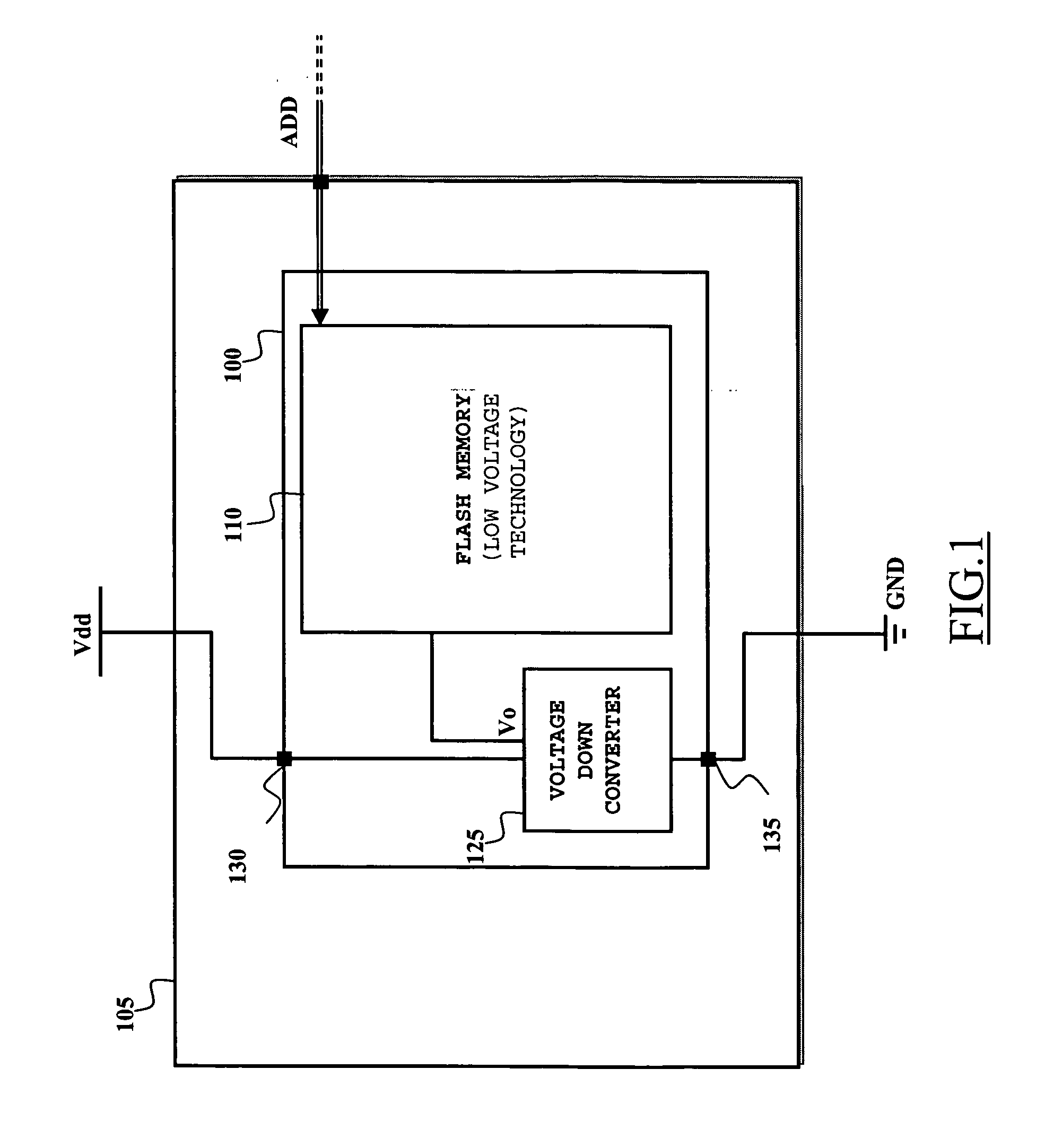
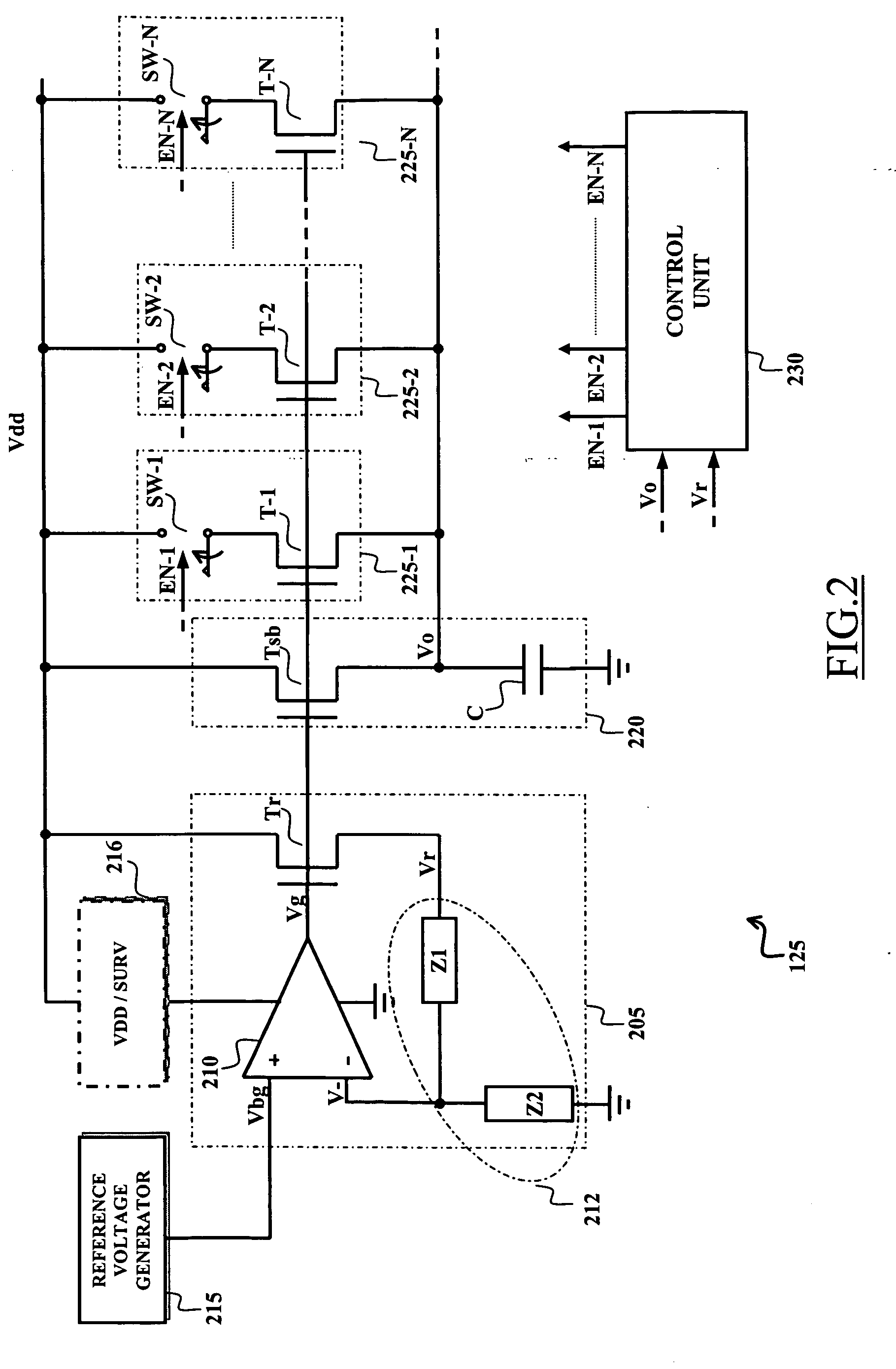
A voltage down converter is provided that includes a voltage regulator and voltage driver circuit branches. The voltage regulator receives a first voltage, has a regulation node providing a regulated second voltage that is lower than the first voltage, and has a control node providing a control voltage corresponding to the second voltage. One voltage driver circuit branch receives the first voltage and includes a variable-conductivity element having a control terminal coupled to the control node for controlling a current sunk by the variable-conductivity element. This one voltage driver circuit branch has a voltage supply node supplying a down-converted voltage corresponding to the second voltage. At least one additional voltage driver circuit branch receives the first voltage and is coupled to the voltage supply node. The additional voltage driver circuit branch includes a further variable-conductivity element having a control terminal coupled to the control node for controlling a current sunk by the further variable-conductivity element, and a switching circuit for selectively enabling the further variable-conductivity element so as to keep the down-converted voltage at a prescribed value depending on the regulated second voltage.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Voltage down converter for high speed memory
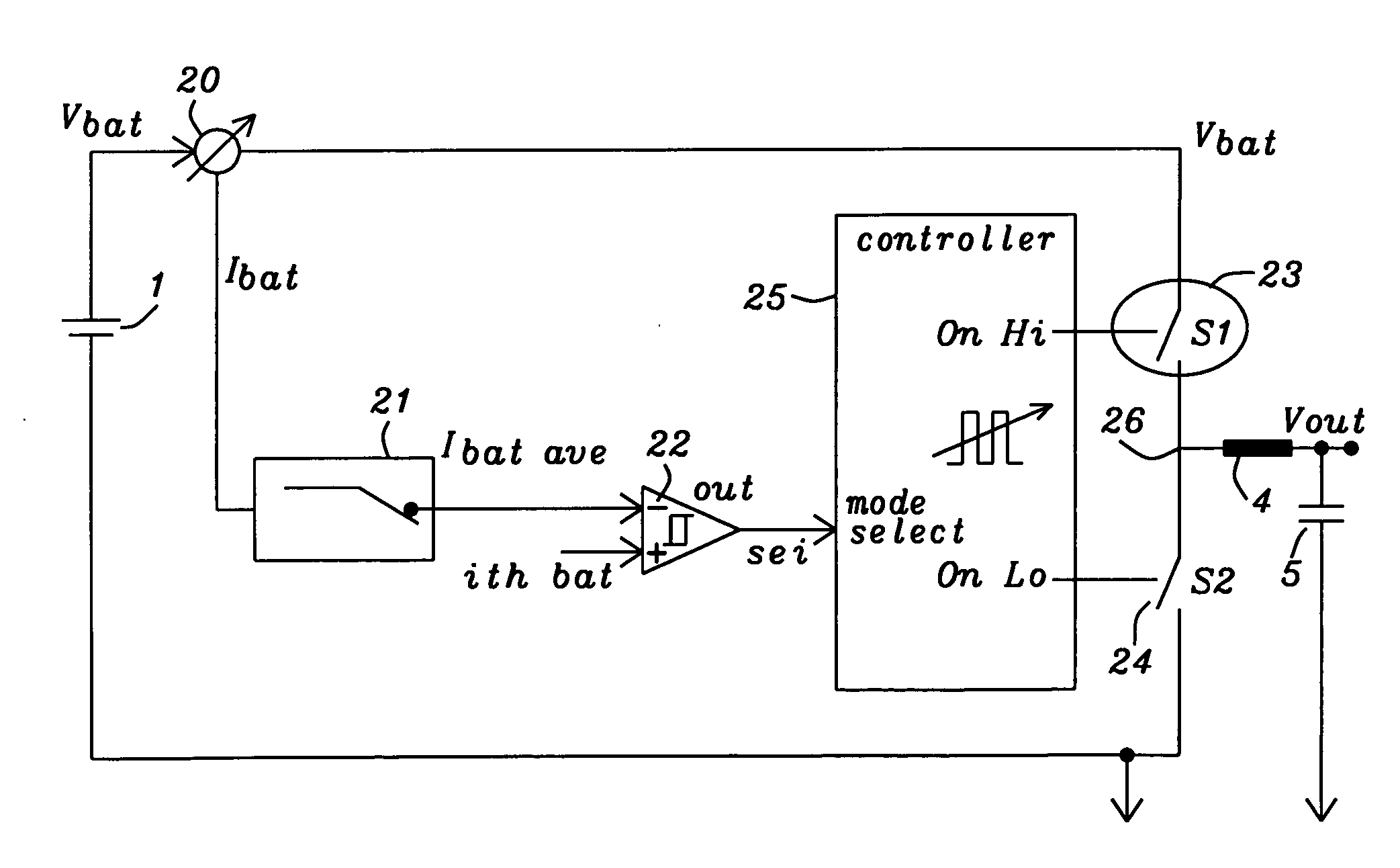
A voltage down converter (VDC) applicable to high-speed memory devices. The VDC includes a steady driver and active driver along with at least one additional transistor. The steady driver and active driver are coupled by a transistor switch during device start-up to provide fast ramp-up to operating voltage and current. After start-up, the steady driver and active drive function to maintain a steady operating voltage and current. An additional transistor is digitally controlled to drive up operating voltage and current upon issuance of an active command representing read, write, and / or refresh of memory. In this manner, the additional transistor provides fast compensation for fluctuations in operating voltage and current brought on by activity in the memory array.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
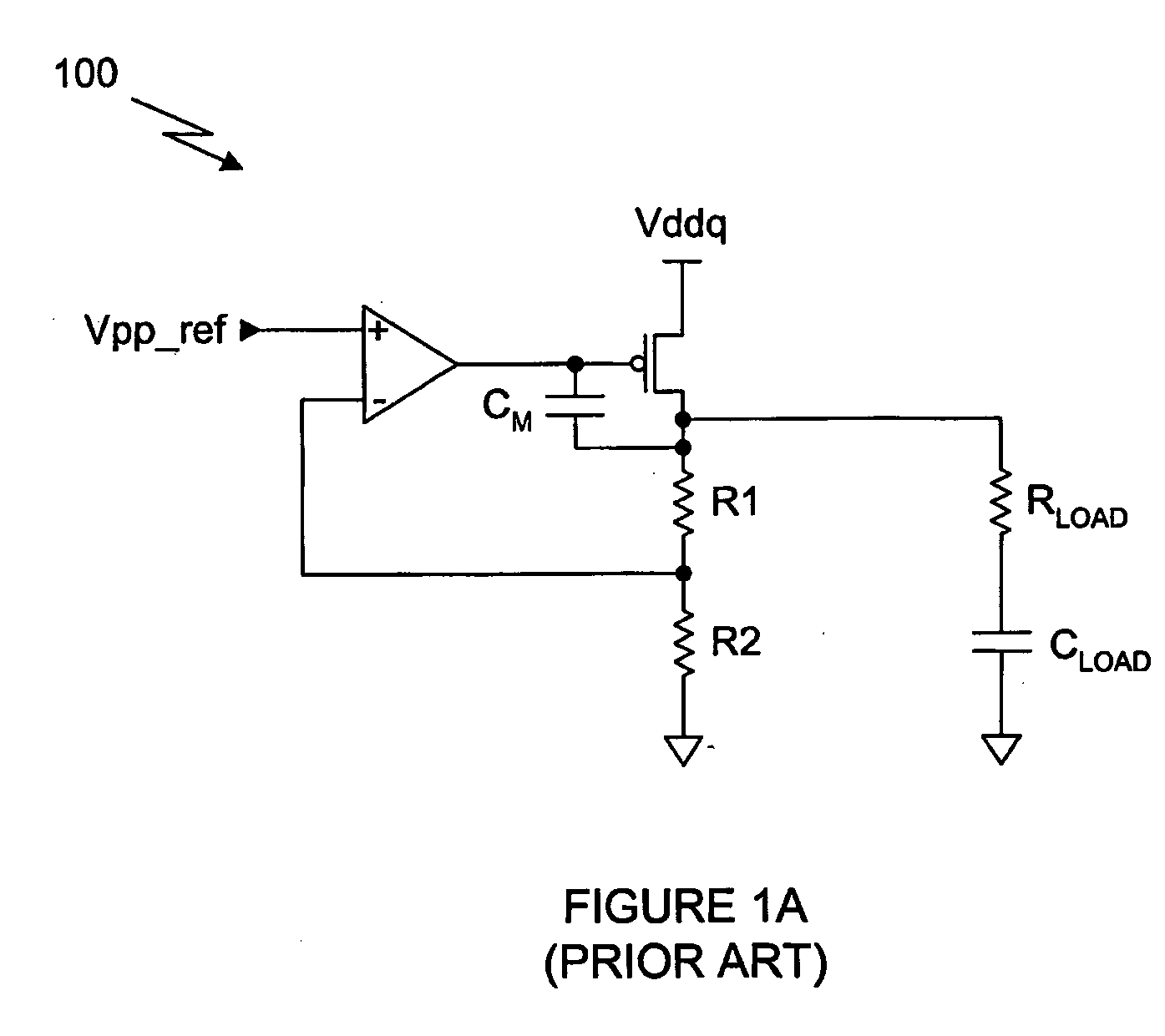
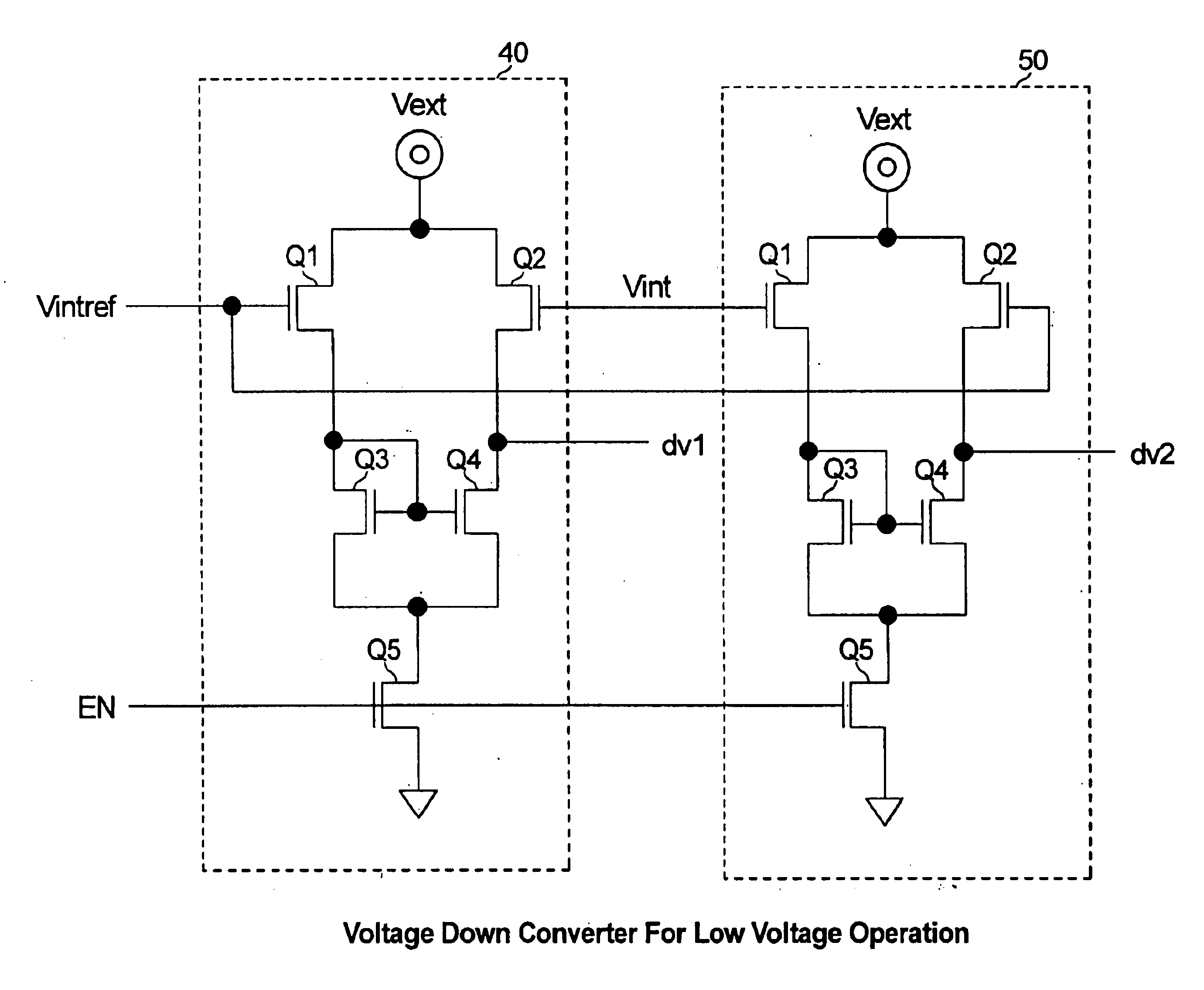
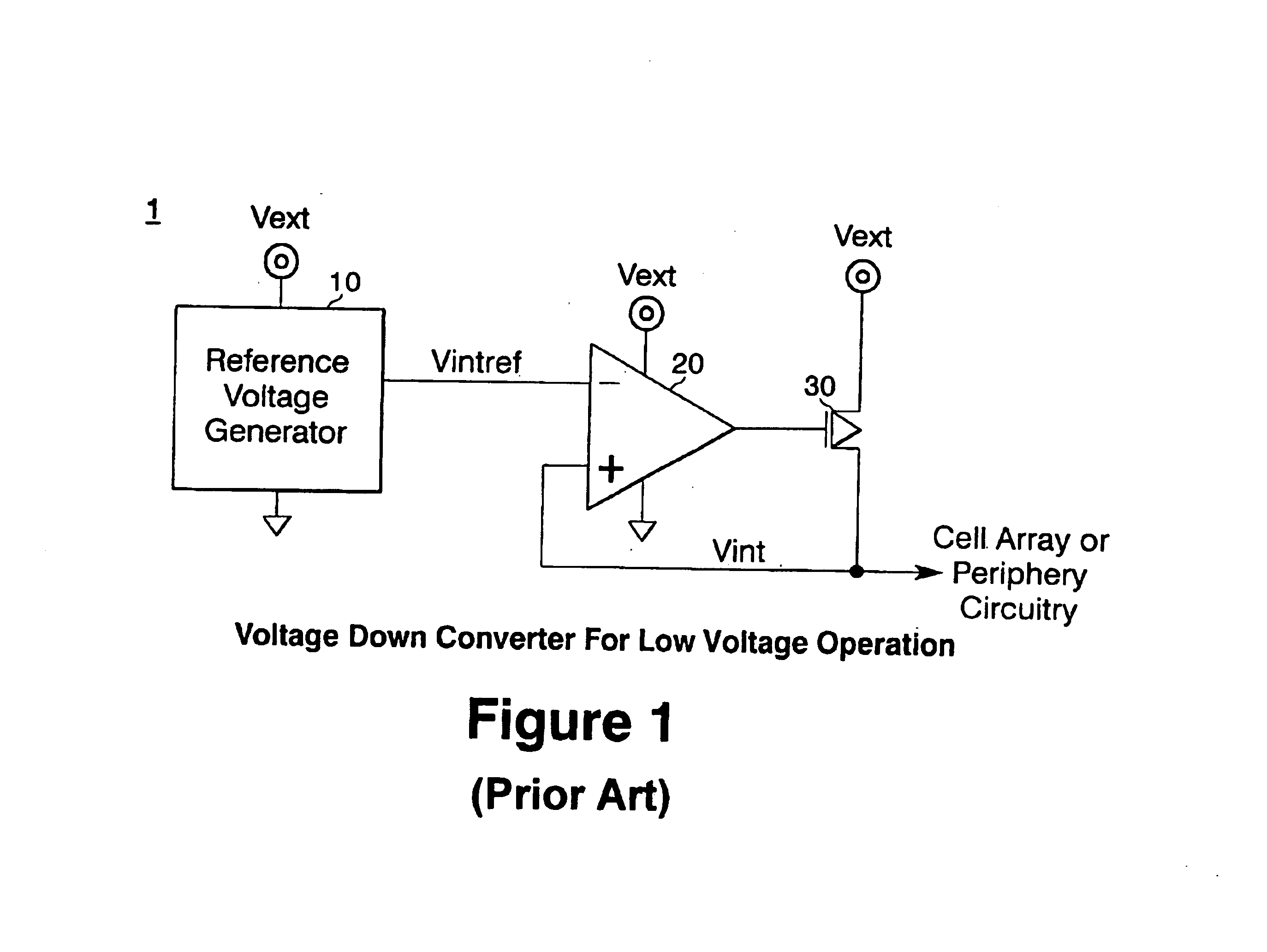
Voltage down converter for low voltage operation
InactiveUS6861872B2Guaranteed uptimeEasily amplifiedBaseband system detailsPulse automatic controlVoltage generatorLow voltage
A voltage down converter for a semiconductor memory device to convert an external voltage to a lower value internal voltage for the device, has a voltage generator that produces a reference voltage corresponding to the value of the internal voltage, a comparator having opposite polarity inputs for producing an amplified output control signal, and a pull-up device operating from the external voltage that receives the control signal from the comparator to produce the internal voltage as an input. A dual source follower is located between the reference voltage generator and comparator and has two sections having cross-coupled inputs which respectively receive the internal reference voltage and the internal voltage to produce output voltages moving in opposite directions, each of which is applied to one input of the comparator, thereby translating the difference between Vintref and Vint to a level in a range that can be better amplified by the comparator.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS6937496B2Solve the real problemGuaranteed uptimeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityDevice material
A semiconductor device having a first circuit block supplied with a first operating voltage, a second circuit block supplied with a second operating voltage, a voltage generating circuit for generating a third operating voltage in response to the first operating voltage, and a third circuit block supplied with the third operating voltage. Preferably, the third operating voltage is generated such that the first operating voltage is increased to a fourth operating voltage by a voltage-up converter, and then the fourth operating voltage is dropped to the third operating voltage by a voltage down-converter. Hence, a power supply operating internally stably in spite of use of a relatively fluctuating voltage can be provided even in the case where a power-supply voltage is dropped.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Buck converter threshold detection for automatic pulse skipping mode
ActiveUS20100007318A1Increase flexibilityEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionTime delaysĆuk converter
Circuits and methods to detect a threshold for entering and leaving a discontinuous current mode of a buck converter have been disclosed. A buck converter is switched to continuous mode if the filtered battery current has reached a defined threshold current Ithccm. In order to expedite the transition from DCM mode to CCM mode the time delay between two or more pulses of a current through an inductor is monitored and the buck converter is switched to CCM mode if this time delay is smaller than a defined threshold.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
AC/DC power converter
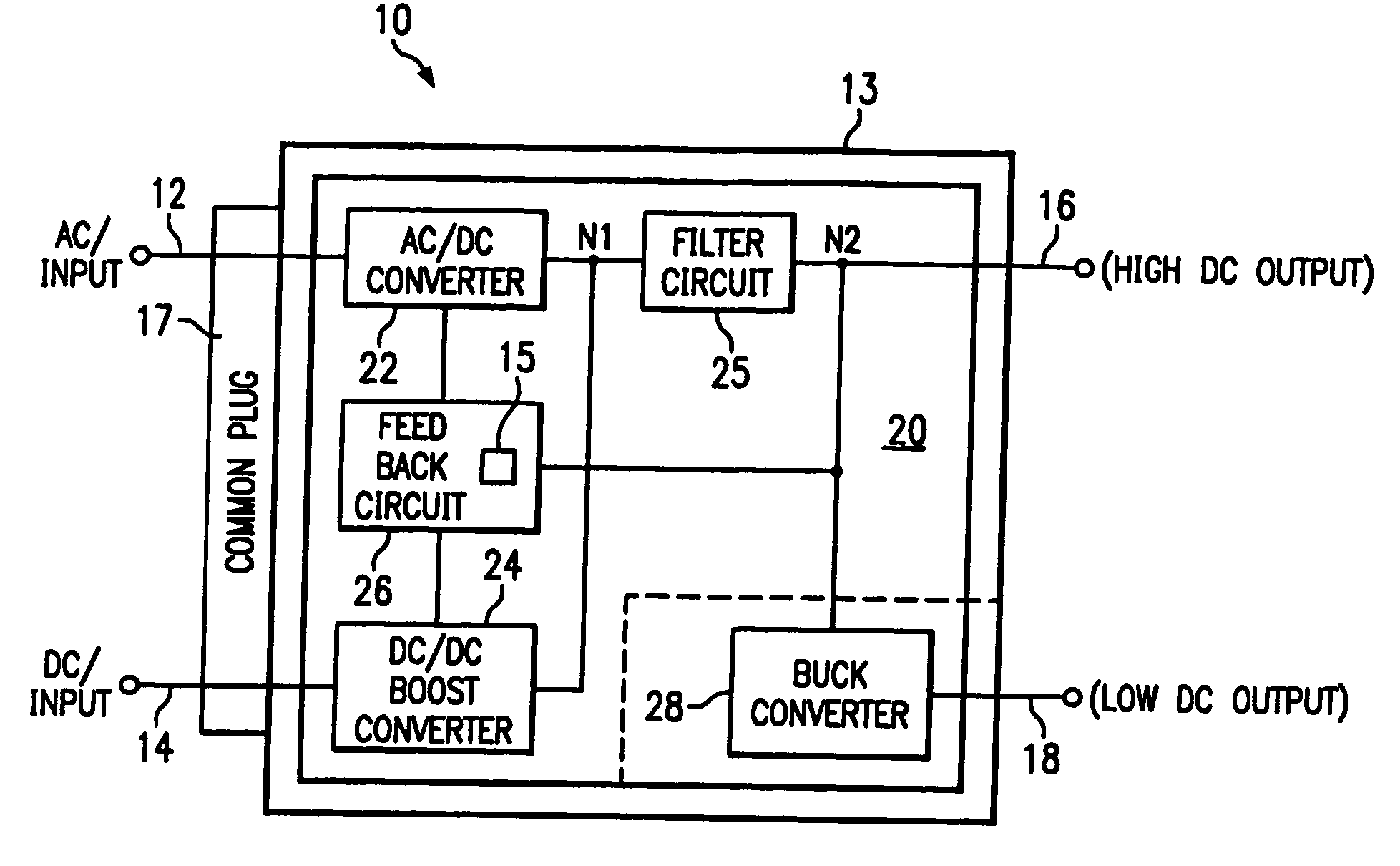
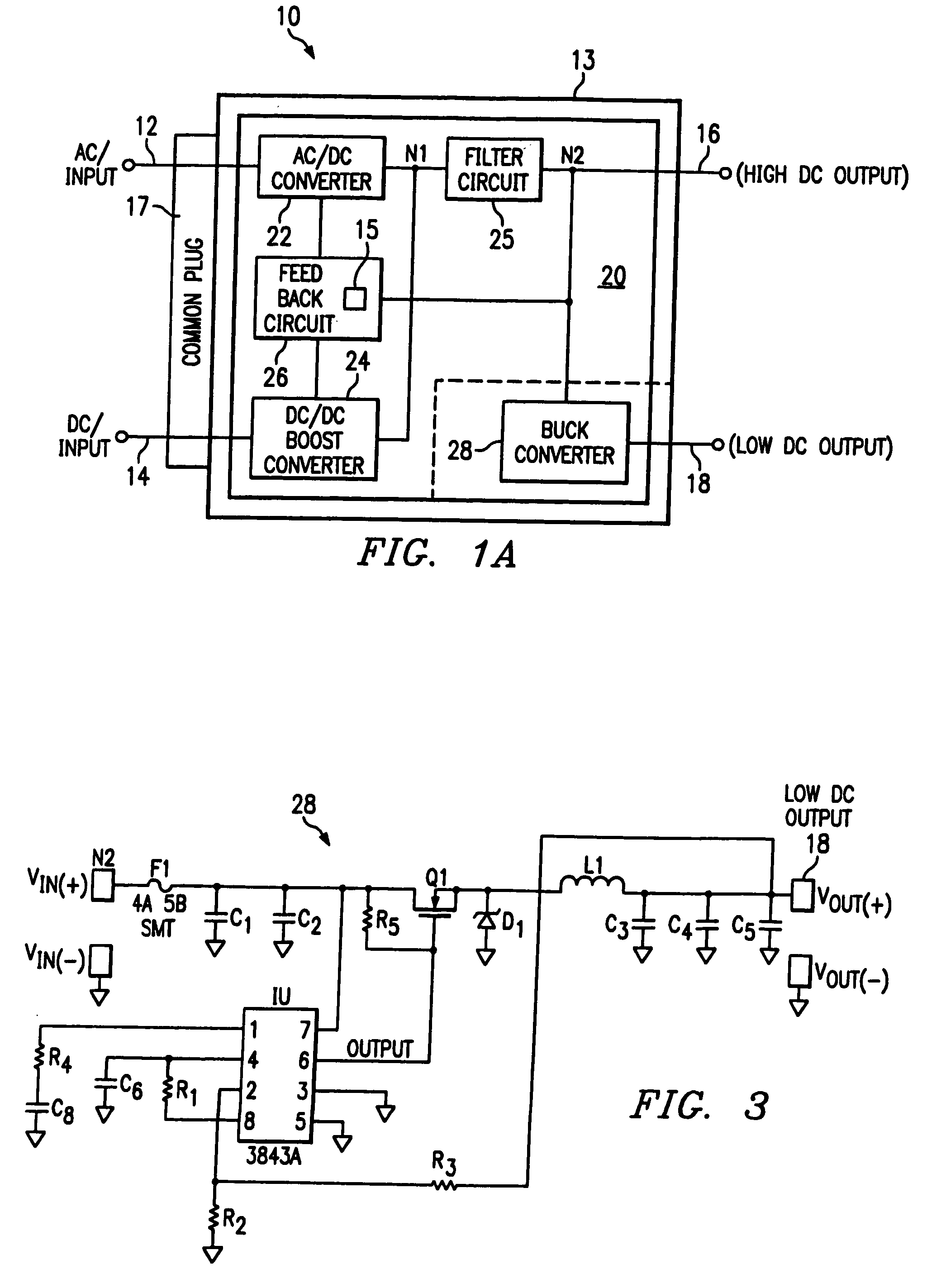
InactiveUS20060007715A1Conversion with intermediate conversion to dcVolume/mass flow measurementBuck converterSystems management
A dual input AC / DC power converter (10) having dual inputs (12, 14) adapted to receive both an AC and DC input and provide a selectable DC voltage output (16) and a second DC output (18). The dual input AC / DC power converter (10) comprises a power converter circuit (20) having an AC-to-DC converter (22), a DC-to-DC booster converter (24), a feedback circuit (26), a filter circuit (25) and a DC-to-DC buck converter (28). Advantageously, the power converter (10) resolves many of system management problems associated with carrying all of the different interface components necessary to power a wide variety of mobile products from either an AC or DC power supply. In addition, the power converter (10) also advantageously includes dual output voltage terminals (16 / 18) to allow for multiple mobile devices of varying power requirements to be powered, simultaneously, by a single converter.
Owner:IGO INC
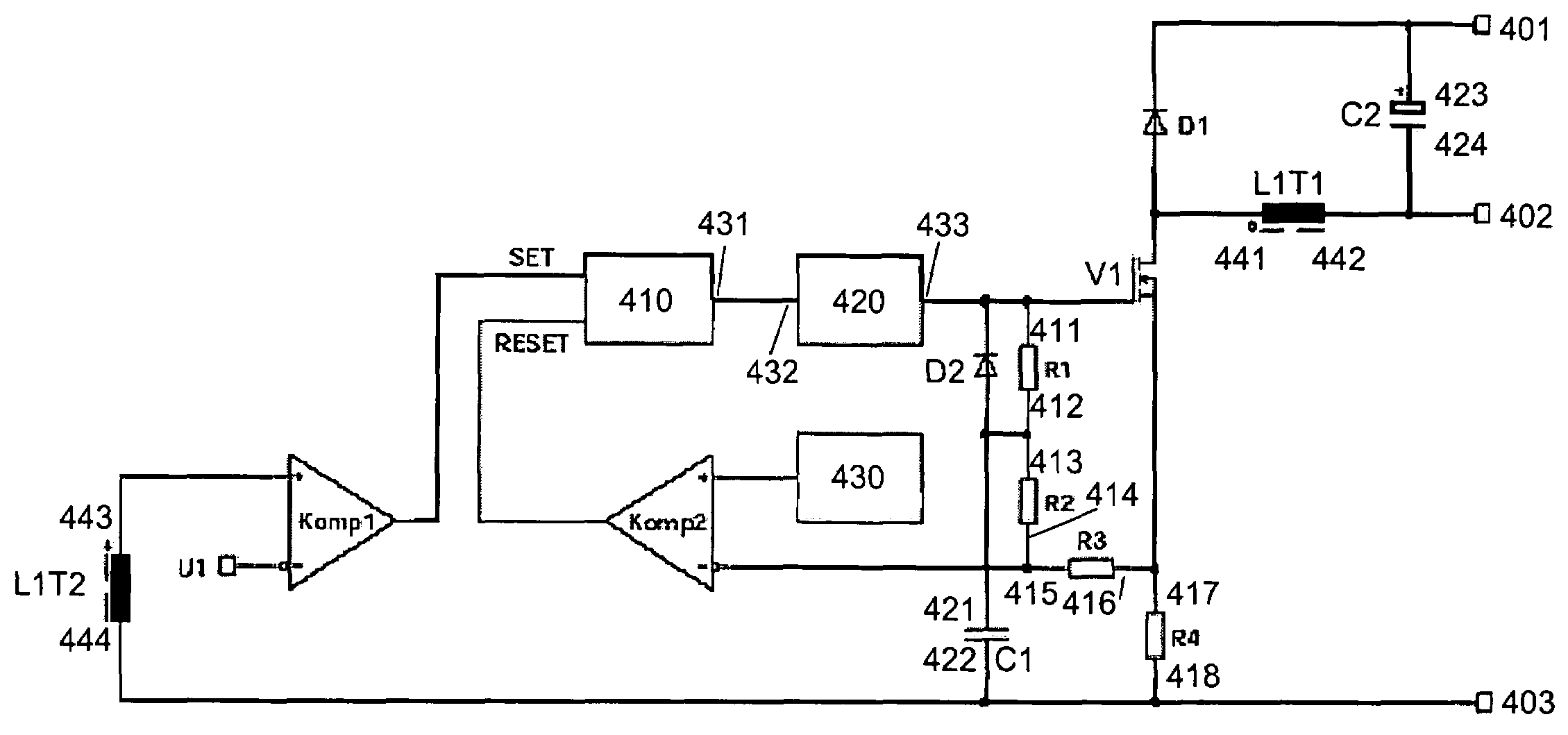
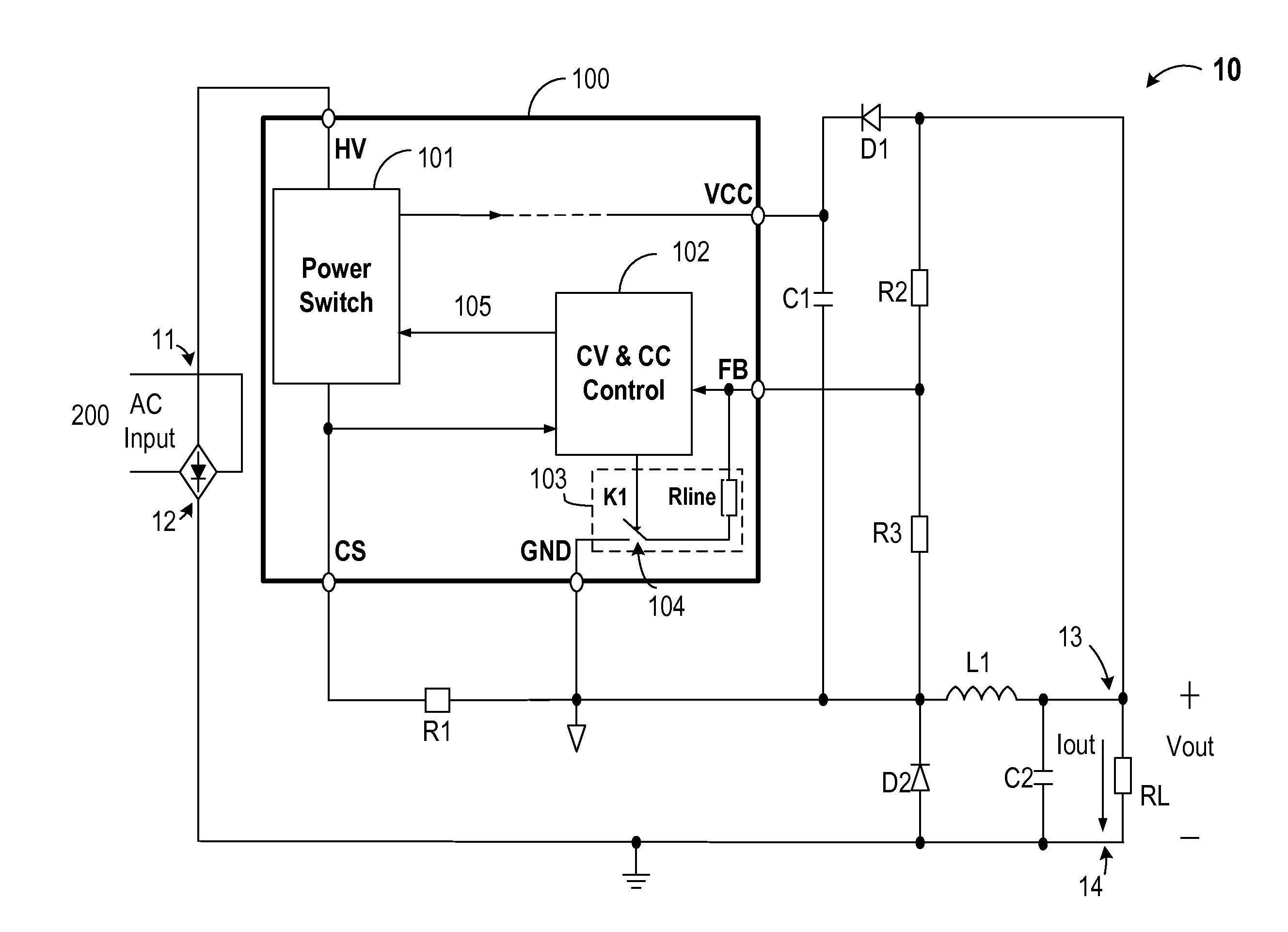
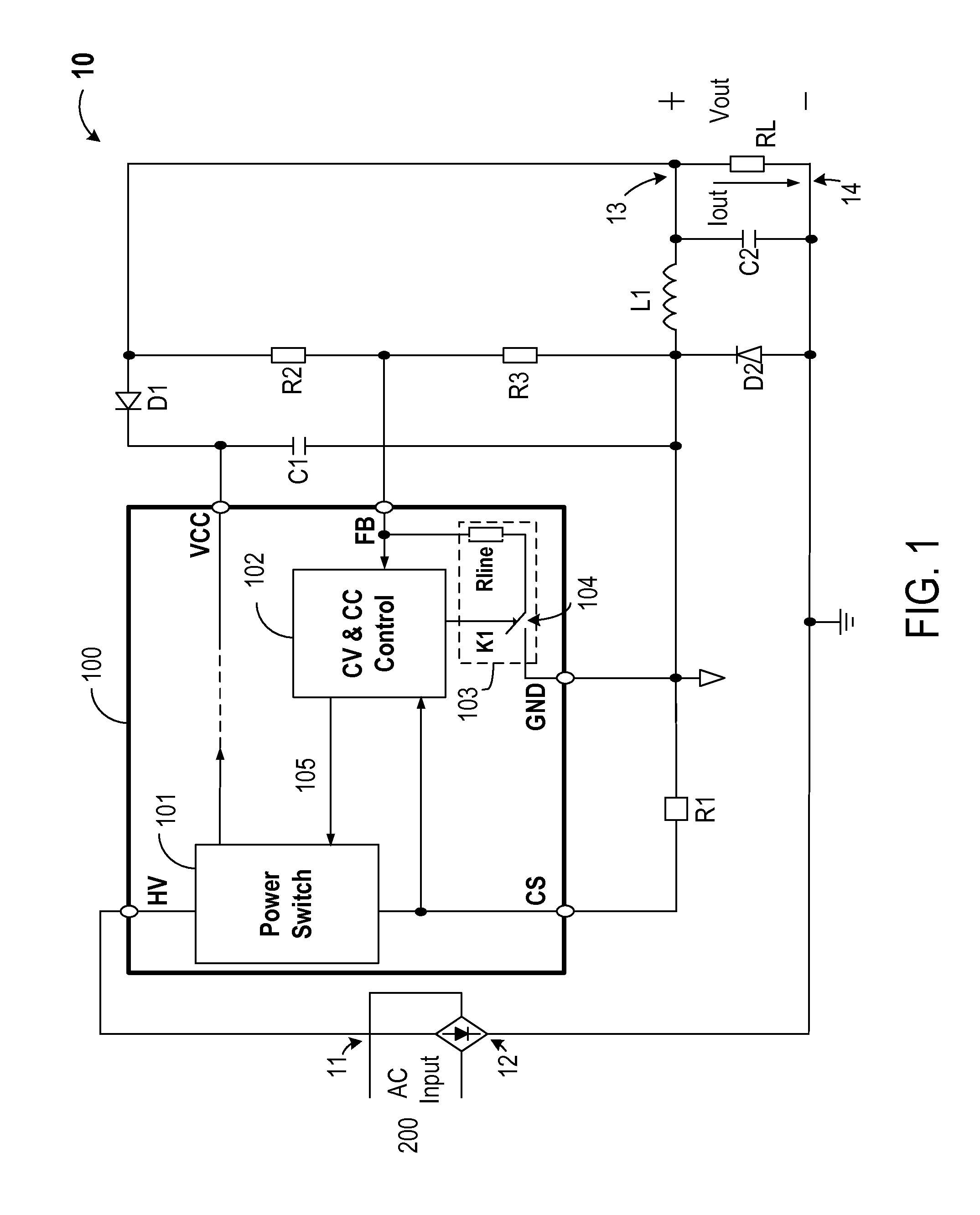
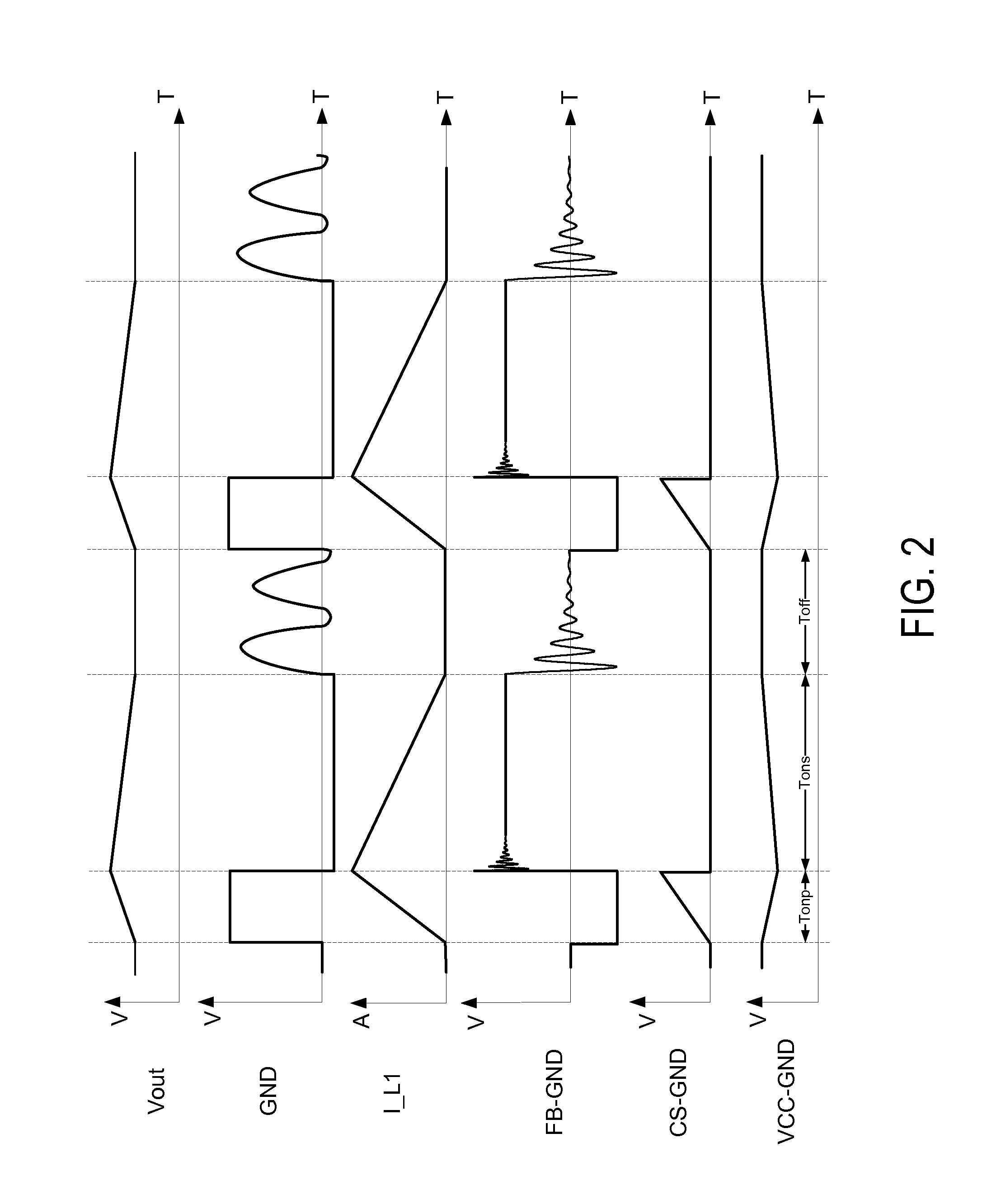
Constant-voltage and constant-current buck converter and control circuit
ActiveUS20140239930A1Reduce voltageAc-dc conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionPower switchingBuck converter
A control circuit is provided for a buck converter that includes at least an inductor coupled to an output of the buck converter. The control circuit includes a power switch configured for coupling to a line voltage and configured for charging the inductor, an input line voltage sampling circuit, and a constant-voltage (CV) and constant-current (CC) control module coupled to the power switch. During a charging period of the inductor, the CV and CC control module is configured to control the power switch to provide a constant output current by maintaining a constant peak inductor current, even when the input line voltage changes. During a discharging period of the inductor, the CV and CC control module is configured to monitor the sensed output voltage to control the power switch to provide a constant output voltage.
Owner:BCD SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Buck converter with surge protection
InactiveUS20100026253A1Avoid complex architectureElectric variable regulationPower conversion systemsCapacitanceZener diode
A buck converter with surge protection comprises a transistor, a voltage clamp circuit, a control circuit, a rectifier diode, an inductor, an output capacitor and a resistor. The transistor is coupled to a input voltage. The voltage clamp circuit has a Zener diode. The Zener diode is coupled to the transistor for limiting gate-to-source voltage of the transistor. The control circuit is used for maintaining a constant output voltage independently of variance of the input voltage. The rectifier diode is used for commutating current maintained by the electromotive force generating at both terminals of the inductor. The inductor is used for storing energy according to the current flowing from the input voltage via the transistor. The output capacitor is used for smoothing a voltage of the inductor. The resistor is applied the smoothed voltage. Hence, the present invention may protect the high-performance power supply from the automotive over-voltage events.
Owner:WANG SHIH YUAN
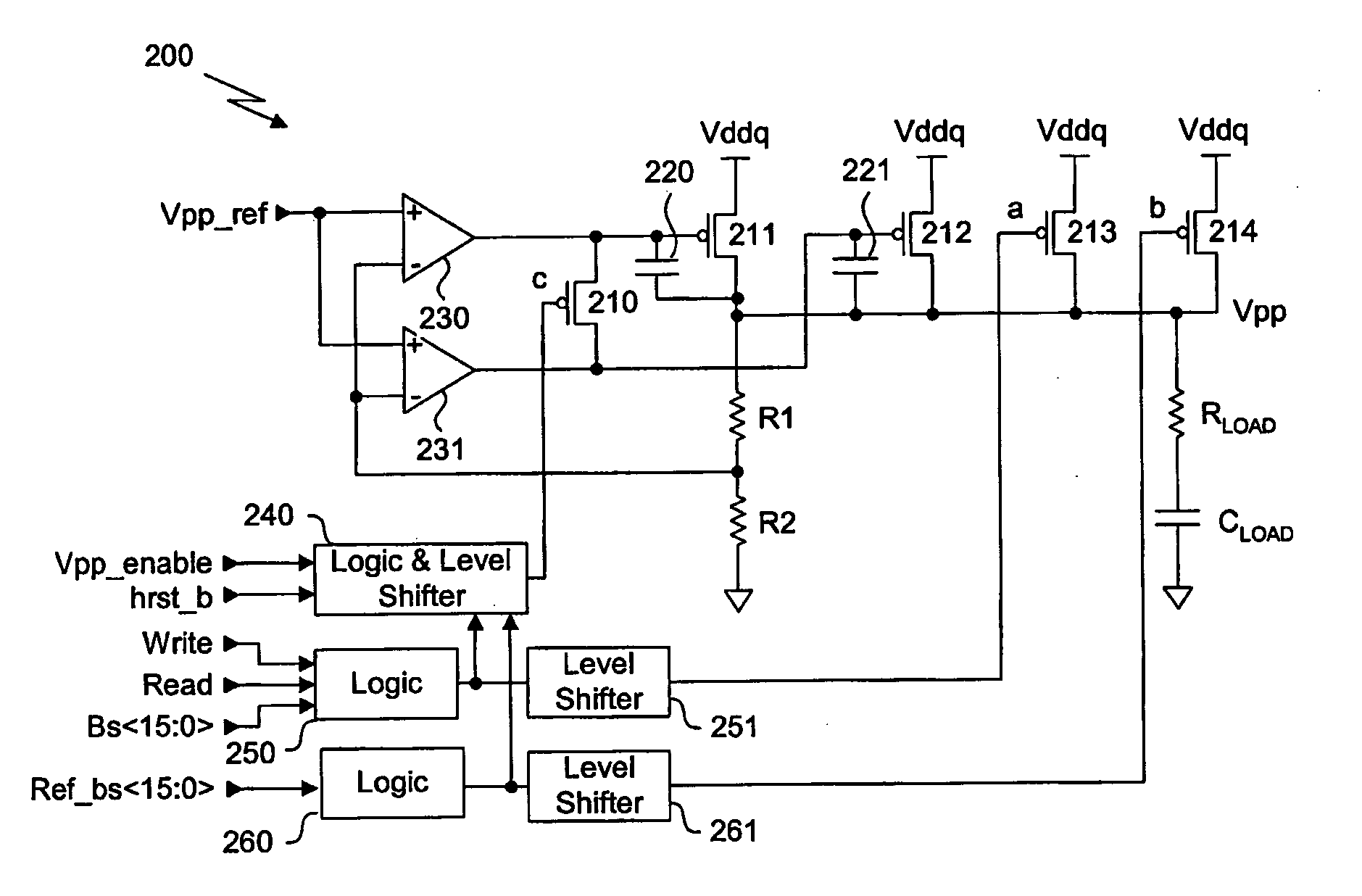
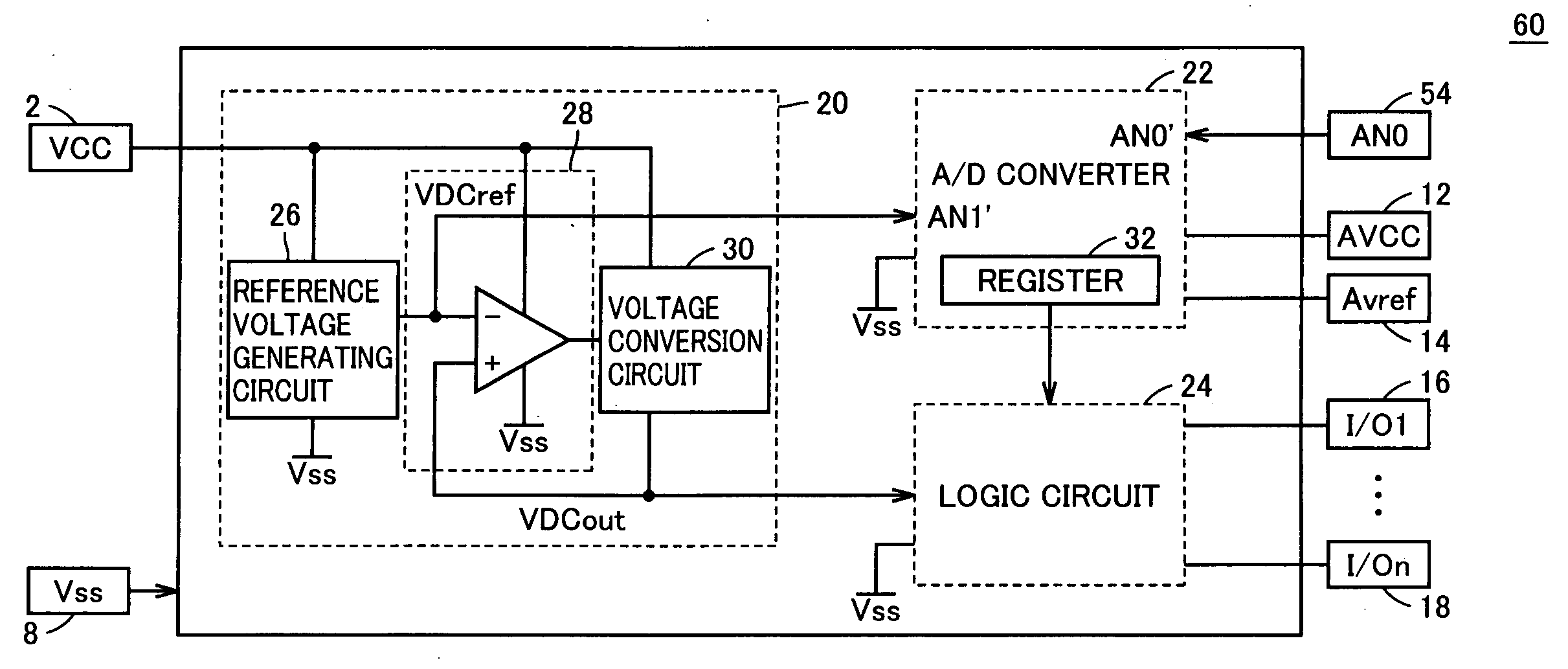
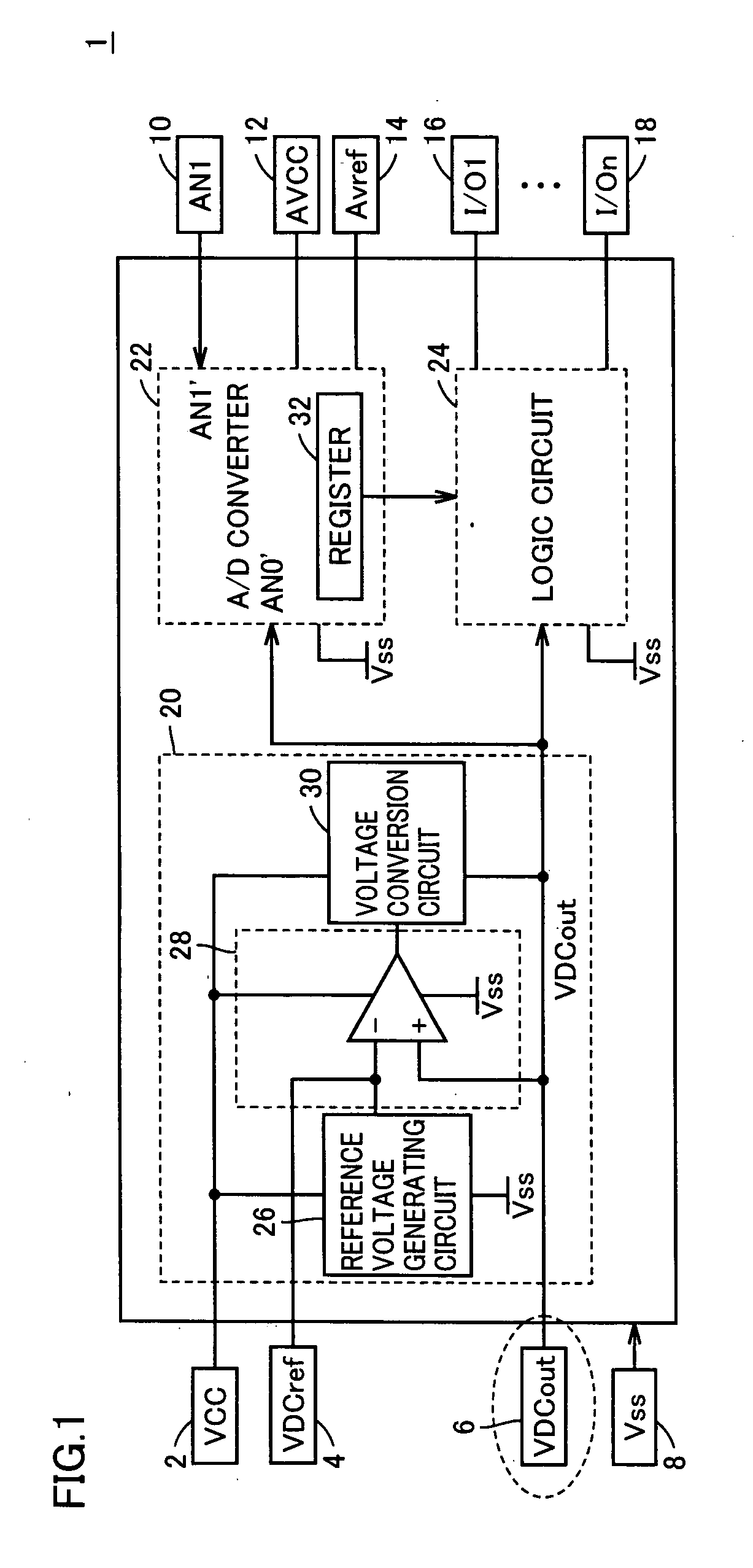
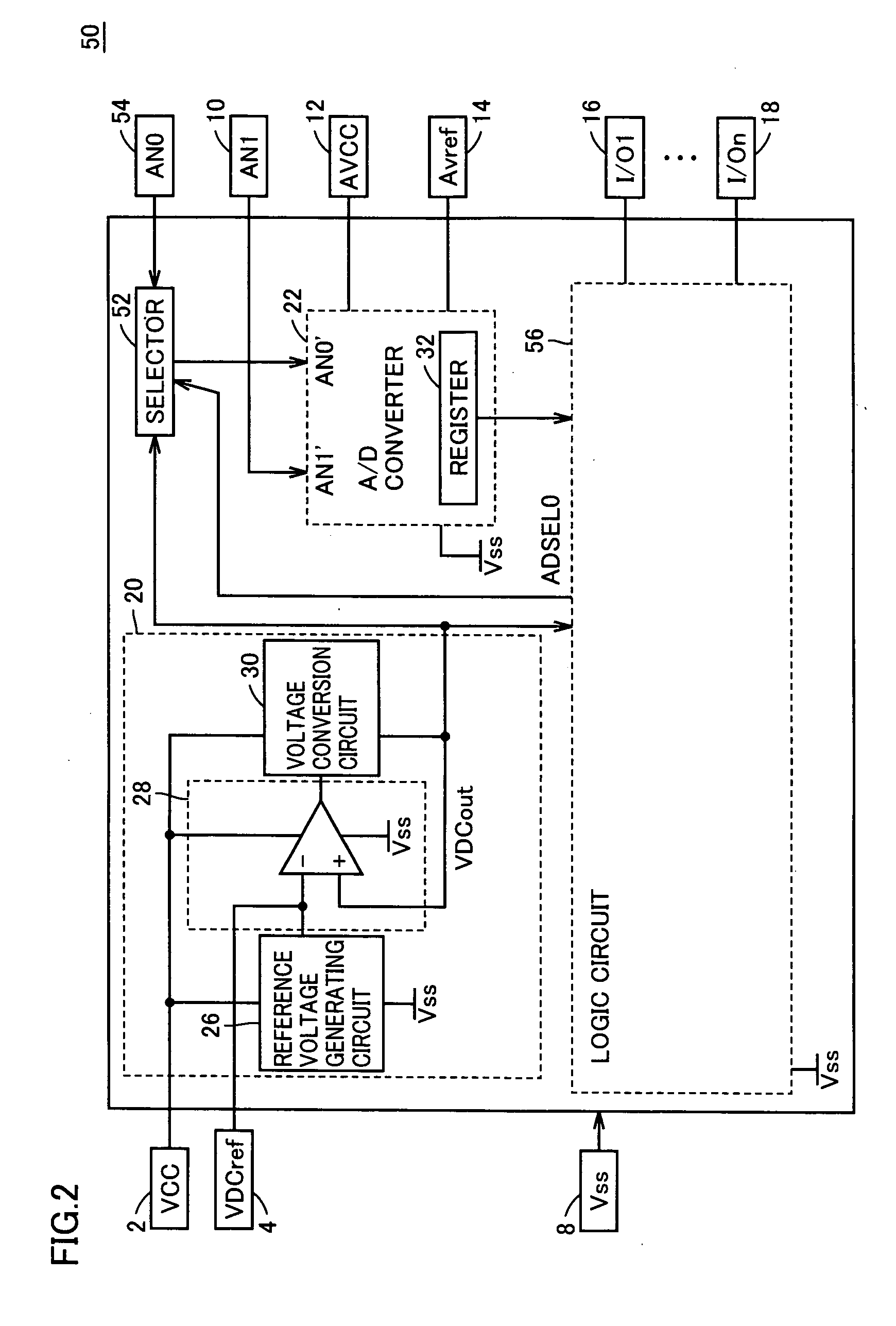
Semiconductor integrated circuit in which voltage down converter output can be observed as digital value and voltage down converter output voltage is adjustable
InactiveUS20050052307A1Reduce in quantityReduce the numberElectric signal transmission systemsAnalog circuit testingChip sizeMan-hour
An output voltage of a VDC circuit is subjected to A / D conversion with an on-chip A / D converter. Accordingly, an output voltage VDCout of the VDC circuit can be observed as a digital value, which facilitates measurement. Reduction in the number of terminals leads to reduction in chip size. In addition, the terminal that has been used for providing voltage VDCout can be used for other purposes. Therefore, a semiconductor integrated circuit allowing for easy mass production test and reduced number of man-hours in the mass production test can be provided.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Avalanche testing at final test of top and bottom FETs of a buck converter
ActiveUS20060170443A1Electrical measurement instrument detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansBuck converterEngineering
An avalanche test circuit for applying an avalanche test signal to a device under test, comprising a series combination of a voltage source and an inductance; a switching device connected in parallel with said series combination; a diode for being connected to a test terminal of said device under test, said diode being connected to a connection point of said inductance and said switching device; a common terminal of said device under test being connected to a connection point of said switching device and said voltage source.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Buck converter having improved transient response to load step down
A synchronous buck converter having an improved transient response during output current includes a first switching transistor connected between an input node and a first node, a second switching transistor connected between the first node and a second node, a series inductor connected between the first node and an output node, an output capacitor connected between the output node and the second node, a first driver circuit operative to turn the first switching transistor one and off according to a variable duty cycle determined by an error signal representing the difference between the voltage output of the converter and a reference voltage, a sensing circuit operative to provide a control signal output when the duty cycle for the first switching transistor is zero, a second drive circuit responsive to the control signal output of the sensing circuit to turn off the second switching transistor and a second sensing circuit operative to provide a second control signal when a dissipating current of the inductor is zero, wherein the second drive circuit is responsive to the second control signal to turn the second switching transistor on when the dissipating current of the inductor is zero.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com